Wavelength dispersion compensating apparatus
a compensating apparatus and wavelength technology, applied in the field of wavelength dispersion (chromatic dispersion) compensating apparatus, can solve the problems of deteriorating signal quality in the system, distortion of pulse waveform, and high manufacturing cost of dispersion compensating fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
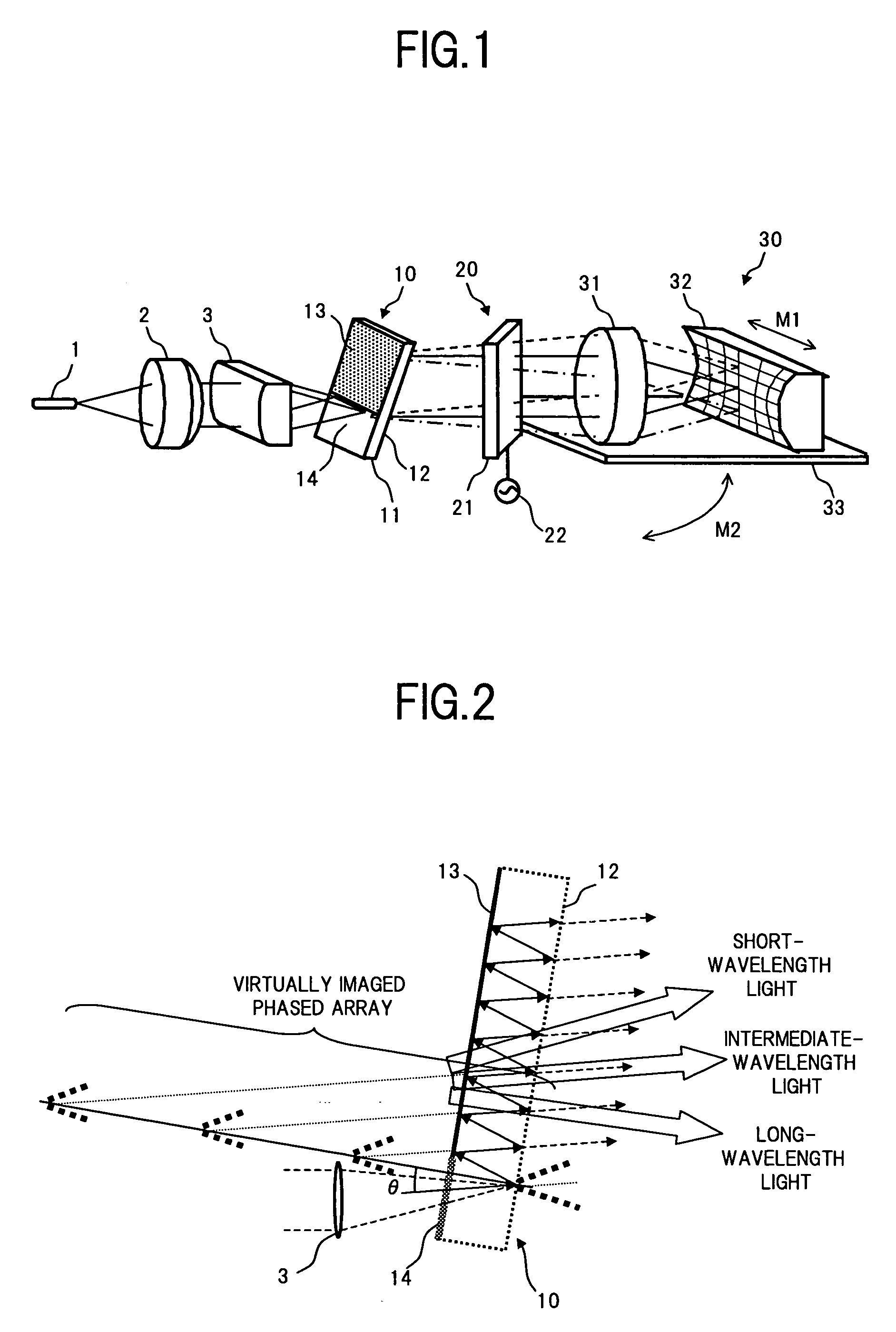
[0053]FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a configuration of a wavelength dispersion (chromatic dispersion) compensating apparatus according to the present invention.
