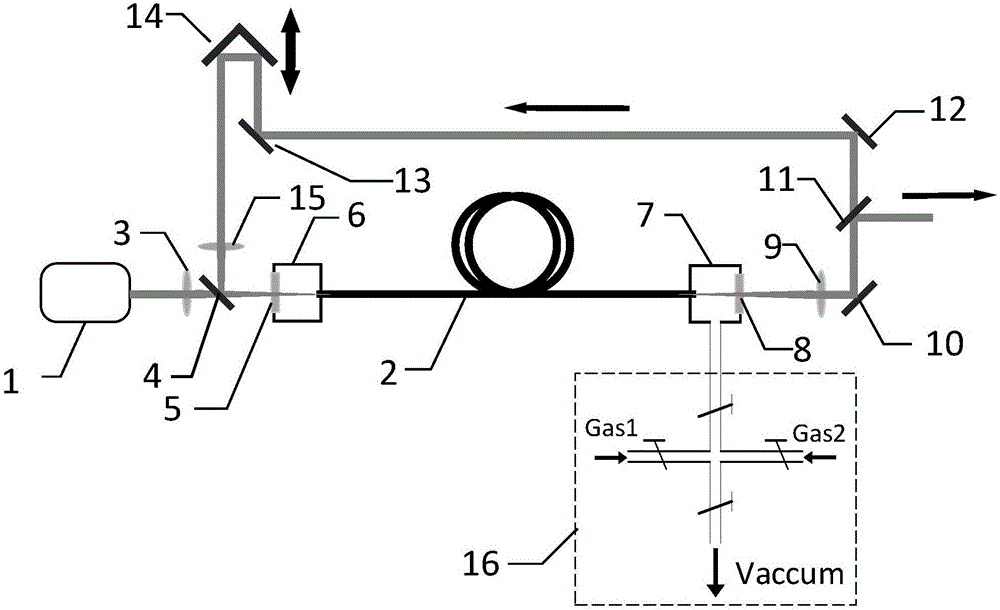
Patents
Literature
219 results about "Raman gain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
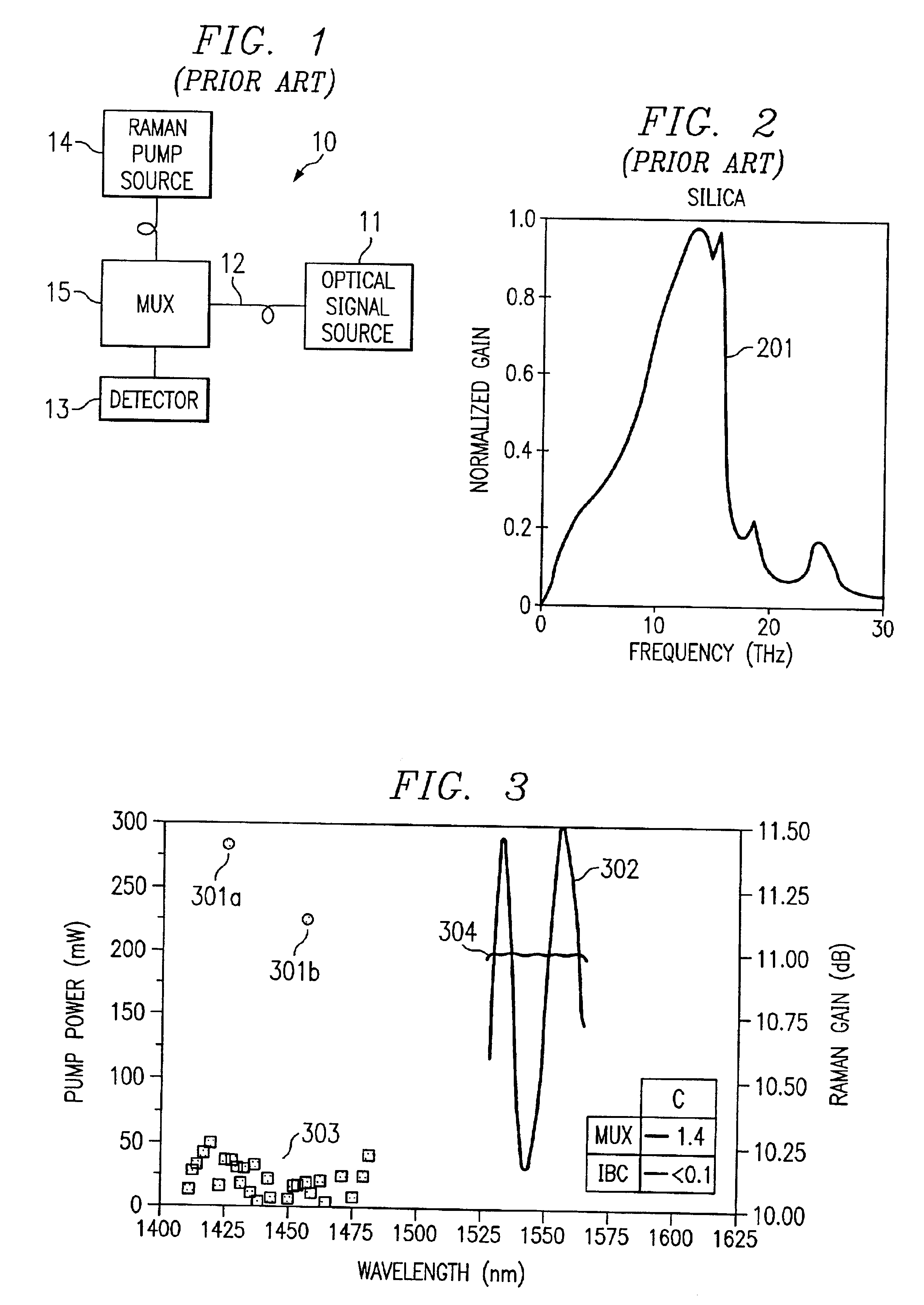
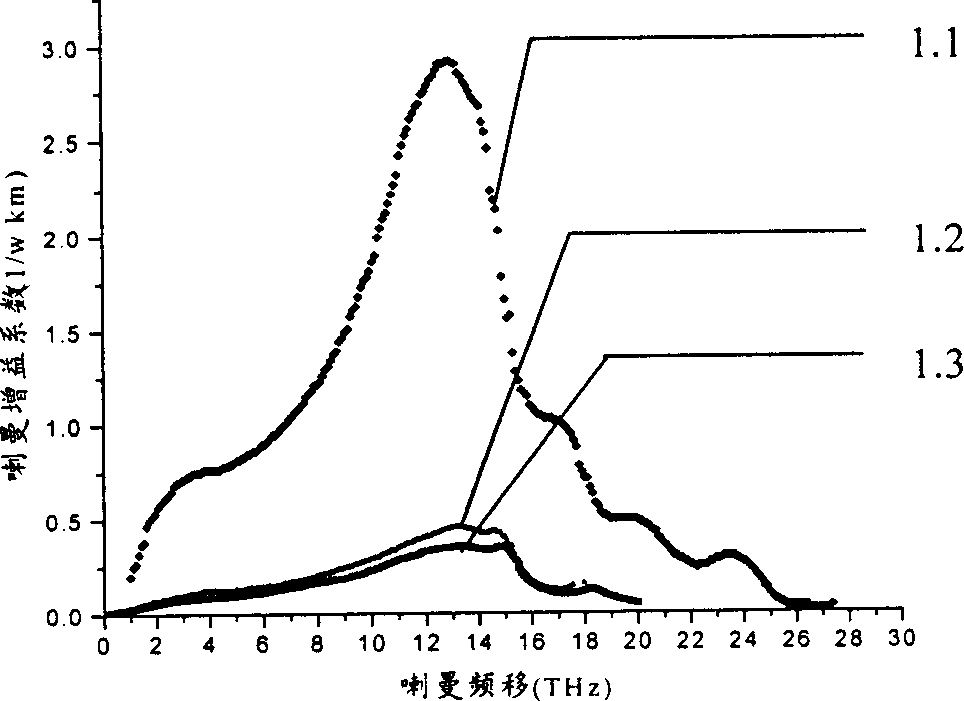
Raman gain is optical gain (amplification) arising from stimulated Raman scattering. It can occur in transparent solid media (e.g. optical fibers), liquids and gases under the influence of intense pump light, and is used in Raman amplifiers and Raman lasers.
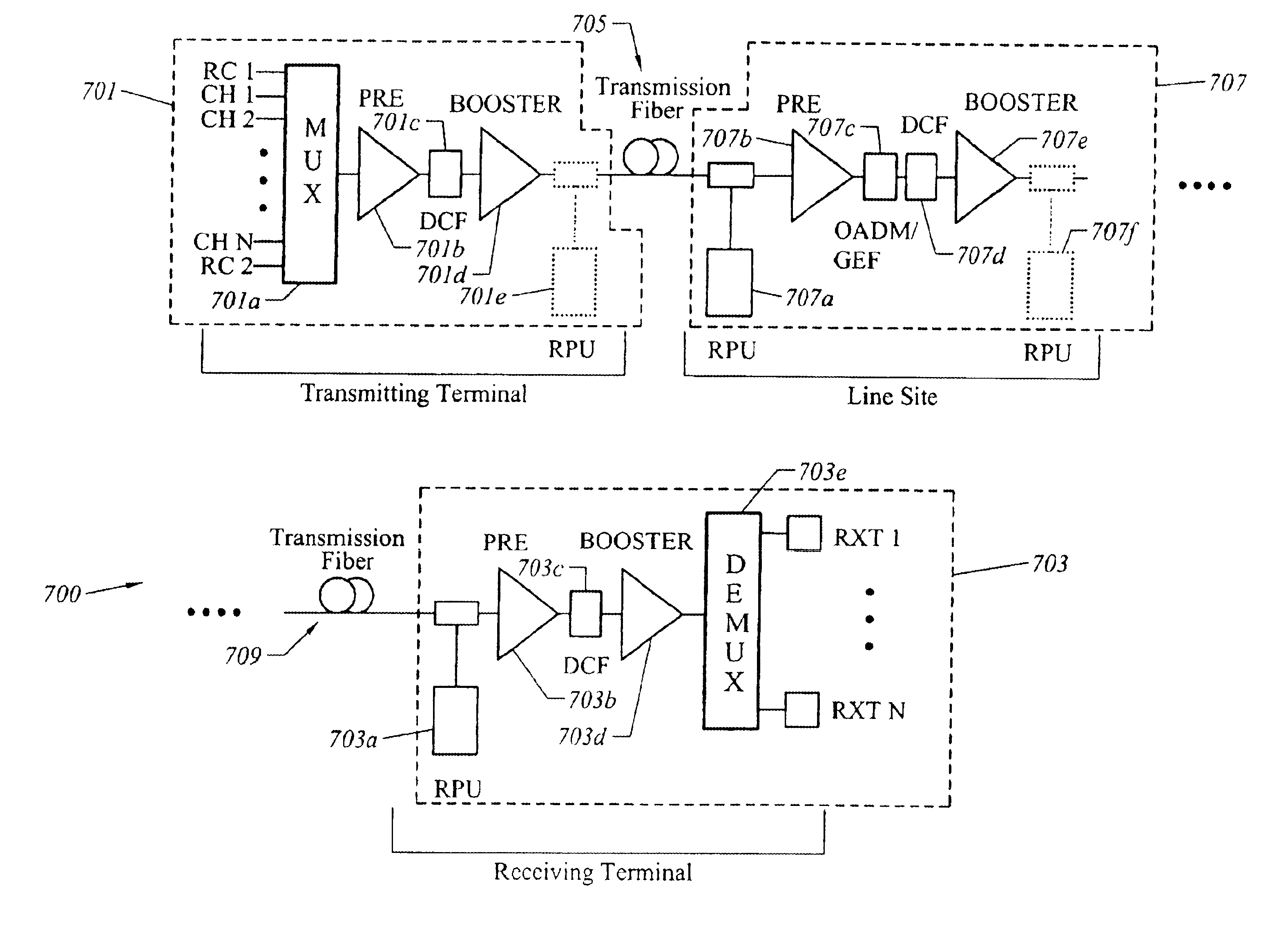
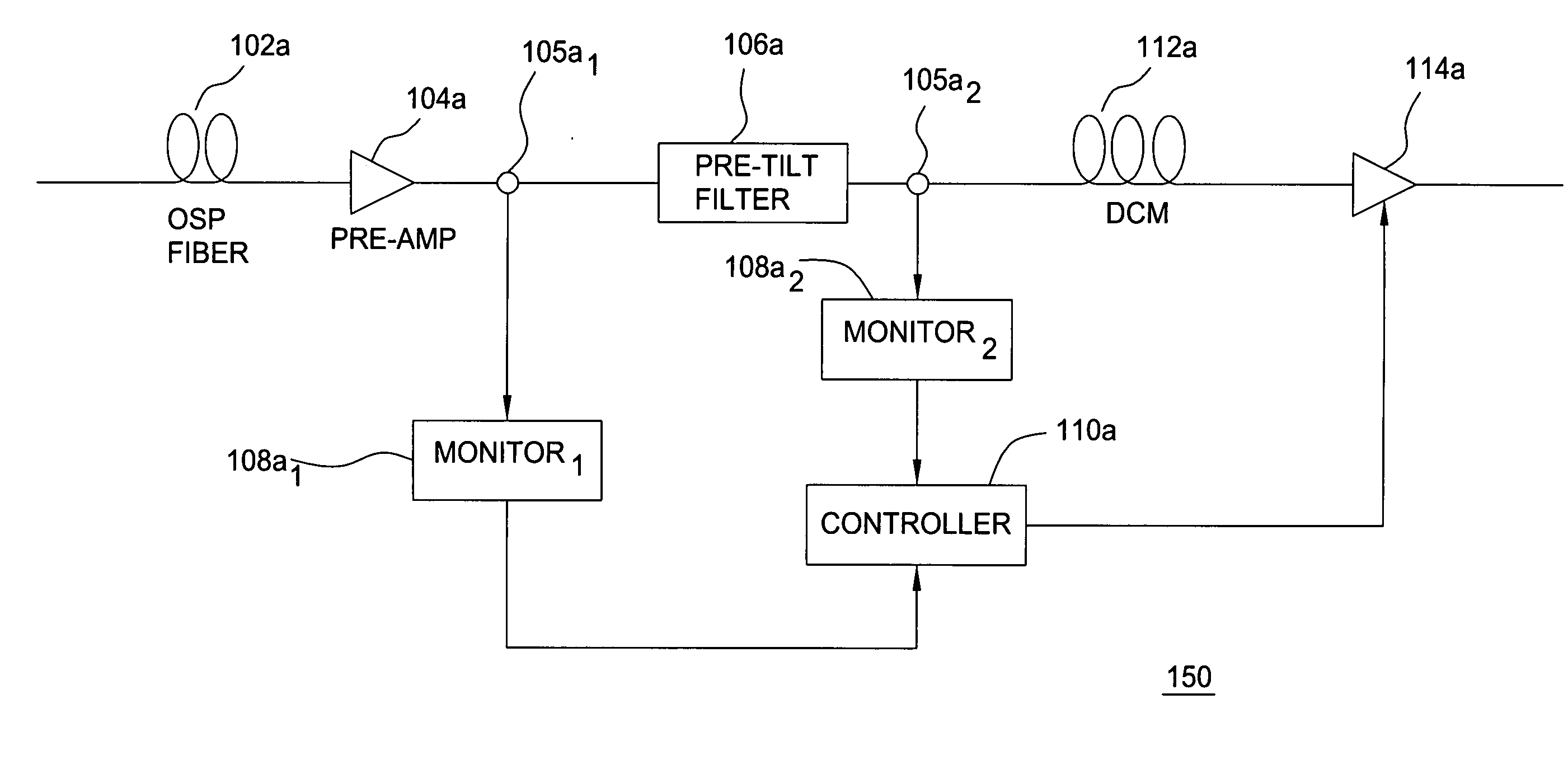
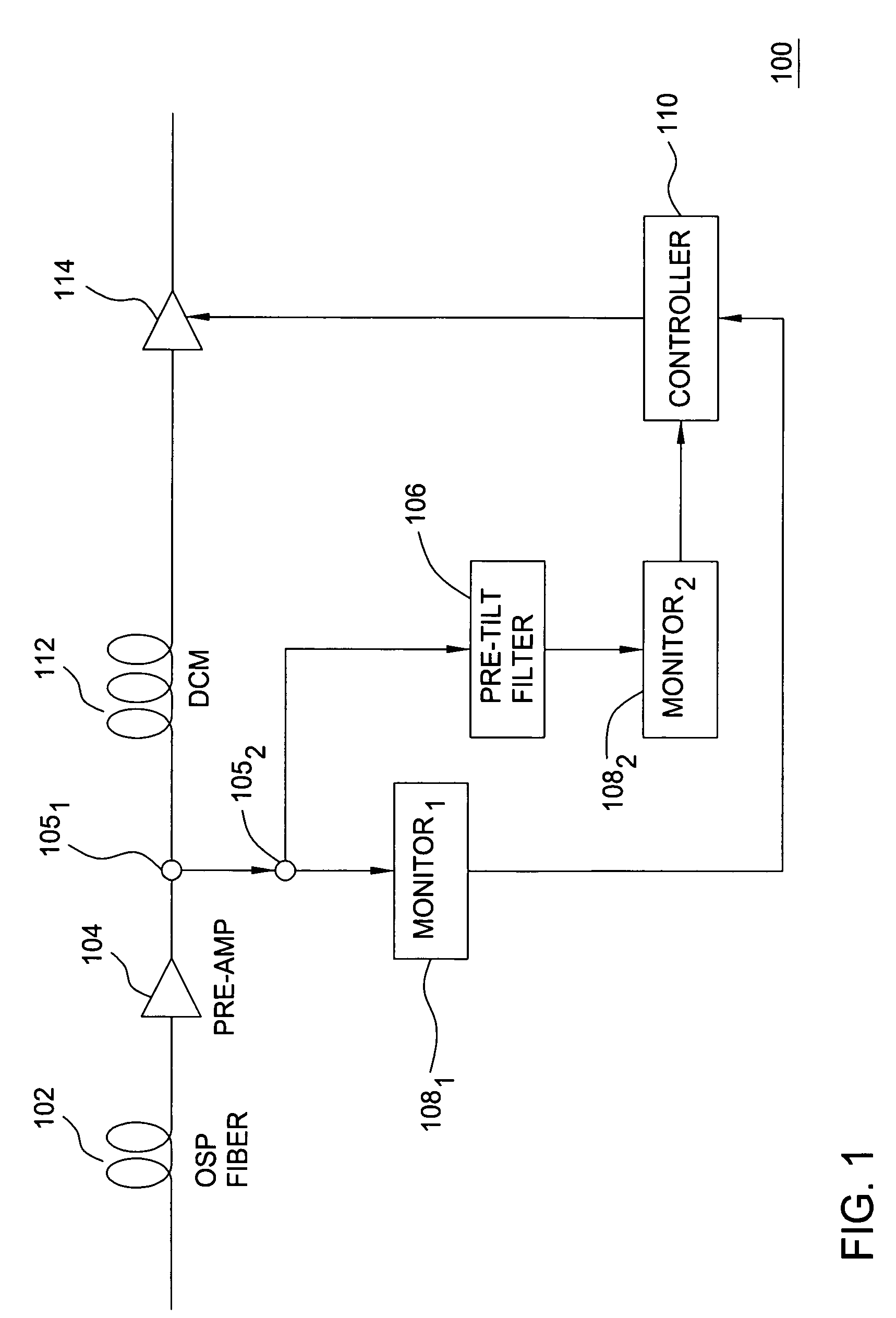
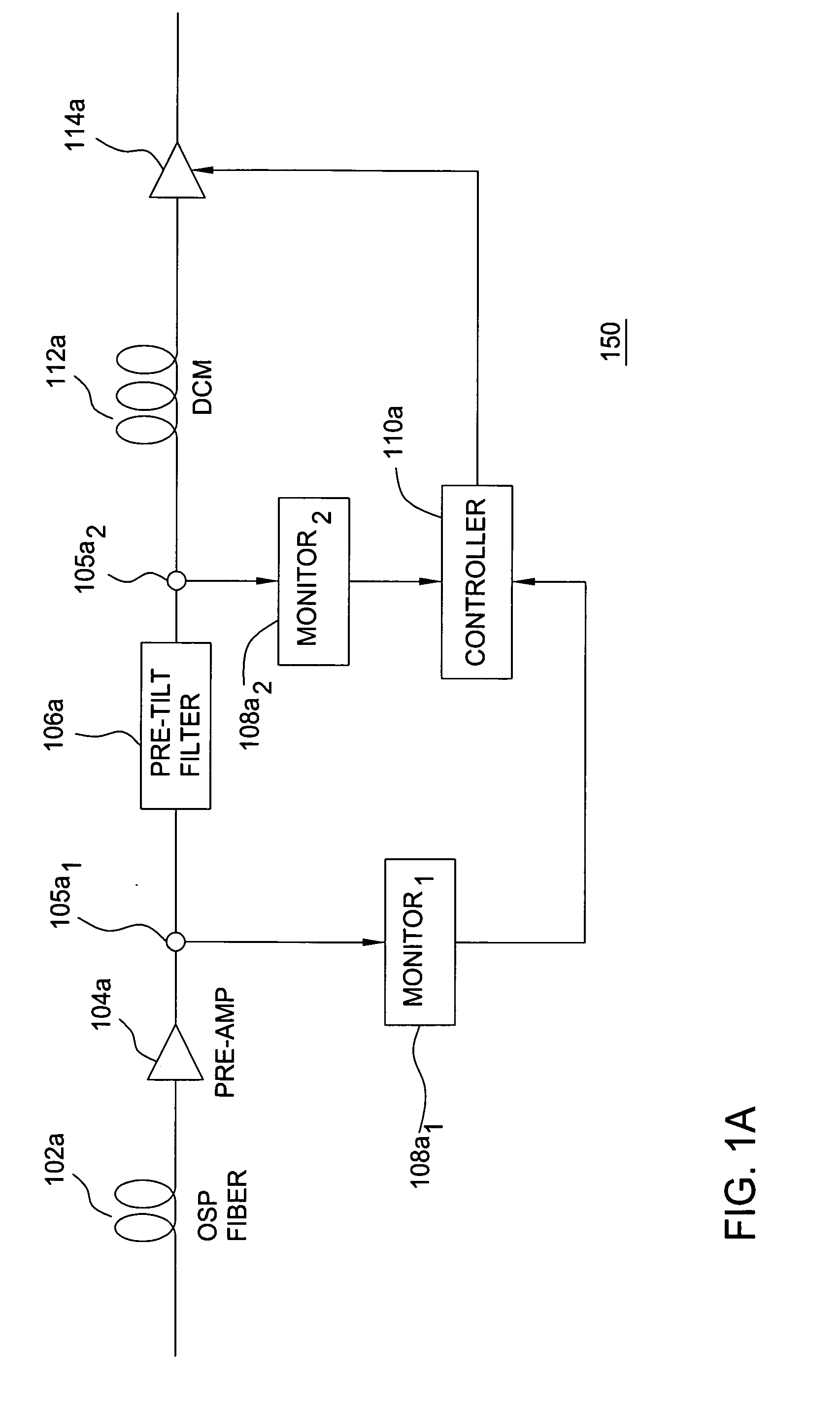
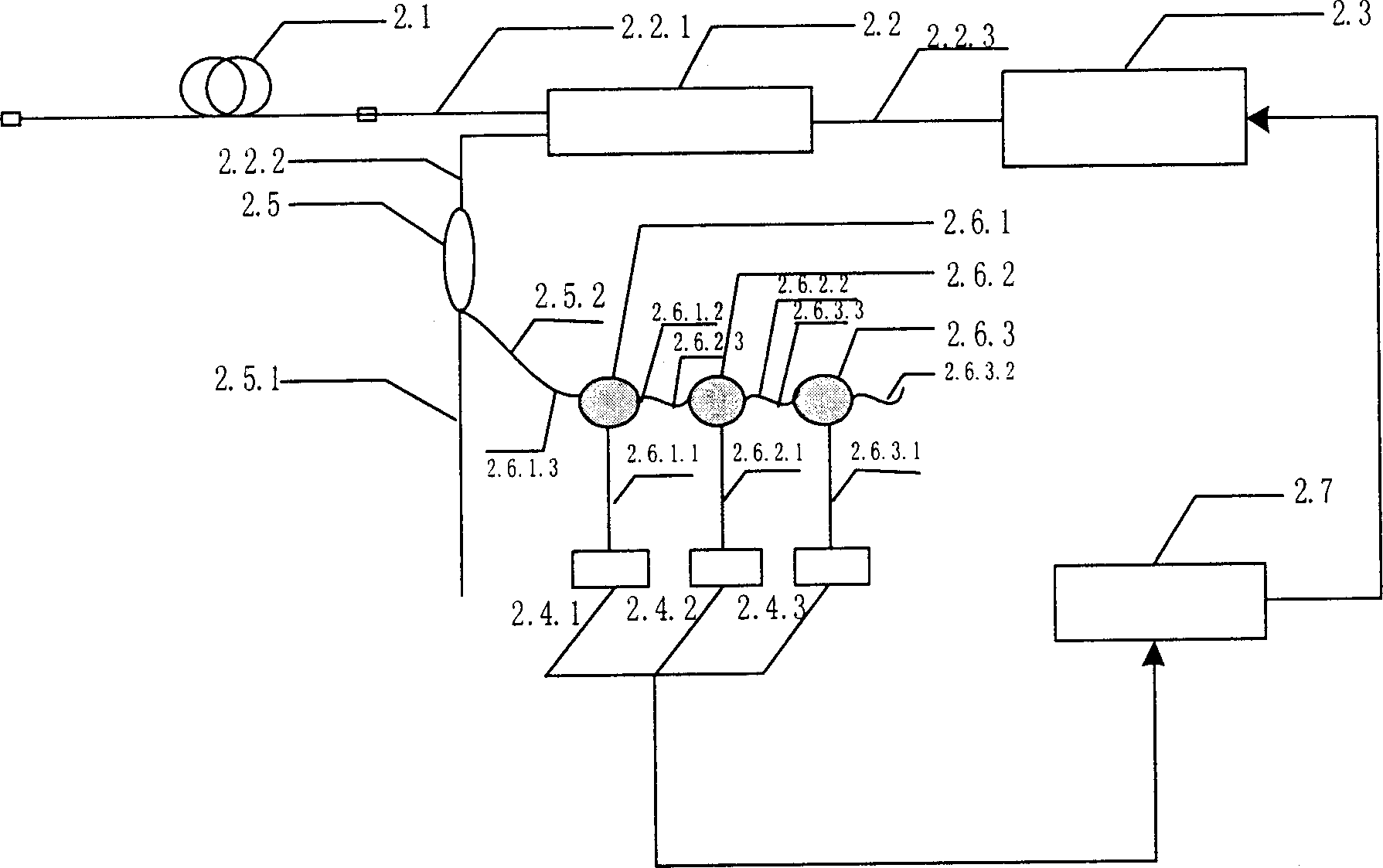
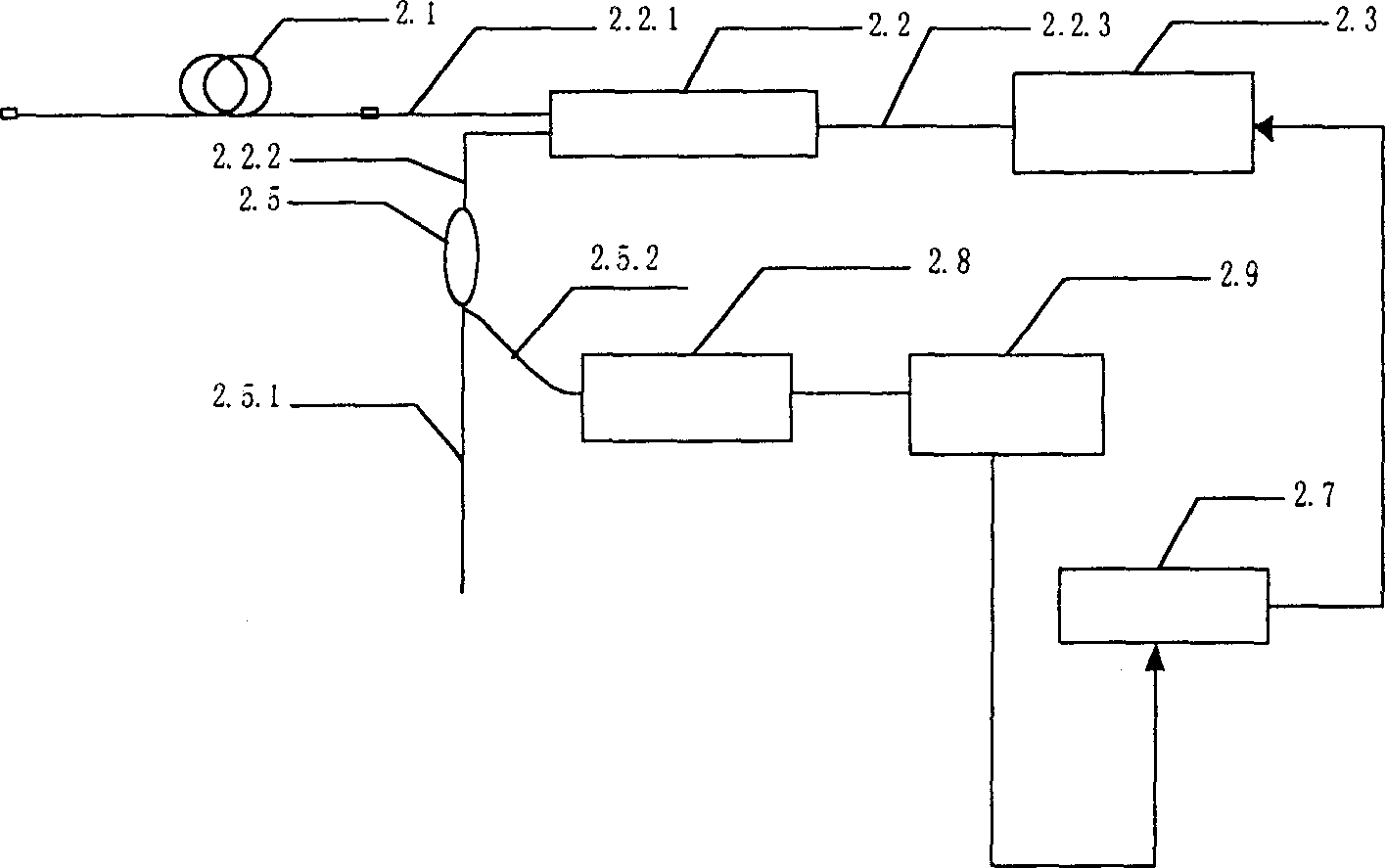
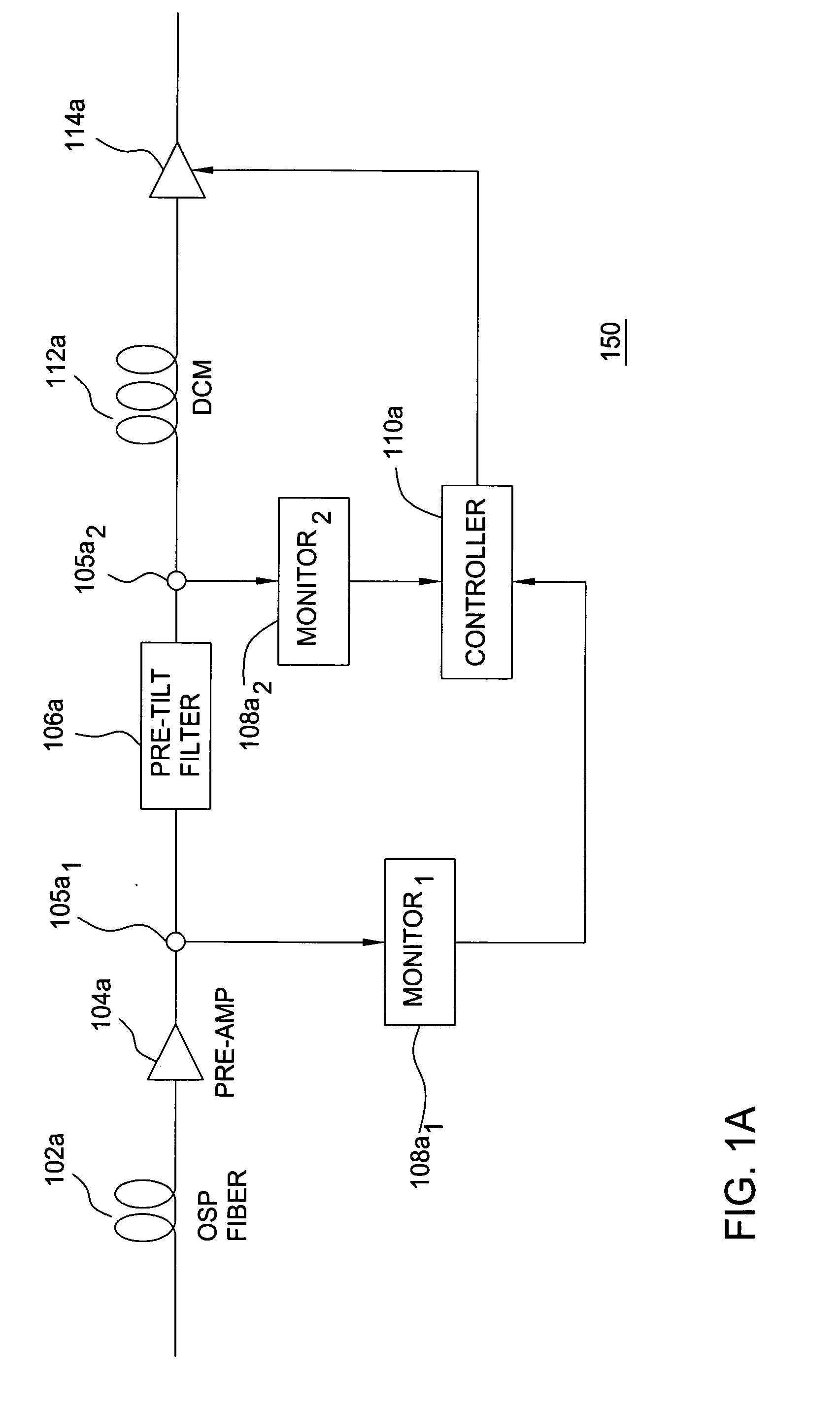
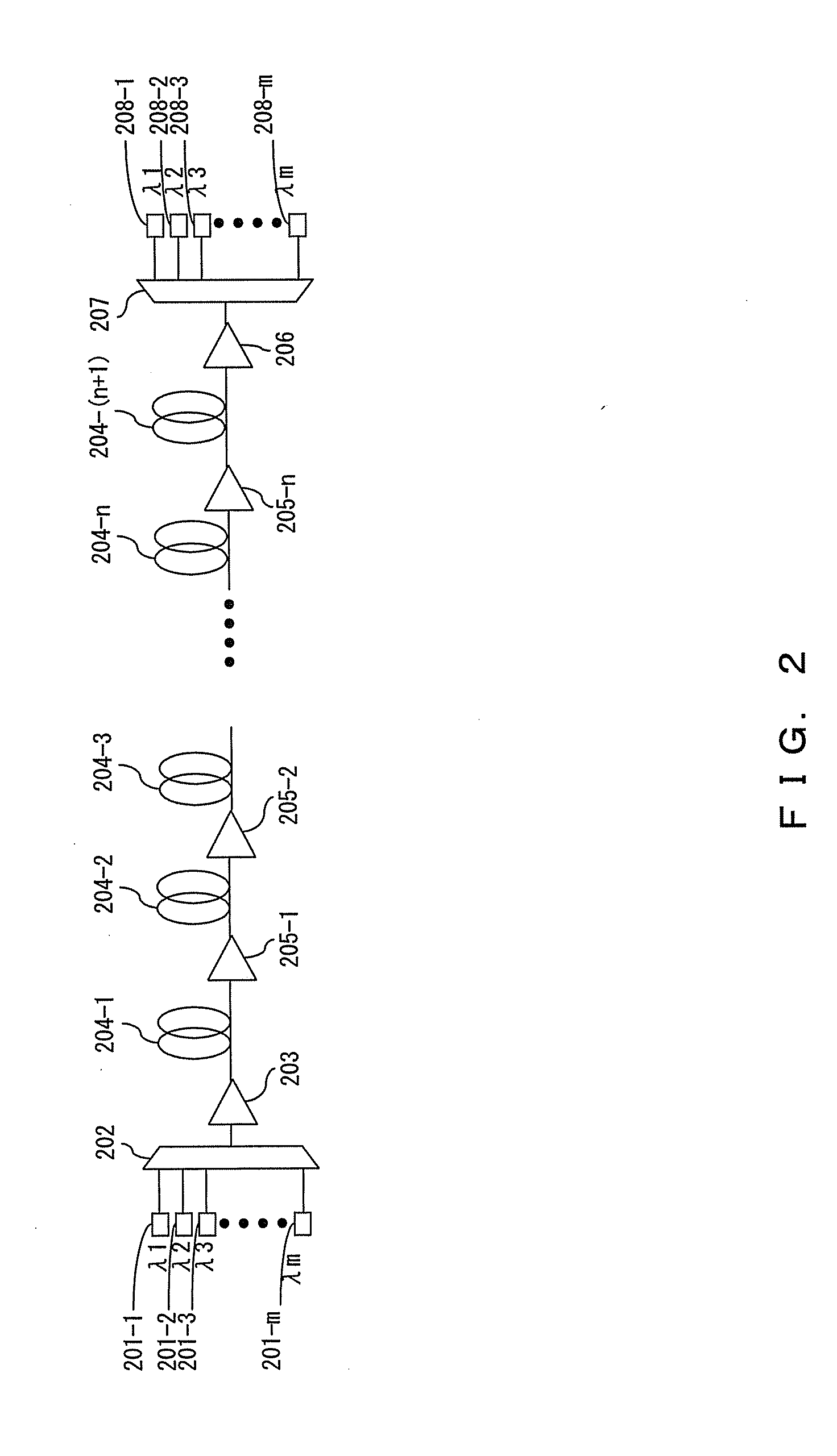
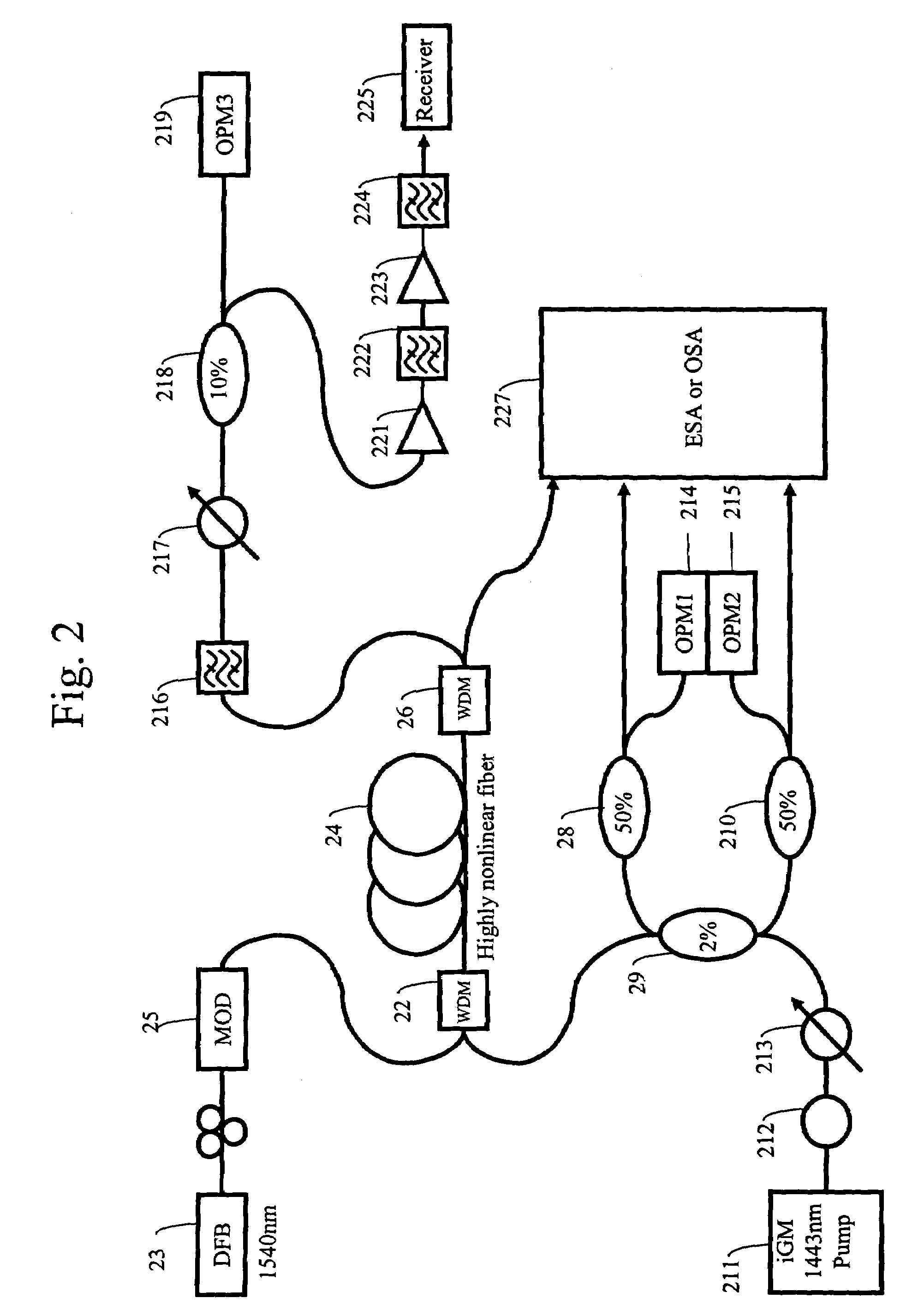
Automatic raman gain and tilt control for ultra-long-distance dense WDM optical communication system
InactiveUS6961522B1Minimizes non-linear effectConstant powerWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionConstant powerErbium doped fiber amplifier
An approach for automatic Raman gain and tilt control for a WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical communication systems is disclosed. An optical fiber carries a plurality of optical signals, in which at least one of the optical signals are reference signals. An optical gain unit (e.g., Raman pump unit) couples to the optical fiber and adjusts the reference signals to compensate, in part, for losses associated with the optical fiber and gain tilt accumulation. Upon detecting and analyzing the reference signals, a controller controls the optical gain unit and outputs a control signal to the optical gain unit based upon the analyzed reference signals. An optical amplifier is connected to the optical fiber and amplifies the optical signals. The optical gain unit provides a nearly constant power per channel at an input of the optical amplifier. Under this approach, a Raman gain control mechanism, combined with the use of gain controlled EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier), allows high transmission capacity over ultra-long distances without optical regeneration and with high flexibility.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for locking Raman gains of target and Raman OFA (optical fiber amplifier)
