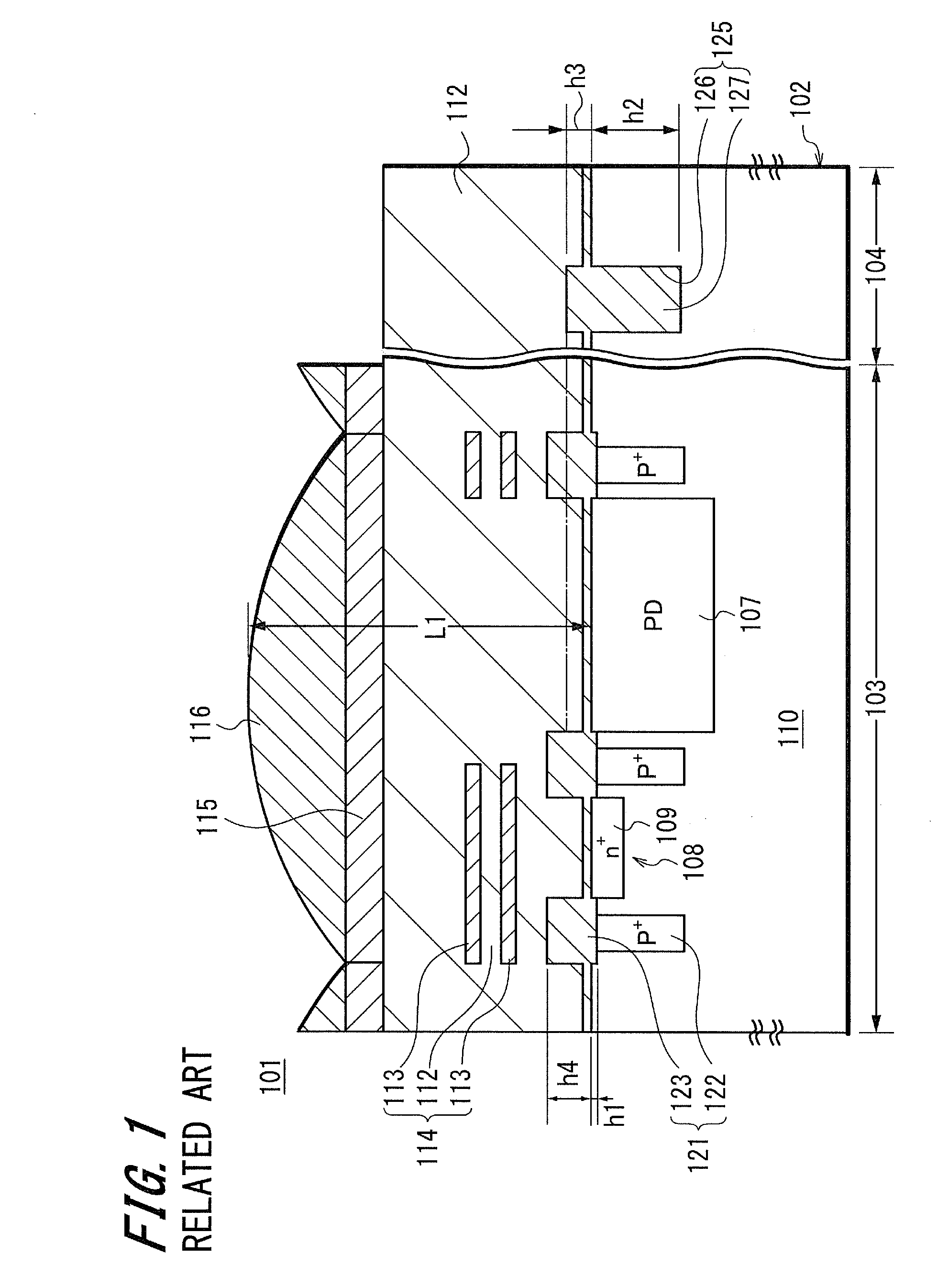
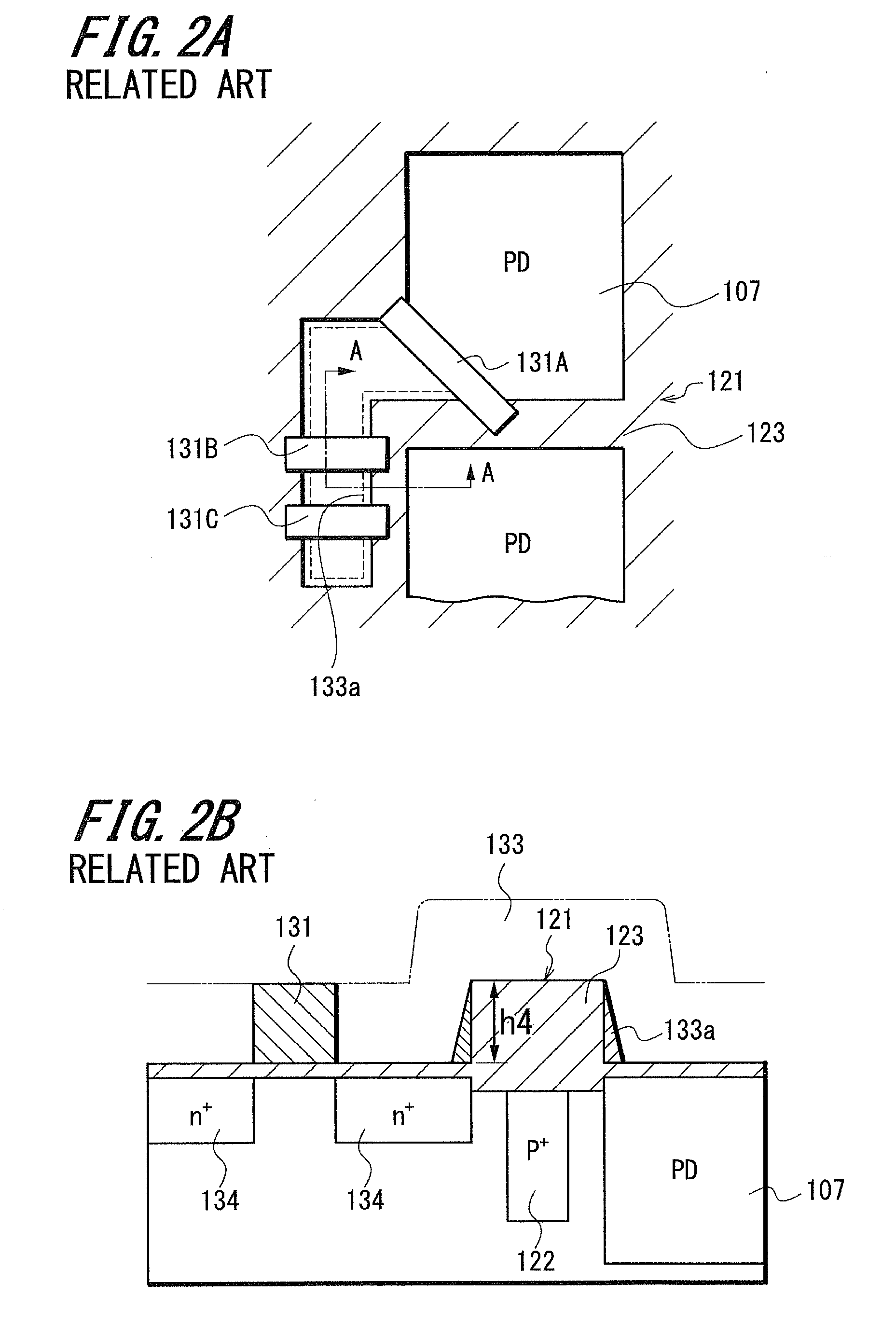
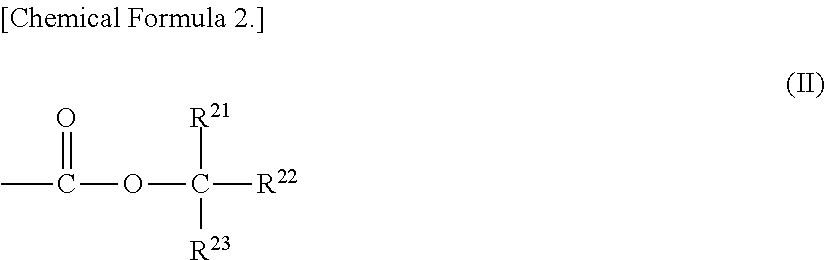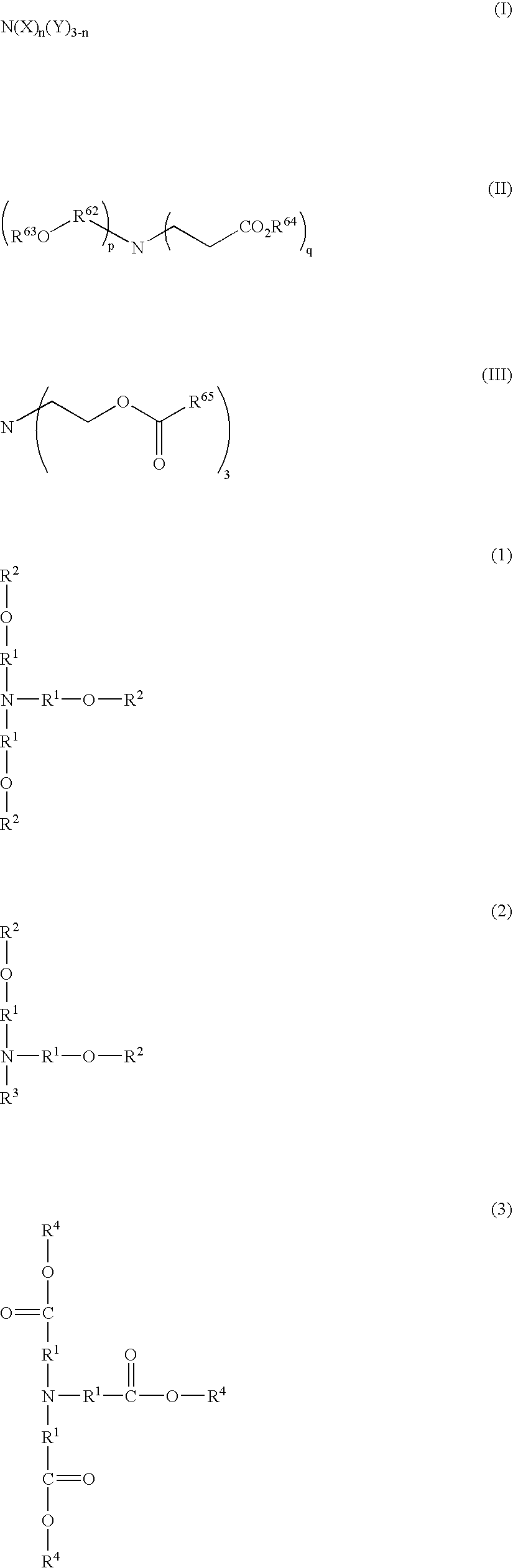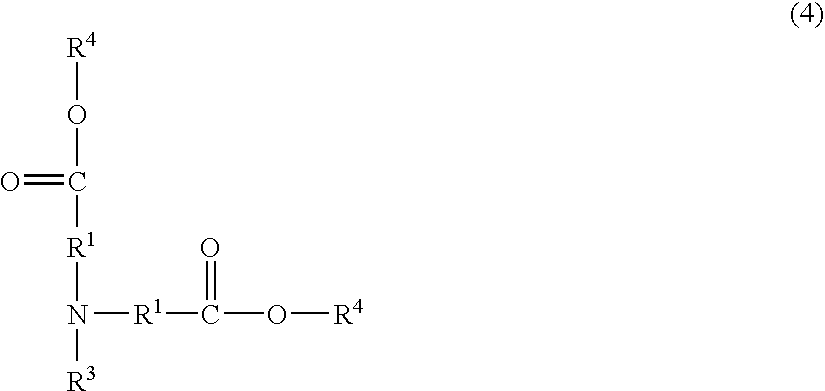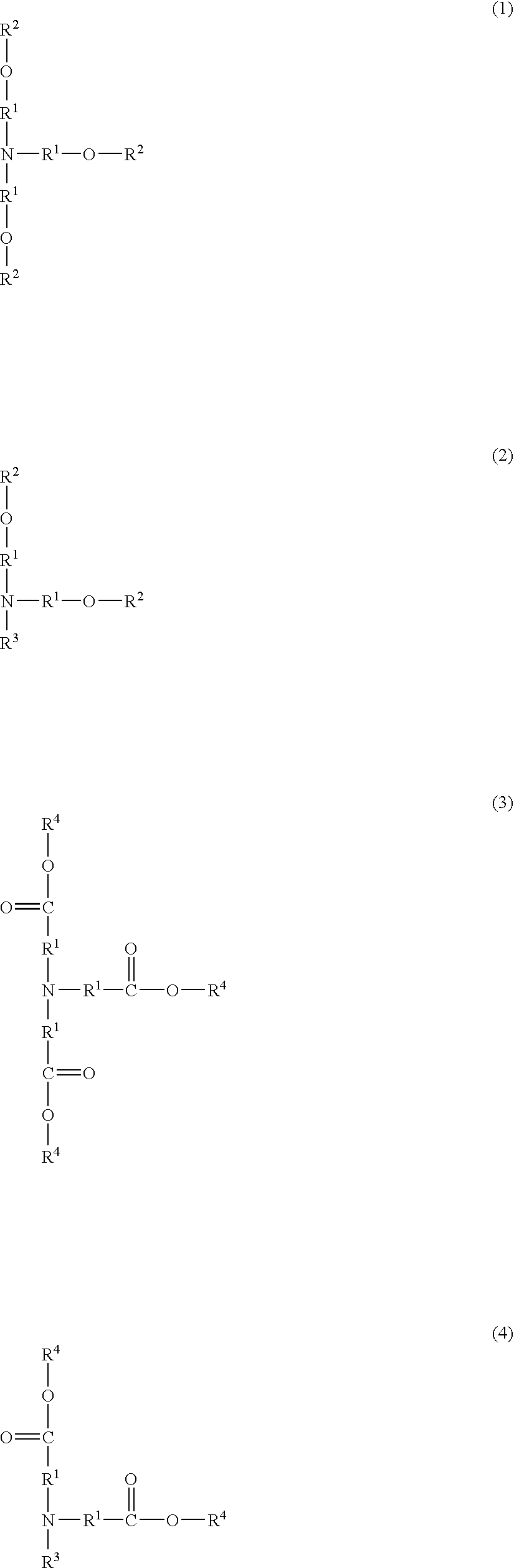Patents
Literature
572results about How to "Reduce film thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
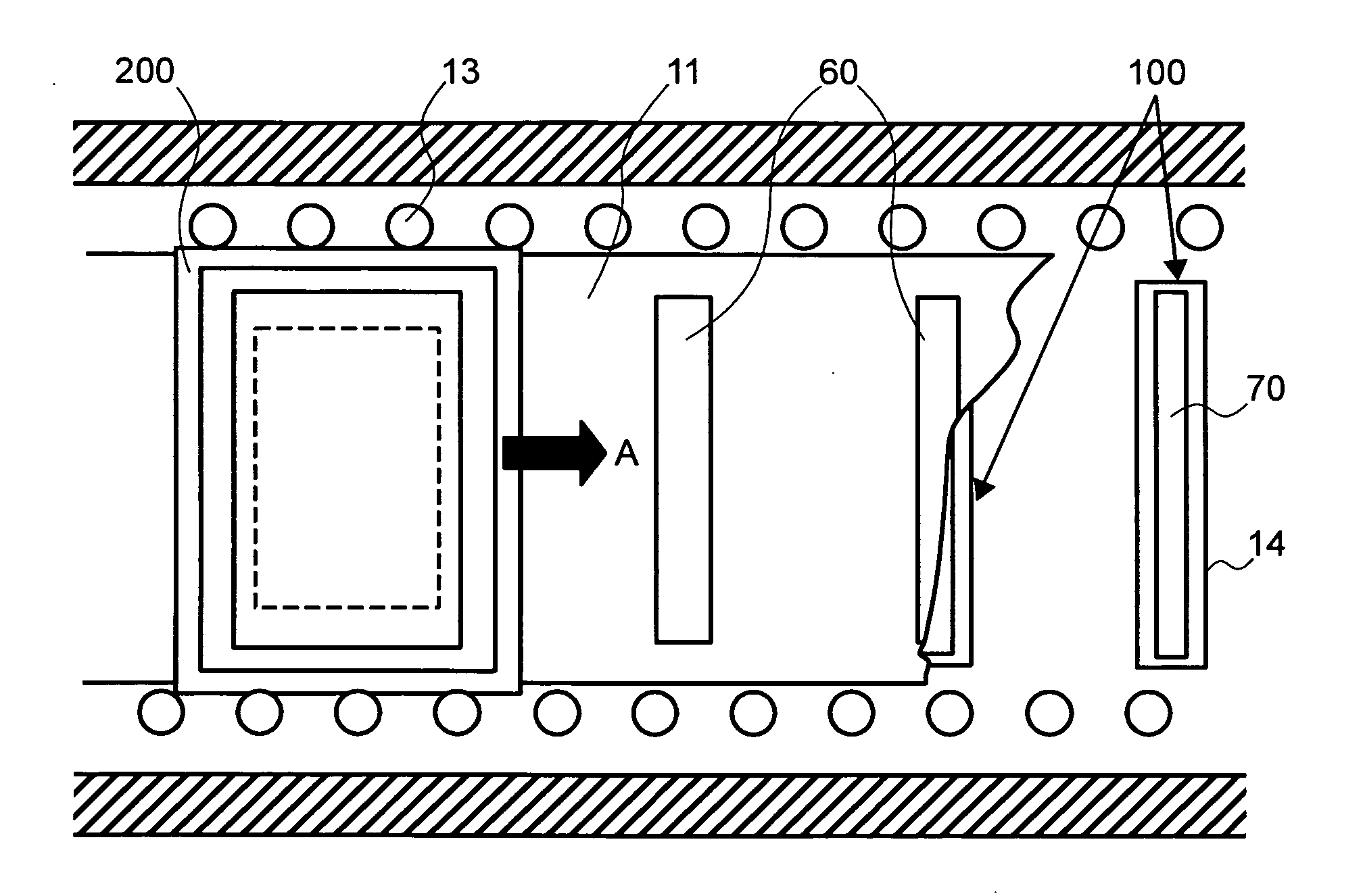
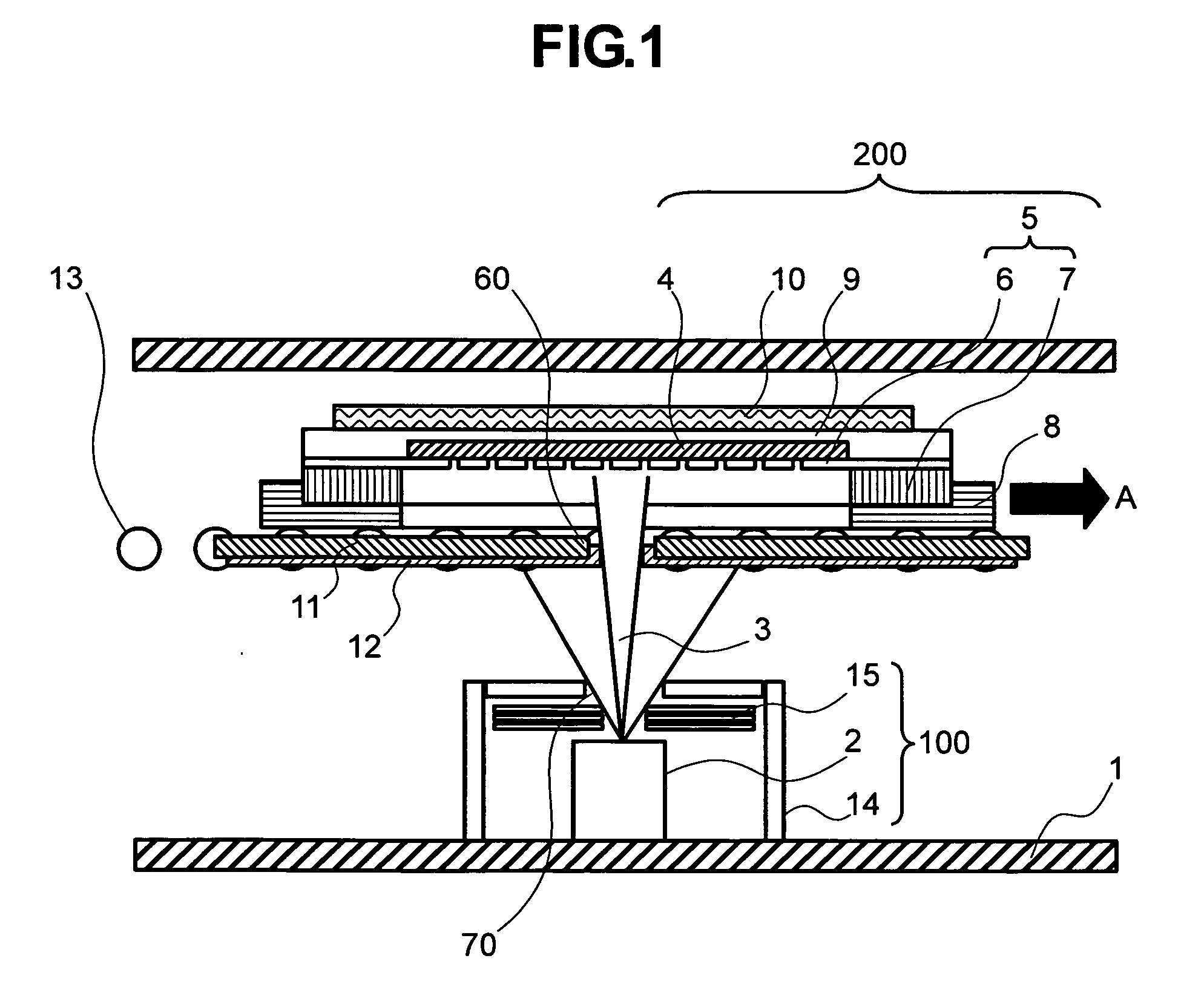
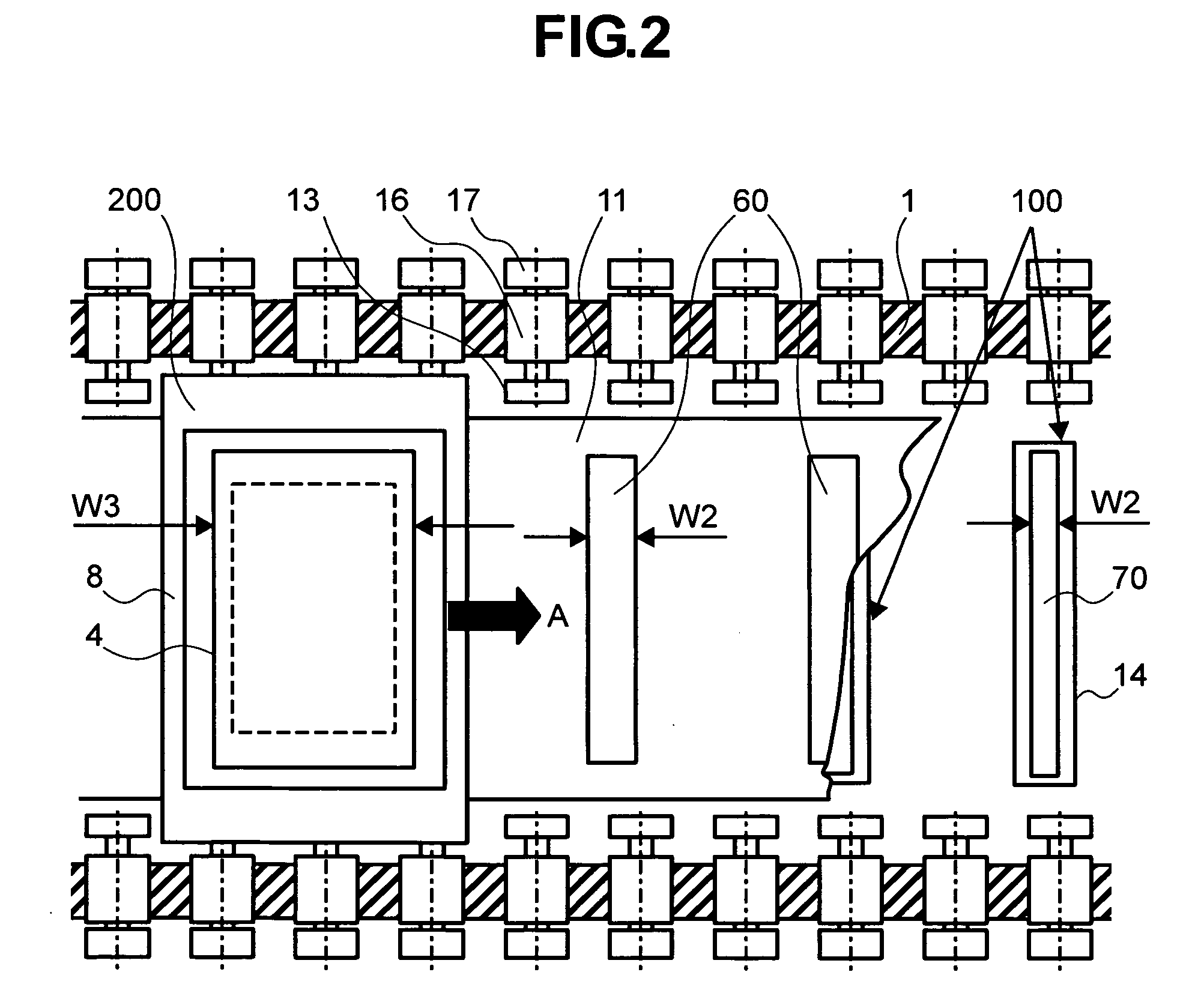
Vapor deposition method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090017192A1Improve cooling effectAvoid misalignmentVacuum evaporation coatingSolid-state devicesGas phaseEvaporation
Provided is a method for moving, in a vacuum chamber carrying therein a fixedly-provided evaporation source, a substrate toward the evaporation source together with a mask closely attached to the substrate surface, and onto the surface substrate, evaporating a material vaporized in the evaporation source through an aperture formed to the mask. In this method of the invention, means for moving the substrate toward the evaporation source is provided with cooling means not to come in contact with but to be in proximity to a surface of the mask on the evaporation source side, and a cooling plate formed with an aperture proximal to the evaporation source is disposed. With such a configuration, the steam of the material coming from the evaporation source is directed to the mask and the substrate through the aperture of the cooling plate. As such, the material film evaporated on the substrate surface shows a satisfactory distribution of film thickness, and any possible misalignment from desired positions of evaporation can be accordingly suppressed.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS +1
Thermal-sprayed metallic conformal coatings used as heat spreaders
InactiveUS20030066672A1Eliminate needHeat dissipationMolten spray coatingScreening gaskets/sealsMolten stateThermal spraying
Heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for an electronic device having an enclosure. An interior surface of the enclosure is covered with a conformal metallic layer which, as disposed in thermal adjacency with one or more heat-generating electronic components or other sources contained within the enclosure, may provide both thermal dissipation and EMI shielding for the device. The layer may be sprayed onto the interior surface in a molten state and solidified to form a self-adherent coating.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090108464A1Well formedImprove manufacturing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padSemiconductor
A first insulating layer including a first contact pad made of conductive polysilicon and a second insulating layer including a second contact pad are formed over a semiconductor silicon layer. After this, a via hole for a through-hole electrode is formed until the via hole penetrates through at least the semiconductor silicon layer and the first contact pad and reaches to the second contact pad.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Electromagnetic interference shield
