Patents
Literature
247 results about "Planar Imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
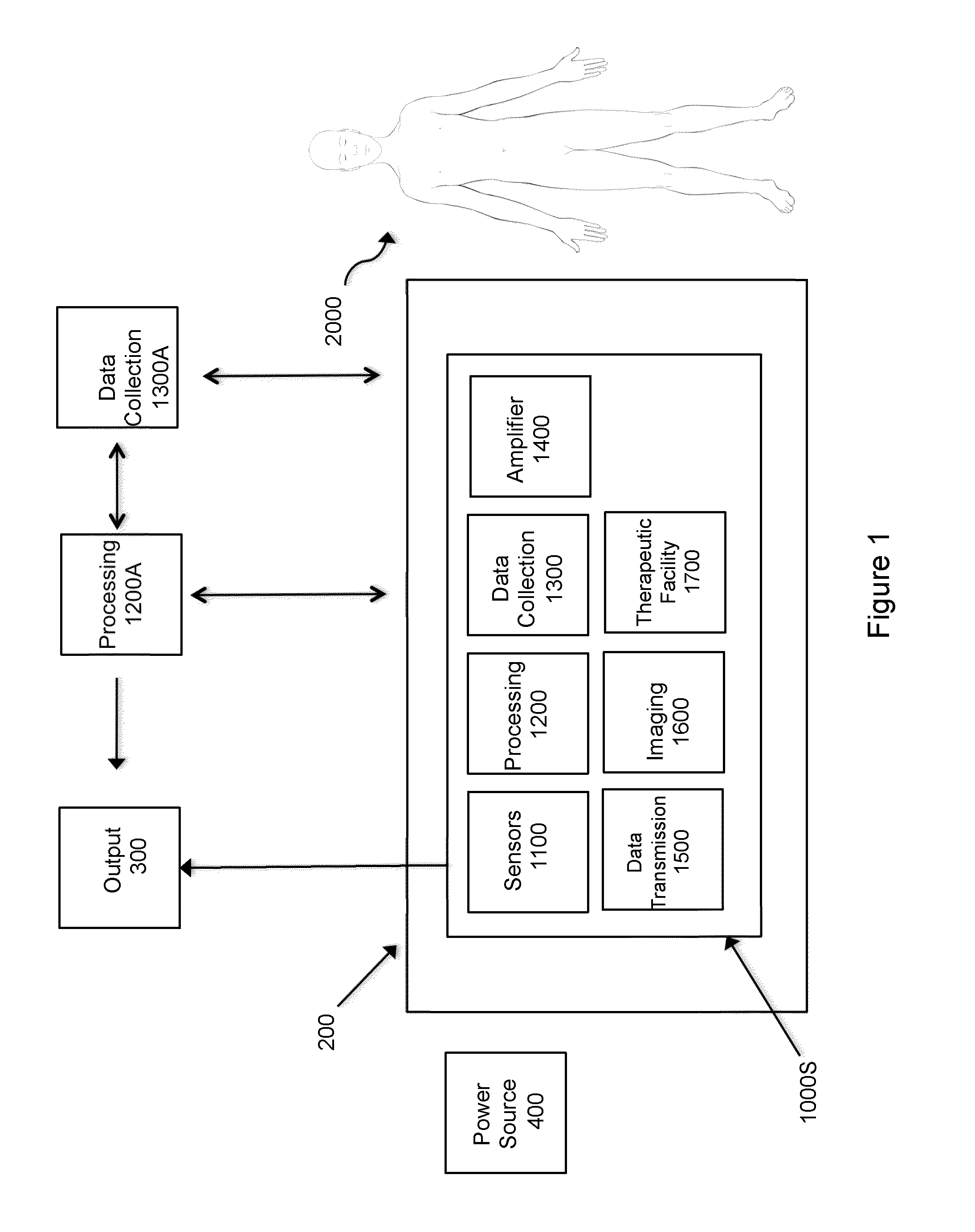
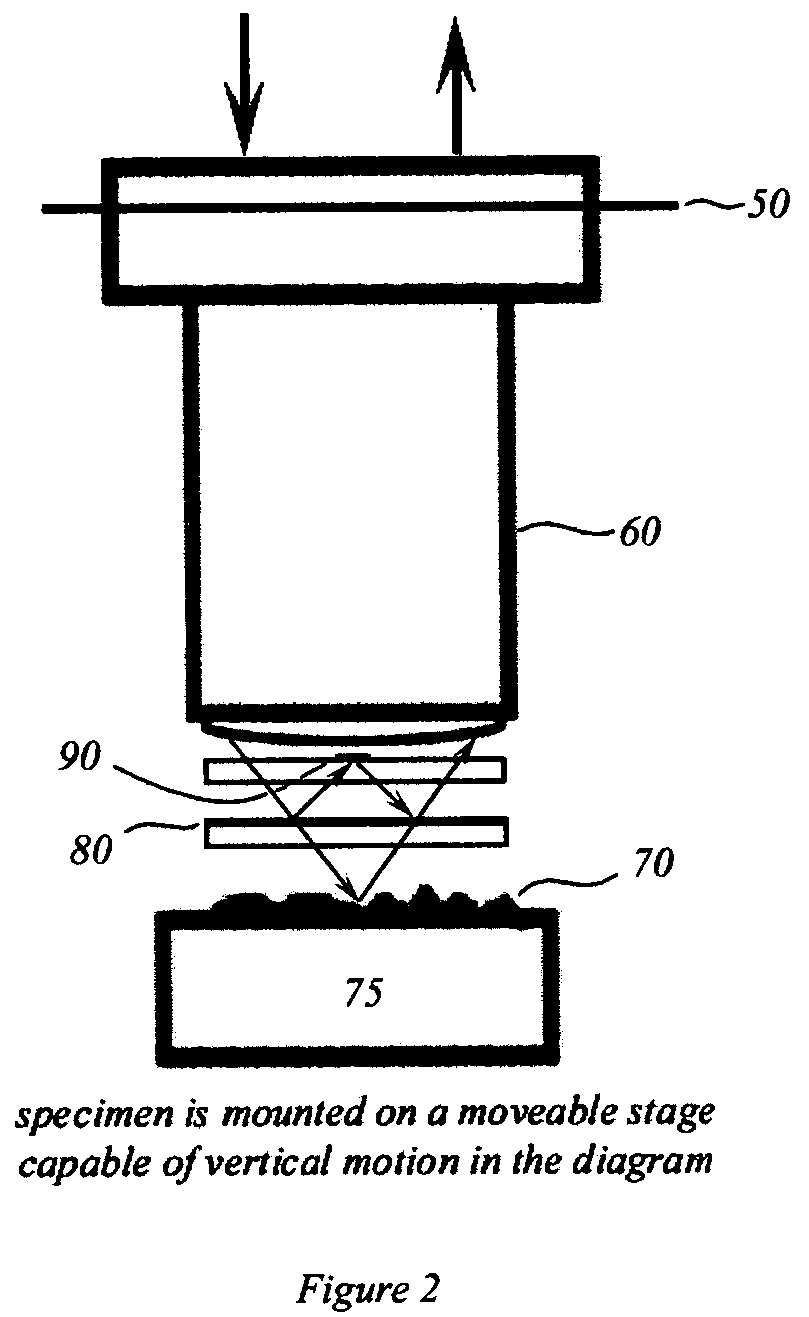
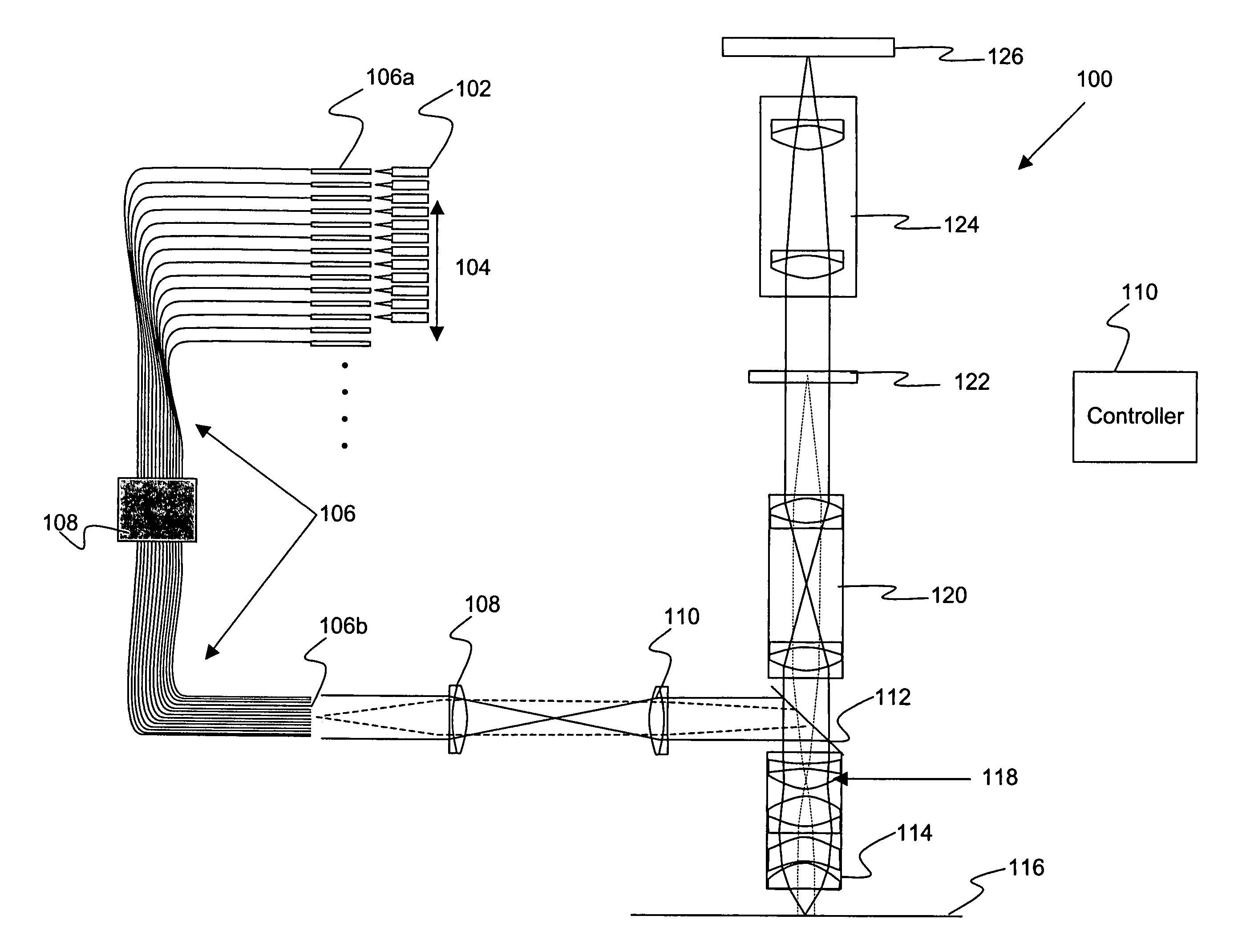
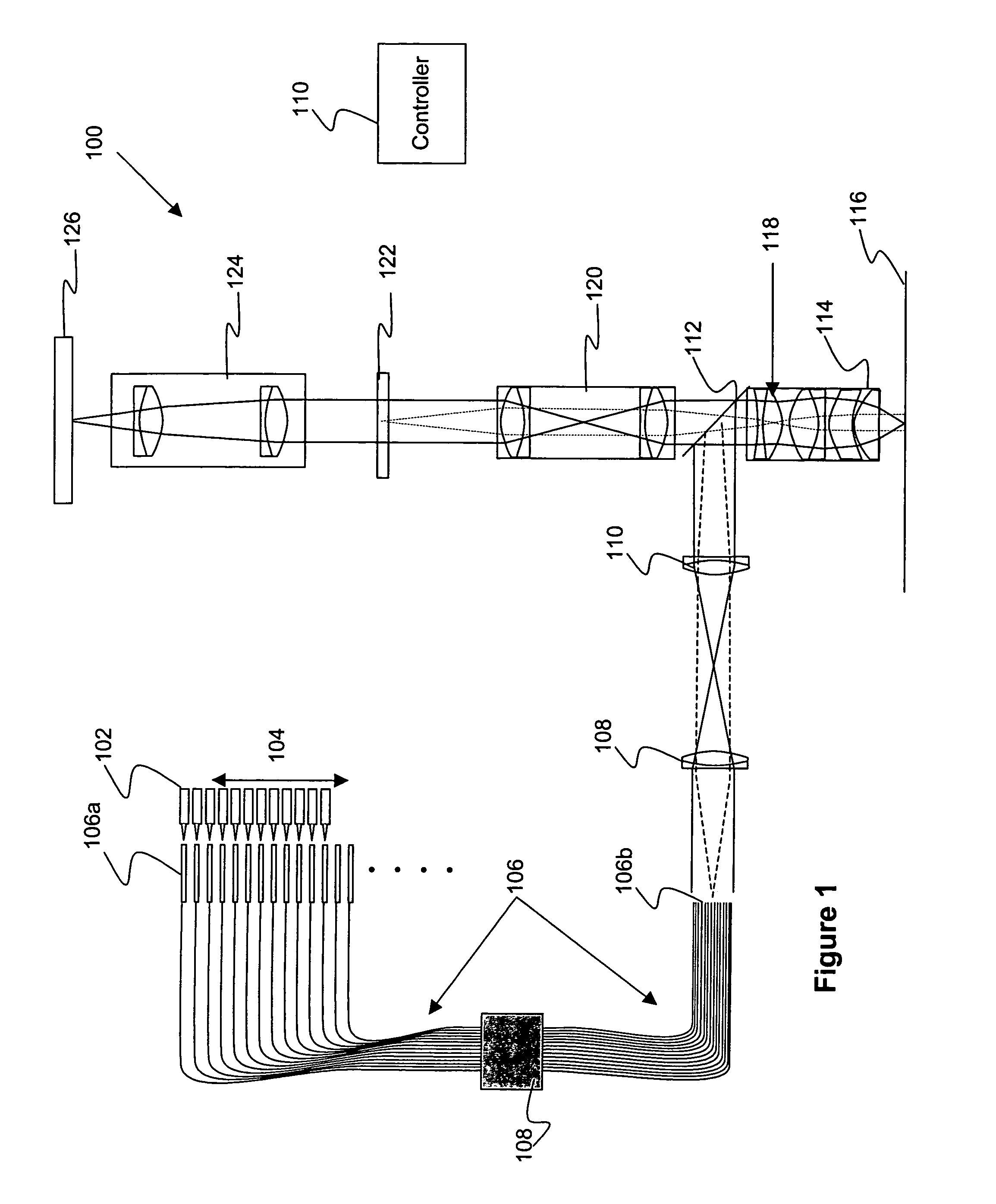
Implementation of a gamma camera to obtain 2D images with no tomographic reconstruction process being involved.
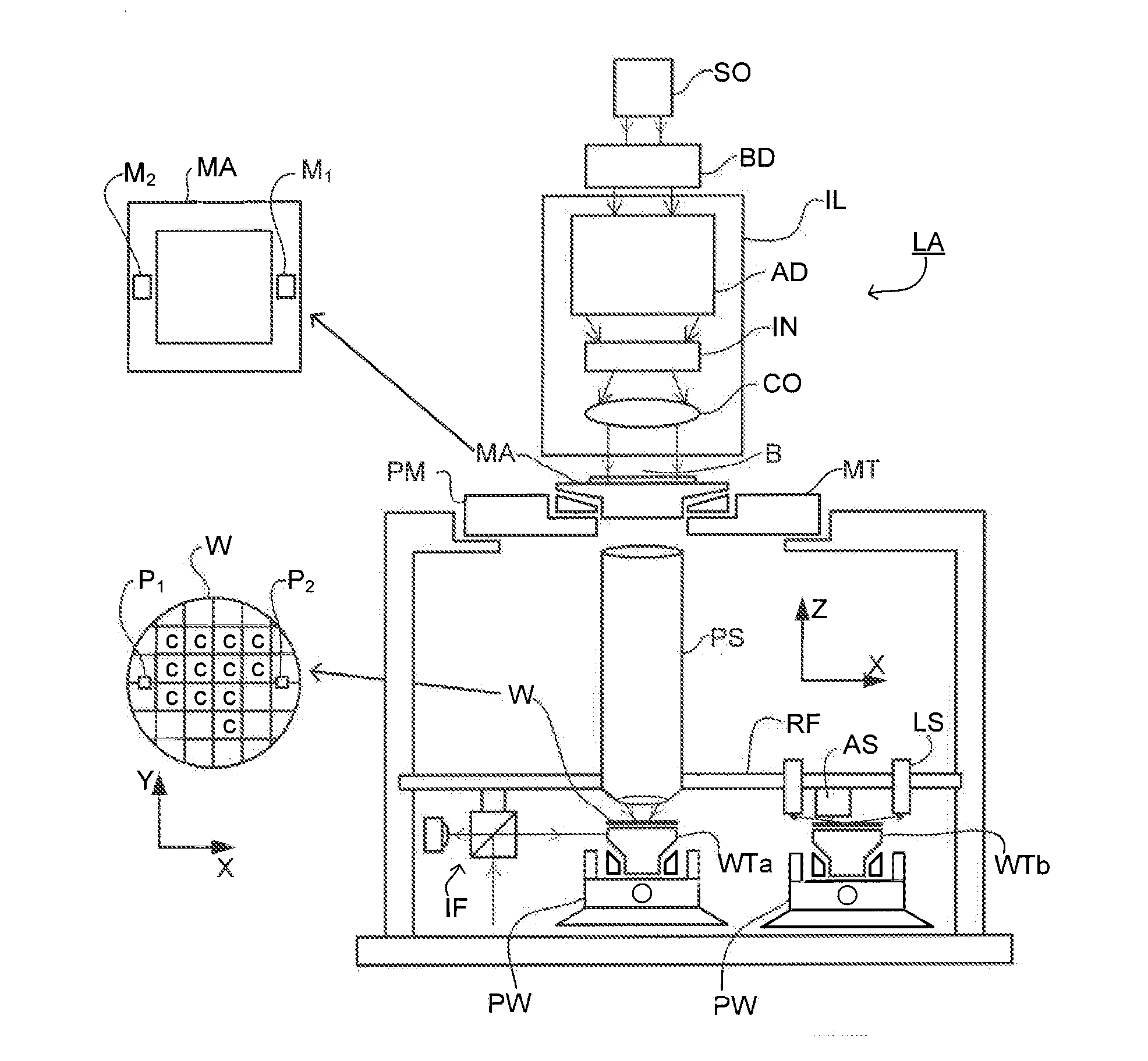
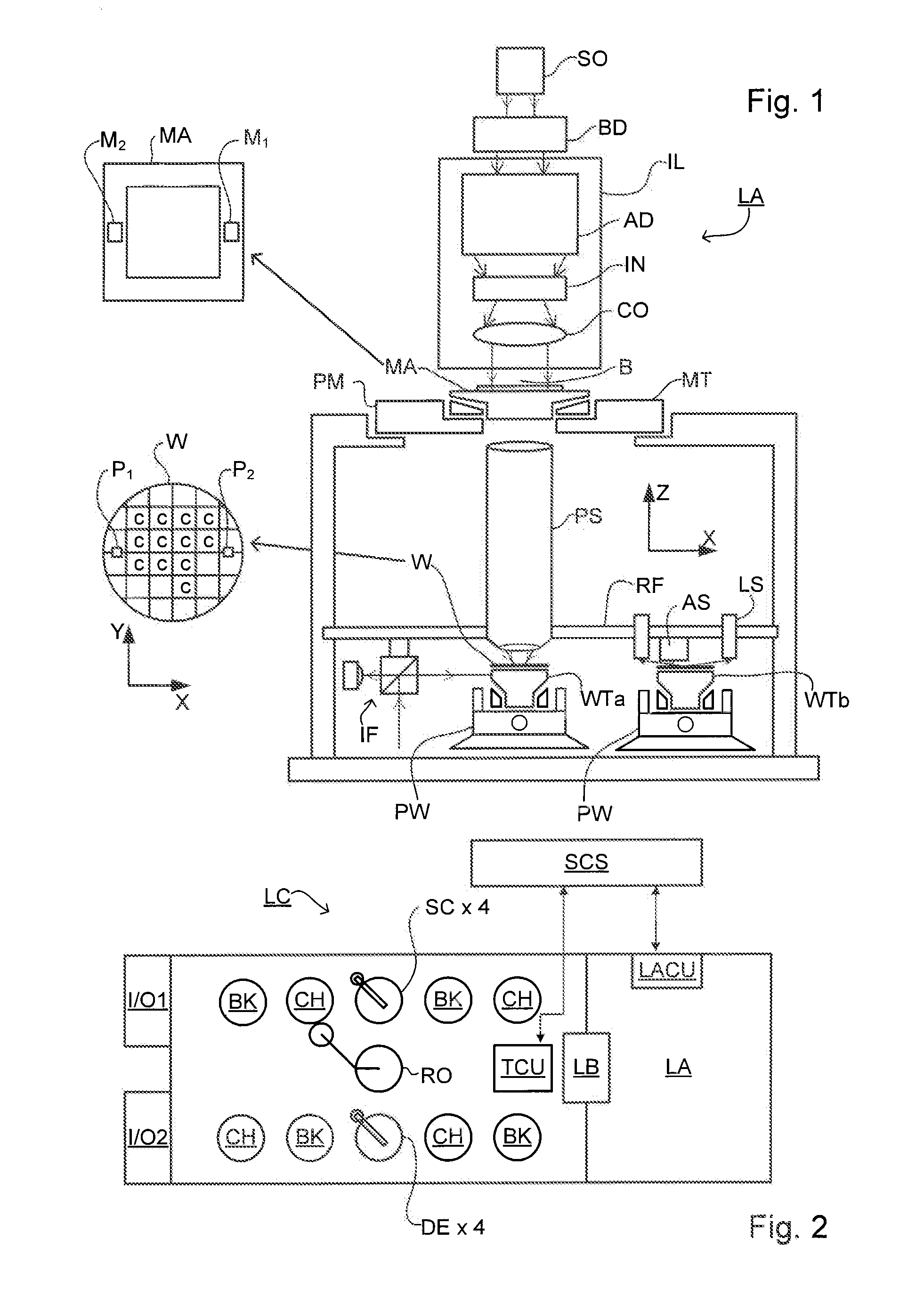
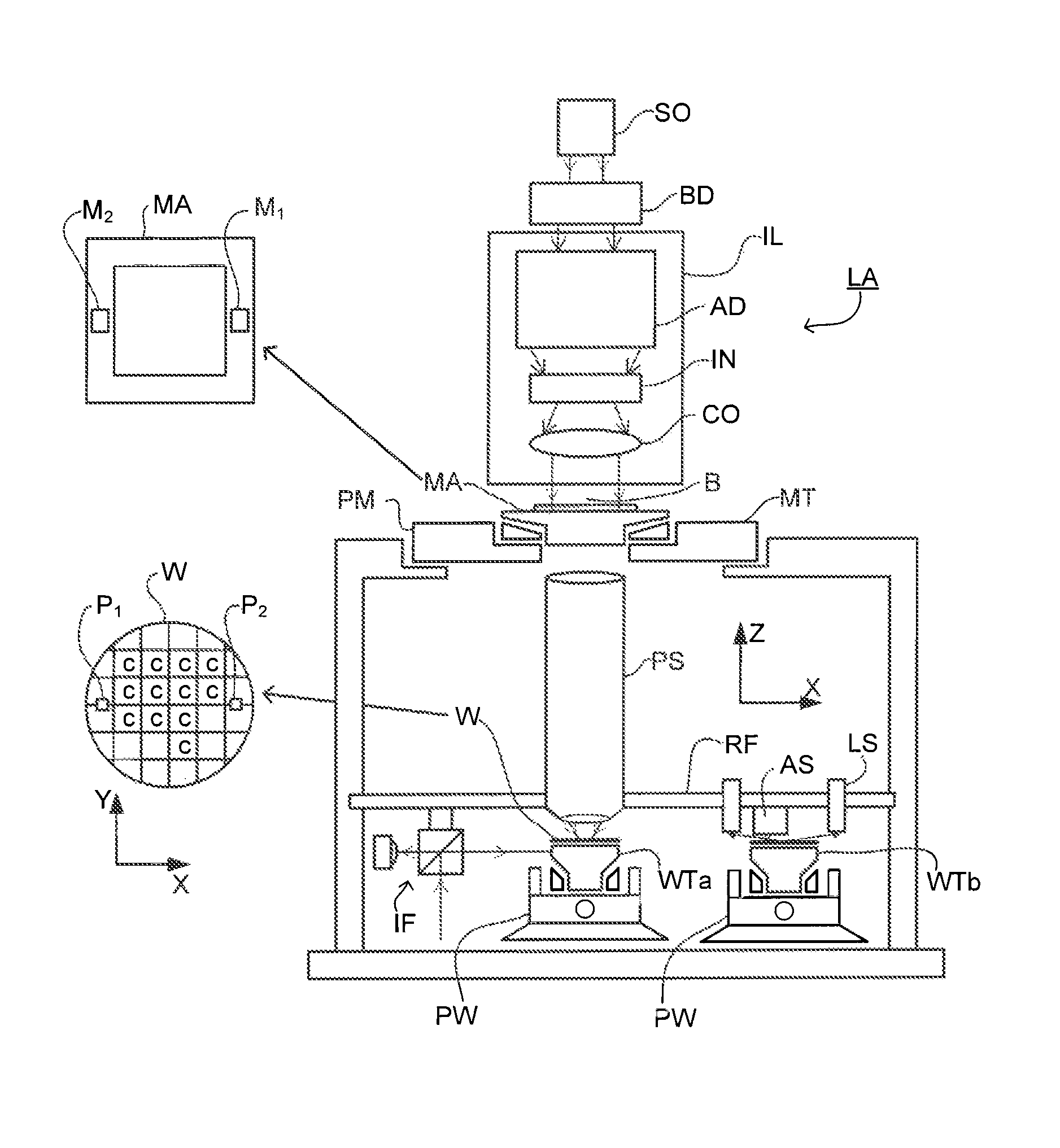
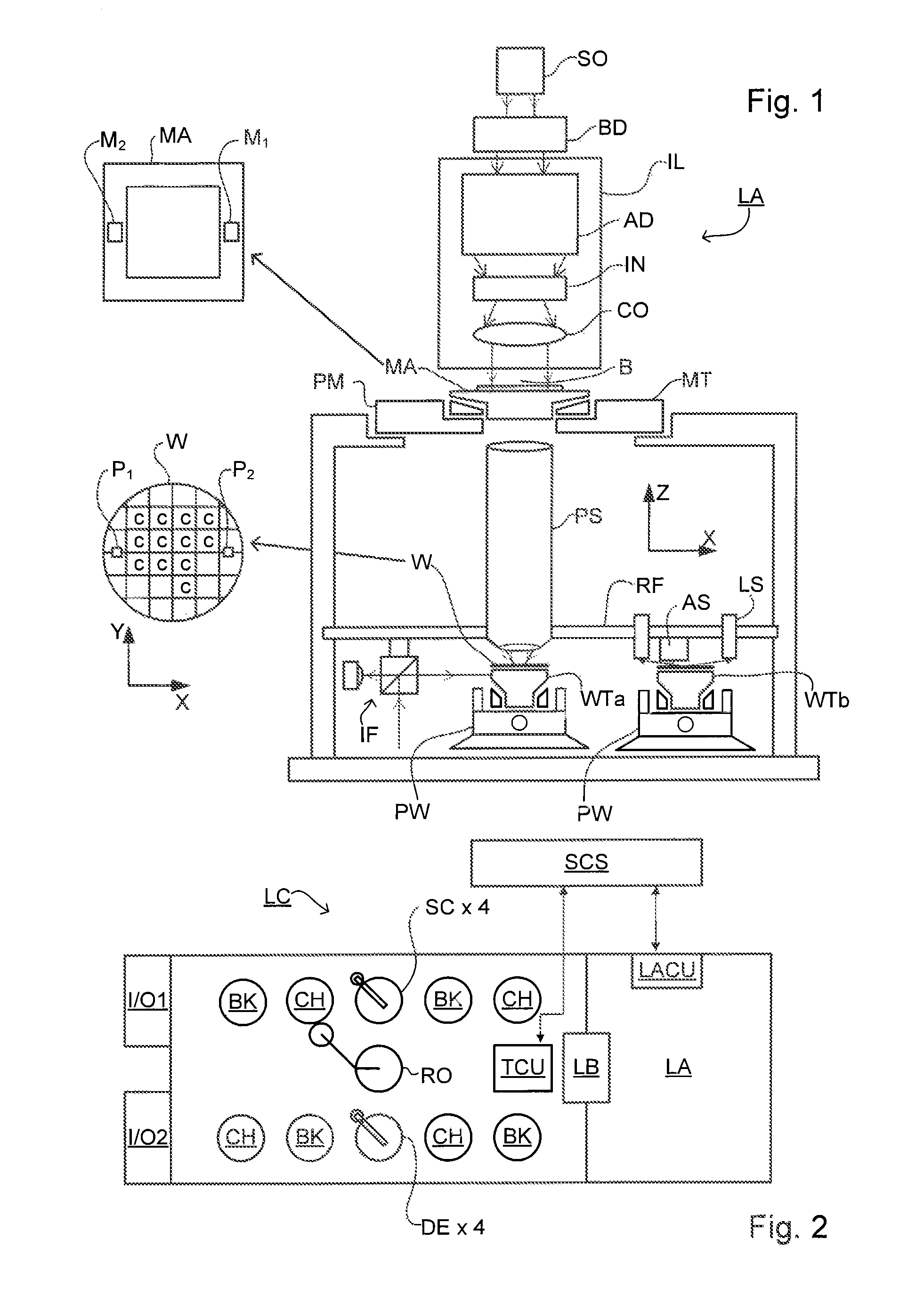
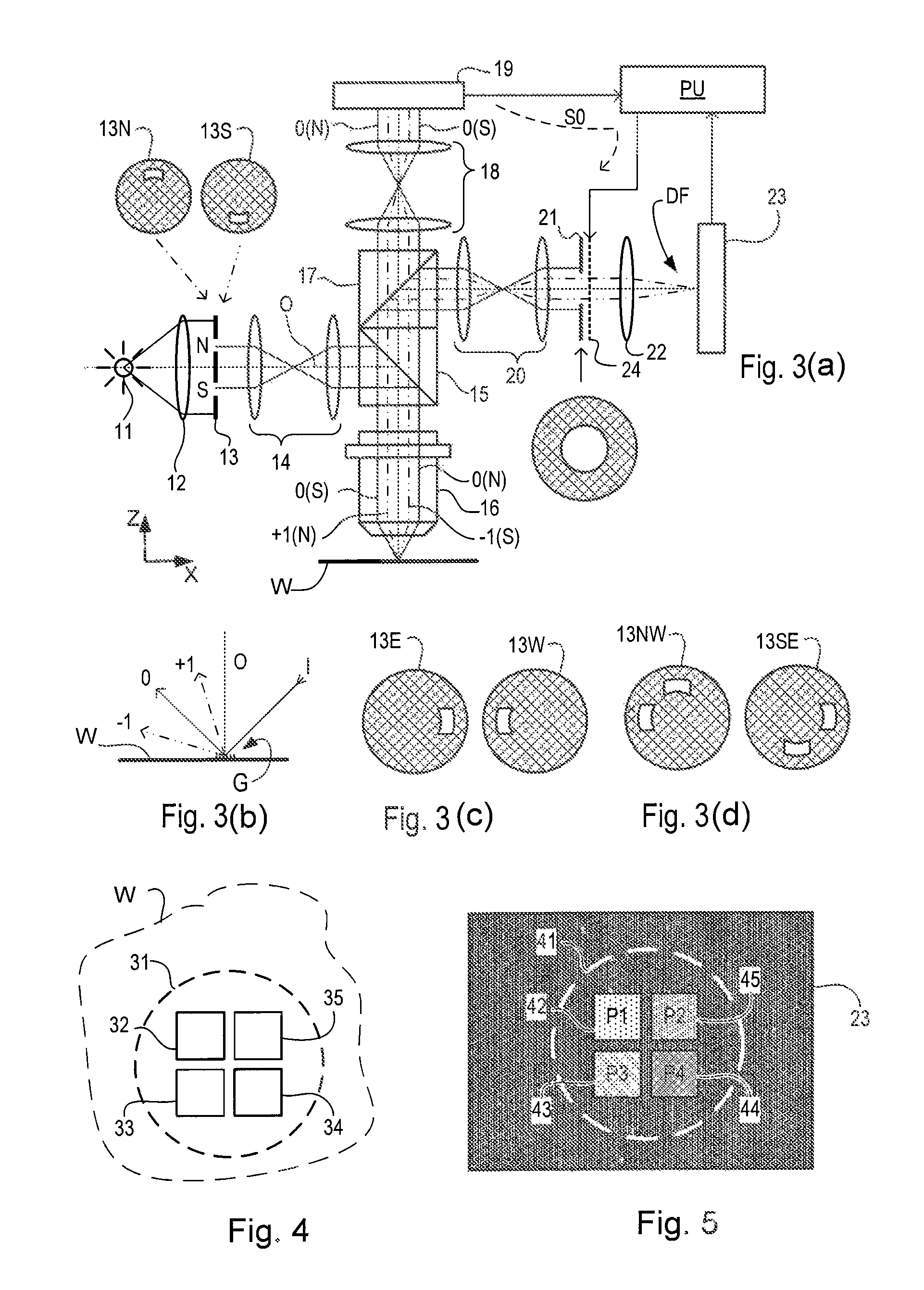
Metrology Method and Inspection Apparatus, Lithographic System and Device Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20120123581A1Improve accuracyImprove throughputPhotomechanical apparatusScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpatial light modulator
Methods are disclosed for measuring target structures formed by a lithographic process on a substrate. A grating structure within the target is smaller than an illumination spot and field of view of a measurement optical system. The optical system has a first branch leading to a pupil plane imaging sensor and a second branch leading to a substrate plane imaging sensor. A spatial light modulator is arranged in an intermediate pupil plane of the second branch of the optical system. The SLM imparts a programmable pattern of attenuation that may be used to correct for asymmetries between the first and second modes of illumination or imaging. By use of specific target designs and machine-learning processes, the attenuation patterns may also be programmed to act as filter functions, enhancing sensitivity to specific parameters of interest, such as focus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
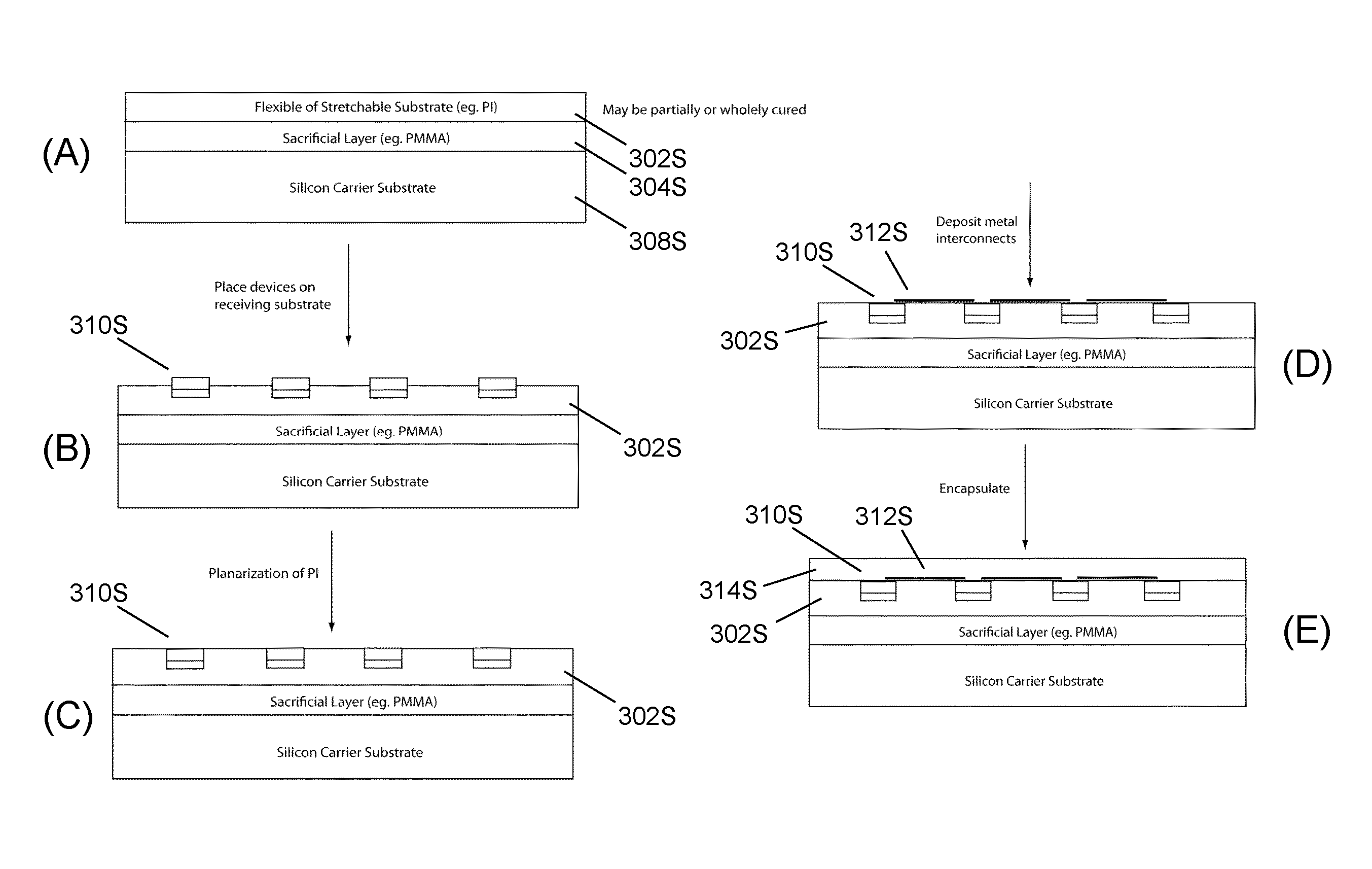
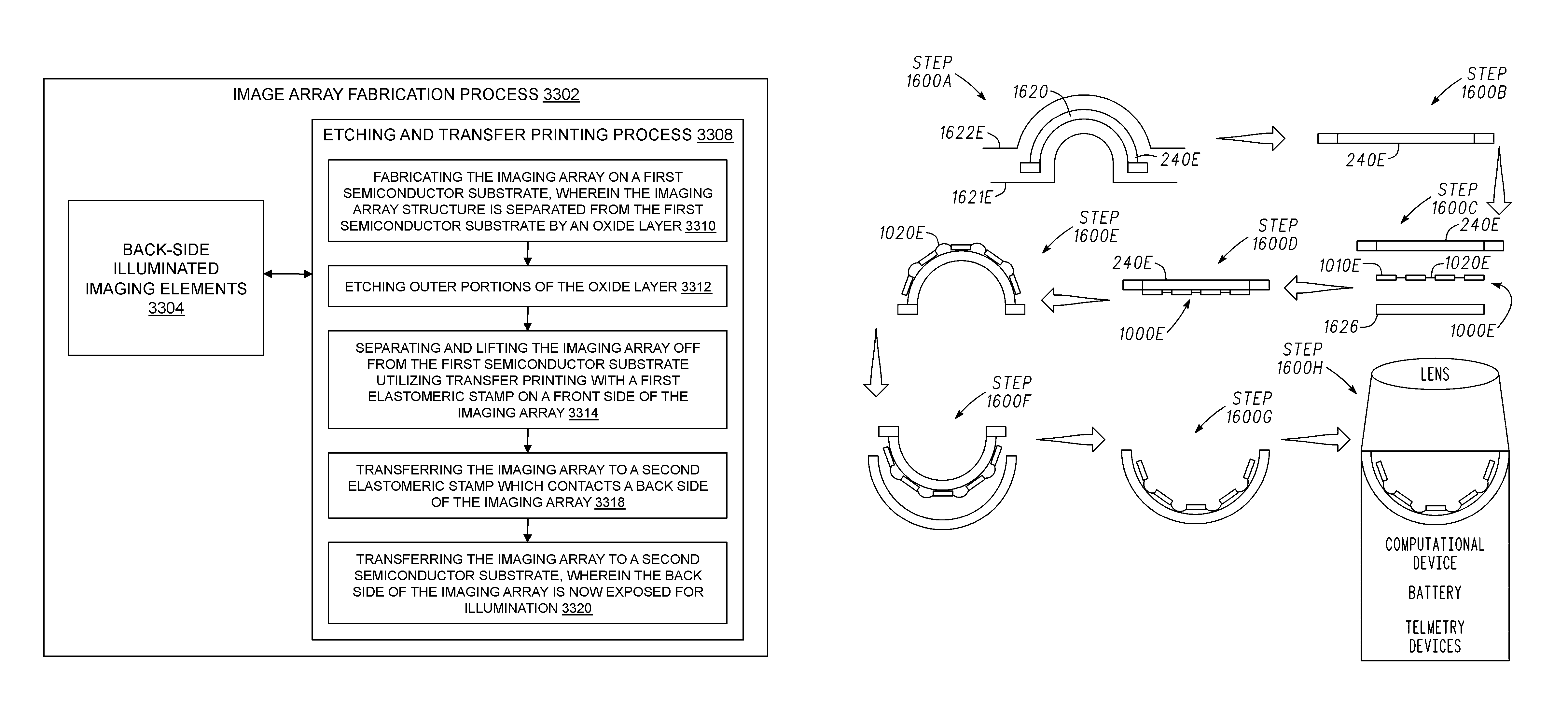
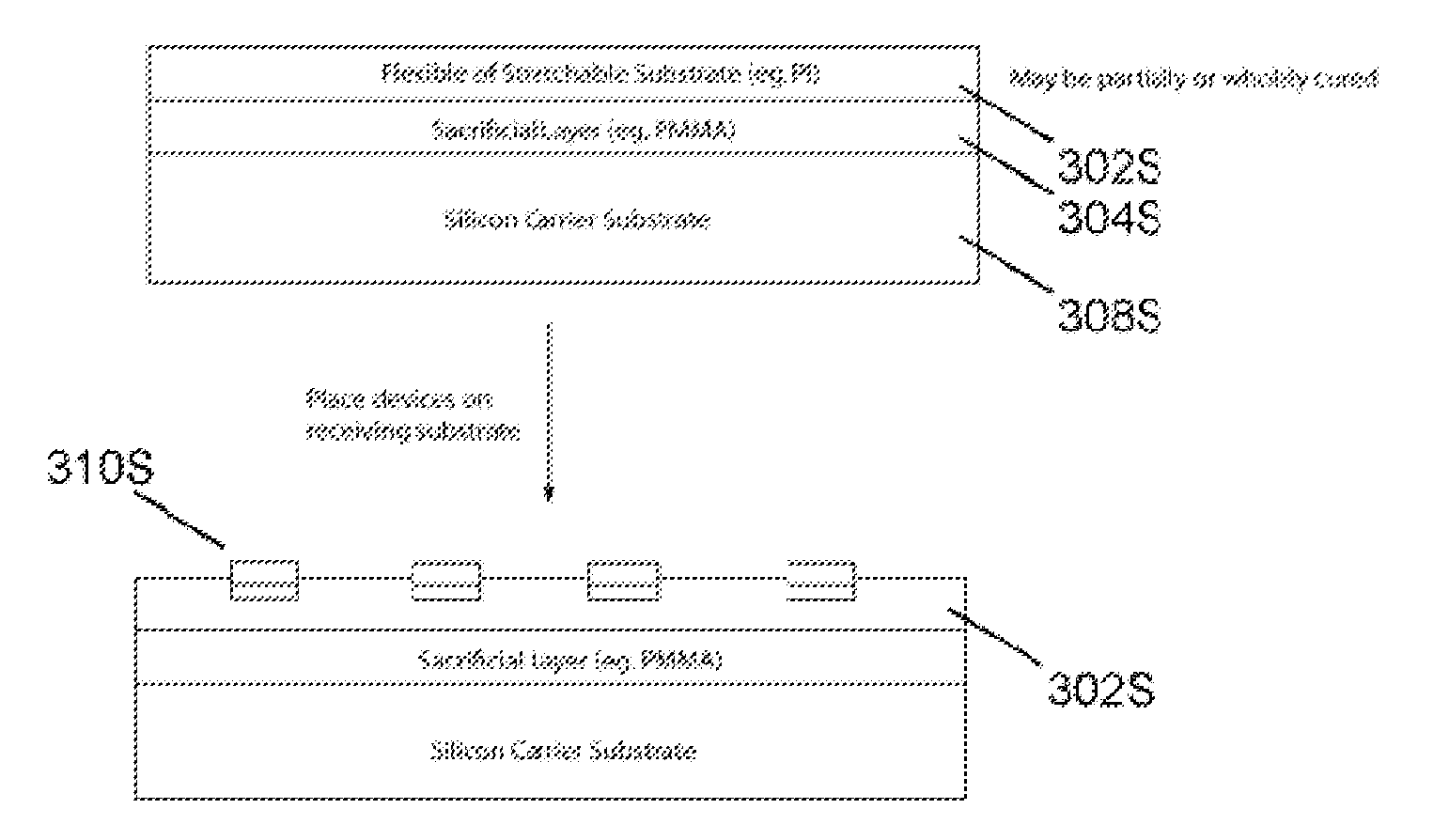
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
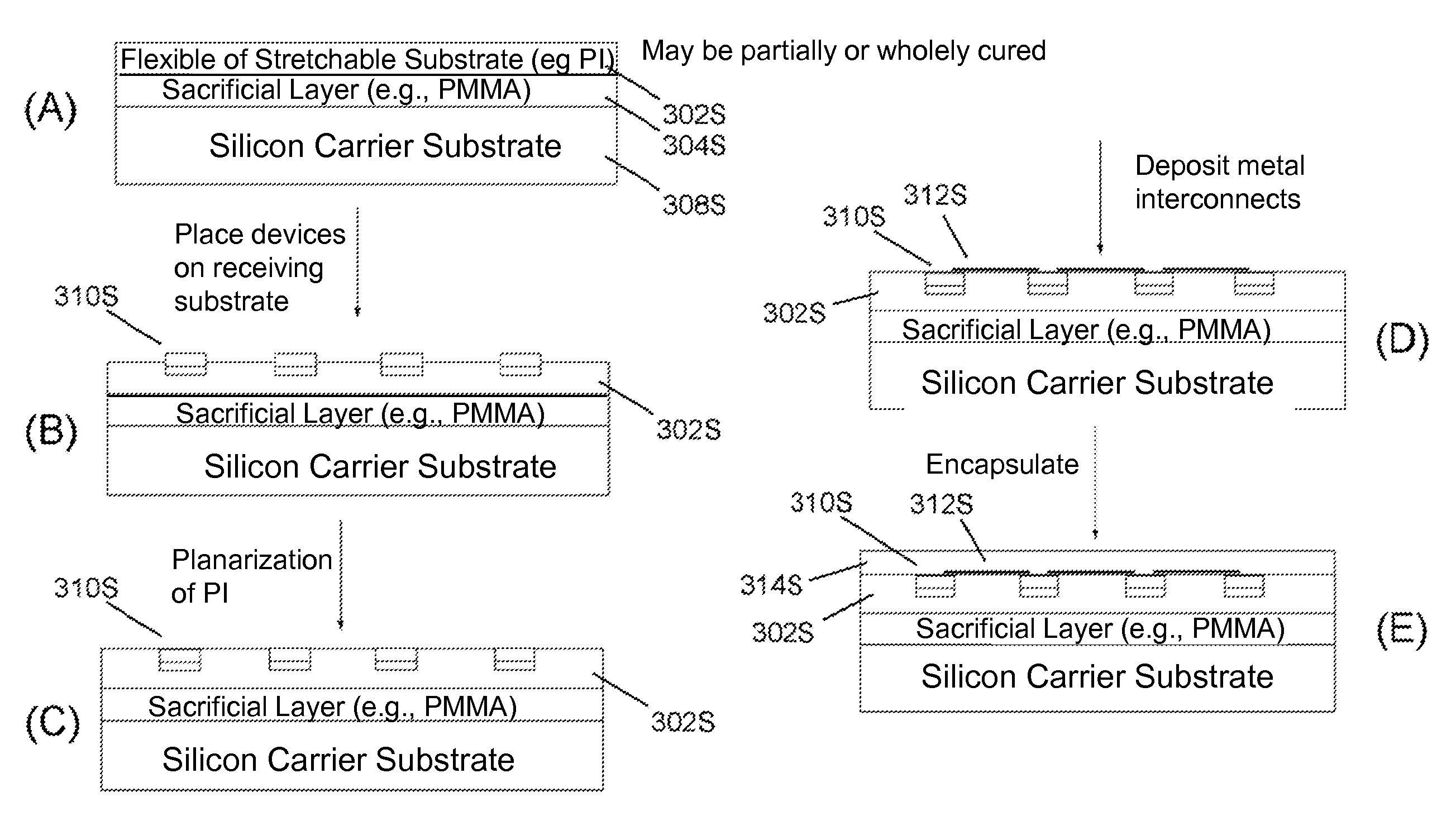
ActiveUS20100178722A1Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionEngineering
System, devices and methods are presented that provide an imaging array fabrication process method, comprising fabricating an array of semiconductor imaging elements, interconnecting the elements with stretchable interconnections, and transfer printing the array with a pre-strained elastomeric stamp to a secondary non-planar surface.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
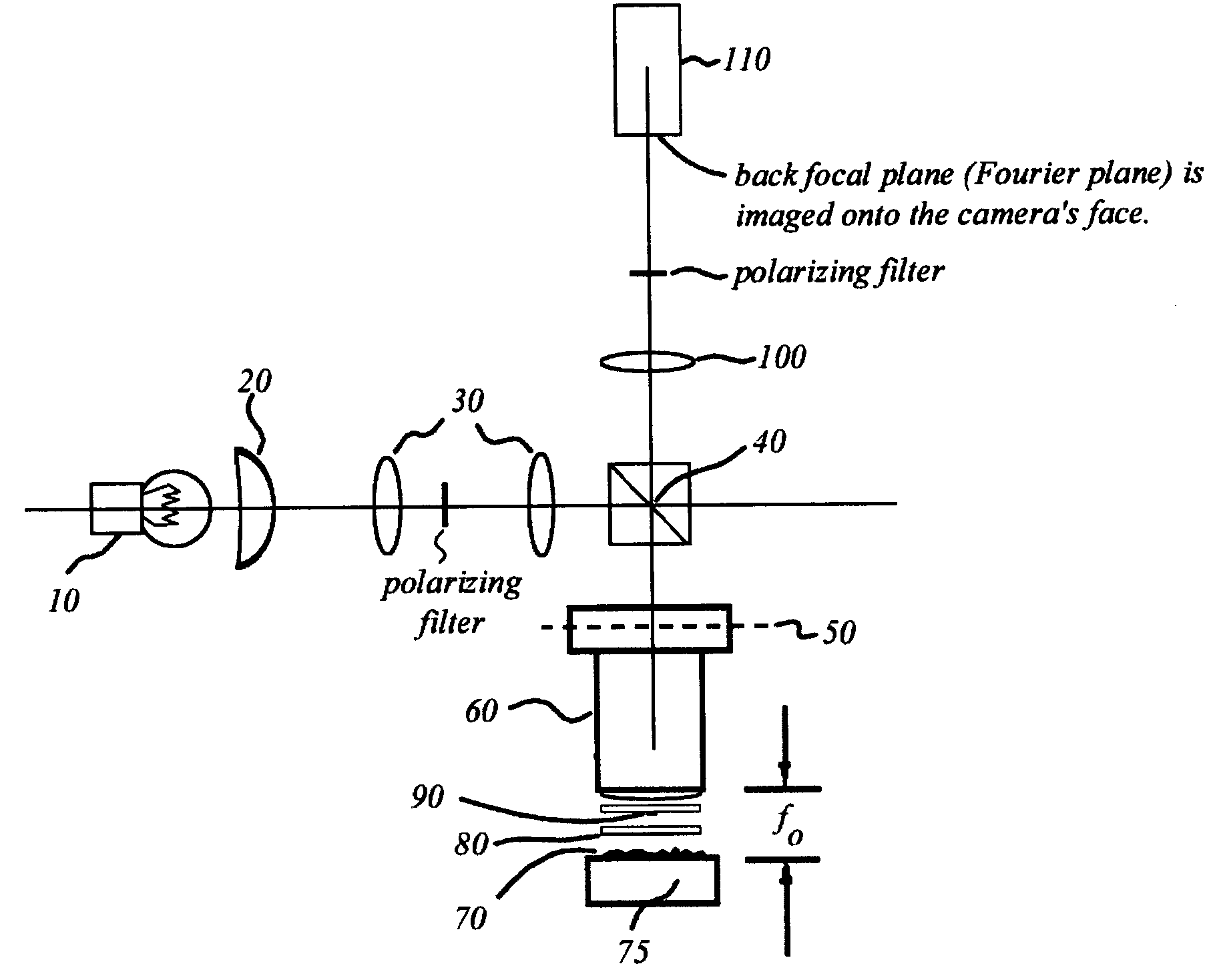
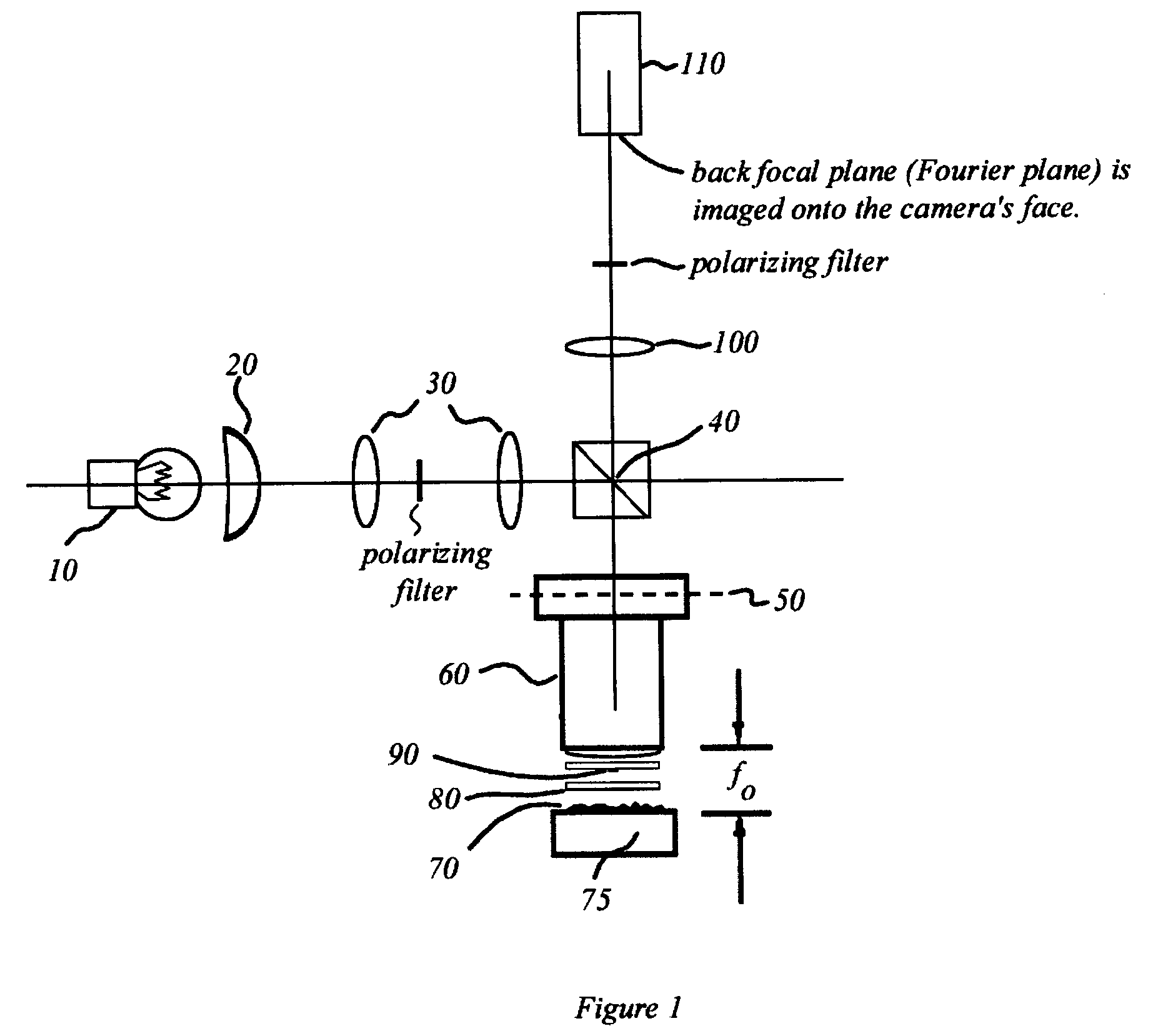
Interferometric back focal plane scatterometry with Koehler illumination
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS20130316487A1Low costReduce reflectionSolid-state devicesAcoustic sensorsEngineeringInterconnection
System, devices and methods are presented that provide an imaging array fabrication process method, comprising fabricating an array of semiconductor imaging elements, interconnecting the elements with stretchable interconnections, and transfer printing the array with a pre-strained elastomeric stamp to a secondary non-planar surface.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS8372726B2Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectCircuit bendability/stretchabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionEngineering
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
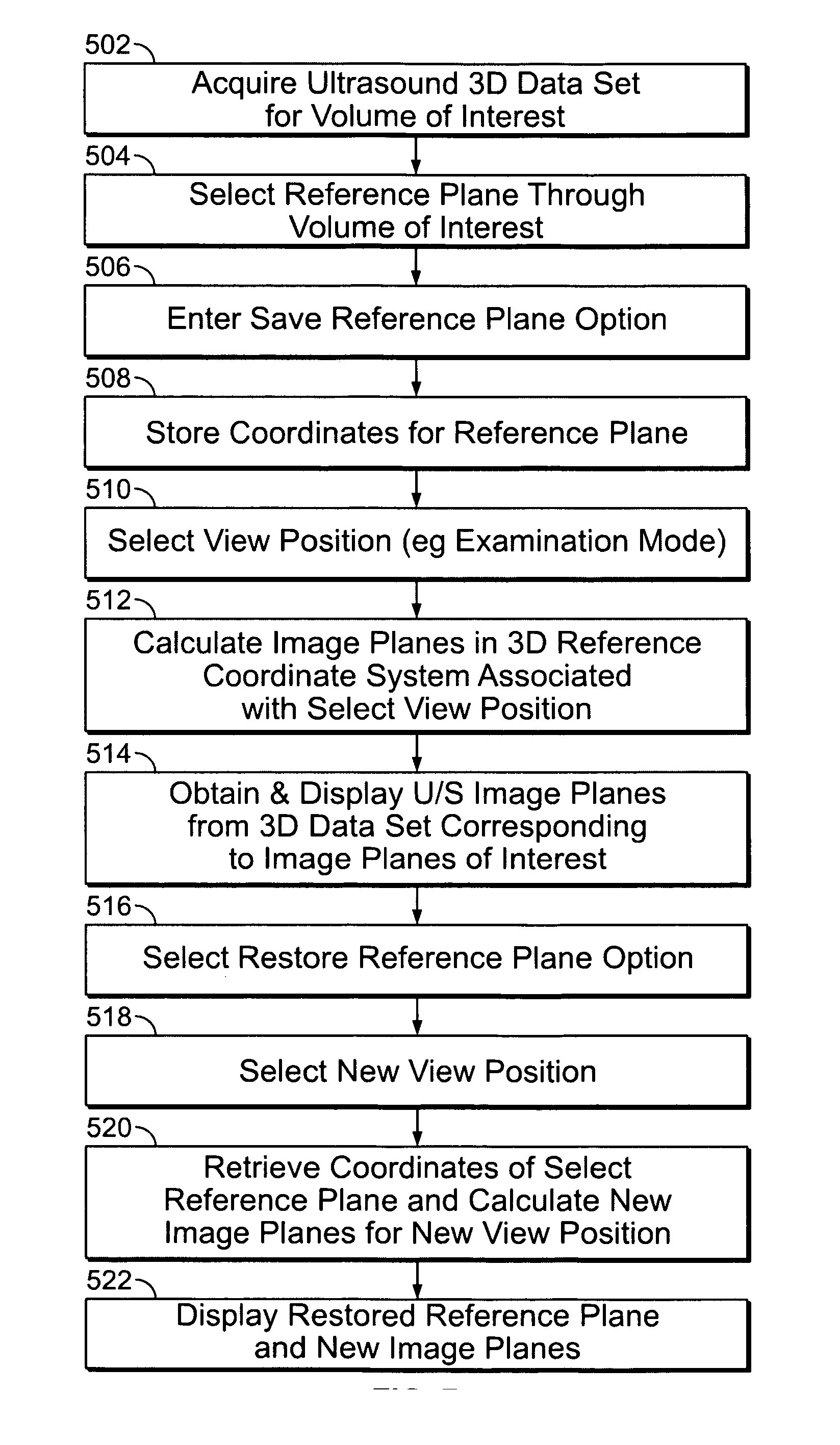
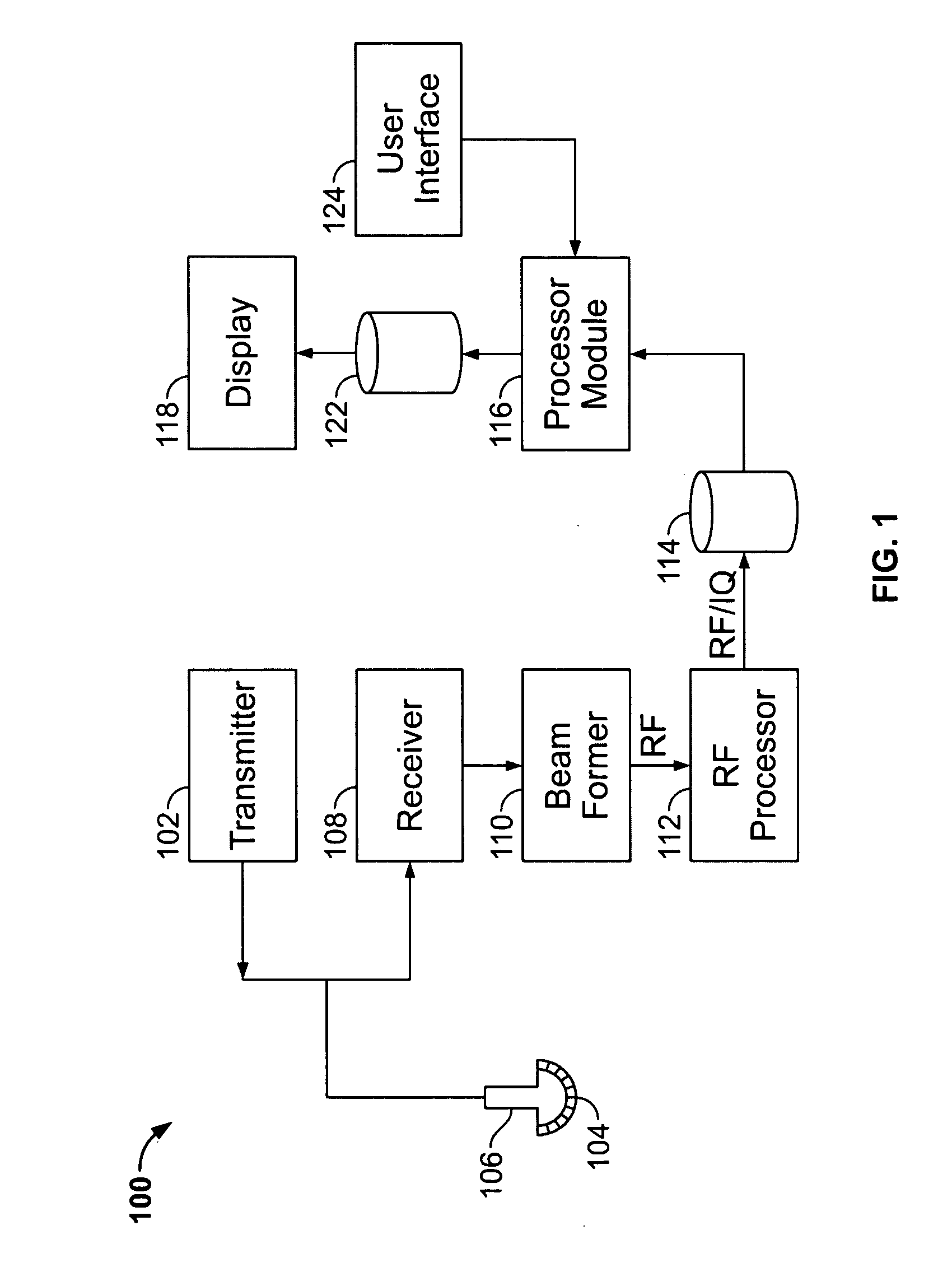
