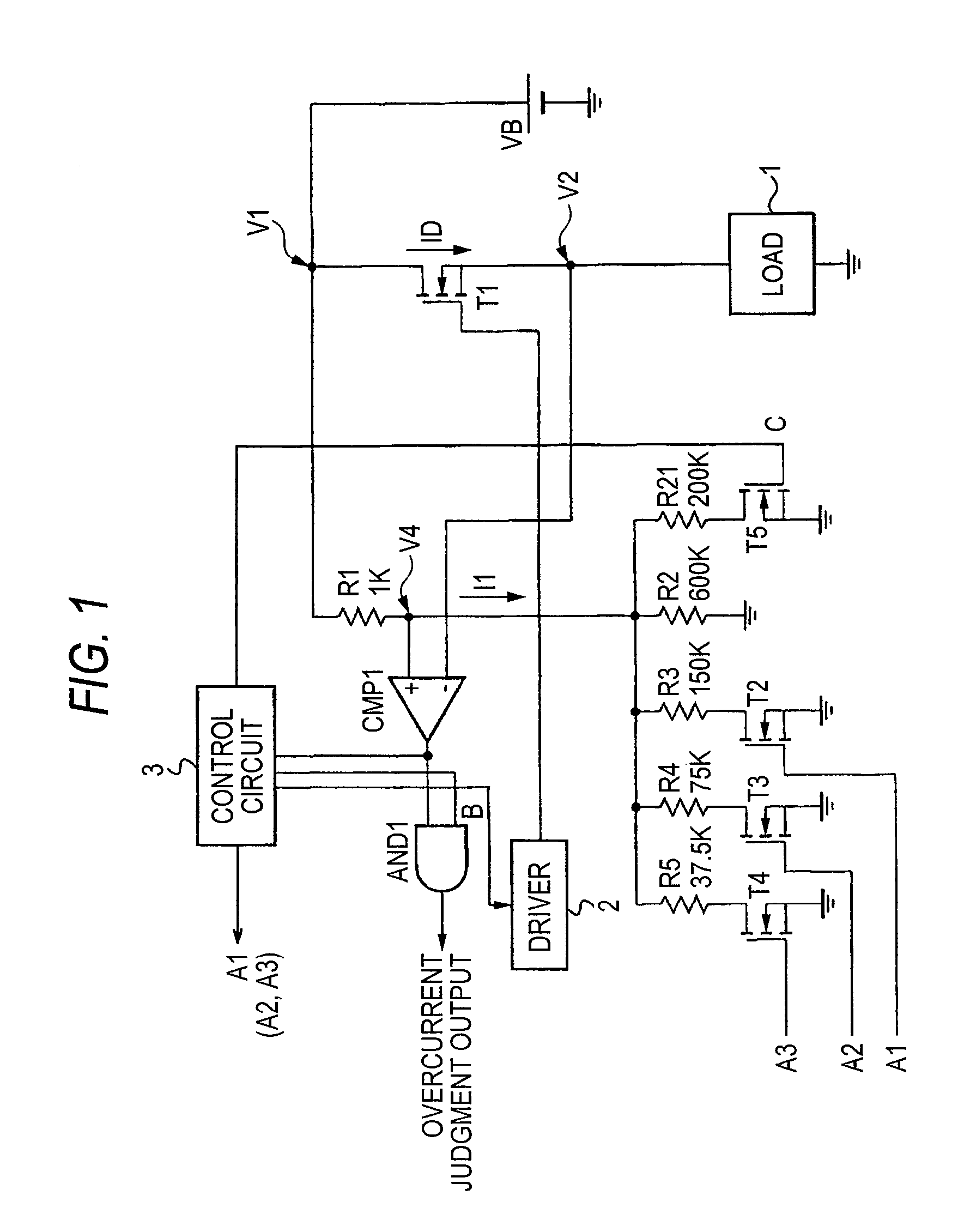
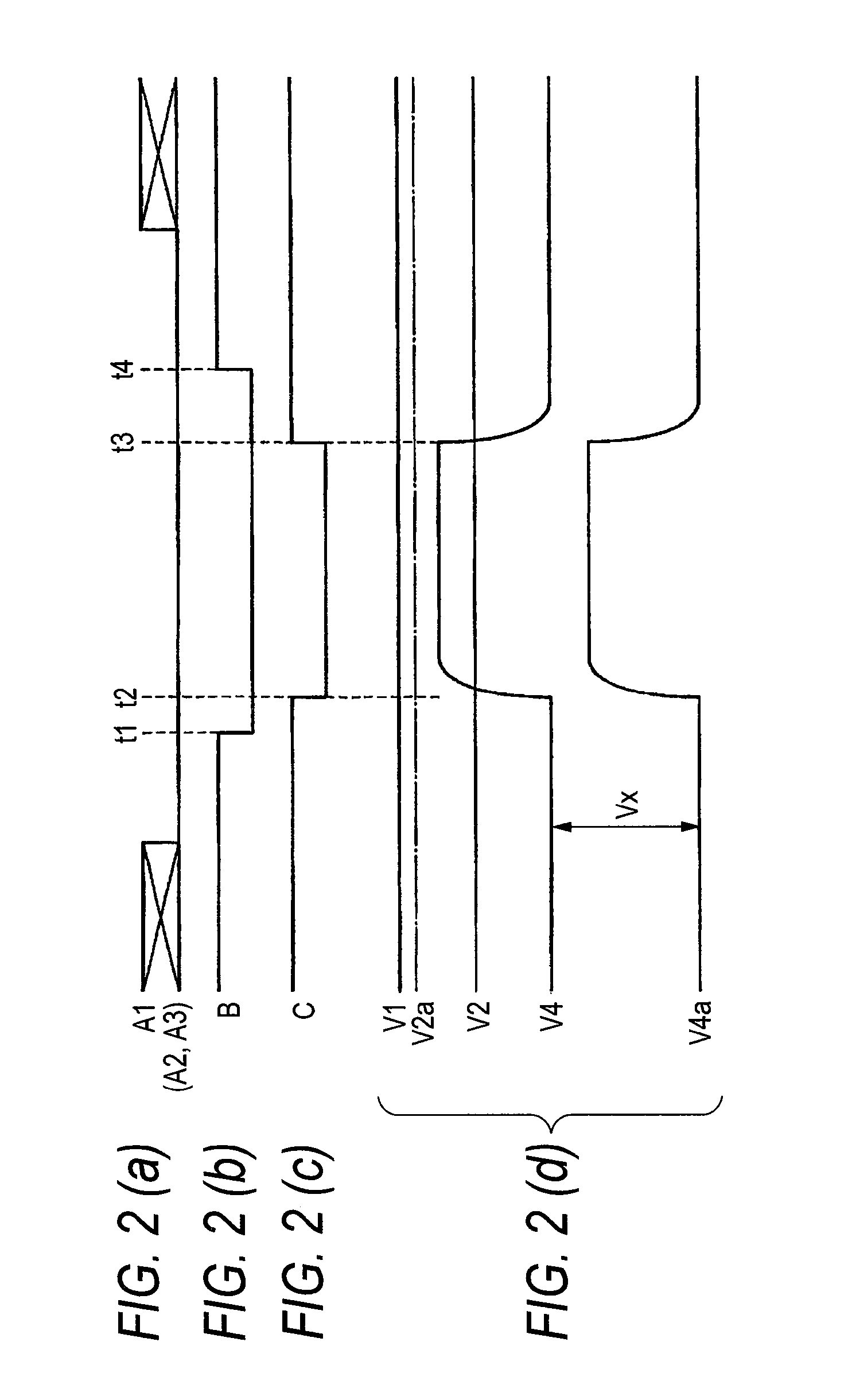
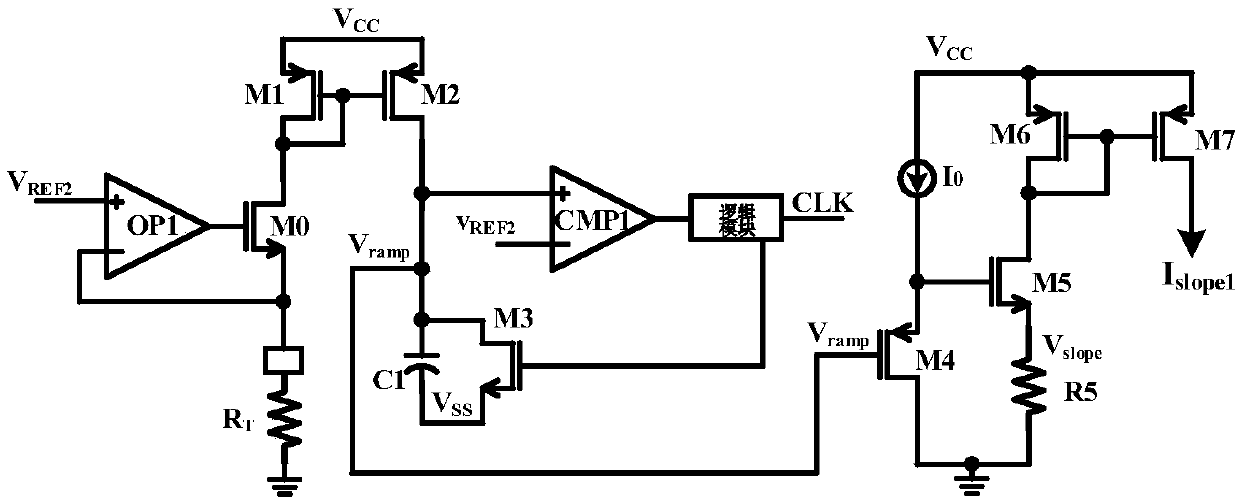
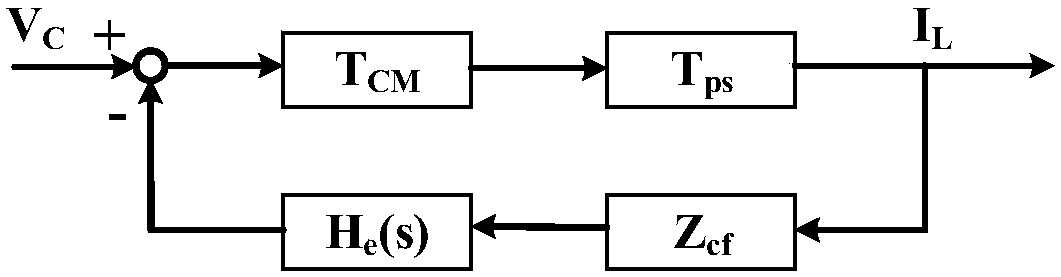
Patents
Literature
2464 results about "Overcurrent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
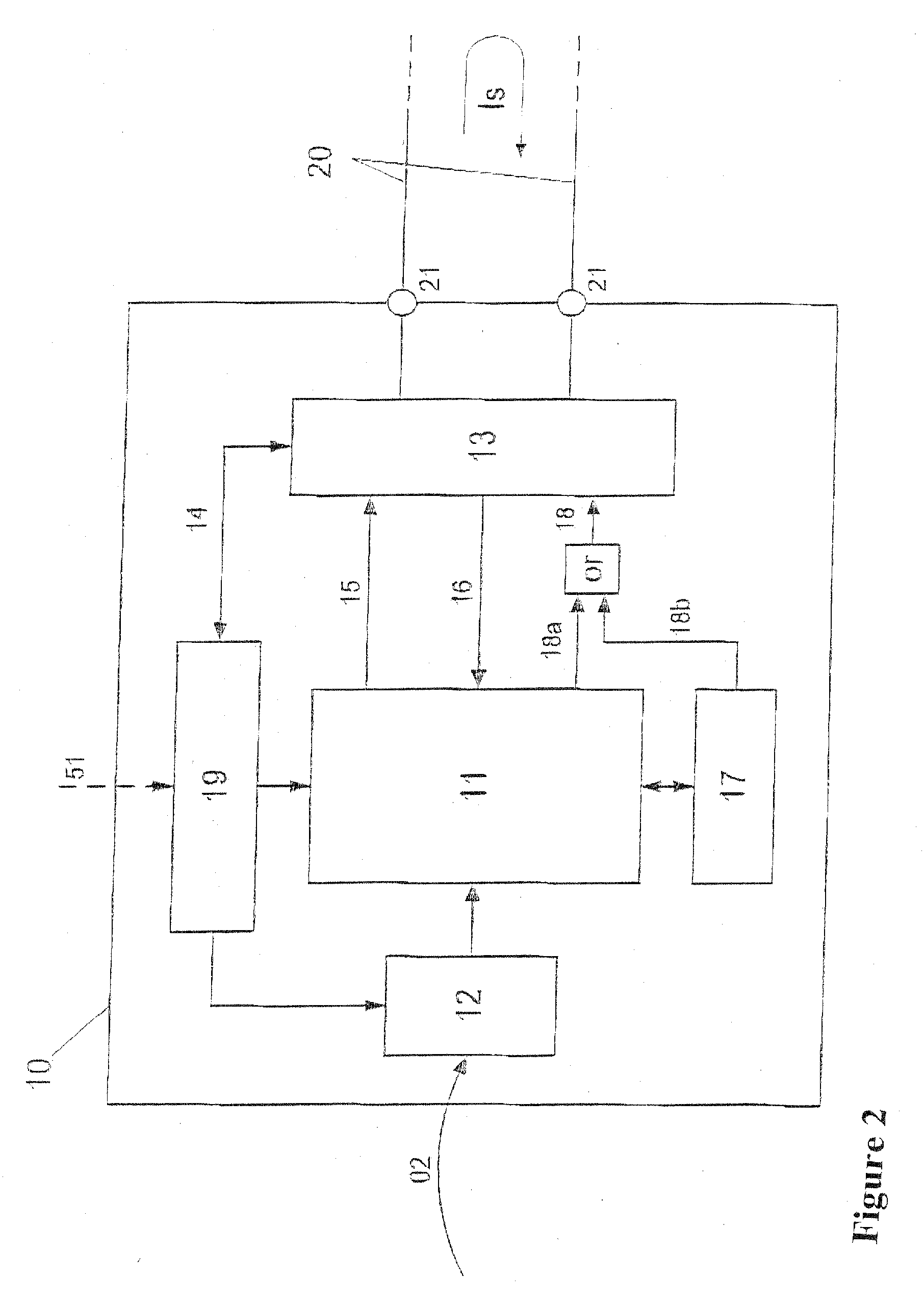
In an electric power system, overcurrent or excess current is a situation where a larger than intended electric current exists through a conductor, leading to excessive generation of heat, and the risk of fire or damage to equipment. Possible causes for overcurrent include short circuits, excessive load, incorrect design, or a ground fault. Fuses, circuit breakers, and current limiters are commonly used overcurrent protection (OCP) mechanisms to control the risks. An overcurrent can be caused by overloading the circuit or by a short circuit, a ground fault, or an arc fault. Circuit breakers and fuses protect circuit wiring from damage caused by overcurrent.
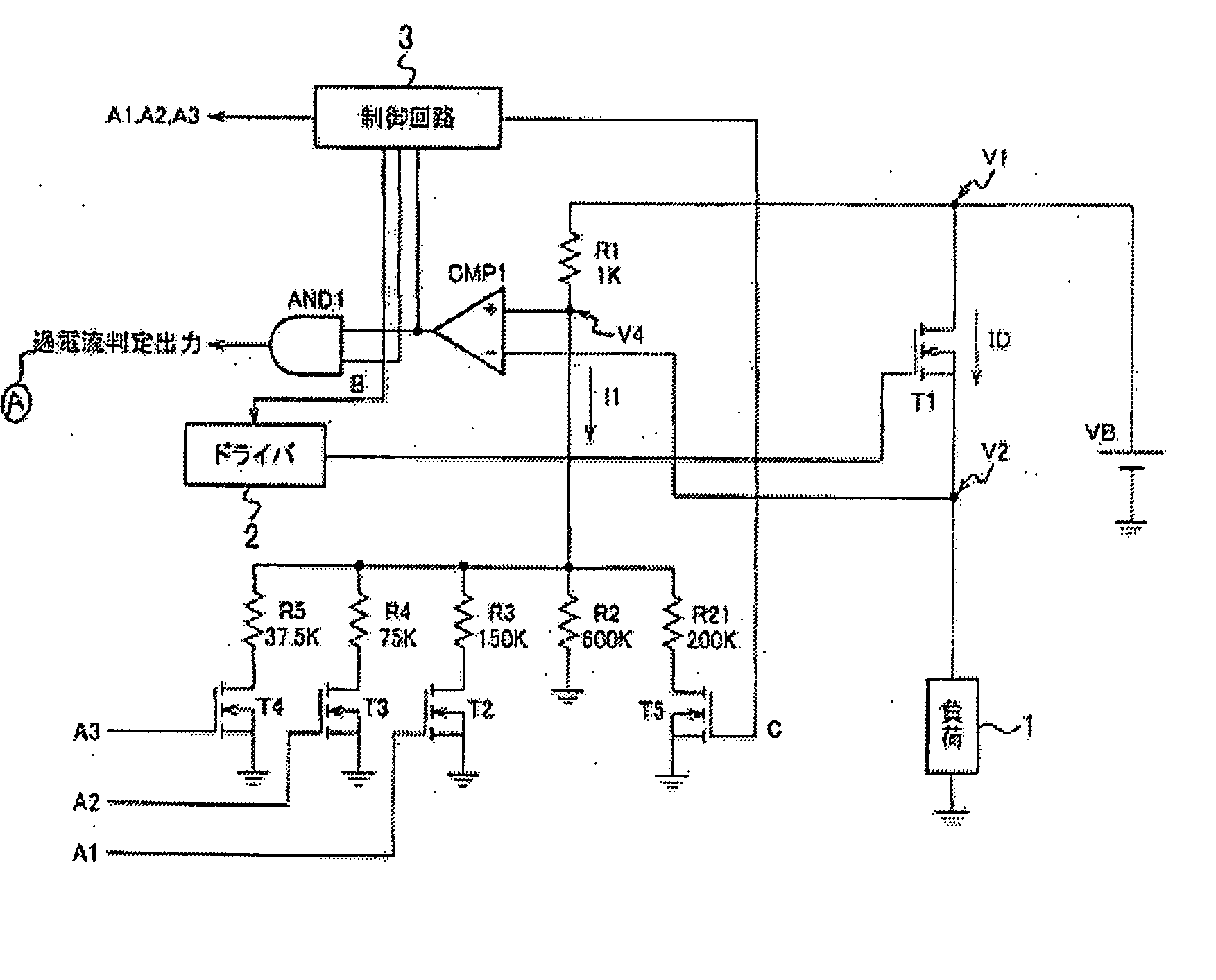
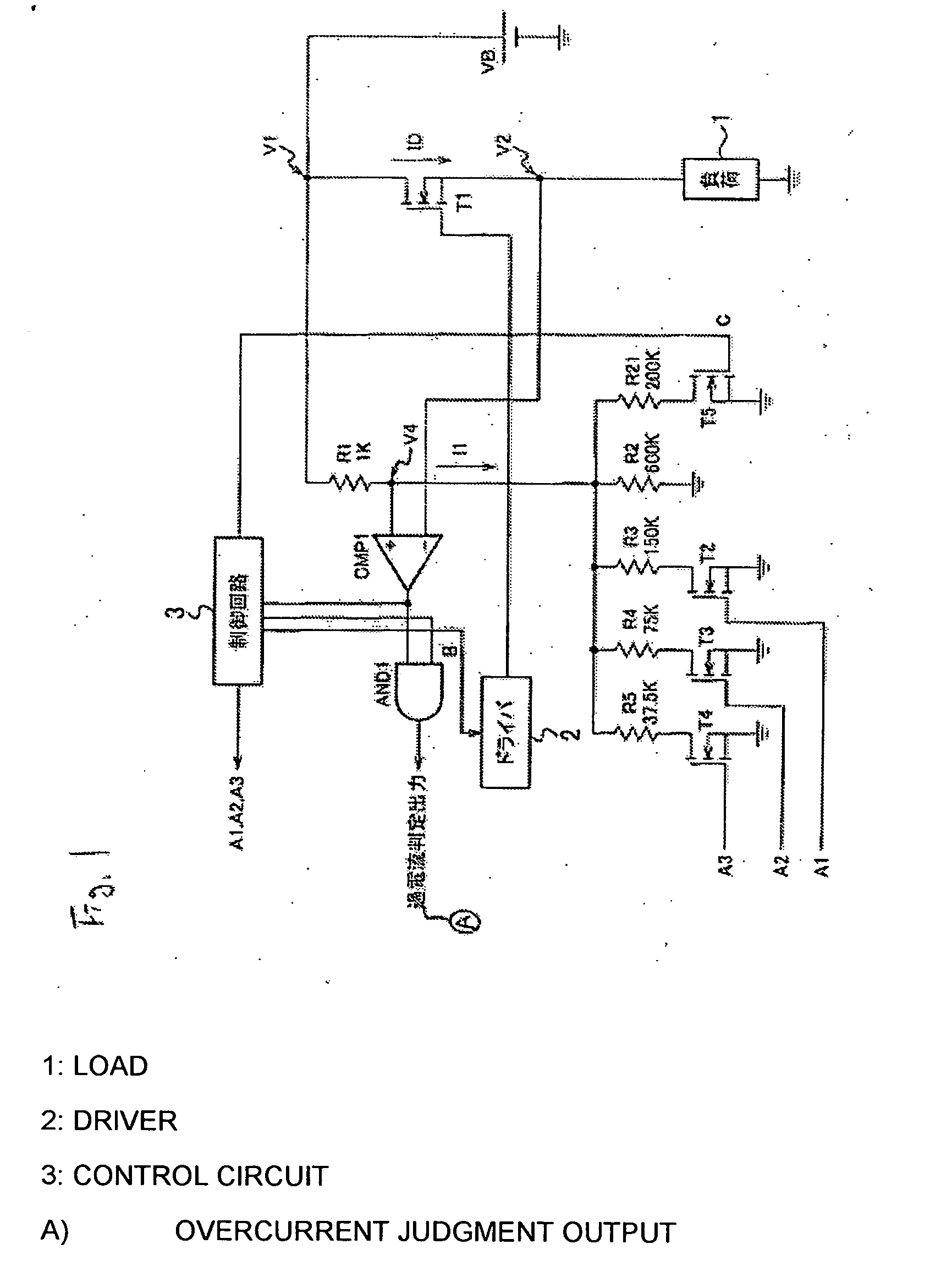
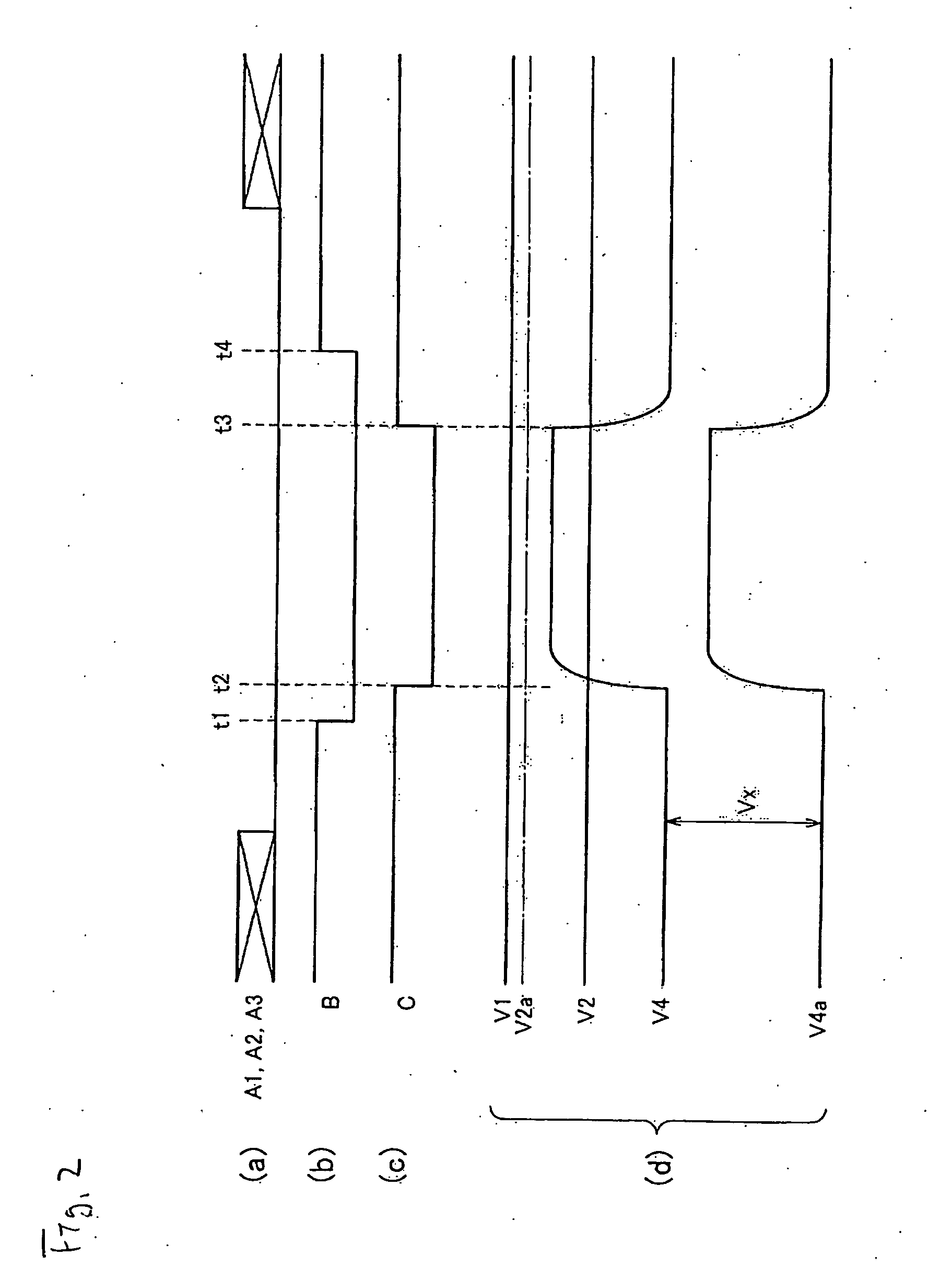
Motor control device and motor control method
InactiveUS7183737B2Improve accuracyCurrent detectionAC motor controlElectric motor controlDriving currentControl signal
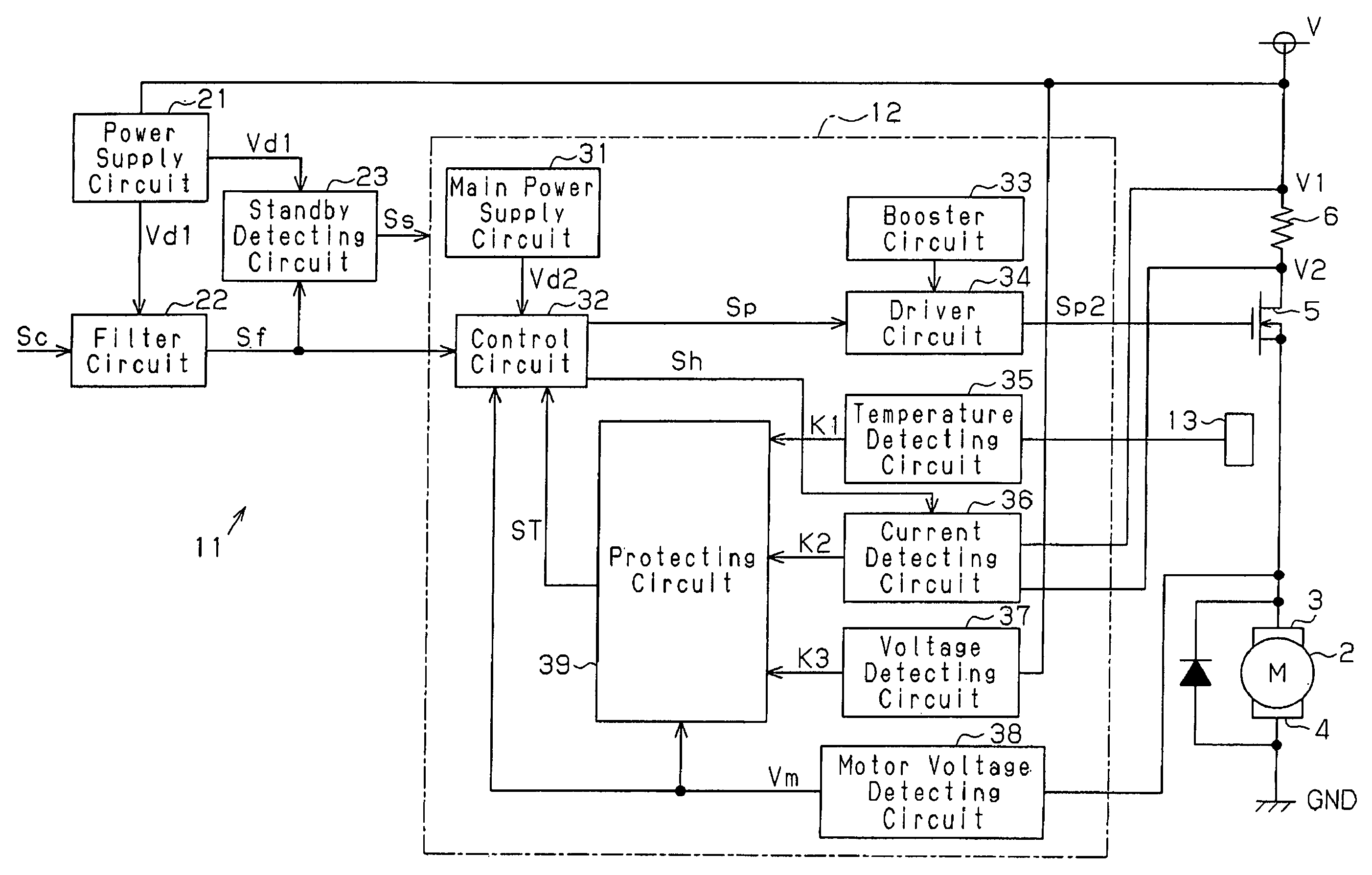
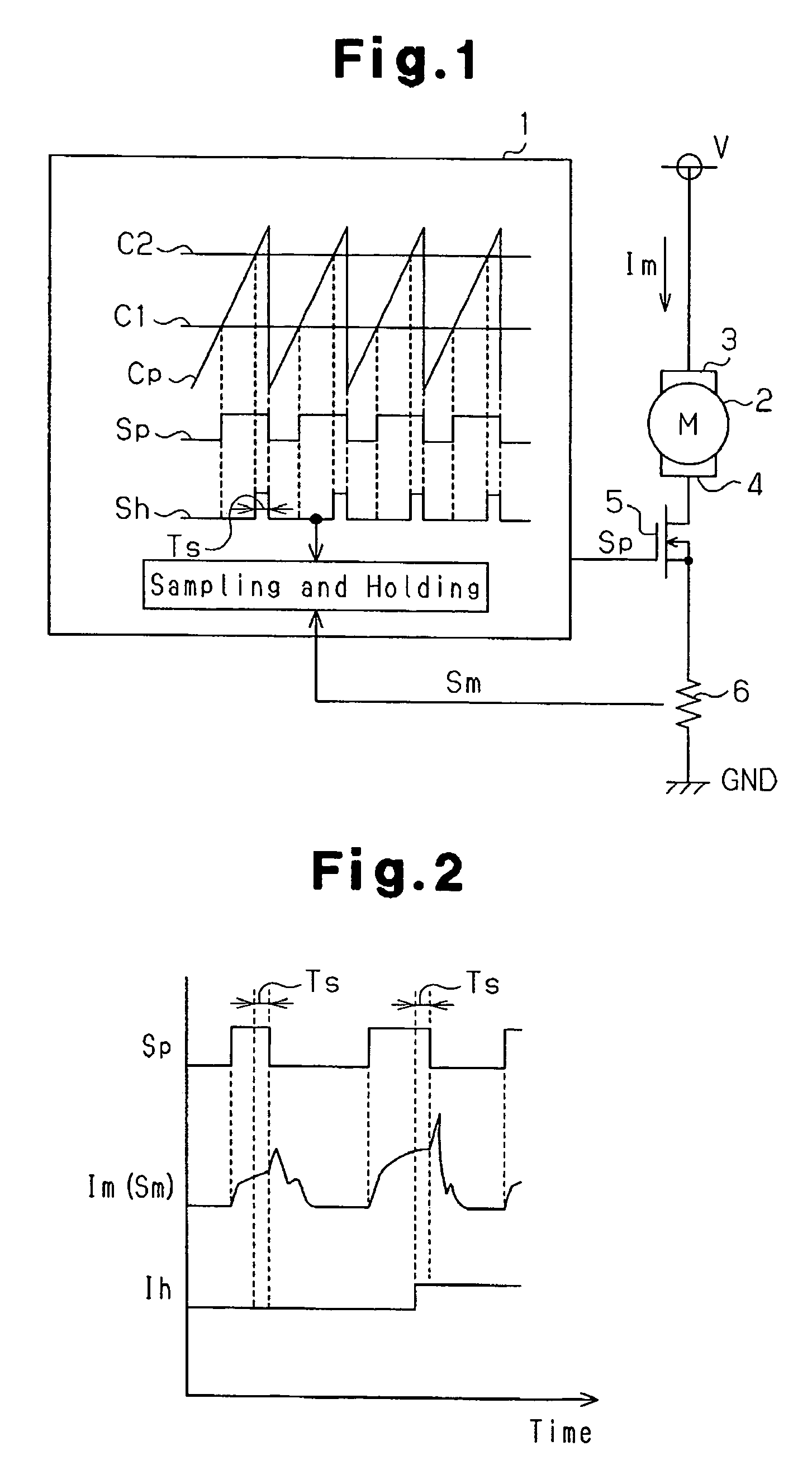
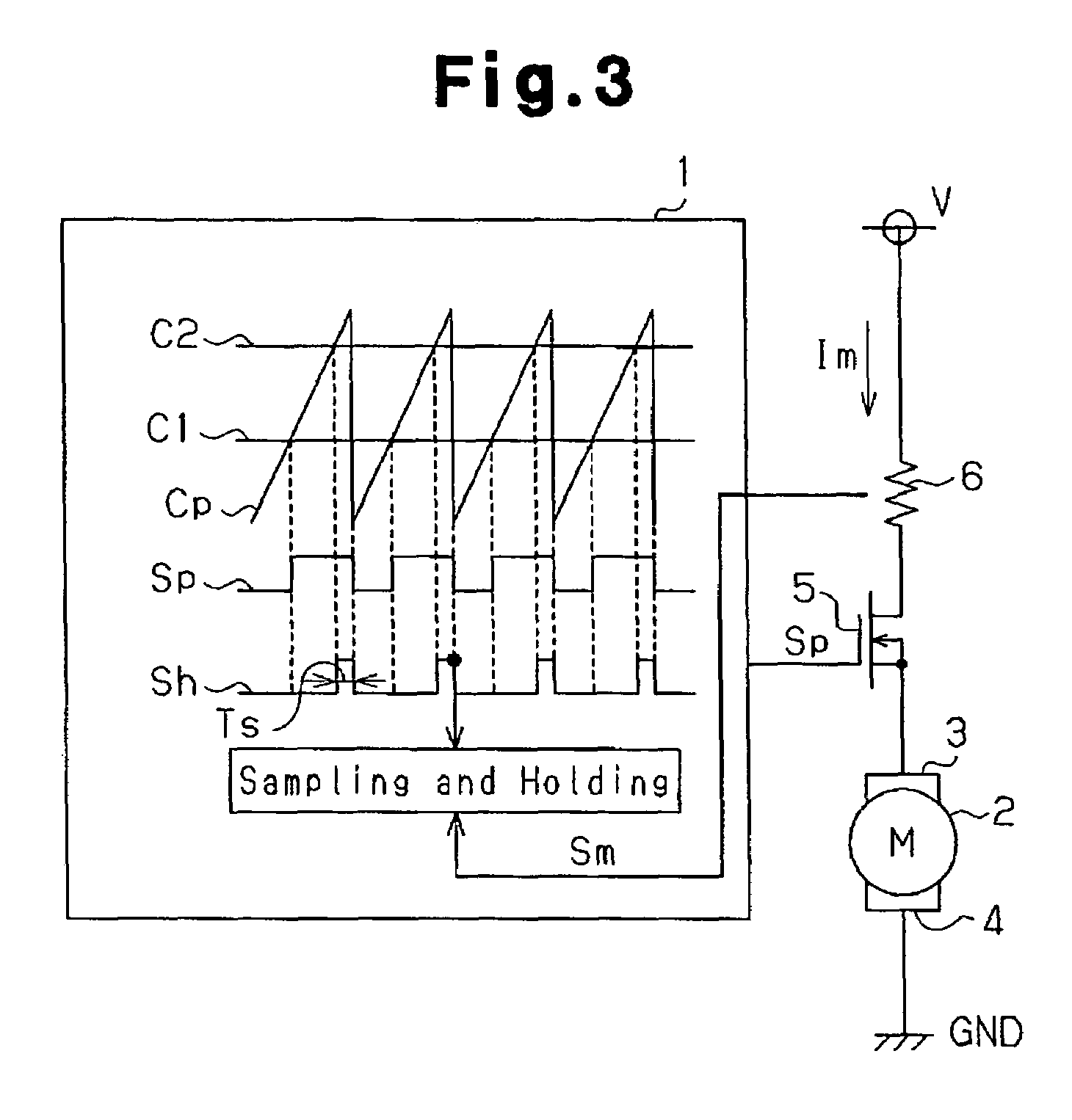
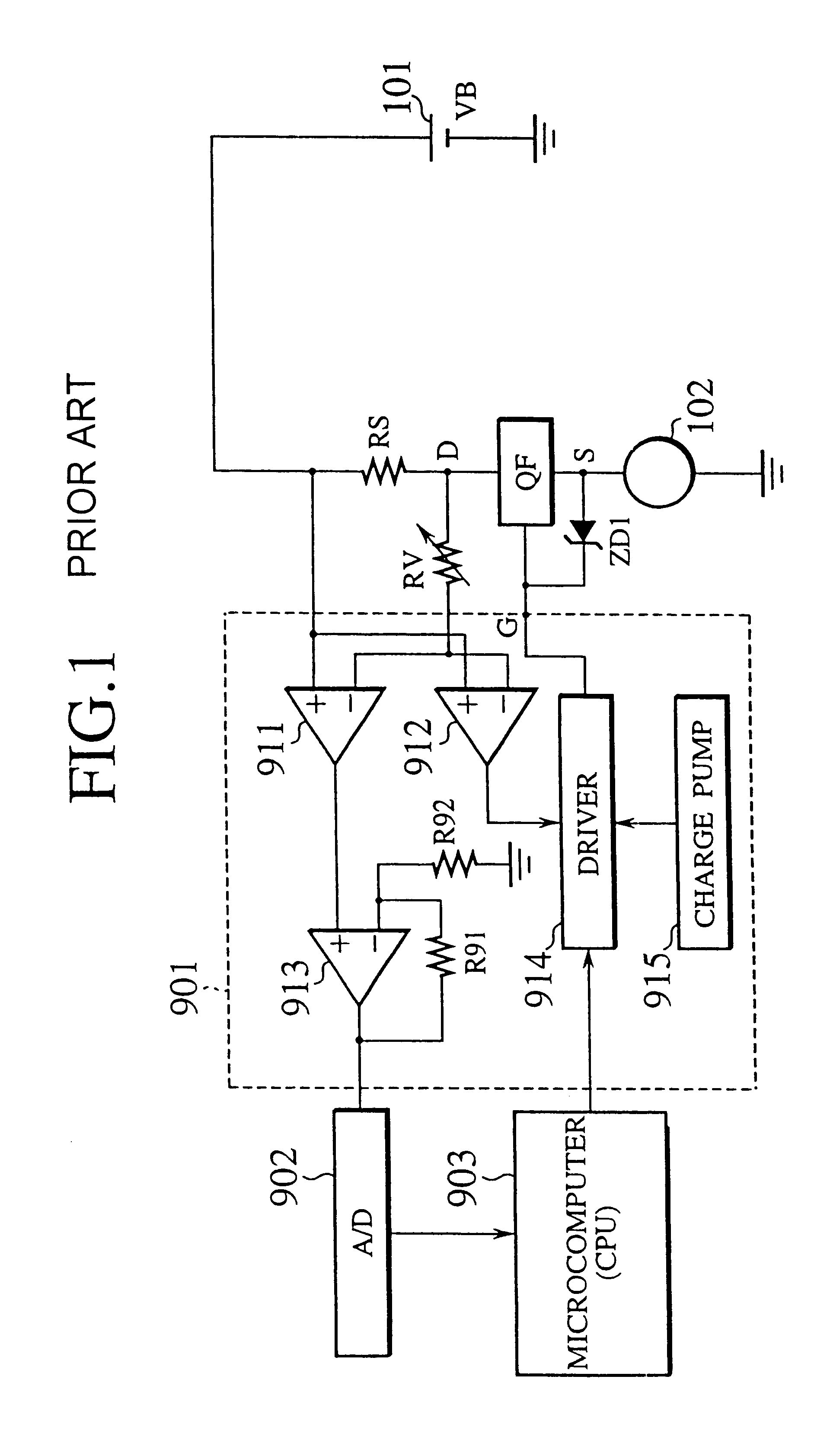
A motor control device selectively turns on or off a drive transistor in-accordance with a PWM control signal Sp, such that a drive current Im supplied to a motor is adjusted. The device also samples and holds a motor current Sm for obtaining a motor current value Ih. With reference to the motor current value Ih, the device protects the motor from an overcurrent. Sampling and holding of the motor current Sm is performed for a sampling and holding time Ts. The sampling and holding time Ts corresponds to a time period between a first point in time when the level of the PWM control signal Sp is switched for turning off the drive transistor and a second point in time that precedes the first point in time by a predetermined period. As a result, the motor current value Ih is detected with high accuracy.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
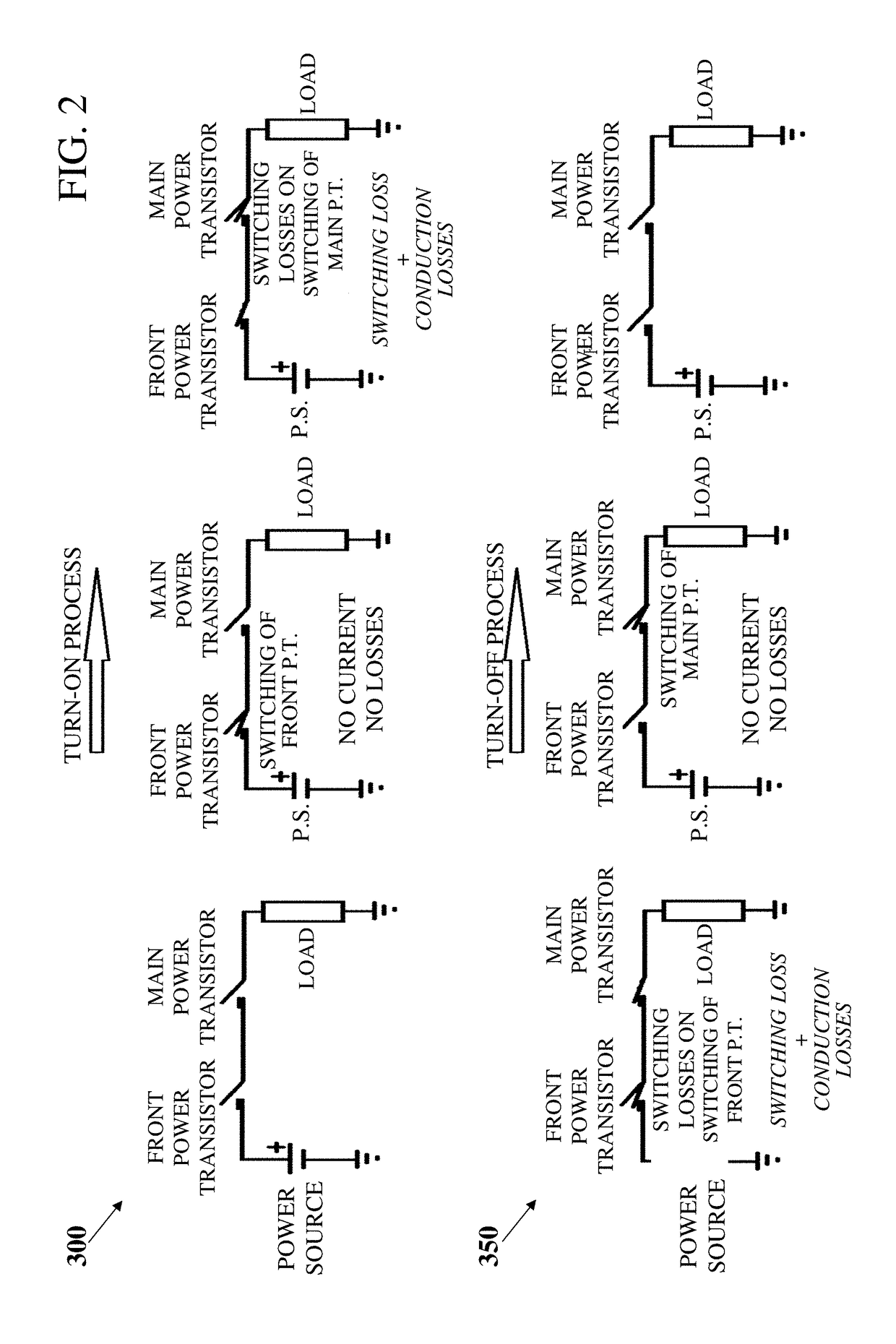
Automatic, Highly Reliable, Fully Redundant Electronic Circuit Breaker That Reduces or Prevents Short-Circuit Overcurrent
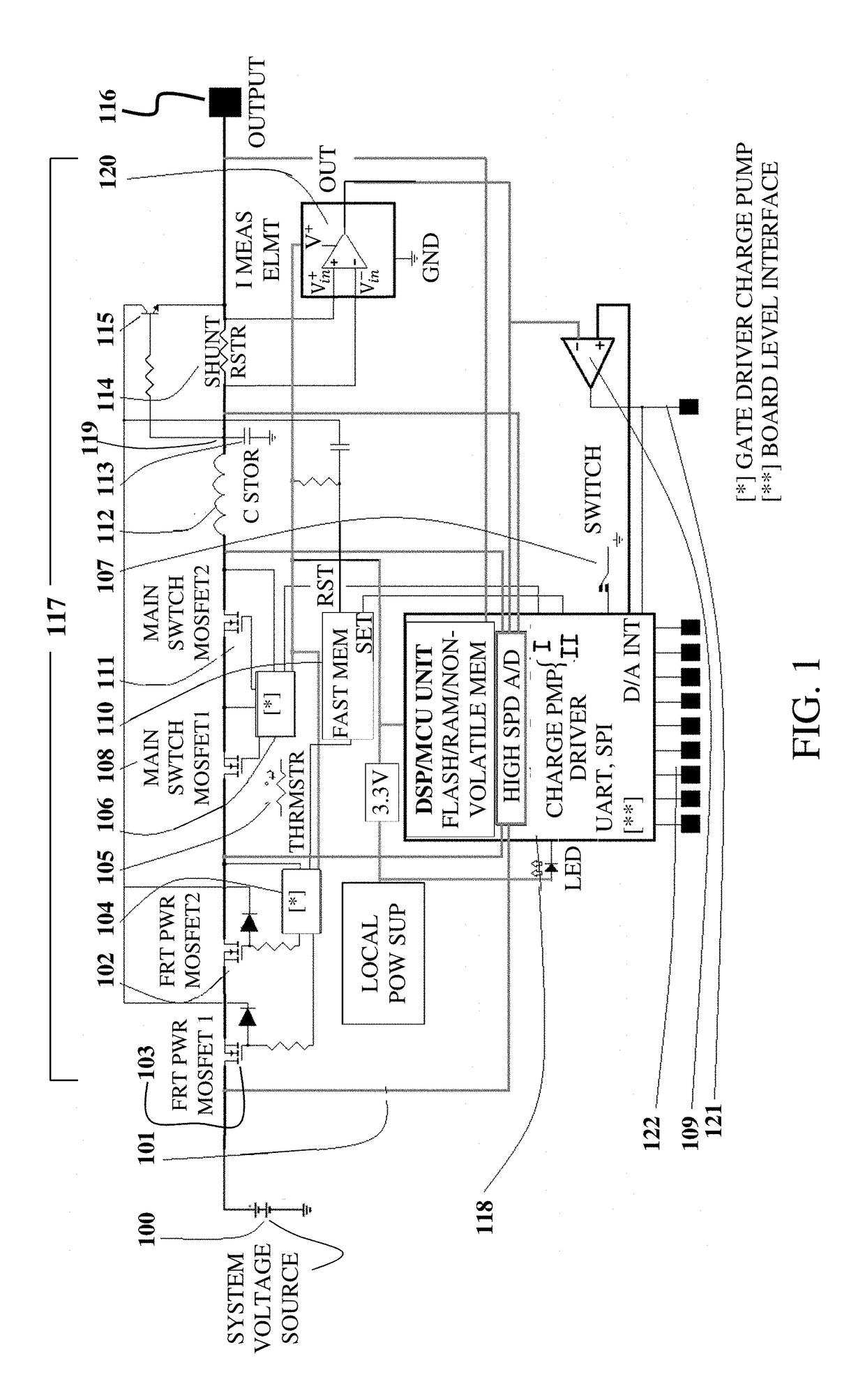
A programmable power (PPSE) switching element including a front power transistor, a main switching transistor, and at least one reverse current blocking transistor in series, a gate of each of which is connected to a gate driver; an inductor and a shunt resistor connected in series with the transistors; a charge storage capacitor connected between ground and a junction located between the inductor and the shunt resistor; a high-speed NPN transistor, a collector of which is connected to the front power transistor and an emitter of which is connected to an output of the main switching transistor via the shunt resistor; a current measurement element in parallel to the shunt resistor; a voltage amplifier; and a high-speed MCU.
Owner:REDLER TECH LTD
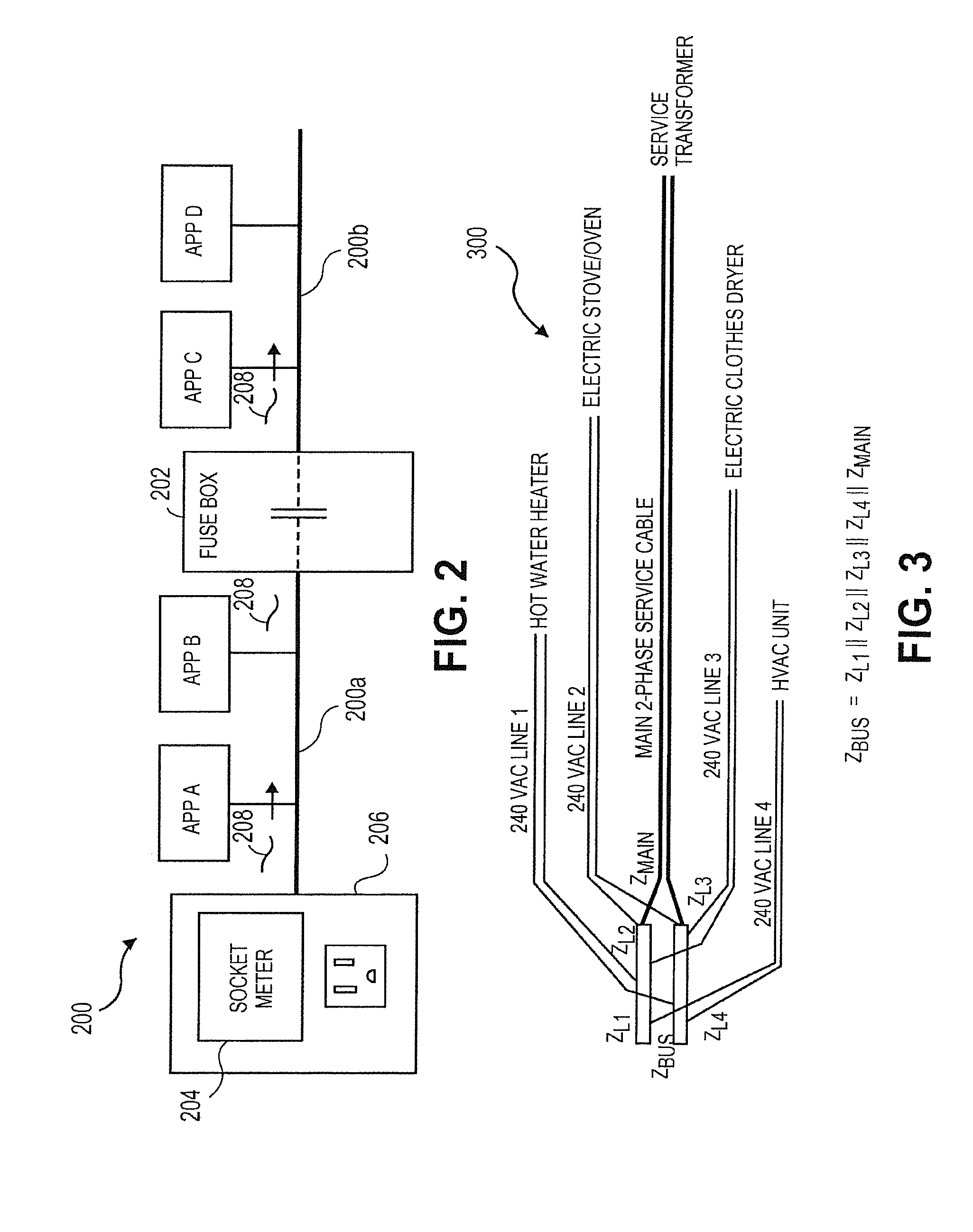
System and method to measure and control power consumption in a residential or commercial building via a wall socket to ensure optimum energy usage therein
InactiveUS20120265586A1Easily measure power usageLess-efficient over timeMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlControl powerOvercurrent
A system and method to measure and control power usage within a residential or commercial building plurality having of electrical circuits electrically connected to an over-current protection device to ensure optimum energy usage therein. The system and method includes a power measurement and control device electrically connected to one of the electrical circuits by which a load draws power that is operable to (i) measure an electrical parameter of the electrical circuits, (ii) compare the measured electrical parameter to an ideal electrical parameter, and (iii) adjust power supplied to one or more of the electrical circuits based on the comparison of the measured electrical parameter and the ideal electrical parameter via a wall socket. The adjustment of power may be automatic or manual deactivation, decrease, and / or increase of power supplied to the electrical circuits via the wall socket so that such is equivalent to or less than the ideal electrical parameter.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