InactiveUS20120037803A1Improve blockageSubstantial transparencyRadiation pyrometryWave amplification devicesMicrowaveElectromagnetic interference
An improved EMI shielded detection system. The disclosed system may include features configured to increase radio wave and microwave absorbance while retaining significant transparency at visible and / or infrared wavelengths, thus increasing EMI shielding efficiency. This may be accomplished through the use of a conductive mesh having appropriately chosen dimensions and spacing, and embedded in a transparent medium. To minimize the impact of the mesh on the effective aperture of the medium, the strands of the mesh may be made relatively narrow, and to provide sufficient shielding despite the narrow strand width, the mesh may be embedded relatively deeply in the medium.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Substrate processing apparatus, method of manufacturing semiconductor device, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS20140357058A1Improve inter-plane uniformity and in-plane uniformity of film thicknessDecrease productivityLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesHydrogenDevice material
There is provided a substrate processing apparatus including: a process chamber configured to accommodate and process a plurality of substrates arranged with intervals therebetween; a first nozzle extending along a stacking direction of the substrates and configured to supply a hydrogen-containing gas into the process chamber; and a second nozzle extending along the stacking direction of the substrates and configured to supply an oxygen-containing gas into the process chamber, wherein the first nozzle includes a plurality of first gas supply holes disposed in a region extending from an upper portion to a lower portion of the first nozzle corresponding to a substrate arrangement region where the substrates are arranged, and the second nozzle includes a plurality of second gas supply holes disposed at an upper portion and a lower portion of the second nozzle to correspond to upper substrates and lower substrates of the substrates.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
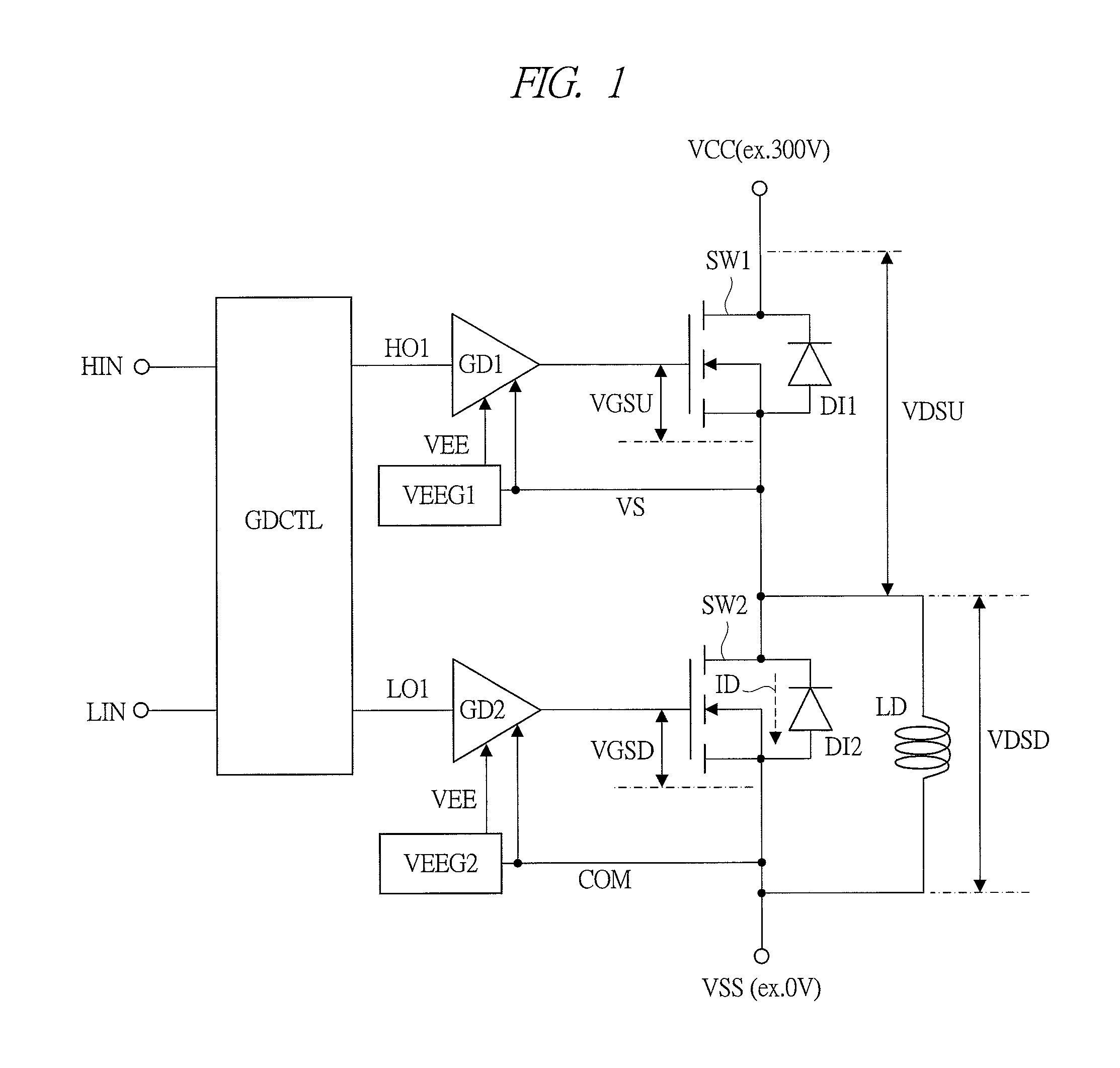
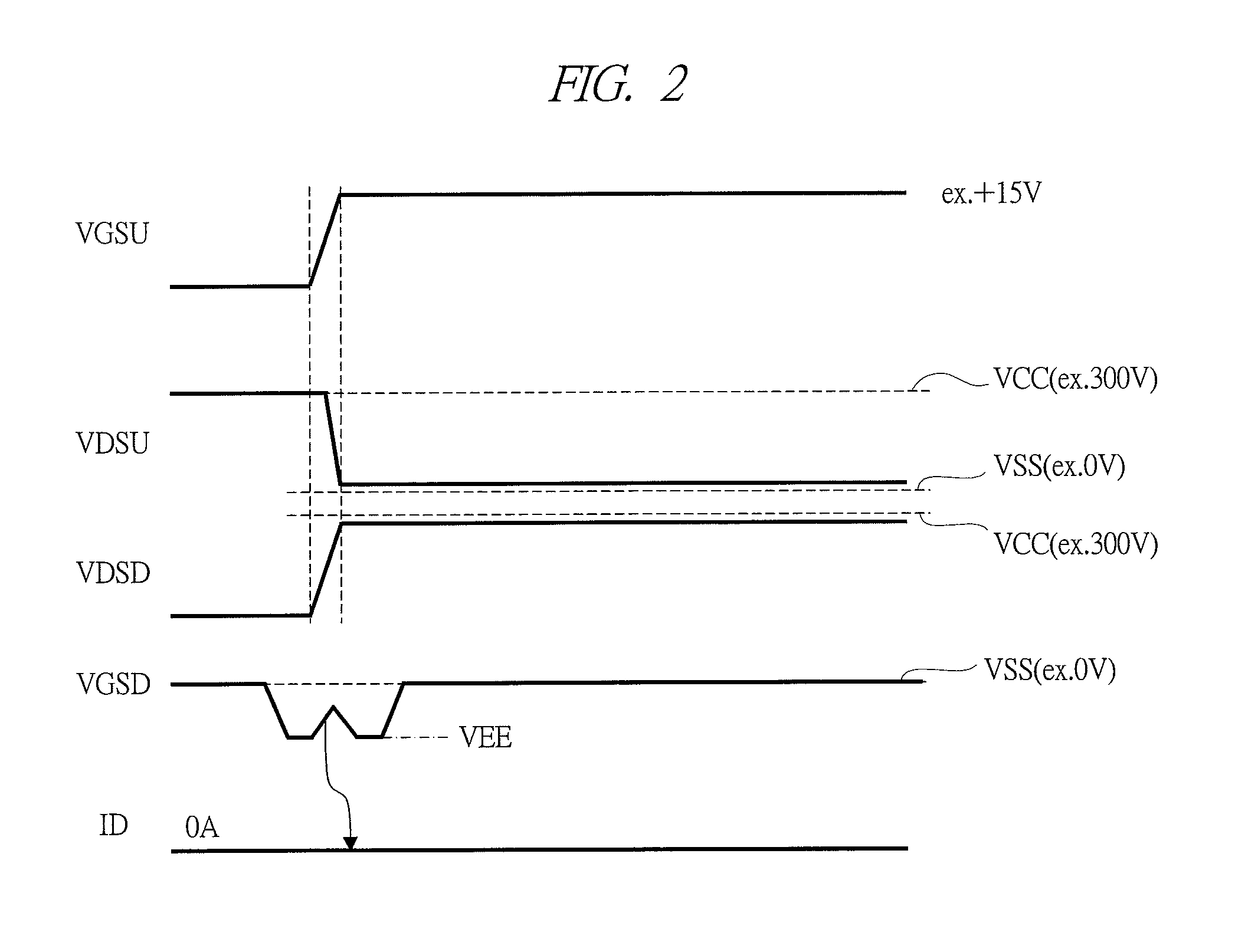
Semiconductor driver circuit and power conversion device
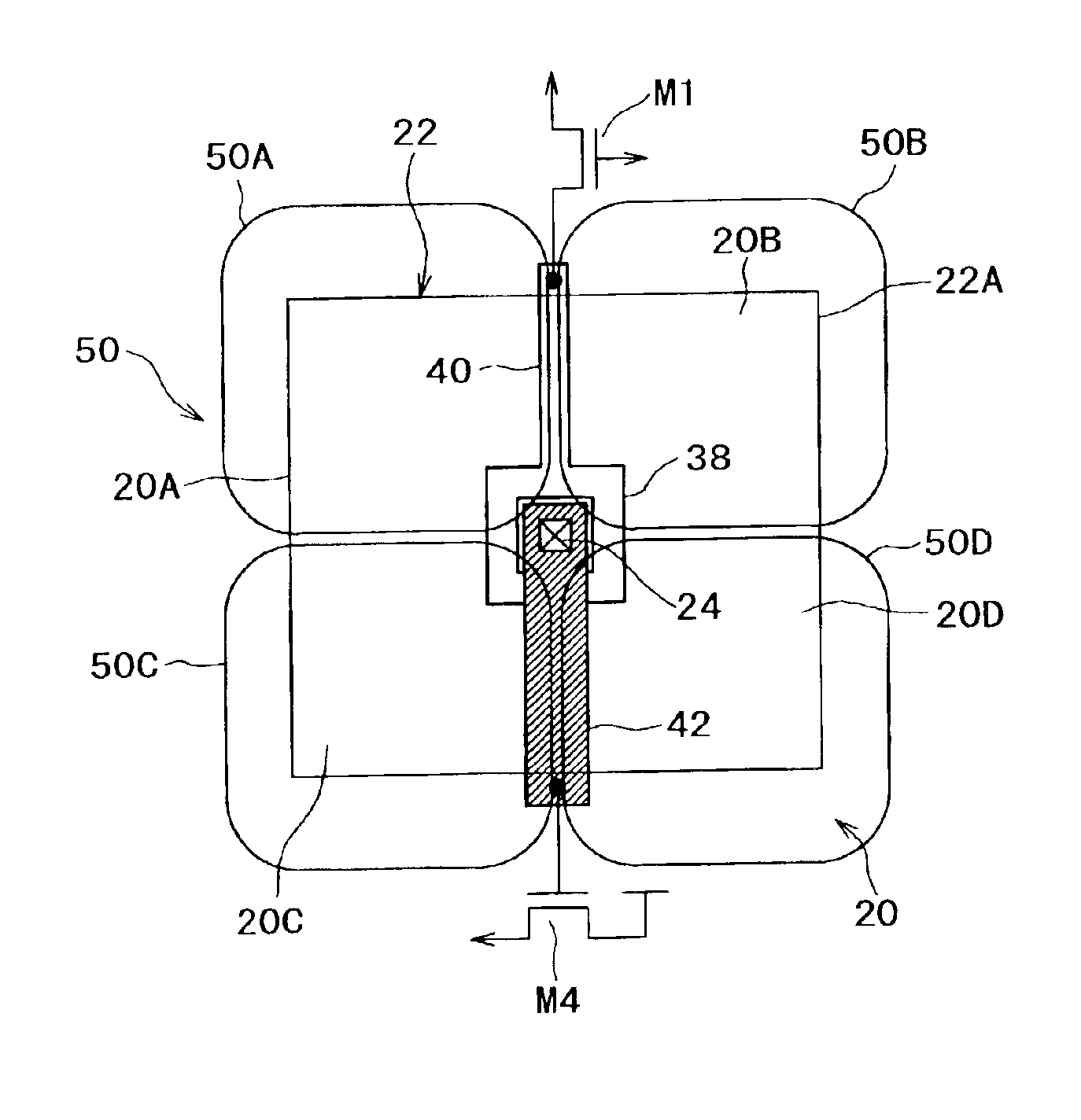
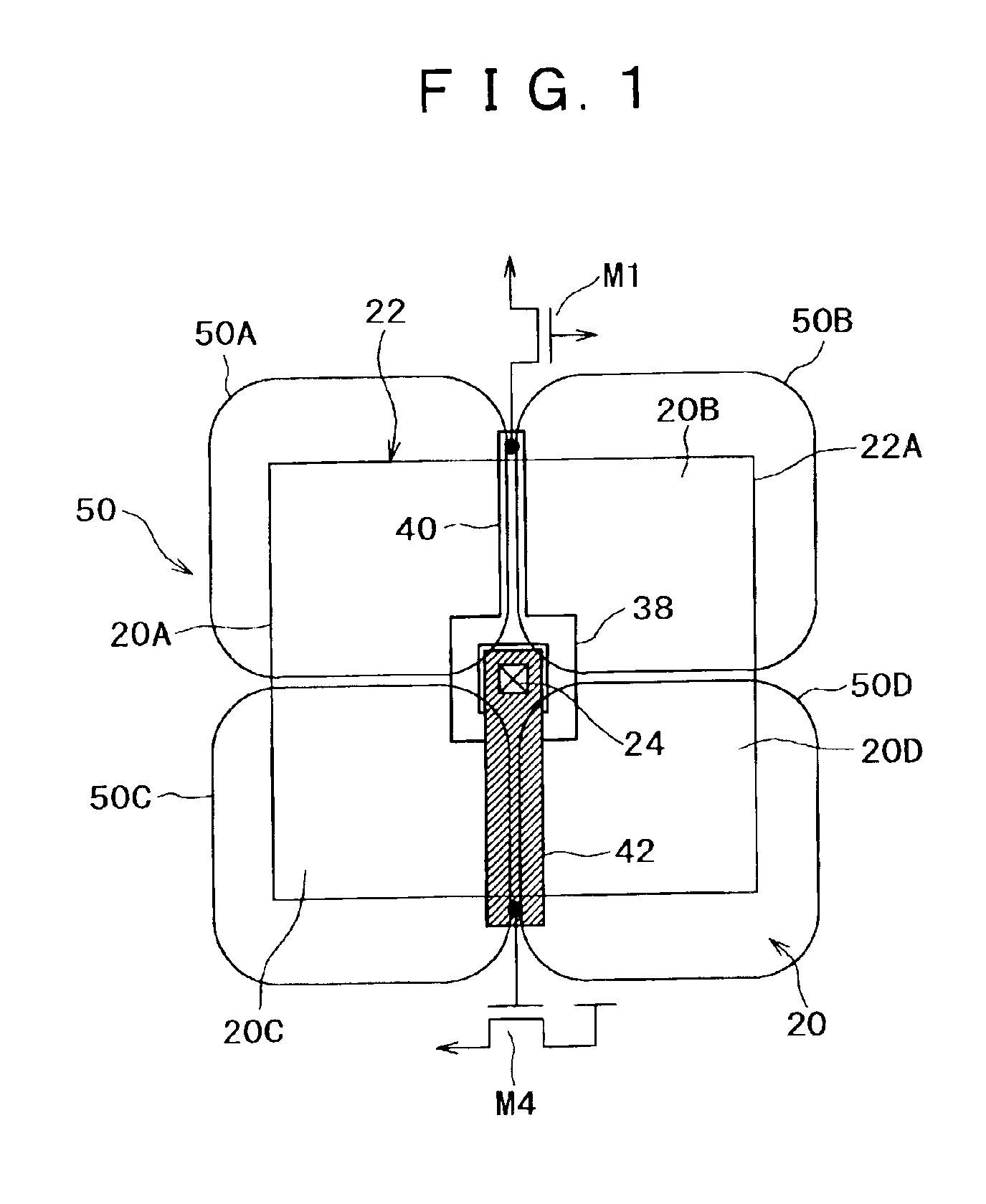
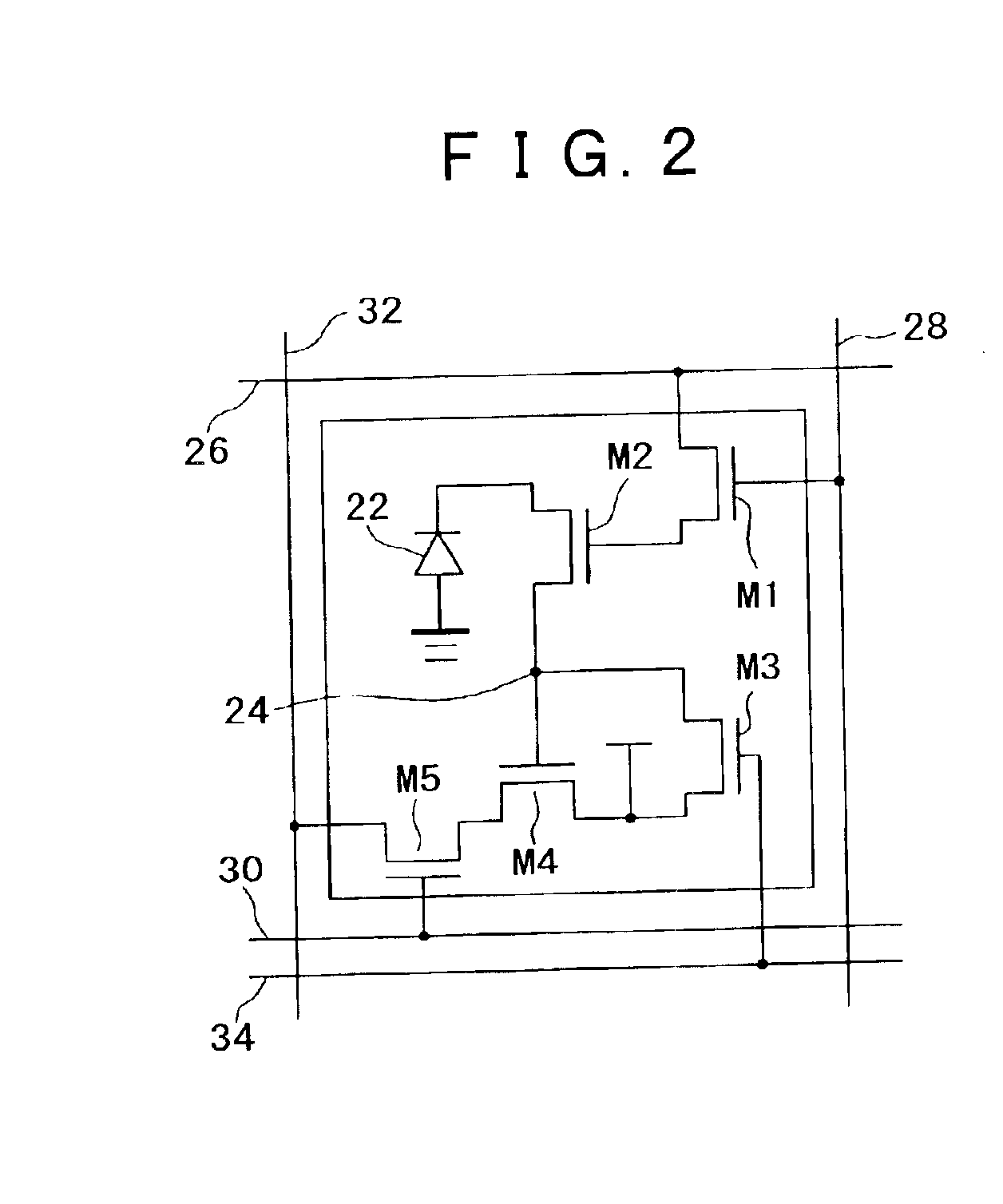
ActiveUS20130265029A1Increase environmental burdenImproved power performanceSolid-state devicesDc-dc conversionCross overGate driver
