Patents
Literature
134results about "Optical transmission with multiple stages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
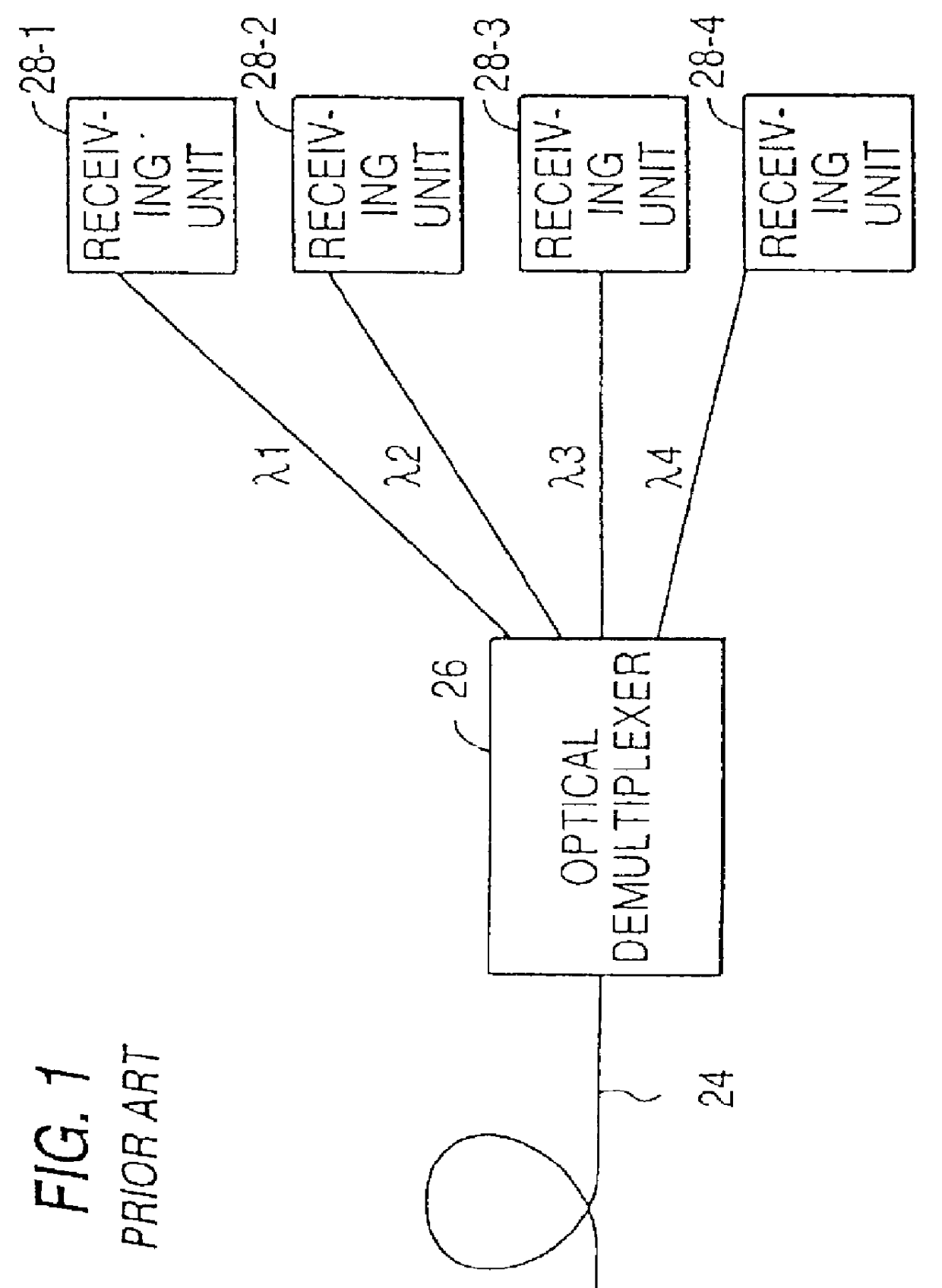
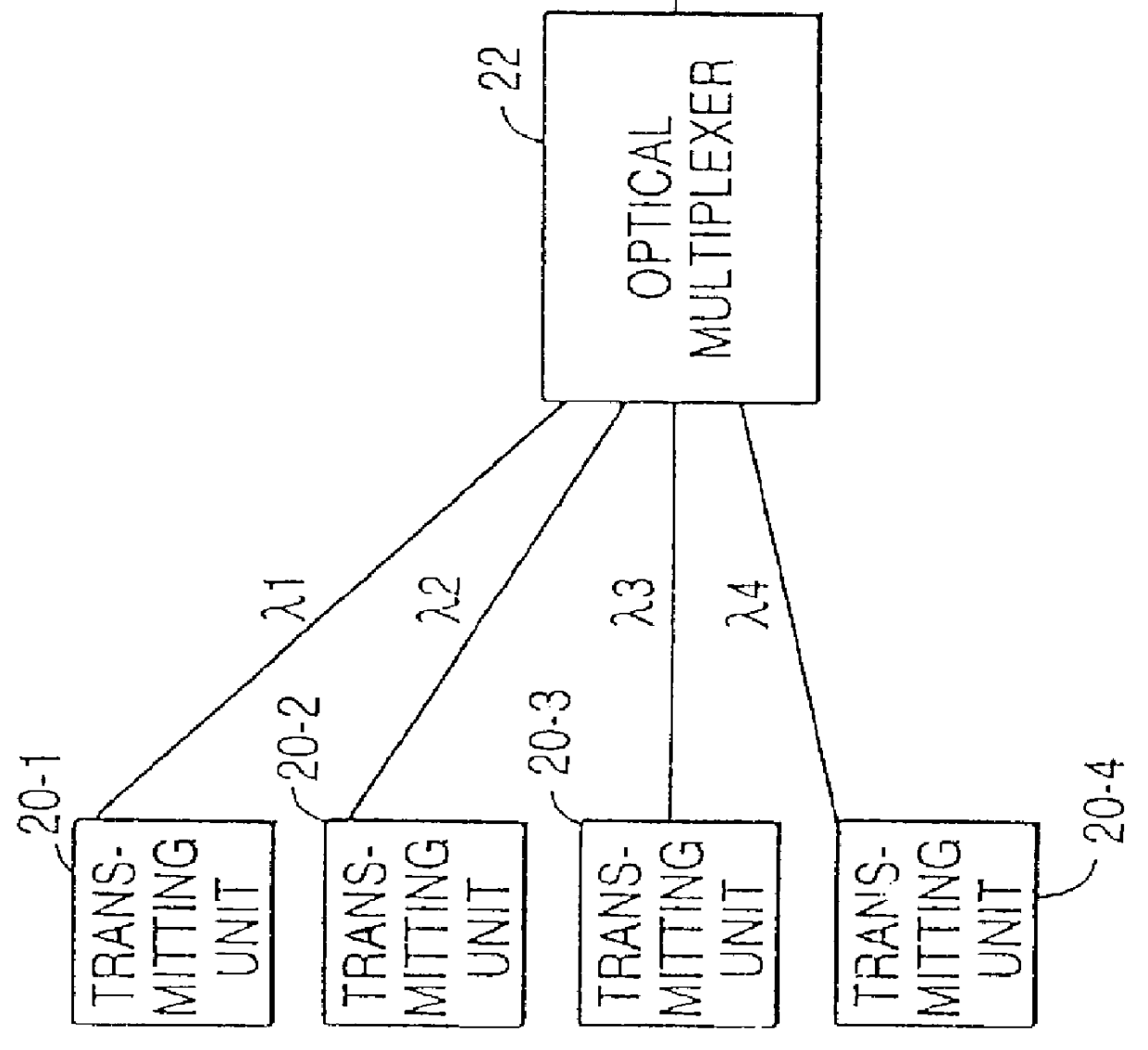
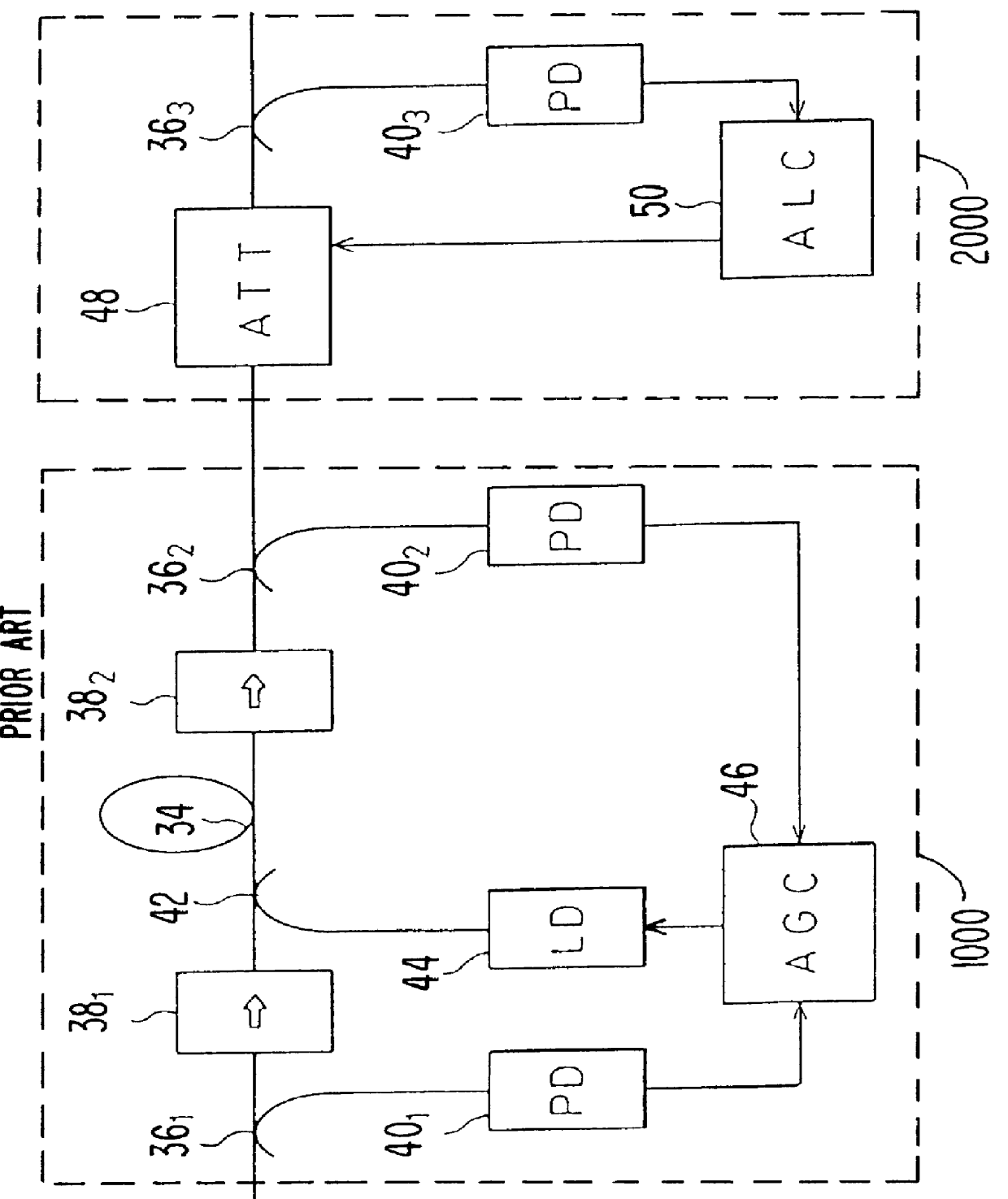
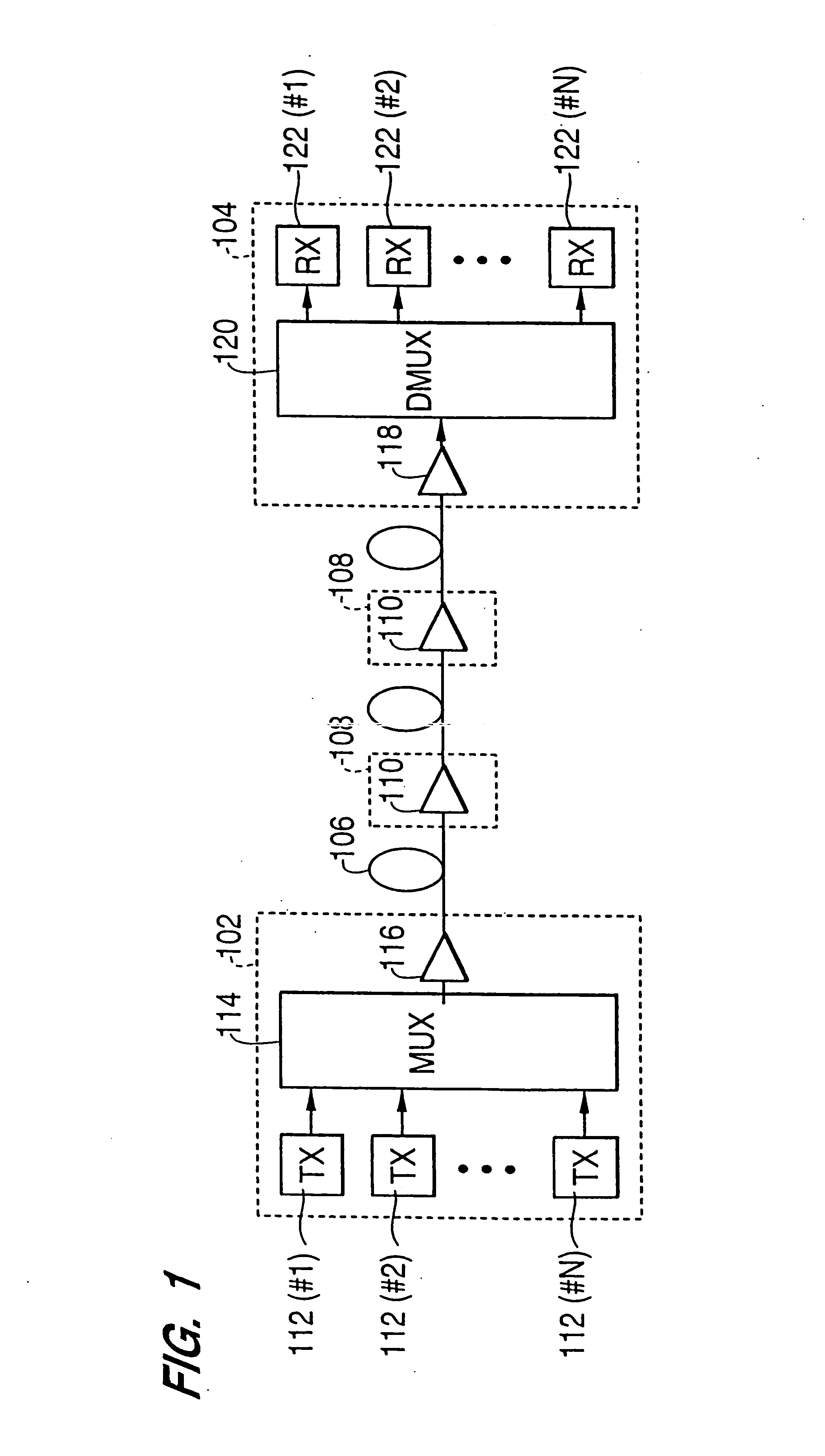
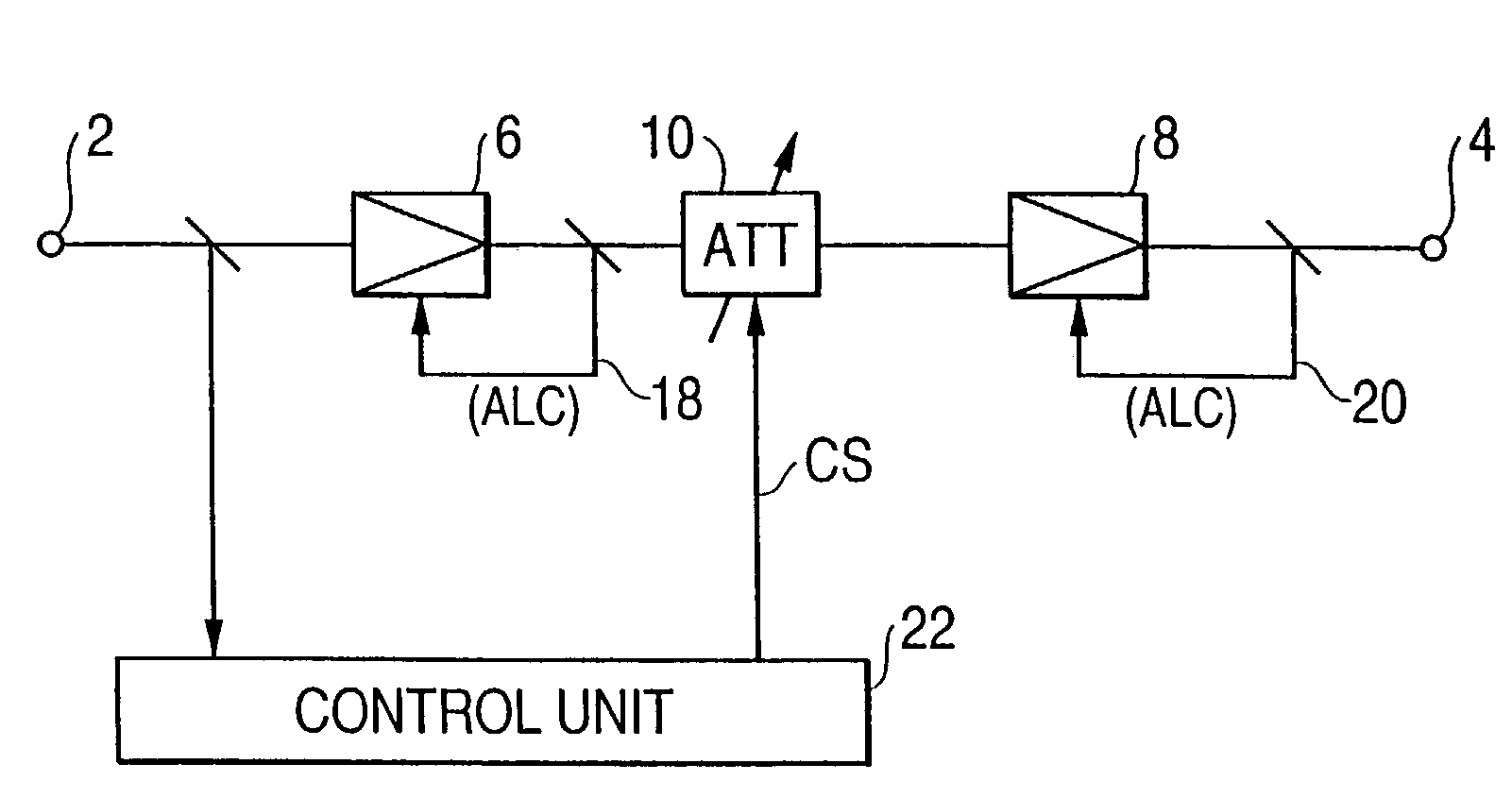
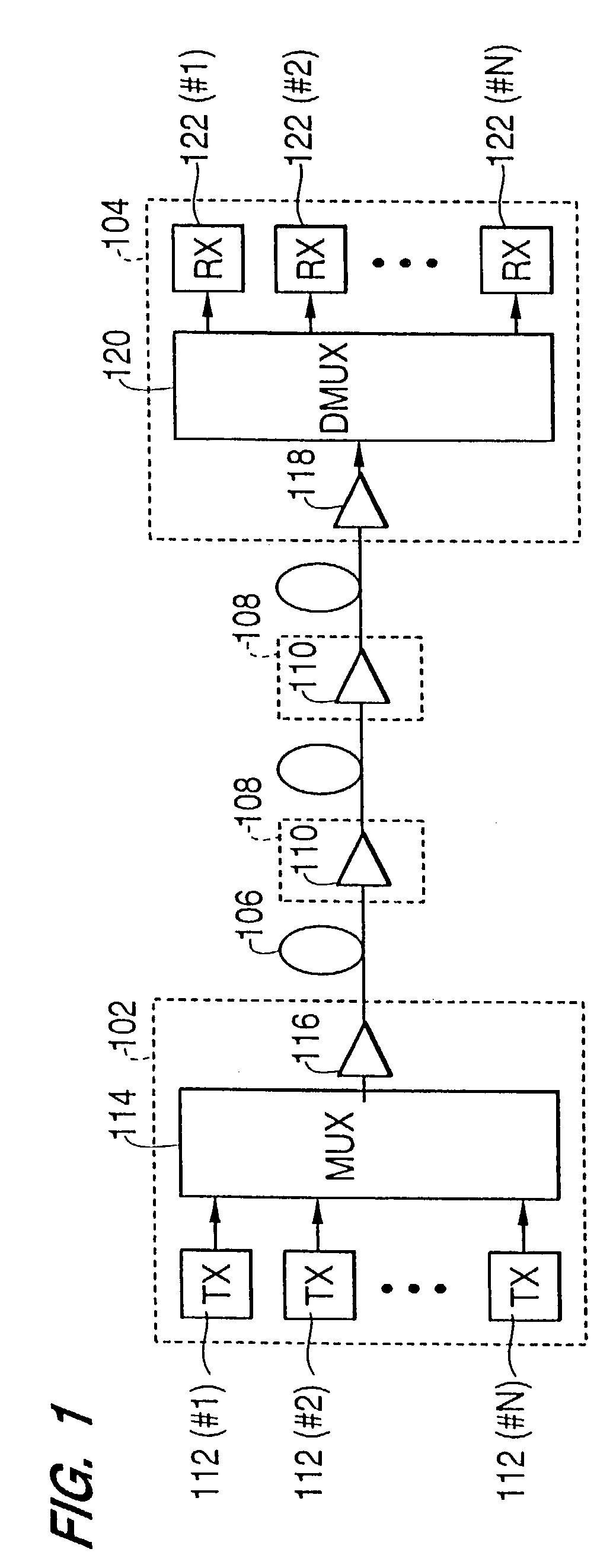
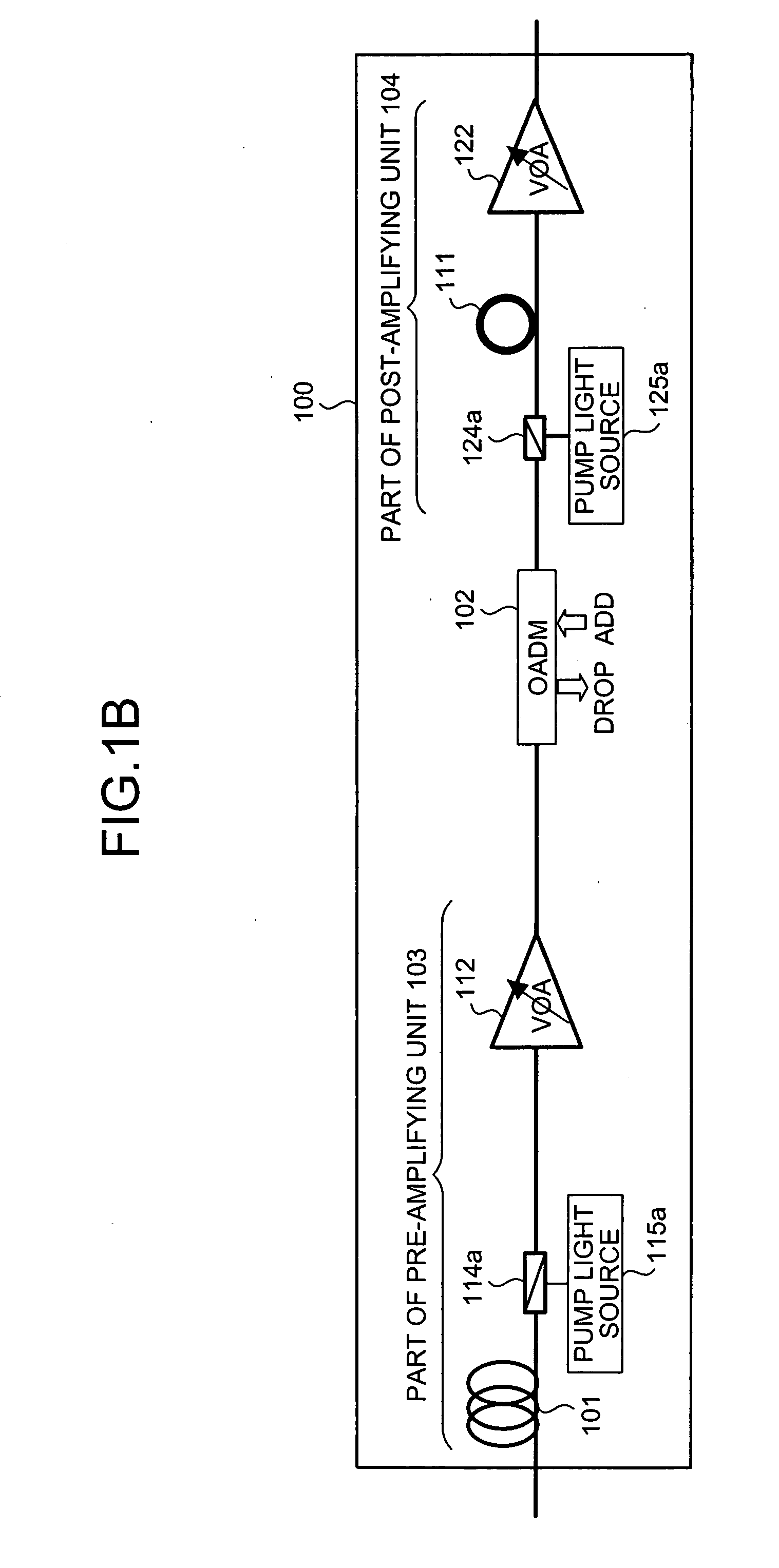
Controller which controls a variable optical attenuator to control the power level of a wavelength-multiplexed optical signal when the number of channels are varied
InactiveUS6025947AReduce degradationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierTransmittance
An optical amplifying apparatus which includes an optical amplifier, an optical attenuator and a controller. The optical amplifier amplifies a light signal having a variable number of channels. The optical attenuator passes the amplified light signal and has a variable light transmissivity. Prior to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal prior to the varying the number of channels. While the number of channels in the light signal is being varied, the controller maintains the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator to be constant. Subsequent to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal subsequent to the varying the number of channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
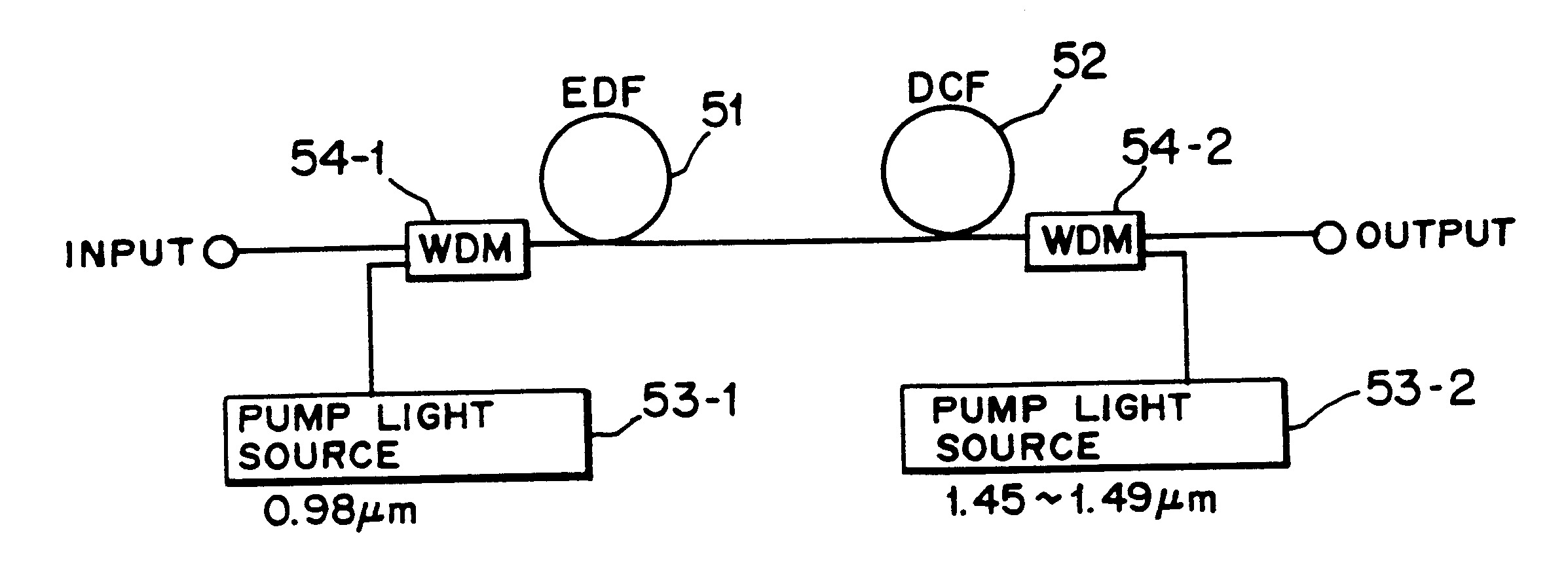
Optical fiber amplifier and dispersion compensating fiber module for optical fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6342965B1Guaranteed uptimeImprove conversion efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical fiber amplifiersRare earth
The invention provides an optical fiber amplifier which assures stable operation of a pump light source and efficiently makes use of residual pump power to achieve improvement in conversion efficiency. The optical fiber amplifier includes a rare earth doped fiber. Pump light from a pump light source is introduced into one end of the rare earth doped fiber by way of a first optical coupler, and residual pump light originating from the pump light and arriving at the other end of the rare earth doped fiber is applied to the other rare earth doped fiber amplifier or the loss compensation of a dispersion compensating fiber by Raman amplification.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
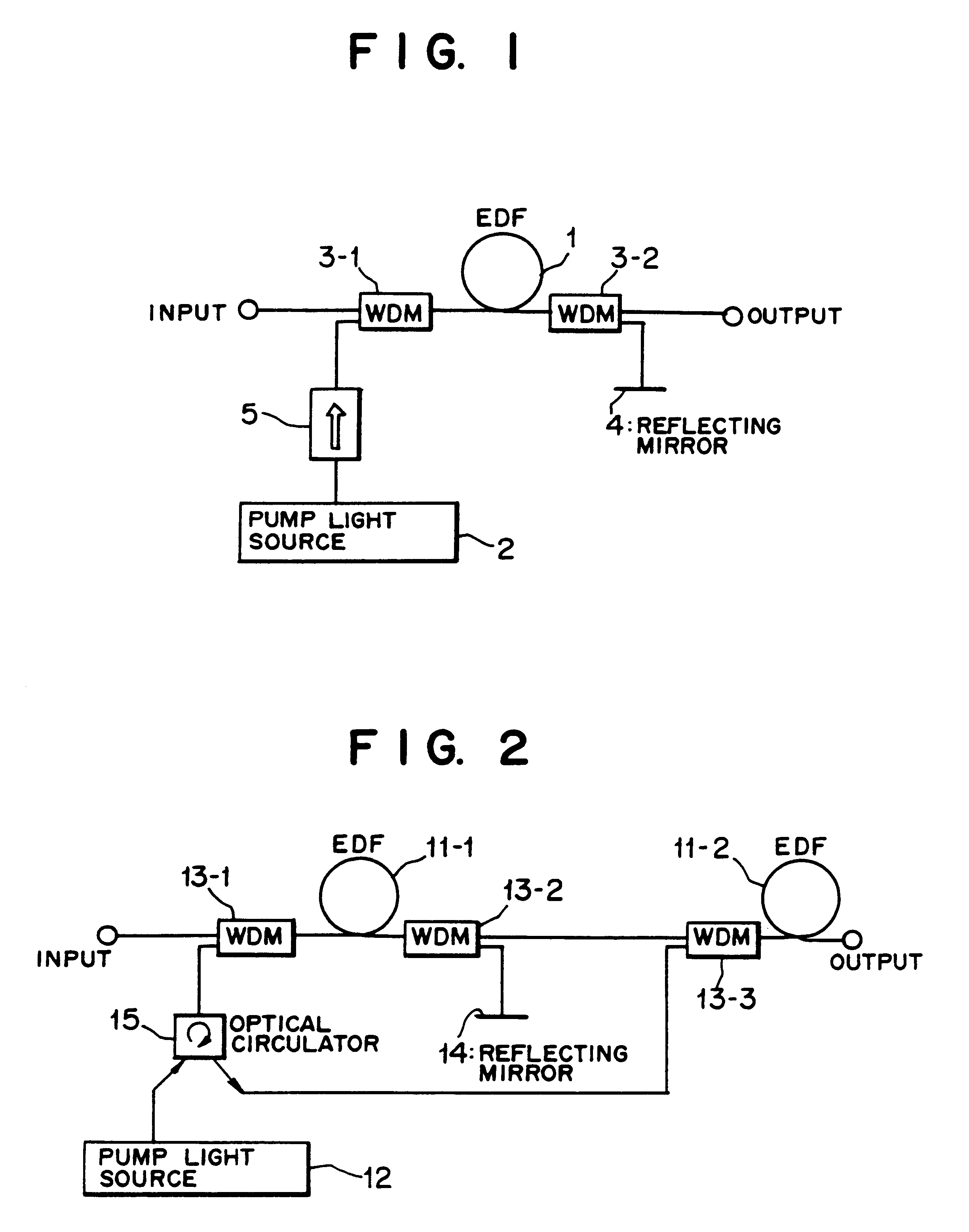
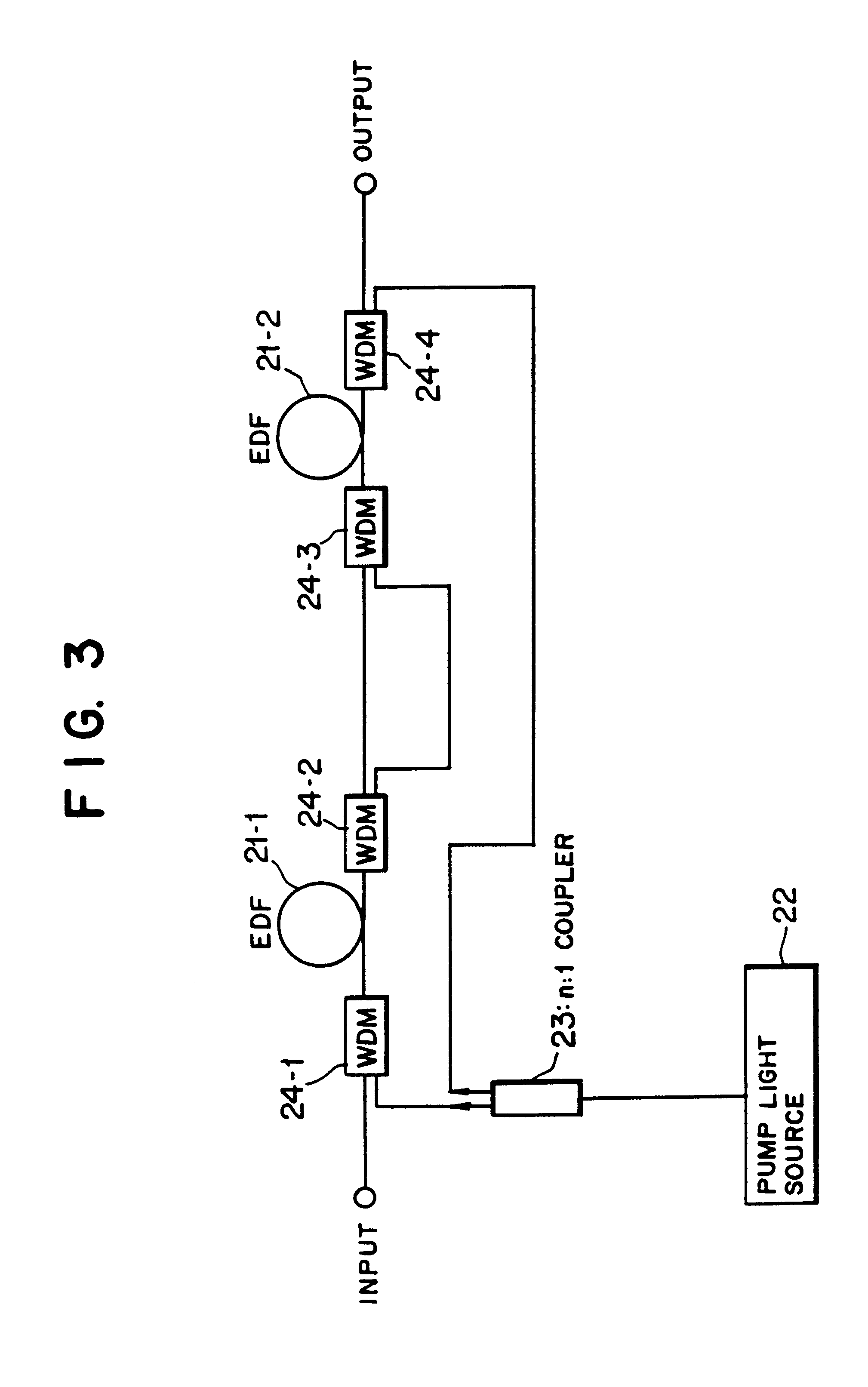
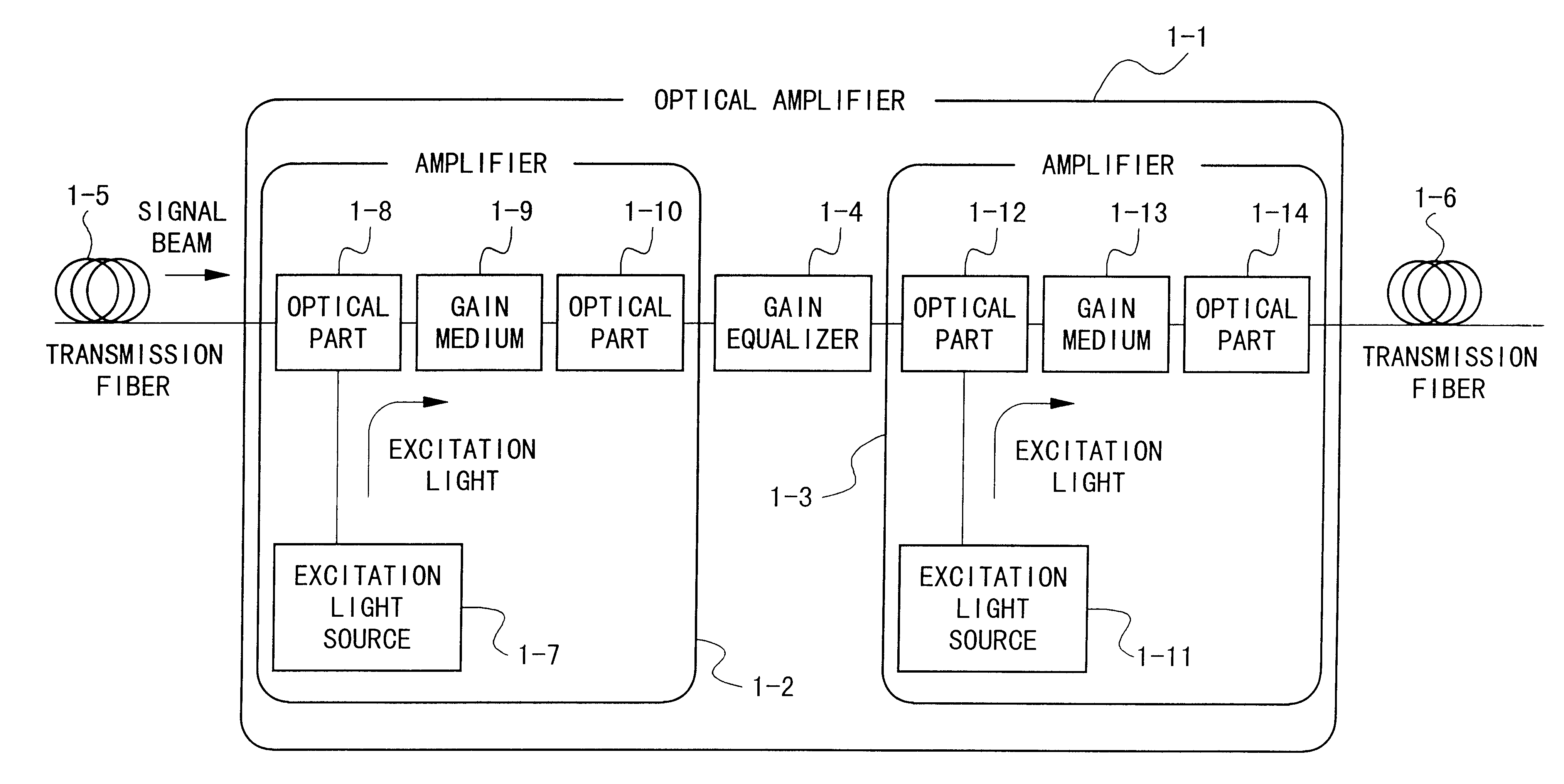
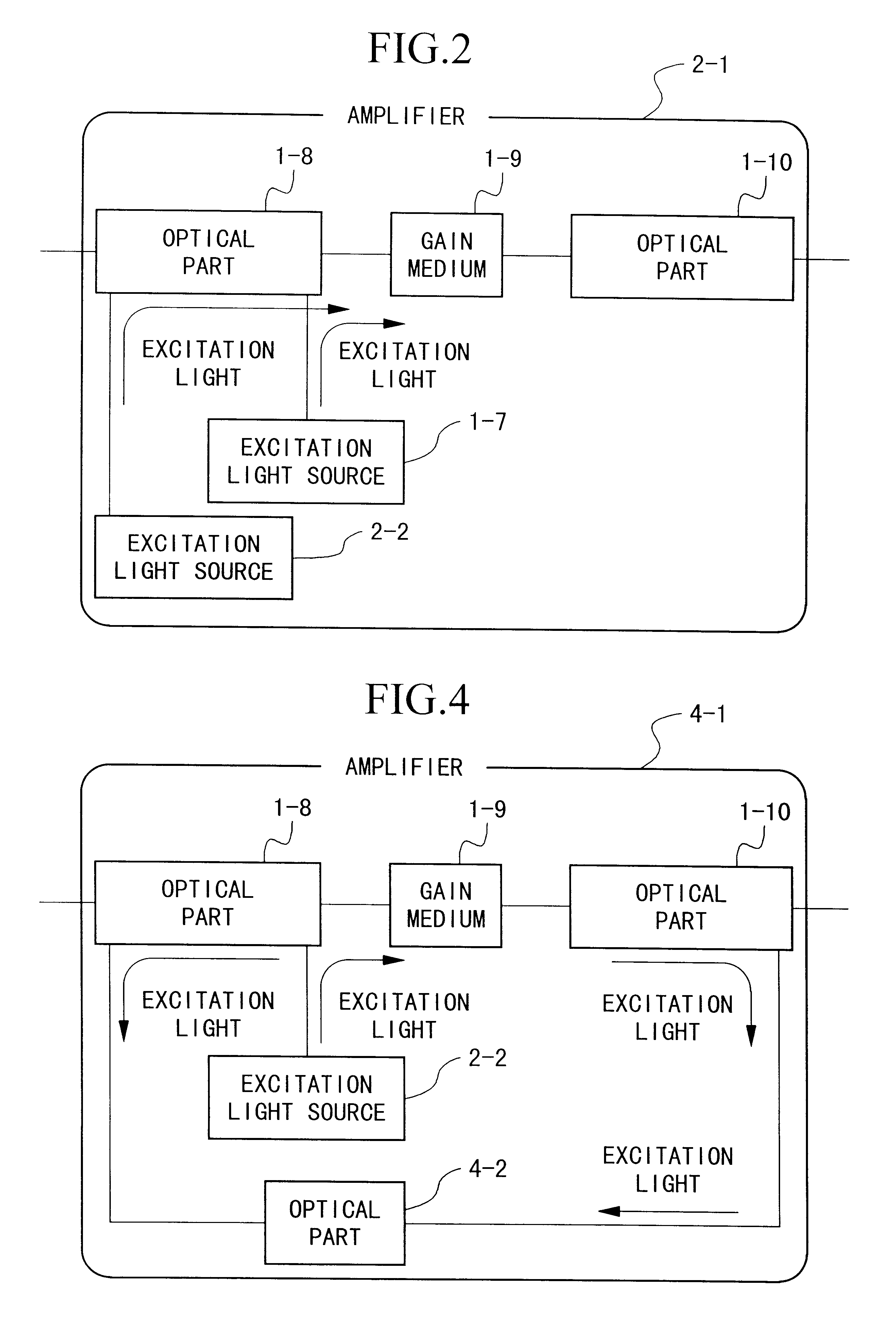
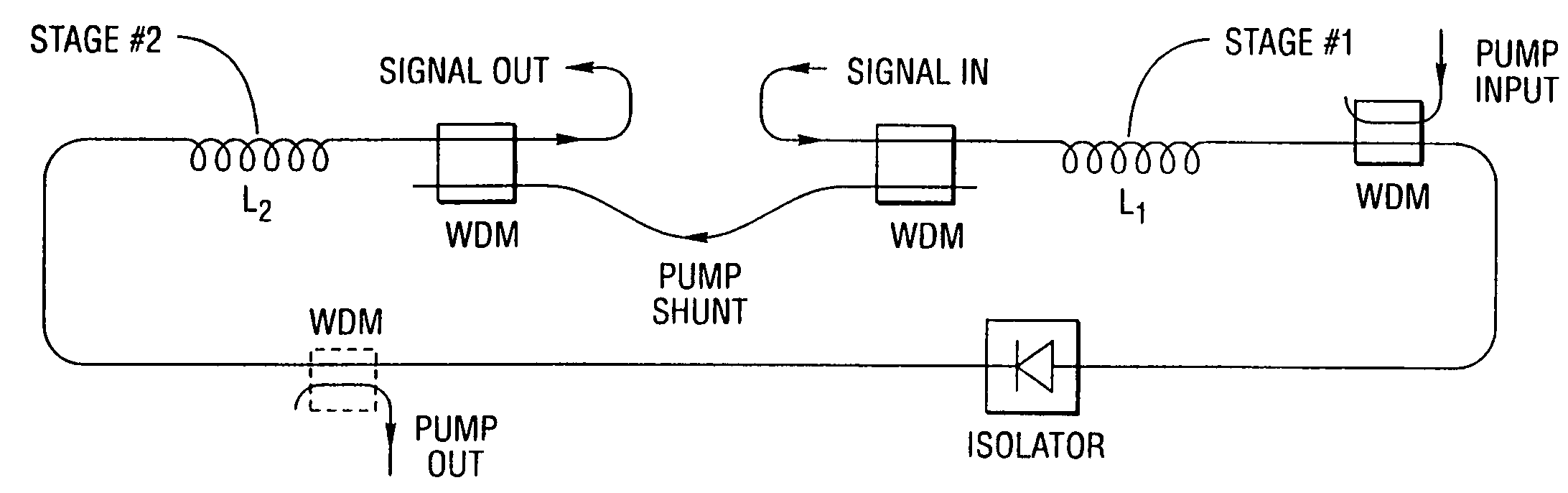
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Multi-stage optical amplifier and broadband communication system
InactiveUS6885498B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberAudio power amplifier
