Patents
Literature
2958 results about "RAID" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
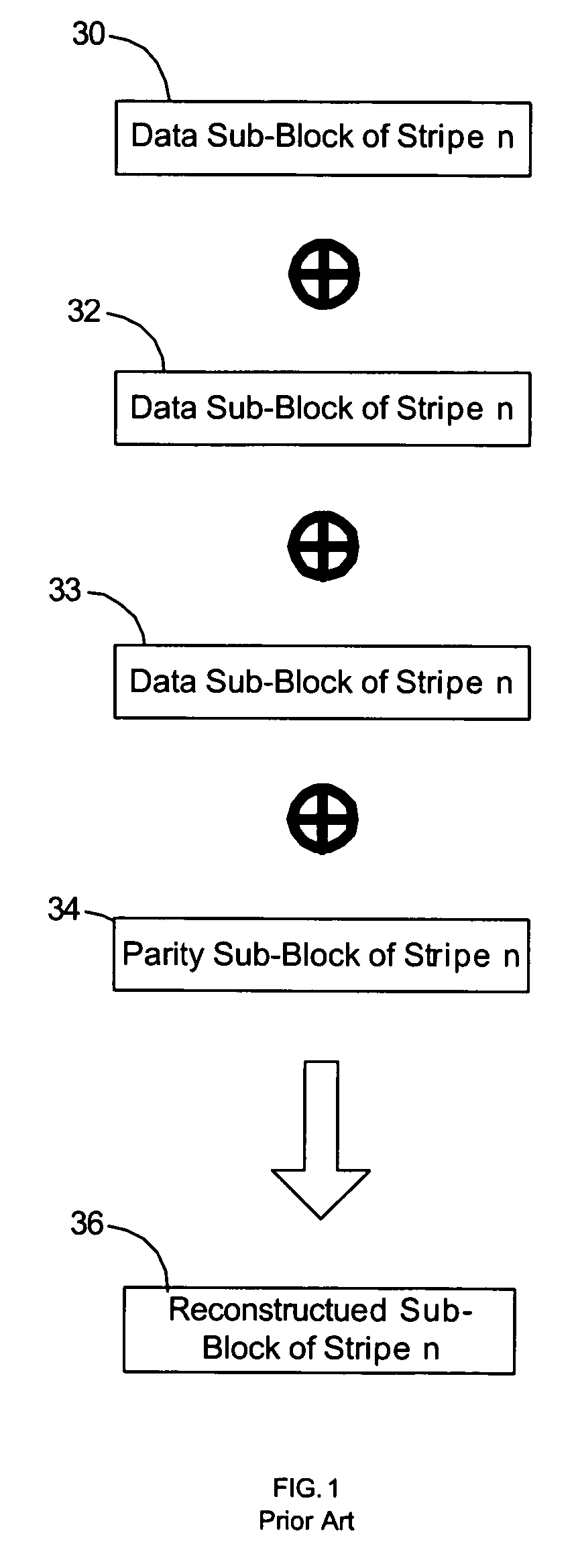
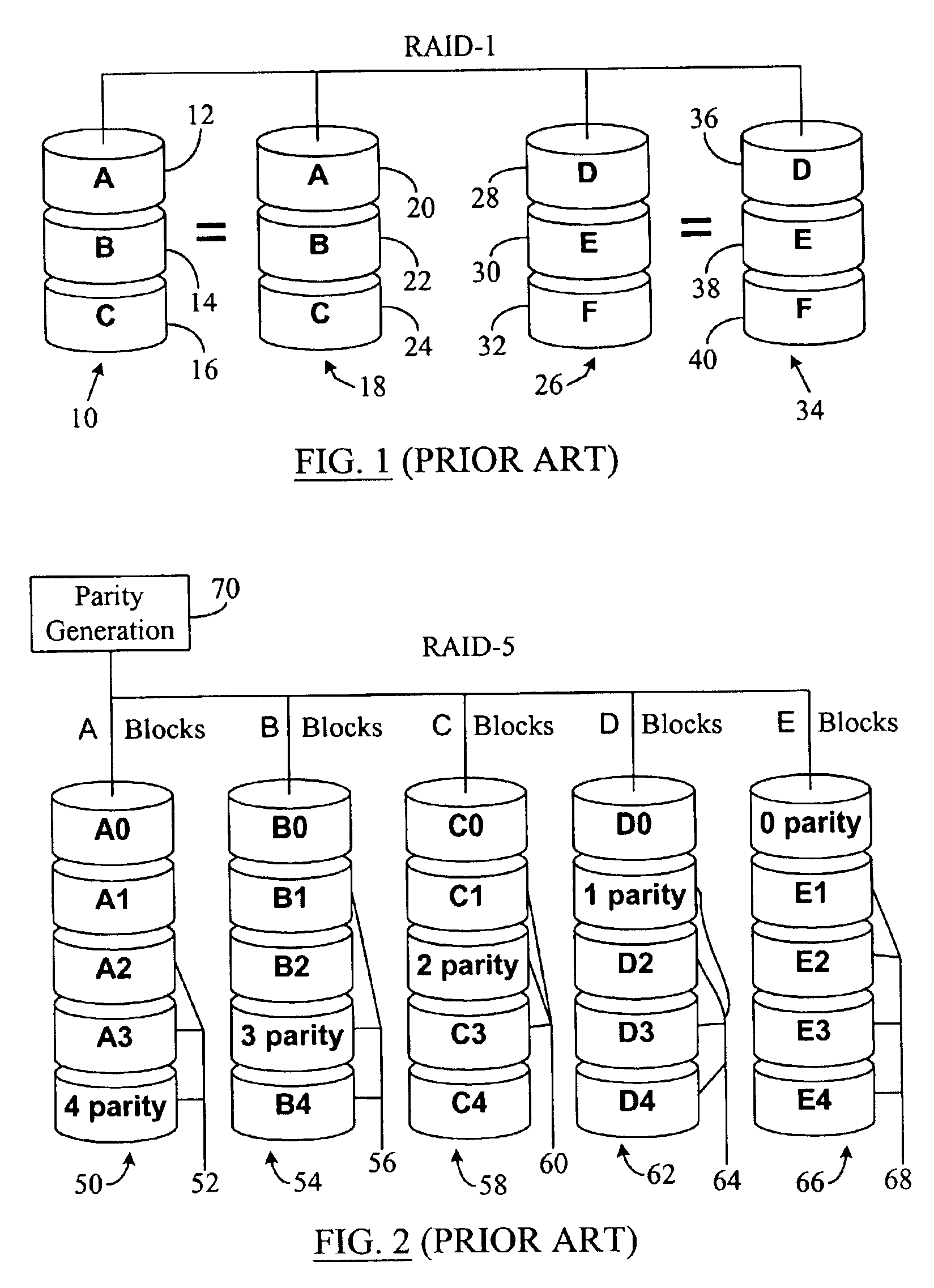
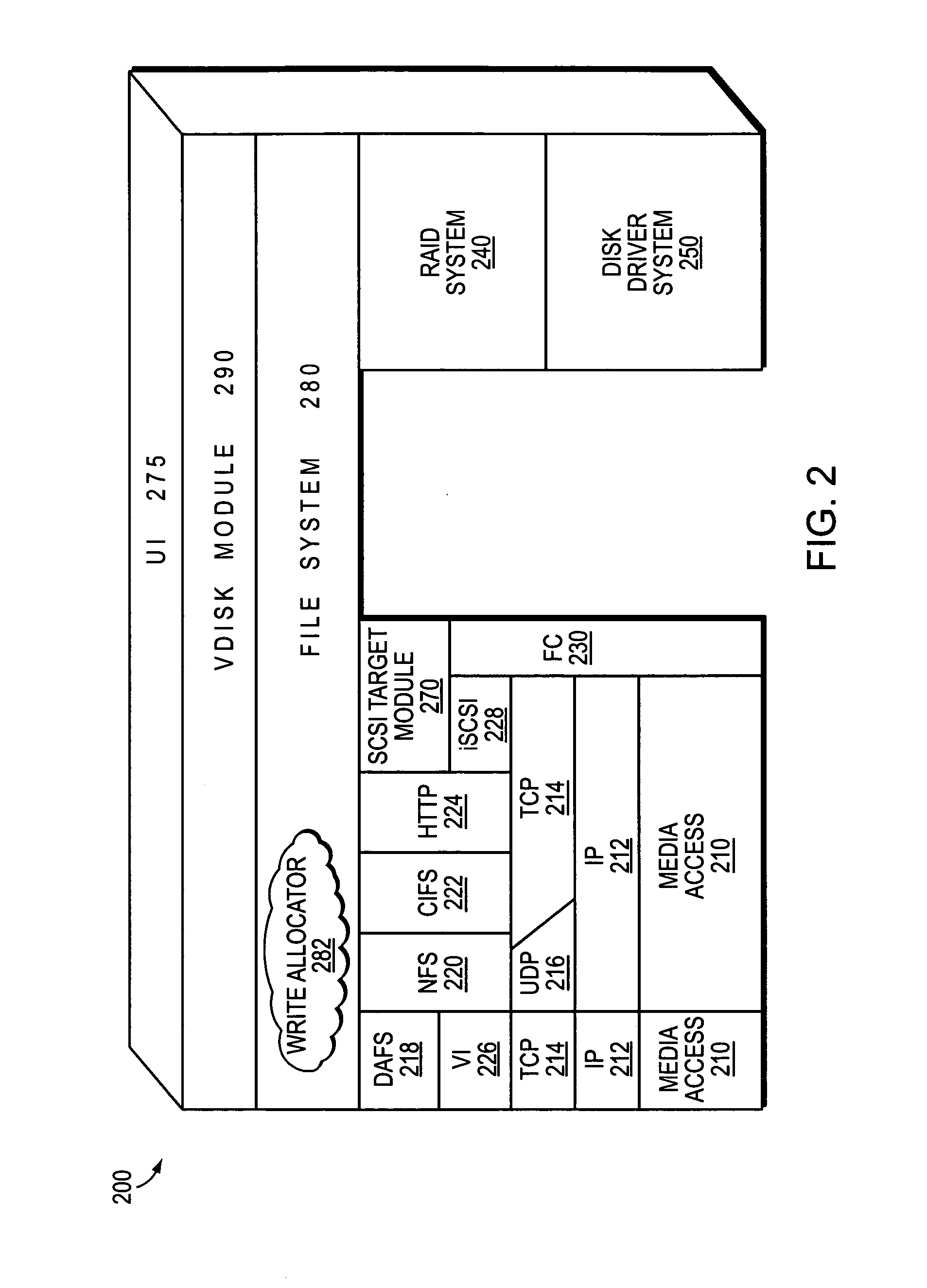
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Drives, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This was in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives referred to as "single large expensive disk" (SLED).
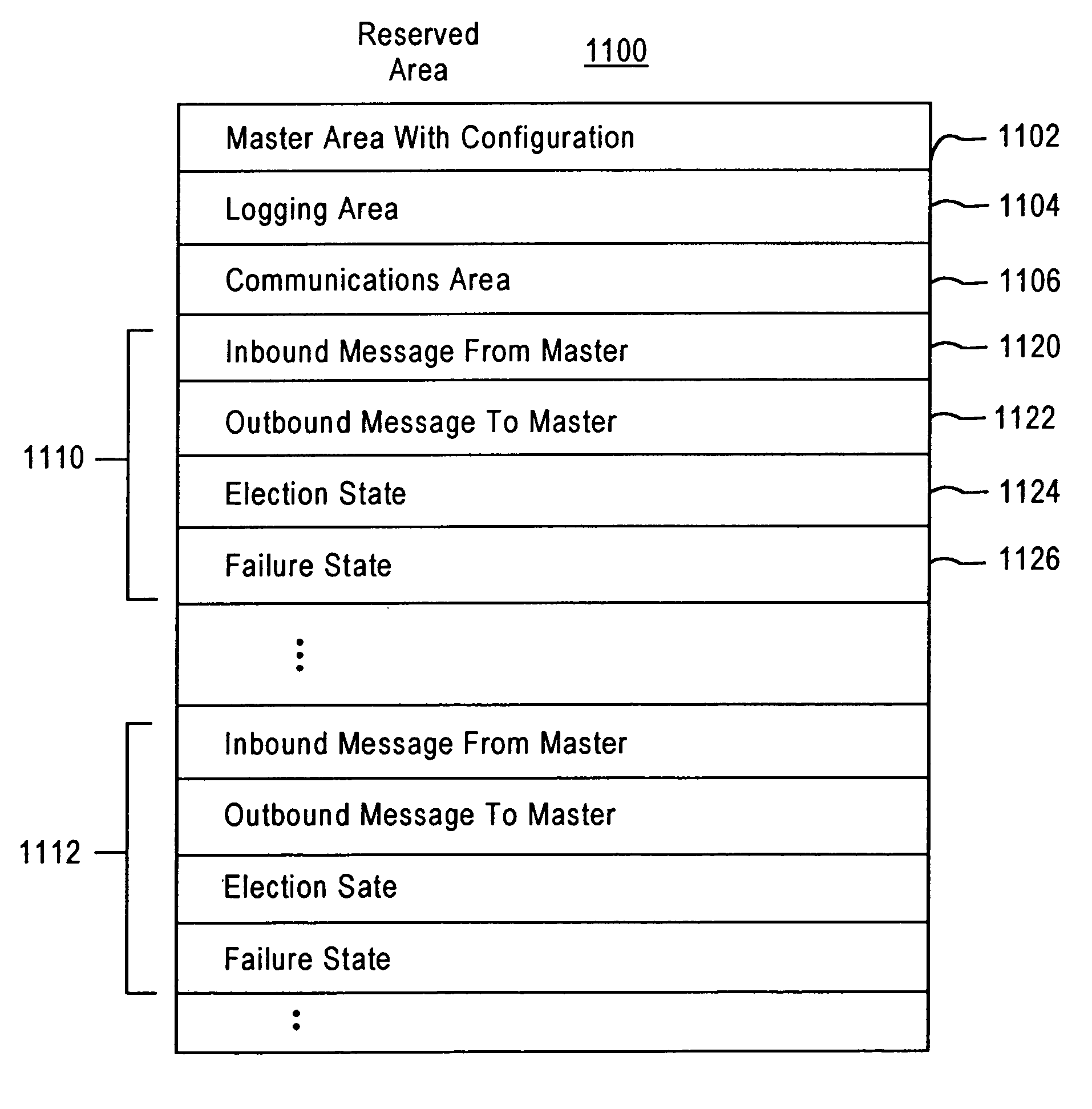
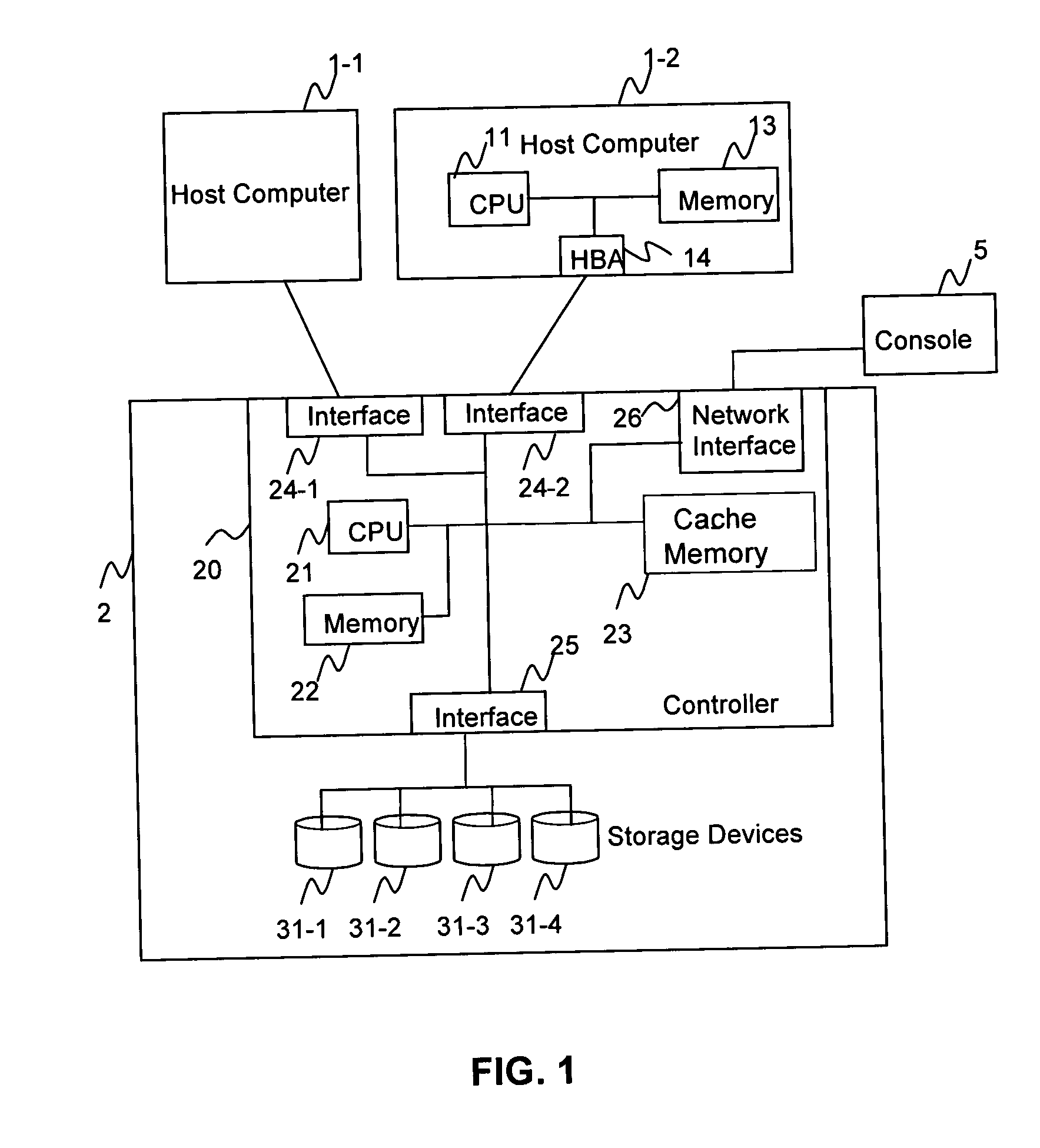
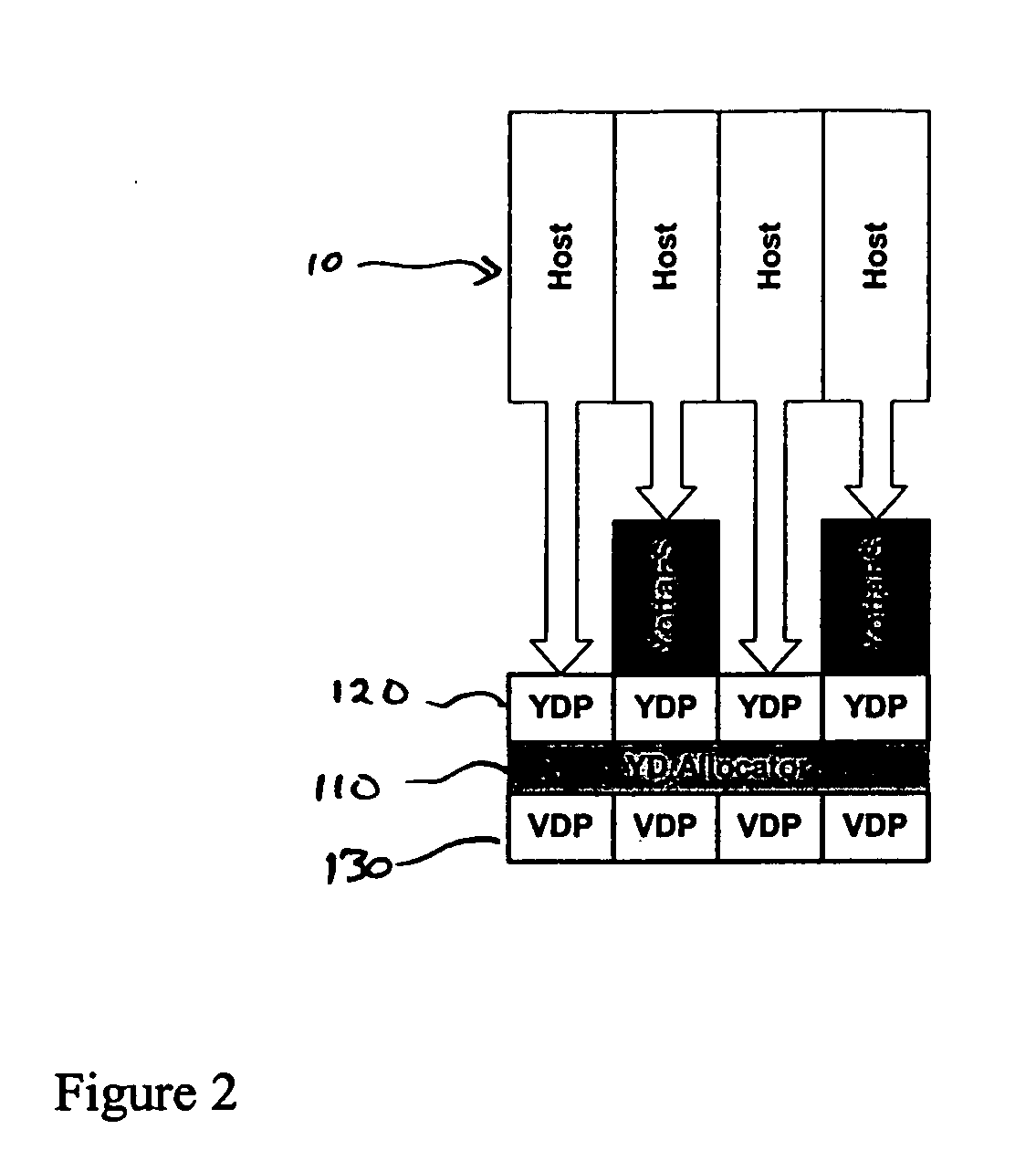
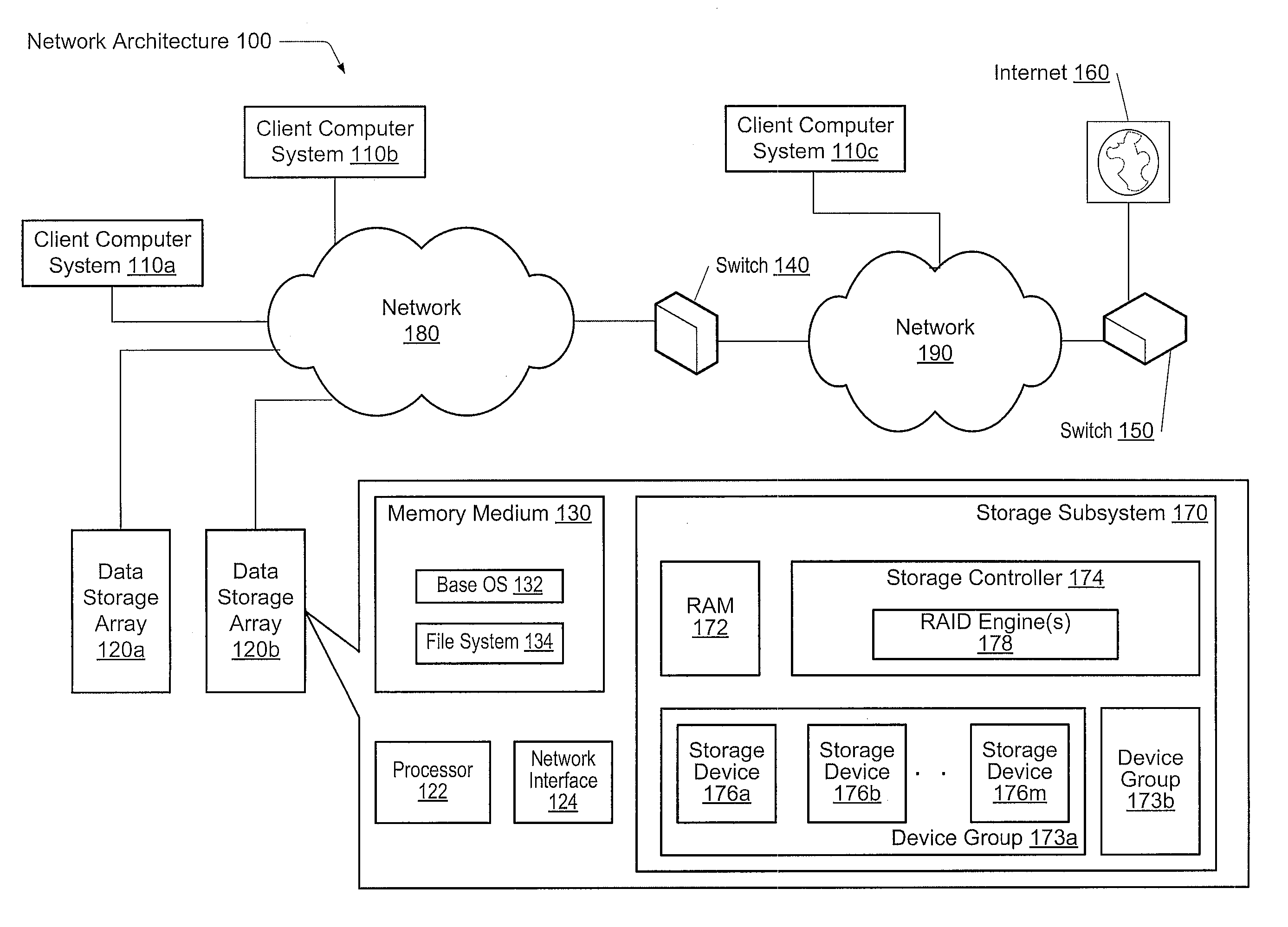
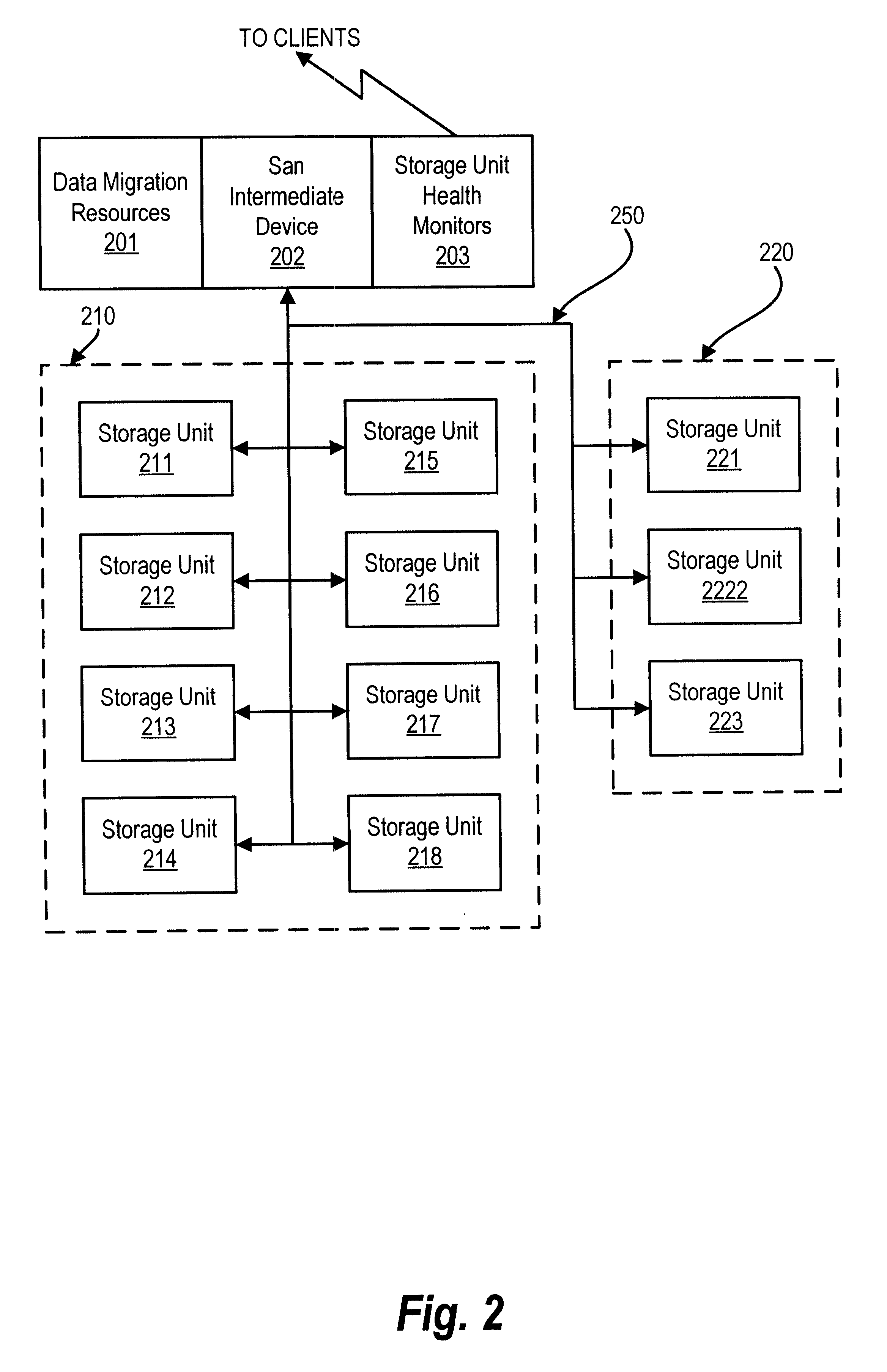
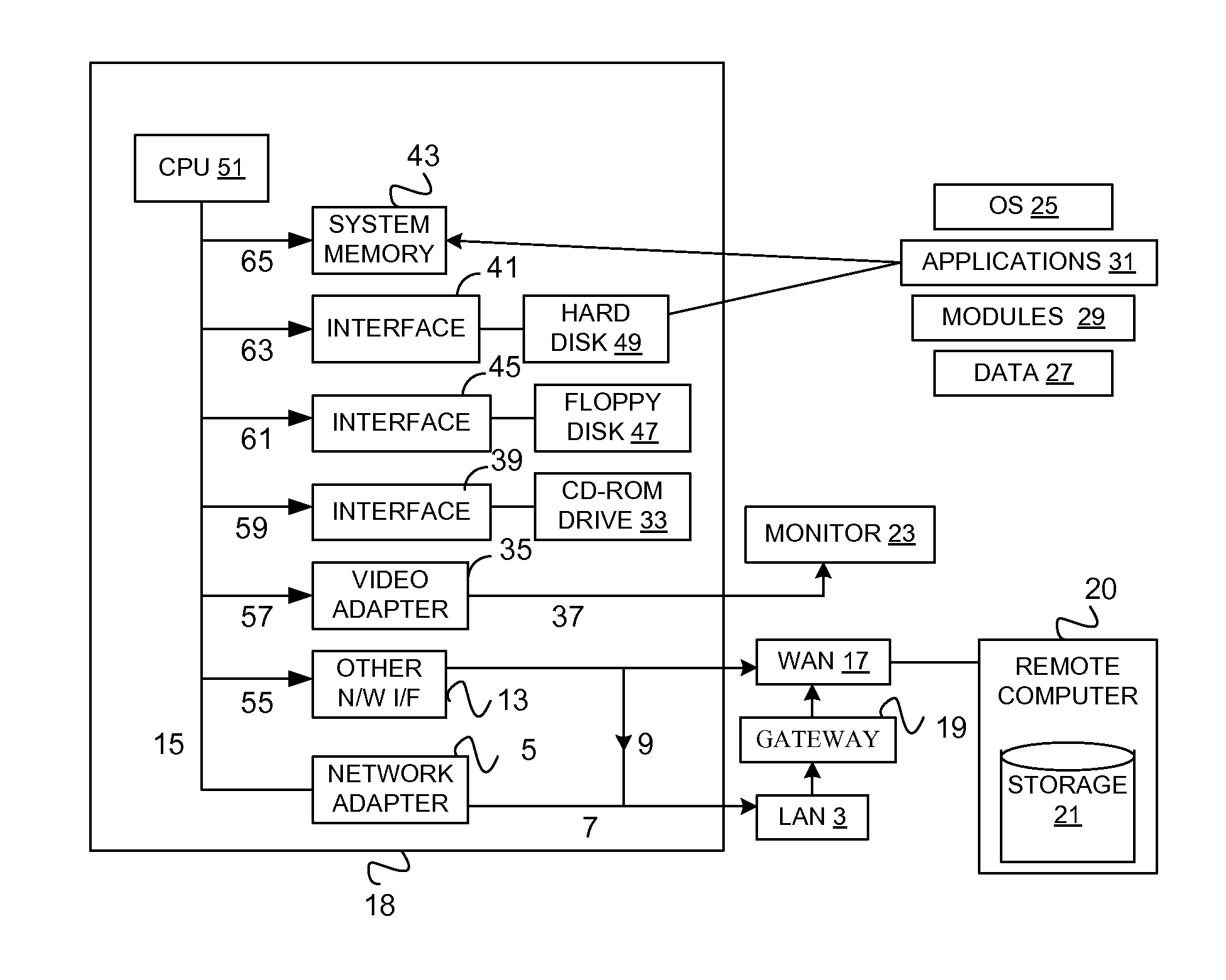
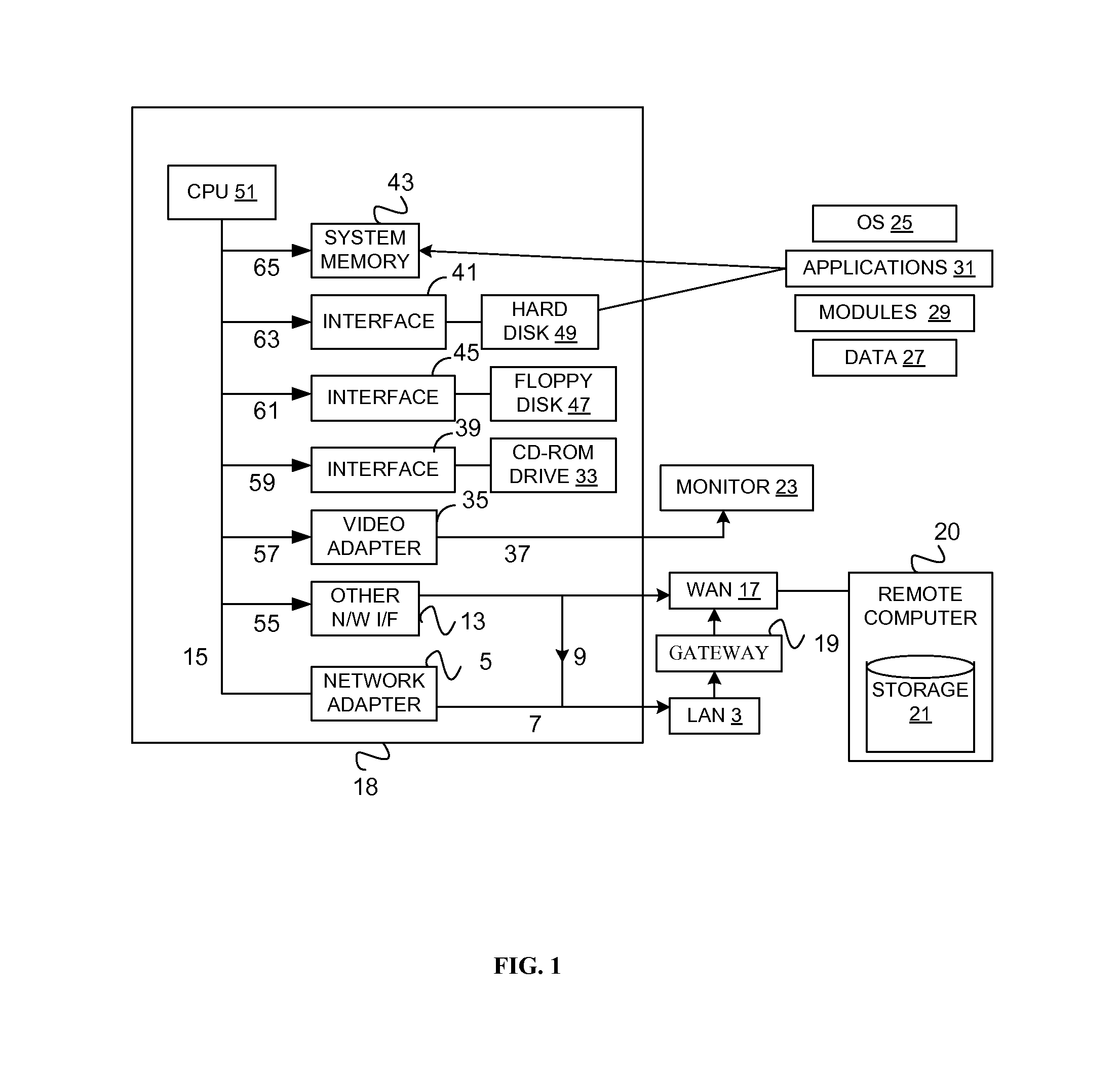
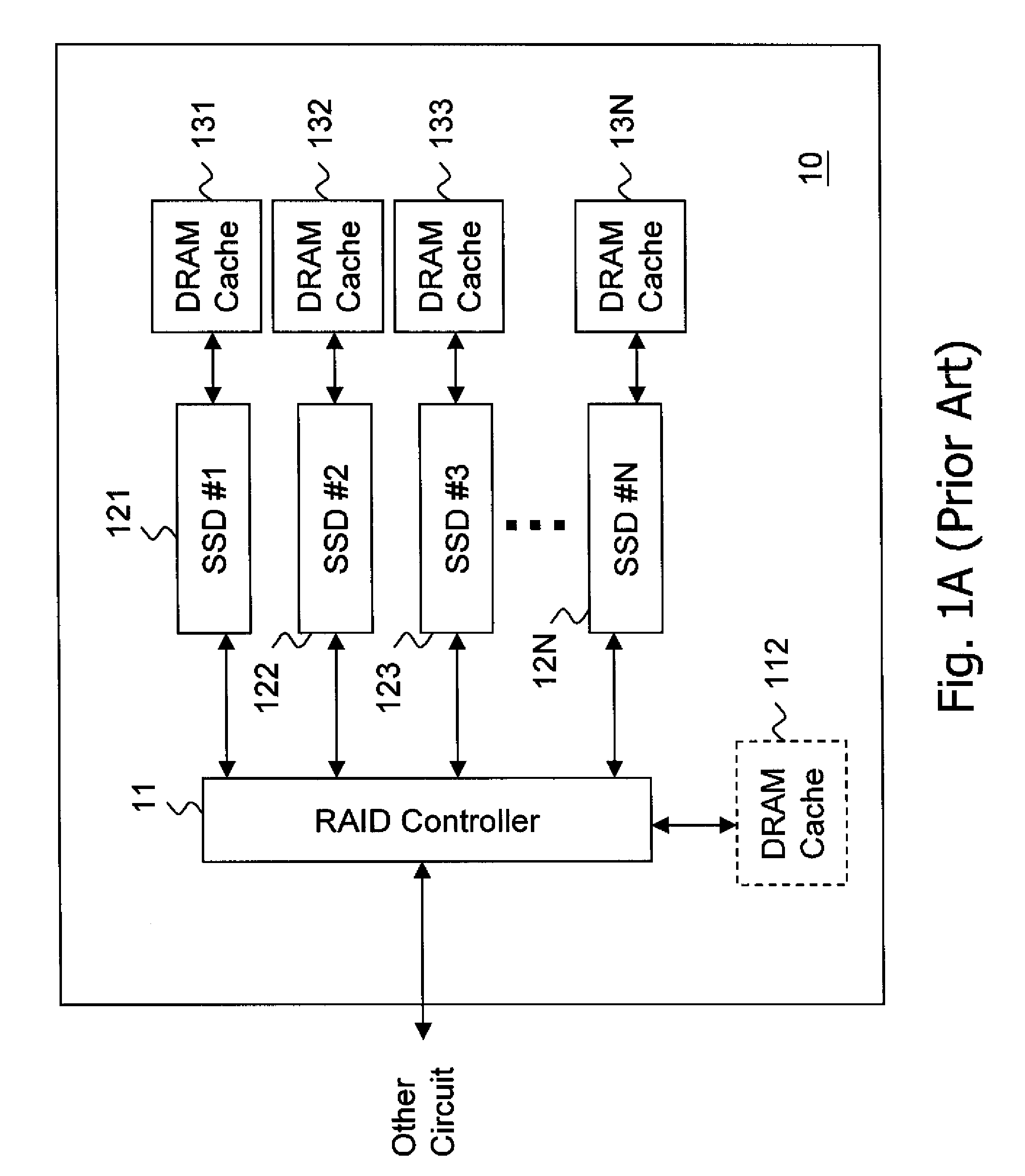
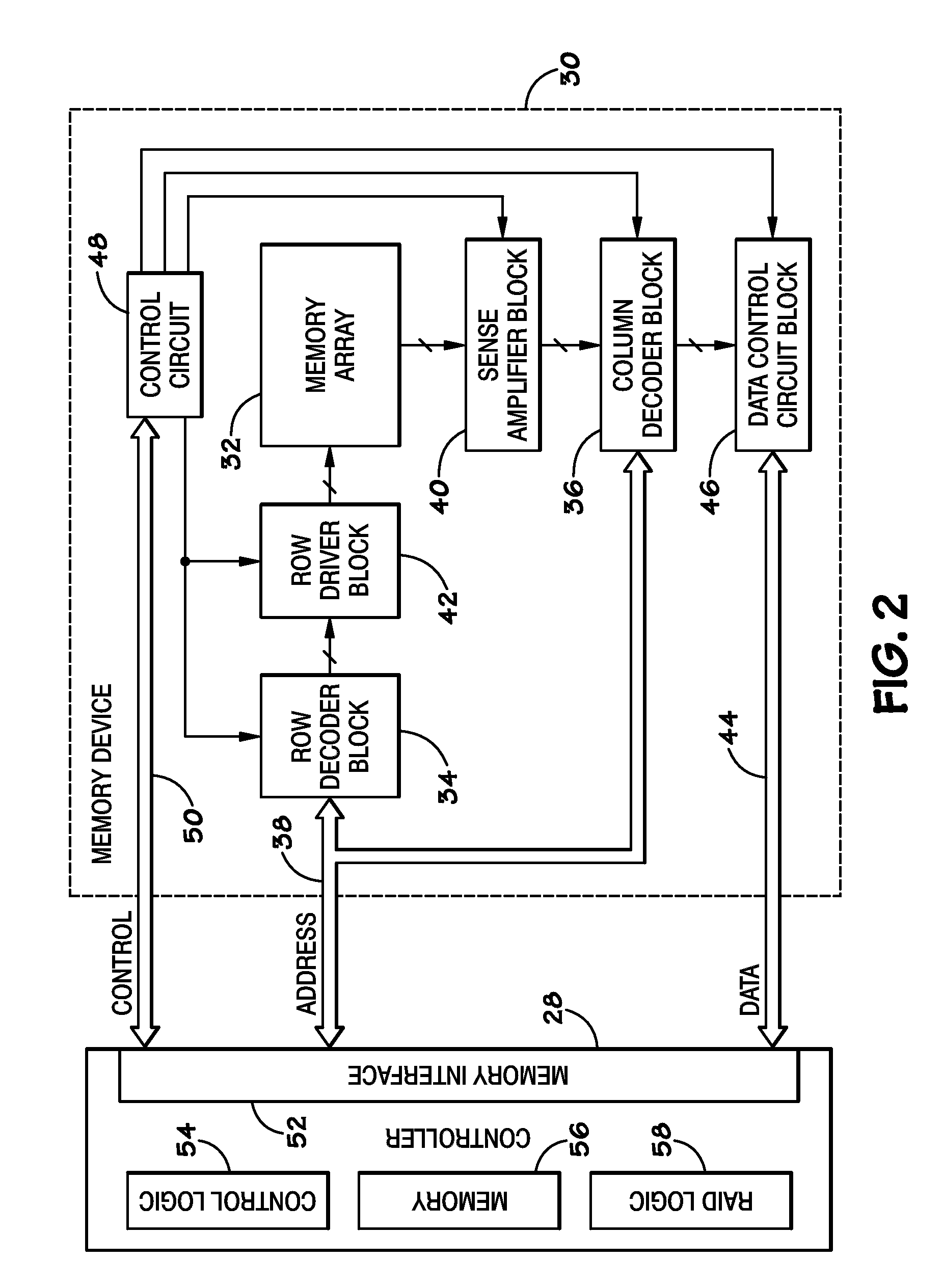
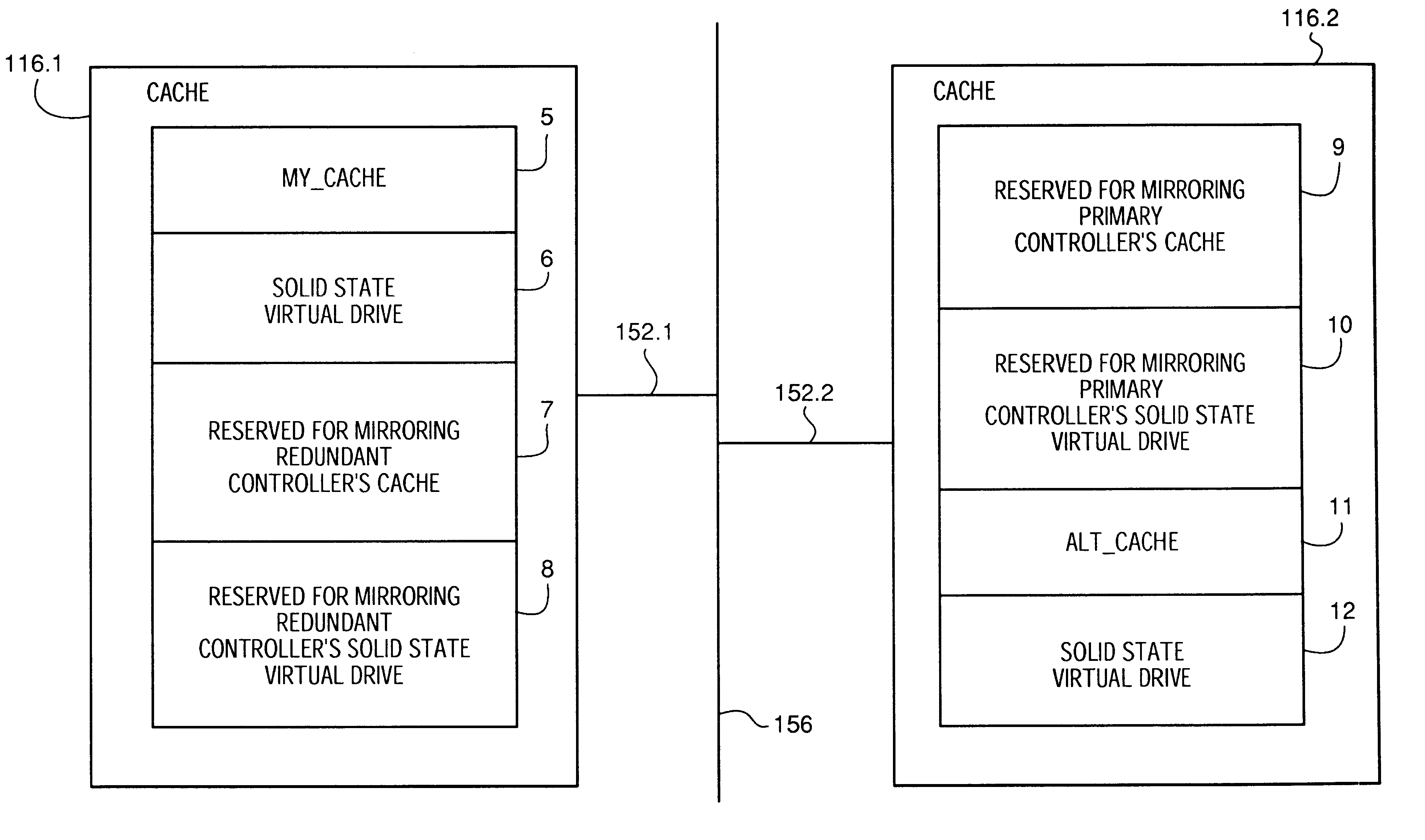
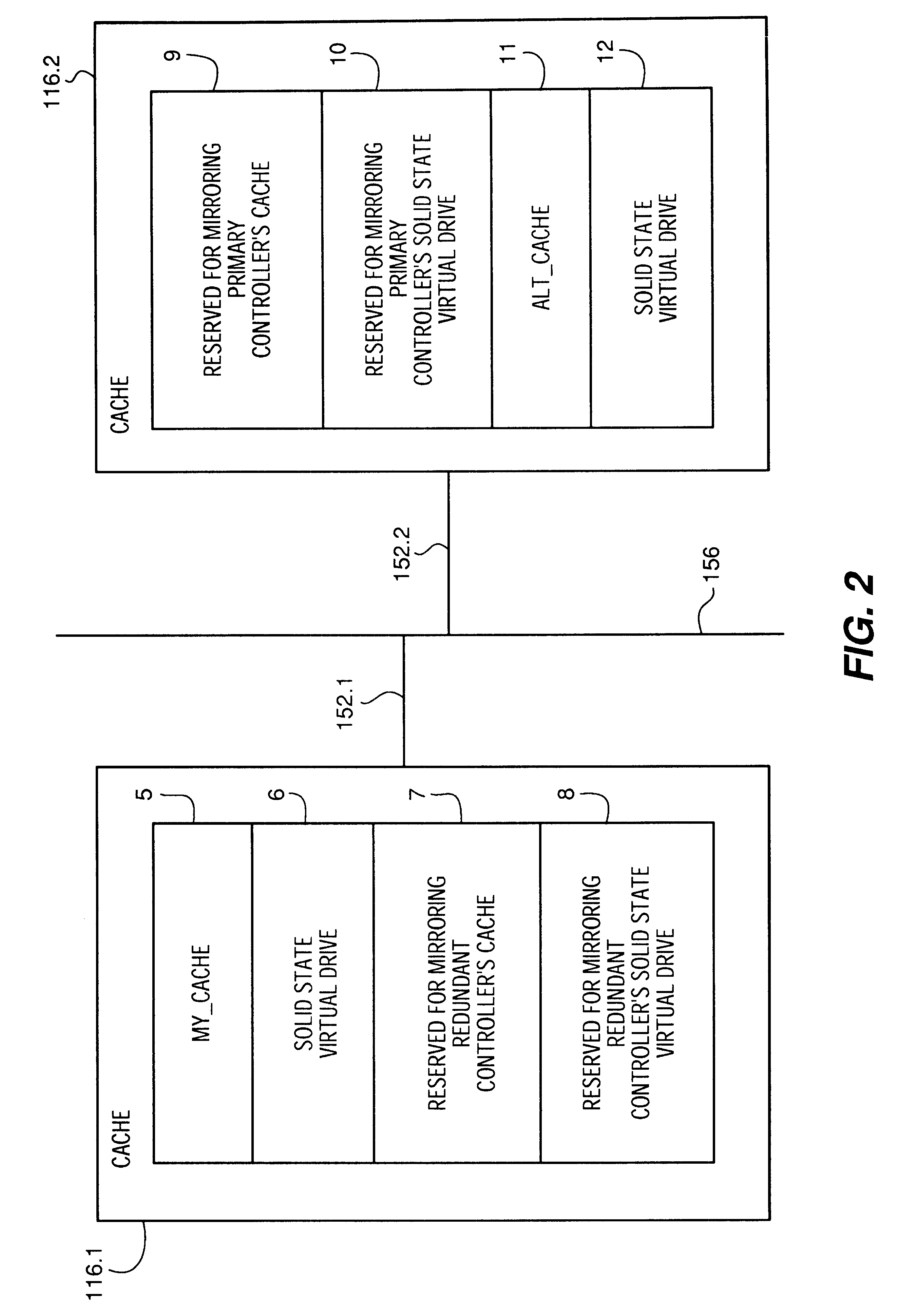