In a power conversion device provided with a power semiconductor device and a semiconductor driver circuit for driving the power semiconductor device, false firing can be prevented, and improvement in reliability can be achieved. The power conversion device is provided with: a first switch element inserted between a power supply voltage and an output node; a second switch element inserted between a ground power supply voltage and the output node; and a gate driver circuit for controlling turning ON / OFF of the second switch element. When the second switch element is controlled to be turned OFF, the gate driver circuit drives a gate-source voltage at, for example, a level of 0 V. However, when the first switch element is shifted from an OFF state to an ON state at a first timing in a state that the gate-source voltage is driven at, for example, the level of 0 V, the gate driver circuit temporarily applies a level of a negative voltage as the gate-source voltage during a first period which crosses over the first timing.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
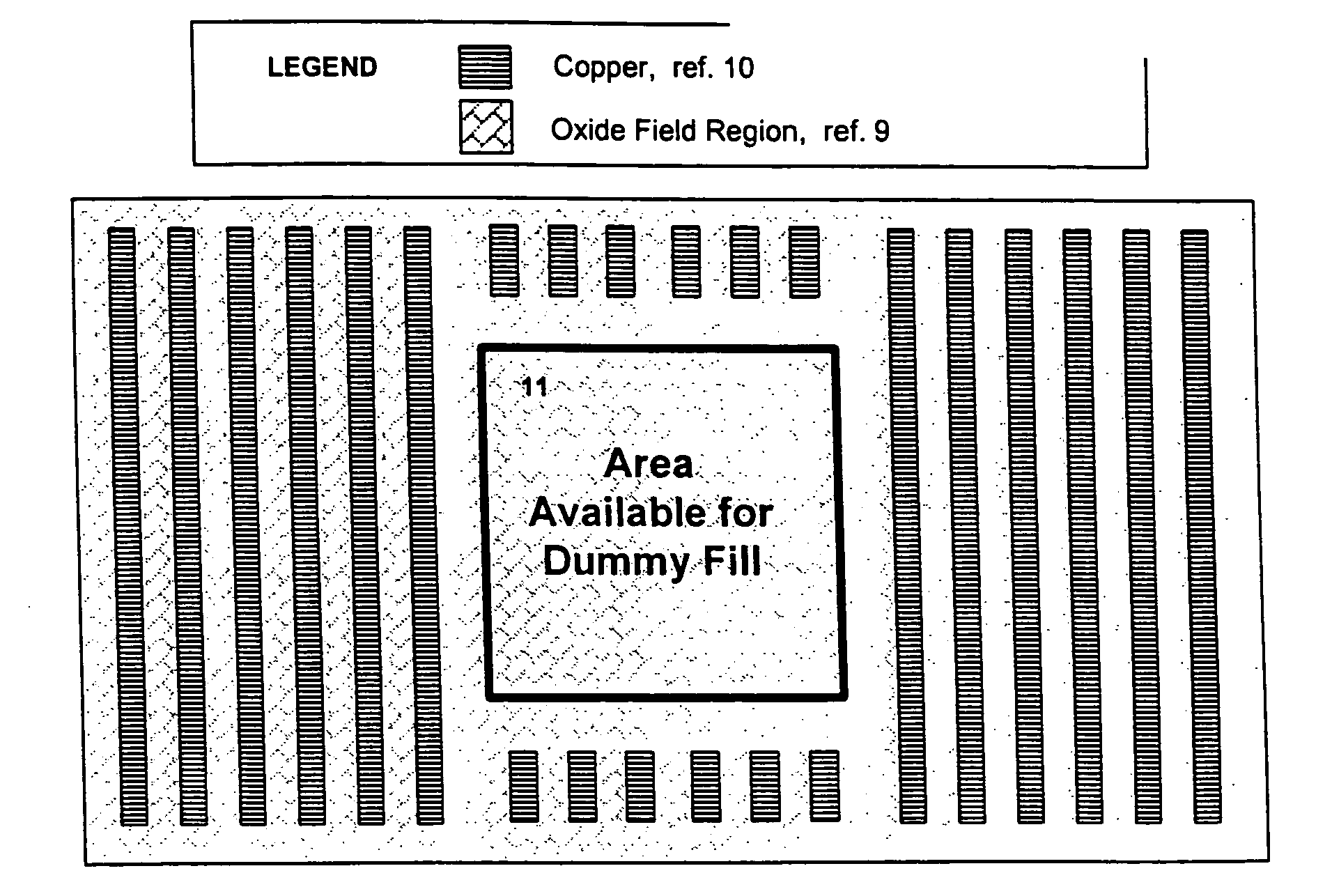
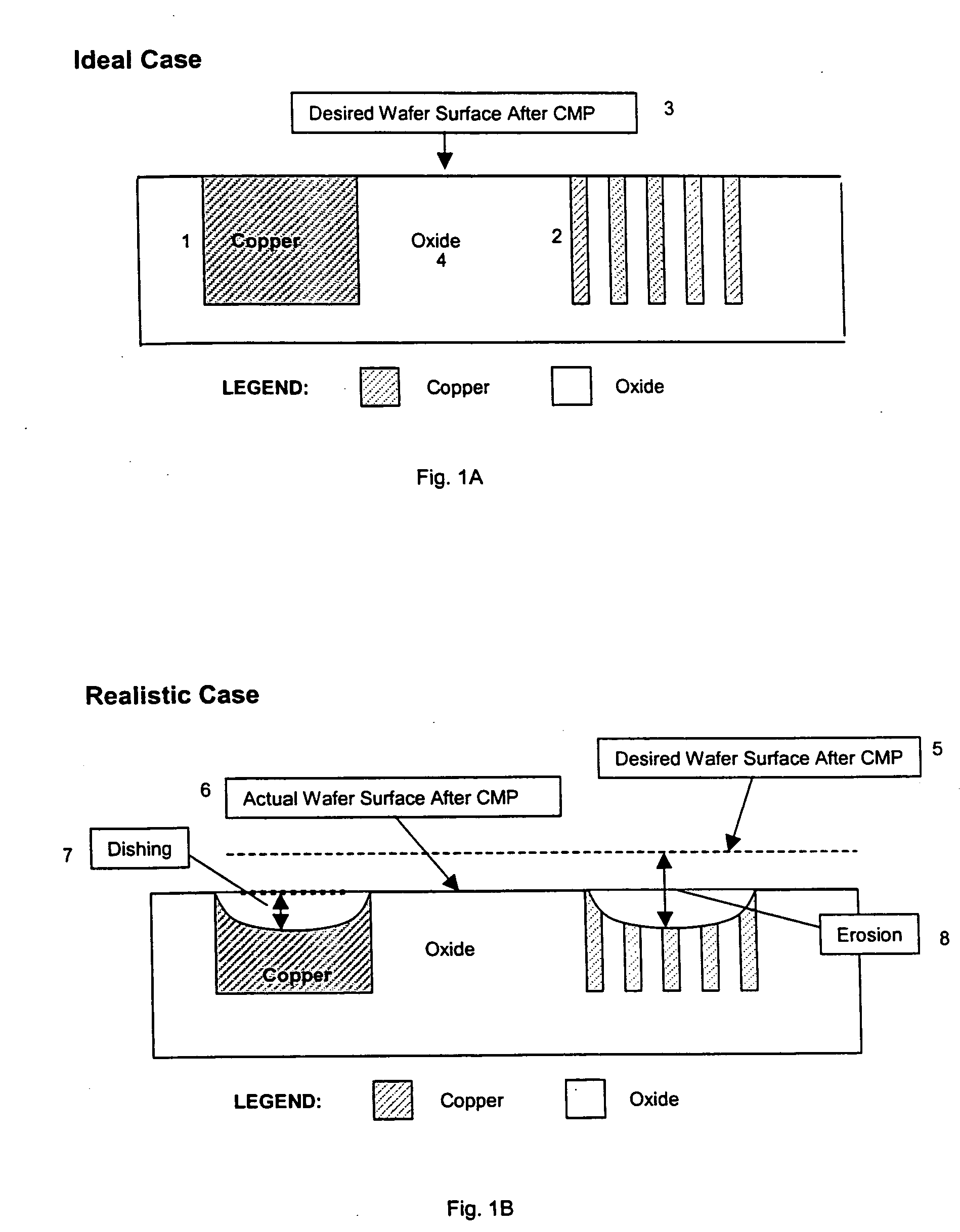
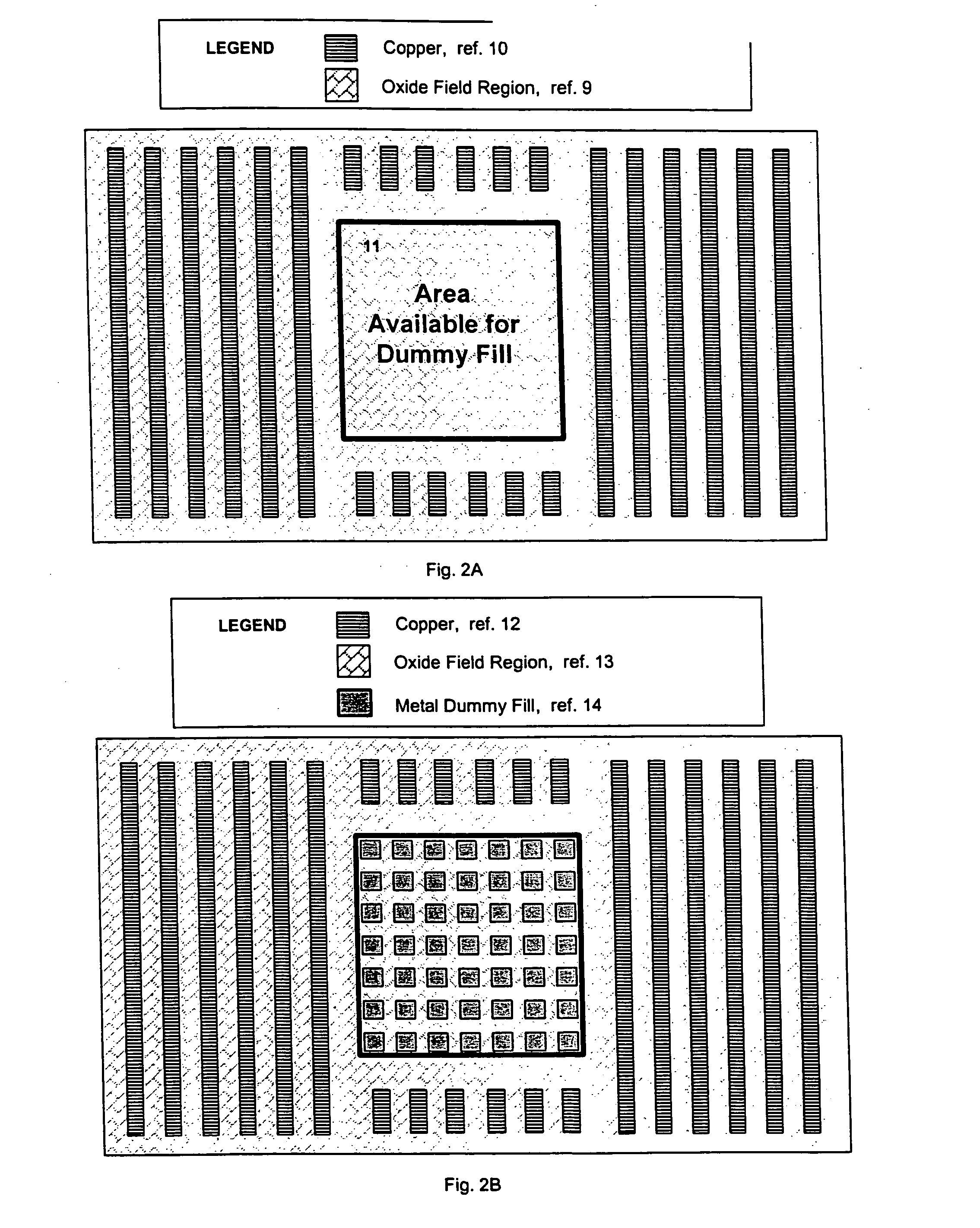
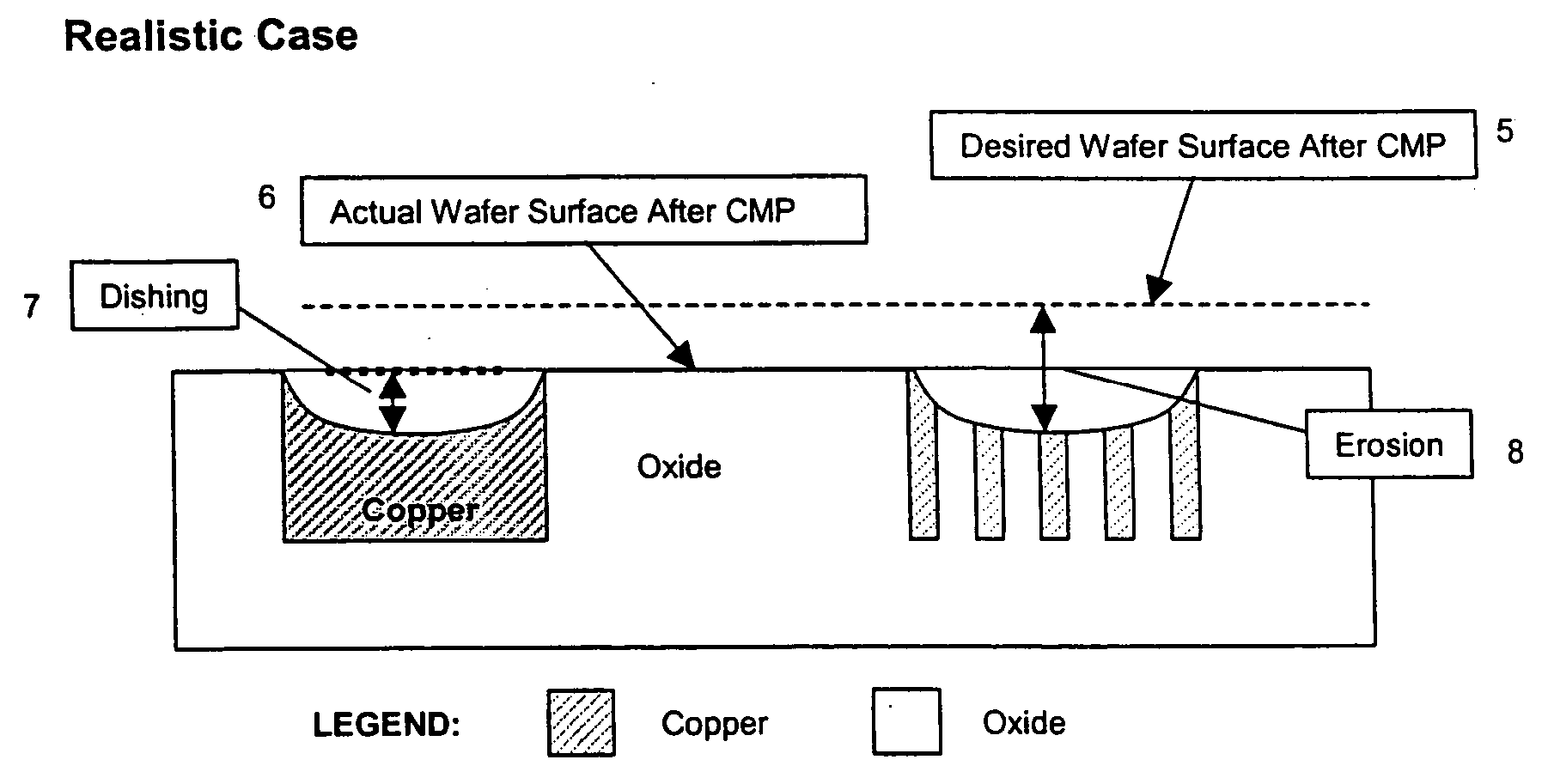
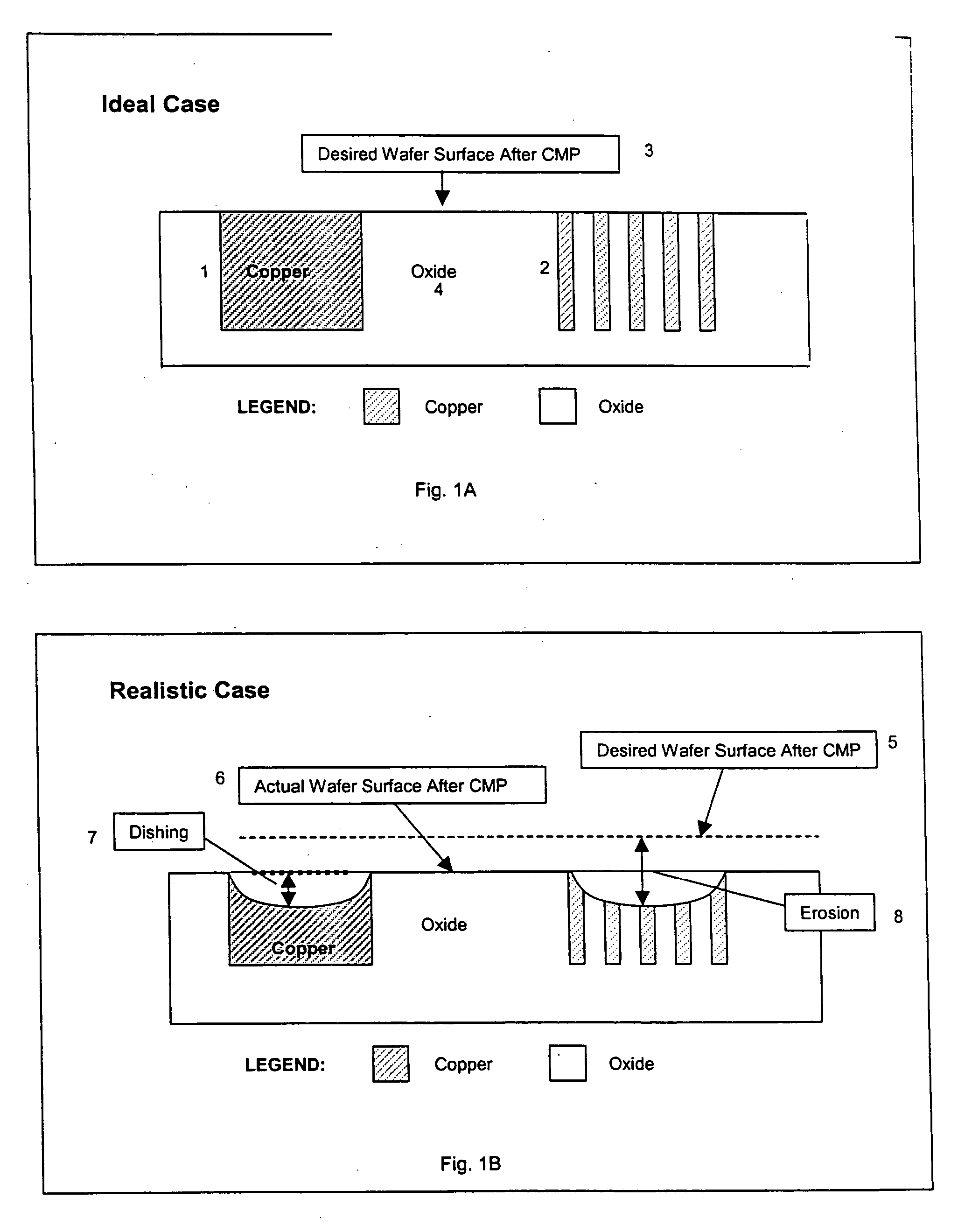
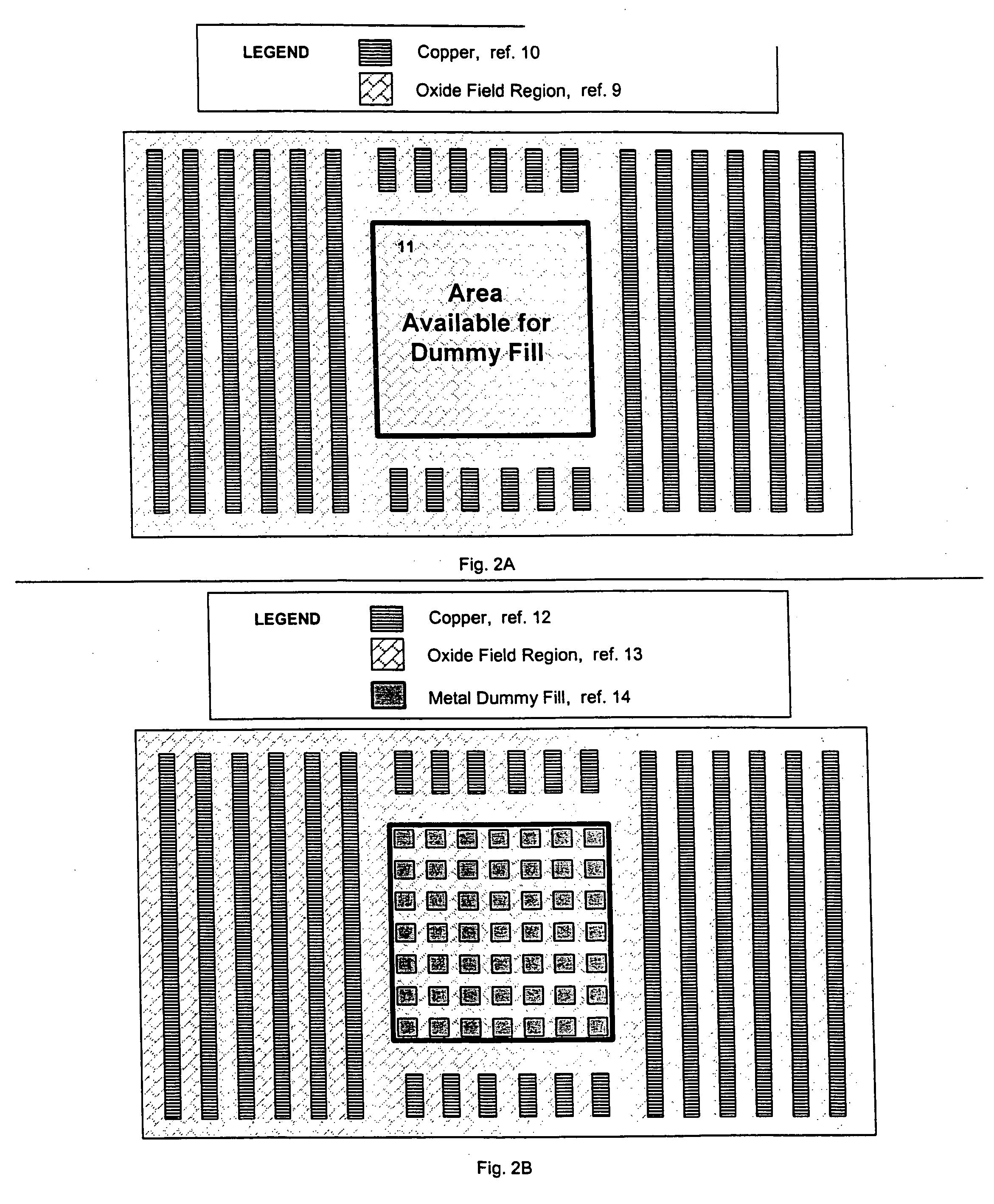
Dummy fill for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050037522A1Minimize full-chip film thickness variationImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingIntegrated circuit layout
A method and system are described to reduce process variation as a result of the electrochemical deposition (ECD), also referred to as electrochemical plating (ECP), and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) processing of films in integrated circuit manufacturing processes. The described methods use process variation and electrical impact to direct the insertion of dummy fill into an integrated circuit.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Dummy fill for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050051809A1Speed up the processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuit manufacturingIntegrated circuit layout
A method and system are described to reduce process variation as a result of the electrochemical deposition (ECD), also referred to as electrochemical plating (ECP), and chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) processing of films in integrated circuit manufacturing processes. The described methods use process variation and electrical impact to direct the insertion of dummy fill into an integrated circuit.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Liquid crystal display with sub-pixel electrodes, and control capacitor electrodes forming control capacitors
InactiveUS6078367AImprove featuresIncrease the areaNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
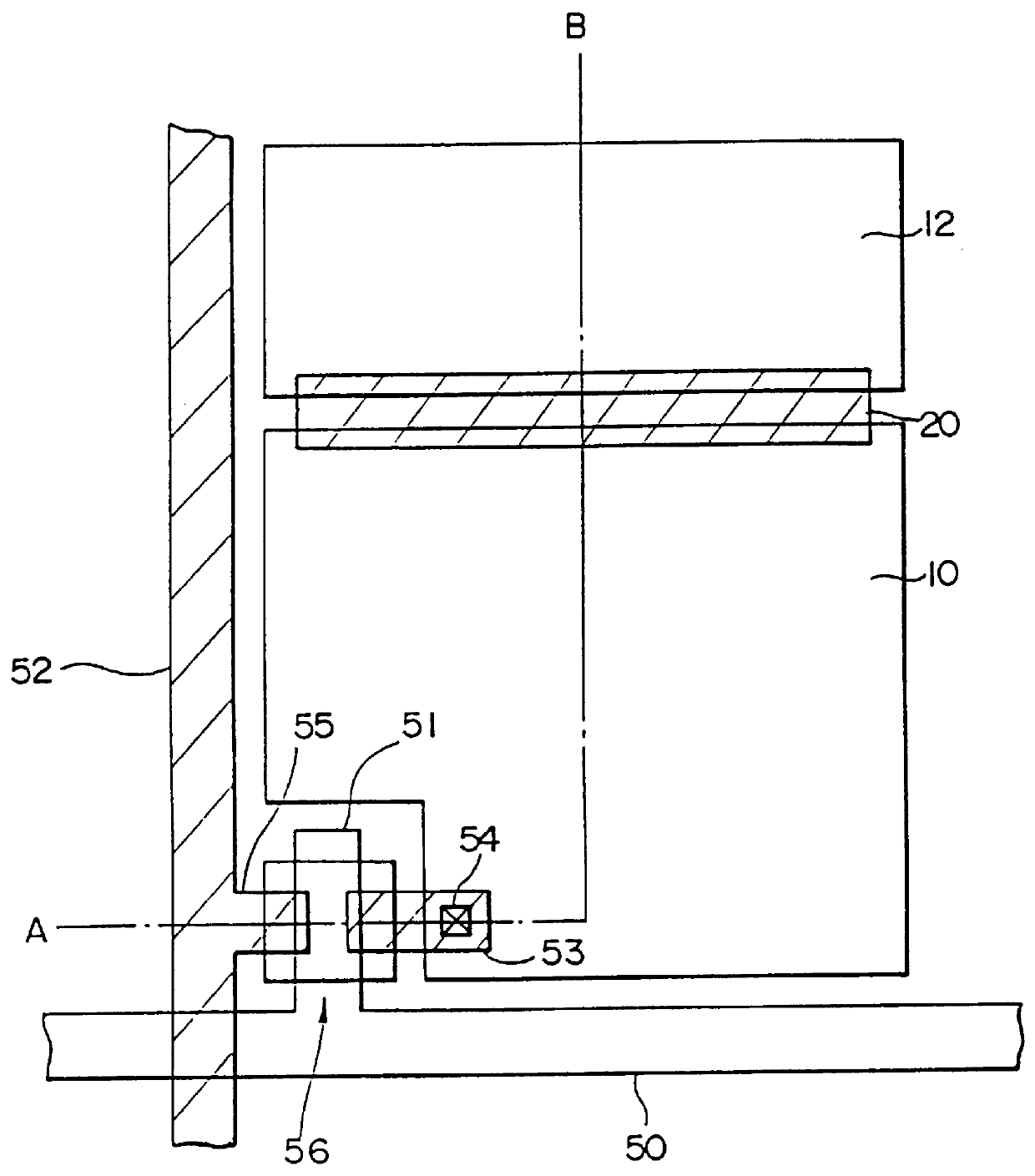
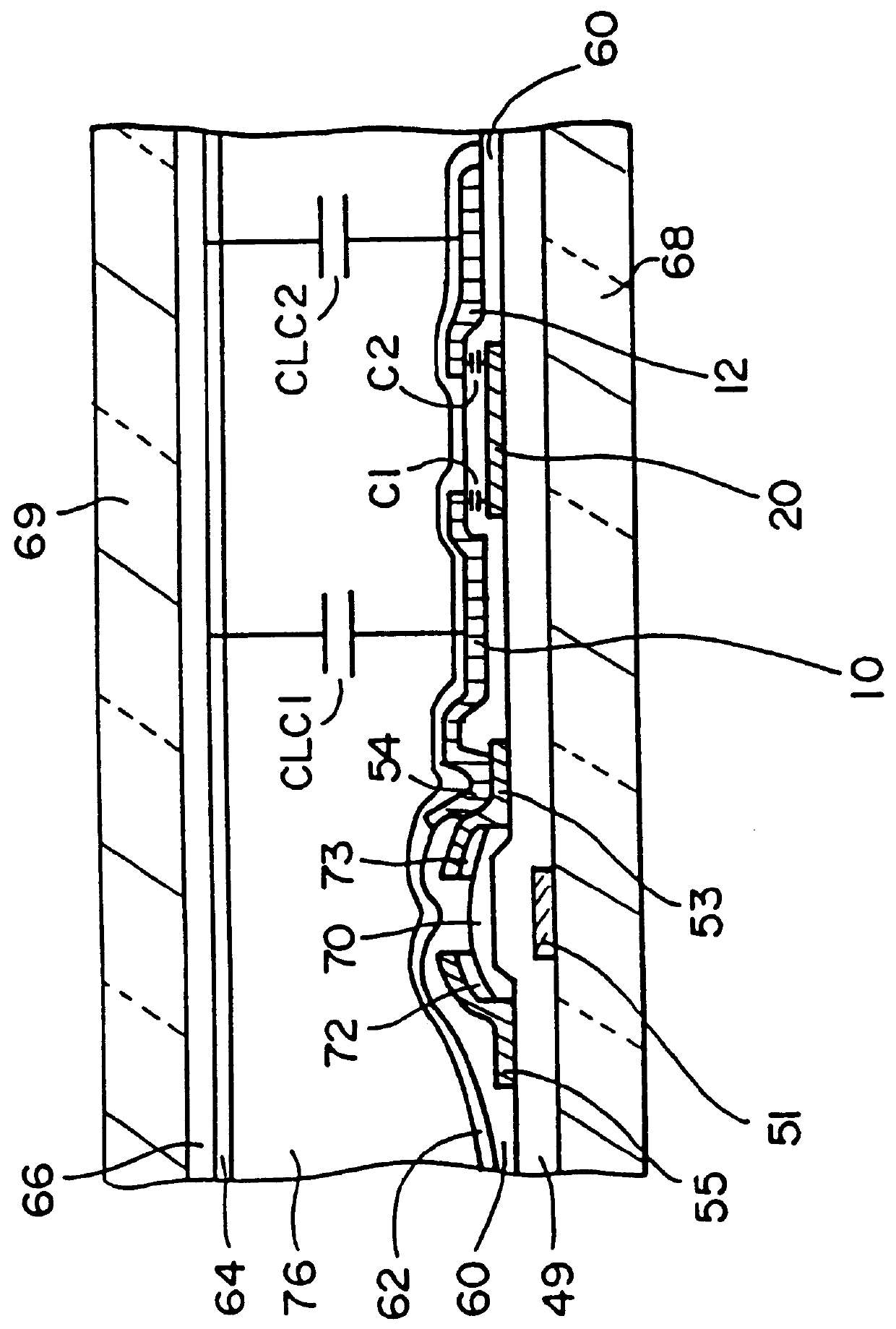
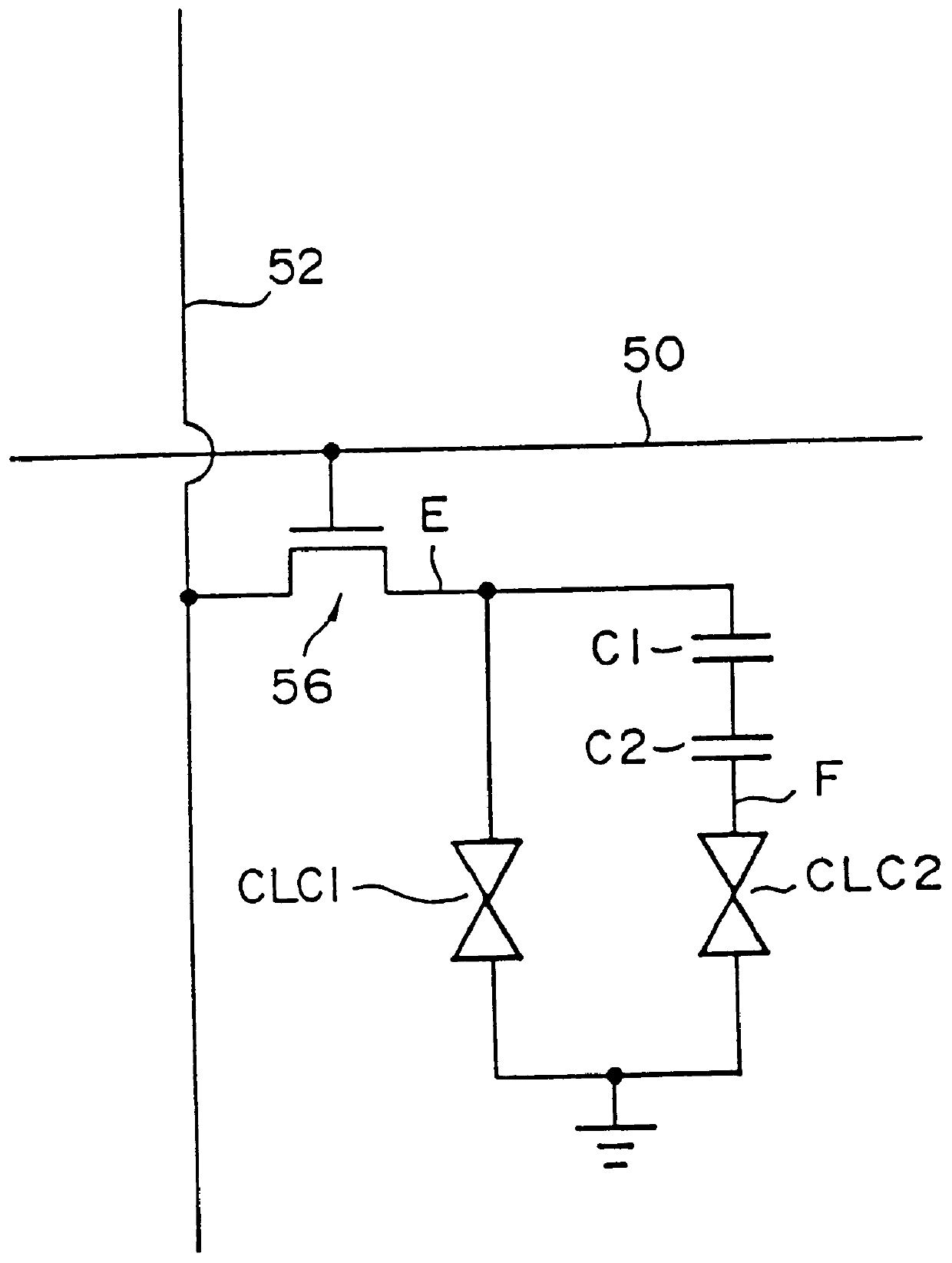
