Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Utility and advantage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
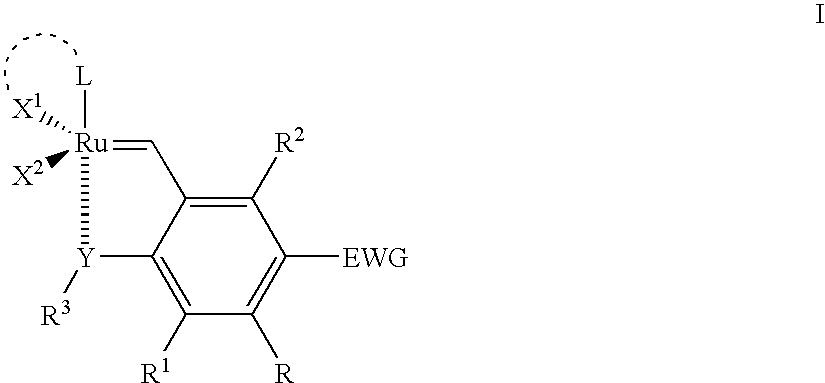
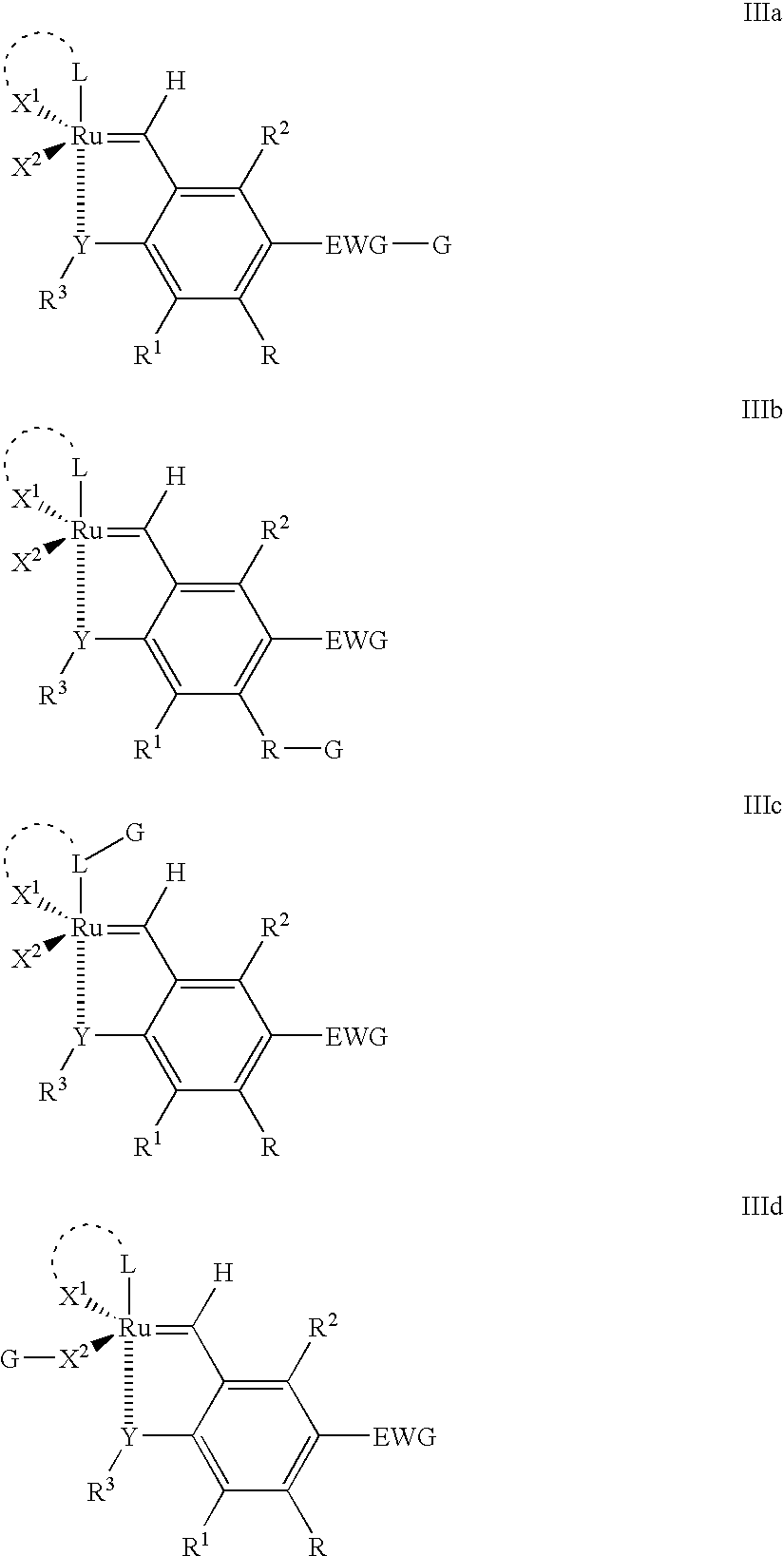
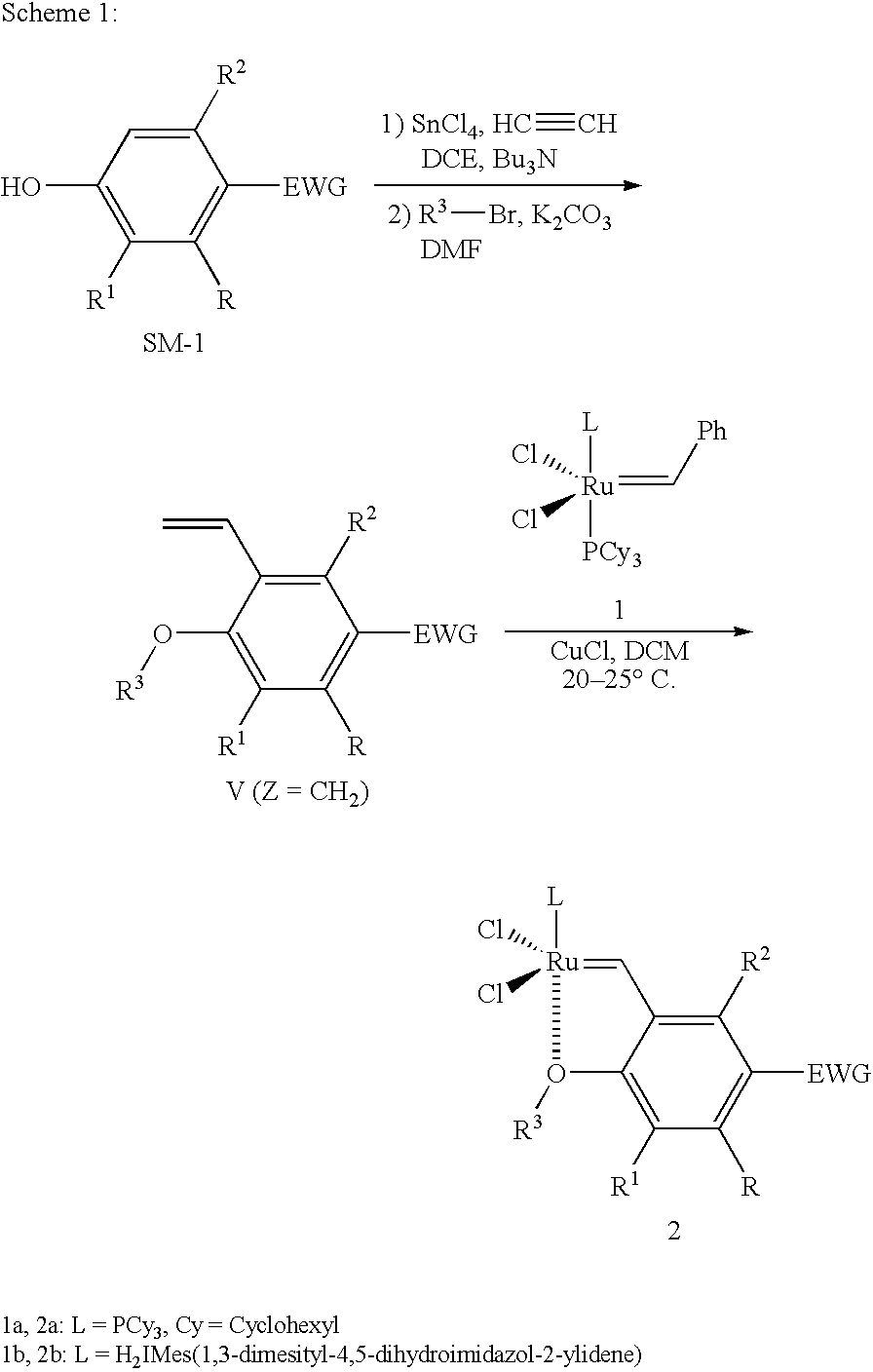
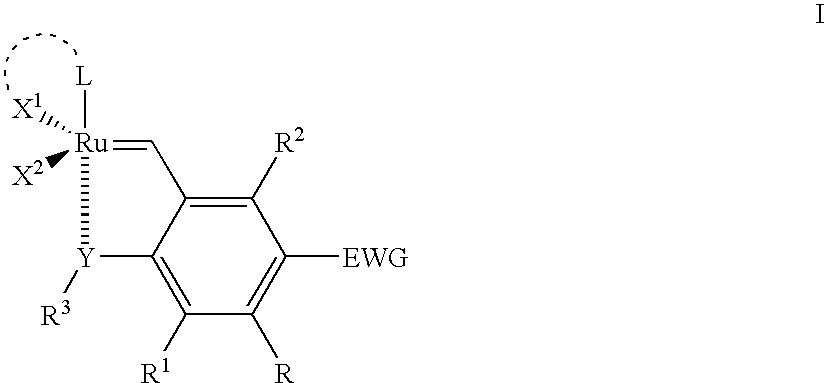
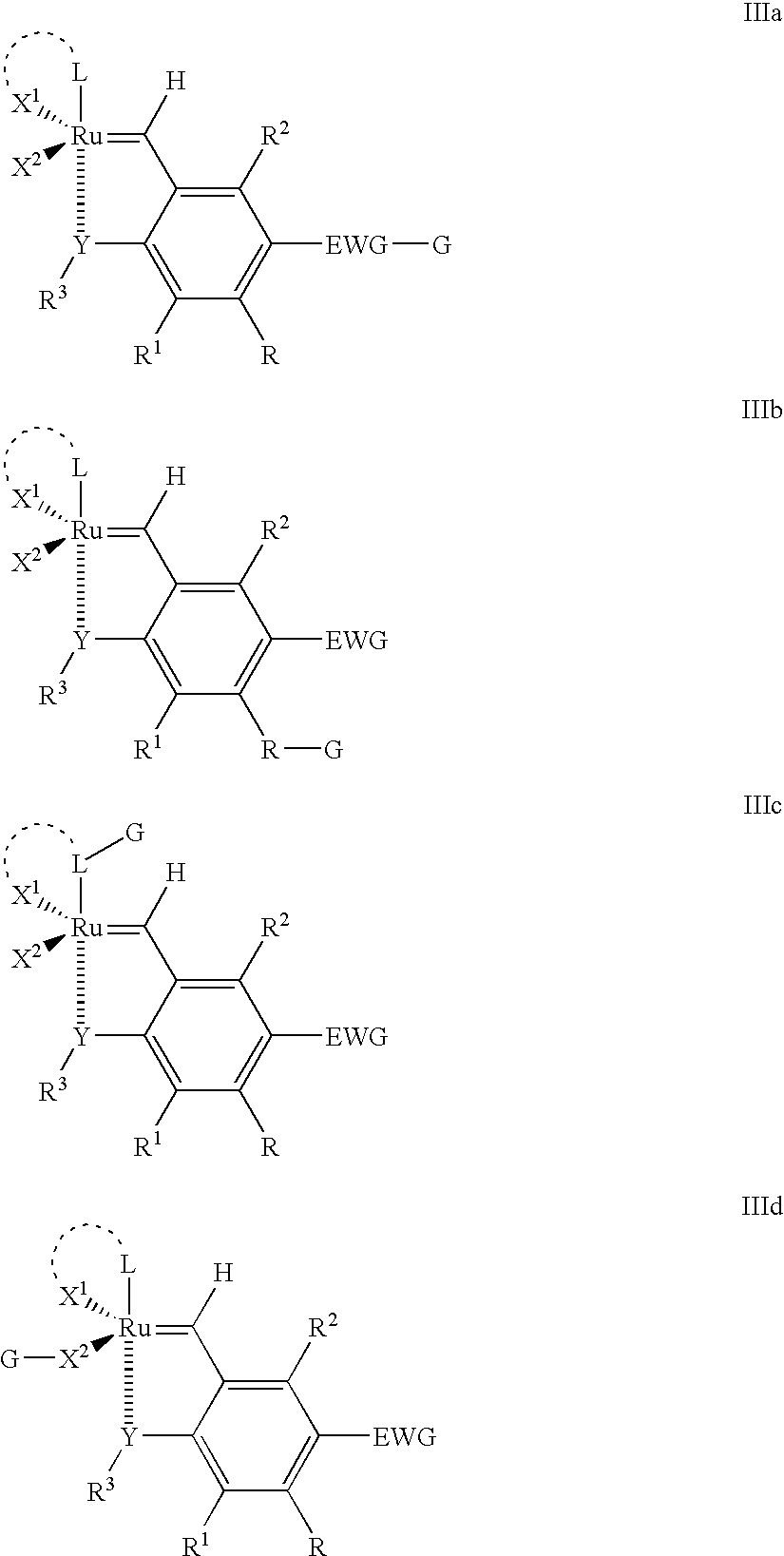
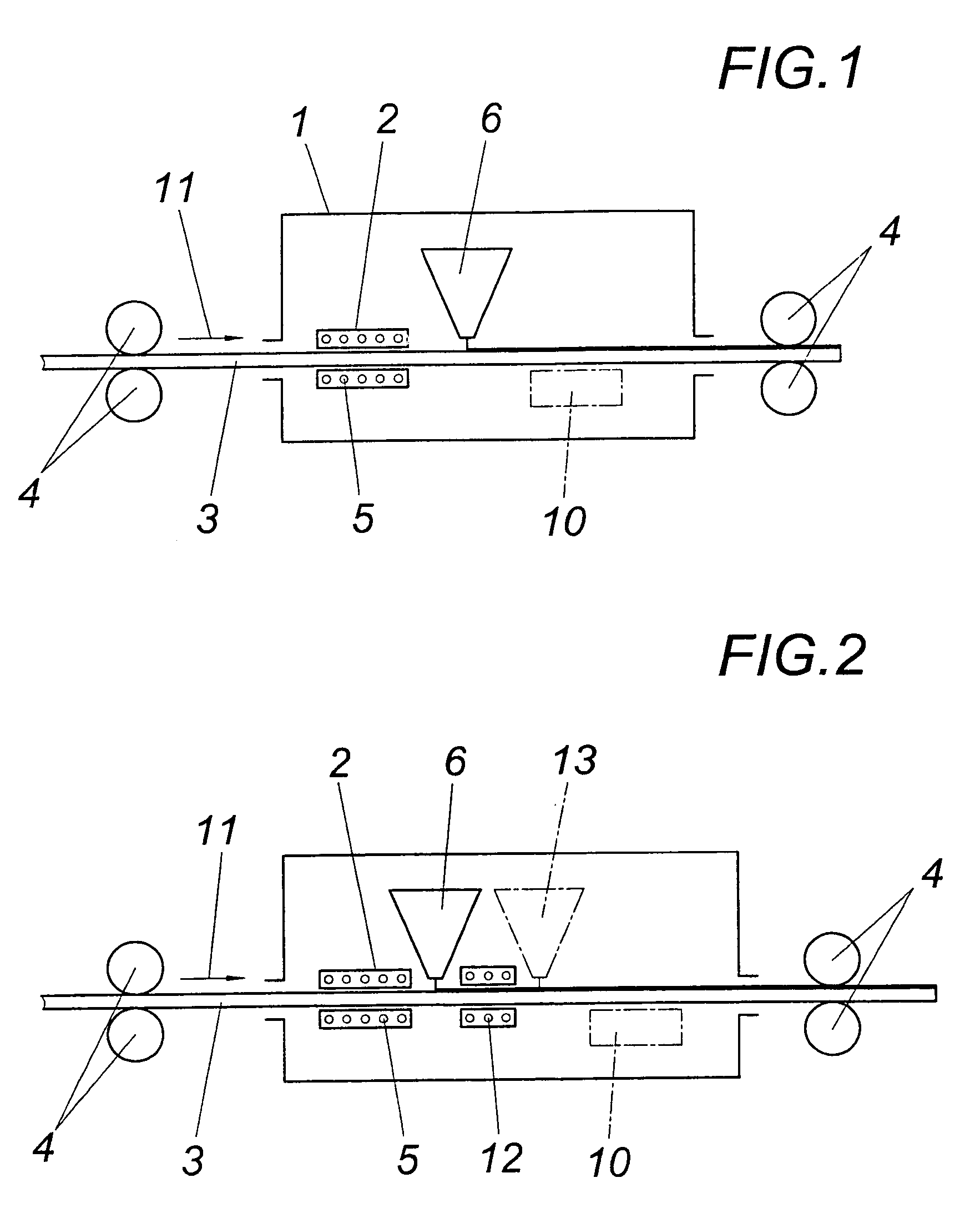
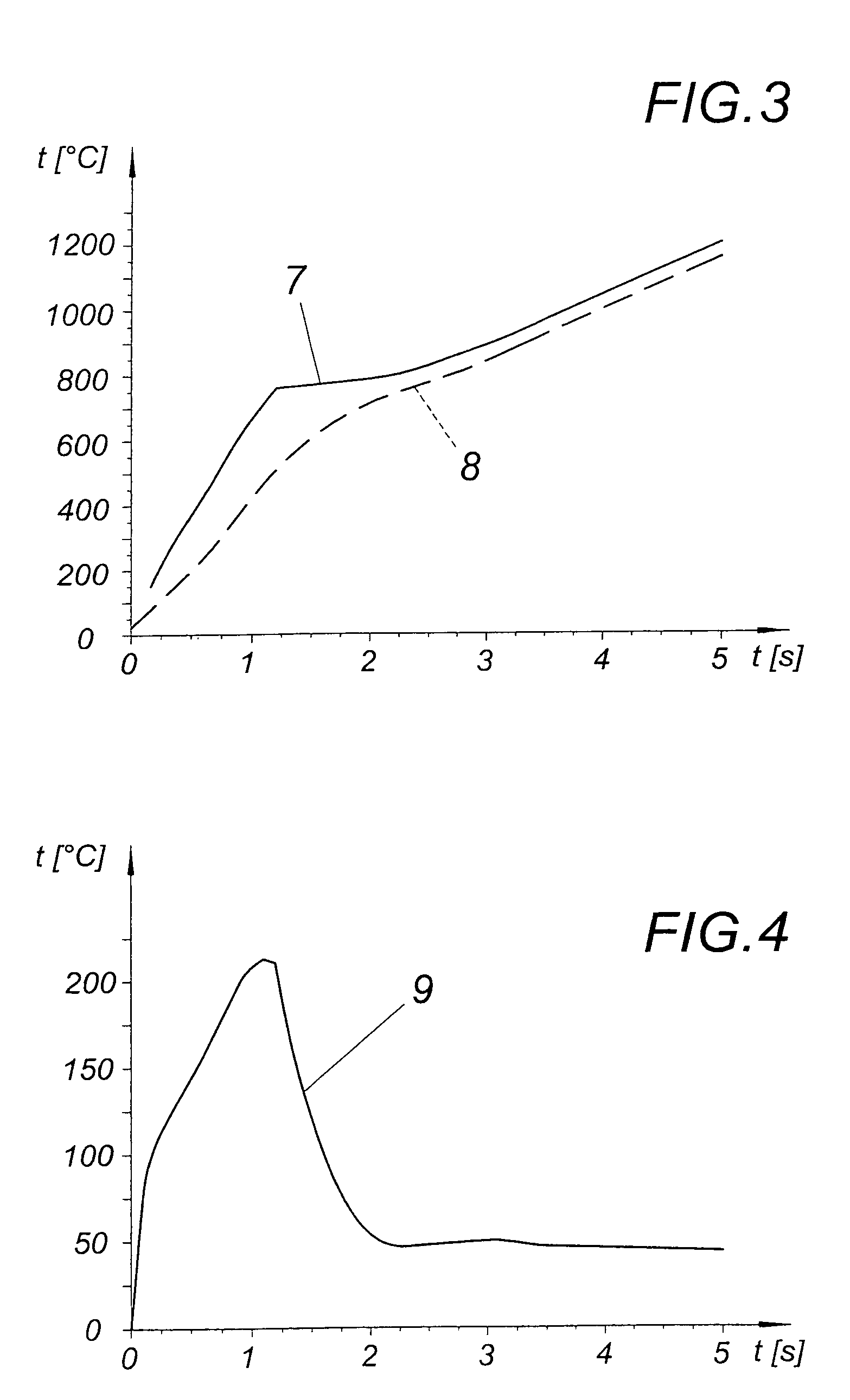
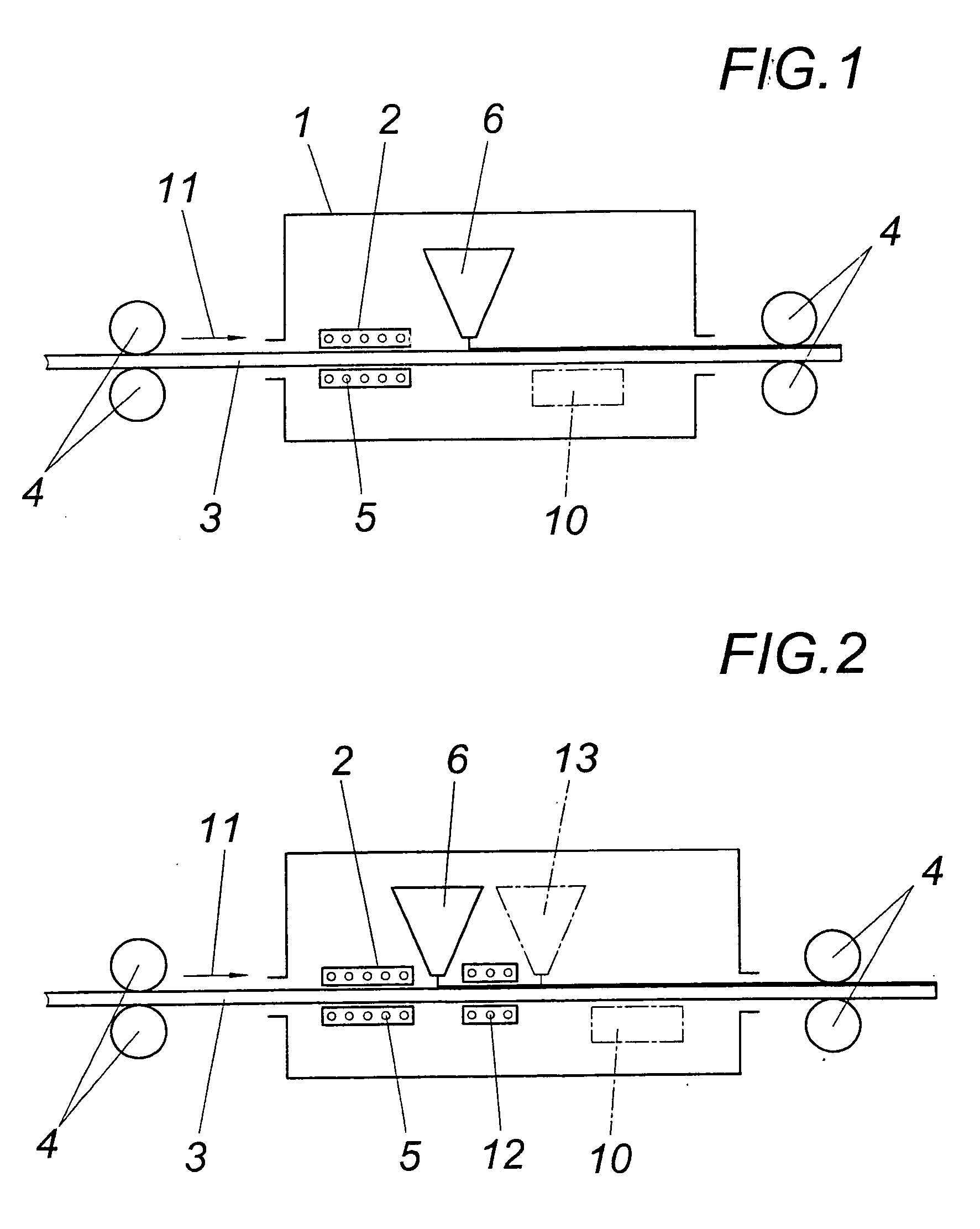
Recyclable ruthenium catalysts for metathesis reactions
ActiveUS20070043180A1Utility and advantageWide applicationRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationAlkeneEfficient catalyst
The invention relates to novel carbene ligands and their incorporated monomeric and resin / polymer linked ruthenium catalysts, which are recyclable and highly active for olefin metathesis reactions. It is disclosed that significant electronic effect of different substituted 2-alkoxybenzylidene ligands on the catalytic activity and stability of corresponding carbene ruthenium complexes, some of novel ruthenium complexes in the invention can be broadly used as catalysts highly efficient for olefin metathesis reactions, particularly in ring-closing (RCM), ring-opening (ROM), ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) and cross metathesis (CM) in high yield. The invention also relates to preparation of new ruthenium complexes and the use in metathesis.