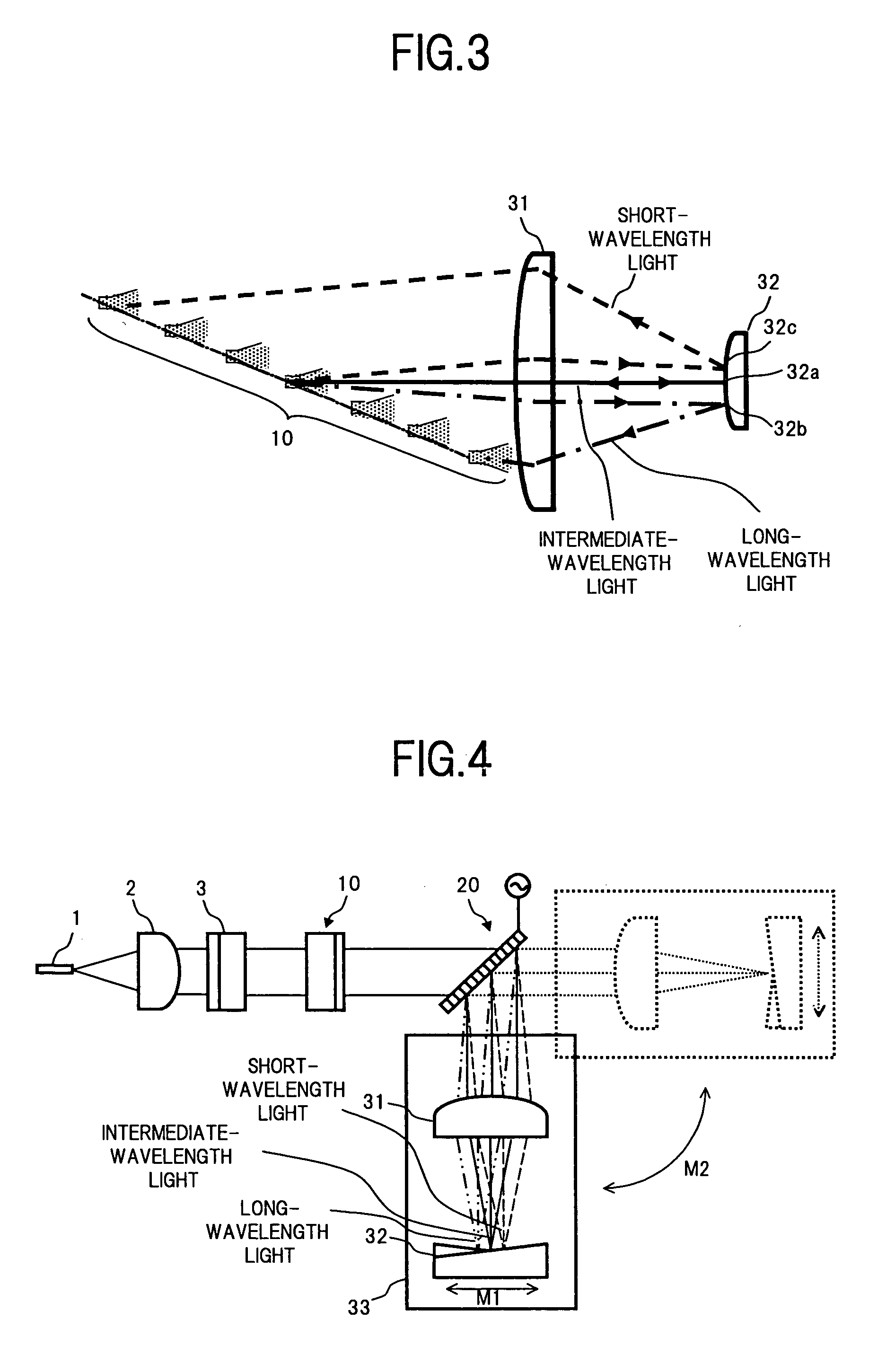
[0054] In FIG. 1, the wavelength dispersion compensating apparatus of the present embodiment comprises for example: a VIPA plate 10; an optical system consisting of an optical fiber 1, a collimate lens 2, and a cylindrical lens 3, which permits a WDM light condensed on one segment to be incident on a transmission area 14 of the VIPA plate 10; a variable dispersion diffraction grating 20 which is given with a light multi-reflected by the VIPA plate 10 and emitted from one of planes of the VIPA plate 10; and a light return apparatus 30 which reflects the light which has passed through the variable dispersion diffraction grating 20 and returns it to the VIPA plate 10 via the variable dispersion diffraction grating 20.