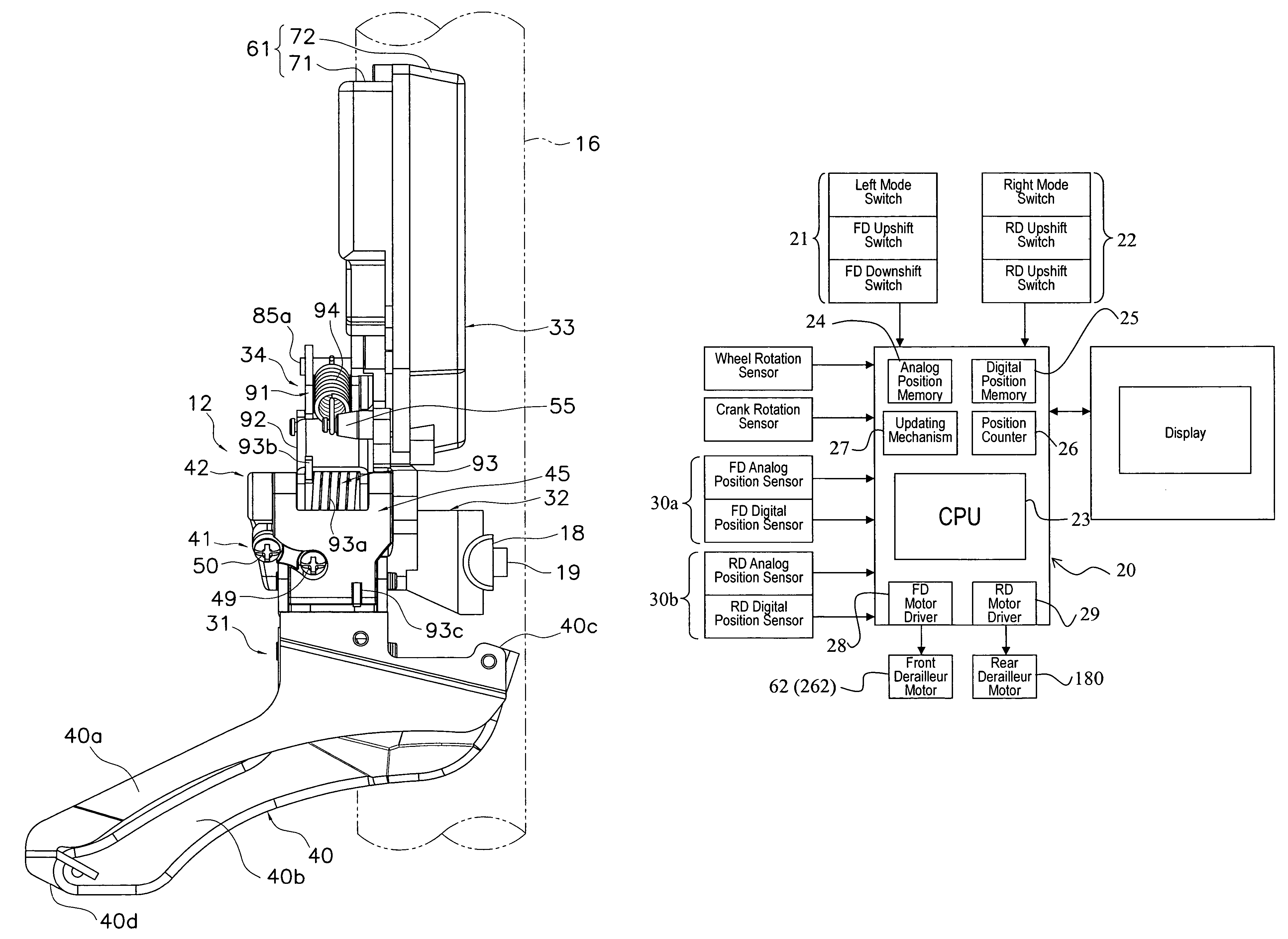
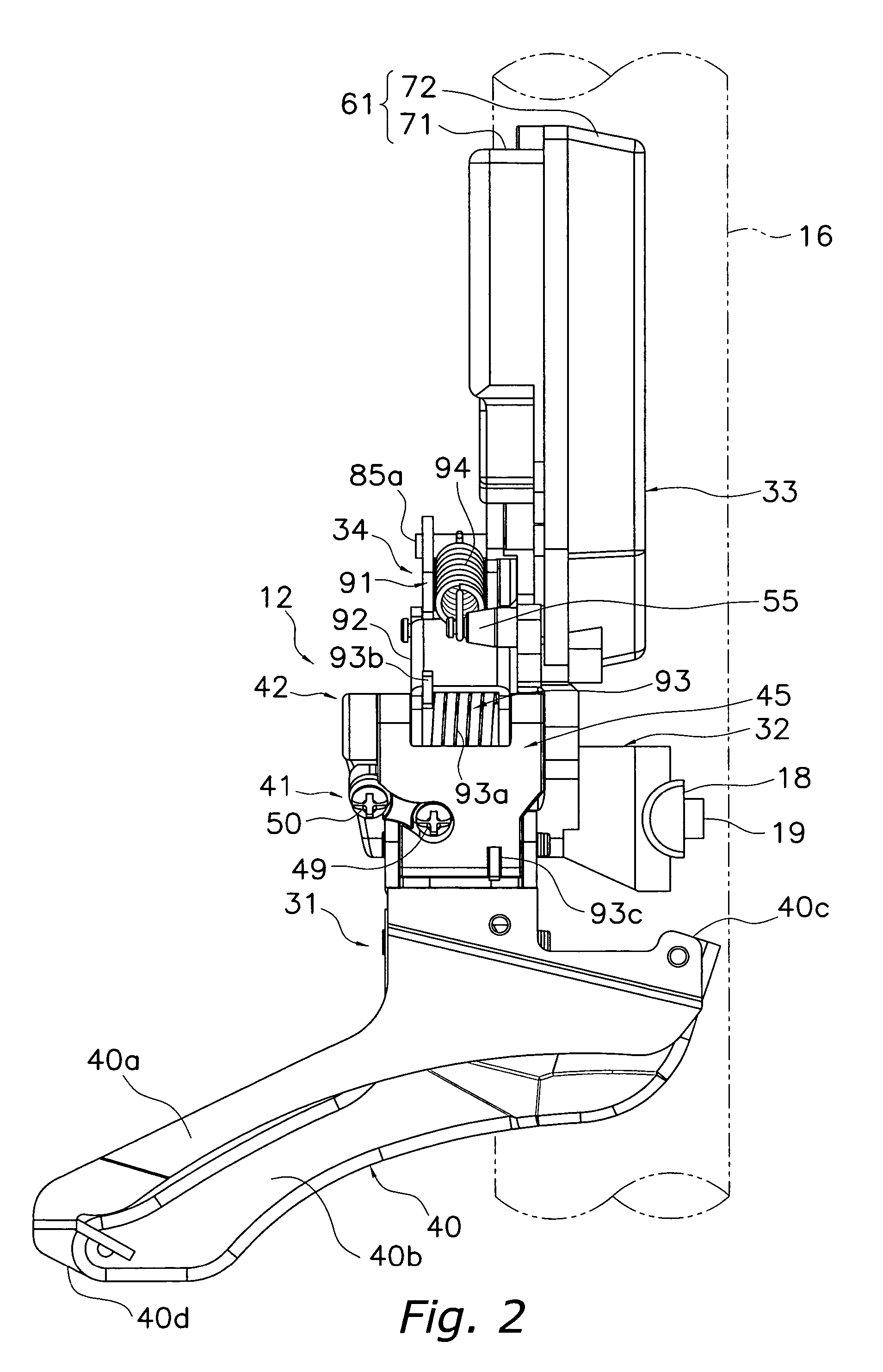
Electric bicycle derailleur
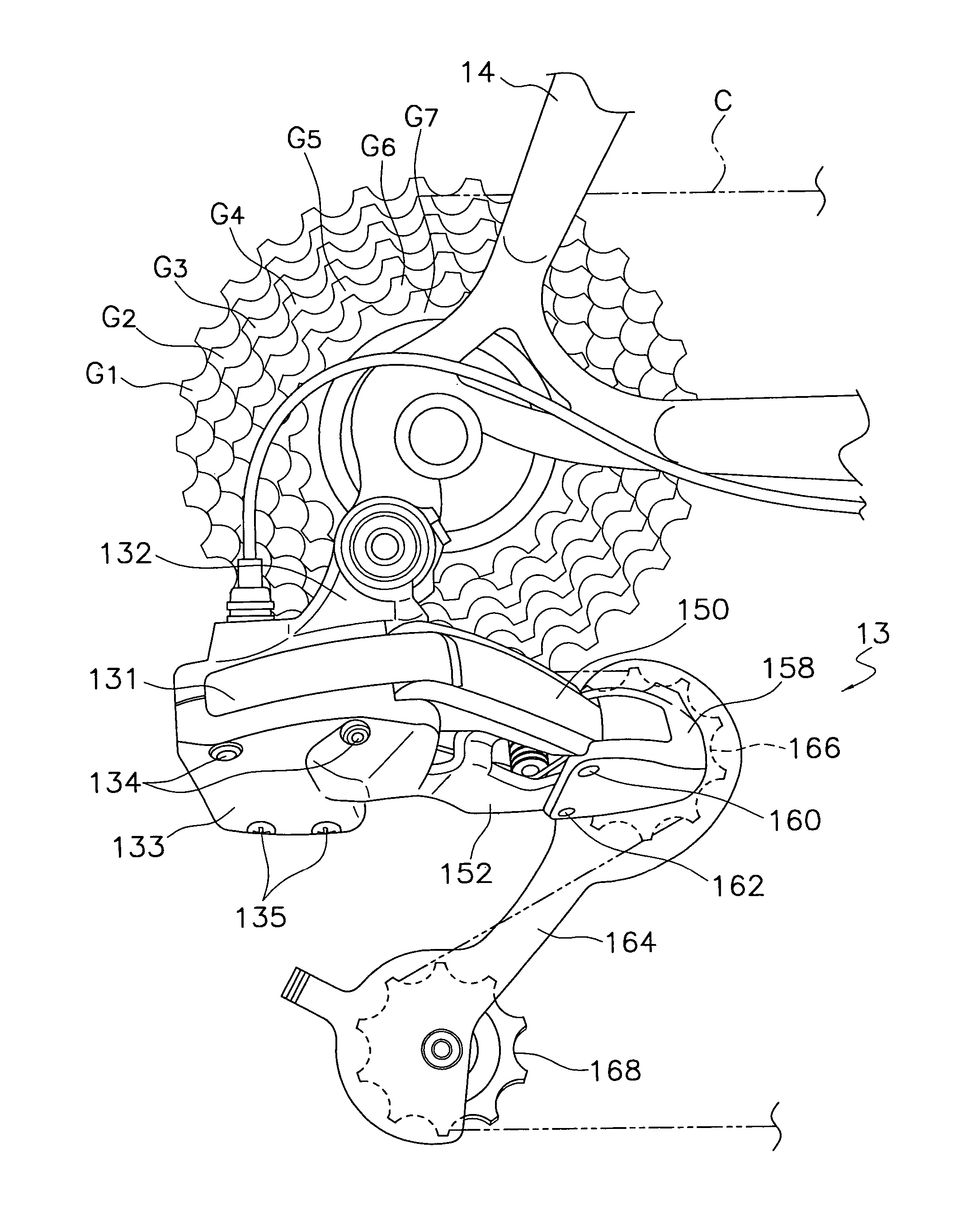
An electric derailleur has a motor unit having a derailleur motor with an output shaft, a position control mechanism and a controller. The output shaft is rotated through a moveable range including a first derailleur shift position and a second derailleur shift position. The position control mechanism is configured and arranged to provide a position signal indicative of an angular position of the output shaft. The controller detects a predetermined lockup position of the derailleur motor occurring at one of the first and second derailleur shift positions. The controller also sets a predetermined stop position for the derailleur motor that is calculated distance prior to the lockup position based on the position signal of the position control mechanism. Thus, the derailleur motor can be calibrated such that a new stop position is set that prevents an overcurrent from occurring in the motor.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Hall-effect current detector
InactiveUS6841989B2Reduce electrostatic noiseNoise shielding can be effectivelySolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesElectricityElectrical conductor
A current detector comprising a current-path conductor assembly and a Hall generator assembly. The current-path conductor assembly includes a sheet-metal current-path conductor and a plastic conductor holder molded in one piece therewith. The Hall generator assembly includes a Hall generator in the form of a semiconductor chip mounted to a metal-made mounting plate, a set of leads electrically connected to the Hall generator, and a plastic encapsulation enveloping the Hall generator and parts of the leads. The Hall generator assembly and the current-path conductor assembly are combined by bonding together the encapsulation of the Hall generator assembly and the conductor holder of the current-path conductor assembly. The conductor holder and the encapsulation are shaped in interfitting relationship to each other, so that when they are united, the Hall generator is positioned to generate a Hall voltage in response to a magnetic field due to the current flowing through the current-path conductor.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Fuse and battery pack containing the fuse
InactiveUS6377432B1Surely interrupt currentEasy to usePrimary cell maintainance/servicingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionOvercurrentEngineering
A fuse is melted and cut off when an overcurrent flows through the fuse. The fuse has a different thermal expansion coefficient metal laminate obtained by laminating a plurality of different thermal expansion coefficient metal plates. When the fuse is melted and cut off by heat of the overcurrent, a mechanical deforming force is applied to a melting portion of the fuse. The mechanical force is caused by the difference between thermal expansion coefficients of the different thermal expansion coefficient metal plates.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
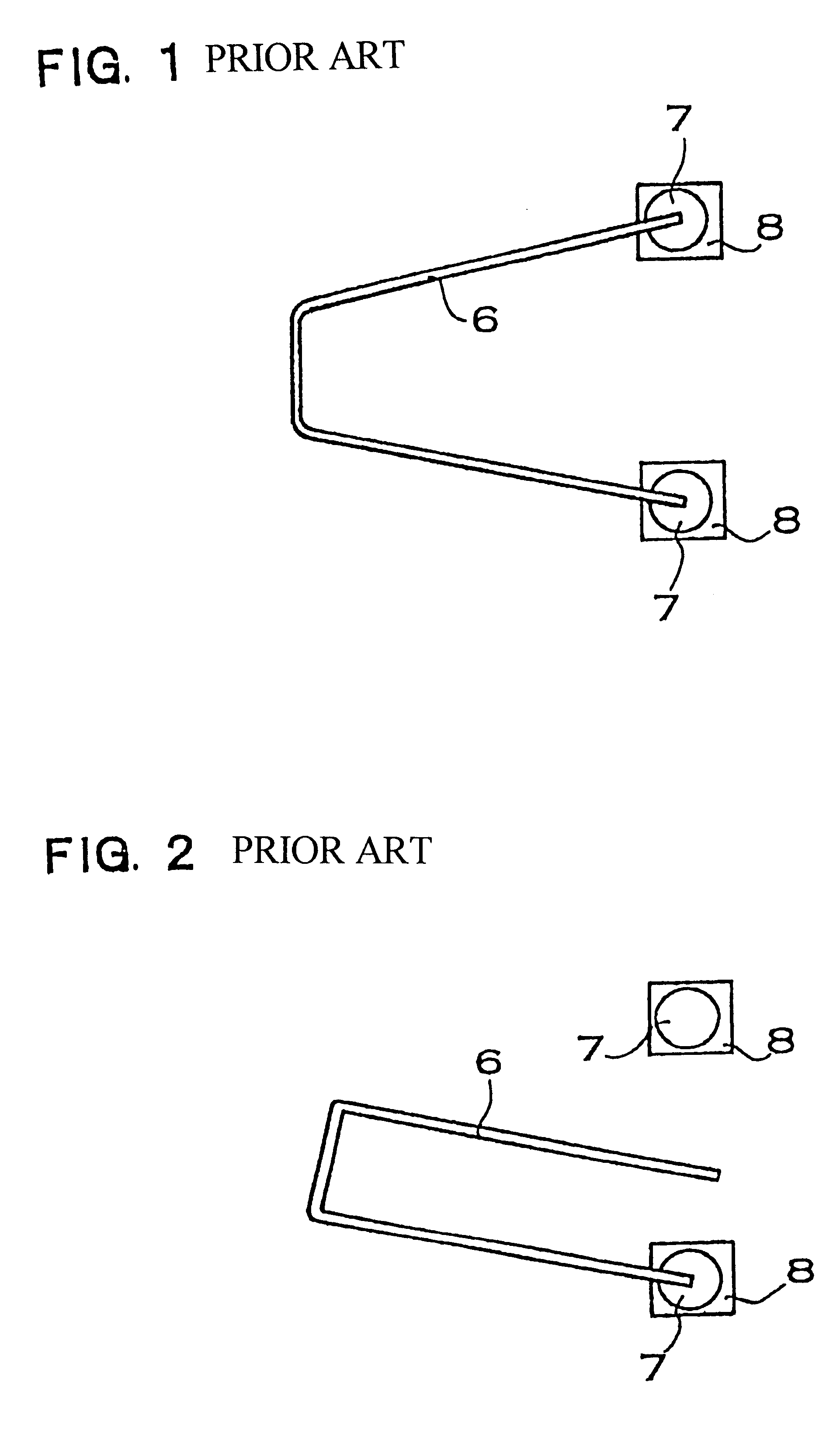
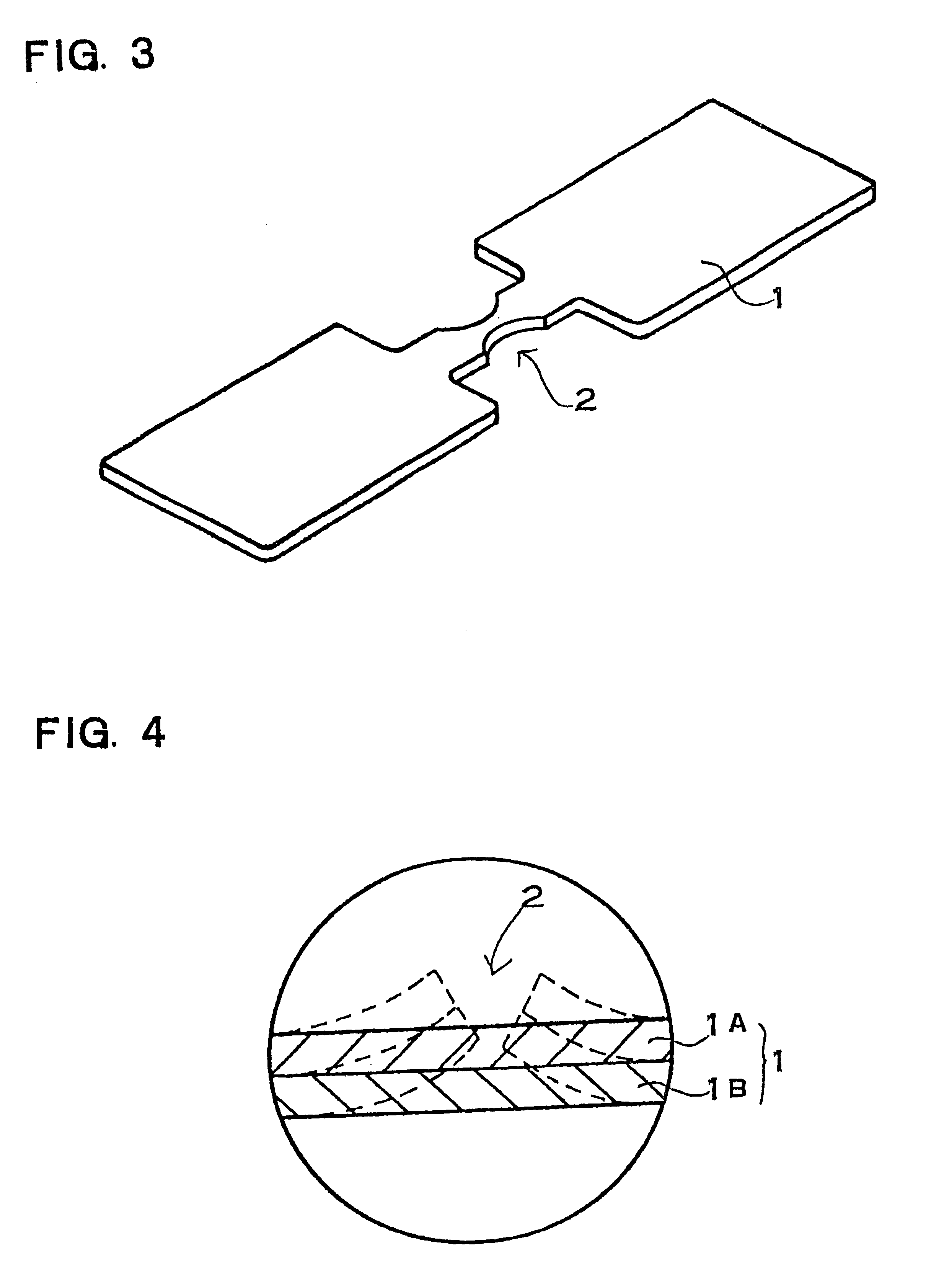
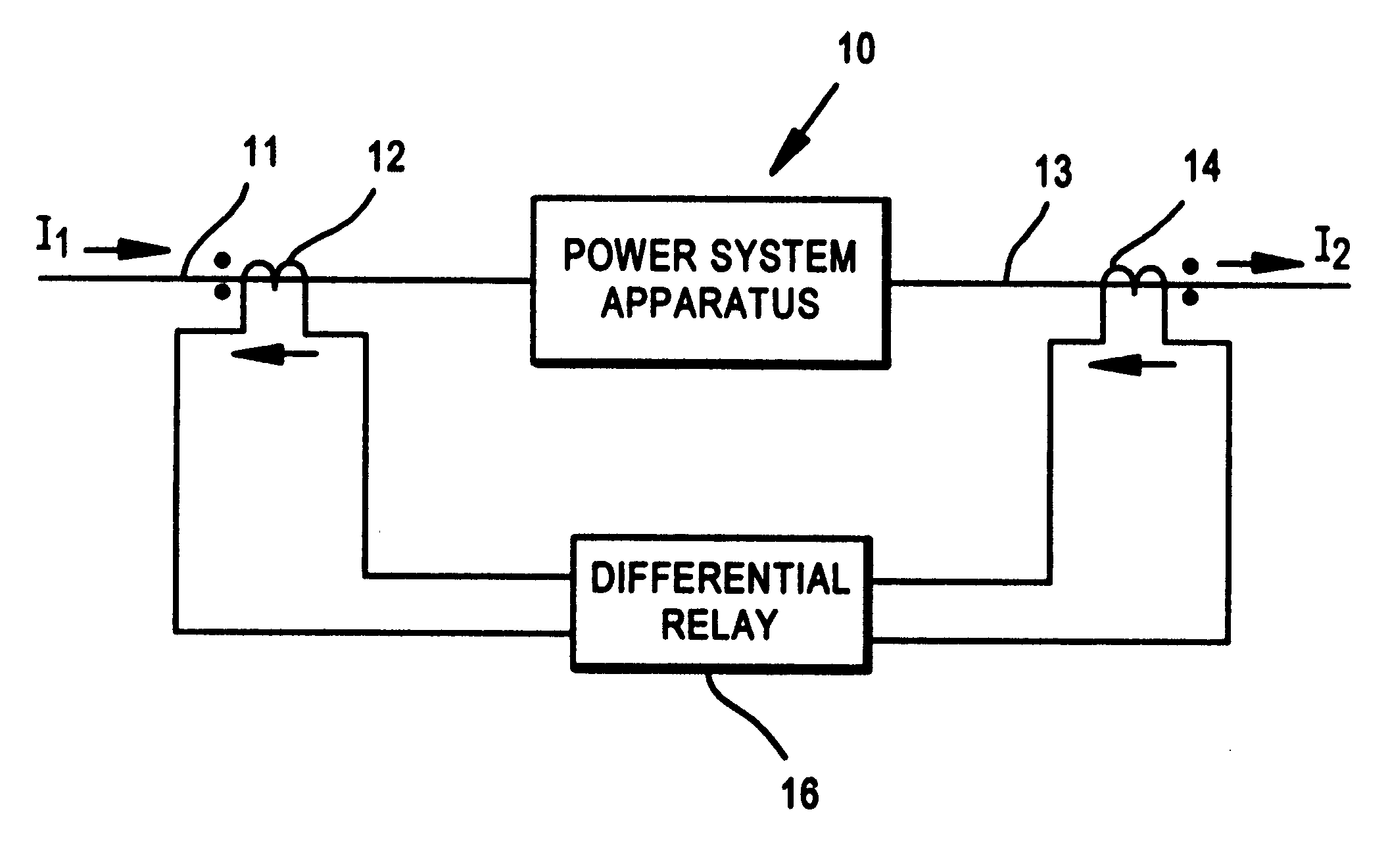
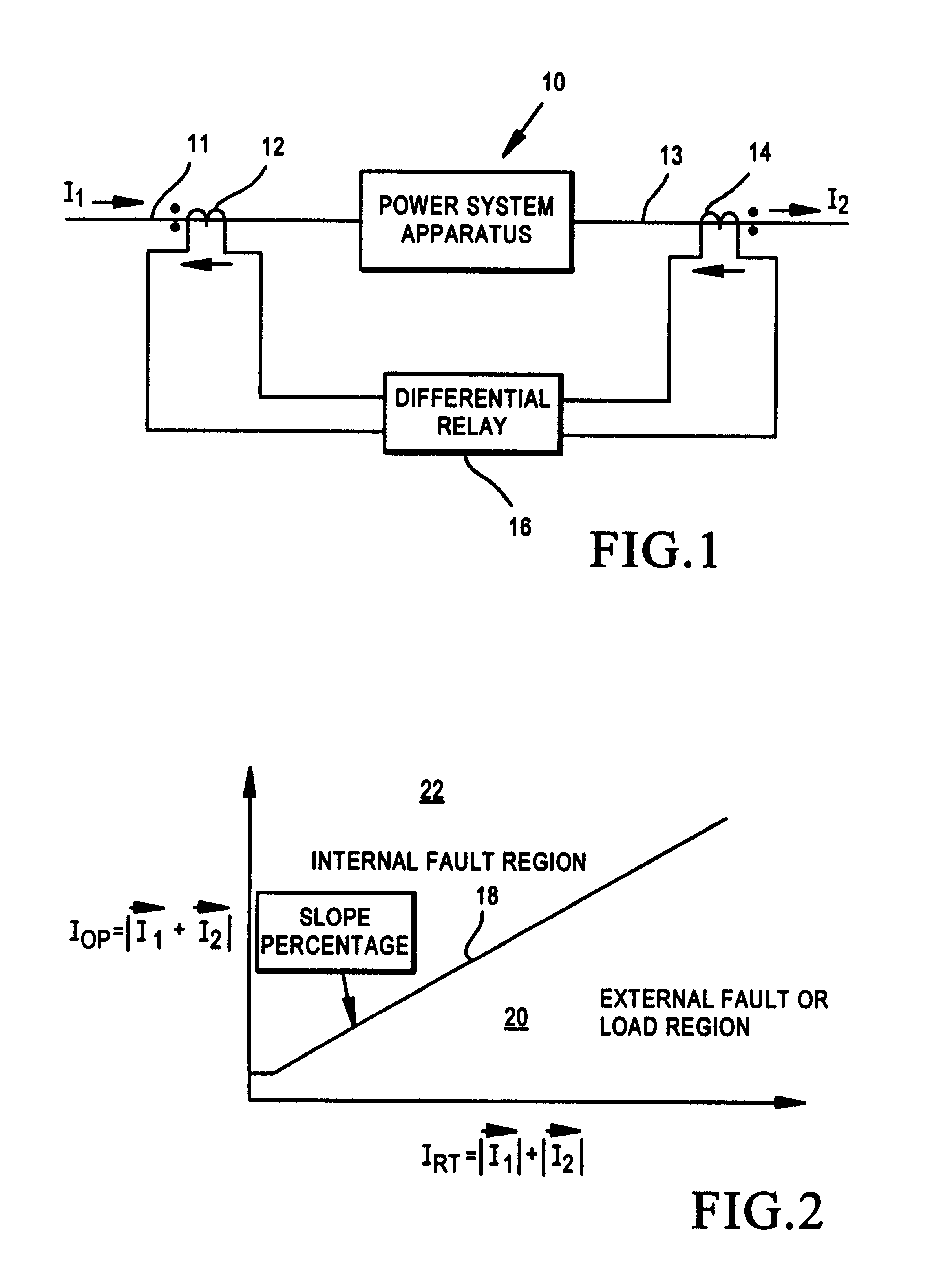
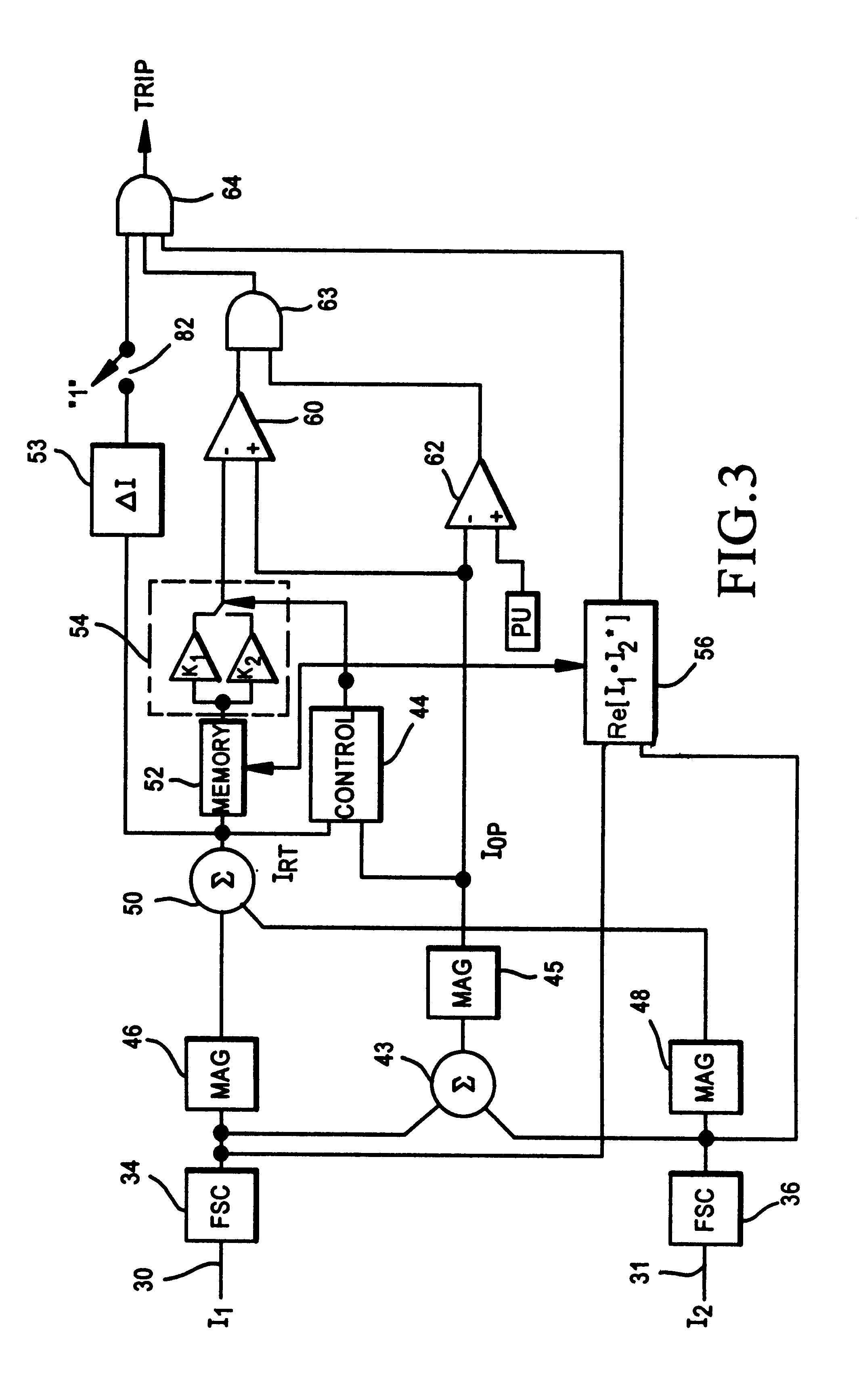
Restraint-type differential relay
InactiveUS6341055B1Preventing tripping signalCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsArrangements responsive to excess currentElectric power systemOvercurrent
