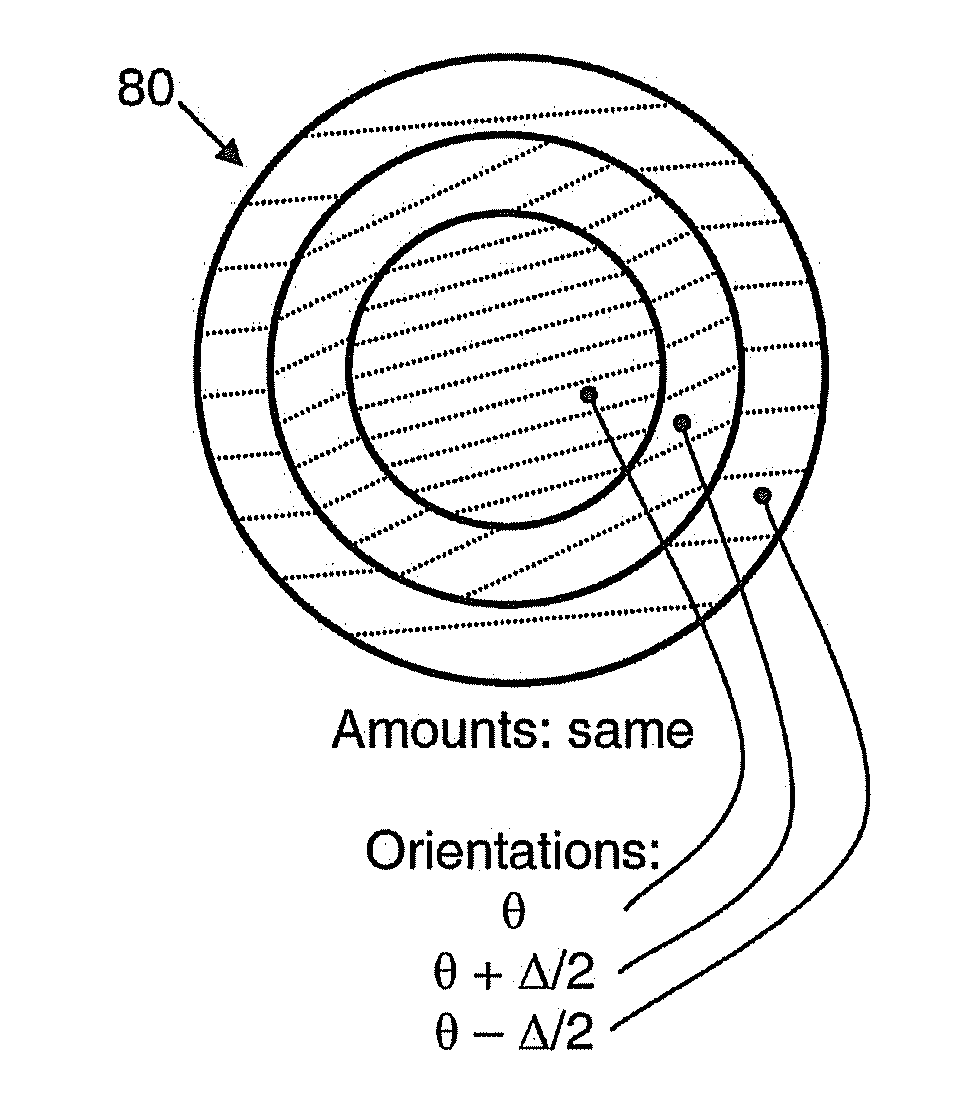
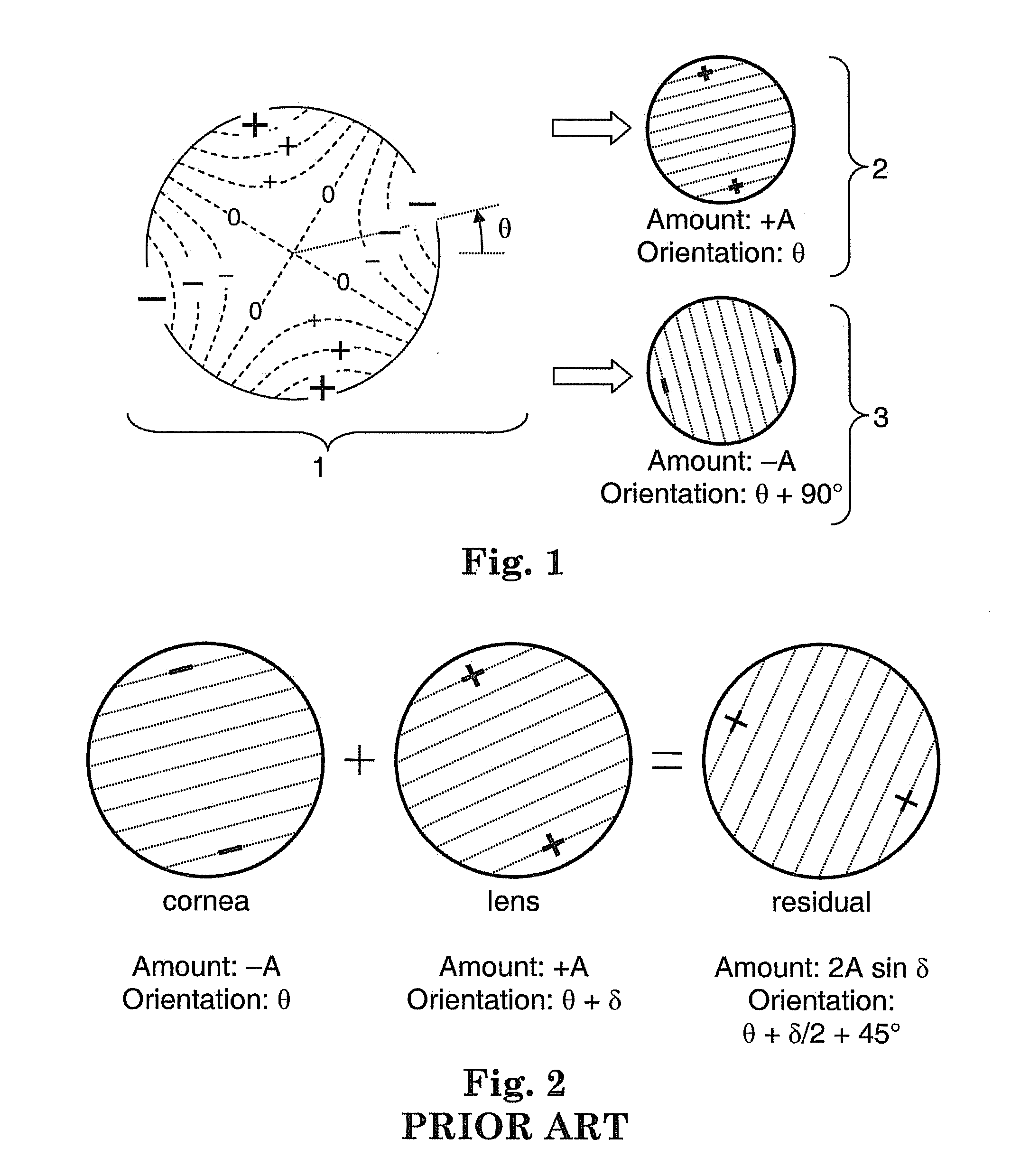
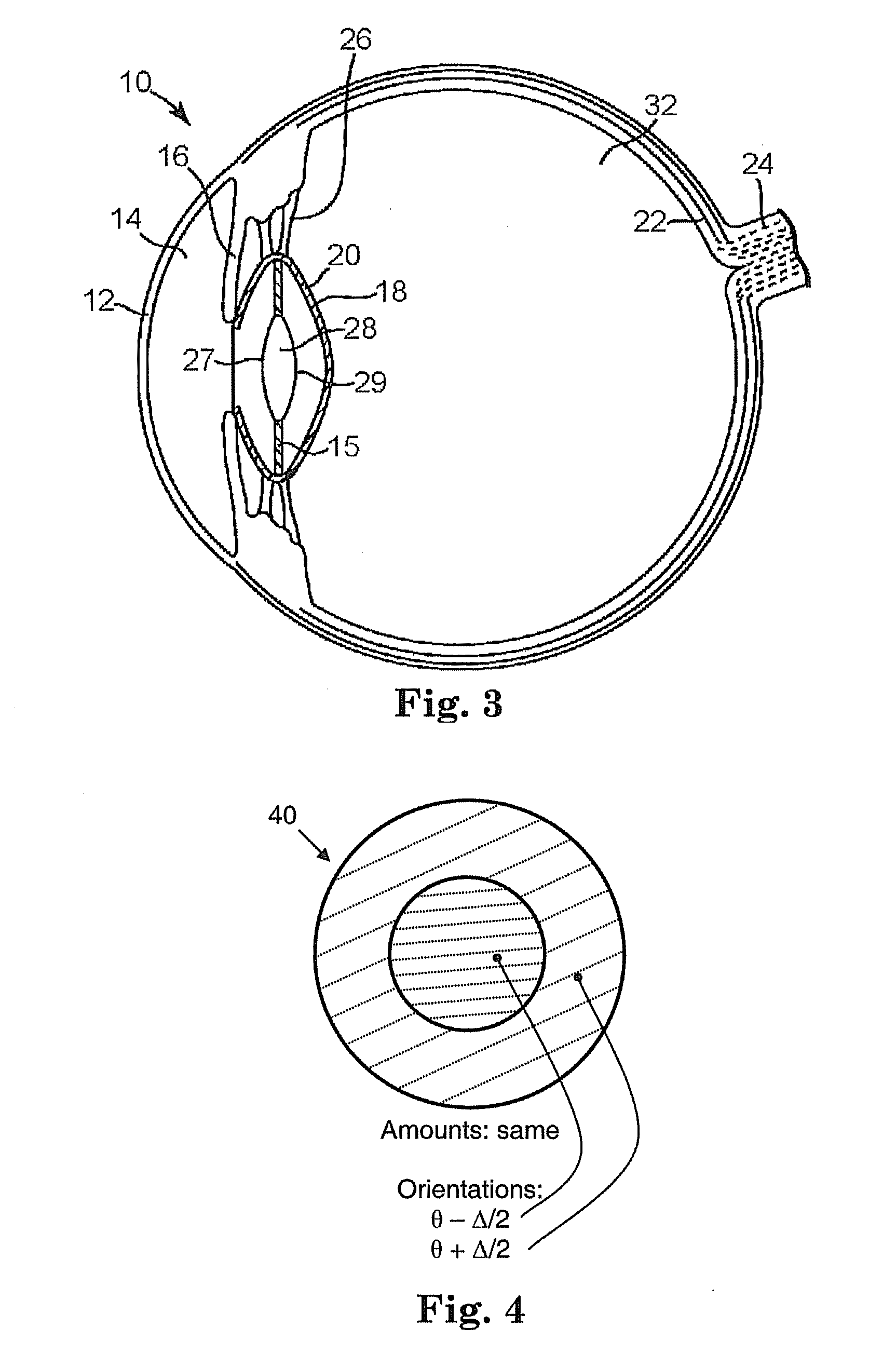
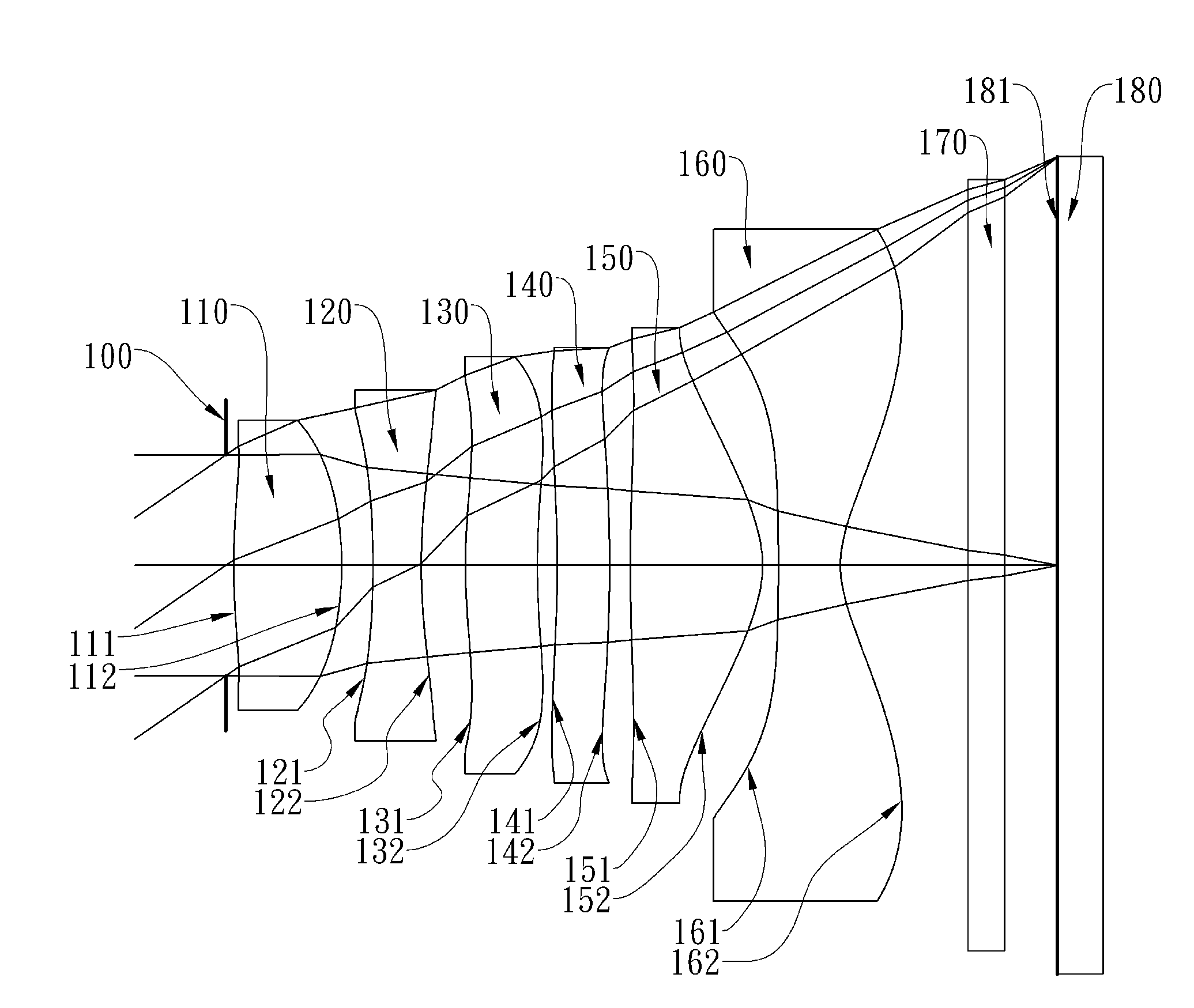
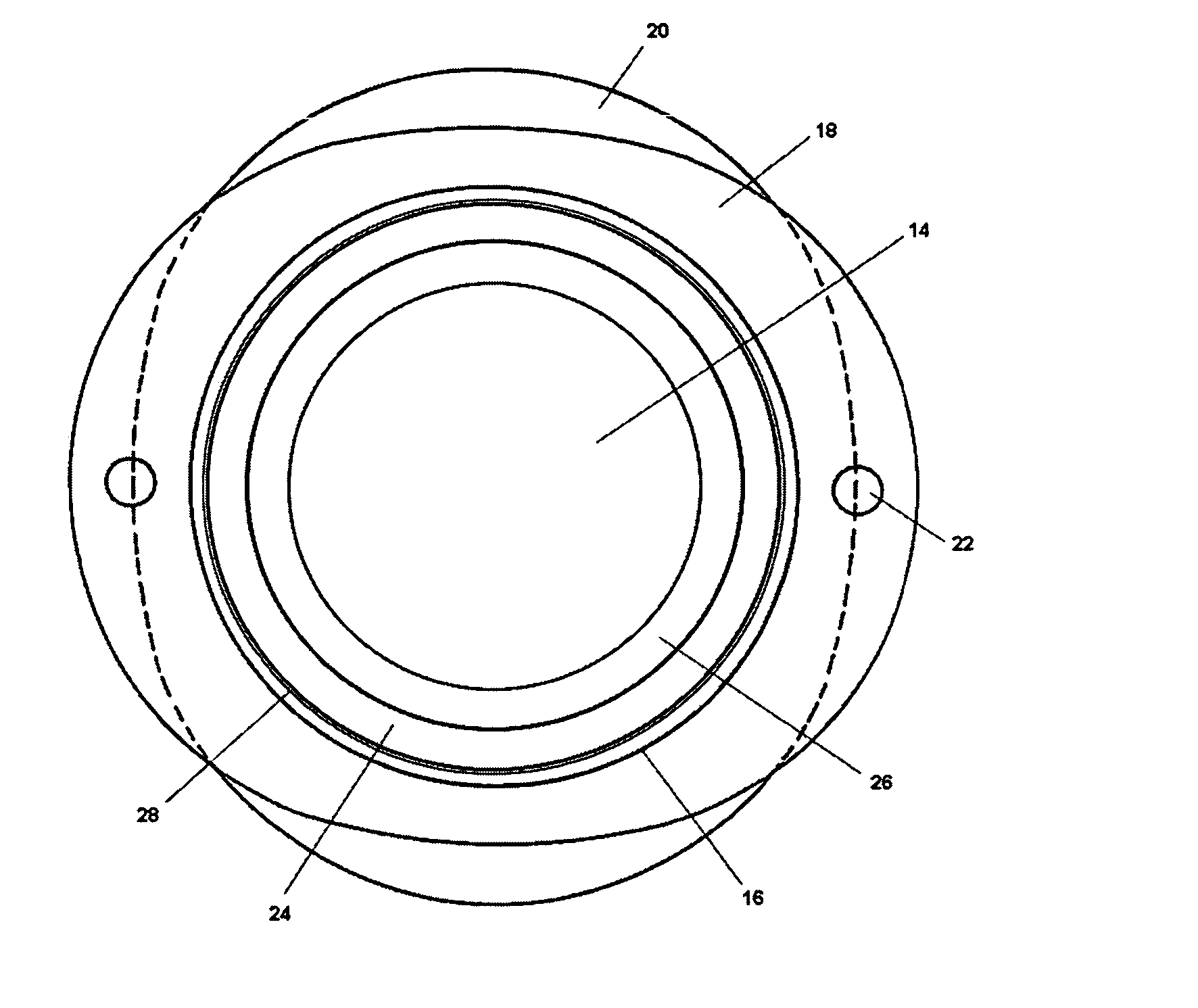
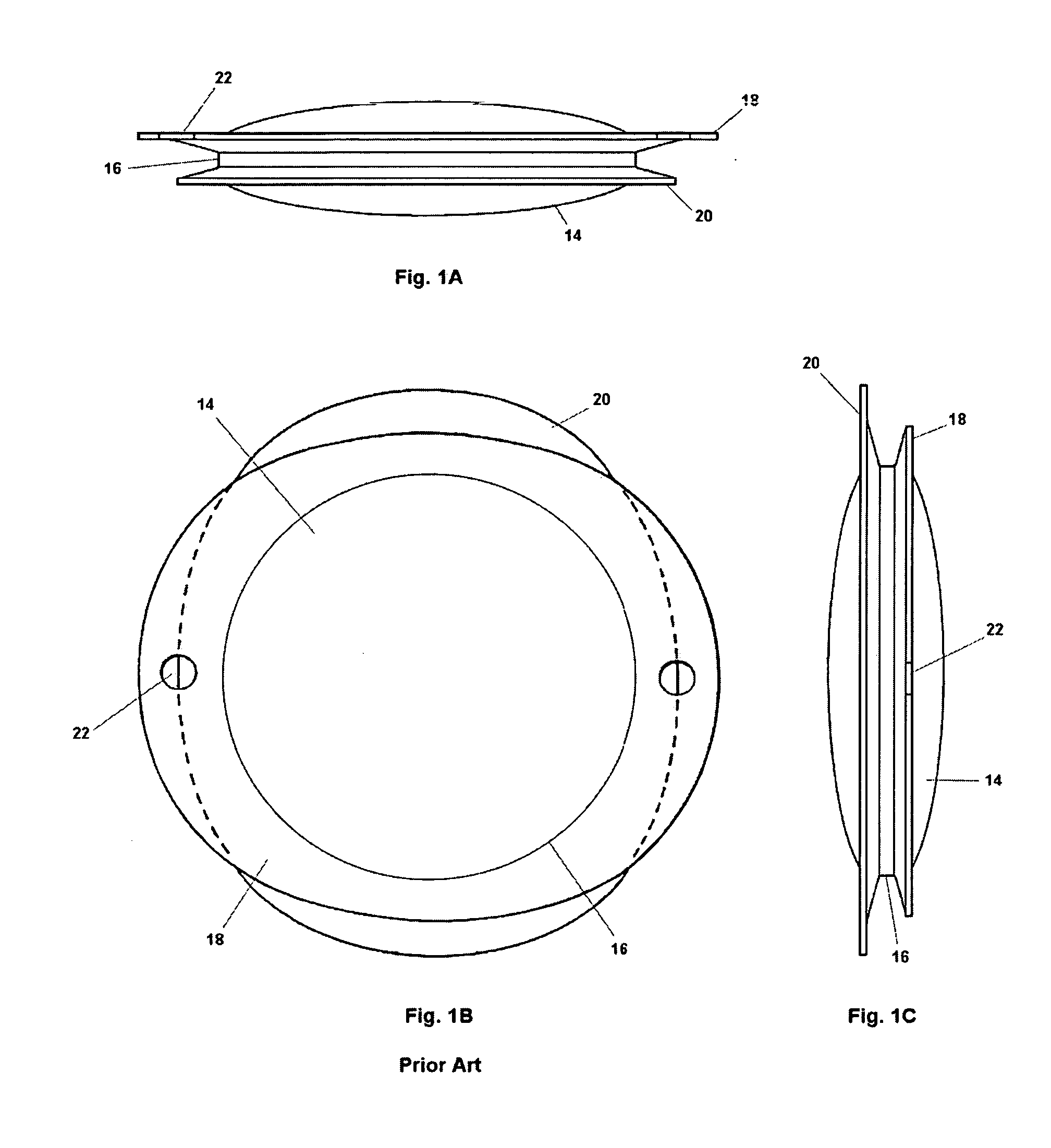
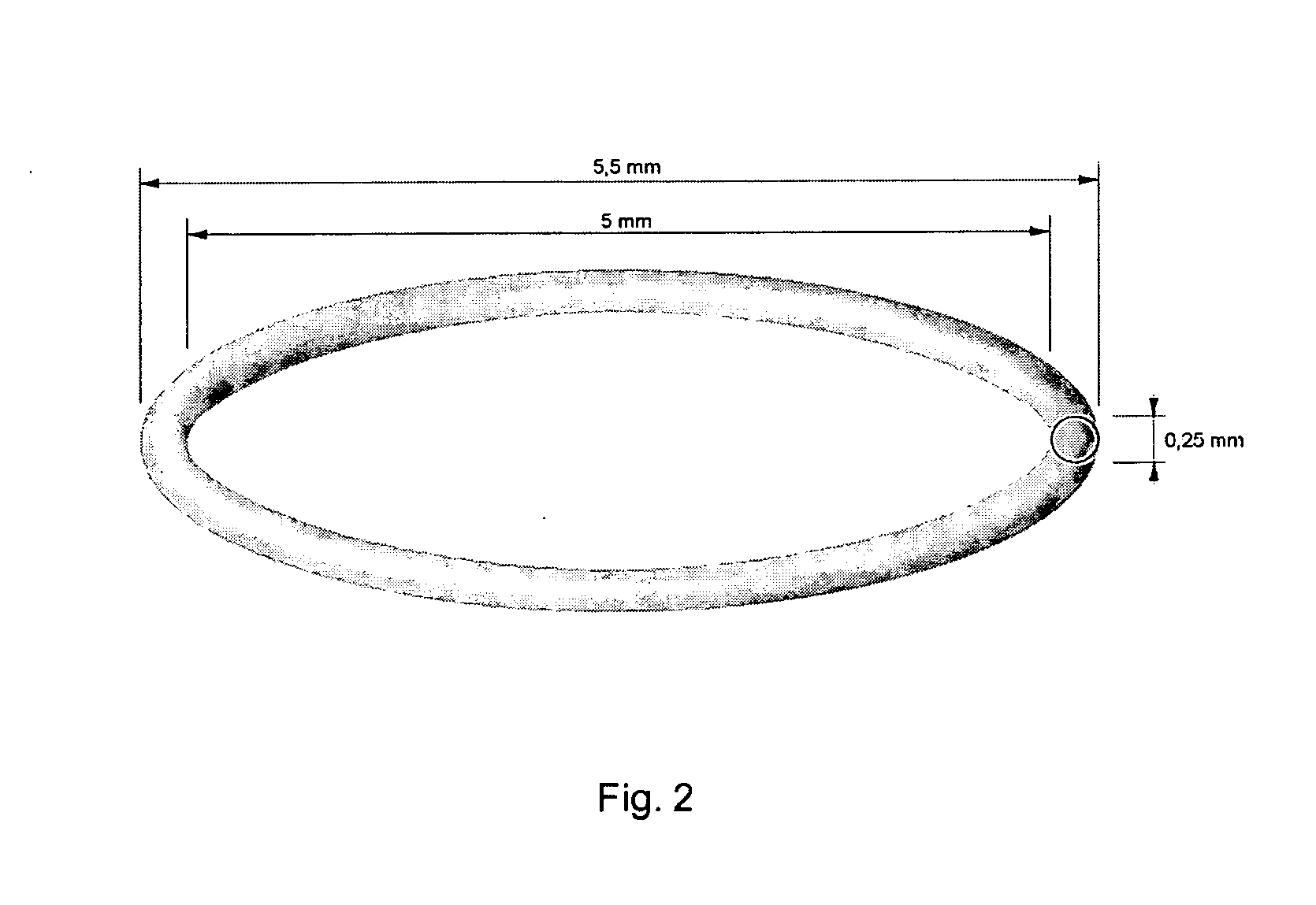
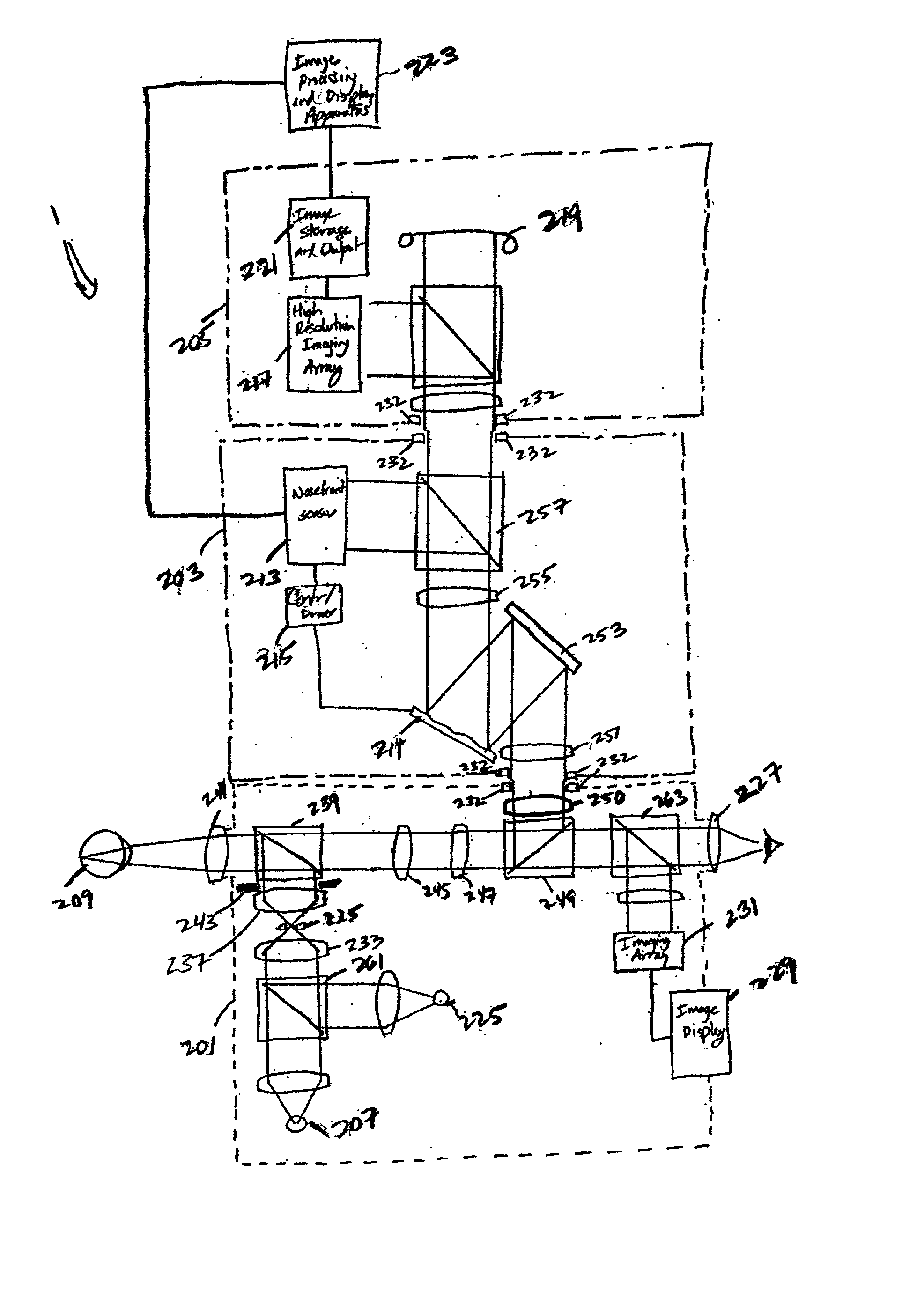
Patents
Literature
2123 results about "Astigmatism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A common vision condition that causes blurred vision.