ActiveCN102307068ADark current has little effectLarge range of valuesLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionAutomatic controlAudio power amplifier
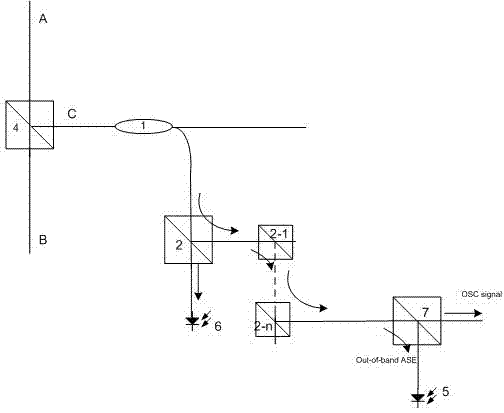
The invention discloses a method for locking Raman gains of a target and a Raman OFA (optical fiber amplifier). The OFA comprises a coupler and a control unit, wherein the control unit comprises a gain locking module; and a detection circuit formed by a filter and an optical power detector is connected between the output end of the coupler and the input end of the control unit. In the method, the control unit is utilized to adjust the power of a pump laser, thus the power of detected OOB (out of band) ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) optical signals is consistent with that of the targeted OOB ASE optical signals, and the amplification gains of the target is locked. The optical path structure of the OFA is simple, the Raman gains can be configured flexibly in accordance with the circuit conditions, and the gains of the Raman OFA can be automatically controlled and locked.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Raman amplifier system and method with integrated optical time domain reflectometer
ActiveUS20140077971A1Security mechanismElectric signal transmission systemsLaser detailsFiberTime domain
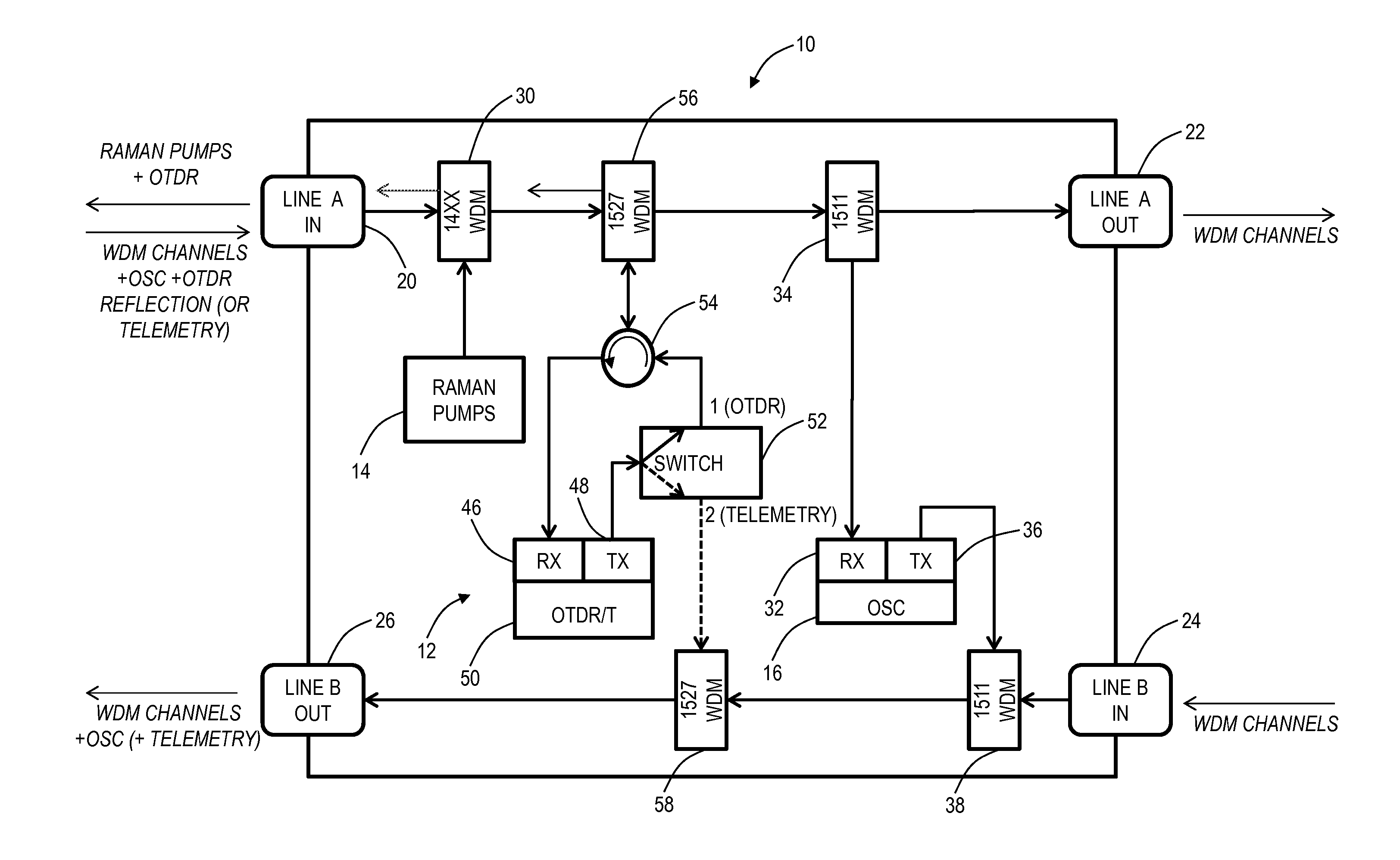
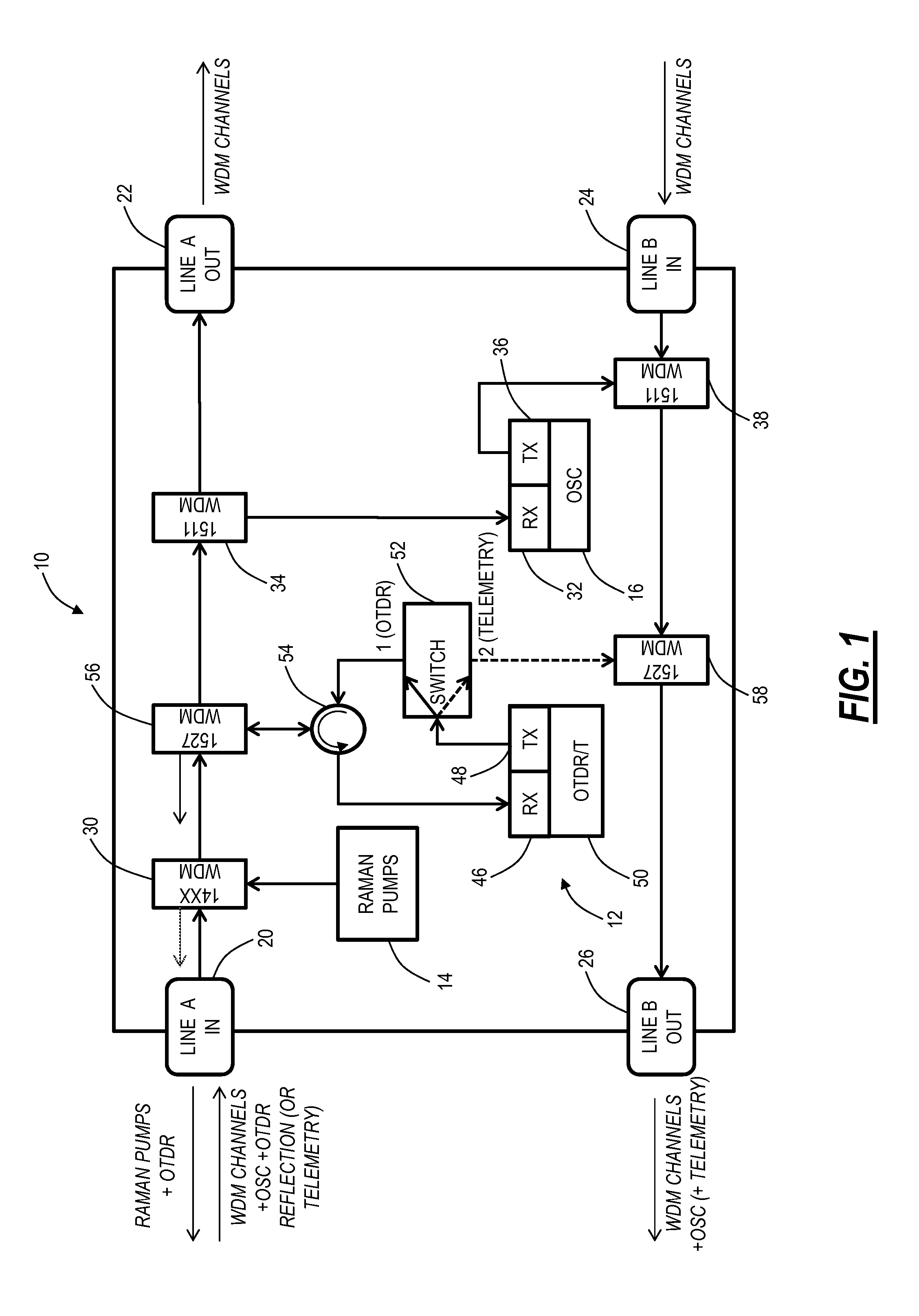
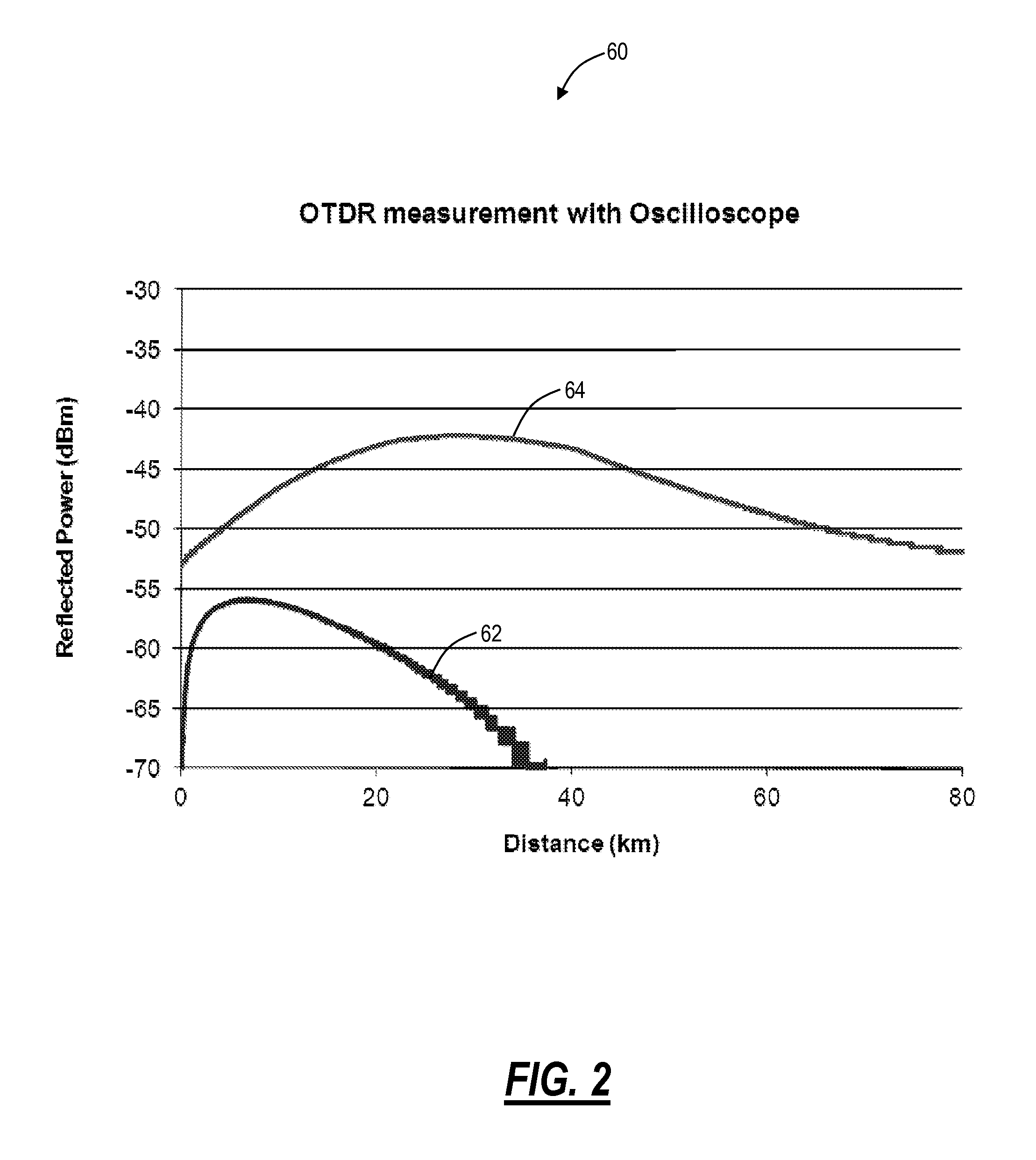
Raman amplifier systems and methods with an integrated Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) for integrated testing functionality include an amplifier system, an OTDR and telemetry subsystem, and a method of operation. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem is configured to operate in an OTDR mode when coupled to a line in port and to operate in a telemetry mode when coupled to a line out port. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem enables on-demand fiber testing while also operating as a telemetry channel that is both a redundant optical service channel (OSC) and provides a mechanism to monitor Raman gain over time. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem minimizes cost and space by sharing major optical and electrical components between the integrated OTDR and other functions on the Raman amplifier.
