Patents
Literature
110 results about "Angular dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
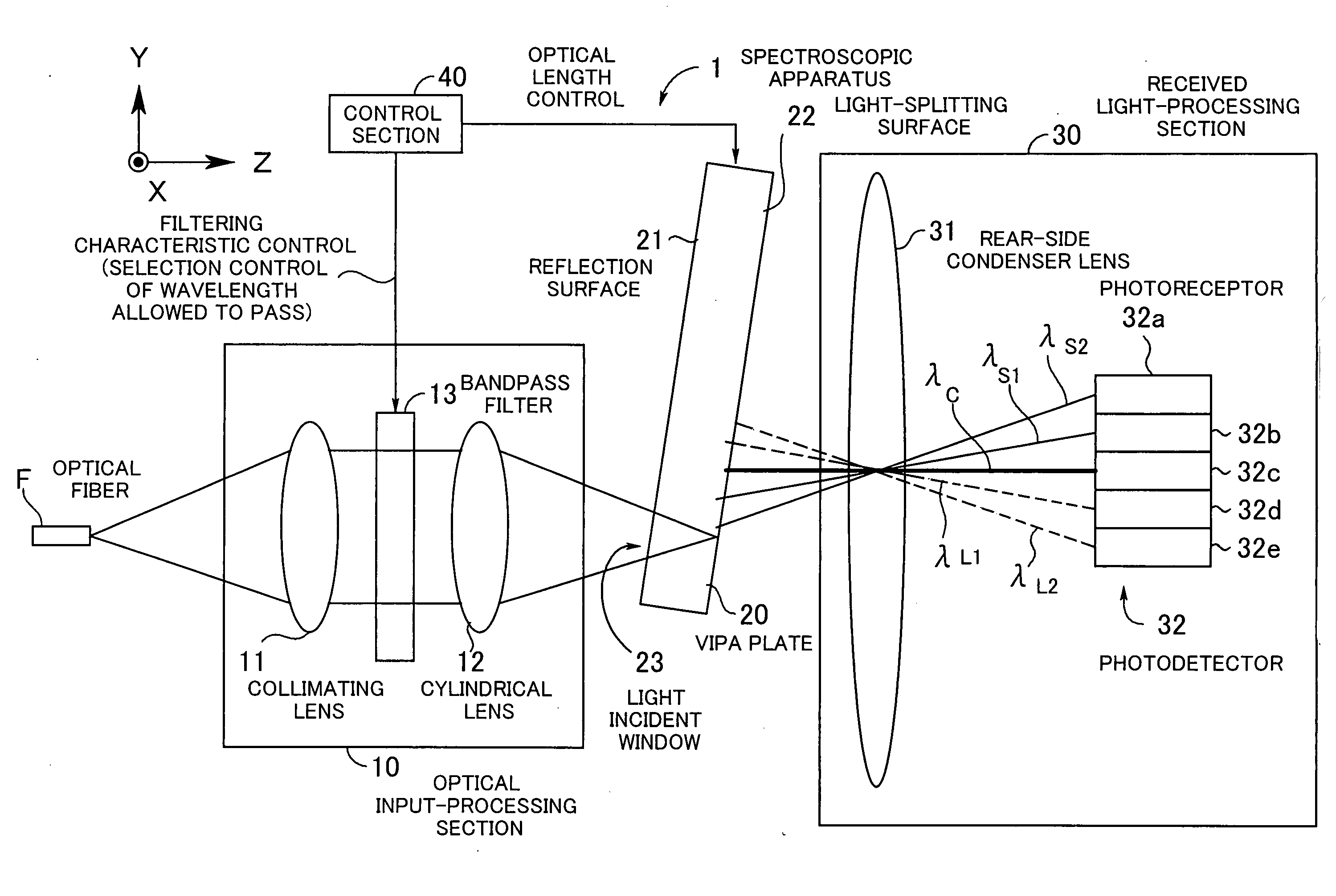
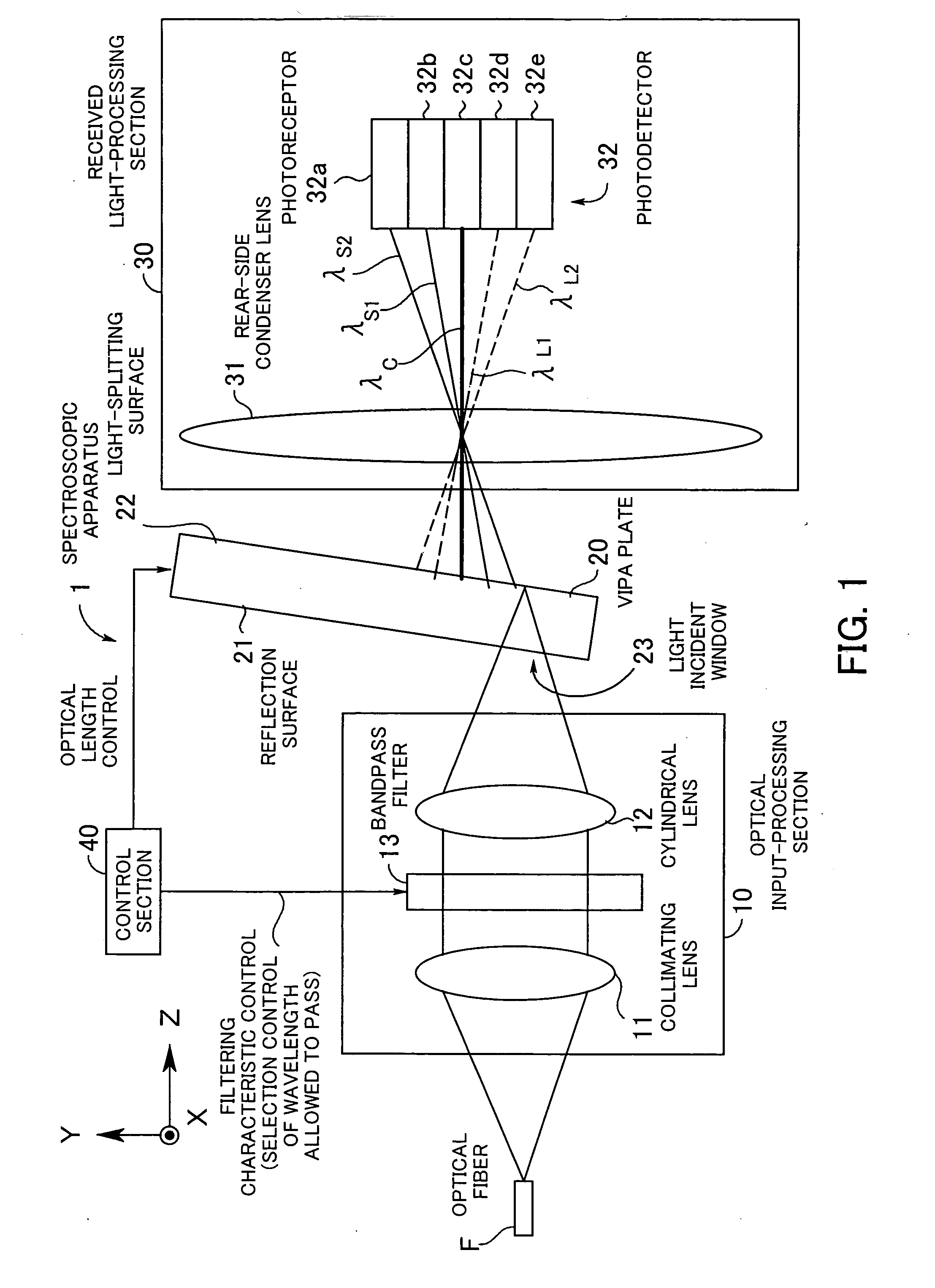
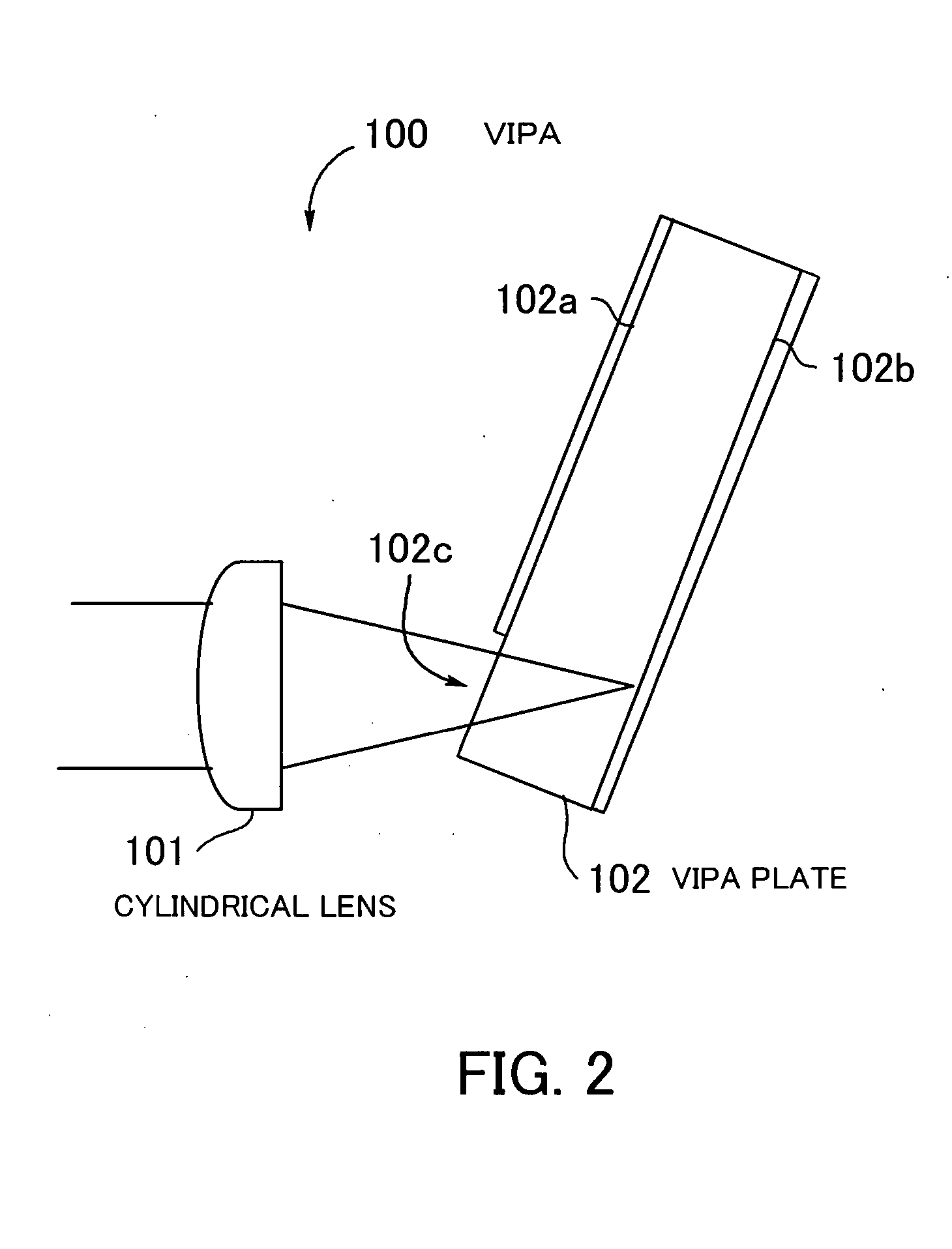
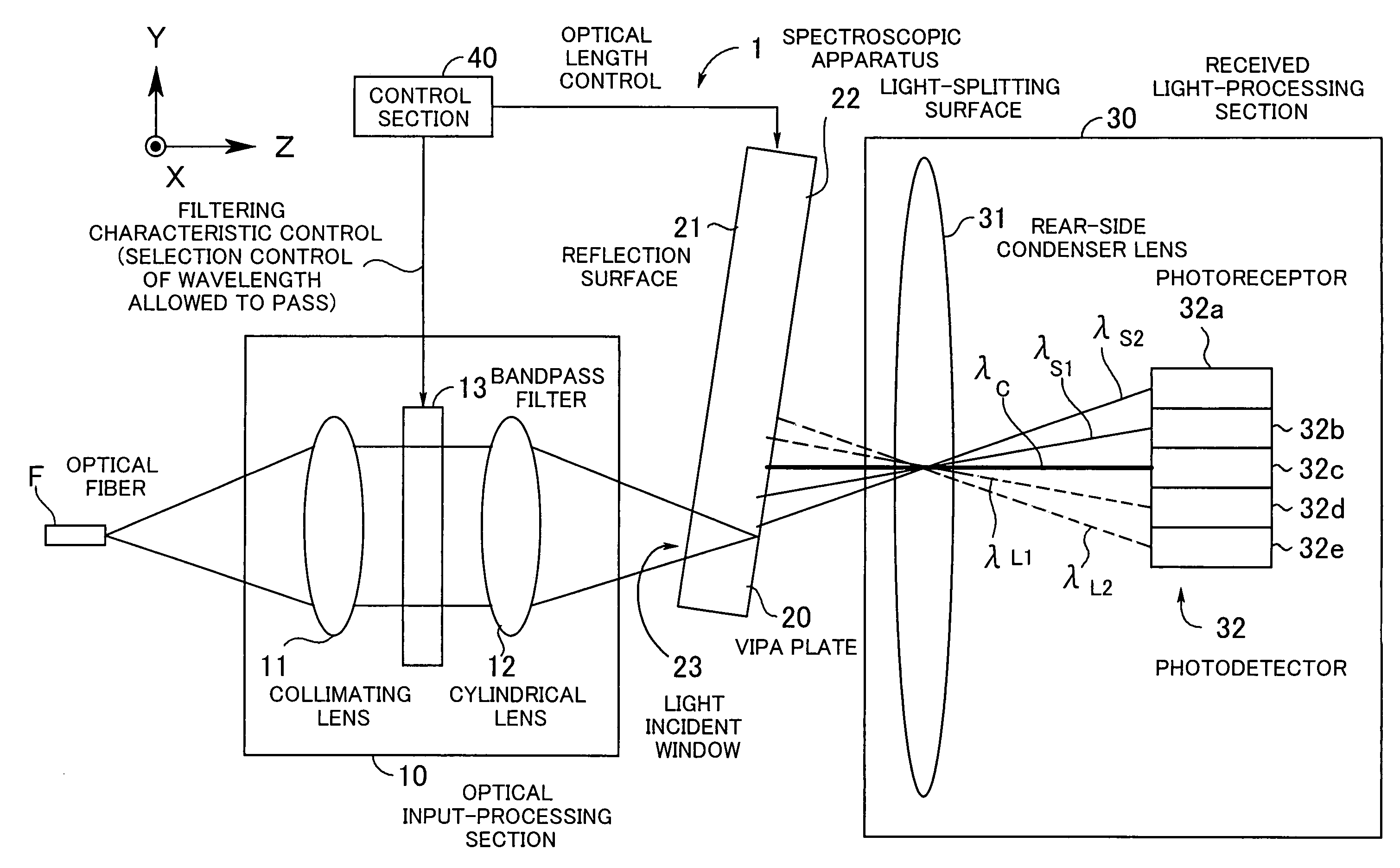
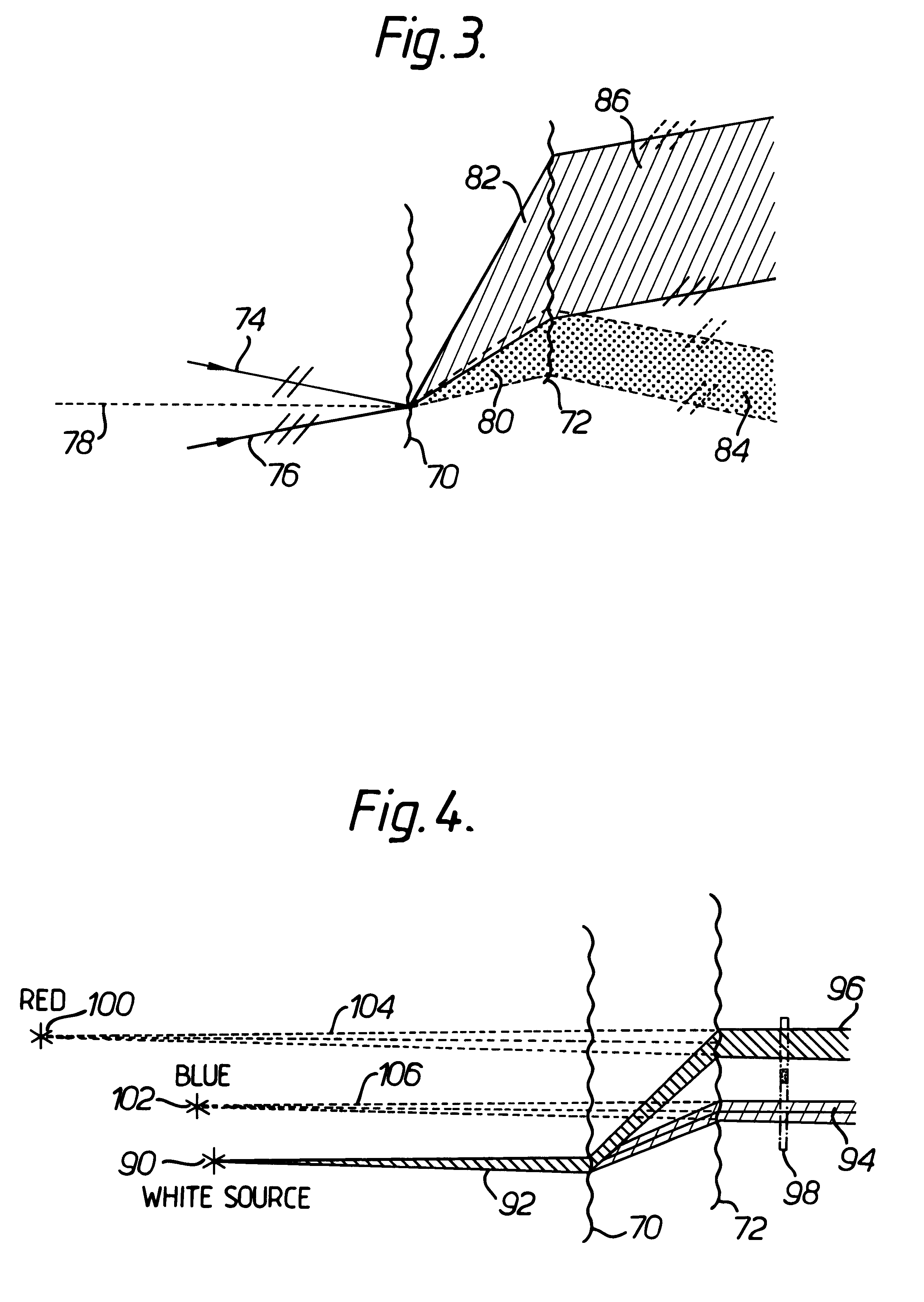
Spectroscopic apparatus
InactiveUS20050046837A1Small sizeLarge angular dispersionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS20090027810A1Low angular dispersionEasy to operateNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
We describe the structure and method of forming a STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer. The device includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20. of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
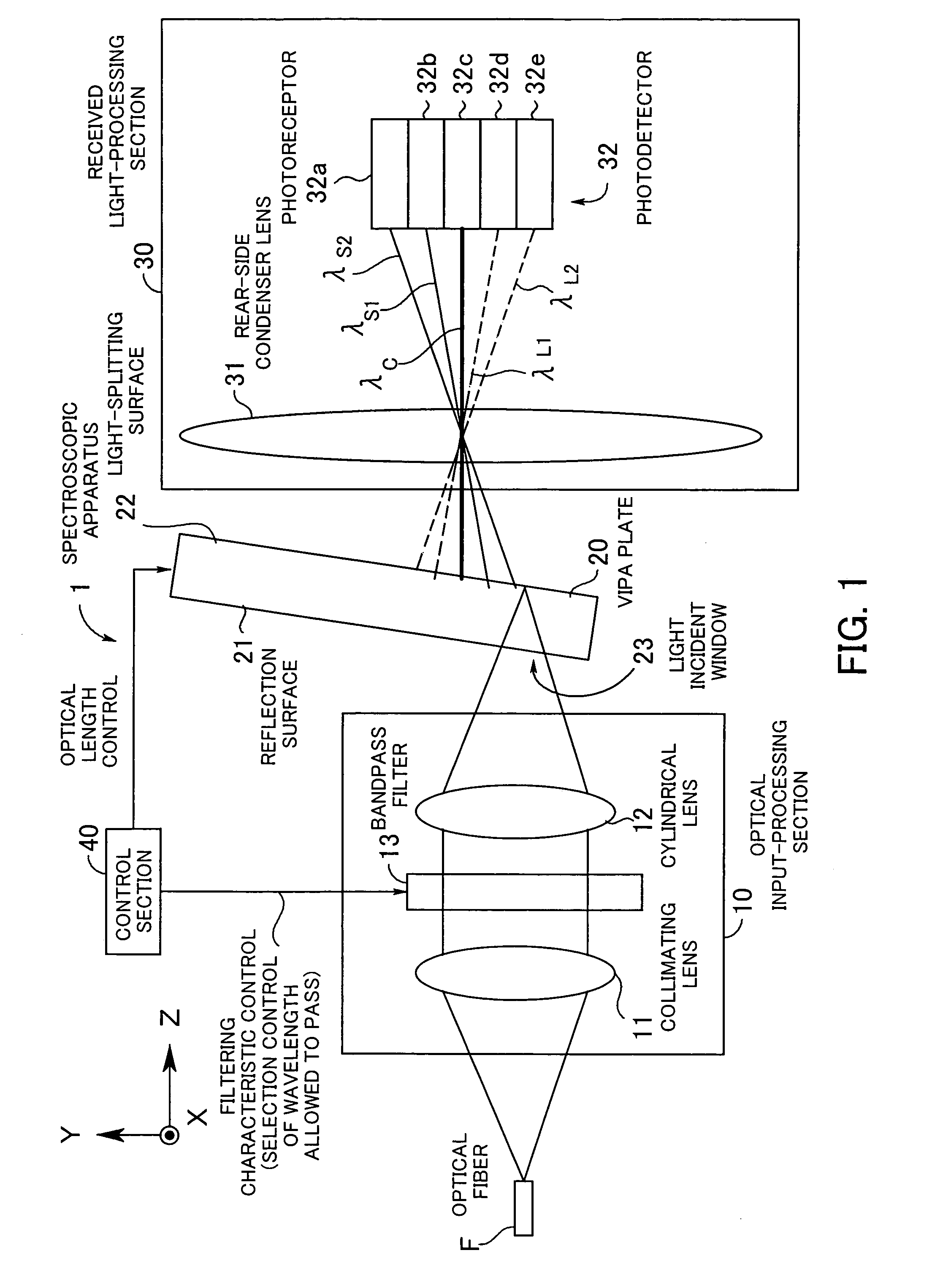
Spectroscopic apparatus
InactiveUS7304798B2Small sizeHigh-precision light-splittingRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBandpass filteringLight beam
A spectroscopic apparatus which is compact in size and performs high-precision light-splitting with a large angular dispersion. An optical input-processing section outputs a filtered transmitted light, using a bandpass filter that transmits only wavelength bands at one period of an input light, and collects the filtered transmitted light to generate a collected beam. An optic includes a first reflection surface and a second reflection surface which are high but asymmetric in reflectivity, and causes the collected beam incident thereon to undergo multiple reflections within an inner region between the first reflection surface and the second reflection surface, to thereby cause split beams to be emitted via the second reflection surface. A received light-processing section performs received light processing of the beams emitted from the optic. A control section variably controls at least one of a filter characteristic of the bandpass filter and an optical length through the optic.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Wavelength manipulation system and method
ActiveUS7092599B2Well formedStatic indicating devicesWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical powerLength wave
A wavelength selective manipulation device and method including: at least a first optical input port for inputting an optical signal including a plurality of wavelength channels; a first wavelength dispersing element for angularly dispersing the wavelength channels of the optical signal into angularly dispersed wavelength signals; an optical power element for focussing in the angularly dispersed dimension the angularly dispersed wavelength signals into a series of elongated spatially separated wavelengths bands; a spatial manipulation element for selectively manipulating the spatial characteristics of the spatially separated wavelength bands to produce spatially manipulated wavelength bands.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
High performance MTJ element for STT-RAM and method for making the same
ActiveUS7750421B2Easy to operateLow dispersionNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSpin angular momentum of lightDamping factor
A STT-MTJ MRAM cell that utilizes transfer of spin angular momentum as a mechanism for changing the magnetic moment direction of a free layer includes an IrMn pinning layer, a SyAP pinned layer, a naturally oxidized, crystalline MgO tunneling barrier layer that is formed on an Ar-ion plasma smoothed surface of the pinned layer and, in one embodiment, a free layer that comprises an amorphous layer of Co60Fe20B20 of approximately 20 angstroms thickness formed between two crystalline layers of Fe of 3 and 6 angstroms thickness respectively or on a single such layer. The free layer is characterized by a low Gilbert damping factor and by very strong polarizing action on conduction electrons. The resulting cell has a low critical current, a high dR / R and a plurality of such cells will exhibit a low variation of both resistance and pinned layer magnetization angular dispersion.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
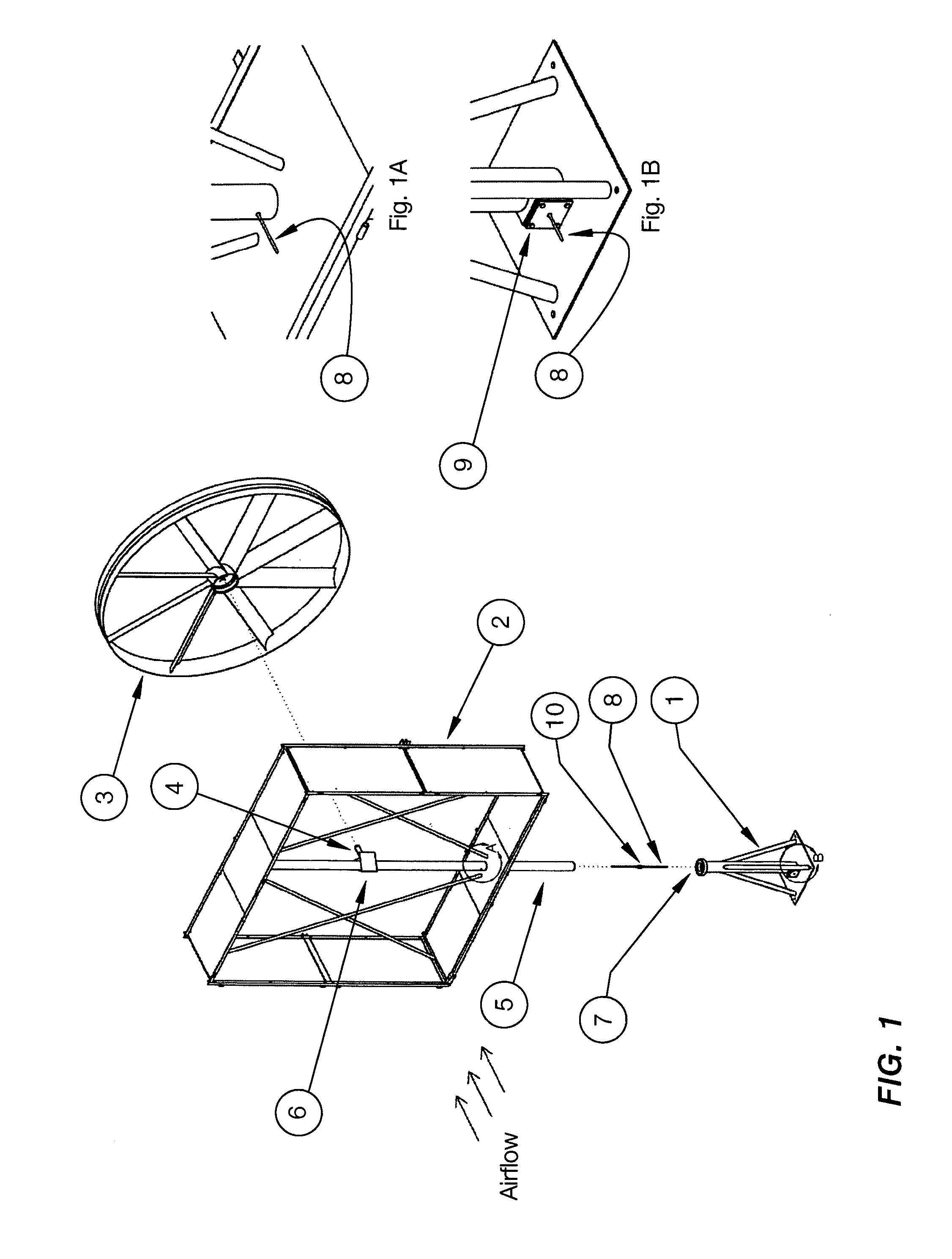
Variable aperture velocity augmented ducted fan wind turbine
InactiveUS7256512B1Exact matchHigh trafficWind motor controlWind motor supports/mountsLeading edgeTrailing edge
A wind powered variable area exit aperture electric generating system having configurable, adjustable duct side walls by which means the ratio between the intake cross-sectional aperture area and the exhaust cross-sectional aperture area may be varied for maximum air molecule flow through the duct, leading to ideal maximum electrical output for any given air mass input. The planar characteristic and angular dispersion of the mutually leading edge coupled extended flaps, and the regular square interior housing result in complementary internal vortices developed at the trailing edge of the planar architectural surfaces.