Owner:ZANNAN SCITECH
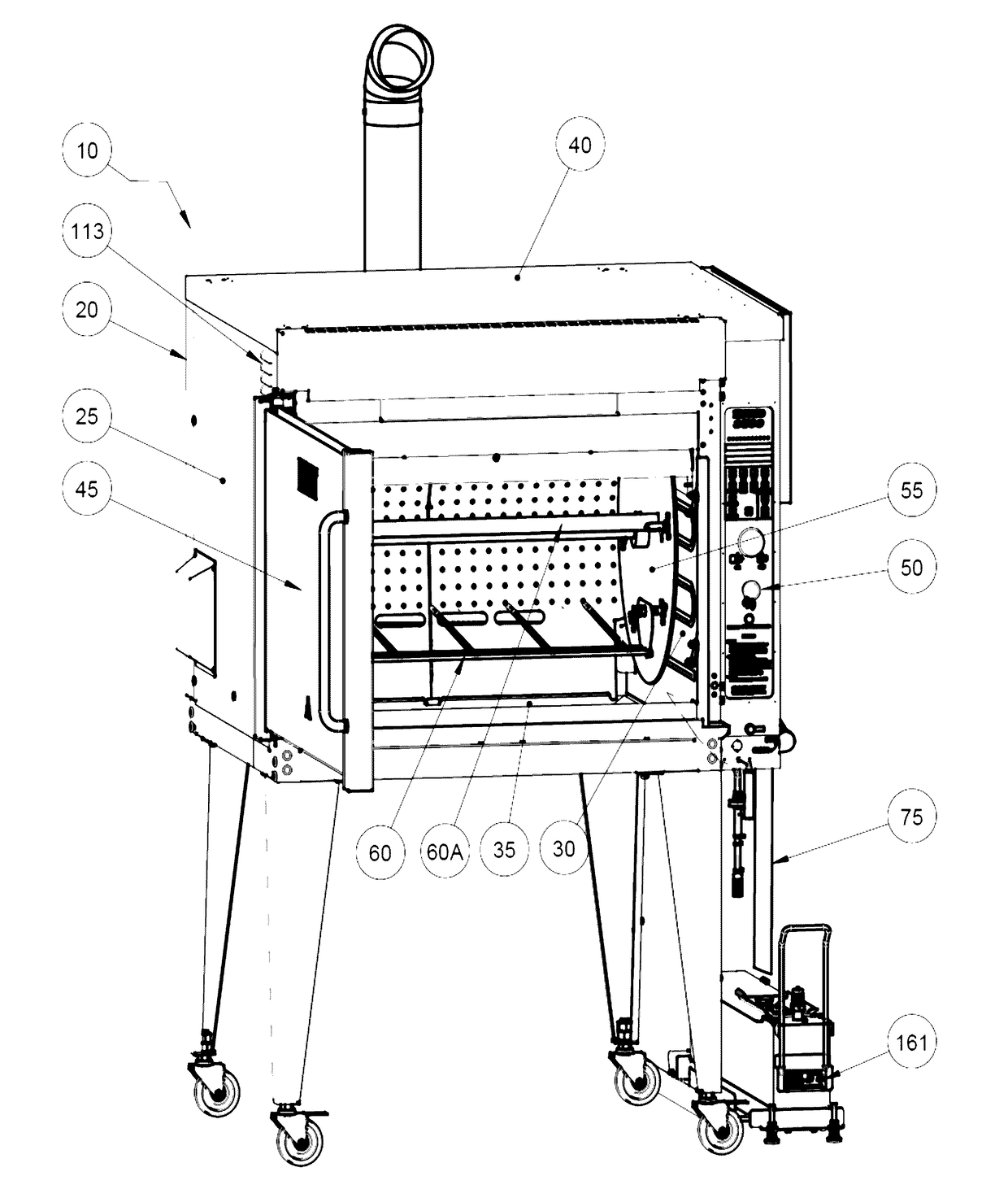
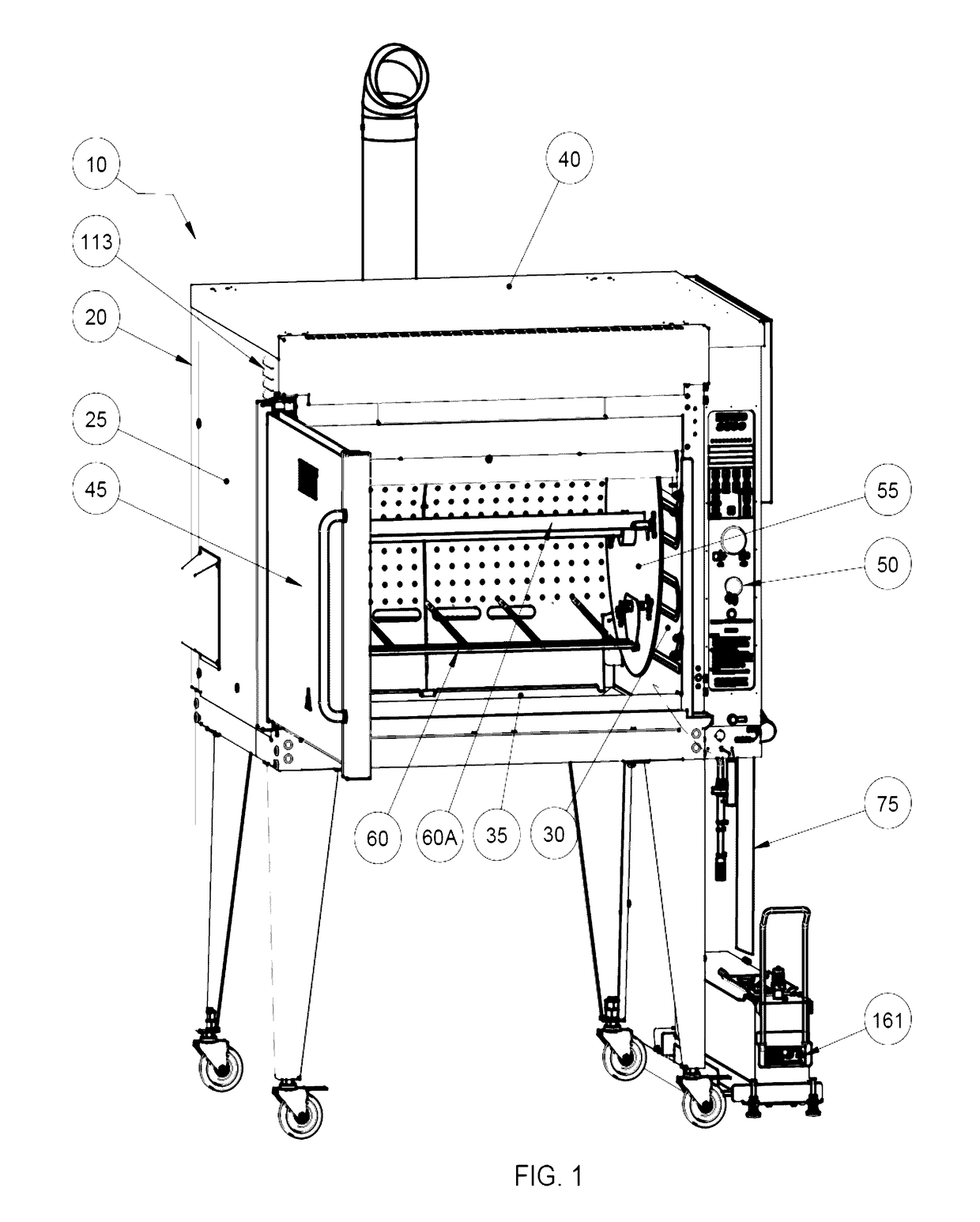
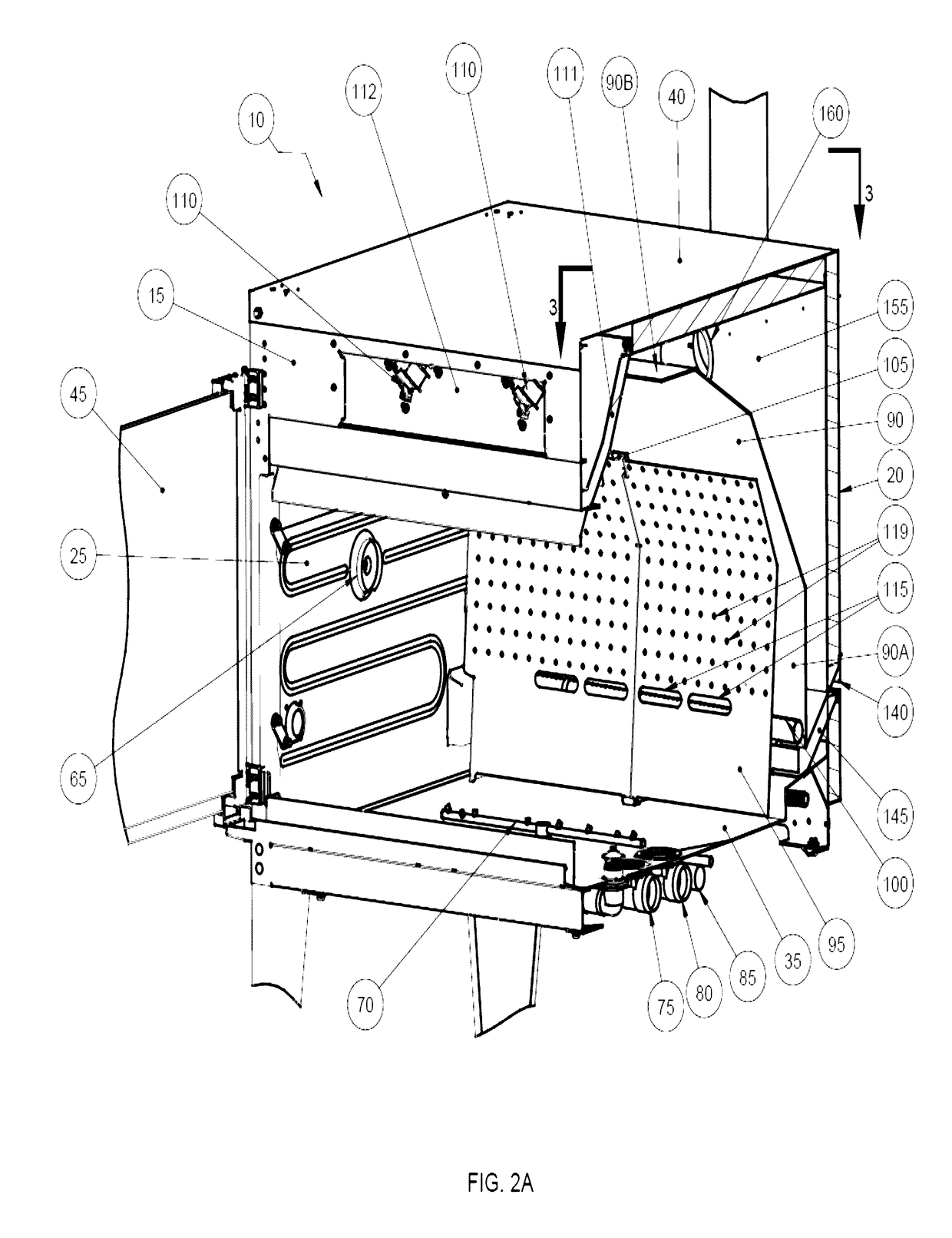
Atmospheric rotisserie burner with convection heating
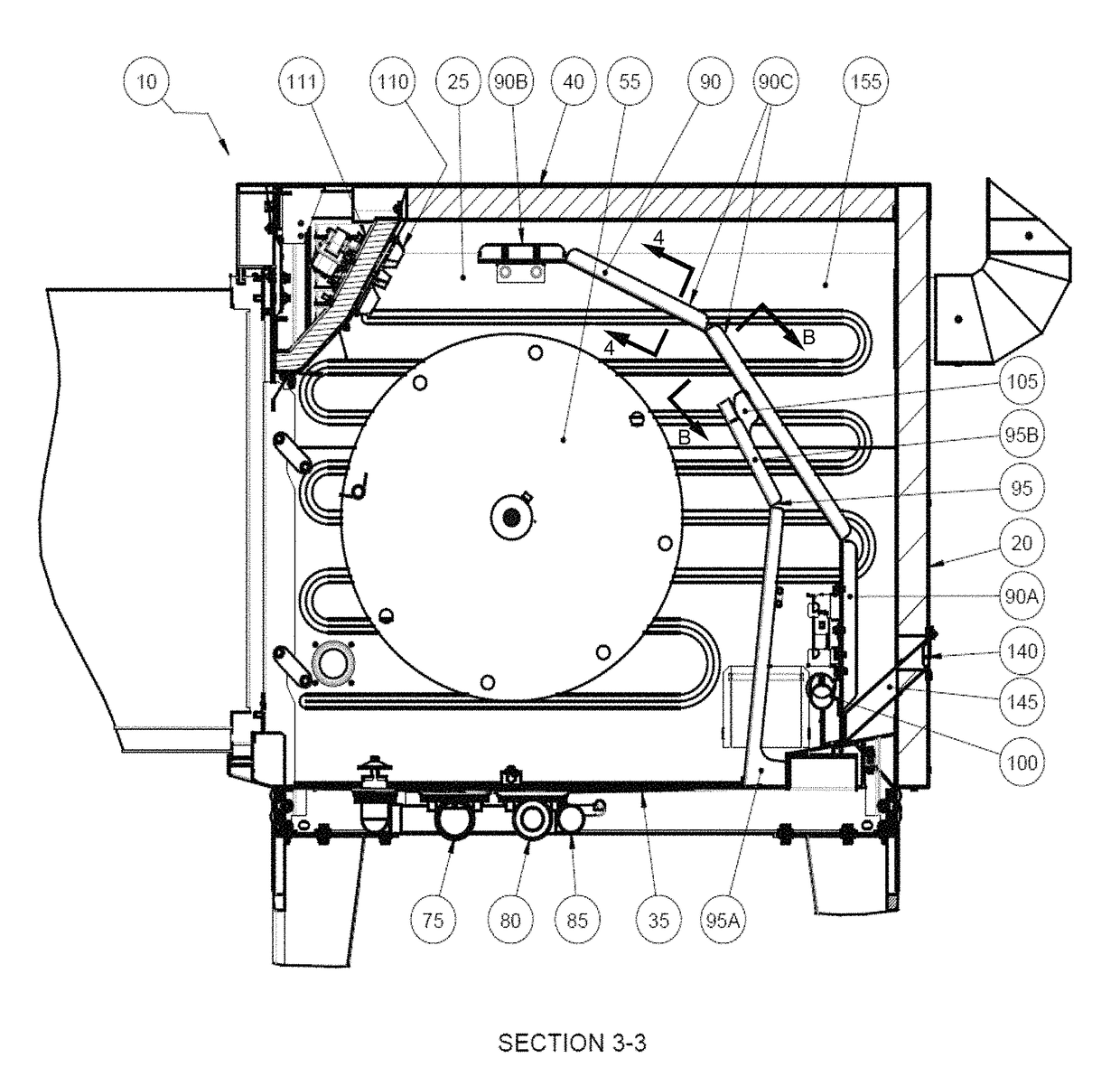
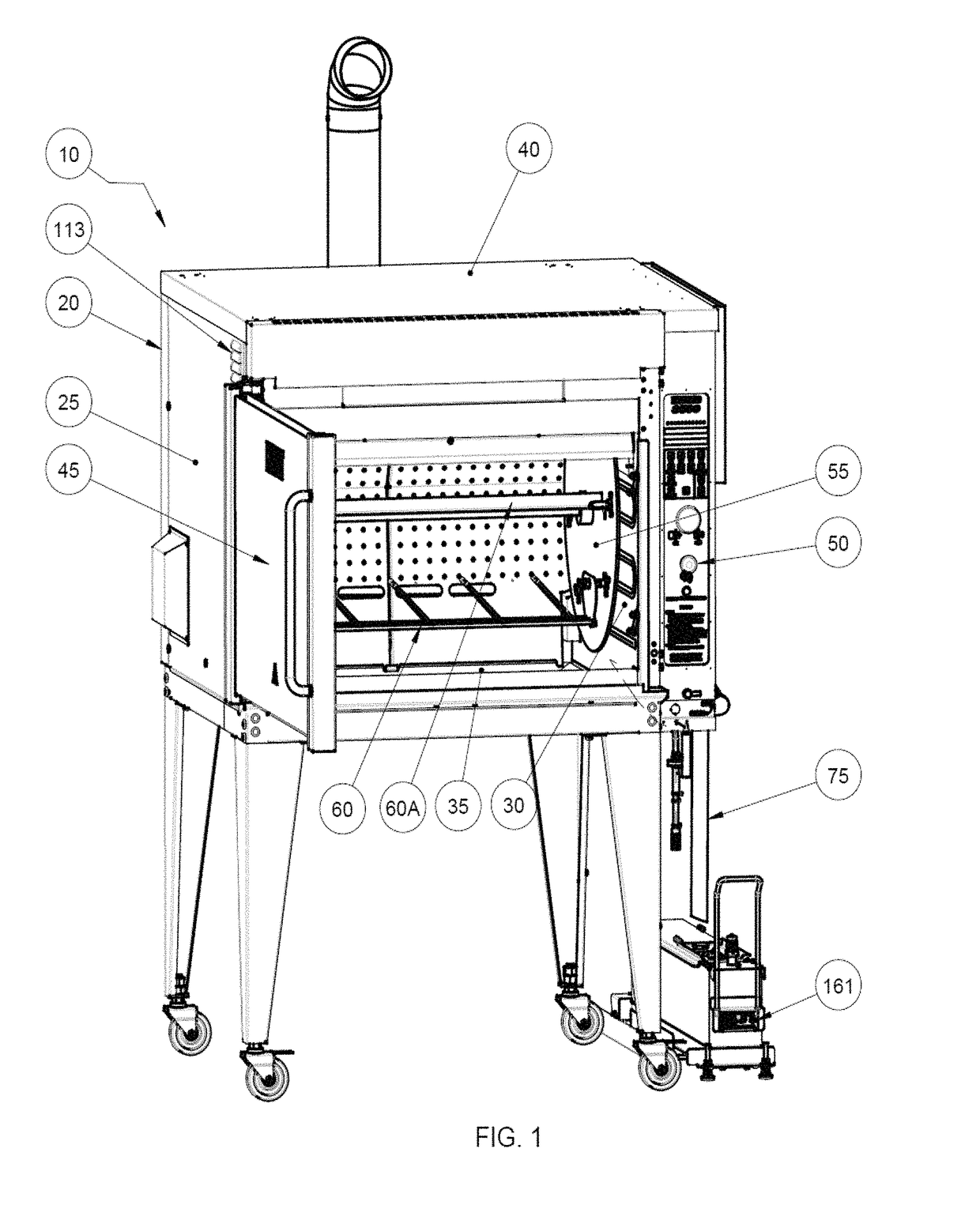
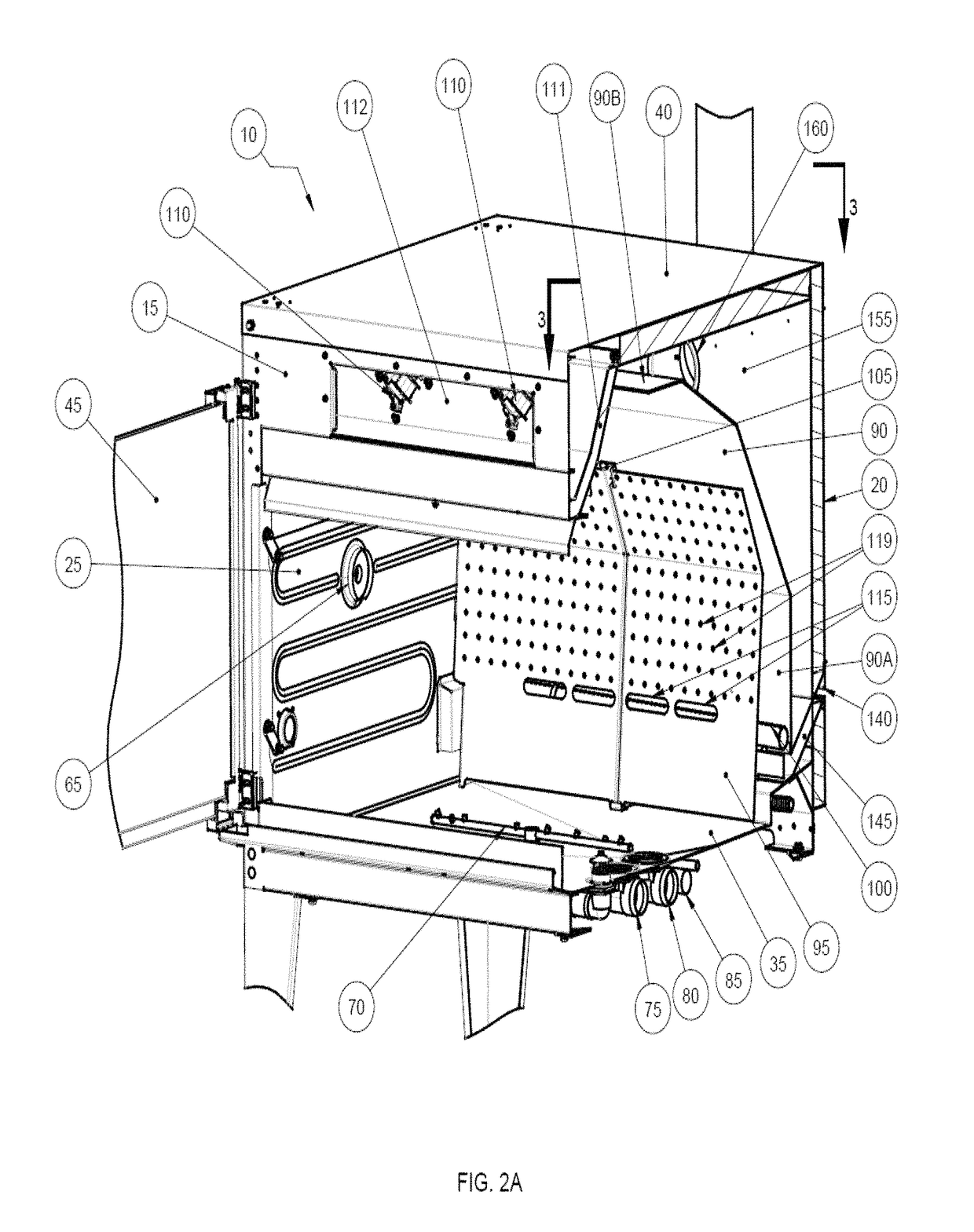
ActiveUS20170079475A1Avoiding flame-out situationUniform temperatureRoasting apparatusFood preparationAir movementEngineering
The present invention provides a device for cooking food that has a cooking cavity defined by a front wall, a back wall that opposes the front wall, two opposing side walls, a ceiling, and a floor that opposes the ceiling; a substrate for supporting a food item, the substrate substantially enclosed by the cavity; a first plenum spanning between the two opposing side walls, said plenum comprising a first segment proximal to the back wall, a second segment proximal to the ceiling, and at least one third segment that joins the first segment and the second segment; a second plenum positioned proximal to but medially displaced from the first plenum; a flame heating element located between the first plenum and the second plenum; and at least one air movement device located proximal to a region in which the front wall and ceiling intersect.
Owner:7794754 CANADA
Electromagnetic interference shield
InactiveUS20120037803A1Improve blockageSubstantial transparencyRadiation pyrometryWave amplification devicesMicrowaveElectromagnetic interference
An improved EMI shielded detection system. The disclosed system may include features configured to increase radio wave and microwave absorbance while retaining significant transparency at visible and / or infrared wavelengths, thus increasing EMI shielding efficiency. This may be accomplished through the use of a conductive mesh having appropriately chosen dimensions and spacing, and embedded in a transparent medium. To minimize the impact of the mesh on the effective aperture of the medium, the strands of the mesh may be made relatively narrow, and to provide sufficient shielding despite the narrow strand width, the mesh may be embedded relatively deeply in the medium.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Atmospheric rotisserie burner with convection heating
ActiveUS10051995B2Utility and advantagePreventing situationRoasting apparatusRoasters/grillsAir movementEngineering
The present invention provides a device for cooking food that has a cooking cavity defined by a front wall, a back wall that opposes the front wall, two opposing side walls, a ceiling, and a floor that opposes the ceiling; a substrate for supporting a food item, the substrate substantially enclosed by the cavity; a first plenum spanning between the two opposing side walls, said plenum comprising a first segment proximal to the back wall, a second segment proximal to the ceiling, and at least one third segment that joins the first segment and the second segment; a second plenum positioned proximal to but medially displaced from the first plenum; a flame heating element located between the first plenum and the second plenum; and at least one air movement device located proximal to a region in which the front wall and ceiling intersect.
