Patents
Literature
1833 results about "Metrology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metrology is the science of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France, when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th Conference Generale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) in 1960.
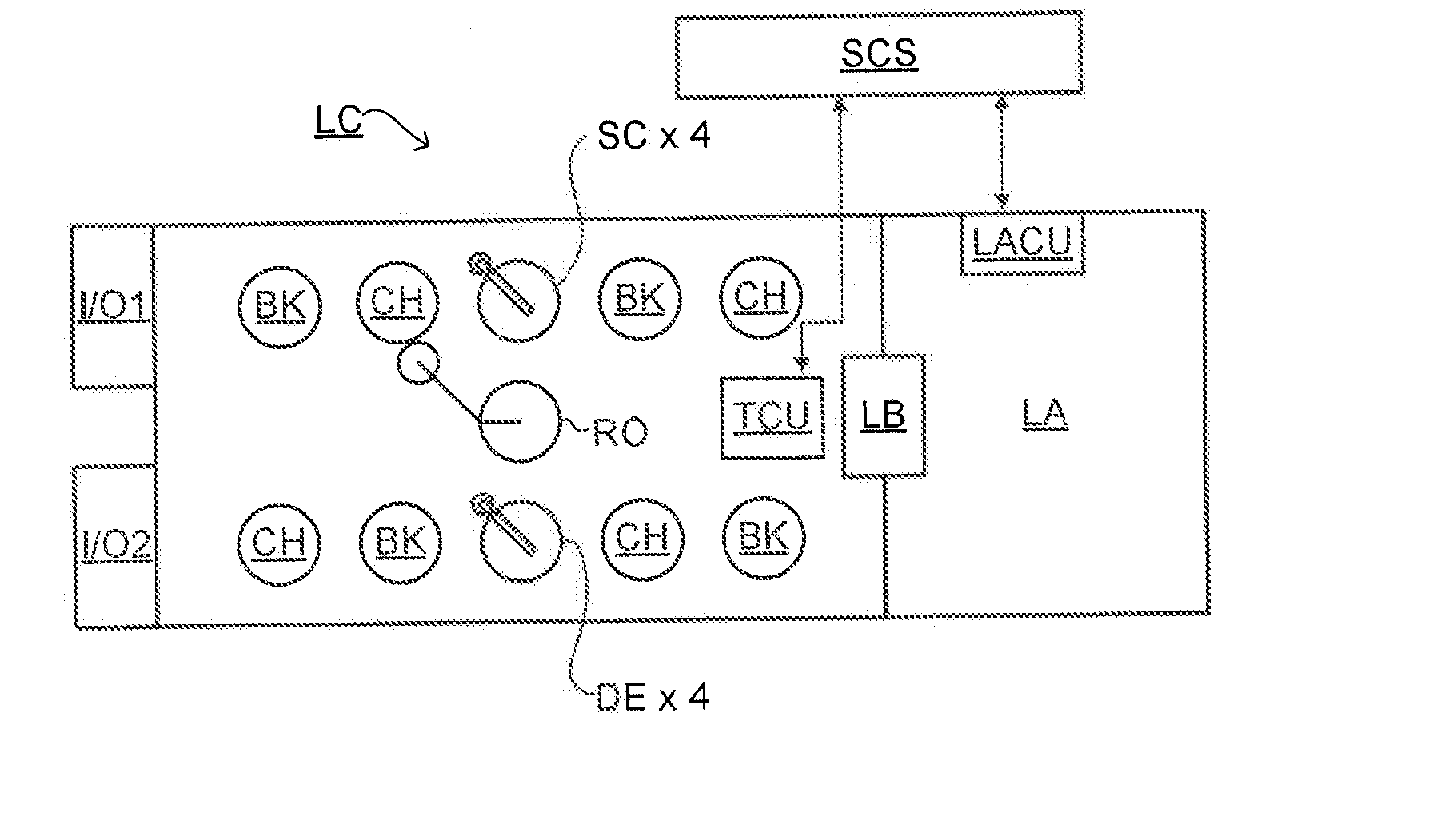
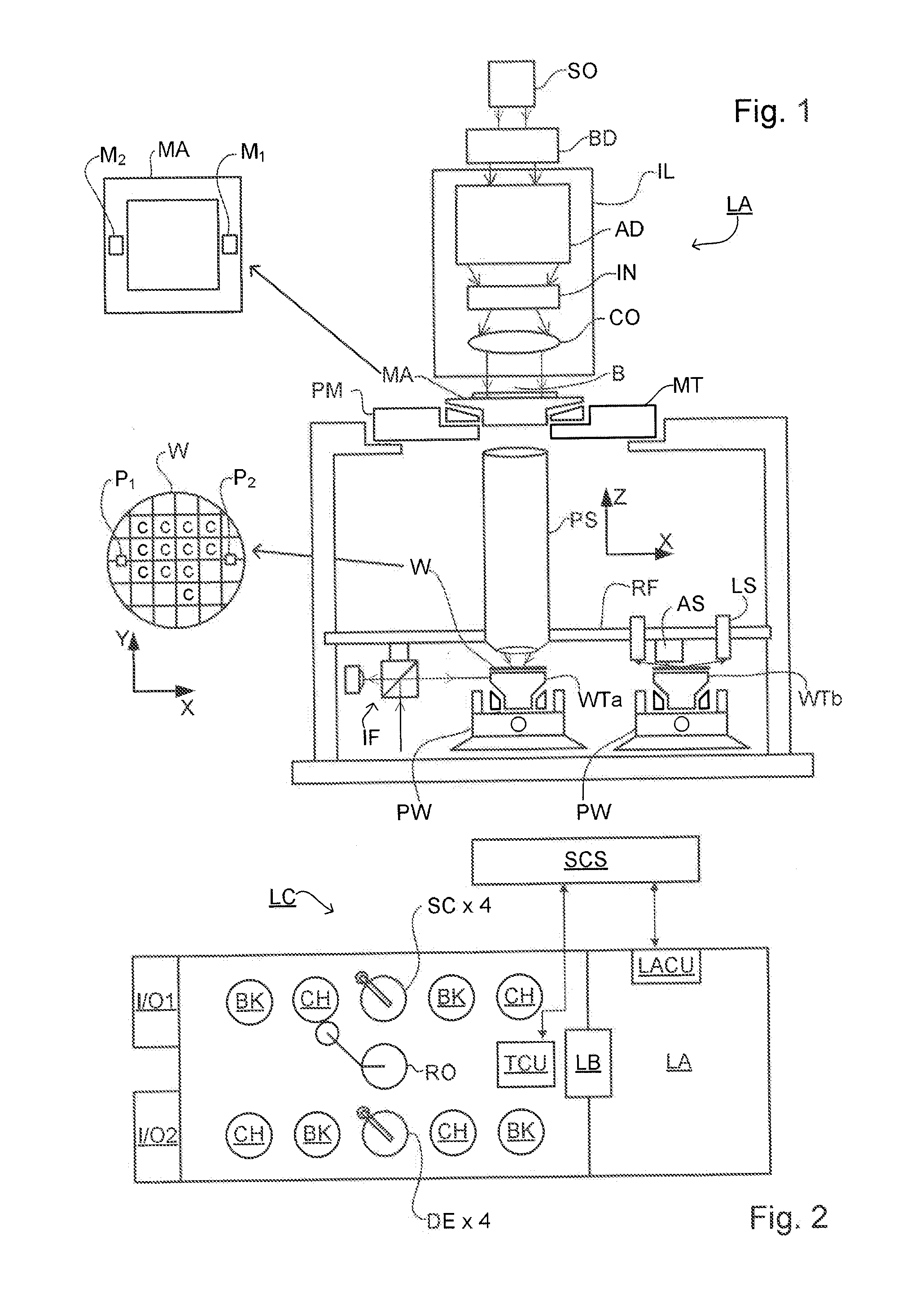
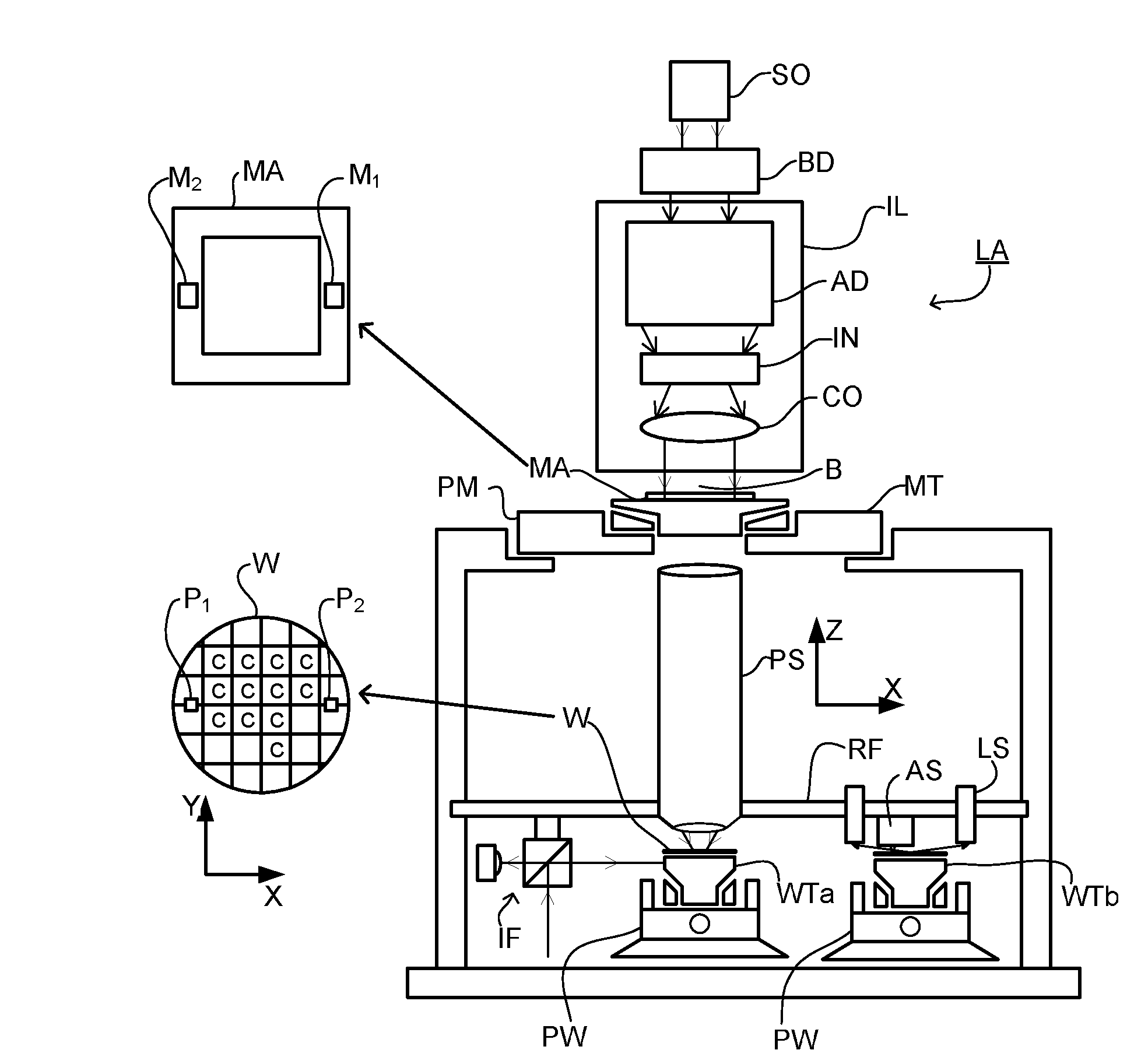
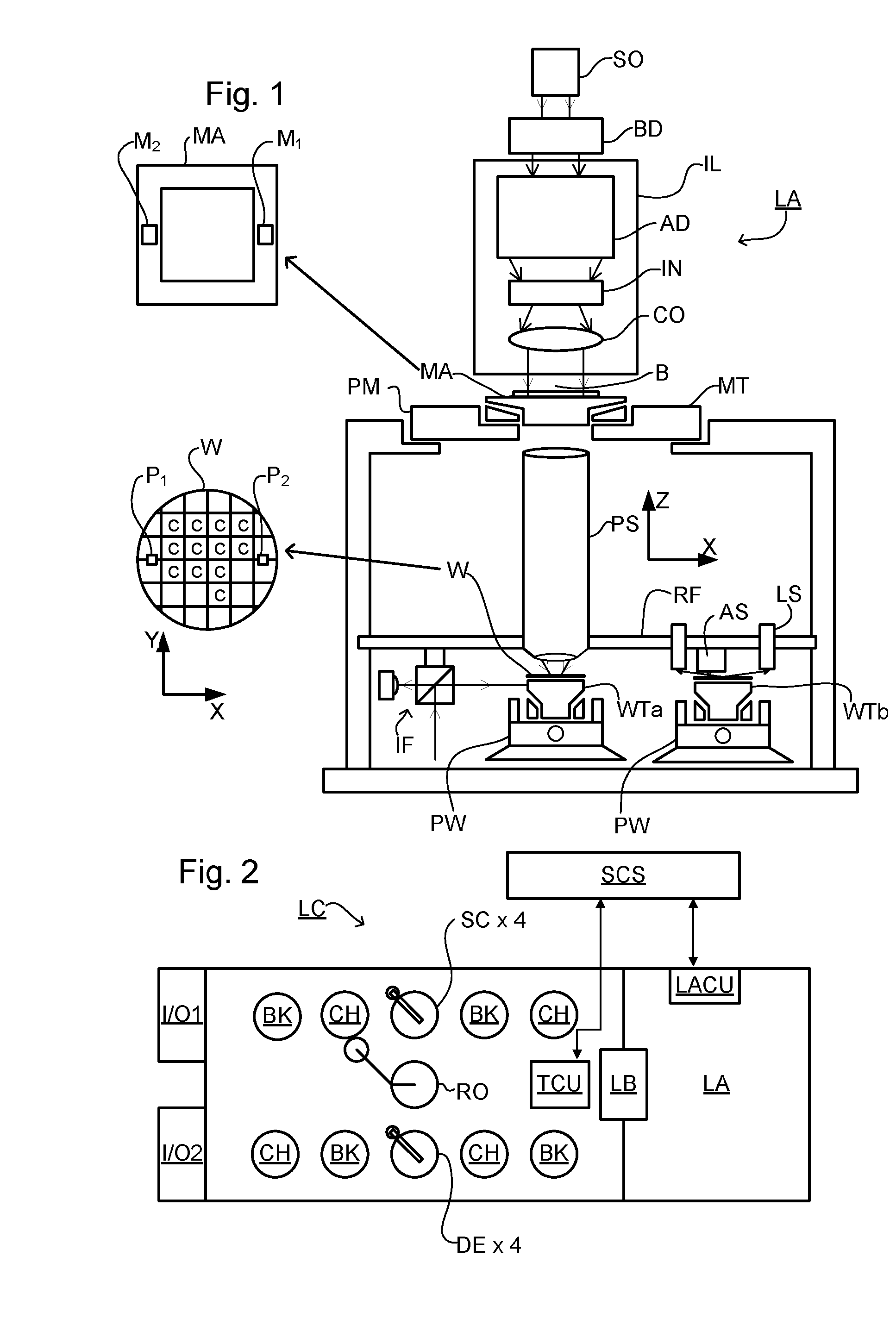
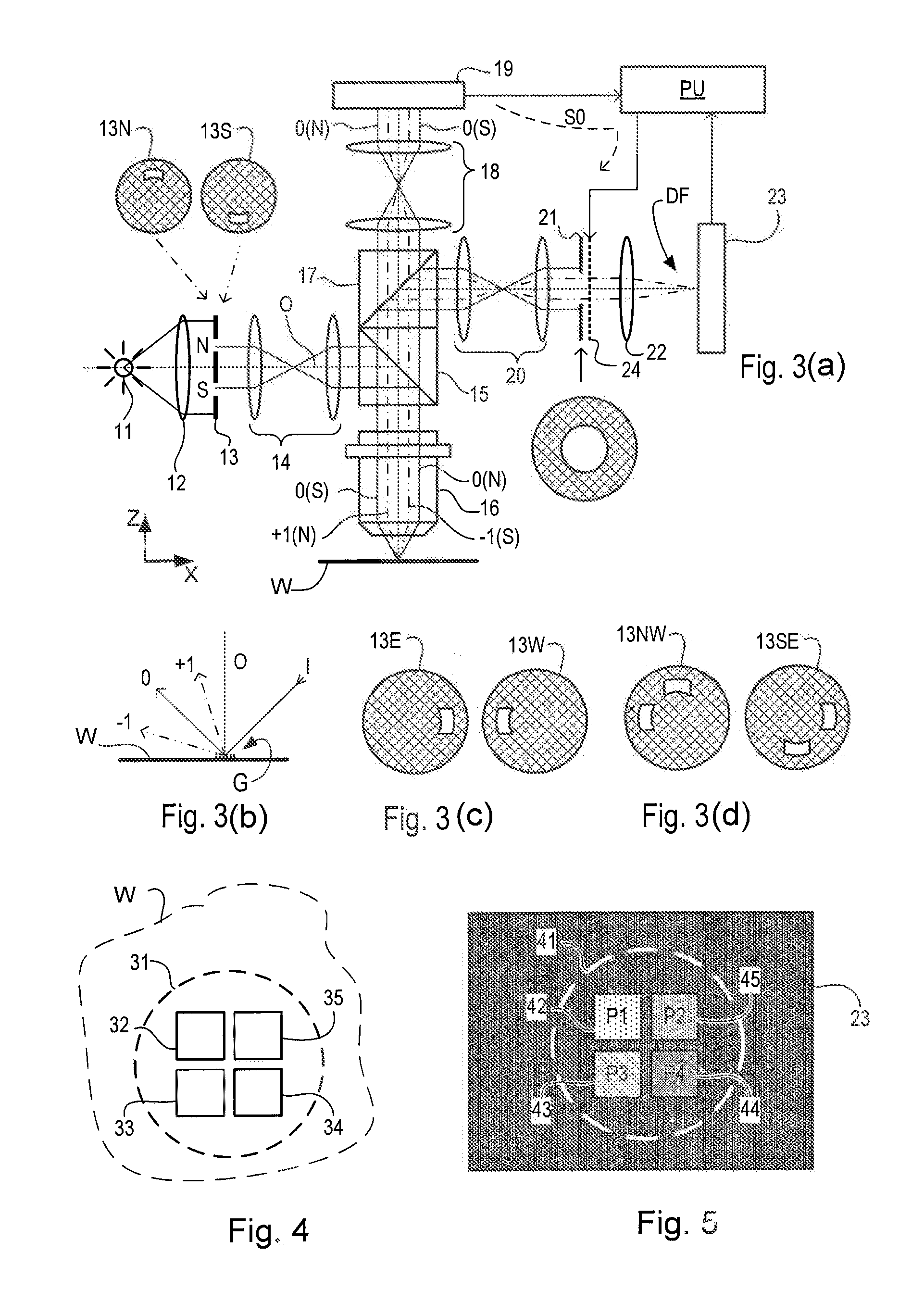
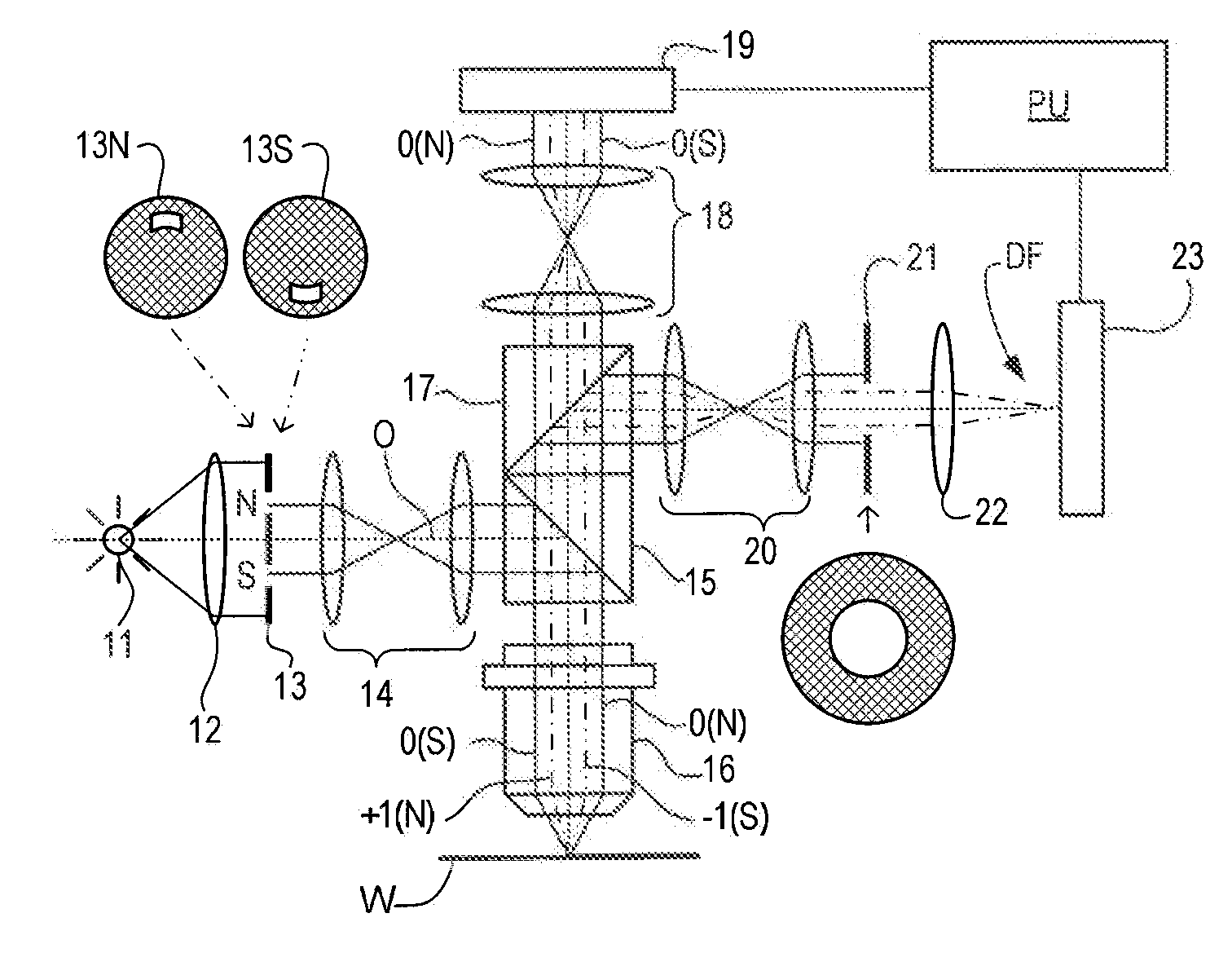
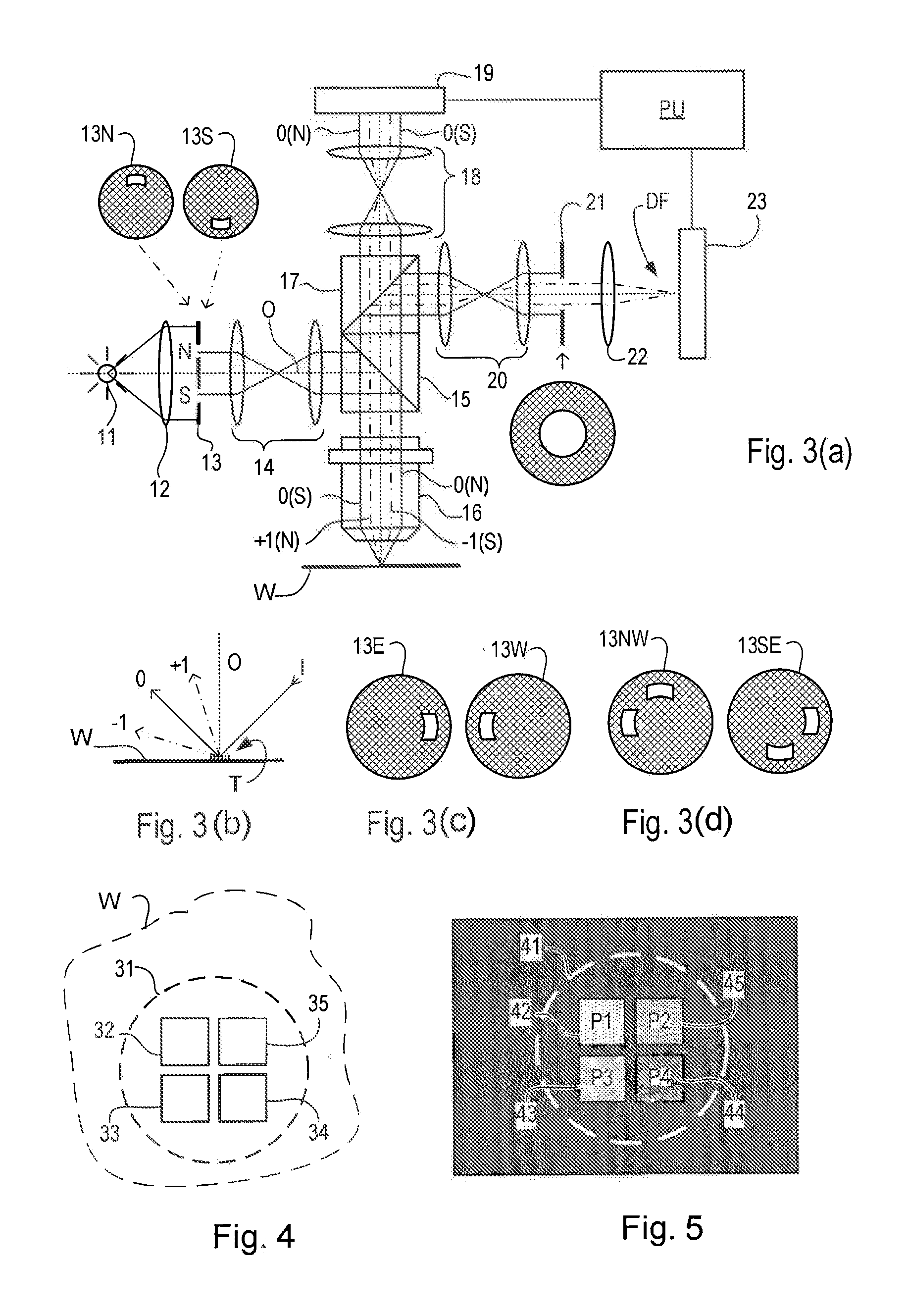
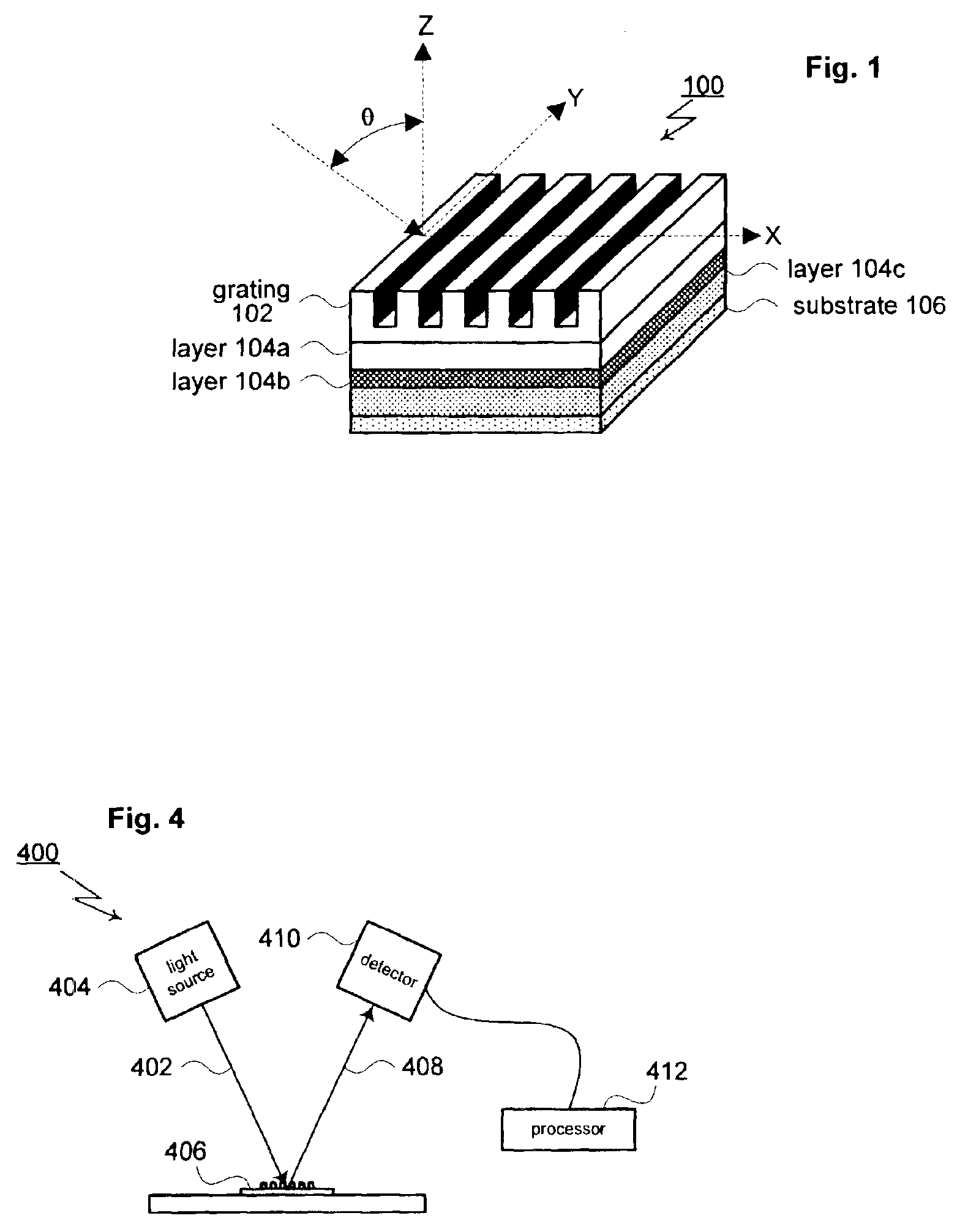
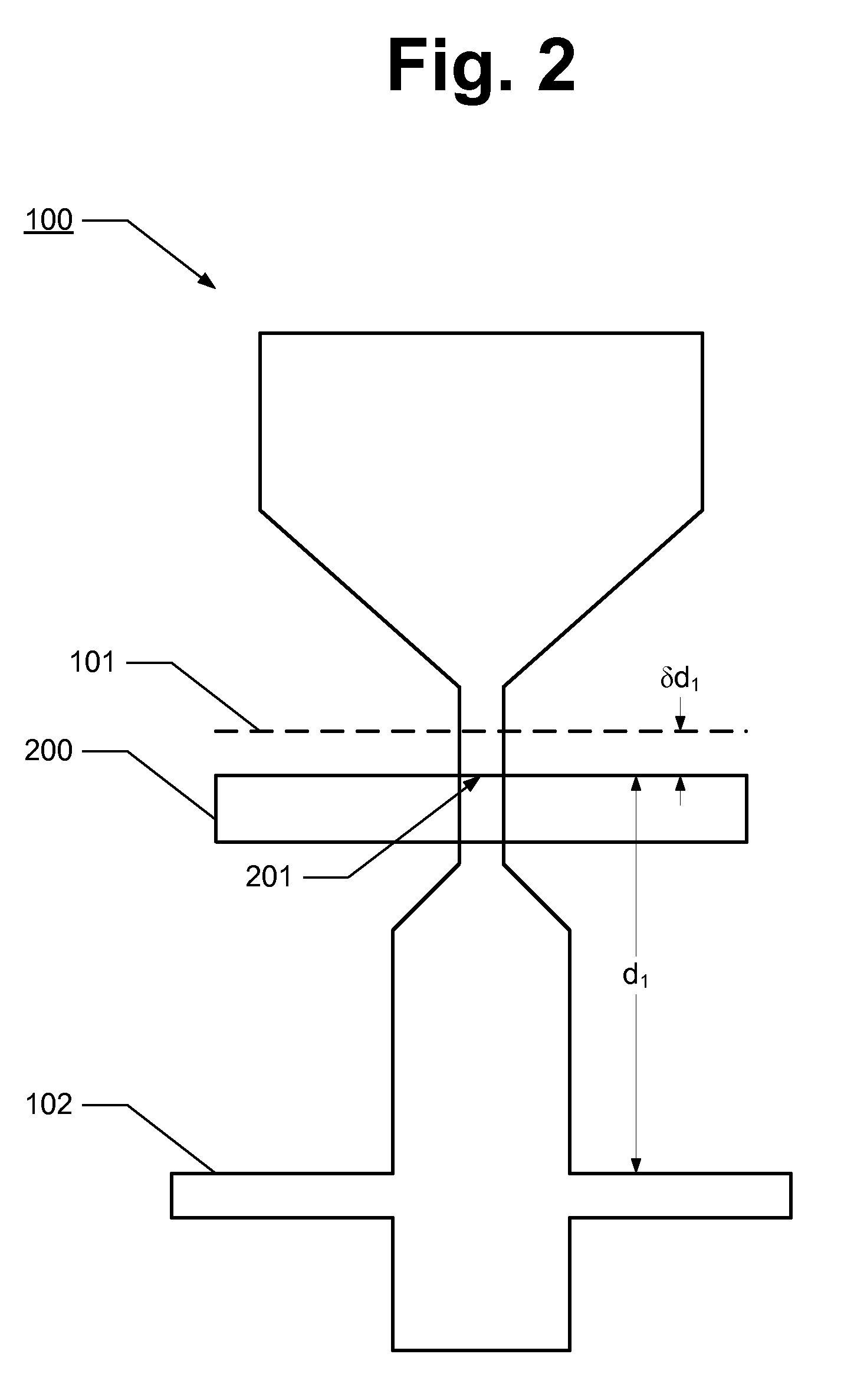
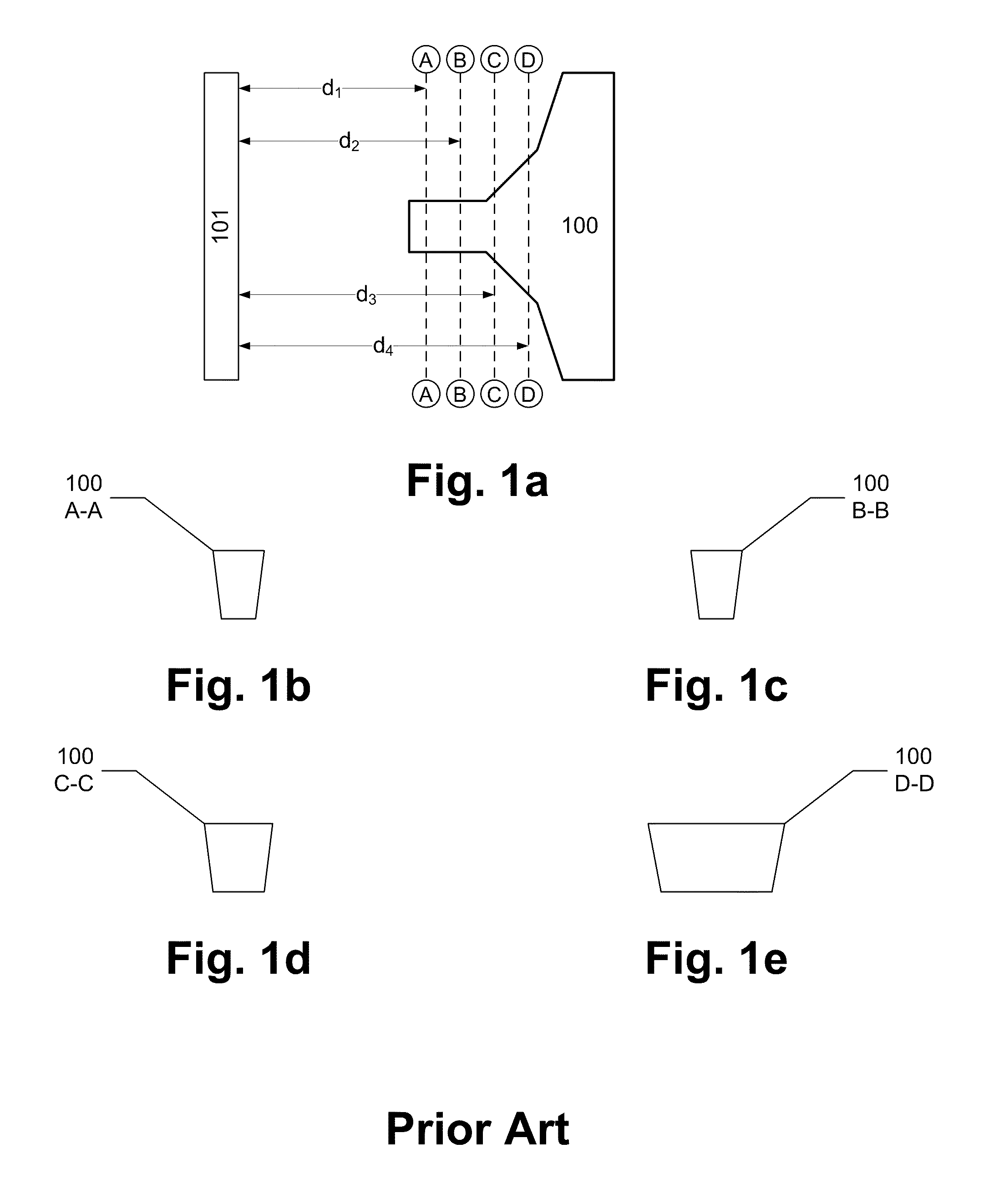
Substrate for Use in Metrology, Metrology Method and Device Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20120044470A1Efficient packagingPhotomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyGrating
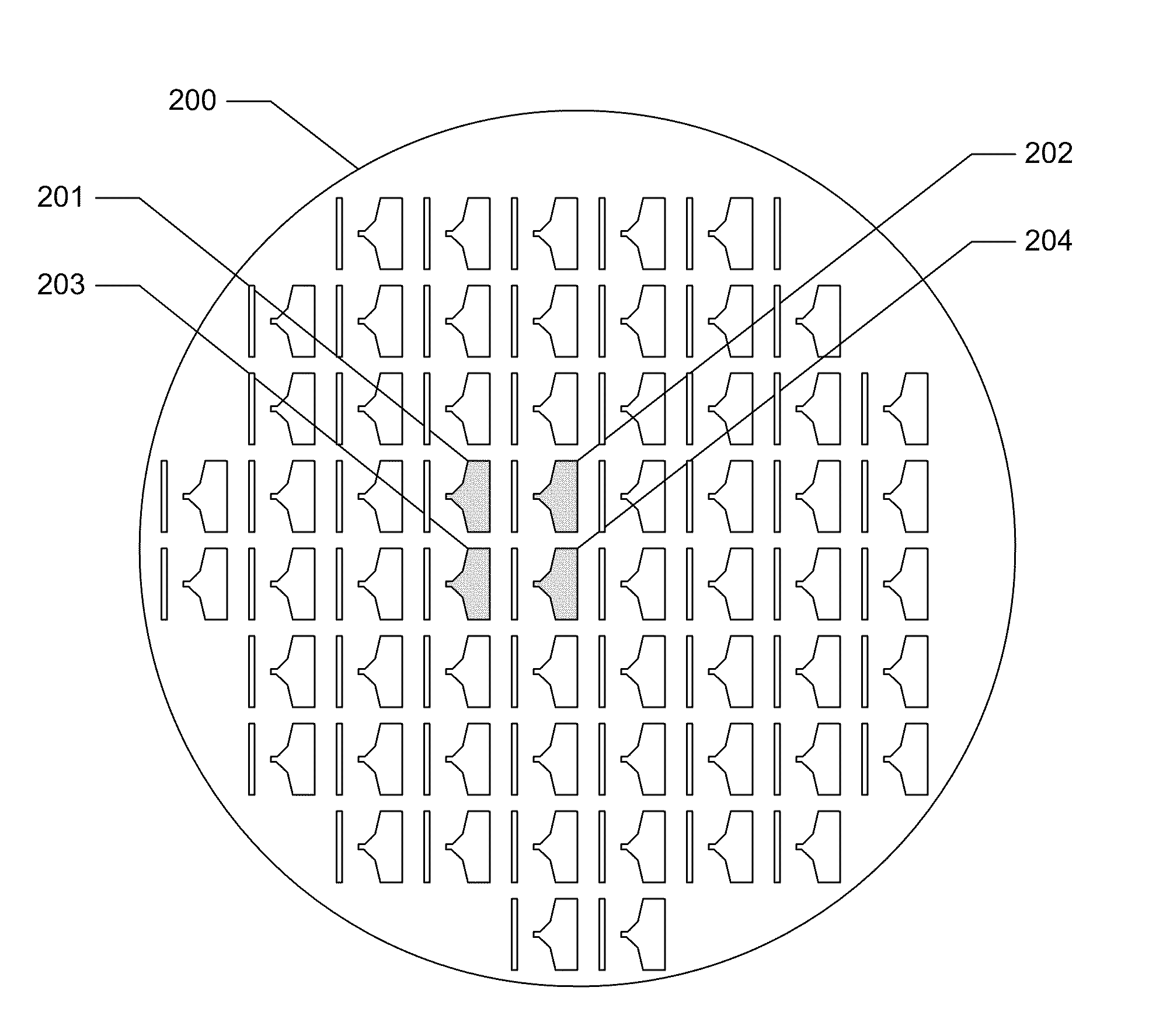
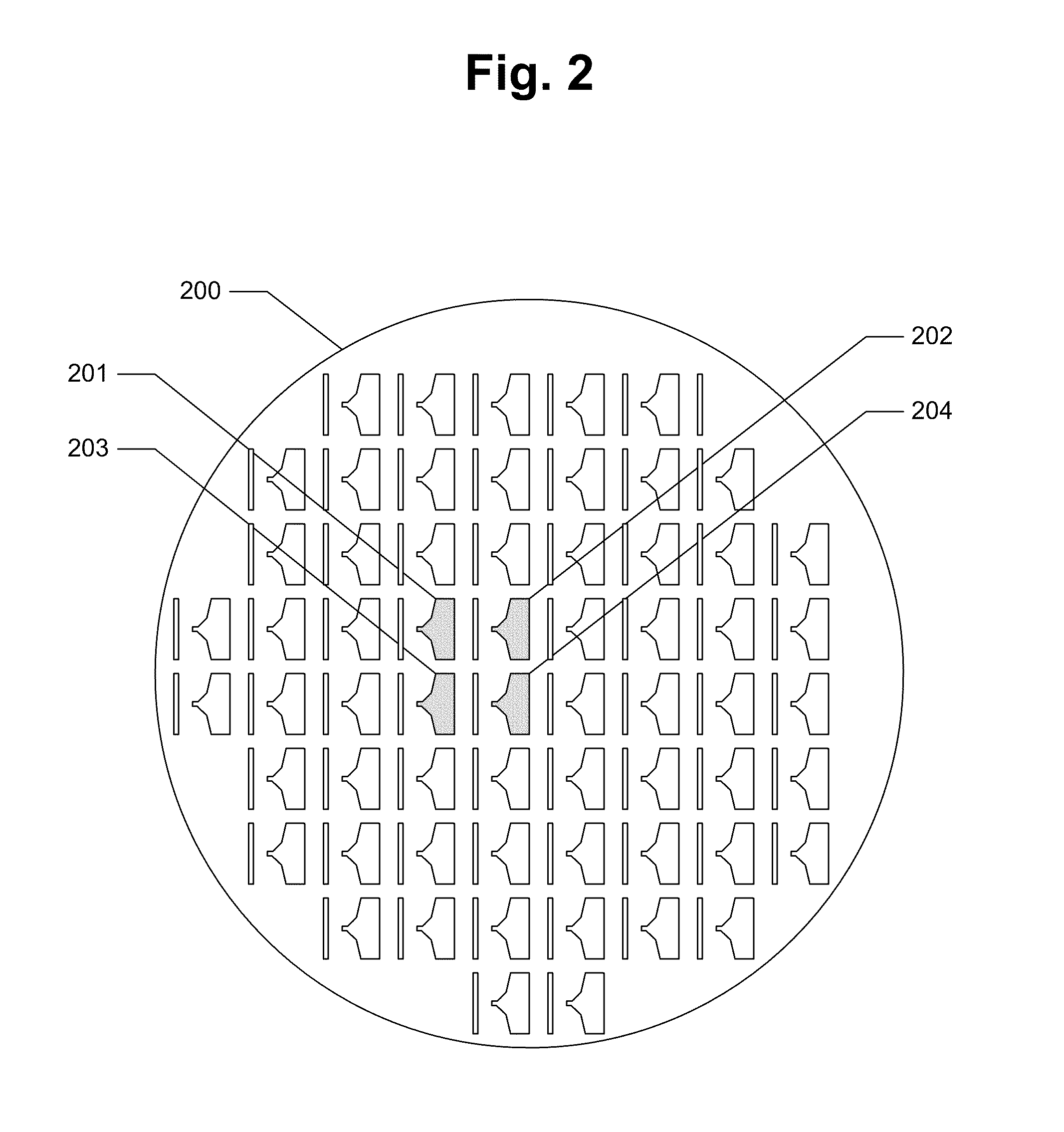
A pattern from a patterning device is applied to a substrate. The applied pattern includes device functional areas and metrology target areas. Each metrology target area comprises a plurality of individual grating portions, which are used for diffraction based overlay measurements or other diffraction based measurements. The gratings are of the small target type, which is small than an illumination spot used in the metrology. Each grating has an aspect ratio substantially greater than 1, meaning that a length in a direction perpendicular to the grating lines which is substantially greater than a width of the grating. Total target area can be reduced without loss of performance in the diffraction based metrology. A composite target can comprise a plurality of individual grating portions of different overlay biases. Using integer aspect ratios such as 2:1 or 4:1, grating portions of different directions can be packed efficiently into rectangular composite target areas.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
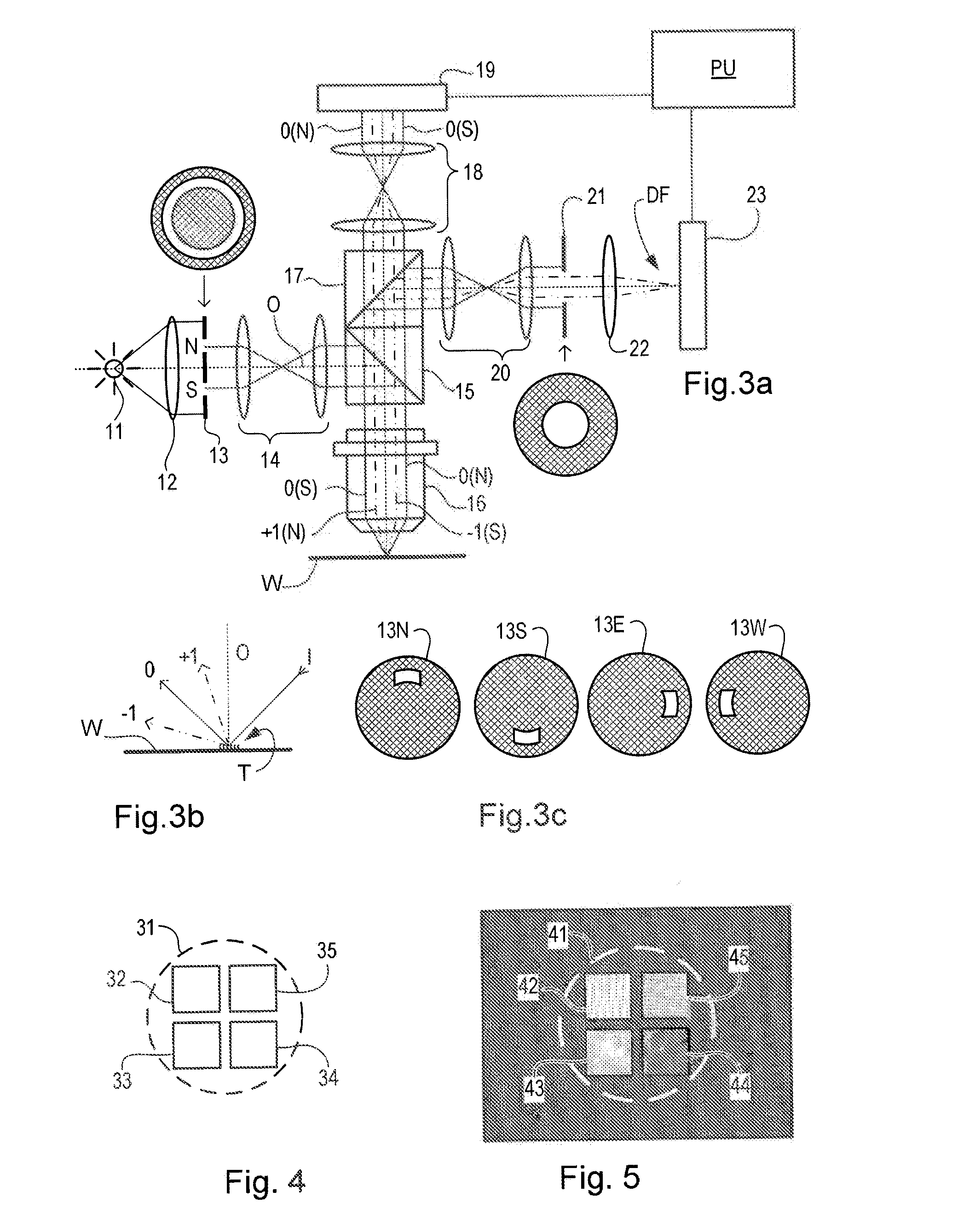
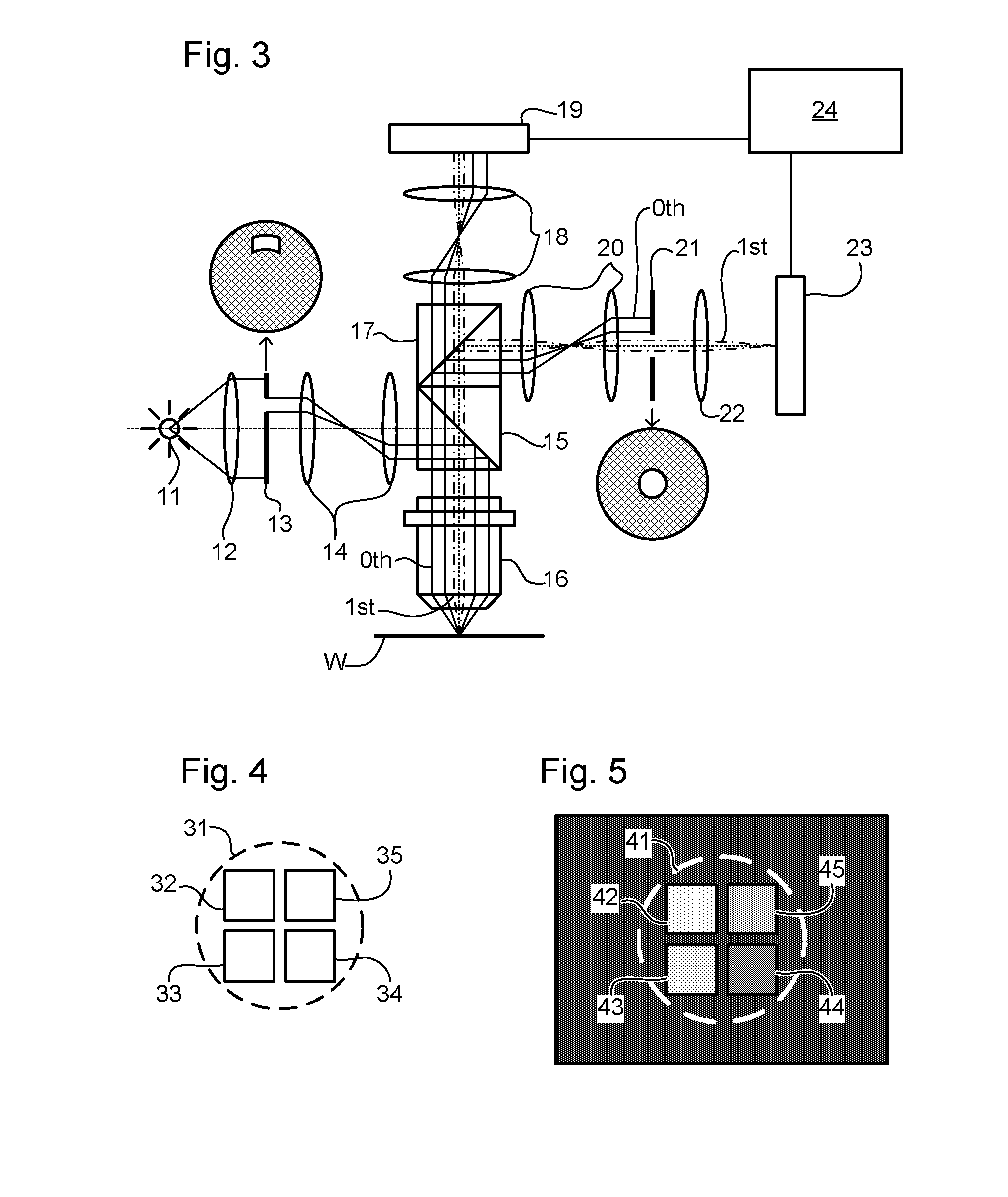
Metrology Method and Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus, Device Manufacturing Method and Substrate
ActiveUS20110043791A1Made preciselySmall targetPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansMetrologyGrating
A metrology apparatus is arranged to illuminate a plurality of targets with an off-axis illumination mode. Images of the targets are obtained using only one first order diffracted beam. Where the target is a composite grating, overlay measurements can be obtained from the intensities of the images of the different gratings. Overlay measurements can be corrected for errors caused by variations in the position of the gratings in an image field.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Metrology Method and Inspection Apparatus, Lithographic System and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20120123581A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputPhotomechanical apparatusScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpatial light modulator
Methods are disclosed for measuring target structures formed by a lithographic process on a substrate. A grating structure within the target is smaller than an illumination spot and field of view of a measurement optical system. The optical system has a first branch leading to a pupil plane imaging sensor and a second branch leading to a substrate plane imaging sensor. A spatial light modulator is arranged in an intermediate pupil plane of the second branch of the optical system. The SLM imparts a programmable pattern of attenuation that may be used to correct for asymmetries between the first and second modes of illumination or imaging. By use of specific target designs and machine-learning processes, the attenuation patterns may also be programmed to act as filter functions, enhancing sensitivity to specific parameters of interest, such as focus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
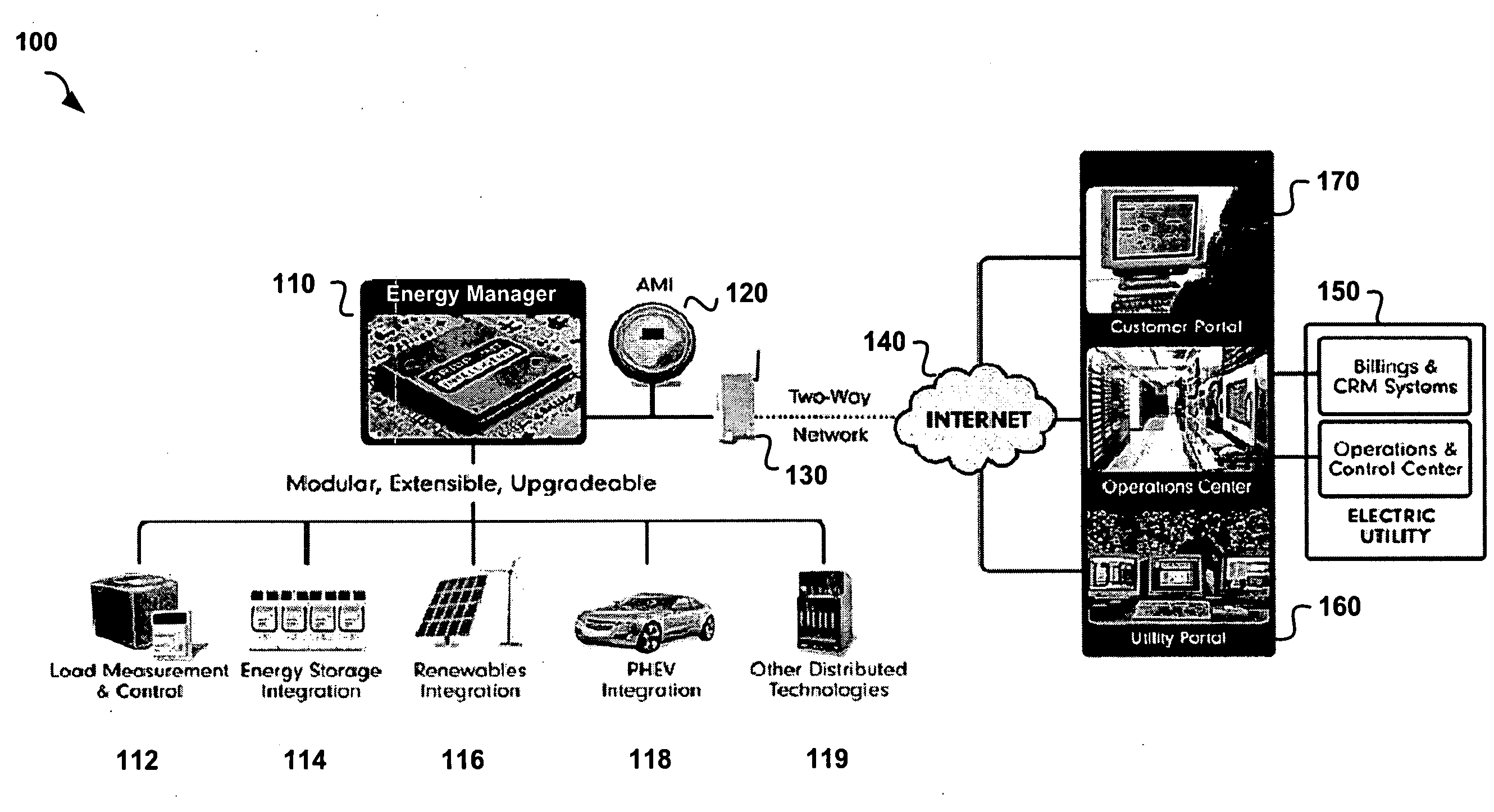
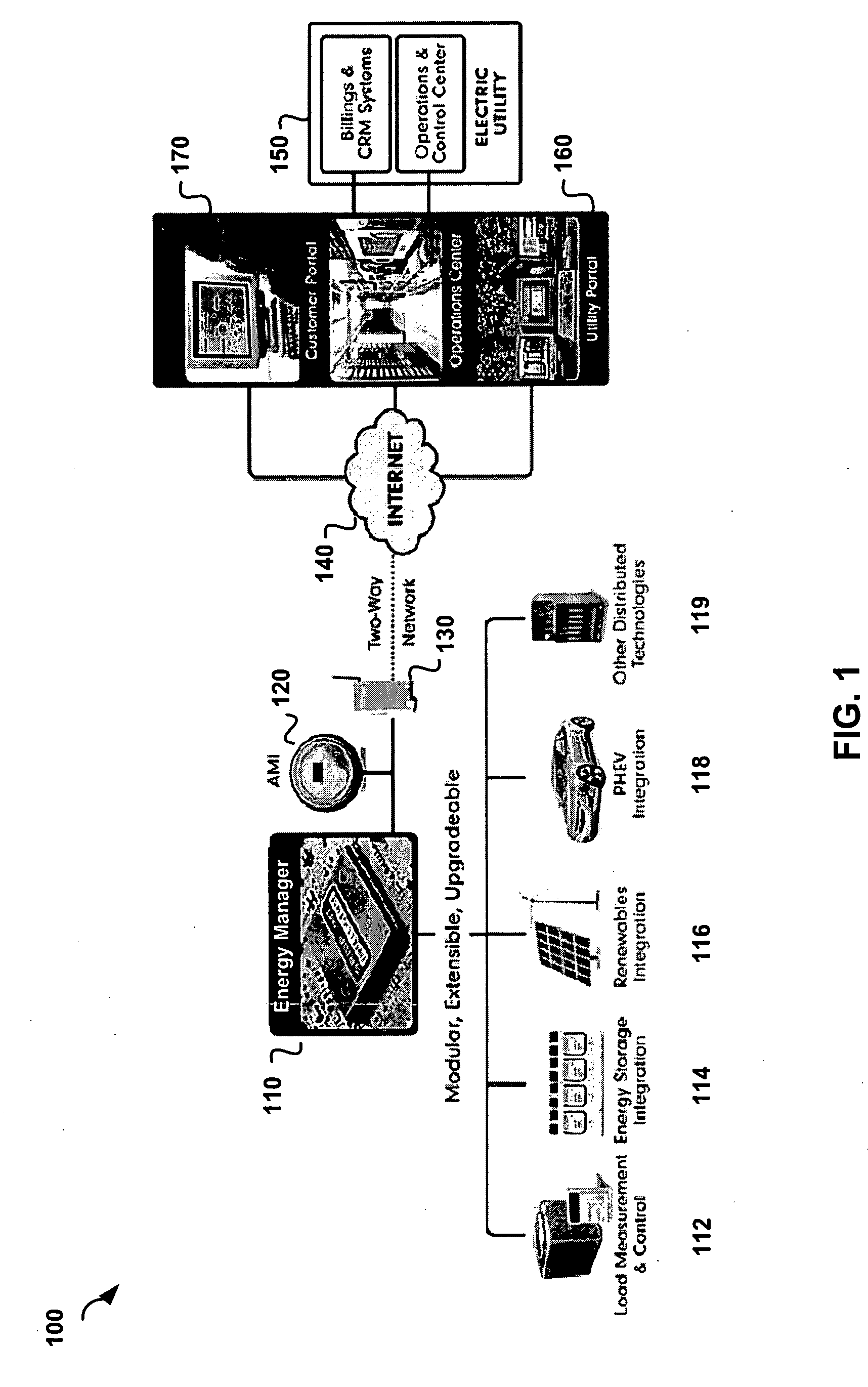
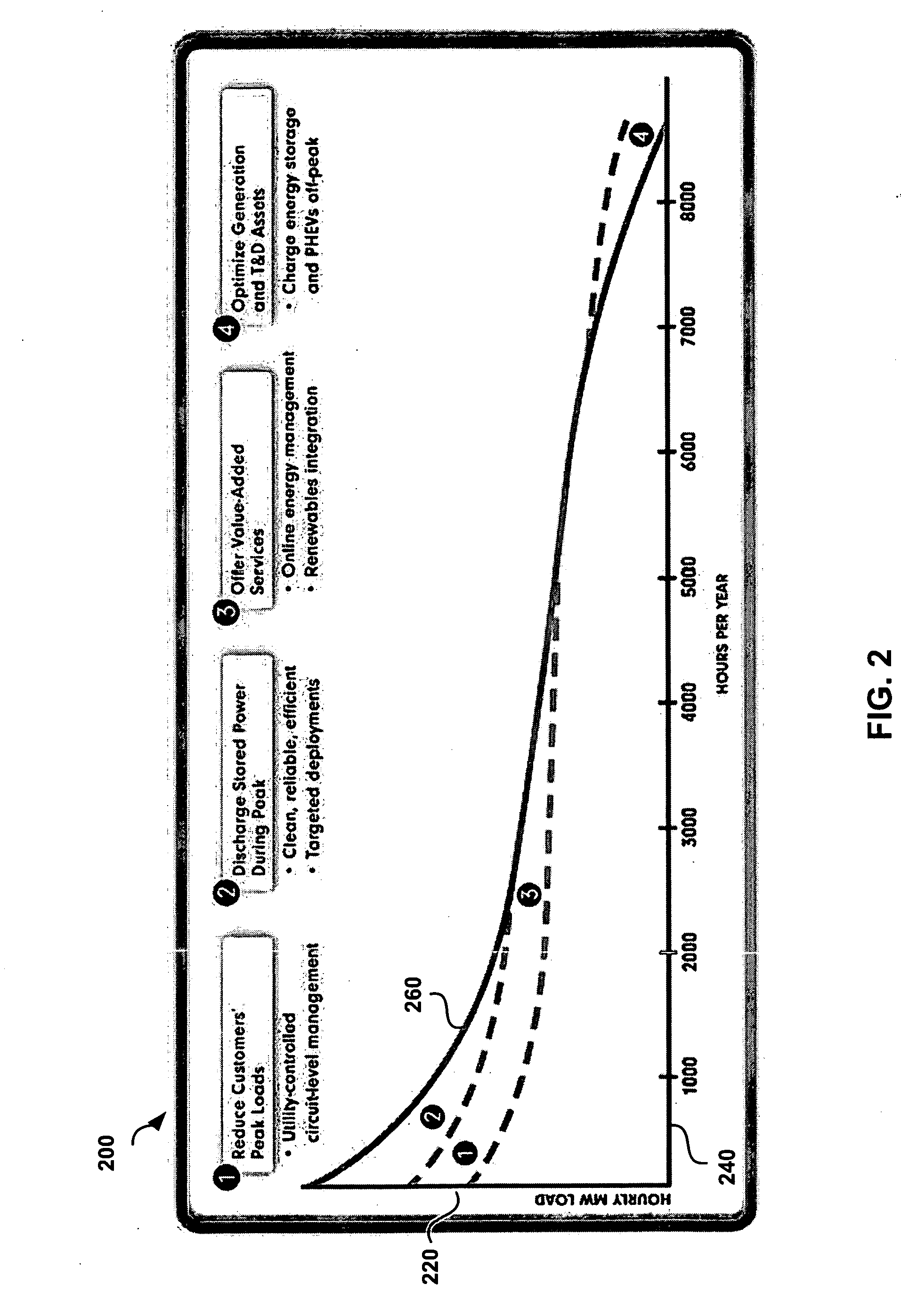
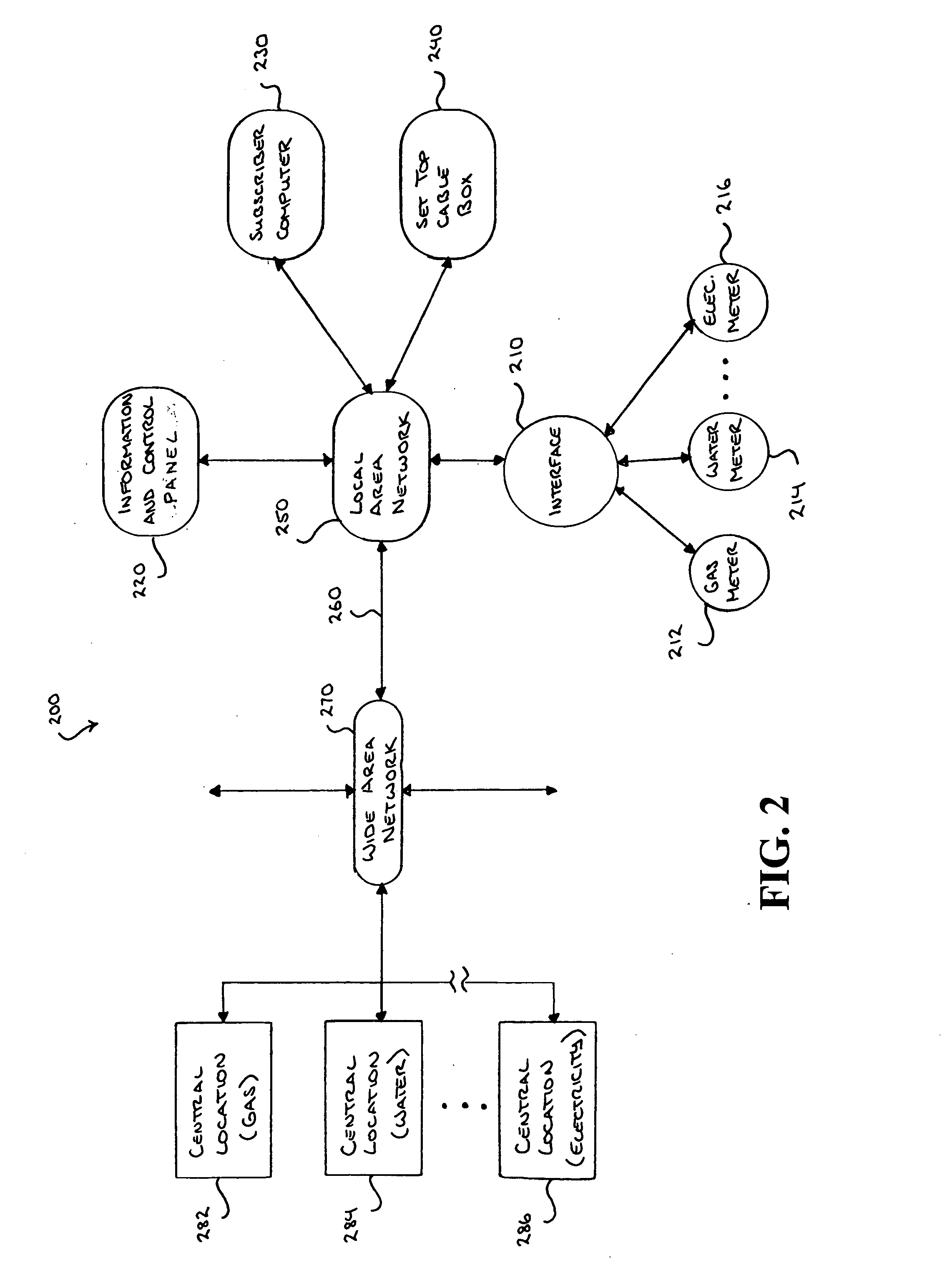
Modular electrical grid interface device
A smart grid gateway which includes a onboard computer programmed to provide load measurement and control of at least one local resource or asset. At least one metrology module is configured to provide metering of the at least one local resource or asset. At least one LAN module is configured to communicate with the at least one local resource or asset. At least one WAN module is configured to communicate with a network operations center.