Owner:MARQUISS WIND POWER
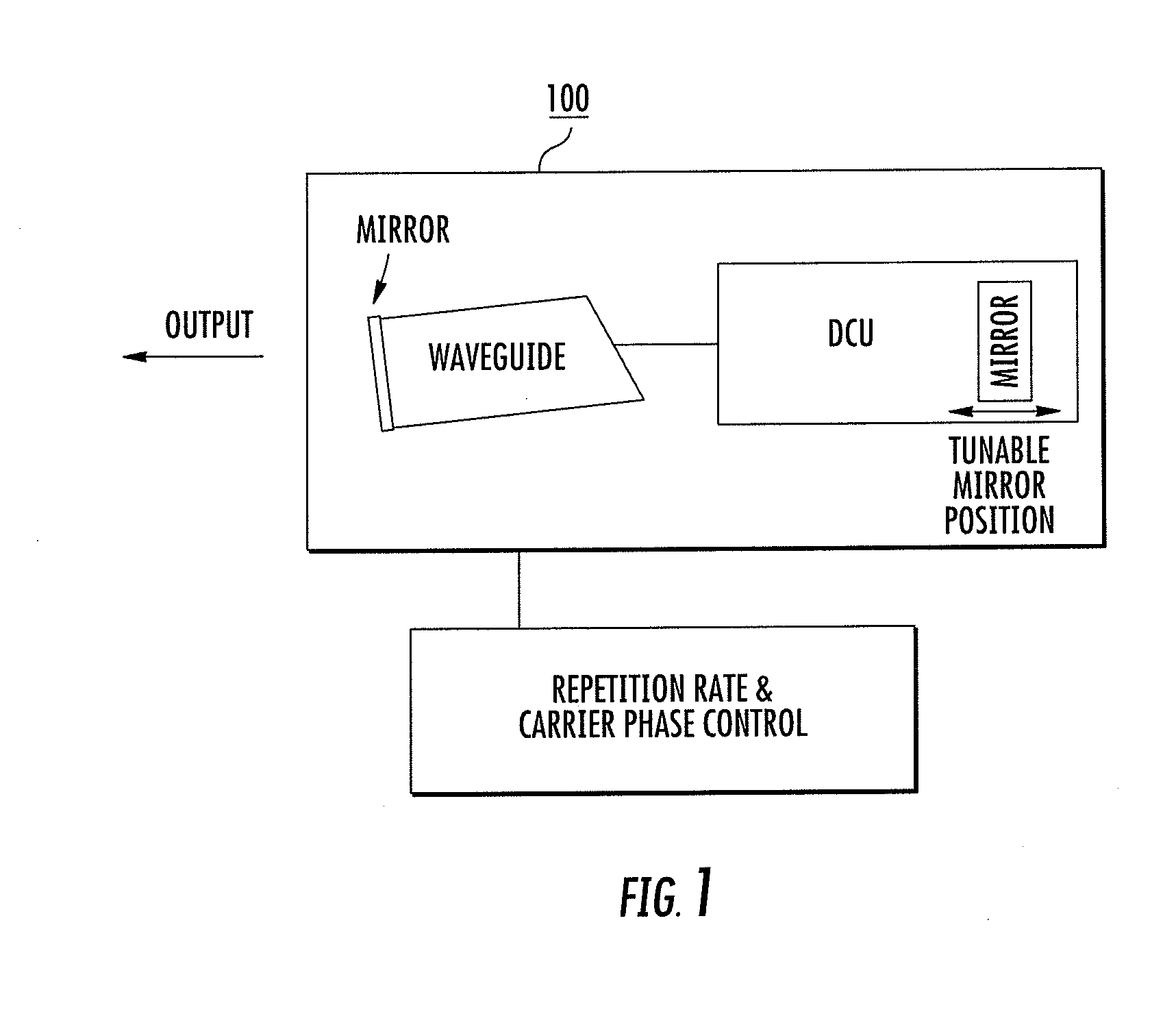
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
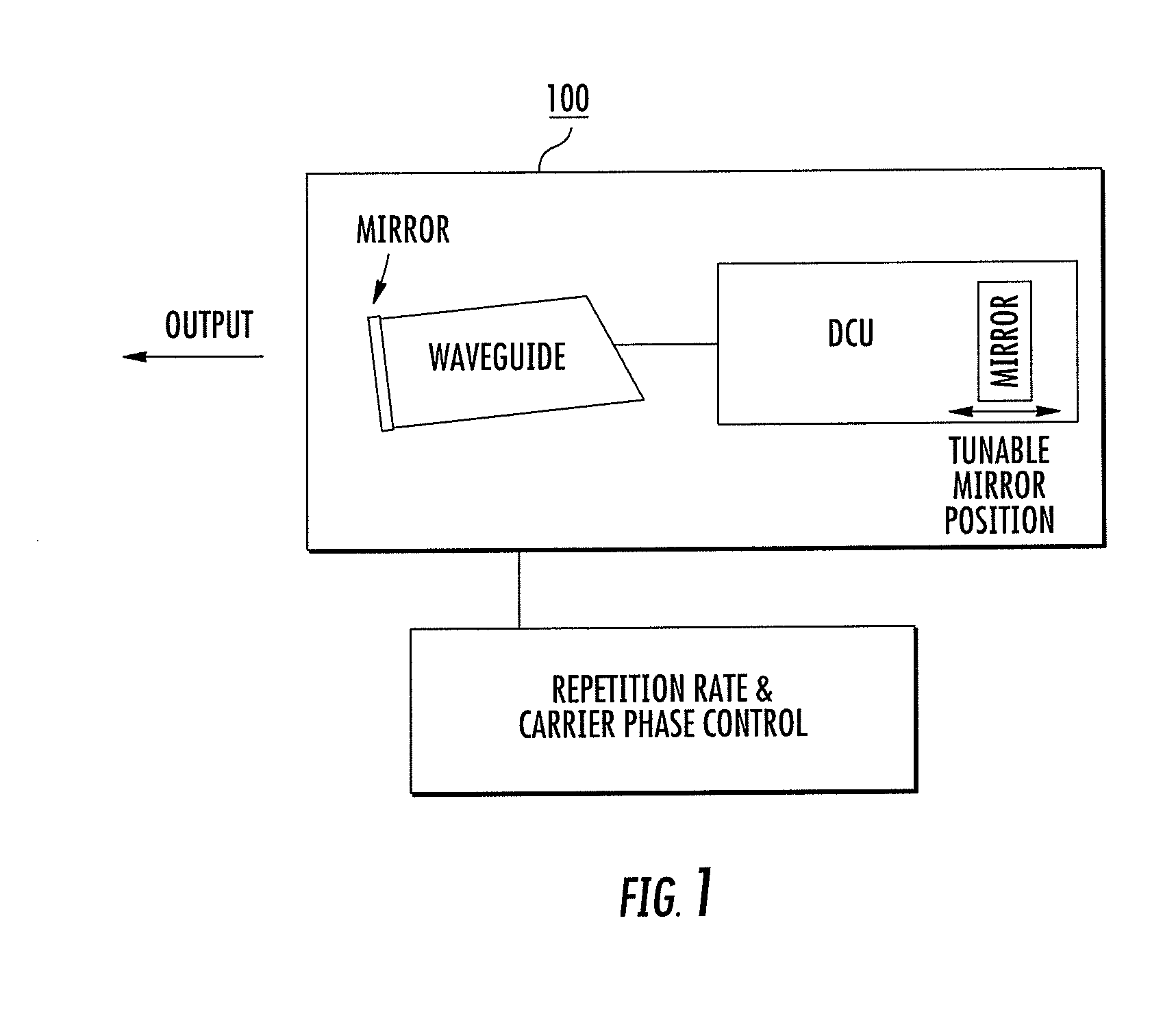
InactiveUS20120133931A1Reduce lossLow-loss bandwidth controlRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Hyper dispersion pulse compressor for chirped pulse amplification systems
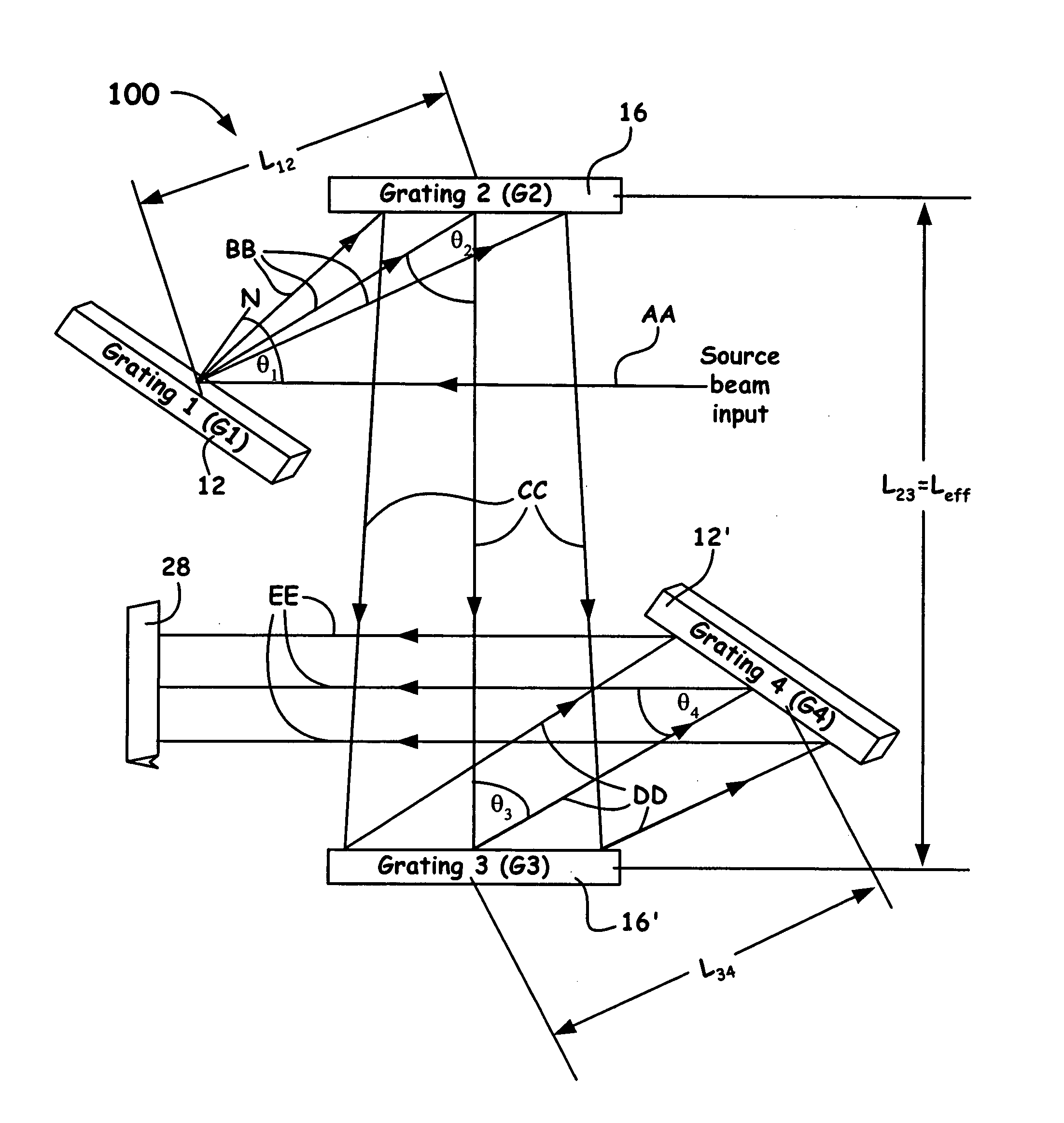
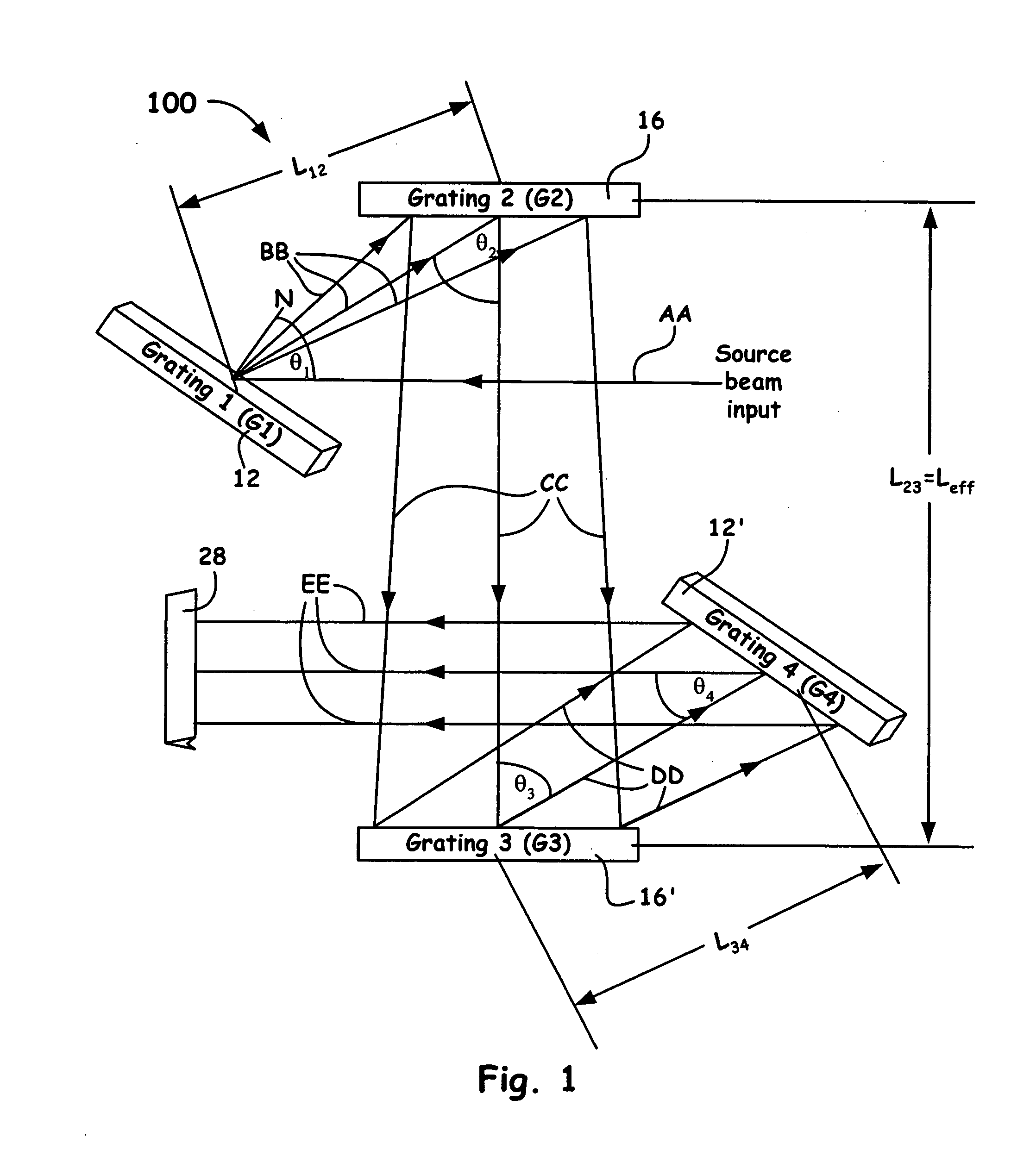
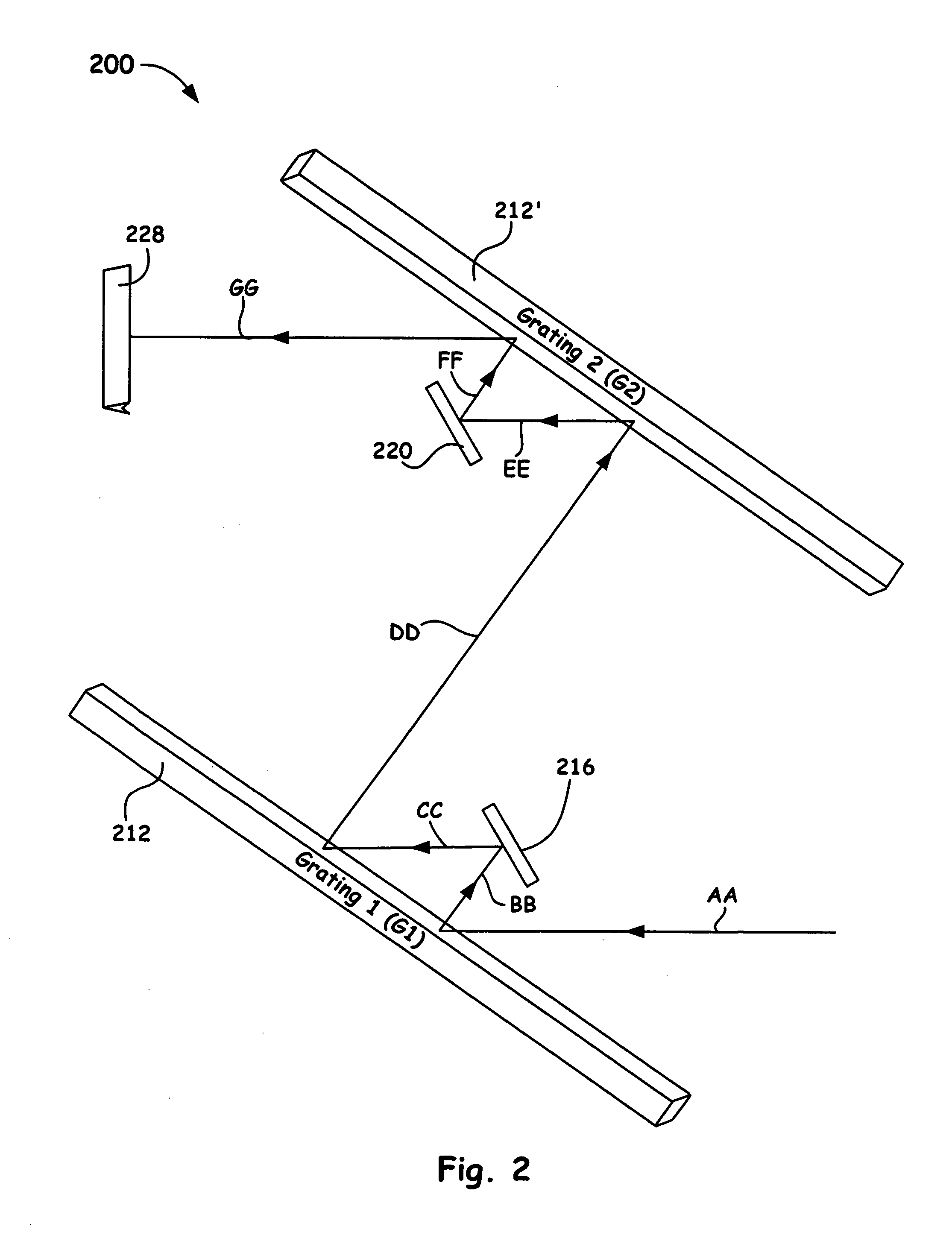
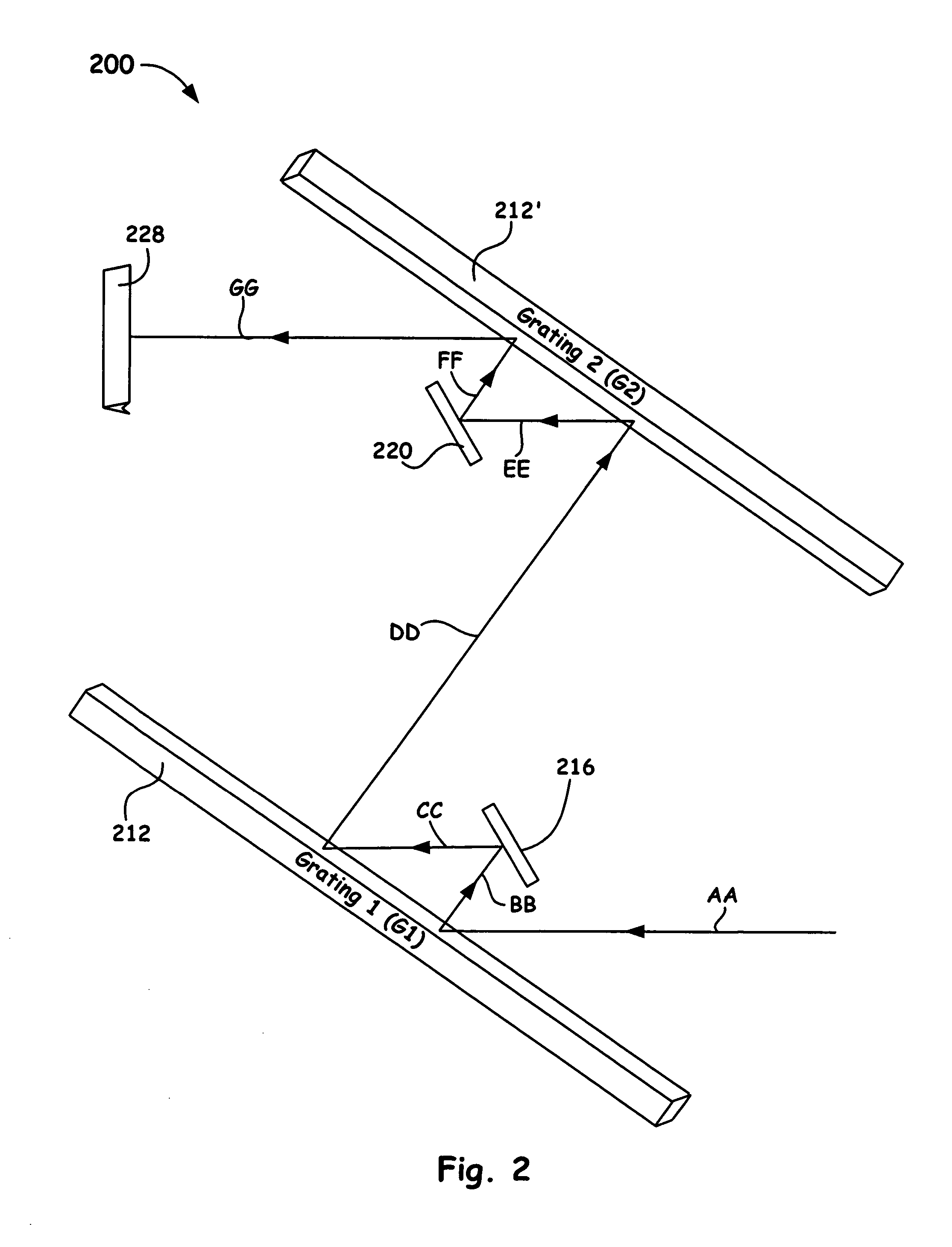
ActiveUS20060050750A1Small compressor footprintReduce system footprintElectric discharge heatingGlass furnace apparatusLight dispersionGrating
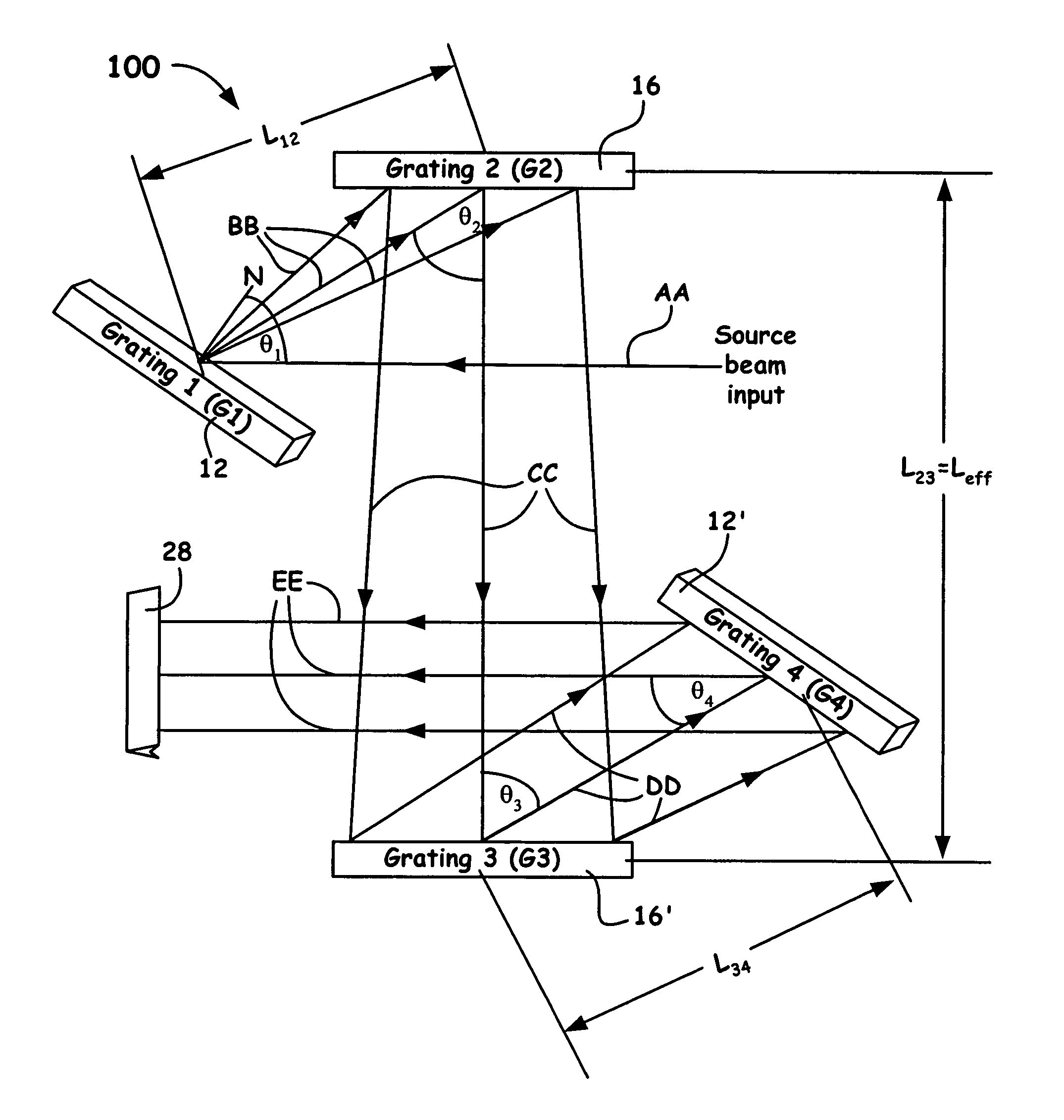
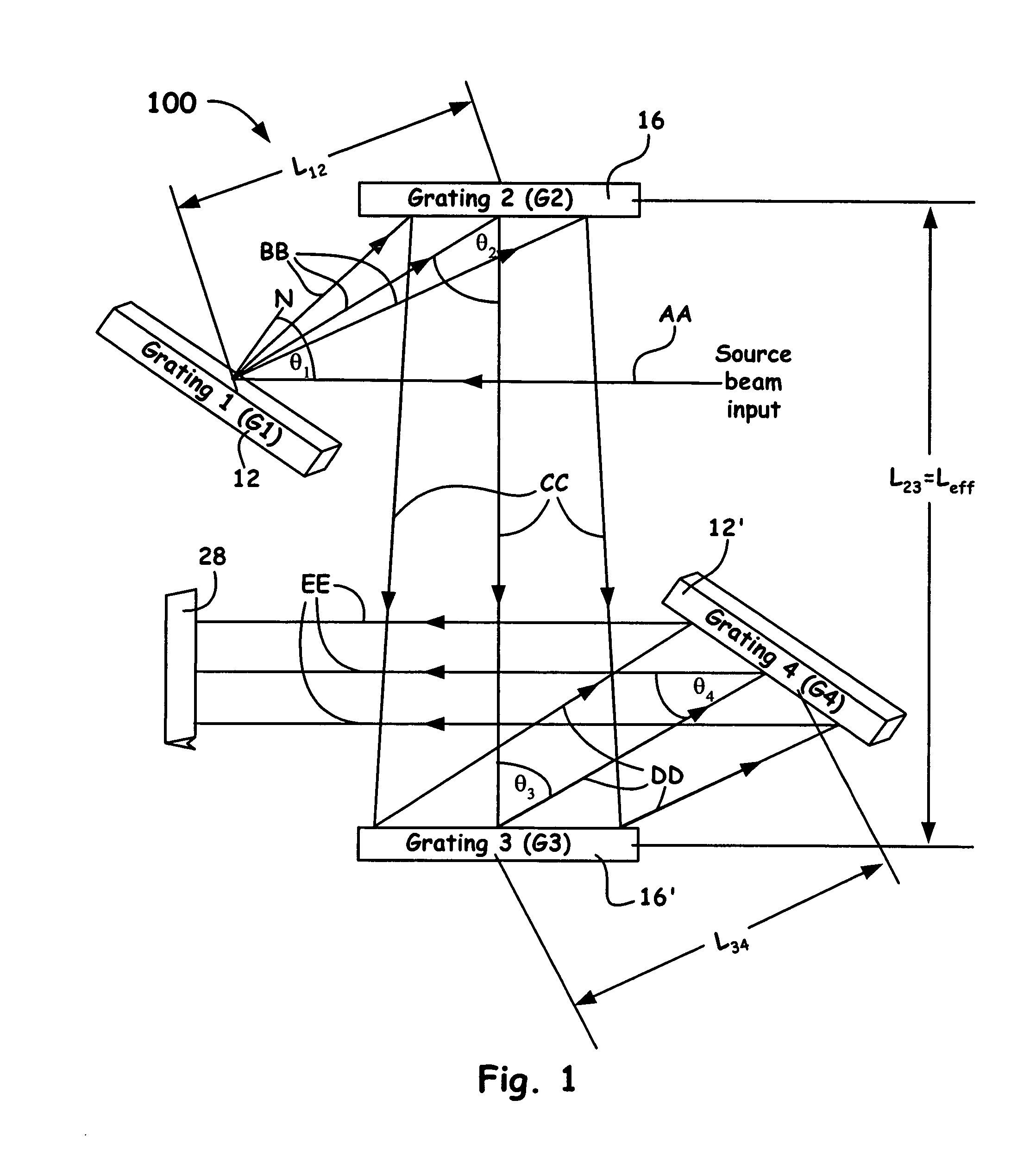
A grating pulse compressor configuration is introduced for increasing the optical dispersion for a given footprint and to make practical the application for chirped pulse amplification (CPA) to quasi-narrow bandwidth materials, such as Nd:YAG. The grating configurations often use cascaded pairs of gratings to increase angular dispersion an order of magnitude or more. Increased angular dispersion allows for decreased grating separation and a smaller compressor footprint.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Harmonic optimization technology
InactiveUS6223458B1Reduce vibrationReduce transmissionMuzzle attachmentGun mountingsVibration controlInertial mass
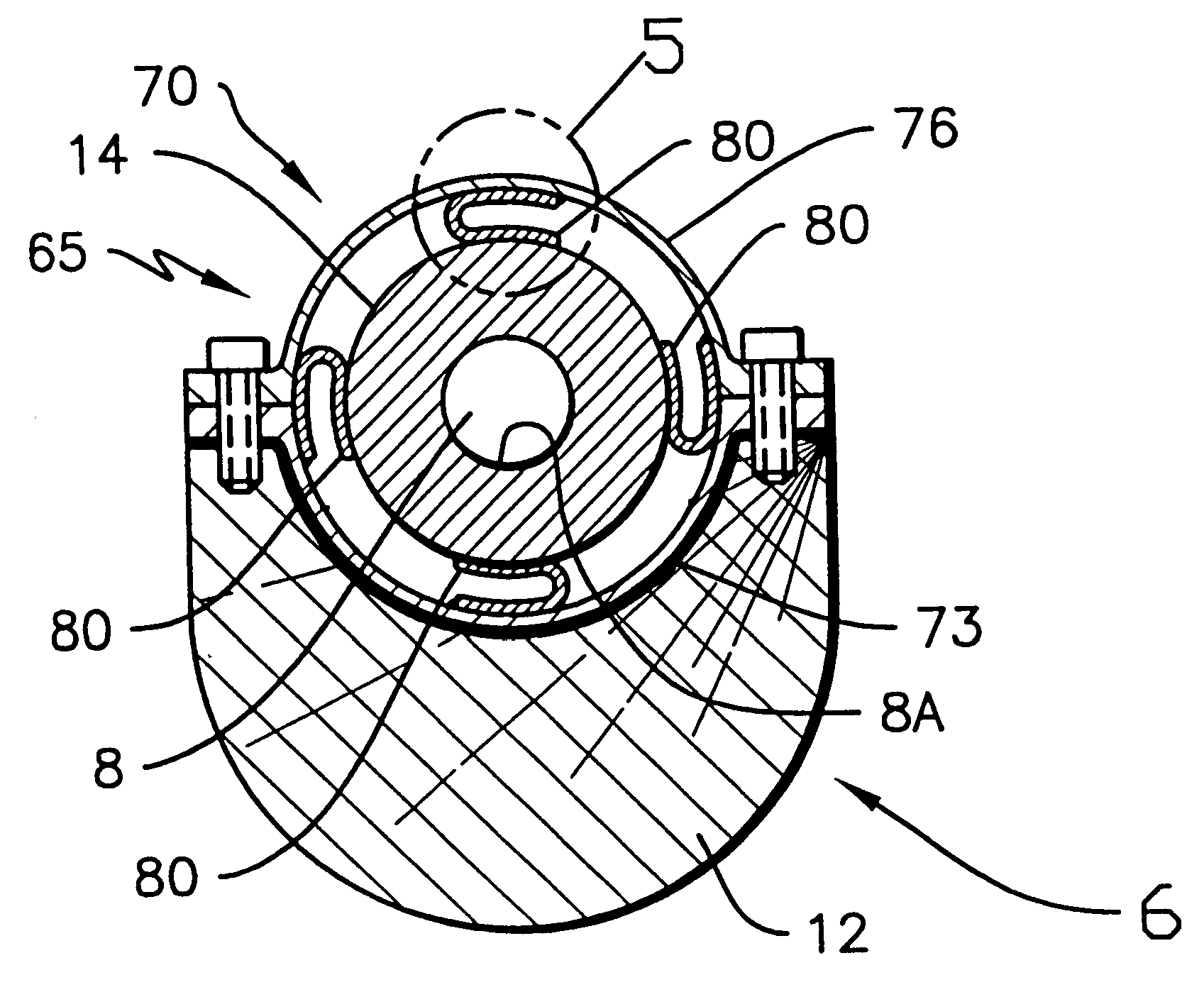
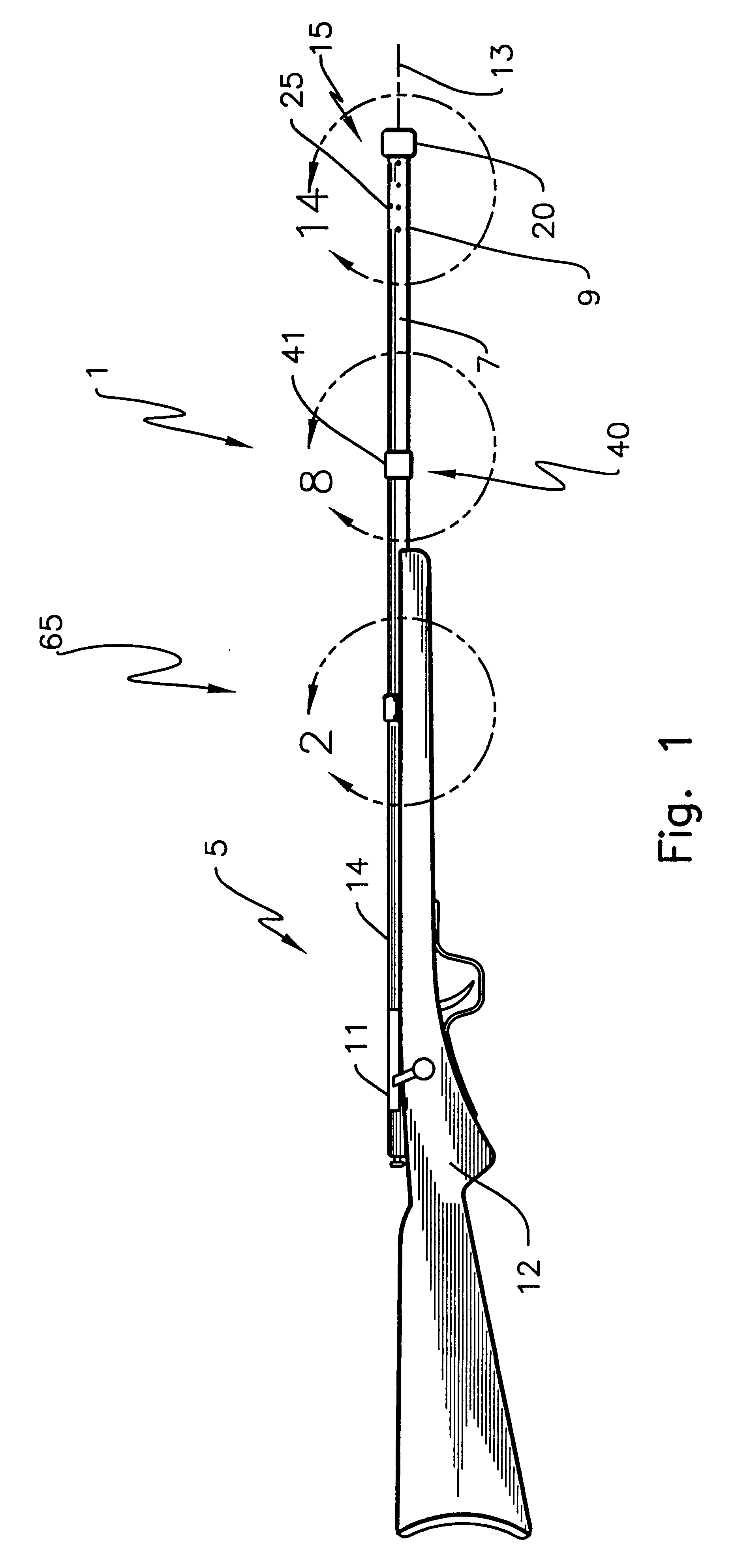
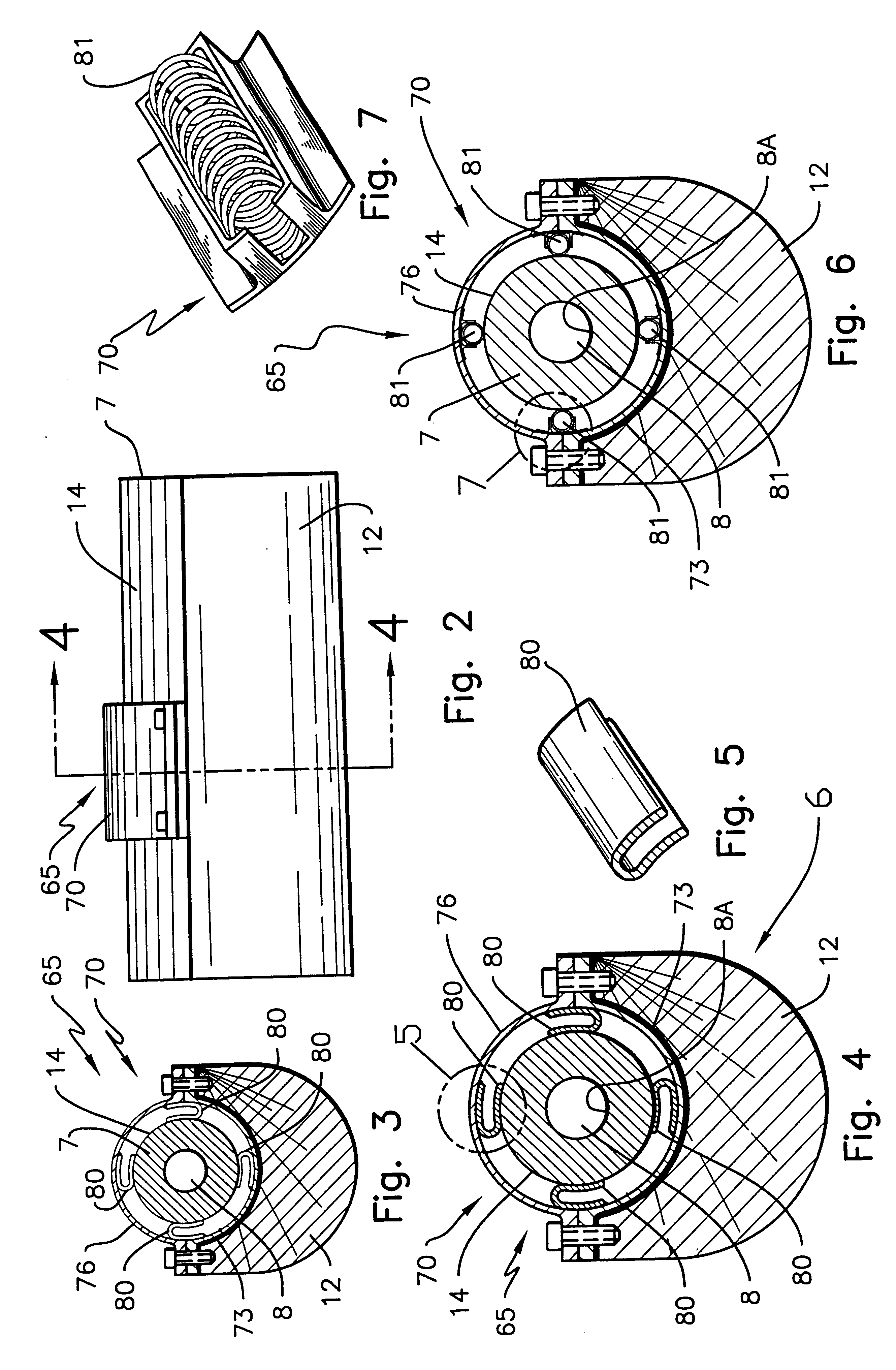
A method and an apparatus or apparatus system for vibration control, by harmonic optimization technology, of vibrations in the cantilever or barrel, portion of a device from which a projectile is fired or launched along the centerline of the cantilever. More particularly this invention relates to rifles, where the rifle barrel is a cantilever portion, and methods and apparatus for increasing the accuracy of firing projectiles. The invention is principally directed to a method and apparatus including a mass device affixed to a flexible cylinder extension at the muzzle end, inertial mass devices, having combustion pressure reduction features, affixed intermediate the muzzle end and the cartridge chamber, and a spring suspension system between barrel and rifle stock affixed proximal to the cartridge chamber. This system decreases the angular dispersion of barrel vibrations at the muzzle resulting from the firing of projectiles through such barrels.
