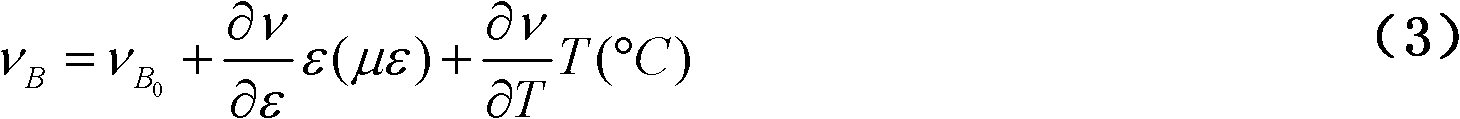Patents
Literature
76results about "Reflectometers using simulated back-scatter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
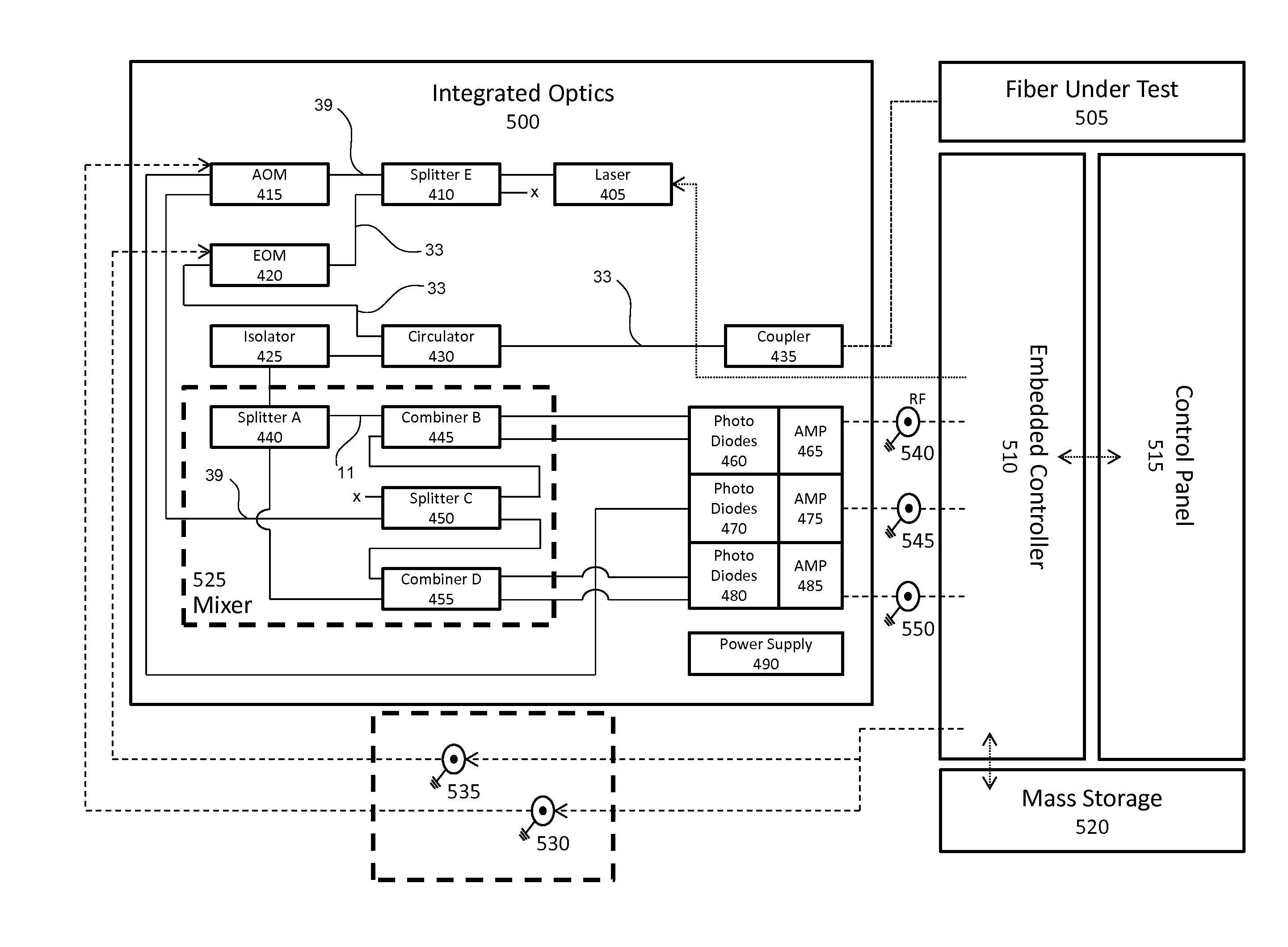