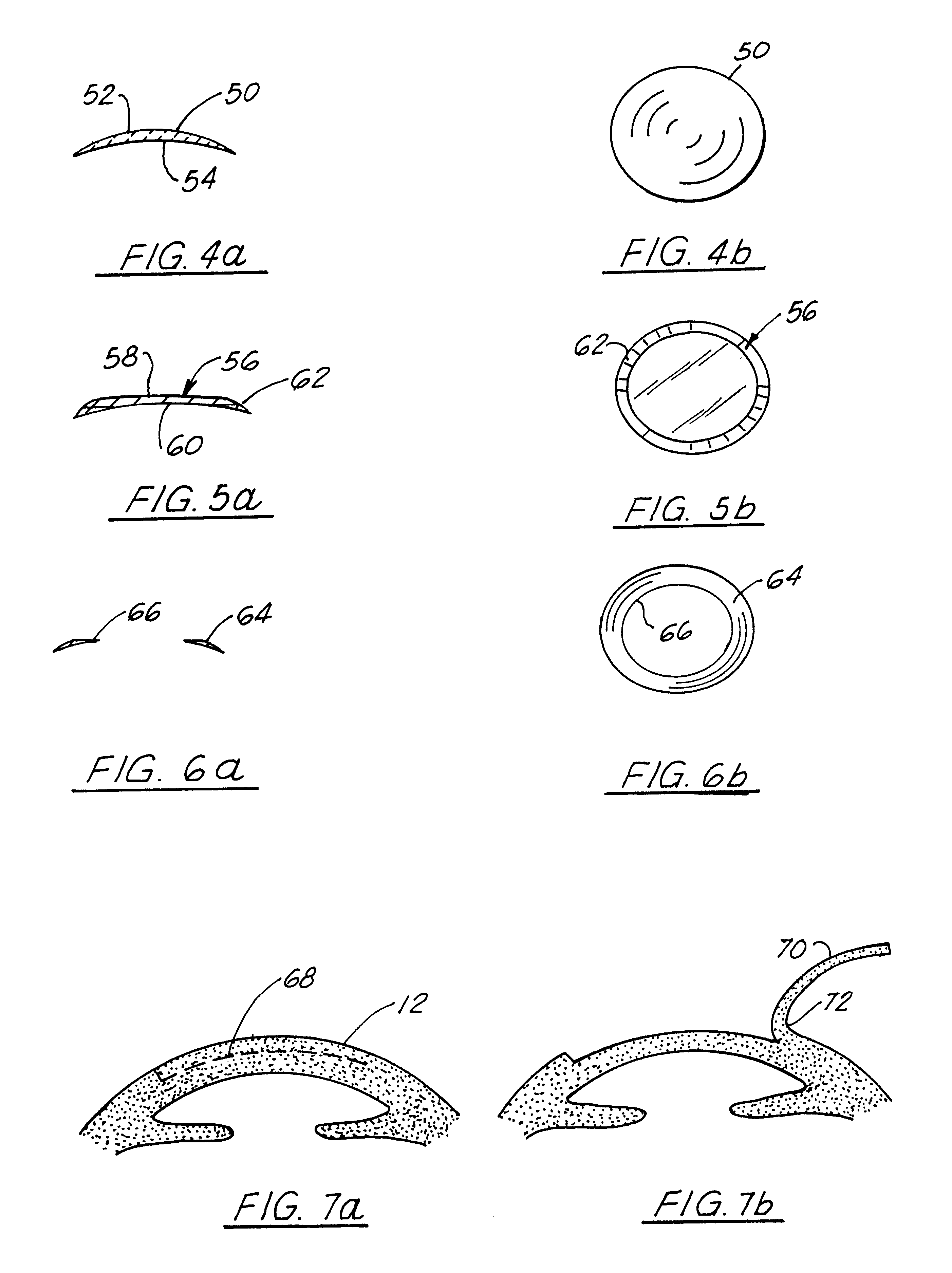
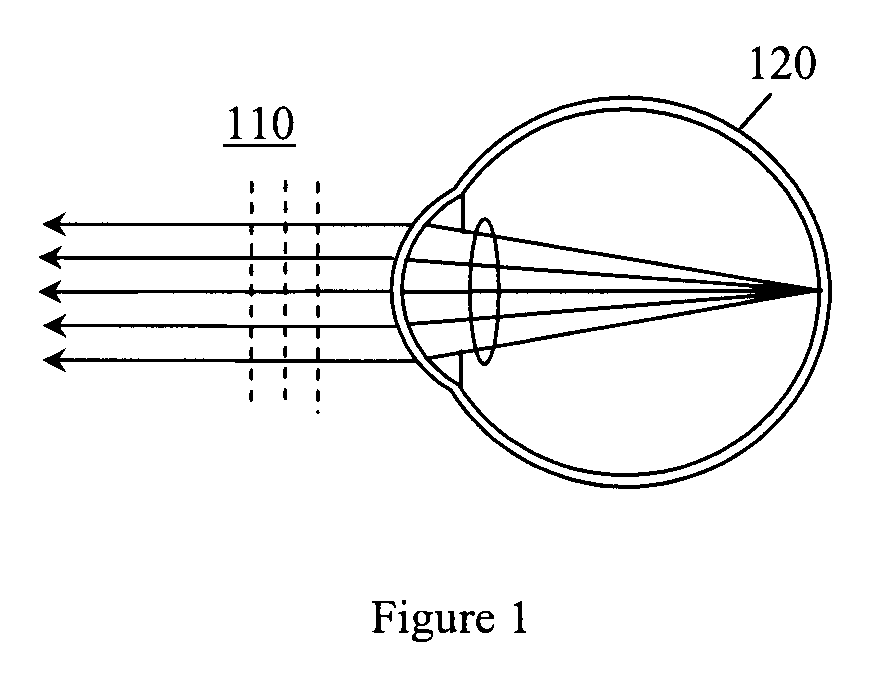
Methods and devices to design and fabricate surfaces on contact lenses and on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations
Methods and devices are described that are needed to design and fabricate modified surfaces on contact lenses or on corneal tissue that correct the eye's optical aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism. The invention provides the means for: 1) measuring the eye's optical aberrations either with or without a contact lens in place on the cornea, 2) performing a mathematical analysis on the eye's optical aberrations in order to design a modified surface shape for the original contact lens or cornea that will correct the optical aberrations, 3) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a contact lens by diamond point turning, three dimensional contour cutting, laser ablation, thermal molding, photolithography, thin film deposition, or surface chemistry alteration, and 4) fabricating the aberration-correcting surface on a cornea by laser ablation.
Owner:BROOKFIELD OPTICAL SYST
Eye mask
InactiveUS20030056281A1Recovering and restoringSimple structureElectrotherapyVibration massageDiseaseFarsightedness
An eye mask has magnetic bodies and self-heating warm members, which are inserted in eye pads on a mask member to be placed over eyeball parts. If required, vibrators and illumination bodies may be additionally placed in the eye pads. Thus, fatigue on the eyes and surroundings thereof can be relieved by the magnetic actions of the magnetic bodies and the warming effects of the warming member, in addition to expected effects of restoring ocular functions, recovering from various ocular diseases, and so on. Furthermore, the surface of each of the eye pads is gradually curved like the inner surface of a sphere. When the eye pads are press-contact to the eyeball parts at predetermined pressures for a long time, the cornea can be warmed by the warming members so that the shape of the cornea can be changed along the shape of the eye pad, resulting in the effects of recovering from eye sight disorder such as pseudo-myopia, moderate farsightedness, or moderate astigmatism.
Owner:HASEGAWA TOKUICHIRO
Methods and systems for optical imaging or epithelial luminal organs by beam scanning thereof
Arrangements, apparatus, systems and systems are provided for obtaining data for at least one portion within at least one luminal or hollow sample. The arrangement, system or apparatus can be (insertable via at least one of a mouth or a nose of a patient. For example, a first optical arrangement can be configured to transceive at least one electromagnetic (e.g., visible) radiation to and from the portion. A second arrangement may be provided at least partially enclosing the first arrangement. Further, a third arrangement can be configured to be actuated so as to position the first arrangement at a predetermined location within the luminal or hollow sample. The first arrangement may be configured to compensate for at least one aberration (e.g., astigmatism) caused by the second arrangement and / or the third arrangement. The second arrangement can include at least one portion which enables a guiding arrangement to be inserted there through. Another arrangement can be provided which is configured to measure a pressure within the at least one portion. The data may include a position and / or an orientation of the first arrangement with respect to the luminal or hollow sample.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Spectroscopic apparatus
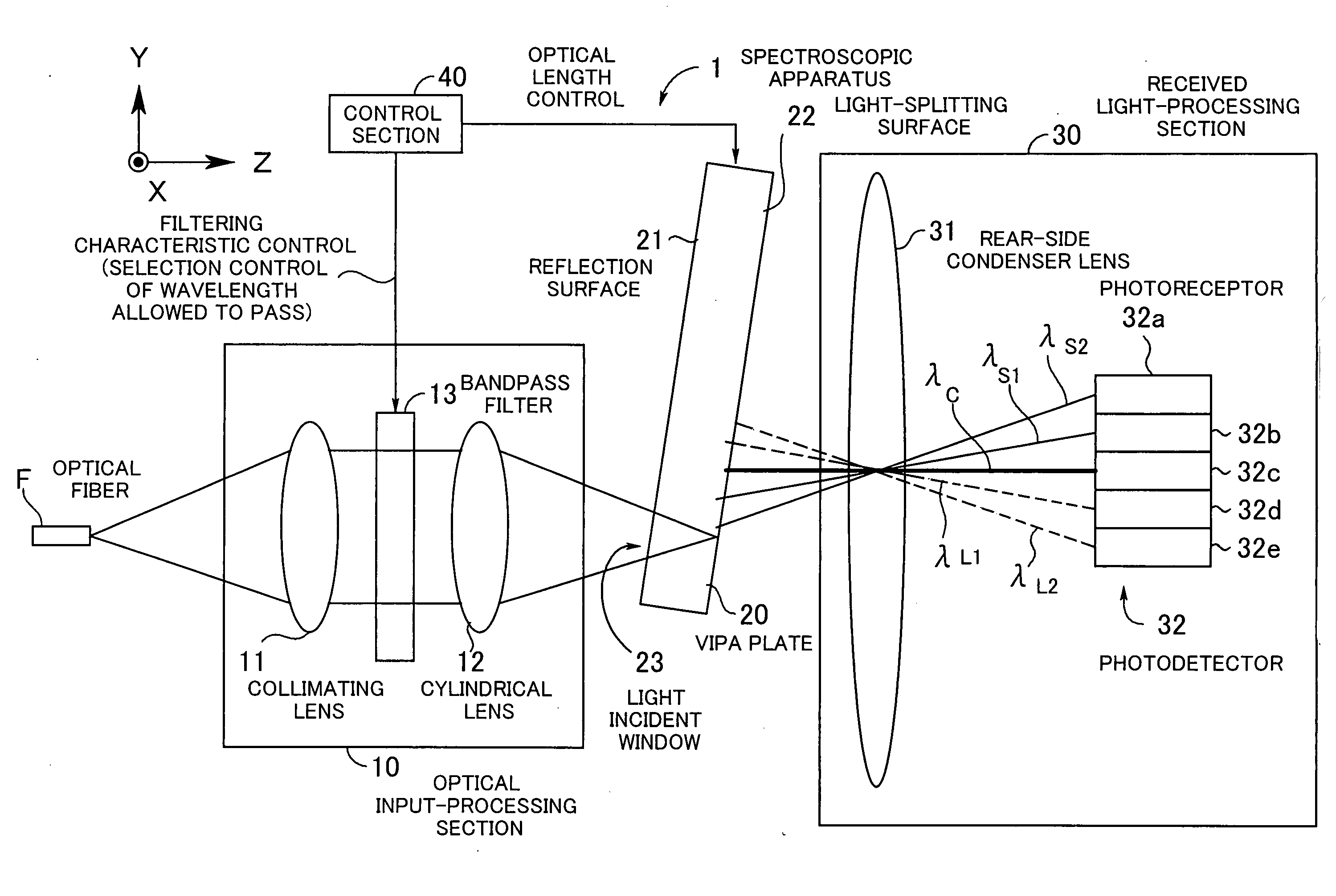
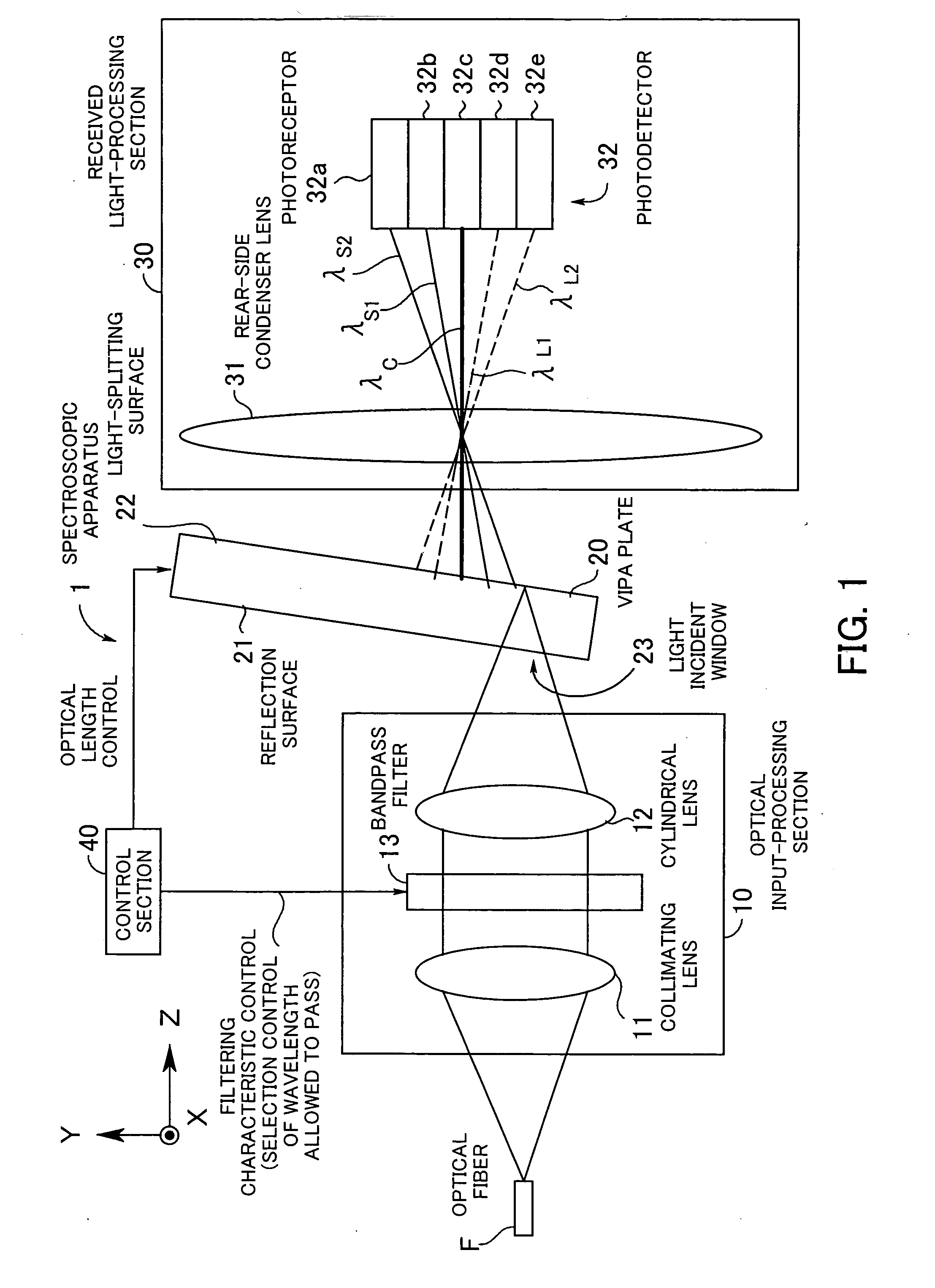
InactiveUS20050046837A1Small sizeLarge angular dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Refraction measuring instrument
