Patents
Literature
2105 results about "Boost converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
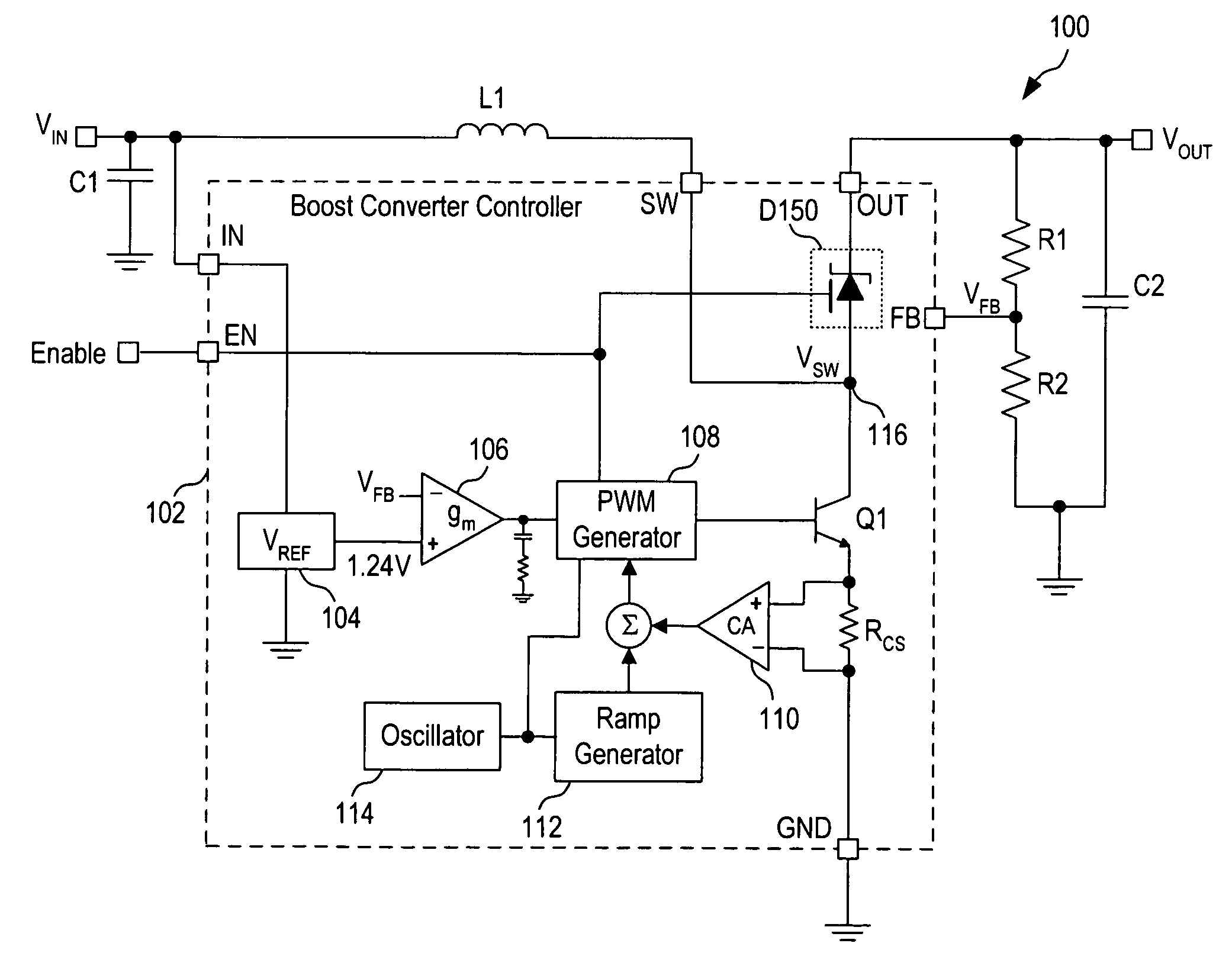
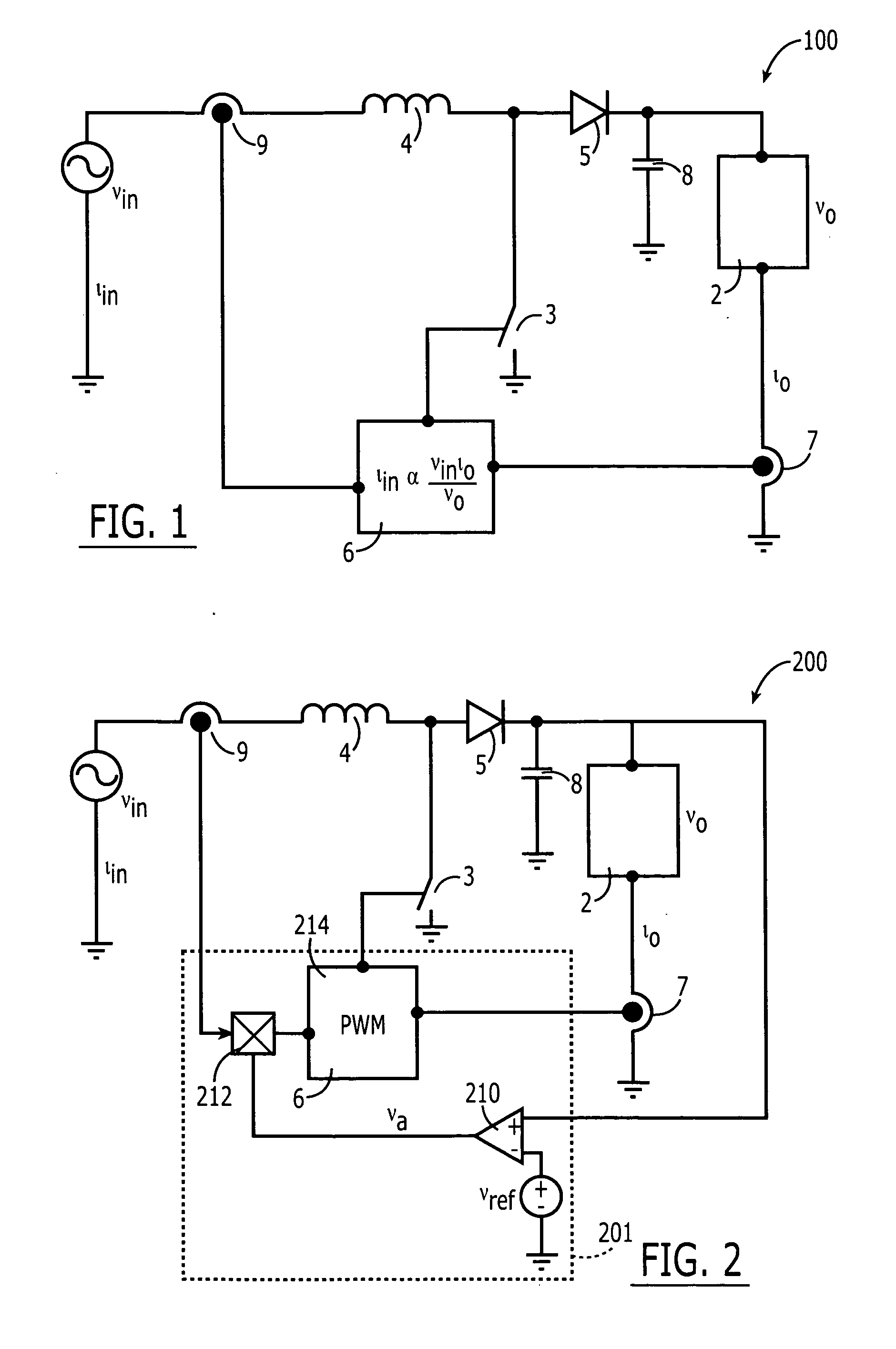
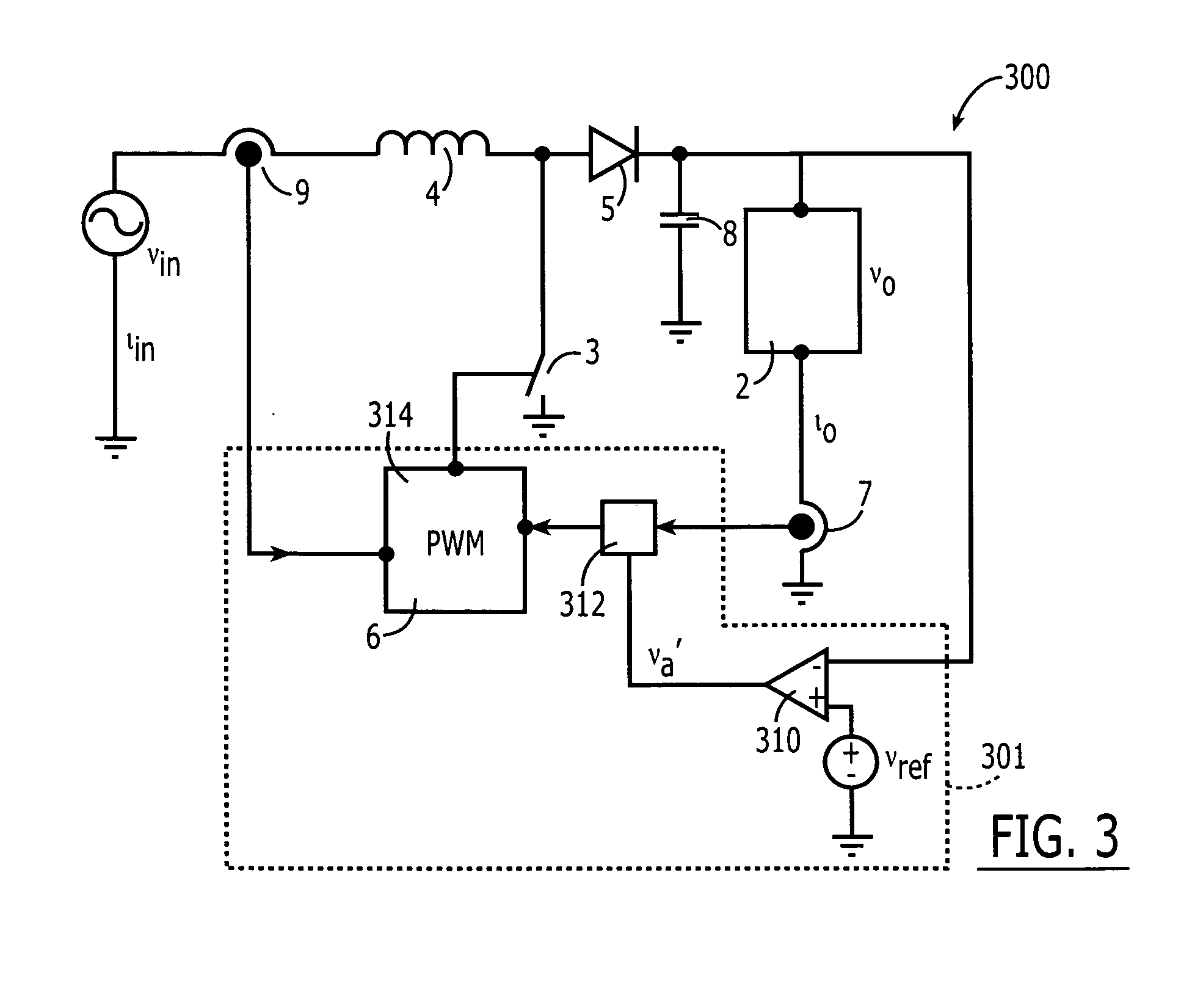
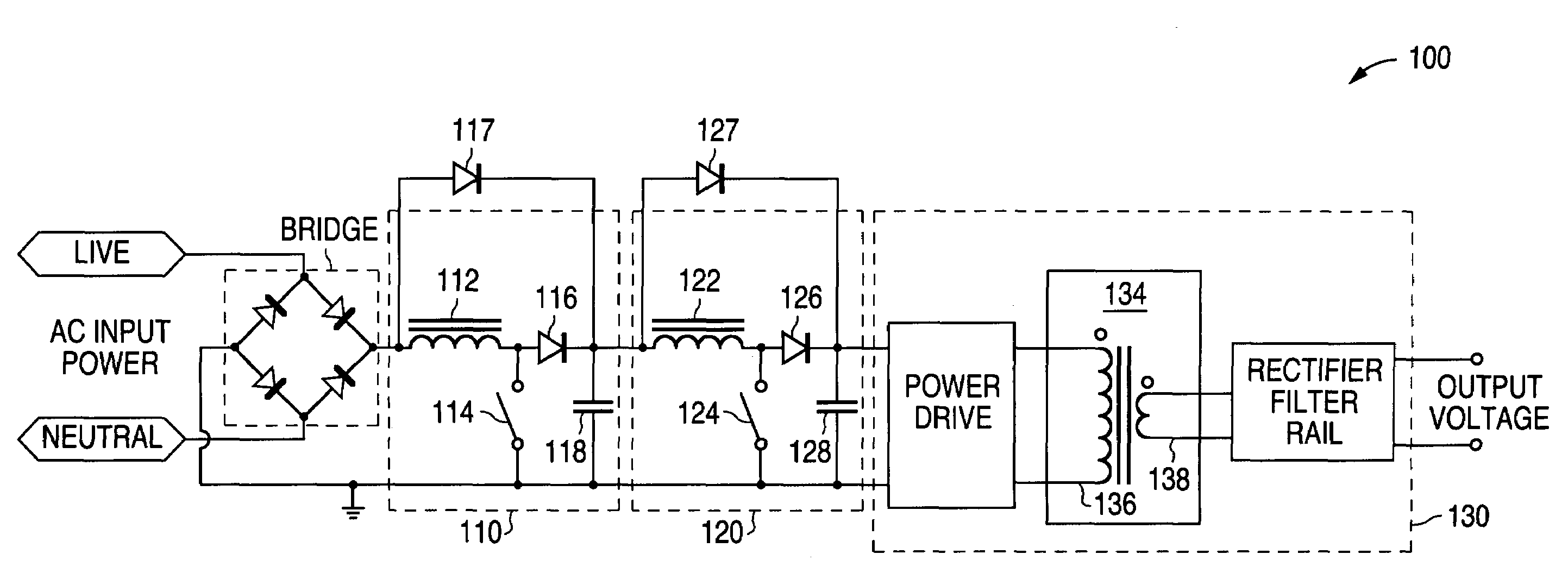
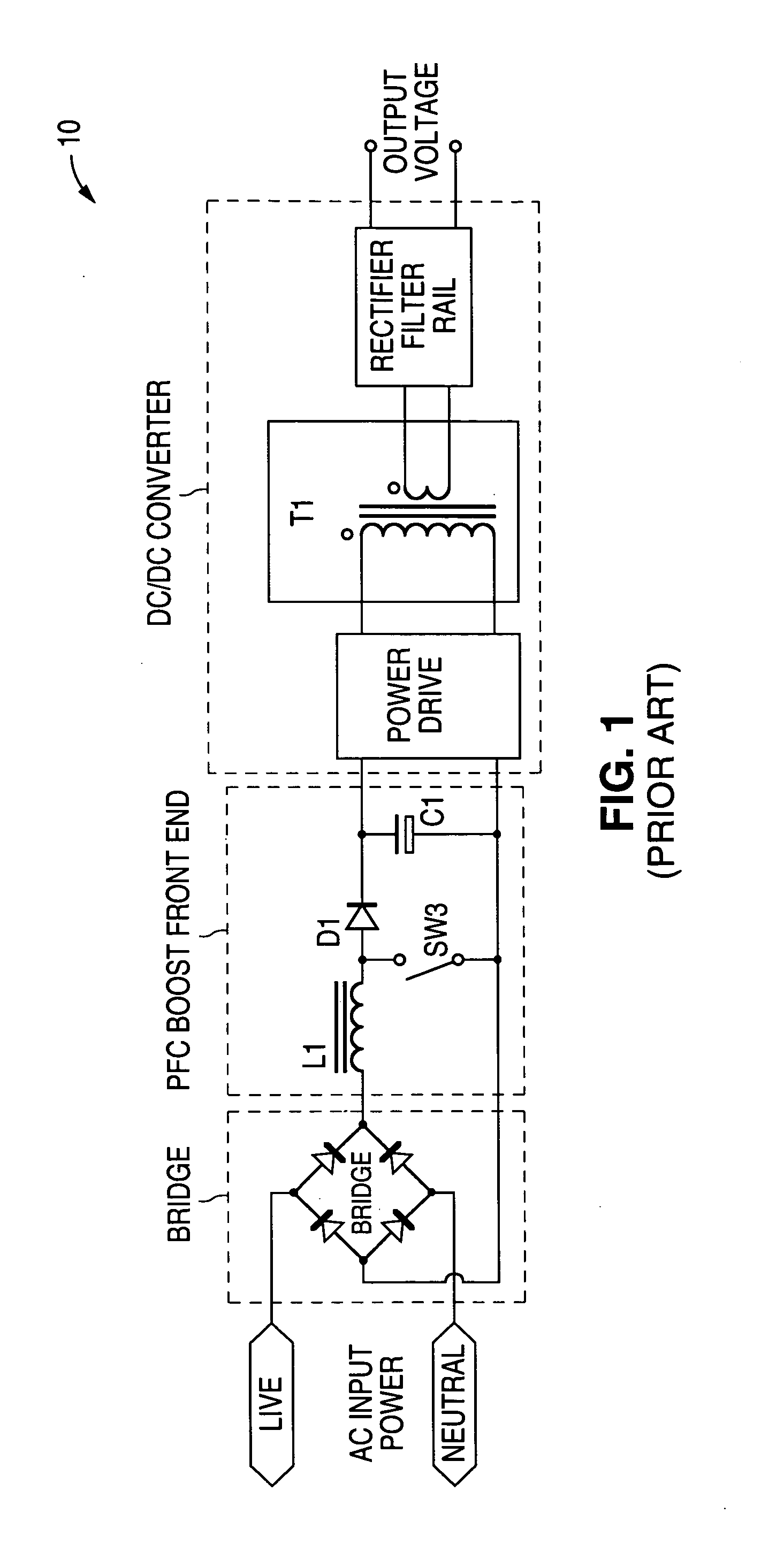
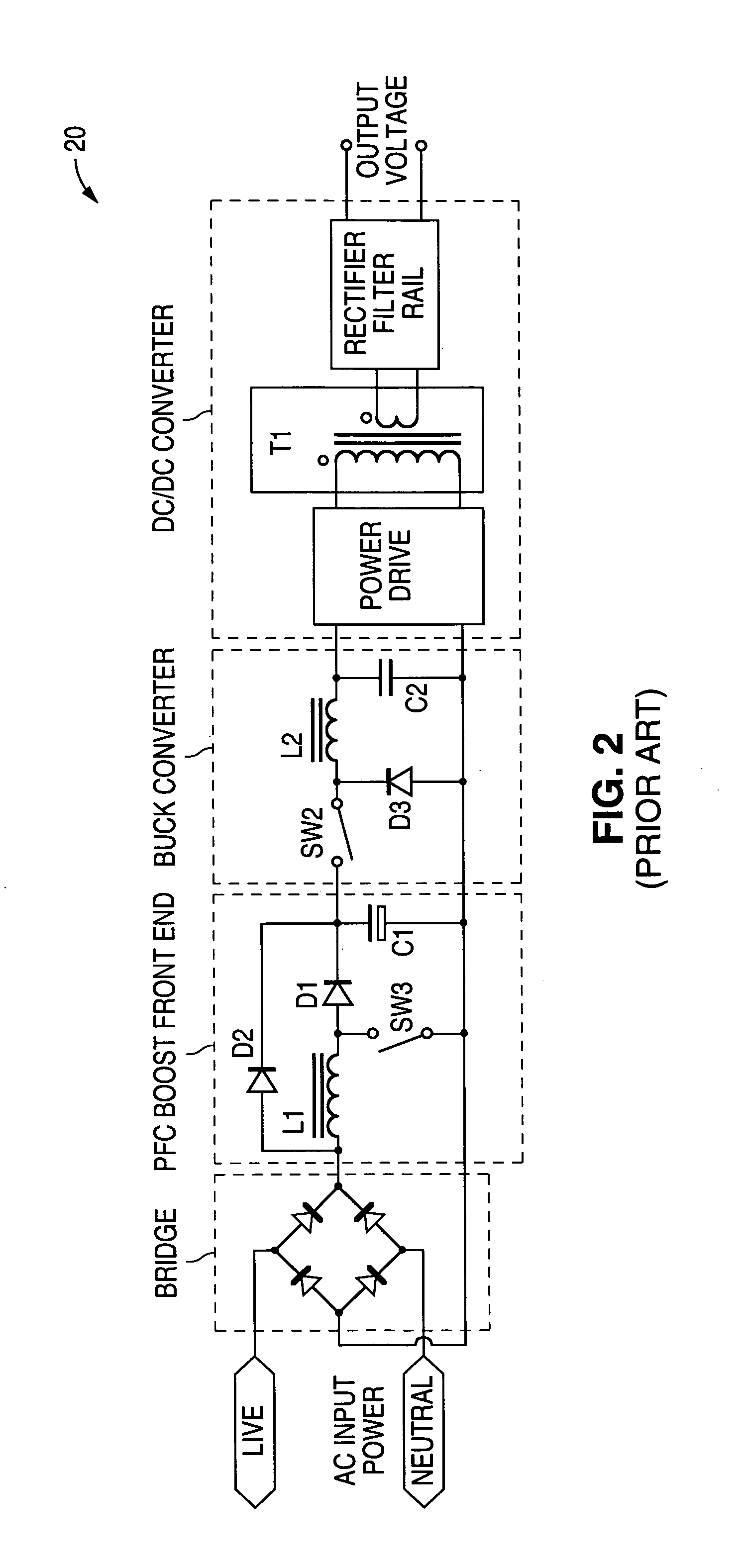
A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage (while stepping down current) from its input (supply) to its output (load). It is a class of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor) and at least one energy storage element: a capacitor, inductor, or the two in combination. To reduce voltage ripple, filters made of capacitors (sometimes in combination with inductors) are normally added to such a converter's output (load-side filter) and input (supply-side filter).
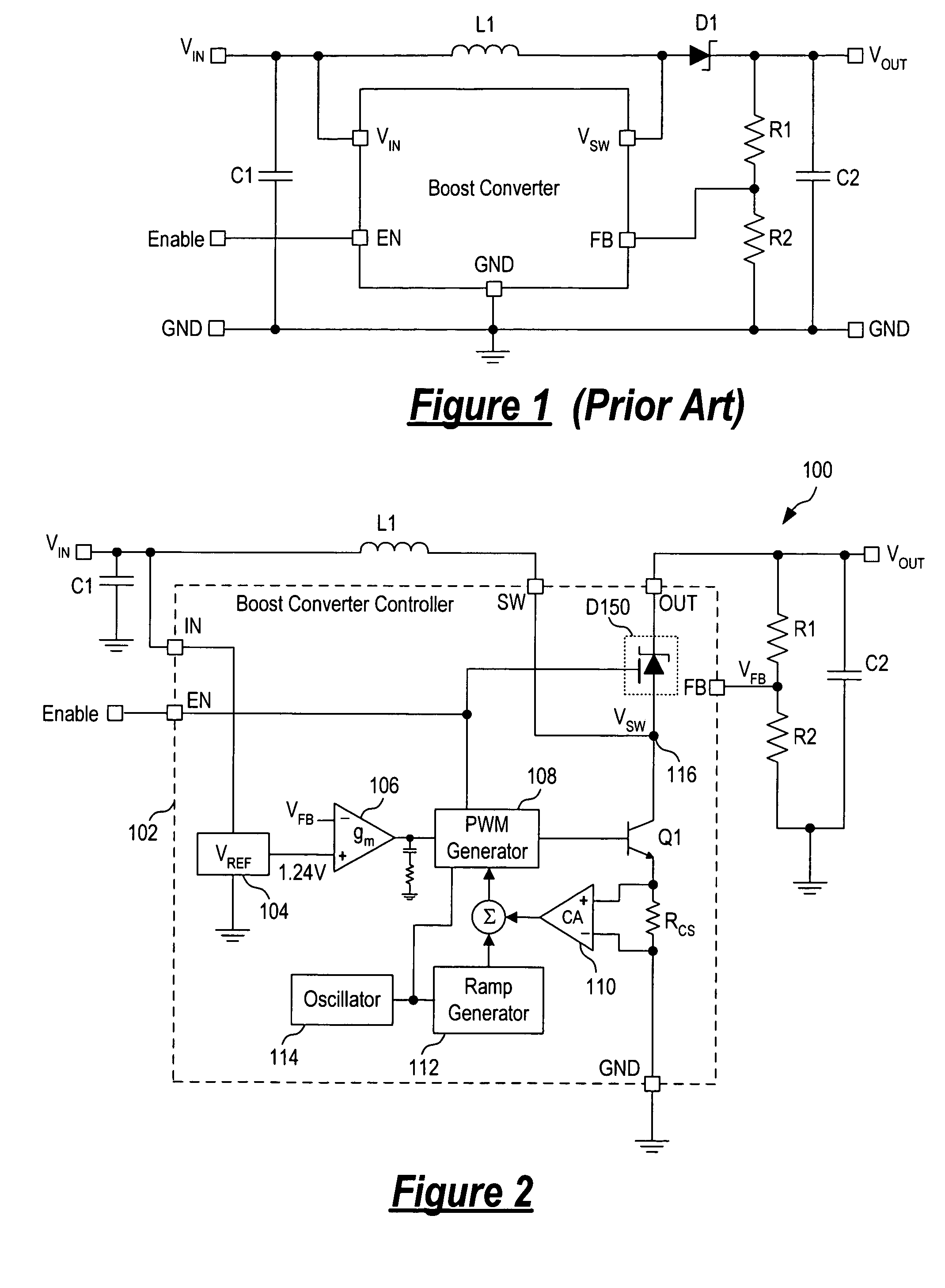
High efficiency power converter
InactiveUS7202653B2Improve efficiencyInhibit currentDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionLinear regulatorReverse current
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Multi-mode renewable power converter system
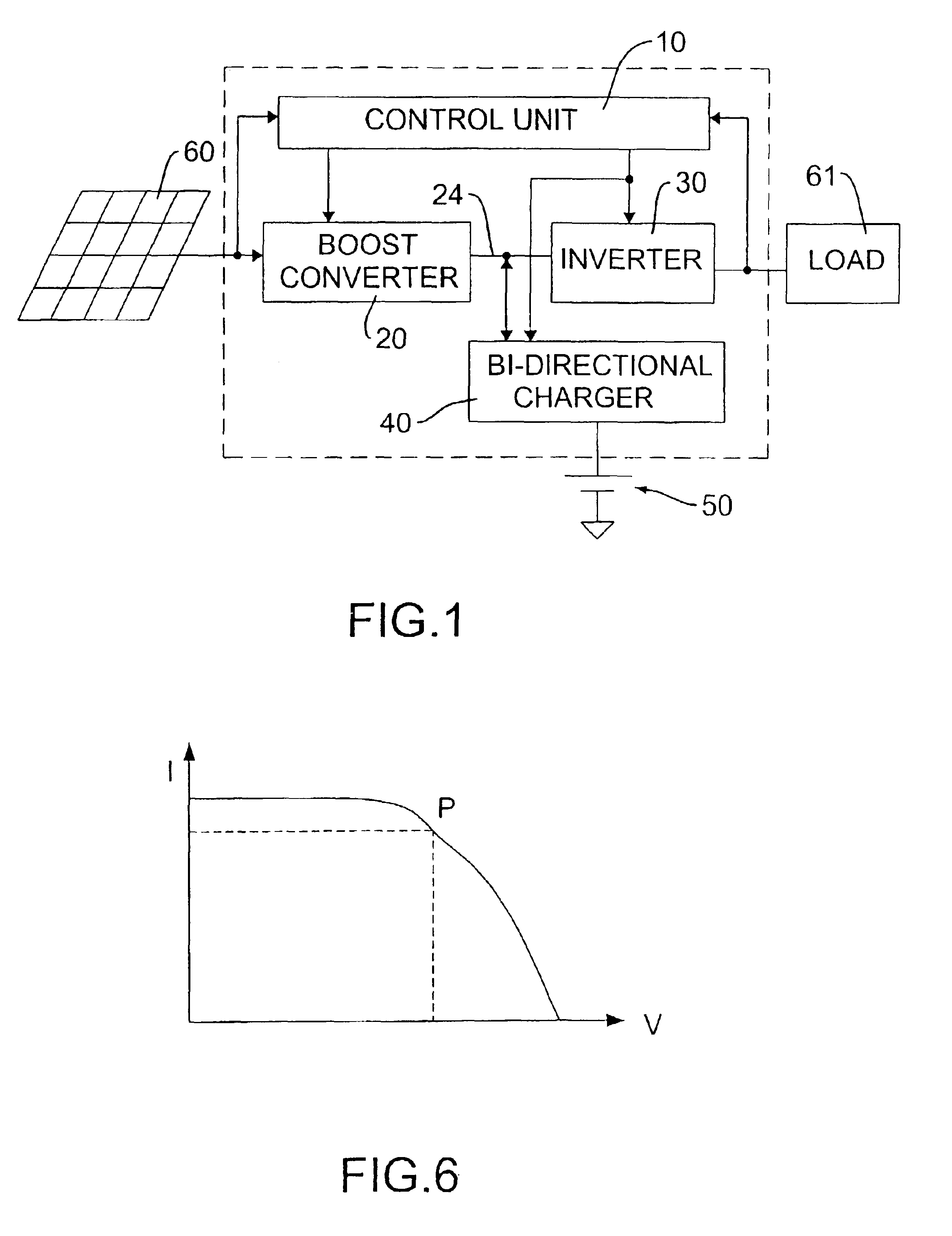
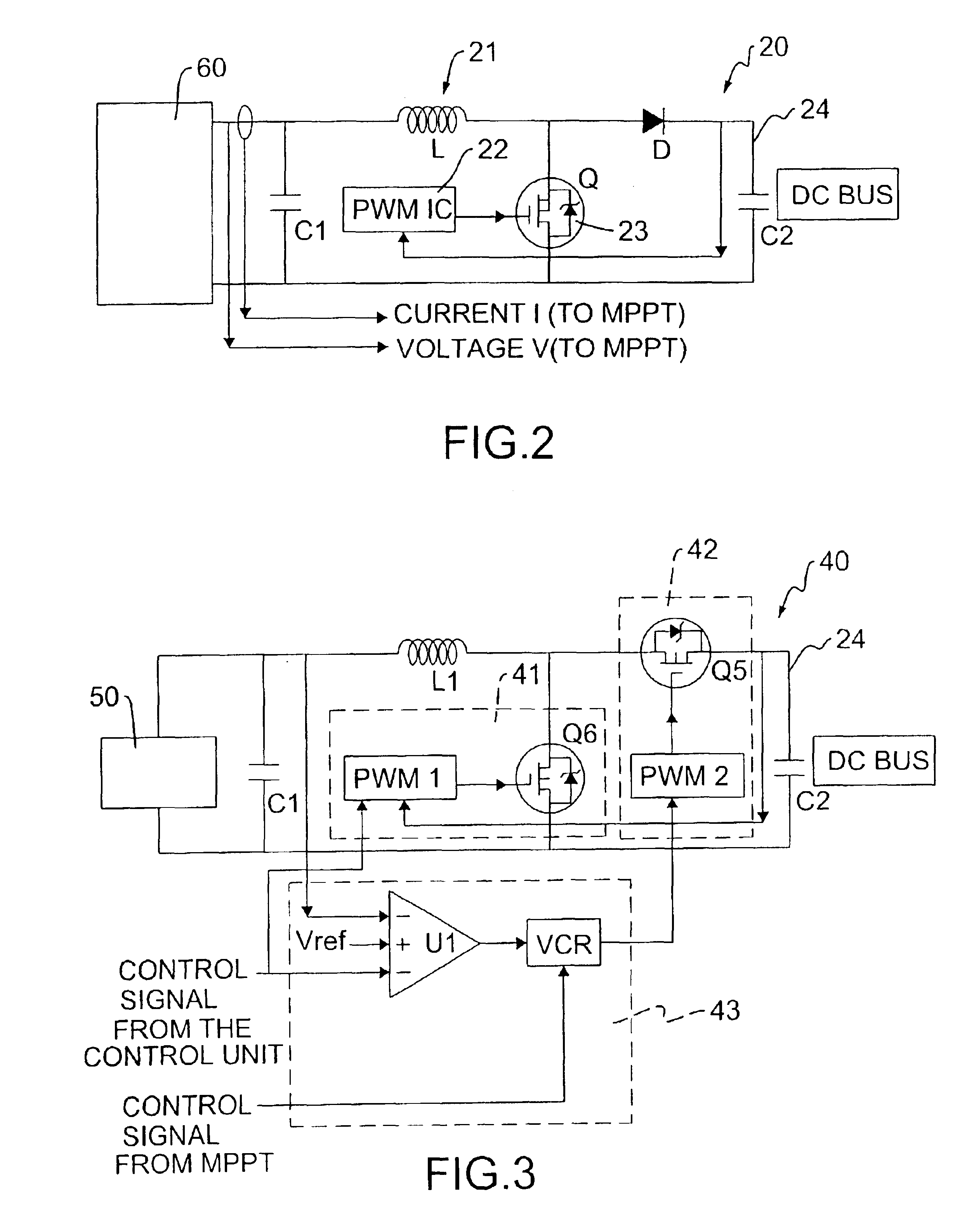
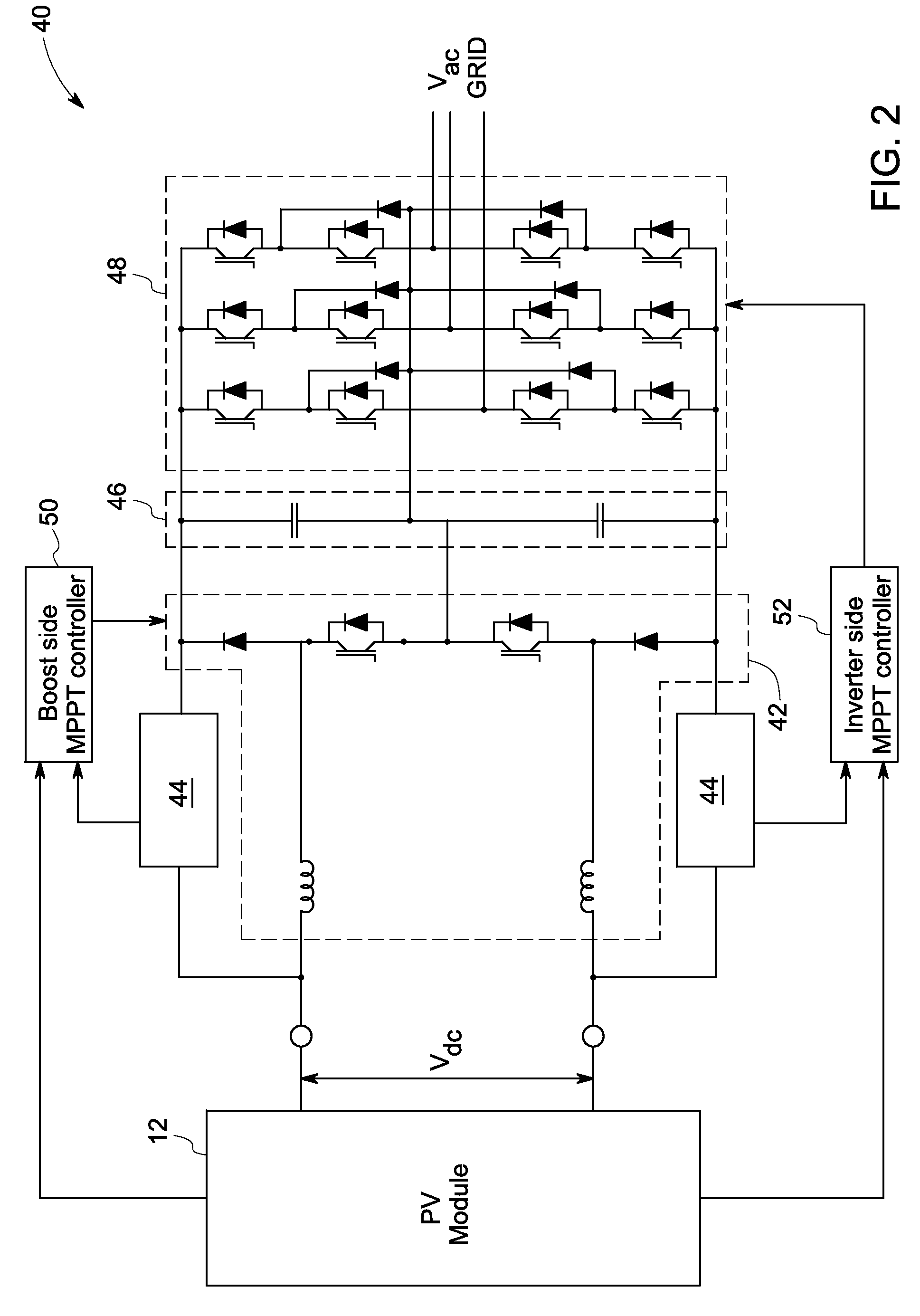
A multi-mode renewable power converter system is disclosed. The system includes a control unit, a boost converter, an inverter and optional bi-directional charger, wherein the boost converter converts DC output of a solar cell or a renewable source to high DC bus voltage, and the inverter converts this DC bus voltage to an AC output. This power converter can be used to support standalone load or grid-connected system with a dynamic maximum power point tracking (MPPT) circuit. The MPPT circuit detects the current and voltage from the solar cell and indicates to the inverter to provide power to the load connected. When the optional bi-directional charger is installed, the MPPT signal is also fed to this charger to make the power efficiency maximized for the system.