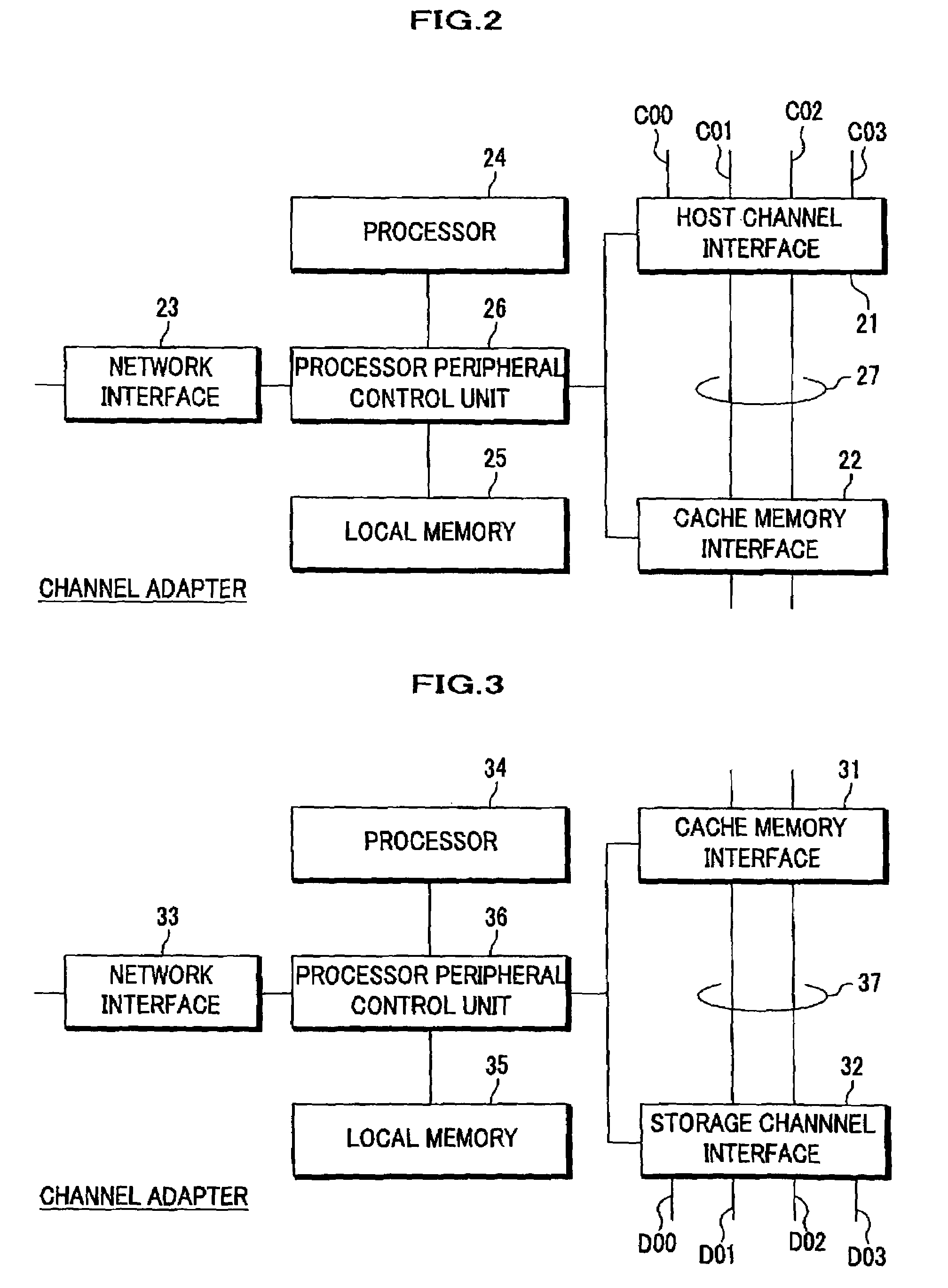
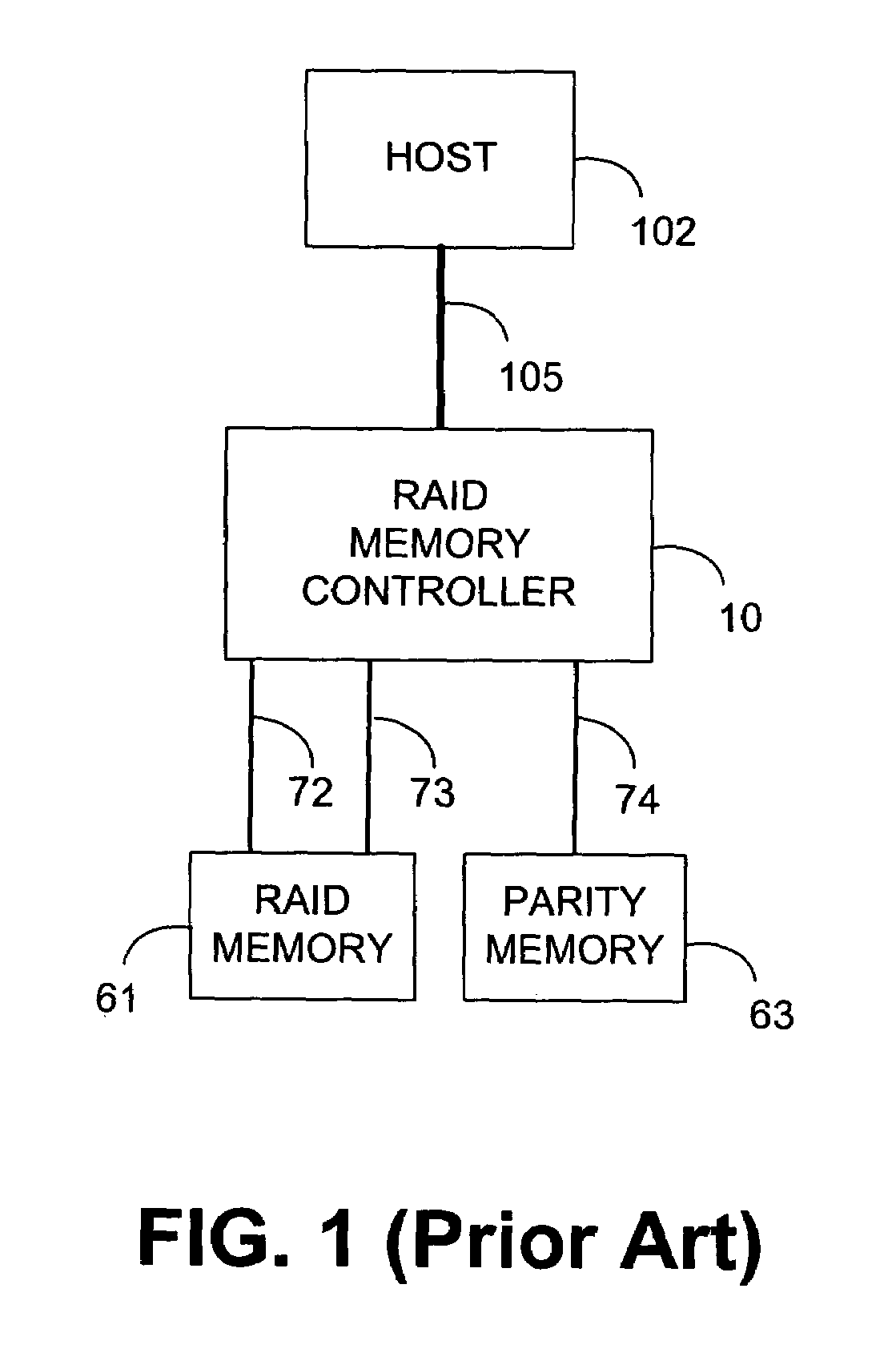
System and method for a reserved memory area shared by all redundant storage controllers
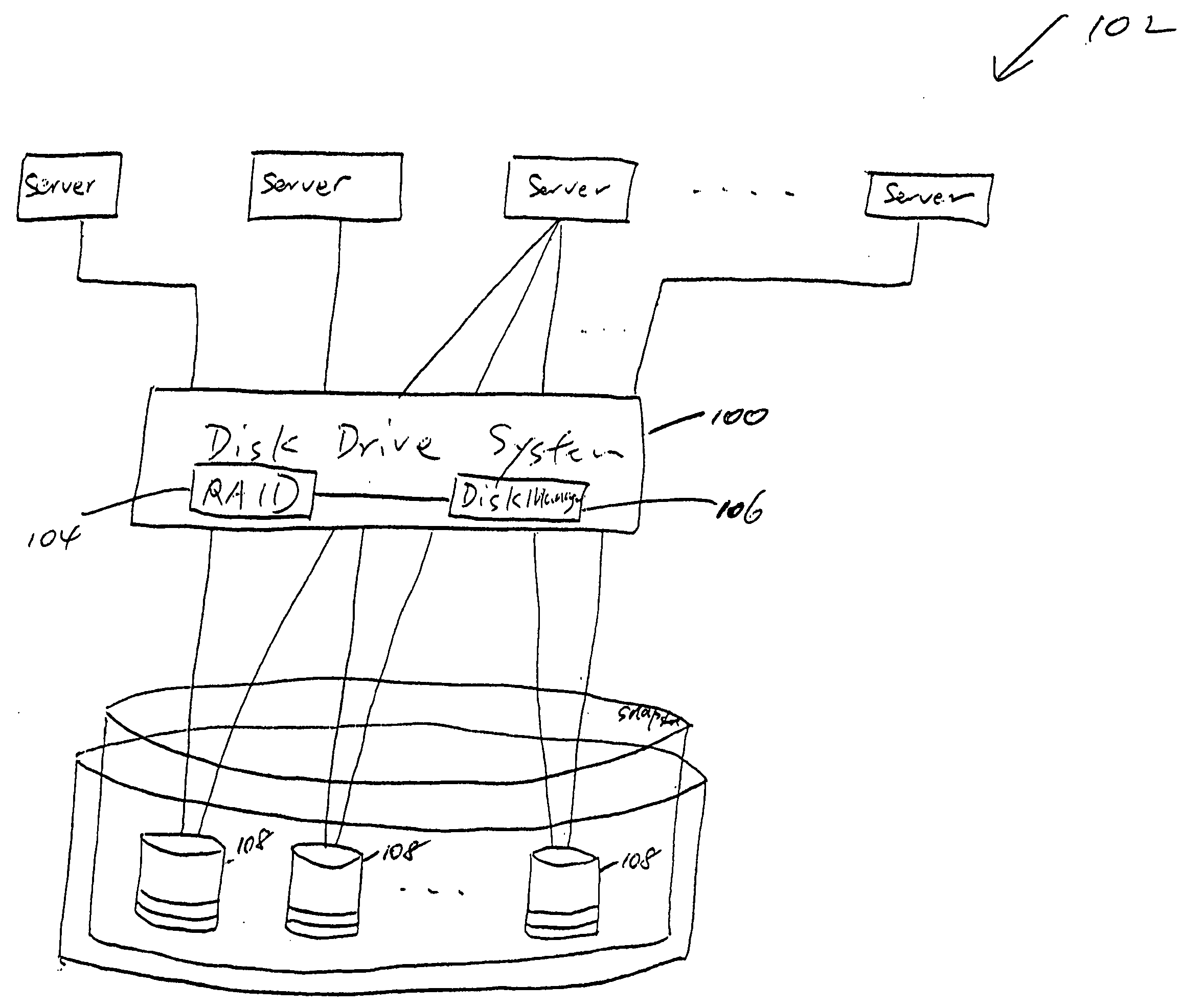
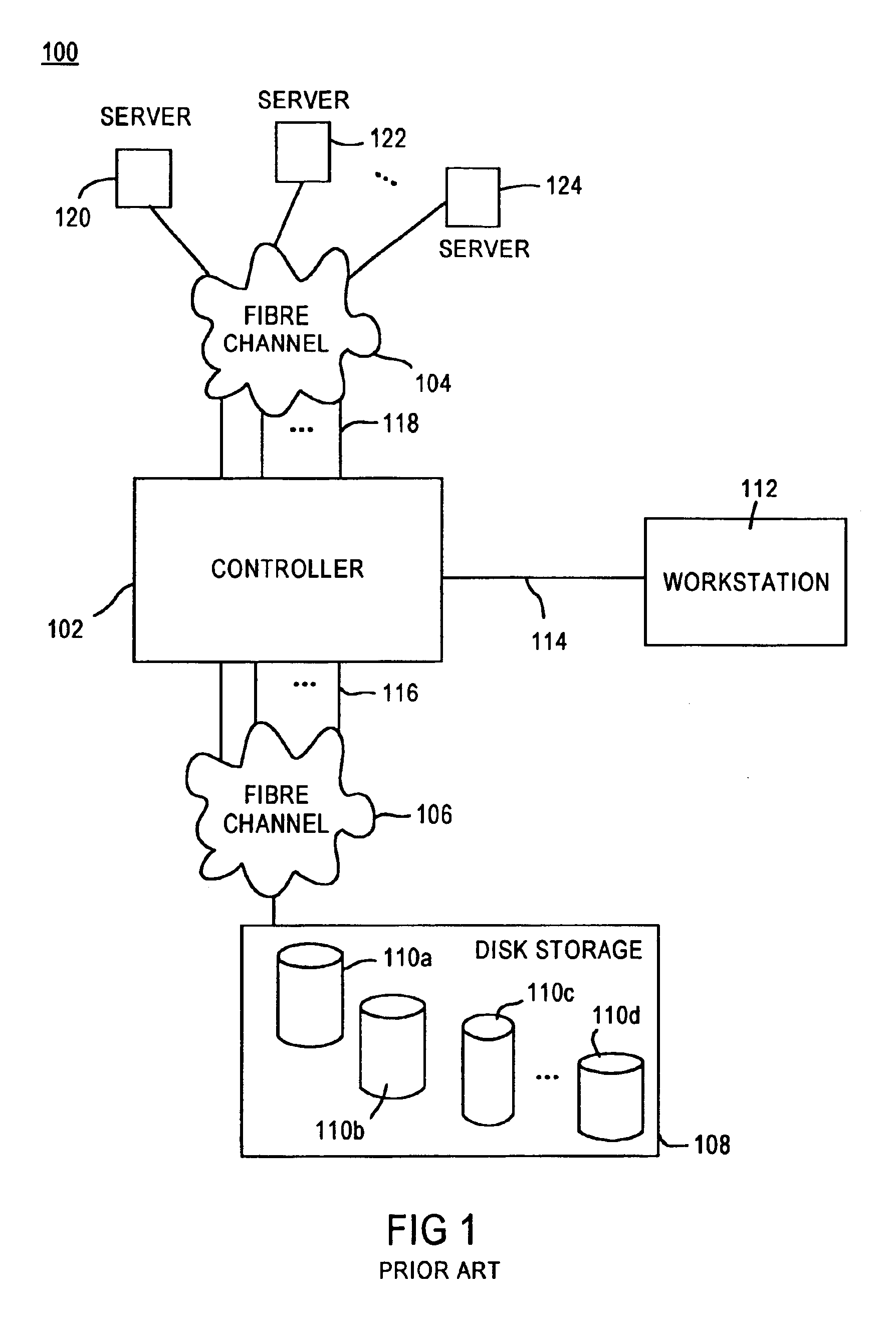
A fibre channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In the event of a failure involving a controller or controller interface, the virtual disks that are accessed via the affected interfaces are re-mapped to another interface in order to continue to provide high data availability. In particular, a common memory storage device is connected to the back-ends of every controller to provide a storage area. In this manner, the common memory storage device can be accessed via operations similar to those a controller already uses to presently access the physical disks which are connected to the back-end of the controllers.
