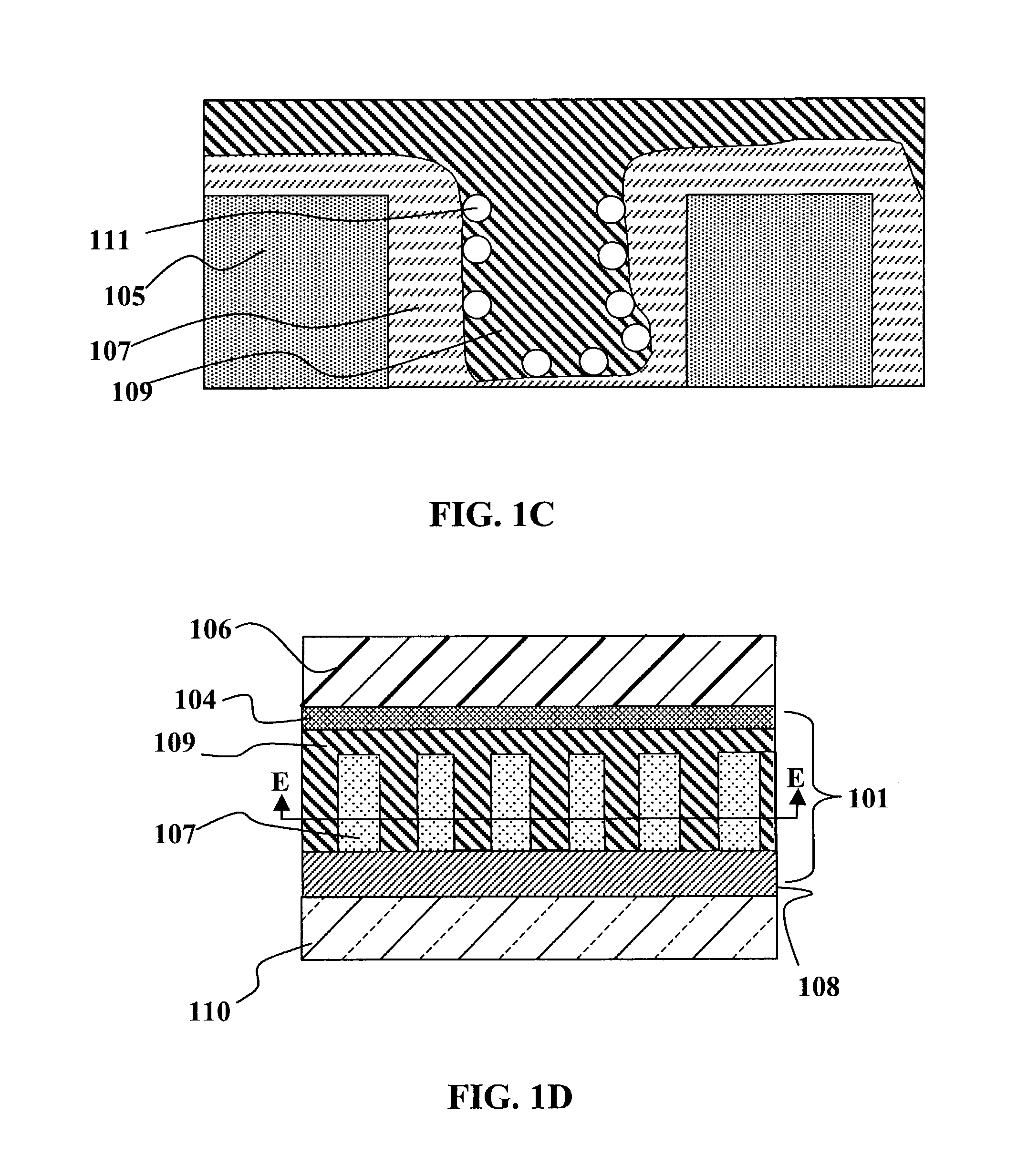
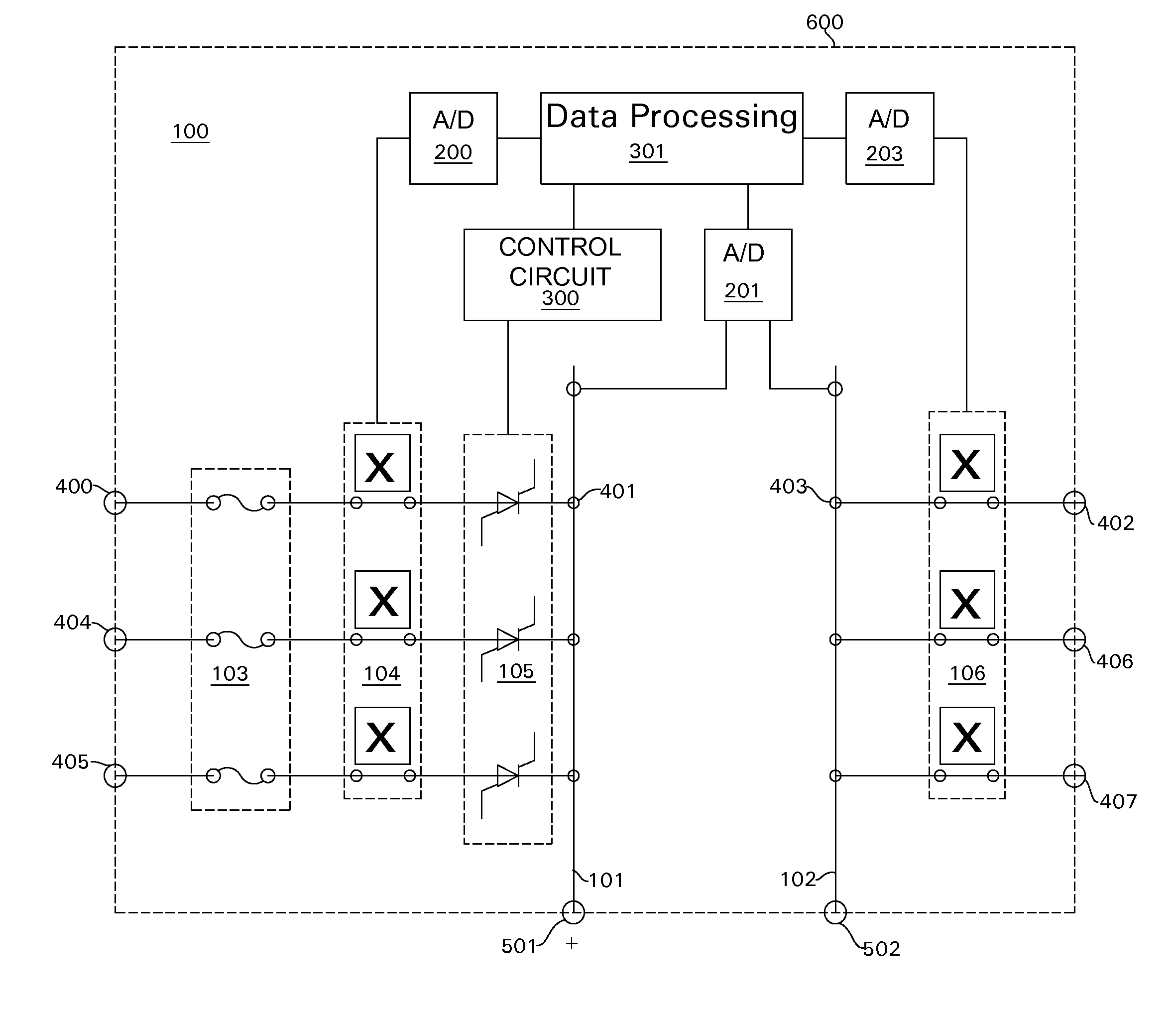
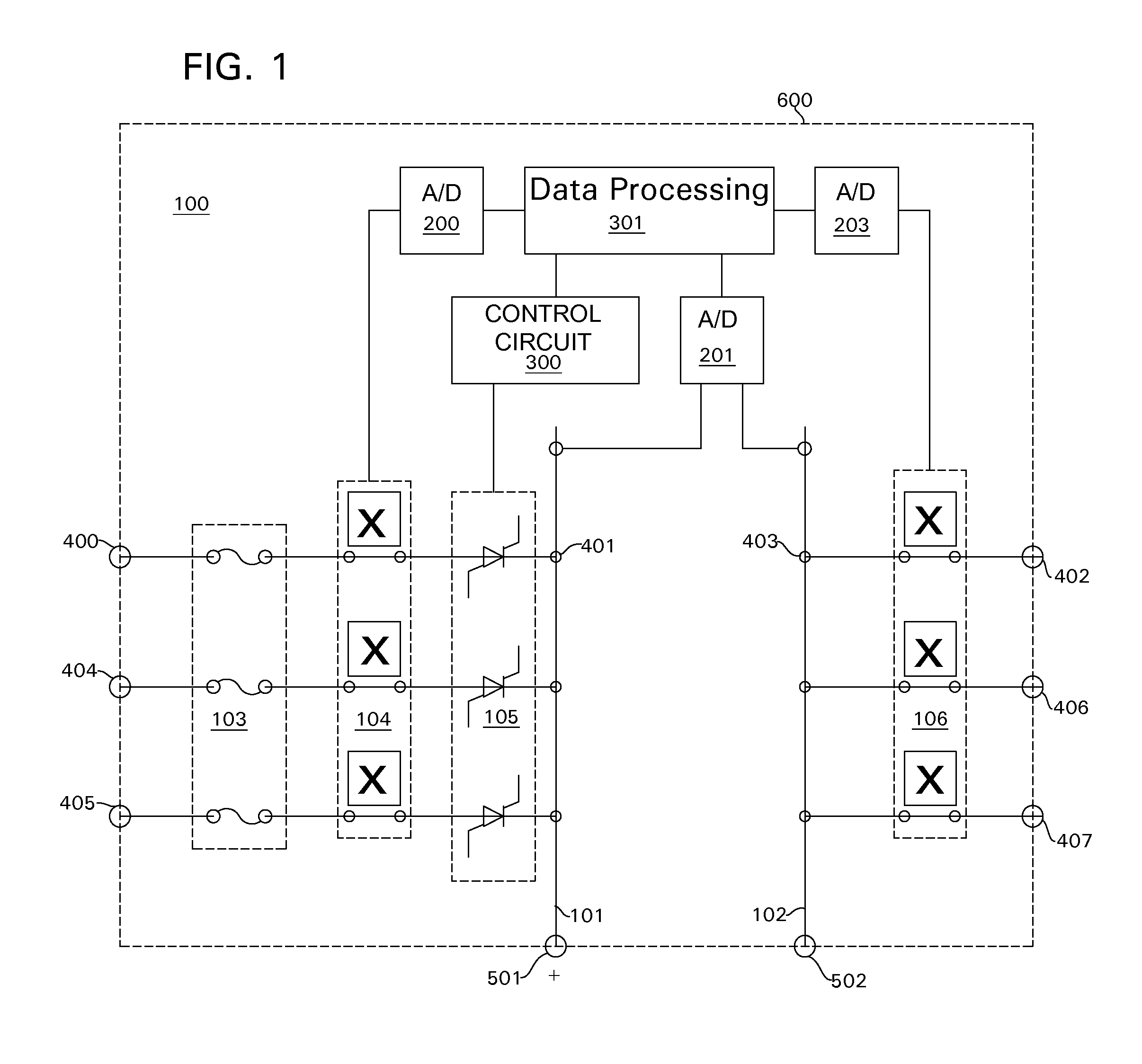
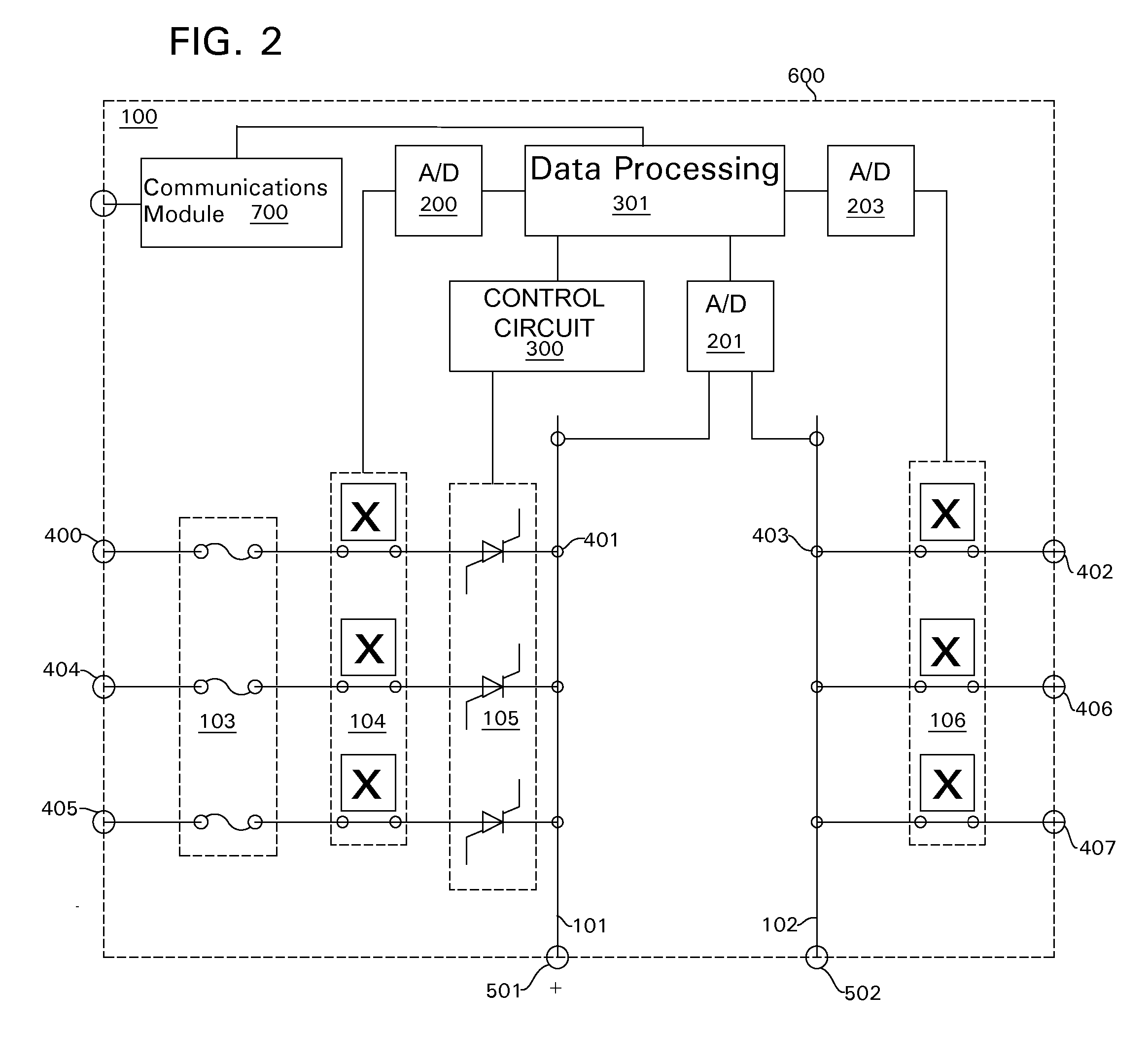
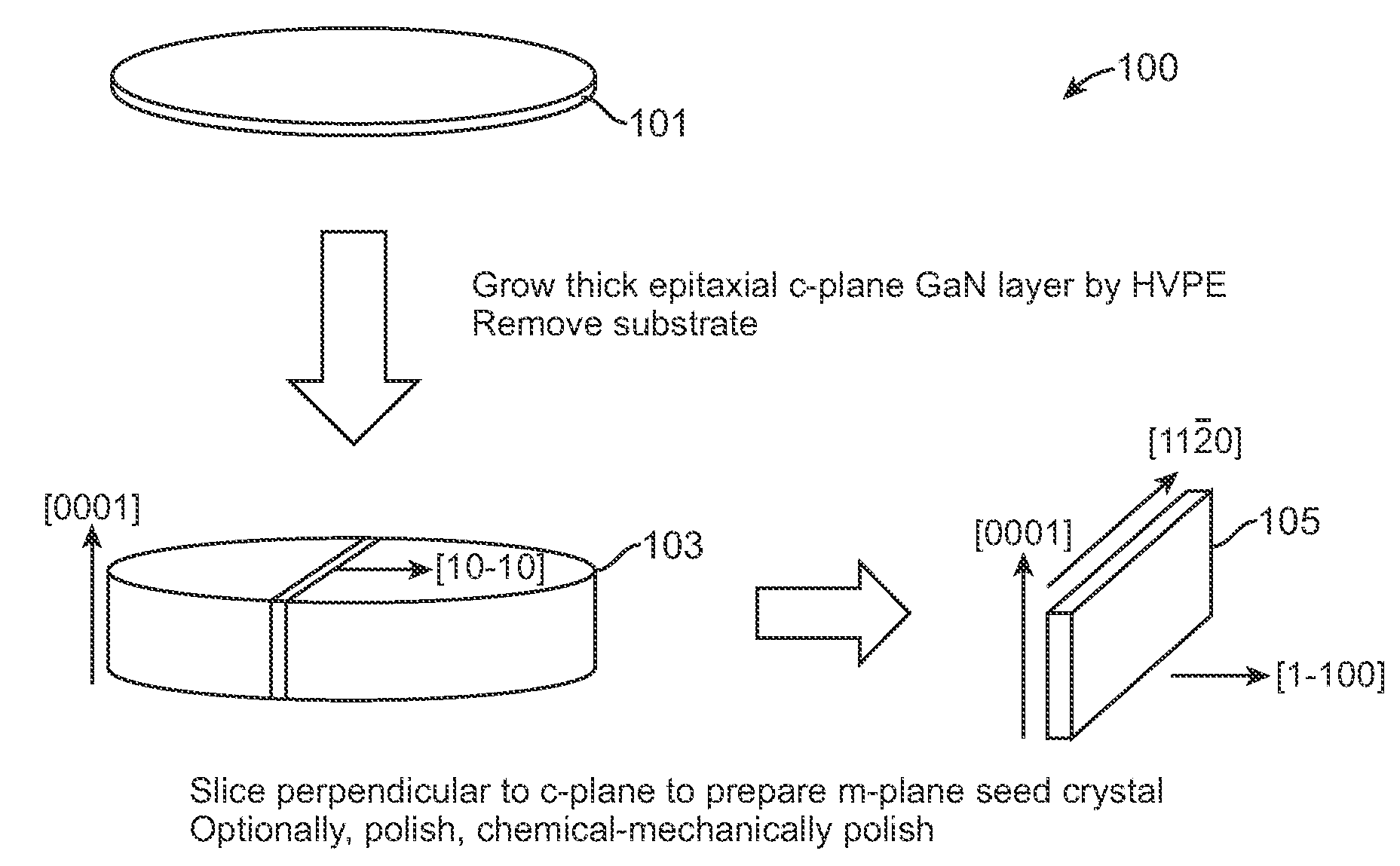
Patents
Literature
37355 results about "Solar cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
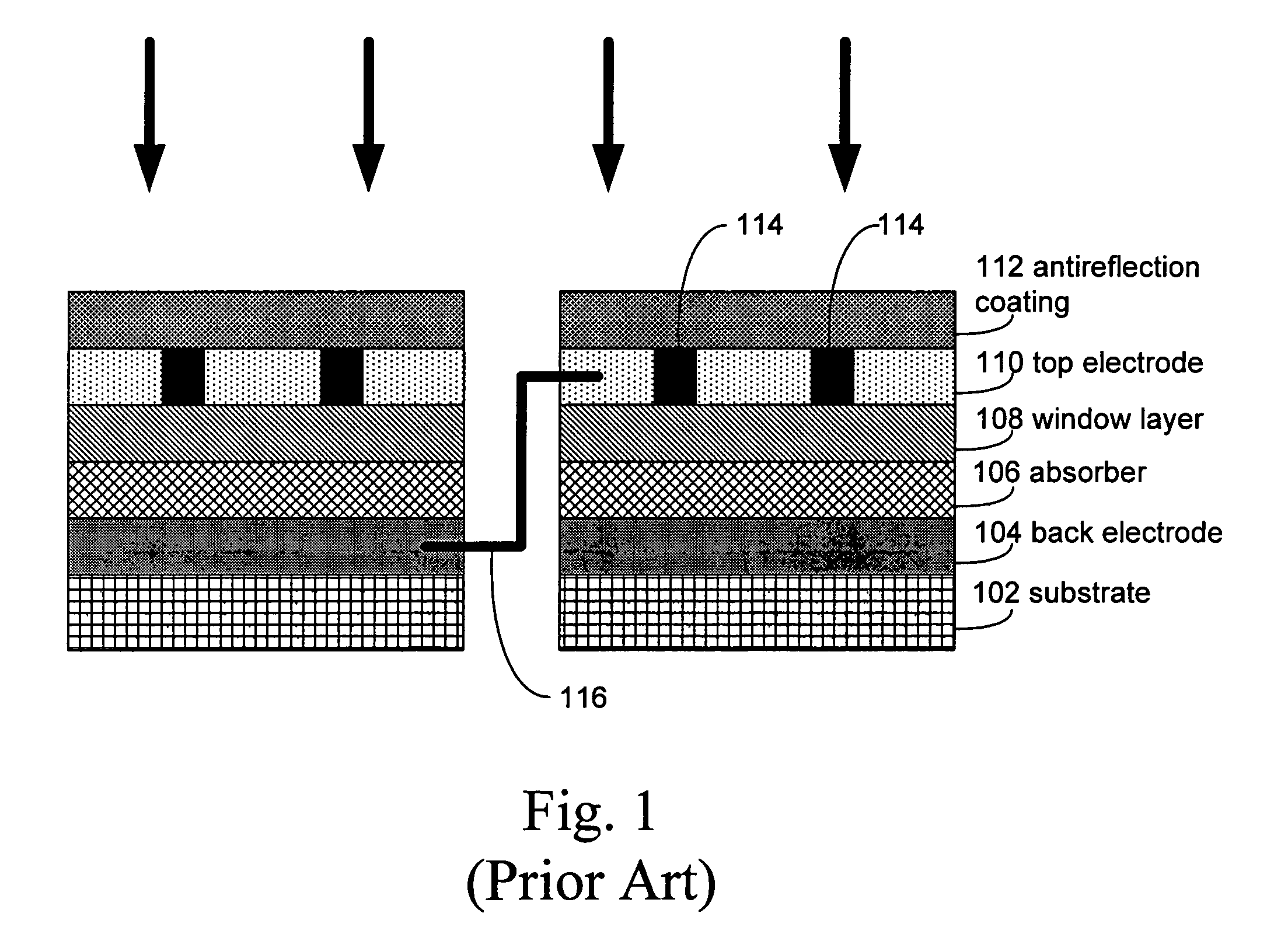
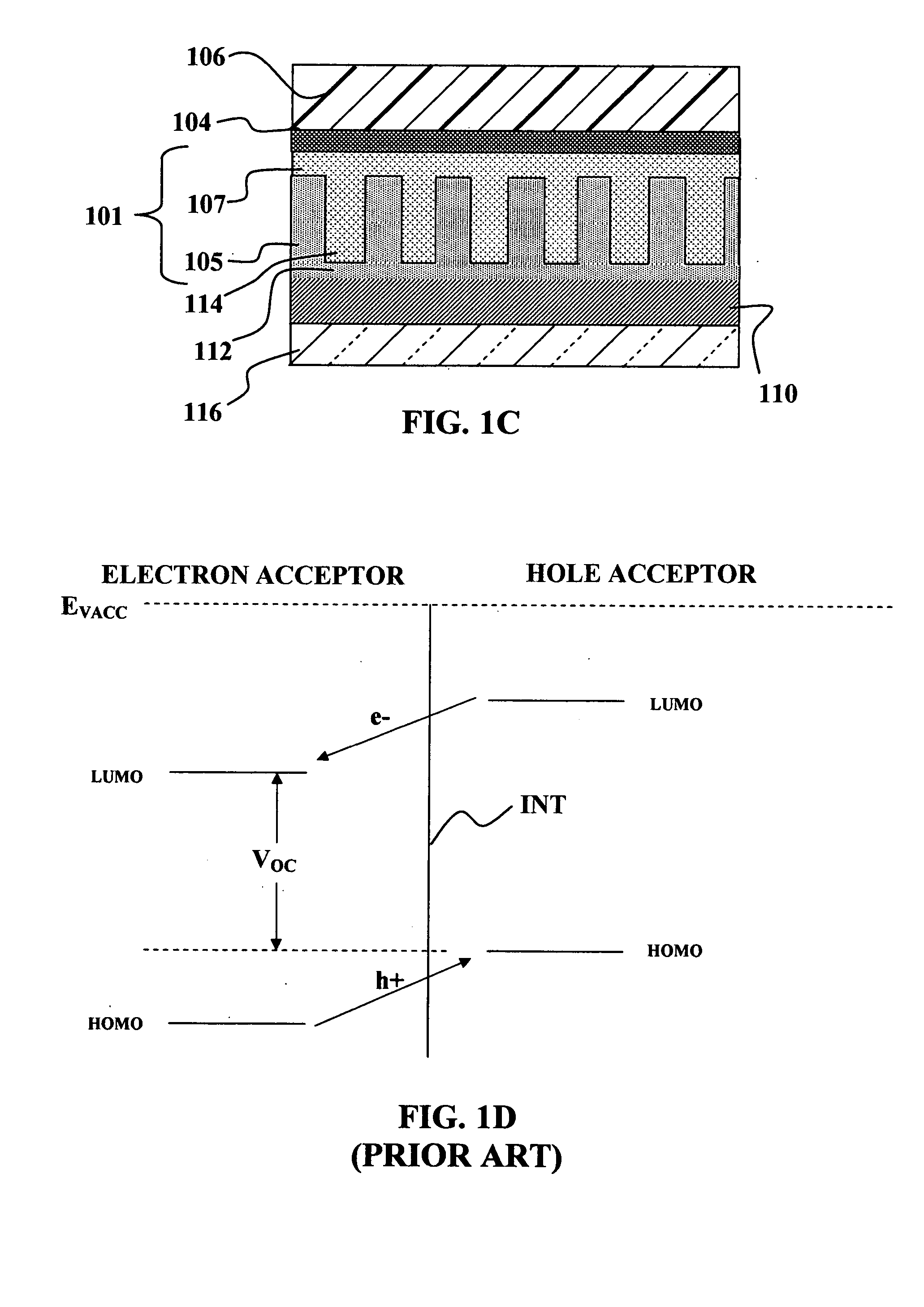
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon. It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or resistance, vary when exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices can be combined to form modules, otherwise known as solar panels. The common single junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.5 to 0.6 volts.
Solar cells using fullerenes
InactiveUS6580027B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSolar cellFullerene
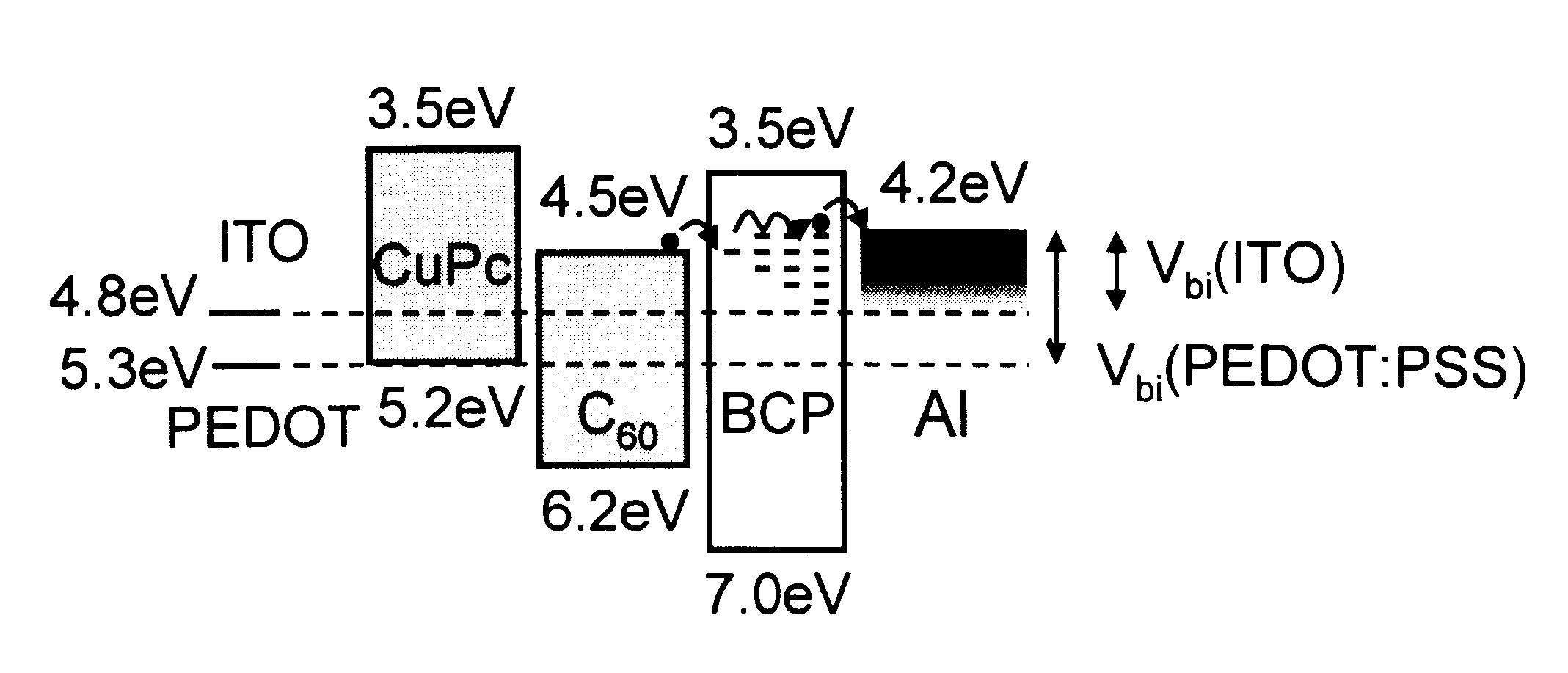
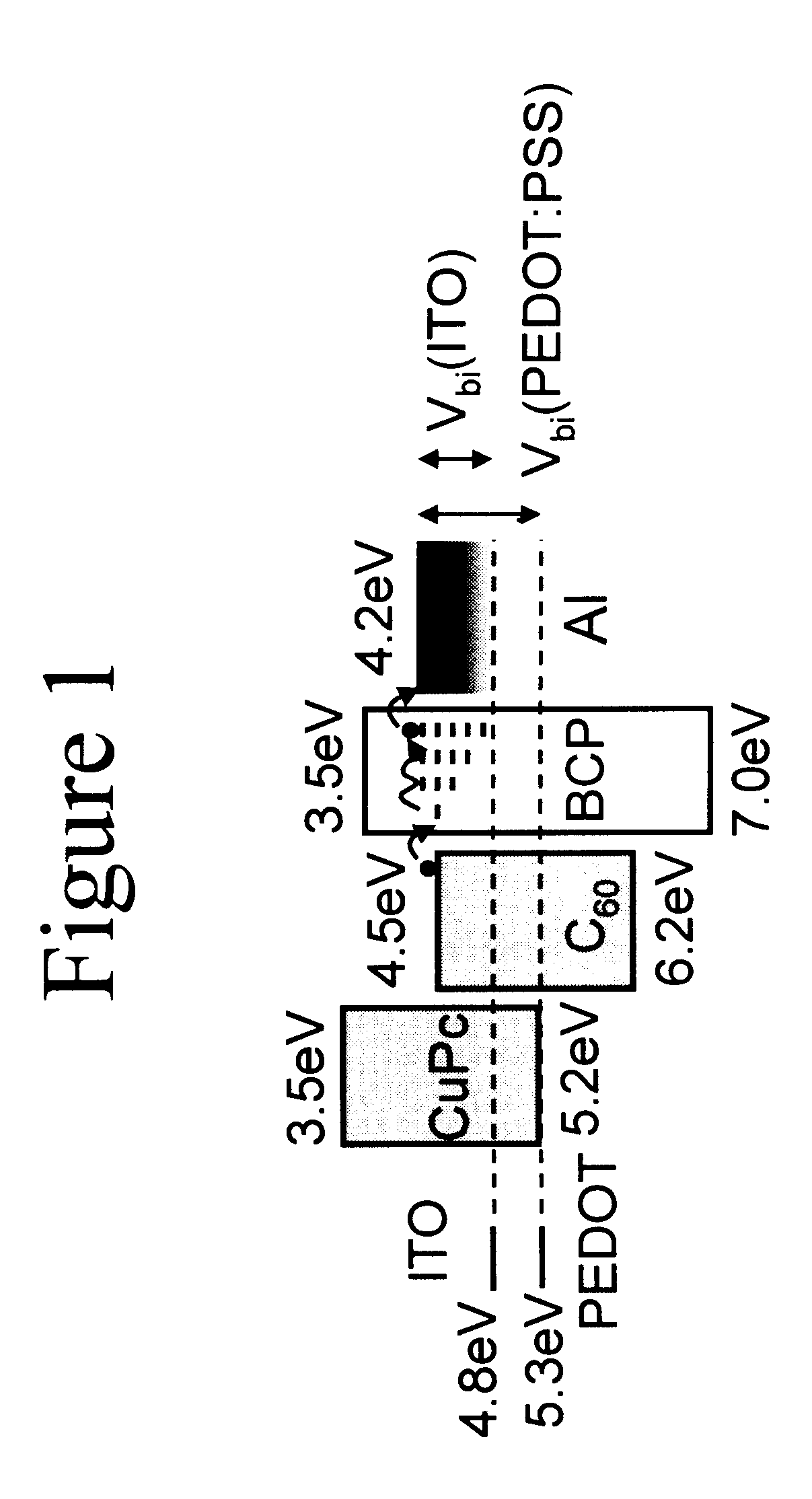
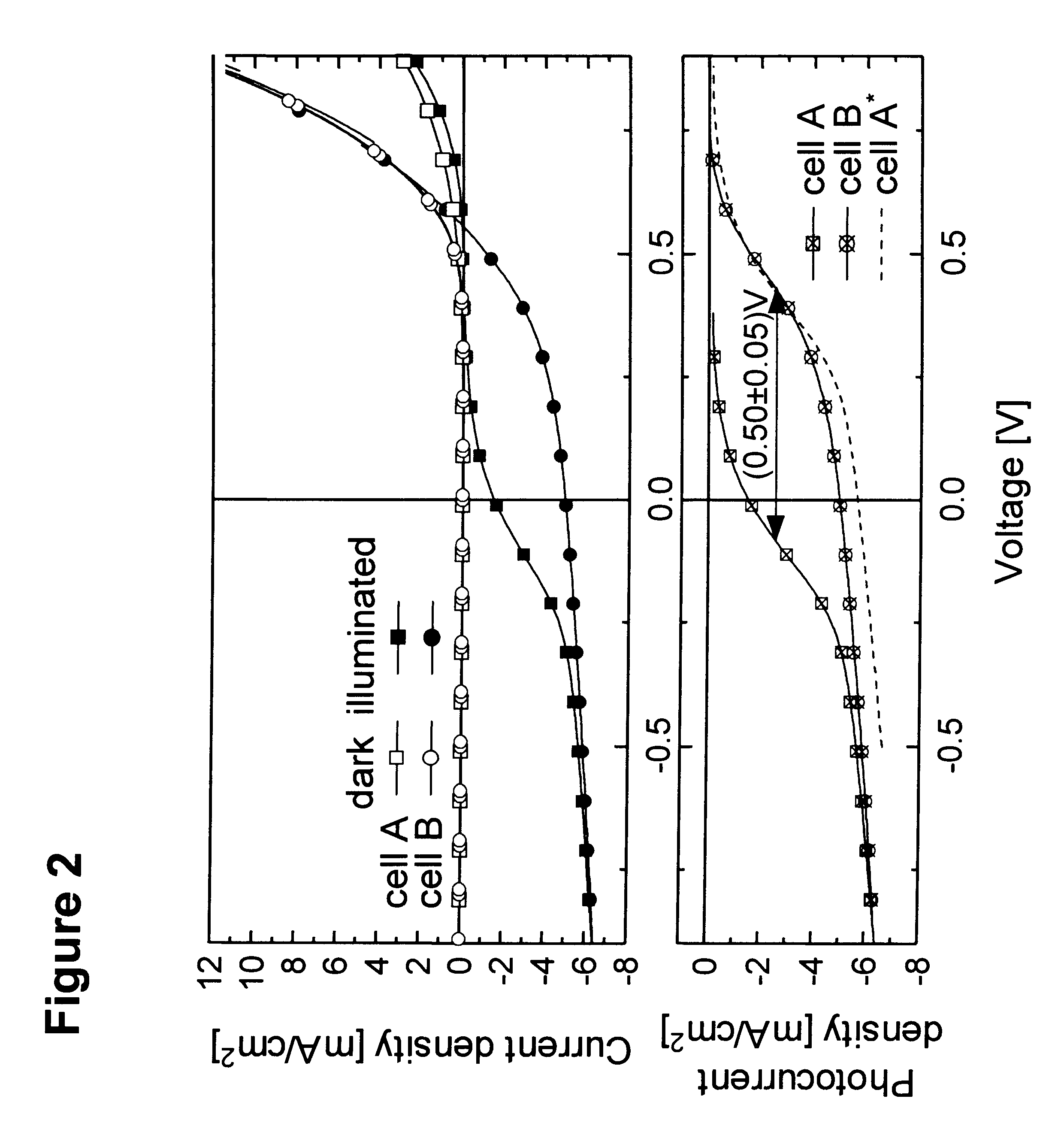
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
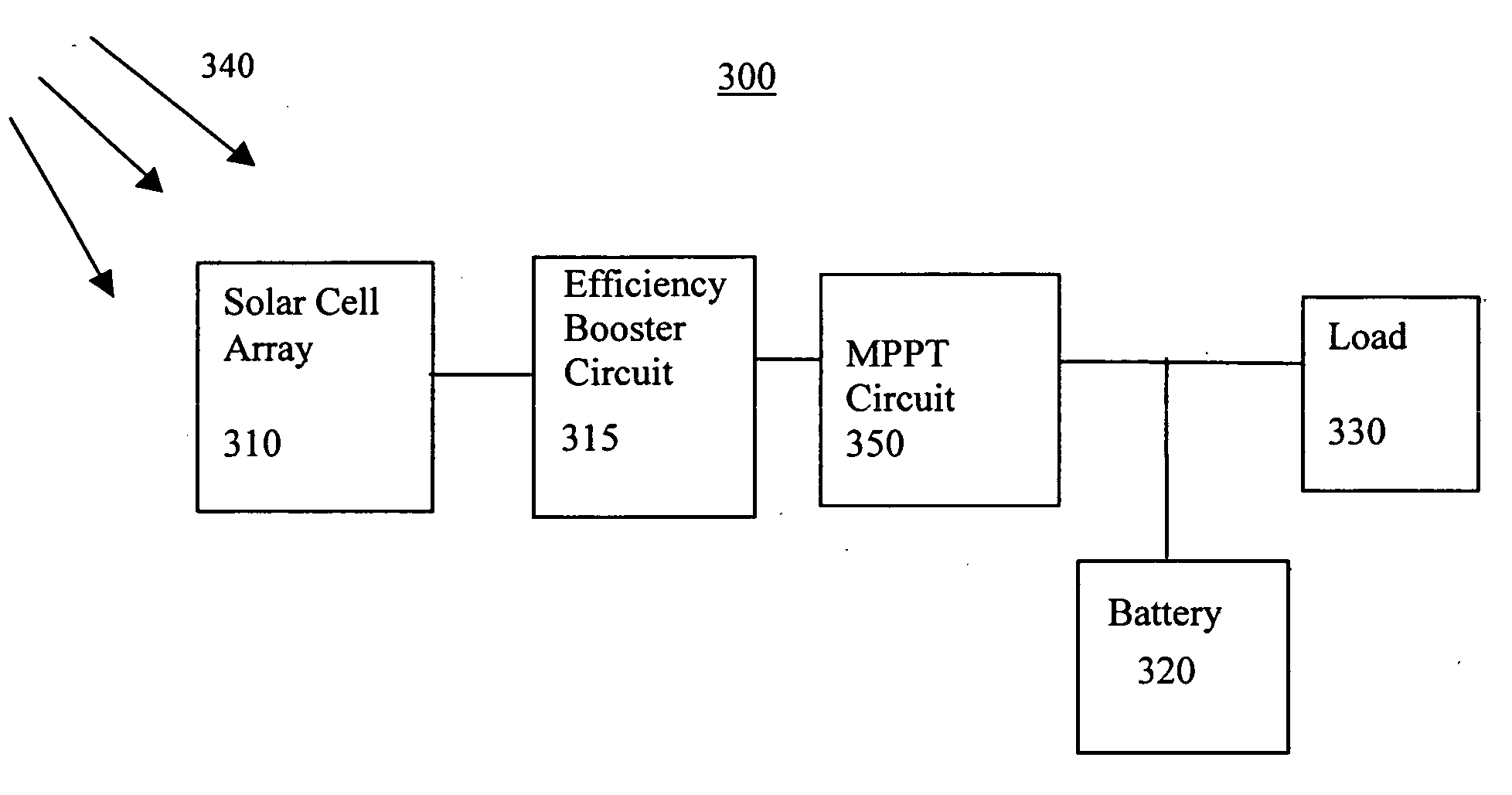
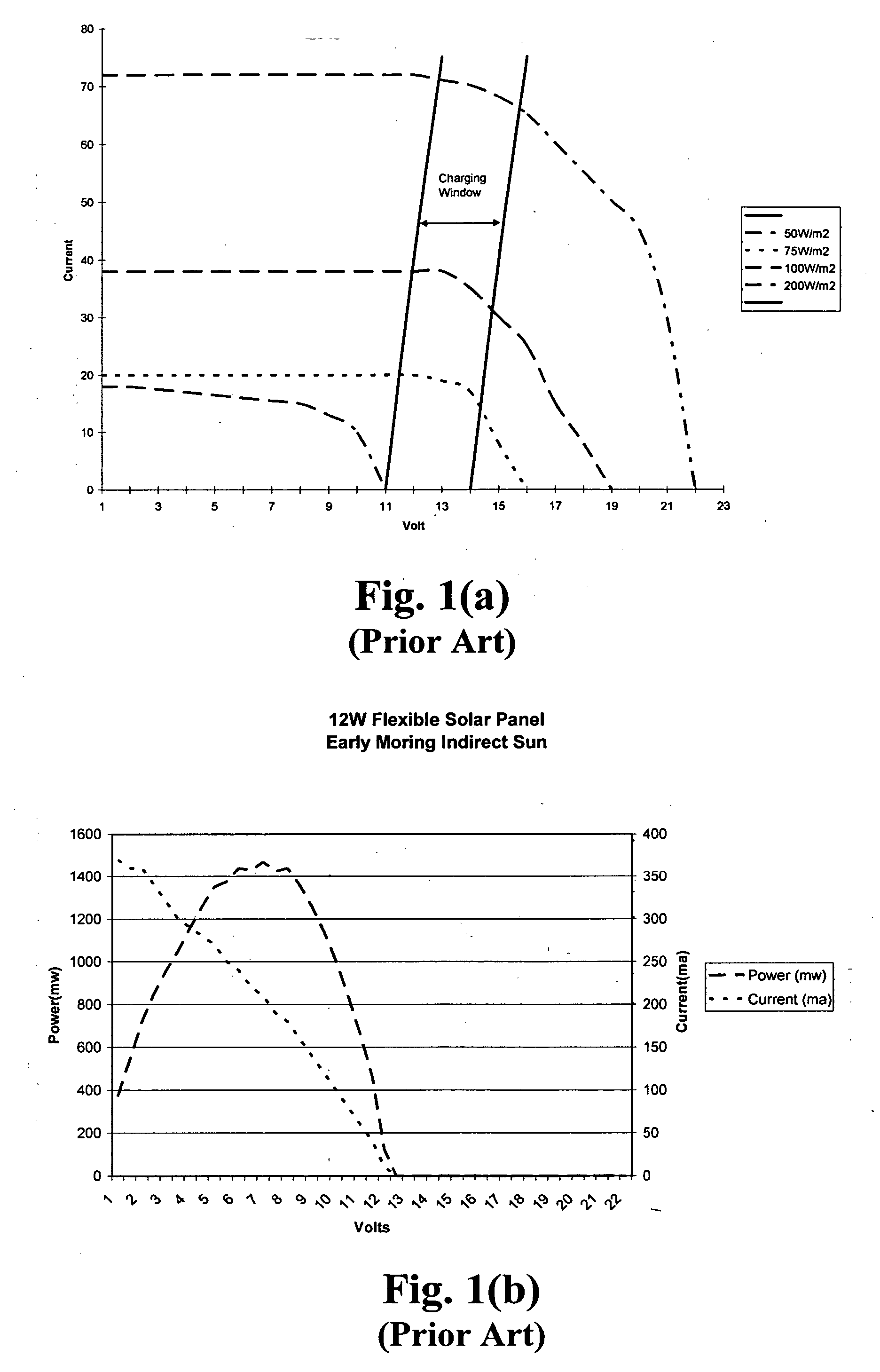
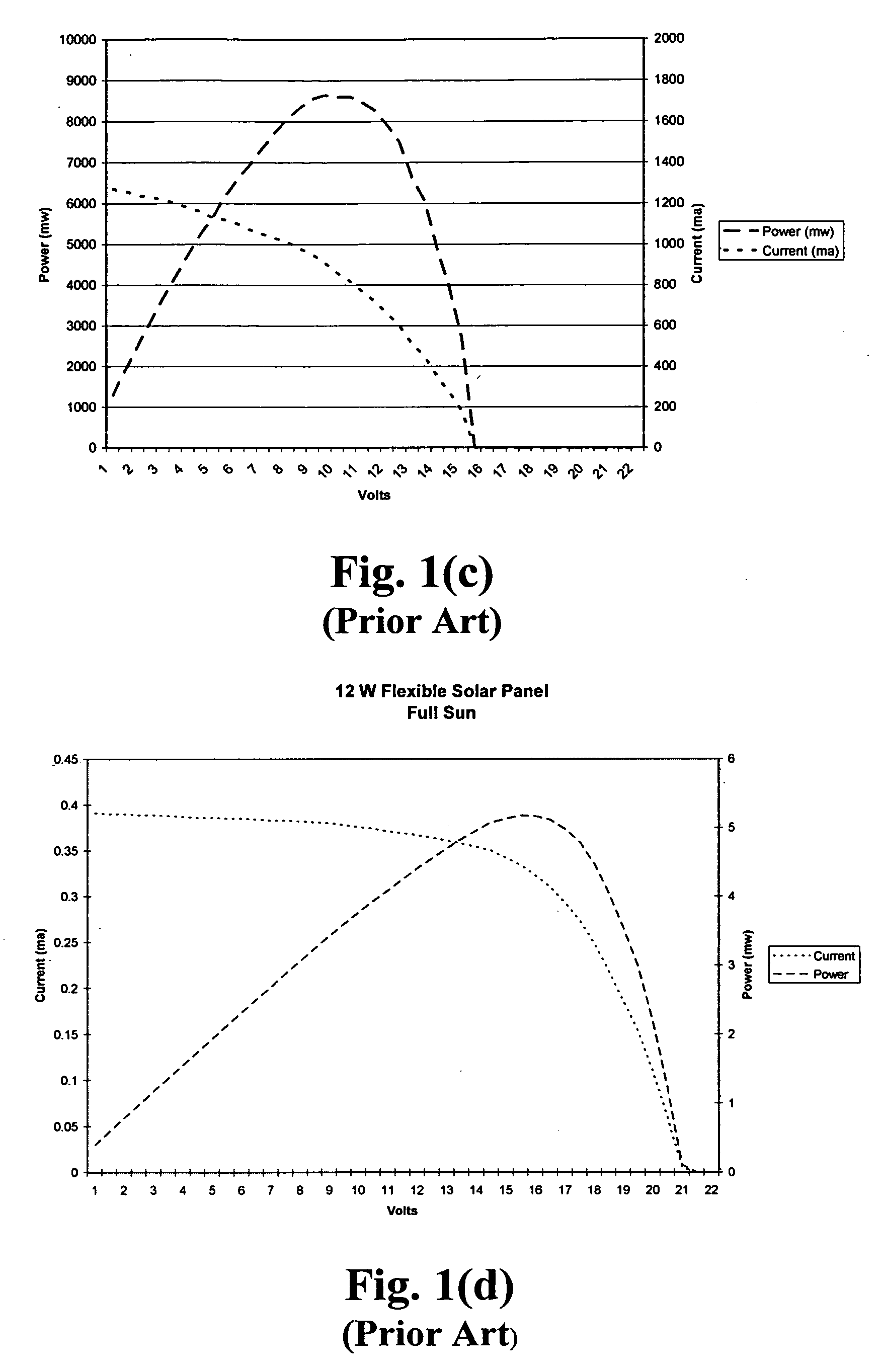
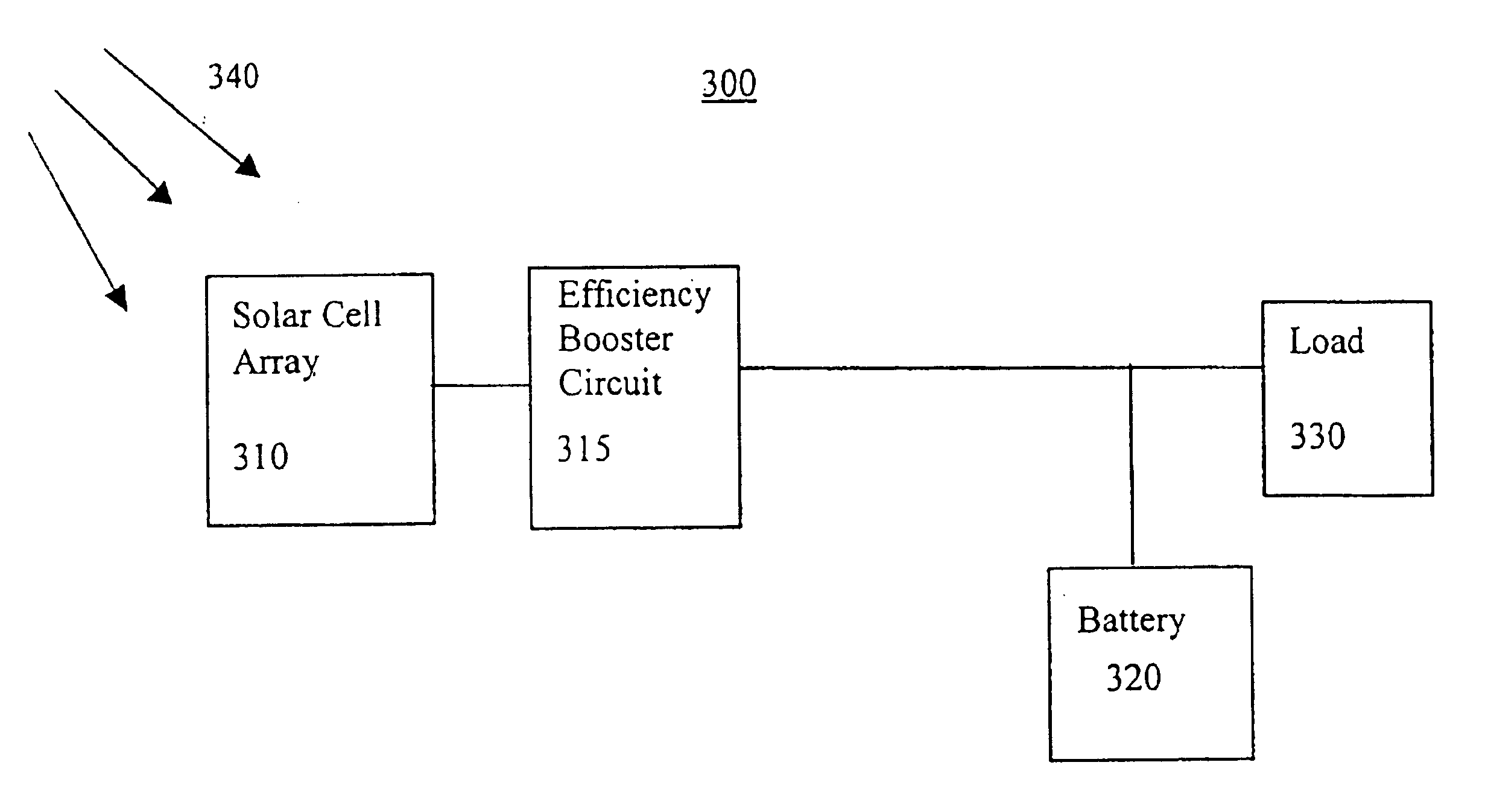
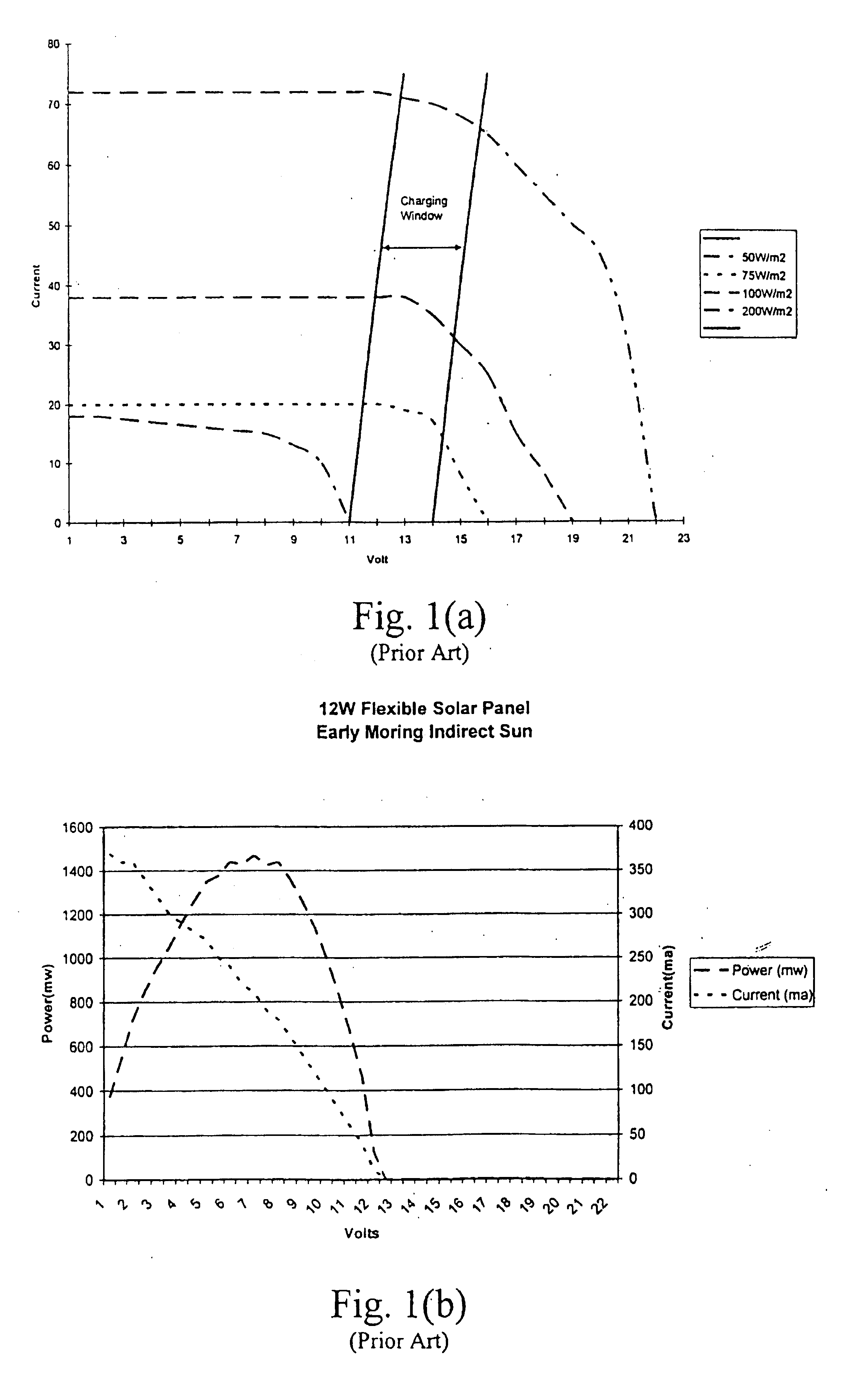
Efficiency booster circuit and technique for maximizing power point tracking
InactiveUS20060174939A1Reduce voltageConsiderable amount of energyBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsSolar cellPoint tracking
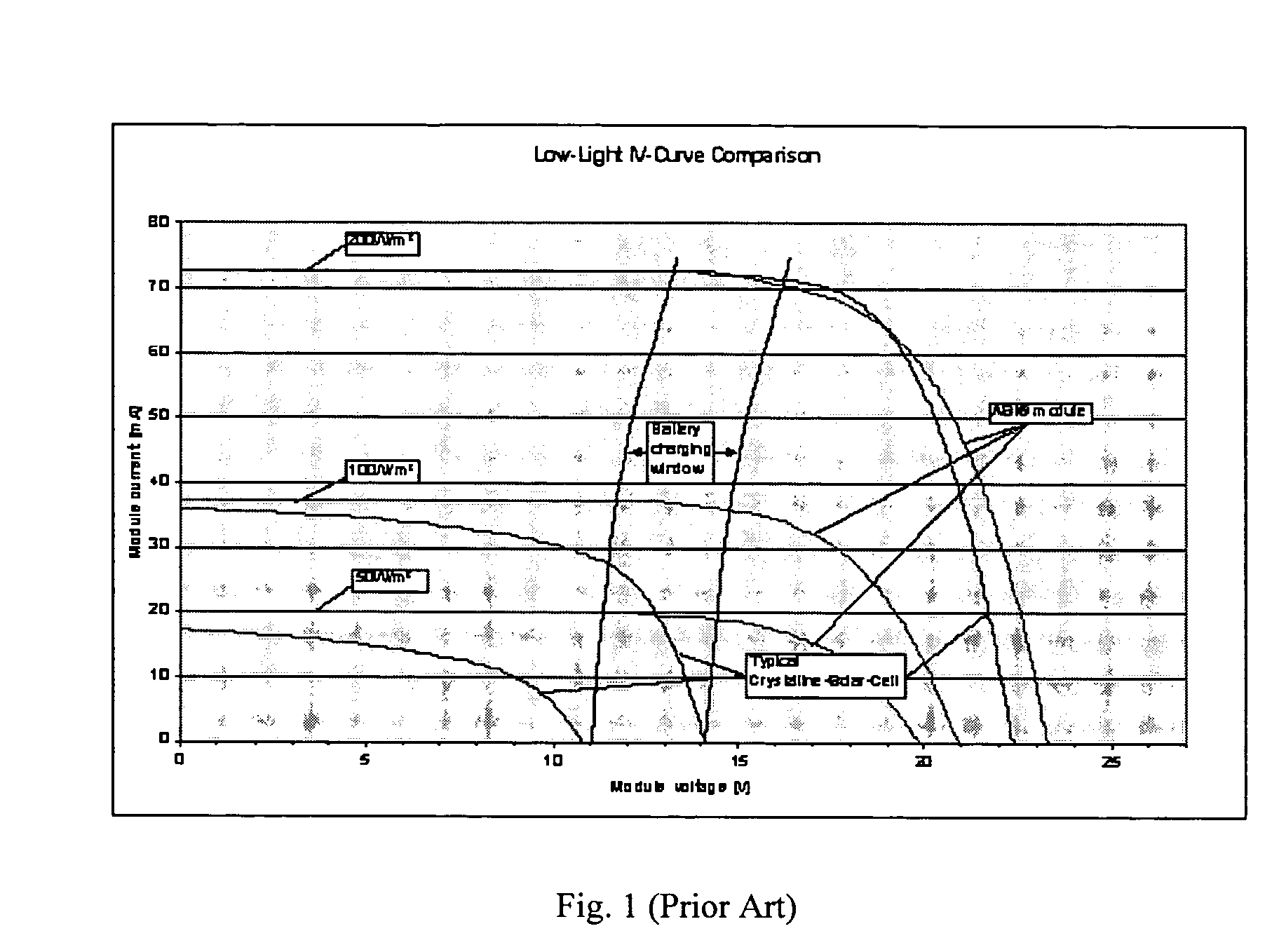
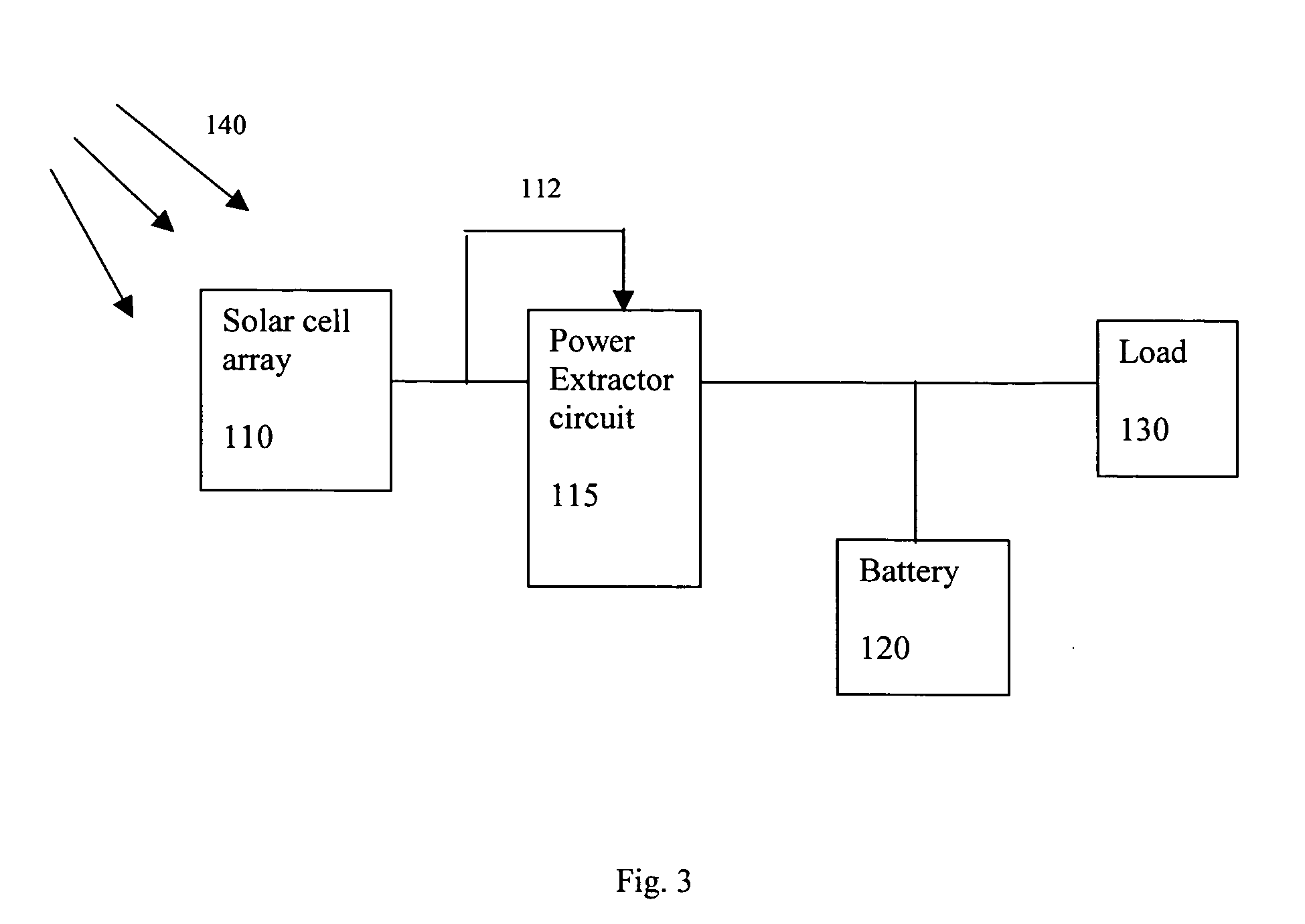
The present invention provides an efficiency booster circuit and accompanying switch mode power conversion technique to efficiently capture the power generated from a solar cell array that would normally have been lost, for example, under reduced incident solar radiation. In an embodiment of the invention, the efficiency booster circuit generates an output current from the solar cell power source using a switch mode power converter. A control loop is closed around the input voltage to the converter circuit and not around the output voltage. The output voltage is allowed to float, being clamped by the loading conditions. If the outputs from multiple units are tied together, the currents will sum. If the output(s) are connected to a battery, the battery's potential will clamp the voltage during charge. This technique allows all solar cells in an array that are producing power and connected in parallel to work at their peak efficiency.
Owner:ISG TECH
Converter circuit and technique for increasing the output efficiency of a variable power source
InactiveUS20060185727A1Not overchargeBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsEngineeringSolar cell
The present invention provides a converter circuit and accompanying switch mode power conversion technique to efficiently capture the power generated from a solar cell array that would normally have been lost, for example, under reduced incident solar radiation. In an embodiment of the invention, the converter circuit generates an output current from the solar cell power source using a switch mode power converter. A control loop is closed around the input voltage to the converter circuit and not around the output voltage. The output voltage is allowed to float, being clamped by the loading conditions. If the outputs from multiple units are tied together, the currents will sum. If the output(s) are connected to a battery, the battery's potential will clamp the voltage during charge. This technique allows all solar cells in an array that are producing power and connected in parallel to work at their peak efficiency.