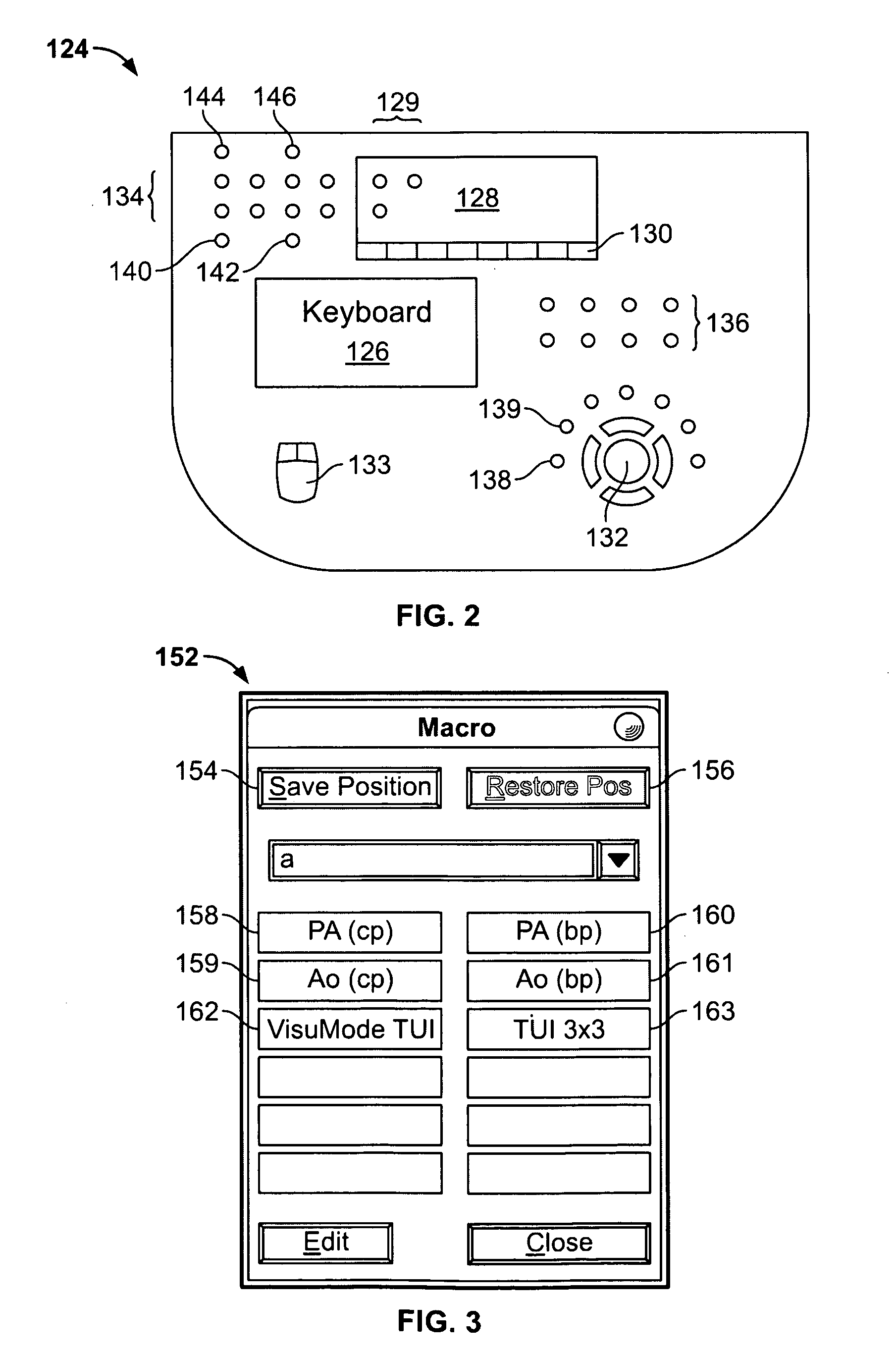
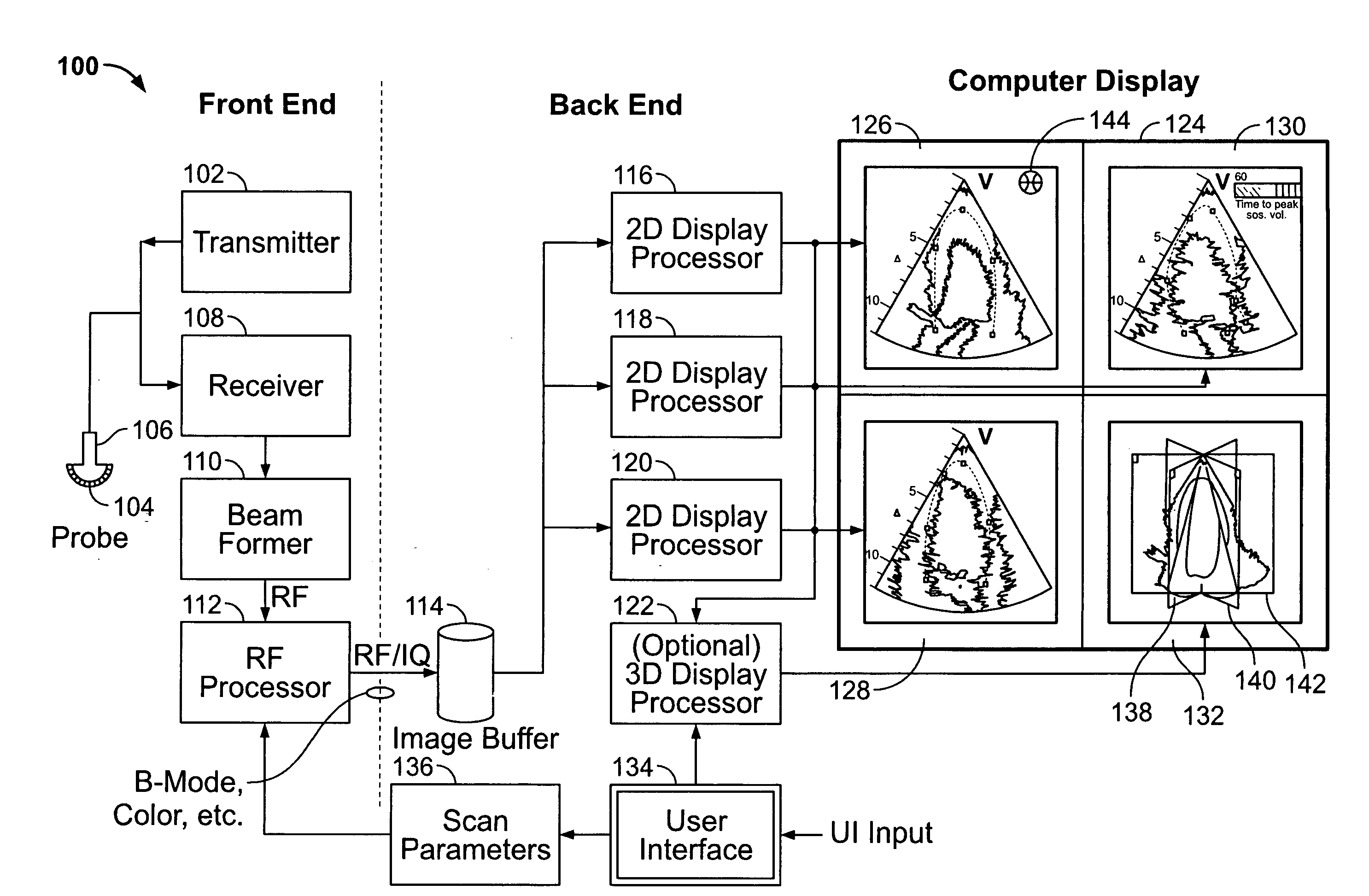
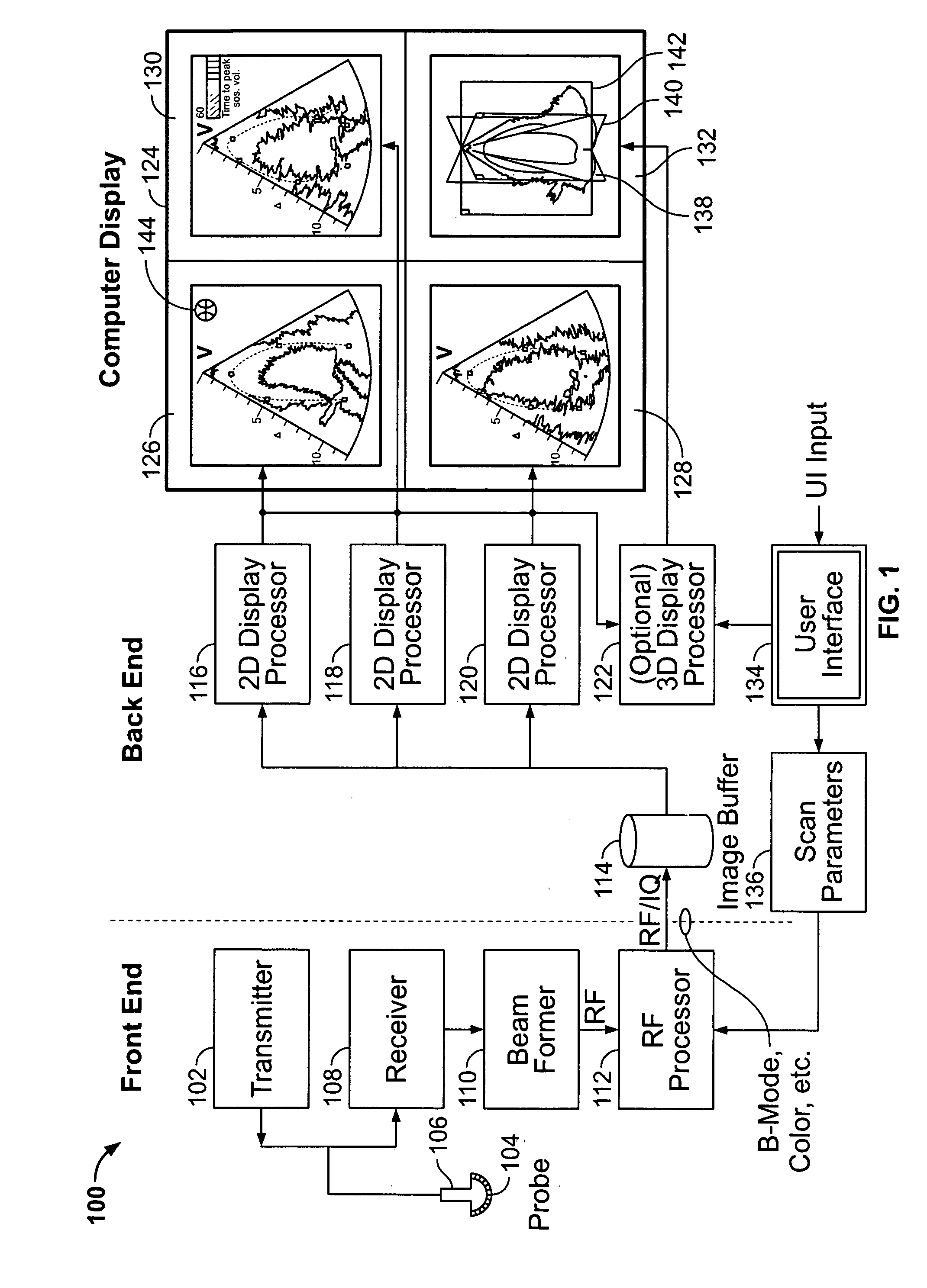
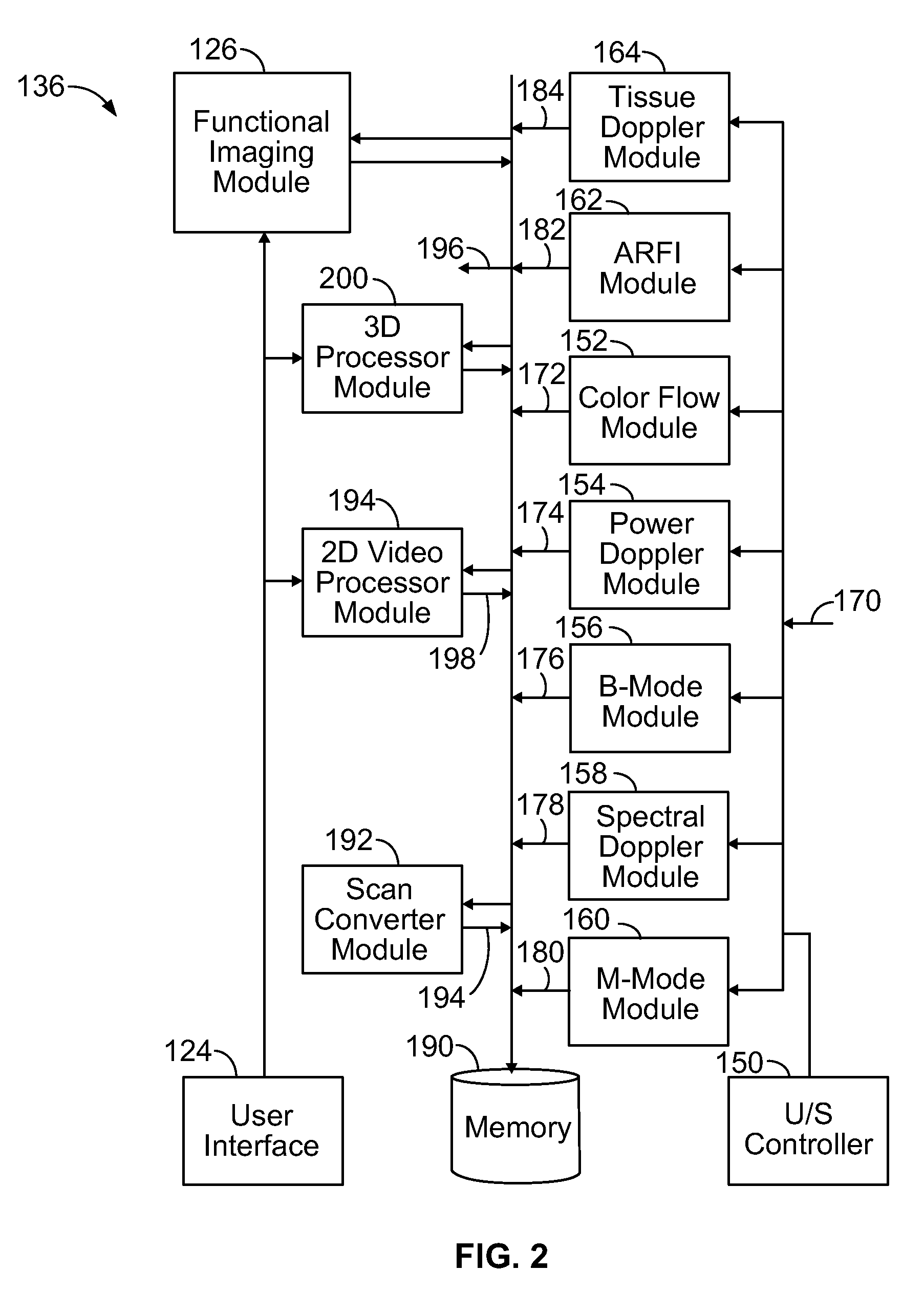
User interface for automatic multi-plane imaging ultrasound system
InactiveUS20070255139A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSonification
A diagnostic ultrasound system is provided for automatically displaying multiple planes from a 3-D ultrasound data set. The system comprises a user interface for designating a reference plane, wherein the user interface provides a safe view position option and a restore reference plane option. A processor module maps the reference plane into a 3D ultrasound data set and automatically calculates image planes based on the reference plane for a current view position and a prior view position. A display is provided to selectively display the image planes associated with the current and prior reference planes. Memory stores the prior reference plane in response to selection of the save reference plane option, while the display switches from display of the current reference plane to restore the prior reference plane in response to selection of the restore reference plane option. Optionally, the memory may store coordinates in connection with the current and prior reference planes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
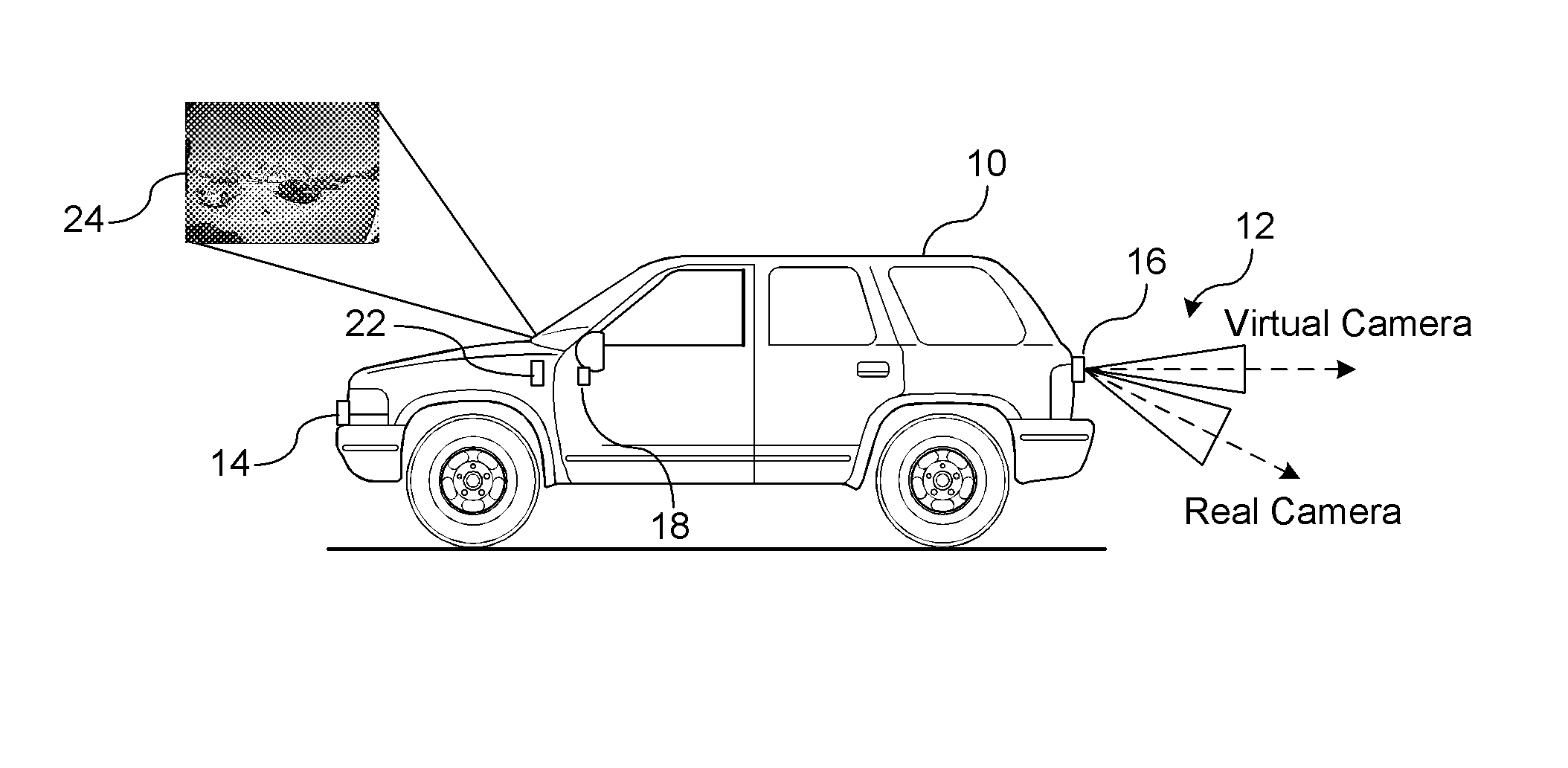
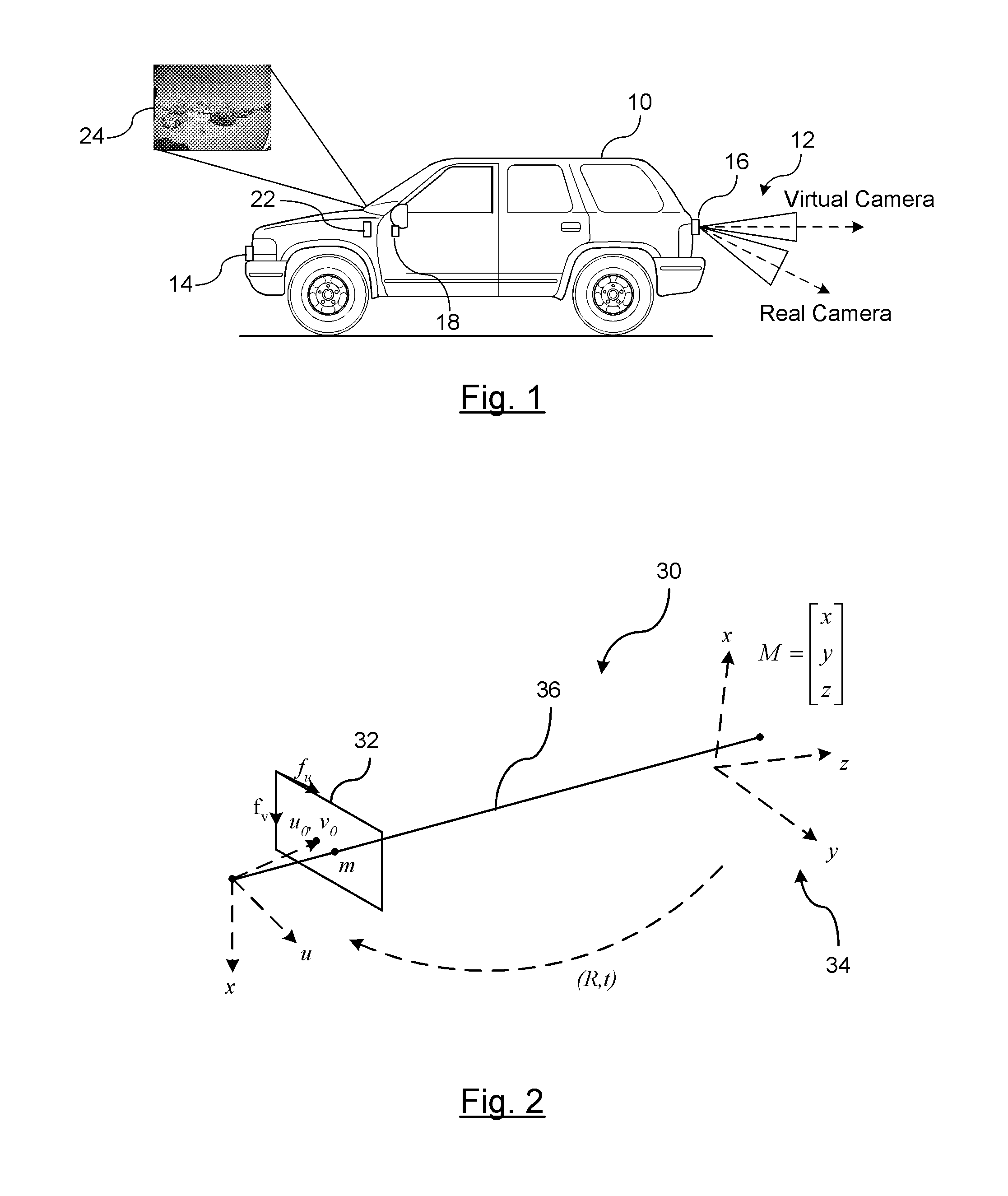
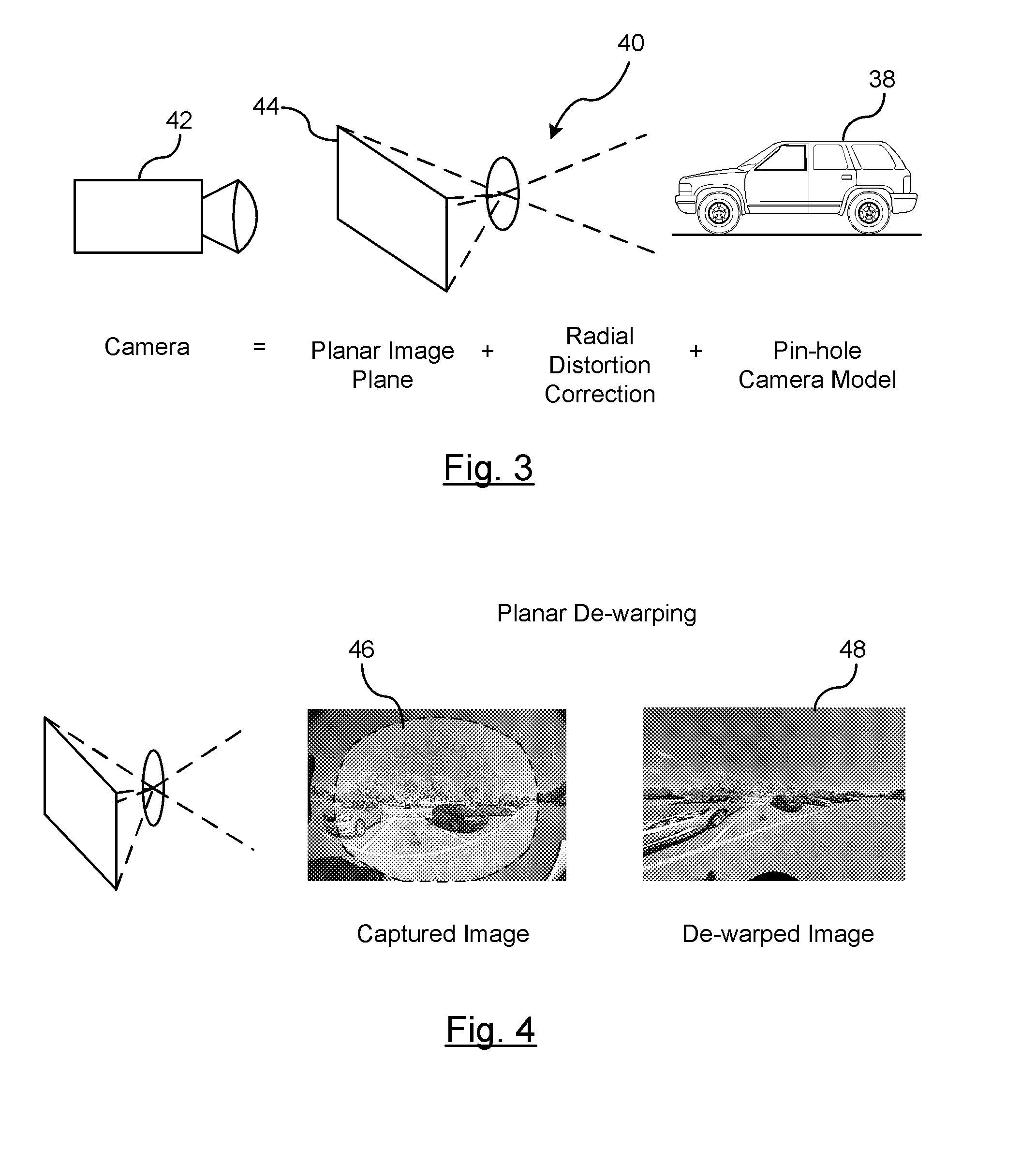
Imaging surface modeling for camera modeling and virtual view synthesis
ActiveUS20140104424A1Enlarge regionEnhances regionImage enhancementImage analysisView synthesisDisplay device
A method for displaying a captured image on a display device. A real image is captured by a vision-based imaging device. A virtual image is generated from the captured real image based on a mapping by a processor. The mapping utilizes a virtual camera model with a non-planar imaging surface. Projecting the virtual image formed on the non-planar image surface of the virtual camera model to the display device.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Sub-diffraction limit image resolution in three dimensions
ActiveUS20110002530A1Character and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsImage resolutionImaging technique
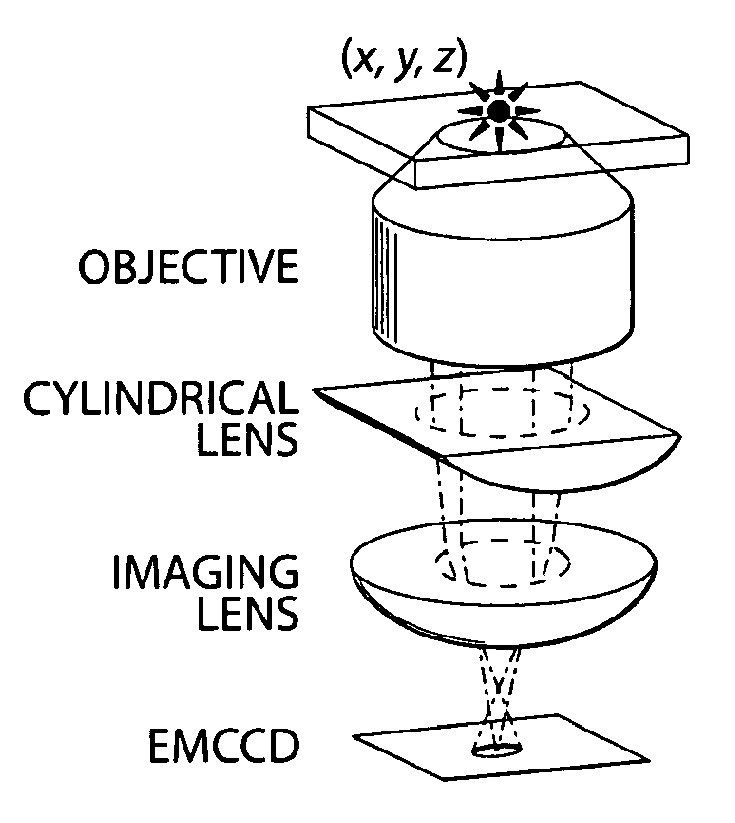
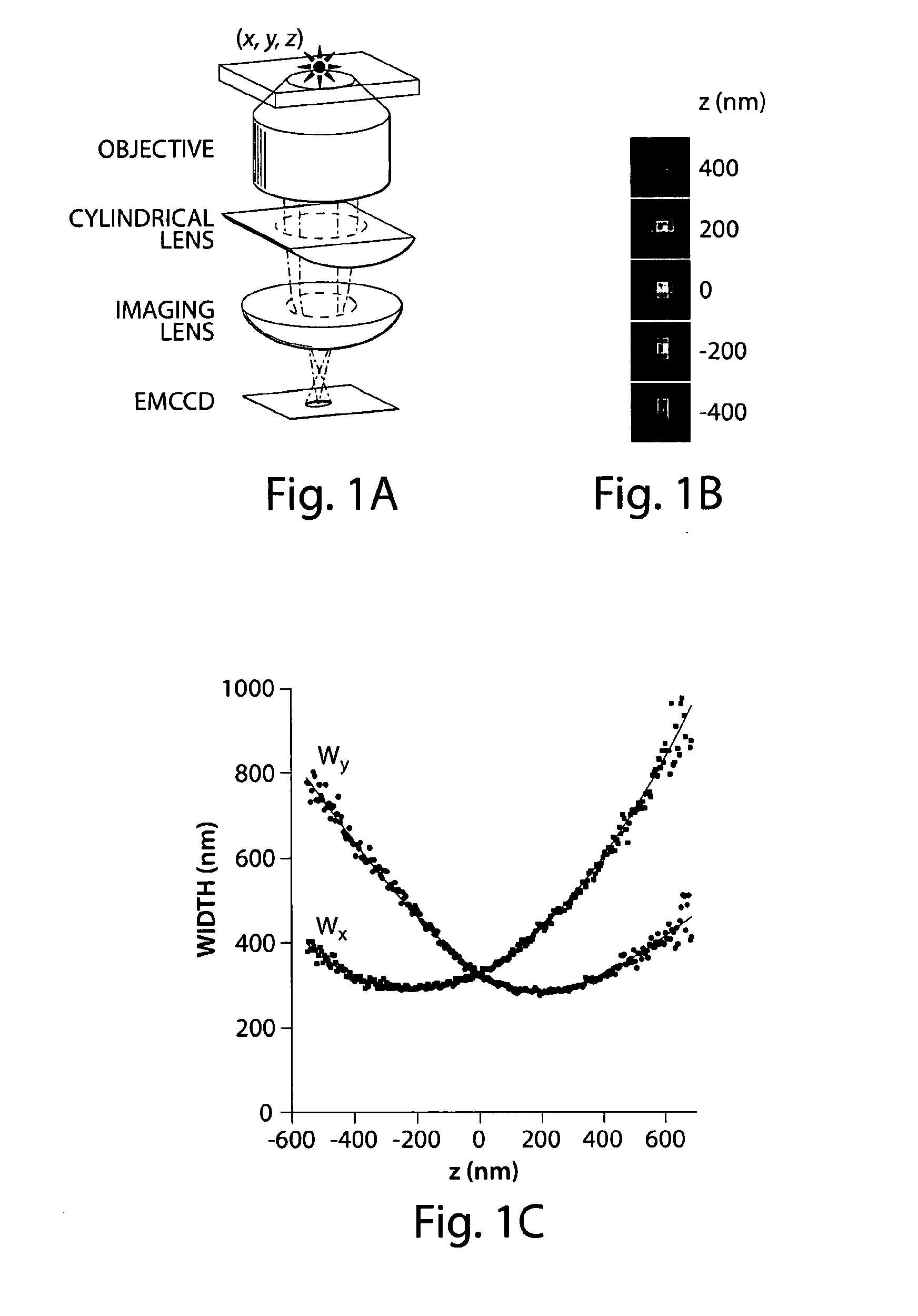
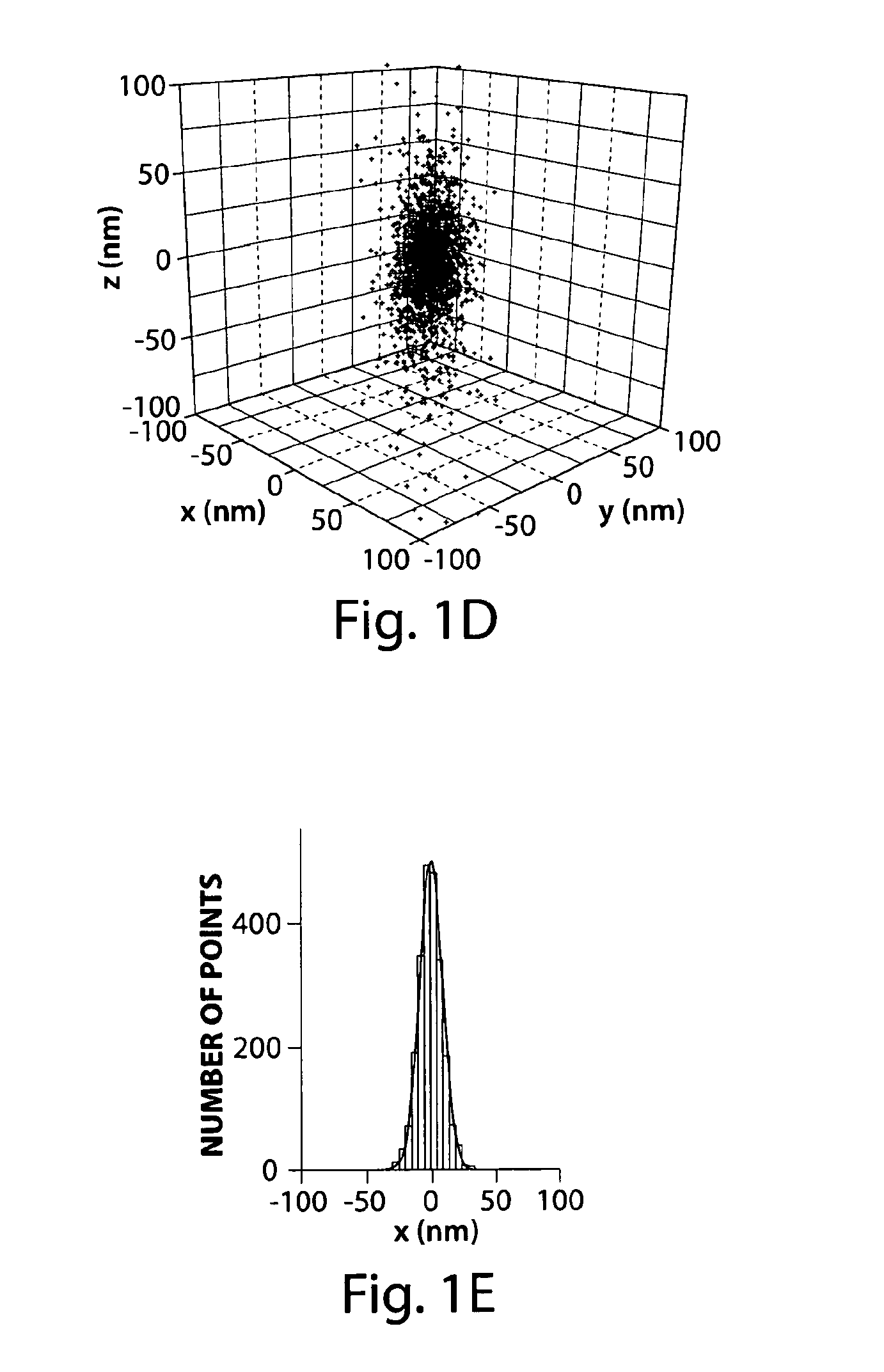
The present invention generally relates to sub-diffraction limit image resolution and other imaging techniques, including imaging in three dimensions. In one aspect, the invention is directed to determining and / or imaging light from two or more entities separated by a distance less than the diffraction limit of the incident light. For example, the entities may be separated by a distance of less than about 1000 nm, or less than about 300 nm for visible light. In some cases, the position of the entities can be determined in all three spatial dimensions (i.e., in the x, y, and z directions), and in certain cases, the positions in all three dimensions can be determined to an accuracy of less than about 1000 nm. In one set of embodiments, the entities may be selectively activatable, i.e., one entity can be activated to produce light, without activating other entities. A first entity may be activated and determined (e.g., by determining light emitted by the entity), then a second entity may be activated and