Owner:VSIP HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for reconstructing data in object-based storage arrays
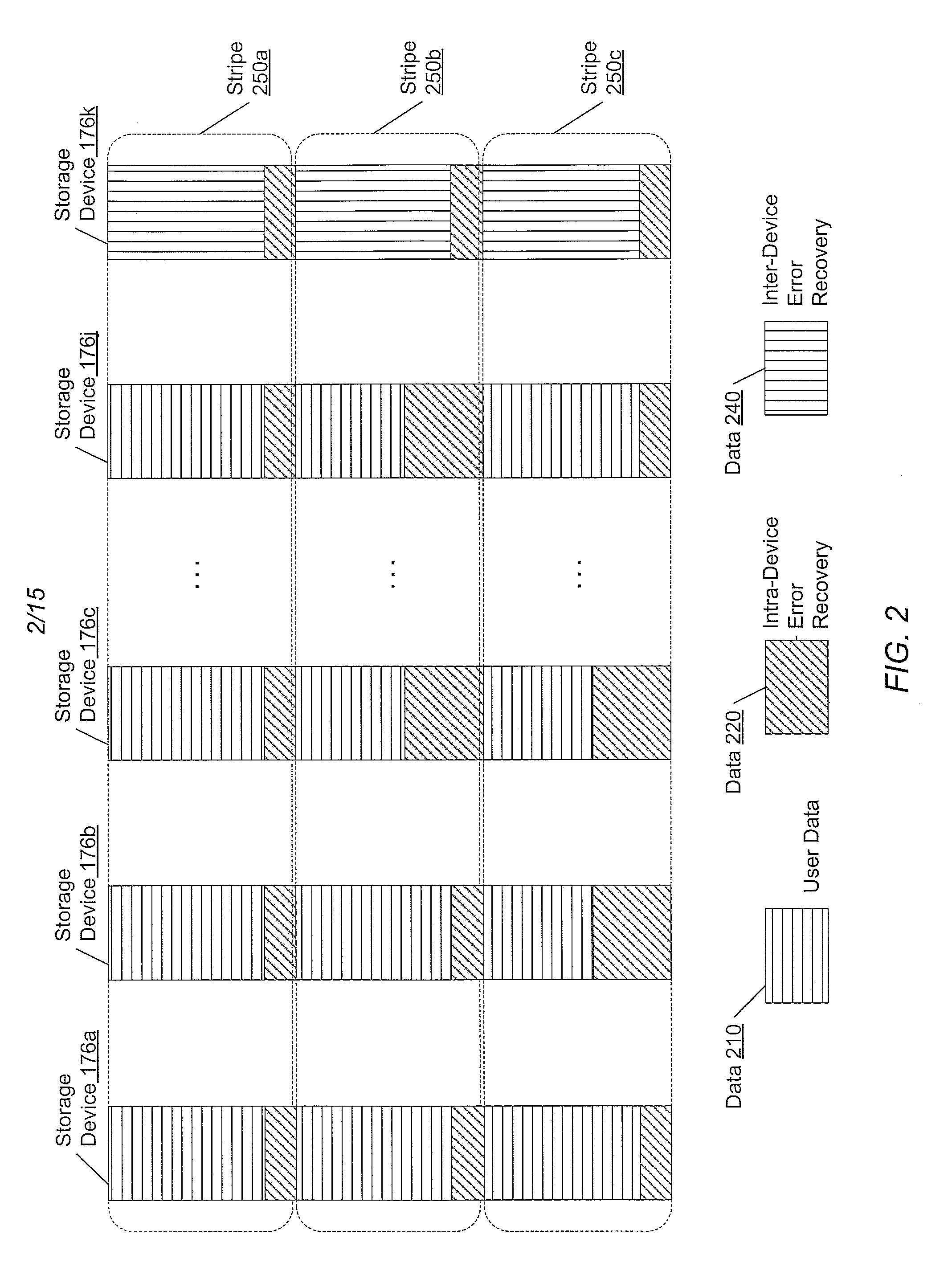
A method and apparatus for placing objects on a storage device of a storage system and reconstructing data of objects in the storage device. The storage system stores data as objects and implements a RAID architecture including a plurality of the storage devices, and a disk controller for processing Object-based Storage Device (OSD) commands. Each object includes data and attribute. Parity data is calculated for reconstructing an object upon occurrence of a storage device failure. Each storage device includes plural stripes each having a predetermined length. Each object is stored in a stripe wherein an attribute is stored in the head of the stripe and data is stored after the attribute. When the object size exceeds the stripe length, the remainder of the object is stored in the next stripe, and when another object is to be stored, an attribute is stored at a head of a further next stripe and data is stored just after the attribute.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
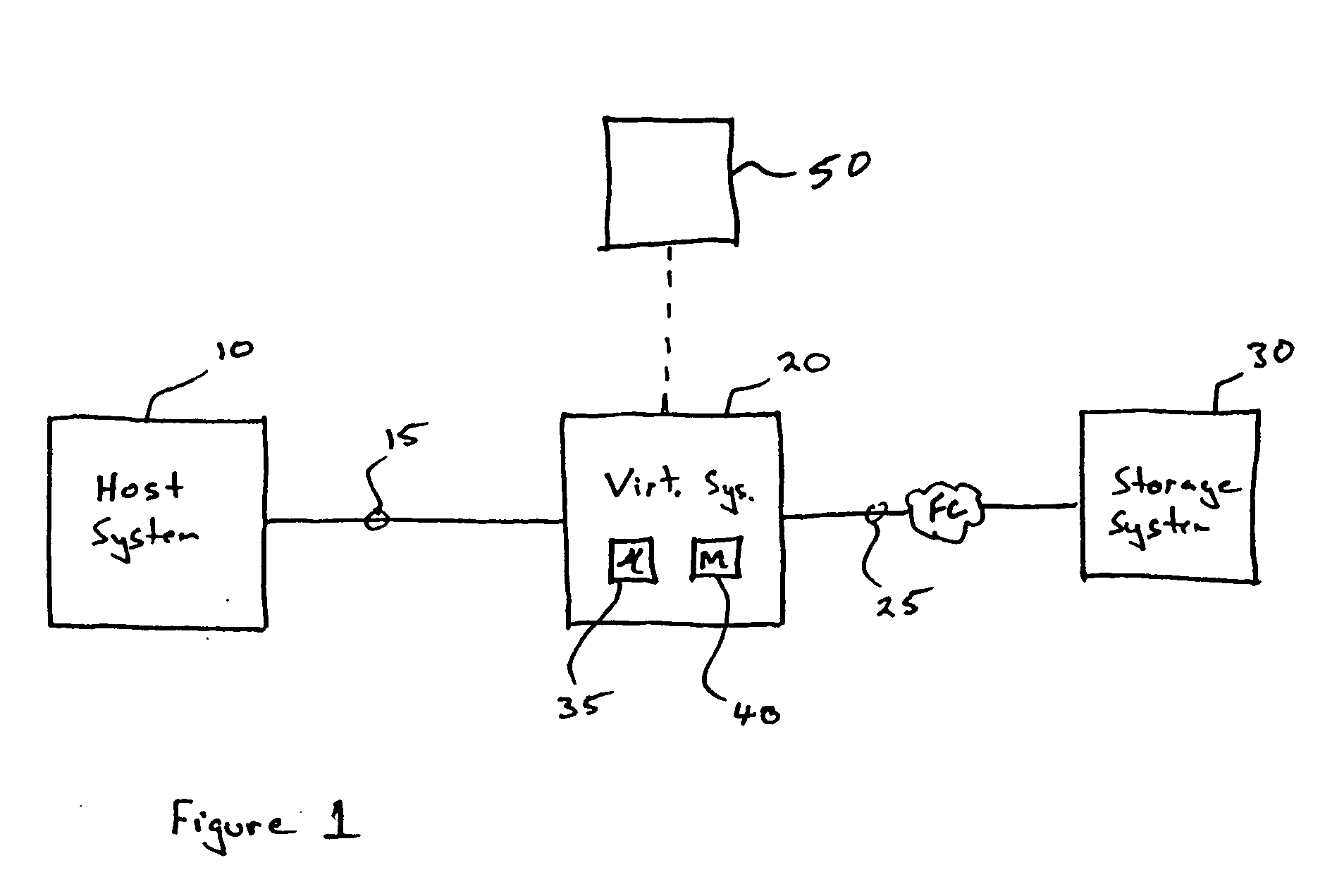
Storage virtualization system and methods
InactiveUS20050125593A1Reduce consumptionWithout impactInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDIslanding
Storage virtualization systems and methods that allow customers to manage storage as a utility rather than as islands of storage which are independent of each other. A demand mapped virtual disk image of up to an arbitrarily large size is presented to a host system. The virtualization system allocates physical storage from a storage pool dynamically in response to host I / O requests, e.g., SCSI I / O requests, allowing for the amortization of storage resources-through a disk subsystem while maintaining coherency amongst I / O RAID traffic. In one embodiment, the virtualization functionality is implemented in a controller device, such as a controller card residing in a switch device or other network device, coupled to a storage system on a storage area network (SAN). The resulting virtual disk image that is observed by the host computer is larger than the amount of physical storage actually consumed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
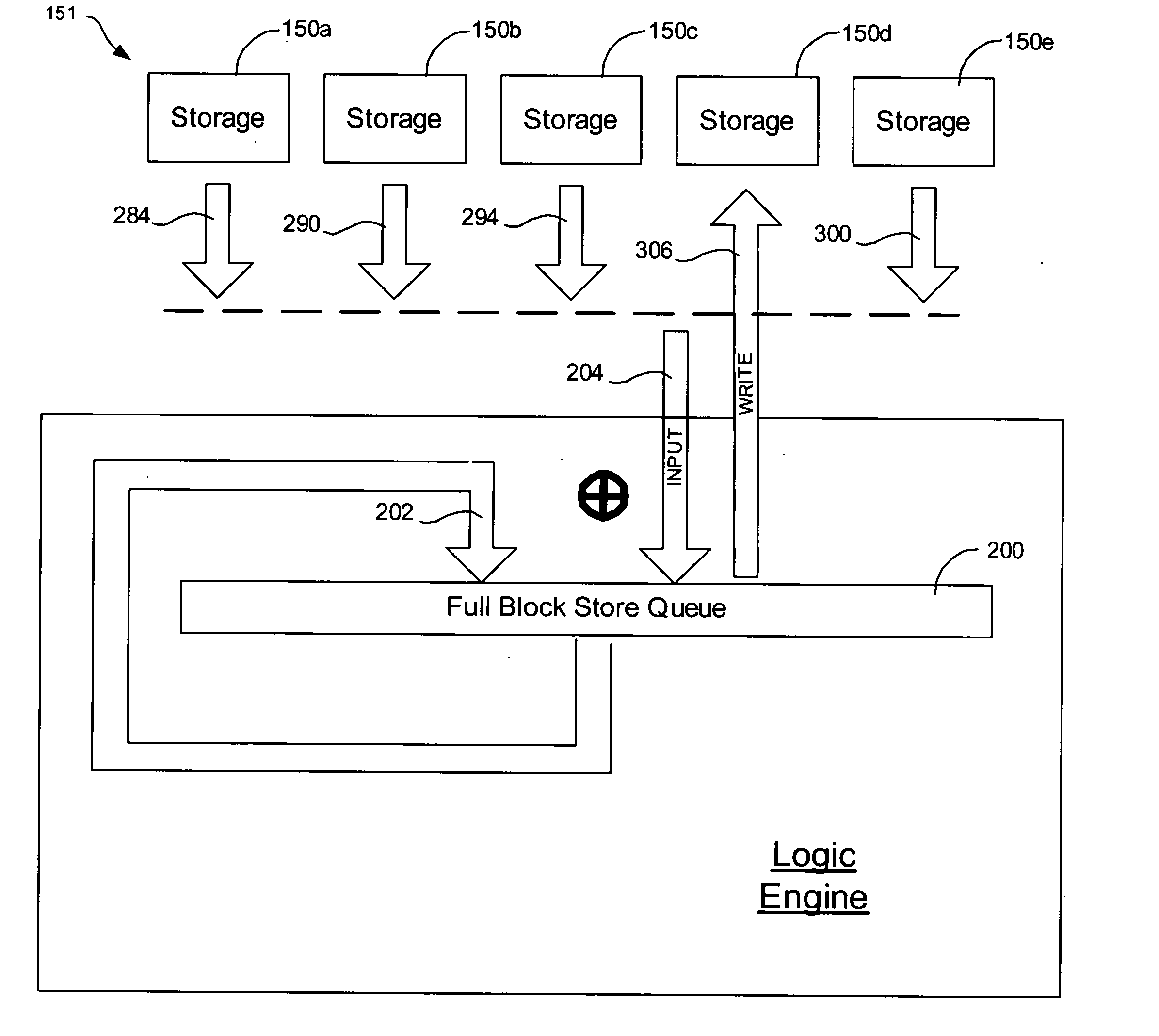
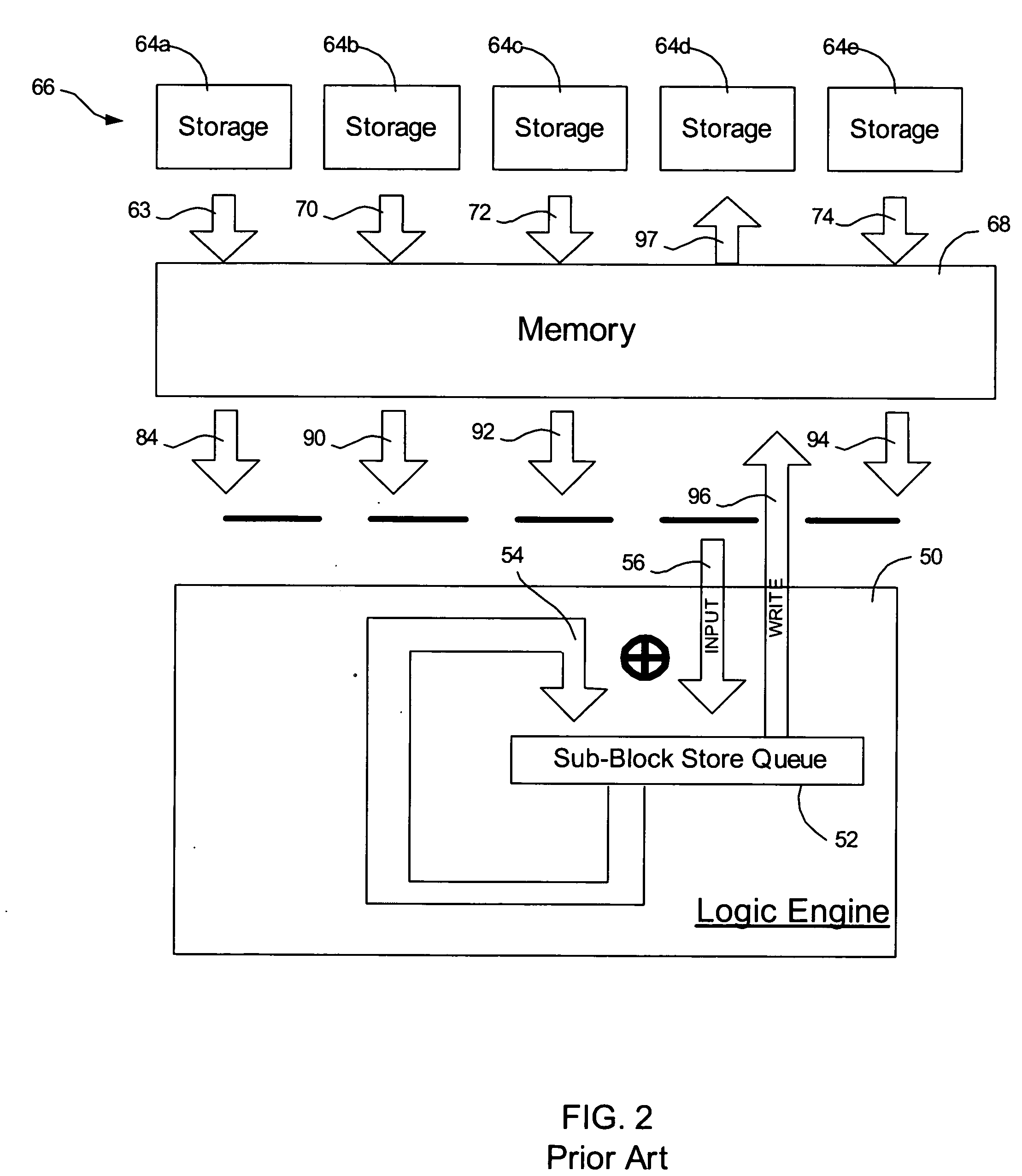
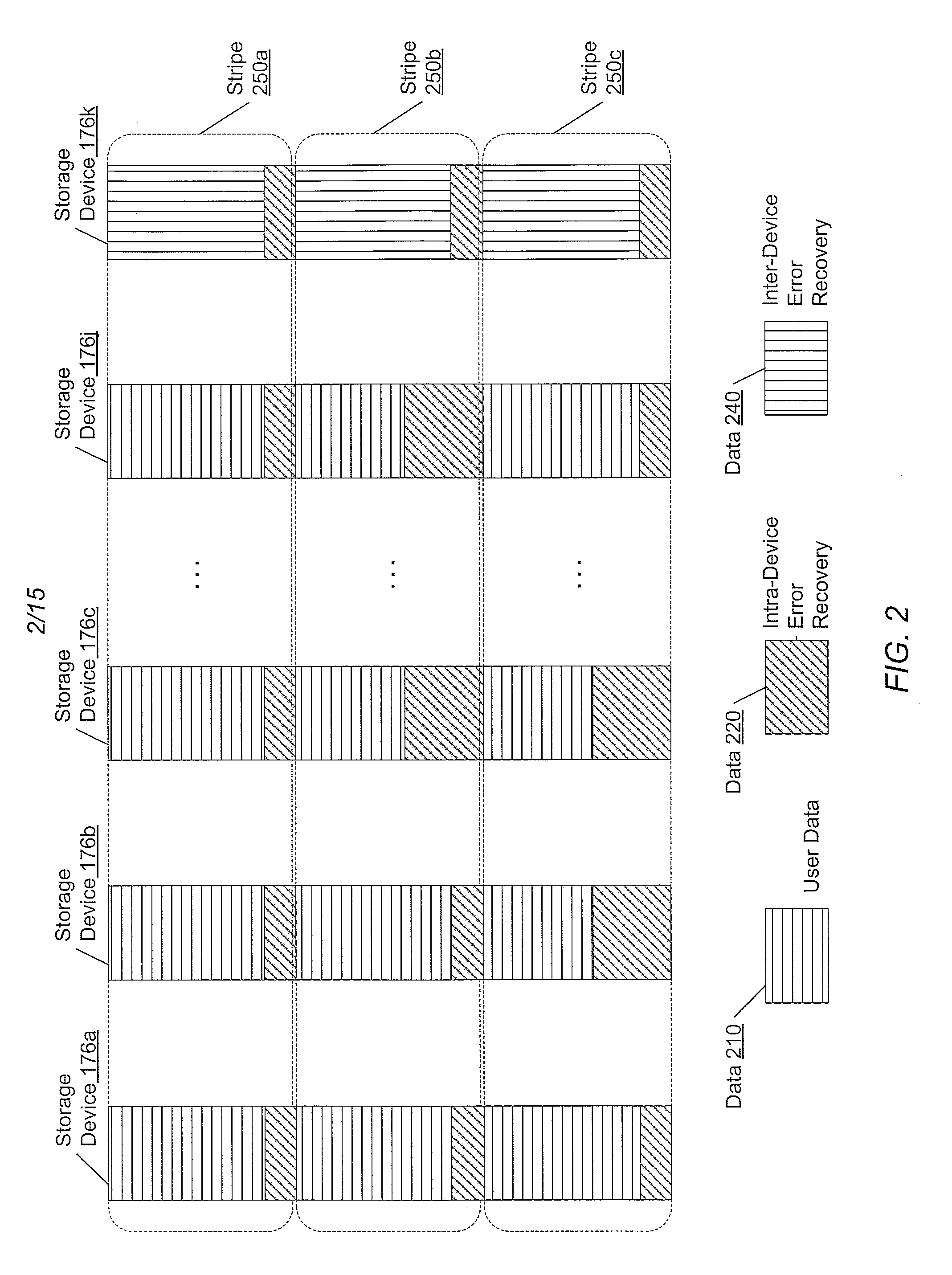
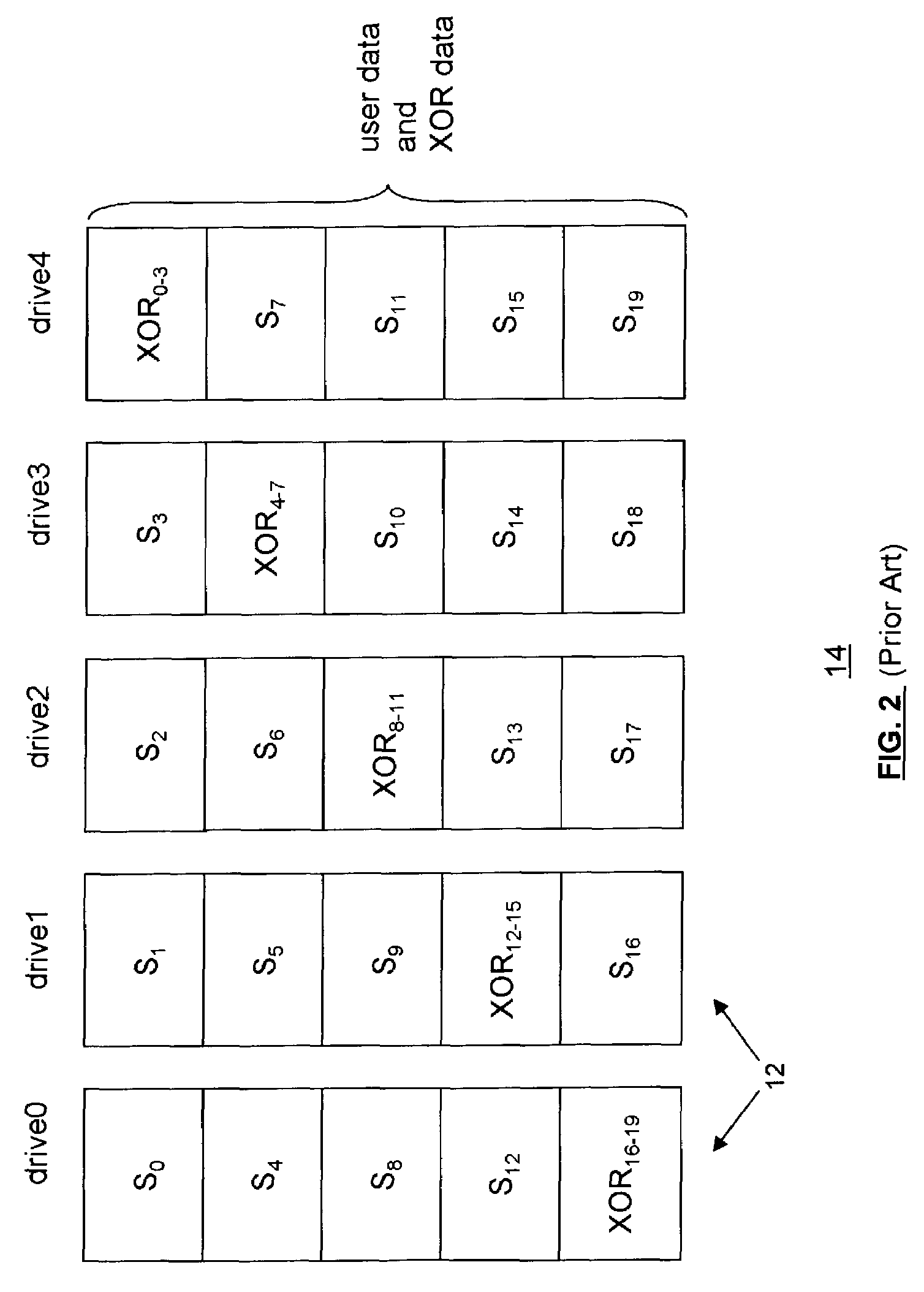
Method, system, and program for managing data organization
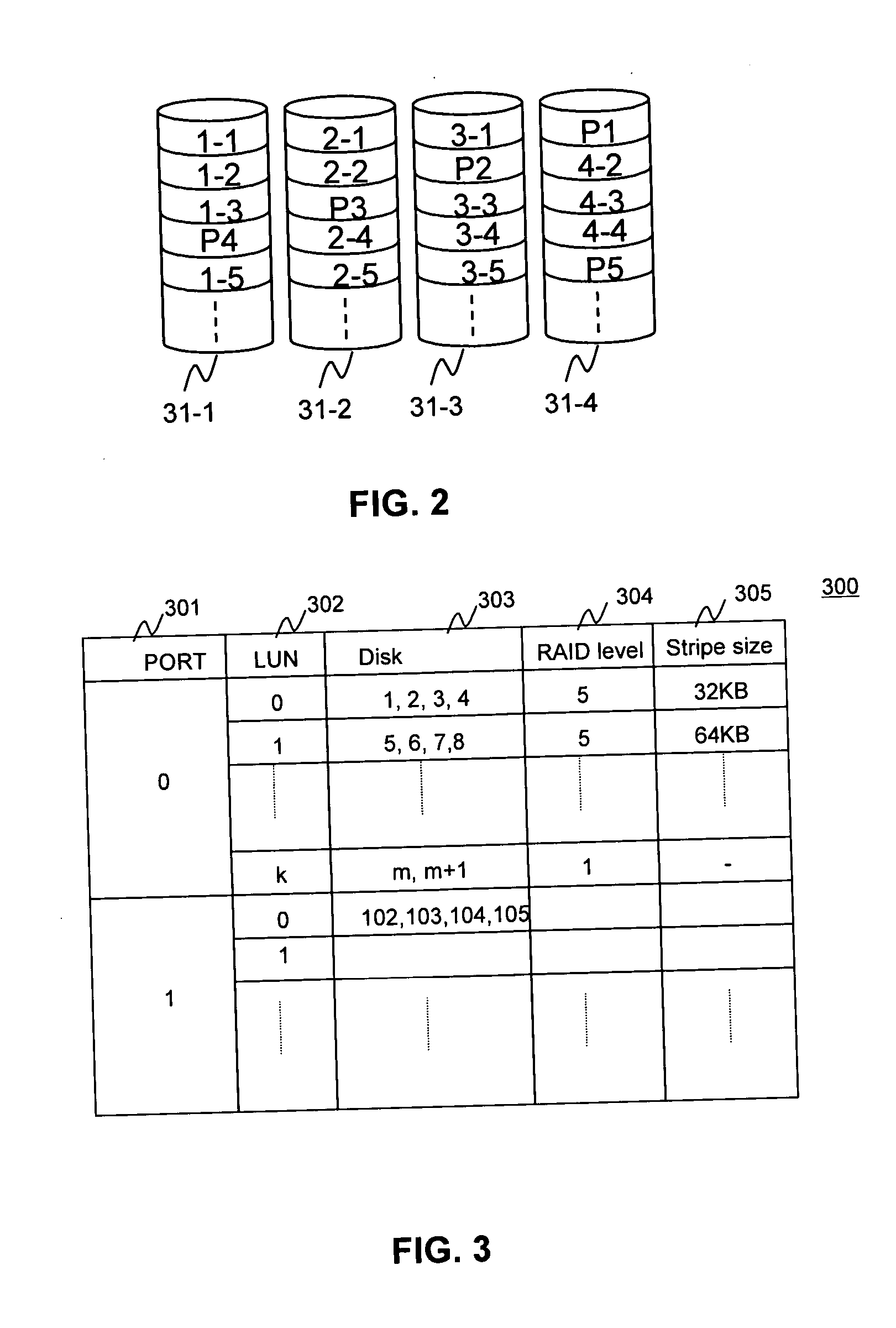
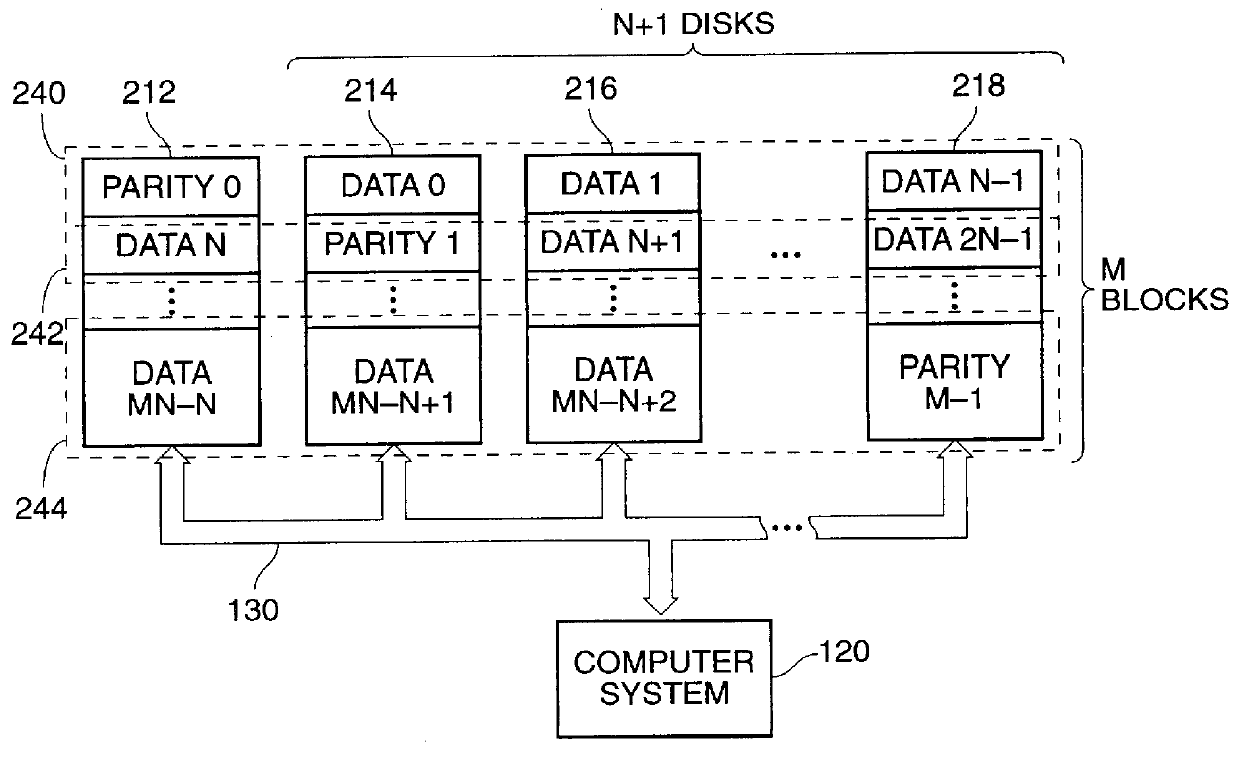
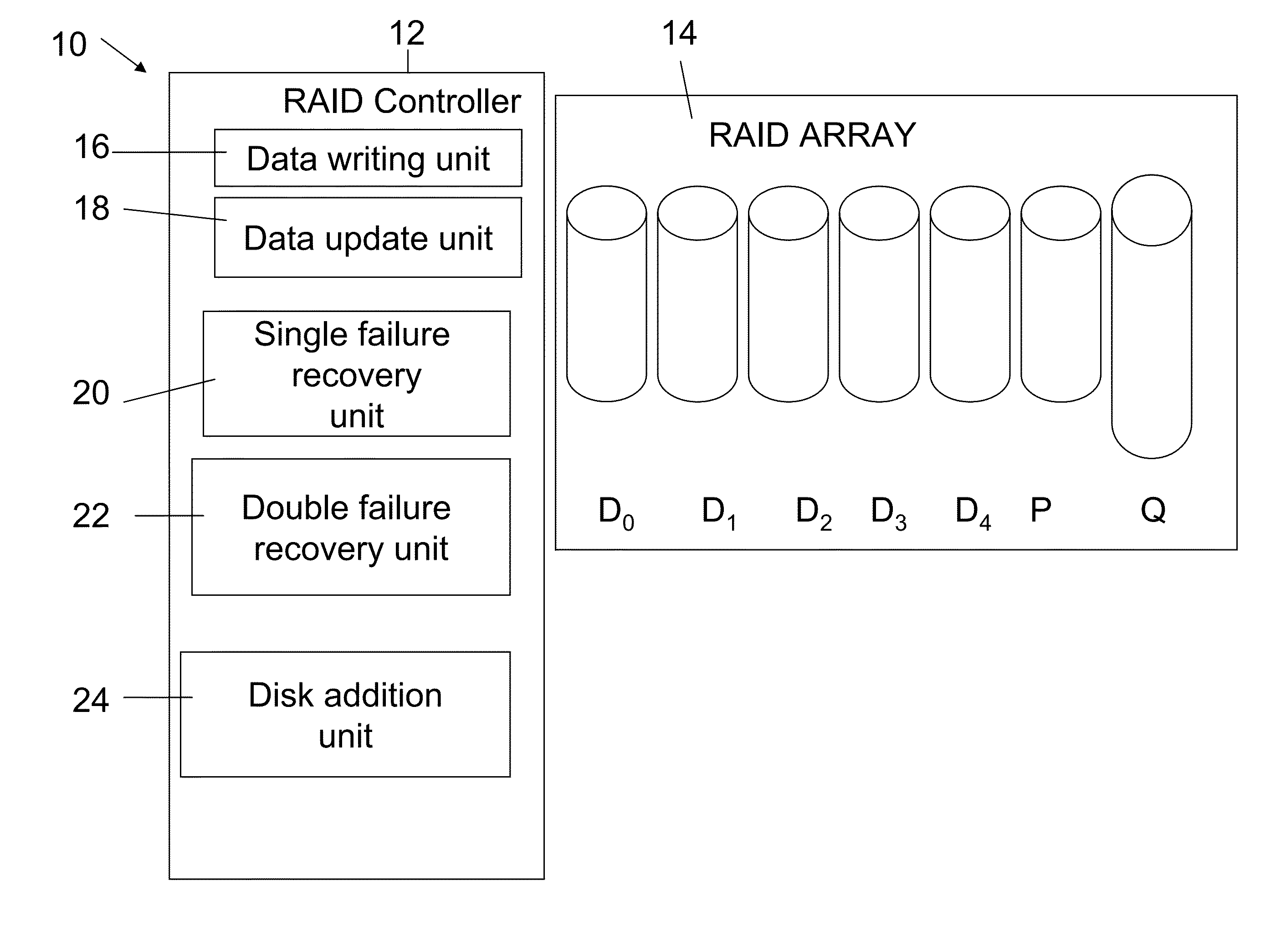
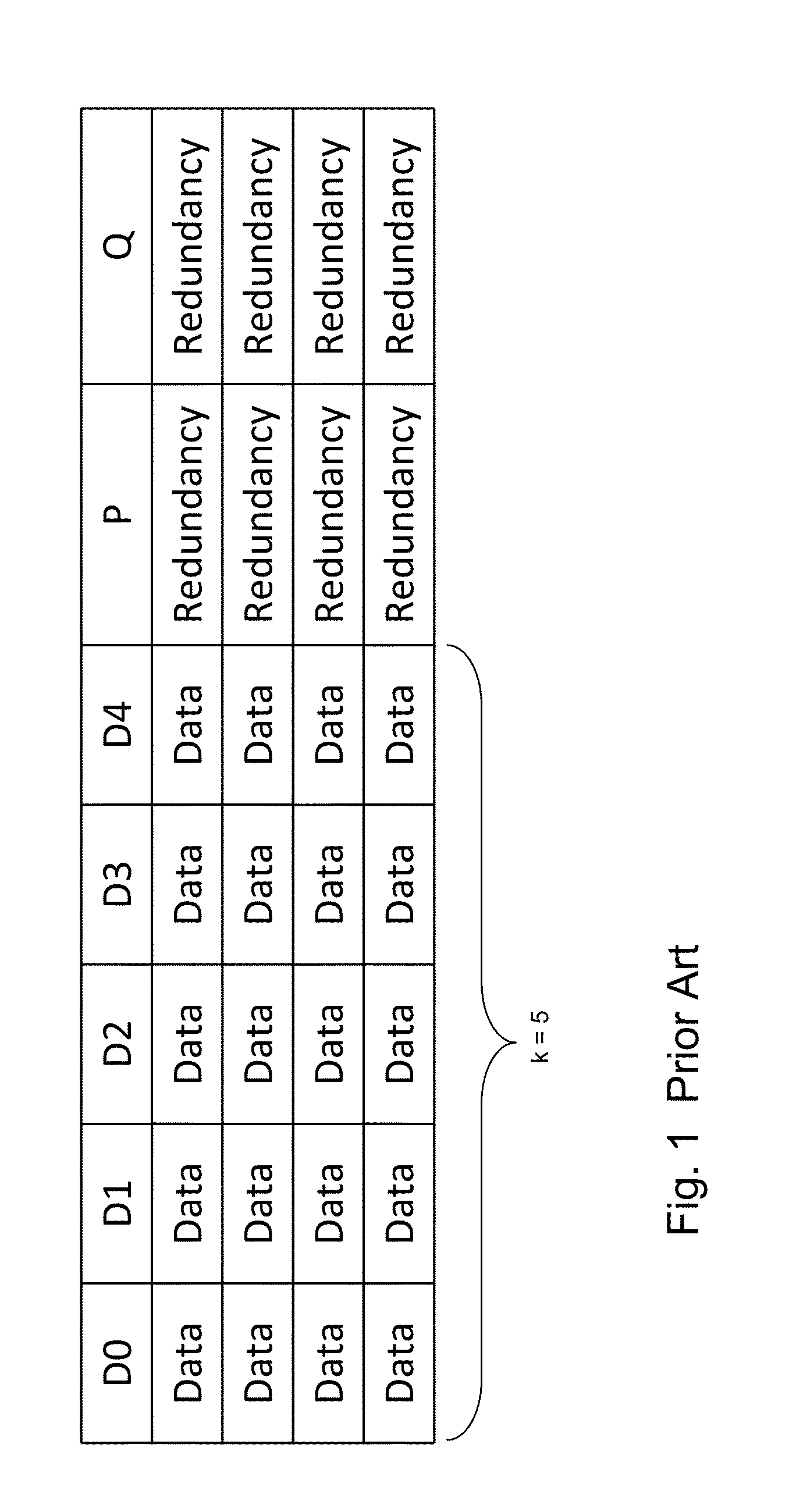
Provided are a method, system, and program for constructing data including reconstructing data organized in a data organization type, such as a Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) organization, for example, which permits data reconstruction In one embodiment, blocks of data are transferred from a stripe of data stored across storage units, such as disk drives in a RAID array, to a logic engine of a storage processor, bypassing the cache memory of the storage processor. A store queue performs a logic function, such as Exclusive-OR, on each block of data as it is transferred from the disk drives, to reconstruct a block of data from the stripe. The constructed block of data may be subsequently transferred to a disk drive of the RAID array to replace a lost block of data in the stripe of data across the RAID array or to replace an old block of parity data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Adaptive raid for an SSD environment
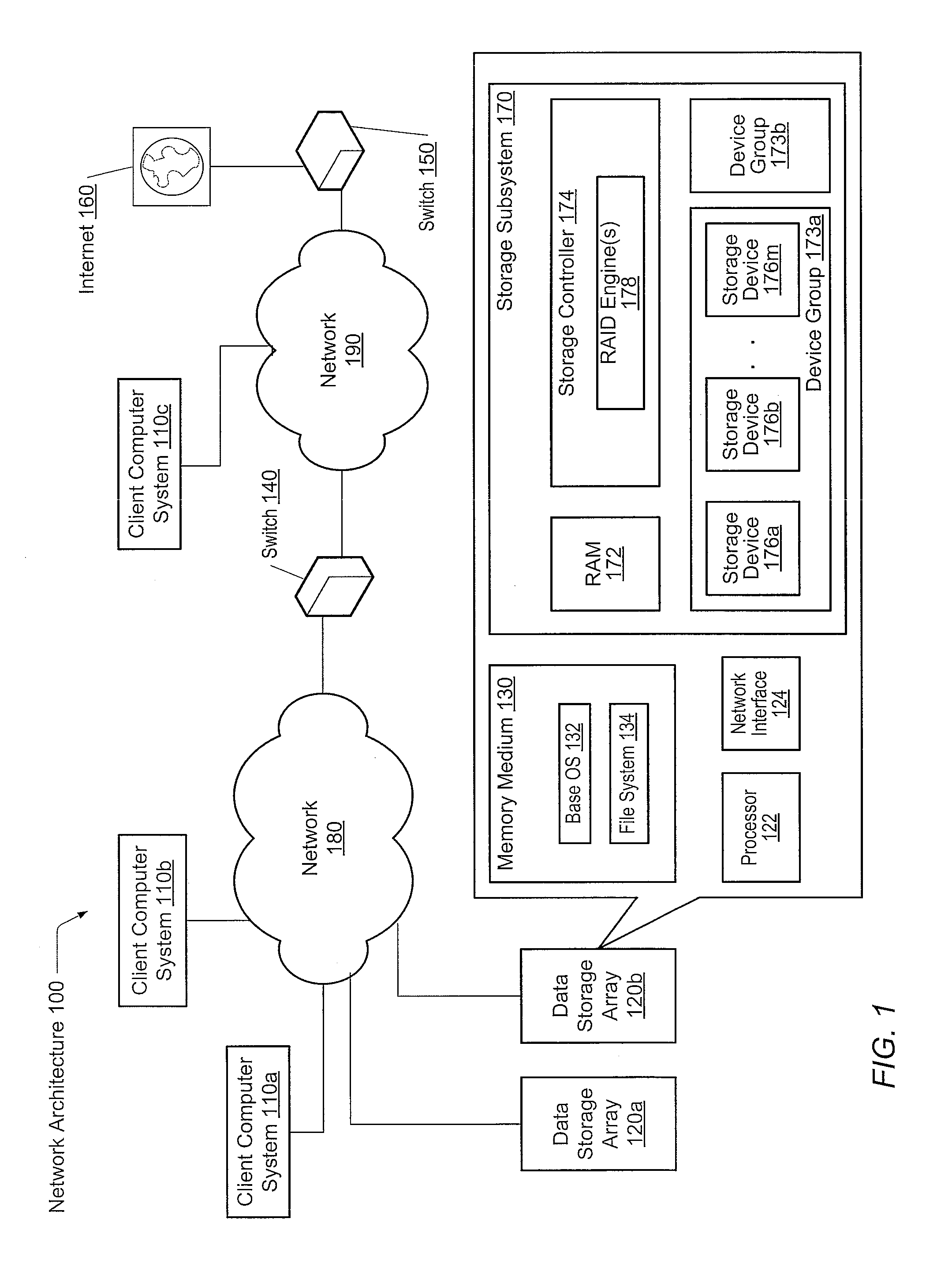