Owner:ISG TECH
Solar cell and method of manufacture
ActiveUS7339110B1Easy to manufactureLess expensiveFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSilicon oxide
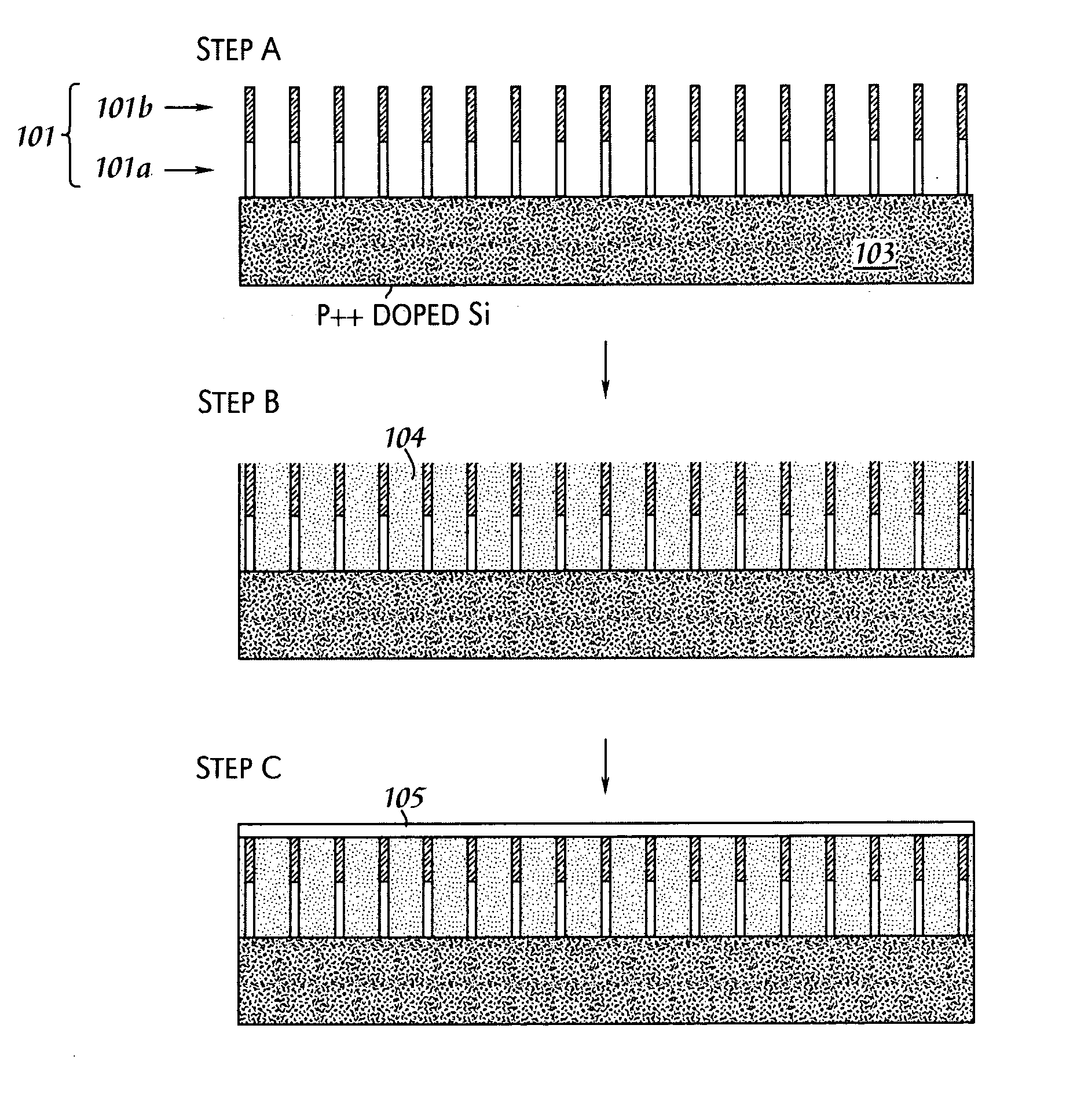
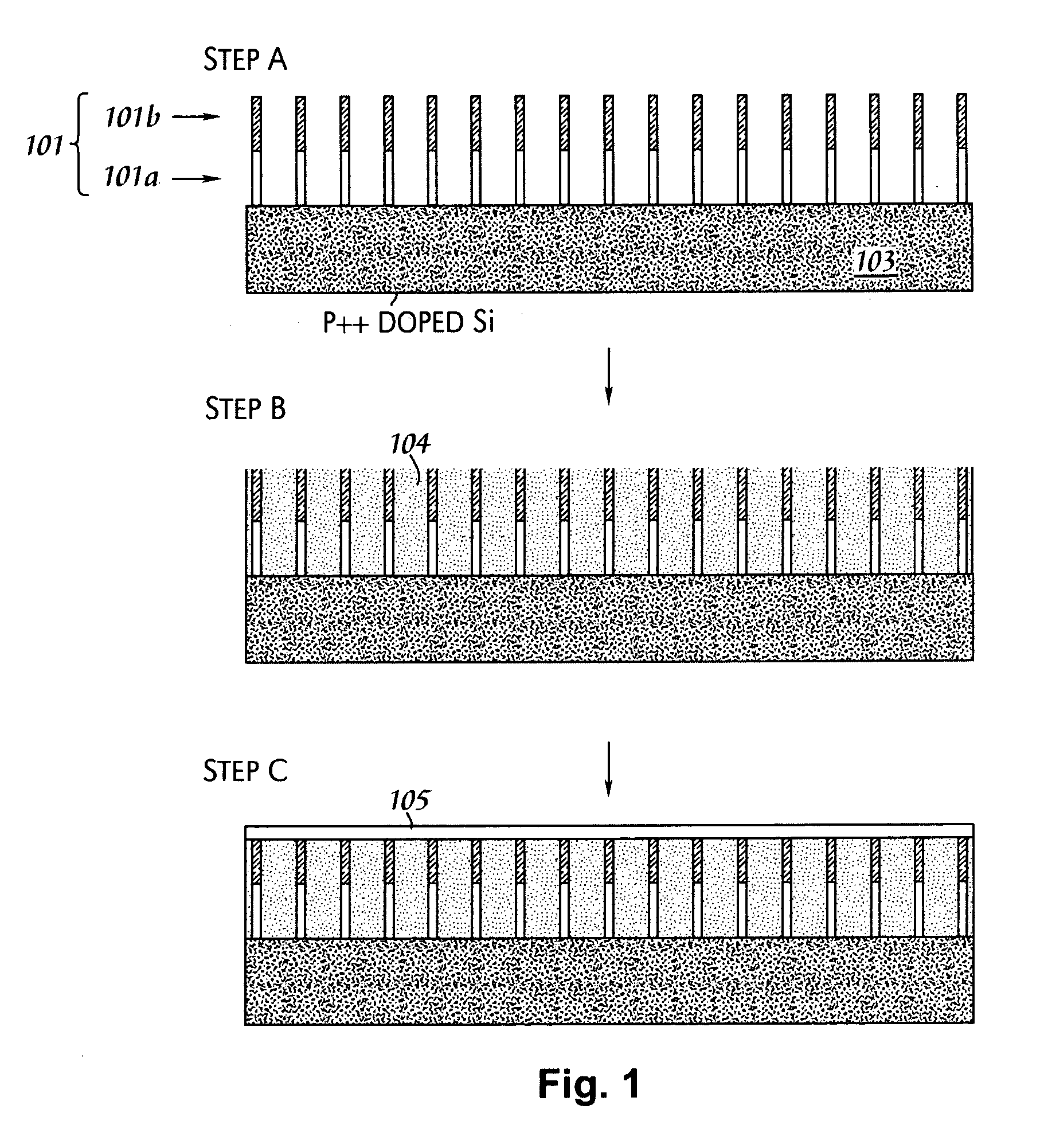
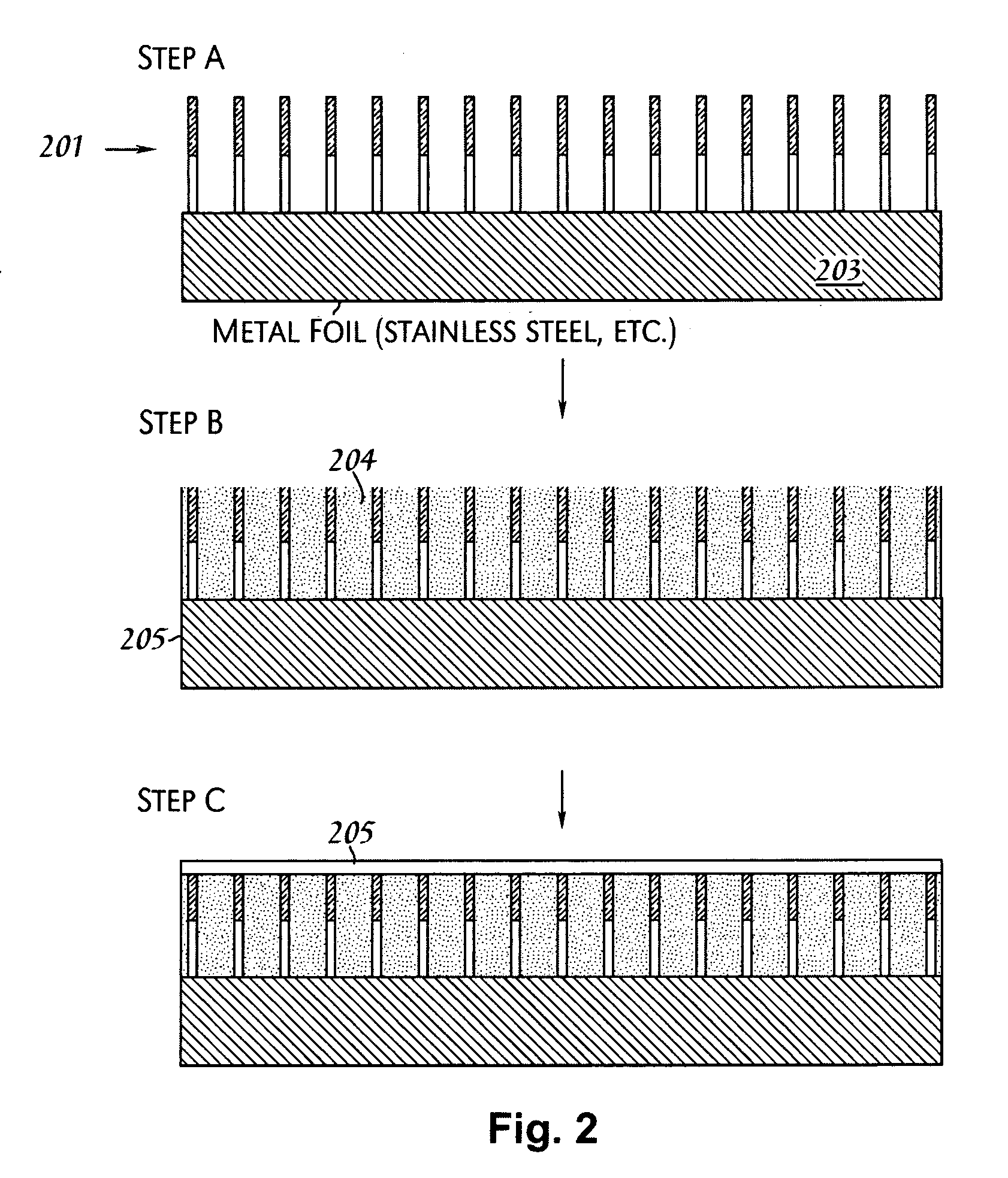
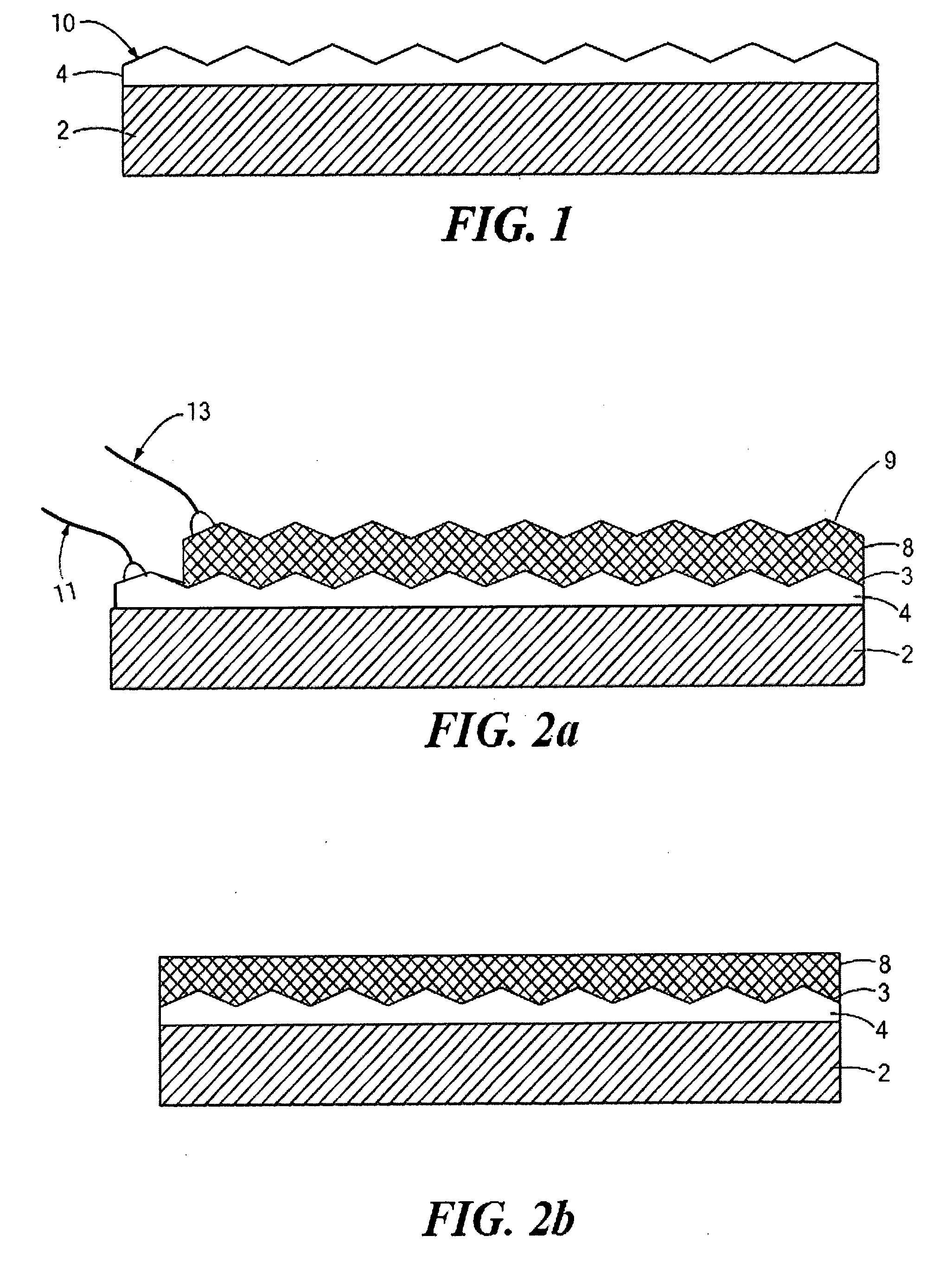
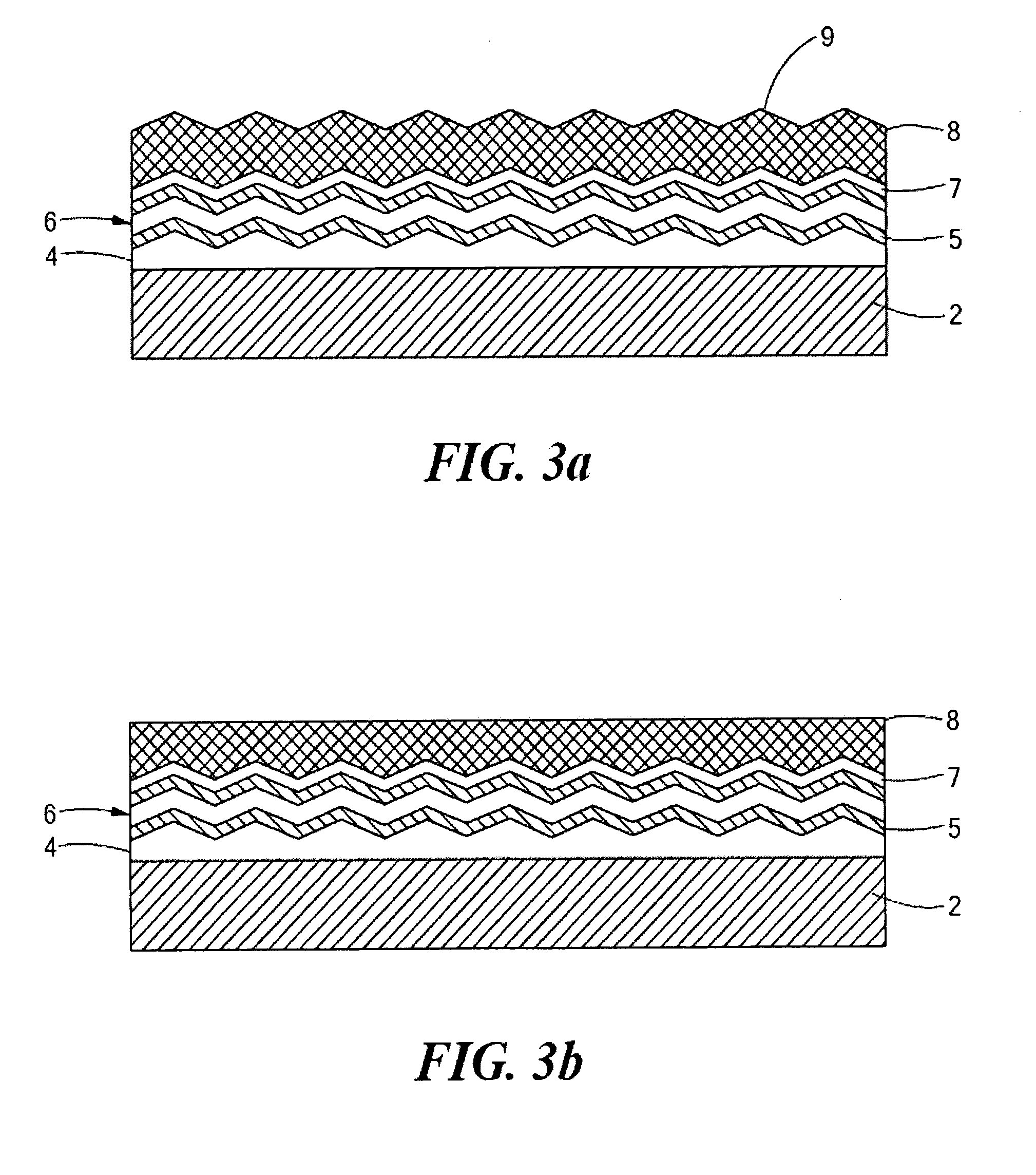
A solar cell that is readily manufactured using processing techniques which are less expensive than microelectronic circuit processing. In preferred embodiments, printing techniques are utilized in selectively forming masks for use in etching of silicon oxide and diffusing dopants and in forming metal contacts to diffused regions. In a preferred embodiment, p-doped regions and n-doped regions are alternately formed in a surface of the wafer in offset levels through use of masking and etching techniques. Metal contacts are made to the p-regions and n-regions by first forming a seed layer stack that comprises a first layer such as aluminum that contacts silicon and functions as an infrared reflector, second layer such titanium tungsten that acts as diffusion barrier, and a third layer functions as a plating base. A thick conductive layer such as copper is then plated over the seed layer, and the seed layer between plated lines is removed. A front surface of the wafer is preferably textured by etching or mechanical abrasion with an antireflection layer provided over the textured surface. A field layer can be provided in the textured surface with the combined effect being a very low surface recombination velocity.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD +1
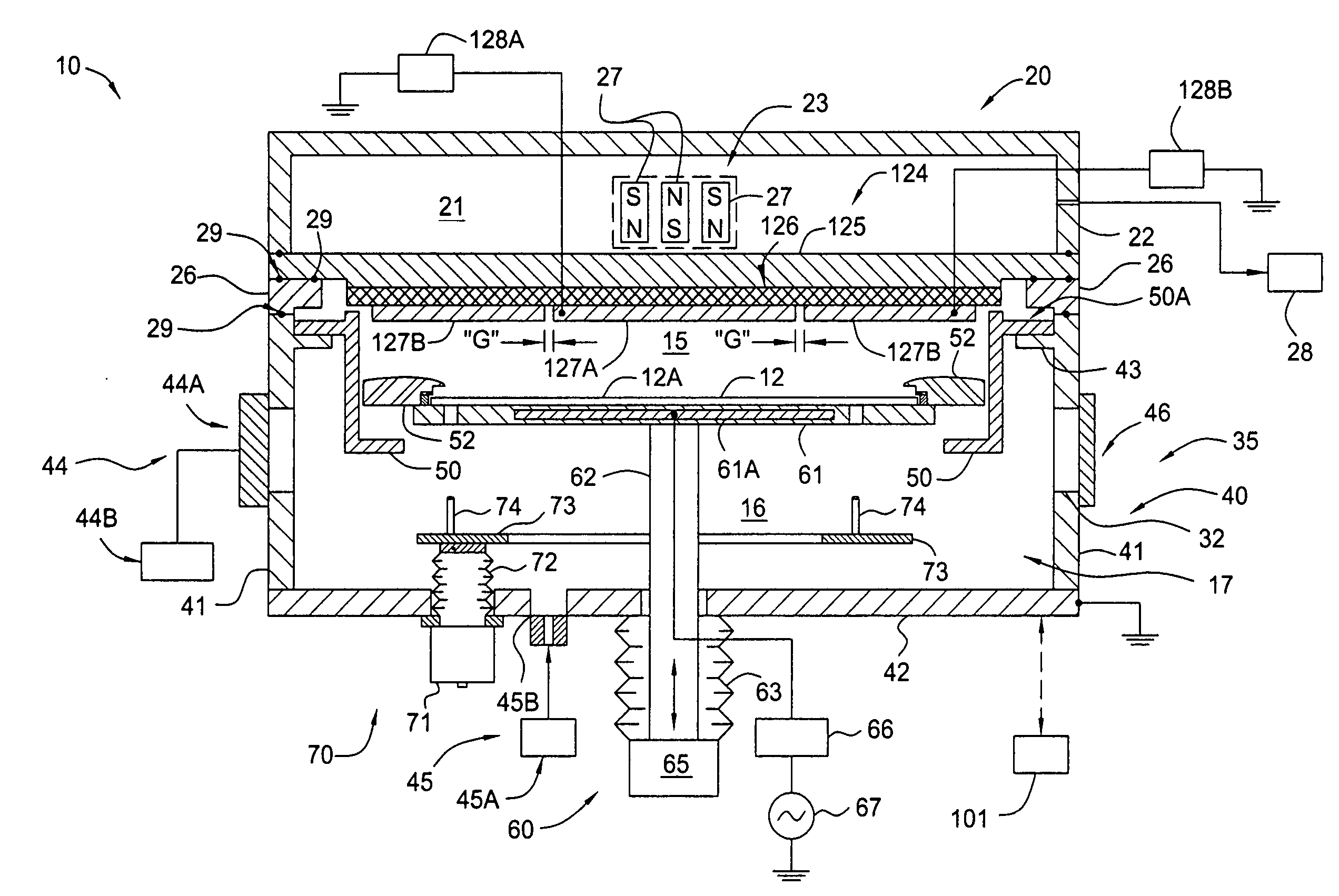
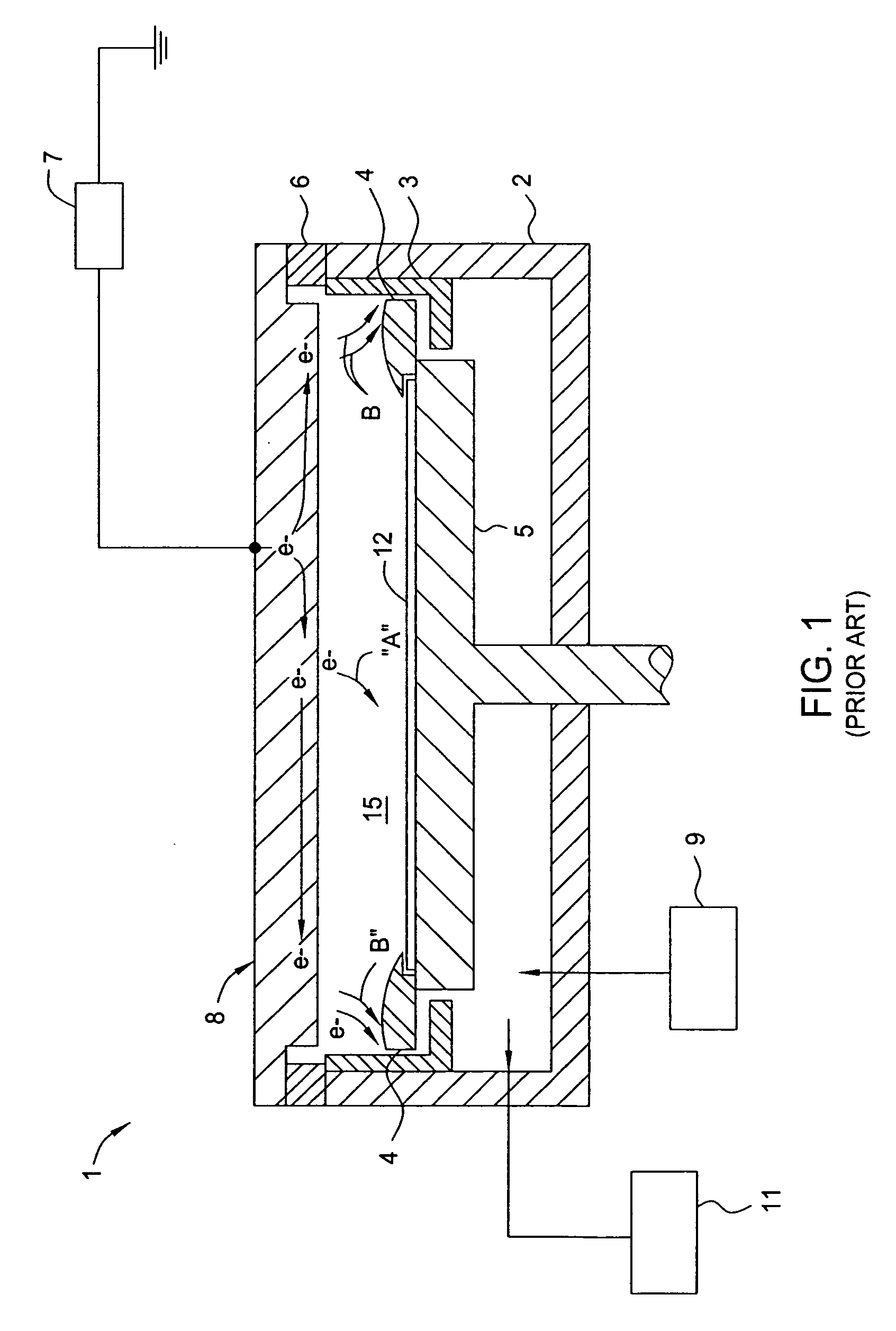
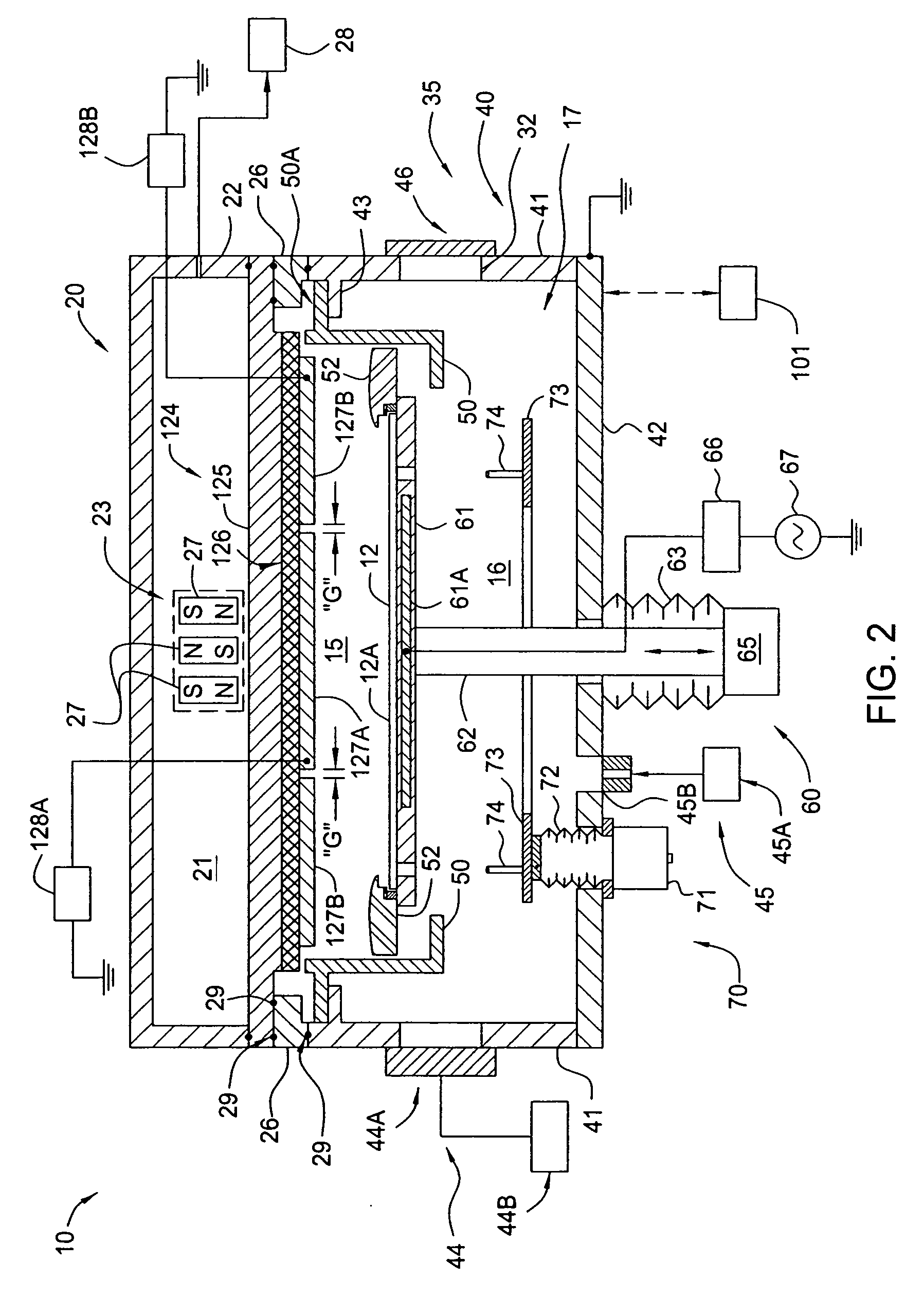
Apparatus for depositing a uniform silicon film and methods for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080305246A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon membraneProduct gas
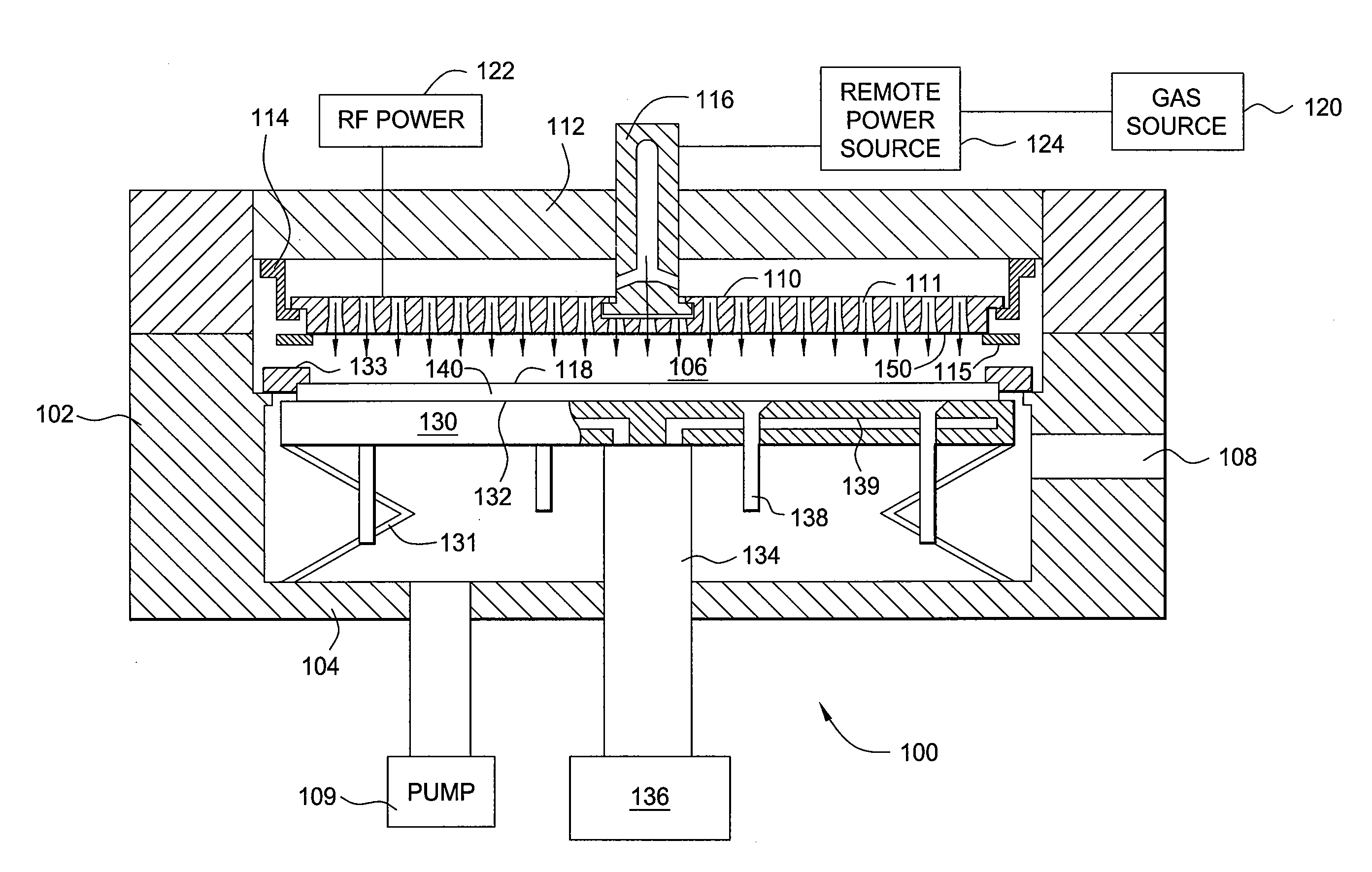
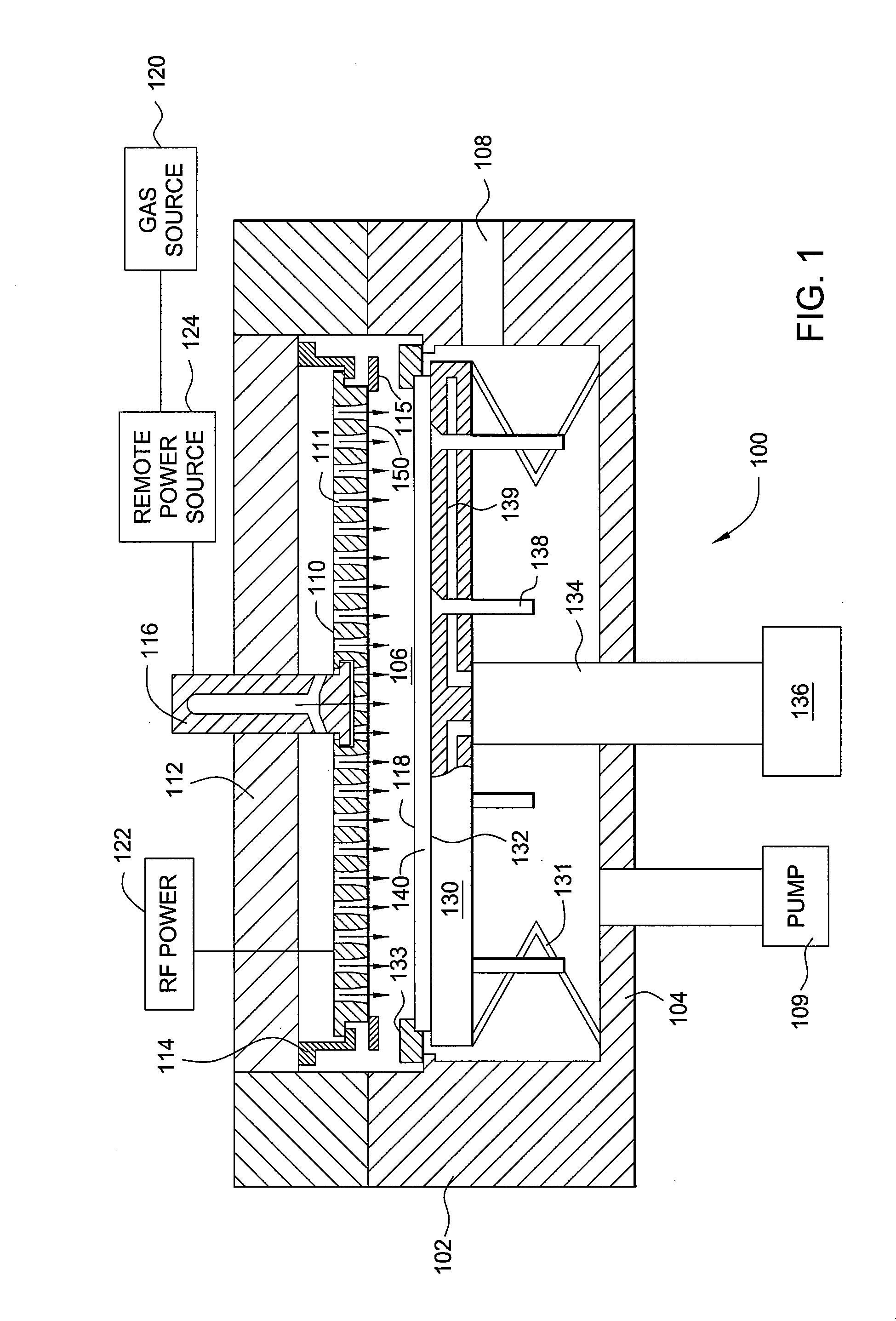
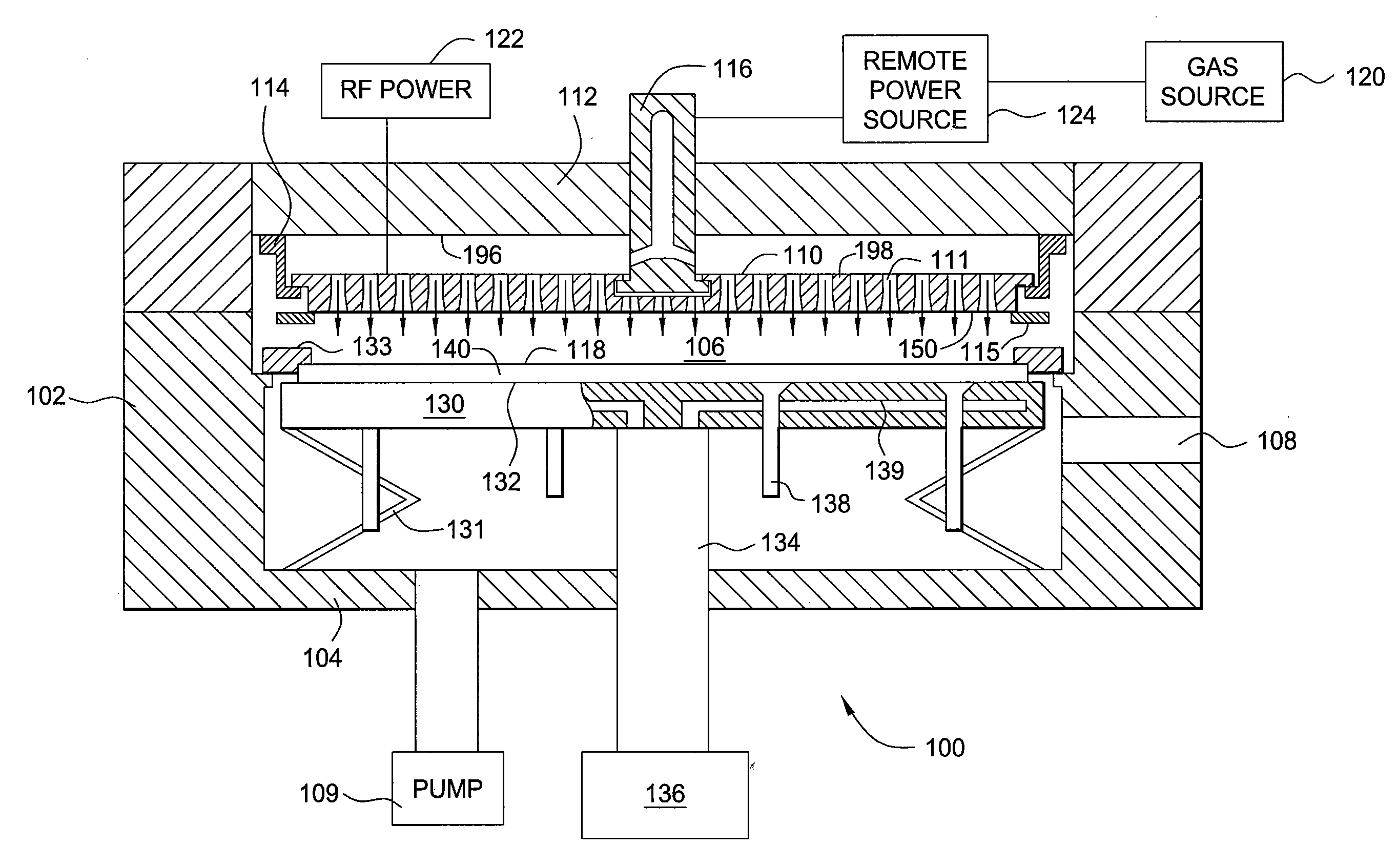
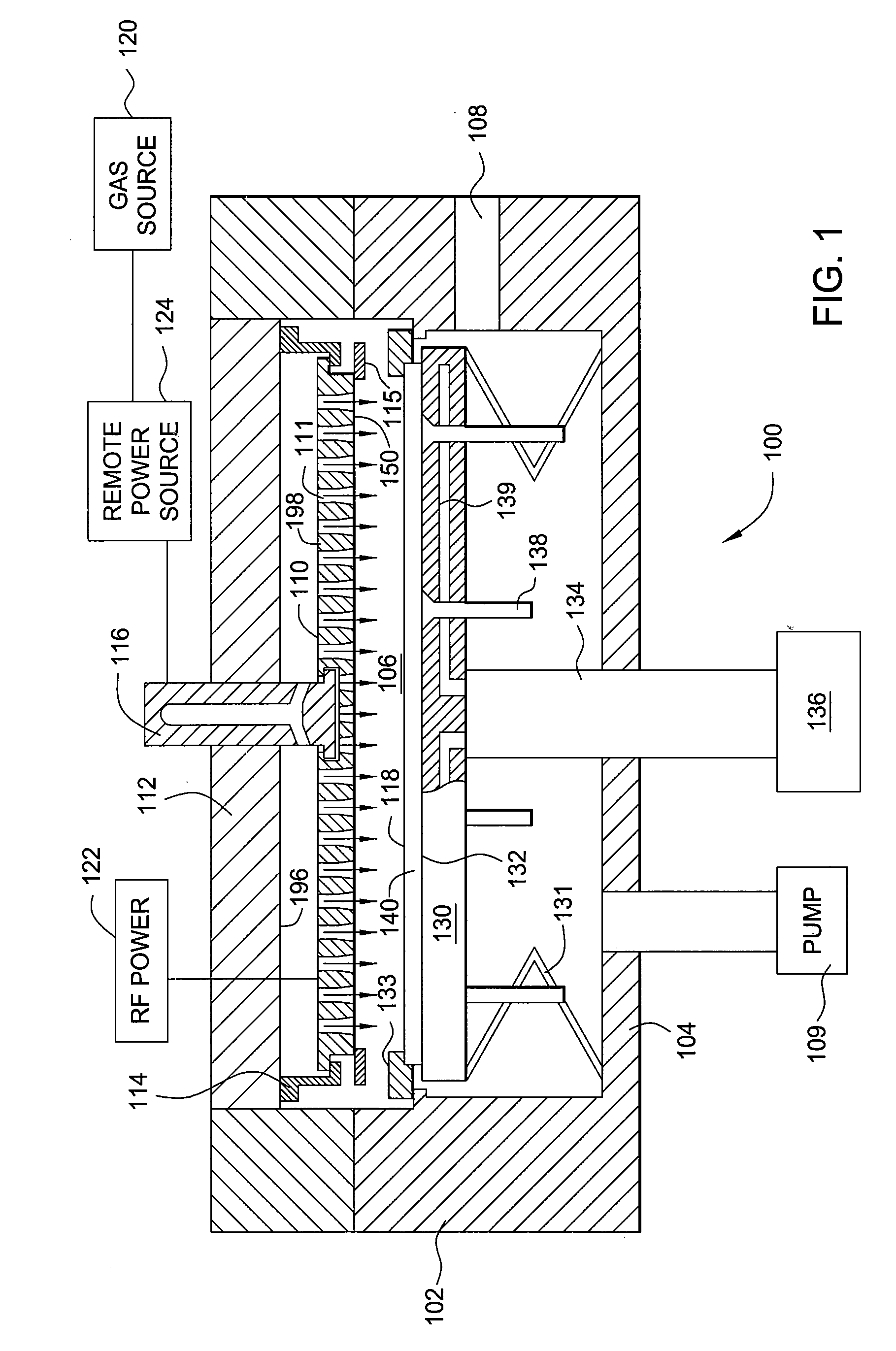
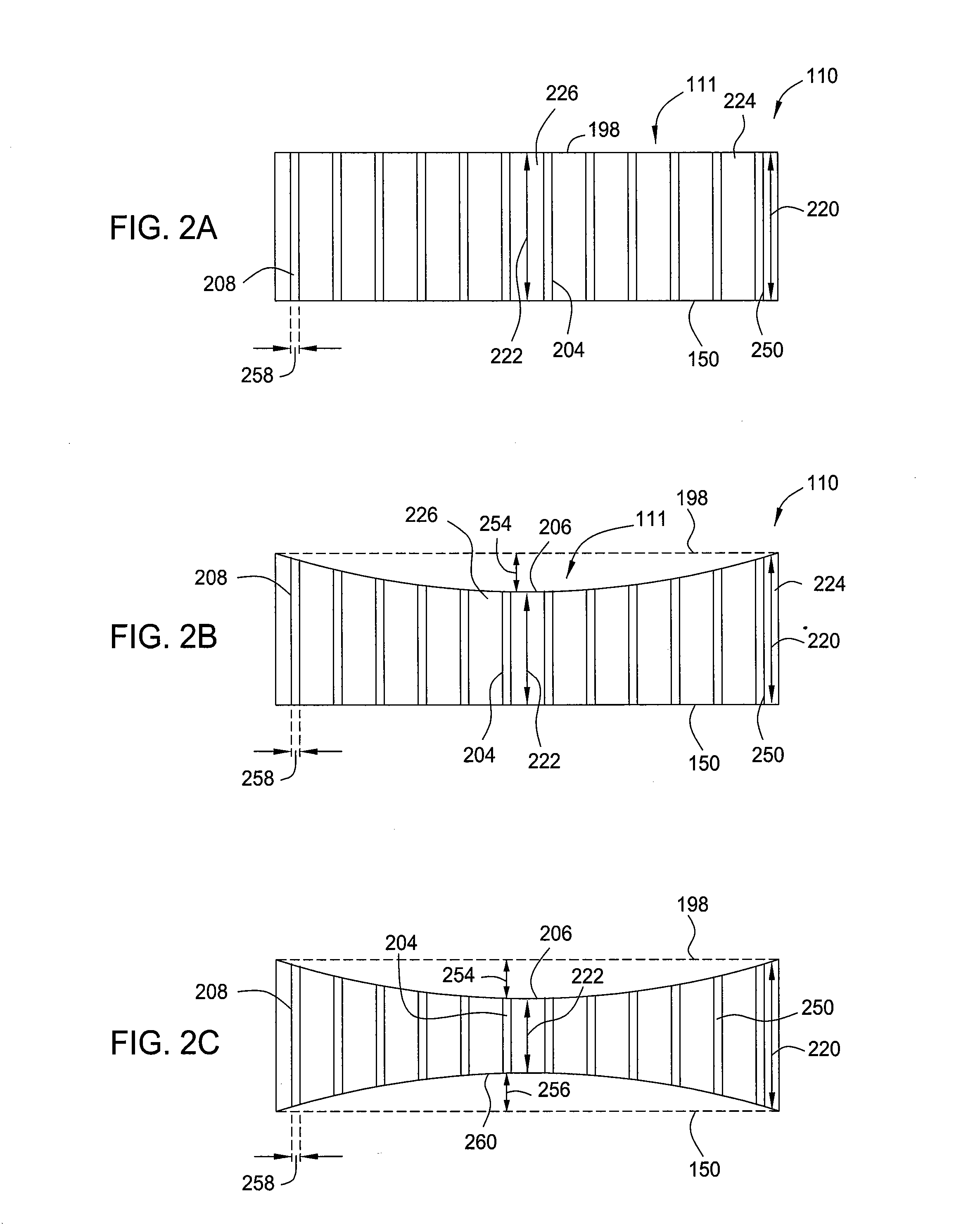
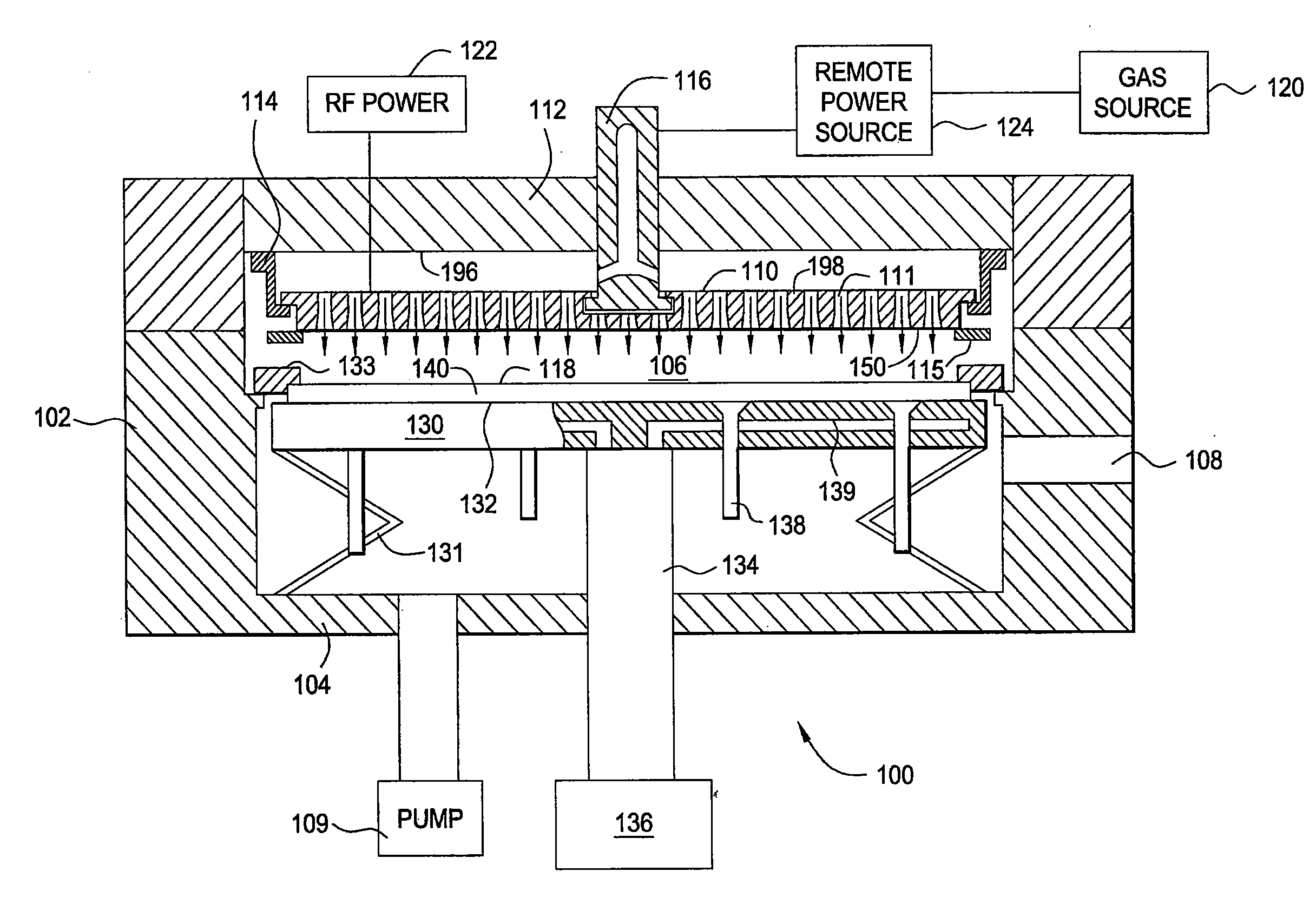
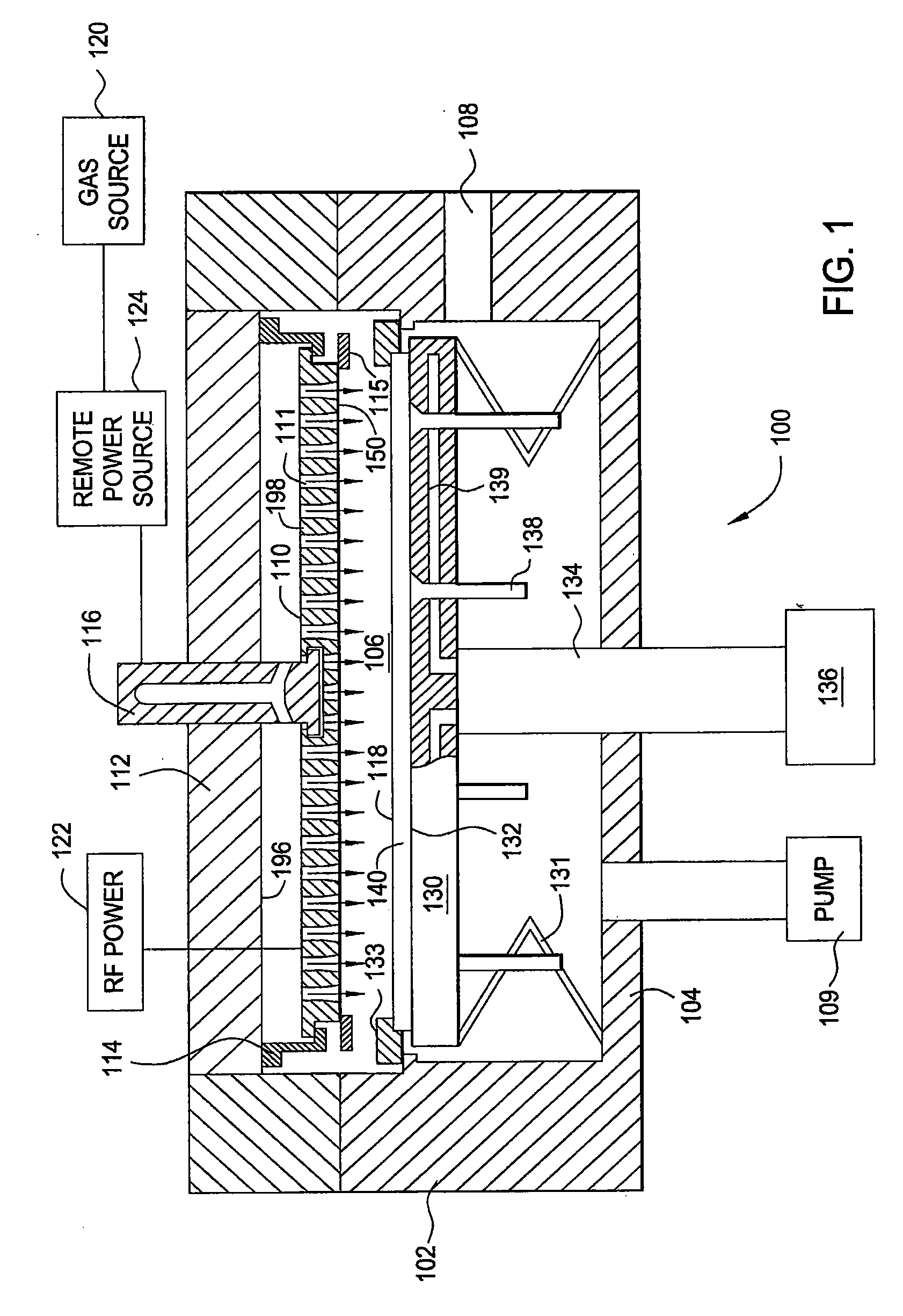
Methods and apparatus having a gradient spacing created between a substrate support assembly and a gas distribution plate for depositing a silicon film for solar cell applications are provided. In one embodiment, an apparatus for depositing films for solar cell applications may include a processing chamber, a substrate support disposed in the processing chamber and configured to support a quadrilateral substrate thereon, and a gas distribution plate disposed in the processing chamber above the substrate support, wherein a bottom surface of the gas distribution plate has a perimeter that includes edges and corners, and wherein the corners of the gas distribution plate are closer to the substrate support than the edges of the gas distribution plate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatus for depositing a uniform silicon film with flow gradient designs
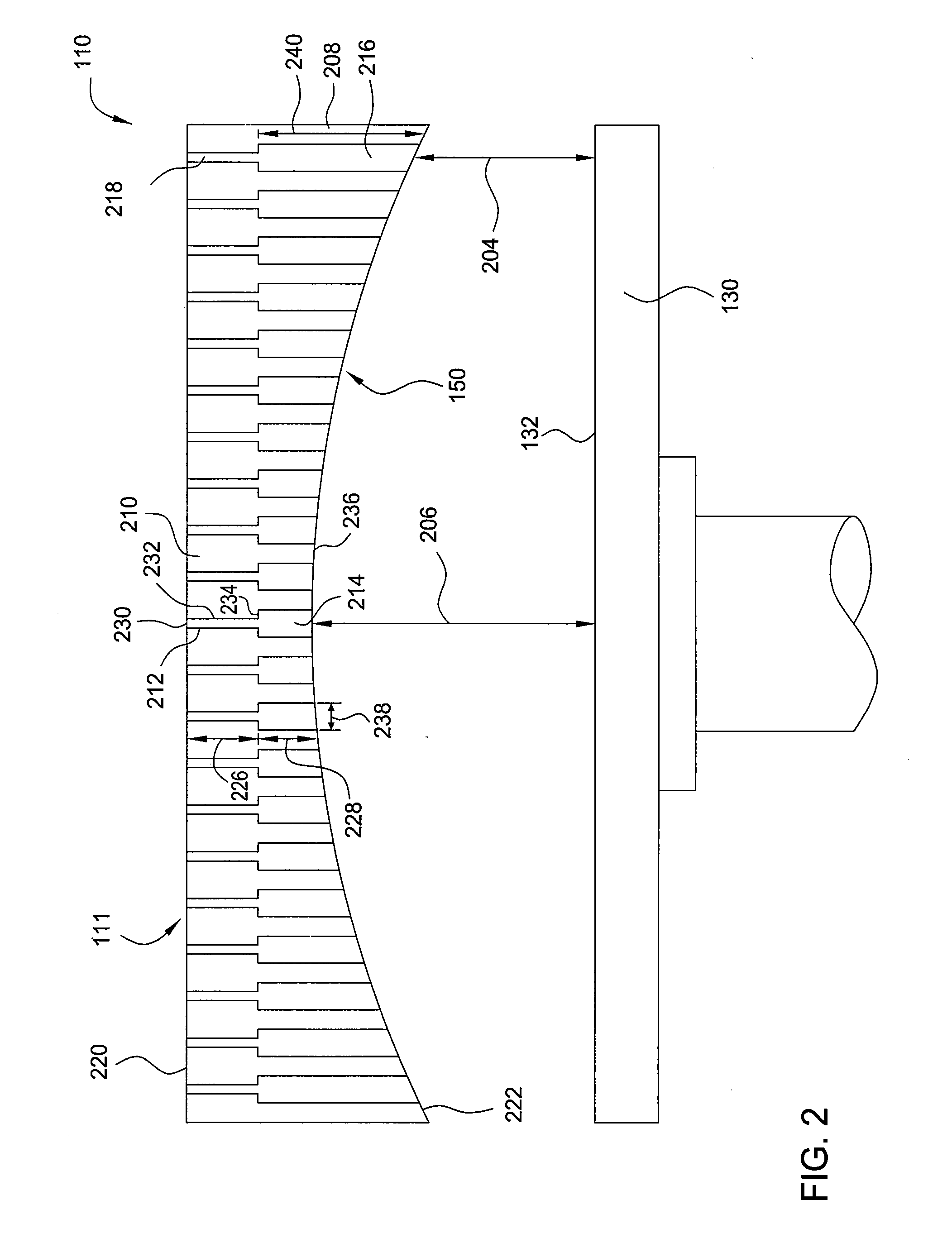
Methods and apparatus having a flow gradient created from a gas distribution plate are provided. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are particularly useful for, but not limited to, depositing a silicon film for solar cell applications. The apparatus for depositing a uniform film for solar cell applications includes a processing chamber, and a quadrilateral gas distribution plate disposed in the processing chamber and having at least four corners separated by four sides. The gas distribution plate further includes a first plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the first plurality of chokes located in the corners, and a second plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the second plurality of chokes located along the sides of the gas distribution plate between the corner regions, wherein the first plurality of chokes have a greater flow resistance than that of the second plurality of chokes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Methods and apparatus for depositing a uniform silicon film with flow gradient designs
InactiveUS20090000551A1Electric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringSolar cell
Methods and apparatus having a flow gradient created from a gas distribution plate are provided. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are particularly useful for, but not limited to, depositing a silicon film for solar cell applications. The apparatus for depositing a uniform film for solar cell applications includes a processing chamber, and a quadrilateral gas distribution plate disposed in the processing chamber and having at least four corners separated by four sides. The gas distribution plate further includes a first plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the first plurality of chokes located in the corners, and a second plurality of chokes formed through the gas distribution plate, the second plurality of chokes located along the sides of the gas distribution plate between the corner regions, wherein the first plurality of chokes have a greater flow resistance than that of the second plurality of chokes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Power extractor circuit