Owner:SCHWINKENDORF KEVIN +1
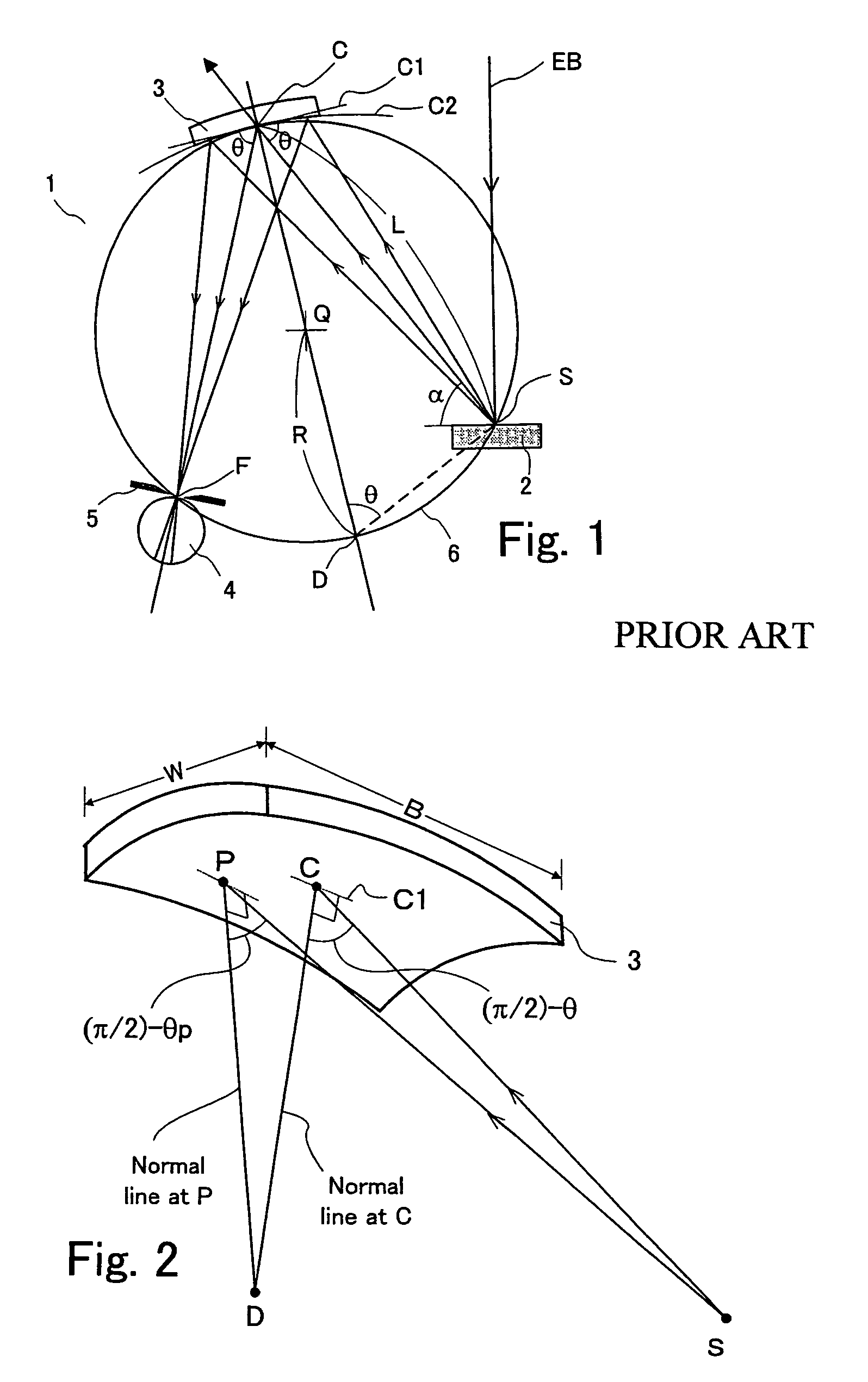
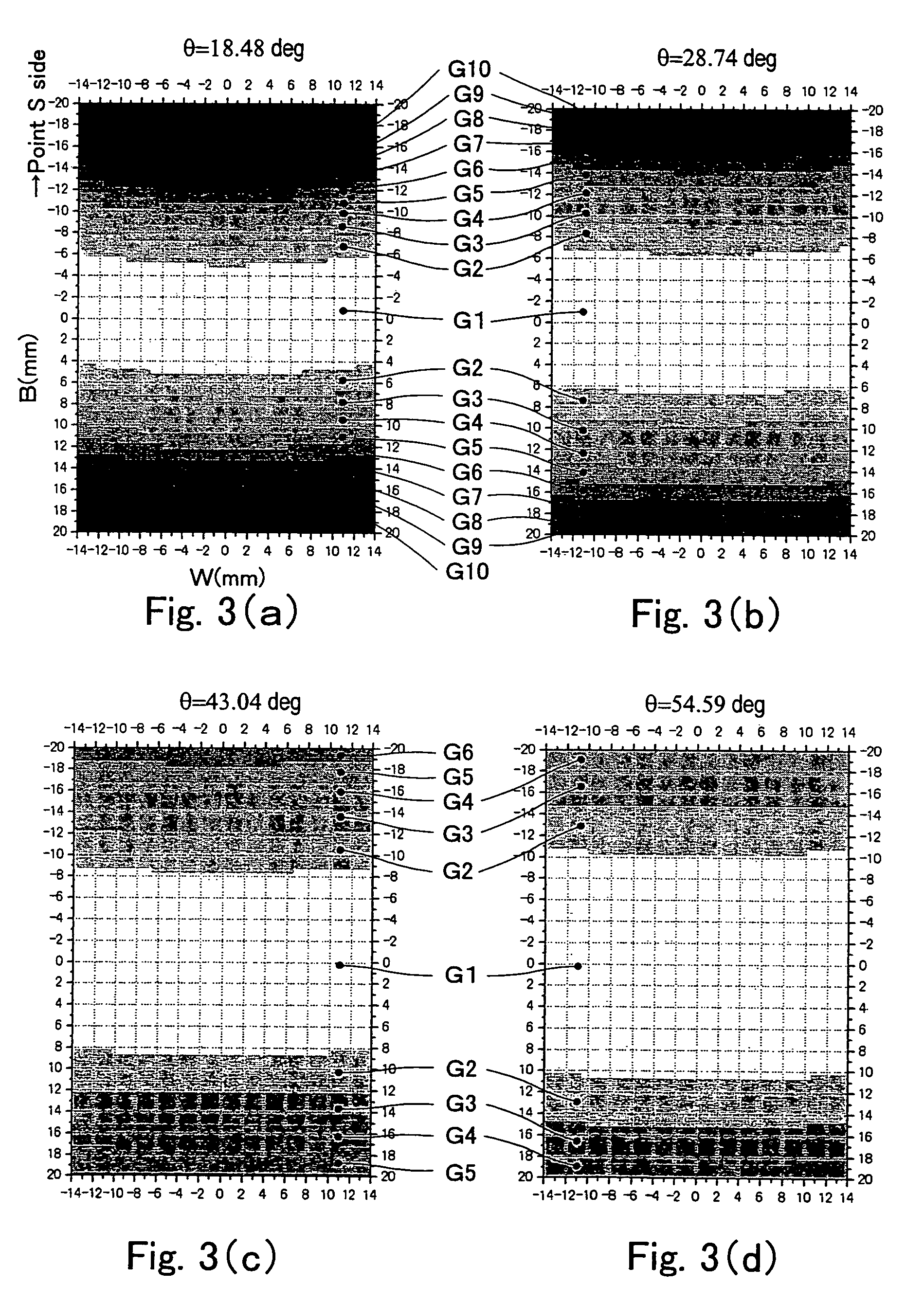
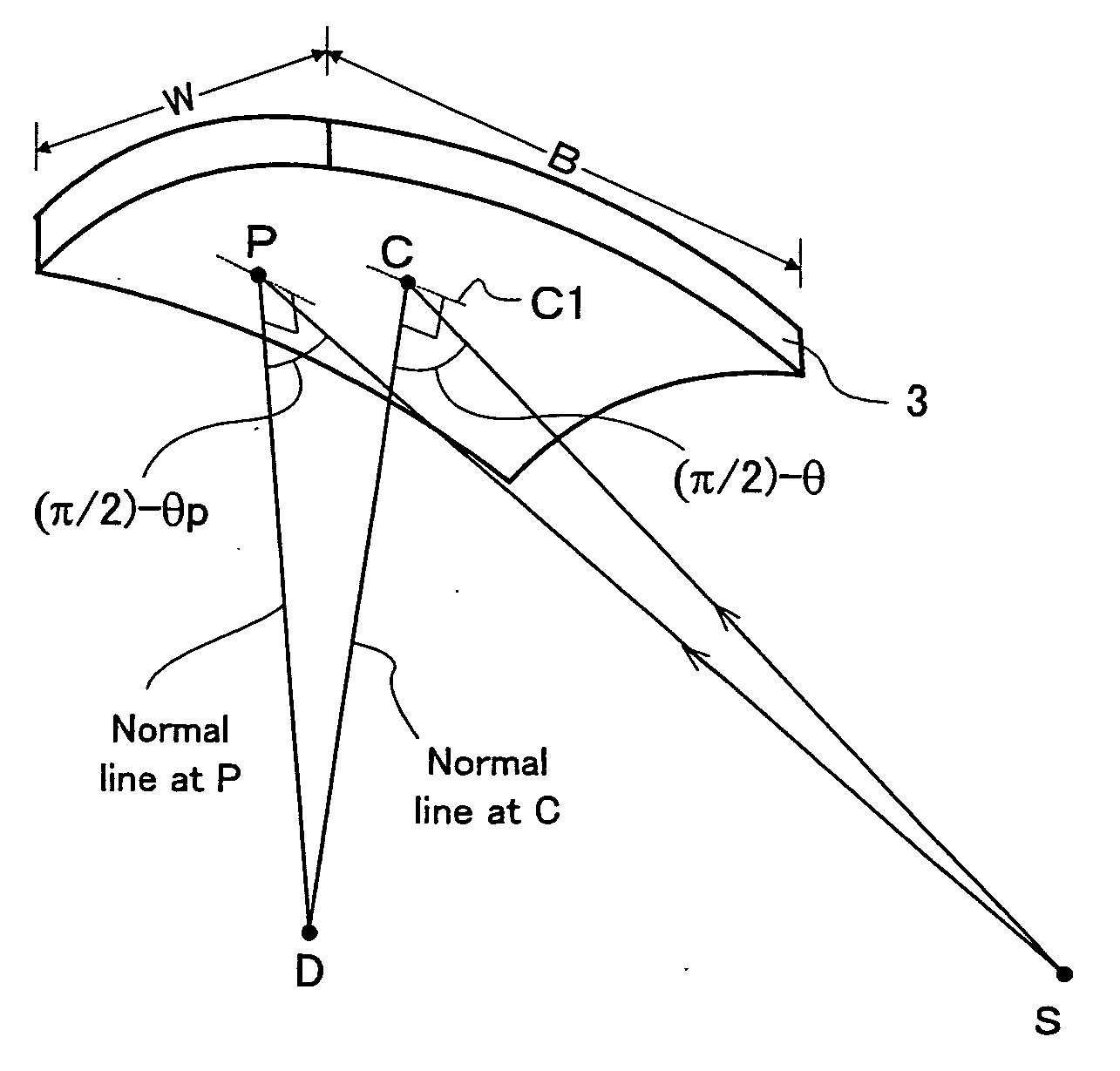
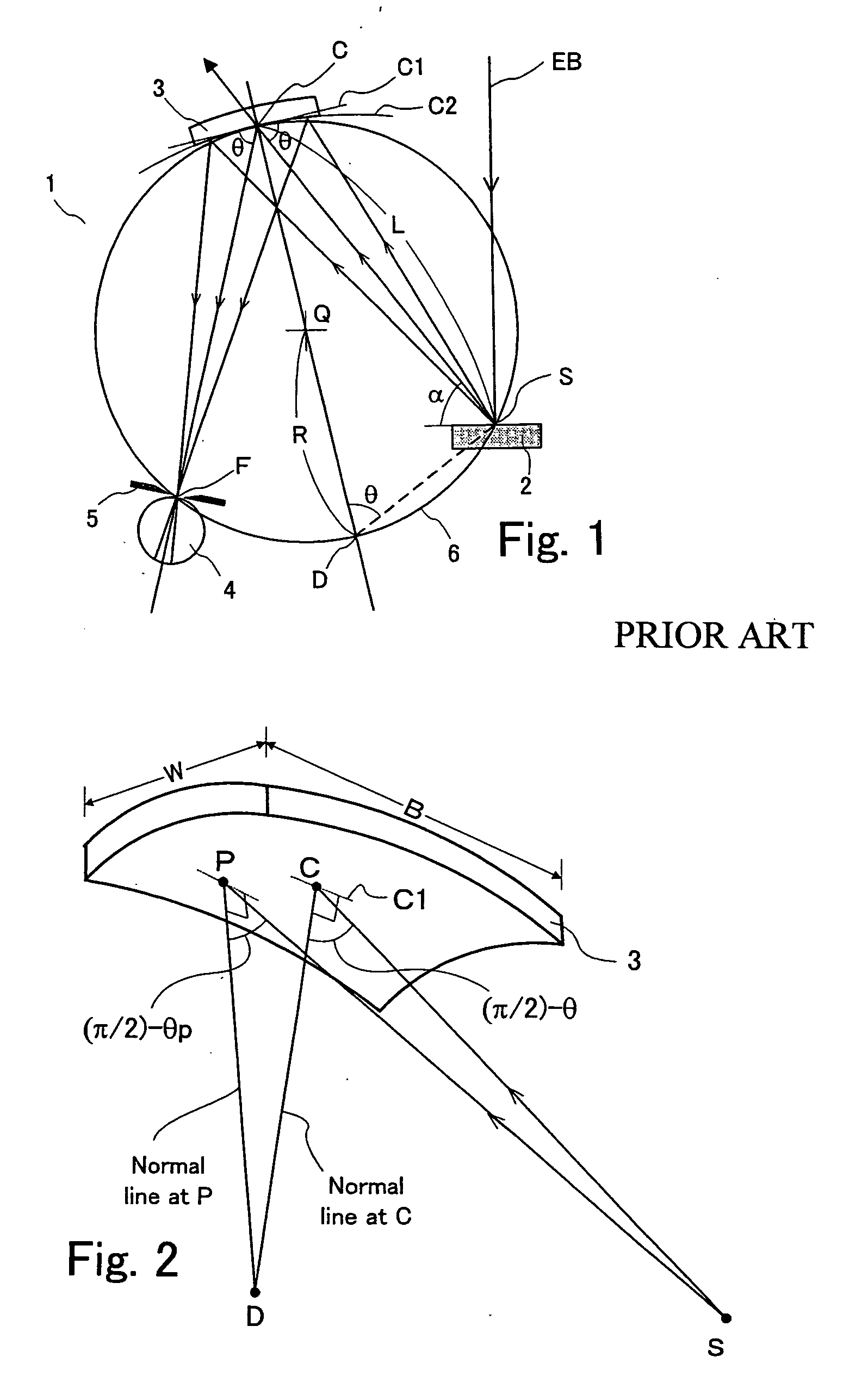
Wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectrometer
InactiveUS7864922B2Performance deteriorationRaise the ratioX-ray spectral distribution measurementElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionX ray spectra
An X-ray spectrometer which uses at least one curved analyzing crystal and which provides improved wavelength resolution of characteristic X-rays used for analysis and improved ratio of characteristic X-rays to background intensity by using only effective diffractive regions of the analyzing crystal. X-ray blocking plates upstand from an end of a crystal support member supporting the analyzing crystal in the direction of angular dispersion of the crystal toward the inside of a Rowland circle. Incident X-rays going from the point X-ray source toward the crystal and X-rays diffracted by the crystal toward an X-ray detector are partially blocked by the X-ray blocking plates. The shielded regions vary according to the incident angle θ of the incident X-rays. Optimum or nearly optimum effective regions of the surface of the crystal can be used at all times.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Optical filtering device
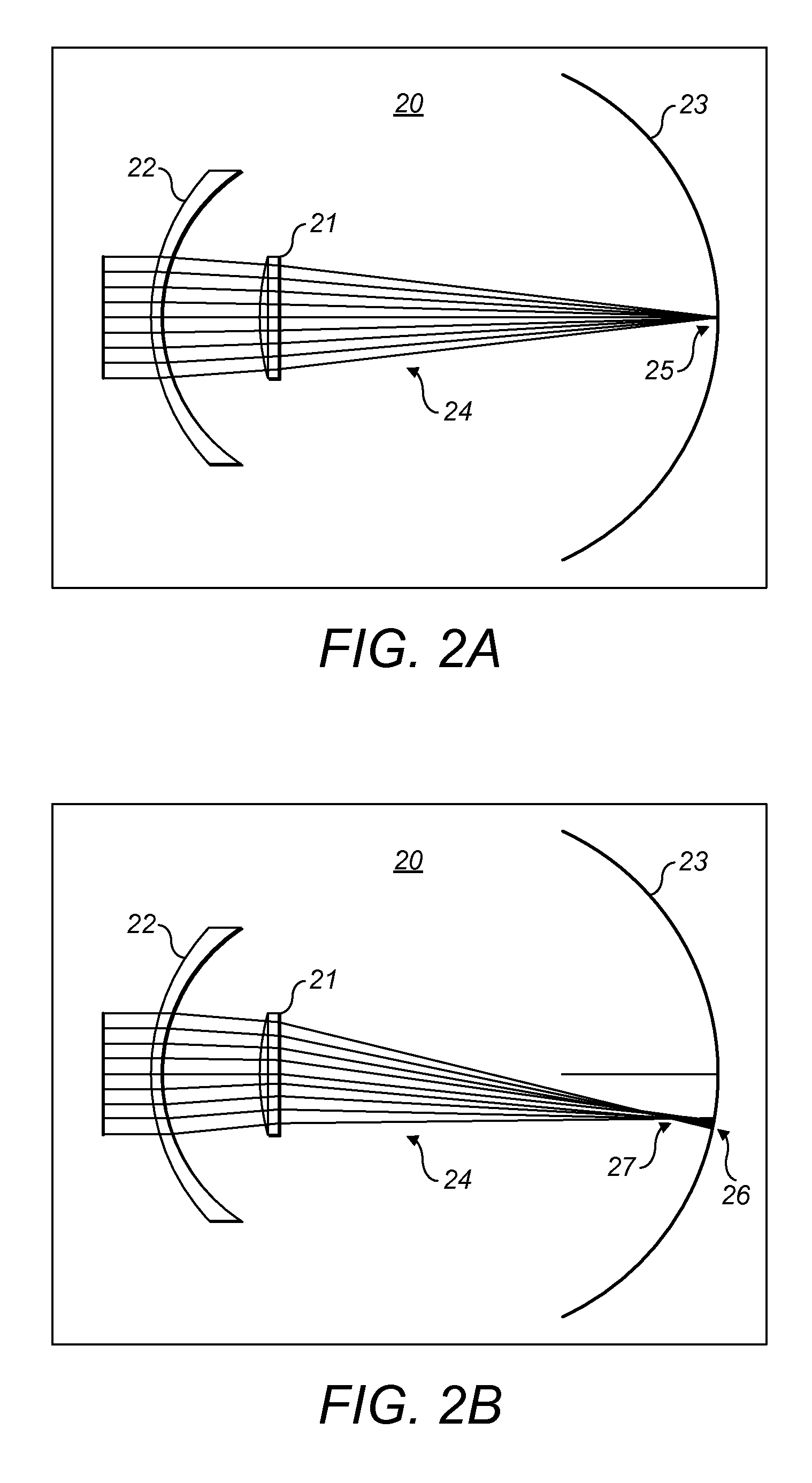
An optical filtering device incorporates first and second prisms, the latter prism counteracting the angular dispersion of the former prism. A spatial light modulator provides a positionally variable optical stop located to block radiation within a wavelength interval and received from a location within a scene. Unobscured radiation from that and other scene locations passes to a camera, which produces an image on a display. Opaque pixels in the stop are positioned to block unwanted light sources. The invention attenuates potentially dazzling monochromatic radiation while retaining radiation at other wavelengths for imaging purposes.