Owner:CIENA
Cascaded pump delivery for remotely pumped erbium-doped fiber amplifiers
ActiveUS20060209394A1Increase volumeWeaken energyLaser detailsFibre transmissionErbium dopingEngineering
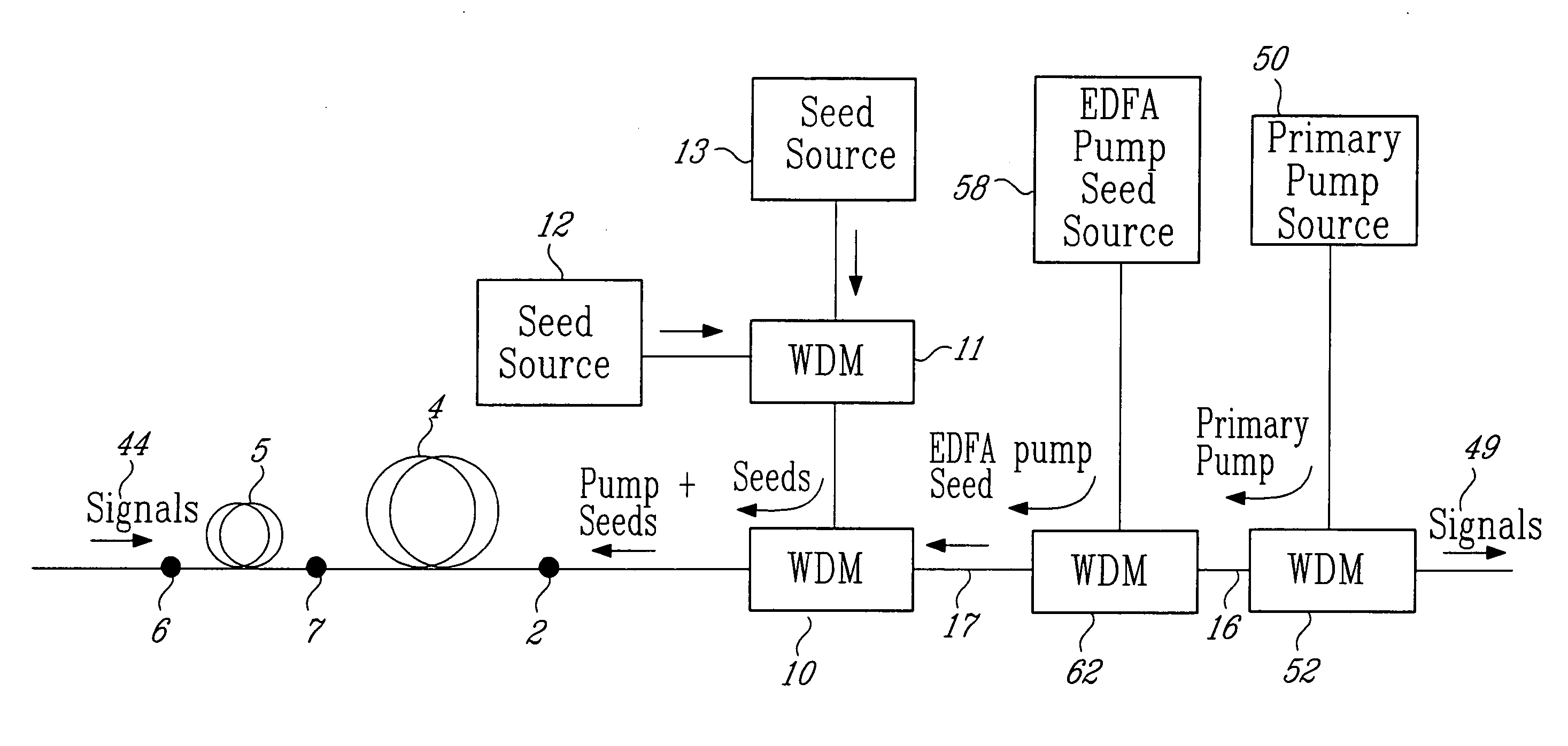
A method for pumping remote optically-pumped fiber amplifiers (ROPAs) in fiber-optic telecommunication systems is disclosed which uses cascaded Raman amplification to increase the maximum amount of pump power that can be delivered to the ROPA. According to the prior art, high power at the ROPA pump wavelength, λp, is launched directly into the fiber and the maximum launch power is limited by the onset of pump depletion by Raman noise and oscillations due to the high Raman gain at ˜(λp+100) nm. In preferred embodiments of the present invention, a ‘primary’ pump source of wavelength shorter than λp is launched into the delivery fiber along with two or more significantly lower-power ‘seed’ sources, among which is included one at λp. The wavelength and power of the seed source(s) are chosen such that, when combined with the high-power primary source, a series, n, where n≧2, of Raman conversions within the fiber ultimately leads to the development of high power at λp. In another embodiment, one or more of the seed sources at wavelengths shorter than λp are replaced by reflecting means to return, into the fiber, backward-travelling amplified spontaneous Raman scattered light resulting from high power in the fiber at a wavelength one Raman shift below the particular seed wavelength. In either case, the high power at λp is developed over a distributed length of the fiber, reaching its maximum some distance into the fiber and exceeding the maximum power possible at that point with the prior art.
Owner:MPB COMM
Method and system for reducing Raman gain tilt error
ActiveUS7038843B2Reduce gain errorLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A method and system in accordance with the present invention greatly reduces the gain error due to Raman gain tilt for individual channels in an optical communication system during a transient event by determining a shift in average power (and thus wavelength) and using the determined shift to alter the average gain in the optical communication system. In various embodiments of the present invention, the average gain of the optical communication system is altered by altering the average gain of an amplifier in the optical communication system. In alternate embodiments of the present invention having an in-line optical filter, the average gain of the optical communication system may be altered by altering the filtering of the optical channels in the optical communication system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser
InactiveCN102354900AShorten the lengthIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringGrating
The invention relates to a random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser which can realize stable, space-irrelevant and continuous laser output, and belongs to the technical field of the optical fiber laser. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser comprises a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber bragg grating, an Er-doped optical fiber, an optical fiber Raman laser and a long monomode optical fiber. The reflection effect of the fiber bragg grating is combined with the distributed Rayleigh scattering effect of the optical fiber to form a distributed random feedback optical resonant cavity; and the light is subjected to gain amplification by an Er-doped optical fiber and the stimulated Raman scattering effect. Compared with the random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser reported before, the threshold value of the pump laser and the length of the monomode optical fiber can be reduced, and the limitation on stimulated emission wavelength and the wavelength number by a Rayleigh gain peak is broken through, thereby realizing the purpose of tuning the laser wavelength. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser is suitable for fields, such as remote optical fiber sensing, remote communication and the like.
Owner:唐山市神州科贸有限公司
Graphite Raman locked mode laser
ActiveCN102104231AImprove applicabilityCompact structureLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringGraphite
The invention relates to a graphite Raman locked mode laser characterized in that laser gain is provided by a stimulated Raman scattering effect with a flexible wavelength and combined with a graphite Raman locked mode device with a wide saturated absorption band to realize locked mode laser output. The whole device of the graphite Raman locked mode laser is formed by a mechanism of combining a stimulated Raman gain medium with the graphite Raman locked mode device, is compact in structure and convenient to integrate and can be applied to a plurality of fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for strengthening atom steam optical filtering signals by combined Raman
ActiveCN101794033AGuaranteed production efficiencyReduce bit error rateNon-linear opticsPrismOptical polarization
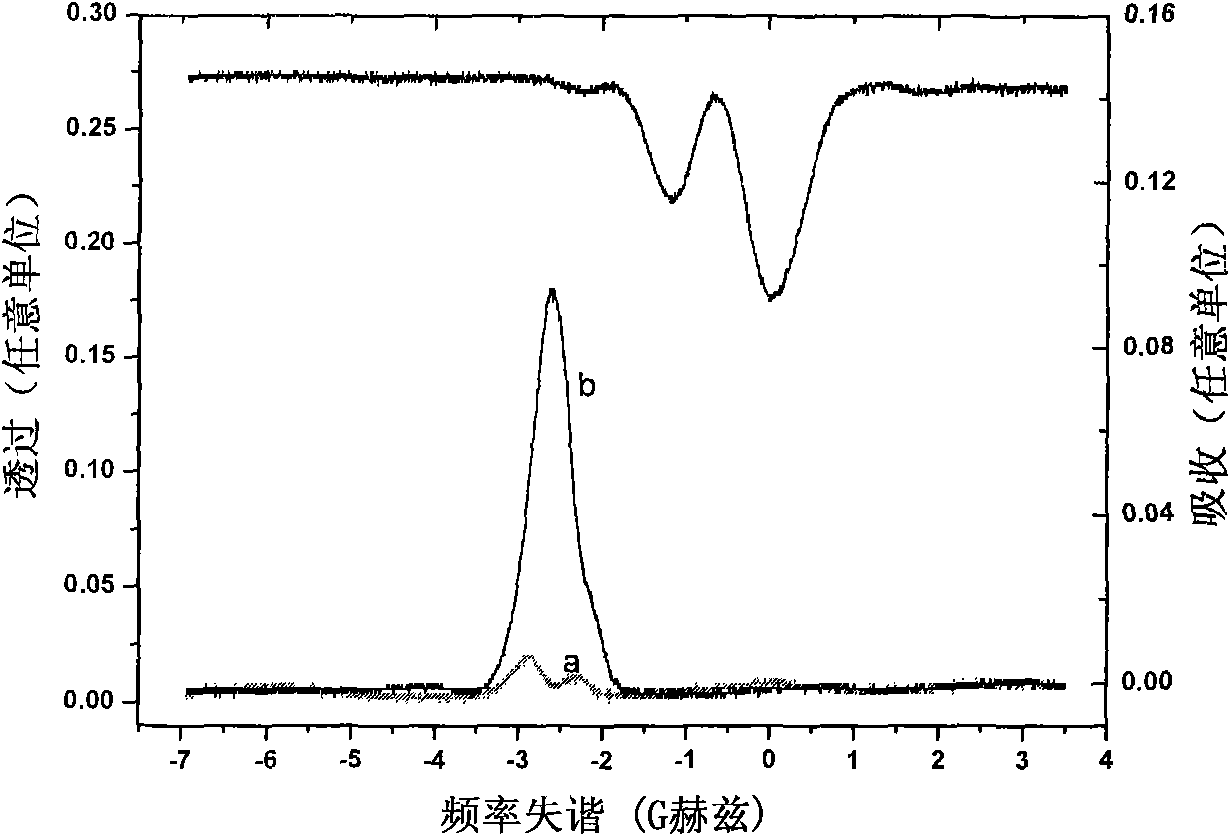
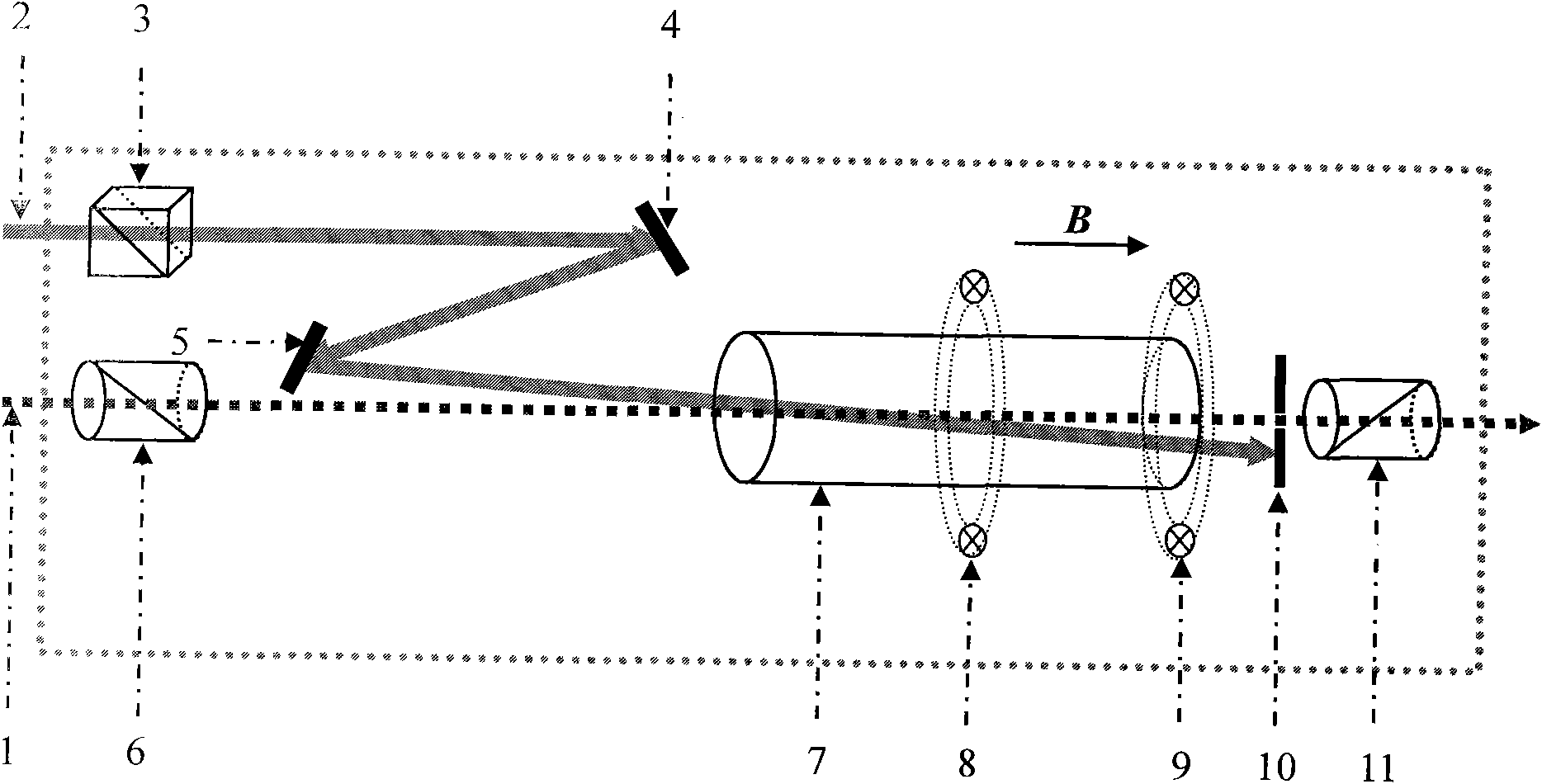
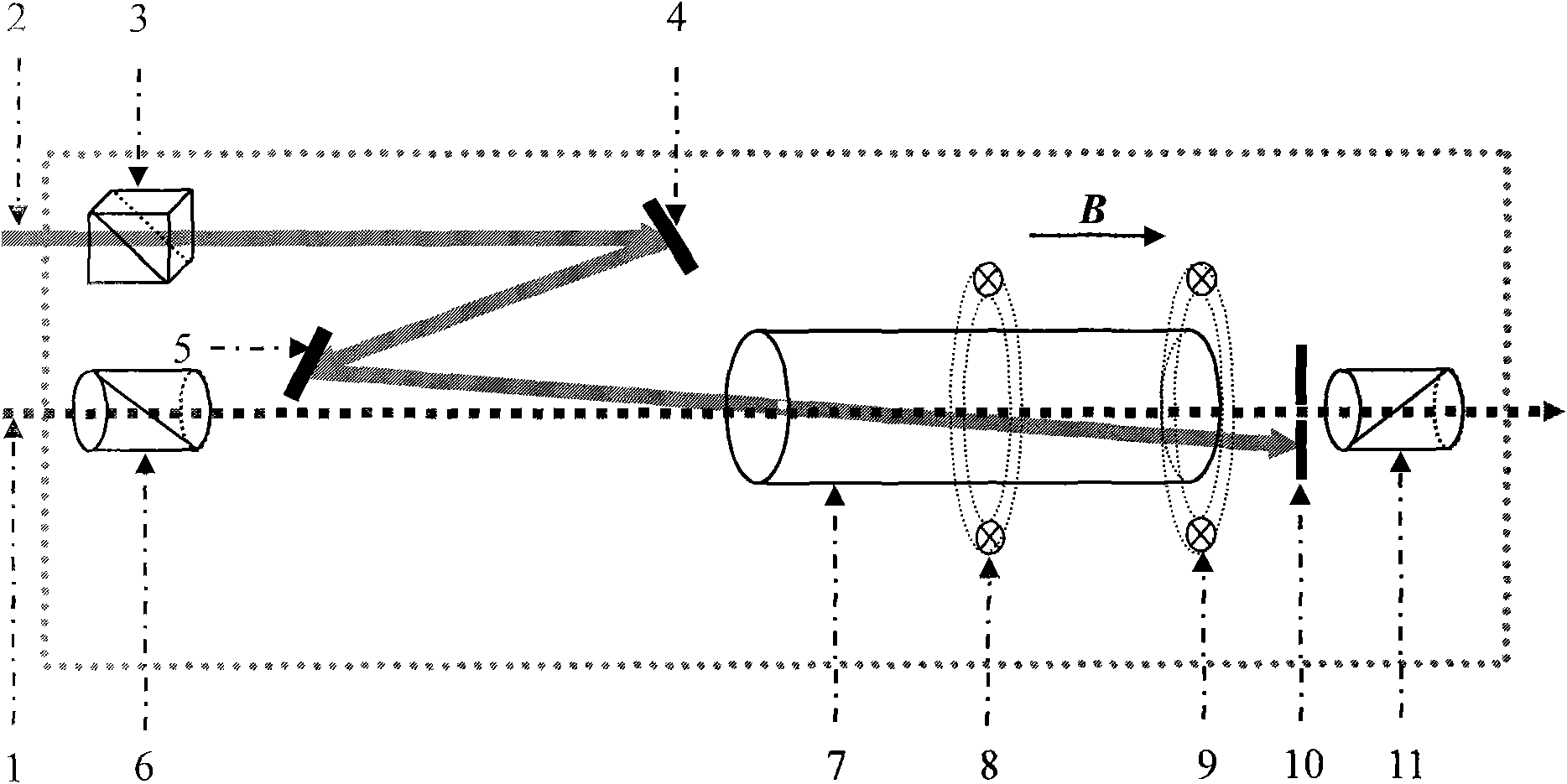
The invention discloses a method and a device for strengthening atom steam optical filtering signals by combined Raman. The method combines two characteristics of atom excited Raman gain and Faraday anomalous dispersion effect of atom steam in a single atom steam bubble. The device for realizing the method comprises a narrow band polarization beam splitter, two holophotes, an atom steam bubble with an external magnetic field with a part of size, an aperture slot with adjustable pore size and a pair of Gran Thomson prisms. In the invention, the atom steam optical filtering signals are strengthened by above 10 times in the atom steam bubble with the external magnetic field with a part of size through vertical direction of weak signal light and pump laser polarization and matching frequency, and scattered light and passband external background light of pumping lasers are inhibited by an optical polarization device, therefore, the device has the advantages of high suppression ratio (-105), adjustable optical filtering wavelength and the like. The invention remarkably enhances the atom steam optical filtering characteristic and the detection sensitivity and has important significance to application in the fields of remote laser communication, free space quantum communication and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
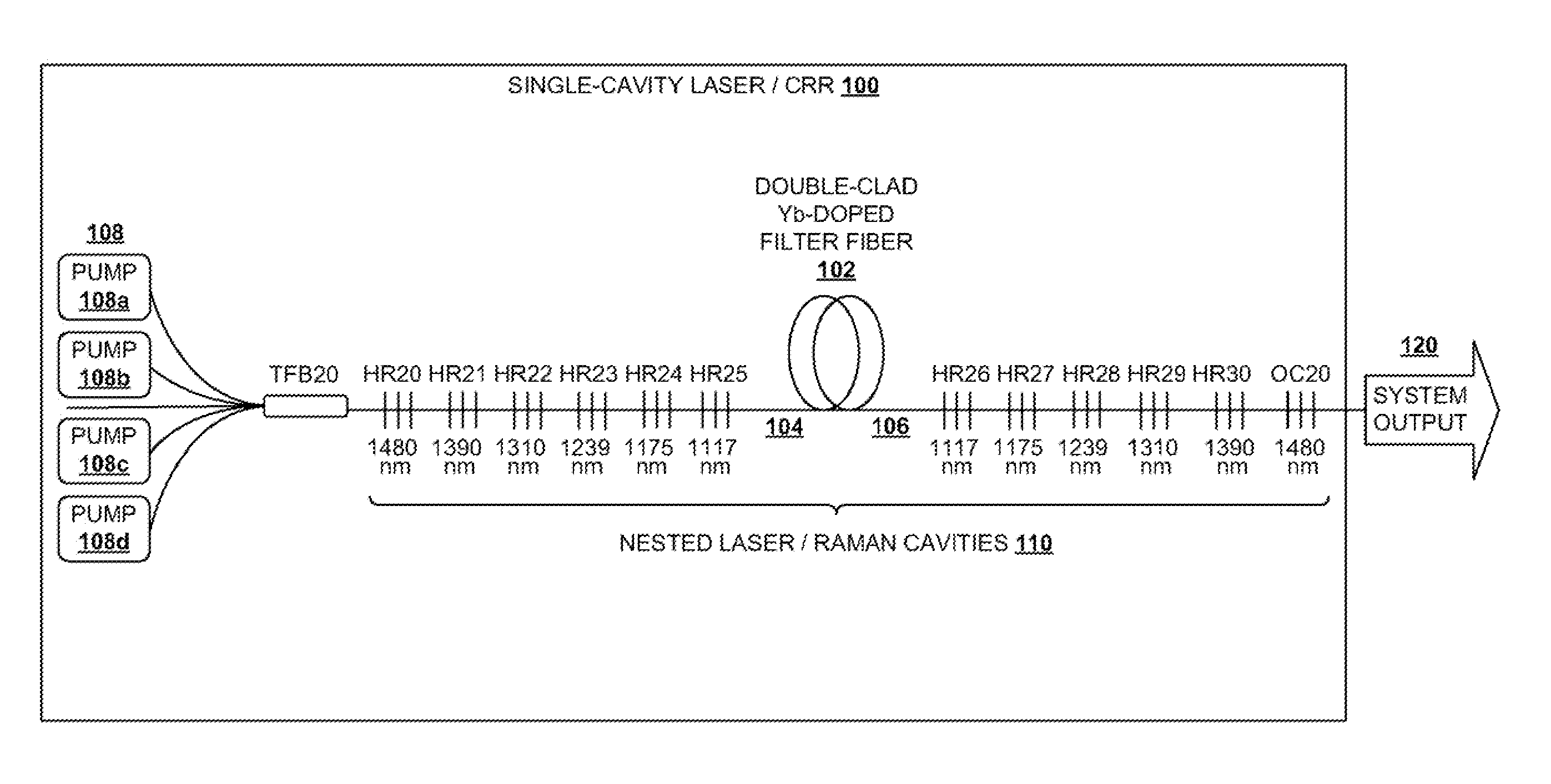
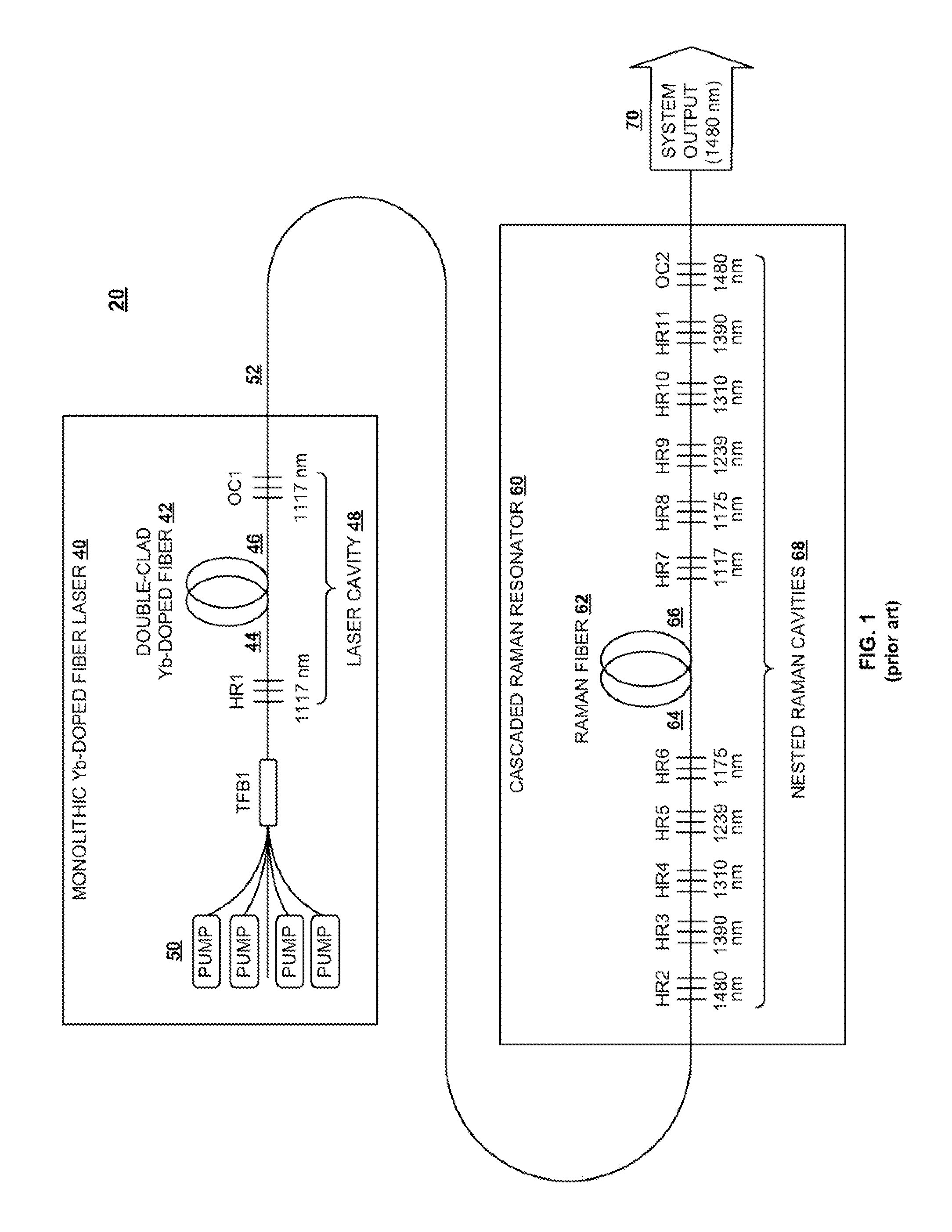
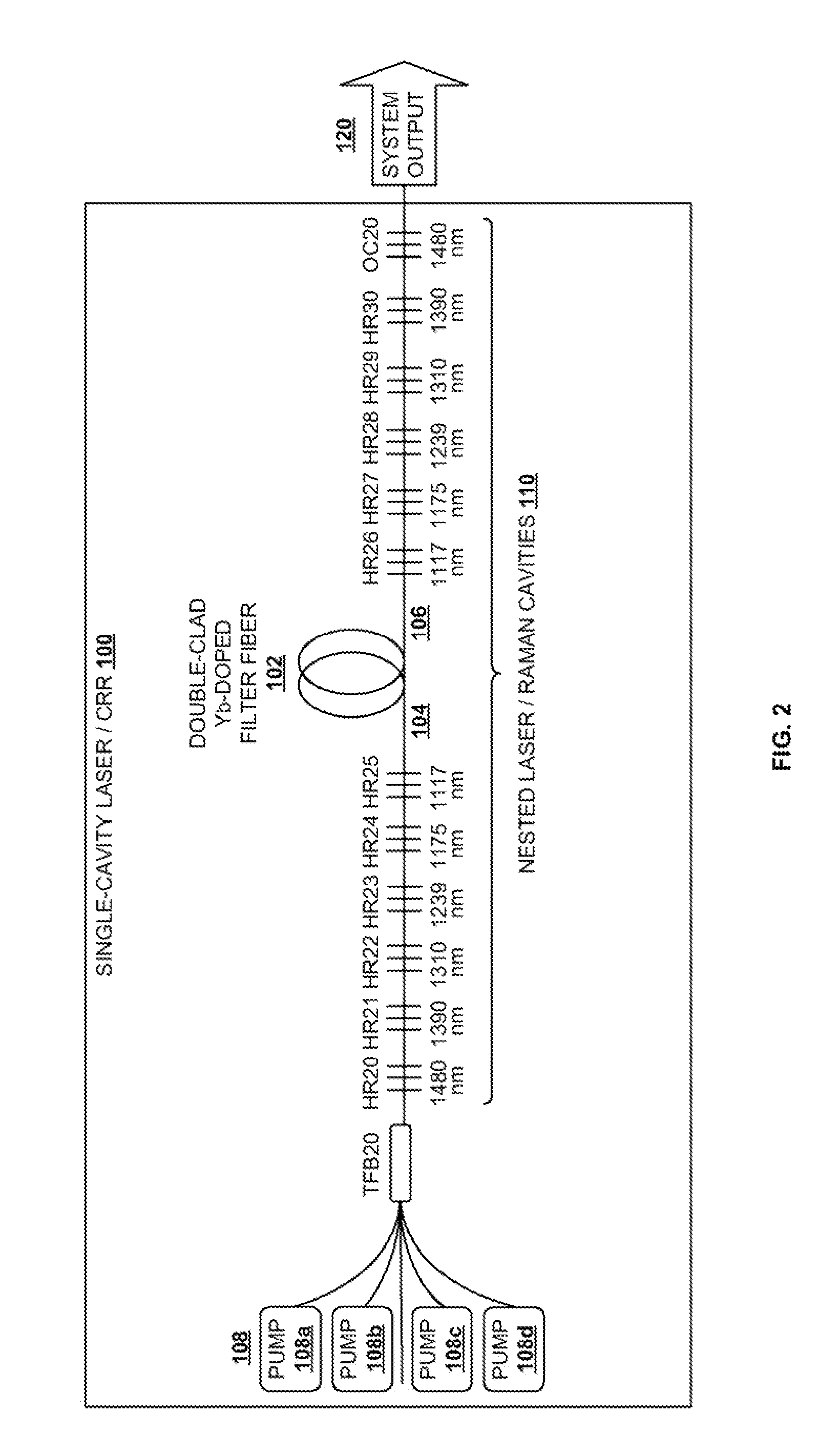
Cascaded Raman Fiber Laser System Based on Filter Fiber
InactiveUS20100290106A1Reduce stepsImprove efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionLength waveFiber laser
A light generation and amplification system includes a length of laser-active filter fiber having a refractive index profile that suppresses unwanted Stokes orders at wavelengths longer than a target wavelength and that has normal dispersion over its operating wavelength. A nested series of reflectors is provided at the fiber's input and output ends, and are configured to provide a nested series of Raman cavities, separated in wavelength by approximately the respective Stokes shifts. The first cavity in the series is a combined cavity that provides laser oscillation due to a combination of ionic gain and feedback at a selected first wavelength and that provides Raman gain to light at the first Stokes shift of the first wavelength when light at the first wavelength has an energy exceeding a Raman scattering threshold. The Raman cavities provide a stepwise transition between the first wavelength and the target wavelength.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Optical fiber for raman amplification
InactiveUS20060033983A1Optimise either the optical or the thermal properties (or both) of an optical fiberImprove thermal stabilityLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialFiberFrequency measurements
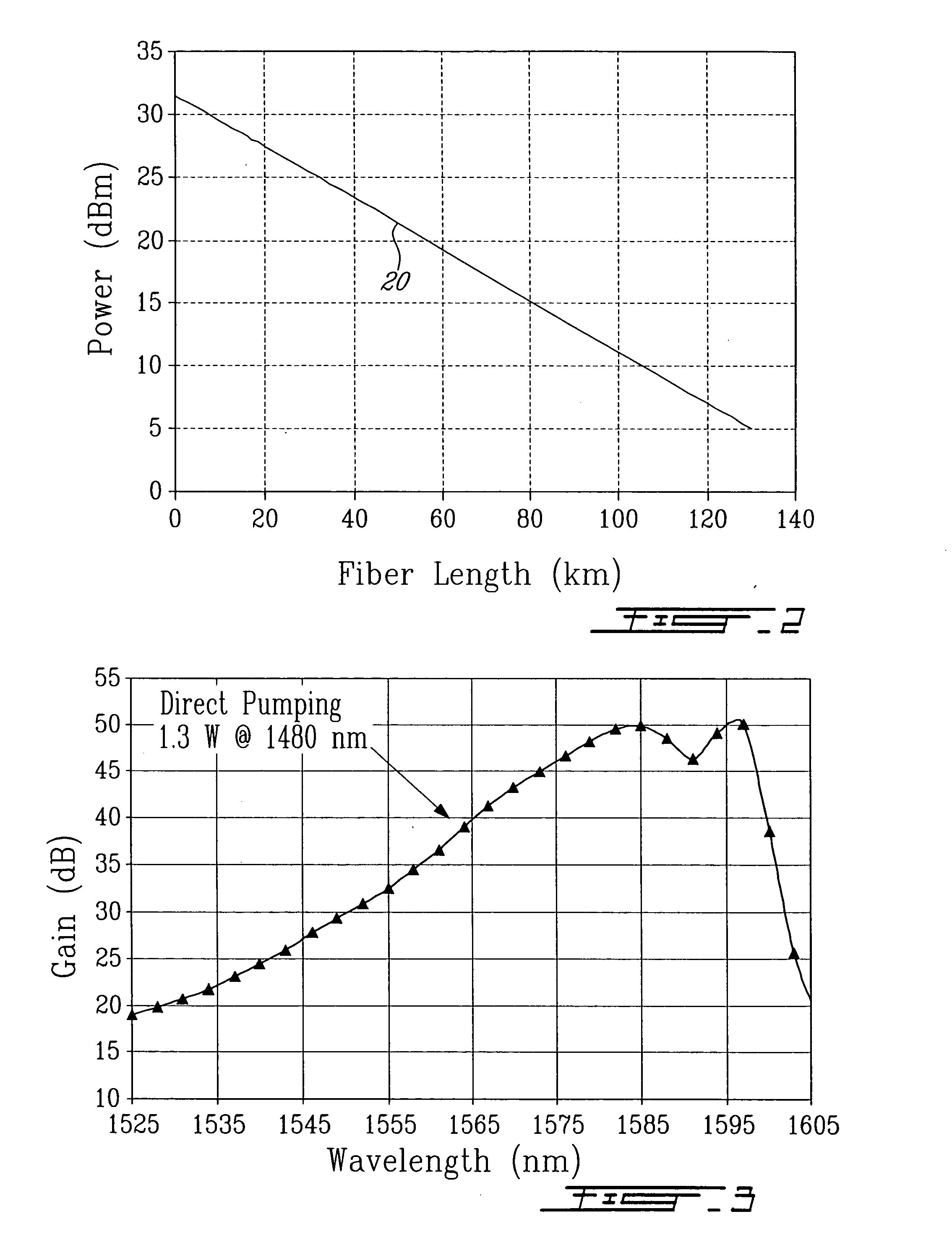
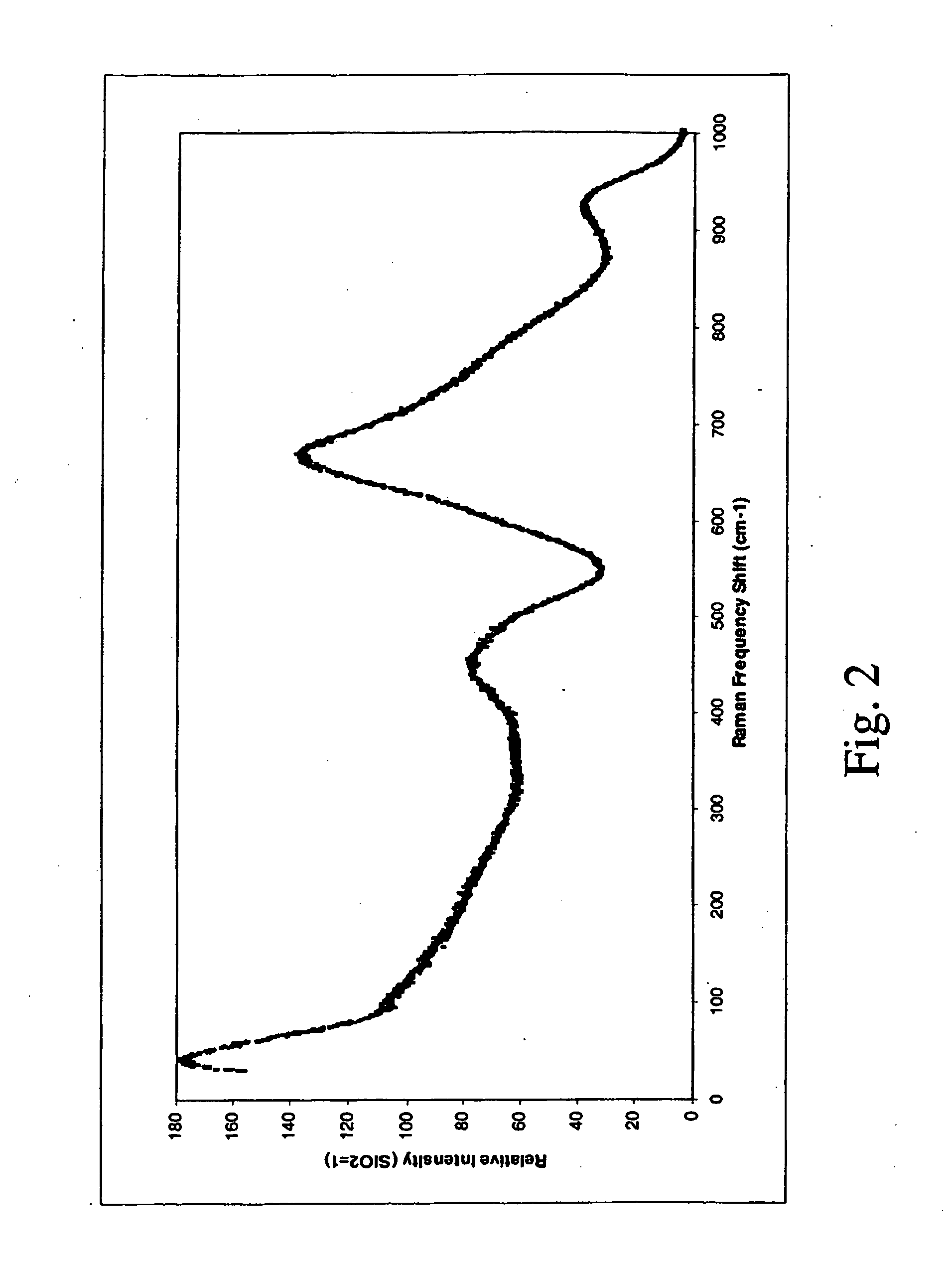
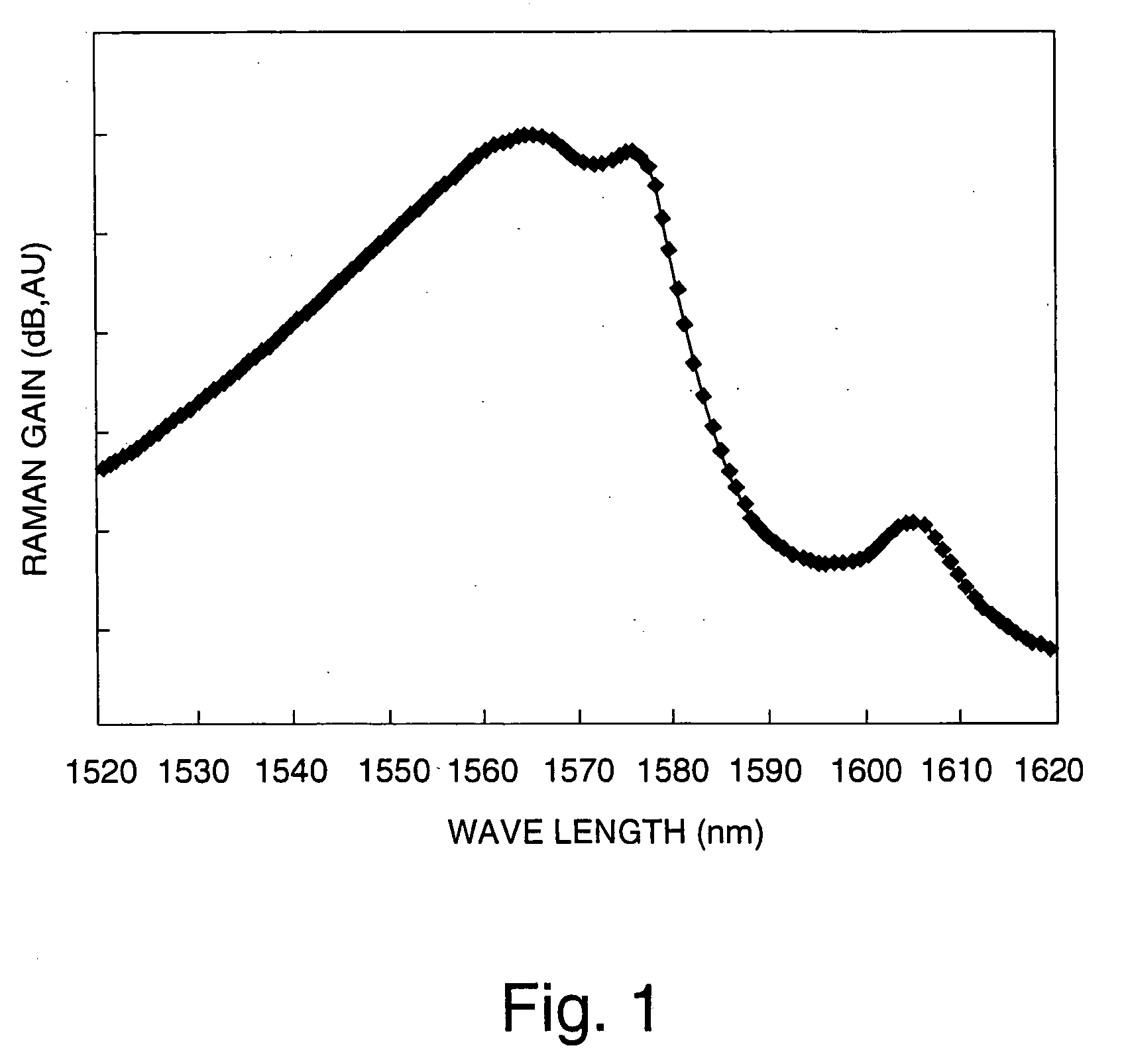