InactiveUS20060001406A1Low powerCaptured powerBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply linesEngineeringSolar cell
The present invention discloses power extractor circuit used to capture the power of a solar cell array during its less-than-optimum conditions. Under reduced incident solar radiation, the low power level supplied by the solar cell array normally would not be adequate to operating a load, but with the presence of the power extractor circuit, the low power generated by the solar panel would be accumulated to a high enough level to overcome the energy barrier of the battery or the load. The power extractor circuit preferably comprises a voltage and current booster circuit, and is designed to operated at all power levels of the solar cell array: low power level to provide the booster function during the low power period of the solar cell array, and high power level to prevent component failure during the normal operation of the solar cell array. Many power extractor circuits can also be installed in series to cover a wide range of power level of the solar cell array. The present invention power extractor circuit can also be used in other power sources to utilize the portion of power which normally would have been lost.
Owner:MATAN STEFAN
Multi-mode renewable power converter system
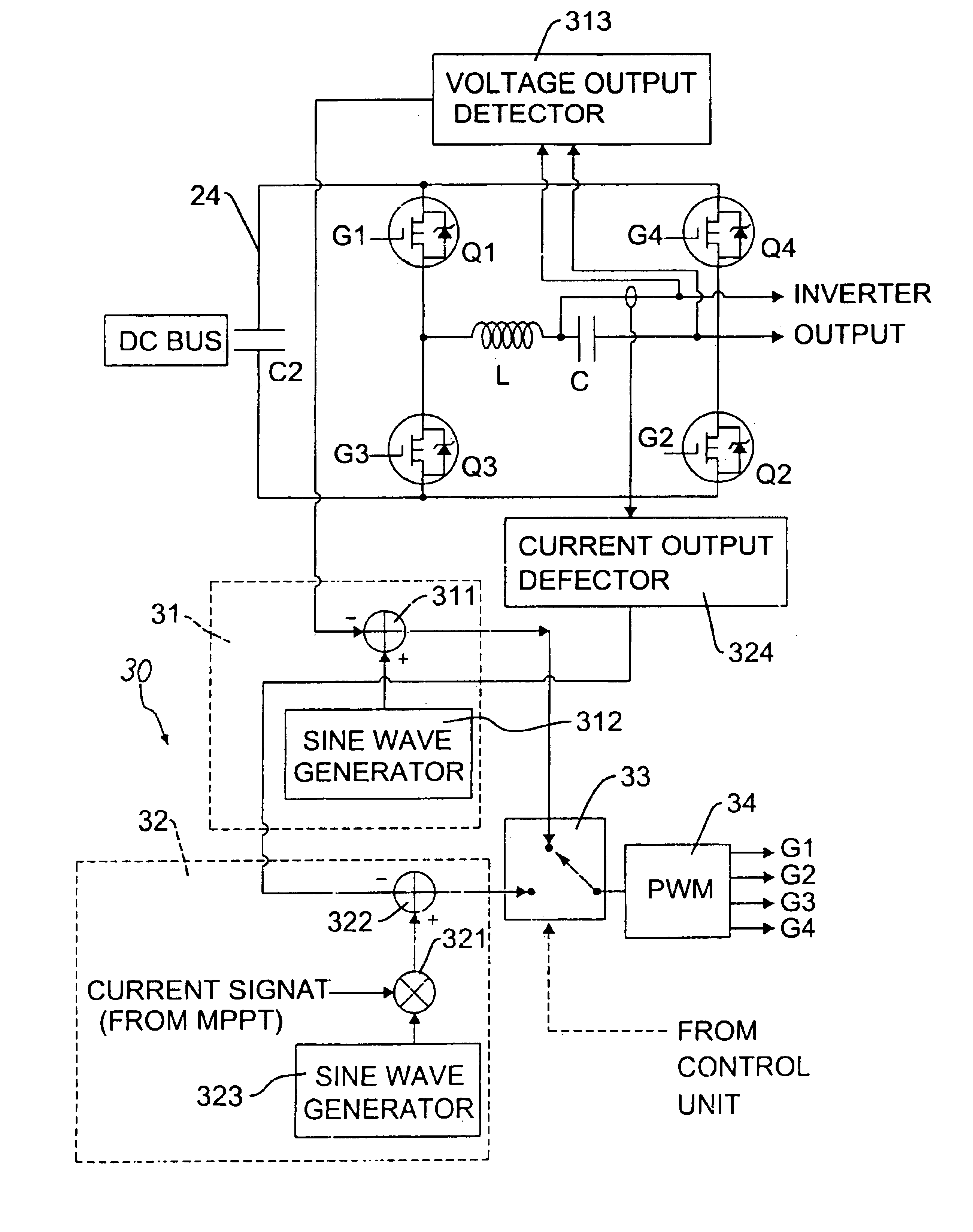
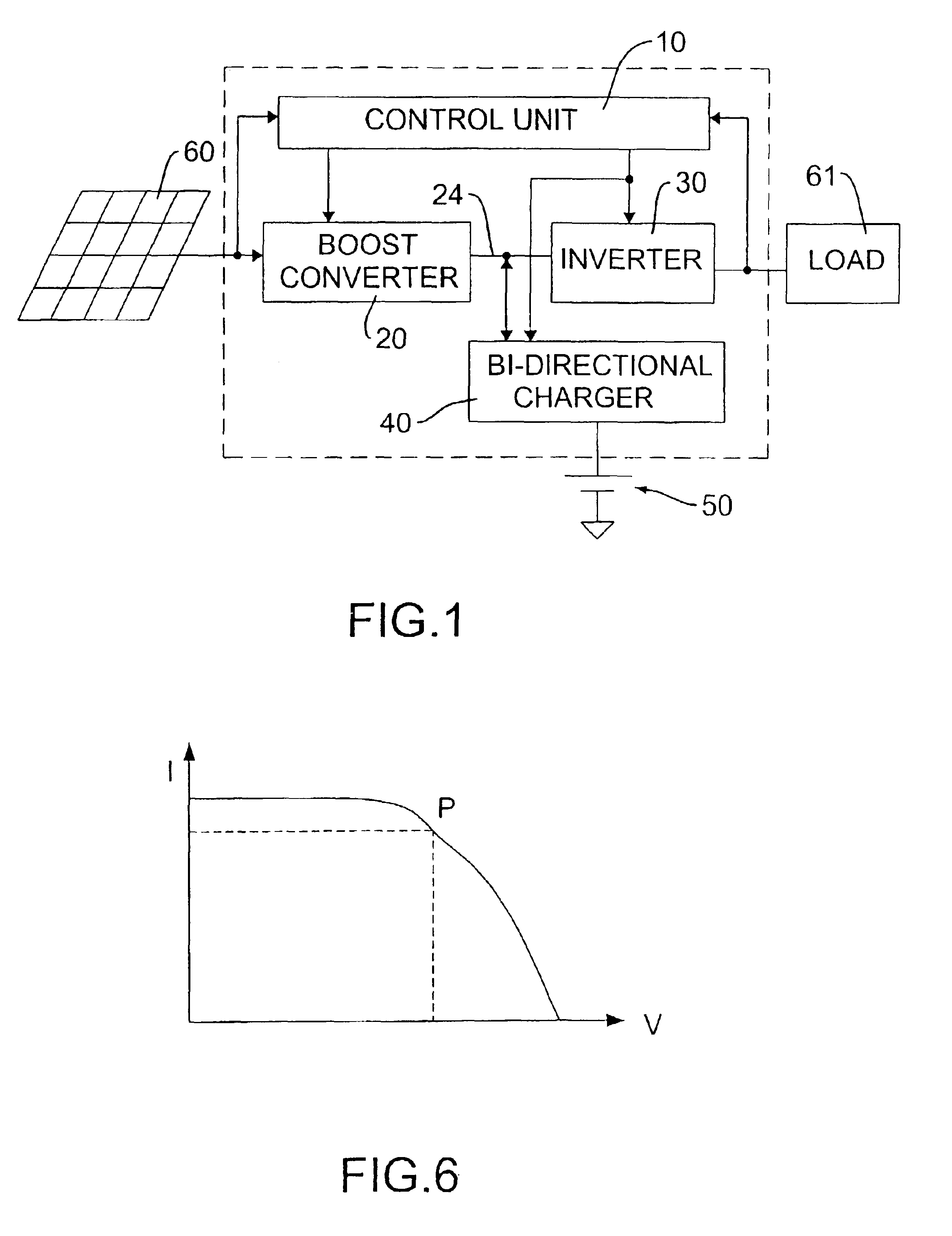
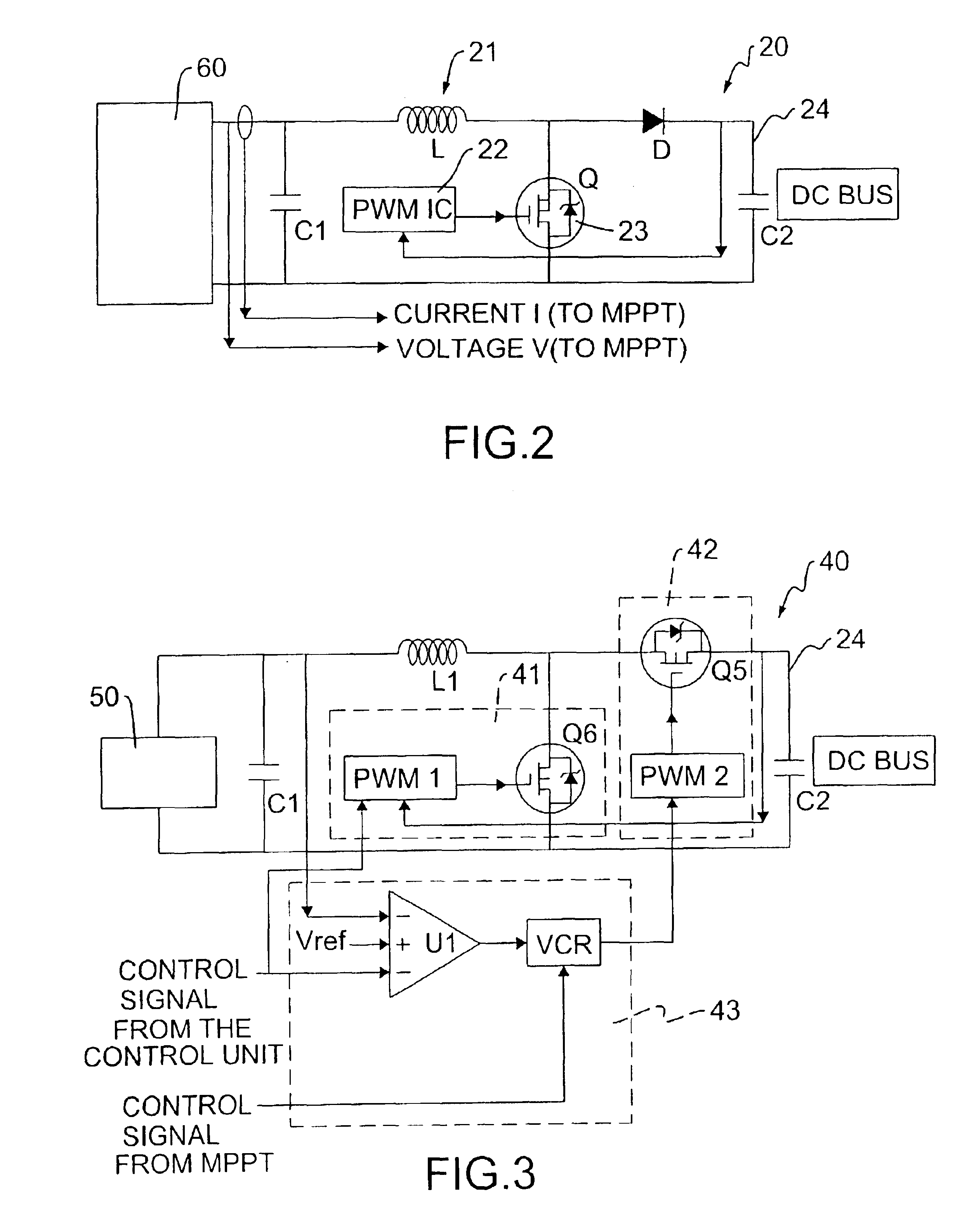
A multi-mode renewable power converter system is disclosed. The system includes a control unit, a boost converter, an inverter and optional bi-directional charger, wherein the boost converter converts DC output of a solar cell or a renewable source to high DC bus voltage, and the inverter converts this DC bus voltage to an AC output. This power converter can be used to support standalone load or grid-connected system with a dynamic maximum power point tracking (MPPT) circuit. The MPPT circuit detects the current and voltage from the solar cell and indicates to the inverter to provide power to the load connected. When the optional bi-directional charger is installed, the MPPT signal is also fed to this charger to make the power efficiency maximized for the system.
Owner:PHOENIXTEC POWER
High efficiency inorganic nanorod-enhanced photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS20060207647A1Reduce weight and sizeImprove reliabilityNanoopticsSemiconductor devicesSolar cellNanostructured materials
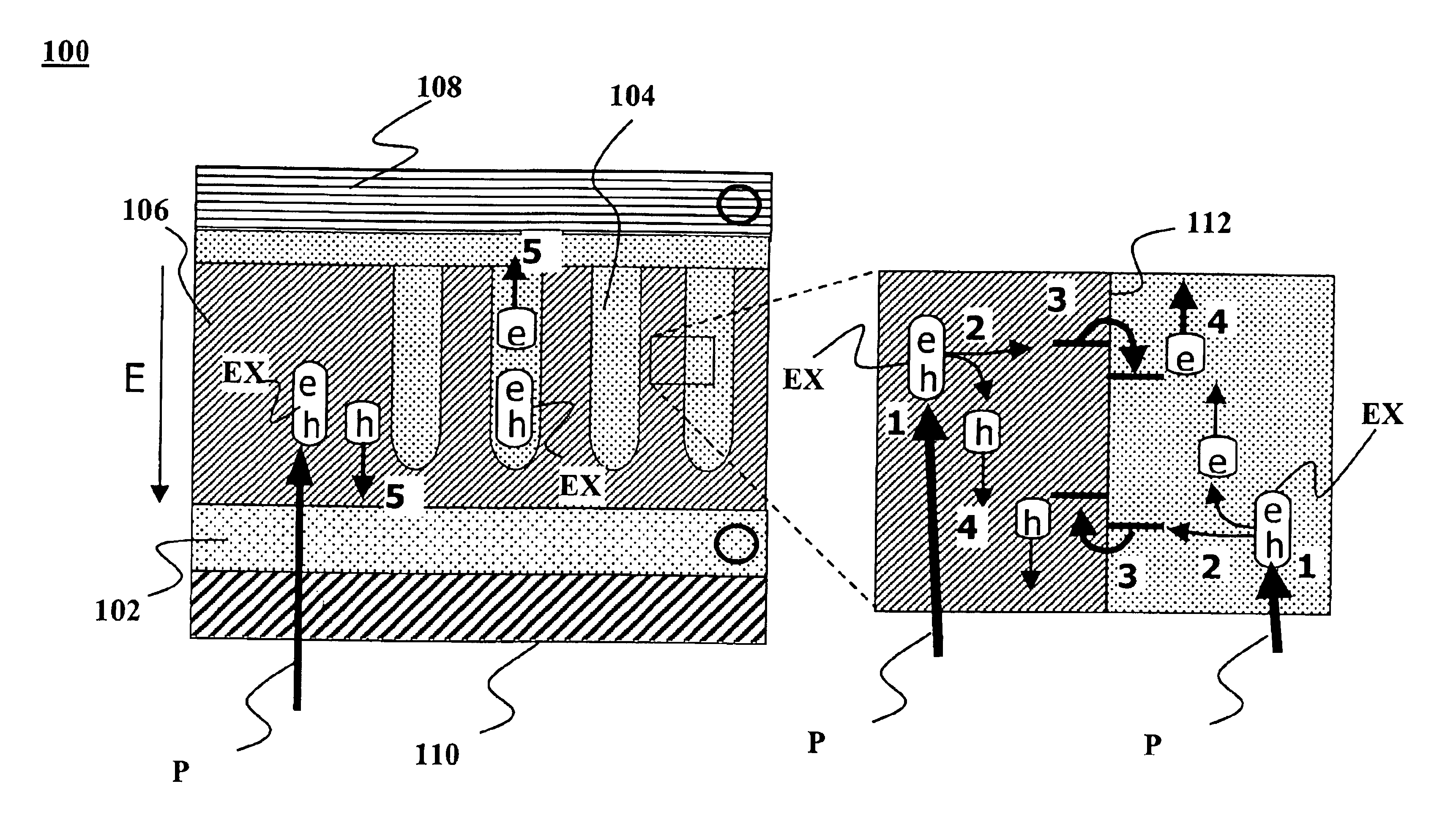
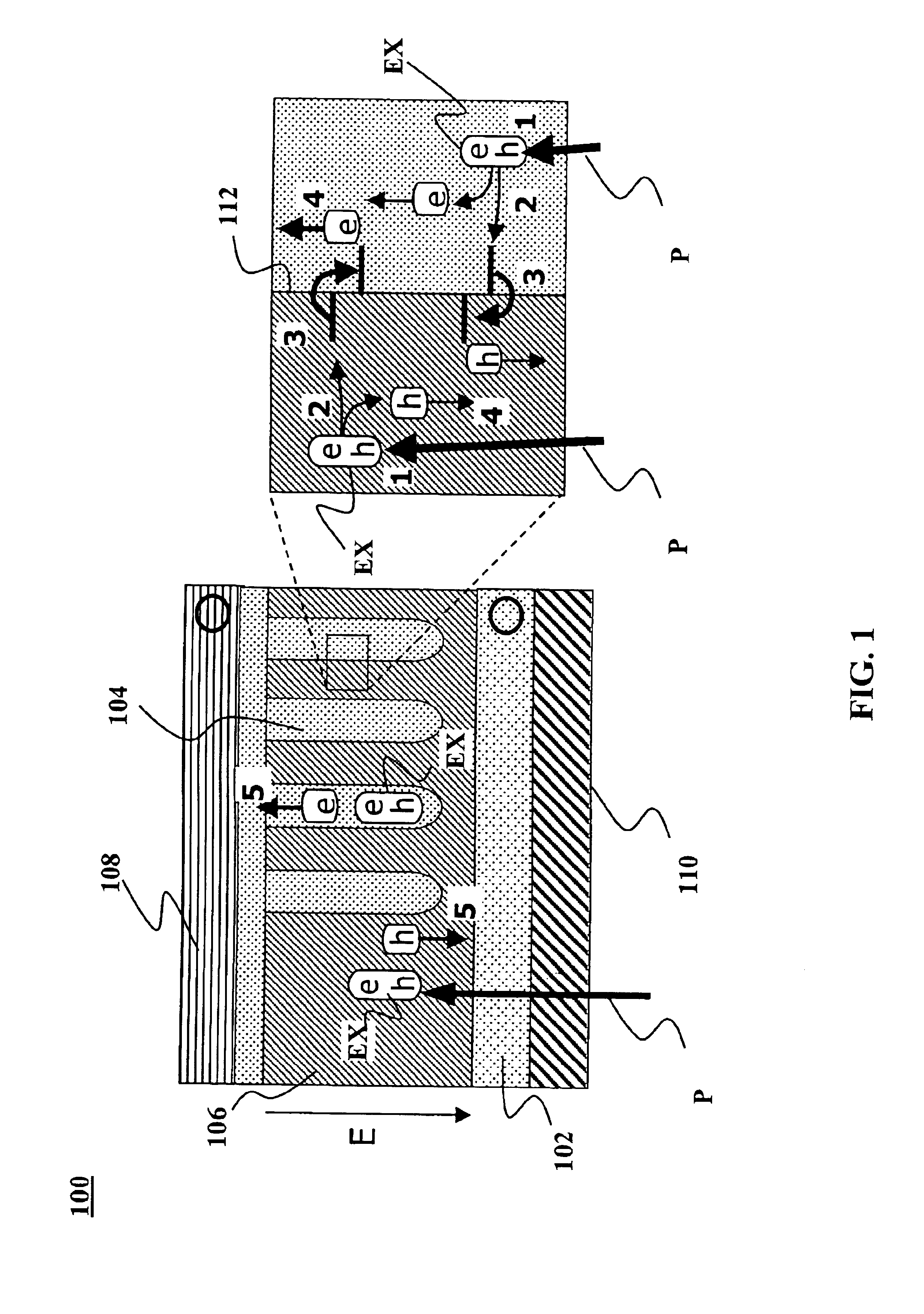
The present invention is directed to photovoltaic devices comprising nanostructured materials, wherein such photovoltaic devices are comprised exclusively of inorganic components. Depending on the embodiment, such nanostructured materials are either 1-dimensional nanostructures or branched nanostructures, wherein such nanostructures are used to enhance the efficiency of the photovoltaic device, particularly for solar cell applications. Additionally, the present invention is also directed at methods of making and using such devices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Nano-architected/assembled solar electricity cell
InactiveUS6852920B2Maximize efficiencyEfficient collectionMaterial nanotechnologyLight-sensitive devicesSolar cellNanostructure
Nano-architected / assembled solar cells and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. The solar cells comprise oriented arrays of nanostructures wherein two or more different materials are regularly arrayed and wherein the presence of two different materials alternates. The two or more materials have different electron affinities. The two materials may be in the form of matrixed arrays of nanostructures. The presence of the two different materials may alternate within distances of between about 1 nm and about 100 nm. An orientation can be imposed on the array, e.g. through solution deposition surfactant templation or other methods.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
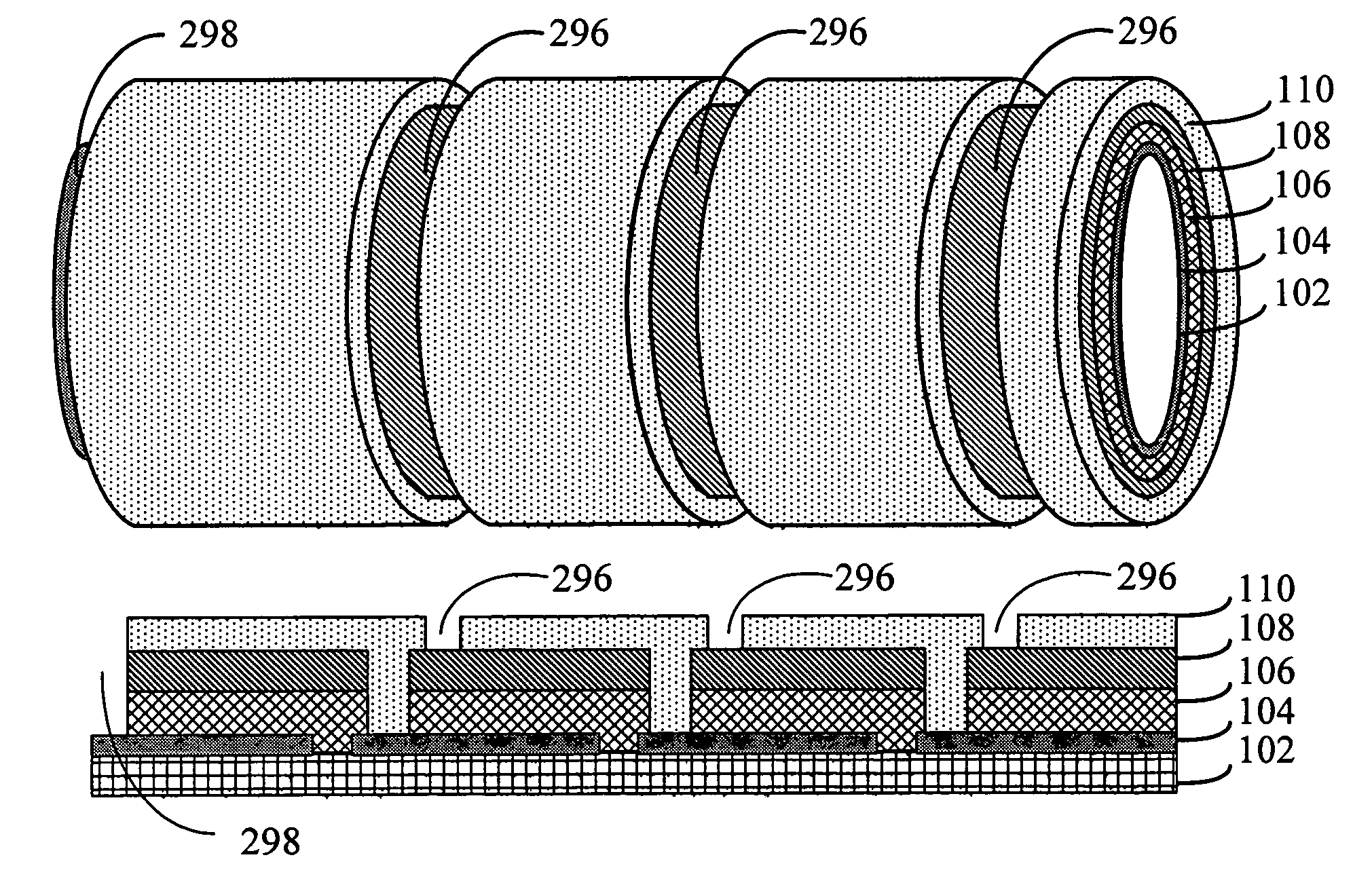
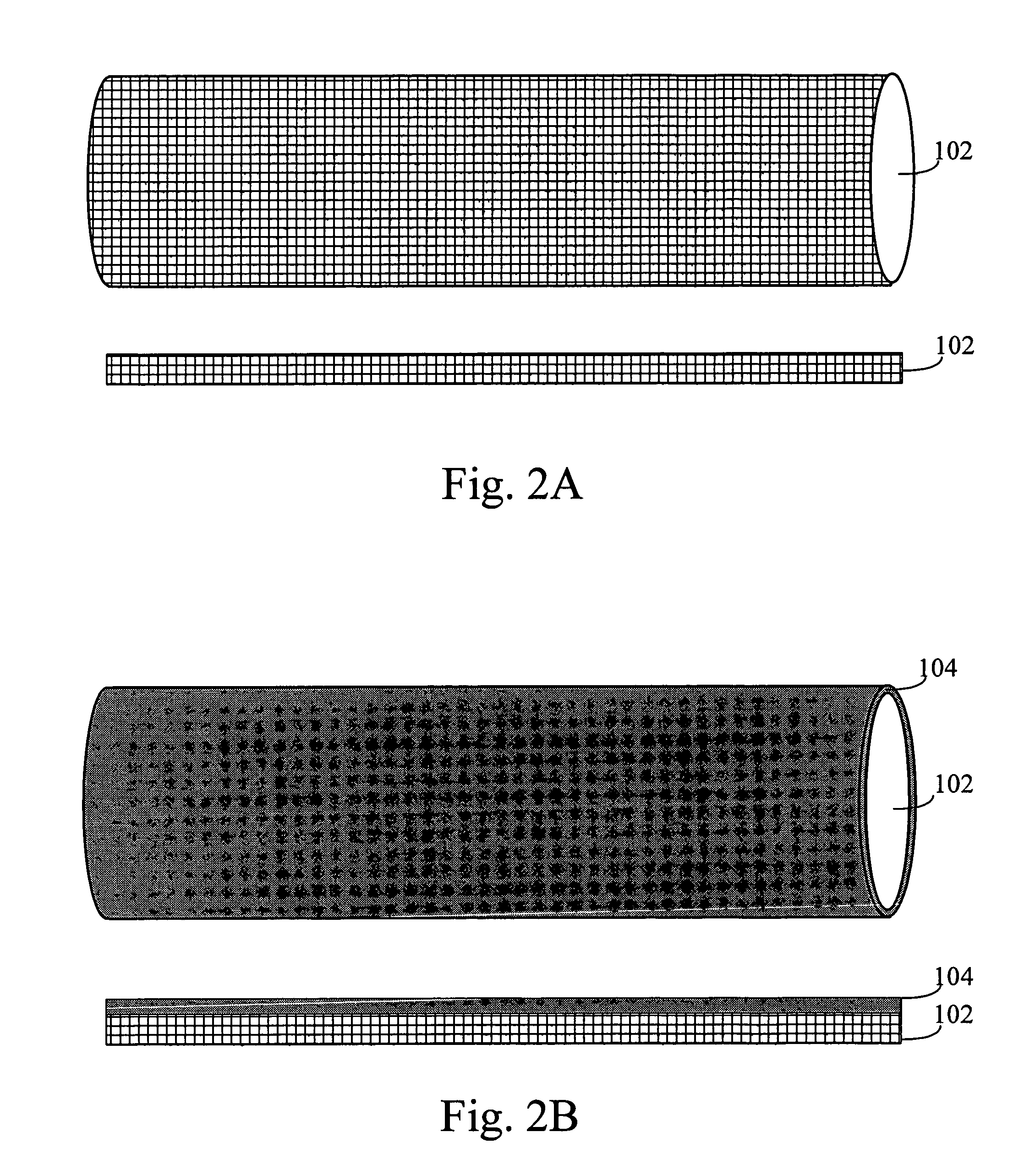
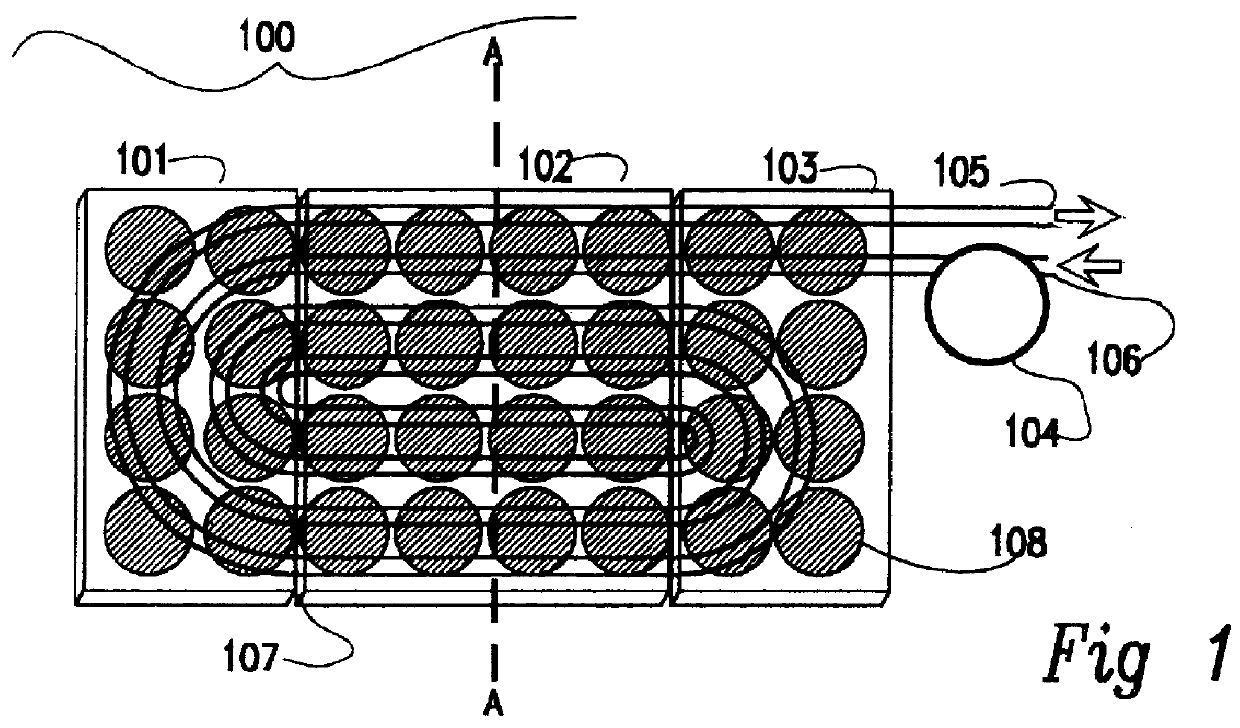
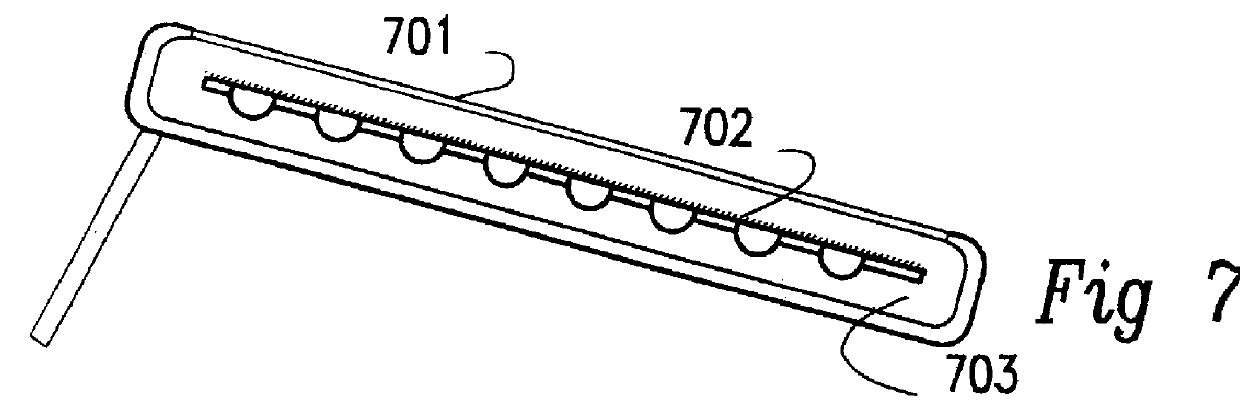
Monolithic integration of cylindrical solar cells
A solar cell unit comprising a substrate and a plurality of photovoltaic cells is provided. The substrate has a first end and a second end. The plurality of photovoltaic cells, which are linearly arranged on the substrate, comprises a first photovoltaic cell and a second photovoltaic cell. Each photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells comprises (i) a back-electrode circumferentially disposed on the substrate, (ii) a semiconductor junction layer circumferentially disposed on the back-electrode, and, (iii) a transparent conductive layer circumferentially disposed on the semiconductor junction. The transparent conductive layer of the first photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells is in serial electrical communication with the back-electrode of the second photovoltaic cell in the plurality of photovoltaic cells.