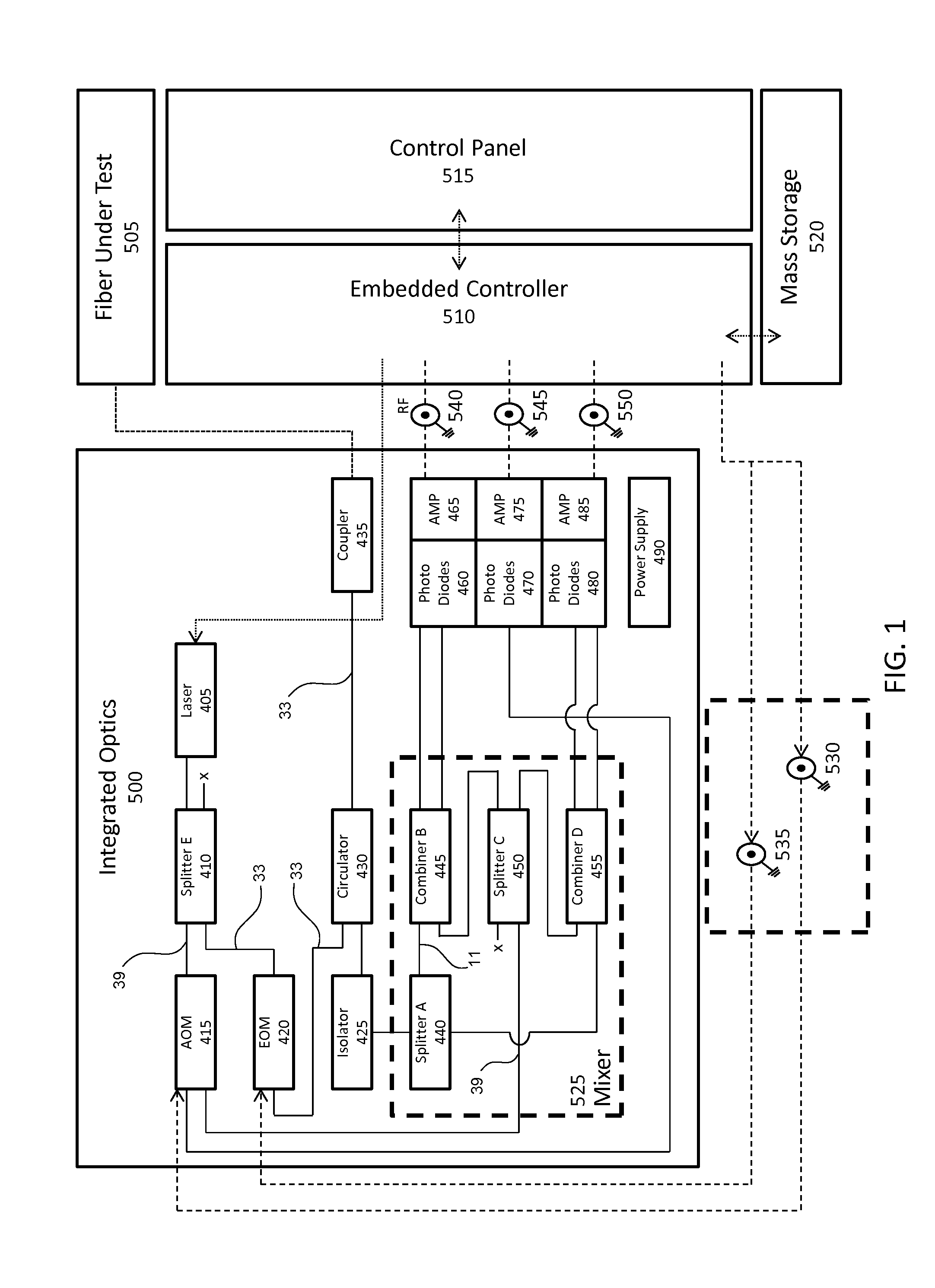
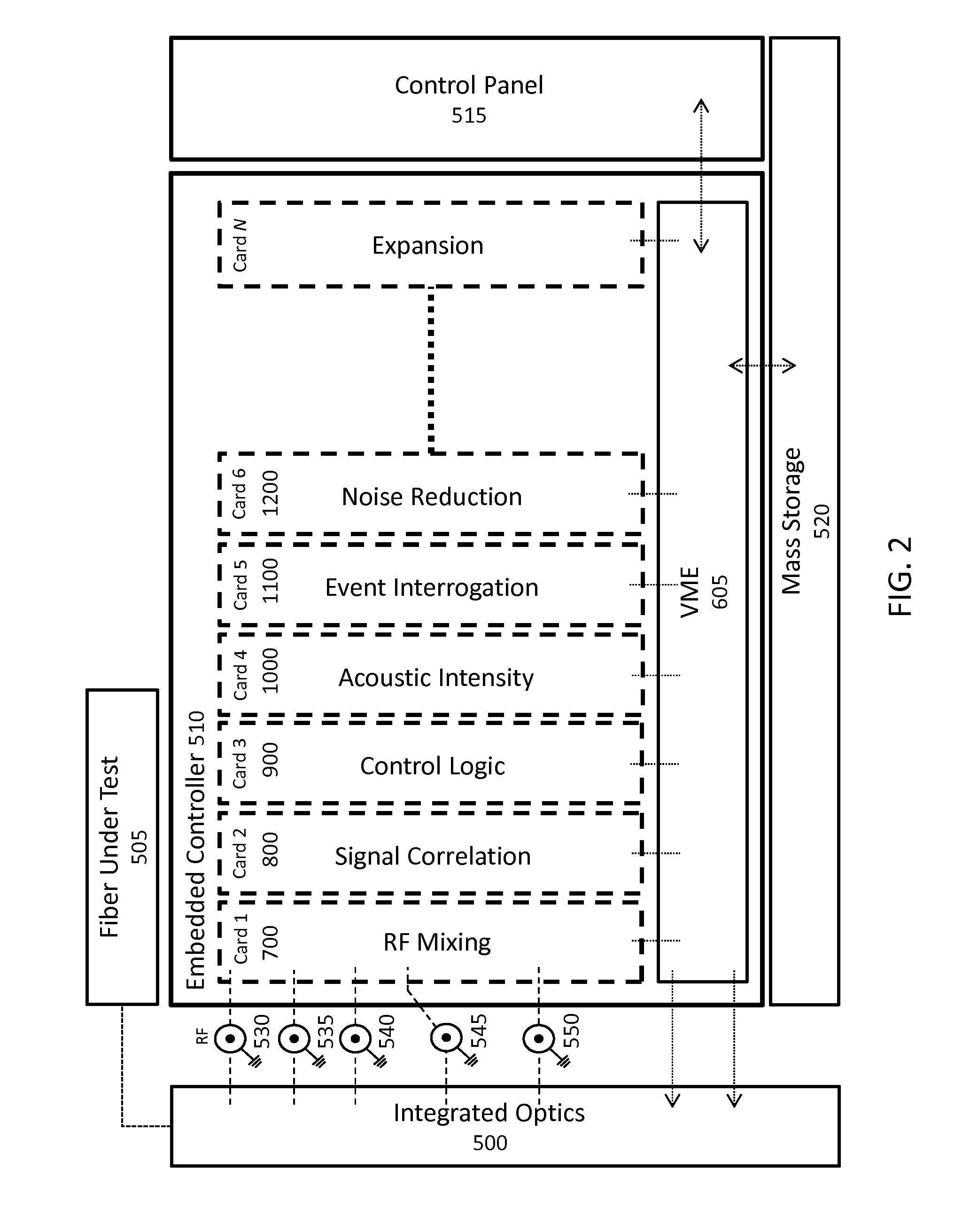
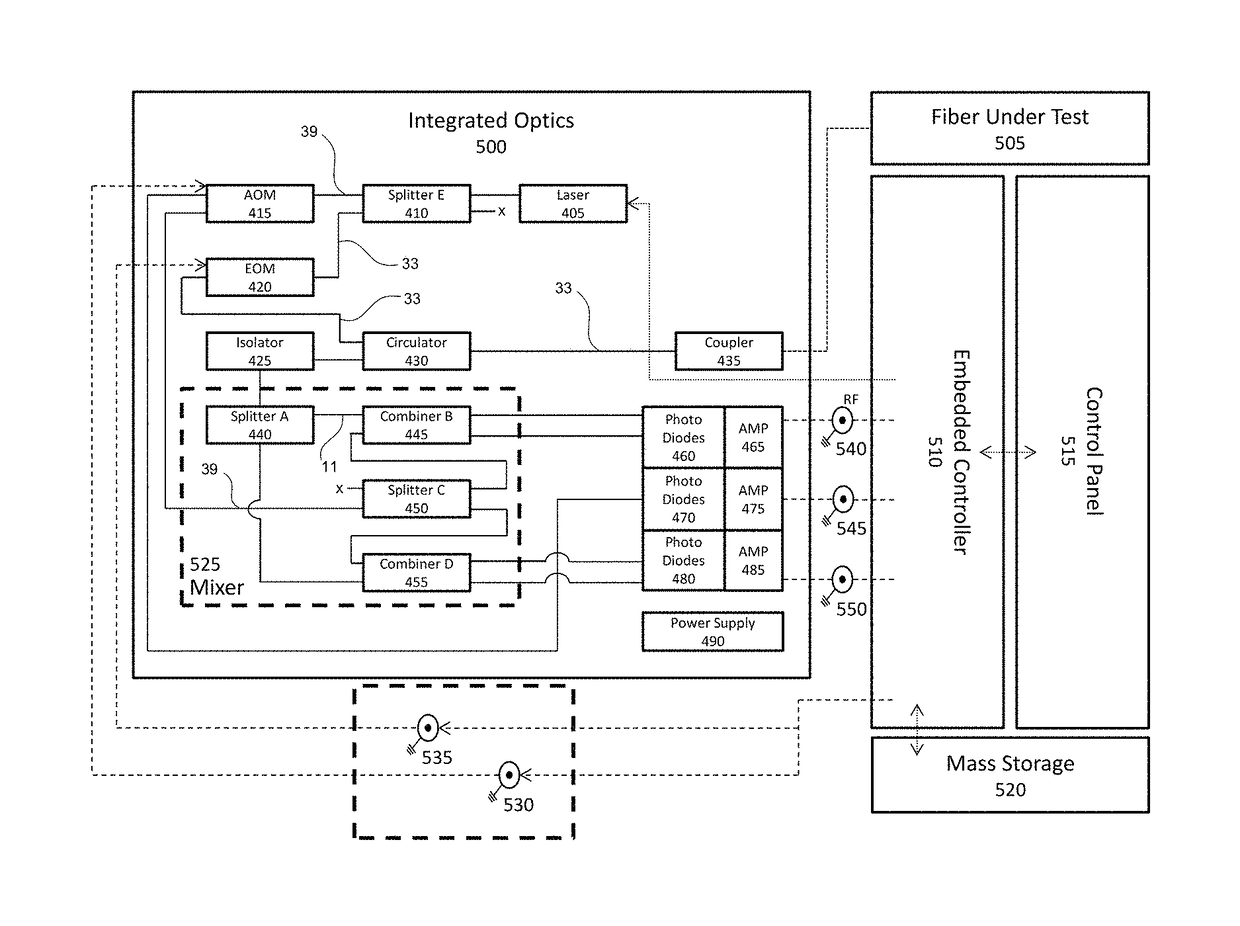
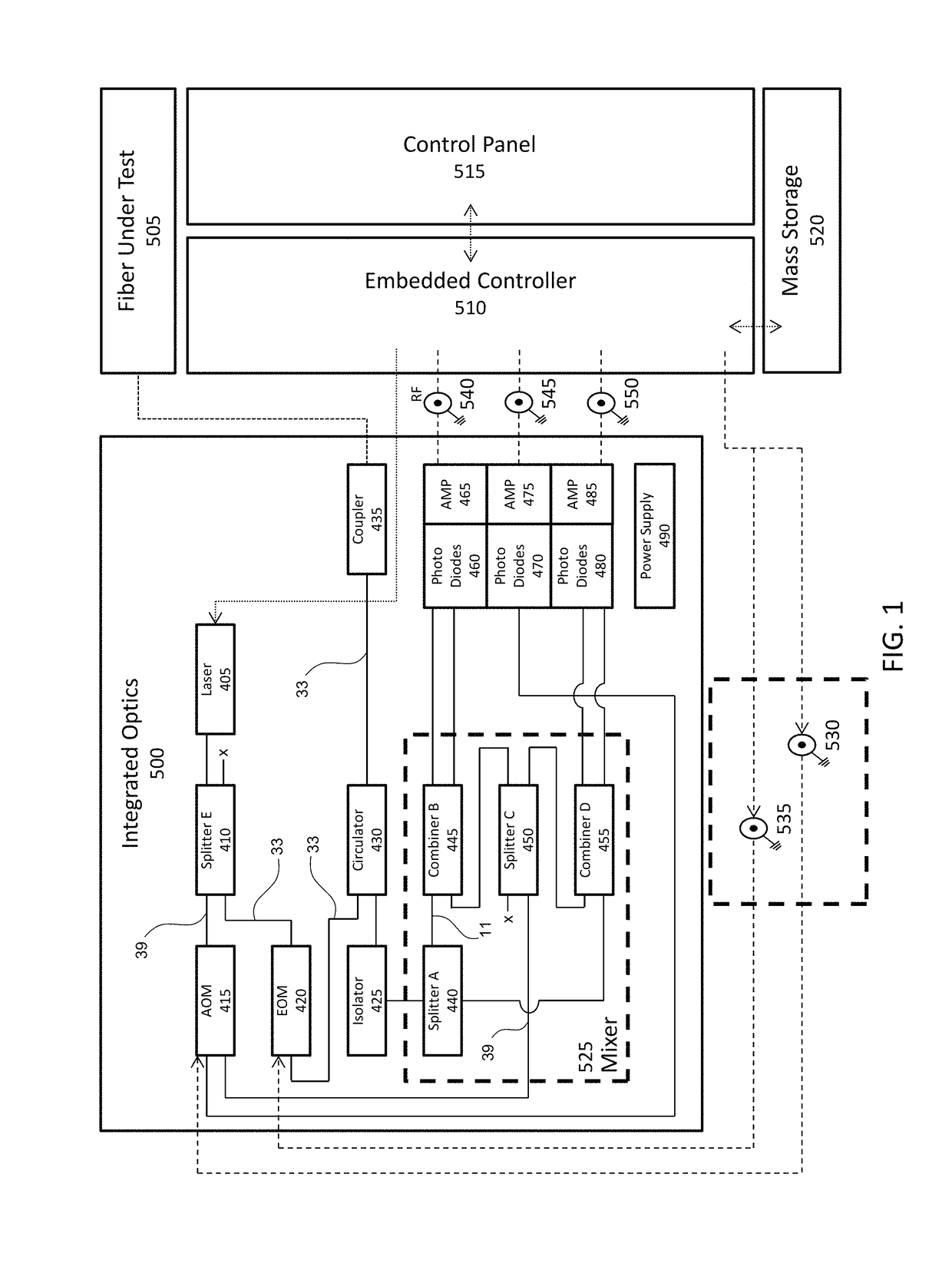
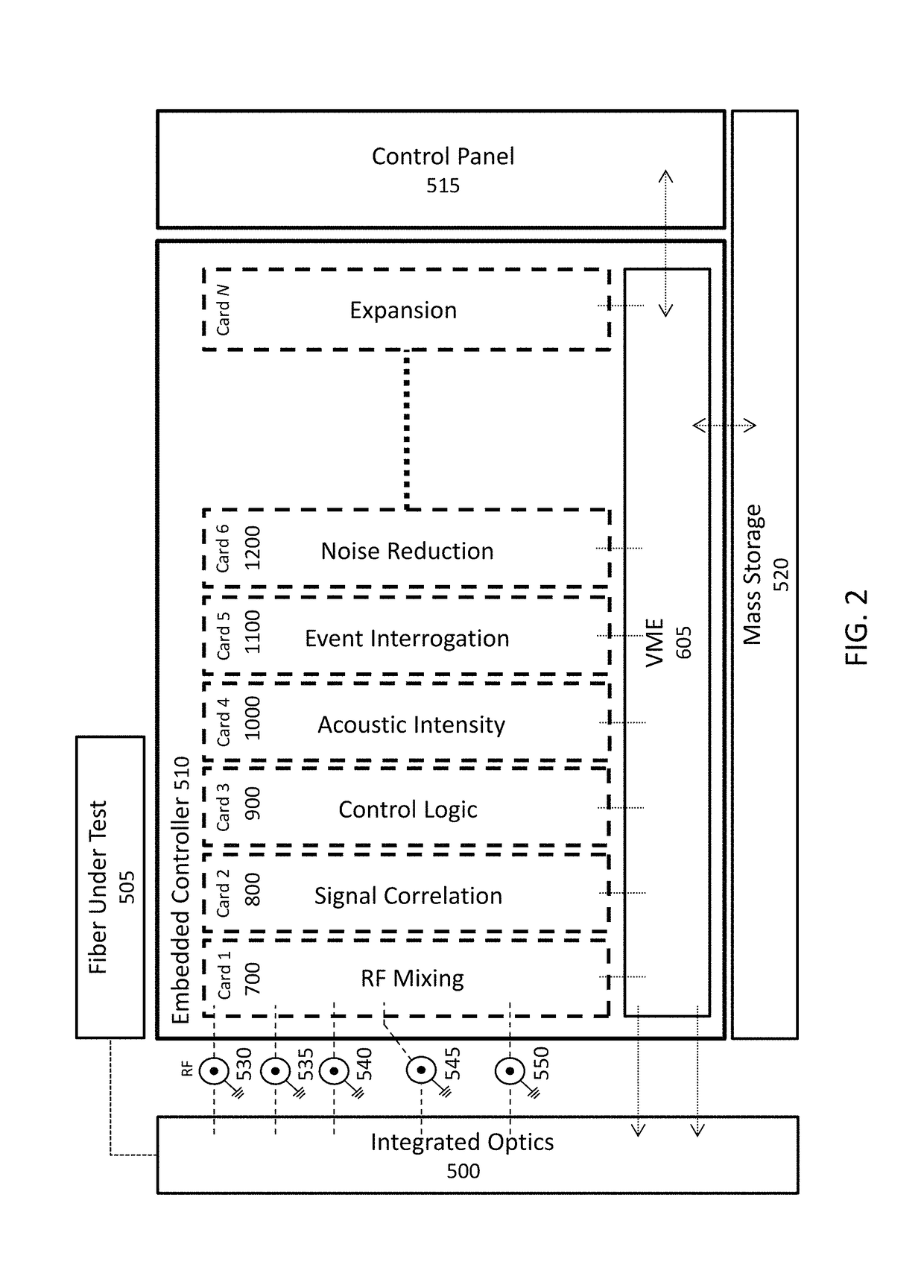