determined. The emitted light may be used to determine the x and y positions of the first and second entities, for example, by determining the positions of the images of these entities, and in some cases, with sub-diffraction limit resolution. In some cases, the z positions may be determined using one of a variety of techniques that uses intensity information or focal information (e.g., a lack of focus) to determine the z position. Non-limiting examples of such techniques include astigmatism imaging, off-focus imaging, or multi-focal-plane imaging.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
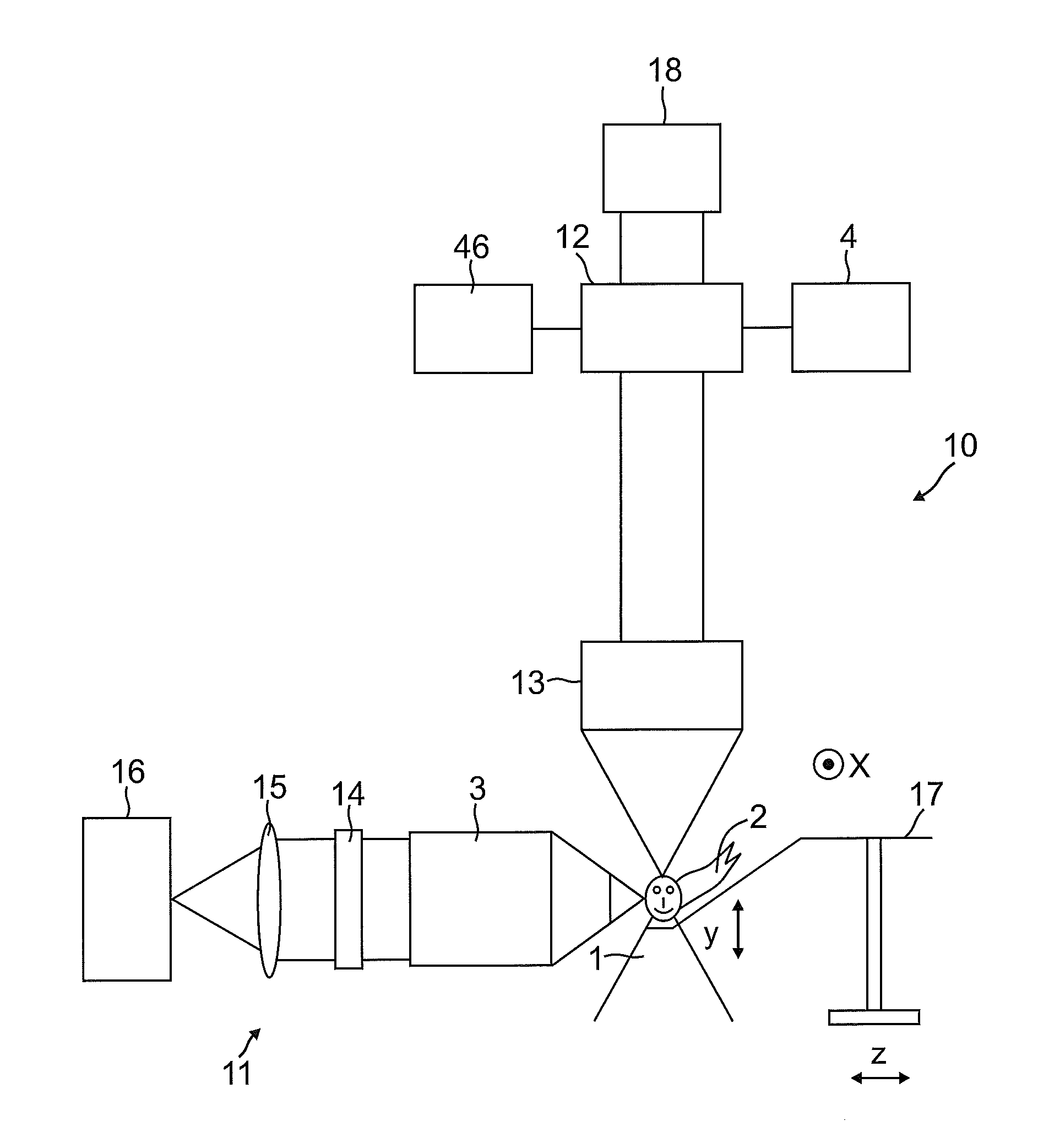
Spim microscope with a sted light sheet
ActiveUS20120098949A1Increase flexibilityMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLight beamOptoelectronics
A STED-SPIM-microscope (Selective Plane Imaging Microscopy) having a y-direction illumination light source and a z-direction detection light camera. An x-scanner generates a sequential light sheet by scanning the illumination light beam in the x-direction. By optionally turning on a STED deactivation light beam the light sheet can optionally be made thinner and therefore the optical resolution can be increased.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Illumination apparatus and methods
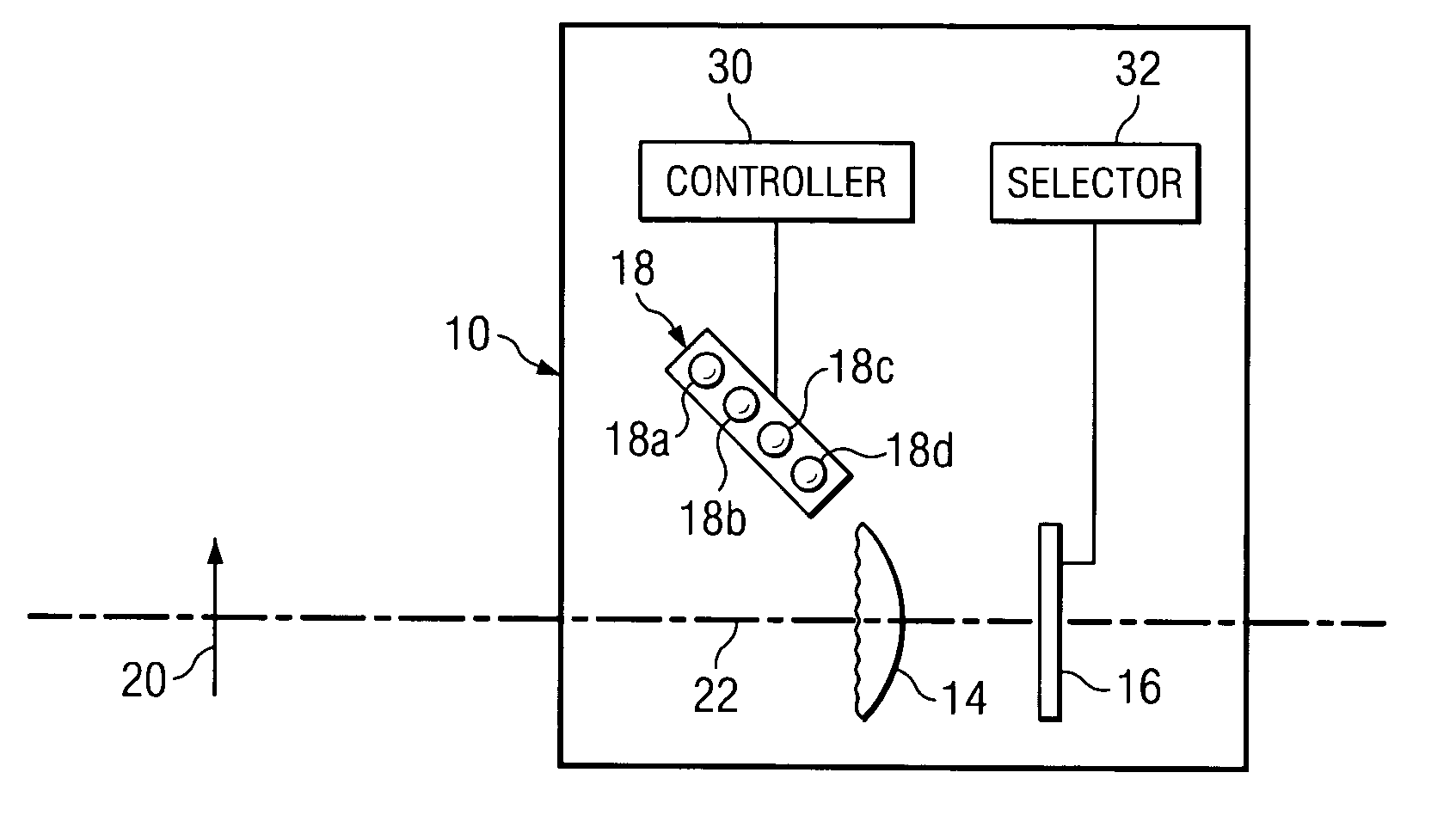
ActiveUS20050141810A1Reduce speckle noiseRemove speckle noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansVisible signalling systemsLight equipmentWafering
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for illuminating a sample, e.g., during an inspection of such sample for defects. In one aspect, the illumination apparatus includes a bundle of fibers that each have a first end and a second end. The illumination apparatus further includes an illumination selector for selectively transmitting one or more incident beams into one or more corresponding first ends of the optical fibers so that the selected one or more incident beams are output from one or more corresponding second ends of the fibers. The illumination apparatus also includes a lens arrangement for receiving the selected one or more incidents beams output from the corresponding one or more second ends of the fibers and directing the selected one or more incident beams towards the sample. The lens arrangement and the fibers are arranged with respect to each other so as to image an imaging plane of the sample at the second ends of the fibers. In one aspect, the incident beams are laser beams. In a specific application of the invention, the sample is selected from a group consisting of a semiconductor device, a semiconductor wafer, and a semiconductor reticle.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
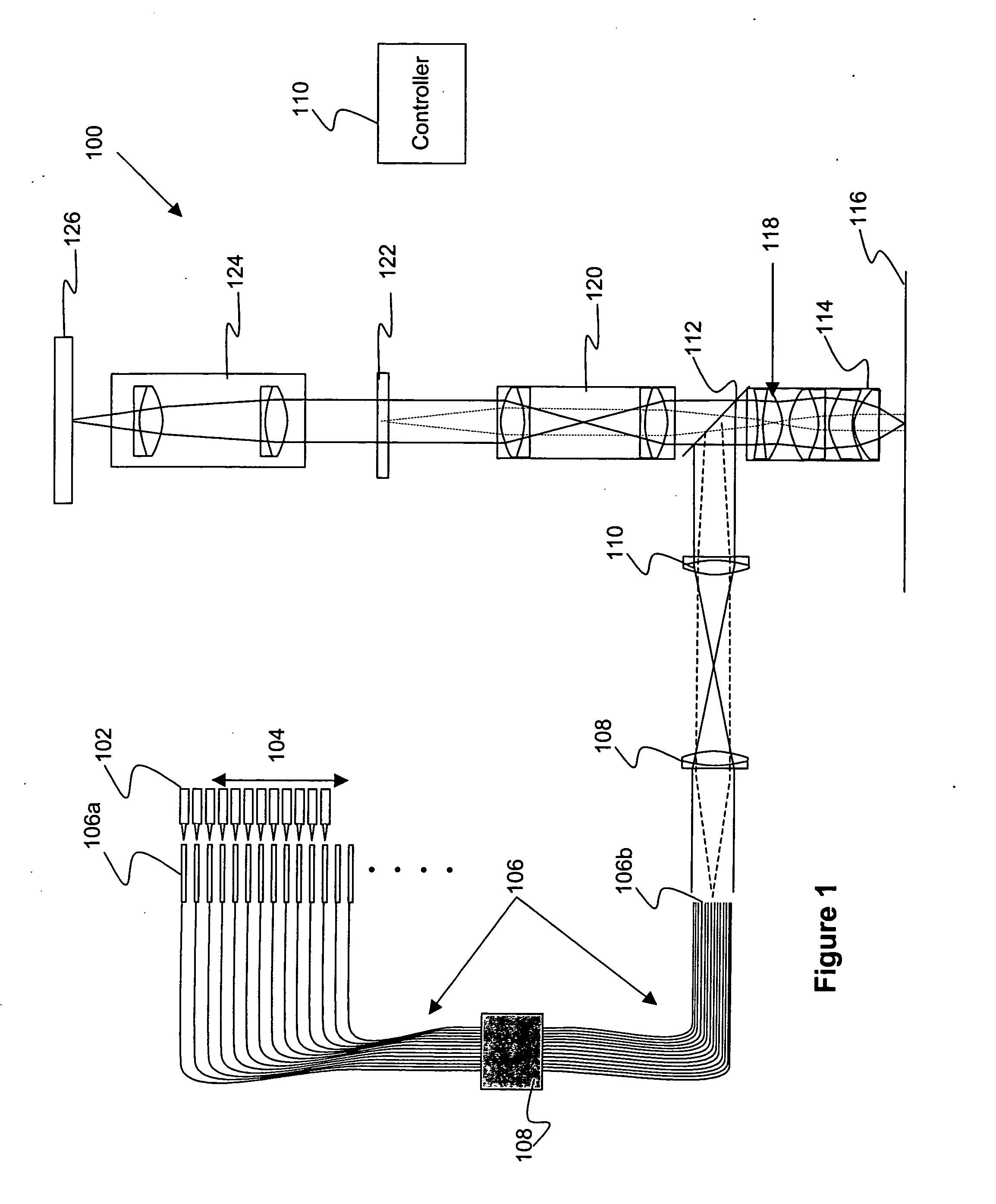
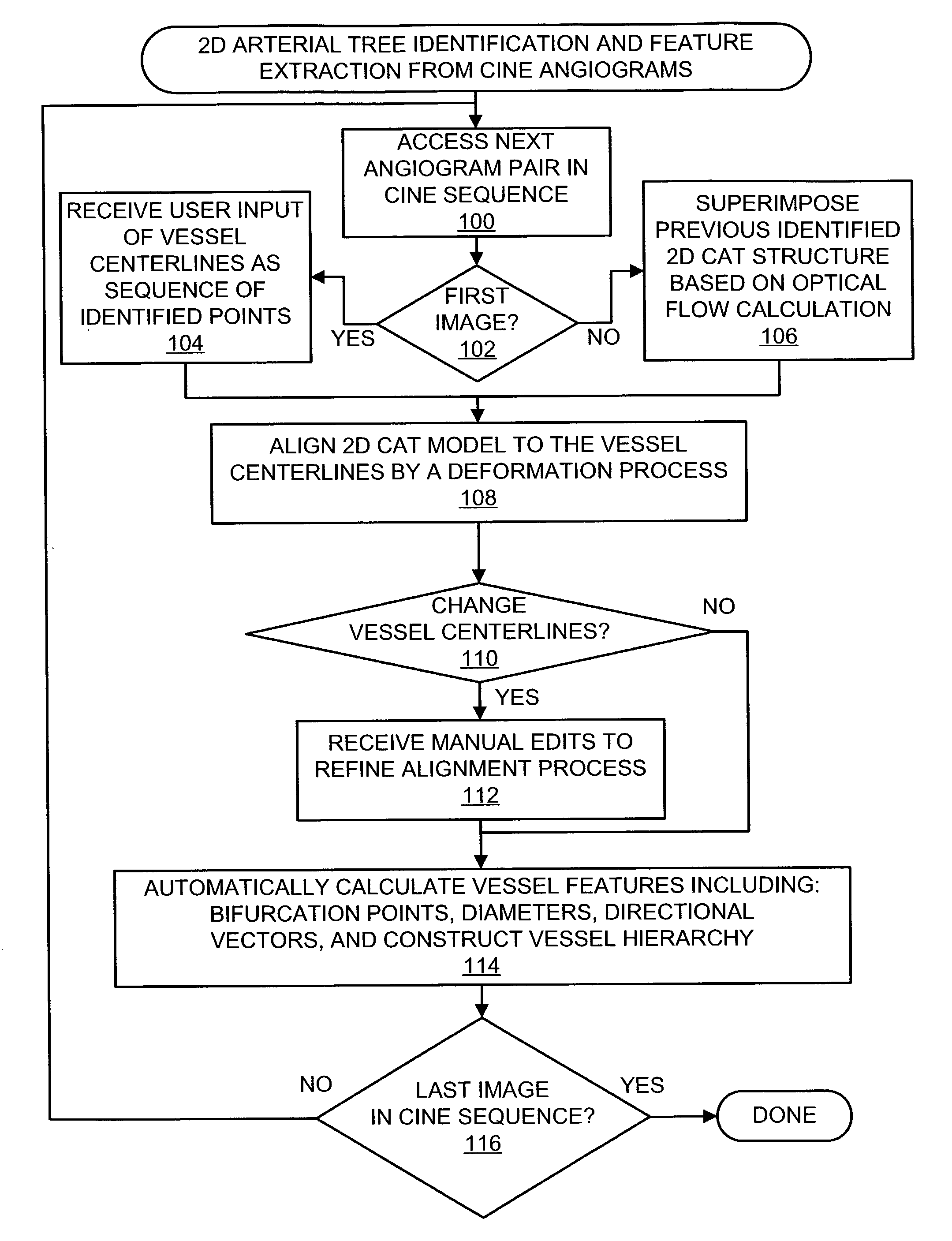
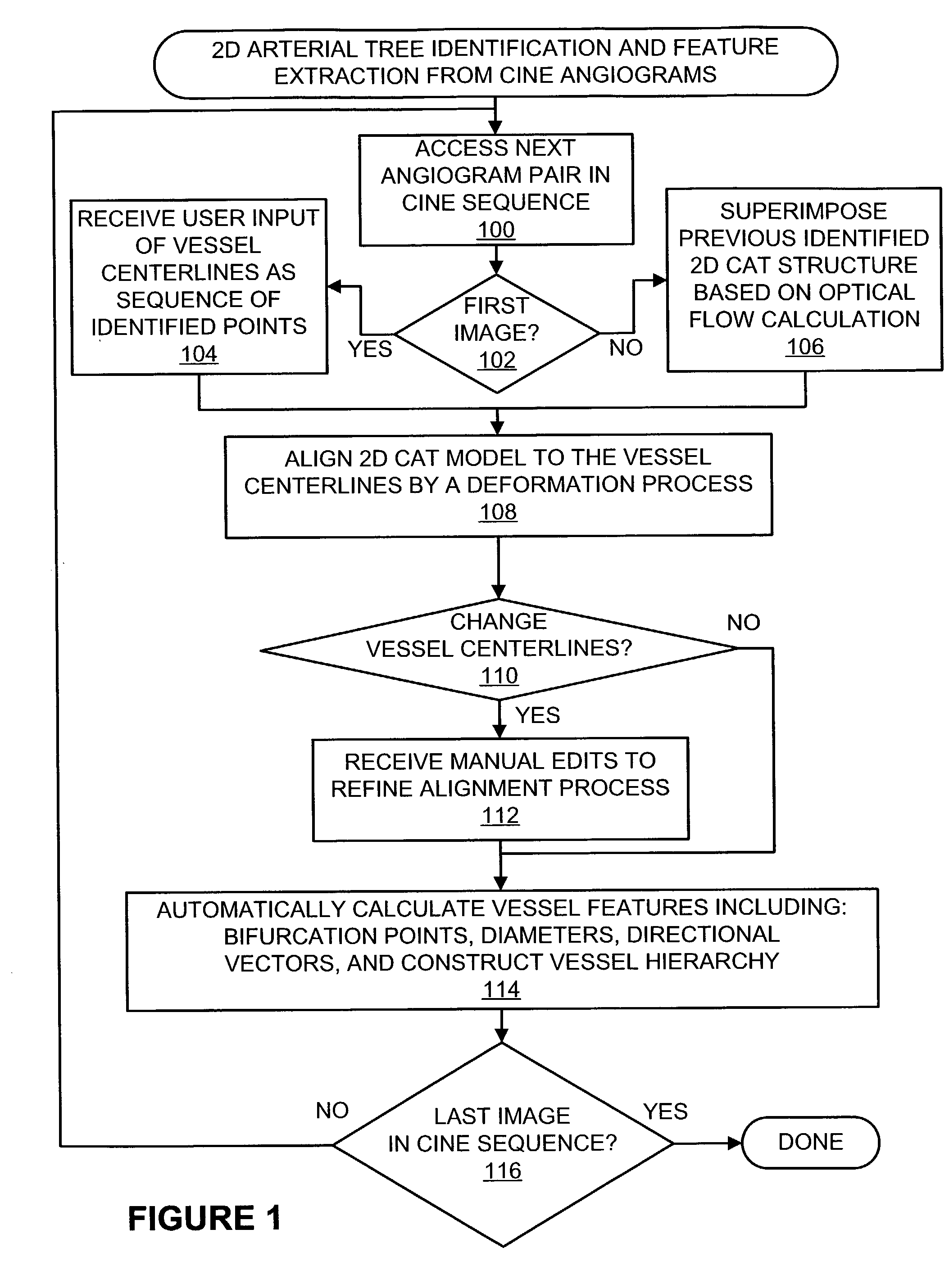
Methods and systems for display and analysis of moving arterial tree structures
ActiveUS7113623B2Improve patient outcomesImprove patient safetyImage enhancementImage analysisKinematicsCardiac cycle
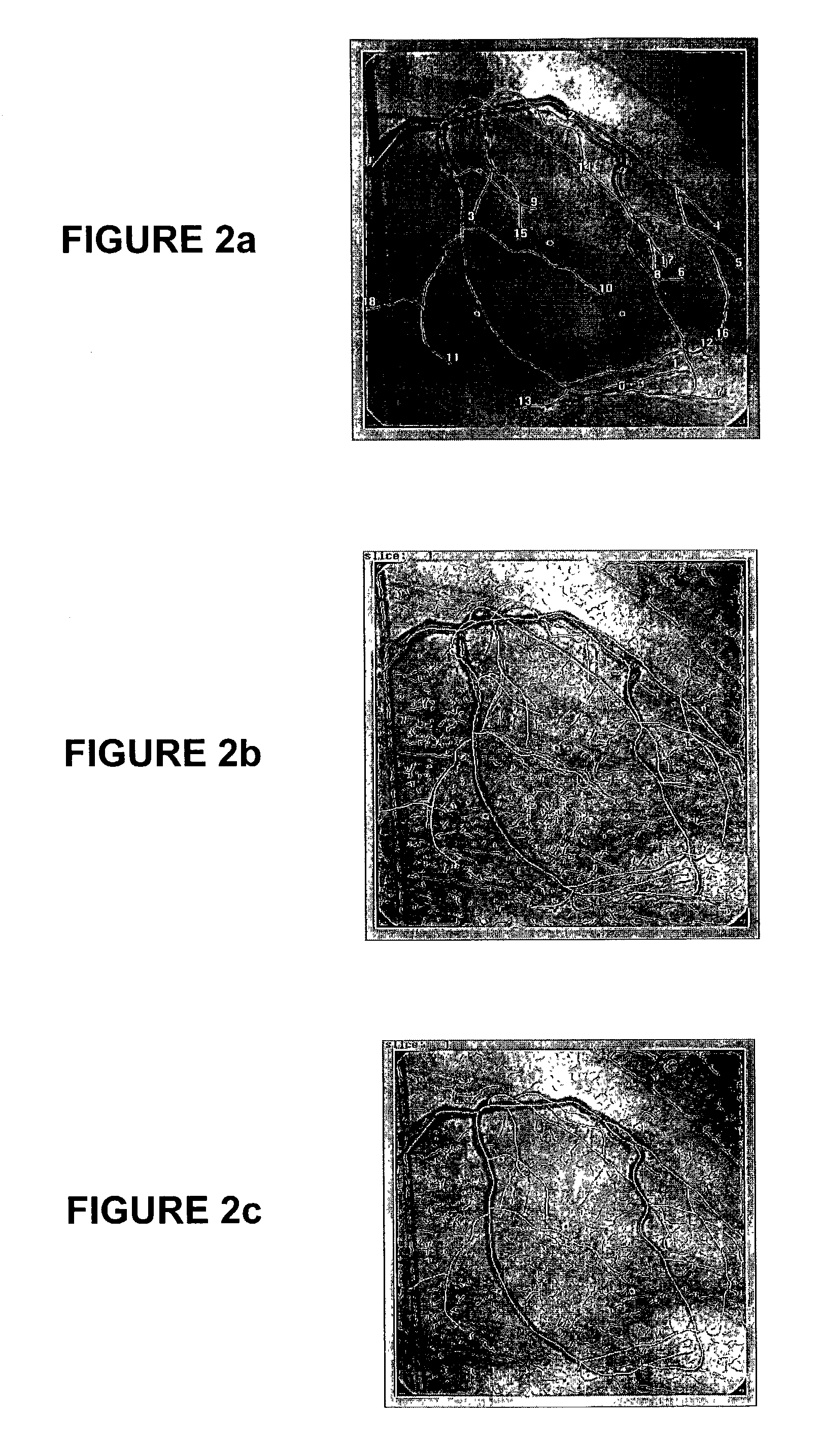