Owner:GRIDPOINT
Metrology Method and Apparatus, and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20120242970A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputPhotomechanical apparatusOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMetrologyGrating
Methods are disclosed for measuring target structures formed by a lithographic process on a substrate. A grating or other structure within the target is smaller than an illumination spot and field of view of a measurement optical system. The position of an image of the component structure varies between measurements, and a first type of correction is applied to reduce the influence on the measured intensities, caused by differences in the optical path to and from different positions. A plurality of structures may be imaged simultaneously within the field of view of the optical system, and each corrected for its respective position. The measurements may comprise first and second images of the same target under different modes of illumination and / or imaging, for example in a dark field metrology application. A second type of correction may be applied to reduce the influence of asymmetry between the first and second modes of illumination or imaging, for example to permit a more accurate overly measurement in a semiconductor device manufacturing process.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
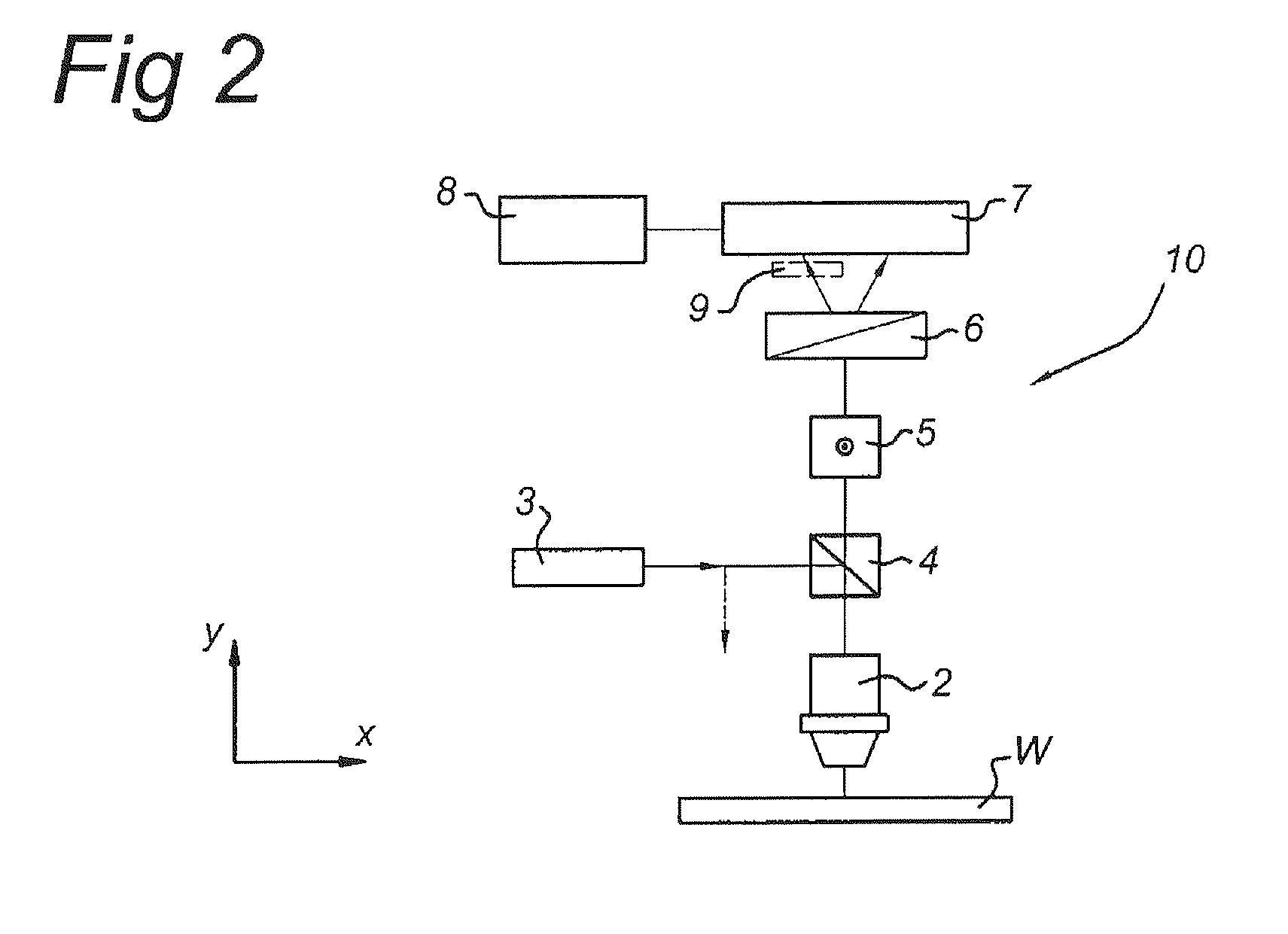
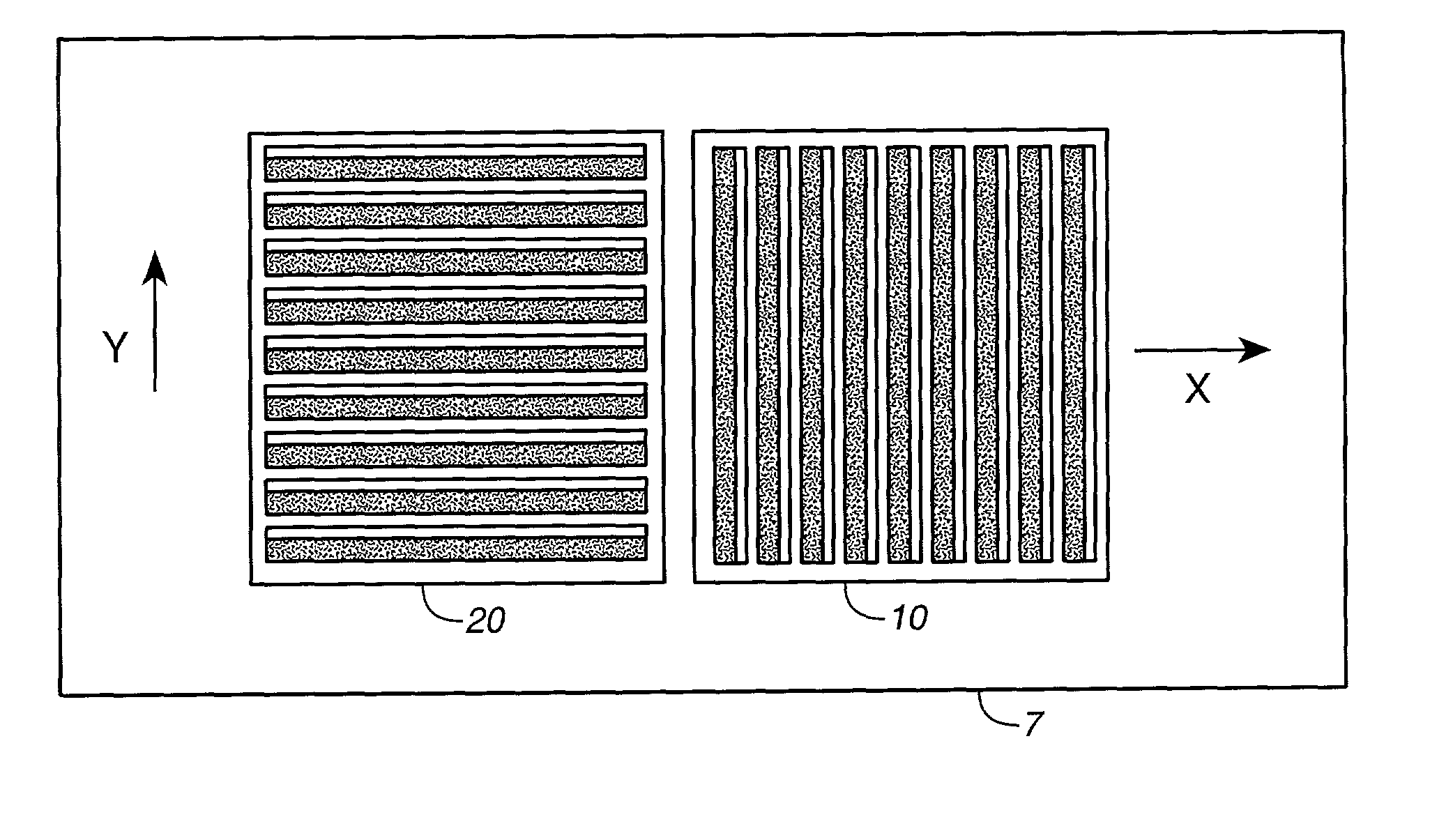
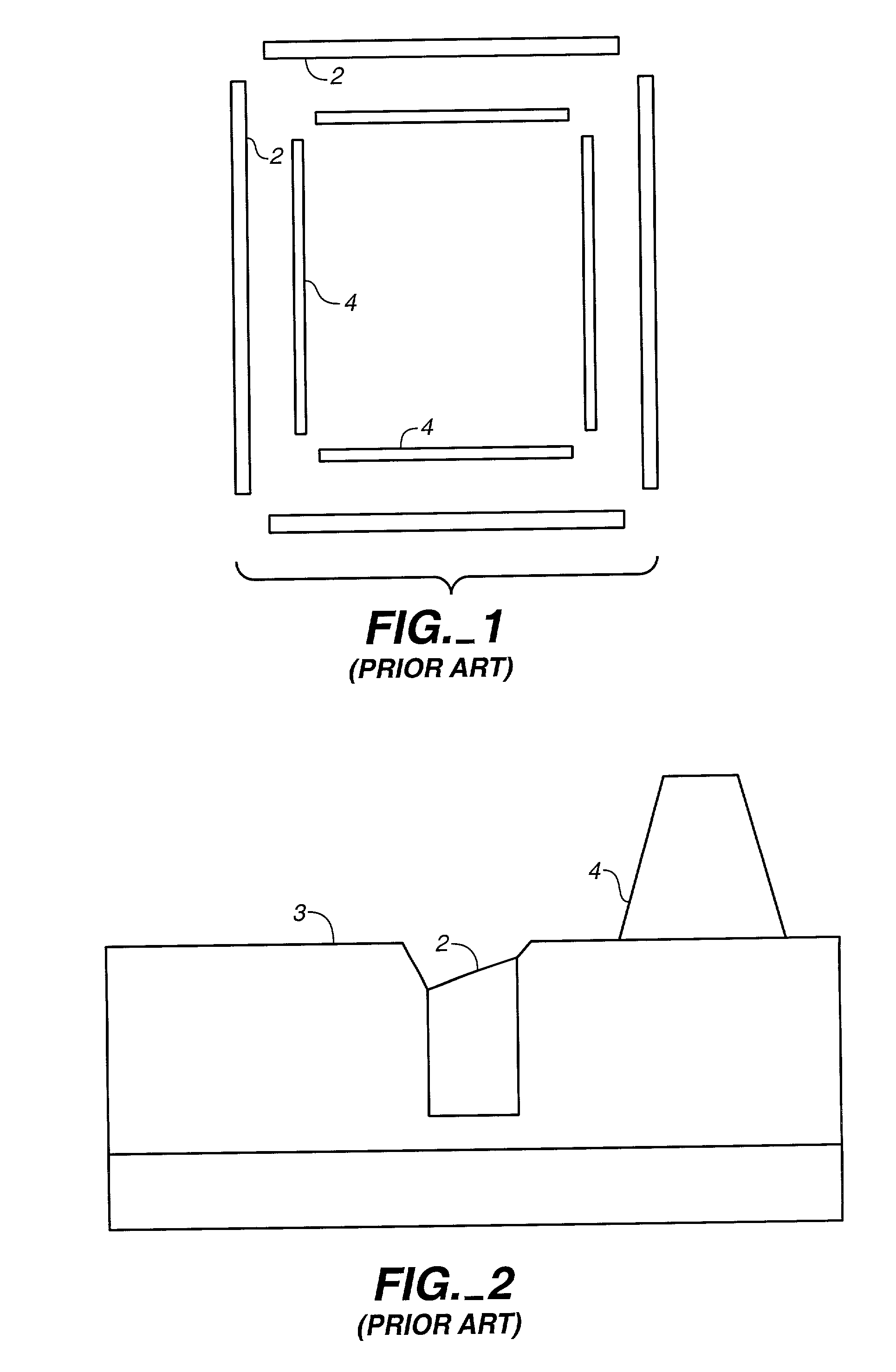
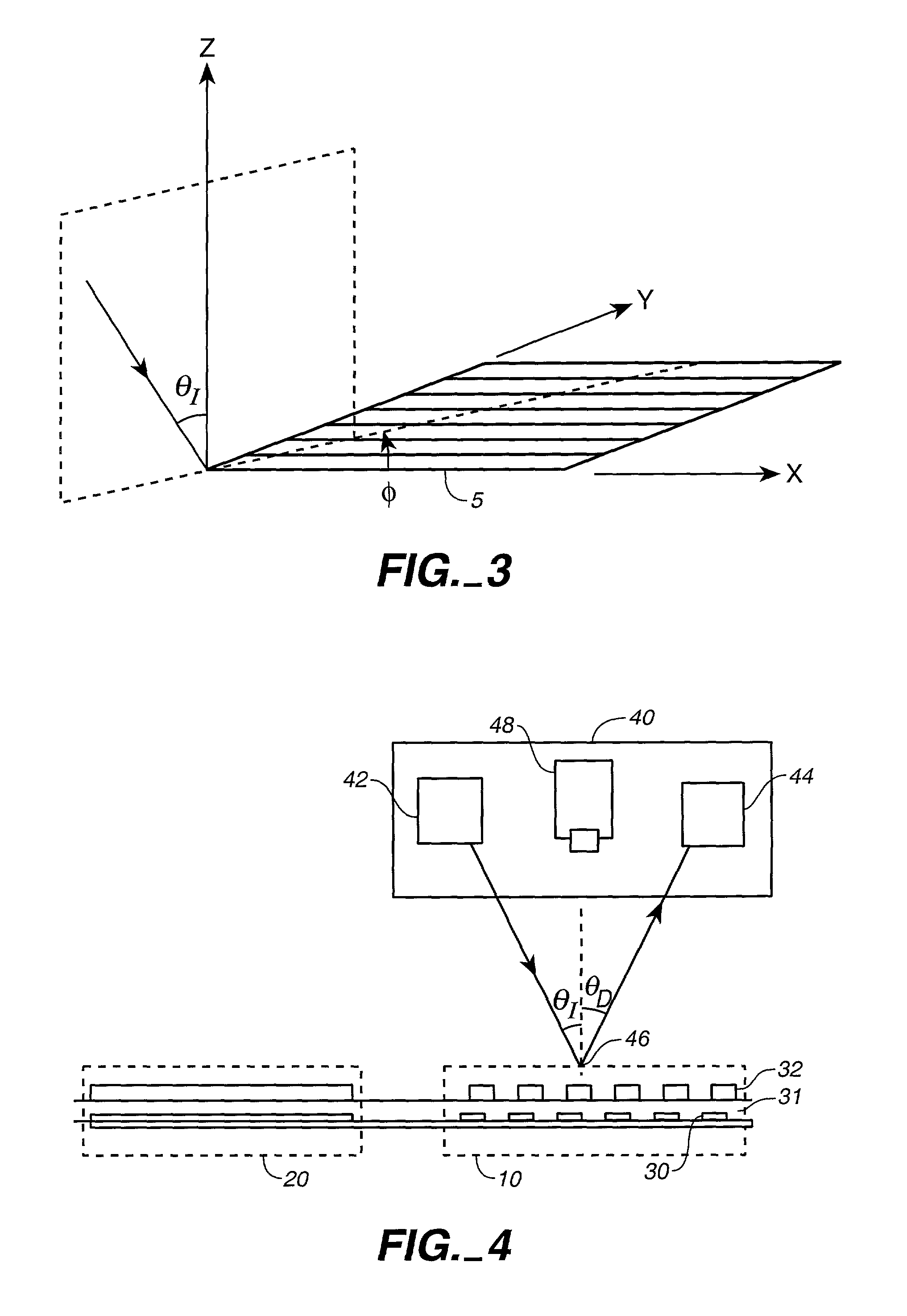
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
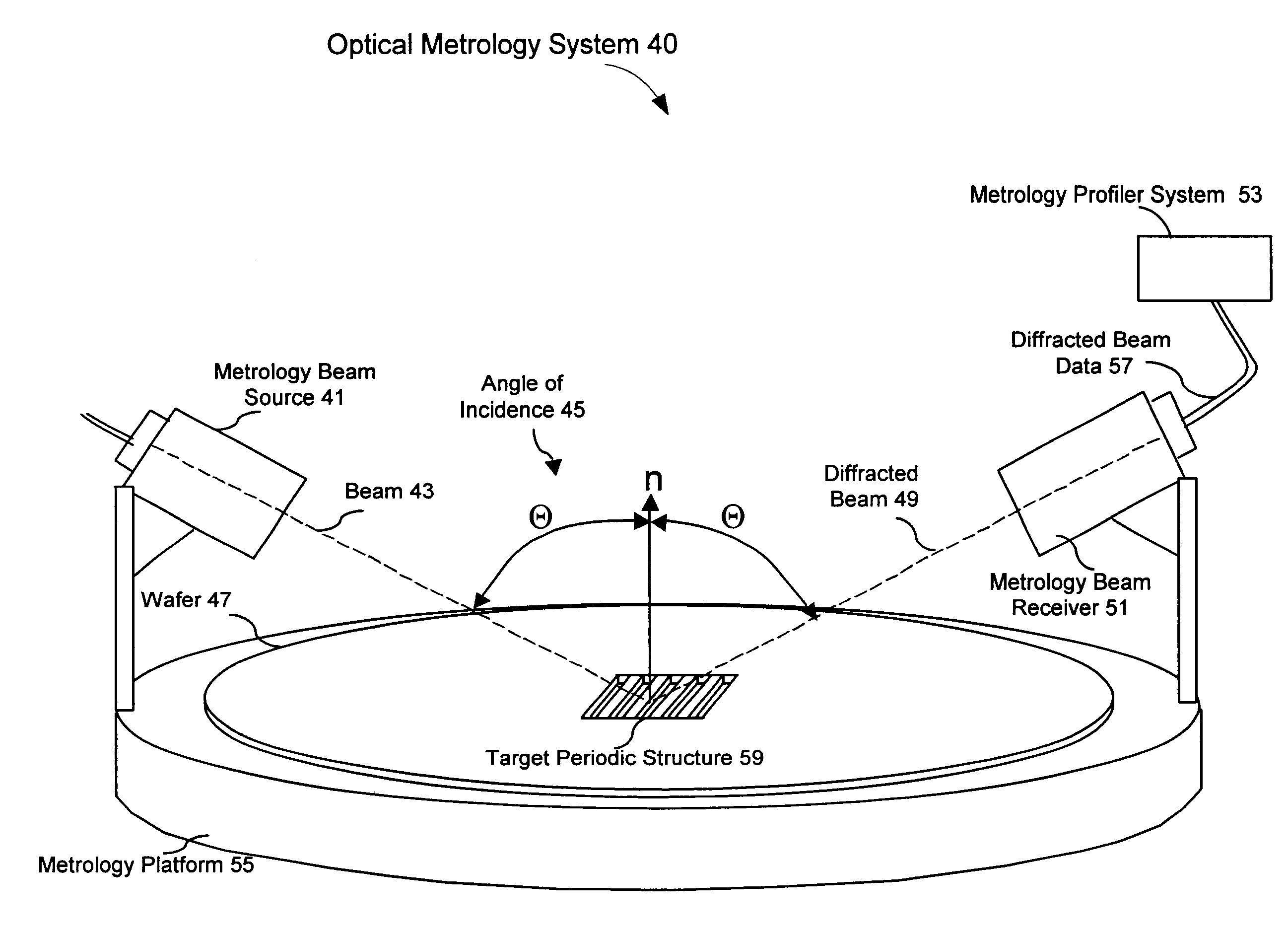
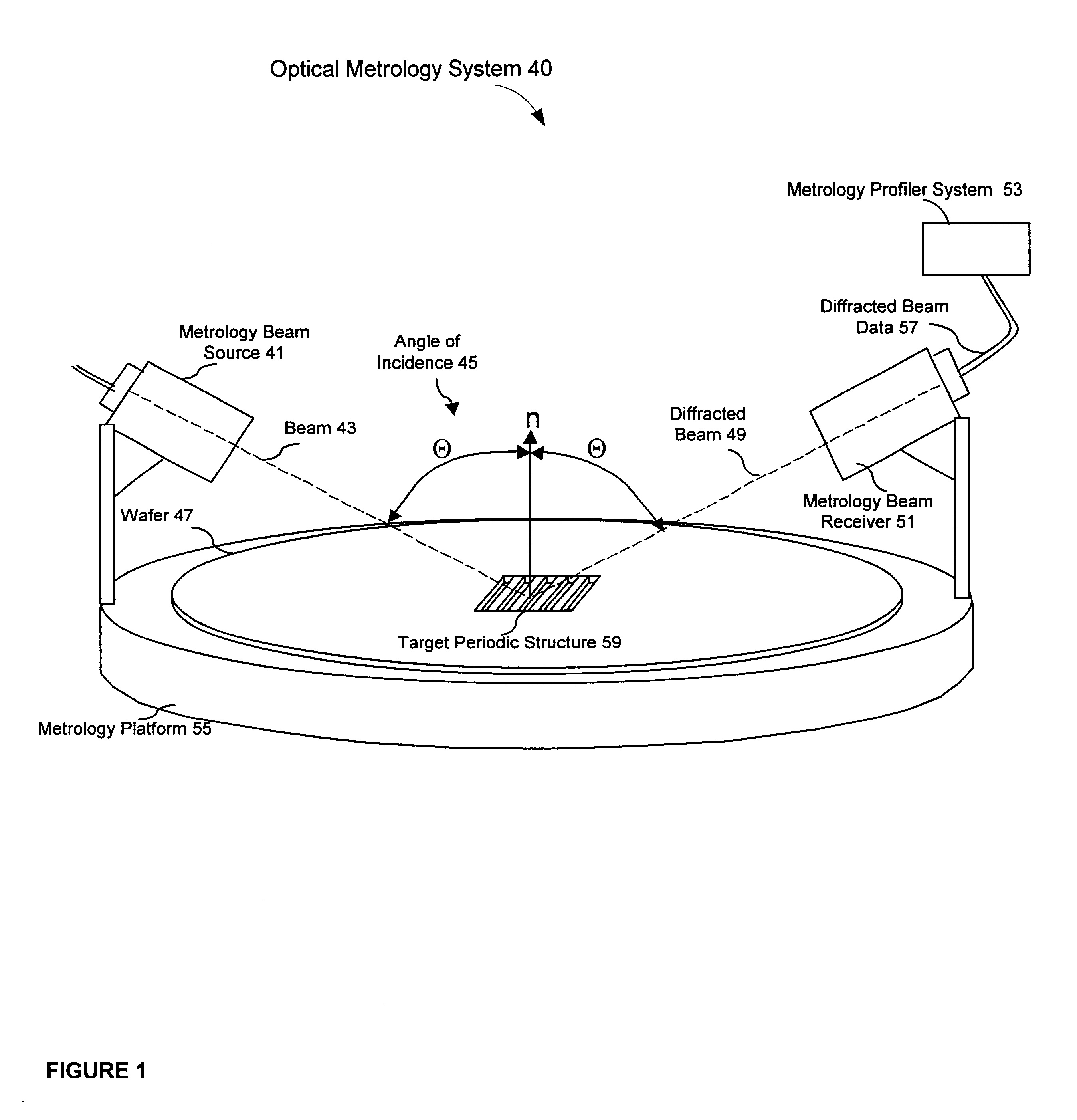
InactiveUS6819426B2Accurate measurementLimited space availableSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Overlay Measurement Apparatus, Lithographic Apparatus and Device Manufacturing Method Using Such Overlay Measurement Apparatus
ActiveUS20110188020A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyLight beam
An overlay measurement apparatus has a polarized light source for illuminating a sample with a polarized light beam and an optical system to capture light that is scattered by the sample. The optical system includes a polarizer for transmitting an orthogonal polarization component that is orthogonal to a polarization direction of the polarized light beam. A detector measures intensity of the orthogonal polarization component. A processing unitise connected to the detector, and is arranged to process the orthogonal polarization component for overlay metrology measurement using asymmetry data derived from the orthogonal polarization component.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Overlay alignment metrology using diffraction gratings
InactiveUS20020158193A1Limited space availableOvercome difficultiesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyAngle of incidence
Alignment accuracy between two or more patterned layers is measured using a metrology target comprising substantially overlapping diffraction gratings formed in a test area of the layers being tested. An optical instrument illuminates all or part of the target area and measures the optical response. The instrument can measure transmission, reflectance, and / or ellipsometric parameters as a function of wavelength, polar angle of incidence, azimuthal angle of incidence, and / or polarization of the illumination and detected light. Overlay error or offset between those layers containing the test gratings is determined by a processor programmed to calculate an optical response for a set of parameters that include overlay error, using a model that accounts for diffraction by the gratings and interaction of the gratings with each others' diffracted field. The model parameters might also take account of manufactured asymmetries. The calculation may involve interpolation of pre-computed entries from a database accessible to the processor. The calculated and measured responses are iteratively compared and the model parameters changed to minimize the difference.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
