Patents
Literature
1263results about How to "Made precisely" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
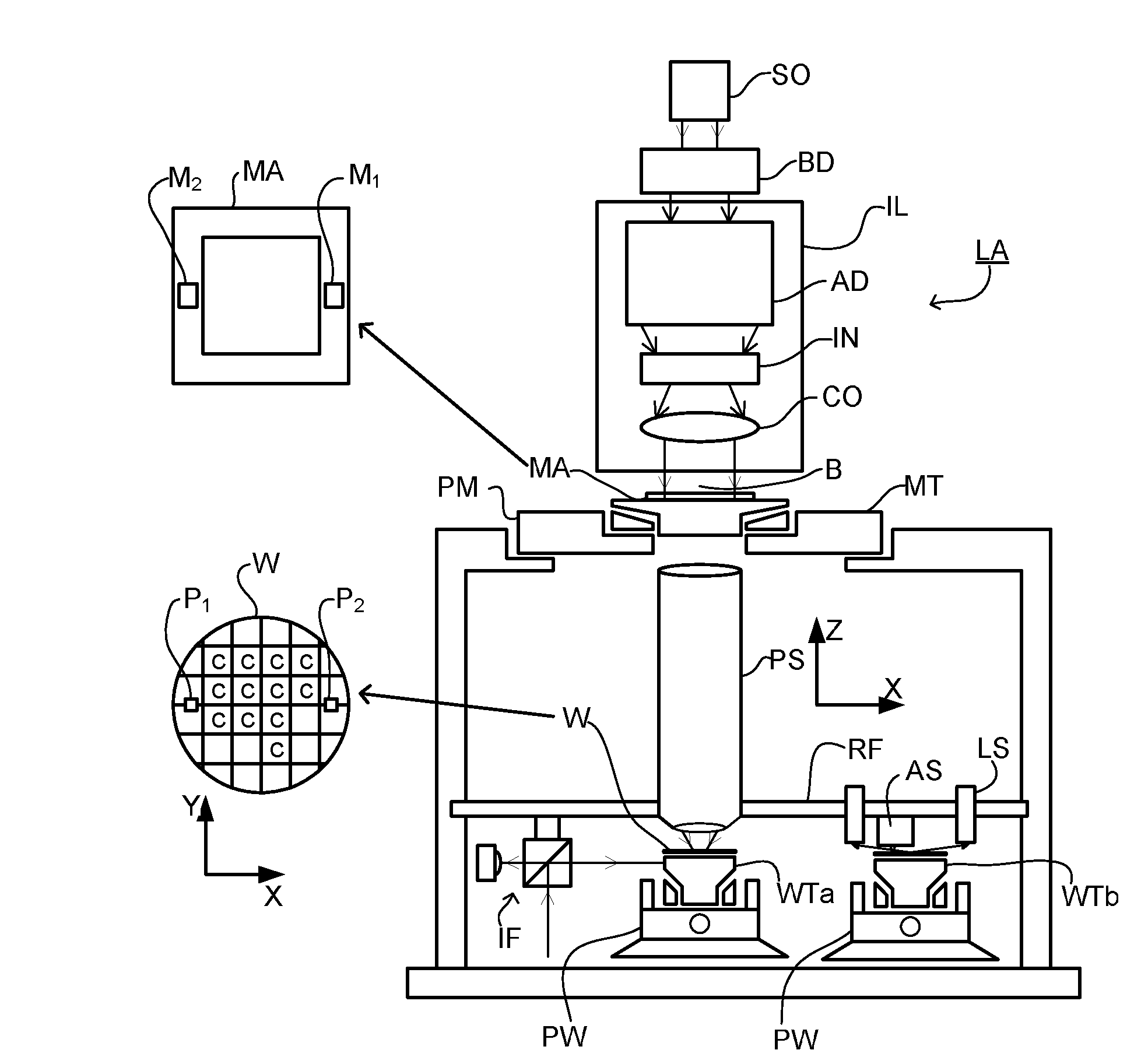
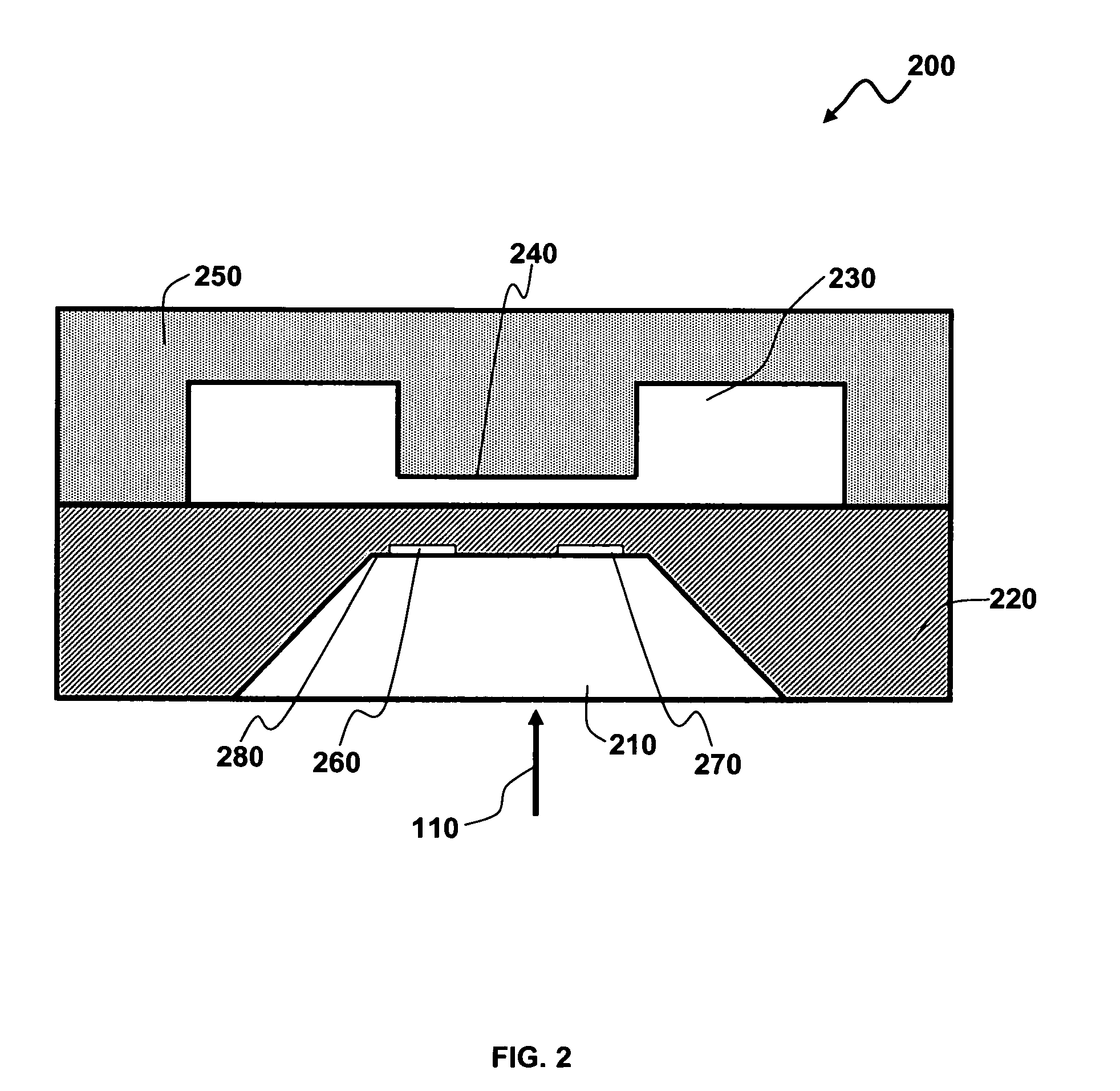
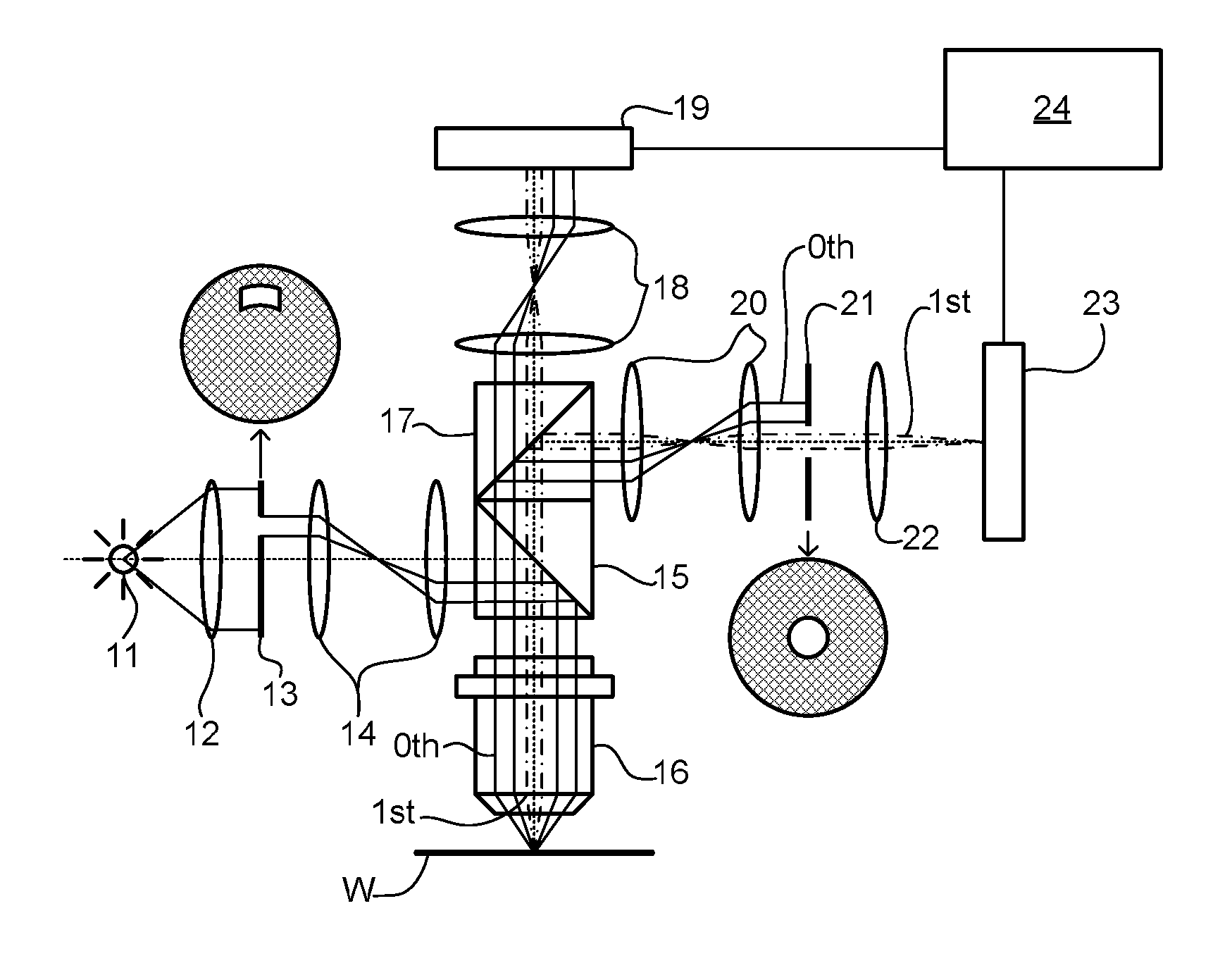
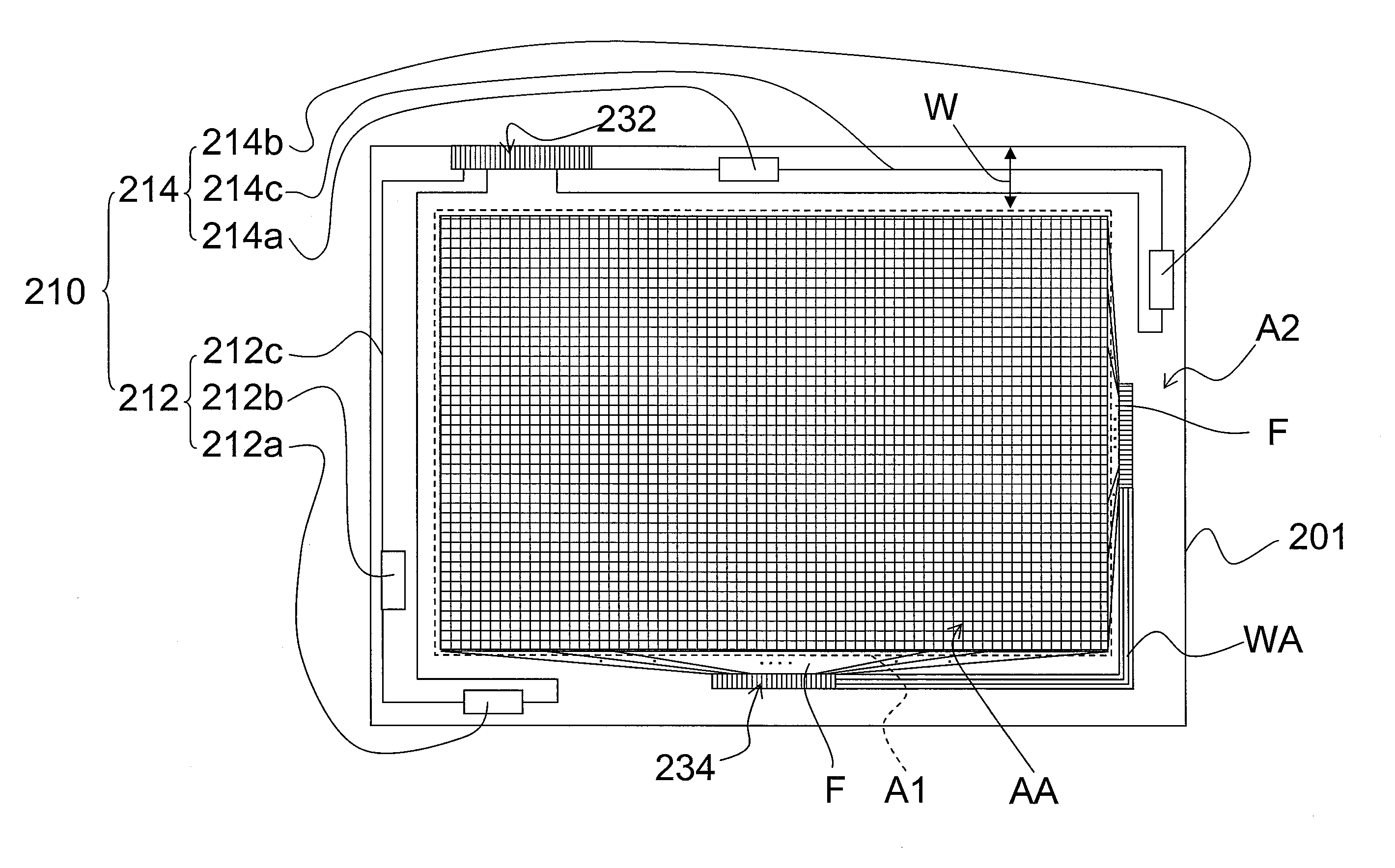
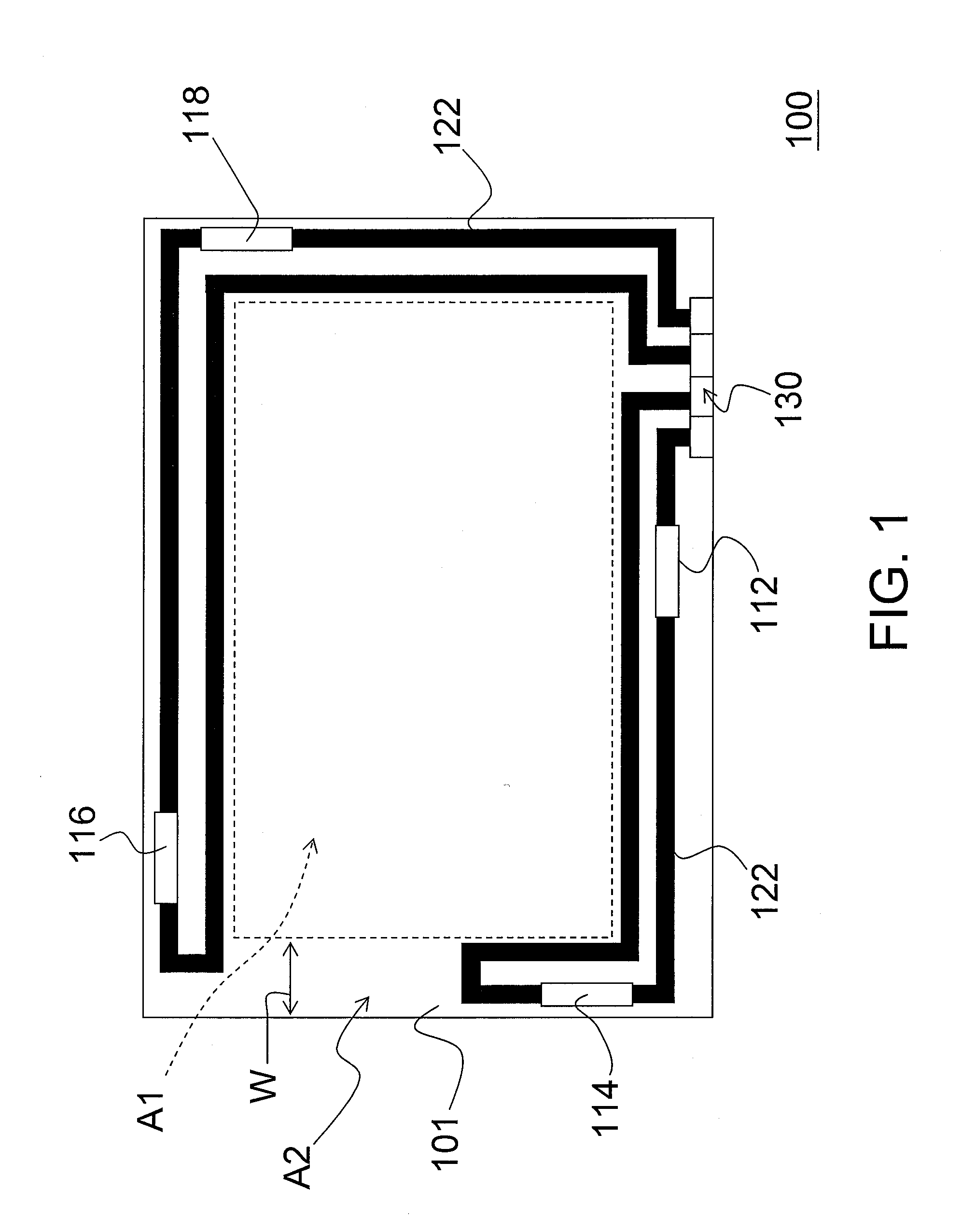
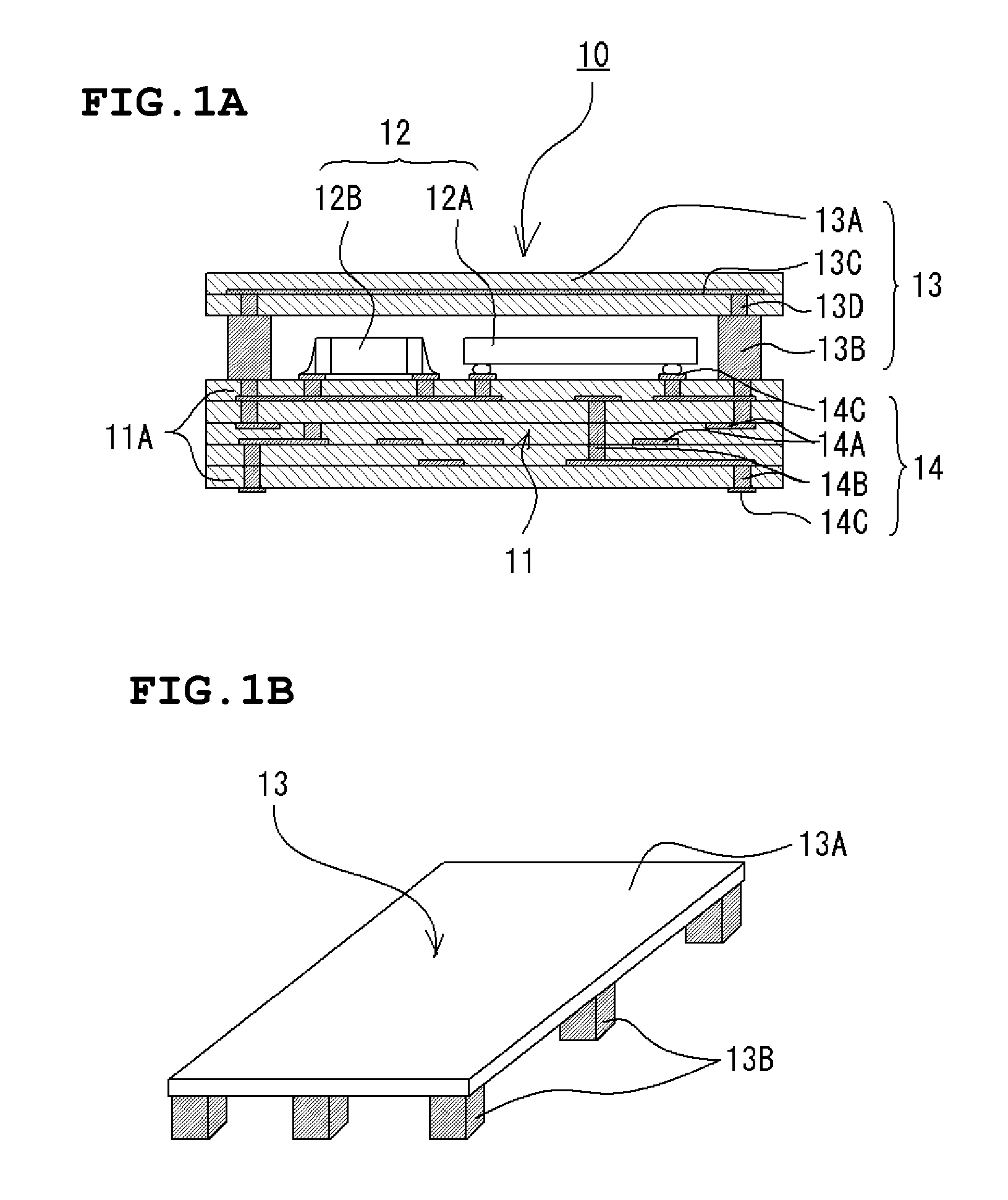
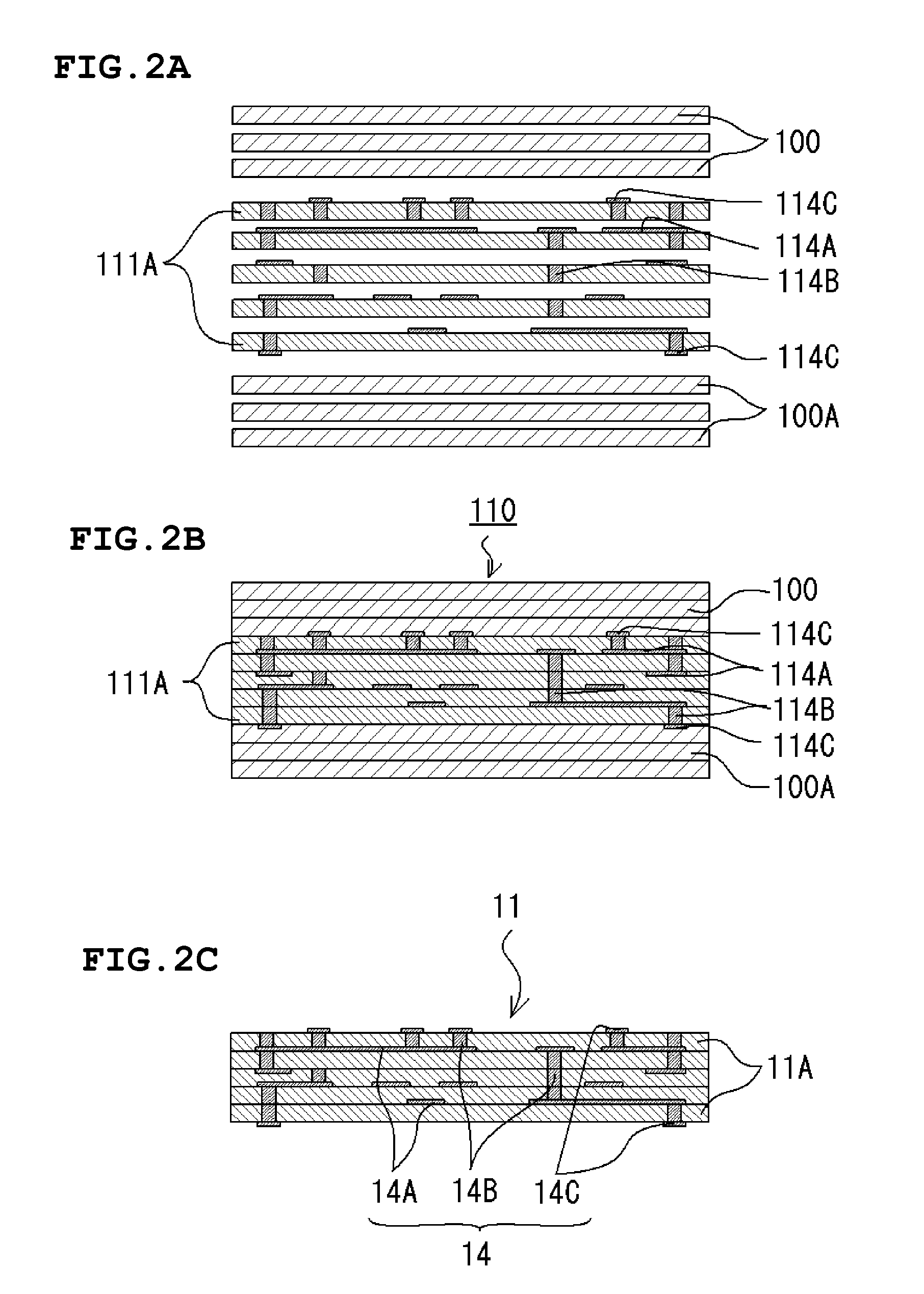
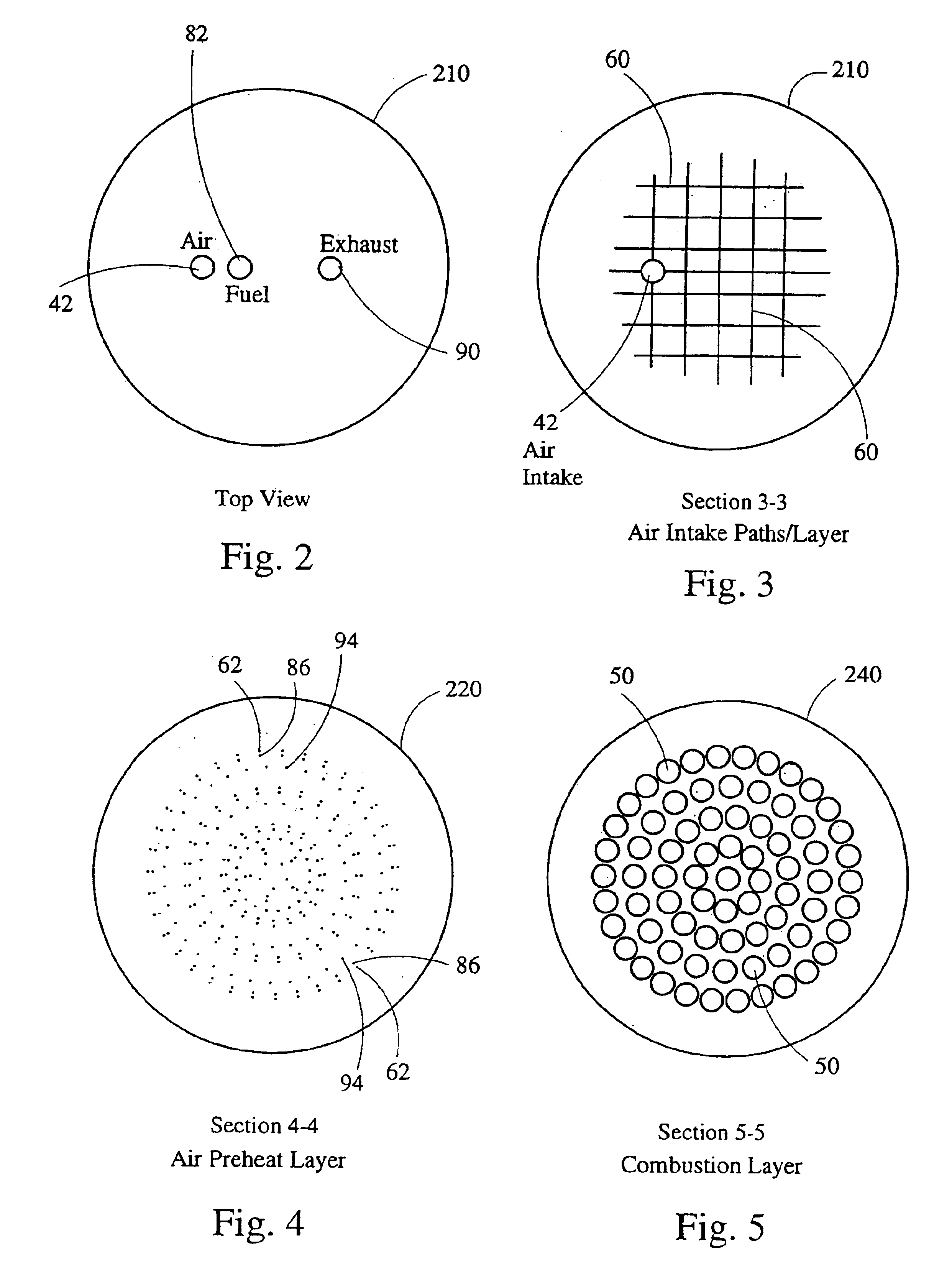
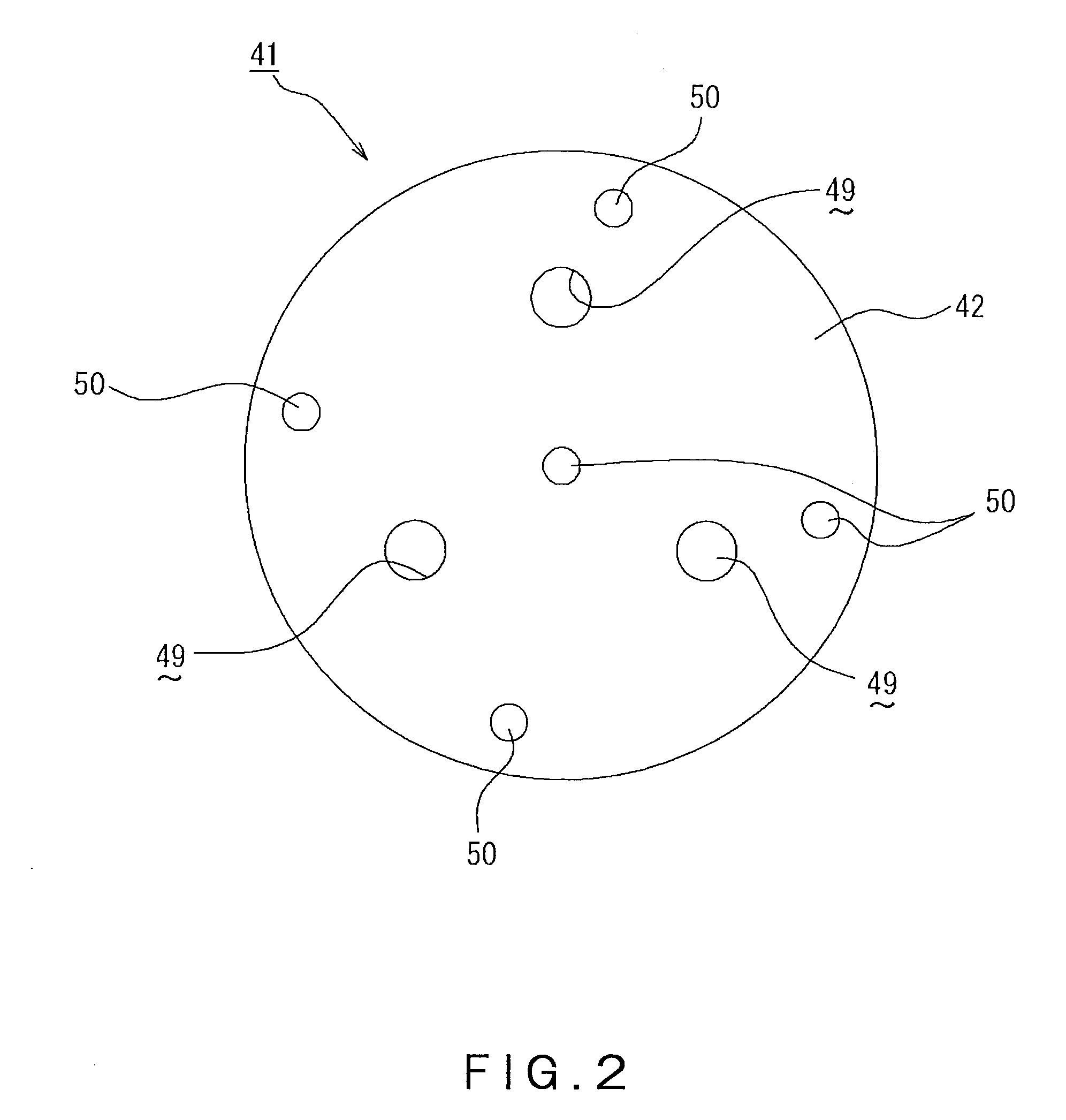
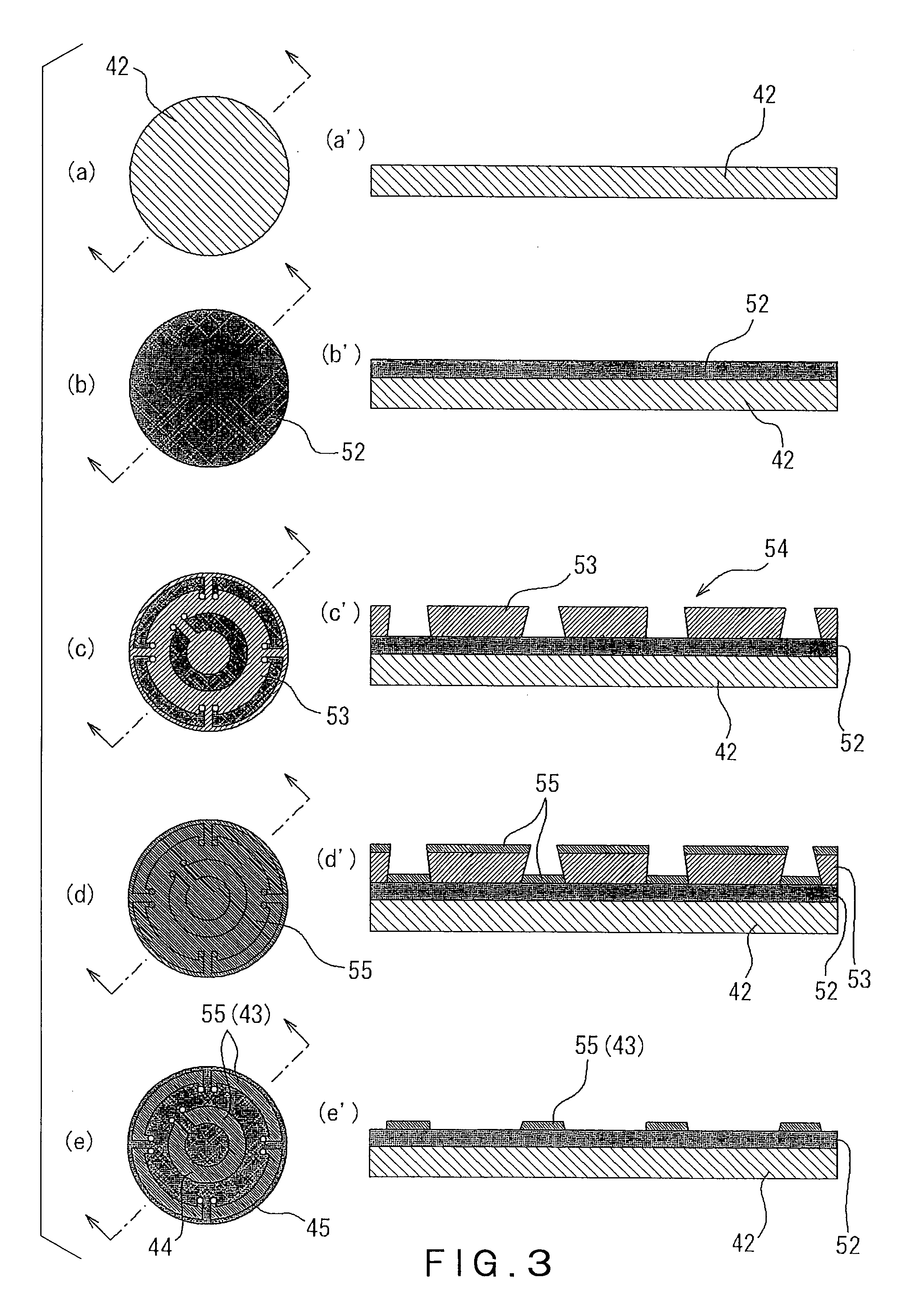
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Device Manufacturing Method and Substrate
ActiveUS20110043791A1Made preciselySmall targetPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansMetrologyGrating
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
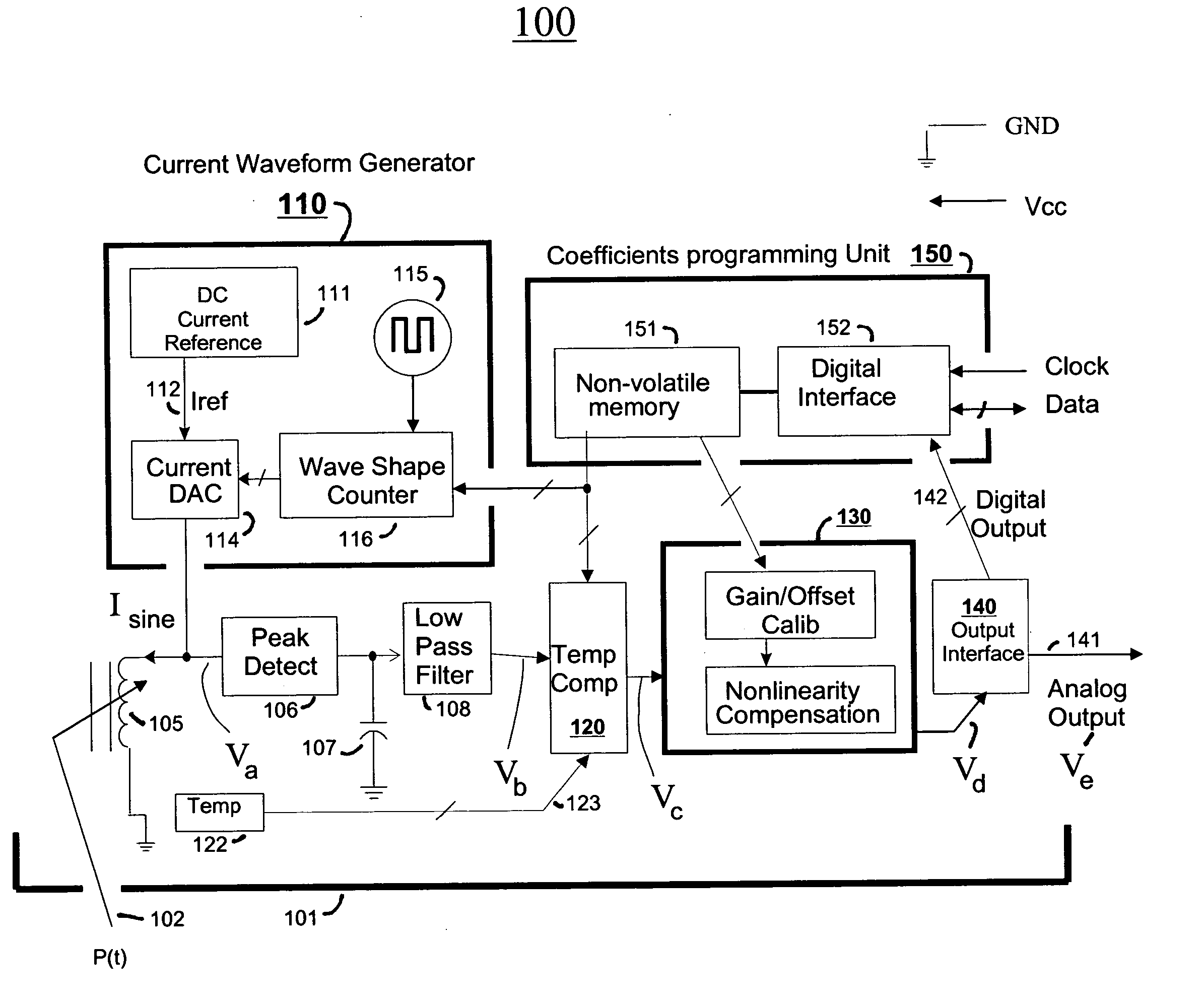
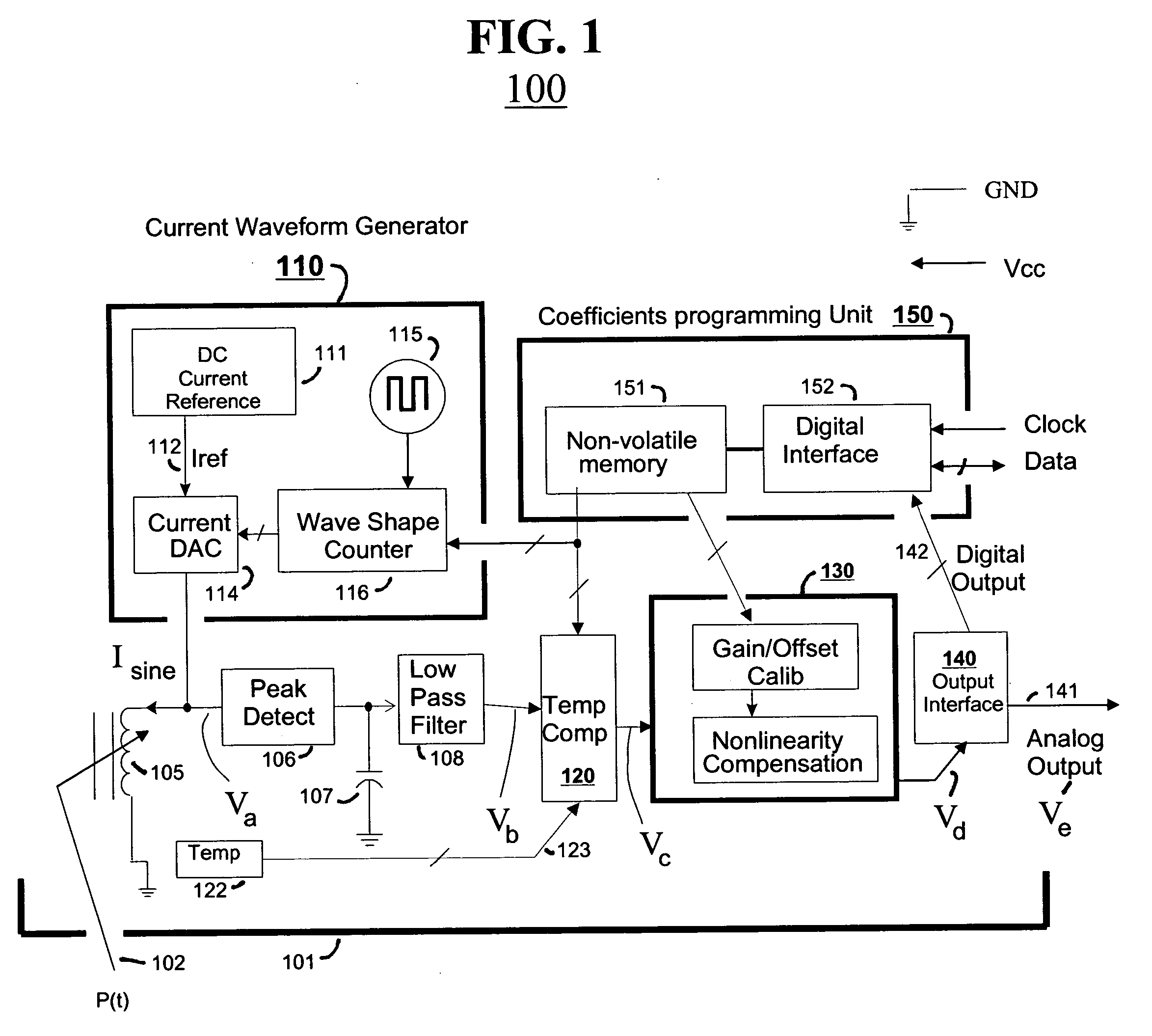
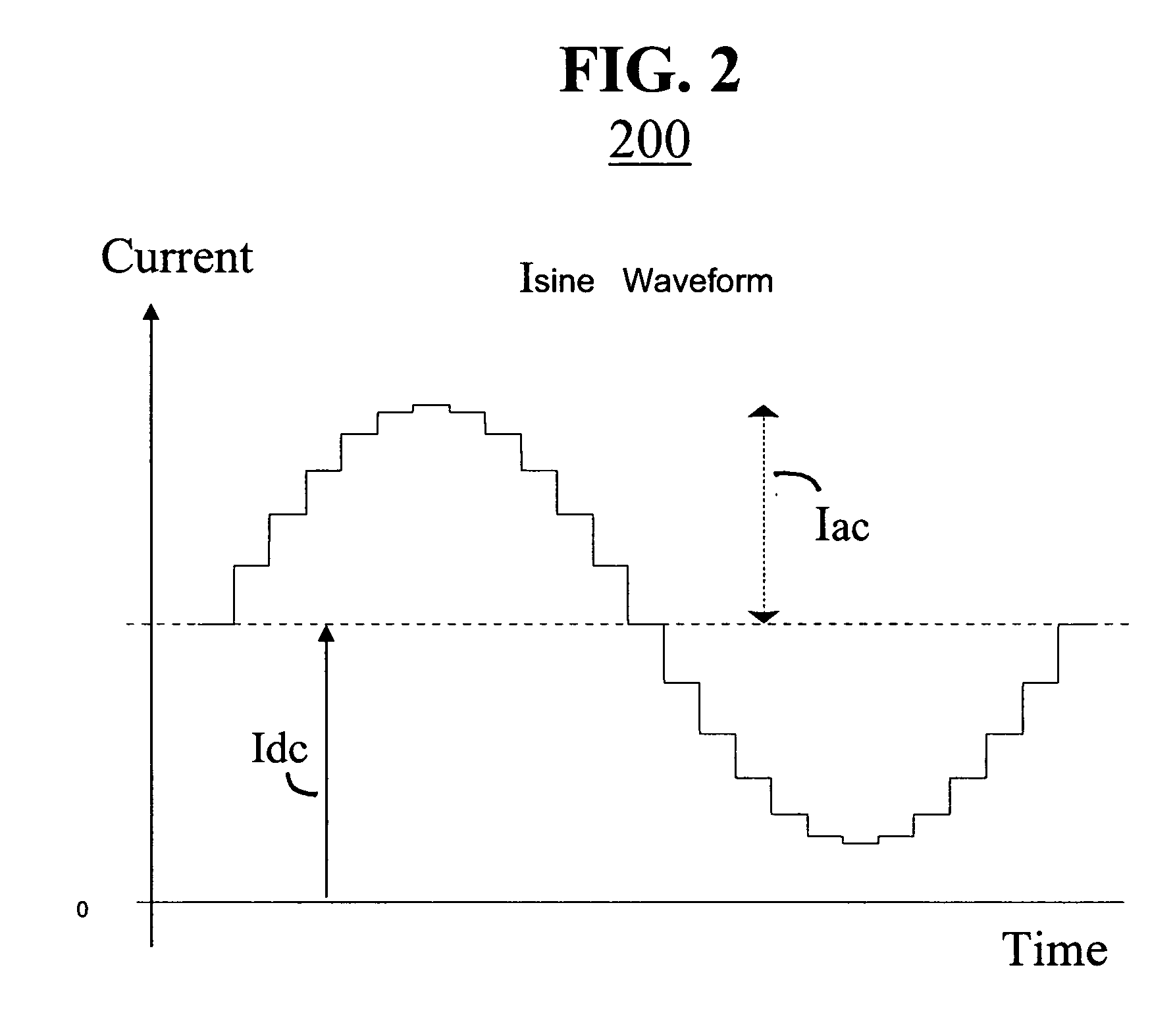
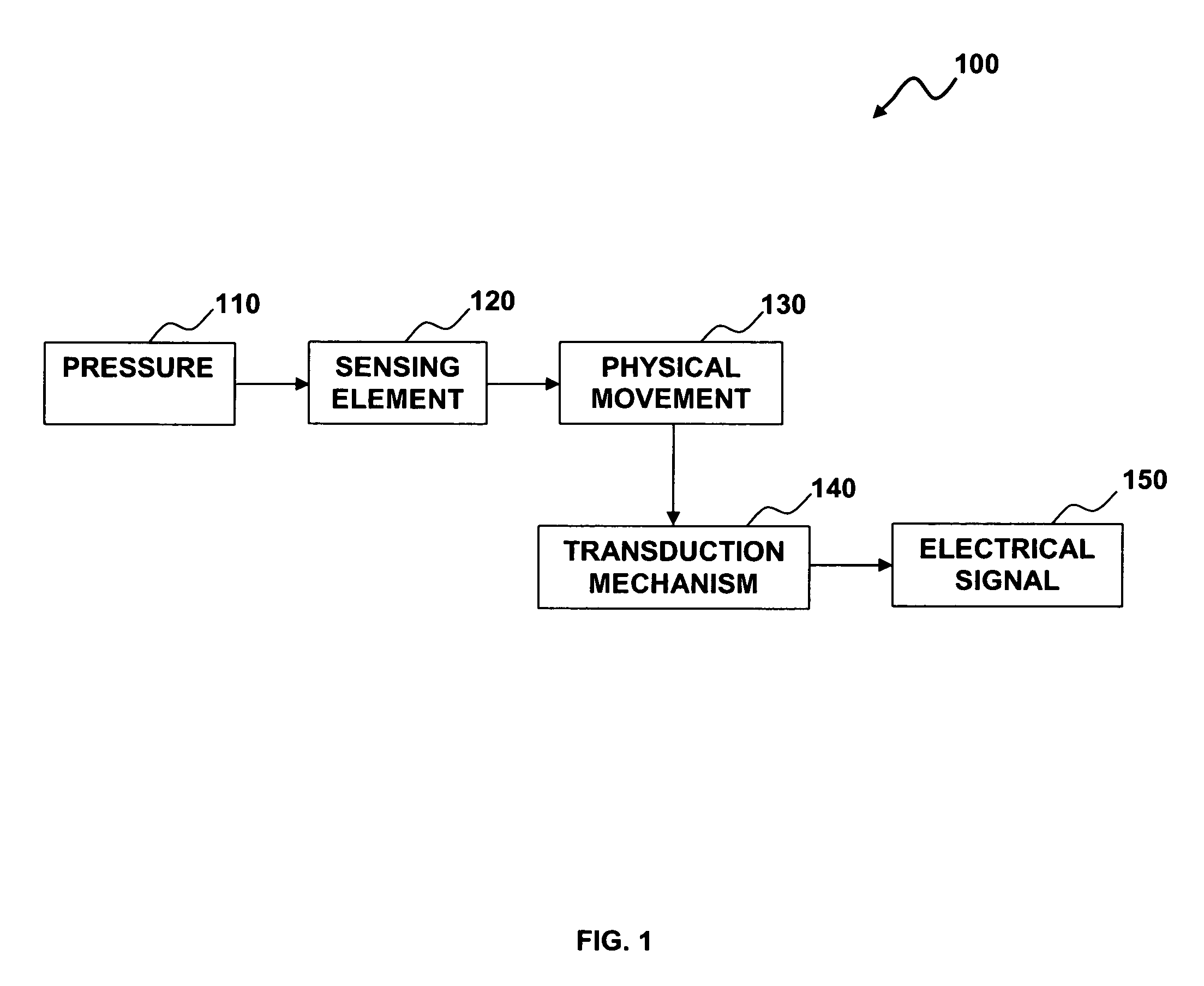
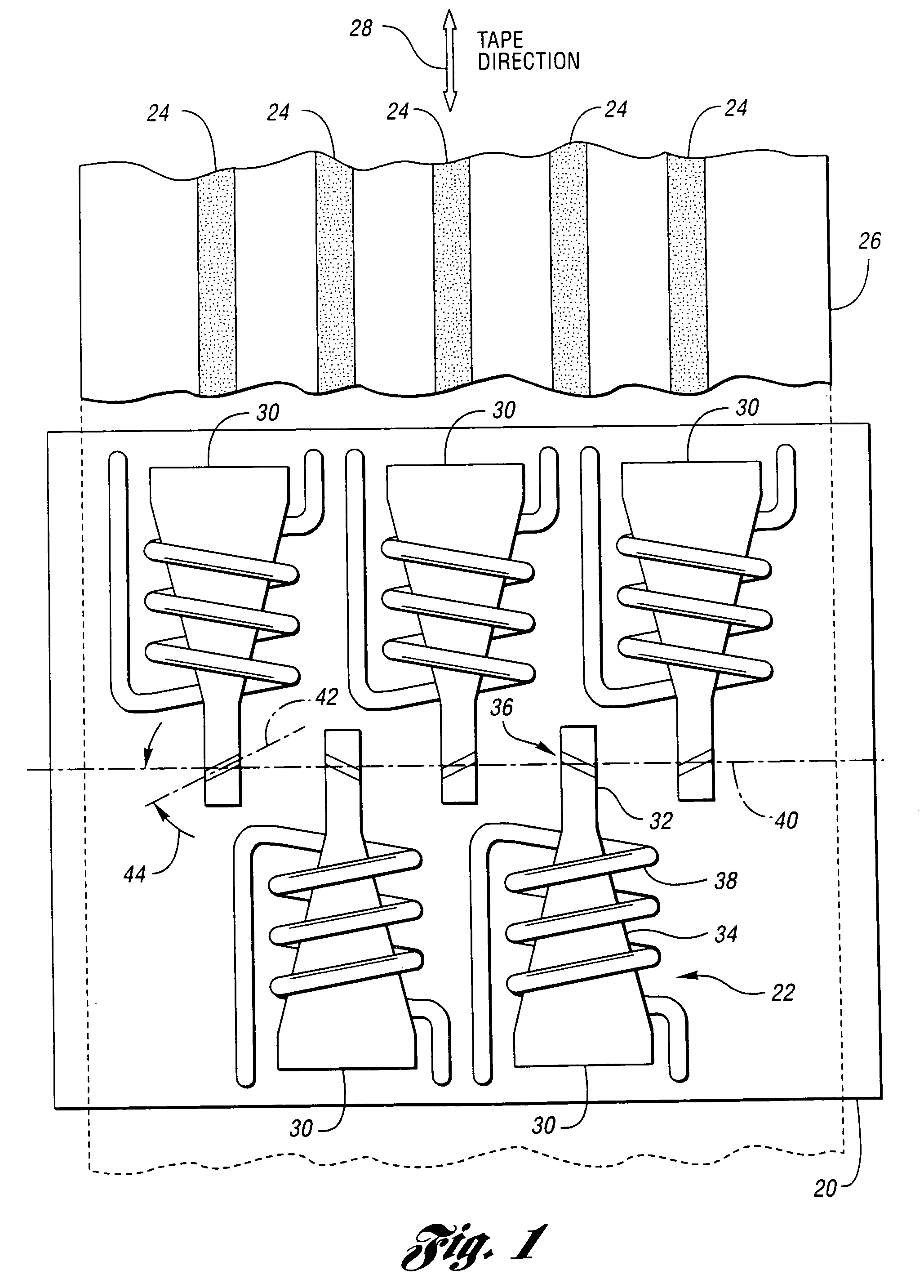
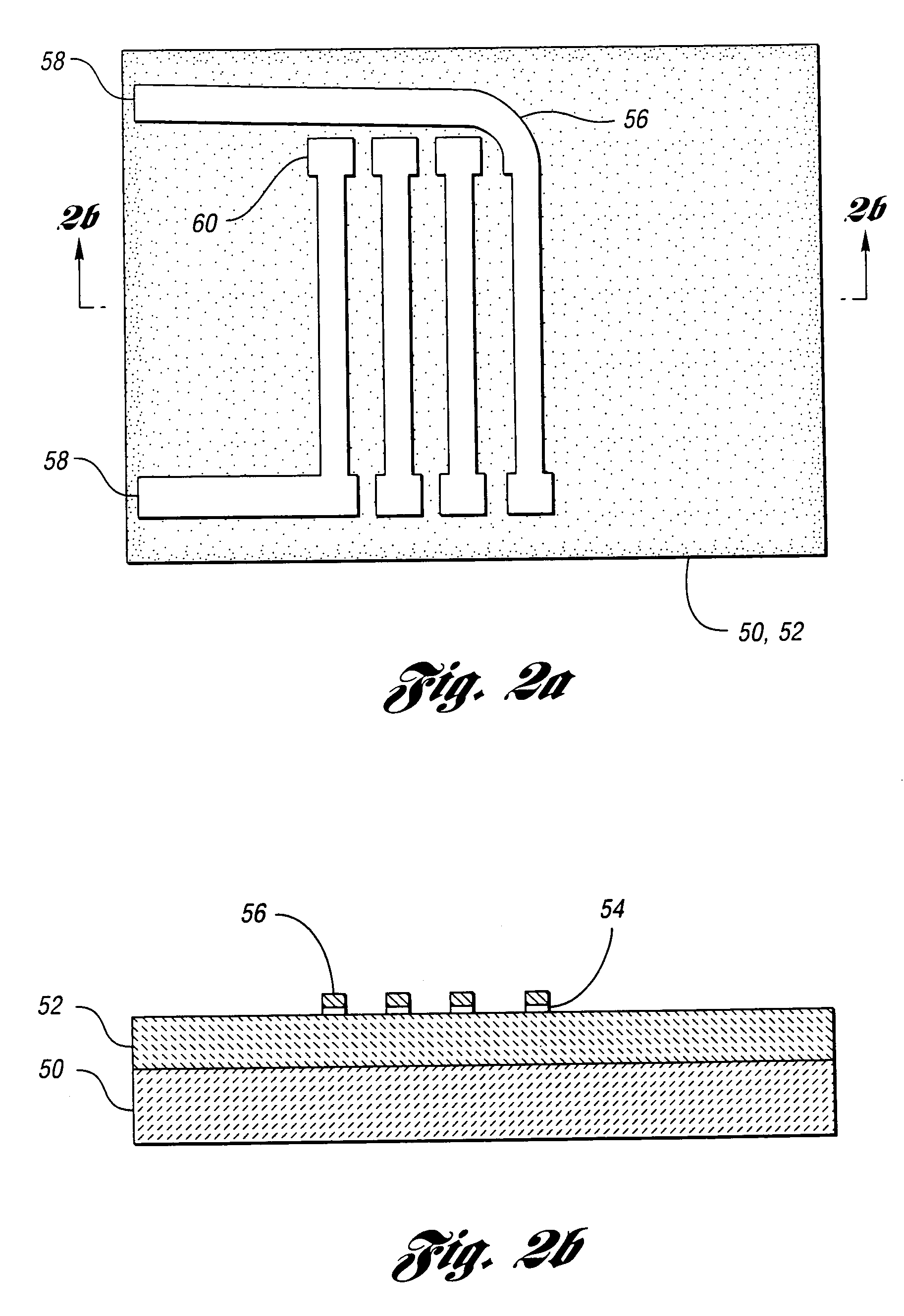
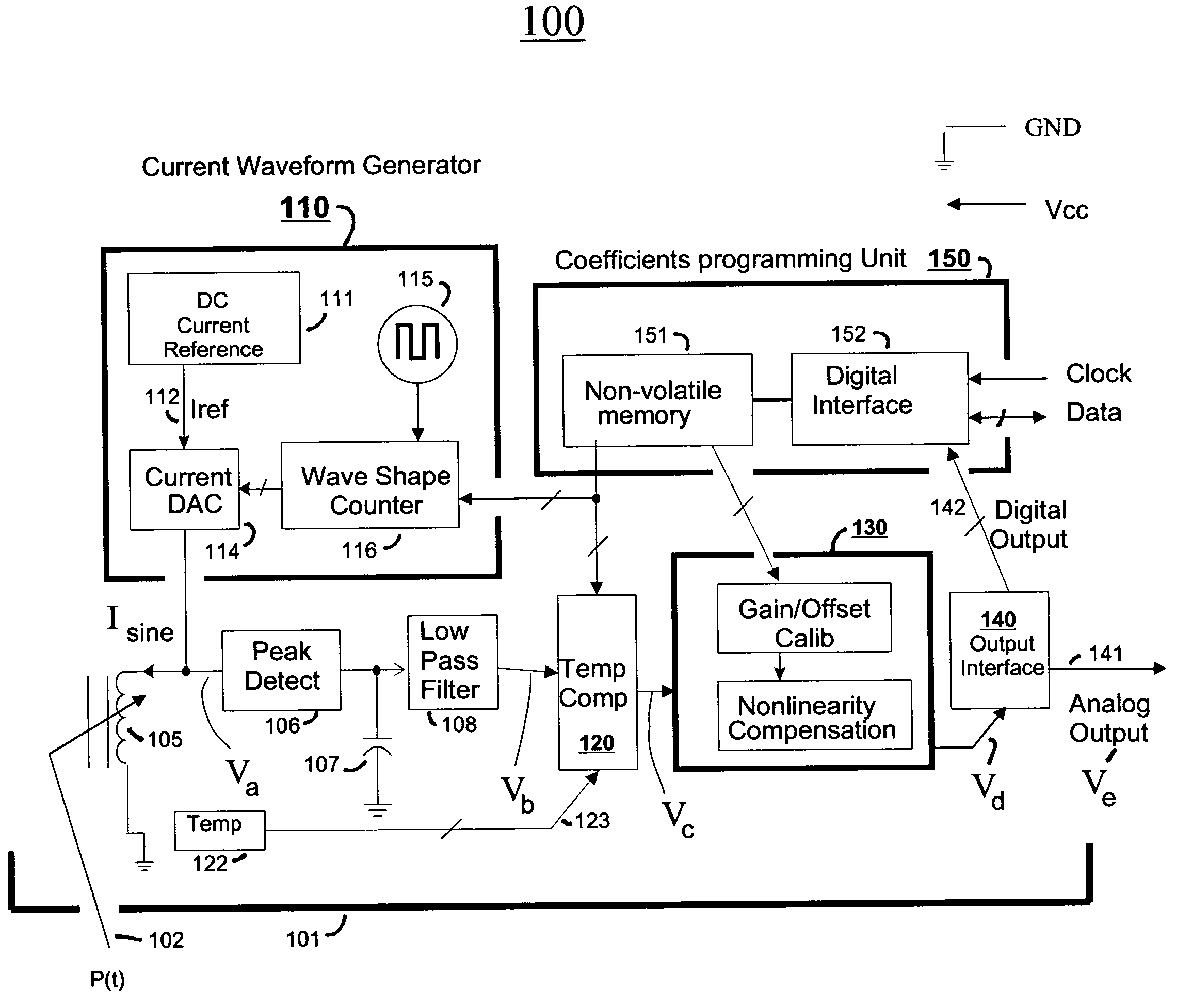
Reactive sensor modules using pade' approximant based compensation and providing module-sourced excitation
ActiveUS20050283330A1High precision measurementLow costSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Reactive sensors typically exhibit nonlinear response to the combination of an excitational signal (e.g., sinusoidally oscillating signal) and a physical parameter under measure (e.g., position of magnetic core member). Such sensors are typically sensitive to temperature variation. Systems and methods are disclosed for compensating for the nonlinear and / or temperature dependant behavior of reactive sensors and for calibrating the post-compensation output signals relative to known samples of the physical parameter under measure (e.g., position). One class of embodiments comprises a housing containing at least part of a reactive sensor, a monolithic integrated circuit and a timing reference (e.g., an oscillator crystal). The integrated circuit includes a waveform generator for generating a sensor exciting signal, a detector for detecting the response of the sensor to the combination of the exciting signal and the under-measure physical parameter, a temperature compensating unit and a Pade' Approximant based, nonlinearity compensating unit. The temperature compensating unit and the Pade' Approximant nonlinearity compensating unit are tuned by use of digitally programmed coefficients. The coefficients calibrate the final output as well as compensating for nonlinearity and temperature sensitivity. A highly accurate measurement of the under-measure physical parameter is made possible even though each of the sensor and compensating circuitry may be relatively simple, compact, and low in cost.