Methods and systems for reconstruction of a three-dimensional representation of a moving arterial tree structure from a pair of sequences of time varying two-dimensional images thereof and for analysis of the reconstructed representation. In one aspect of the invention, a pair of time varying arteriographic image sequences are used to reconstruct a three-dimensional representation of the vascular tree structure as it moves through a cardiac cycle. The arteriographic image sequences maybe obtained from a biplane imaging system or from two sequences of images using a single plane imaging system. Another aspect of the invention then applies analysis methods and systems utilizing the three-dimensional representation to analyze various kinematic and deformation measures of the moving vascular structure. Analysis results may be presented to the user using color coded indicia to identify various kinematic and deformation measures of the vascular tree.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS9123614B2Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectAcoustic sensorsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionEngineering
System, devices and methods are presented that provide an imaging array fabrication process method, comprising fabricating an array of semiconductor imaging elements, interconnecting the elements with stretchable interconnections, and transfer printing the array with a pre-strained elastomeric stamp to a secondary non-planar surface.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
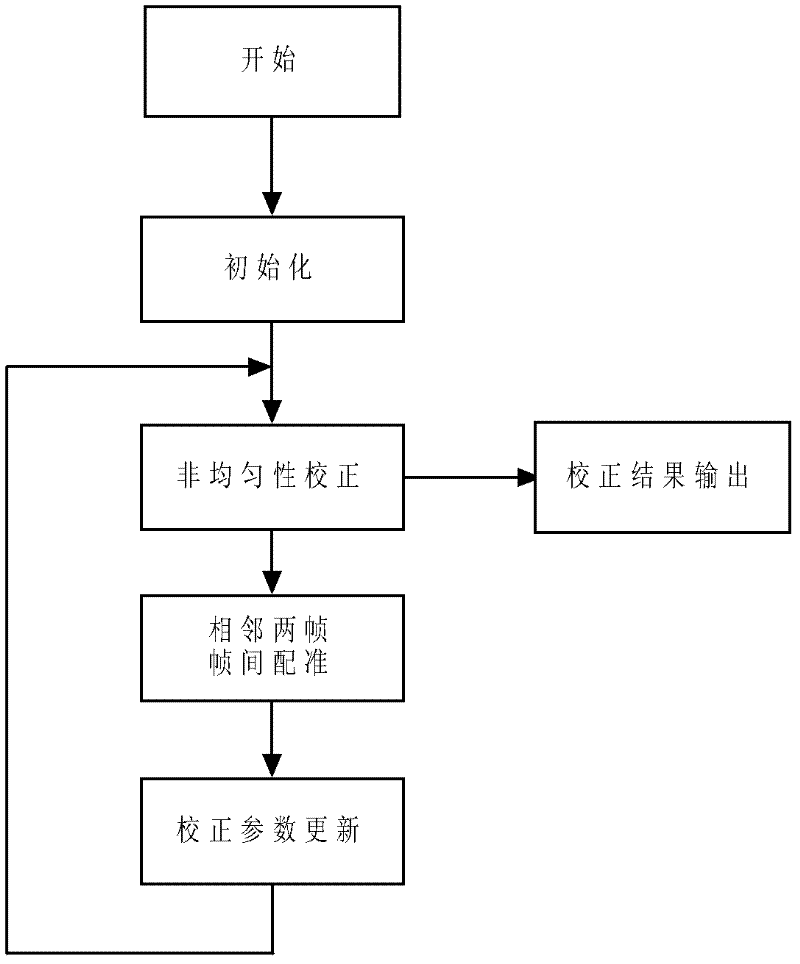
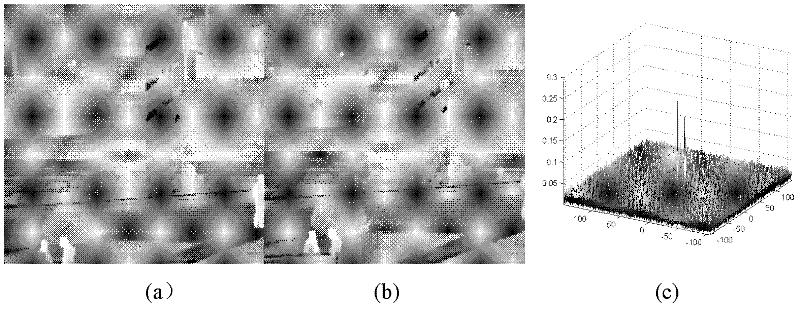
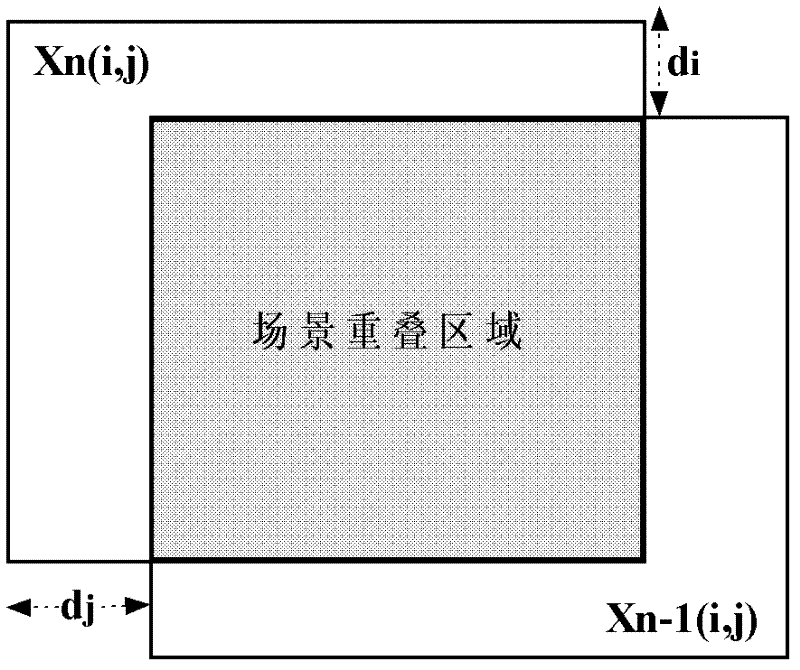
Rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method
InactiveCN102538973APrevent erroneous updatesBug update avoidanceRadiation pyrometryPhase correlationSteep descent
The invention discloses a rapidly converged scene-based non-uniformity correction method, wherein the aim of non-uniformity correction is achieved by minimizing interframe registration error of two adjacent images. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: initializing gain and offset correction parameters and acquiring an uncorrected original image; acquiring a new uncorrected original image, and carrying out non-uniformity correction on the new uncorrected original image and the previous uncorrected original image by utilizing the current non-uniformity correction parameters; obtaining relative displacement, scene correlation coefficient and interframe registration error of two corrected images by utilizing an original point masking phase correlation method; and updating correction parameters along the negative gradient direction by adopting a steepest descent method. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high correction accuracy, fast convergence speed, no ghost effect and low calculated amount and storage content and is especially applicable to being integrated into an infrared focal plane imaging system, and the effect of improving imaging quality, environmental suitability and time stability of an infrared focal plane array is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
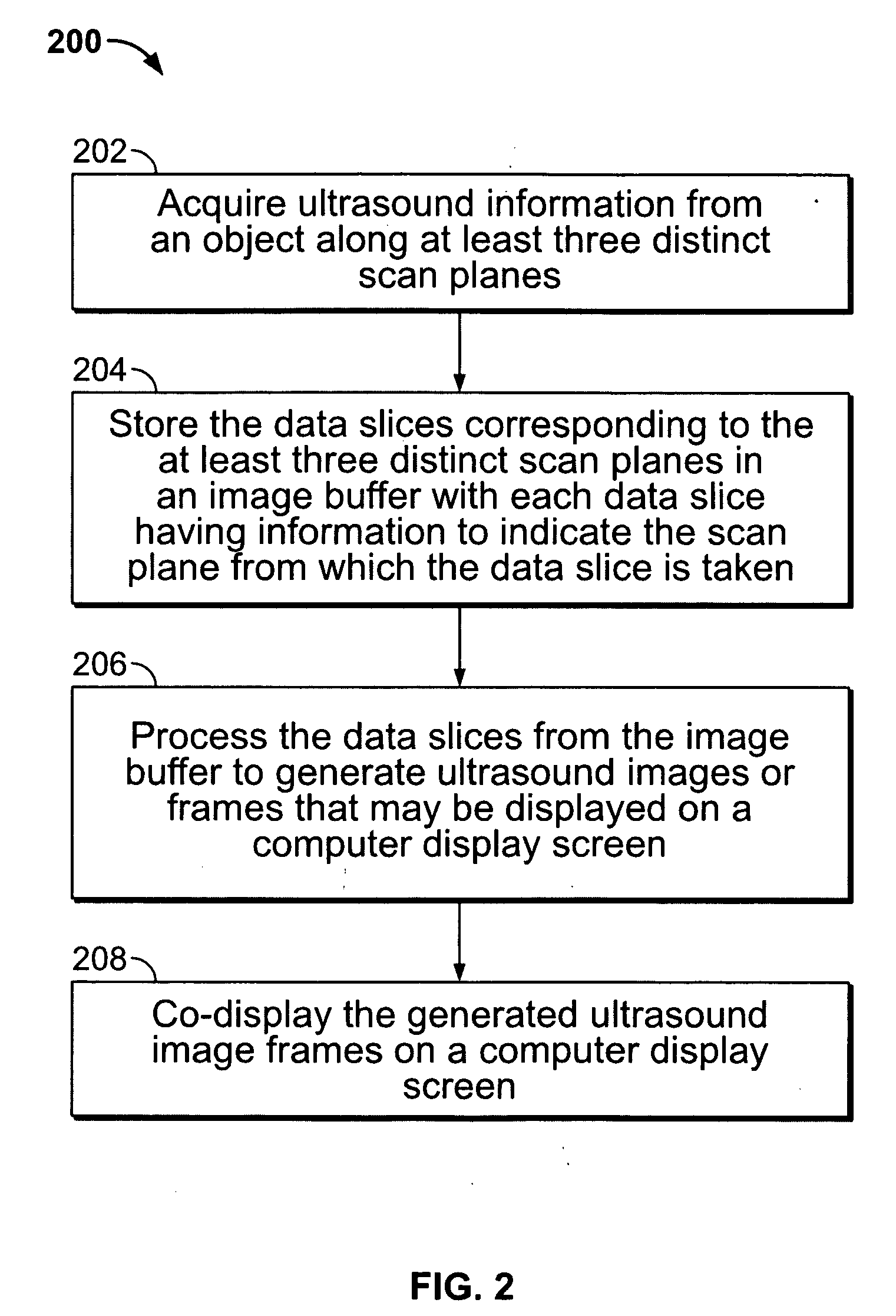
Method and apparatus for real time ultrasound multi-plane imaging
ActiveUS20050283078A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationDisplay device
An ultrasound system is provided that includes a probe for successively acquiring ultrasound information from an object along at least three distinct scan planes. The scan planes intersect one another along an axis extending from the probe through the object. A memory is included for storing data slices corresponding to the at least three distinct scan planes based on the ultrasound information. Also included is a processor that accesses the memory to select and obtain the data slices and generates ultrasound images based on the data slices. A display is included for co-displaying the ultrasound images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and applications of non-planar imaging arrays