A multi-stage optical amplifier includes at least a distributed Raman amplifier fiber and a discrete amplifier fiber. The amplifier is configured to be coupled to at least one signal source that produces a plurality of signal wavelengths λs; and at least a first pump source that produces one or more pump beam wavelengths λp. A signal input port is coupled to the amplifier. A signal output port is coupled to the amplifier. The distributed Raman and discrete amplifier fibers are positioned between the signal input port and the signal output port. A first pump input port is coupled to a first end of the distributed Raman amplifier fiber. A second pump input port is coupled to a second end of the distributed Raman amplifier fiber. The first end is located closer to the signal input port than the second end. A third pump input port is coupled to the discrete amplifier fiber.
Owner:NEPTUNE SUBSEA IP LTD
Controller which controls a variable optical attenuator to control the power level of a wavelength-multiplexed optical signal when the number of channels are varied
InactiveUS6144485AReduce degradationWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierTransmittance
An optical amplifying apparatus which includes an optical amplifier, an optical attenuator and a controller. The optical amplifier amplifies a light signal having a variable number of channels. The optical attenuator passes the amplified light signal and has a variable light transmissivity. Prior to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal prior to the varying the number of channels. While the number of channels in the light signal is being varied, the controller maintains the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator to be constant. Subsequent to varying the number of channels in the light signal, the controller varies the light transmissivity of the optical attenuator so that a power level of the amplified light signal is maintained at an approximately constant level that depends on the number of channels in the light signal subsequent to the varying the number of channels.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Data in motion storage system and method
ActiveUS20170280211A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical cavityWaveguide
A data storage system is disclosed that includes a recirculating loop storing data in motion. The data may be carried by a signal via the loop including one or more satellites or other vessels that return, for example by reflection or regeneration, the signals through the loop. The loop may also include a waveguide, for example an optical fiber, or an optical cavity. Signal multiplexing may be used to increase the contained data. The signal may be amplified at each roundtrip and sometimes a portion of the signal may be regenerated.