A system and method for adaptive RAID geometries. A computer system comprises client computers and data storage arrays coupled to one another via a network. A data storage array utilizes solid-state drives and Flash memory cells for data storage. A storage controller within a data storage array is configured to determine a first RAID layout for use in storing data, and write a first RAID stripe to the device group according to the first RAID layout. In response to detecting a first condition, the controller is configured to determine a second RAID layout which is different from the first RAID layout, and write a second RAID stripe to the device group according to the second layout, whereby the device group concurrently stores data according to both the first RAID layout and the second RAID layout.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
Method for allocating files in a file system integrated with a RAID disk sub-system
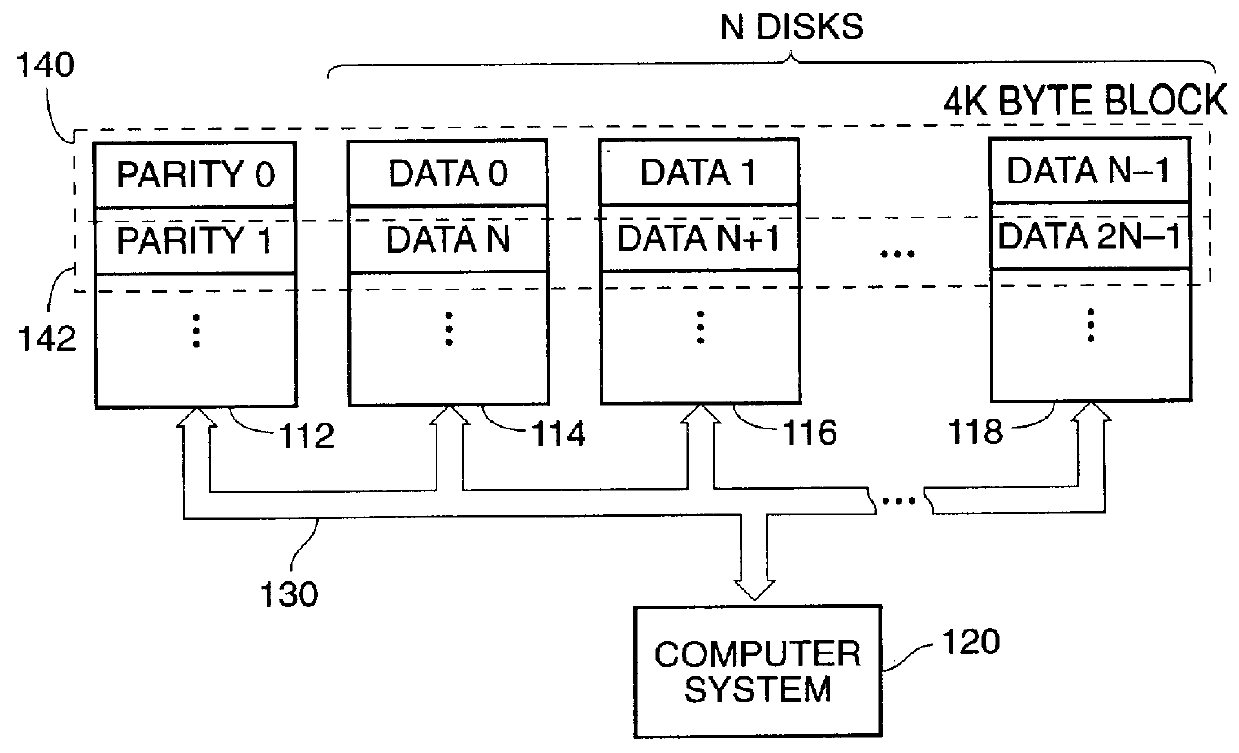
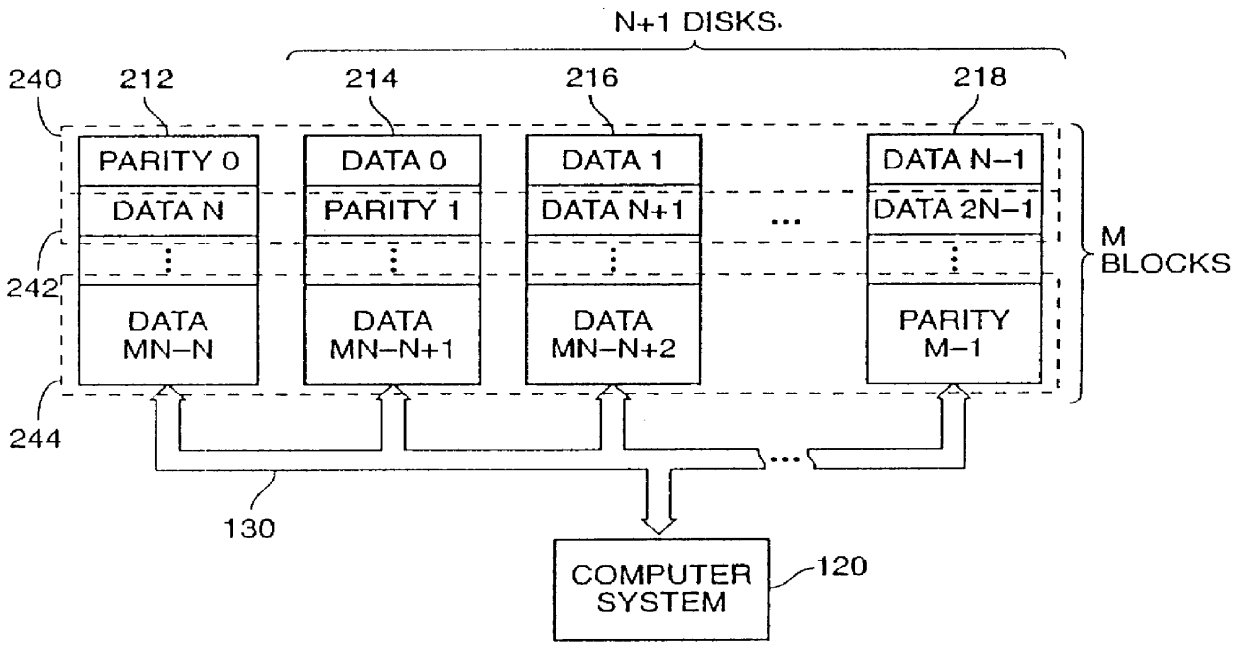
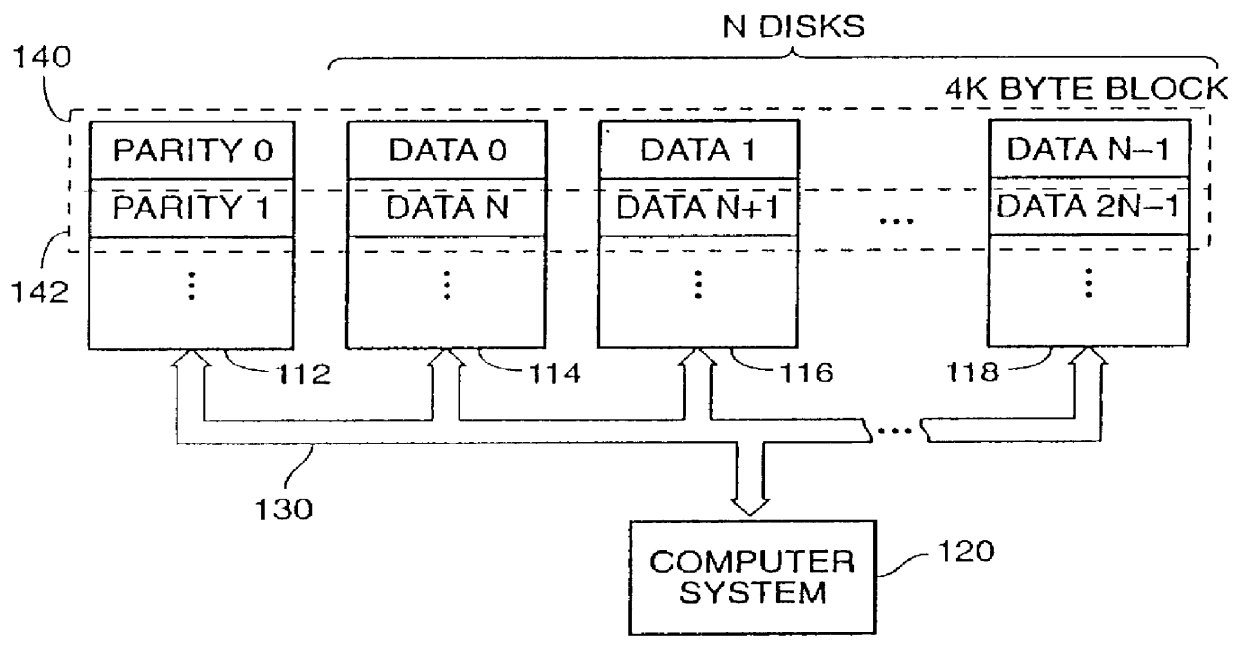
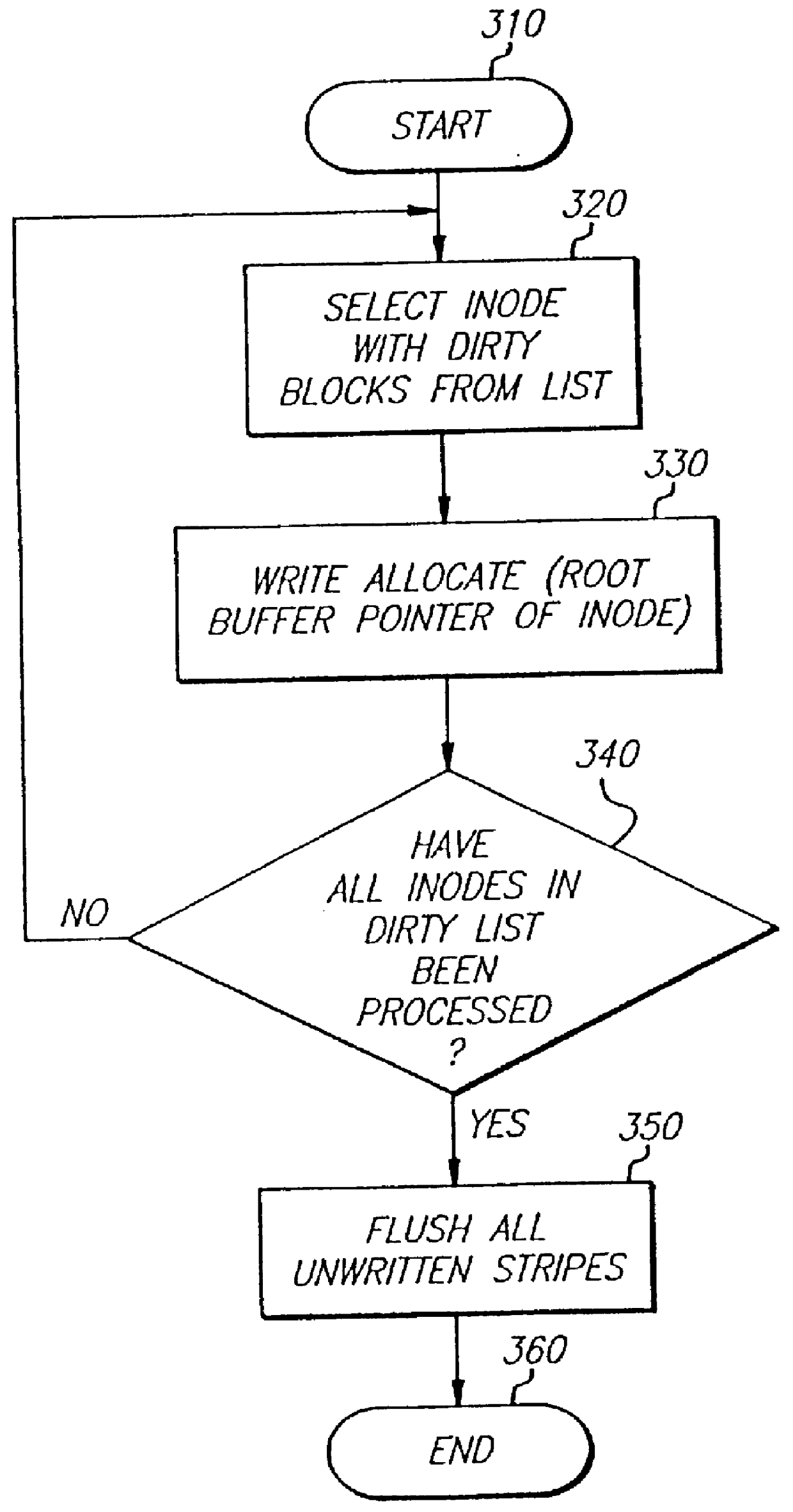
The present invention is a method for integrating a file system with a RAID array that exports precise information about the arrangement of data blocks in the RAID subsystem. The file system examines this information and uses it to optimize the location of blocks as they are written to the RAID system. Thus, the system uses explicit knowledge of the underlying RAID disk layout to schedule disk allocation. The present invention uses separate current-write location (CWL) pointers for each disk in the disk array where the pointers simply advance through the disks as writes occur. The algorithm used has two primary goals. The first goal is to keep the CWL pointers as close together as possible, thereby improving RAID efficiency by writing to multiple blocks in the stripe simultaneously. The second goal is to allocate adjacent blocks in a file on the same disk, thereby improving read back performance. The present invention satisfies the first goal by always writing on the disk with the lowest CWL pointer. For the second goal, a new disk is chosen only when the algorithm starts allocating space for a new file, or when it has allocated N blocks on the same disk for a single file. A sufficient number of blocks is defined as all the buffers in a chunk of N sequential buffers in a file. The result is that CWL pointers are never more than N blocks apart on different disks, and large files have N consecutive blocks on the same disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
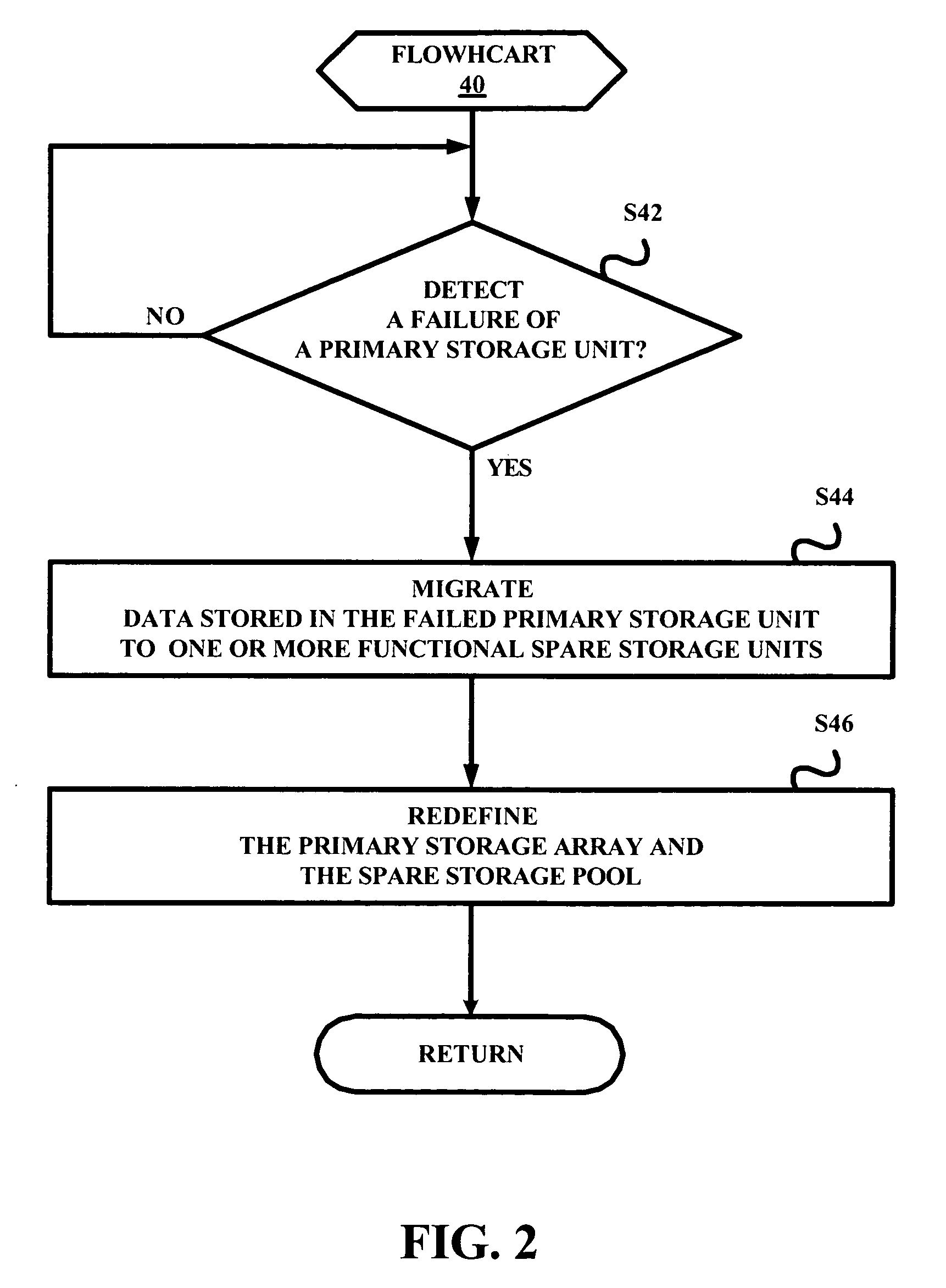
Method and apparatus for storage unit replacement in non-redundant array
InactiveUS6598174B1Lower performance requirementsMaintaining accessMemory loss protectionReliability/availability analysisRAIDData storing
A method and apparatus used in a storage network facilitates the protection of data in, and replacement of, storage devices about to fail before the failure happens. In a network that includes a set of storage devices organized as a non-redundant (for example RAID 0) array, a storage device about to fail in the non-redundant array can be replaced by another storage device, typically from a pool of spares. The method includes detecting a condition of a first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. Conditions which are detected according to various embodiments indicate that the first particular storage device is suffering events indicating that it is likely to fail, or otherwise suffering from reduced performance. The conditions are detected for example, by the receipt of a signal from the storage device itself, or by the monitoring of statistics concerning the performance of the storage device. The method further provides for selecting a particular spare storage device, which can be used in place of the first particular storage device. In response to detecting the condition, data stored in the first particular storage device is migrated to the second particular storage device, and the second particular storage takes the place of the first particular storage device in the non-redundant array. The first particular storage device can then be gracefully removed from the network without loss of service to the clients computers.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
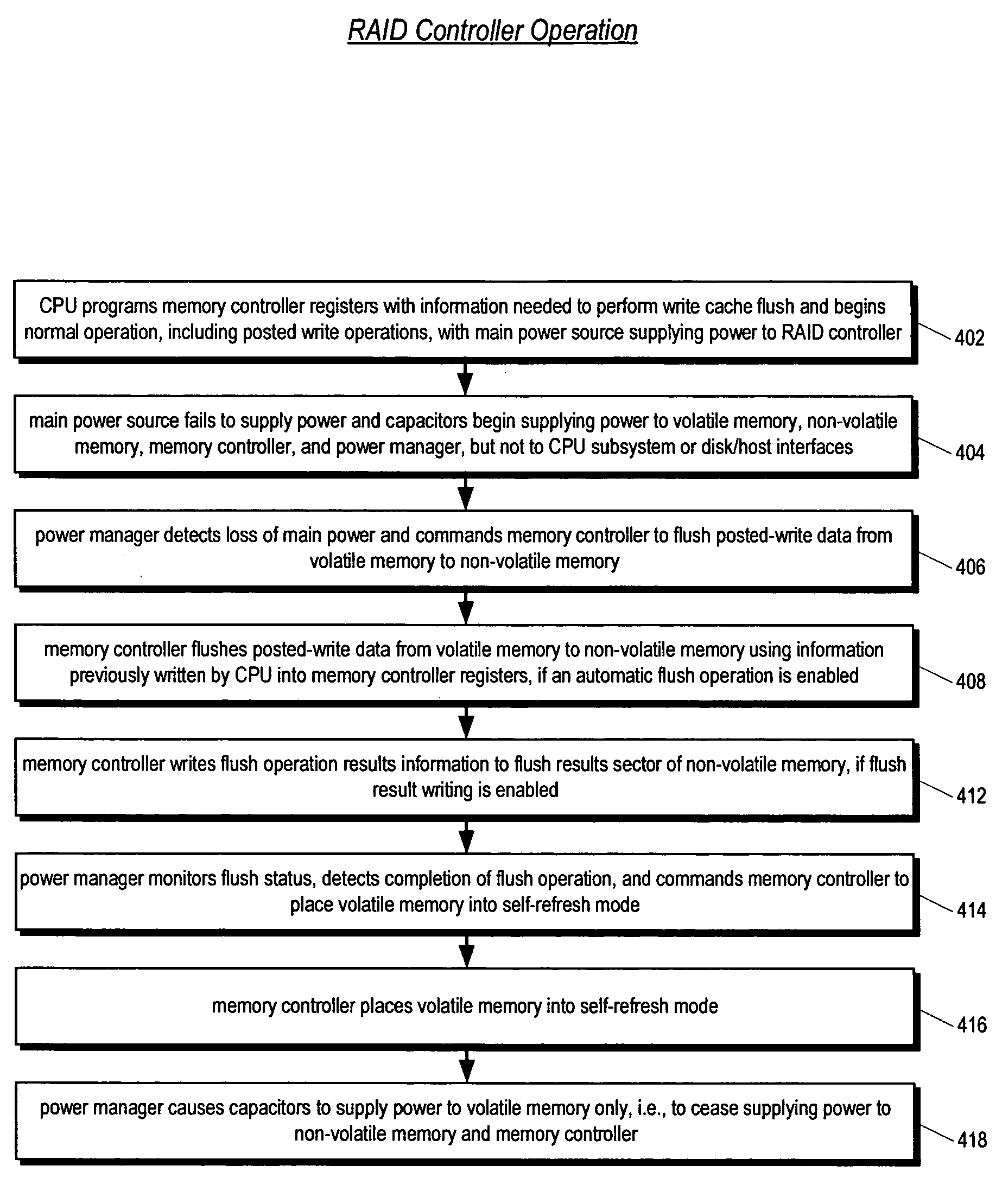