Owner:7794754 CANADA
Light emitting device having organic light emitting material with mixed layer
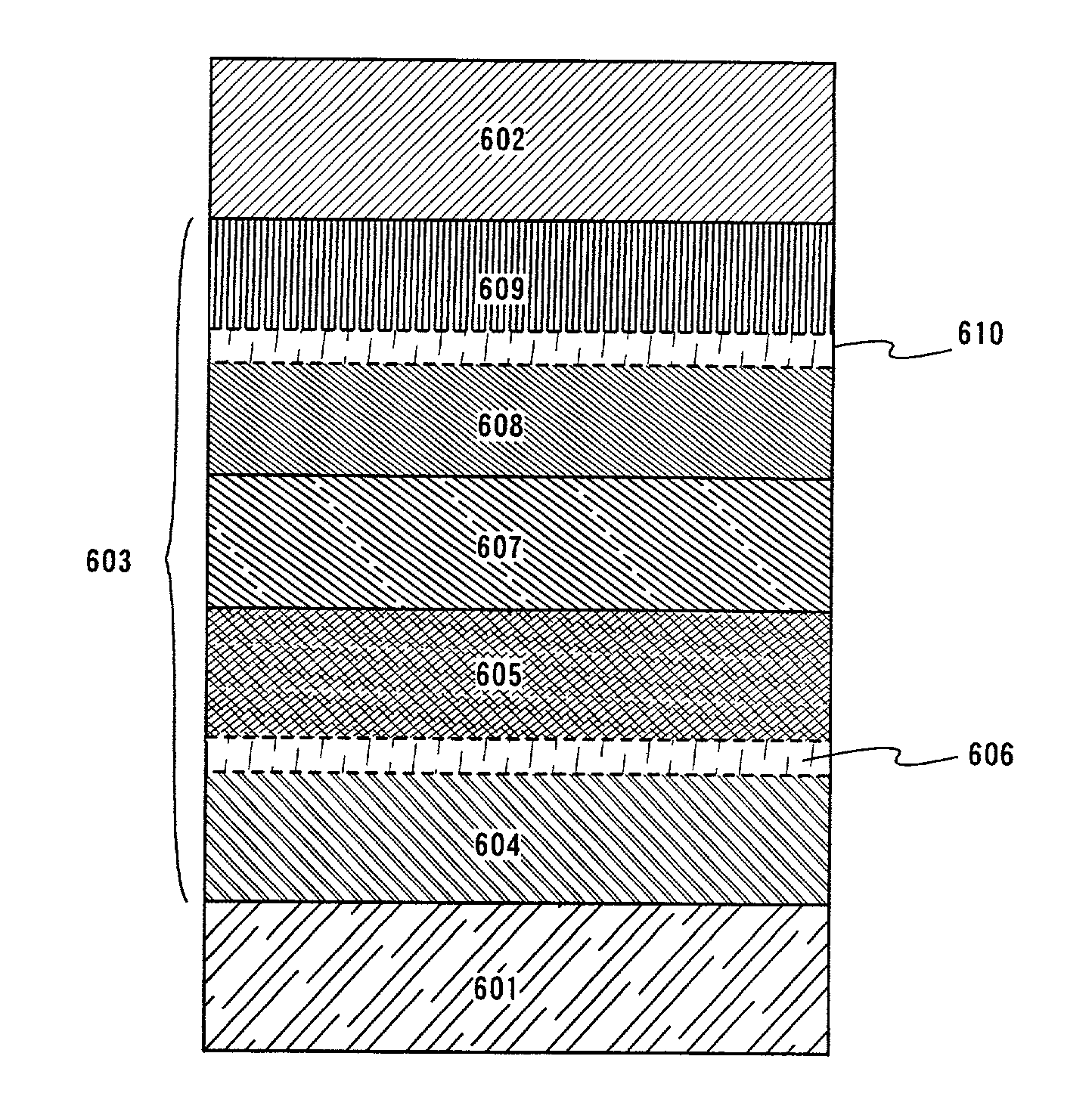
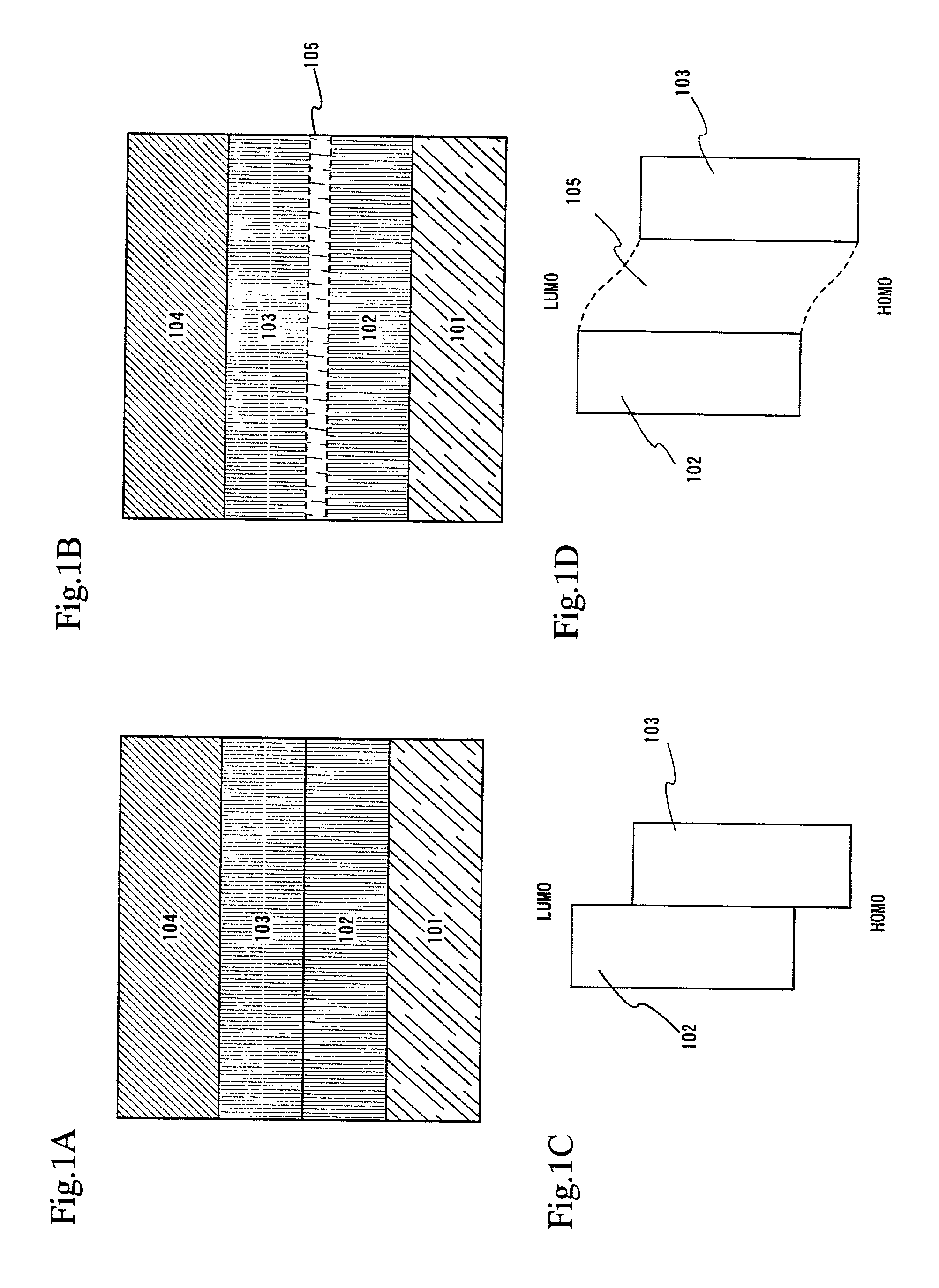
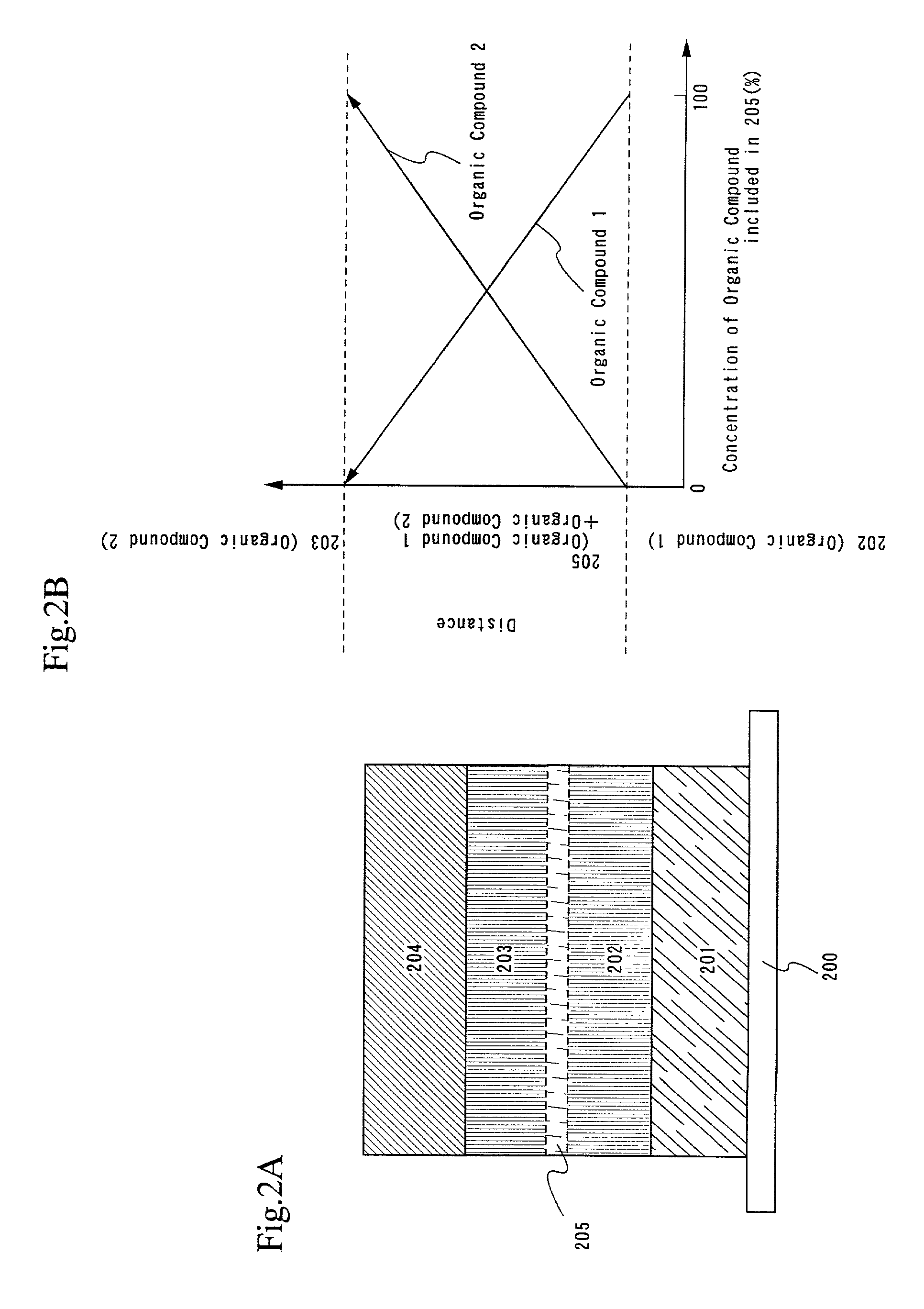
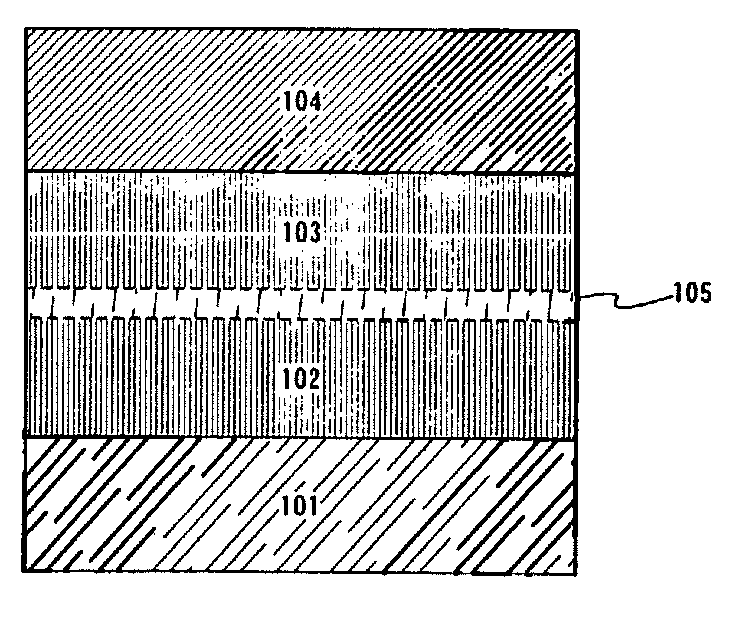
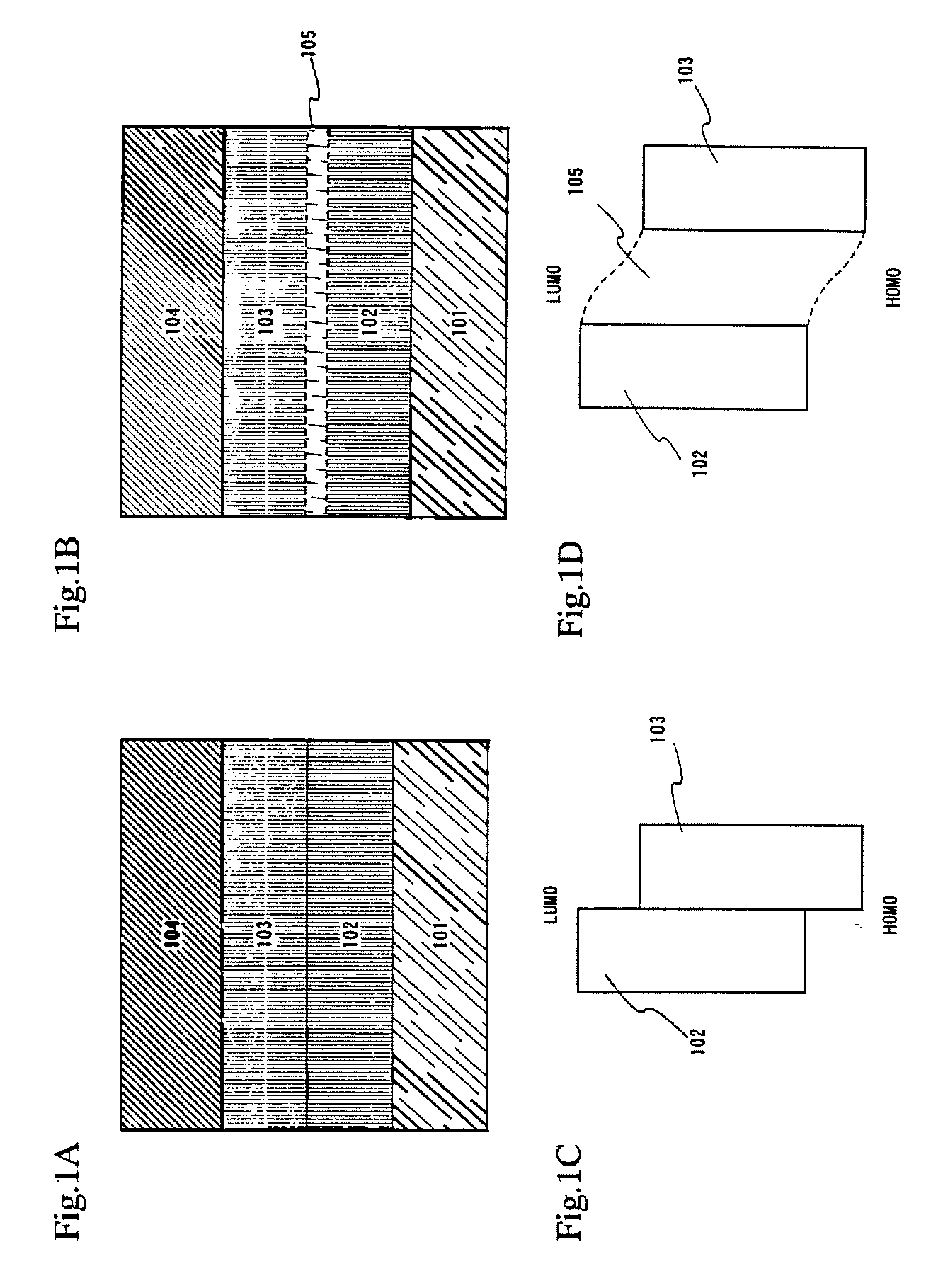
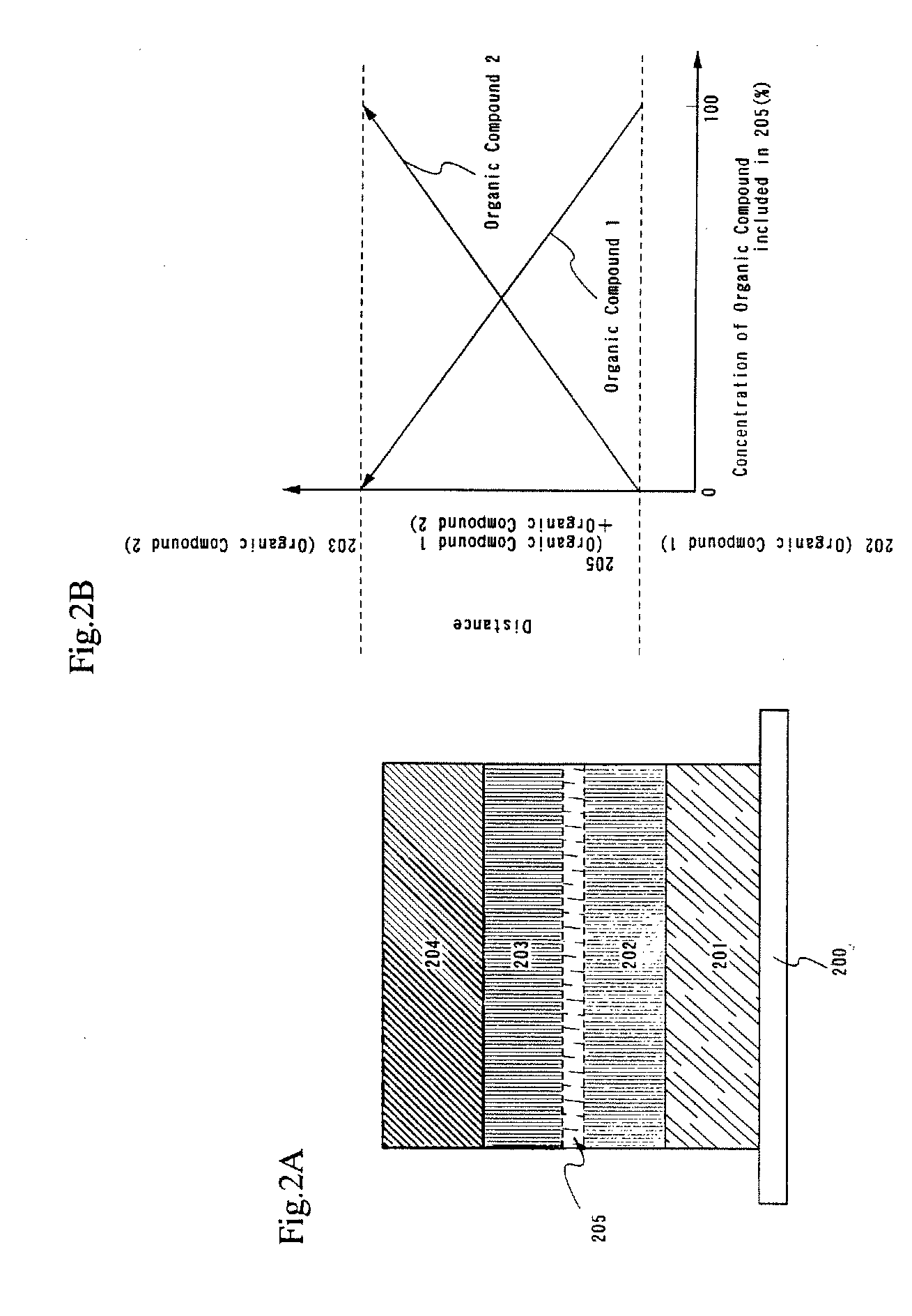
InactiveUS7342355B2Reduce the driving voltageLonger heating element lifetimeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic compoundLight emitting device
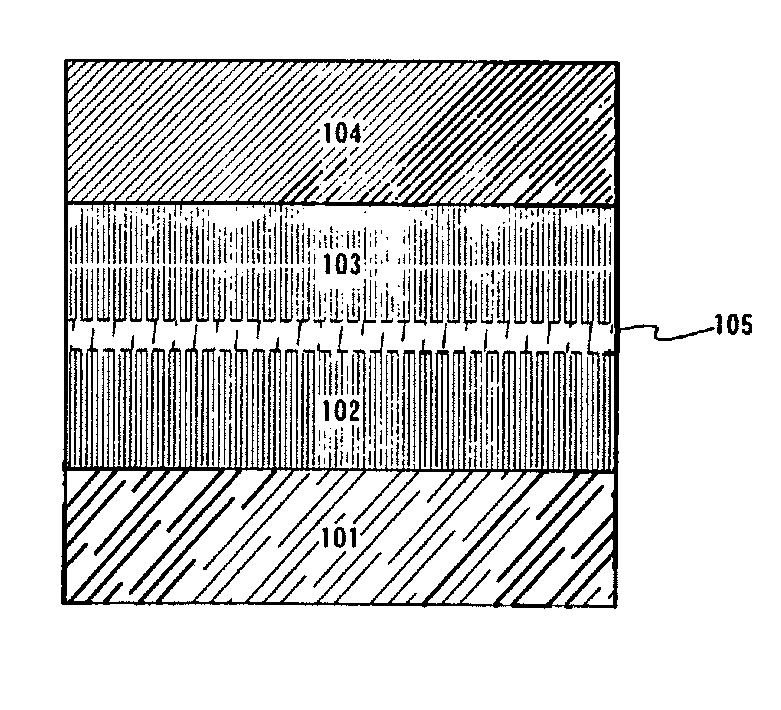
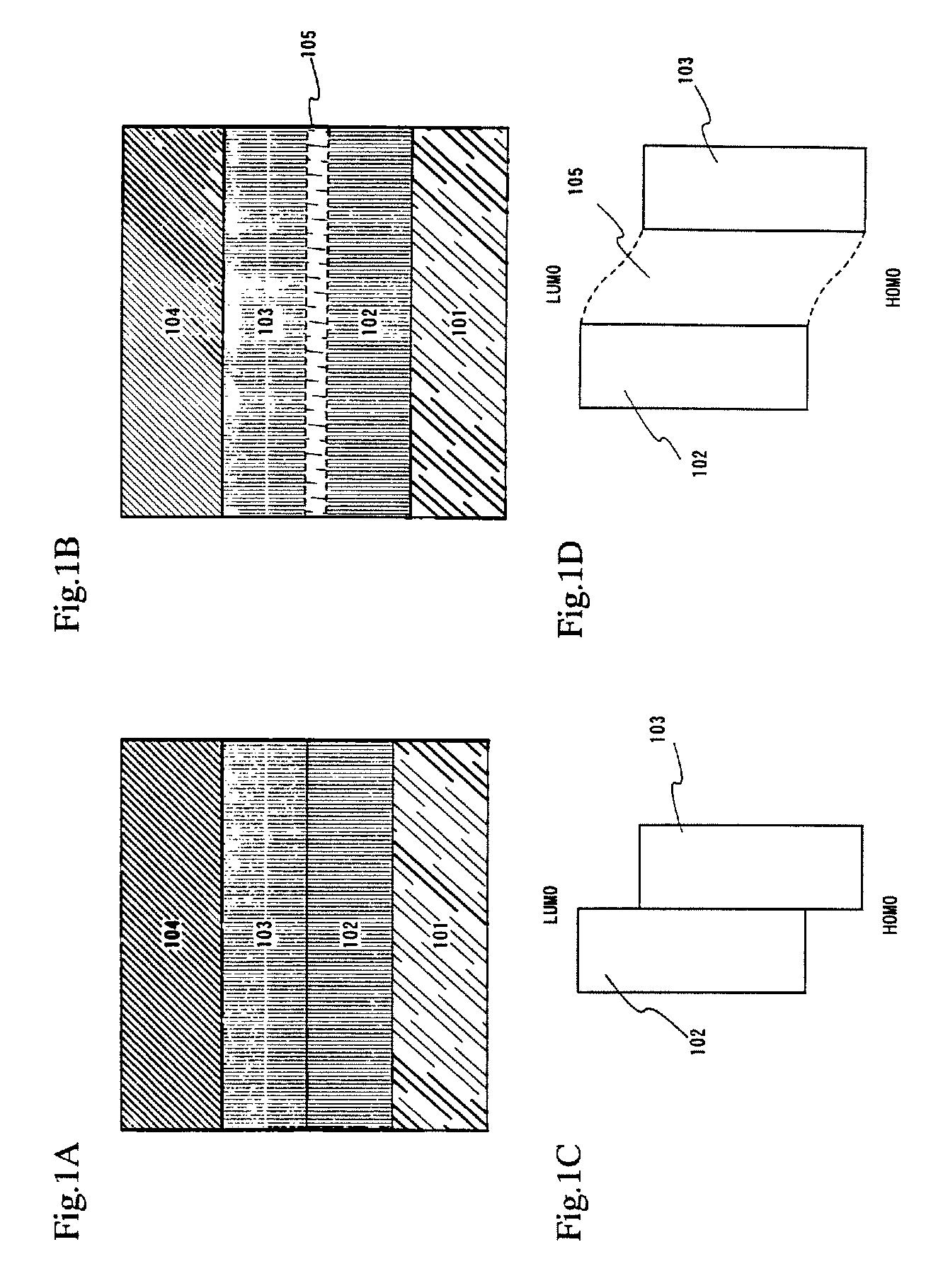
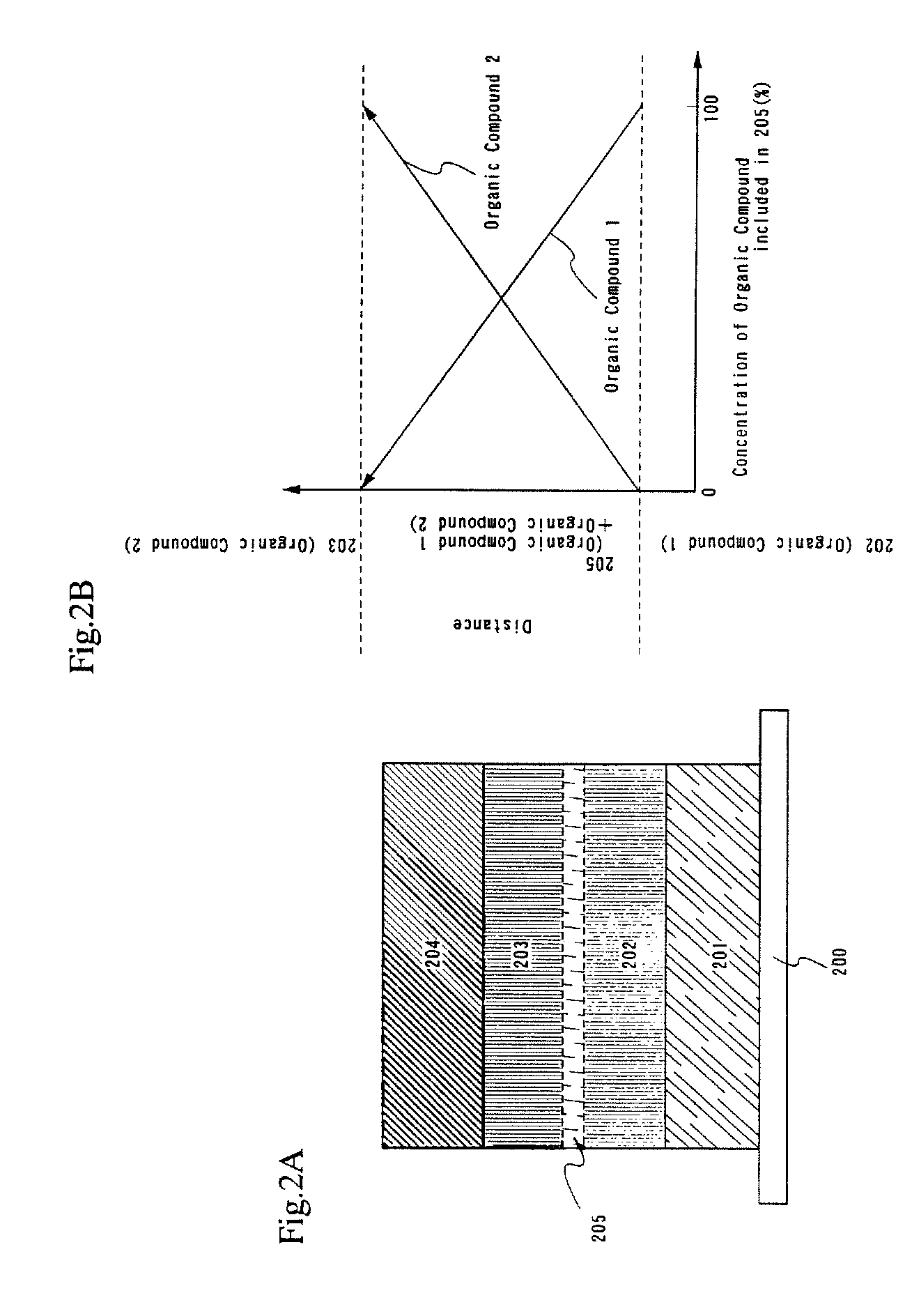
A light emitting device is provided which has a structure for lowering energy barriers at interfaces between layers of a laminate organic compound layer. A mixed layer (105) composed of a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (1) (102) and a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (2) (103) is formed at the interface between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103). The energy barrier formed between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103) thus can be lowered.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for fabricating a biochip using the high density carbon nanotube film or pattern
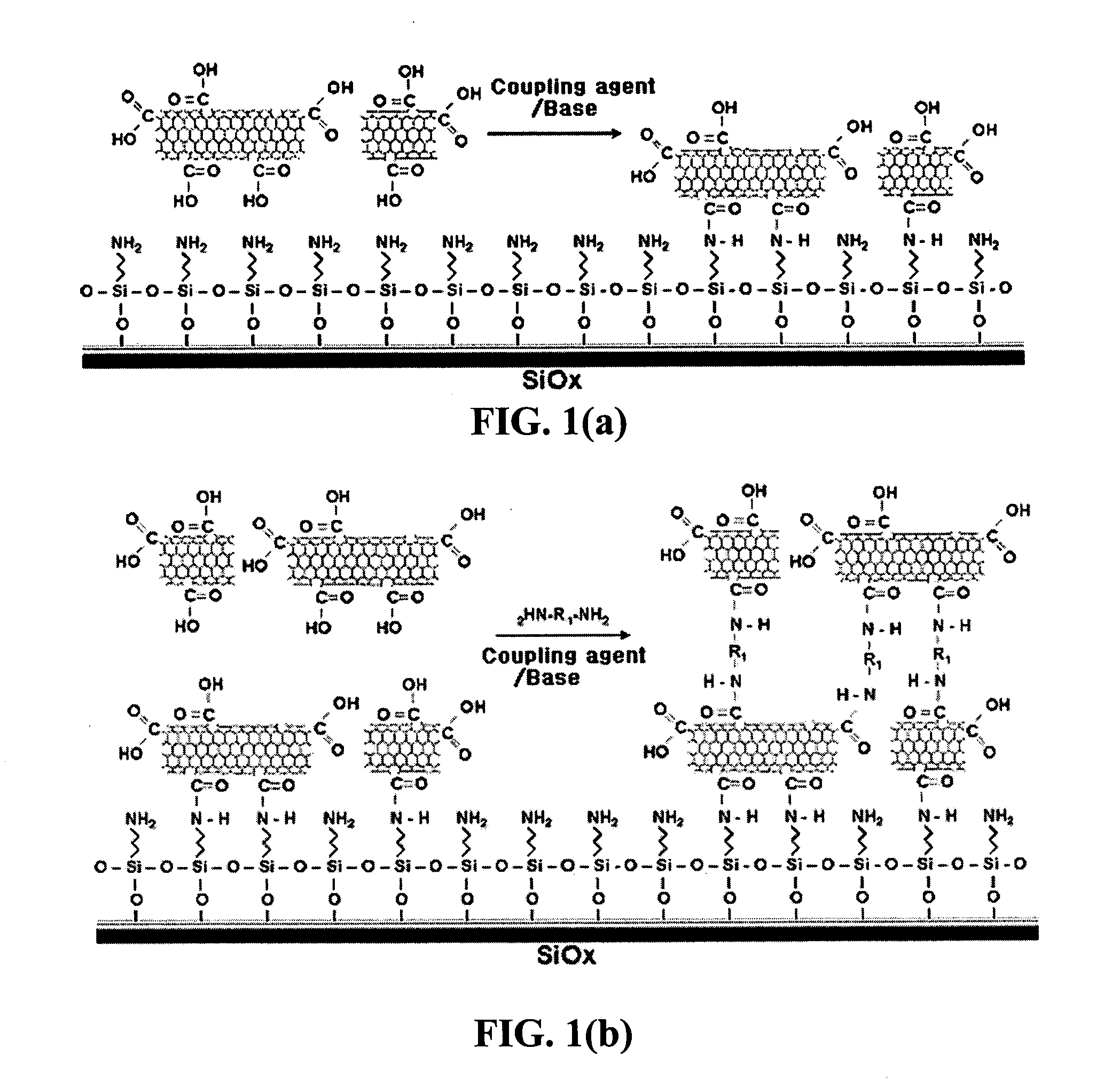
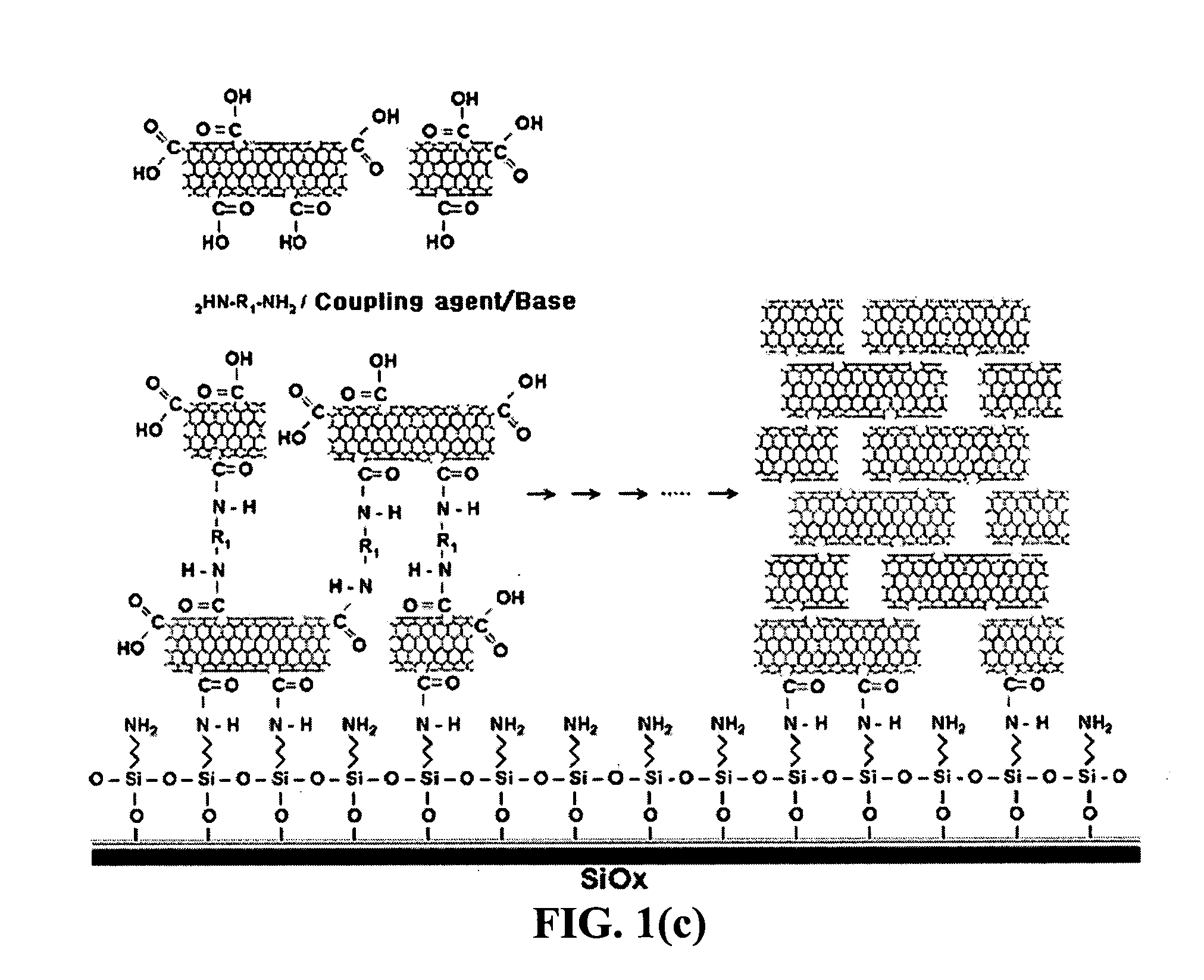
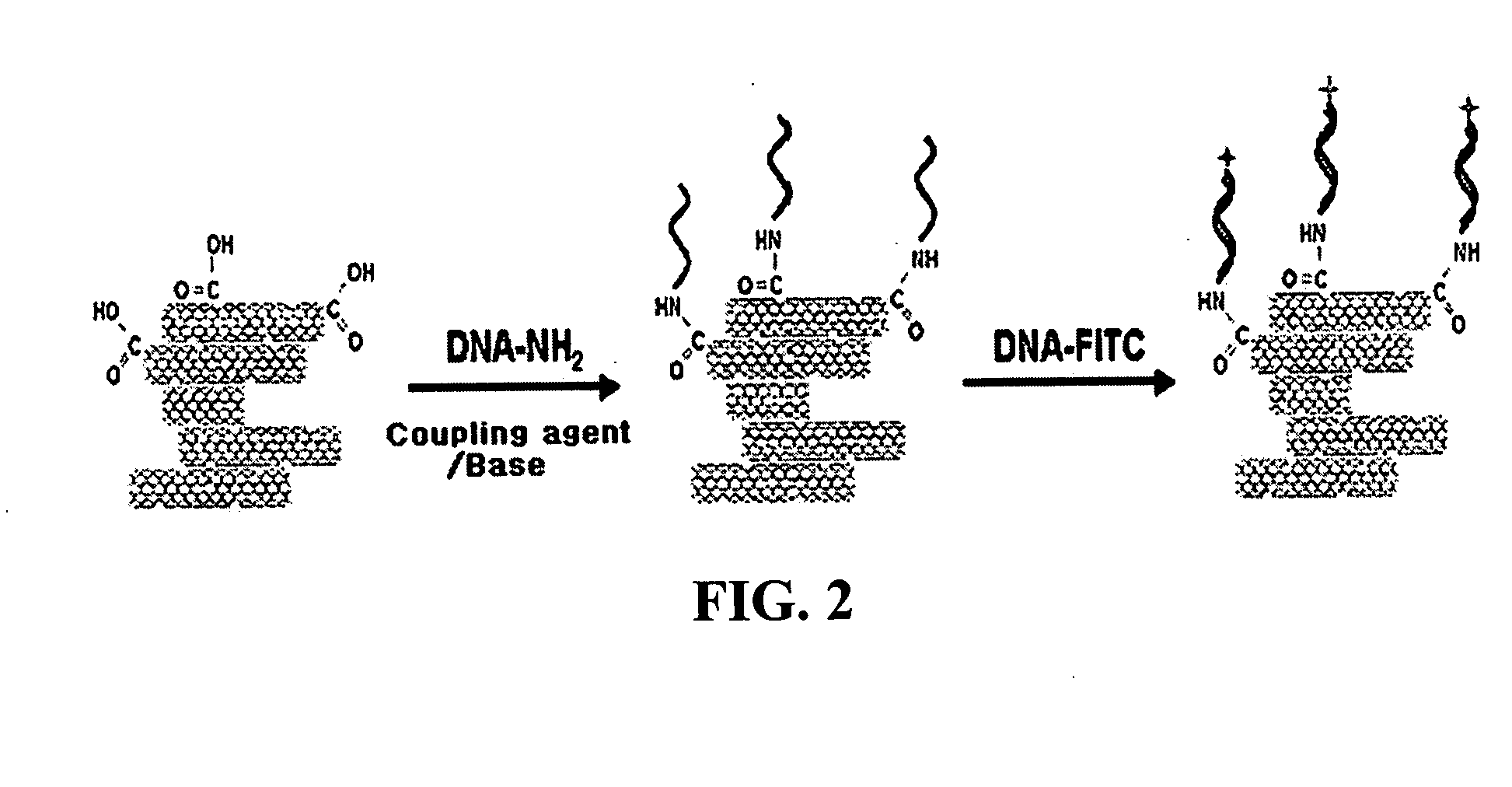
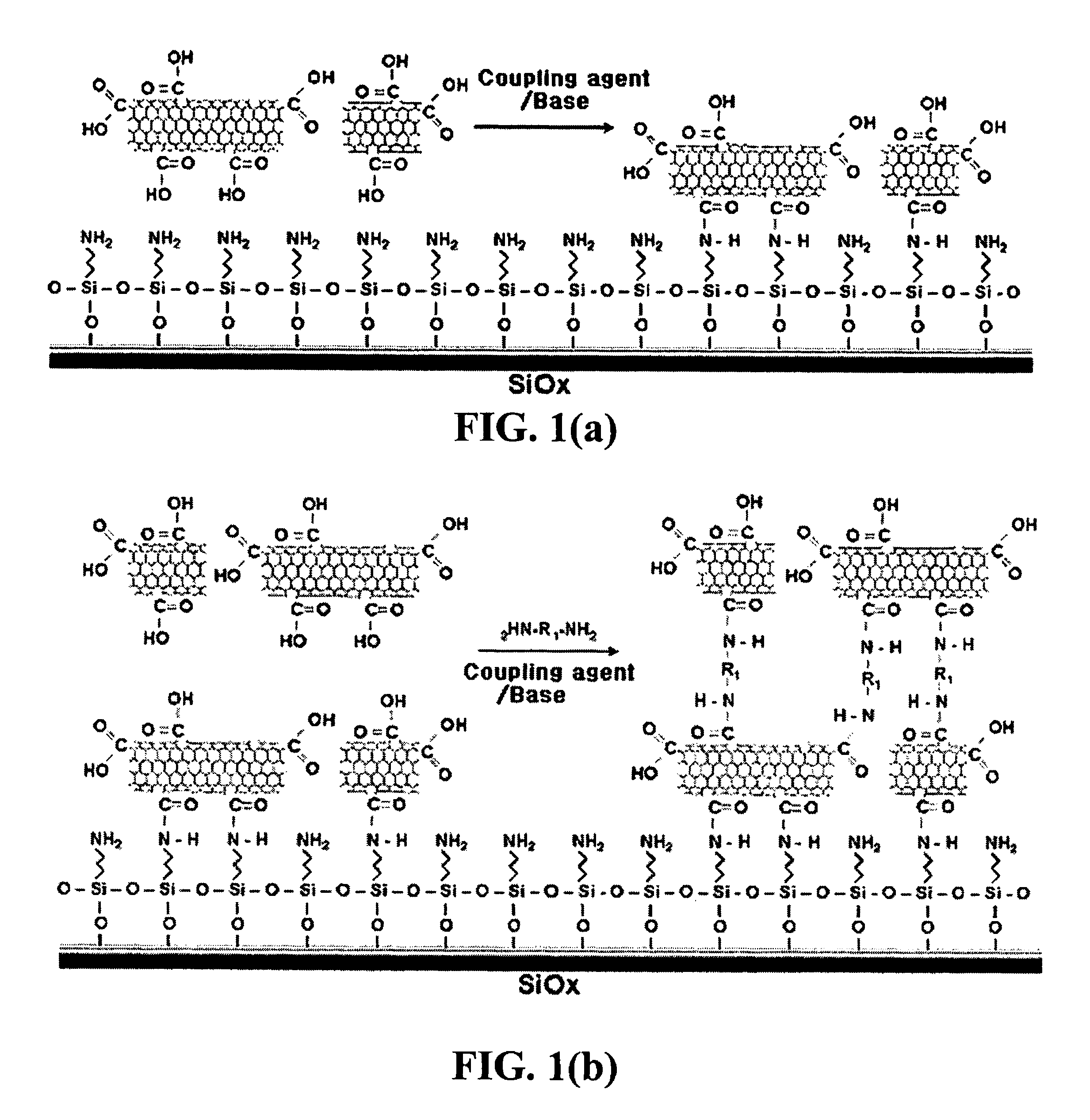
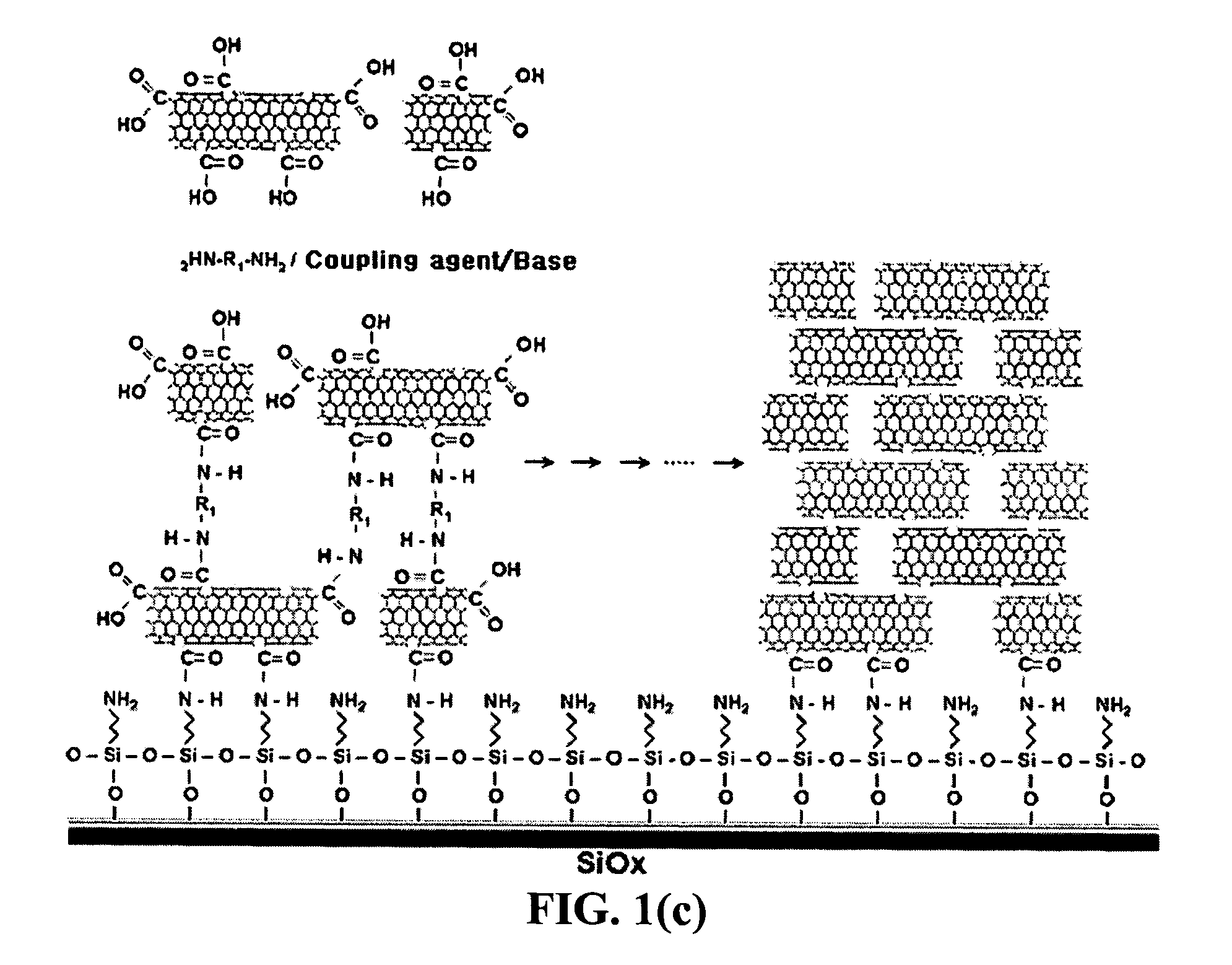
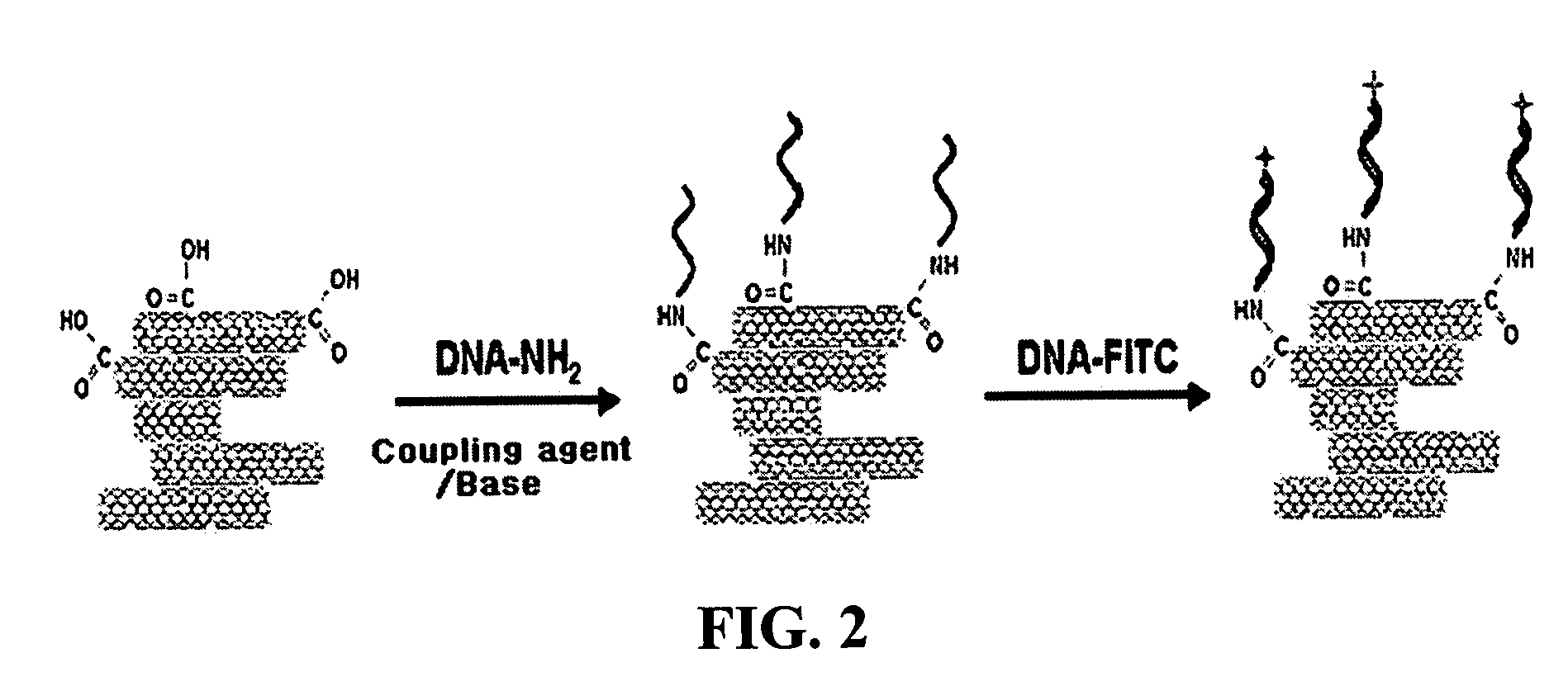
InactiveUS20050019791A1Improve defectsUtility and advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical conductorFluorescence
The present invention relates to a CNT-biochip comprising a bio-receptor which is attached by means of an exposed chemical functional group on a surface of a high density CNT film or pattern which is produced by laminating repeatedly carbon nanotubes (CNT) by chemical bond on the substrate modified with amine groups, and a method for fabricating the same. According to the present invention, it is possible to fabricate various types of CNT-biochips by chemical or physicochemical bonding of various bio-receptors to a CNT pattern (or film) containing exposed carboxyl groups or a CNT pattern (or film) modified by various chemical functional groups. Also, it is possible to fabricate a CNT-biochip comprising bio-receptors attached evenly with high density on a surface of a CNT film where chemical functional groups are abundant and present evenly. Further, the CNT-biochip is applicable to next generation biochips which measure an electrical or electrochemical signal using both conductor and semiconductor properties of the CNT, thereby not needing labeling. Particularly, upon fluorescent measurement of DNA hybridization using the CNT-DNA chip according to the present invention, it is possible to show more distinct signals, thereby producing excellent results. The CNT-DNA chip is useful for genotyping, mutation detection, pathogen identification and the like.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