Owner:NKB PROPERTIES MANAGEMENT LLC
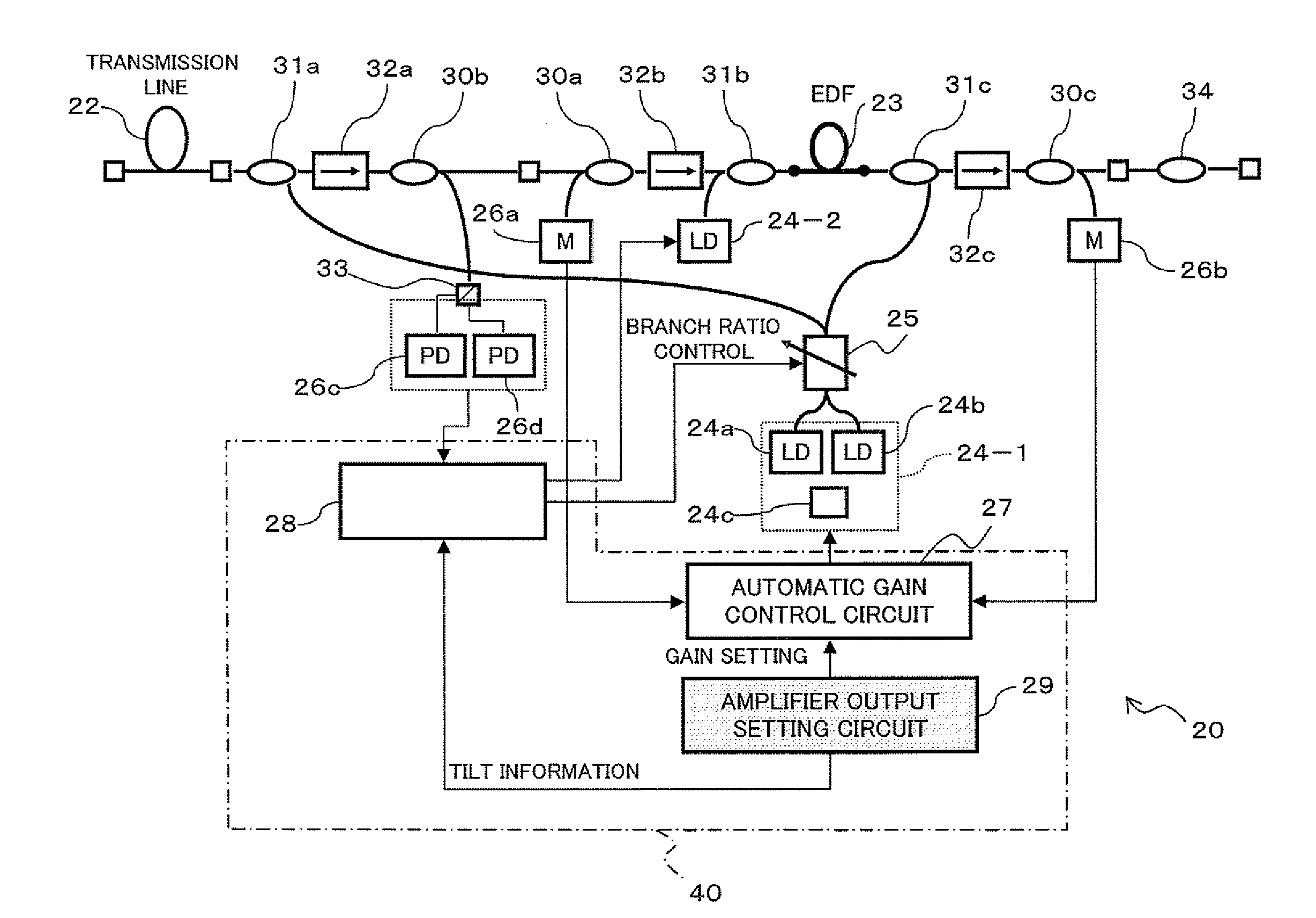
Optical amplifier
InactiveUS20060087723A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredOptical transmission with multiple stagesFibre transmissionOptical isolatorSignal light
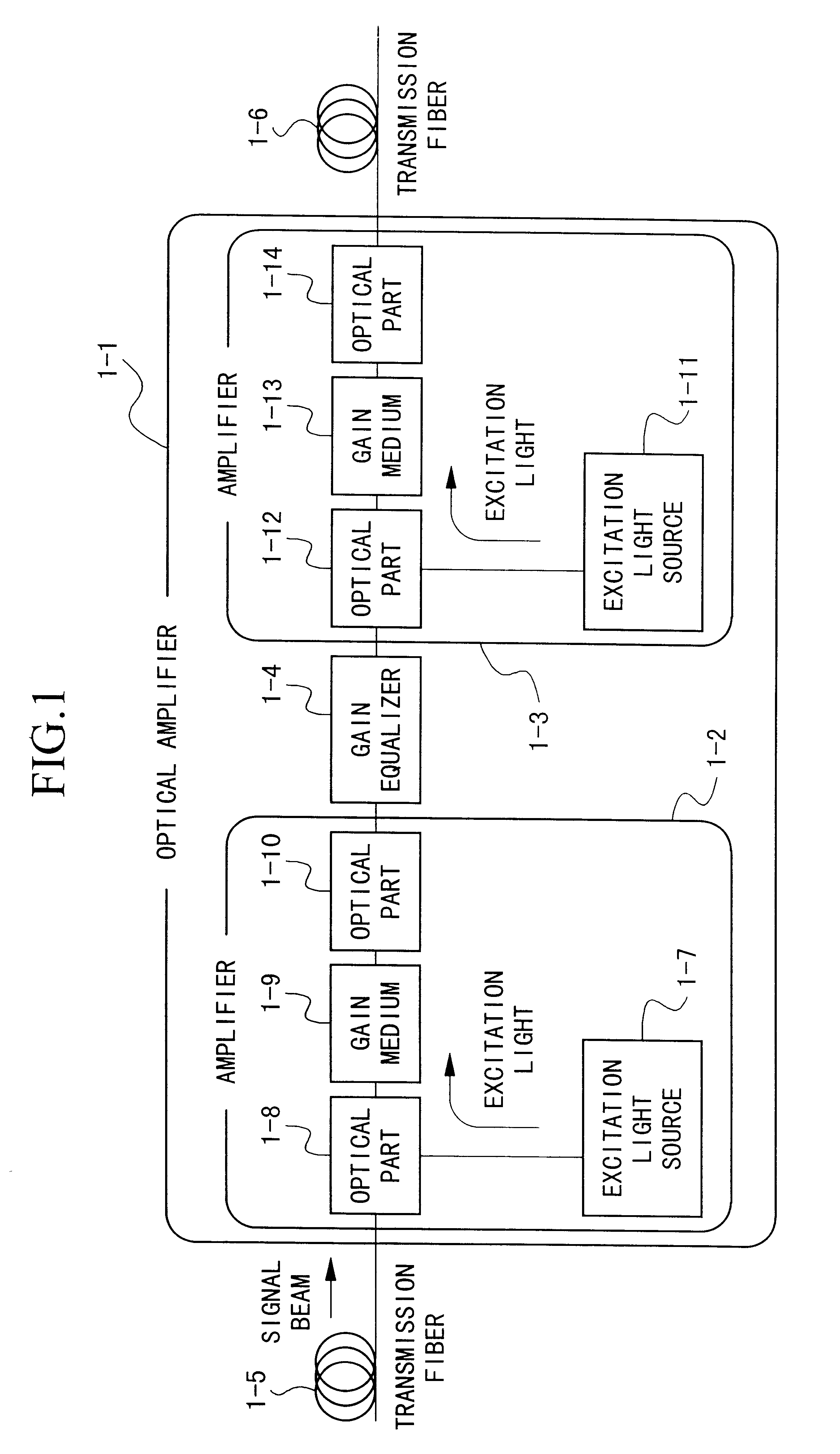
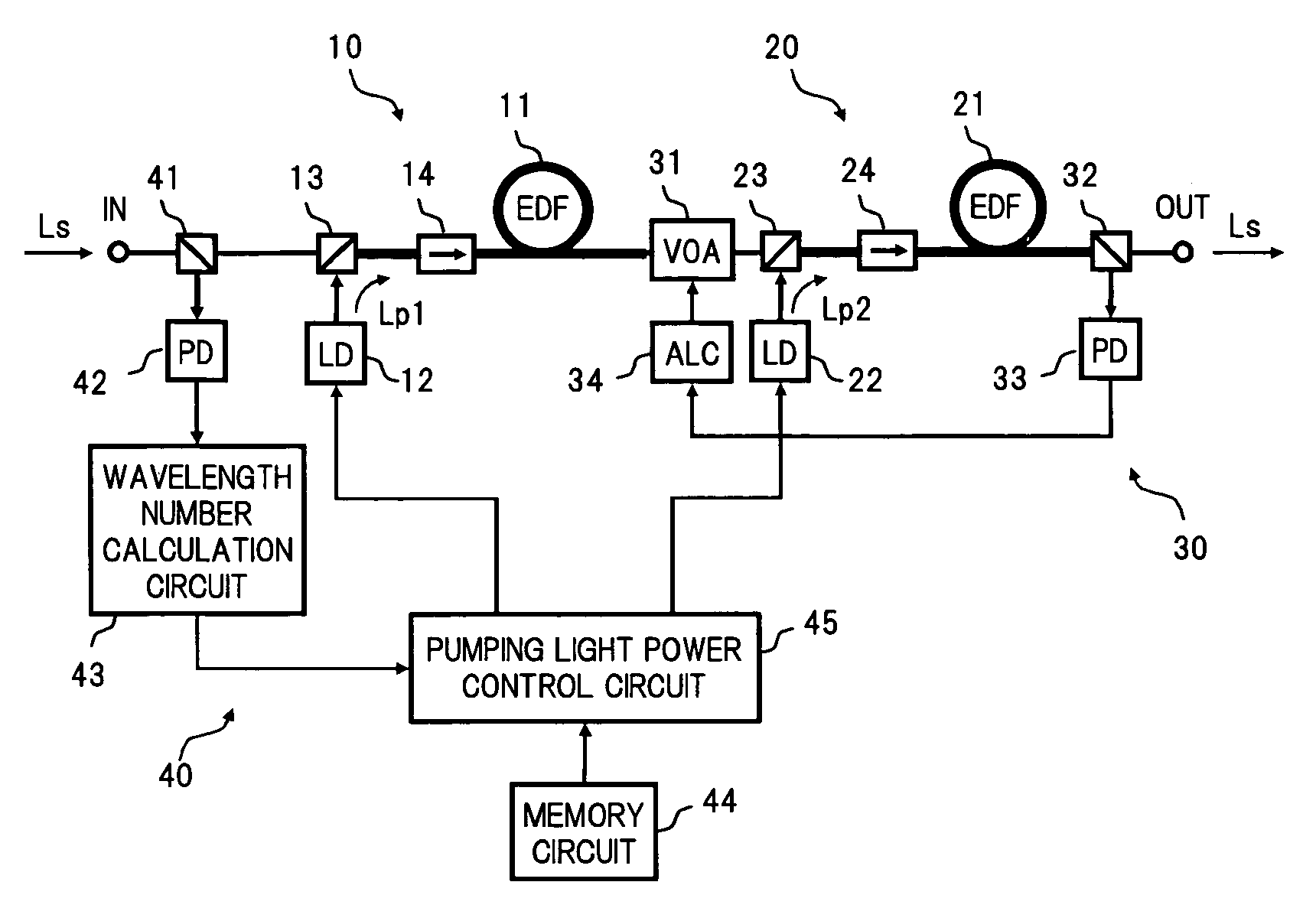
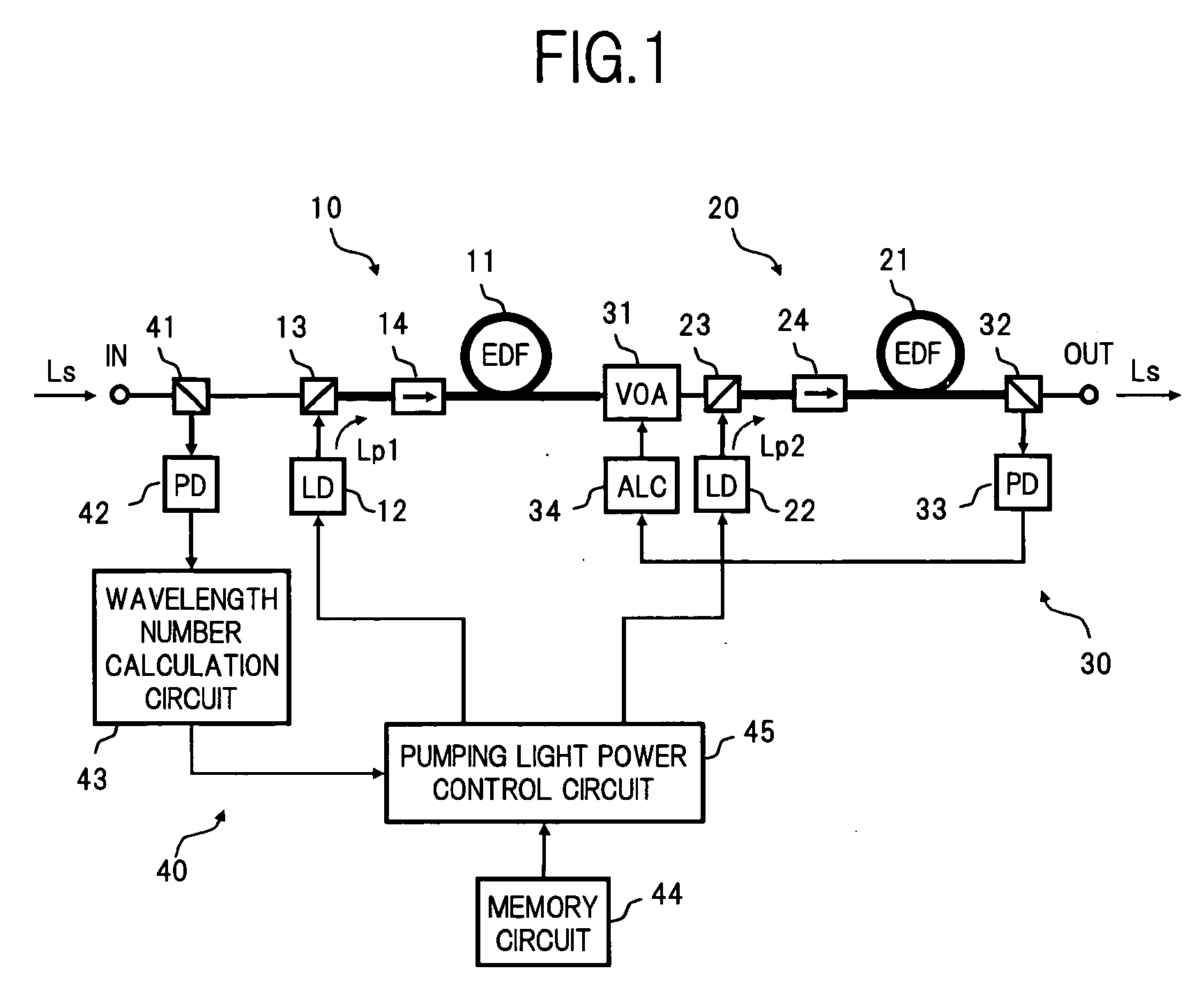
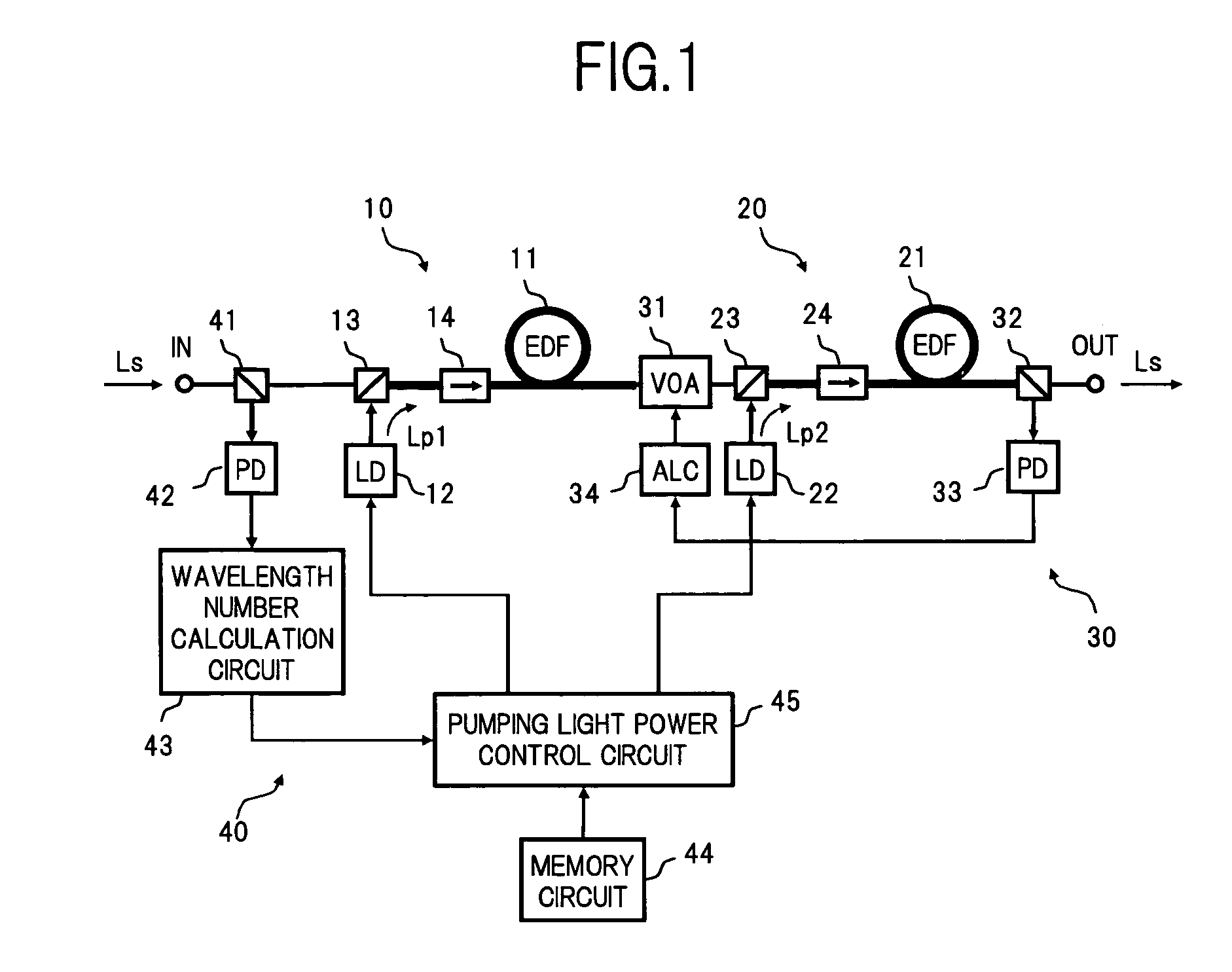
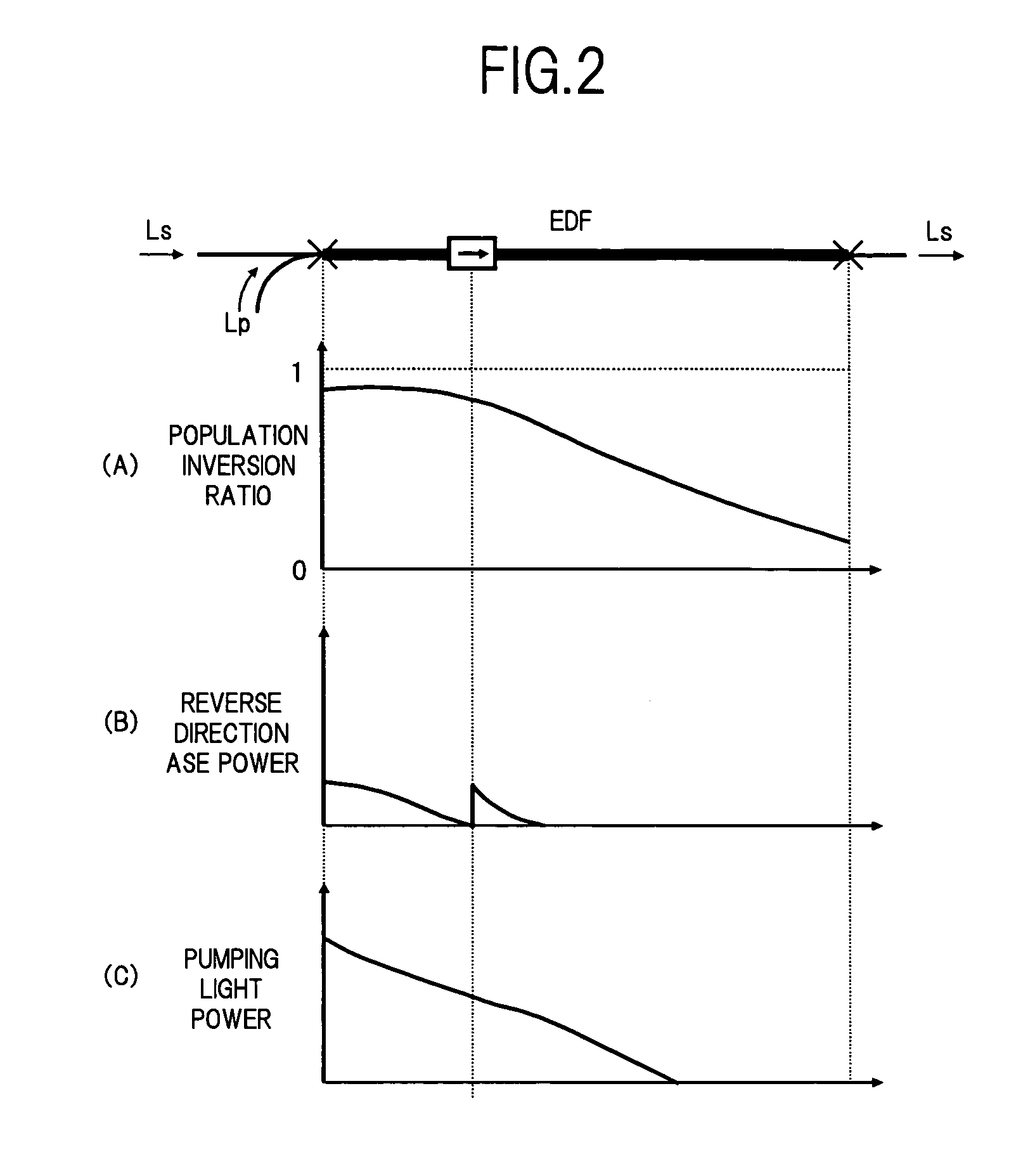
An optical amplifier of the invention comprises first and second optical amplification sections connected in a cascade manner between an input terminal and an output terminal. Optical isolators which block C-band ASE travelling in an opposite direction to L-band signal light, are inserted on the amplification medium of each of the optical amplification sections. A constant gain control section calculates the number of wavelengths based on the input power of signal light, and controls the pumping light power of each optical amplification section at a constant slope with respect to the number of wavelengths, so that the respective gains in the optical amplification sections corresponding to the number of wavelengths each become constant. As a result, it is possible to maintain flat gain wavelength characteristics even when receiving input of WDM light where the number of wavelengths varies rapidly over a wide range.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplifier and optical amplification method
ActiveUS7123404B1Solve problemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesMultiplexingOptical attenuator
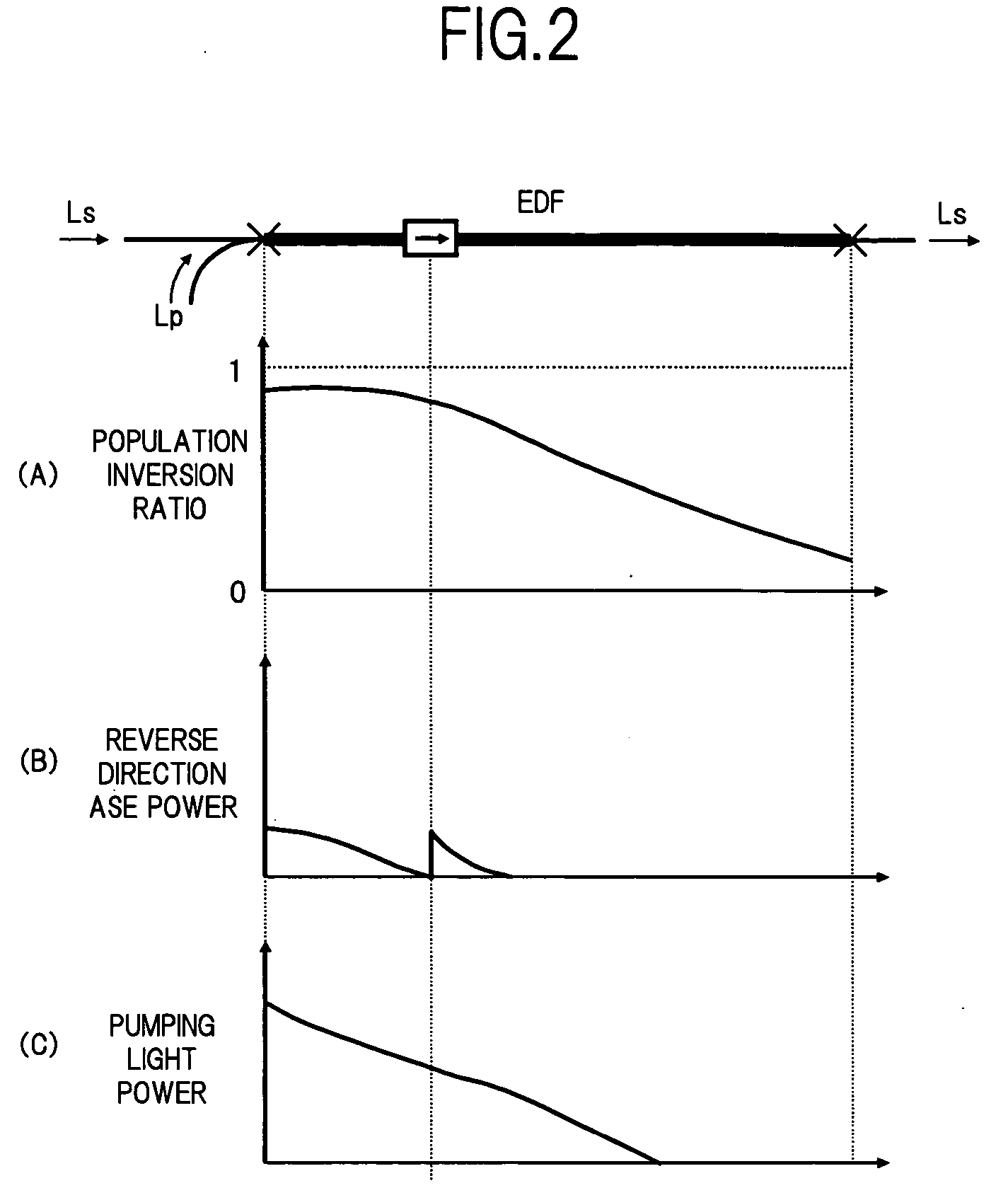
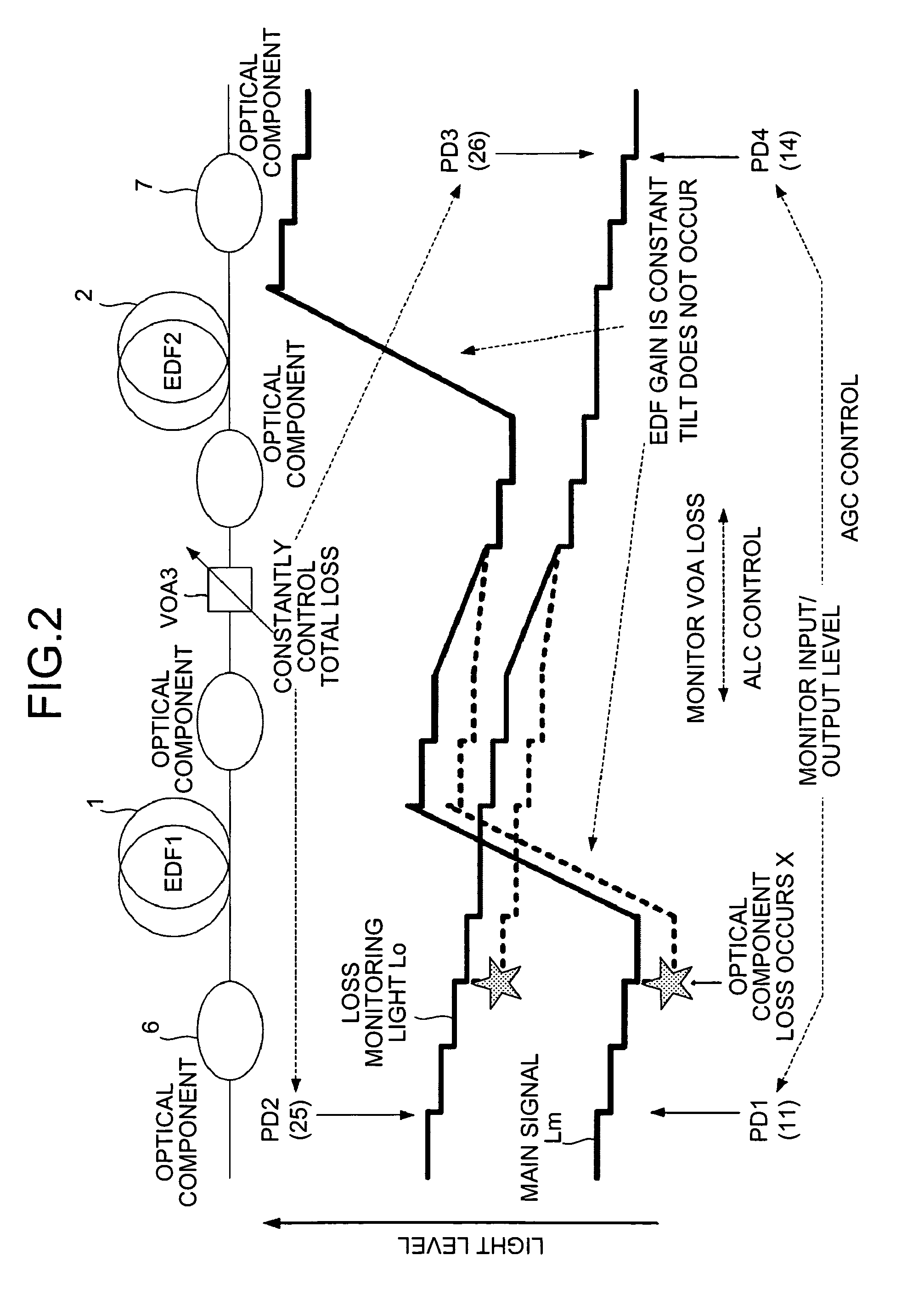
An optical amplifier includes an output unit that outputs a loss monitoring light having a wavelength that causes neither absorption nor gain with respect to each of the wavelengths of a light signal to be amplified with EDFs; a multiplexing unit that multiplexes the loss monitoring light with the light signal at an input stage of the light signal; a demultiplexing unit that demultiplexes the loss monitoring light from multiplexed light signal at an output stage of the light signal; a detecting unit that detects intensity of loss monitoring light at the input stage and intensity of loss monitoring light at the output stage; a calculating unit that calculates, based on the intensities, a loss of the loss monitoring light that has occurred between the input stage and the output stage; and a control unit that controls, based on the loss, the variable optical attenuator.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplifier and gain tilt compensation method
InactiveUS20030039026A1Reliable compensationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