A differential relay for protecting a power apparatus portion of a power system, such as a bus line, includes incoming and outgoing power lines on which incoming and outgoing currents are present. The incoming and outgoing currents of each phase are applied through current transformers and then through filtering and normalizing circuits prior to application to the differential relay. The differential relay includes a circuit for determining the presence of an external fault, and maintains security by avoiding a tripping action of the relay for said external faults. Further, the relay includes circuits which in response to the external fault evolving to an internal fault alters the operation of a portion of the relay, by increasing the gain for the restraint current, enabling a directional element for supervision of the differential relay, and for extending the immediate post-fault value of restraint current, and adding a time delay for a selected period of time, all of which are used to identify an external fault evolving into an internal fault.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
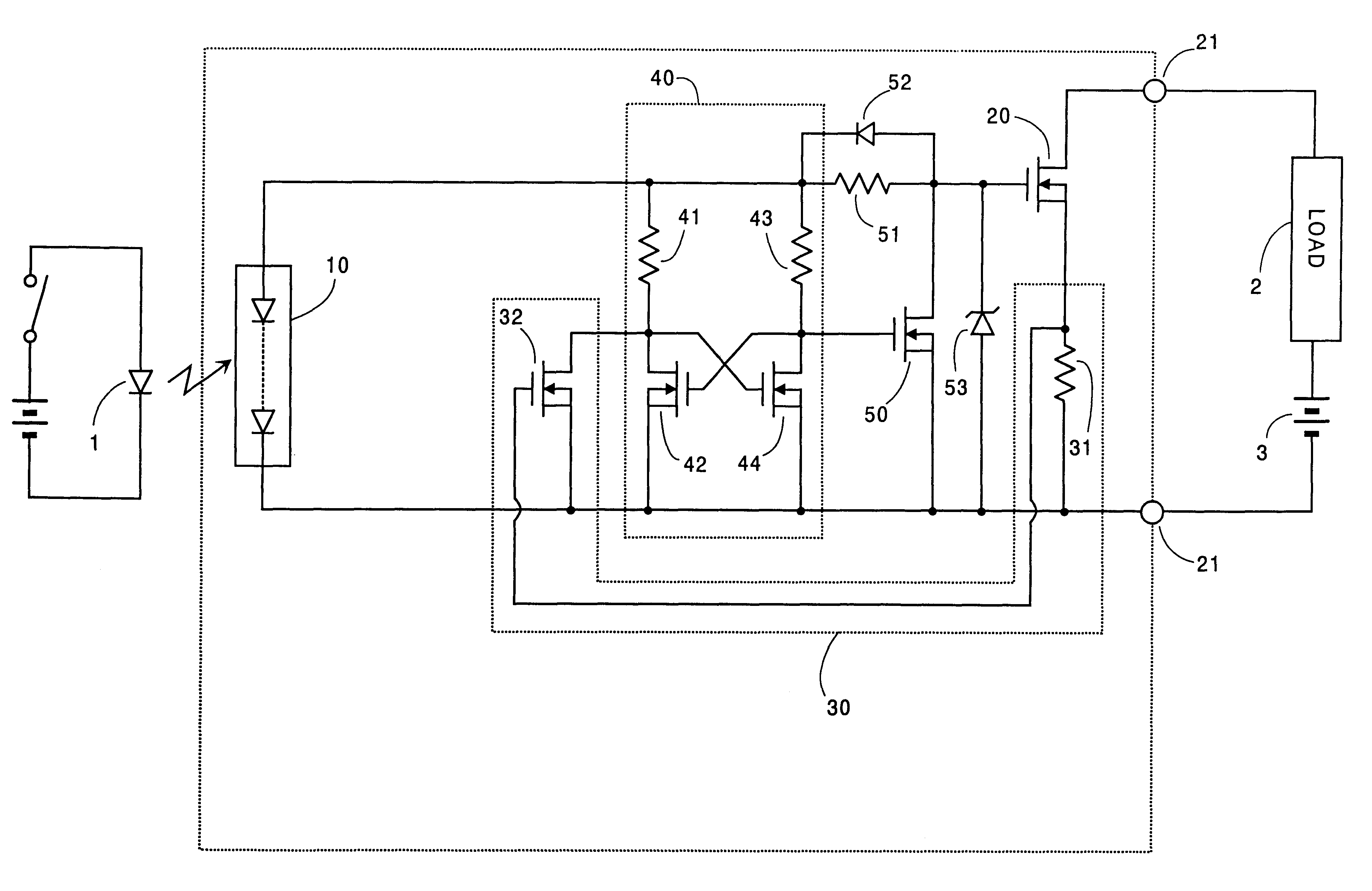
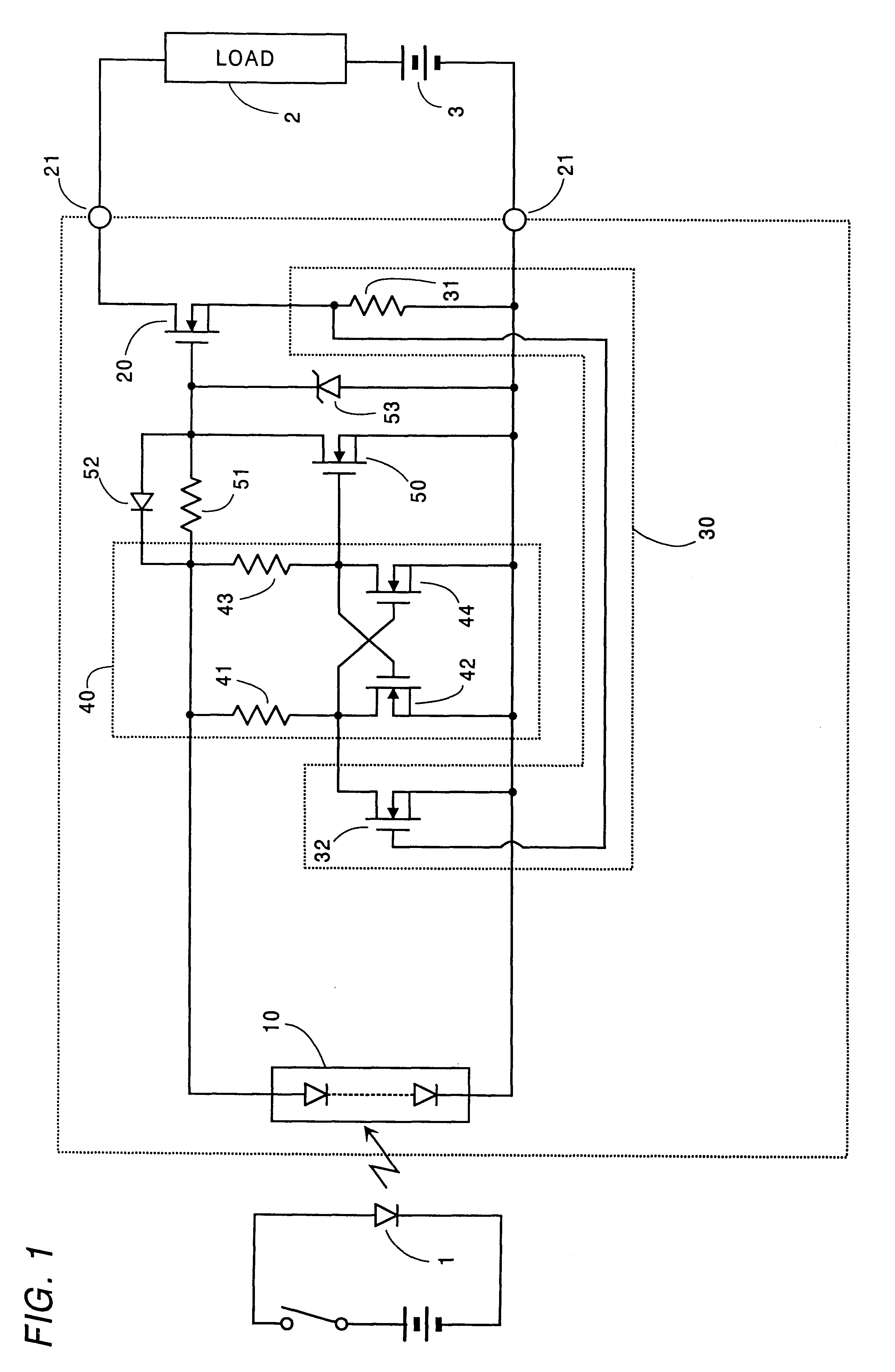
Light responsive semiconductor switch with shorted load protection
InactiveUS6339236B1Low working voltageSuccessful and reliable interruptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCurrent limitingOvercurrent
An improved light responsive semiconductor switch with shorted load protection capable of successfully interrupting a load overcurrent. The switch is includes an output transistor which is triggered by a photovoltaic element to connect a load to a power source thereof, and an overcurrent sensor which provides an overcurrent signal upon seeing an overcurrent condition in the load. A shunt transistor is connected in series with a current limiting resistive element across the photovoltaic element to define a shunt path of flowing the current from the photovoltaic element through the current limiting resistive element away from the output transistor. A latch circuit is included to be energized by the photovoltaic element and to provide an interruption signal once the overcurrent signal is received and hold the interruption signal. The interruption signal turns on the shunt transistor so as to flow the current from the photovoltaic element through the shunt path, thereby turning off the output transistor for interruption of the overcurrent. The current limiting resistive element is connected in series with the shunt transistor to limit the current from the photovoltaic element when the shunt transistor is turned on, thereby providing a supply voltage from the photovoltaic element to the latch circuit. Thus, the latch circuit is enabled to keep providing the interruption signal for reliable interruption of the overcurrent.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Electronically commutated motor (ECM) and method of controlling an ecm
InactiveUS20070024225A1Protection from damageProtection from destructionCommutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringLimit value
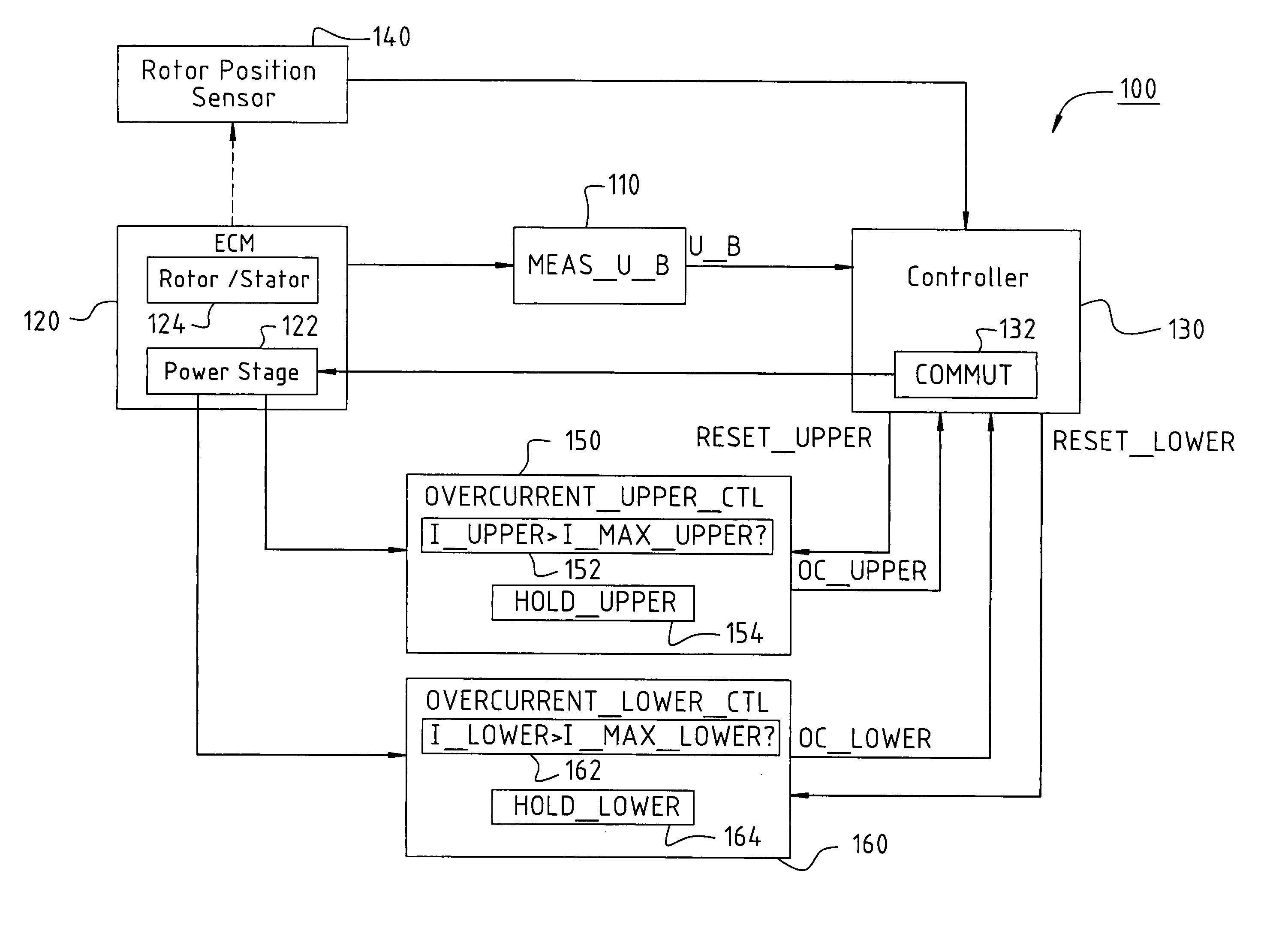
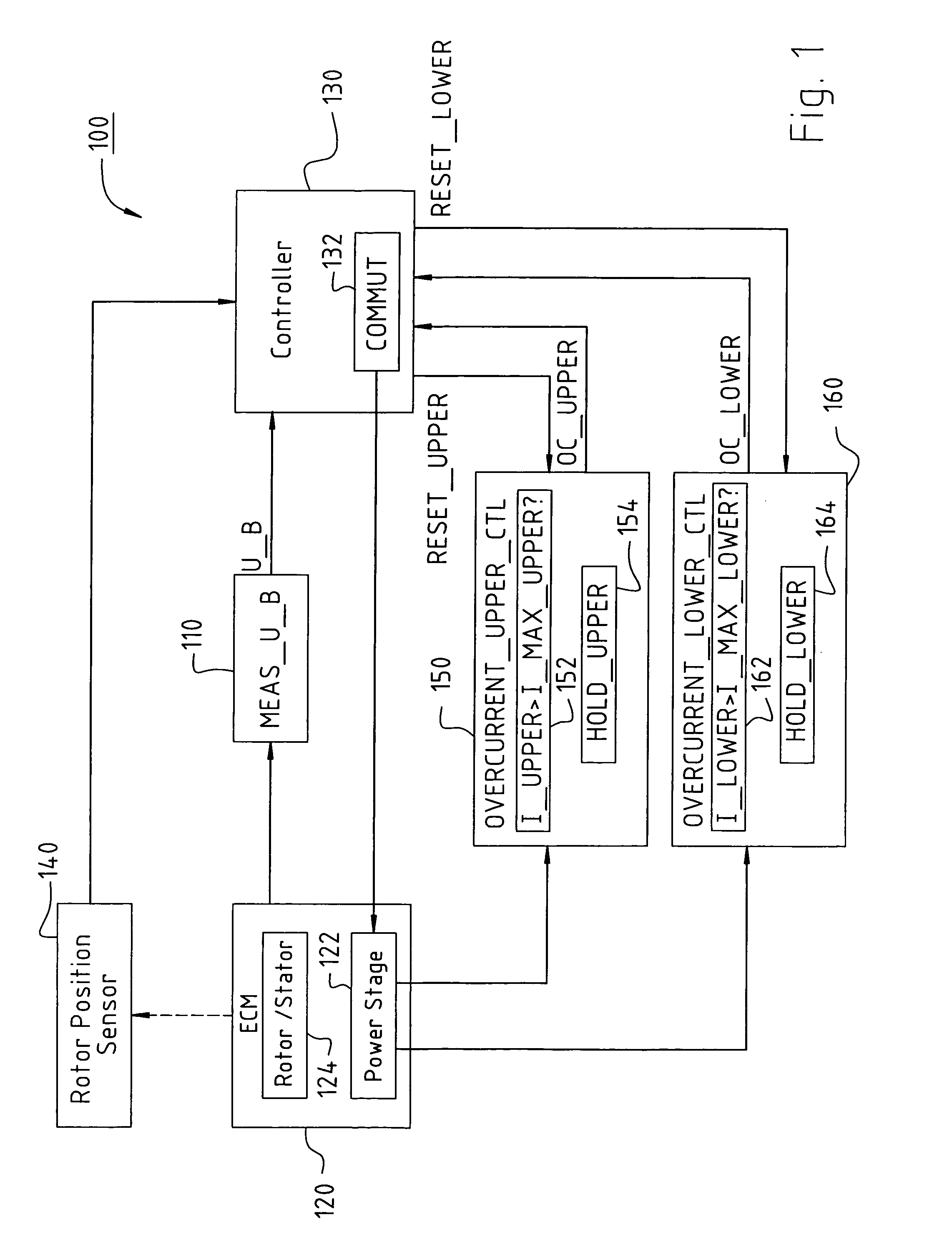
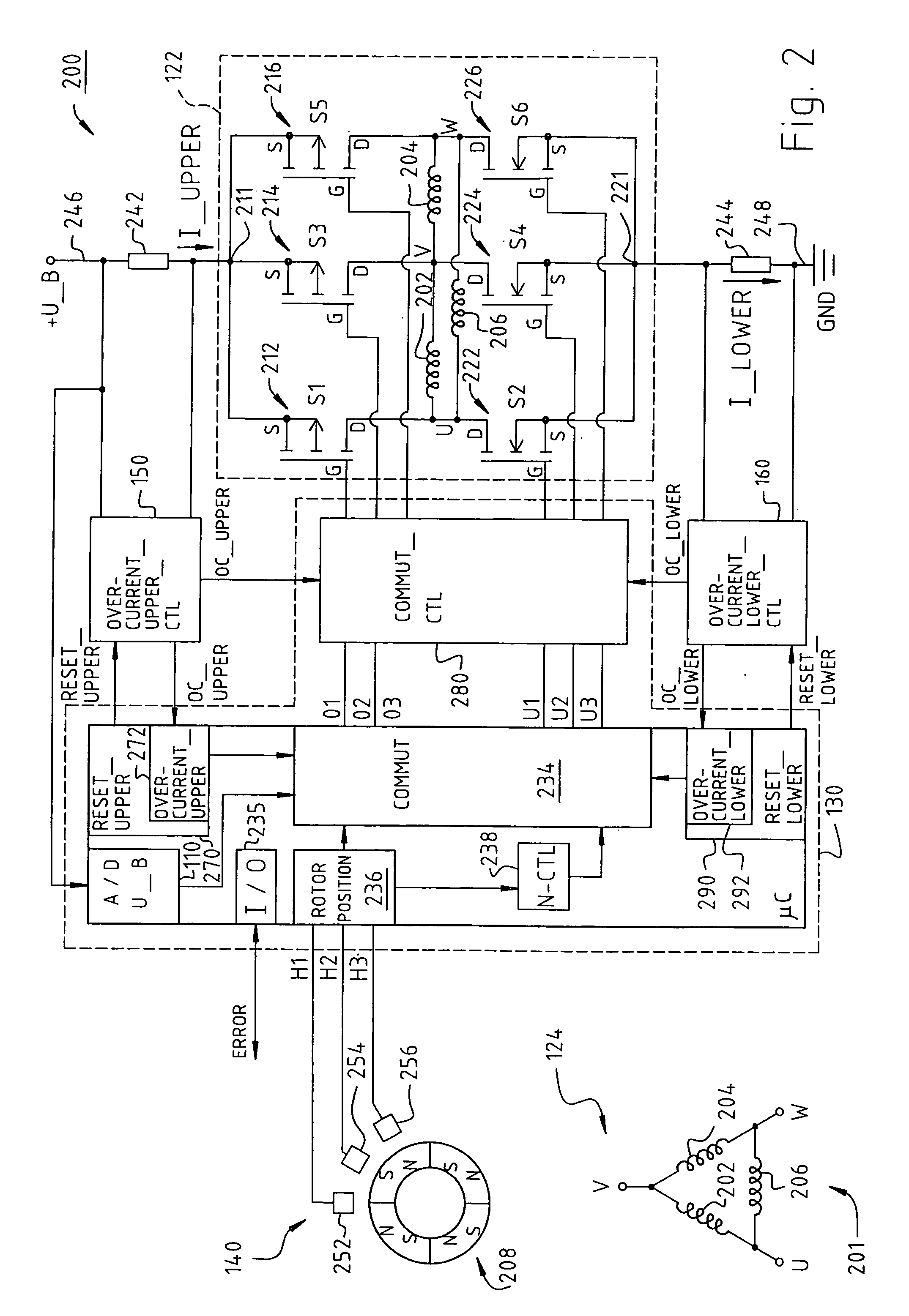
An electronically commutated motor comprises a rotor (208); a stator (201) electromagnetically interacting with the rotor (208), which stator is formed with a stator winding (202, 204, 206); a power stage (122) controlling the currents flowing in the stator winding (202, 204, 206) during operation; at least one current measuring element (242, 244) for sensing a measured value for the currents (I_UPPER, I_LOWER) flowing in the power stage, and an overcurrent measuring element (152, 162) for evaluating an associated measured value and for sensing a current whose absolute value exceeds a predetermined limit value (I_MAX_UPPER, I_MAX_LOWER); a holding element (154, 164) associated with the overcurrent measuring element (152, 162), configured, when an overcurrent occurs in the associated current measuring element (242, 244), to generate an overcurrent signal (OC_UPPER, OC_LOWER), to store the signal, and to deliver a signal to the power stage (122).
Owner:EBM PAPST ST GEORGEN & -
Semiconductor active fuse for AC power line and bidirectional switching device for the fuse
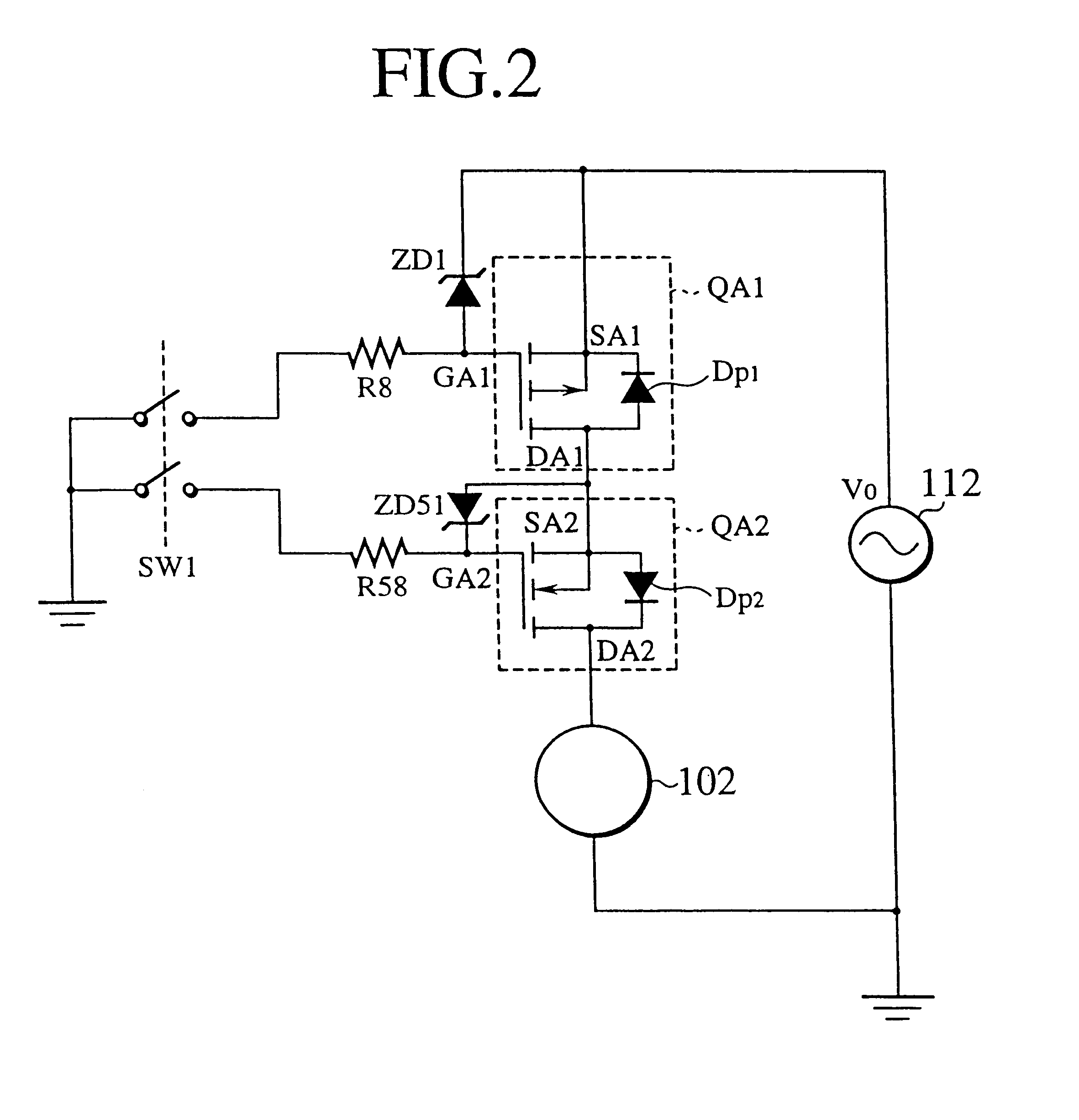