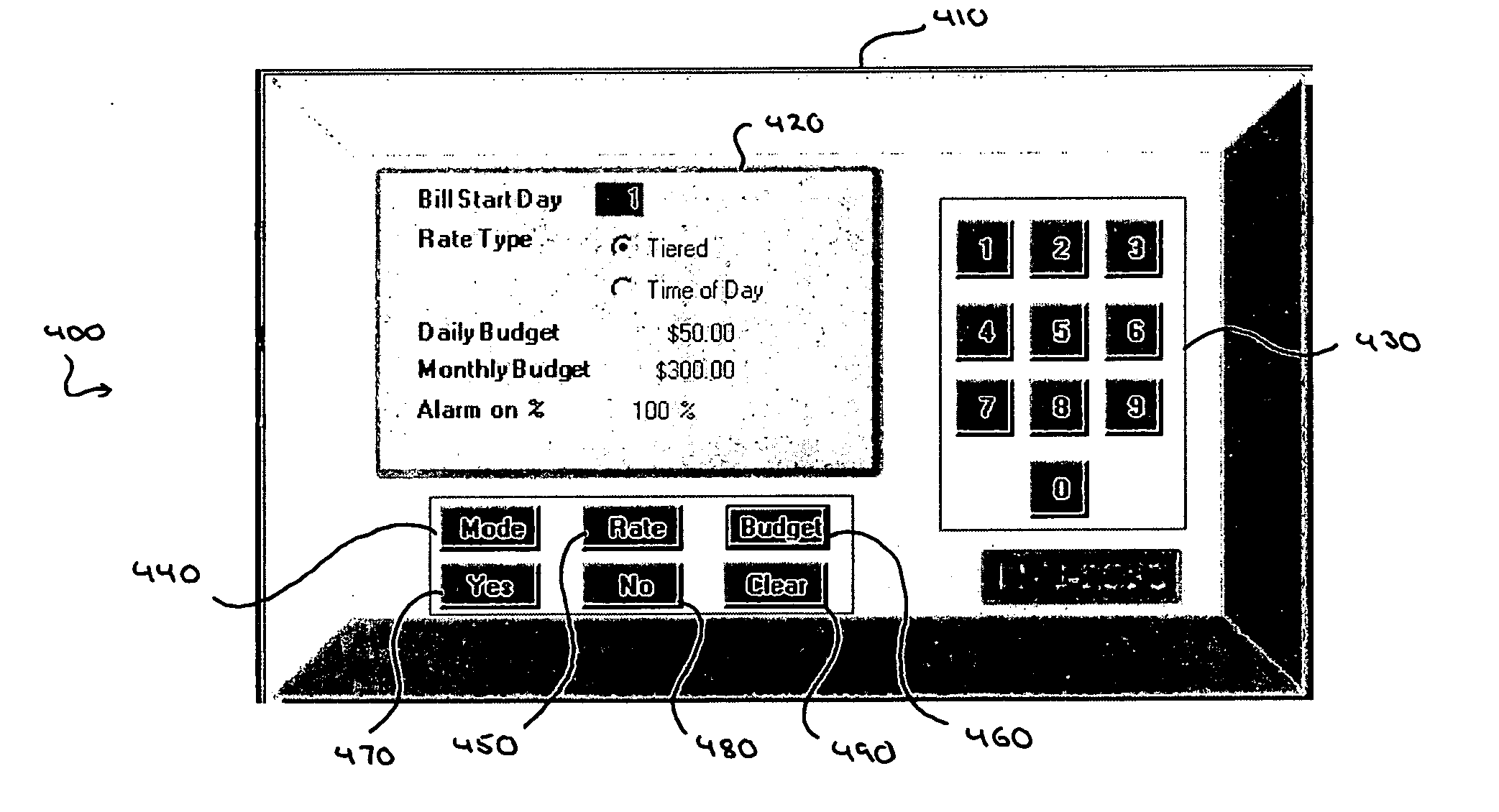
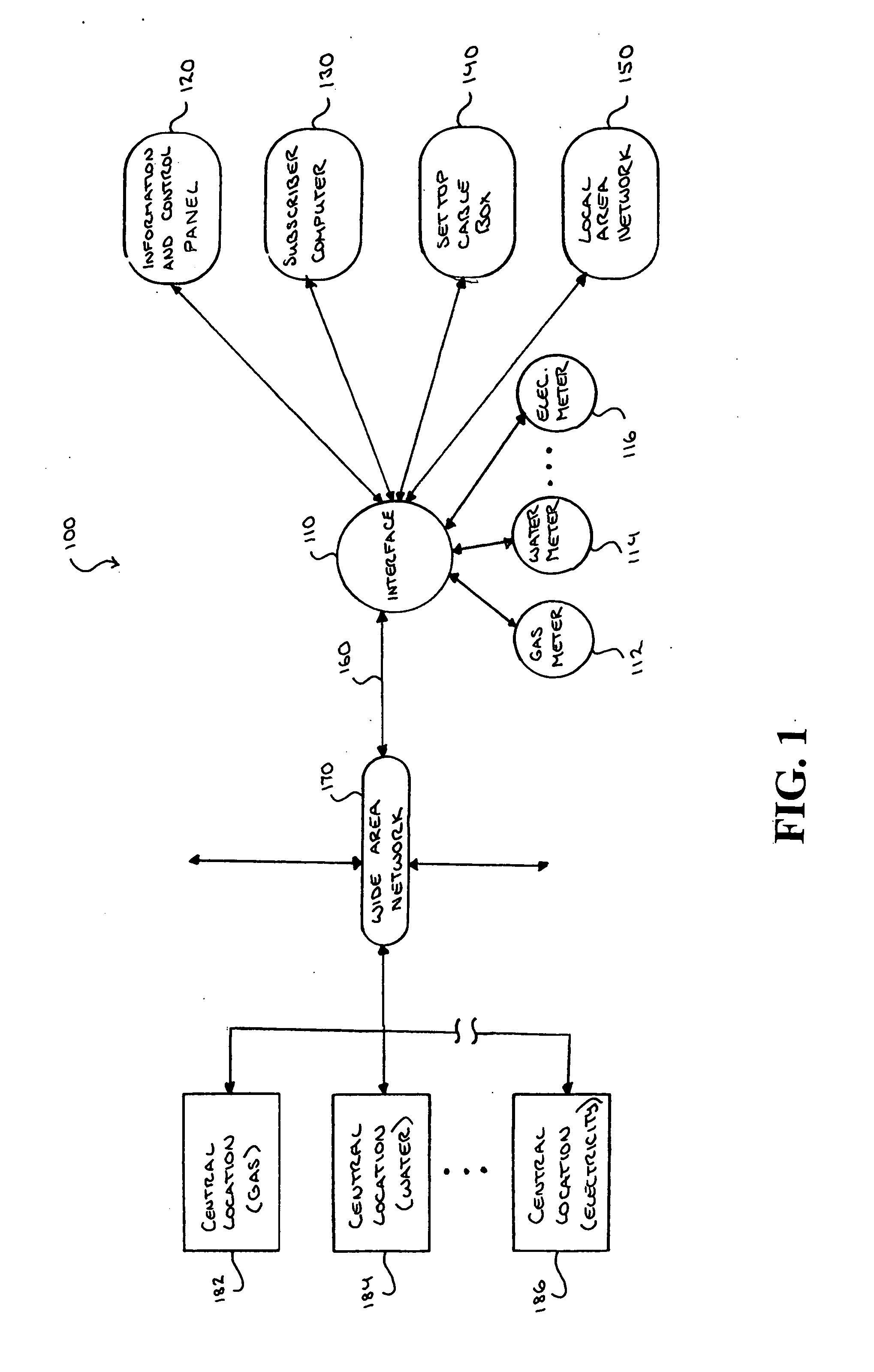
Integrated metrology systems and information and control apparatus for interaction with integrated metrology systems
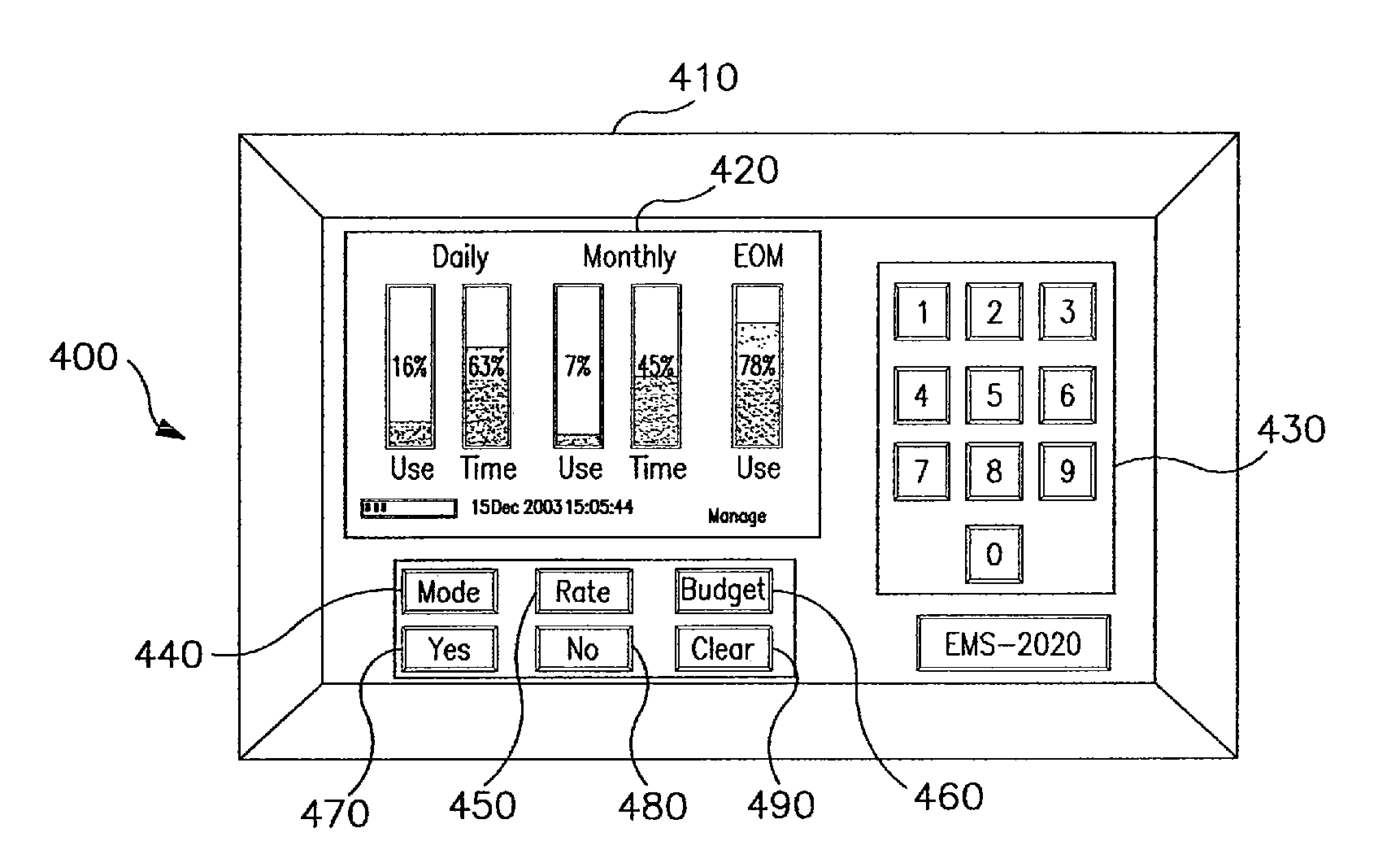
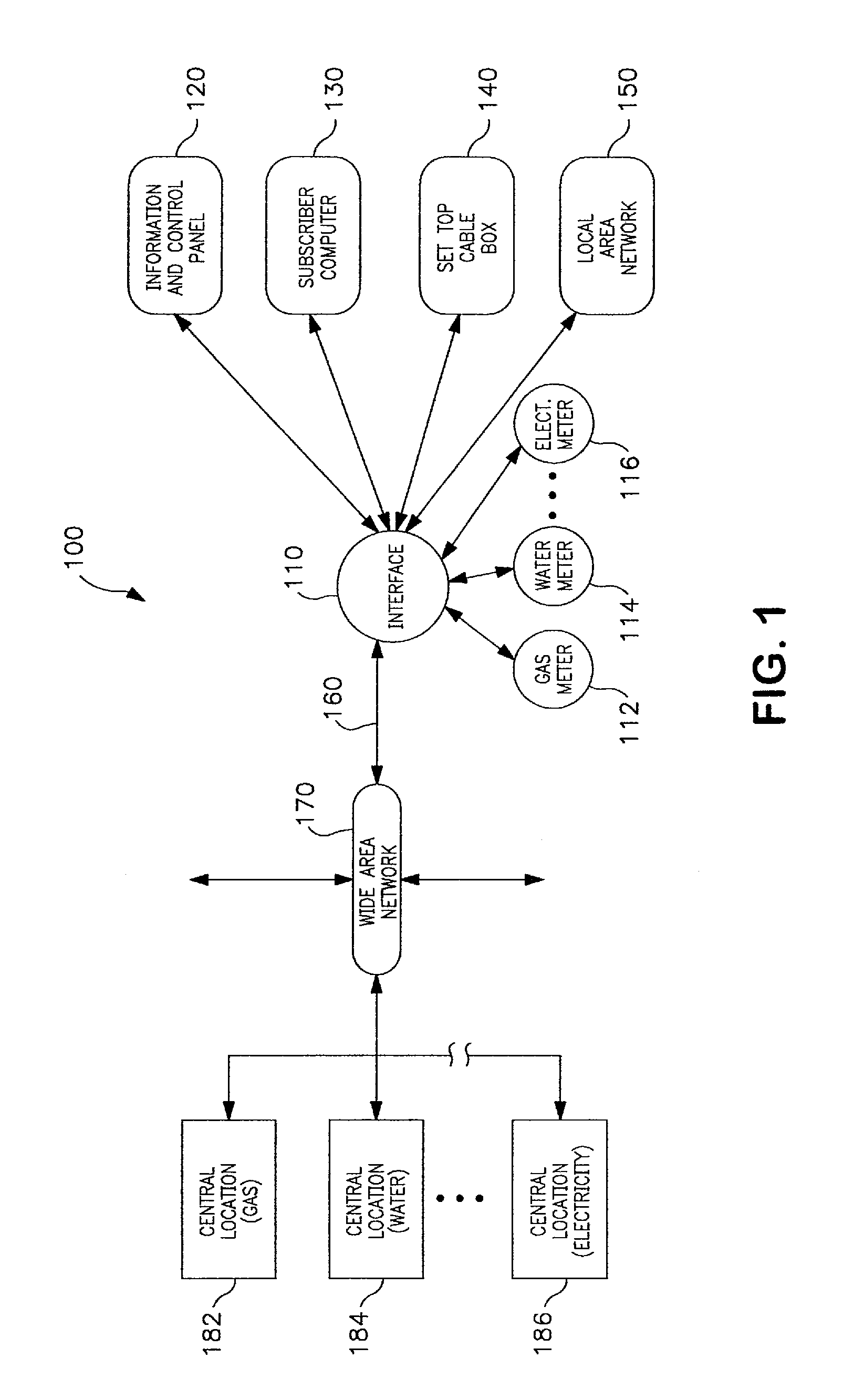
ActiveUS7379791B2Increase profitabilityPositive economic advantagesLevel controlNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTelecommunications linkMetrology
A system is disposed at a location of a utility commodity subscriber for informing the subscriber of and controlling utility commodity usage. The system includes utility meters, an information and control apparatus, and a first and second data communication link. The meters measure usage and and generate usage signals. The information and control apparatus includes a microprocessor, a memory, a clock, and a user interface. The first data communication link is between the utility meters and the information and control apparatus and the second data communication link is between the information and control apparatus and one or more central locations. The second communication link also provides rate information to the information and control apparatus and utility commodity usage data to the central location. The microprocessor computes an accumulated cost of utility commodity for a predetermined period of time. Information related to the accumulated cost is output to the subscriber.
Owner:ENERGYCITE INC
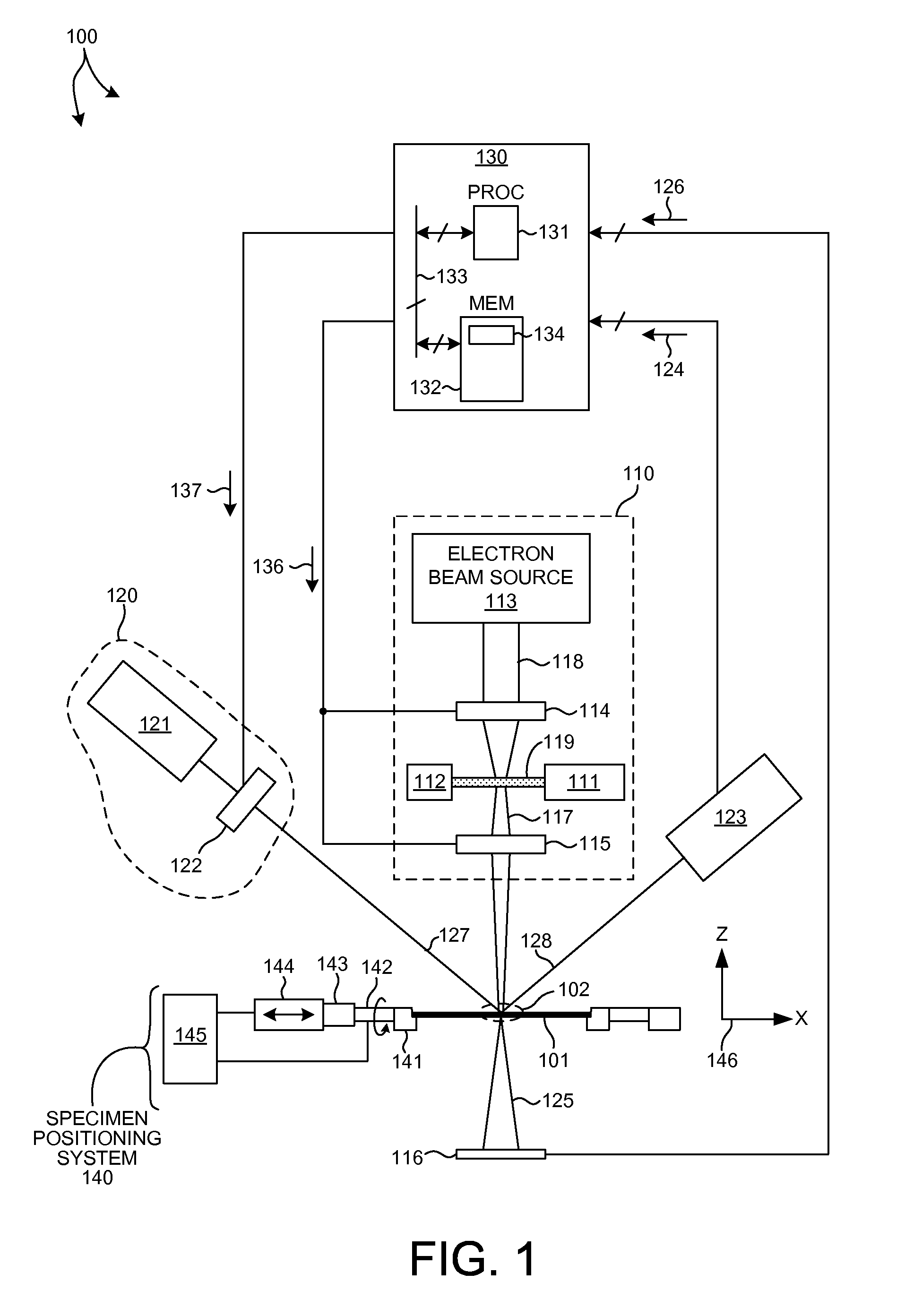
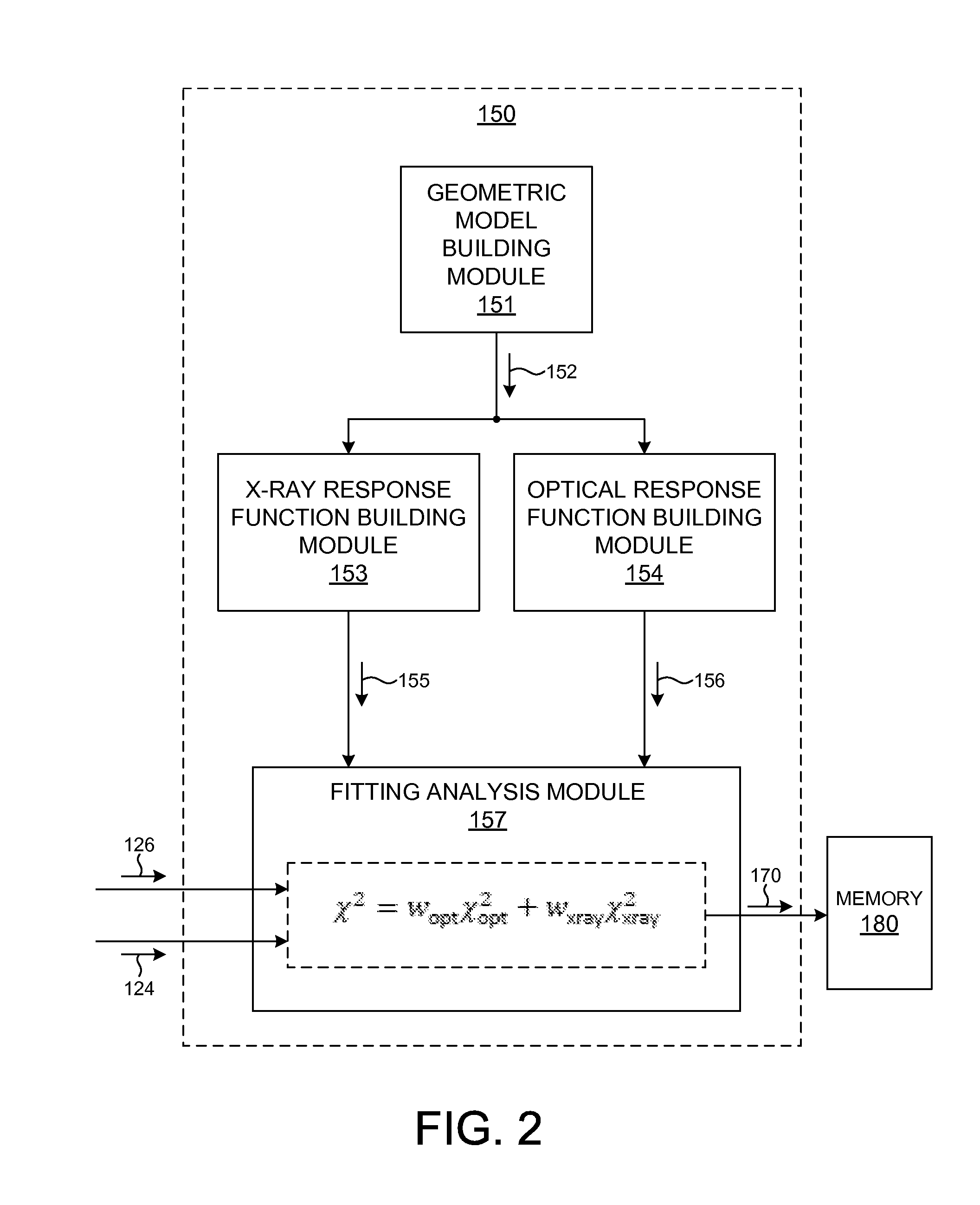
Metrology Tool With Combined X-Ray And Optical Scatterometers
ActiveUS20130304424A1Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setMetrology
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous optical scattering and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with optical scatterometry measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements based on models that share at least one geometric parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
Integrated metrology systems and information and control apparatus for interaction with integrated metrology systems
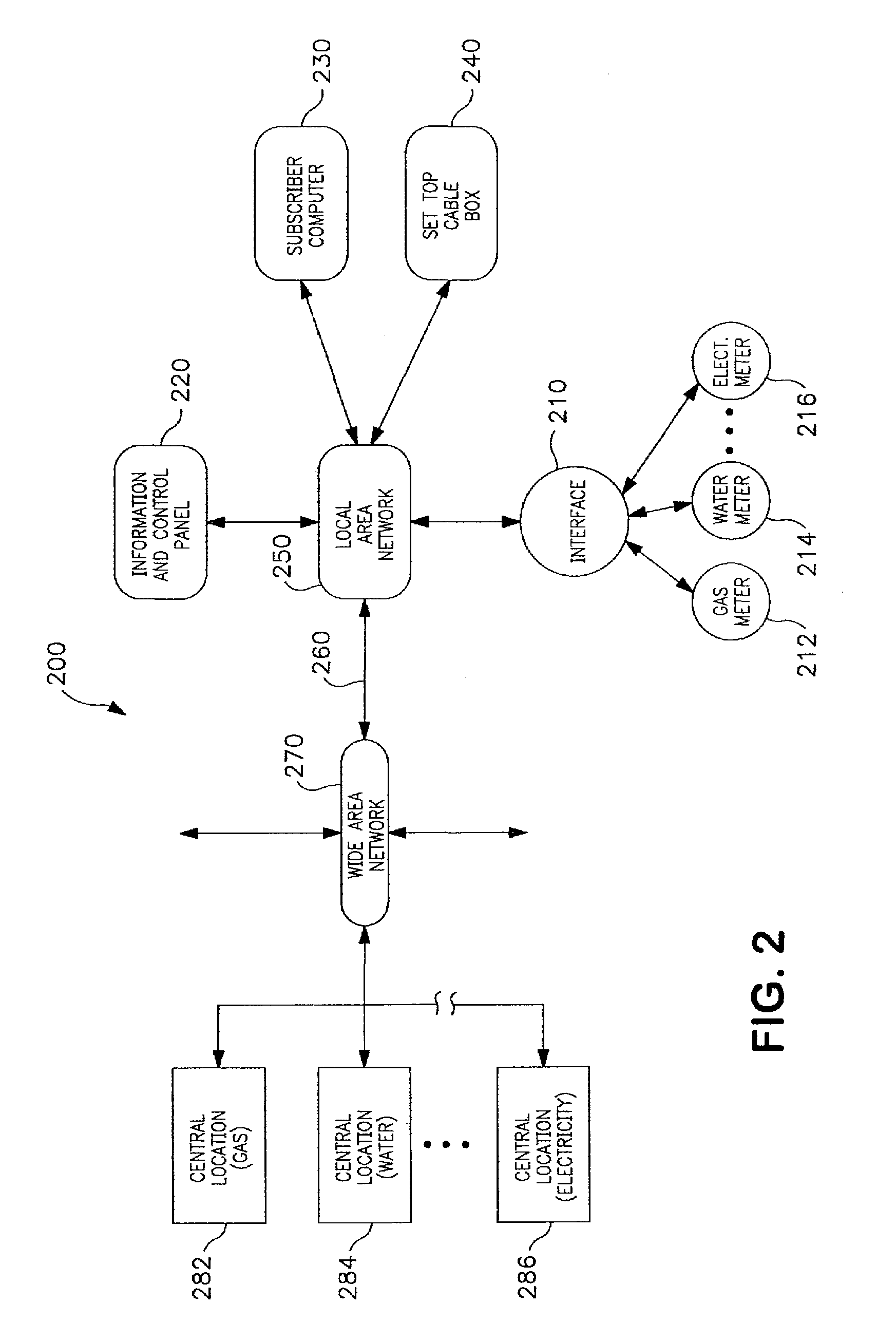
ActiveUS20060031180A1Increase profitabilityPositive economic advantagesElectric signal transmission systemsLevel controlTelecommunications linkMetrology
A system is disposed at a location of a utility commodity subscriber for informing the subscriber of utility commodity cost and usage and for controlling utility commodity usage. The system includes one or more utility meters, an information and control apparatus, a first data communication link, and a second data communication link. The one or more meters measure usage of one or more utility commodity and for generating one or more usage signals including a measurement of the subscriber's usage of the one or more utility commodities. The information and control apparatus includes a microprocessor, a memory, a clock, and a user interface, for inputting and outputting information. The first data communication link is between the one or more utility meters and the information and control apparatus and provides the one or more usage signals to said information and control apparatus for storage in the memory. The second data communication link is between the information and control apparatus and one or more central locations associated with the one or more utility commodity. The second communication link also provides rate information related to usage of the one or more utility commodity from the one or more central location to the information and control apparatus and provides utility commodity usage data from the information and control apparatus to the one or more central location. The microprocessor computes an accumulated cost of one or more utility commodity for a predetermined period of time according to the clock, the one or more usage signal, and the rate information. Information related to the accumulated cost is provided to the user interface for output to the subscriber.