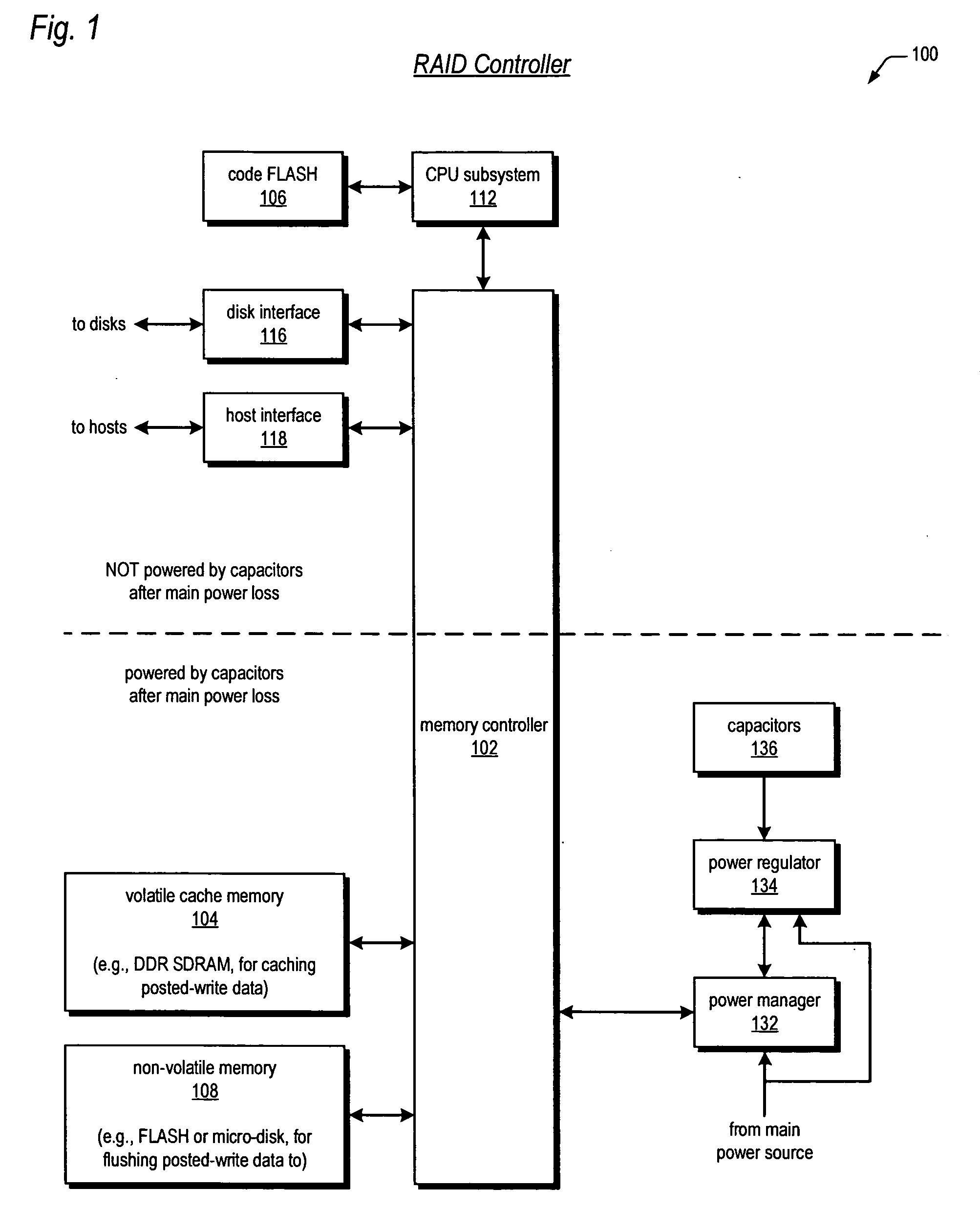
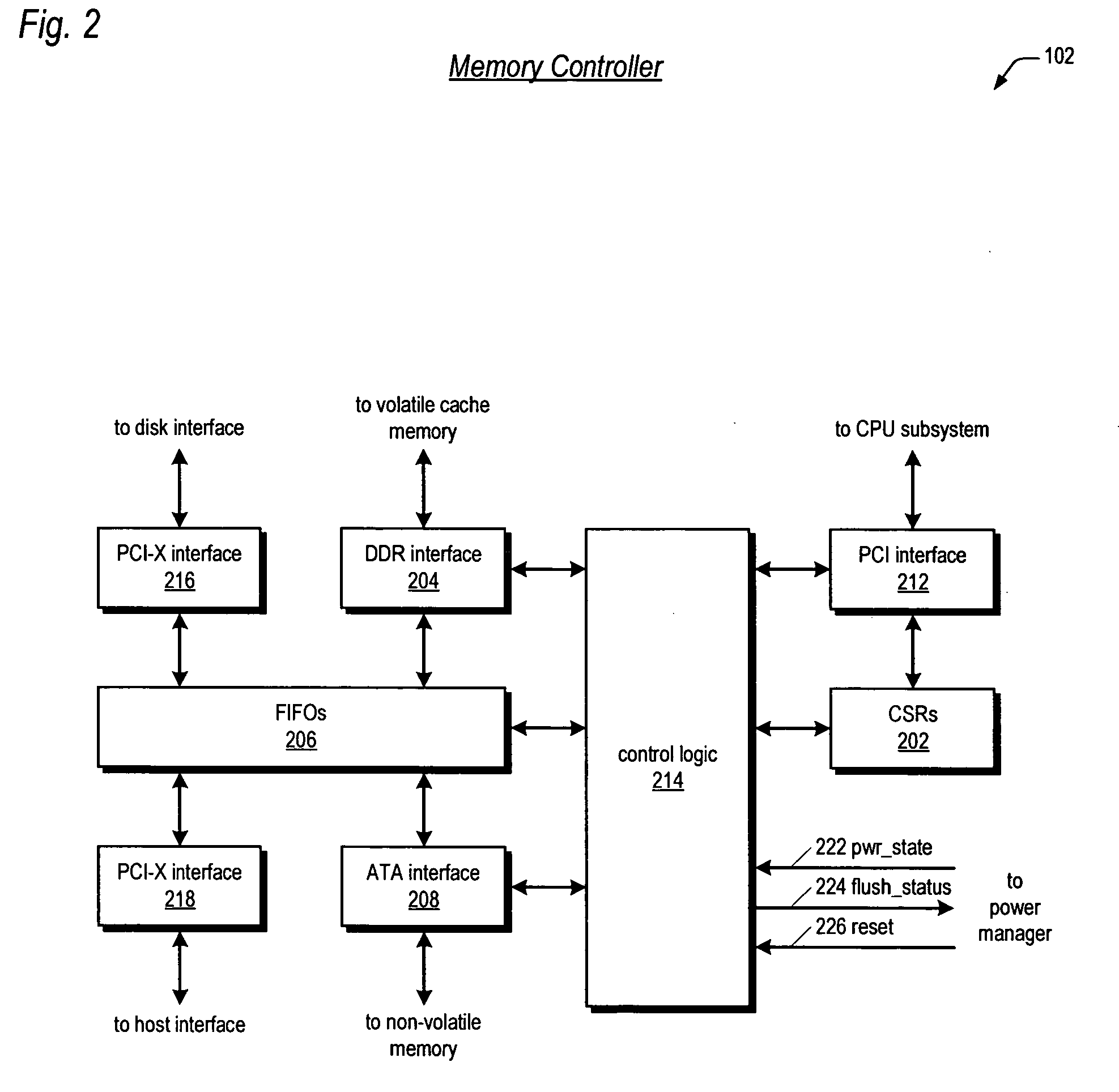
Raid controller using capacitor energy source to flush volatile cache data to non-volatile memory during main power outage
InactiveUS20060015683A1Reduces amount of energy storage capacity requirementLess expensiveEnergy efficient ICTMemory loss protectionRAIDStored energy
A write-caching RAID controller is disclosed. The controller includes a CPU that manages transfers of posted-write data from host computers to a volatile memory and transfers of the posted-write data from the volatile memory to storage devices when a main power source is supplying power to the RAID controller. A memory controller flushes the posted-write data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory when main power fails, during which time capacitors provide power to the memory controller, volatile memory, and non-volatile memory, but not to the CPU, in order to reduce the energy storage requirements of the capacitors. During main power provision, the CPU programs the memory controller with information needed to perform the flush operation, such as the location and size of the posted-write data in the volatile memory and various flush operation characteristics.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
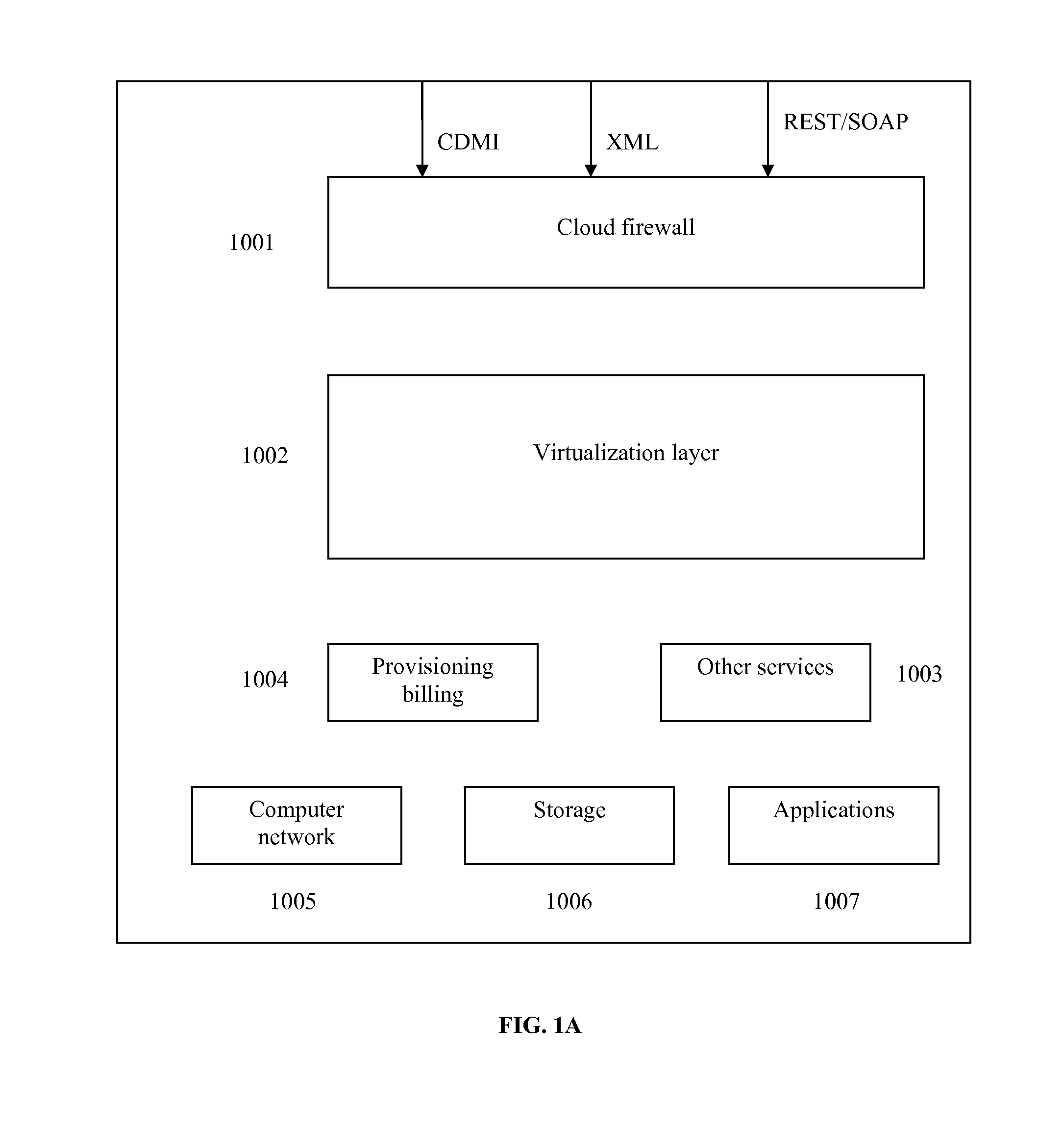
Distributed virtual storage cloud architecture and a method thereof
ActiveUS20130204849A1Prevent lockInput/output to record carriersDigital data information retrievalThird partyVirtualization
The present disclosure relates to a distributed information storage system which functions as virtual cloud storage overlay on top of physical cloud storage systems. The disclosure discloses transparently solving all the data management related security, virtualization, reliability and enables transparent cloud storage migration, cloud storage virtualization, information dispersal and integration across disparate cloud storage devices operated by different providers or on-premise storage. The cloud storage is owned or hosted by same or different third-party providers who own the information contained in the storage which eliminates cloud dependencies. This present disclosure functions as a distributed cloud storage delivery platform enabling various functionalities like cloud storage virtualization, cloud storage integration, cloud storage management and cloud level RAID.
Owner:CHACKO PETER
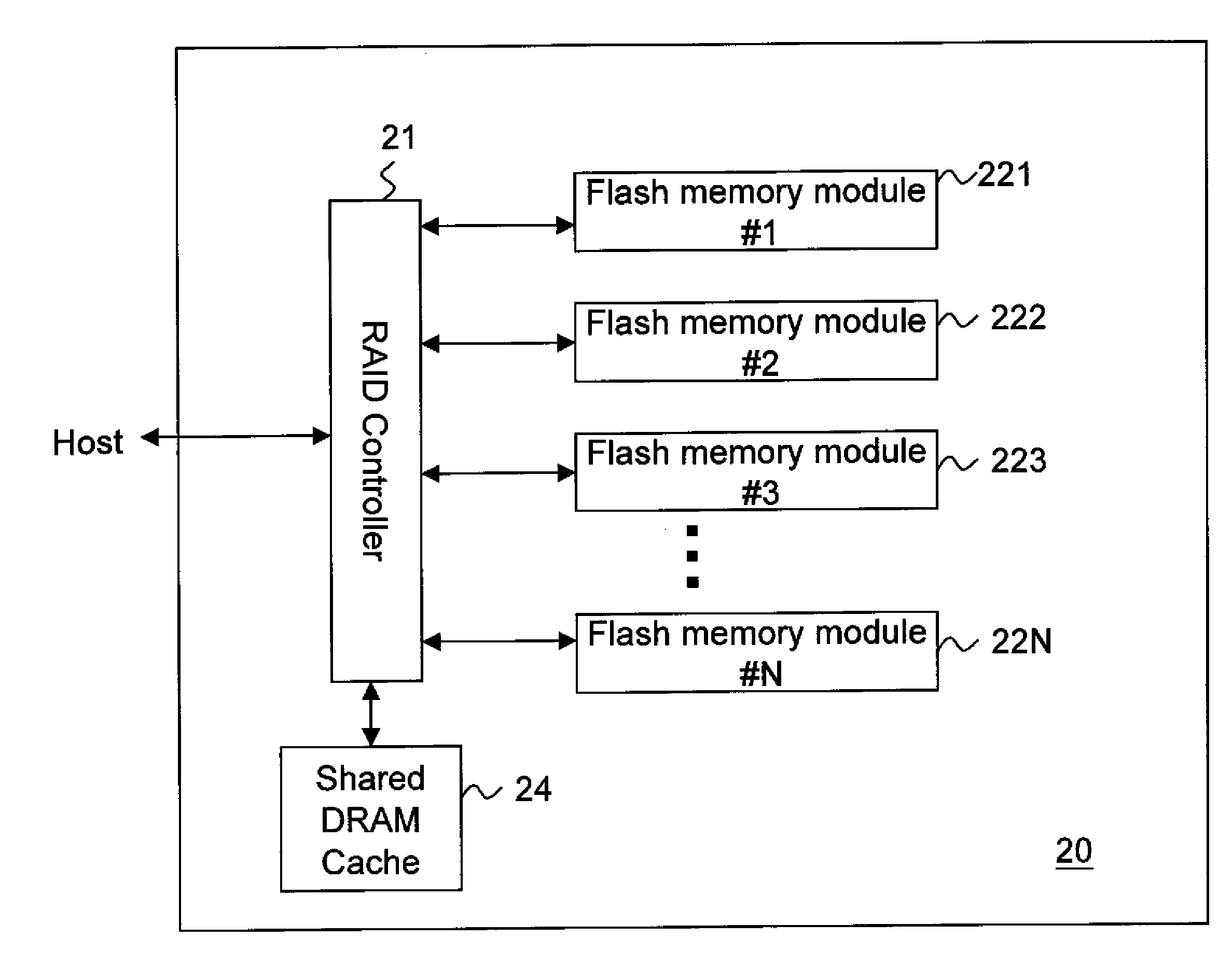
Non-volatile memory storage system
InactiveUS20100125695A1Speed up data transferCost-effective structureMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDComputer science
The present invention discloses a flash memory storage system, comprising at least one RAID controller; a plurality of flash memory cards electrically connected with the RAID controller; and a cache memory electrically connected with the RAID controller and shared by the RAID controller and the flash memory cards. The cache memory efficiently enhances the system performance. The storage system may comprise more RAID controllers to construct a nested RAID architecture.
Owner:NANOSTAR CORP
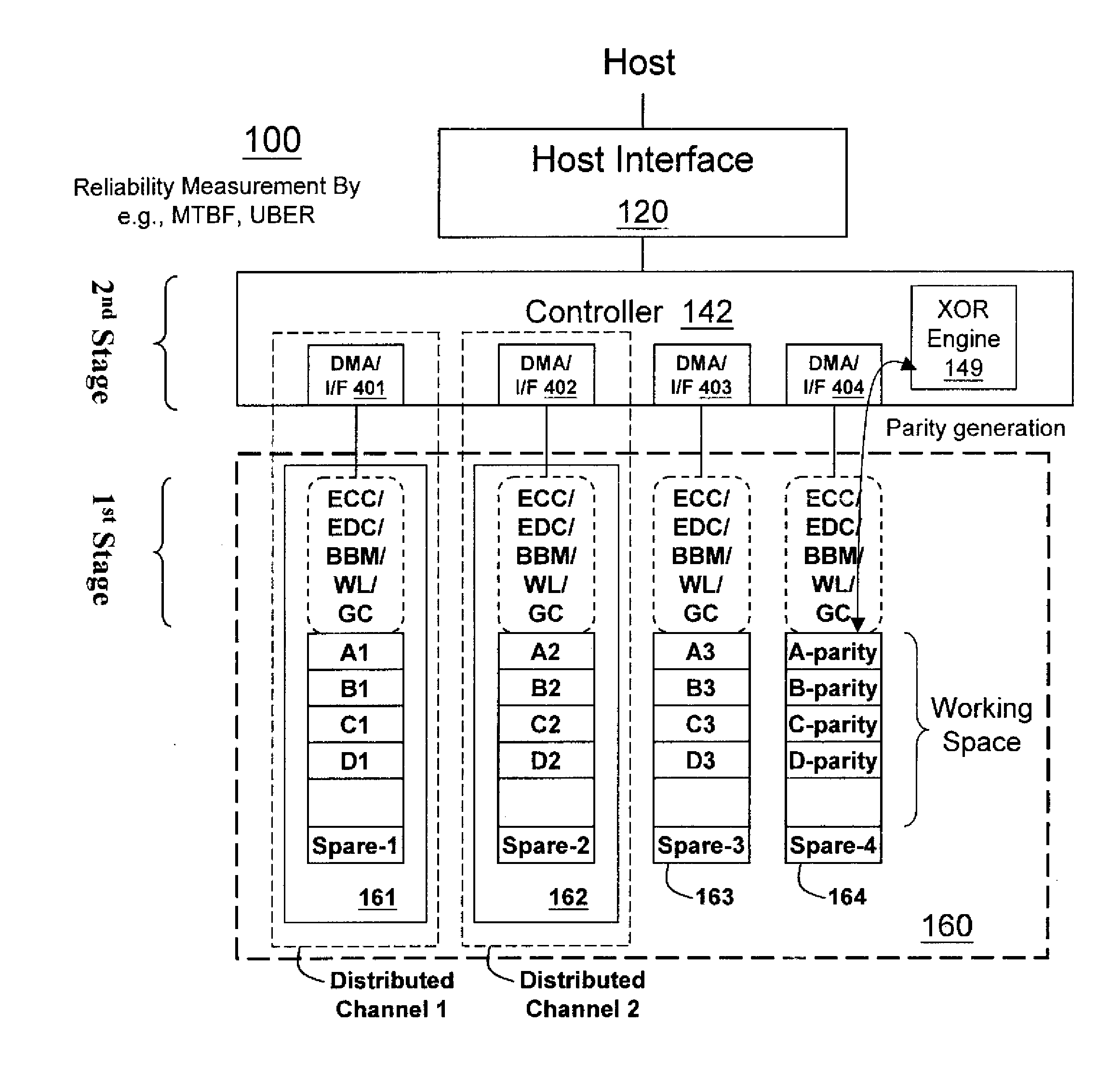
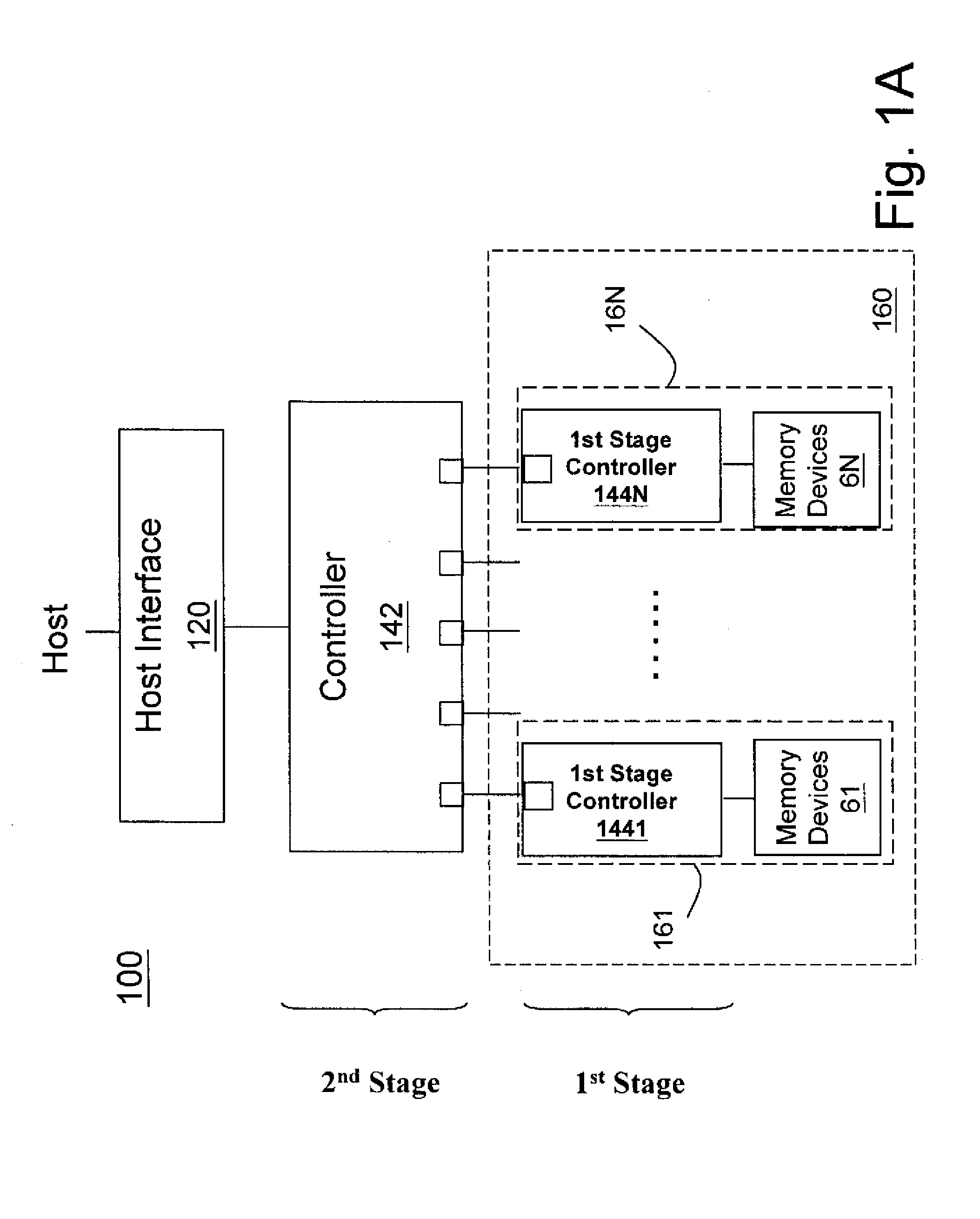
Non-volatile memory data storage system with reliability management
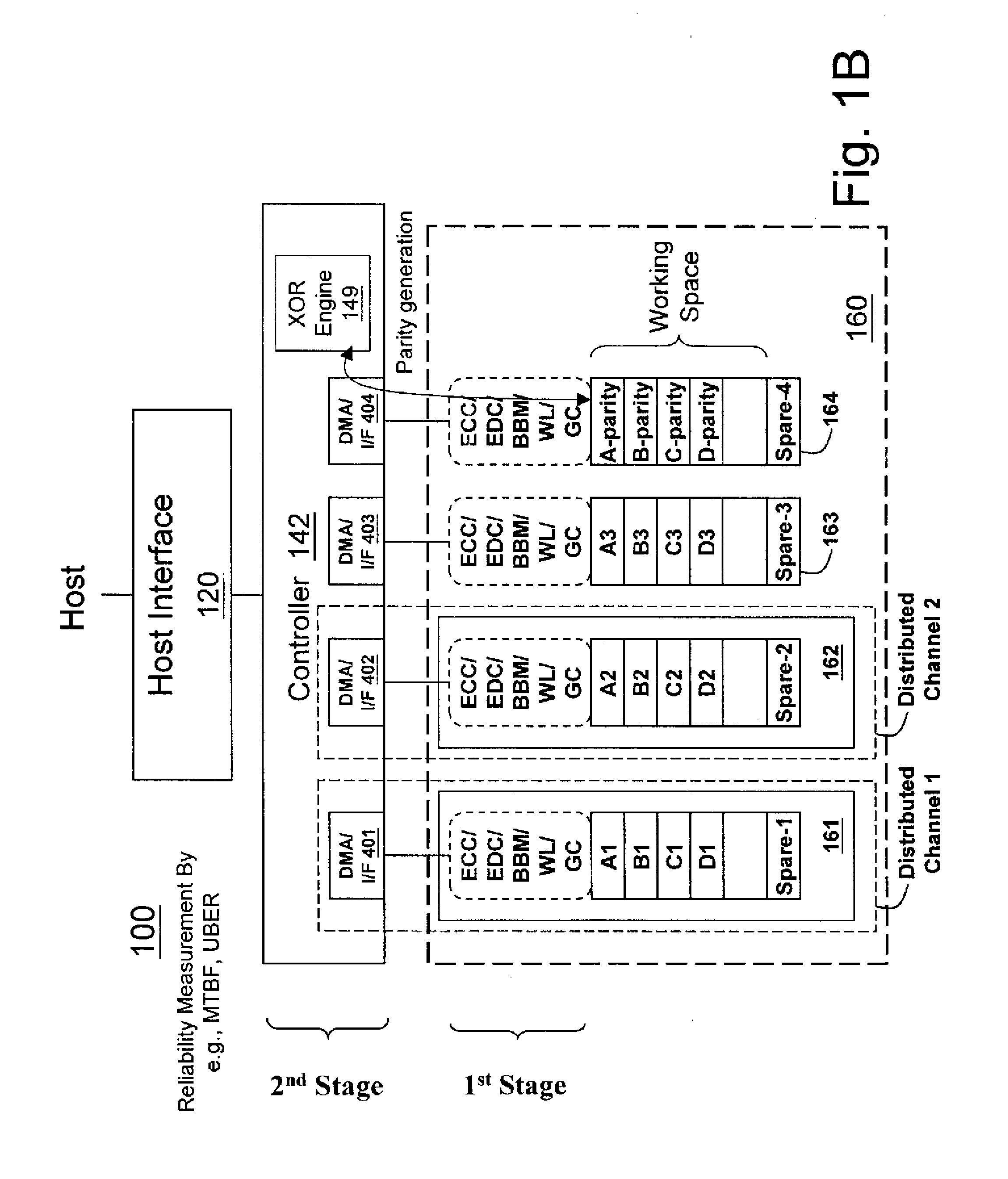
InactiveUS20100017650A1Improve reliabilityReliable managementMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDData recovery
A non-volatile memory data storage system, comprising: a host interface for communicating with an external host; a main storage including a first plurality of flash memory devices, wherein each memory device includes a second plurality of memory blocks, and a third plurality of first stage controllers coupled to the first plurality of flash memory devices; and a second stage controller coupled to the host interface and the third plurality of first stage controller through an internal interface, the second stage controller being configured to perform RAID operation for data recovery according to at least one parity.