Owner:PHOENIXTEC POWER
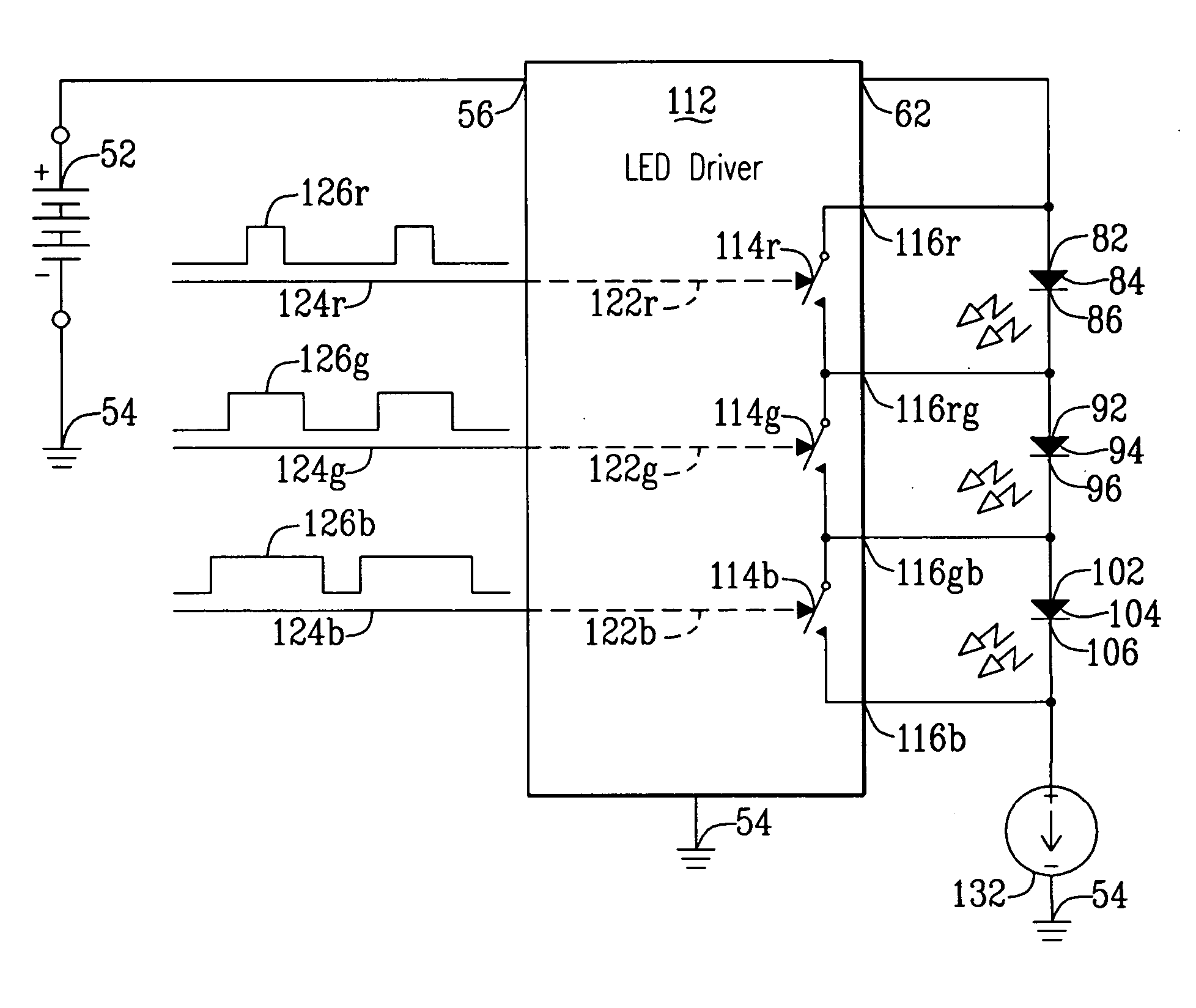
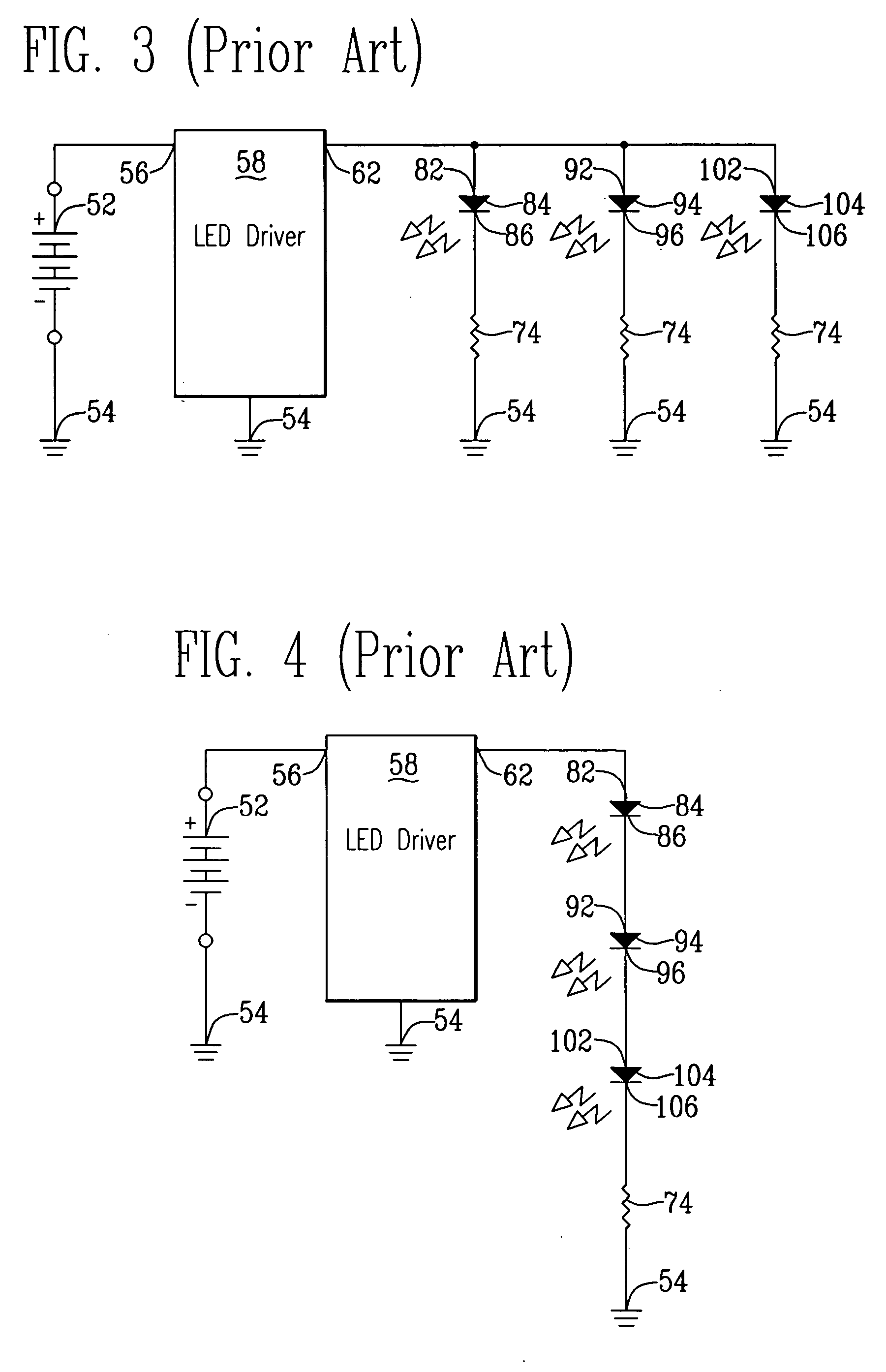
Method and IC driver for series connected R, G, B LEDs
ActiveUS20050243022A1Minimal costAccurate powerElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesBoost converterCurrent generator
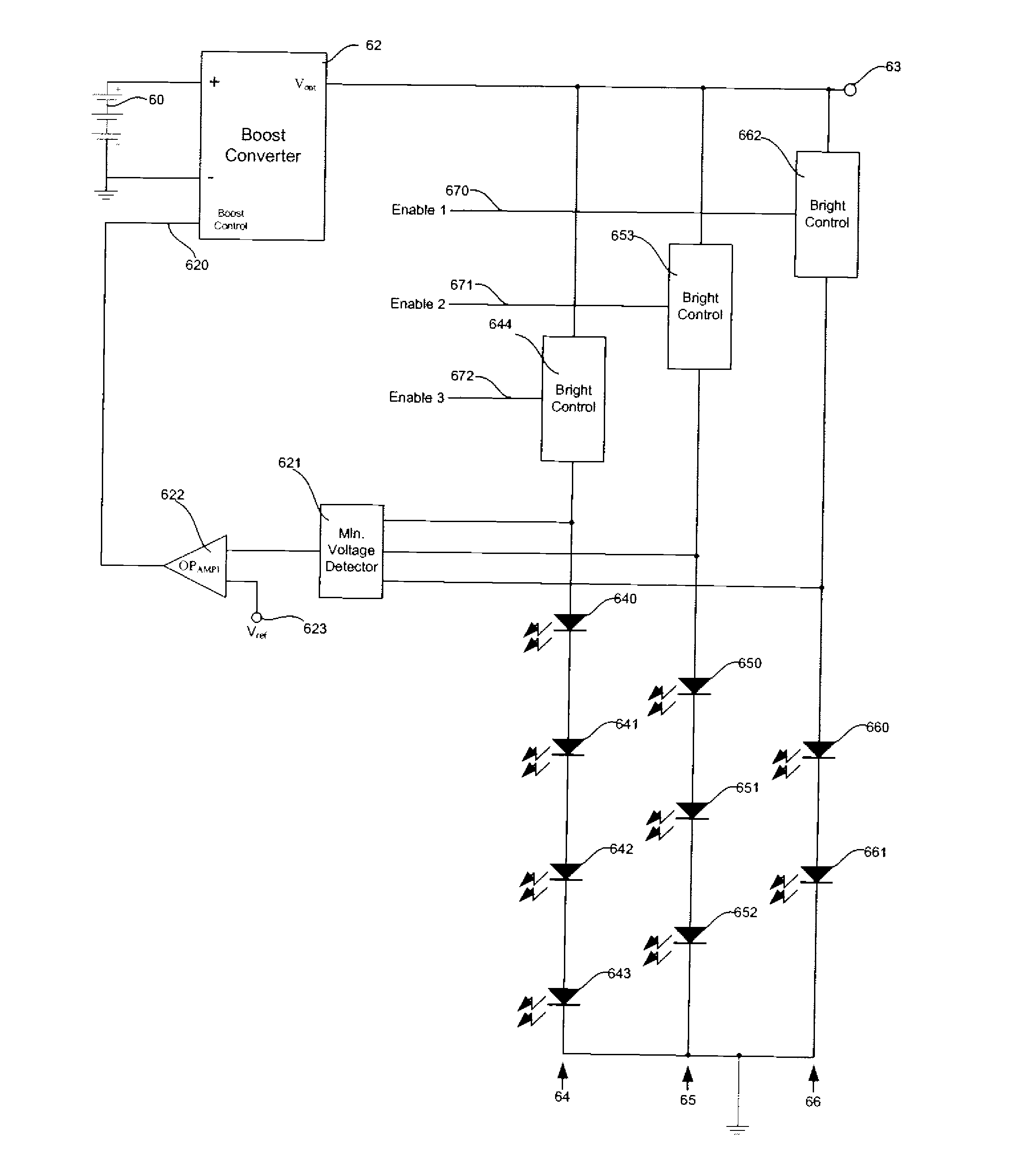
A LED driver is connectible to several series connected RGB LEDs which connect in series with a current generator. A plurality of LED switches are respectively connectible across one RGB LED. Each LED switch, operating in response to a binary signal is either open to permit electrical current to flow through the RGB LED, or closed to shunt current around that RGB LED. By varying respective duty cycles of the binary signals the LED driver is adapted for controlling operation of the combined RGB LEDs so they emit differing colors of light. An adaptive boost converter LED driver continuously adjusts voltage applied across the series connected RGB LEDs to be only that required for operating those LEDs through which open LED switches permit current to flow.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
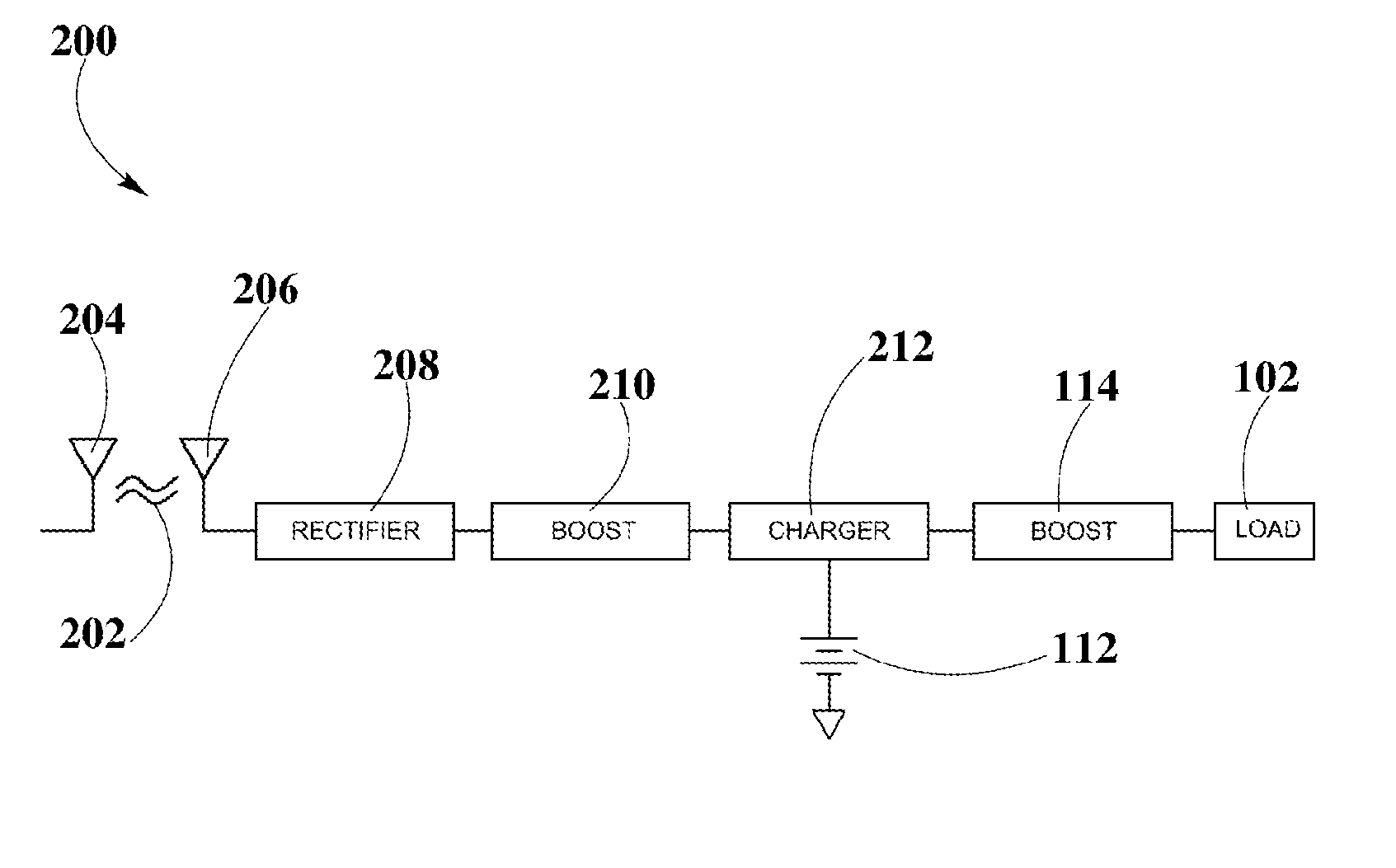
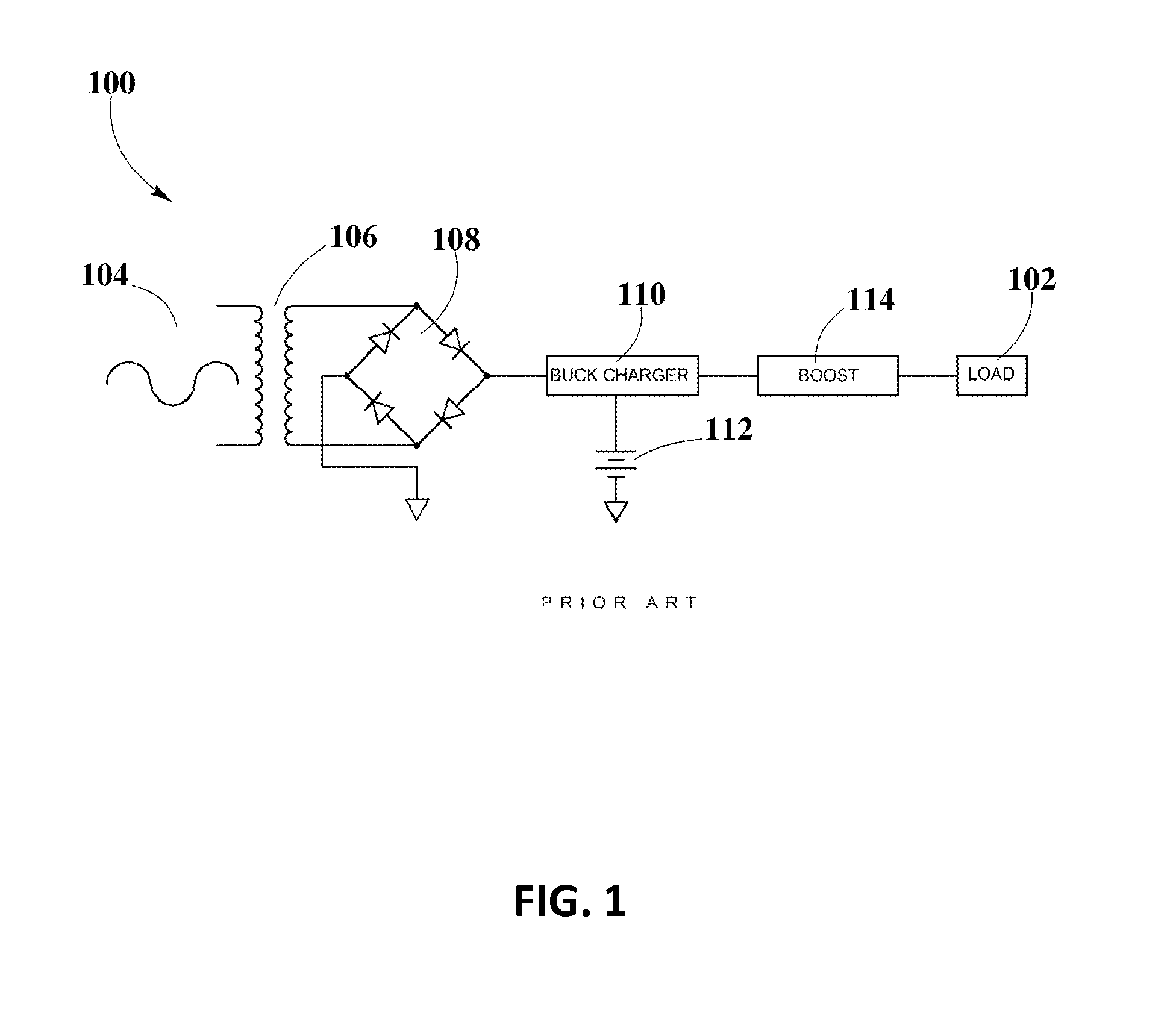
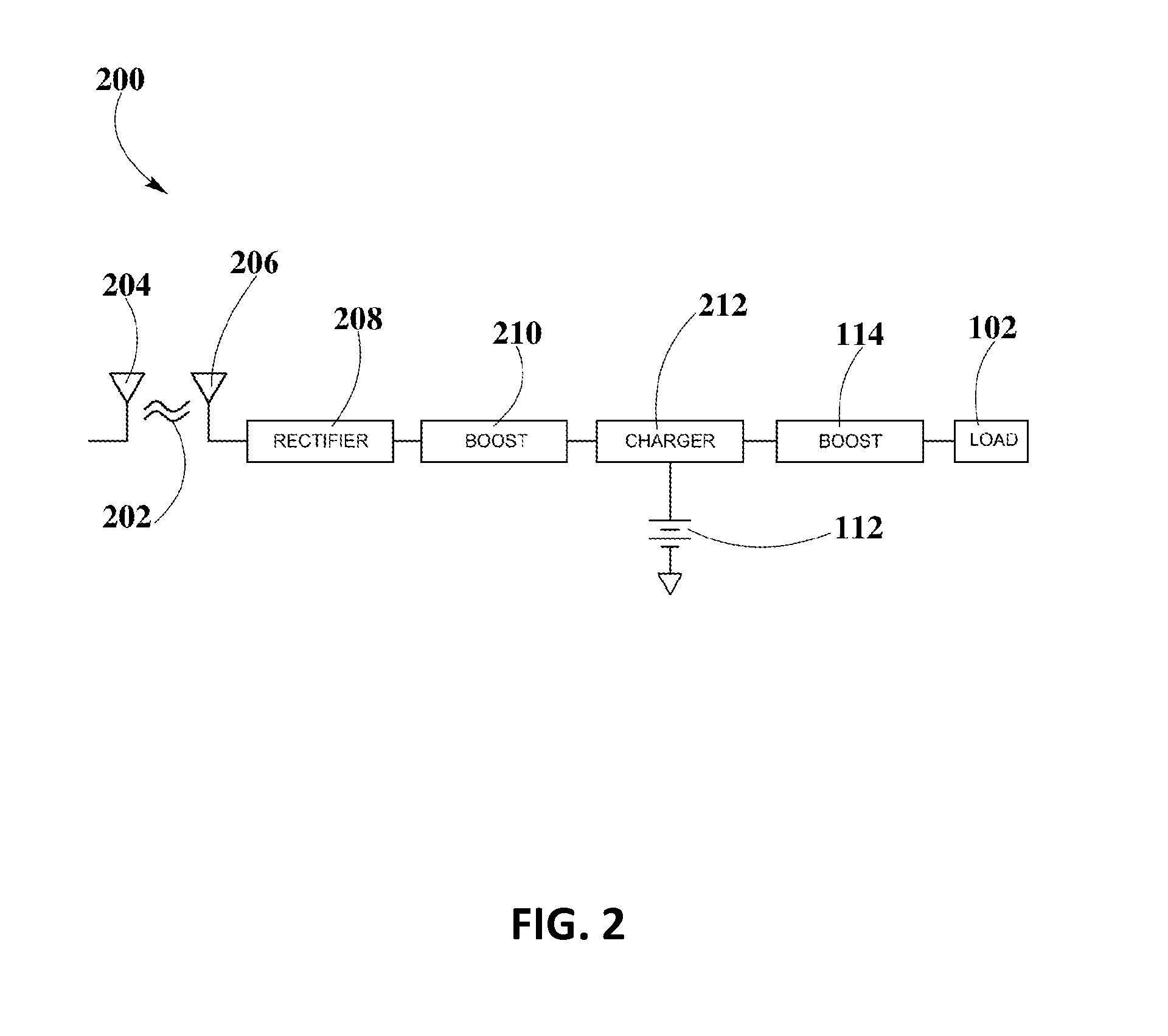
Boost-Charger-Boost System for Enhanced Power Delivery
InactiveUS20150326072A1Dc network circuit arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsElectric power transmissionEngineering
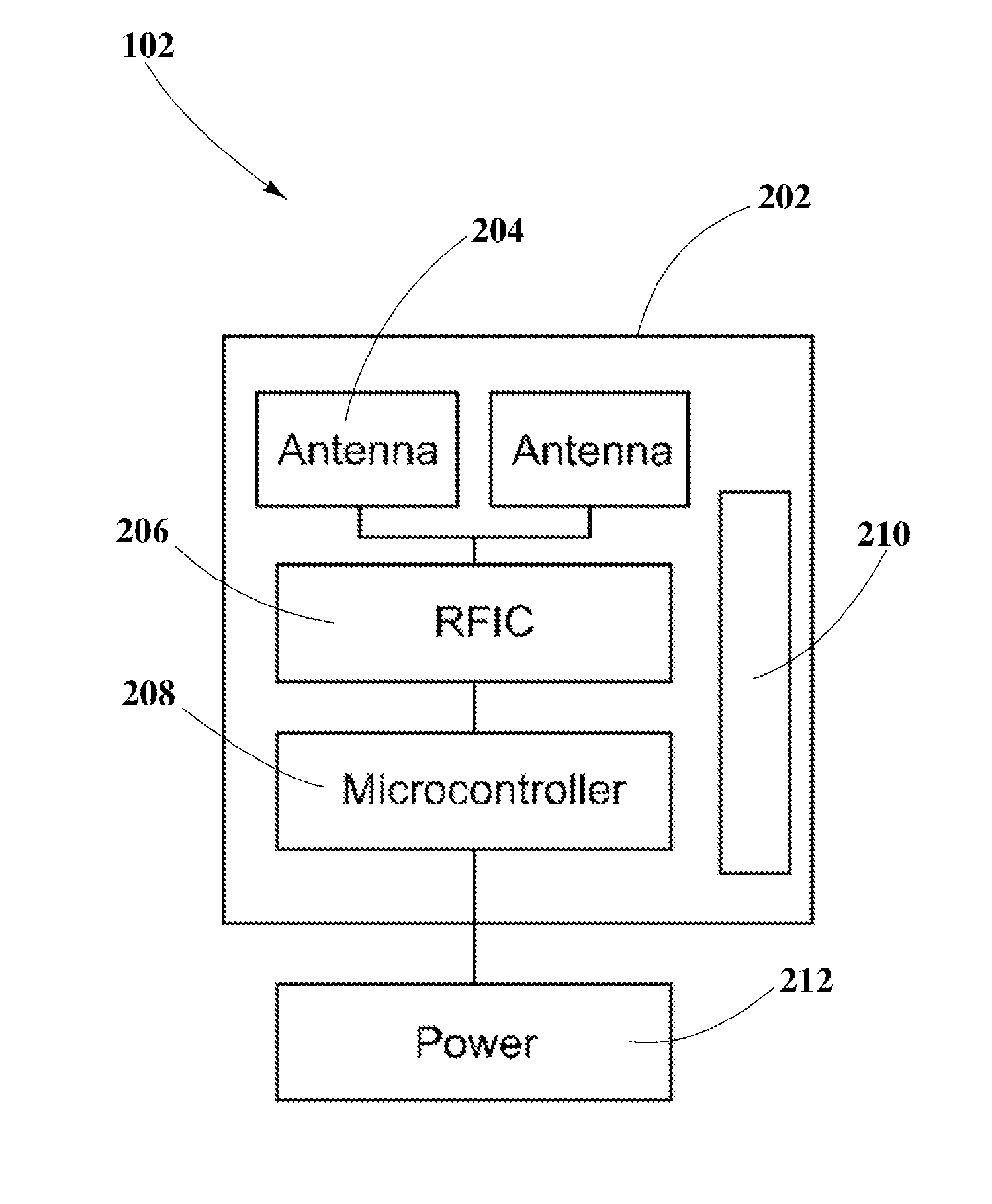
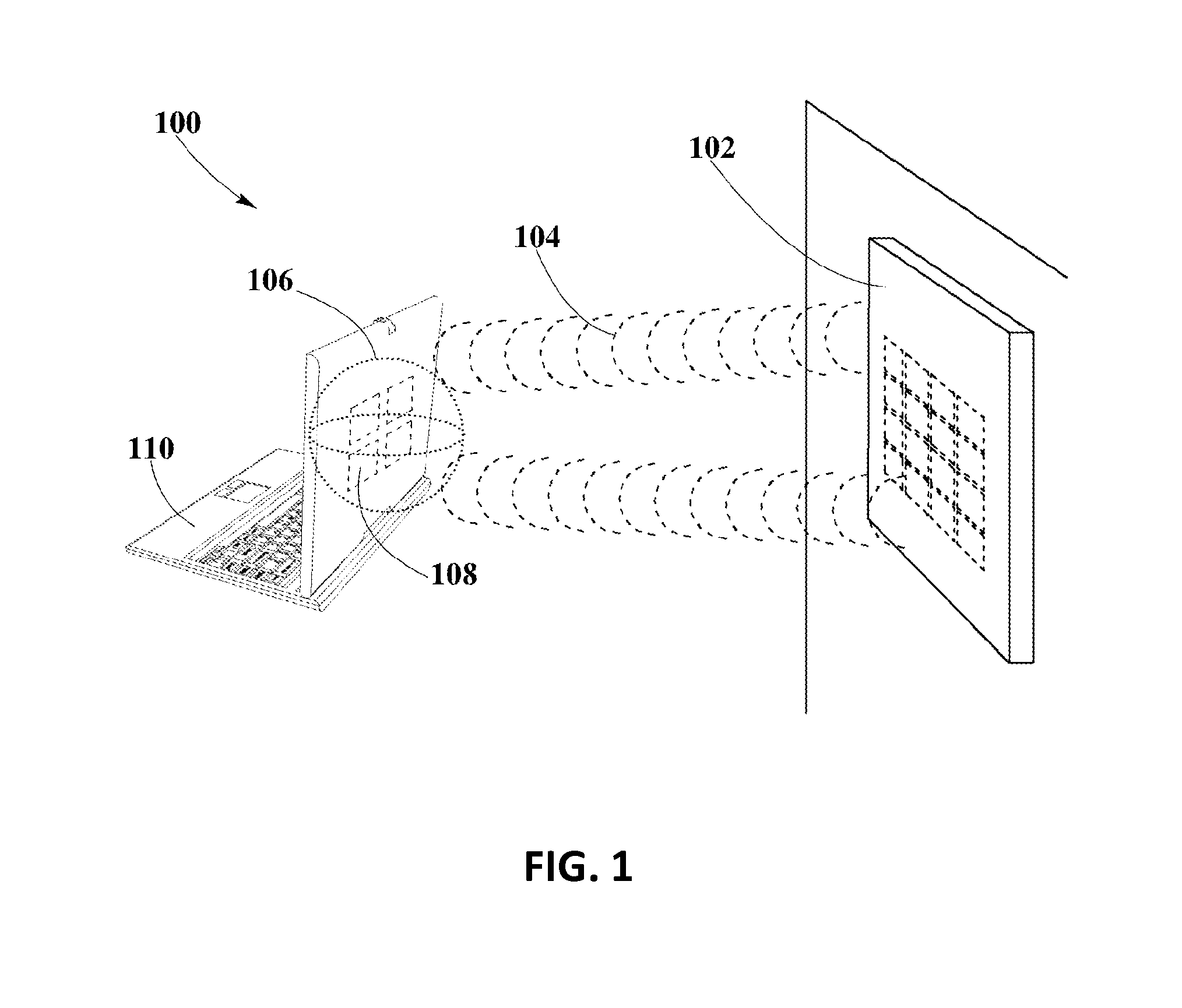
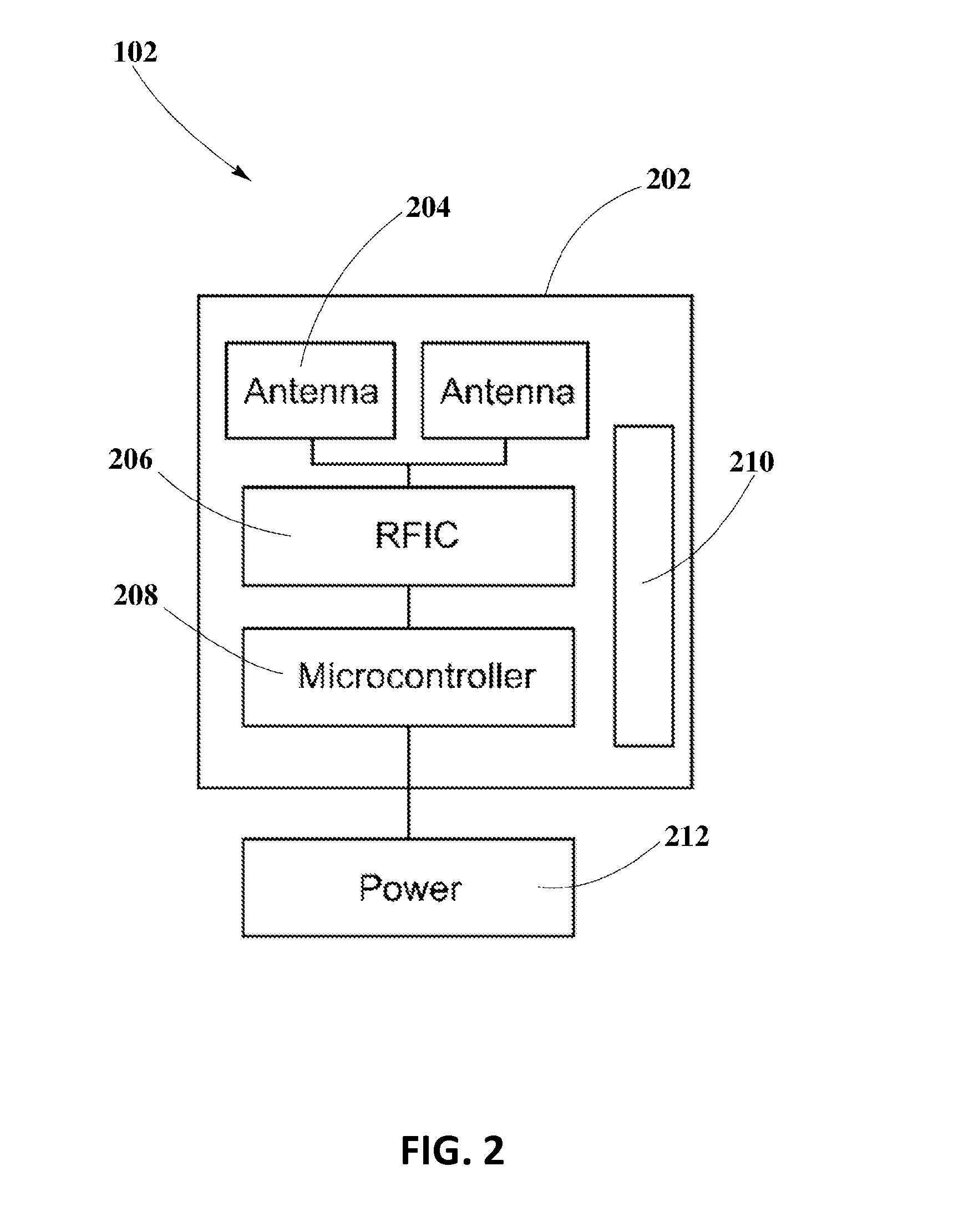
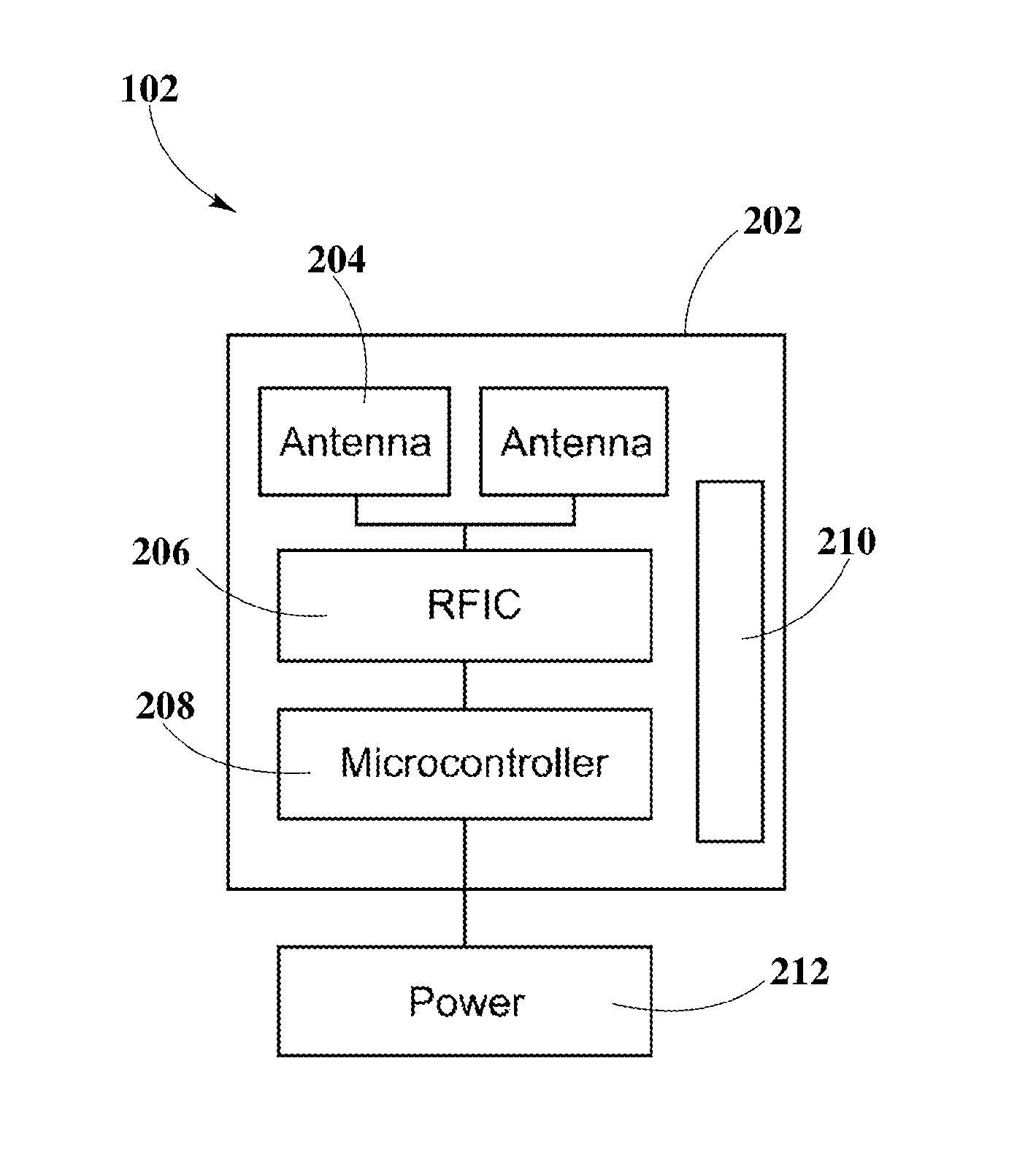
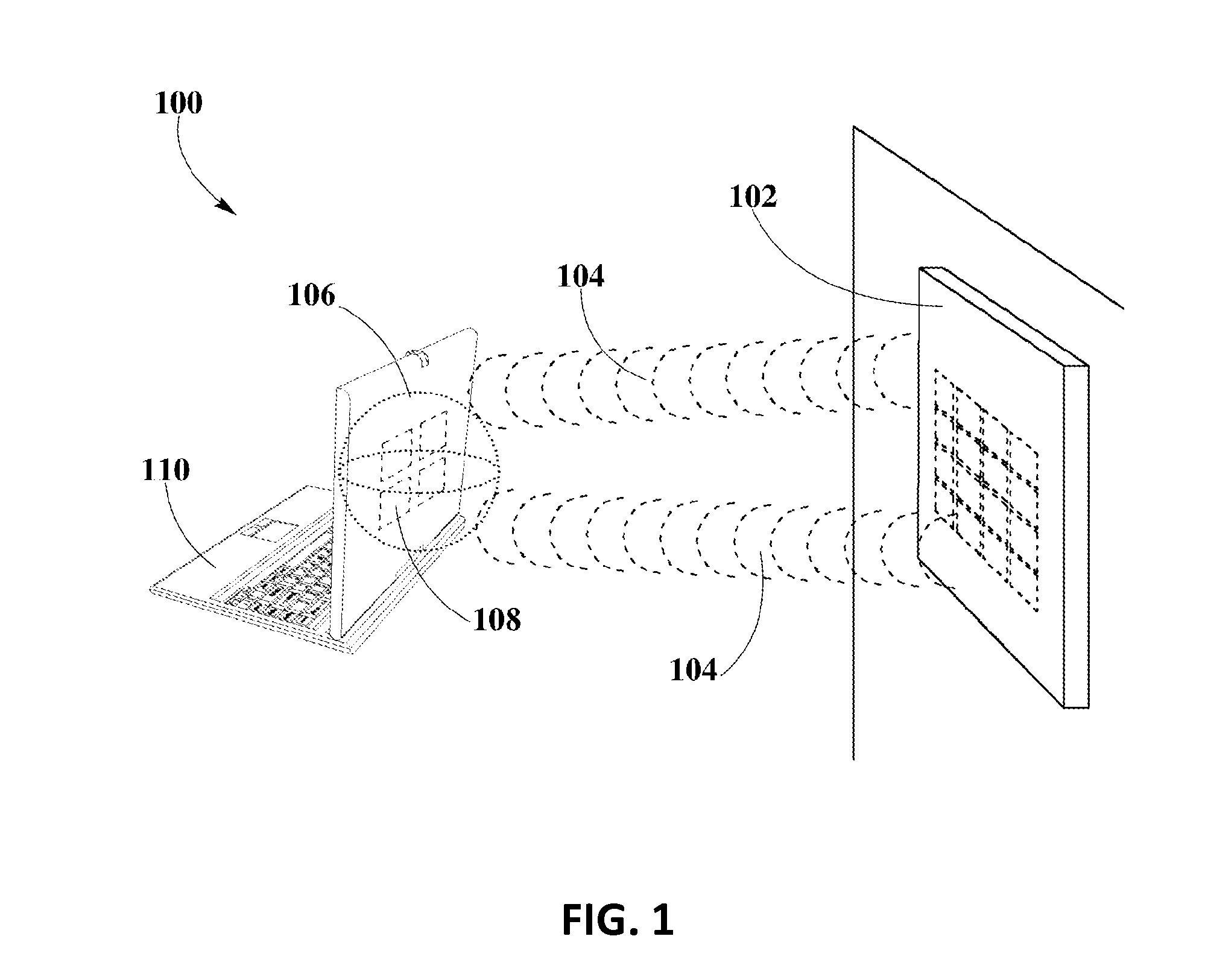
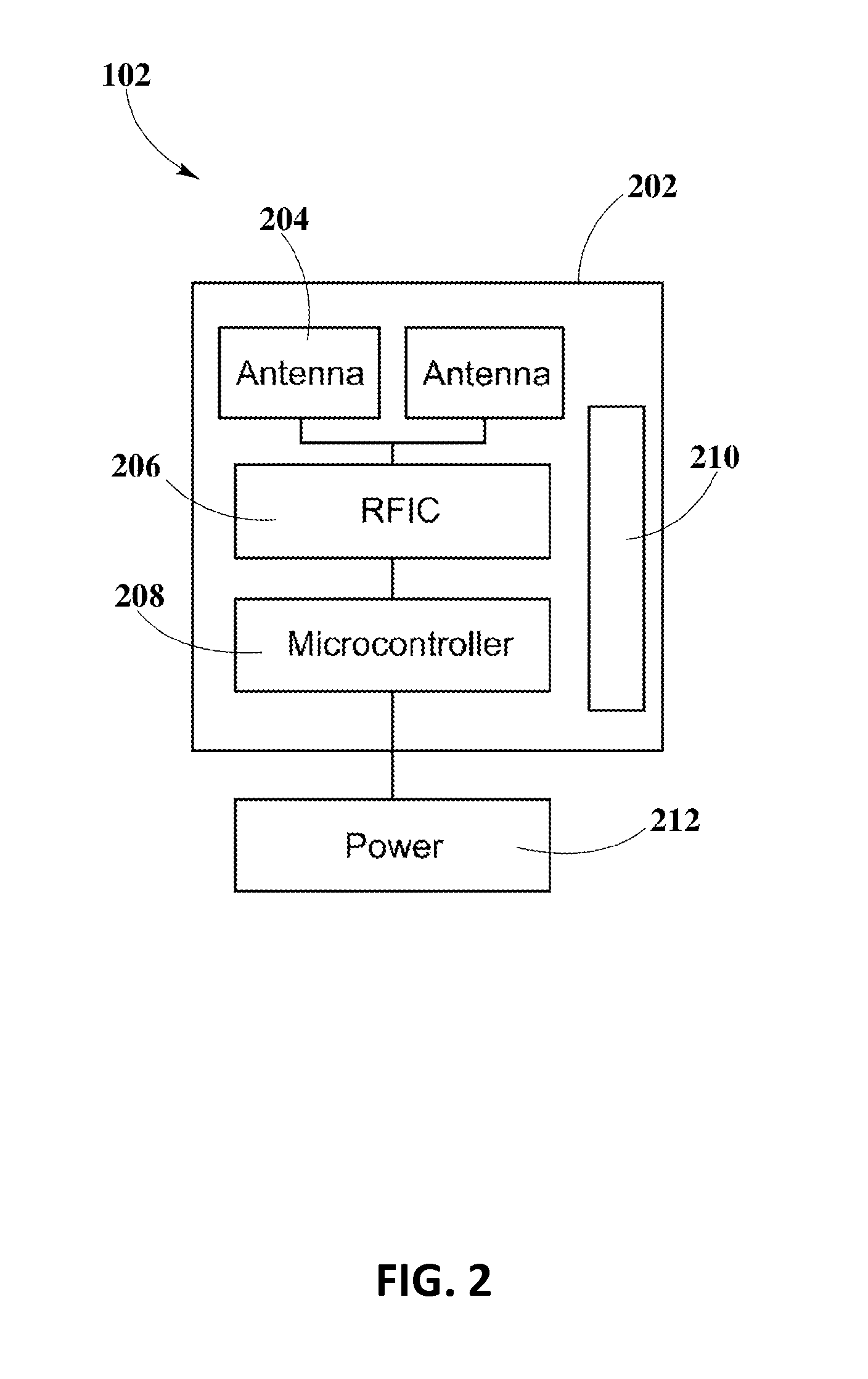
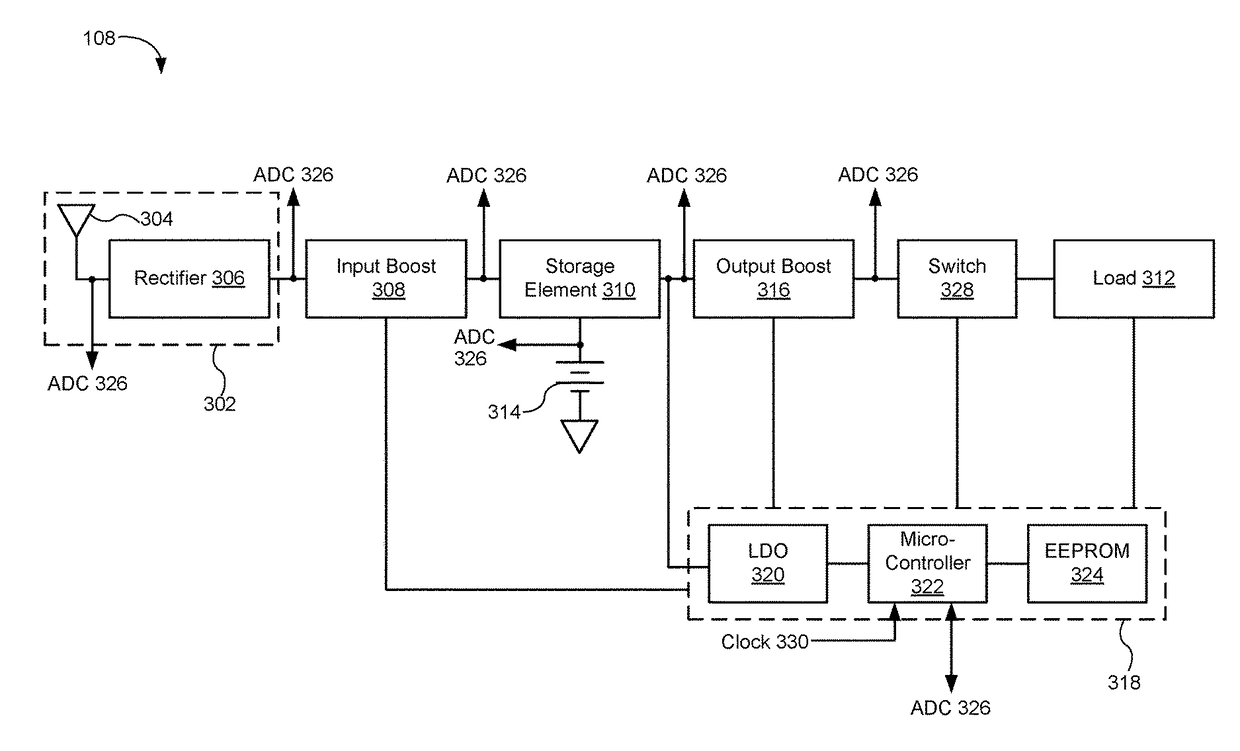
A controlled-power delivery system may operate with RF waves for supplying continuous and suitable power to a load. The controlled-power delivery system may include one or more receiving antennas, one or more rectifiers, a first boost converter, a charger, a storage element, and a second boost converter. The first boost converter may step up the rectified DC voltage obtained from the receiving antenna and rectifier to supply a suitable voltage level that can be used for charging the storage element. The second boost converter may increase the voltage from the storage element to a suitable level that may satisfy the power requirements of the load. The charger in conjunction with the first and second boost converters may be configured to allow a plurality of modes of operation for delivering power to the load and charging the storage element.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
Methods and Systems for Maximum Power Point Transfer in Receivers
InactiveUS20150326070A1Increase powerMaximize power extractedBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power transmissionEngineering
A MPPT management method in a receiver used for wireless power transmission may include the monitoring of the power extracted from RF waves at a dedicated antenna element in the receiver; detecting MPPT at an intelligent input boost converter in the receiver; comparing the detected MPPT with MPPT tables stored or calculated within a main system micro-controller in the receiver; adjusting the MPPT at the intelligent boost converter to find a suitable maximum peak that may enable an optimal power extraction from RF waves.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
