Patents
Literature
1739 results about "Zener diode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
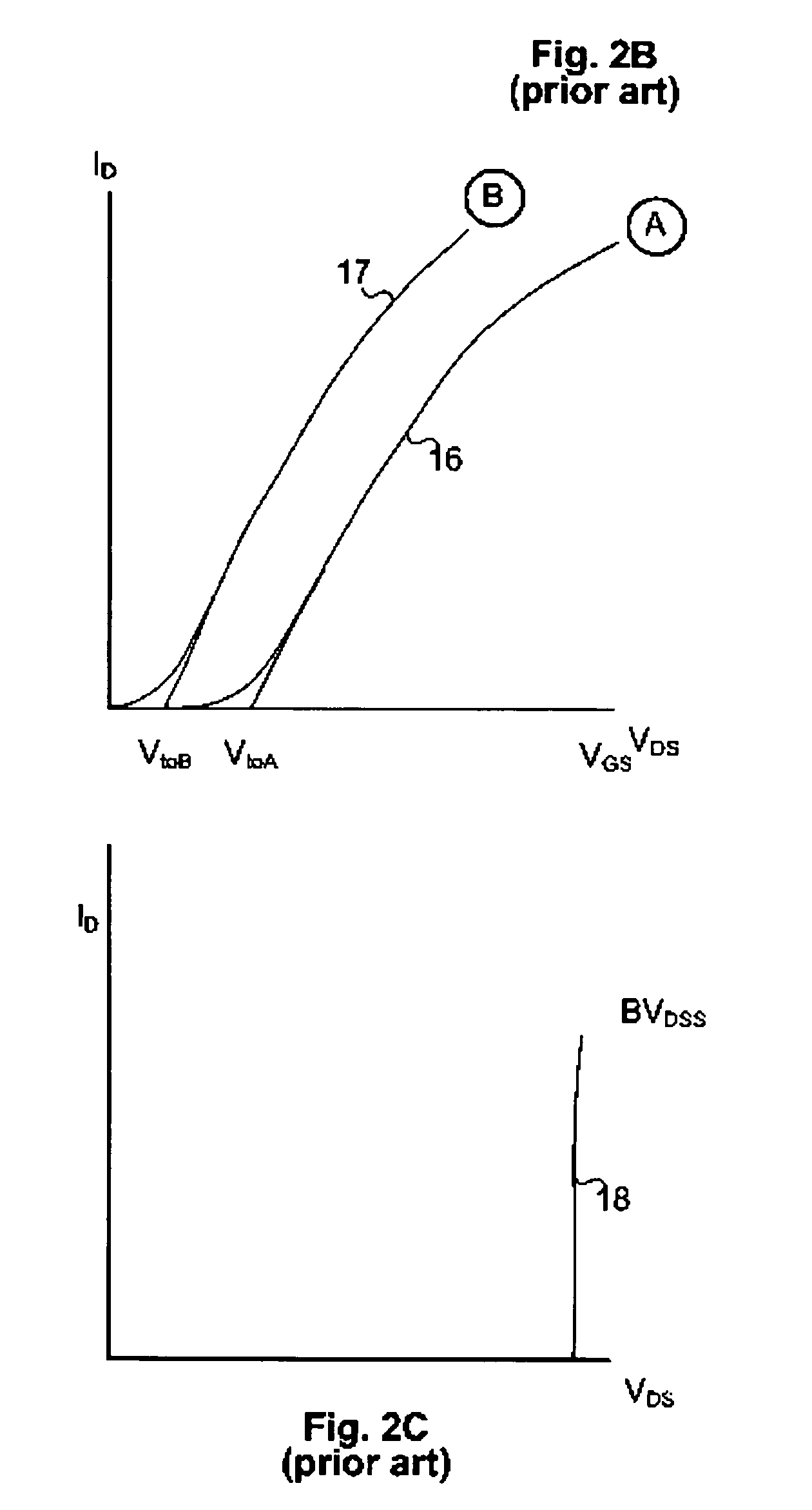
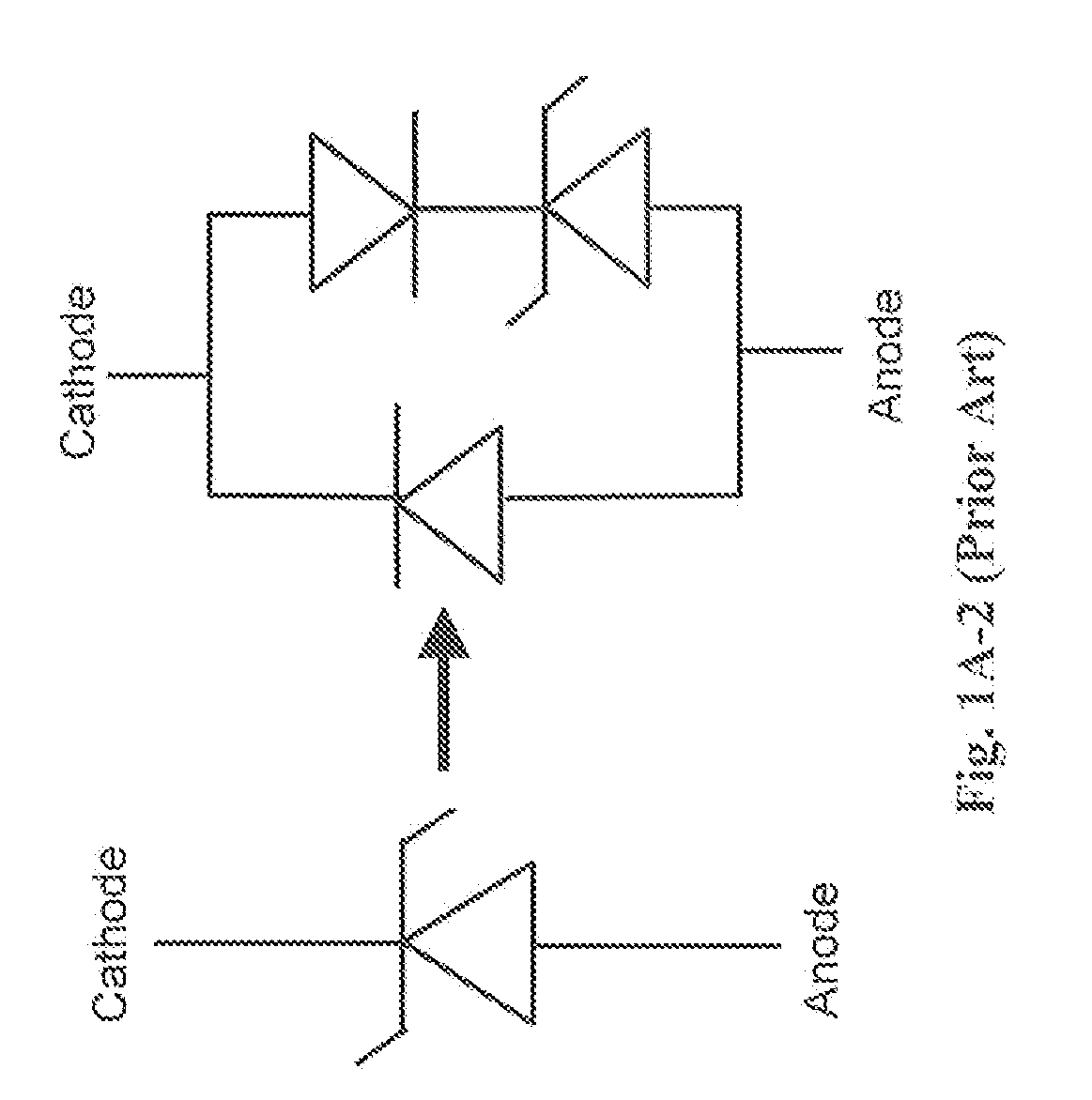
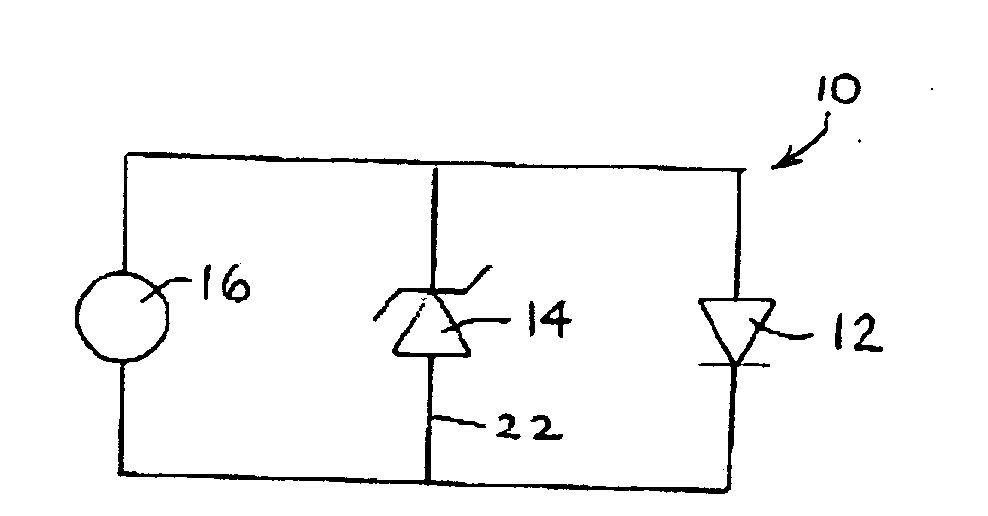
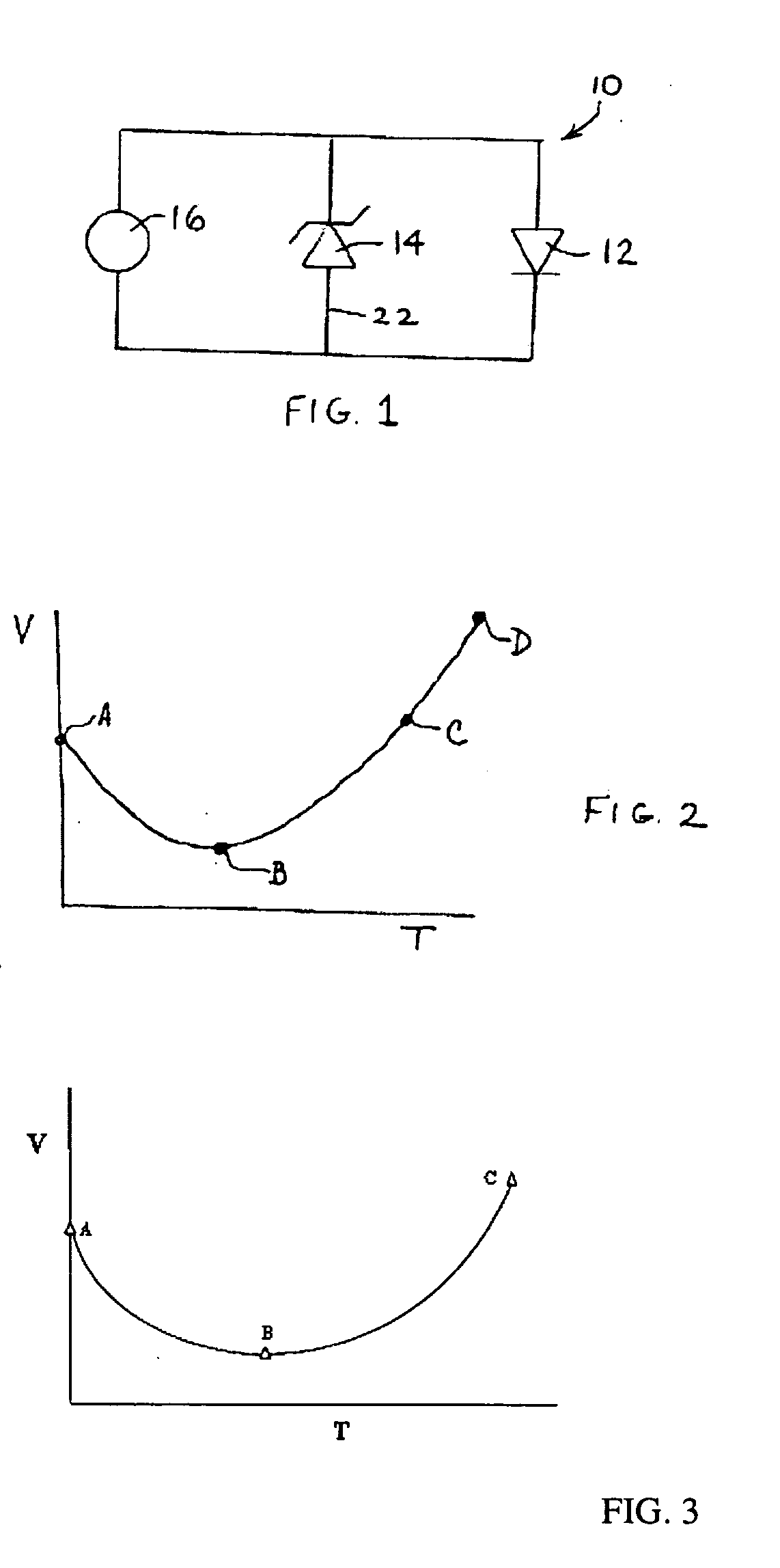
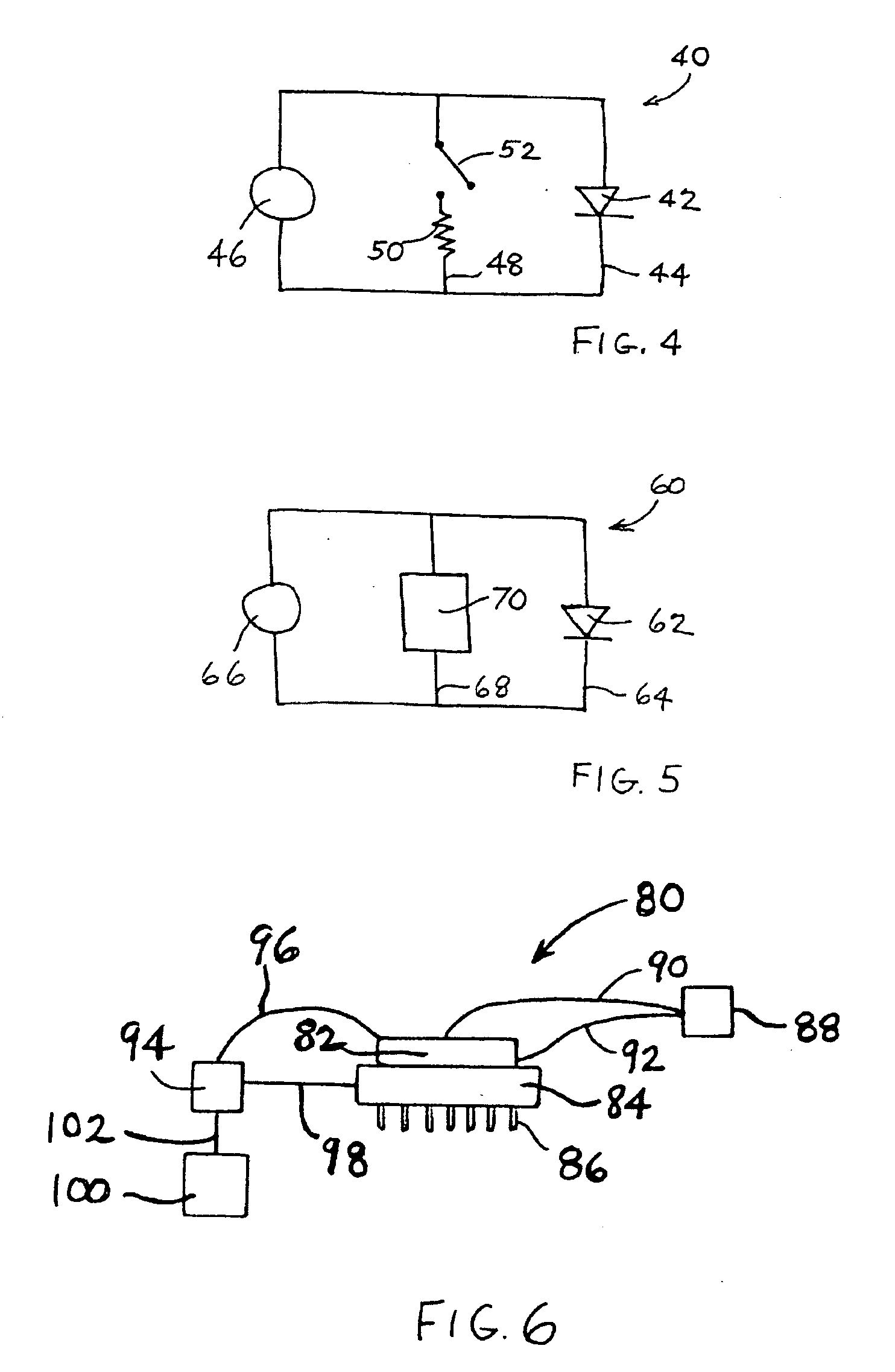
A Zener diode is a type of diode that allows current to flow not only from its anode to its cathode, but also in the reverse direction, when the voltage across its terminals exceeds the Zener voltage, a characteristic of the device. This effect is known as the Zener effect, after Clarence Zener, who first described the phenomenon.
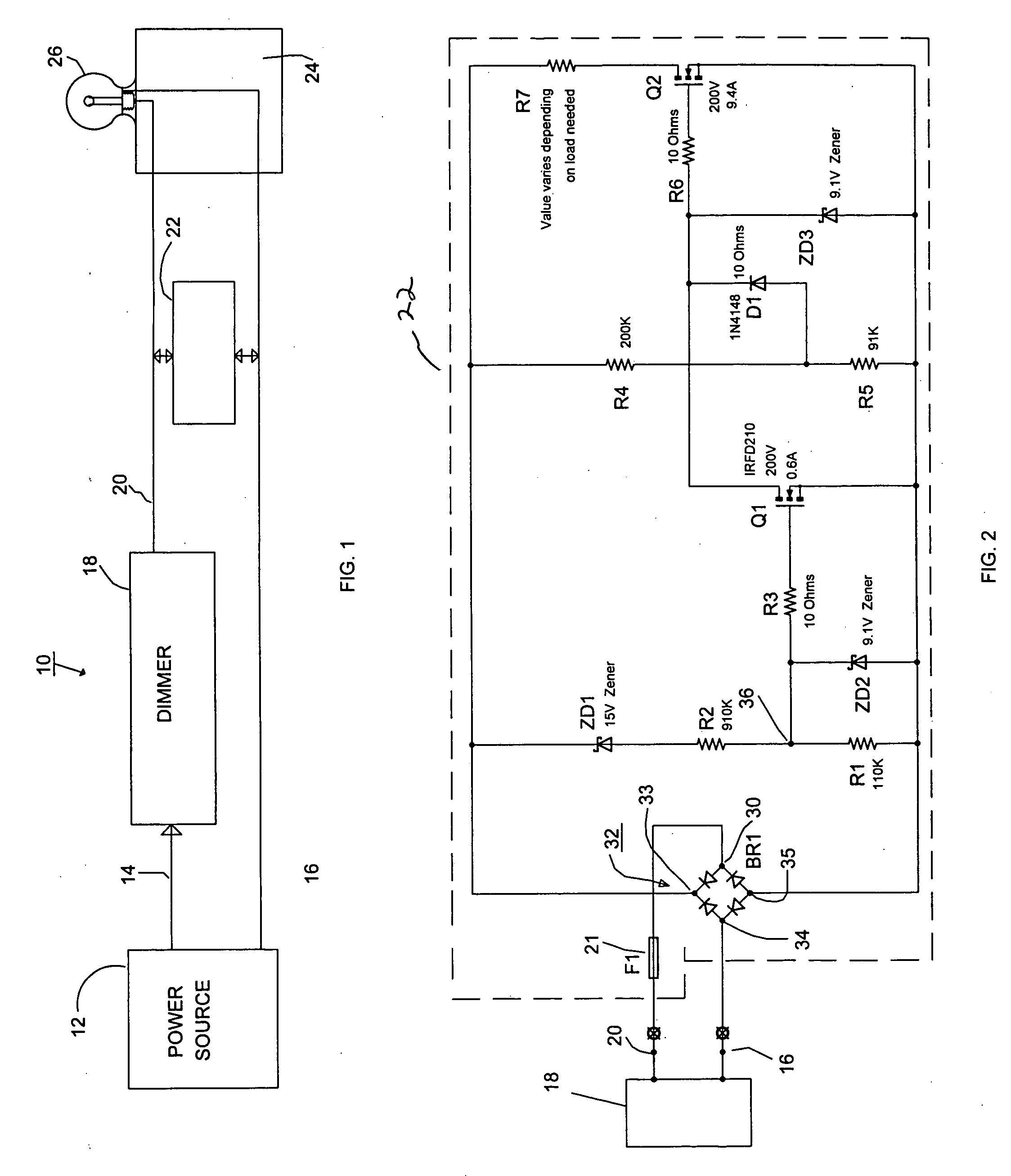
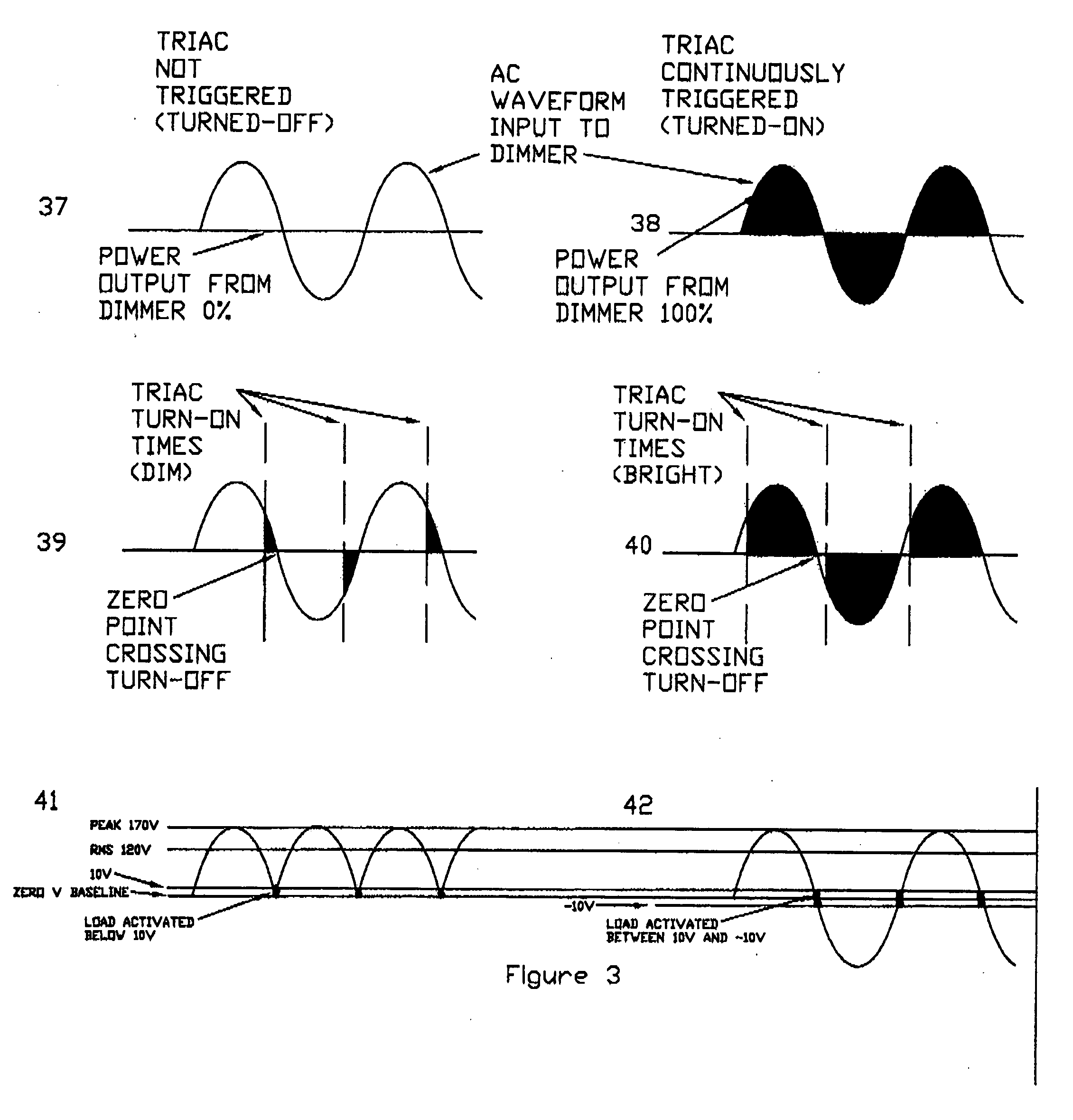
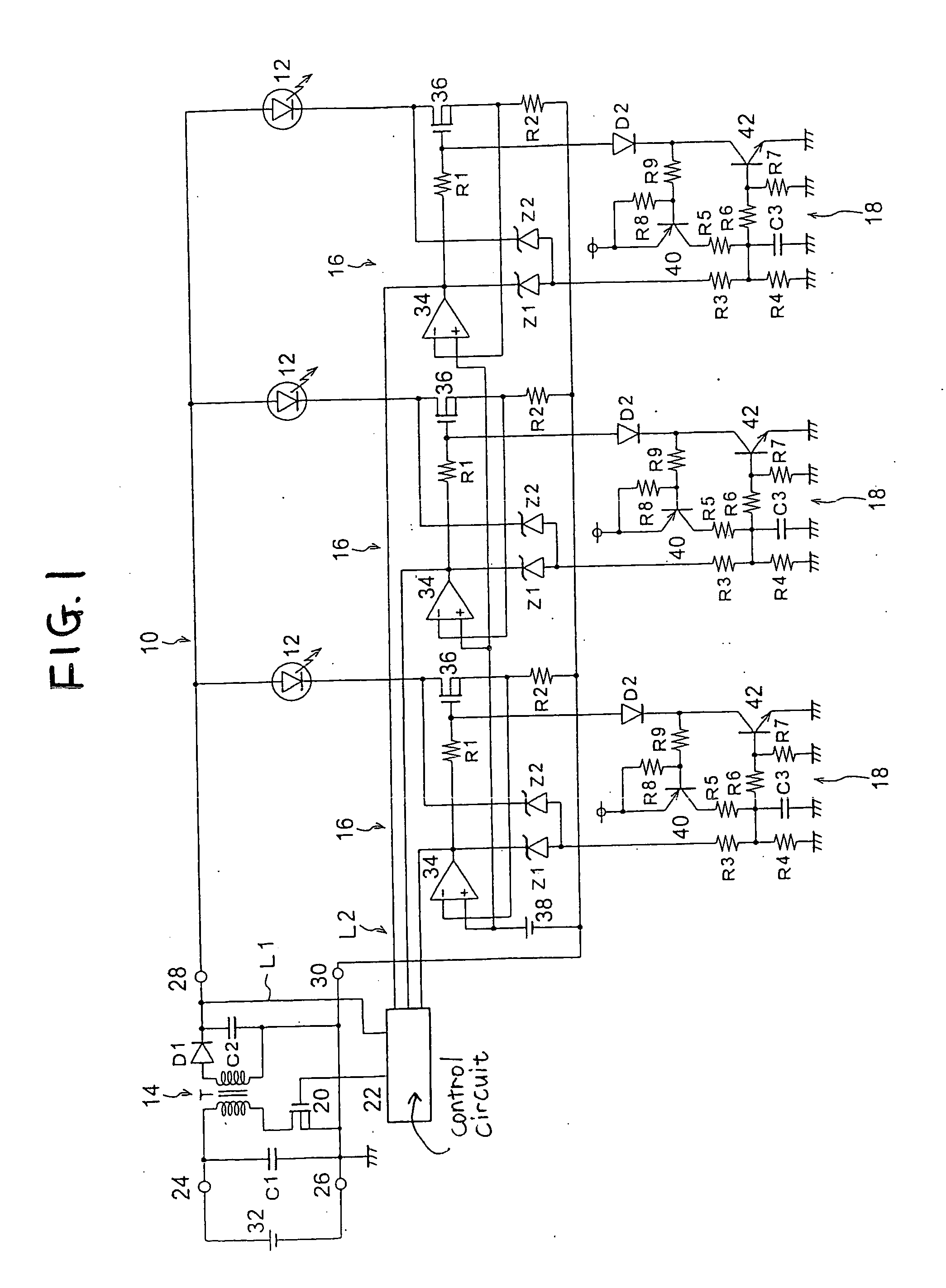
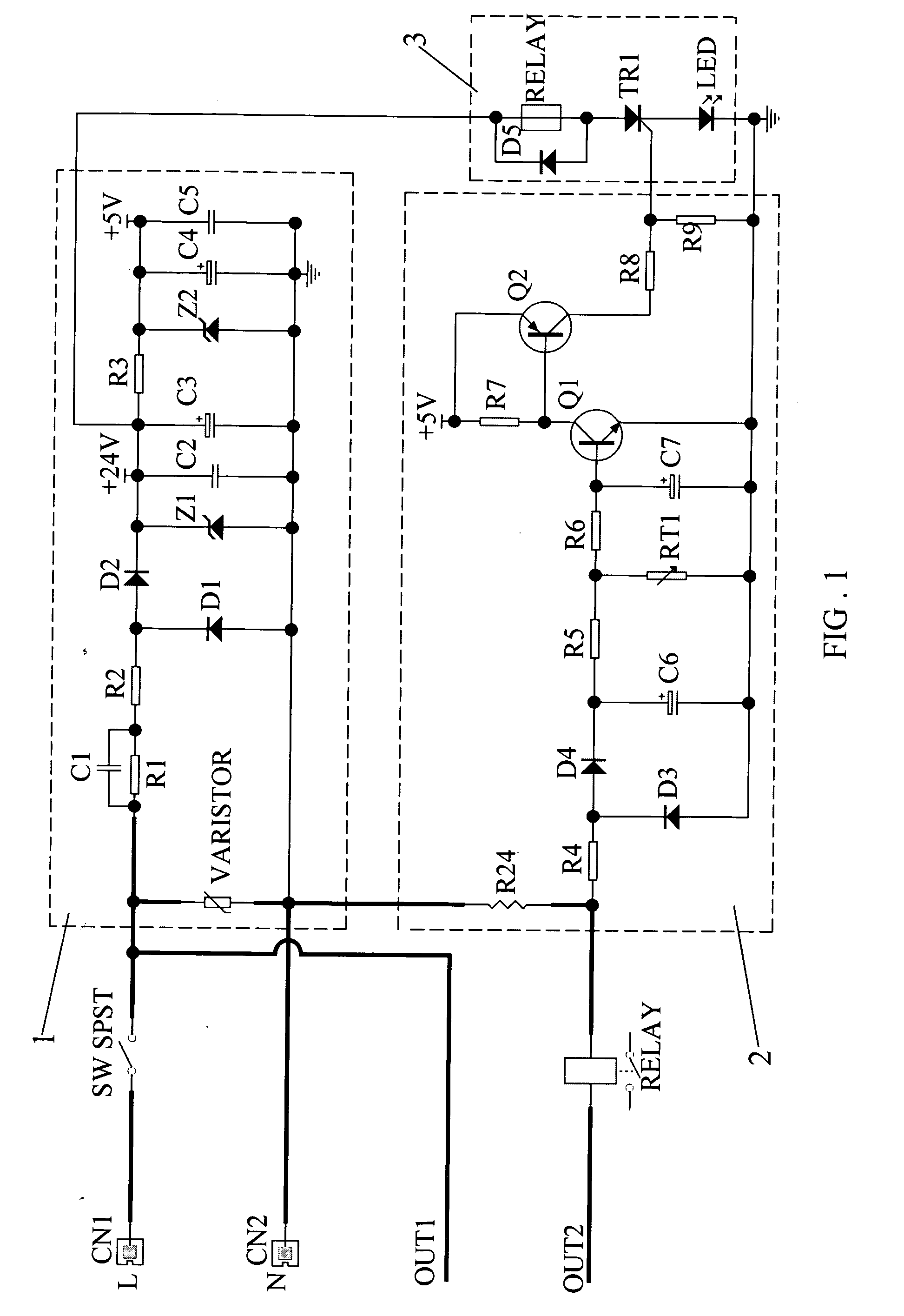
Dimmer circuit for LED
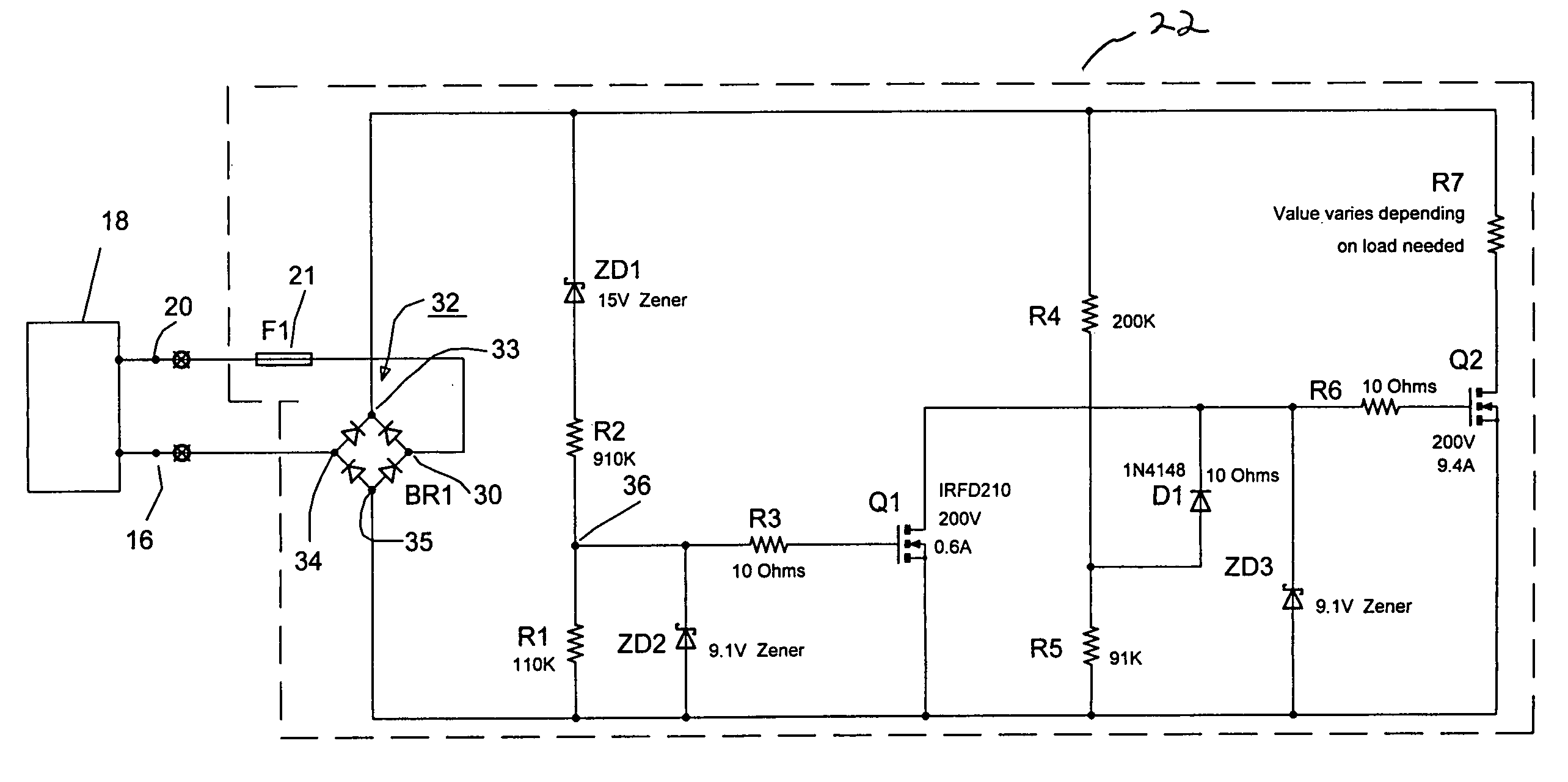
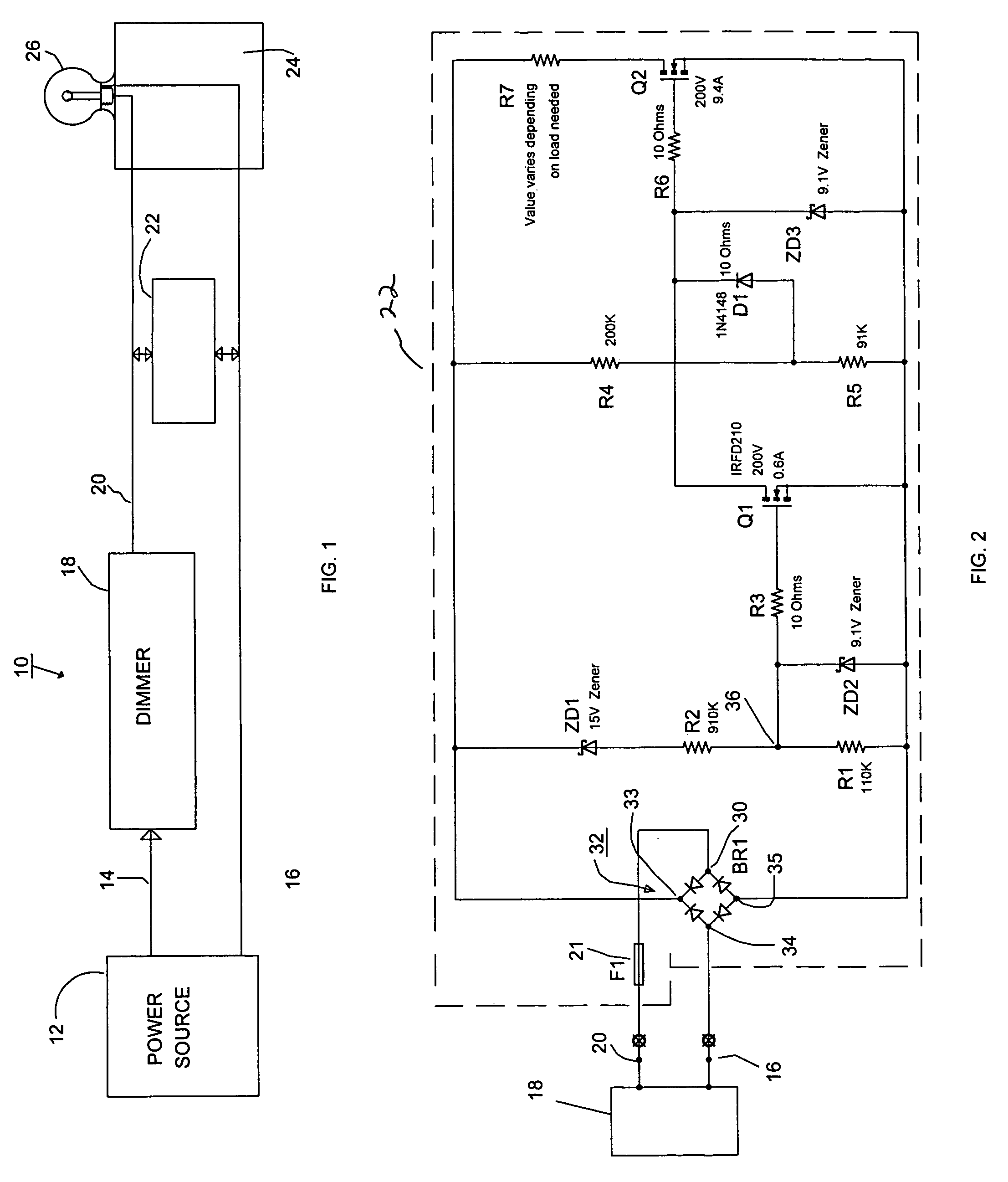
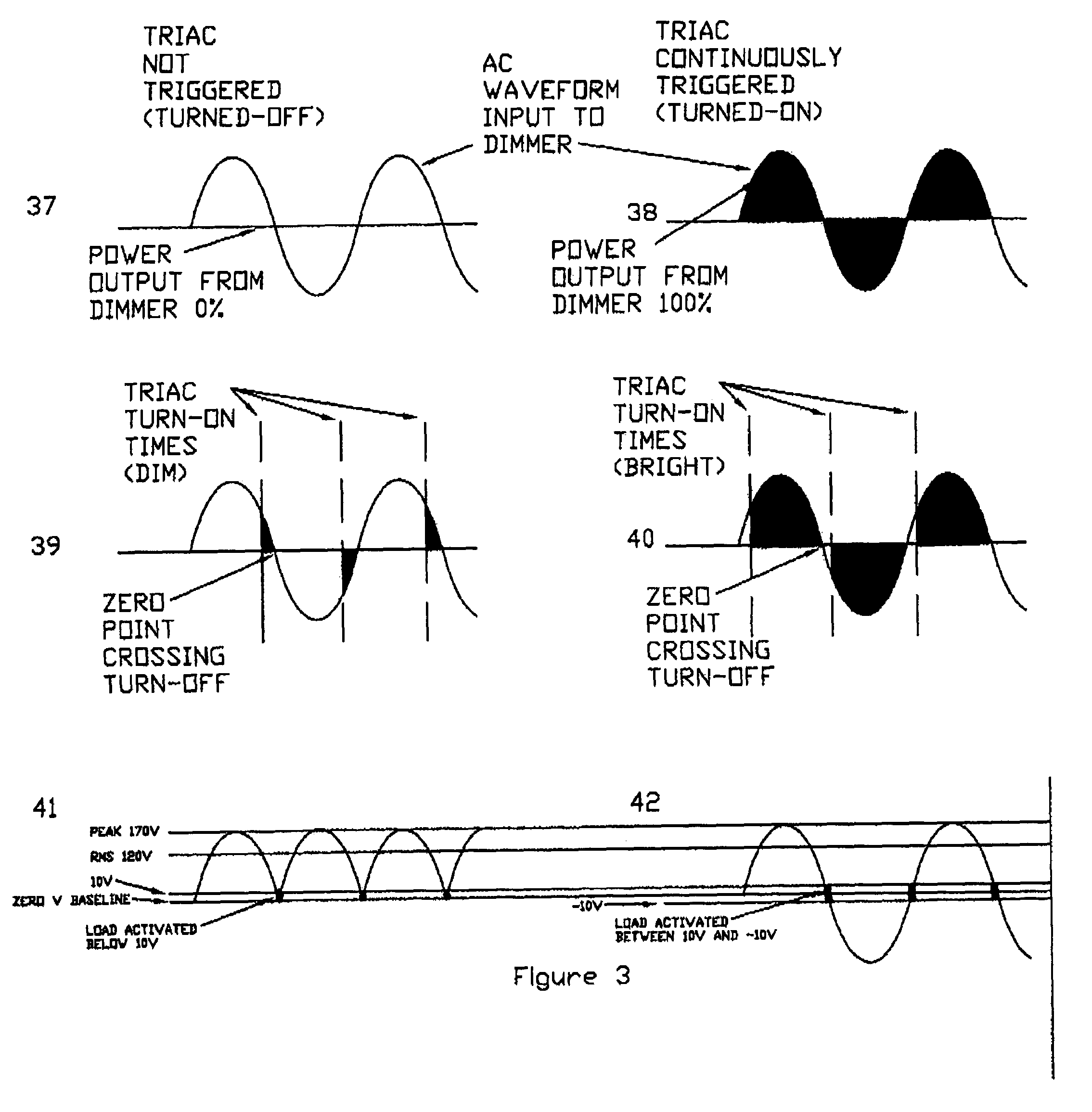
InactiveUS7102902B1Low heat generationReduce heatAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcMOSFETZener diode
The AC output from a source is rectified and applied to a resistor / Zener diode circuit connection which determines the magnitude of the rectified voltage applied via a circuit to a first MOSFET device. The inverted output of the first MOSFET device is applied to the gate electrode of a second MOSFET device in a manner such that the second MOSFET device is ON even when the AC output passes through zero. The output of the second MOSFET device is connected to a resistor which determines the magnitude of the load applied to the dimmer.
Owner:LEDTRONICS
LED array primary display light sources employing dynamically switchable bypass circuitry