ActiveUS20160027834A1Low costLess reflection and diffraction defectSolid-state devicesAcoustic sensorsInterconnectionEngineering
System, devices and methods are presented that provide an imaging array fabrication process method, comprising fabricating an array of semiconductor imaging elements, interconnecting the elements with stretchable interconnections, and transfer printing the array with a pre-strained elastomeric stamp to a secondary non-planar surface.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
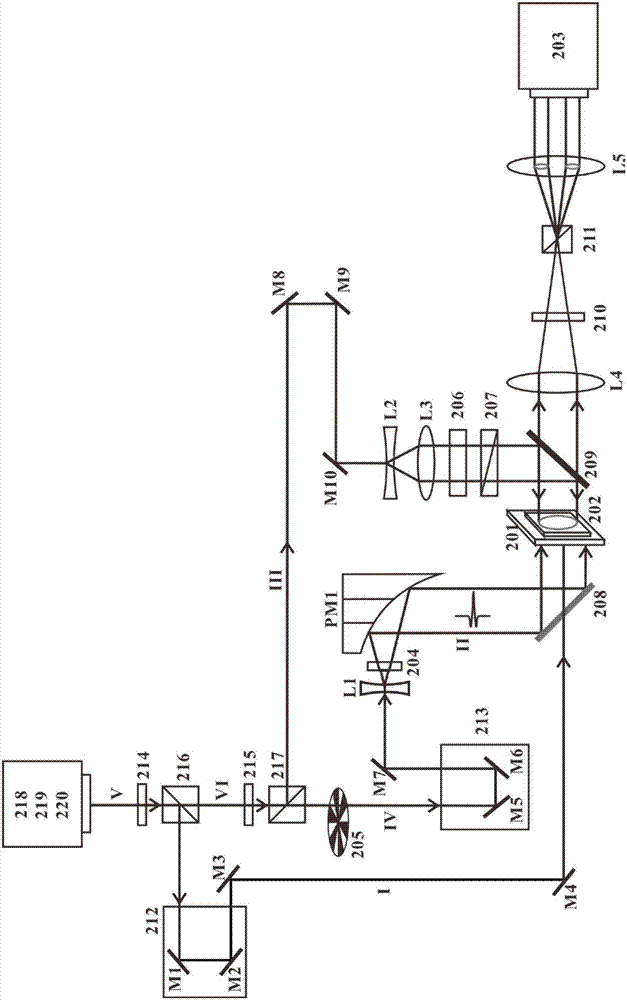
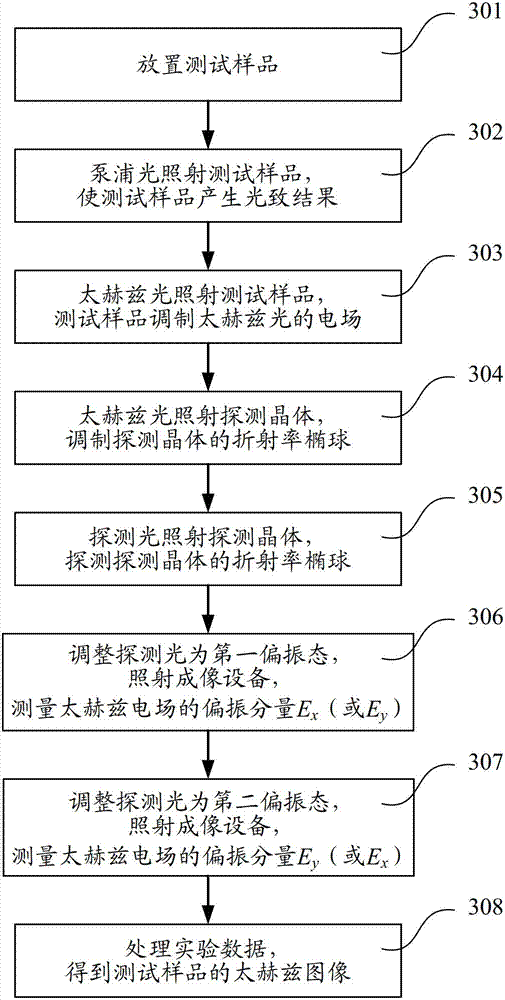
Terahertz time-space resolution imaging system, imaging method and application thereof
The invention relates to a terahertz time-space resolution imaging system. The system comprises a sample placing frame, a detection crystal, a pump light generator, a terahertz light generator, a detection light generator and an imaging device, wherein the detection crystal is located at one side of an exit surface of the sample placing frame; the pump light generator is used for generating a pump light to illuminate a test sample; the terahertz light generator is used for generating a terahertz light to illuminate the test sample, illuminating the detection crystal after acquiring information of the test sample and modulating an index ellipsoid of the detection crystal; the detection light generator is used for generating a detection light to illuminate the detection crystal, detecting the index ellipsoid of the detection crystal and indirectly acquiring the information of the test sample; and the imaging device is located into a light path after the detection light passes through the detection crystal and is used for collecting a terahertz image of the test sample. According to the terahertz time-space resolution imaging system, a terahertz focal plane imaging technique is introduced into a terahertz time resolution spectral measurement system, the time-space resolution imaging measurement on a luminescent property of the test sample is realized, the four-dimensional spectral information is acquired, and the comprehensive and accurate observation on a time-space evolution process of the luminescent property of the test sample is realized.
Owner:BEIJING YUANDA HENGTONG TECH DEV CO LTD
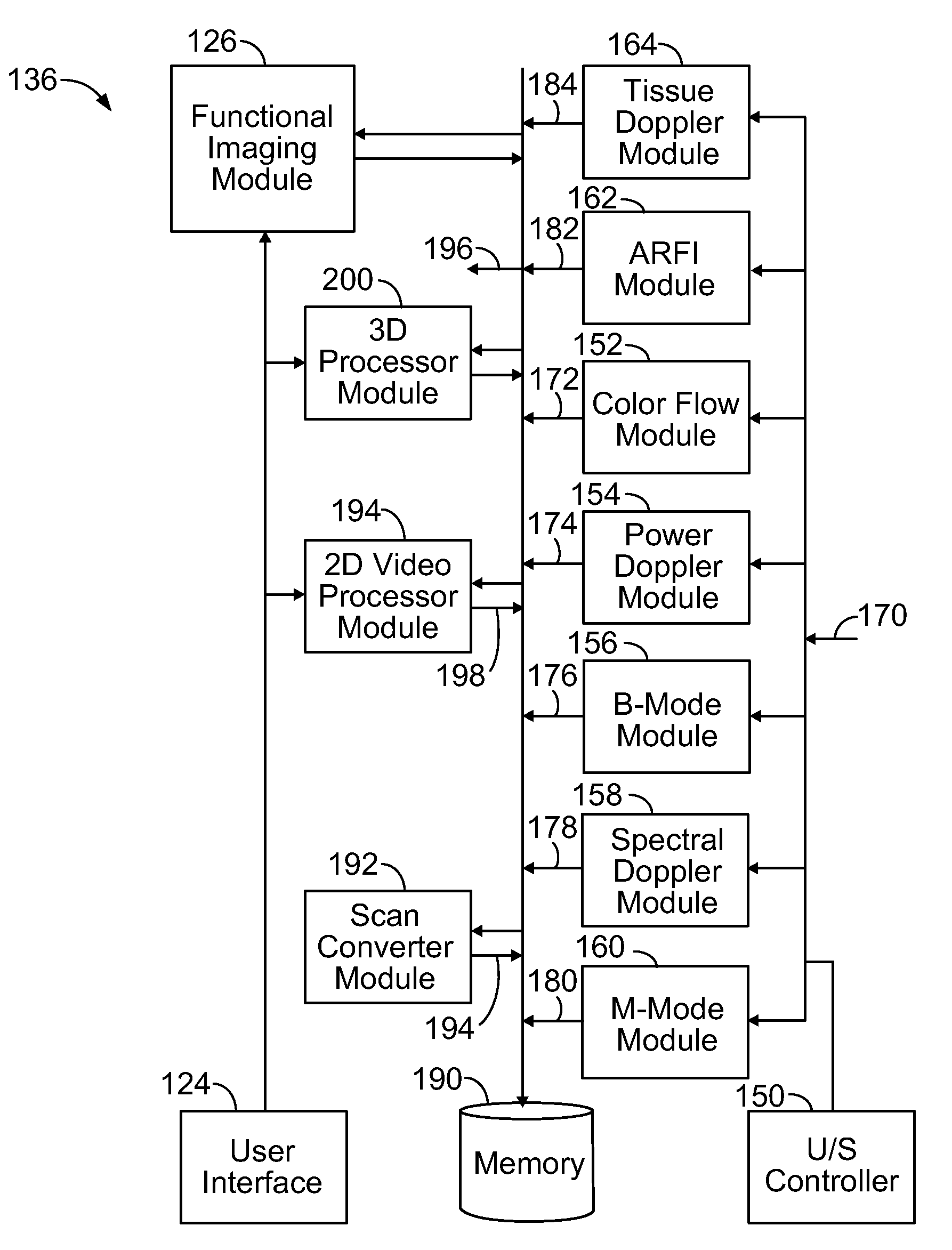
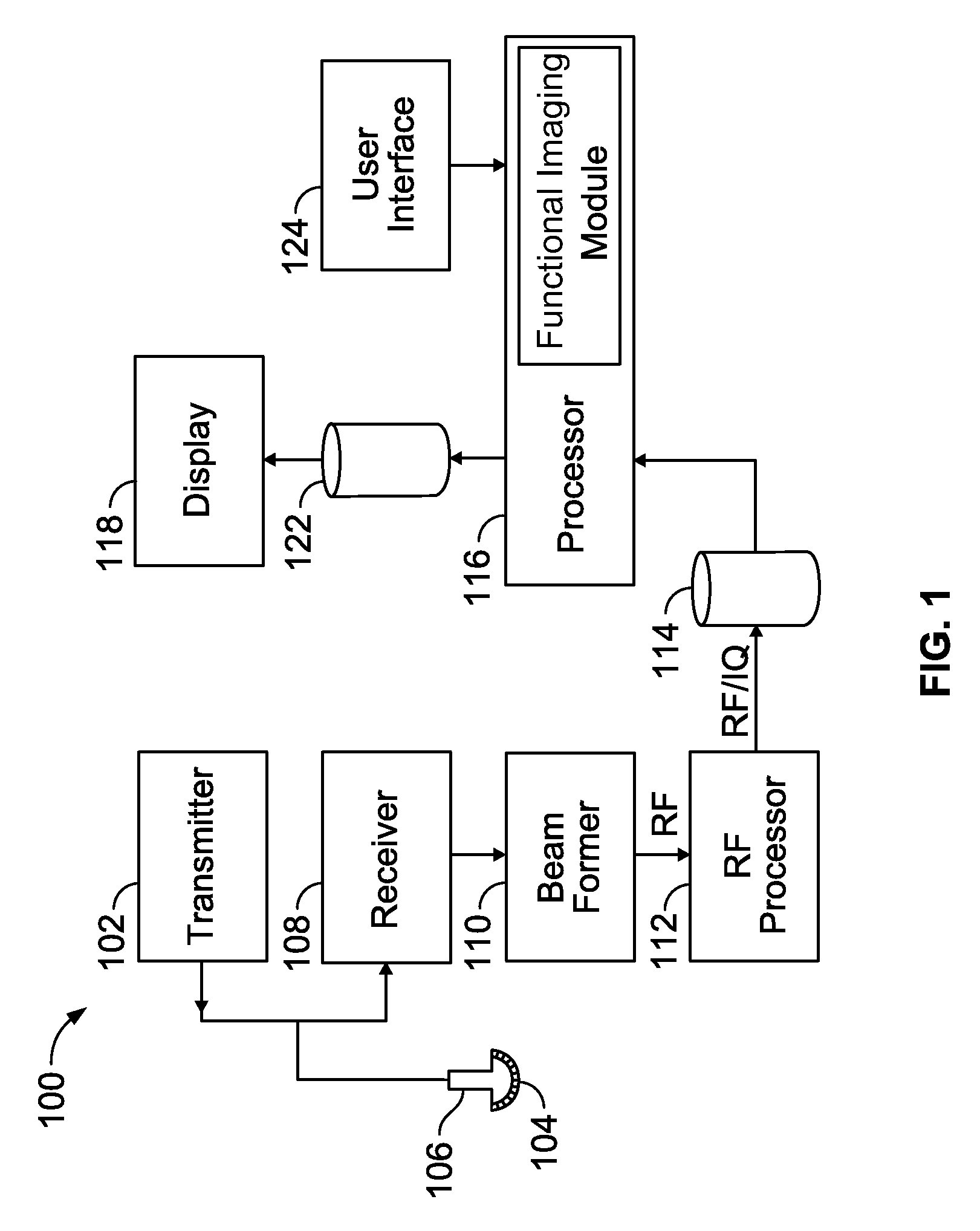
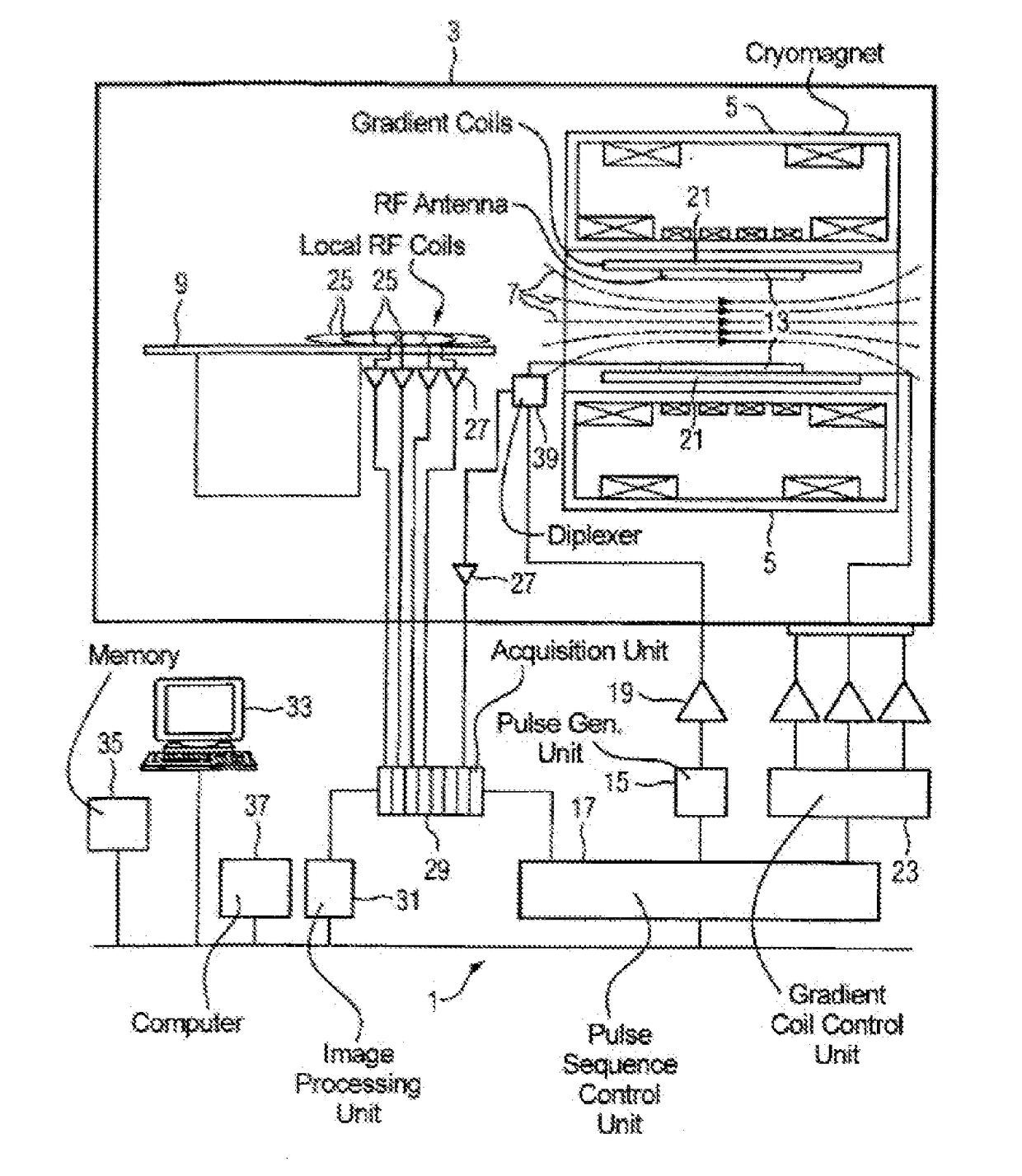
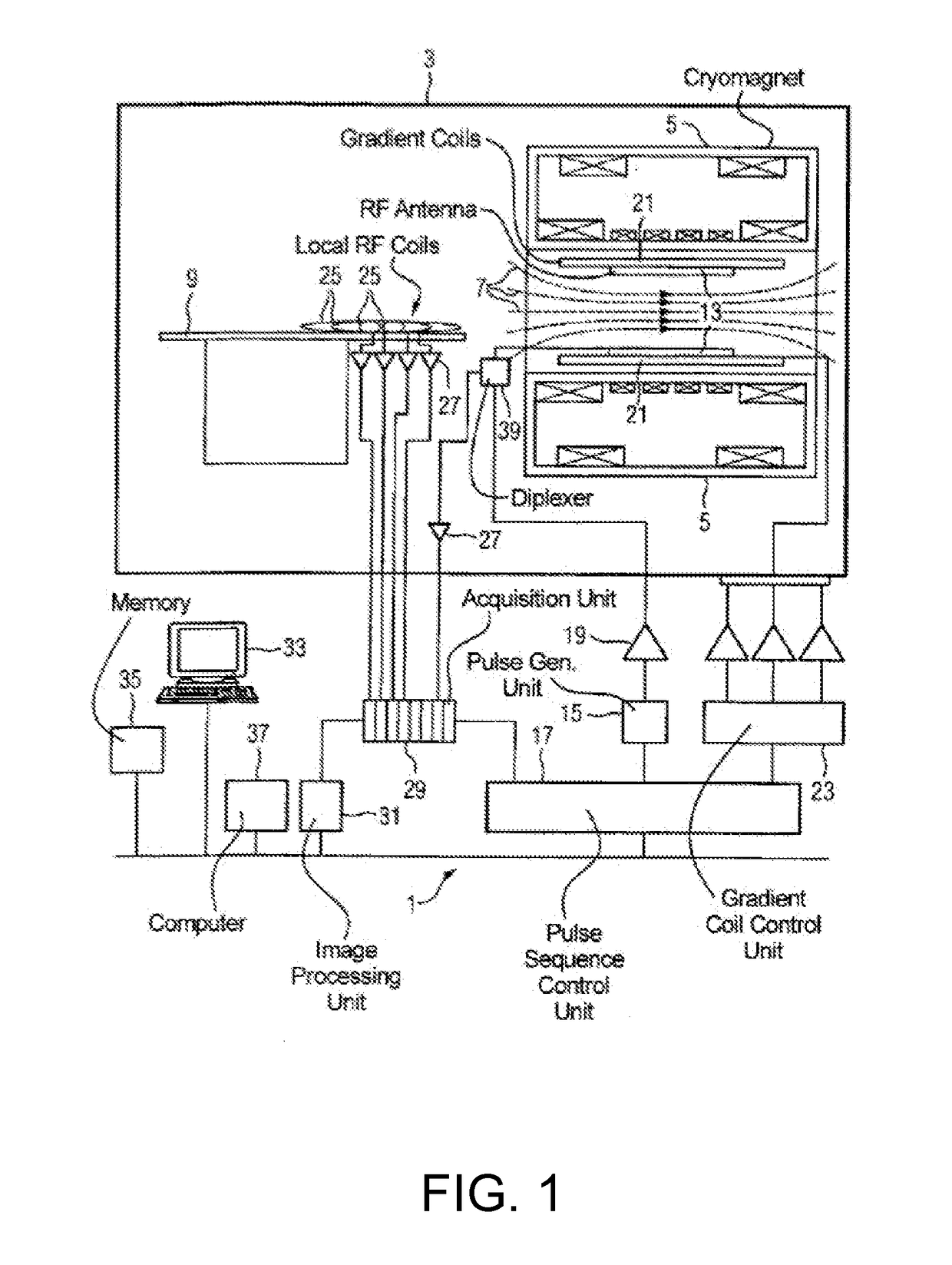
System and methods for improved real time functional magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9116219B1Suppress physiological noiseWiden meansMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionBlood oxygenation level dependentParallel imaging
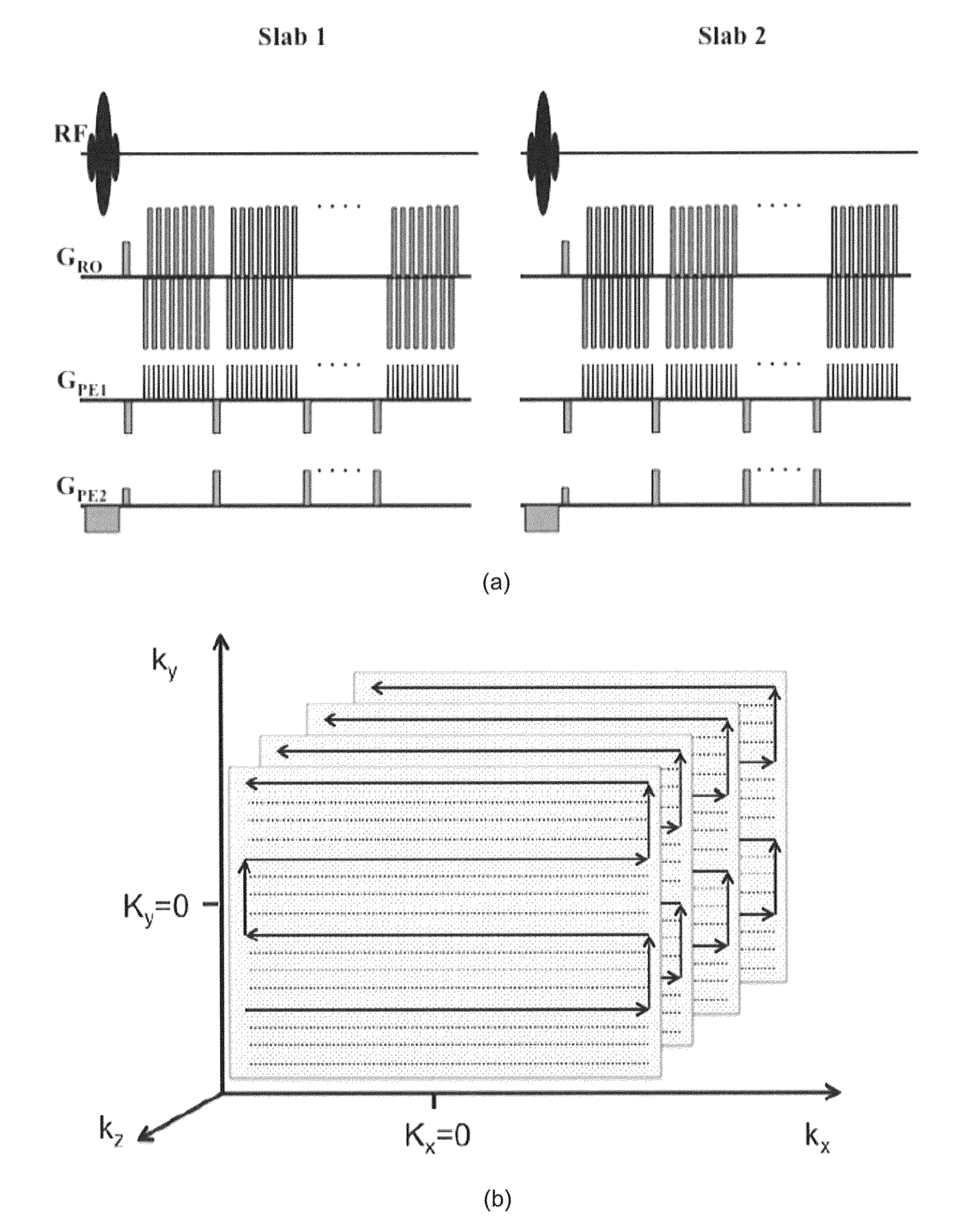
A system and methods for high-speed functional magnetic resonance imaging using multi-slab echo-volumar imaging (EVI), specifically a combination of multi-slab excitation and single-shot 3D encoding with parallel imaging to reduce geometrical image distortion and blurring, and to increase blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) sensitivity compared to conventional echo-planar imaging (EPI).