Raman amplifier having an optical fiber made of a tellurite glass is disclosed. The tellurite glass has at least two further metal oxides, the metals of said respective two oxides being selected from a first group of Nb, W, Ti, Tl, Ta, and Mo and from a second group of Nb, W, Ti, Pb, Sb, In, Bi, Tl, Ta, Mo, Zr, Hf, Cd, Gd, La, and Ba. The so obtained fiber has improved optical (Raman gain) and / or thermal (thermal stability index) properties. Alternatively, the tellurite based glass compositions of the fiber have at least one additional metal oxide, where the metal is selected among Nb, Ti, Tl, Ta, and Mo, the glass showing a particularly high Raman gain. The maximum Raman gain of these glasses is typically higher than 100 times of the maximum Raman gain of pure silica and the respective total cross-section of the Raman spectrum is typically greater than 100 times the total cross-section of pure silica, in the frequency measurement range of 200 cm−1 to 1080 cm−1.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Raman amplifier and optical relay transmission system
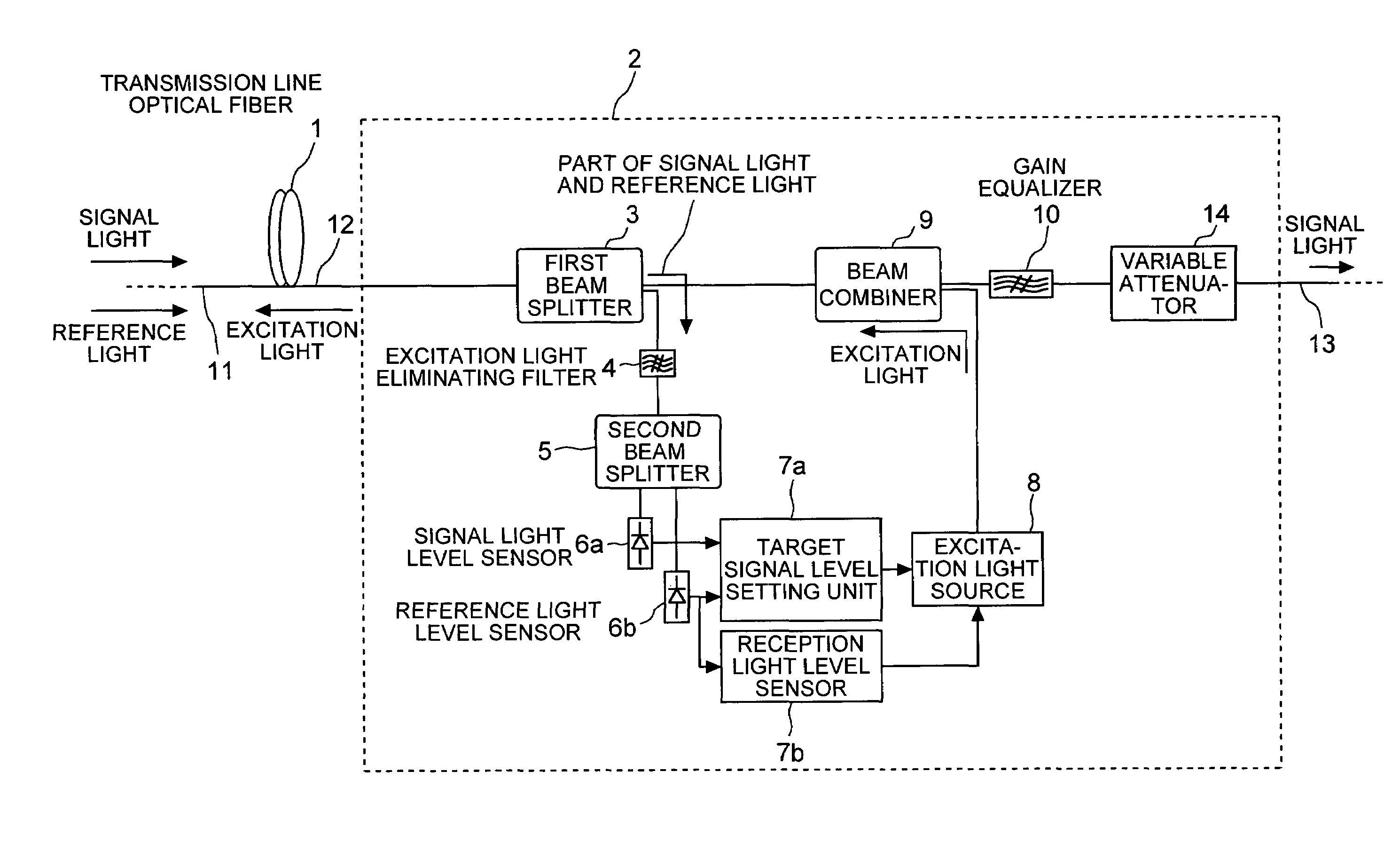
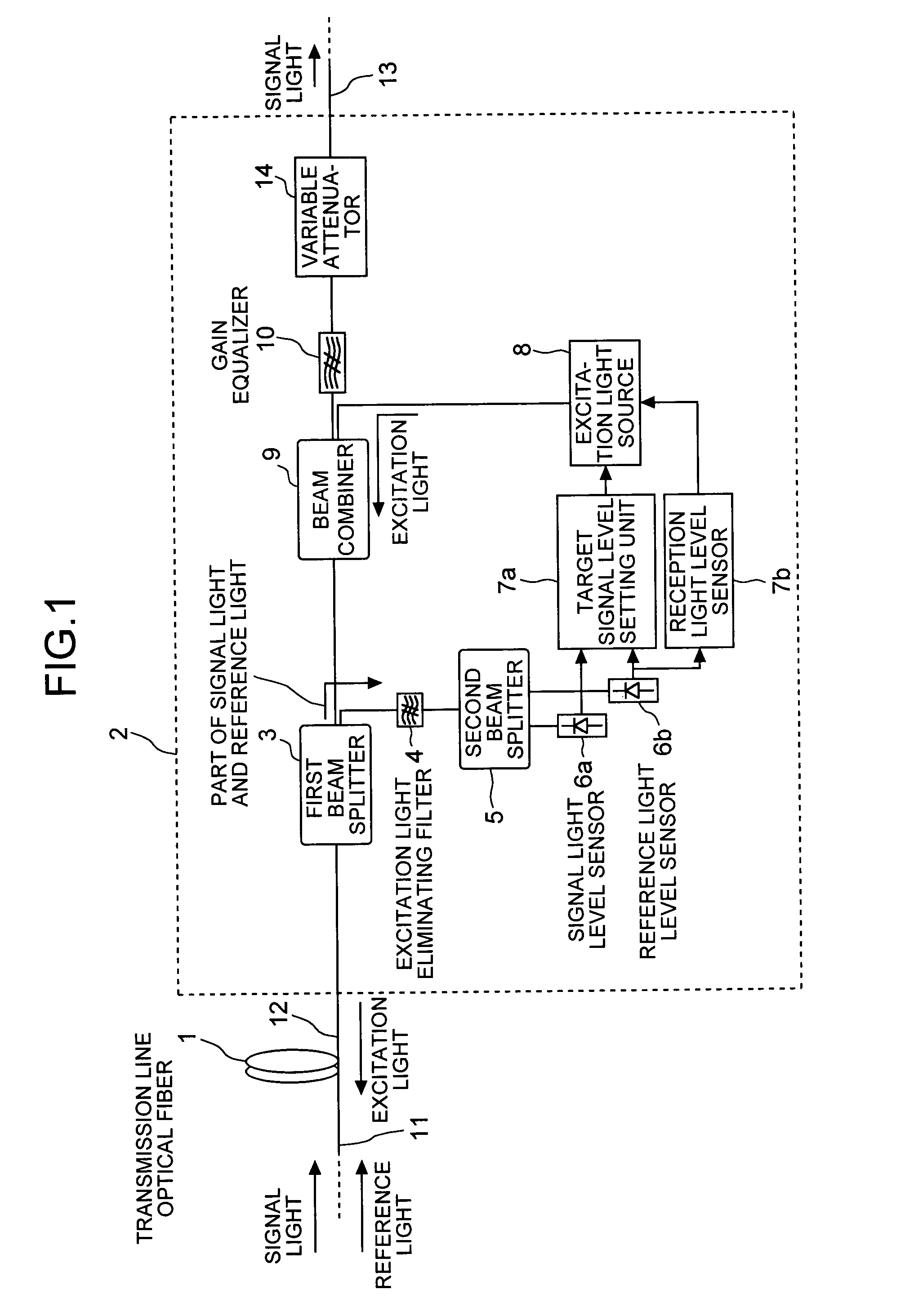
ActiveUS20050099676A1Solve problemsLaser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBeam splitterRaman amplifiers
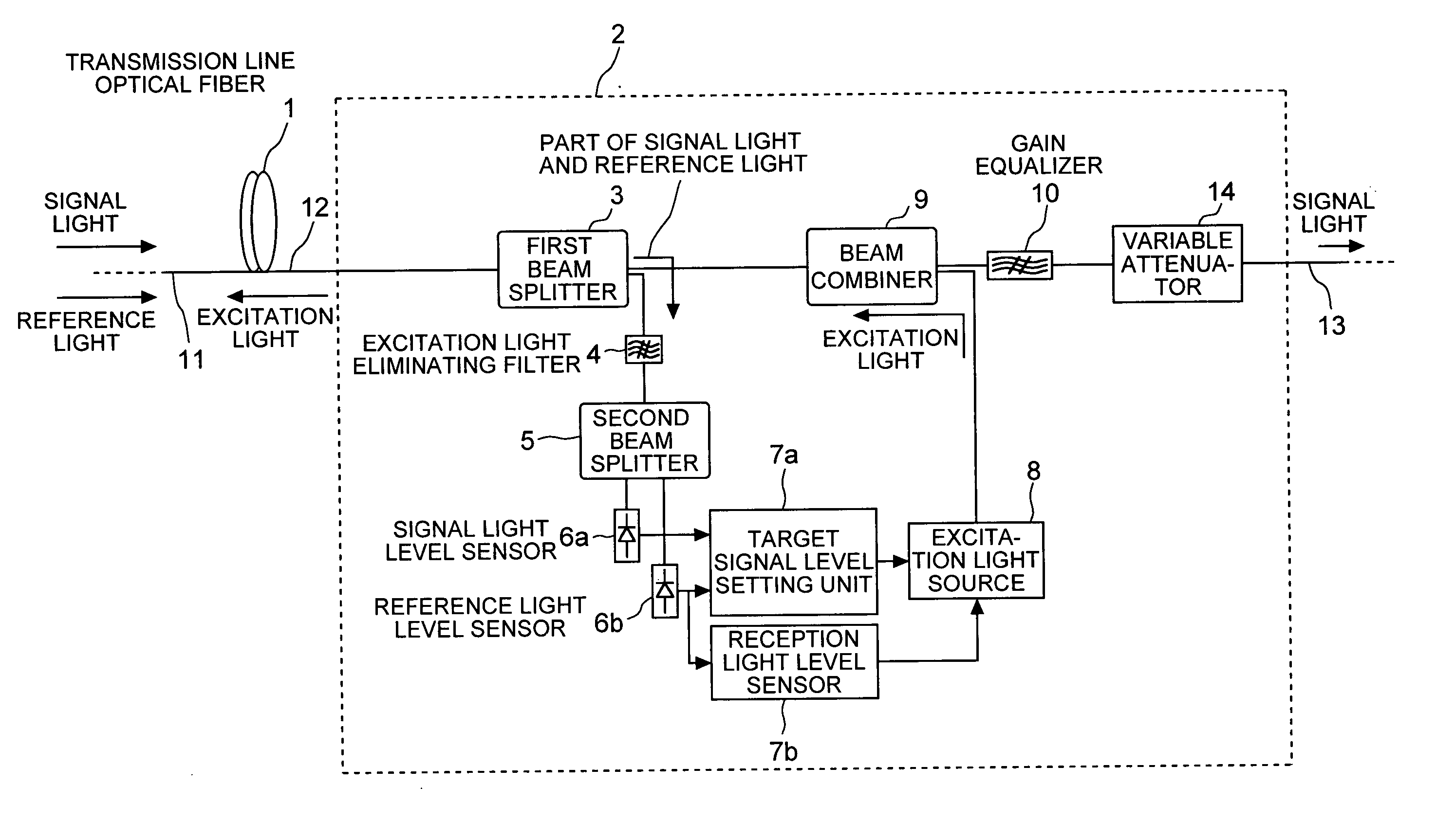
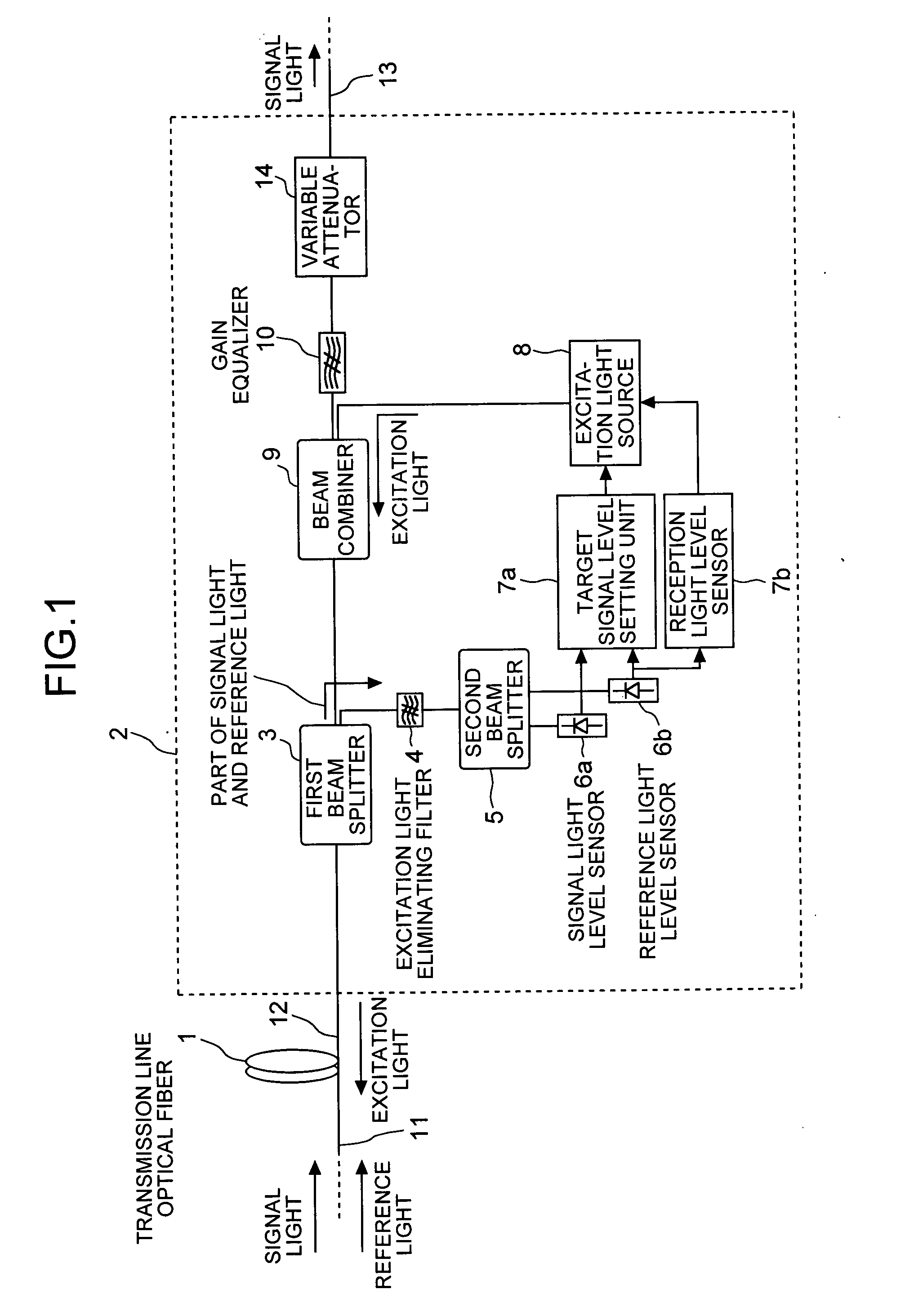
An optical fiber propagates and amplifies a second signal light that is a wavelength-multiplexed signal of a first signal light of a plurality of wavelengths and a reference light that is out of a wavelength range of amplification. An excitation light source outputs an excitation light for amplifying the second signal light. A beam splitter splits a portion of the second signal light into the first signal light and the reference light. A signal light level detecting unit detects a level of the first signal light. A reference light level detecting unit detects a level of the reference light. A signal level setting unit calculates a target value for constantly maintaining a Raman gain, and controls the output level of the excitation light in such a way that the first signal level matches with the target value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
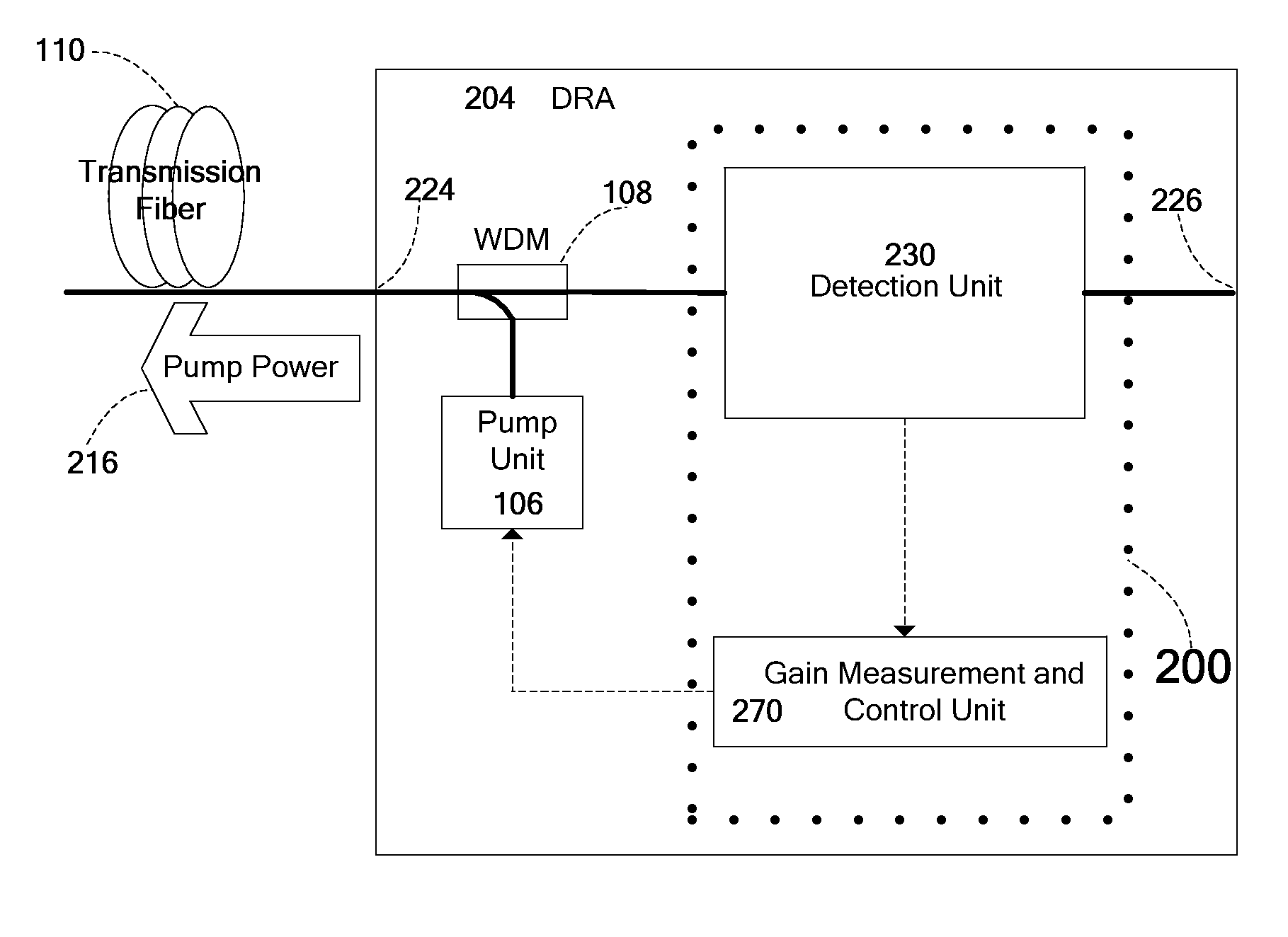
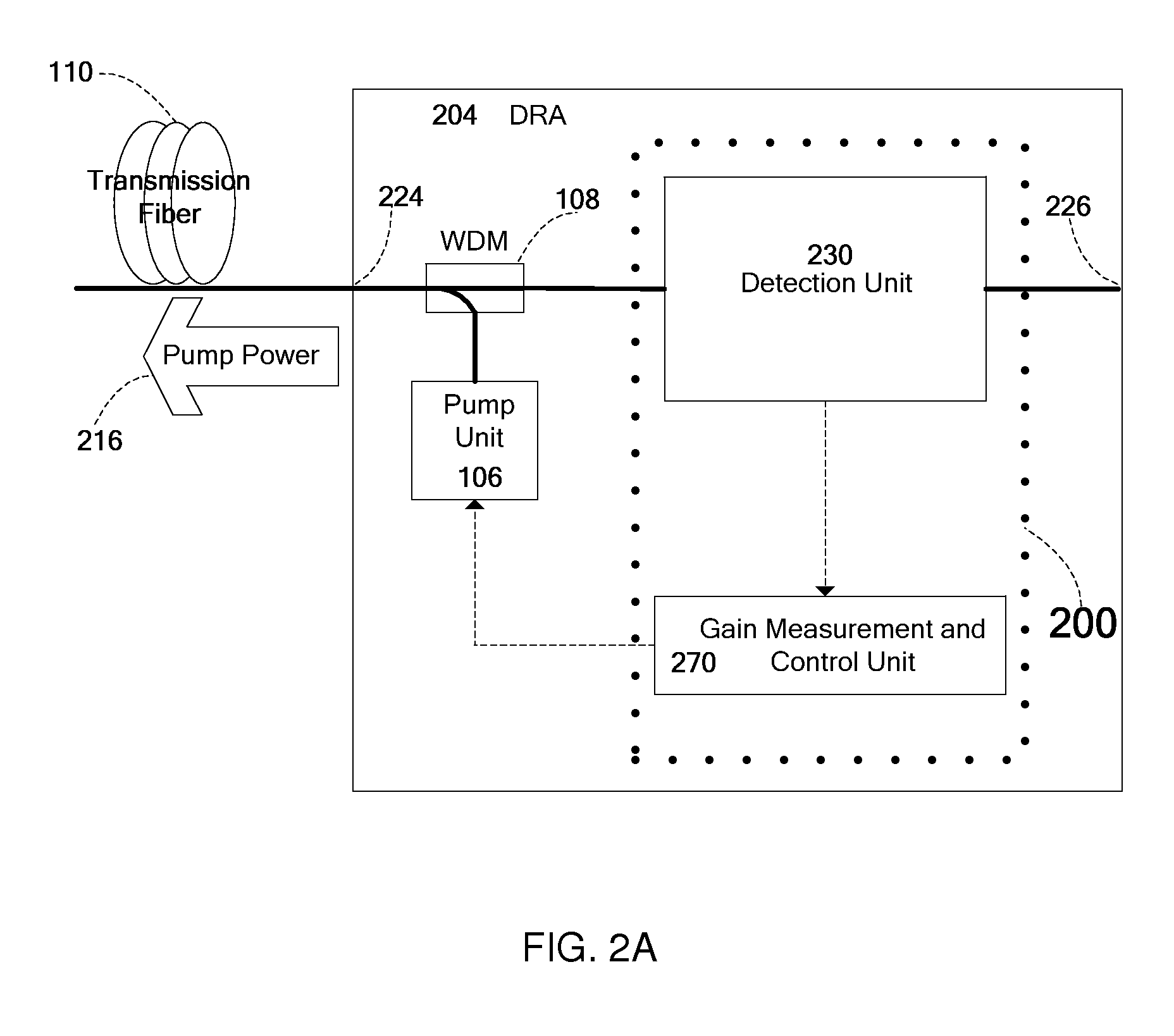
Automatic measurement and gain control of distributed Raman amplifiers
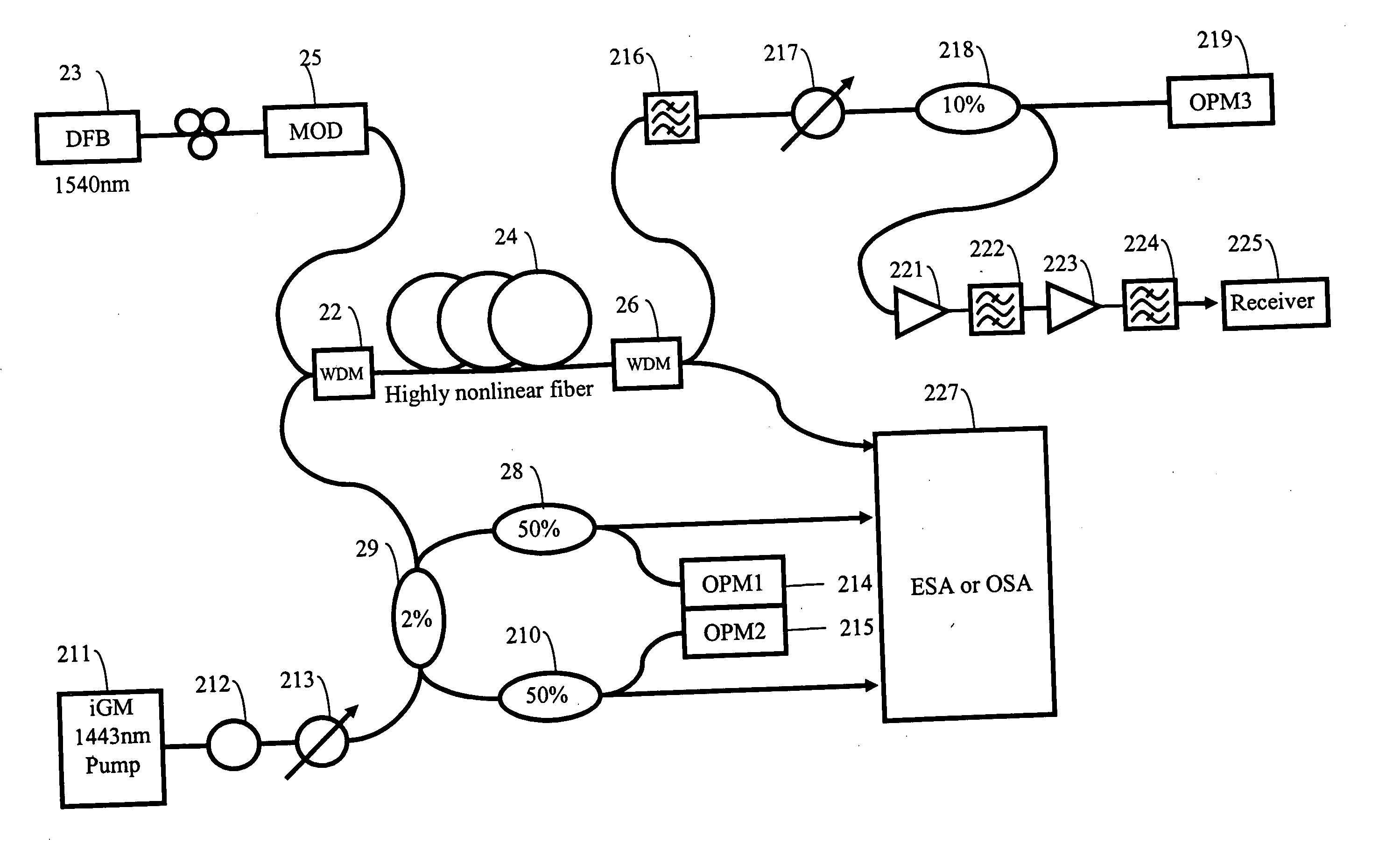
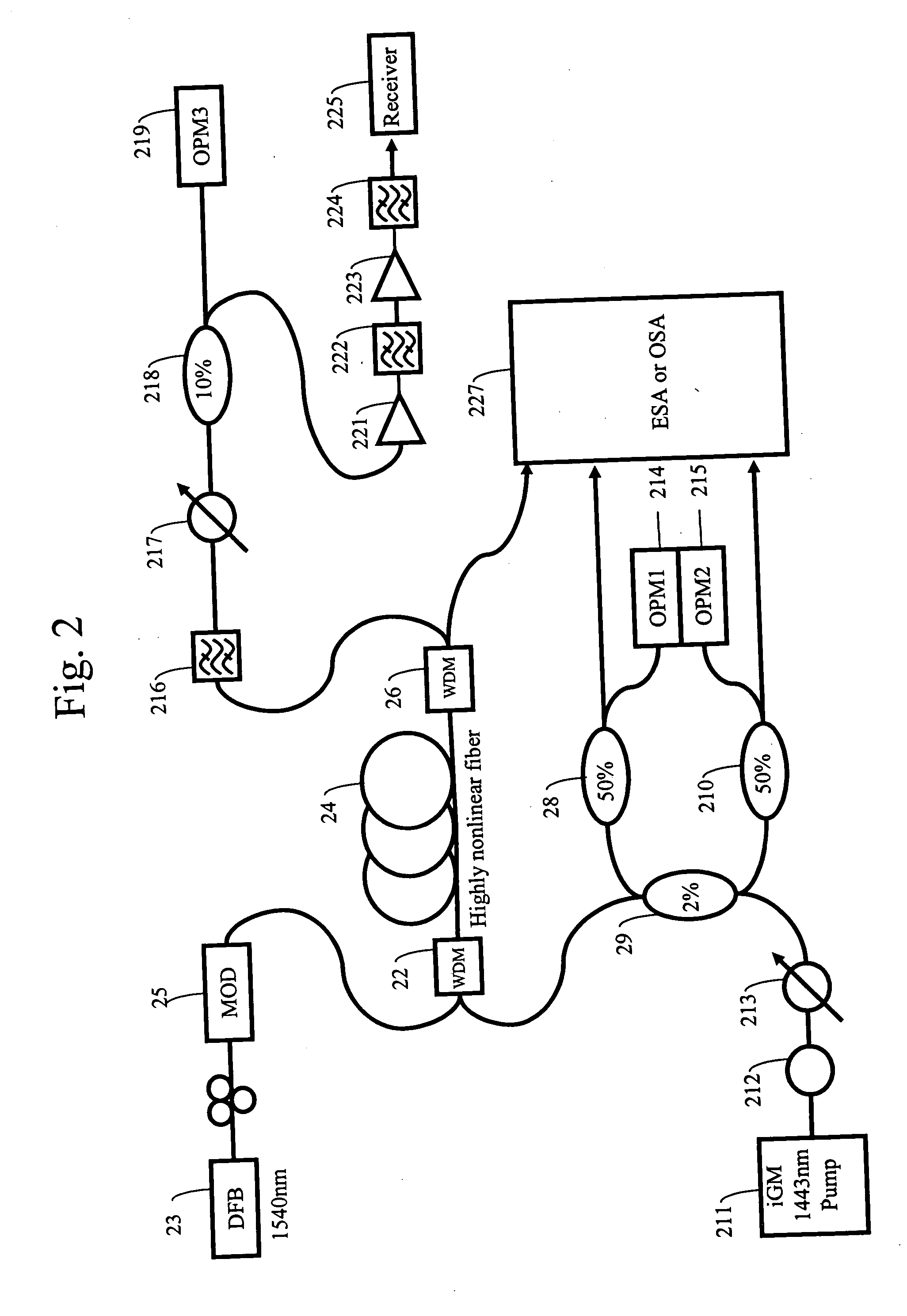
ActiveUS8643941B2Laser using scattering effectsFibre transmissionOptical power meterRaman amplifiers
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC +1
Raman fiber amplifier and automatic gain control method thereof
The invention an automatic gain control method of a Raman fiber amplifier. The automatic gain control method includes extracting in-band or out-of-band ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) power; adjusting power of a pumping laser to enable output power of the Raman fiber amplifier (RFA) and ASE power generated by the RFA to tend to meeting a formula (3): PaseT=10*log(KG*10(Pout / 10)+CG), wherein PaseT, Pout refer to theoretical value of the ASE power generated by the RFA and the Raman output power respectively, and unit is dBm; G refers to Raman gain, and unit is dB; KG and CG refer to slope and intercept value under the gain. The automatic gain control method is wide in application range, can be used for gain control of Raman amplifiers small in input light power change and can be applied to gain control of Raman amplifiers quite wide in input light power change range.
Owner:WUXI TACLINK OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
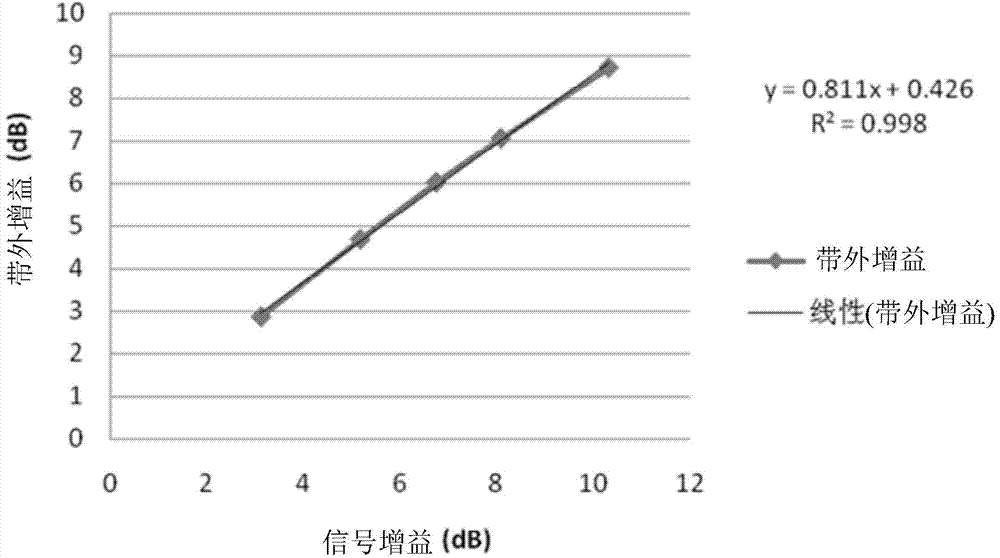
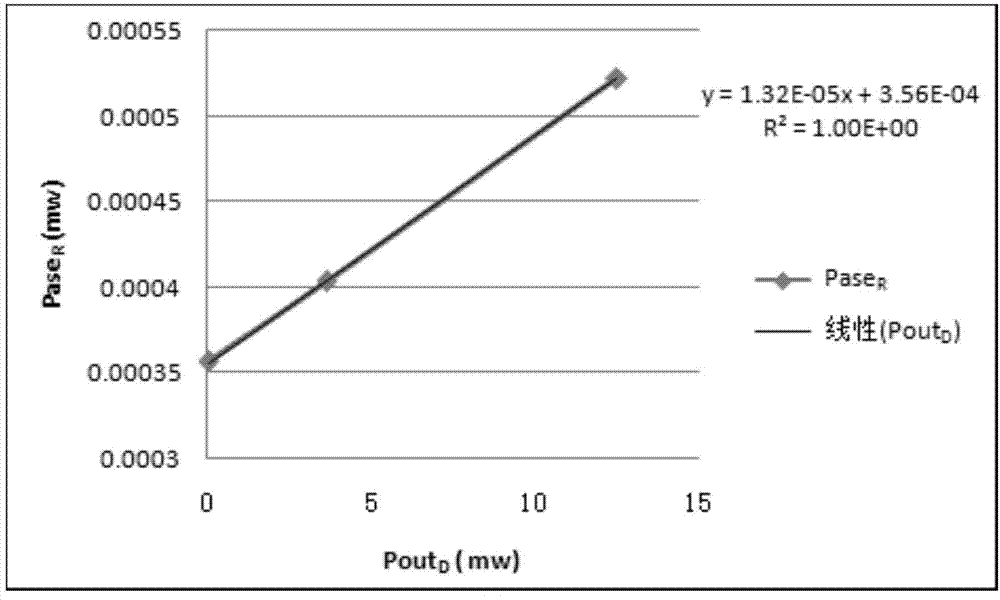
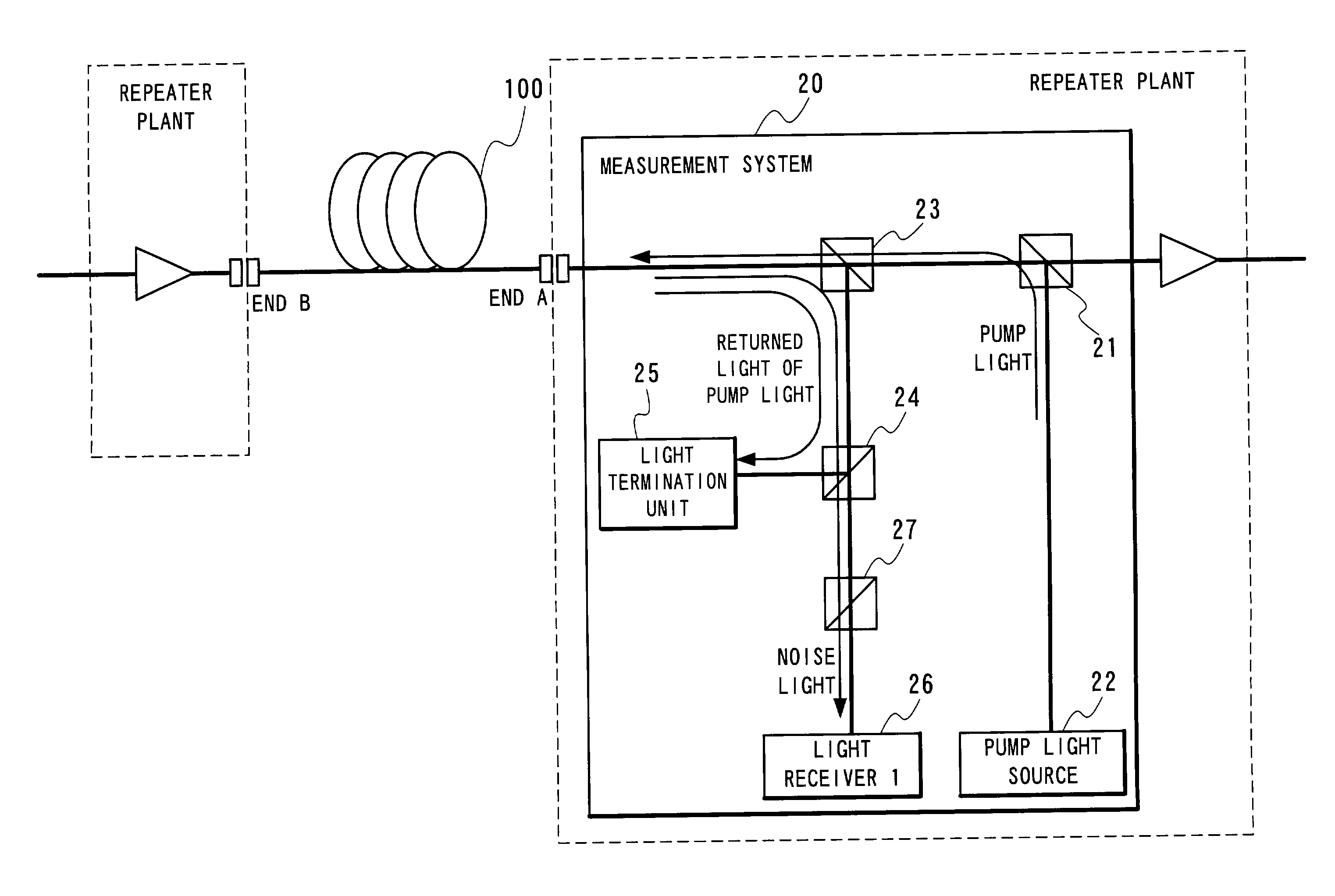
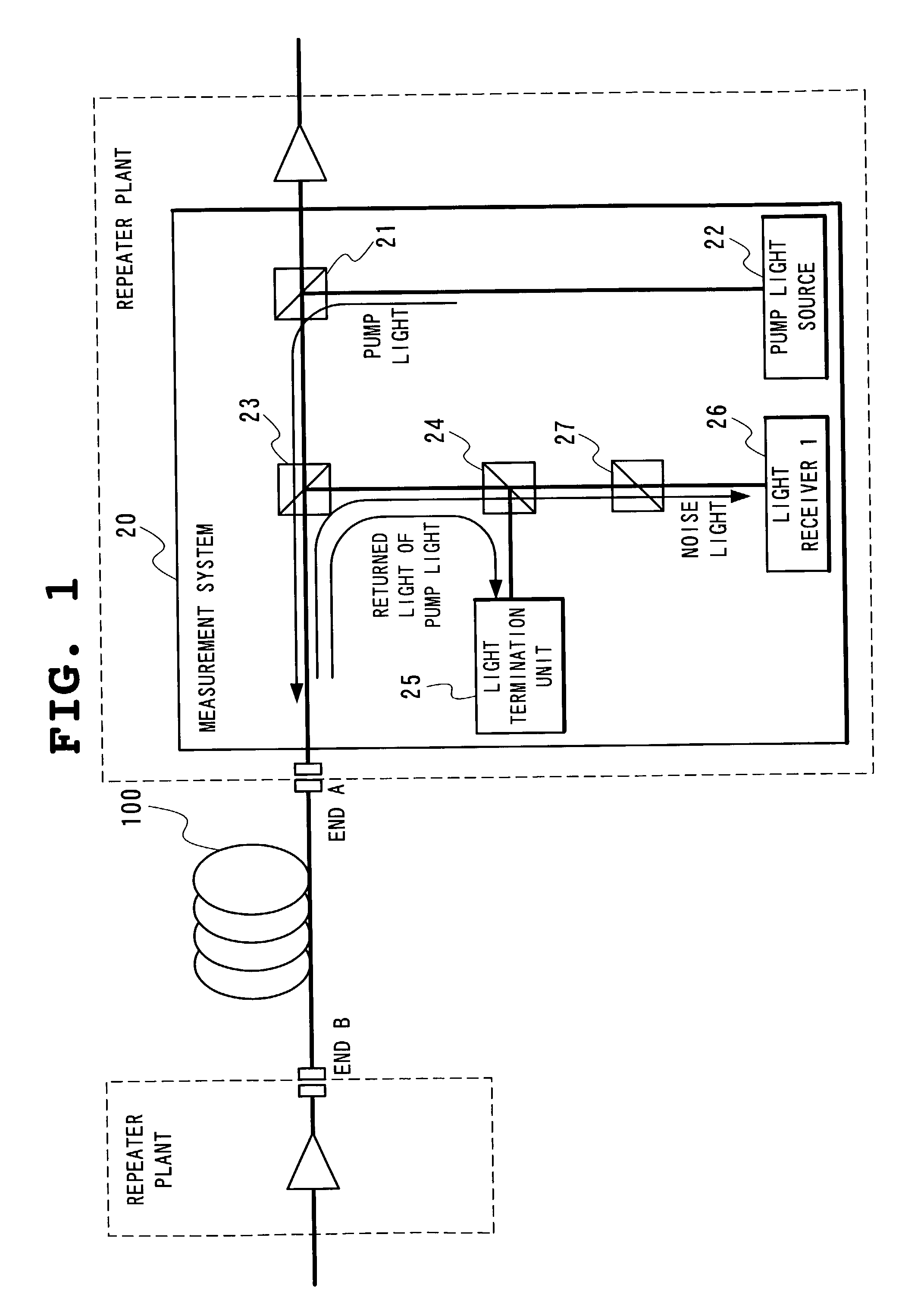
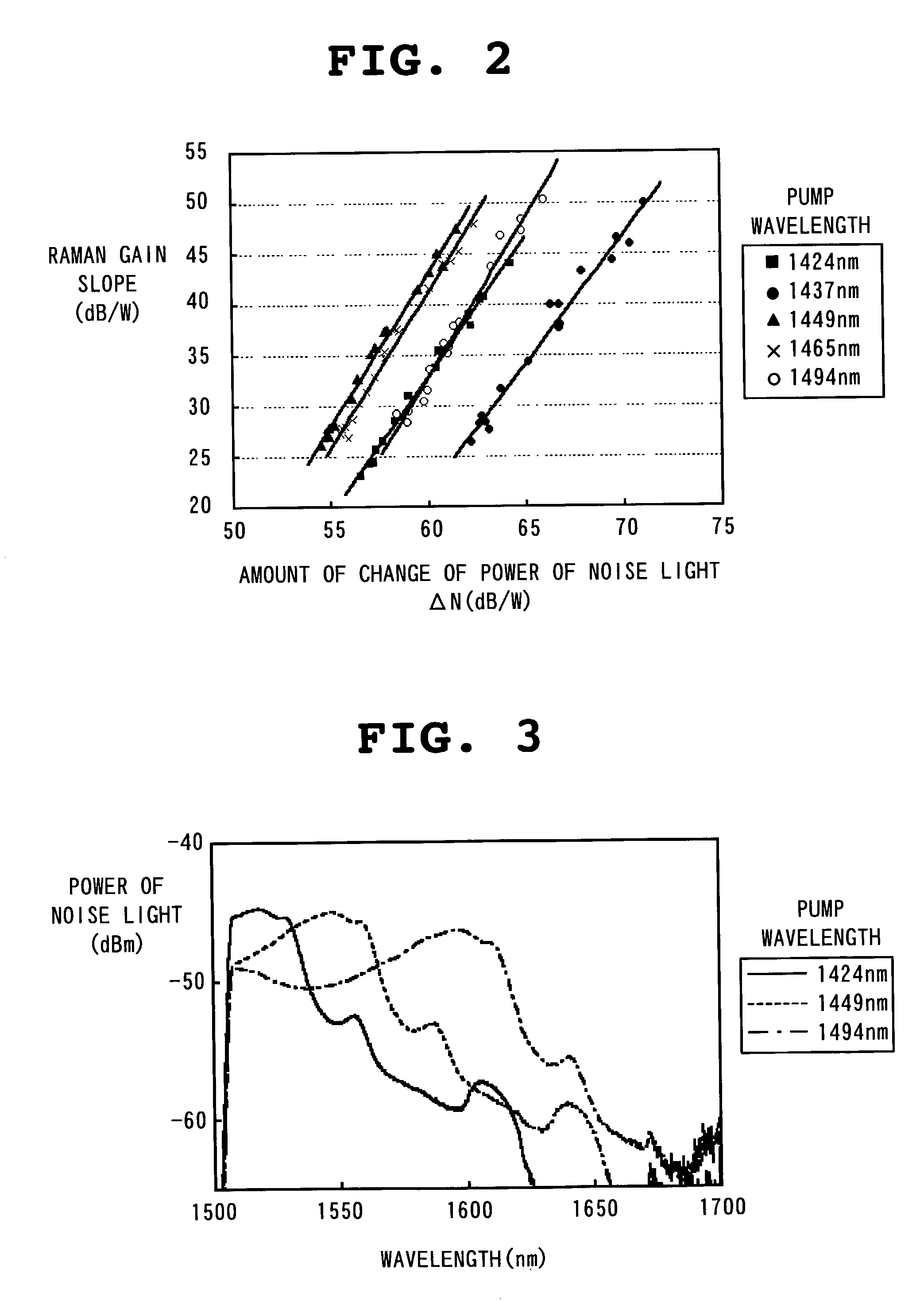
Optical fiber transmission system, raman gain slope measuring device and raman gain slope measuring method
InactiveUS7061665B2High cost performanceImprove workabilityLaser using scattering effectsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMeasurement deviceOptical power
In Raman gain slope measurement method and device measures Raman gain slope which is a value obtained by normalizing a gain generated by Raman amplification caused by pump light incident on an optical fiber by optical power of the pump light in question. The method and device measures the power of noise light and operates based on a relationship between the optical power of pump light incident on an optical fiber and the optical power of the measured noise light generated by the application of the pump light, Raman gain slope of the optical fiber in question is thus calculated.