InactiveUS20060215111A1Small sizeReduce weightRefractometersSkiascopesMeasuring instrumentBeam splitting
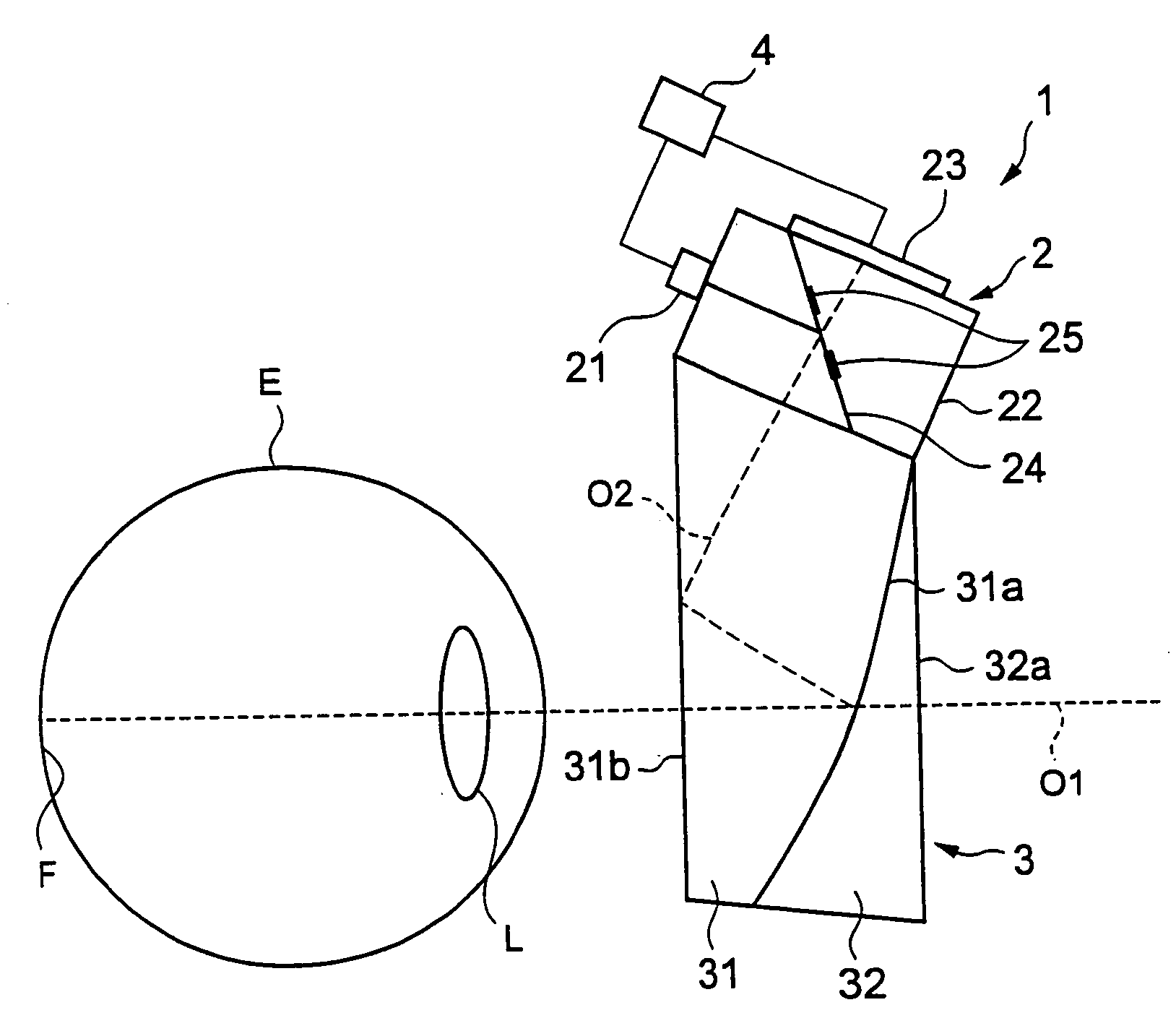
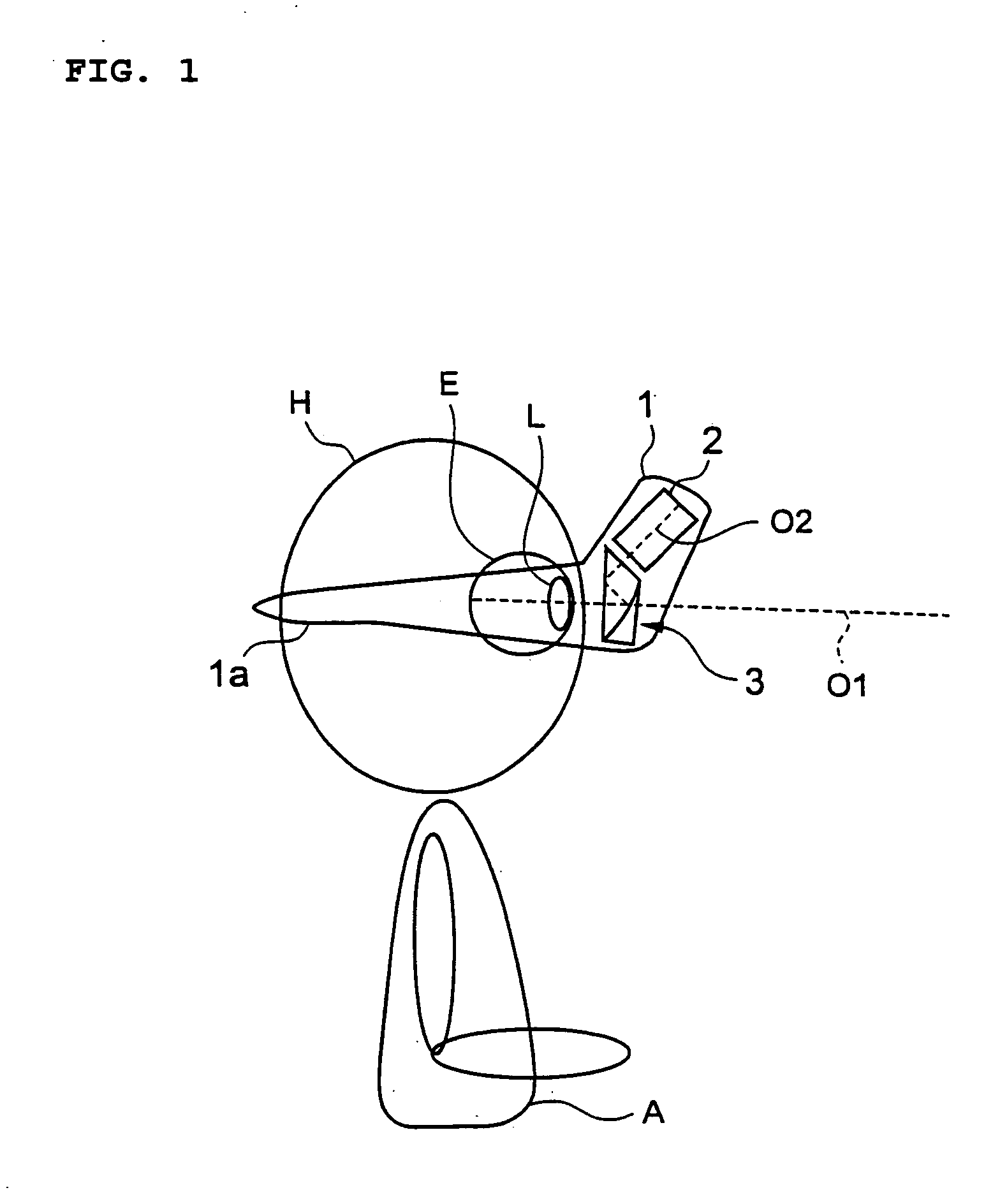
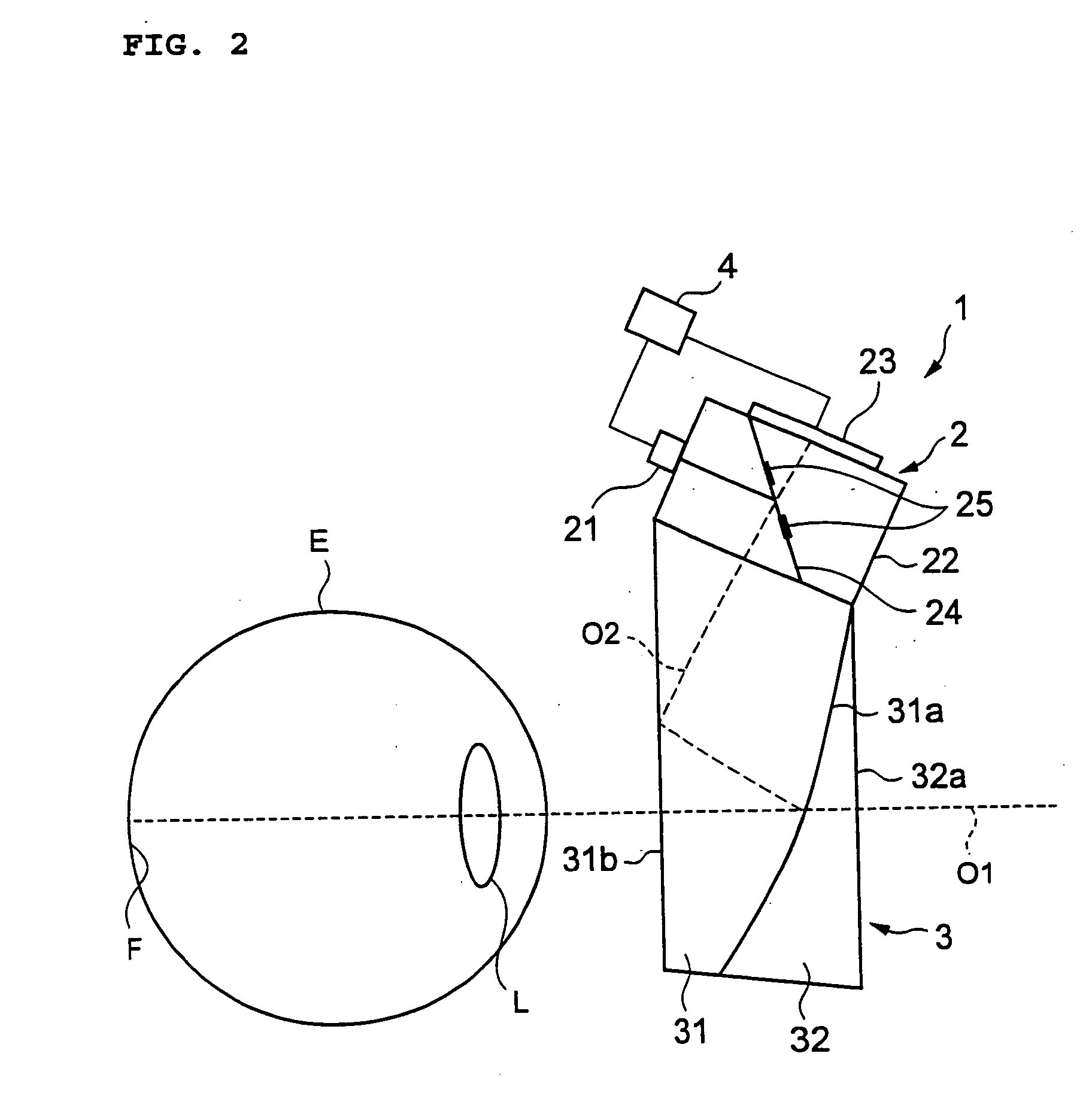
A refraction measuring instrument for measuring the refraction of an eye to be examined while the subject is viewing an external object in a more natural posture. A measuring light beam from a light source 21 is reflected from a mirror 25, shaped into a beam with a ring cross section, directed to a free curved surface prism 31 along an optical axis O2, reflected from a surface 31b and a beam splitting surface 31a, guided to an eye E along an optical axis O1 together with the visible light from outside the instrument, and form a ring pattern on the fundus F. The measurement beam reflected from the fundus F is received by a CCD 23 through the free curved surface prism 31 and a prism 22, and a ring pattern is imaged. A calculation control device 4 analyzes the imaged ring pattern and calculates the sphericity, the degree of astigmatism, and the astigmatic axis angle. For measurement, the subject A wears the refraction measuring instrument 1 on the head H through a wearing section 1a.
Owner:KK TOPCON
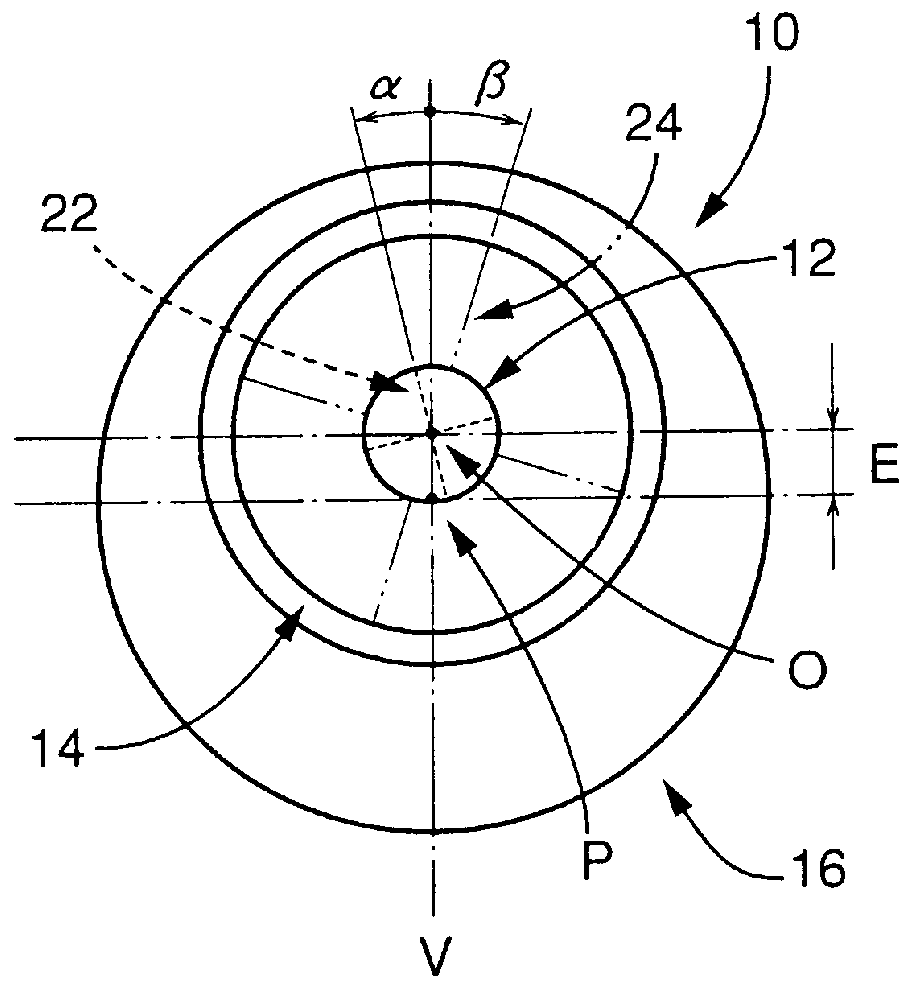
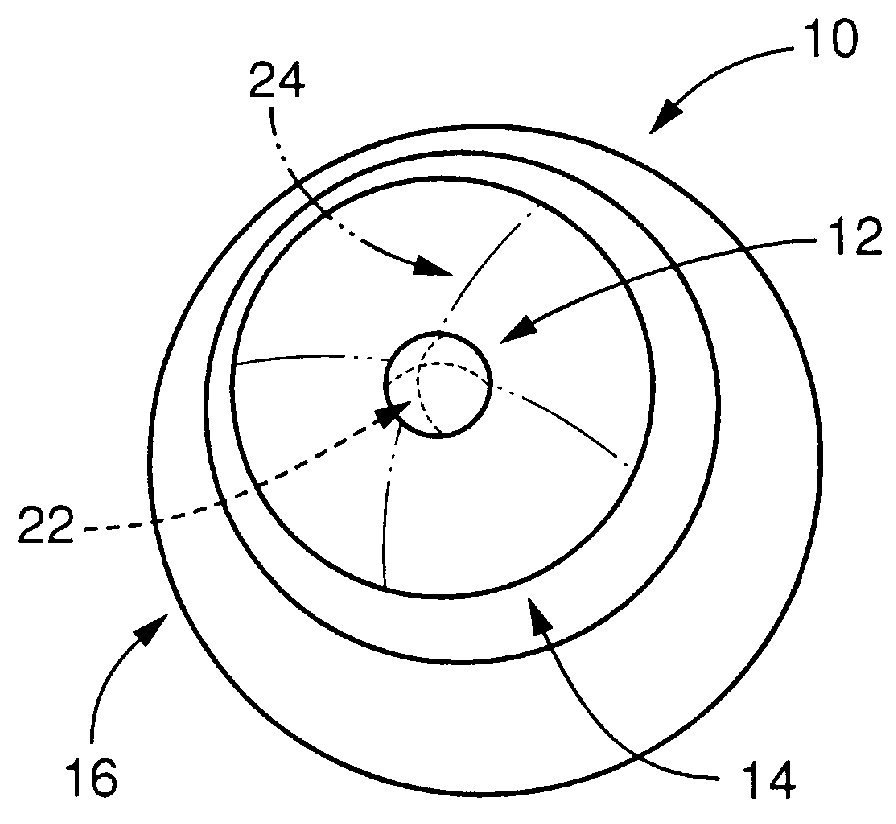
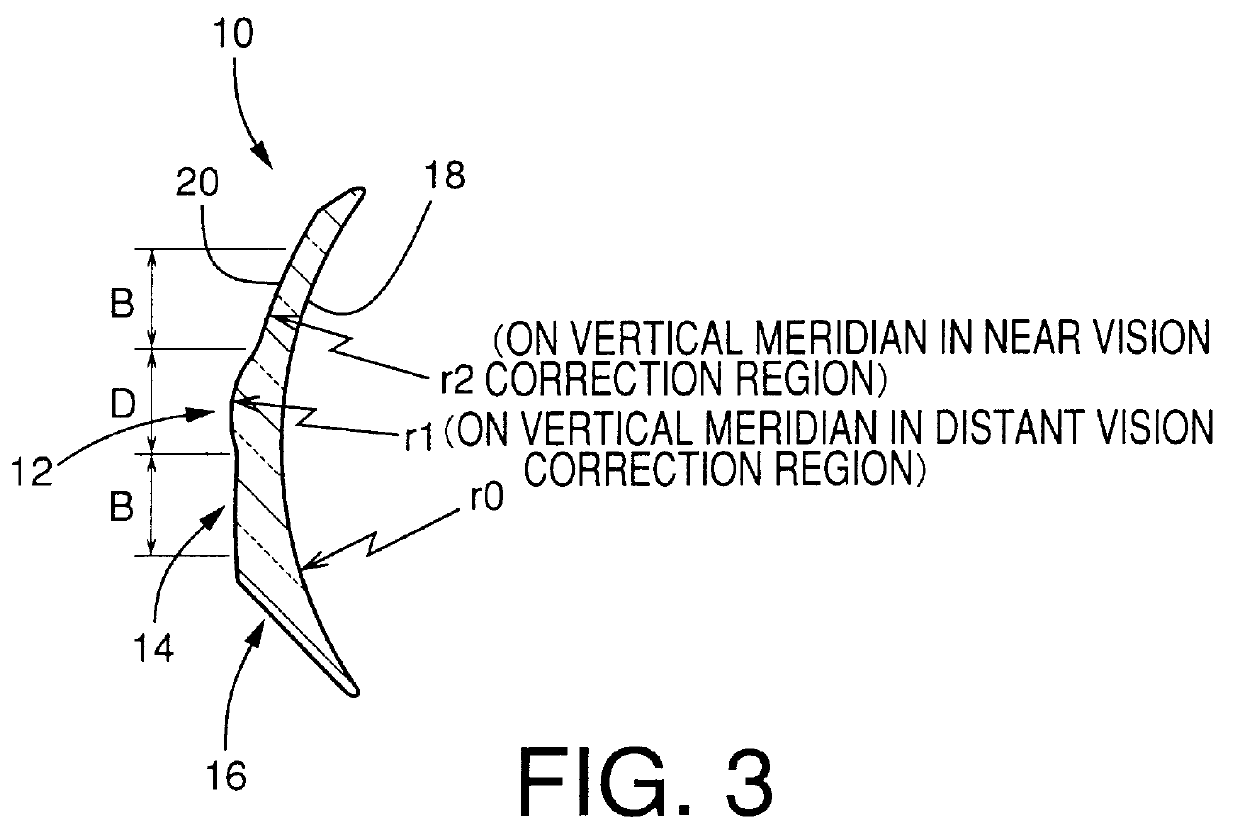
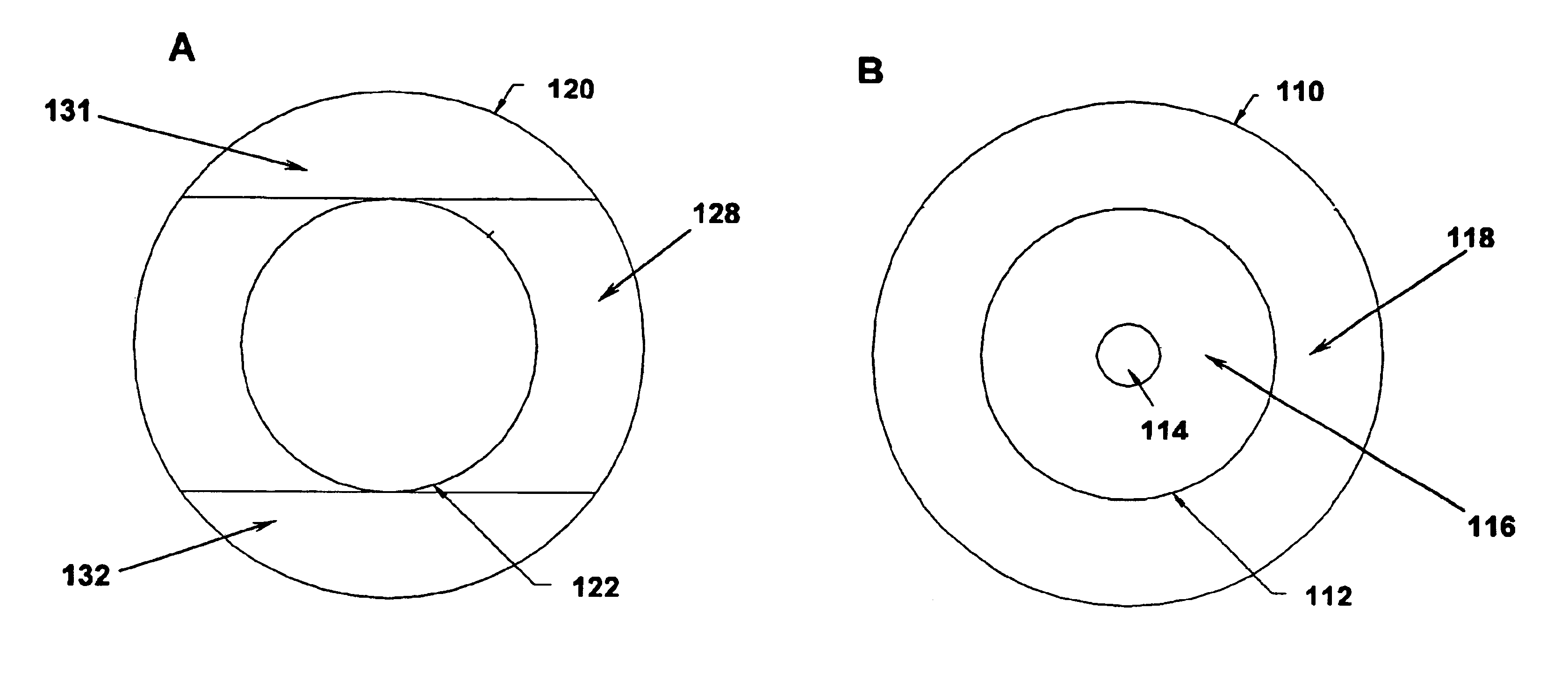
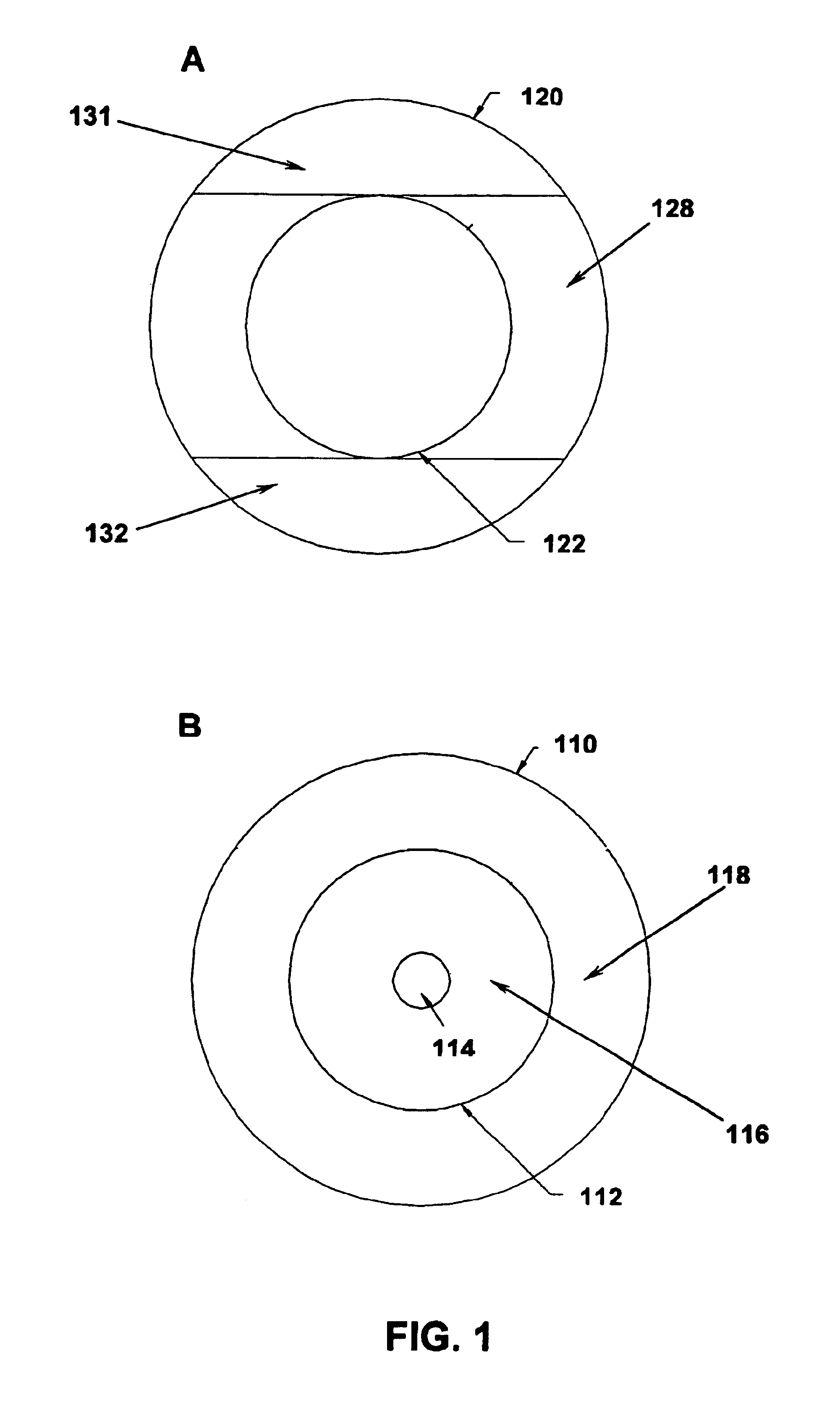
Toric multifocal lens having different astigmatism corrective optical powers in respective vision correction regions, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6142625AEasy to produceImprove stabilitySpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsOptical powerStigmatism
A toric multifocal lens including a plurality of vision correction regions having centers on a common optical center axis, the plurality of vision correction regions providing respective different values of a spherical optical power, each of the plurality of vision correction regions having an optical power for correction of astigmatism, wherein the improvement comprises: at least one of a cylindrical optical power and a cylindrical axis orientation which determine the optical power for correction of astigmatism being different in at least two different vision correction regions of the plurality of vision correction regions, so that the at least two different vision correction regions have respective different values of the optical power for correction of astigmatism.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Method and apparatus for creating ocular surgical and relaxing incisions
ActiveUS20080281303A1Improve accuracyImprove precisionLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLight beamTarget tissue
A system and method of treating target tissue in a patient's eye, which includes generating a light beam, deflecting the light beam using a scanner to form first and second treatment patterns, delivering the first treatment pattern to the target tissue to form an incision that provides access to an eye chamber of the patient's eye, and delivering the second treatment pattern to the target tissue to form a relaxation incision along or near limbus tissue or along corneal tissue anterior to the limbus tissue of the patient's eye to reduce astigmatism thereof.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Super wide-angle panoramic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6611282B1Without significant loss of image qualityEliminate aberrationsTelevision systemsTelescopesWide fieldViewpoints
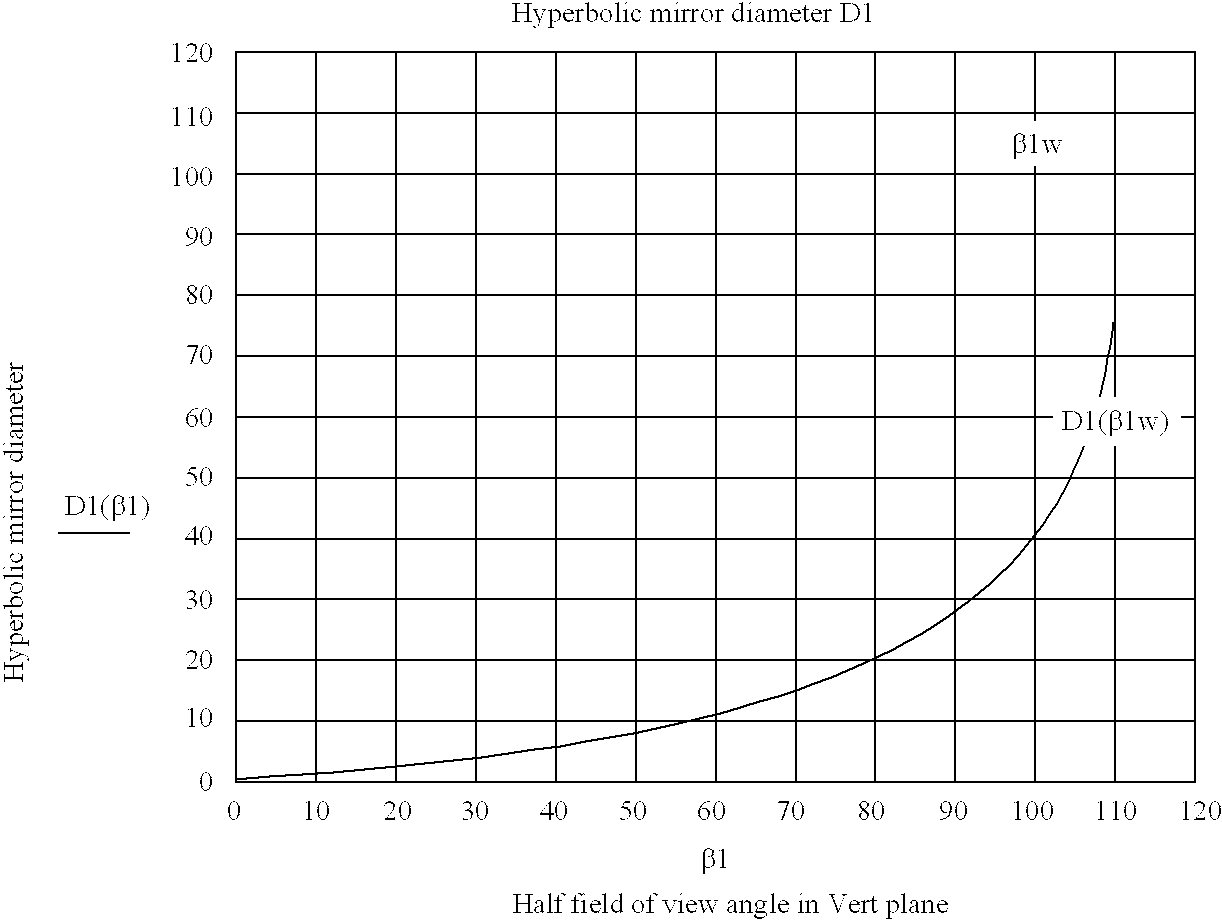
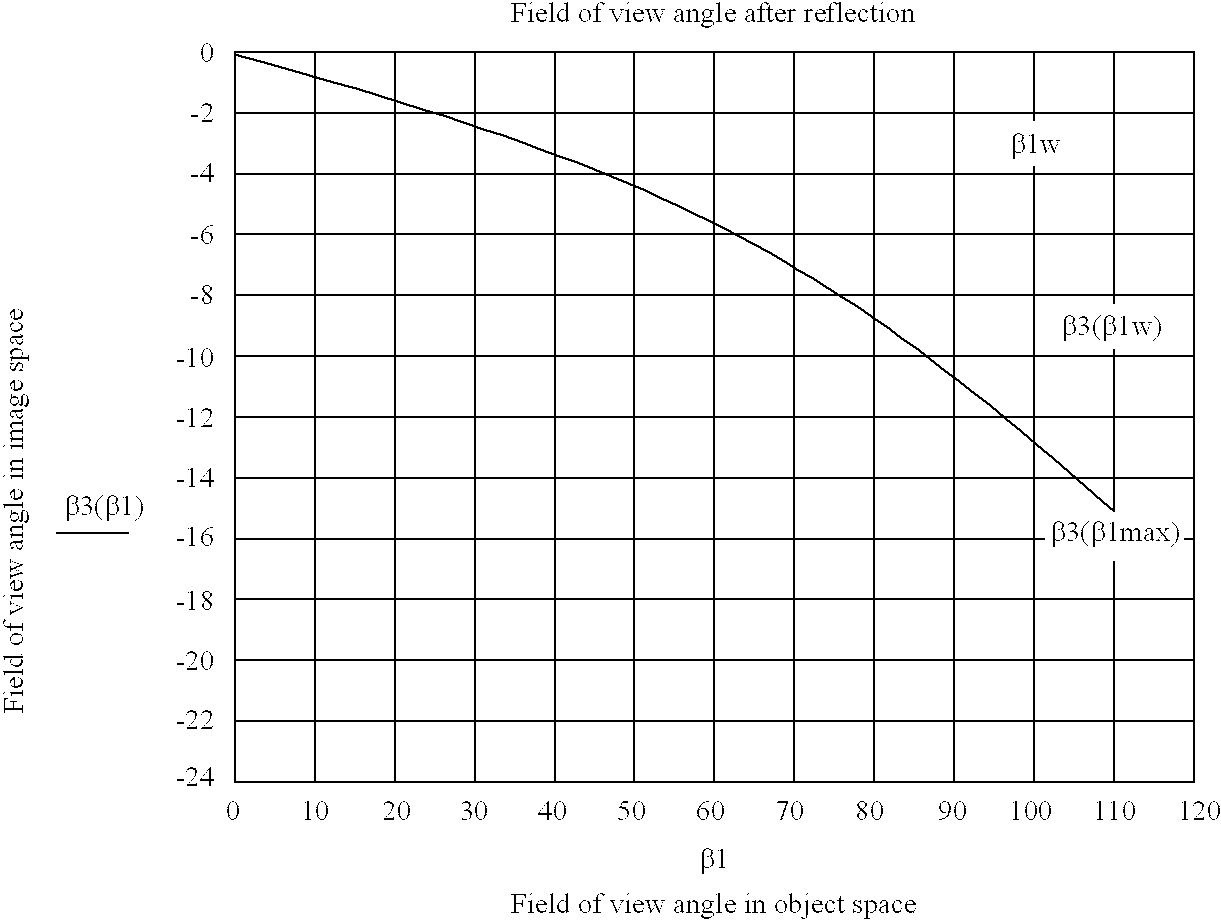