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC +1
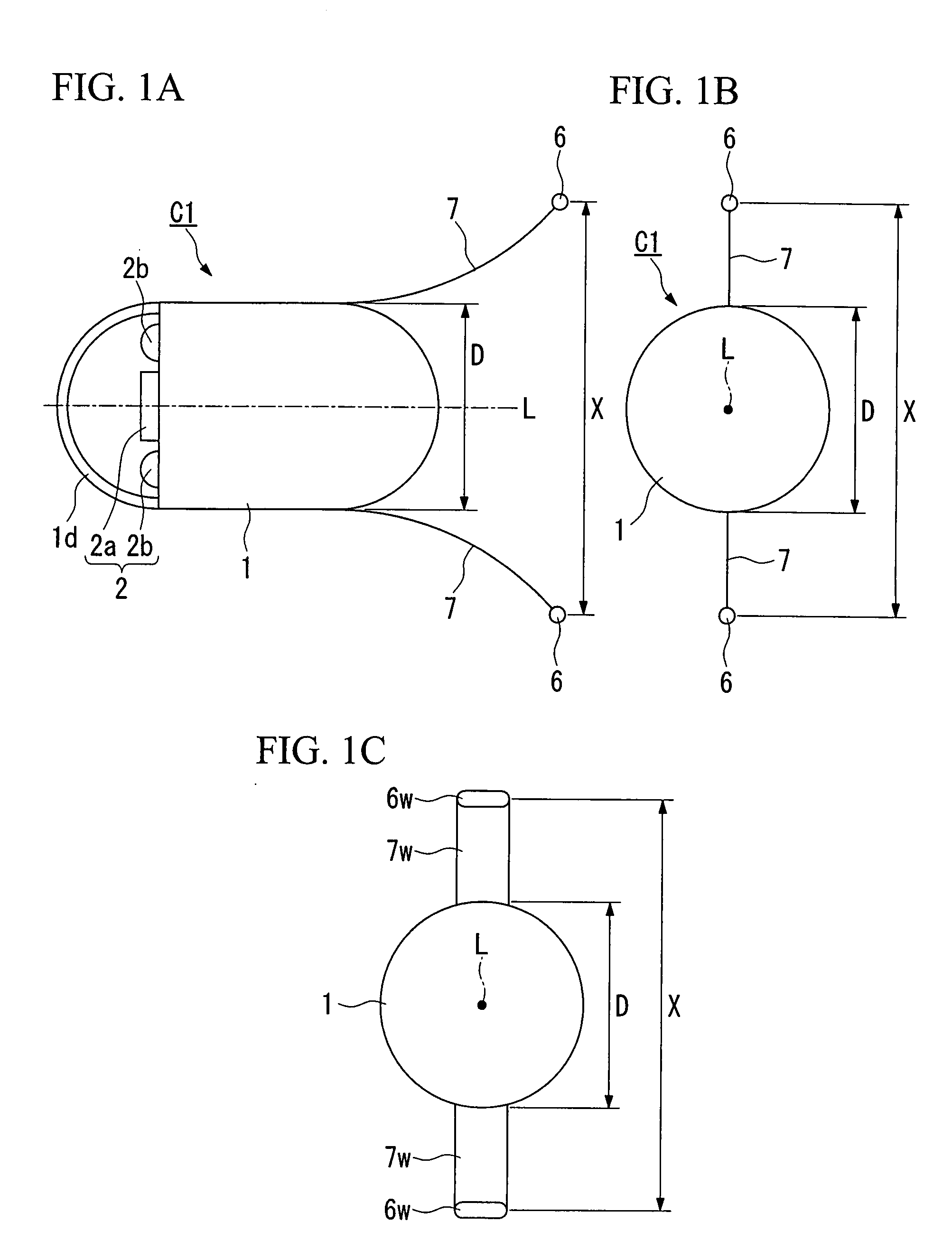
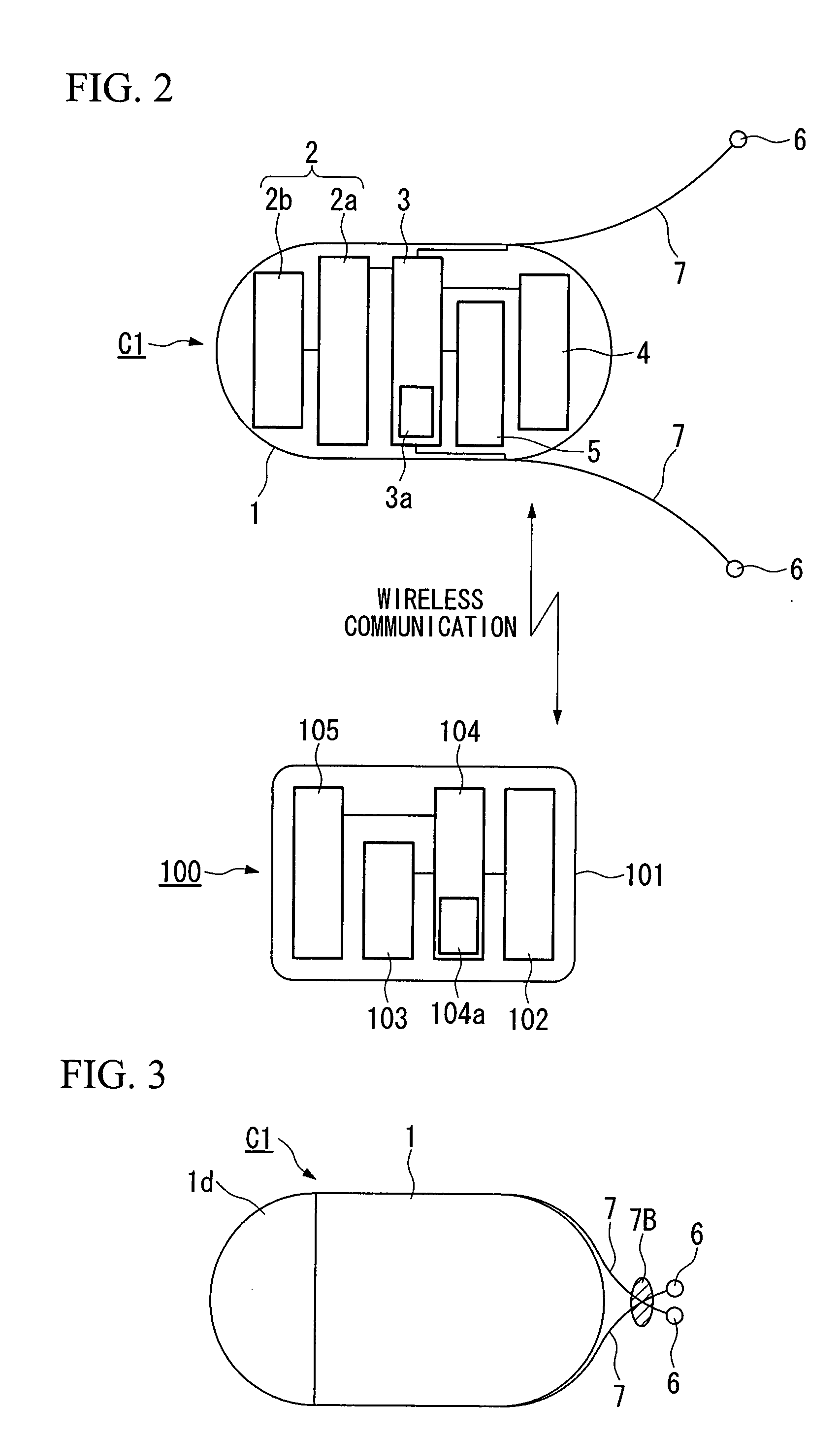
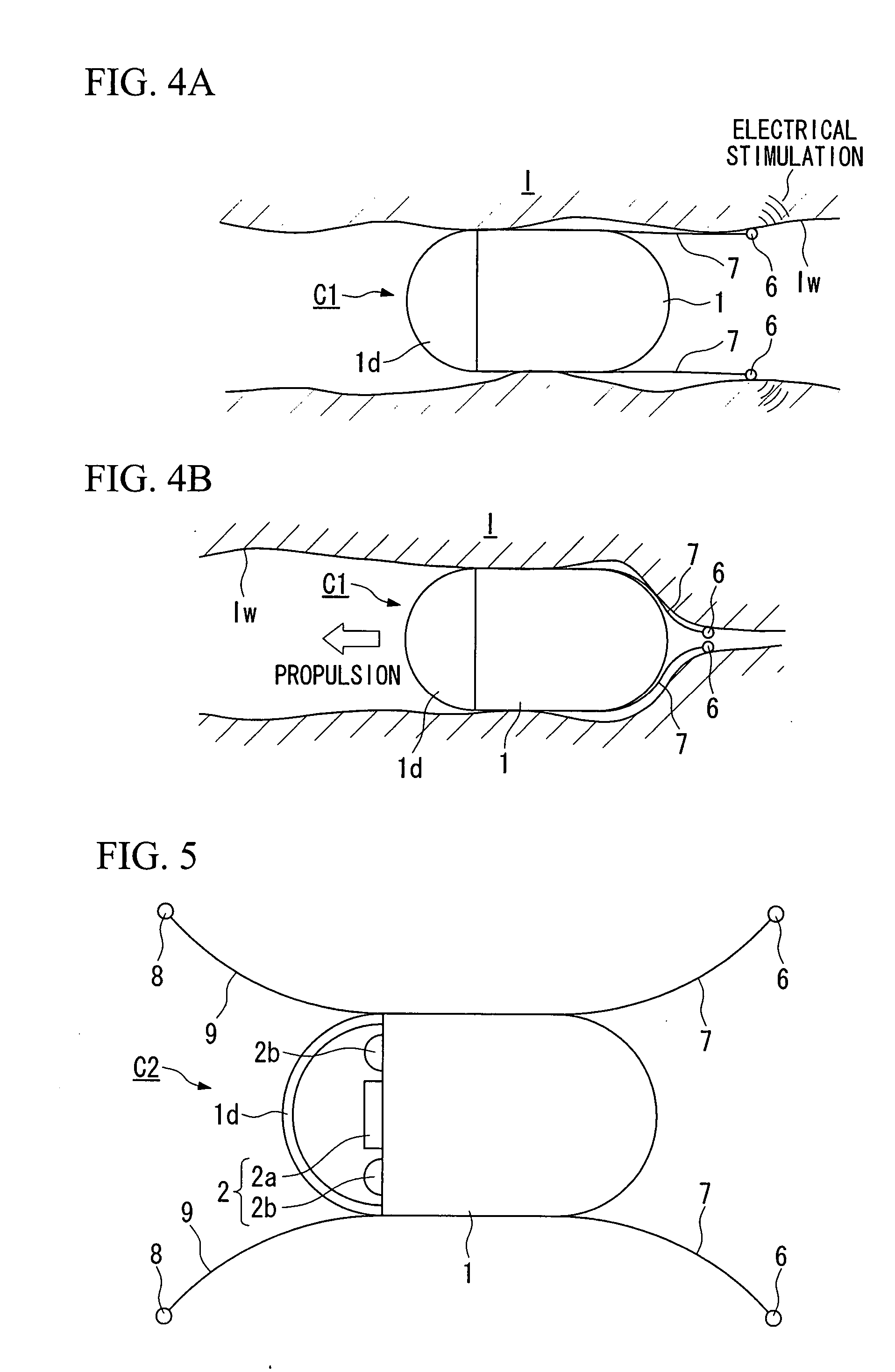
Capsulu type medical device
ActiveUS20070161851A1Increase the areaElasticityElectrotherapyEndoscopesIn vivoElectrical stimulations
A capsule type medical device is of a type of a capsule type medical device that is introduced inside the living body to gather in-vivo information, and comprises a capsule shaped casing; an in-vivo information acquisition device for acquiring the in-vivo information; a communication device for sending the in-vivo information acquired by the in-vivo information acquisition device to outside of the living body by wireless; at least one pair of first electrodes provided in a vicinity of one end along an axis of the casing for giving electric stimulation to body tissue in the living body; a first current control device for sending current to the first electrodes; and an interelectrode distance variation device for changing a distance between the electrodes.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
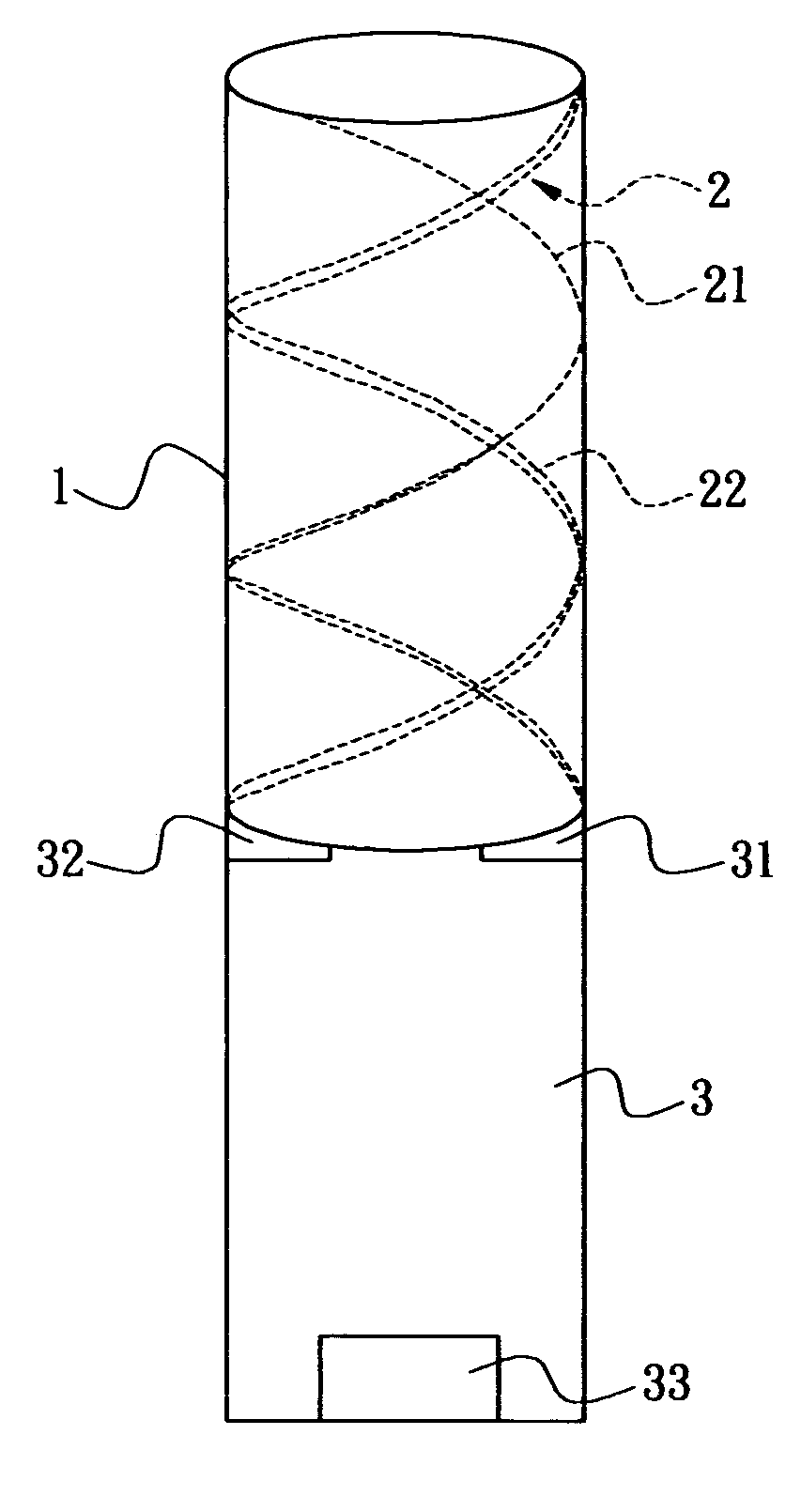
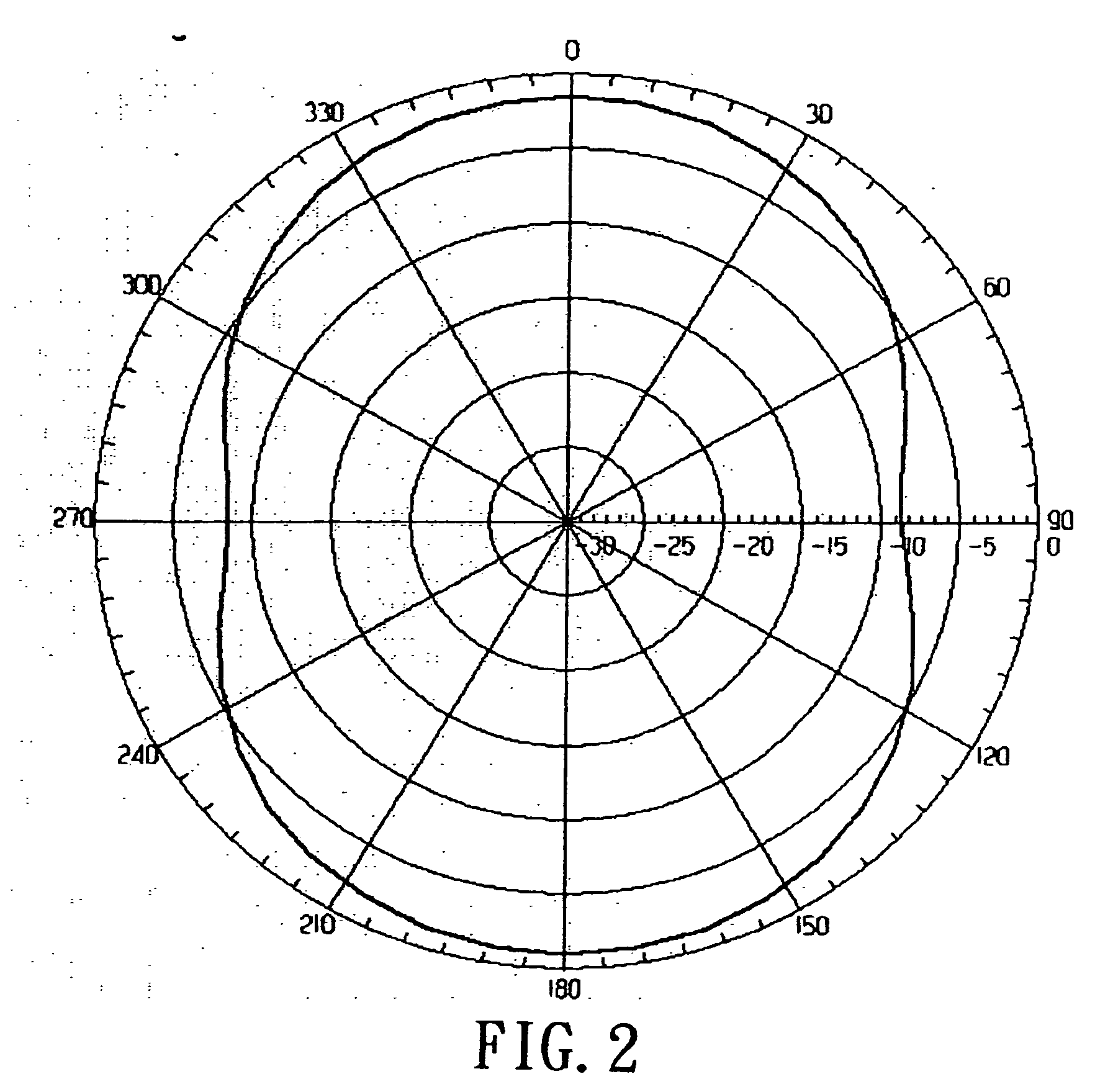
Circular-polarization dipole helical antenna
InactiveUS20060232493A1Quick fine-tuningReduce lossRadiating elements structural formsHelical antennasElectrical conductorPhase difference
A circular-polarization dipole helical antenna is used for electronic device and satellite terminal and includes a base, and an antenna conductor arranged on surface of the base. The antenna conductor includes a plurality of metal conductors with high Q value and anti-oxidation property and continuously and helically coated on surface of the base. The base is made of low loss and high dielectric constant material. An unbalance-to-balance circuit module connects two signal-feeding ends to the base with phase difference of 180 degree. The problems of narrow bandwidth, low efficiency, complicated structure and precise manufacture can be solved.
Owner:CIREX TECH CORP
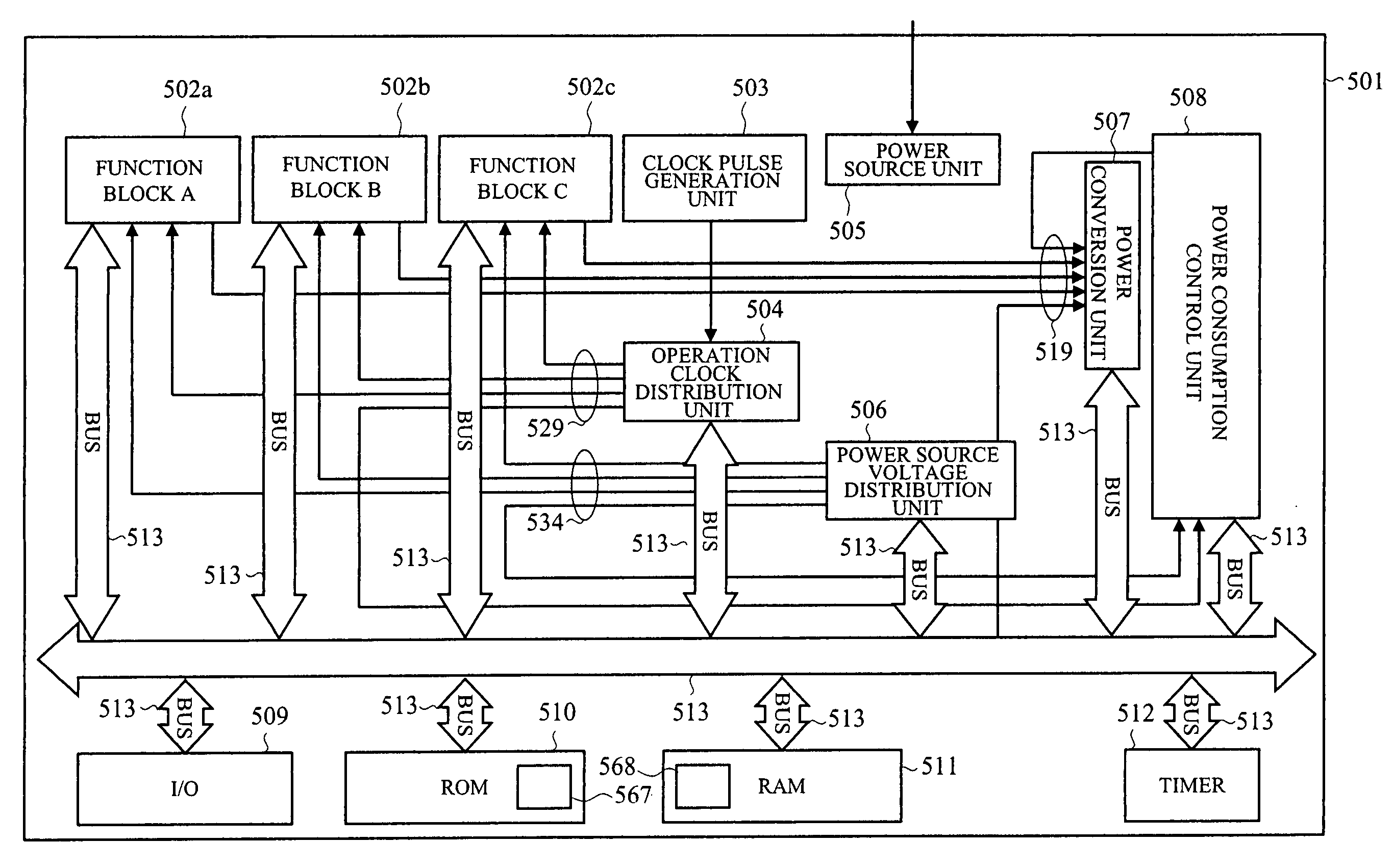
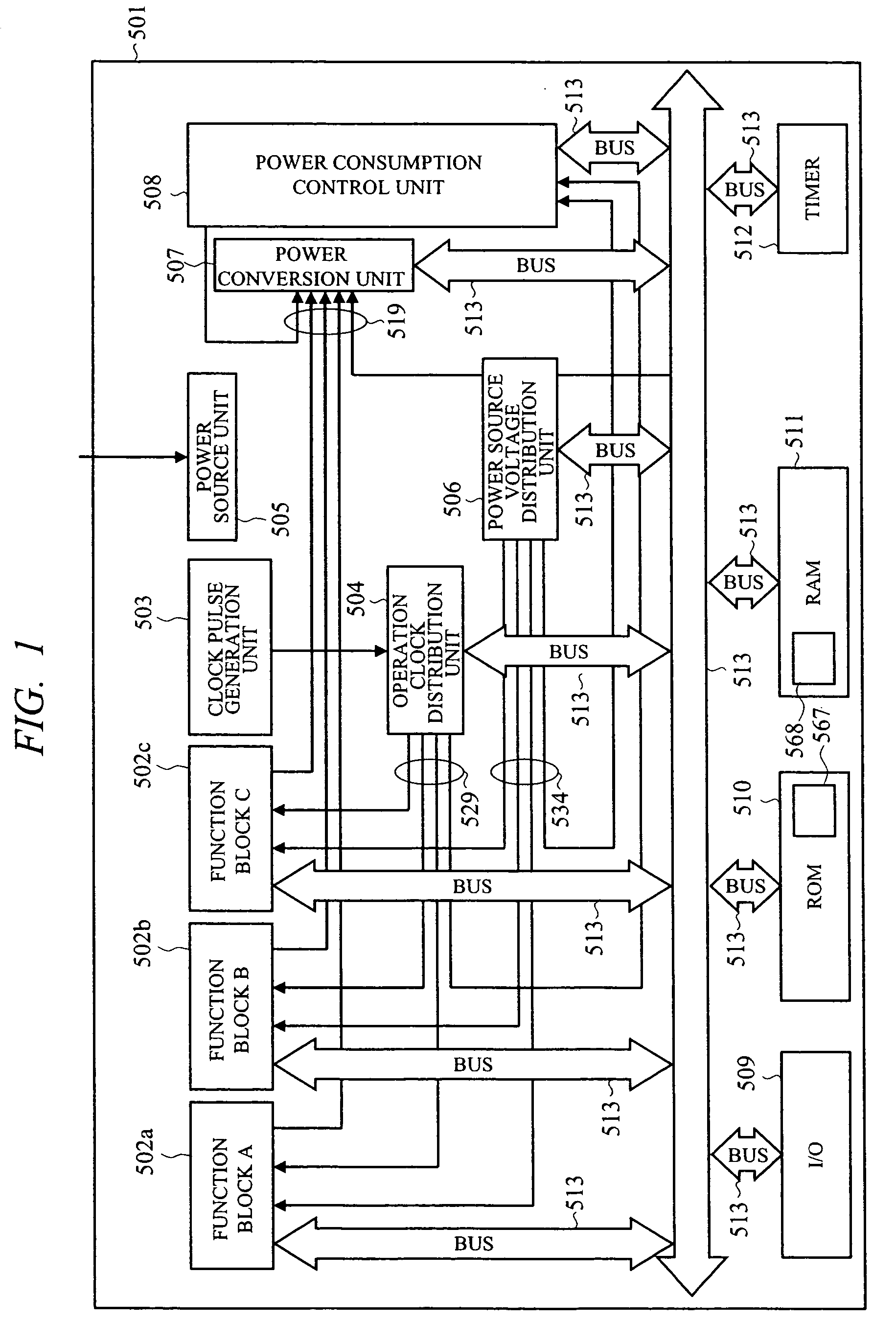
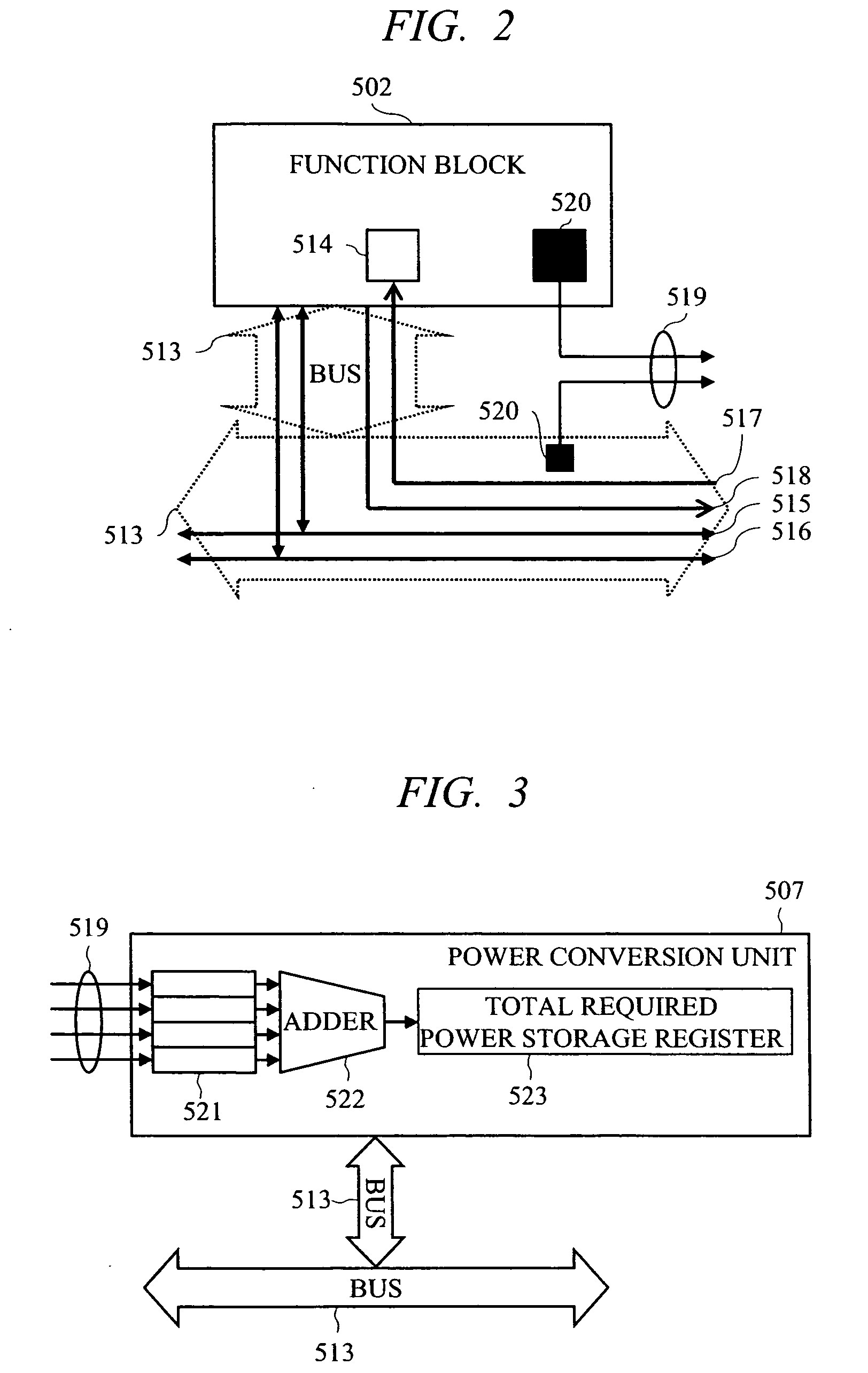