Owner:THE SEC OF STATE FOR DEFENCE IN HER BRITANNIC MAJESTYS GOVERNMENT OF THE UK OF GREAT BRITAIN & NORTHERN IRELAND
Wavelength-dispersive X-ray spectrometer
InactiveUS20100284513A1Performance deteriorationRaise the ratioX-ray spectral distribution measurementElectric discharge tubesImage resolutionX-ray
An X-ray spectrometer which uses at least one curved analyzing crystal and which provides improved wavelength resolution of characteristic X-rays used for analysis and improved ratio of characteristic X-rays to background intensity by using only effective diffractive regions of the analyzing crystal. X-ray blocking plates upstand from an end of a crystal support member supporting the analyzing crystal in the direction of angular dispersion of the crystal toward the inside of a Rowland circle. Incident X-rays going from the point X-ray source toward the crystal and X-rays diffracted by the crystal toward an X-ray detector are partially blocked by the X-ray blocking plates. The shielded regions vary according to the incident angle θ of the incident X-rays. Optimum or nearly optimum effective regions of the surface of the crystal can be used at all times.
Owner:JEOL LTD
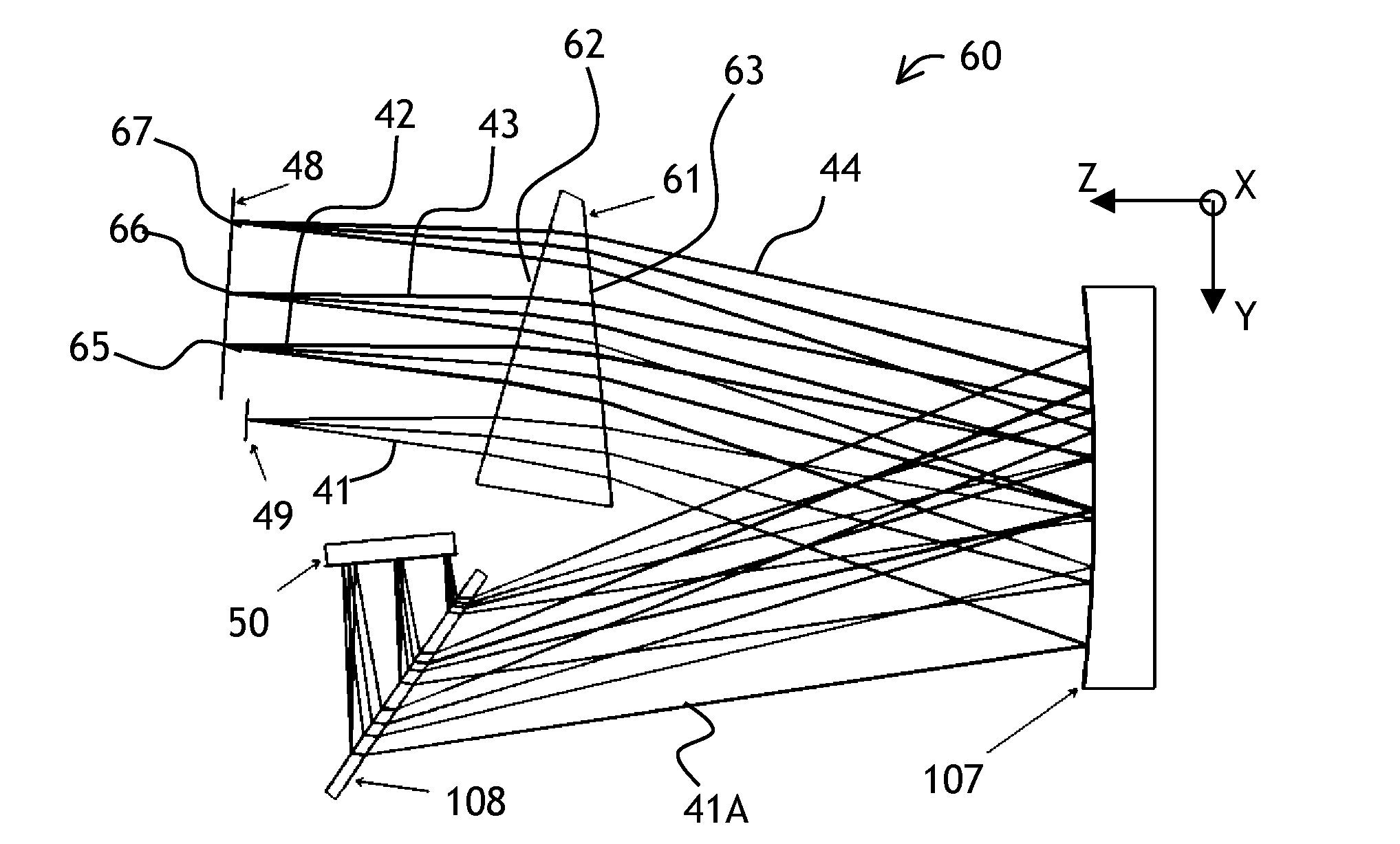
Wavelength dispersing device
InactiveUS20090273840A1Reduce widthSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsReflex reflectorsOptical aberrationLength wave
A compact wavelength dispersing device and a wavelength selective optical switch based on the wavelength dispersing device is described. The wavelength dispersing device has a folding mirror that folds the optical path at least three times. A focal length of a focusing coupler of the device is reduced and the NA is increased, while the increased optical aberrations are mitigated by using an optional coma-compensating wedge. A double-pass arrangement for a transmission diffraction grating allows further focal length and overall size reduction due to increased angular dispersion.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
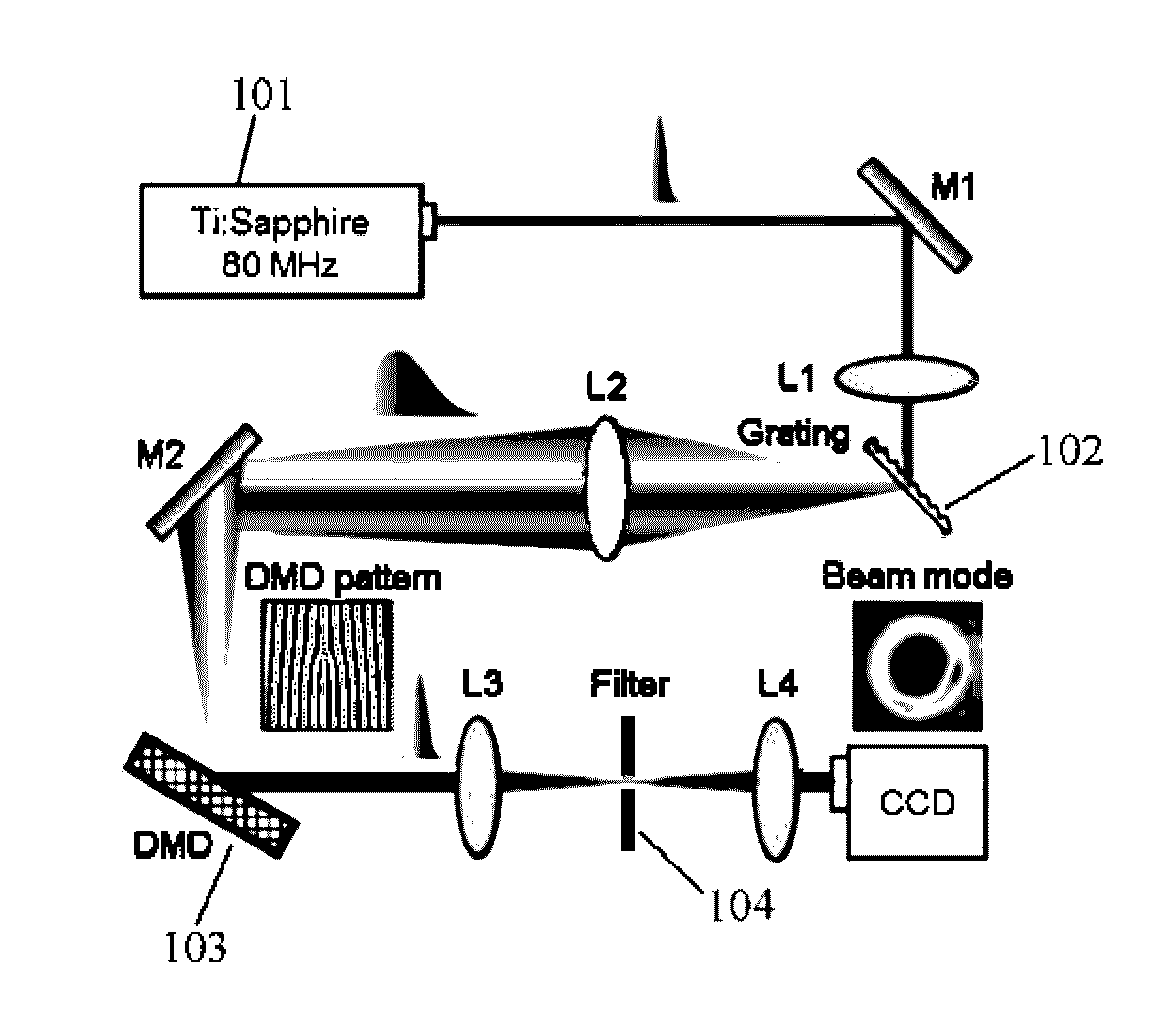
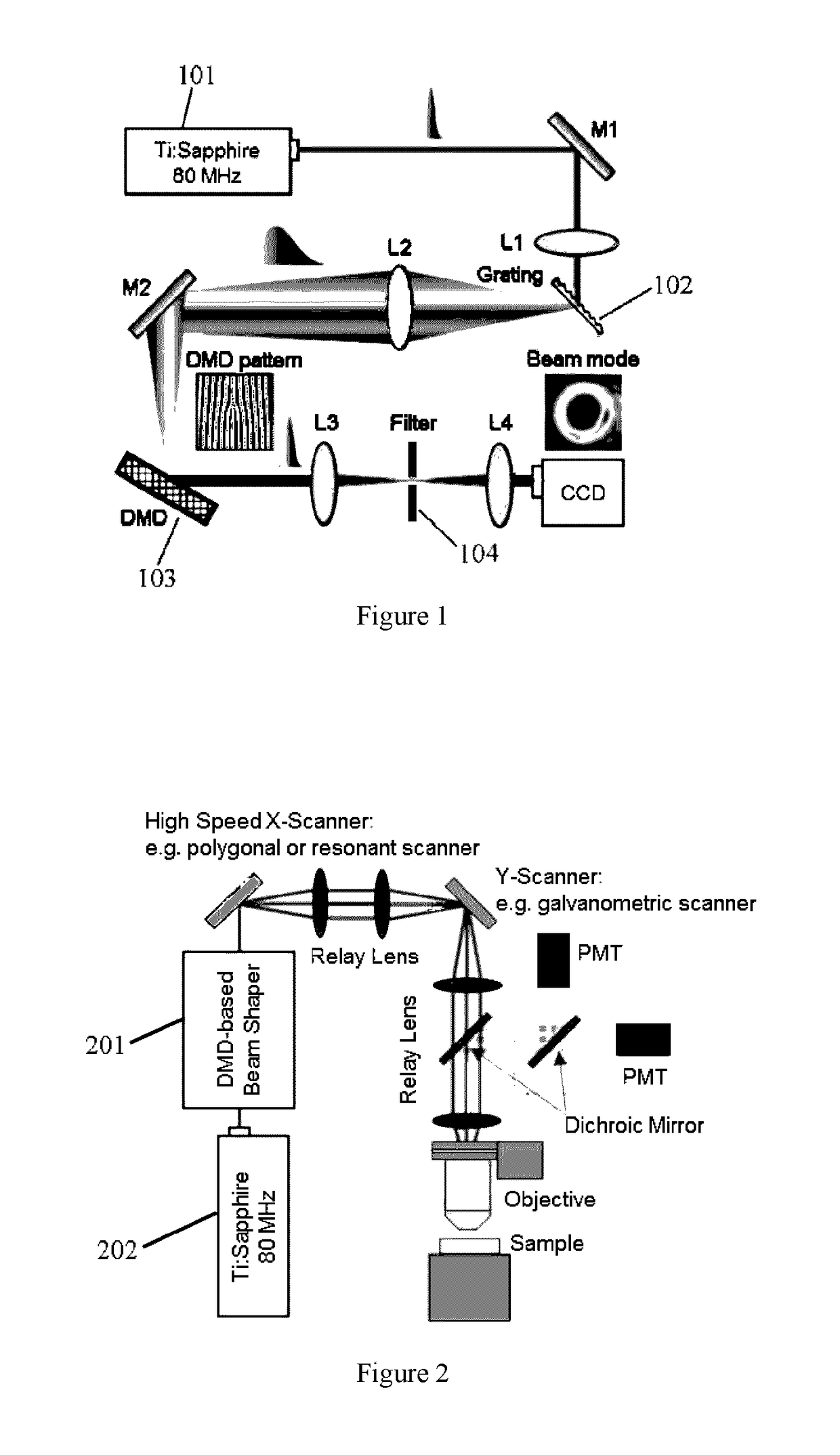
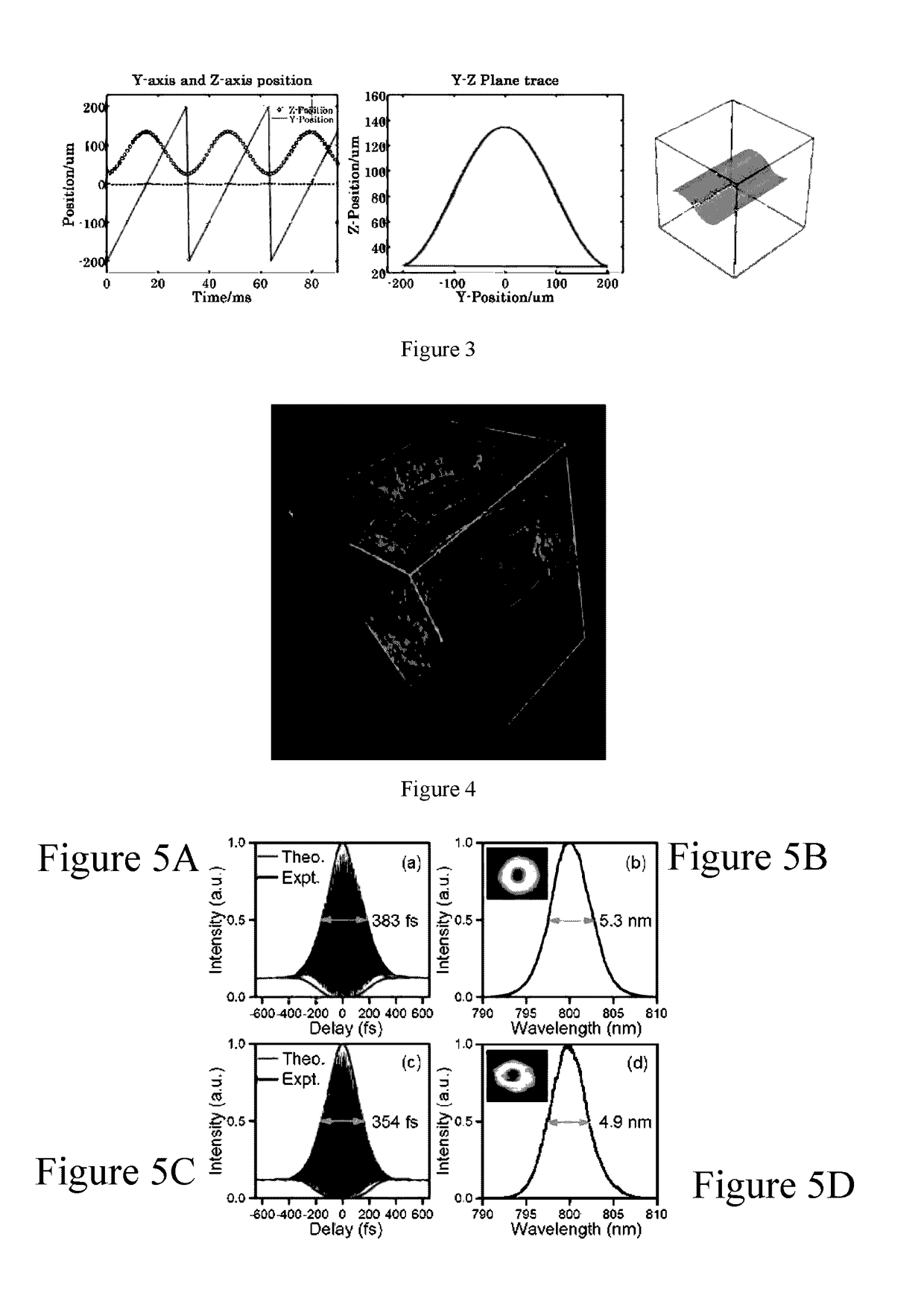
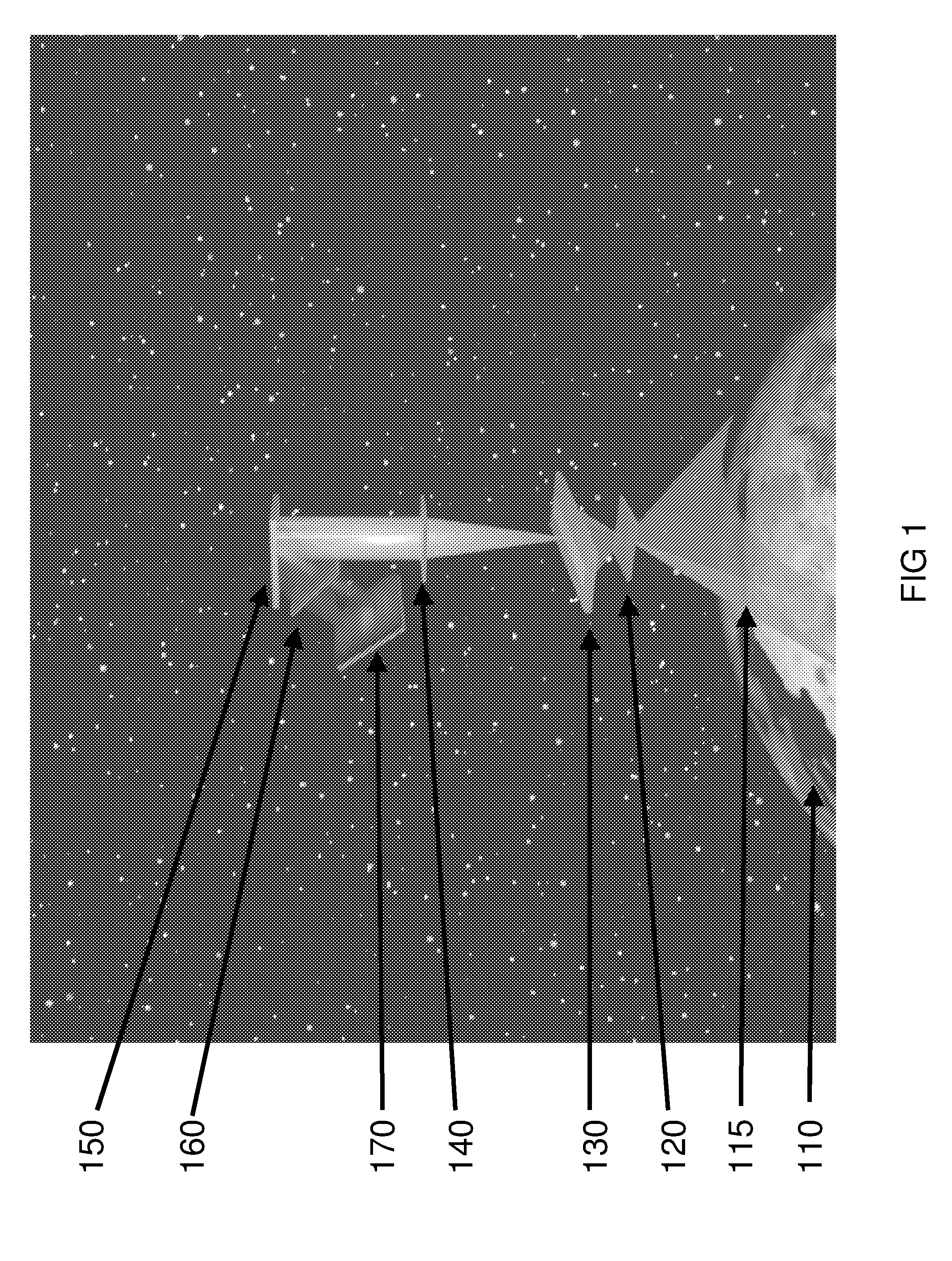
High-speed Binary Laser Beam Shaping and Scanning
ActiveUS20170082845A1High shapingHigh scanning rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrequency spectrumLight beam
A device for shaping and scanning an ultrafast laser beam including a laser source configured to output a pulsed laser beam containing different frequency spectrum; a digital micromirror device (DMD) consisting of a plurality of micromirrors, configured to receive the laser beam and shape the received laser beam with a first angular dispersion; and a dispersion compensation unit, arranged before or after the DMD, configured to transfer the laser beam from the laser source to the DMD with a second angular dispersion for neutralizing the first angular dispersion.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for producing a diffraction grating
ActiveUS20150034591A1Easy to manufactureBeneficial stray light characteristicRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationResistAngular dispersion
A manufacturing method for a grating is disclosed for the angular dispersion of light impinging the grating. The grating comprises tapered structures and cavities. A cavity width and / or corrugation amplitude is varied for achieving a desired grating efficiency according to calculation. A method is disclosed for conveniently creating gratings with variable cavity width and / or corrugation amplitude. The method comprises the step of anisotropically etching a groove pattern into a grating master. Optionally a replica is produced that is complementary to the grating master. By variation of an etching resist pattern, the cavity width of the grating may be varied allowing the optimization towards different efficiency goals.
Owner:STICHTING NEDERLANDSE WETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK INSTN +1
Intraocular Lens with Fresnel Prism
InactiveUS20120277857A1Reduce impactReduce dispersionIntraocular lensDiffraction effectIntraocular lens
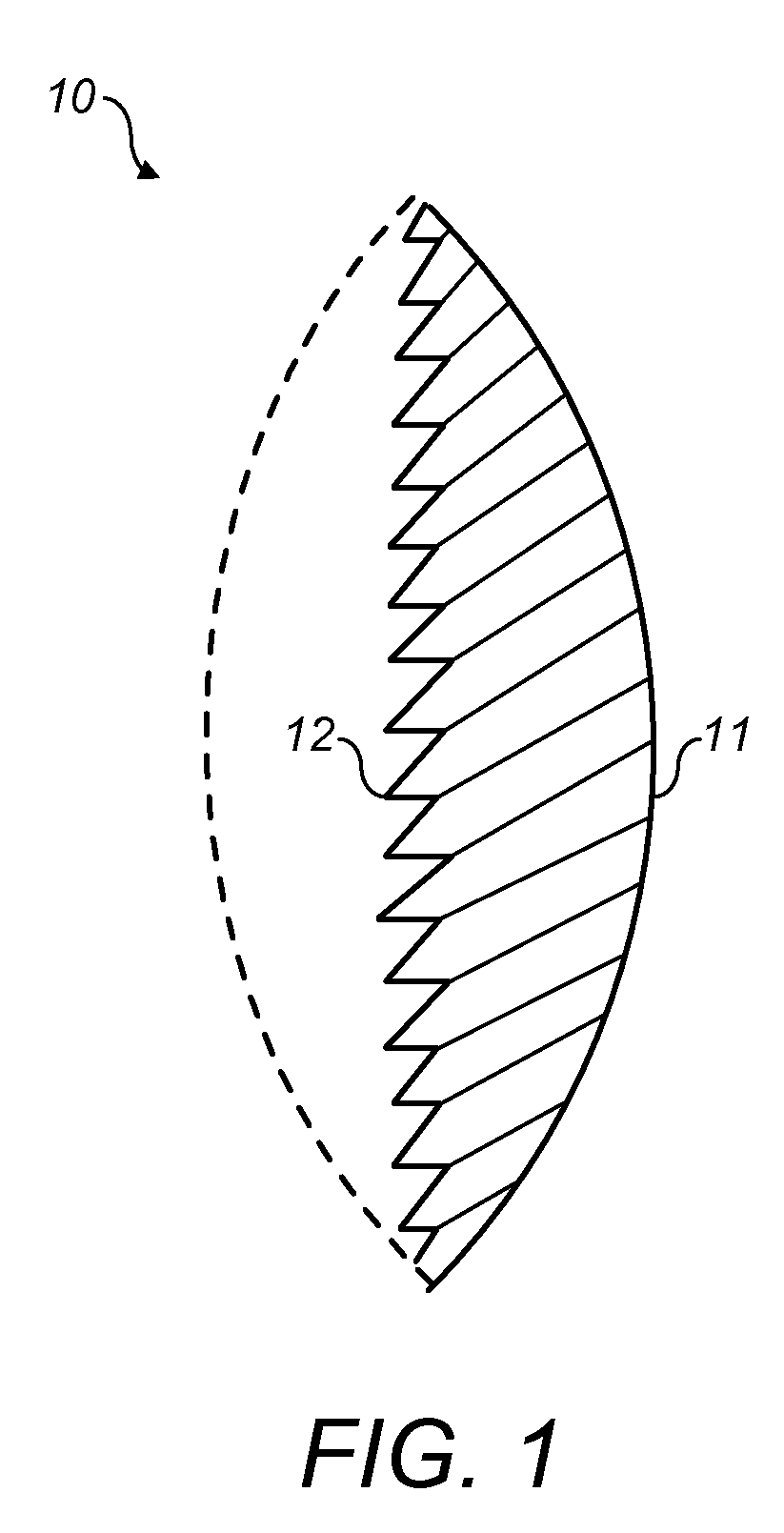
An intraocular lens is described which comprises, as one face thereof, a linear Fresnel prism array with facets angled relative to the optical axis of the lens so as to deviate light incident thereon to an off-axis position. The facets are modified so as to reduce at least one of diffraction effects and astigmatism associated with the Fresnel prism. In particular, by varying the pitch of the prism elements across the array, which may comprise varying their size, a diffraction grating effect can be reduced or negated, such that light is not diffracted into undesirable orders and multiple images can be avoided. Furthermore, chromatic angular dispersion associated with the diffraction grating effect may be reduced. The pitch variation can be random. By varying the angle of the facets across the array, astigmatism that would otherwise result from the presence of the Fresnel prism can also be compensated.