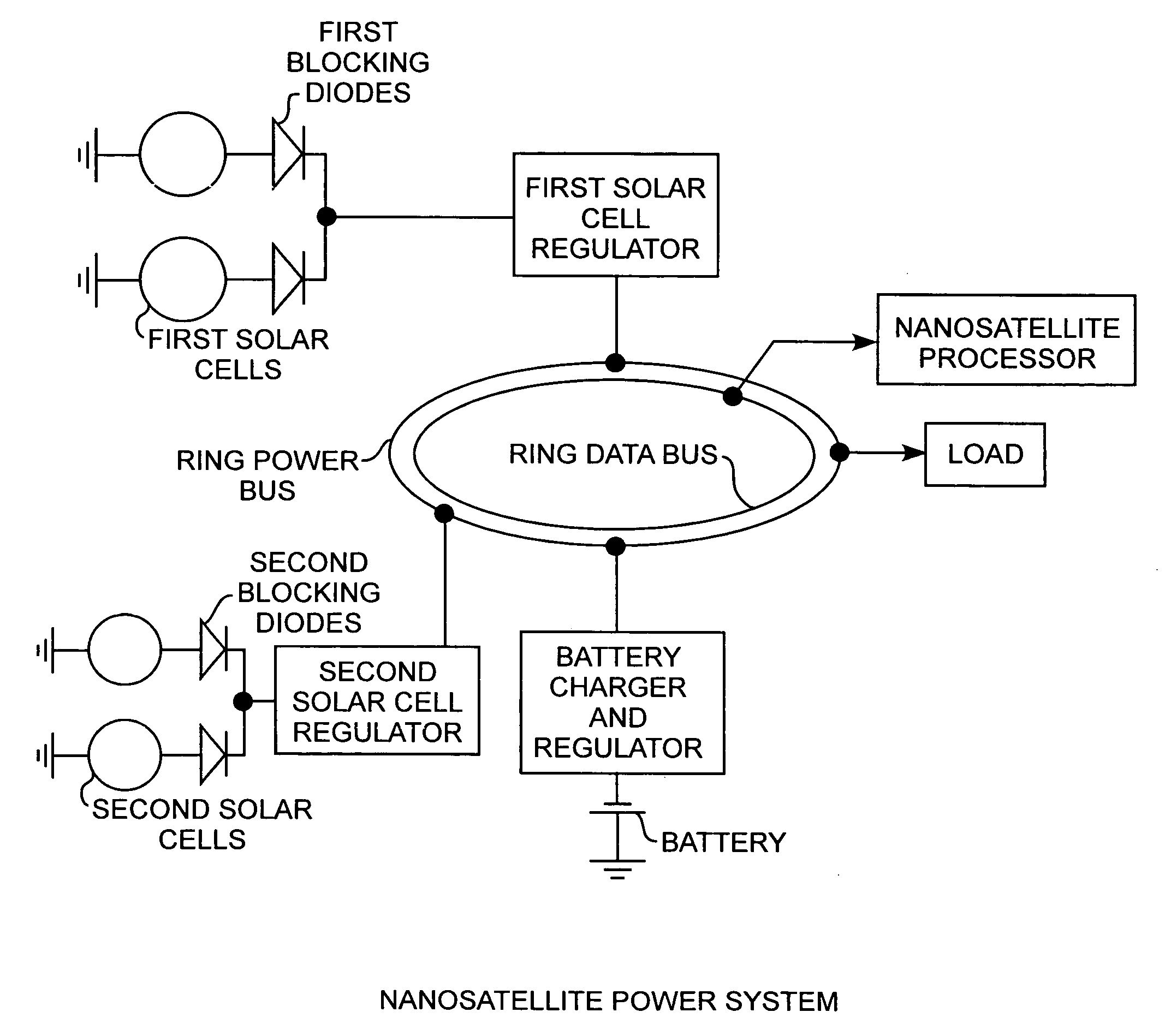
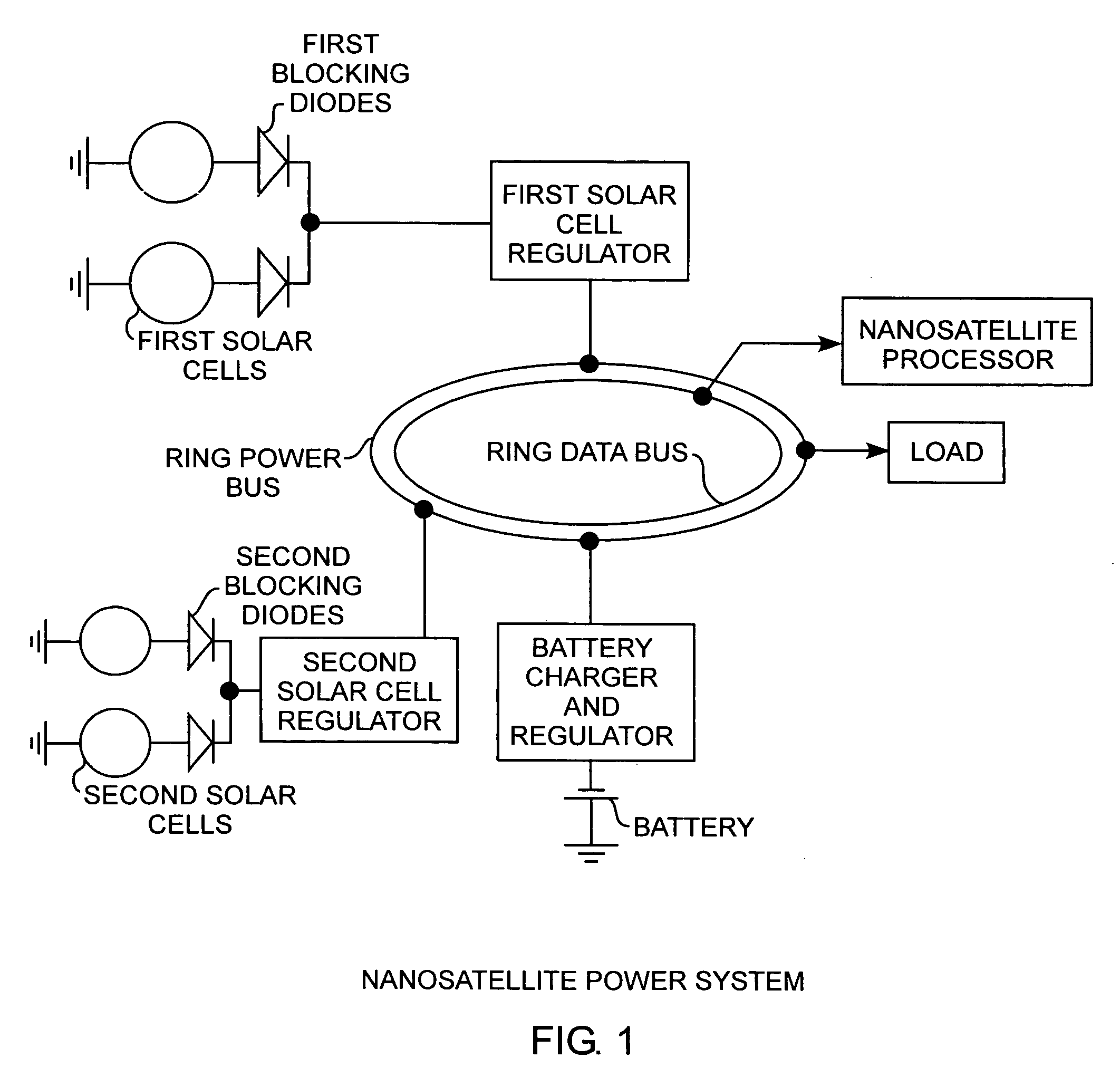
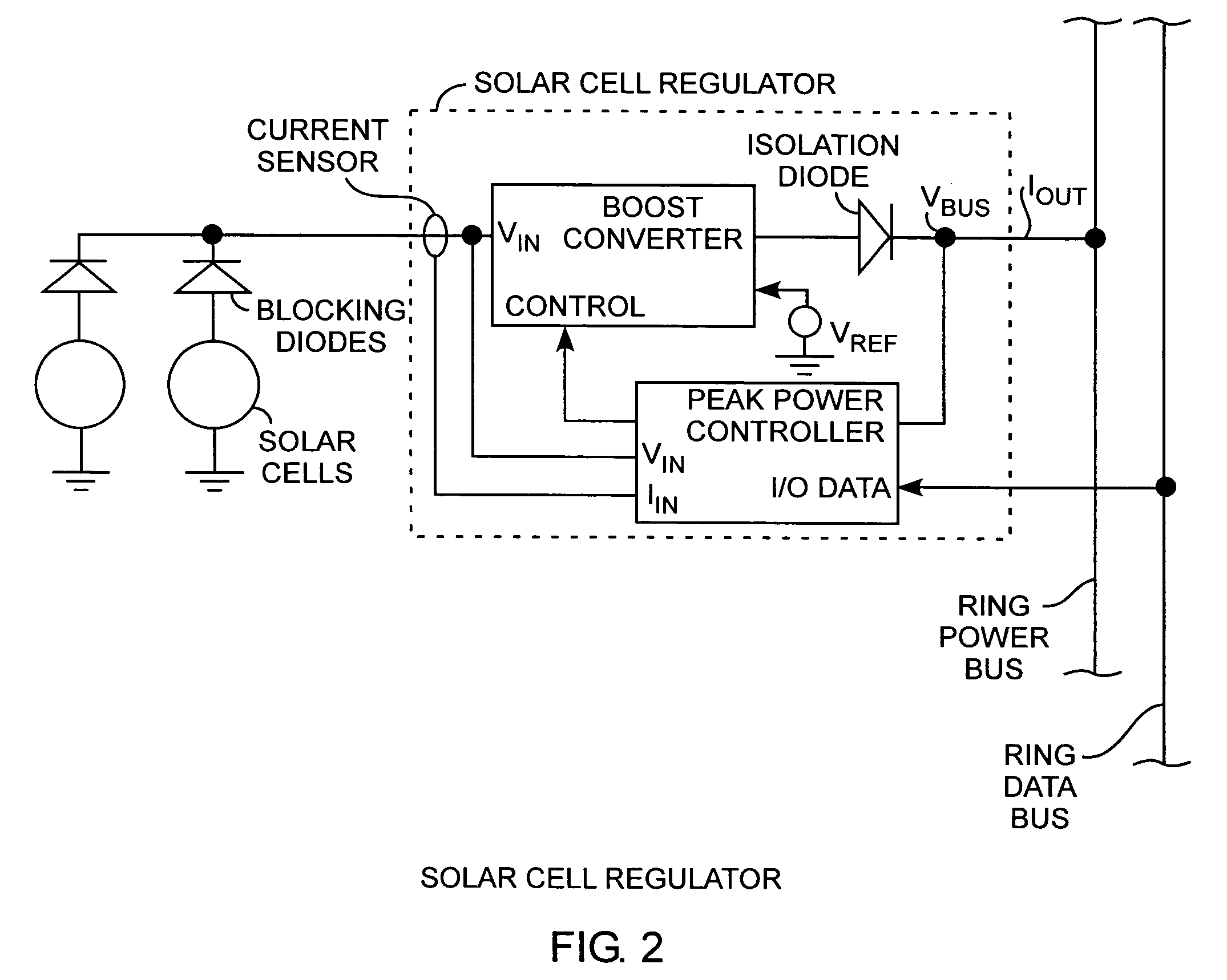
Nanosatellite solar cell regulator
A solar cell regulator in a nanosatellite includes a pulse width modulated DC-DC boost converter and a peak power tracking controller for converting solar cell power to bus power for charging of system batteries and powering loads while the controller controls the pulse width modulation operation of the converter for sensing solar cell currents and voltages along a power characteristic curve of the solar cell for peak power tracking, for determining any power data point, including a peak power point, an open circuit voltage point, and a short circuit current point along the power characteristic curve of the solar cell, and for communicating the power data to a satellite processor for monitoring the performance of the solar cell during operational use of the satellite.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
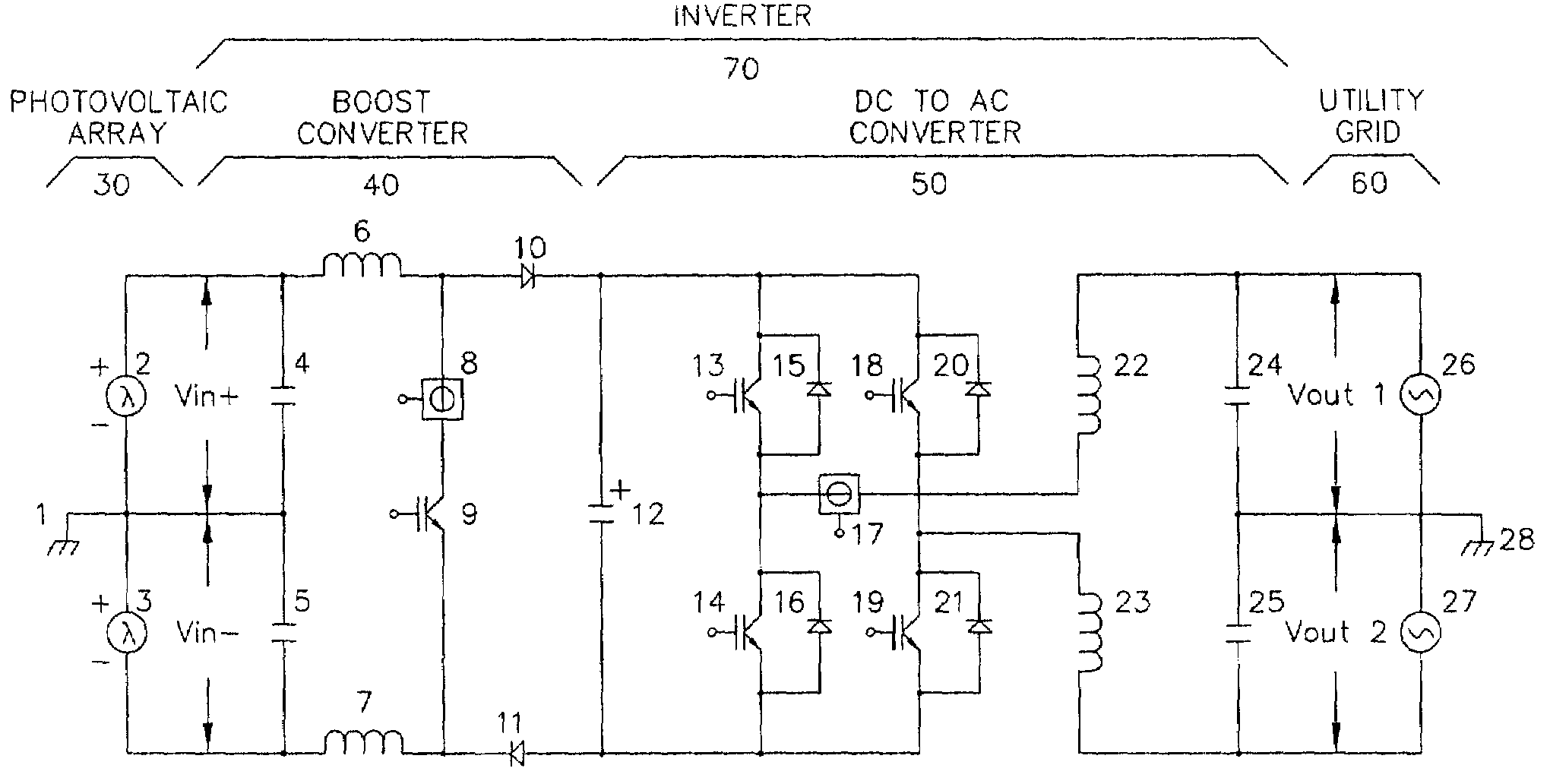
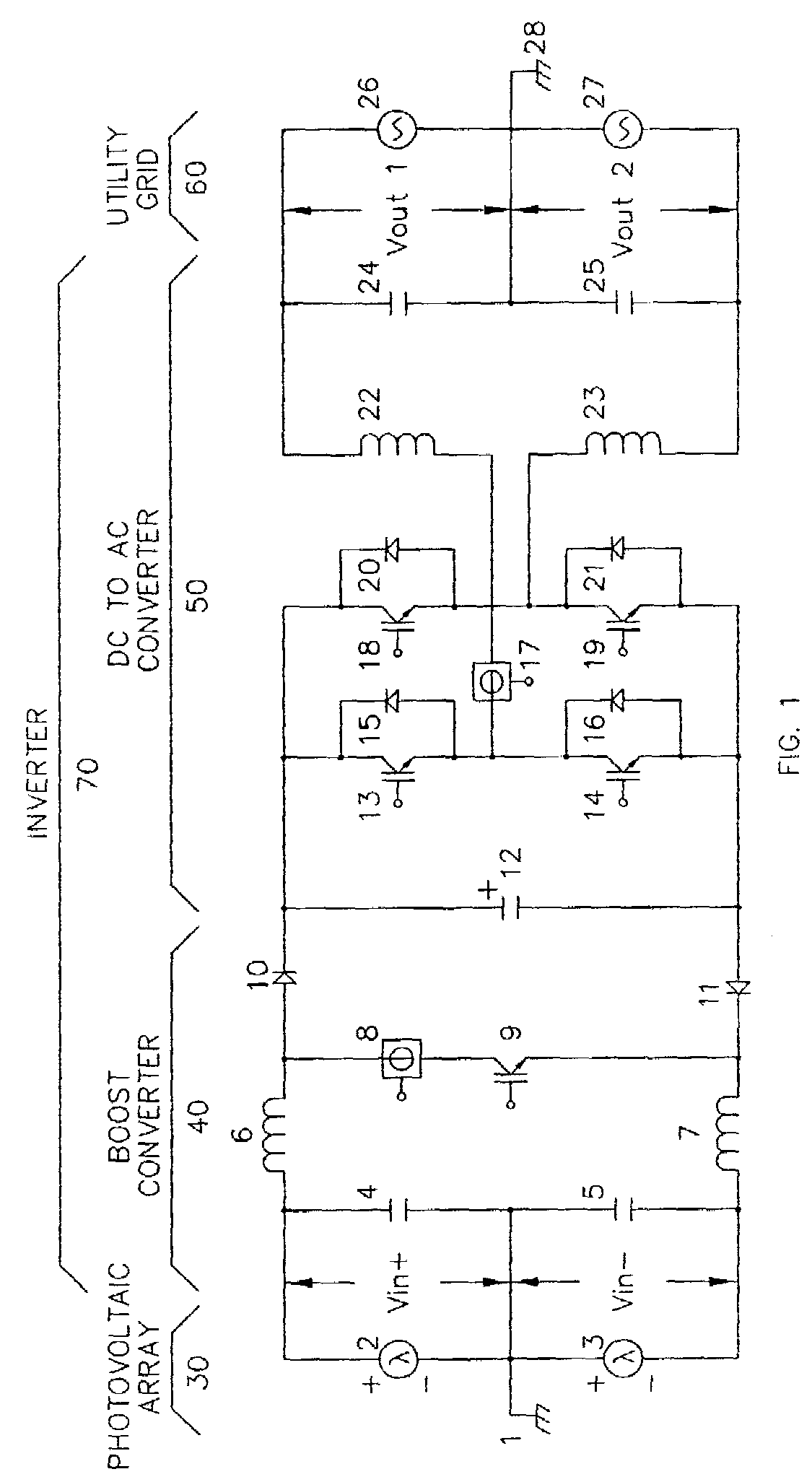
DC to AC inverter with single-switch bipolar boost circuit
InactiveUS7099169B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower inverterPerformance enhancement
This invention improves the performance and lowers the cost of DC to AC inverters and the systems where these inverters are used. The performance enhancements are most valuable in renewable and distributed energy applications where high power conversion efficiencies are critical. The invention allows a variety of DC sources to provide power thru the inverter to the utility grid or directly to loads without a transformer and at very high power conversion efficiencies. The enabling technology is a novel boost converter stage that regulates the voltage for a following DC to AC converter stage and uses a single semiconductor switching device. The AC inverter output configuration is either single-phase or three-phase.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
Enhanced Receiver for Wireless Power Transmission
ActiveUS20150326069A1Reduce power levelAdjusting operationBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemMicrocontrollerConverters
An enhanced receiver for wireless power transmission is disclosed. The receiver may be able to convert RF waves into continuous, stable and suitable voltage or power that can be used for charging or powering an electronic device. The receiver may include an antenna array for extracting and rectifying power from RF waves or pockets of energy. An input boost converter in the receiver may step up and stabilize the rectified voltage, while charging a storage element in the receiver. An output boost converter in the receiver may step up the output voltage of the storage element to deliver continuous and suitable power or voltage to a load. A microcontroller in the receiver may perform power measurements at different nodes or sections to adjust the operation of the input and output boost converters so that load power requirements can be satisfied at all times.