Owner:SOLYNDRA RESIDUAL TRUST
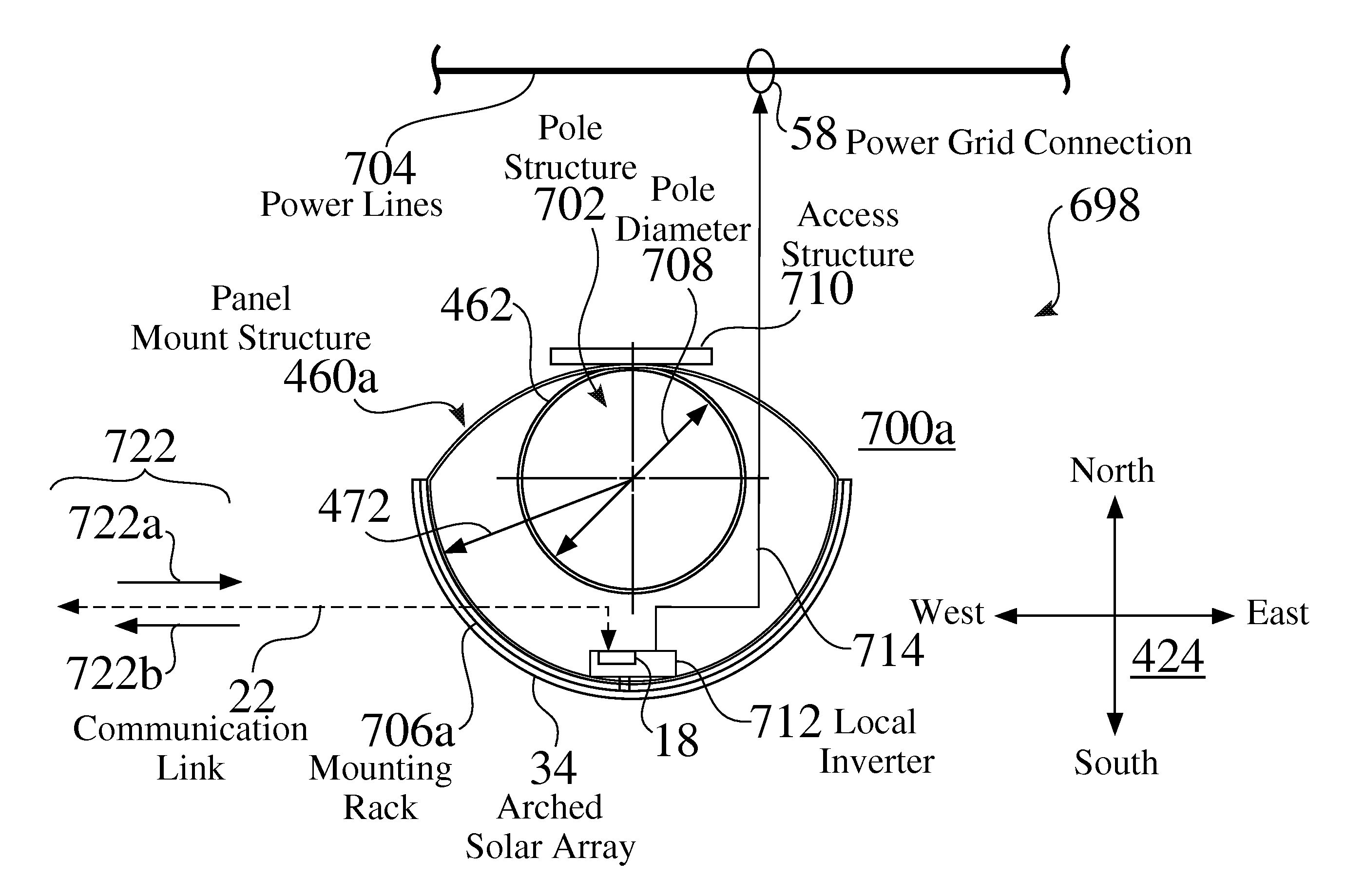
Pole-mounted power generation systems, structures and processes
ActiveUS20130038124A1Photovoltaic supportsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionAlternating current
Solar power systems and structures are mountable to a power distribution structure, e.g. a power pole or tower, which supports alternating current (AC) power transmission lines. An exemplary power generation structure is fixedly attached to and extends from the power distribution structure, and comprises a mounting rack. A solar array, comprising at least one solar panel, is affixed to the mounting rack. A DC to AC invertor is connected between the DC outputs of the solar array and the AC power transmission lines. The length of the solar array is generally in alignment with the power distribution structure, and the width of the solar array is greater than half the is circumference of the power distribution structure. The mounting rack and solar array may preferably be rotatable, such as based on any of location, time of day, or available light.
Owner:ACCURATE SOLAR POWER LLC
Solution-based fabrication of photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS20050183767A1Improve overall utilizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleSolar cell
An ink for forming CIGS photovoltaic cell active layers is disclosed along with methods for making the ink, methods for making the active layers and a solar cell made with the active layer. The ink contains a mixture of nanoparticles of elements of groups IB, IIIA and (optionally) VIA. The particles are in a desired particle size range of between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter, where a majority of the mass of the particles comprises particles ranging in size from no more than about 40% above or below an average particle size or, if the average particle size is less than about 5 nanometers, from no more than about 2 nanometers above or below the average particle size. The use of such ink avoids the need to expose the material to an H2Se gas during the construction of a photovoltaic cell and allows more uniform melting during film annealing, more uniform intermixing of nanoparticles, and allows higher quality absorber films to be formed.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
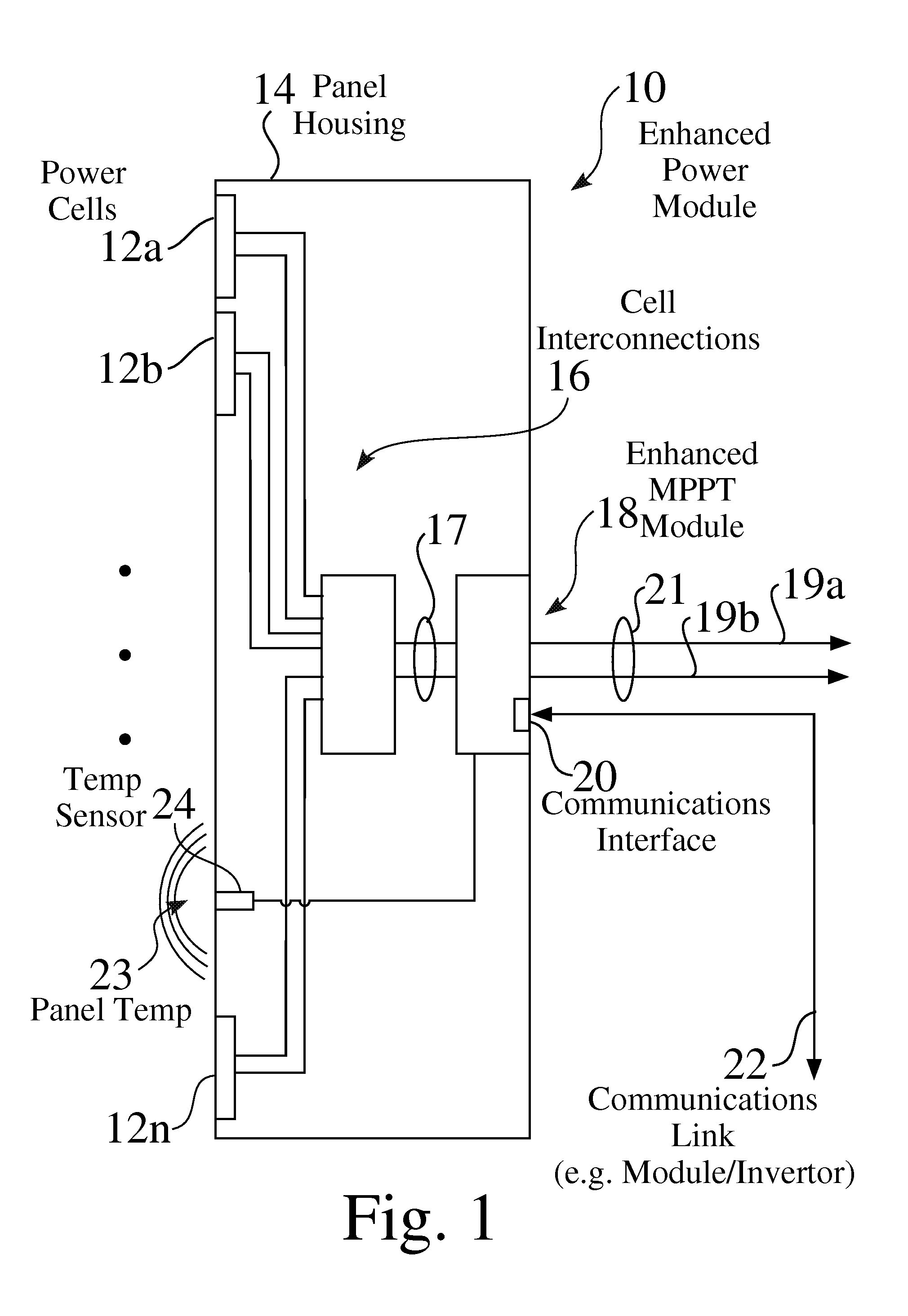
Device For Distributed Maximum Power Tracking For Solar Arrays
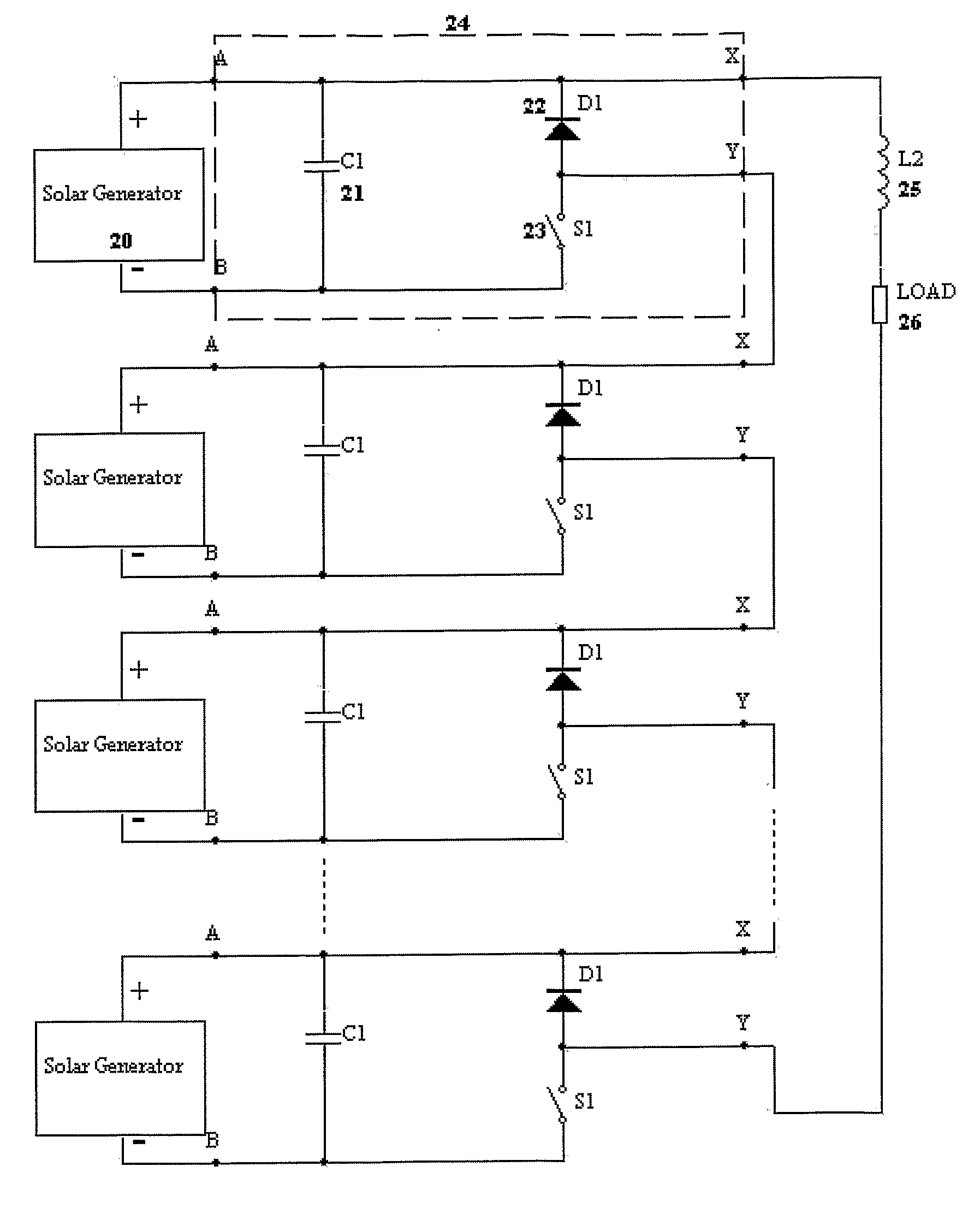
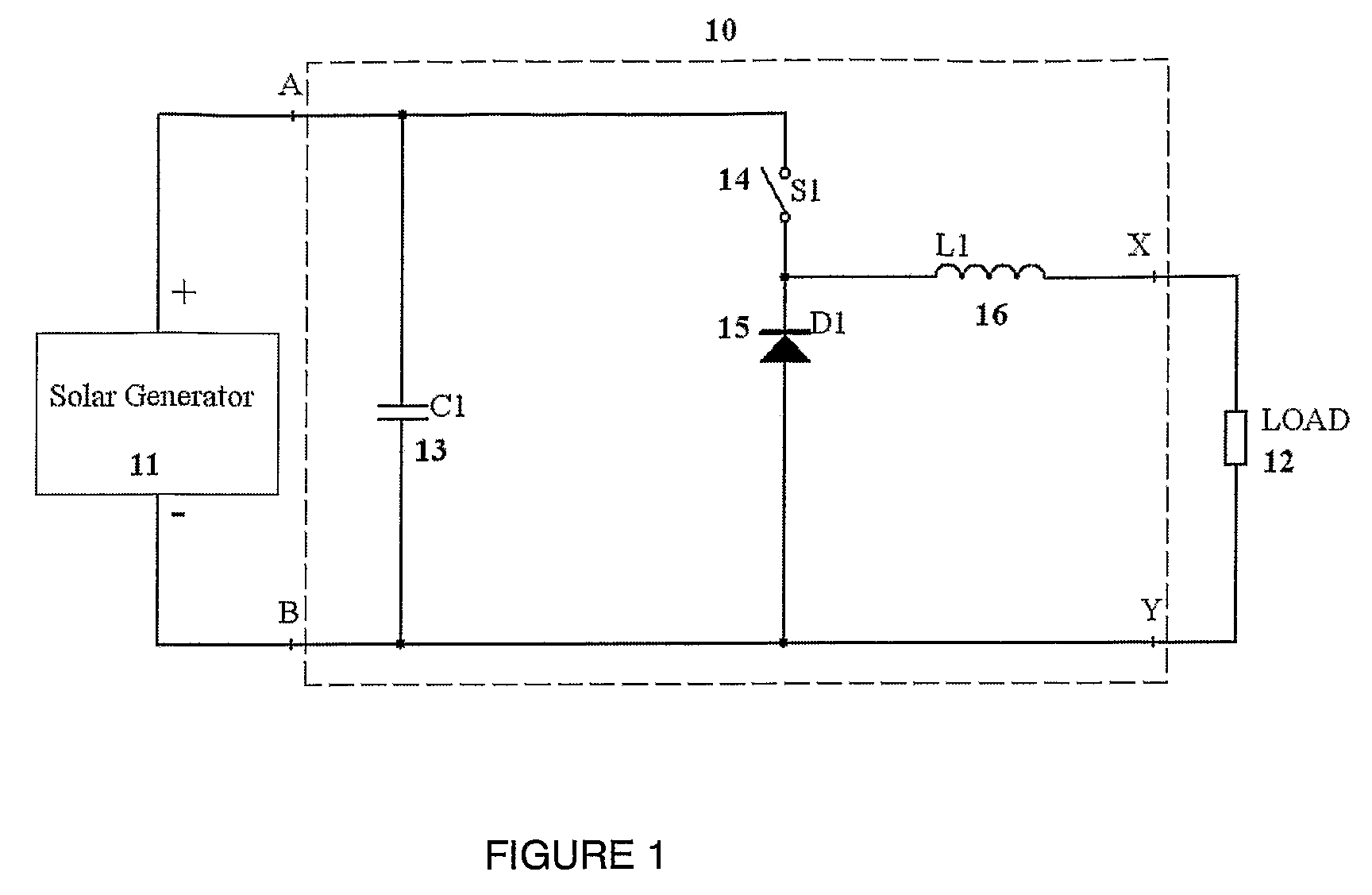
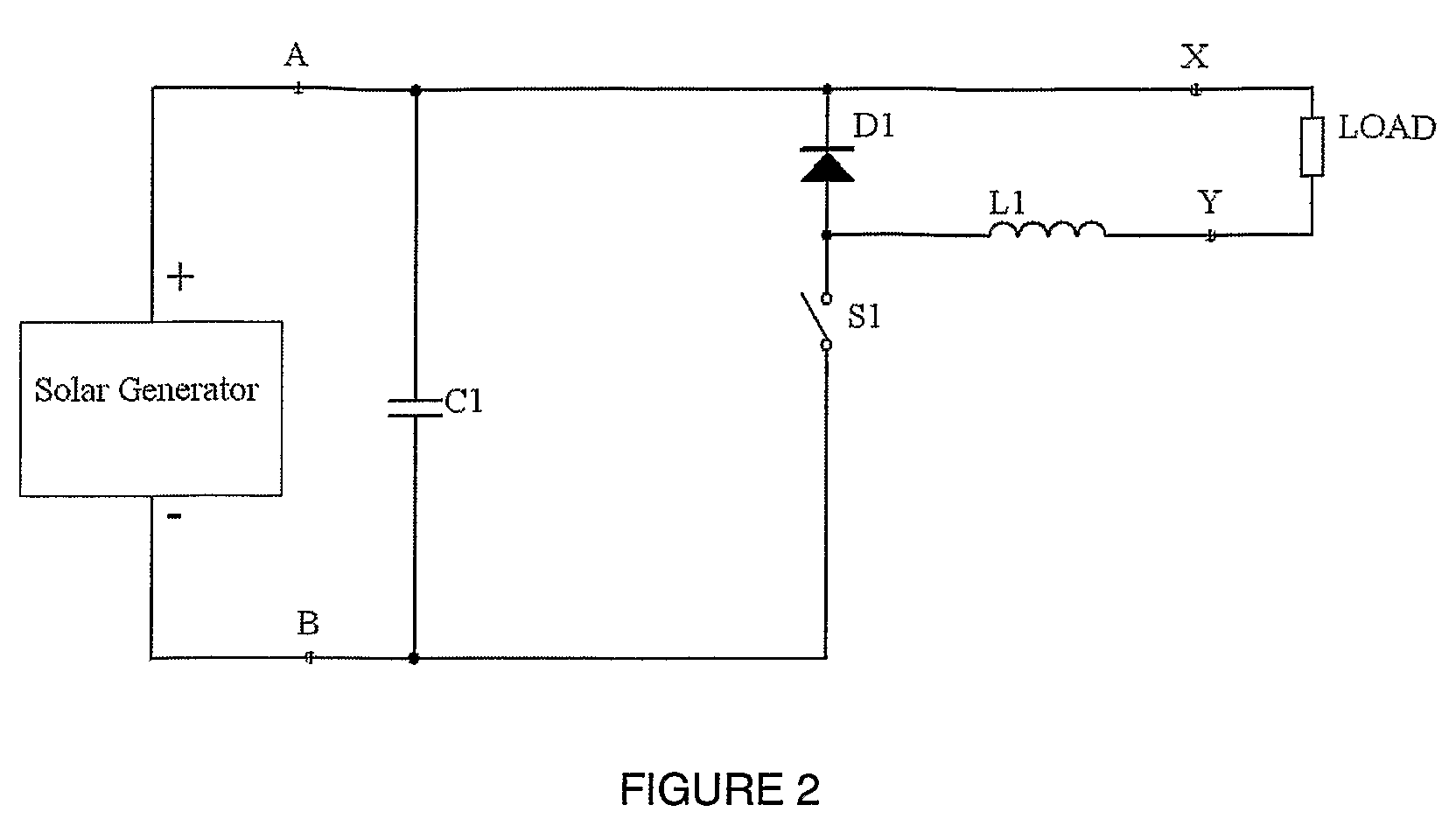
ActiveUS20080303503A1Dc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsSolar generatorElectrical battery
The present invention is a system for providing power from solar cells whereby each cell or cell array is allowed to produce its maximum available power and converted by an operatively connected DC / DC converter. Each cell or cell array has its own DC / DC converter. In one form the system for providing power from solar cells includes one or more solar generators wherein each of said solar generators has one to nine solar cells; a maximum power tracker operatively associated with each solar generator, each of said maximum power tracker includes a buck type DC / DC converter without an output inductor, each of said maximum power trackers are operatively connected in series with each other; an inductor operatively connected to the series connected maximum power trackers; and means for providing electrical power from the inductor to load means, wherein each of said maximum power trackers is controlled so that the operatively associated solar generator operates at its maximum power point to extract maximum available power.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Method of processing a substrate using a large-area magnetron sputtering chamber with individually controlled sputtering zones
InactiveUS20070056843A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention generally provides a method for processing a surface of a substrate in a physical vapor deposition (PVD) chamber that has a sputtering target that has separately biasable sections, regions or zones to improve the deposition uniformity. In general, aspects of the present invention can be used for flat panel display processing, semiconductor processing, solar cell processing, or any other substrate processing. In one aspect, each of the target sections of the multizone target assembly are biased at a different cathodic biases by use of one or more DC or RF power sources. In one aspect, each of the target sections of the multizone target assembly are biased at a different cathodic biases by use of one power source and one or more resistive, capacitive and / or inductive elements. In one aspect, the processing chamber contains a multizone target assembly that has one or more ports that are adapted deliver a processing gas to the processing region of the PVD chamber. In one aspect, the processing chamber contains a multizone target assembly that has one or more magnetron assemblies positioned adjacent to one or more of the target sections.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
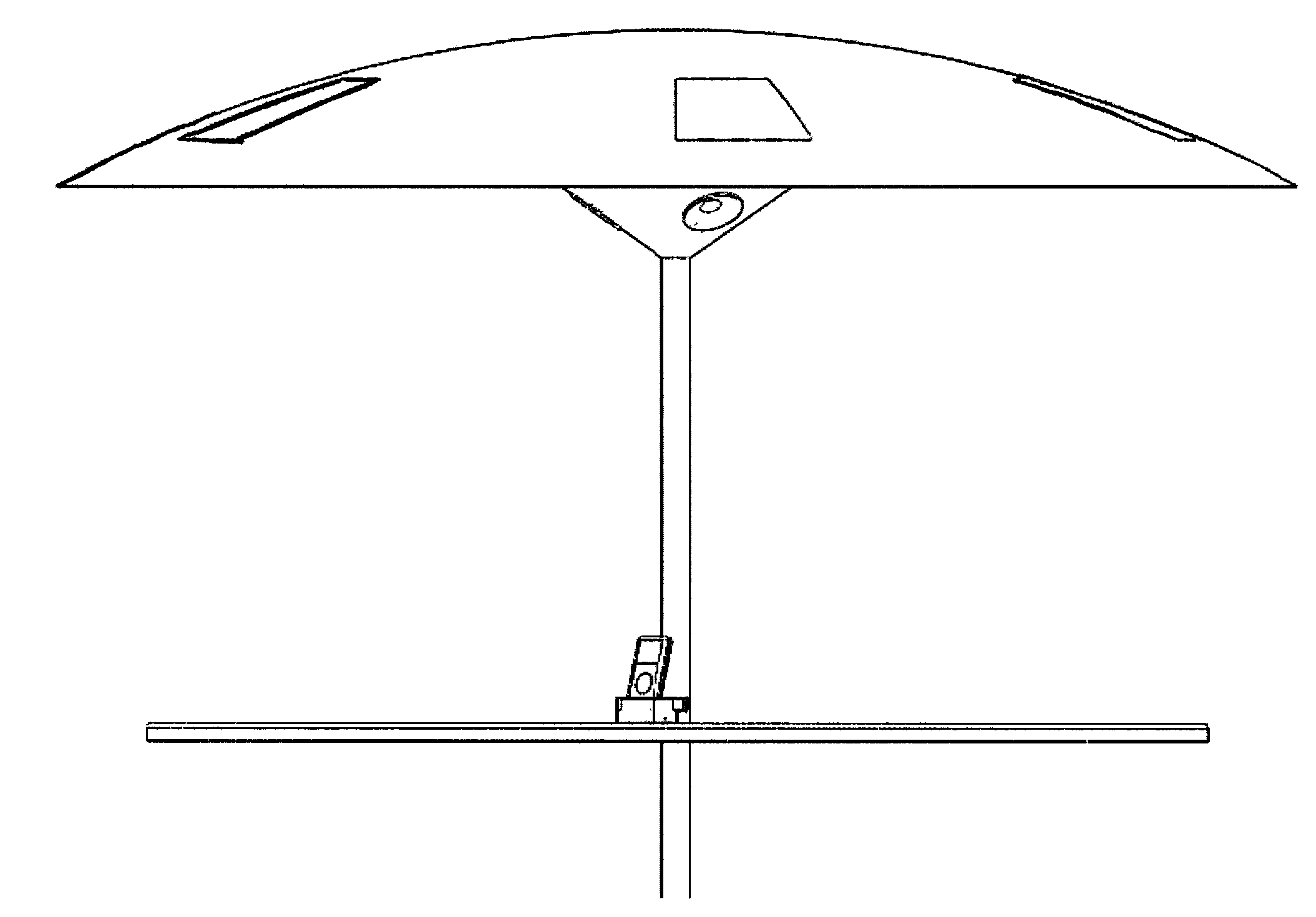
Solar-powered media system and apparatus
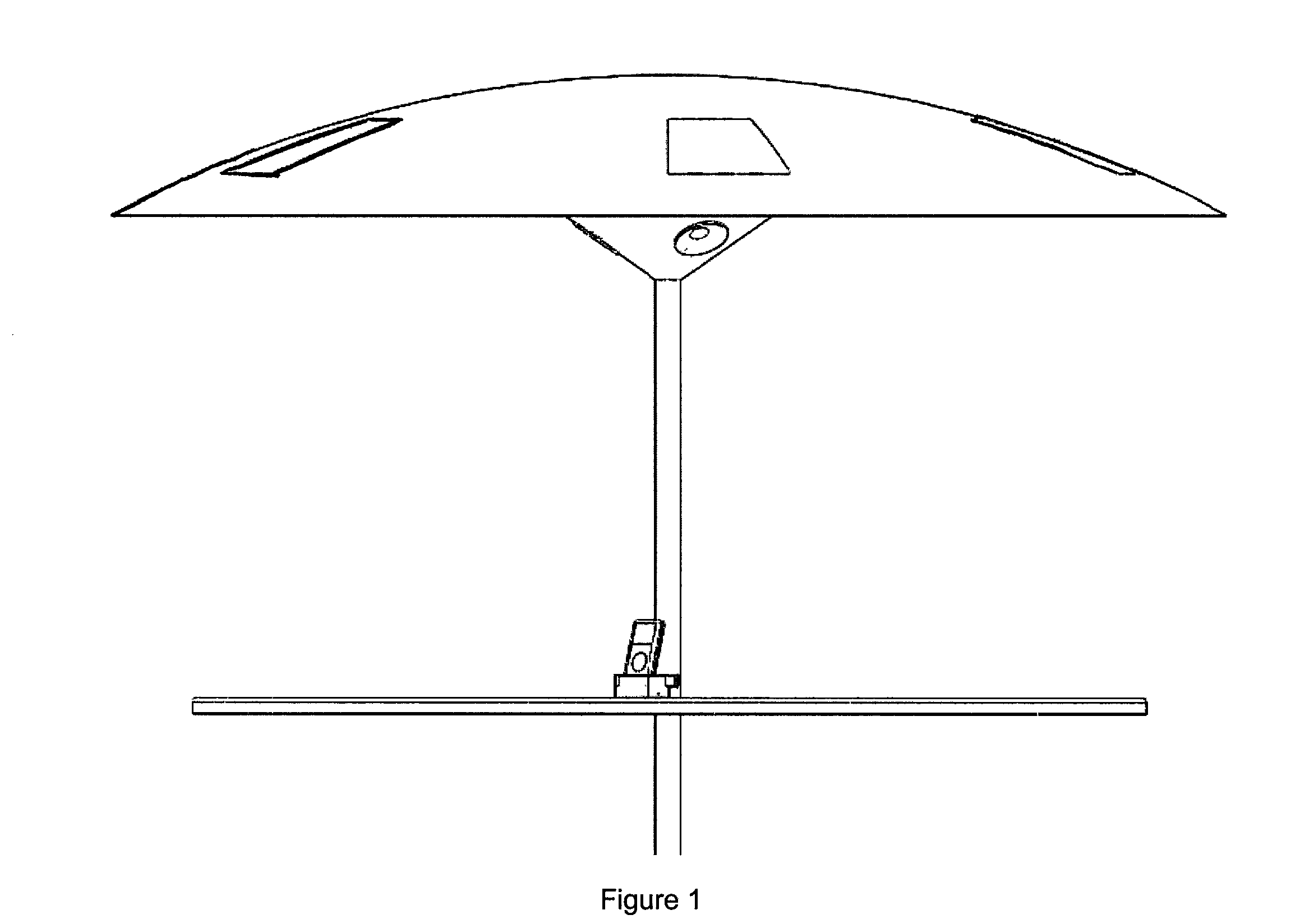
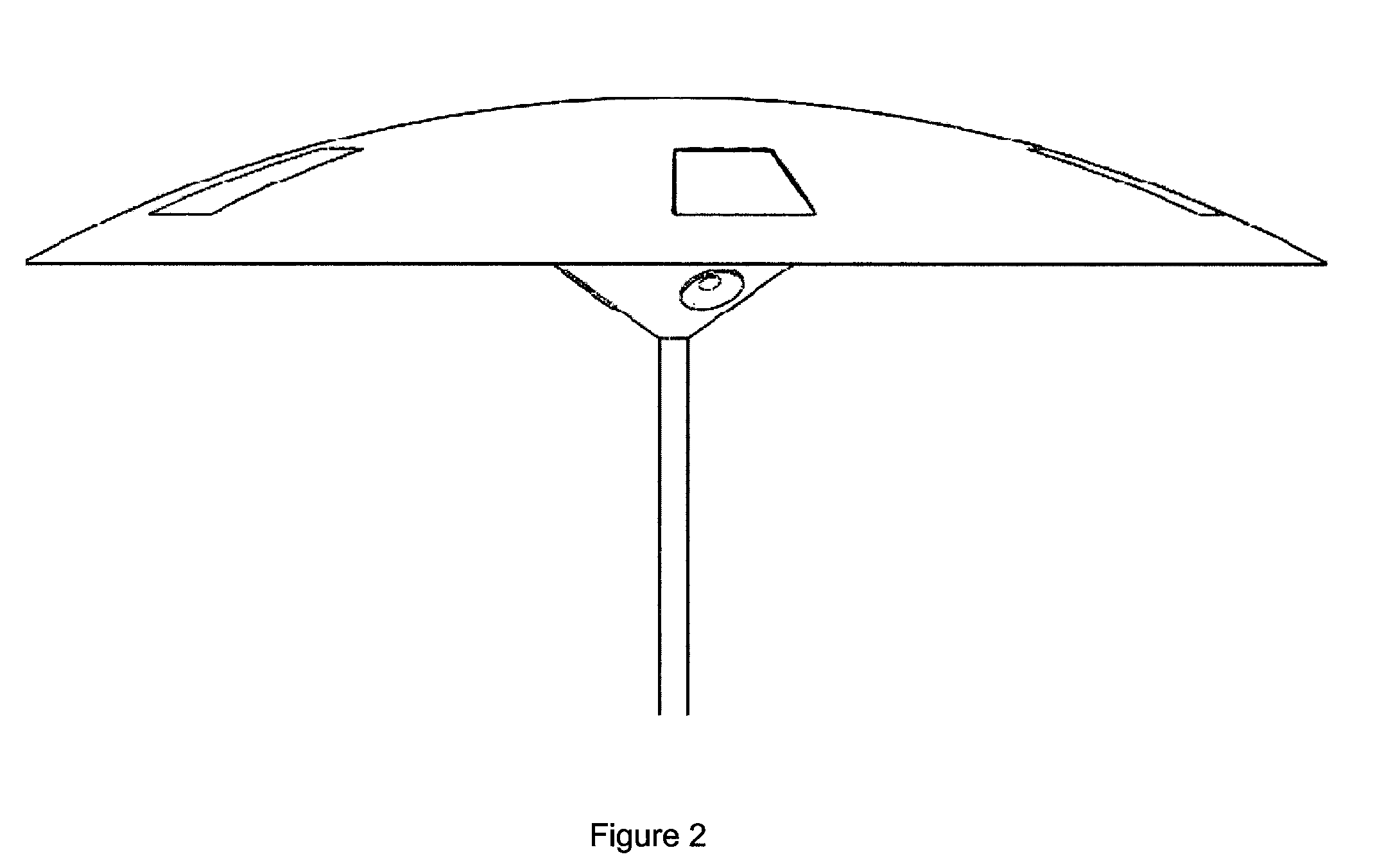
Solar-powered media systems and apparatuses are disclosed. The solar-powered media systems and apparatuses comprise shade structures, solar cells, energy storage devices, electronics and / or circuitry, docking stations, wireless communications devices, and audio and / or visual components capable of outputting media content. One aspect of the solar-powered media system and apparatus pertains to shade structures, which provide shade for one or more users. Another aspect of the disclosure pertains to energy storage devices, which store electrical energy to power the solar-powered media system. Another aspect of the disclosure pertains to docking stations, which allow communication and electrical energy transfer between various devices. Another aspect of the disclosure pertains to audio & visual components capable of outputting media content for one or more users. Another aspect of the disclosure pertains to solar cells integrated into or attached to the said shade structure. All aspects can be utilized alone or in combination with one another.