A bidirectional switching device has a first main semiconductor element and a second main semiconductor element. The first main semiconductor element has a first main electrode connected to an ungrounded side of an AC power source, and a second main electrode. The first main semiconductor element contains a first parasitic diode whose cathode region is connected to the first main electrode and whose anode region is connected to the second main electrode. The second main semiconductor element has a third main electrode connected to the second main electrode, and a fourth main electrode connected to a load. The second main semiconductor element contains a second parasitic diode whose anode region is connected to the third main electrode and whose cathode region is connected to the fourth main electrode. A current flowing from the first main semiconductor element toward the second main semiconductor element passes through the second parasitic diode, and a current flowing from the second main semiconductor element toward the first main semiconductor element passes through the first parasitic diode. The bidirectional switching device is used to form a semiconductor active fuse for an AC power system. The semiconductor active fuse is capable of detecting an overcurrent without a shunt resistor, which was connected in series to a power supply cable, thereby minimizing heat dissipation as well as a conduction loss. The semiconductor active fuse is capable of easily and speedily detecting not only an overcurrent caused by a dead short but also an abnormal current caused by an incomplete short circuit failure having a certain extent of short-circuit resistance, and breaking alternating current in an AC power supply cable.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Abnormality detecting device of electric power converting device and abnormality detecting method
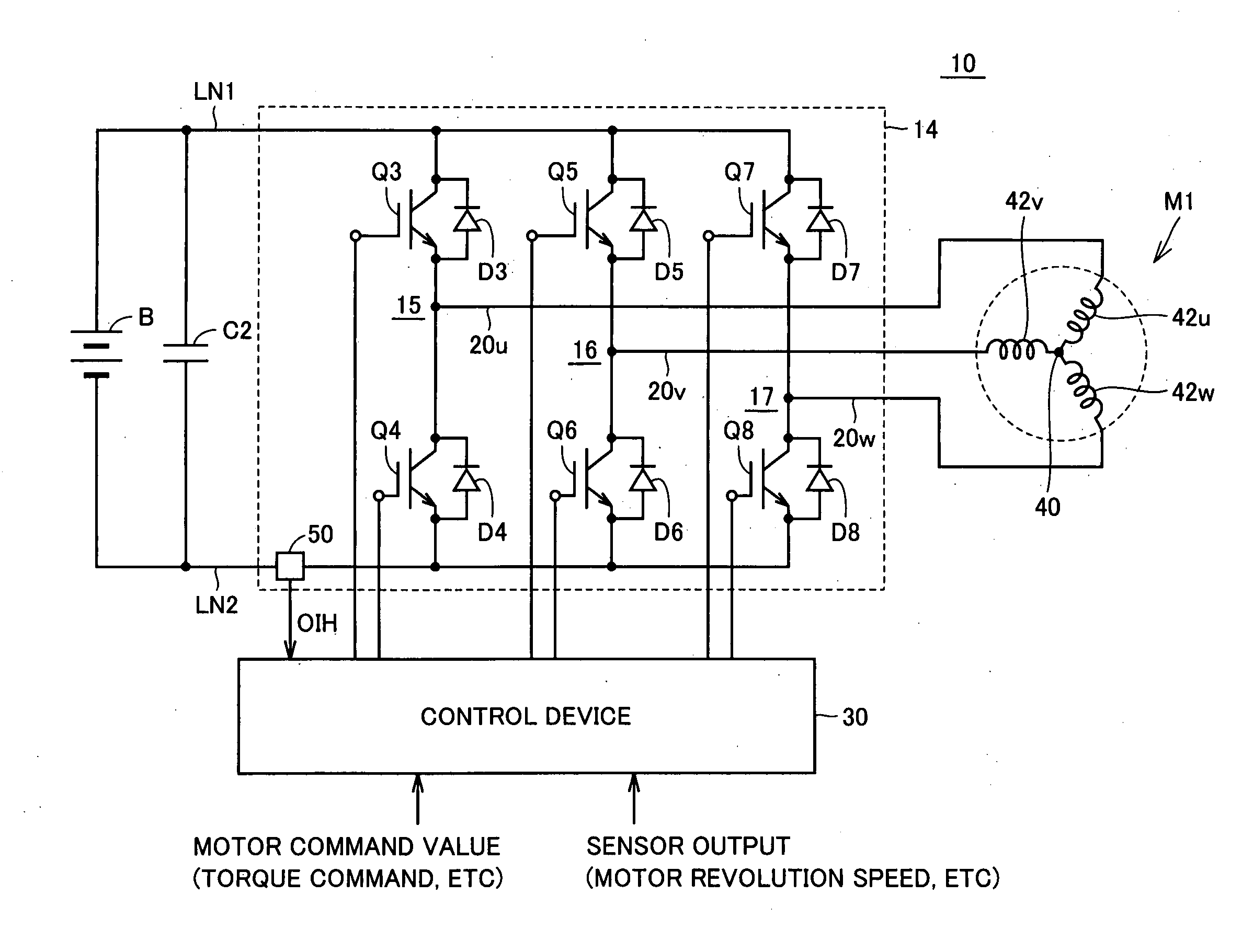
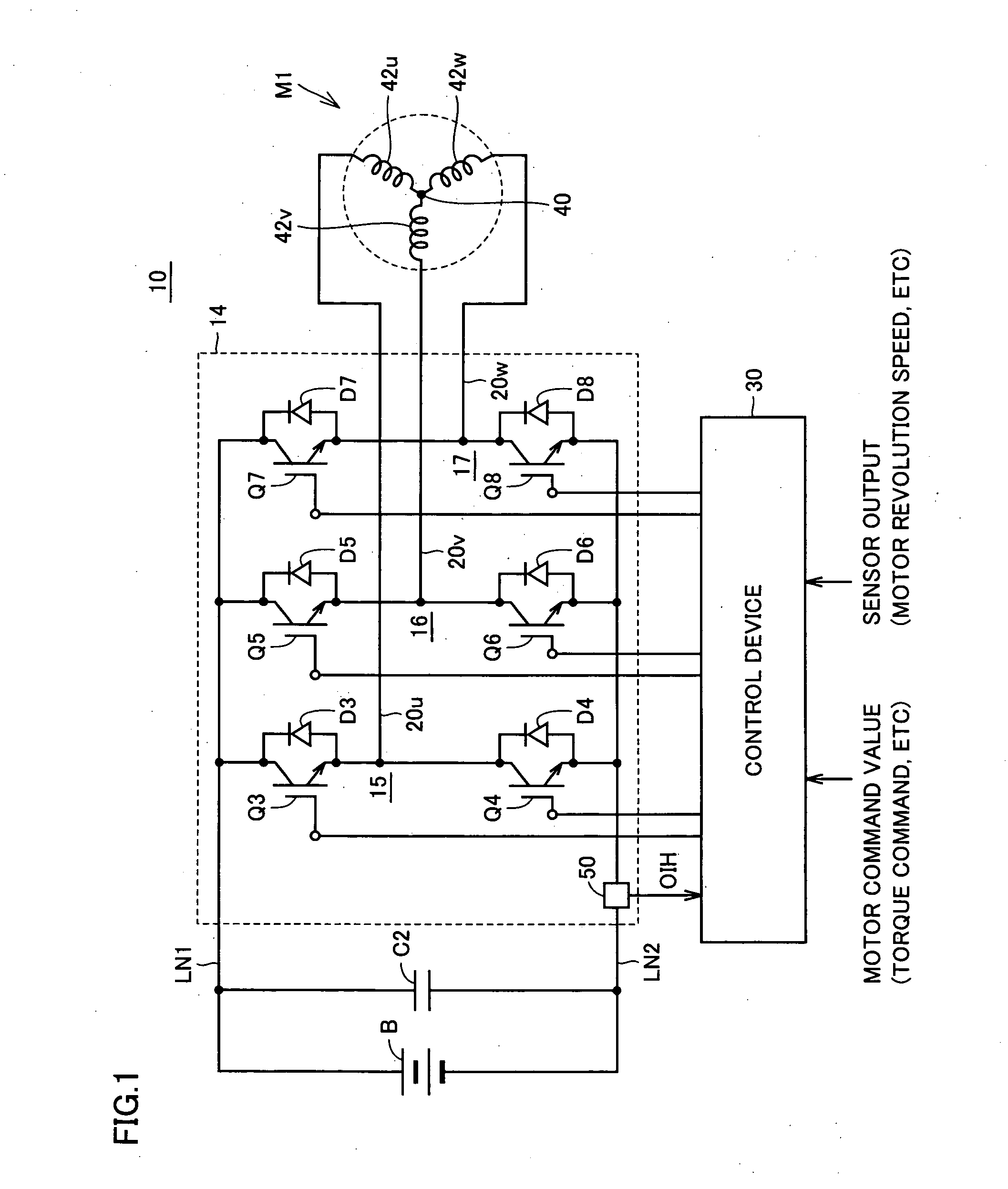
ActiveUS20090009920A1Accurately determineDC motor speed/torque controlAsynchronous induction motorsOvercurrentInverter
Each of three-phase arm of an inverter has first and second switching elements connected in series together at a connection point to the corresponding phase coil of the three-phase motor. Control device turns on the first switching element of the i-th (i is a natural number smaller than four) for a predetermined time period, and determines that the second switching element of the i-th arm has a short fault, when an overcurrent exceeding a predetermined threshold is detected within the predetermined time period. The predetermined time period is shorter than a time period from a time point of turning on the first switching element of the i-th arm to a time point of attaining the predetermined threshold by a current flowing through a path extending from a power supply line through the second switching element of the remaining arm other than the i-th arm to a ground line.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electric bicycle derailleur
InactiveUS20050239587A1Easy CalibrationAvoid overuseChain/belt transmissionGearingOvercurrentElectric machinery
An electric derailleur has a motor unit having a derailleur motor with an output shaft, a position control mechanism and a controller. The output shaft is rotated through a moveable range including a first derailleur shift position and a second derailleur shift position. The position control mechanism is configured and arranged to provide a position signal indicative of an angular position of the output shaft. The controller detects a predetermined lockup position of the derailleur motor occurring at one of the first and second derailleur shift positions. The controller also sets a predetermined stop position for the derailleur motor that is calculated distance prior to the lockup position based on the position signal of the position control mechanism. Thus, the derailleur motor can be calibrated such that a new stop position is set that prevents an overcurrent from occurring in the motor.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
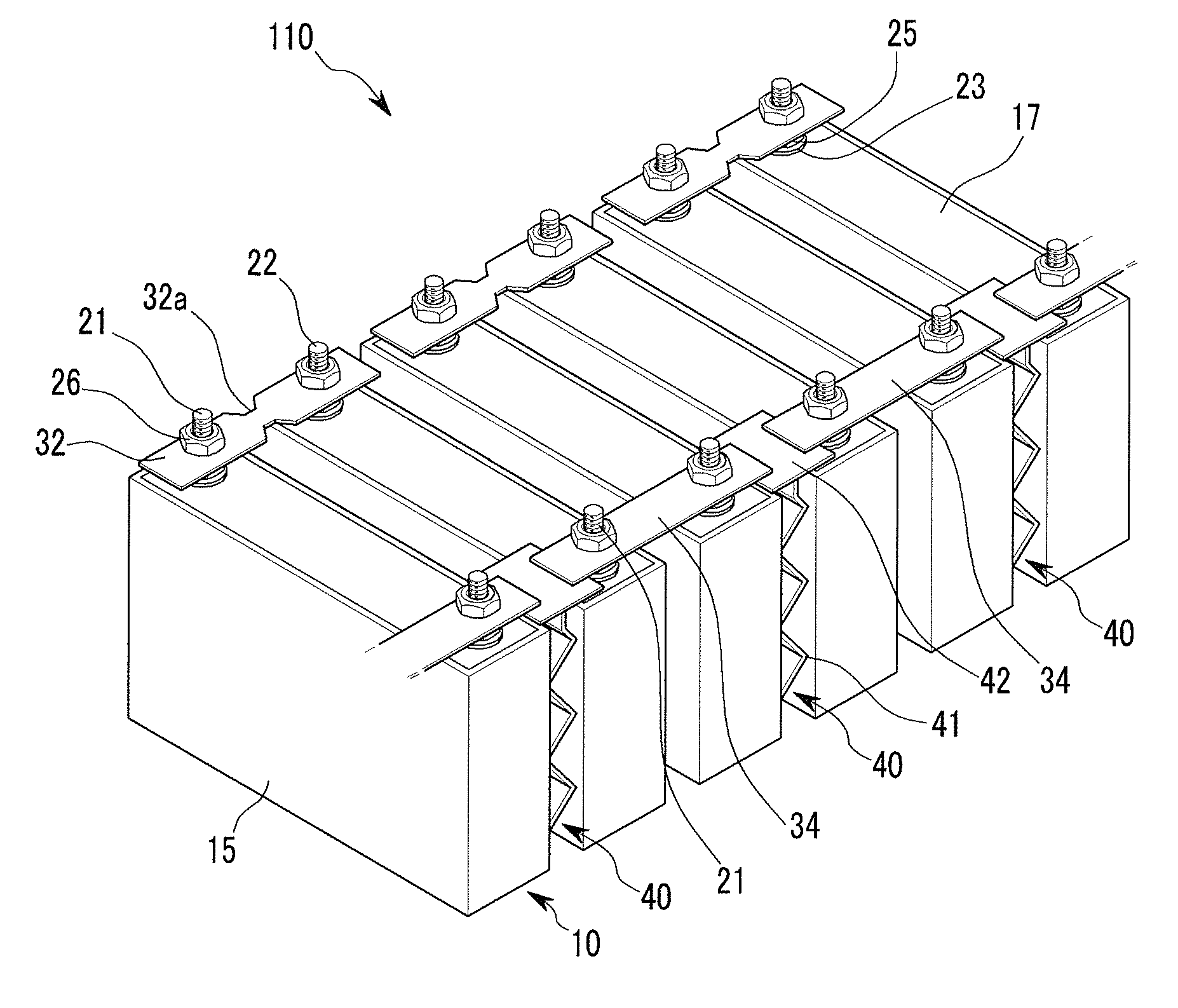