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
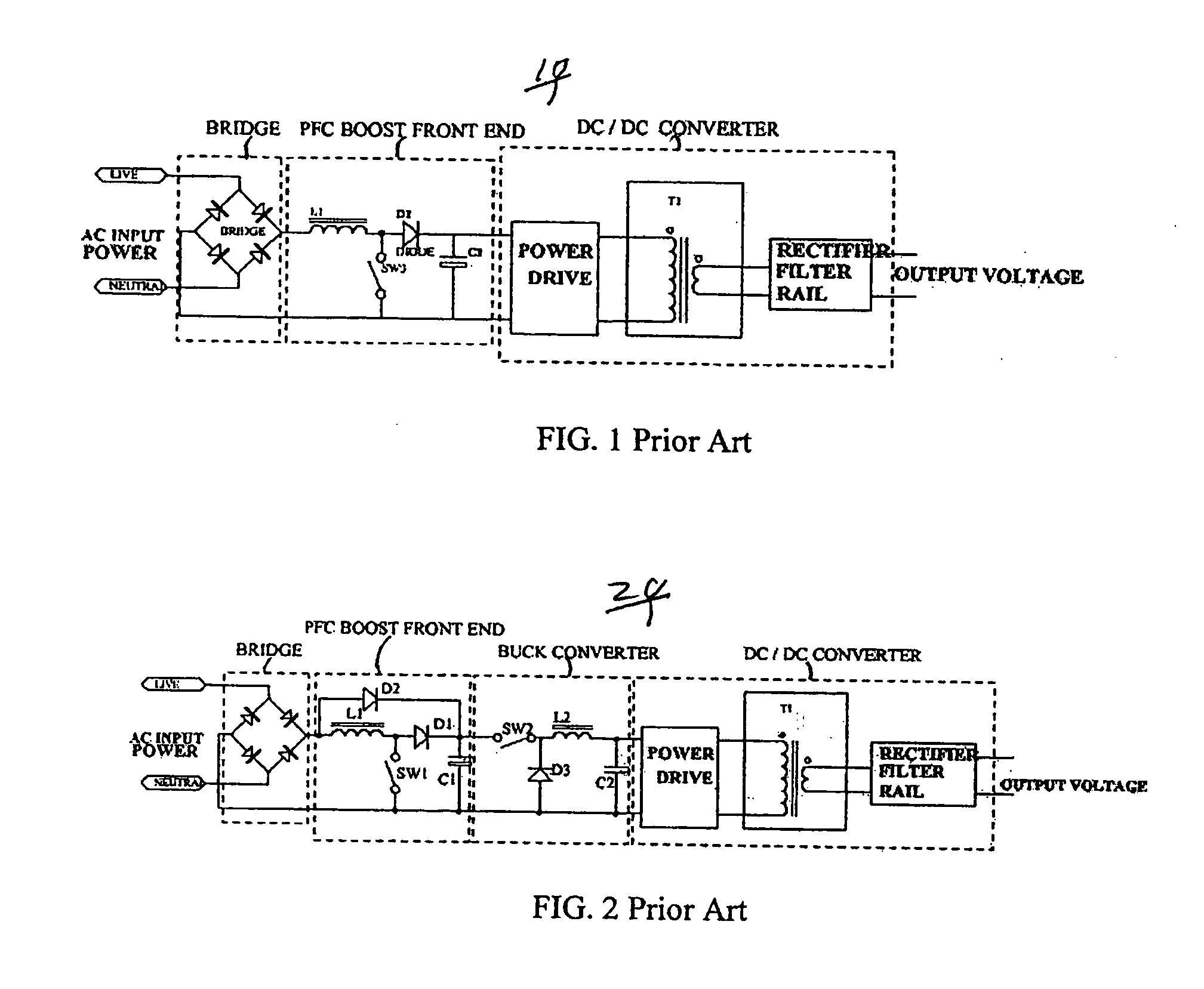
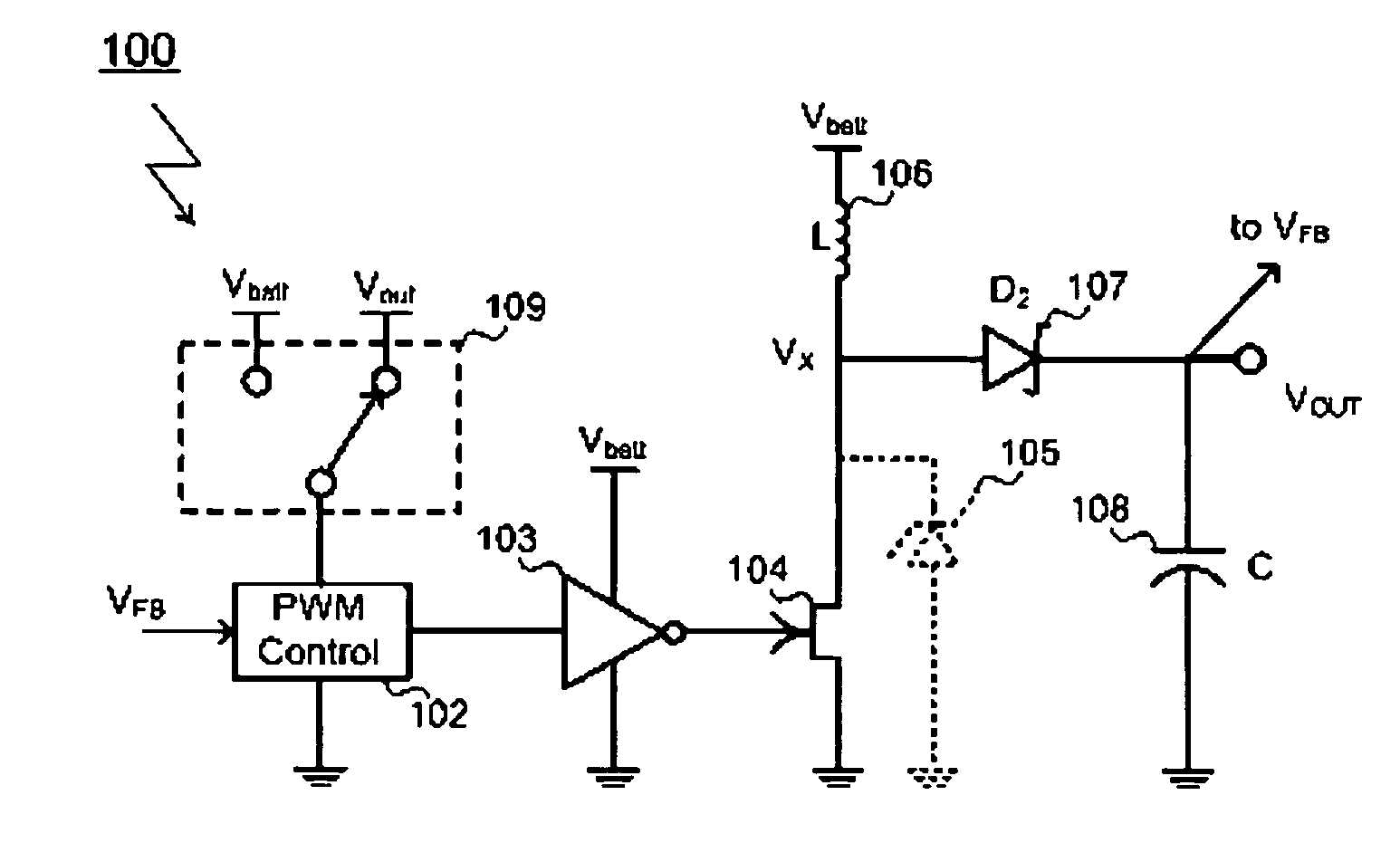
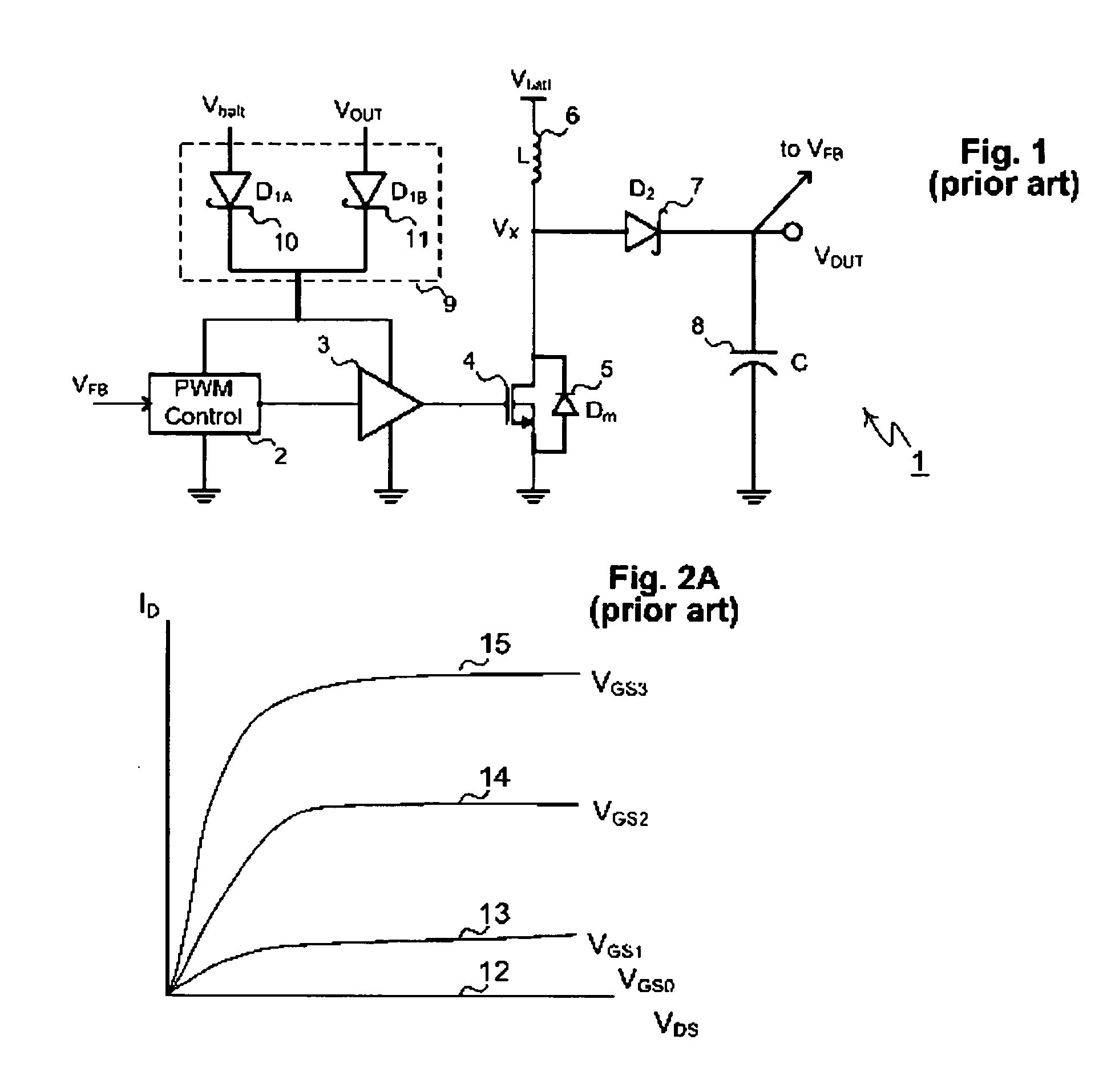
Circuit for maintaining hold-up time while reducing bulk capacitor size and improving efficiency in a power supply
InactiveUS20050030772A1Improve efficiencyReducing voltage operating rangeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
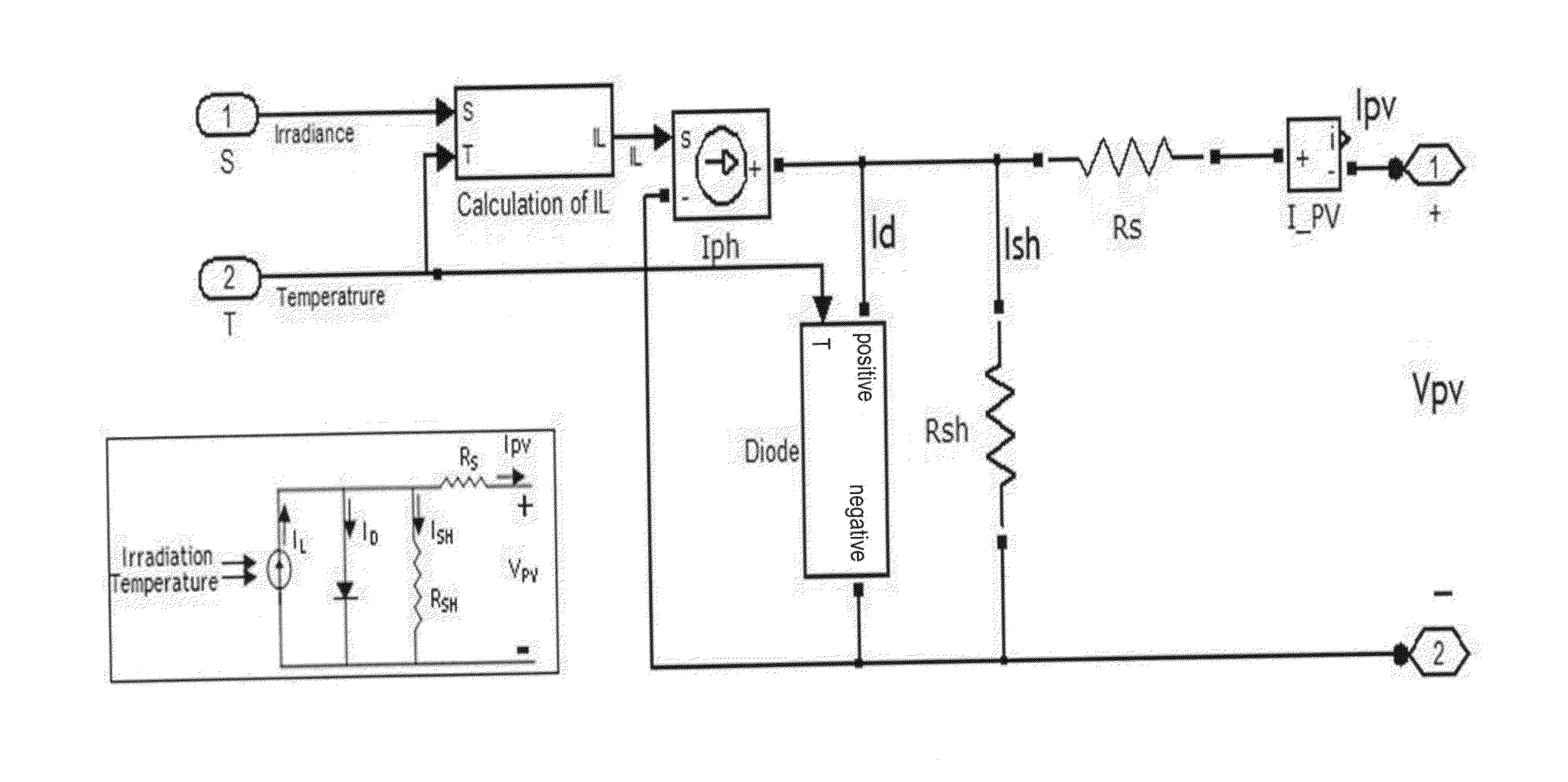
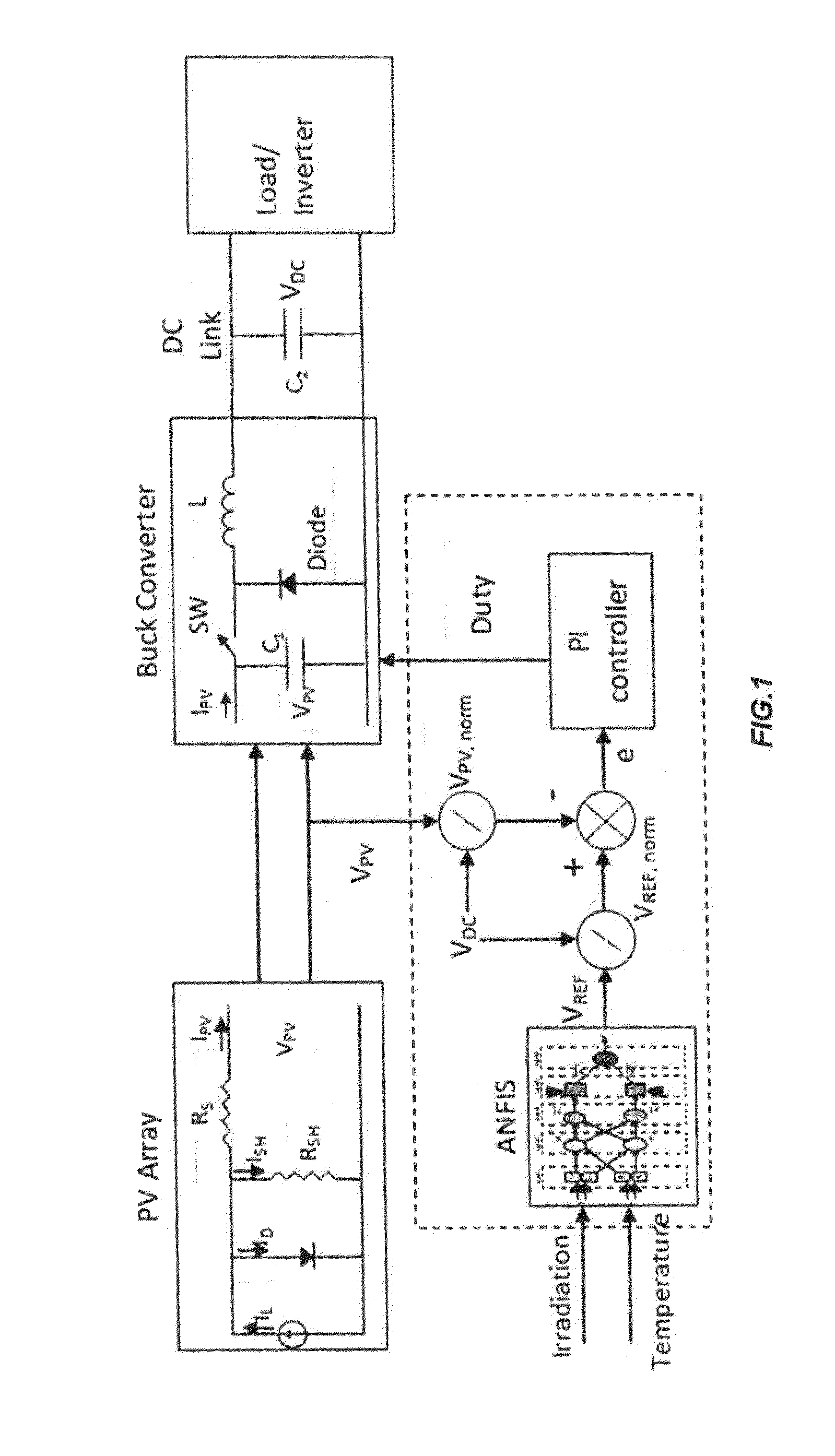
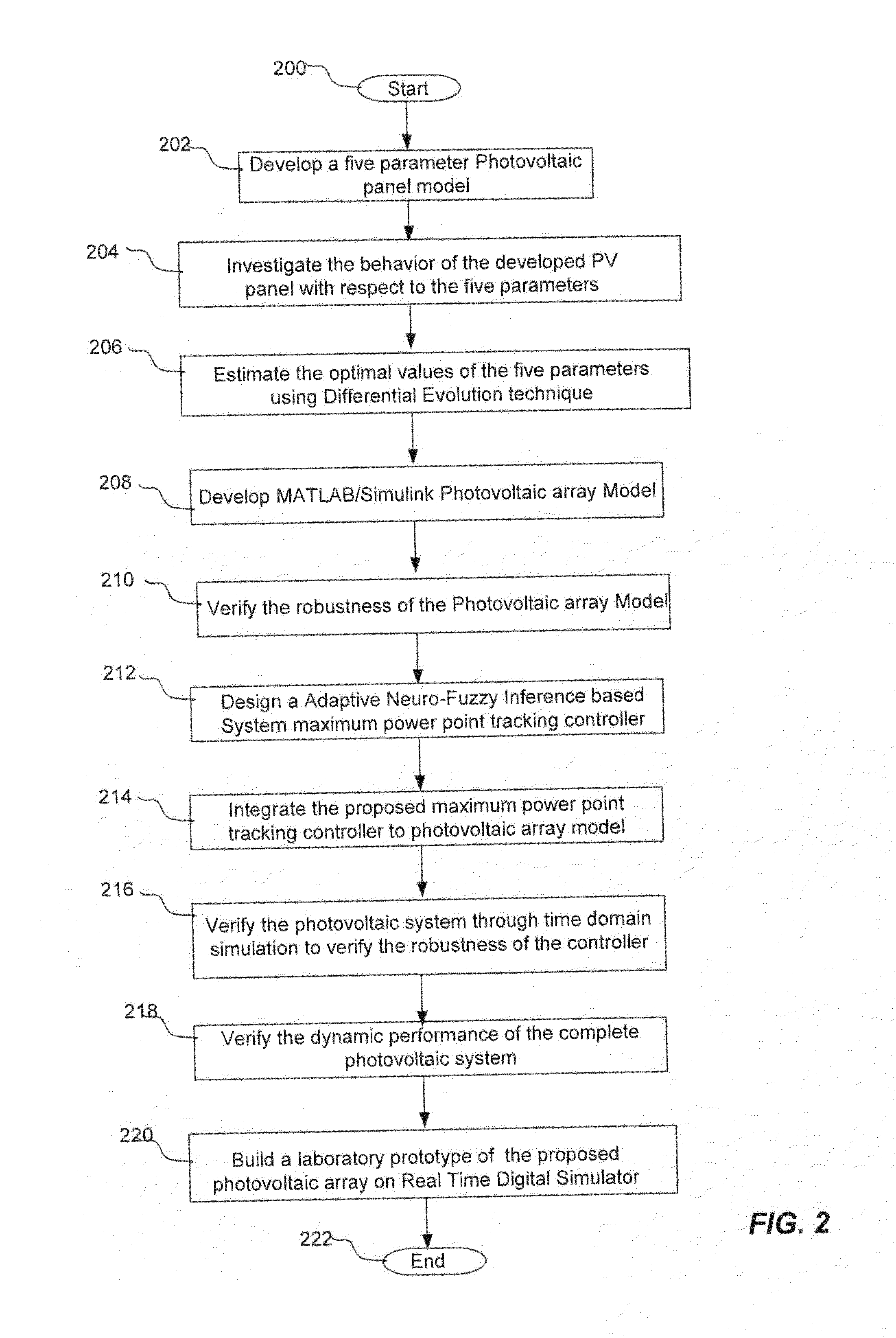
Photovoltaic systems with maximum power point tracking controller
ActiveUS20150188415A1Simulator controlAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsFuzzy inferenceEngineering
A system and a method provide a photovoltaic system which regenerates the output characteristics of the photovoltaic at different ambient condition with high precision under all environmental conditions. The photovoltaic system includes a photovoltaic array, a buck / boost converter, a DC link capacitor to connect the buck / booster converter to a load / inverter, an adaptive network-based fuzzy inference maximum power point tracking controller, a voltage control loop, a proportional integral controller to maintain the output voltage of the photovoltaic array to the reference voltage by adjusting the duty ratio of buck / boost converter.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
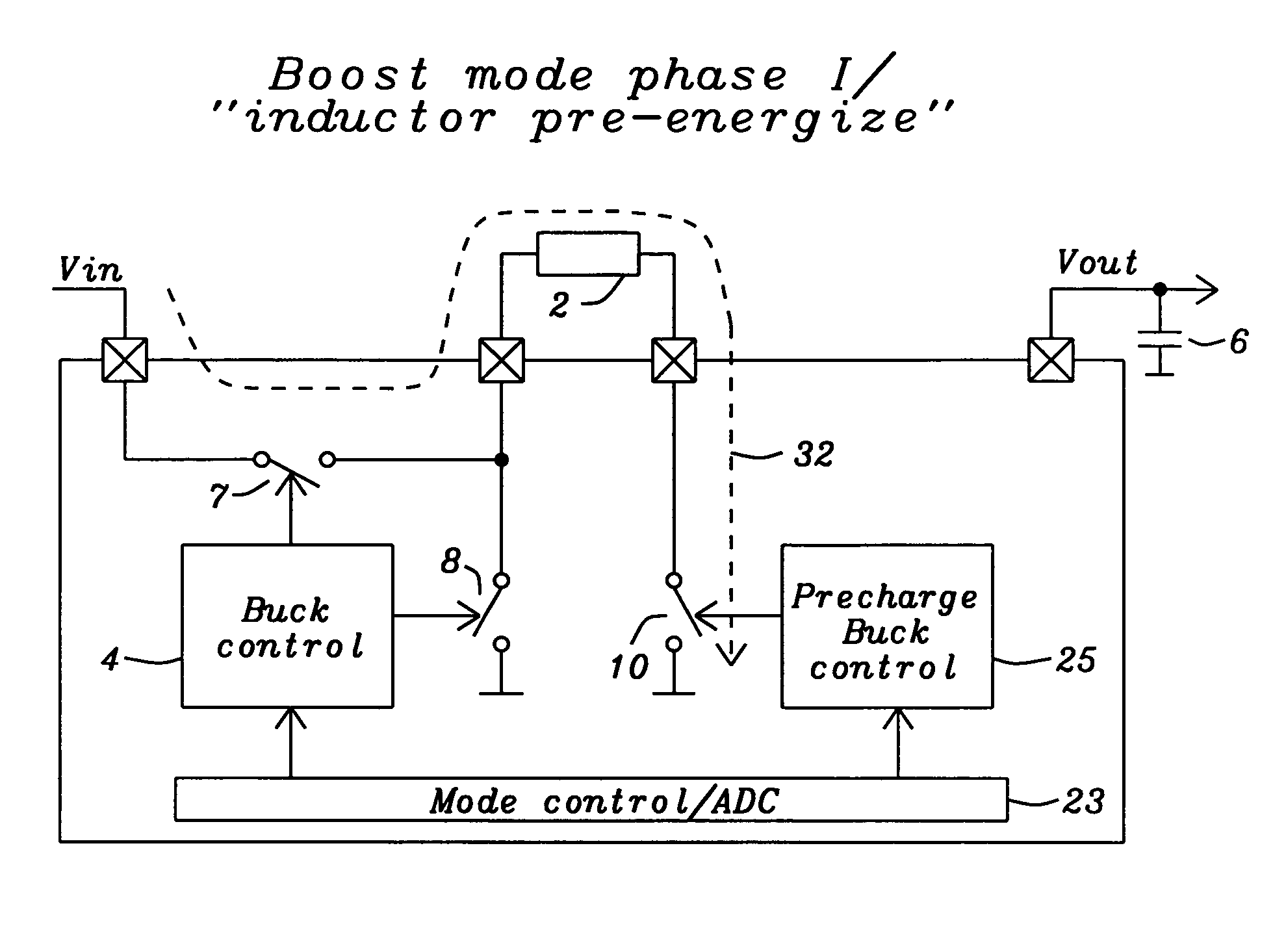
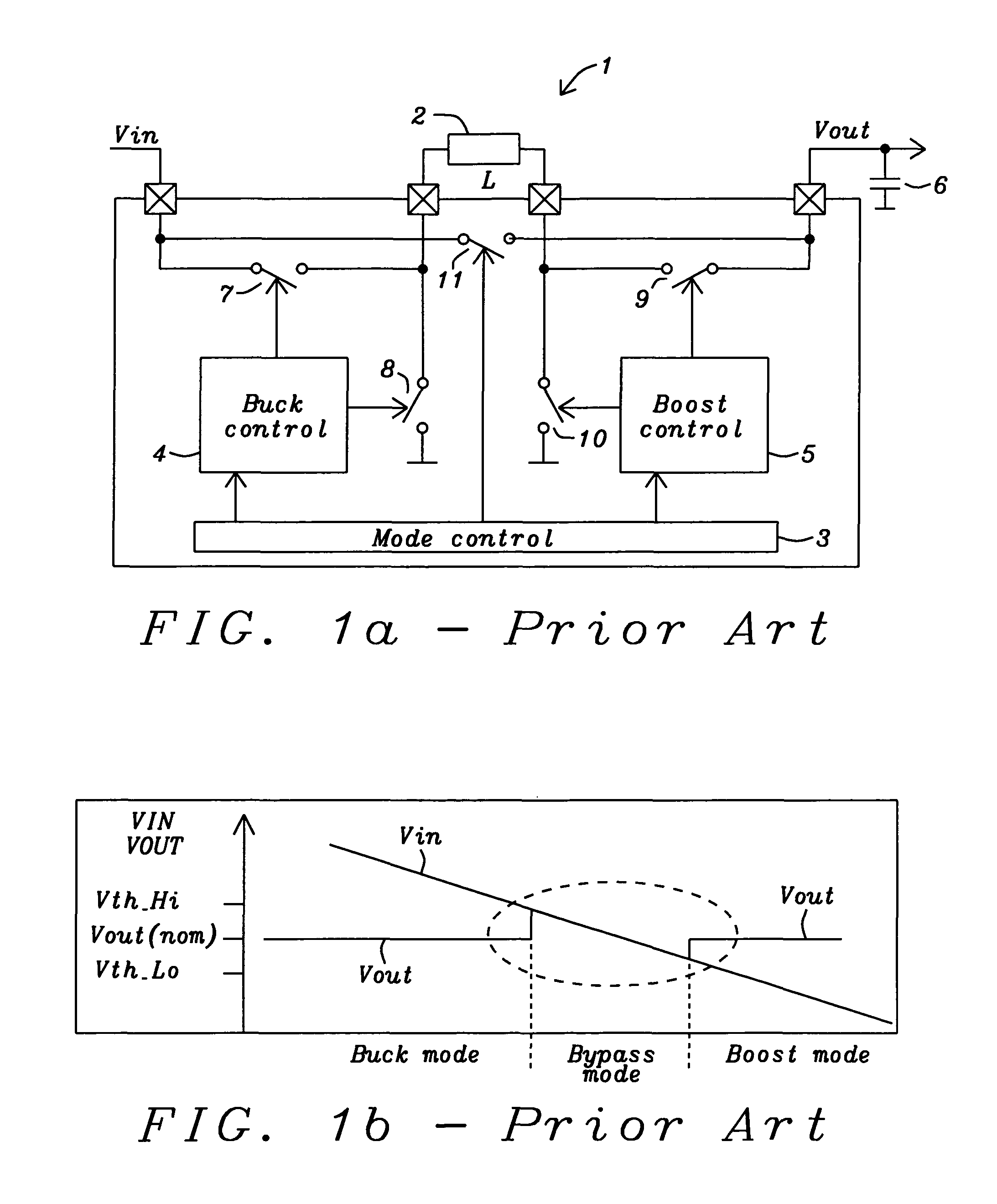
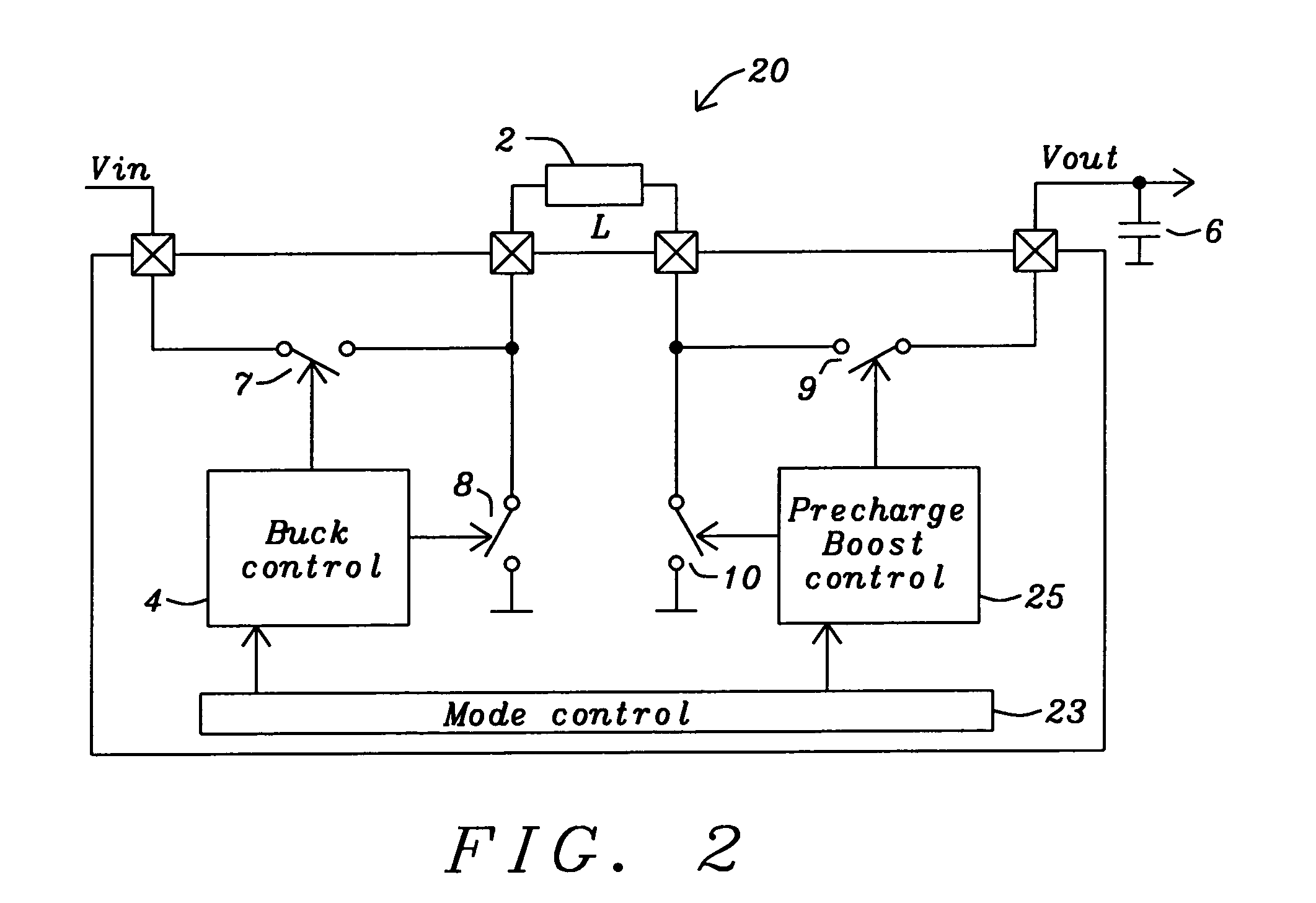
Buck converter with inductor pre-energizing
ActiveUS7804282B2Simple control circuitDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationBuck converterĆuk converter
Circuits and methods to achieve a buck-boost converter, capable to achieve a constant output voltage by pre-charging of an inductor if the input voltage is close to the output voltage has been achieved. The prior art problem of output voltage variations occurring while the input voltage is close to the output voltage is avoided. In case the input voltage is lower than a defined threshold voltage or the duty cycle exceeds a defined maximum allowable level, the inductor of the converter is pre-charged followed by boosting of the energy of the inductor to the output of the converter. In both modes the control loops of the buck converter can be used for buck duty cycle control. The duration of the pre-charge depends upon the level of the input voltage, the lower the input level is the longer is the pre-charge performed.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation using a common duty-cycle timing signal