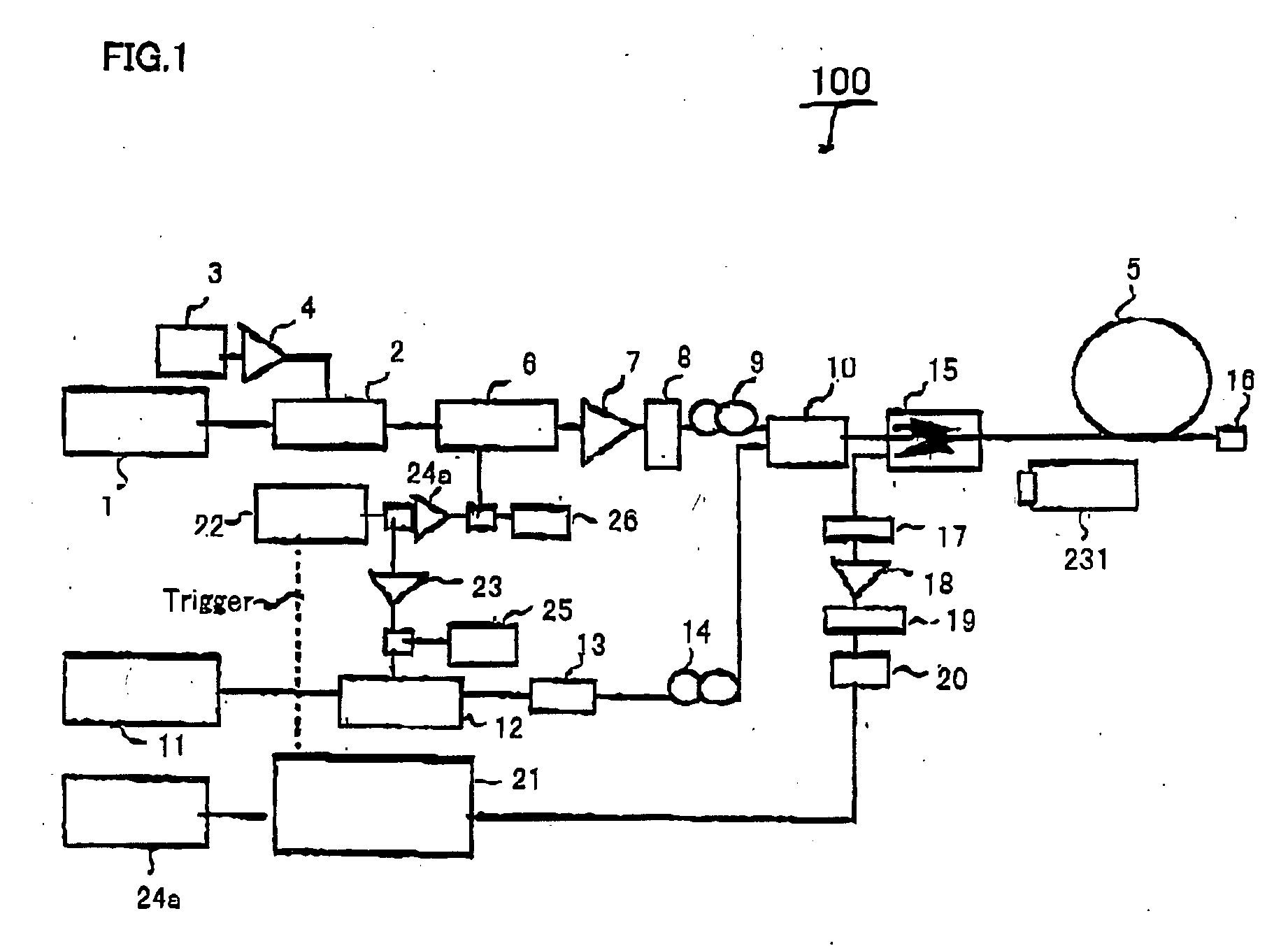
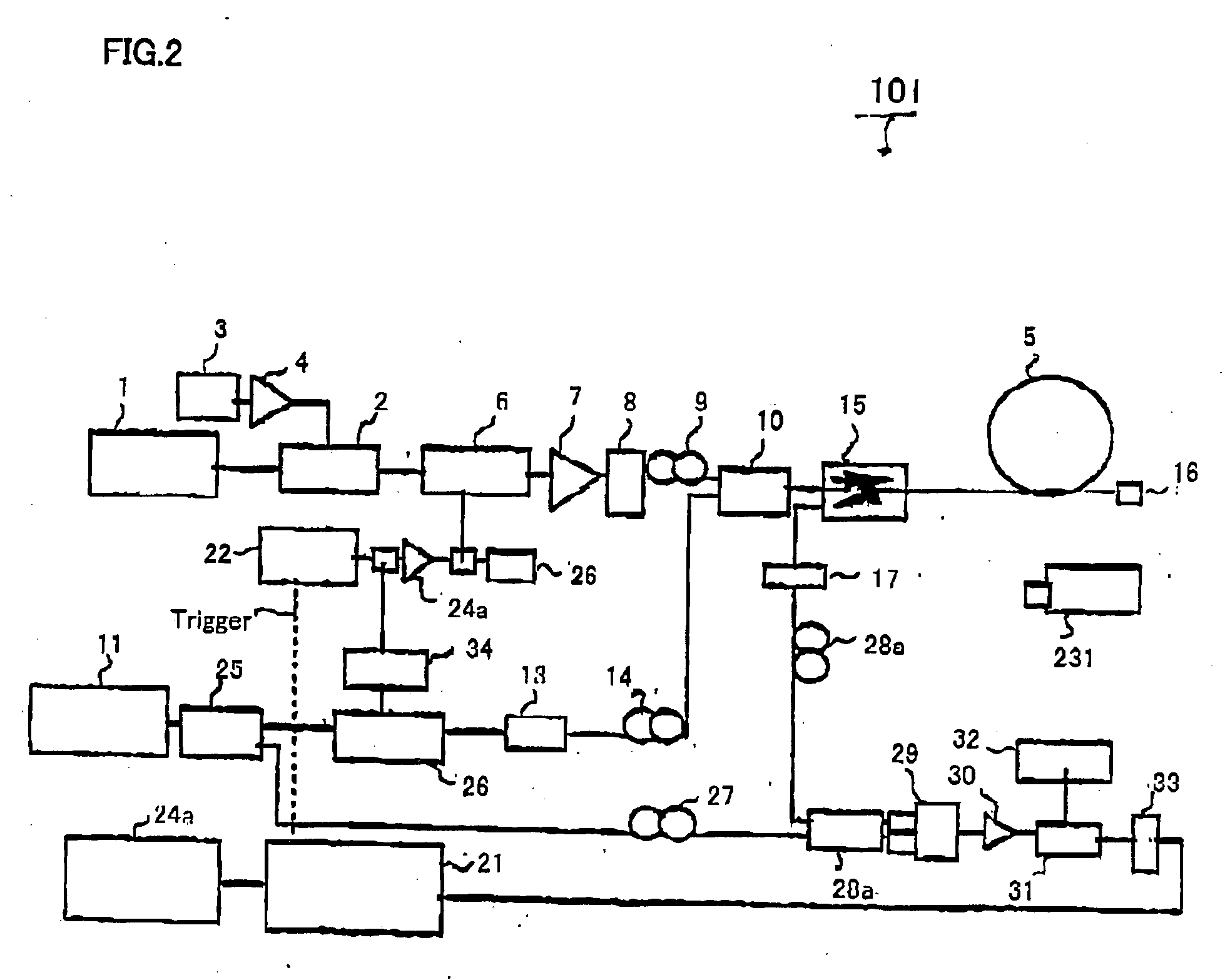
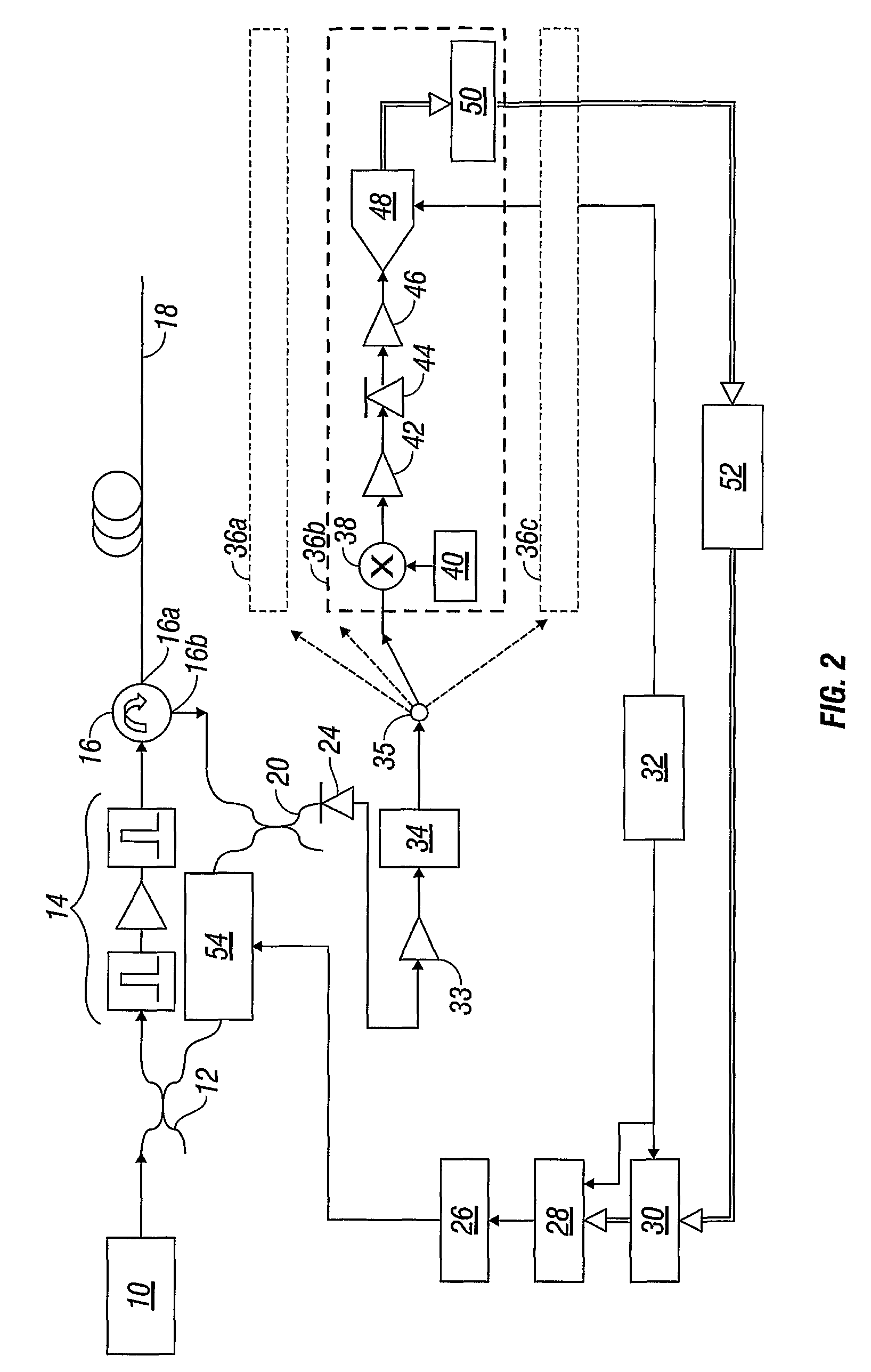
Real-time fiber optic interferometry controller
ActiveUS20160191163A1Increase