A system for capturing super wide-angle panoramic images. In particular, a two-reflector system is disclosed which is substantially self-correcting in which optical aberrations are substantially eliminated, such as field curvature, astigmatism and the like. Moreover, the super wide-angle panoramic imaging apparatus of the invention captures a super-wide field of view from a substantially single reference viewpoint. The invention provides a substantially compact viewpoint, while also having a substantially flat and stigmatic image plane, in the context of a super wide-angle panoramic system. Devices and methods for capturing panoramic images of super wide-angle scenes are provided. In a particular embodiment of the invention, two reflectors are provided (e.g., one a hyperboloidal mirror, the other a concave ellipsoidal or spherical mirror), a relay system (e.g., optics such as a mirror, a lens, a pinhole and the like) and an image sensor (e.g., an electronic photo-sensor, a film and the like).
Owner:REMOTEREALITY
Image capturing lens assembly
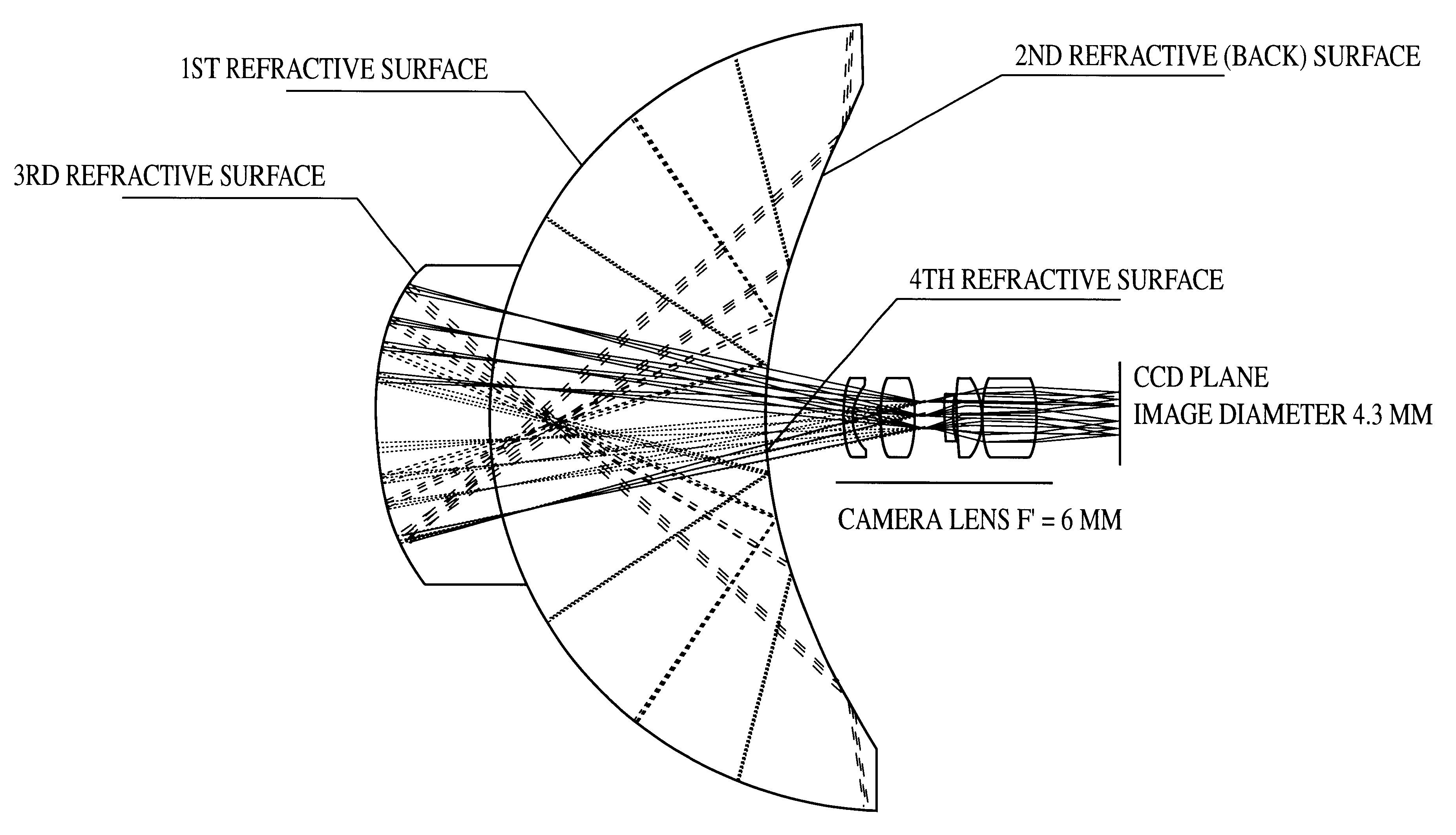
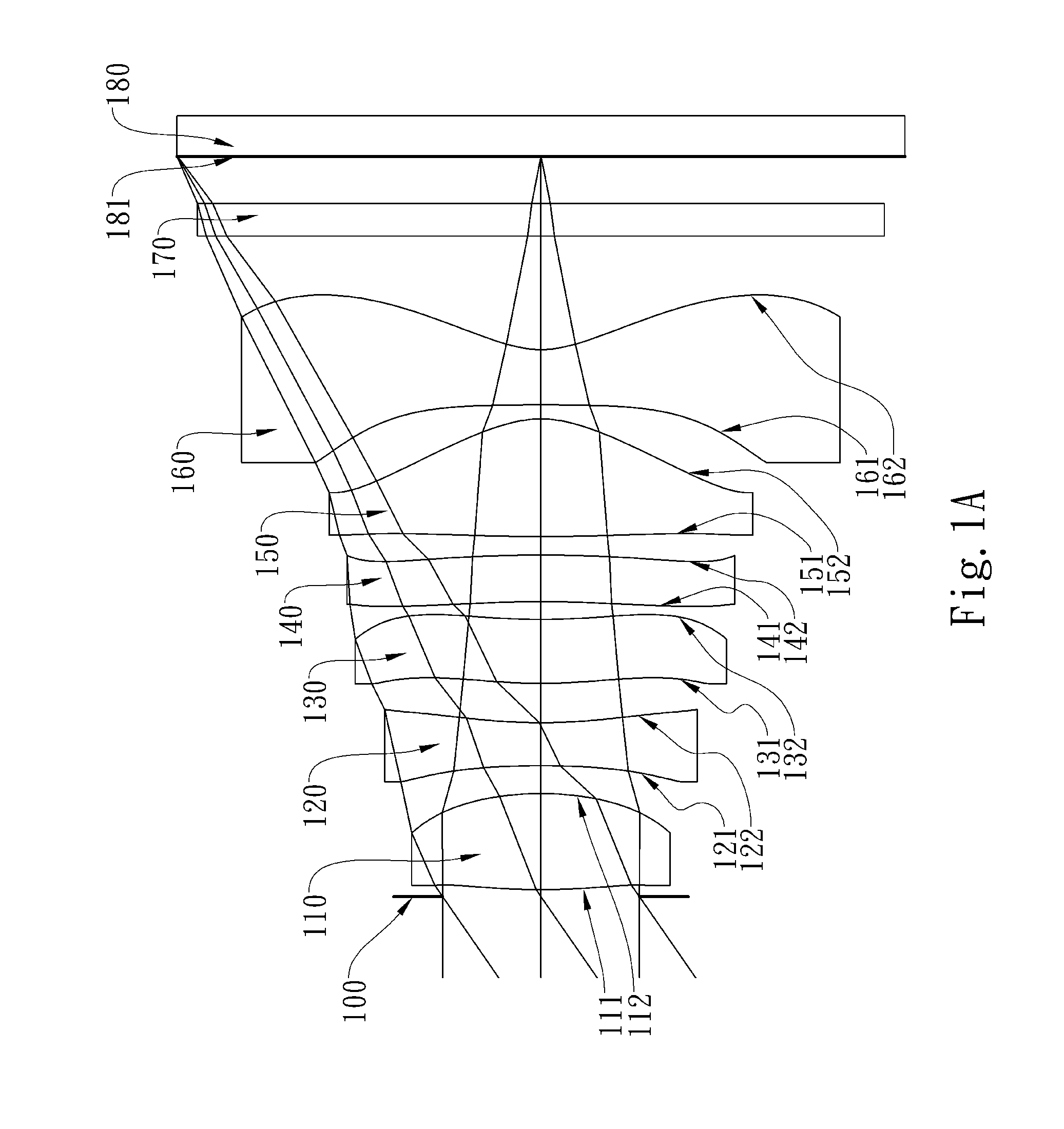
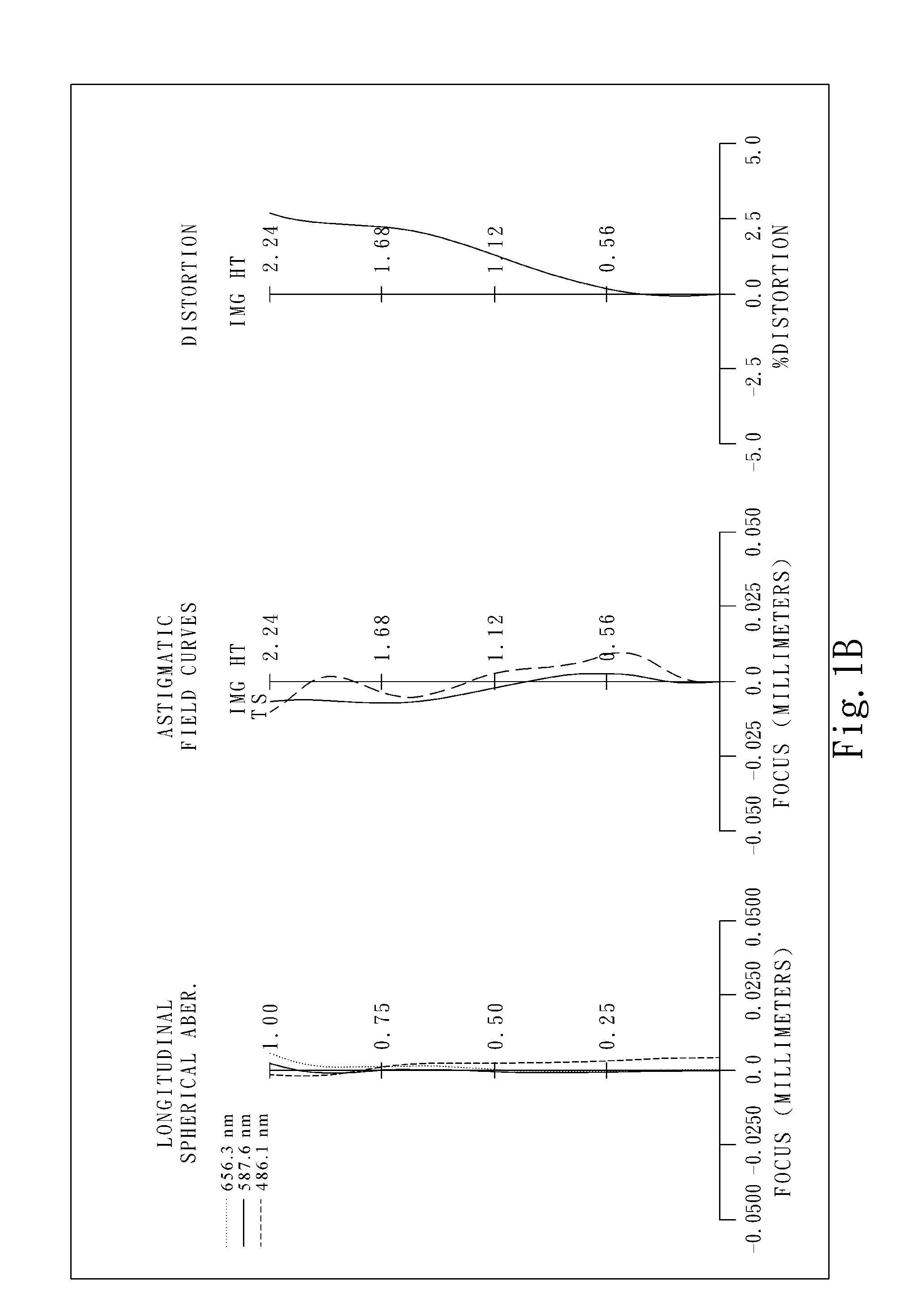
ActiveUS20120194726A1High image resolutionReduce track lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionAstigmatism
This invention provides an image capturing lens assembly, in order from an object side to an image side comprising: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element having at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; a fifth lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, and the fifth lens element is made of plastic; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, and the sixth lens element is made of plastic. By such arrangement, the photo-sensitivity and the total track length of the image capturing lens assembly can be reduced. Furthermore, the aberration and astigmatism of the assembly can be effectively corrected for obtaining higher image resolution.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
High performance corneal inlay
A corneal inlay protects ocular structures from harmful wavelengths of light while maintaining acceptable color cosmetics, color perception, overall light transmission, photopic vision, scotopic vision, color vision, and / or cirdadian rhythms. The corneal inlay can also include a pinhole effect to increase depth of focus. In some embodiments, the corneal inlay can also correct refractive errors including, but not limited to, higher order aberration, lower order aberration, myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and / or presbyopia.
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
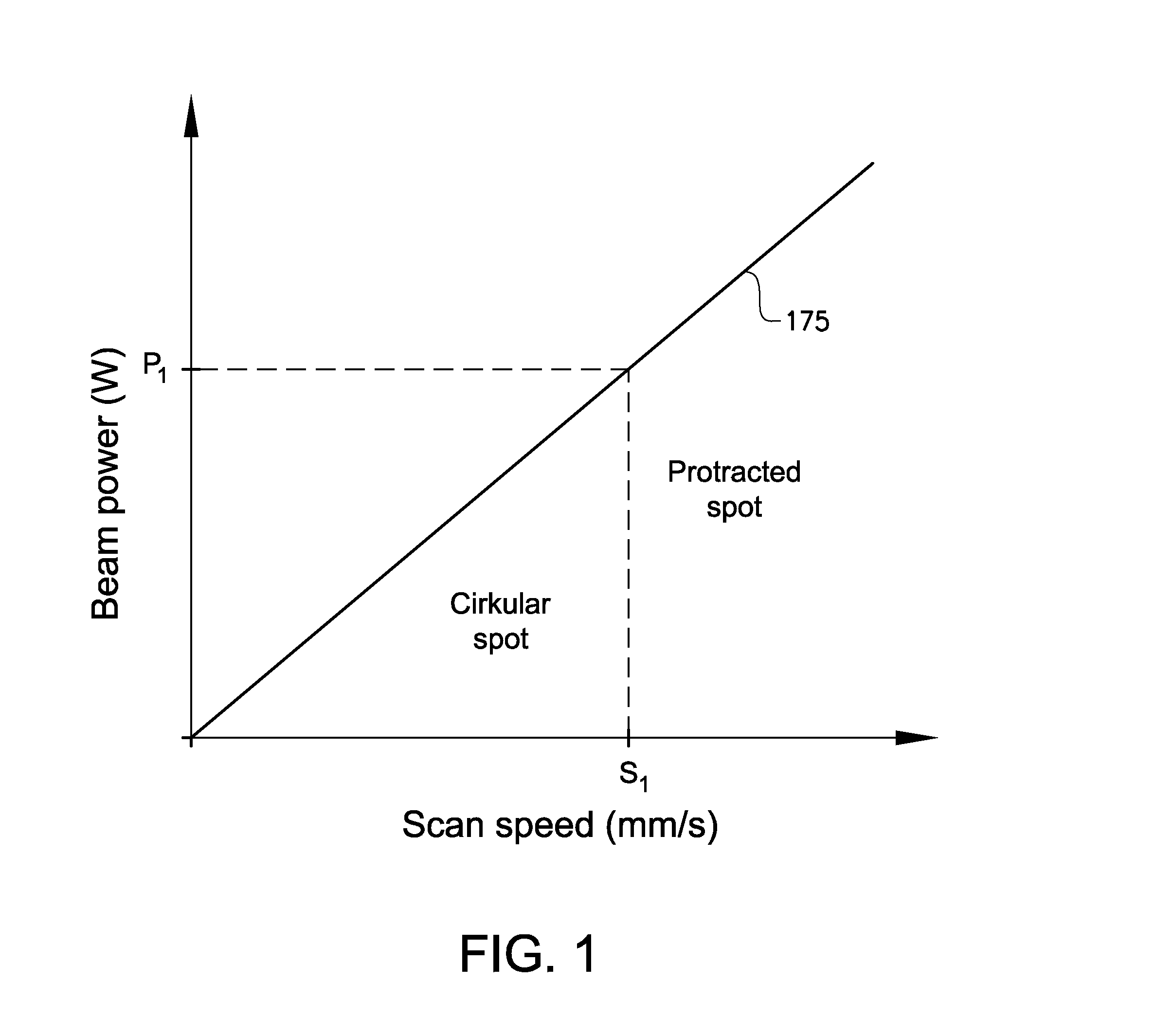
Method for fusing a workpiece
InactiveUS20150283613A1Increase powerSolve the slow scanning speedAdditive manufacturing apparatusAuxillary shaping apparatusEngineeringHigh energy beam
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to a method for welding a workpiece comprising the steps of: making a first weld at a first position on said workpiece with a high energy beam, deflecting the high energy beam with at least one deflection lens for making a second weld at a second position on said workpiece, focusing the high energy beam on said workpiece with at least one focusing lens, shaping the high energy beam on said workpiece with at least one astigmatism lens so that the shape of the high energy beam on said workpiece is longer in a direction parallel to a deflection direction of said high energy beam than in a direction perpendicular to said deflection direction of said high energy beam. The invention is also related to the use of an astigmatism lens and to a method for forming a three dimensional article.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Corneal implant and method of manufacture
Prosthetic implants designed to be implanted in the cornea for modifying the cornea curvature and altering the corneal refractive power for correcting myopia, and myopia with astigmatism, such implants formed of a micro-porous hydrogel material.