Owner:ENERGYCITE INC
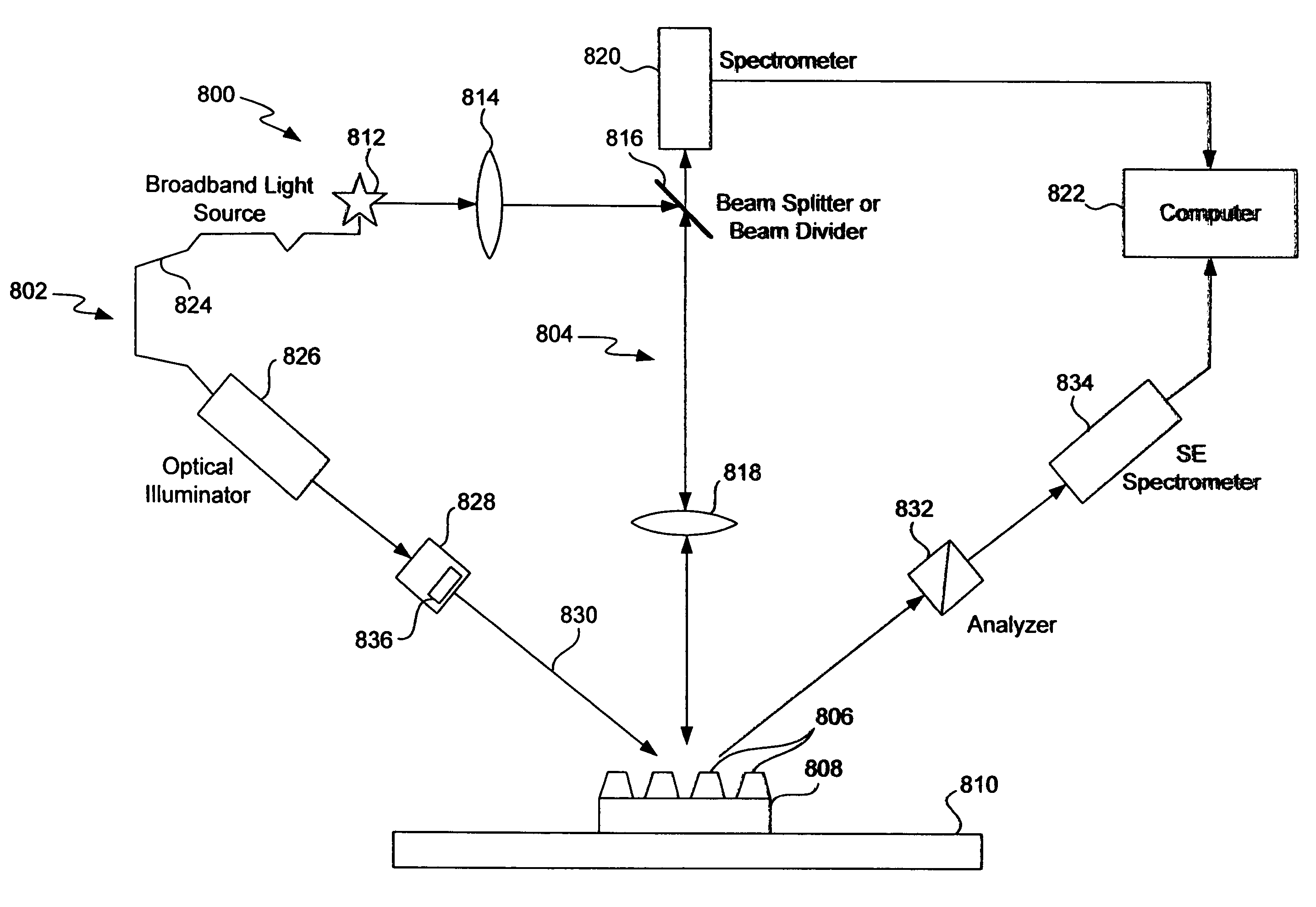
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Integrated use of model-based metrology and a process model
ActiveUS20140172394A1Predictive result is improvedSimple processPhotomechanical apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationMetrologyModel method
Methods and systems for performing measurements based on a measurement model integrating a metrology-based target model with a process-based target model. Systems employing integrated measurement models may be used to measure structural and material characteristics of one or more targets and may also be used to measure process parameter values. A process-based target model may be integrated with a metrology-based target model in a number of different ways. In some examples, constraints on ranges of values of metrology model parameters are determined based on the process-based target model. In some other examples, the integrated measurement model includes the metrology-based target model constrained by the process-based target model. In some other examples, one or more metrology model parameters are expressed in terms of other metrology model parameters based on the process model. In some other examples, process parameters are substituted into the metrology model.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
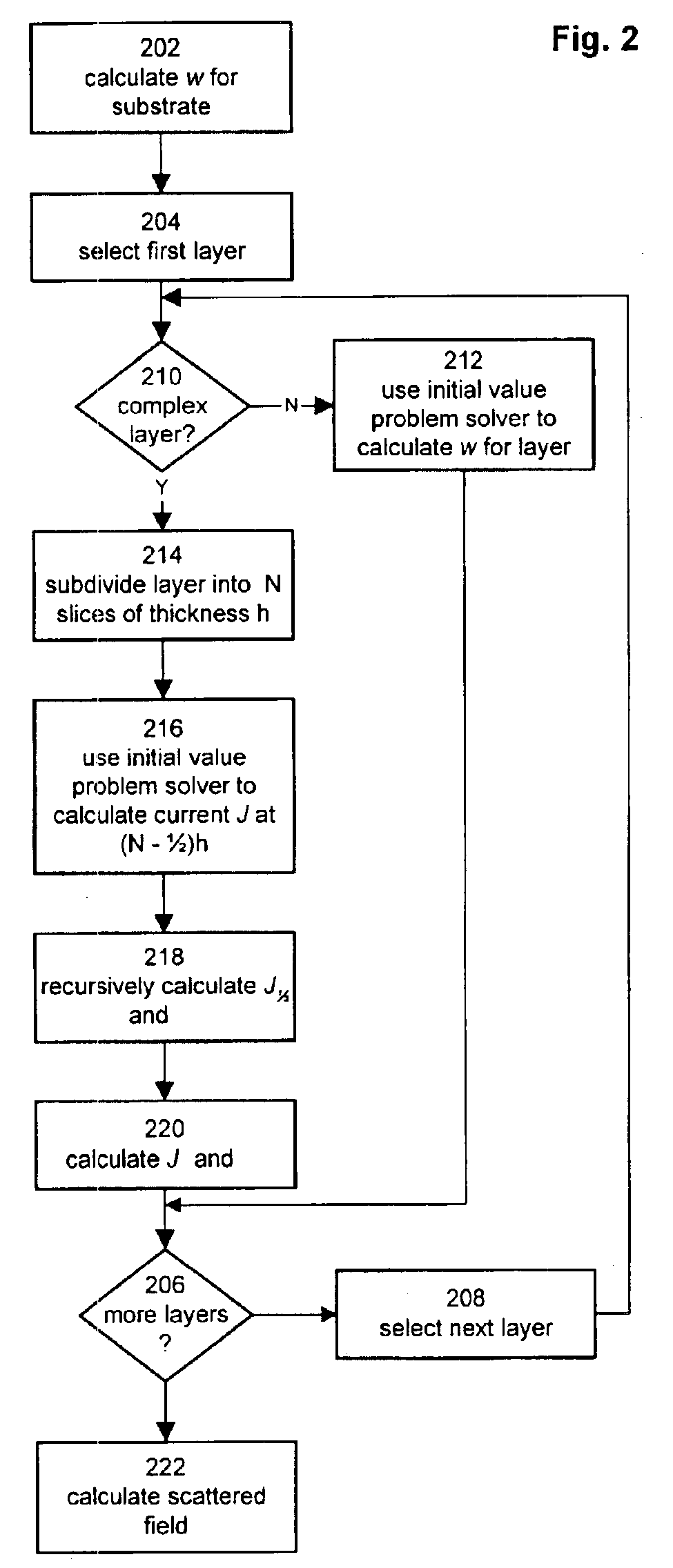
CD metrology analysis using a finite difference method
ActiveUS6919964B2Directly computeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetrologyDirect evaluation
A method for modeling diffraction includes constructing a theoretical model of the subject. A numerical method is then used to predict the output field that is created when an incident field is diffracted by the subject. The numerical method begins by computing the output field at the upper boundary of the substrate and then iterates upward through each of the subject's layers. Structurally simple layers are evaluated directly. More complex layers are discretized into slices. A finite difference scheme is performed for these layers using a recursive expansion of the field-current ratio that starts (or has a base case) at the lowermost slice. The combined evaluation, through all layers, creates a scattering matrix that is evaluated to determine the output field for the subject.
Owner:THERMA WAVE INC
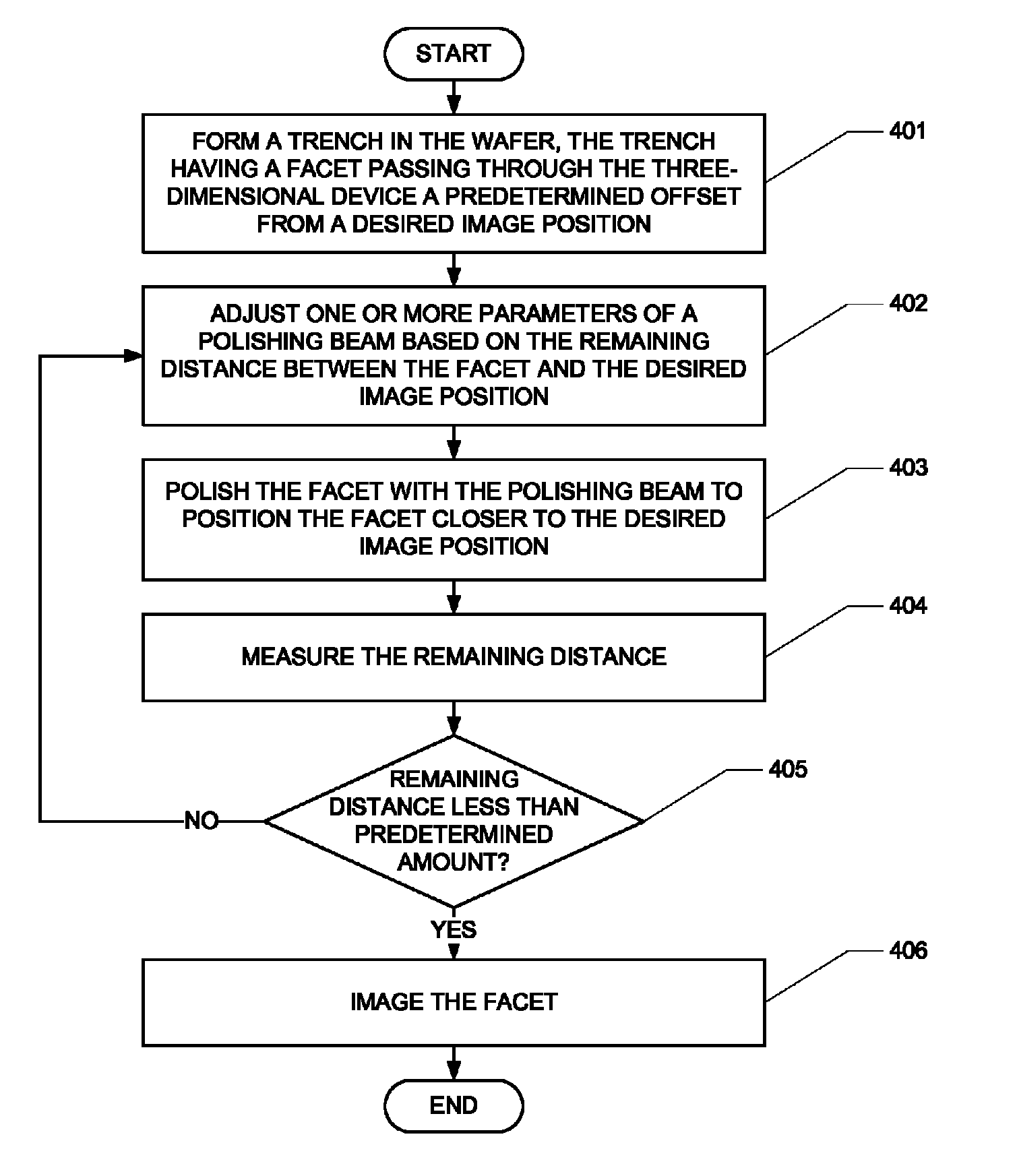
Precise metrology with adaptive milling
ActiveUS8222599B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyEngineering
A method of measuring a three-dimensional device in a wafer is provided. The method comprises the step of forming a trench in the wafer. The trench has a facet passing through the three-dimensional device a predetermined offset from a desired image position. The method further comprises iteratively, until a remaining distance between the facet and the desired image position is less than a predetermined threshold, adjusting one or more parameters of a polishing beam based on the remaining distance, polishing the facet with the polishing beam to position the facet closer to the desired image position, and measuring the remaining distance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
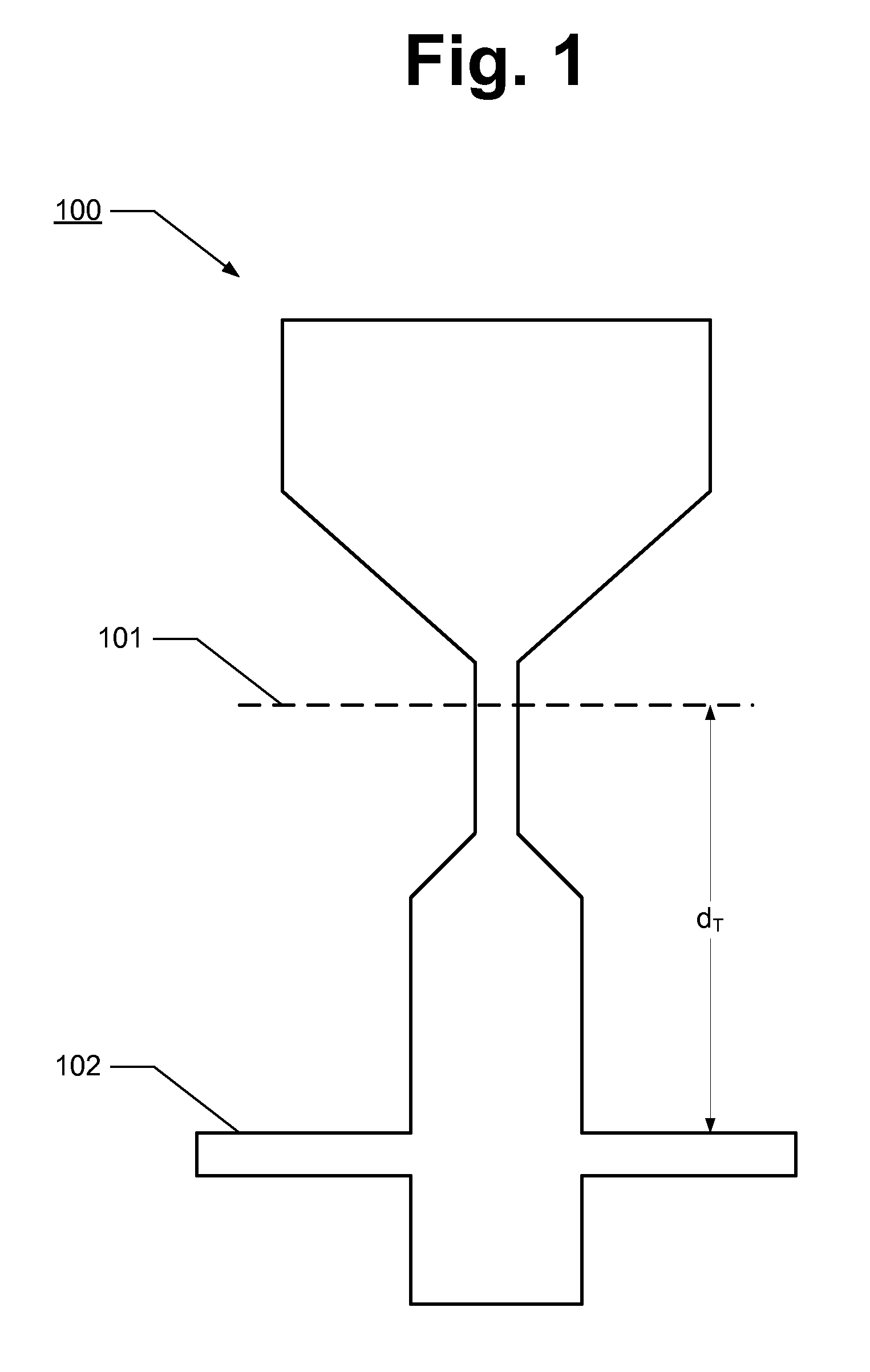
Metrology and 3D reconstruction of devices in a wafer
InactiveUS8097846B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyEngineering
A method for measuring three-dimensional devices in a wafer comprises the step of obtaining a plurality of cross-sectional images of a corresponding plurality of three-dimensional devices in the wafer. The plurality of three-dimensional devices have essentially identical geometries. Each cross-sectional image is obtained from a plane in the corresponding three-dimensional device at a predetermined distance from a fiducial mark thereof. The predetermined distance is different for each of the plurality of cross-sectional images. The method further comprises the step of determining the geometries of the plurality of three-dimensional devices based on the cross-sectional images thereof.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