ActiveUS7336056B1Remove overlapSmooth transitEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionIntegratorBuck converter
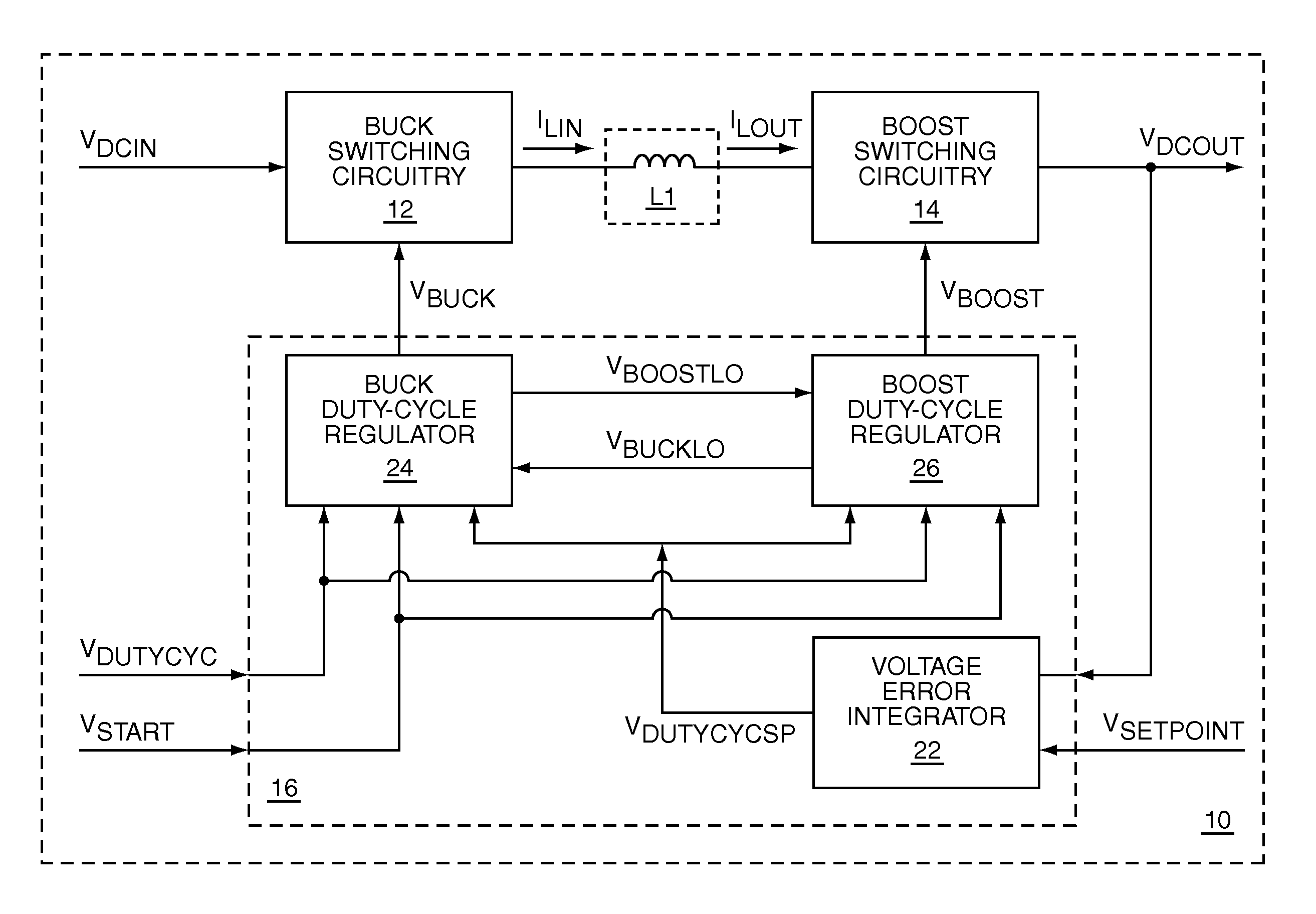
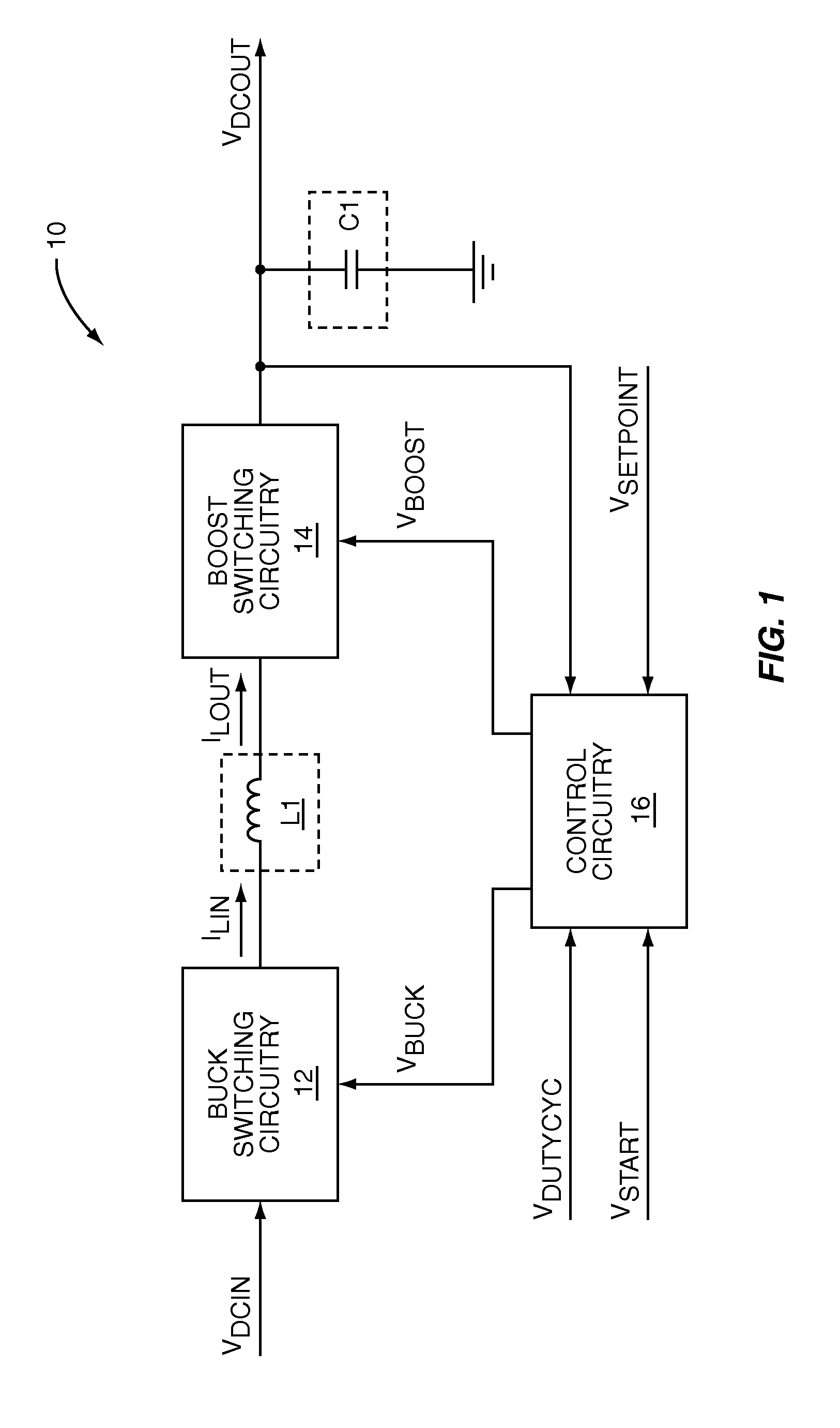
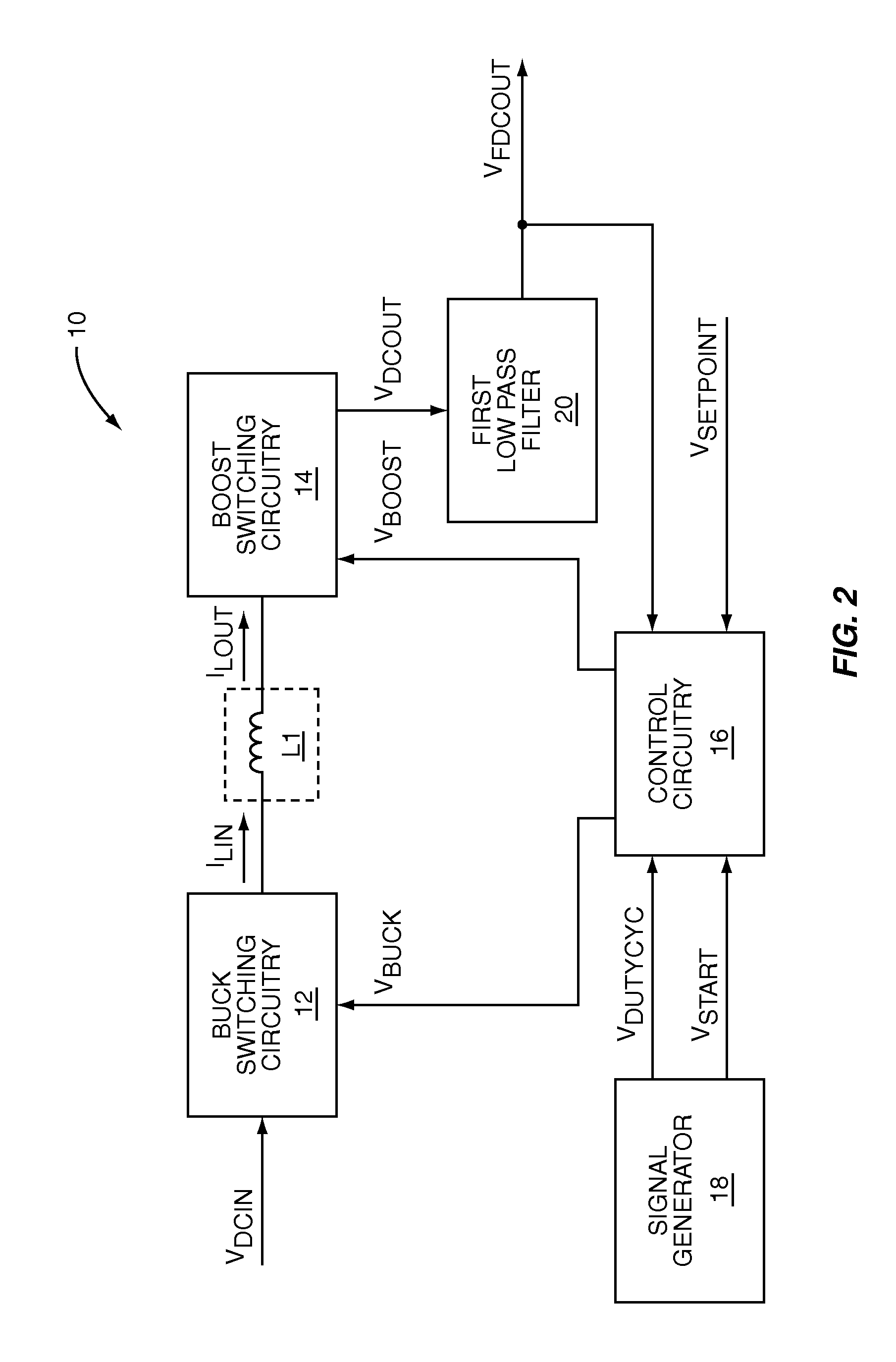
The present invention is a switching power converter that supports both a boost mode of operation and a buck mode of operation, uses one energy storage element, transitions smoothly between boosting and bucking, and avoids simultaneous boosting and bucking. The switching power converter uses a common duty-cycle timing signal and a common duty-cycle setpoint signal to provide a smooth transition between boosting and bucking, and to eliminate overlap between boosting and bucking. A voltage input error integrator is used to integrate out errors between an output voltage and a setpoint voltage to provide the common duty-cycle setpoint signal. Duty-cycle error integrators are used to integrate out errors between the common duty-cycle setpoint signal and the actual duty-cycle of either the buck converter or the boost converter. Non-overlapping boost operating and buck operating ranges are provided by the common duty-cycle setpoint signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
System for producing electric power from renewable sources and a control method thereof
InactiveUS7952897B2Reduction of this drawbackPrecise maintenancePower supply linesDc-dc conversionOperating pointElectric power system
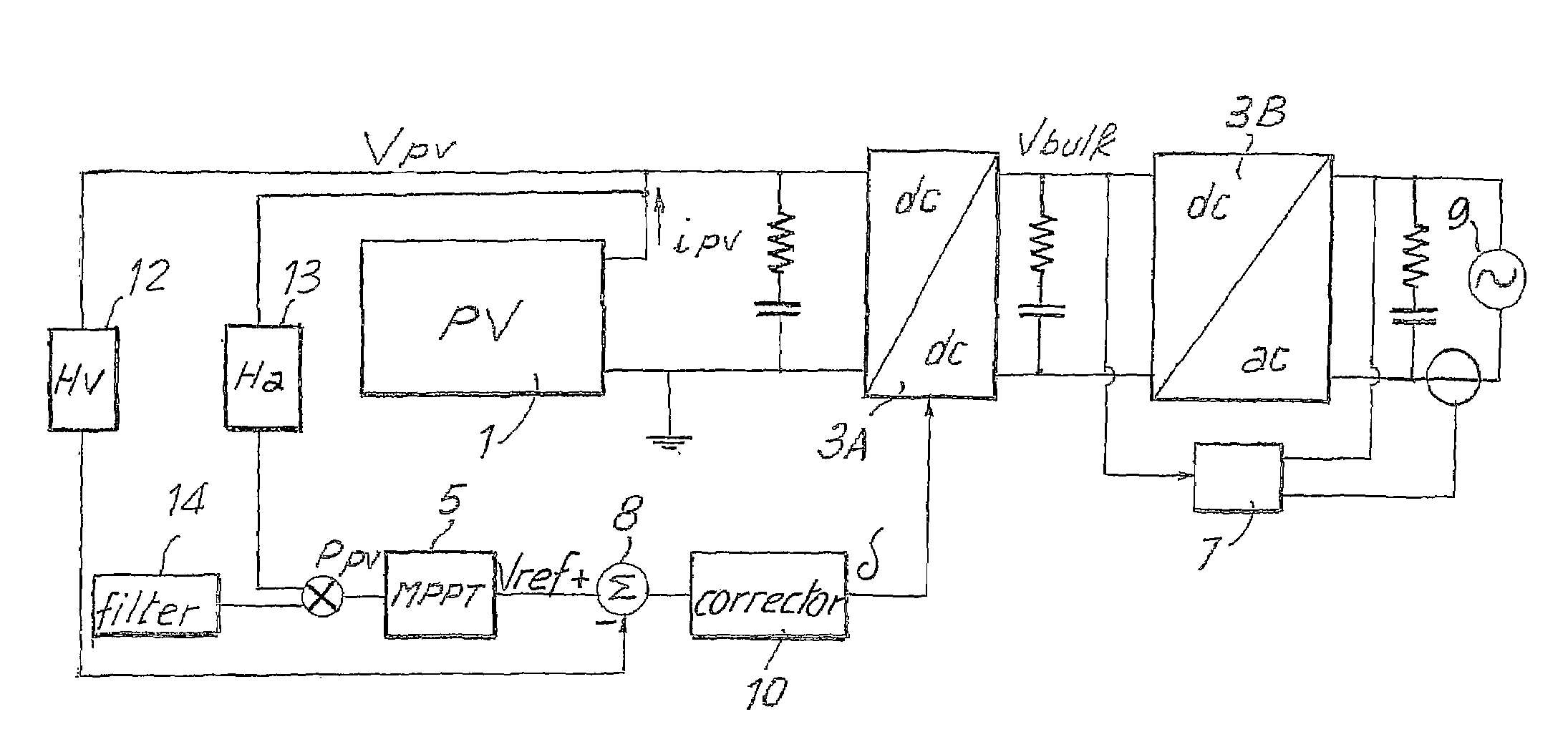
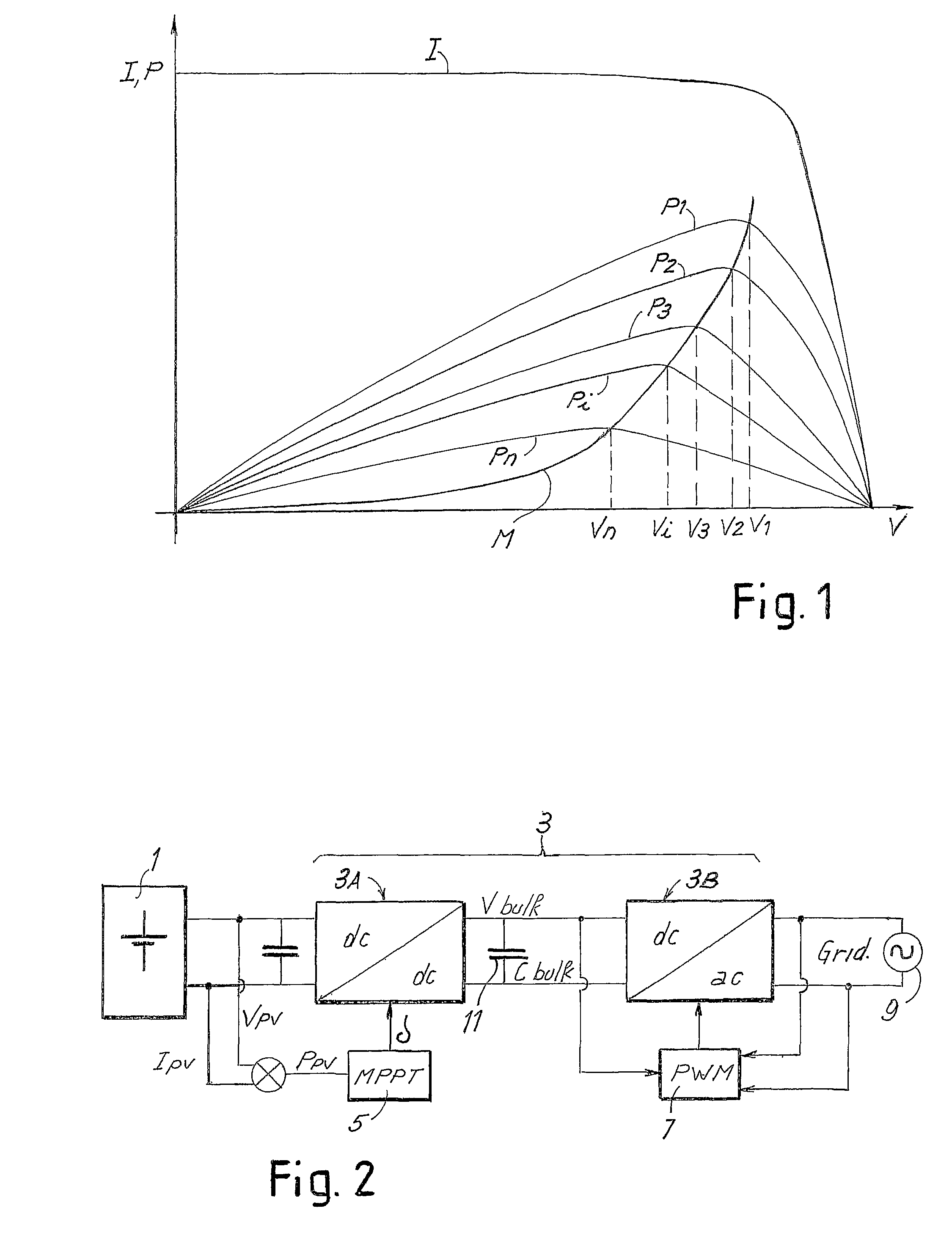
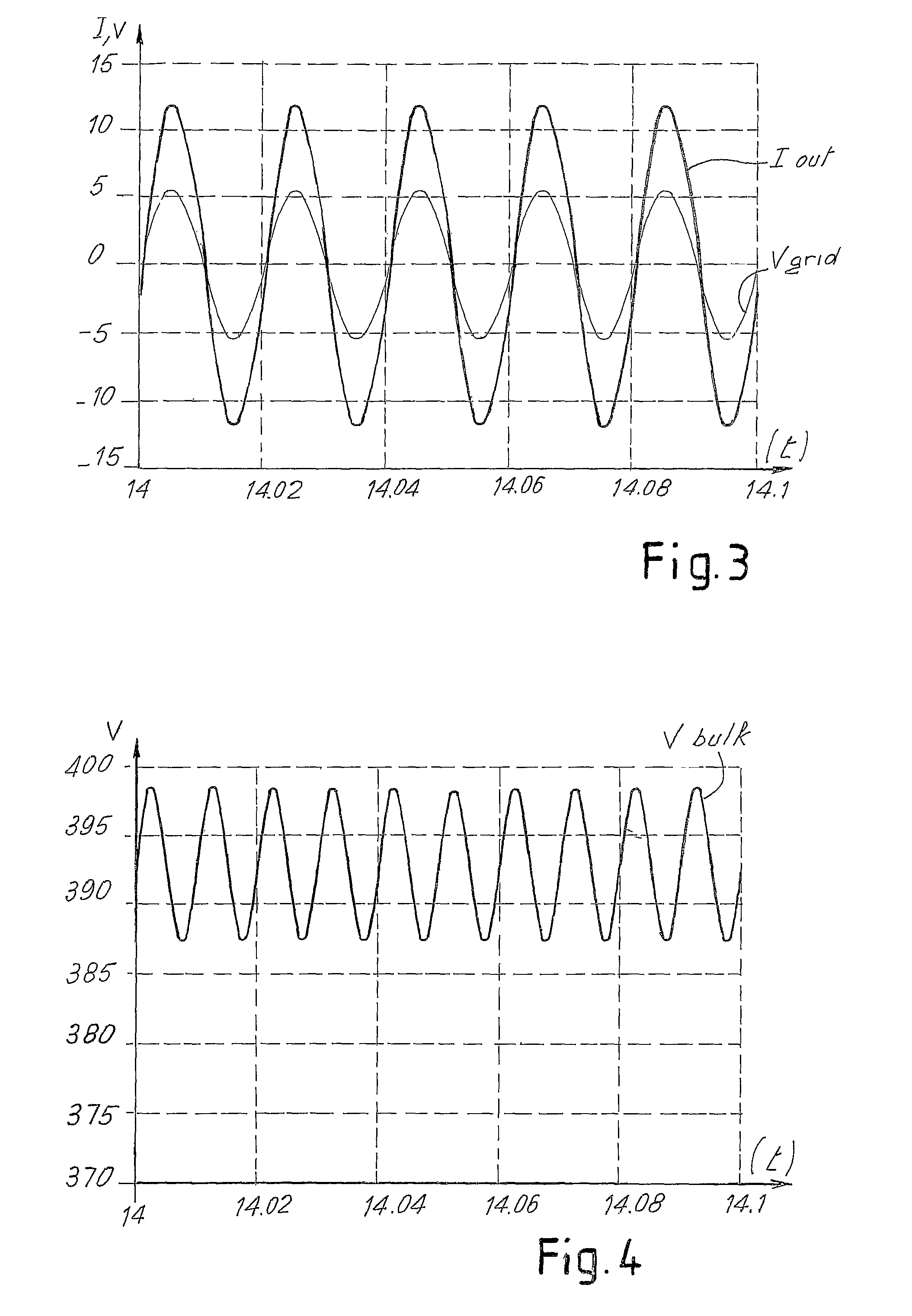
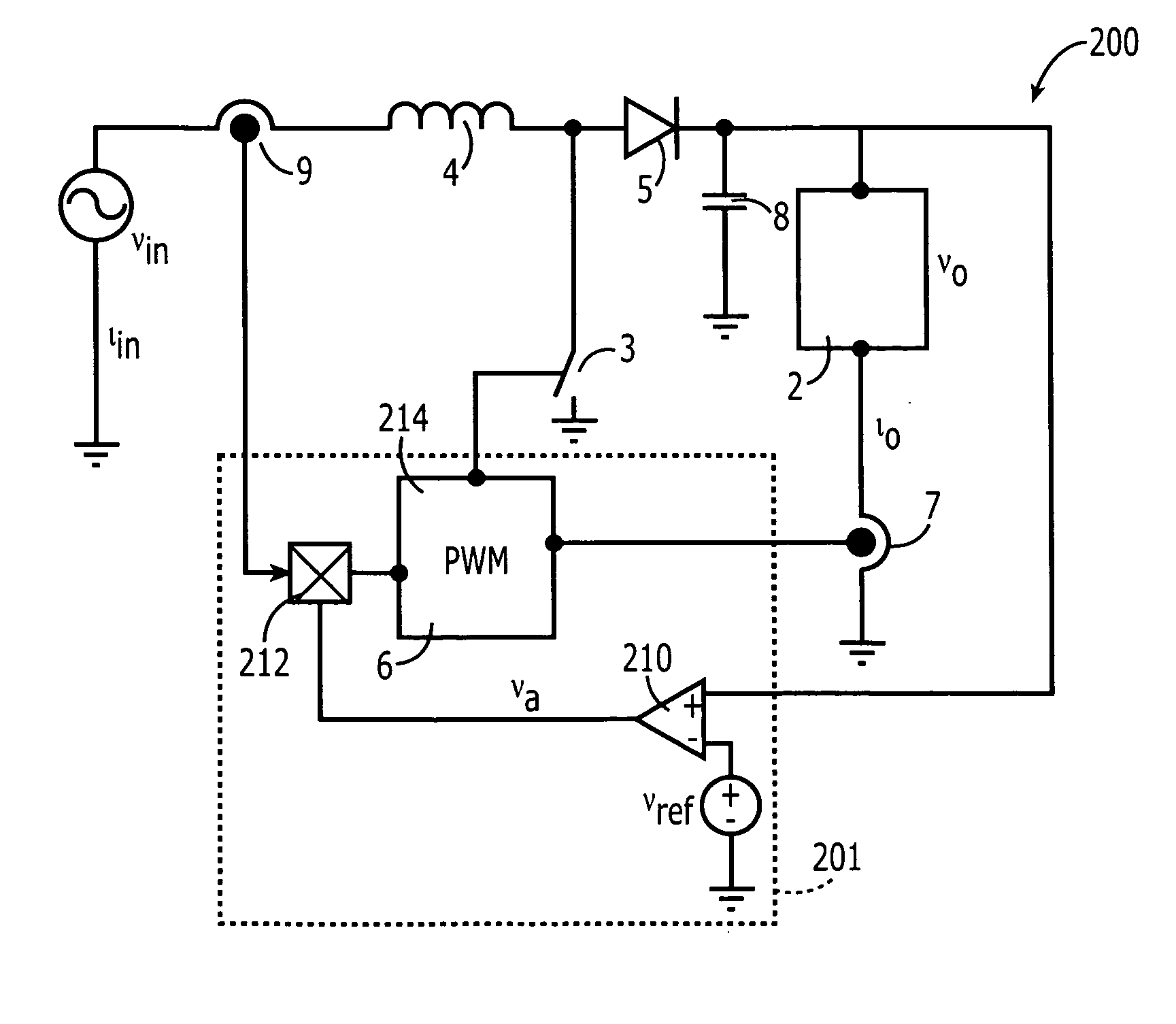
Described herein is a system for generating electric power, comprising: an electric-power source (1) having a preferential point of operation; a double-stage inverter (3A, 3B), which transfers the energy from said source to an external a.c.-voltage electrical network (9); a block (5) for identification of the preferential point of operation, which supplies a reference signal according to the conditions of operation of the electric-power source and to the preferential point of operation of said source; a corrector block (10), provided for setting the parameter for control of the boost converter (3A) of the double-stage inverter (3A, 3B) as a function of the reference signal and of a signal of actual operation of said electric-power source, and for maintaining the source in the proximity of the preferential point of operation.