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 01652 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 27, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 27, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 17, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 00463 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 3, 1997A liquid crystal display element, a manufacturing method(s) thereof, and electronic devices (utilizing this element) which can improve, through a simple process, the visual angle characteristics, and the like, of liquid crystal panels is provided. A first control capacitor electrode (20) is included, provided below first and second sub-pixel electrodes (10, 12) and a protective insulating film (60). Also, control capacitors C1 and C2 are formed by the first and second sub-pixel electrodes (10, 12), and the first control capacitor electrode (20), through the protective insulating film (60). The visual angle characteristics of the liquid crystal panels are improved by the provision of the control capacitors C1 and C2. An increase in processes can be prevented, because the first control capacitor electrode (20) can be formed by a material identical to that of the source electrode. Moreover, the surface area of the control capacitor electrode can be miniaturized, and the aperture rate, and the like, can be improved, as a result of being able to make the protective insulating film (60) even thinner than the gate insulating film (49).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Solid-state imaging device, production method thereof, and electronic device
InactiveUS20090256226A1Additional processing stepReduce film thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid-statePeripheral
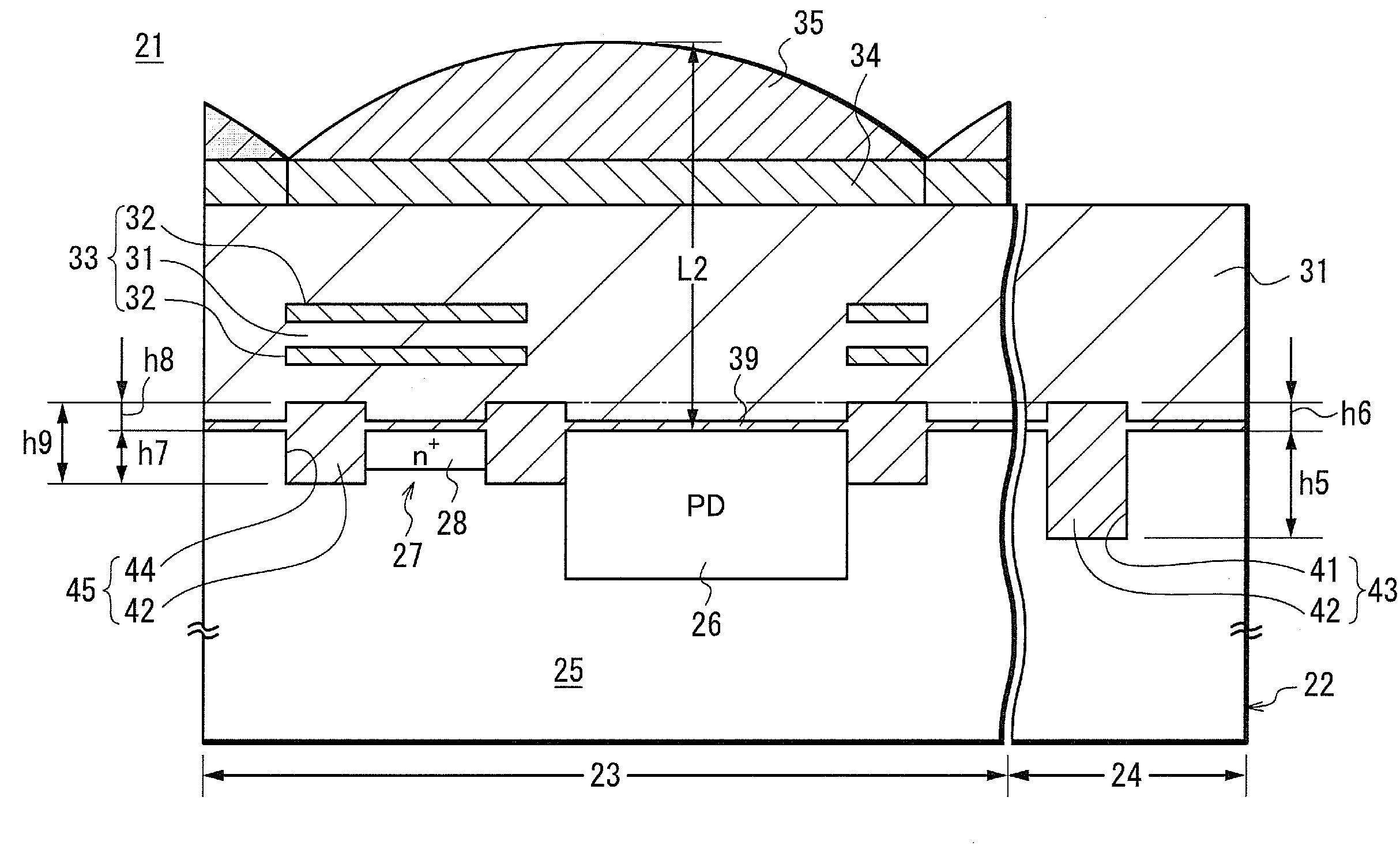
Disclosed is a solid-state imaging device which includes a pixel section, a peripheral circuit section, a first isolation region formed with a STI structure on a semiconductor substrate in the peripheral circuit section, and a second isolation region formed with the STI structure on the semiconductor substrate in the pixel section. The portion of the second isolation region buried into the semiconductor substrate is shallower than the portion buried into the semiconductor substrate of the first isolation region, and the height of the upper face of the second isolation region is equal to that of the first isolation region. A method of producing the solid-state imaging device and an electronic device provided with the solid-state imaging devices are also disclosed.
Owner:SONY CORP
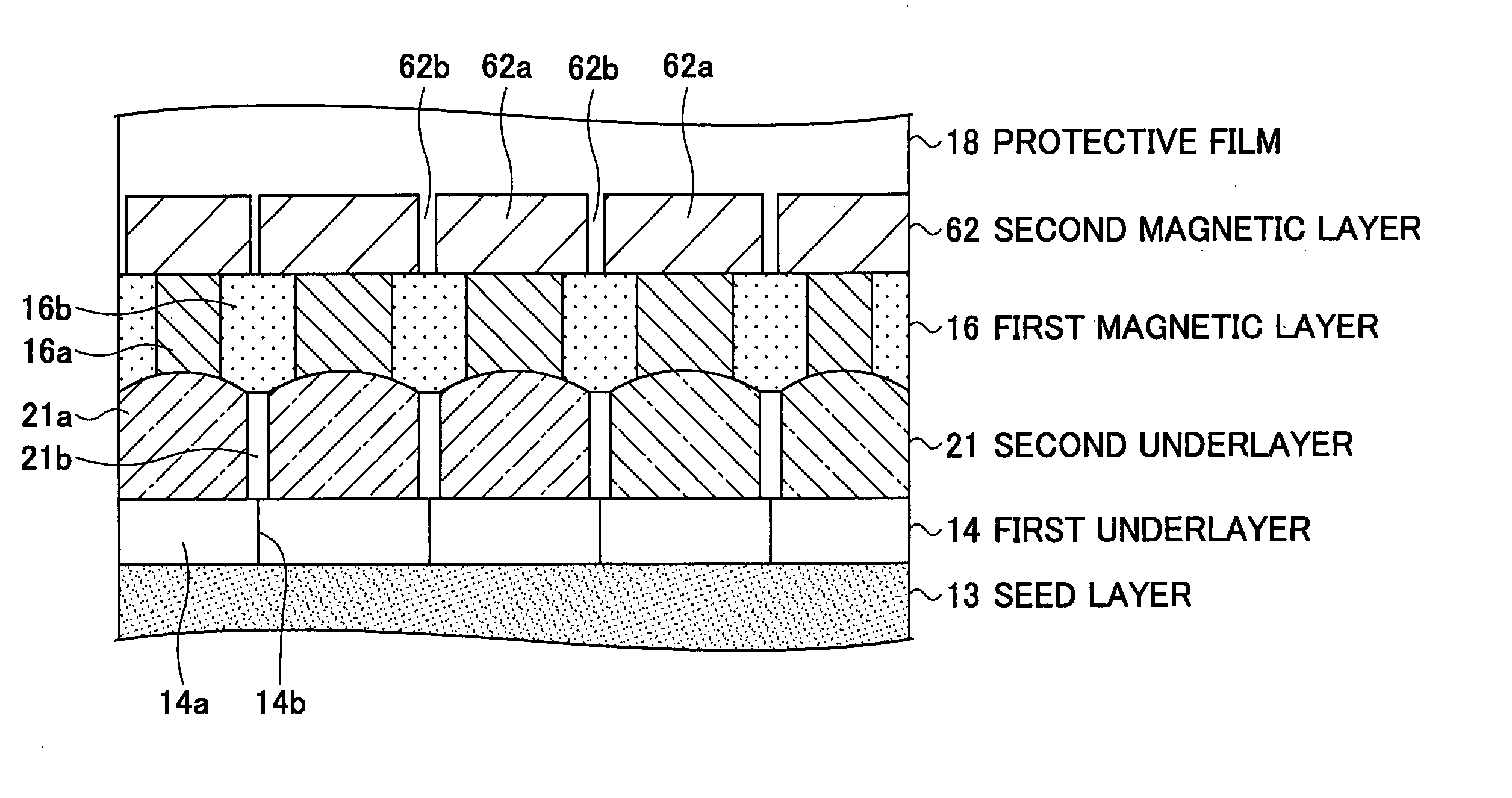
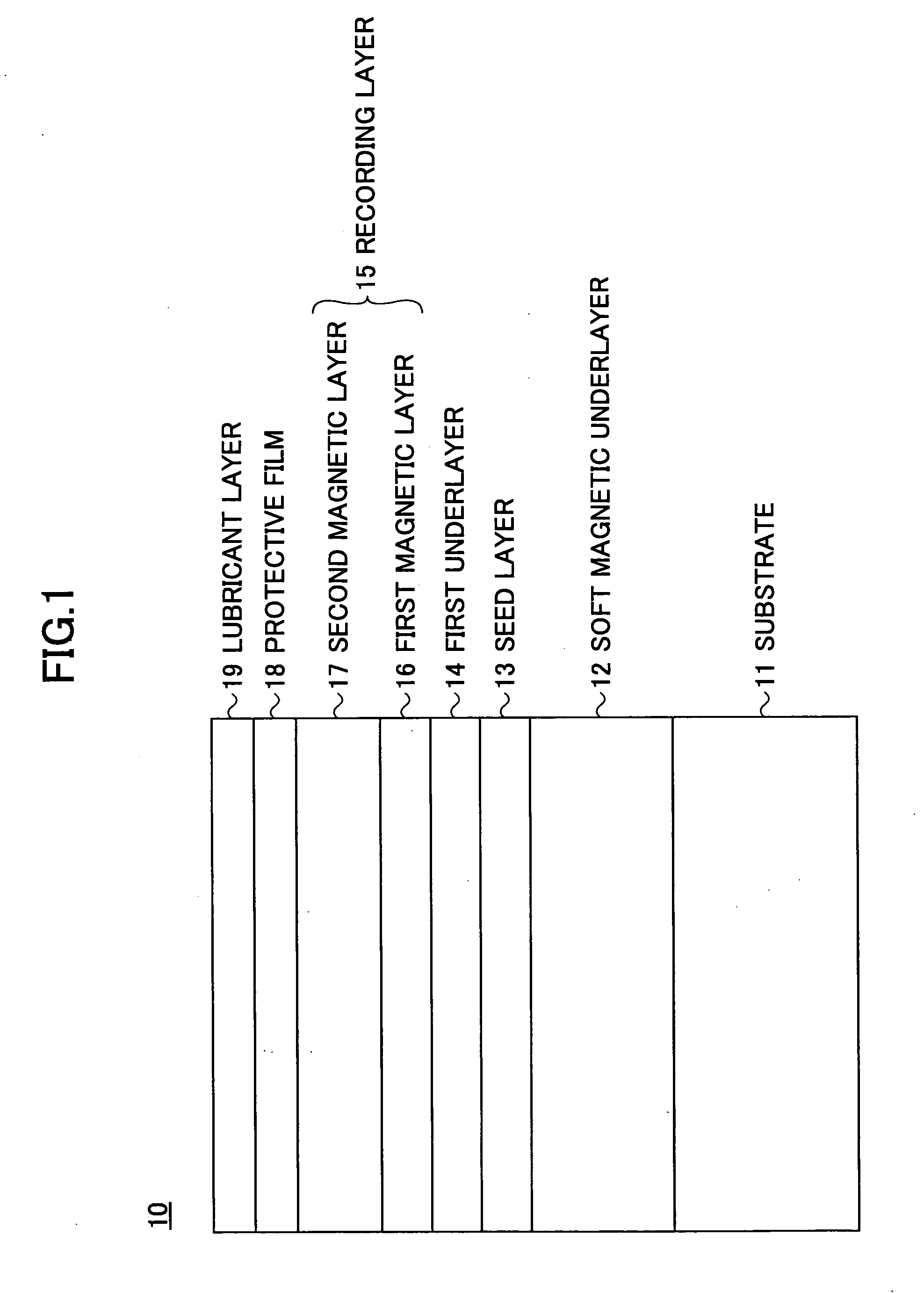
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic storage device
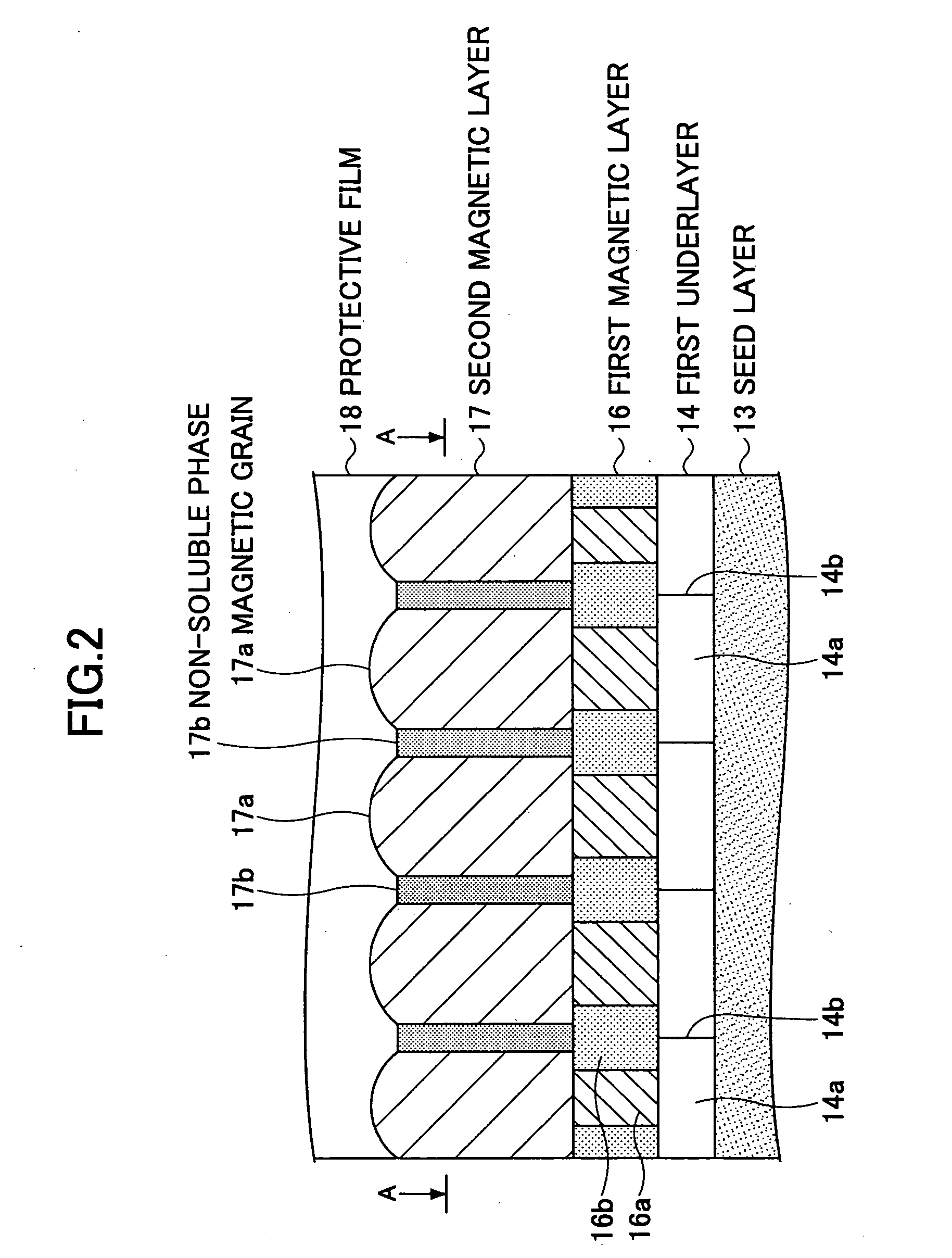
InactiveUS20060222902A1Medium noise is reducedImprove signal-to-noise ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh densityMagnetic storage