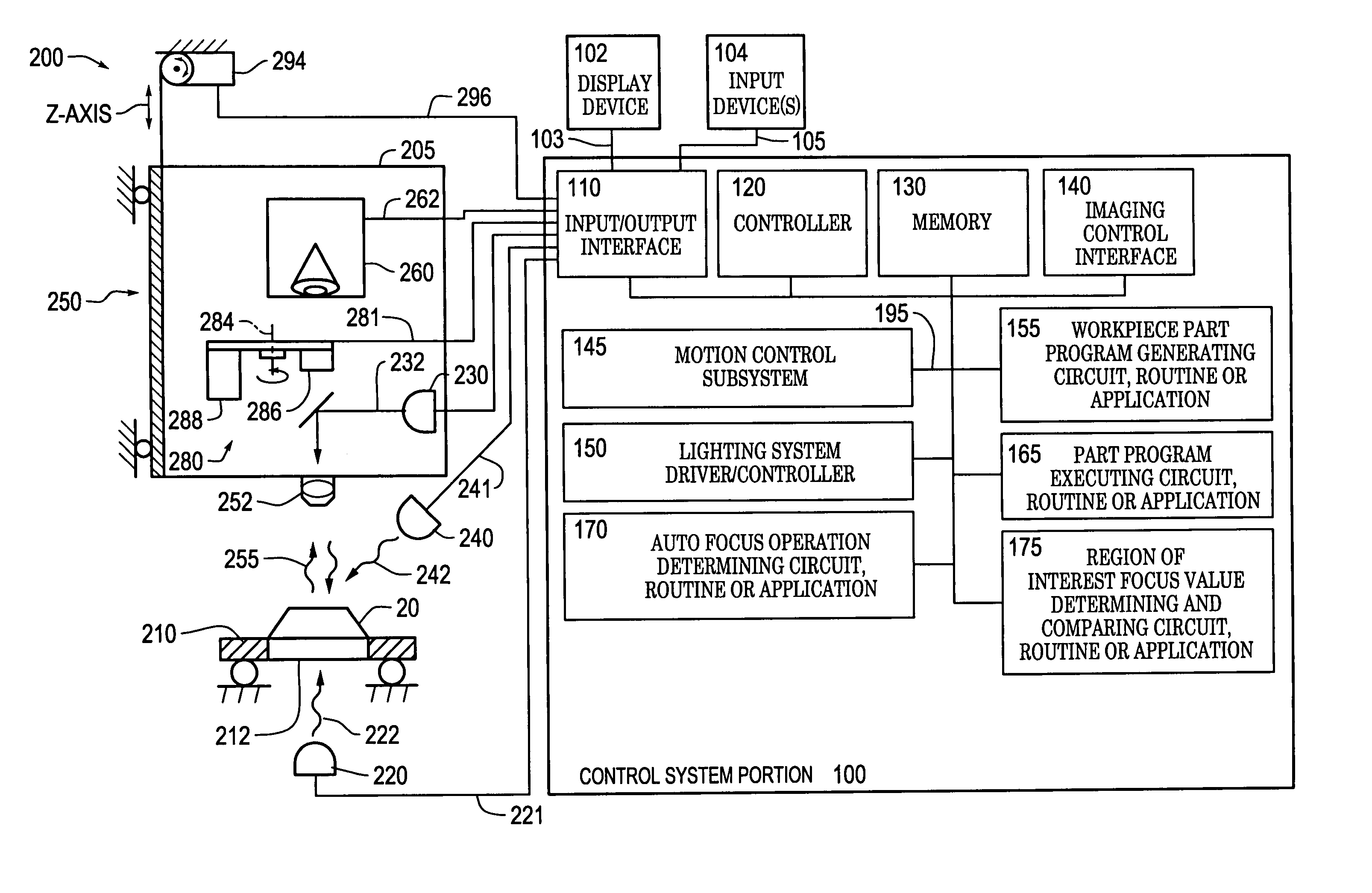
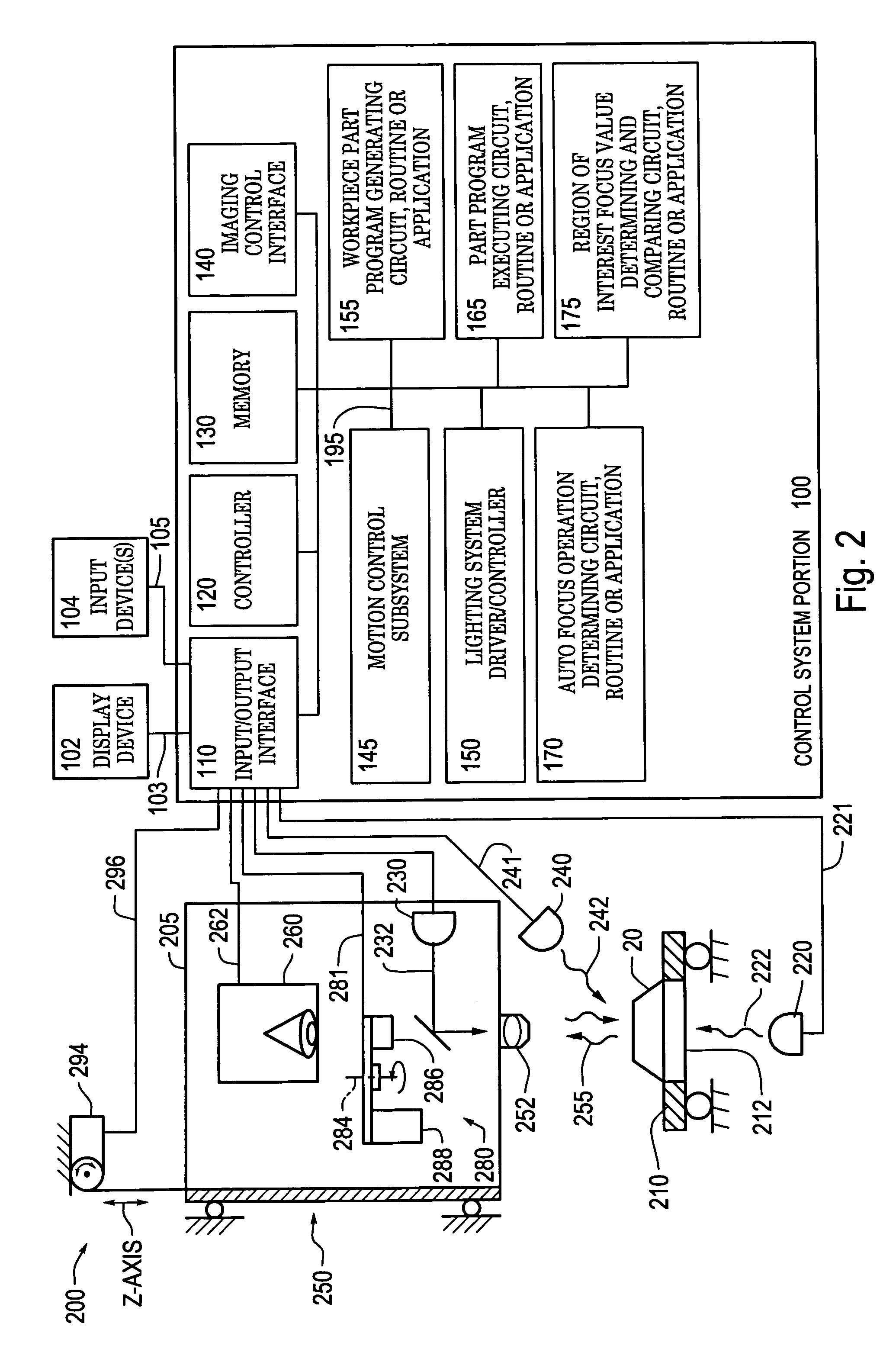
Systems and methods for rapidly automatically focusing a machine vision inspection system
ActiveUS7030351B2Increase speedAccurate autofocusTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesMachine visionMetrology
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
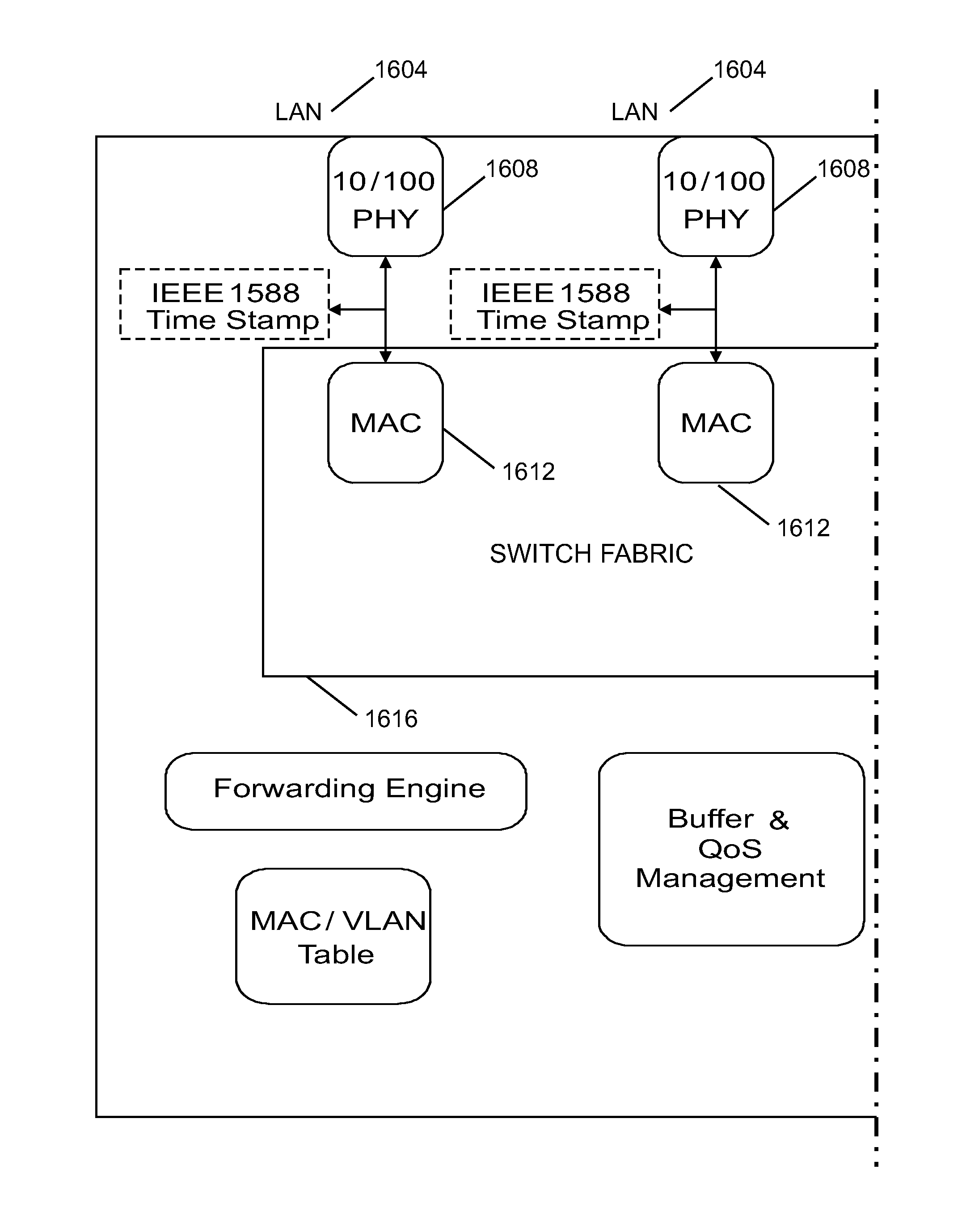
Method and apparatus for synchronizing measurements taken by multiple metrology devices
ActiveUS8630314B2Accuracy issueEasy to integrateTime-division multiplexUsing optical meansComputer hardwareMetrology
Apparatus includes at least two devices that communicate with each other, wherein a first one of the at least two devices having an IEEE 1588 precision time protocol interface, the interface including one or more components configured for communications in both a wired manner and a wireless manner with a second one of the at least two devices. The second one of the at least two devices having an IEEE 1588 precision time protocol interface, the interface including one or more components configured for communications in both a wired manner and a wireless manner with the first one of the at least two devices. Wherein one of the at least two devices includes a master clock and the other one of the at least two devices includes a slave clock, wherein the master clock communicates a time to the slave clock and the slave clock is responsive to the communicated time from the master clock to adjust a time of the slave clock if necessary to substantially correspond to the time of the master clock, thereby time synchronizing the at least two devices together.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
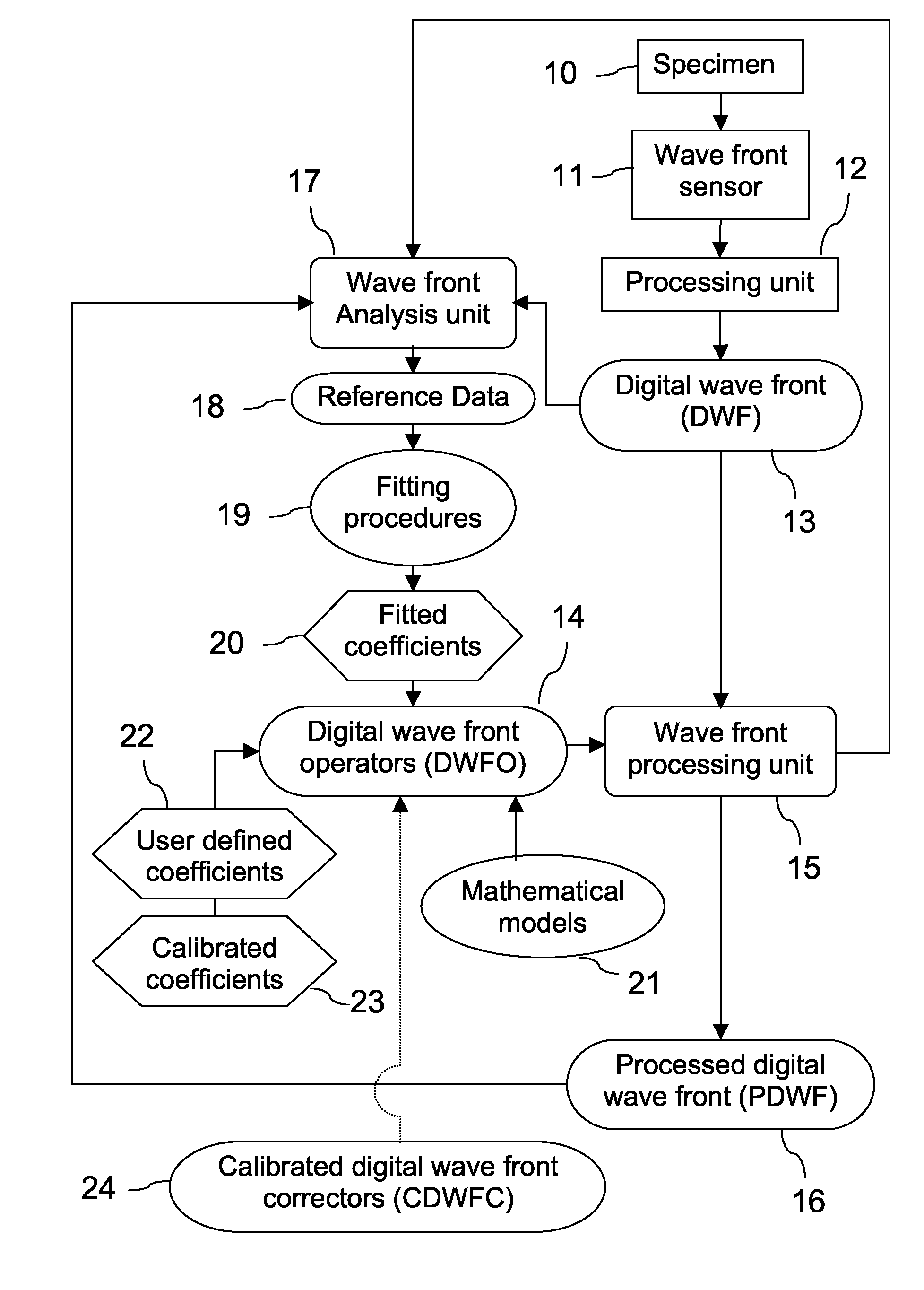
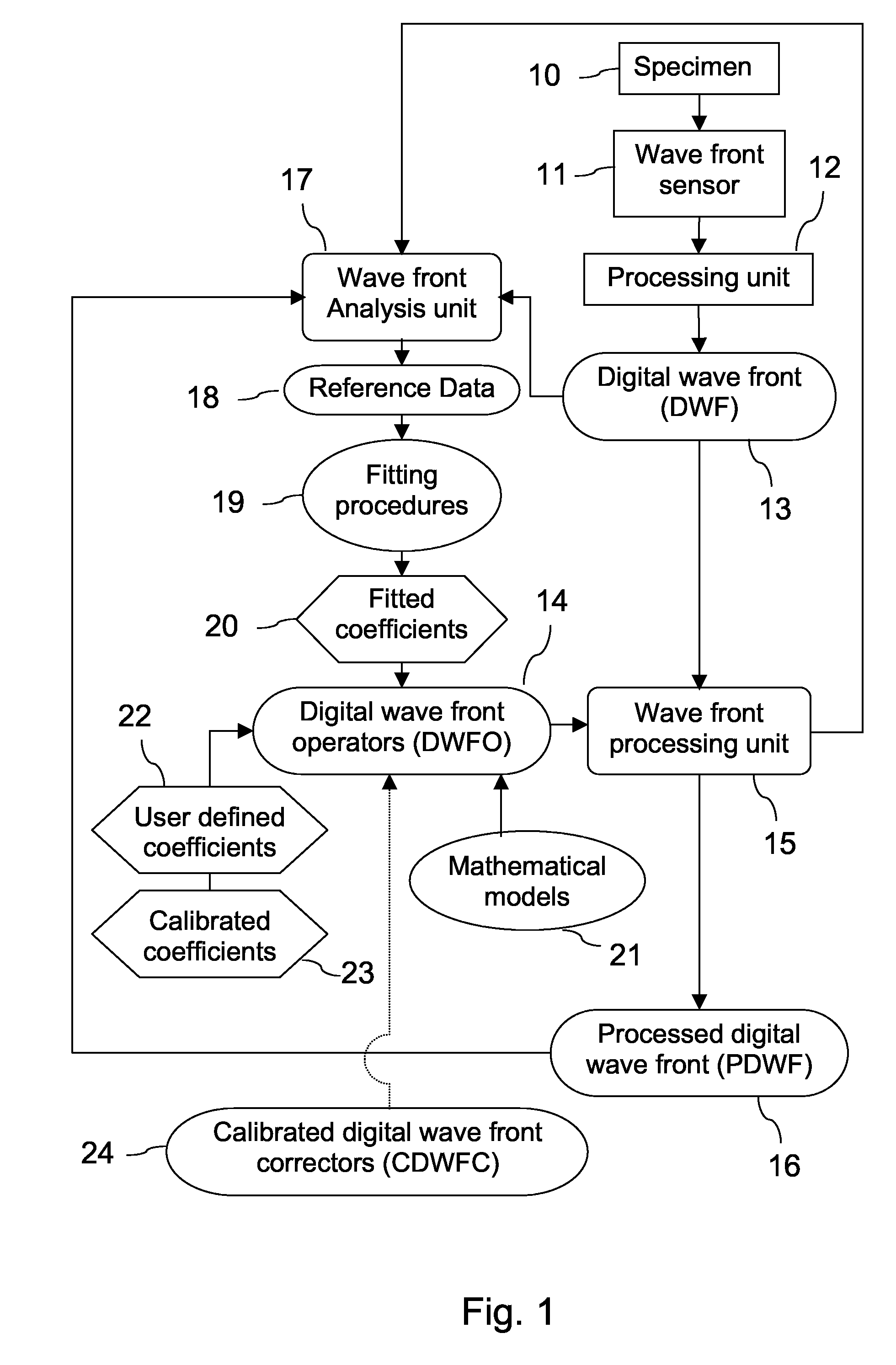
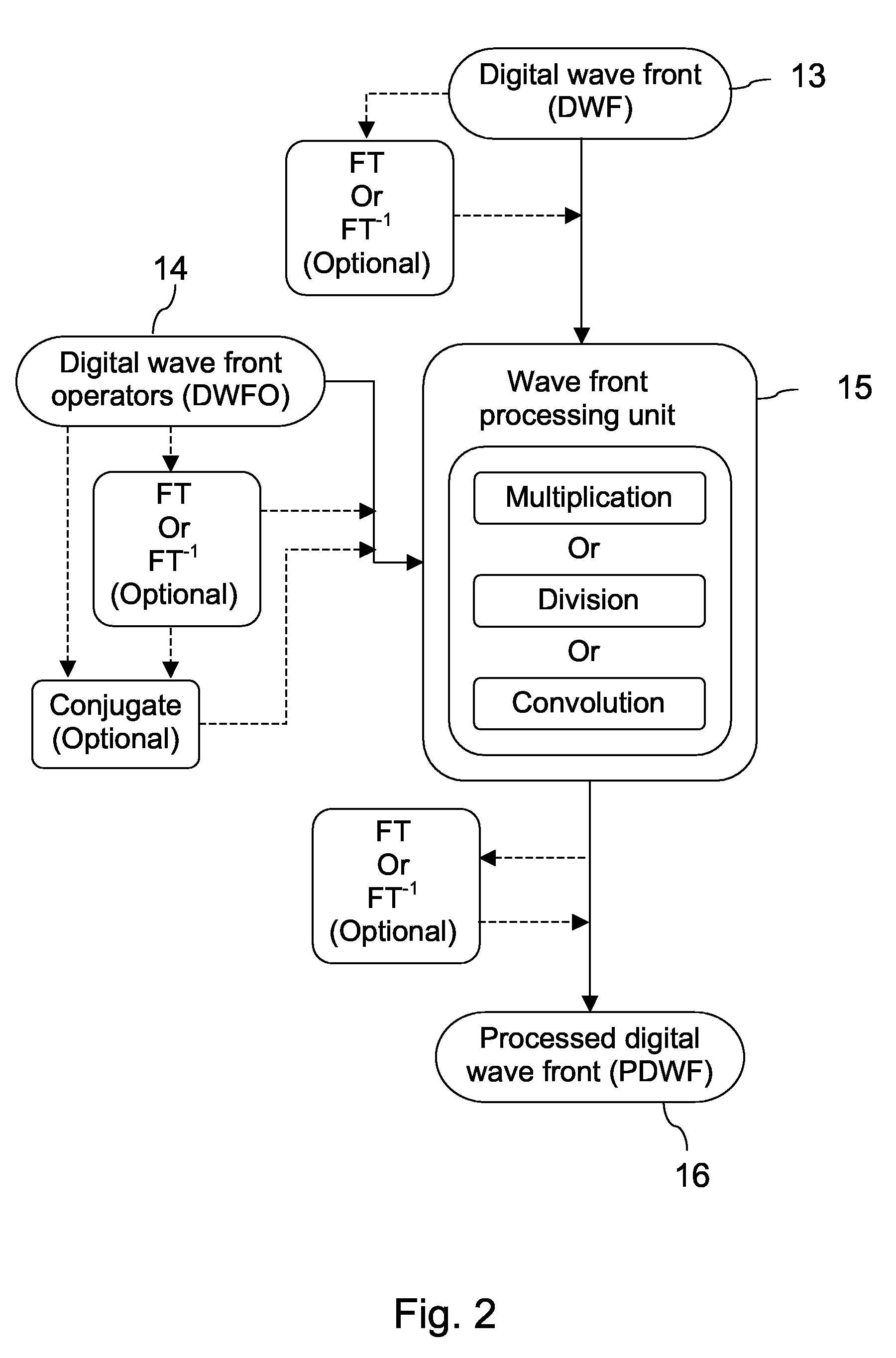
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
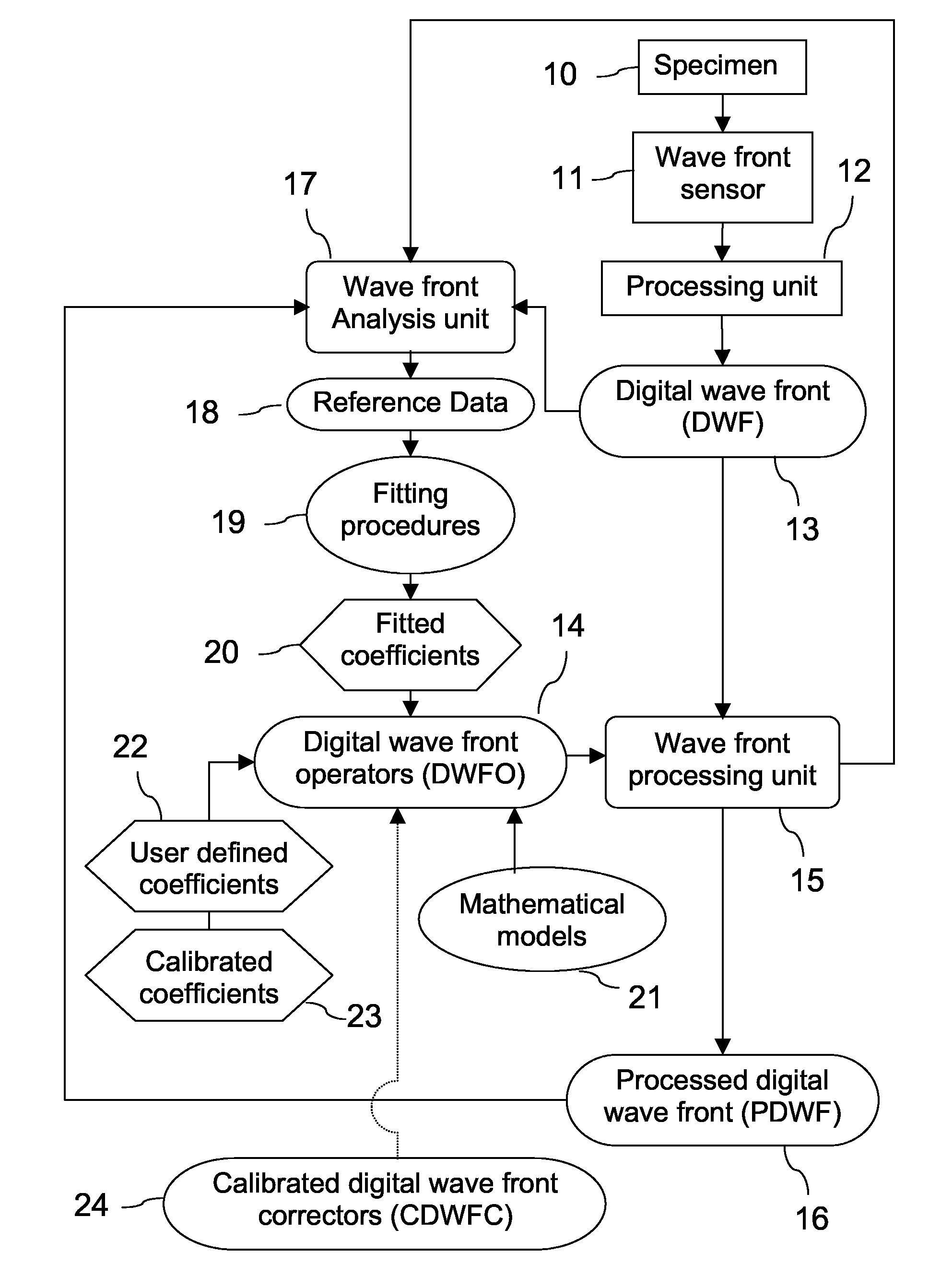
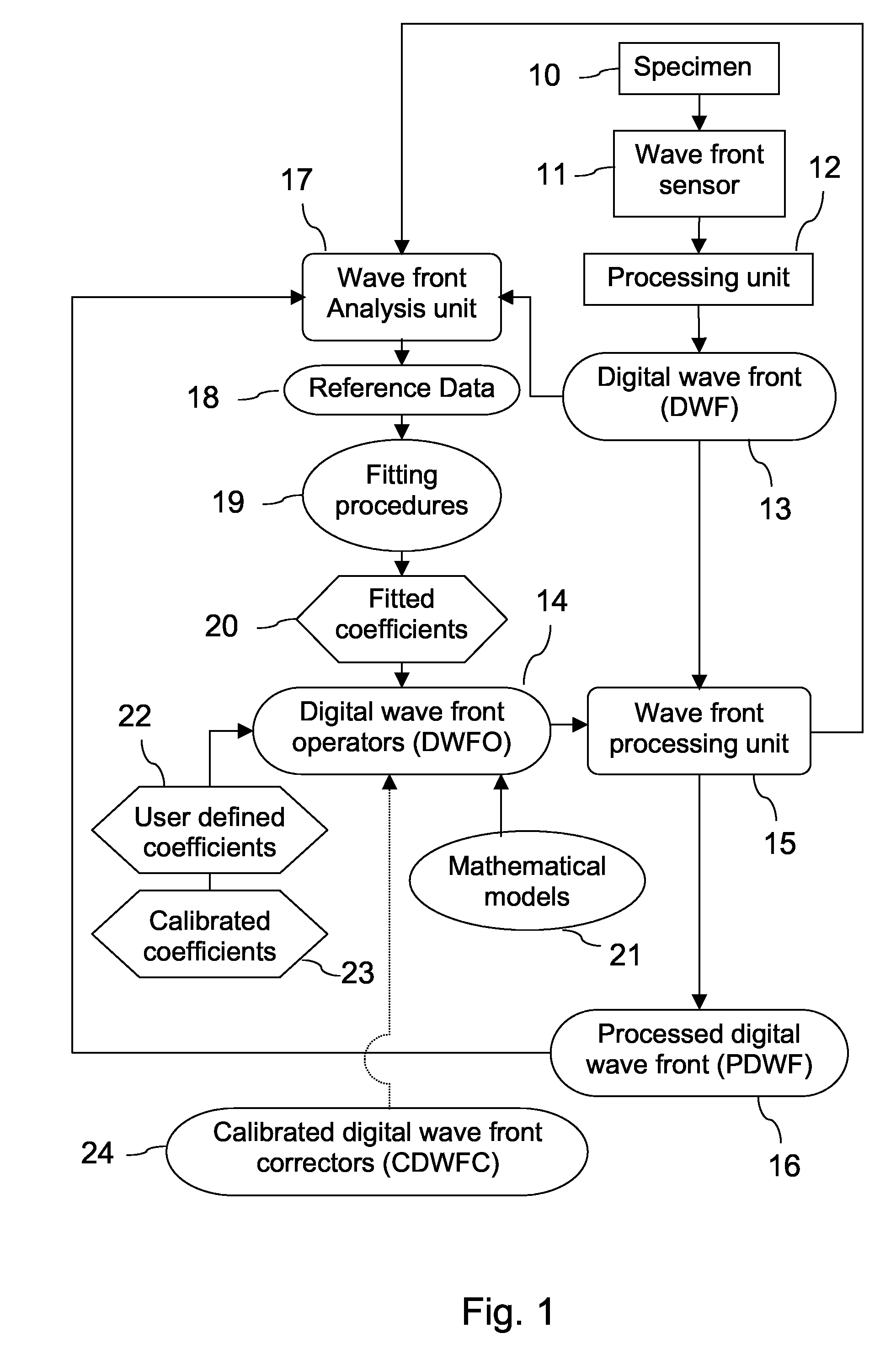
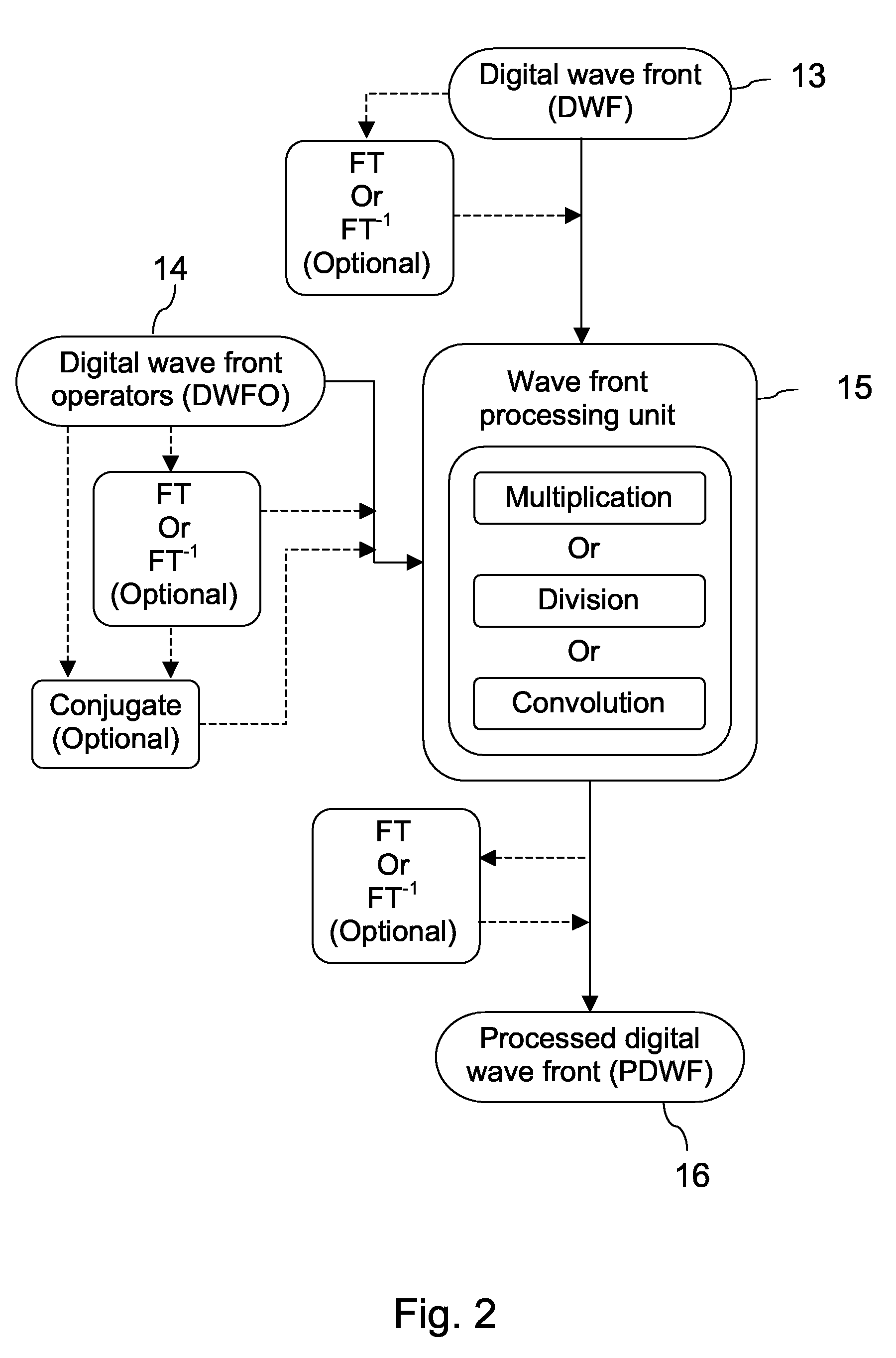
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
Design driven inspection or measurement for semiconductor using recipe
InactiveUS6886153B1Reduces instrument setup timeReduce setup timeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMetrologySemiconductor
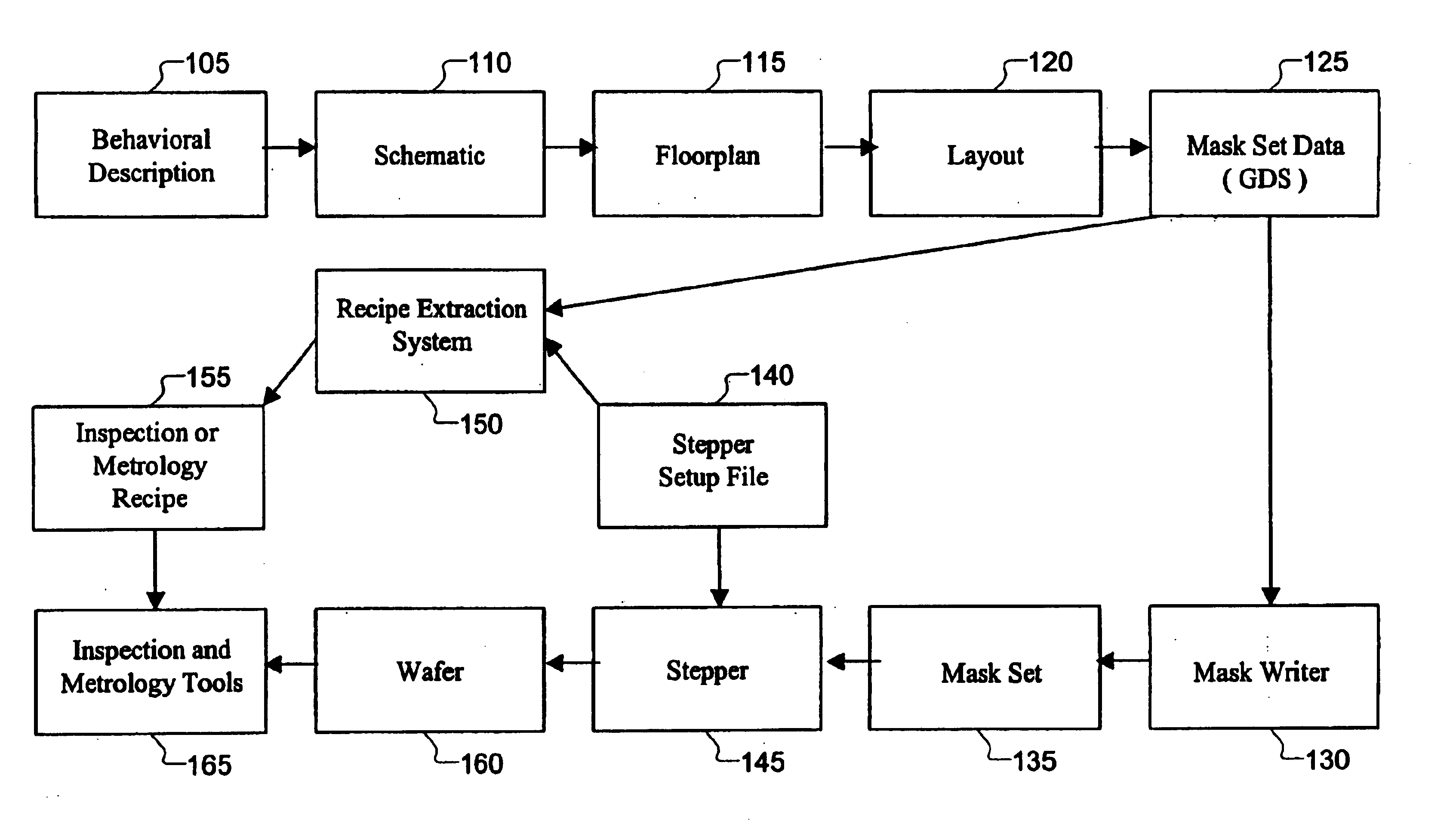
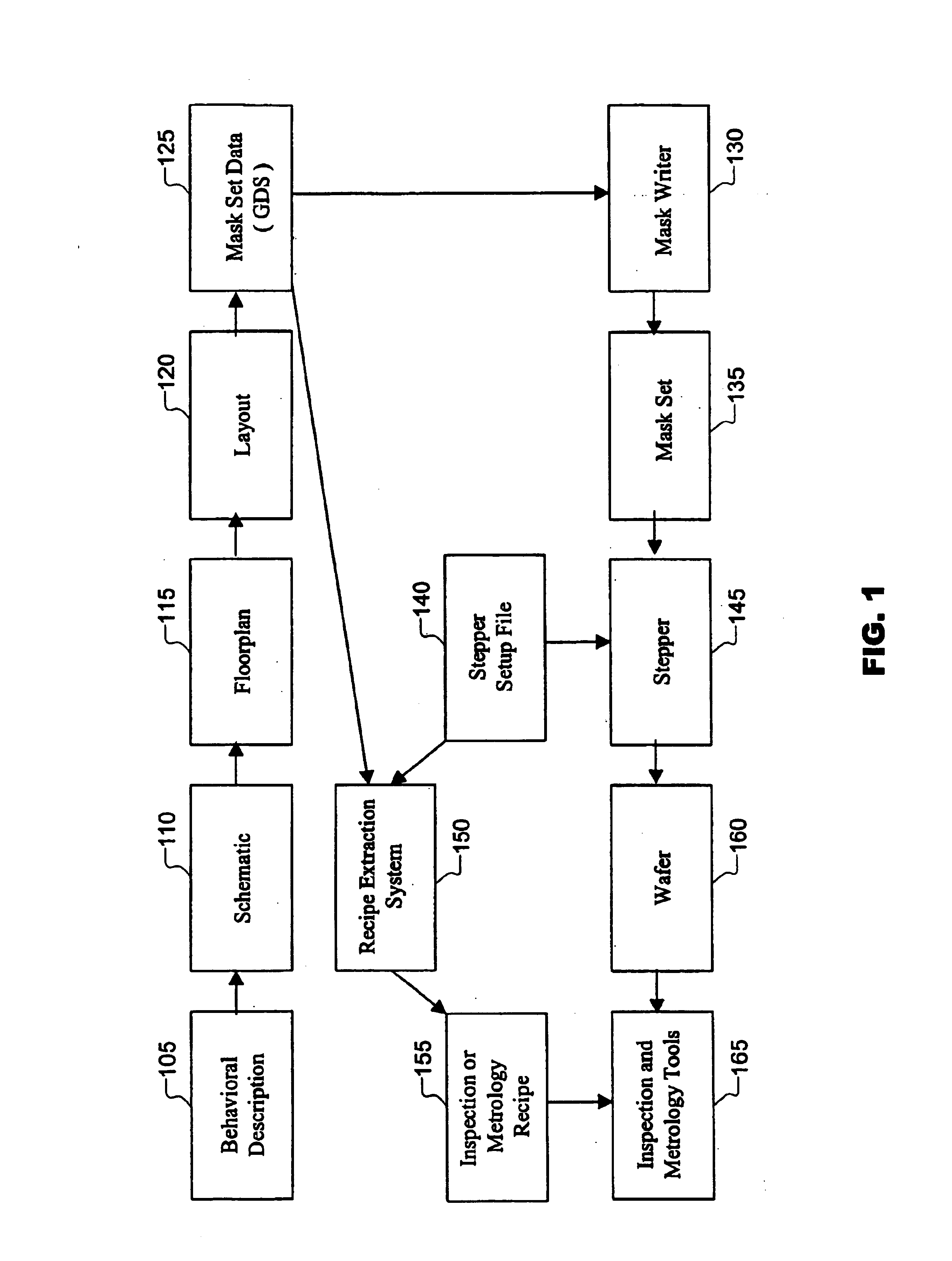
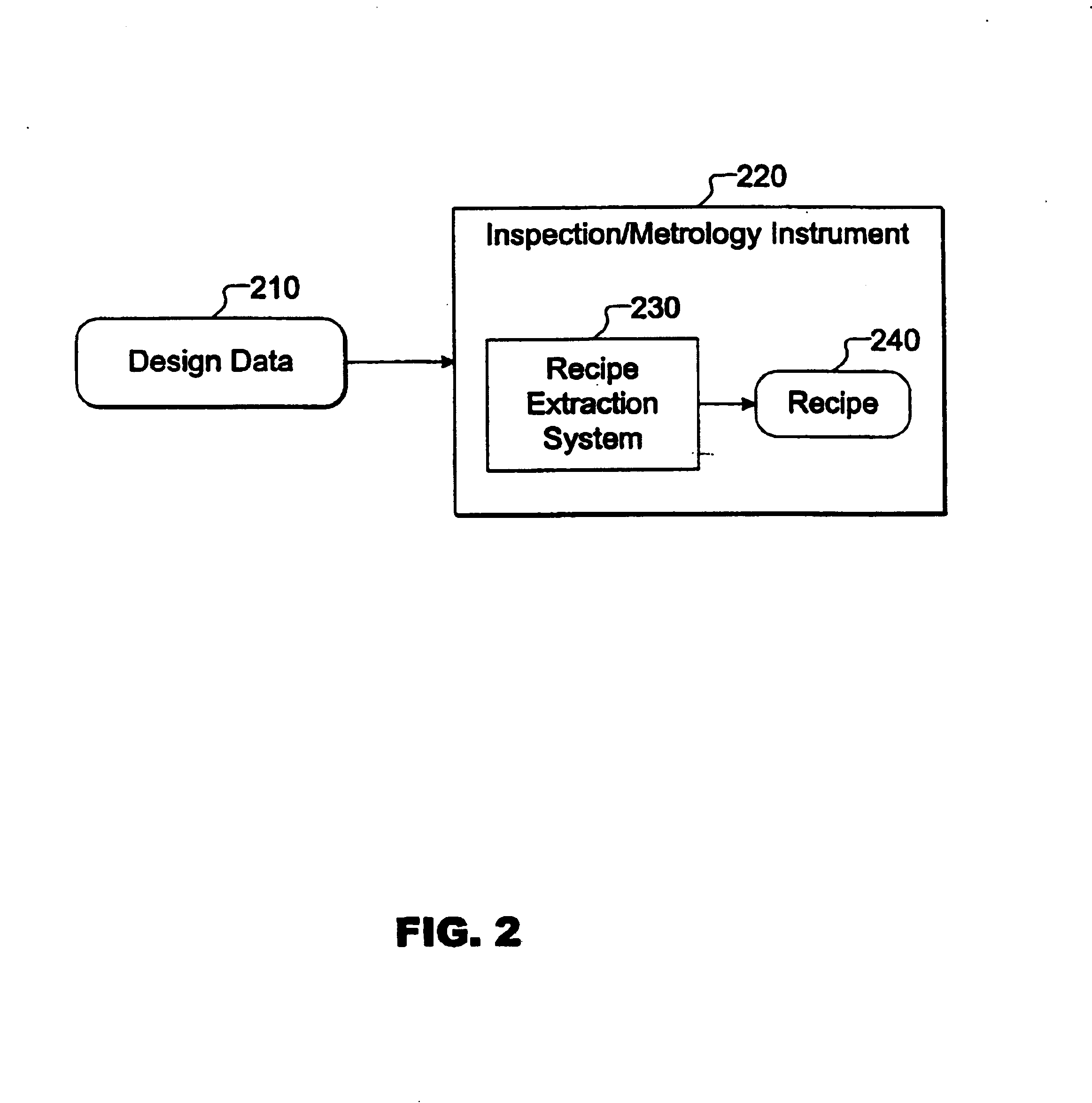
Design driven inspection / metrology methods and apparatus are provided. A recipe is a set of instructions including wafer processing parameters, inspection parameters, or control parameters for telling an inspection / metrology system how to inspect / measure a wafer. Design data is imported into a recipe extraction system that recognizes instances of target structures and configures recipe parameters accordingly, thereby reducing manual instrument setup time, improving inspection / measurement accuracy, and improving fabrication efficiency.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
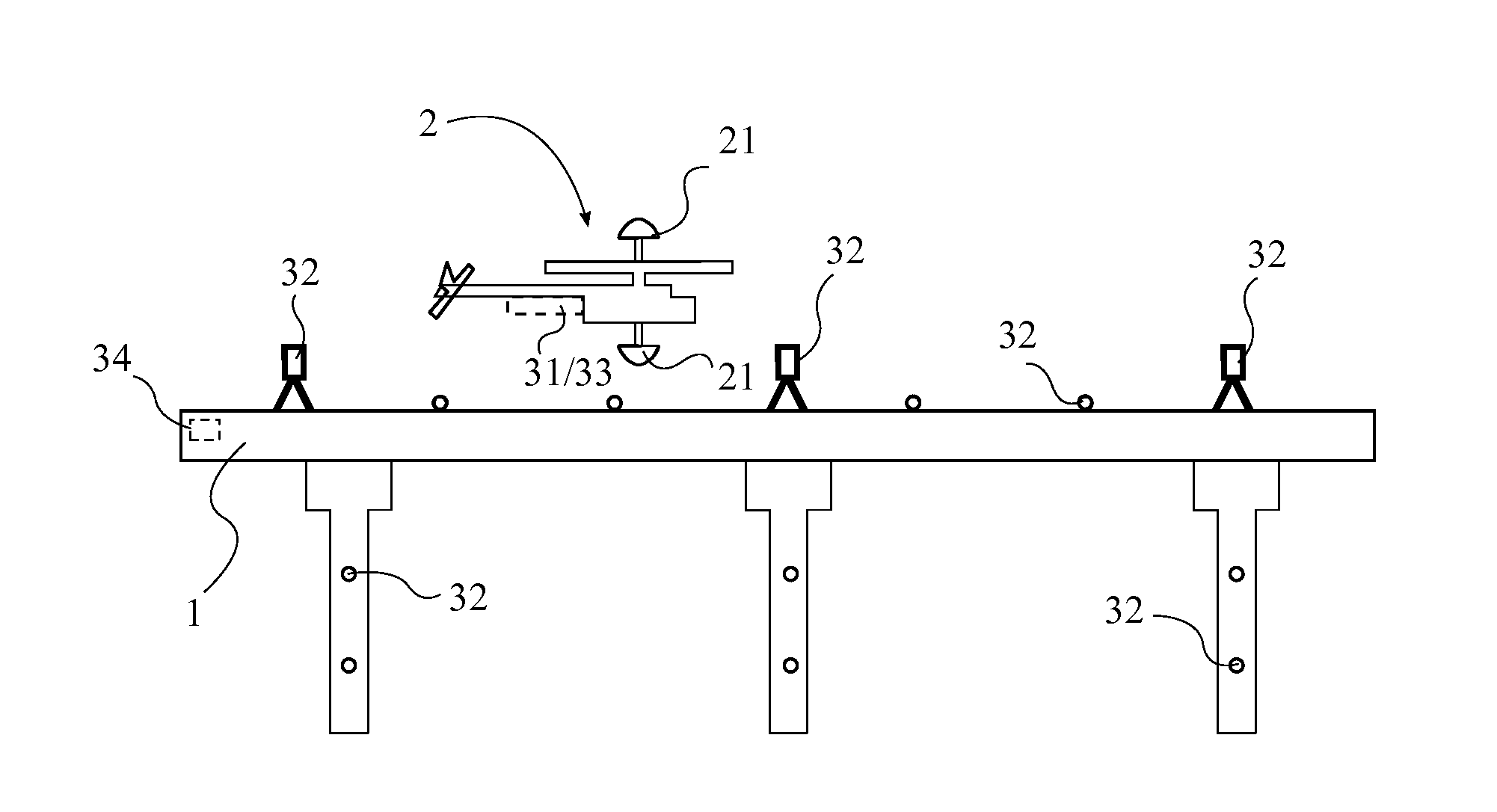
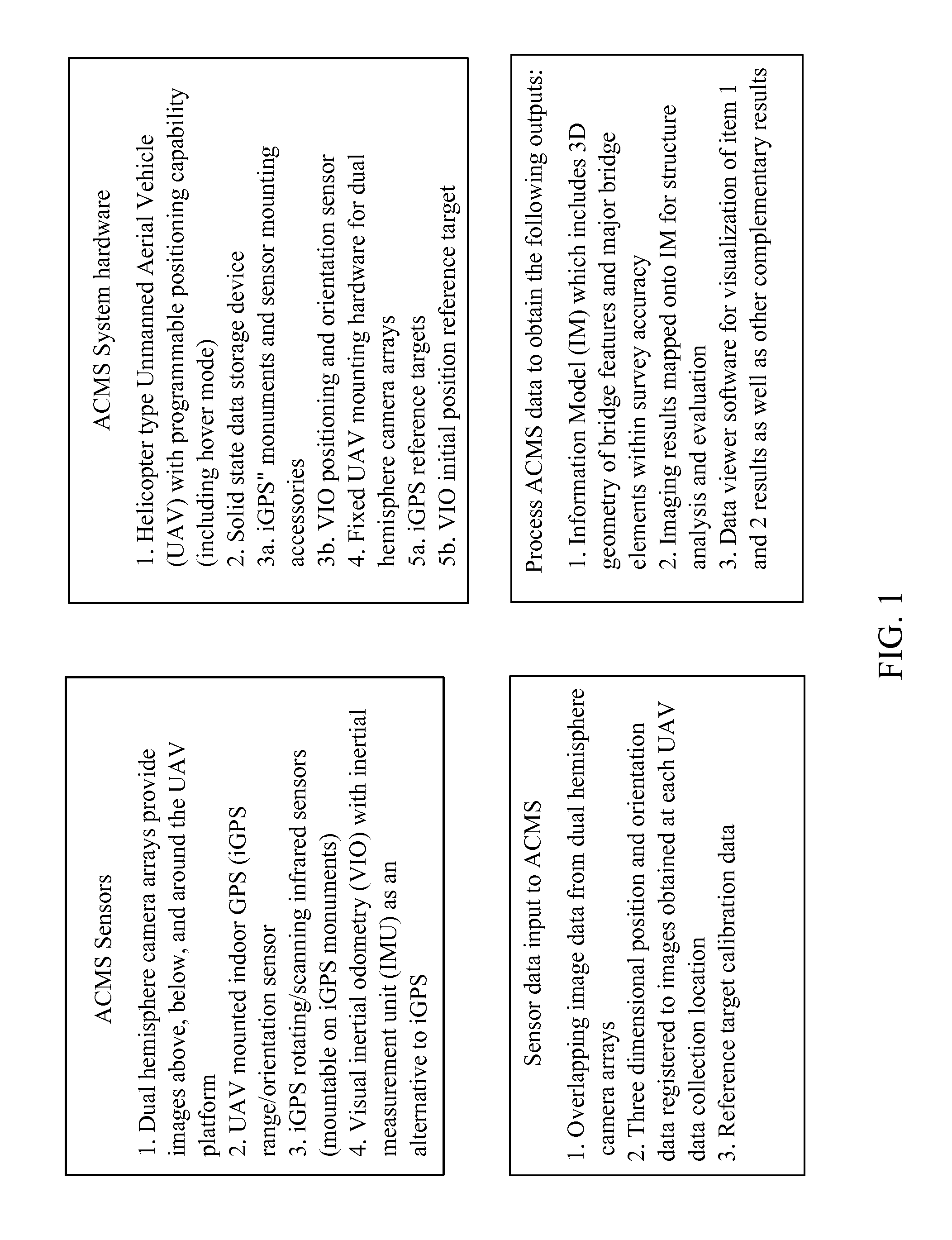
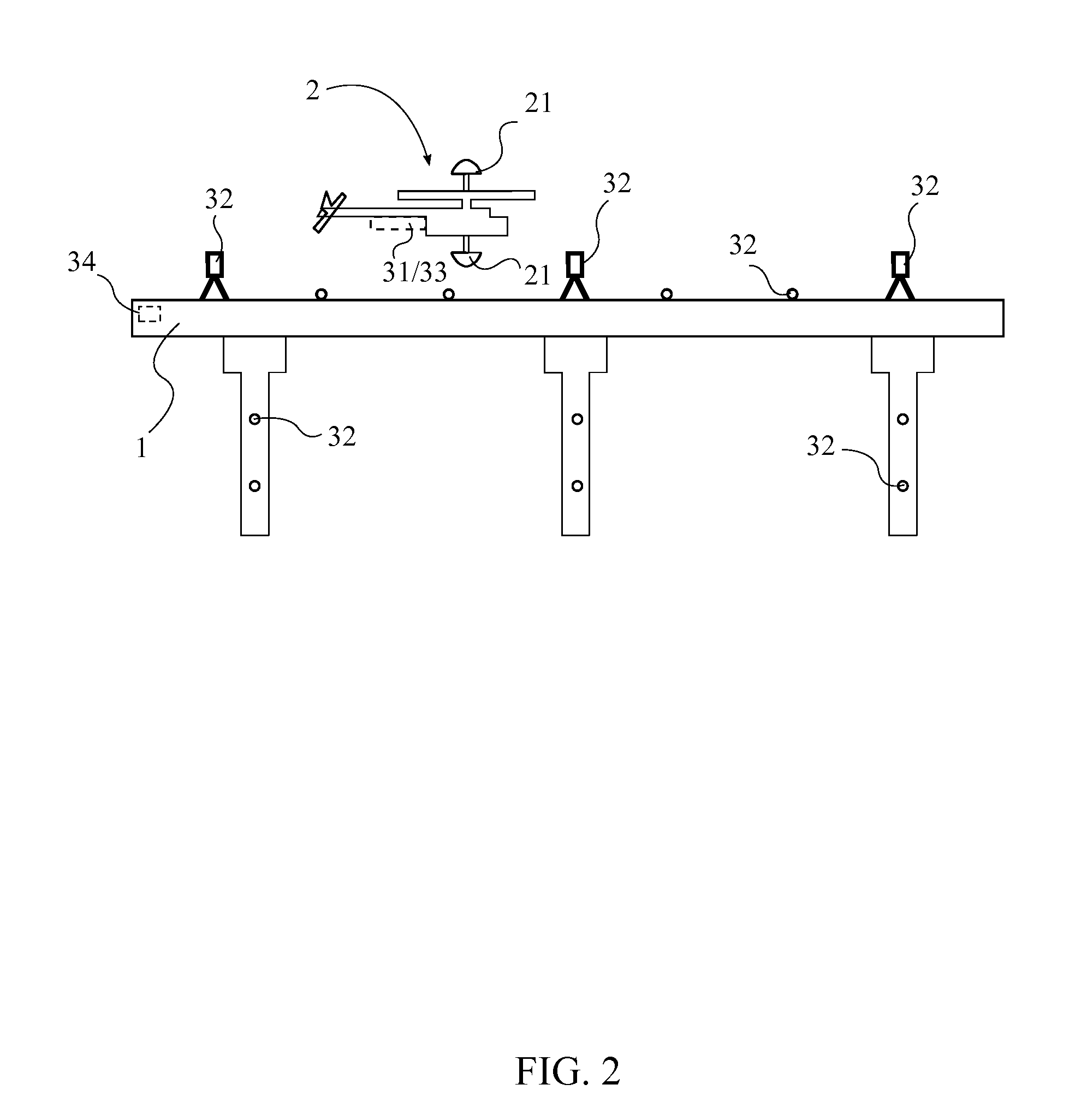
System and Method of Automated Civil Infrastructure Metrology for Inspection, Analysis, and Information Modeling
A system and method of automated civil infrastructure metrology for inspection, analysis, and information modeling utilizes an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) equipped with a position tracking system and digital cameras to capture a plurality of images of a structure to be inspected. The UAV is flown in a scan pattern around the structure while continually capturing images of the structure while position and orientation data is also recorded and linked for each of the images. Image processing and pattern recognition software algorithms are used to analyze the images and create an information model of the structure which is then used to carry out a virtual inspection of the structure in a three dimensional software environment.