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and power consumption control device
ActiveUS20070083779A1Guaranteed uptimeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsPower modePower budget
To perform execution scheduling of function blocks so as to control the total required power of the function blocks within a supplyable power budget value, and thereby realize stable operations at low power consumption. Function block identifiers are allotted to all the function blocks, and to a RAM area that a power consumption control device can read and write, a list to store identifiers and task priority, power mode value showing power states, and power mode time showing the holding time of power states can be linked. A single or plural link lists for controlling the schedules of tasks operating on the function blocks, a link list for controlling the function block in execution currently in high power mode, a link list for controlling the function block in stop currently in stop mode, and a link list for controlling the function block in execution currently in low power mode are allotted, and thereby the power source and the operation clock are controlled by the power consumption control device.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
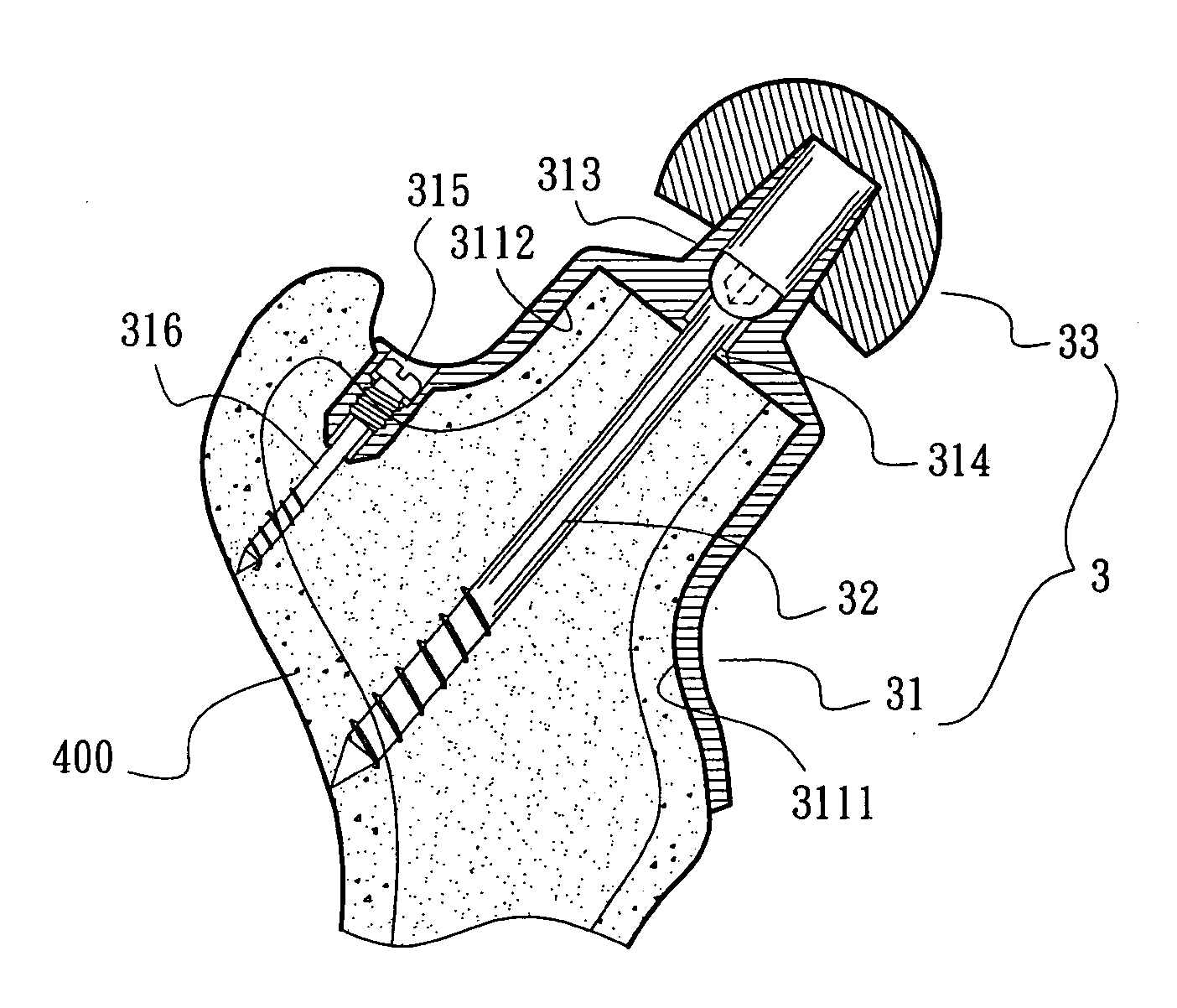
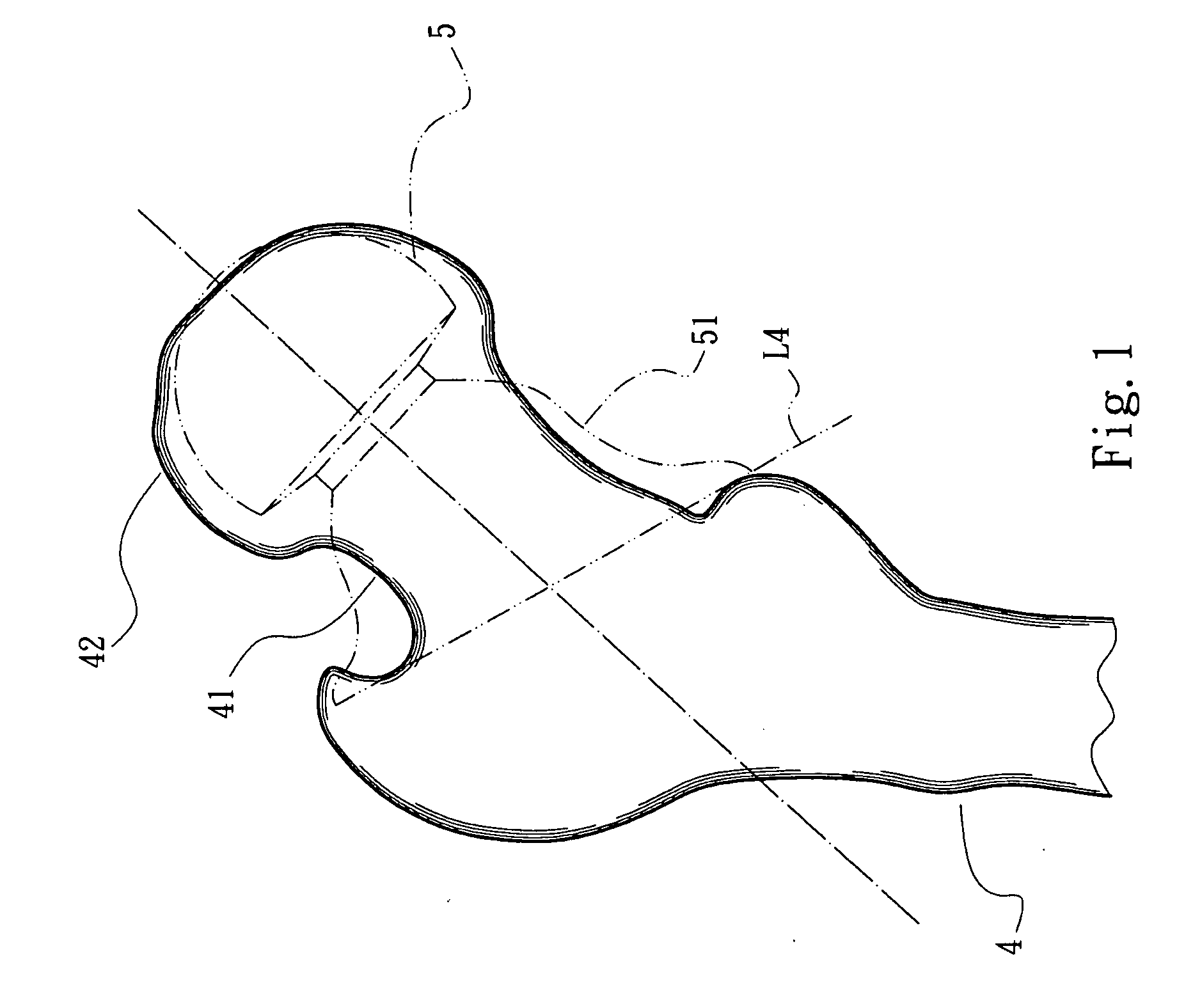
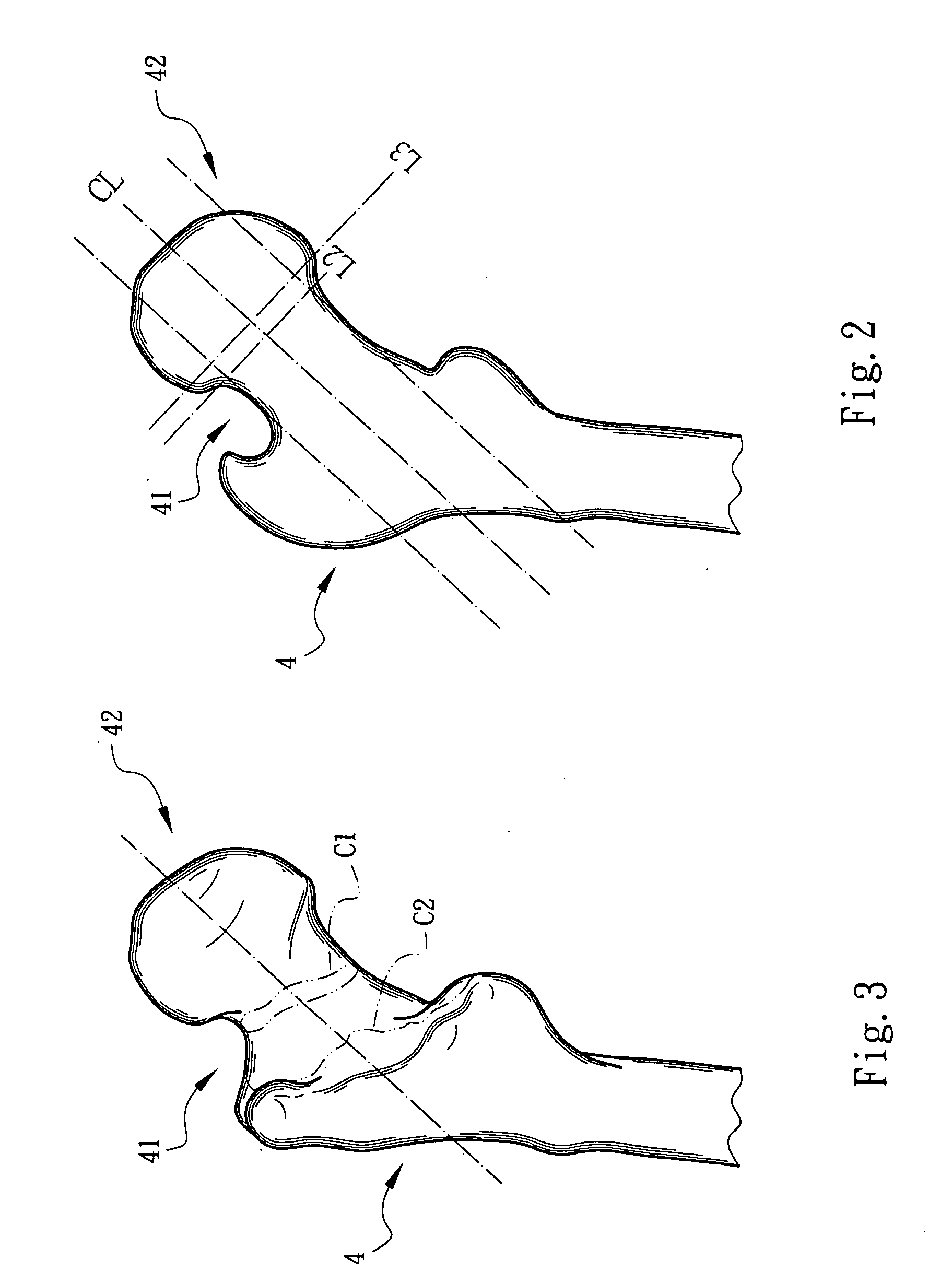
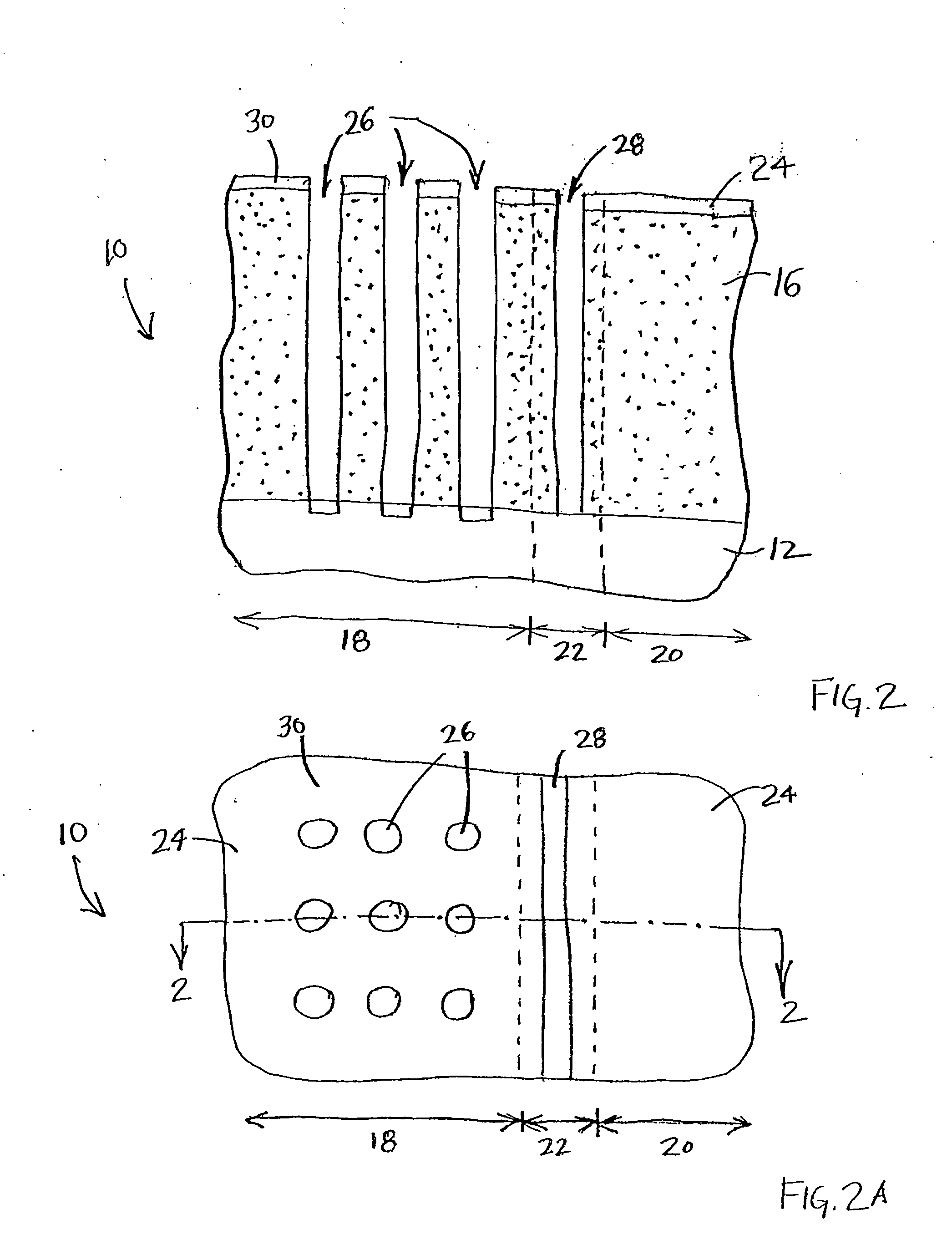
Femoral head prosthesis assembly and operation instruments thereof
InactiveUS20100168866A1Improve fitImprove the quality of operationSurgeryJoint implantsRight femoral headFemoral head prosthesis
A femoral head prosthesis assembly and operation instruments thereof. The operation instruments include a hollow femoral neck holder with a configuration adapted to the surface configuration of the femoral neck and a shaper blade for cutting a replacement end of the femur into a predetermined configuration. A guide tube is disposed on a top face of the femoral neck holder. A transverse slot is formed on the femoral neck holder for indicating a femoral head cutting line. The femoral head prosthesis assembly includes a cap body and an artificial femoral head. A root section of the cap body has an inner surface in conformity to the surface of the femoral neck. A top section of the cap body has a cross section adapted to that of the replacement end. The cap body can be precisely securely bonded with the replacement end of the femur.