Owner:REVISION OPTICS
Drug delivery implants for inhibition of optical defects
InactiveUS20100114309A1Avoid side effectsInhibition releaseSenses disorderEye surgeryFar-sightednessHomatropine
An implant for use with an eye comprises an implantable structure and a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent is deliverable from the structure into the eye so as to therapeutically effect and / or stabilize a refractive property of the eye. In many embodiments, the refractive property of the eye may comprise at least one of myopia, hyperopia or astigmatism. The therapeutic agent can comprise a composition that therapeutically effects or stabilizes the refractive property of the eye. The therapeutic agent may comprise at least one of a mydriatic or a cycloplegic drug. For example, the therapeutic agent may include a cycloplegic that comprises at least one of atropine, cyclopentolate, succinylcholine, homatropine, scopolamine, or tropicamide. In many embodiments, a retention element can be attached to the structure to retain the structure along a natural tissue surface.
Owner:MATI THERAPEUTICS
Toric intraocular lens with modified power characteristics
An intraocular lens for correcting or reducing the astigmatism of a cornea includes an optical element that has optical properties and characteristics that make it tolerant of rotational misalignment, when compared to a comparable lens having a uniform astigmatism orientation across its entire optical element, leading to more relaxed tolerances for a surgeon that implants the lens. The optical element of the toric ophthalmic lens has meridians associated therewith, including a high power meridian and a low power meridian orthogonal to the high power meridian. The optical element has at least one radially modulated meridian along which power monotonically varies with increasing radial position.
Owner:ABBOTT MEDICAL OPTICS INC
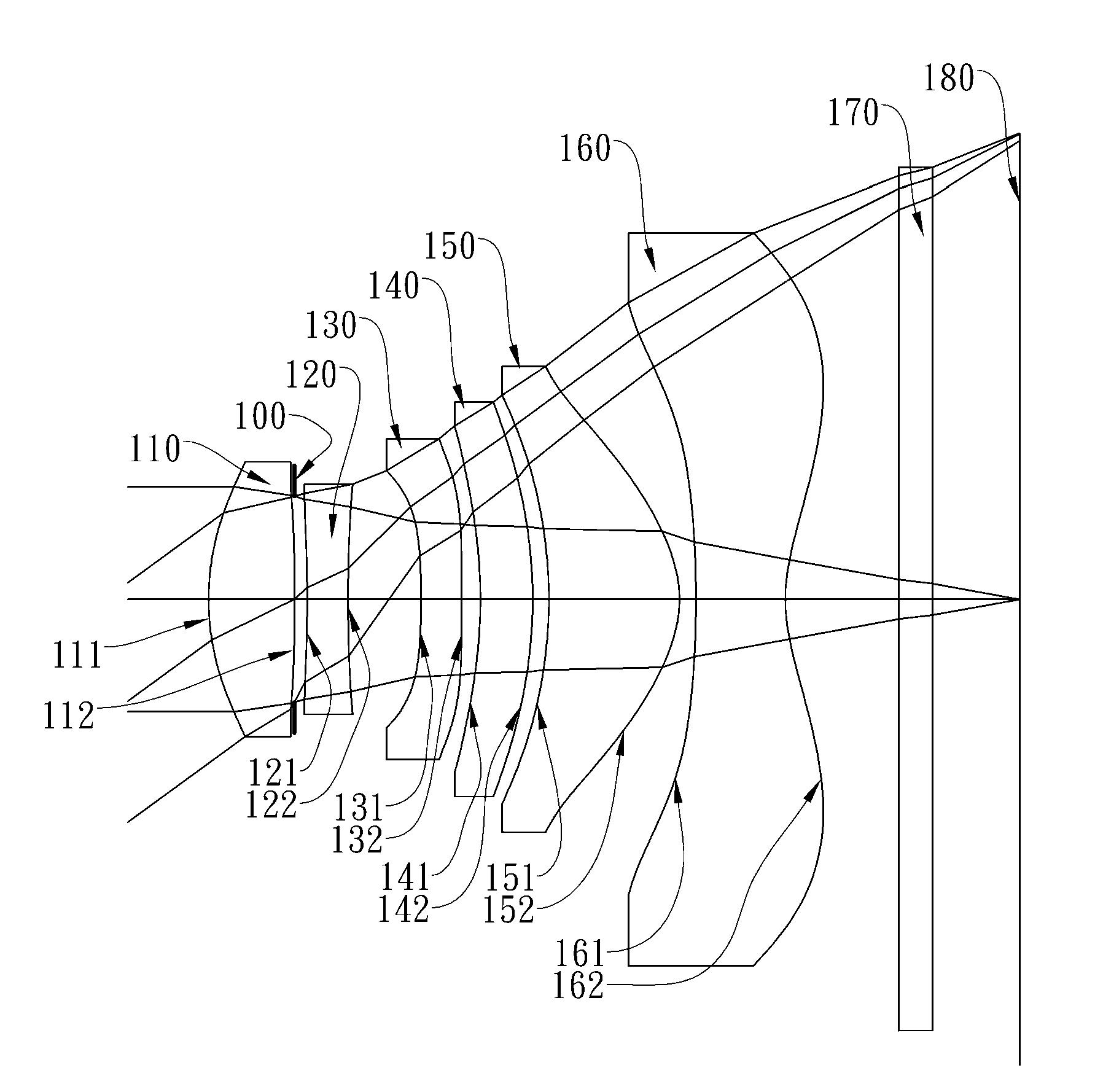
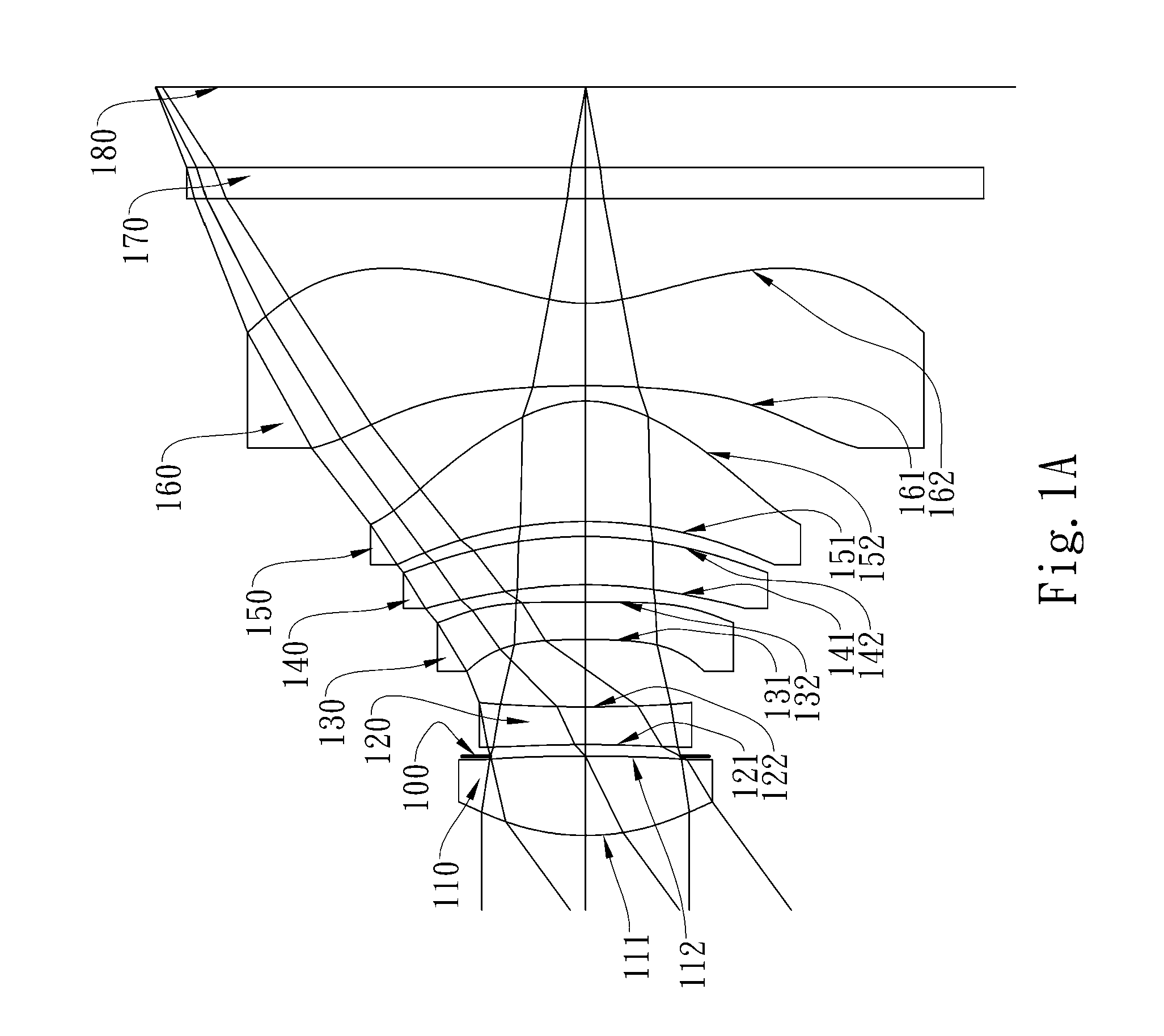
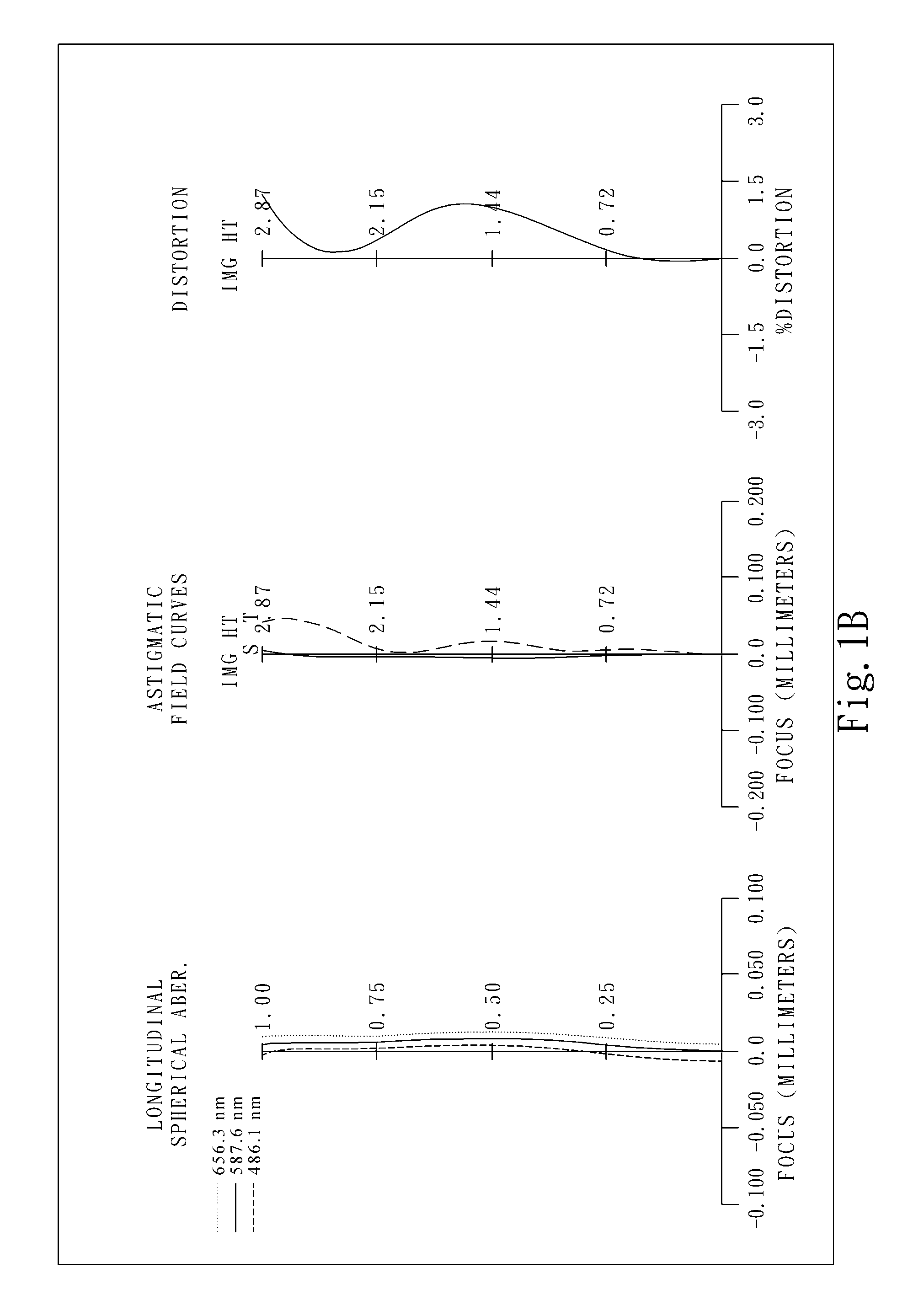
Optical image capturing lens assembly
The present disclosure provides an optical image capturing lens assembly comprising, in order from an object side to an image side: a first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex image-side surface; a second lens element; a third lens element; a fourth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; a fifth lens element, at least one of an object-side surface and an image-side surface thereof being aspheric; and a sixth lens element with negative refractive power having a concave image-side surface, at least one of an object-side surface and the image-side surface thereof being aspheric, at least one inflection point being formed on at least one of the surfaces thereof. With the aforementioned arrangements, the sensitivity of the optical system can be attenuated while the aberration and astigmatism can be effectively corrected to improve the image quality.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Modular intraocular implant
An adjustable ocular insert to be implanted during refractive cataract surgery and clear (human) crystalline lens refractive surgery and adjusted post-surgically. The implant comprises relatively soft but compressible and resilient base annulus designed to fit in the lens capsule and keep the lens capsule open. Alternatively the annulus may be placed in the anterior or posterior chamber. The annulus can include a pair of opposed haptics for secure positioning within the appropriate chamber. A rotatable annular lens member having external threads is threadedly engaged in the annulus. The lens member is rotated to move the lens forward or backward so to adjust and fine-tune the refractive power and focusing for hyperopia, myopia and astigmatism. The intraocular implant has a power range of approximately +3√0π−3 diopters.
Owner:EGGLESTON HARRY C
Lithographic projection apparatus and a device manufacturing method
A lithographic apparatus wherein a dipole illumination mode used for printing a line pattern, is arranged to provide quadrupole illumination. Radiation emanating from the two additional poles and passing the mask pattern without being affected by diffraction is prevented from reaching the wafer by a radiation blocking aperture disposed in the projection system. Astigmatism aberration due to lens heating associated with the dipole illumination mode is reduced by lens heating associated with the additional poles of the quadrupole illumination mode.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Toric multifocal contact lenses
The present invention provides a toric multifocal contact lens having a cylindrical optical power to correct astigmatism vision errors and a multifocal power to compensate for presbyopia. A toric multifocal contact lens of the invention has a central axis, an anterior surface having a first central optical zone, and an opposite posterior surface having a second central optical zone. The first central optical zone and the second central optical zone combine to provide a cylindrical optical power to correct astigmatism vision errors and a multifocal power to compensate for presbyopia.
Owner:ALCON INC
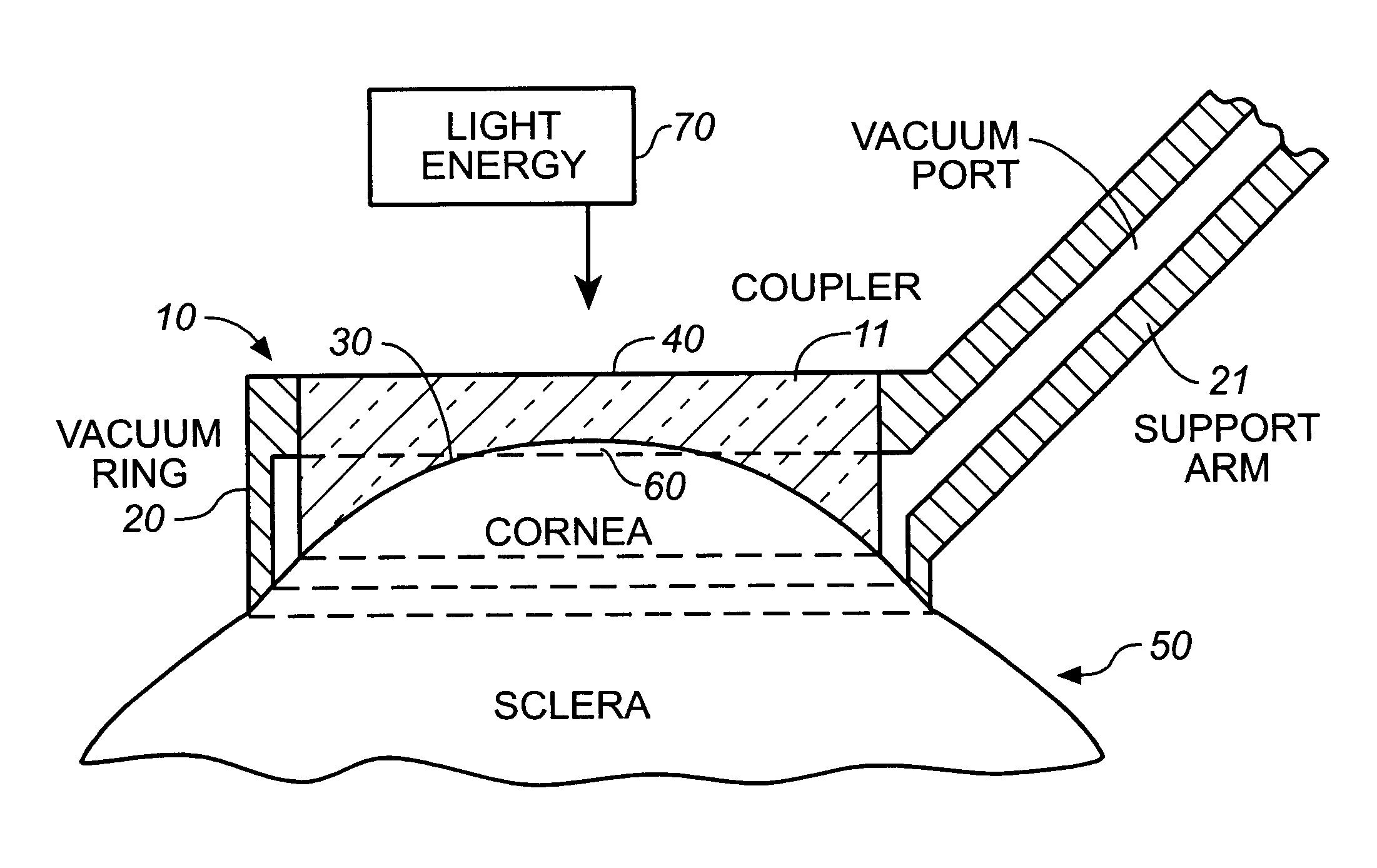
Apparatus for cornea reshaping
InactiveUS6342053B1Prevent accidental contactImprove protectionLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingOcular refractionOptical energy
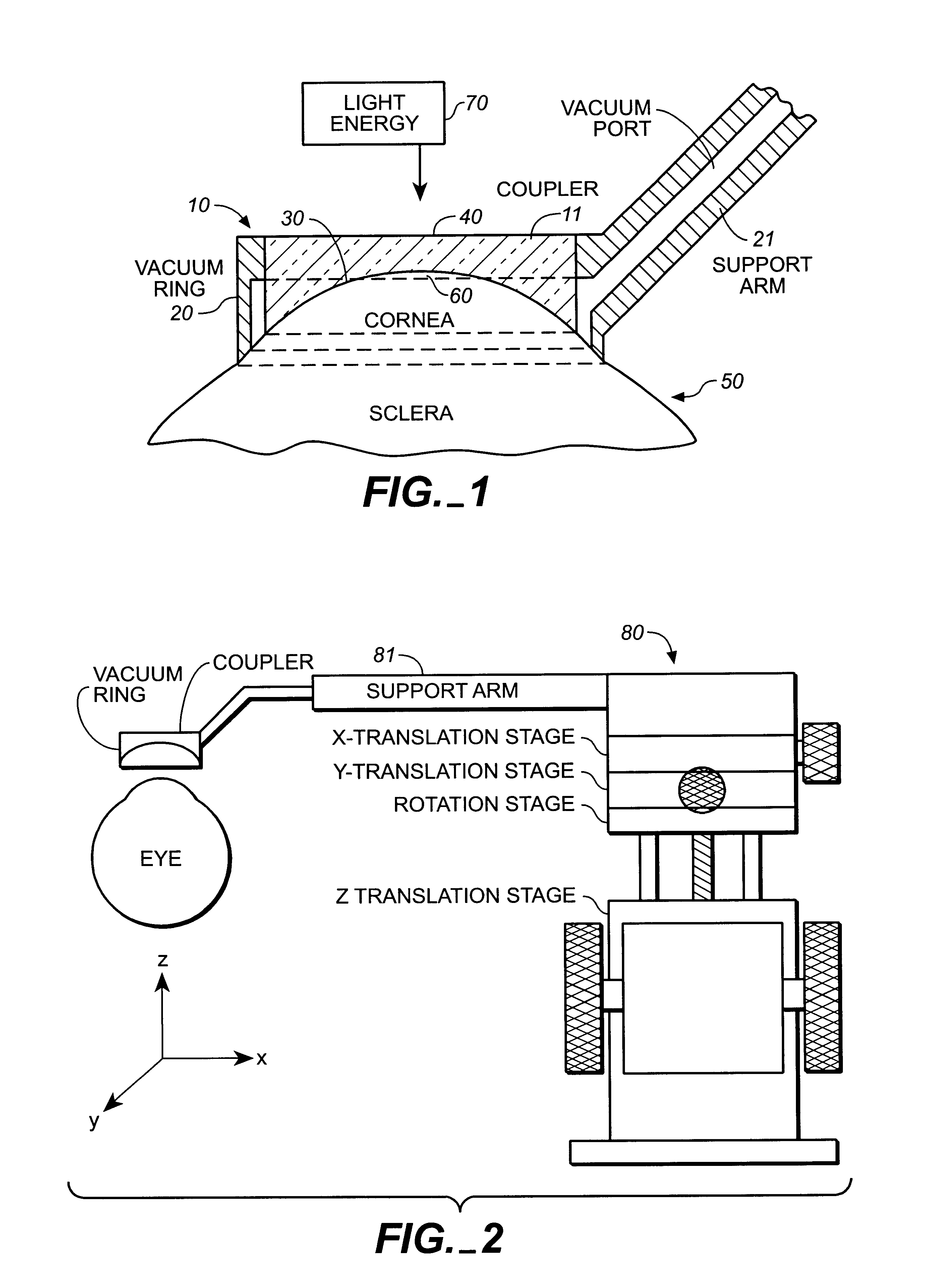
An apparatus is described for use in combination with a noninvasive ophthalmological method for cornea reshaping in order to correct ocular refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. This apparatus is called a coupler and it is made of a material which is substantially transparent to the light energy used to reshape the cornea. The coupler conducts heat from the anterior portion of the cornea during the heating of the stroma by the light energy. The reshaping is enhanced by the coupler as it has a corneal engaging surface with a radius of curvature which approximates the desired emmetropic shape of the cornea. In addition to being a heat sink and template for the eye, the coupler also acts as a positioner and restrainer of the eye by attaching itself to the eye via an annular suction ring. Finally, the coupler also acts as a mask to prevent accidental exposure of the central optic zone to any light energy during the cornea reshaping procedure.