Owner:RAYNER INTRAOCULAR LENSES
Apparatus for generating tera-Hertz wave and tuning method
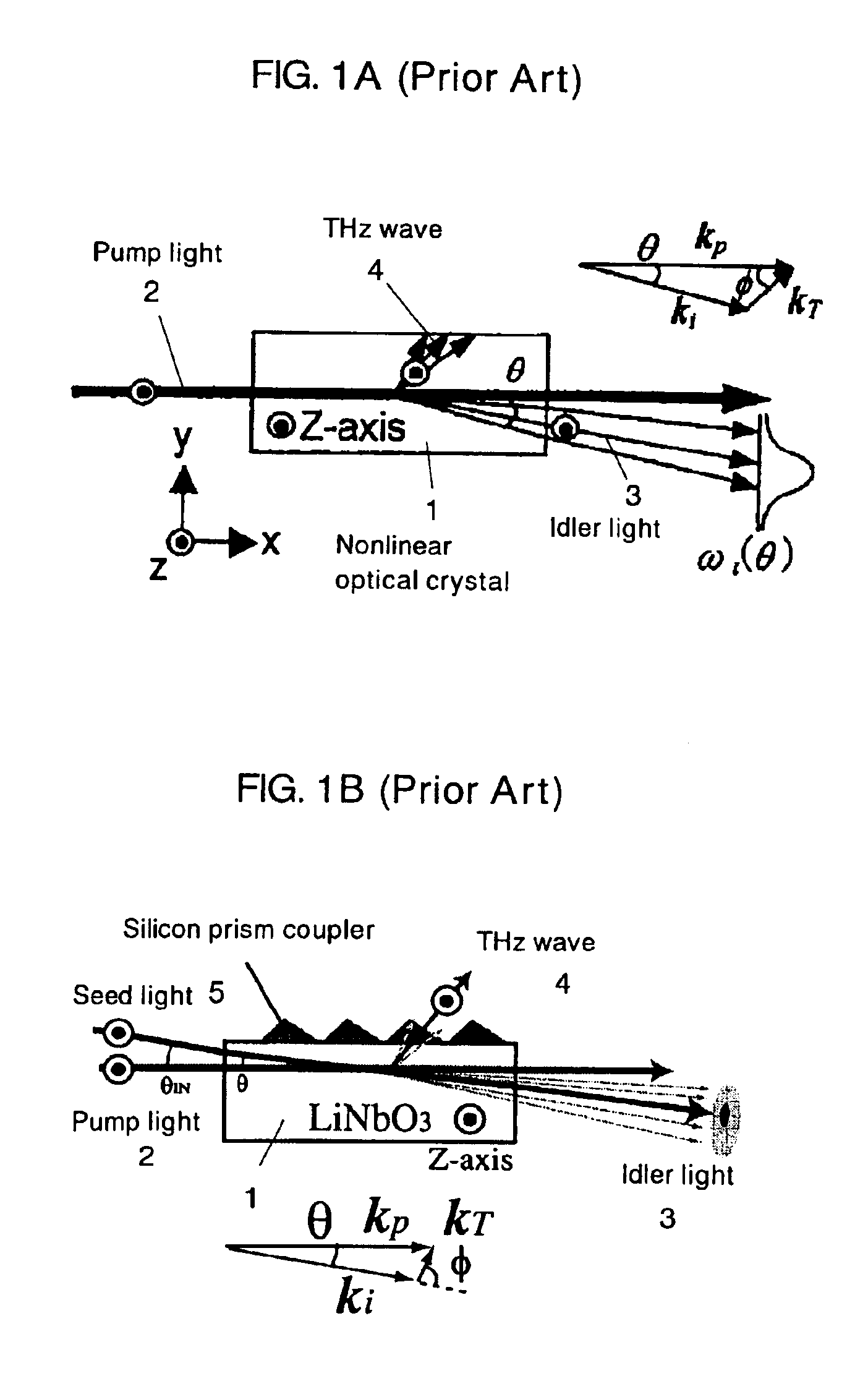
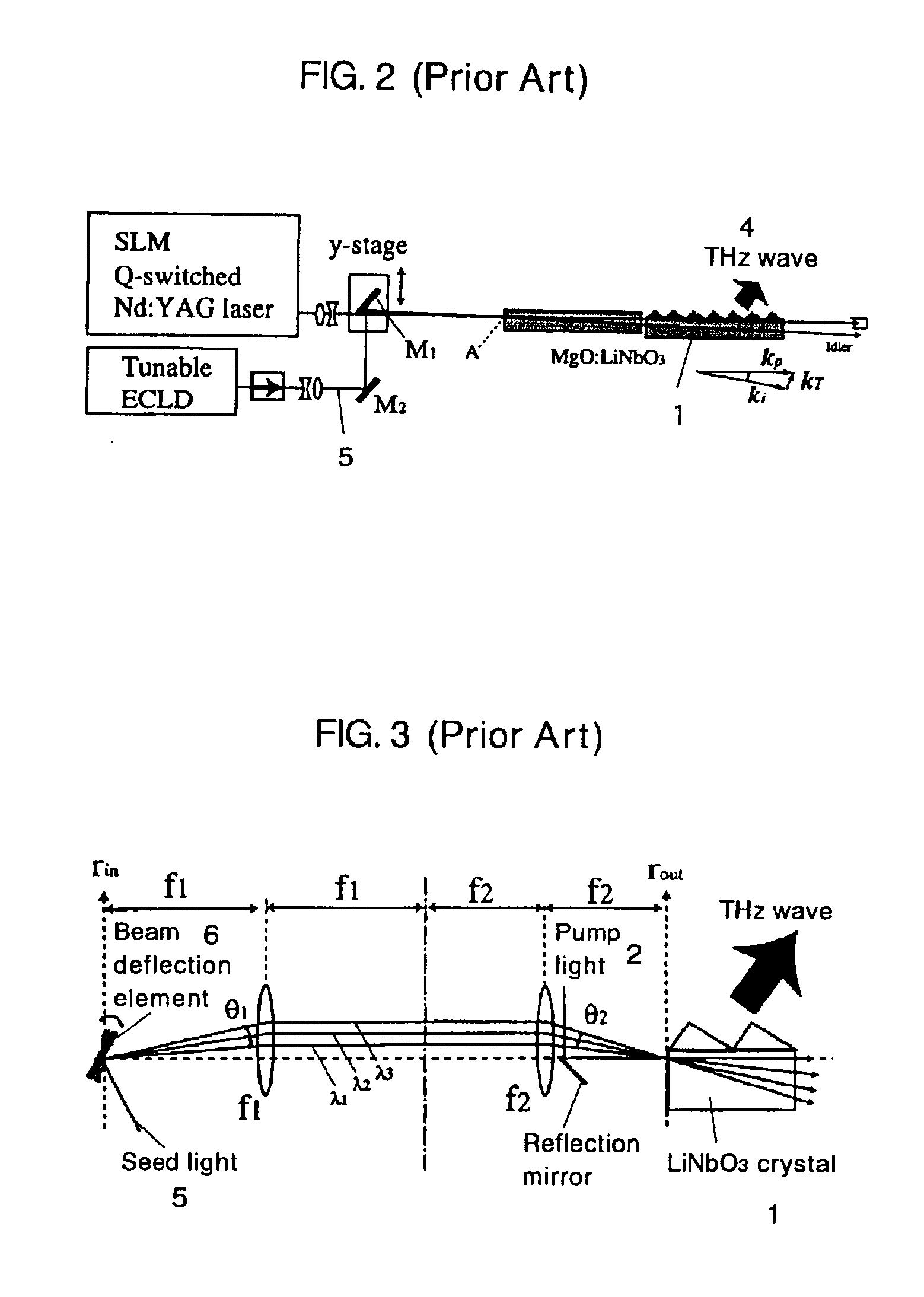
InactiveUS6903341B2Easy to adjustLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryNonlinear optical crystalWavelength
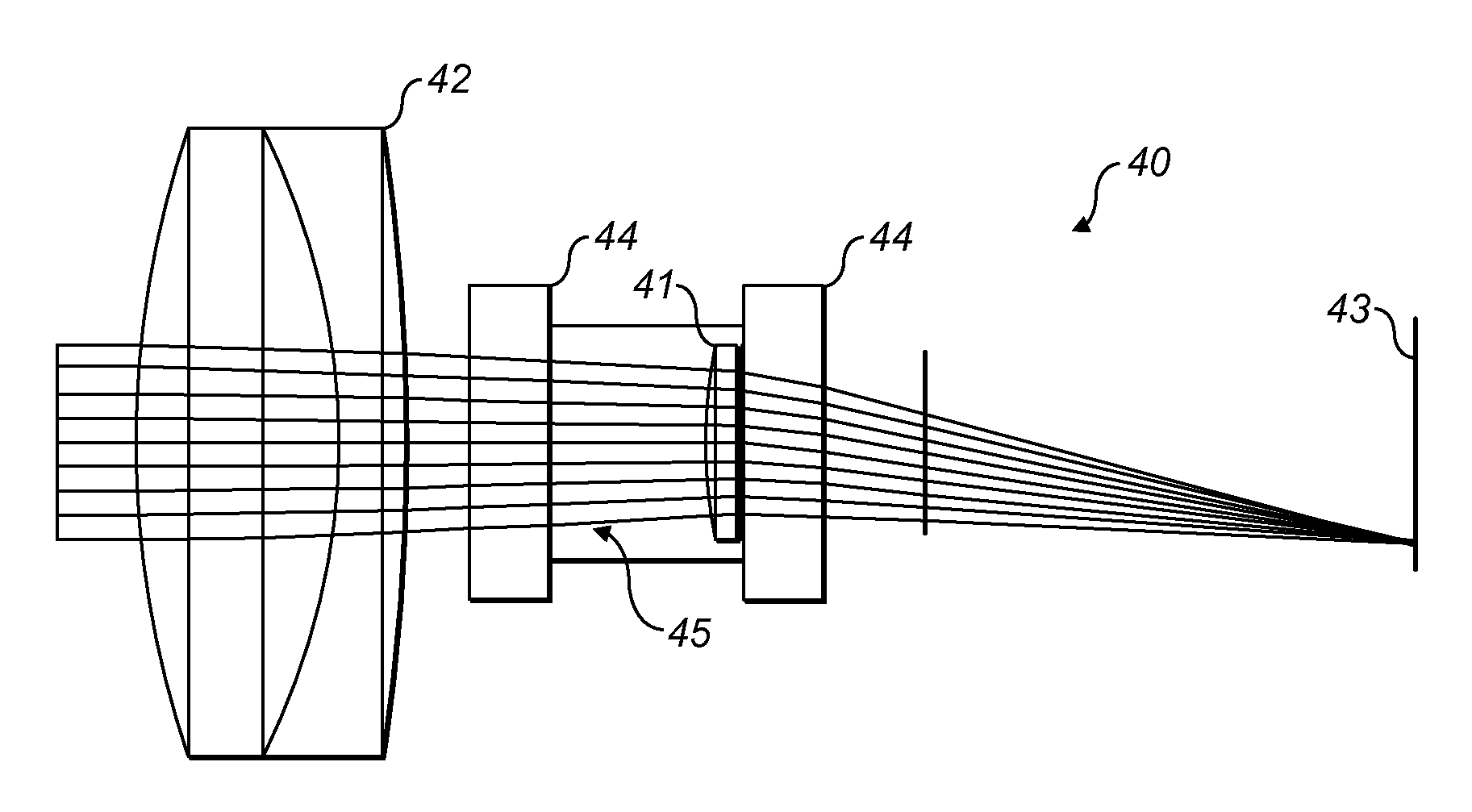
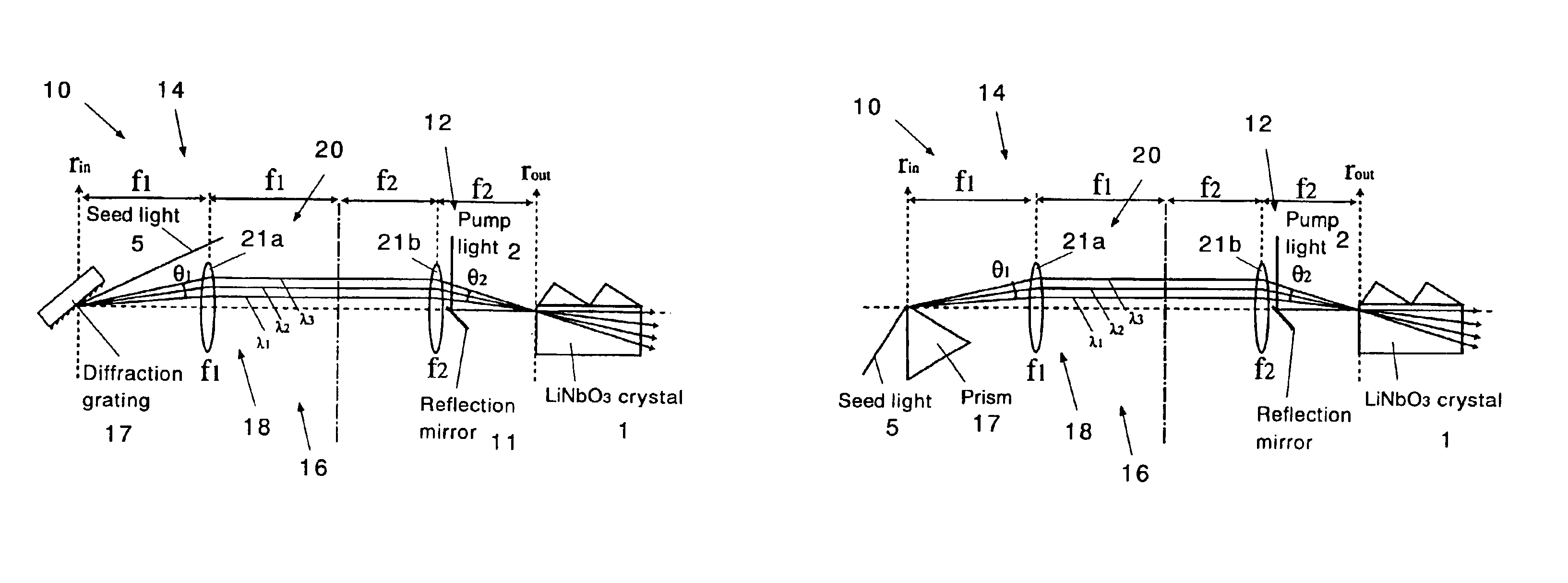
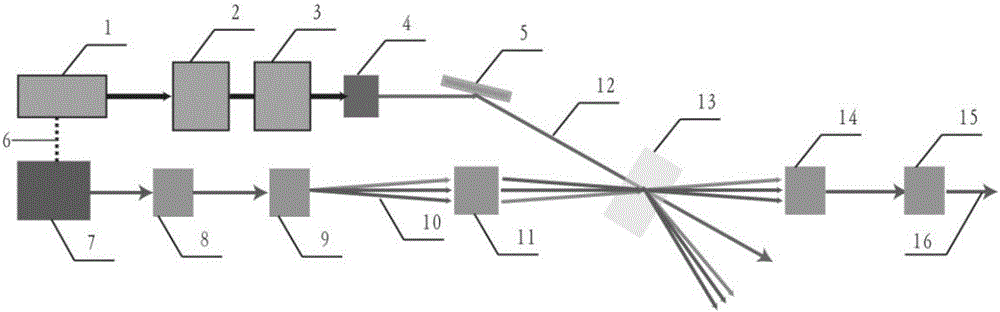
There are disclosed a nonlinear optical crystal 1 which can generate a THz wave by a parametric effect; a pump light incidence apparatus 12 for allowing a pump light 2 to be incident upon the nonlinear optical crystal; and a seed light injection apparatus 14 for injecting a seed light 5 having a variable frequency in a generation direction of an idler light 3 generated by the pump light. The seed light injection apparatus 14 comprises angle dispersion compensation means 16 set so that an incidence angle θIN of the seed light upon the nonlinear optical crystal 1 substantially equals to a desired phase matching condition regardless of a wavelength.
Owner:RIKEN
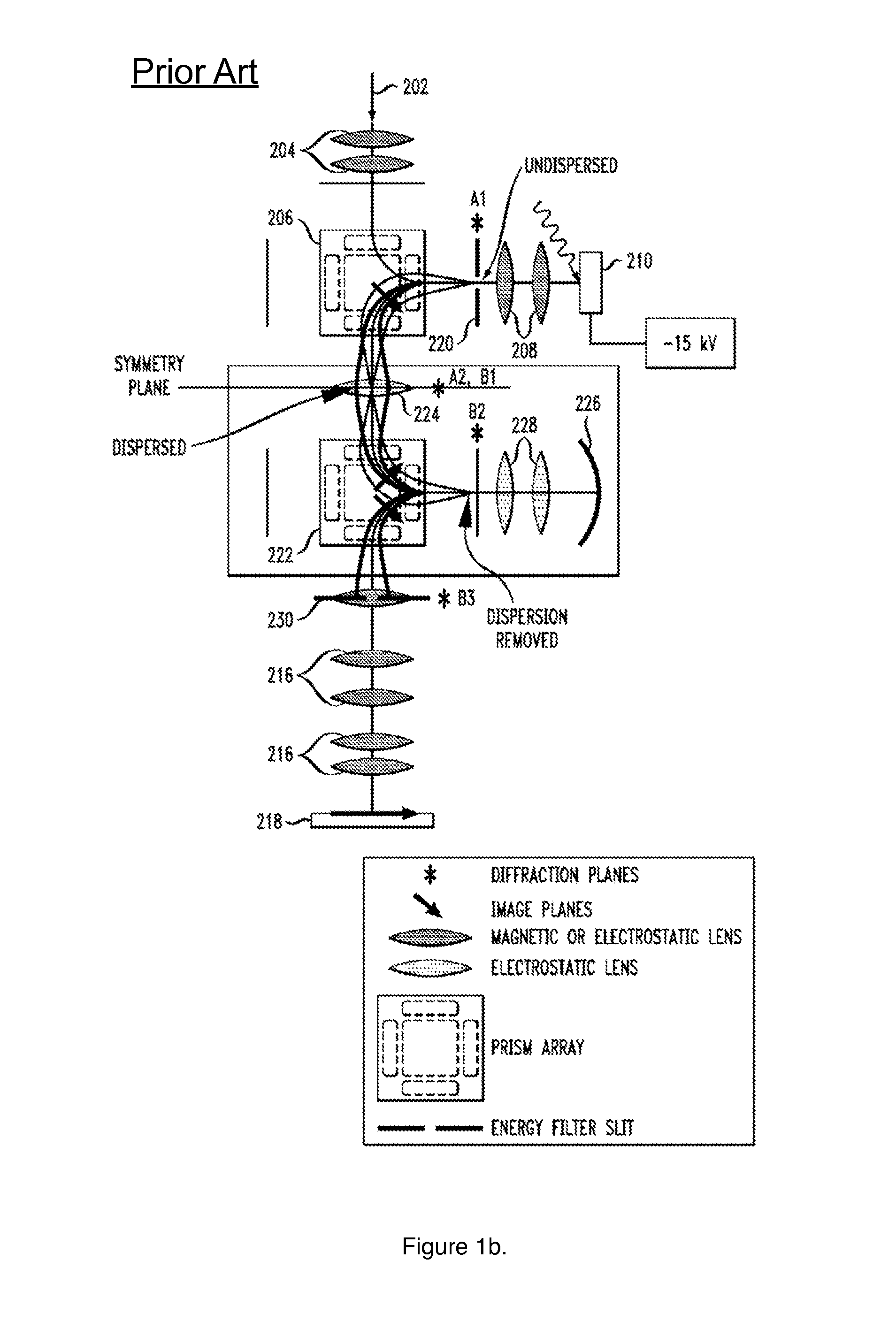
Aberration-corrected and energy-filtered low energy electron microscope with monochromatic dual beam illumination
ActiveUS8729466B1Excessive aberrationStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam sourceHigh energy beam
One embodiment relates to an apparatus for correcting aberrations introduced when an electron lens forms an image of a specimen and simultaneously forming an electron image using electrons with a narrow range of electron energies from an electron beam with a wide range of energies. A first electron beam source is configured to generate a lower energy electron beam, and a second electron beam source is configured to generate a higher energy electron beam. The higher energy beam is passed through a monochromator comprising an energy-dispersive beam separator, an electron mirror and a knife-edge plate that removes both the high and low energy tail from the propagating beam. Both the lower and higher energy electron beams are deflected by an energy-dispersive beam separator towards the specimen and form overlapping illuminating electron beams. An objective lens accelerates the electrons emitted or scattered by the sample. The electron beam leaving the specimen is deflected towards a first electron mirror by an energy-dispersive beam separator, which introduces an angular dispersion that disperses the electron beam according to its energy. A knife-edge plate, located between the beam separator and first electron mirror, is inserted that removes all of the beam with energy larger and smaller than a selected energy and filters the beam according to energy. One or more electron lenses focus the electron beam at the reflection surface of the first electron mirror so that after the reflection and another deflection by the same energy-dispersive beam separator the electron beam dispersion is removed. The dispersion-free and energy-filtered electron beam is then reflected in a second electron mirror which corrects one or more aberrations of the objective lens. After the second reflection, electrons are deflected by the magnetic beam separator towards the projection optics which forms a magnified, aberration-corrected, energy-filtered image on a viewing screen.
Owner:ELECTRON OPTICA
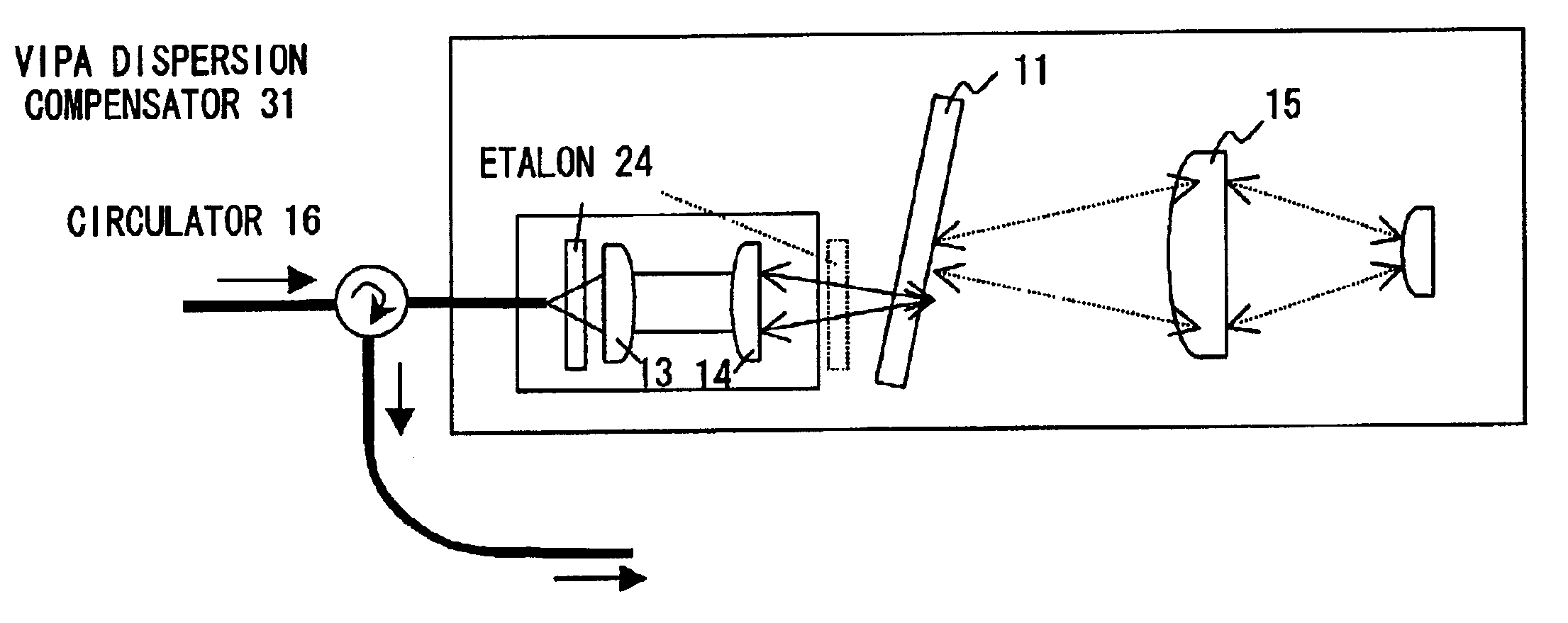
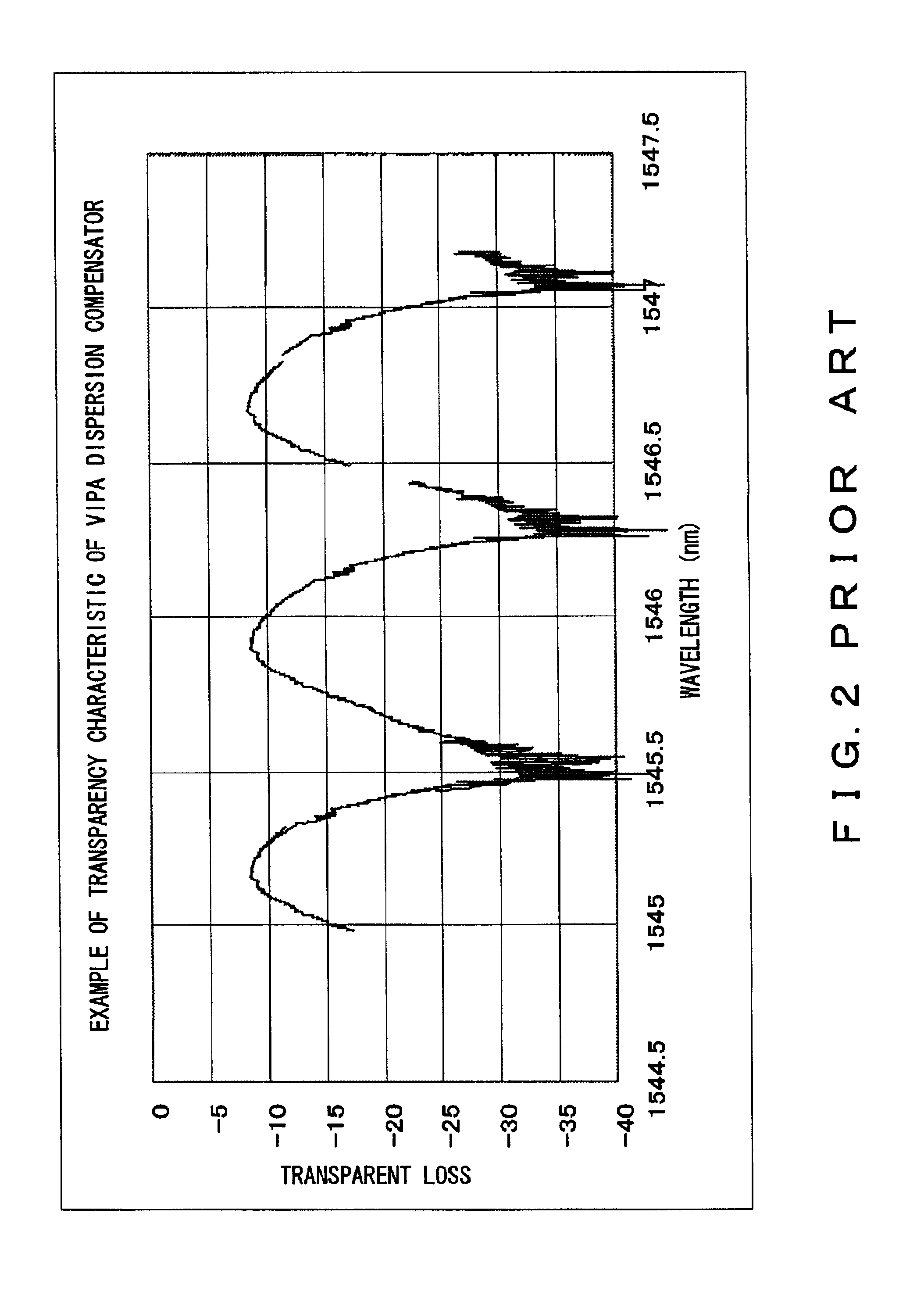
Wavelength dispersion compensating apparatus
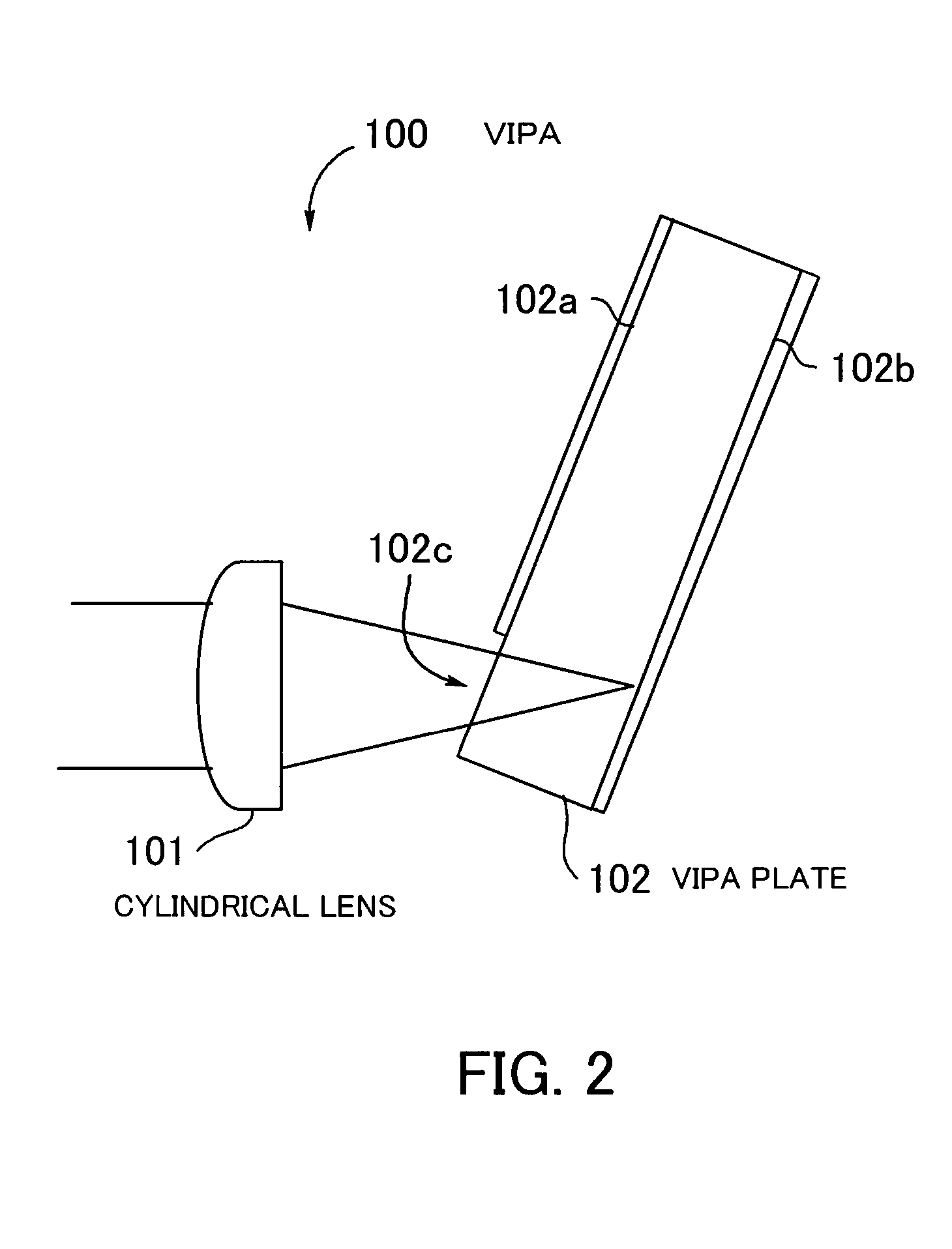
A wavelength dispersion compensating apparatus of the invention comprises: a VIPA plate capable to output incident lights at different angles according to wavelengths; a variable dispersion diffraction grating which can angularly disperse the lights of respective wavelengths output from the VIPA plate, in a direction substantially perpendicular to a direction of angular dispersion in the VIPA plate and also capable to change an amount of the angular dispersion; a light return apparatus which condenses the output lights from the variable dispersion diffraction grating and reflects them by a mirror, to return them to the VIPA plate side; and a stage rotation mechanism which rotates a movable stage on which the lens and the mirror are mounted, according to a diffraction angle in the variable dispersion diffraction grating, so as to enable wavelength dispersion and wavelength dispersion slope to be given to a WDM light, to be changed independently. As a result, it becomes possible to compensate for, over a wide wavelength band, the wavelength dispersion and wavelength dispersion slope of the WDM light, which are propagated through an optical fiber to be accumulated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Hyper dispersion pulse compressor for chirped pulse amplification systems