Owner:SHIH GRANT LU SUN
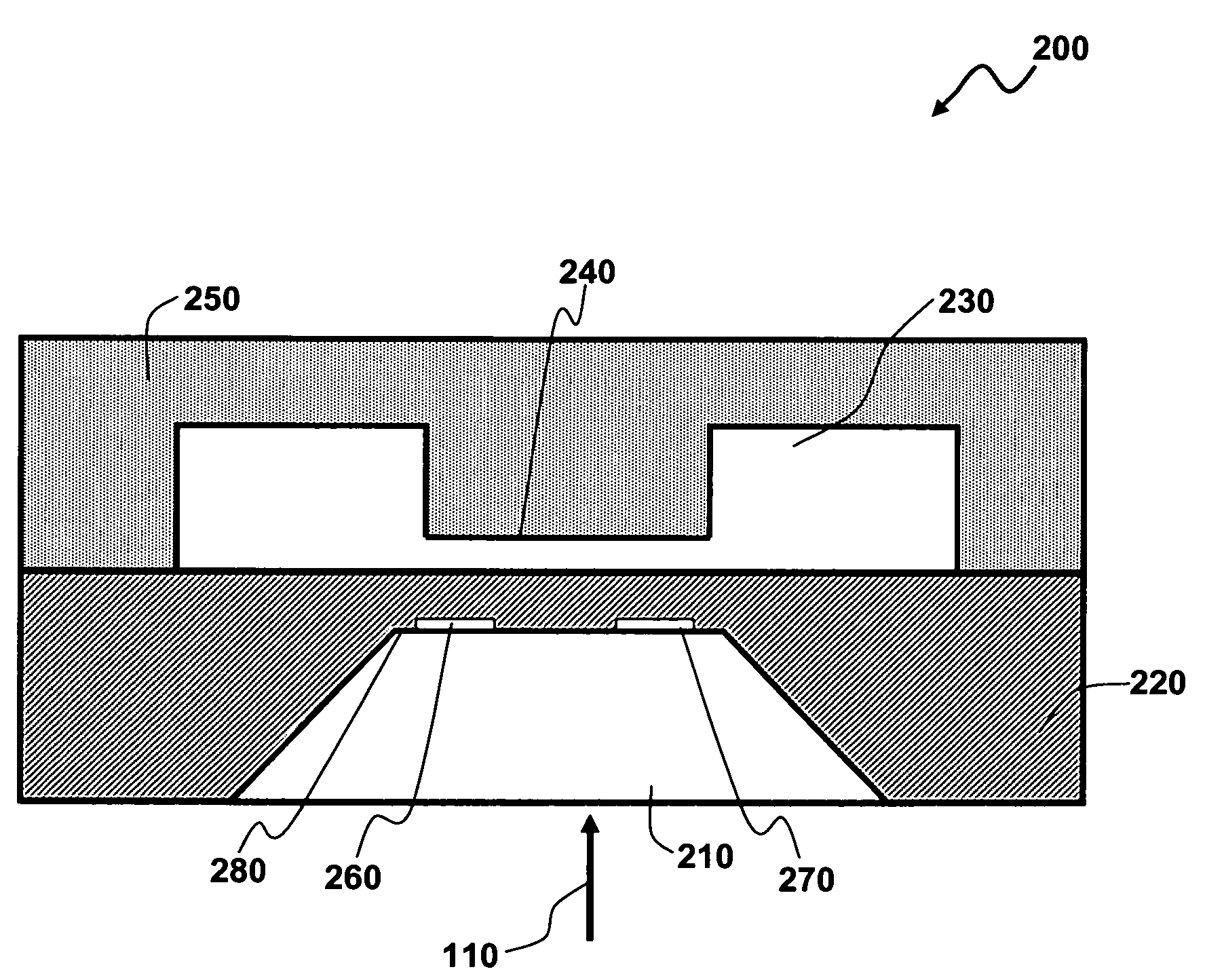
Dual span absolute pressure sense die
InactiveUS7503221B2Accurate measurementSmall voltageFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationMultiple fluid pressure valves simultaneous measurementPressure senseHigh pressure
An absolute pressure sensor includes a sense die with a reference chamber on a top side thereof. The reference chamber comprises a precisely fabricated beam that limits the travel of a diaphragm. The beam can be positioned in a cap or cover member of the sense die, thereby allowing the sense die diaphragm to move freely for a particular distance. Over this distance, the sense die will have one sensitivity. When the sense die is pressurized to a certain point, the diaphragm moves until it contacts the beam member in the cap or cover. When the diaphragm hits the beam, the sensitivity of the sense die changes, thereby allowing a smaller voltage out for the greater pressure in. Such an arrangement permits the sensor to provide a function that accurately measures low pressure and measures a higher pressure without utilizing a linear scale.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
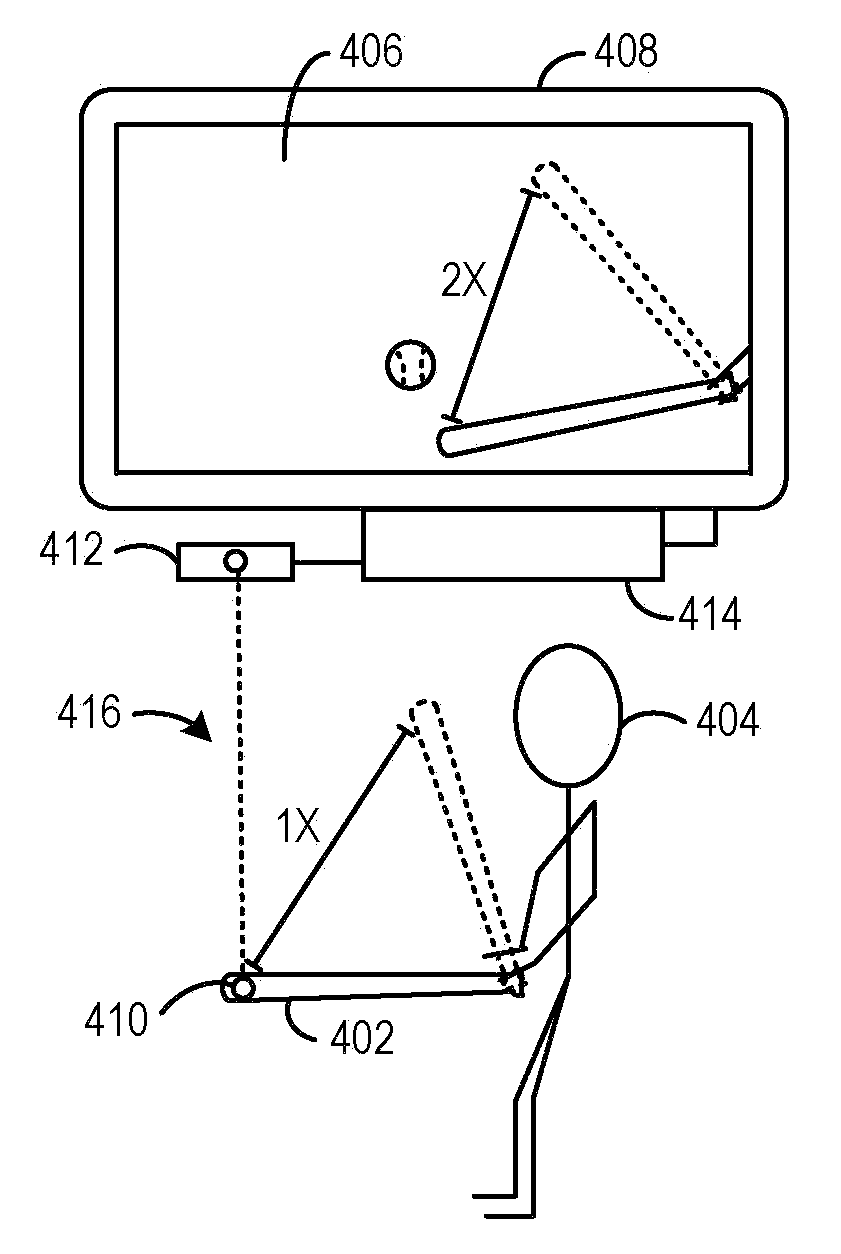
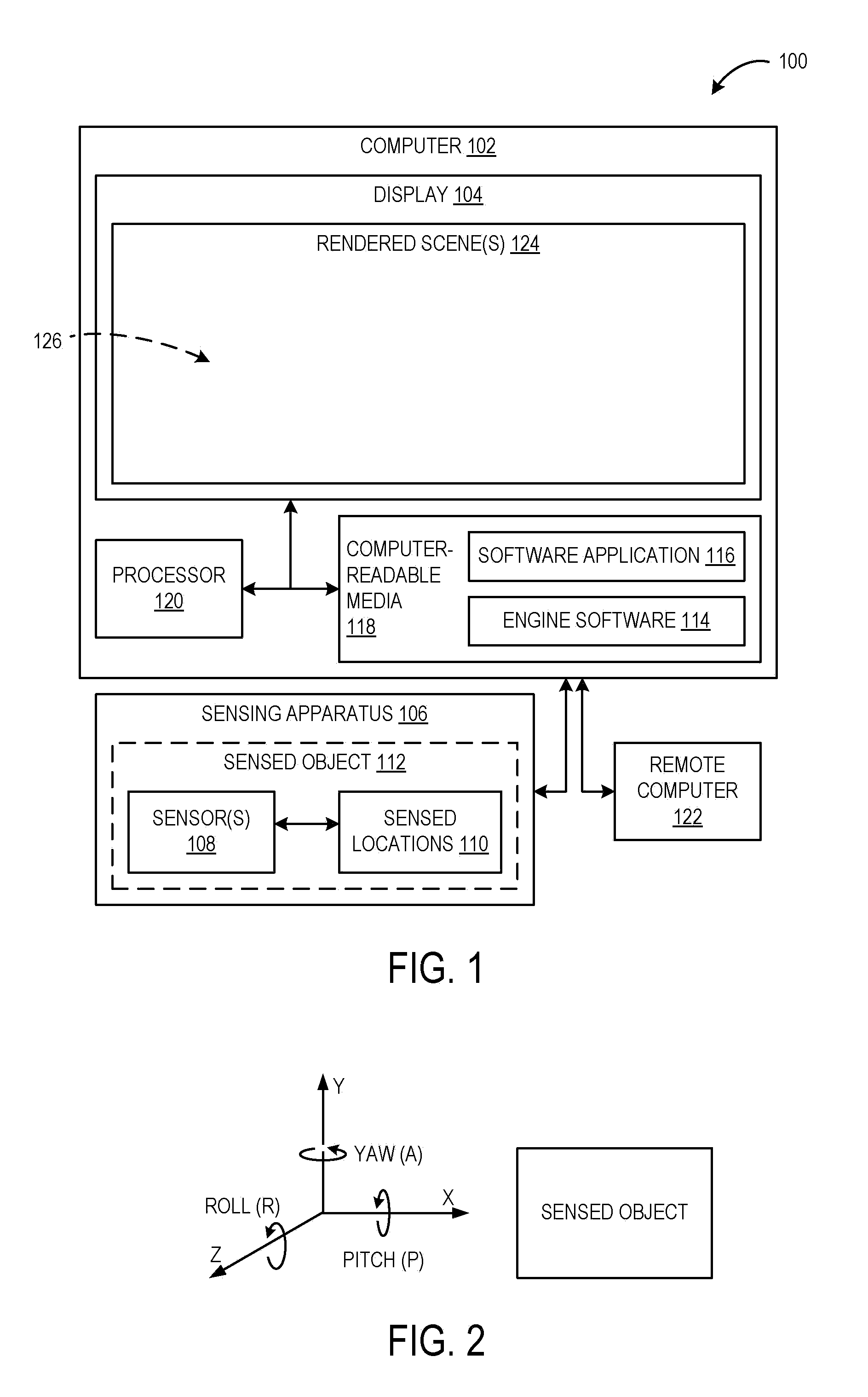
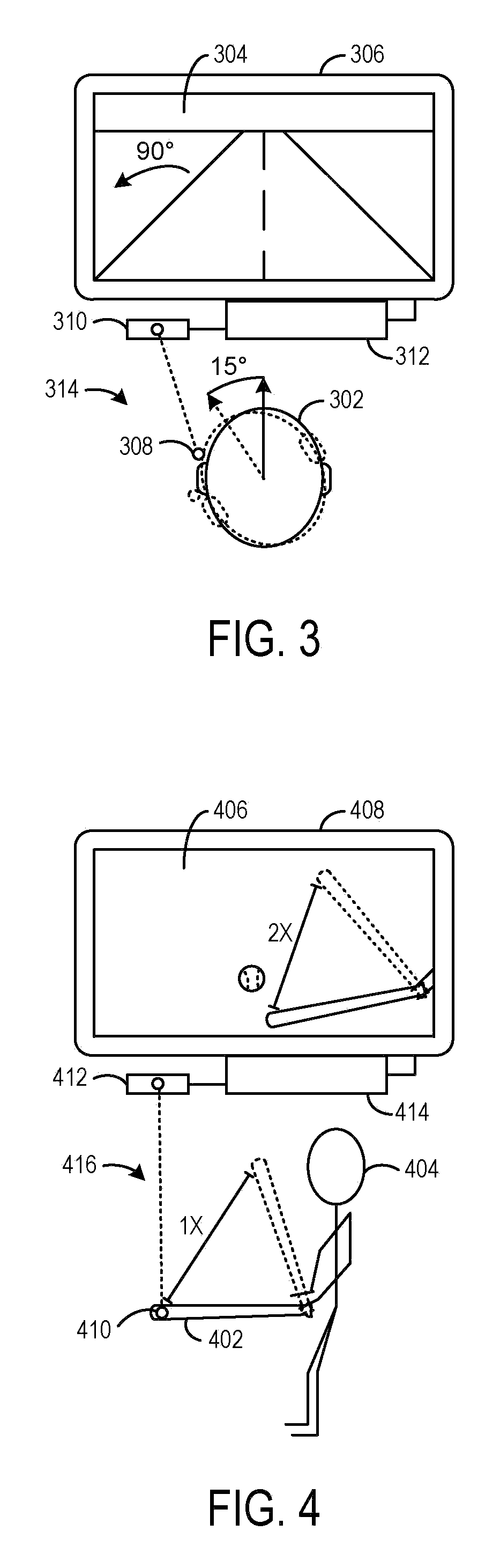
Approach for Merging Scaled Input of Movable Objects to Control Presentation of Aspects of a Shared Virtual Environment
InactiveUS20080211771A1Authenticity of be improveAccurately simulateCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo gamesApplication softwareUser control
A system for controlling operation of a computer. The system includes, a sensing apparatus configured to obtain positional data of a sensed object controllable by a first user, such positional data varying in response to movement of the sensed object, and engine software operatively coupled with the sensing apparatus and configured to produce control commands based on the positional data, the control commands being operable to control, in a multi-user software application executable on the computer, presentation of a virtual representation of the sensed object in a virtual environment shared by the first user and a second user, the virtual representation of the sensed object being perceivable by the second user in a rendered scene of the virtual environment, where the engine software is configured so that the movement of the sensed object produces control commands which cause corresponding scaled movement of the virtual representation of the sensed object in the rendered scene that is perceivable by the second user.
Owner:NATURALPOINT
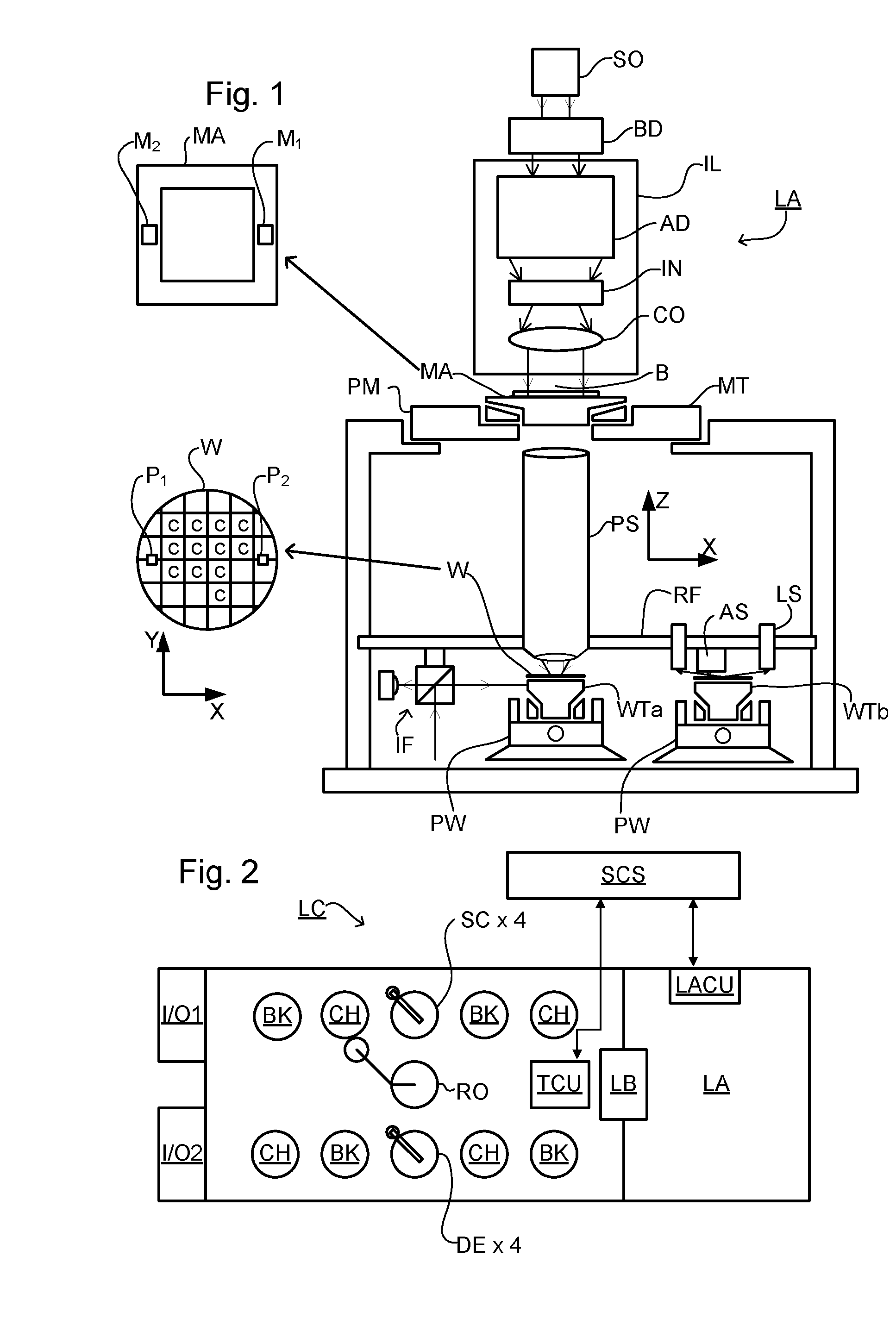
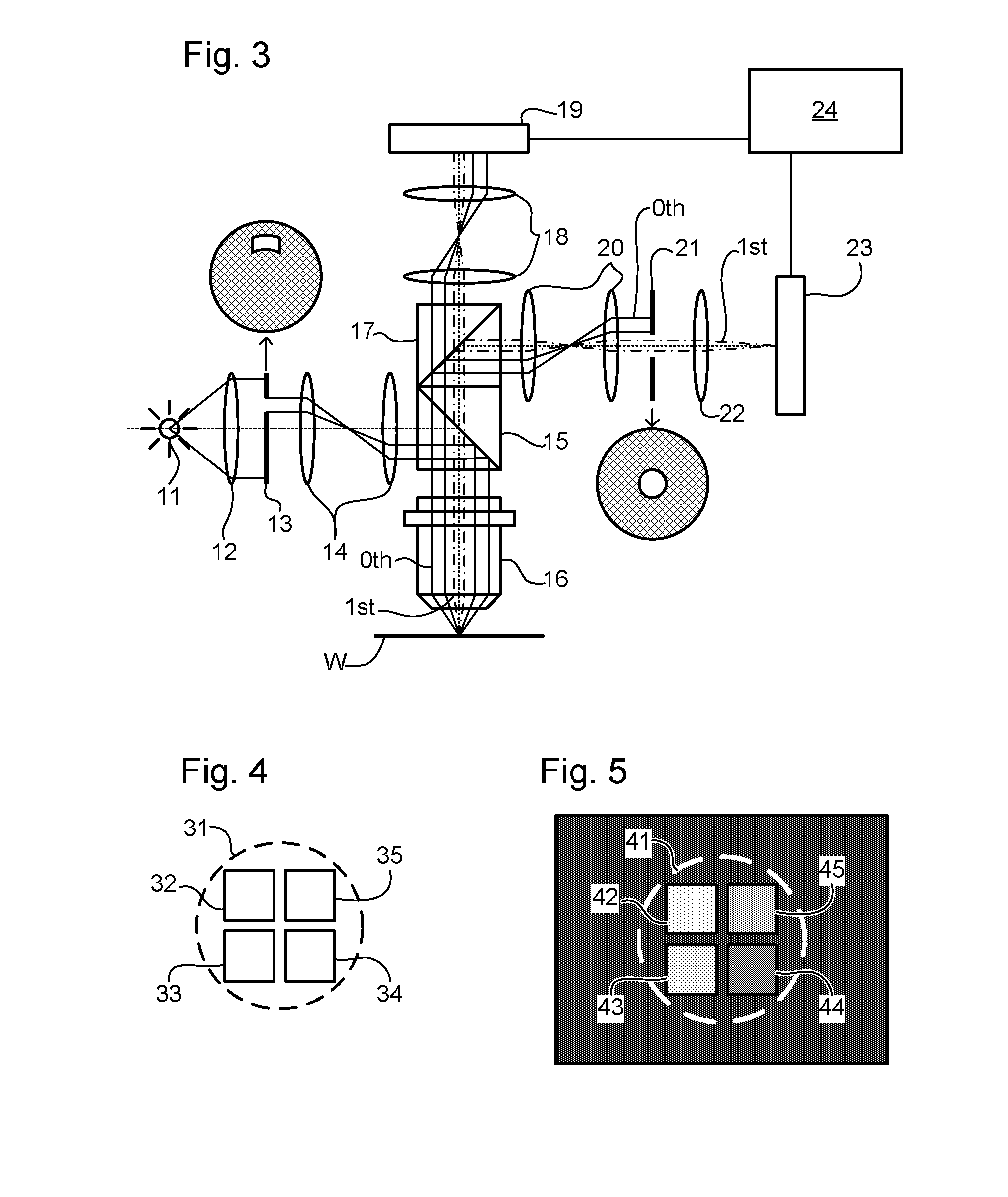
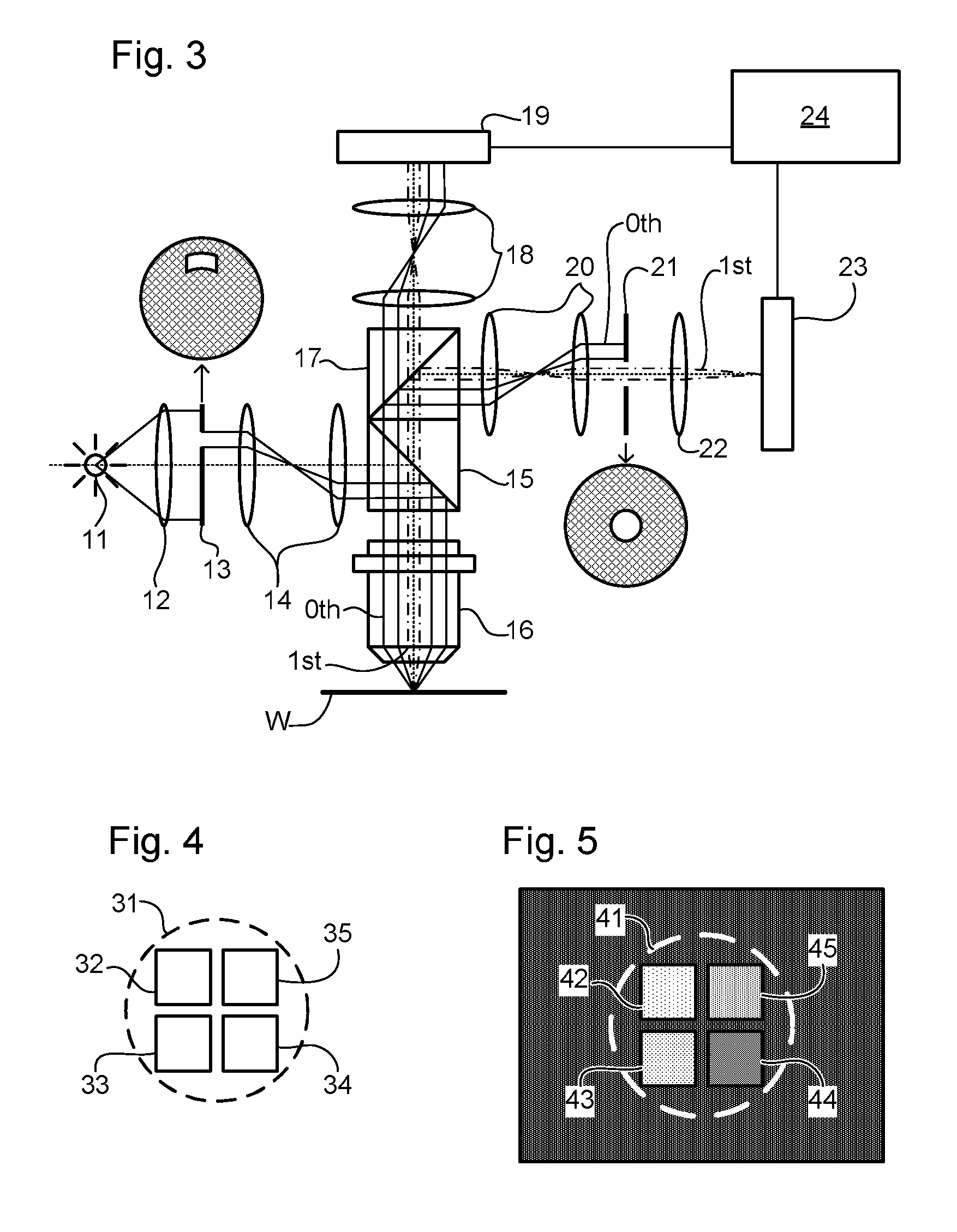
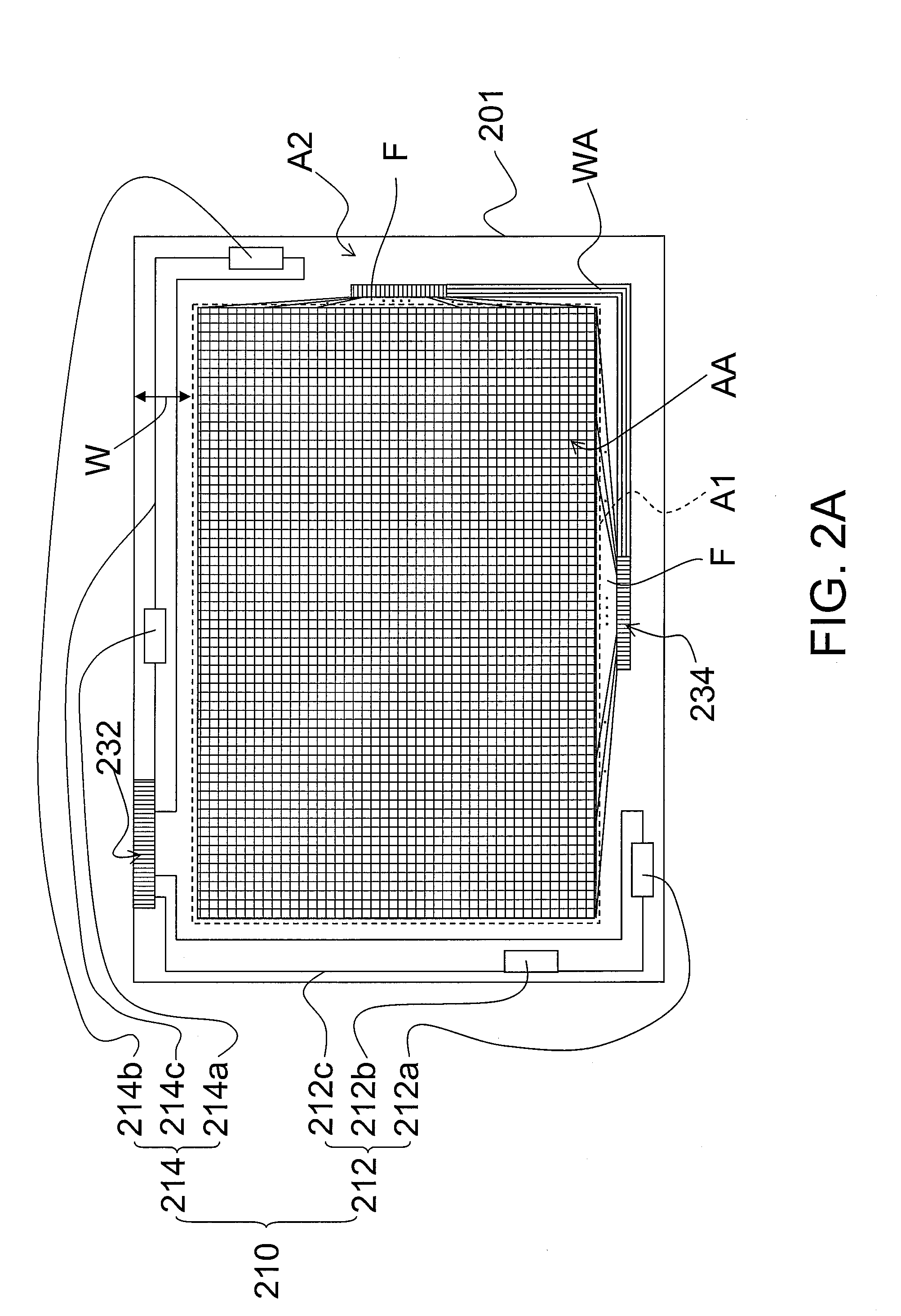
Metrology method and apparatus, lithographic apparatus, device manufacturing method and substrate
ActiveUS8411287B2Made preciselyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansGratingMetrology
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
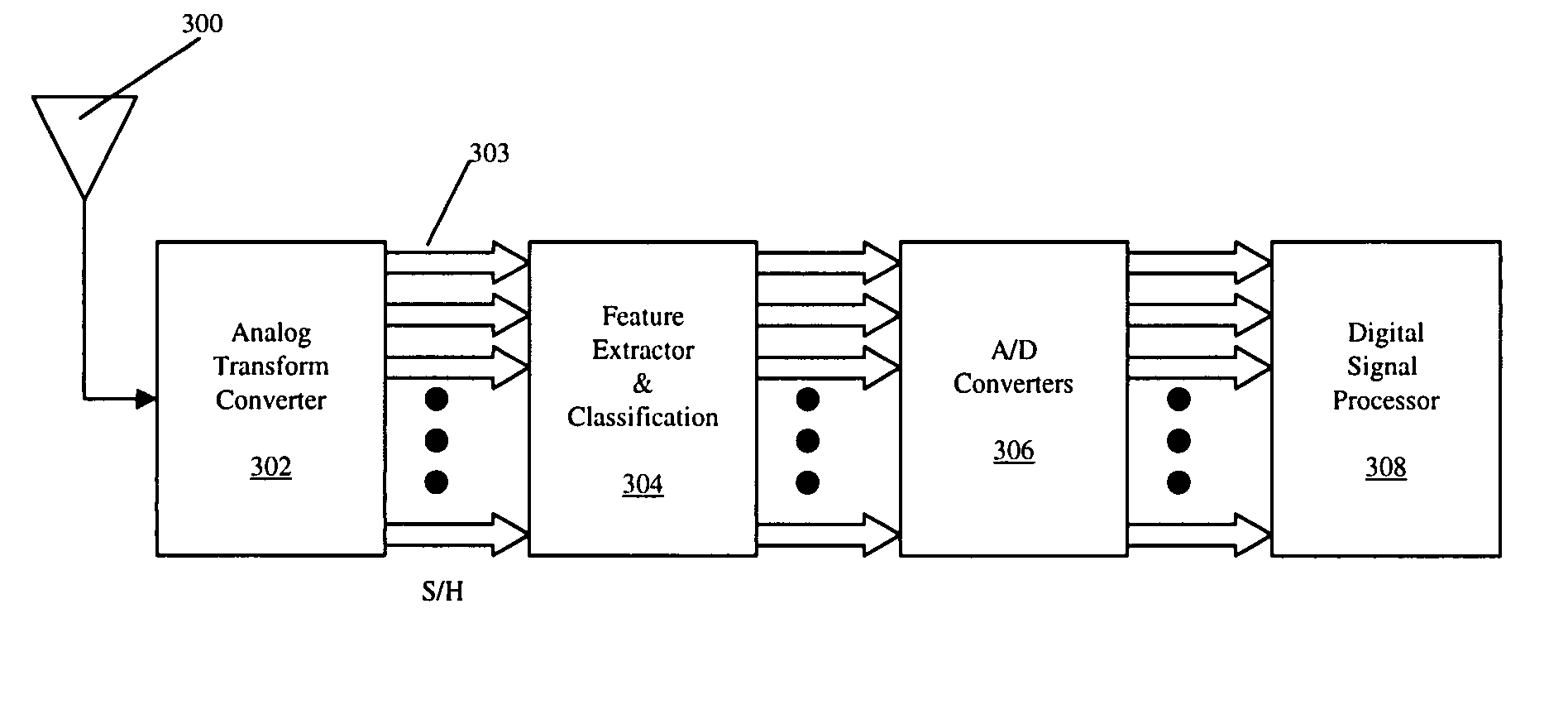
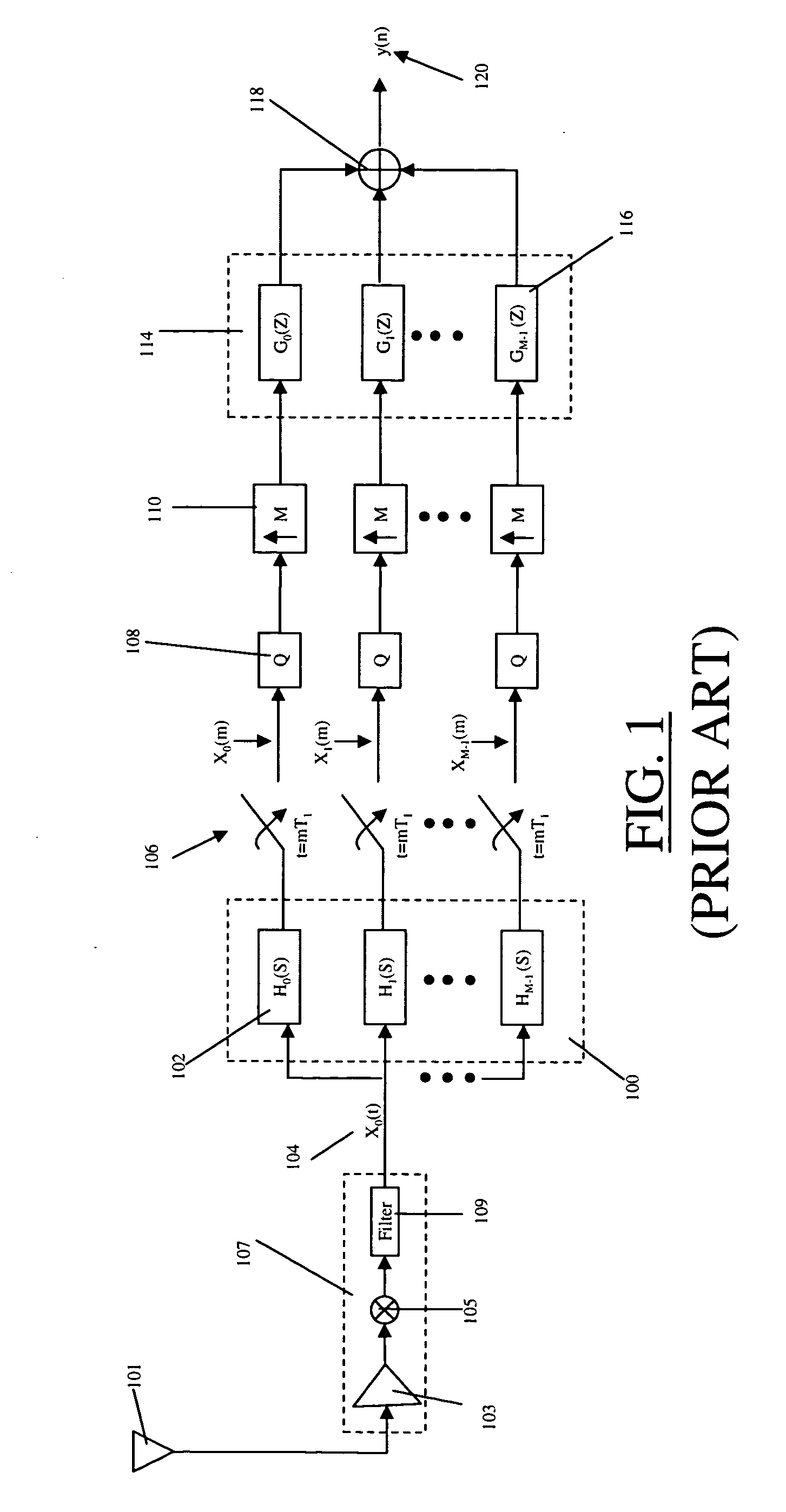
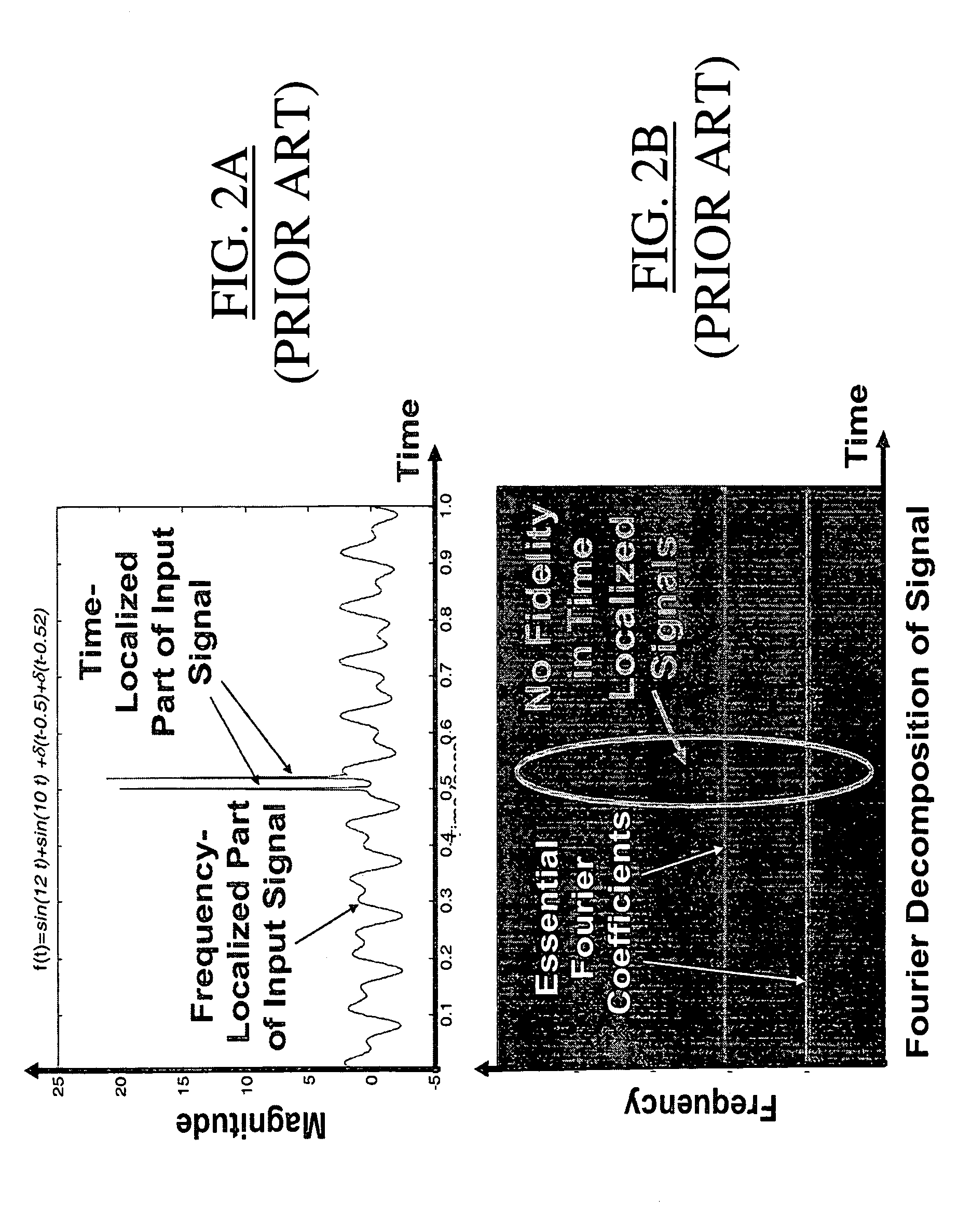
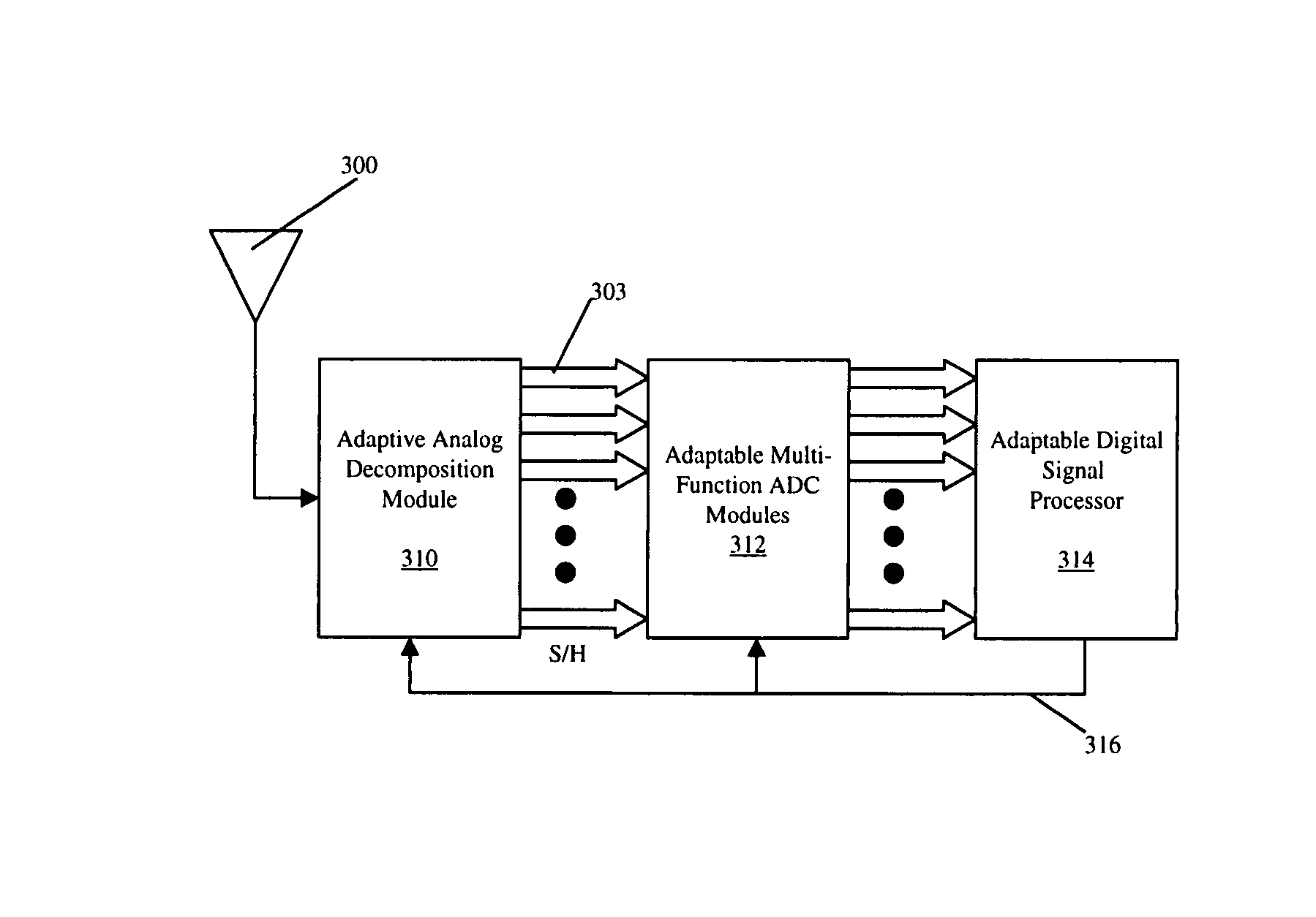
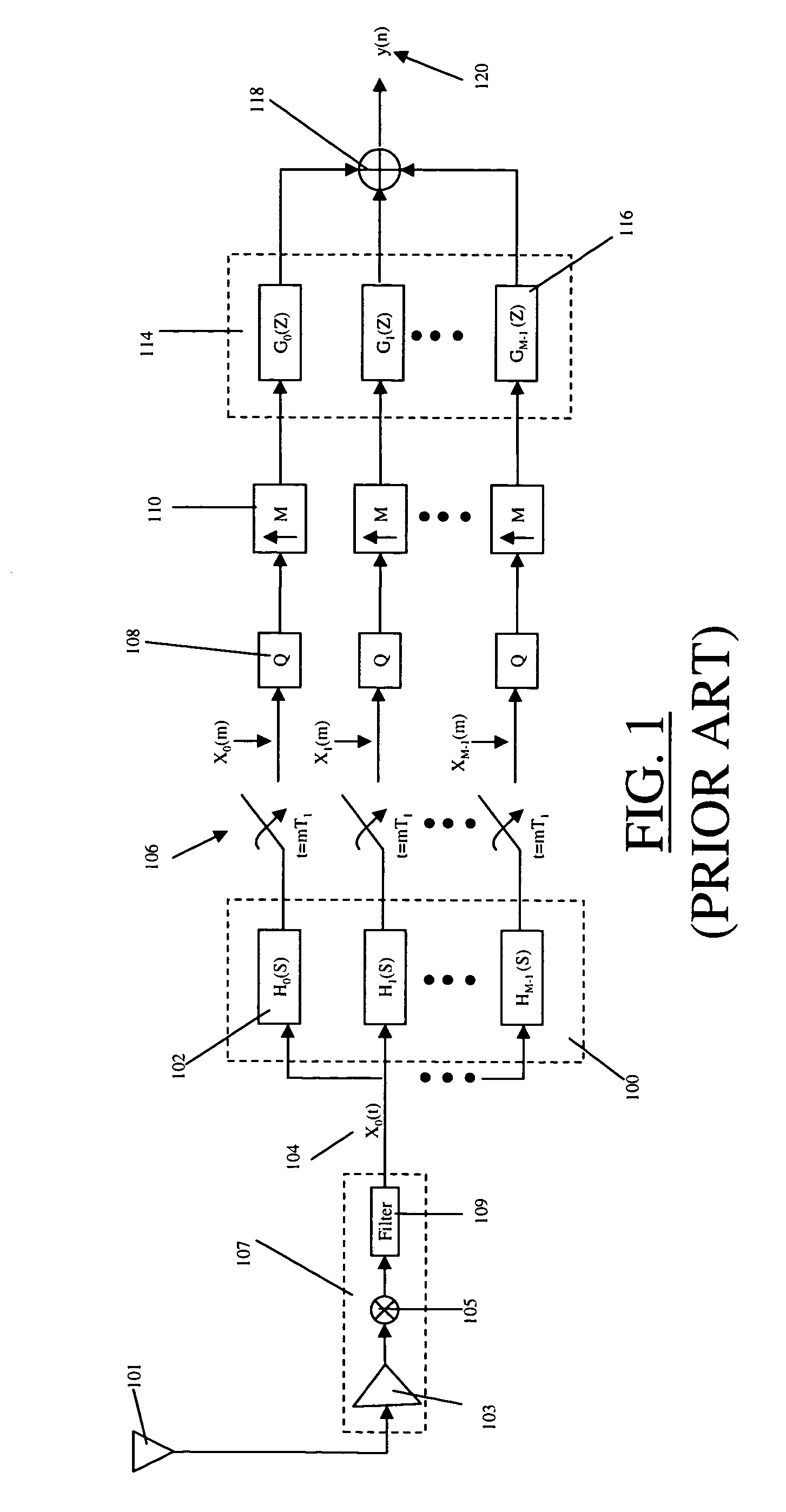
Adaptive, intelligent transform-based analog to information converter method and system
InactiveUS20050156775A1Made preciselyImprove detection rateElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFeature extractionAnalog signal