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium for enabling high density recording is disclosed. The perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate on which a soft magnetic underlayer, a seed layer made of a non-crystalline material, an underlayer made of Ru or an Ru alloy including Ru as a main component, and a recording layer including a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer. The first and second magnetic layers include a plurality of magnetic grains having easy magnetization axes in a substantially perpendicular direction with respect to the substrate surface, and first and second nonmagnetic non-soluble phases segregating the magnetic grains of the first and second magnetic layers, respectively. The first magnetic layer includes the first non-soluble phase at a first atomic concentration that is higher than a second atomic concentration of the second non-soluble phase in the second magnetic layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Semiconductor light emitting element
ActiveCN101237013AIncrease reflectionReduce absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureLight-emitting diode
The present invention provides a semiconductor light emitting element realizing lower resistance, higher output, higher power efficiency, higher mass productivity and lower cost of the element using a light transmissive electrode for an electrode arranged exterior to the light emitting structure. A semiconductor light emitting element including a light emitting section, a first electrode, and a second electrode on a semiconductor structure including first and second conductive type semiconductor layers, the first and the second electrodes being arranged on the first conductive type semiconductor layer and a second conductive type semiconductor layer of the light emitting section, respectively; and a light transmissive insulating film formed on at least one part of the second conductive type semiconductor layer; wherein the second electrode includes a first layer of a light transmissive conductive film for covering at least one part of the second conductive type semiconductor layer and a second layer which is arranged on at least one part of the light transmissive insulating film and which conducts to the first layer; a light reflecting part is formed on a surface side of the first layer, and aboundary region of the light transmissive insulating film and the semiconductor structure; and the second layer side surface of the light transmissive insulating film is distant from the semiconductor structure than the surface of the first layer.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Magneto-optical recording medium and reproducing method thereof
InactiveUS20050002318A1Effectively transferred and readGood effectMechanical recordingRecord information storageControl layerCoupling
A magneto-optical recording medium, including a recording layer, a transfer control layer magnetically coupled to the recording layer, and a reproduction layer. The recording layer includes a recording magnetic domain in which information is recorded by a magnetization direction vertical to the surface of the film. The reproduction layer includes a reproduction magnetic domain in which information in the recording layer is transferred and formed as a magnetization direction by magnetic