The optical amplifier realizes EDFA amplification of optical signals in new bands (the S+- and S-bands), at wavelengths of 1450 to 1530 nm. The amplifier uses multiple erbium-doped fibers to amplify optical signals at wavelengths of 1450 to 1530 nm. Each of the multiple optical filters is interposed between the individual erbium-doped fibers. The sum of the transmission characteristics of the multiple filters is identical to an inverted EDF wavelength gain characteristic at wavelengths of 1450 to 1530 nm which is then shifted to the direction that the transmission increases.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Gain and signal level adjustments of cascaded optical amplifiers
InactiveUS20060198017A1Easy maintenanceLow lightOptical transmission with multiple stagesFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierOptical amplifier
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Gain and signal level adjustments of cascaded optical amplifiers
InactiveUS7061666B2Optical transmission with multiple stagesFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierOptical amplifier
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplifier
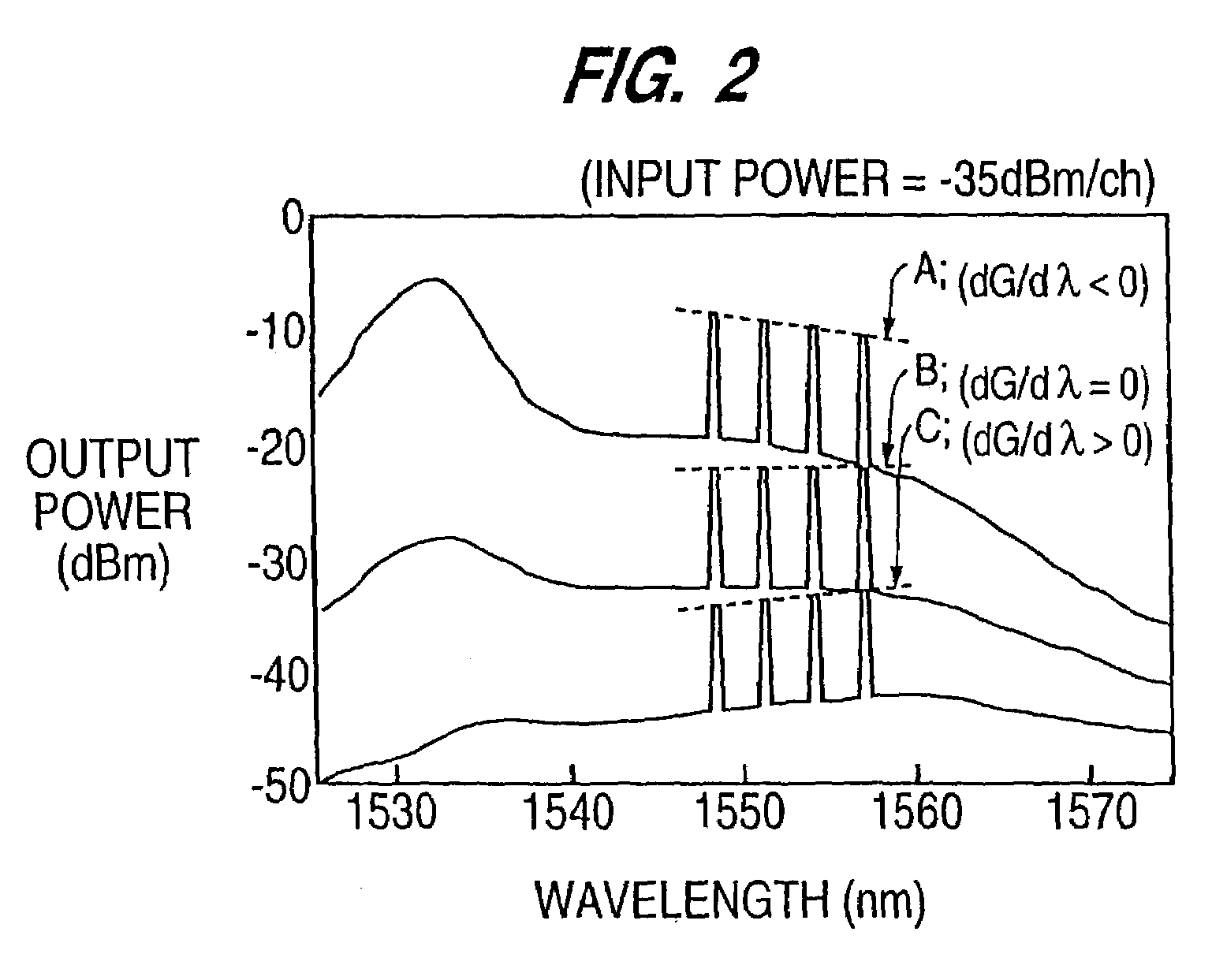
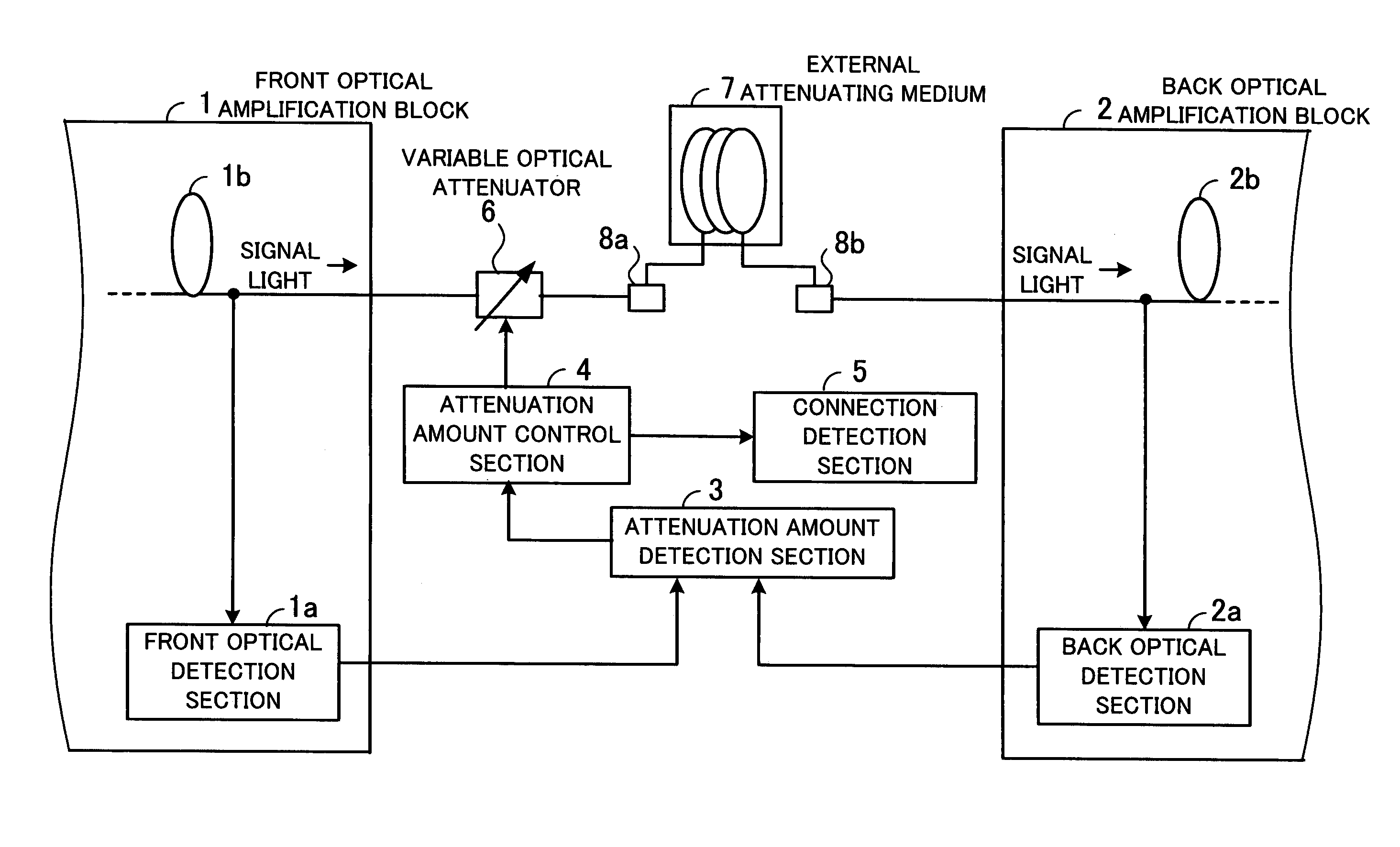
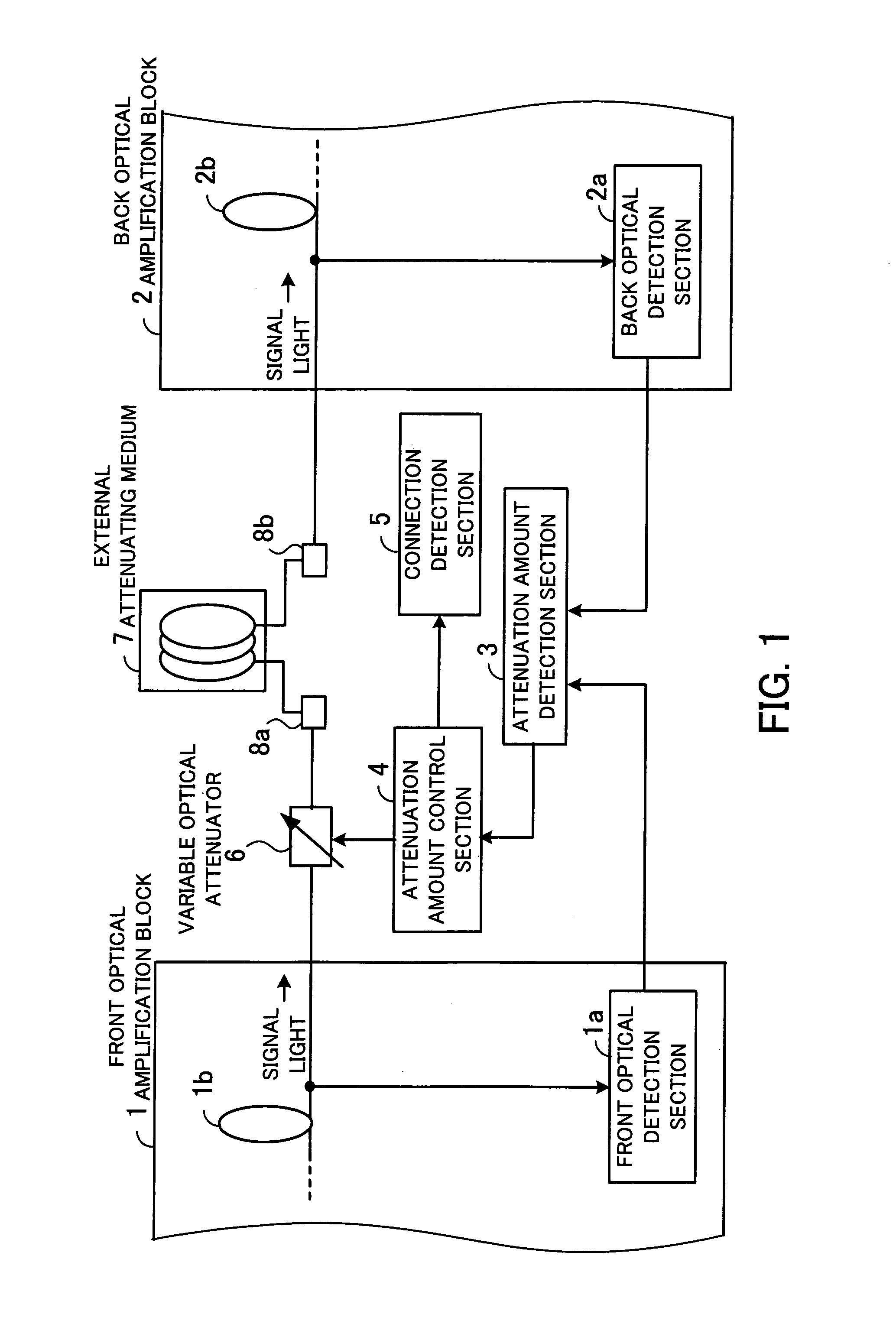
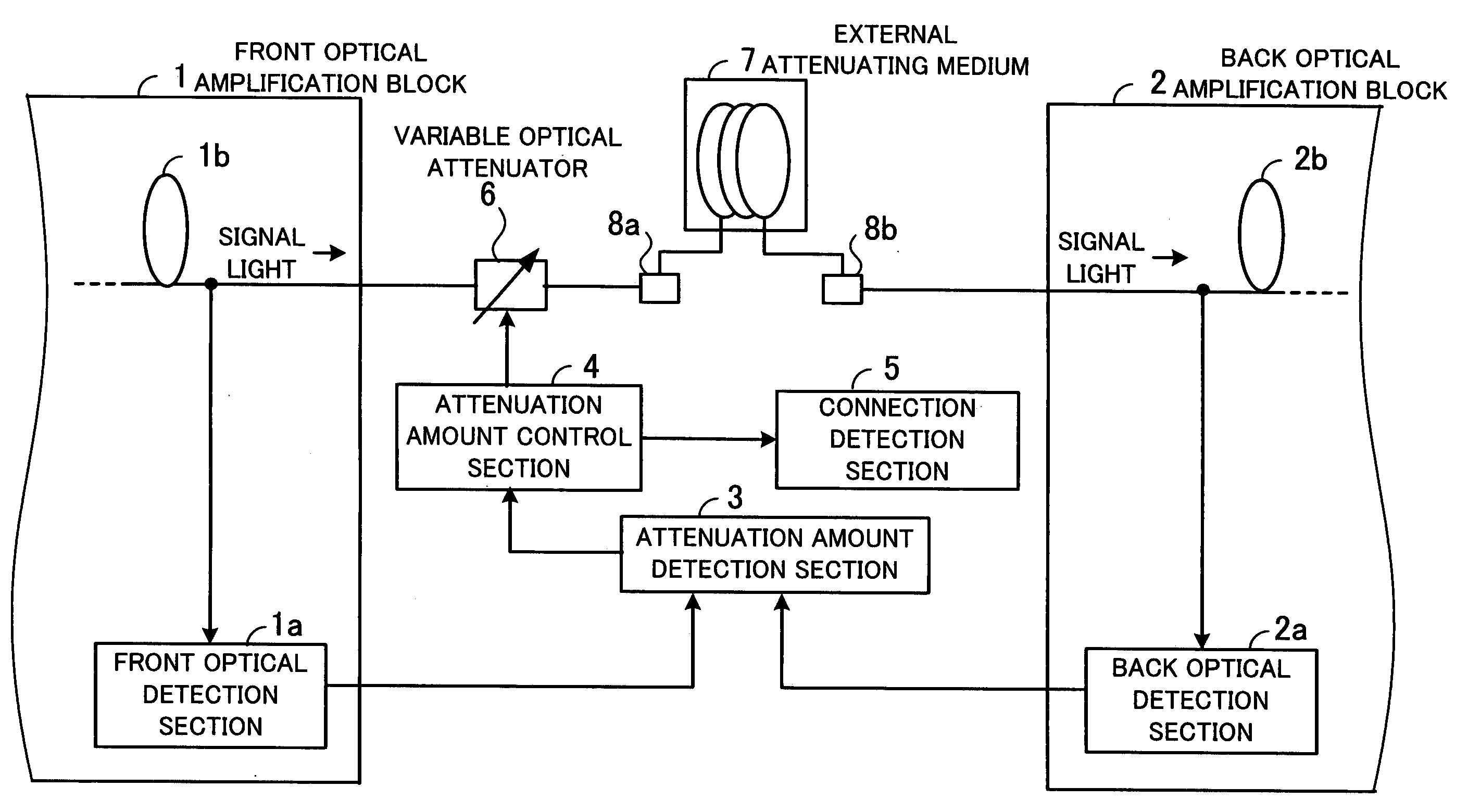
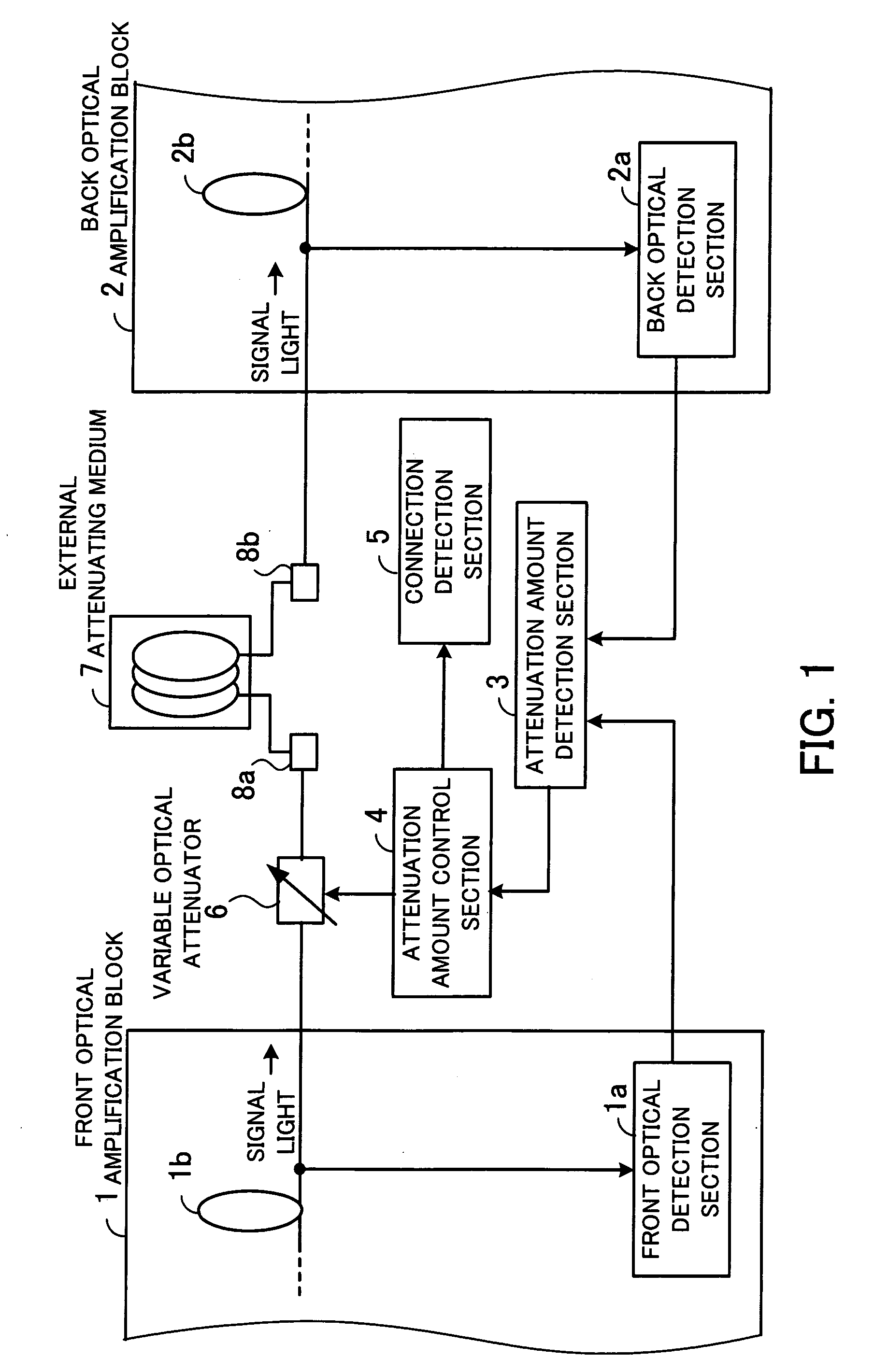
ActiveUS7215464B1Increase powerEliminate needLaser detailsOptical transmission with multiple stagesUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
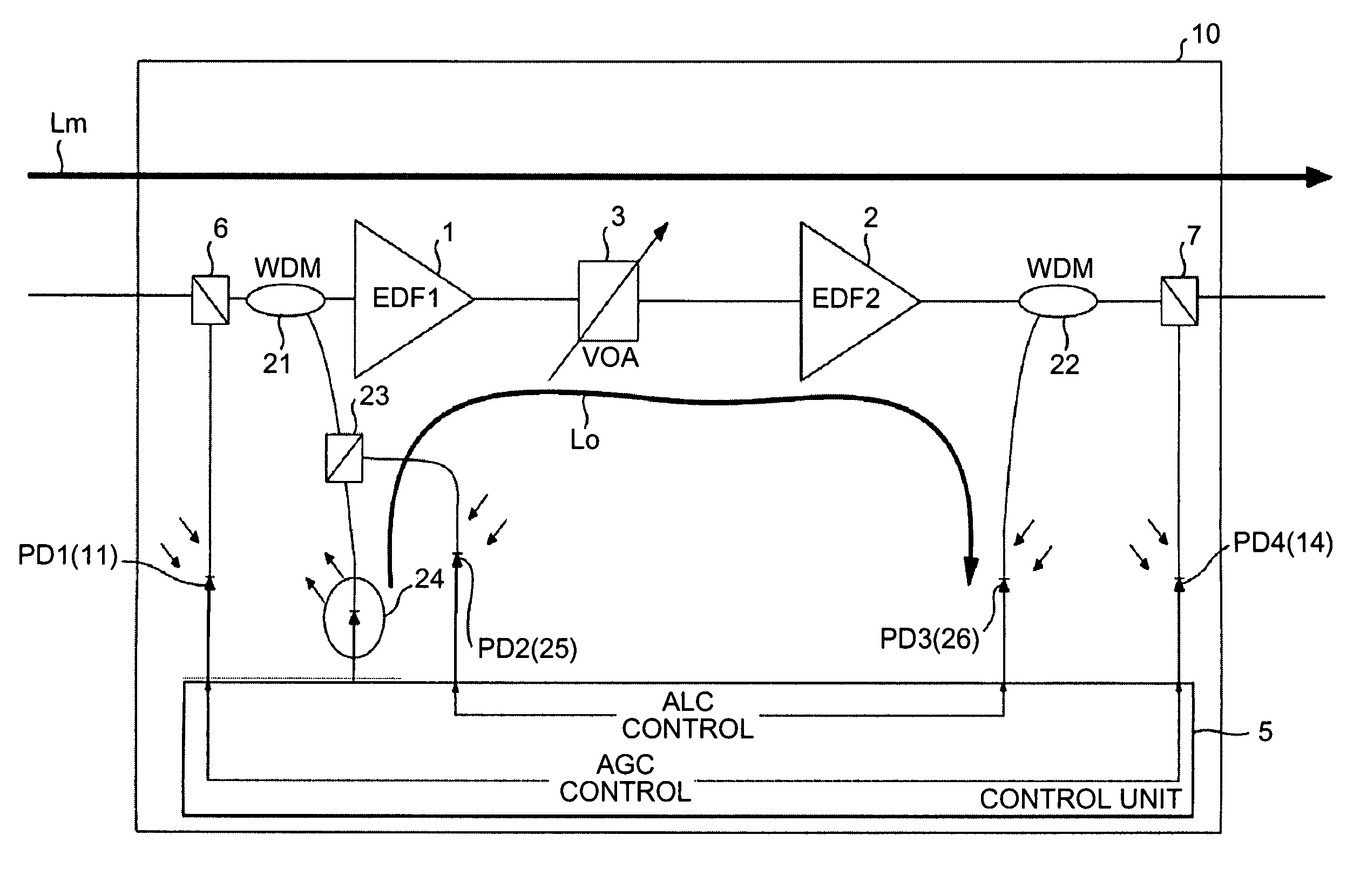
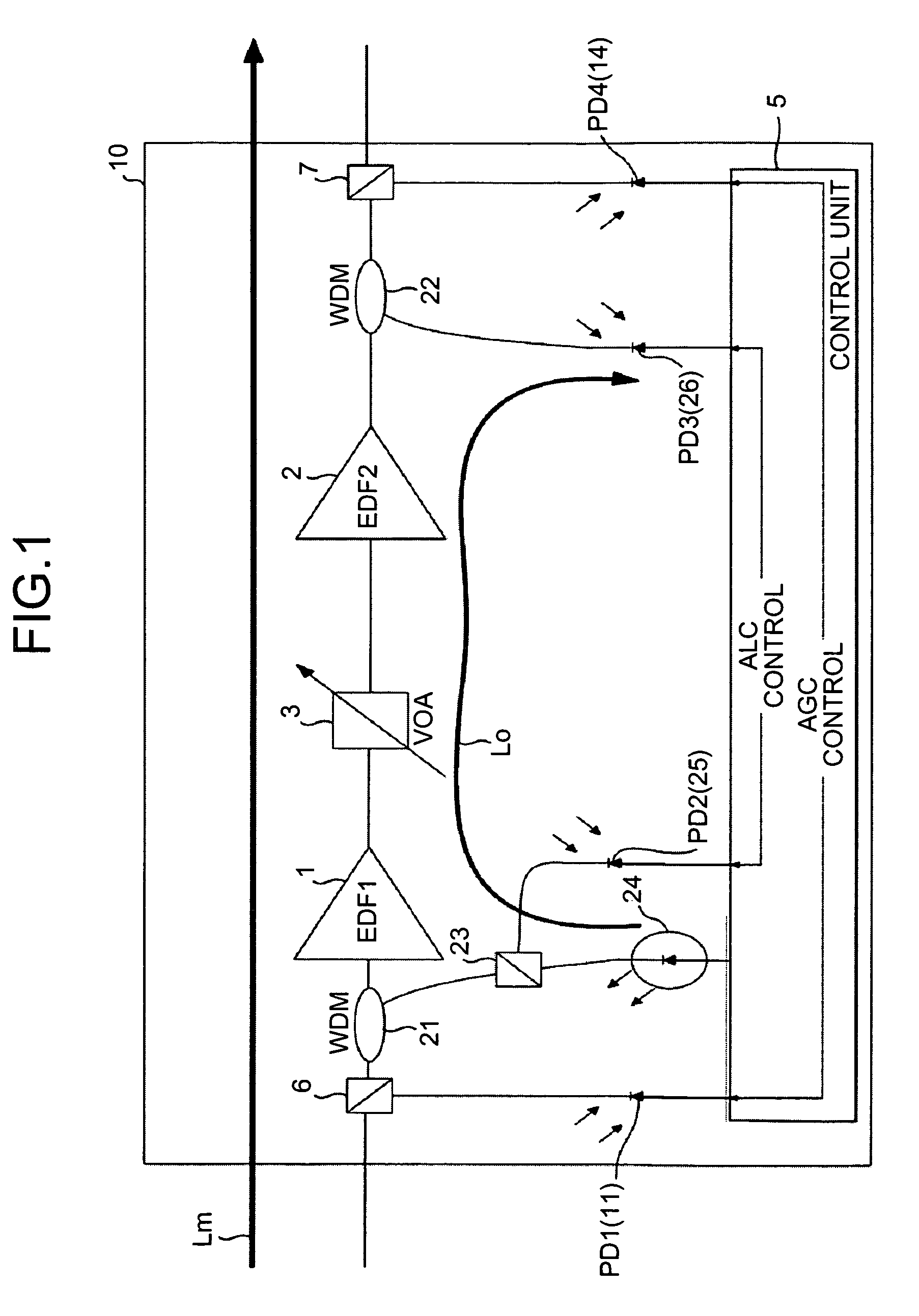
Optical amplifier which can eliminate the need for an optical detection section before an external attenuating medium, can prevent SN degradation, and can reduce power required for pumping light. An attenuation amount detection section detects an amount of signal light attenuation caused by a variable optical attenuator and the external attenuating medium connected in series, by means of a front optical detection section provided before the variable optical attenuator and the external attenuating medium and a back optical detection section provided thereafter. An attenuation amount control section controls the variable optical attenuator such that the amount of signal light attenuation detected by the attenuation amount detection section is kept constant. A connection detection section detects a connection or disconnection of the external attenuating medium in accordance with the amount of signal light attenuation obtained when the amount of attenuation caused by the variable optical attenuator is minimized.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
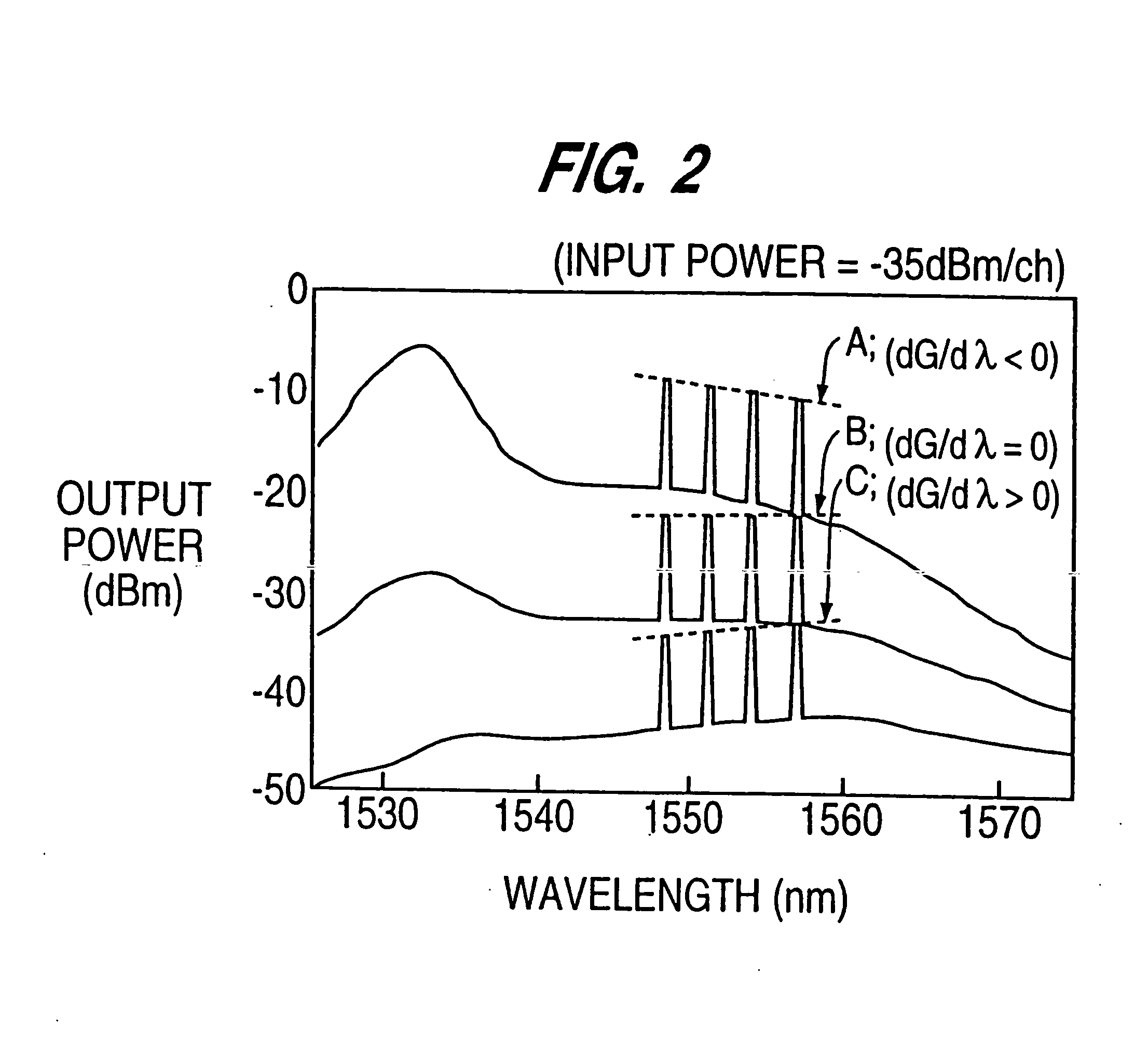
Compensation Of Gain Variations In A Multistage Optical Amplifier