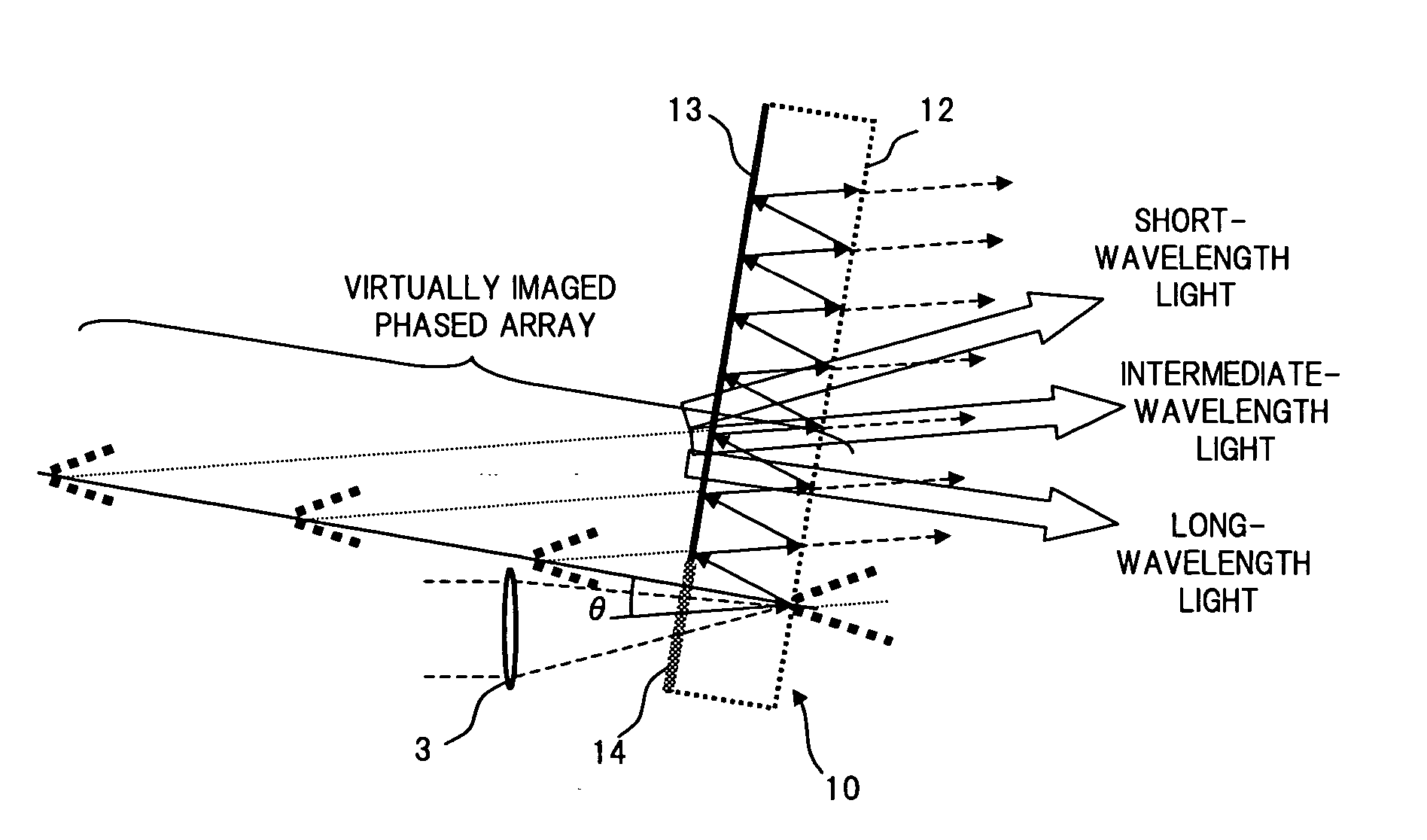
[0055] As with the conventional configuration shown in the above described FIG. 18, the VIPA plate 10 has...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com