Owner:MARICI HLDG THE NETHERLANDS BV
Solar inverter and control method
ActiveUS8184460B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionControl signalEngineering
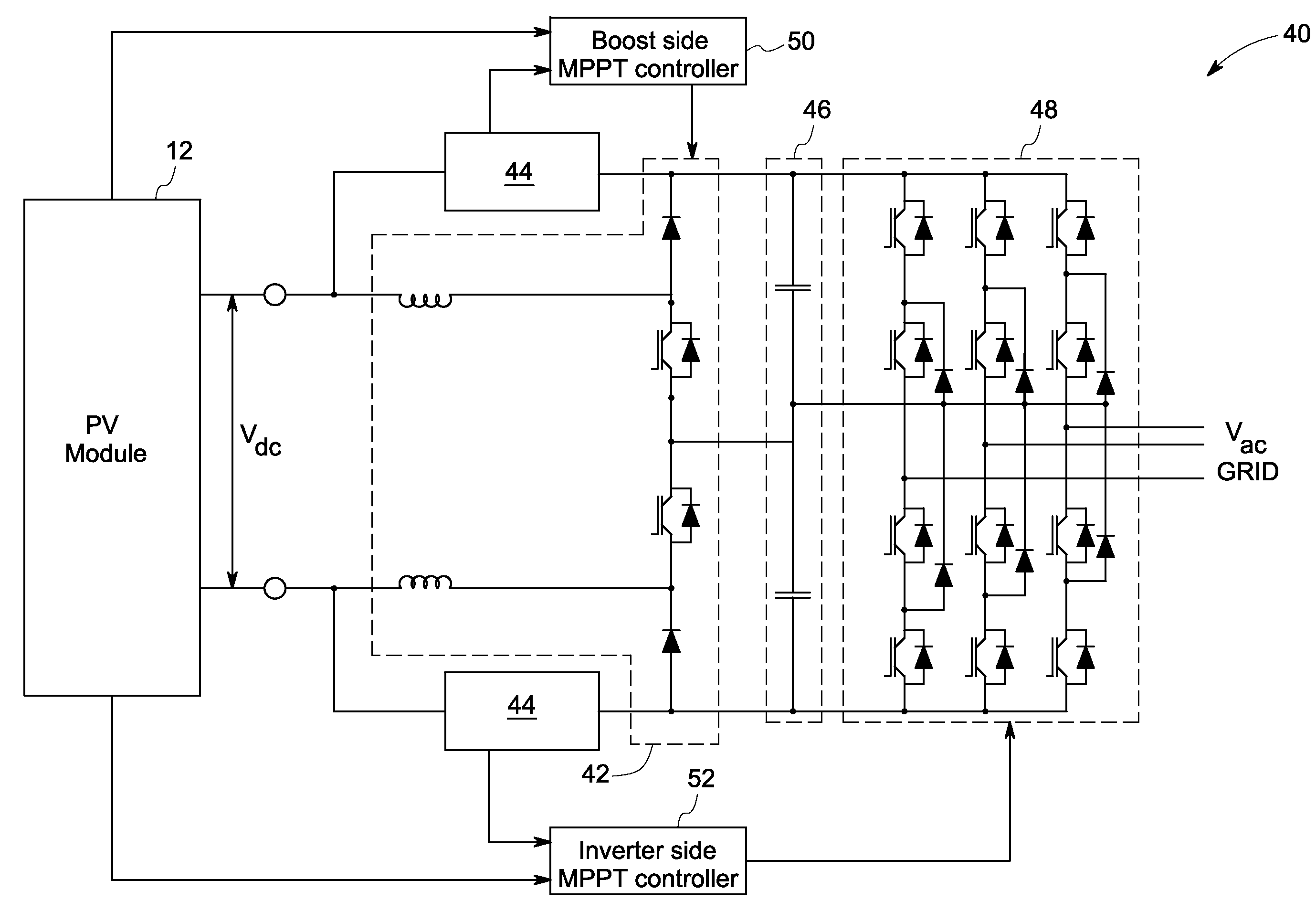
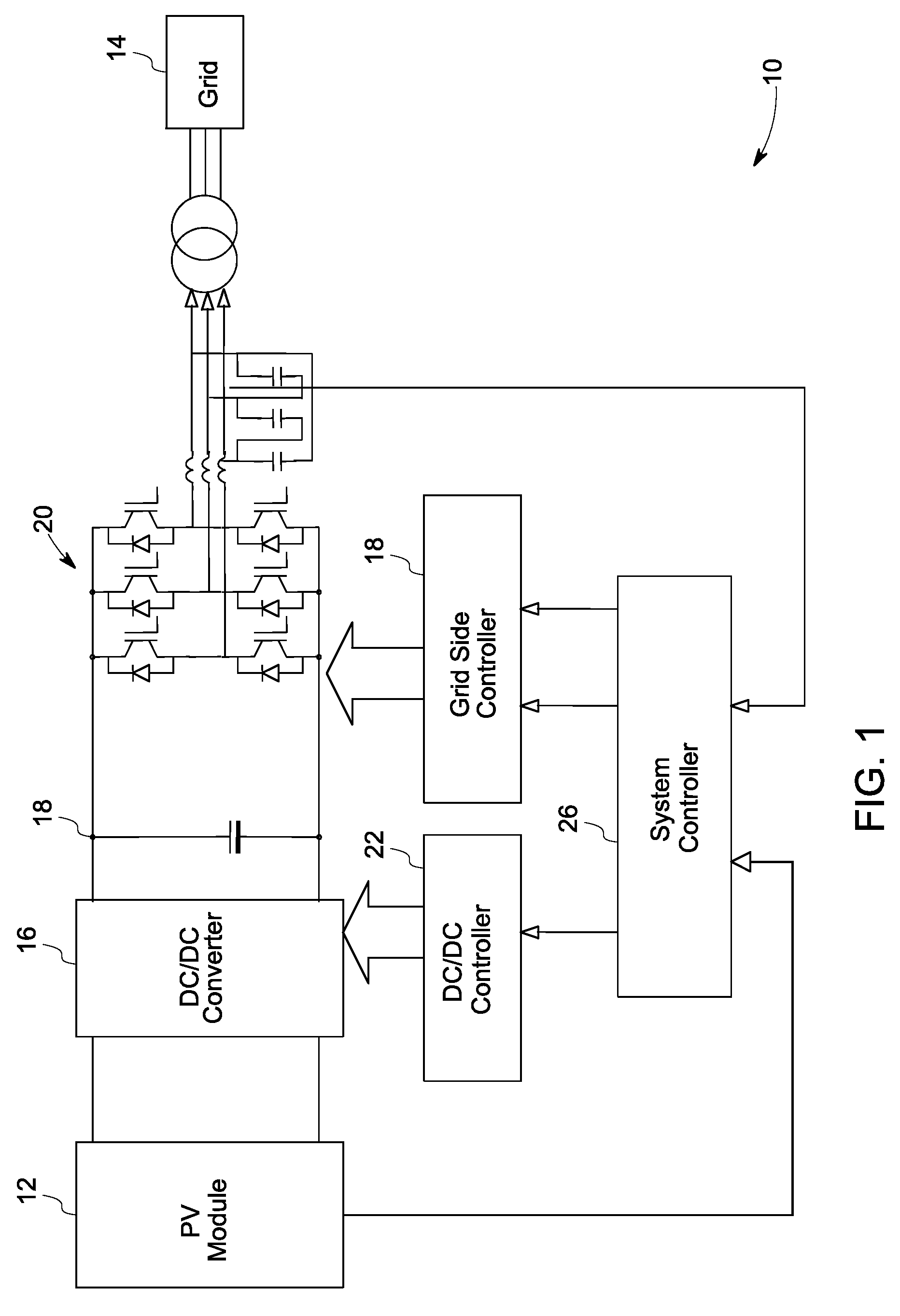
A power generation system including a photovoltaic (PV) module to generate direct current (DC) power is provided. The system includes a controller to determine a maximum power point for the power generation system and a boost converter for receiving control signals from the controller to boost the power from the PV module to a threshold voltage required to inject sinusoidal currents into the grid. A DC to alternating current (AC) multilevel inverter is provided in the system to supply the power from the PV module to a power grid. The system also includes a bypass circuit to bypass the boost converter when an input voltage of the DC to AC multilevel inverter is higher than or equal to the threshold voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High-Frequency Power MESFET Boost Switching Power Supply
InactiveUS20080186004A1Lower on-resistanceLow off-state drain leakageTransistorDc-dc conversionMOSFETHigh frequency power
A MESFET based boost converter includes an N-channel MESFET connected to a node Vx. An inductor connects the node Vx to a battery or other power source. The node Vx is also connected to an output node via a Schottky diode or a second MESFET or both. A control circuit drives the MESFET (and the second MESFET) so that the inductor is alternately connected to ground and to the output node. The maximum voltage impressed across the low side MESFET is optionally clamped by a Zener diode. In some implementations, the MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET. The MOSFET is switched off during sleep or standby modes to minimize leakage current through the MESFET. The MOSFET is therefore switched at a low frequency compared to the MESFET and does not contribute significantly to switching losses in the converter. In other implementations, more than one MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET, the MOSFETs being switched off during periods of inactivity to suppress leakage currents.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Enhanced receiver for wireless power transmission
Owner:ENERGOUS CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for a hybrid battery configuration for use in an electric or hybrid electric motive power system
InactiveUS7049792B2Optimize power systemImprove power densityMotor/generator/converter stoppersBatteries circuit arrangementsHigh energyElectric vehicle
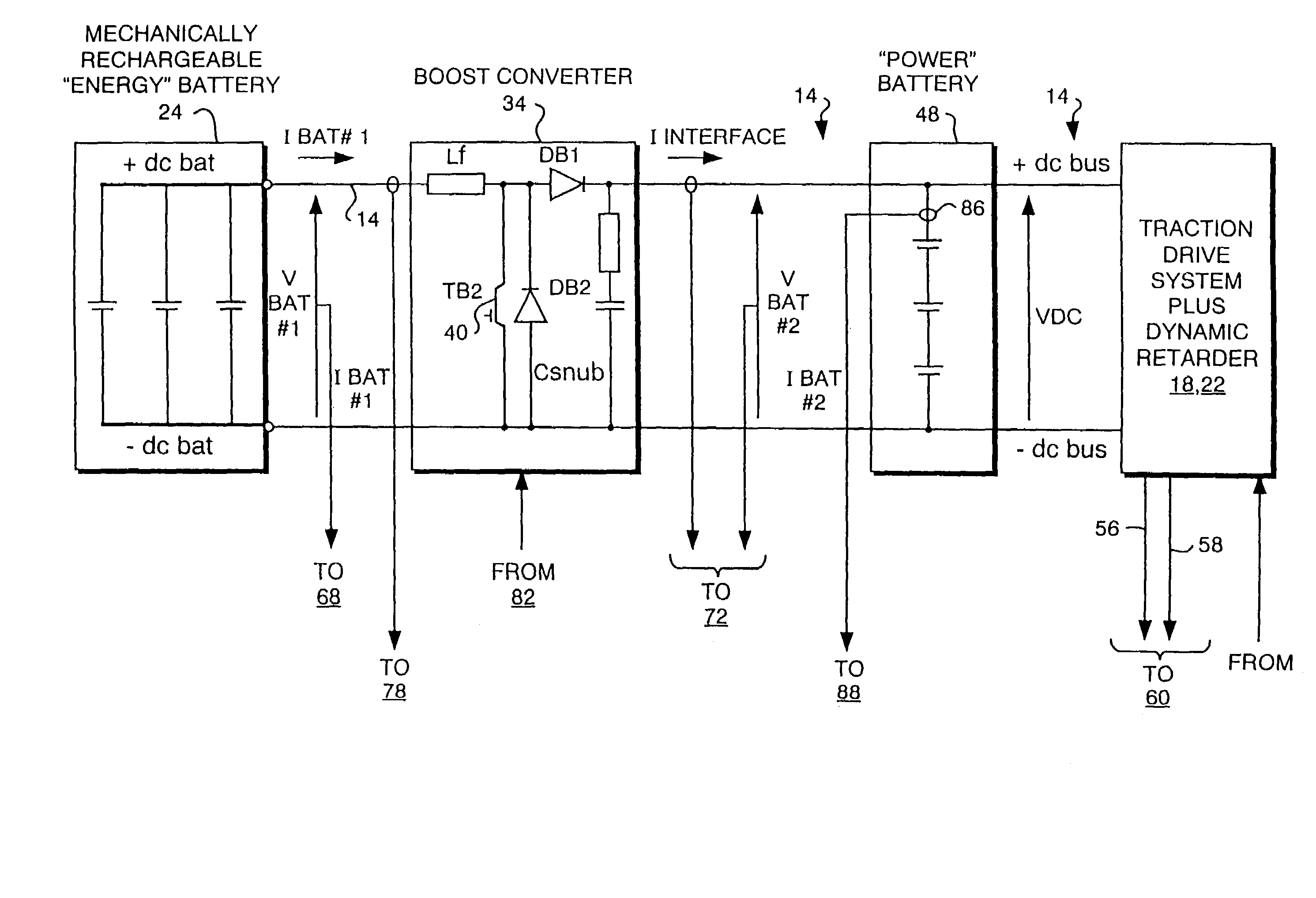
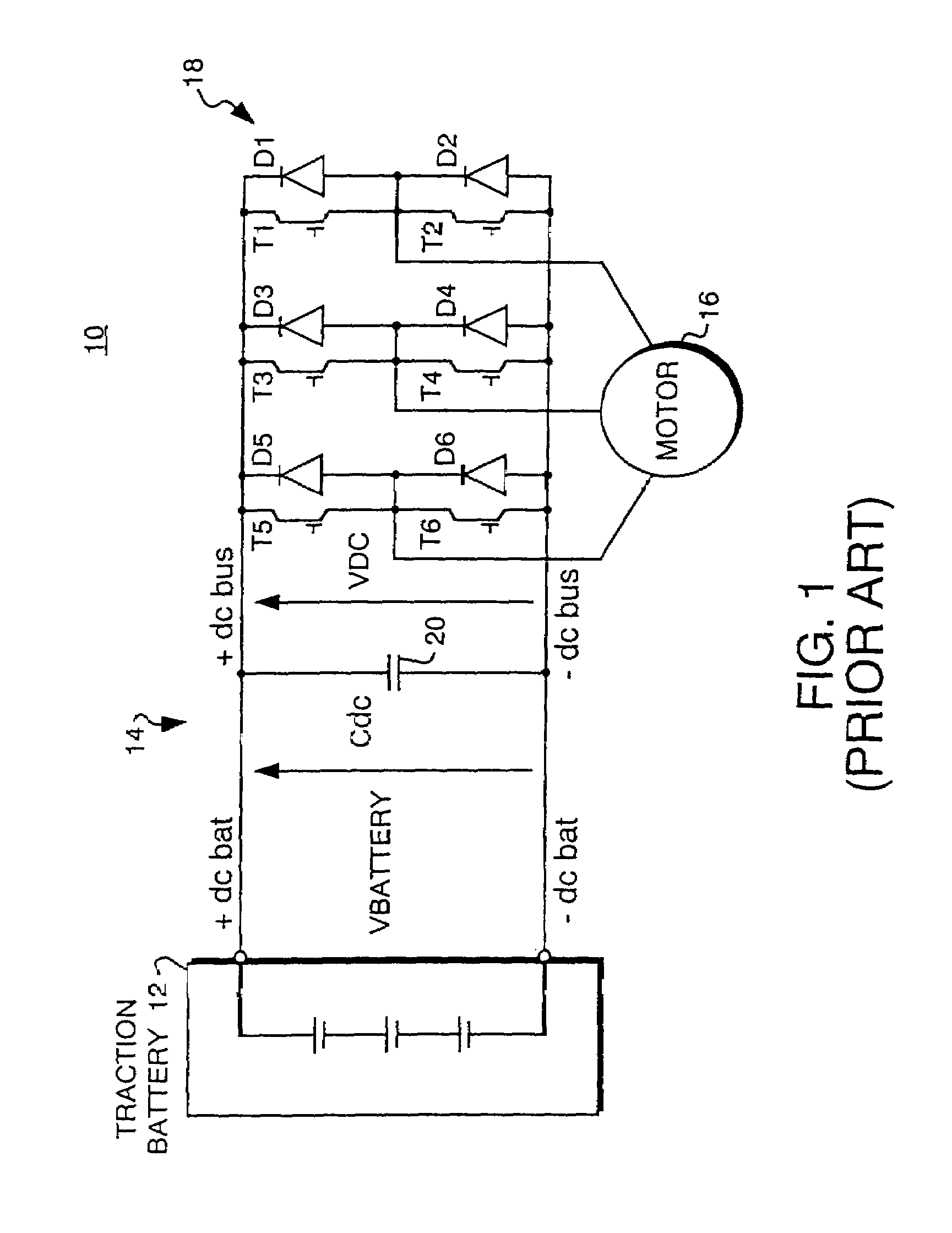
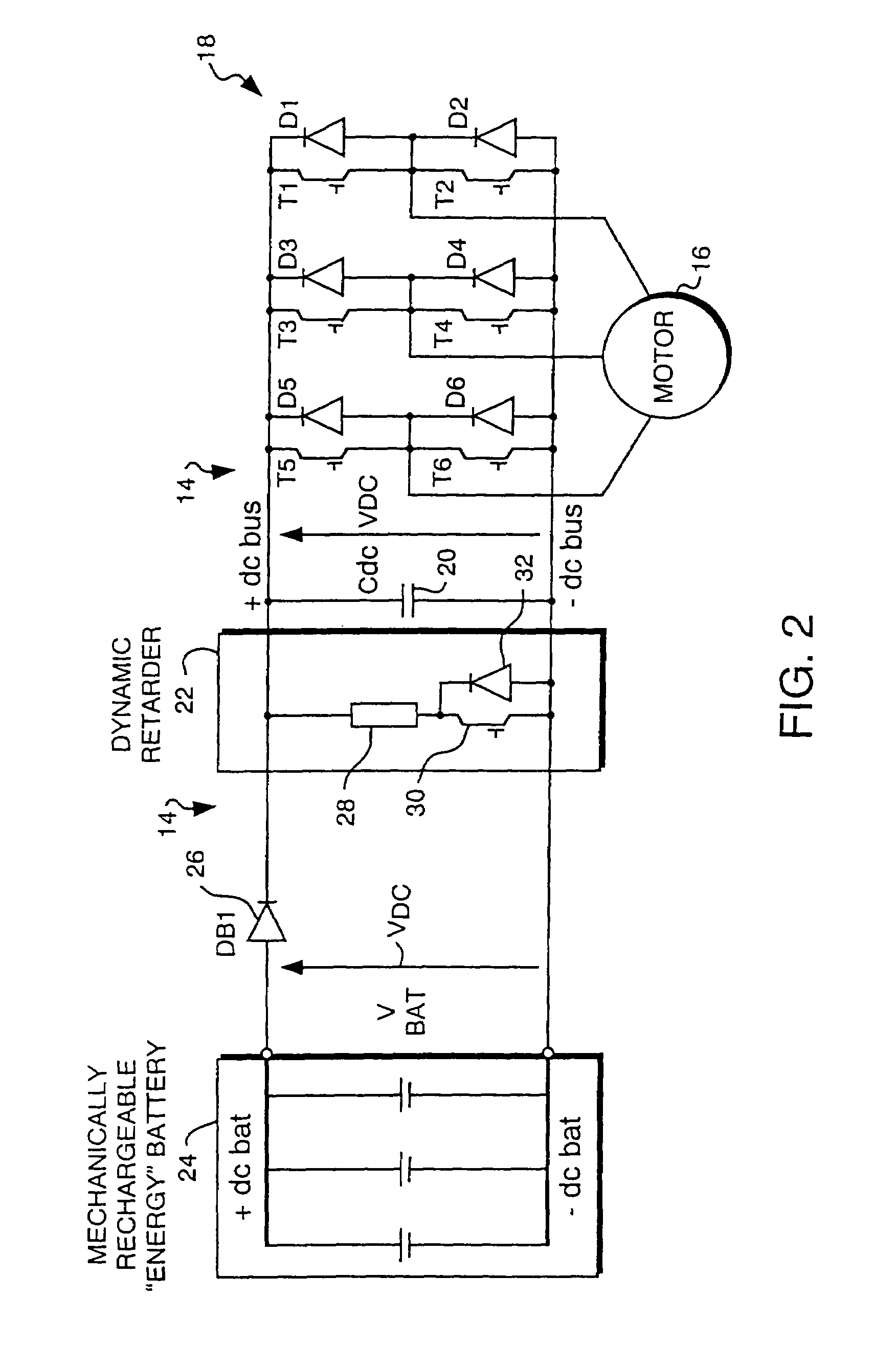
A power system for an electric motor drive such as may be used in an electrically propelled vehicle incorporates the combination of a high power density battery and a high energy density battery to provide an optimal combination of high energy and high power, i.e., a hybrid battery system. The hybrid battery system in one form includes components which prevent electrical recharge energy from being applied to the high energy density battery while capturing regenerative energy in the high power density battery so as to increase an electric vehicle's range for a given amount of stored energy. A dynamic retarding function for absorbing electrical regenerative energy is used during significant vehicle deceleration and while holding speed on down-hill grades, to minimize mechanical brake wear and limit excessive voltage on the battery and power electronic control devices. The high energy density battery coupled in circuit with a boost converter, a high power density battery, a dynamic retarder, and an AC motor drive circuit. The hybrid battery system is controlled by a hybrid power source controller which receives signals from a vehicle system controller using current and voltage sensors to provide feedback parameters for the closed-loop hybrid battery control functions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction
ActiveUS7266001B1Small sizeReduce Harmonic DistortionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionAverage currentEngineering
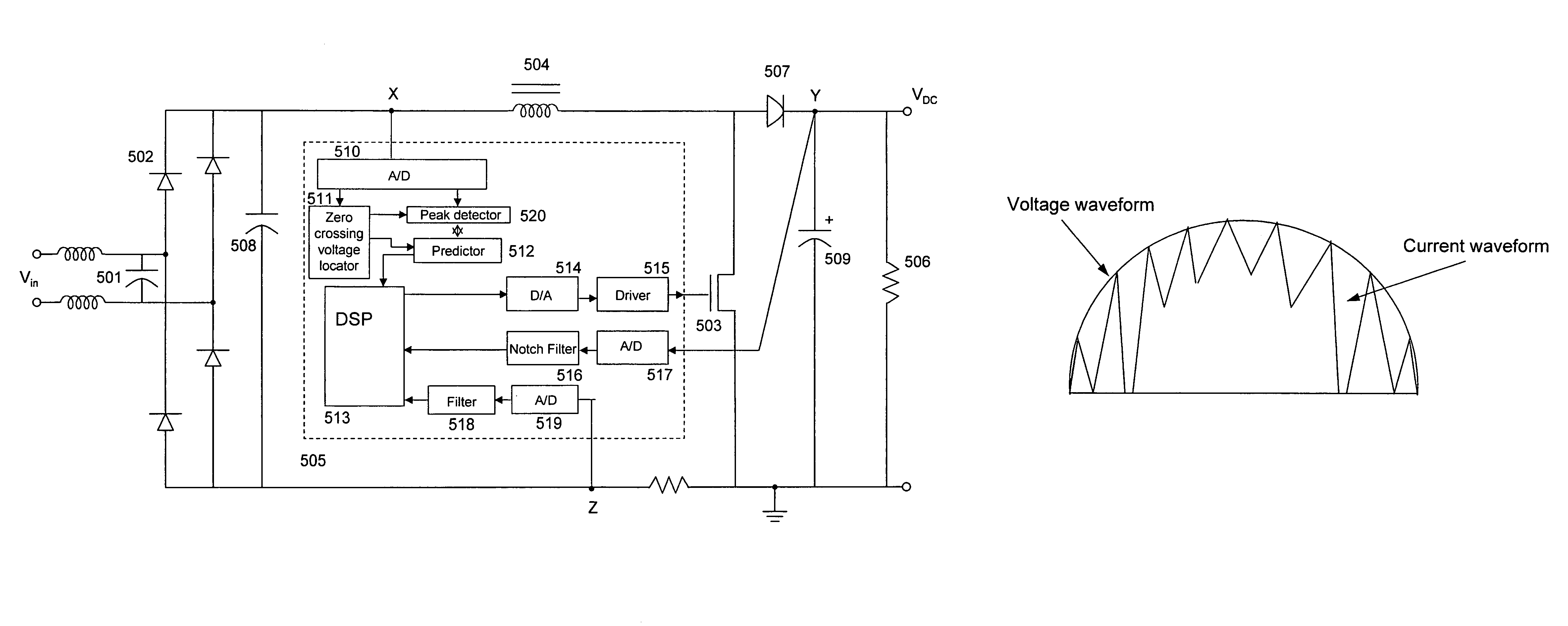
In a method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction in mixed operation modes, a frequency of the input voltage is obtained by detecting the zero crossing points of the input voltage. A peak of the input voltage is obtained by detecting input voltage with 90 degree phase. Thus, the present invention predicts the input voltage by its frequency and peak and the characteristic of the sine wave. A digital signal processor computes the duty and frequency of a boost switch, switching the operation mode of the boost converter among continuous mode, critical mode and discontinuous mode according to input voltage or the load. According to another aspect, the operation is switched to critical mode from the average current mode when a zero current is detected before the charging and recharging cycle of the boost switch is finished.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Switching regulator with automatic multi mode conversion
ActiveUS7944191B2Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl theoryBoost converter
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for efficient switching regulators that adapt automatically to, and operate with, input voltages that are above, below, or equal to the output voltage. The disclosed switching regulators demonstrate advantages of both buck and boost converters at high efficiency.
Owner:MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Photovoltaic module-mounted ac inverter
ActiveUS20080285317A1Total current dropIncrease the ripple frequencyConversion constructional detailsElectric power transfer ac networkEngineeringTransistor
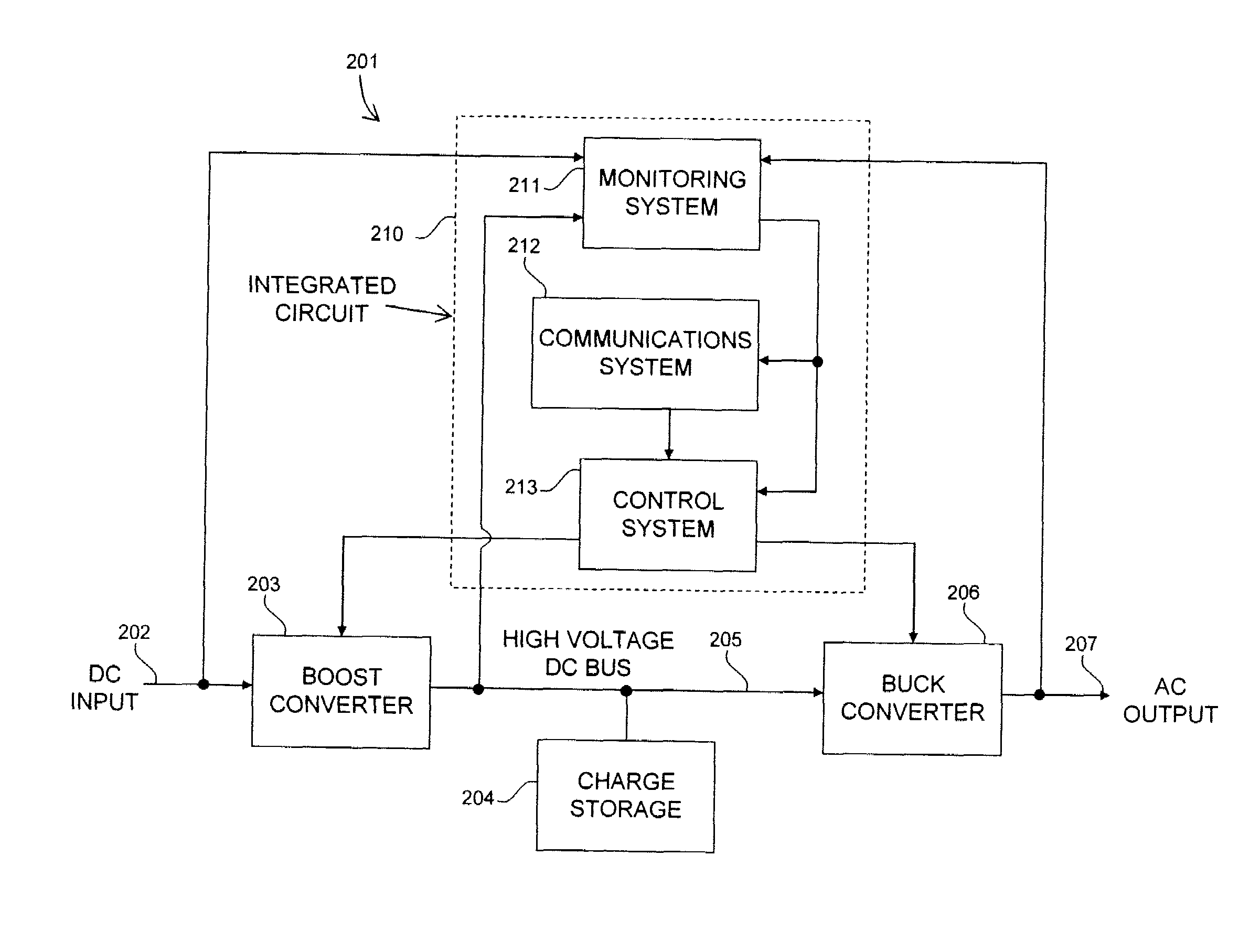
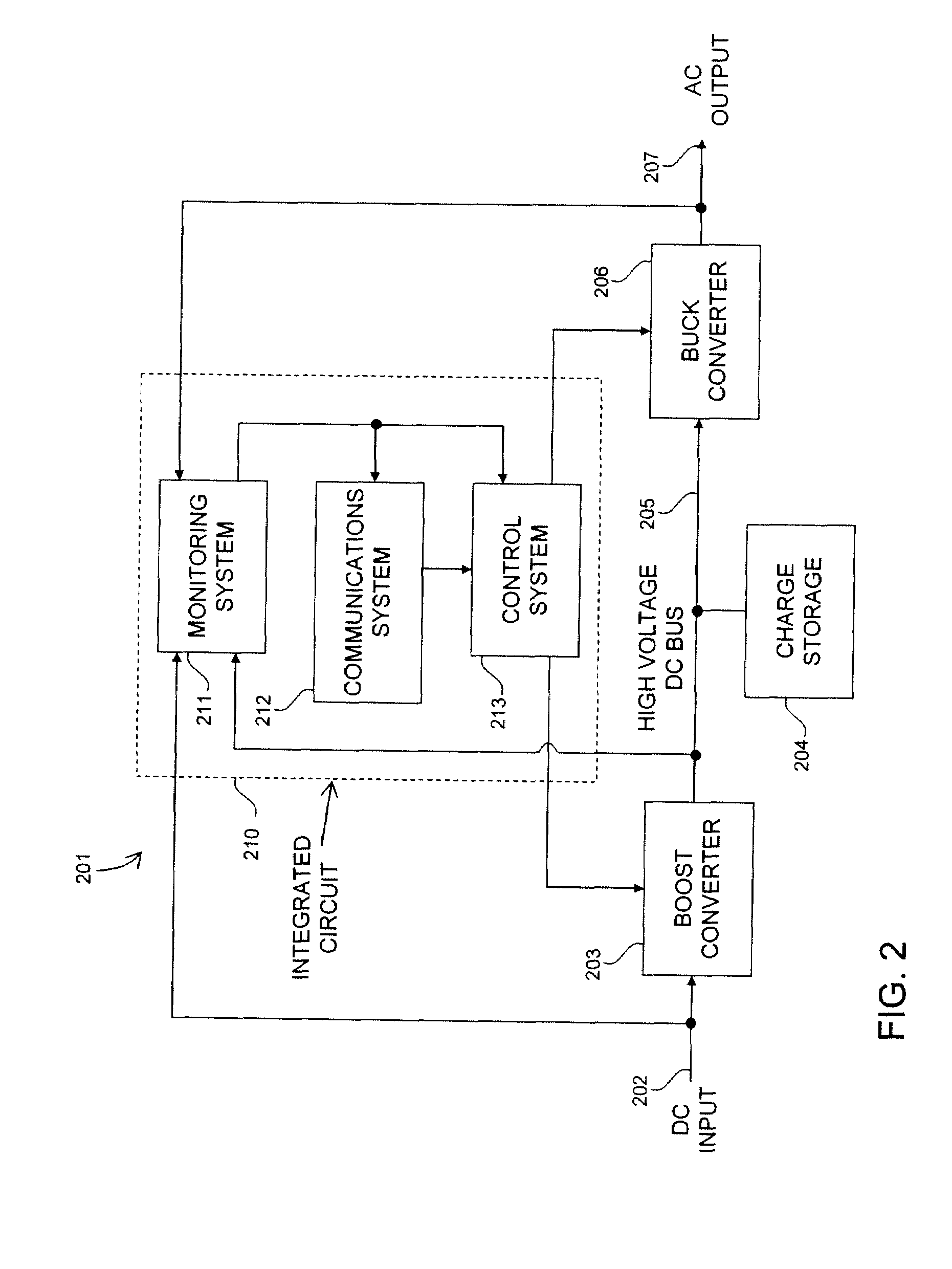
A photovoltaic module-mounted AC inverter circuit uses one or more integrated circuits, several power transistors configured as switches, several solid-dielectric capacitors for filtering and energy storage, several inductors for power conversion and ancillary components to support the above elements in operation. The integrated circuit includes all monitoring, control and communications circuitry needed to operate the inverter. The integrated circuit controls the activity of pulse-width modulated power handling transistors in both an input boost converter and a single-phase or multi-phase output buck converter. The integrated circuit also monitors all power processing voltages and currents of the inverter and can take appropriate action to limit power dissipation in the inverter, maximize the available power from the associated PV module and shut down the inverter output if the grid conditions so warrant. The integrated circuit implements power line communications by monitoring the AC wiring for signals and generating communications signals via the same pulse-width modulation system used to generate the AC power. Communications is used to report inverter and PV module status information, local identification code and to allow for remote control of inverter operation.
Owner:ENPHASE ENERGY
Non-synchronous boost converter including switched schottky diode for true disconnect
ActiveUS20060176029A1Avoid conductionTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionLDMOSControl signal
A non-synchronous boost converter includes a switched Schottky diode to rectify the switched output voltage of the boost converter where the switched Schottky diode has forward conduction blocking capability. The switched Schottky diode has an anode terminal coupled to receive the switched output voltage, a cathode terminal providing the output DC voltage, and a gate terminal coupled to receive a control signal. The control signal has a first state for turning the switched Schottky diode on where the switched Schottky diode conducts current when forward biased and a second state for turning the switched Schottky diode off where forward conduction of the switched Schottky diode is blocked even when the diode is forward biased. The switched Schottky diode can be a JFET controlled or an LDMOS gate controlled Schottky diode. Furthermore, the switched Schottky diode can be formed on-chip or off-chip of the controller circuit of the boost converter.
Owner:MICREL
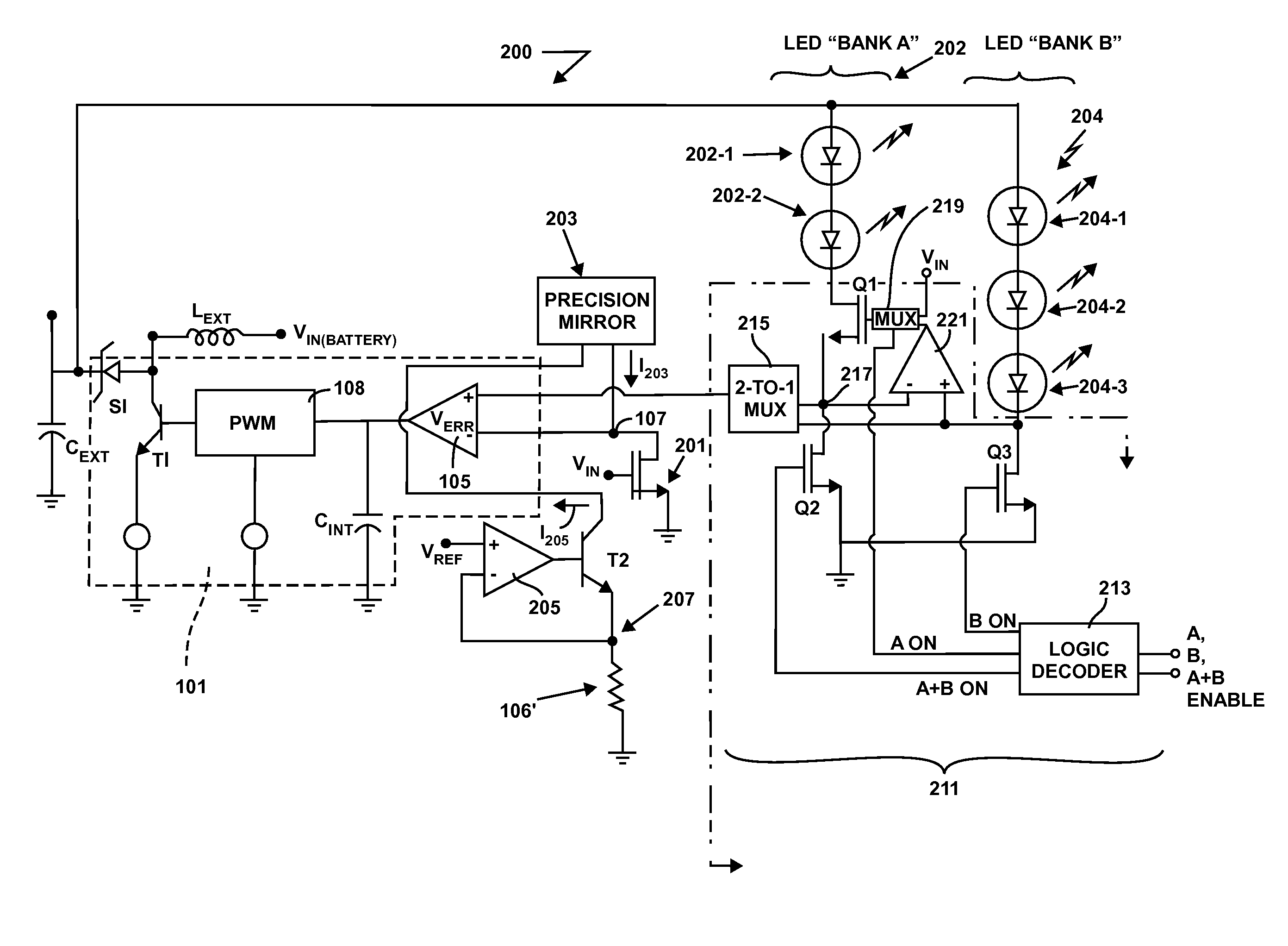
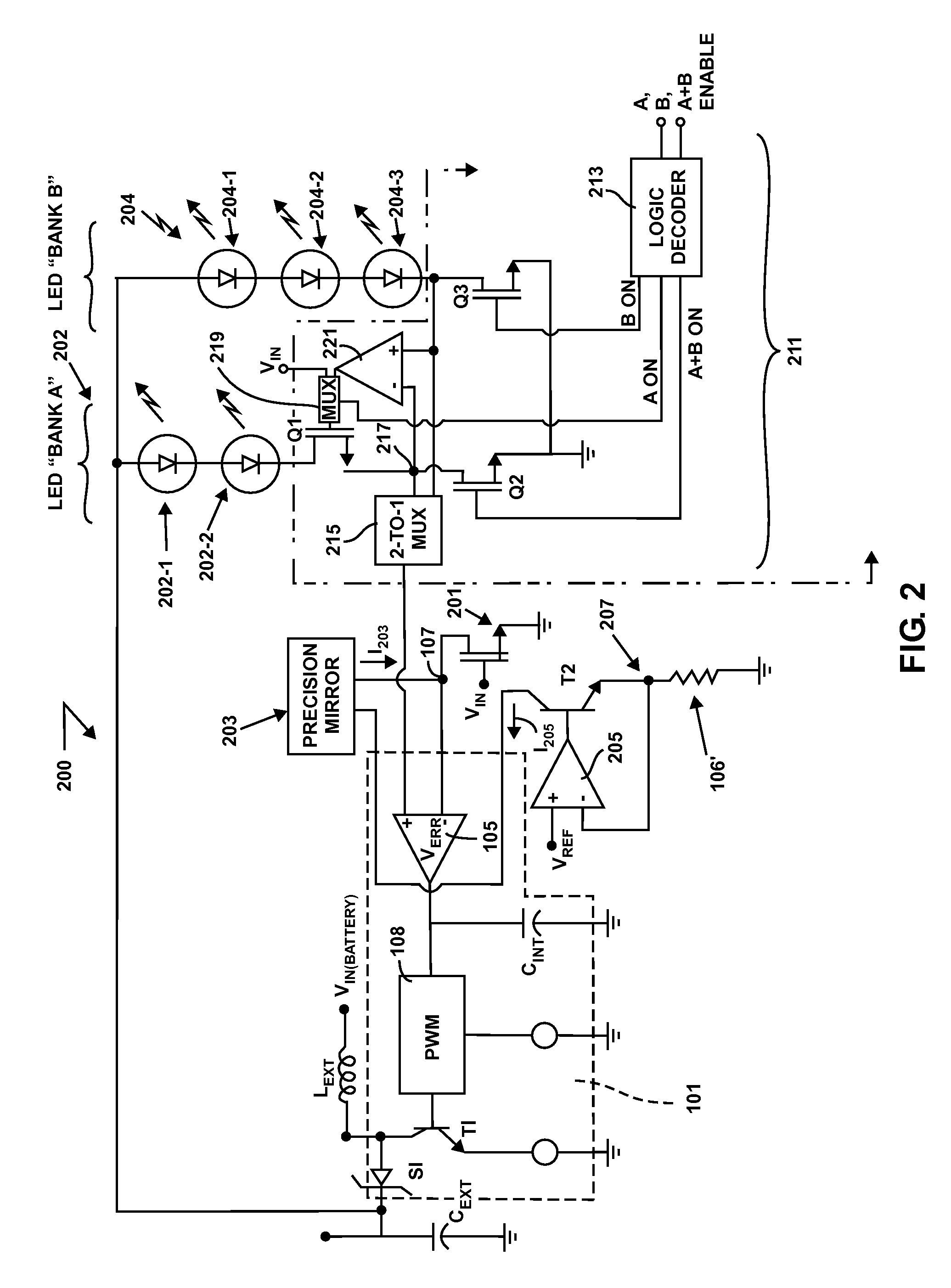
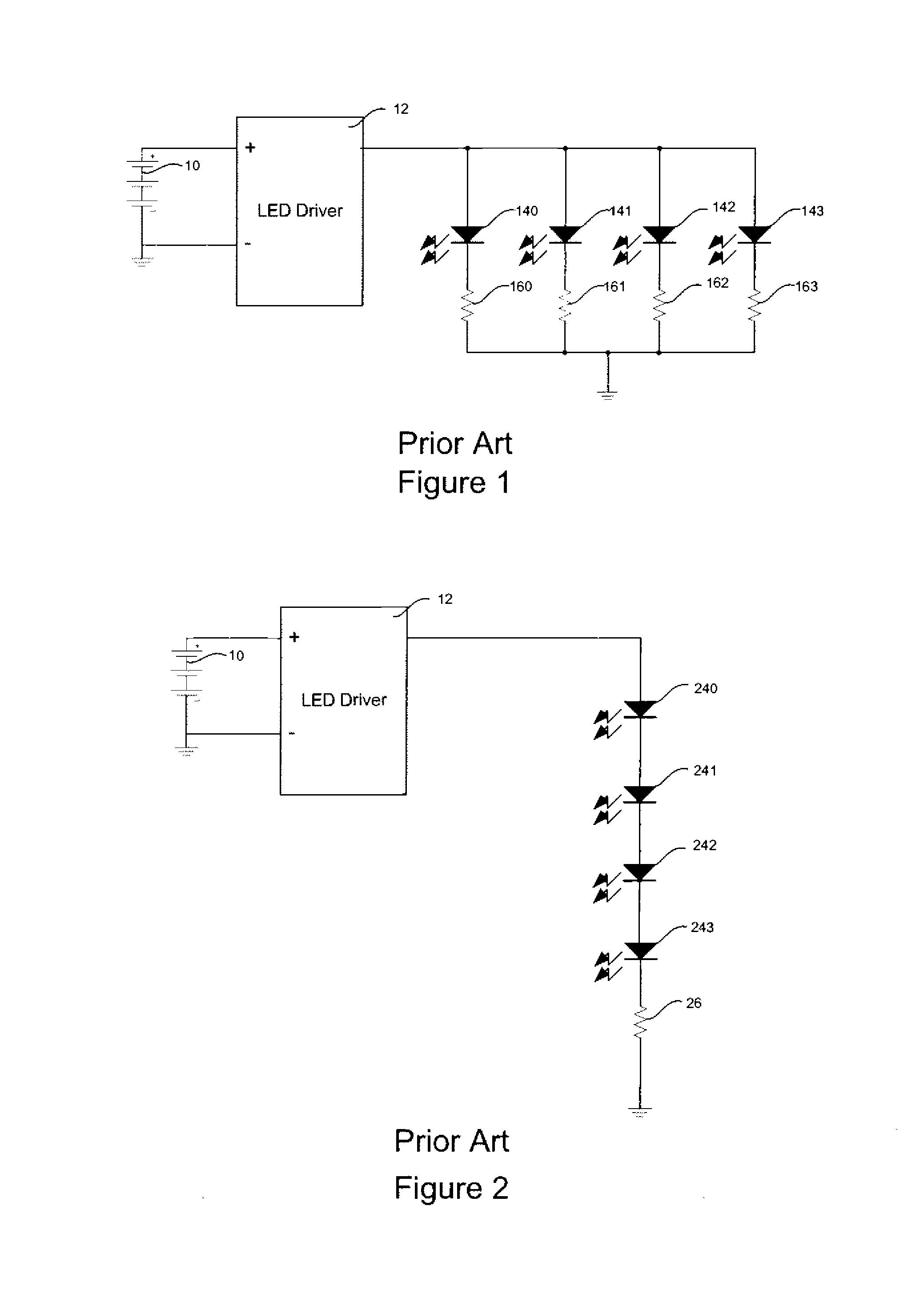
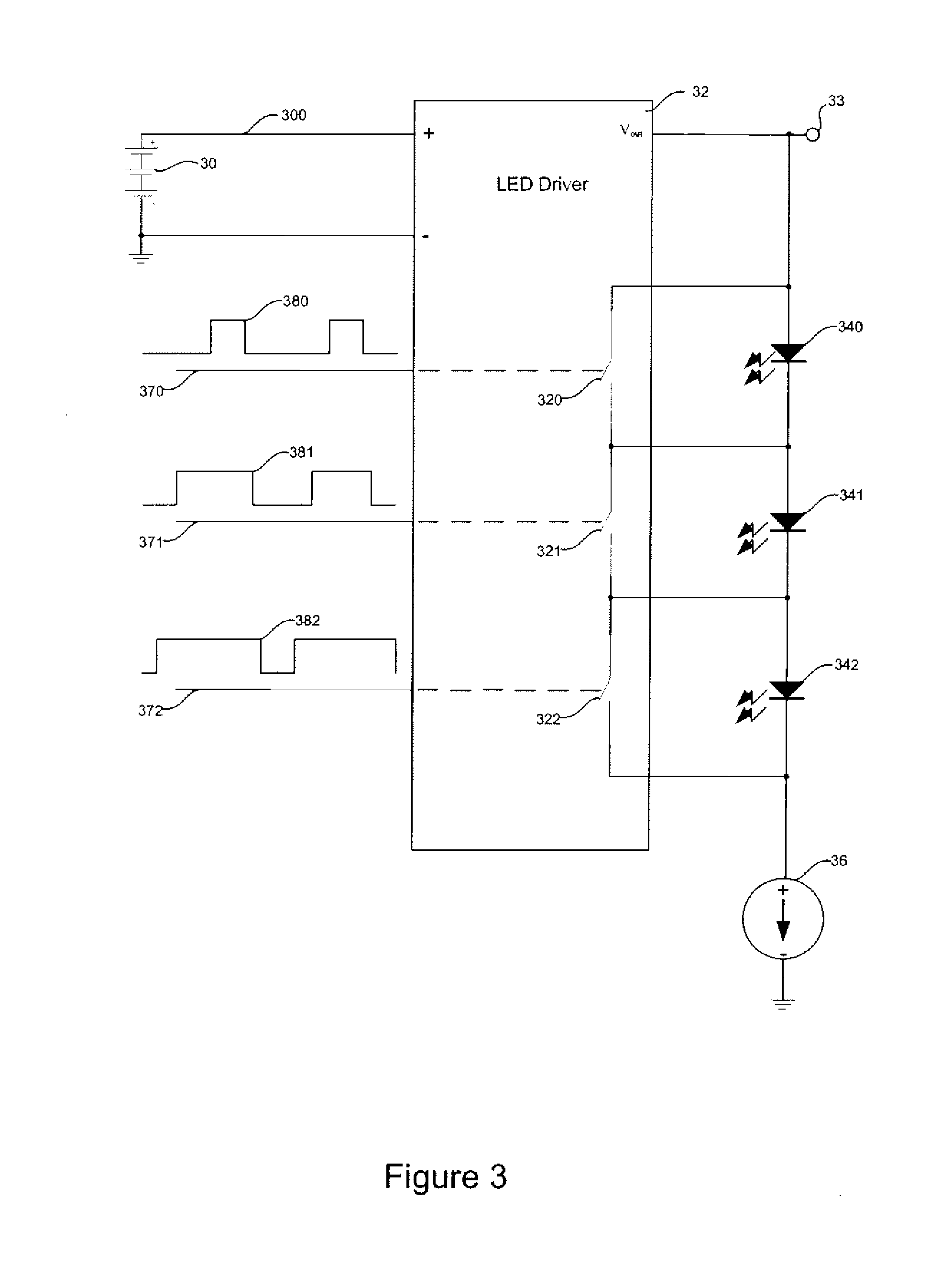
Light emitting diode driver circuit
Describe is a device for a multiplexing, output current-sensed, boost converter circuit which may be used as an LED driver. A boost converter LED driver circuit using a single set of passive external LC components for controlling the current through, and thus the output of, one and more than one bank of LEDs. The present invention allows for regulated current in one and more than one bank of LEDs by sensing current in the controller. The output voltage of a switcher adjusts it's level automatically until the current to the LEDs is set to the desired LED threshold requirement.