The present invention provides an adaptive, intelligent transform based Analog to Information Converter (AIC) for wideband signals by directly converting an analog signal to information (e.g., features, decisions). This direct conversion is achieved by (i) capturing most of the information of a wideband signal via hardware / software implemented mathematical transformations, (ii) effectively removing unwanted signals such as jammer and interfere from the input signal, and (iii) using novel algorithms for highly accurate decision making and feature extraction (e.g., high probability of detection with low probability of false alarm). The jump in the improvement over today's state-of-the-art is in terms of effective and optimum signal information extraction at high-speed.
Owner:HRL LAB
Adaptive, intelligent transform-based analog to information converter method and system
InactiveUS7324036B2Effectively removing unwanted signalsMade preciselyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionFeature extractionAnalog signal
The present invention provides an adaptive, intelligent transform based Analog to Information Converter (AIC) for wideband signals by directly converting an analog signal to information (e.g., features, decisions). This direct conversion is achieved by (i) capturing most of the information of a wideband signal via hardware / software implemented mathematical transformations, (ii) effectively removing unwanted signals such as jammer and interfere from the input signal, and (iii) using novel algorithms for highly accurate decision making and feature extraction (e.g., high probability of detection with low probability of false alarm). The jump in the improvement over today's state-of-the-art is in terms of effective and optimum signal information extraction at high-speed.
Owner:HRL LAB
System for calculating IOL power
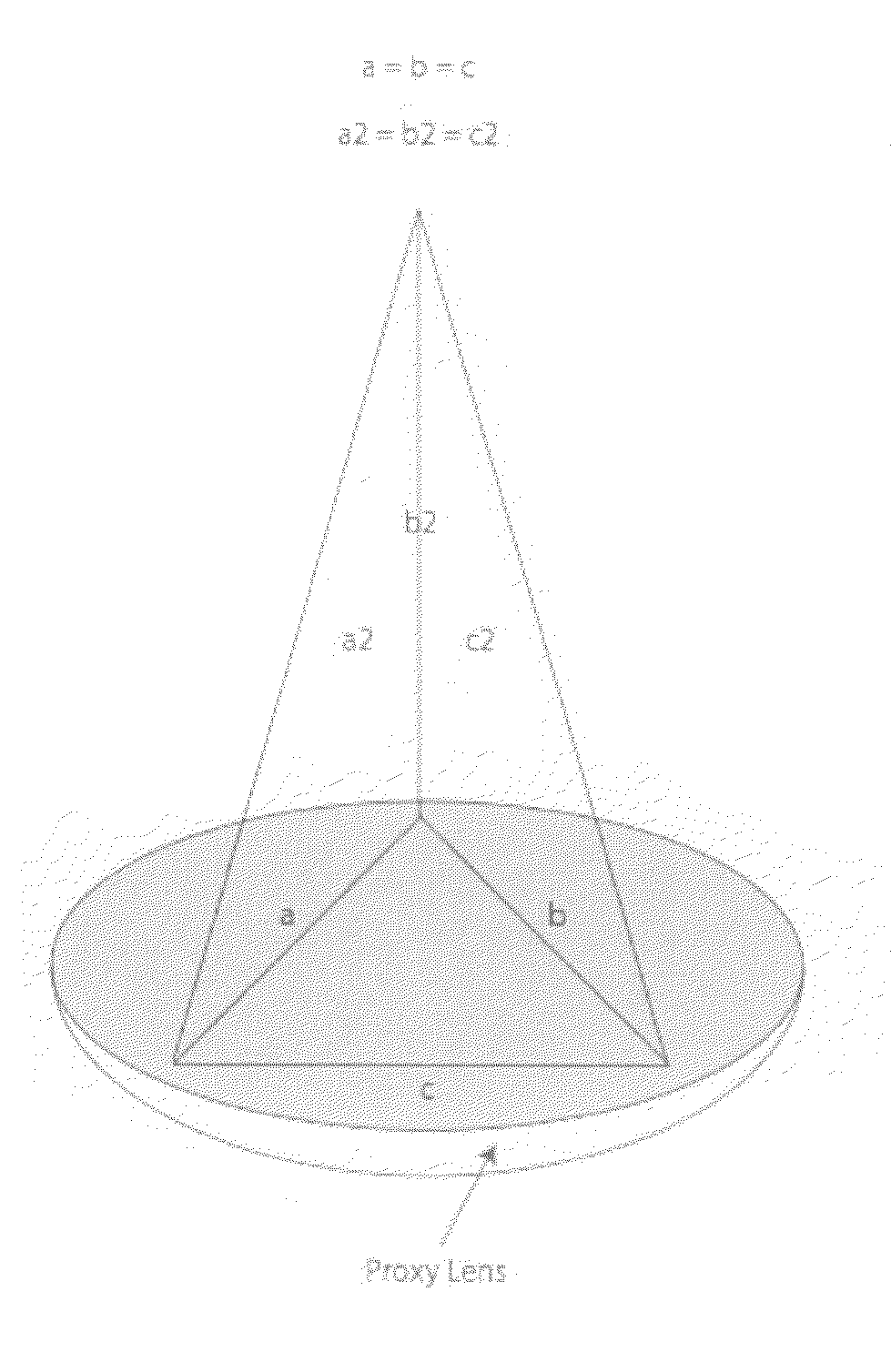
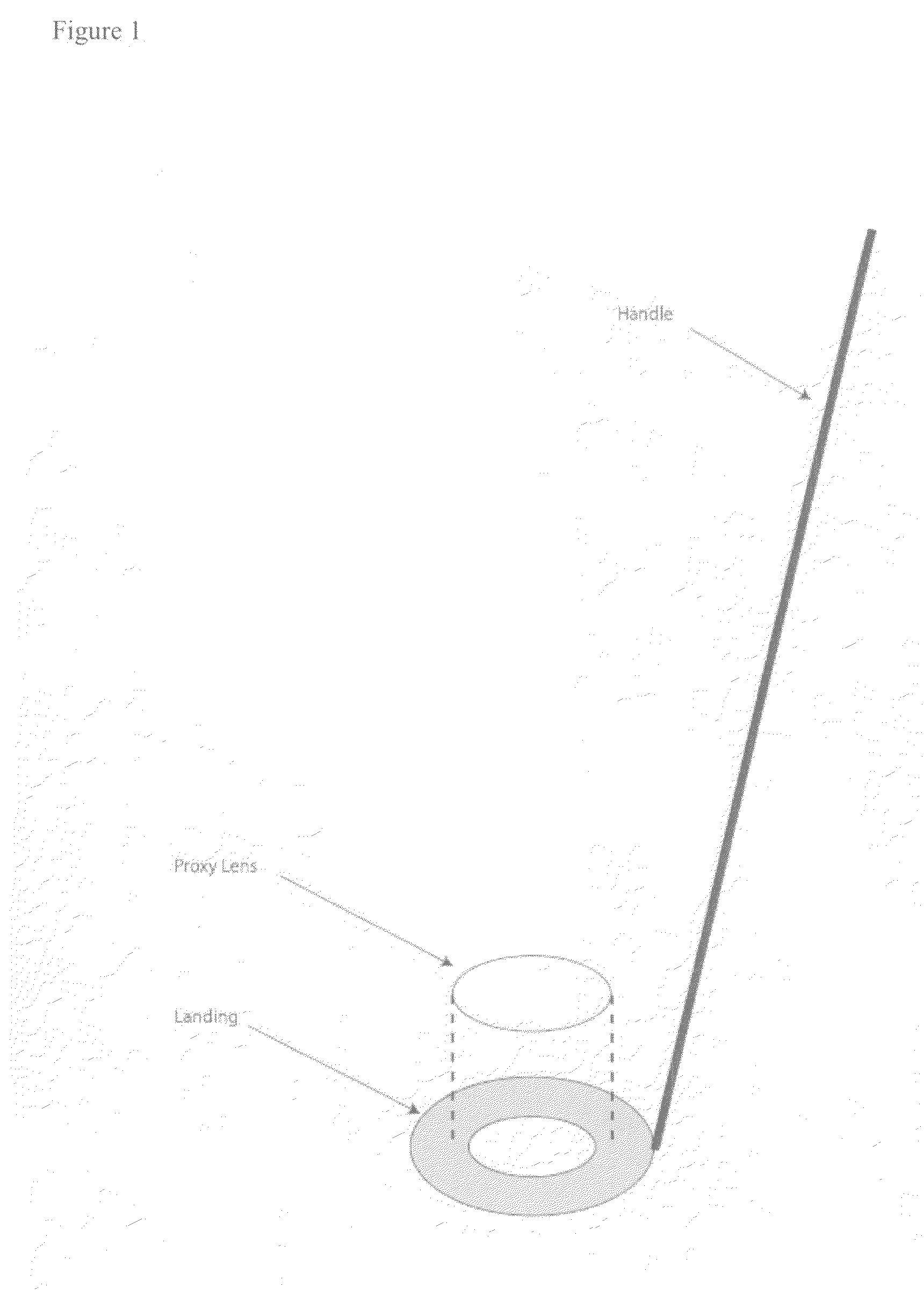
InactiveUS20080004610A1Improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellnessReduce probabilityEye surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive measurementsCamera lens
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus to improve human ophthalmic surgery patient wellness and surgical procedural outcome of both indicated cataract surgery and elective surgeries with the implantation of permanent standard intraocular lens (IOL) and new technology intraocular lens (NTIOL). The present invention further relates to measurement of refraction intra-operatively to validate or obviate the pre-operative calculations and thus selection of the IOL or NTIOL and allow for a correction to be made intra-operatively before the permanent IOL or NTIOL is implanted. Specifically, several embodiments of the invention pertain to a disposable, temporary Proxy Lens apparatus that are used for in situ refractive measurements, an Insertion Tool apparatus to manipulate the Proxy Lens within the optical path for the refractive measurement and a Refractometer apparatus to perform the refractive measurements.
Owner:MILLER DAVID +4
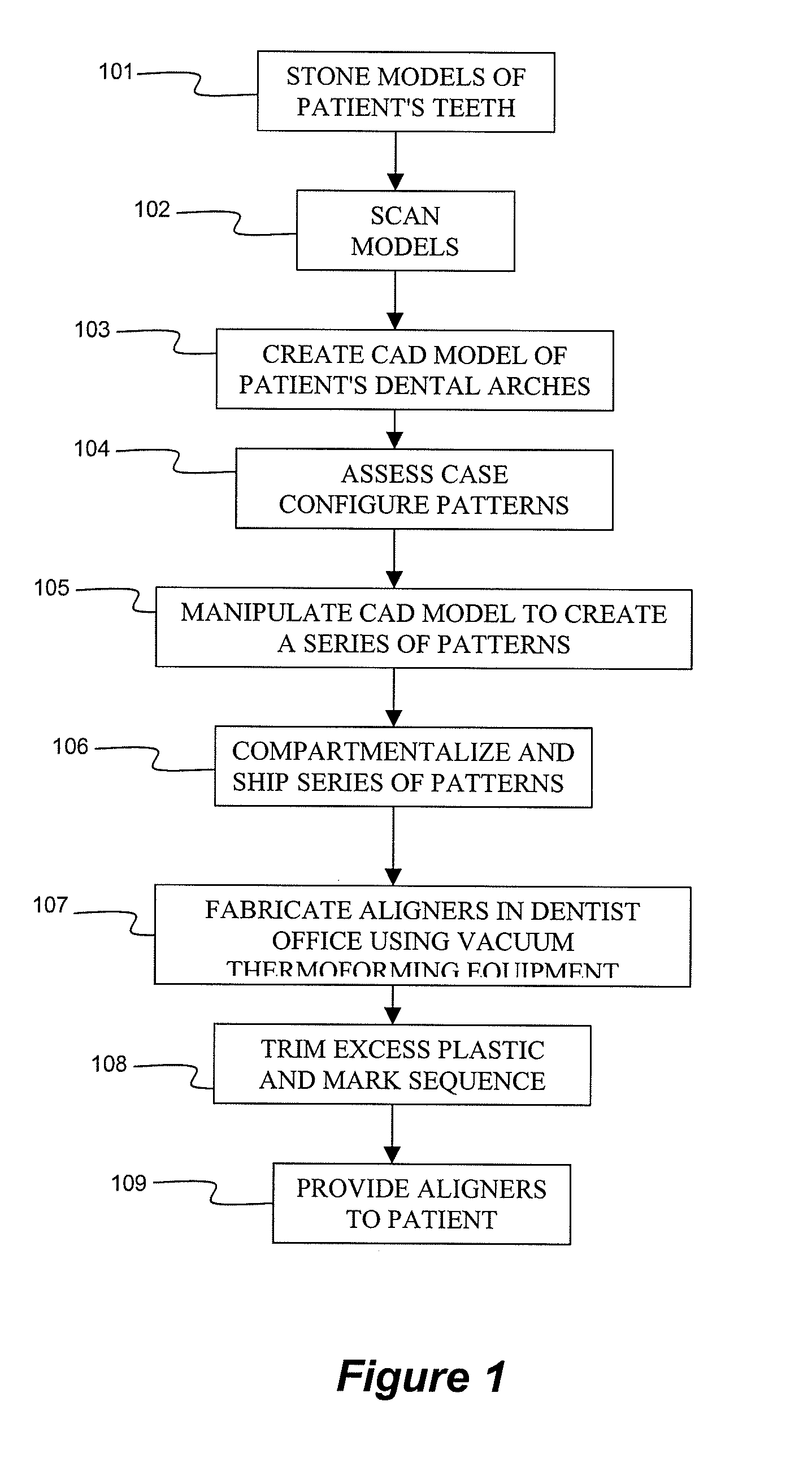
System and method for fabricating orthodontic aligners
InactiveUS20080050692A1Made preciselyImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusLaser cuttingEngineering
The present invention is directed to a method of fabricating a successive set of patterns representing incremental stages of an orthodontic treatment plan, and then sending all or a portion of the successive patterns at the same time to the dentist. The dentist is provided with a vacuum machine for thermoforming a set of aligners as negative impressions of the positive teeth patterns. A polymeric sheet is inserted into a vacuum forming machine and sucked down over the positive pattern, forming a polymeric shell with cavities shaped to receive the teeth and resiliently bias or reposition at least some of the teeth into alignment with the aligner cavities. When the aligner is formed and while still on the stereolithographic plastic pattern, excess portions of the aligner polymeric material are trimmed using manual tools and / or a laser cutting machine.