Owner:SCOTT MICHAEL L
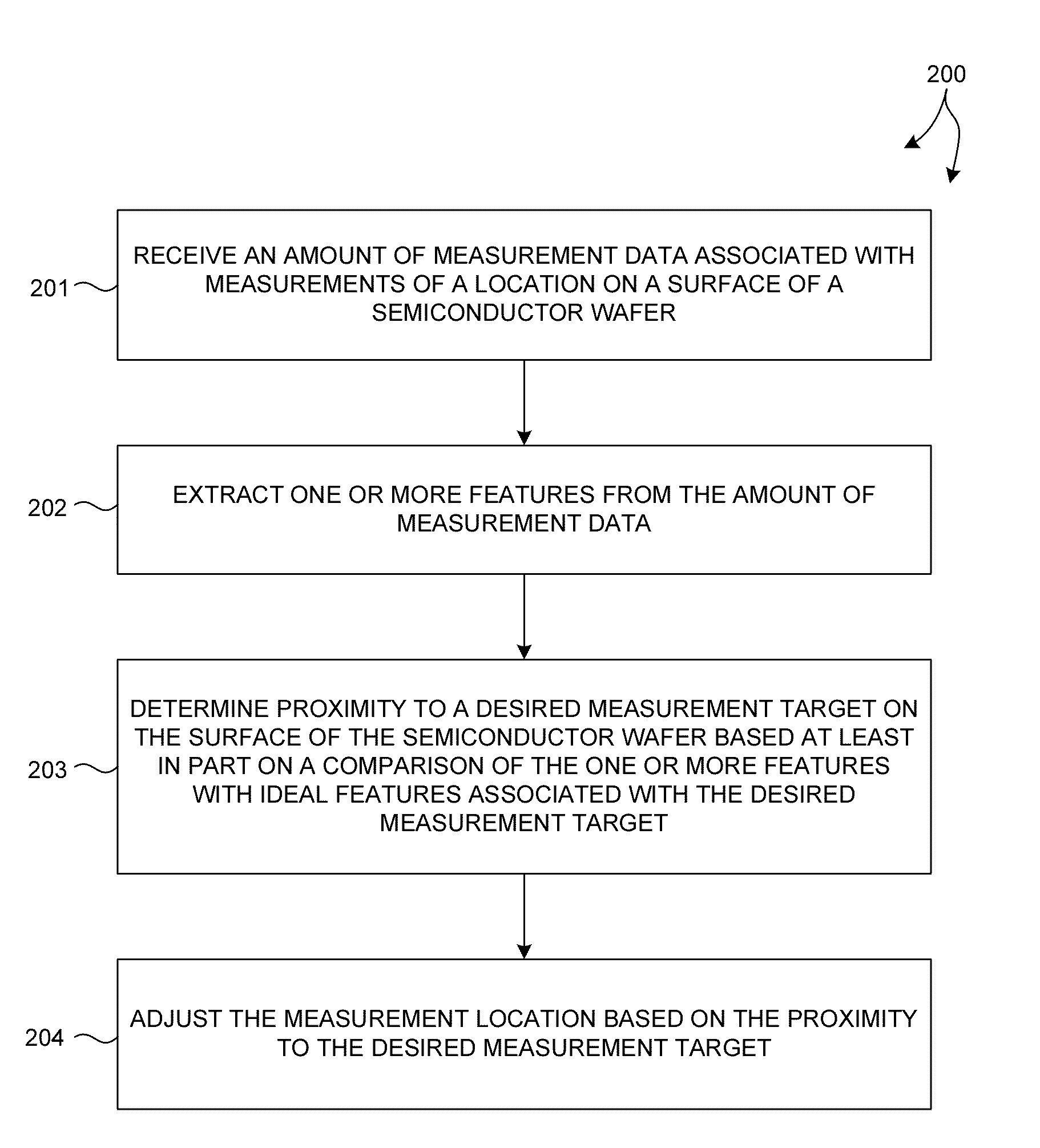
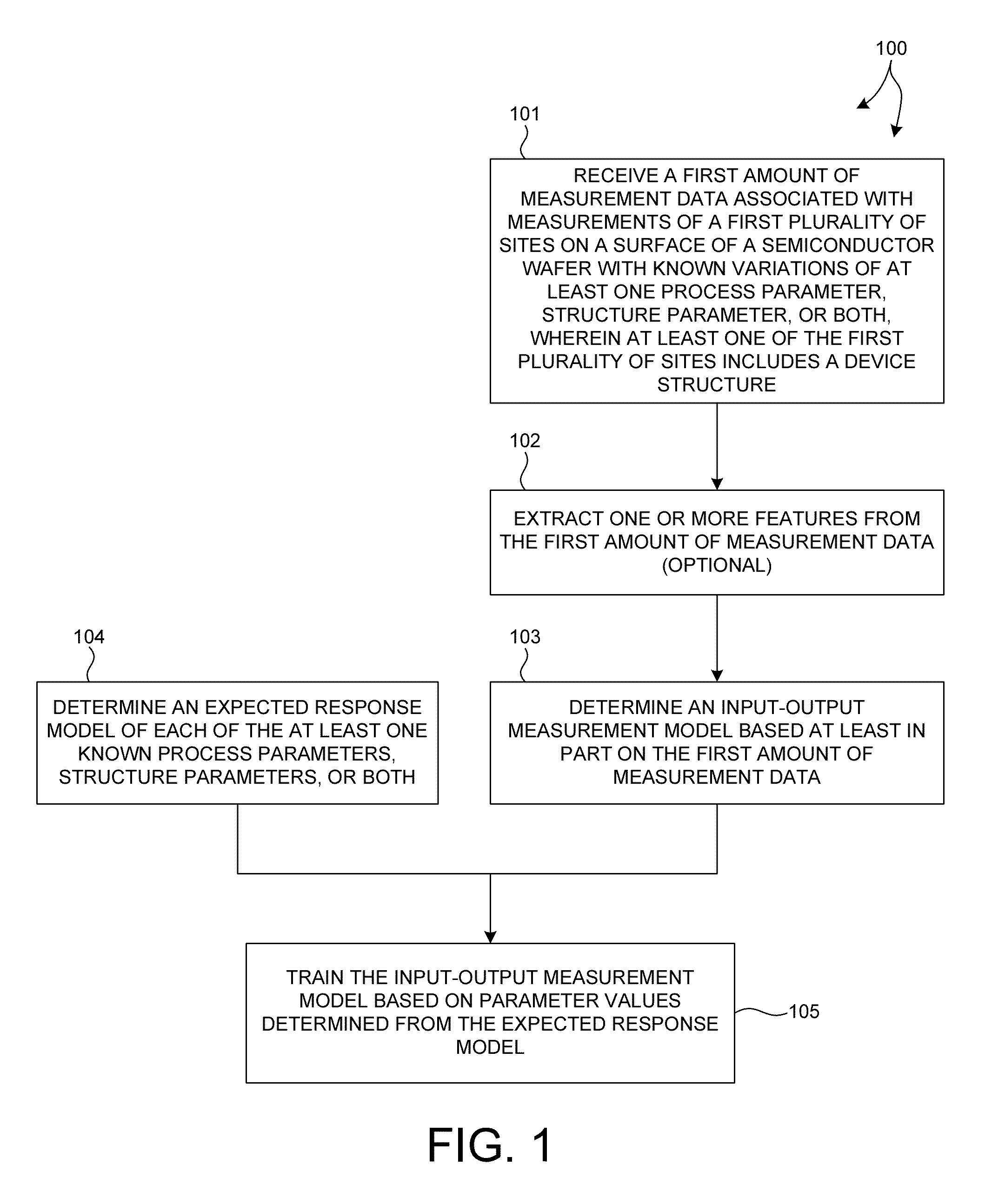
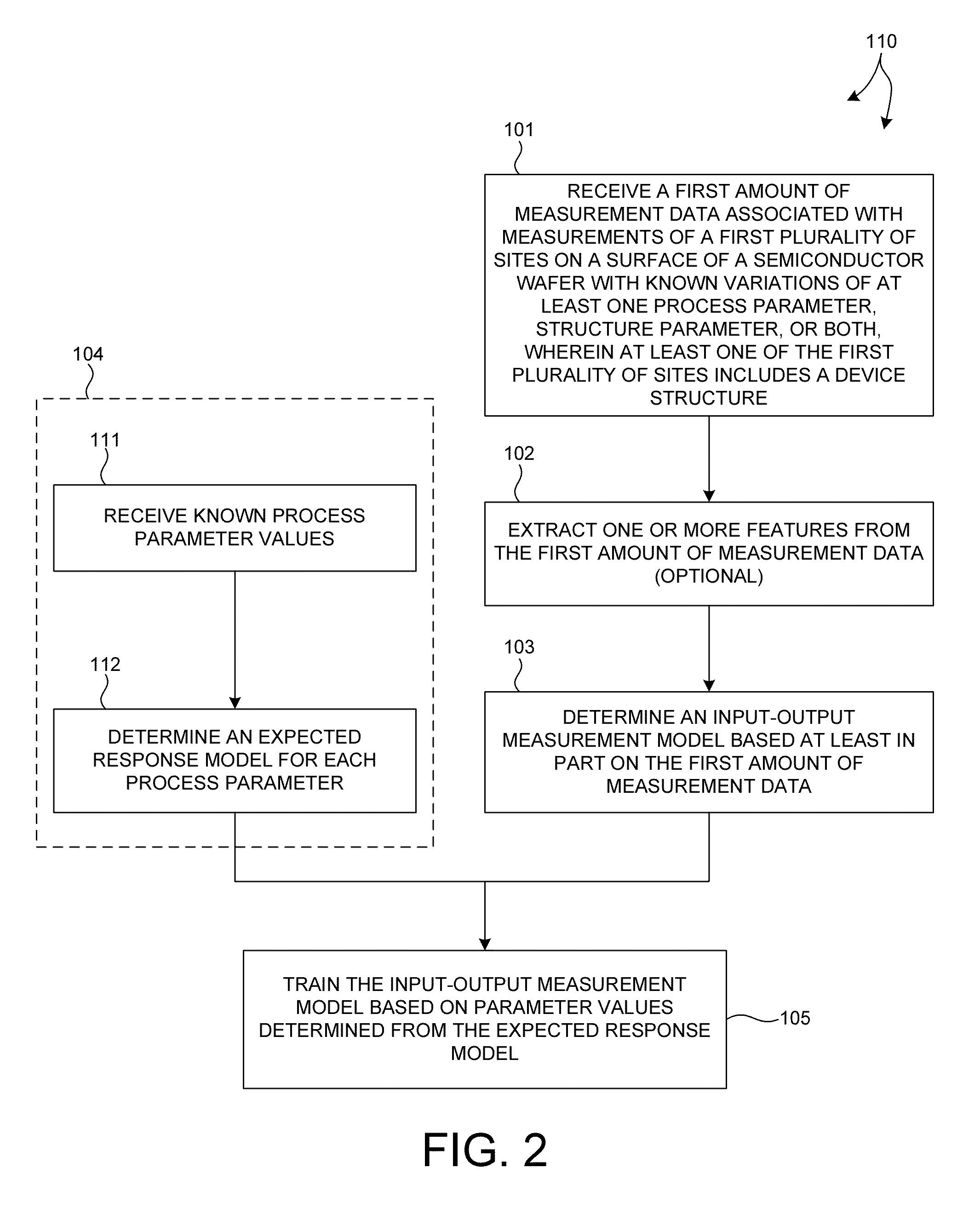
On-device metrology
ActiveUS20140316730A1Accurate measurementAvoid poor resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesMetrologyComputation process
Methods and systems for performing semiconductor metrology directly on device structures are presented. A measurement model is created based on measured training data collected from at least one device structure. The trained measurement model is used to calculate process parameter values, structure parameter values, or both, directly from measurement data collected from device structures of other wafers. In some examples, measurement data from multiple targets is collected for model building, training, and measurement. In some examples, the use of measurement data associated with multiple targets eliminates, or significantly reduces, the effect of under layers in the measurement result, and enables more accurate measurements. Measurement data collected for model building, training, and measurement may be derived from measurements performed by a combination of multiple, different measurement techniques.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
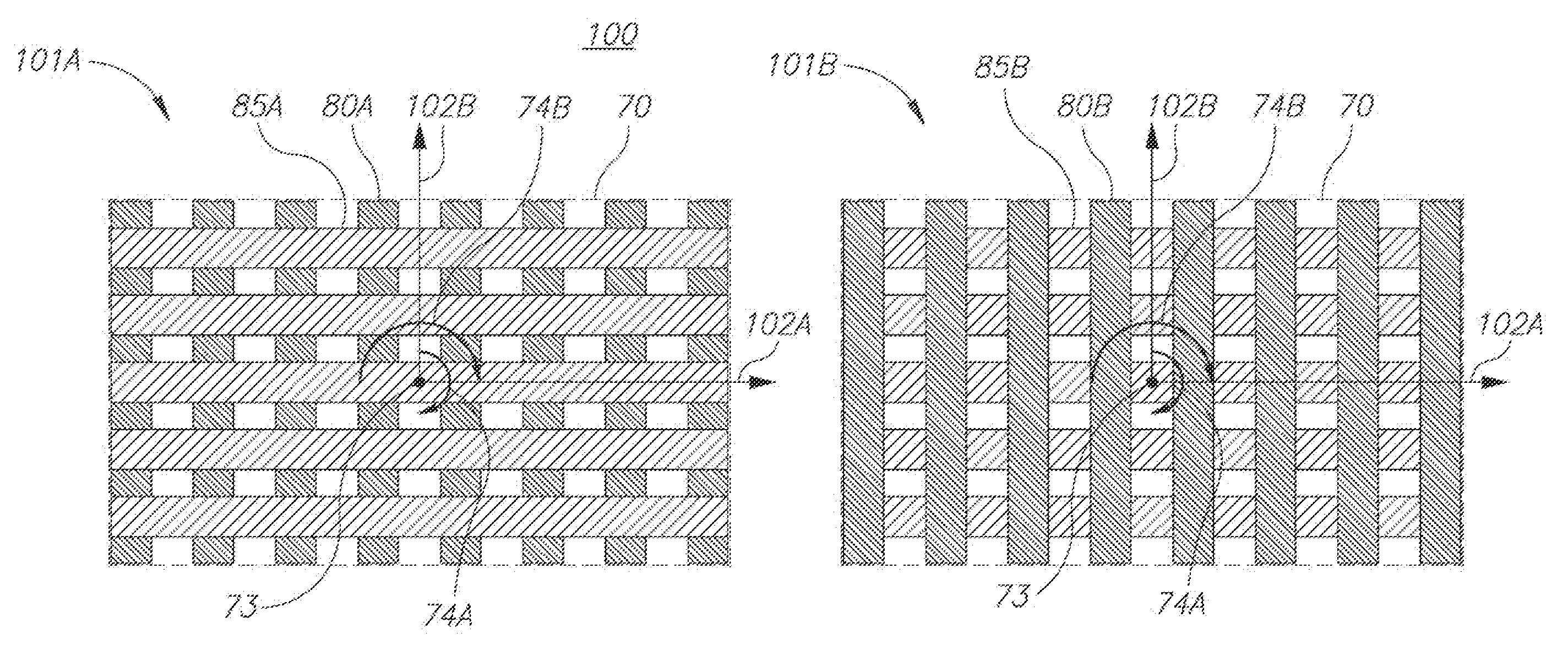
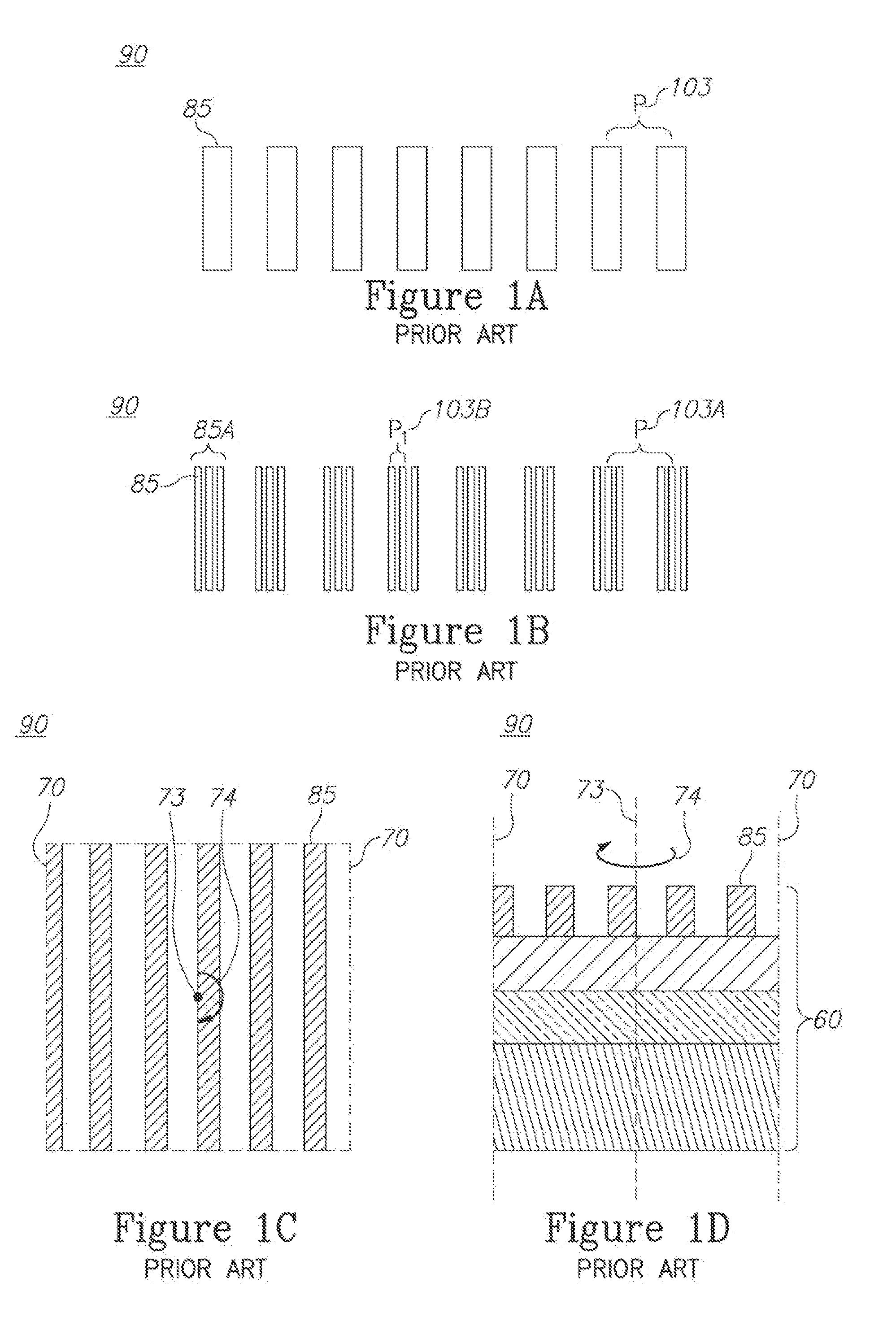
Symmetric target design in scatterometry overlay metrology
ActiveUS20150204664A1Photomechanical apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansMetrologyPhase shifted
Metrology methods, systems and targets are provided, which implement a side by side paradigm. Adjacent cells with periodic structures are used to extract the overlay error, e.g., by introducing controllable phase shifts or image shifts which enable algorithmic computation of the overlay. The periodic structures are designed to exhibit a rotational symmetry to support the computation and reduce errors.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Scatterometry-Based Imaging and Critical Dimension Metrology
ActiveUS20150300965A1Improve the measurement effectMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiffraction orderMetrology
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures and materials based on scatterometry measurement data are presented. Scatterometry measurement data is used to generate an image of a material property of a measured structure based on the measured intensities of the detected diffraction orders. In some examples, a value of a parameter of interest is determined directly from the map of the material property of the measurement target. In some other examples, the image is compared to structural characteristics estimated by a geometric, model-based parametric inversion of the same measurement data. Discrepancies are used to update the geometric model of the measured structure and improve measurement performance. This enables a metrology system to converge on an accurate parametric measurement model when there are significant deviations between the actual shape of a manufactured structure subject to model-based measurement and the modeled shape of the structure.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
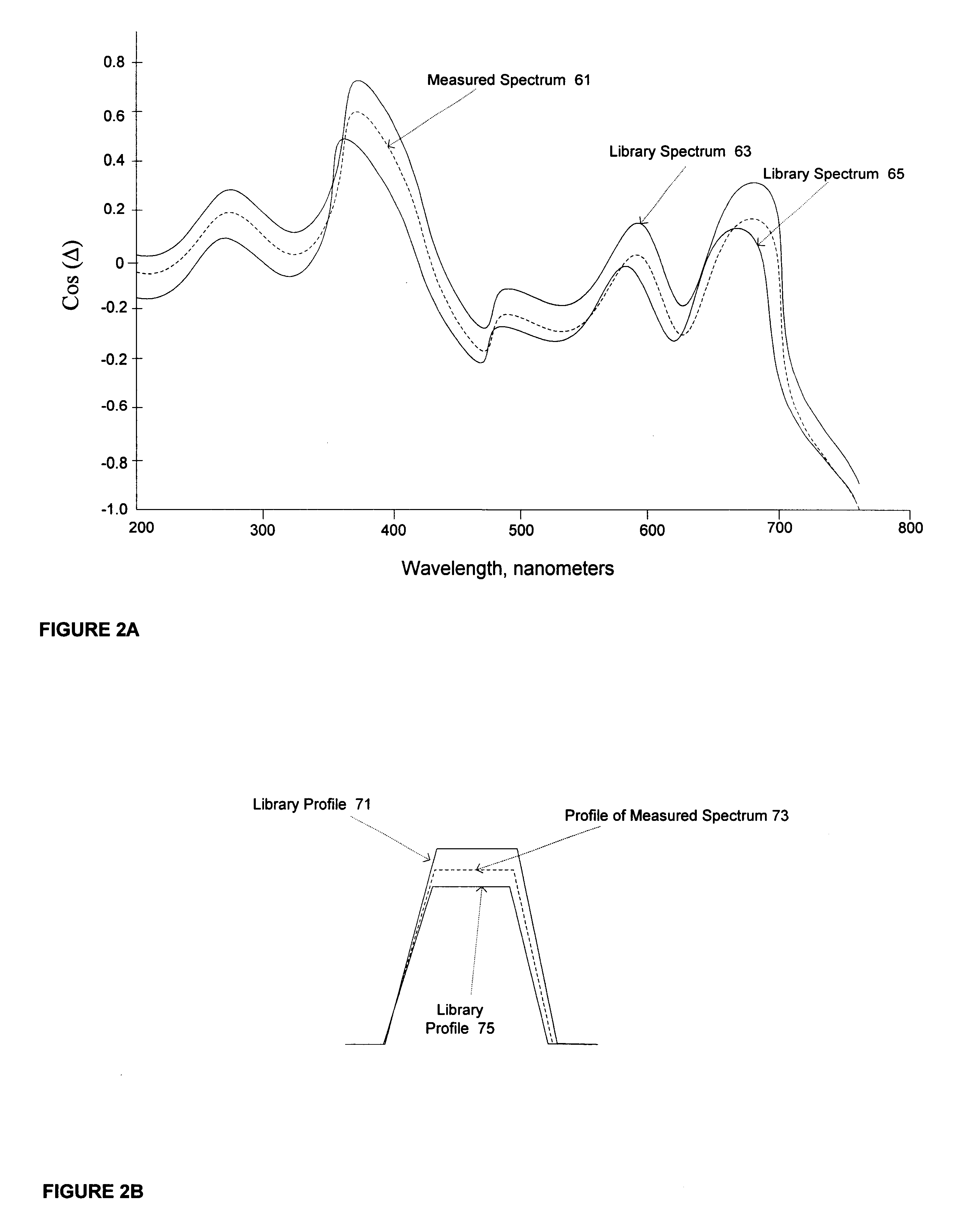
Profile refinement for integrated circuit metrology
InactiveUS6609086B1Minimize cost functionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceScattering properties measurementsMetrologyData space
The present invention includes a method and system for determining the profile of a structure in an integrated circuit from a measured signal, the signal measured off the structure with a metrology device, selecting a best match of the measured signal in a profile data space, the profile data space having data points with a specified extent of non-linearity, and performing a refinement procedure to determine refined profile parameters. One embodiment includes a refinement procedure comprising finding a polyhedron in a function domain of cost functions of the profile library signals and profile parameters and minimizing the total cost function using the weighted average method. Other embodiments include profile parameter refinement procedures using sensitivity analysis, a clustering approach, regression-based methods, localized fine-resolution refinement library method, iterative library refinement method, and other cost optimization or refinement algorithms, procedures, and methods. Refinement of profile parameters may be invoked automatically or invoked based on predetermined criteria such as exceeding an error metric between the measured signal versus the best match profile library.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON US HOLDINGS INC
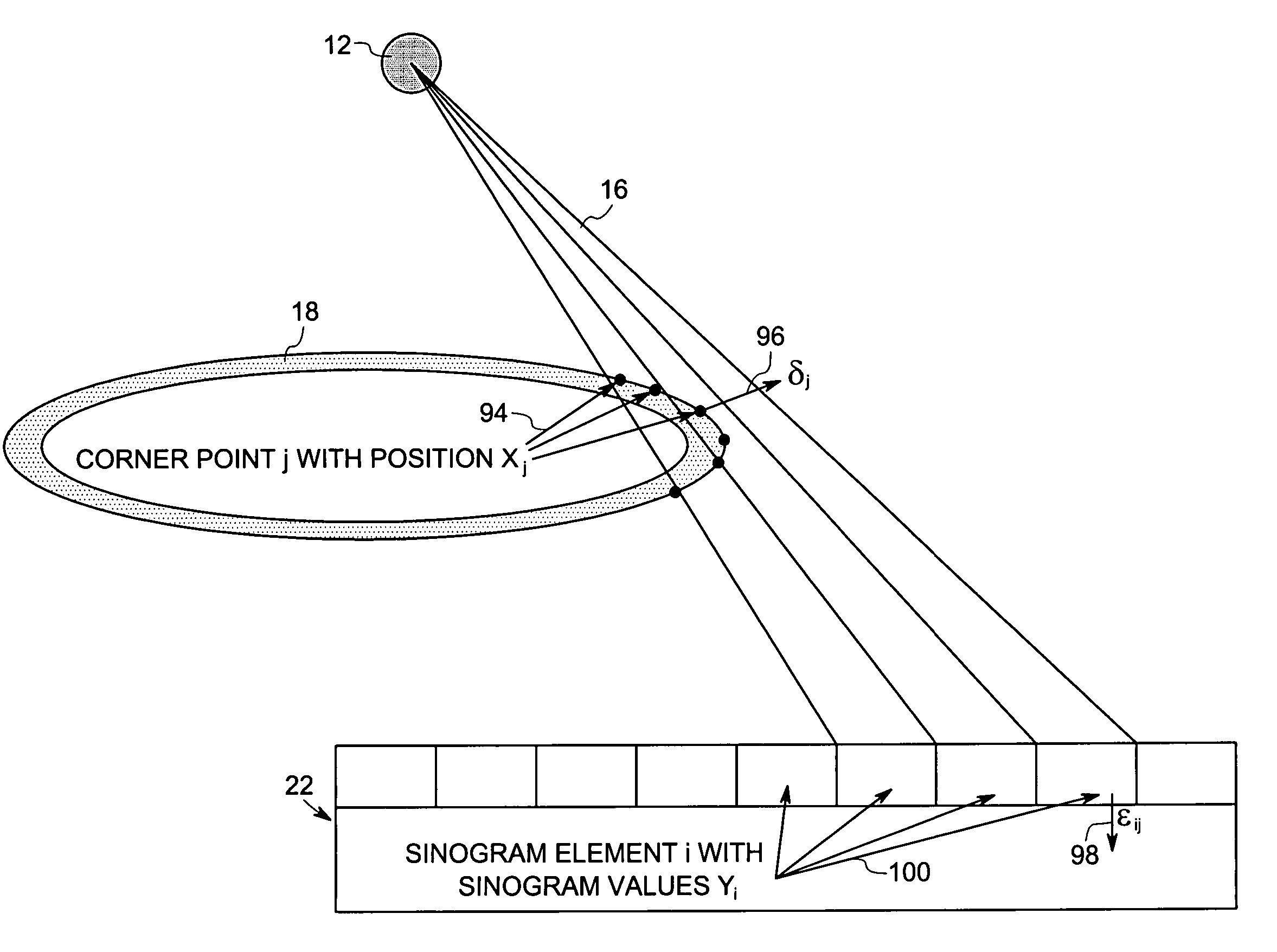
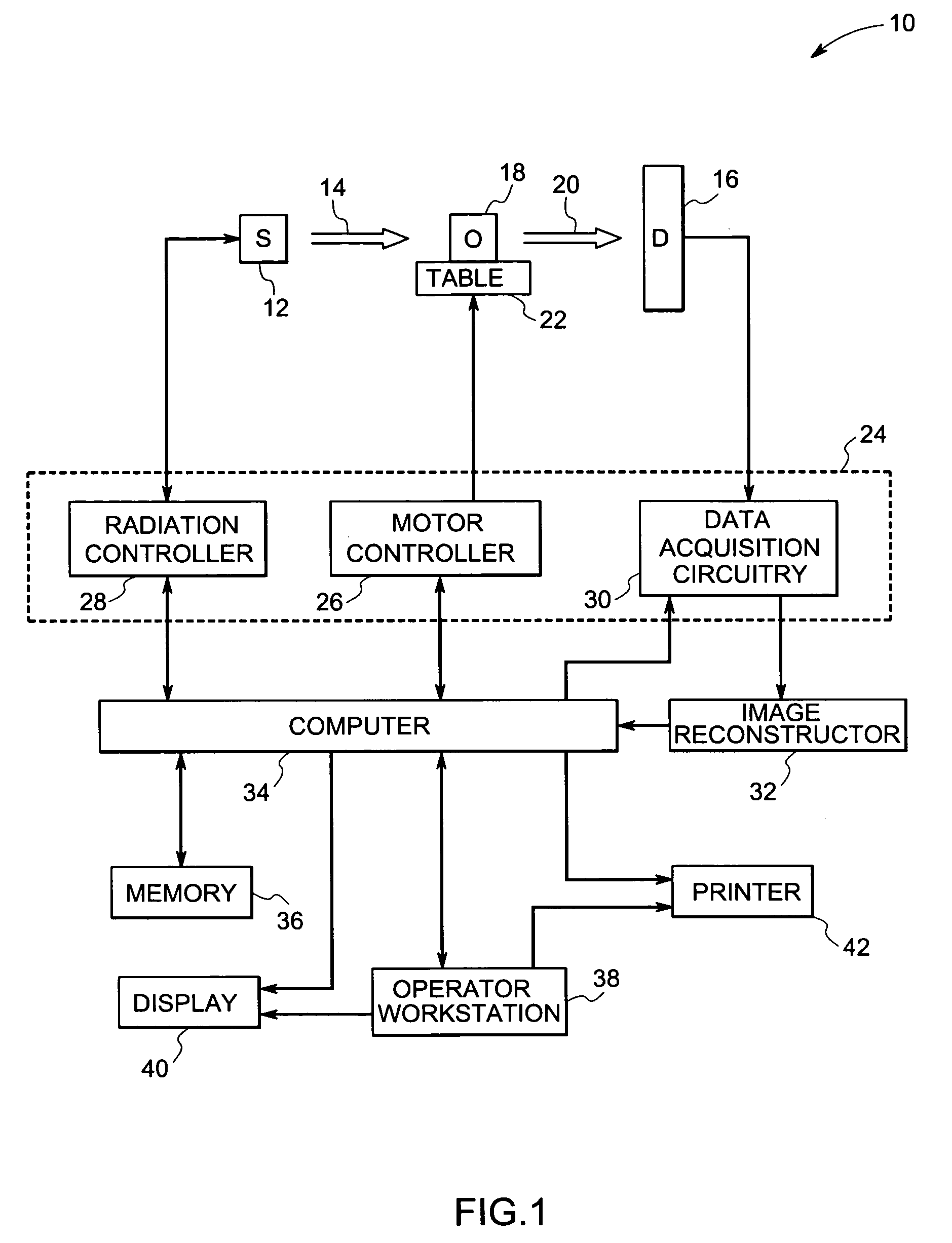
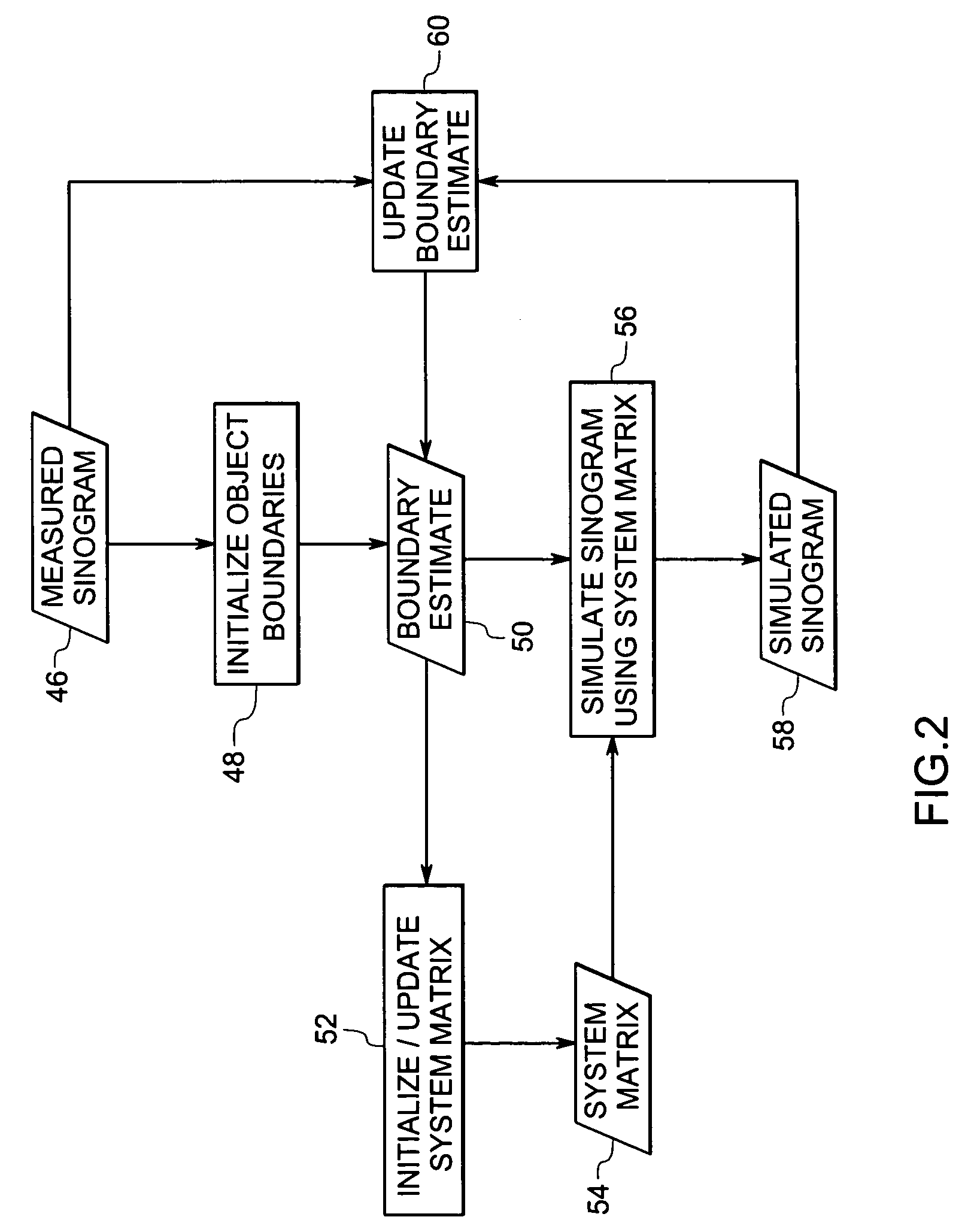
System and method for boundary estimation using CT metrology
InactiveUS7203267B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMetrologyAlgorithm
A technique is provided for CT reconstruction for use in CT metrology. The boundary based CT reconstruction method includes the steps of initializing a boundary of an object to obtain a boundary estimate, defining a forward model based on the boundary estimate, linearizing the forward model to obtain a system matrix and implementing an iterative image reconstruction process using the system matrix to update the boundary estimate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
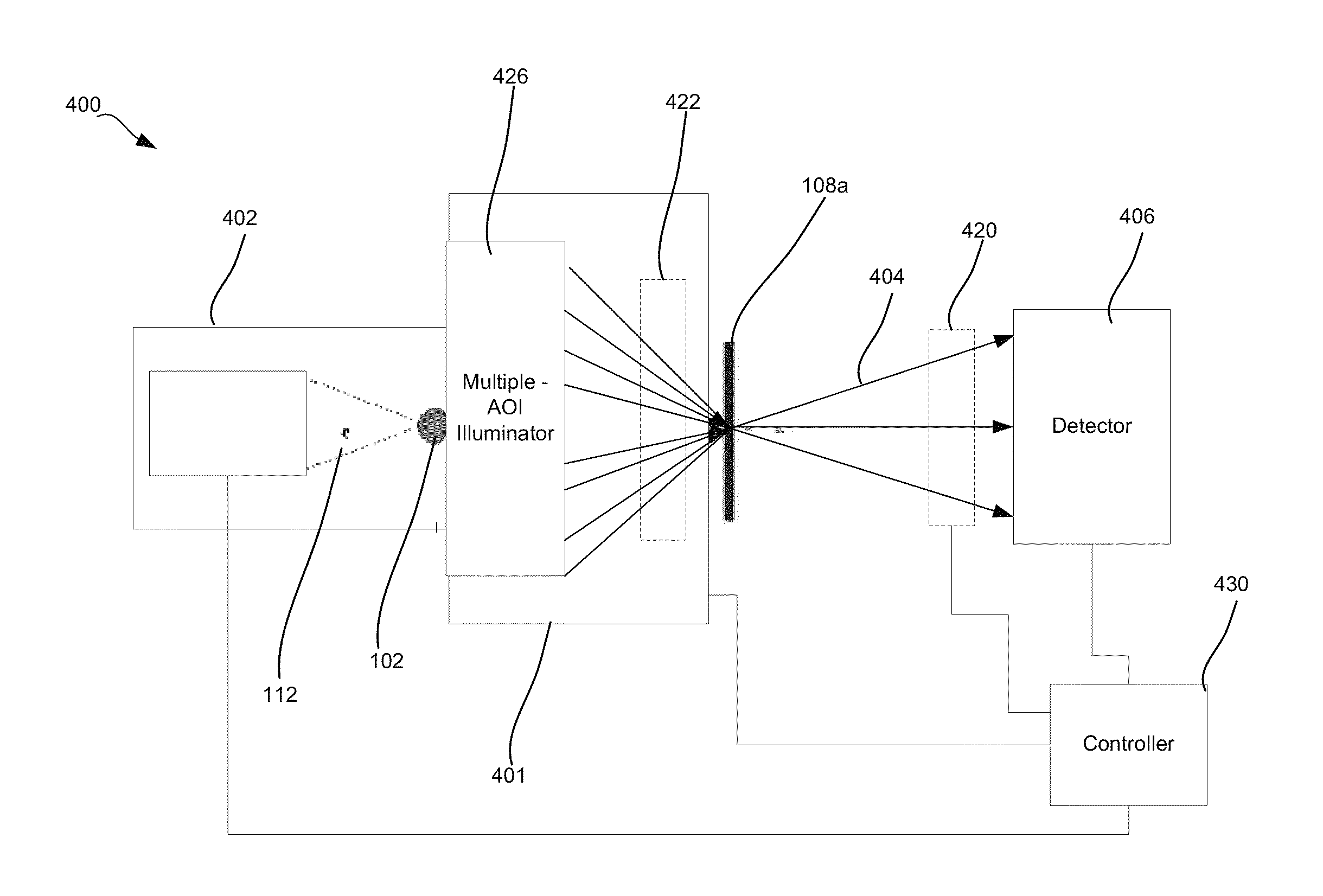
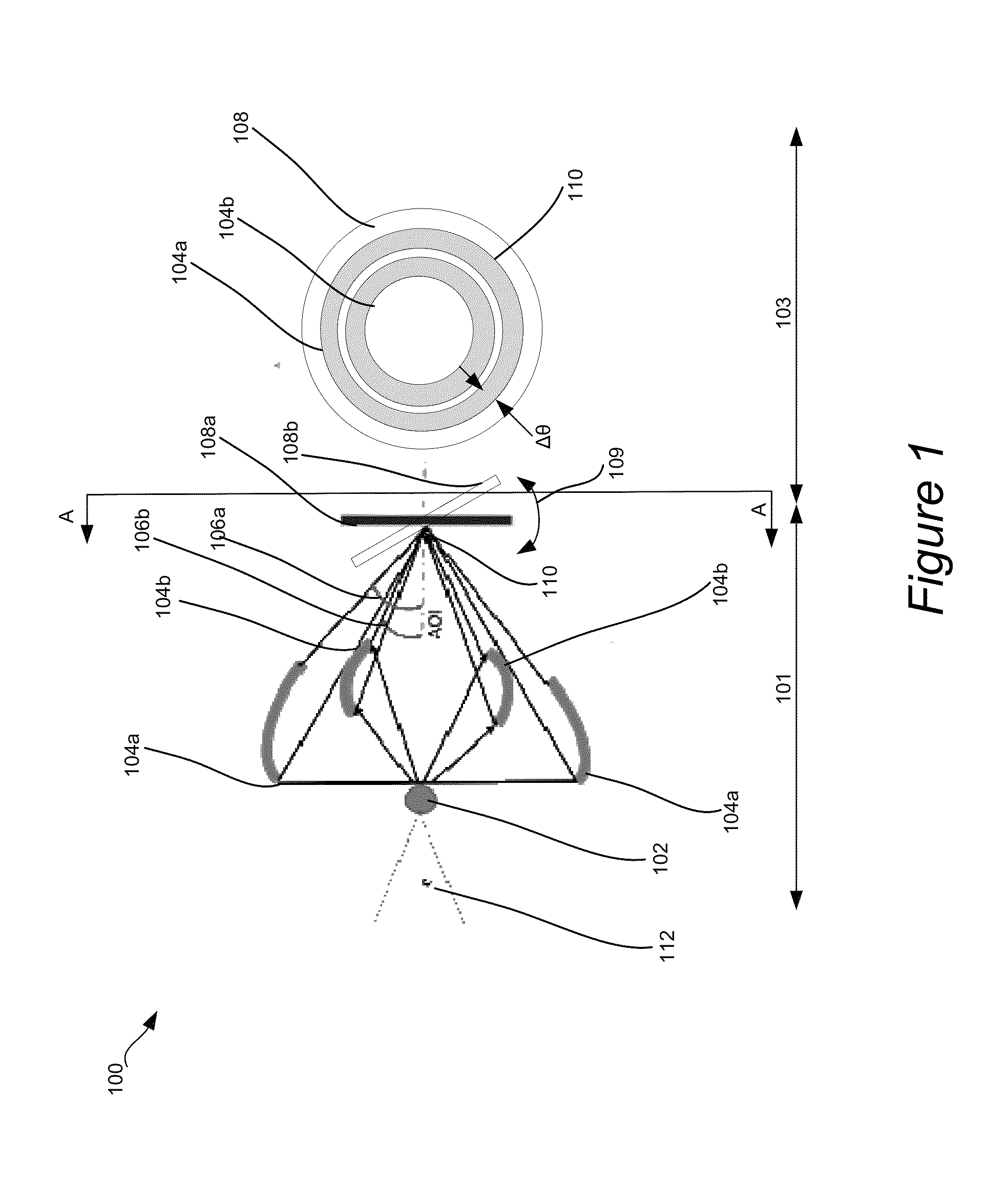
Small-angle scattering x-ray metrology systems and methods
ActiveUS20150110249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationTesting semiconductor materialsSoft x rayMetrology
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for performing small angle x-ray scattering metrology. This system includes an x-ray source for generating x-rays and illumination optics for collecting and reflecting or refracting a portion of the generated x-rays towards a particular focus point on a semiconductor sample in the form of a plurality of incident beams at a plurality of different angles of incidence (AOIs). The system further includes a sensor for collecting output x-ray beams that are scattered from the sample in response to the incident beams on the sample at the different AOIs and a controller configured for controlling operation of the x-ray source and illumination optics and receiving the output x-rays beams and generating an image from such output x-rays.
Owner:KLA CORP
Metrology Methods, Metrology Apparatus and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20170184981A1Precise structureIncrease the angle of incidenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAction spectrumMetrology
Hybrid metrology apparatus (1000, 1100, 1200, 1300, 1400) measures a structure (T) manufactured by lithography. An EUV metrology apparatus (244, IL1 / DET1) irradiates the structure with EUV radiation and detects a first spectrum from the structure. Another metrology apparatus (240, IL2 / DET2) irradiates the structure with second radiation comprising EUV radiation or longer-wavelength radiation and detects a second spectrum. Using the detected first spectrum and the detected second spectrum together, a processor (MPU) determines a property (CD / OV) of the structure. The spectra can be combined in various ways. For example, the first detected spectrum can be used to control one or more parameters of illumination and / or detection used to capture the second spectrum, or vice versa. The first spectrum can be used to distinguish properties of different layers (T1, T2) in the structure. First and second radiation sources (SRC1, SRC2) may share a common drive laser (LAS).
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Multiple precursor showerhead with by-pass ports
ActiveUS8361892B2Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyEngineering
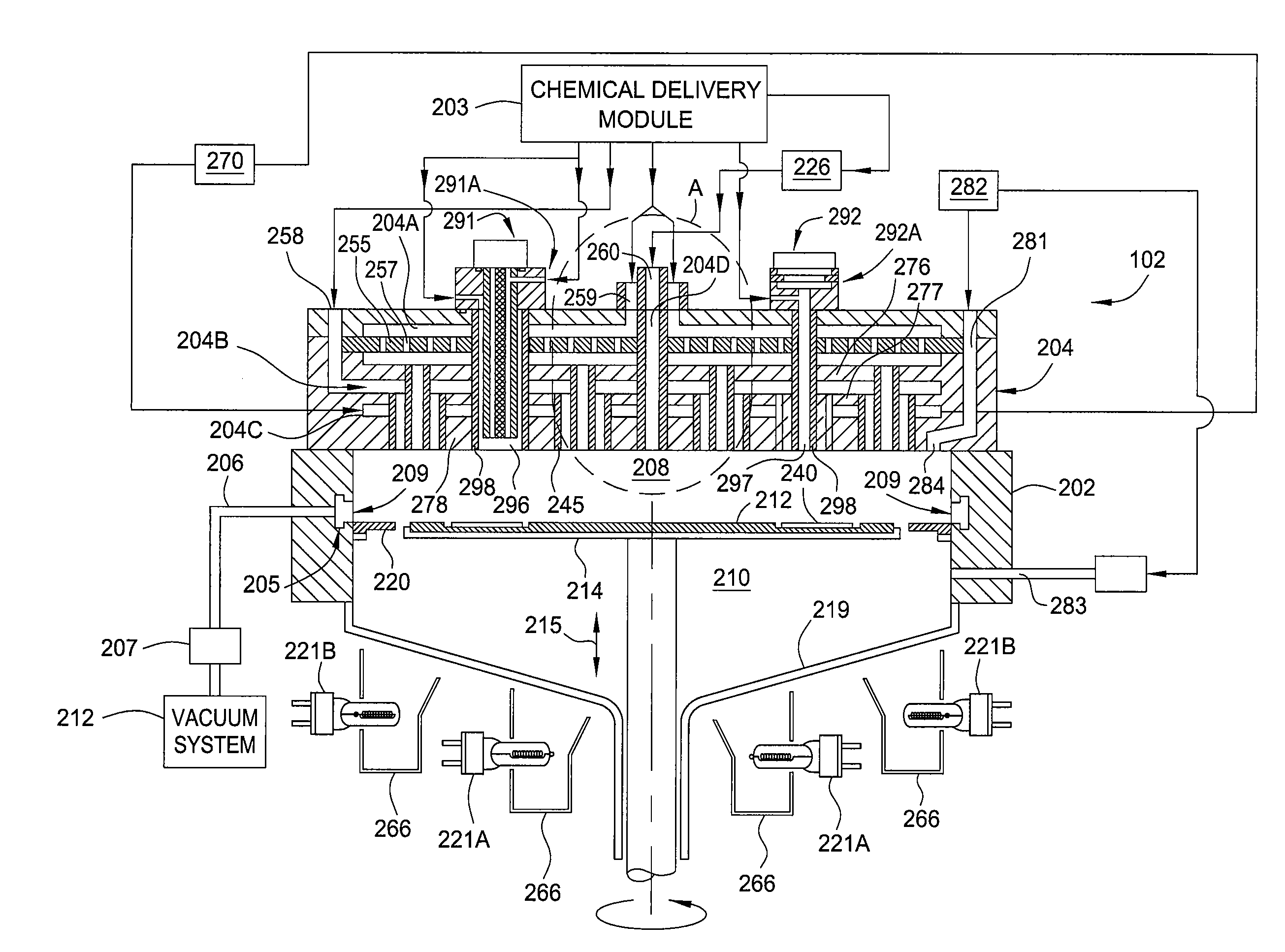
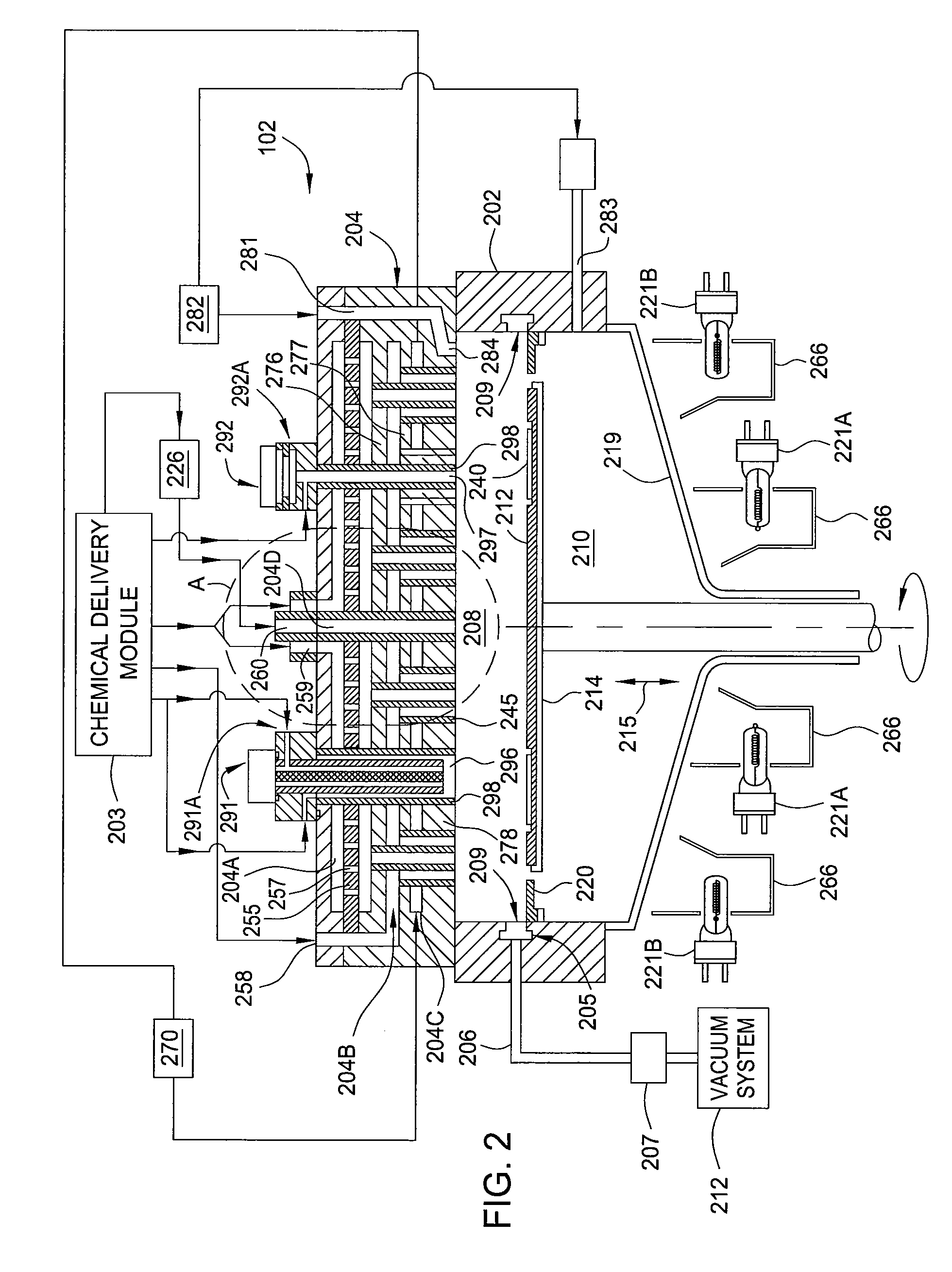
A method and apparatus that may be utilized for chemical vapor deposition and / or hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) deposition are provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus a processing chamber that includes a showerhead with separate inlets and channels for delivering separate processing gases into a processing volume of the chamber without mixing the gases prior to entering the processing volume. In one embodiment, the showerhead includes one or more cleaning gas conduits configured to deliver a cleaning gas directly into the processing volume of the chamber while by-passing the processing gas channels. In one embodiment, the showerhead includes a plurality of metrology ports configured to deliver a cleaning gas directly into the processing volume of the chamber while by-passing the processing gas channels. As a result, the processing chamber components can be cleaned more efficiently and effectively than by introducing cleaning gas into the chamber only through the processing gas channels.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and methods for detecting overlay errors using scatterometry
Disclosed is a method for determining an overlay error between at least two layers in a multiple layer sample. A sample having a plurality of periodic targets that each have a first structure in a first layer and a second structure in a second layer is provided. There are predefined offsets between the first and second structures. Using a scatterometry overlay metrology, scatterometry overlay data is obtained from a first set of the periodic targets based on one or more measured optical signals from the first target set on the sample. Using an imaging overlay metrology, imaging overlay data is obtained from a second set of the periodic targets based on one or more image(s) from the second target set on the sample.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com