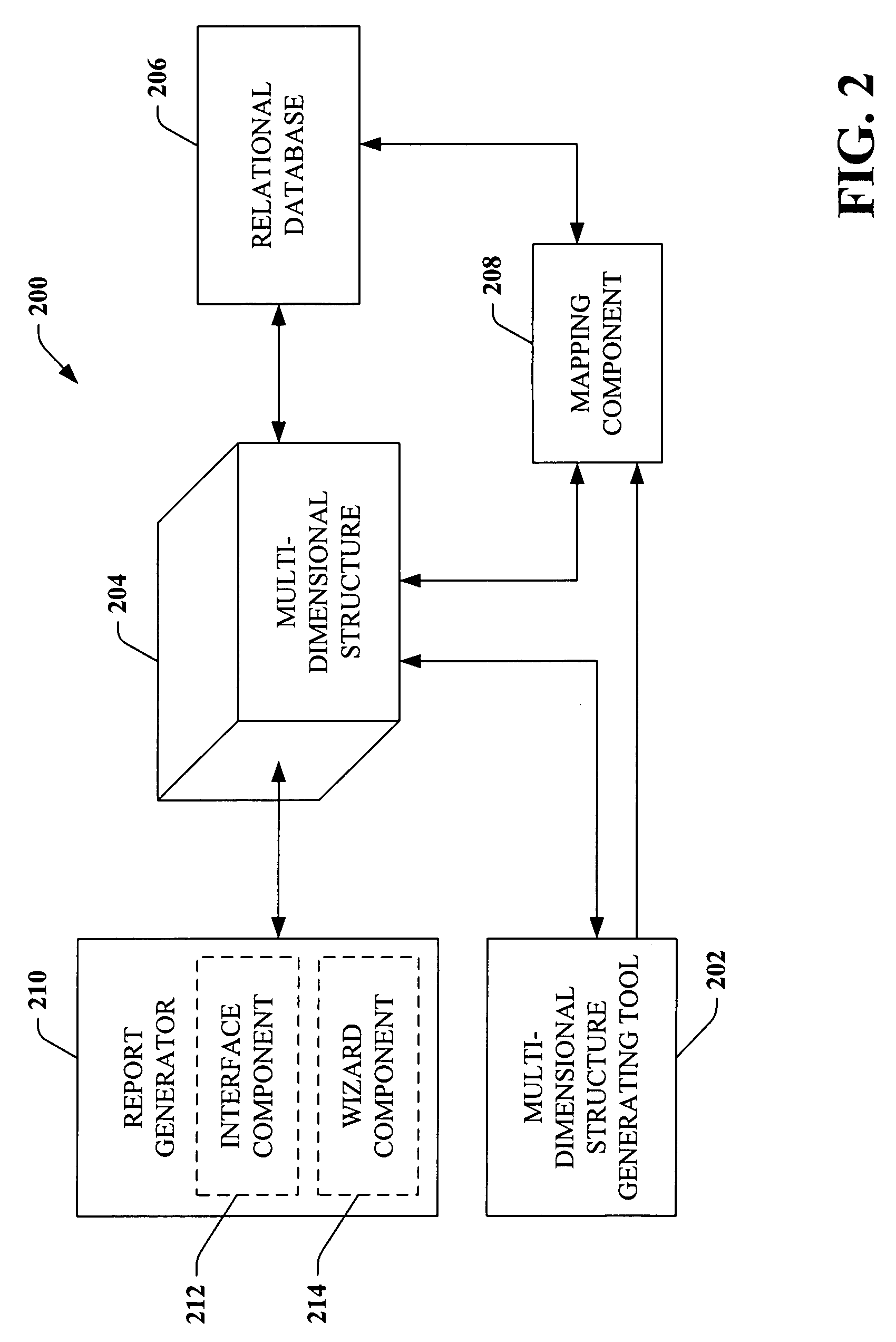
Relational reporting system and methodology
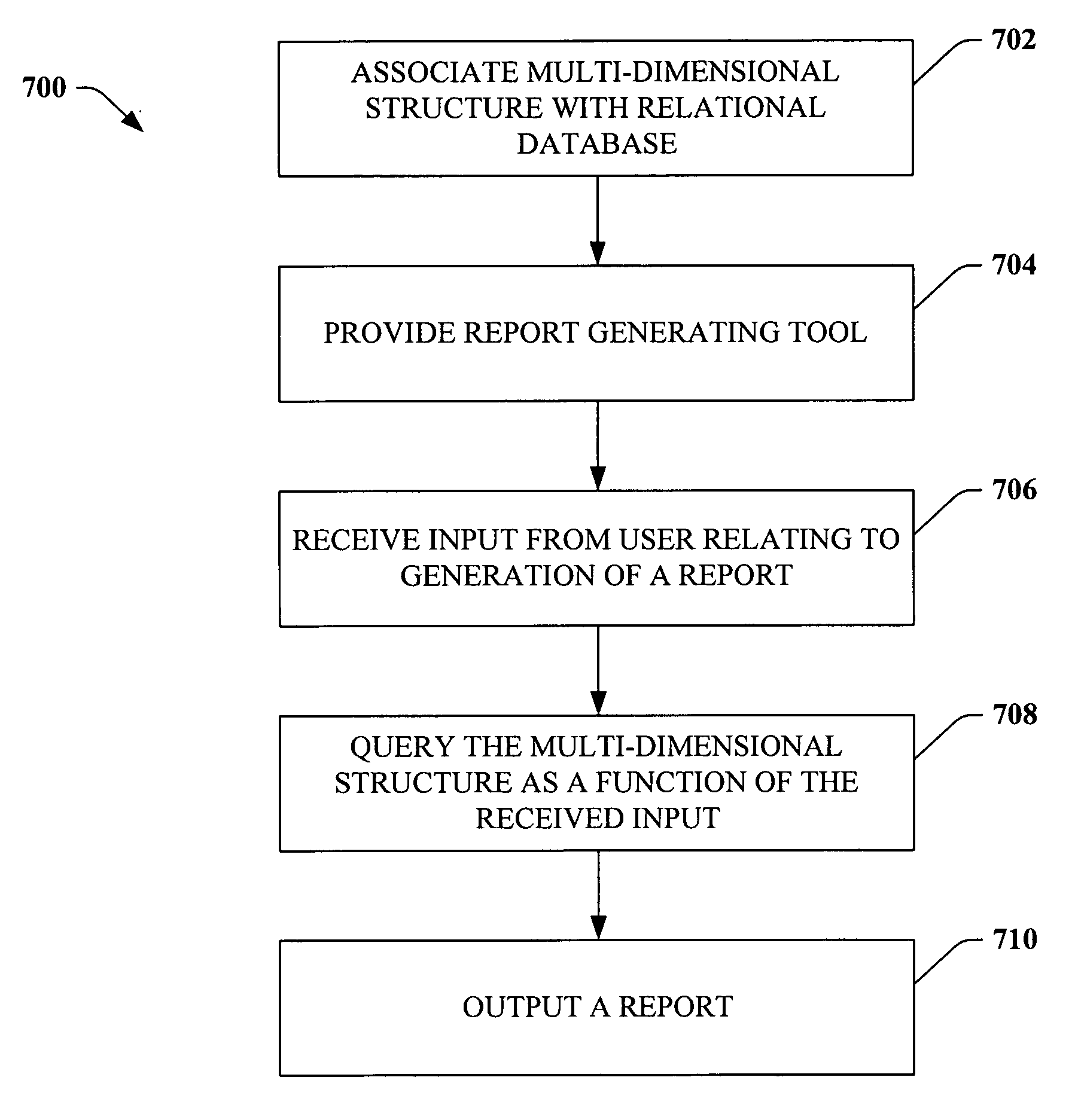
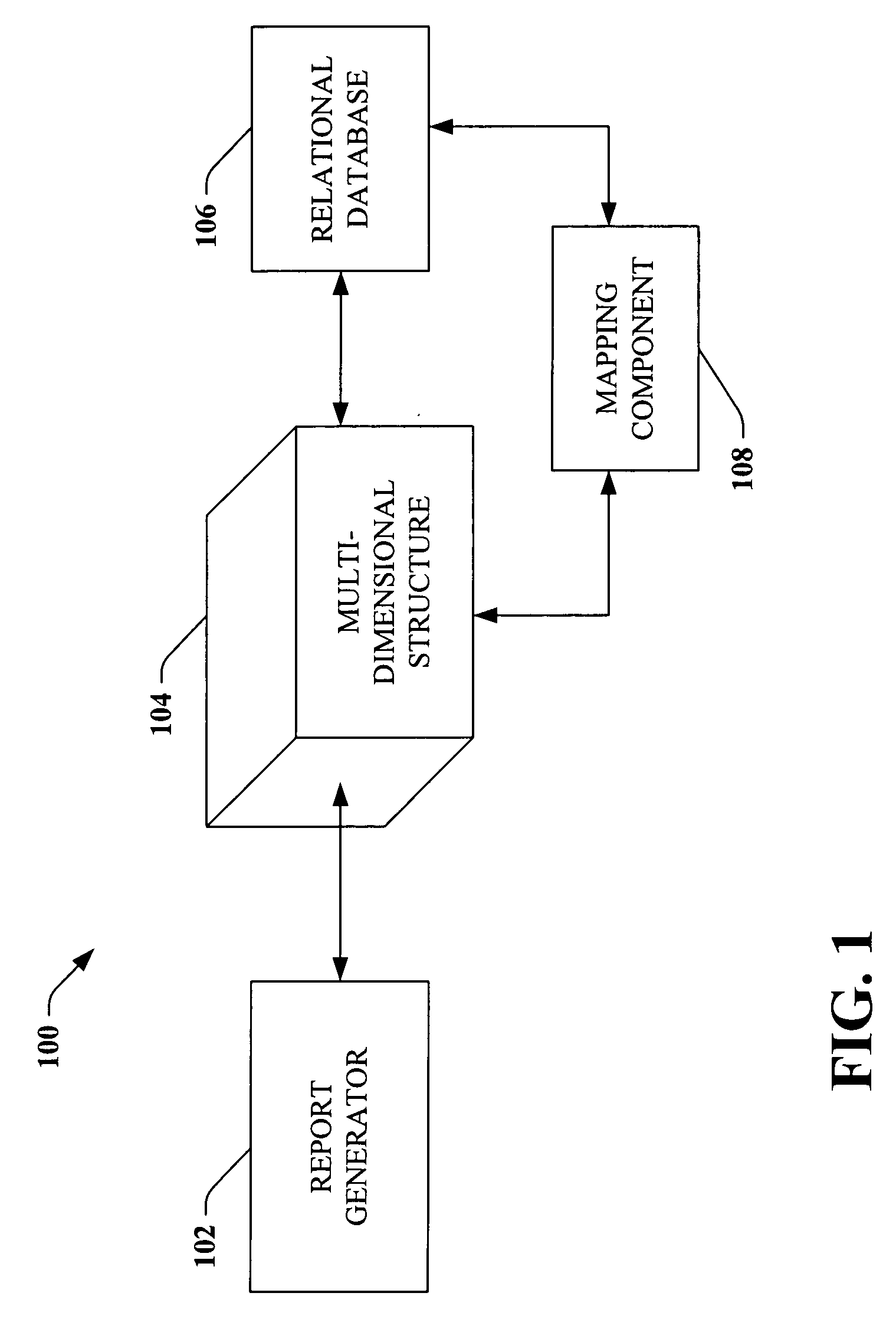
InactiveUS20060010156A1Utility and advantageReduce redundant dataMulti-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseMulti dimensional
A system that facilitates generating a report based upon data within a relational database comprises a mapping component that utilizes mapping functions to associate a multi-dimensional structure with the relational database. A report generator communicates with the multi-dimensional structure to obtain data relating to the relational database and generates a report that includes the obtained data. For example, the mapping component can utilize measure groups to effectuate the association between the multi-dimensional structure and the relational database.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
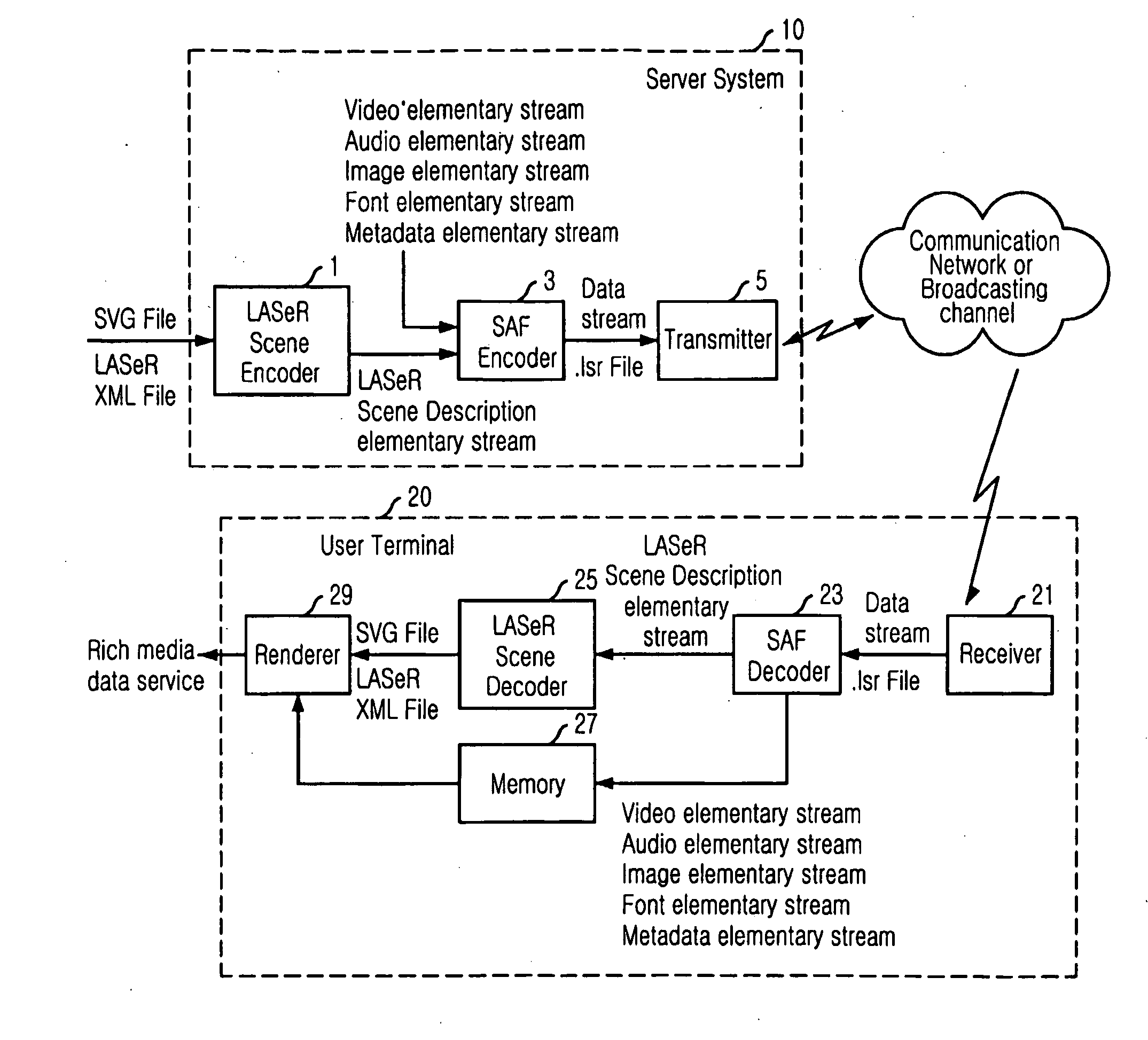
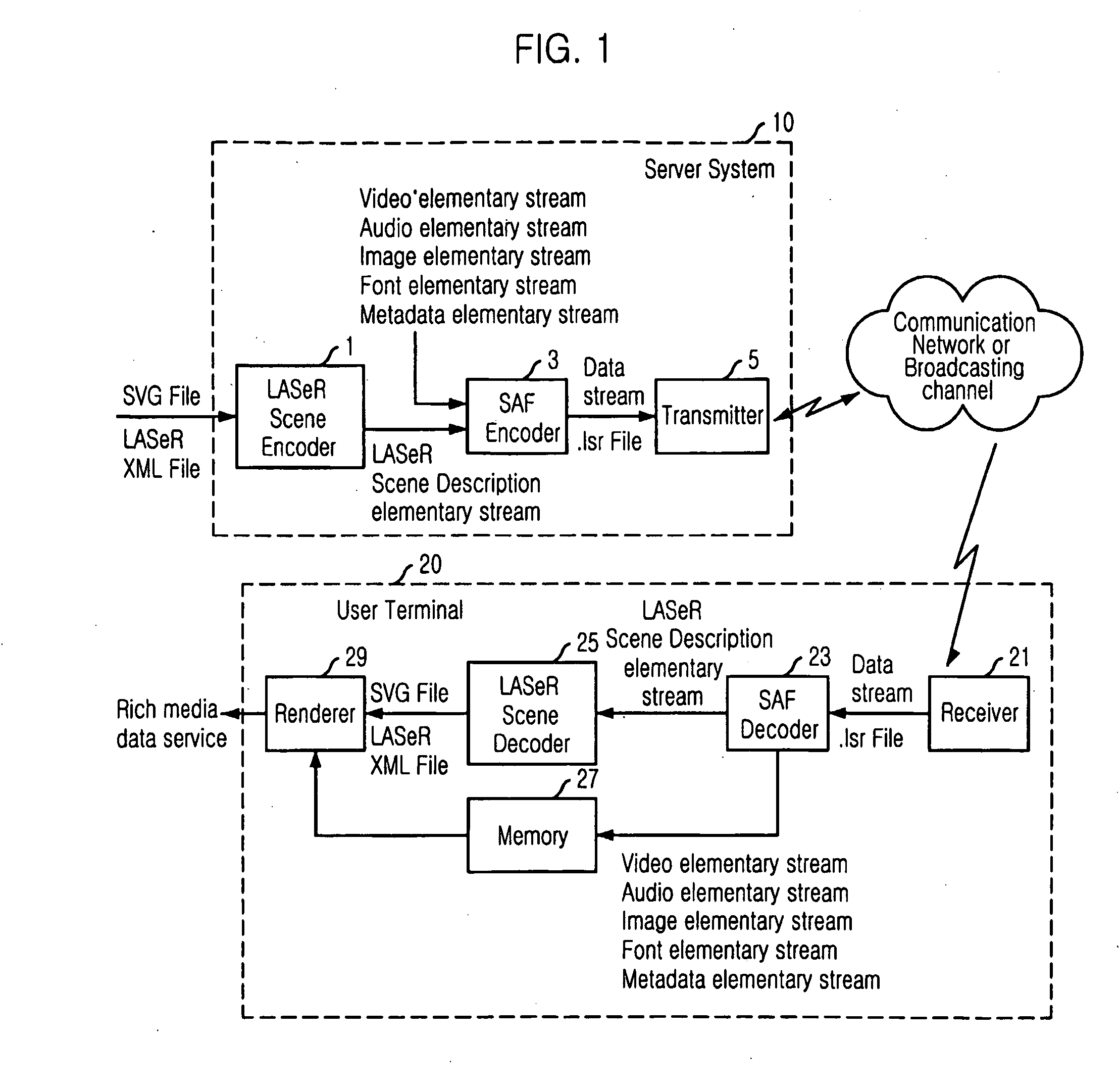
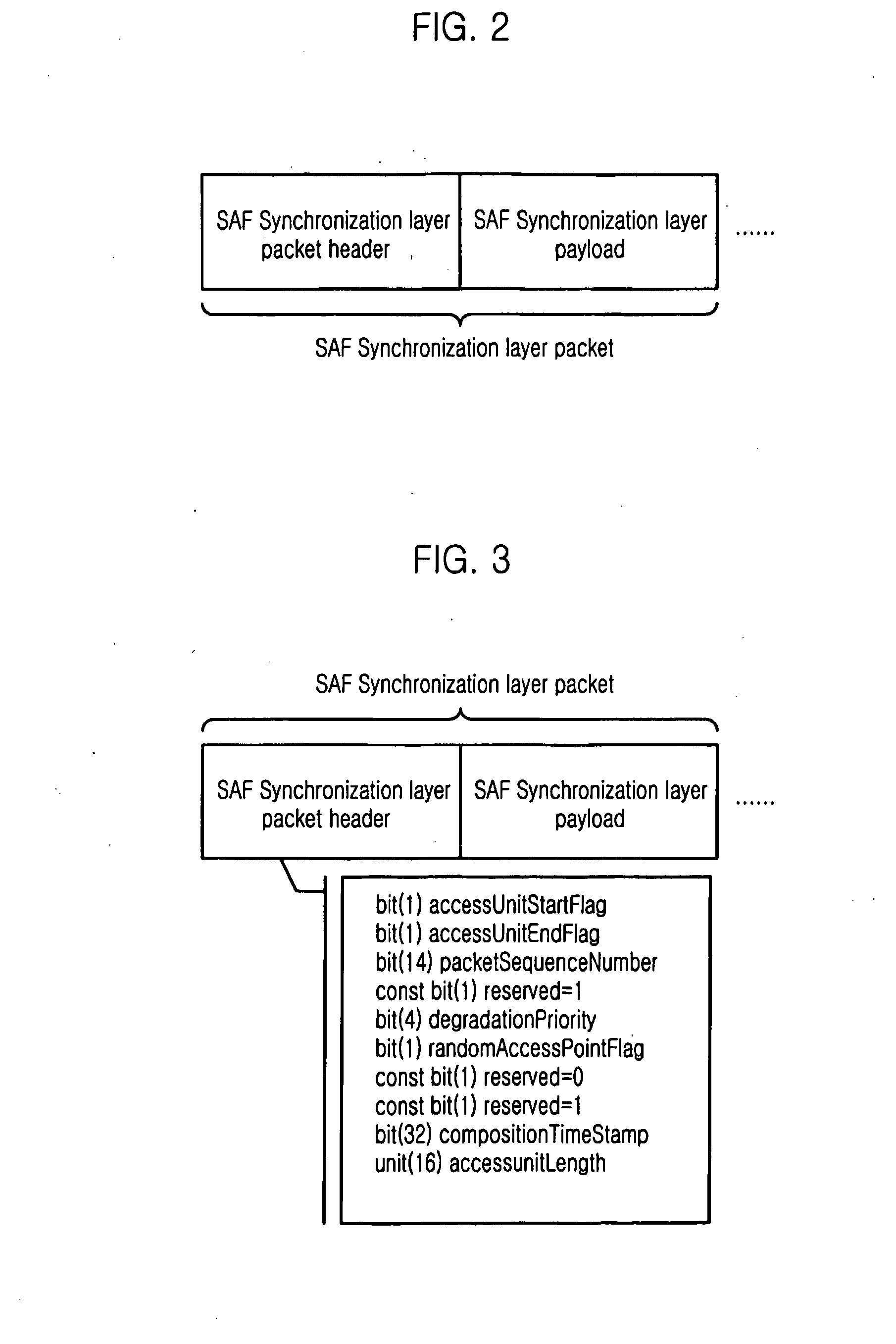
Saf Synchronization Layer Packet Structure and Server System Therefor
InactiveUS20090003389A1Simple and effectiveEasily integratePipe supportsTime-division multiplexData transmissionPacket payload
Provided is a Simple Aggregation Format (SAF) synchronization packet structure including a SAF synchronization packet header and a SAF synchronization packet payload and multiplexing diverse element streams which include a scene description elementary stream. The SAF synchronization packet header includes time information related to an access unit included in the SAF synchronization packet payload, and the SAF synchronization packet payload includes header information on the access unit and payload information indicating the access unit. Since the present invention can multiplex diverse elementary streams effectively and simply into one data stream, synchronized data transmission is possible. Since the present invention accommodates a synchronization layer packet of the MPEG-4 system, it can be easily integrated with the MPEG-4 system and utilize the advantage of the MPEG-4 synchronization layer packet such as the concept of an access unit or a degradation priority.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
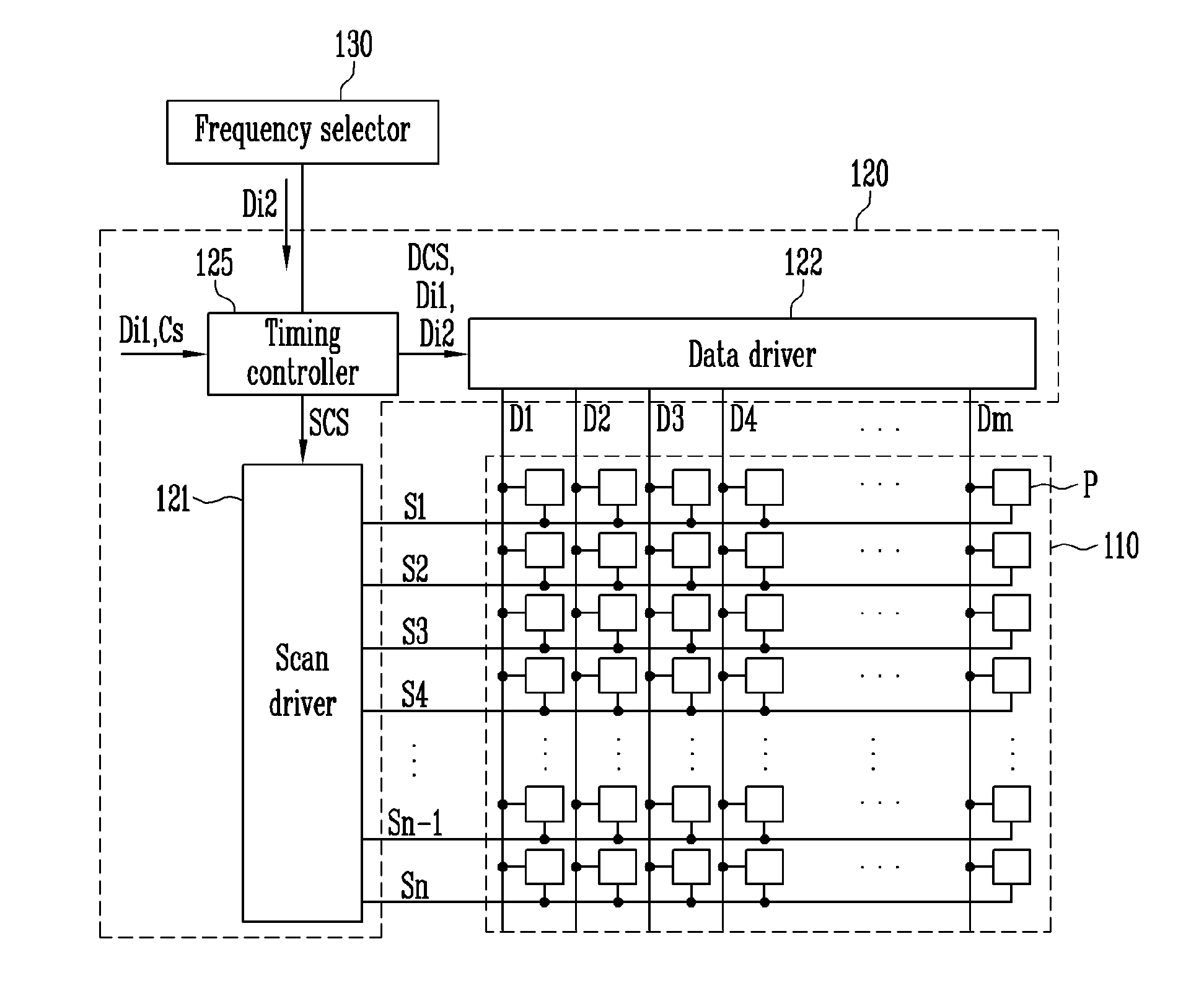
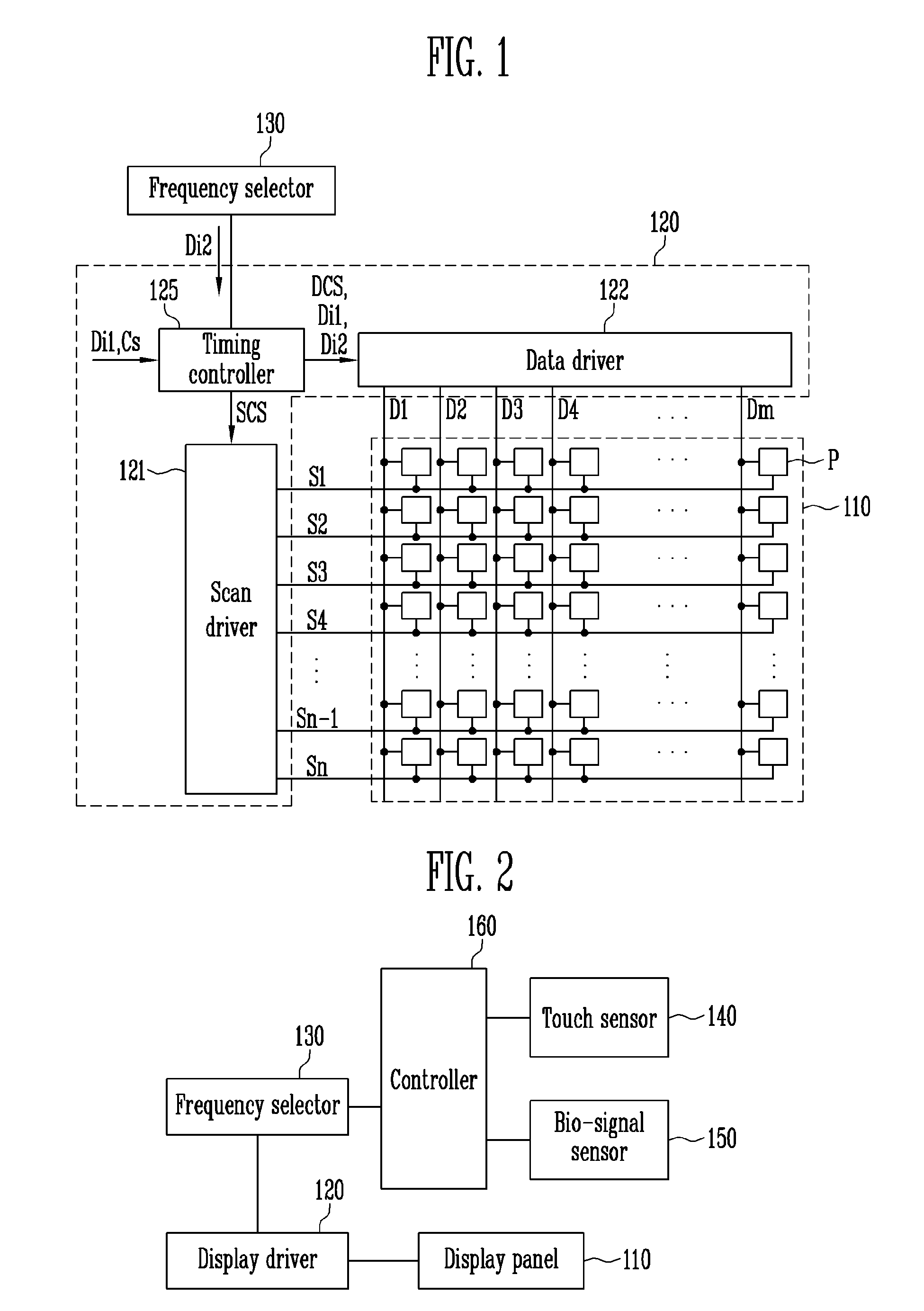
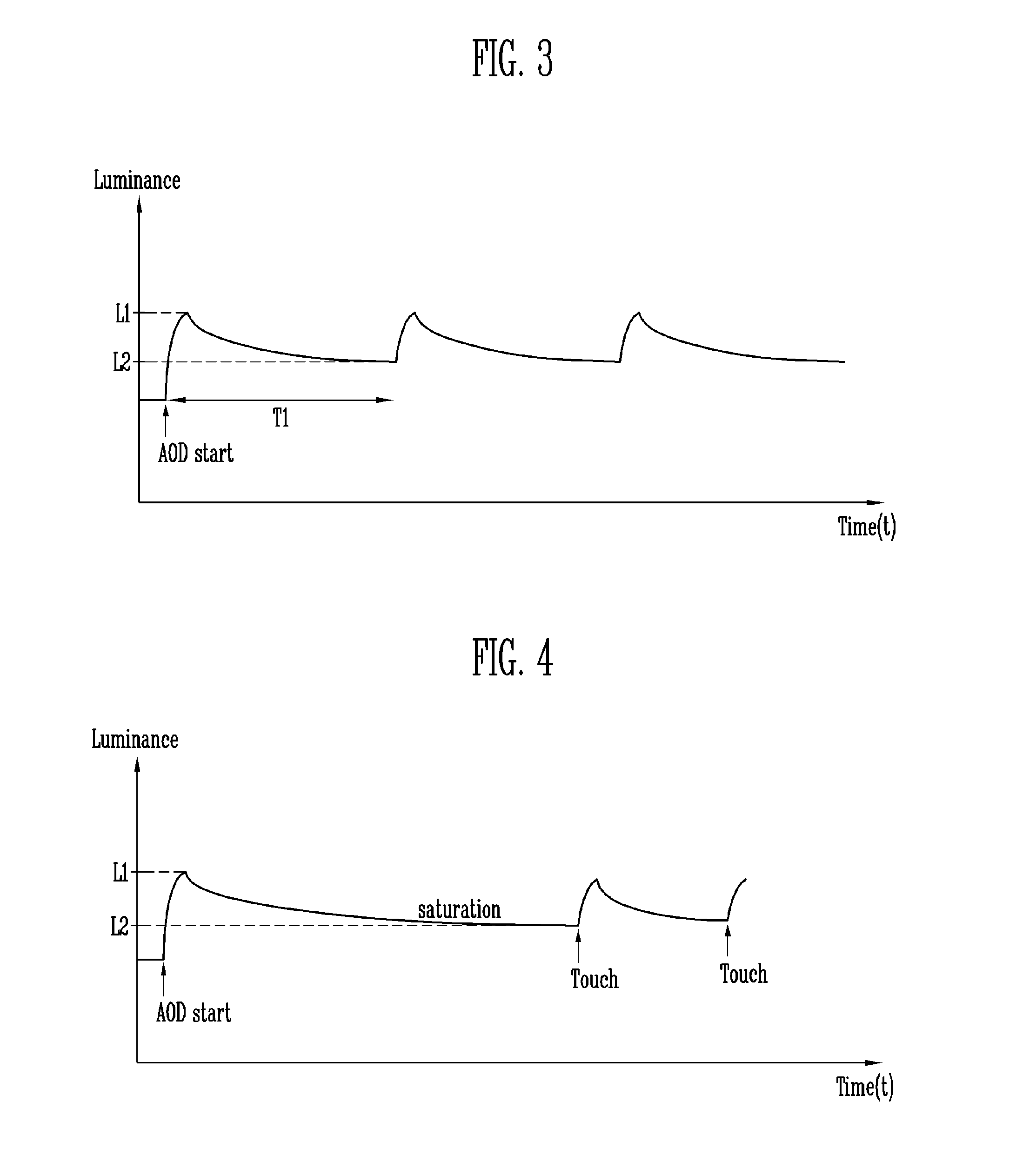
Display device having reduced power consumption and driving method therefor
ActiveUS20170053592A1Reduce power consumptionResolution problemInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceData signal