Owner:HARRISON SOREN DAVID
Solar concentrator for heat and electricity
InactiveUS6080927AIncrease productionAvoid overall overheatingSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringSolar cell
PCT No. PCT / NZ95 / 00084 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 14, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 08683 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 21, 1996A solar concentrator for producing usable power as heat and / or electricity uses a self-steering heliostat 1502 to concentrate solar radiation 1509 onto an absorbing surface such as, or including, a solar cell array 1511 capable of absorbing power from the radiation, meanwhile removing heat (such as from long-wave infra-red radiation or resistive losses) from the surface with fluid heat transfer means 1503, 1504, then making effective use of that low-grade heat. Thus the solar cell array is kept relatively cool and a larger proportion of the solar energy incident on the reflector unit is used. The invention uses electricity 1506 from the solar cells to move a transporting fluid through a heat exchanger 1504. Excess electricity may be available for local storage or use 1510, or feeding 1512 to the power distribution grid. Applications include warming swimming pools 1501, heating hot-water supplies using excess electricity, or warming, lighting and ventilating open spaces.
Owner:JOHNSON COLIN FRANCIS
Solar power generation apparatus, solar power generation system, and method of manufacturing solar power generation apparatus
InactiveUS20050121067A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple structurePV power plantsDc-dc conversionManufacturing cost reductionAc power system
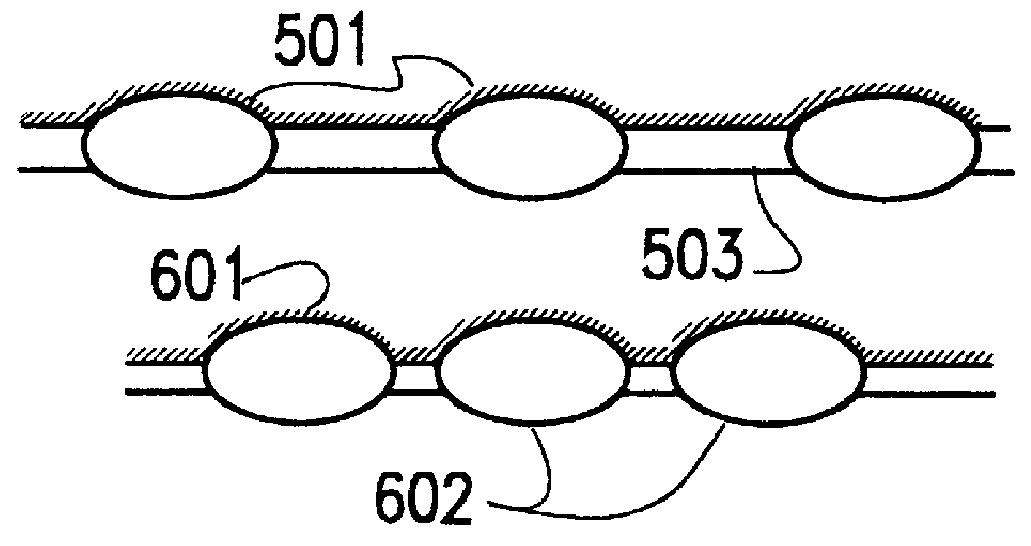
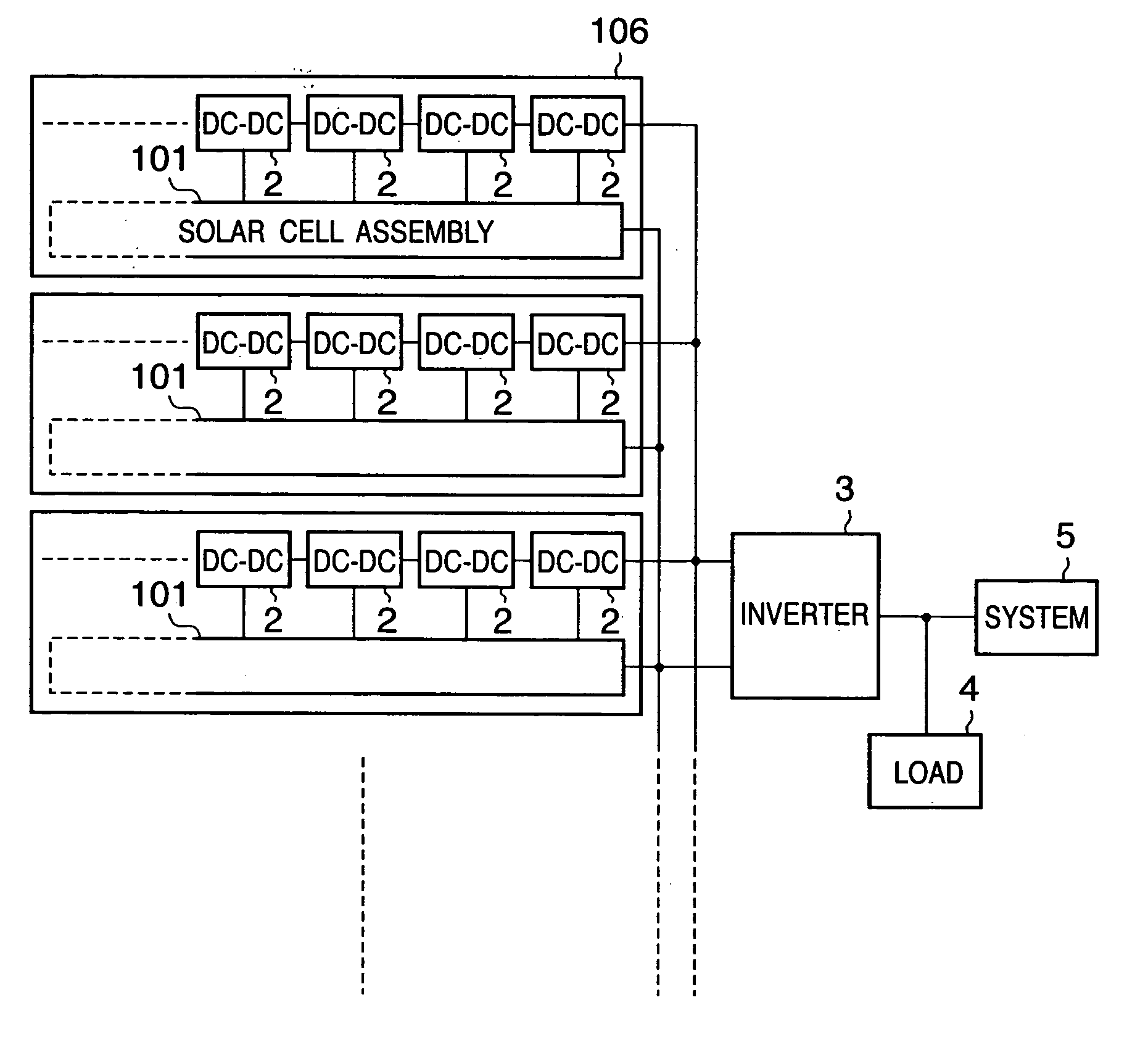
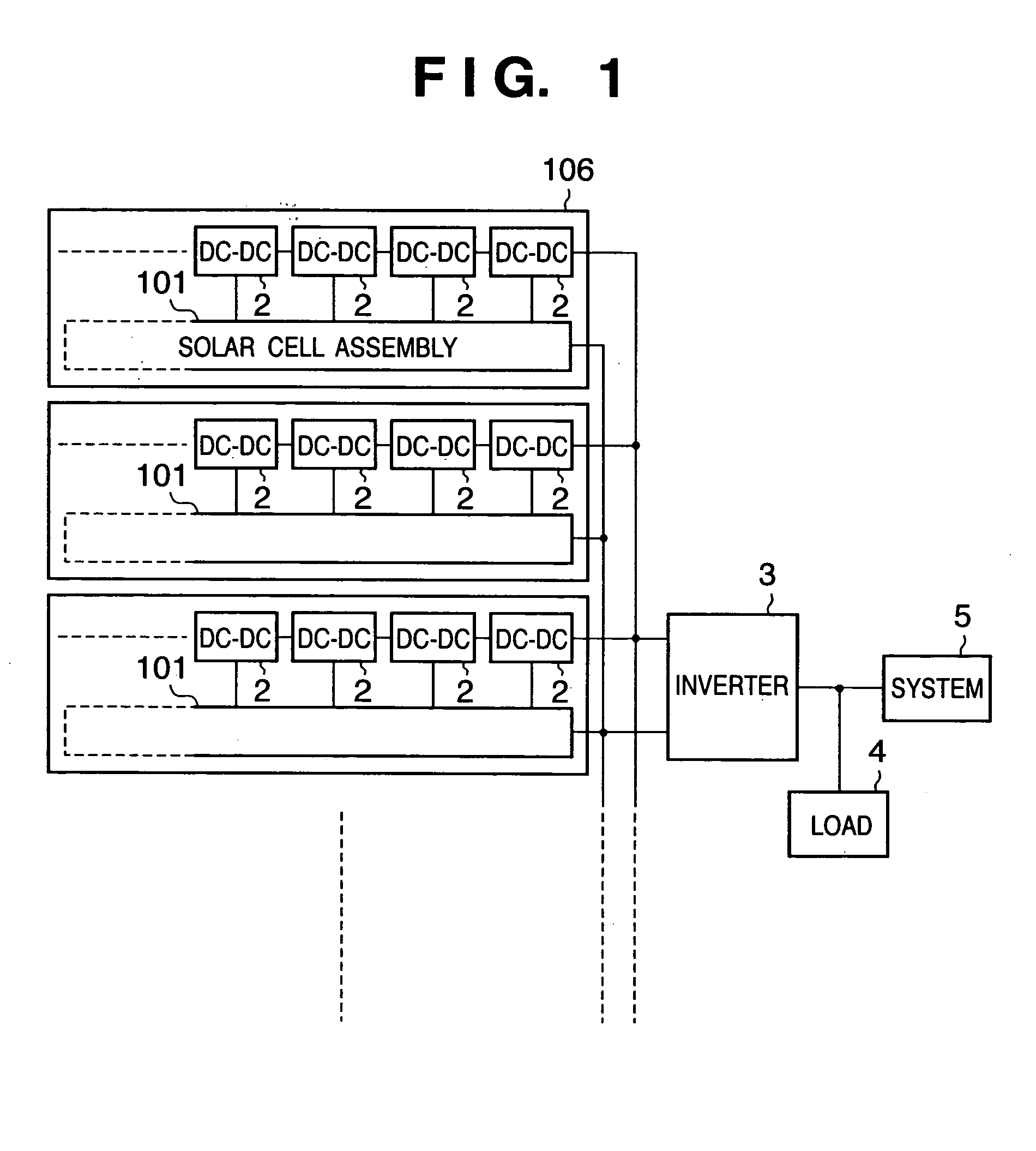
A solar cell assembly including a plurality of solar cells is formed on a common substrate, and a DC / DC converter which converts the output from the solar cell is connected to each solar cell to constitute a solar power generation apparatus. The output from the solar power generation apparatus is converted into an AC power by an inverter and supplied to a load or commercial AC power system. Since the arrangement is simplified, the manufacturing cost can be reduced, and the influence of partial shade or a variation in characteristic decreases.
Owner:CANON KK
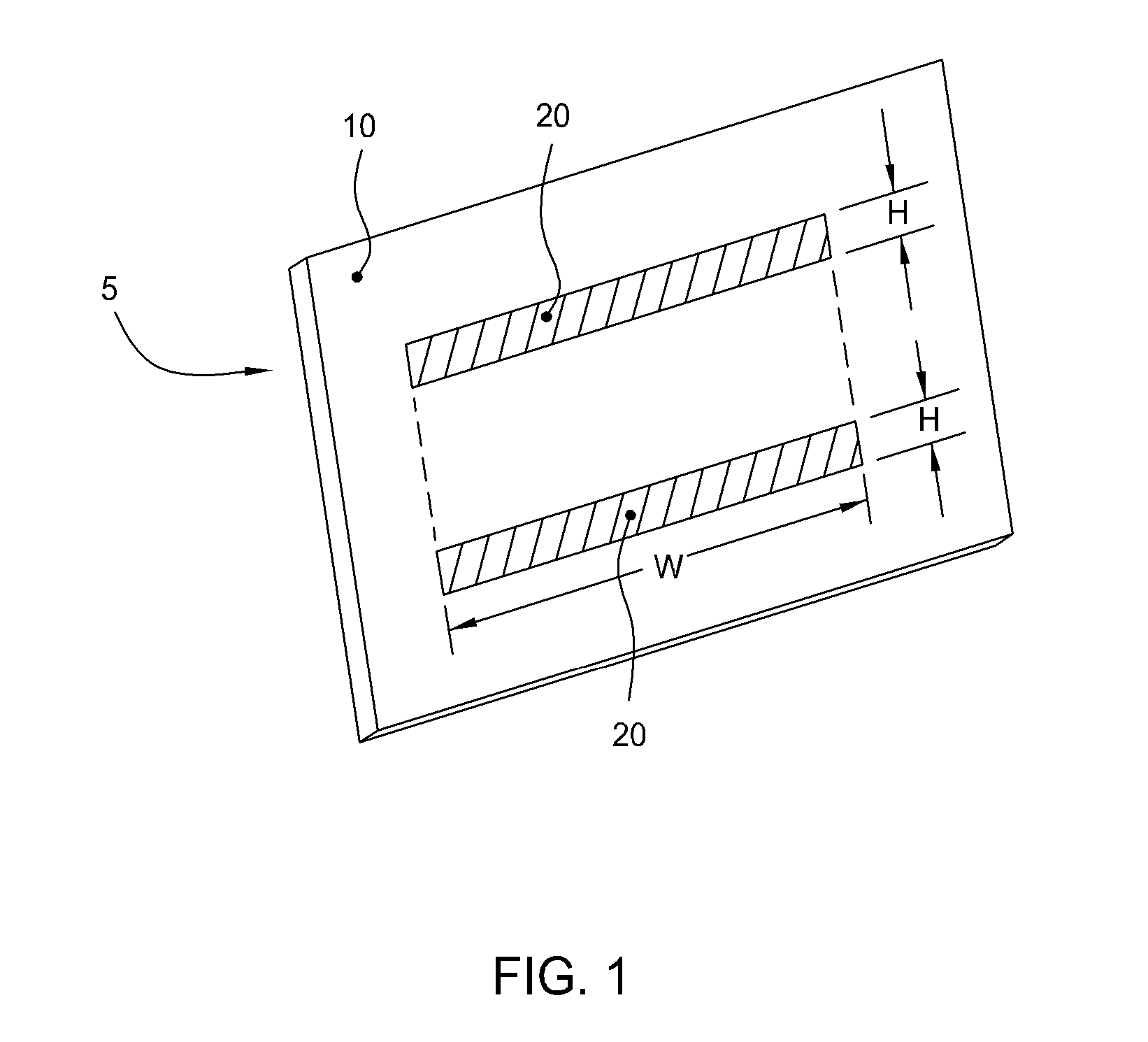
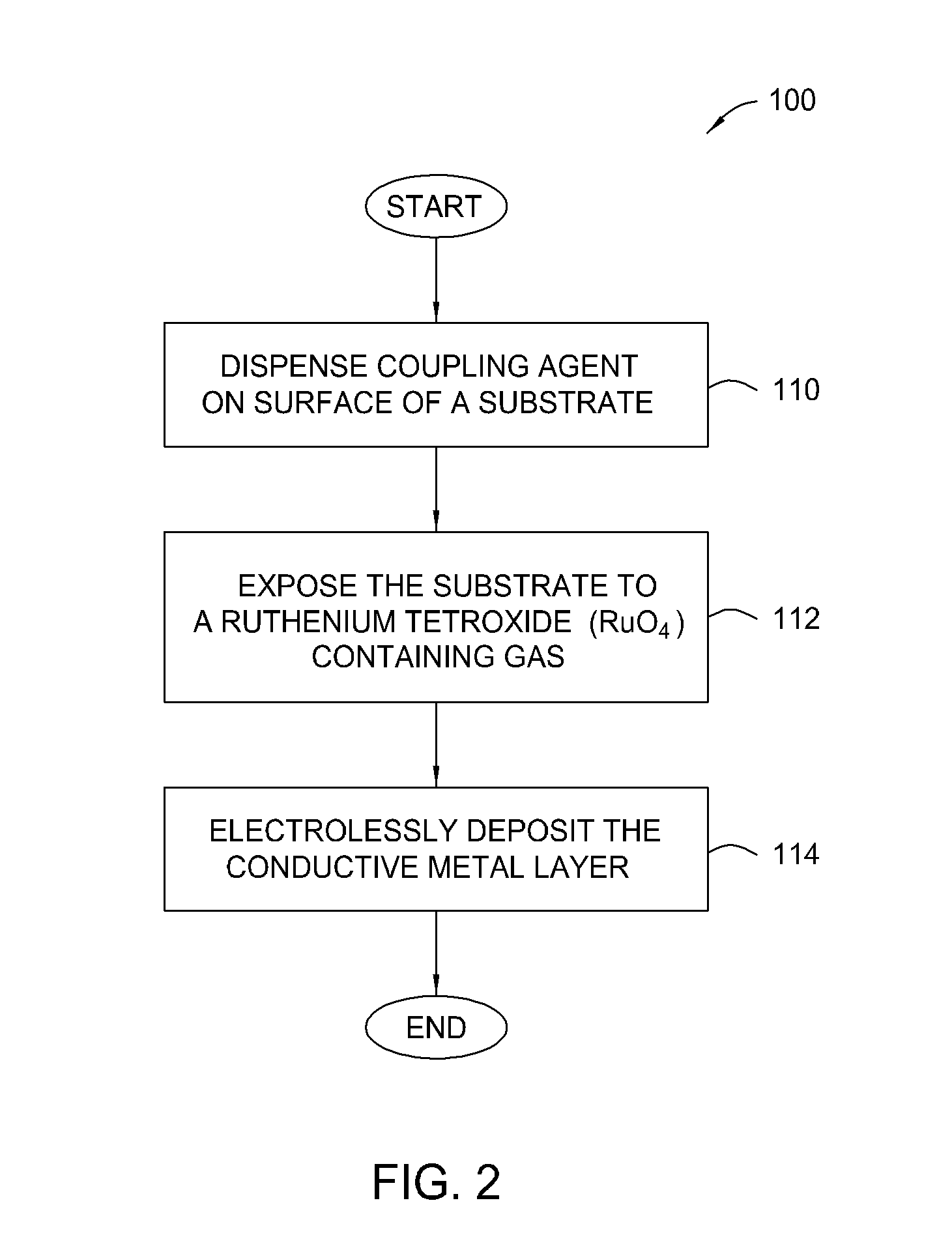
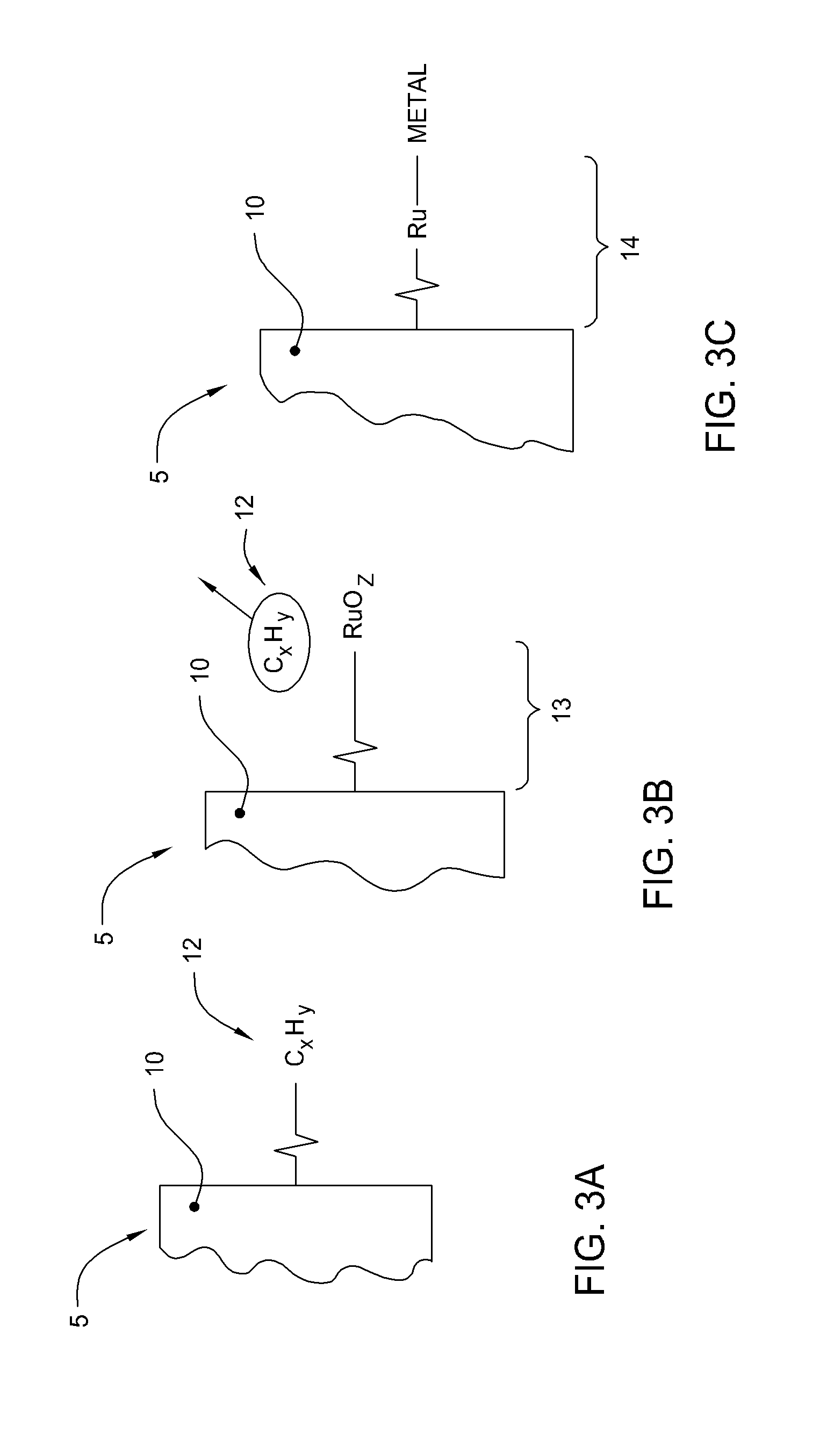
Patterned electroless metallization processes for large area electronics
The present invention generally provides an apparatus and method for selectively forming a metallized feature, such as an electrical interconnect feature, on a electrically insulating surface of a substrate. The present invention also provides a method of forming a mechanically robust, adherent, oxidation resistant conductive layer selectively over either a defined pattern or as a conformal blanket film. Embodiments of the invention also generally provide a new chemistry, process, and apparatus to provide discrete or blanket electrochemically or electrolessly platable ruthenium or ruthenium dioxide containing adhesion and initiation layers. In general, aspects of the present invention can be used for flat panel display processing, semiconductor processing, solar cell device processing, or any other substrate processing, being particularly well suited for the application of stable adherent coating on glass as well as flexible plastic substrates. This invention may be especially useful for the formation of electrical interconnects on the surface of flat panel display or solar cell type substrates where the line sizes are generally larger than semiconductor devices or where the formed feature are not generally as dense.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
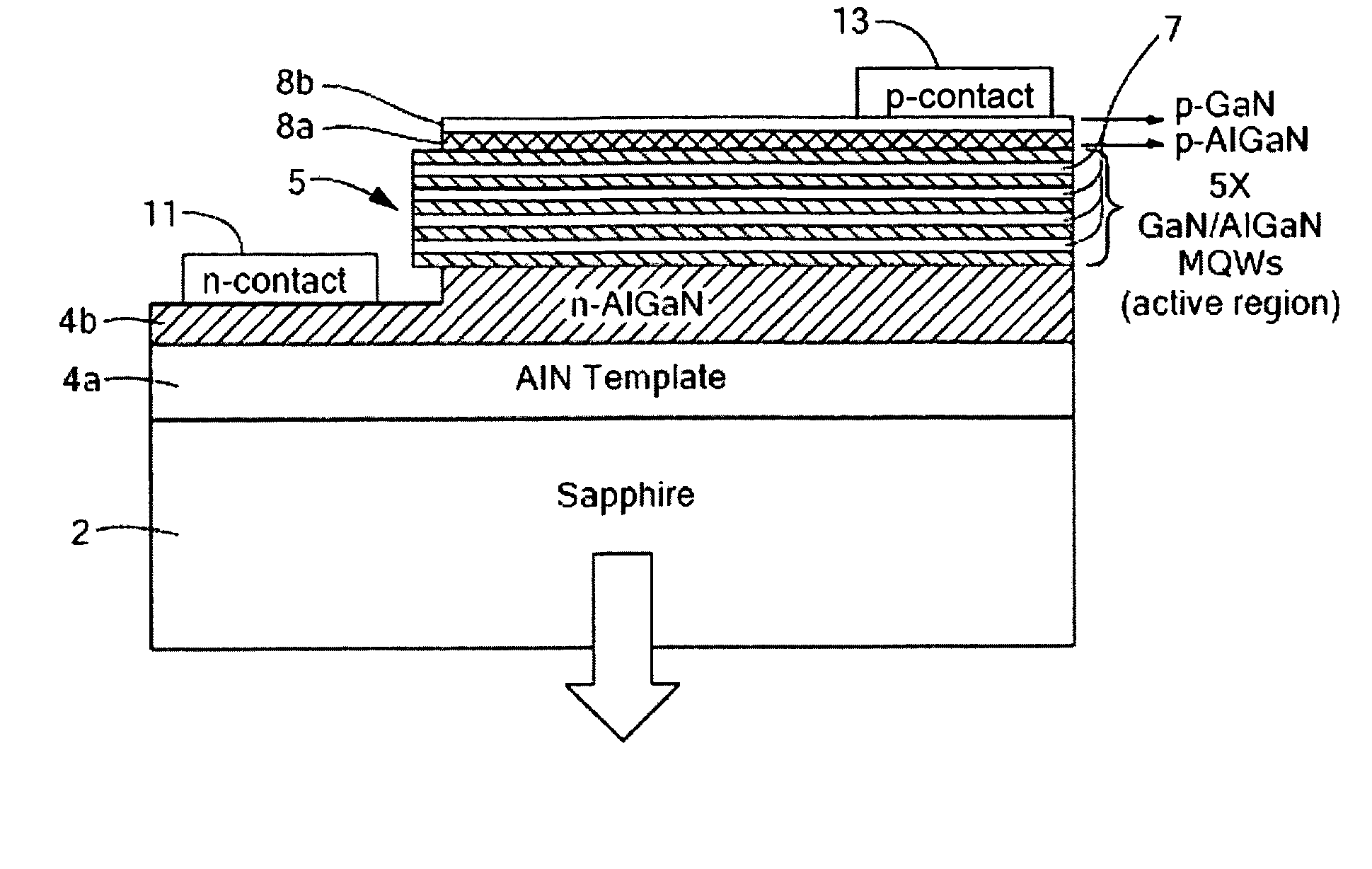
Optical devices featuring textured semiconductor layers
ActiveUS20070120141A1Accelerate escapeLight extraction efficiencySolid-state devicesNanoopticsQuantum efficiencyPhosphor
A semiconductor sensor, solar cell or emitter, or a precursor therefor, has a substrate and one or more textured semiconductor layers deposited onto the substrate. The textured layers enhance light extraction or absorption. Texturing in the region of multiple quantum wells greatly enhances internal quantum efficiency if the semiconductor is polar and the quantum wells are grown along the polar direction. Electroluminescence of LEDs of the invention is dichromatic, and results in variable color LEDs, including white LEDs, without the use of phosphor.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Photovoltaic devices fabricated by growth from porous template
Photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. A device may be characterized by an architecture where two more materials having different electron affinities are regularly arrayed such that their presence alternates within distances of between about 1 nm and about 100 nm. The materials are present in a matrix based on a porous template with an array of template pores. The porous template is formed by anodizing a layer of metal. A photovoltaic device may include such a porous template disposed between a base electrode and a transparent conducting electrode. A first charge-transfer material fills the template pores, A second (complementary) charge-transfer material fills additional space not occupied by the first charge-transfer material.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
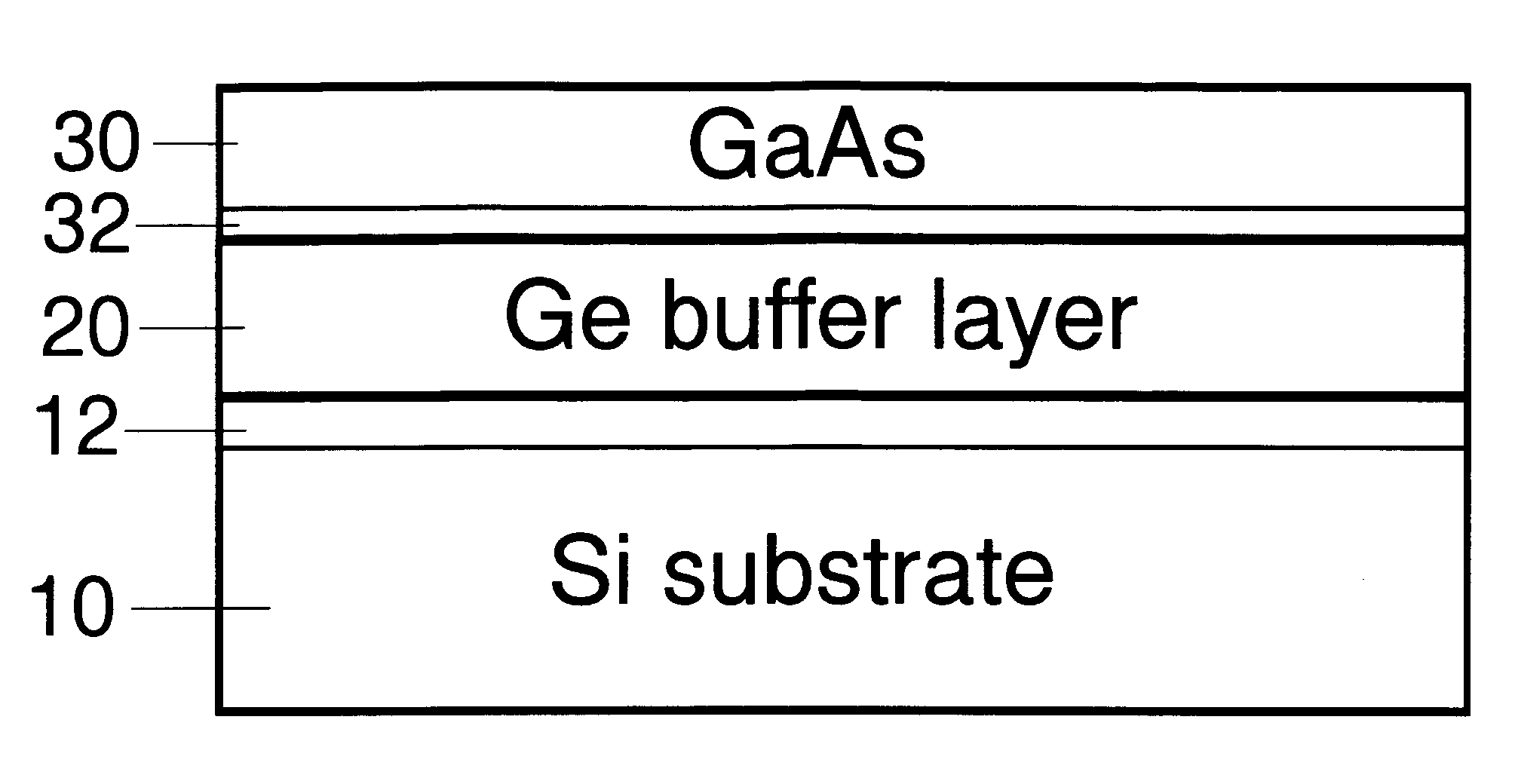
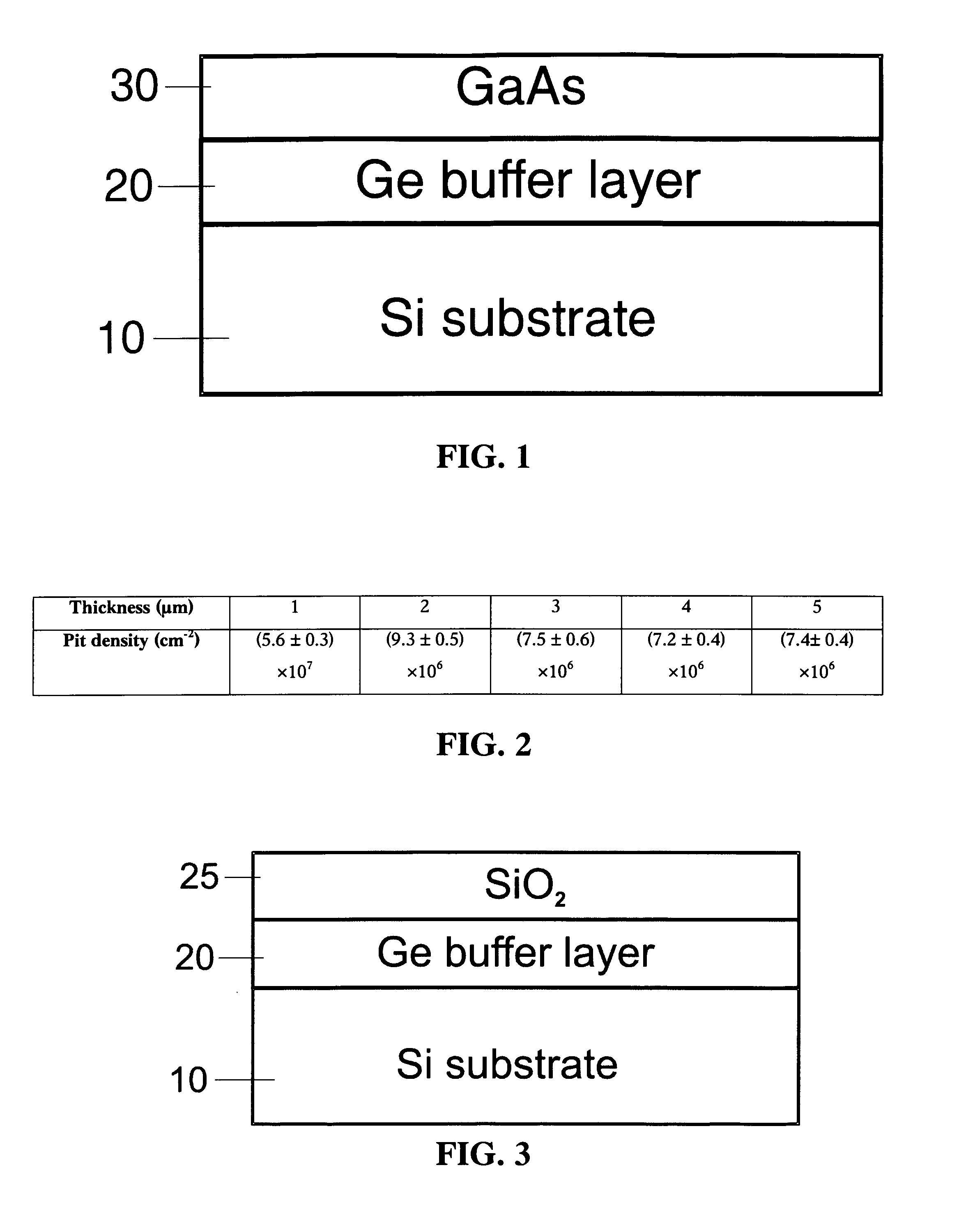
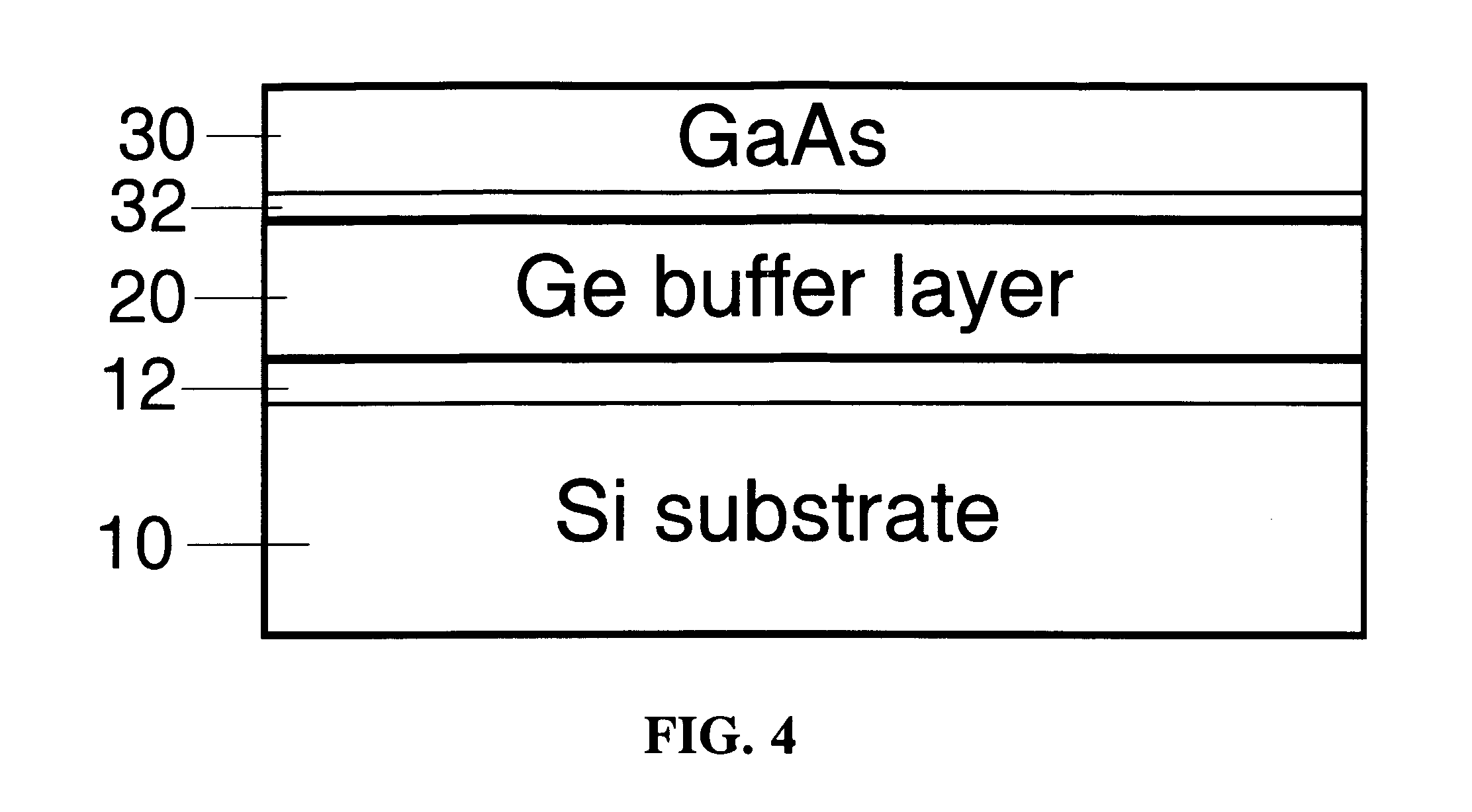
Method for Producing Virtual Ge Substrates for III/V-Integration on Si(001)
InactiveUS20070231488A1Fast epitaxial growthCheap methodSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField-effect transistorSolar cell
Relaxed germanium buffer layers can be grown economically on misoriented silicon wafers by low-energy plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, in conjunction with thermal annealing and / or patterning, the buffer layers can serve as high-quality virtual substrates for the growth of crack-free GaAs layers suitable for high-efficiency solar cells, lasers and field effect transistors.