coupling. The direction of magnetization of the recording magnetic domain of the recording layer and the direction of magnetization of the transfer control layer corresponding to the recording magnetic domain are in opposite directions in at least part of the range of temperatures less than a transfer temperature where the reproduction magnetic domain is transferred to the reproduction layer. The Curie point temperature of the transfer control layer is higher than this transfer temperature.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
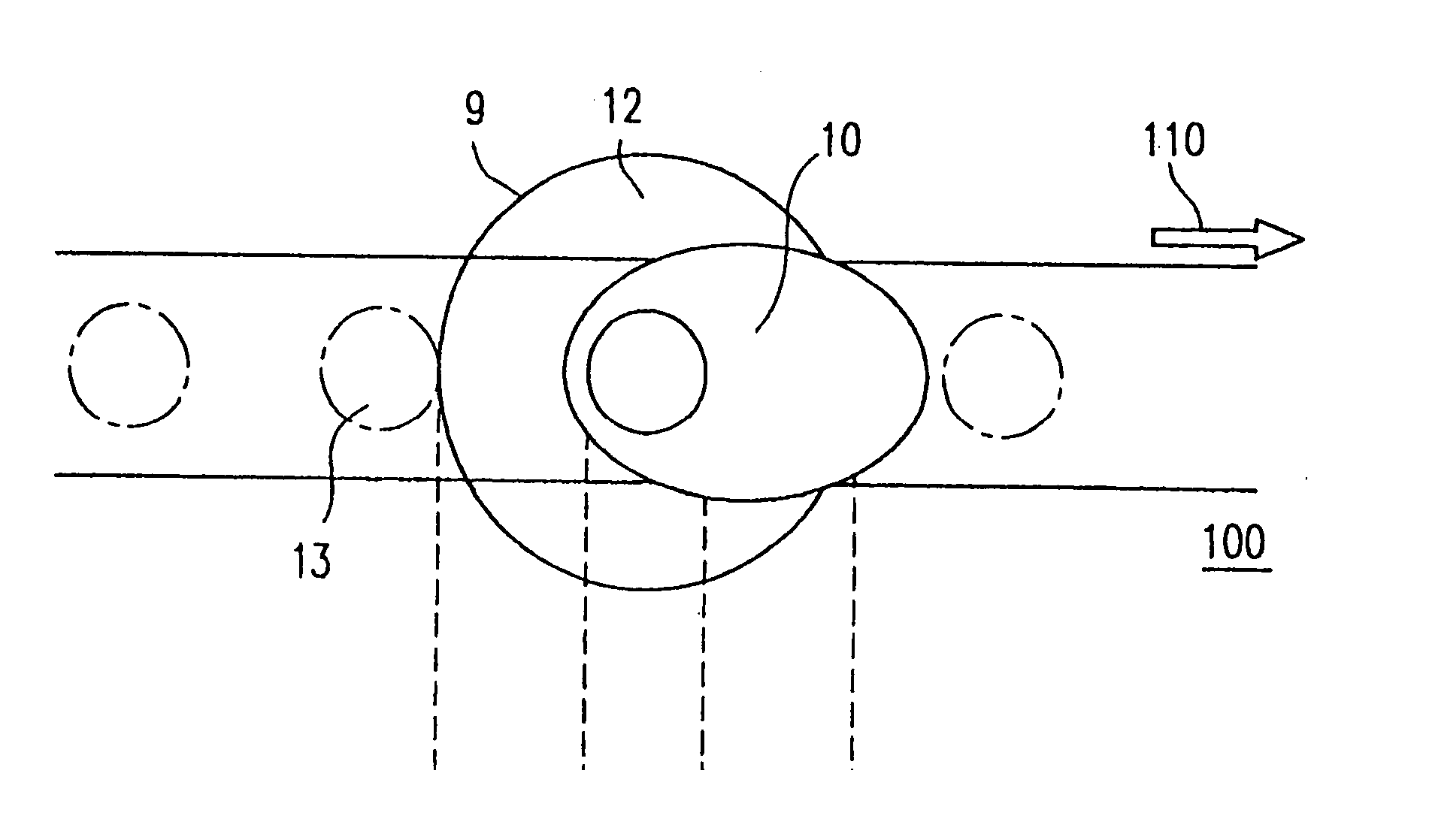
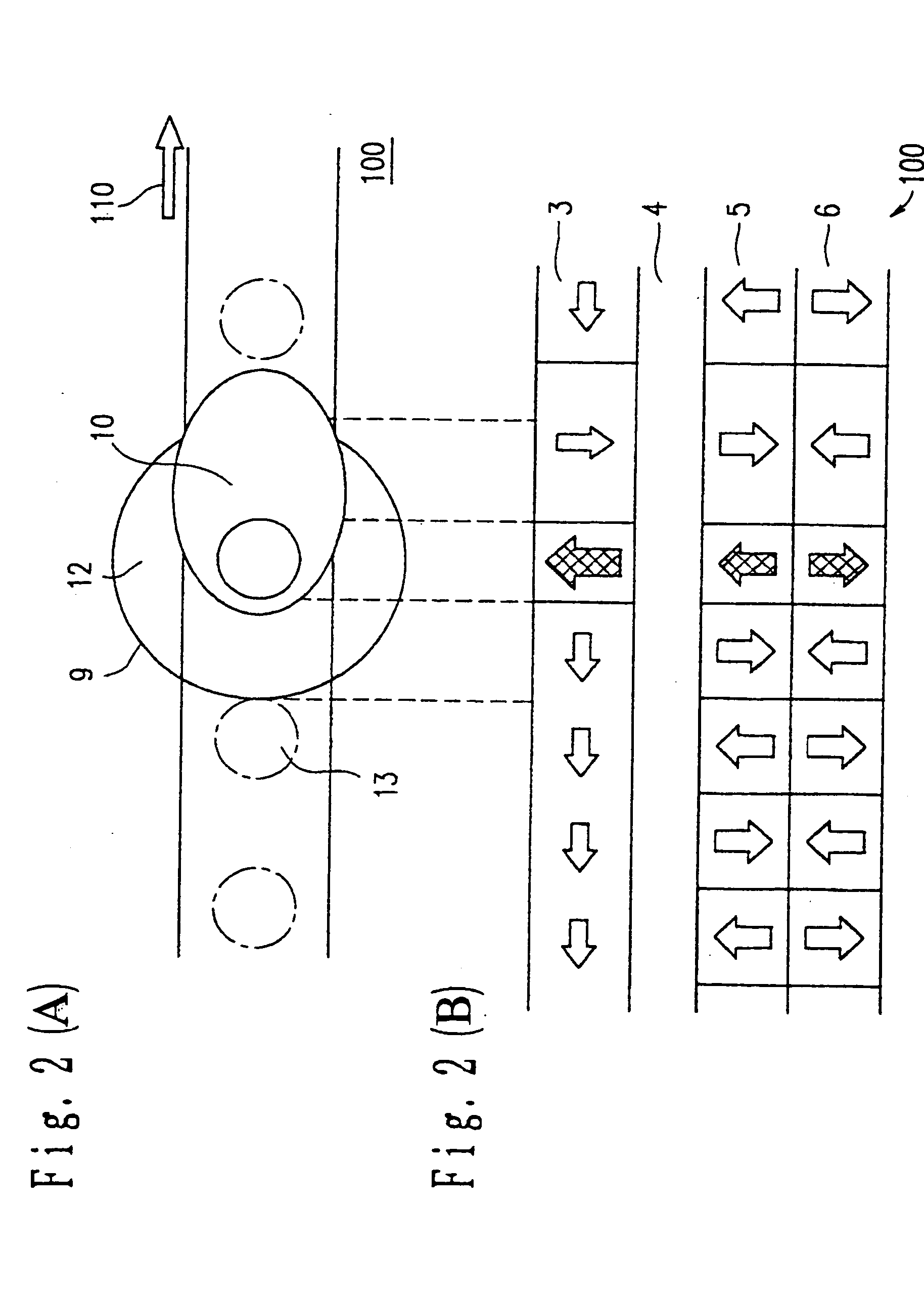
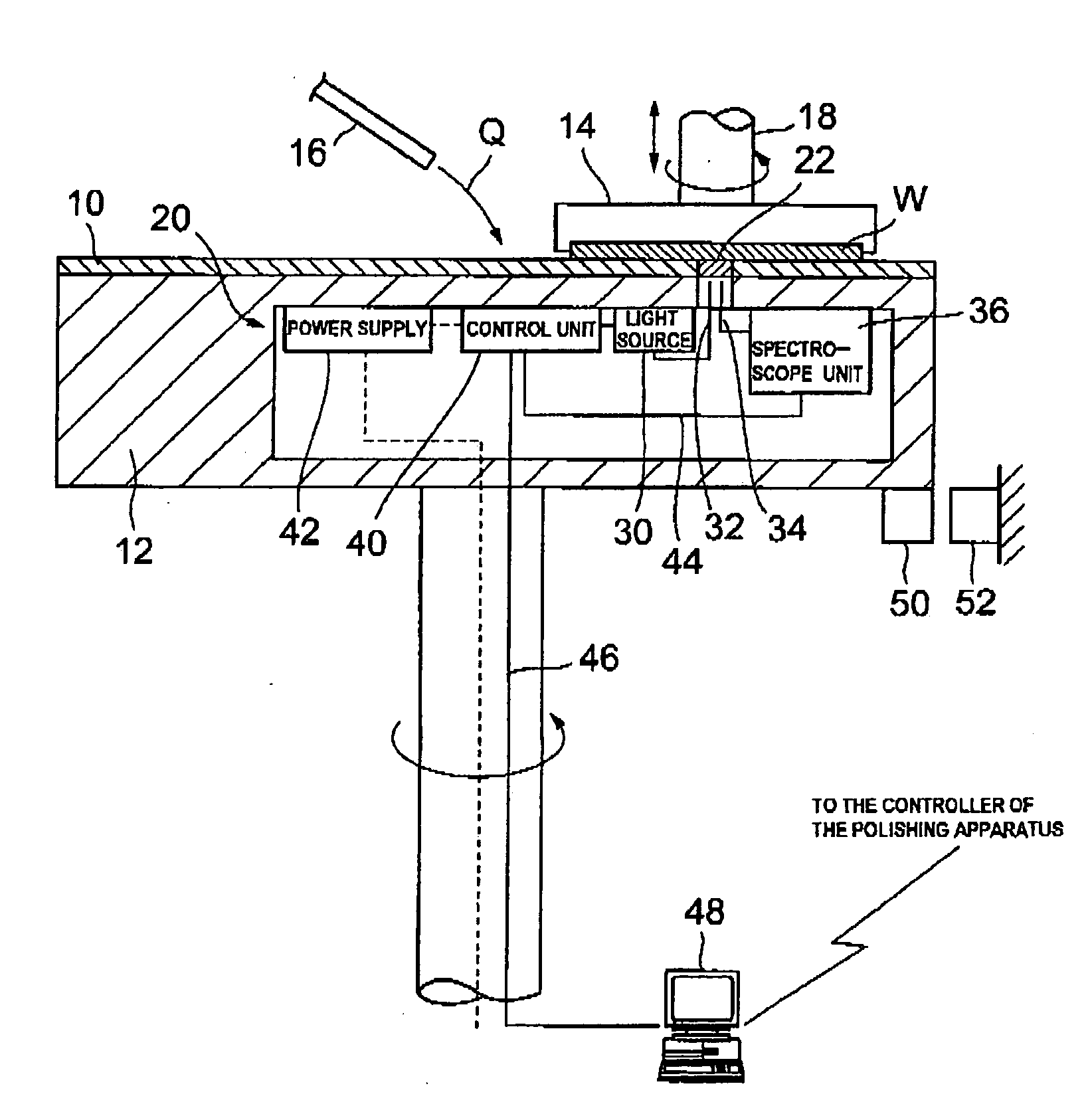
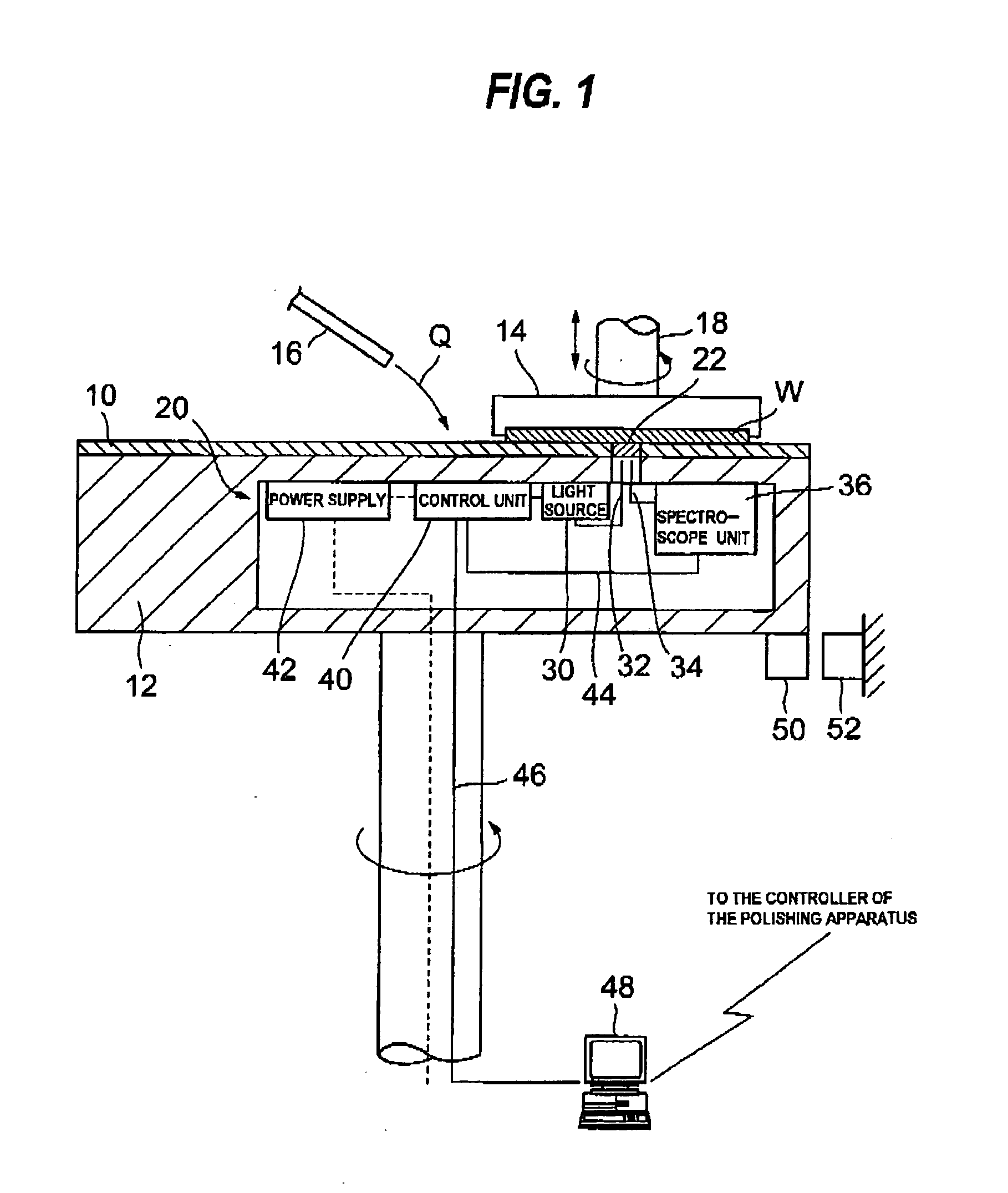
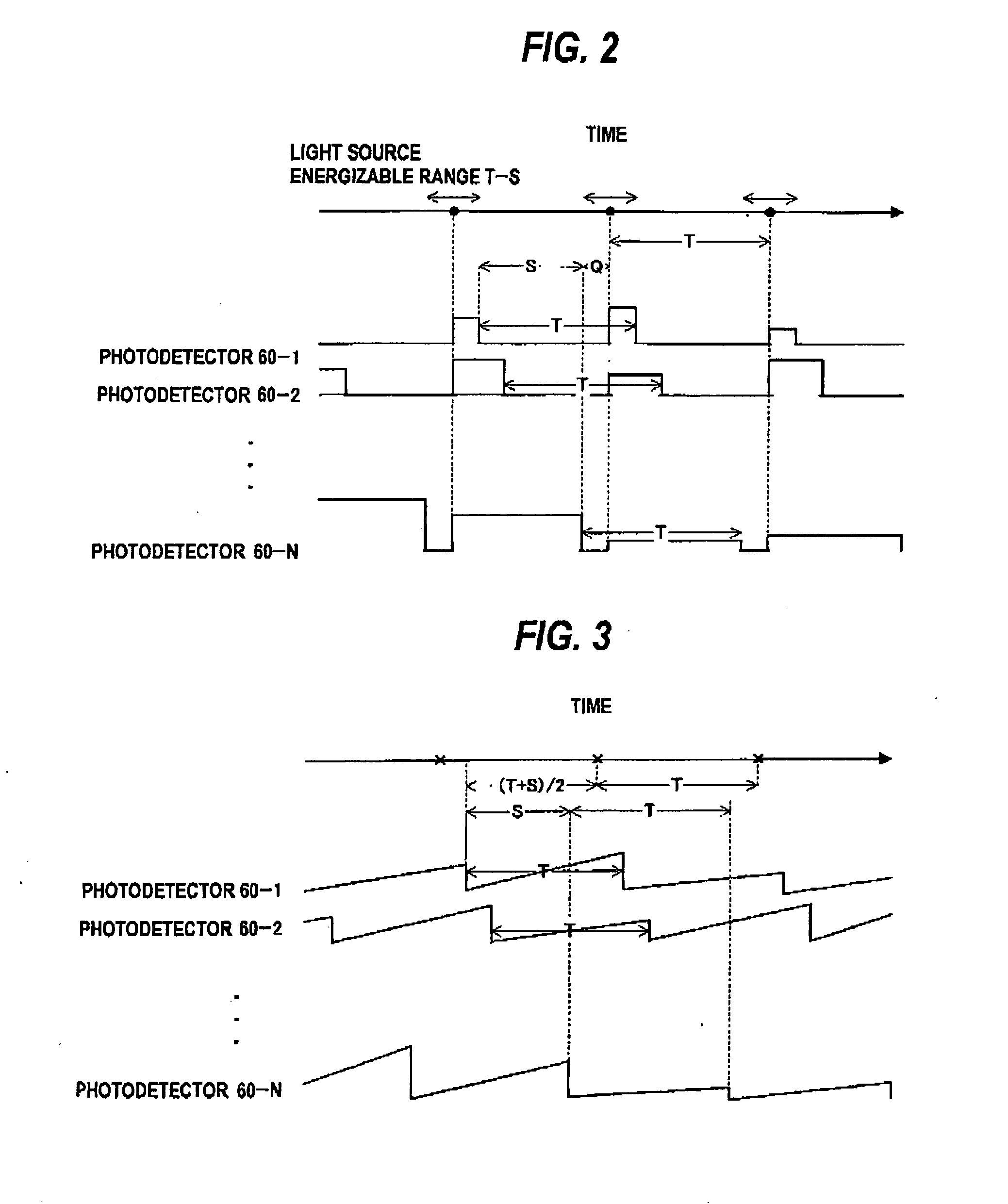
Processing end point detection method, polishing method,and polishing apparatus
ActiveUS20100015889A1Accurate polishing end point detectionUniform film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesLength waveArtificial intelligence
The present invention relates to a processing end point detection method for detecting a timing of a processing end point (e.g., polishing stop, changing of polishing conditions) by calculating a characteristic value of a surface of a workpiece (an object of polishing) such as a substrate. This method includes producing a spectral waveform indicating a relationship between reflection intensities and wavelengths at a processing end point, with use of a reference workpiece or simulation calculation, based on the spectral waveform, selecting wavelengths of a local maximum value and a local minimum value of the reflection intensities, calculating the characteristic value with respect to a surface, to be processed, from reflection intensities at the selected wavelengths, setting a distinctive point of time variation of the characteristic value at a processing end point of the workpiece as the processing end point, and detecting the processing end point of the workpiece by detecting the distinctive point during processing of the workpiece.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +1
Electrowetting device and varifocal lens, optical pickup device, optical recording/reproduction device, droplet operation device, optical element, zoom lens, imaging device, light modulating
InactiveUS20080100905A1Drive voltage causing an equal change in focal length may be reducedReduce film thicknessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesStatic indicating devicesOptical pickupEngineering
Disclosed is an electrowetting device. The electrowetting device includes a conductive or polar liquid material, and an electrode applying voltage to the liquid material through a dielectric layer. In the electrowetting device, the dielectric layer is formed as an anodized portion made of a metal oxide formed by anodizing the electrode, and a voltage applying unit applying voltage between the electrode and the liquid material and a polar capacitor are placed between the electrode and the liquid material.