ActiveUS8068522B2Small footprintReduce system footprintElectric discharge heatingGlass furnace apparatusGratingChirped pulse amplification
A grating pulse compressor configuration is introduced for increasing the optical dispersion for a given footprint and to make practical the application for chirped pulse amplification (CPA) to quasi-narrow bandwidth materials, such as Nd:YAG. The grating configurations often use cascaded pairs of gratings to increase angular dispersion an order of magnitude or more. Increased angular dispersion allows for decreased grating separation and a smaller compressor footprint.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Frequency comb source with large comb spacing
InactiveUS8571075B2Reduce lossEasy to adjustRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
A frequency comb laser providing large comb spacing is disclosed. At least one embodiment includes a mode locked waveguide laser system. The mode locked waveguide laser includes a laser cavity having a waveguide, and a dispersion control unit (DCU) in the cavity. The DCU imparts an angular dispersion, group-velocity dispersion (GVD) and a spatial chirp to a beam propagating in the cavity. The DCU is capable of producing net GVD in a range from a positive value to a negative value. In some embodiments a tunable fiber frequency comb system configured as an optical frequency synthesizer is provided. In at least one embodiment a low phase noise micro-wave source may be implemented with a fiber comb laser having a comb spacing greater than about 1 GHz. The laser system is suitable for mass-producible fiber comb sources with large comb spacing and low noise. Applications include high-resolution spectroscopy.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
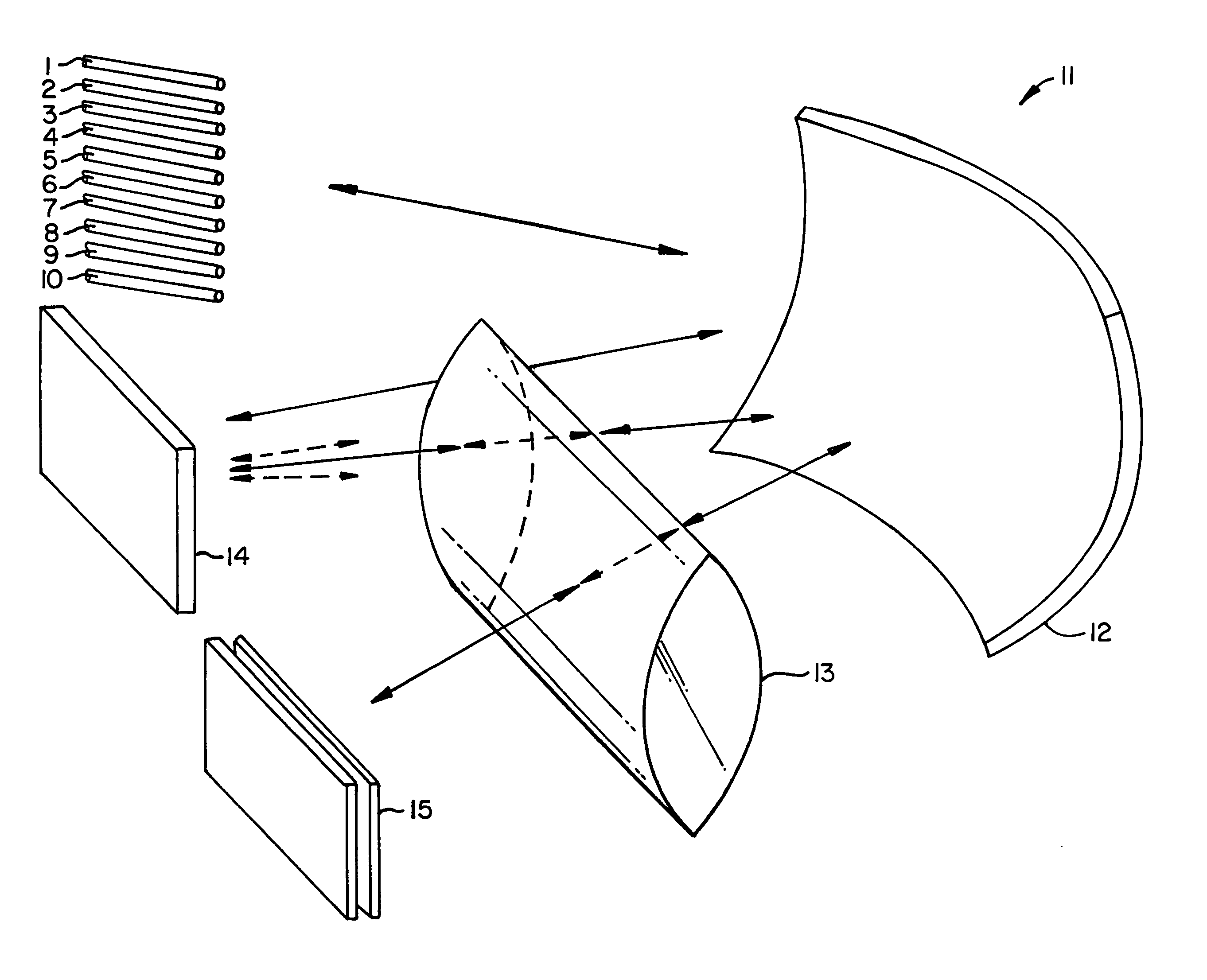
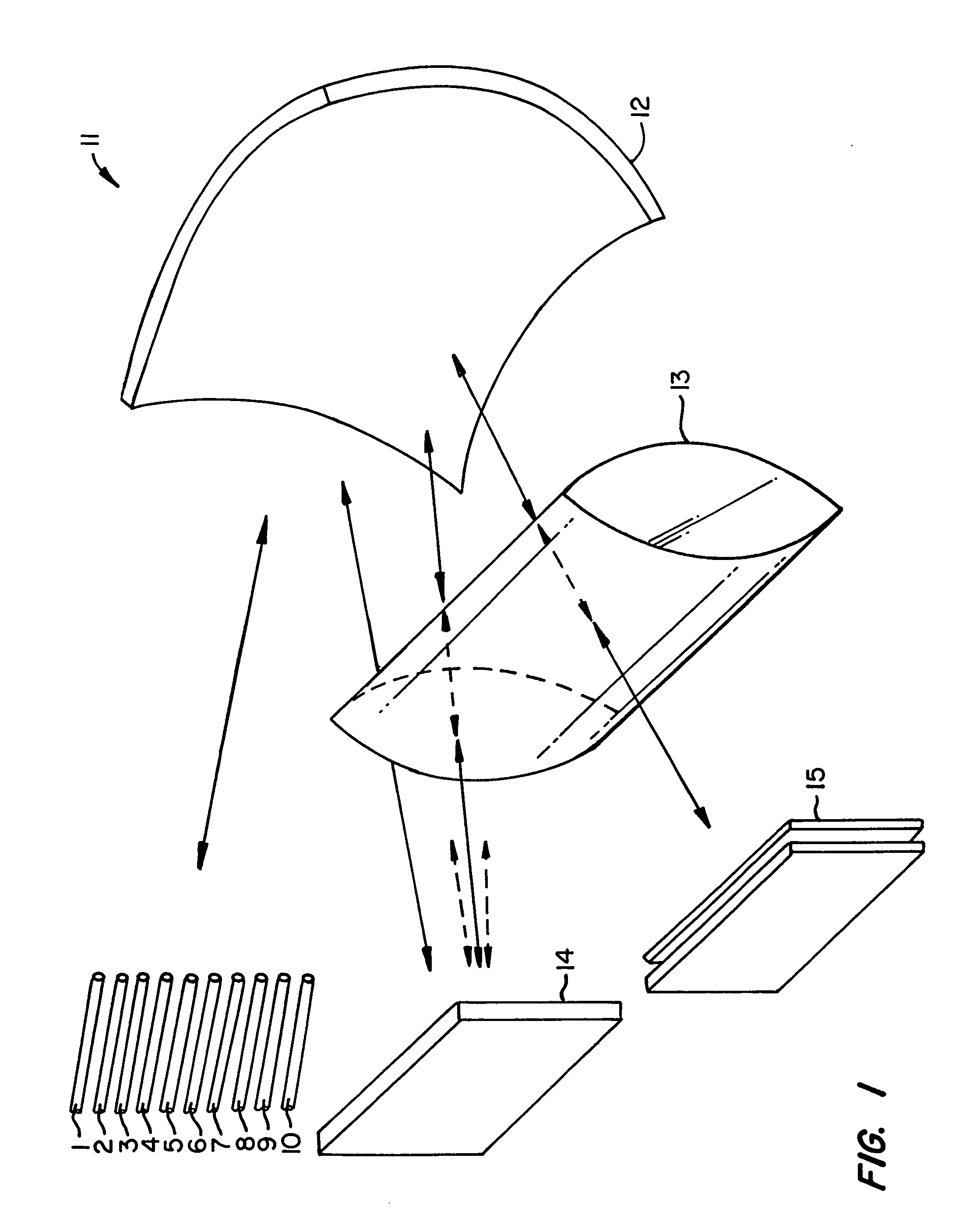
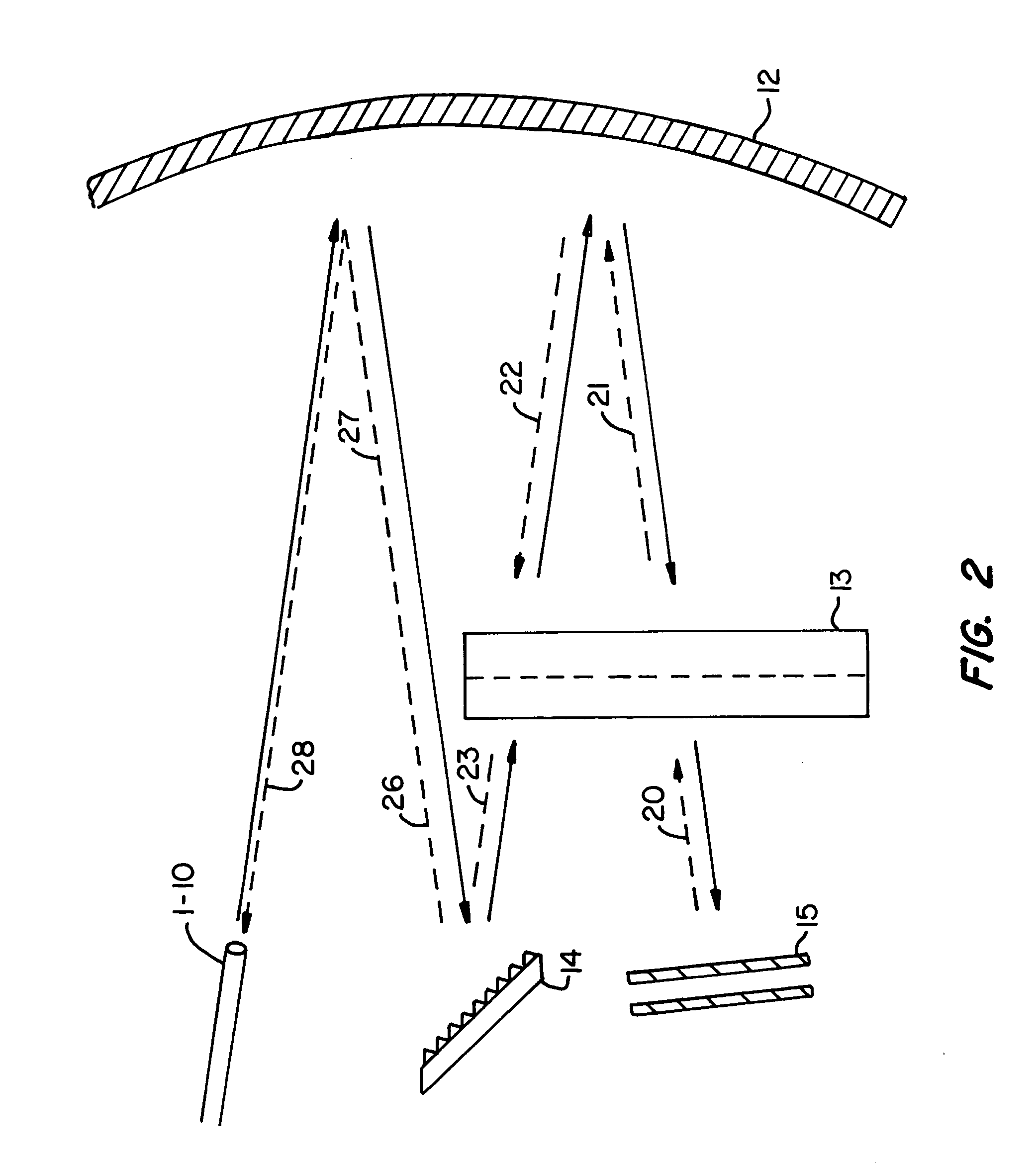
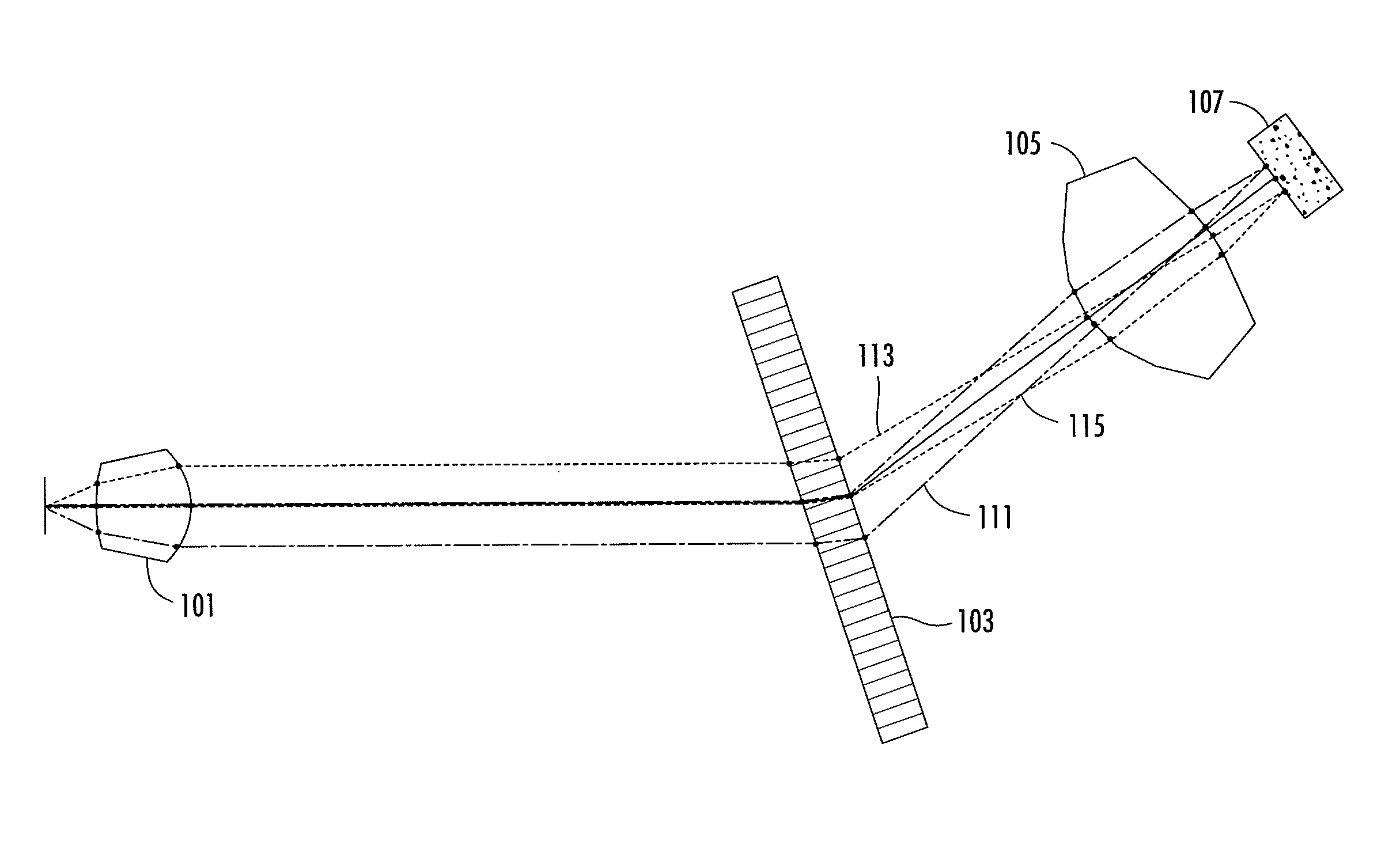
Multiple-wavelength spectroscopic apparatus
ActiveUS7359051B2Low costEffective controlRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMultiwavelength spectroscopyLength wave
In a multi-wavelength spectroscopic apparatus using diffraction gratings, a first diffraction grating is a diffraction grating with diffraction efficiencies of p-polarized light and s-polarized light being equal on a short wavelength side of an operating wavelength range, and a second diffraction grating is a diffraction grating with diffraction efficiencies of p-polarized light and s-polarized light being equal on a long wavelength side of an operating wavelength range. By performing dispersion with two such diffraction gratings, it is possible to enlarge the amount of angular dispersion, and to produce a spectroscopic apparatus, which cancels wavelength dependencies of the diffraction efficiencies and has a small wavelength dependency of the diffraction efficiency.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Wavelength selective switch
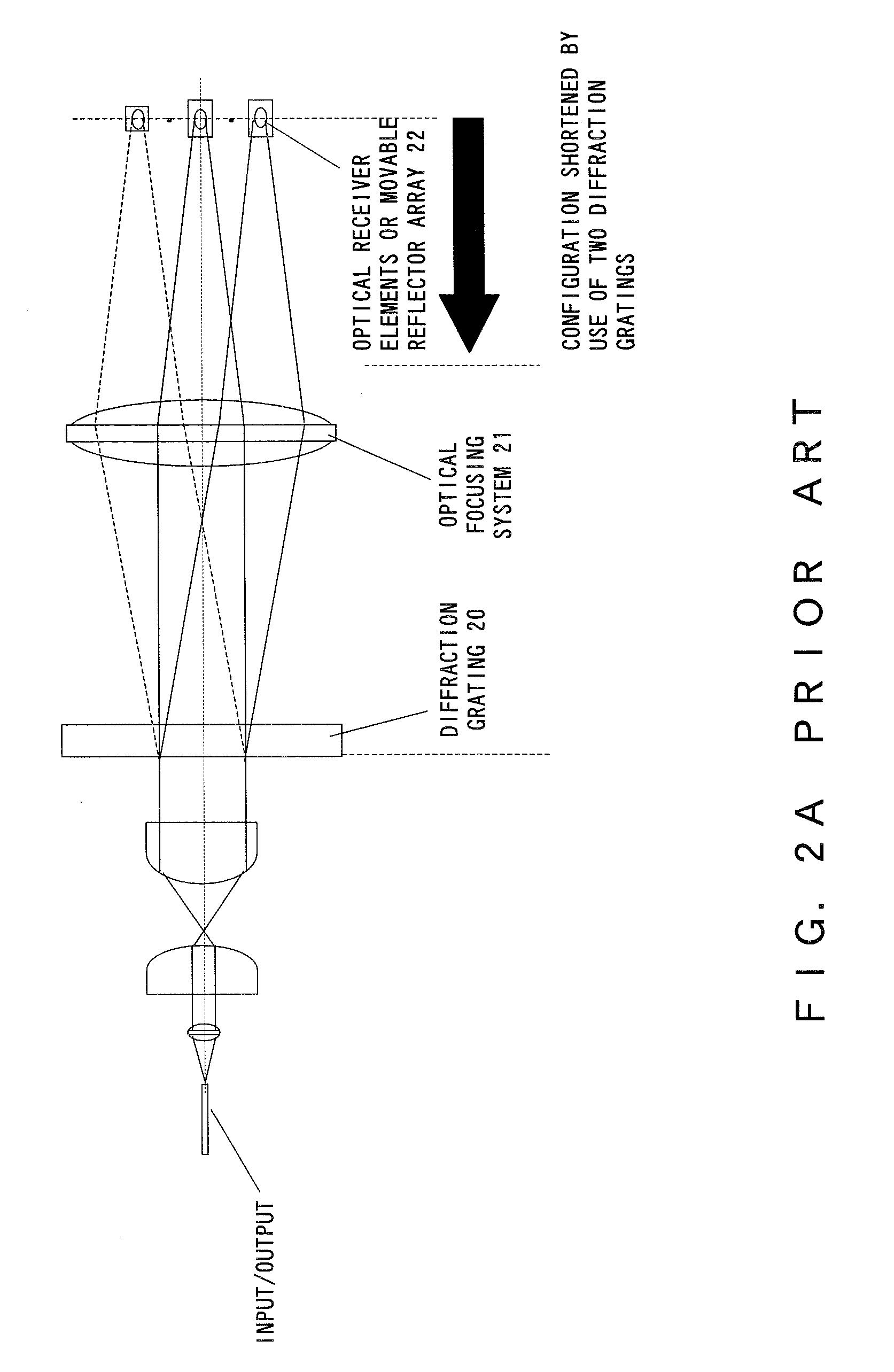
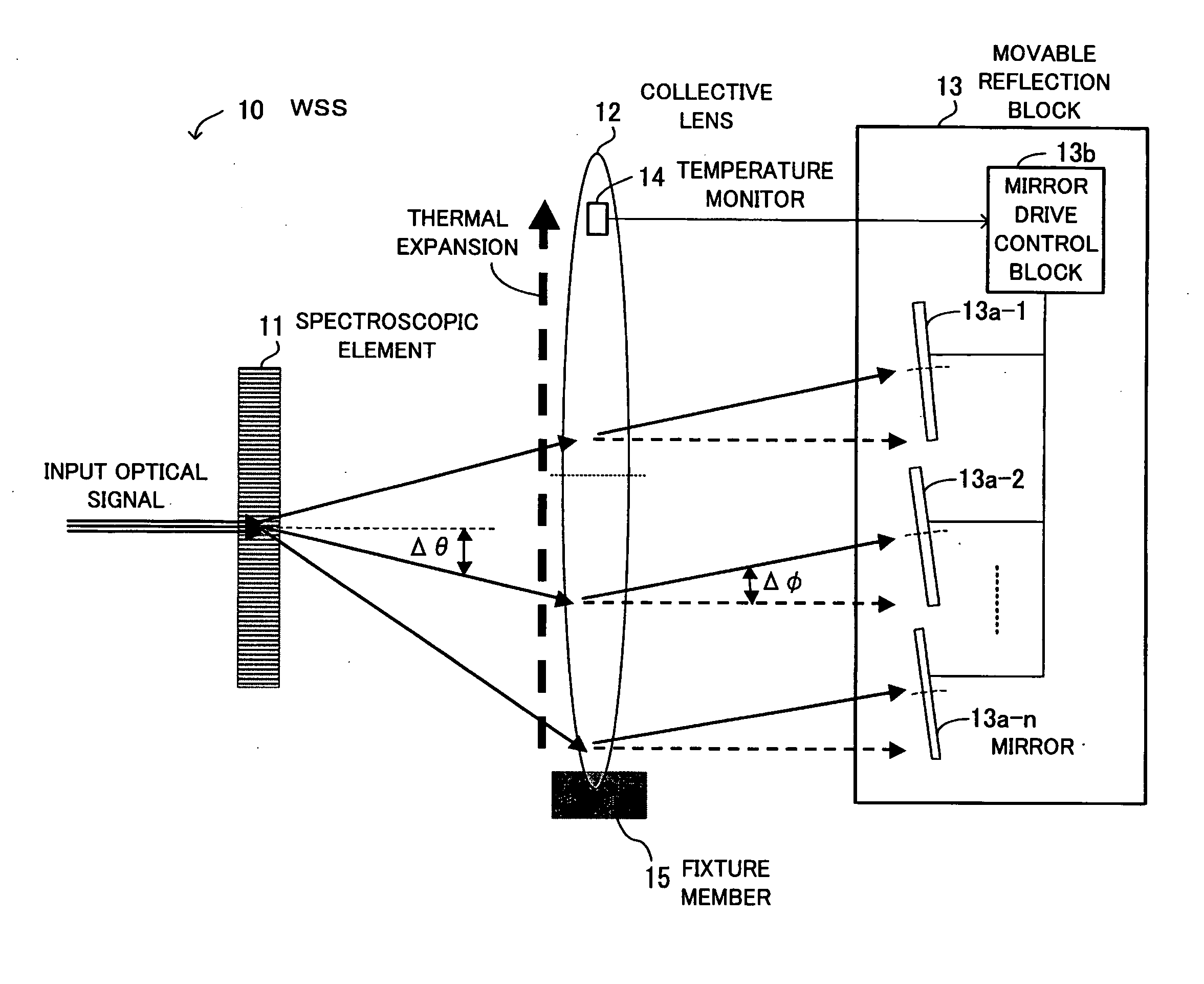
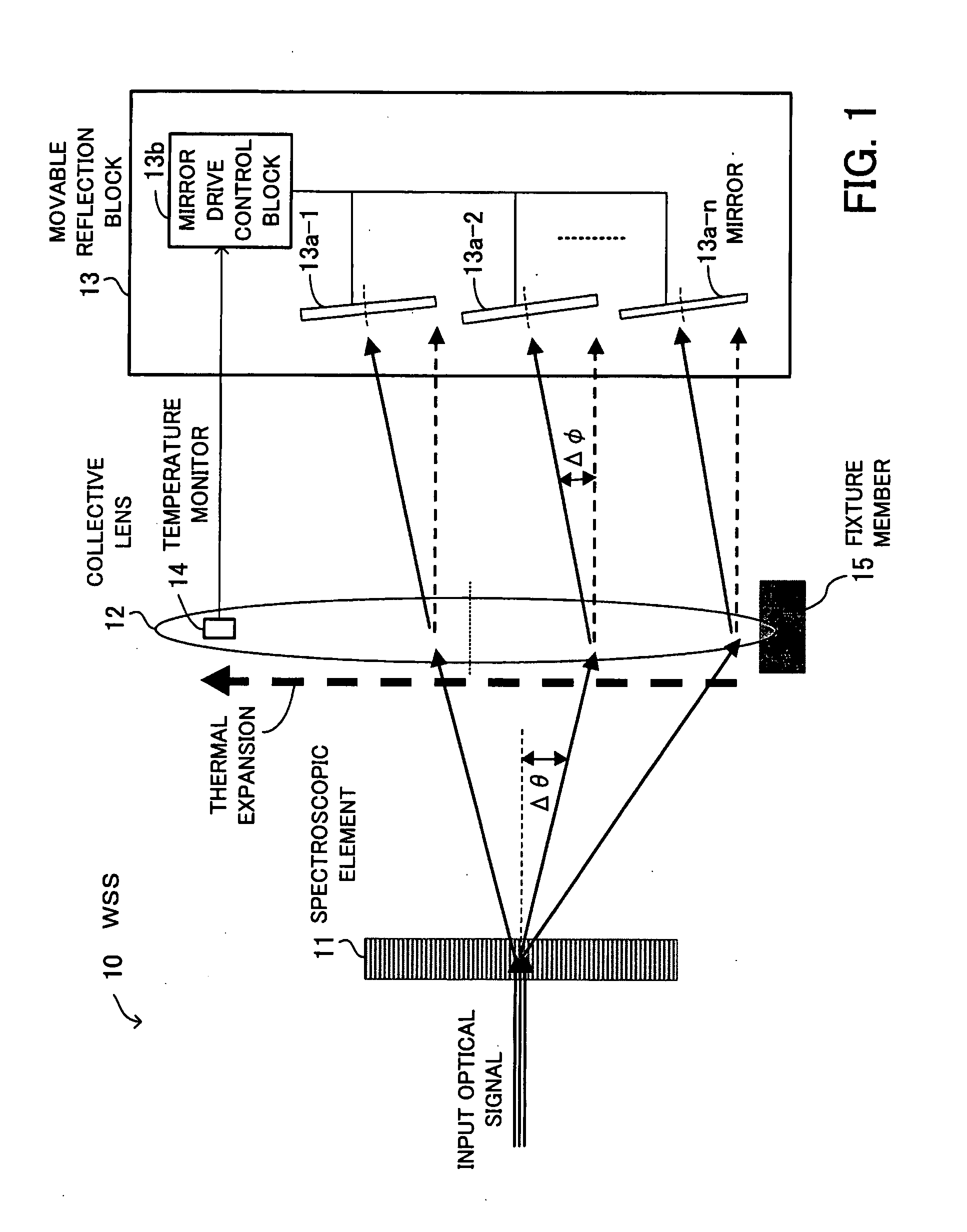
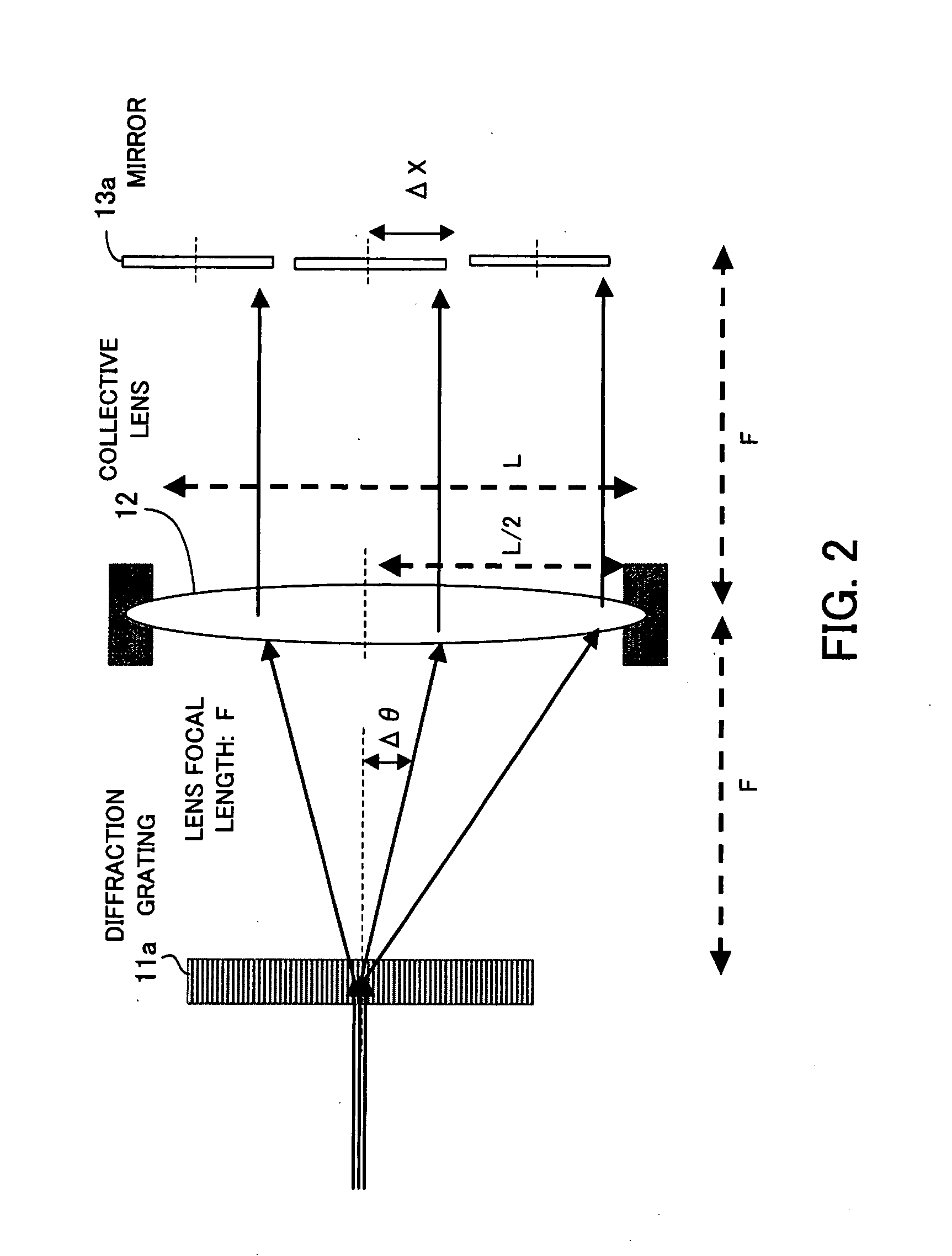
ActiveUS20080239444A1Effectively suppress the degradation of pass band characteristicsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesLength waveAngular dispersion
A wavelength selective switch for suppressing degradation of pass band characteristics when the temperature rises. The wavelength selective switch includes a spectroscopic element for separating input light and providing angular dispersion depending on wavelengths, a collective lens for gathering light output from the spectroscopic element, and a movable reflection block which includes a plurality of mirrors arranged in the direction of angular dispersion made by the spectroscopic element, changes the angles of the mirrors in a direction differing from the direction of angular dispersion, and reflects the light coming from the collective lens. The collective lens is fixed at one end with respect to the direction of angular dispersion, expands with heat in a direction in which it is not fixed when the temperature rises, and outputs the light in a direction opposite to the direction in which the angle of light output from the spectroscopic element changes.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Compact Bragg reflector type concave diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer and designing method thereof