A display device may include a display panel, a data driver transmitting a data signal, a scan driver sequentially transmitting a scan signal, a frequency selector for selecting a driving frequency for image display, selecting a low frequency if the image displayed on the display panel is a first image and selecting a normal frequency if the image displayed on the display panel is not the first image, the normal frequency being higher than the low frequency. The display device also includes a timing controller for controlling the data driver and the scan driver based on the selected driving frequency. The timing controller may control the data driver and the scan driver such that luminance of the display panel on which the first image is displayed is periodically changed according to the low frequency if the image displayed on the display panel is the first image.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
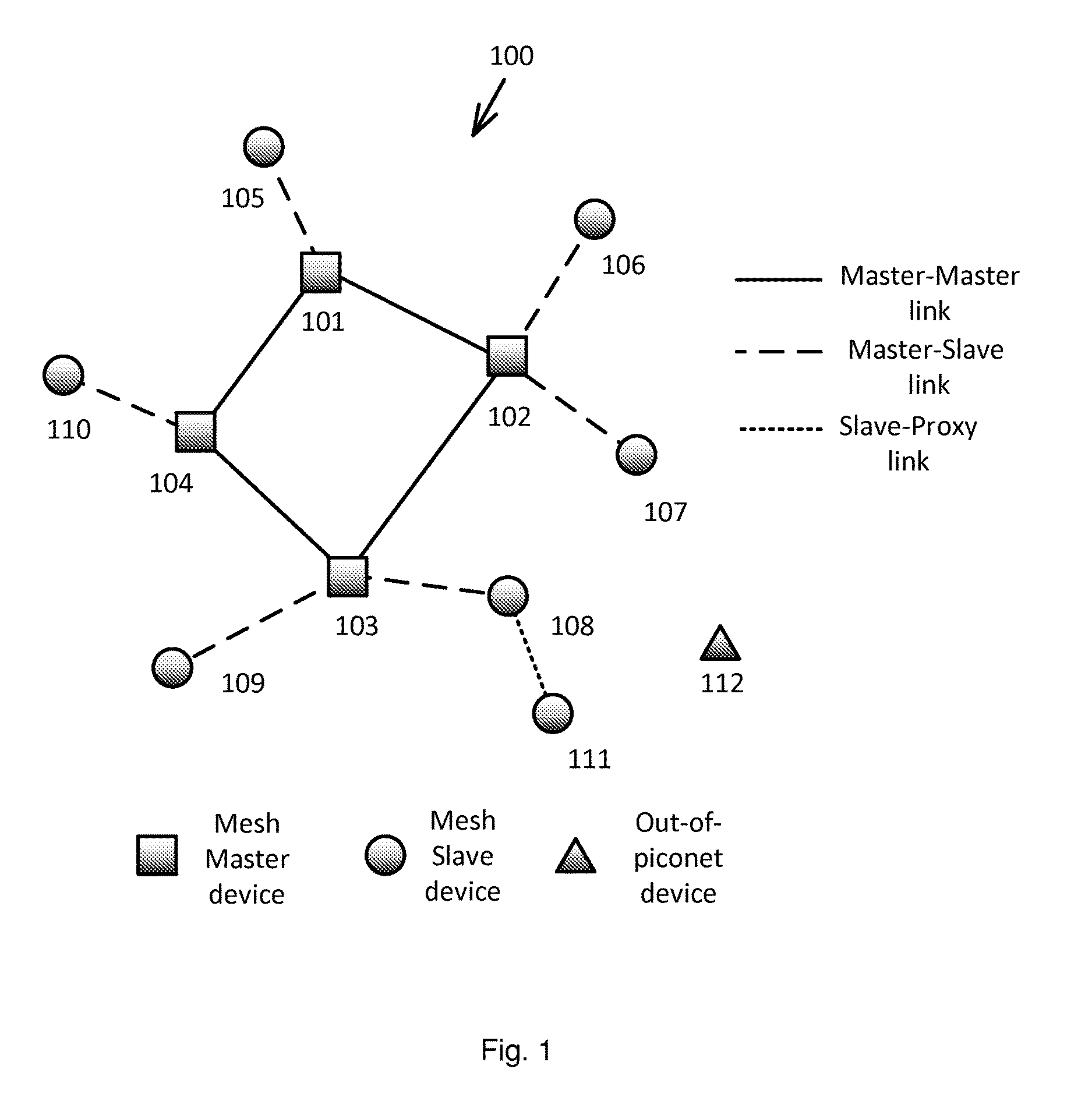
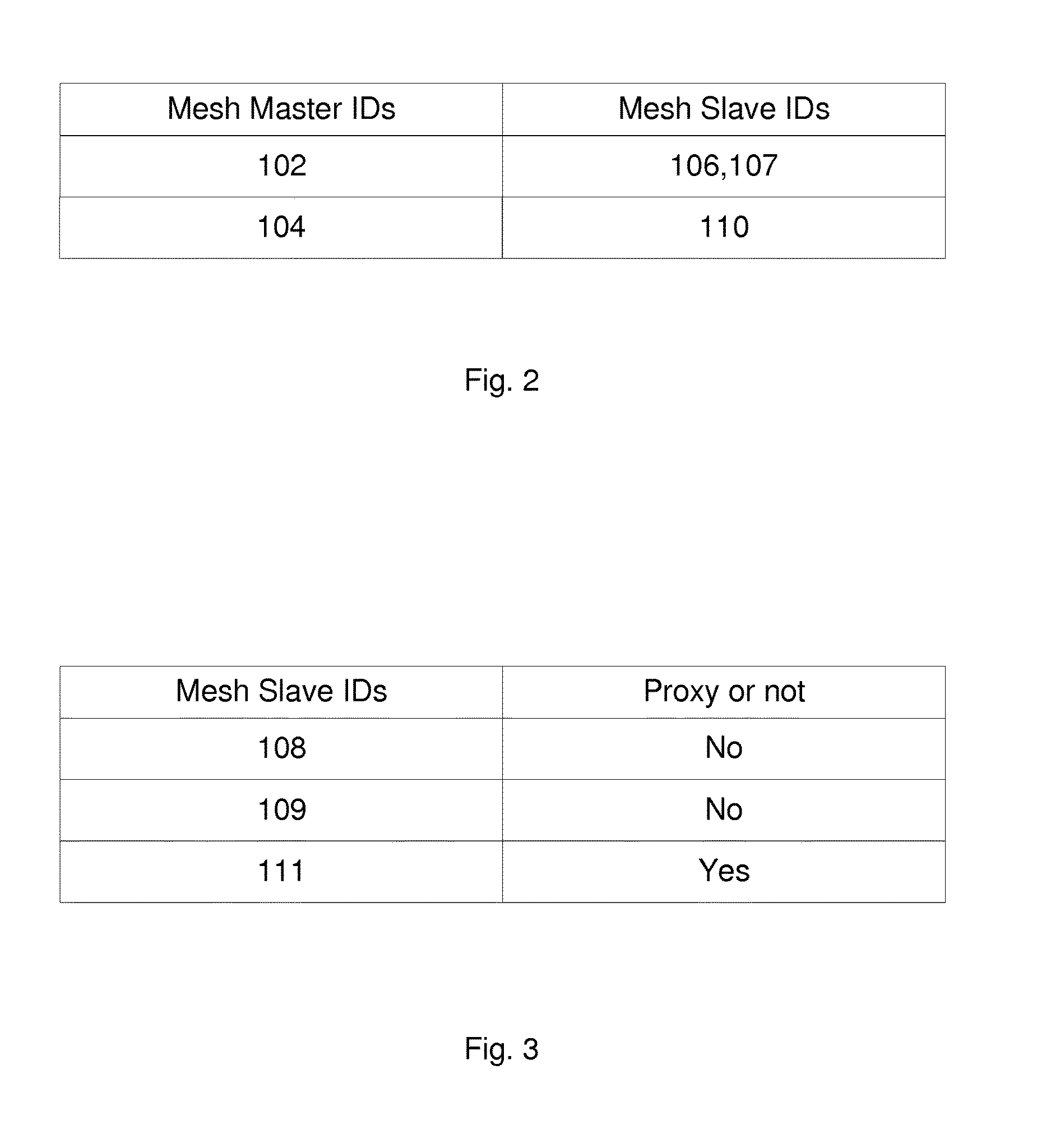
A Master Device and Methods Therein
InactiveUS20160380778A1Optimize networkExtended service lifeSpecial service provision for substationNetwork traffic/resource managementComputer hardwareUnicast
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
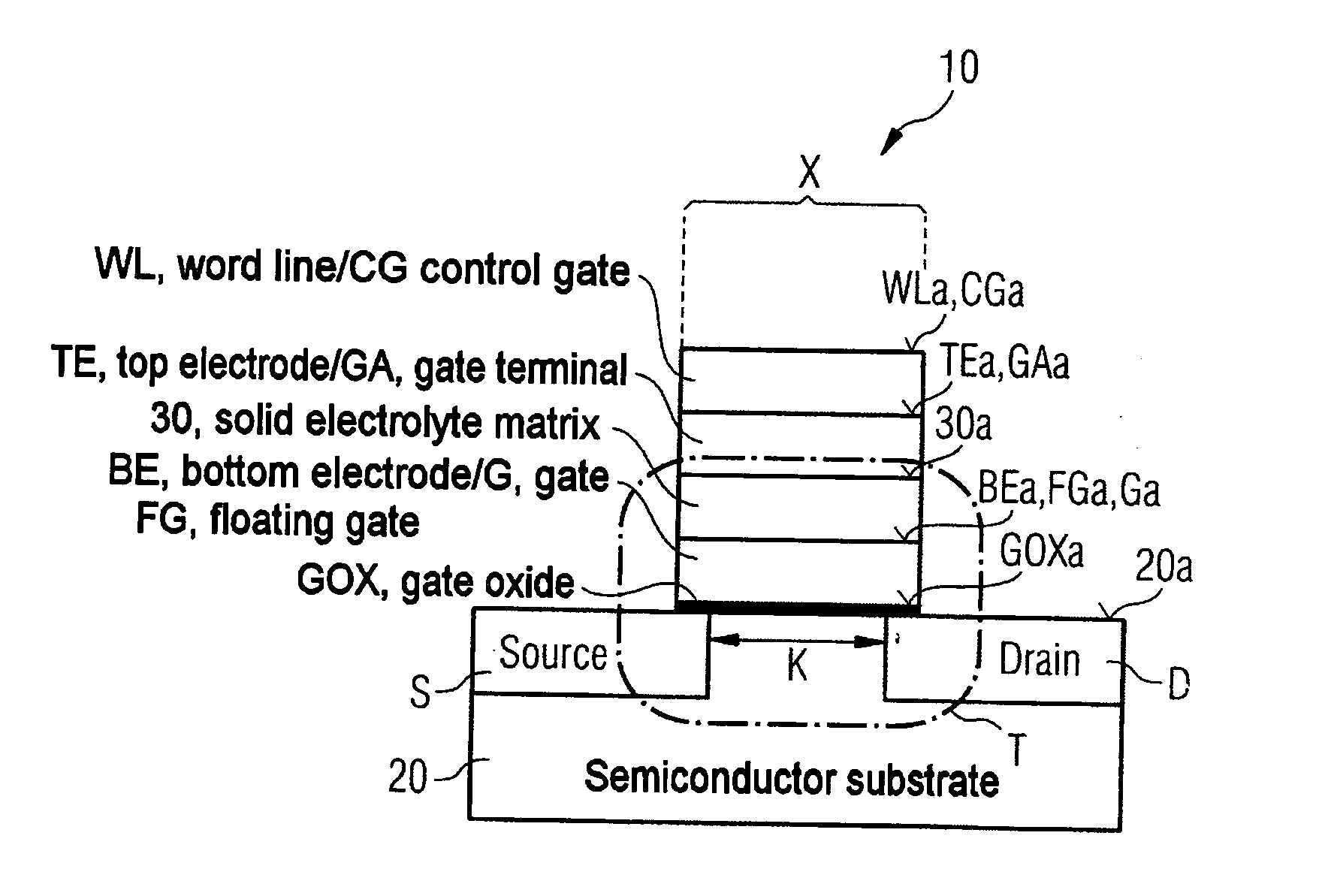
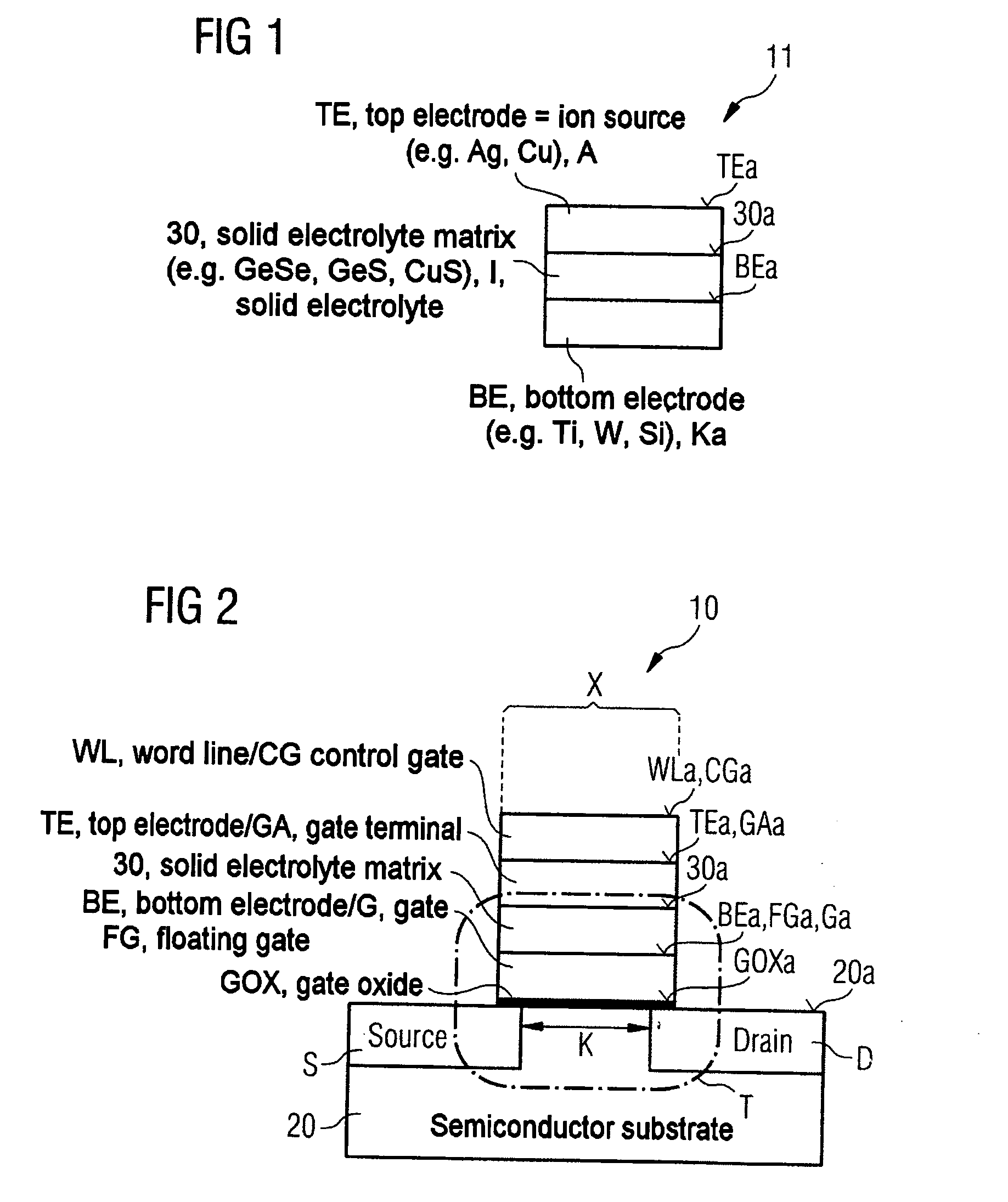
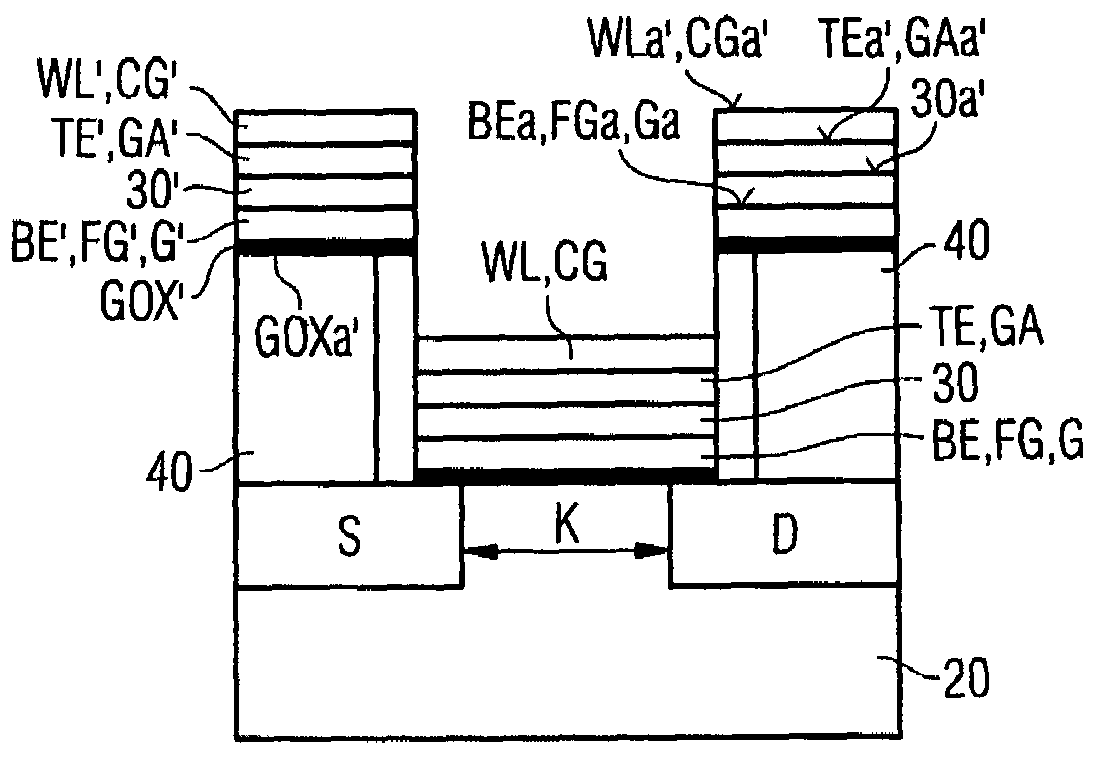
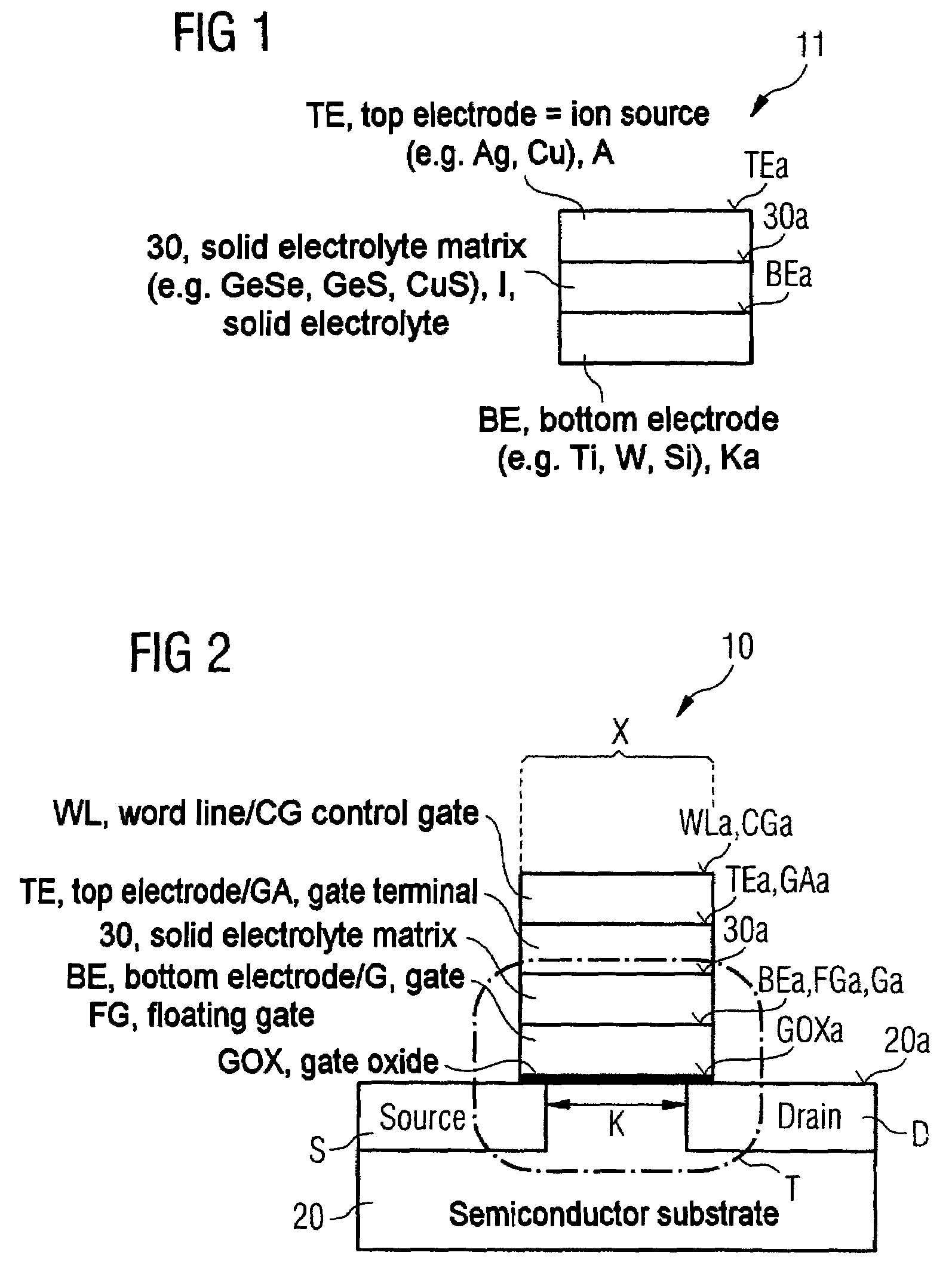
Method for fabricating a semiconductor memory cell
InactiveUS20050201143A1Easy to manufactureIncrease spaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSemiconductor
Semiconductor memory cell and also a corresponding fabrication method are described, in which a first or bottom electrode device of the memory element of the semiconductor memory cell according to the invention and the gate electrode device of the underlying field effect transistor as selection transistor of the semiconductor memory cell are formed as the same material region or with a common material region.
Owner:ADESTO TECH
Scalable apparatus and method for increasing throughput in multiple level minimum logic networks using a plurality of control lines
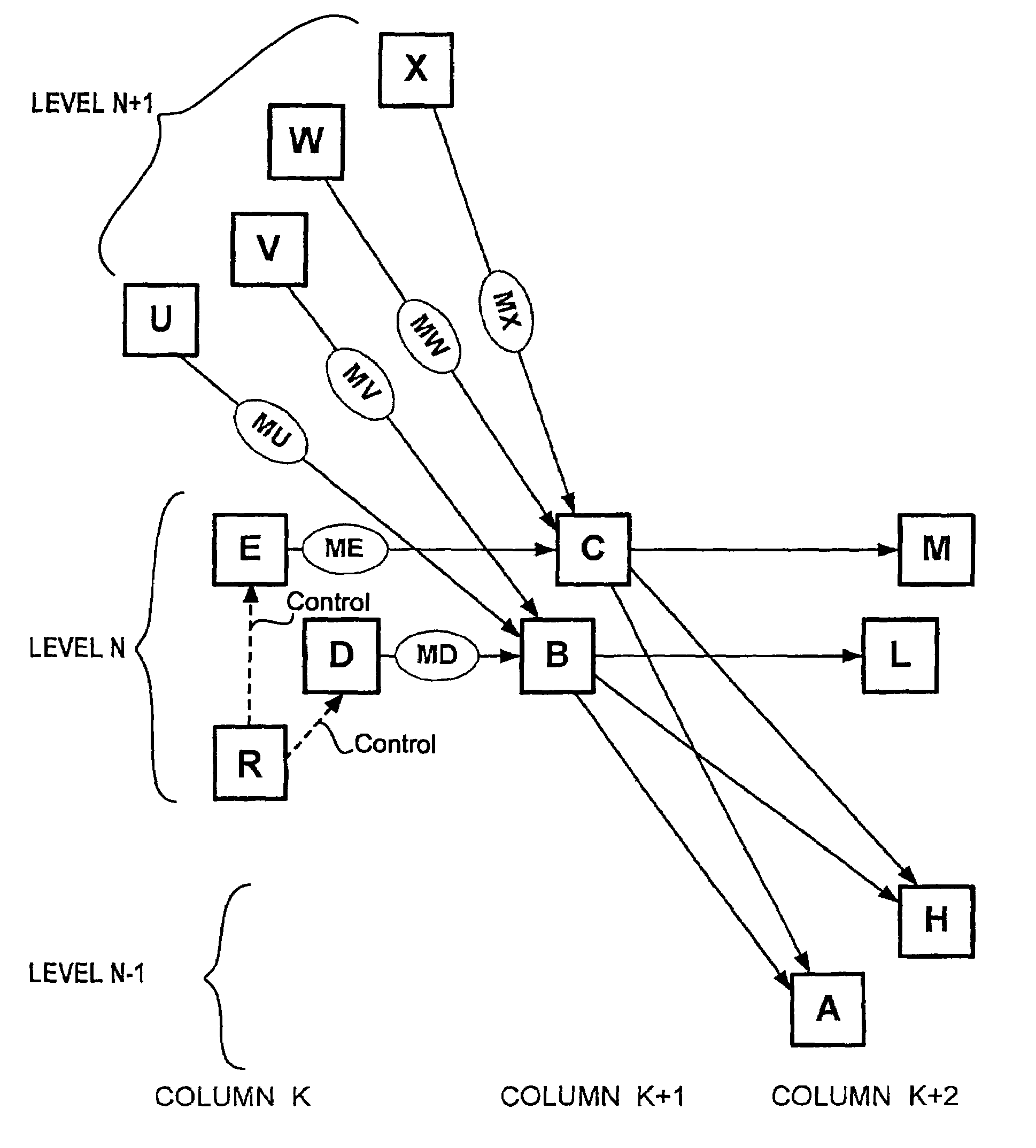
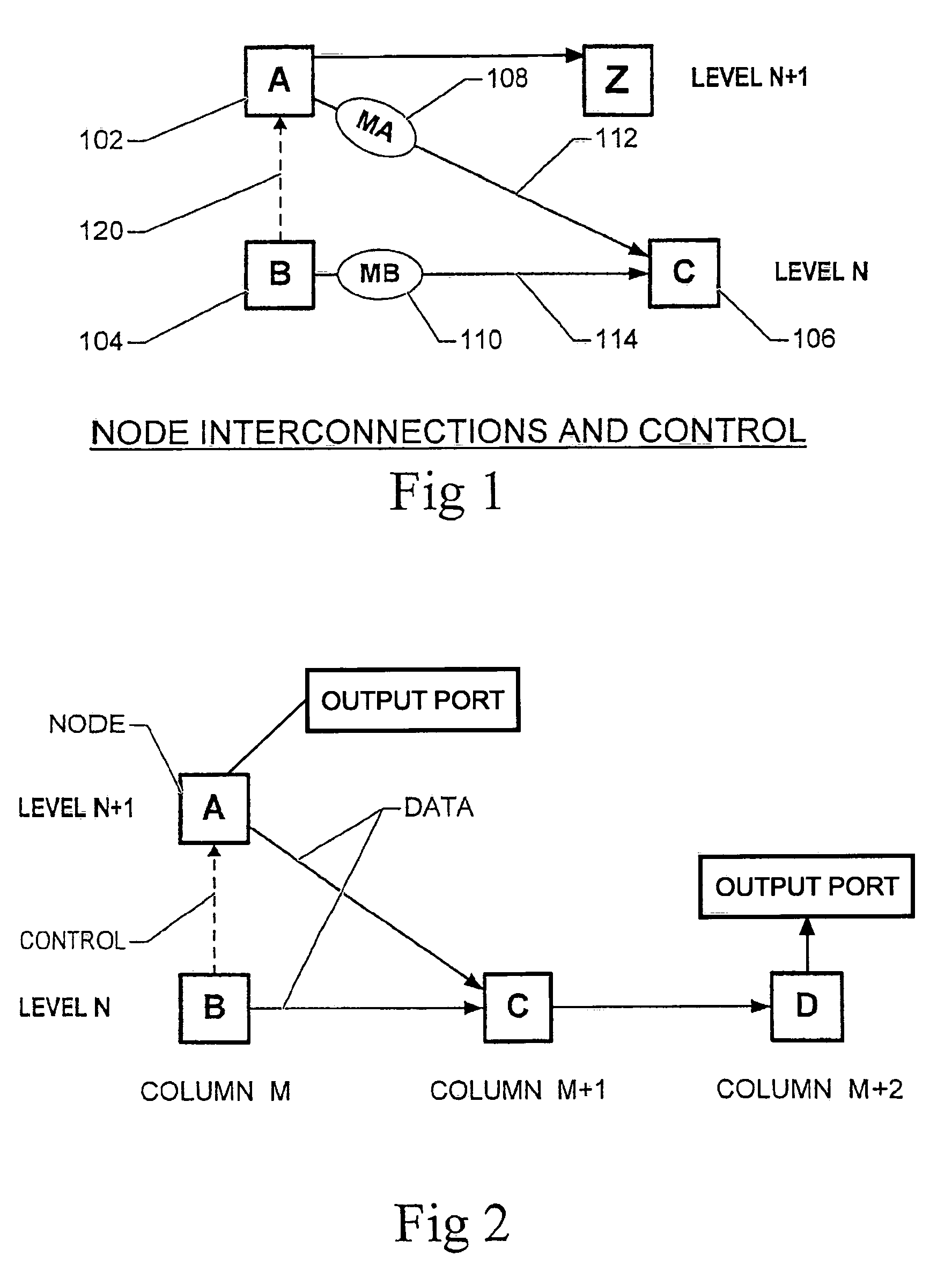
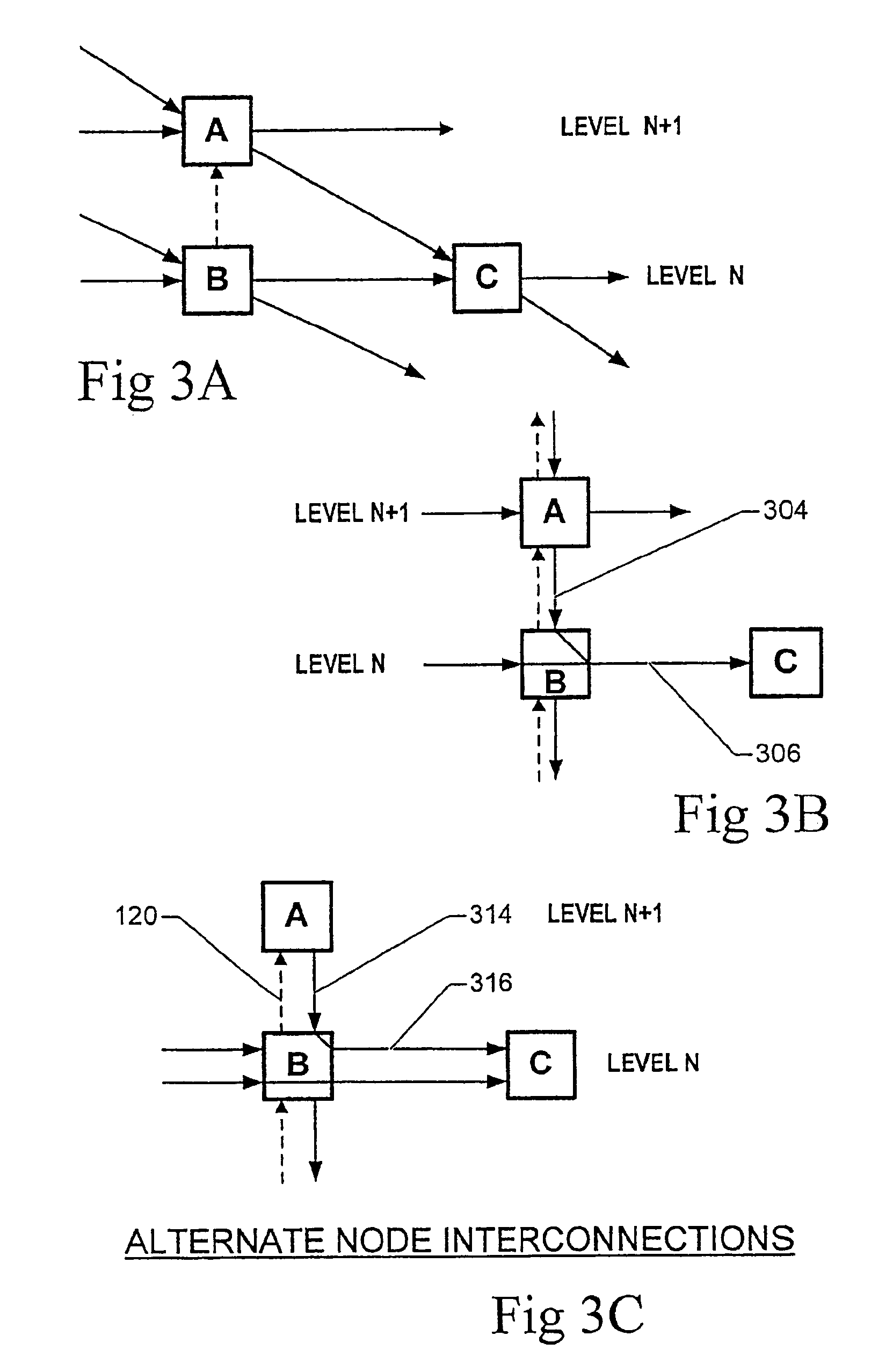
InactiveUS7221677B1Information receiveImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsLevel structureControl line
A network or interconnect structure which includes a plurality of nodes which are interconnected within a hierarchical multiple level structure. The level of each node is determined by the position of the node within the structure and data messages move from node to node from a source level to a destination level. Each node within the interconnect structure is capable of receiving simultaneous data messages at its input ports from any other node and the receiving node is able to transmit each of the received data messages through its output ports to separate nodes in the interconnect structure to one or more levels below the level of the receiving node.