InactiveUS20020043943A1Reduce heat outputEasy burn-out element replacementElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBlack outEffect light
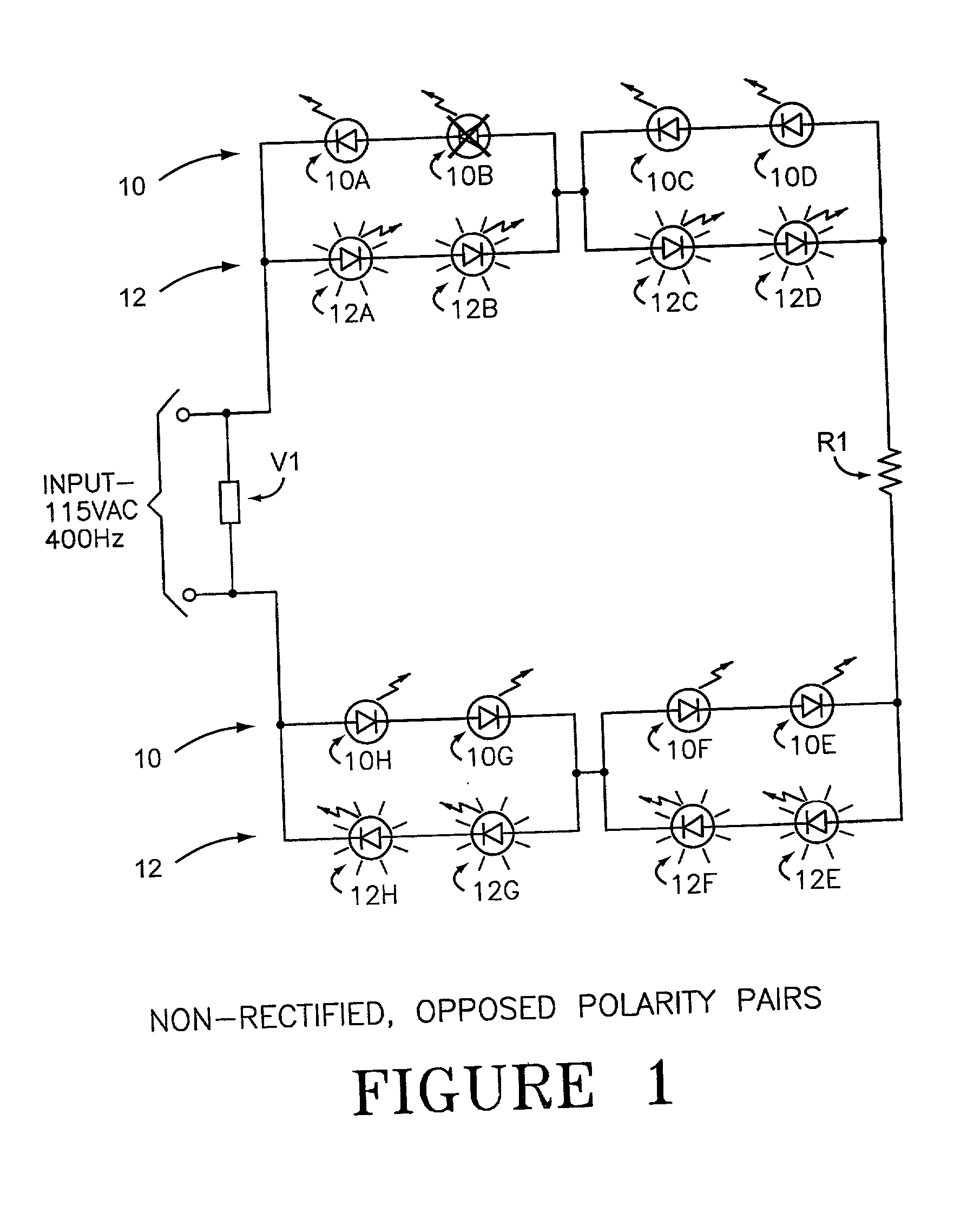
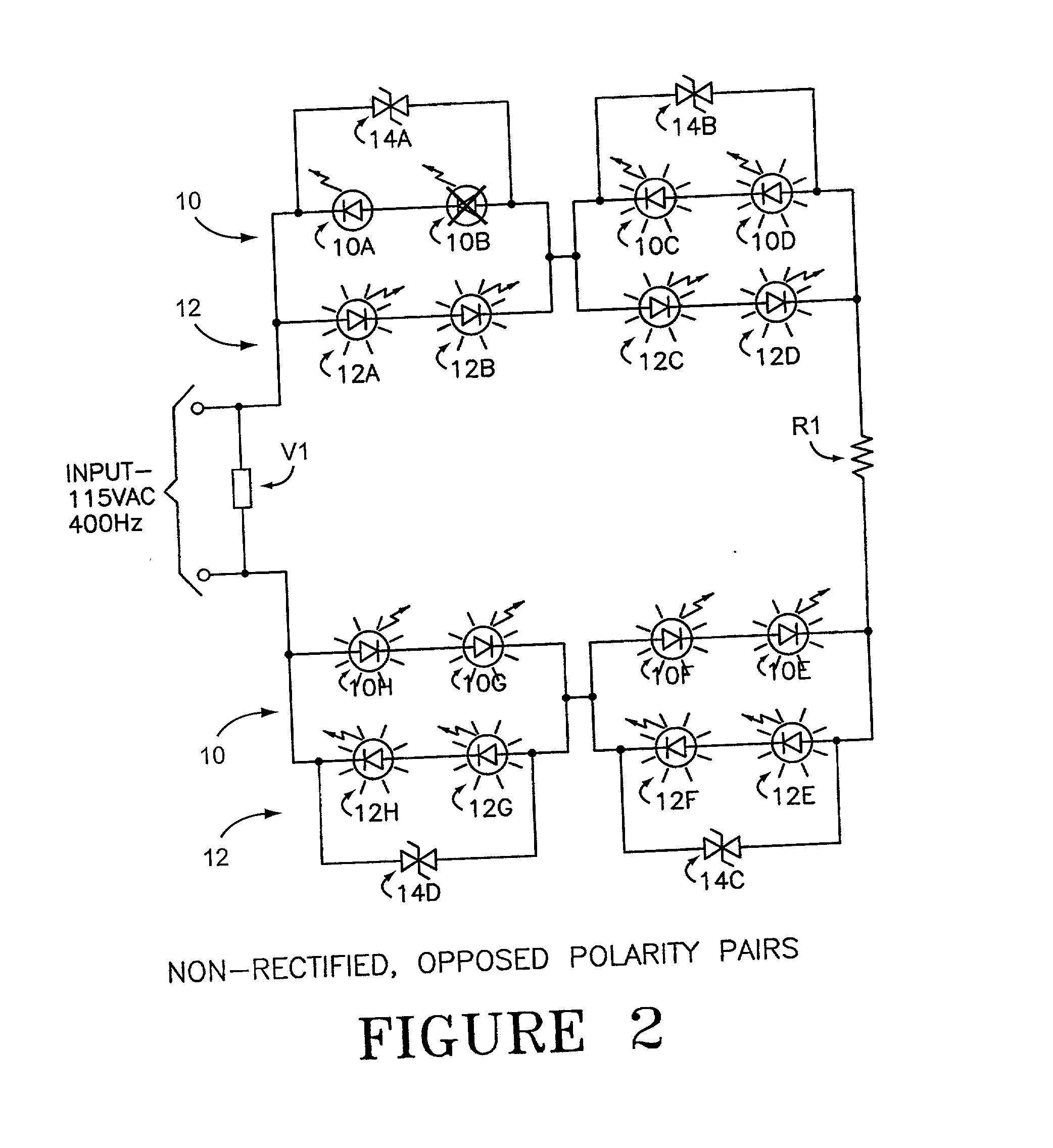
The invention comprises use of Dynamically Switchable Bypass (DSB) elements in association with one or more Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) in arrays for illumination circuits to provide rugged, reliable lighting. The DSBs are selected from Transient Voltage Suppressors, including Silicon, Metal Oxide Varistors, and Multi Layer Varistors as well as Zener Diodes. The DSBs are not used as circuit protecting devices, but rather as alternative paths for electric current to bypass failed LEDs. Bi-directional TVSs are used as alternative electric paths for circuits using Alternating Current (AC) and parallel LED arrays that light on both phases of AC. Zener Diodes are used in parallel to, but in the opposite polarity orientation to, one or more LEDs in DC or rectified AC circuits. The inventive paired DSB / LED elements overcomes the black-out problems of prior series LED illumination systems, making possible the use of robust LEDs in illumination systems where reliability, long life, low power consumption, low heat output, resistance to shock, vibration, and humidity, and self-diagnosis are important. The DSB elements have breakdown voltages slightly higher than the LED(s) they support, so that when an LED fails, the conduction through the DSB begins. Because the conduction voltage of the DSB so nearly matches the conduction voltage of the LED(s), the remainder of the circuit continues to function as normal. The system is self-diagnostic in that any LED failure presents itself as a dark LED rather than as a whole string of dark LEDs. DSBs may be used with incandescent bulbs.