flexibilityImprove utilizationReflectometers using simulated back-scatterSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFiberMultiplexing
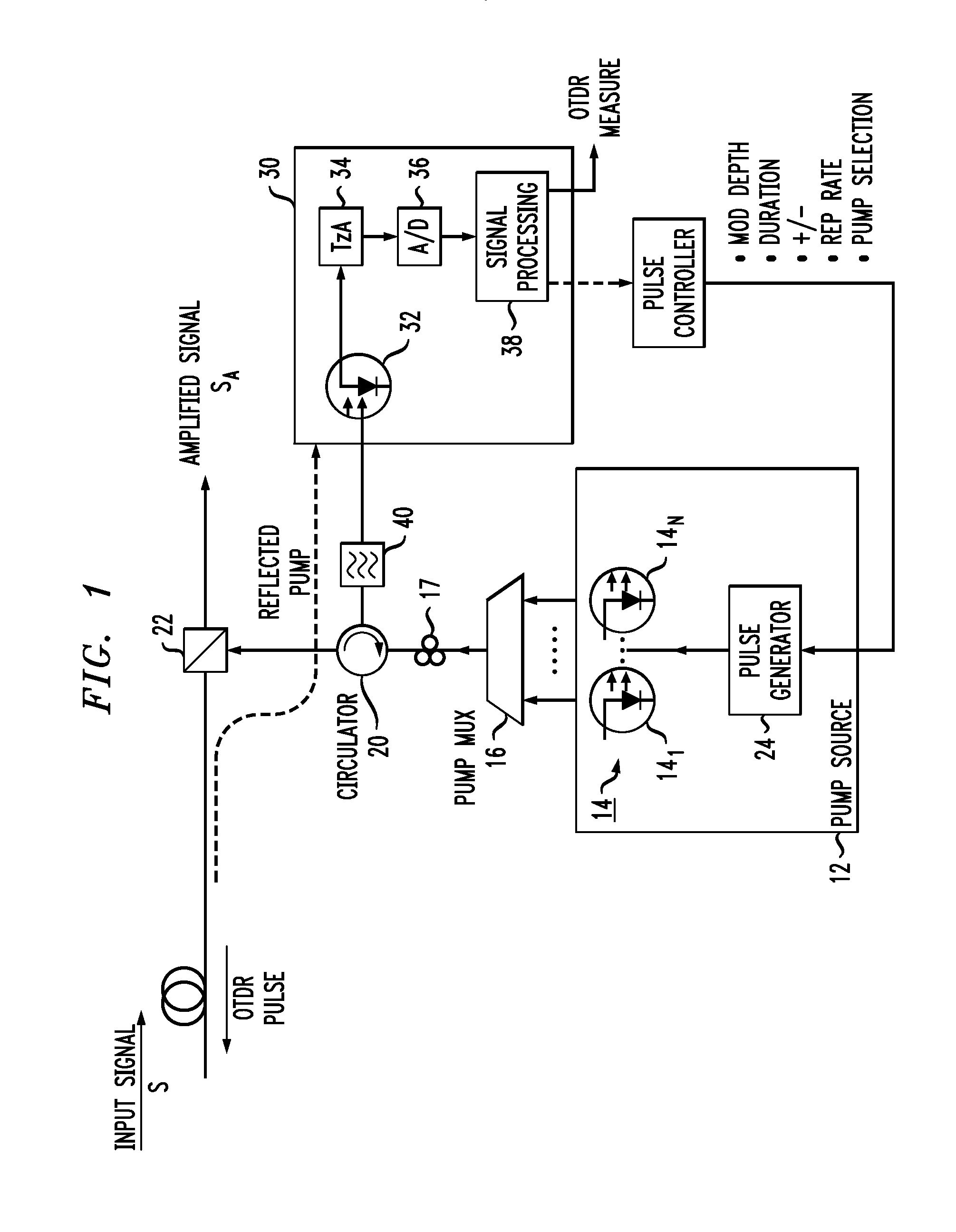
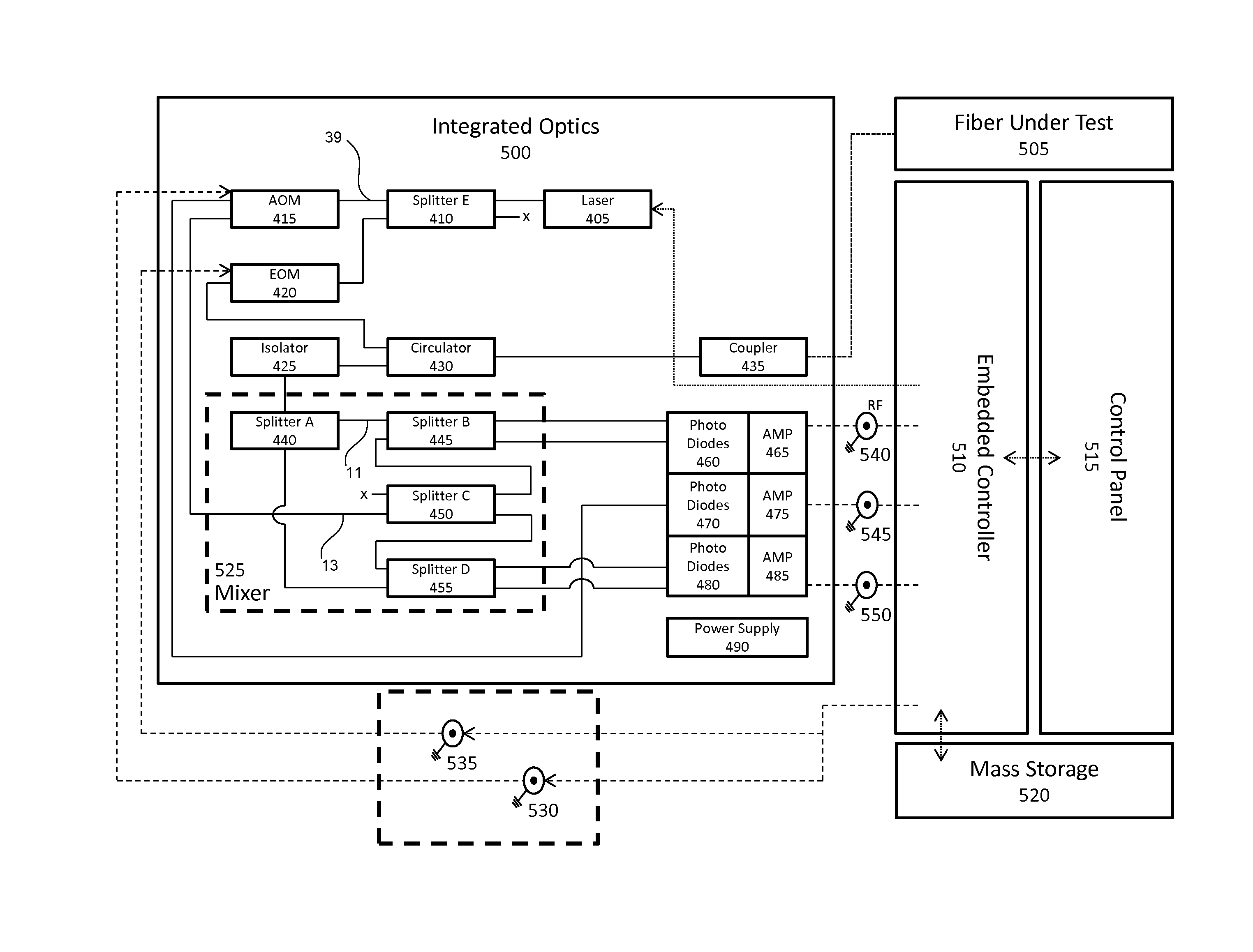