Owner:NEC CORP
Raman amplifier and optical relay transmission system
ActiveUS7068421B2Laser using scattering effectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBeam splitterRaman amplifiers
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Continuously tunable laser device based on stimulated Raman scattering effect
InactiveCN106169696AImprove conversion efficiencyCompact conversion efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsSpectroscopyStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a continuously tunable laser device based on a stimulated Raman scattering effect. The laser device comprises a semiconductor laser pump source with fiber-coupled output, an end face pump light beam coupling system composed of a first convex lens and a second convex lens, an injection lens, a laser gain medium (or a bonding crystal), a Q-switched device, an optical tuning device, a middle lens, a Raman gain medium and an output lens. A method for achieving continuously tunable laser by the laser device comprises the steps of stimulating the laser gain medium with a wide emission line by the semiconductor pump source with a specific wavelength to generate fundamental frequency light, continuously tuning the frequency of the fundamental frequency light by using the optical tuning device, and when the fundamental frequency light enters a Raman resonant cavity, shifting the frequency of the fundamental frequency light to be continuously tunable laser with the longer wavelength for outputting via stimulated Raman scattering. The laser device expands the wavelength range of the continuously tunable laser, and has wide applications in aspects of spectroscopy, biomedicine and pollution monitoring.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Optical fiber for Raman amplification, optical fiber coil, Raman amplifier, and optical communication system
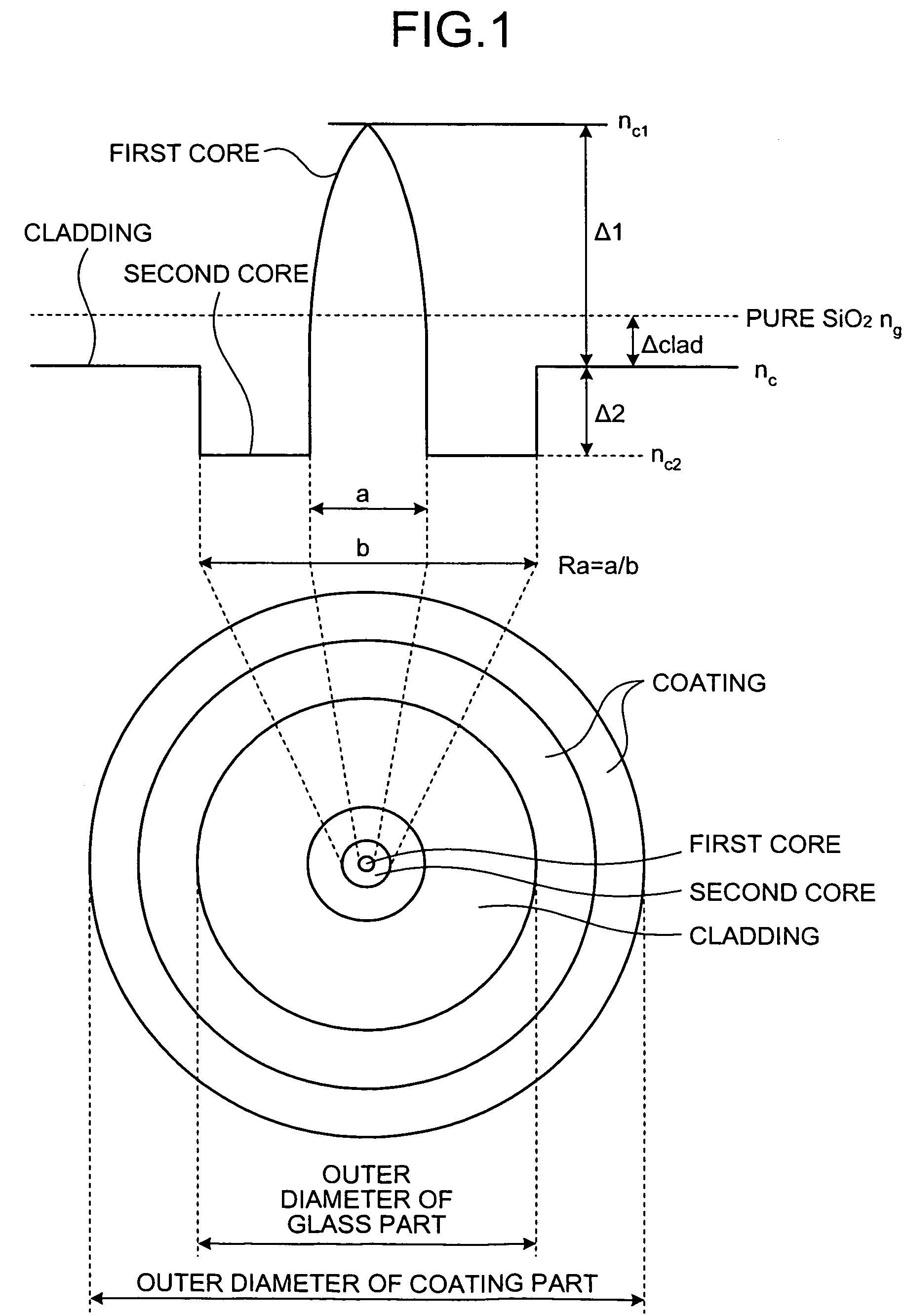
ActiveUS7248399B2Easy to useUse light energyLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCommunications systemZero-dispersion wavelength
An optical fiber for Raman amplification amplifies a signal light with a pumping light. A chromatic dispersion at a wavelength of 1,550 nm is in a range between −70 ps / nm / km and −30 ps / nm / km. Raman gain efficiency with a pumping light of 1,450 nm is equal to or more than 5 (W×km)−1. Nonlinear coefficient at the wavelength of 1,550 nm is equal to or less than 5.0×10−9 W−1. Zero-dispersion wavelength is neither at a wavelength of the signal light nor at a wavelength of the pumping light. Cut-off wavelength is equal to or less than the wavelength of the pumping light.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
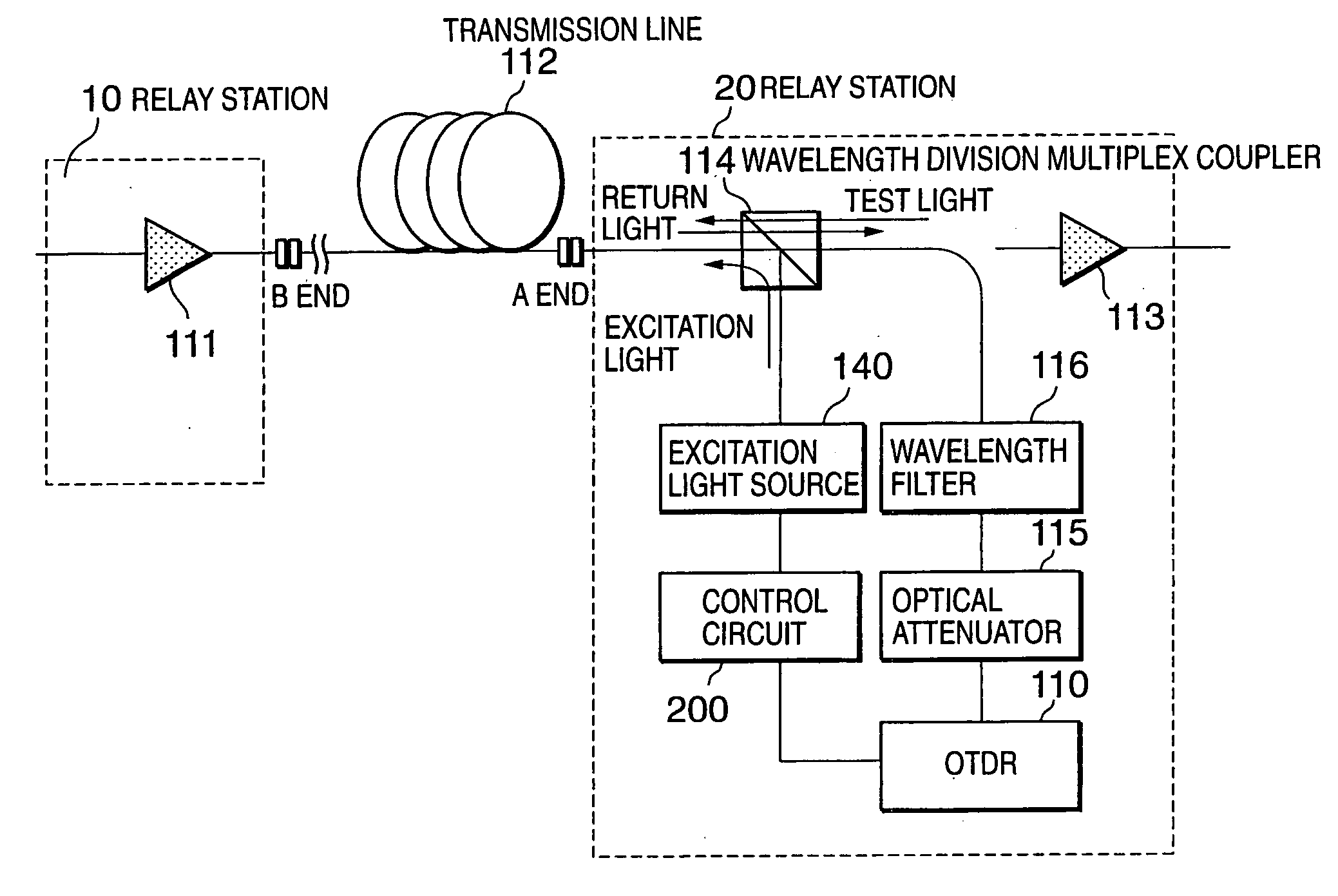
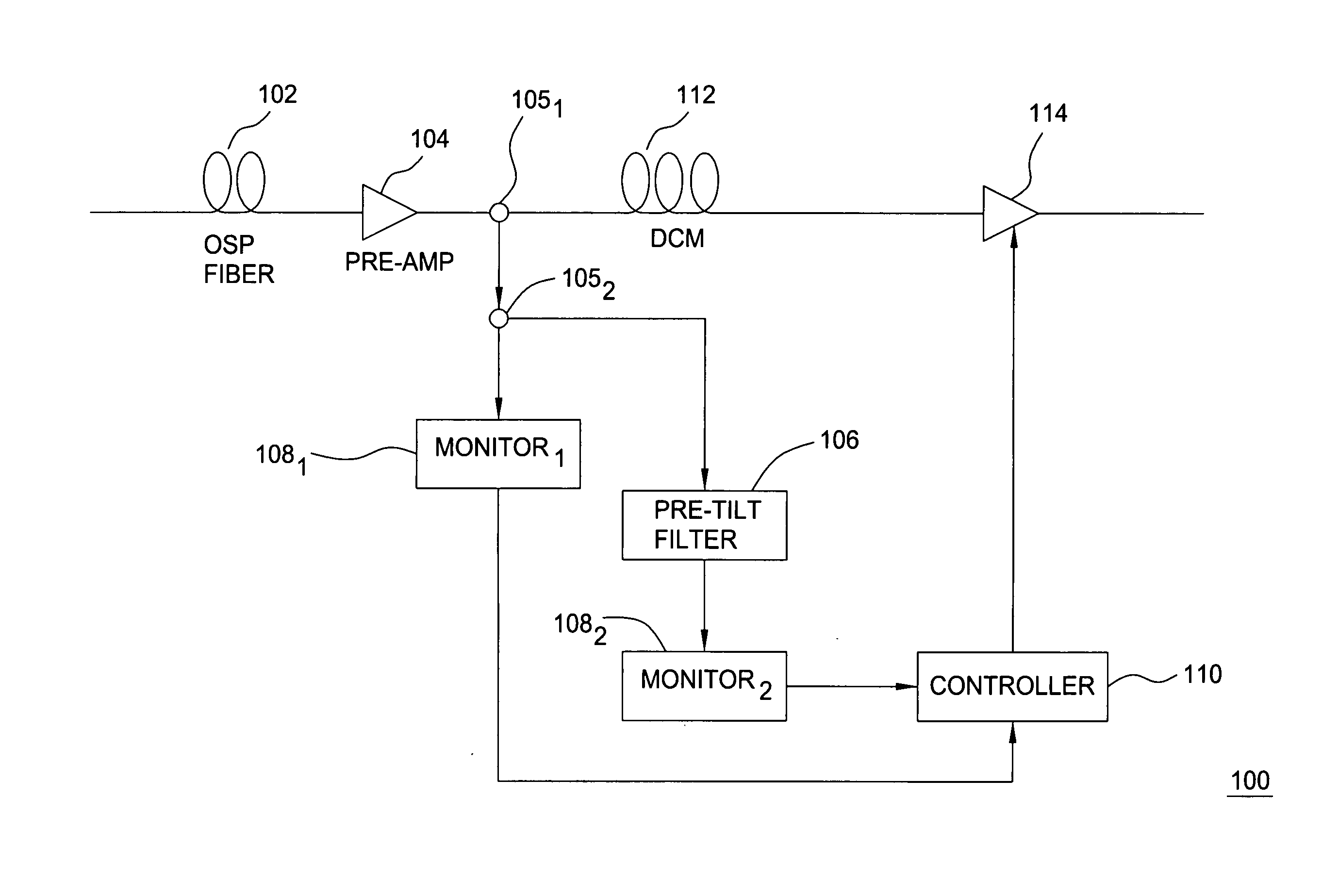
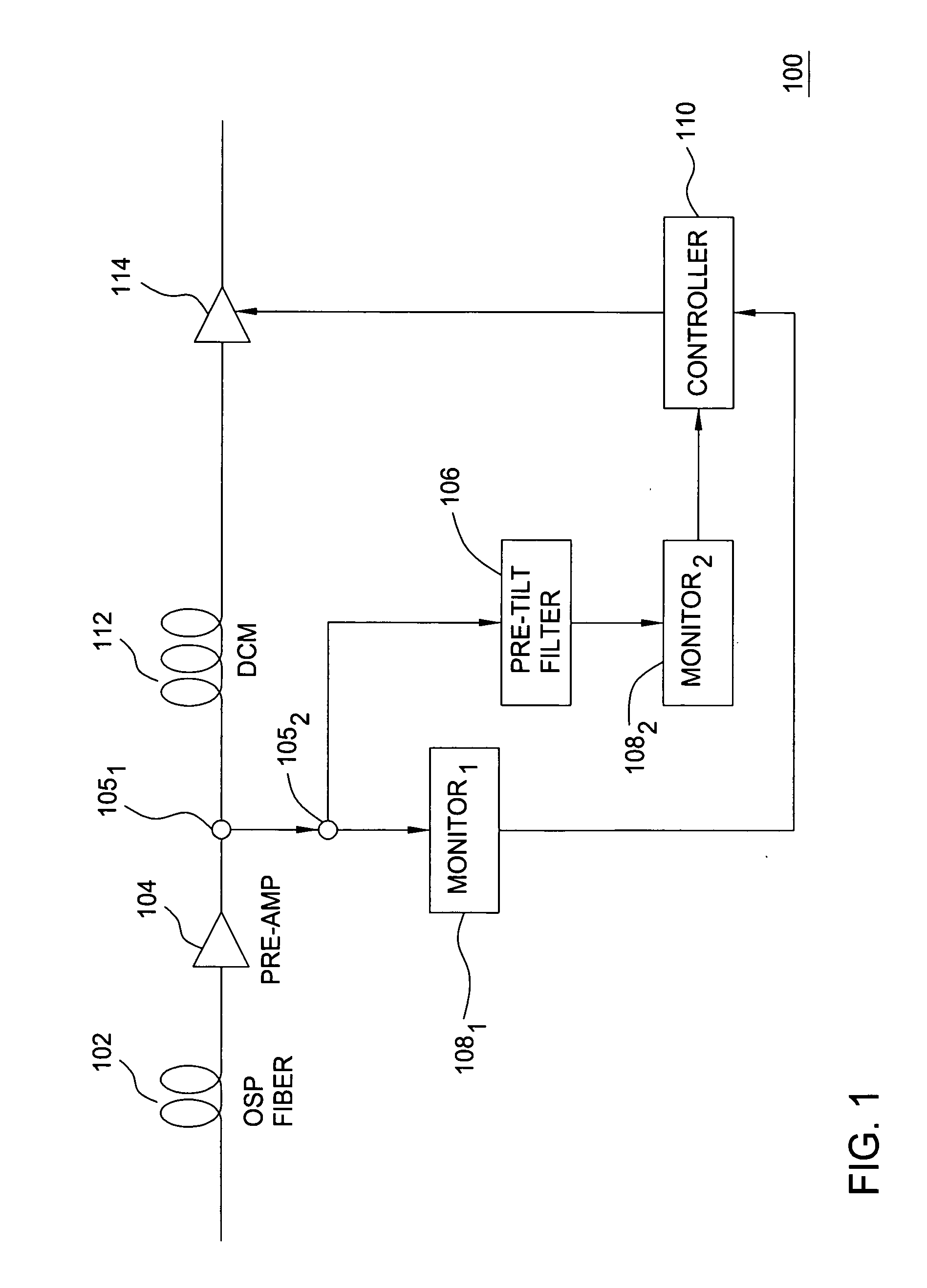
Method and apparatus for measuring Raman gain, method and apparatus for controlling Raman gain, and Raman amplifier
InactiveUS20040160664A1Laser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansWavelength filterControl signal
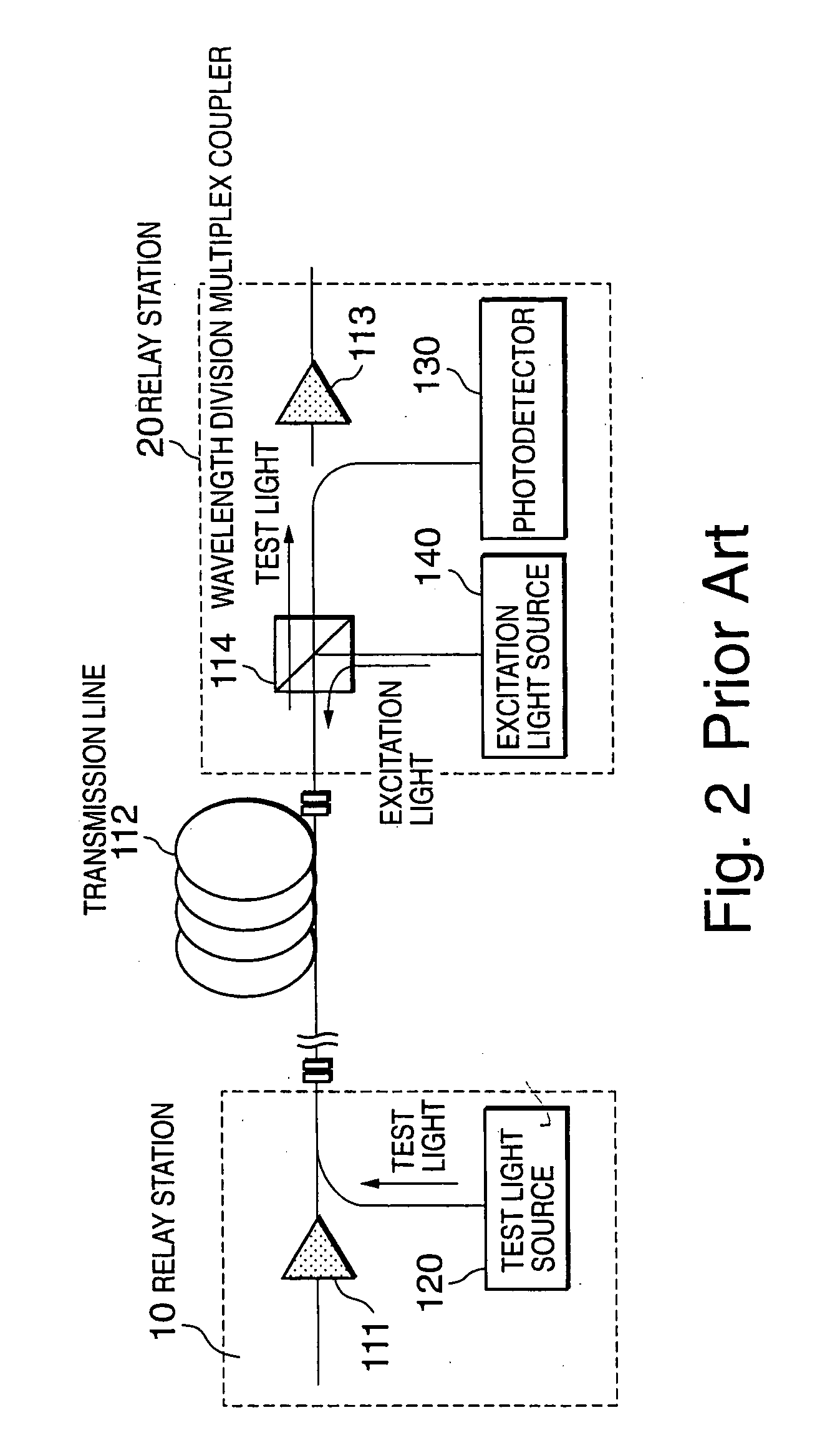
A Raman amplifier of the present invention includes a loss measuring unit (110) for measuring loss distribution of an object of measurement by OTDR based on reflected light with respect to outputted test light; an optical coupler (114) in which the test light is supplied to a first input terminal thereof and one of output terminals thereof is connected to an optical fiber transmission line; a wavelength filter (116) inserted between the loss measuring unit (110) and the optical coupler (114); a control circuit (200) for generating a control signal for reducing an error signal obtained by comparing a Raman gain obtained with a reference value; and an excitation light source (140) for changing an excitation light power based on the control signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
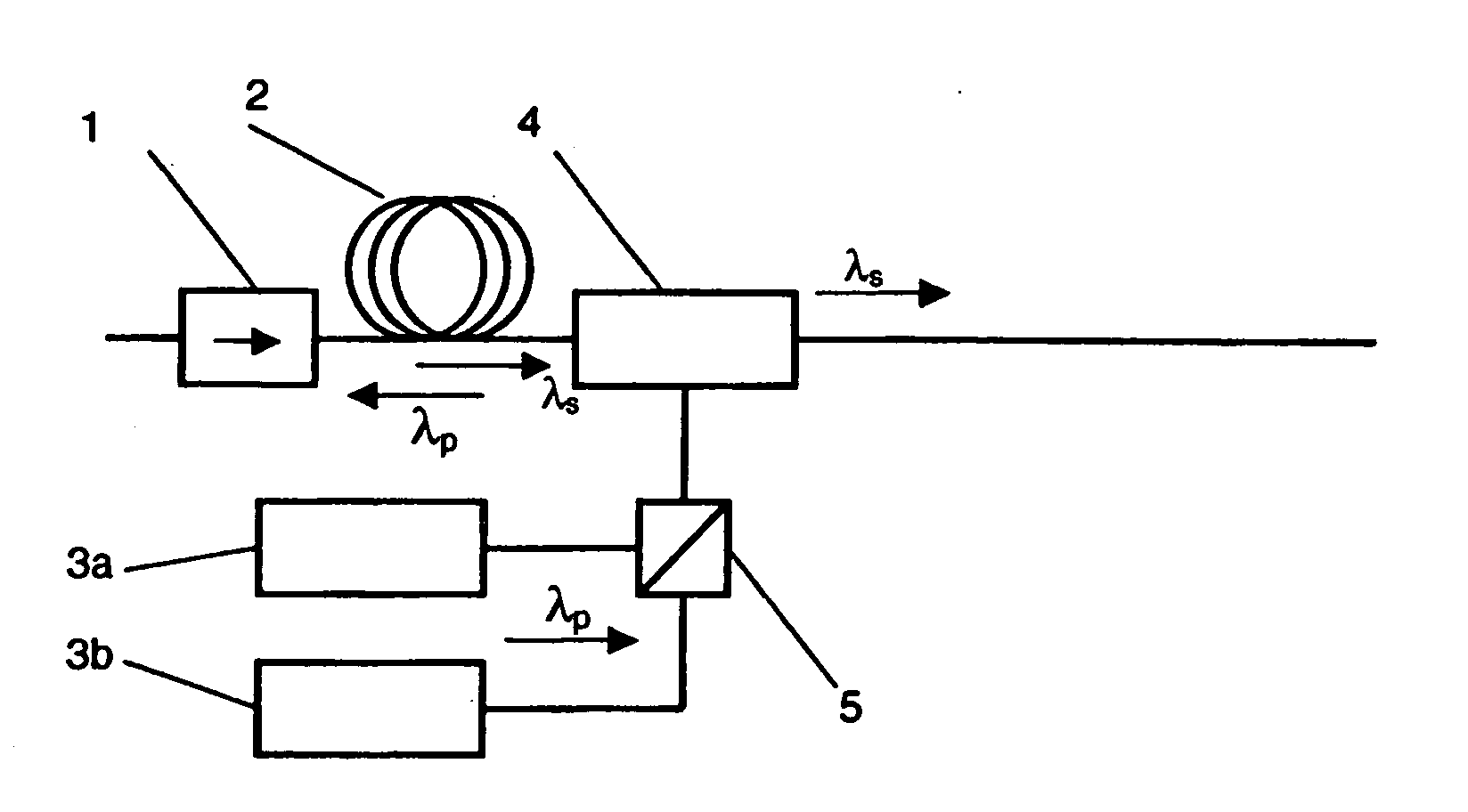
Raman amplifier, pump source for use in a raman amplifier and method for amplifying an optical signal
ActiveUS20050105165A1Accurately determineImprove system performanceLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionOptical powerRaman amplifiers
A method, pump and Raman amplifier control an amount of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) produced by the Raman amplifier pump so as to regulate a power penalty experienced by a receiver due to the SBS. A multi-mode semiconductor laser produces a multi-mode pump light having a dominate mode at a predetermined wavelength. At least a portion of the multi-mode pump light is coupled to a Raman gain medium in a forward pumping direction. A reflection sensor monitors reflected light that is at least partially reflected from said Raman gain medium. The reflection sensor has a passband characteristic that passes optical power of a dominate SBS peak of said reflected light, but suppresses other SBS peaks that are offset in wavelength from said dominate SBS peak. The optical power of the dominate SBS peak is compared to an optical power of the multi-mode pump light, and it is determined whether a result of the comparing step is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Dynamically spectrally tailored raman pump laser
InactiveUS6907051B1Easy to adjustIncrease desireLaser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionFrequency spectrumRaman pump
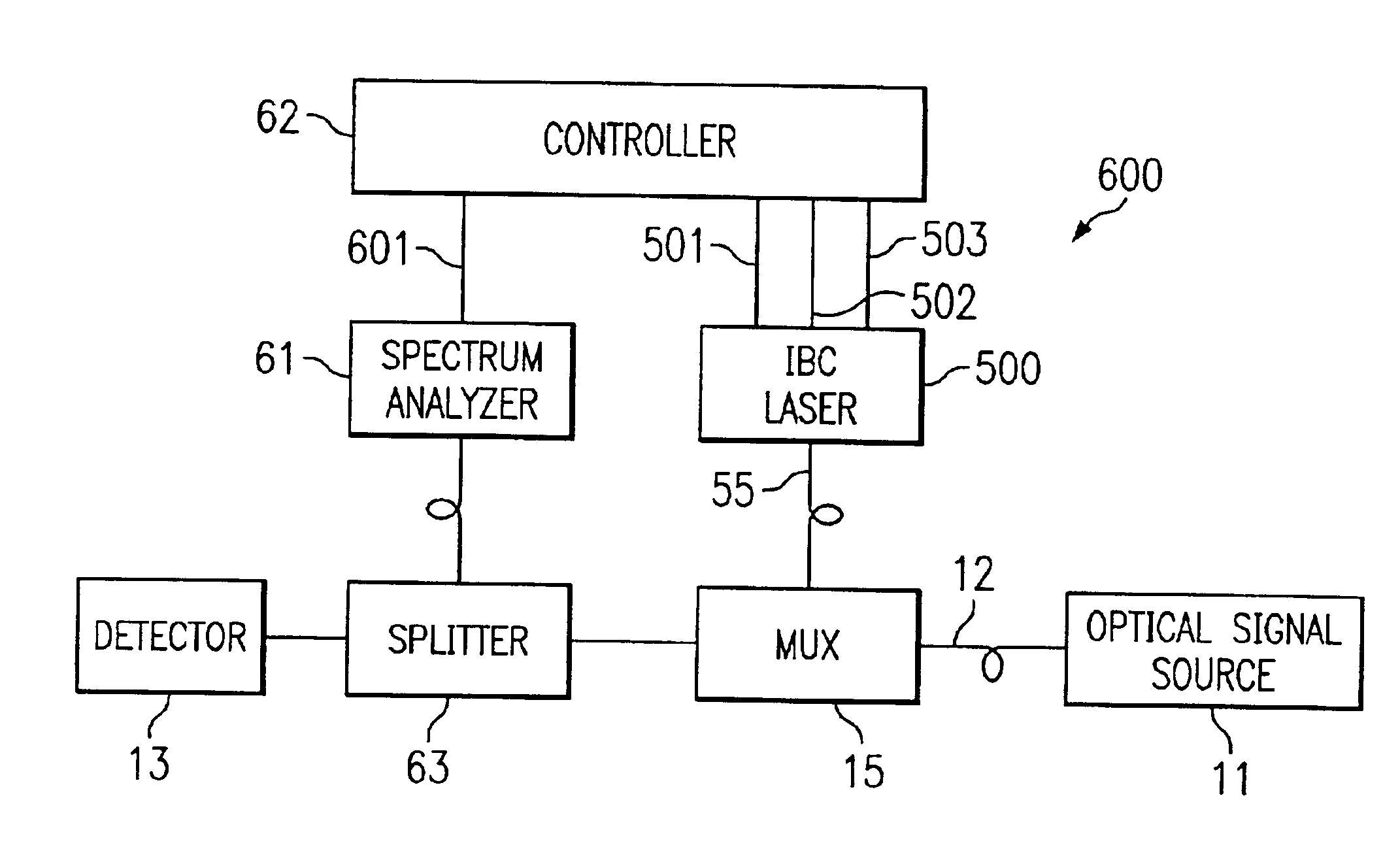
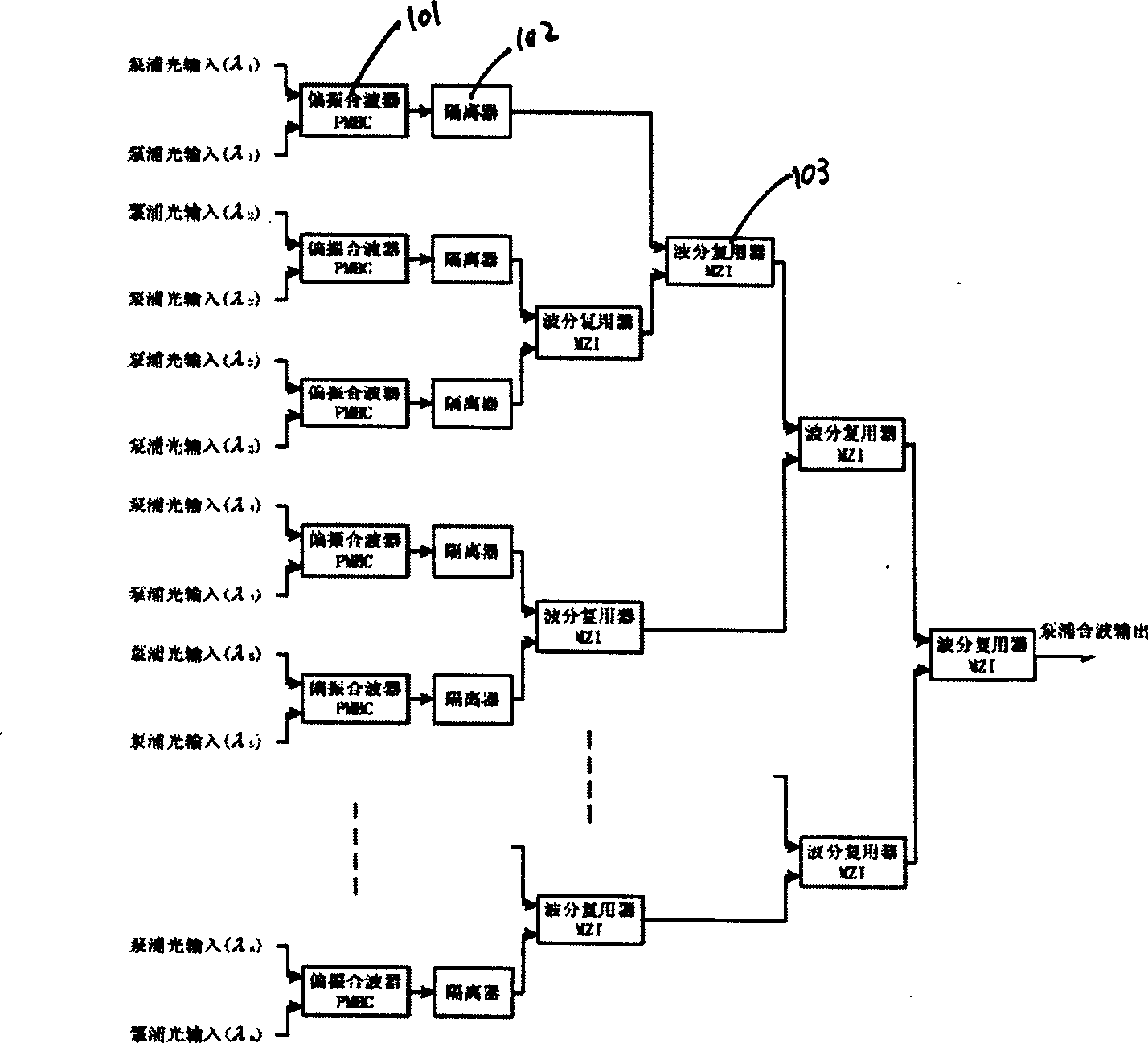
The present invention is directed to a system and method which provide a Raman pump which is spectrally tailored in response to feedback from control structure associated with the Raman pump source. In certain embodiments of the present inventions, an incoherently beam combined laser (IBC) is utilized to provide a spectrally tailored Raman pump. In these embodiments, emitters in an emitter array are either individually addressable or block addressable to facilitate adjustment of emitter output power. By adjustment of the output power, the Raman pump may be spectrally tailored. The spectral tailoring can occur by employing suitable control algorithms to algorithms to dynamically maintain reasonably flat Raman gain.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