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
Direct current combiner box with power monitoring, ground fault detection and communications interface
InactiveUS20060237058A1Save a lot of timeShorten the timeBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsCommunication interfaceDc current
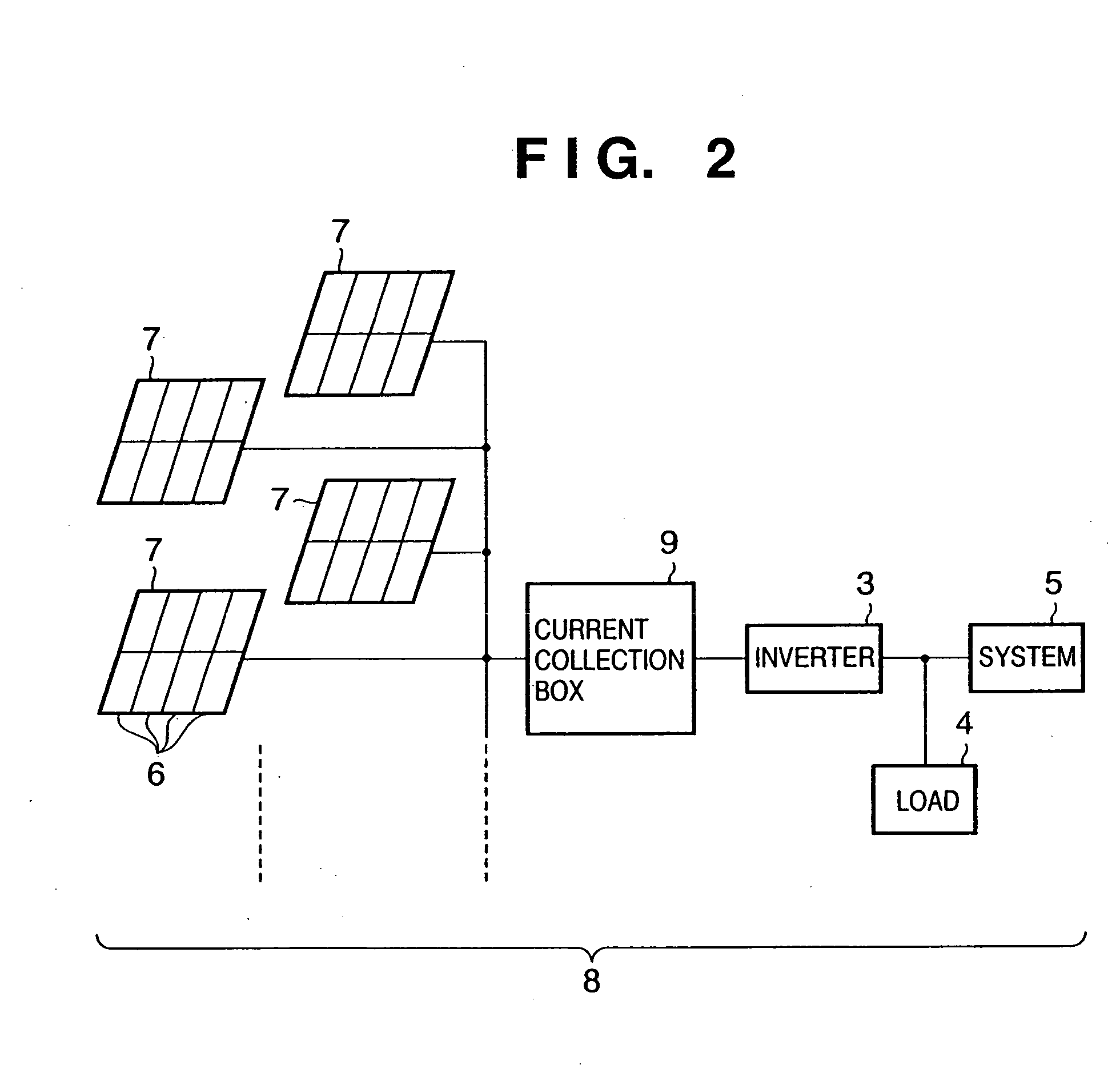
A combiner box is used to collect direct current from solar panels or other energy sources. The combiner box integrates all means necessary for ground fault detection, current monitoring, voltage monitoring, and power monitoring. The combiner box may include a communication interface suitable for Web enabled monitoring, electronic notifications of system status, and / or remote control of system functions. In one embodiment, the combiner box uses integrated circuits and printed circuit board technology to achieve new efficiencies in manufacturing, installation and system analysis at the string level. A separate hand piece may be used by installers to test the performance of the combiner box, installation of the solar panels, performance of the solar panels and connections between the solar panels and the combiner box.
Owner:ENERGY RECOMMERCE
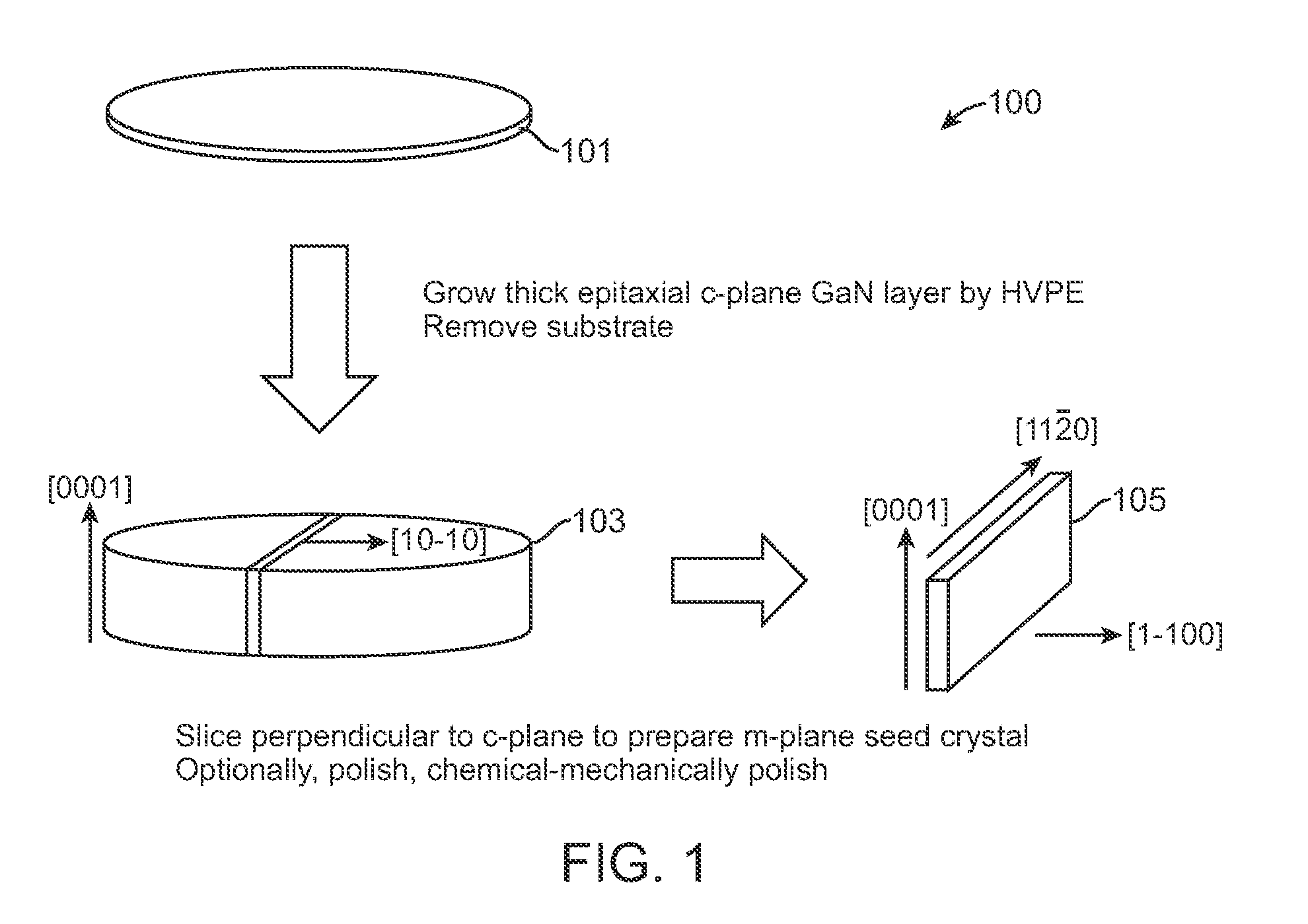
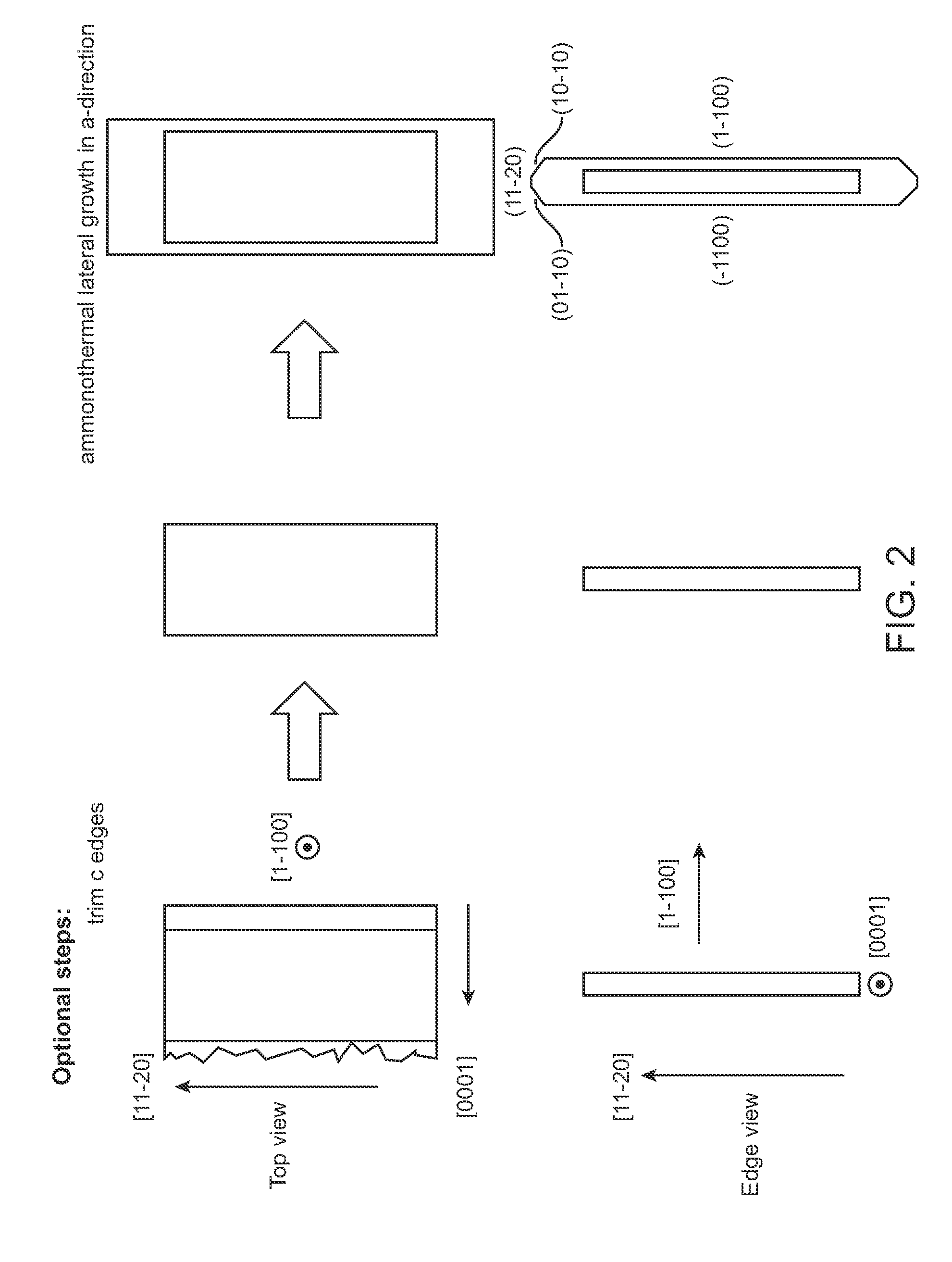
High quality large area bulk non-polar or semipolar gallium based substrates and methods
InactiveUS20100003492A1Great area of substrateCost-effective manufacturingPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialPhotodetectorSolar cell
A large area nitride crystal, comprising gallium and nitrogen, with a non-polar or semi-polar large-area face, is disclosed, along with a method for making. The crystal is useful as a substrate for a light emitting diode, a laser diode, a transistor, a photodetector, a solar cell, or for photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen generation.
Owner:SORAA
Photovoltaic devices fabricated from nanostructured template
Photovoltaic devices, such as solar cells, and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. A device may be characterized by an architecture having a nanostructured template made from an n-type first charge transfer material with template elements between about 1 nm and about 500 nm in diameter with about 1012 to 1016 elements / m2. A p-type second charge-transfer material optionally coats the walls of the template elements leaving behind additional space. A p-type third charge-transfer material fills the additional space volumetrically interdigitating with the second charge transfer material.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
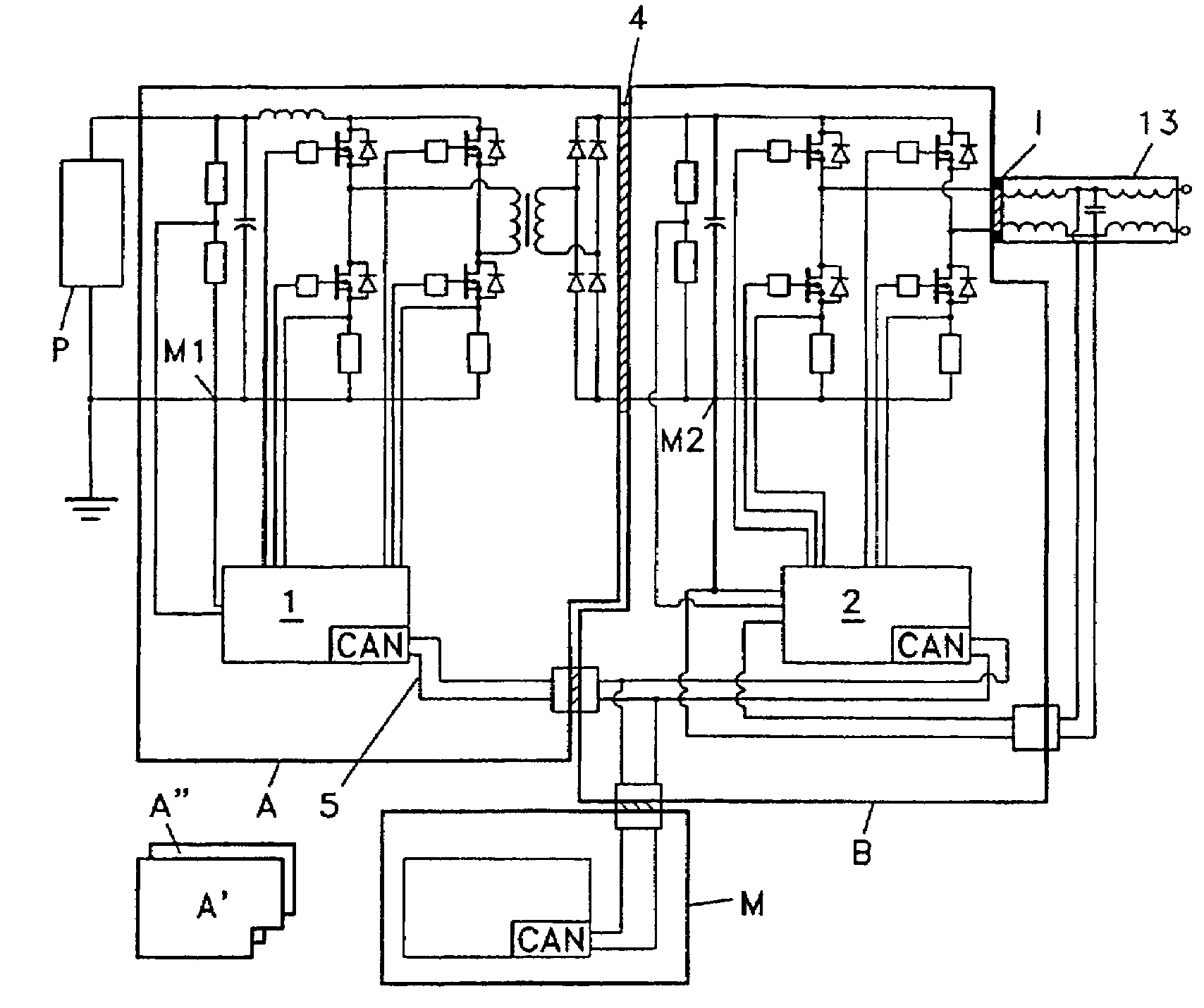
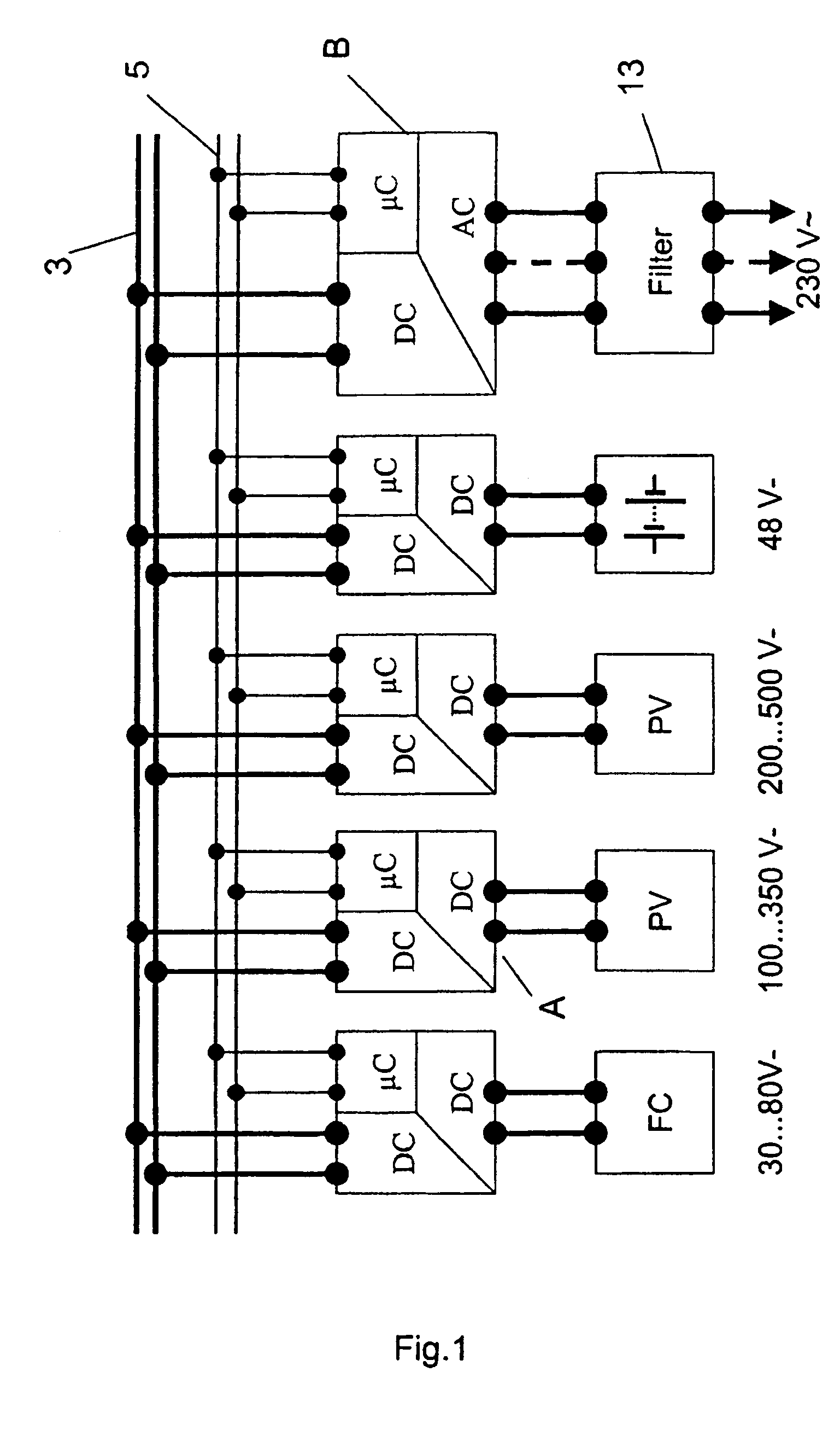
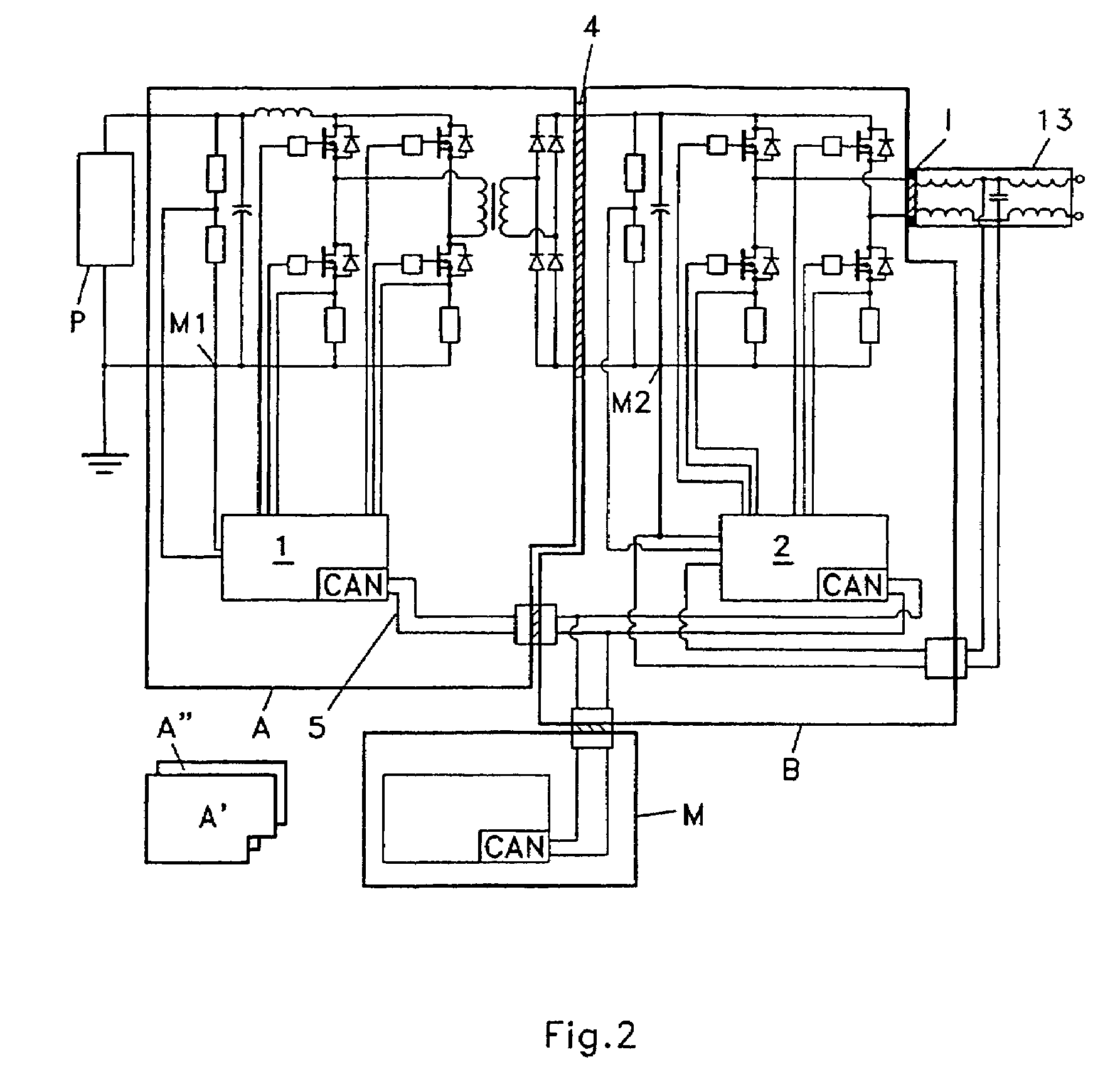
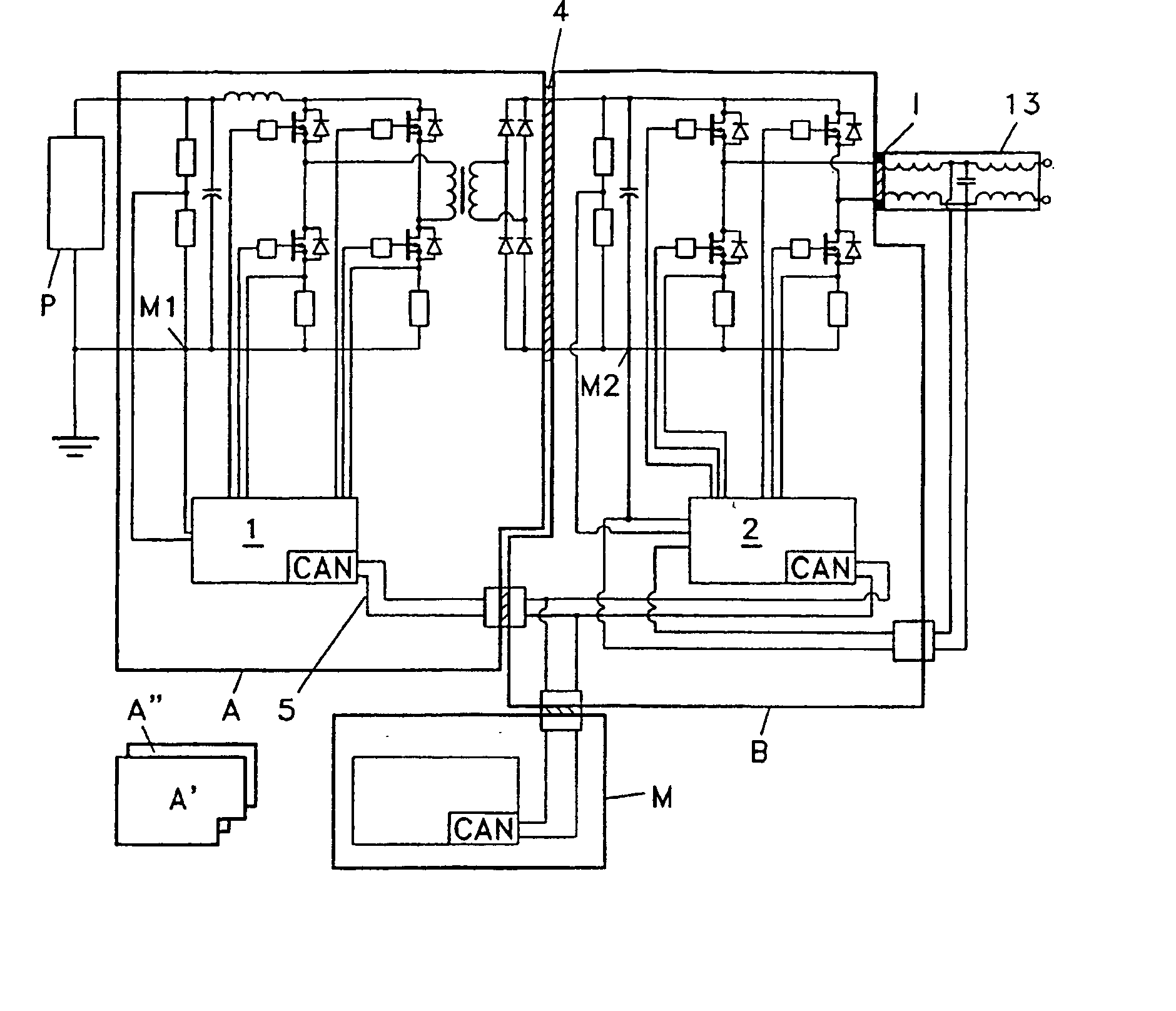
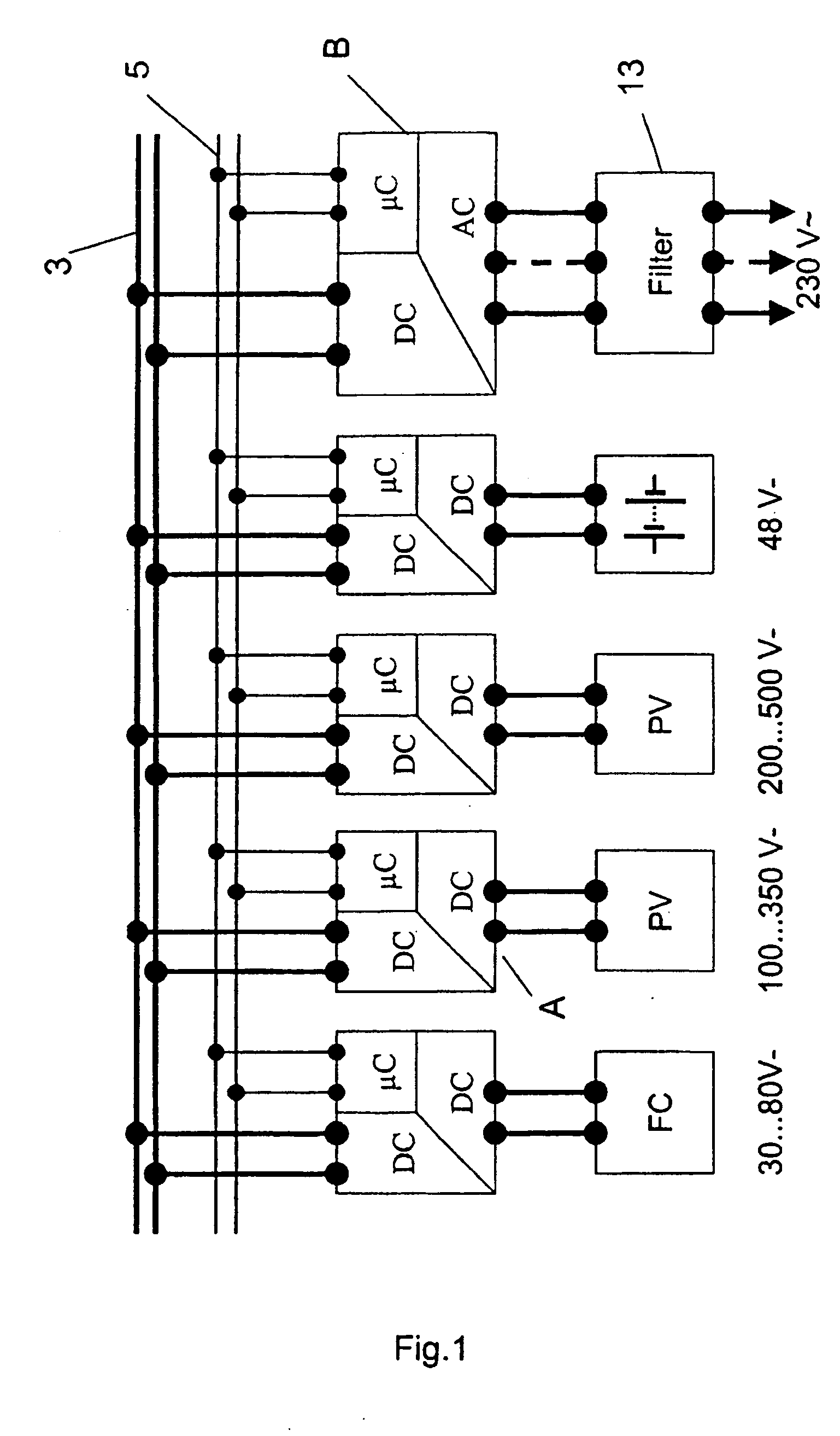
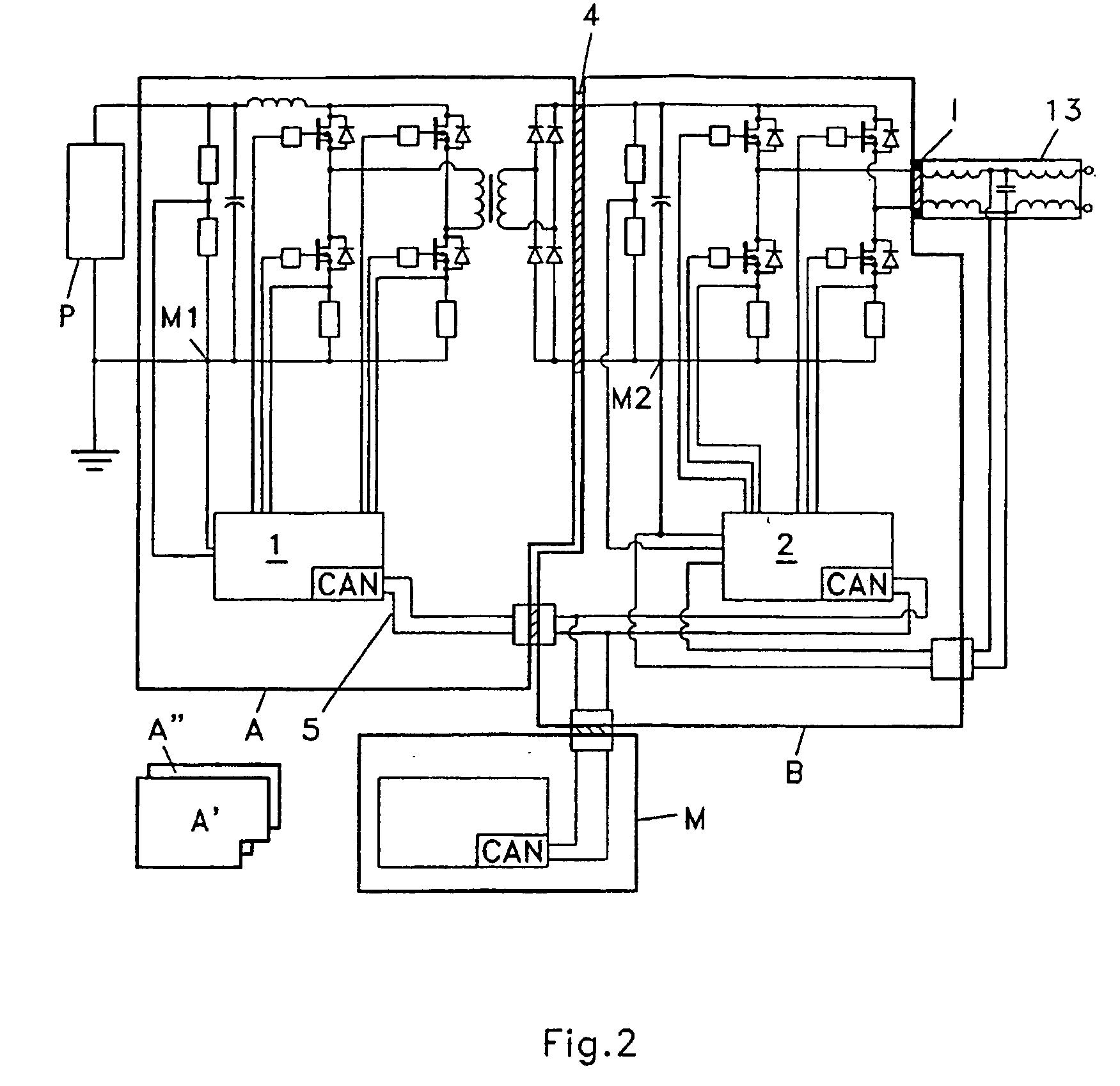
Power converter
ActiveUS7339287B2Easy to controlDc network circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTransformerEngineering
A power converter for converting energy from a green power unit as e.g. a solar cell into energy fed into the commercial grid is described. The object is to provide a versatile modularized power converter with eased access to control of the power switches. Another object is to improve the electrical efficiency. This is achieved by using an independent controller on a DC / DC module and an independent controller on a DC / AC module, whereby the two independent controllers communicate with each other and the outside world by means of a communication bus. Further, the DC / DC module of the power converter comprises a transformer which transfers energy from the DC / DC module to the DC / AC module. This design enables independent control of the modules and eases controllability of the power switches in order to suppress retroaction from pulsations generated on the mains when supplying energy to a single phase grid. Hereby the electrical efficiency of the power converter is increased. Also, an active snubber circuit is described which further increase the efficiency.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Power converter