ActiveUS20080037109A1Reduce variationLaser detailsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierEngineering
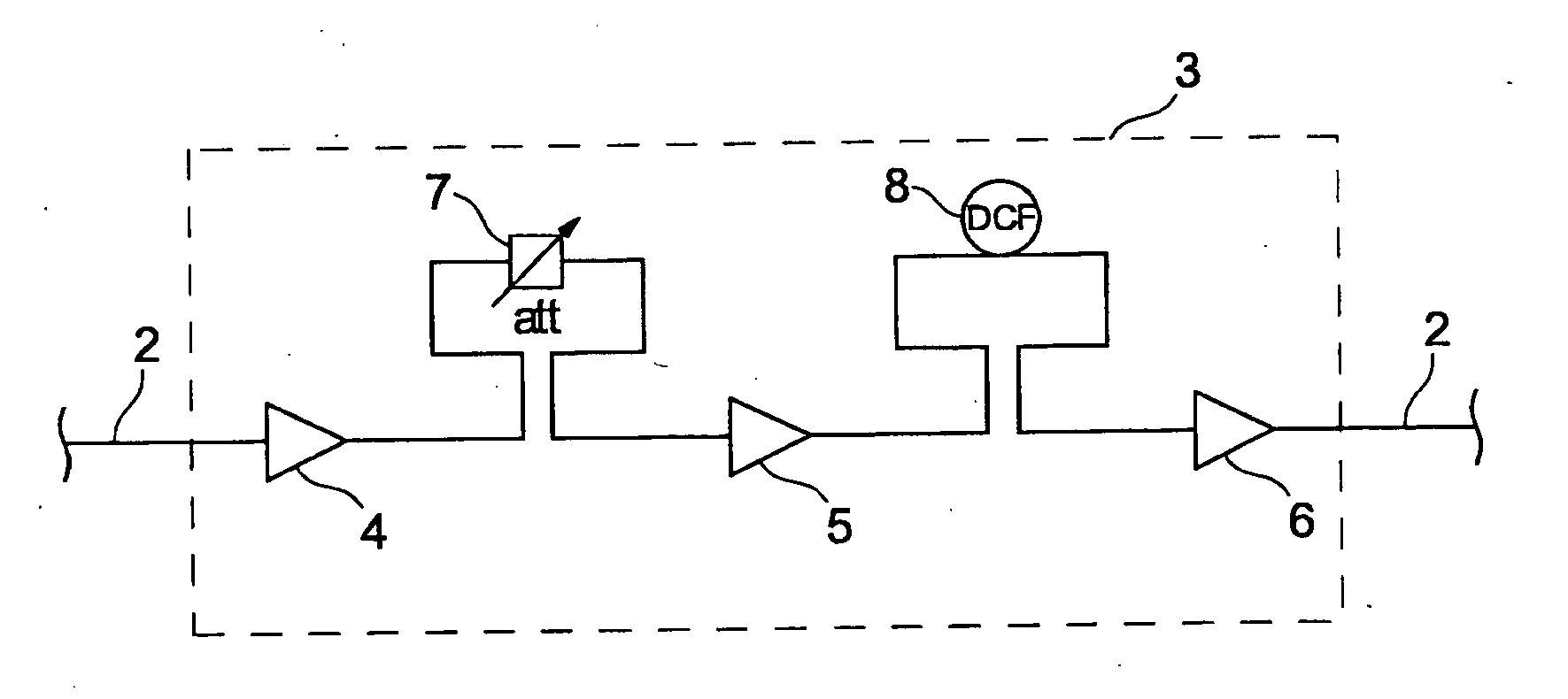
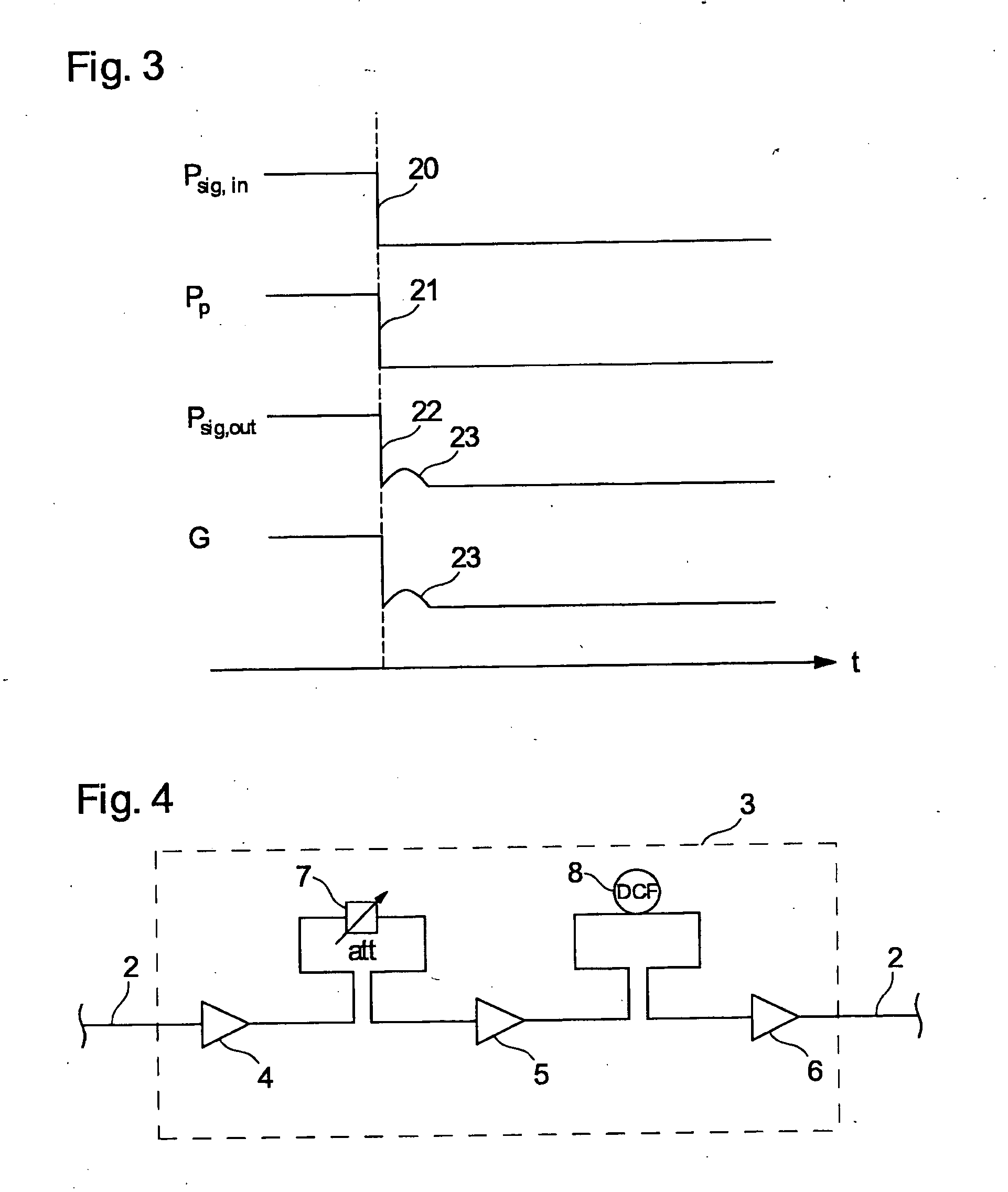
There is described a method for compensation of gain variations in a multistage optical amplifier, for the amplification of an optical wavelength multiplex signal, comprising several amplifier stages in series, each with at least one pumping device. Gain variation occurring after a switching process can easily be compensated for, when the power jump expected at the second amplifier stage is determined and, depending thereon, a new pump power is calculated for the corresponding pump device, the new pump power is set for the pump device before the power jump arrives at the input of the second stage.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
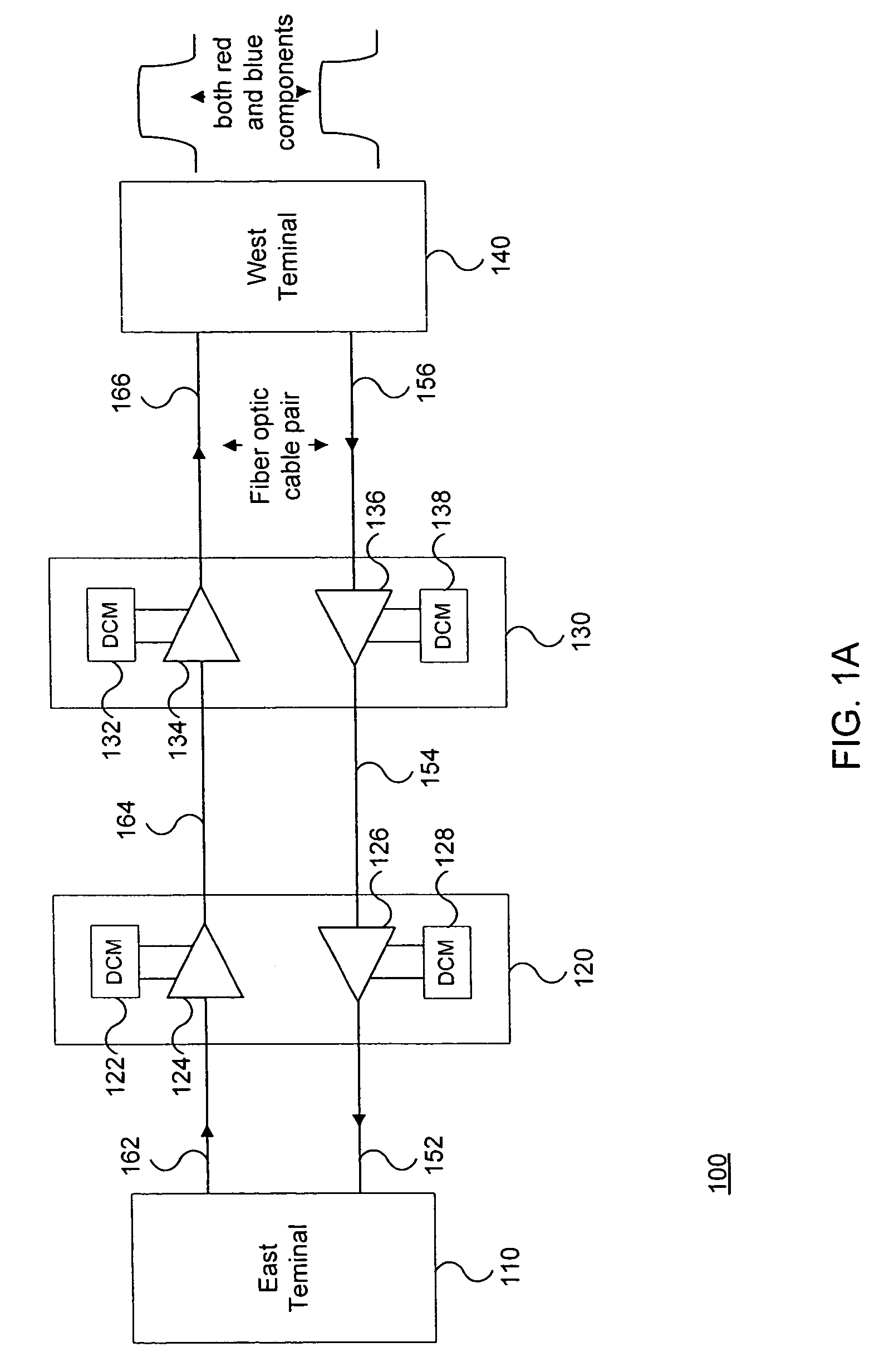
Bidirectional communication system
ActiveUS7512343B2Time-division multiplexOptical transmission with multiple stagesCommunications systemFiber chromatic dispersion
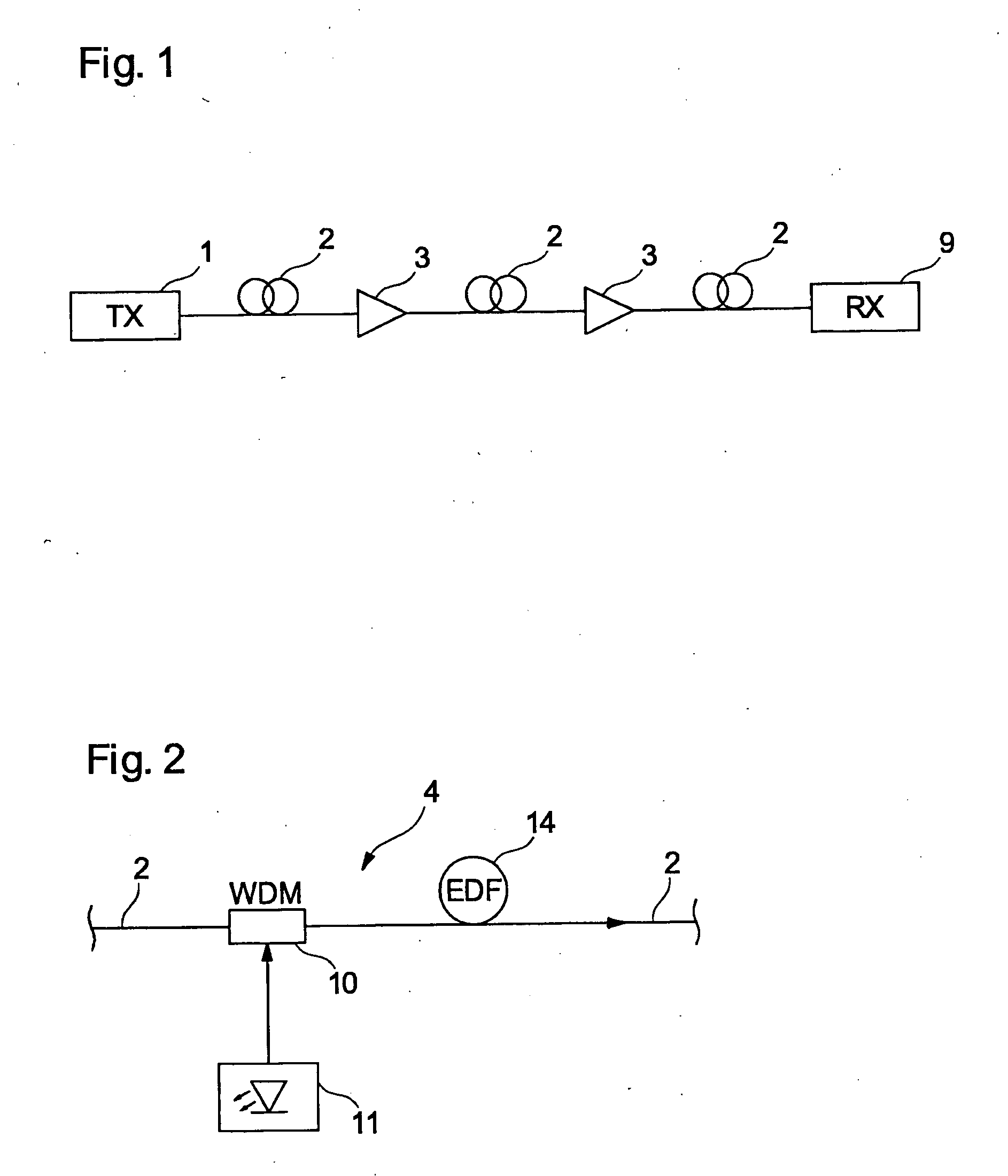
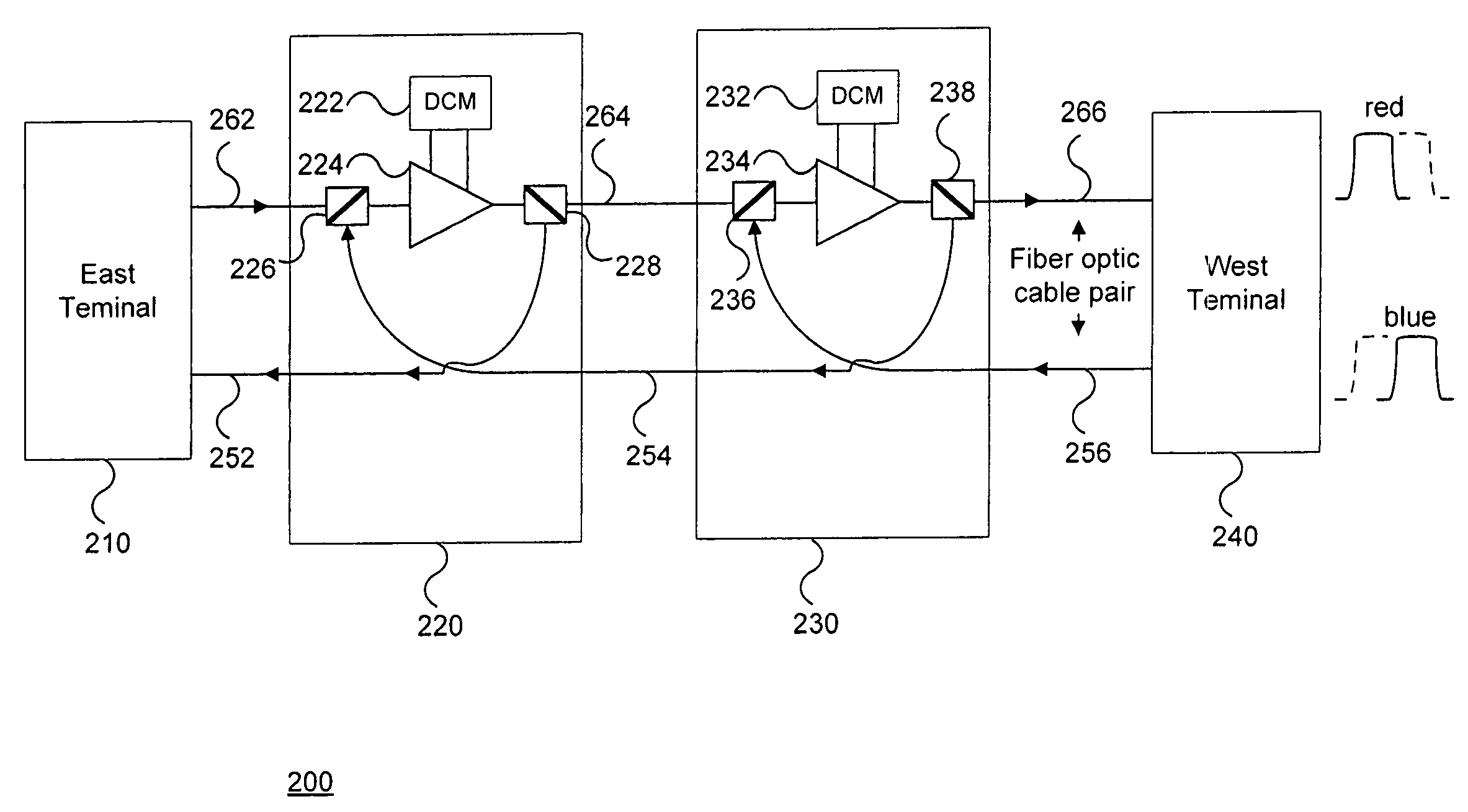
A bidirectional communication system is disclosed. A single optical line amplifier is used to amplify signals in both the east and west directions. Additionally, a single dispersion compensation module is used to compensate for fiber dispersion in both directions. Using a single optical line amplifier and a single dispersion compensation module for both directions allows for reduction in the number of optical line amplifiers used in a given network.
Owner:CIENA
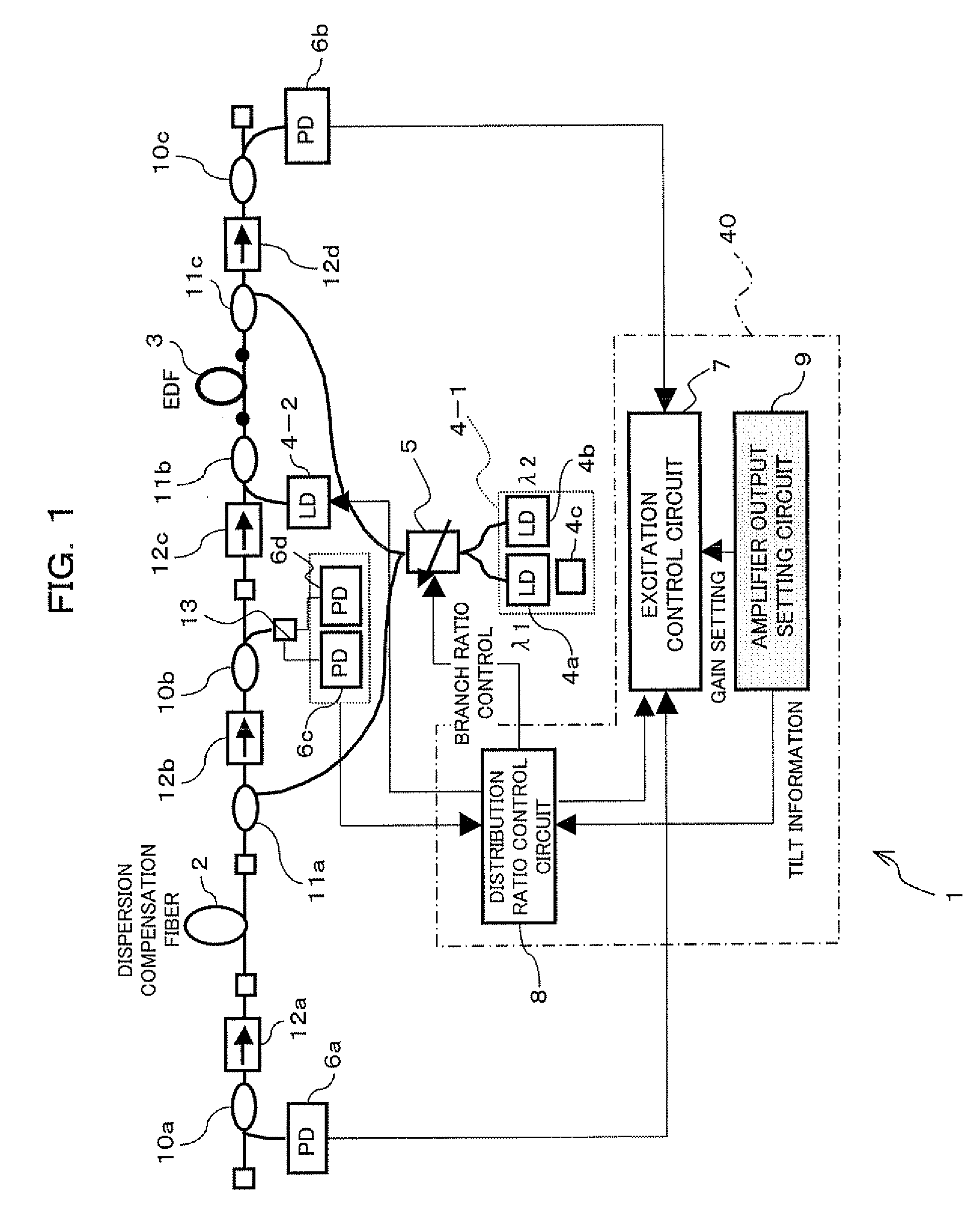
Optical amplifier, optical amplification repeater and pump light supply control method
InactiveUS20070268569A1Improve efficiencyImprove noise characteristicsLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberRare earth
There is provided an optical amplifier including a Raman amplification medium, a rare earth doped fiber located at a latter stage of the Raman amplification medium, a first pump light outputting unit for outputting pump light with a plurality of wavelengths, a variable distribution element for distributing the pump light with the plurality of wavelengths, outputted from the first pump light outputting unit, to the Raman amplification medium and the rare earth doped fiber in a variable distribution ratio for each wavelength, and a control unit for individually controlling the distribution ratio of the pump light with the plurality of wavelengths in the variable distribution element and the power of the pump light with the plurality of wavelengths from the first pump light outputting unit in accordance with a wavelength arrangement of each of signal lights wavelength-multiplexed into the wavelength-multiplexed signal light.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