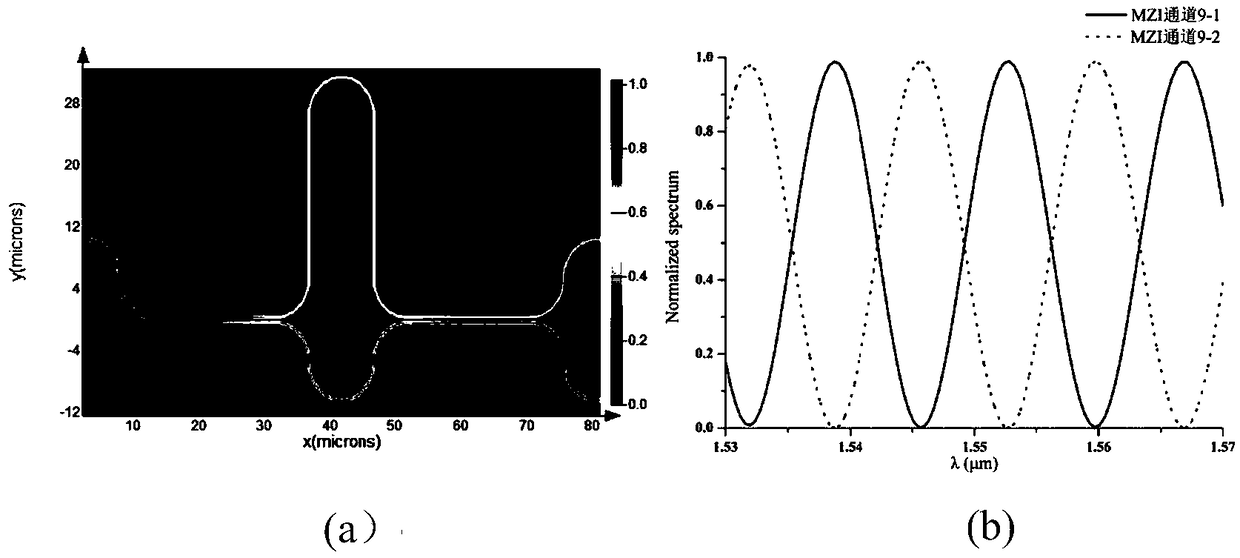
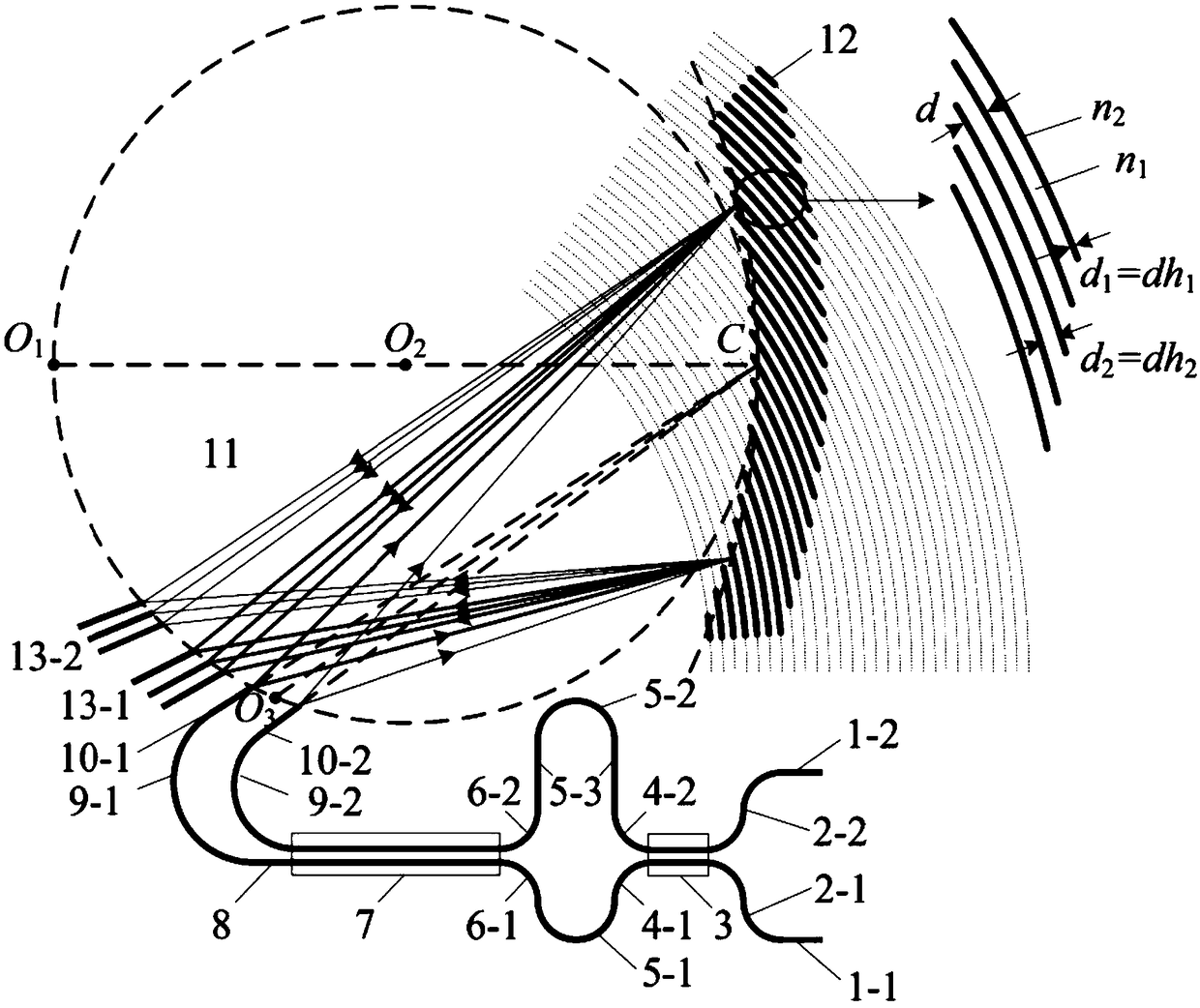
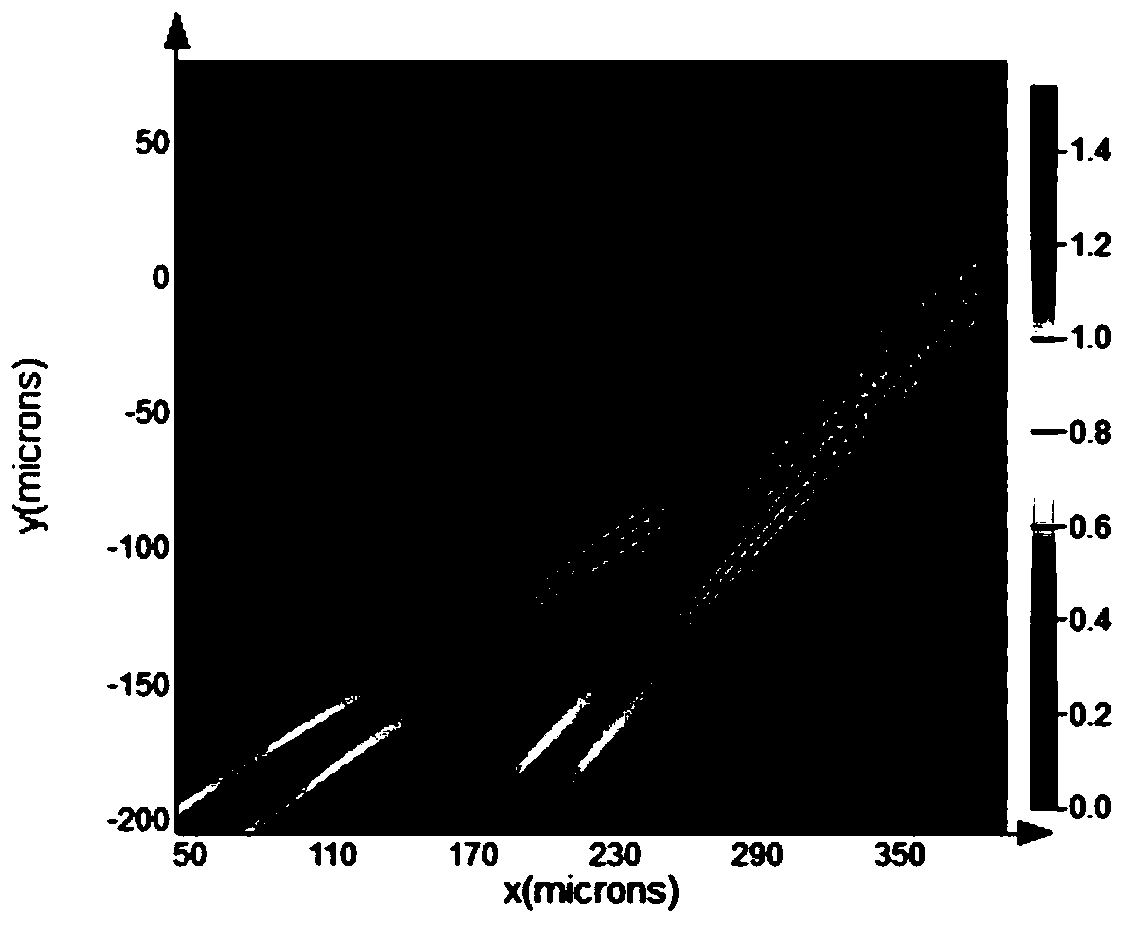
The invention discloses a compact Bragg reflector type concave diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer and a designing method thereof. The compact Bragg reflector type concave diffractiongrating wavelength division multiplexer includes an MZI interleaving filter, two input waveguides, a Bragg reflector-type concave diffraction grating, a free transmission region and two output waveguide arrays. The designing method includes that firstly the incident angle relationship between the two input waveguides relative to the grating tooth surface is determined according to the angular dispersion relationship of the Bragg reflector-type concave diffraction grating; secondly, structural parameters of the MZI interleaving filter are determined by a designed concave grating wavelength interval; and finally the designing of the compact Bragg reflector type concave diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer design cascaded with the MZI interleaving filter is realized. Compared with the conventional concave diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexers, the odd and even channel light outputted by the MZI interleaving filter are respectively incident on the diffractiongrating at different angles, and the output light frequency of the wavelength division multiplexer is halved using the MZI interleaving filter at an interval, the circumferential length of the Rolandcircle is fully utilized, the size of the device is effectively reduced, and the complexity of the process is lowered.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
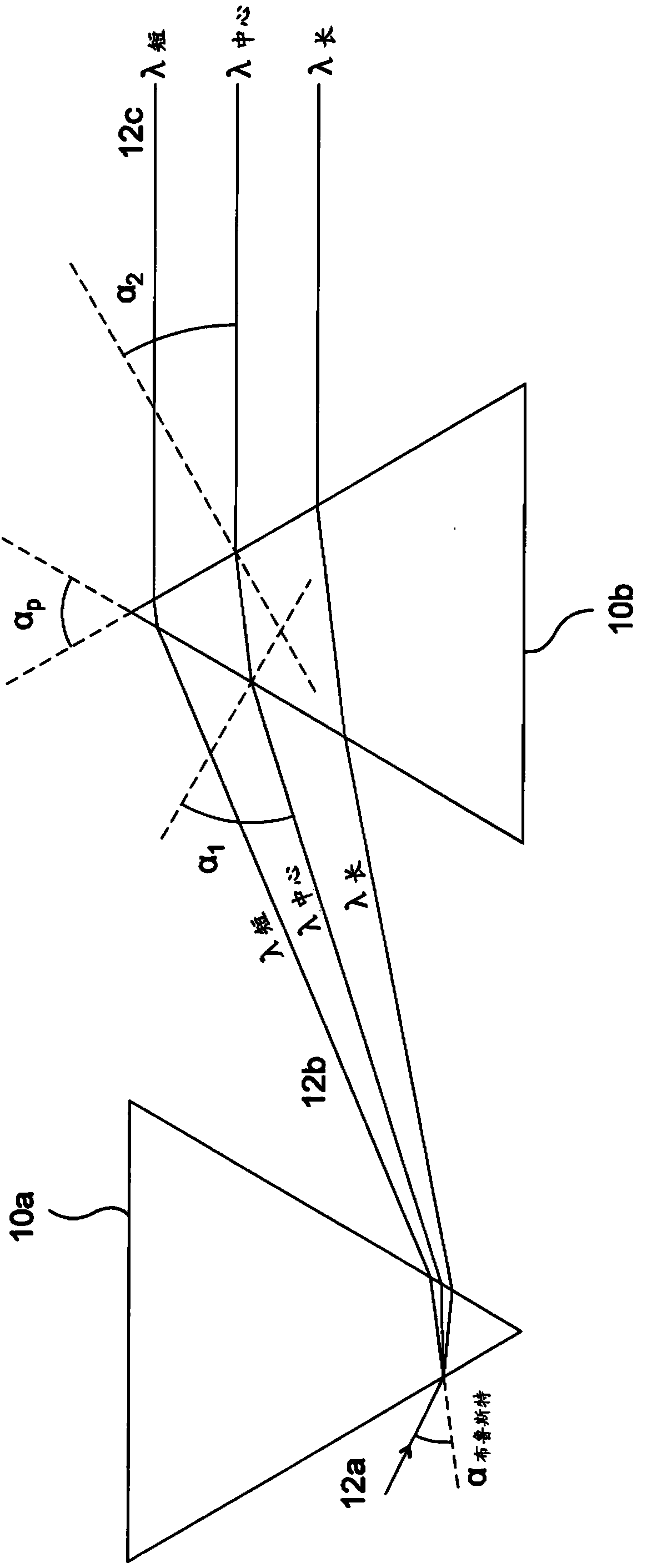
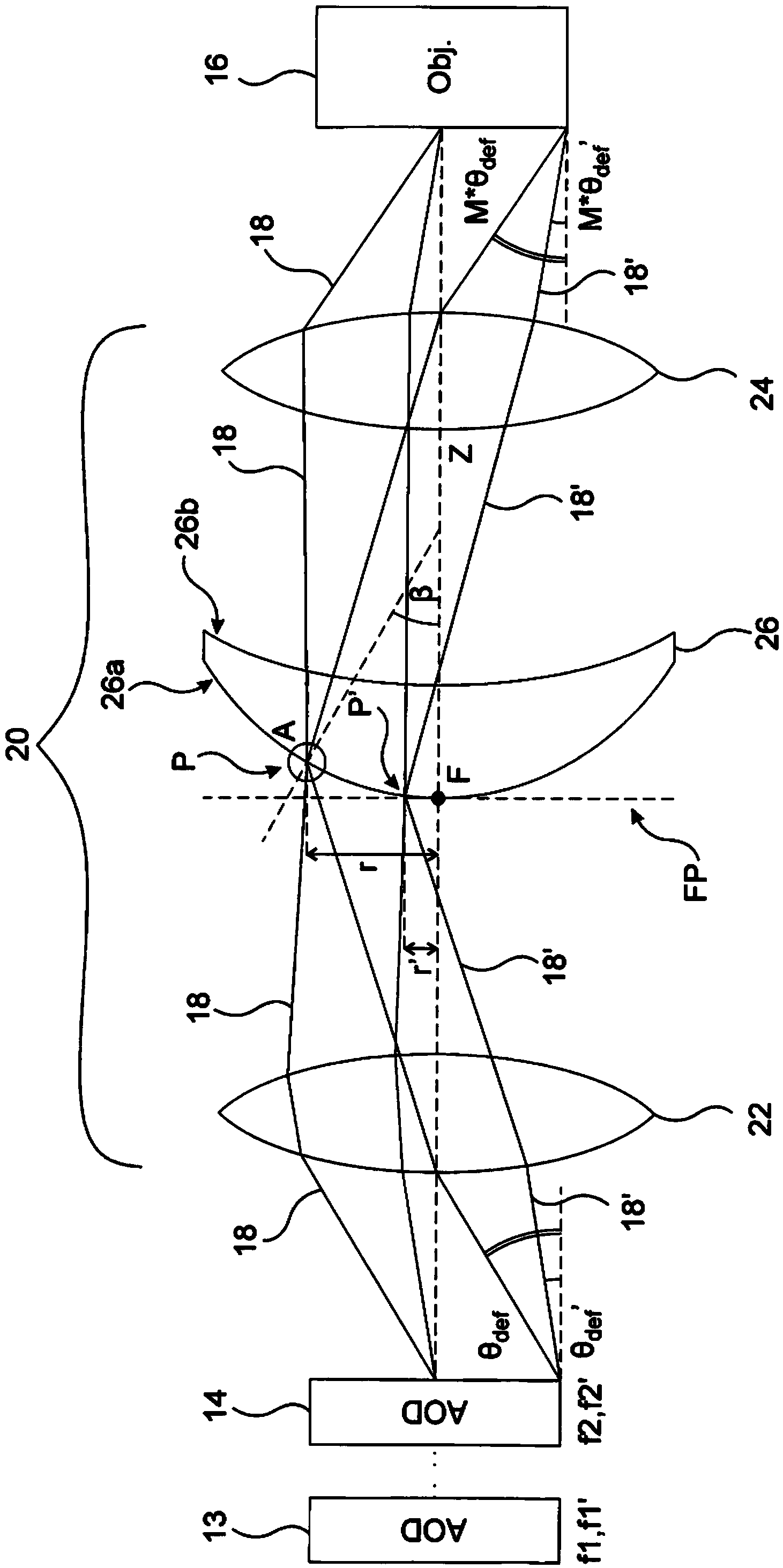
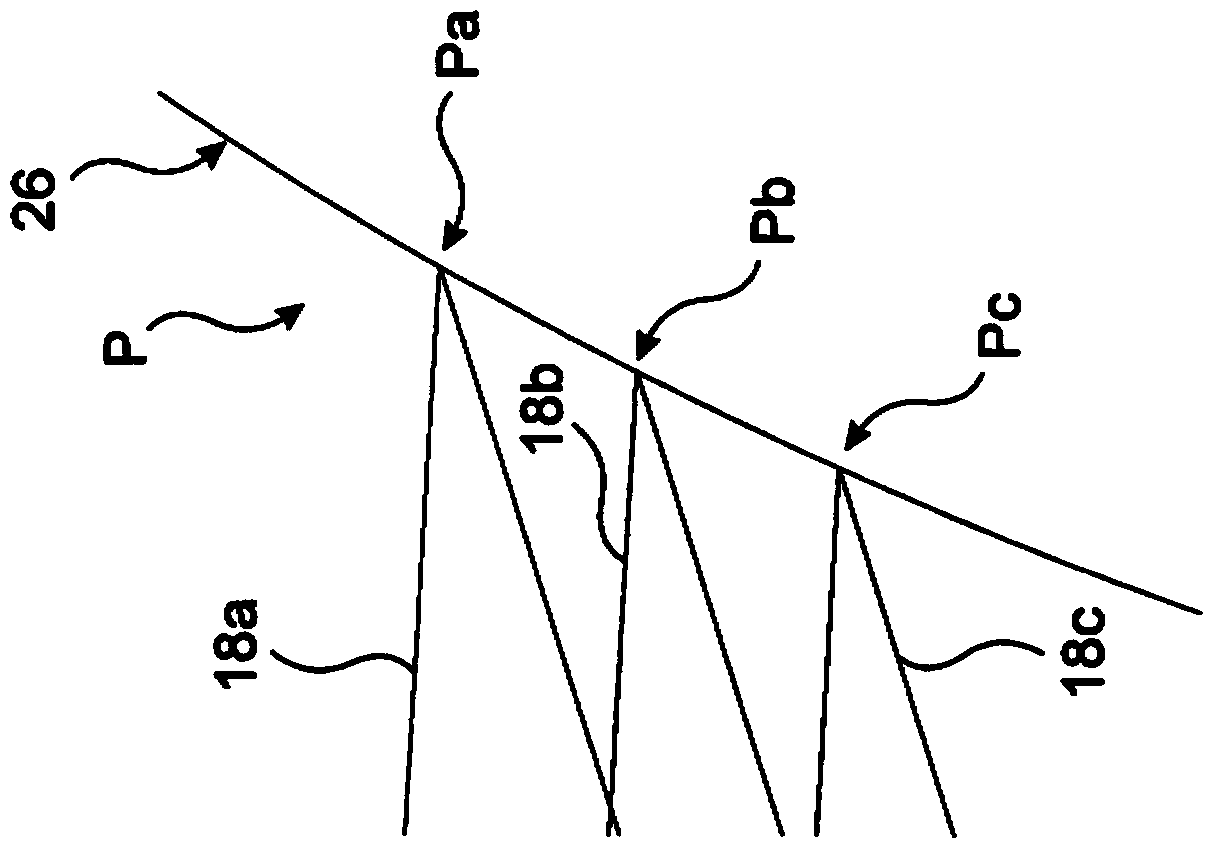
Compensator system and method for compensating angular dispersion
The invention relates to a compensator system adapted to compensate for the angular dispersion of electromagnetic beams deflected by at least one acousto-optic deflector of an optical system, wherein the angular dispersion of each deflected beam is dependent on the deflection angle obtained by the deflecting acoustic frequency of the acousto-optic deflector, characterised in that the compensator system comprises: - a first lens group for spatially separating the deflected beams of different deflection angle and angular dispersion by focusing the beams substantially into the focal plane, - a compensator element having a first surface and a second surface, and being arranged such that the first surface of the compensator element lies substantially in the focal plane of the first lens group, and the first and second surfaces of the compensator element have nominal radiuses R1 and R2 that together work as prisms with tilt angles beta and prism opening angles alphap that vary with the distance from the optical axis so as to compensate for the angular dispersion of the spatially separated deflected beams, - a second lens group arranged so as to substantially parallelise the different wavelength components of each deflected beam exiting the compensator element while maintaining the angular variation of the beams deflected at different acoustic frequencies. The invention further relates to method for compensating for the angular dispersion of electromagnetic beams deflected by at least one acousto-optic deflector of an optical system, wherein the angular dispersion of each deflected beam is dependent on the deflection angle obtained by the deflecting acoustic frequency, characterised by - spatially separating the deflected beams of different deflection angle and angular dispersion by focusing the beams via a first lens group substantially into the focal plane of the first lens group, - compensating for the angular dispersion of the spatially separated deflected beams in accordance with the angular dispersion of the given beam, - substantially parallelising the spectral components of each deflected beam while maintaining the angular variation of the beams deflected at different acoustic frequencies.