Owner:LASER BIOTECH +1
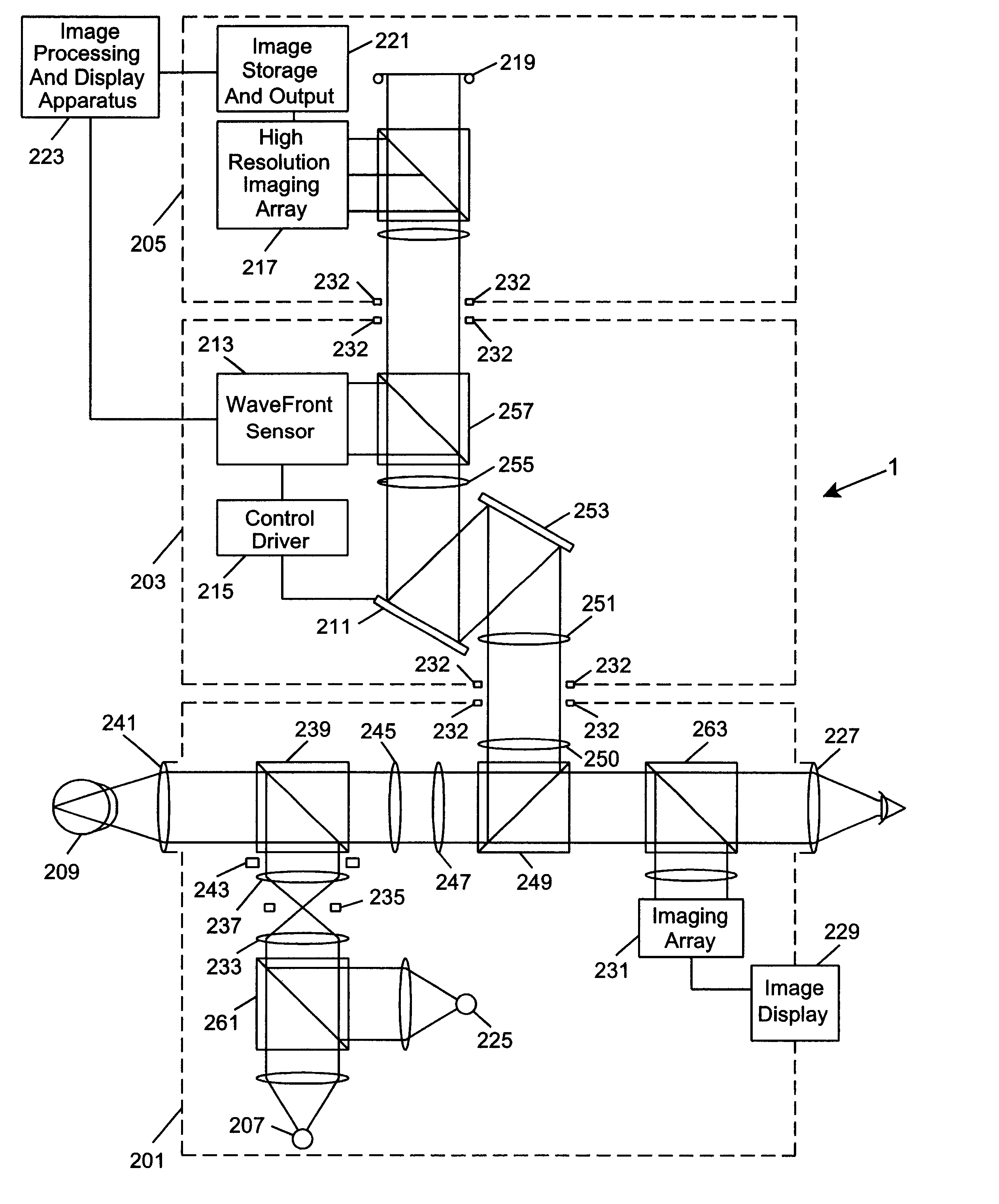
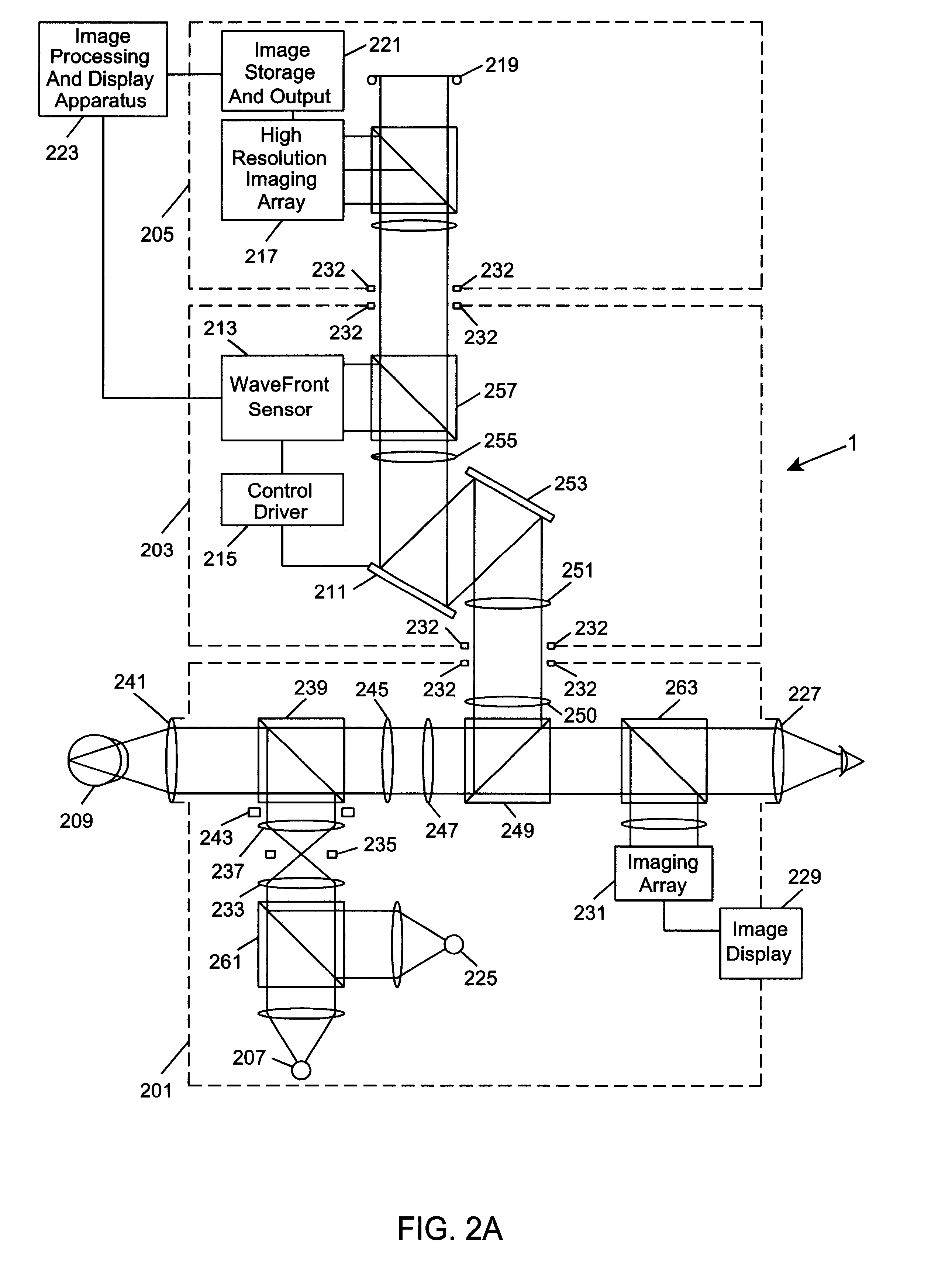
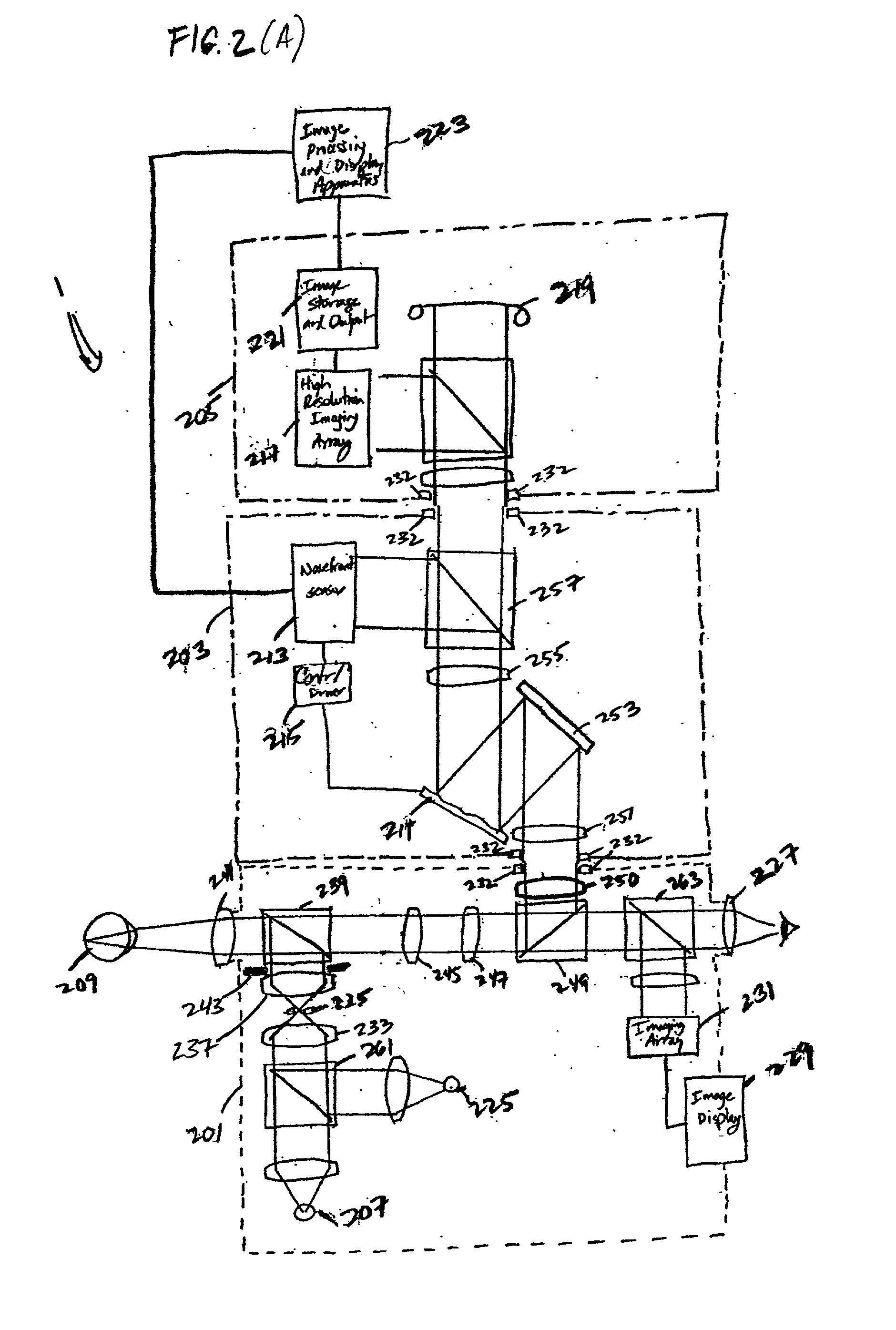
Ophthalmic instrument having an integral wavefront sensor and display device that displays a graphical representation of high order aberrations of the human eye measured by the wavefront sensor
An improved ophthalmic instrument including an integral wavefront sensor and display device, wherein the wavefront sensor measures phase aberrations in reflections directed thereto to characterize aberrations of the eye and is operably coupled to the display device, which displays a graphical representation of the aberrations of the eye. Such graphical representation may include: two dimensional contour maps that graphically depict contribution of pre-specified terms (such as spherical aberration, astigmatism and coma) for the aberrations of the eye, coefficients corresponding to such pre-specified terms that characterize the aberrations of the eye, or predefined two-dimensional icons that provide a general graphical depiction of such prespecified terms. Such graphical representations provide the practitioner with valuable information characterizing the high order optical errors of the eye (which is far beyond the diopter information typically provided by current ophthalmic instruments) for use in diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities and disease in the eye.
Owner:ADAPTIVE OPTICS ASSOC
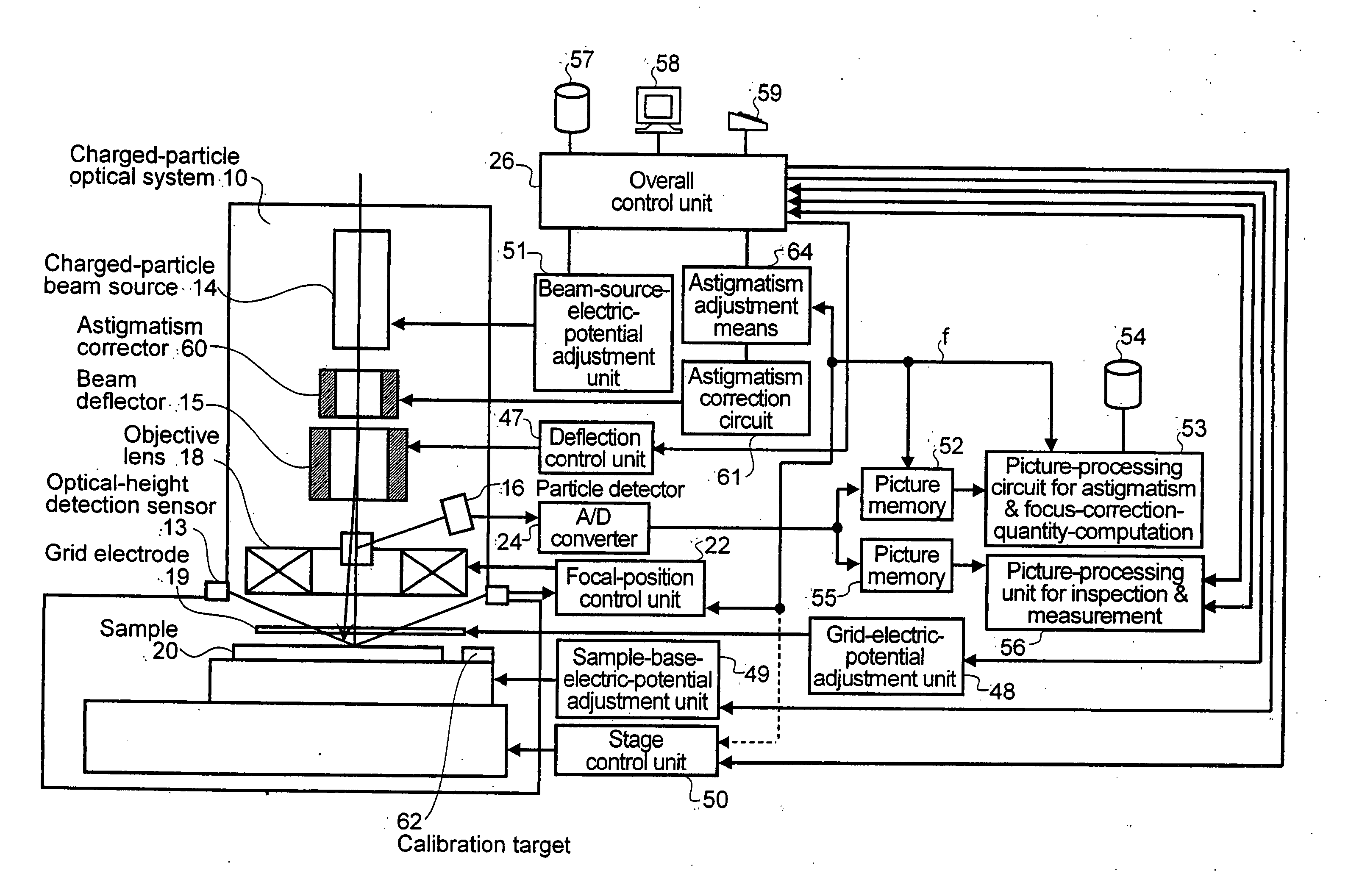
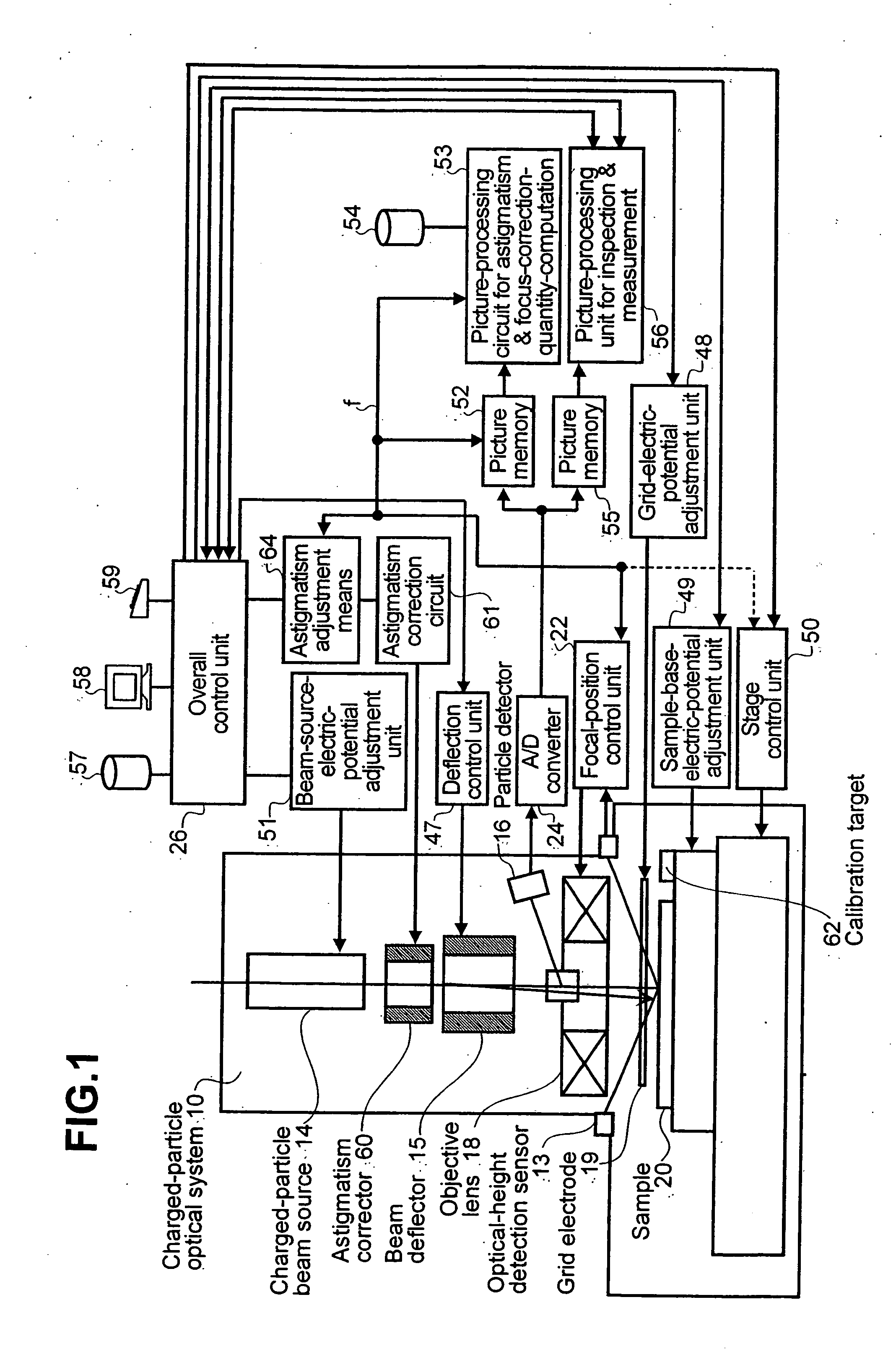
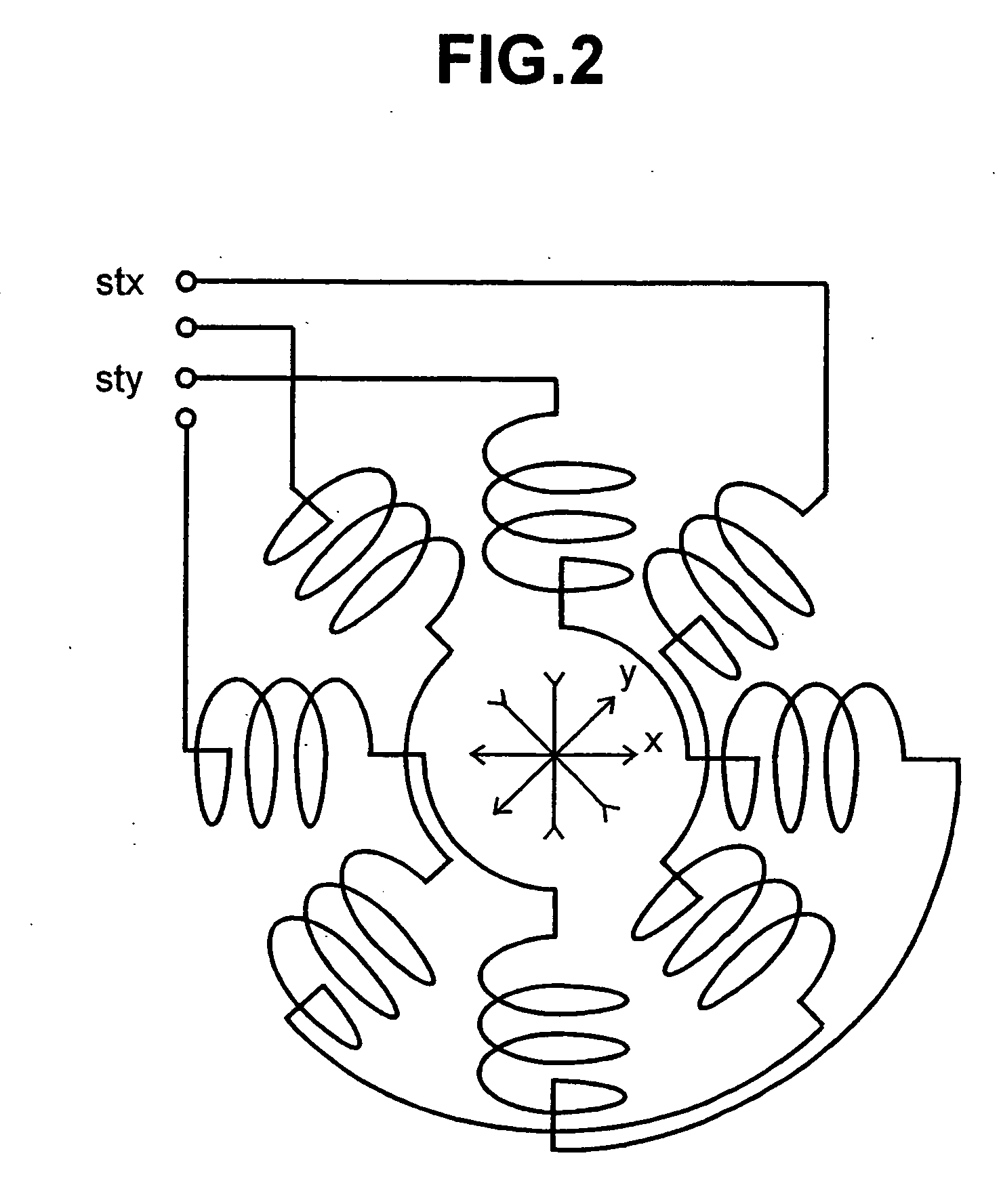
Charged-particle beam apparatus and method for automatically correcting astigmatism and for height detection
InactiveUS20060060781A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesAstigmatismCharged particle beam
Charged-particle beam arrangements (e.g., apparatus and methods) for automatically correcting astigmatism and for height detection.