Owner:SONY CORP
Display device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110198624A1Uniform film shapeReduce film thicknessElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
A display device includes an array of light emitting cells. Each light emitting cell includes first and second electrodes, and an organic light emitting layer located between the first and second electrodes. Banks are above the first electrode that partition the organic light emitting layer to define each of the light emitting cells. First and second light emitting cells are adjacent to one another and located in a peripheral region of the array. The first light emitting cell is closer to a center of the array than the second light emitting cell. A first bank borders the first light emitting cell and the second light emitting cell. An inclination angle of an innermost sidewall of the first bank that is adjacent the first light emitting cell is greater than an inclination angle of an outermost sidewall of the first bank that is adjacent the second light emitting cell.
Owner:JOLED INC
Cellulose ester film, its manufacturing method, polarizing plate, and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6844033B2Good moisture vapor transmittanceGood dimensional stabilityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveCelluloseLiquid-crystal display
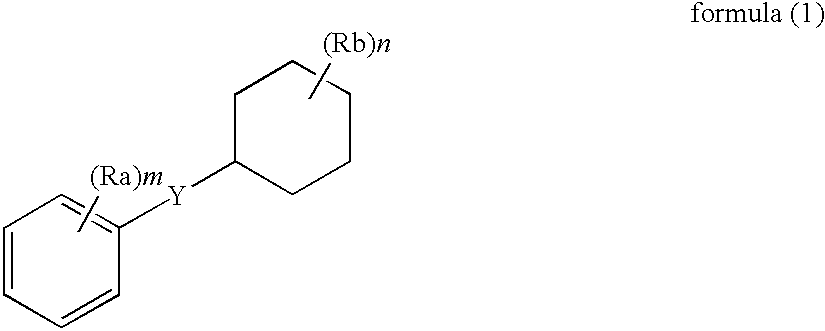
A cellulose ester film and its manufacturing method are disclosed, the cellulose ester film comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1) in an amount of from 1 to 30% by weight, wherein Y represents an ester bond or a divalent organic group containing an ester bond, RTA and Rd independently represent a substituent, and m and n independently represent an integer of 0 to 5, provided that when m or n is not less than 2, plural Ras or Rbs may be the same or different.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Surface capacitive touch panel and its fabrication method
InactiveUS20110199330A1Reduce film thicknessImprove film thickness uniformityTransmission systemsPrinted circuit manufactureCapacitive sensingTouch panel
A surface capacitive touch panel includes a transparent substrate, a decorative layer, a metal trace pattern layer, and a passivation layer. The decorative layer and the capacitive sensing electrode layer are formed on the transparent substrate. The metal trace pattern layer is formed on the capacitive sensing electrode layer. The decorative layer is disposed at a position substantially overlapping the metal trace pattern layer.
Owner:WINTEK CHINA TECH LTD +1
Lithium secondary cell
InactiveUS6228532B1Reduce film thicknessElectrode carriers/collectorsActive material electrodesPolyelectrolyteHydrogen atom
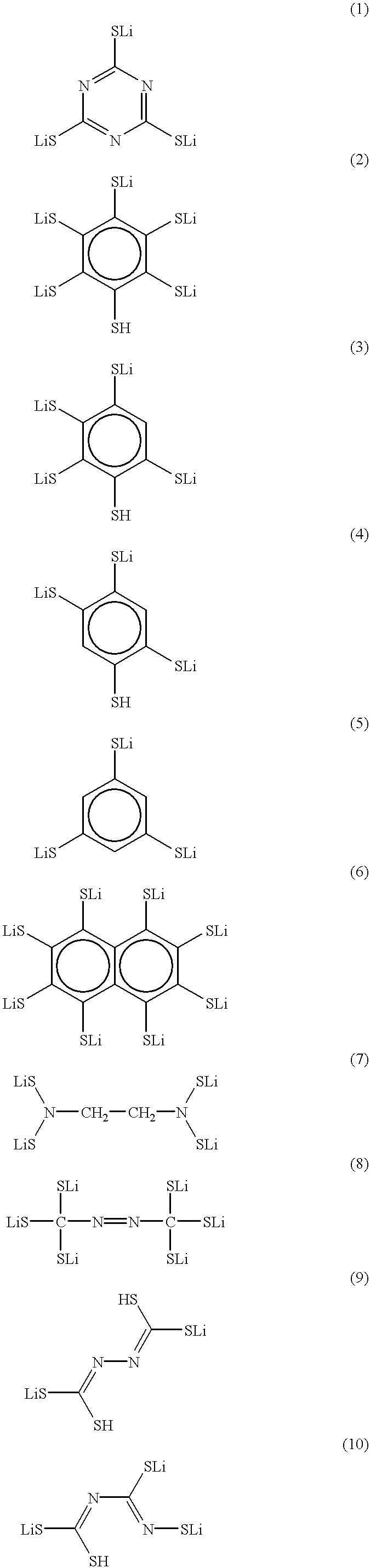
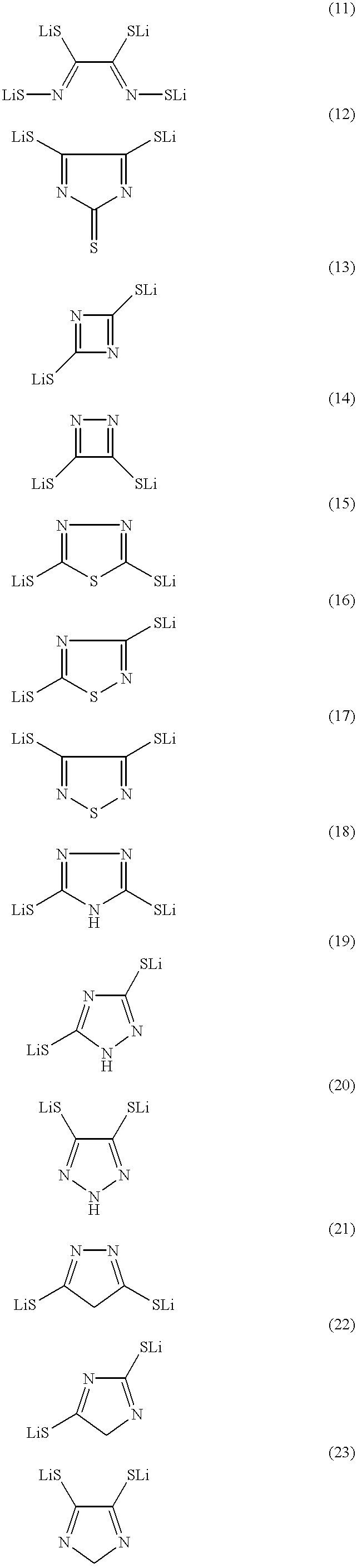
There is provided a lithium polymer secondary cell in which reduction of the film thickness of a solid electrolyte can be realized. The lithium ion secondary cell consists essentially of a composite electrode as a positive electrode having a positive electrode layer, containing a mercaptide compound and a conductive material, carried on a collector; the hydrogen atom of at least one mercapto group in the mercaptide compound being substituted with a lithium atom; a polyelectrolyte; and a lithium negative electrode.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080303968A1Lower resistanceReduce the overall diameterTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
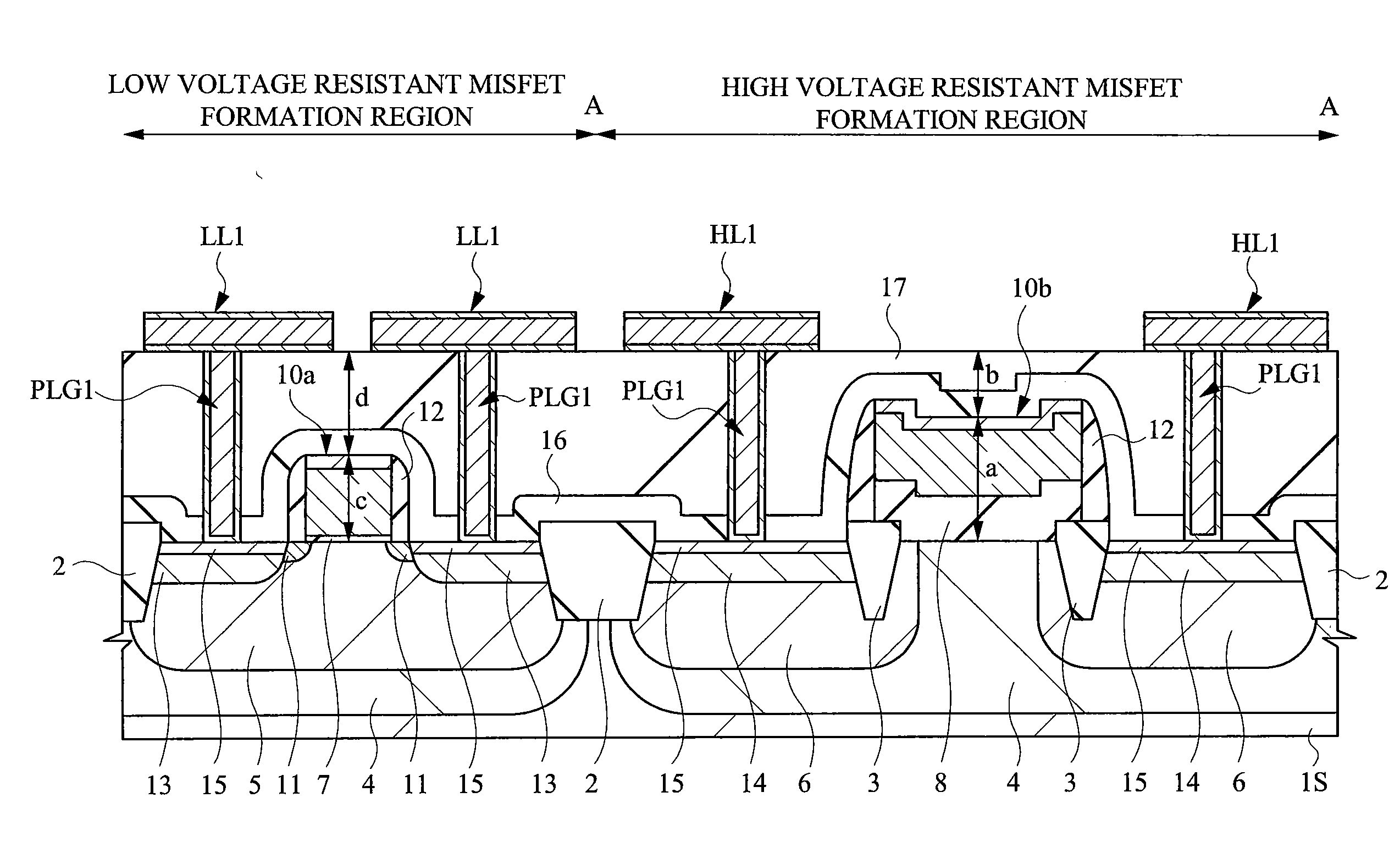
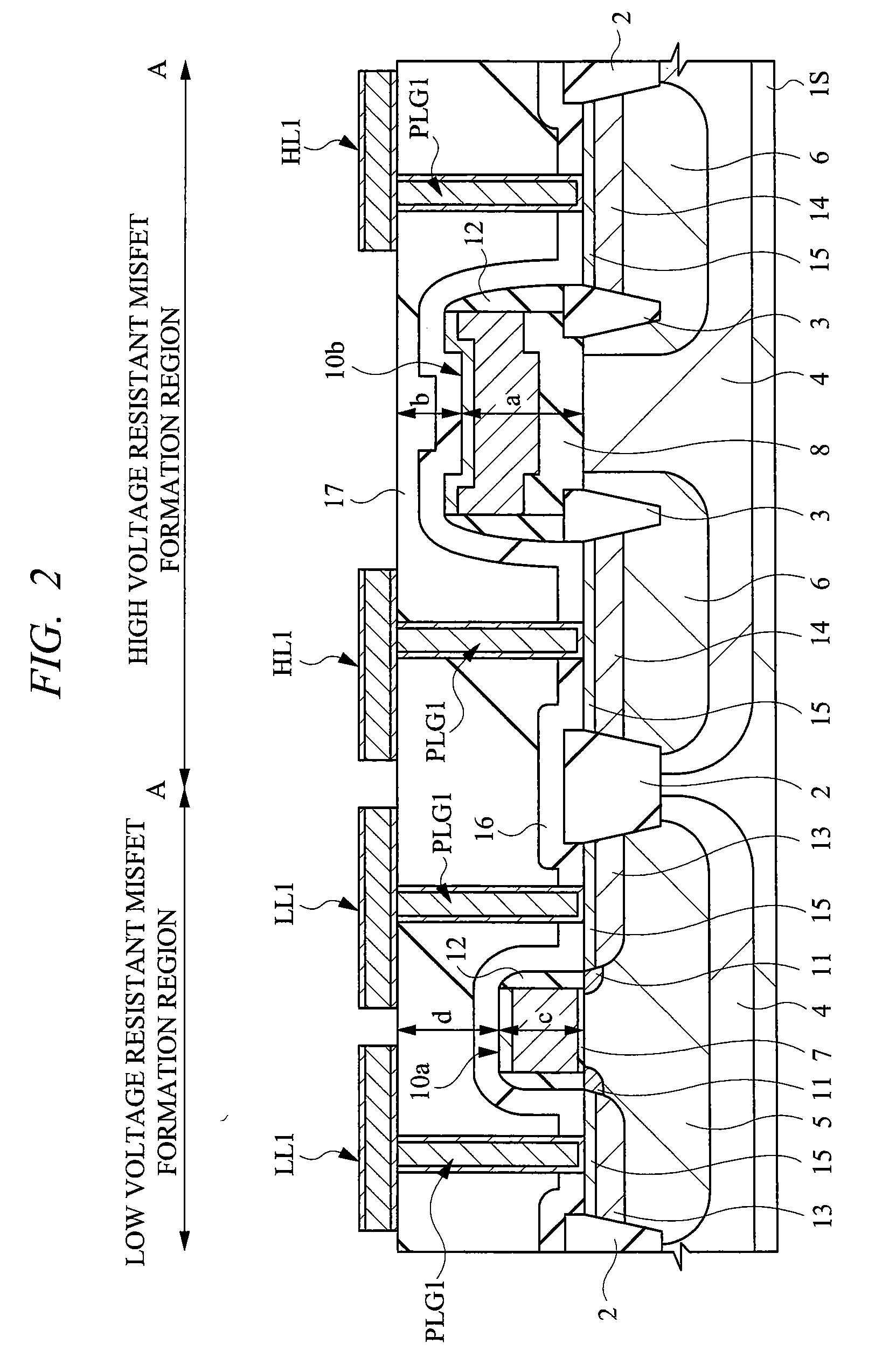
In an LCD driver, in a high voltage resistant MISFET, end portions of a gate electrode run onto electric field relaxing insulation regions. Wires to become source wires or drain wires are formed on an interlayer insulation film of the first layer over the high voltage resistant MISFET. At this moment, when a distance from an interface between a semiconductor substrate and a gate insulation film to an upper portion of the gate electrode is defined as “a”, and a distance from the upper portion of the gate electrode to an upper portion of the interlayer insulation film on which the wires are formed is defined as “b”, a relation of a>b is established. In such a high voltage resistant MISFET structured in this manner, the wires are arranged so as not to be overlapped planarly with the gate electrode of the high voltage resistant MISFET.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS6900480B2Light transmission efficiency is improvedEasy to controlTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
A solid-state imaging device having, in each of unit pixels, an on-chip microlens composed of plural convex lens parts for each of photoelectric conversion elements provided on a semiconductor chip is disclosed. A floating diffusion part and a signal-charge read gate for taking out a signal charge from the photoelectric conversion element are provided on a region positioned in a boundary of each convex lens part of the on-chip microlens. A wiring for the floating diffusion part and a wiring for the read gate are provided along the respective boundaries of the convex lens parts of the on-chip microlens. In this device, the film thickness of the on-chip microlens can be reduced with regard to the area of each unit pixel, thereby facilitating the process control and enhancing the light transmission efficiency. It is also possible to enhance the circuit wiring efficiency in each unit pixel while avoiding any incomplete charge transfer to consequently improve the picture quality.