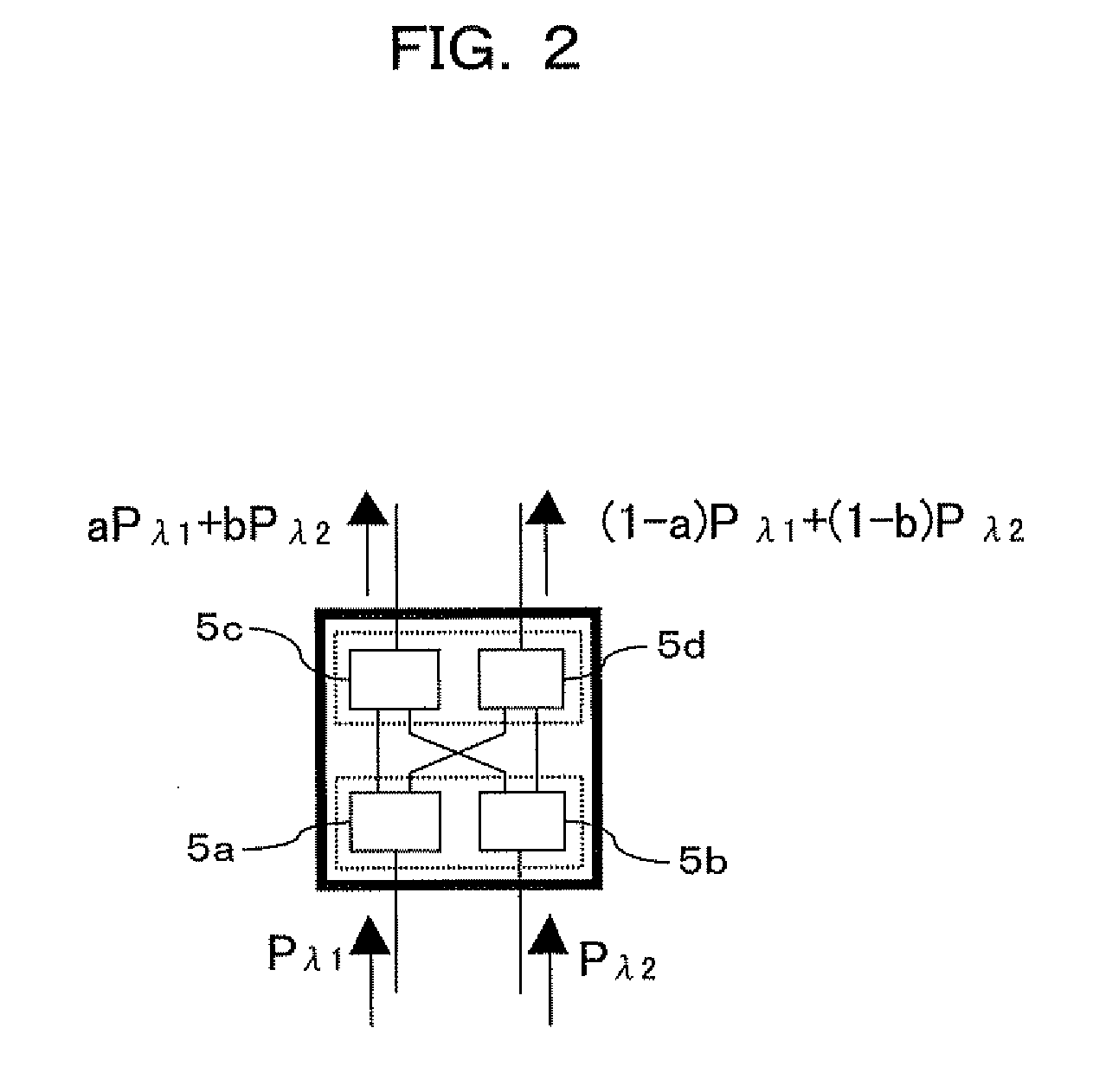
Independently variable first and second order polarization mode dispersion compensator
InactiveUS7003183B1Polarising elementsOptical transmission with multiple stagesPolarization mode dispersionIndustrial engineering
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fiber-optic compensation for dispersion, gain tilt, and band pump nonlinearity
InactiveUS6985283B1Simple system implementationCost-effectiveLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesErbium dopingInstability
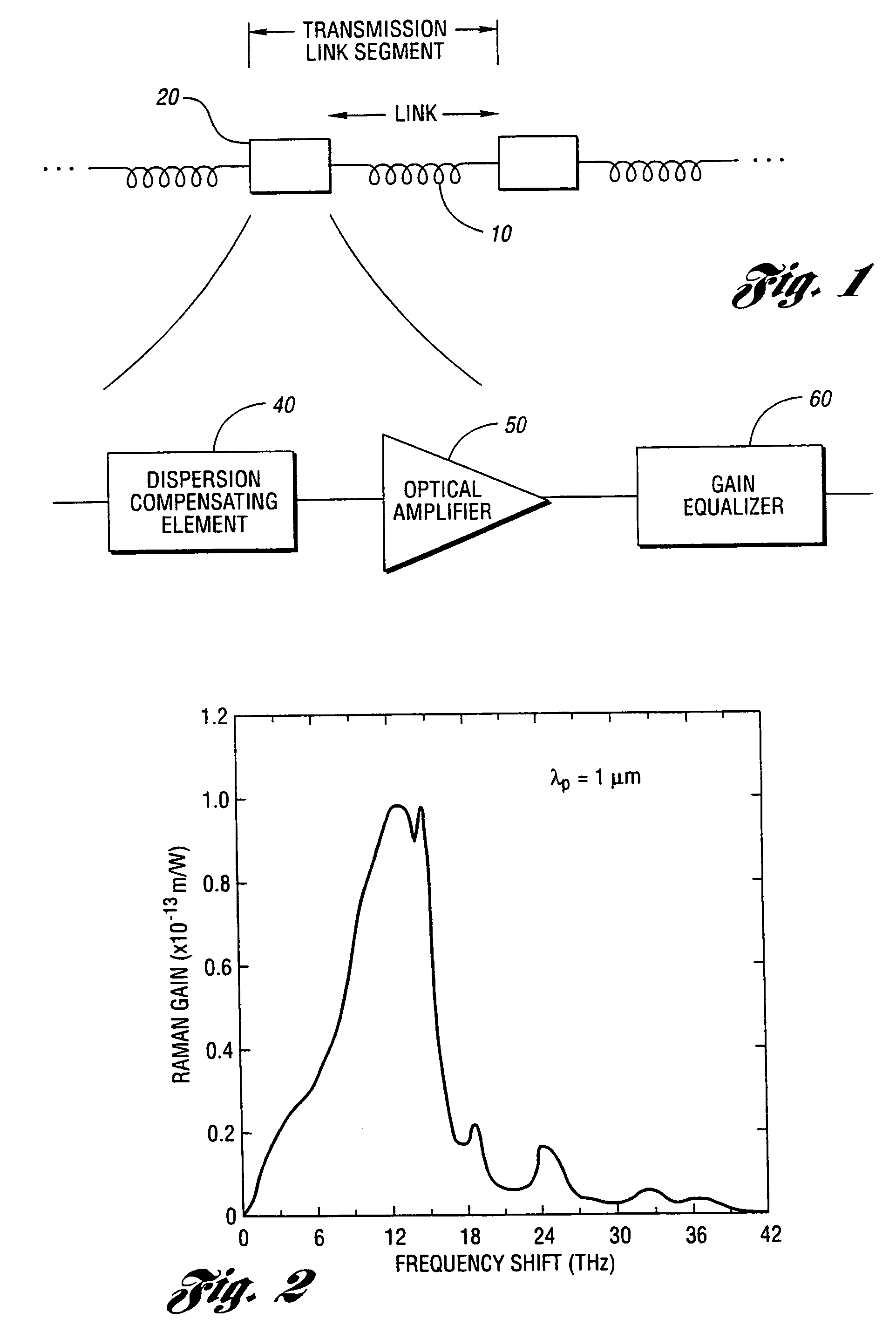
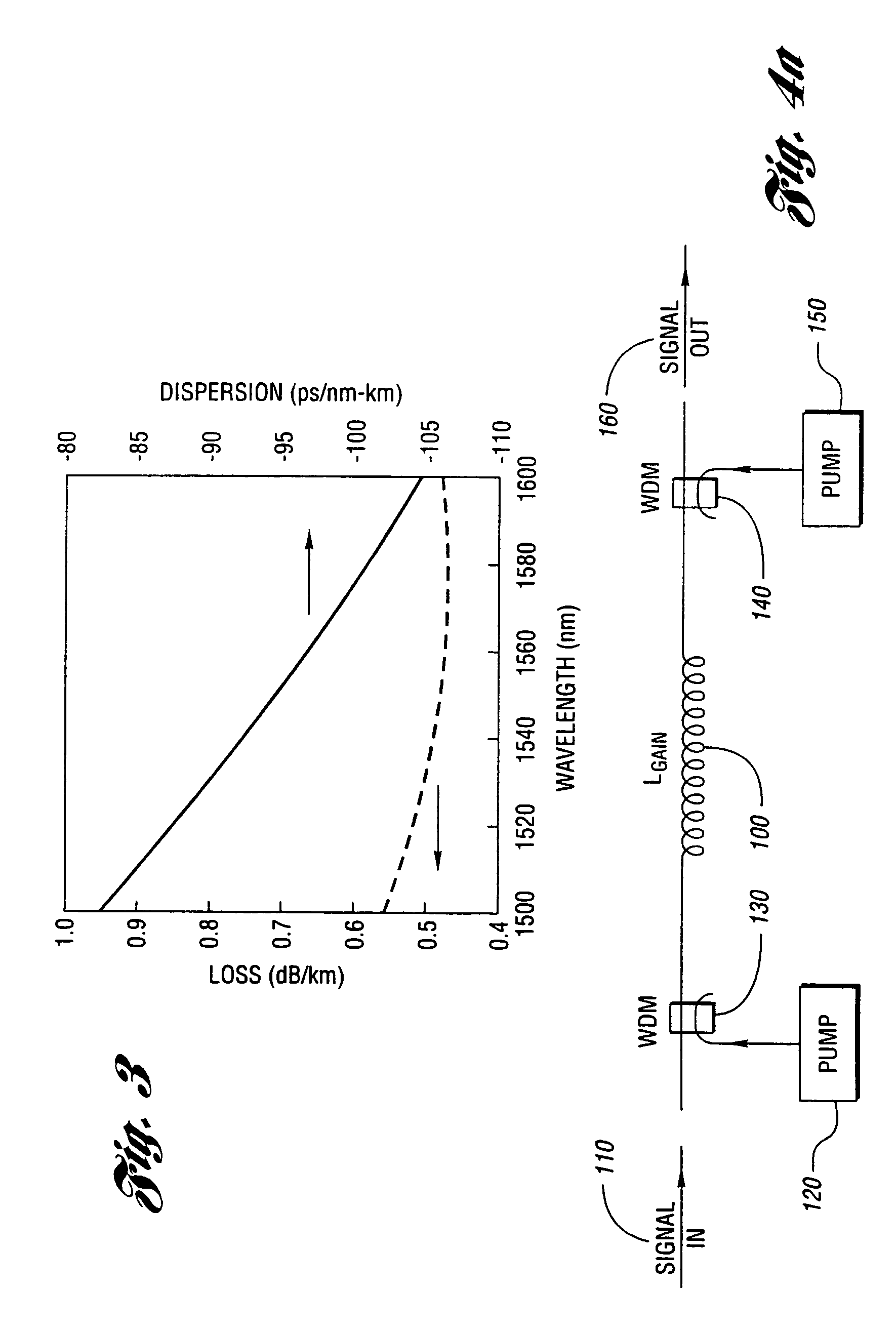
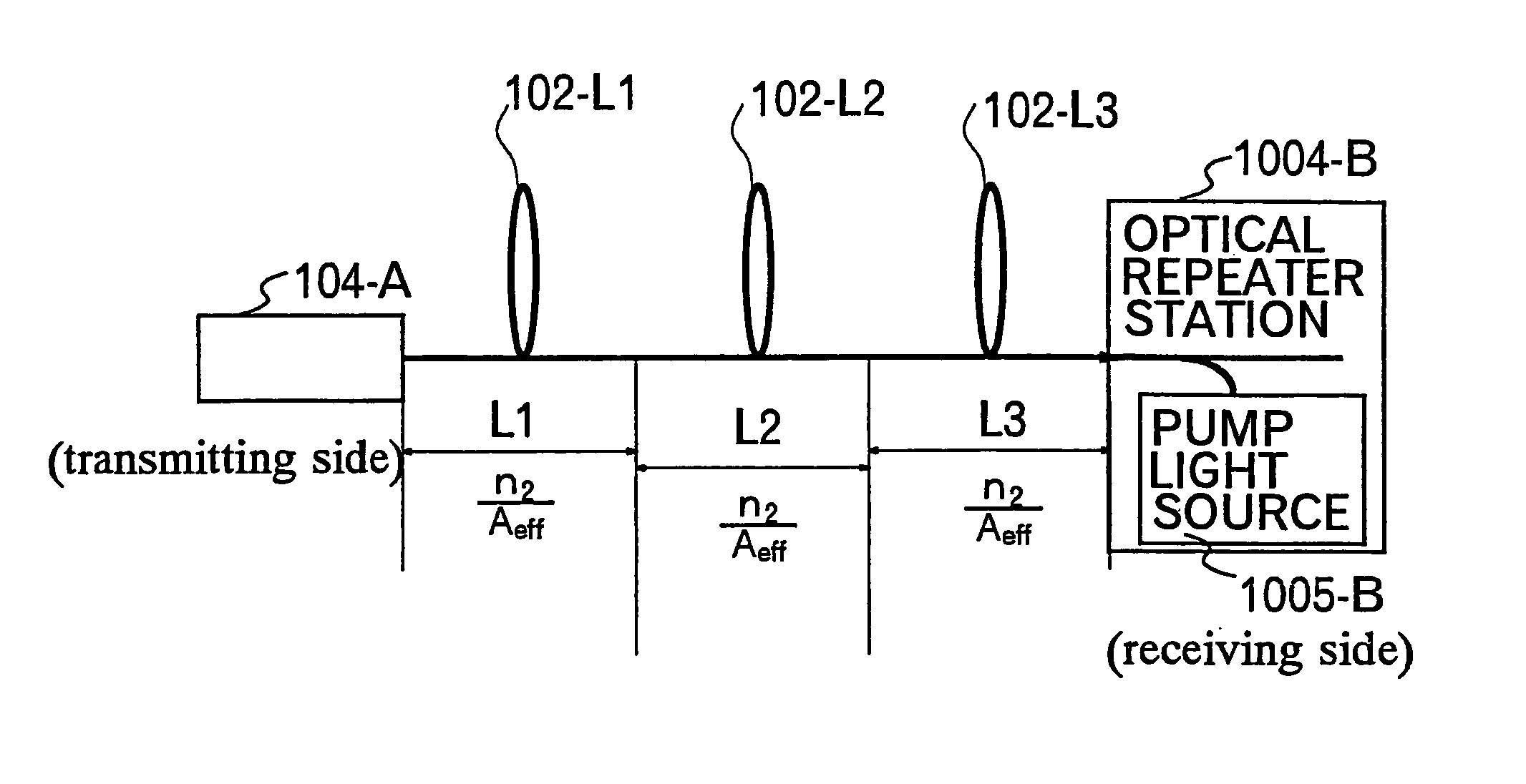
An apparatus and method are described for combining optical amplification and dispersion compensation in a Raman amplifier. A Dispersion-Managing Raman Amplifier (DMRA) combines Raman amplification with dispersion compensation by selecting the length and dispersion of the gain fiber to balance the dispersion of the link. This gain fiber is also single-mode at the signal and pump wavelengths. The pumping level is adjusted to balance the losses from the gain fiber and transmission link, while the pumping configuration is selected to remain within the 3 dB loss length for the pumping light. When the amplifier is split into two segments, the two segments may be joined by an isolator, a gain equalization element, and / or an optical add / drop multiplexer. For WDM transmission systems based on dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF), operation in the “violet band” between 1430–1530 nm is based on Raman amplification. By using a DMRA, a dispersion and nonlinearity managed system can be implemented. In particular, 4WM does not phase match in such a system, and modulation instability is absent in the transmission link. Furthermore, gain equalization can be added to the DMRA by cascading one or two Mach-Zehnder frequency filters. The invention also includes a method for symmetrically adding channels below and above the C-band, the gain tilt within the C-band can be minimized. Therefore, a roughly equal number of channels should be placed in the short-wavelength S-band and the long-wavelength L-band to minimize the Raman energy exchange in the C-band. Also, whereas C- and L-bands can be amplified using erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, the S-band can use either discrete or distributed Raman amplifiers. To minimize the interaction between pumps for different bands, alternate band pumps can be spatially dispersed and / or cross-polarized. The distributed Raman amplification can be achieved by pumping the transmission line with discrete laser diodes or by a Raman oscillator.