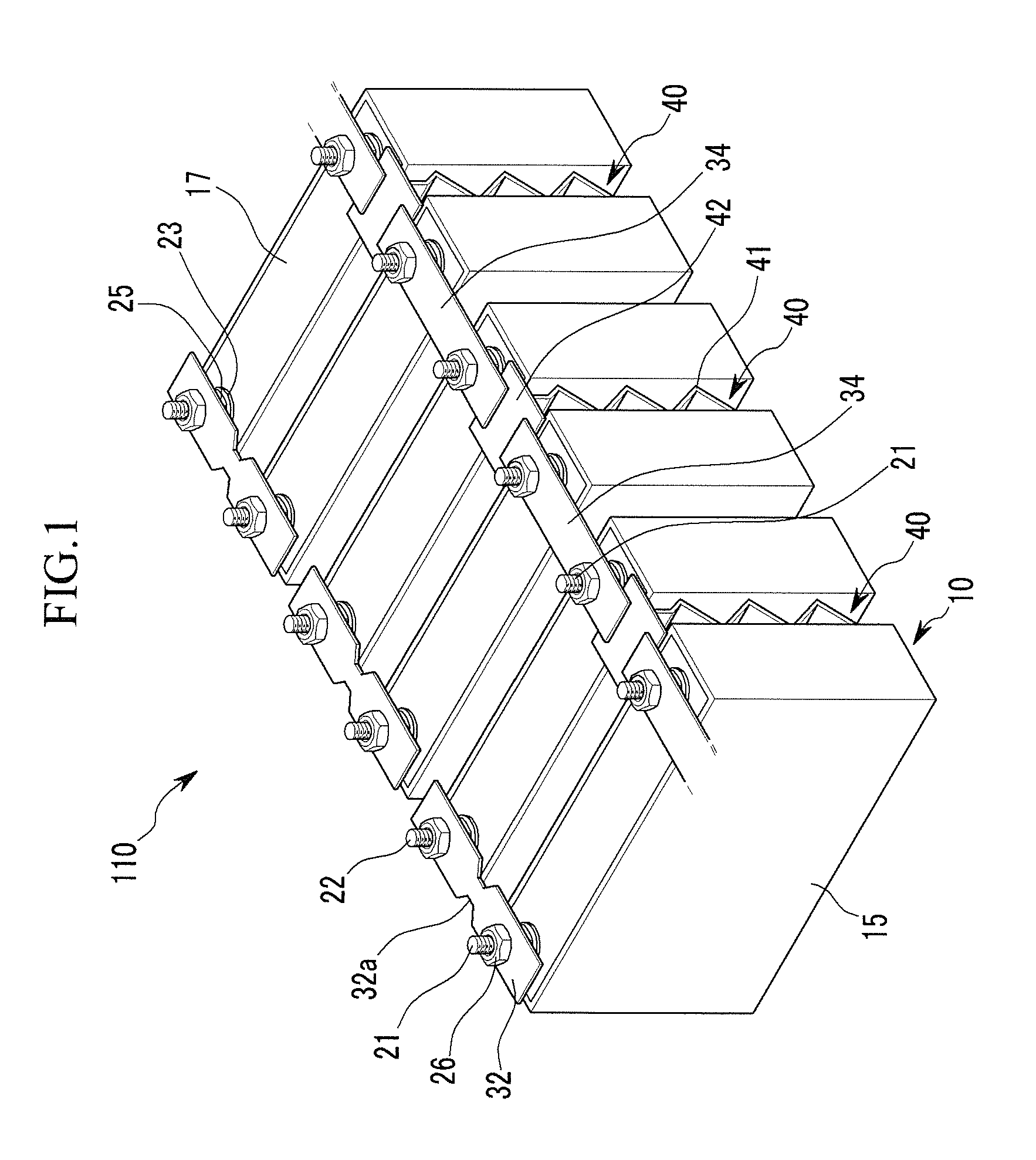
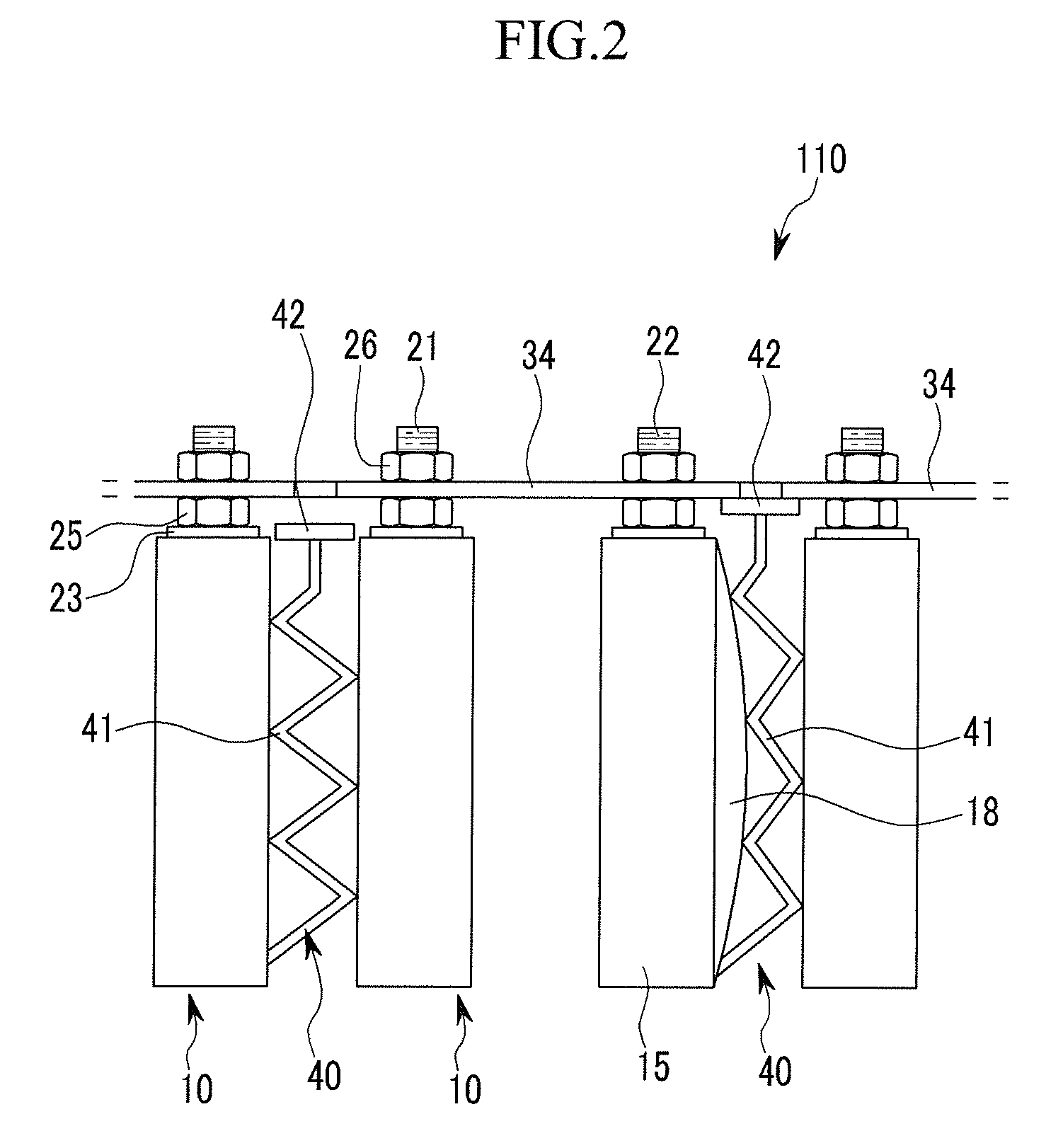
Battery module
ActiveUS20110039147A1Improve securityPrimary cell to battery groupingCurrent conducting connectionsOvercurrentRechargeable cell
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
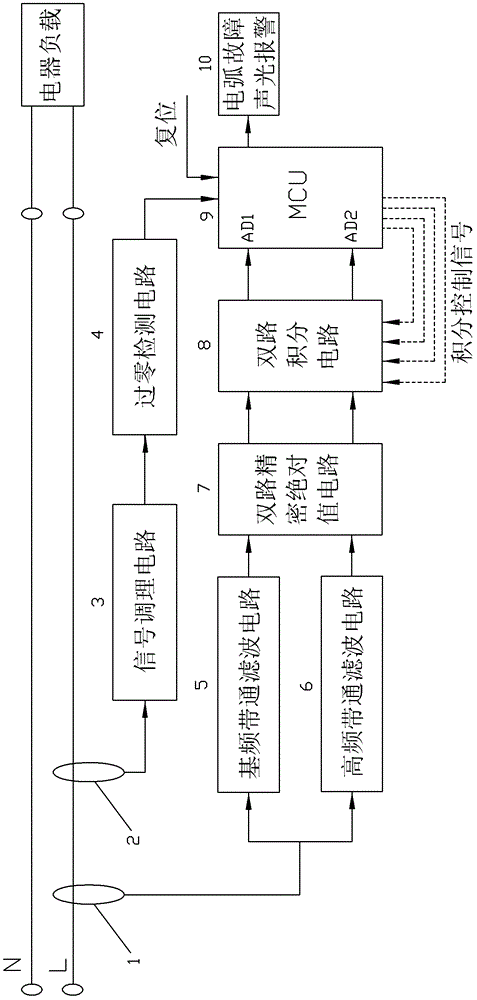
Low-voltage arc fault detection method
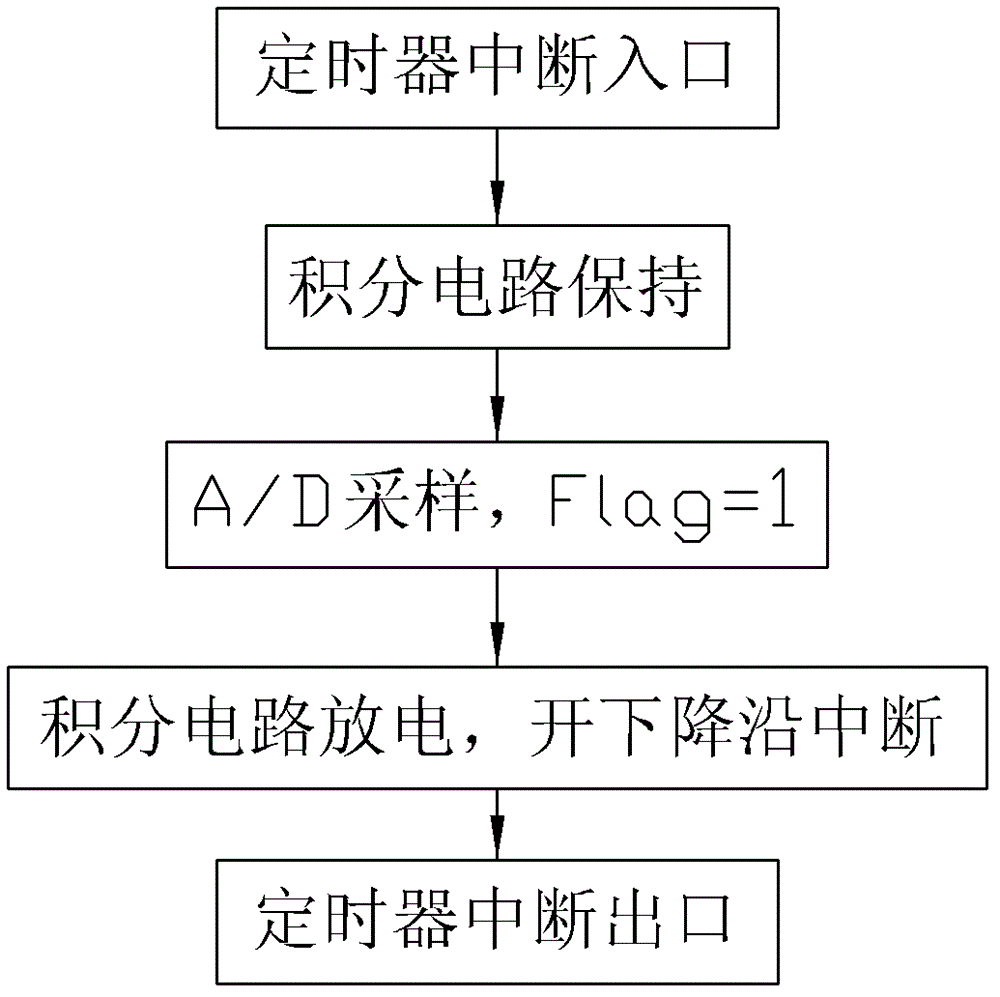
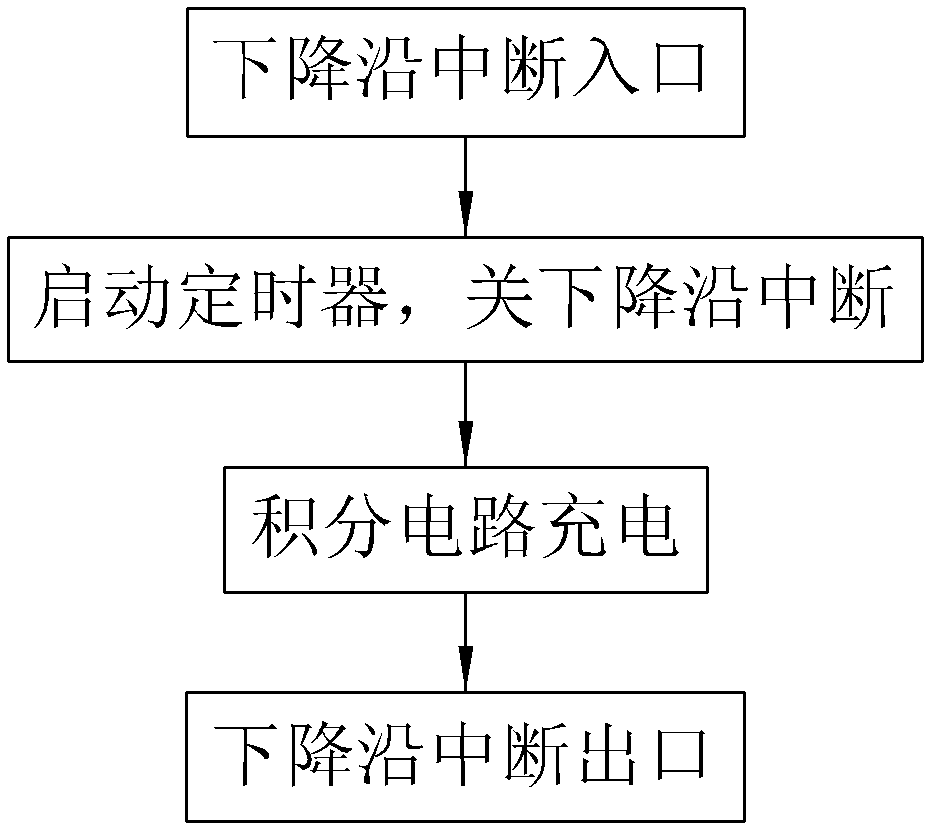
InactiveCN102749533AImprove reliabilityAvoid misuseCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingLow voltageCurrent sensor
A low-voltage arc fault detection method comprises collecting current signals in a loop through a current sensor, obtaining fundamental frequency analog signals and high frequency analog signals, achieving accumulating calculation of the fundamental frequency analog signals and high frequency analog signals of power frequency cycle through an integrating circuit, an interrupt trigger and a timer, and further obtaining higher harmonic occupancy. According to the method, whether arc faults occur is judged by real-time monitoring of change characteristics of the line current higher harmonic occupancy and calculation of over-limit times of the higher harmonic occupancy, normal arc and fault arc which are generated by some special electric appliance loads and normal on-off action are distinguished by judging whether higher harmonic occupancy changes caused by the arc faults are periodic and judging occurring frequency, occurrence of the arc faults can be detected in real time, the method is not limited by an installing position, malfunction caused by disturbance of operating arc generated by normal circuit opening and closing and loads such as a switch power and a dust collector can be avoided well, and the reliability is high.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Method for the transmission of signals in a bus system, superposed on a direct supply voltage
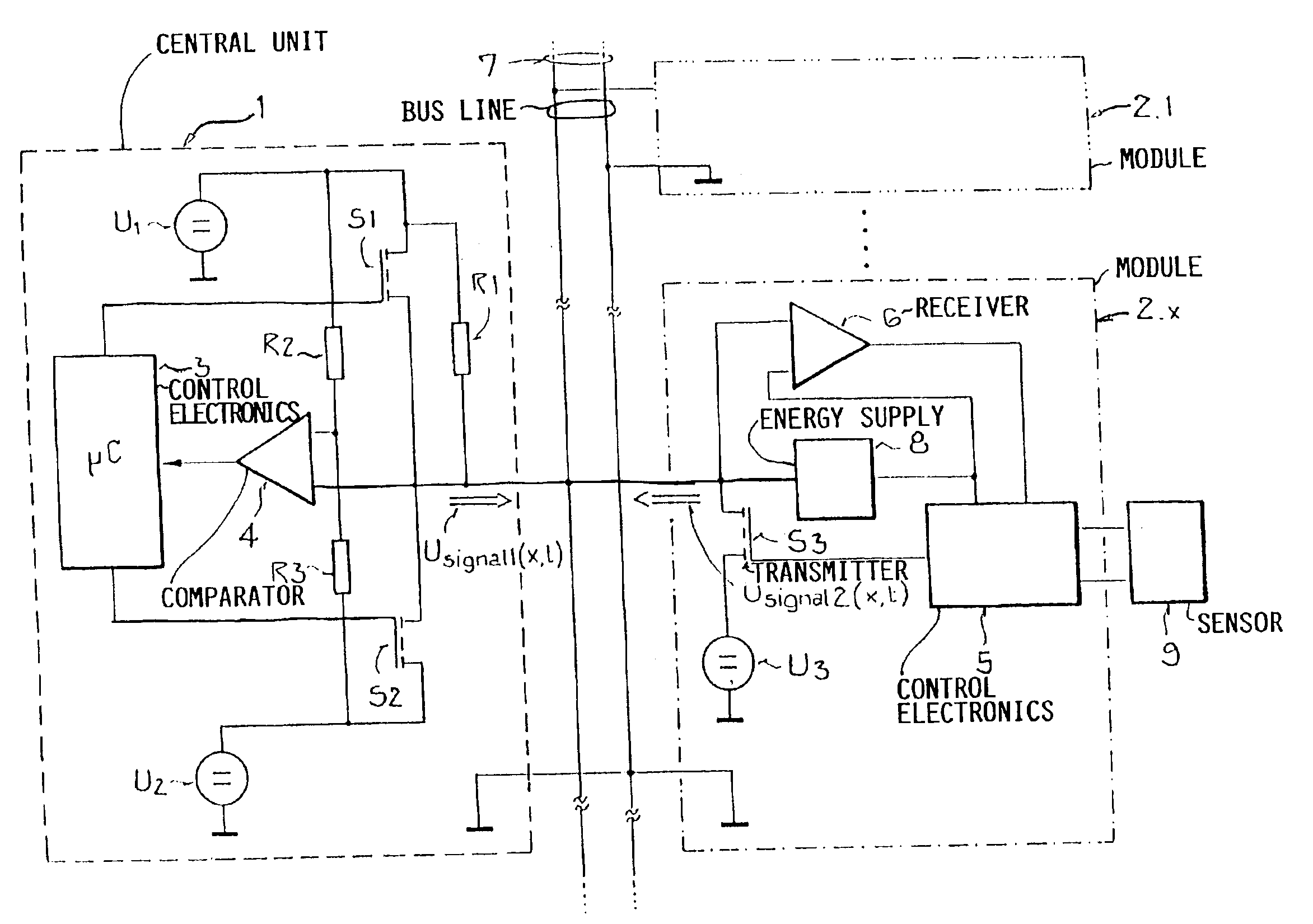
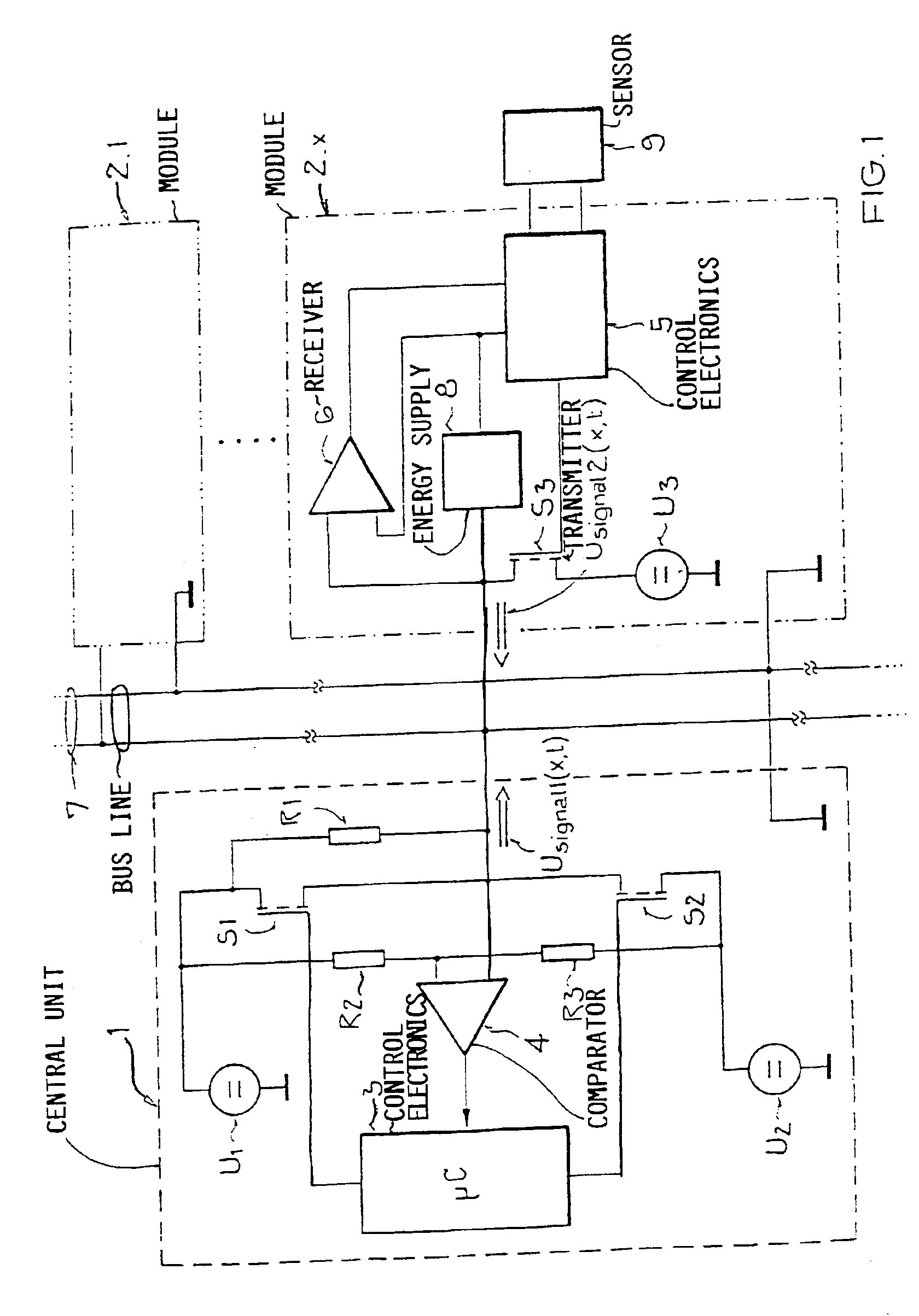
InactiveUS6870282B1Easy to carryIncrease rangeBatteries circuit arrangementsInsulated cablesOvercurrentBus
Previously in a bus system, voltage signals were transmitted from the central unit to the modules, which could reply thereto by variation of the current input. A disadvantage thereby is the relatively high susceptibility to interference of the current input, which itself already must be kept relatively small due to the energy consumption, as well as the correspondingly high effort and expense for an error-free recognition of the signals transmitted from the modules in the central unit. It is now suggested, that the modules also answer to the central unit by means of voltage signals superposed on the direct supply voltage, whereby for the time duration of the signal transmission by the modules, the central unit provides the direct supply voltage to the bus line over a resistor, so that the voltage signal of the module can be detected in the central unit on the bus line on the side of the resistor facing away from the direct supply voltage. A preferred application for bus systems in motor vehicles, especially for a sensor data bus, is provided.
Owner:CONTI TEMIC MICROELECTRONIC GMBH +1
Semiconductor aggregate substrate and semiconductor device with fuse structure to prevent breakdown
Electrostatic breakdown is avoided during fabrication of individual semiconductor devices using a semiconductor aggregate substrate. The semiconductor aggregate substrate is comprised of a large wafer. A plurality of sections are provided on the surface of the wafer, which are divided by division lines. A display active matrix circuit is integrally formed in each of the segments through normal IC production processing. Guard ring patterns are provided so that they surround the individual display active matrix circuits. A connection pattern is also provided for commonly connecting the guard ring patterns adjoining each other through the division lines. The connection pattern has opening structures for dealing with an external overcurrent on both sides of the division lines. The opening structures are constituted by, for example fuse patterns.