Owner:STC UNM
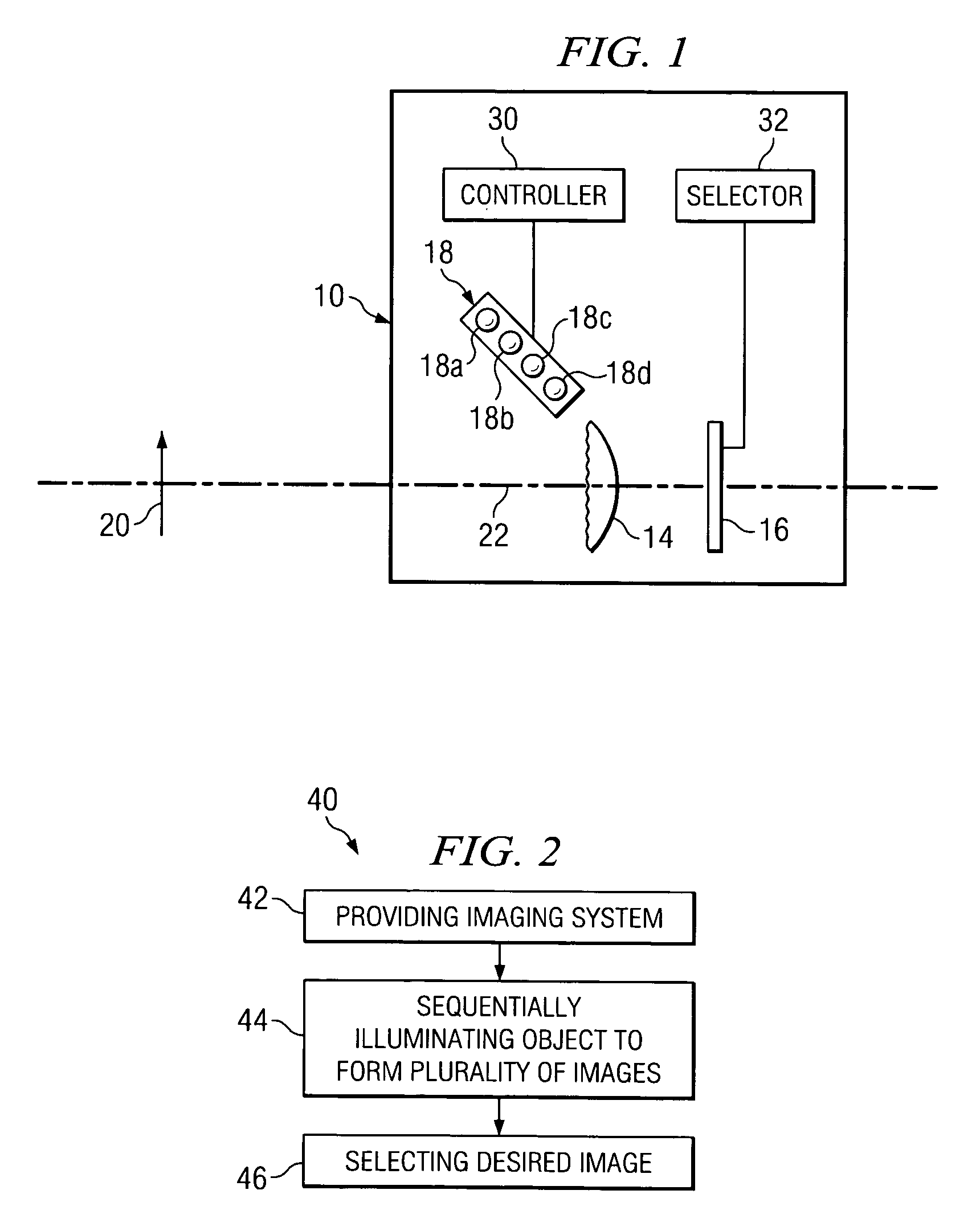
Imaging system with large depth of field
InactiveUS7106511B2Decrease apertureTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryCamera lensDepth of field
An optical imaging system and method for achieving a large depth of field without decreasing the relative aperture of an imaging lens. The imaging system has a light source for sequentially illuminating an object to be imaged with light of different ones of a plurality of wavelengths, and an imaging lens that has a focal length that varies with the wavelength of the light that illuminates the object. For each wavelength of light by which the object is illuminated, the imaging lens will image a different object plane onto an image receiving unit, and the image receiving unit will capture one well-focused, high resolution image of the object.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
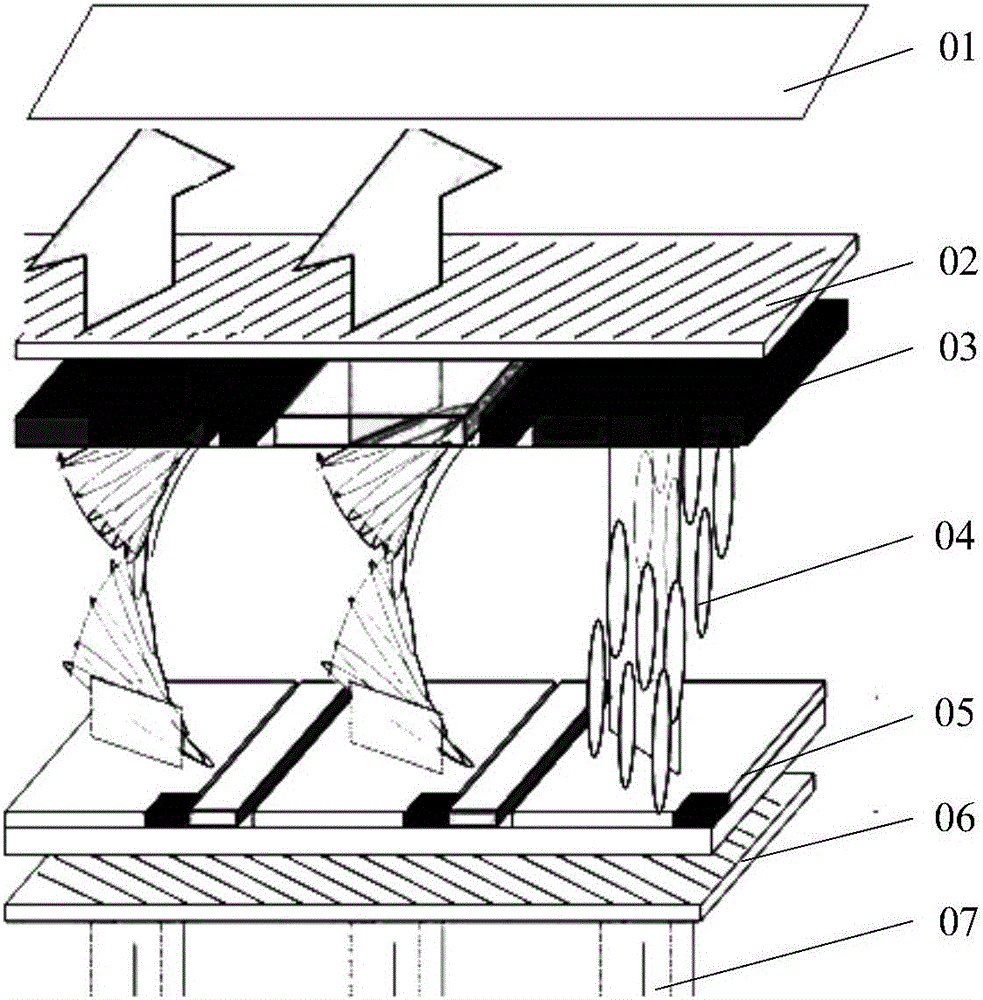
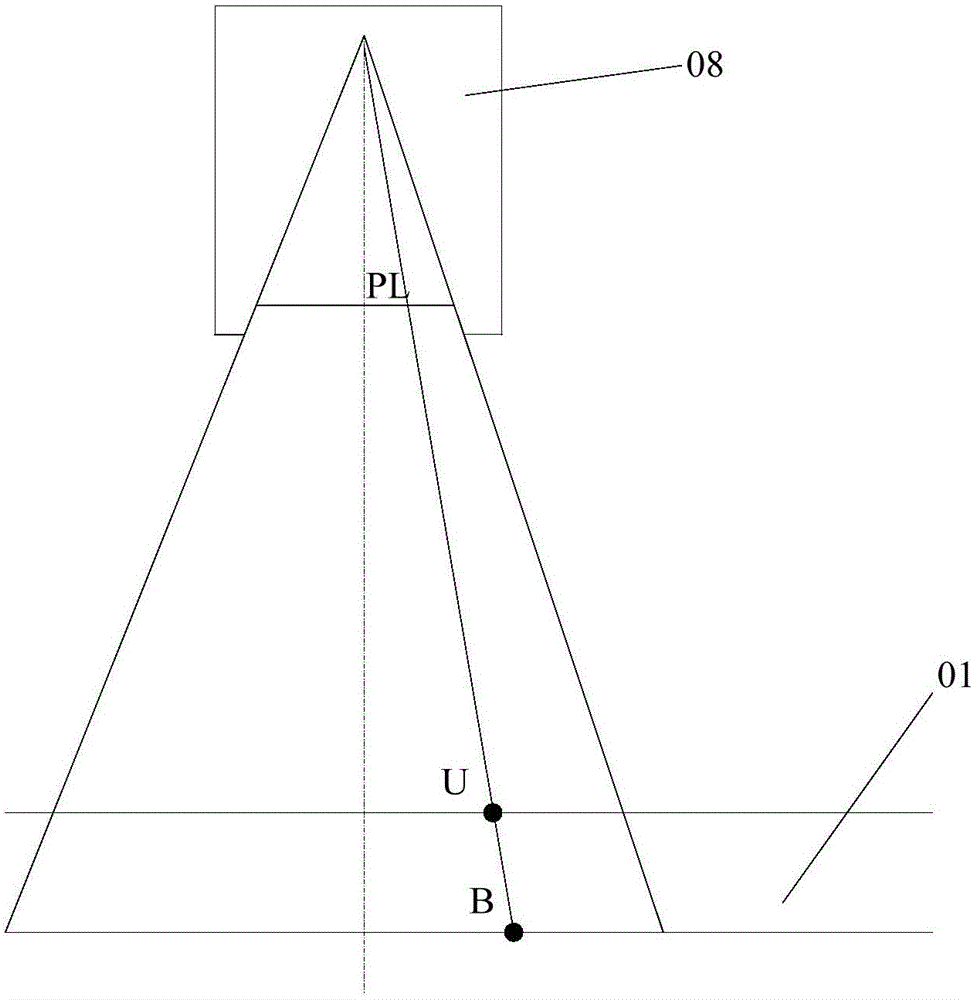
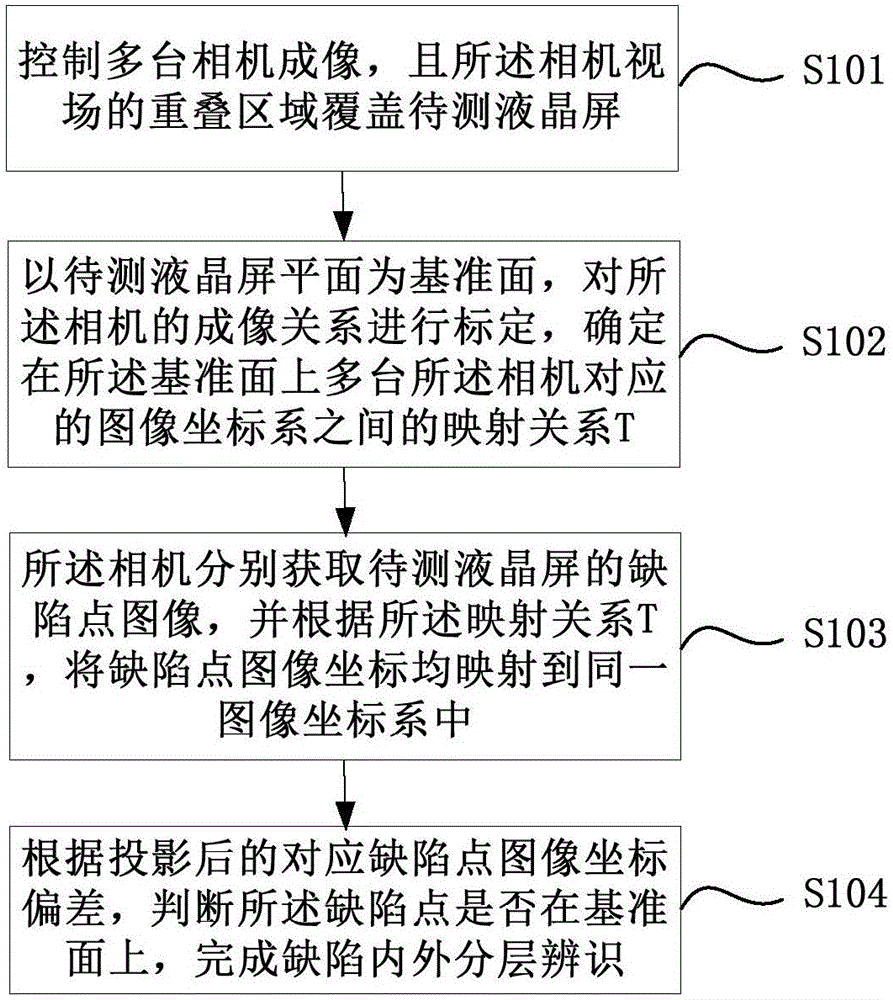
Liquid crystal screen defect layered positioning method and device
ActiveCN105842885ADistinguishing Interference QuicklySimple production processNon-linear opticsCamera imageStereoscopic imaging
The invention relates to an embodiment disclosing a liquid crystal screen defect layered positioning method and device; the method comprises the following steps: controlling a plurality of cameras for imaging, wherein a camera view field overlap area covers a to-be-detected liquid crystal screen; using the to-be-detected liquid crystal screen surface as the reference surface, calibrating a mapping relation T between each camera image coordinate system; respectively mapping defect point image coordinates corresponding to each camera into the same image coordinate system according to the mapping relation T; determining whether the defect is on the reference surface or not according to the mapped corresponding defect point image coordinate deviation, and identifying inner / outer layer defects; in addition, using a mapping relation G between the camera image coordinates and object space coordinates to accurately calculate the defect point depth coordinate, thus determining the defect layer. Using various cameras to form the visual system, so the plane image defect detection can be improved to form stereo imaging, thus determining detect points and plane positions, obtaining depth information, completing defect points inner / outer layer positioning and grading, helping to remove interferences, and guiding technology improvement so as to ensure liquid crystal screen quality.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
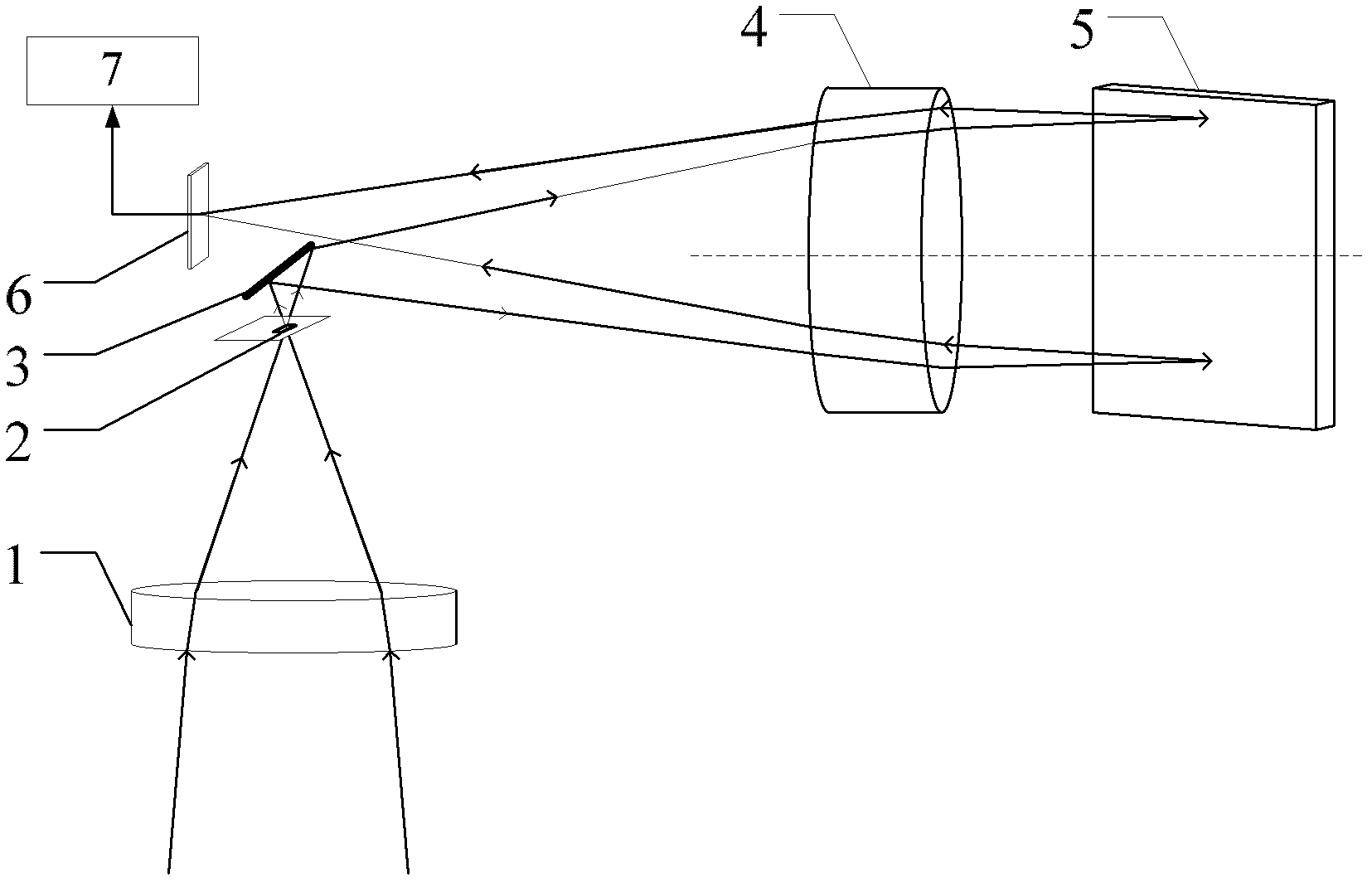
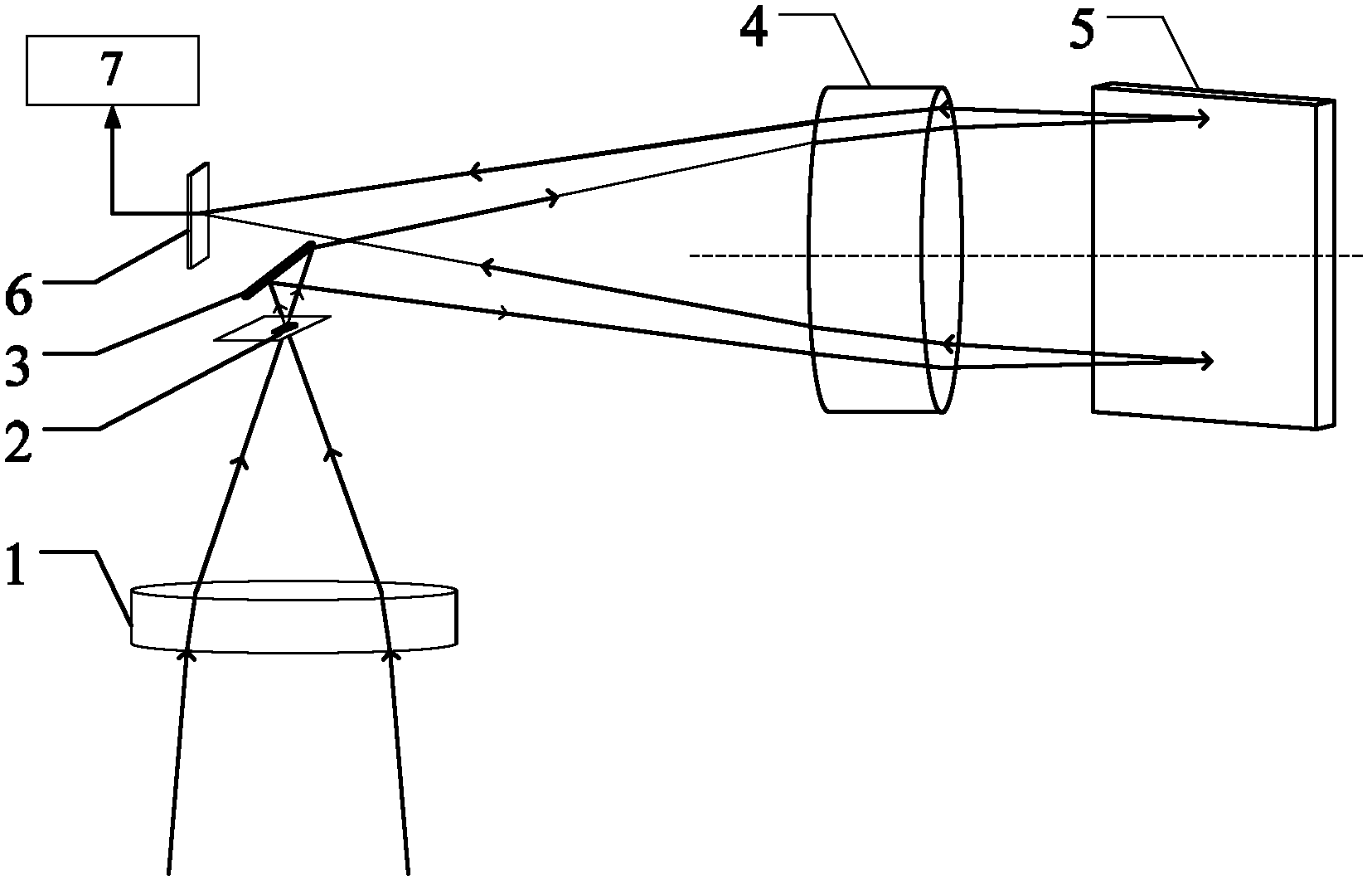
Raster imaging spectrometer
InactiveCN102620827ASimple structureImprove stabilityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotovoltaic detectorsGrating
The invention provides a raster imaging spectrometer which comprises a preposed receiving optics unit, a light split imaging unit comprising an entrance slit, a plane mirror, a collimating-focusing system and a raster, and a spectral signal processing unit comprising an area array photoelectric detector and a signal processing system. The entrance slit is arranged at the focal point of an emergent light ray of the preposed receiving optics unit; the emergent light ray of the preposed receiving optics unit penetrates through the entrance slit to be capable of reaching the reflecting surface of the plane mirror; the collimating-focusing system is arranged on the reflected light ray of the plane mirror and is coaxial with the raster; the reflected light ray of the raster on the plane mirror passes through the collimating-focusing system-collimated emergent light ray; the area array photoelectric detector is positioned at the focal point of the diffracted light ray of the emergent light ray focused by the collimating-focusing system, of the raster; and an output end of the area array photoelectric detector is connected with an input end of the signal processing system. The raster imaging spectrometer provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple in structure, high in stability, high in spectral resolution, small in volume, low in price, capable of planar imaging, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
System and method for functional ultrasound imaging
A system and method for functional ultrasound imaging are provided. The method includes obtaining ultrasound image data acquired from a multi-plane imaging scan of an imaged object. The ultrasound image data defines a plurality of image planes. The method also includes determining functional image information for the imaged object from two-dimensional tracking information based on the plurality of image planes and generating functional ultrasound image data for the imaged object using the functional image information.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
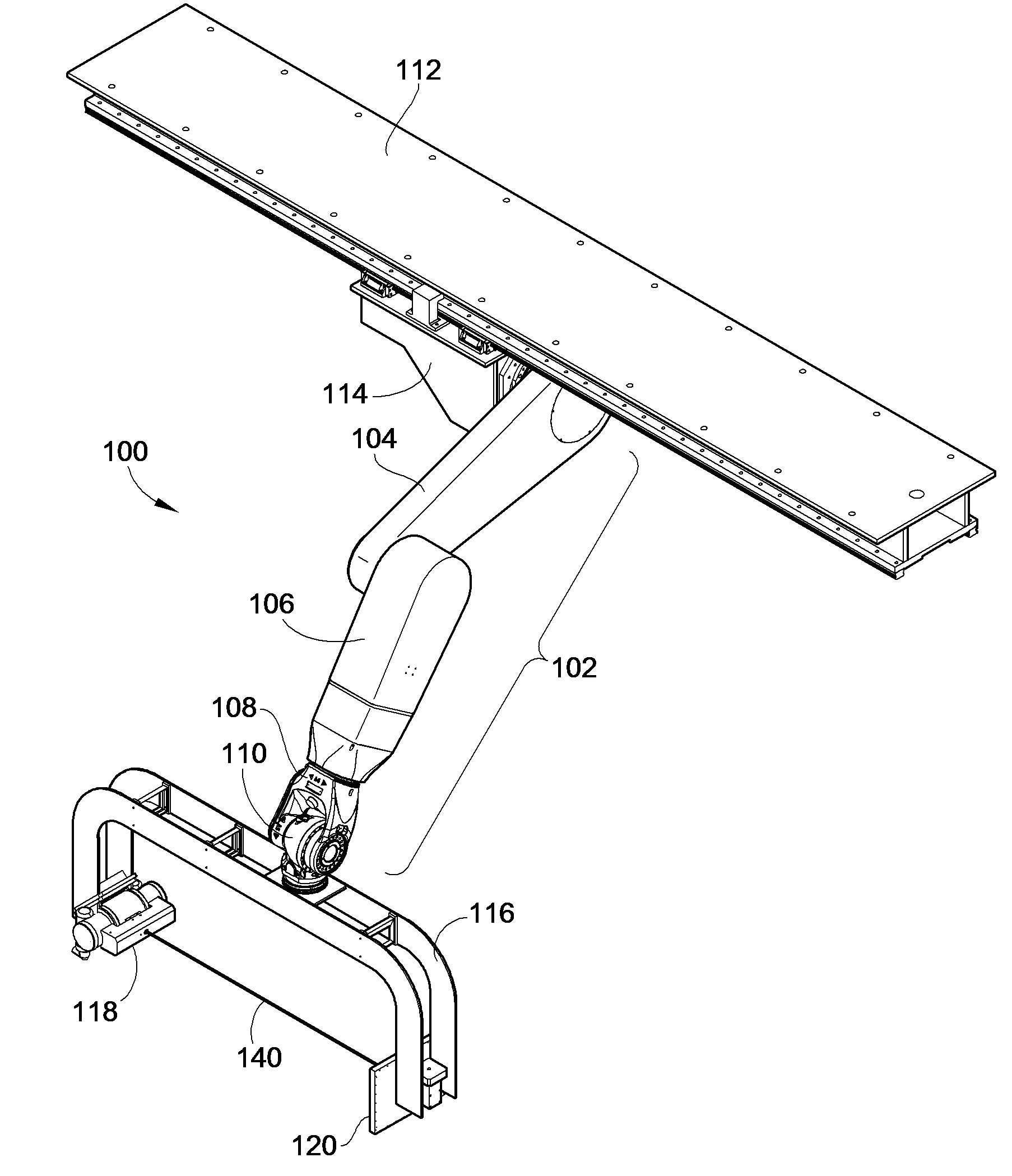