Owner:IDD AEROSPACE
High-Frequency Power MESFET Boost Switching Power Supply
InactiveUS20080186004A1Lower on-resistanceLow off-state drain leakageTransistorDc-dc conversionMOSFETHigh frequency power
A MESFET based boost converter includes an N-channel MESFET connected to a node Vx. An inductor connects the node Vx to a battery or other power source. The node Vx is also connected to an output node via a Schottky diode or a second MESFET or both. A control circuit drives the MESFET (and the second MESFET) so that the inductor is alternately connected to ground and to the output node. The maximum voltage impressed across the low side MESFET is optionally clamped by a Zener diode. In some implementations, the MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET. The MOSFET is switched off during sleep or standby modes to minimize leakage current through the MESFET. The MOSFET is therefore switched at a low frequency compared to the MESFET and does not contribute significantly to switching losses in the converter. In other implementations, more than one MESFET is connected in series with a MOSFET, the MOSFETs being switched off during periods of inactivity to suppress leakage currents.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Multiple use LED light fixture
ActiveUS20100014289A1Guaranteed high quality outputReduce riskMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceHeat managementComputer module
The invention provides a multi-use light fixture that includes a light engine, a rugged housing, and an external power supply removeably embedded within an optional external enclosure. The light fixture includes several novel heat management features designed to reduce the risk of failure and thereby increase the reliability of the light fixture. The light engine includes groups of light modules, each having a light emitting diode (LED) and a zener diode. The housing includes an internal gap defined between the a circuit board and the housing. The housing also includes an arrangement of external fins and vents that dissipate heat generated by the light engine. The lens cover includes a plurality of inlets to supply ambient air into the fixture. During operation, heat is generated by the light modules, namely the LEDs, and then is transferred along a first flow path through a main body portion of the housing and the fins for dissipation to ambient and a second air flow path whereby ambient air flows through the light engine to increase the performance and efficiency of the light engine.
Owner:ELECTRALED
Voltage regulating devices in LED lamps with multiple power sources
ActiveUS20110057572A1Reduce materialReduce inventory costsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesZener diodeVoltage regulation
LED driver circuits containing voltage reducing devices, voltage regulating devices, and voltage converting devices are disclosed as the main components to provide power to LEDs. The LED driver circuits are designed to work with a ballast, mains alternating current voltage, direct current voltage, and electromagnetic induction power. The voltage regulating devices can be a resistor in series with at least one zener diode or a voltage regulator both in parallel with and providing power to the LEDs. The LEDs can also be anti-parallel diode pairs consisting of one diode and one LED or two LEDs, or the LEDs can be anti-parallel diode string pairs consisting of diodes and LEDs or all LEDs. The LED driver circuits will be incorporated into LED replacement lamps, and in particular to LED lamps to replace fluorescent lamps for use with existing ballasts and other power sources where the ballast may be removed or bypassed.
Owner:DENOVO LIGHTING
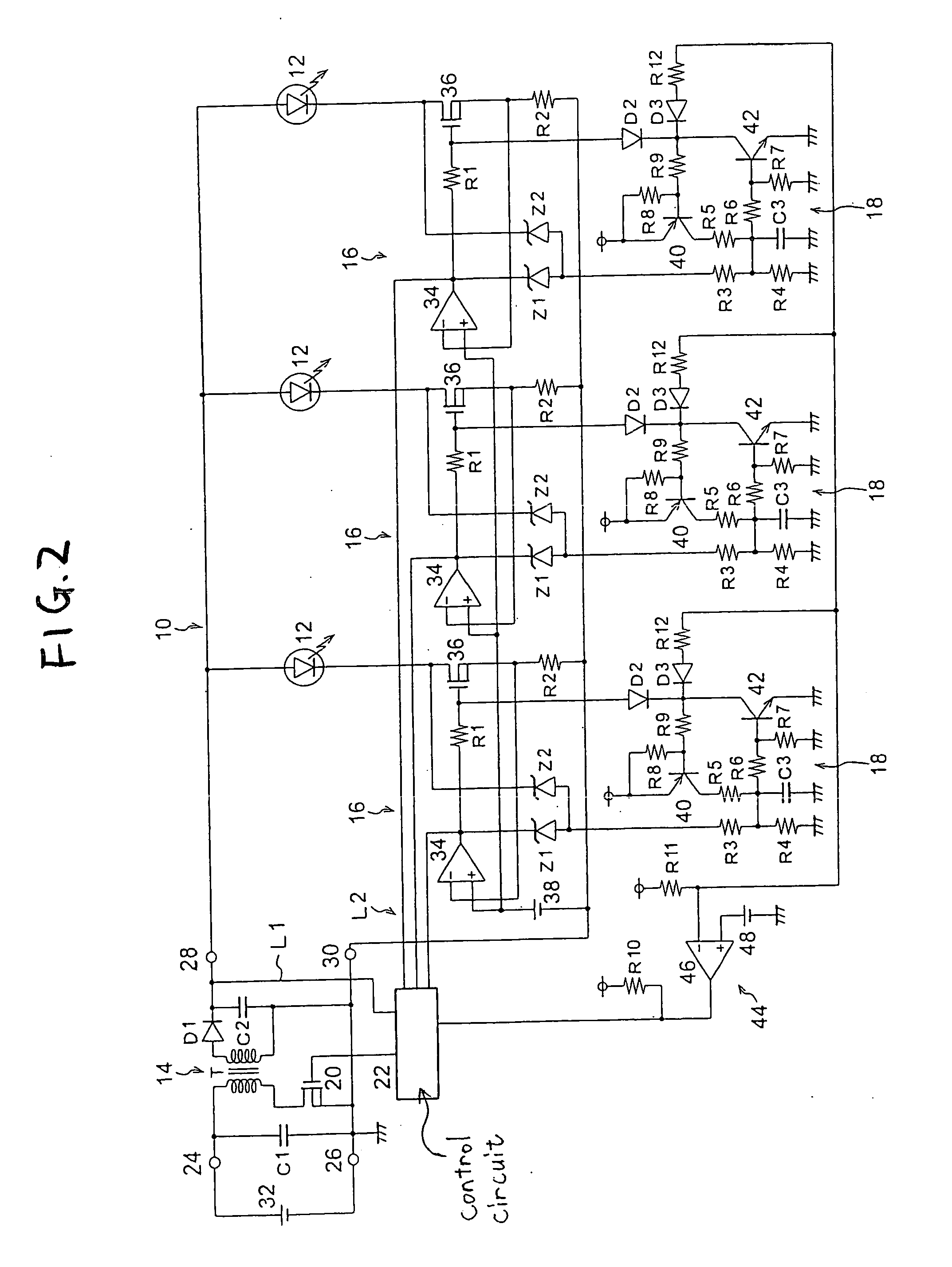
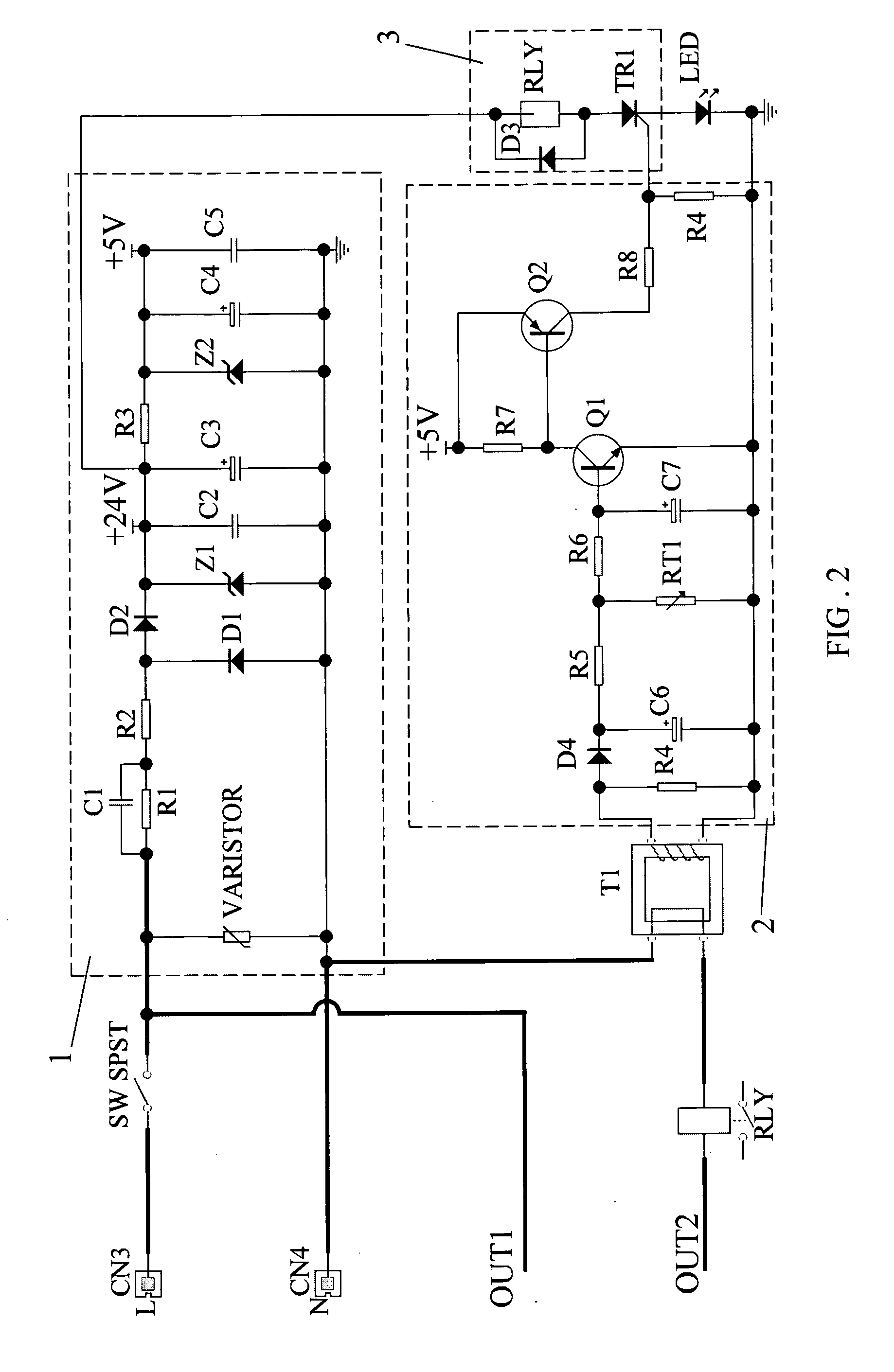
Dimmer circuit for LED
InactiveUS20060192502A1Low heat generationReduce heatAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcMOSFETDimmer
The AC output from a source is rectified and applied to a resistor / Zener diode circuit connection which determines the magnitude of the rectified voltage applied via a circuit to a first MOSFET device. The inverted output of the first MOSFET device is applied to the gate electrode of a second MOSFET device in a manner such that the second MOSFET device is ON even when the AC output passes through zero. The output of the second MOSFET device is connected to a resistor which determines the magnitude of the load applied to the dimmer.
Owner:LEDTRONICS
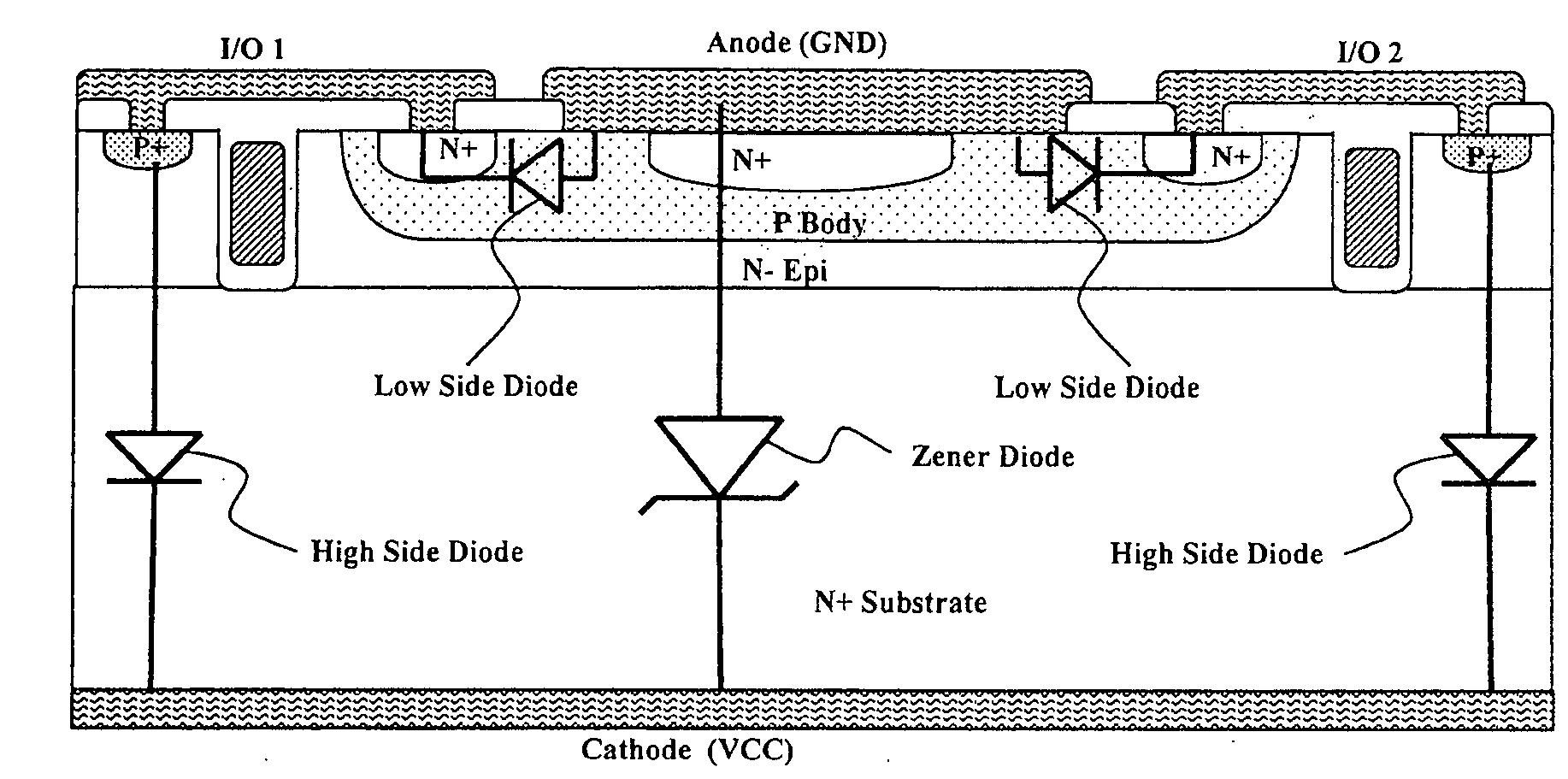
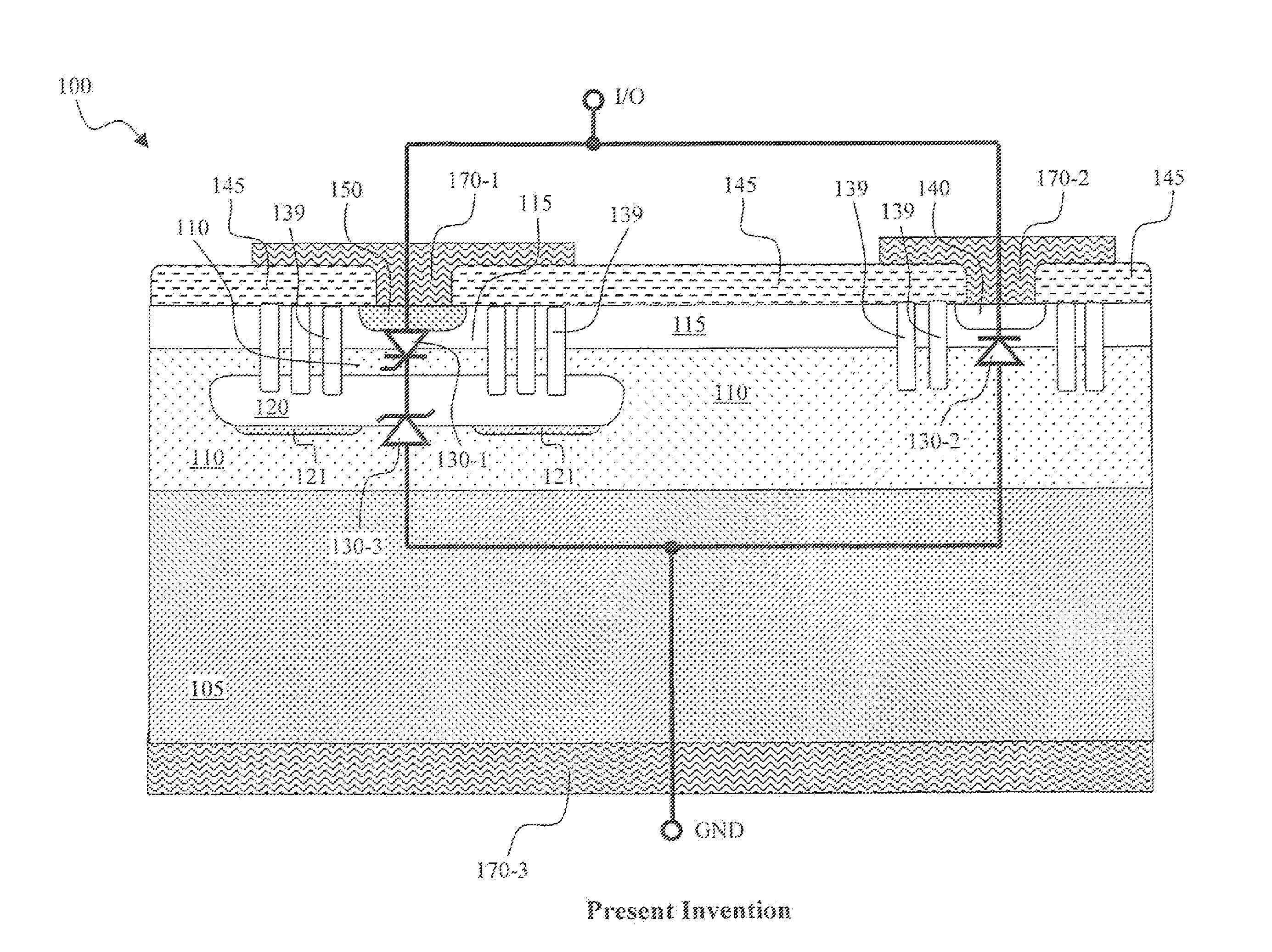
Optimized configurations to integrate steering diodes in low capacitance transient voltage suppressor (TVS)
ActiveUS20090045457A1Reduced lateral areaReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceZener diode
A transient-voltage suppressing (TVS) device disposed on a semiconductor substrate including a low-side steering diode, a high-side steering diode integrated with a main Zener diode for suppressing a transient voltage. The low-side steering diode and the high-side steering diode integrated with the Zener diode are disposed in the semiconductor substrate and each constituting a vertical PN junction as vertical diodes in the semiconductor substrate whereby reducing a lateral area occupied by the TVS device. In an exemplary embodiment, the high-side steering diode and the Zener diode are vertically overlapped with each other for further reducing lateral areas occupied by the TVS device.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Electrically-programmable integrated circuit antifuses
InactiveUS6897543B1Reduces drain-to-source resistanceIncrease resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh resistanceZener diode
Integrated circuit antifuse circuitry is provided. A metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) antifuse transistor serves as an electrically-programmable antifuse. In its unprogrammed state, the antifuse transistor is off and has a relatively high resistance. During programming, the antifuse transistor is turned on which melts the underlying silicon and causes a permanent reduction in the transistor's resistance. A sensing circuit monitors the resistance of the antifuse transistor and supplies a high or low output signal accordingly. The antifuse transistor may be turned on during programming by raising the voltage at its substrate relative to its source. The substrate may be connected to ground through a resistor. The substrate may be biased by causing current to flow through the resistor. Current may be made to flow through the resistor by inducing avalanche breakdown of the drain-substrate junction or by producing Zener breakdown of external Zener diode circuitry connected to the resistor.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
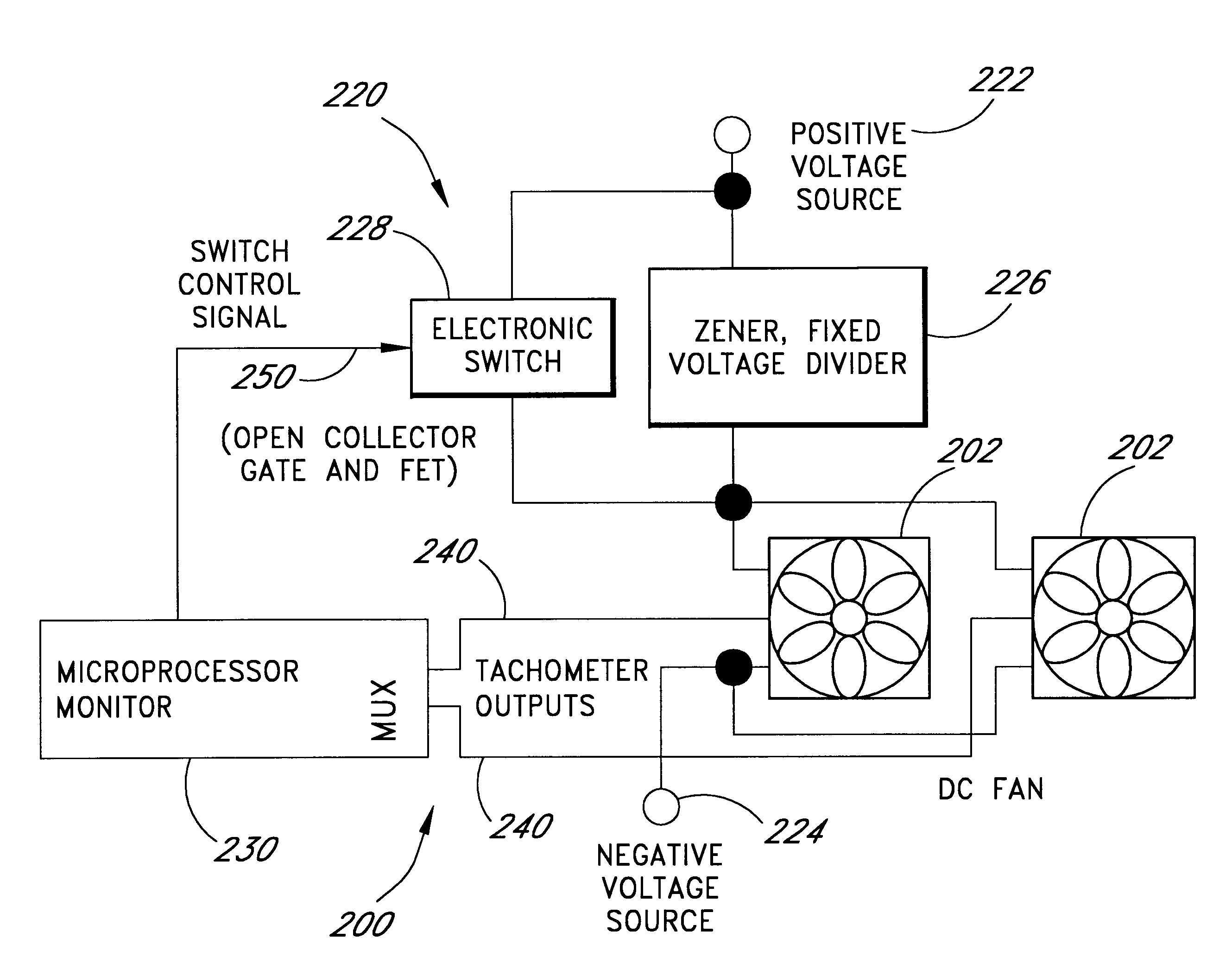
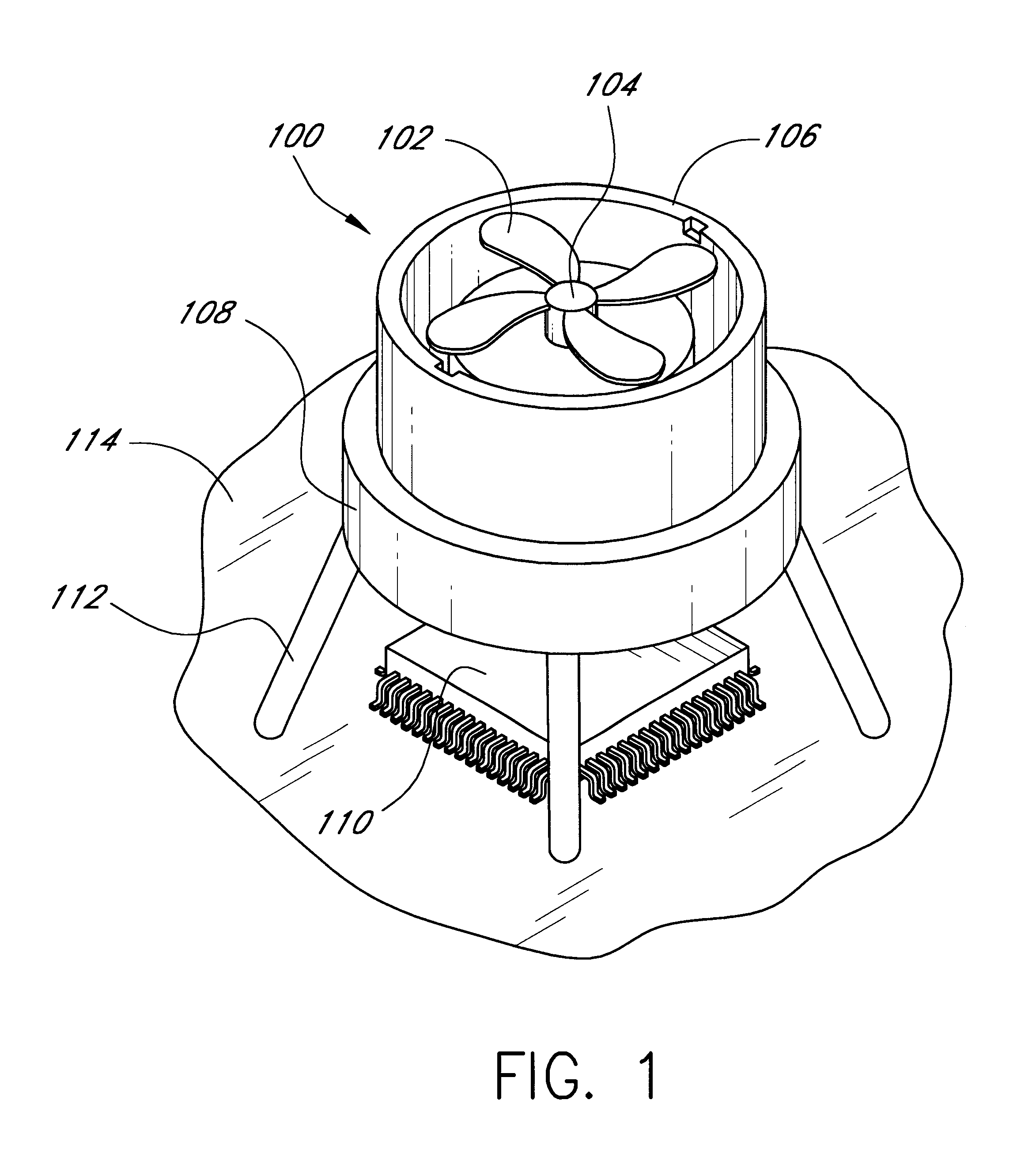
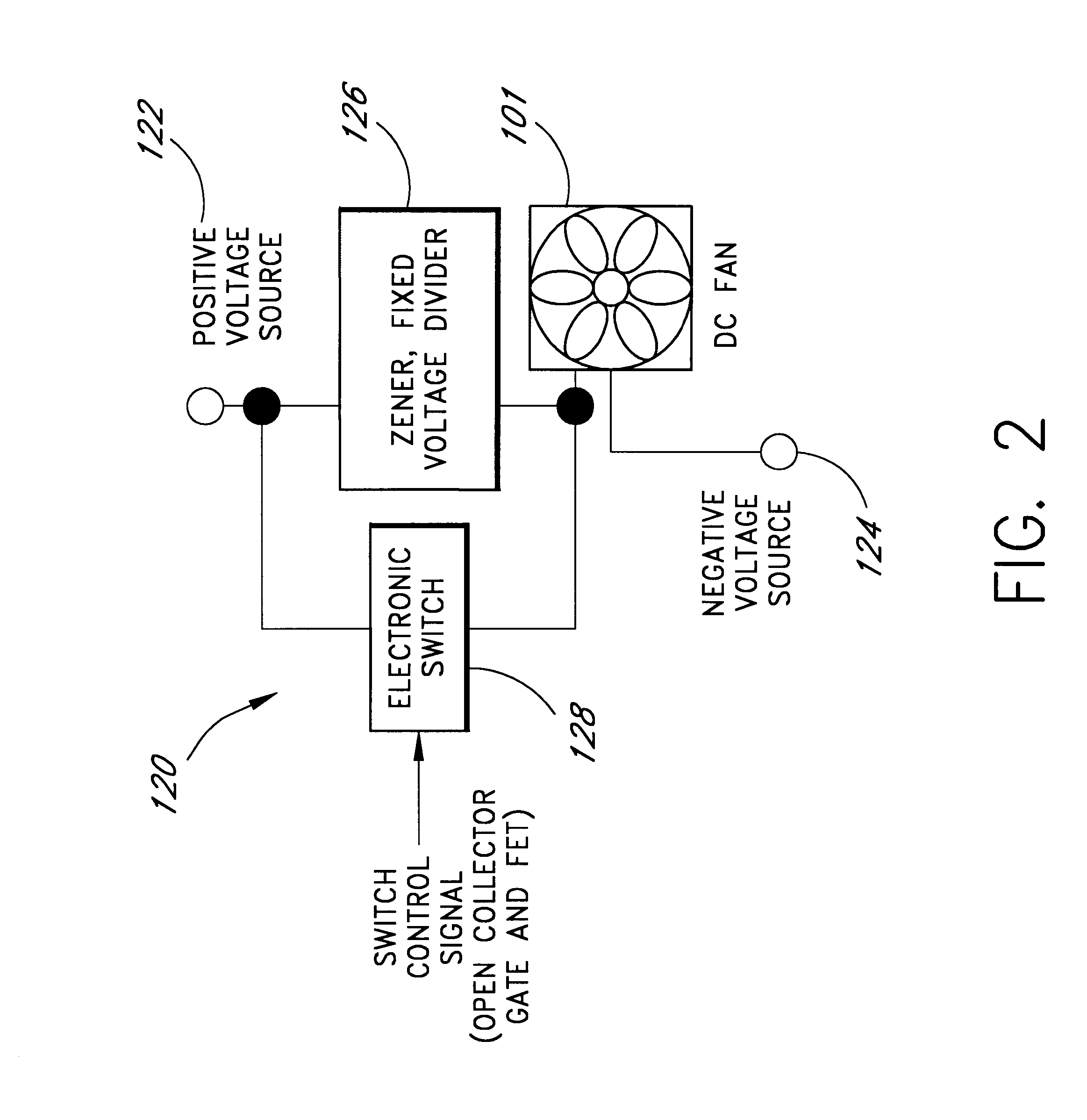
Computer fan speed control system
InactiveUS6247898B1Reduce stepsReduce voltageDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlSpeed control systemZener diode
A cooling system for cooling components of a computer is provided. The cooling system includes a DC fan which operates at a speed which is substantially proportional to the voltage that is applied to the fan. A zener diode voltage divider is connected in series between a voltage source and a first input of the fan. The second input of the fan is connected to a reference voltage source. A switch is also connected in series between the voltage source and the first voltage input of the fan so as to be connected in parallel with the zener diode voltage divider. When the switch is in a first position, the voltage produced by the voltage source is applied directly to the fan allowing the fan to operate at a first speed. When the switch is in a second position, the voltage from the voltage source is applied to the first input of the fan through the zener diode such that the first input of the fan receives a second voltage that is less than the first voltage thereby causing the fan to operate at a second speed. The zener diode voltage divider is substantially current independent such that the voltage drop across the zener diode is substantially independent of the current that is drawn by the fan.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Electrical circuit for delivering power to consumer electronic devices
InactiveUS20170099011A1Lower resistanceReduce conductionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLow voltageFull wave
An electrical circuit for providing electrical power for use in powering electronic devices, such as monitors, televisions, white goods, data centers, and telecom circuit boards, is described herein. The electrical circuit includes a voltage reduction circuit and a rectifier circuit for delivering input power signal to the voltage reduction circuit. The voltage reduction circuit is configured to receive an input power signal and generate an output power signal at a lower voltage level. The rectifier circuit includes a full wave bridge rectifier coupled to the electrical power source, a Zener based charging circuit coupled to the full wave bridge rectifier, a voltage divider coupled to the Zener based charging circuit and the full wave bridge rectifier, and an output terminal coupled to the full wave bridge rectifier, the Zener based charging circuit, and the voltage divider for delivering the input power signal to the voltage reduction circuit.