Owner:SONY CORP
Switching power supply as well as control circuit and method thereof
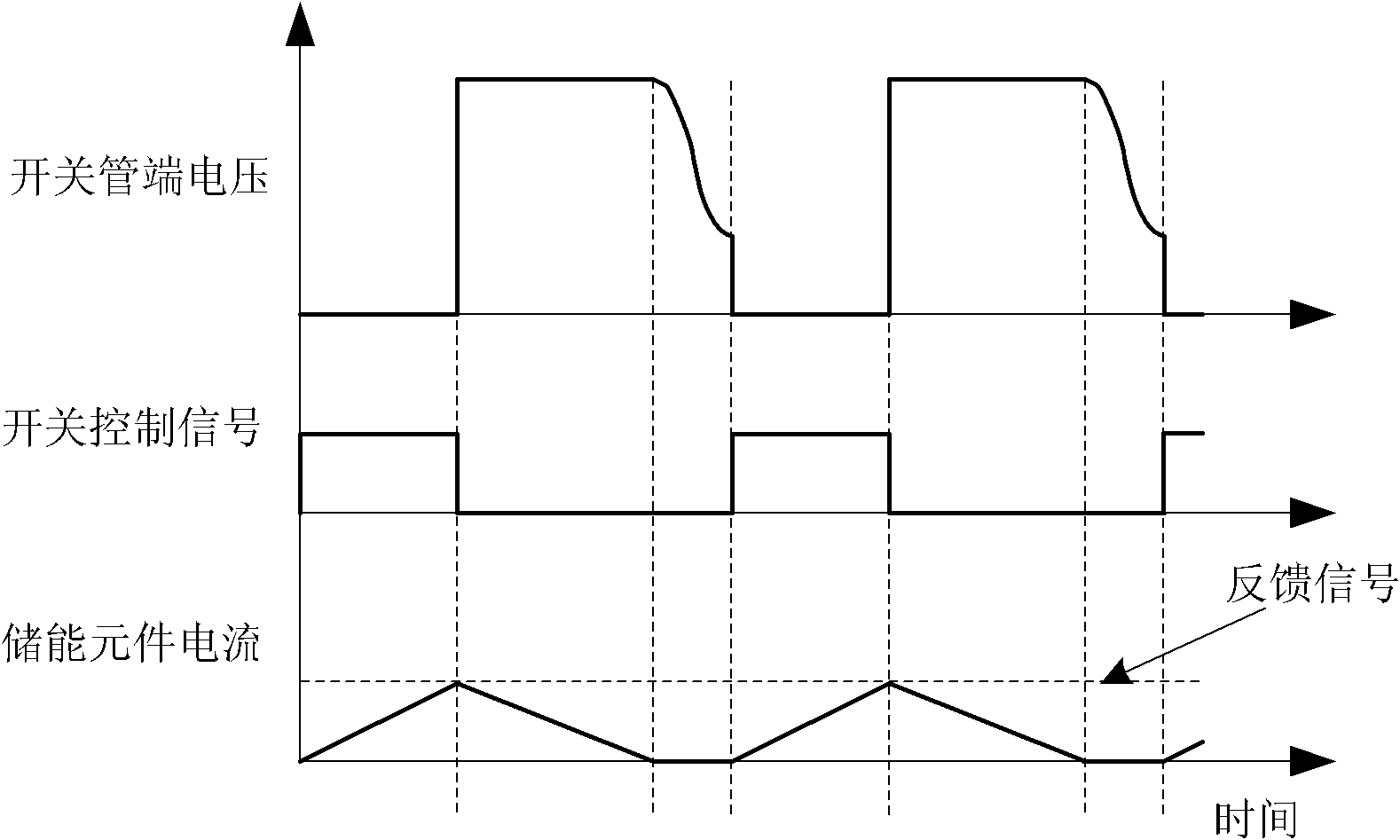
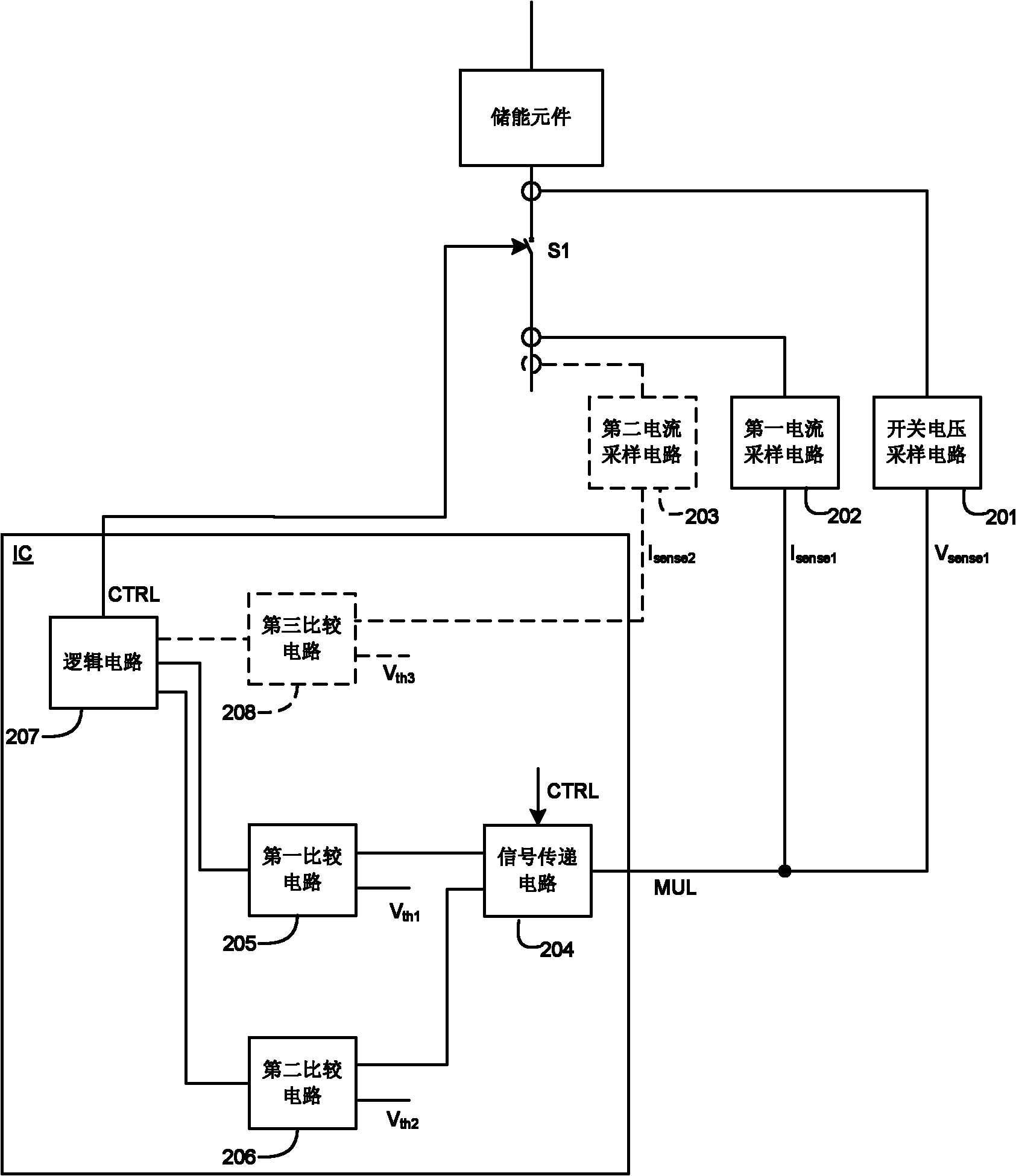
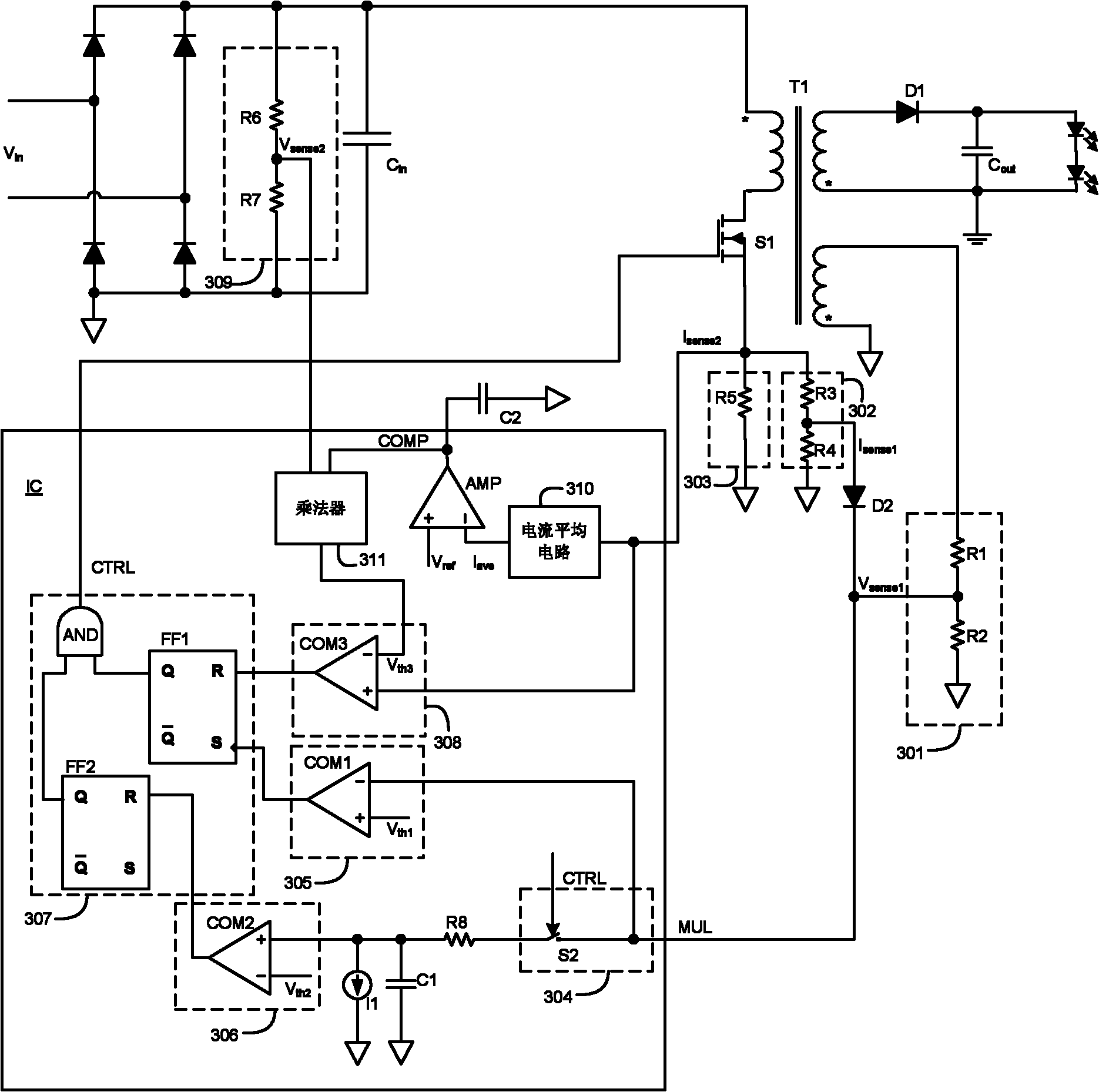
The invention discloses a switching power supply and a control circuit and method thereof. The control circuit is provided with multi-functional pins for receiving first current sampling signals and switching voltage sampling signals. The control circuit is used for comparing signals on the multi-functional pins with a second threshold value when a switching tube is switched on; and the control circuit is used for comparing the signals on the multi-functional pins with a first threshold value when the switching tube is switched off, thus controlling switch-on and switch-off of the switching tube. The control circuit is used for receiving second current sampling signals and switching off the switching tube when the second current sampling signals are more than a third threshold value. The first current sampling signals independent of the second current sampling signals are used for realizing overcurrent protection, thus the limited value of overcurrent can be adjusted, thereby providing sufficient protection for the switching power supply. In addition, the multi-functional pins are used for receiving the first current sampling signals and the switching voltage sampling signals simultaneously, thus simplifying the circuit and saving the cost and the volume.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Charging fault diagnosis and safety detection system and method of electric vehicle
InactiveCN109450006AImprove securityReduce workloadCharging stationsElectric powerOvervoltageOvercurrent
The invention discloses a charging fault diagnosis and safety detection system and method of an electric vehicle. The system comprises a BMS, a CAN wire, a VCU, a vehicle charger, a DC charging pile,an AC charging pile, a battery, a vehicle charging interface, a charging interface, a charging gun and a charging fault diagnosis and safety detection system, and the charging fault diagnosis and safety detection system comprises a signal acquisition unit, a national standard memory, a processing unit, a human-machine interaction interface and a relay. The method includes steps: the charging faultdiagnosis and safety detection system is externally connected between the vehicle charging interface and the charging interface of the charging gun, the connection to an electric vehicle charging system is realized through the CAN wire, and through collection of message information, acquired by the VCU, of the BMS and communication messages of the DC charging pile and the AC charging pile and comparison with an electric vehicle charging national standard, the reason of charging failure is determined, and charging is finished after occurrence of problems of overcurrent and overvoltage of charging. According to the system and the method, the charging detection efficiency and the charging security of electric vehicles can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power generation using batteries with reconfigurable discharge
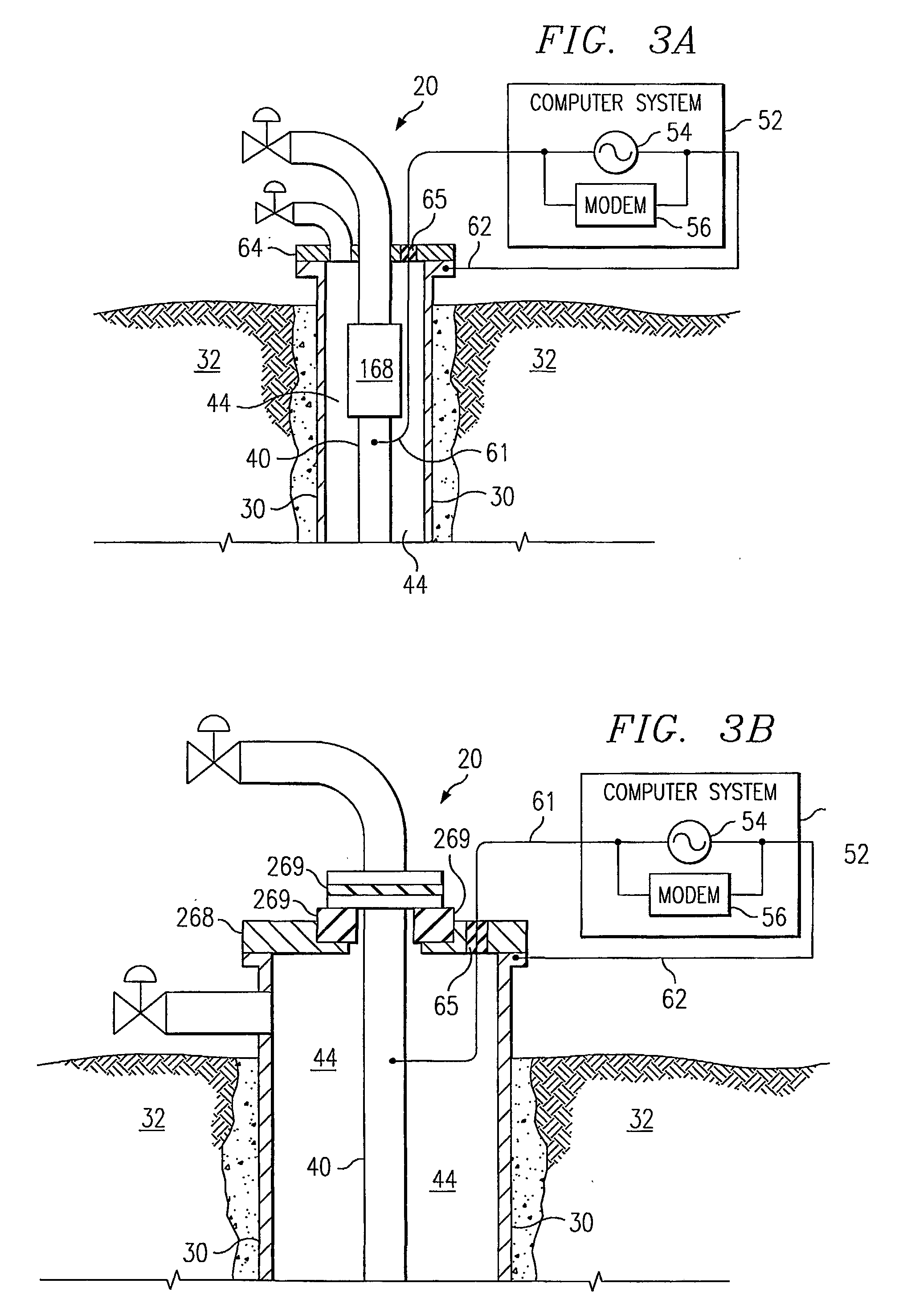
A petroleum well (20) for producing petroleum products that incoroprates a system adapted to provide power to a down-hole device (50) in the well (20). The system comprises a current impedance device (70) and a downhole power storage device (112). The current impedance device (70) is positioned such that when a time-varying electrical current is transmitted through the portion of a piping structure (30 and / or 40) a voltage potential forms between one side (81) of the current impedance device (70) and another side (82) of the current impedance device (70). The device (112) is adapted to be electrically connected to the piping structure (30 and / or 40) across the voltage potential formed by the current impedance device (70), is adapted to be recharged by the electrical current, and is adapted to be electrically connected to the downhole device (50) to provide power to the downhole device (50) as needed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Display device and its driving method
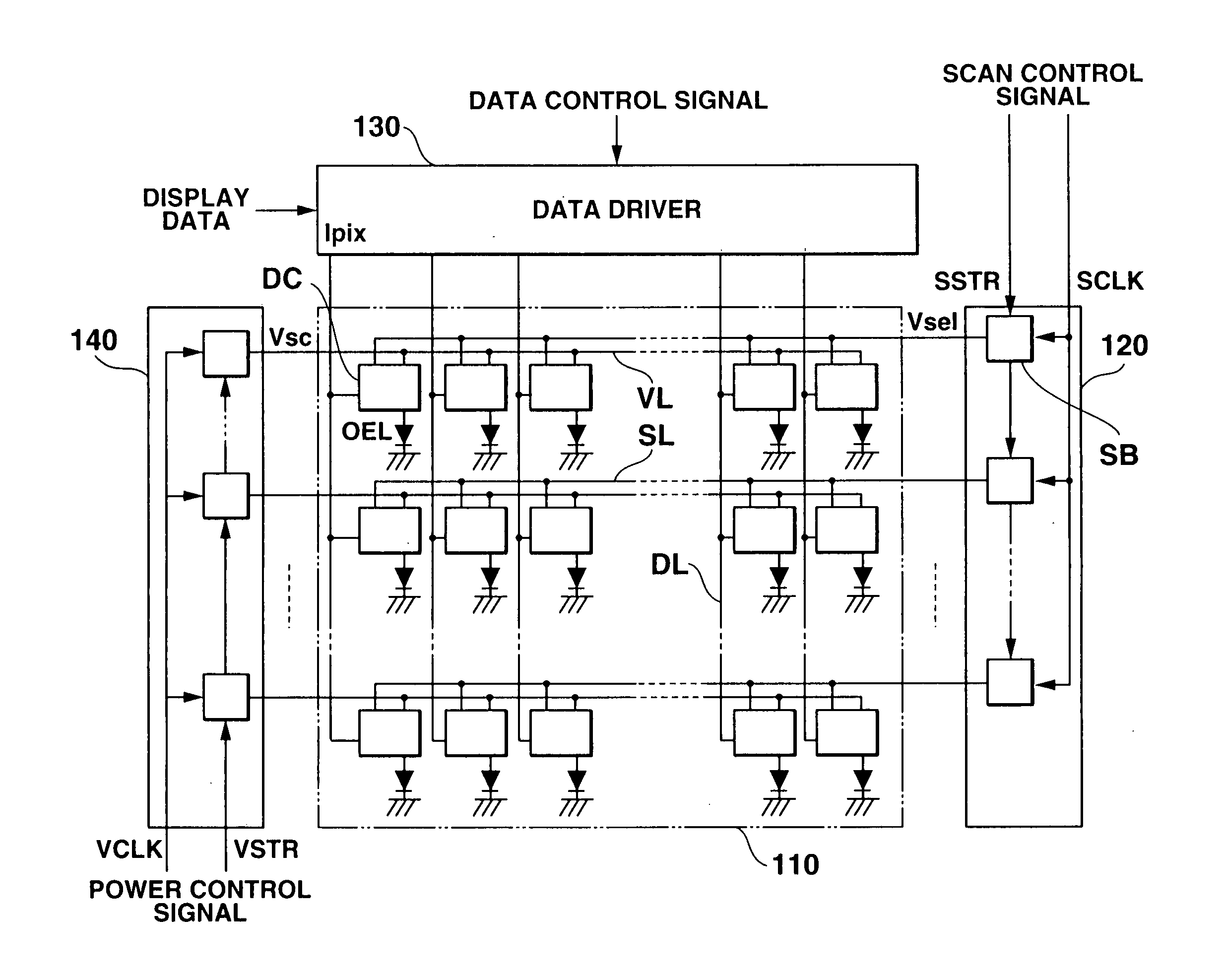
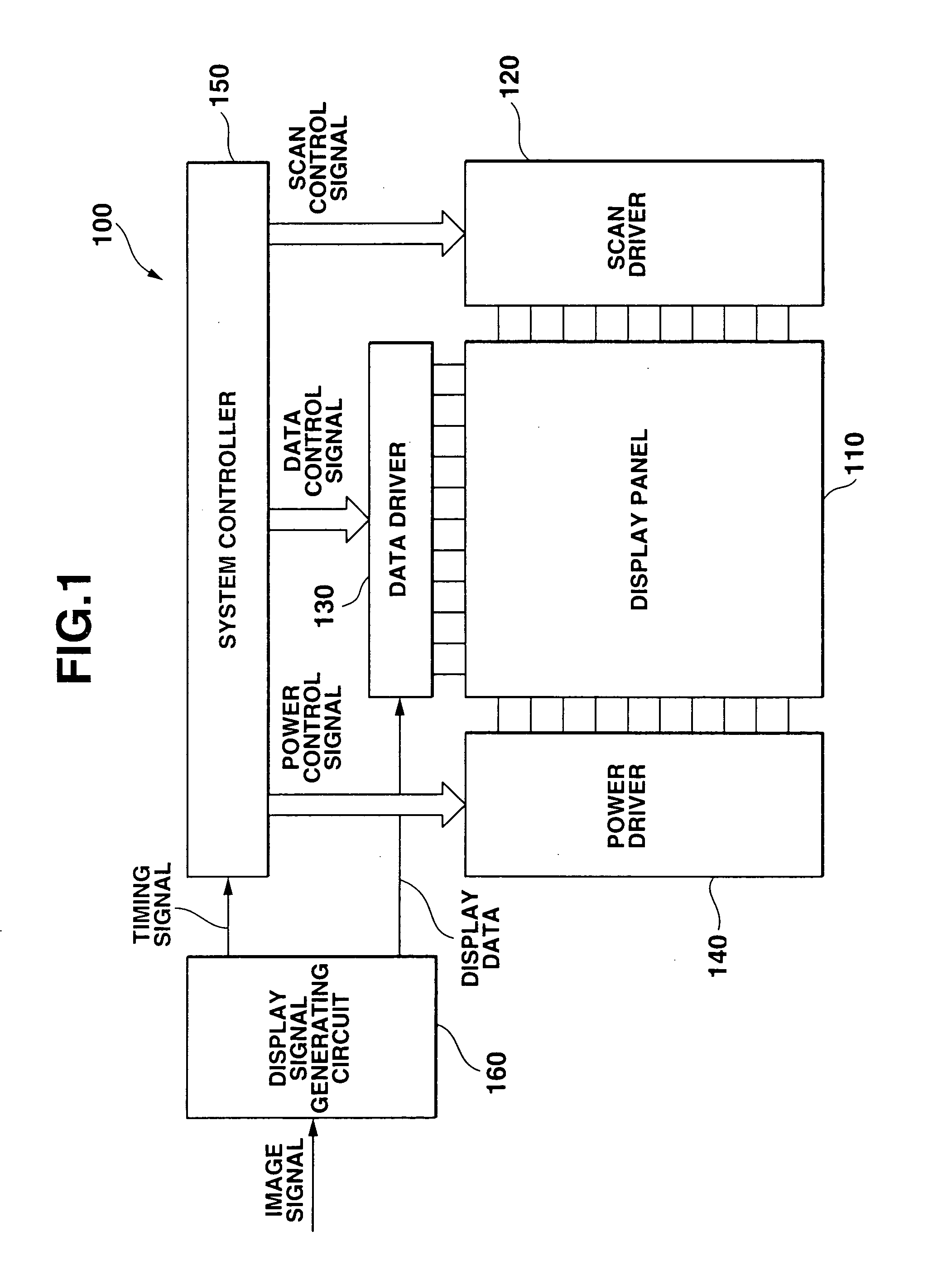
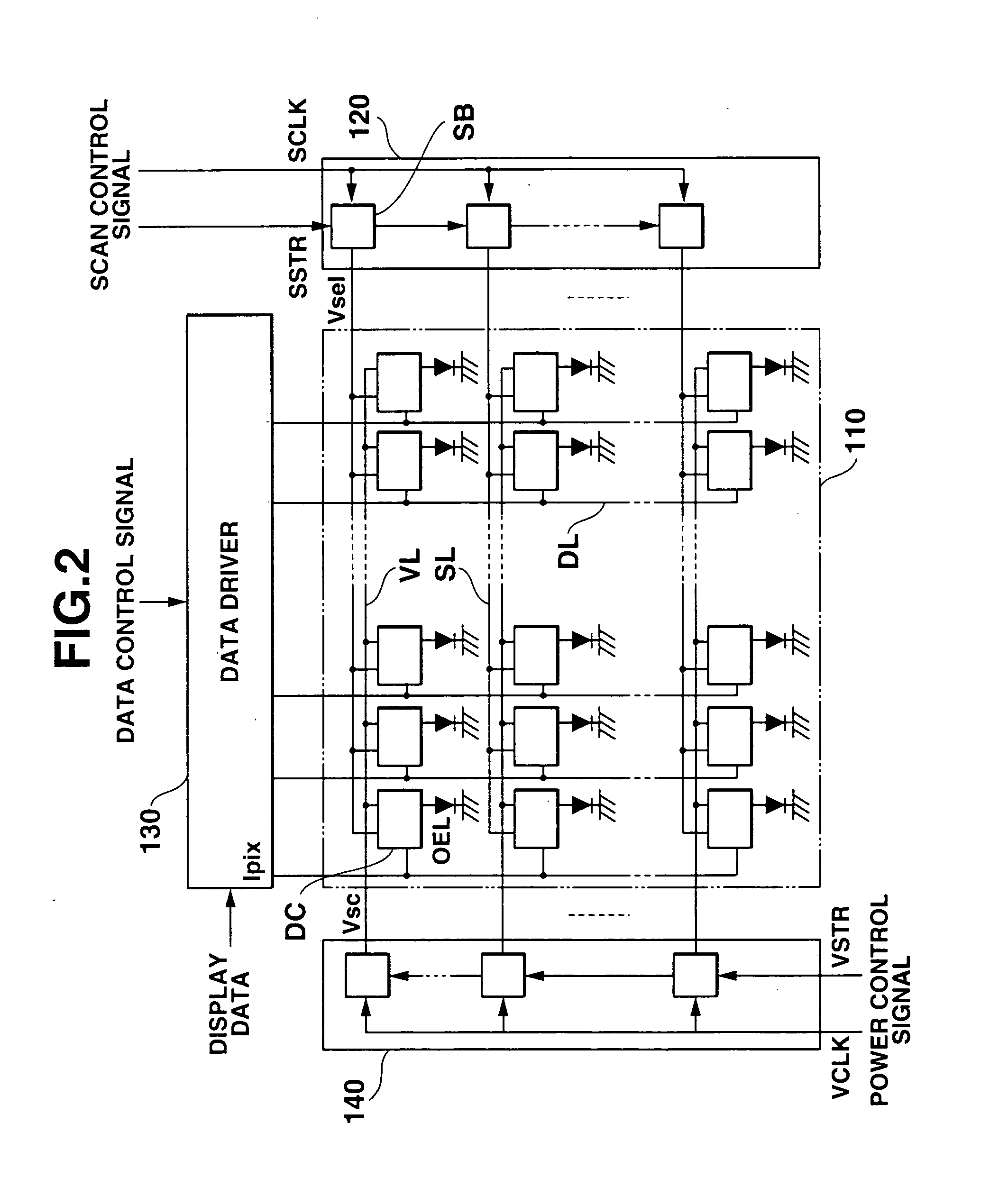
ActiveUS20050225518A1Good display qualitySuppress increase in power consumptionStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesWrite currentEngineering
A display panel (110) comprises a plurality of optical elements (OEL) each having a pair of electrodes and performing an optical operation according to current passing between the pair of electrodes, a current line (DL), a switch circuit (Tr2) that passes a write current (Ia) with a predetermined current value through the current line (DL) during a selection time (Tse) and stops passing current during a non-selection time (Tnse), and a current storage circuit (Tr1, Tr2, Cs, Cp) that stores current data according to the current value of the write current (Ia) passing through the current line (DL) during the selection time (Tse) and that supplies a drive current (Ib) having a current value, which is obtained by subtracting a predetermined offset current (Ioff) from the current value of the stored write current (Ia), to the optical elements (OEL) during the non-selection time (Tnse). The current storage circuit (Tr1, Tr2, Cs, Cp) includes a first capacitor device (Cs) to which an electrical charge corresponding to the write current (Ia) is written and a second capacitor device (Cp) to which an electrical charge corresponding to offset current (Ioff) is written, and the second capacitor device (Cp) has a capacitive value, which is equal to or larger than the first capacitor device (Cs).
Owner:SOLAS OLED LTD
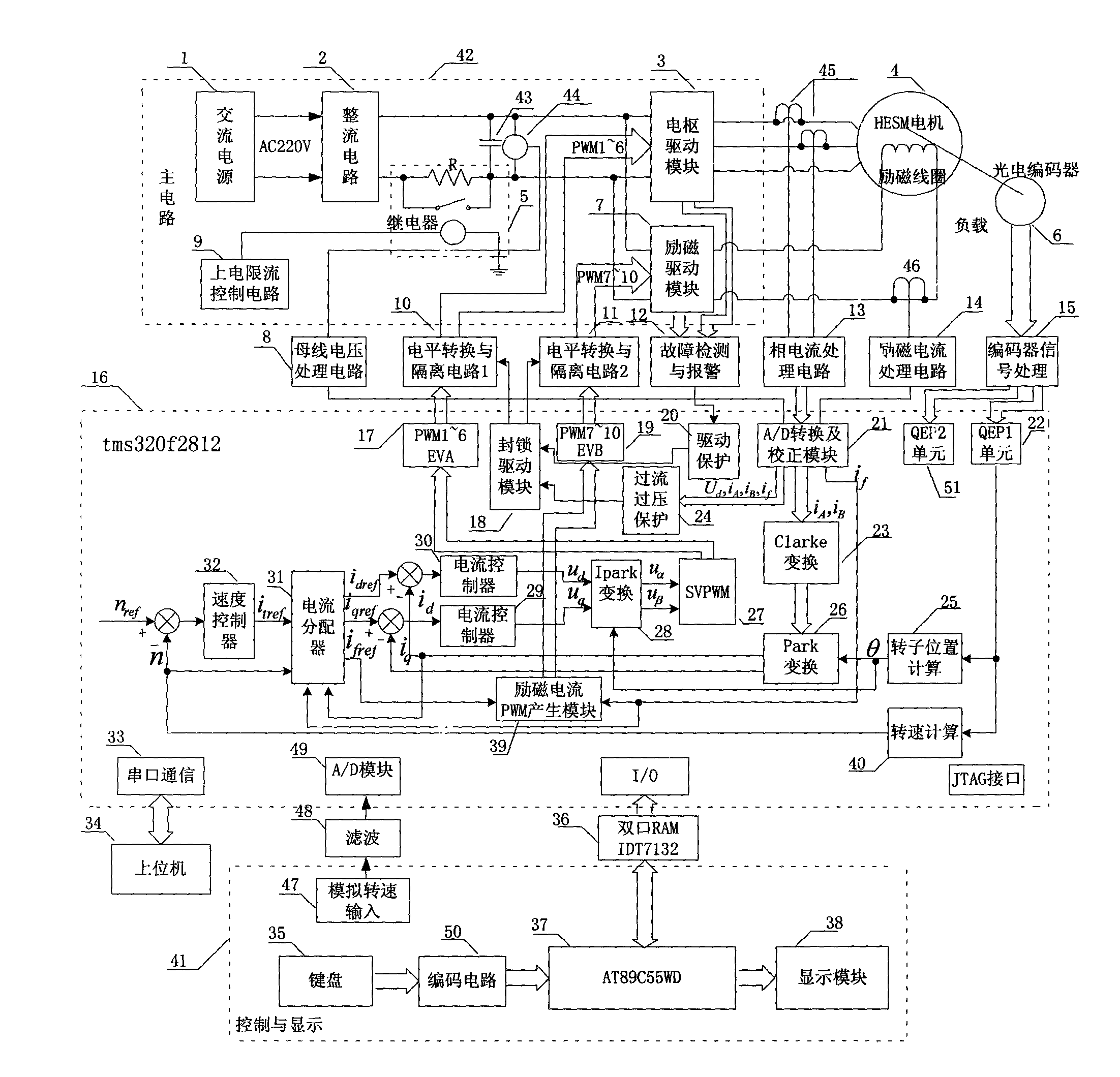
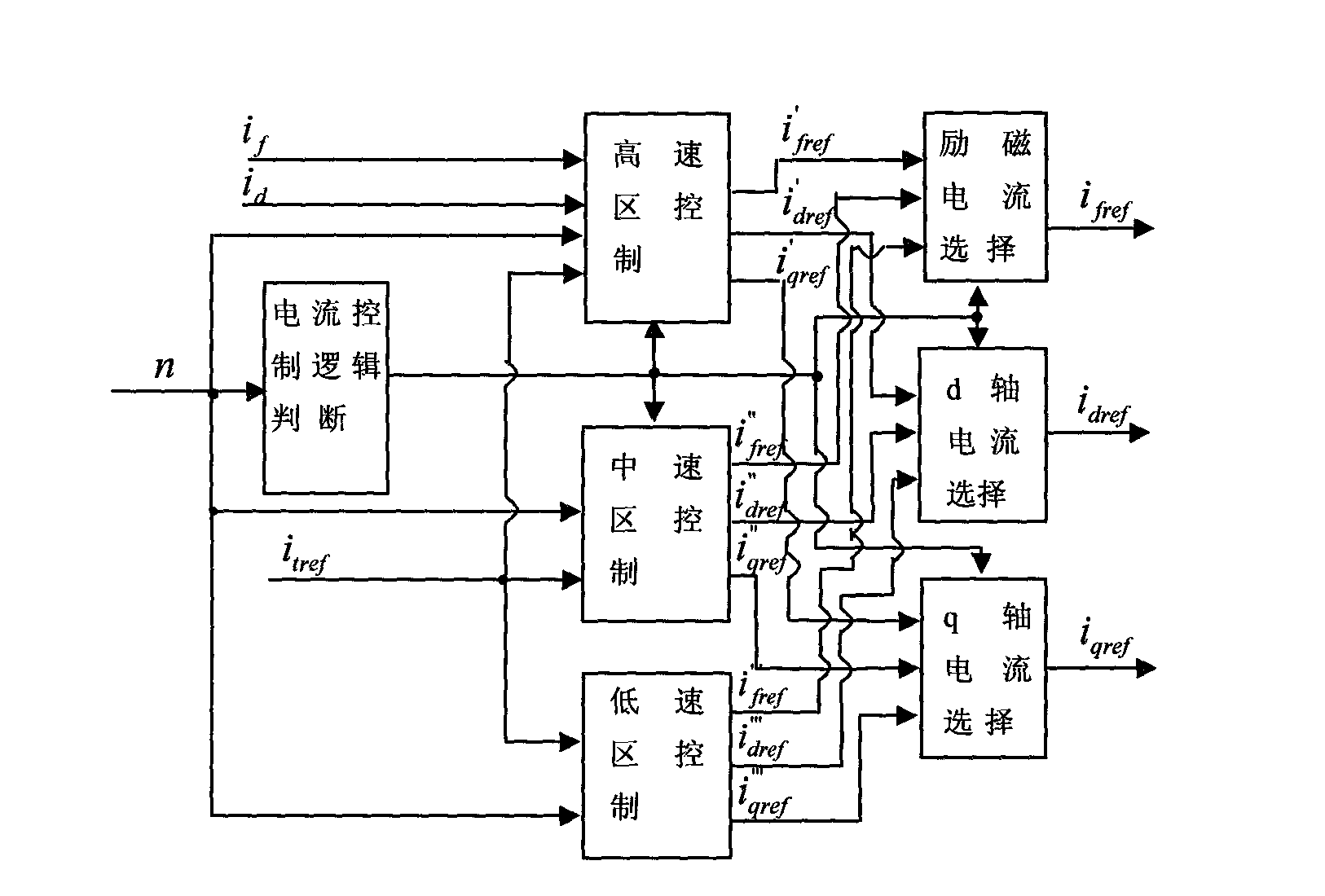
Wide range speed control system and current distribution method for hybrid excitation synchronous machine
InactiveCN102324882AIncrease starting torqueShort transition timeVector control systemsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsLow speedConstant power
The invention discloses a wide range speed control system and current distribution method for a hybrid excitation synchronous machine. A control policy is applied to armature drive and excitation drive simultaneously. When the motor is in the starting period, a rated forward magnetism strengthening current is applied to the exciting winding to increase the starting torque of the motor, so that the motor obtains electromagnetic torque exceeding the rated torque under the condition of no overcurrent, and the transition time of motor starting is shortened. When the motor is in the low speed operating interval, if the motor load exceeds the rated load, the electromagnetic torque of the motor is increased by applied the forward magnetism strengthening current, so that the motor obtains excessive loading capacity under the condition of no overcurrent and no overheat. When the motor operates at high speed, a constant power operating interval far above the rated rotating speed can be obtainedby applying an appropriate reverse exciting current to HESM (Hybrid Excitation Synchronous Machine) and performing weak magnetic regulation on the d-axis armature current.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
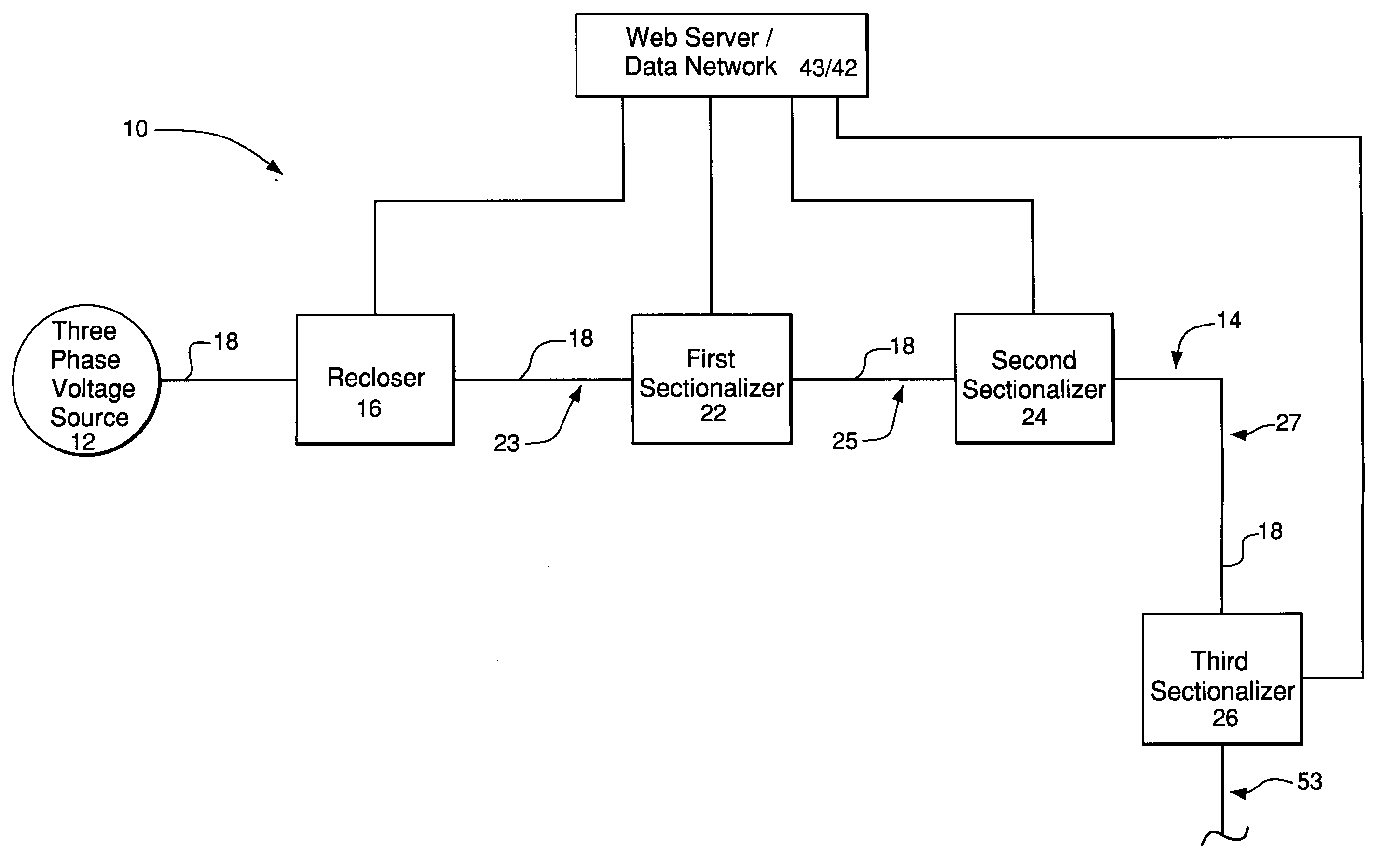
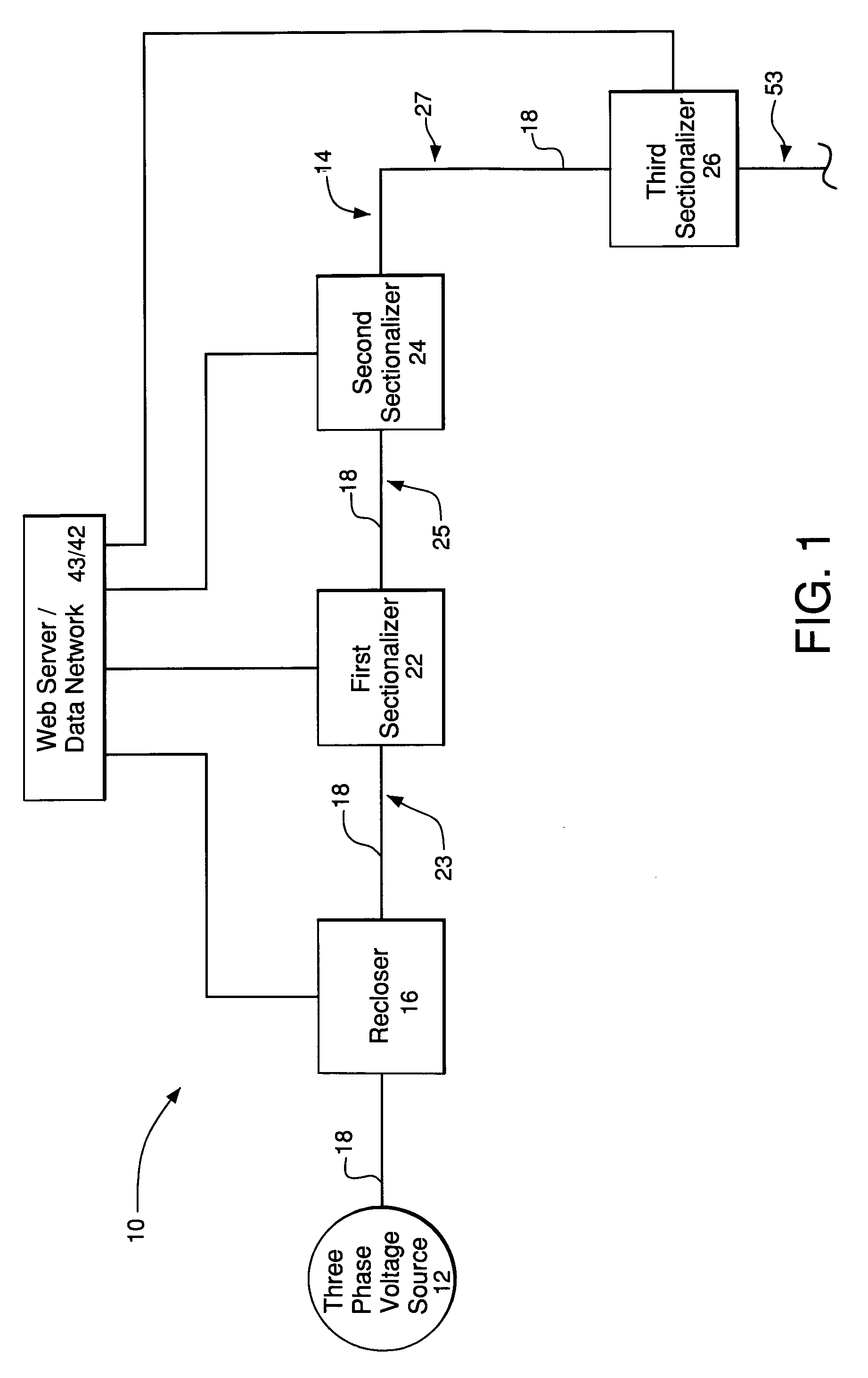
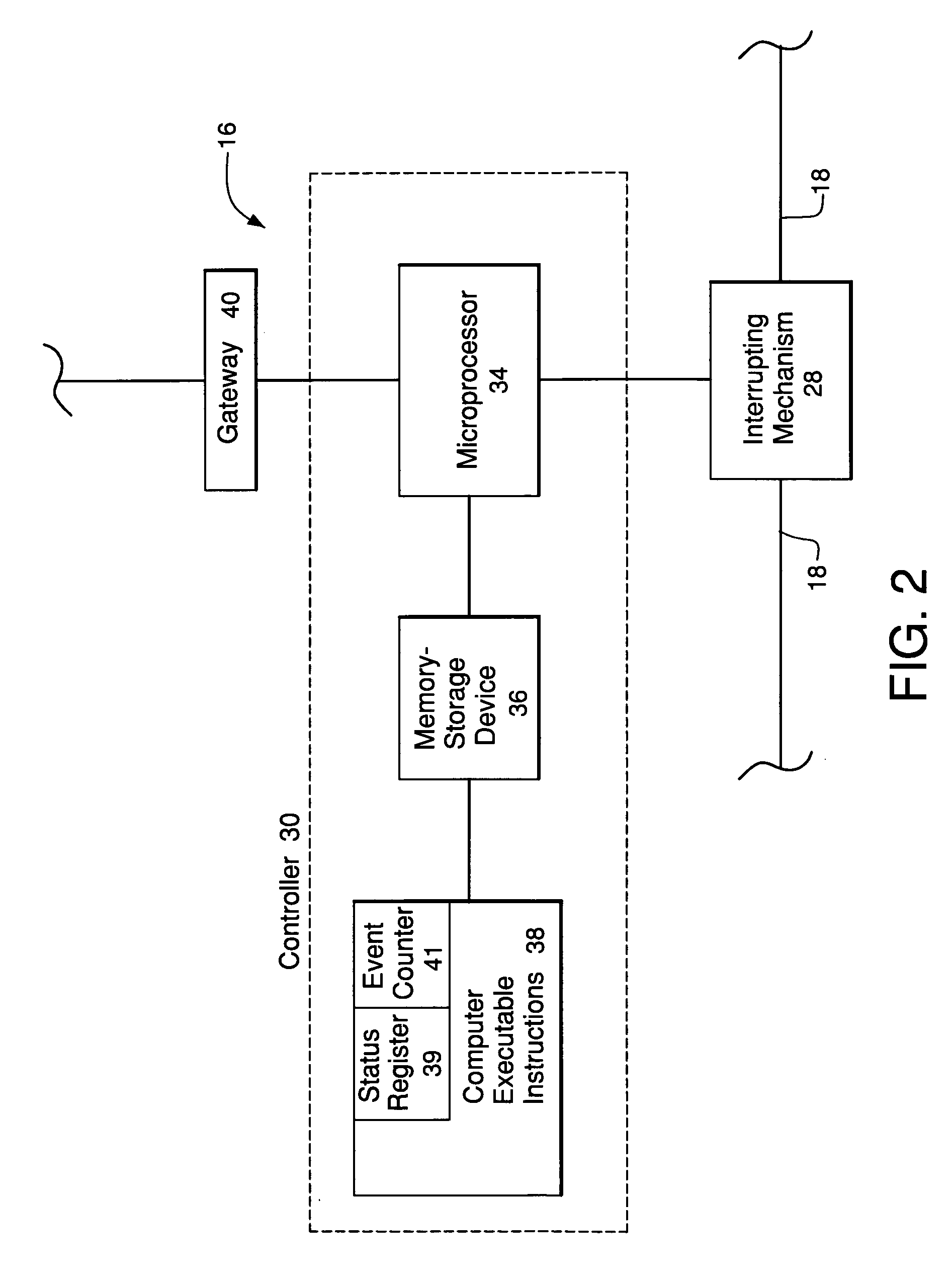
Adaptive protection system for a power-distribution network
ActiveUS7110231B1Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionFeeder lineOvercurrent
A preferred embodiment of a system comprises a recloser electrically coupled to a voltage source of a power-distribution network and adapted to isolate a section of a distribution feeder of the power-distribution network from the voltage source in response to an overcurrent condition in the section of the distribution feeder. The system also comprises a sectionalizer electrically coupled to the section of the distribution feeder. The sectionalizer and the recloser are adapted to communicate via a data network and the recloser is responsive to control inputs sent to the recloser from the sectionalizer over the data network.