Owner:HILLIARD JACK KEITH
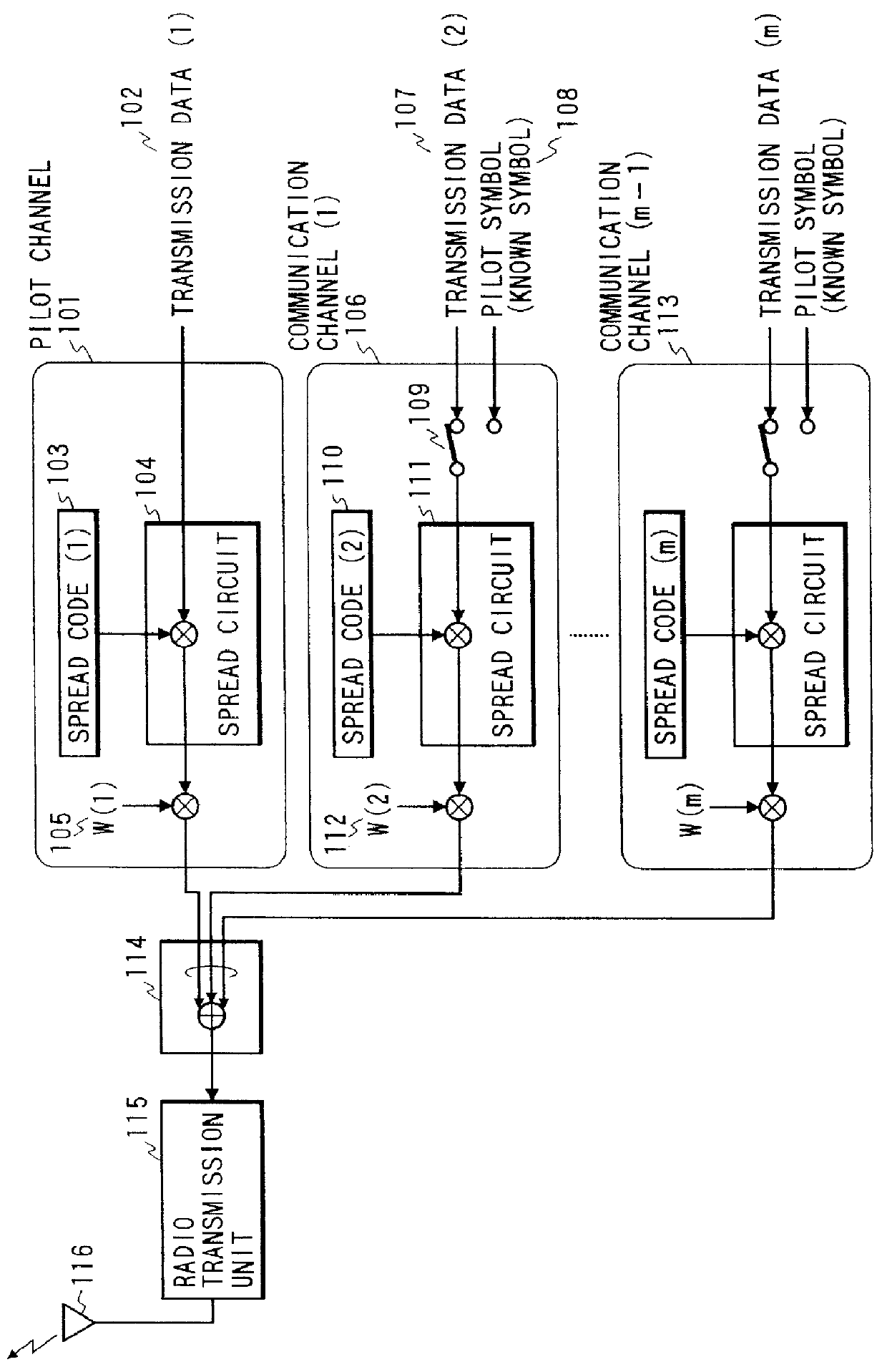
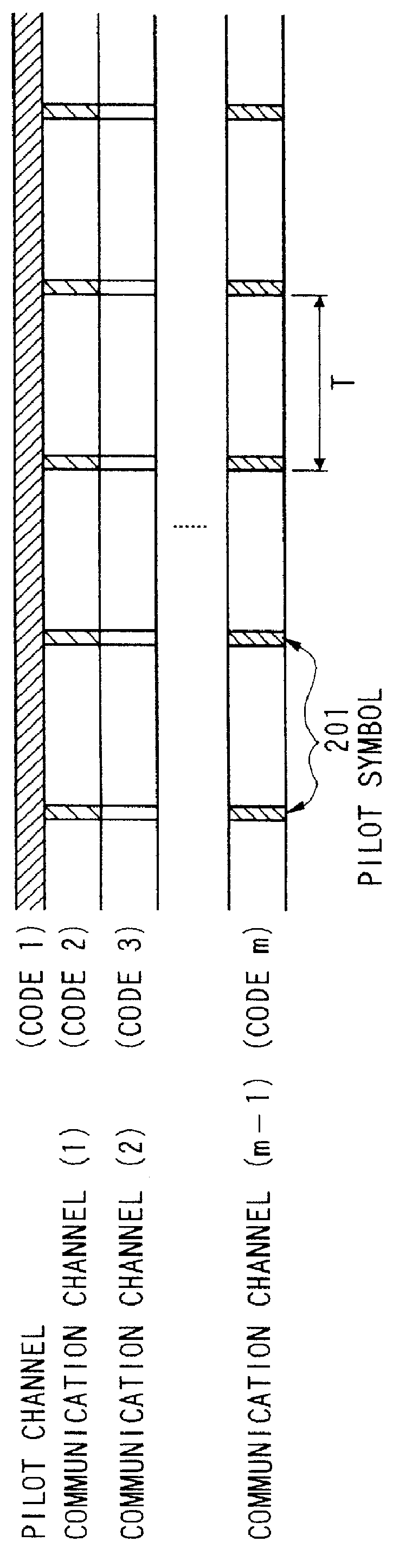
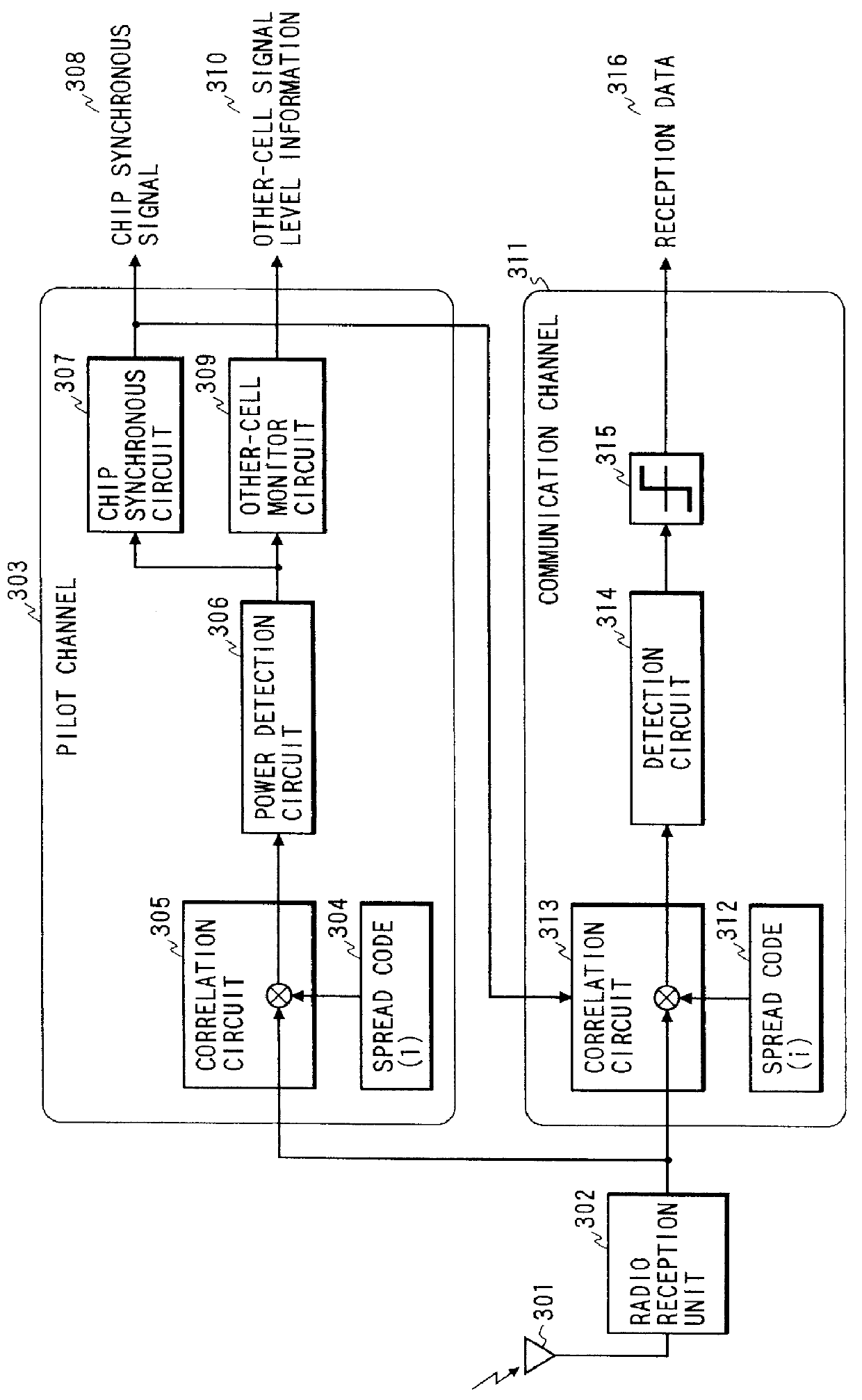
CDMA cellular radio transmission system
InactiveUS6028852AIncrease powerImprove reliabilityPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCellular radioEngineering
A base station transmits, in addition to a pilot channel, signals which are multiplexed with pilot symbols inserted in the respective signals in communication channels. As the transmission of the pilot channel as a reference signal for coherent detection is unnecessary with high power so as to attain high reliability, the pilot channel can be transmitted with low power by means of weight in comparison with the communication channel, so that interference with the communication channel of any other station is reduced. Moreover, accurate coherent detection can be made from the pilot symbol inserted in the communication channel on the mobile station side.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
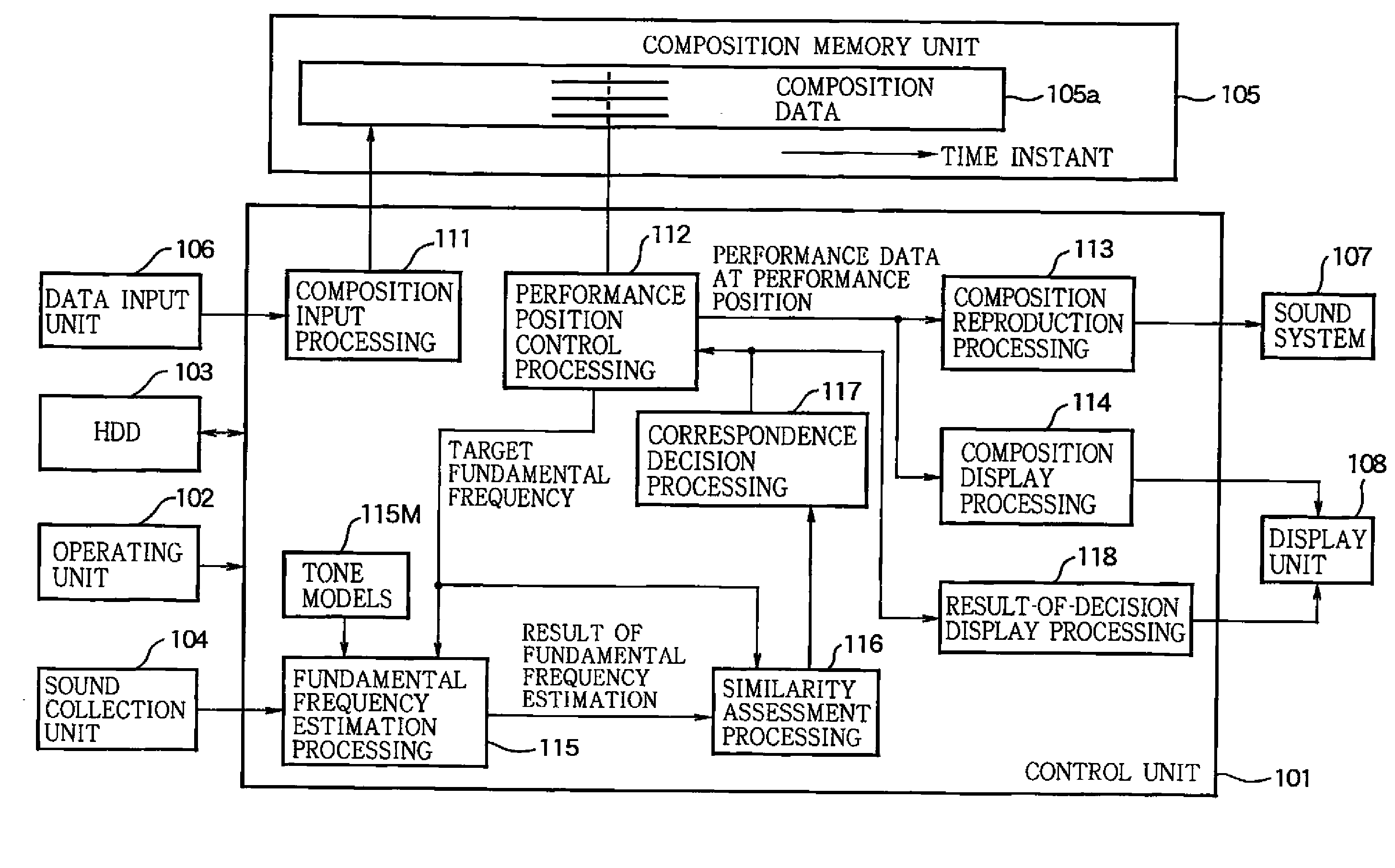
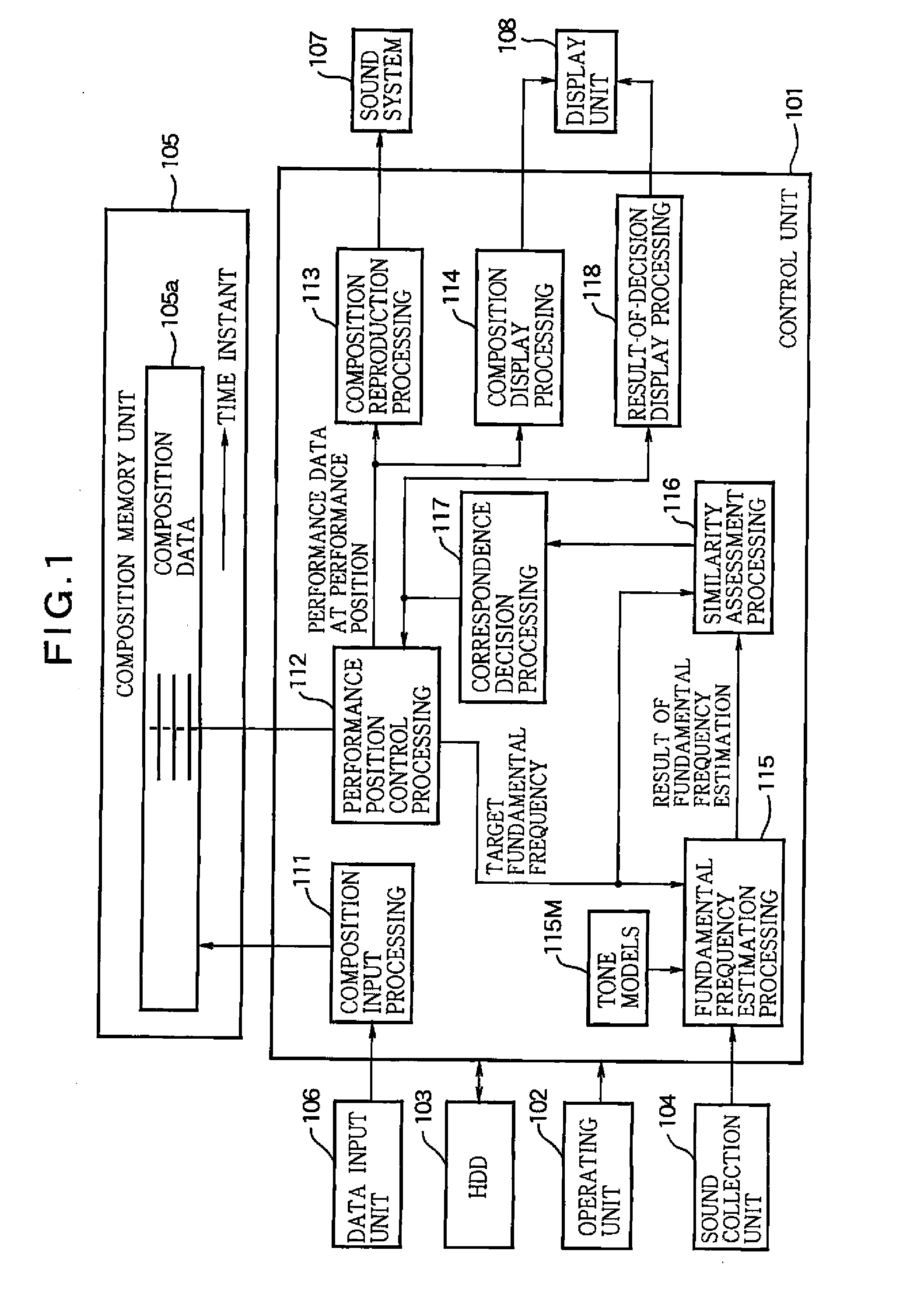
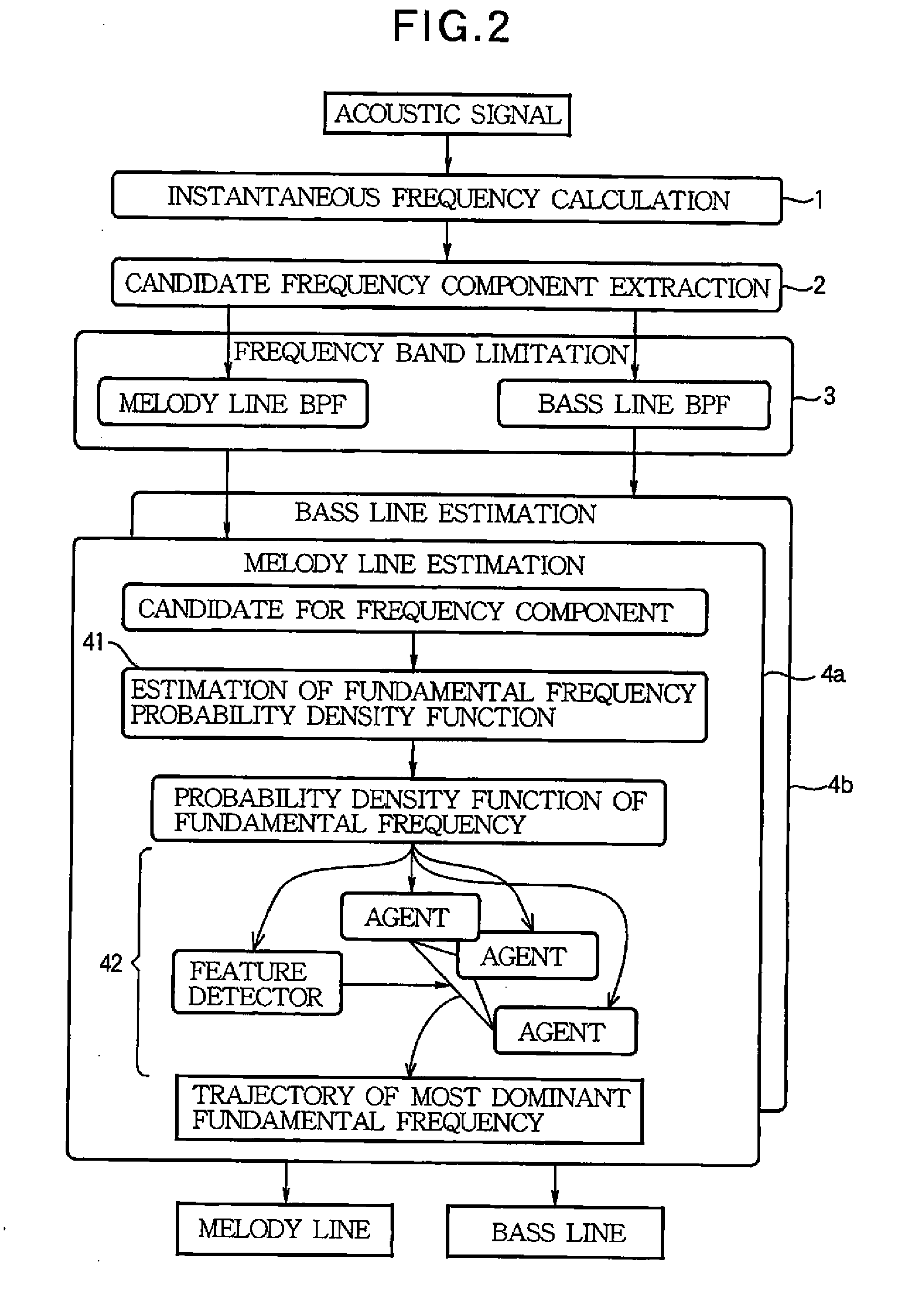
Sound analysis apparatus and program
InactiveUS20080202321A1Made preciselyHigh-precision estimationElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsWeight valueFundamental frequency
A sound analysis apparatus employs tone models which are associated with various fundamental frequencies and each of which simulates a harmonic structure of a performance sound generated by a musical instrument, then defines a weighted mixture of the tone models to simulate frequency components of the performance sound, further sequentially updates and optimizes weight values of the respective tone models so that a frequency distribution of the weighted mixture of the tone models corresponds to a distribution of the frequency components of the performance sound, and estimates the fundamental frequency of the performance sound based on the optimized weight values.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Touch display panel and display apparatus
InactiveUS20110080376A1Manufacturing precision is very highLow transmitting line resistanceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsTouch SensesMedia layer
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
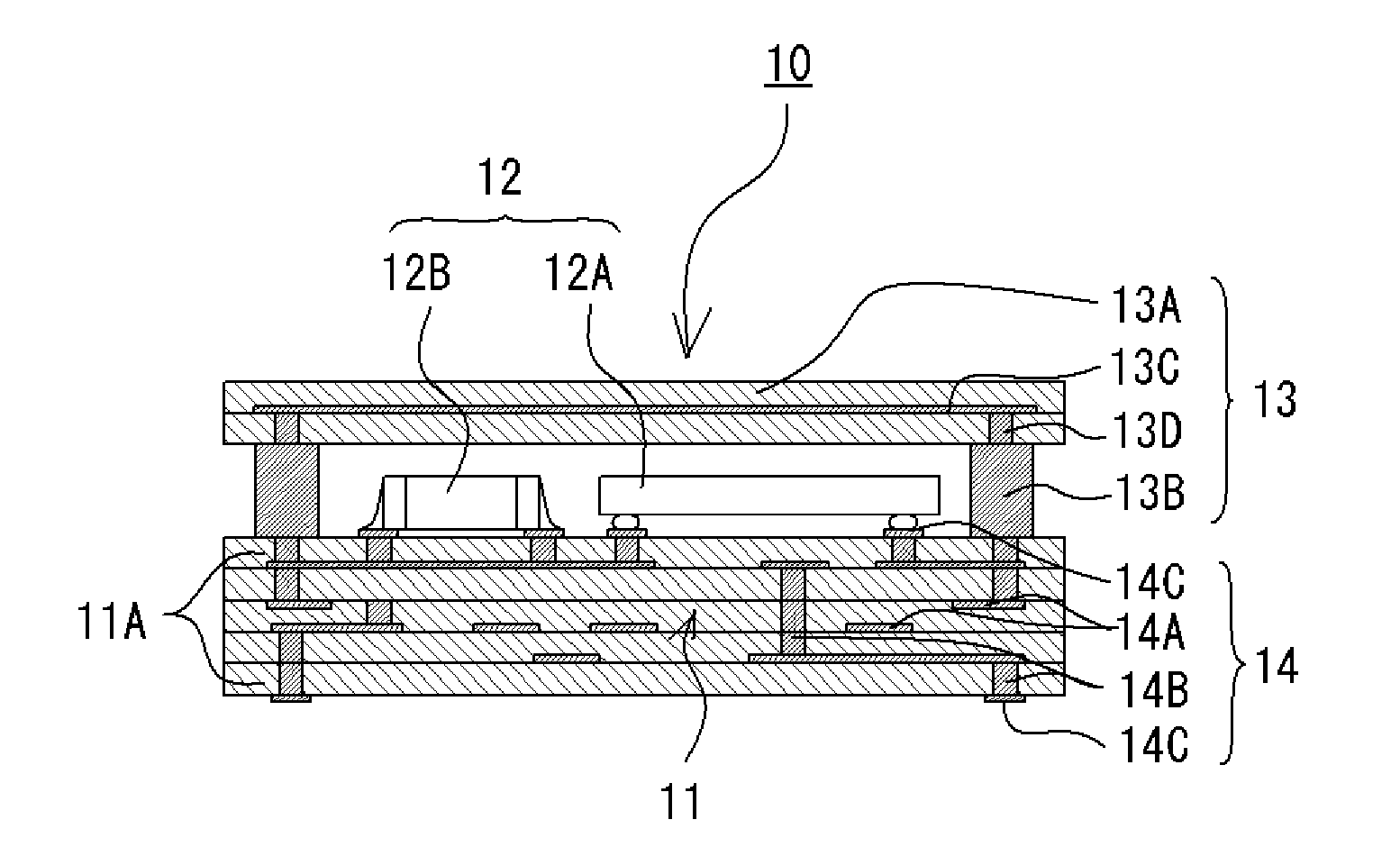
Electronic component and its manufacturing method
ActiveUS20070221399A1Reduce heightAccurately fabricateMagnetic/electric field screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionEngineeringSurface mounting
An electronic component includes a wiring board having a wiring pattern, a surface mount device mounted on an upper surface of the wiring board, and a cap arranged to cover the wiring board. The cap includes a top portion made of a flat ceramic member, and a leg portion made of a columnar member having a height similar to a height of the surface mount devices.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
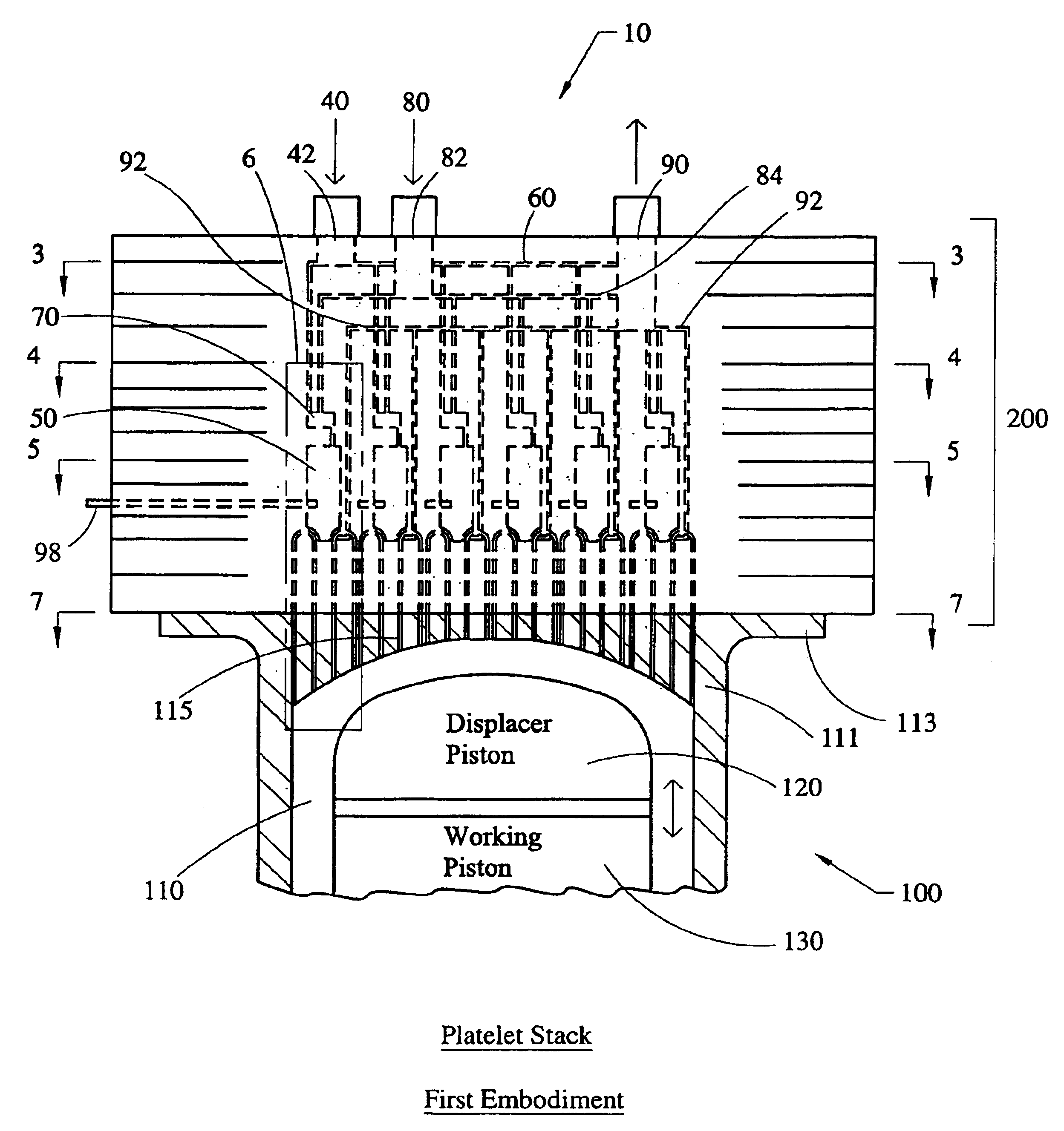
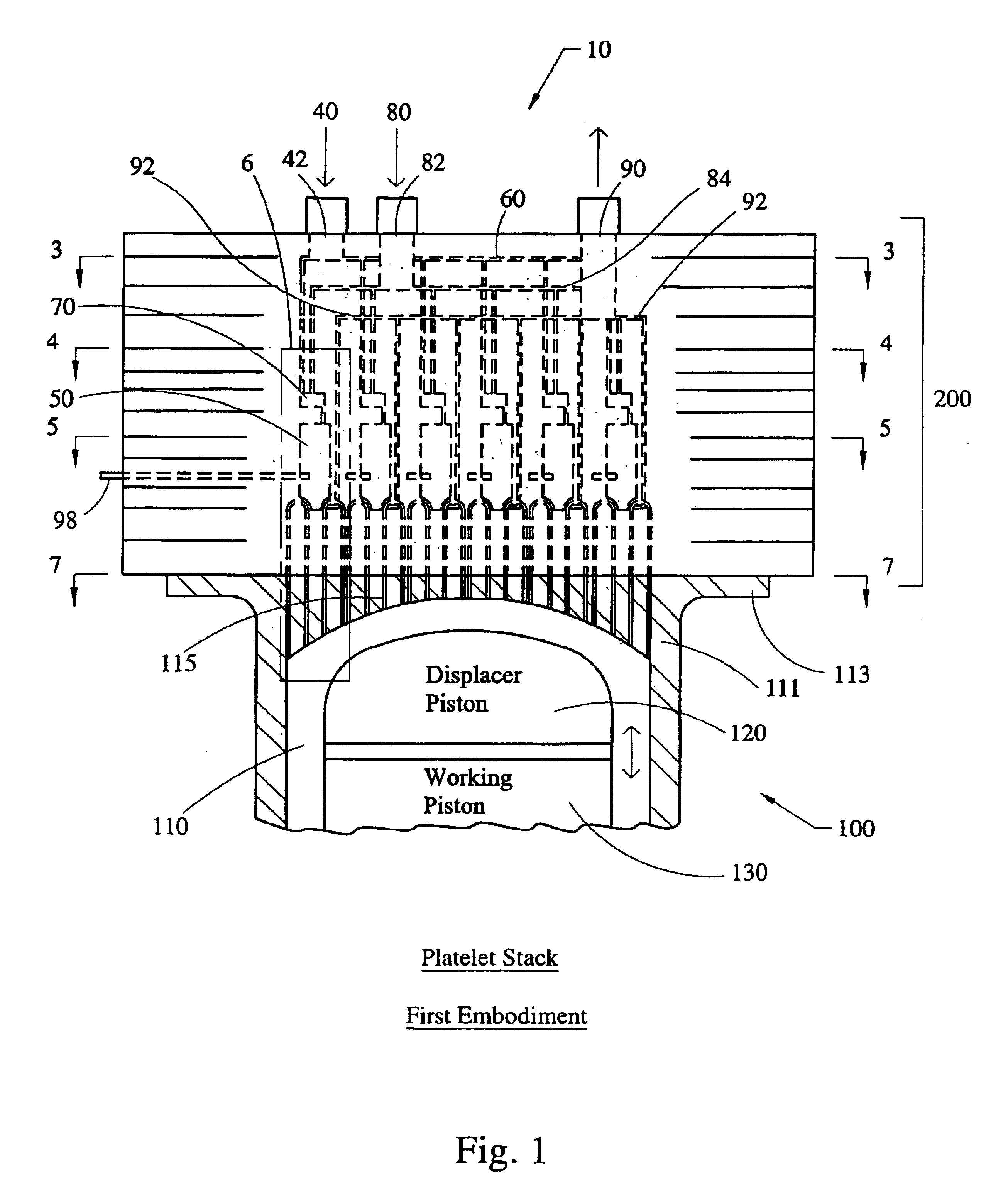
Stirling engine having platelet heat exchanging elements
InactiveUS6931848B2Guaranteed uptimeEfficient heat transferSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringStaged combustion
The present invention provides heat exchanging elements for use in Stirling engines. According to the present invention, the heat exchanging elements are made from muliple platelets that are stacked and joined together. The use of platelets to make heat exchanging elements permits Stirling engines to run more effiecient because the heat transfer and combustion processes are improved. In one embodiment, multi-stage combustion can be introduced with platlets, along with the flexibility to use different types of fuels. In another embodiment, a single component constructed from platelets can provide the heat transfer rquirements betweeen the combustion gas / working gas, working gas in the regenerator and the working gas / coolant fluid of a Stirling engine. In another embodiment, the platelet heat exchanging element can recieve solar energy to heat the Stirling engine's working gas. Also, this invention provides a heat exchanging method that allows for multiple fluids to flow in opposing or same direction.