Owner:INTERACTIC HLDG LLC
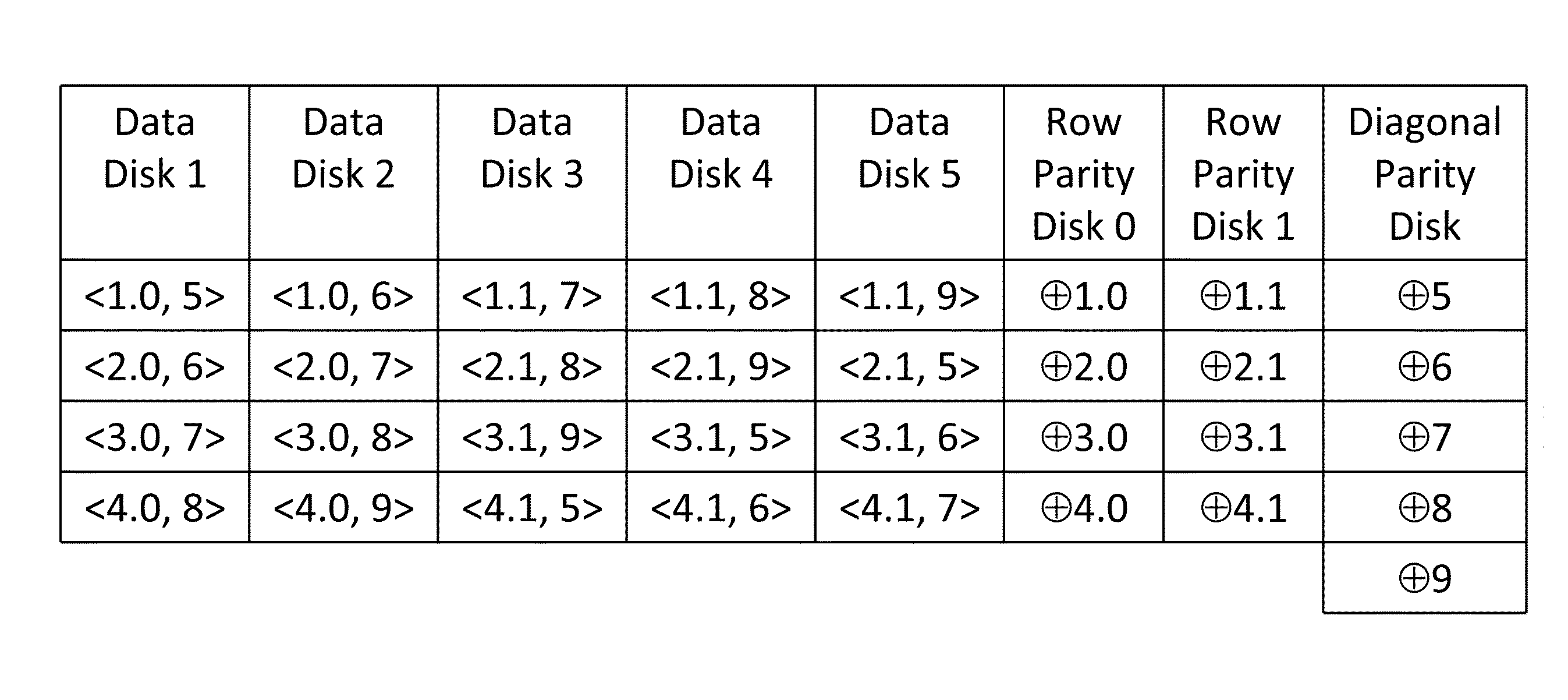
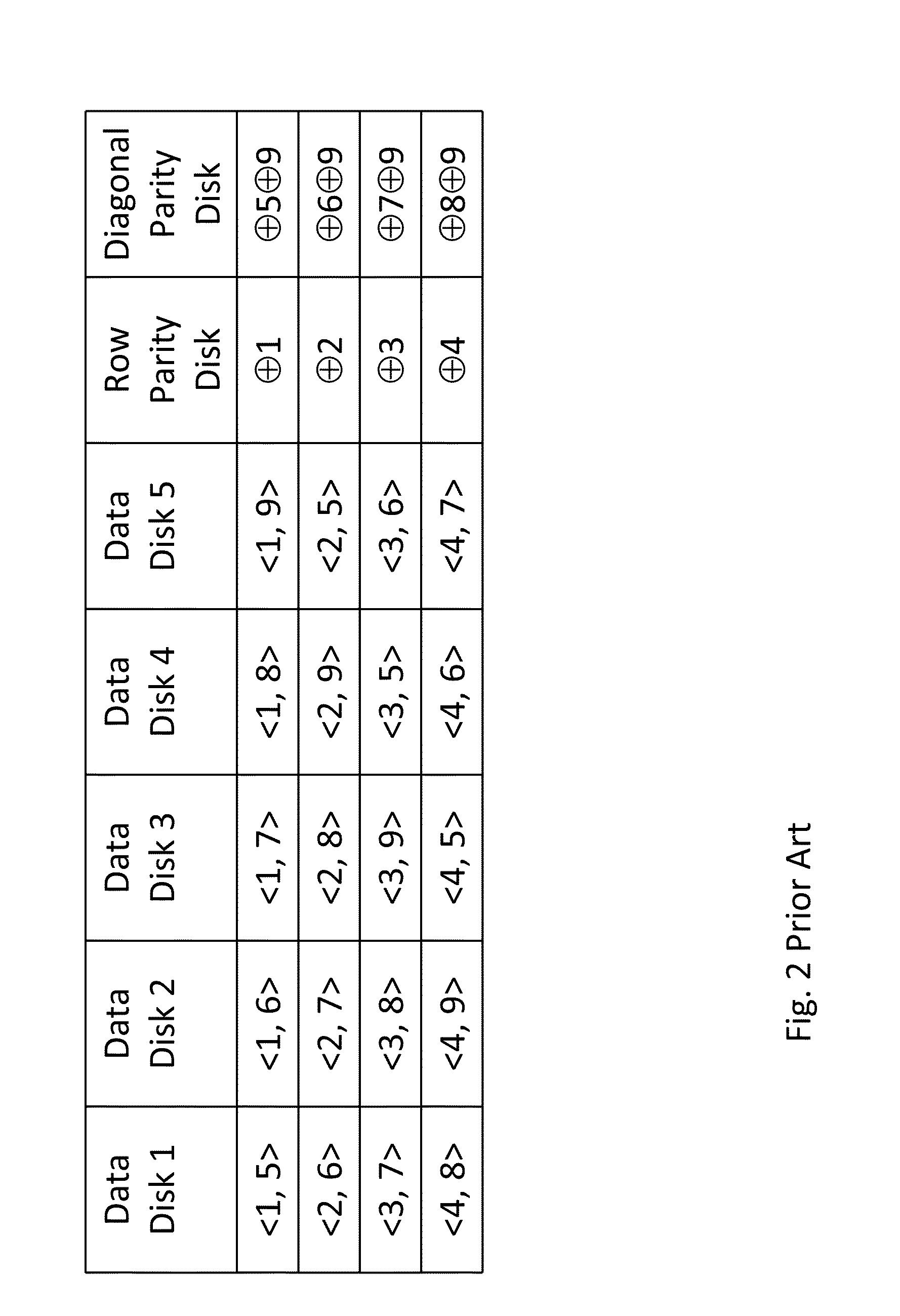
Method and system for storing data in raid memory devices
ActiveUS8990495B2Reduce overheadUtility and advantageRedundant data error correctionMemory systemsRAID
A redundant array of independent disk (RAID) memory storage system comprising data storage blocks arranged in a first plurality of data rows and a second plurality of data columns, wherein parity data is stored in additionally defined parity blocks, and wherein numbers of data blocks in respective columns are different, to accommodate the additional diagonal parity data block that the geometry of the system requires. The system is suitable for an SSD array in which sequential disk readout is not required.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
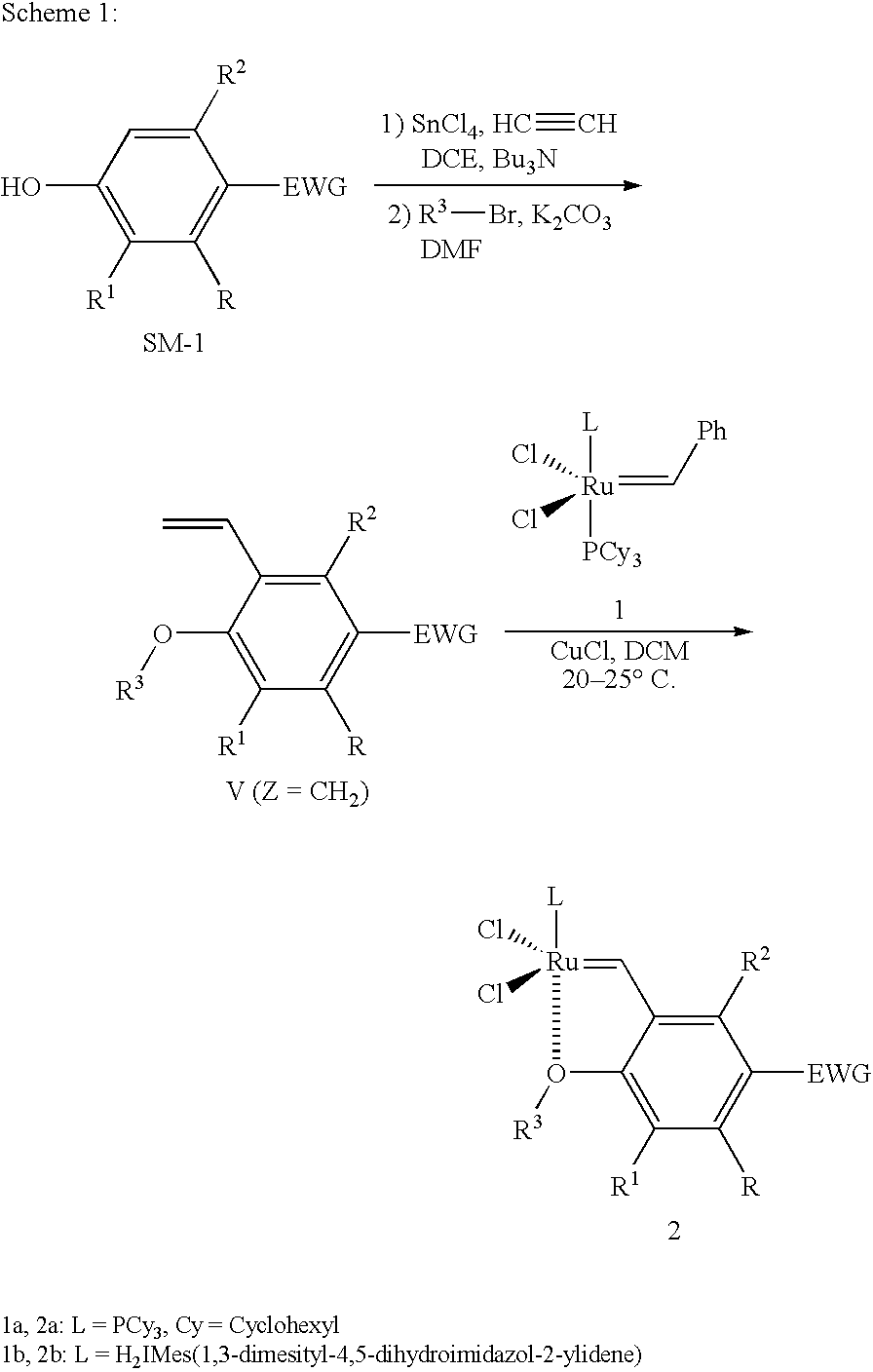
Recyclable ruthenium catalysts for metathesis reactions
ActiveUS7632772B2Utility and advantageLittle or no traceRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationCarbeneAlkene
The invention relates to novel carbene ligands and their incorporated monomeric and resin / polymer linked ruthenium catalysts, which are recyclable and highly active for olefin metathesis reactions. It is disclosed that significant electronic effect of different substituted 2-alkoxybenzylidene ligands on the catalytic activity and stability of corresponding carbene ruthenium complexes, some of novel ruthenium complexes in the invention can be broadly used as catalysts highly efficient for olefin metathesis reactions, particularly in ring-closing (RCM), ring-opening (ROM), ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) and cross metathesis (CM) in high yield. The invention also relates to preparation of new ruthenium complexes and the use in metathesis.
Owner:ZANNAN SCITECH
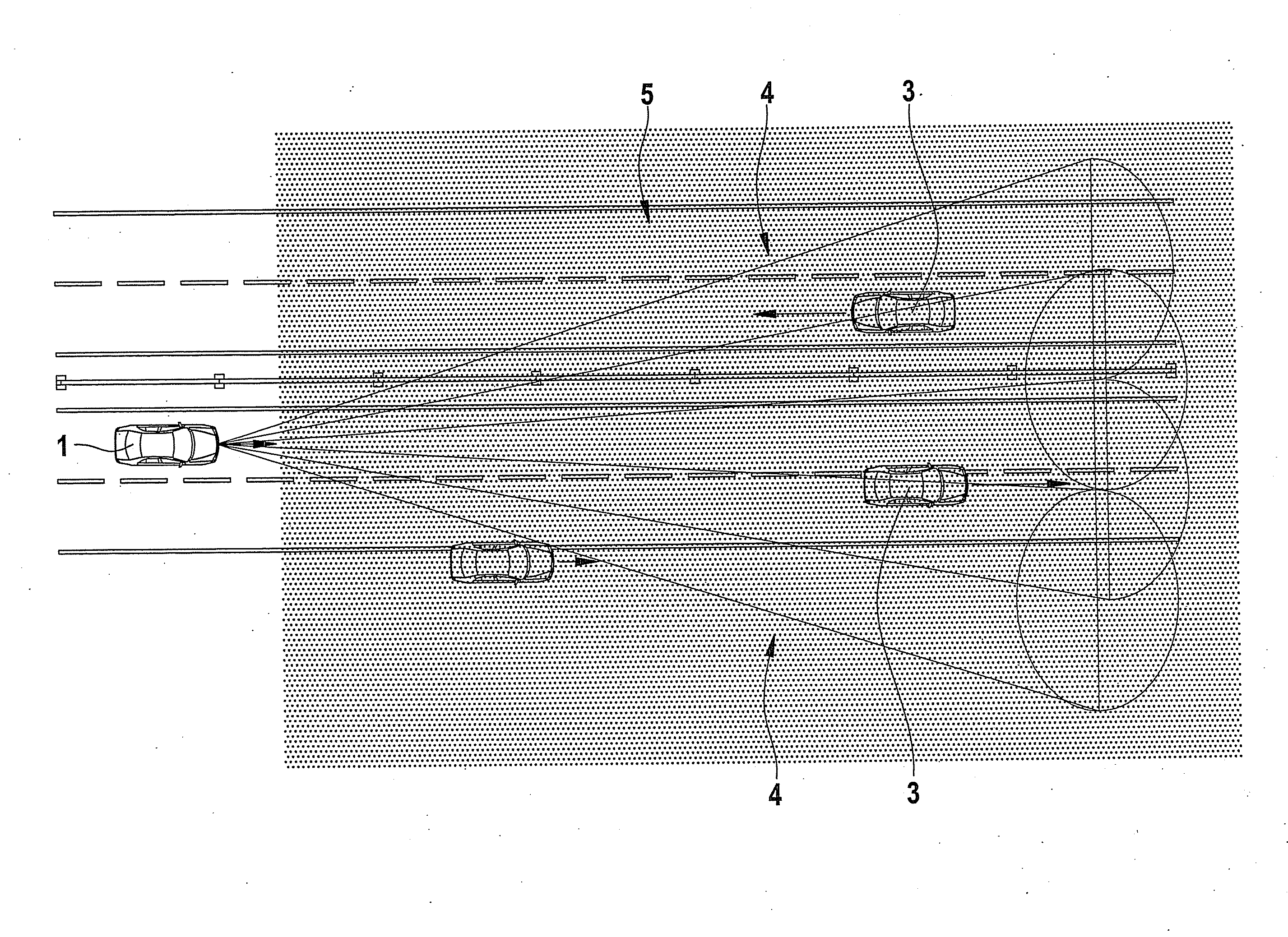
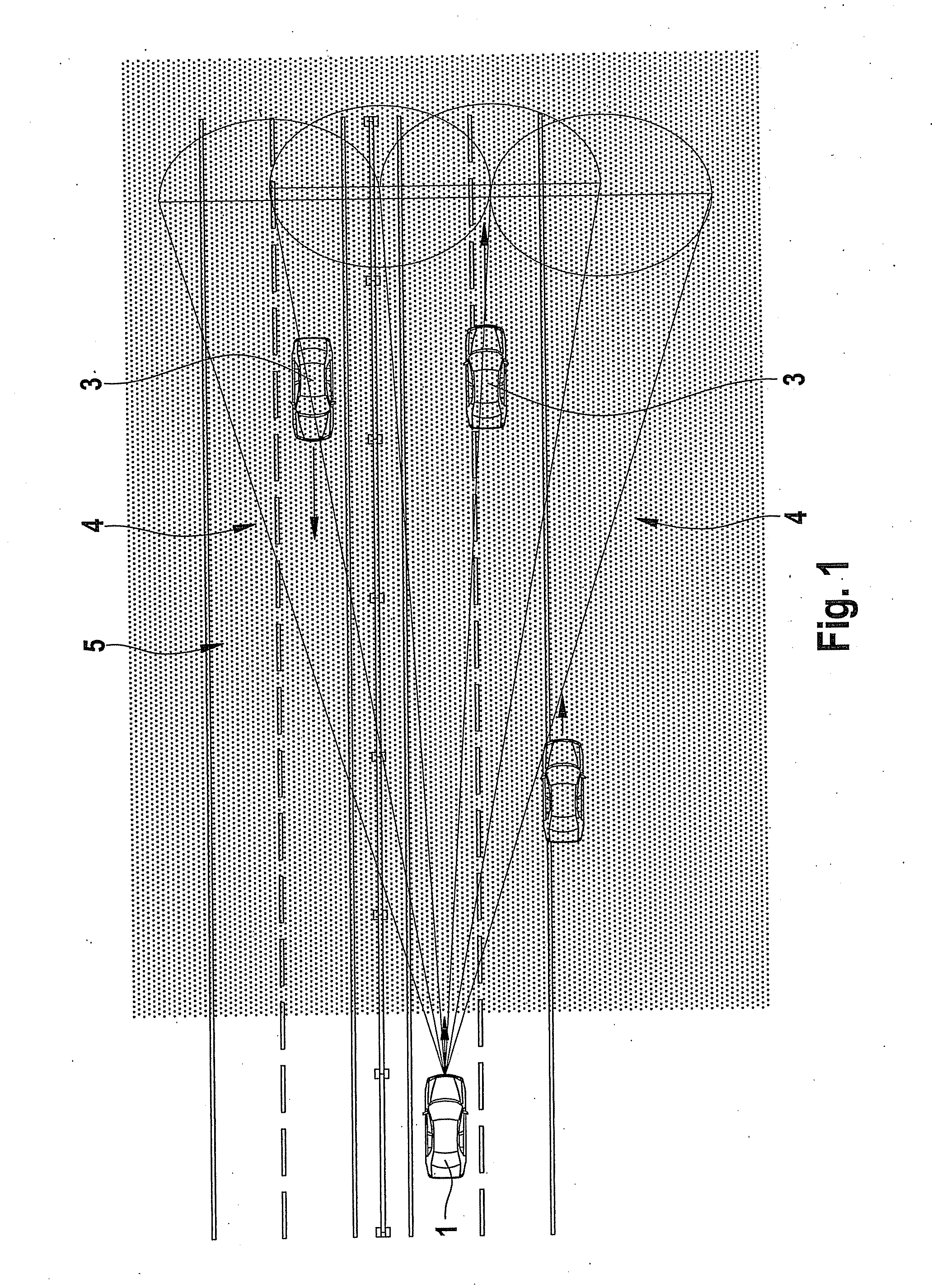
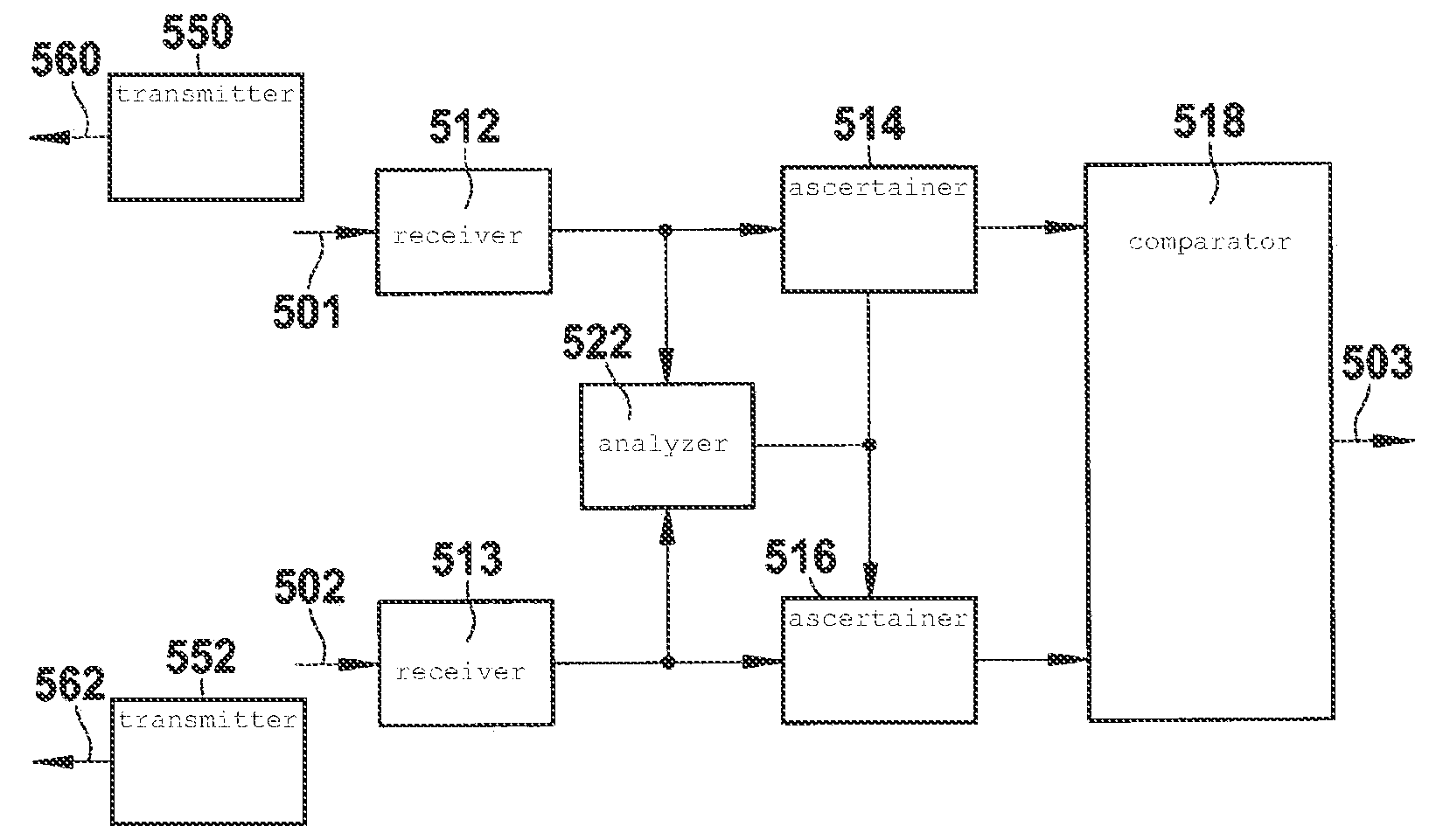
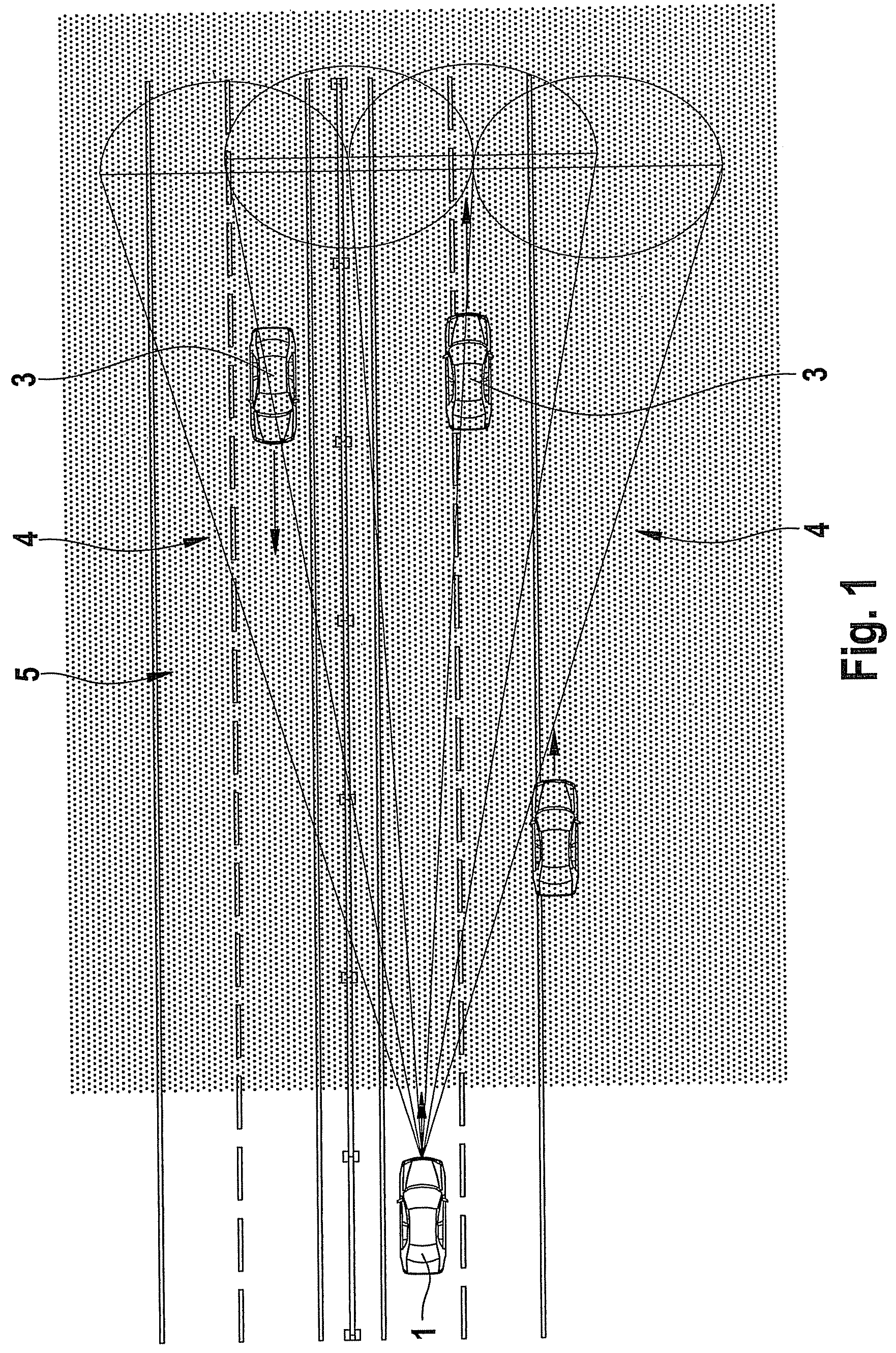
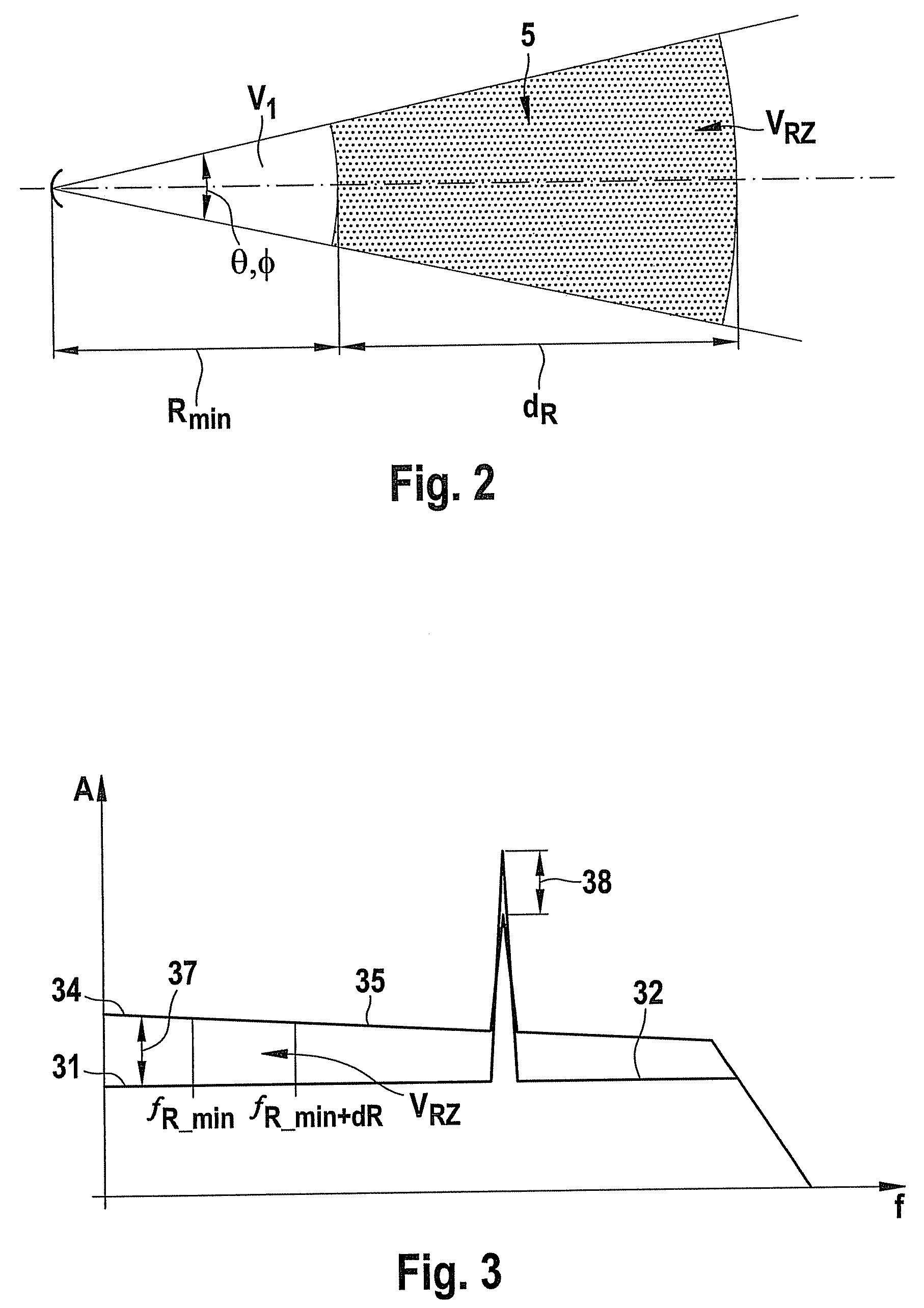
Method and device for detecting precipitation by radar
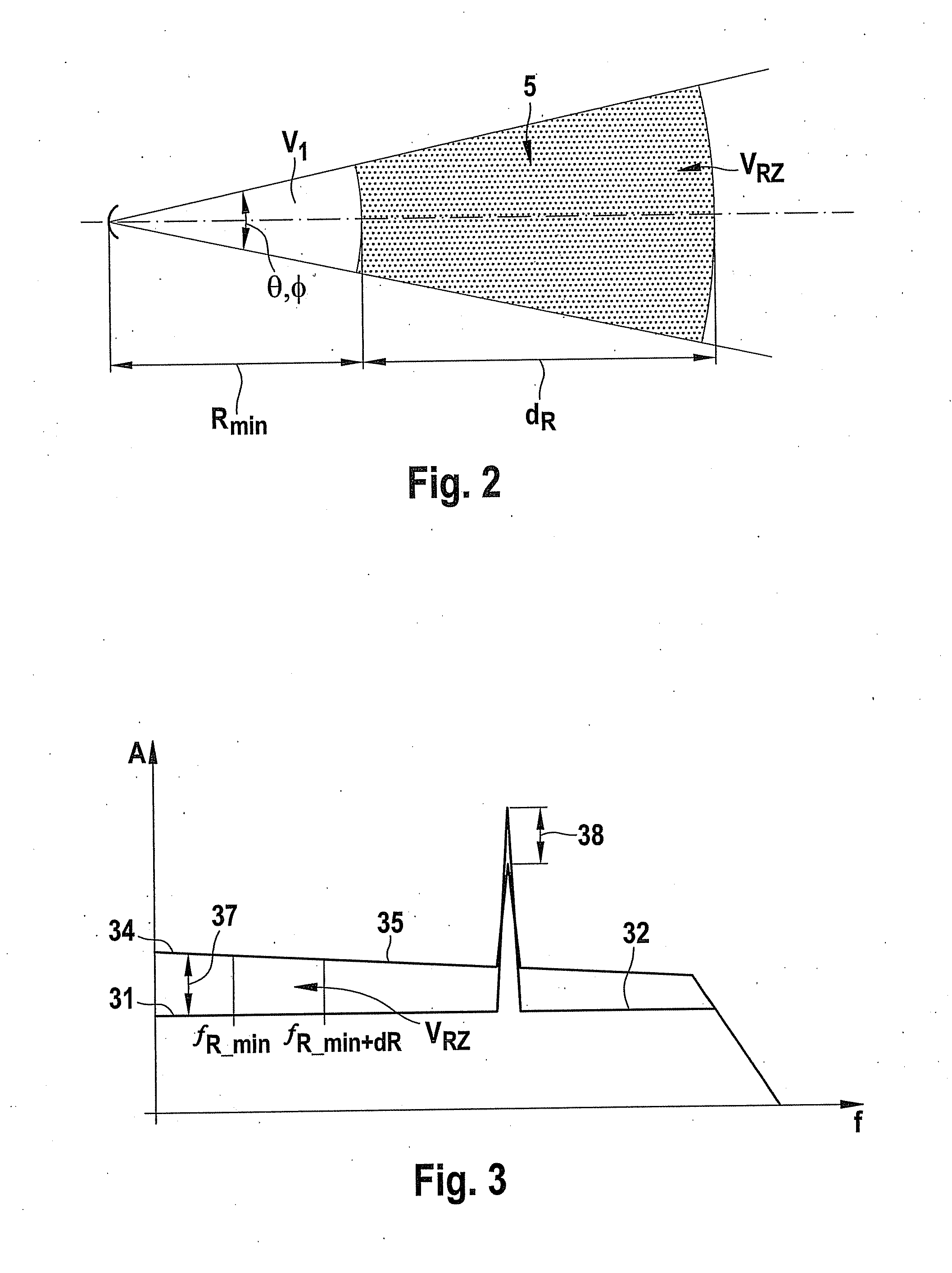
InactiveUS20100309041A1Improve accuracyIncrease flexibilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationRadar signalsPrecipitation
A method for detecting precipitation in a region monitored by radar beams includes ascertaining a first average power of a first backscattered radar signal, ascertaining a second average power of a second backscattered radar signal, and detecting an existence of a homogenous medium when the average powers conform.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Packing source data packets into transporting packets with fragmentation
InactiveUS20110116394A1Optimize advantageUtility and advantageNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemTelecommunications link
A communication system and method are disclosed for transmitting packets of information in at least one first format over a communications link that utilizes packets of information in a second format. In certain embodiments, the packets of information in a first format are converted to packets of information in the second format prior to transmission via the communications link by packing and fragmenting the information in the first format in a coordinated manner. Embodiments may also utilize packing subheaders and fragmentation control bits in the packing and fragmentation processes.