Owner:NEPTUNE SUBSEA IP LTD +1
Optical fiber cable
InactiveUS7099541B2Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesOptical fiber cableNonlinear phase shift
An optical fiber cable including a plurality of optical fibers, each optical fiber having a characteristic value in a middle field which is larger than characteristic values in fields other than the middle field of the optical fiber. The characteristic value in a respective field is a nonlinear refractive index of the optical fiber in the field divided by an effective cross section of the optical fiber in the field. The middle field and the characteristic value in the middle field are set as a combination to suppress a nonlinear phase shift generated in light transmitted through the plurality of optical fibers.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20060222367A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesMultiplexerOptical add-drop multiplexer
An optical transmission apparatus includes an optical add drop multiplexer (OADM) that adds / drops an optical signal to / from a transmission path. The optical transmission apparatus further includes a pump light multiplexer and a dispersion compensation fiber that are located downstream of the OADM on the transmission path. The optical transmission apparatus is configured to house a pump light source connectable to the pump light multiplexer to Raman amplify an optical signal in the dispersion compensation fiber.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
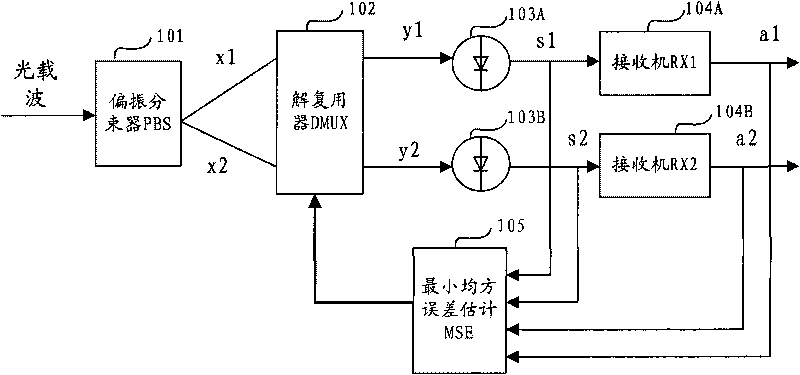
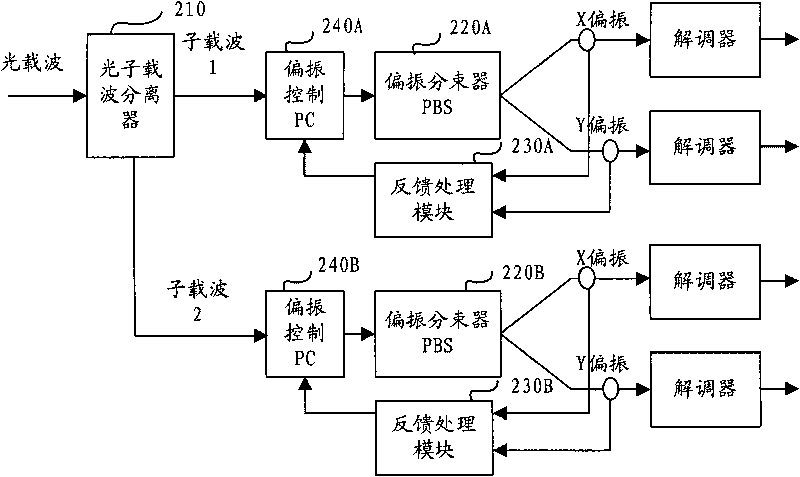
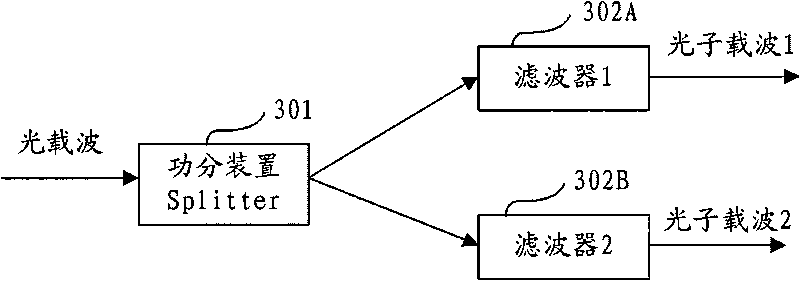
Method, device and system for photolyzing, polarizing and multiplexing optical carrier
InactiveCN101729149ALower requirementReduce complexityPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical transmission with multiple stagesMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for photolyzing, polarizing and multiplexing an optical carrier, which relate to the technical field of optical communication, and can improve the frequency spectrum utilization ratio of the system, improve the tolerance limits of chromatic dispersion CD and polarization mode dispersion PMD, and simultaneously reduce the device requirement and the complexity of a receiving end. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises the following steps of: separating the optical carrier into more than two paths of photon carriers at the receiving end; respectively photolyzing, polarizing and multiplexing each path of photon carrier into two paths of optical signals to be demodulated; and using the optical signals to be demodulated as feedback input signals, and respectively correspondingly regulating the incident angle of each path of photon carrier. Through the device photolyzing more than two paths of photon carriers and combining photolysis, polarization and multiplexing, the embodiment of the invention enables an optical carrier signal to be decomposed into more than four paths in an optical modulation format to be processed, and a DQPSK demodulator can be directly used on an optical wave for carrying out time delay interference detection to obtain an output signal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Fiber amplifier and control method thereof
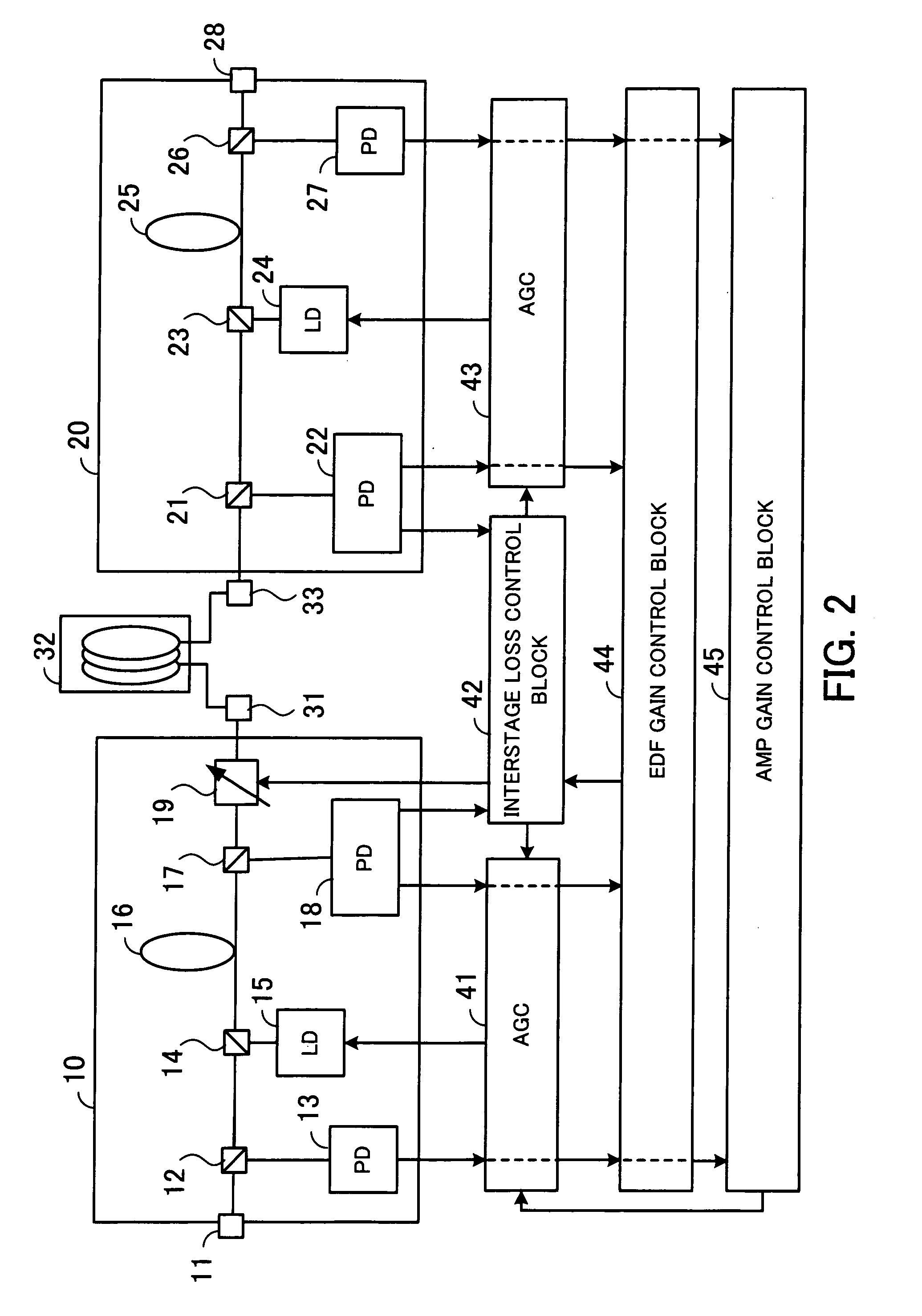
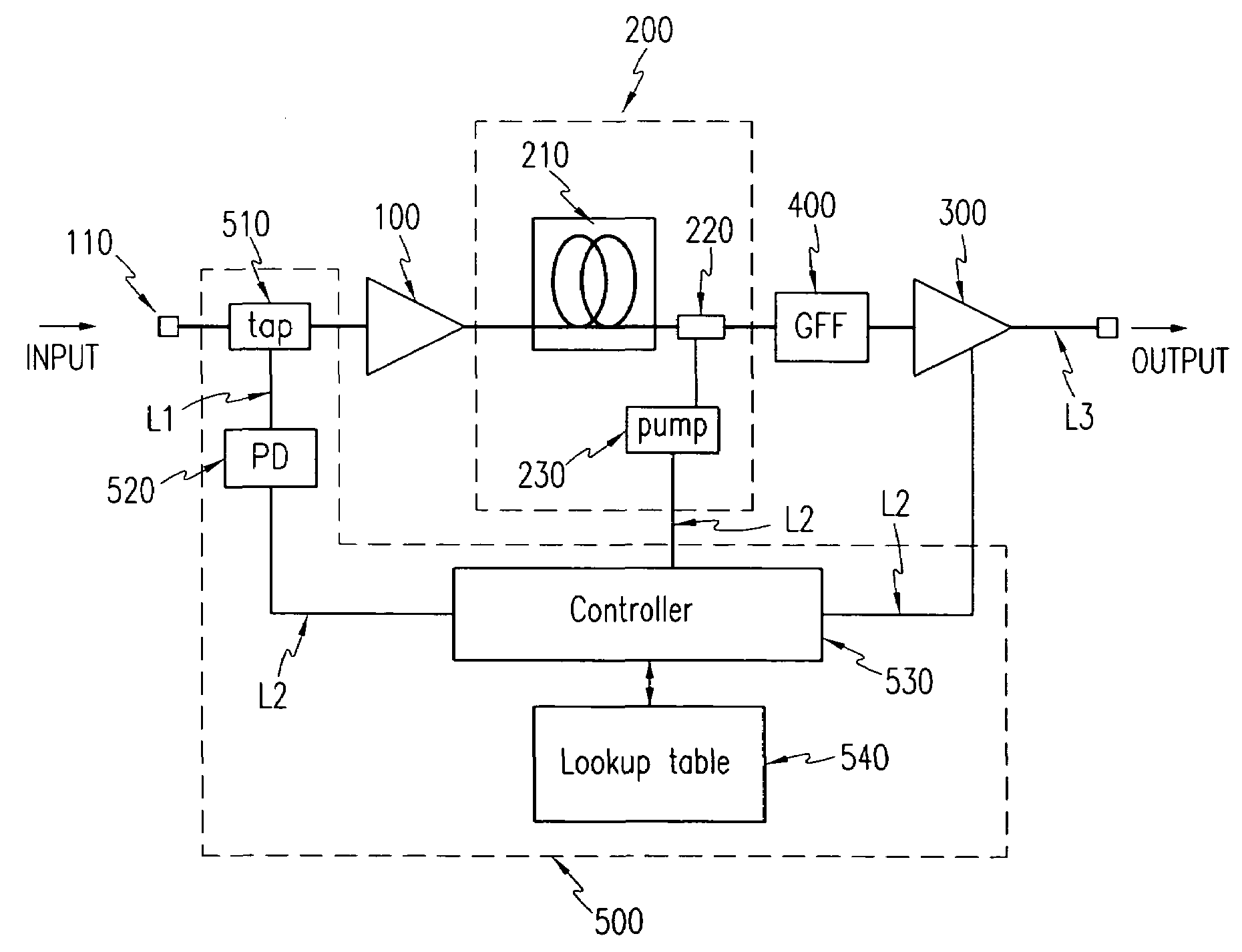
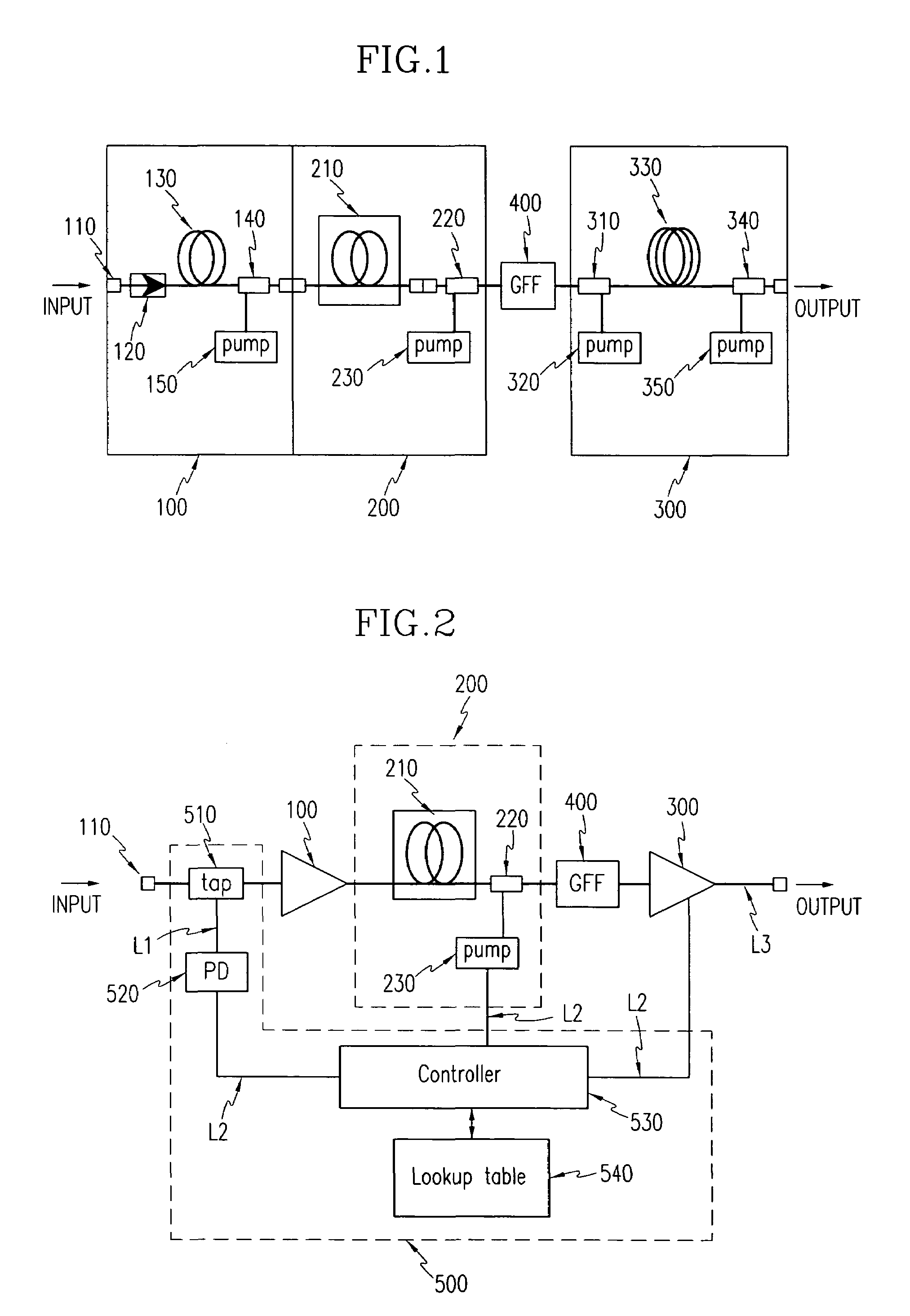
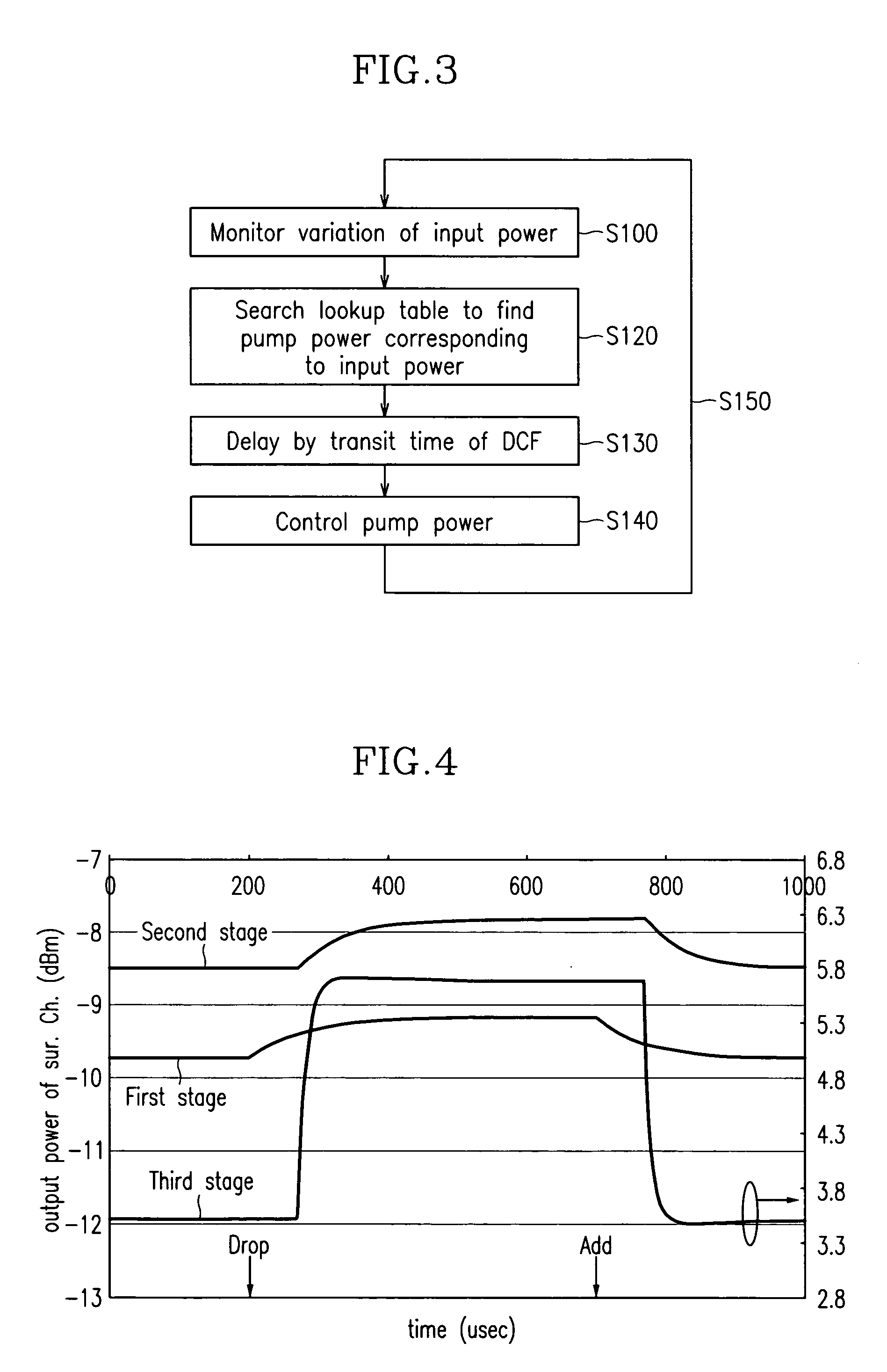
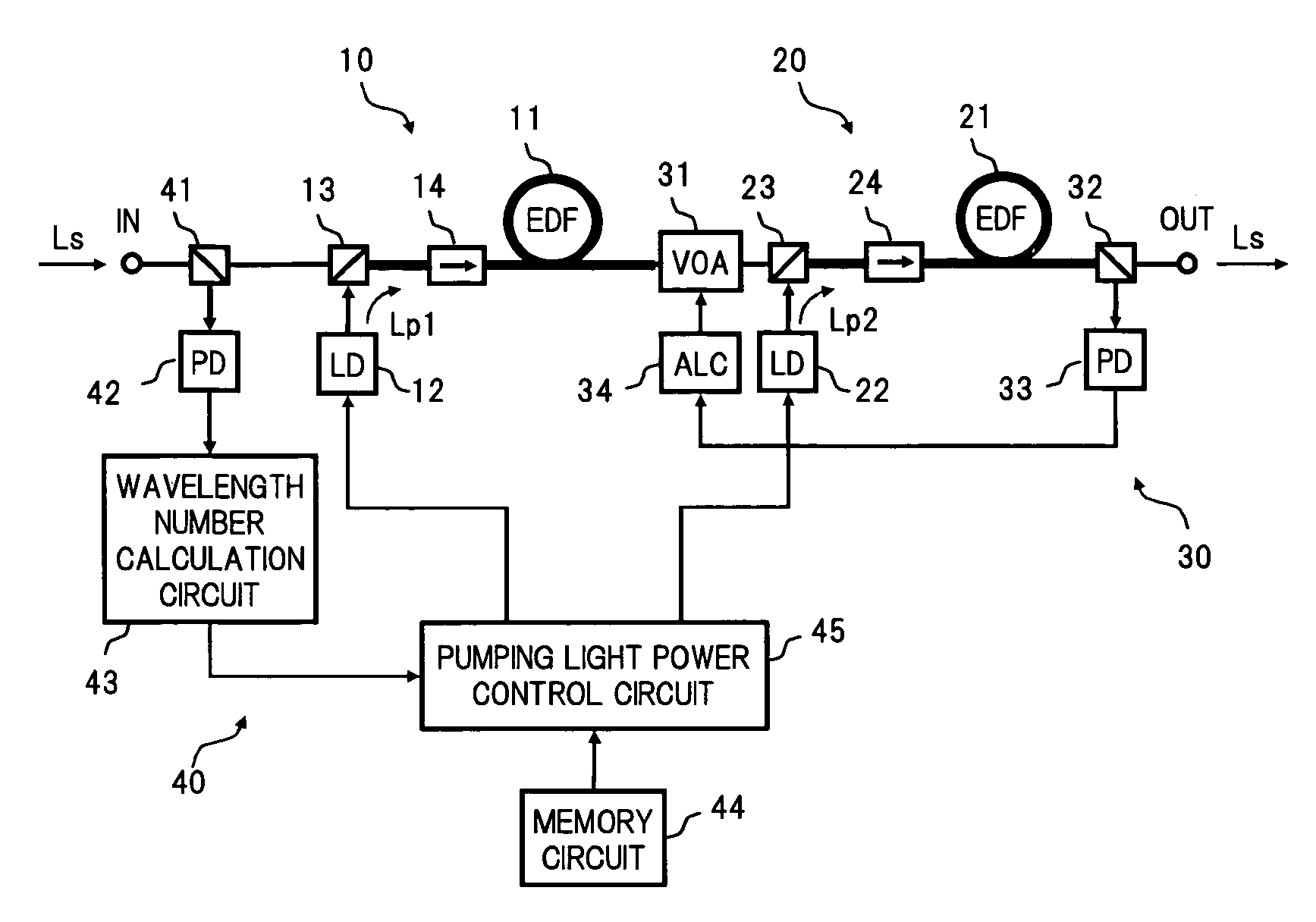
InactiveUS7038841B2Constant outputReduce transient effectsLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierThree stage
A method for realizing, in a fiber amplifier with three stages of amplifiers, automatic gain control in which a constant gain is obtained when channels are varied, and automatic level control in which a constant output per channel is obtained when a light power is varied because of variations in span loss. A light power or another light power of a specific wavelength is monitored to determine when variations in these light powers take place, current values of pump laser diodes appropriate for an input is read from a lookup table, and pump laser diodes are driven. During this operation, a pump power of the first stage amplifier is constantly maintained, and those of the second or third stage amplifier are controlled.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Broadband optical fiber
InactiveUS20030118304A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBroadbandWide band
Provided is an optical fiber that is in particular suitable for Raman amplification. An effective area at a wavelength of 1570 nm is in a range of 35 mum2 to 45 mum2, an absolute value of a dispersion slope at the wavelength is equal to or less than 0.04 ps / nm2 / km, and a dispersion value at the wavelength is in a range of 5 ps / nm / km to 10 ps / nm / km. It is desirable that a refractive index profile contains at least one annular region between a center core and a cladding region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical amplifier
ActiveUS20070109630A1Increase powerEliminate needLaser detailsOptical transmission with multiple stagesUltrasound attenuationSignal light
Optical amplifier which can eliminate the need for an optical detection section before an external attenuating medium, can prevent SN degradation, and can reduce power required for pumping light. An attenuation amount detection section detects an amount of signal light attenuation caused by a variable optical attenuator and the external attenuating medium connected in series, by means of a front optical detection section provided before the variable optical attenuator and the external attenuating medium and a back optical detection section provided thereafter. An attenuation amount control section controls the variable optical attenuator such that the amount of signal light attenuation detected by the attenuation amount detection section is kept constant. A connection detection section detects a connection or disconnection of the external attenuating medium in accordance with the amount of signal light attenuation obtained when the amount of attenuation caused by the variable optical attenuator is minimized.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