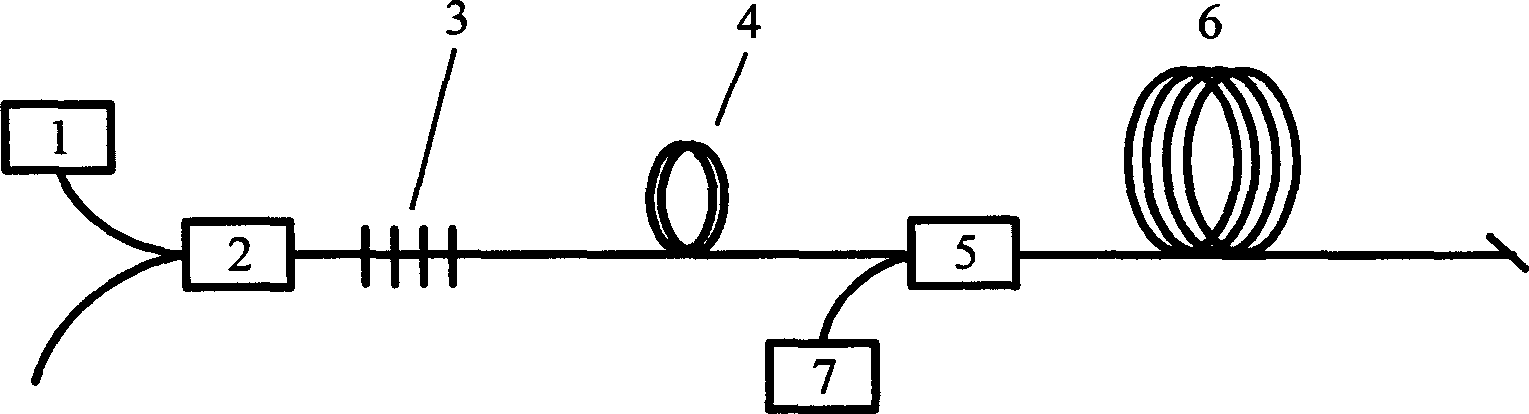
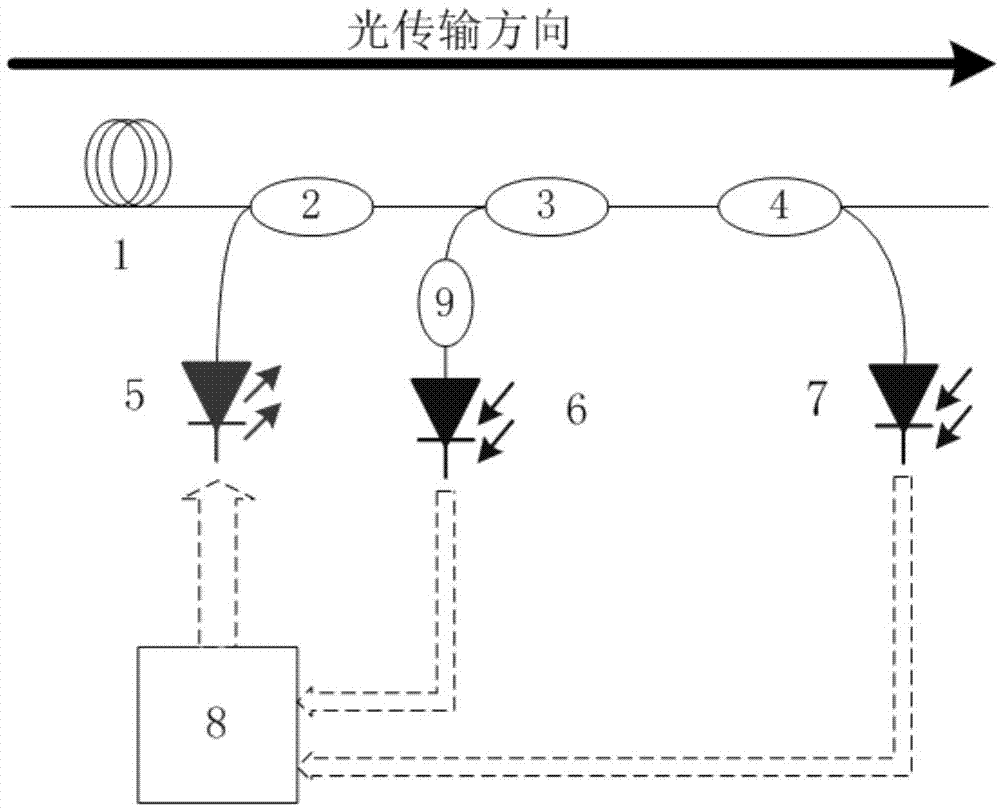
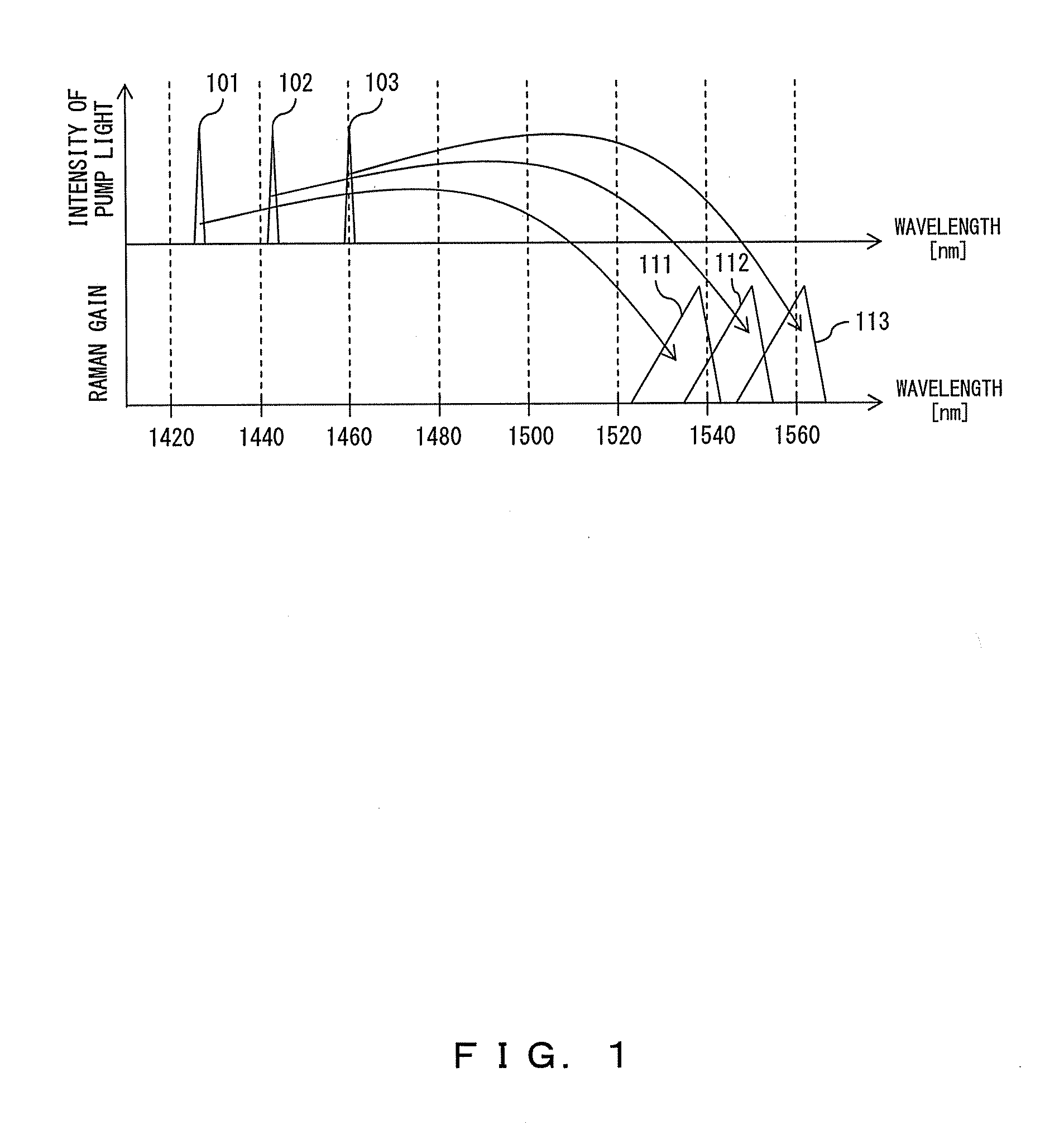
Raman gain real time kinetic control and compensation method and its Raman optical-fibre amplifier
InactiveCN1412616ARaman gain remains constantSimple structureLaser using scattering effectsElectromagnetic transmissionAutomatic controlBand-pass filter
The present invention mainly utilizes the spontaneous raidation noise of backward pump, i.e. light power level of ASE to implement autoamtic control of Raman gain of Raman optical-fibre amplifier andcompensation. Its Raman optical-fibre amplifier is characterized by that at the signal light detection place a combination of filter and photoelectric detector for detecting the backward ASE power ofRaman optical fibre amplifier nearby dirrerent wavelength is added, the output of the photoelectric detector is connected with control unit of automatic regulation of gain of Raman amplifier.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Method and system for reducing Raman gain tilt error
ActiveUS20050041977A1Reduce gain errorLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
A method and system in accordance with the present invention greatly reduces the gain error due to Raman gain tilt for individual channels in an optical communication system during a transient event by determining a shift in average power (and thus wavelength) and using the determined shift to alter the average gain in the optical communication system. In various embodiments of the present invention, the average gain of the optical communication system is altered by altering the average gain of an amplifier in the optical communication system. In alternate embodiments of the present invention having an in-line optical filter, the average gain of the optical communication system may be altered by altering the filtering of the optical channels in the optical communication system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
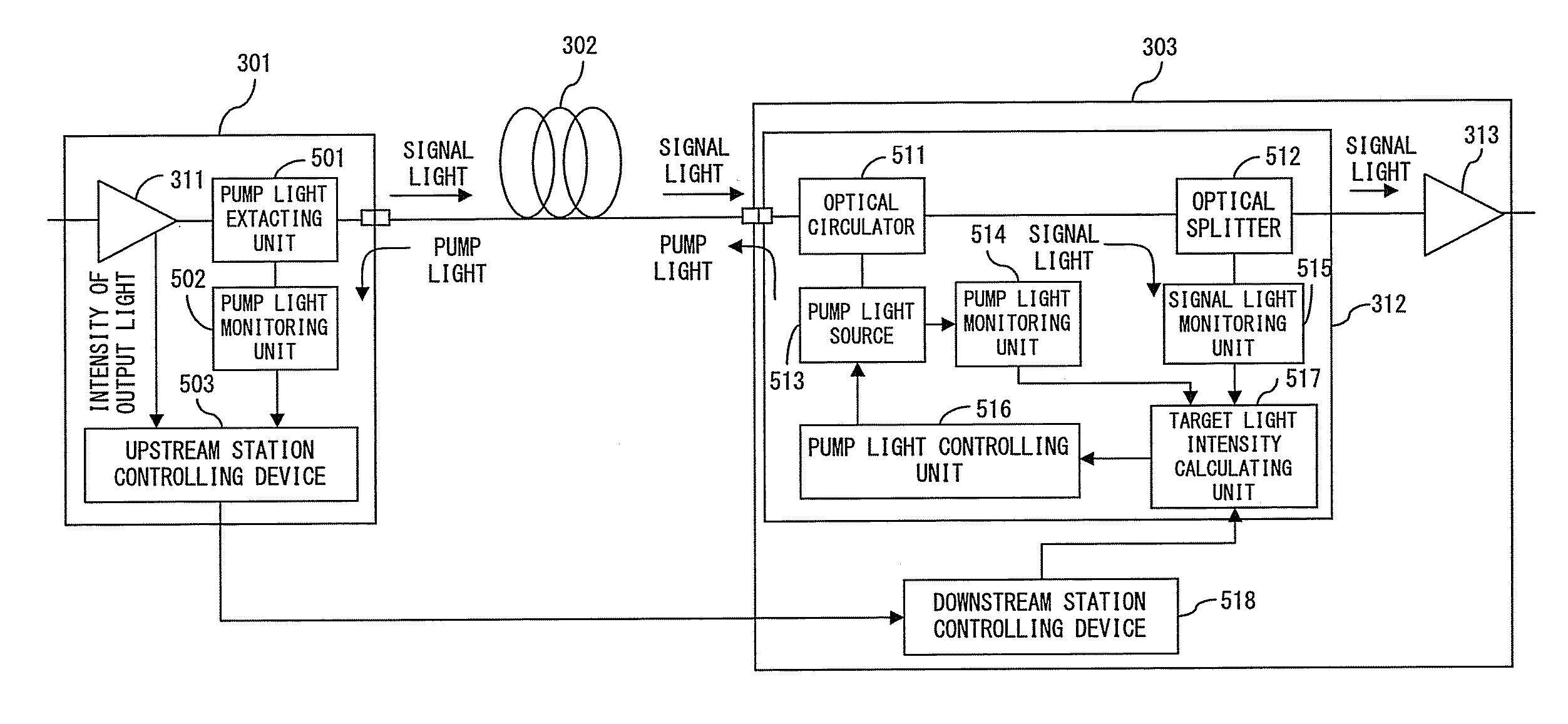
Raman amplifier
InactiveUS20080123180A1Satisfactory gain characteristicImprove estimation accuracyLaser detailsElectromagnetic repeatersFiberAudio power amplifier
When pump light is supplied to a transmission line fiber from a downstream station toward an upstream station and signal light from the upstream station is Raman-amplified, a corresponding intensity of amplified spontaneous scattering light is calculated from a required Raman gain by using a correlation between a Raman gain and the intensity of amplified spontaneous scattering light that occurs with Raman amplification, and further a target light intensity is calculated from the obtained intensity of the amplified spontaneous scattering light and the intensity of the amplified signal light. Then, the intensity of the pump light is controlled so that the intensity of light, which is measured by the downstream station, becomes equivalent to the target light intensity.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Random fiber laser with tunable wavelength
InactiveCN102437500AImprove slope efficiencyWavelength tunableLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionRandom laserSeeds source
The invention discloses a random fiber laser system with tunable wavelength, belonging to the laser device field. According to the system, first pump source laser with tunable wavelength and a series of low energy seed source laser are injected into a fiber, through a series of Raman amplification effects, distributed Raman amplification light is generated in a transmission fiber, and distributedRayleigh backward diffusion light forms random laser after Raman amplification. A random laser in the invention can realize continuous tunable wavelength. In a selectable scheme, after first Raman amplification, residual energy of a first pump source or a first seed source is fed back to the fiber for reuse, and slope efficiency of a finally formed random laser is raised. The system can control aRaman gain and a shape of a Raman gain spectrum through additional seed light, reduce a threshold of the laser, and raise output power.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
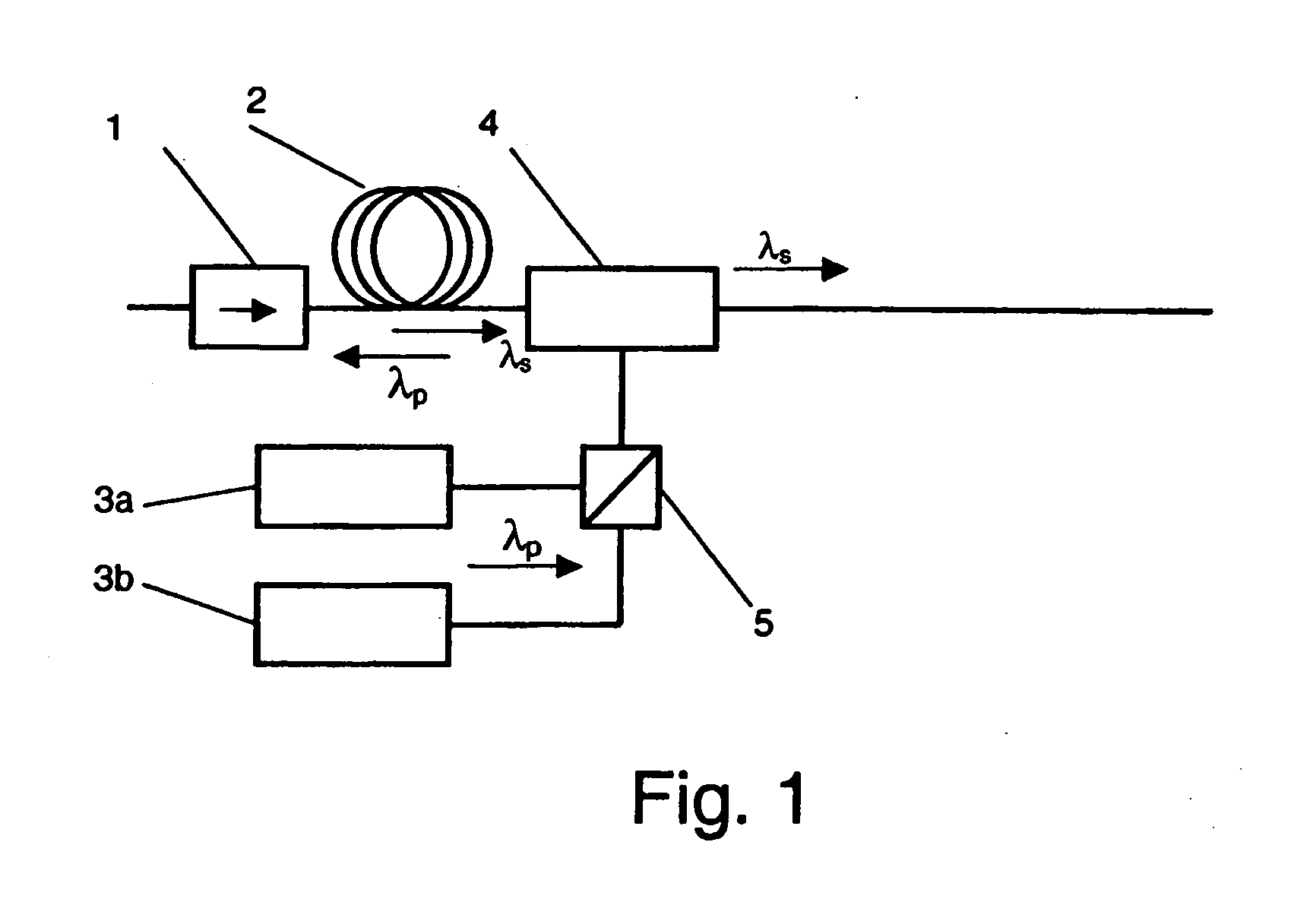
Raman amplifier, pump source for use in a raman amplifier and method for amplifying an optical signal
ActiveUS7206123B2Improve system performanceAddress limitationsLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionRaman amplifiersOptical power
A method, pump and Raman amplifier control an amount of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) produced by the Raman amplifier pump so as to regulate a power penalty experienced by a receiver due to the SBS. A multi-mode semiconductor laser produces a multi-mode pump light having a dominate mode at a predetermined wavelength. At least a portion of the multi-mode pump light is coupled to a Raman gain medium in a forward pumping direction. A reflection sensor monitors reflected light that is at least partially reflected from said Raman gain medium. The reflection sensor has a passband characteristic that passes optical power of a dominate SBS peak of said reflected light, but suppresses other SBS peaks that are offset in wavelength from said dominate SBS peak. The optical power of the dominate SBS peak is compared to an optical power of the multi-mode pump light, and it is determined whether a result of the comparing step is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Random fiber laser of semiconductor laser cascaded pump
InactiveCN102231476AReduce output powerIncreased Raman Gain BandwidthExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor laser excitation apparatusRayleigh scatteringRefractive index