Owner:WI LAN INC
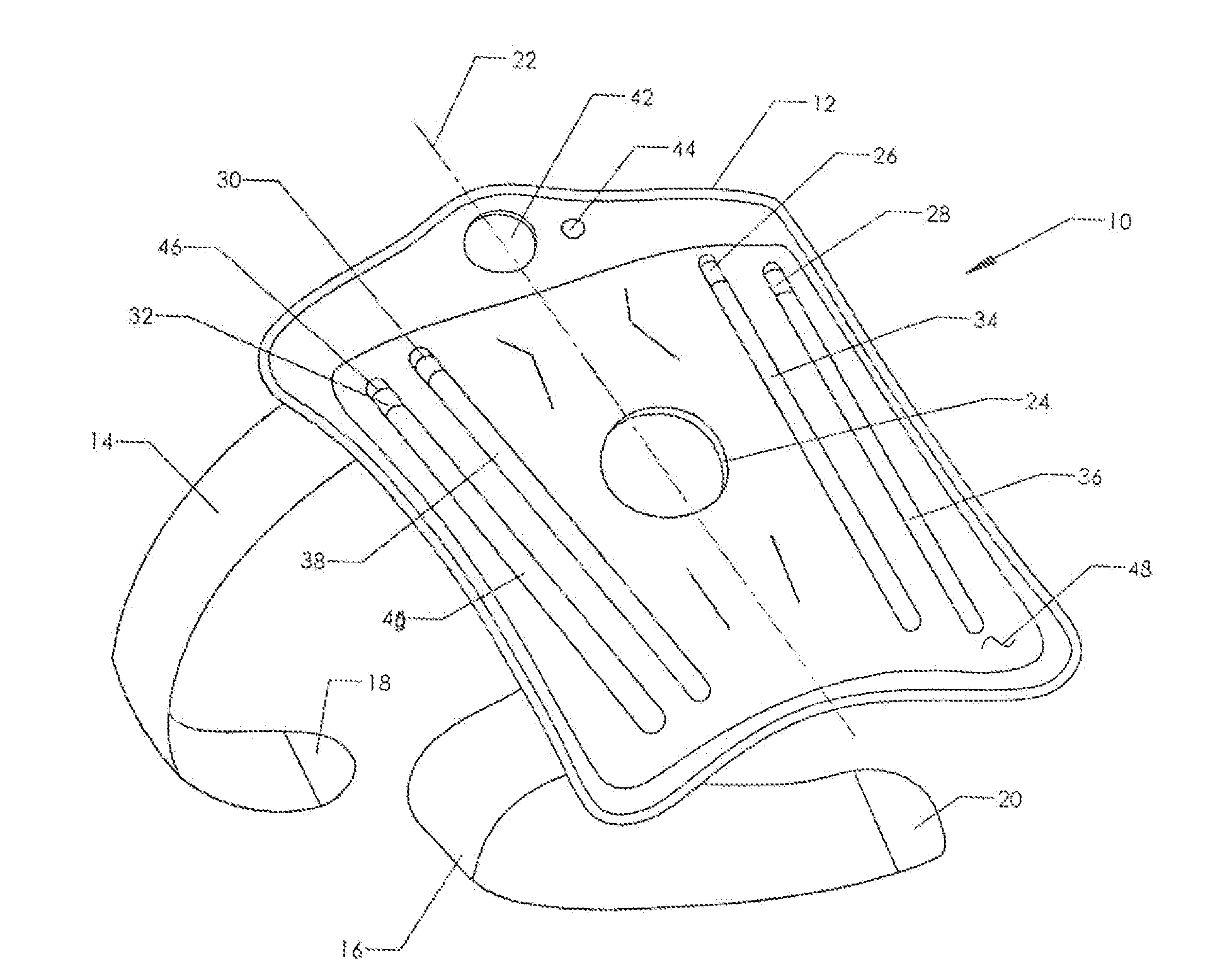
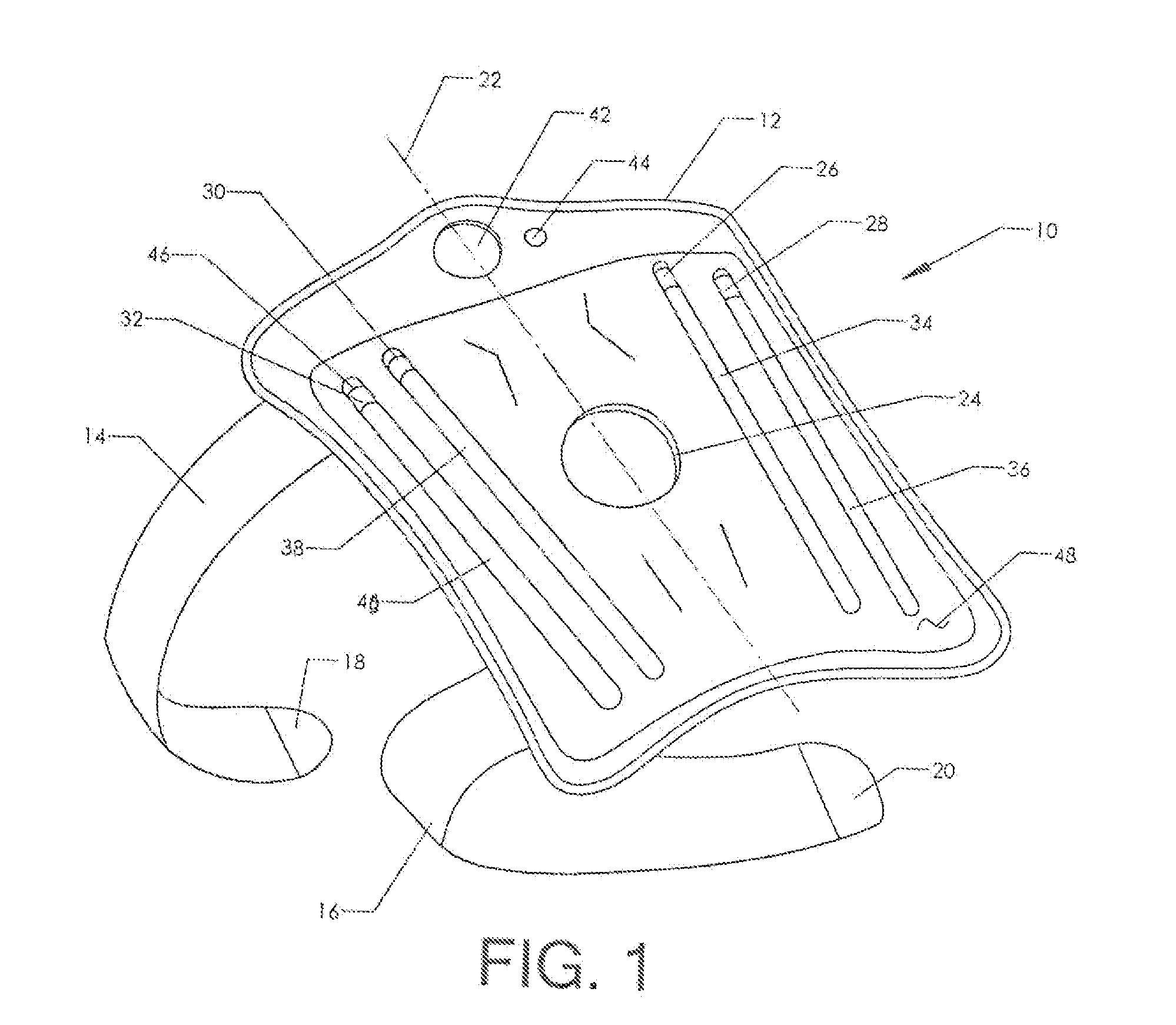
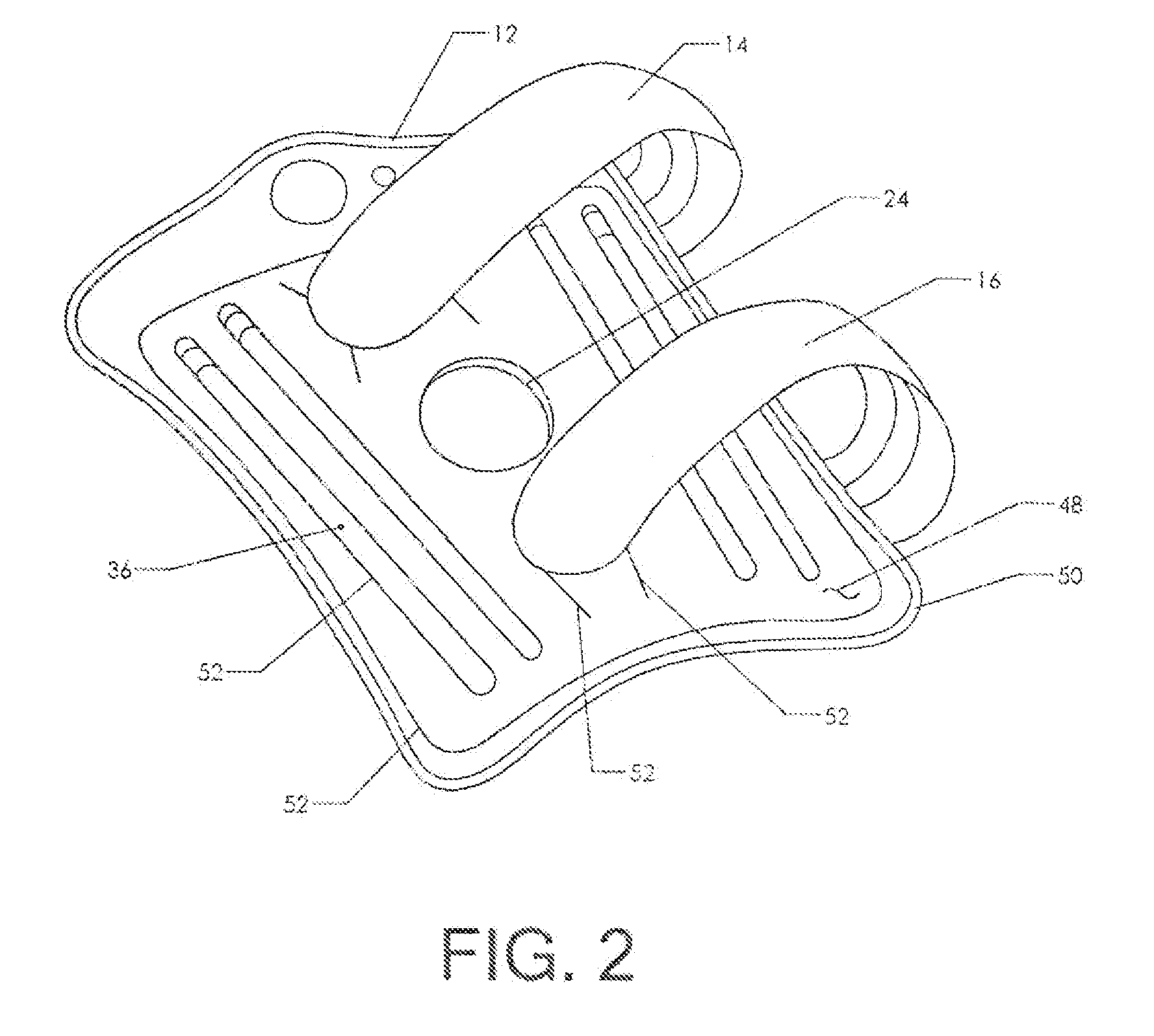
Pneumatic Knee Brace with Removable Stays
ActiveUS20140330184A1Easy to disassembleImprove rigidityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTherapeutic coolingMedicineKnee Joint
A reconfigurable knee brace which is particularly suitable for cold therapy. The brace includes a large wrap which fits over the front of the leg and wraps around the knee. Two or more securing straps are provided to hold the wrap in place. Once in position, an internal air bladder can be inflated to secure the fit. The user inflates the air bladder using an included squeeze pump and selectively deflates the bladder using a release button. One or more removable stays are positioned on the left and right lateral sides of the knee. When the stays are in position, the knee is held in place and cannot flex or extend. However, the stays are made removable. Once the stays are removed, the knee is able to flex and extend (though it is still stabilized by the encircling wrap).
Owner:KILBEY BRIAN E
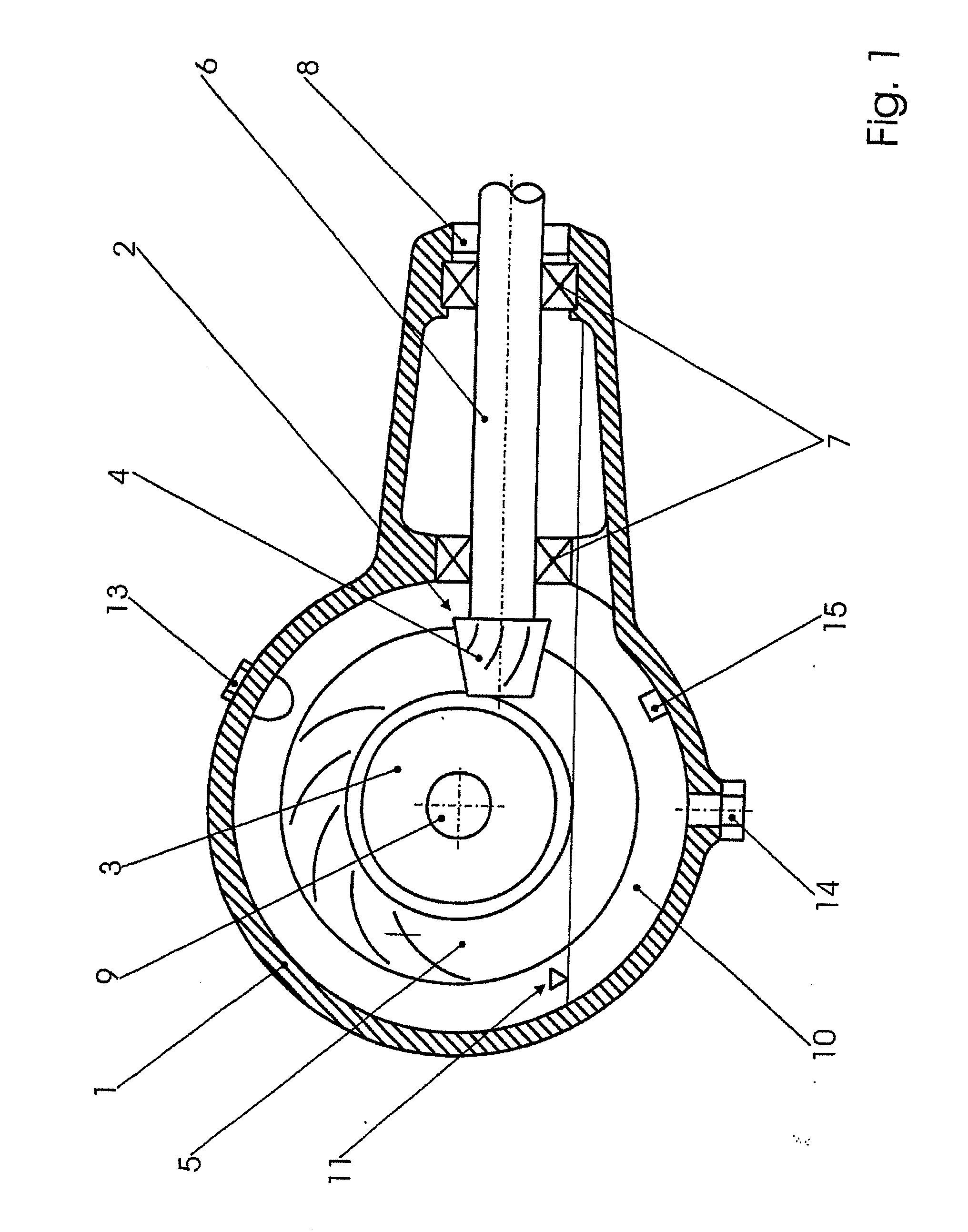
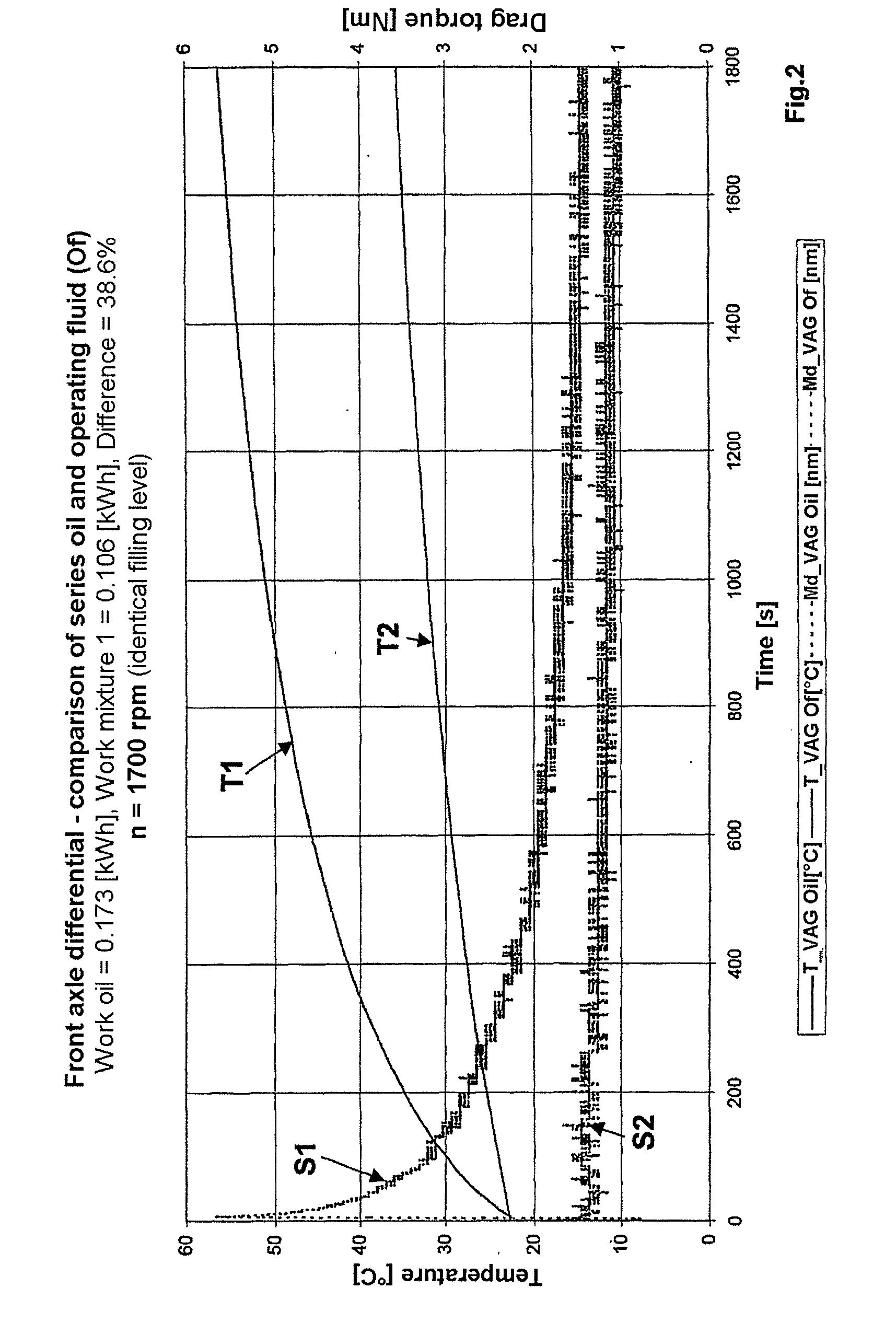
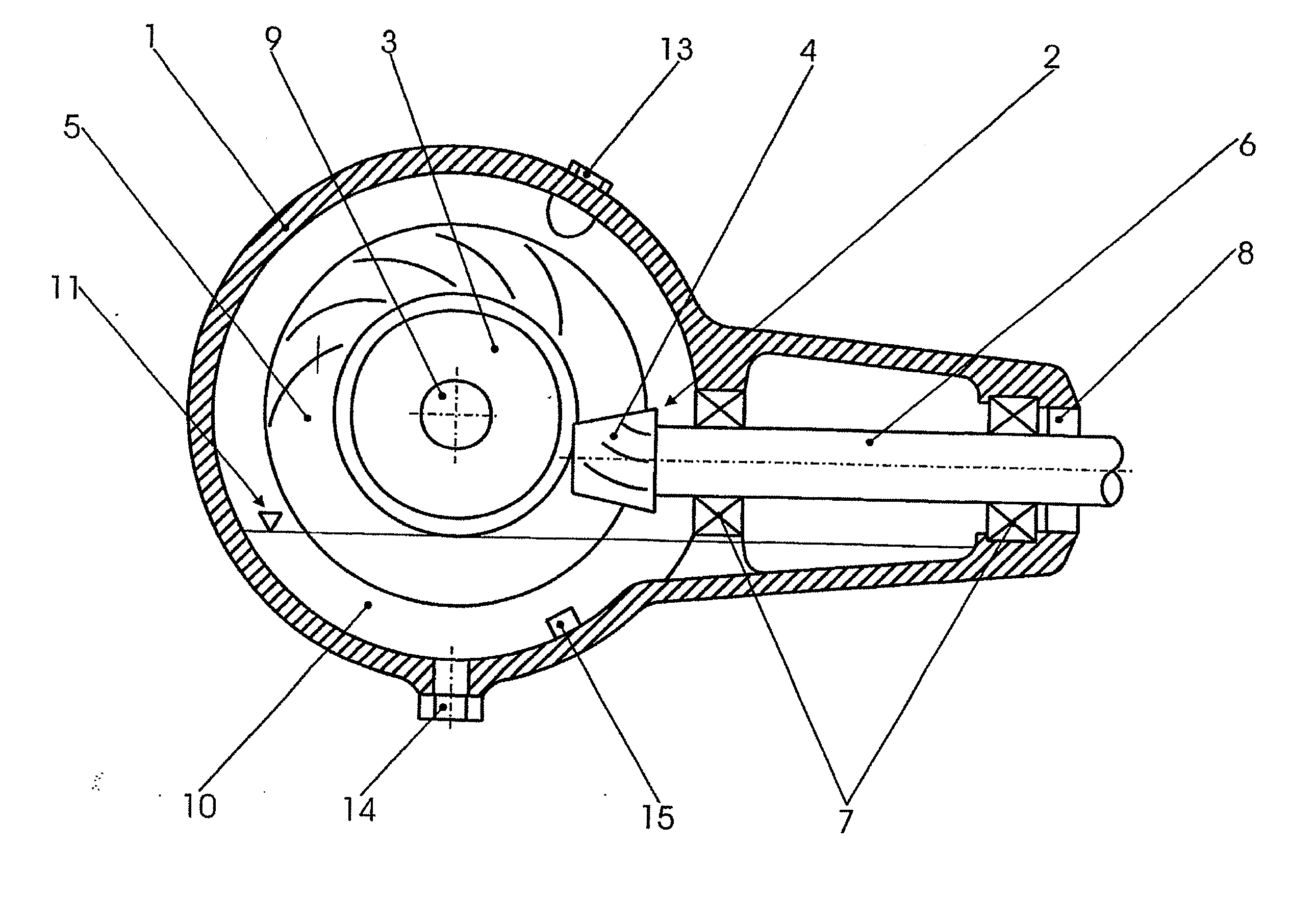
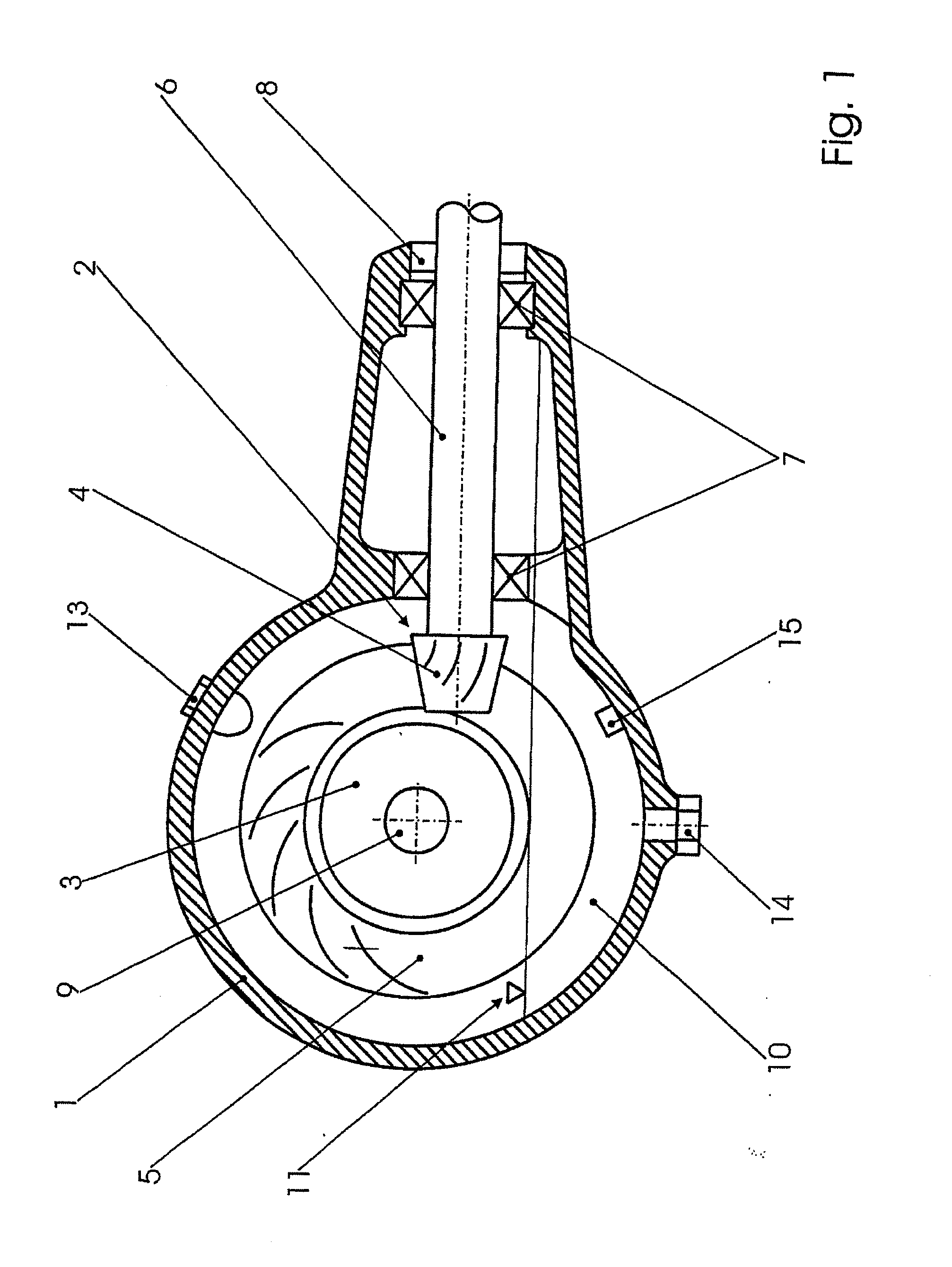
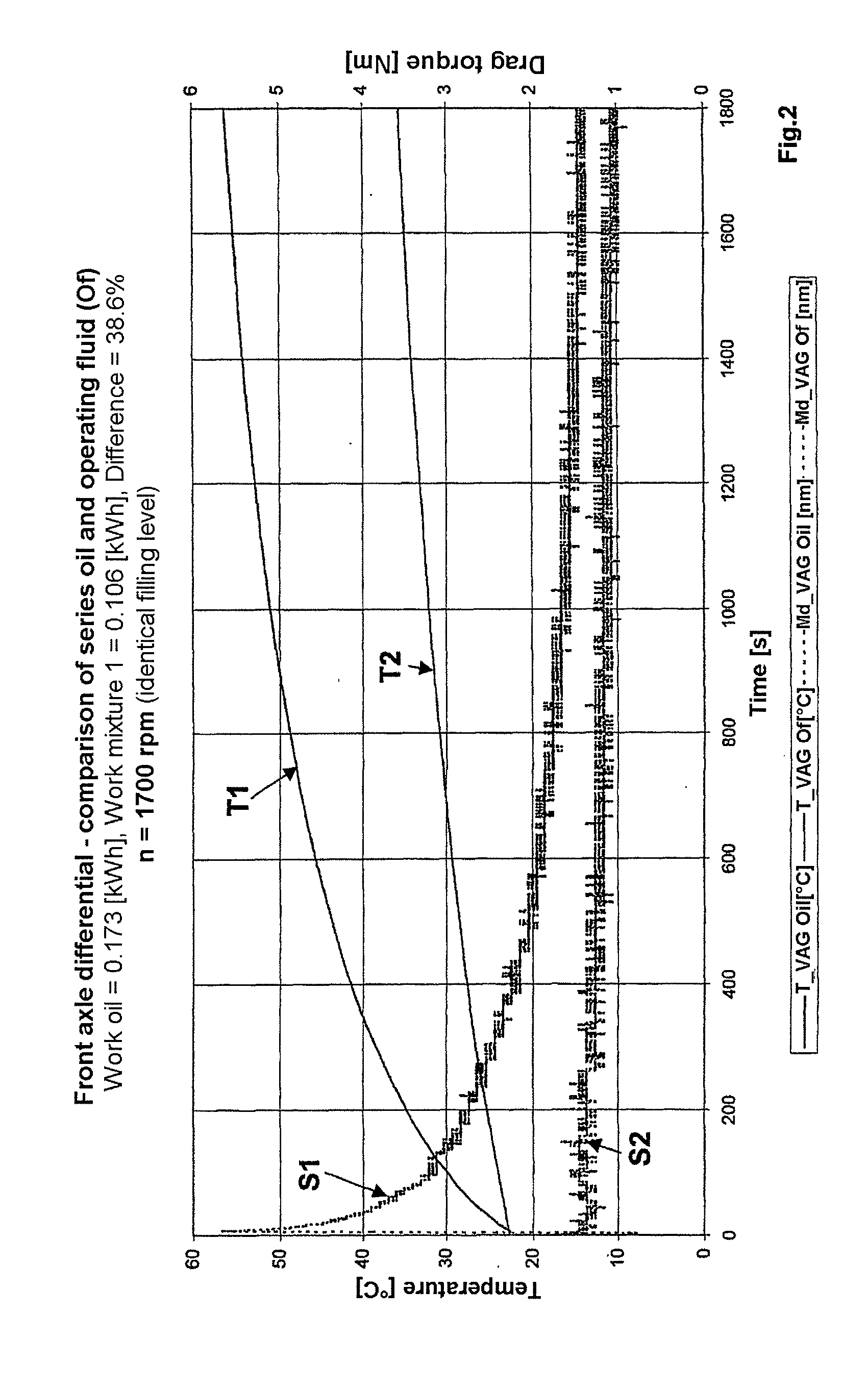
Operable transmission, working fluid for such a transmission, and method for commissioning the same
InactiveUS20090277298A1Less installation spaceHigh levelMetal rolling stand detailsVacuum evaporation coatingWorking fluidMicrometer
An operable transmission comprising toothed wheels. In order to operate the transmission with a lubricant and coolant which is environmentally friendly while providing improved heat dissipation and temperature-independent viscosity, the transmission contains a mixture of water and a glycol or similar, in which graphite particles are suspended. The mixture contains 40 to 60 percent per weight of the glycol and 2 to 25 percent by weight of graphite in the form of flaky graphite particles having a grain size of less than 12 micrometers, the remainder being composed of water and other admixtures and / or additives. Also disclosed are the lubricant and coolant as well as a method for starting a transmission operated with the lubricant and coolant.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
Method for fabricating a semiconductor memory cell
InactiveUS7214587B2Easy to manufactureIncrease spaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSemiconductor
Semiconductor memory cell and also a corresponding fabrication method are described, in which a first or bottom electrode device of the memory element of the semiconductor memory cell according to the invention and the gate electrode device of the underlying field effect transistor as selection transistor of the semiconductor memory cell are formed as the same material region or with a common material region.