Owner:WATANABE MASAHIRO +3
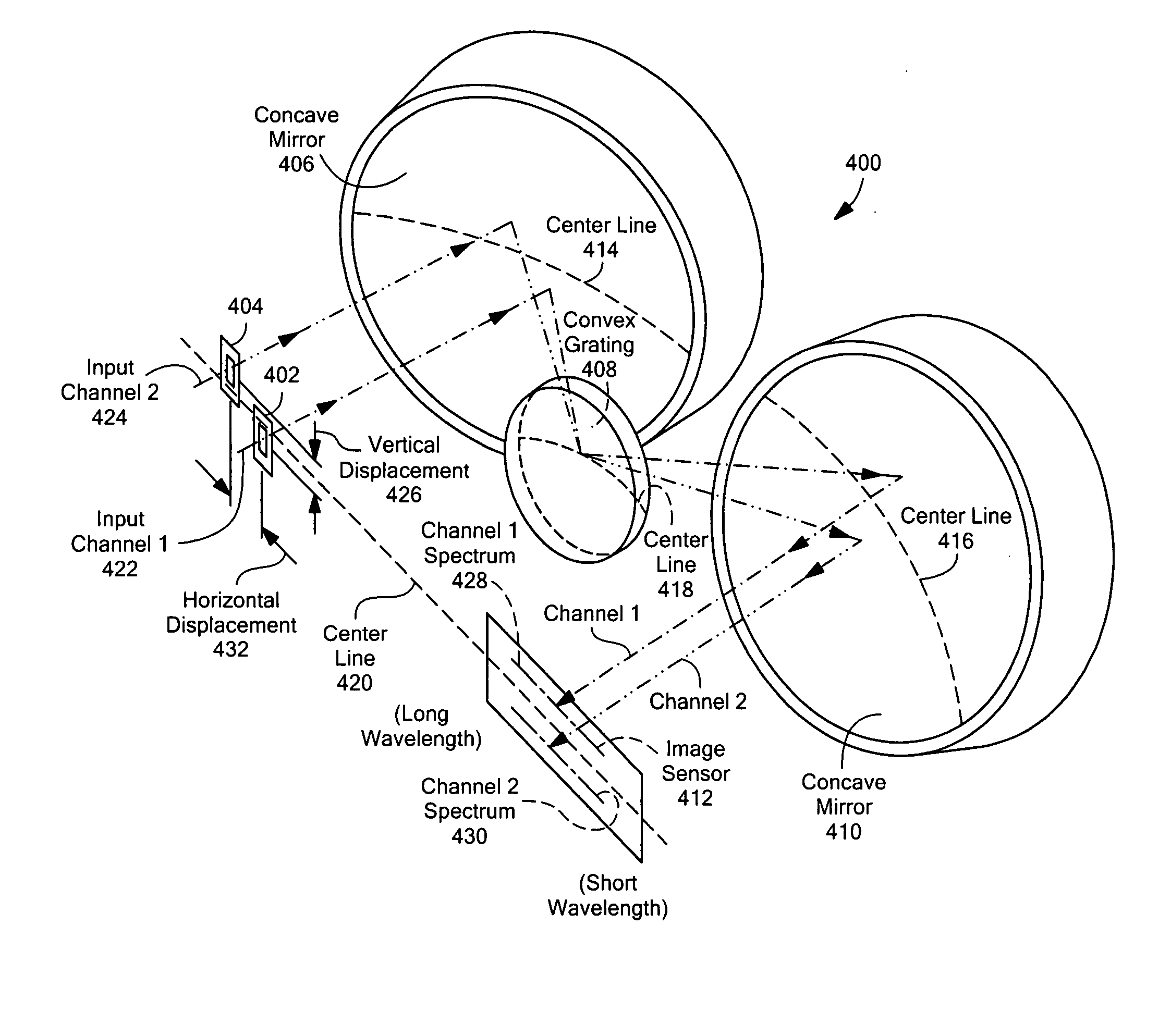
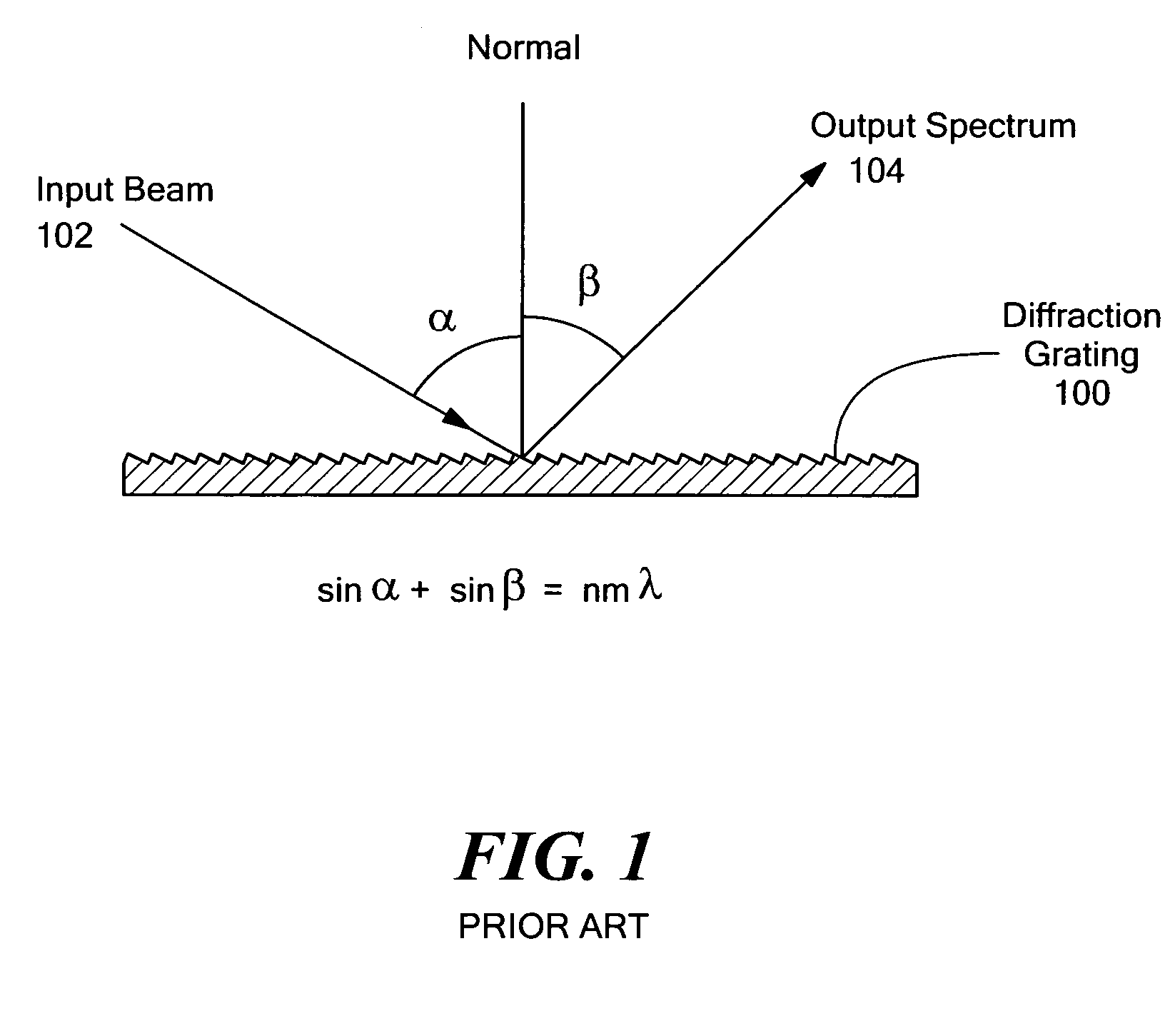
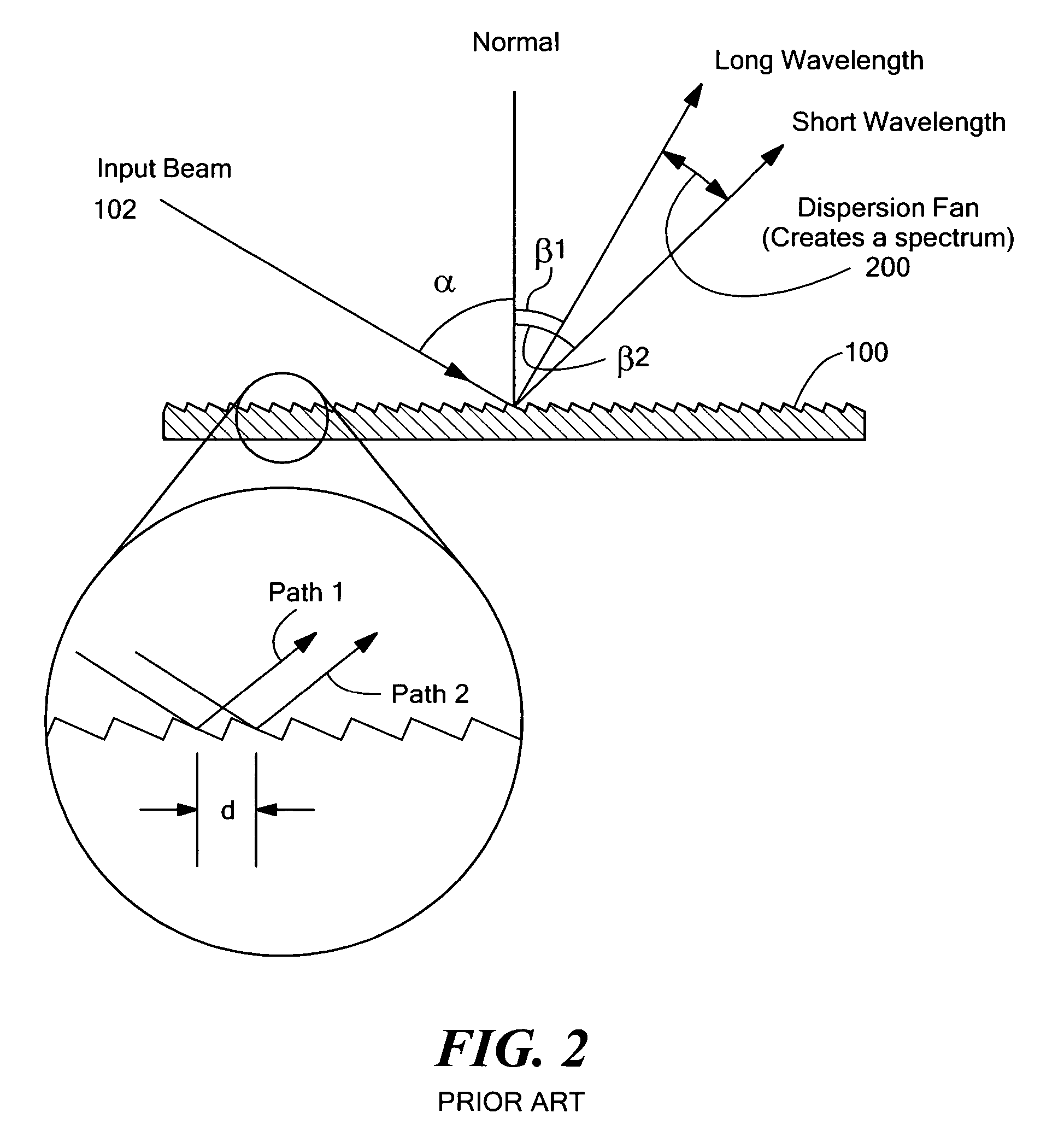
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
A multi-spectrum, multi-channel imaging spectrometer includes two or more input slits or other light input devices, one for each of two or more input channels. The input slits are vertically and horizontally displaced, with respect to each other. The vertical displacements cause spectra from the two channels to be vertically displaced, with respect to each other, on a single image sensor on a stationary image plane. The horizontal displacements cause incident light beams from the respective input channels to strike a convex grating at different respective incidence angles and produce separate spectra having different respective spectral ranges. A retroflective spectrometer includes a convex grating that, by diffraction, disperses wavelengths of light at different angles and orders approximately back along an incident light beam. A single concave mirror reflects both the input channel and the dispersed spectrum. A prism, set of mirrors, beam splitters or other optical element(s) folds the input channel(s) of a spectrometer to enable the input(s) to be moved away from the plane of the image sensor, thereby enabling a large camera or other device to be attached to the spectrometer without blocking the input(s). A mounting mechanism enables a curved optical element to be adjusted through lateral and transverse translations, without requiring a gimbal mount.
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
Iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source
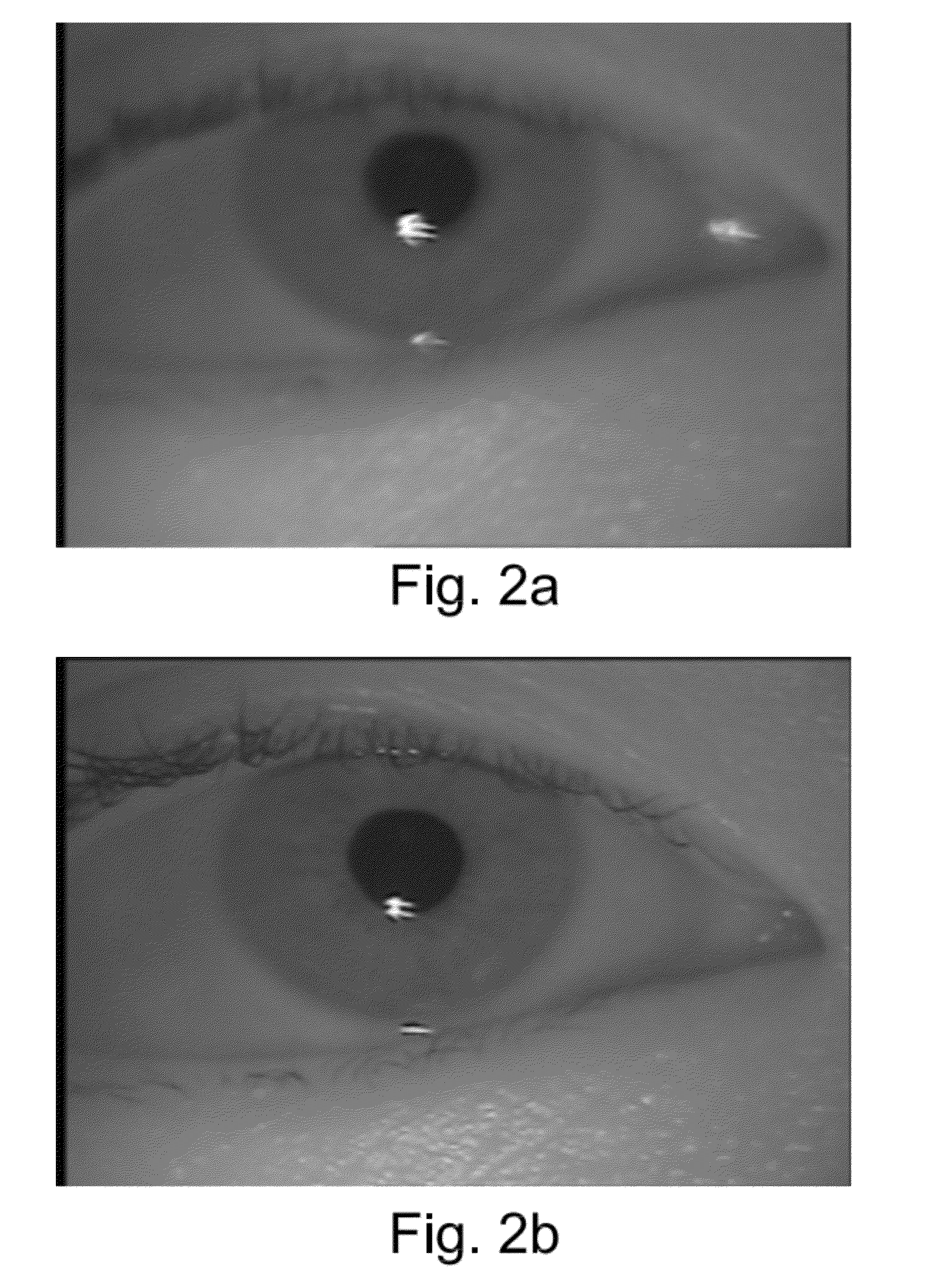
An iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source to assess both the resolution of the iris patterns and the direction of focus adjustment. The corneal reflection results in two virtual images on the meridional and the sagittal planes. These virtual images are formed behind the cornea and close to the iris. Yet, both are projected onto the same location and result in a composite glint area. In addition, the shape of the glint area of a non-coaxial light source varies with different camera focus settings. Furthermore, due to the high intensity of the glint area, the shape can be easily observed, and the size and the shape of the glint area can be used to determine the resolution of the iris image and the direction of focus adjustment, respectively.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
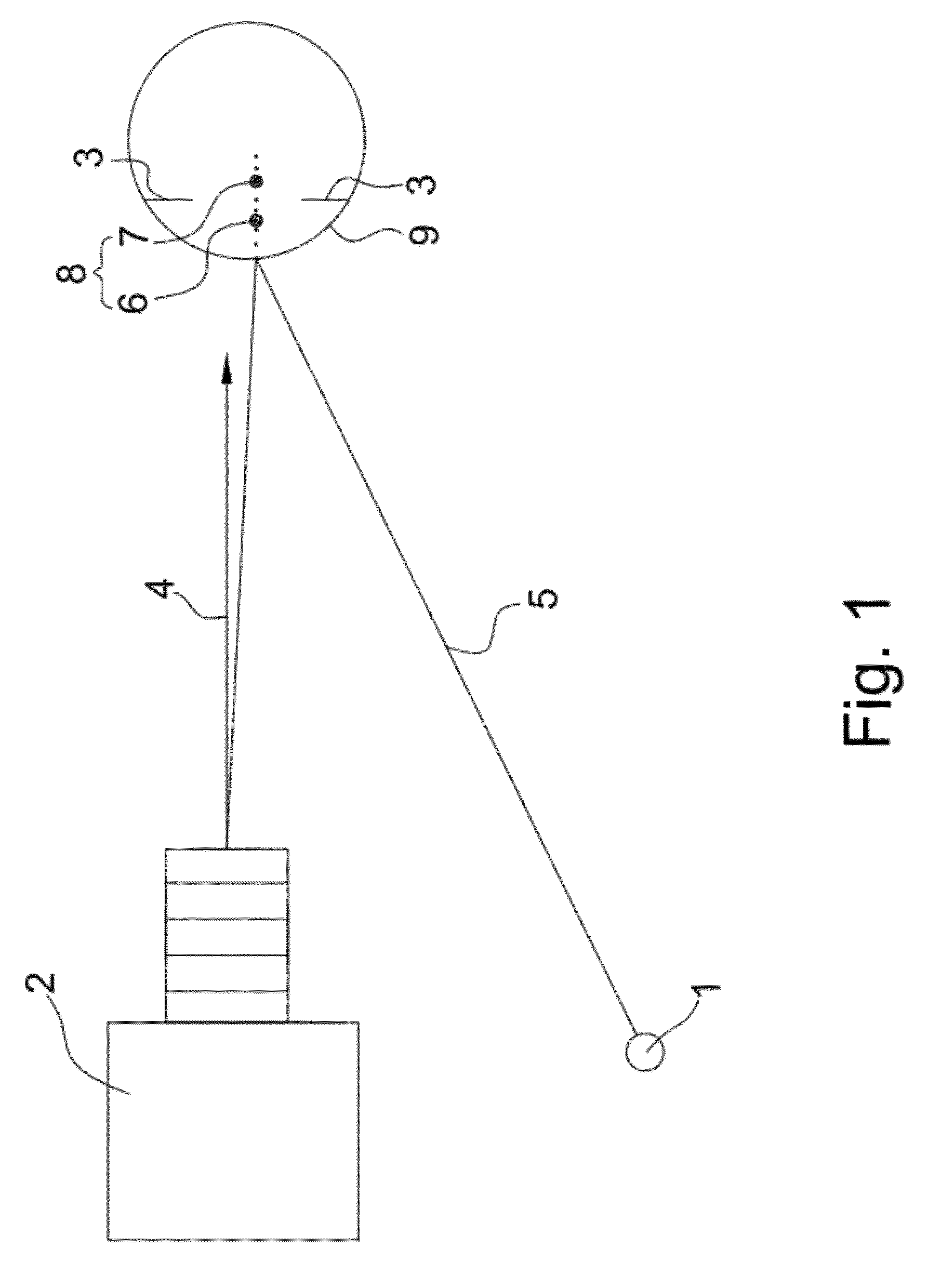
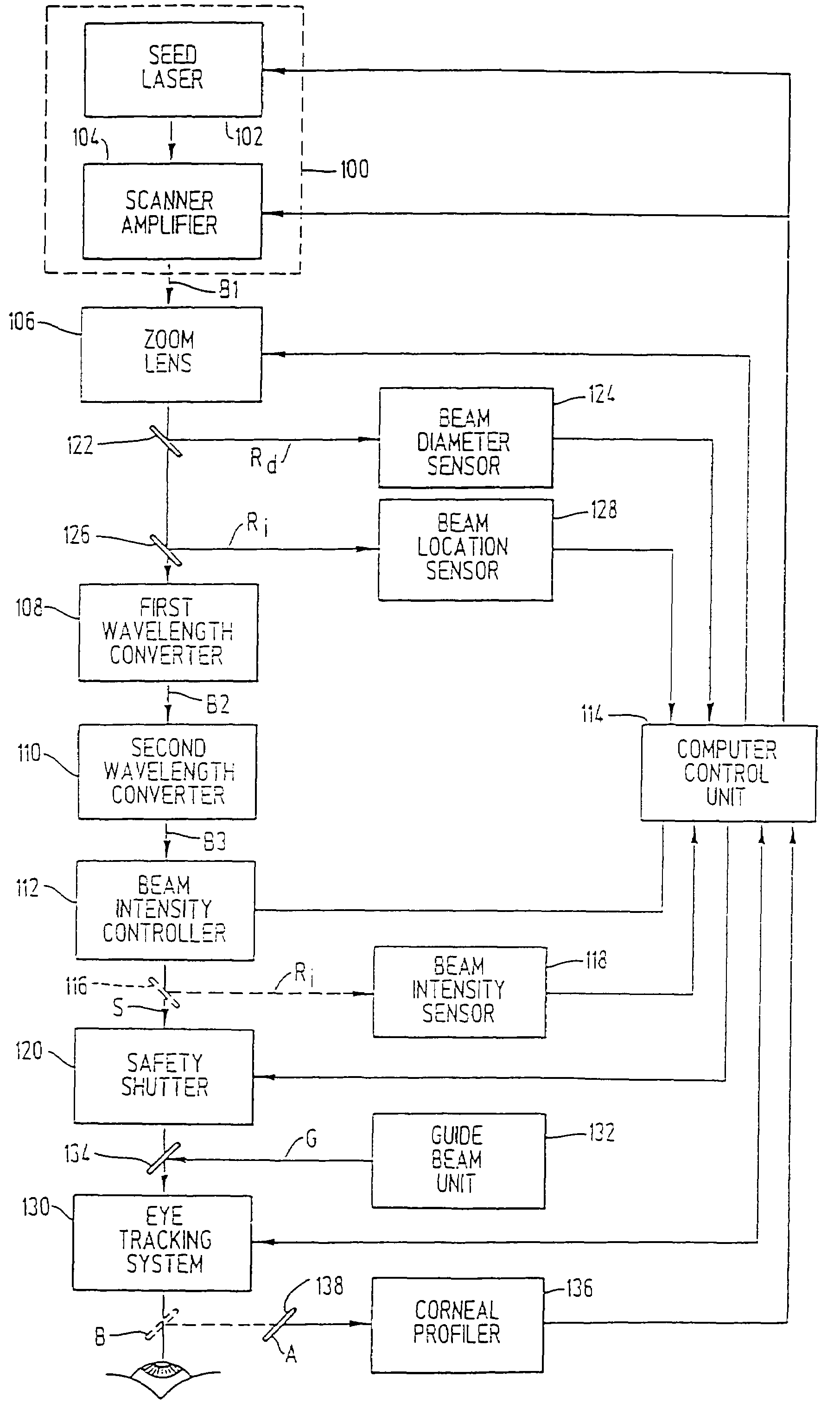
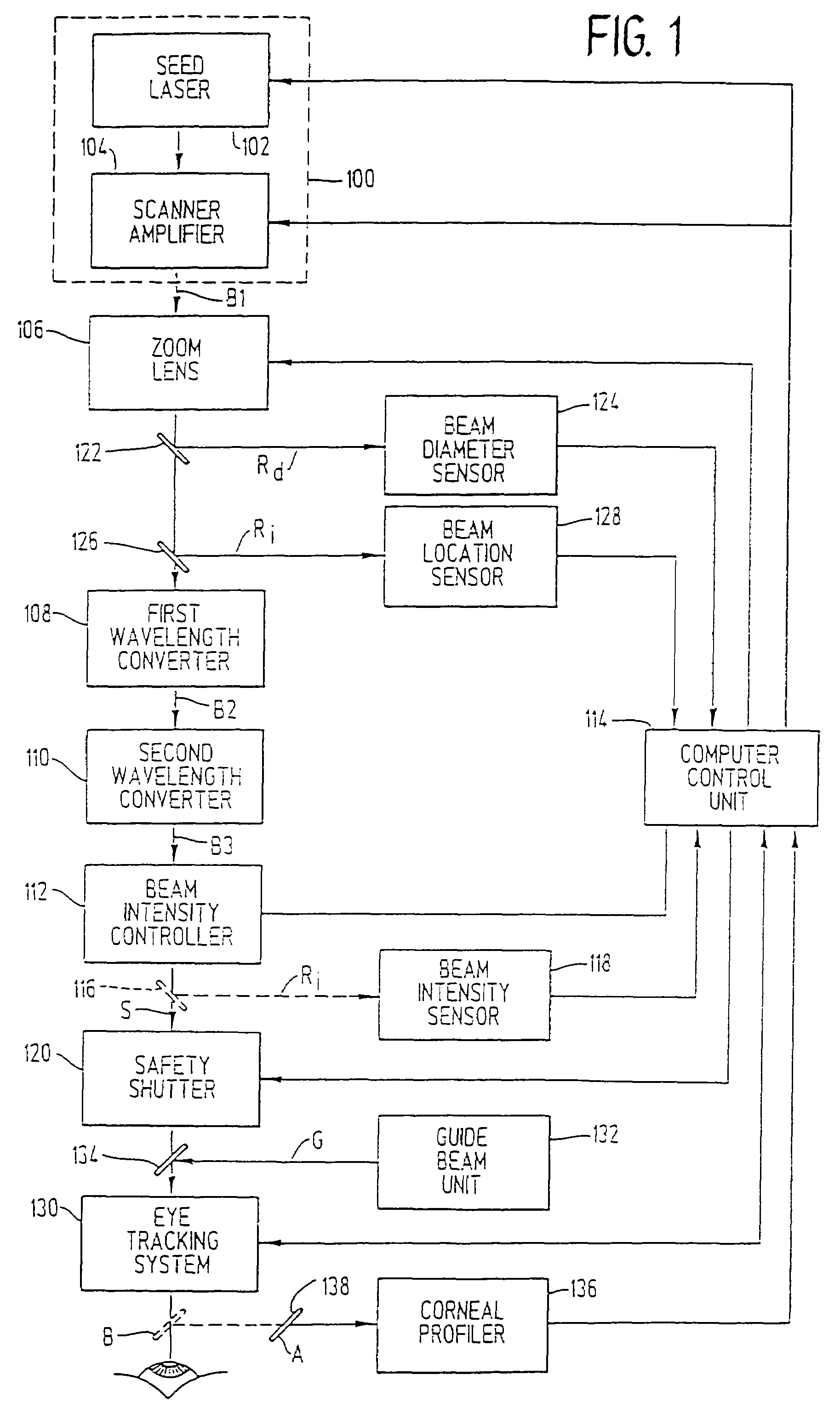
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
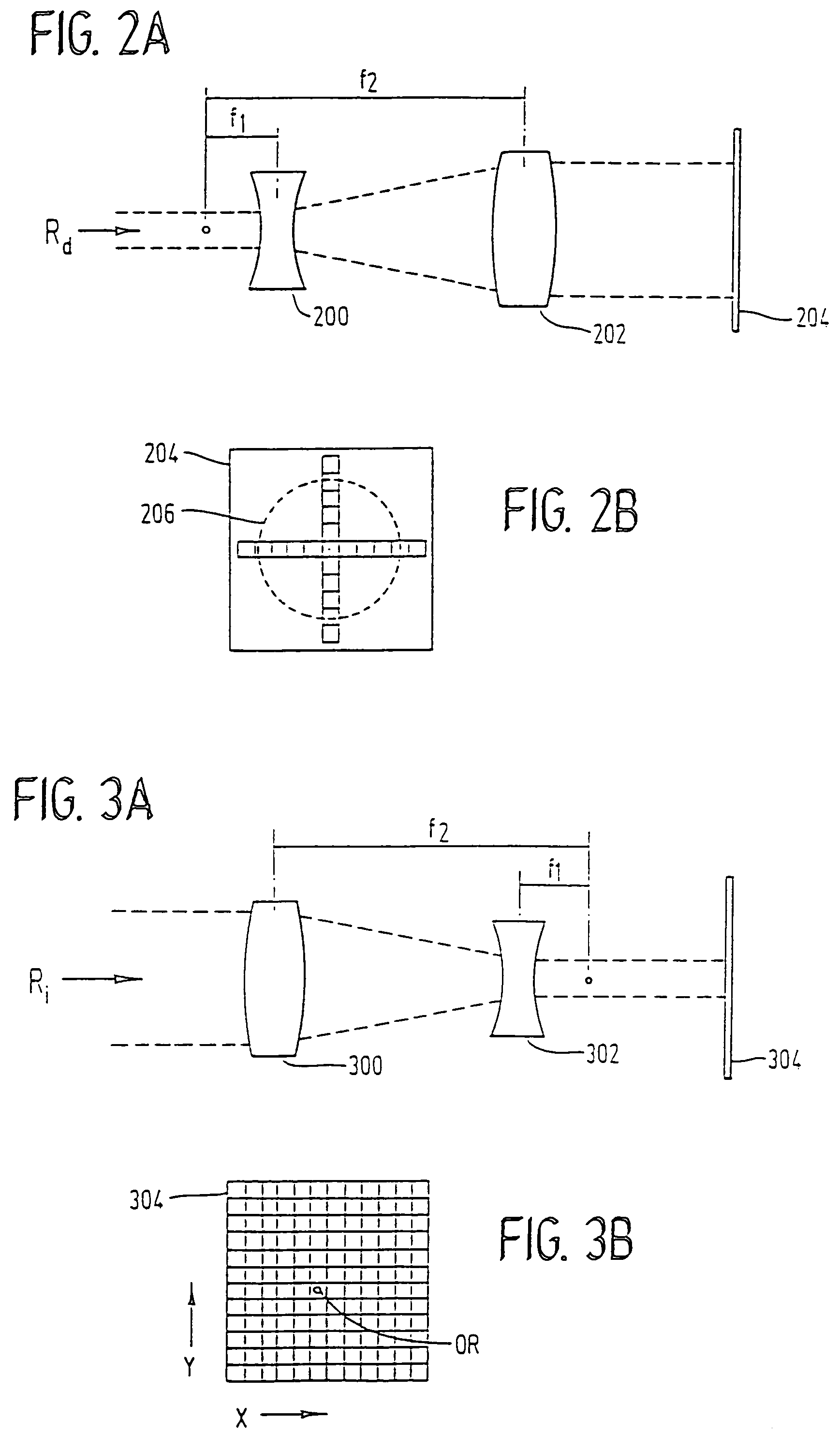
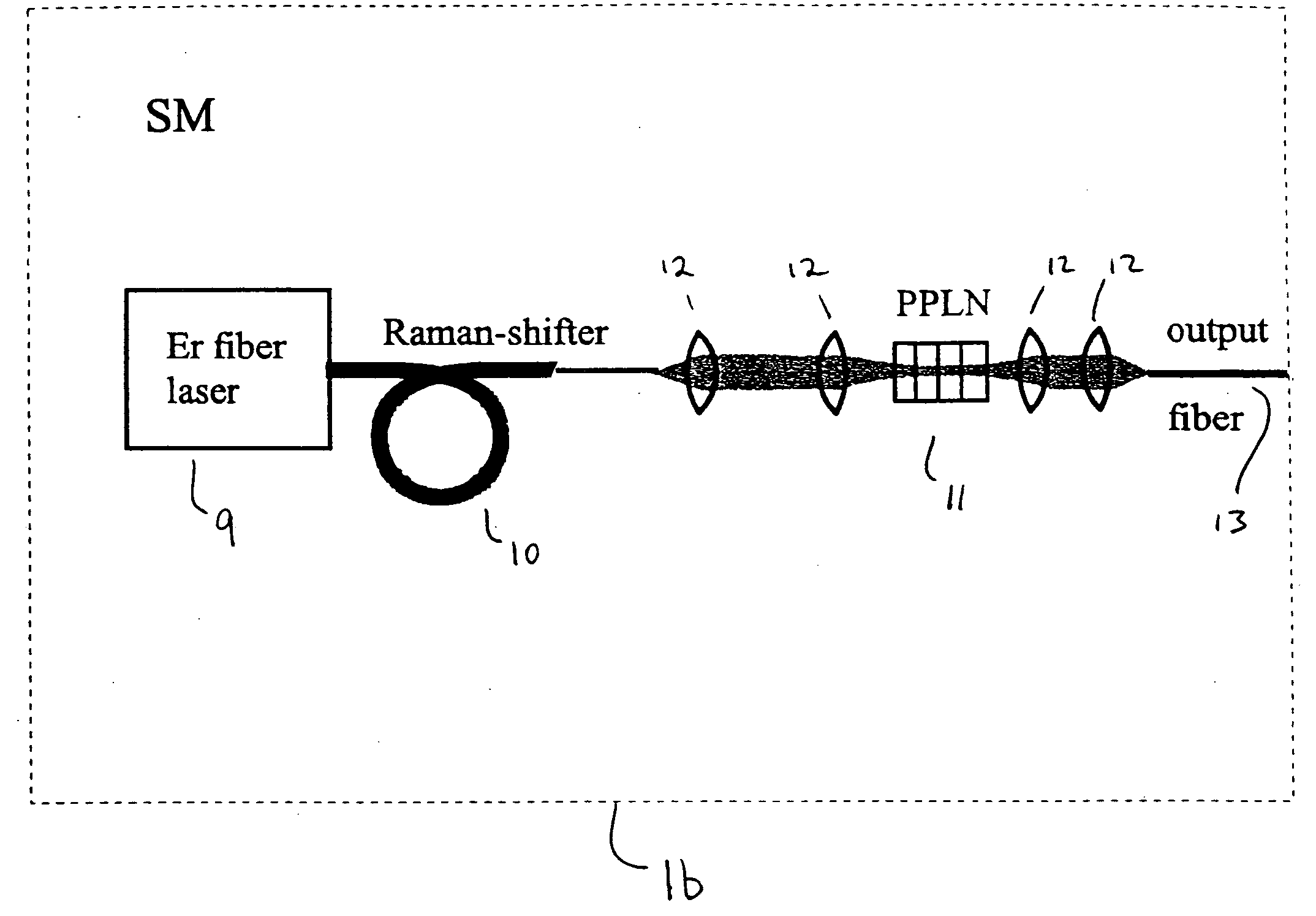
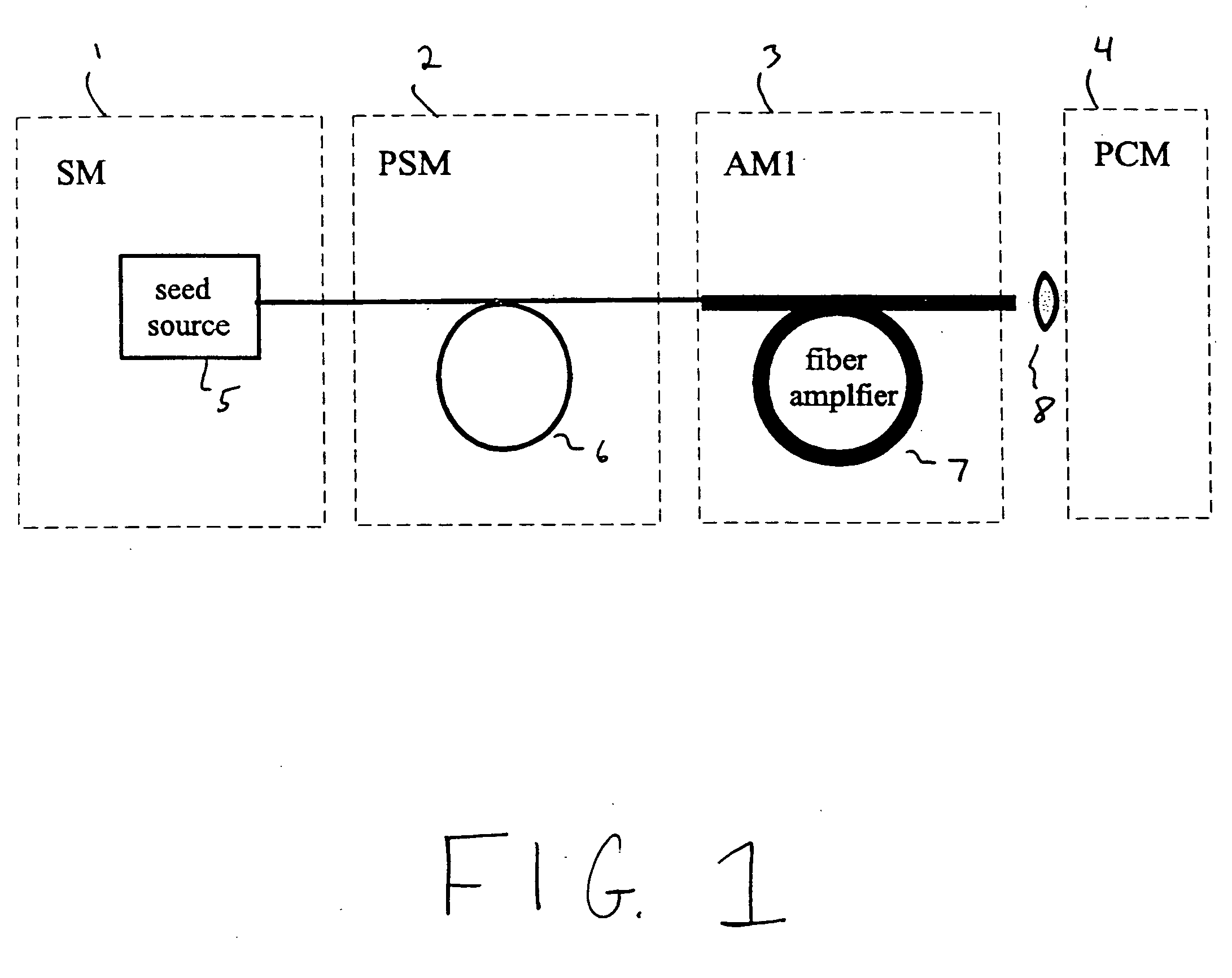
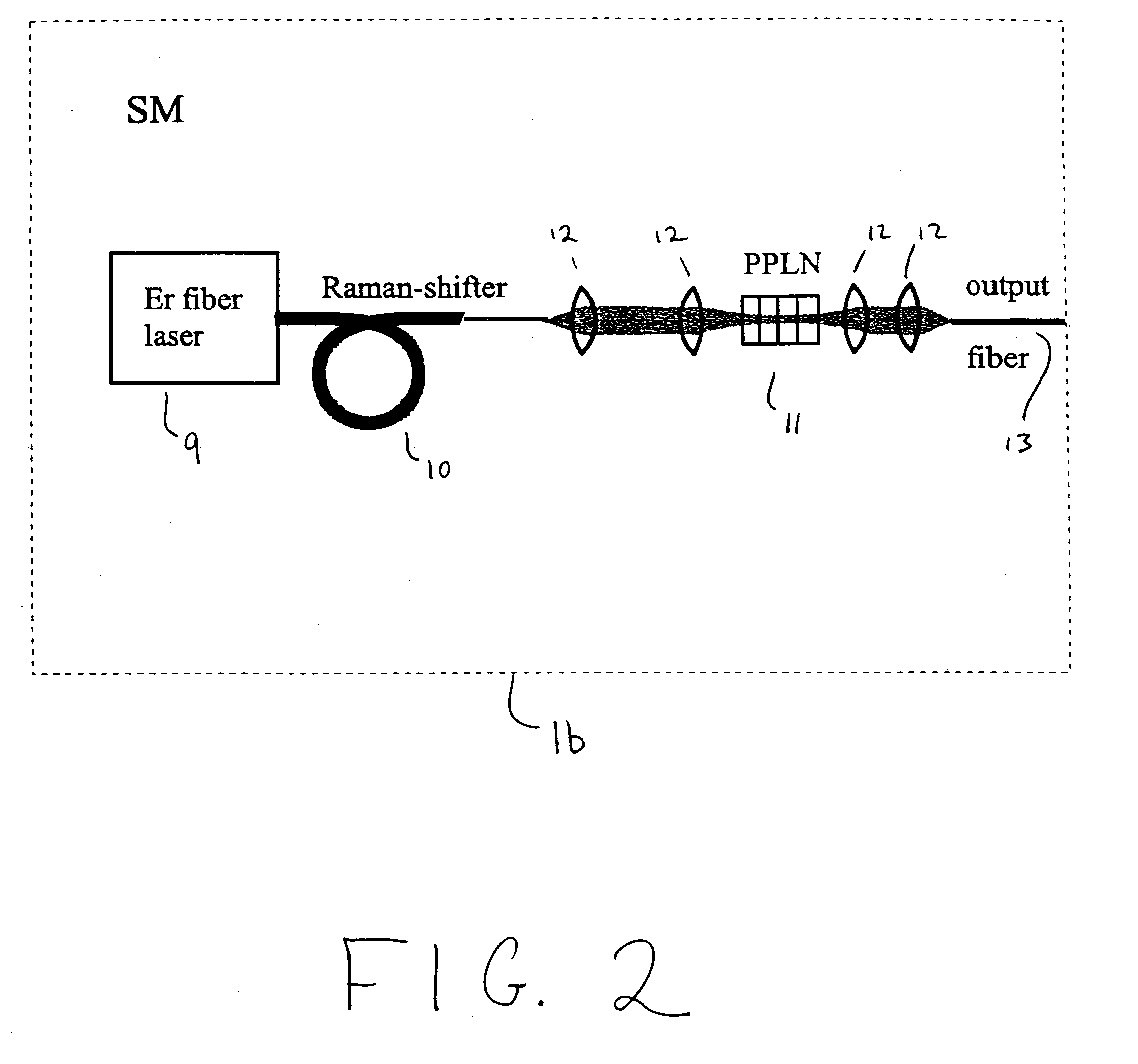
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS20050163426A1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. Dispersive broadening is introduced by dispersive pulse stretching in the presence of self-phase modulation and gain, resulting in the formation of high-power parabolic pulses. In addition, dispersive broadening is also introduced by simple fiber delay lines or chirped fiber gratings, resulting in a further increase of the energy handling ability of the fiber amplifiers. The phase of the pulses in the dispersive delay line is controlled to quartic order by the use of fibers with varying amounts of waveguide dispersion or by controlling the chirp of the fiber gratings. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used. A particularly compact implementation of the whole system uses fiber oscillators in conjunction with fiber amplifiers. Additionally, long, distributed, positive dispersion optical amplifiers are used to improve transmission characteristics of an optical communication system. Finally, an optical communication system utilizes a Raman amplifier fiber pumped by a train of Raman-shifted, wavelength-tunable pump pulses, to thereby amplify an optical signal which counterpropogates within the Raman amplifier fiber with respect to the pump pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Bag-in-the-lens intraocular lens with removable optic and capsular accommodation ring
Owner:TASSIGNON MARIE JOSE B
Method of treating the human eye with a wavefront sensor-based ophthalmic instrument