The invention provides a random fiber laser system and belongs to the novel laser device field. In the system, a traditional single-mode fiber is taken as a laser medium, and a cascaded semiconductor laser is taken as pump light which is coupled to the fiber along an opposite direction from a middle point of the fiber. Photon is in propagation in the fiber, scattering is generated because of nonuniform random refractive index, and distributed Rayleigh scattering is formed. The pump light provides distributed Raman gain along the fiber. When total gain is greater than total loss, backward scattered photon is amplified to generate laser. Frequency of random laser is a result of frequency of last grade pump light shifting downward with 13 THz. By properly selecting pump light, output of the random laser in a whole fiber transparent window is realized. By using cascaded semiconductor laser as the pump light, not only is Raman gain spectrum bandwidth increased, but also Raman gain form is controlled. Thereby the random laser in the invention has the characteristics of controllable mode, super-long transmission, low threshold, high output power and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Raman distributed feedback fiber laser and high power laser system using the same
ActiveCN103597675ALaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionGratingHigh power lasers
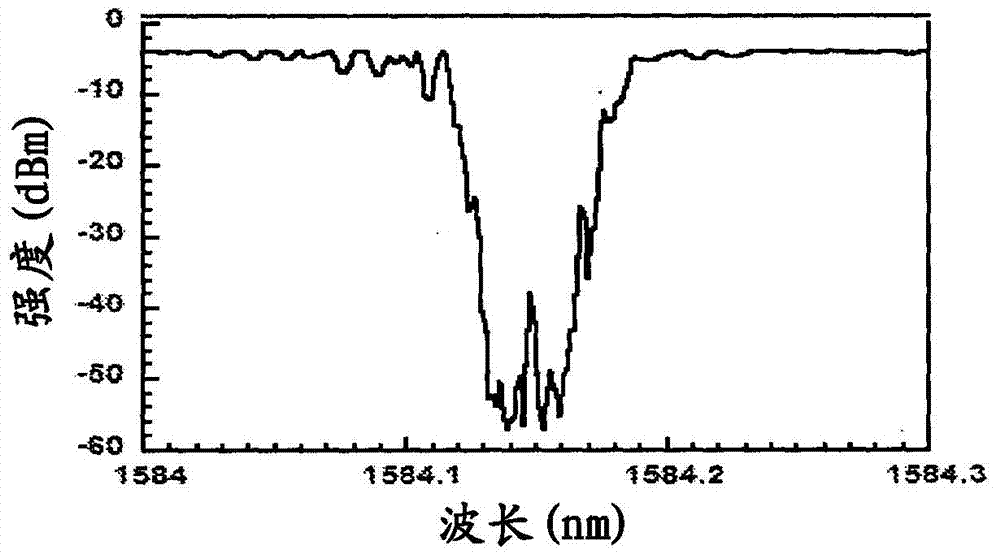
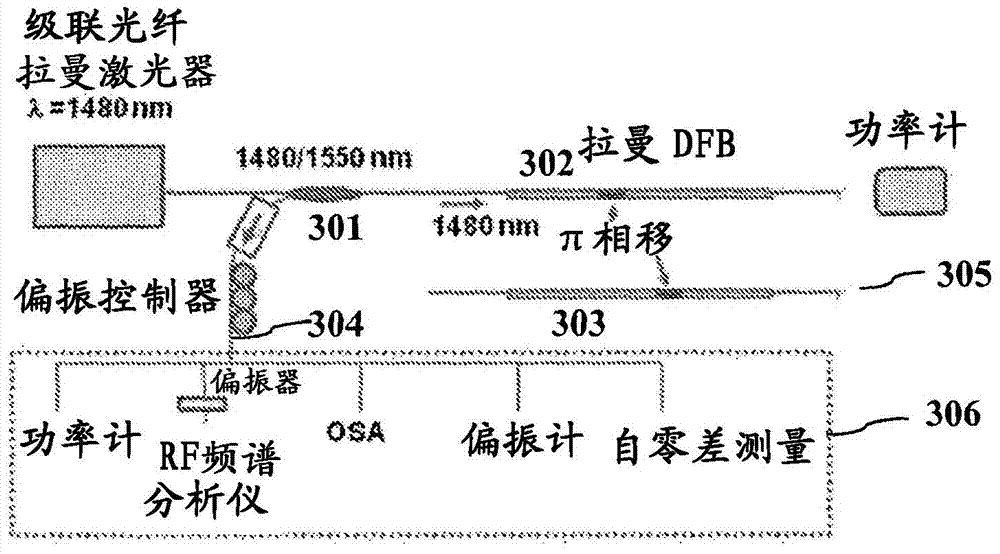
A Raman distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser is disclosed. It includes a pump source and a Raman gain fiber of a length smaller than 20 cm containing a distributed feedback (DFB) grating with a discrete phase structure located within no more than 10 % off the center of the grating and wherein the Raman DFB fiber laser generates a laser signal with an optical spectrum, which has an optical bandwidth at half maximum optical intensity of less than 1 gigahertz (GHz) (wherein a maximum intensity frequency is different from the frequency of the pump laser). The Raman laser includes compensation for the nonlinear phase change due to Kerr effect and thermal effect resulting from absorption of the optical field, thus enhancing the conversion efficiency.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Reman optical fibre amplifier with dynamic gain wave control
InactiveCN1472585AReduce the change of signal optical powerAvoid Large Nonlinear EffectsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNon-linear opticsLaser arrayOptoelectronics
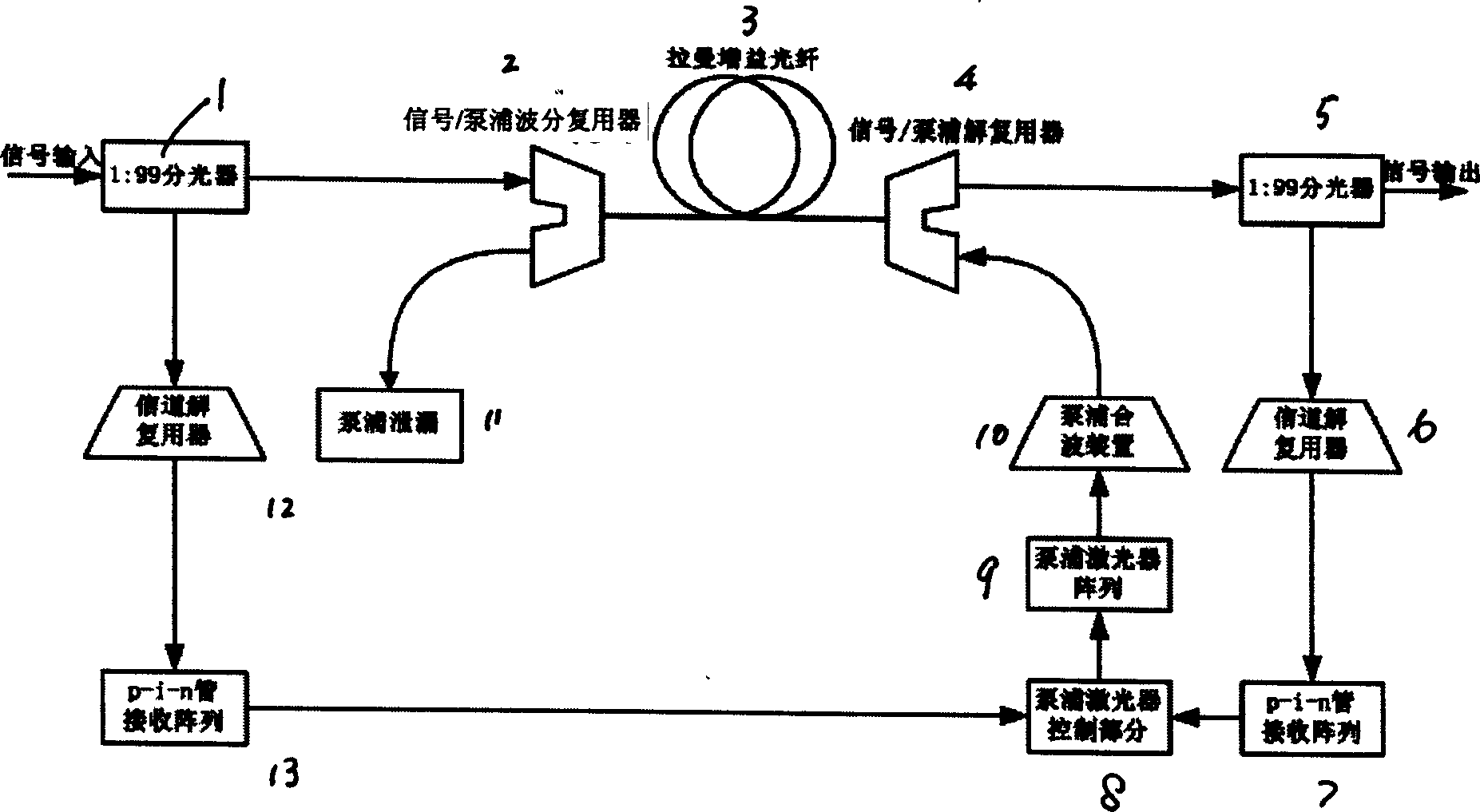
An amplifier includes two parts as Raman amplifying part consists of a set of pumping laser array, pumping wave combining device, a section of Raman gain optical fibre, signal / pumping multiplexer and demultiplexer and signal demultiplexer; gain feedback control device consists of signal input-output power measurement and pumping laser controller. As discrete Raman optical fibre amplifier, it can realize C+L waveband 1428-1604 nm dispersion compensation by applying dispersion compensating fibre as Raman gain media and realize gain spectrum smooth and fluctuation control for optical signal waveband by controlling output power of N number of pumping lasers in 14xxnm.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
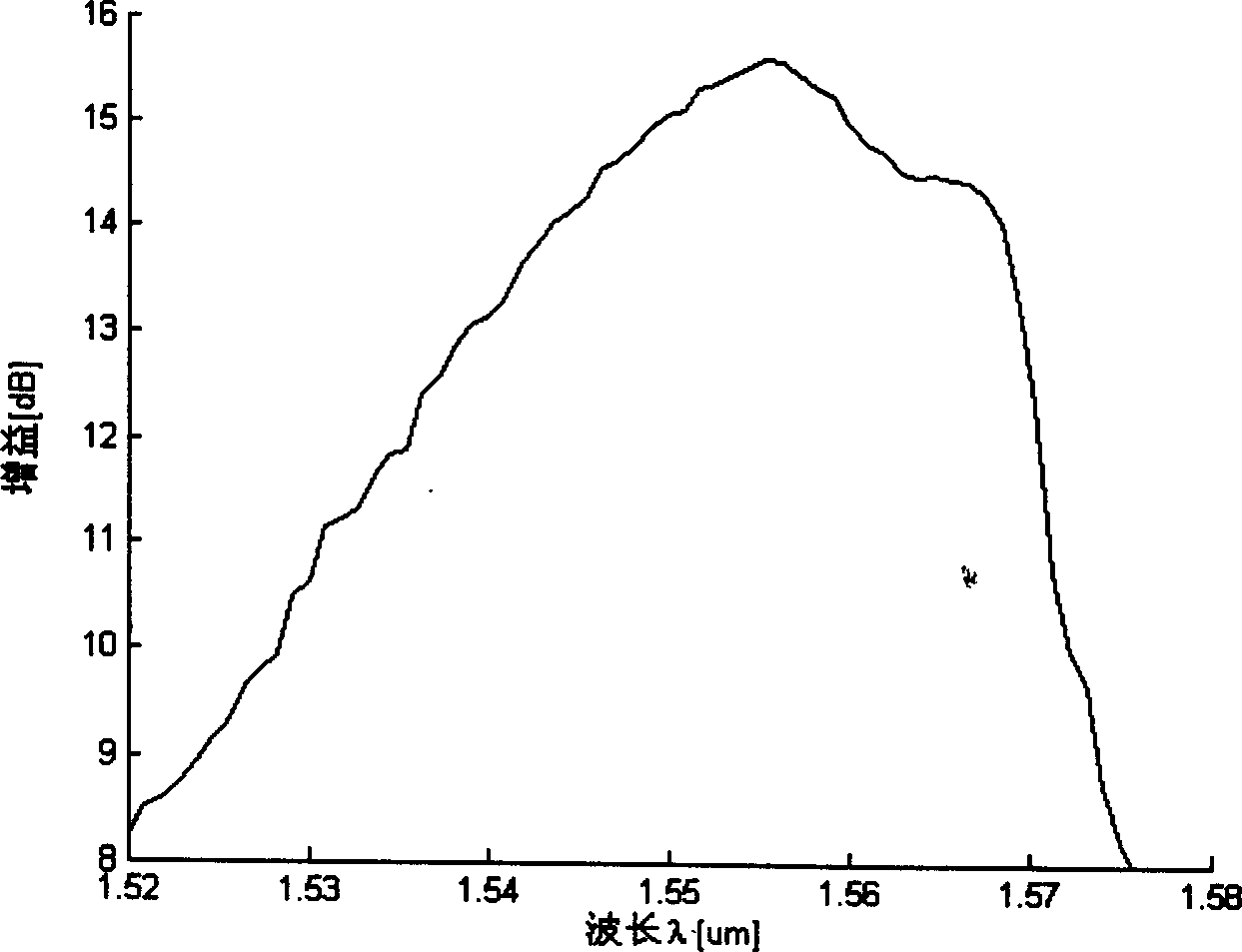
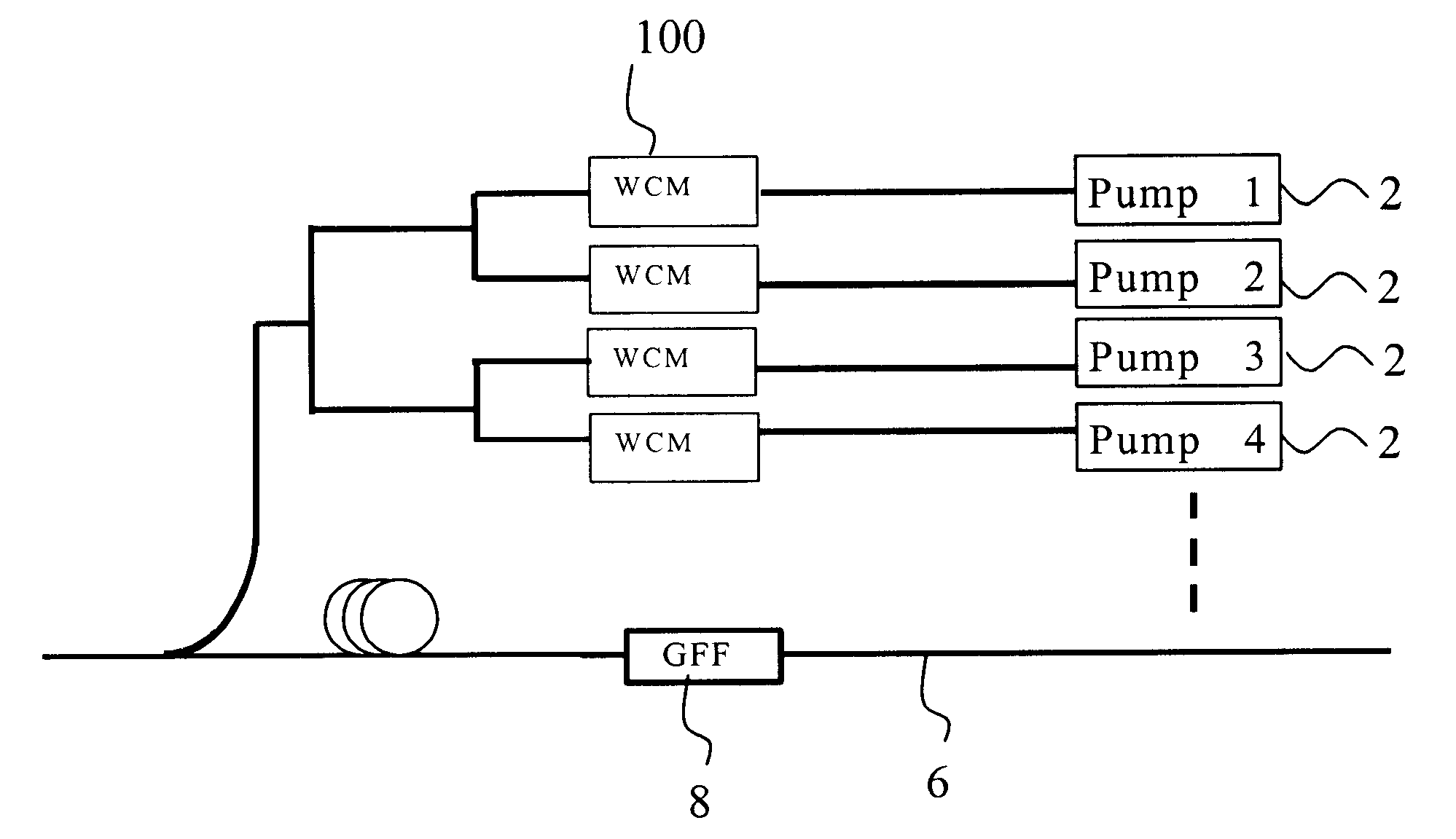
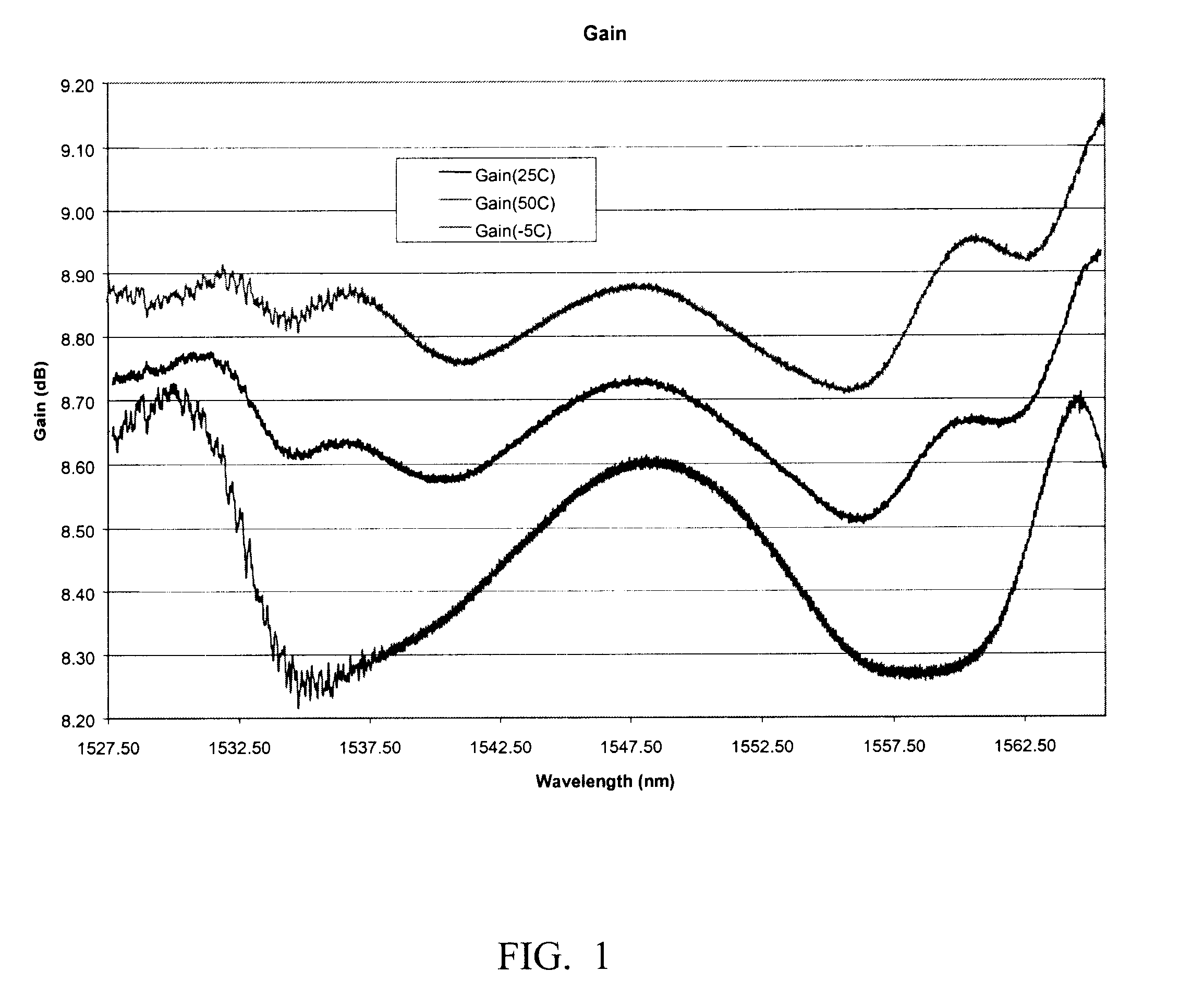
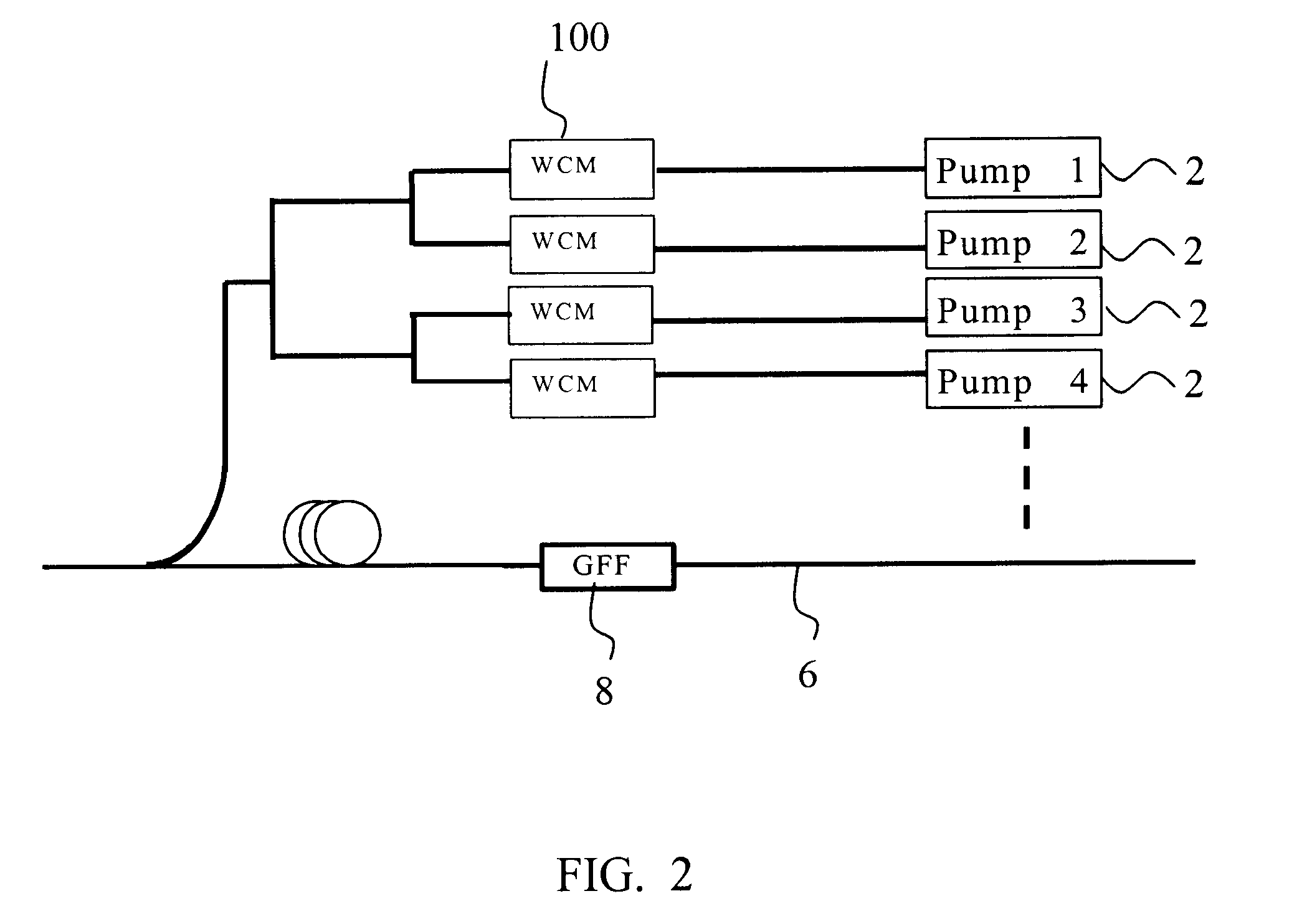
Method and system for controlling Raman gain flatness sensitivity to pump laser wavelength variation
An exemplary embodiment of the invention is a Raman amplifier for use in an optical communications network. The Raman amplifier includes a plurality of pump lasers and a plurality of wavelength control modules, each associated with one of the pump lasers. Each wavelength control module includes a fiber Bragg grating optically coupled to a respective one of the plurality of pump lasers. The fiber Bragg grating receives a pump laser output from one of the pump lasers and generates a wavelength control module output. A temperature sensor is in thermal contact with the fiber Bragg grating and generates a temperature signal indicative of a temperature of the fiber Bragg grating. A controller is operatively connected to the temperature sensor and generates a control signal in response to the temperature signal. A thermal regulator is in thermal contact with the fiber Bragg grating and adjusts the temperature of the fiber Bragg grating in response to the control signal. The controller adjusts the temperature of the fiber Bragg grating to reduce sensitivity of Raman gain flatness to variation in a wavelength of the pump laser output.
Owner:CIENA
Tunable medium-infrared optical fiber mixed gas cascaded Raman laser
ActiveCN106253047AHigh strengthIncrease distanceLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthStimulate raman scattering
The invention discloses a tunable medium-infrared optical fiber mixed gas cascaded Raman laser, which comprises a near-infrared tunable laser pumping source, an input coupling module, an input gas cavity, a hollow-core optical fiber, an output gas cavity, an output guiding element and a coupling output mirror which are sequentially arranged along an optical path, and further comprises a feedback system, wherein the hollow-core optical fiber is filled with two mixed Raman gain gases which is used for making pump light undergo stimulated Raman scattering to generate first-stage Raman laser and making the first-stage Raman laser undergo stimulated Raman scattering to generate second-stage Raman laser in medium-infrared band; and the feedback system is used for guiding the first-stage Raman laser and the second-stage Raman laser in medium-infrared band which are transmitted by the coupling output mirror into an input window. The tunable medium-infrared optical fiber mixed gas cascaded Raman laser has the advantages of narrow line width, tunable property, low pump threshold, high conversion efficiency and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com