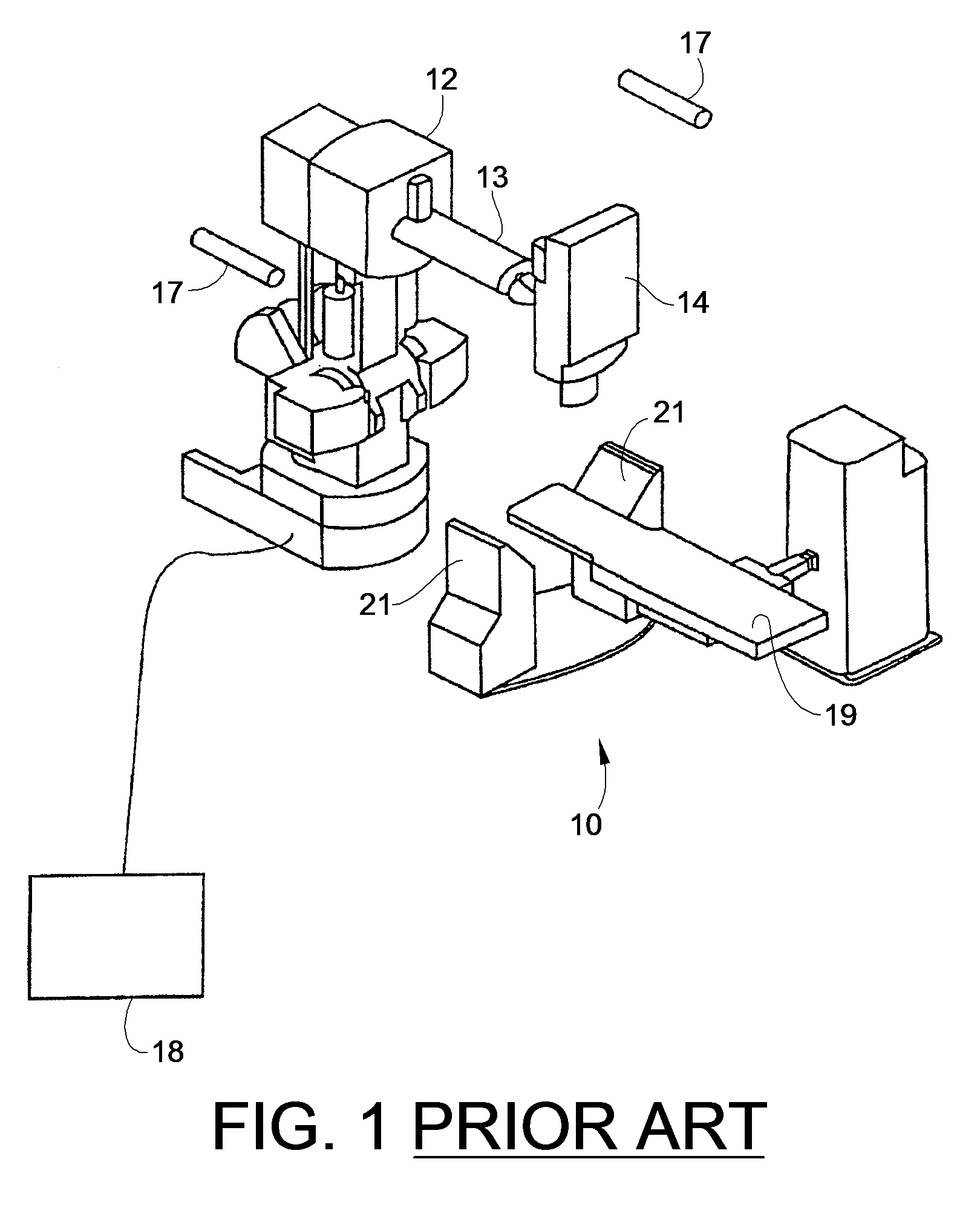
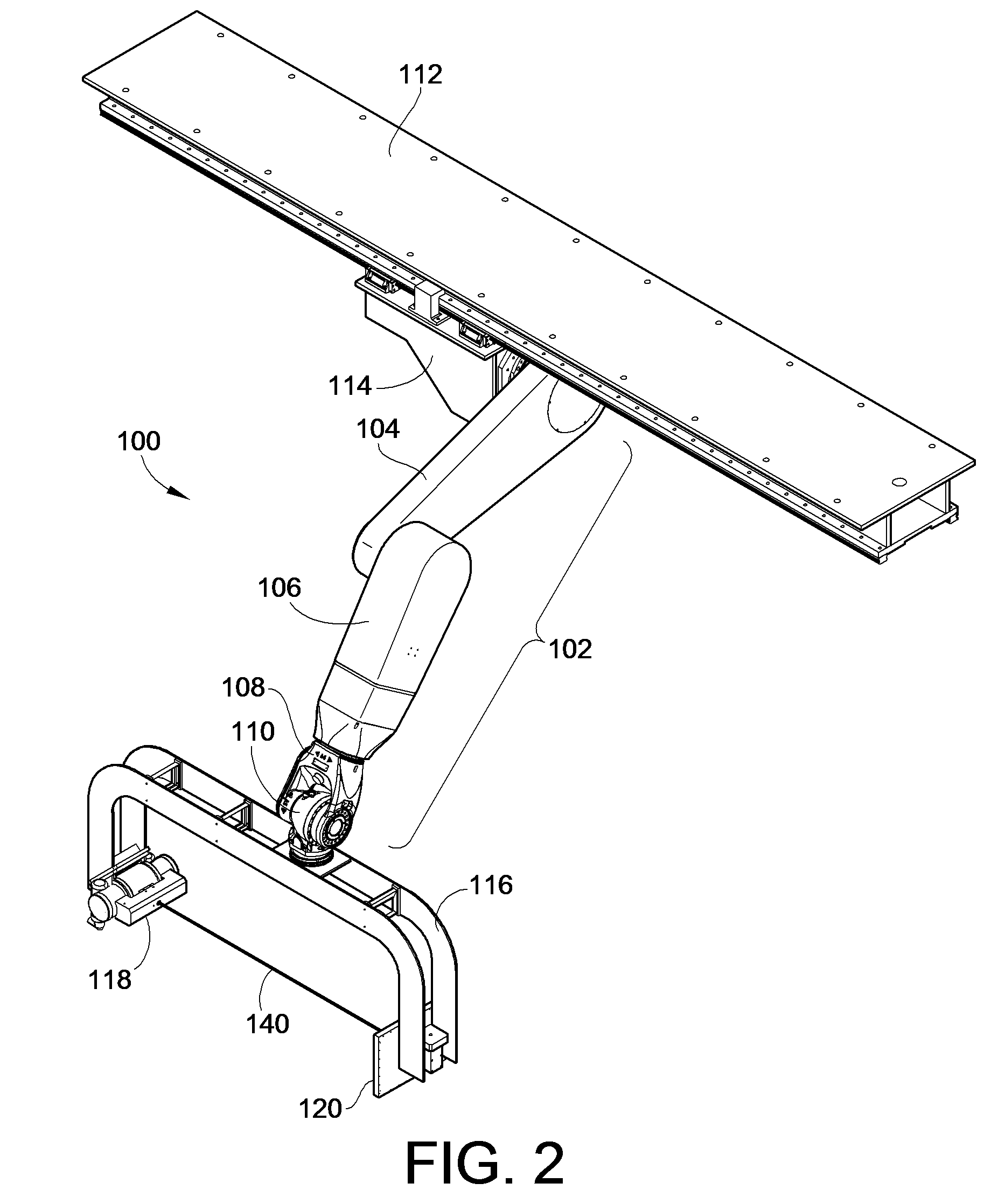
Imaging positioning system having robotically positioned D-arm
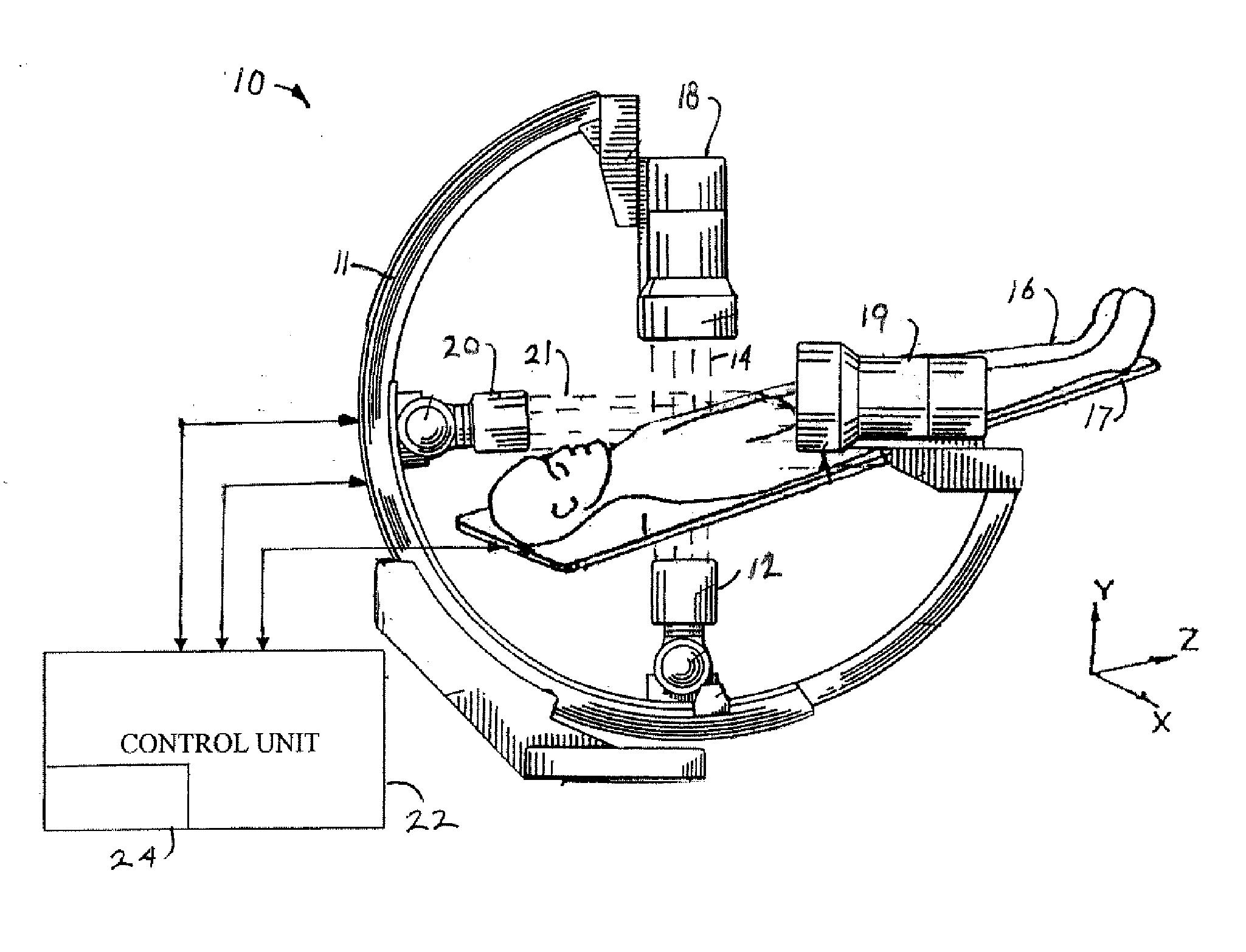
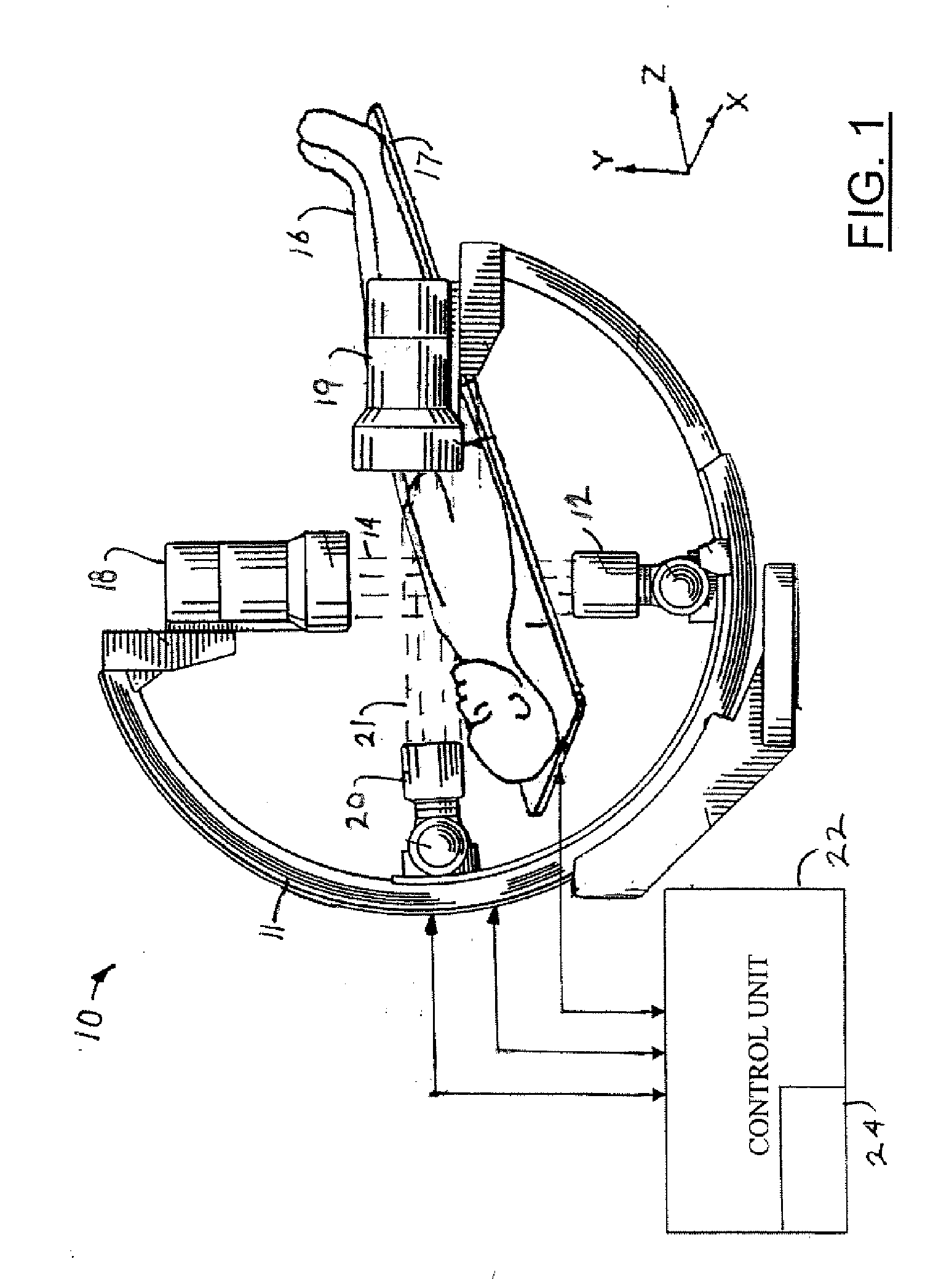
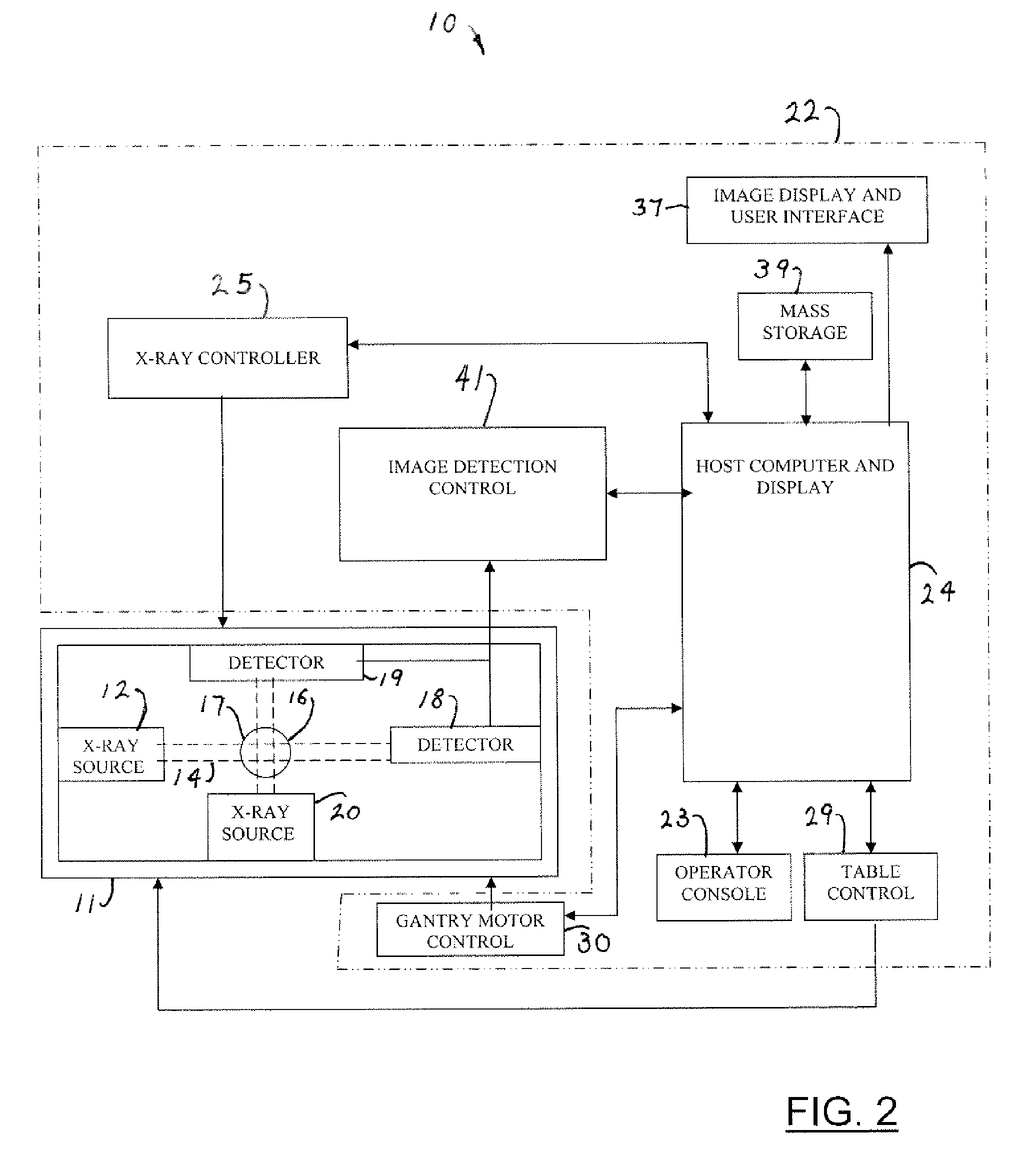
InactiveUS7695192B2Maximize available spacePrecise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDynamic fieldRobotic arm
An imaging positioning system having a robotically positioned support structure is provided. By utilizing a robotic arm, imaging along multiple planes within a patient treatment room without having to move the patient is provided. Such a configuration allows multiple axis x-ray imaging, cone beam CT acquisitions having a dynamic field of view, and PET imaging within the treatment room. Rotation of the imaging panel on the support structure allows the imaging system to simulate a gantry rotation when a fixed beam is used for treatment. Beam line x-ray imaging is also provided by tilting the imaging panel or by moving the support structure on which the x-ray source is positioned. Laser distance scanning for collision avoidance and force torque sensing movement enhance the safety thereof. The support structure may be in the form of a ring along which the imaging components may move.
Owner:FIRST MIDWEST BANK +1
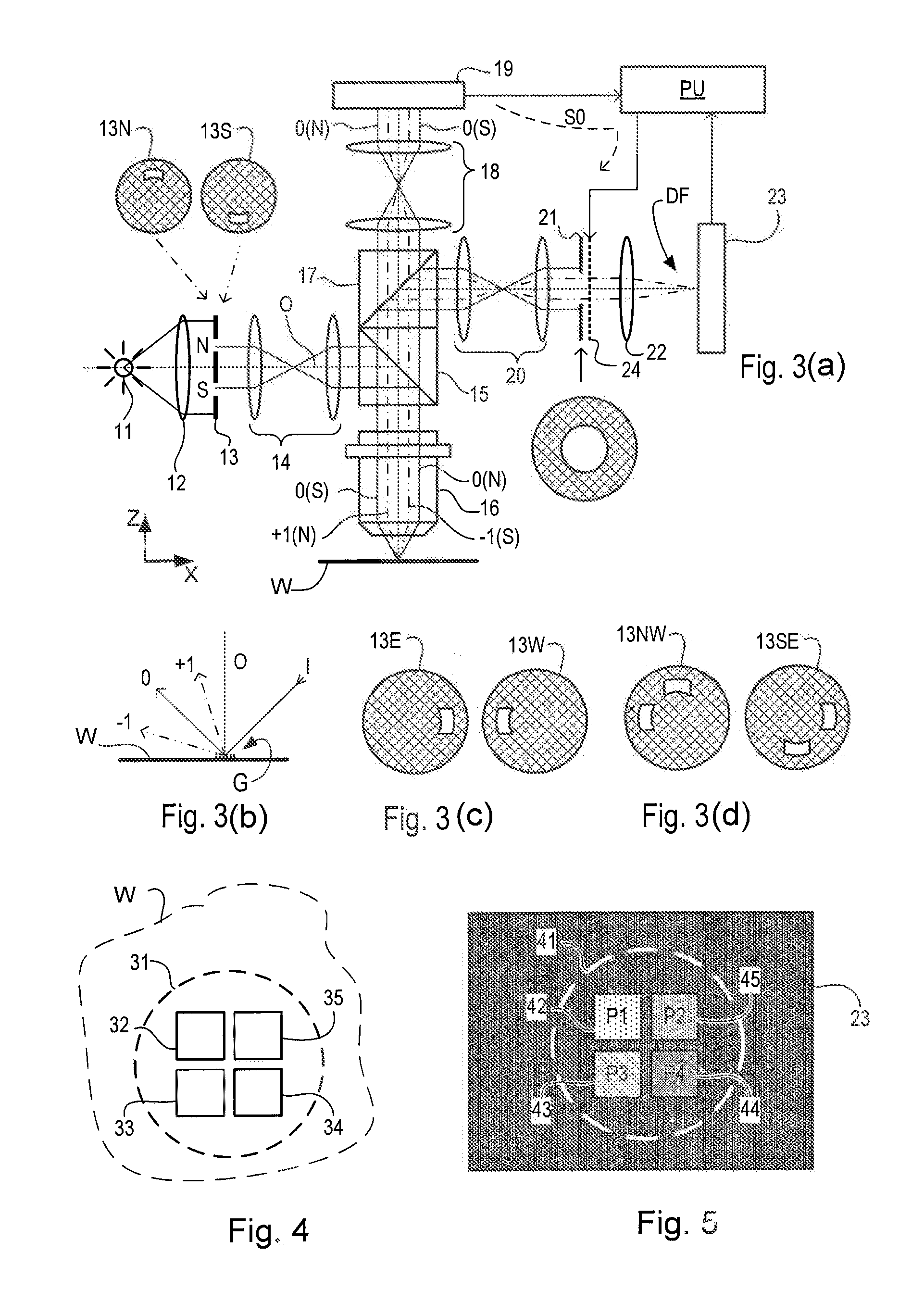
Tracking region-of-interest in nuclear medical imaging and automatic detector head position adjustment based thereon
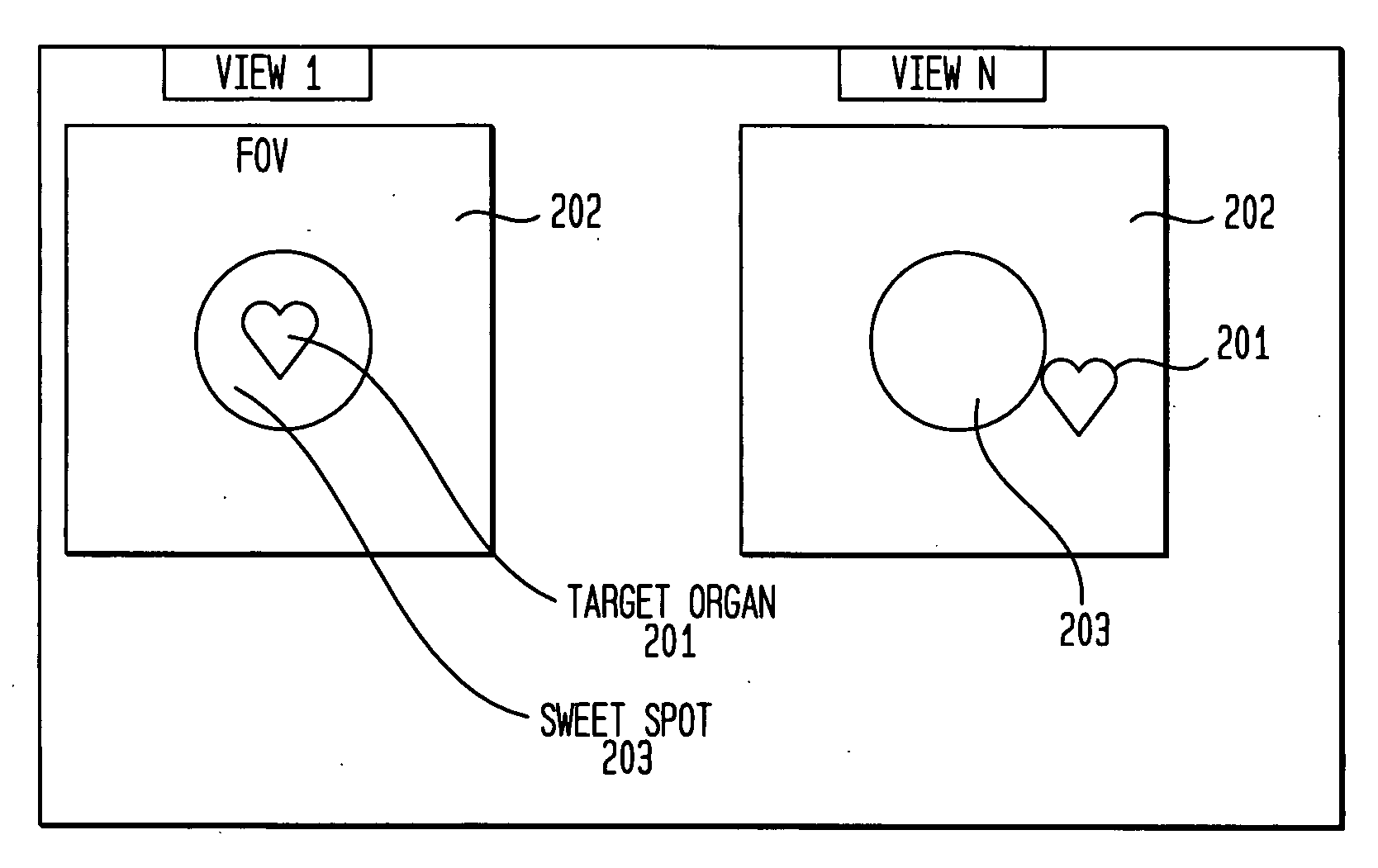
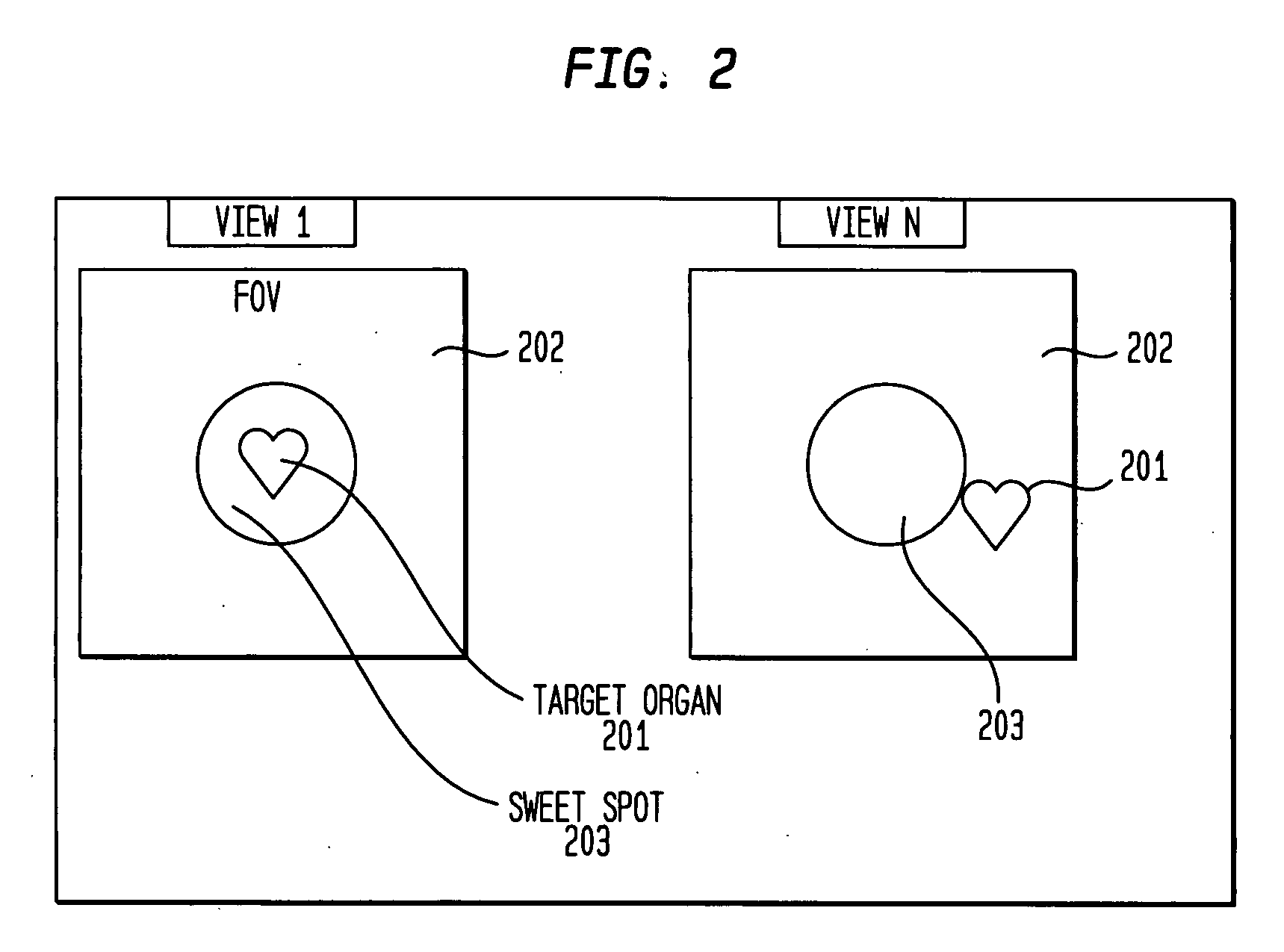
A method and system for automatically identifying and tracking a ROI over all planar acquisition view angles of a nuclear imaging system, such as a gamma camera used for SPECT or planar imaging. Temporal intensity variation in emission projection imaging is measured to identify a region of interest (ROI) such as the myocardium. The method automatically tracks the location of the ROI over different planar view angles and adapts detector head orbit and positioning to bring the ROI within a predefined preferred area or so-called “sweet spot” within the FOV of a collimator attached to the front of a scintillation detector surface. After initial positioning of the detector head by the user, the system automatically tracks the ROI location as the detector head(s) rotate about the patient and re-position the detector head(s) appropriately to maintain the ROI within the optimal collimation area of the detector FOV.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
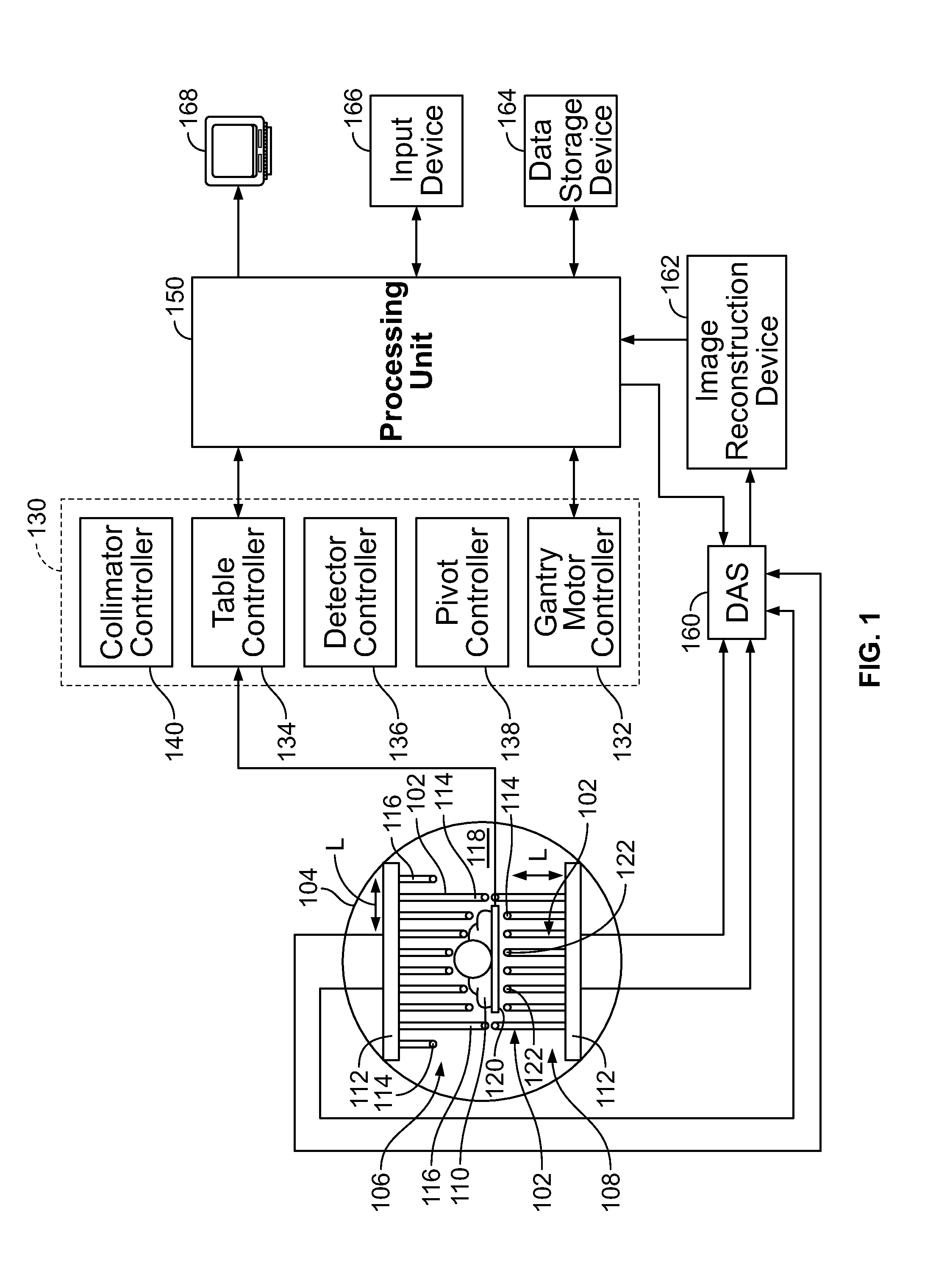
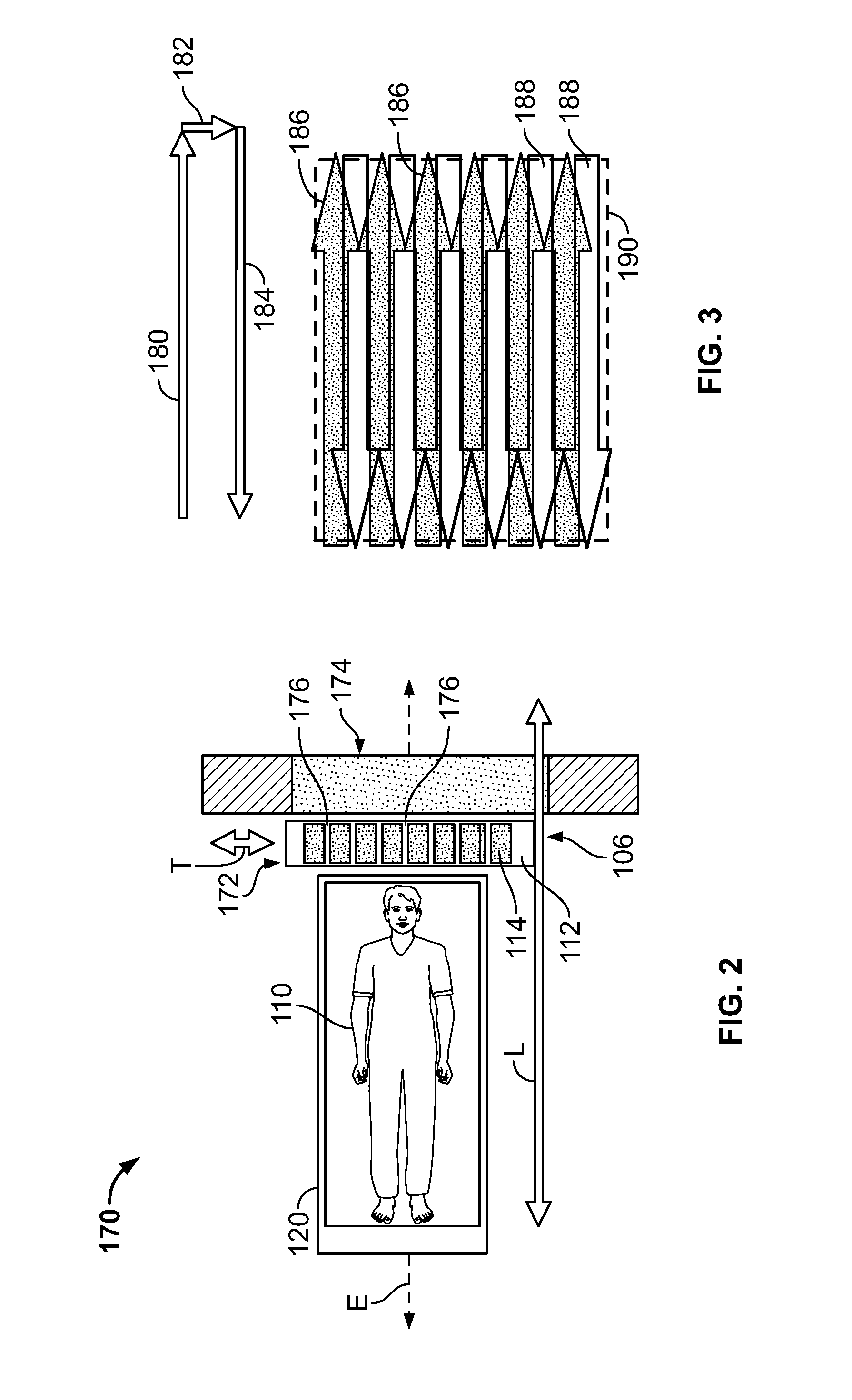
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving detector heads
ActiveUS20150094573A1Patient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsPhotonSingle-photon emission computed tomography
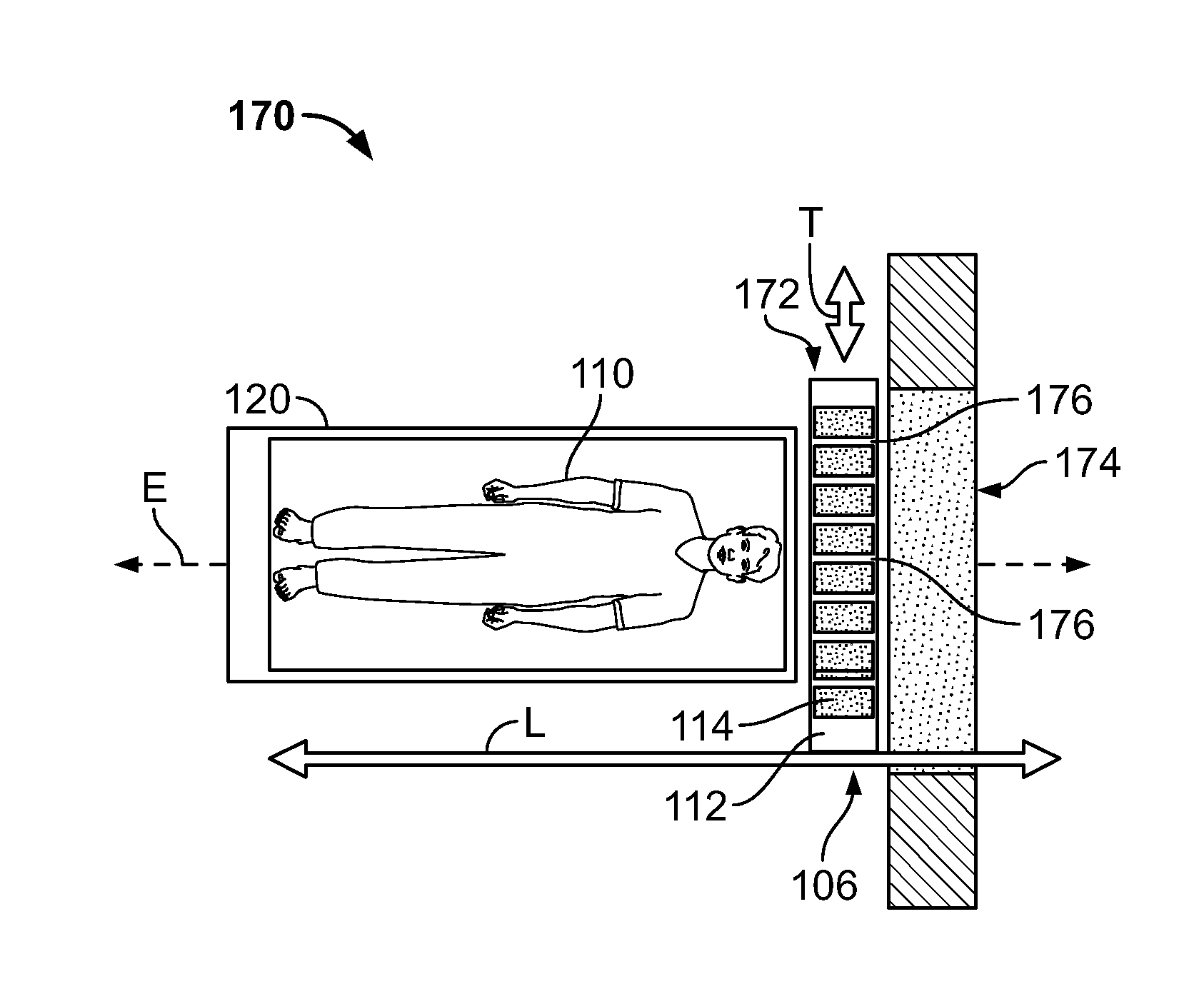
Systems and methods for planar imaging with detectors having moving heads are provided. One system includes a gantry having an opening therethrough, a patient table movable through the opening of the gantry along an examination axis, and a plurality of detector units mounted to the gantry and aligned in a row transverse to the examination axis. The plurality of detector units are spaced apart from each other, wherein the spacing forms gaps between adjacent detector units. The plurality of detector units are configured to acquire Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) data. The system further includes a controller configured to control movement of the patient table and the plurality of detector units to acquire two-dimensional (2D) SPECT data, wherein the plurality of detector units remain in a fixed relative orientation with respect to each other when acquiring the 2D SPECT data and move together to acquire the 2D SPECT data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
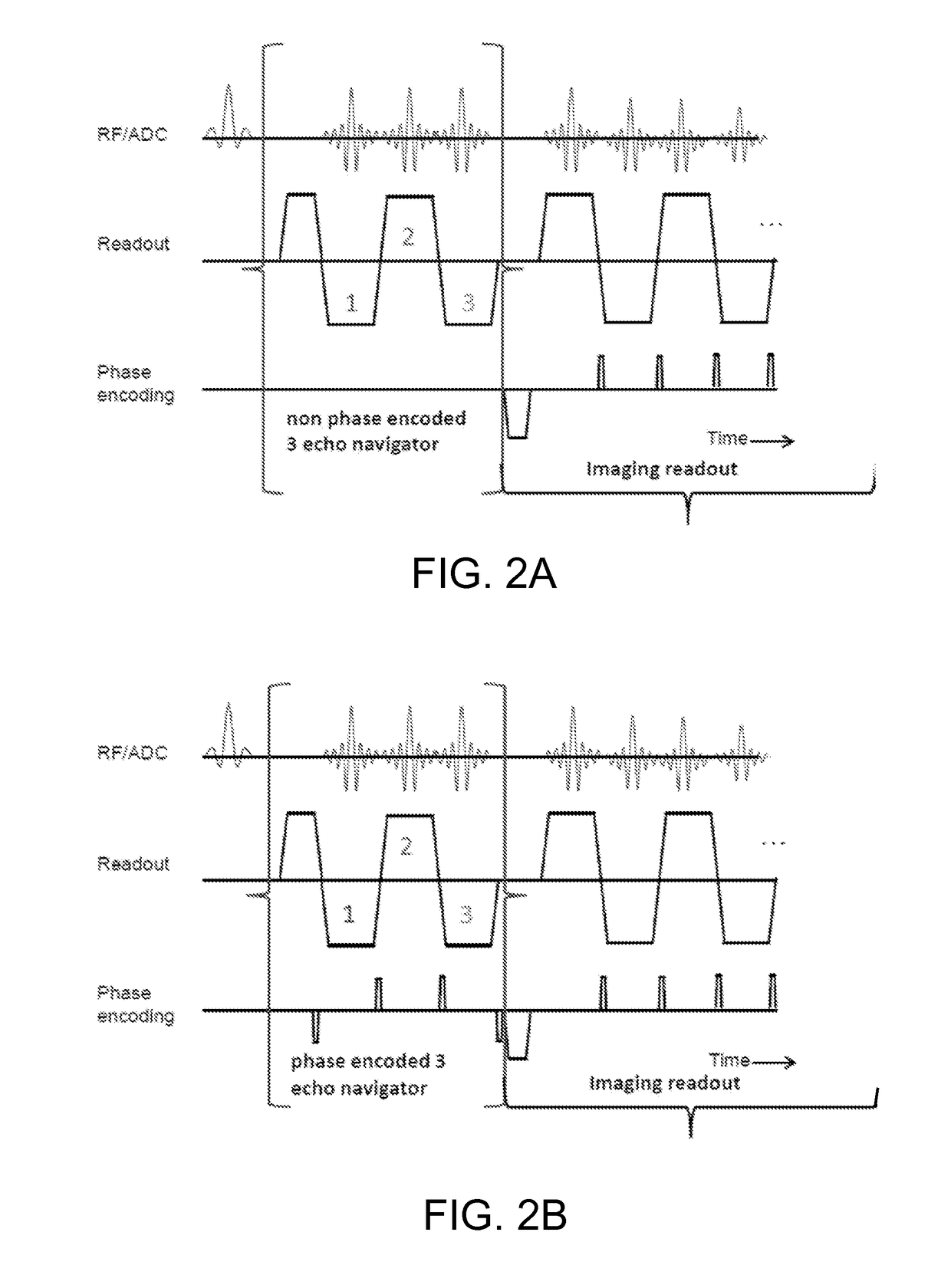
Navigator-Based Data Correction For Simultaneous Multislice MR Imaging
ActiveUS20170089999A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to correctImage enhancementImage analysisData setElectrical polarity
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for providing improved simultaneous multislice echo planar imaging (EPI) with navigator-based correction of image data for B0 drift and N / 2 ghosting. The correction is based on two types of multi-echo phase-encoded navigator sequences having opposite readout gradient polarities, and optionally also uses a non-phase-encoded navigator sequence. One or more navigator sequences can be generated between each RF excitation pulse and the subsequent EPI readout sequence. A dynamic off-resonance in k-space technique can be used to correct for B0 drift, and a modified slice GRAPPA technique that is based on odd and even kernels can provide slice-specific correction for N / 2 ghosting effects for the EPI MR image data sets. Various patterns of navigator sequences and / or interpolation of navigator data can be used to improve accuracy of the image data corrections.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and System for Scatter Correction During Bi-Plane Imaging with Simultaneous Exposure