Owner:FREEMAN MICHAEL H FREE
Transient voltage/current protection system for electronic circuits associated with implanted leads
A transient voltage / surge current protection system is provided for electronic circuits associated with implanted leads. In particular, a transient voltage suppressor such as a diode, a zener diode, a transorb, a surge protector, varistor components or the like, is placed in parallel with the electronic circuits to thereby divert harmful surge current and bypass the electronic circuit during an external defibrillation event or during an applied therapeutic shock, such as from an ICD.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
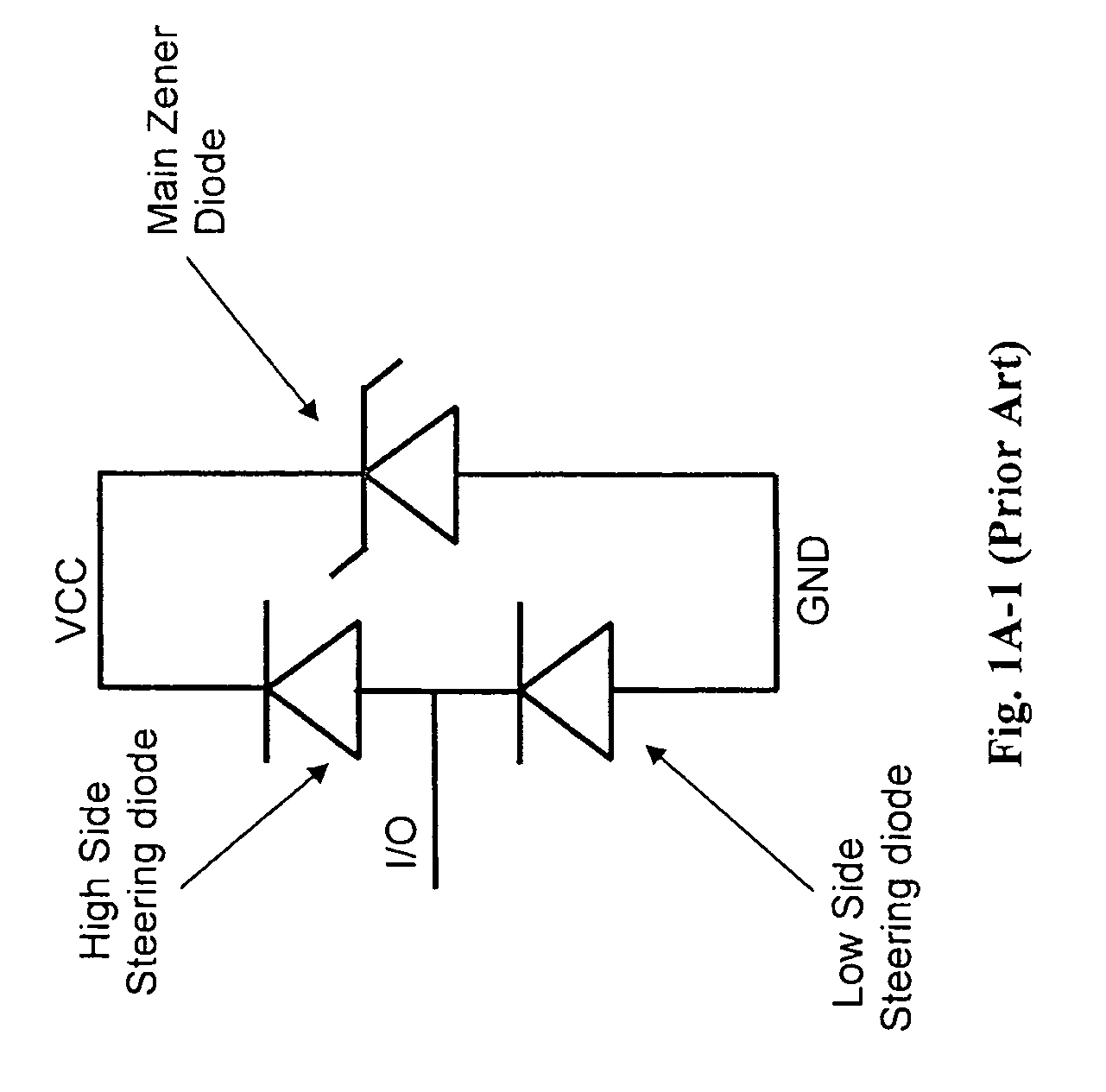
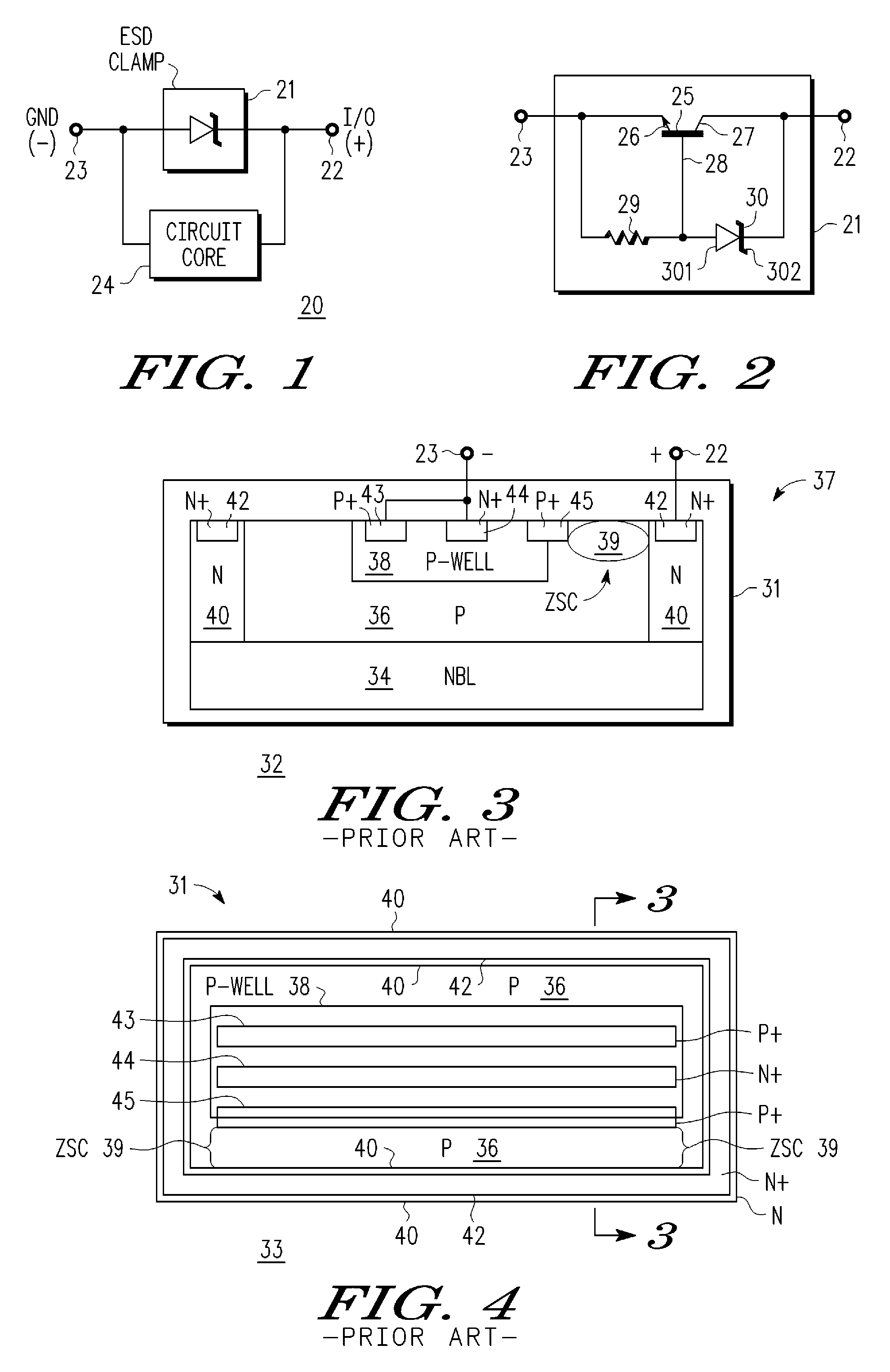
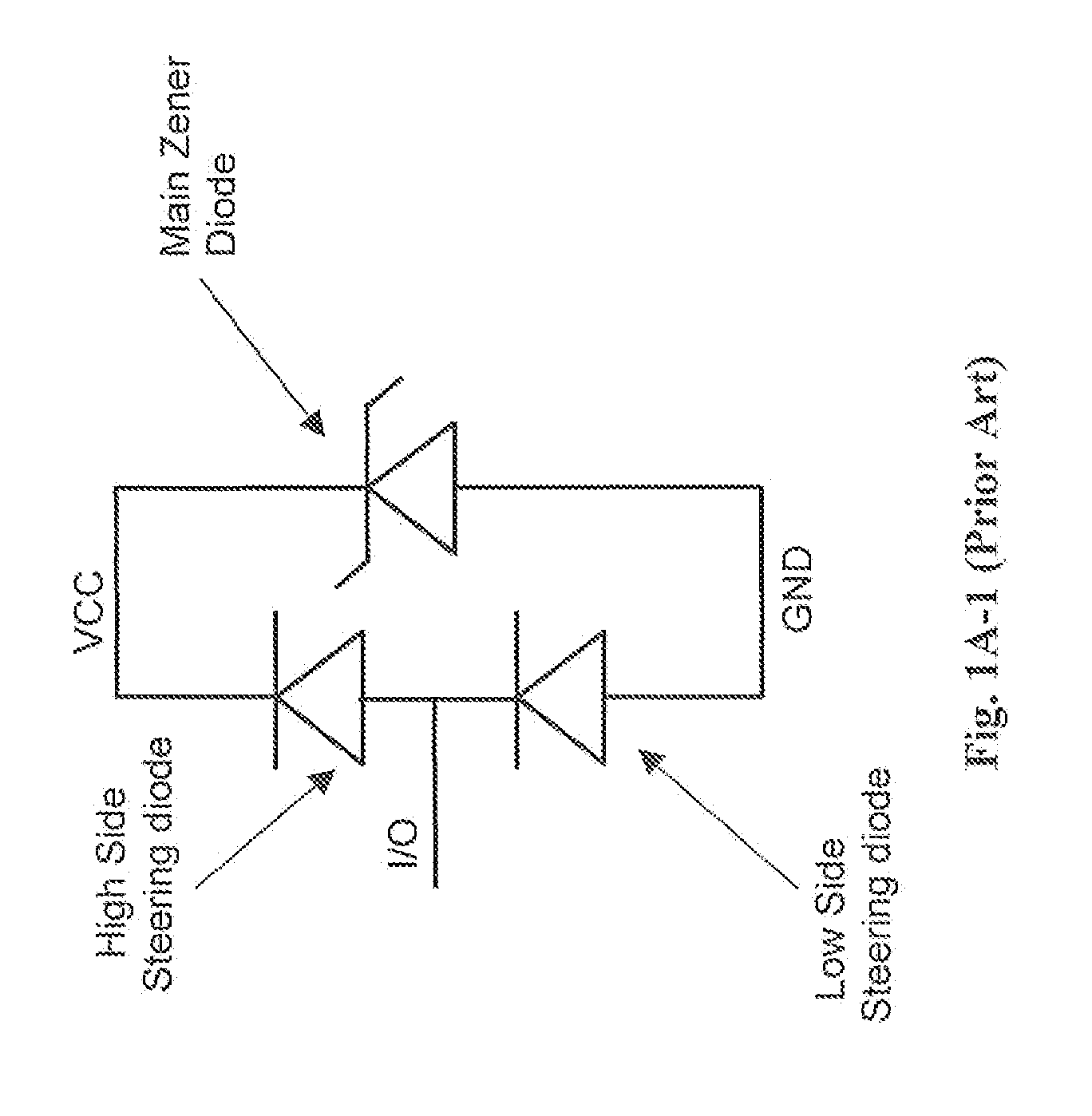
Complementary zener triggered bipolar ESD protection
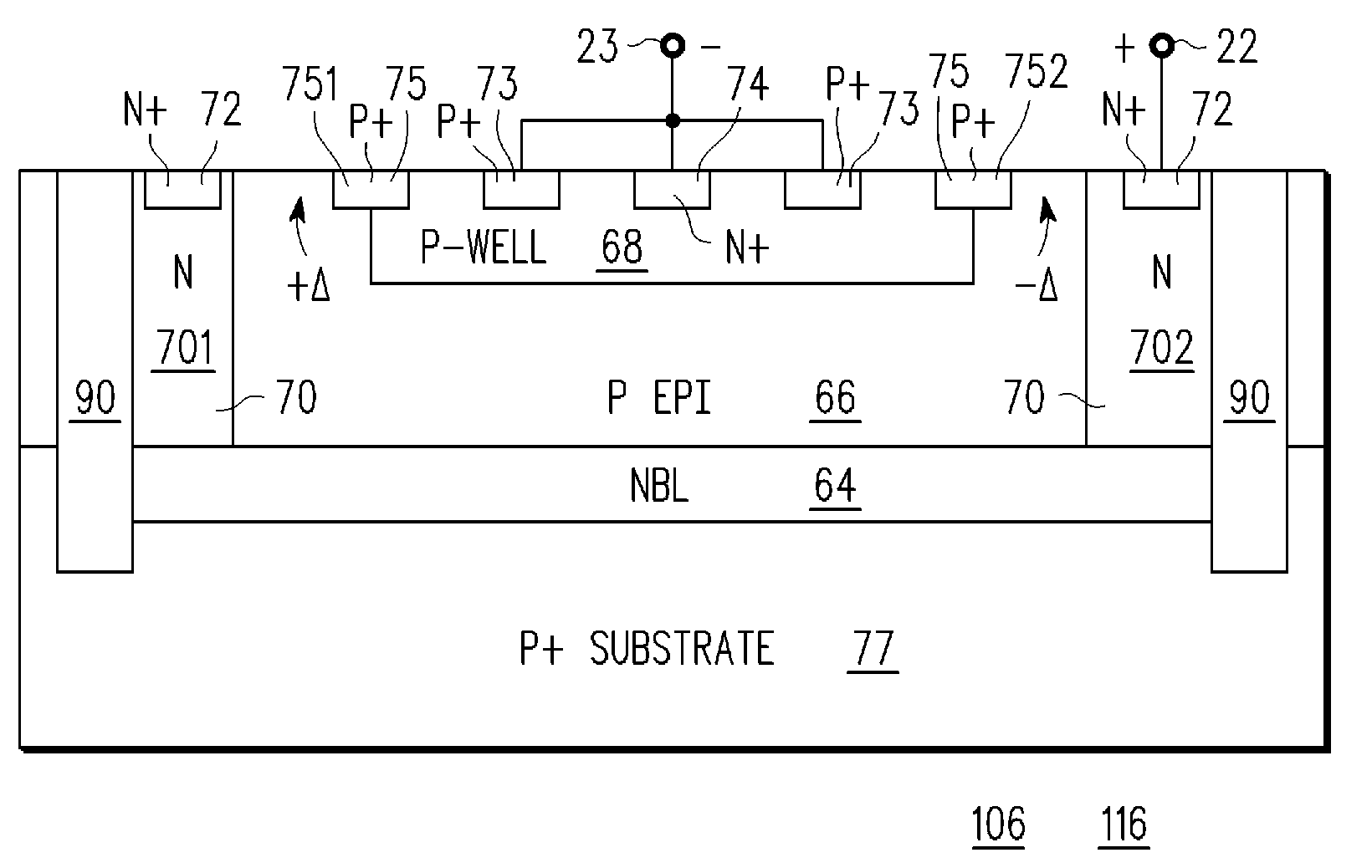
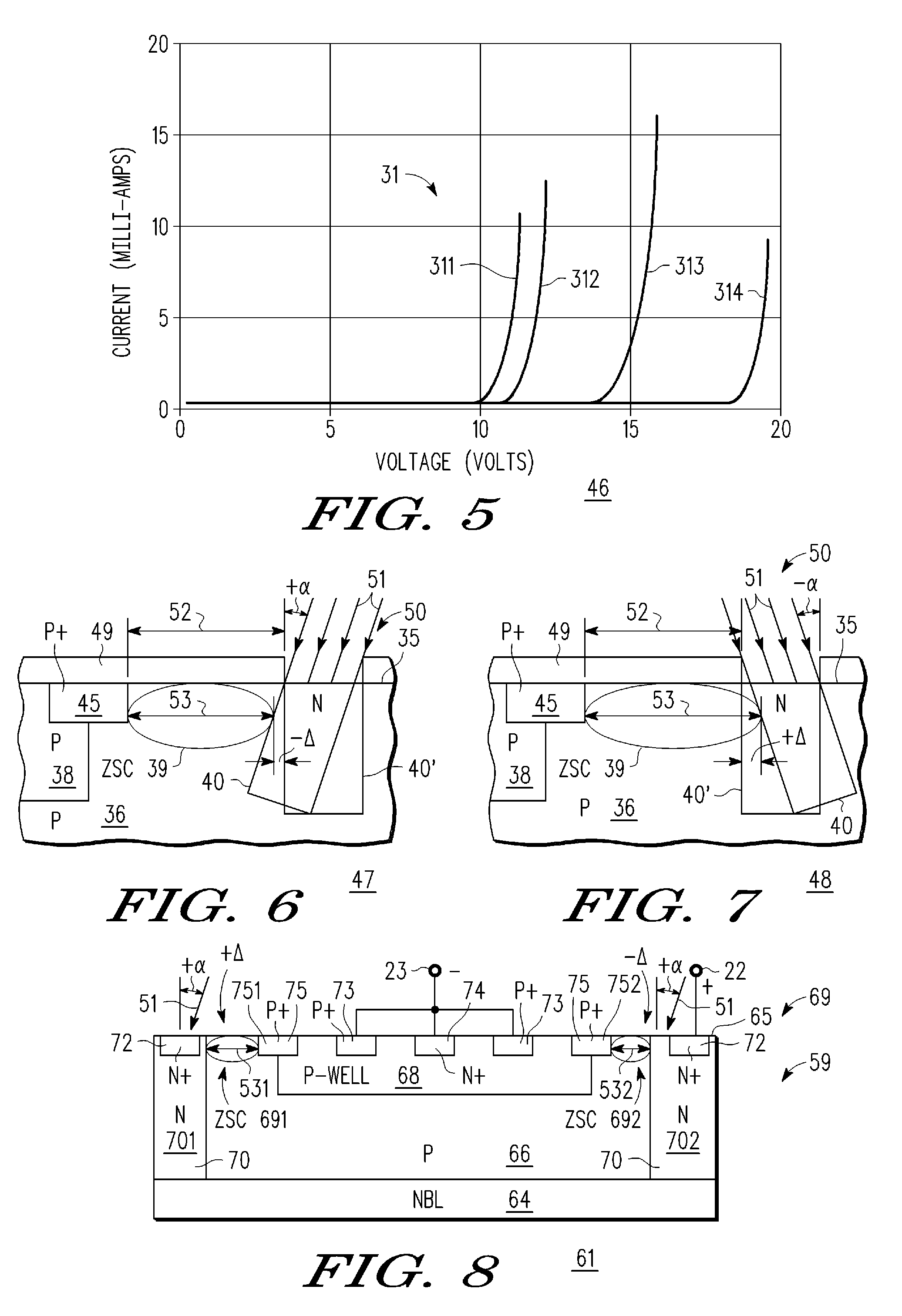
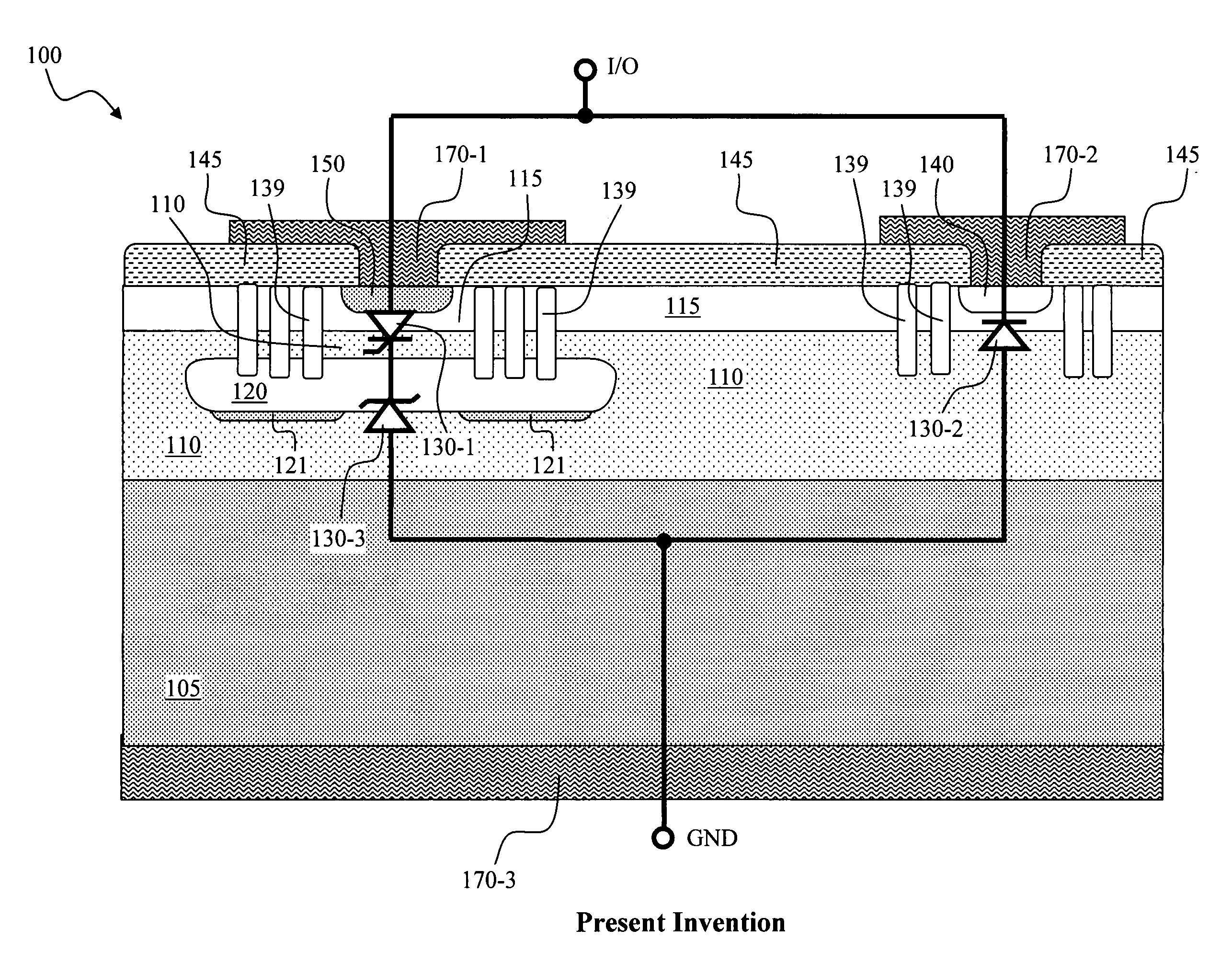
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection clamp (61) for I / O terminals (22, 23) of integrated circuits (ICs) (24) comprises an NPN bipolar transistor (25) coupled to an integrated Zener diode (30). Variations in the break-down current-voltage characteristics (311, 312, 313, 314) of multiple prior art ESD clamps (31) in different parts of the same IC chip is avoided by forming the anode (301) of the Zener (30) in the shape of a base-coupled P+ annular ring (75) surrounded by a spaced-apart N+ annular collector ring (70) for the cathode (302) of the Zener (30). Even though an angled implant (51, 86, 98) used to form the N+ annular collector ring (70) causes location dependent variations in the width (53) of the Zener space charge (ZSC) region (69), the improved annular shaped clamp (61) always has a portion that initiates break-down at the design voltage so that variations in the width (53) of the ZSC region (69) do not cause significant variations in the clamp's current-voltage characteristics (611, 612, 613, 614).