Owner:DISENCO +1
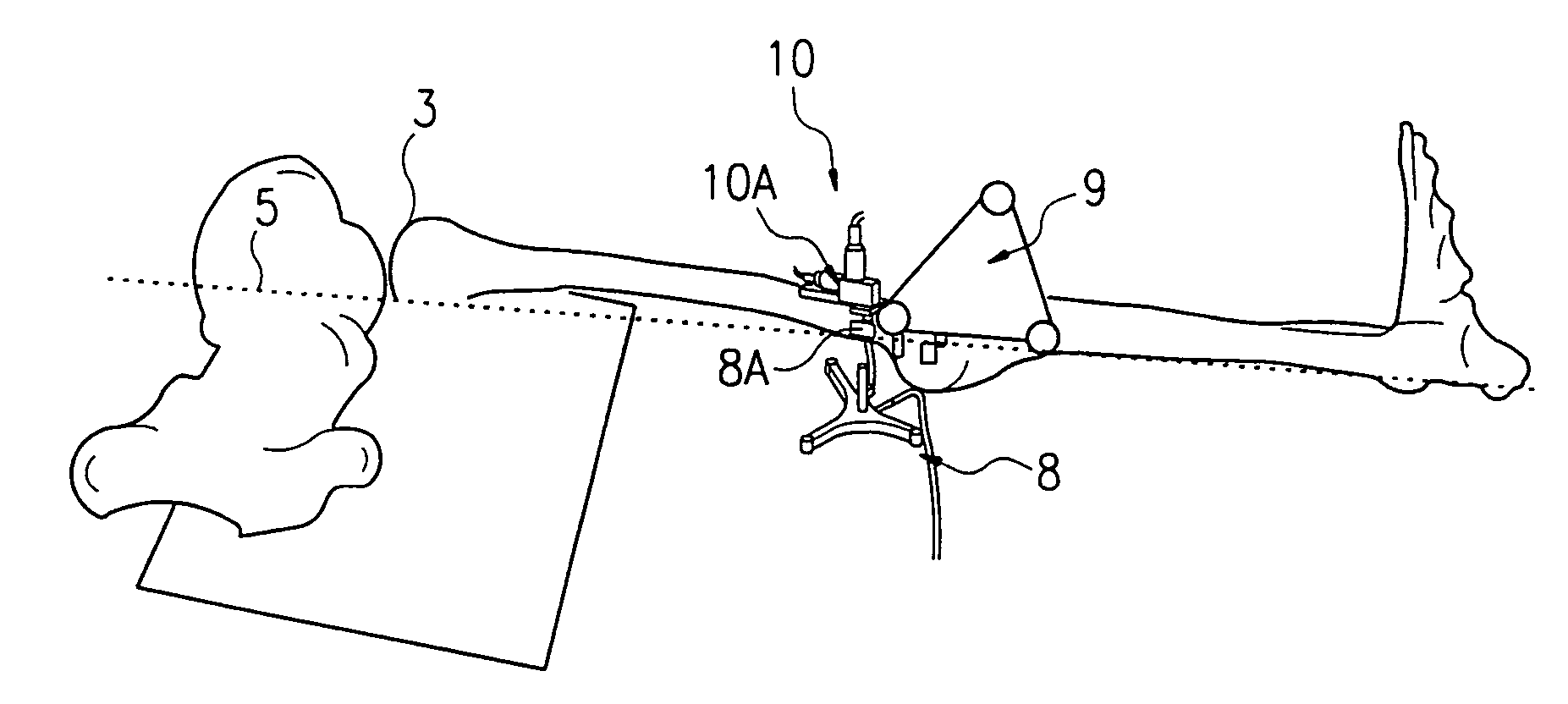
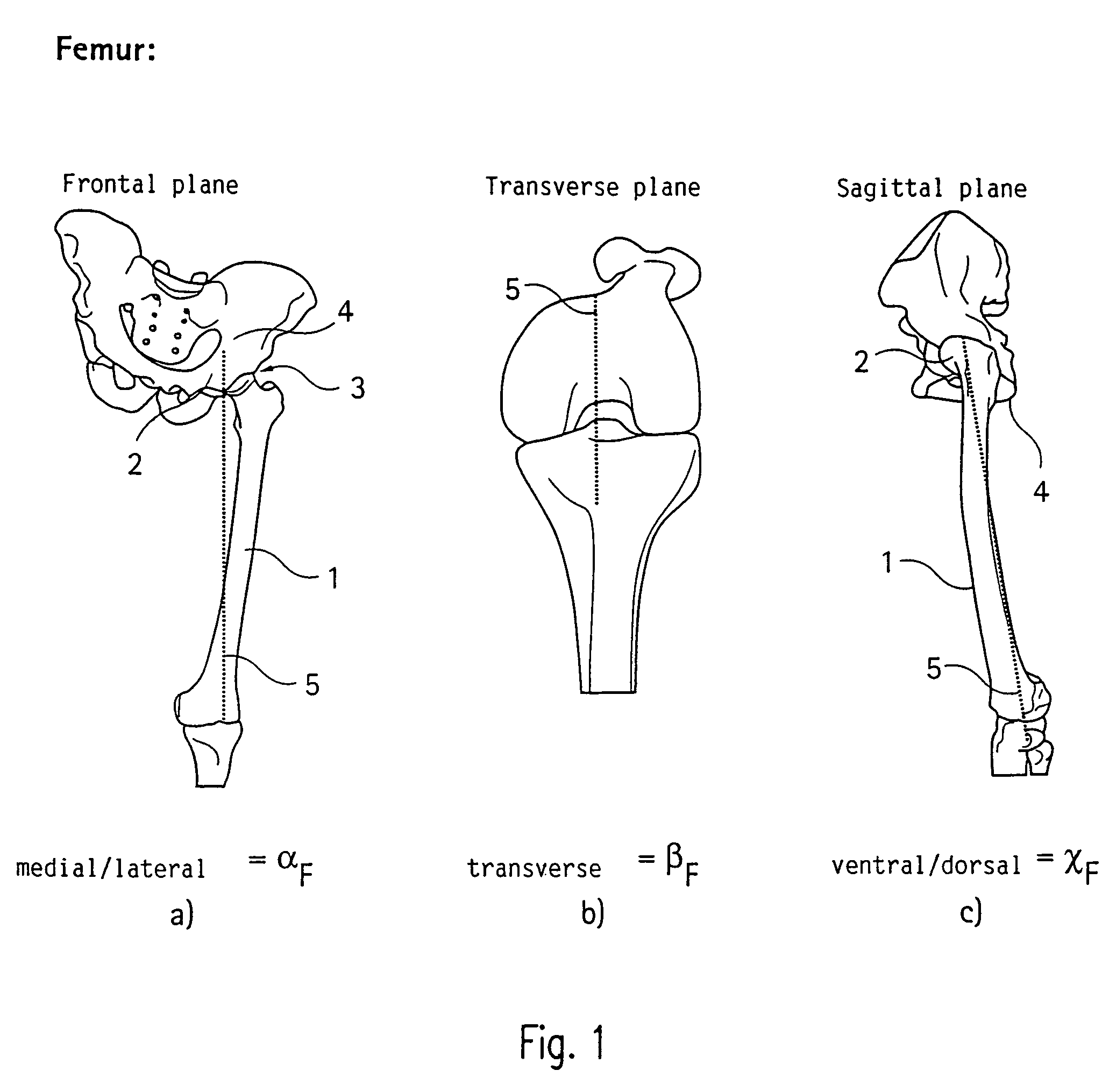
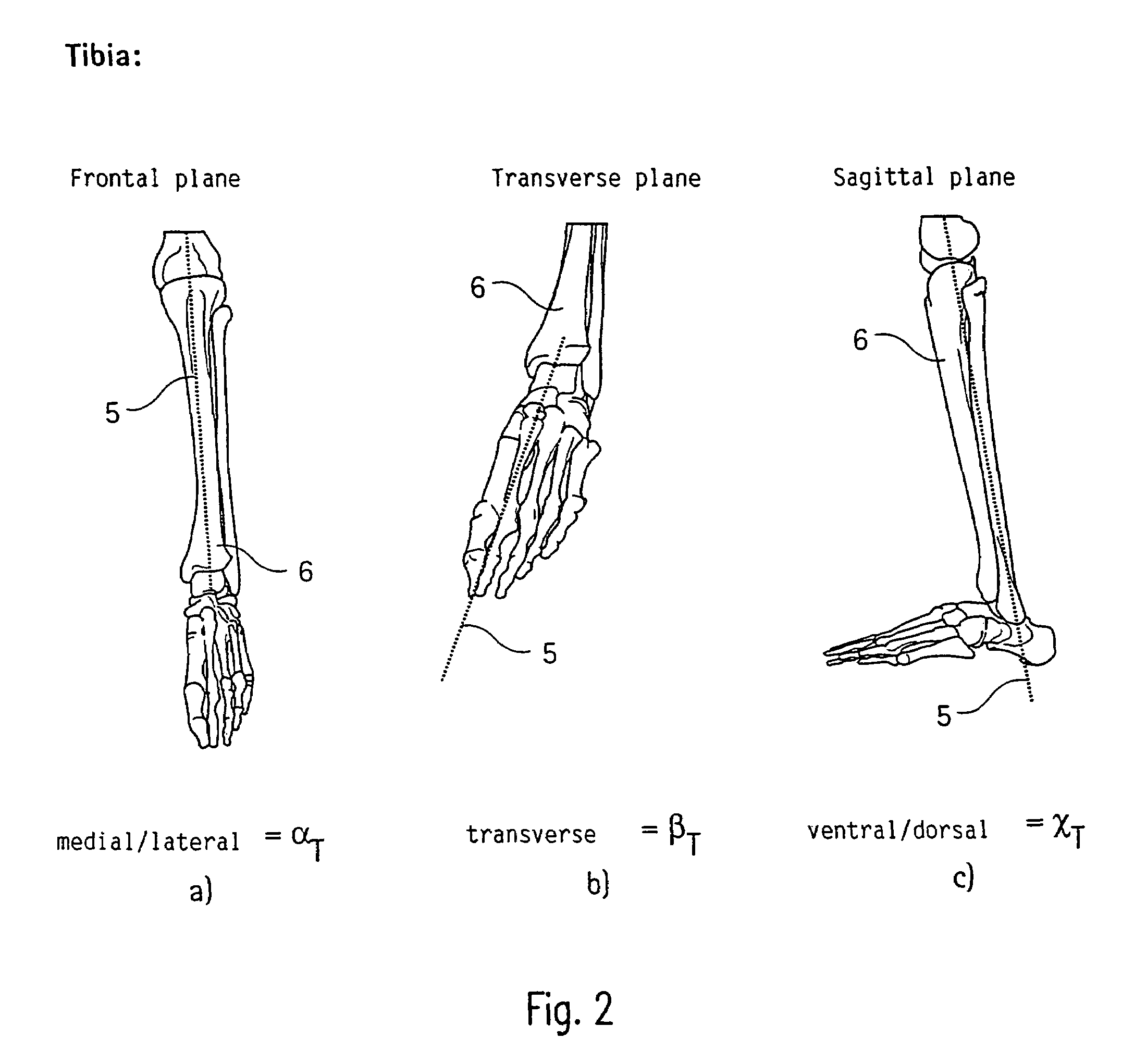
Method and apparatus for finding the position of a mechanical axis of a limb
InactiveUS7611520B2Rapidly and easily to locateDetermination of its position would be fairly trivialSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationMeasurement deviceMeasurement point
A method of finding the position of a mechanical axis running in the longitudinal direction through a limb that is rotatably supported by its first end in a center of rotation that is not fixed and is not accessible for the mechanical determination of coordinates, by means of an optical coordinate-measurement device with an indicator to detect measurement-point coordinates in one rotational position of the limb such that, for each rotational position, a multi-point indicator rigidly attached near the second end of the limb signals several measurement-point coordinates, and, from the sets of measurement-point coordinates detected in a plurality of rotational positions, at least one group is selected that can be assigned to the same site of the center of rotation, and the measurement-point-coordinate sets assigned to this site of the center of rotation are used to calculate the mechanical axis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
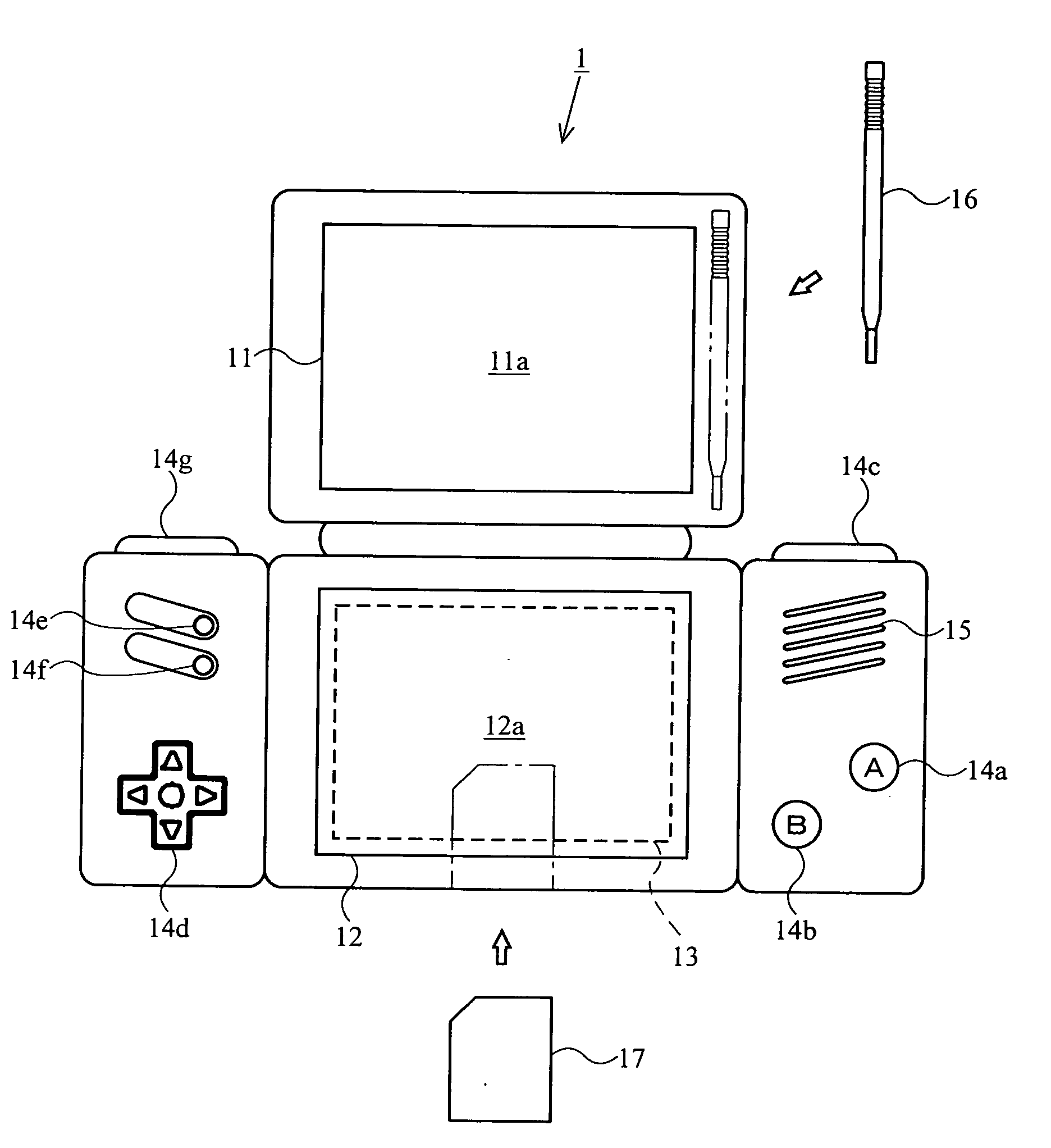
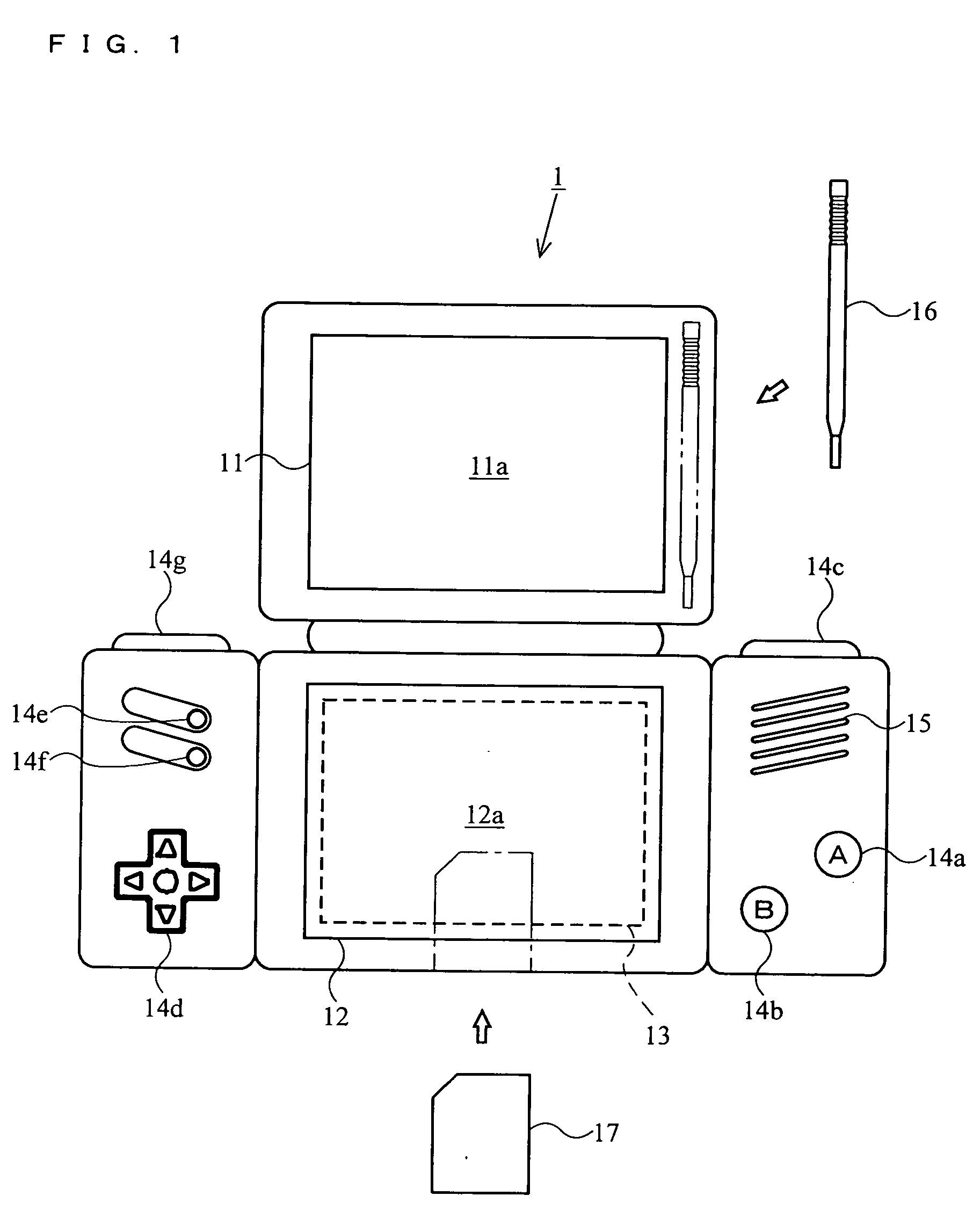
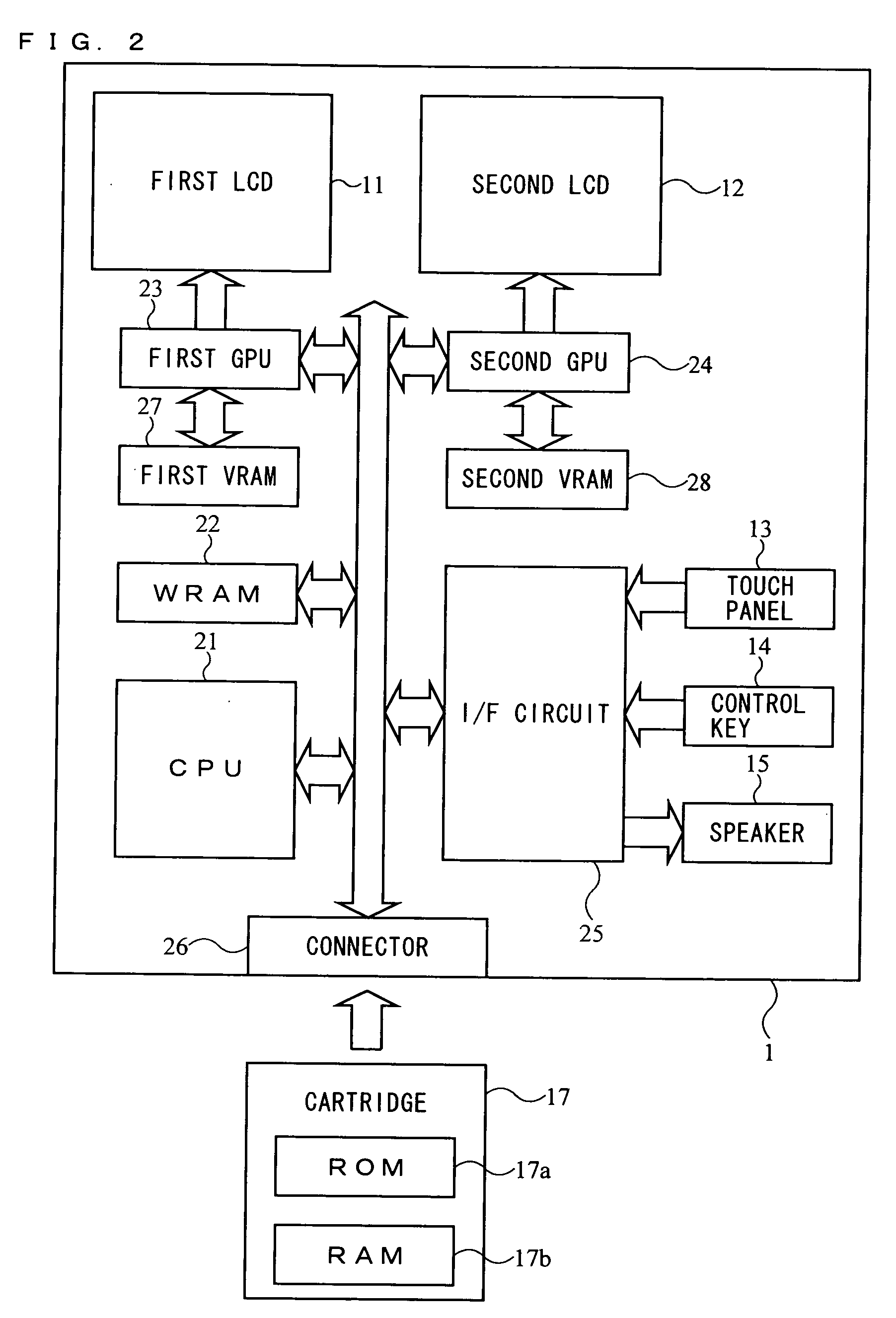
Recording medium storing video game program and video game device
ActiveUS20050215323A1Made preciselyMaintain operabilityVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsHuman–computer interactionTouch panel
The player gives a change in the input through a touch operation to a character pattern P2 displayed on a second display screen 12a covered by a touch panel. The character pattern P2 is associated with a player character P1 displayed on a first display screen 11a, and is displayed on a larger scale than the player character P1. The player character P1 is moved according to the change in the input. Thus, the present invention provides a video game played on a dual-screen video game device with a novel operation in which the player can accurately specify an intended position.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Hot plate and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20080011737A1Improved in uniformity in heating valueMore uniformly heatedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHot plates heating arrangementsEngineeringMetal
A hot plate for heating a substrate placed on the hot plate. The hot plate comprises a silicon base having pin insertion holes through which support pins for supporting a substrate from below and elevating the substrate above the hot plate pass; a heater composed of a resistor made of a metal film deposited on the back surface of the silicon base; and a temperature sensor, composed of a resistor made of a metal film deposited on the back or front surface of the silicon base. The front surface of the silicon base has gap-making protrusions for making a gap between the hot plate and a substrate placed on the gap-making protrusions.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
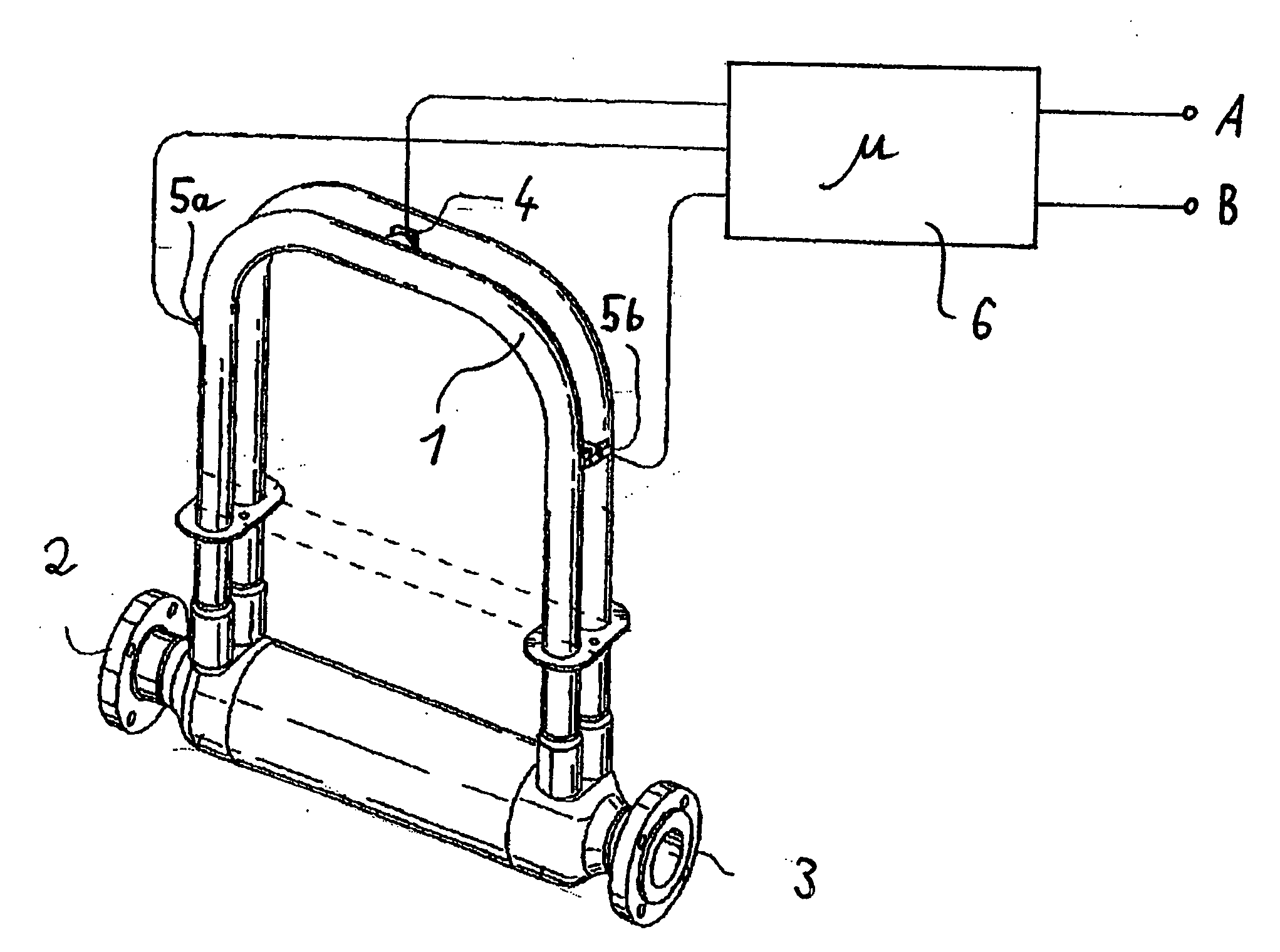
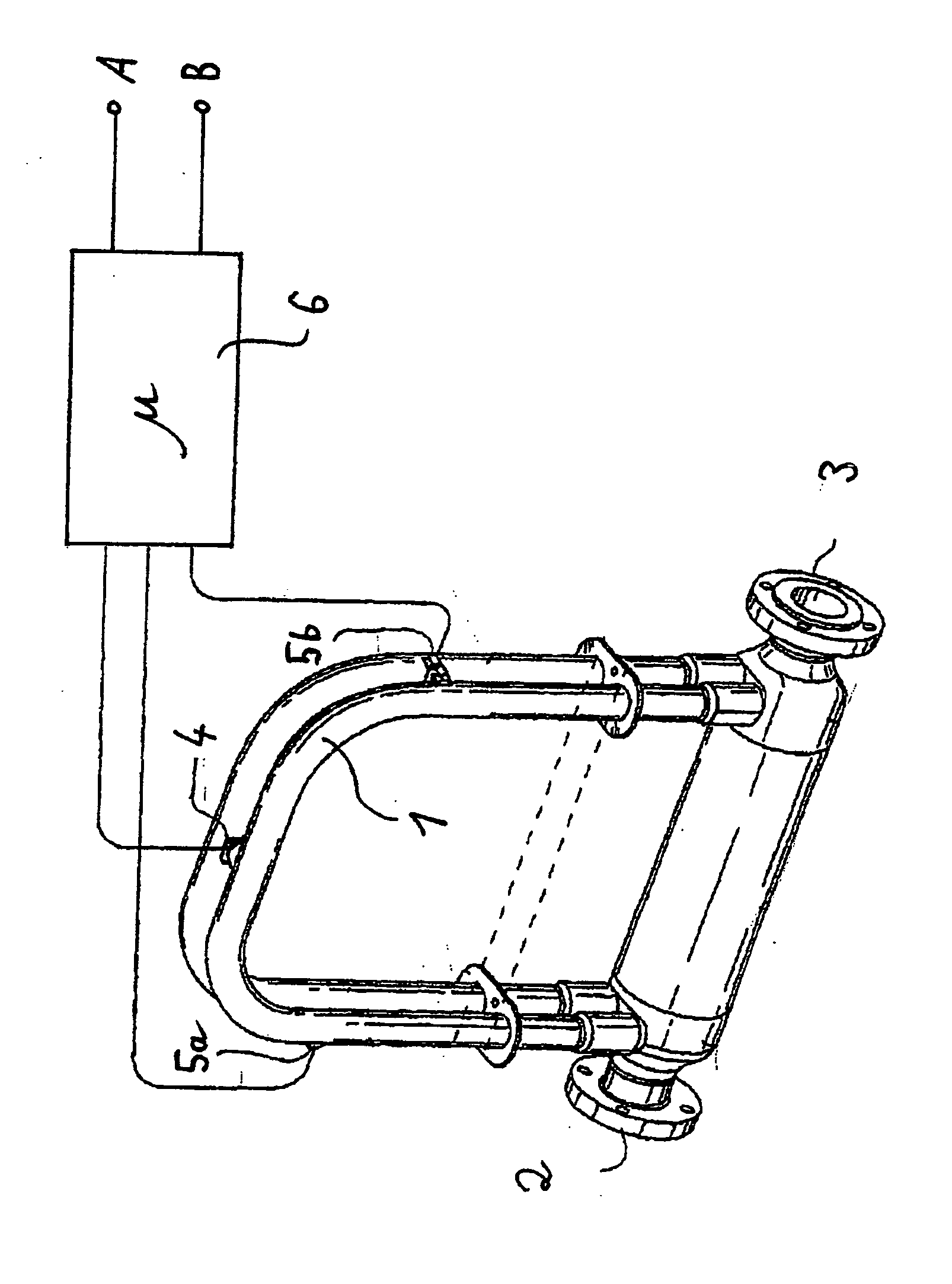
Method for operating a vibratory measuring instrument, and corresponding instrument
InactiveUS20100011882A1Made preciselyAccurate signalVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusTesting/calibration for volume flowMeasuring instrumentClassical mechanics
A method for operation of a vibratory measurement instrument comprises flowing a fluid through at least one measurement tube; causing the measuring tube to oscillate mechanically using an oscillation production unit; detecting an oscillation behavior of the tube using at least one oscillation sensor; determining at least one of a mass flow, a viscosity, and a density in a narrowband frequency range based on the oscillation behavior; evaluating at least one of the mass flow, the viscosity, and the density using signal processing of an electronics unit; and evaluating the oscillation behavior at least at times in a broadband frequency range using the electronics unit.