Owner:MICREL
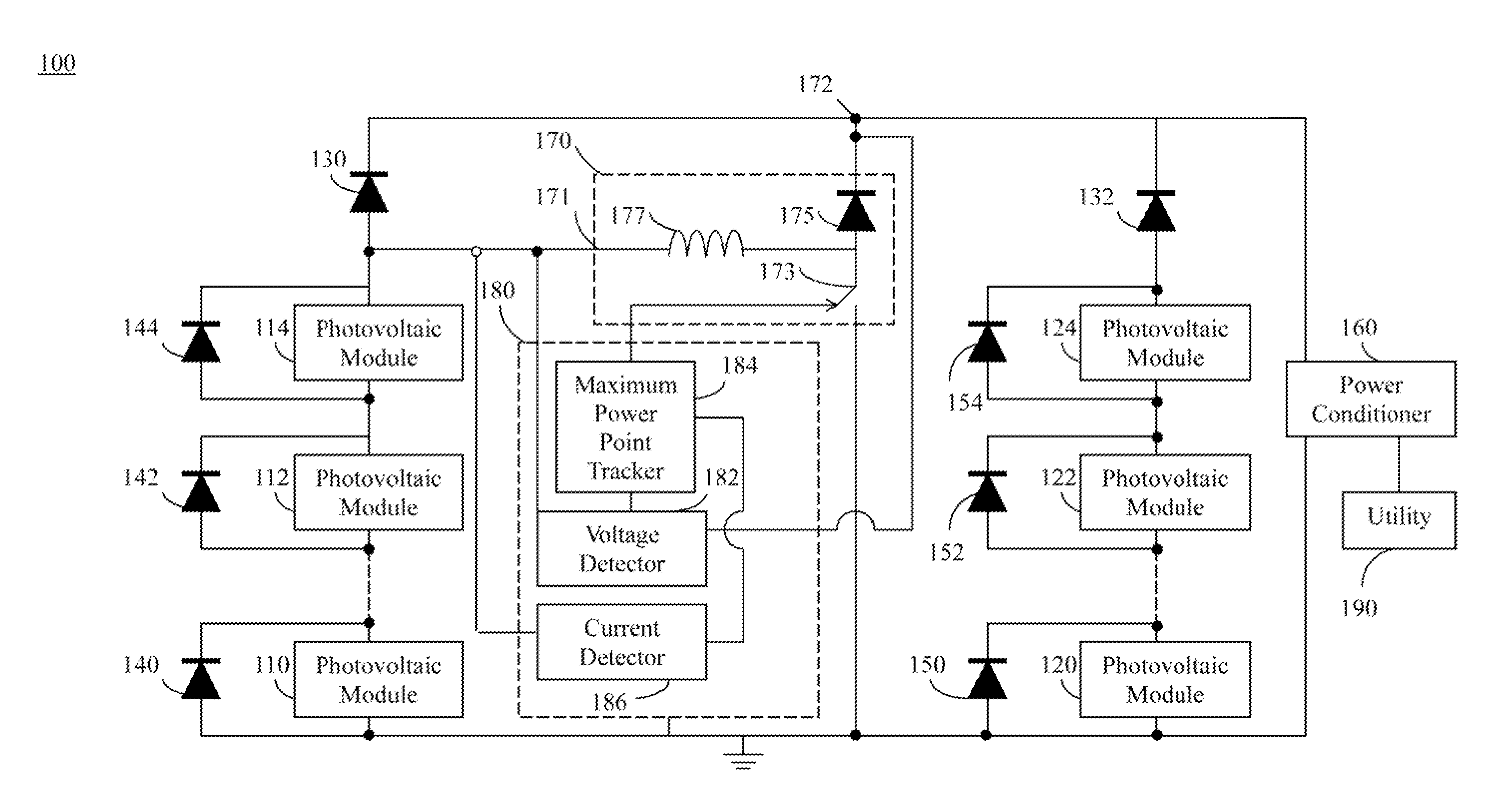
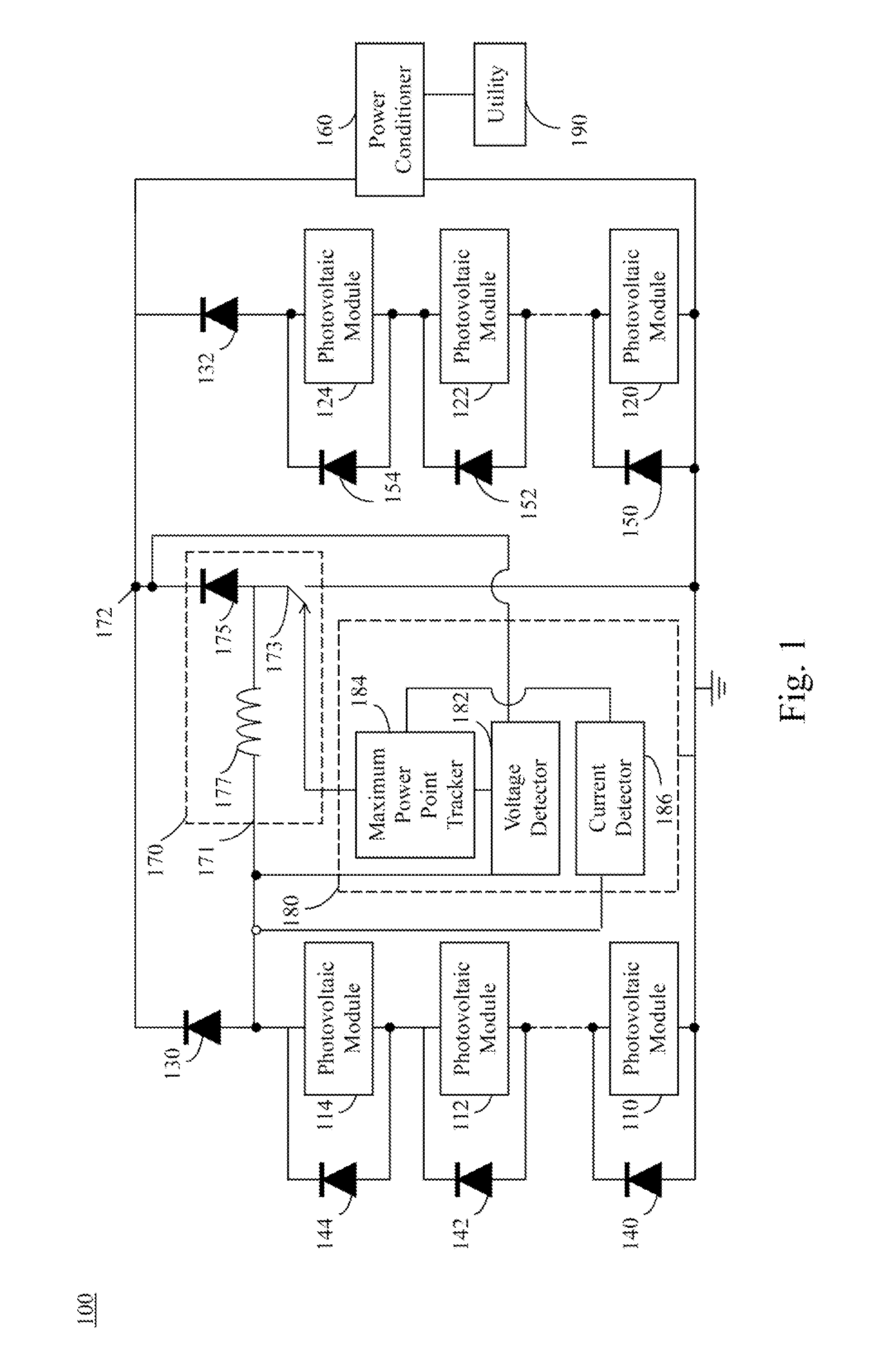
Photovoltaic system and boost converter thereof
A photovoltaic system is disclosed herein, which includes a blocking diode, a string of photovoltaic modules, a boost converter and a controller. The photovoltaic modules are connected in series with the blocking diode. A voltage input terminal of the boost converter is connected to an anode of the blocking diode, and a voltage output terminal of the boost converter is connected to a cathode of the blocking diode. In use, the controller can drive the boost converter when the blocking diode is cut off.
Owner:DU PONT APOLLO
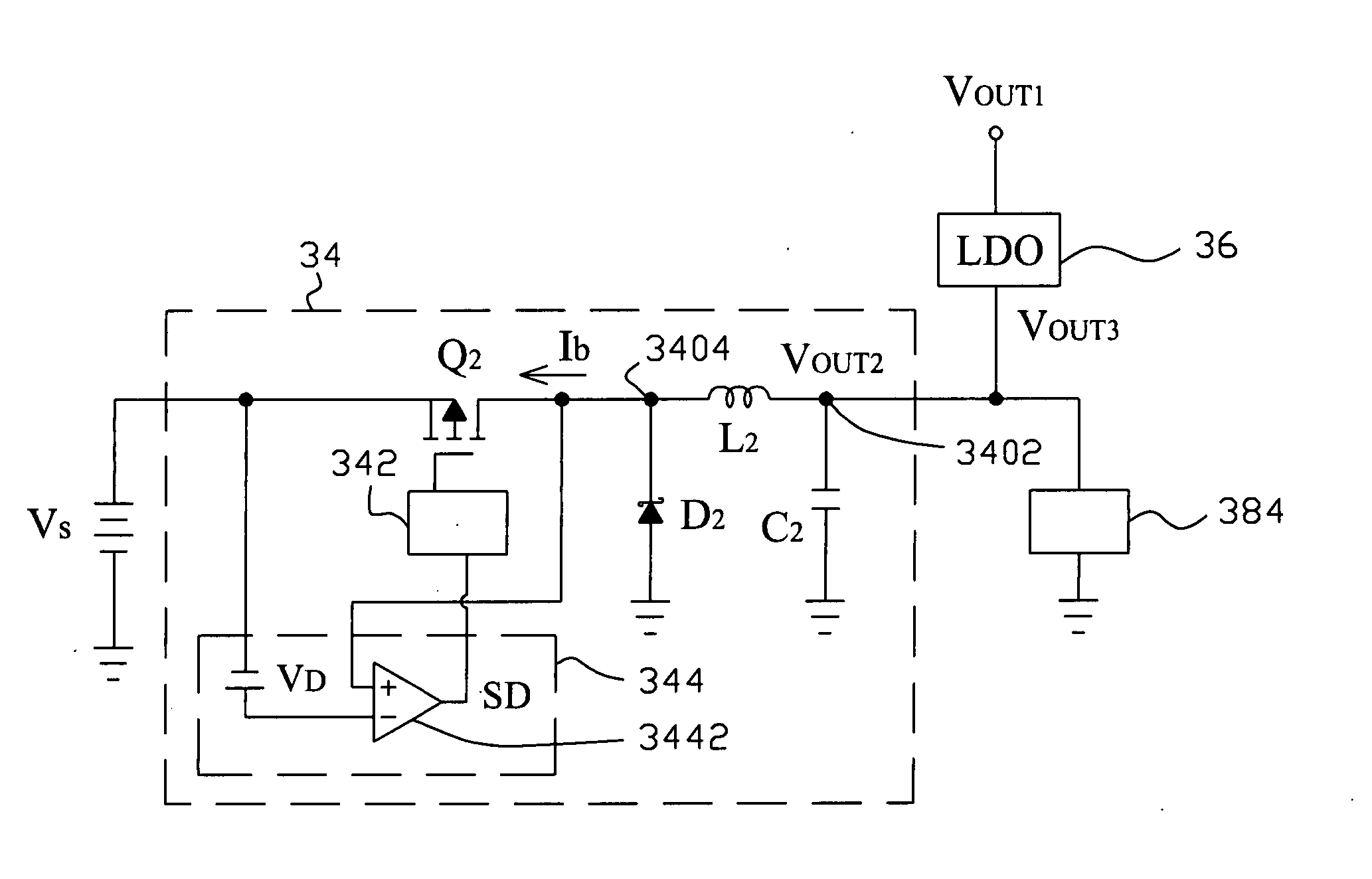
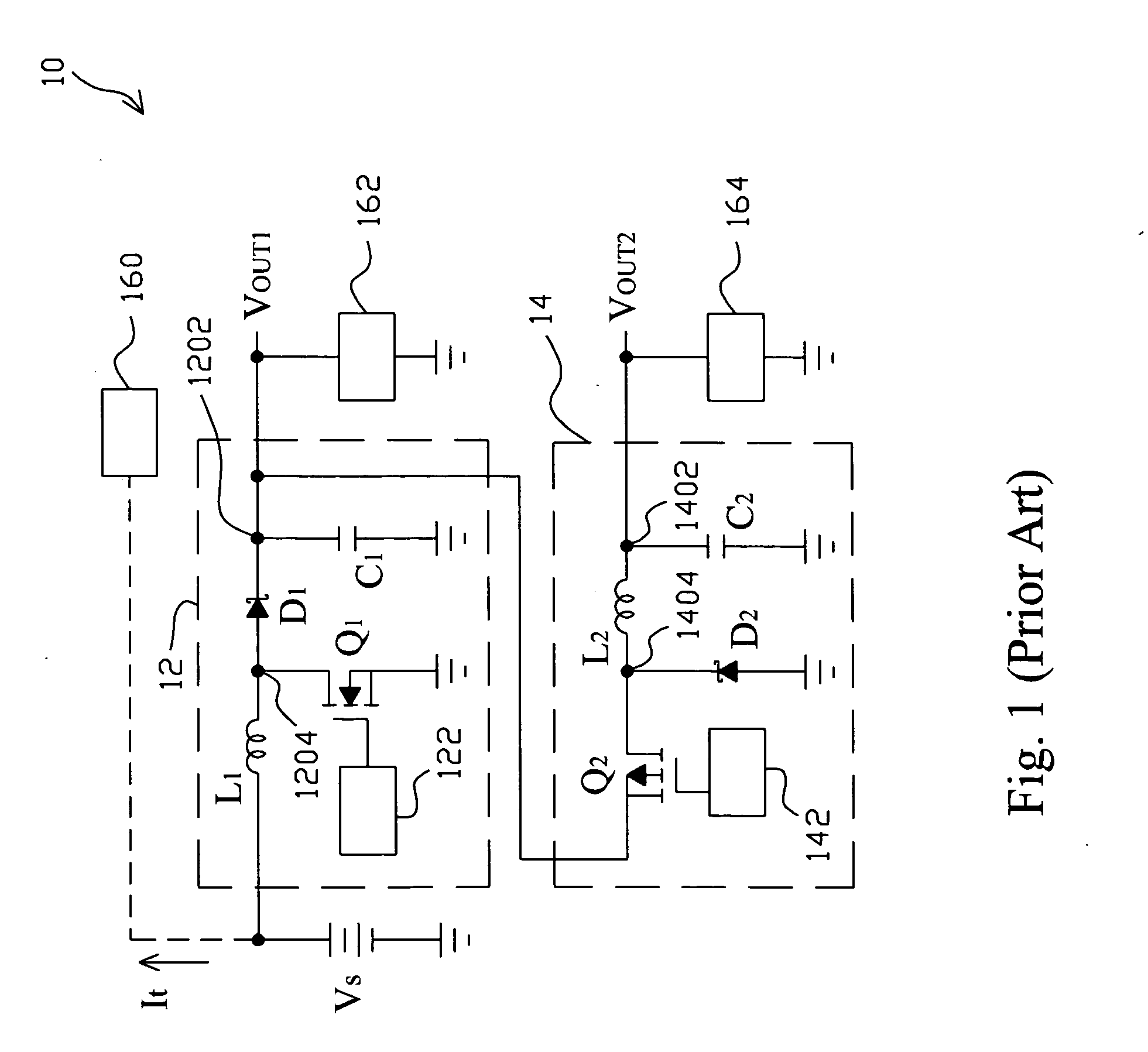
Efficiency improved voltage converter
InactiveUS20050017701A1Improve efficiencyAvoid flowElectric variable regulationVoltage converterBuck converter
A voltage converter improves the efficiency thereof by connecting a boost converter and an LDO regulator with a buck converter in parallel. The boost converter boosts up a supply voltage to generate a first output voltage at a first output, and the buck converter bucks down the supply voltage to generate a second output voltage at a second output. When the second output voltage is lower than a threshold, the LDO regulator converts the first output voltage to a third voltage at said second output.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
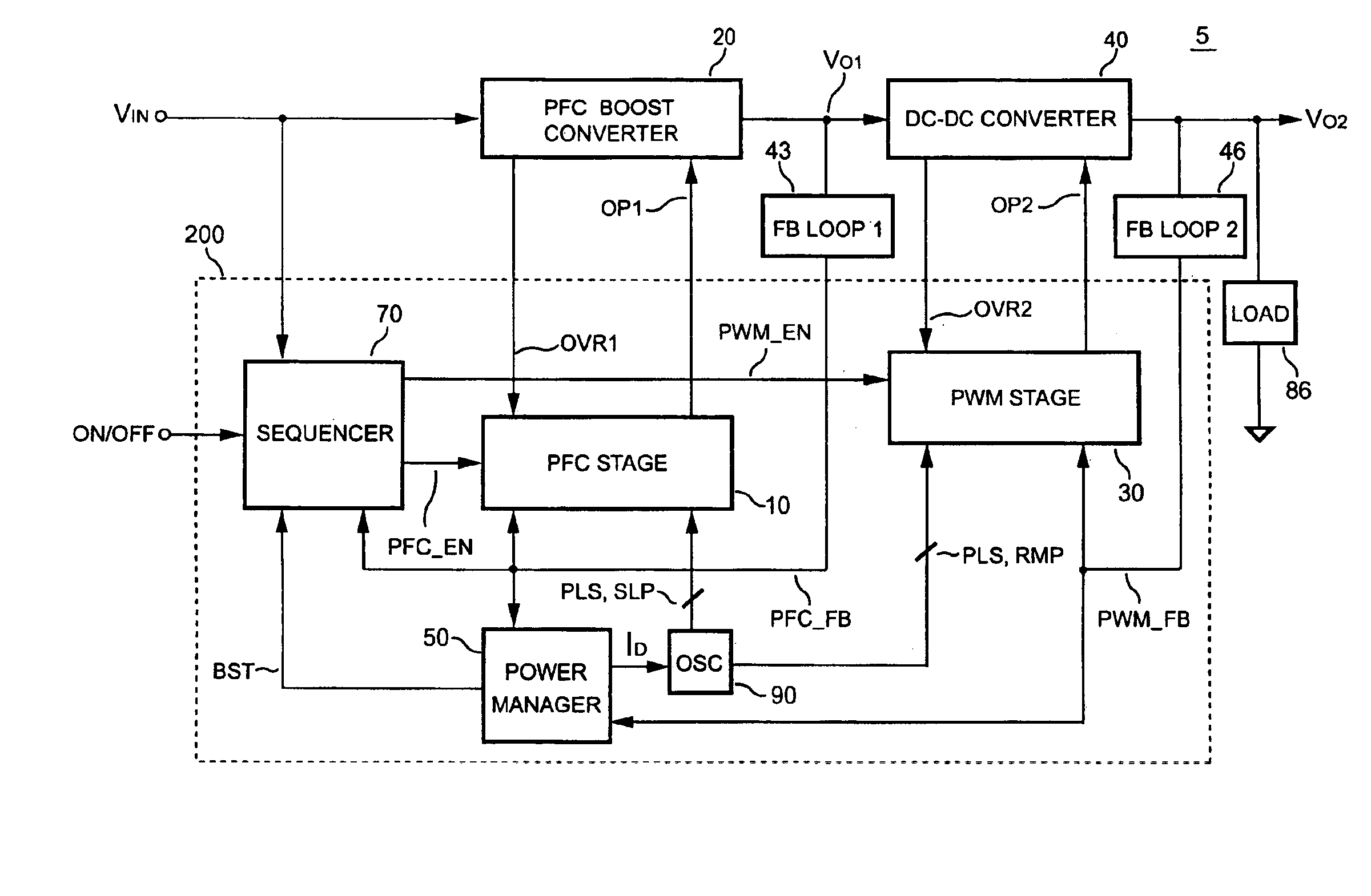
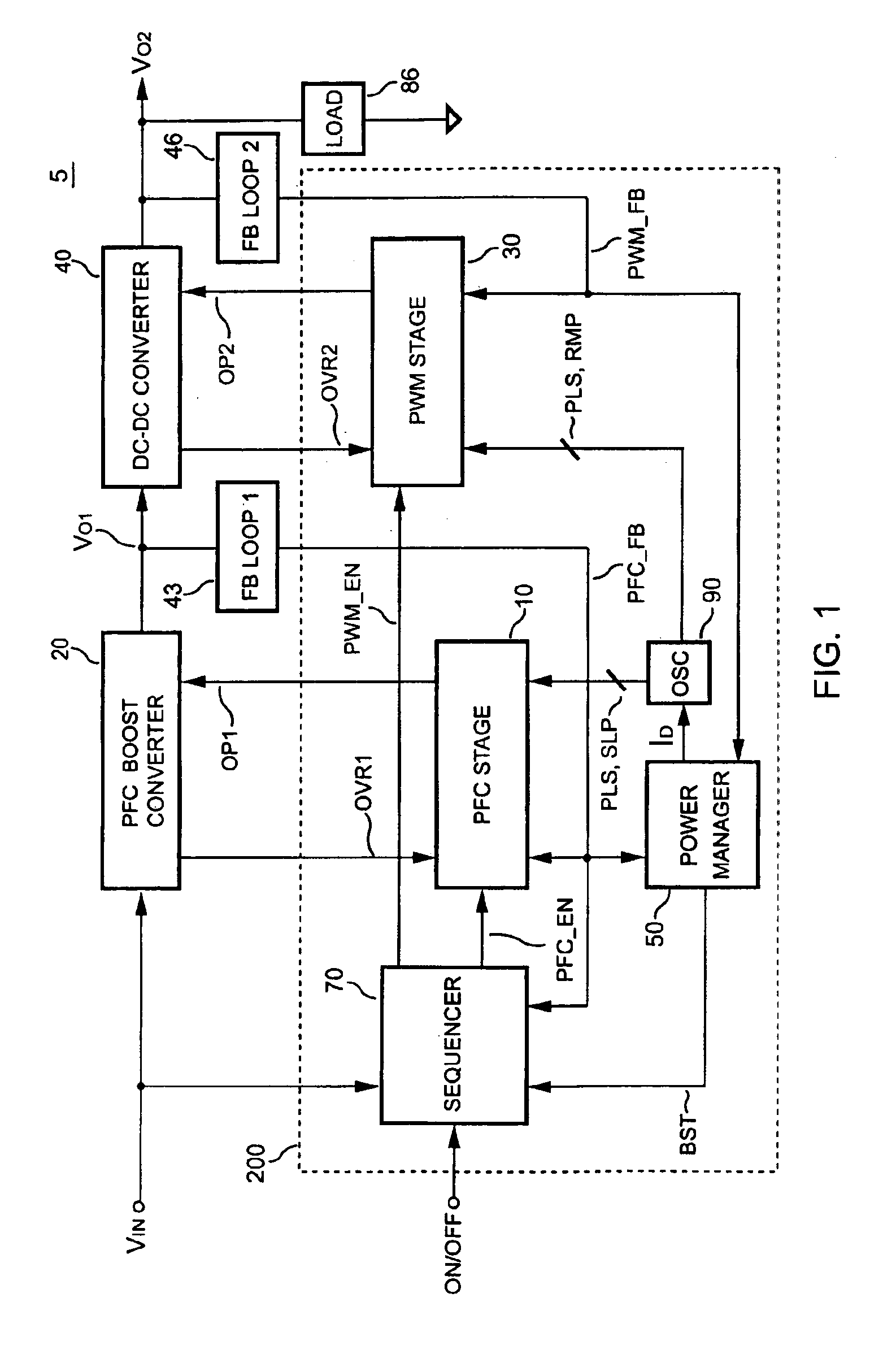
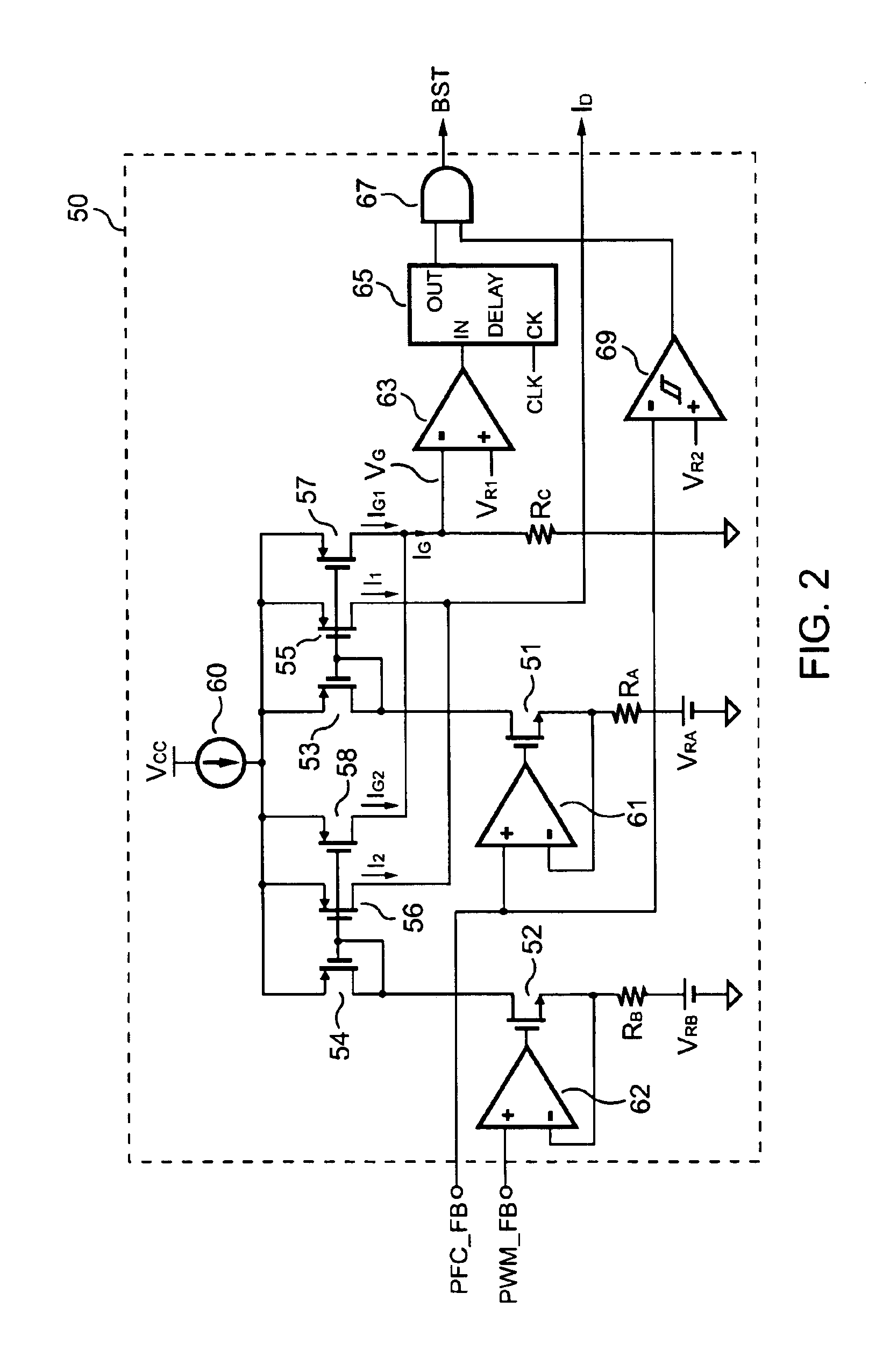
PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching
InactiveUS6903536B2Reduce switching noiseIncrease the pulse widthEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDead timeSwitching signal
The present invention discloses a PFC-PWM controller having interleaved switching. A PFC stage generates a PFC signal for switching a PFC boost converter of a power converter. A PWM stage generates a PWM signal for switching a DC-to-DC converter of the power converter. The PFC-PWM controller includes a power manager for generating a discharge current and a burst-signal. Under light-load conditions, the discharge current decreases in proportion to a load of the power converter. The burst signal is utilized to disable the PFC signal in a suspended condition for power saving. A pulse width of the pulse-signal ensures a dead time to spread switching signals, such as the PFC and PWM signals, and reduces switching noise. When the discharge current decreases, the pulse width of the pulse-signal will increase and a frequency of the pulse-signal will decrease correspondingly. This further reduces power consumption under light-load and zero-load conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
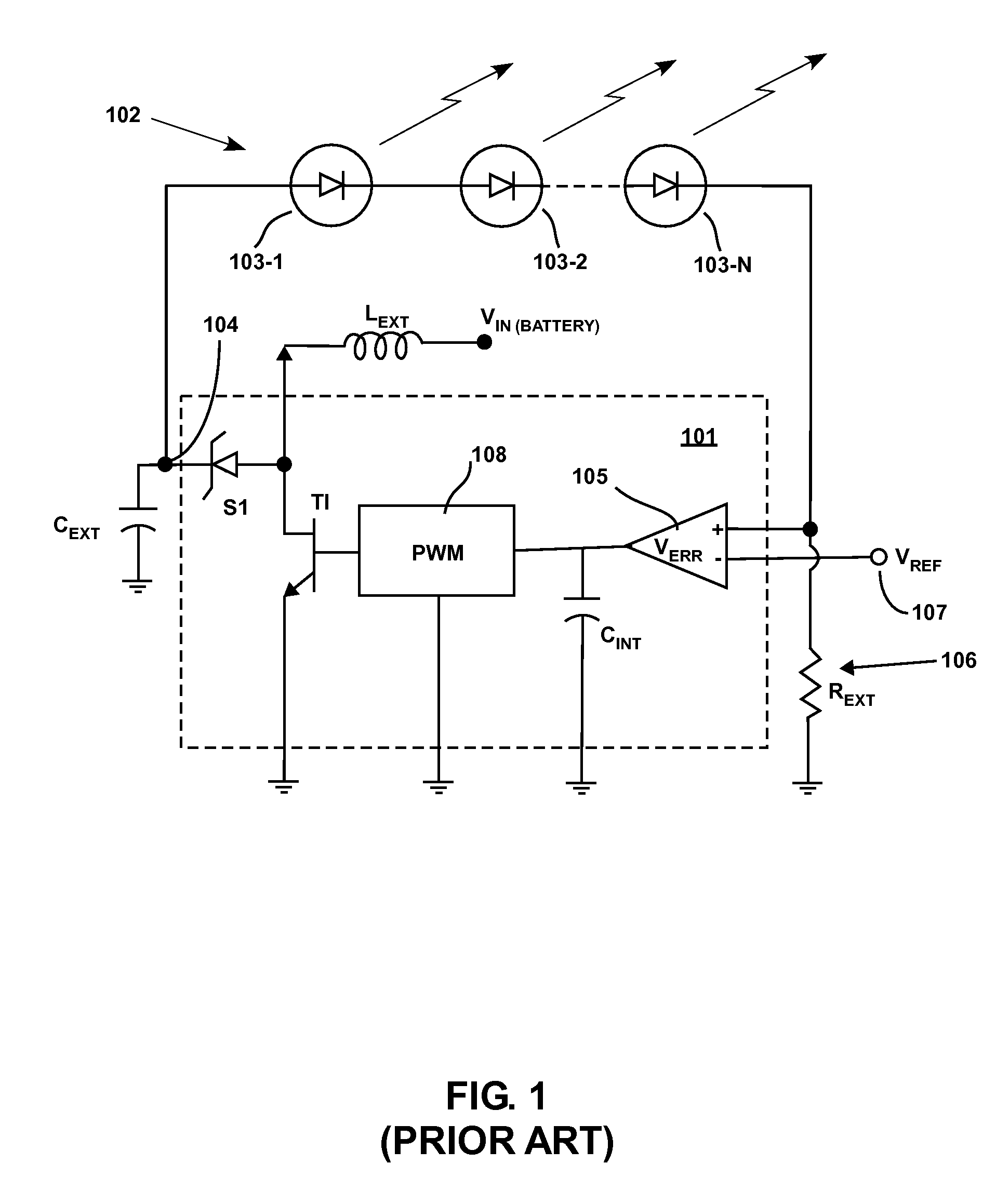
Driving parallel strings of series connected LEDs
InactiveUS20080001547A1Batteries circuit arrangementsElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringBoost converter
Systems and methods are described that provide an efficient and cost-effective LED driver for controlling strings of LEDs. Embodiments described include an LED driver that comprises an adaptive boost converter and current source that cooperate to provide a desired light output from energized LEDs. Systems and methods are also described that modulate the excitation of the LEDs using a pulsed signal to obtain brightness control. Techniques are described for controlling the operation of individual LEDs in a string of LEDs such that a desired level of light output can be achieved. Embodiments are described in which multicolored LEDs can be included in strings of LEDs and excitation of the individual LEDs can be controlled to obtained a desired color of output.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Power converter apparatus and methods using output current feedforward control
InactiveUS20060043942A1Fast load transient responseReduce the amount requiredDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringInductor
A controller for a boost converter includes a first current sense input configured to receive an inductor current sense signal representative of a current in the inductor and a second current sense input configured to receive an output current sense signal representative of an output current of the boost converter. The controller further includes a control circuit configured to be coupled to a boost switch of the boost converter and to control the boost switch responsive to the received inductor current sense signal to force an input current of the boost converter directly proportional to the output current and to an input voltage of the boost converter and inversely proportional to an output voltage of the boost converter. The invention may be embodied as apparatus or methods.