ActiveUS20050275386A1Reduce Harmonic DistortionSimple processDc network circuit arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsElectric forceElectricity
A power converter for converting energy from a green power unit as e.g. a solar cell into energy fed into the commercial grid is described. The object is to provide a versatile modularized power converter with eased access to control of the power switches. Another object is to improve the electrical efficiency. This is achieved by using an independent controller on a DC / DC module and an independent controller on a DC / AC module, whereby the the two independent controllers communicate with each other and the outside world by means of a communication bus. Further, the DC / DC module of the power converter comprises a transformer which transfers energy from the DC / DC module to the DC / AC module. This design enables independent control of the modules and eases controllability of the power switches in order to suppress retroaction from pulsations generated on the mains when supplying energy to a single phase grid. Hereby the electrical efficiency of the power converter is increased. Also, an active snubber circuit is described which further increase the efficiency.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
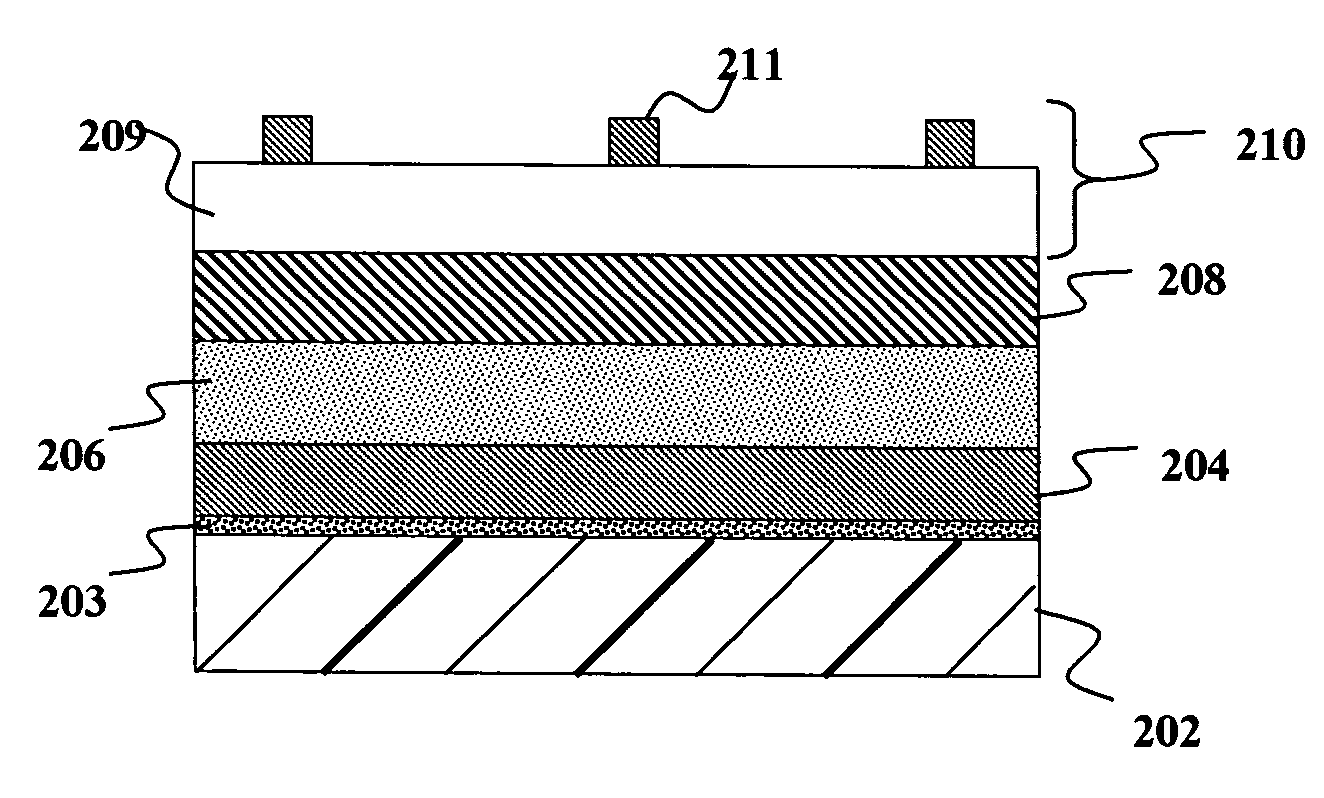
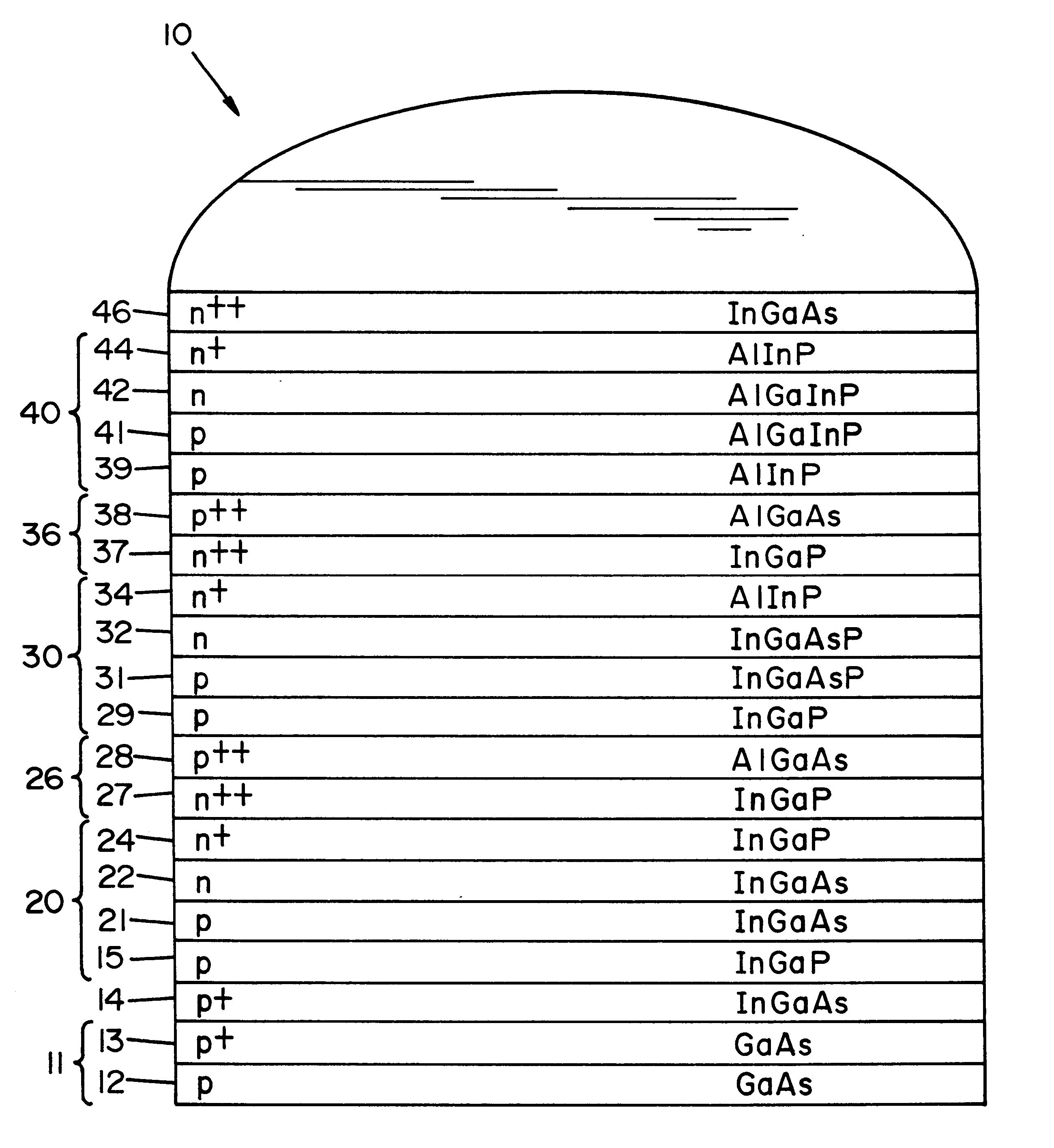
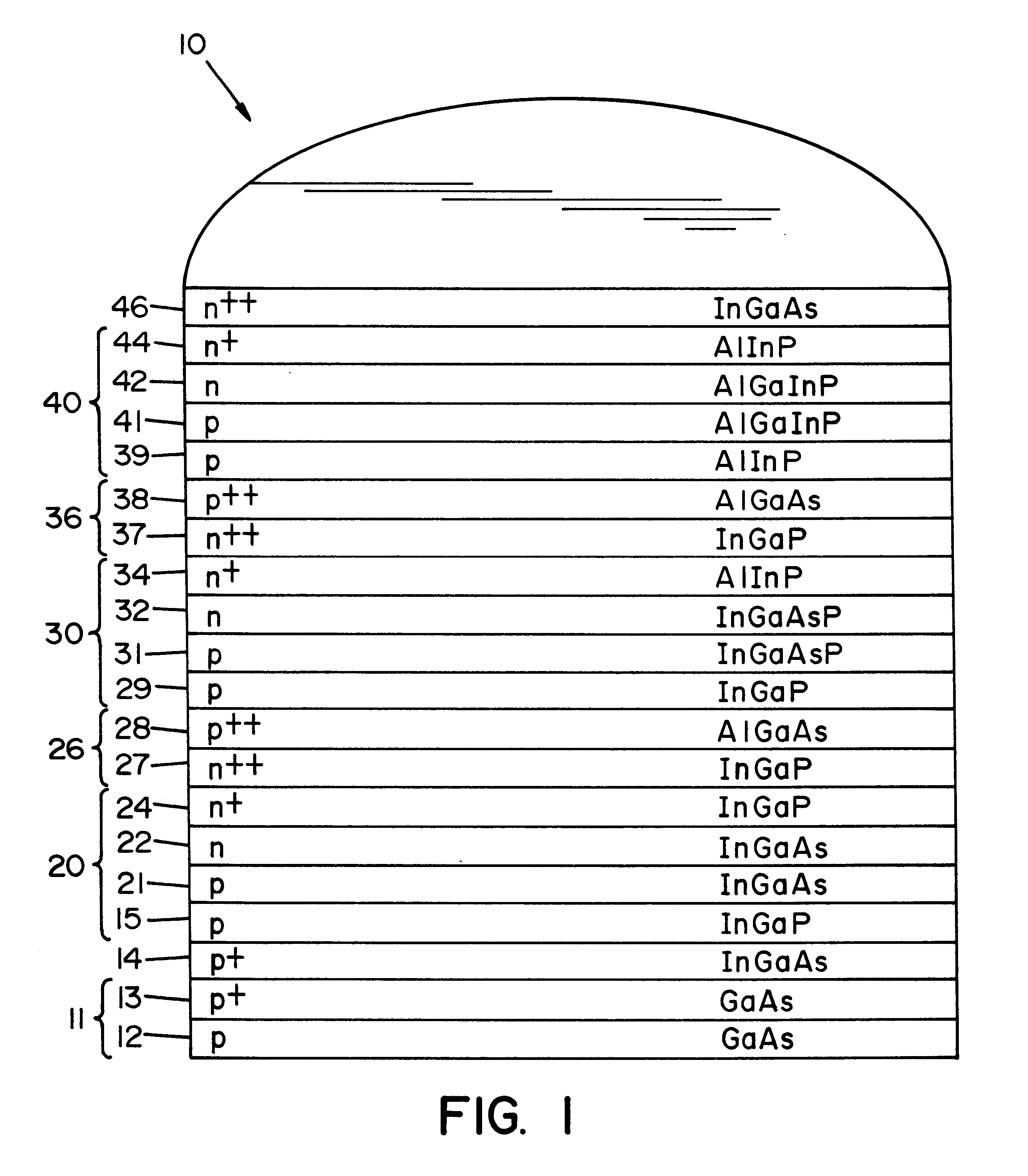
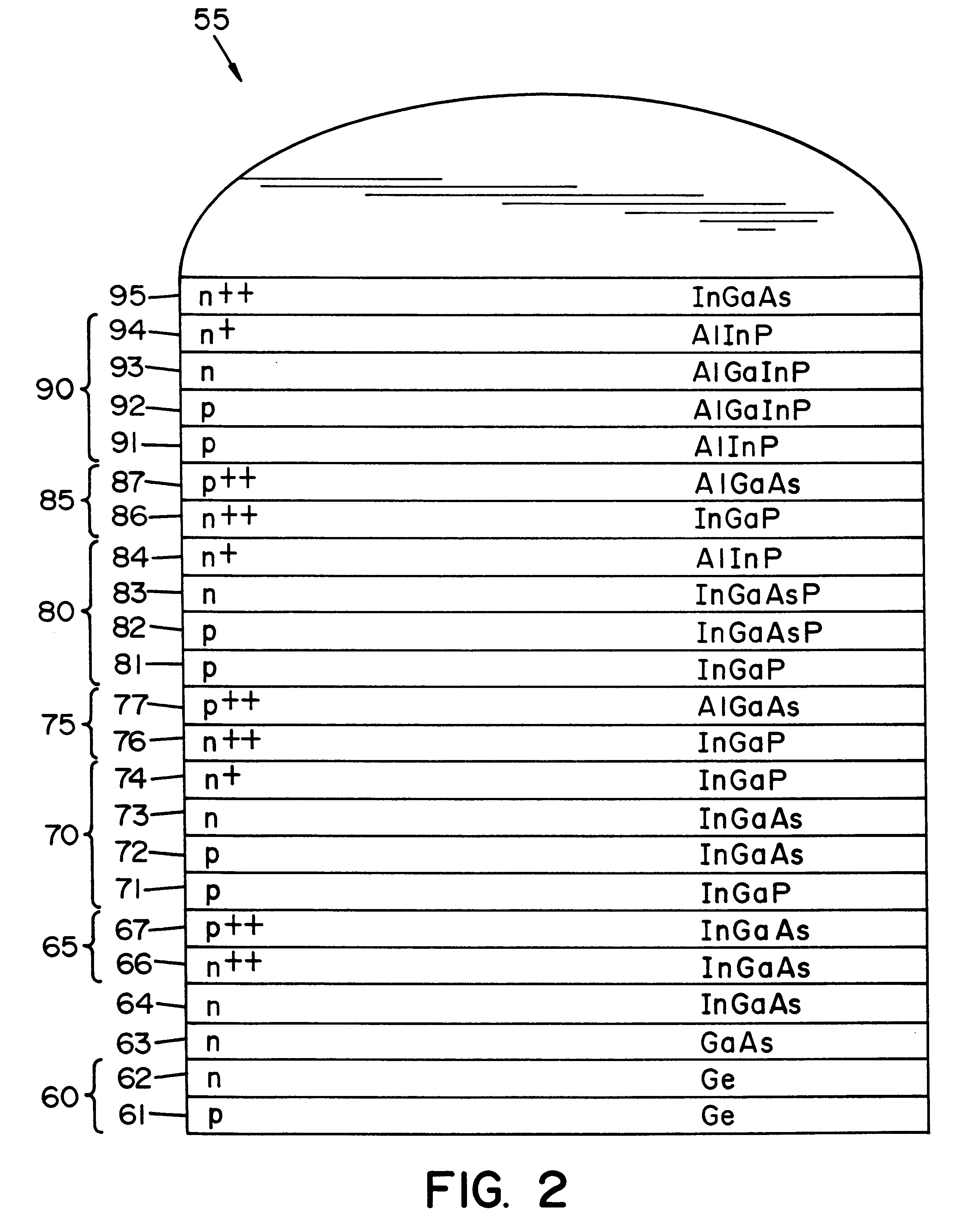
Multi-junction photovoltaic cell
InactiveUS6660928B1Useful radiation hardnessCell efficiency and power densityPV power plantsSolid-state devicesLattice mismatchSolar cell
A solar cell comprising a substrate, a buffer layer, a first subcell, a second subcell, and a third subcell, where said first subcell, said second subcell, and said third subcell are lattice matched, and where said substrate is lattice mismatched with said first, second, and third subcells.
Owner:ESSENTIAL RES
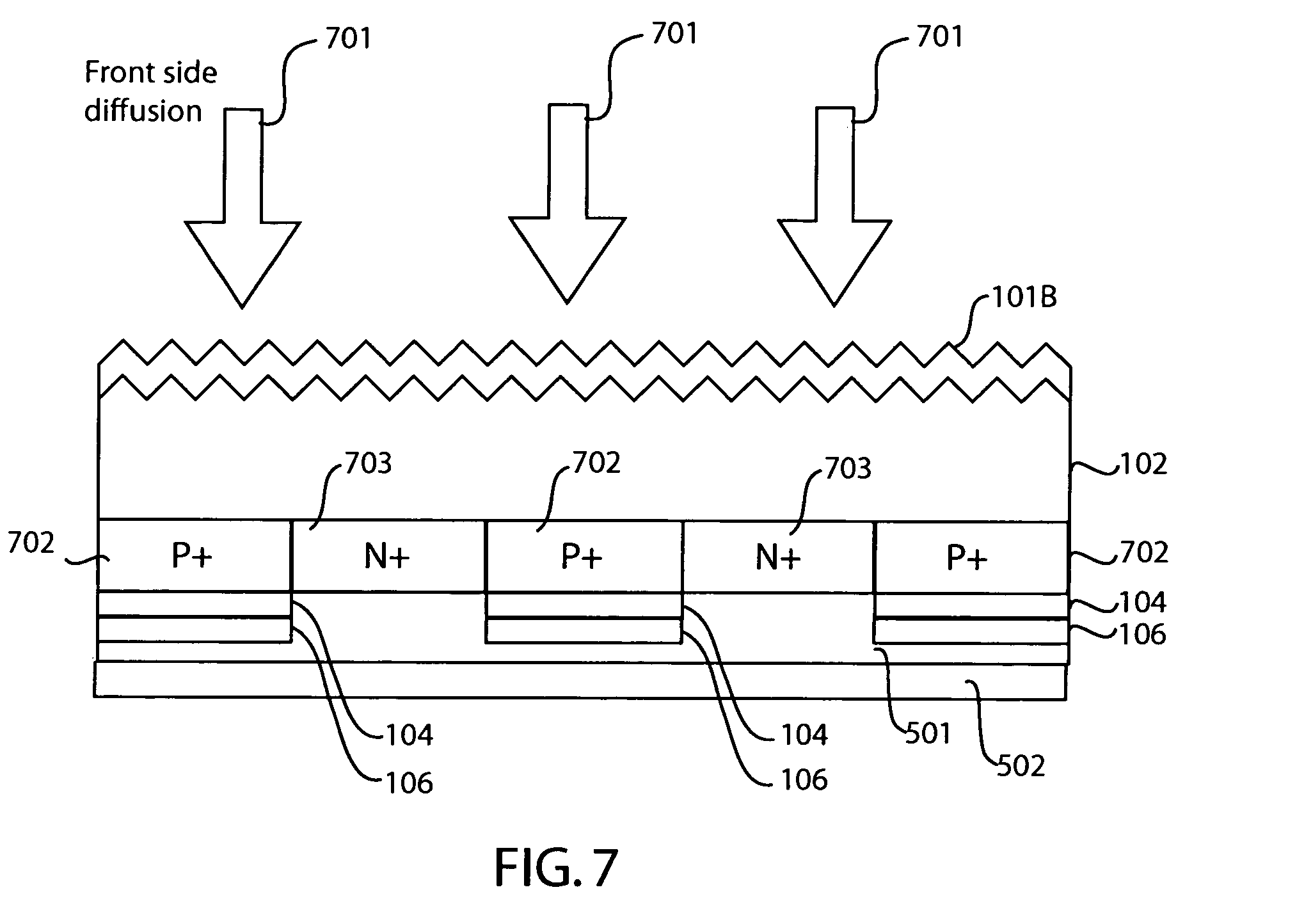
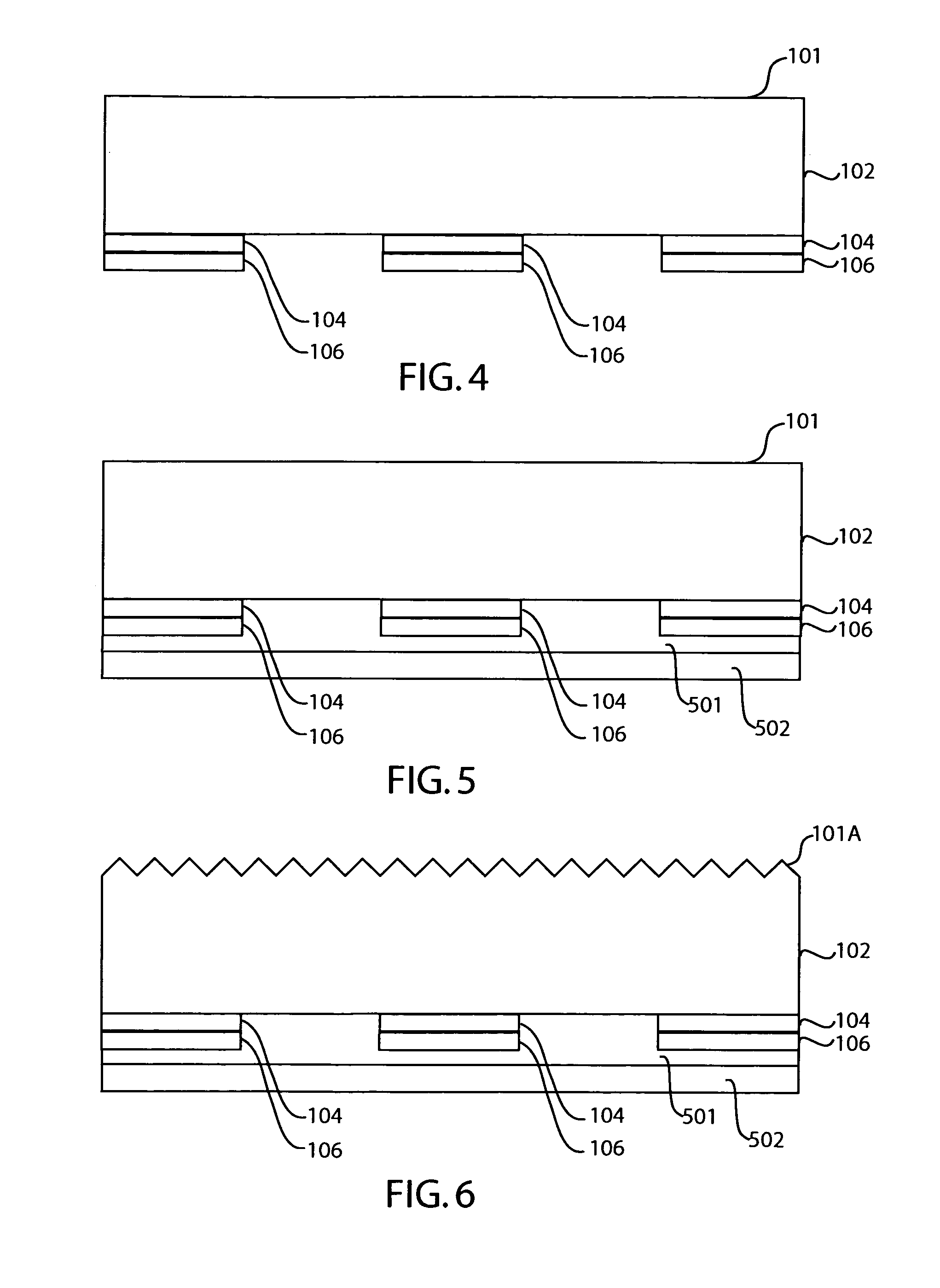
Use of doped silicon dioxide in the fabrication of solar cells
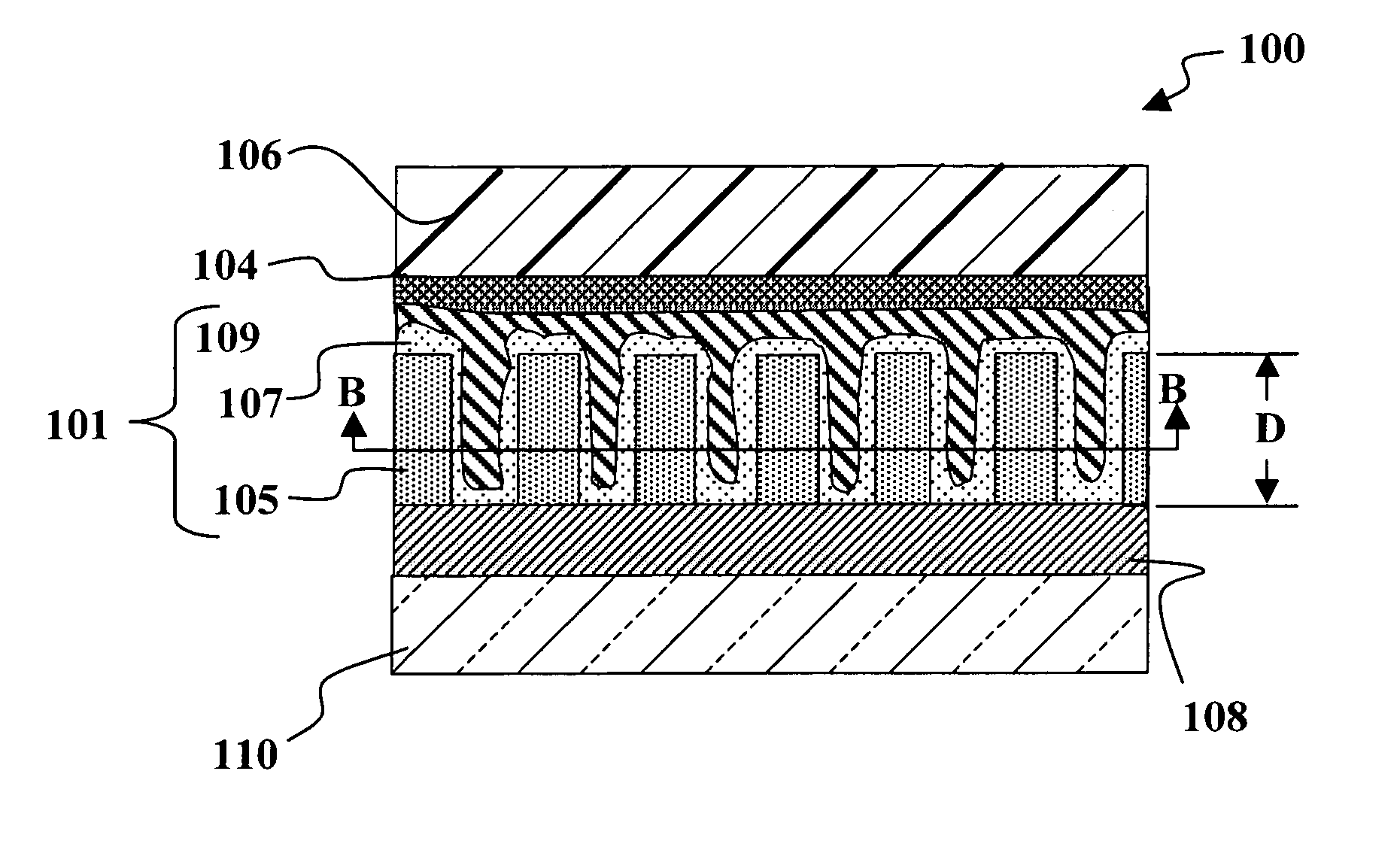
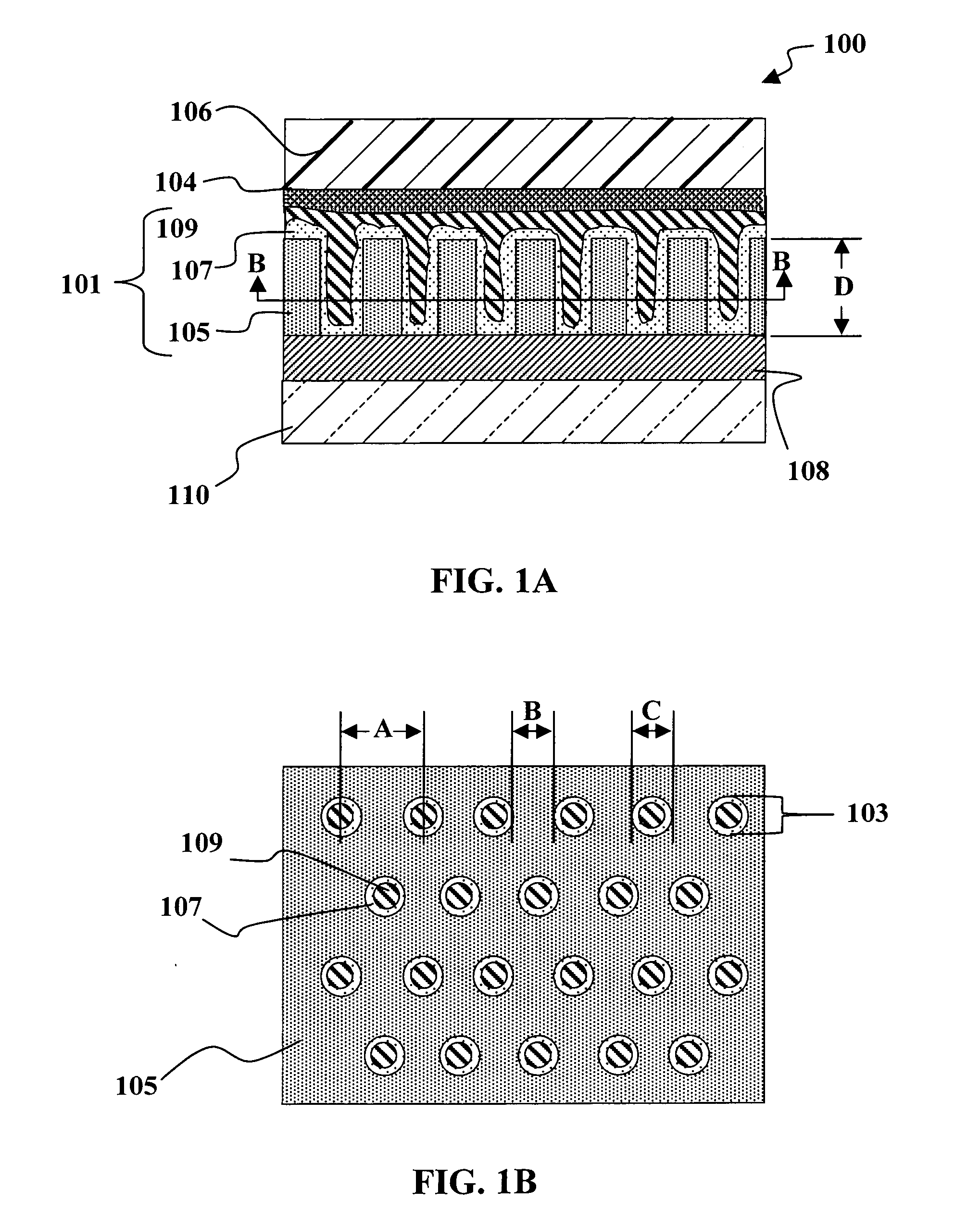
In one embodiment, a method of forming doped regions in a substrate of a back side contact solar cell includes the steps of depositing a first doped oxide layer on a back side of a substrate, depositing a first undoped oxide layer over the first doped oxide layer, diffusing a first dopant from the first doped oxide layer into the substrate to form a first doped region in the substrate, and diffusing a second dopant into the substrate by way of a front side of the substrate, wherein the diffusion of the first dopant and the second dopant into the substrate are performed in-situ. The method may further include the steps of patterning the first doped and undoped oxide layers to expose portions of the back side of the substrate and depositing a second doped and undoped oxide layers on the back side of the substrate.
Owner:MAXEON SOLAR PTE LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com