Owner:SONY CORP
Film
InactiveUS20100304062A1Easy to processIncrease chanceSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The present invention provides a uniaxially oriented multilayer film comprising at least (i) a layer (A) and (ii) a layer (B), wherein said layer (A) comprises a linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) comprising (e.g. selected from):—a multimodal LLDPE produced using a Ziegler Natta catalyst (znLLDPE), or—a LLDPE produced using a single site catalyst (mLLDPE) or—a mixture of a mLLDPE and a multimodal znLLDPE, said layer (B) comprises a multimodal LLDPE, and said multilayer film is in the form of a stretched film which is uniaxially oriented in the machine direction (MD) in a draw ratio of at least 1:3.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
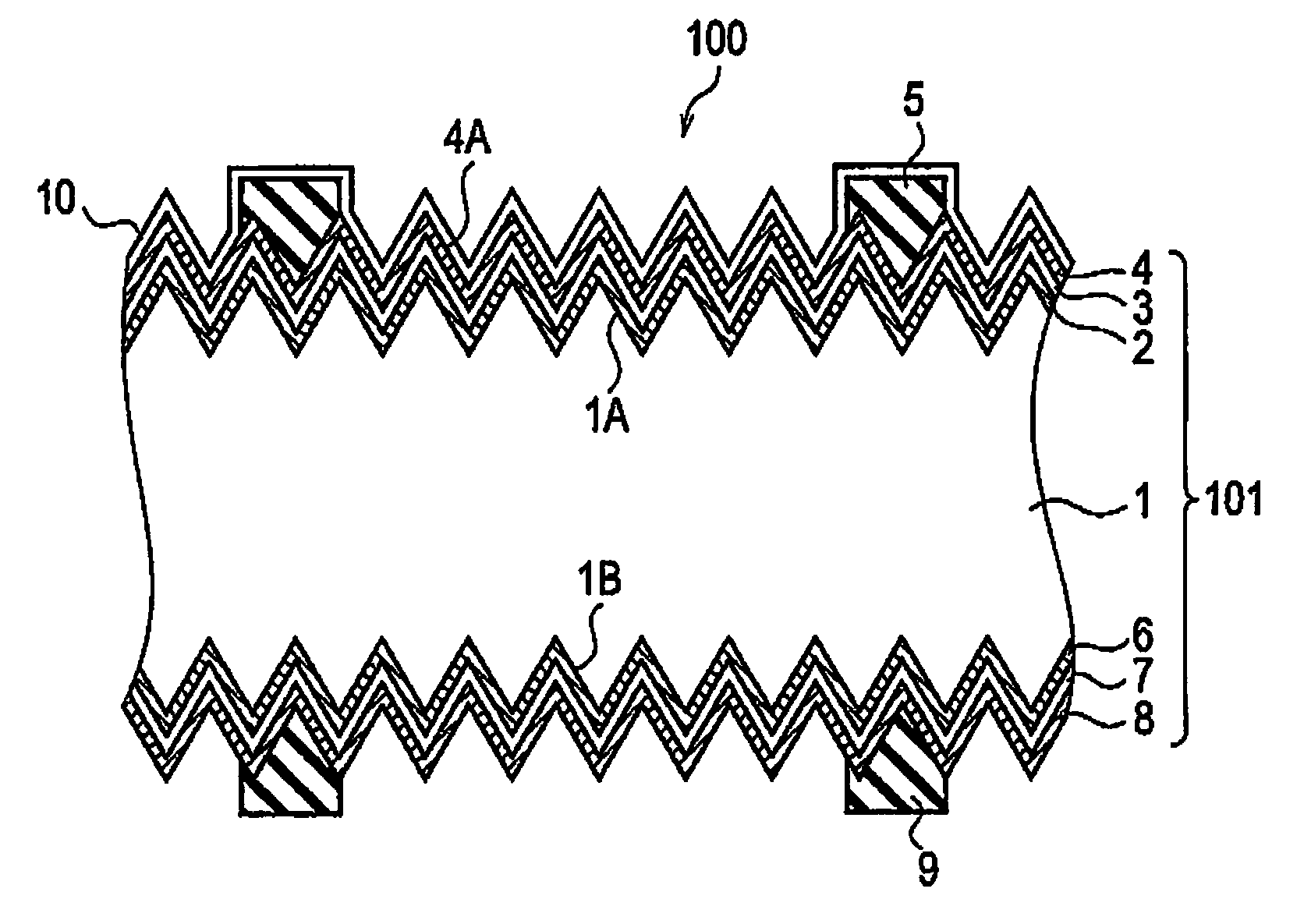
Solar cell module
InactiveUS20100006147A1Relieve pressureReduce warpagePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A solar cell module includes: a photoelectric conversion body 101 having an uneven surface on a light-entering surface; and a protection layer 10 made of a resin and provided to cover the uneven surface. In a cross section of the protection layer 10 taken in parallel to a light-entering direction, a thickness W2 of a projected portion on the uneven surface is smaller than a thickness W1 of a recessed portion on the uneven surface.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Pigment dispersion, coloring composition for color filter, color filter, liquid crystal display and organic EL display
ActiveCN101541898AImprove transmittanceIncrease contrastOptical filtersPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusDispersion stabilityPigment dispersion
Disclosed is a pigment dispersion exhibiting both high contrast and adequate dispersion stability, wherein a granulated pigment is used. Also disclosed is a coloring composition for color filters having good developability, which uses the pigment dispersion. Specifically disclosed is a pigment dispersion containing a pigment, a solvent and a dispersing agent, which is characterized in that the dispersing agent contains a block copolymer composed of a block A having an affinity for solvents and a block B having a functional group containing a nitrogen atom. This pigment dispersion is also characterized in that the dispersing agent has an amine number of not less than 80 mgKOH / g but not more than 150 mgKOH / g in terms of the effective solid content. Also specifically disclosed is a use of such a pigment dispersion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Method for manufacturing soi wafer and soi wafer
InactiveUS20060051945A1Quality improvementPerfectness is highSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystallinityIon implantation
The present invention provides a method of producing an SOI wafer, comprising at least steps of forming an oxygen ion-implanted layer by implanting oxygen ions into a silicon wafer from one main surface thereof, subjecting the silicon wafer to oxide film-forming heat treatment to convert the oxygen ion-implanted layer into a buried oxide film, and thereby producing an SOI wafer having an SOI layer on the buried oxide film, wherein when the buried oxide film is formed in the silicon wafer, the buried oxide film is formed so that a thickness thereof is thicker than a thickness of the buried oxide film which the SOI wafer to be produced has, and thereafter the silicon wafer in which the thicker buried oxide film is formed is subjected to a heat treatment to reduce the thickness of the buried oxide film. Thereby, there can be provided a method of producing an SOI wafer in which a high quality SOI wafer having a buried oxide film of which a film thickness is thin and perfectness is high and an SOI layer of which crystallinity and surface quality are extremely good can be produced by using SIMOX method.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Liquid crystal polyester composition and electronic circuit board using the same
ActiveUS8465670B2High viscosityReduce film thicknessLiquid crystal compositionsPrinted circuit aspectsPolyesterVolume average
To provide a liquid crystal polyester composition which is suited for use as a material for forming a liquid crystal polyester film having excellent thermal conductivity. Also, an excellent electronic circuit board is provided by using an insulating film obtained from the liquid crystal polyester composition. The liquid crystal polyester composition of the present invention is composed of a liquid crystal polyester, a solvent and a thermally conductive filler. The thermally conductive filler is contained in the amount of 50 to 90 volume % based on the total amount of the liquid crystal polyester and the thermally conductive filler, and the thermally conductive filler contains 0 to 20 volume % of a first thermally conductive filler having a volume average particle diameter of 0.1 μm or more and less than 1.0 μm, 5 to 40 volume % of a second thermally conductive filler having a volume average particle diameter of 1.0 μm or more and less than 5.0 μm and 40 to 90 volume % of a third thermally conductive filler having a volume average particle diameter of 5.0 μm or more and 30.0 μm or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Dehumidifying element, and adsorbing element used for the dehumidifying element
InactiveUS20060086125A1Improve heat transfer performanceFacilitate actionDomestic cooling apparatusIsotope separationSorbentSingle plate
In a dehumidification unit comprising alternate laminations of an adsorption element (1) which supports an adsorbent and which is provided with a first air ventilation passage (3) and a cooling element (2) which is provided with a second air ventilation passage (4), the first air ventilation passage (3) of the adsorption element (1) and the second air ventilation passage (4) of the cooling element (2) are adjacently formed, with a single plate member (P) lying between the first and second air ventilation passages (3, 4). As a result of such arrangement, as compared with a structure in which the air ventilation passages (3, 4) are adjacently formed with two plate members lying therebetween, the performance of heat transfer between the air ventilation passages (3, 4) is further improved, and the action of absorbing and removing heat of adsorption is promoted, whereby the dehumidification capability of the dehumidification unit is maintained at high levels over a long period of time. Furthermore, the dehumidification unit is made compact relative to its height direction by an amount corresponding to reduction in the number of plate members lying between the first air ventilation passage (3) and the second air ventilation passage (4), and cost savings are provided because of reduction in the number of component members.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Method of forming resist pattern and negative tone-development resist composition
ActiveUS20110262864A1Improve hydrophilicityPromote formationPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSolubilityResist
A method of forming a resist pattern, including: forming a resist film on a substrate using a resist composition containing a base component (A) which exhibits decreased solubility in an organic solvent under action of an acid and an acid-generator component (B) which generates an acid upon exposure, conducting exposure of the resist film, and patterning the resist film by a negative tone development using a developing solution containing an organic solvent, wherein the base component (A) includes a resin component (A1) containing a structural unit (a0) derived from an acrylate ester containing an acid decomposable group which generates an alcoholic hydroxy group by the action of acid to thereby exhibit increased hydrophilicity.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Resist composition
InactiveUS6916593B2Small sizeReduce film thicknessRadiation applicationsDiazo compound compositionsResistChemical compound
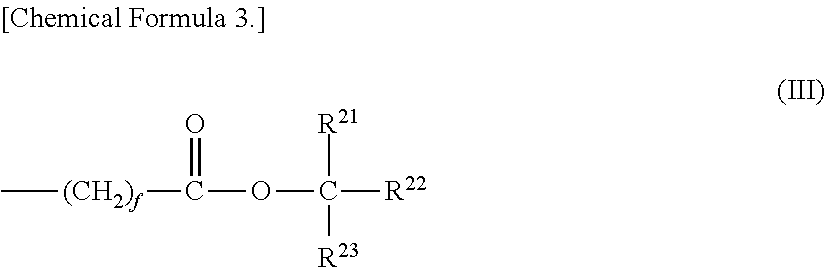
Although use of a nitrogen-containing compound as a basic compound component of a resist composition makes it possible to ease the T-top problem at an acid dissociation constant pKa falling within a range of 2 to 6, it is accompanied with the problem that the reaction, that is, acid diffusion upon use of a highly-reactive acid-labile group cannot be controlled. In order to overcome this problem, one or more basic compounds selected from those represented by the following formulas (I) to (III) and (1) to (4) are employed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
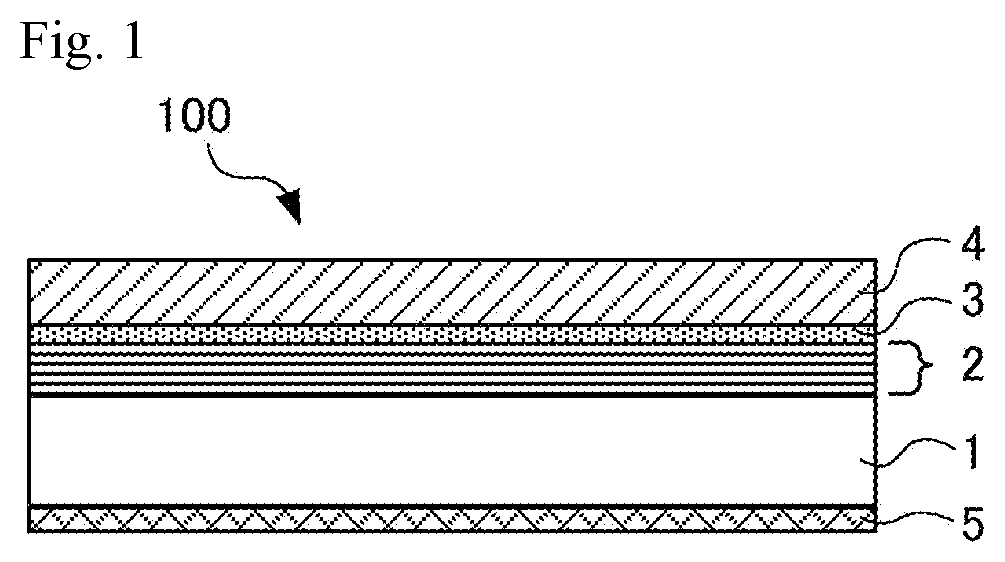
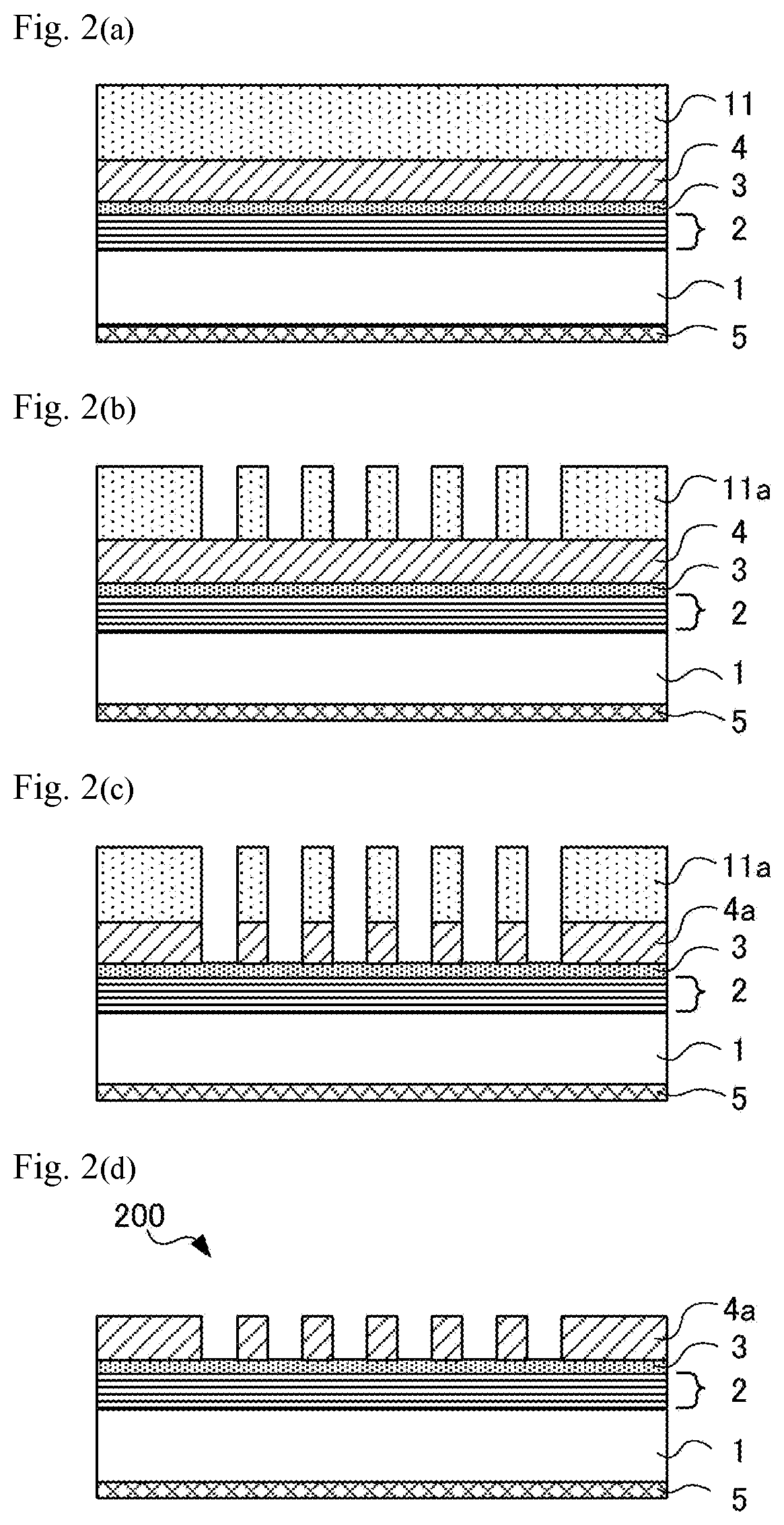
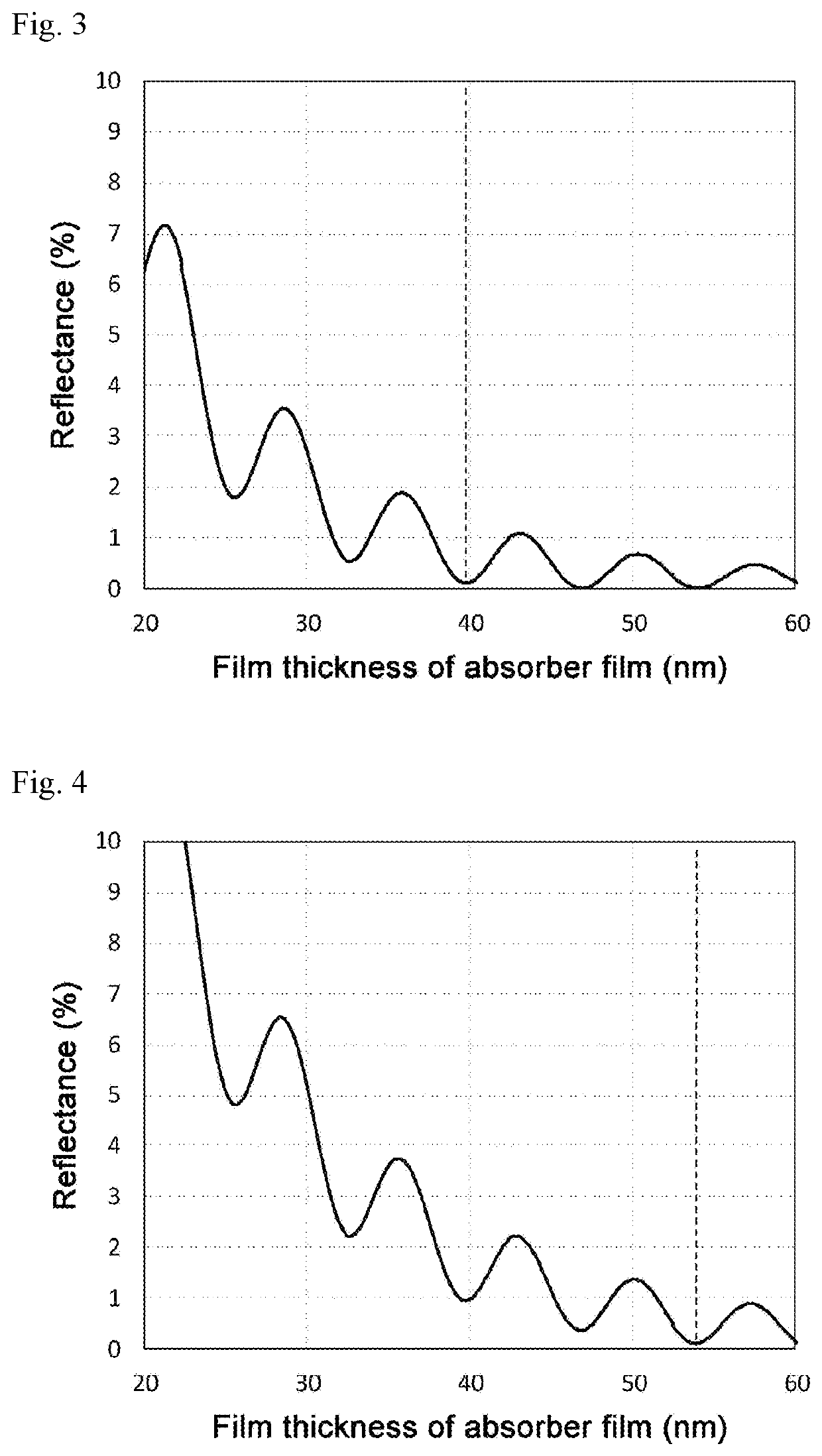
Reflective mask blank, reflective mask and manufacturing method thereof, and semiconductor device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20190384157A1Fine and highly accurate absorber patternStable cross-sectional shapePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistShadow effect
Provided are a reflective mask blank and a reflective mask, which are able to reduce the shadowing effects of EUV lithography and form a fine pattern. As a result, a semiconductor device can be stably manufactured with high transfer accuracy. The reflective mask blank comprises a multilayer reflective film and an absorber film in that order on a substrate, and the absorber film comprises a material comprising an amorphous metal comprising at least one or more elements among cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni).
Owner:HOYA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com