Owner:LAMBDA AMERICAS
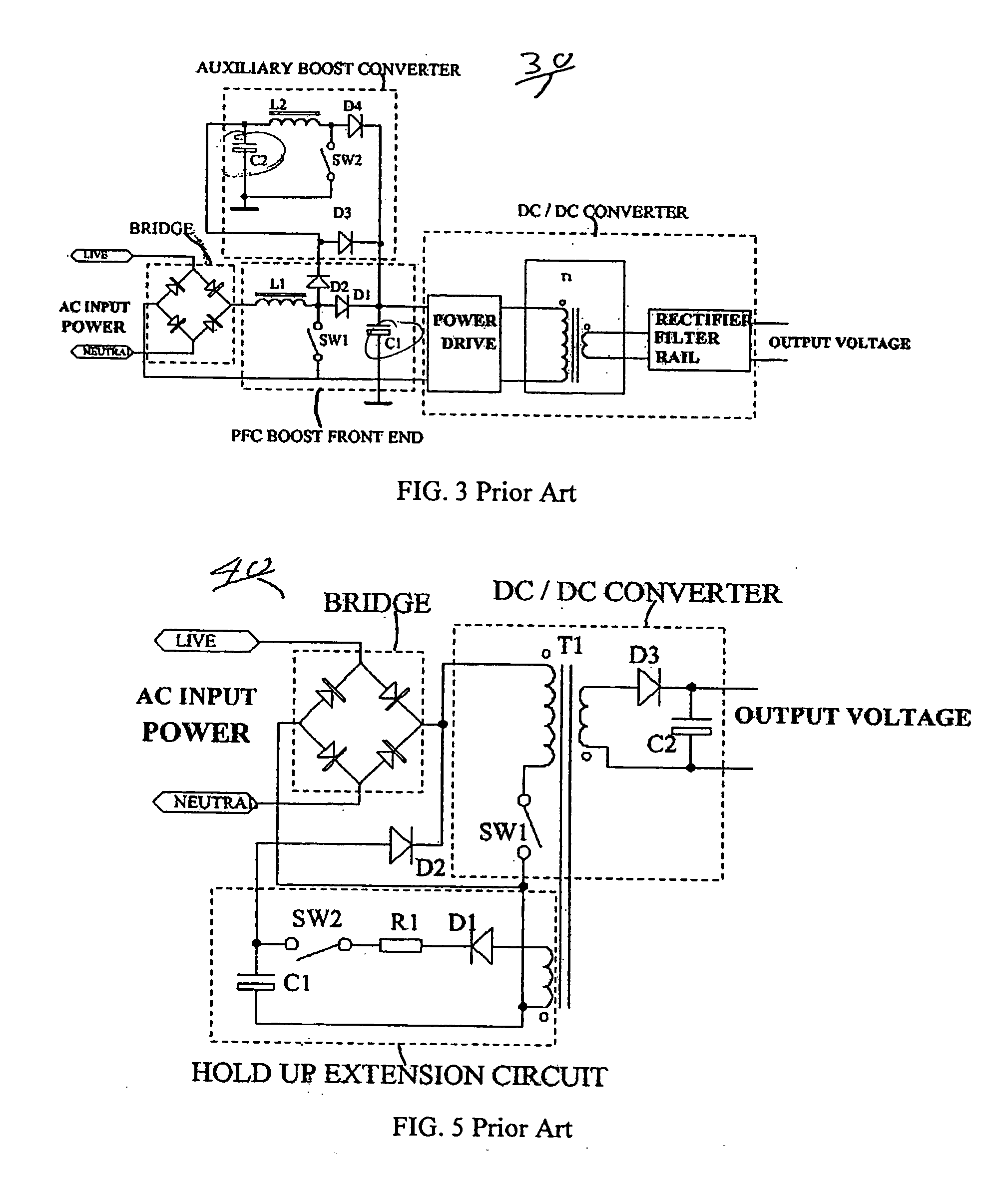
Circuit for maintaining hold-up time while reducing bulk capacitor size and improving efficiency in a power supply
InactiveUS7061212B2Improve efficiencyReduces peak current and voltage stressEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceDc dc converter
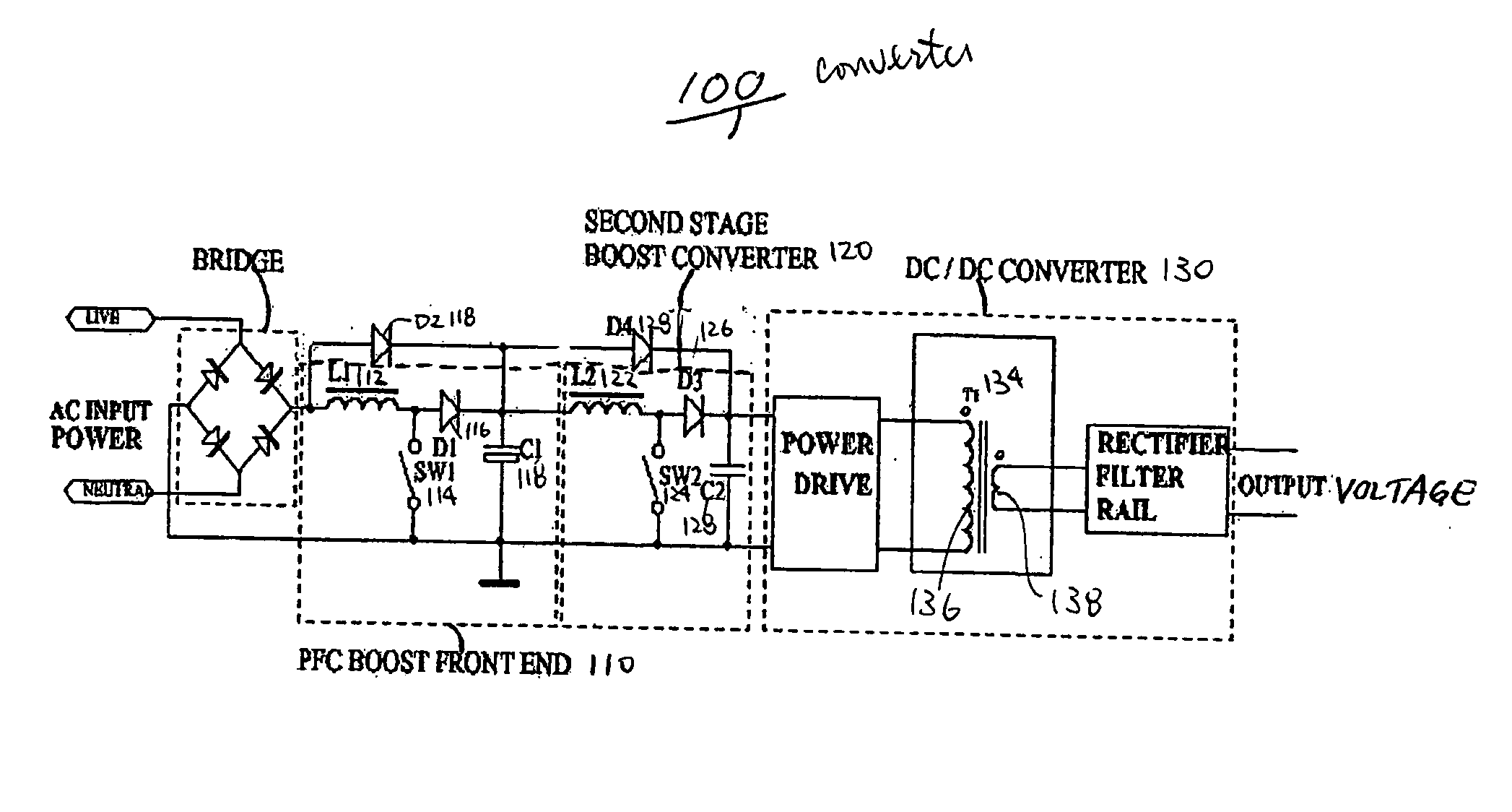
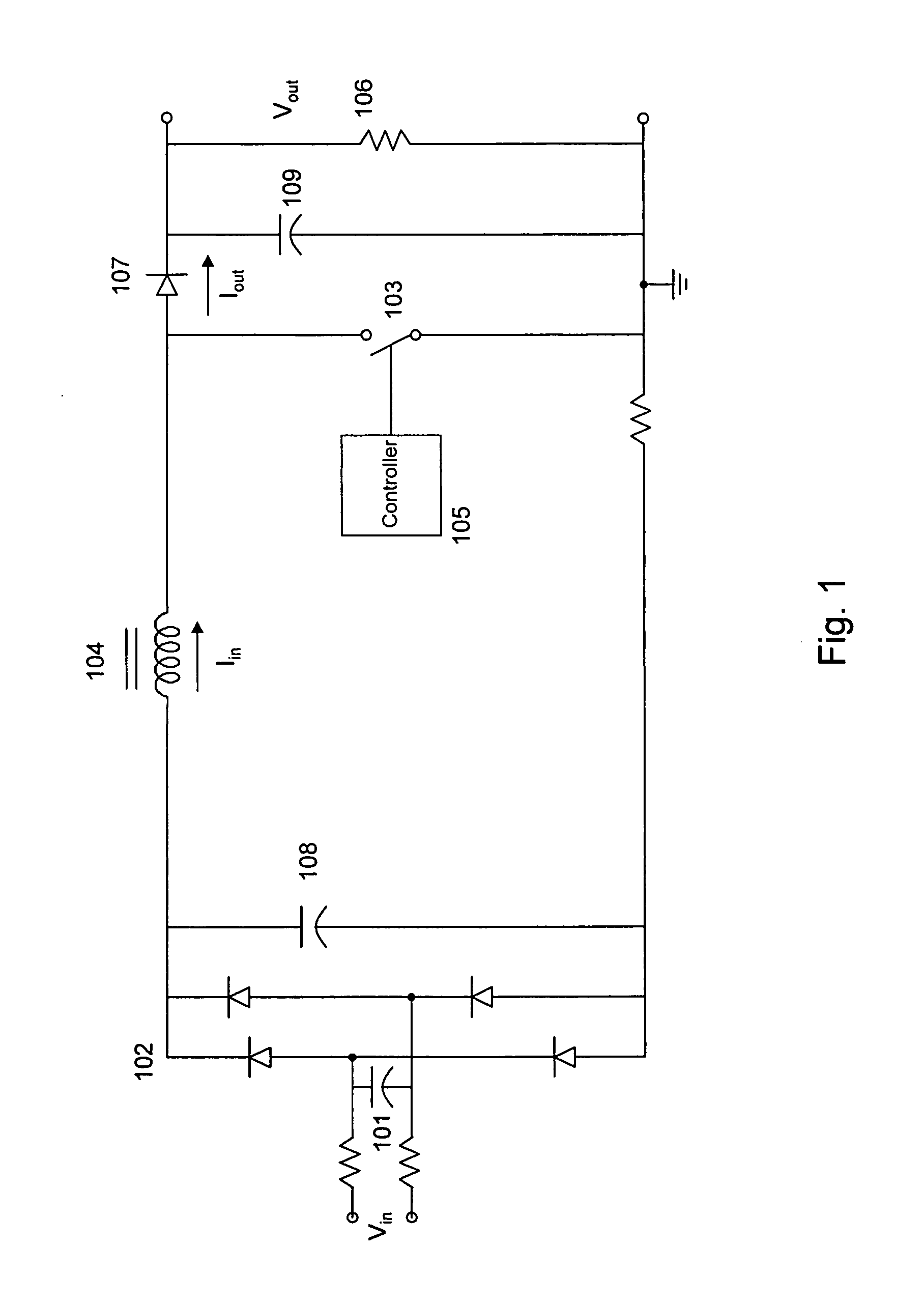
A circuit that utilizes most of the energy stored in the bulk capacitor of an AC to DC or DC to DC converter power supply by providing an intermediate converter between a first stage boost converter and a DC-DC converter. When the bulk voltage starts to fall during the hold-up time, the intermediate converter boosts the falling voltage to maintain the regulated DC input to the DC to DC converter while reducing the operating range and increasing the operating duty cycle, so as to increase efficiency, reduce peak current and voltage stresses. The circuit also reduces the size of the output filter components and reduces the size of the bulk capacitance by up to half.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
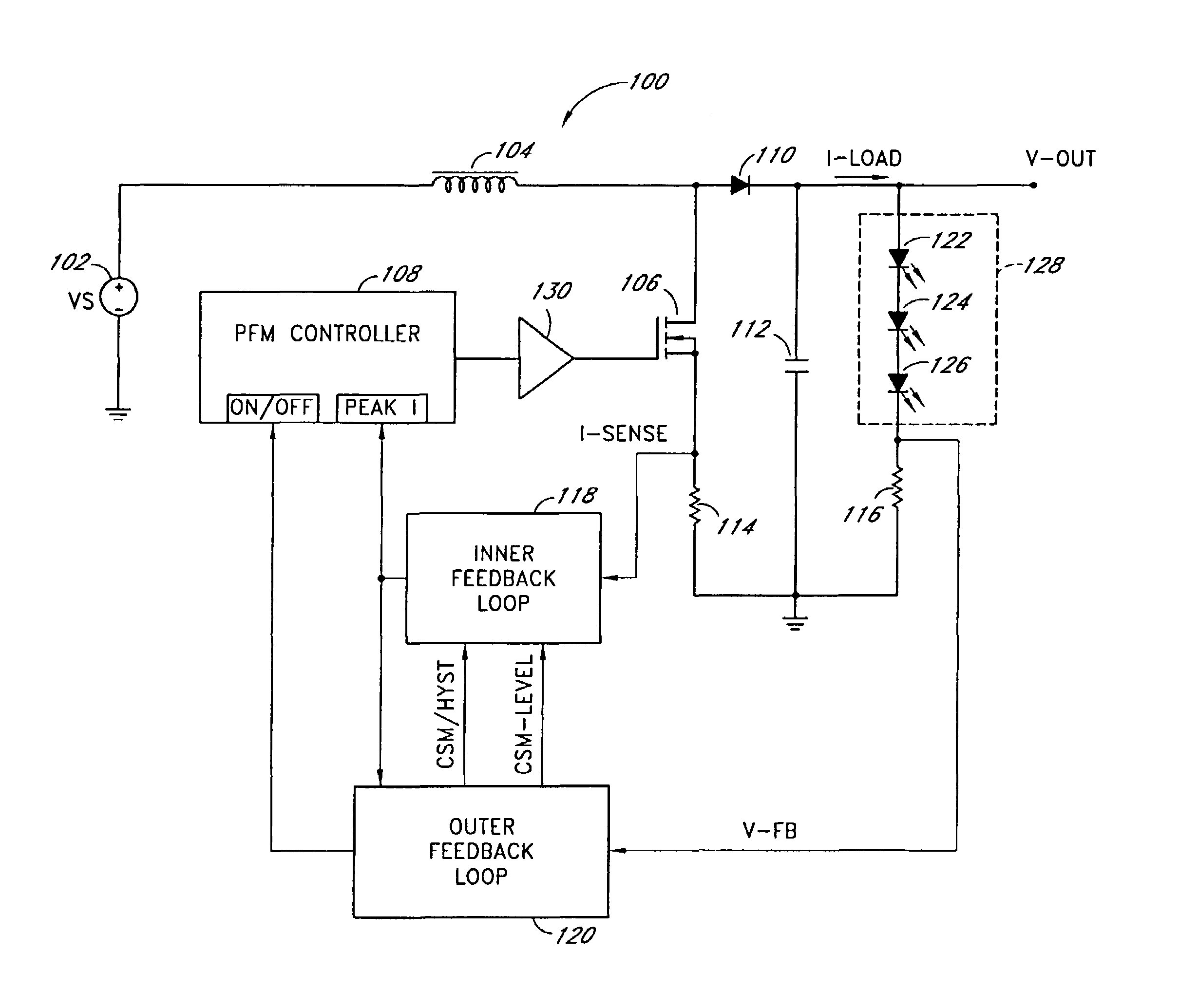
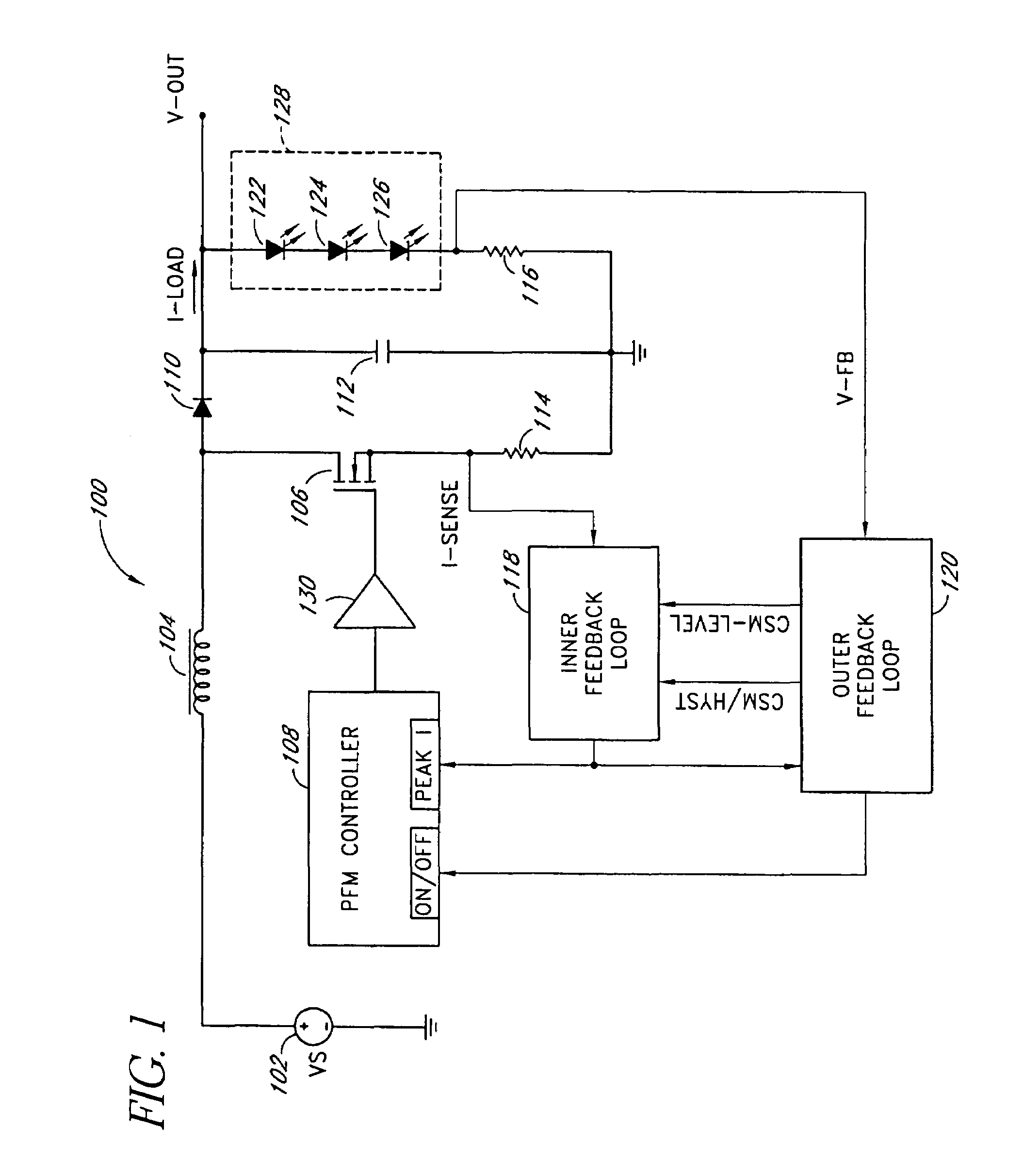
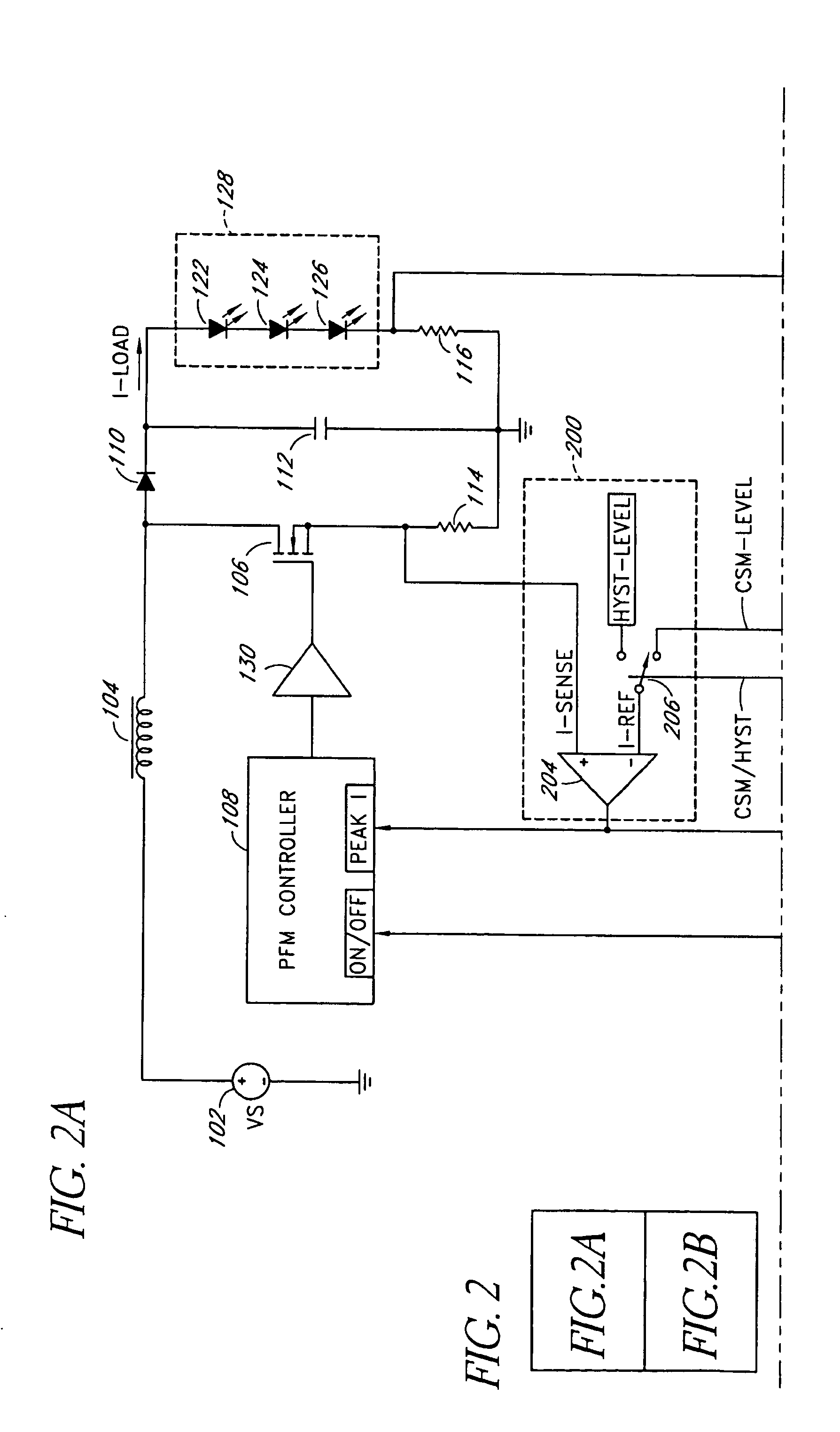
Dual-mode PFM boost converter
InactiveUS7102340B1Conduction loss downReduce switching lossesElectric lighting sourcesDc-dc conversionSwitched currentDual mode
A dual-mode pulse frequency modulation boost converter operates in a hysteretic mode during light load currents to regulate an output voltage using a substantially fixed peak switching current and operates in a continuous mode during heavy load currents to regulate the output voltage using a variable peak switching current. The boost converter senses load power to automatically switch between the hysteretic mode and the continuous mode.
Owner:MICROSEMI
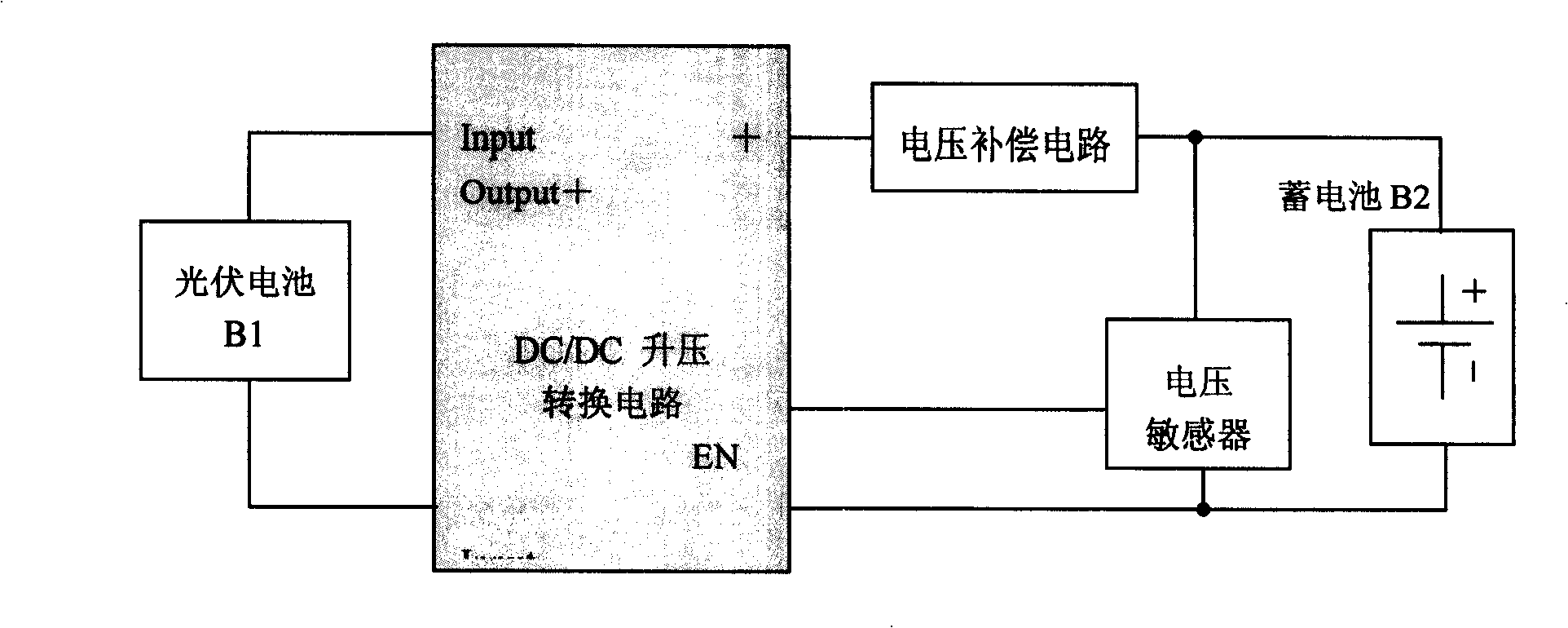
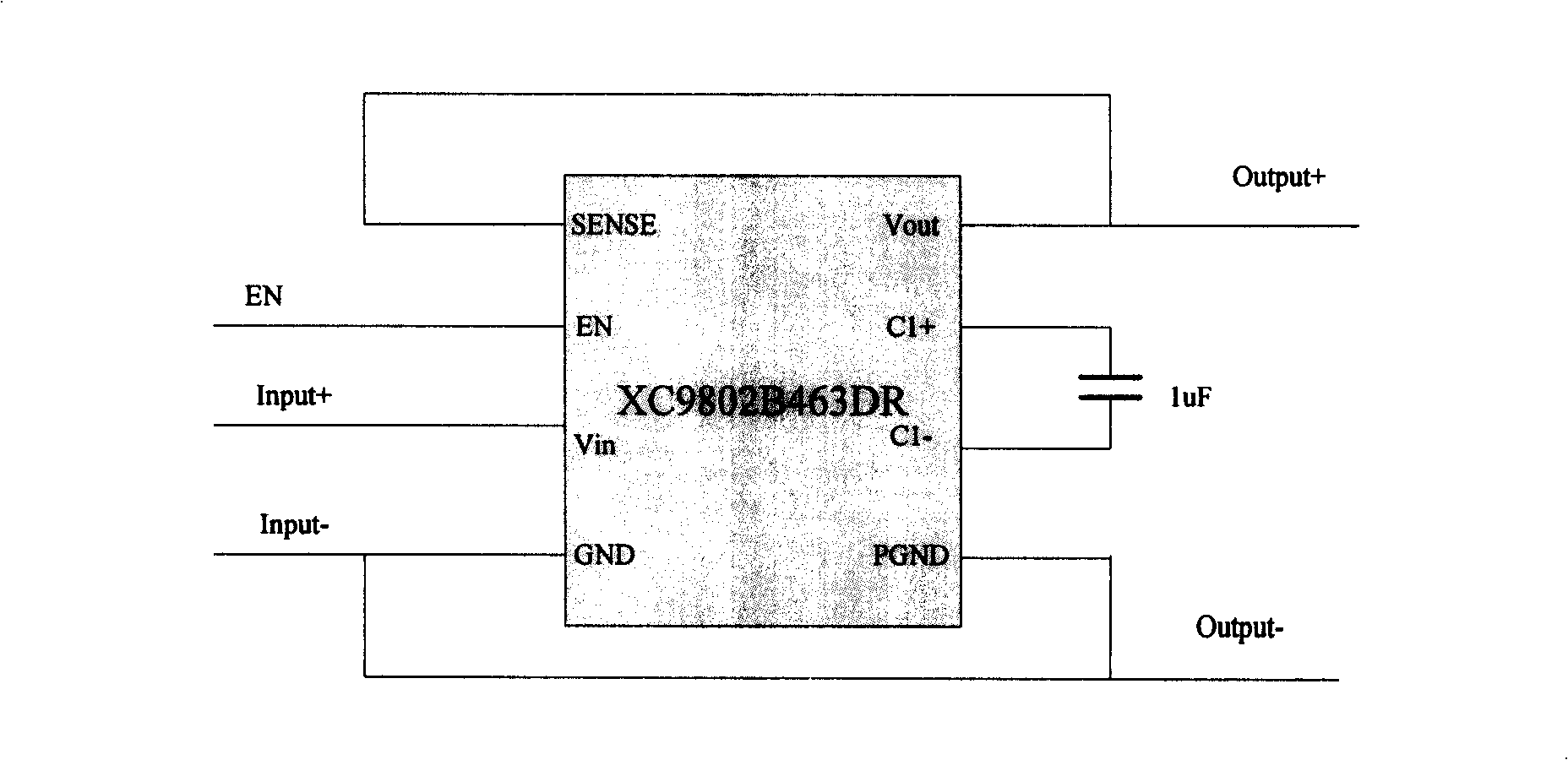
Photovoltaic battery- DC / DC voltage boosting convert charging method
InactiveCN101257221AAvoid overchargingRealize chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerOvervoltageElectricity
The invention relates to a photovoltaic cell -DC / DC boost conversion charge method which belongs to battery technique field. The method includes: 1) a portable equipment accumulator voltage is detected by a voltage sensor, when lows to full charge capacity, the voltage sensor makes DC / DC boost converter starting DC / DC conversion, and electricity quantity flows from photovoltaic current to lithium battery for charging; 2) when the portable equipment accumulator is in full charge capacity state, accumulator need not charge again, the voltage sensor makes DC / DC boost converter forbidding DC / DC conversion, thereby, the portable equipment accumulator is protected and over charge phenomena is prevented. The method can be realized simply, and has short reaction time, high efficiency, overvoltage protection and anti-counterblast protection.
Owner:BEIJING HI TECH WEALTH INVESTMENT DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com