Owner:FEMTONICS
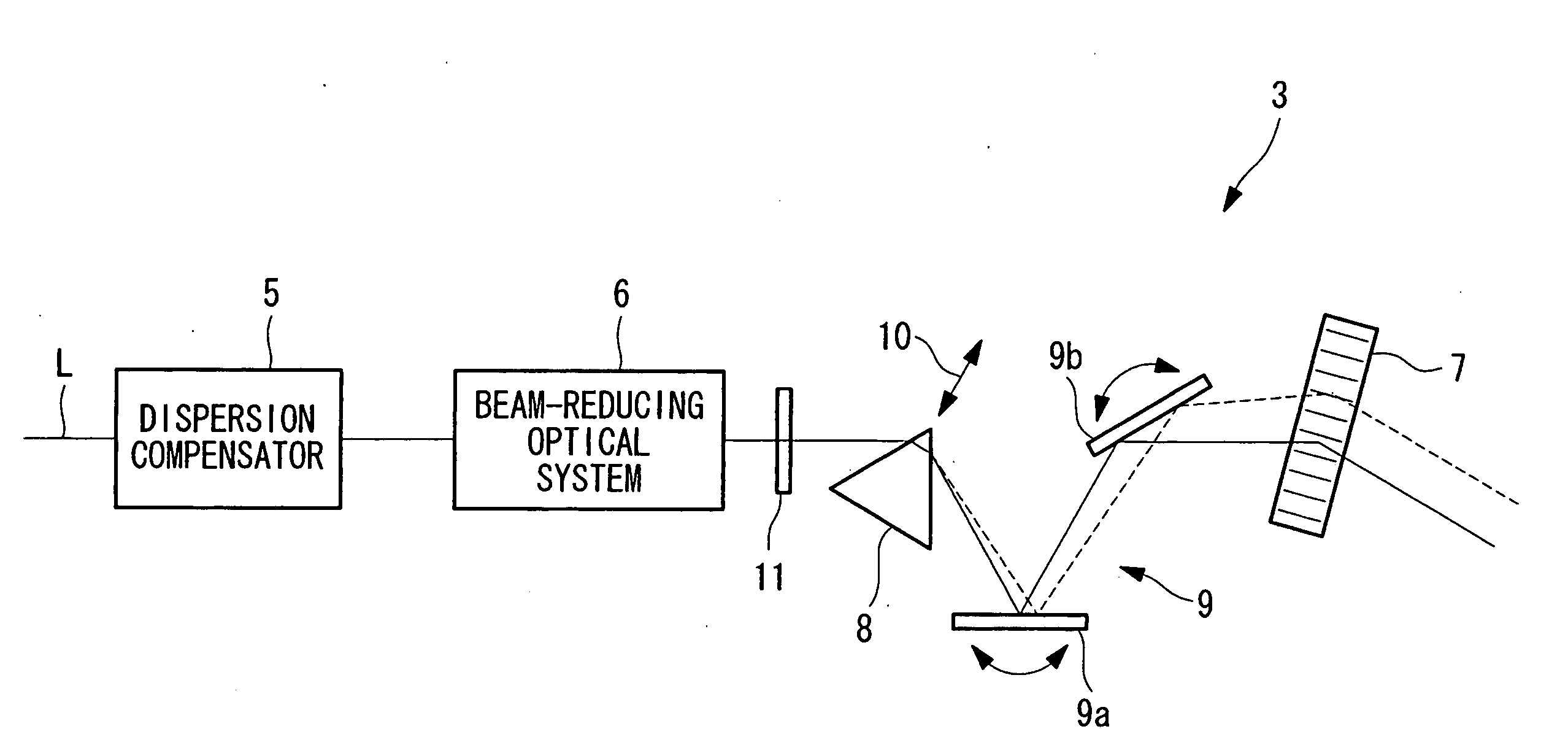
Laser microscope
InactiveUS20090290209A1Reduce variationSimple configurationMicroscopesNon-linear opticsAcousto optic deflectorLaser Microscopy
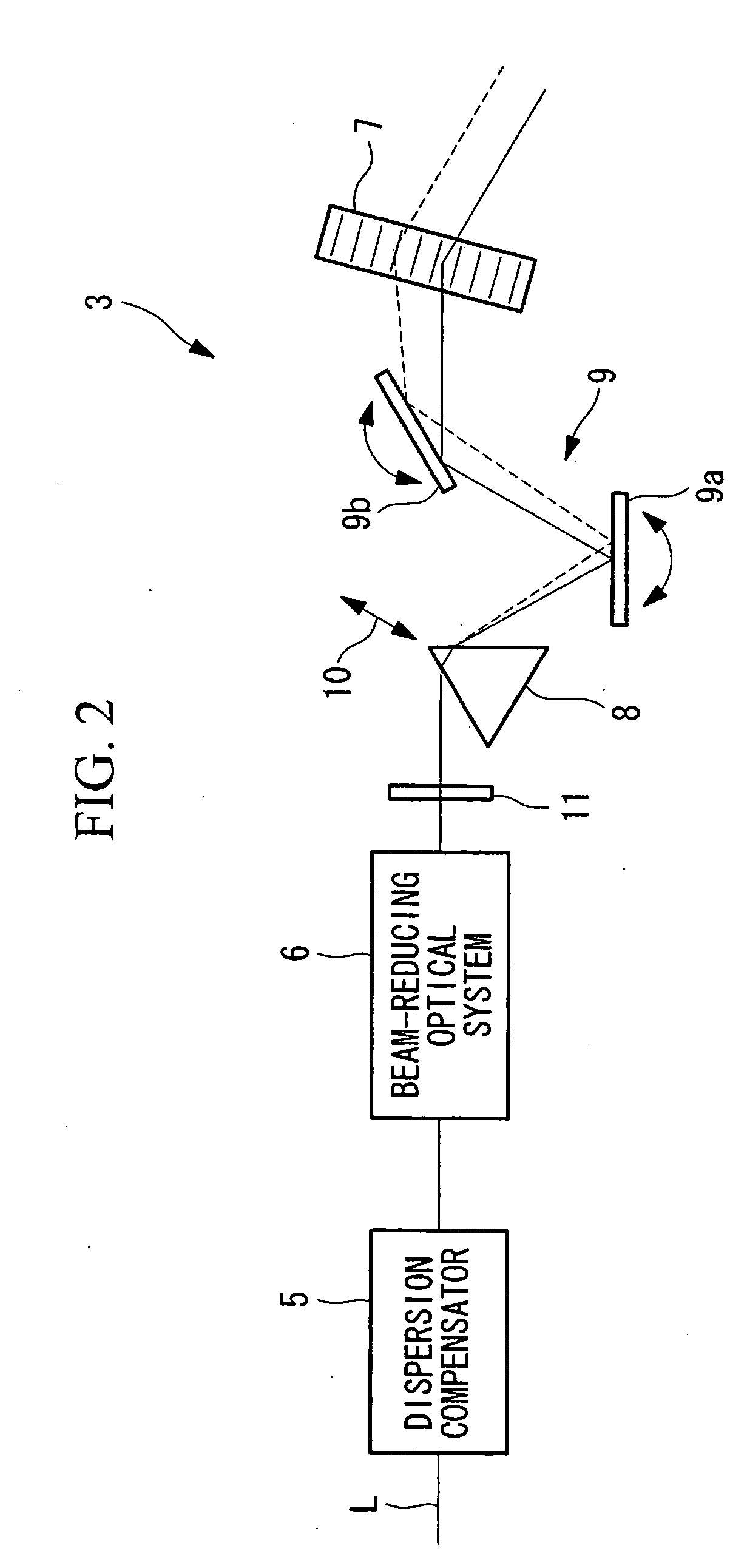
It is an object to perform high-precision observation by compensating group-velocity-delay dispersion and angular dispersion with a simple structure. The invention provides a laser microscope 1 including a light source; an acousto-optic deflector 7 that deflects ultrashort-pulse laser light L emitted from the light source; an angular-dispersion element 8, disposed in front of or after the acousto-optic deflector 7, that applies angular dispersion in a direction opposite to the acousto-optic deflector 7; and a group-velocity-delay dispersion-amount adjusting unit 10 that adjusts the amount of dispersion compensation by moving the angular-dispersion element 8 so as to vary the optical path length at each wavelength between the angular-dispersion element 7 and the acousto-optic deflector 8.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Grating wavefront inclined dispersion compensation device
ActiveCN107727250ARemove the influence of applied effectsReduce system errorOptical elementsGratingBlazed grating
The invention discloses a grating wavefront inclined dispersion compensation device, which comprises a first blazed grating, an Offner optical system, and a second blazed grating or a right-angle reflector. The grating wavefront inclined dispersion compensation device compensates for temporal stretching and spatial stretching caused by a grating angular dispersion effect, and ensures that the time-space dispersion of a light beam is zero when the light beam reaches a working surface. Compared with the traditional wavefront inclination acquisition technology based on gratings, the grating wavefront inclination compensation device fundamentally eliminates the influence of the grating angular dispersion effect on the application effect of a wavefront inclination technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Open-loop wavelength selective external resonator and beam combining system
InactiveCN107078465ASemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsExternal cavity laserPolarizer
Owner:TRUMPF LASER GMBH CO KG
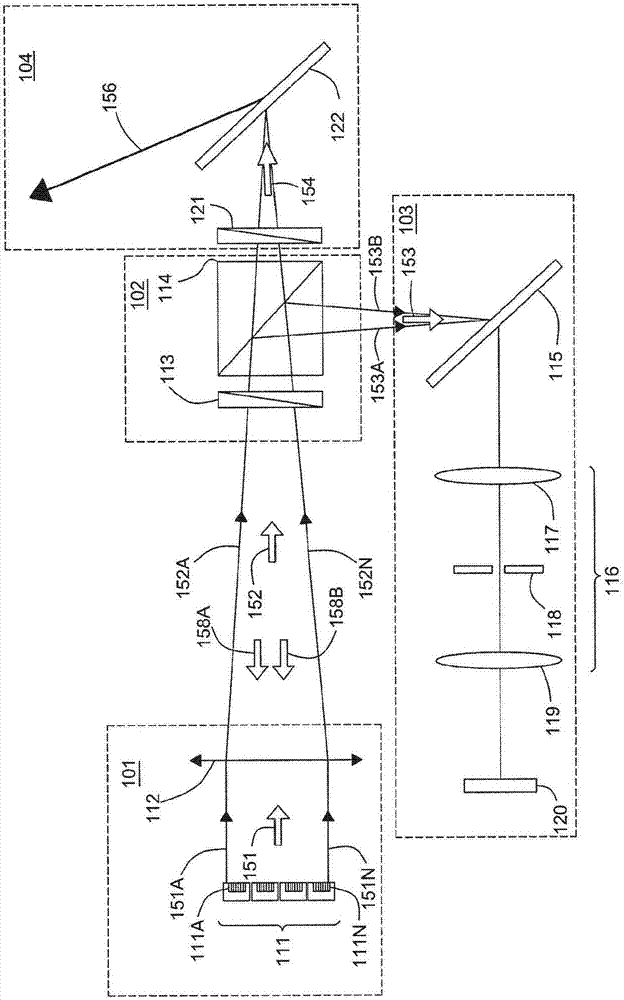
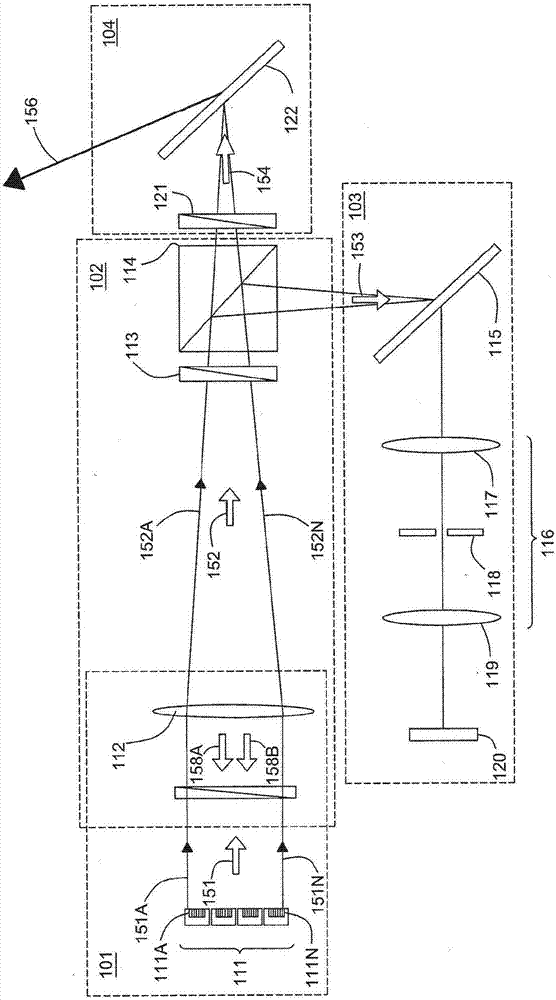
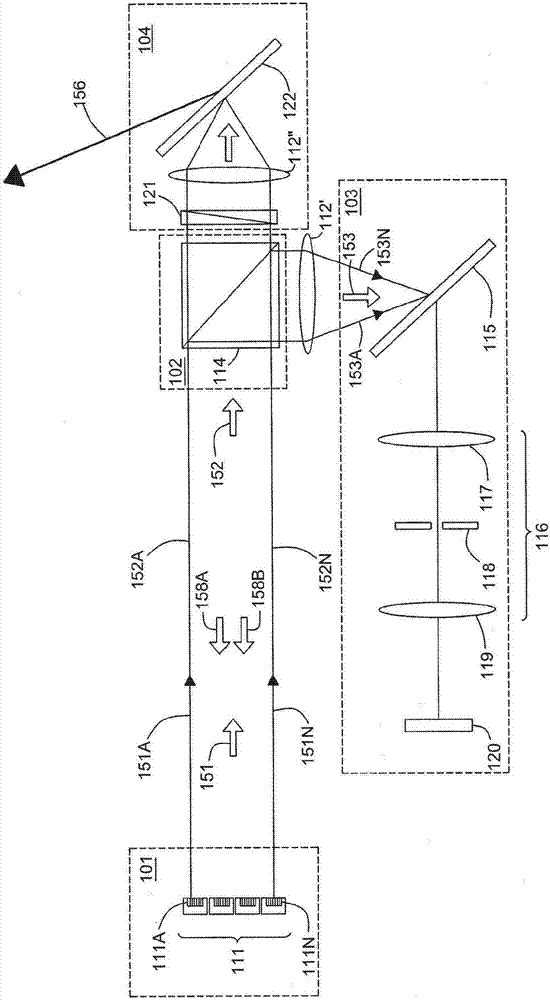
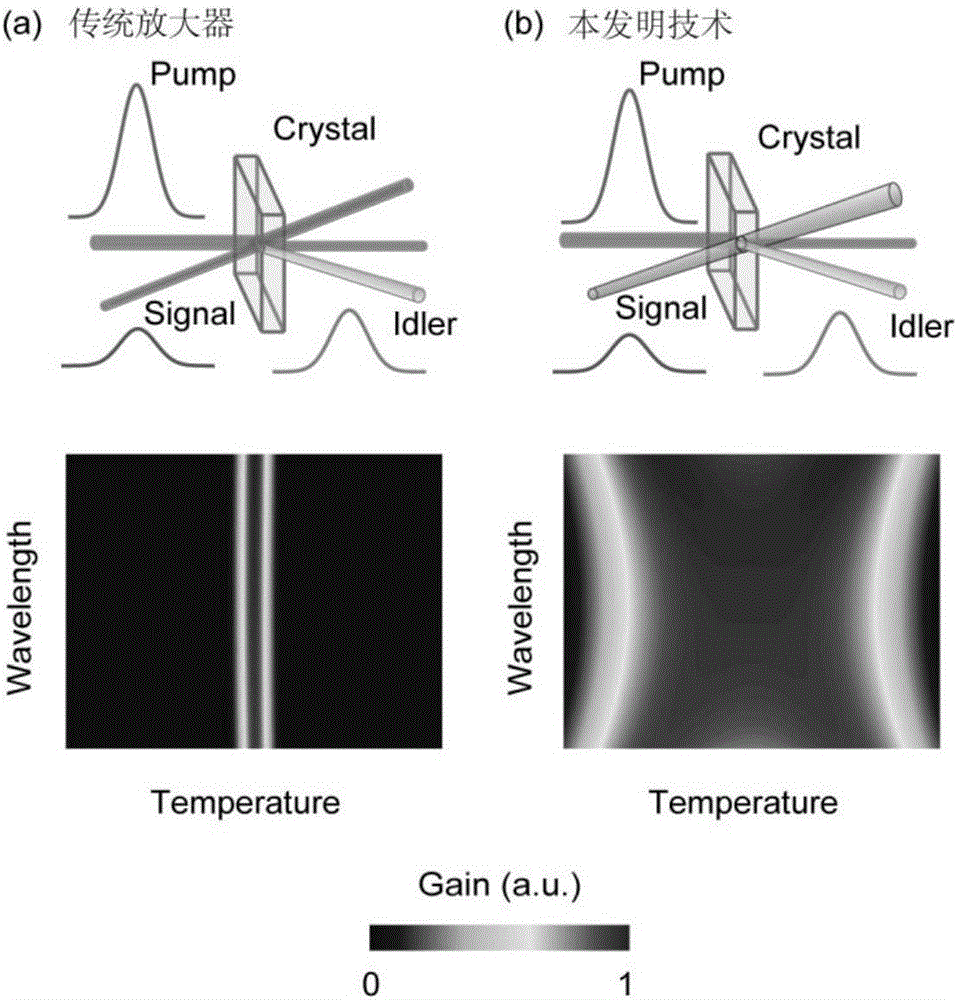
Temperature-and-wavelength-insensitive optical parametric chirped-pulse amplifier
ActiveCN106410577AHigh average power pulse outputSupport outputActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsGratingImage transfer
The invention provides a temperature-and-wavelength-insensitive optical parametric chirped-pulse amplifier, which is formed by a pump light path, a signal light path and an amplifier. The pump light path comprises a neodymium-doped yttrium vanadate regenerative amplifier, a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet amplifier, a first image transfer system and a frequency doubling crystal. The signal light path comprises a titanium-sapphire regenerative amplifier, a pulse stretcher and a pulse compressor. The amplifier is a nonlinear crystal amplifier. The temperature-and-wavelength-insensitive optical parametric chirped-pulse amplifier is characterized in that a chirp signal light beam and a pump light beam are input to the nonlinear crystal amplifier at a non-colinear angle larger than 5 DEG C; and through optimization of groove number of a first grating, the signal light beam is modified by angular dispersion. The temperature-and-wavelength-insensitive optical parametric chirped-pulse amplifier has the advantages of being insensitive to both temperature and wavelength, and meanwhile, paves the way for synchronously improving the peak power and mean power of an ultra-short ultra-intense laser system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
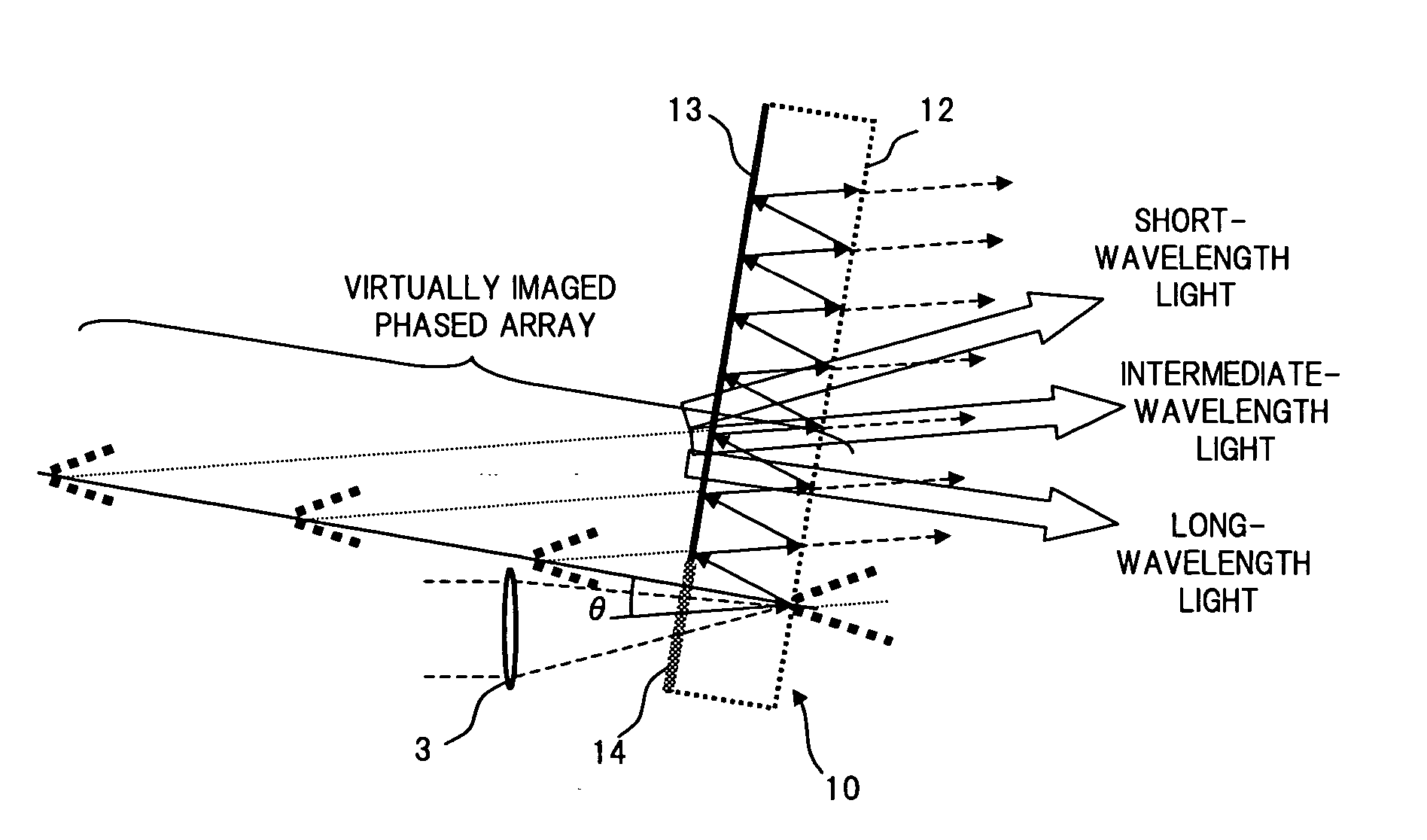
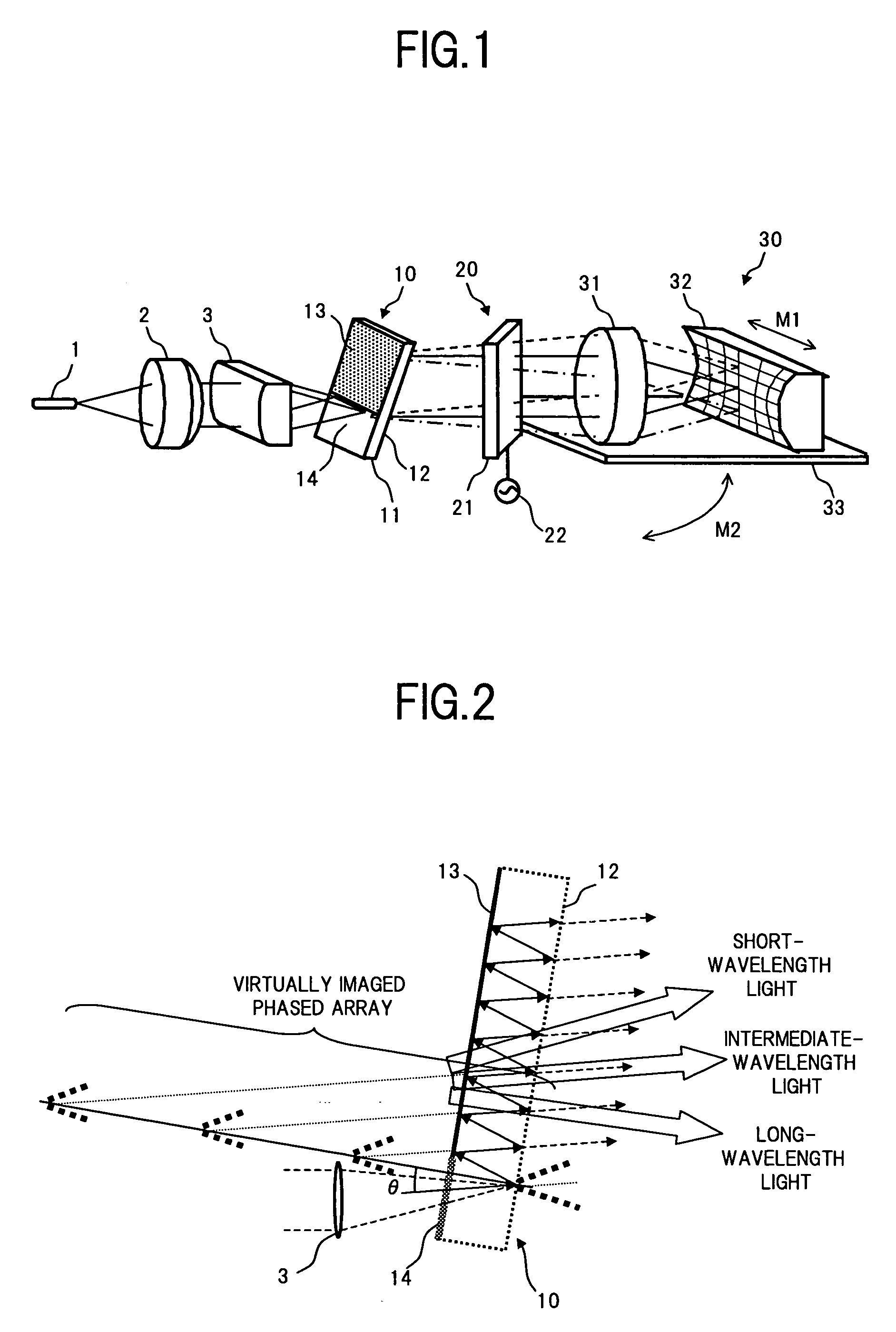
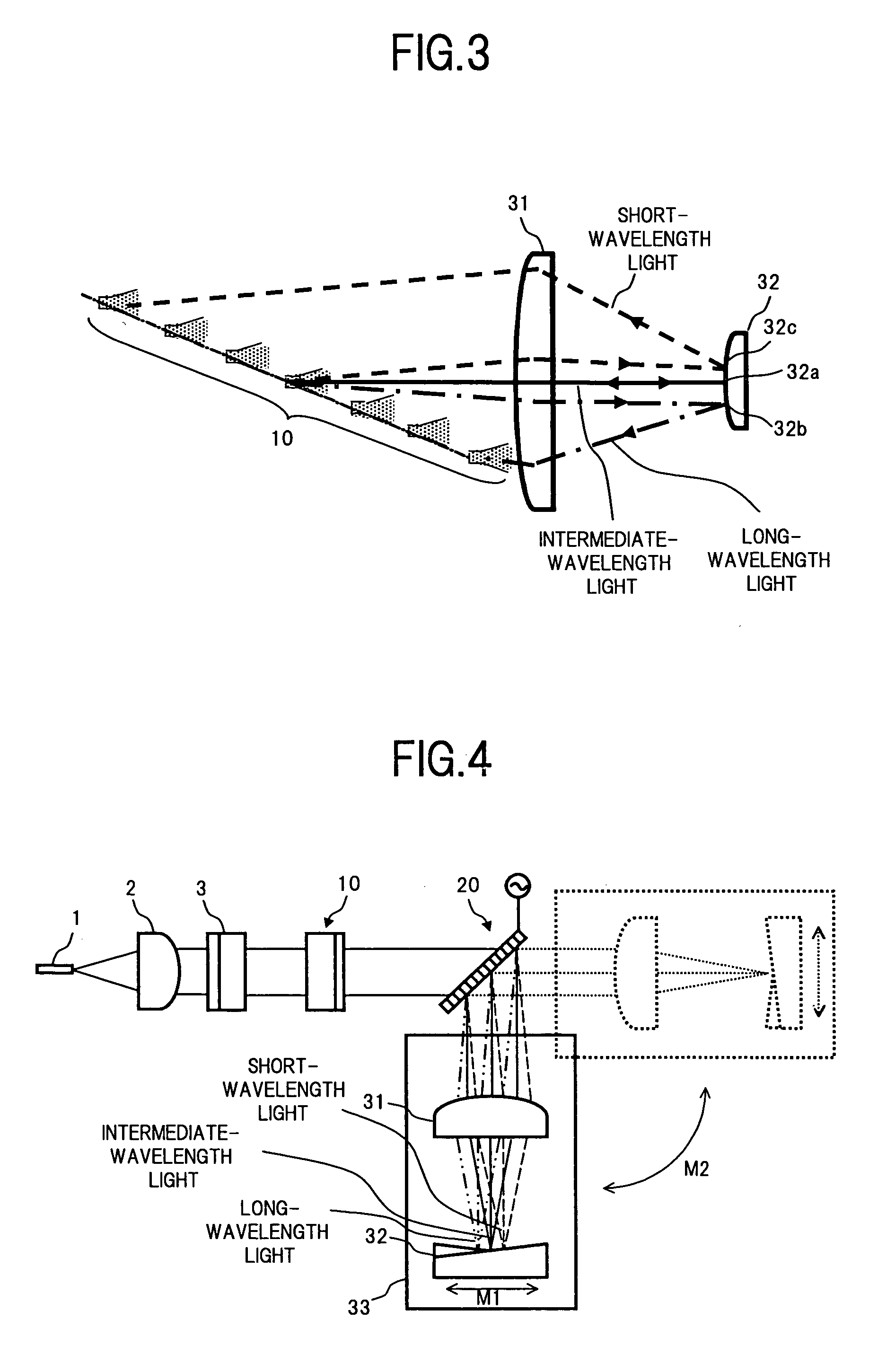
Optical apparatus and device
InactiveUS6900940B2Improving wavelength characteristicPrismsWavelength-division multiplex systemsParallel plateLength wave
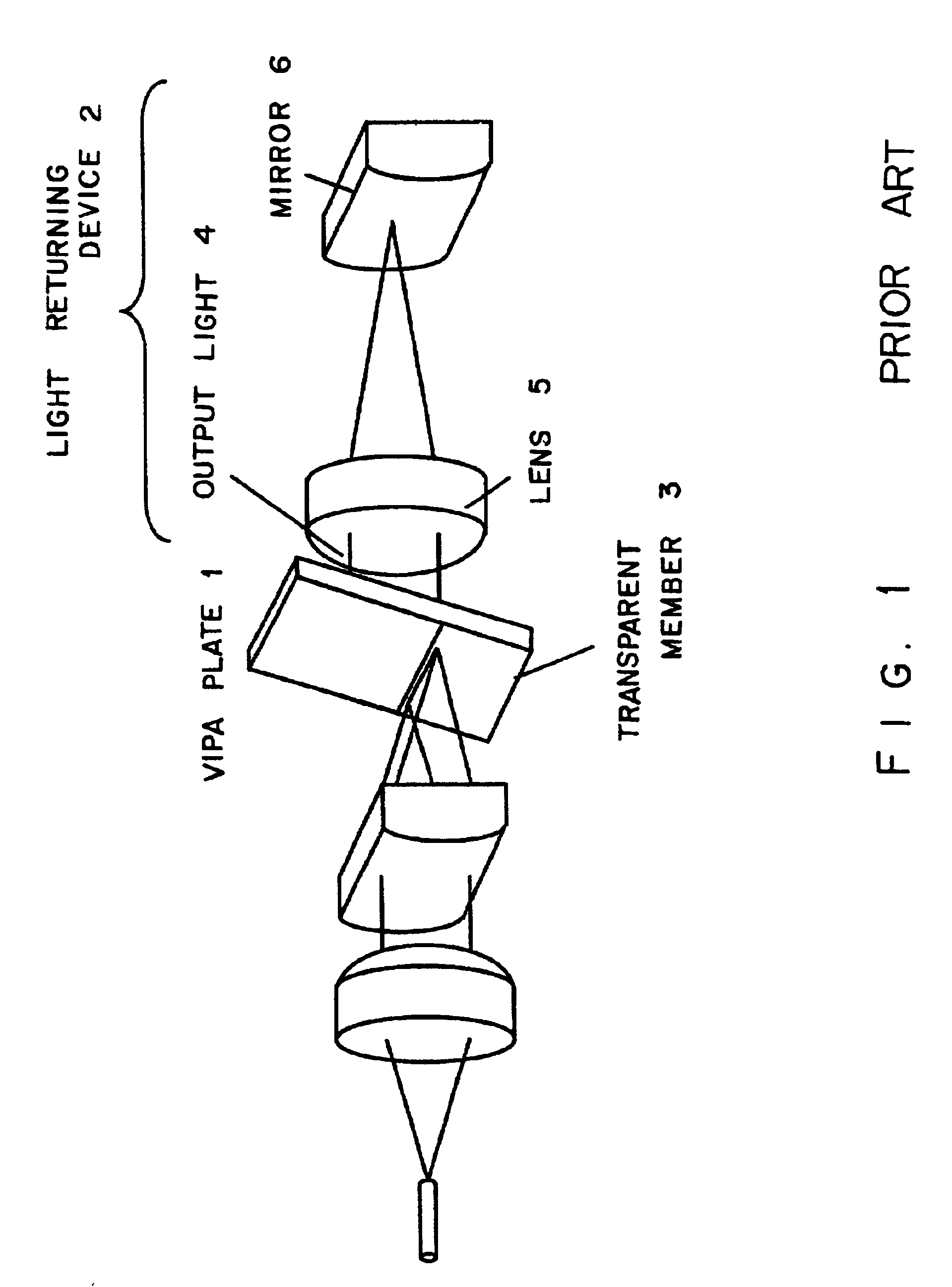
A VIPA plate having a configuration where a translucent reflection film and a total reflection film are respectively arranged on one side and the other side of a transparent parallel plate can be used as a wavelength dispersion compensator by using a special mirror and a lens. However, the transparency characteristic of the wavelength dispersion compensator using such a VIPA plate is a periodical characteristic which is asymmetric with a central wavelength in a wavelength regime. Accordingly, not parallel light but converged or diverged light having angular dispersion is input to an etalon plate, so that a filter whose transparency characteristic is an asymmetric periodical characteristic which is reverse to the VIPA plate is configured for the central wavelength in the wavelength regime. With this filter, the transparency characteristic of the wavelength dispersion compensator using the VIPA plate is optimized.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com