Owner:ADESTO TECH
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7915807B2Reduce the driving voltageLonger heating element lifetimeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsLight emitting device
A light emitting device is provided which has a structure for lowering energy barriers at interfaces between layers of a laminate organic compound layer. A mixed layer (105) composed of a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (1) (102) and a material that constitutes an organic compound layer (2) (103) is formed at the interface between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103). The energy barrier formed between the organic compound layer (1) (102) and the organic compound layer (2) (103) thus can be lowered.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light Emitting Device and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20080111481A1Reduce the driving voltageLonger heating element lifetimeDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsOrganic compound
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for fabricating a biochip using the high density carbon nanotube film or pattern
InactiveUS8067341B2Improve defectsUtility and advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical conductorCarbon nanotube
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Clutch engaging and disengaging apparatus
InactiveUS6345710B1Utility and advantageInexpensive, deformation-resistantFluid actuated clutchesMachines/enginesMobile vehiclePlastic materials
The cylinder of a cylinder and piston unit in the friction clutch engaging / disengaging apparatus of a power train for use in a motor vehicle is assembled of two separately produced coaxial tubular walls. The outer wall is made of a plastic material and is of one piece with an extension serving to supply pressurized hydraulic fluid from a pump or another source to the plenum chamber for the reciprocable annular piston between the two walls. The inner wall is made of sheet metal and one of its end portions is separably coupled to one end portion of the outer wall by snap action. Such one end portion of the outer wall is separably secured to a support, usually the transmission case in the power train of the motor vehicle.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Optical device
InactiveUS7068345B2Efficient developmentUtility and advantageLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsOptical propertyDisplay device
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Operable transmission, working fluid for such a transmission, and method for commissioning the same
ActiveUS20120304792A1Less installation spaceHigh levelGearboxesPortable liftingWorking fluidGear wheel
An operable transmission comprising toothed wheels. In order to operate the transmission with a lubricant and coolant which is environmentally friendly while providing improved heat dissipation and temperature-independent viscosity, the transmission contains a mixture of water and a glycol or similar, in which graphite particles are suspended. The mixture contains 40 to 60 percent per weight of the glycol and 2 to 25 percent by weight of graphite in the form of flaky graphite particles having a grain size of less than 12 micrometers, the remainder being composed of water and other admixtures and / or additives. Also disclosed are the lubricant and coolant as well as a method for starting a transmission operated with the lubricant and coolant.
Owner:MAGNA STEYR FAHRZEUGTECHN
Method for producing a stratified composite material
InactiveUS7156149B2Utility and advantageNone have achieved superiorPretreated surfacesCoatingsSurface layerSolid particle
A method is described for producing a stratified composite material, with a layer of sinterable solids particles being applied to a strip-like metal carrier and being sintered with liquid phase by the supply of heat continuously in the forward feed direction. In order to provide simplified production conditions it is proposed that the metal carrier is heated continuously in the forward feed direction with a temperature profile which decreases towards lower temperatures from a maximum temperature above the melting temperature of the solids particles in the region of a surface layer receiving the particle layer towards a core layer of the metal carrier, and that the particle layer is sintered at least in a layer resting on the metal carrier by a heat transmission from the heated metal carrier.
Owner:MIBA GLEITLAGER GMBH
Method for producing a stratified composite material
InactiveUS20050281946A1Low amount of workLow thermal energyPretreated surfacesCoatingsSurface layerLiquid phase
A method is described for producing a stratified composite material, with a layer of sinterable solids particles being applied to a strip-like metal carrier and being sintered with liquid phase by the supply of heat continuously in the forward feed direction. In order to provide simplified production conditions it is proposed that the metal carrier is heated continuously in the forward feed direction with a temperature profile which decreases towards lower temperatures from a maximum temperature above the melting temperature of the solids particles in the region of a surface layer receiving the particle layer towards a core layer of the metal carrier, and that the particle layer is sintered at least in a layer resting on the metal carrier by a heat transmission from the heated metal carrier.
Owner:MIBA GLEITLAGER GMBH
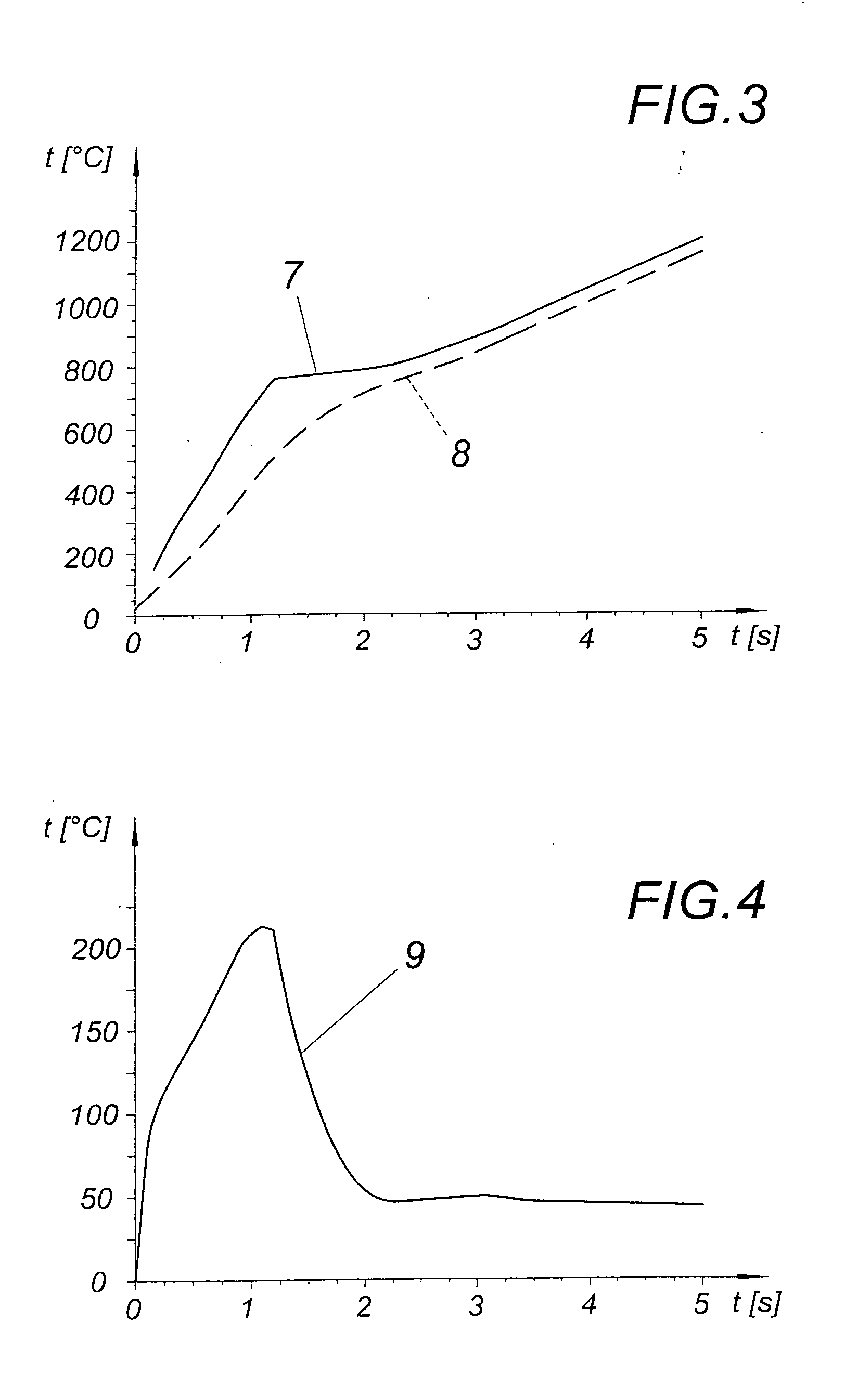
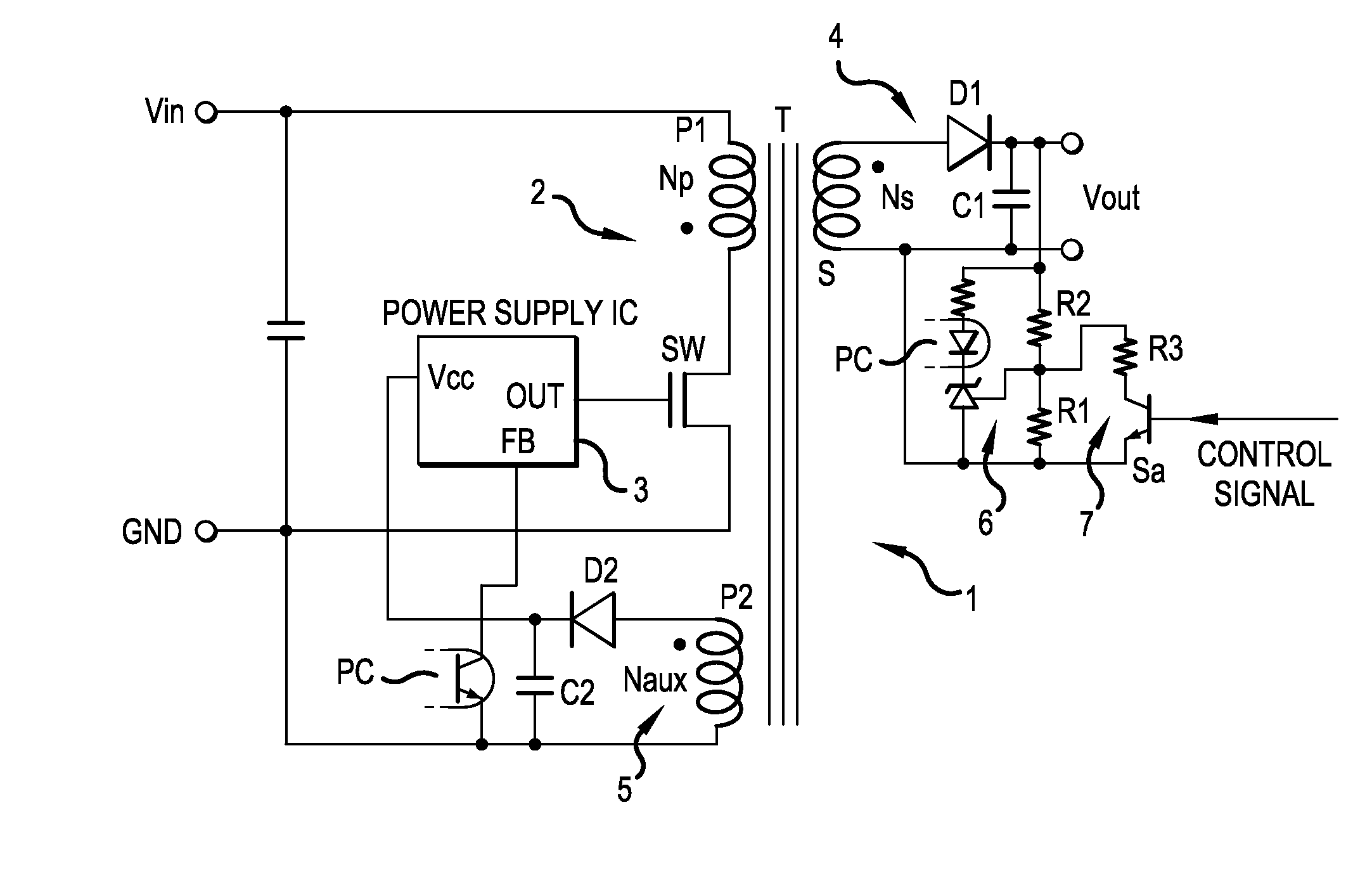
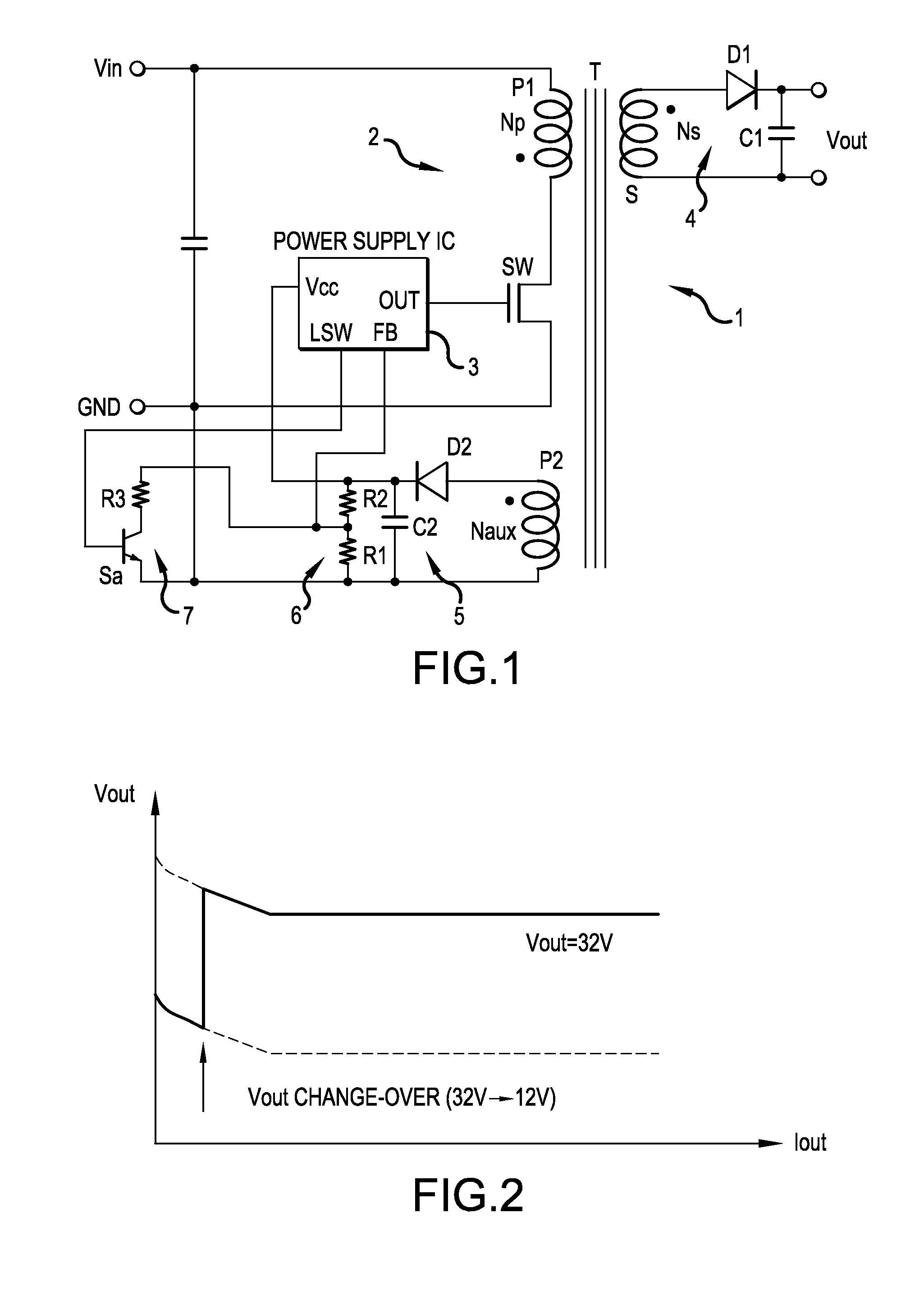
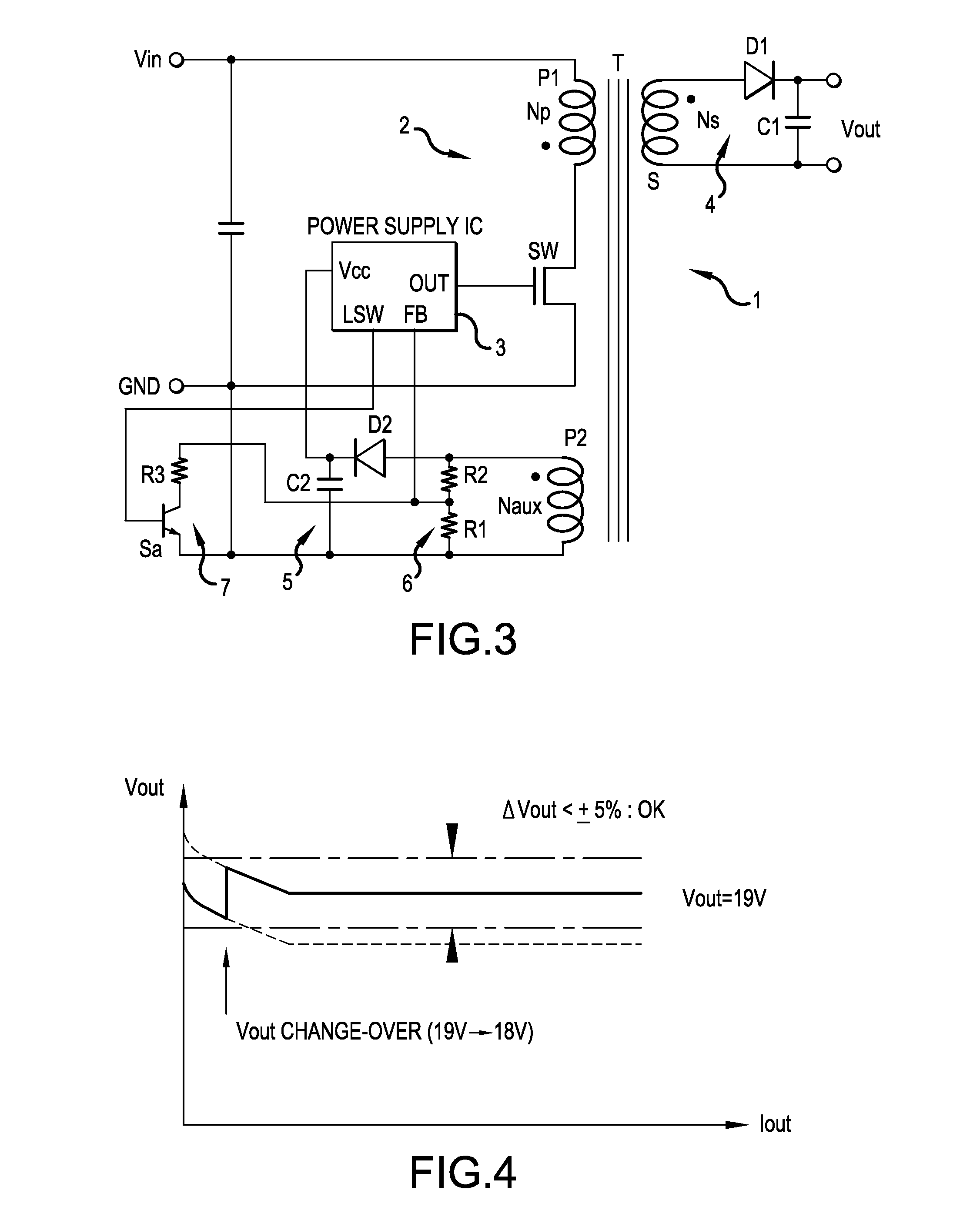
Isolated switching power supply
ActiveUS20150078040A1Simple constructionReadily and surely detectEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionAC powerSwitching power
An isolated switching power supply can include a switching element connected to an input power supply, a control circuit that ON / OFF-drives the switching element and generates an AC power in a secondary winding and in an auxiliary winding of the isolation transformer, an output circuit that rectifies the AC power generated in the on a secondary winding of the isolation transformer and outputs the rectified power, an internal power supply circuit that generates a driving power supply voltage for the control circuit from the AC power generated in the auxiliary winding, an output voltage detecting circuit that feeds back an output monitoring voltage obtained from the driving power supply voltage to the control circuit to control the ON / OFF driving of the switching element by the control circuit and an output voltage controller that changes a level of the output monitoring voltage obtained from the driving power supply voltage.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
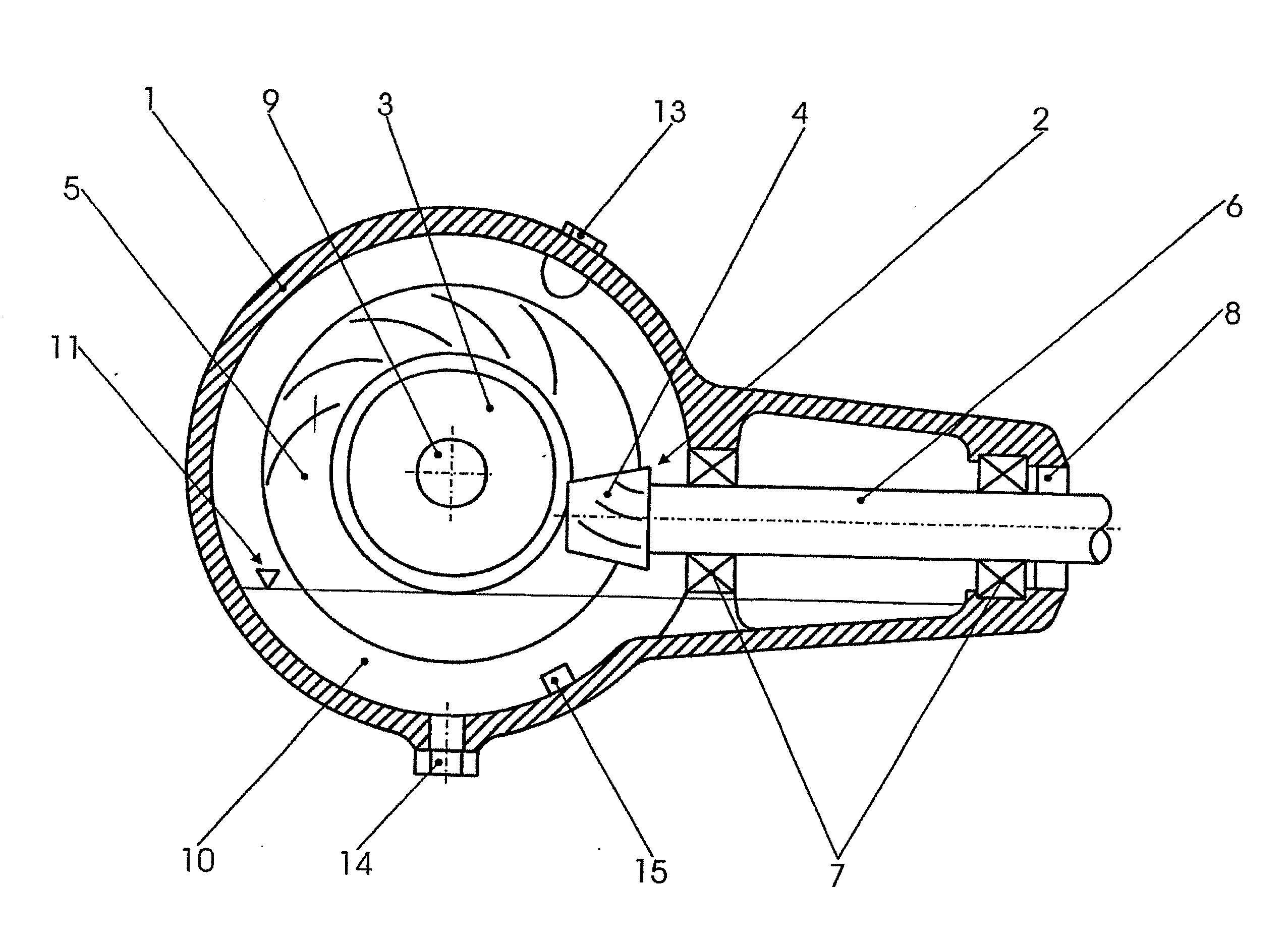
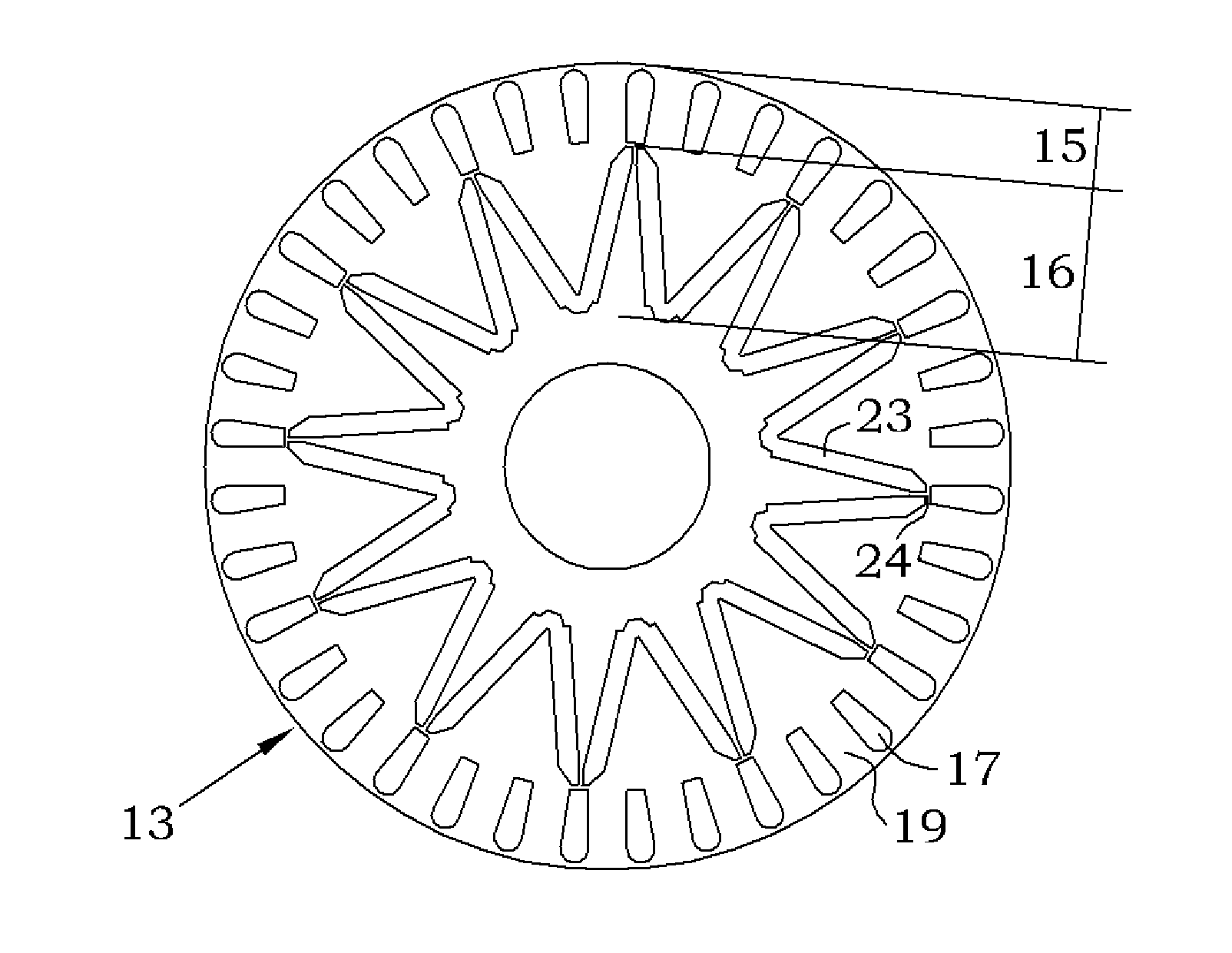
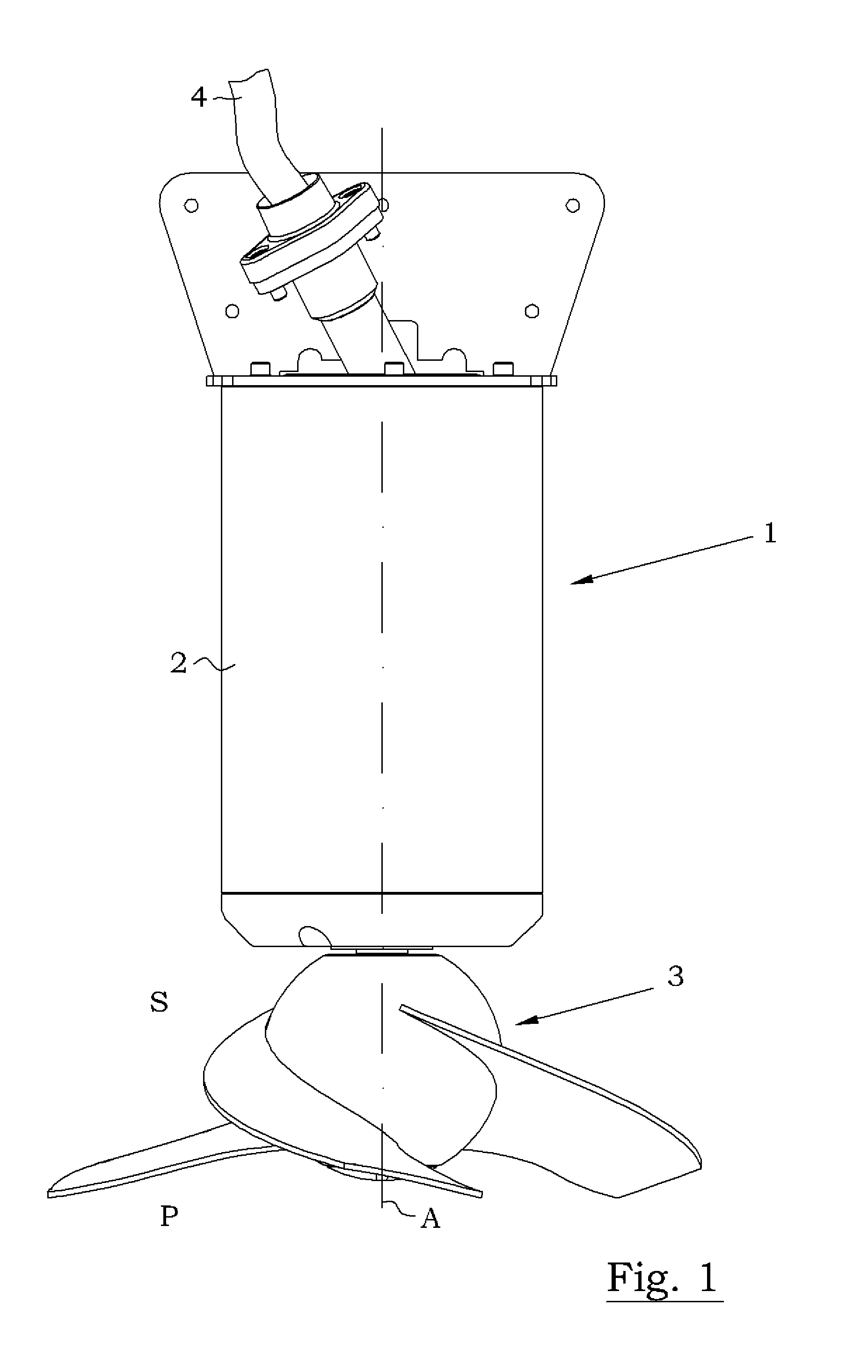
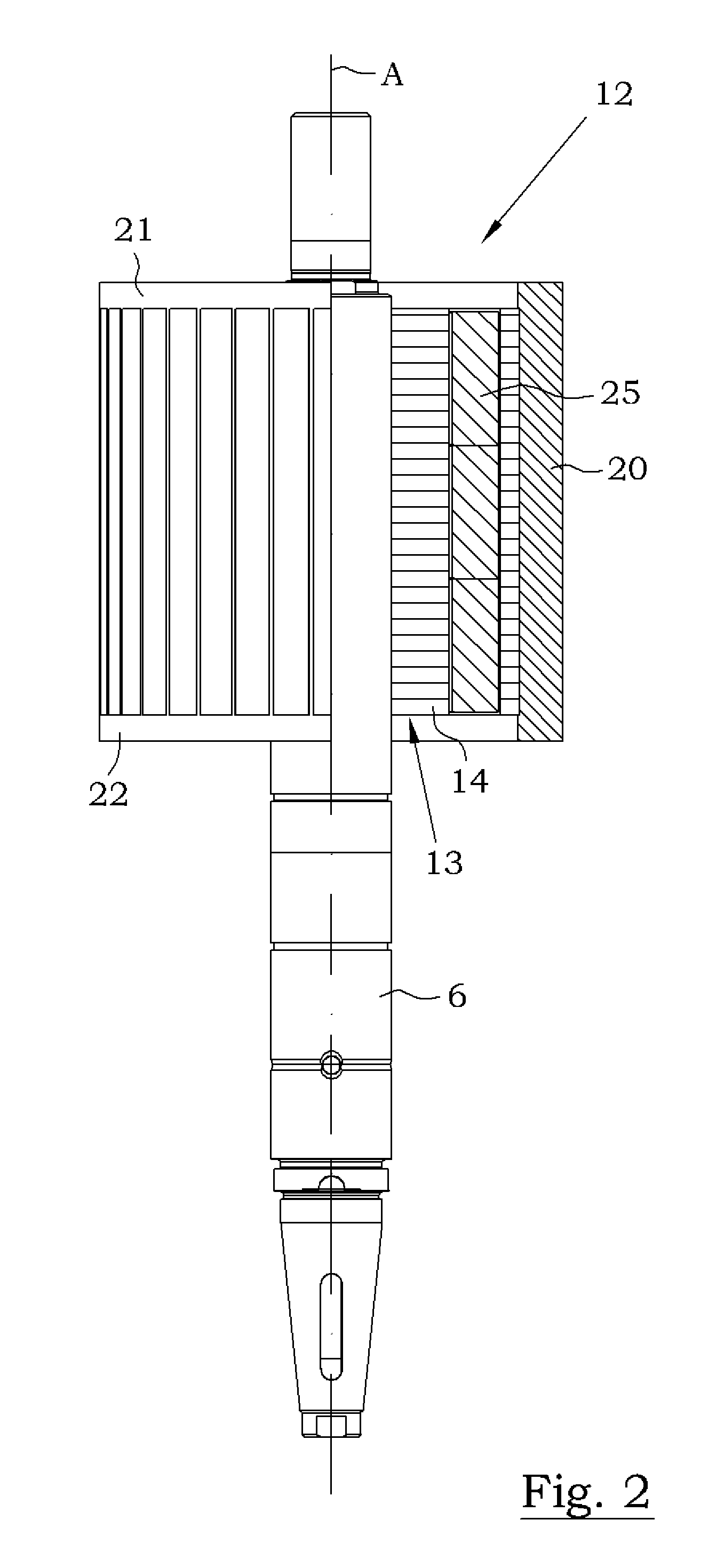
Mixer assembly
InactiveUS20110249528A1Decreased stator current lossImprove efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsTransportation and packagingHybrid typeDrive shaft
A mixer assembly for generating and maintaining a motion within a volume of liquid, the mixer assembly including a motor, a drive shaft and a propeller connected to the drive shaft. When the propeller is in operation, it is driven by the motor and rotates about a propeller axis. The mixer assembly's motor comprises a stator and a hybrid type rotor. The hybrid rotor includes a rotor core comprising an annular radially outer section of asynchronous type and an annular radially inner section of synchronous type arranged radially inside the annular radially outer section.
Owner:XYLEM IP HLDG
Method and device for detecting precipitation by radar
InactiveUS8558730B2Improve accuracyIncrease flexibilityICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAcousticsPrecipitation
A method for detecting precipitation in a region monitored by radar beams includes ascertaining a first average power of a first backscattered radar signal, ascertaining a second average power of a second backscattered radar signal, and detecting an existence of a homogenous medium when the average powers conform.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com