Owner:ABB INC
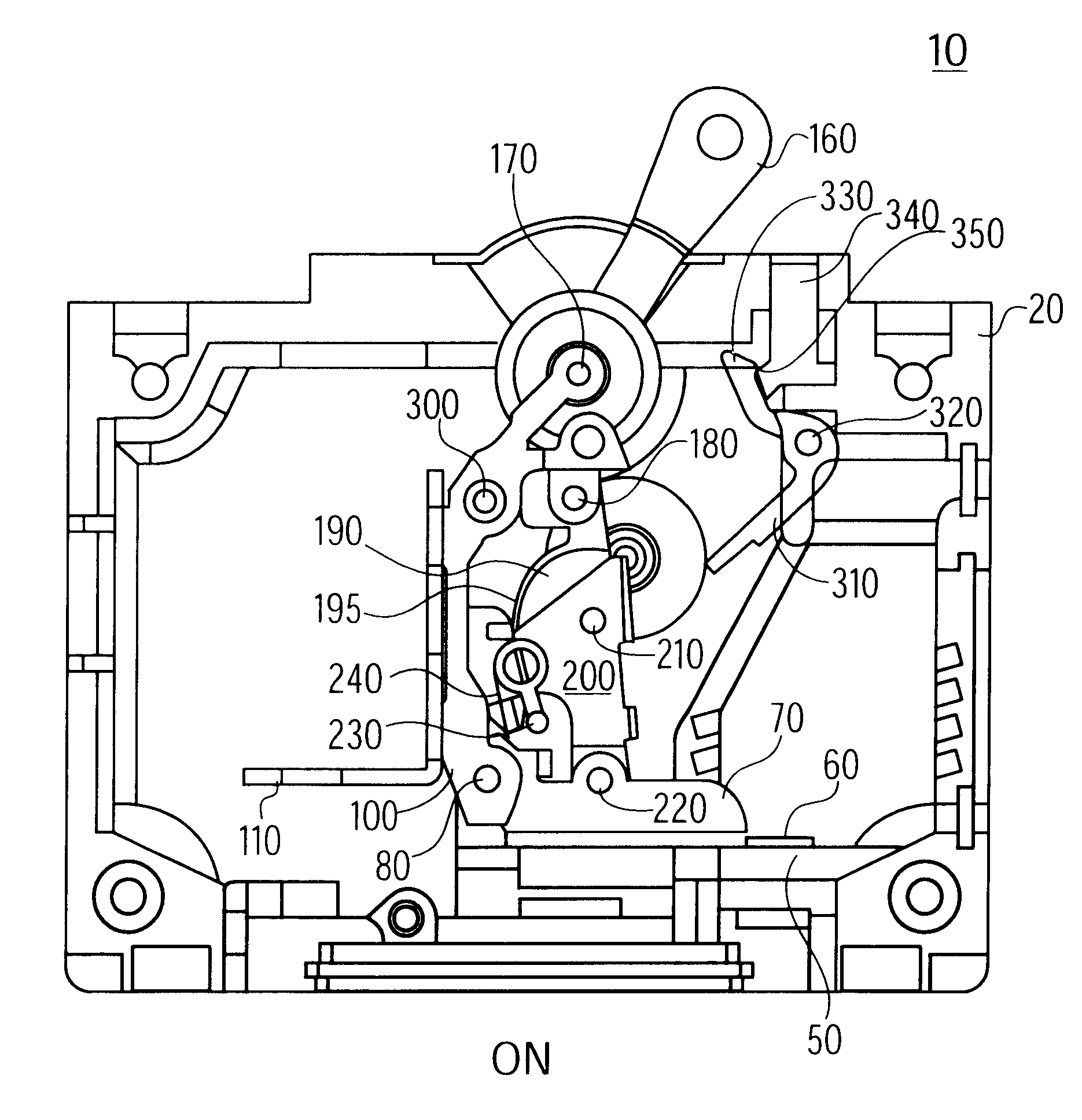
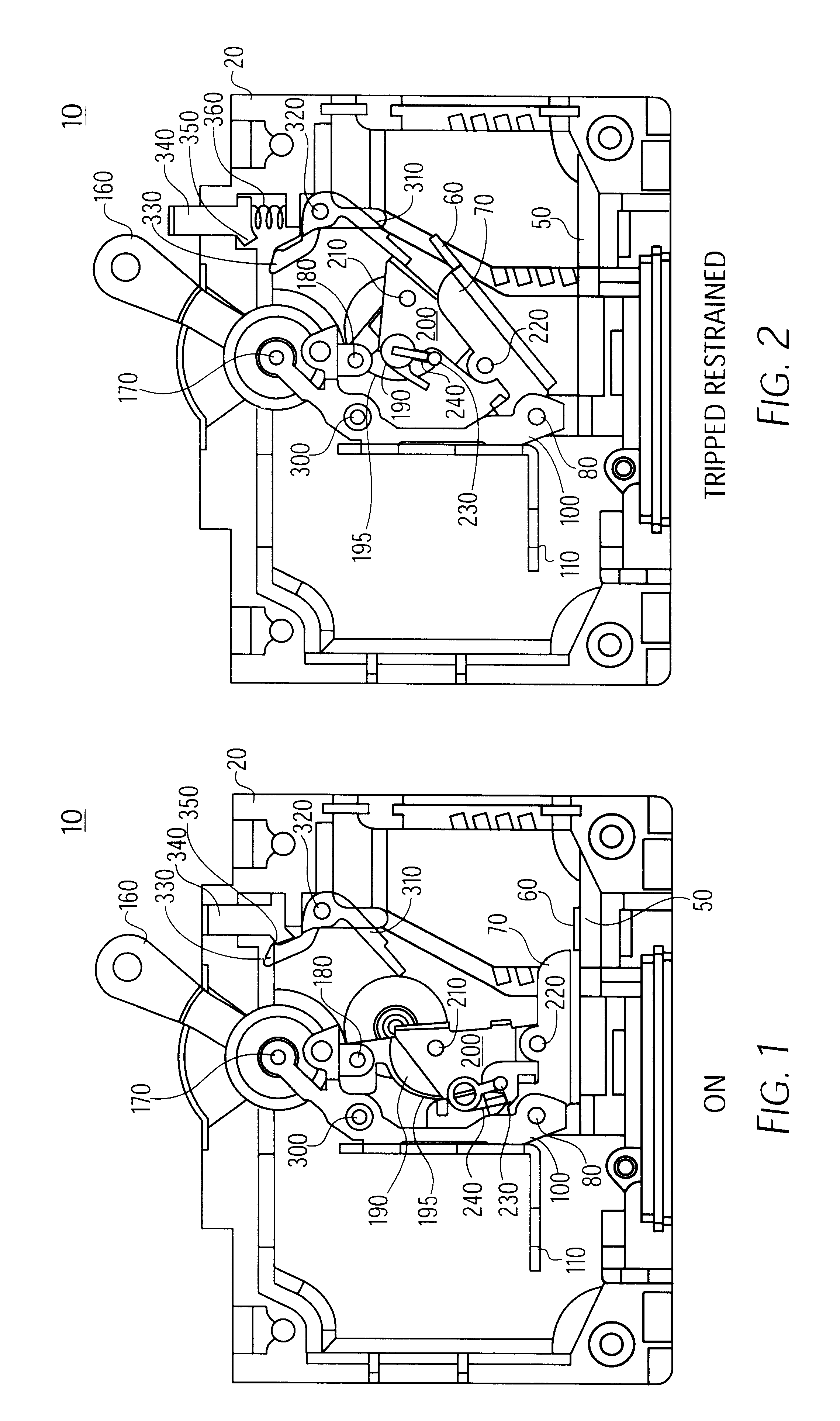
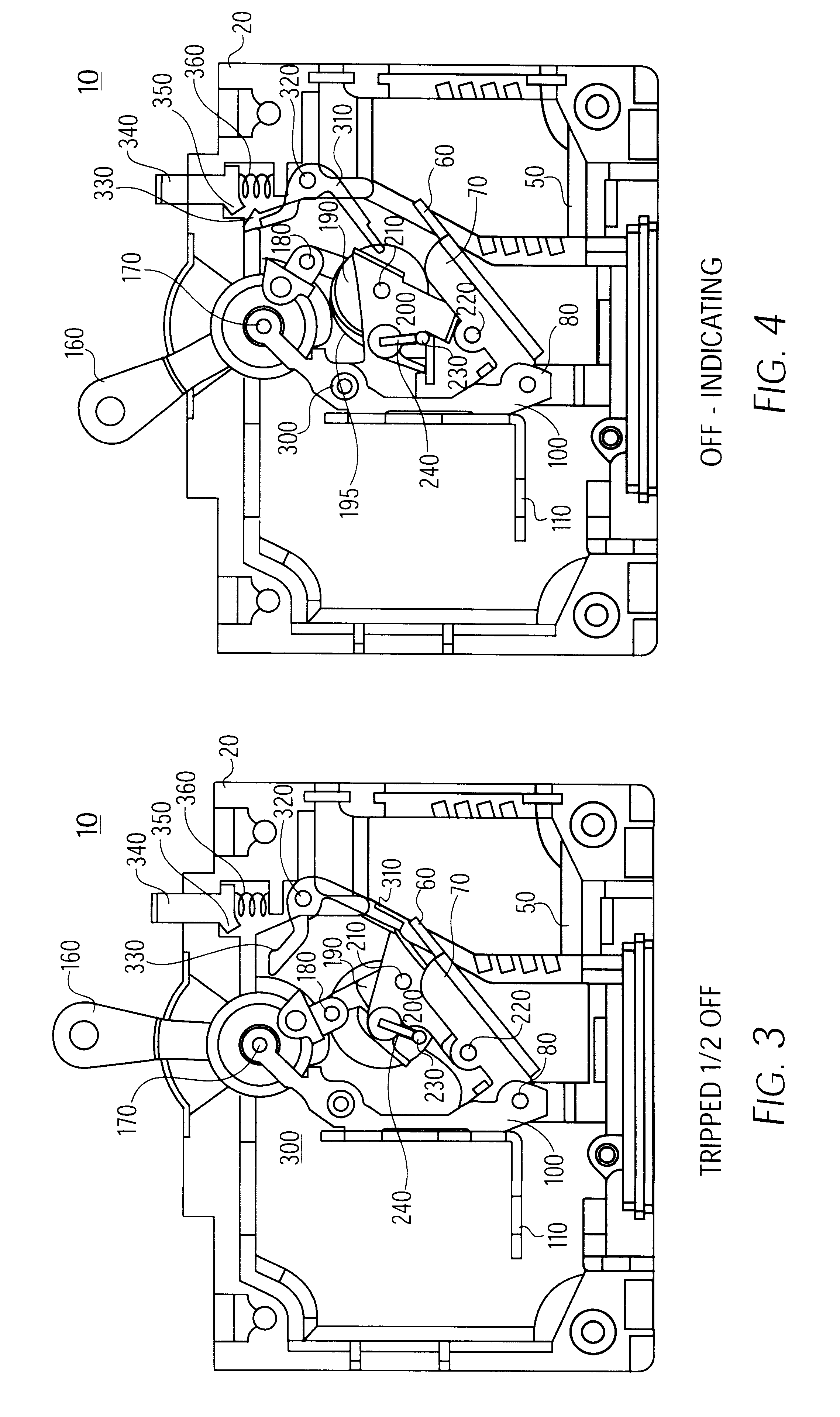
Trip indicating circuit breaker
A circuit breaker having an external trip indicator, having a circuit breaker housing, a trip mechanism within the housing, sensing a trip condition and being responsive thereto to mechanically break an electrical circuit, an indicator, having a selectively operable retaining mechanism and being biased outward from the circuit breaker housing, and a linkage, sensing a trip condition of the trip mechanism and selectively releasing the selectively operable retaining mechanism to allow the indicator to move outwardly from the housing. The external trip indicator is operated by sensing an overcurrent condition with the trip mechanism, breaking the electric circuit in response to the overcurrent, sensing a mechanical movement of the trip mechanism, and thereby releasing a positional restraint on the mechanical indicator; and allowing the mechanical indicator to protrude from the housing. The external trip indicator is reset by first resetting the trip mechanism and then displacing the mechanical indicator into the housing.
Owner:AIRPAX
Battery module
ActiveCN101997131AImprove securityCurrent conducting connectionsSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsOvercurrentShort circuit
A battery module including a plurality of rechargeable batteries including a case and terminals protruding outside of the case; a first connecting member electrically connecting first terminals of neighboring rechargeable batteries and including a fuse unit configured to disconnect the first terminals of the neighboring rechargeable batteries when an overcurrent is generated; a plurality of second connecting members electrically connecting second terminals of the neighboring rechargeable batteries to terminals of connected rechargeable batteries; and a shorting member configured to generate a short circuit by connecting neighboring second connecting members to each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD +1
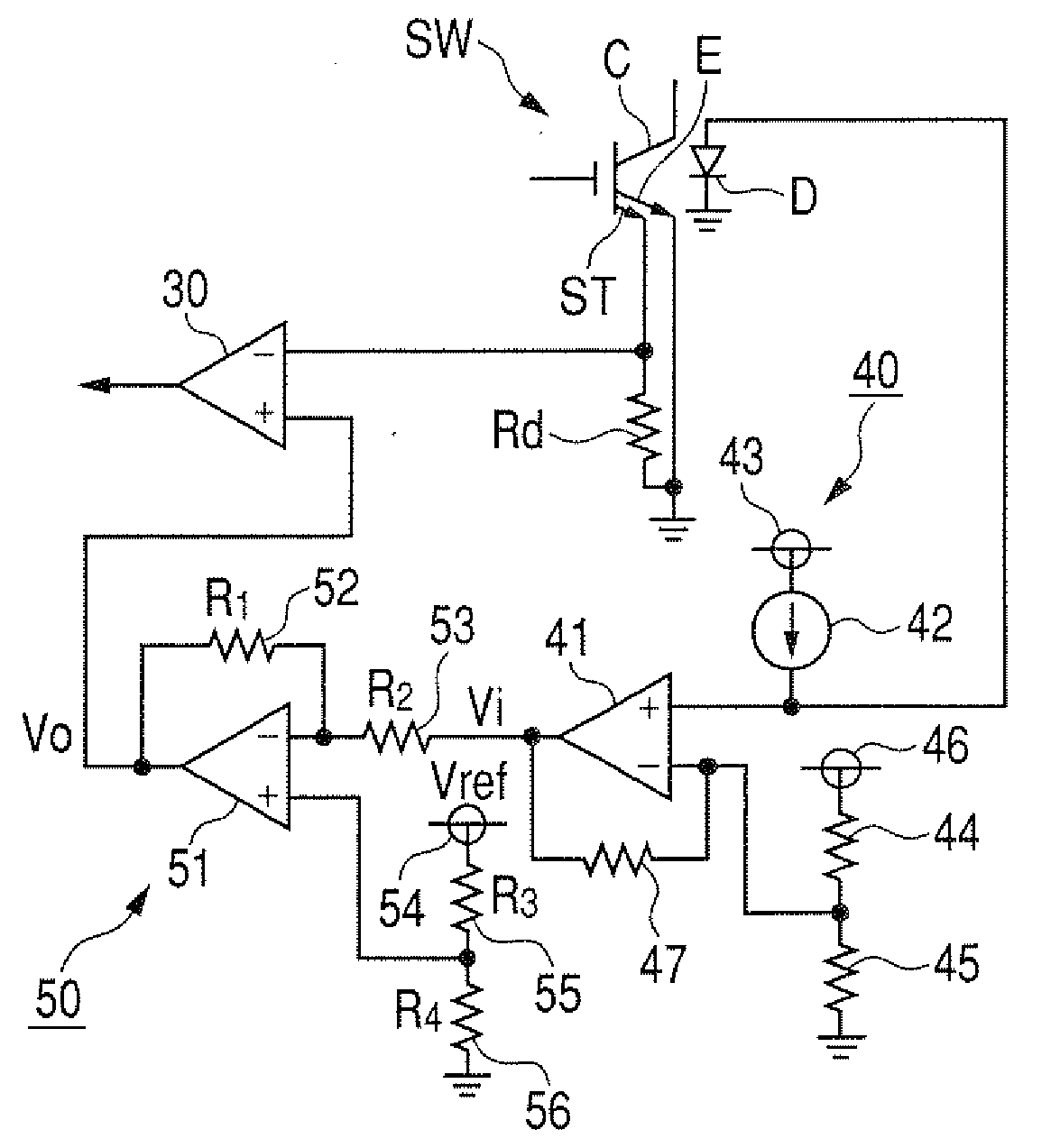
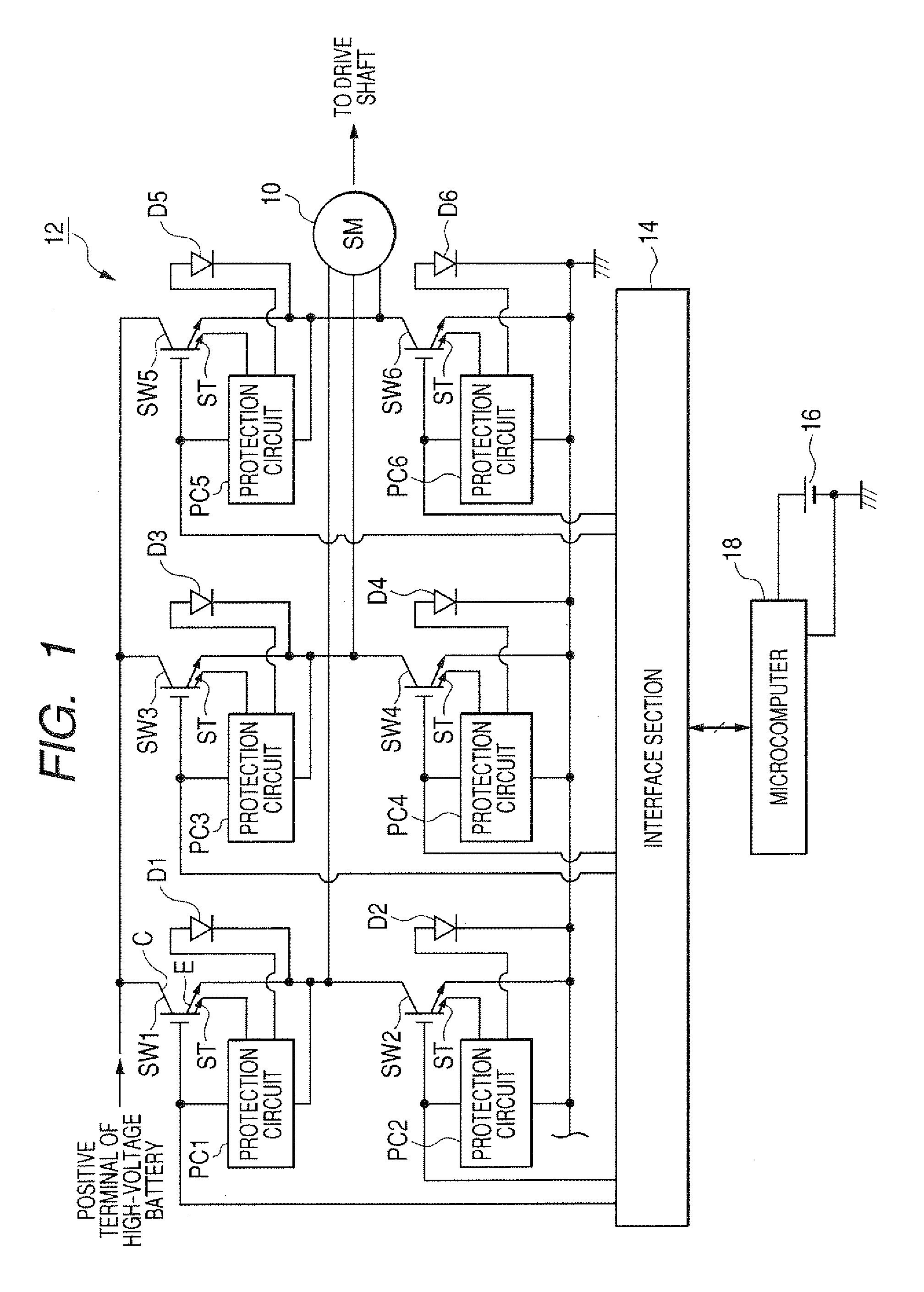
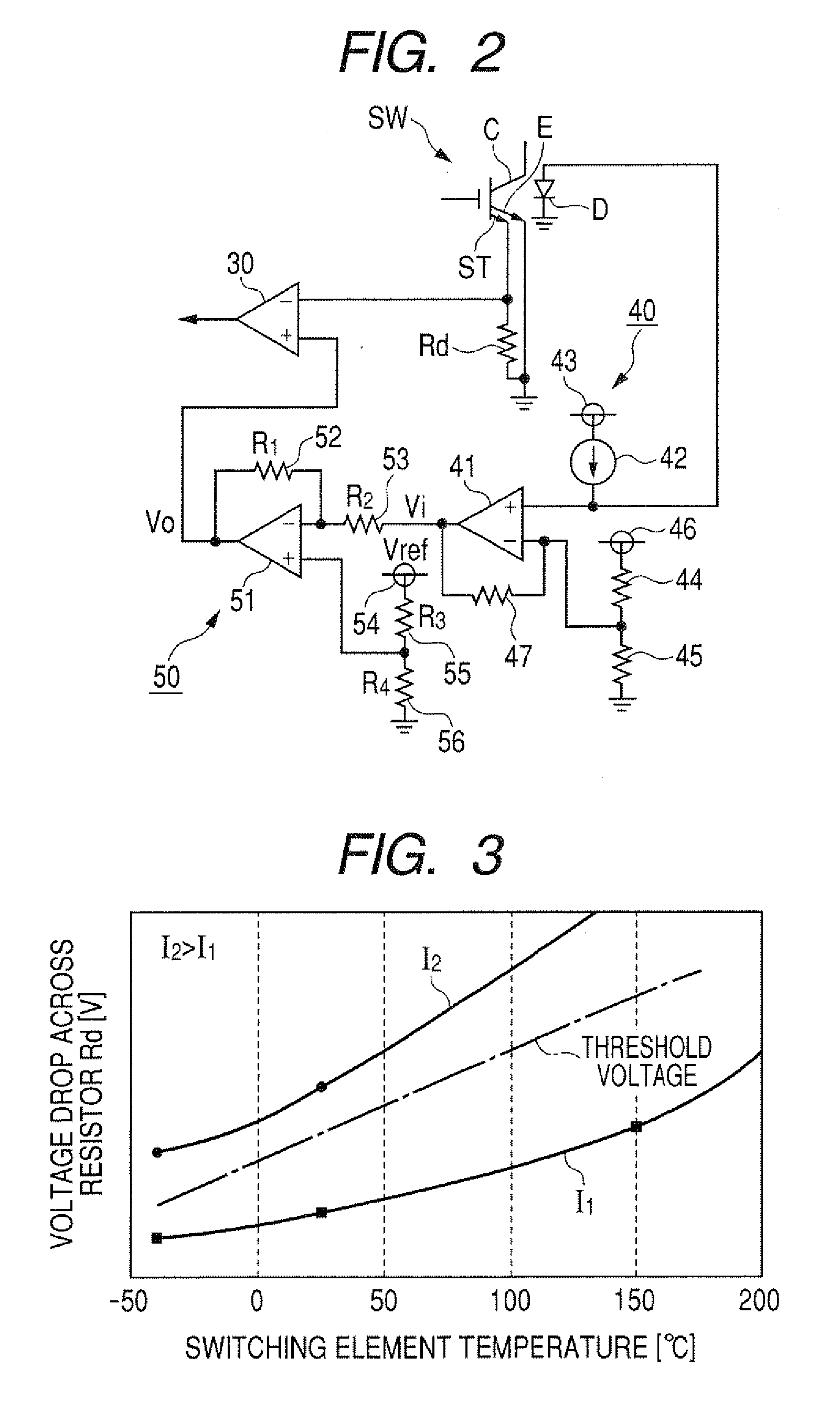
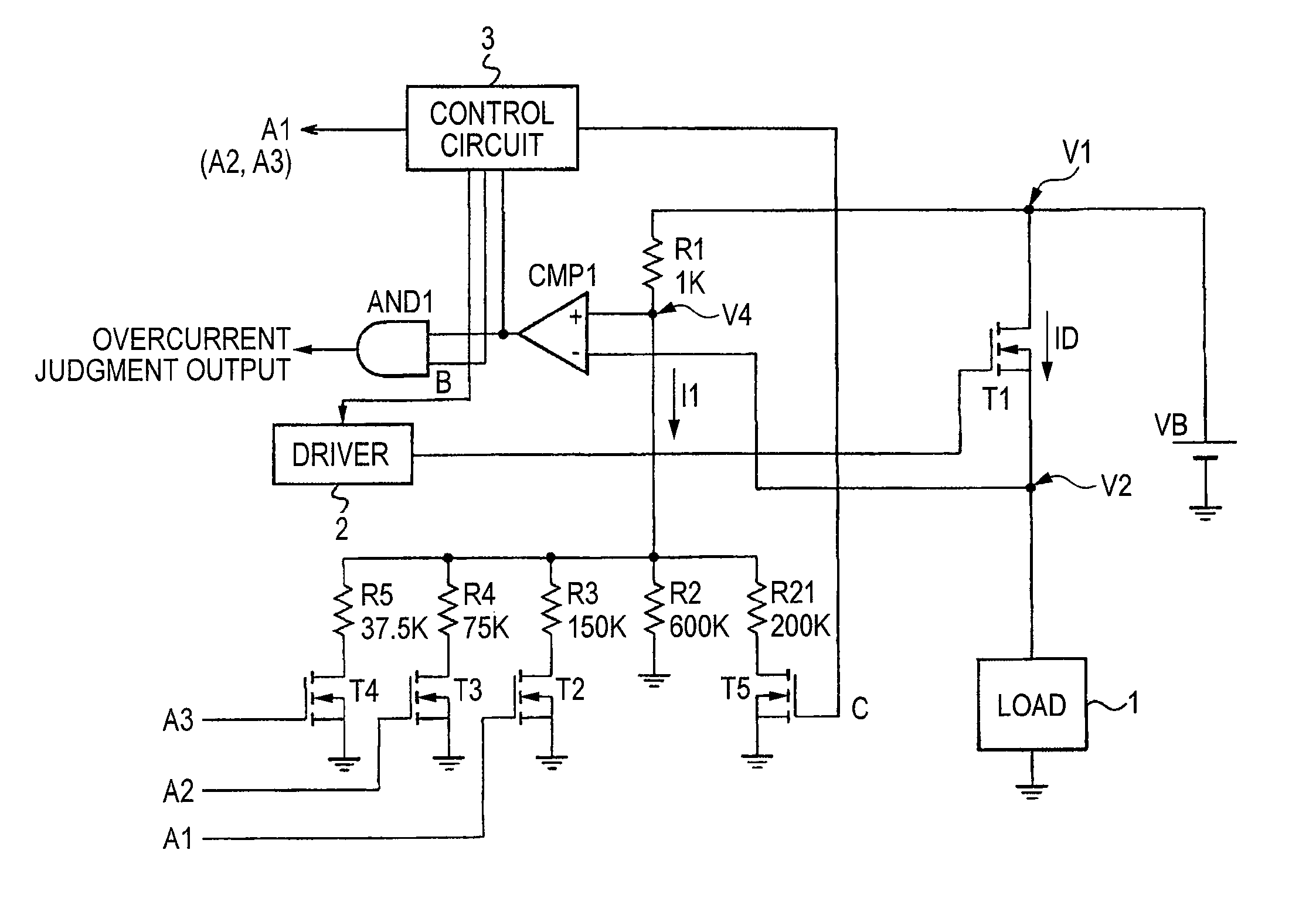
Switching element overcurrent protection circuit which operates within a high-voltage system that incorporates the switching element
ActiveUS20080100978A1Simple circuit configurationMade preciselyElectronic switchingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionOvercurrentEngineering
A circuit for detecting excessive current flow through a switching element derives an electrical quantity relating to a condition of the switching element and correlated with the current level, and compares the magnitude of that electrical condition quantity with a threshold value corresponding to the maximum allowable level of current. A temperature detection signal indicative of the switching element temperature is converted to a compensation signal having a temperature characteristic which is modified from that of the temperature detection signal, and which is utilized to compensate the magnitude comparison operation against inaccuracy caused by a temperature dependency of the electrical condition quantity.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Load driving device with diagnosing unit for overcurrent detector
InactiveUS7457089B2Improve protectionPrevent erroneous overcurrent detectionParameter calibration/settingTransistorOvercurrentSemiconductor
A load driving device for controlling a driving and a stop of a load through on / off switching of a semiconductor device under the control of a driving circuit, includes an overcurrent detecting unit that compares, with a prescribed judgment voltage, an inter-electrode voltage which is generated when a current flows between a first electrode and a second electrode of the semiconductor device, and judges that an overcurrent is flowing through the semiconductor device when the inter-electrode voltage is higher than the judgment voltage, and a diagnosing unit that performs a diagnosis as to whether the overcurrent detecting unit is operating normally in a state that the semiconductor device is a on-state. When the diagnosing unit judges that the overcurrent detecting unit is not operating normally, the diagnosing unit outputs an instruction signal for turning off the semiconductor device, to the driving circuit.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
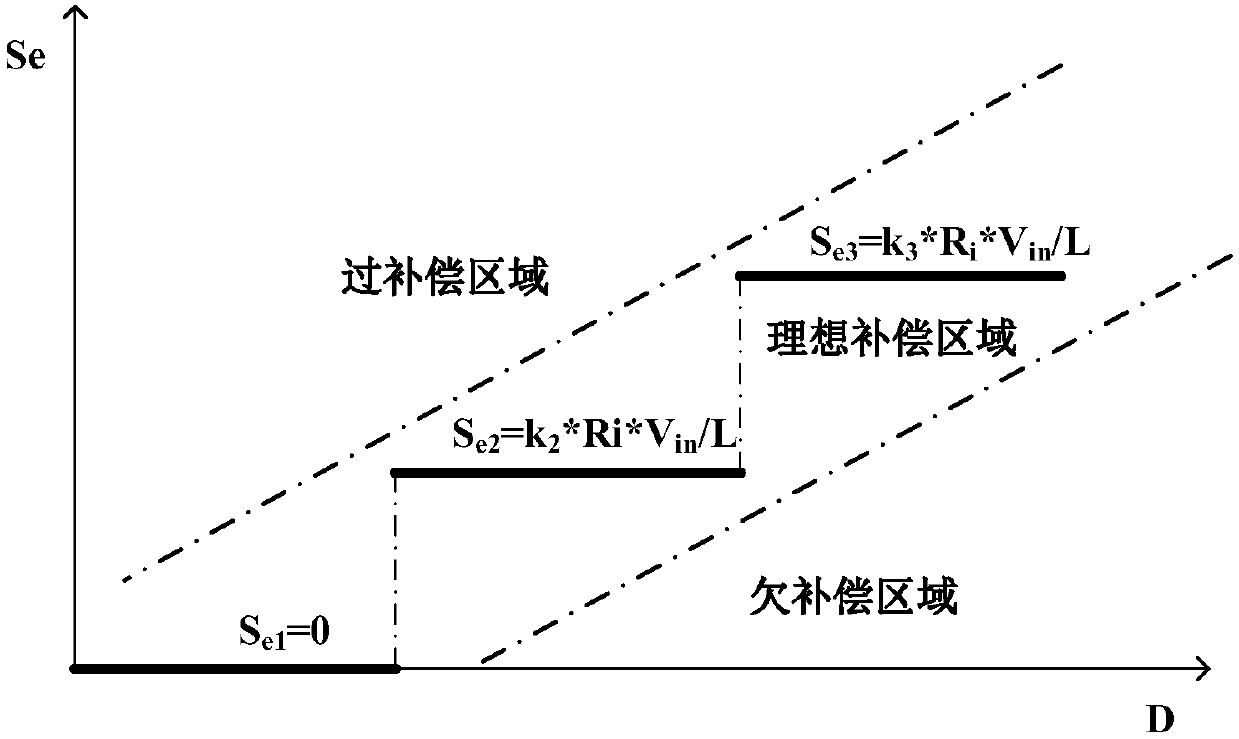
Segmented slope compensation circuit applicable to BUCK converter
ActiveCN107707103AHigh precisionStable jobAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPower conversion systemsCapacitanceSystem stability
A segmented slope compensation circuit applicable to a BUCK converter belongs to the technical field of an electronic circuit. An oscillator circuit is used for introducing output voltage informationof the BUCK converter, a negative input end voltage of an operational amplifier is clamped to a positive input end voltage thereof, a first capacitor is charged by a current mirror, the negative inputend voltage, namely a slop voltage signal, of the operational amplifier is obtained, the slop voltage signal is compared with a second reference voltage to obtain a periodic slope voltage signal, a slope current generation circuit is used for generating compensation slopes with different slope rates under different duty ratios, a slope voltage correlated to the duty ratios is generated on a sampling resistor after passing through a slope summing circuit, and a base current compensation circuit is used for stabilizing a system. Compared with a traditional slope compensation circuit, the segmented slope compensation circuit has the advantages that the system stability is improved by employing different slope compensation rates under different duty ratios; and with the adoption of a triode as a buffer, the segmentation accuracy is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Load driving device