Owner:NXP USA INC
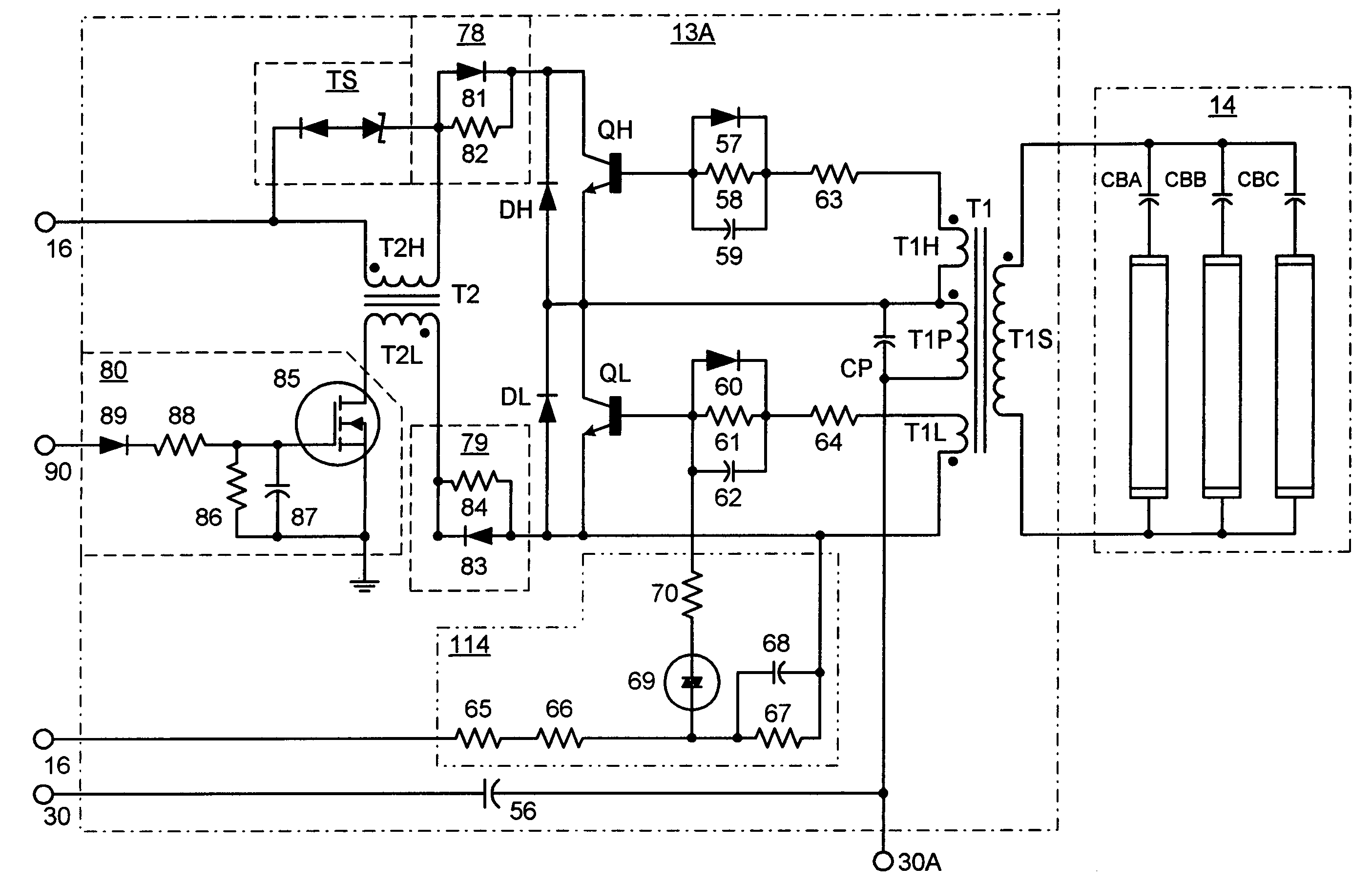
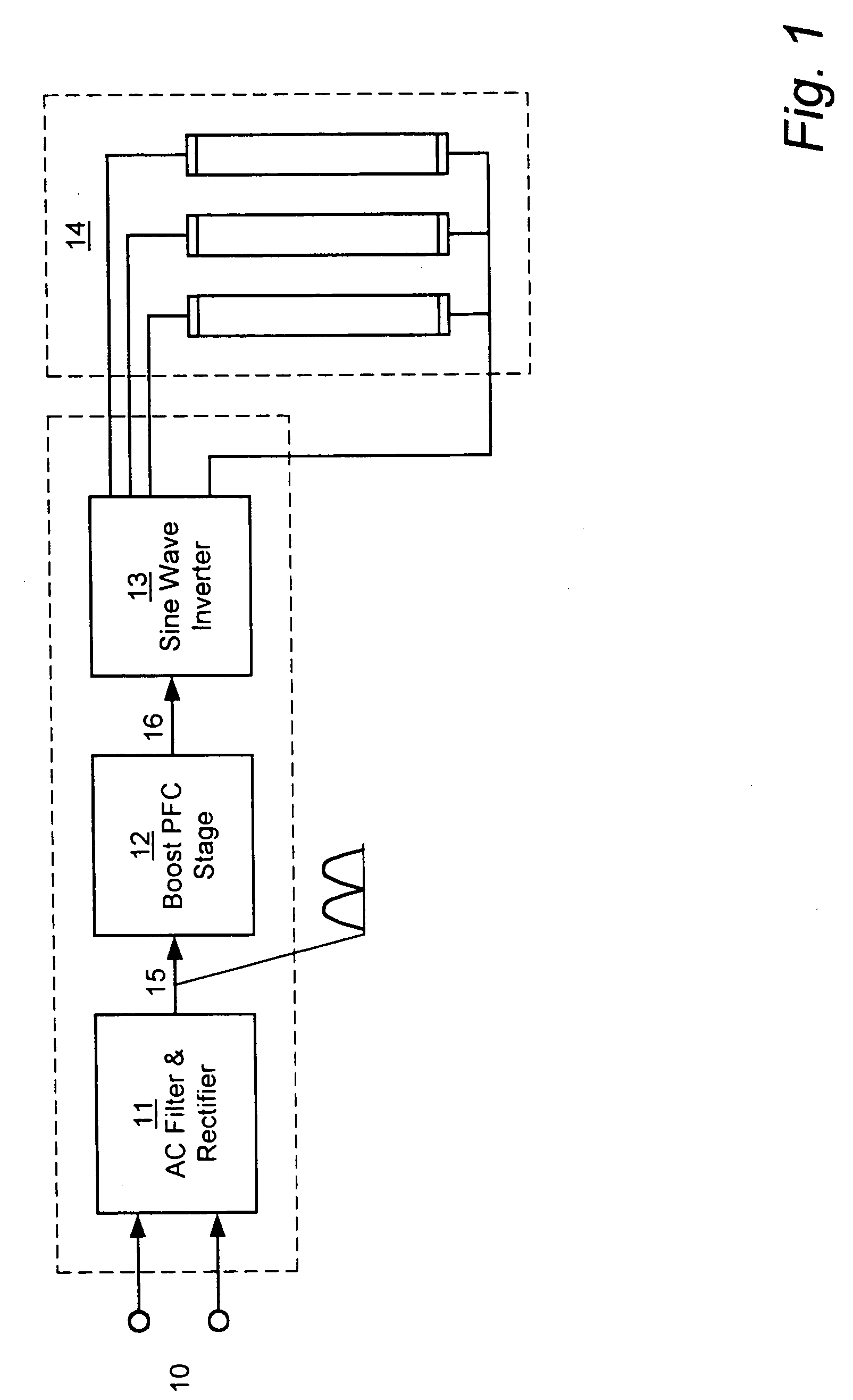
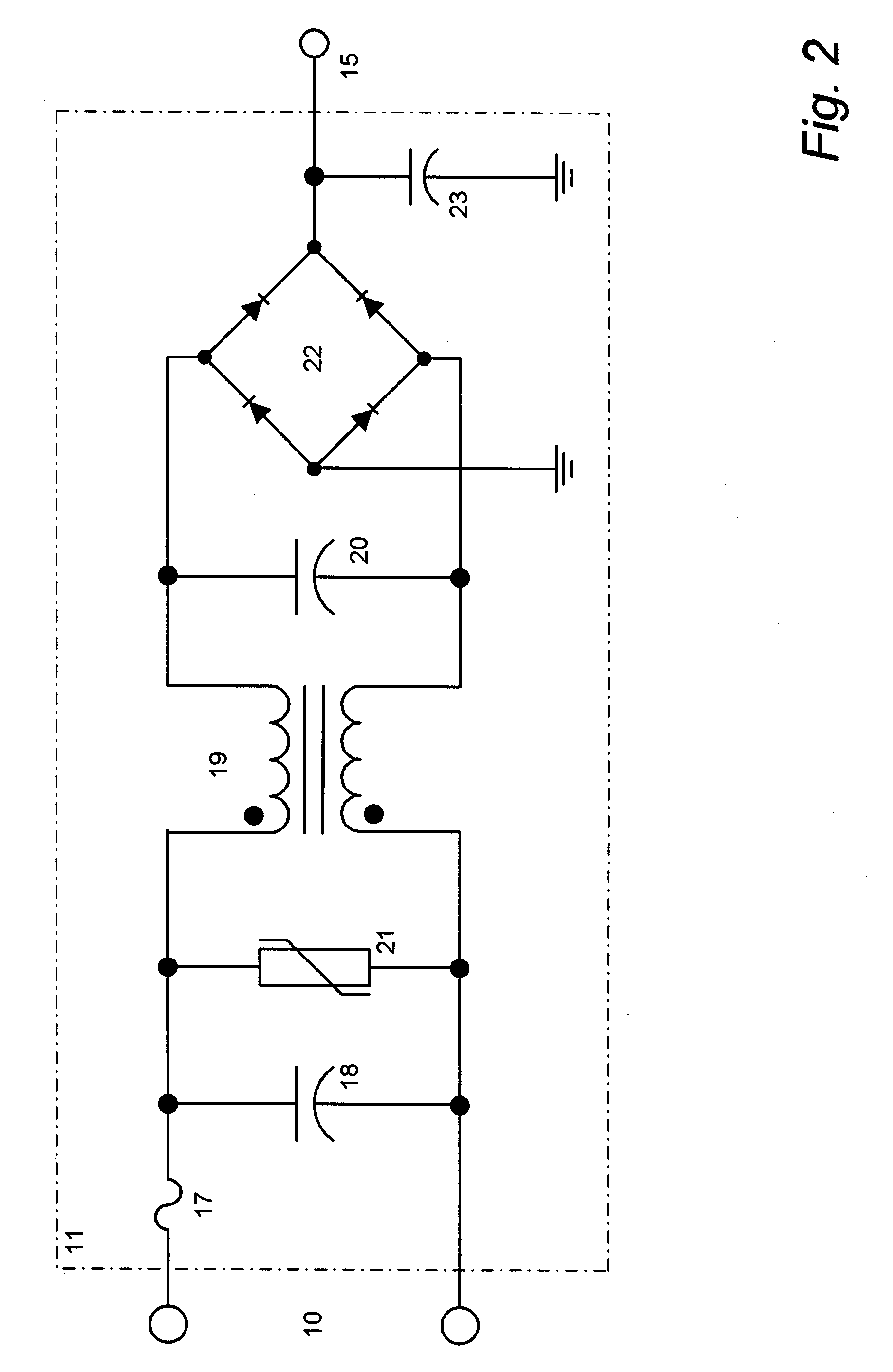
Instant start electronic ballast with universal AC input voltage
InactiveUS7061188B1Improve unit efficiencyLimit power lossElectric heatingElectric light circuit arrangementZener diodeEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic ballast that energizes fluorescent lamps connected in a parallel configuration. The ballast employs a power factor correcting boost converter that can be used over a wide range of AC line voltages to provide regulated power to a self-oscillating sine wave inverter that drives the fluorescent lighting load at high frequencies. The inverter employs special networks that limit a certain type of shoot-through current, and thus improve the efficiency of the unit. Also included is a restart circuit that limits power losses during the zero lamp condition, by periodically interrupting the inverter operation when the zero lamp state is detected. To improve operation of the power factor correcting circuitry over the wide range of AC line voltages, a DC offset is added to the sampled AC voltage at the higher AC line voltages by Zener diode based coupling circuit.
Owner:TECHN CONSUMER PRODS
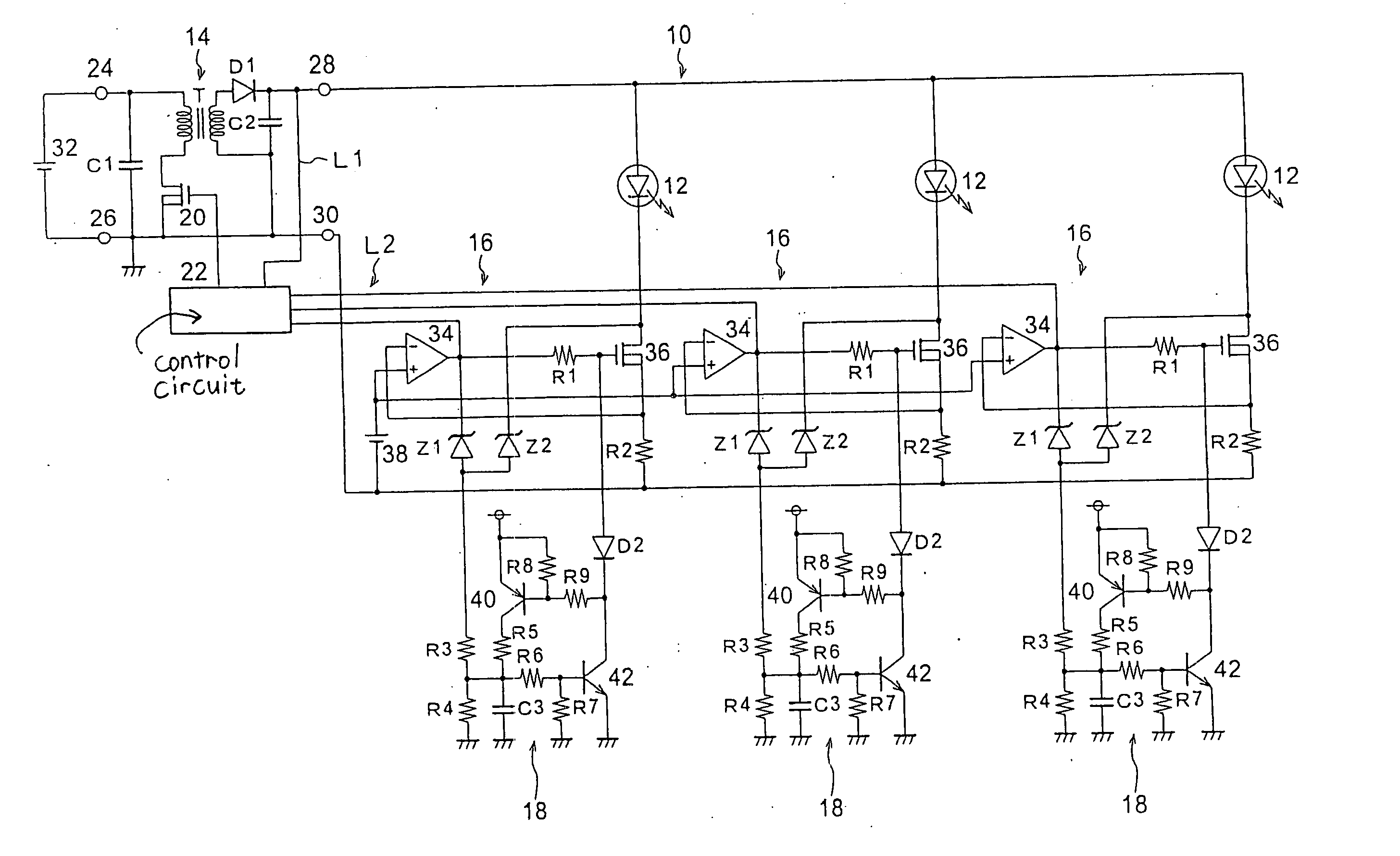
Lighting control circuit for vehicle lamps
InactiveUS20060082332A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesZener diodeVoltage regulation
The supply of a predetermined current to LEDs is controlled by using series regulators. In accordance with the controlled states of the series regulators, a switching regulator adjusts an output voltage relative to the LEDs to the maximum voltage. When a ground fault occurs at the anode of one of the LEDs, and when a short circuit occurs at the output terminal of the switching regulator and the output voltage drops abnormally, the operation of the switching regulator is halted. When the gate voltage of an NMOS transistor is raised due to the disconnection of one of the LEDs, or when the drain voltage of the transistor is raised due to a short circuit at one of the LEDs, a Zener diode becomes conductive and an NPN transistor and a PNP transistor are rendered on. Then, a current flows through a diode, and as the gate voltage has been lowered, the operation of the NMOS transistor is halted, so that the remaining, normal LEDs are protected when an abnormality occurs.