InactiveUS20060083351A1Improve imaging rateEquivalent imaging ratesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation diagnosticsX-raySample image
A method for x-ray scatter correction during simultaneous bi-plane imaging using digital image processing. The basic concept includes correcting the image from each plane by combining it with an image of the scatter generated from the exposures of the opposite plane in such a way that the scatter effects are removed. The correction image is formed by sampling images from the detector with only the x-ray exposure of the scatter producing plane being active. These sampled images of scatter are processed to form the scatter correction image. The scatter correction image is stored in an image memory so that it is available for combination with subsequent x-ray images to remove scatter distortion.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Illumination apparatus and methods
ActiveUS7319229B2Reduce speckle noiseRemove speckle noiseMaterial analysis by optical meansVisible signalling systemsLight equipmentDevice material
Disclosed are apparatus and methods for illuminating a sample, e.g., during an inspection of such sample for defects. In one aspect, the illumination apparatus includes a bundle of fibers that each has a first end and a second end. The illumination apparatus further includes an illumination selector for selectively transmitting one or more incident beams into one or more corresponding first ends of the optical fibers so that the selected one or more incident beams are output from one or more corresponding second ends of the fibers. The illumination apparatus also includes a lens arrangement for receiving the selected one or more incidents beams output from the corresponding one or more second ends of the fibers and directing the selected one or more incident beams towards the sample. The lens arrangement and the fibers are arranged with respect to each other so as to image an imaging plane of the sample at the second ends of the fibers. In one aspect, the incident beams are laser beams. In a specific application of the invention, the sample is selected from a group consisting of a semiconductor device, a semiconductor wafer, and a semiconductor reticle.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Fluorescent optical sheet microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN105300941ALarge field of viewHigh spatio-temporal resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceImage resolution
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Metrology method and inspection apparatus, lithographic system and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS9140998B2Improve accuracyImprove throughputScattering properties measurementsDigital computer detailsUltrasound attenuationSpatial light modulator
Methods are disclosed for measuring target structures formed by a lithographic process on a substrate. A grating structure within the target is smaller than an illumination spot and field of view of a measurement optical system. The optical system has a first branch leading to a pupil plane imaging sensor and a second branch leading to a substrate plane imaging sensor. A spatial light modulator is arranged in an intermediate pupil plane of the second branch of the optical system. The SLM imparts a programmable pattern of attenuation that may be used to correct for asymmetries between the first and second modes of illumination or imaging. By use of specific target designs and machine-learning processes, the attenuation patterns may also be programmed to act as filter functions, enhancing sensitivity to specific parameters of interest, such as focus.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
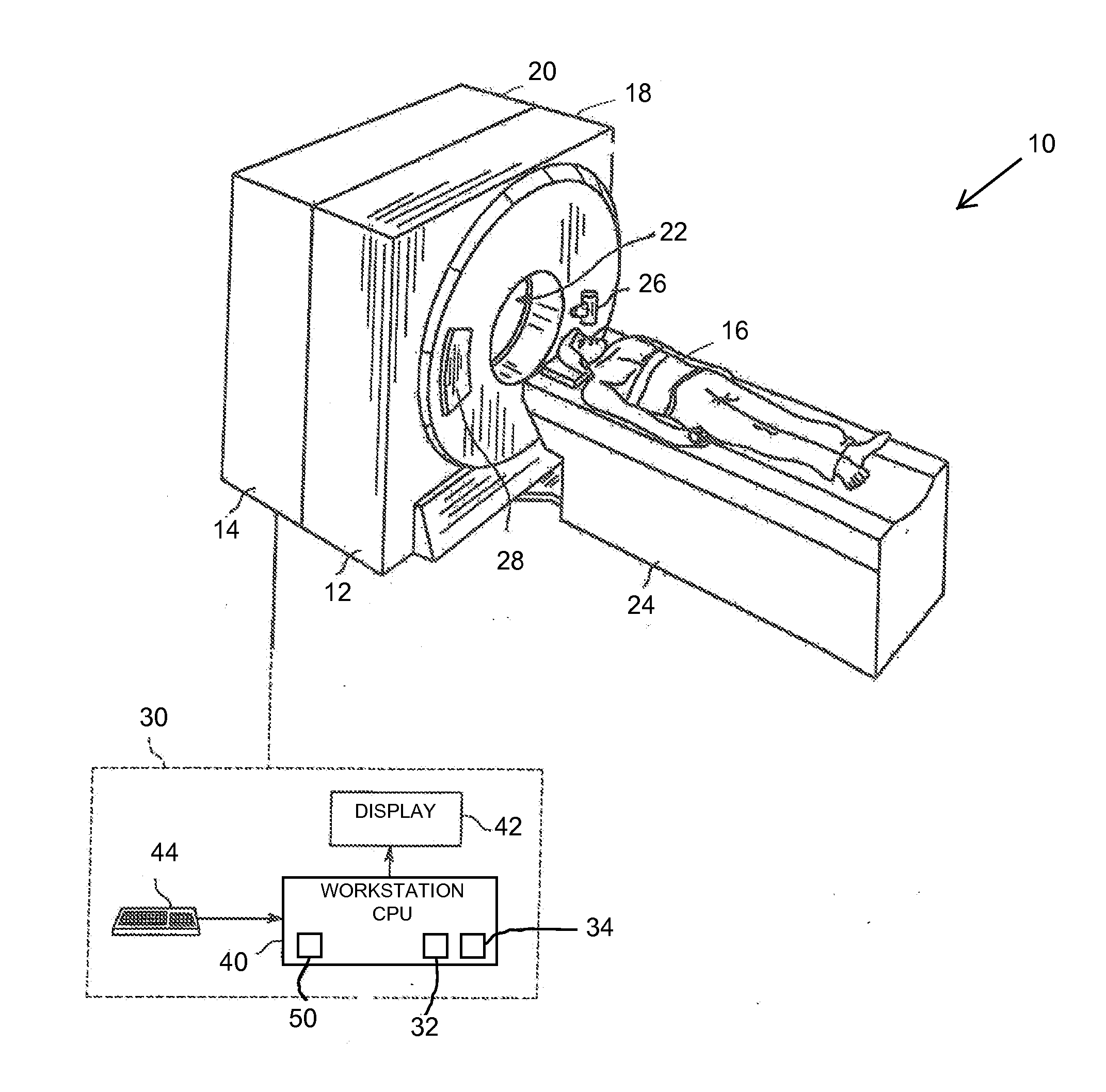
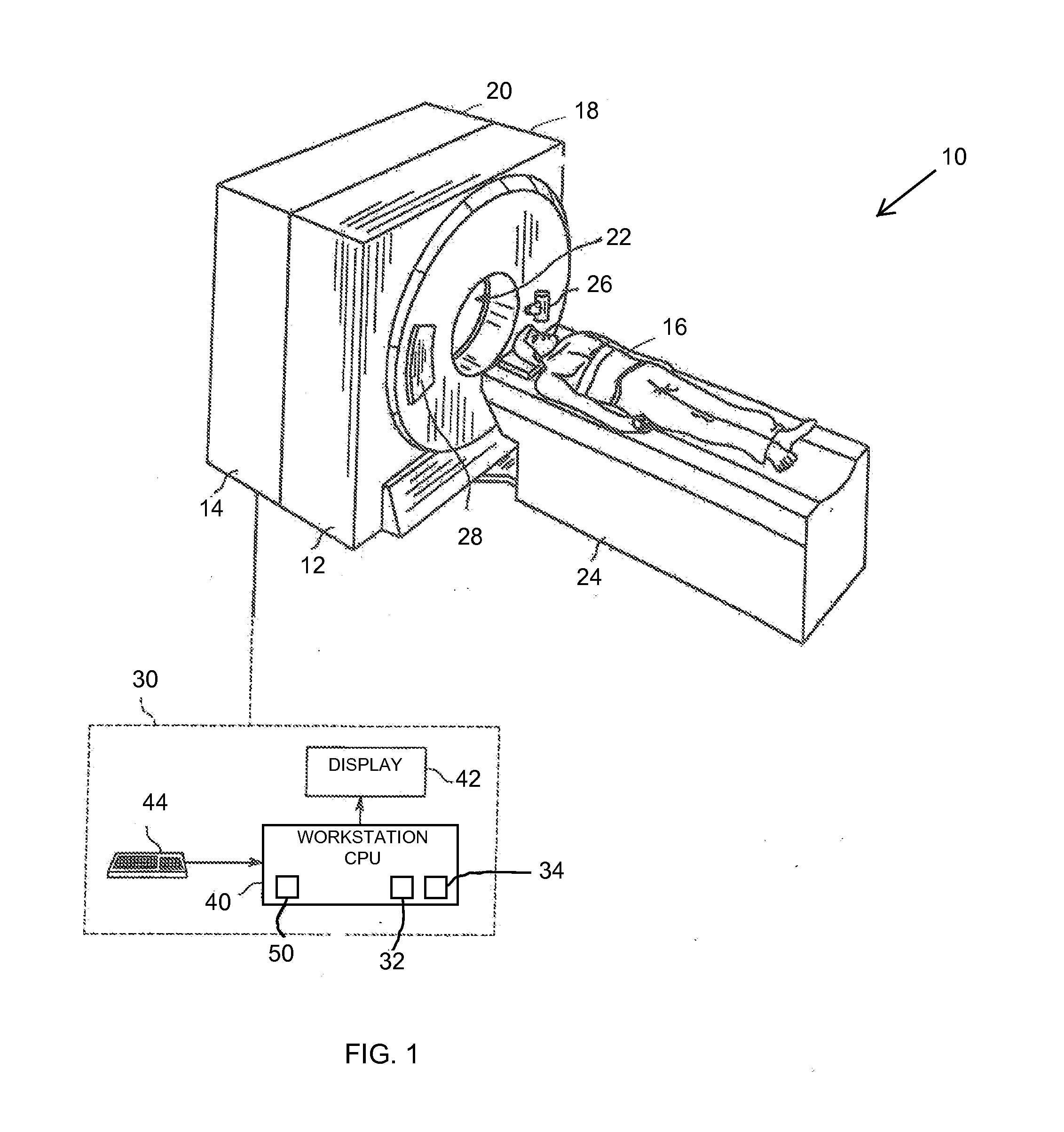
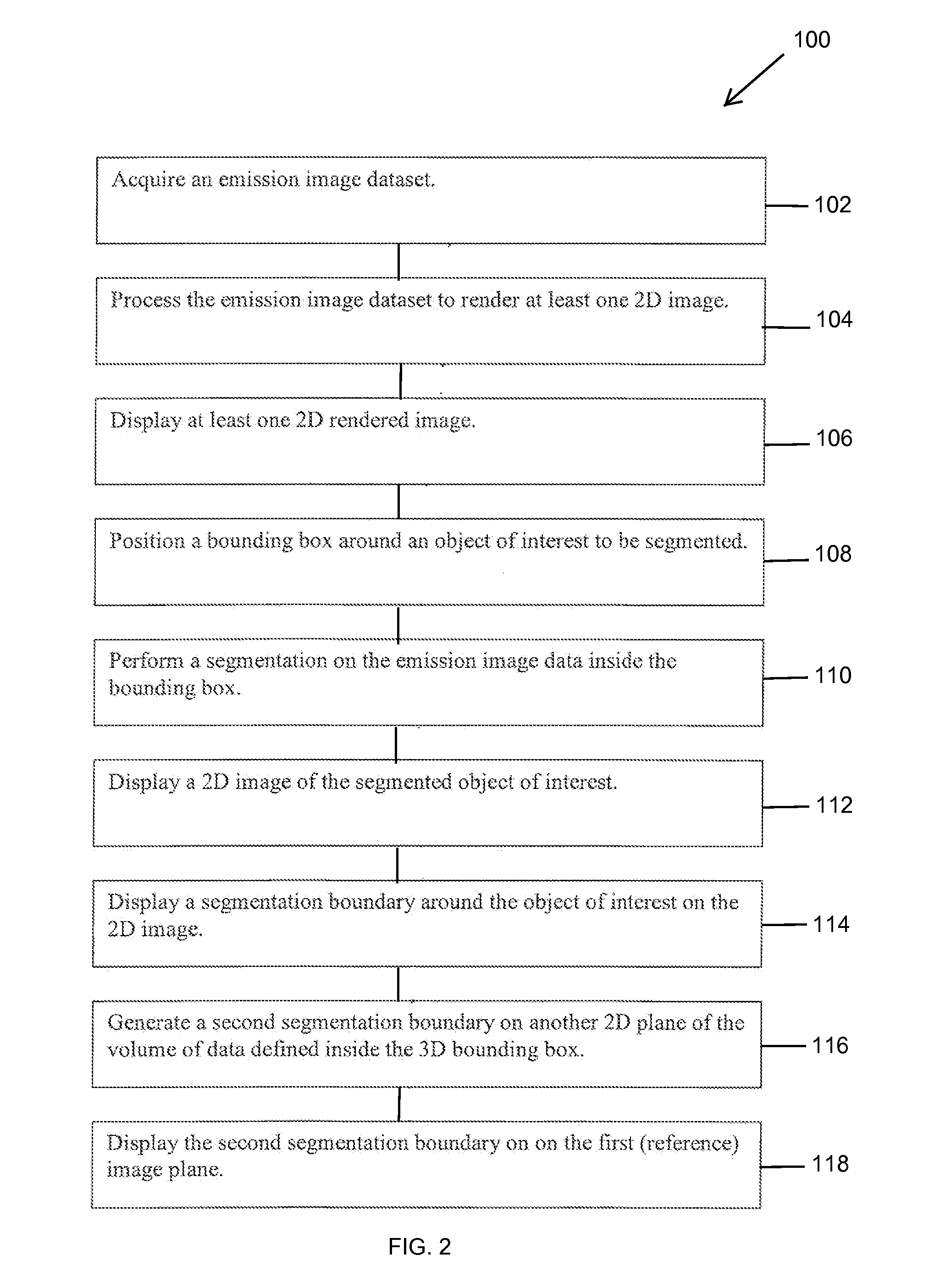
Methods and system for displaying segmented images
A method for displaying a segmented two-dimensional (2D) image includes obtaining a three-dimensional (3D) volume dataset corresponding to an imaged volume along a viewing plane, segmenting an object of interest within 3D volume to generate a plurality of segmented two-dimensional (2D) images along the viewing plane, selecting a reference image for viewing from the plurality of segmented 2D images, and displaying the reference image, the reference image having a first segmentation boundary drawn around the object of interest and a second segmentation boundary drawn around the object of interest, the first segmentation boundary being derived from the segmentation performed on the reference image and the second segmentation boundary being derived from the segmentation performed on at least one non-reference image of the plurality of segmented 2D images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com