Owner:NANOSTAR CORP
Flash devices with raid
InactiveUS20090172335A1Improve reliabilityImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTRAIDHard disc drive
Methods and apparatus of the present invention include multiple flash storage devices that are configured to form a single storage device that is flexible and scalable. Reliability and performance are improved while keeping the power consumption benefits compared to conventional hard disk drives.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
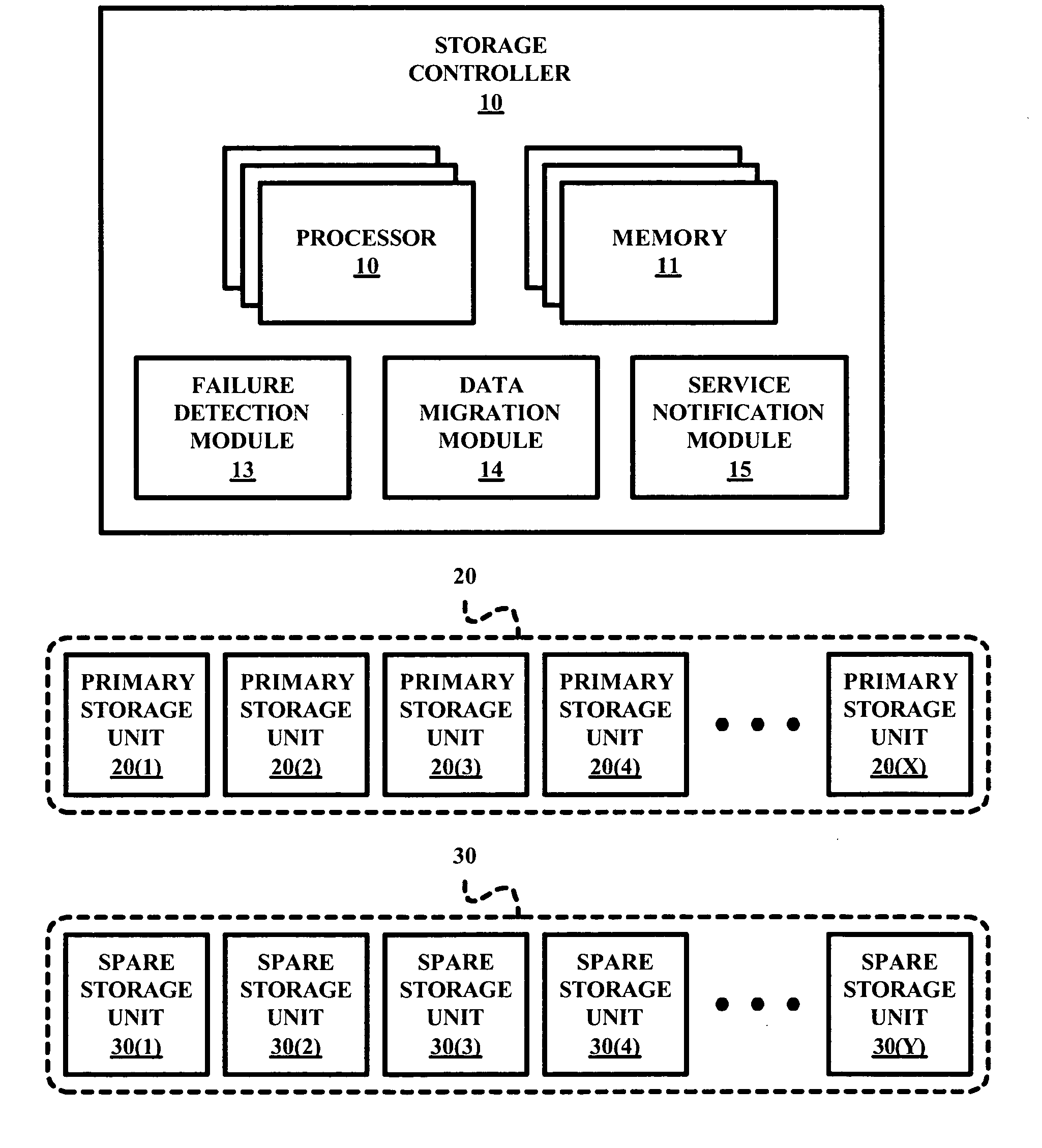
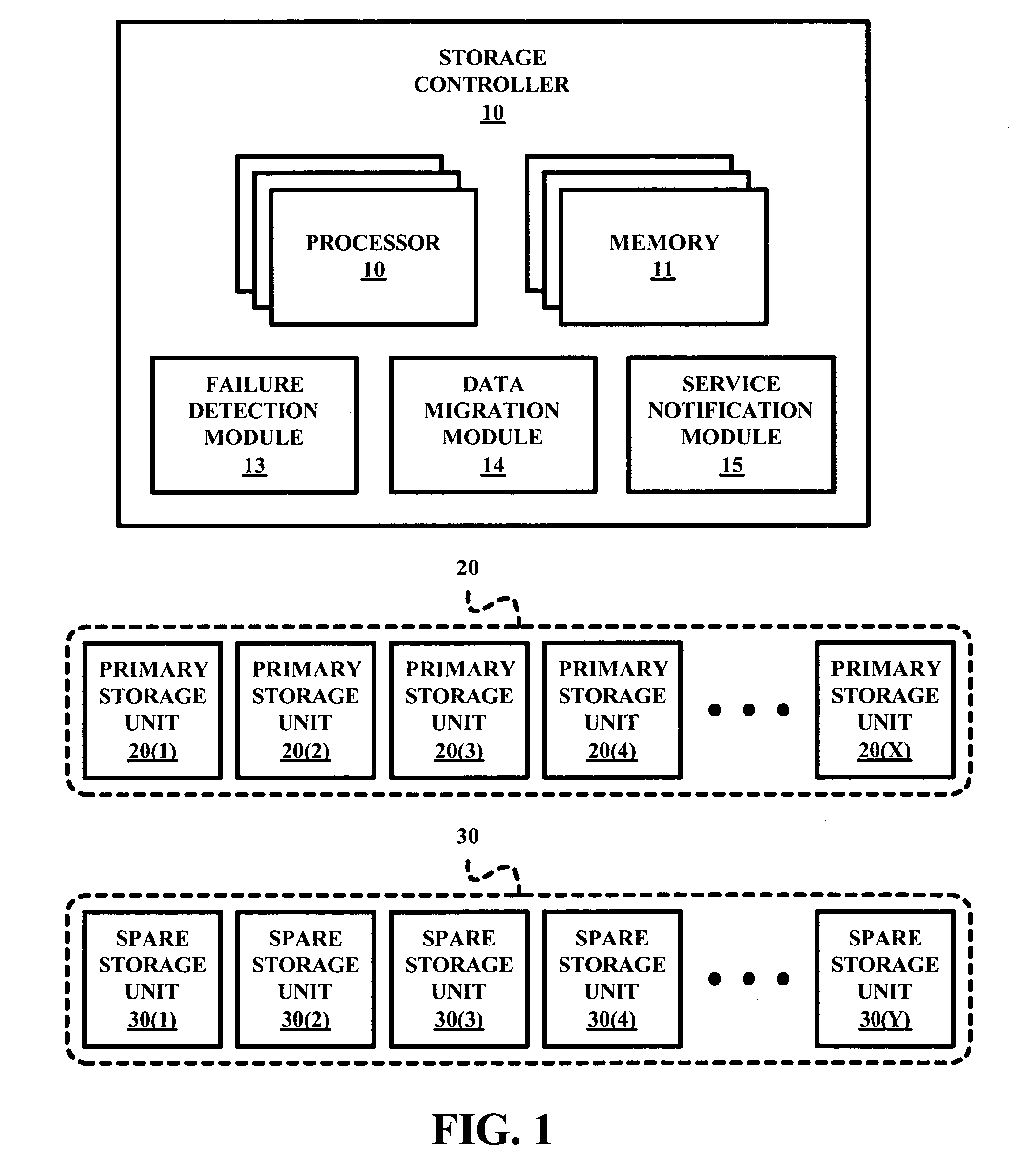
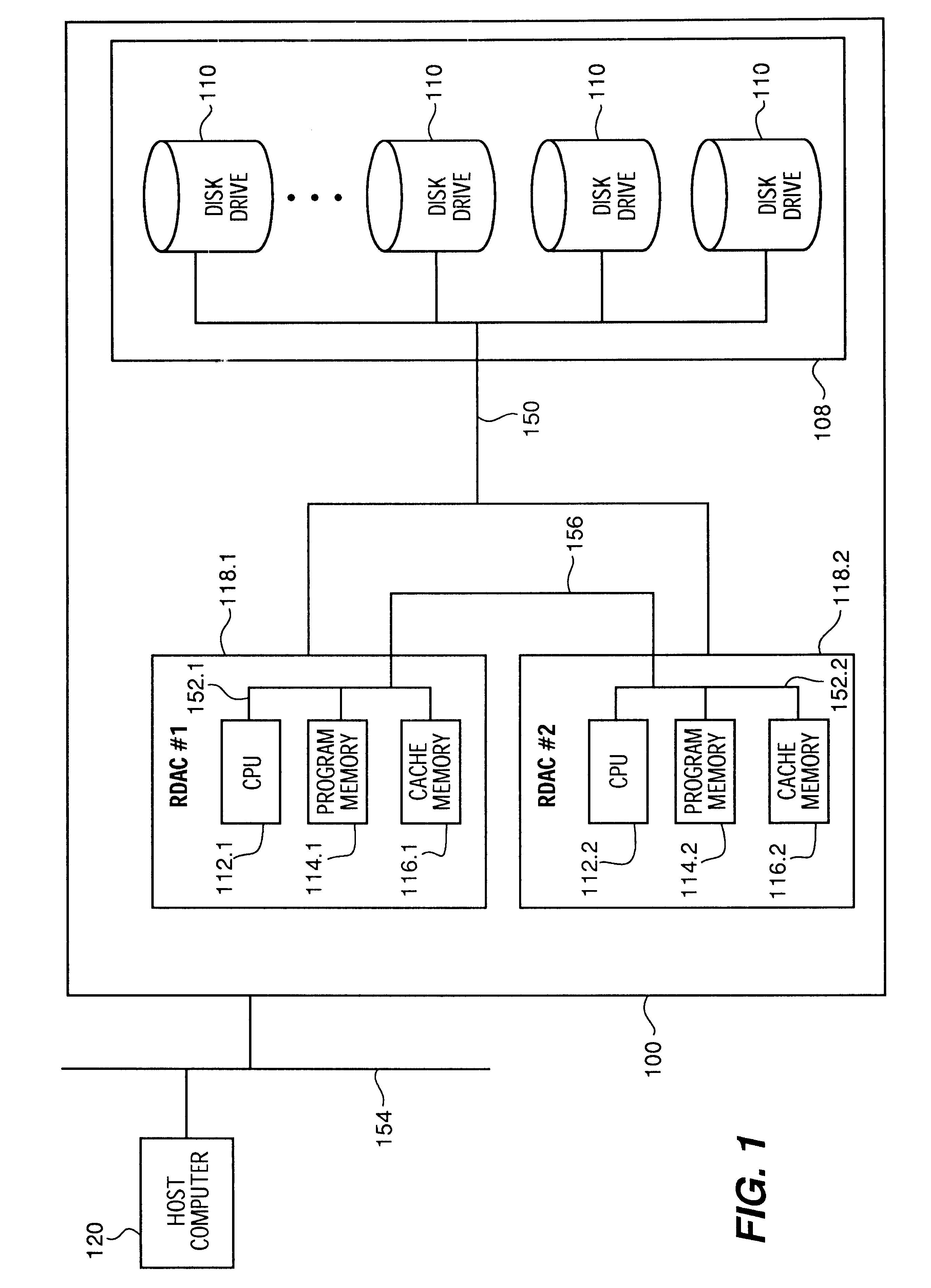
Management method for spare disk drives a RAID system
A RAID system employs a storage controller, a primary storage array having a plurality of primary storage units, and a spare storage pool having one or more spare storage units. A method of operating the storage controller in managing the primary storage array and the spare storage pool involves a testing by the storage controller of at least one repair service threshold representative of one or more operational conditions indicative of a necessity to repair at least one of the primary storage array and the spare storage unit, and a selective initiation by the storage controller of a repair service action for repairing one of the primary storage array and the spare storage unit based on the testing of the at least one repair service threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
On-chip shared memory based device architecture
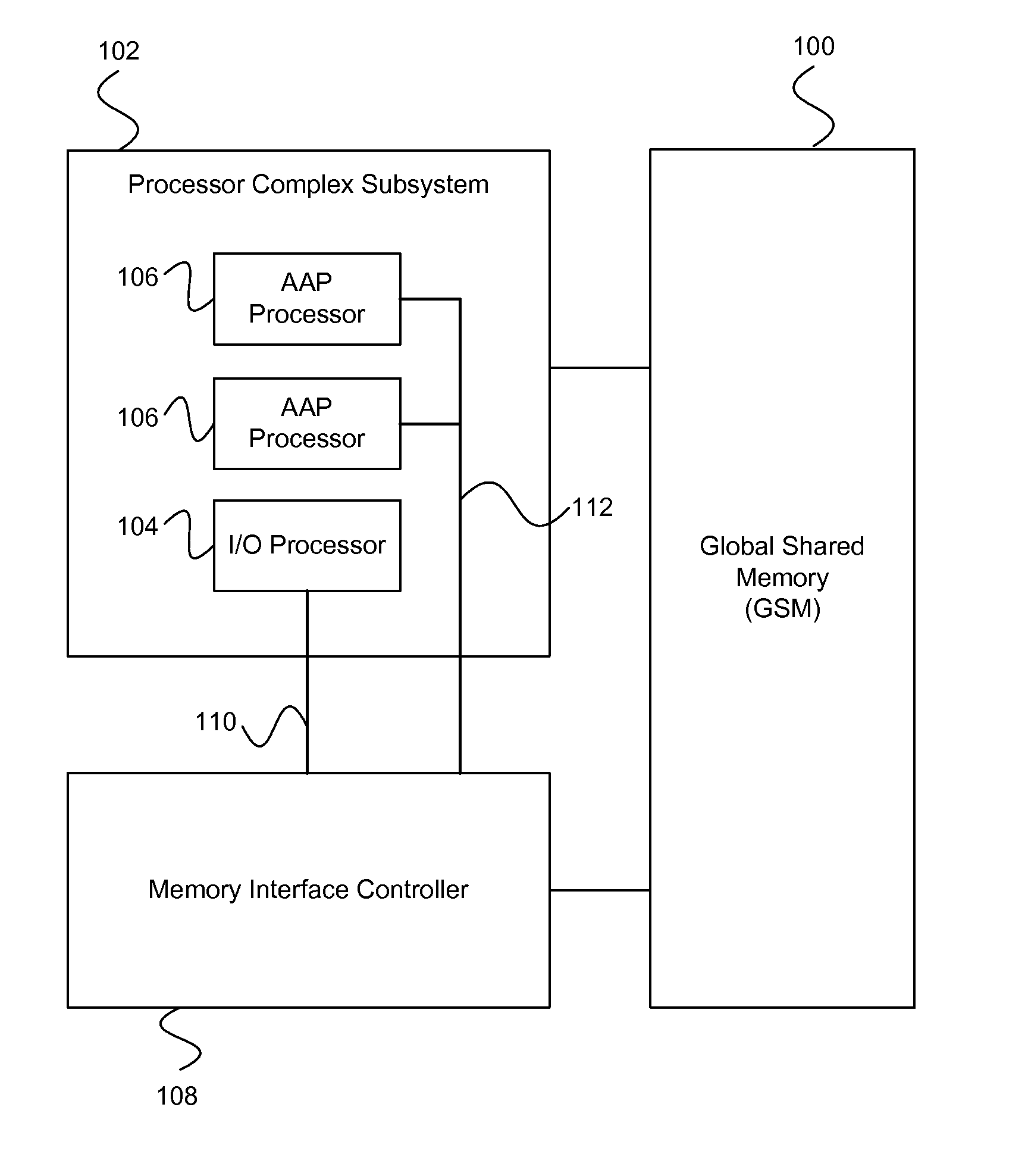
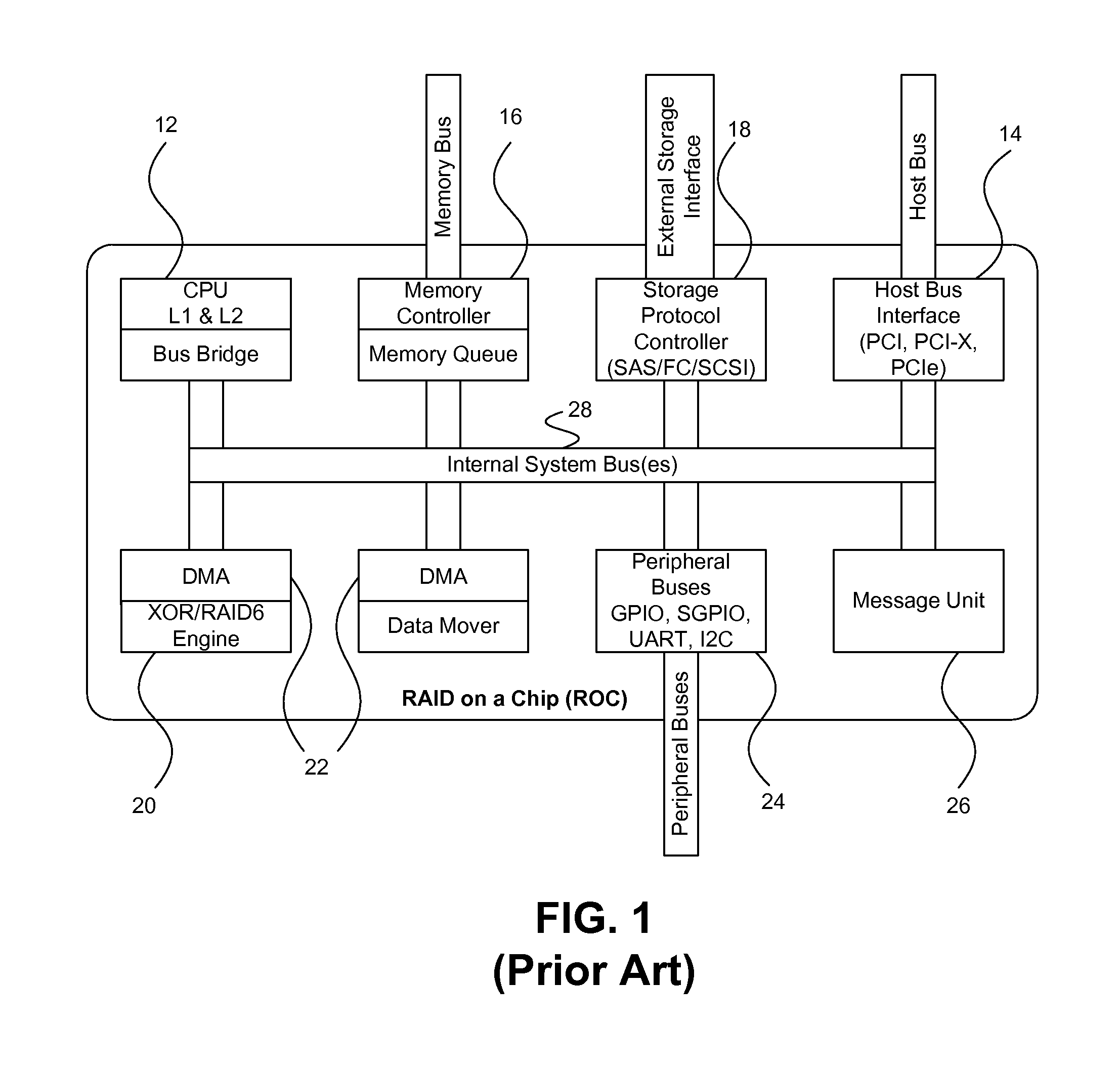
ActiveUS7743191B1Reduce disadvantagesLow costRedundant array of inexpensive disk systemsRecord information storageExtensibilityRAID
A method and architecture are provided for SOC (System on a Chip) devices for RAID processing, which is commonly referred as RAID-on-a-Chip (ROC). The architecture utilizes a shared memory structure as interconnect mechanism among hardware components, CPUs and software entities. The shared memory structure provides a common scratchpad buffer space for holding data that is processed by the various entities, provides interconnection for process / engine communications, and provides a queue for message passing using a common communication method that is agnostic to whether the engines are implemented in hardware or software. A plurality of hardware engines are supported as masters of the shared memory. The architectures provide superior throughput performance, flexibility in software / hardware co-design, scalability of both functionality and performance, and support a very simple abstracted parallel programming model for parallel processing.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
Adaptive RAID for an SSD environment
A system and method for adaptive RAID geometries. A computer system comprises client computers and data storage arrays coupled to one another via a network. A data storage array utilizes solid-state drives and Flash memory cells for data storage. A storage controller within a data storage array is configured to determine a first RAID layout for use in storing data, and write a first RAID stripe to the device group according to the first RAID layout. In response to detecting a first condition, the controller is configured to determine a second RAID layout which is different from the first RAID layout, and write a second RAID stripe to the device group according to the second layout, whereby the device group concurrently stores data according to both the first RAID layout and the second RAID layout.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
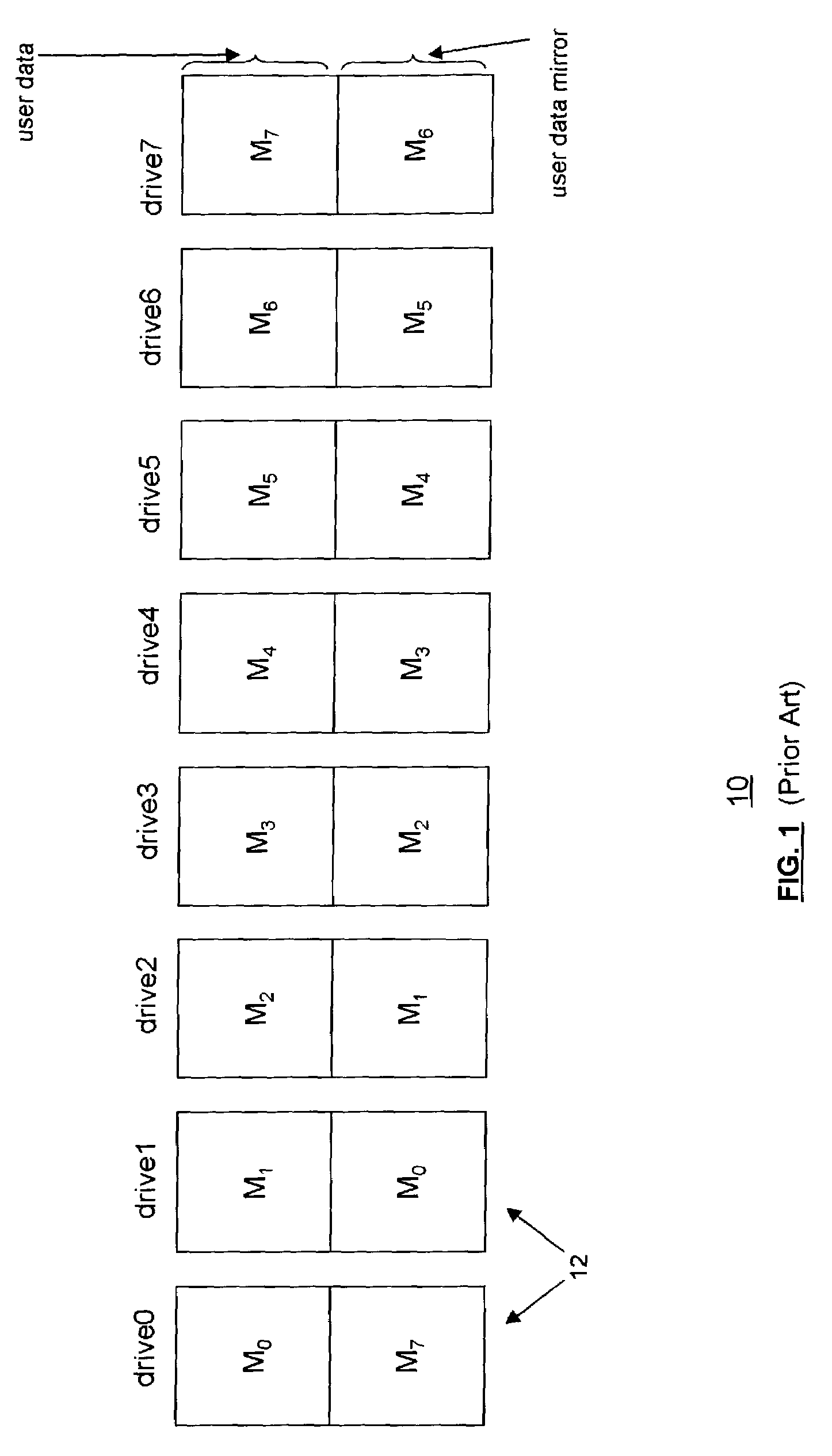
Accelerated RAID with rewind capability
InactiveUS7076606B2Increase exposureImprove read performanceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsRAIDData store
A method for storing data in a fault-tolerant storage subsystem having an array of failure independent data storage units, by dividing the storage area on the storage units into a logical mirror area and a logical stripe area, such that when storing data in the mirror area, duplicating the data by keeping a duplicate copy of the data on a pair of storage units, and when storing data in the stripe area, storing data as stripes of blocks, including data blocks and associated error-correction blocks.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Method for allocating files in a file system integrated with a raid disk sub-system
A method is disclosed for integrating a file system with a RAID array that exports precise information about the arrangement of data blocks in the RAID subsystem. The file system examines this information and uses it to optimize the location of blocks as they are written to the RAID system. Thus, the system uses explicit knowledge of the underlying RAID disk layout to schedule disk allocation. The method uses separate current-write location (CWL) pointers for each disk in the disk array where the pointers simply advance through the disks as writes occur. The algorithm used has two primary goals. The first goal is to keep the CWL pointers as close together as possible, thereby improving RAID efficiency by writing to multiple blocks in the stripe simultaneously. The second goal is to allocate adjacent blocks in a file on the same disk, thereby improving read back performance. The method satisfies the first goal by always writing on the disk with the lowest CWL pointer. For the second goal, a new disks chosen only when the algorithm starts allocating space for a new file, or when it has allocated N blocks on the same disk for a single file. A sufficient number of blocks is defined as all the buffers in a chunk of N sequential buffers in a file. The result is that CWL pointers are never more than N blocks apart on different disks, and large files have N consecutive blocks on the same disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
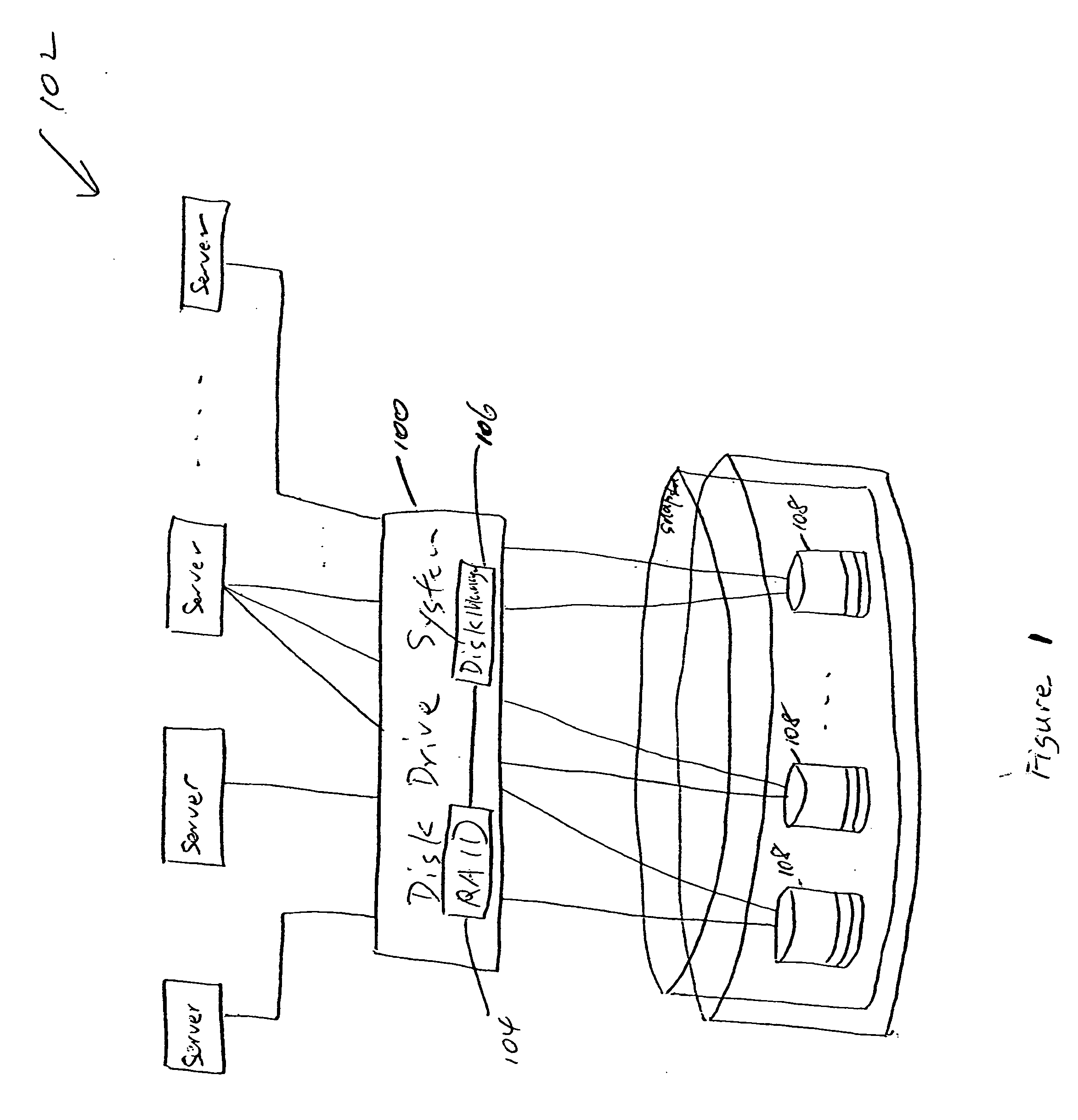
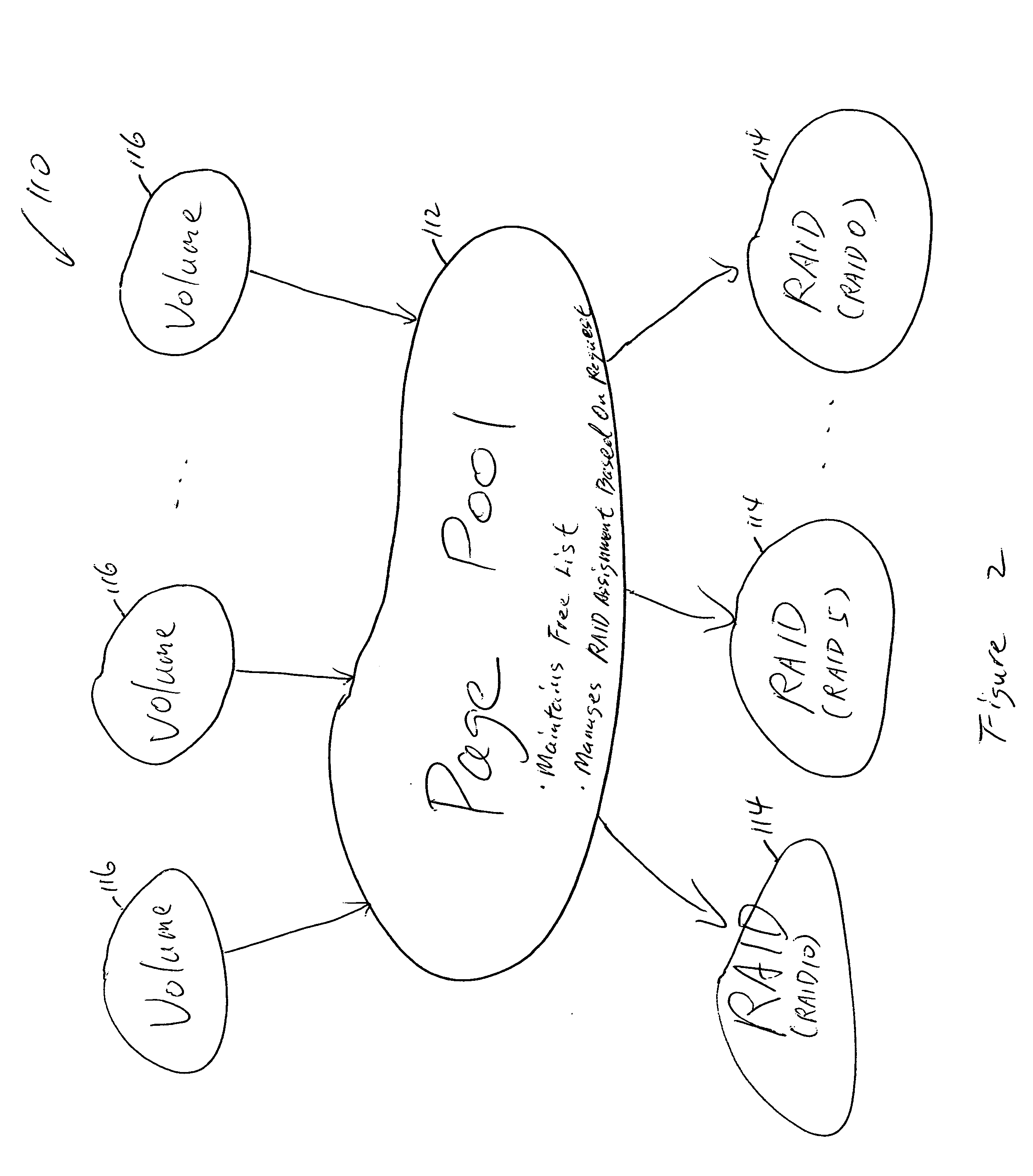
Virtual disk drive system and method
ActiveUS20050055603A1Useful operationInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDDynamic data
A disk drive system and method capable of dynamically allocating data is provided. The disk drive system may include a RAID subsystem having a pool of storage, for example a page pool of storage that maintains a free list of RAIDs, or a matrix of disk storage blocks that maintain a null list of RAIDs, and a disk manager having at least one disk storage system controller. The RAID subsystem and disk manager dynamically allocate data across the pool of storage and a plurality of disk drives based on RAID-to-disk mapping. The RAID subsystem and disk manager determine whether additional disk drives are required, and a notification is sent if the additional disk drives are required. Dynamic data allocation and data progression allow a user to acquire a disk drive later in time when it is needed. Dynamic data allocation also allows efficient data storage of snapshots / point-in-time copies of virtual volume pool of storage, instant data replay and data instant fusion for data backup, recovery etc., remote data storage, and data progression, etc.