Owner:KOITO MFG CO LTD
Tvs with low capacitance & forward voltage drop with depleted scr as steering diode
A transient-voltage suppressing (TVS) device disposed on a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type. The TVS includes a buried dopant region of a second conductivity type disposed and encompassed in an epitaxial layer of the first conductivity type wherein the buried dopant region extends laterally and has an extended bottom junction area interfacing with the underlying portion of the epitaxial layer thus constituting a Zener diode for the TVS device. The TVS device further includes a region above the buried dopant region further comprising a top dopant layer of a second conductivity type and a top contact region of a second conductivity type which act in combination with the epitaxial layer and the buried dopant region to form a plurality of interfacing PN junctions constituting a SCR acting as a steering diode to function with the Zener diode for suppressing a transient voltage.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Magnetic storage device
InactiveUS7218550B2Reduce power consumptionReduce complexityRead-only memoriesDigital storageMagnetic storageZener diode
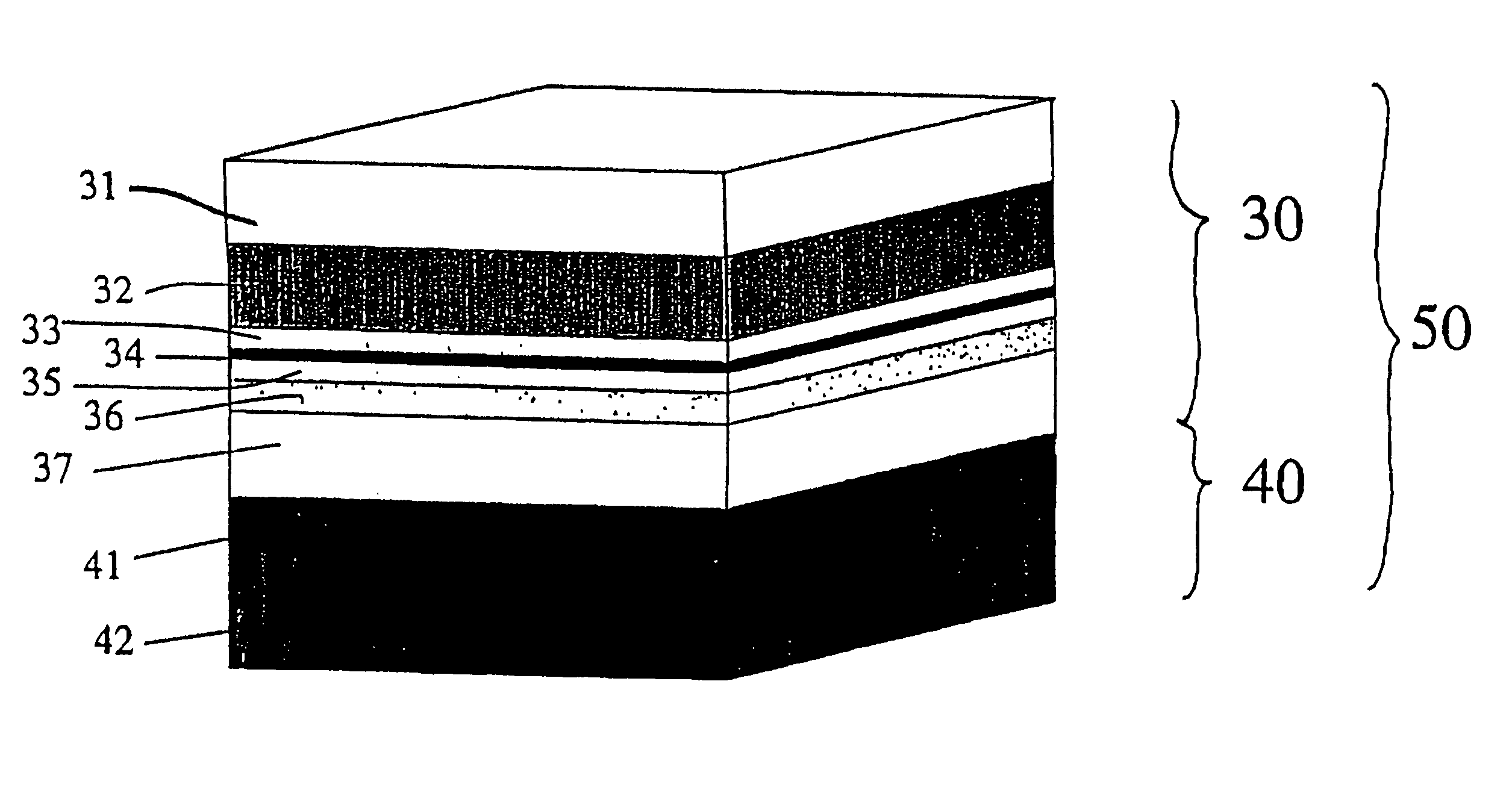
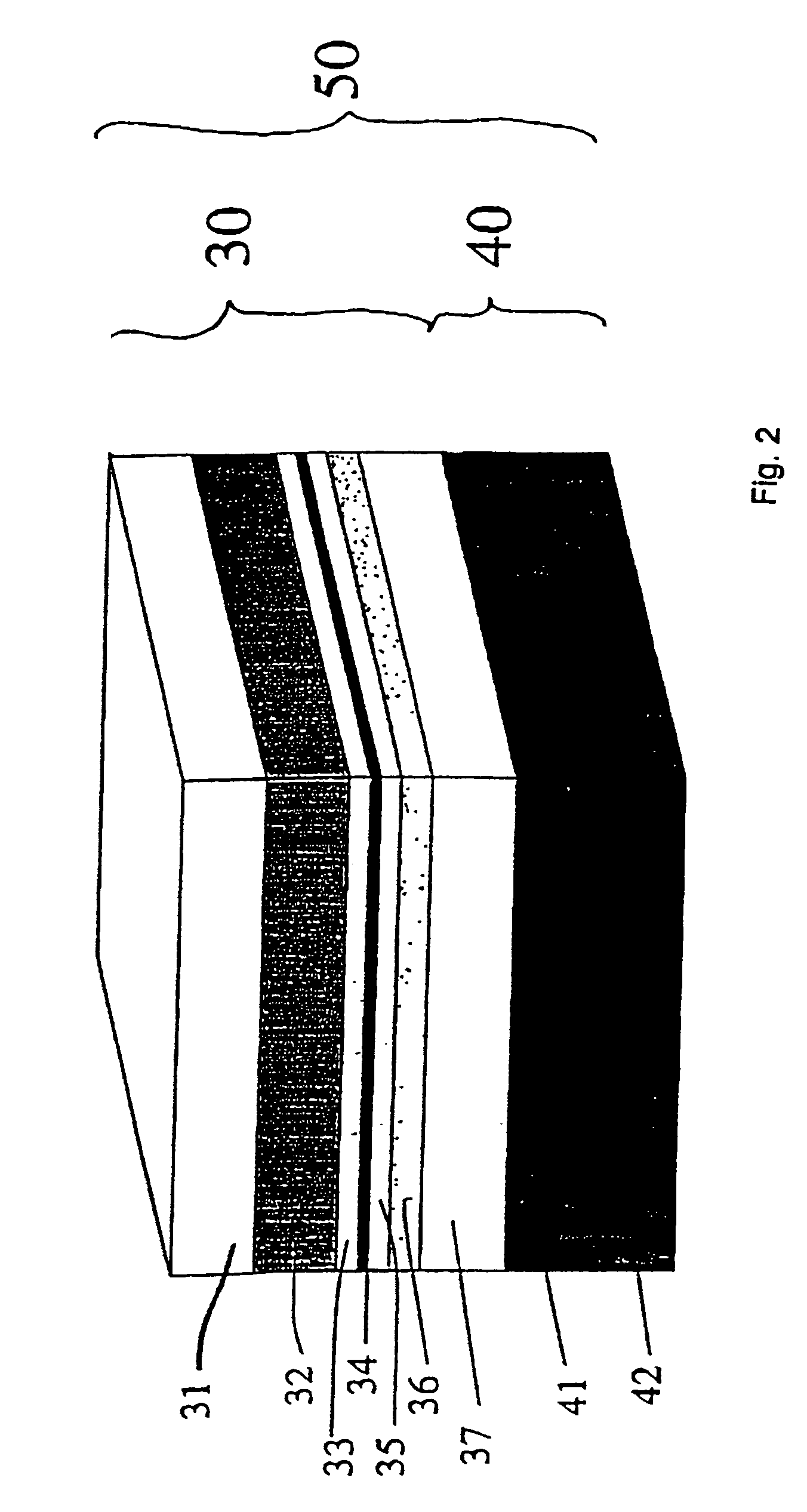
A magnetic storage device comprises an array of magnetic memory cells (50). Each cell (50) has, in electrical series connection, a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) (30) and a Zener diode (40). The MTJ (30) comprises, in sequence, a fixed ferromagnetic layer (FMF) (32), a non-magnetic spacer layer (33), a tunnel barrier layer (34), a further spacer layer (35), and a soft ferromagnetic layer (FMS) (36) that can change the orientation of its magnetic moment. The material type and thickness of each layer in the MTJ (30) is selected so that the cell (50) can be written by applying a voltage across the cell, which sets the orientation of the magnetic moments of the FMF (32) and FMS (36) relative to one another. The switching is effected by means of an induced exchange interaction between the FMS and FMF mediated by the tunneling of spin-polarised electrons in the MTJ (30). The cell (50) therefore has low power consumption during write operations allowing for fast writing and dense integration of cells (50) in an array. The mechanism used to control the array to write and sense the information stored in the cells (50) is simplified.
Owner:SONY CORP
LED thermal management system and method
ActiveUS20100134024A1Low heat generationEasy to operateElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementZener diodeEngineering
A thermal management system for reducing or eliminating heat-mediated degradation of LED performance and / or operating life. The system may include a thermal controller arranged to respond to an LED operating condition, and to responsively limit temperature in the LED. The thermal controller in one implementation includes a bypass circuit containing a bypass control element, such as a varistor, Zener diode, or antifuse device, and arranged to divert current from flowing to the LED so that the LED remains in a cool state, e.g., below 75° C. The system may be arranged to (I) at least partially attenuate the power supplied to an LED so as to reduce heat generation in such LED and maintain the LED below a threshold temperature and / or (II) remove heat from the LED to maintain temperature of the LED below a threshold temperature.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
TVS with low capacitance & Forward voltage drop with depleted SCR as steering diode
A transient-voltage suppressing (TVS) device disposed on a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type. The TVS includes a buried dopant region of a second conductivity type disposed and encompassed in an epitaxial layer of the first conductivity type wherein the buried dopant region extends laterally and has an extended bottom junction area interfacing with the underlying portion of the epitaxial layer thus constituting a Zener diode for the TVS device. The TVS device further includes a region above the buried dopant region further comprising a top dopant layer of a second conductivity type and a top contact region of a second conductivity type which act in combination with the epitaxial layer and the buried dopant region to form a plurality of interfacing PN junctions constituting a SCR acting as a steering diode to function with the Zener diode for suppressing a transient voltage.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Switching control circuit and switching power-supply apparatus
ActiveUS20110175587A1Increase the number ofReduce the number of terminalsDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationZener diodeEngineering
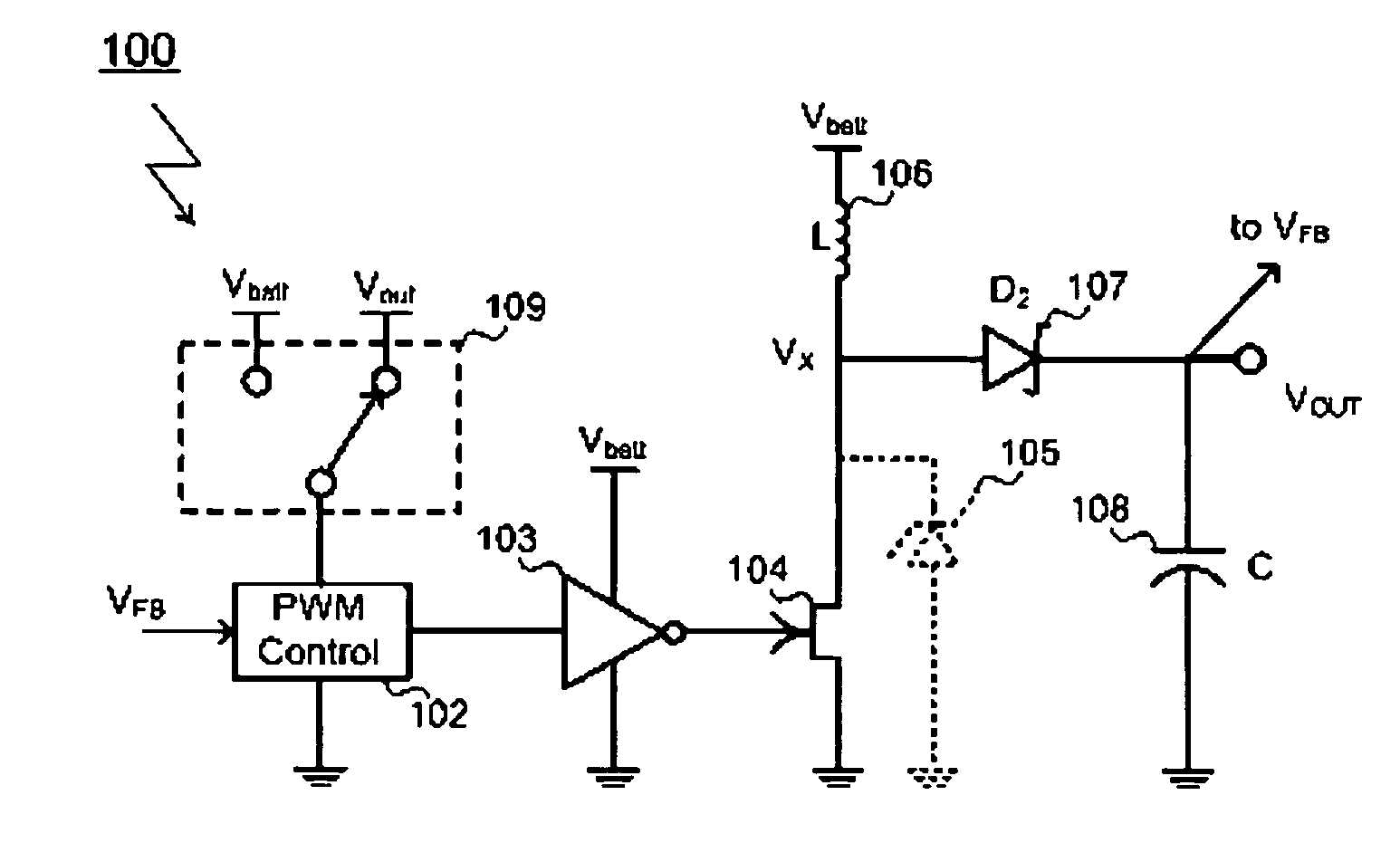
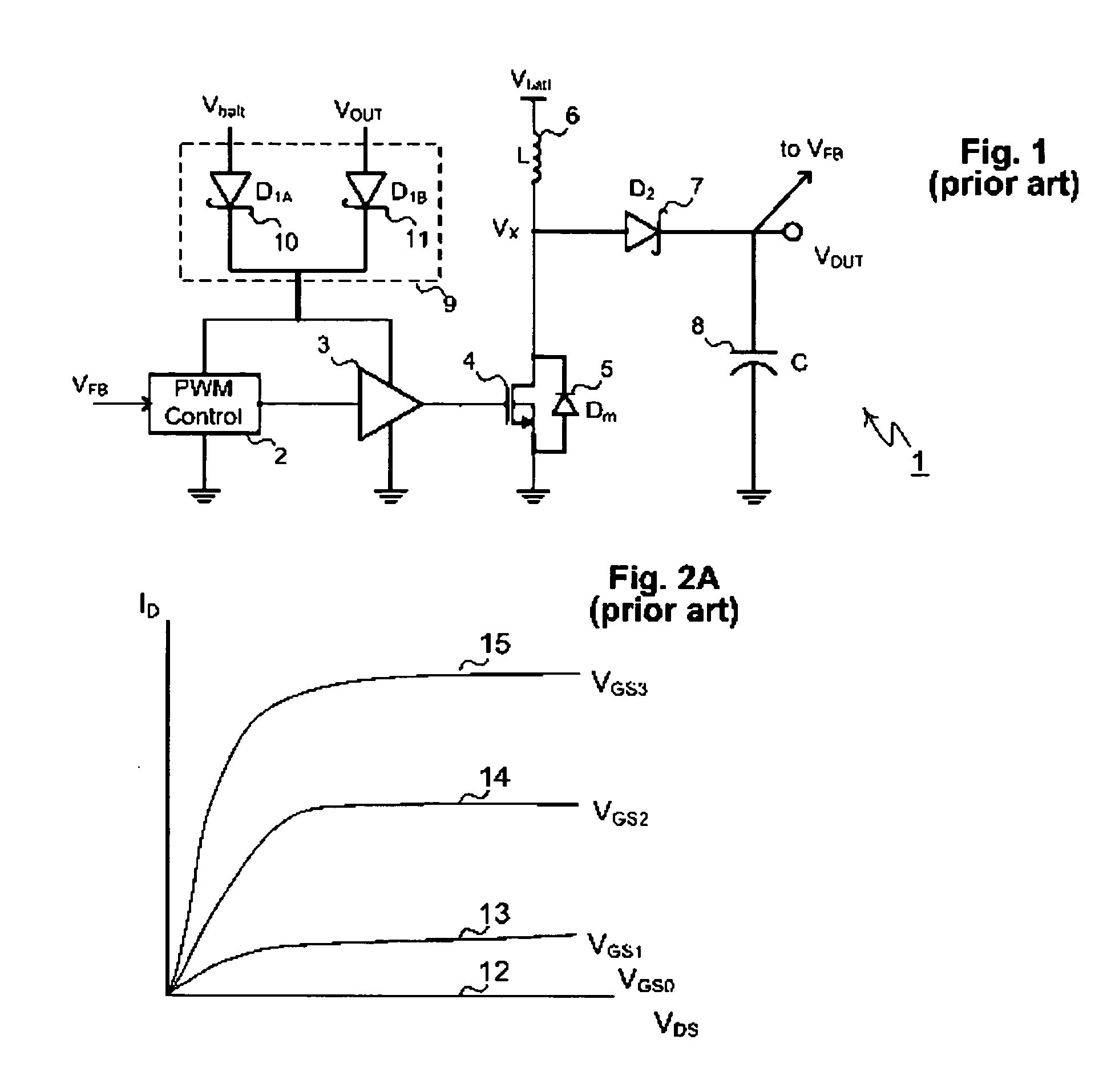
A switching power-supply apparatus and a switching power supply circuit in which a feedback signal is input from a feedback circuit to a feedback terminal of a switching control IC includes a capacitor and a Zener diode connected between the feedback terminal and a ground terminal. The Zener diode is a selectively connected external circuit. A voltage of the feedback terminal during an overcurrent operation changes depending on whether or not the external circuit is present. A return / latch determination circuit detects the voltage of the feedback terminal to switch between an automatic return system and a latch system in an overcurrent operation state.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Light emitting device
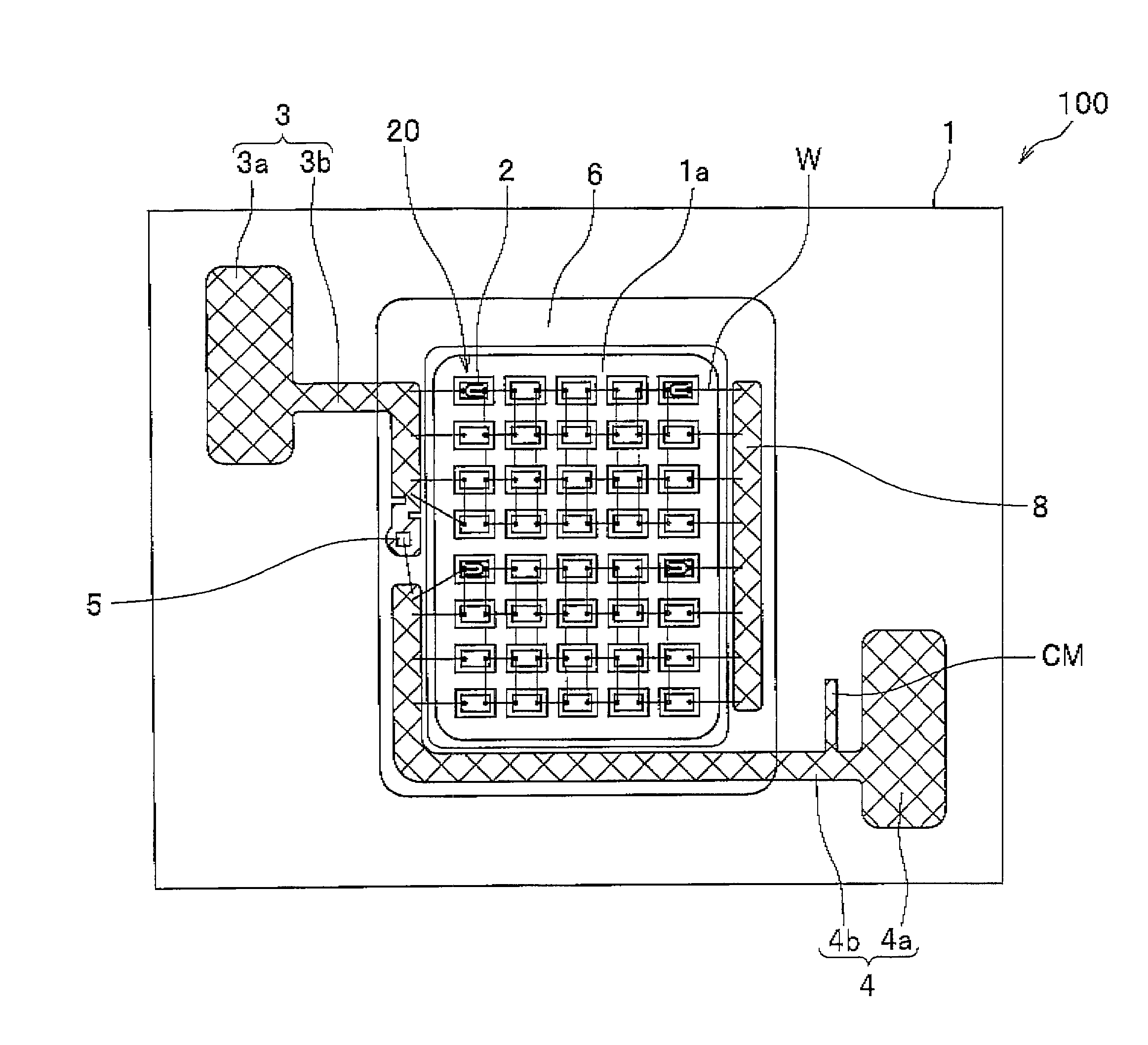
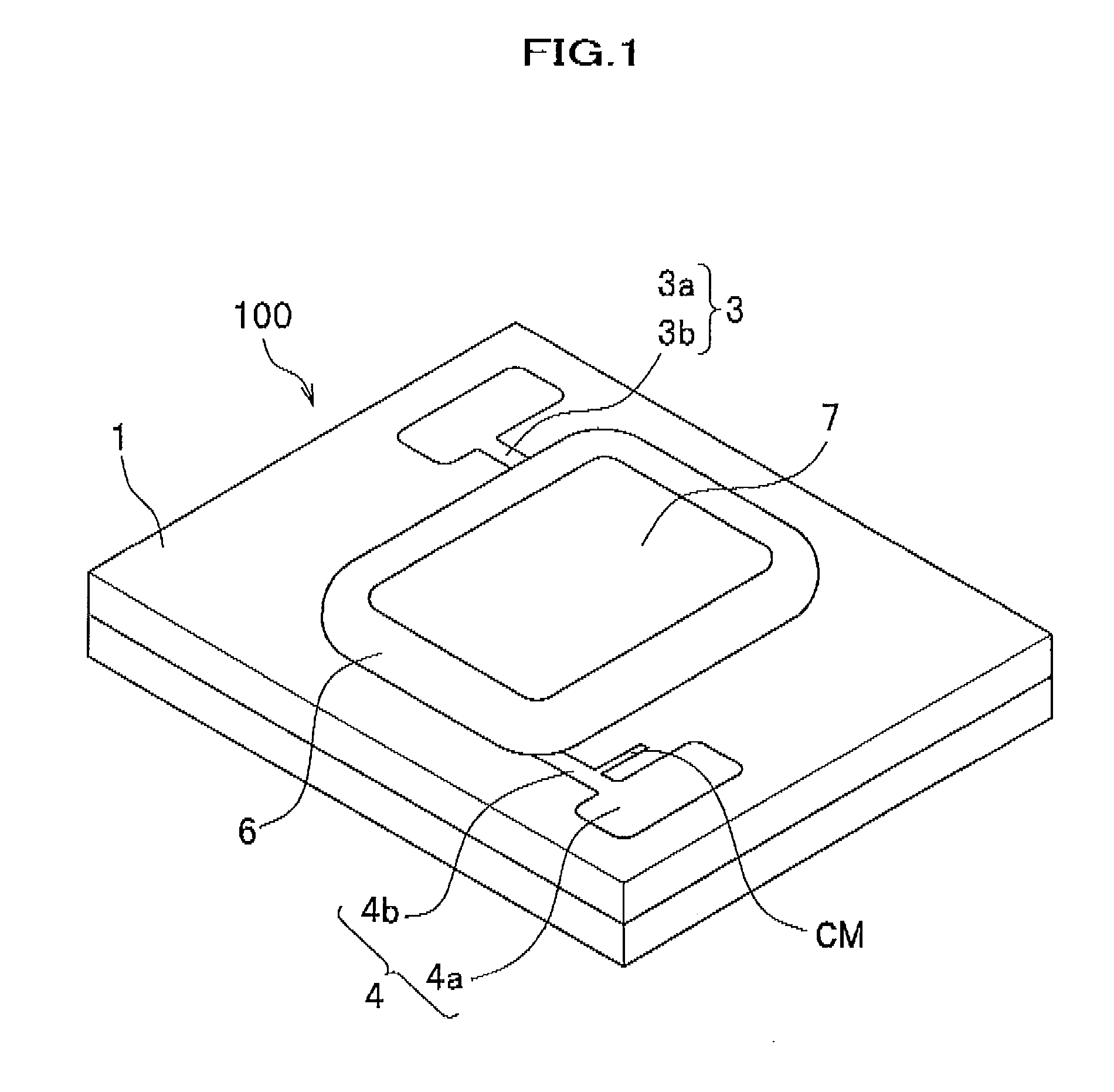
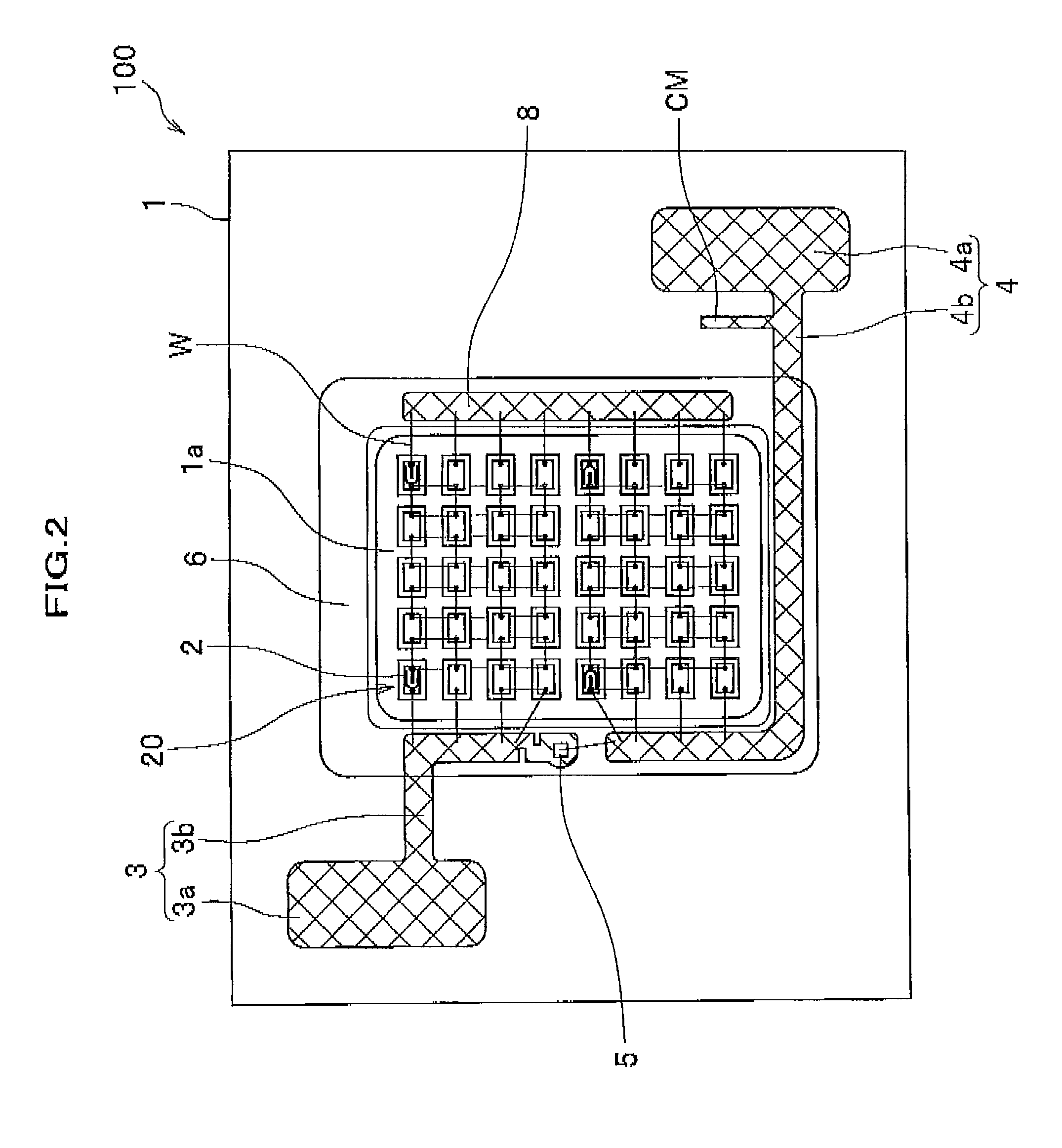
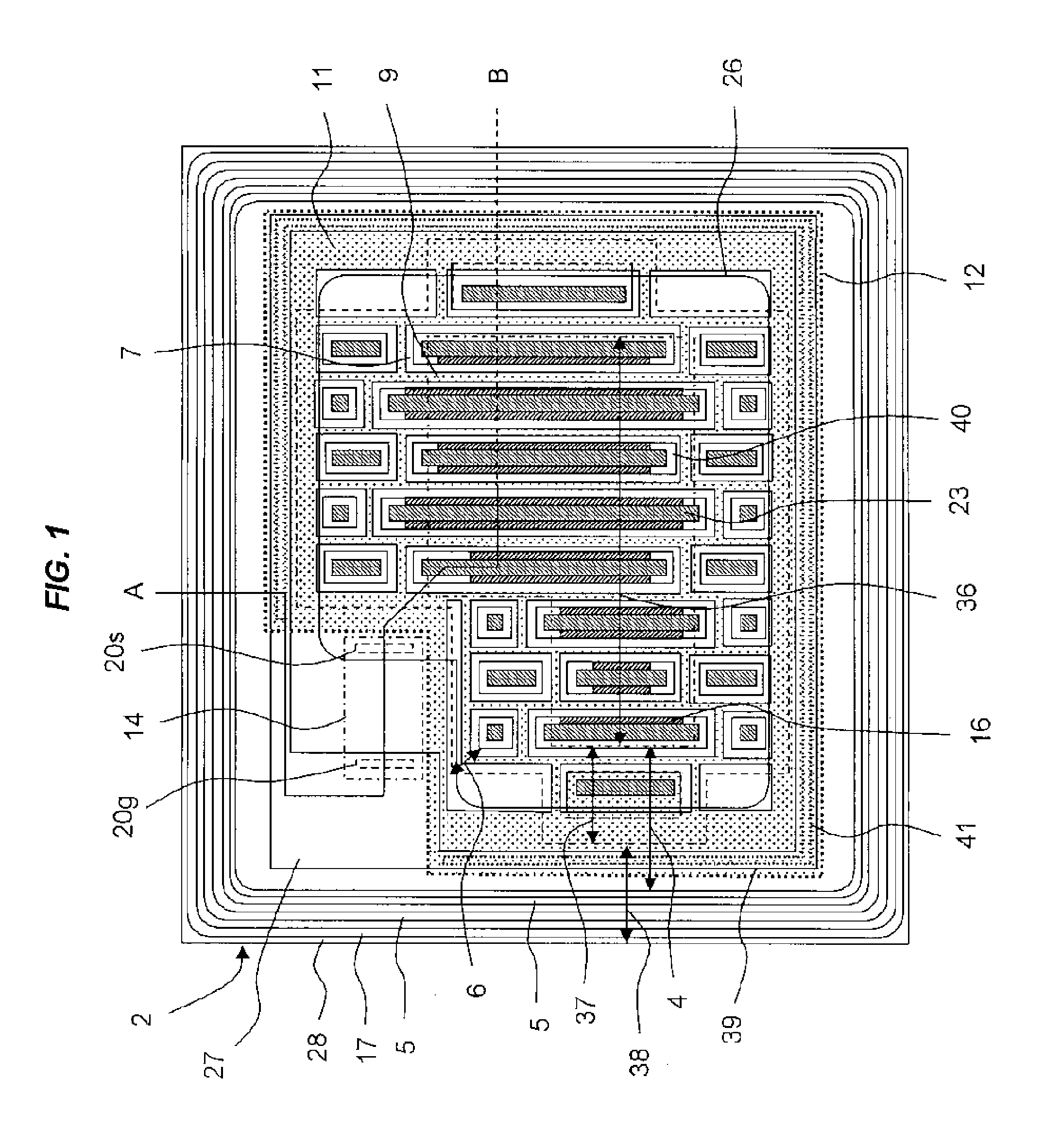
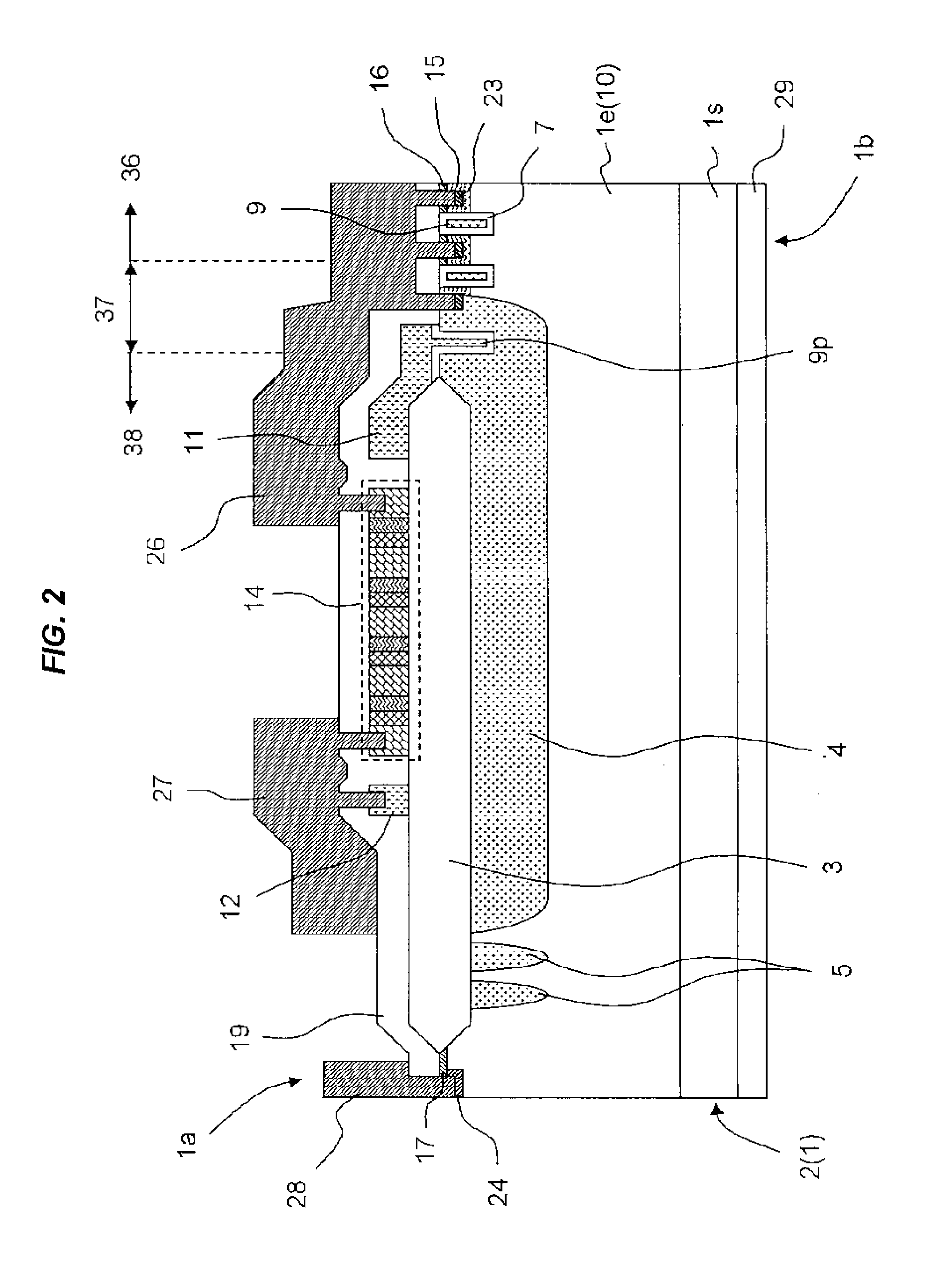
ActiveUS20110254022A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedLoss in output lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesZener diodeLight emitting device