Owner:ABB PATENT GMBH
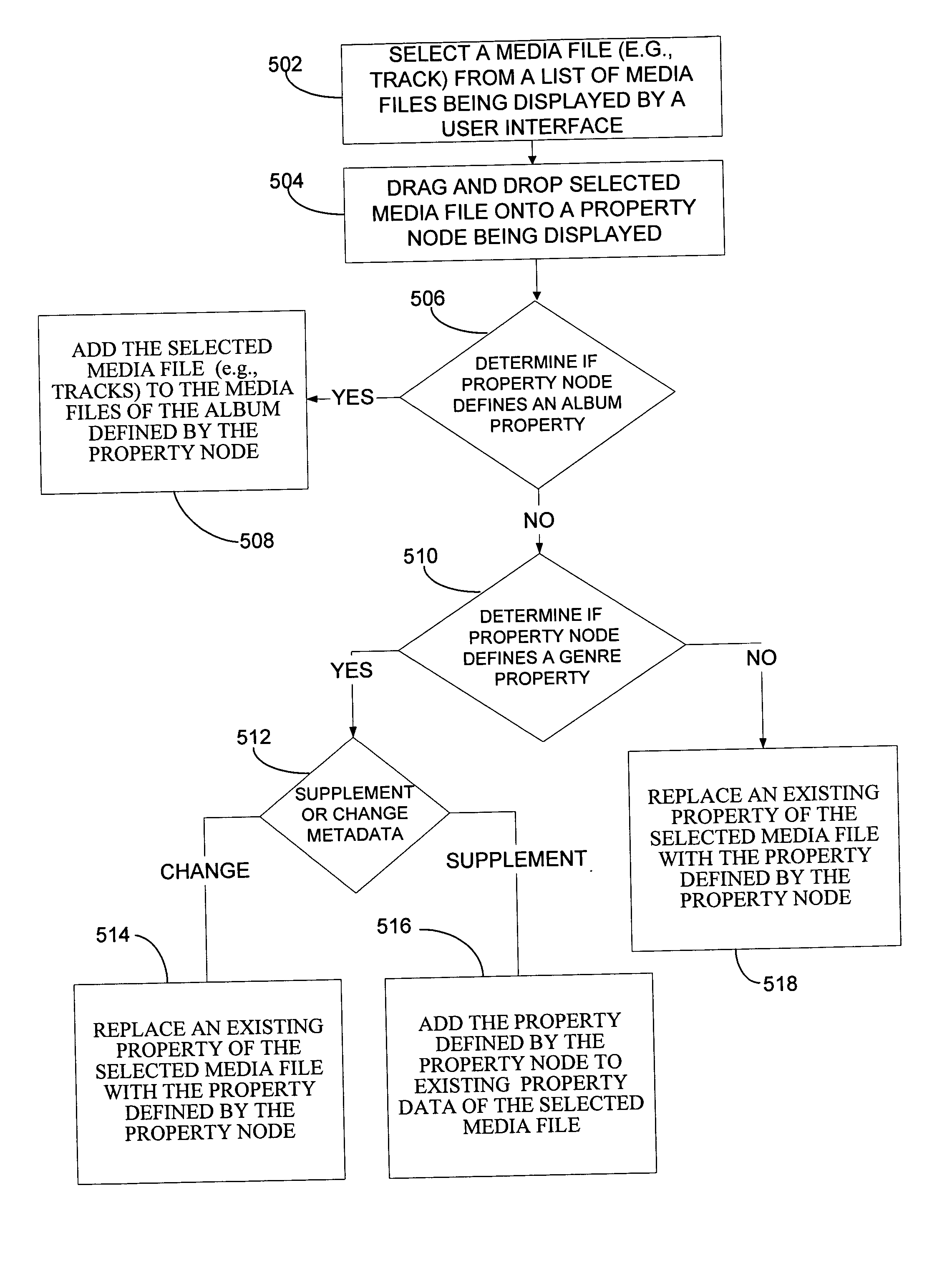
Drag and drop metadata editing
InactiveUS20050010589A1Improve user experienceLess laborMetadata audio data retrievalDigital data processing detailsDrag and dropGraphics
A method and system for modifying metadata of one or more media files via a drag and drop operation. A media library stores one or more media files. A graphical user interface displays the one or more media files in the media library via a display. The graphical user interface allows a user to select one or more media files from the media files being displayed. The user interface allows a user to drag and drop the one or more selected media files onto a property node that defines a property the user would like to incorporate into the metadata of one or more selected media files. Dropping the one or more selected media files onto the property node modifies the metadata of the media file to correspond to the property defined by the property onto which the one or more selected media files were dropped.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
High track density magnetic recording head
ActiveUS7130152B1High track densityMade preciselyManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsTrack densityMagnetic media
Closer spacing of elements for writing multiple tracks onto a magnetic media increases the areal density of stored information. A thin film multiple track recording head includes recording gaps in a plane parallel with the head substrate. This configuration allows for flexible placement of the elements within the head, improved control of recording gap geometry, and alternating azimuth gap angles.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
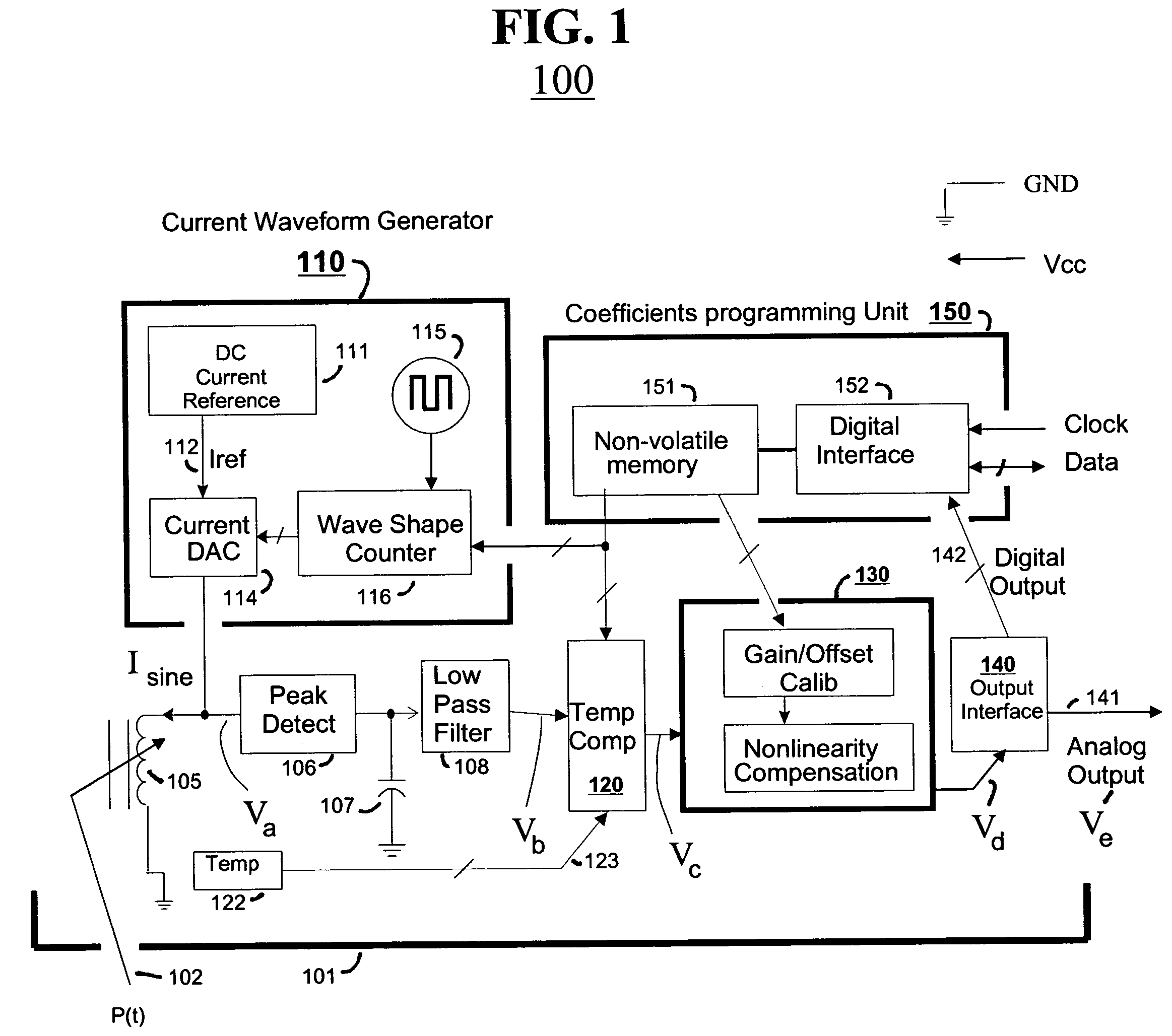
Reactive sensor modules using Pade' Approximant based compensation and providing module-sourced excitation
ActiveUS7006938B2High precision measurementLow costSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsIntegrated circuitNon linear response
Reactive sensors typically exhibit nonlinear response to temperature variation. Systems and methods are disclosed for compensating for the nonlinear and / or temperature dependent behavior of reactive sensors and for calibrating the post-compensation output signals relative to known samples of the physical parameter under measure. One call of embodiments includes a housing containing at least part of a reactive sensor, a monolithic integrated circuit and a timing reference. The integrated circuit includes a waveform generator for generating a sensor exciting signal, a detector for detecting the response of the sensor to the combination of the exciting signal and the under-measure physical parameter, a temperature compensating unit and the Pade Approximant nonlinearity compensating unit are tuned by use of digitally programmed coefficients. The coefficients calibrate the final output as well as compensating for nonlinearity and temperature sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC +1
Optical function device with photonic band gap and/or filtering characteristics
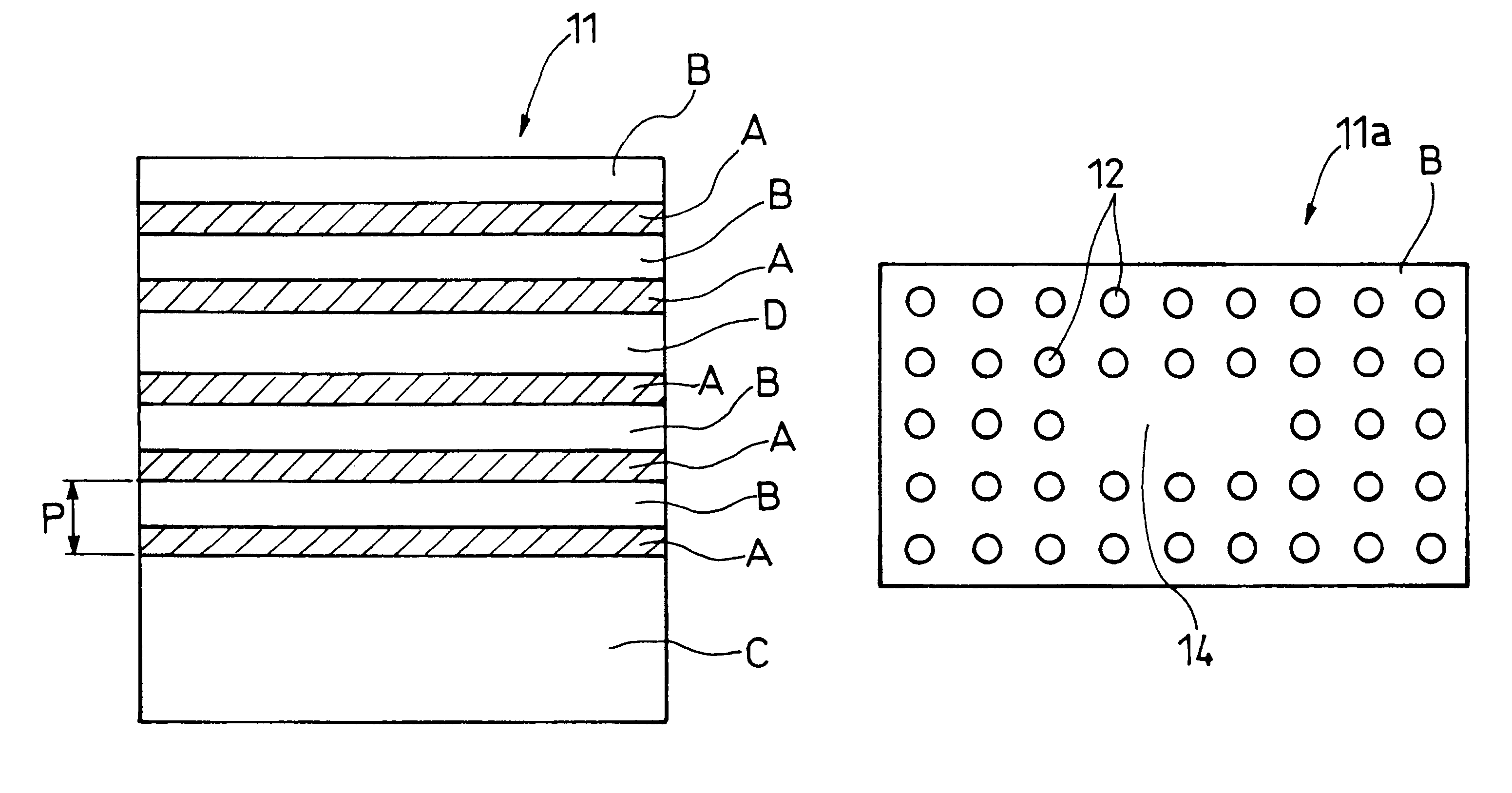
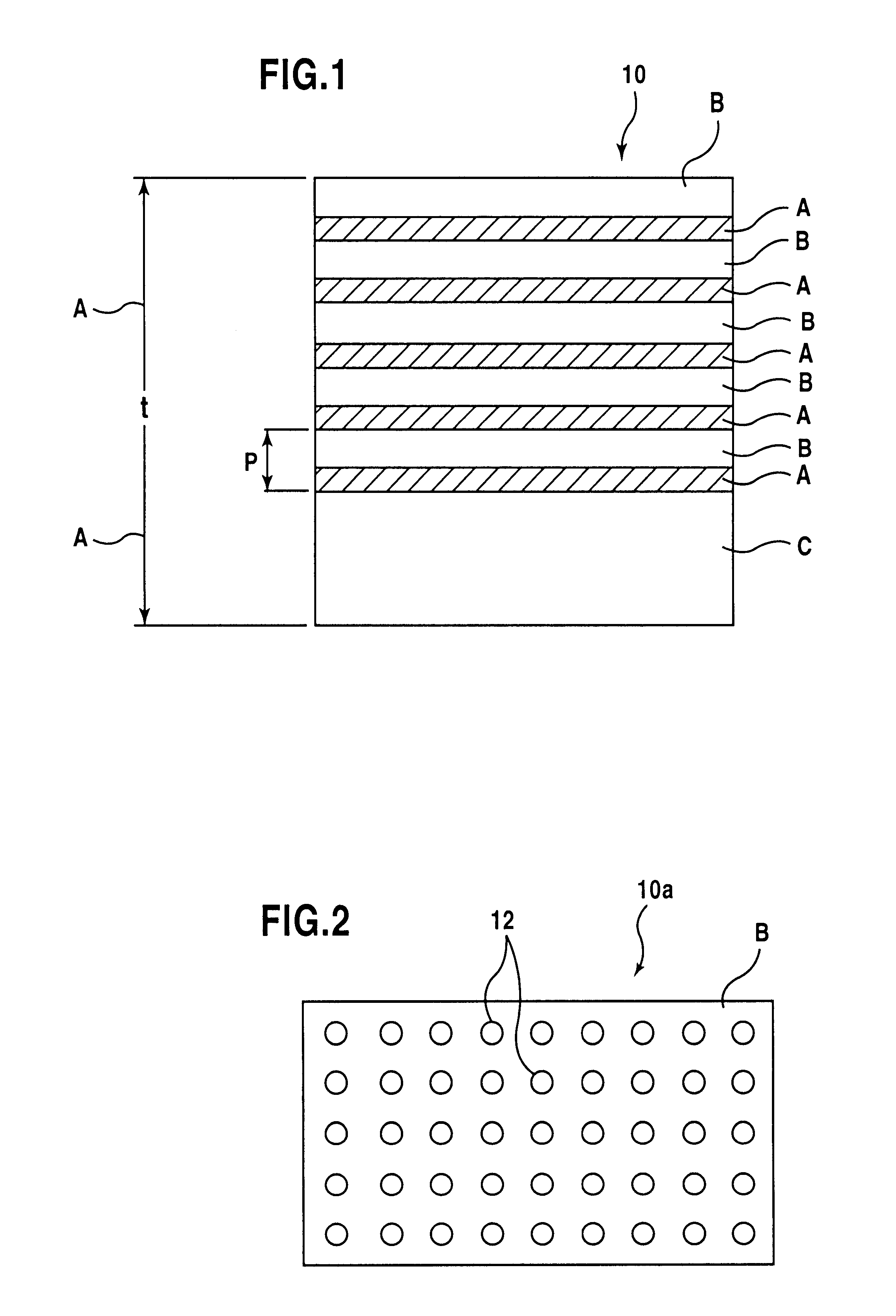
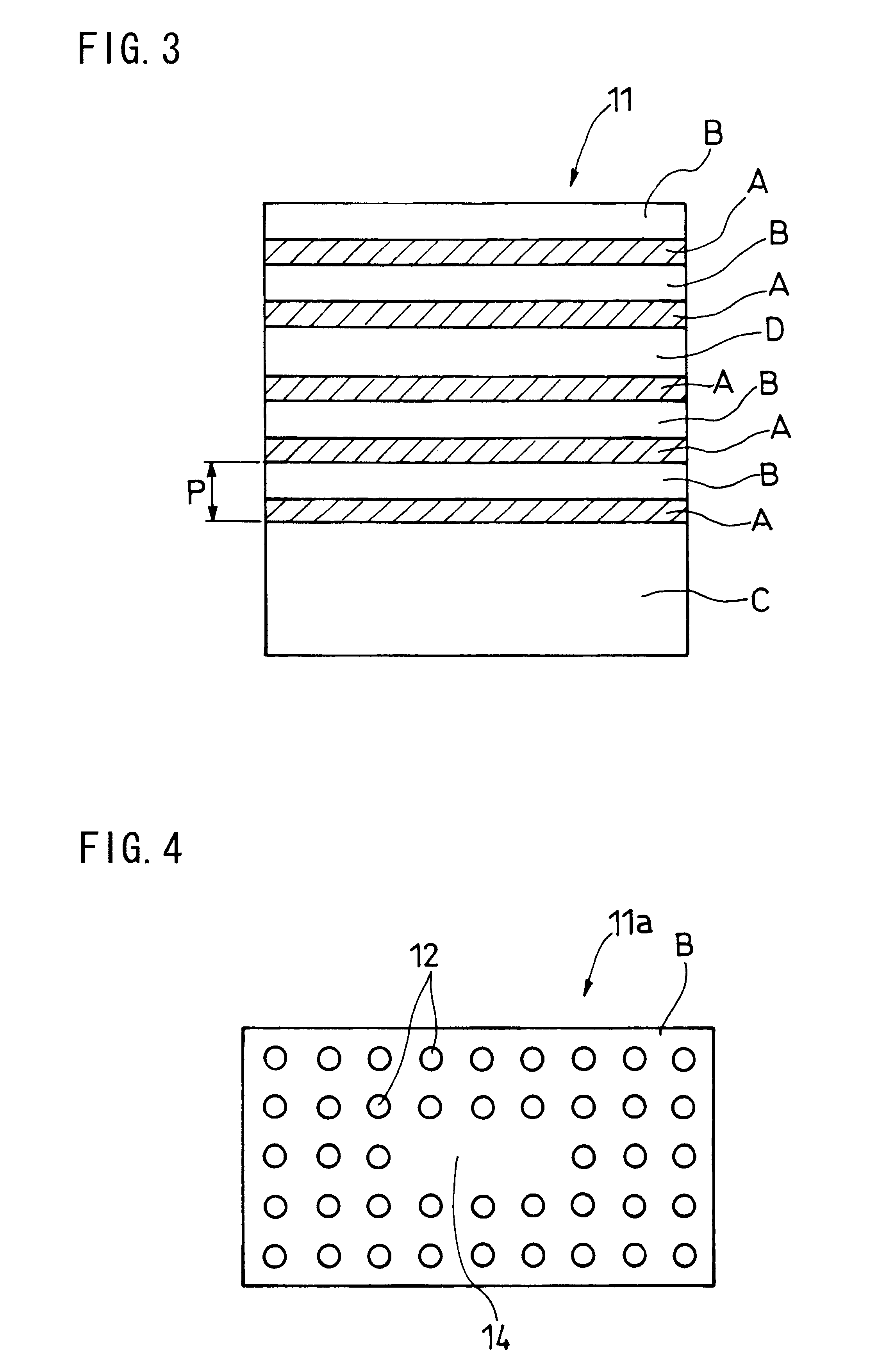
A stacked material free from a degraded quality of crystal, formed with a precise periodicity, and fabricated without relying on the vapor phase growth method is provided. An optical function device using the stacked material is also provided. A starting stacked material composed of two alternate layers (A), (B) having different refractive indexes is stacked over two periods or more by a substrate bonding method to provide a multi-periodic stacked structure.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Substrate dicing method
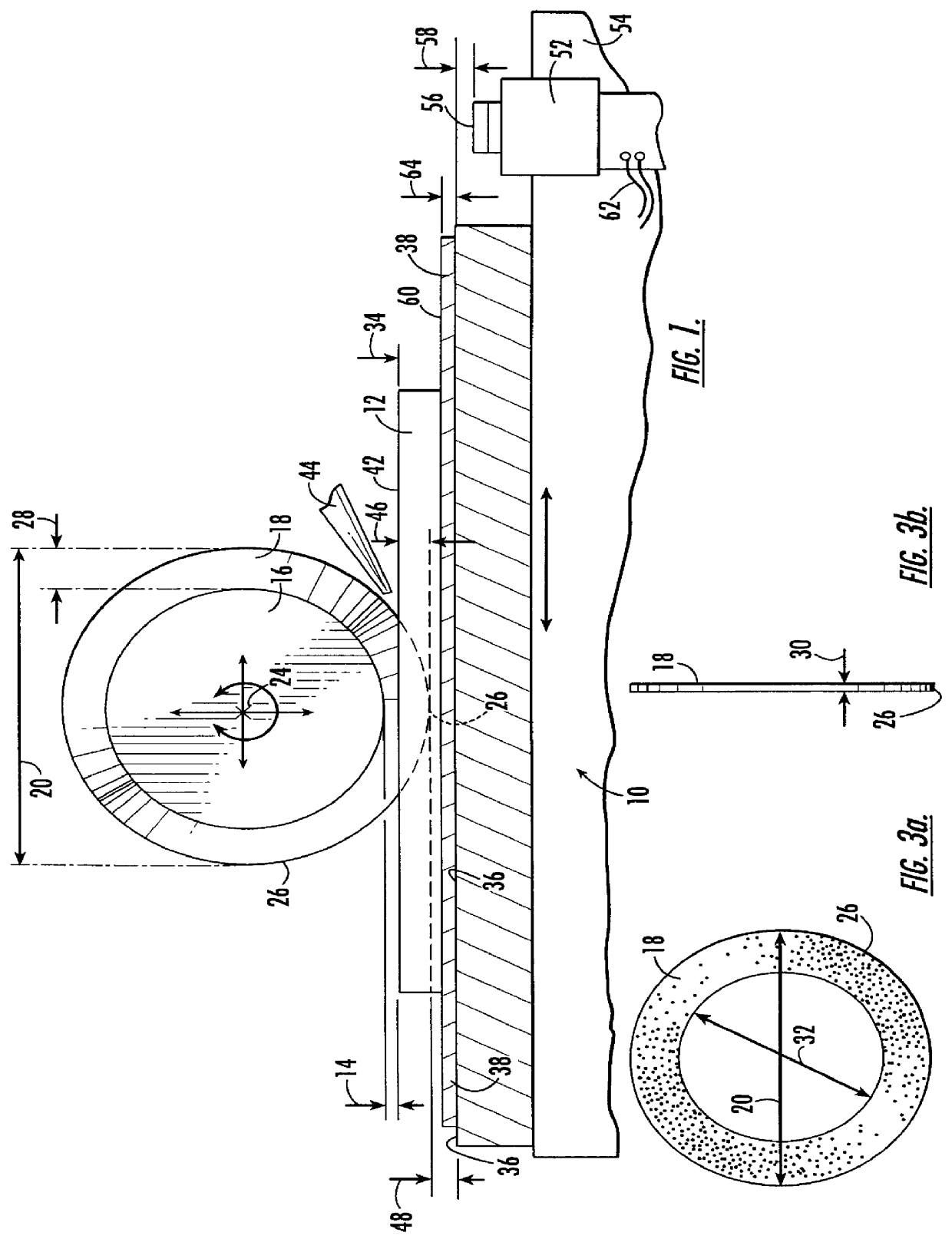
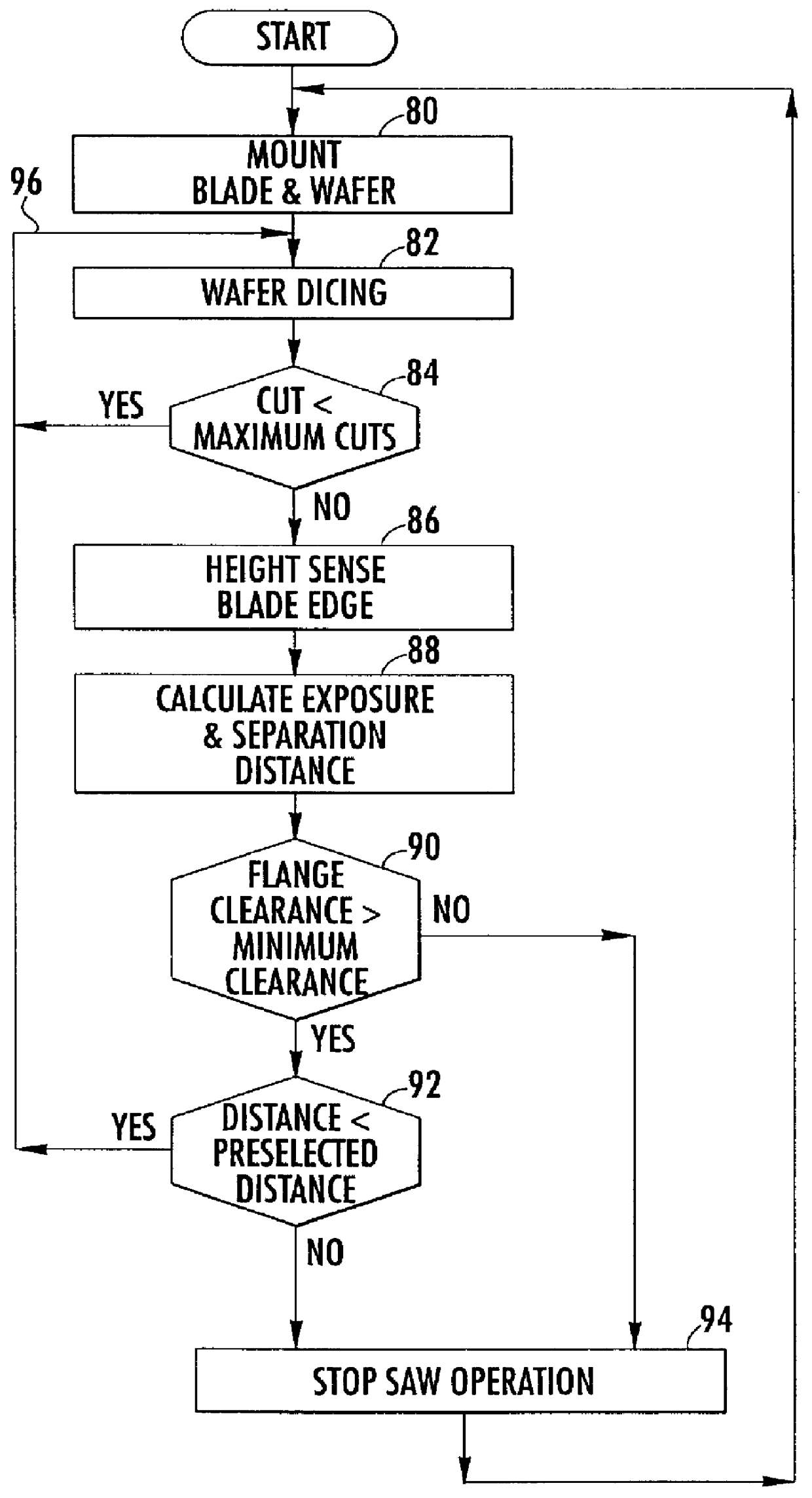
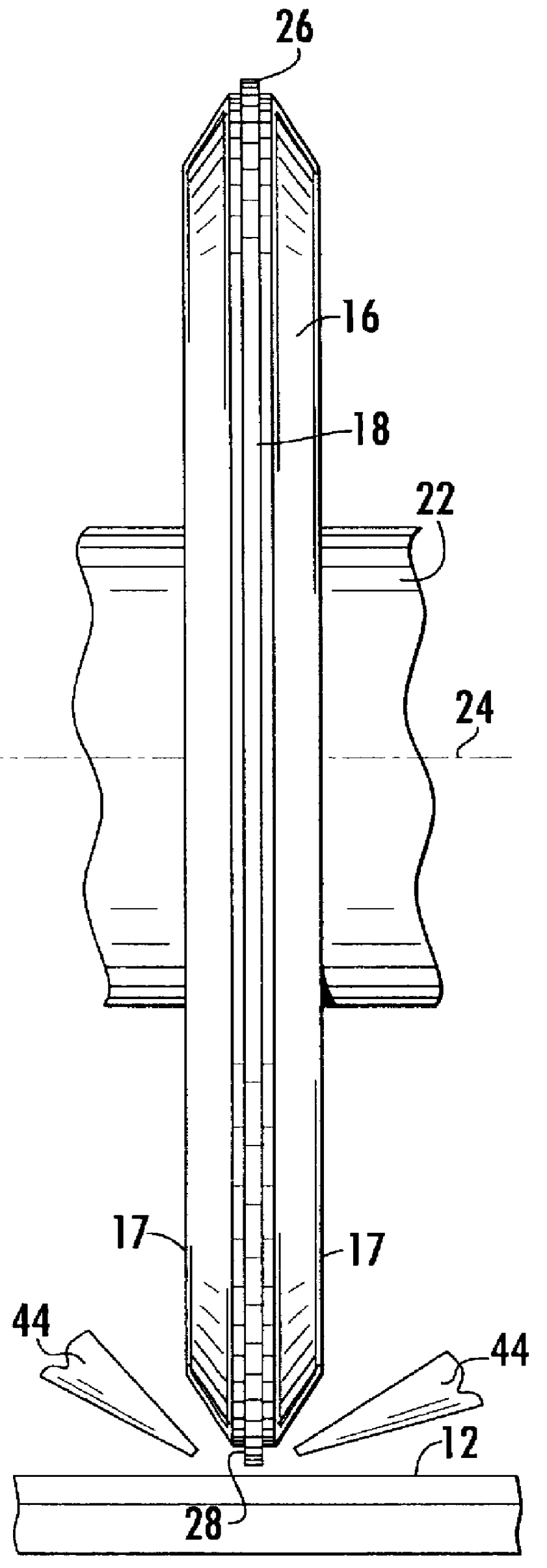
InactiveUS6152803AEffective movementShorten the timeMetal sawing accessoriesGrinding feed controlKnife bladesLocation data
A programmable dicing saw is operable with movement of its spindle and work surface for aligning a dicing blade juxtaposed between flanges on the spindle and dicing a substrate along a predetermined blade path. By locating the center of the substrate, an efficient movement of the blade relative to the substrate center rather than the work surface center saves time. Locating the center of the blade includes aligning opposing substrate edges and edge location data entry into a processor for calculation of the substrate center and control based on the substrate center. In addition, prior to cutting along the edges of the substrate, the dicing blade is first aligned for travel parallel to and proximate the edge of the substrate, and an alignment offset is provided to the programmable dicing saw for laterally moving the blade toward the center of the substrate prior to making a cut and avoiding damage to the blade and substrate that typically results when the blade slides along the substrate edge rather than cutting into the substrate. In addition, by knowing the substrate center location, an arcuate cut can be accurately made into the substrate by making multiple straight cuts with a rotation of the substrate about its center between each cut. A flange clearance is monitored by measuring the blade exposure after a preselected number of cuts during the substrate dicing, and a minimum flange clearance permitted before blade movement toward the substrate is automatically stopped.
Owner:THERMOCARBON
Alert flags for data cleaning and data analysis
InactiveUS20050028046A1Made preciselyMoreError detection/correctionData miningData profilingData structure
A data structure and methods for generating and using the data structure which contains cleaning attribute flags for each field of a database record which has been modified by a data cleaning operation. The flags may are used to determine if a pattern, cluster or trend identified during data mining of the cleaned data is likely to have been influenced by the data cleaning process, especially to a degree which leads to identification of false trends, patterns, or clusters.
Owner:IBM CORP
Highly selective doped oxide etchant
InactiveUS20070207622A1High densityImprove etch selectivityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidOrganic acid
Etch solutions for selectively etching doped oxide materials in the presence of silicon nitride, titanium nitride, and silicon materials, and methods utilizing the etch solutions, for example, in the construction of container capacitor constructions are provided. The etch solutions are formulated as a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and an organic acid having a dielectric constant less than water, optionally with an inorganic acid, and a pH of 1 or less.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
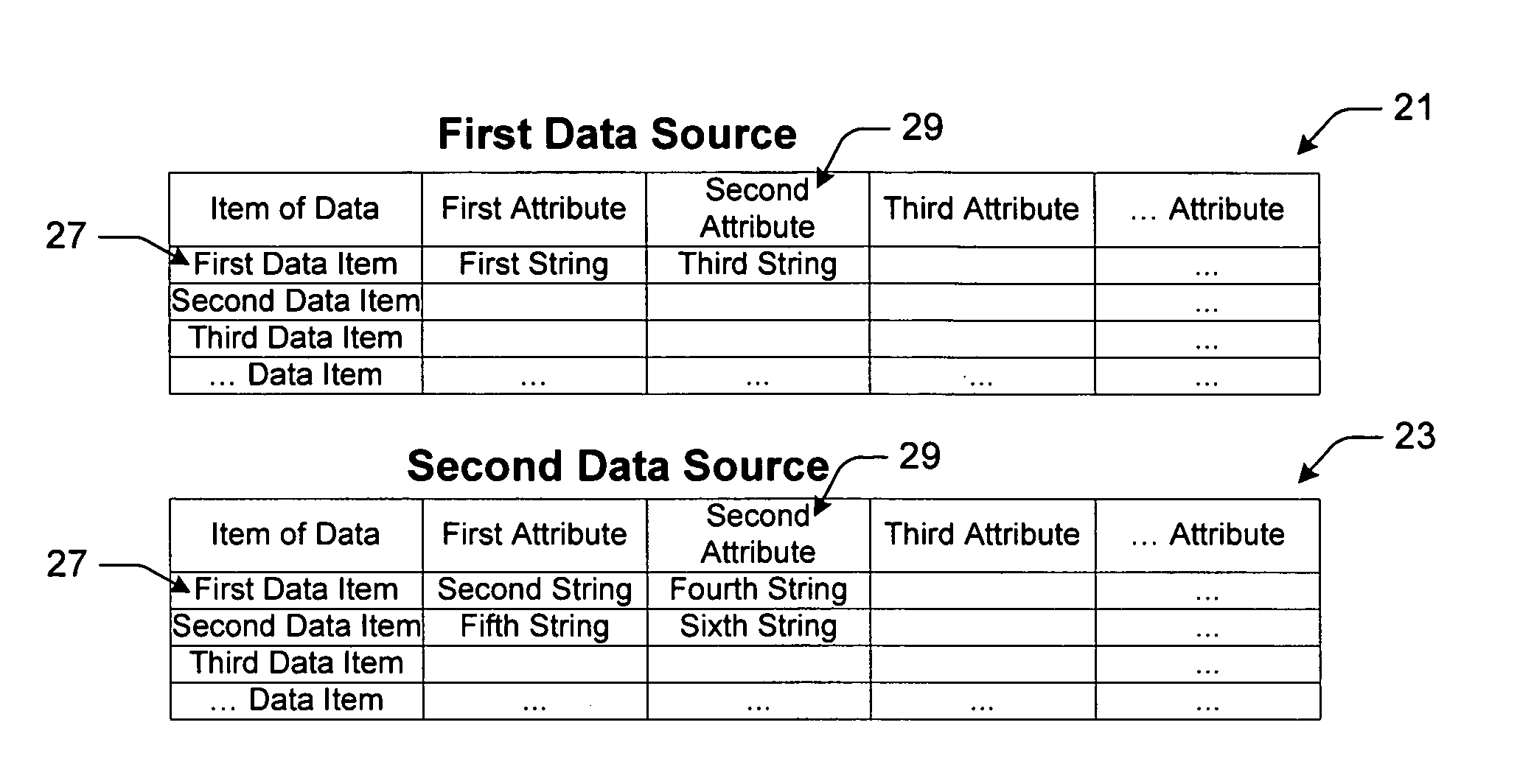
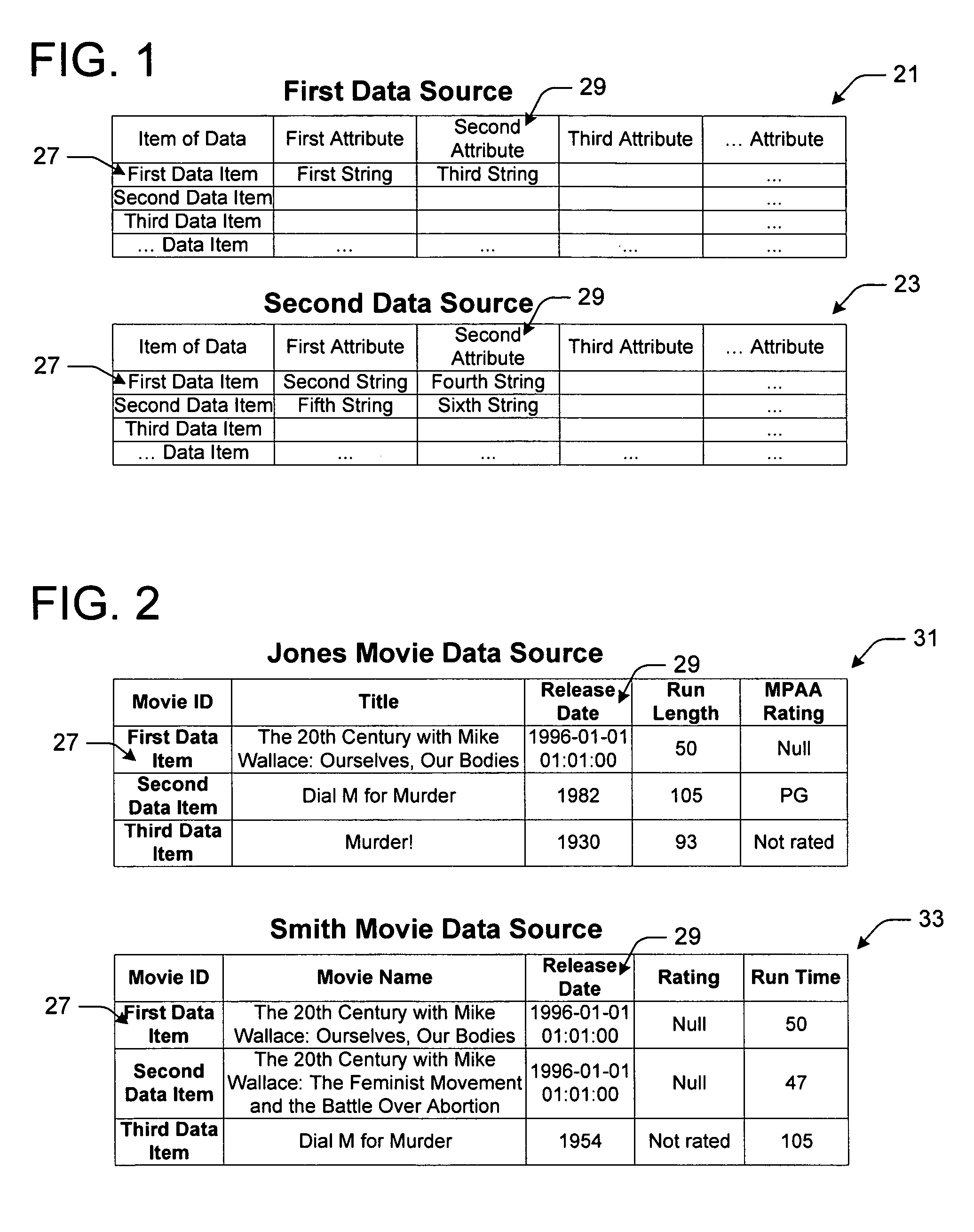
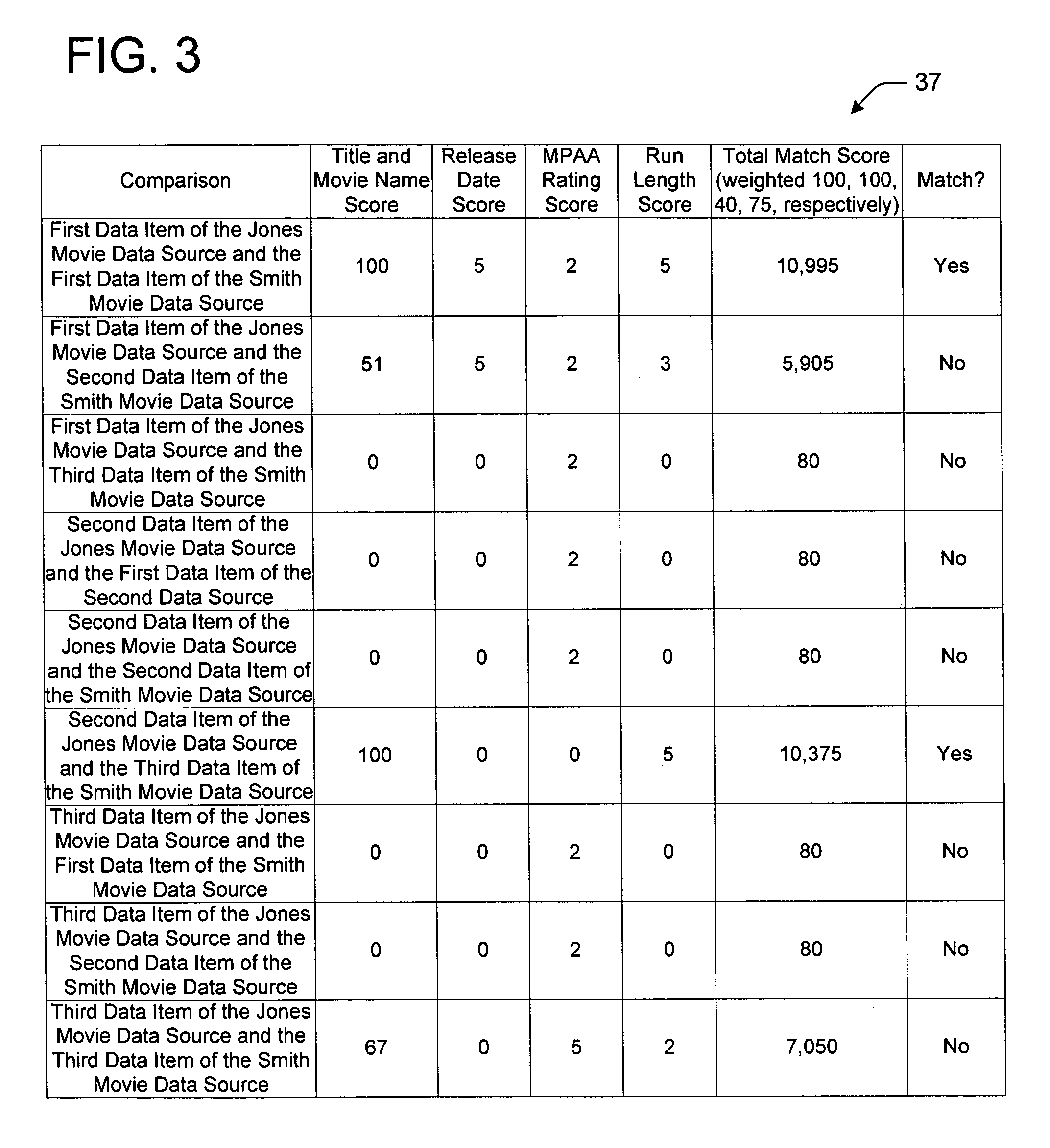
Methods, computer readable mediums and systems for linking related data from at least two data sources based upon a scoring algorithm
InactiveUS7644077B2Reliance has been minimizedReduce dependenceData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsScoring algorithmData source
A method for linking related data, such as metadata, from at least two data sources. The method includes formatting items of data of the data sources according to attributes. The method also executes a scoring algorithm for one or more of the attributes to generate a score for one or more sets of the formatted items of data, each of the sets includes an item of data from one data source and an item of data from another data source. Finally the method identifies related items of data of the separate data sources based upon the generated scores to facilitate linking related data of the two data sources. The method may also provide a link between data items of the data sources.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com