Owner:DELL INT L L C
Secure data storage in raid memory devices
ActiveUS20130124776A1Reduce overheadUtility and advantageMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionRAIDComputer architecture
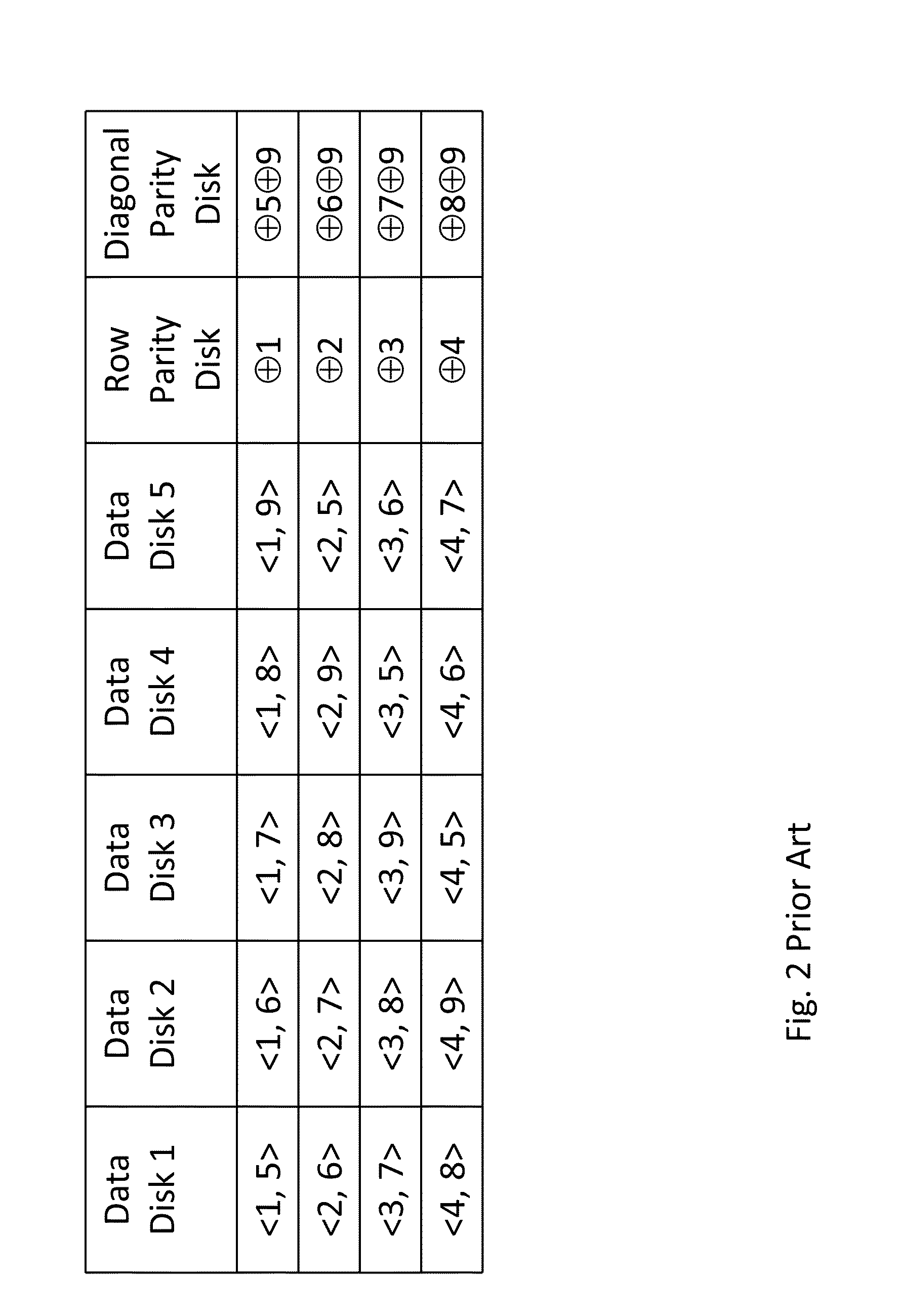
A redundant array of independent disk (RAID) memory storage system comprising data storage blocks arranged in a first plurality of data rows and a second plurality of data columns, wherein parity data is stored in additionally defined parity blocks, and wherein numbers of data blocks in respective columns are different, to accommodate the additional diagonal parity data block that the geometry of the system requires. The system is suitable for an SSD array in which sequential disk readout is not required.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
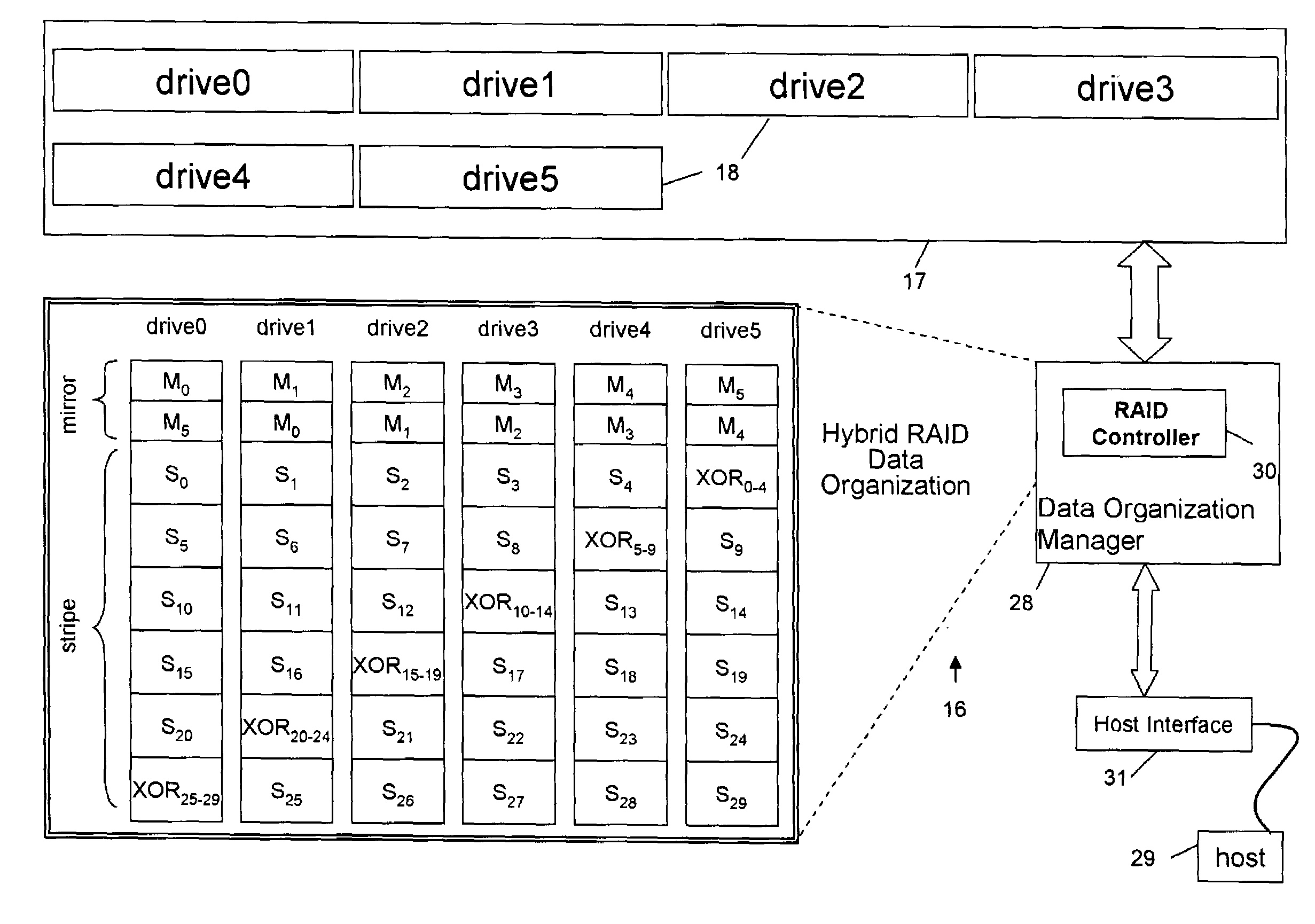
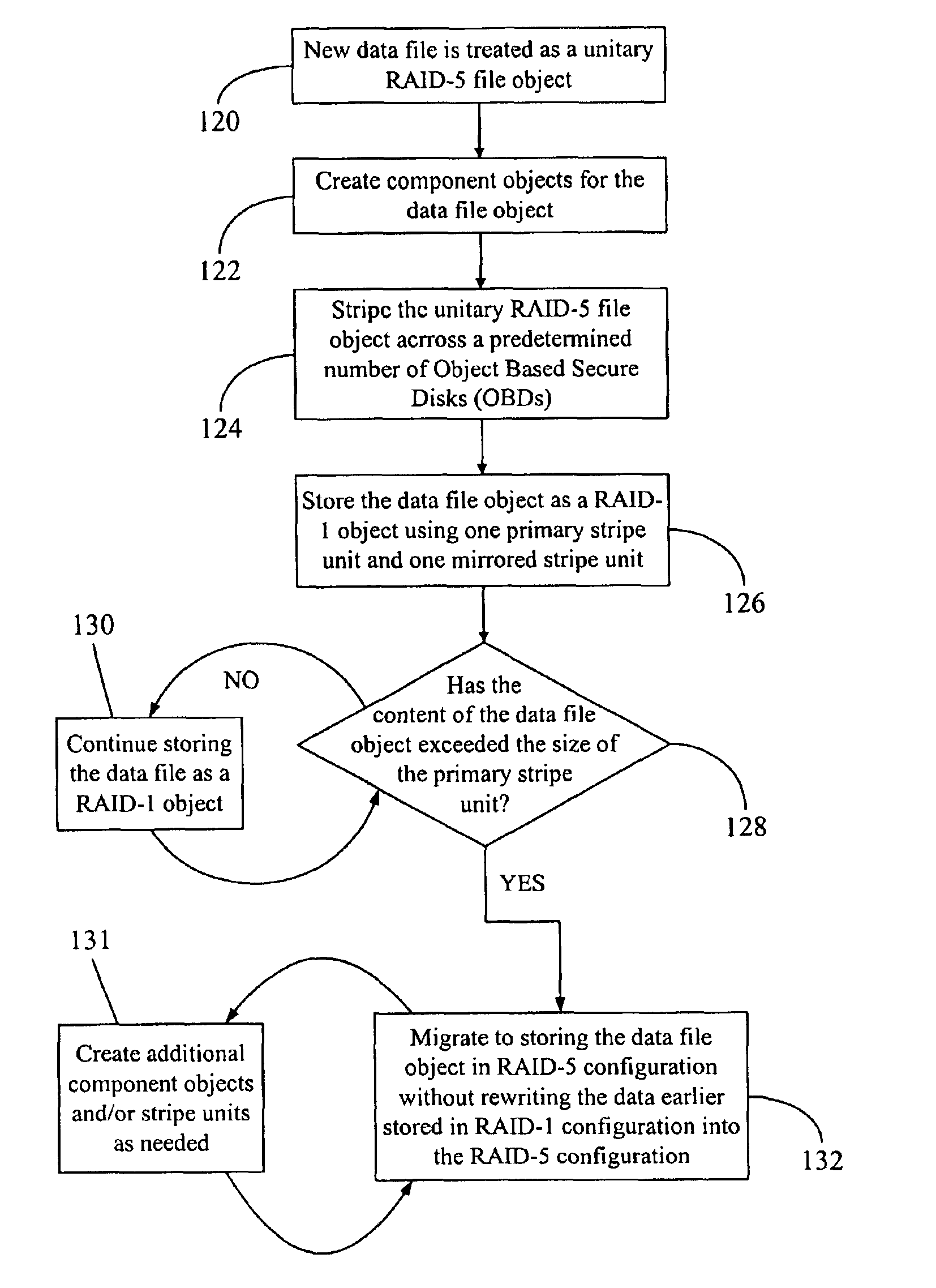
Data file migration from a mirrored RAID to a non-mirrored XOR-based RAID without rewriting the data
InactiveUS6985995B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityData processing applicationsMemory loss protectionRAIDObject based
A data storage methodology wherein a data file is initially stored in a format consistent with RAID-1 and RAID-X and then migrated to a format consistent with RAID-X and inconsistent with RAID-1 when the data file grows in size beyond a certain threshold. Here, RAID-X refers to any non-mirrored storage scheme employing XOR-based error correction coding (e.g., a RAID-5 configuration). Each component object (including the data objects and the parity object) for the data file is configured to be stored in a different stripe unit per object-based secure disk. Each stripe unit may store, for example, 64 KB of data. So long as the data file does not grow beyond the size threshold of a stripe unit (e.g., 64 KB), the parity stripe unit contains a mirrored copy of the data stored in one of the data stripe units because of the exclusive-ORing of the input data with “all zeros” assumed to be contained in empty or partially-filled stripe units. When the file grows beyond the size threshold, the parity stripe unit starts storing parity information instead of a mirrored copy of the file data. Thus, the data file can be automatically migrated from a format consistent with RAID-1 and RAID-X to a format consistent with RAID-X and inconsistent with RAID-1 without the necessity to duplicate or rewrite the stored data.
Owner:PANASAS INC
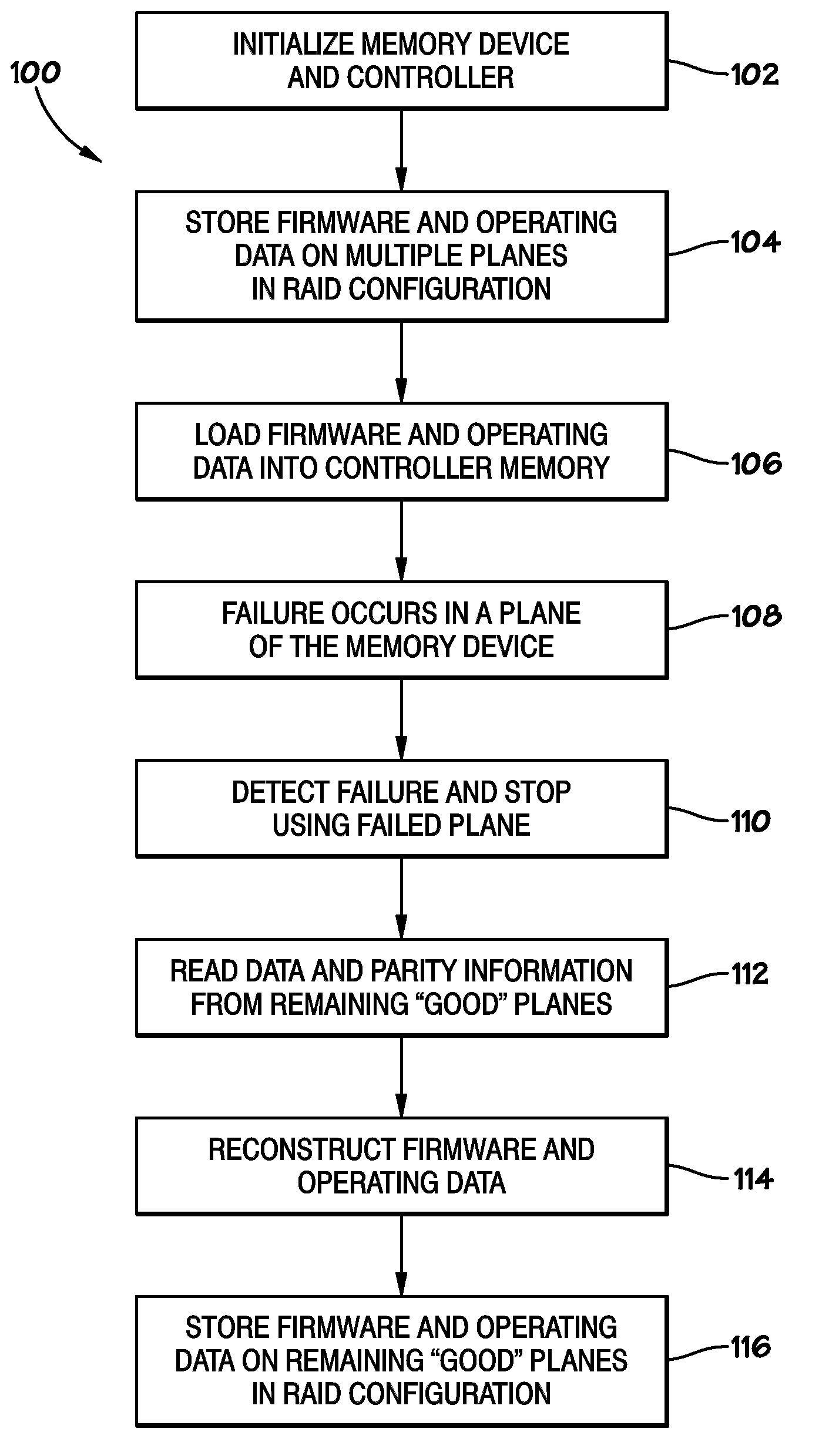
Systems and Methods for Storing and Recovering Controller Data in Non-Volatile Memory Devices
Systems and methods are disclosed for storing the firmware and other data of a flash memory controller, such as using a RAID configuration across multiple flash memory devices or portions of a single memory device. In various embodiments, the firmware and other data used by a controller, and error correction information, such as parity information for RAID configuration, may be stored across multiple flash memory devices, multiple planes of a multi-plane flash memory device, or across multiple blocks or pages of a single flash memory device. The controller may detect the failure of a memory device or a portion thereof, and reconstruct the firmware and / or other data from the other memory devices or portions thereof.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System and method for a redundant communication channel via storage area network back-end
InactiveUS6883065B1Redundancy and robustness in systemInput/output to record carriersFault responseFailoverRAID
A fiber channel storage area network (SAN) provides virtualized storage space for a number of servers to a number of virtual disks implemented on various virtual redundant array of inexpensive disks (RAID) devices striped across a plurality of physical disk drives. The SAN includes plural controllers and communication paths to allow for fail-safe and fail-over operation. The plural controllers can be loosely-coupled to provide n-way redundancy and have more than one independent channel for communicating with one another. In particular, respective portions from each of the back-end physical disk drives within the SAN are used as one of these alternative communication channels to pass messages between controllers. Such an alternative communications channel provides even further redundancy and robustness in the system.
Owner:INNOVATIONS IN MEMORY LLC
Apparatus and method to provide virtual solid state disk in cache memory in a storage controller
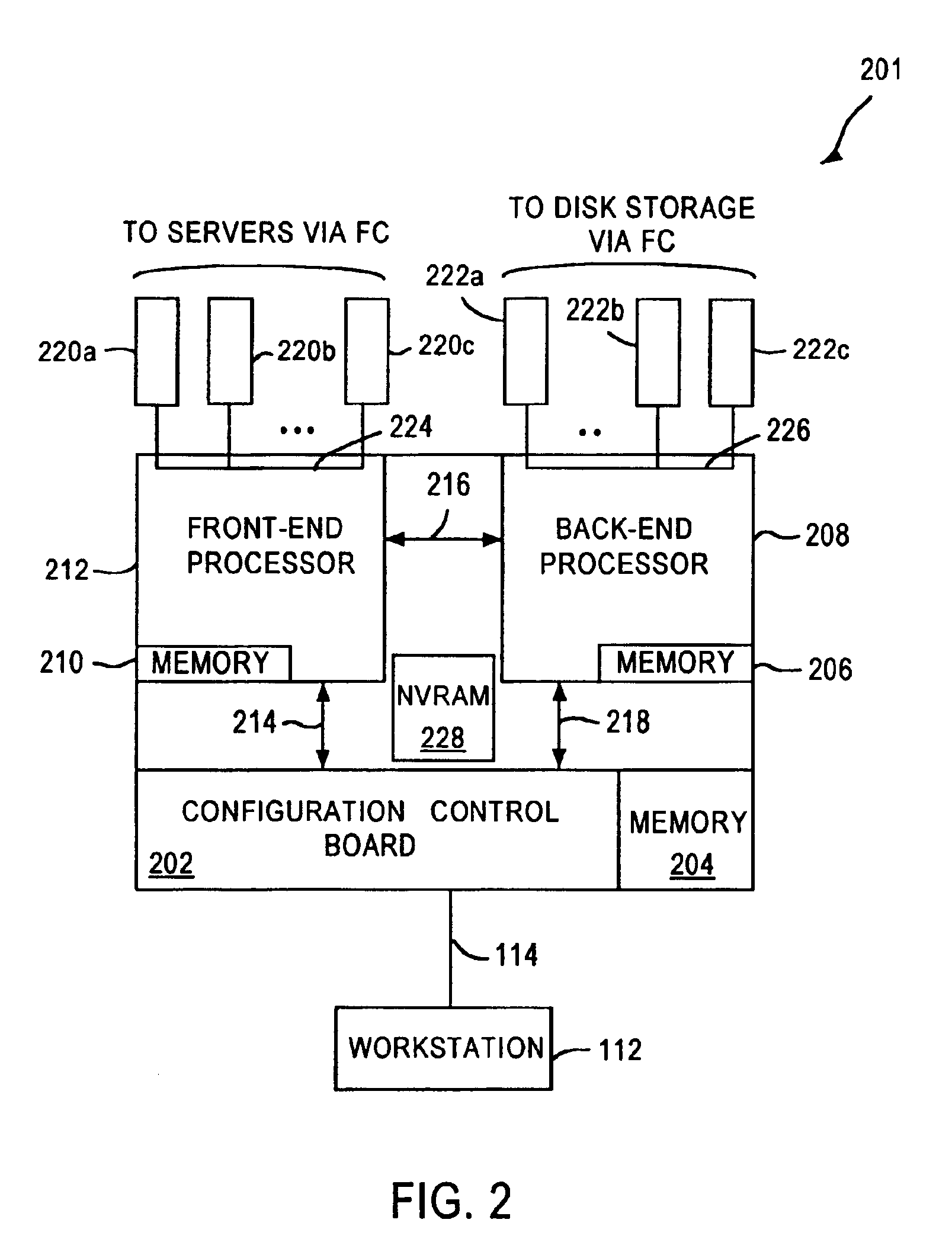
InactiveUS6567889B1Reduce in quantityImprove I/O performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersRAIDControl store
A portion of a storage controller's cache memory is used as a virtual solid state disk storage device to improve overall storage subsystem performance. In a first embodiment, the virtual solid state disk storage device is a single virtual disk drive for storing controller based information. In the first embodiment, the virtual solid state disk is reserved for use by the controller. In a second embodiment, a hybrid virtual LUN is configured as one or more virtual solid state disks in conjunction with one or more physical disks and managed using RAID levels 1-6. Since the hybrid virtual LUN is in the cache memory of the controller, data access times are reduced and throughput is increased by reduction of the RAID write penalty. The hybrid virtual LUN provides write performance that is typical of RAID 0. In a third embodiment, a high-speed virtual LUN is configured as a plurality of virtual solid state disks and managed as an entire virtual RAID LUN. Standard battery backup and redundant controller features of RAID controller technology ensure virtual solid state disk storage device non-volatility and redundancy in the event of controller failures.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
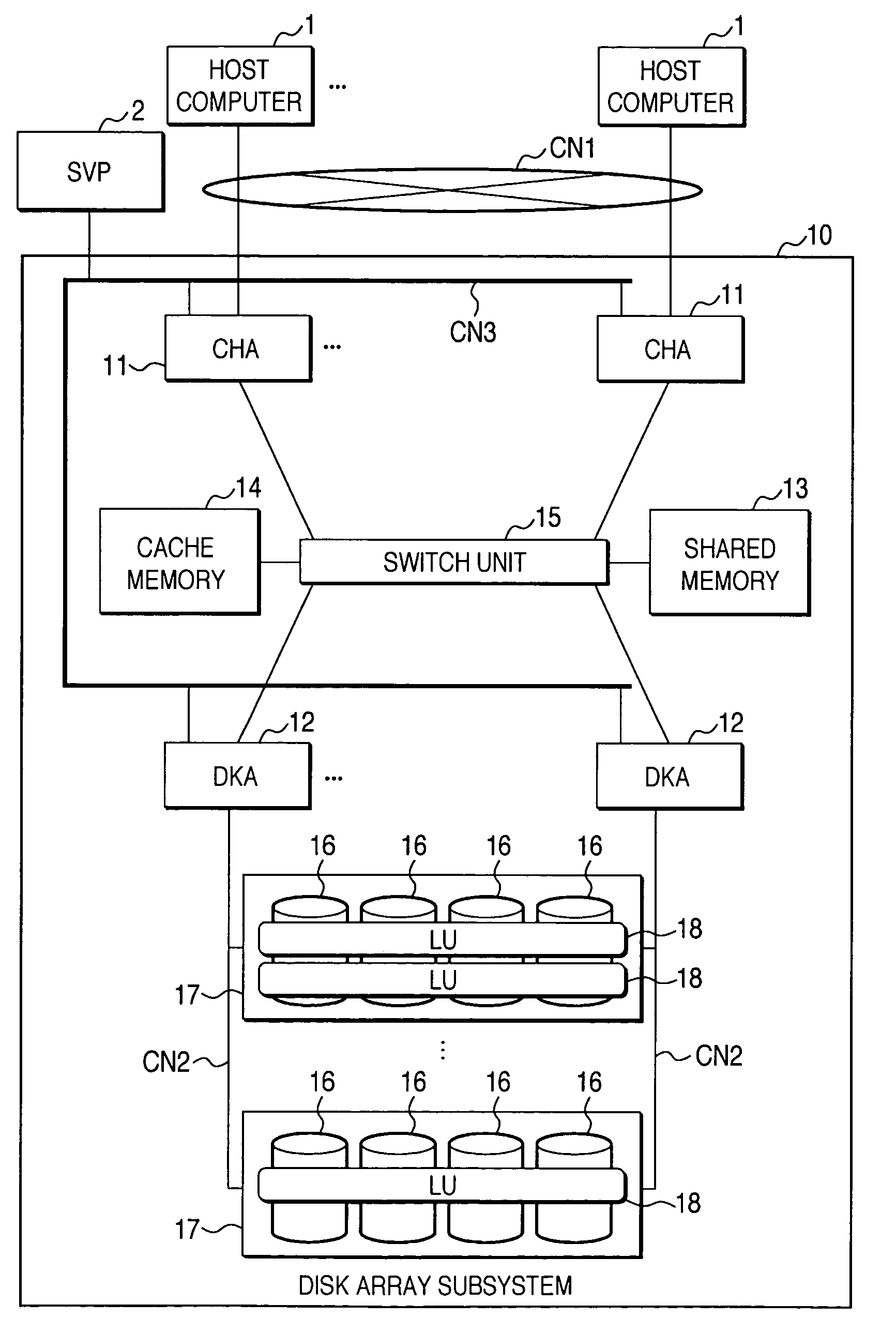
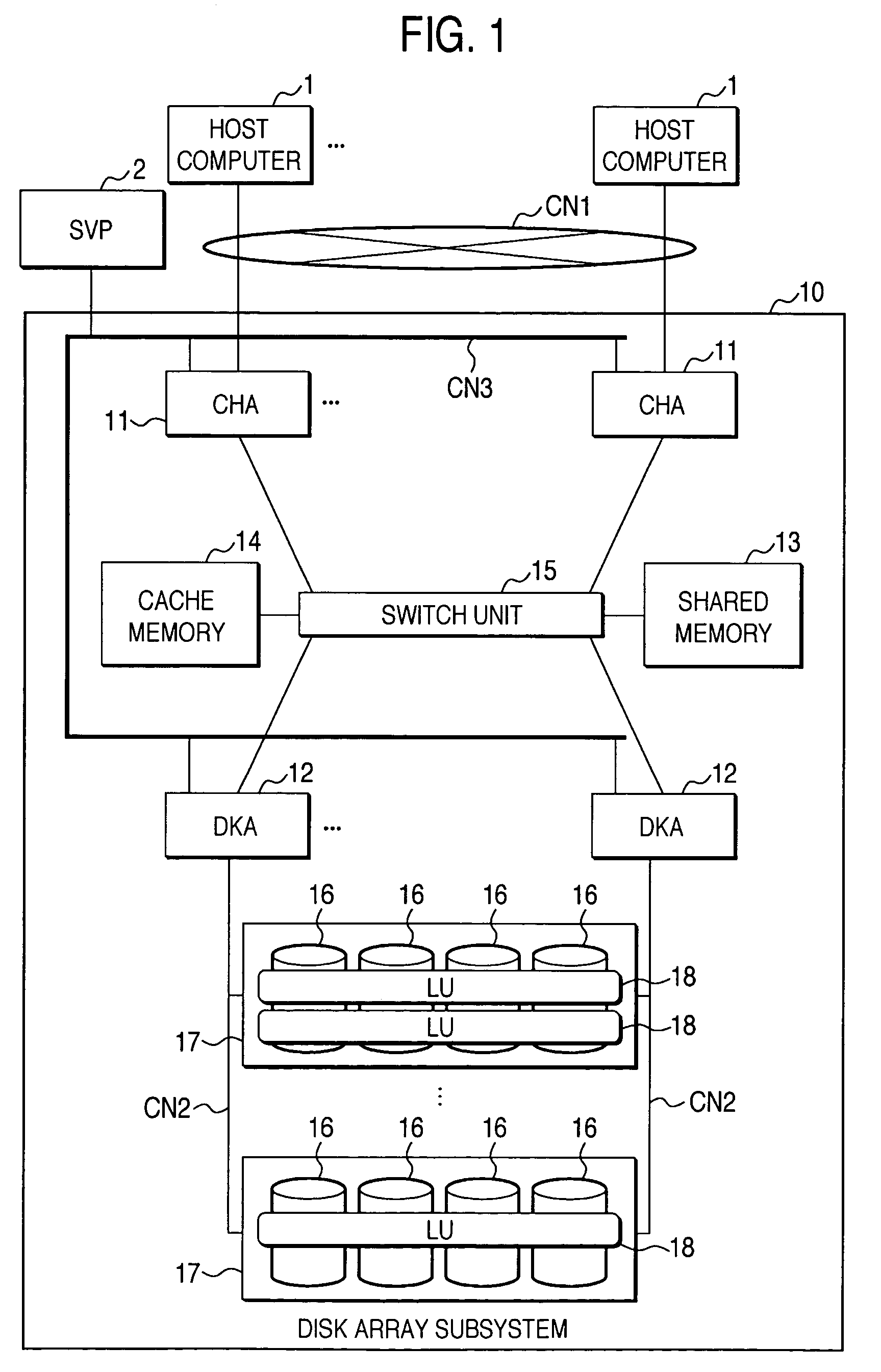
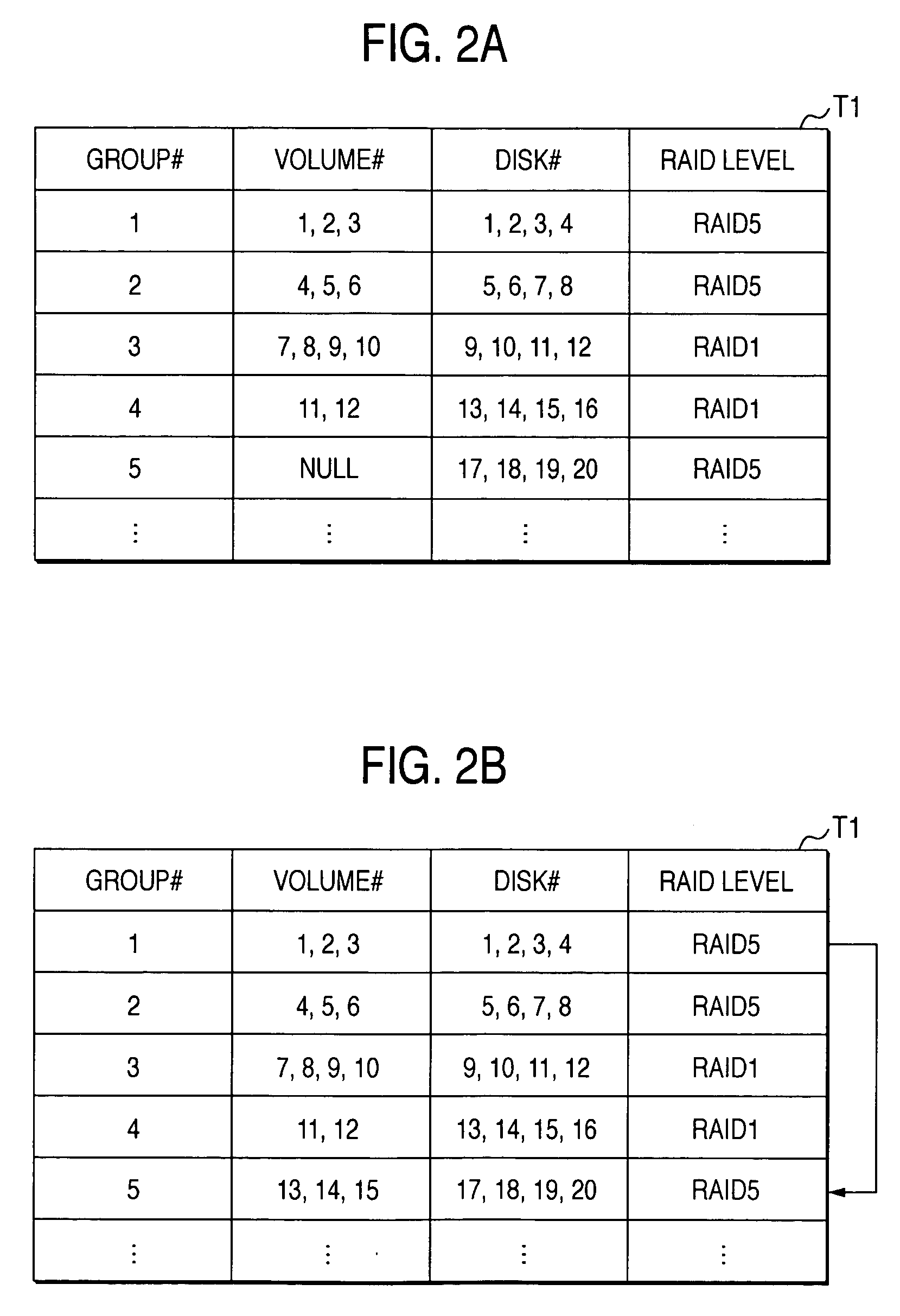
Disk array system and a method of avoiding failure of the disk array system
ActiveUS7028216B2Avoid failureReduce the likelihood of occurrenceInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionRAIDDisk array