InactiveUS20070103832A1Prevent erroneous overcurrent detectionImprove protectionTransistorParameter calibration/settingOvercurrentDevice material
A load driving device for controlling a driving and a stop of a load through on / off switching of a semiconductor device under the control of a driving circuit, includes an overcurrent detecting unit that compares, with a prescribed judgment voltage, an inter-electrode voltage which is generated when a current flows between a first electrode and a second electrode of the semiconductor device, and judges that an overcurrent is flowing through the semiconductor device when the inter-electrode voltage is higher than the judgment voltage, and a diagnosing unit that performs a diagnosis as to whether the overcurrent detecting unit is operating normally in a state that the semiconductor device is a on-state. When the diagnosing unit judges that the overcurrent detecting unit is not operating normally, the diagnosing unit outputs an instruction signal for turning off the semiconductor device, to the driving circuit.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
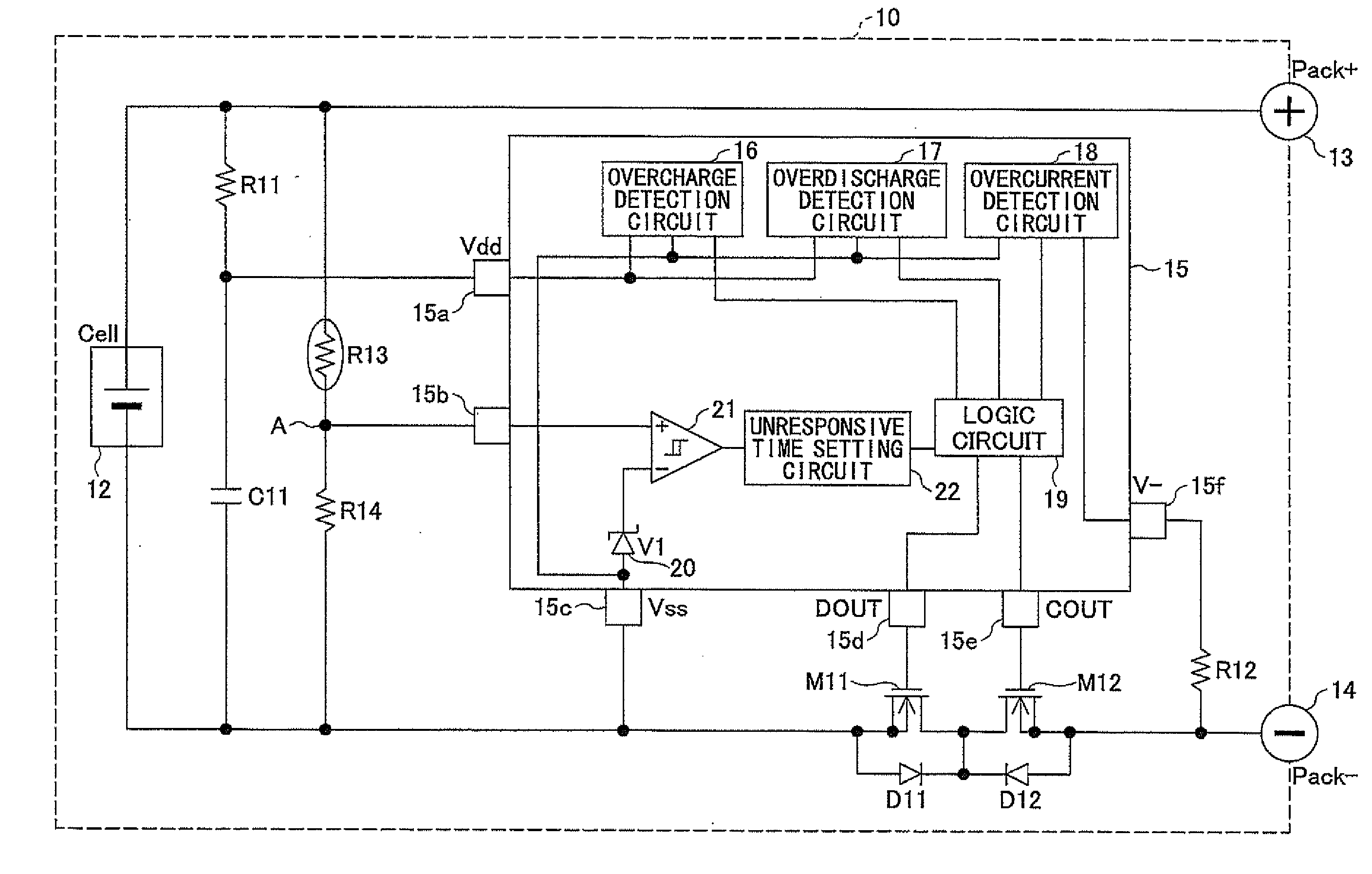
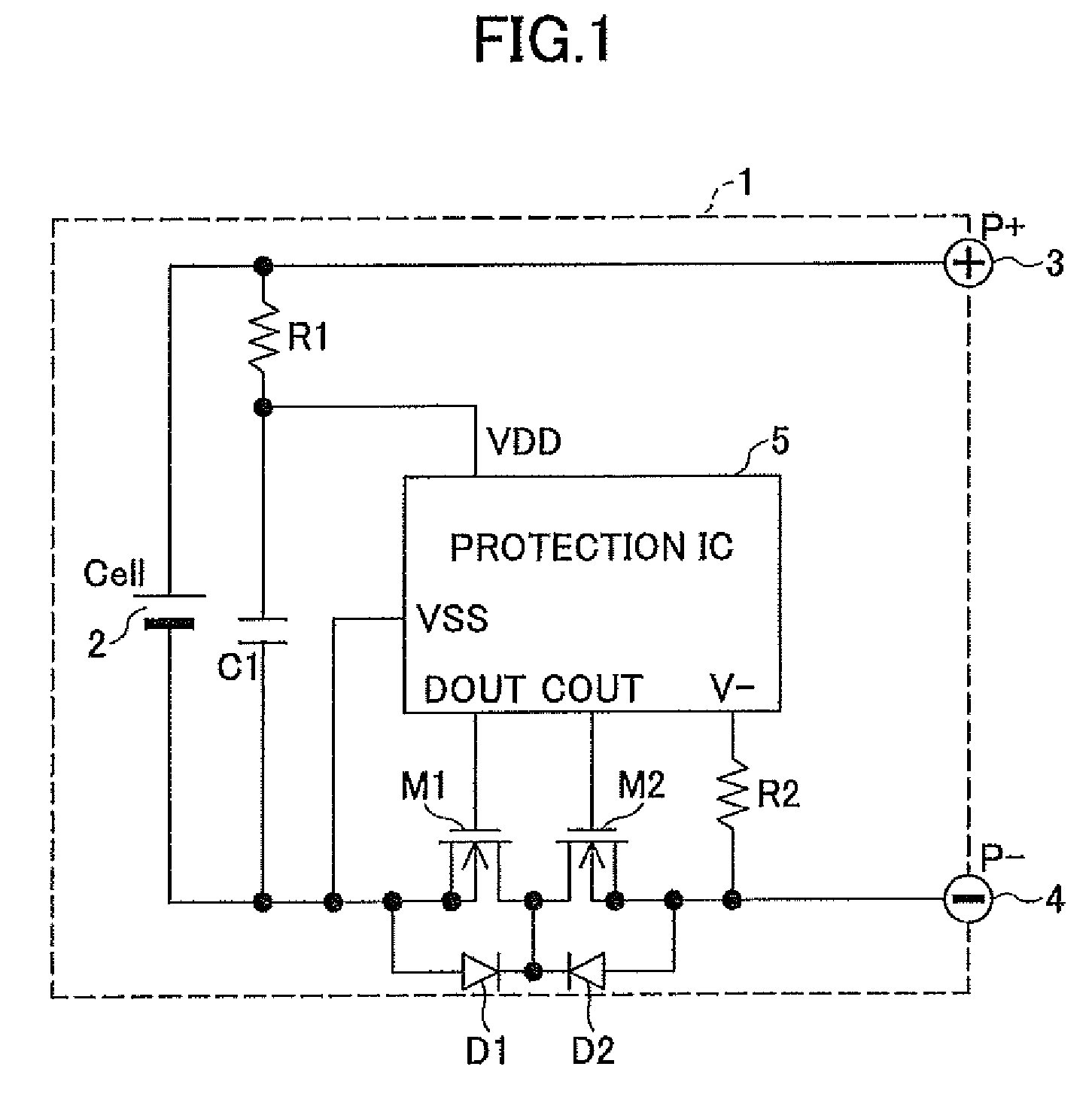
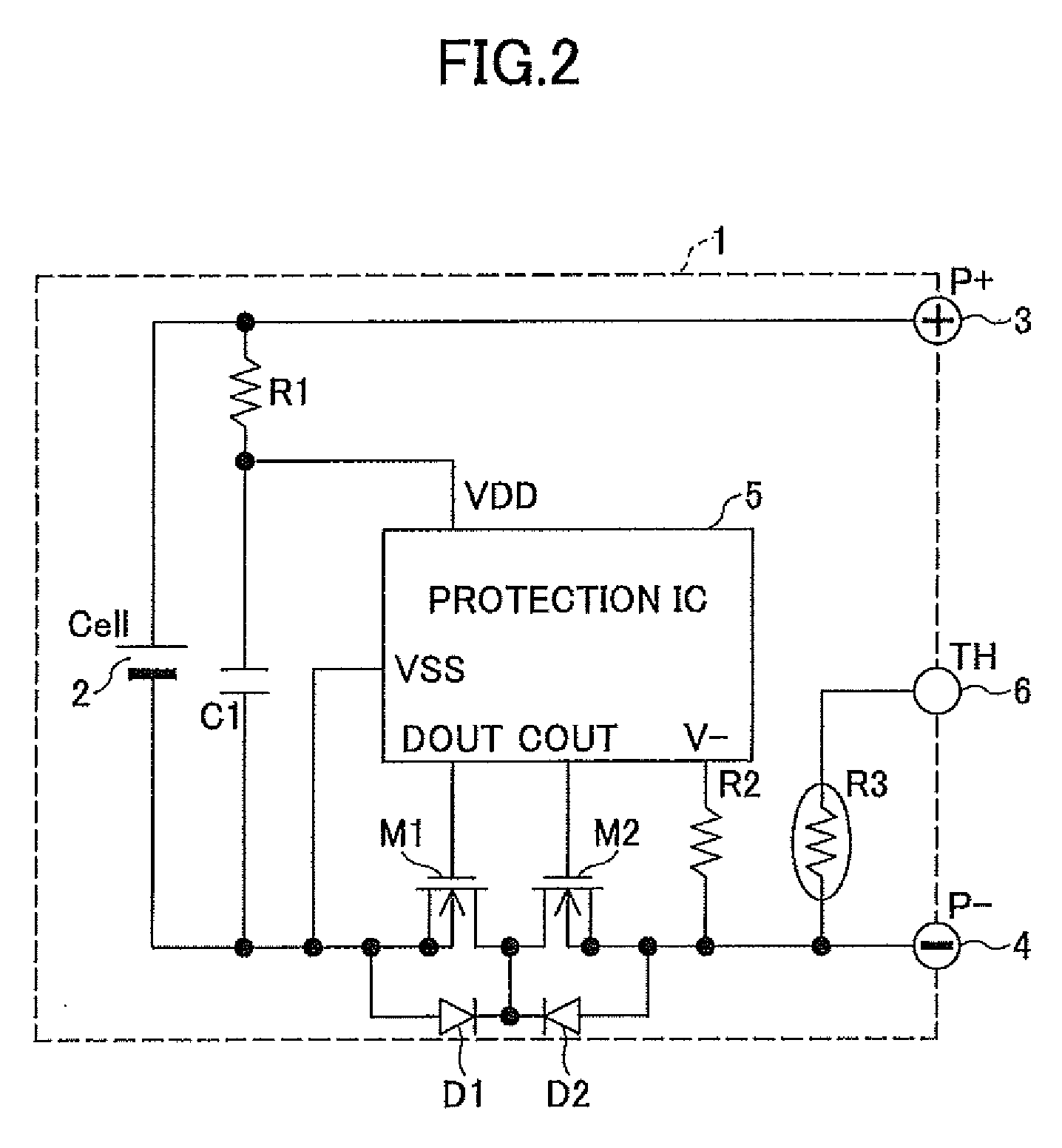
Battery Pack Having Protection Circuit for Secondary Battery
A battery pack has first through third external terminals connected to positive and negative power supply terminals and a voltage detection terminal, respectively. A secondary battery is connected between the first external terminal and the third external terminal. A protection circuit controls ON / OFF of first and second switching elements provided on a wiring between the secondary battery and a load or a charge device by detecting an overcharge, an overdischarge and an overcurrent of the secondary battery. A first thermistor is connected between the second external terminal and the third external terminal. A series circuit containing a second thermistor and a resistor is provided in parallel to the secondary battery. A third switching element is connected between the second external terminal and the third external terminal. The protection circuit turns on the third switching element and short-circuits between the second external terminal and the third external terminal when a detection is made by the second thermistor that a temperature of the secondary battery exceeds a predetermined temperature.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Circuit for safe forwarding of an analog signal value
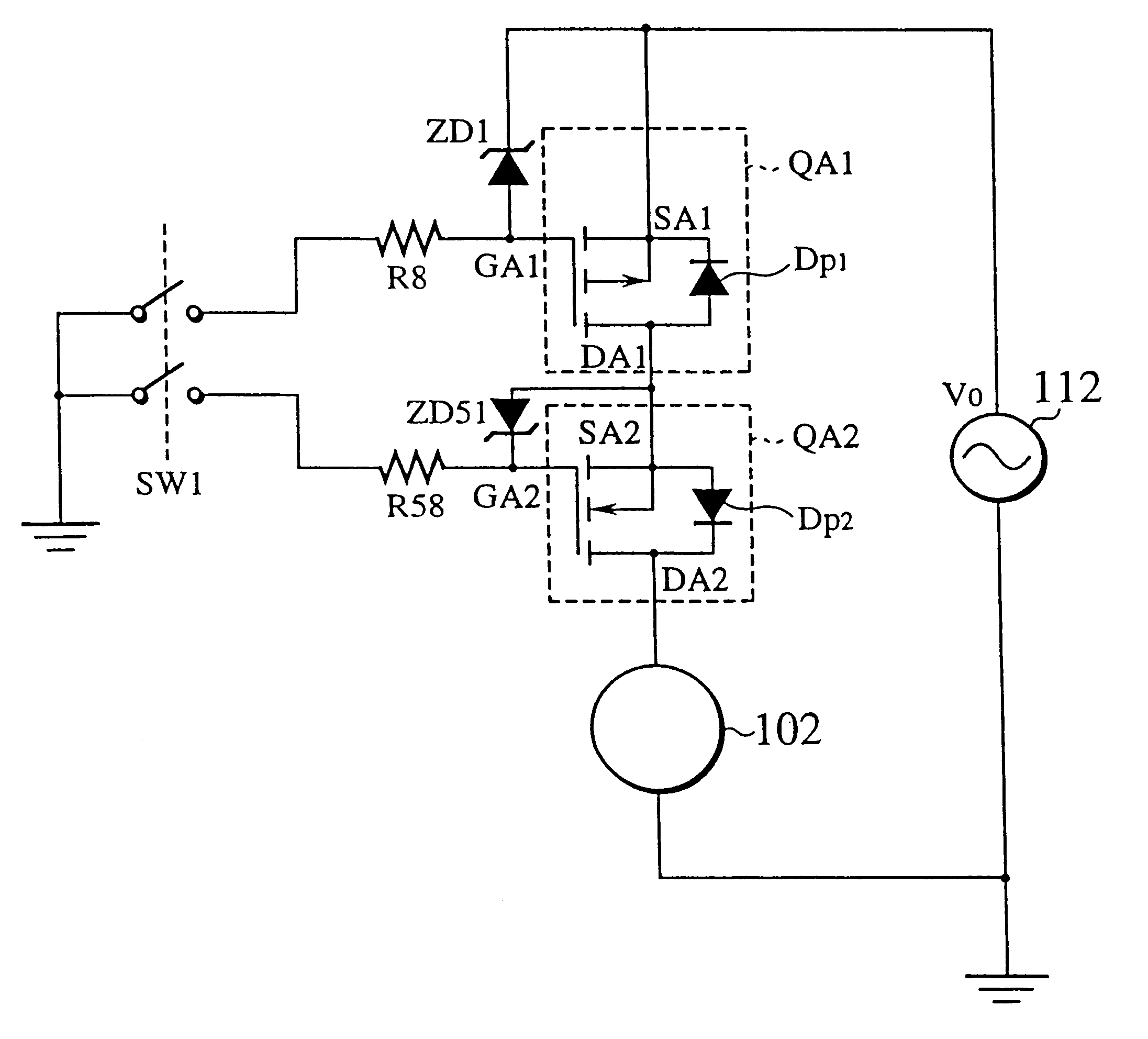
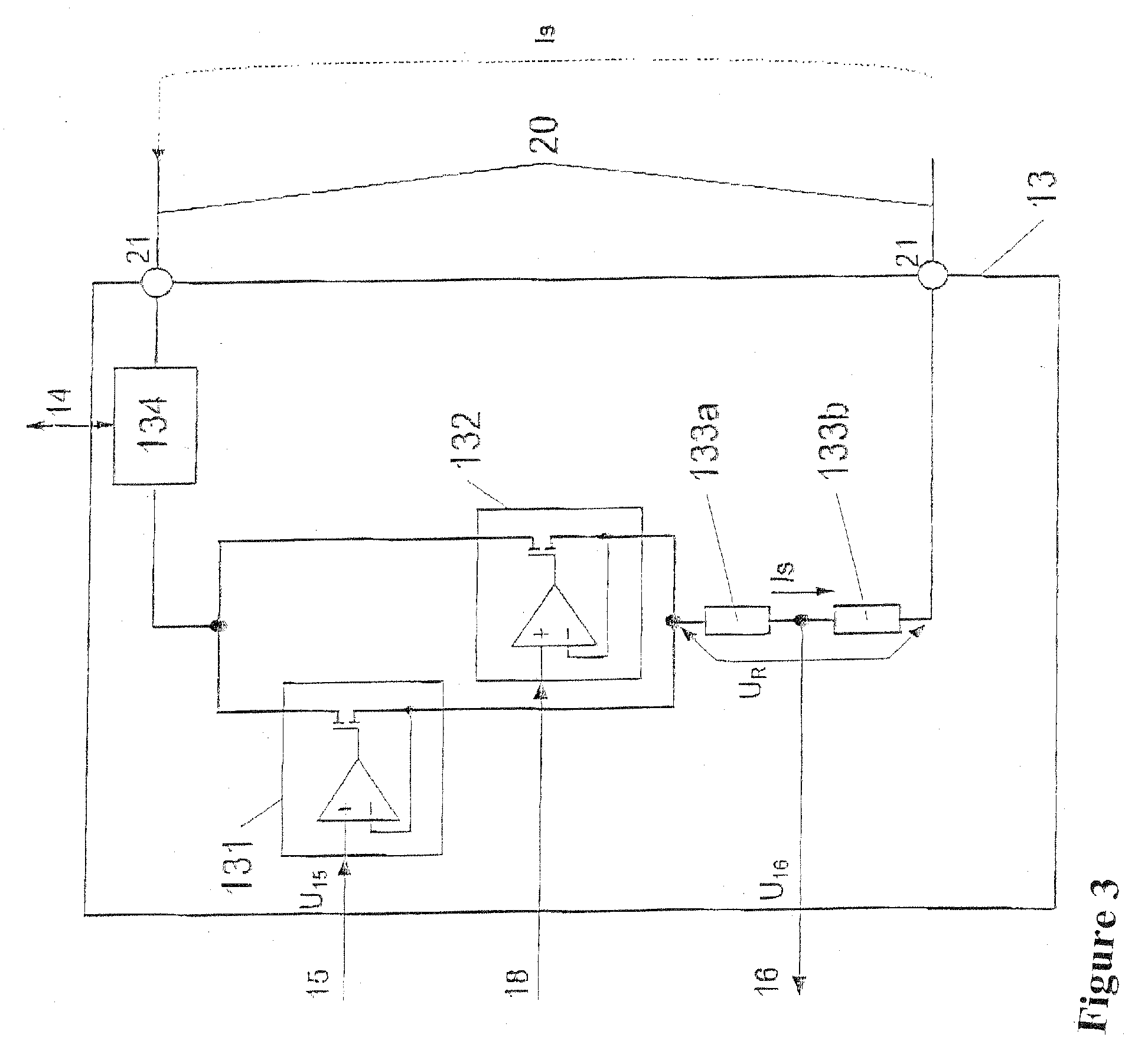
ActiveUS20080007307A1Improve functional safetyIncrease probabilityProgramme controlOscillations generatorsIntrinsic safetyExplosion protection
In a circuit for safe forwarding of a physical or technical variable between at least two systems in communication with one another, which variable is represented by the value of a loop current (Is), which is adjusted by a control unit (11) by means of a current output circuit (13) in a current loop (20, 60), the current output circuit (13) has at least two parallel-connected final control elements (131, 132), controllable by the control circuit (11), as current sources for mutually independent adjustment of a value of the loop current (Is). The final control elements (131, 132) are in series with at least two likewise series-connected measurement resistors (133a, 133b). The voltage, proportional to the loop current (Is), dropping via at least one but not all of the at least two measurement resistors is fed back to the control unit (11), which compares the value of this voltage with the corresponding value of the loop current, which value is specified to at least one of the final control elements, and in the event of deviations, via a predeterminable threshold, allocates an fault value corresponding to the NAMUR recommendation NE043 to the loop current via the first final control element (131), and in the case of failure of the first final control element (131) via the second final control element (132). A monitoring circuit (17) is provided, which in the event of failure of the control unit (11) allocates an fault value that likewise corresponds to the NAMUR recommendation NE043 to the loop current via the second final control element (132). The invention, compared to embodiments based on the principle of redundance, thus makes it possible to disclose a more-favorable embodiment for monitoring and signalling faults, which makes do with only one current path. The circuit may be designed in that way. By additional wiring, the demands in terms of explosion protection by intrinsic safety, functional safety (up to at least SIL 2), HART communication, and a standardized interface in accordance with NAMUR recommendation NE43 with an upper fault current (greater than 21 mA) and a lower fault current (less than 3.6 mA) and an active mode (current source) and passive mode (current sink) can be met at the same time.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com