There is presented a light emitting device, having plural light emitting elements disposed on a substrate, in which a protection element, such as a zener diode, can be disposed at an appropriate position. The light emitting device includes: a substrate; a light emitting section having plural light emitting elements disposed in a mounting area on the substrate; a positive electrode and negative electrode each having a pad section and wiring section to apply voltage to the light emitting section through the wiring sections; a protection element disposed at one of the positive electrode and negative electrode and electrically connected with the other one electrode; and a light reflecting resin formed on the substrate such as to cover at least the wiring sections and the protection element, wherein the wiring sections are formed along the periphery of the mounting area such that one end portions thereof are adjacent to each other.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Semiconductor device
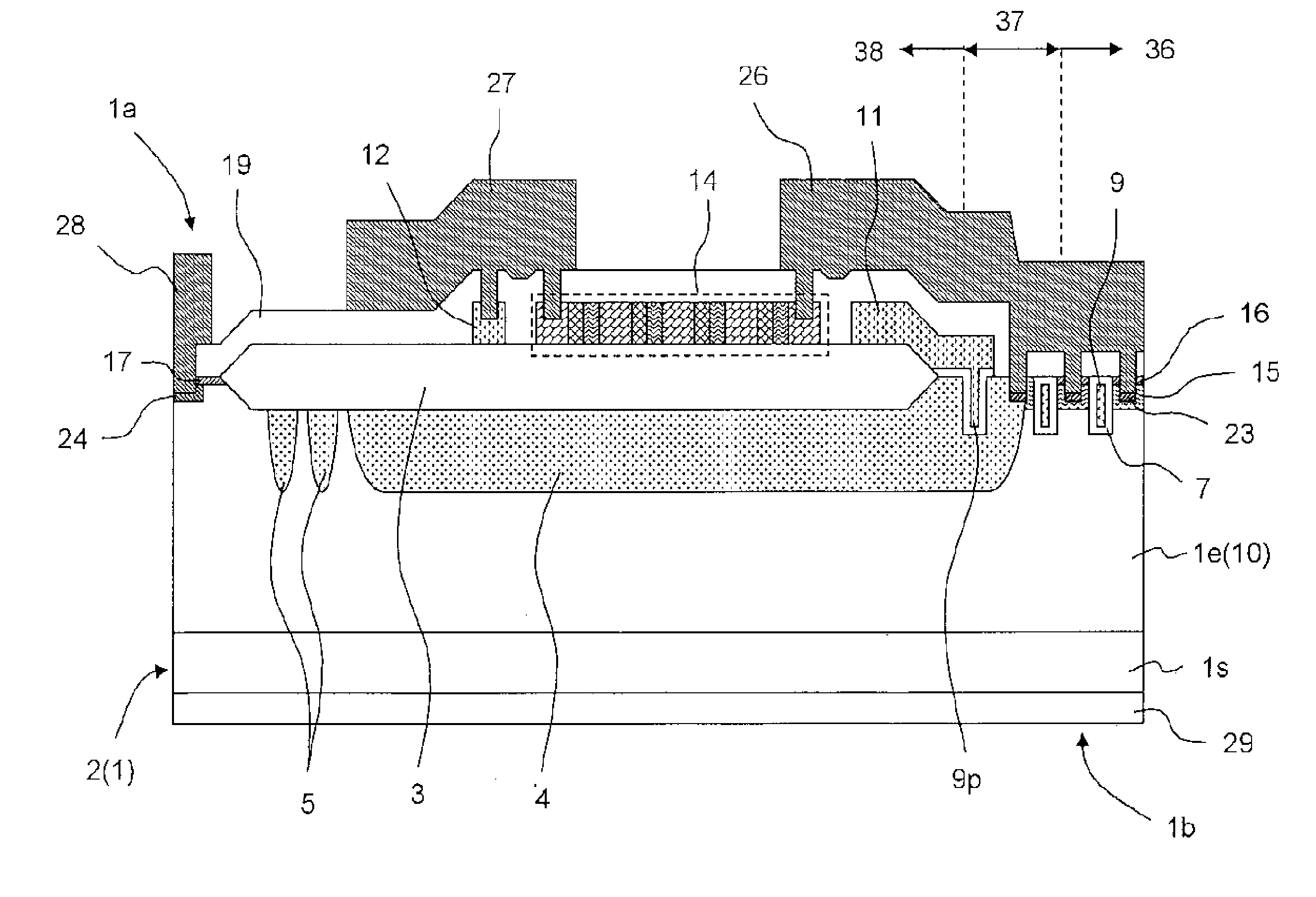
InactiveUS20120049187A1Reliable manufacturingEffectively prevent deteriorationSolid-state devicesDiodeZener diodeMiniaturization
Accompanying the miniaturization of a gate electrode of a trench gate power MOSFET, the curvature of the bottom part of the trench increases, and thereby, electric fields concentrate on the part and deterioration of a gate oxide film (insulating film) occurs. The deterioration of the gate insulating film is more likely to occur when the gate side bias is negative in the case of an N-channel type power MOSFET and when the gate side bias is positive in the case of a P-channel type power MOSFET.The present invention is a semiconductor device including an insulating gate power transistor etc. in a chip, wherein a gate protection element includes a bidirectional Zener diode and the bidirectional Zener diode has a plurality of P-type impurity regions (or a P-type impurity region) having different concentrations so that the withstand voltage with its gate side negatively biased and the withstand voltage with the gate side positively biased are different from each other.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
LED lamp
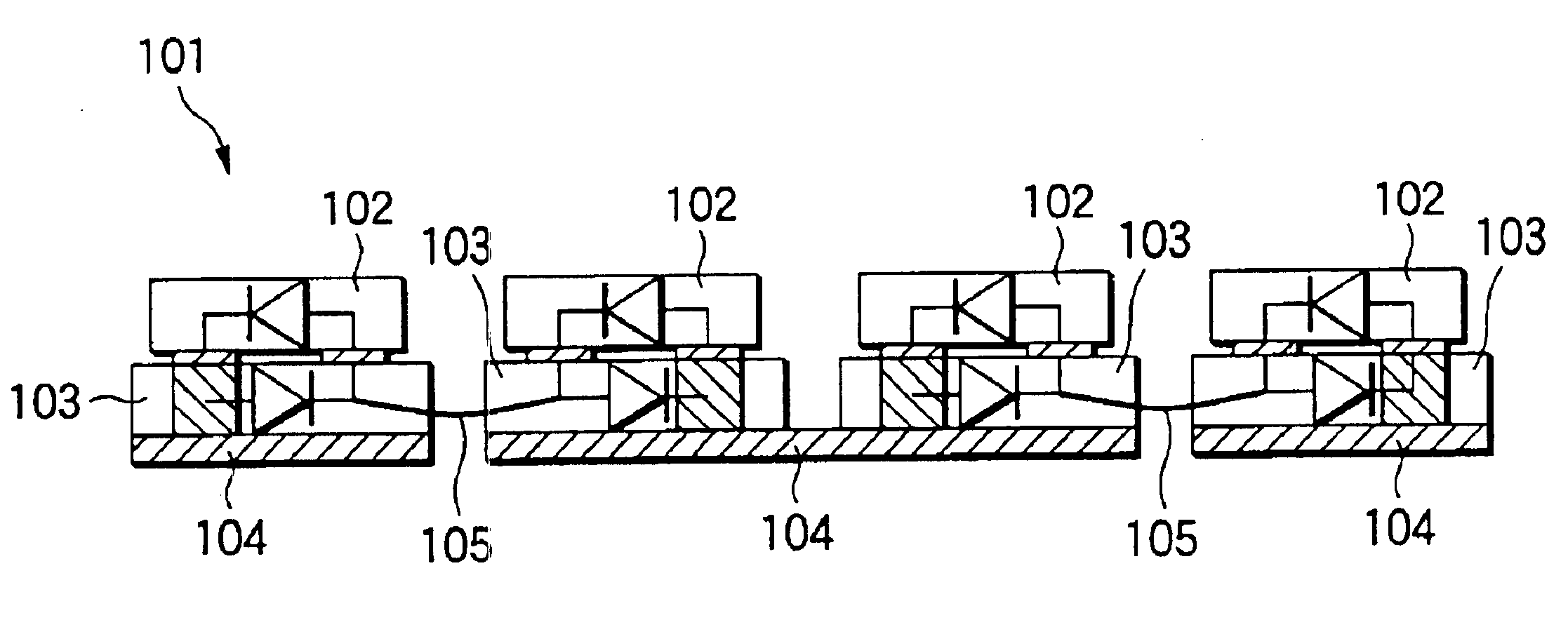
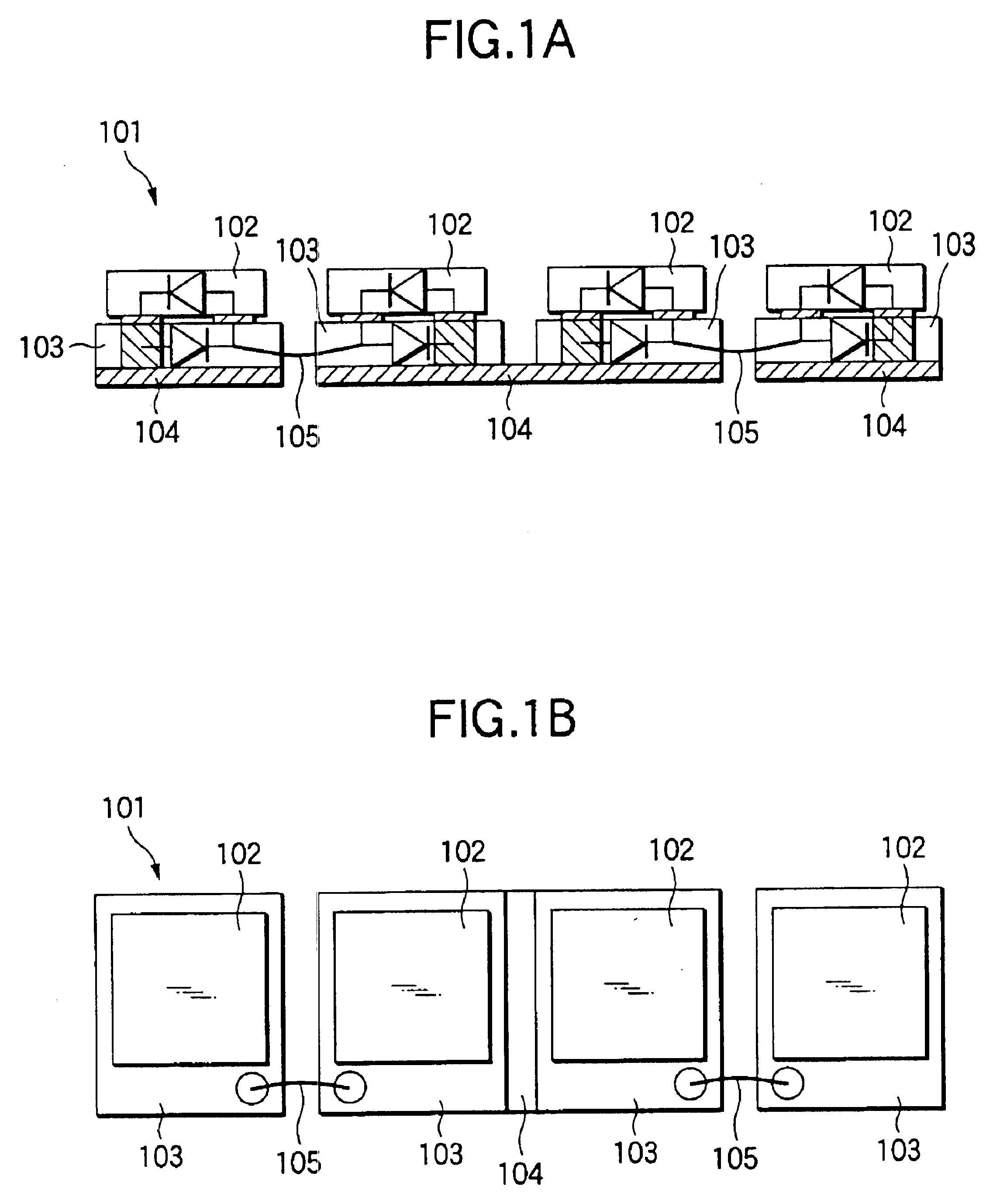
InactiveUS6841931B2High strengthImprove cooling effectDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesMiniaturizationZener diode
In an LED lamp, a Zener diode is mounted on a copper plate, and a GaN-based light-emitting element is mounted on the Zener diode with an electrode of the element being oriented facedown. Two Zener diodes close to the center of the LED lamp are mounted on a common copper plate, thereby interconnecting the two light-emitting elements in series. Consequently, a Zener diode is connected to the respective two Zener diodes by means of a wire serving as a conductive member. Four light-emitting elements are connected in series, so that four light-emitting elements are connected in series, thus completing a circuit configuration. In this way, use of the Zener diodes for interconnection purpose enables a reduction in the number of minimum required wires. It is better to connect the wire to the upper surfaces of the Zener diodes, thereby obviating a necessity for a redundant wire space and enabling miniaturization of the LED lamp.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Bipolar resistive-switching memory with a single diode per memory cell
According to various embodiments, a resistive-switching memory element and memory element array that uses a bipolar switching includes a select element comprising only a single diode that is not a Zener diode. The resistive-switching memory elements described herein can switch even when a switching voltage less than the breakdown voltage of the diode is applied in the reverse-bias direction of the diode. The memory elements are able to switch during the very brief period when a transient pulse voltage is visible to the memory element, and therefore can use a single diode per memory cell.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Electrically-programmable integrated circuit antifuses
InactiveUS7272067B1Reduces drain-to-source resistanceIncrease resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Integrated circuit antifuse circuitry is provided. A metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) antifuse transistor serves as an electrically-programmable antifuse. In its unprogrammed state, the antifuse transistor is off and has a relatively high resistance. During programming, the antifuse transistor is turned on which melts the underlying silicon and causes a permanent reduction in the transistor's resistance. A sensing circuit monitors the resistance of the antifuse transistor and supplies a high or low output signal accordingly. The antifuse transistor may be turned on during programming by raising the voltage at its substrate relative to its source. The substrate may be connected to ground through a resistor. The substrate may be biased by causing current to flow through the resistor. Current may be made to flow through the resistor by inducing avalanche breakdown of the drain-substrate junction or by producing Zener breakdown of external Zener diode circuitry connected to the resistor.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Composite field effect transistor
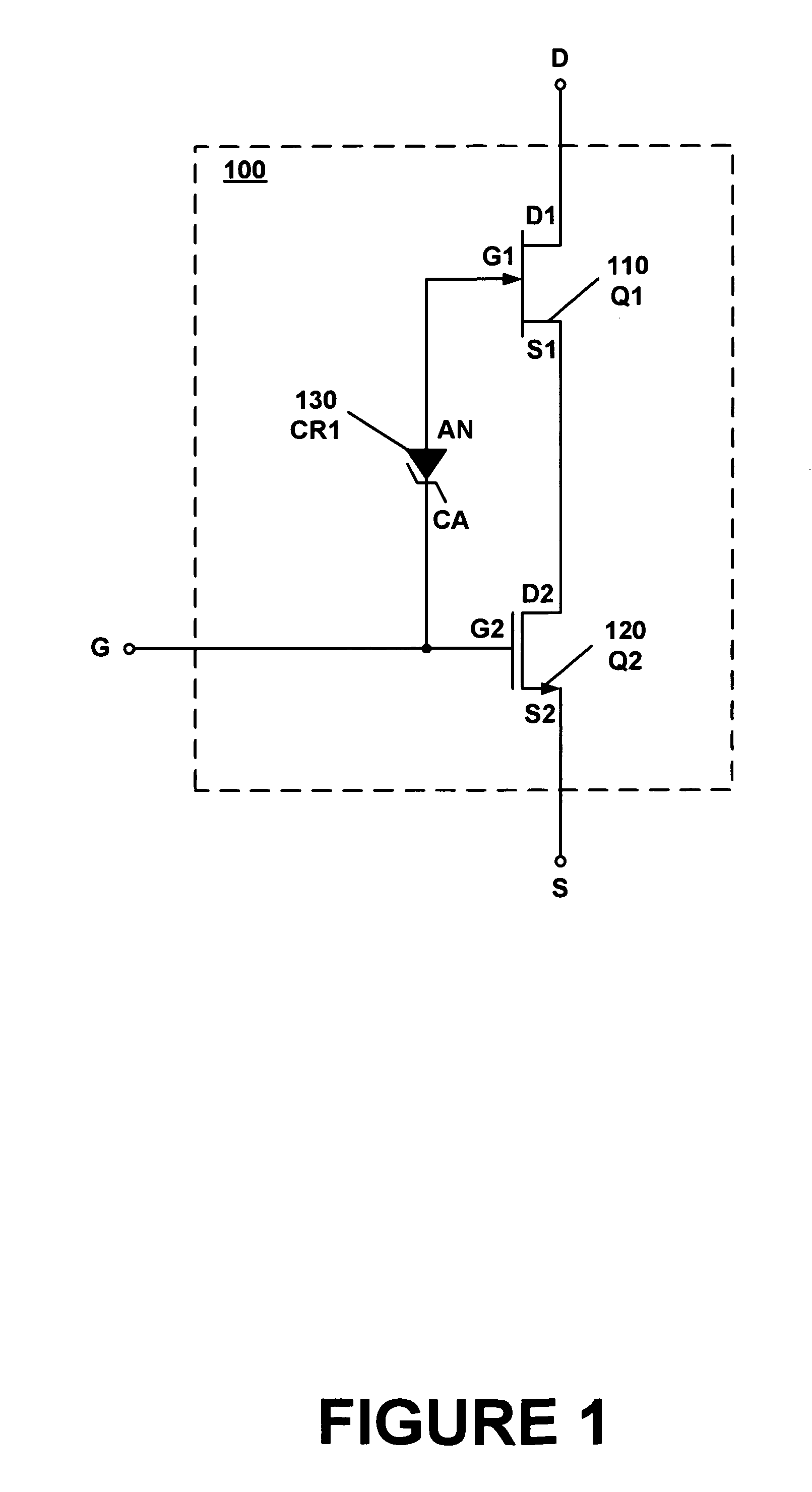
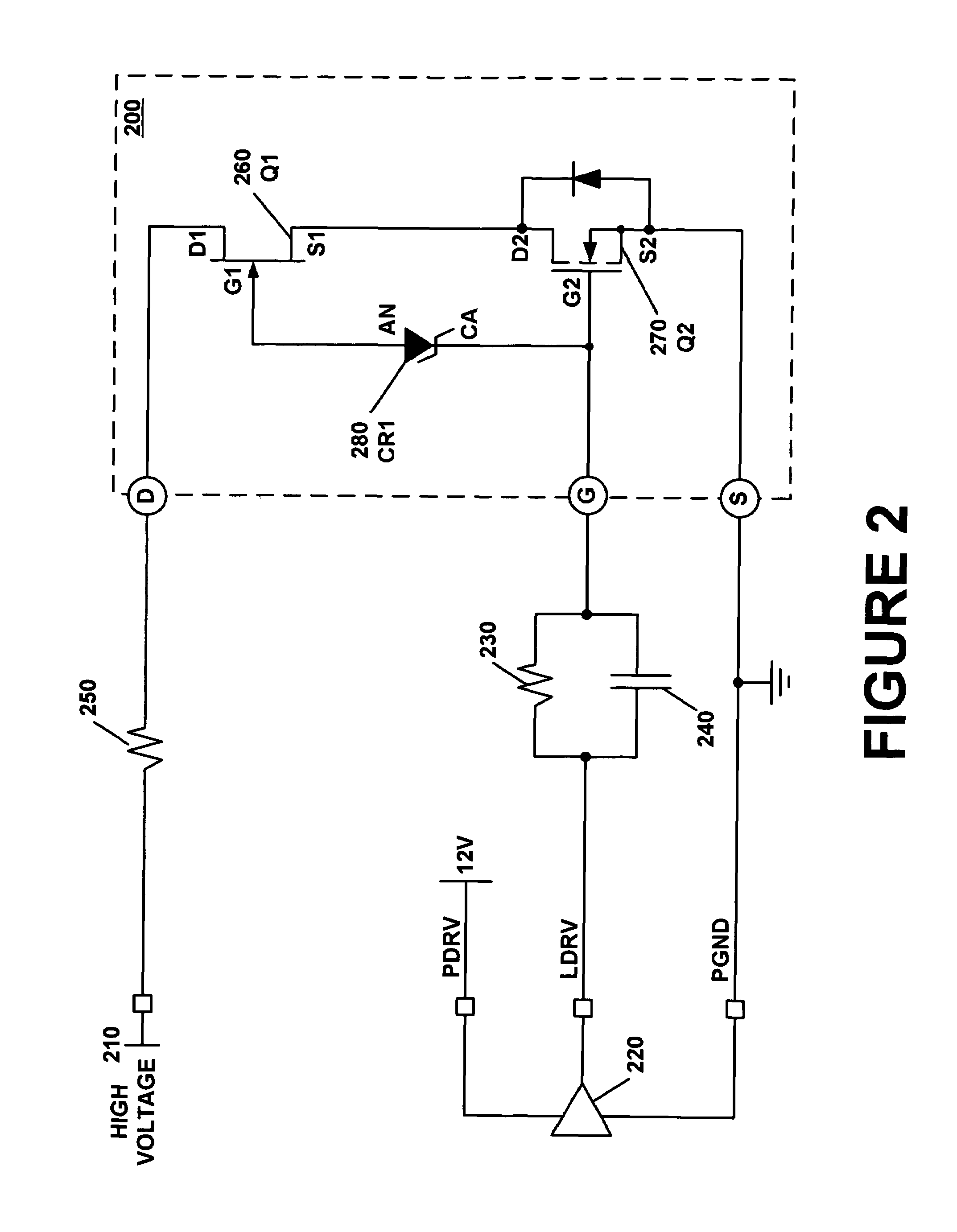
A composite field effect transistor, in accordance with one embodiment, includes a zener diode, a junction field effect transistor and a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor. A gate of the junction field effect transistor is coupled to an anode of the zener diode. A cathode of the zener diode is coupled to a gate of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor. A drain of the metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor is coupled to a source of the junction field effect transistor.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Semiconductor laser apparatus and manufacturing method thereof