An improved method for treating the eye includes the step of providing an ophthalmic instrument including an integral wavefront sensor. The wavefront sensor measures phase aberrations in reflections directed thereto to characterize aberrations of the eye. The wavefront sensor may be operably coupled to a display device, which displays a graphical representation of the aberrations of the eye. Such graphical representation may include: two dimensional contour maps that graphically depict contribution of pre-specified terms (such as spherical aberration, astigmatism and coma) for the aberrations of the eye, coefficients corresponding to such pre-specified terms that characterize the aberrations of the eye, or predefined two-dimensional icons that provide a general graphical depiction of such pre-specified terms. Such graphical representations provide the practitioner with valuable information characterizing the high order optical errors of the eye (which is far beyond the diopter information typically provided by current ophthalmic instruments) for use in diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities and disease in the eye. In addition, the wavefront sensor may be part of an adaptive optical subsystem that compensates for the phase aberrations measured therein to provide phase-aligned images of the eye for capture by an image capture subsystem. Such images may be used by practitioner in diagnosis and treatment of abnormalities and disease in the eye.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
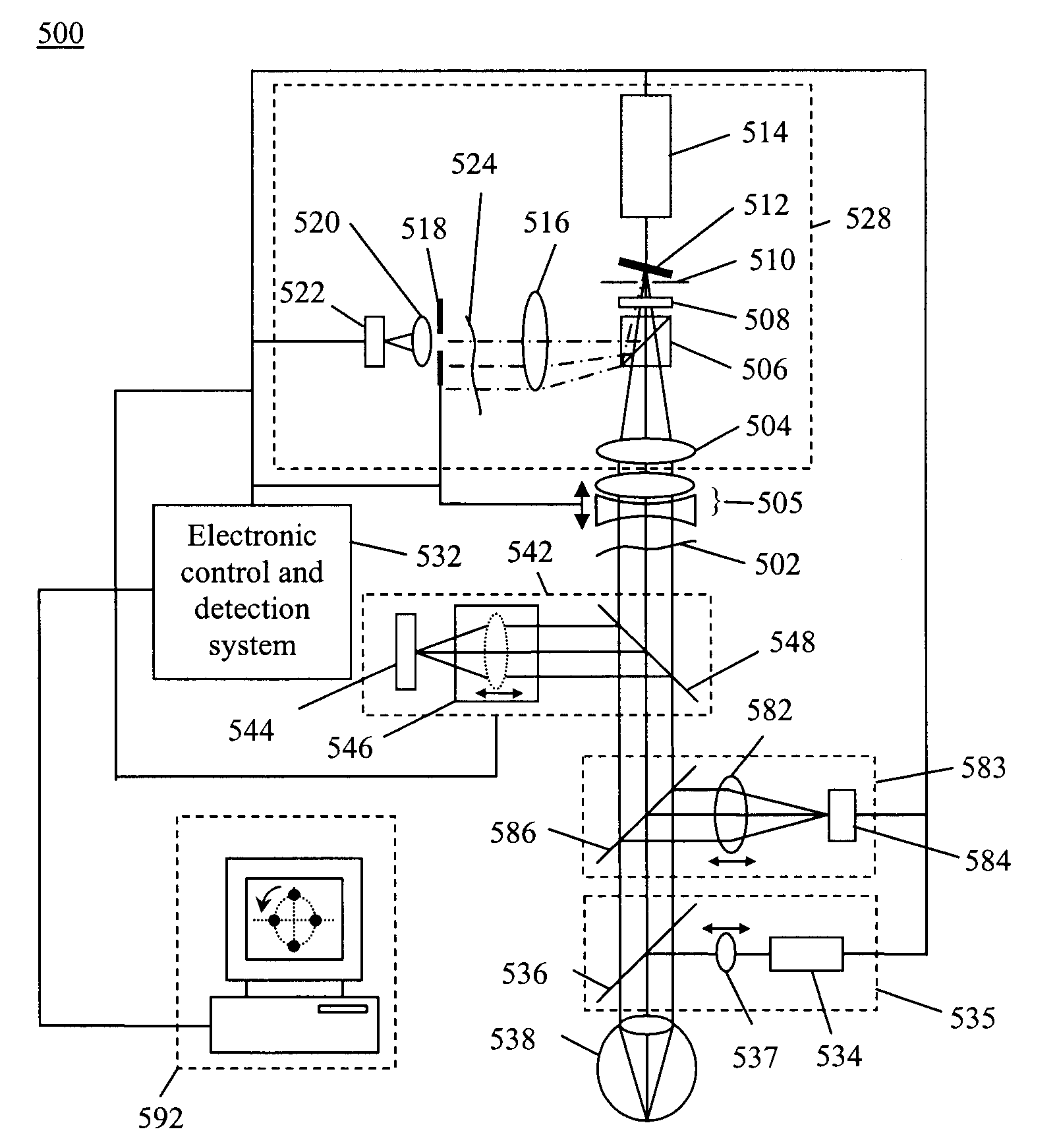
Optimizing vision correction procedures
InactiveUS20100110379A1Easy to measureOut noiseOptical measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringWavefront sensorCylindroma
In one embodiment, an apparatus for optimizing vision correction procedures comprising: a narrow beam of light directed to a patient's retina; a dynamic defocus and compensation offsetting device configured to offset the defocus of a wavefront from an eye, a wavefront sensor configured to measure the local tilt of a number of subwavefronts sampled around an annular ring (the diameter of which can be dynamically changed) over the wavefront with the defocus offset; and a display device configured to display a two dimensional (2D) data points pattern in real time with each data point location representing a corresponding local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts. A proper defocus offset, not passive compensation, can reveal the predominant feature(s) of other wavefront aberration component(s), thus enabling a refractive surgeon to fine tune the vision correction procedure and minimize the remaining wavefront aberration(s) in real time. Meanwhile, by sampling the wavefront around annular rings and displaying the local tilt of the sampled subwavefronts on a monitor in the form of a 2D data points pattern, a refractive ophthalmic surgeon can easily correlate the measurement result to the two major refractive errors, namely spherical and cylinder refractive errors, including the axis of astigmatism.
Owner:CLARITY MEDICAL SYST
Method and apparatus for improving safety during exposure to a monochromatic light source
A method and apparatus are disclosed for improving bodily safety during exposure to an eye hazardous monochromatic treatment light source by diverging the light, such as with a diffusing unit attached to the light source distal end so that the radiance of the light exiting the distal end is an eye safe level. At a first position of the light source distal end substantially in contact with an outer surface of a target, the energy density of an exit beam from the distal end is suitable for effecting a desired treatment, and at a second non-contact position of the distal end the exit beam energy density is significantly less than a value suitable for effecting the treatment. In an additional embodiment, the diverging or diffusing unit has a device for evacuating vapors or particles from the target.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
Methods of obtaining ophthalmic lenses providing the eye with reduced aberrations
InactiveUS20060158611A1Reduce aberrationImprove visual qualitySpectales/gogglesEye treatmentOptical aberrationCapsular bag
An intraocular lens comprises optical part configured to be implanted in an eye of a subject. The intraocular lens further comprises at least one aspheric surface configured, in combination with a lens in the capsular bag of an eye, to reduce an aberration of a wavefront passing the eye. The aberrations may include astigmatism, coma, and / or spherical aberrations. An aberration of the intraocular lens may be expressed as a linear combination of Zernike polynomial terms that may include a Zernike coefficient a11. The Zernike coefficient a11 may be selected to reduce a spherical aberration of a wavefront passing the eye and / or to compensate for an average value resulting from a predetermined number of estimations of the Zernike coefficient a11 in a population of corneas and capsular bag lenses.
Owner:PIERS PATRICIA ANN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com