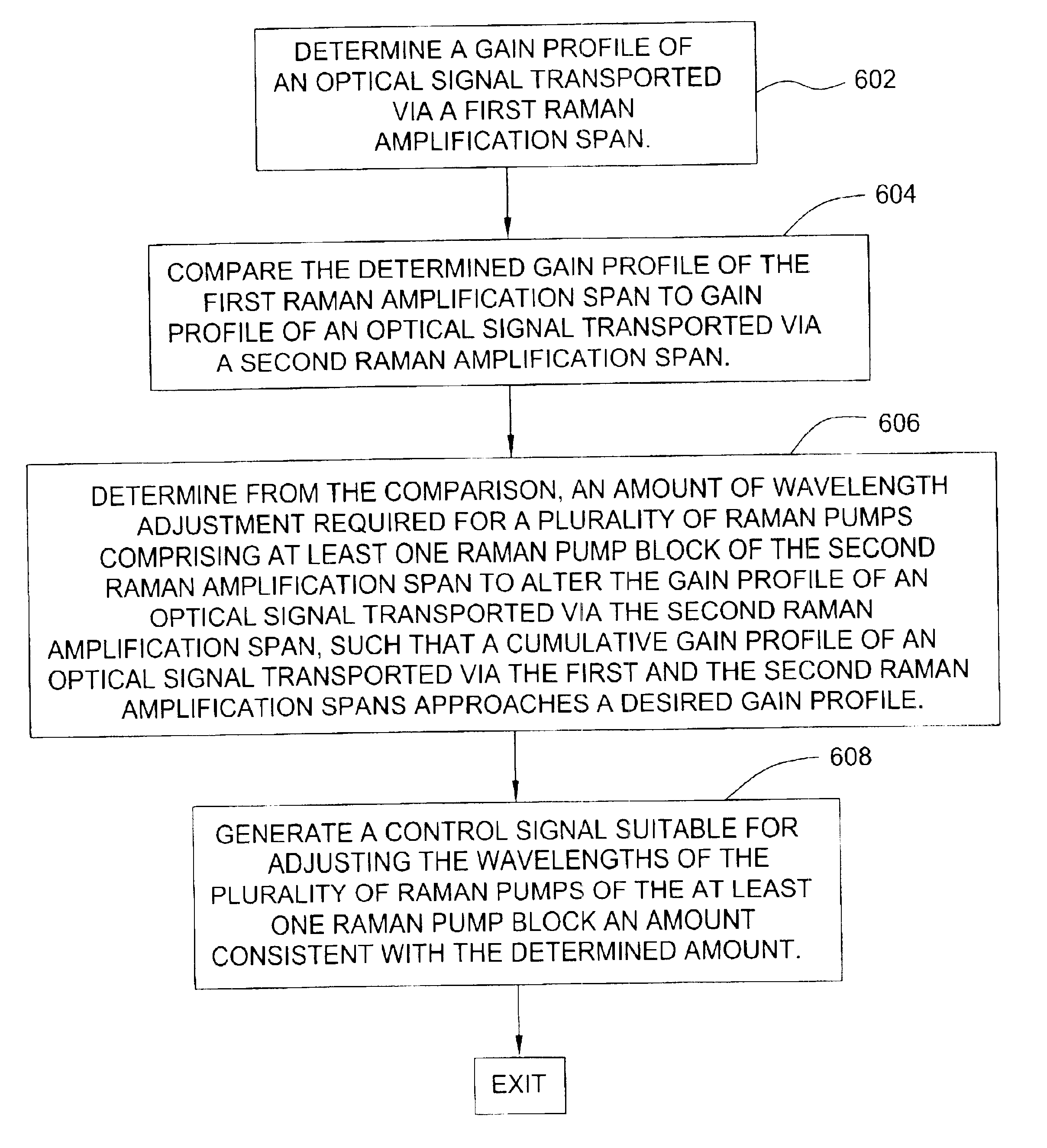
Method, apparatus and system for reducing gain ripple in a raman-amplified WDM system
InactiveUS6859306B2Reducing gain rippleLaser detailsOptical transmission with multiple stagesControl signalLength wave
A method, apparatus and system for reducing gain ripple in a Raman-amplified WDM system includes determining a gain profile of an optical signal transported via a first Raman amplification span in a Raman-amplified WDM system, comparing the determined gain profile to a gain profile of an optical signal transported via a second Raman amplification span, determining, from the comparison, an amount of wavelength adjustment required for a plurality of Raman pumps comprising at least one Raman pump block of the second Raman amplification span to alter the gain profile of an optical signal transported via the second Raman amplification span, such that a cumulative gain profile of an optical signal transported via the first and the second Raman amplification spans approaches a desired gain profile, and generating a control signal suitable for adjusting the wavelengths of the plurality of Raman pumps of the at least one Raman pump block an amount consistent with the determined amount.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Cascaded raman pump for raman amplification in optical systems
InactiveUS20050259315A1Enhanced signalLaser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesNonlinear parametersPump wave
A pumping module having a cascaded Raman laser for Raman amplified optical transmission systems. Non-linear parametric phenomena, such as Raman-assisted three-wave mixing, in Raman amplified signals from a cascaded Raman pump are strongly reduced by substantially suppressing from the output spectrum of the Raman pump the emission peaks at wavelengths shorter than that of the desired pumping wave on a specific wavelength λn, and within a given spacing from λn. The pumping non-zero dispersion fibres have zero dispersion between the wavelength range of the transmission signal and the wavelength range of the pump signal.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Optical amplifier control
InactiveUS6643055B1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierControl circuit
A system and method for controlling the output power of an optical amplifier in a node in a network, wherein the output power of the amplifier is controlled via a pump laser in a control circuit. The node reads a supervisory channel comprising information on how to control the amplifier. The node then uses the information for the control of the amplifier.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Optical signal varying devices, systems and methods
InactiveUS6839522B2Flexible operationIncrease lossLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
Raman assisted EDFA system and method
InactiveUS20050180757A1Improve noiseReduce the required powerOptical transmission with multiple stagesElectromagnetic transmissionAudio power amplifierCommunications system
A system, amplifier and method are provided for amplifying an optical signal in an optical communications system where spans between amplifiers may vary. The system includes a Raman amplifier variable gain portion and an EDFA gain portion. The amount of Raman amplifier gain is chosen to trade off accumulation of noise with accumulation of multi-path interference. This variable Raman gain is used to equalize the loss of each span so that the amount of optical power supplied at the input of the EDFA gain portion is substantially constant throughout the system.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS SUBSEA COMM LLC
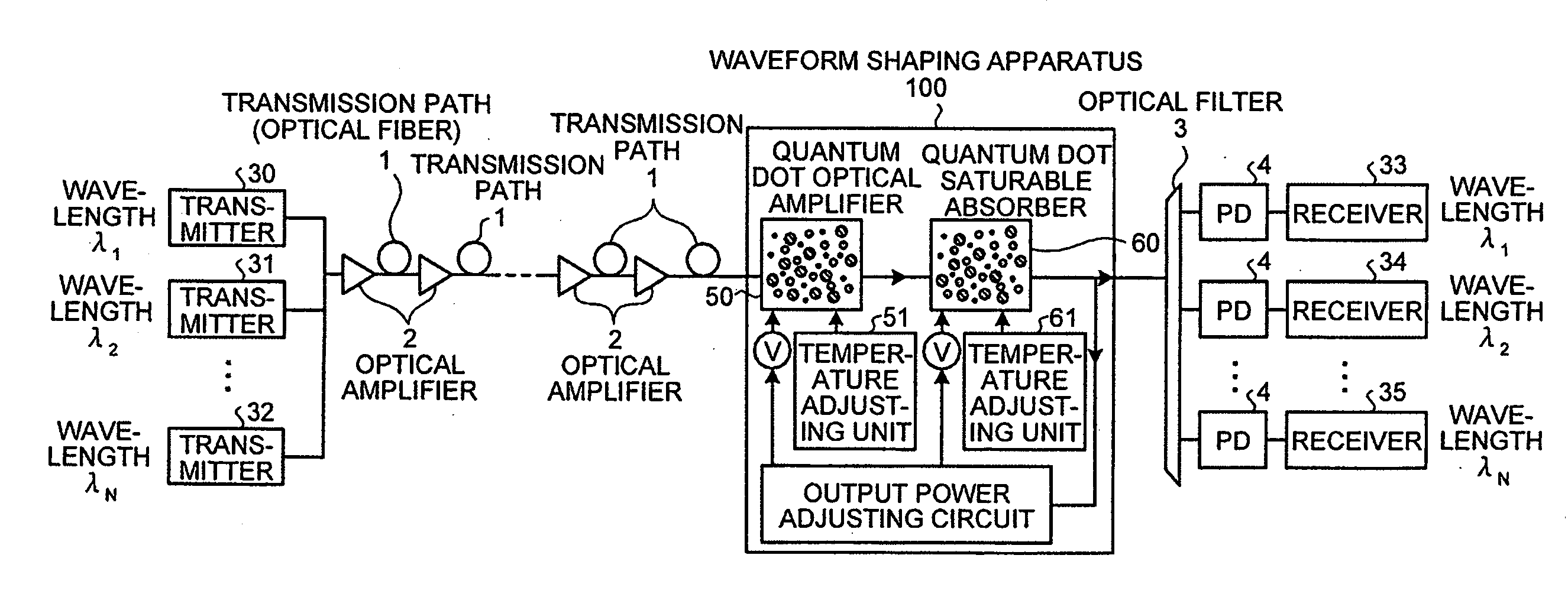
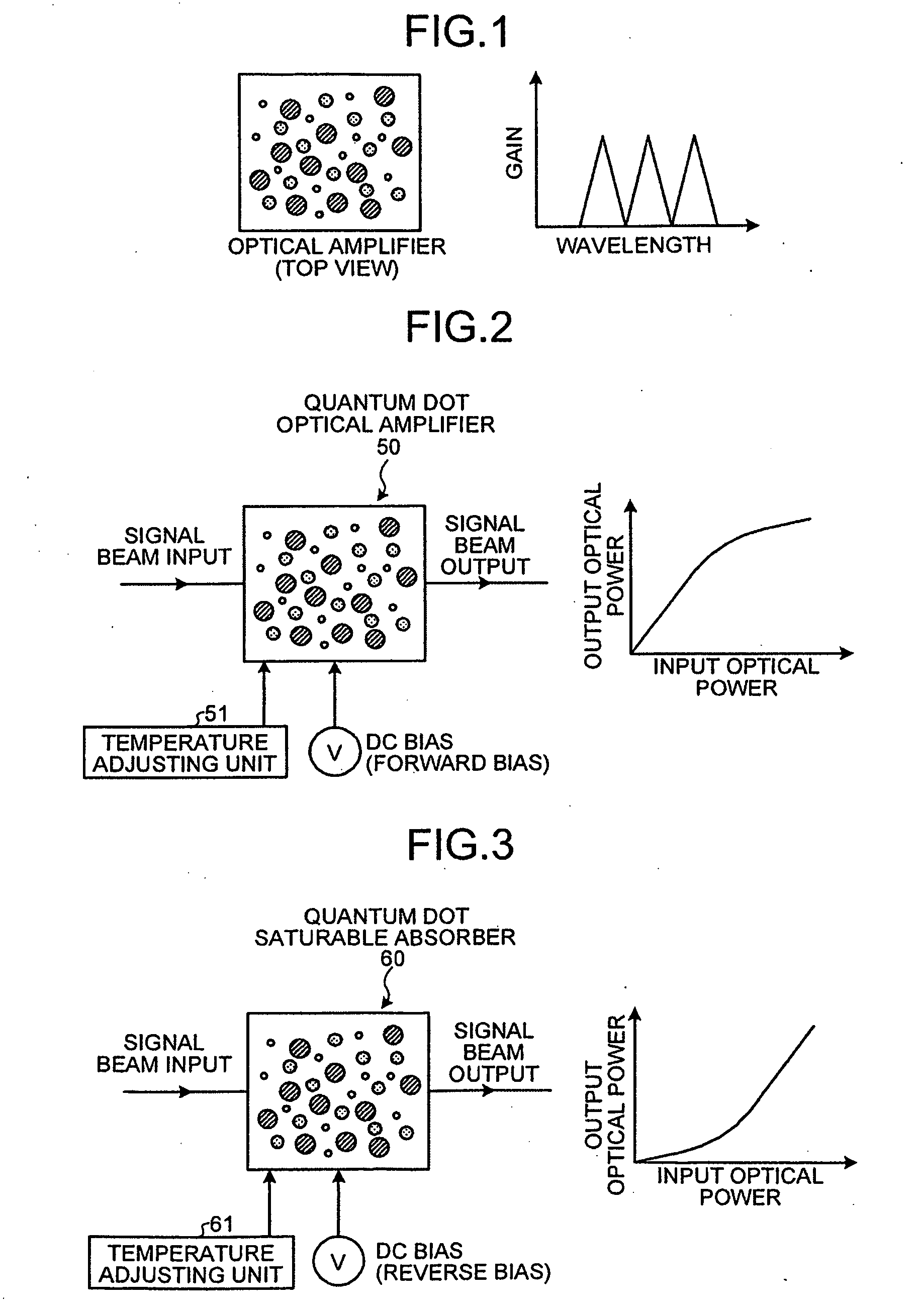
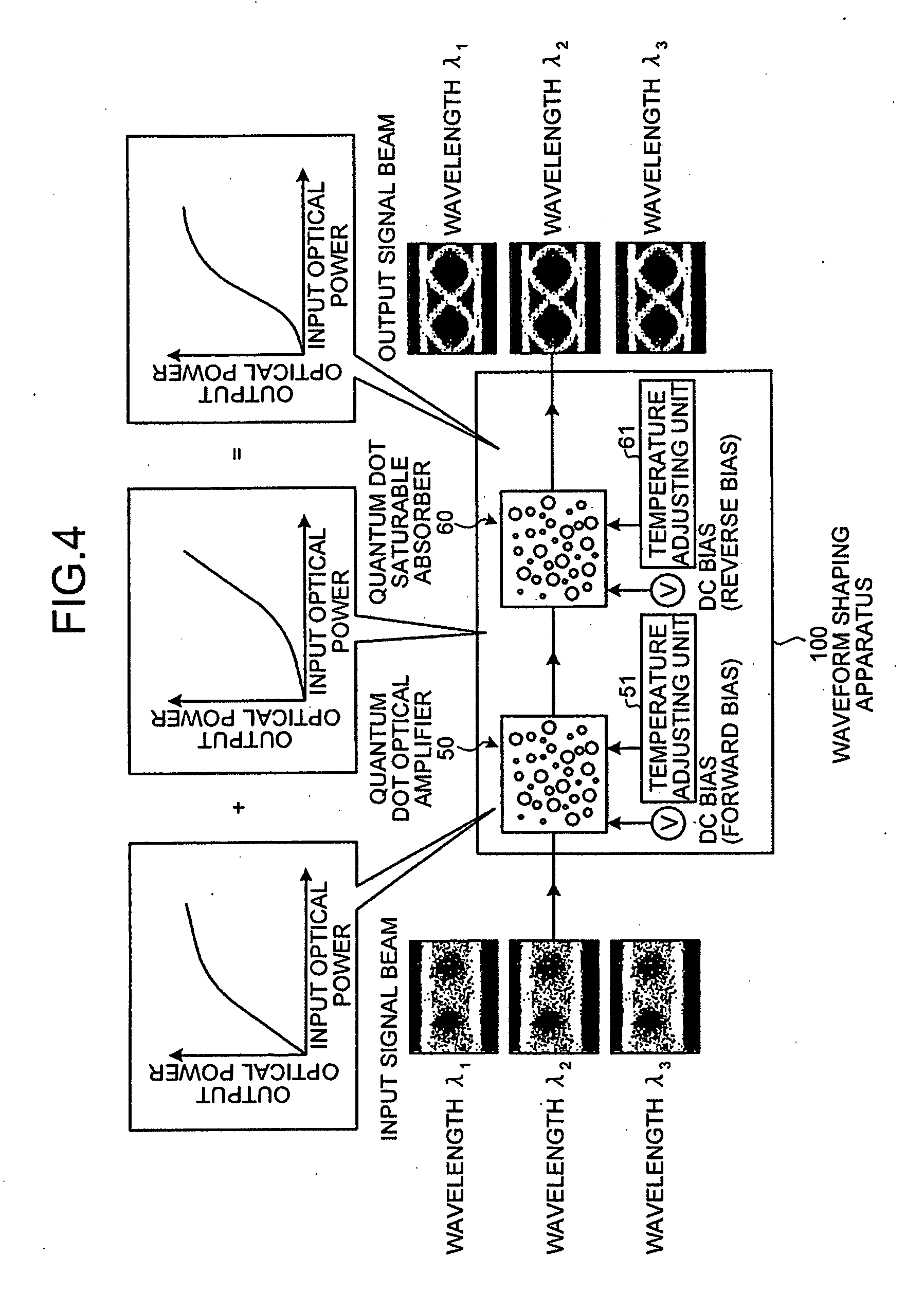
Waveform shaping apparatus, optical transmission system, and waveform shaping method
ActiveUS20080232817A1Solve problemsLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAbsorption factorWaveform shaping
A waveform shaping apparatus includes a quantum dot optical amplifier in which an amplification factor of input signal beams saturates if the optical power of the signal beams is equal to or greater than a predetermined value; and a quantum dot saturable absorber in which an absorption factor of the input signal beams saturates if the optical power of the signal beams is under a predetermined value. The quantum dot optical amplifier and the quantum dot saturable absorber are connected in series with a transmission path of the signal beams, and shape the waveform of the signal beams. Voltages applied to the quantum dot optical amplifier and the quantum dot saturable absorber, respectively, are adjusted based on the optical power of the signal beams.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical amplifier
InactiveUS7085043B2Improve efficiencyGain in each of the optical amplifications sections can be made constantOptical transmission with multiple stagesFibre transmissionOptical isolatorSignal light
An optical amplifier of the invention comprises first and second optical amplification sections connected in a cascade manner between an input terminal and an output terminal. Optical isolators which block C-band ASE travelling in an opposite direction to L-band signal light, are inserted on the amplification medium of each of the optical amplification sections. A constant gain control section calculates the number of wavelengths based on the input power of signal light, and controls the pumping light power of each optical amplification section at a constant slope with respect to the number of wavelengths, so that the respective gains in the optical amplification sections corresponding to the number of wavelengths each become constant. As a result, it is possible to maintain flat gain wavelength characteristics even when receiving input of WDM light where the number of wavelengths varies rapidly over a wide range.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com