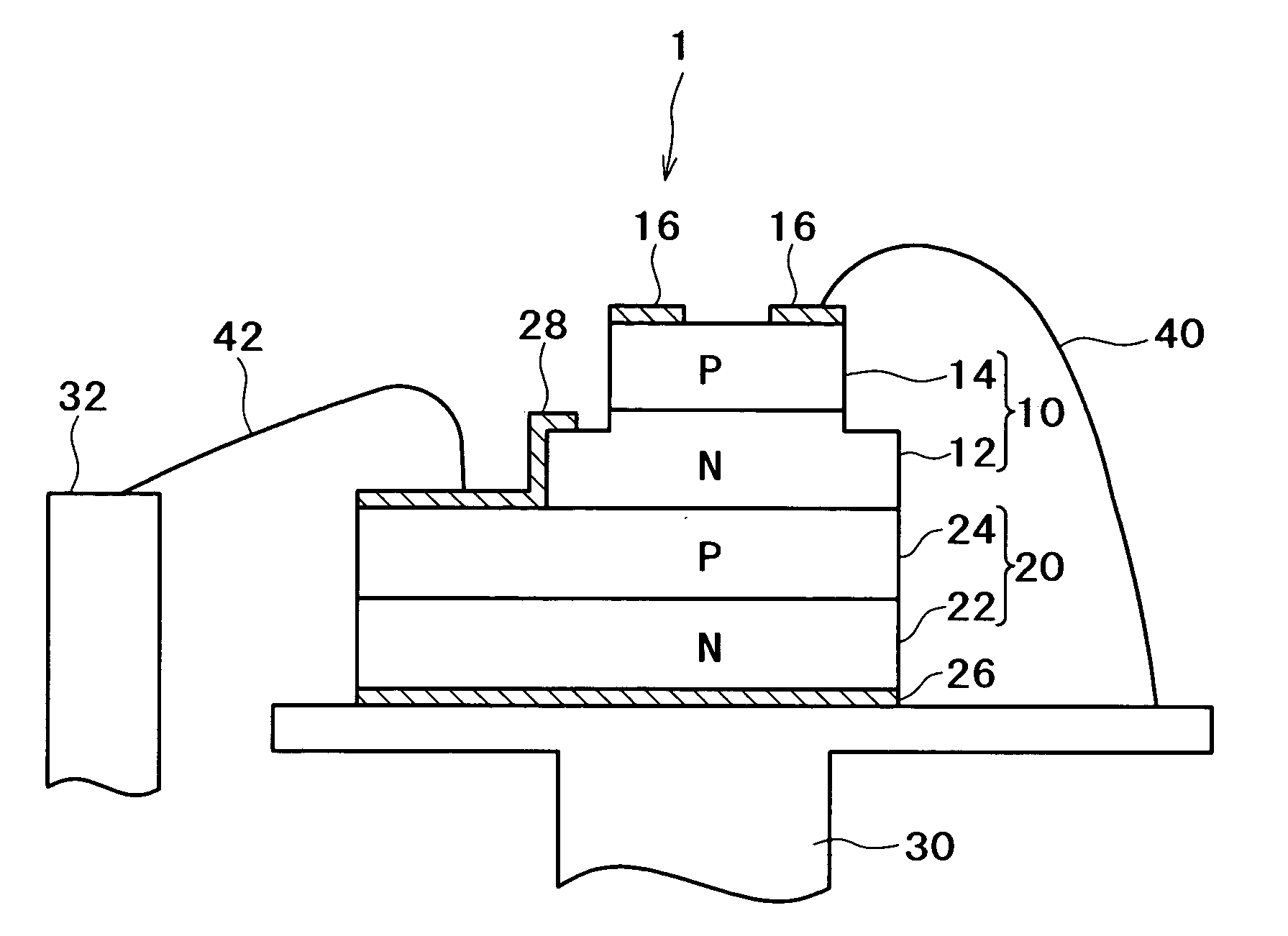
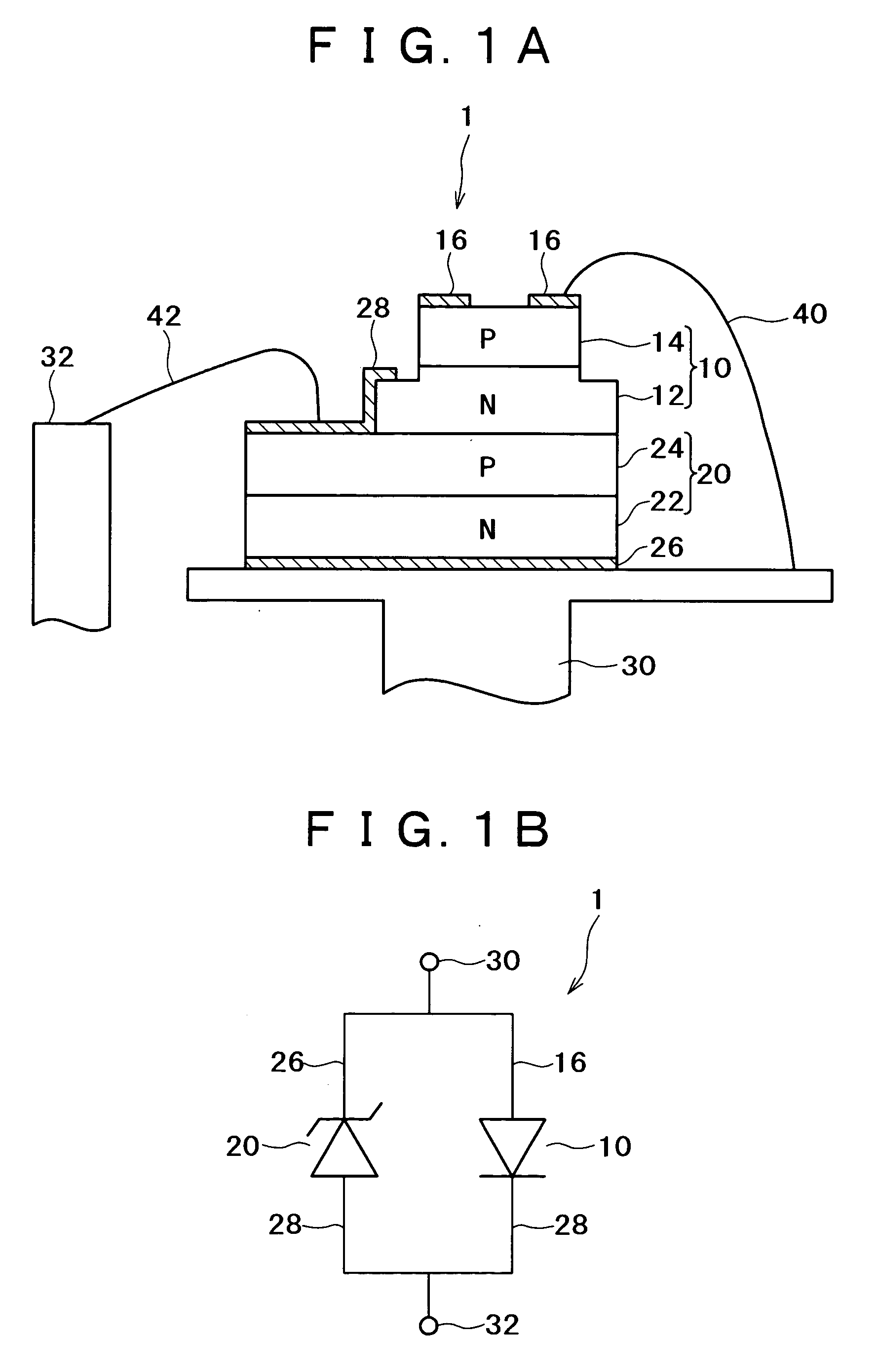
ActiveUS20050271107A1Improve resistance to static voltage break downImprove reliabilityLaser detailsSolid-state devicesZener diodePhysics
A semiconductor laser apparatus has a Zener diode containing a first semiconductor region of a first conduction type and a second semiconductor region of a second conduction type joined with the first semiconductor region, and a vertical-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser diode stacked above the Zener diode and containing at least a first mirror layer of a first conduction type, a second mirror layer of a second conduction type and an active region sandwiched between the first and second mirror layers. The first semiconductor region and the second mirror layer are electrically connected and the second semiconductor region and the first mirror layer are electrically connected.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Light-emitting semiconductor device having an overvoltage protector, and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20060056123A1Simpler and more compactLess-expensive constructionSolid-state devicesEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentOvervoltageZener diode
An LED includes a light-generating semiconductor region having an active layer sandwiched between two confining layers of opposite conductivity types for generating light. A cathode is arranged centrally on one of the opposite major surfaces of the semiconductor region from which is emitted the light. A reflector of electroconductive material is formed on the other major surface of the semiconductor region for reflecting the light back toward the light-emitting surface of the semiconductor region. For protecting the LED against breakdown from overvoltages, a zener diode is employed which takes the form of a baseplate having two semiconductor regions of opposite conductivity types sandwiched between a pair of electrodes in the form of metal layers. The protector baseplate is integrated with the light-generating semiconductor region by joining one of the metal layers to the reflector under heat and pressure, thus serving as both mechanical support and overvoltage protector for the LED.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Power converter having a low voltage regulator powered from a high voltage source
InactiveUS6233165B1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionTransformerLow voltage
A power supply arrangement including a transformer and a switching element coupled to a primary winding of the transformer and a power supply. The power supply includes a capacitor having a first terminal coupled to a junction of the primary winding and the switching element and a first diode coupled between the capacitor and an output node. The power supply further includes a discharge element, such as a resistor or a diode, coupled between the junction of the first diode and the capacitor and a power supply common. A voltage regulator, such as a Zener diode, is connected to the output node to produce a regulated voltage powered by the voltage applied to the transformer primary winding, with the regulated voltage being used to power the control circuitry.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Light-adjusting and current-limiting control circuit
InactiveUS20080258631A1Low costSmall sizeDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesDIACSilicon-controlled rectifier
A light-adjusting and current-limiting control circuit for a lamp includes a sampling circuit formed of a manganese-copper line or a current transformer, a power circuit provided with resistors, capacitors, diodes, a Varistor and a zener diode, a signal adjusting circuit composed of diodes, resistors, a varistor, triacs and capacitors, and a control output circuit having a thyristor, diodes, a relay and an LED. The control output circuit can be replaced with a light-adjusting input circuit, a chip processor control circuit, a zero-crossing detection circuit and a two-way silicon controlled rectifier control output circuit 5. Thus, the invention has a low cost, a small size and an excellent precision, compared to conventional ones.
Owner:FUMONG TECH SHENZHEN
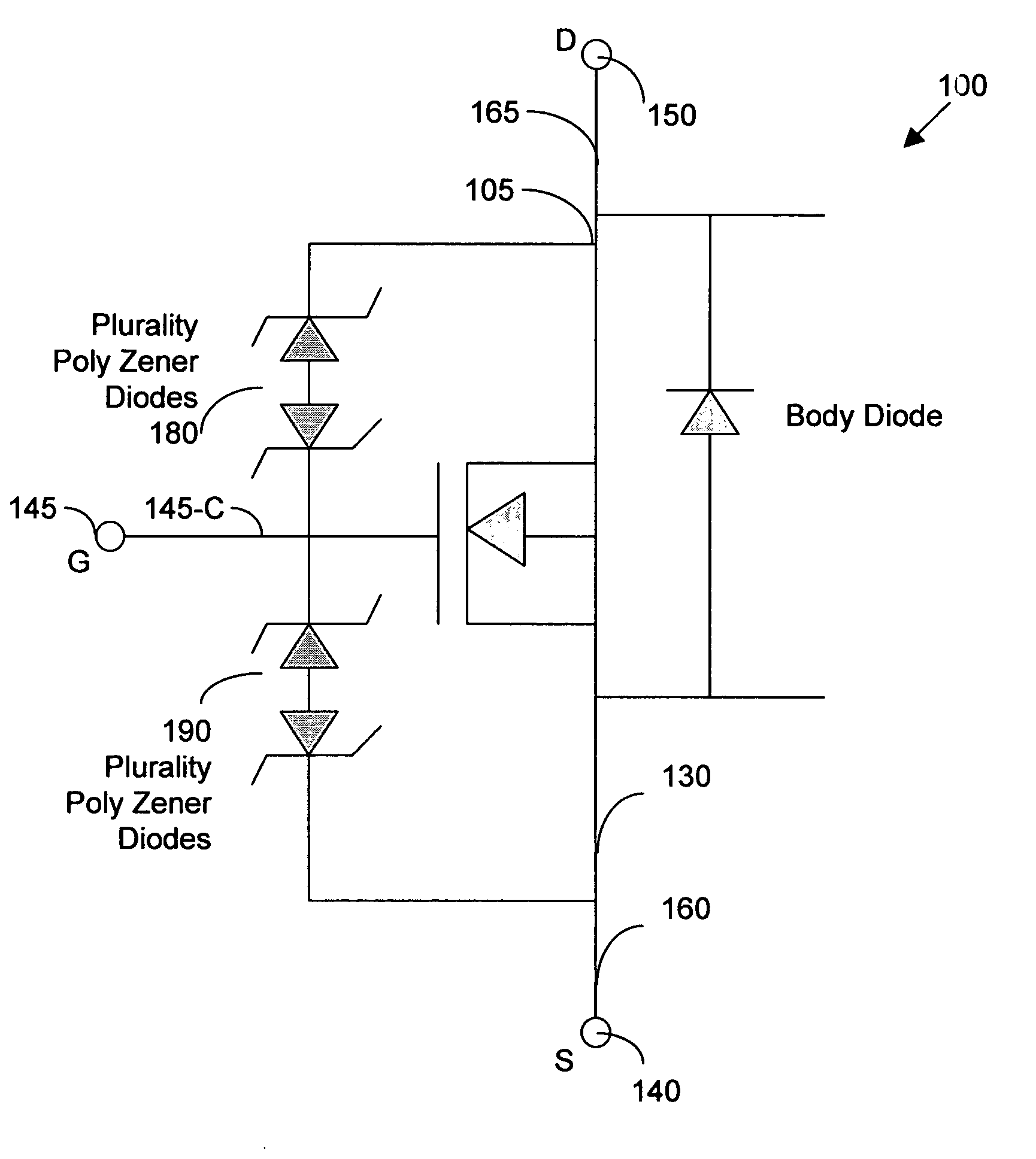
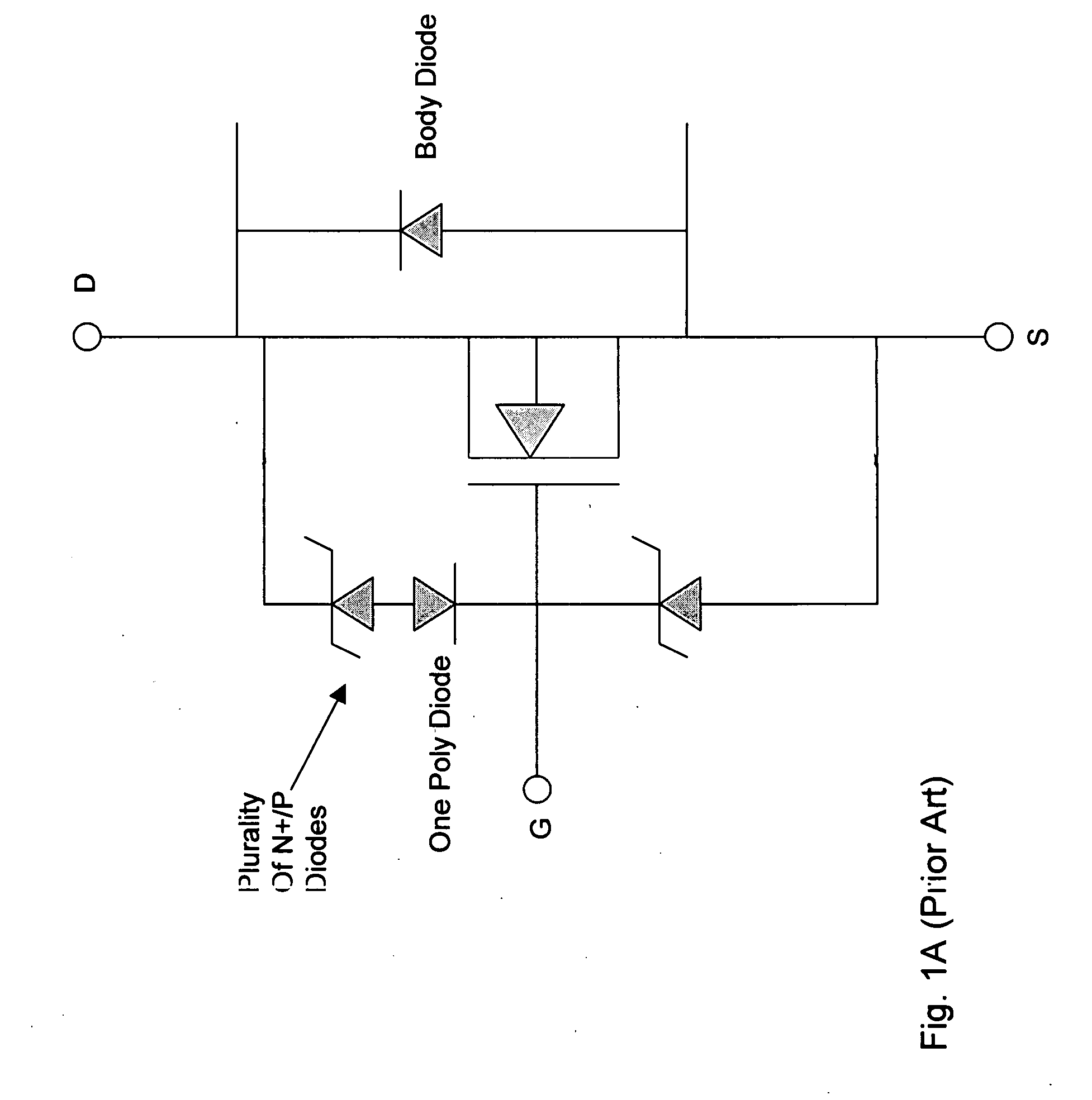
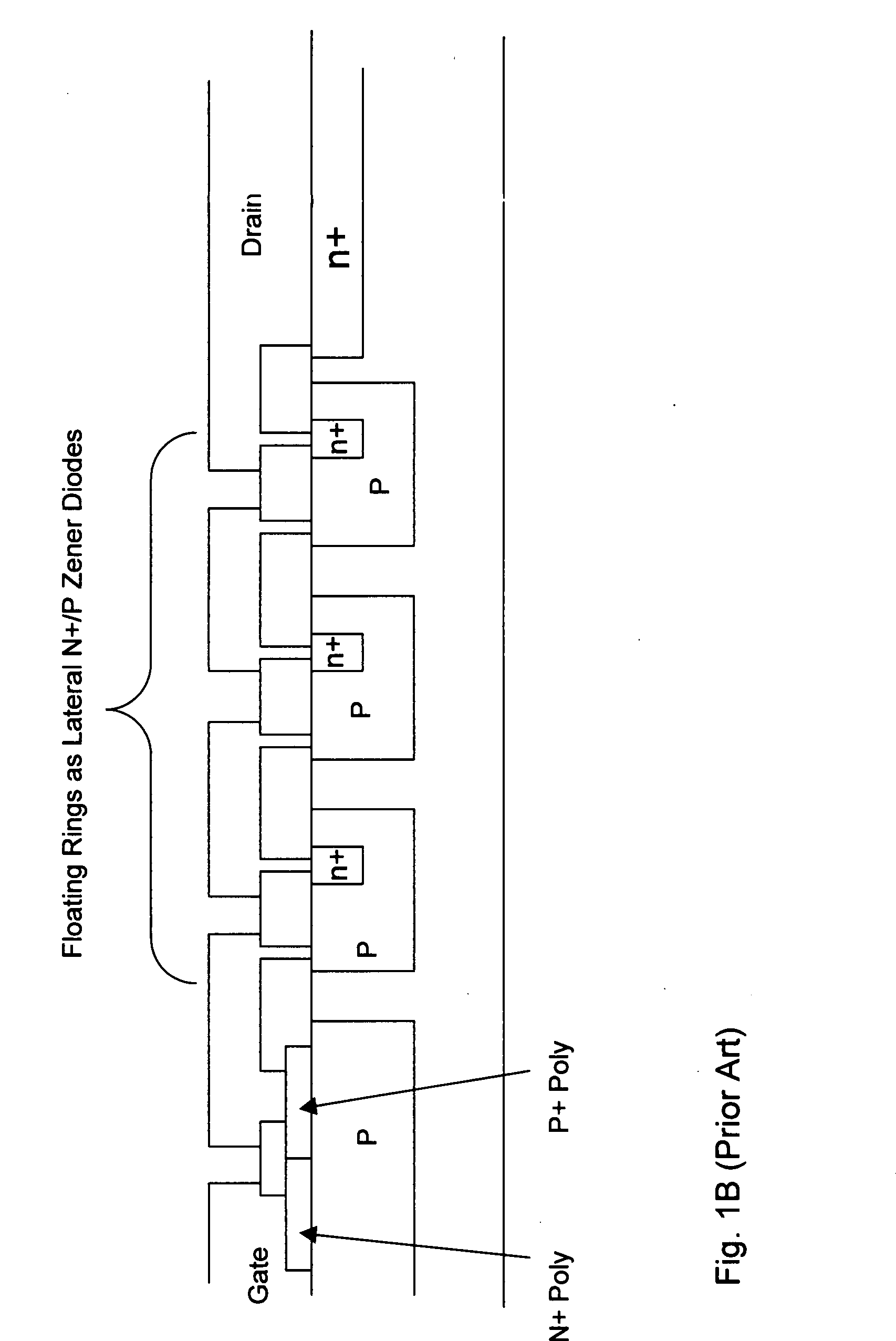
Trenched MOSFETs with improved gate-drain (GD) clamp diodes
ActiveUS20080258224A1Prevent channelingLower breakdown voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDopantInsulation layer
A MOSFET device that includes a first Zener diode connected between a gate metal and a drain metal of said semiconductor power device for functioning as a gate-drain (GD) clamp diode. The GD clamp diode includes multiple back-to-back doped regions in a polysilicon layer doped with dopant ions of a first conductivity type next to a second conductivity type disposed on an insulation layer above the MOSFET device, having an avalanche voltage lower than a source / drain avalanche voltage of the MOSFET device wherein the Zener diode is insulated from a doped region of the MOSFET device for preventing a channeling effect. The MOSFET device further includes a second Zener diode connected between a gate metal and a source metal of the MOSFET device for functioning as a gate-source (GS) clamp diode, wherein the GD clamp diode includes multiple back-to-back doped regions in the polysilicon layer doped with dopant ions of a first conductivity type next to a second conductivity type disposed on the insulation layer above the MOSFET device having a lower breakdown voltage than a gate oxide rupture voltage of the MOSFET device.
Owner:FORCE MOS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com