The invention is intended to reduce disk access during data transfer from a disk in which occurrence of failure is anticipated to a spare disk as much as possible so that occurrence of double-failure is prevented in advance. When occurrence of failure in a disk which configures a RAID group, contents stored in the disk is copied to the spared disk. Simultaneously, another RAID group is paired with the above described RAID group and a secondary volume is provided therein. A write request is directed to the secondary volume. A differential bitmap controls a update data. Data which is not updated is read out from the primary volume, and data which is already updated is read from the secondary volume. When data transfer is completed, contents stored in the secondary volume are copied to the primary volume.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
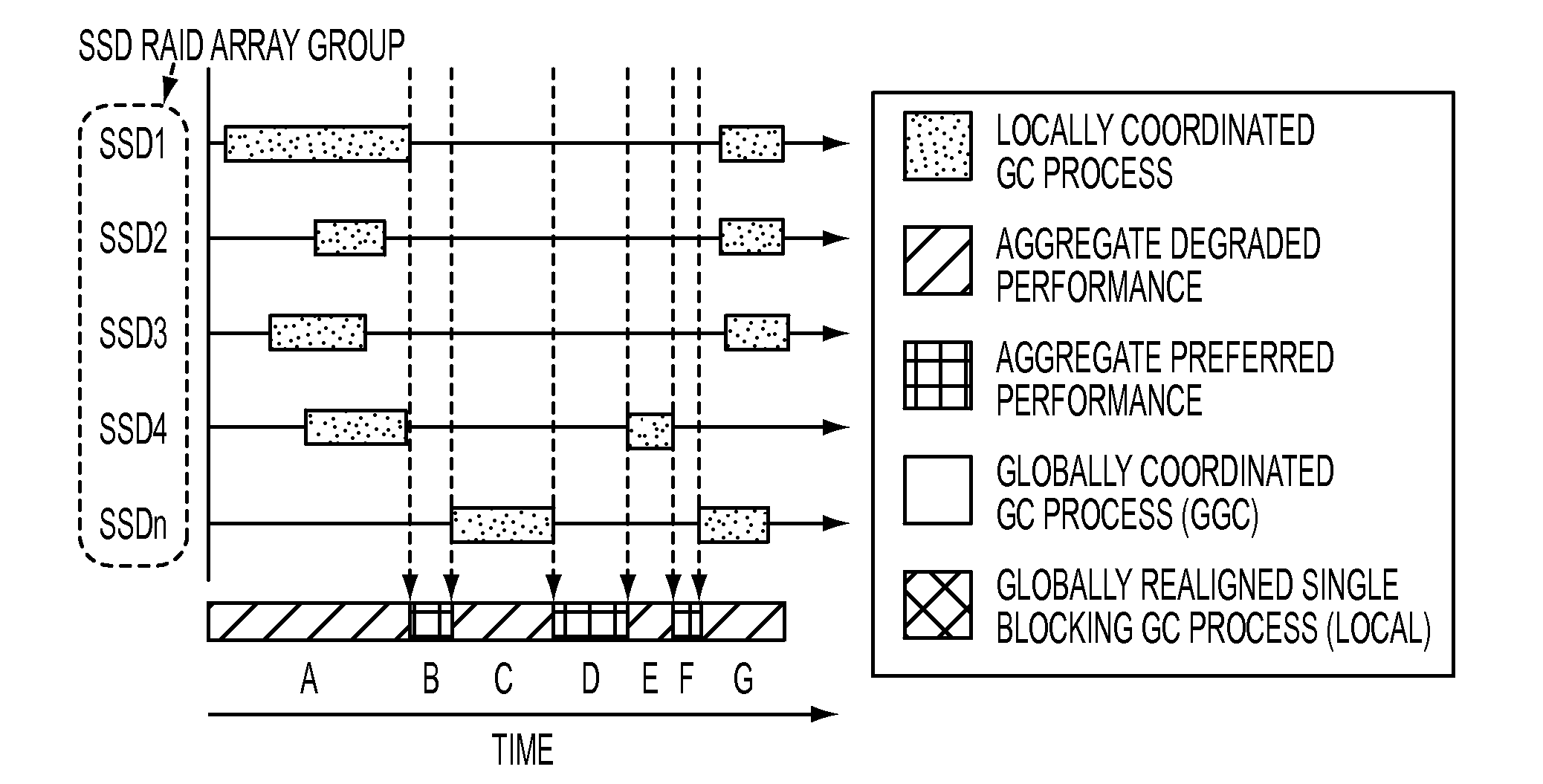
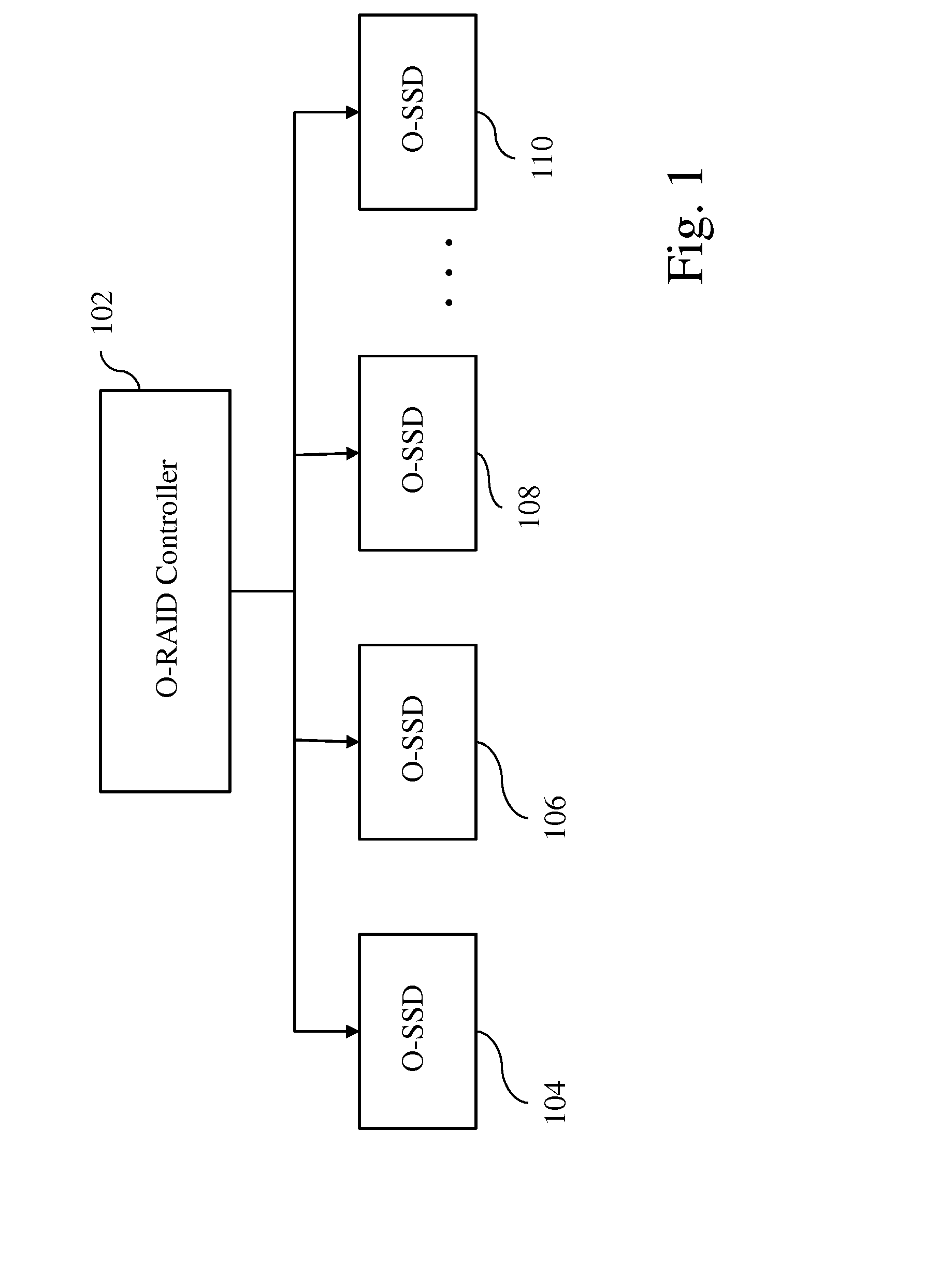
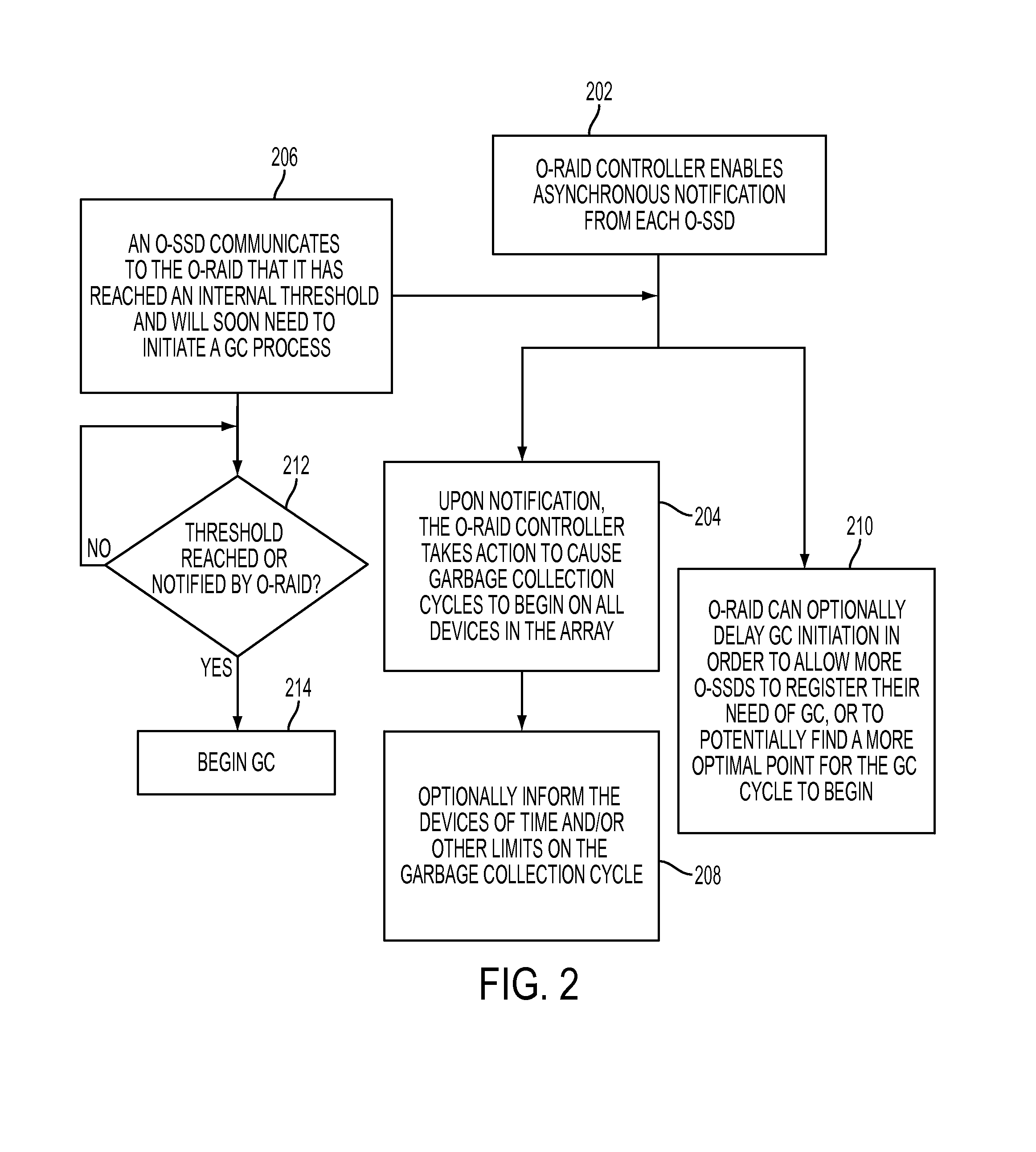
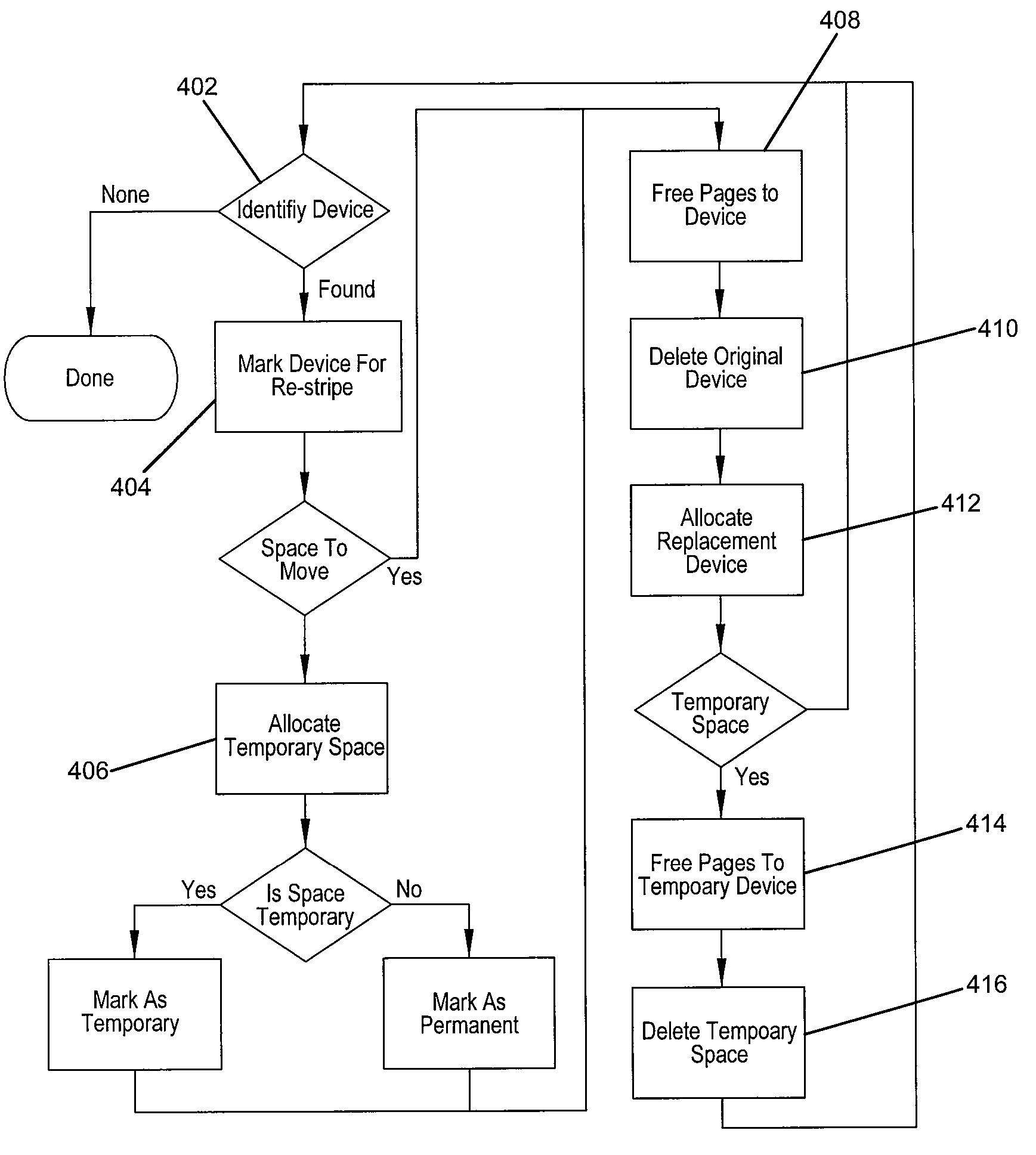
Coordinated garbage collection for raid array of solid state disks
ActiveUS20120036309A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDWaste collection
An optimized redundant array of solid state devices may include an array of one or more optimized solid-state devices and a controller coupled to the solid-state devices for managing the solid-state devices. The controller may be configured to globally coordinate the garbage collection activities of each of said optimized solid-state devices, for instance, to minimize the degraded performance time and increase the optimal performance time of the entire array of devices.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
System and method for raid management, reallocation, and restriping
Owner:DELL INT L L C
Storage system using flash memory modules logically grouped for wear-leveling and RAID
A storage system using flash memories includes a storage controller and plural flash memory modules as storage media. Each flash memory module includes at least one flash memory chip and a memory controller for leveling erase counts of blocks belonging to the flash memory chip. The storage controller combines the plural flash memory modules into a first logical group, translates a first address used for accessing the flash memory modules belonging to the first logical group to a second address used for handling the first address in the storage controller, and combines the plural first logical groups into a second logical group.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
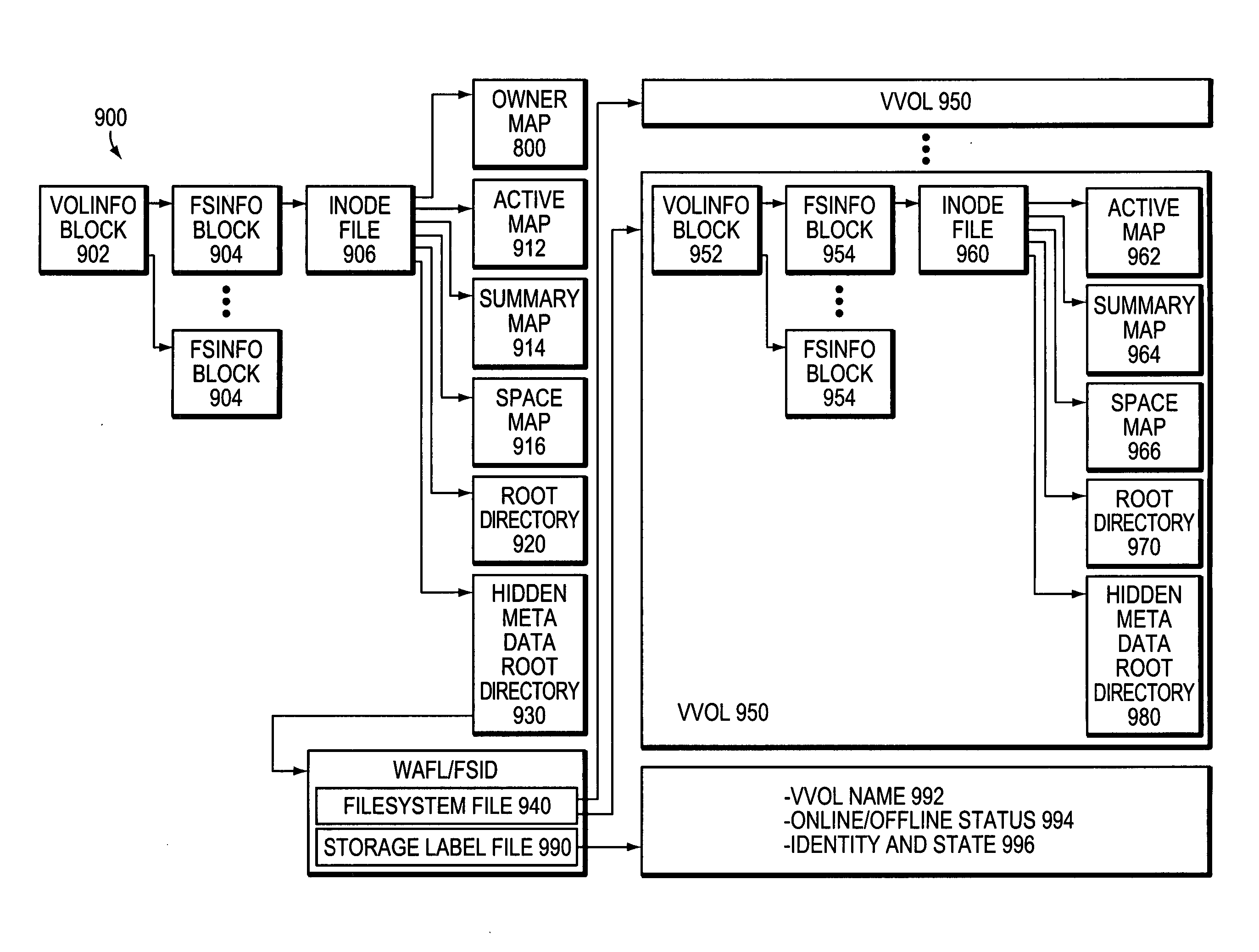
Extension of write anywhere file system layout
ActiveUS20050246401A1Avoid partialFlexible sizeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsRAIDFile system
A file system layout apportions an underlying physical volume into one or more virtual volumes (vvols) of a storage system. The underlying physical volume is an aggregate comprising one or more groups of disks, such as RAID groups, of the storage system. The aggregate has its own physical volume block number (pvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that pvbn space. Each vvol has its own virtual volume block number (vvbn) space and maintains metadata, such as block allocation structures, within that vvbn space. Notably, the block allocation structures of a vvol are sized to the vvol, and not to the underlying aggregate, to thereby allow operations that manage data served by the storage system (e.g., snapshot operations) to efficiently work over the vvols. The file system layout extends the file system layout of a conventional write anywhere file layout system implementation, yet maintains performance properties of the conventional implementation.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
User configurable raid system with multiple data bus segments and removable electrical bridges
InactiveUS6076142ACarrier constructional parts dispositionError detection/correctionMass storageModem device
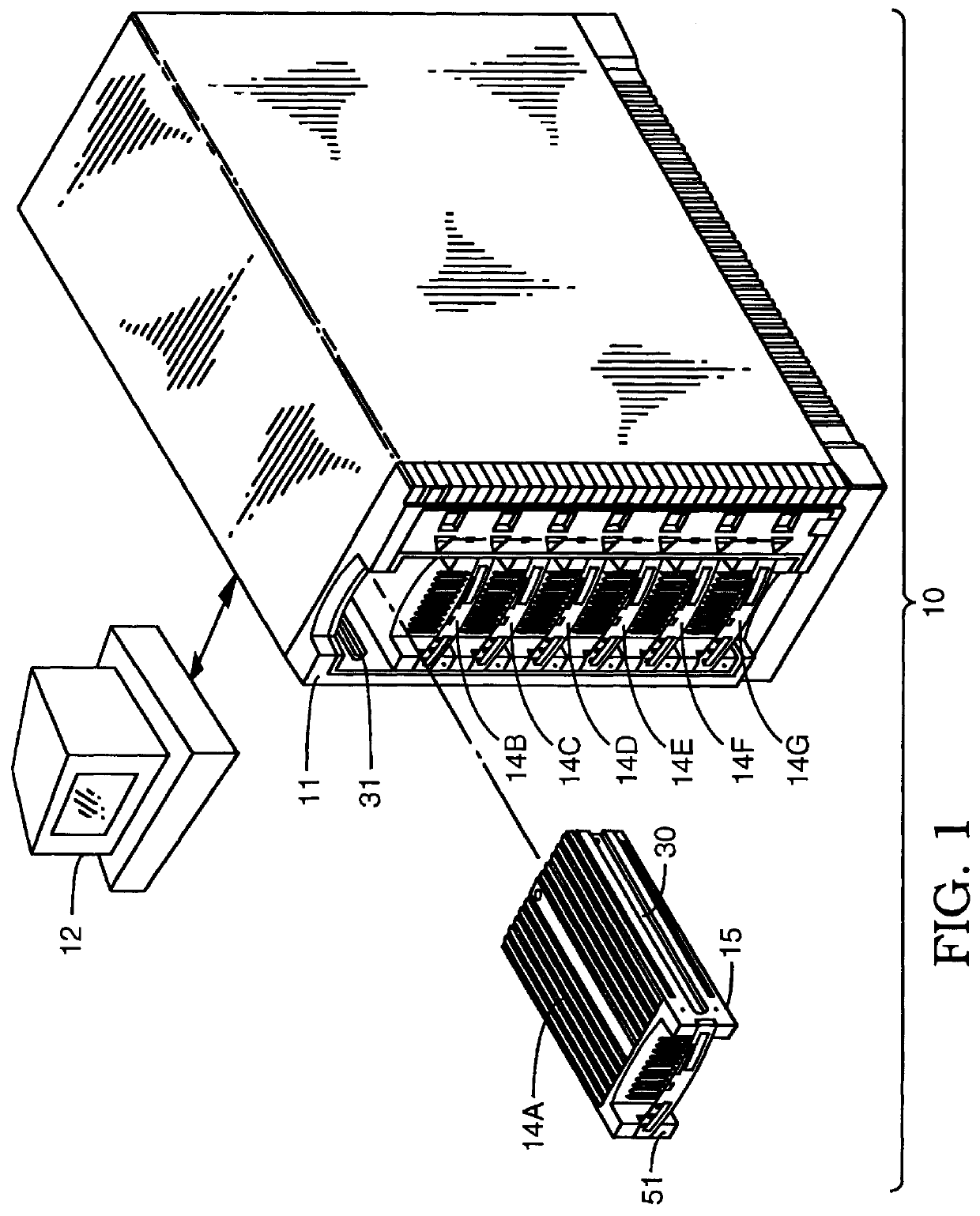
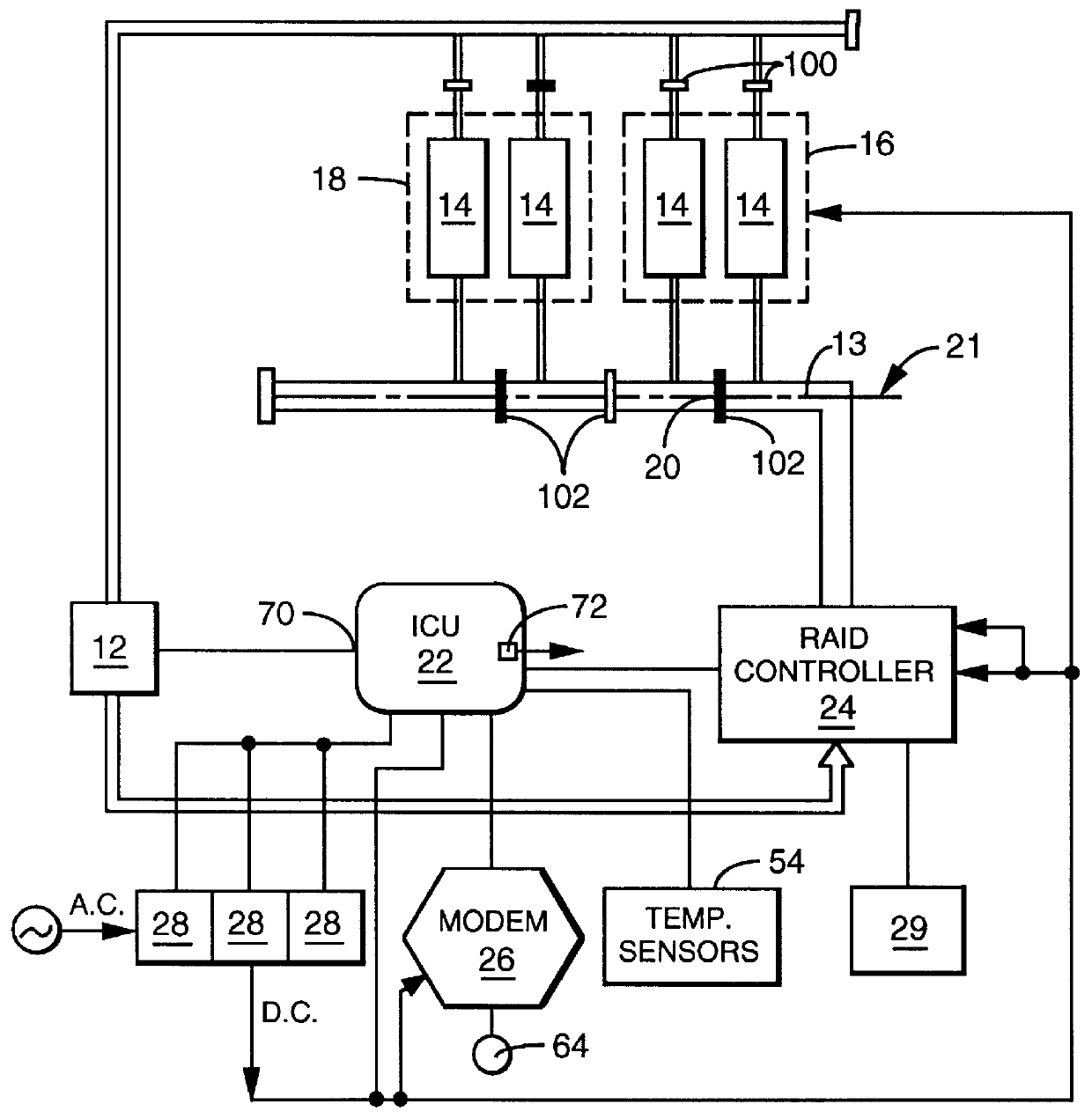
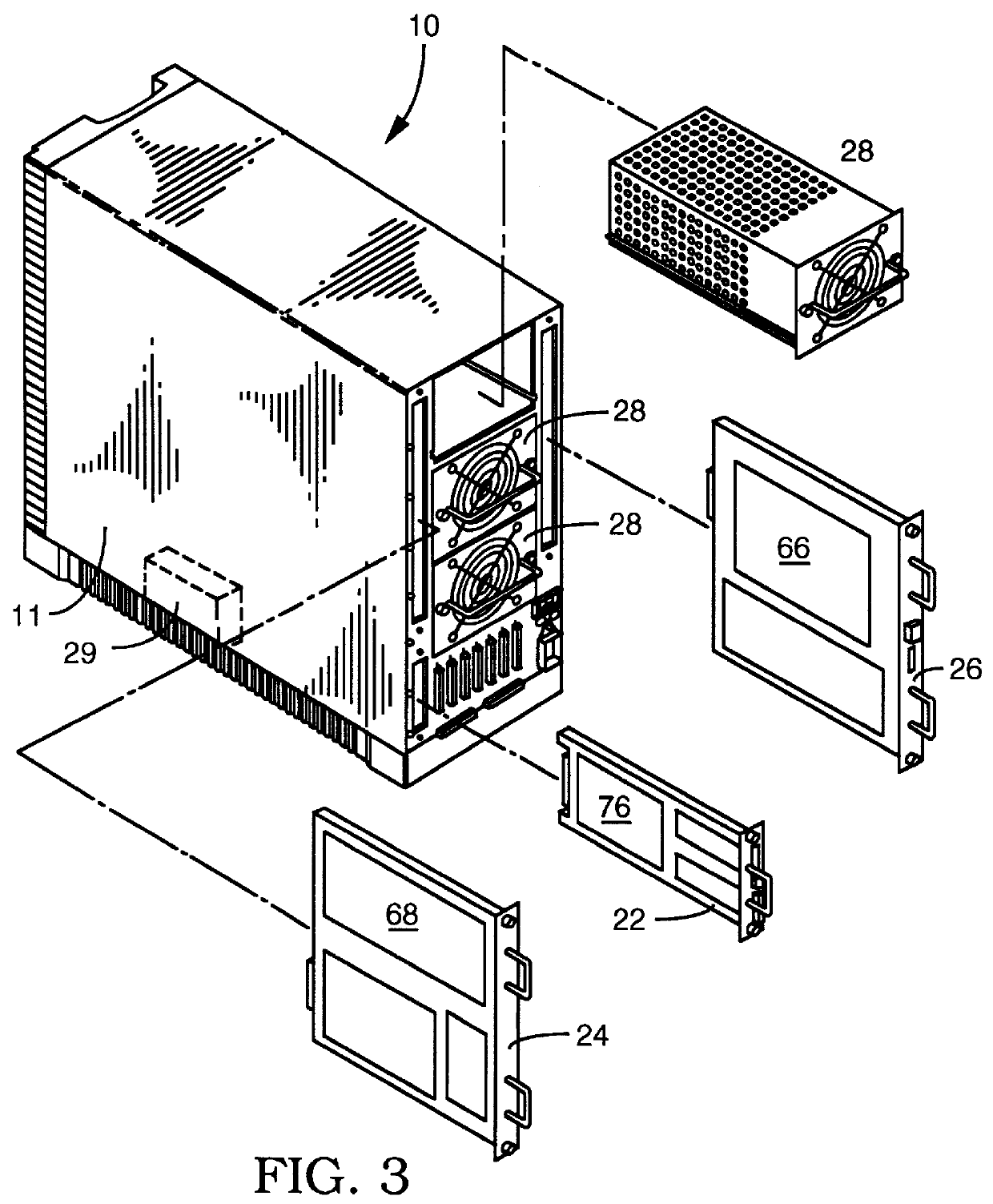
A user configurable RAID system designed to provide RAID functions as well as mass storage functions in a non-RAID mode. Flexibility is built into the system to allow the user to configure the SCSI bus to which removable drive modules are connected into one or more channels to define some of the drive modules in a RAID set and others as stand-alone drives which are independently operated or logically grouped and operated in a non-RAID mode. Removable internal SCSI bridges allow the SCSI bus to be configured into one or more channels. In the RAID mode, the system is configured to prevent a wrong drive from being removed from the system in the event of a drive failure. The system automatically unlatches only the failed drive. The RAID system includes an intelligent control unit ("ICU"), a RAID controller and a modem. The ICU allows the system administrator to access the RAID system Monitor Utility so that the status of the system may be monitored and its configuration changed. The ICU also monitors the failure status of the various components of the system. The ICU has a built-in pager feature that can be configured with the Monitor Utility to page the system administrator via the modem when a component or system failure is encountered. The RAID controller controls the functions of the RAID set as programmed and configured using the Monitor Utility. The Monitor Utility may be remotely accessed using a computer via the modem. Redundant removable power supply and fan units are provided to improve system integrity. The removable power supply and fan units are configured such when the unit is plugged into the system housing, the fan is first turned on and the power through the unit is allowed to stabilize before turning on the power supply to begin providing DC power to the components in the system. A set of manual release buttons are provided for manually unlatching the drive modules from the system housing. A locking mechanism is provided for simultaneously locking all the manual release buttons.
Owner:MICRONET TECH
RAID memory system
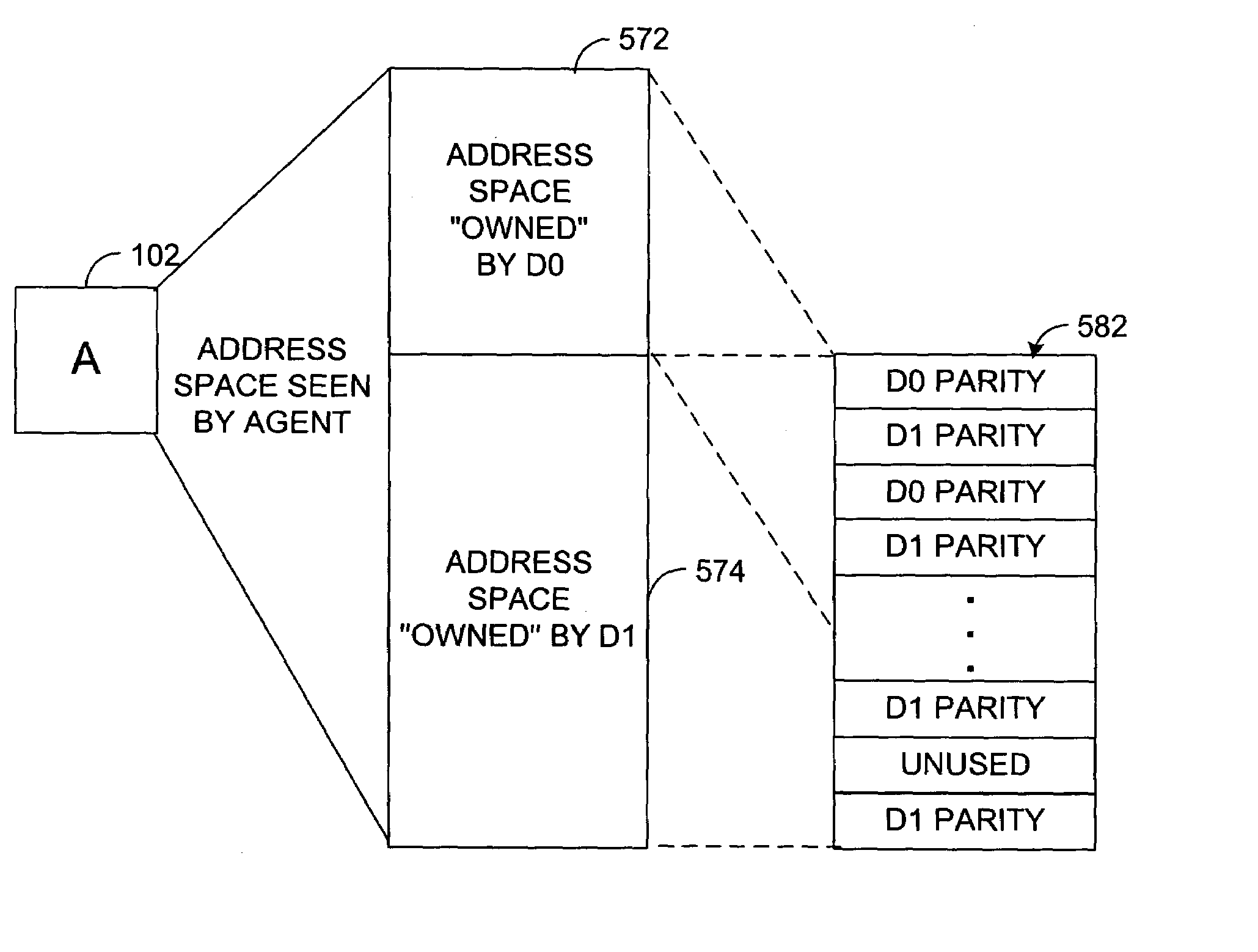
Embodiments of the present invention are broadly directed to a memory system. In one embodiment, a first data memory is coupled to a first memory controller and a second data memory is coupled to a second memory controller. A parity memory is coupled to a parity controller, the parity controller being directly coupled to both the first memory controller and the second memory controller. Parity data control logic is configured to store and retrieve parity information associated with data stored in both the first data memory and the second data memory, the parity data control logic configured to interleave within the parity memory parity data associated with data stored in the first data memory with parity data associated with data stored in the second data memory.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com