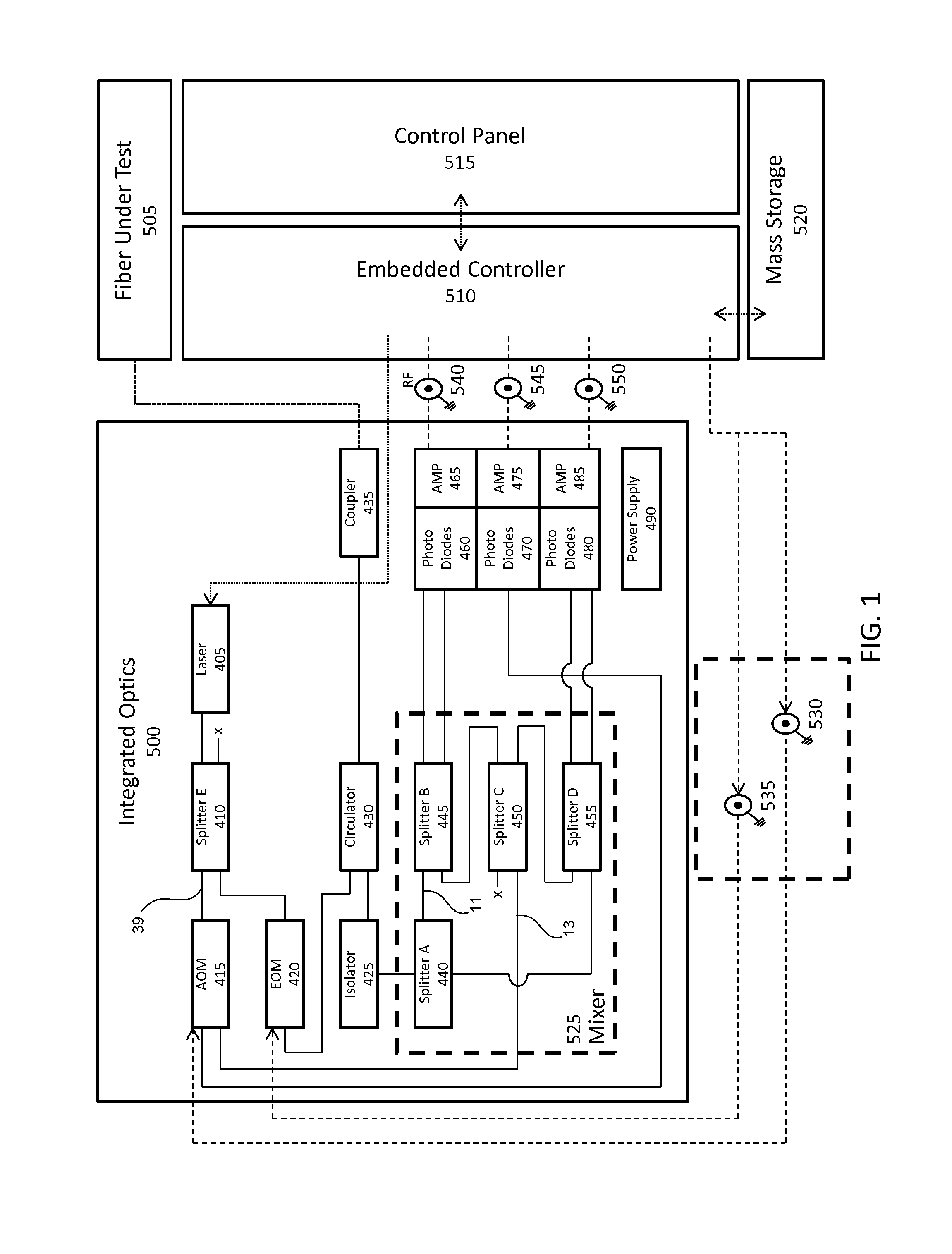
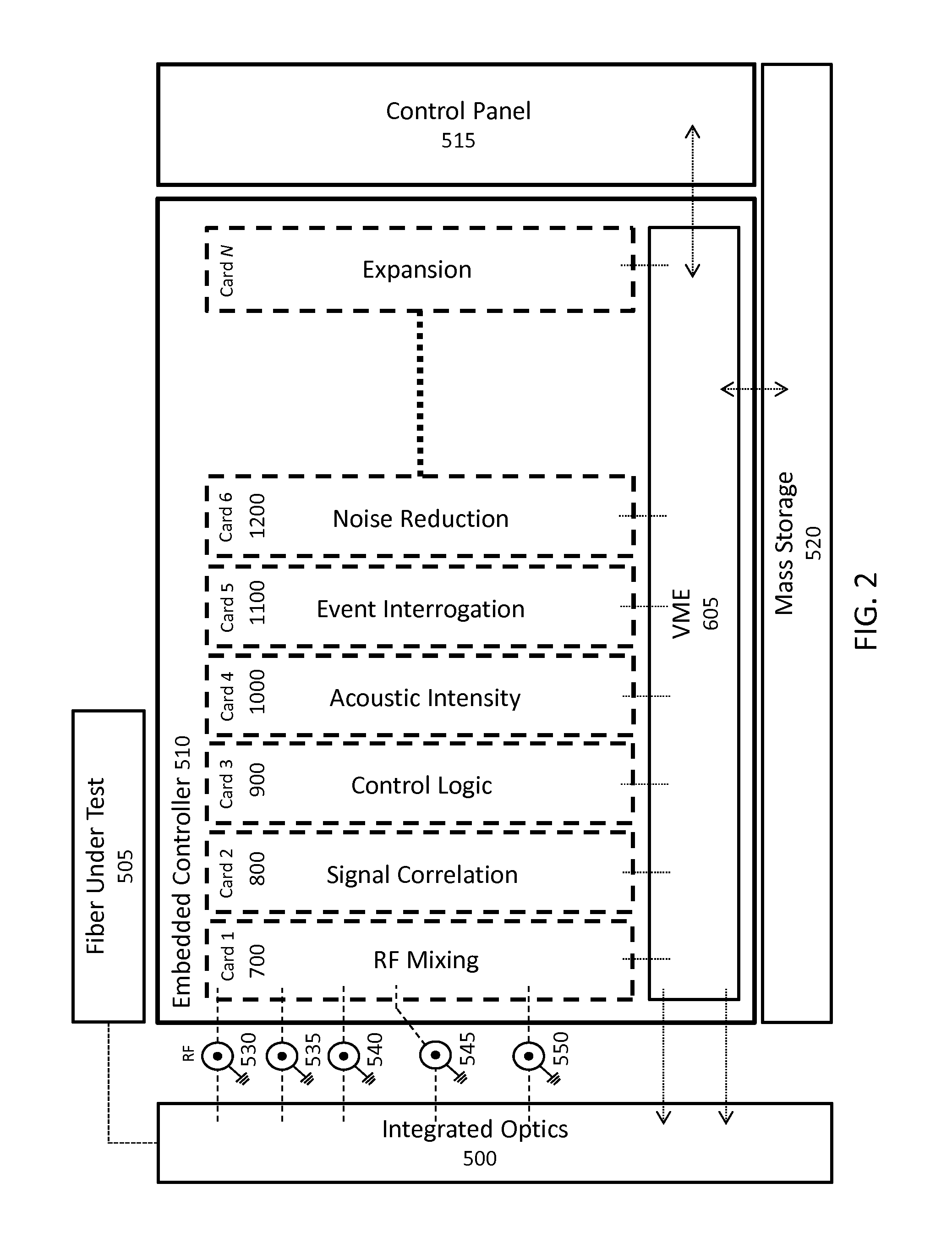
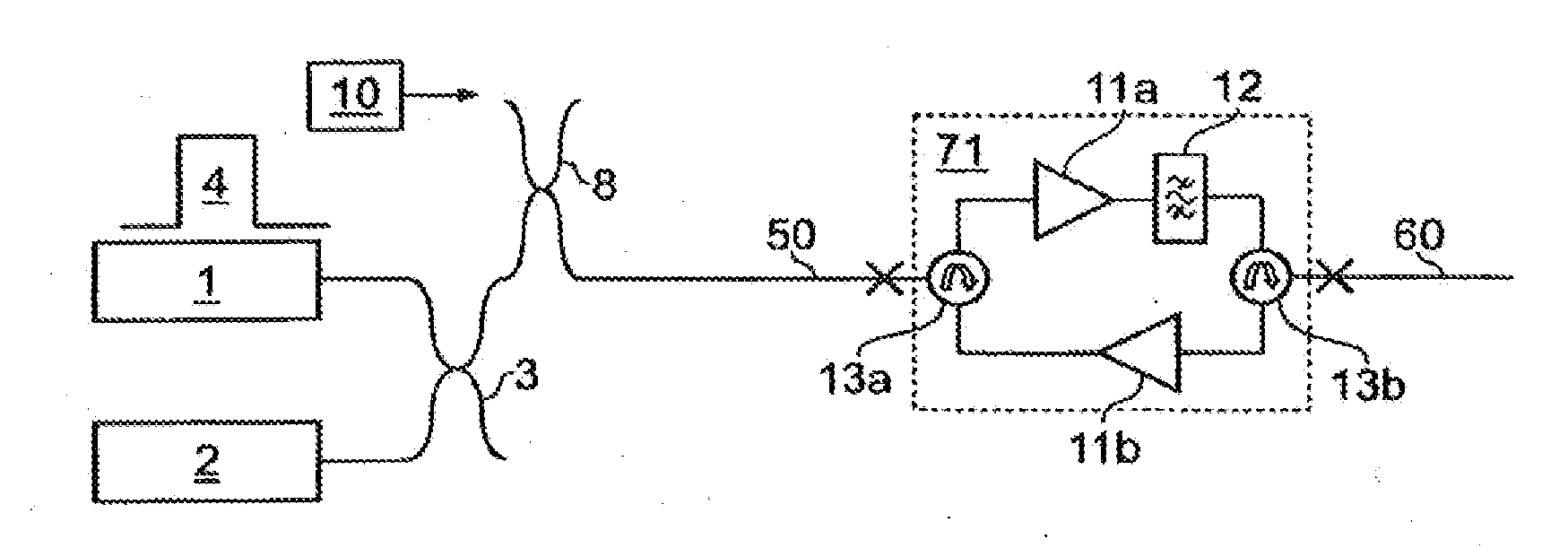
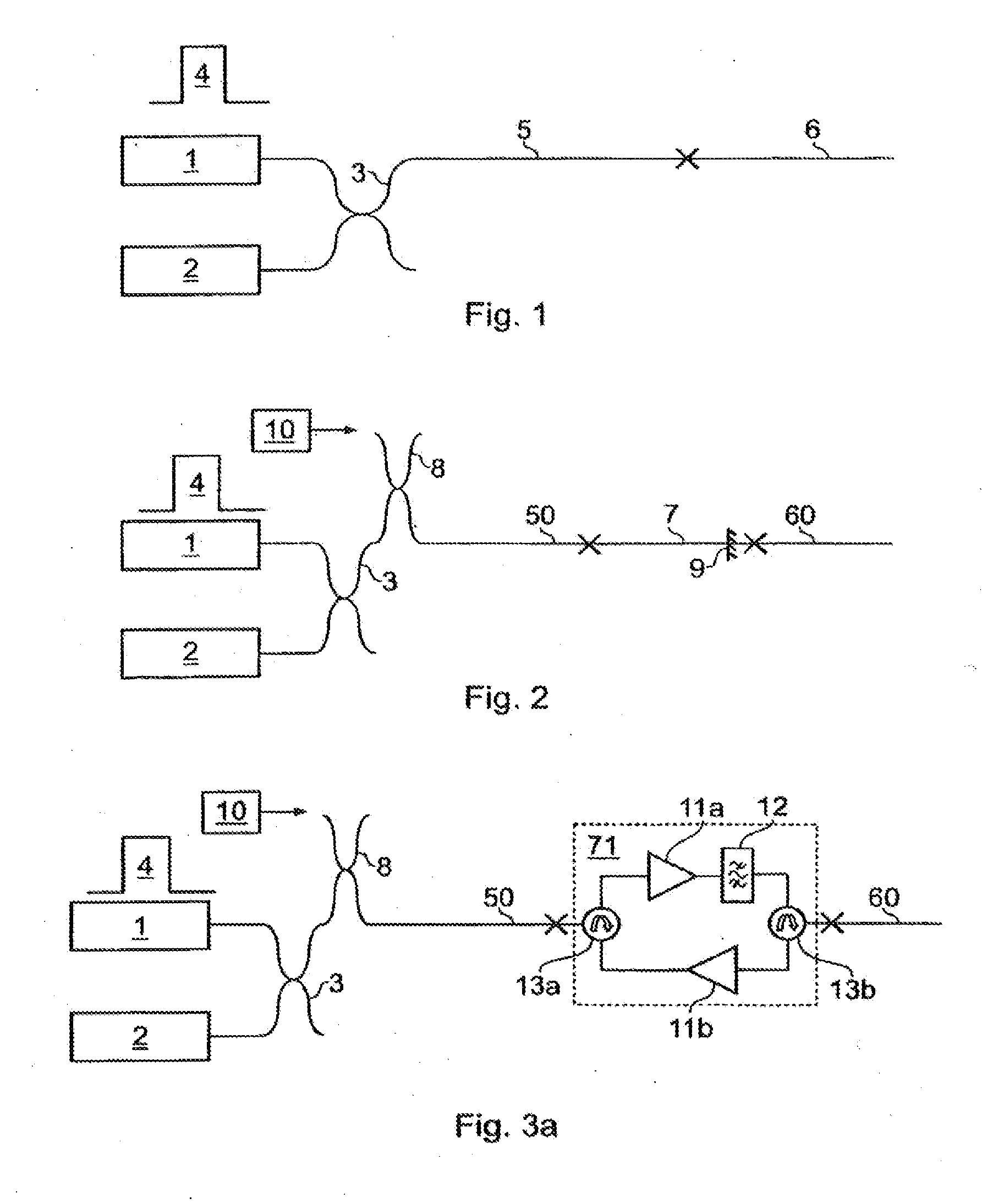
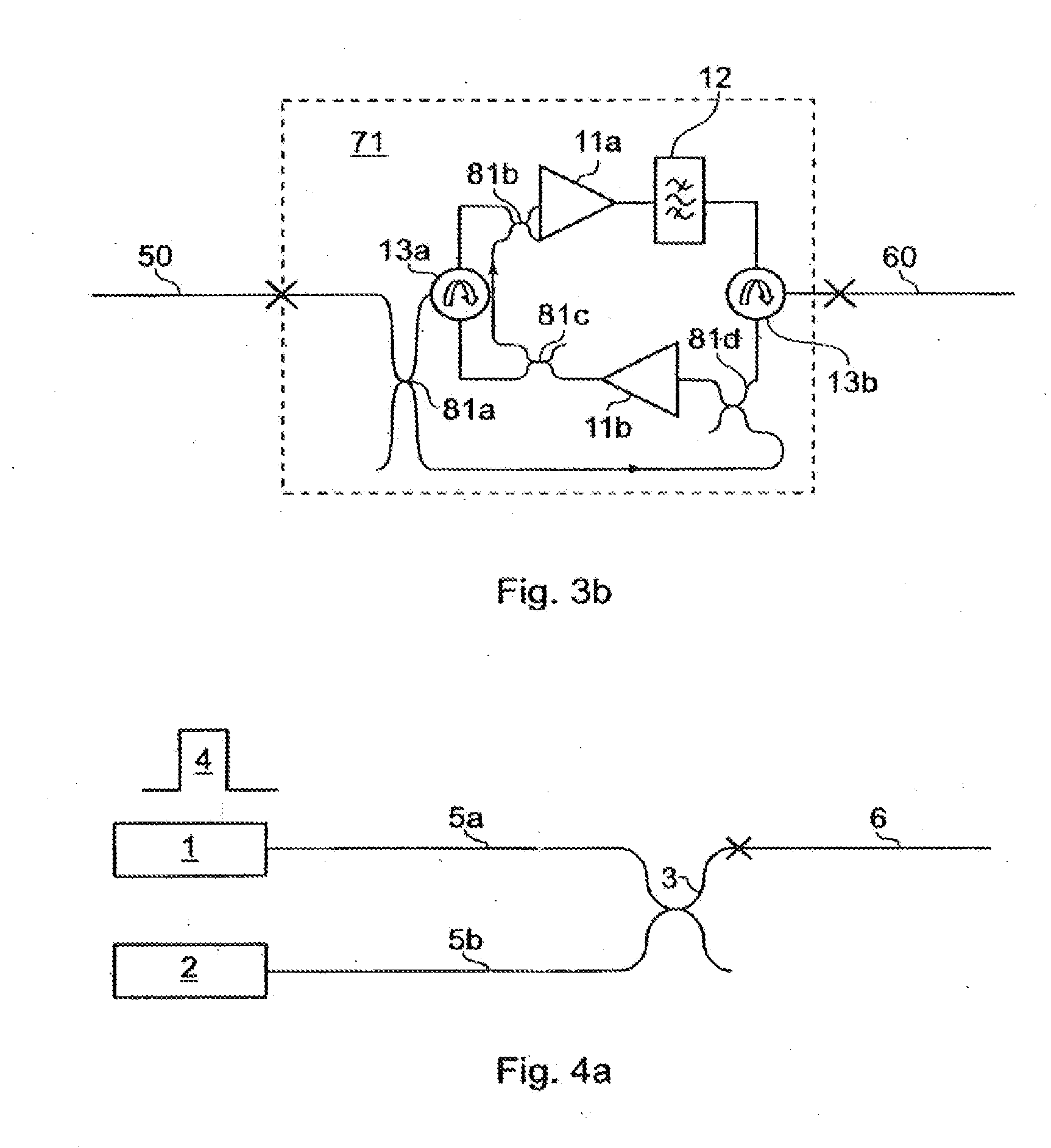
A modular fiber optic interferometry control system and method for extracting information from superimposed waves is disclosed. The system comprises a first module for converting a radio frequency input to a multiplexed binary data stream, a second module for correlating a pseudo random number (PRN) reference with a received PRN code modulated backscattered signal, and a third module comprising control logic. In some embodiments the system further comprises one or more of a fourth module for generating a power stream, a fifth module for event interrogation, and a sixth module for noise reduction.
Owner:ADELOS INC
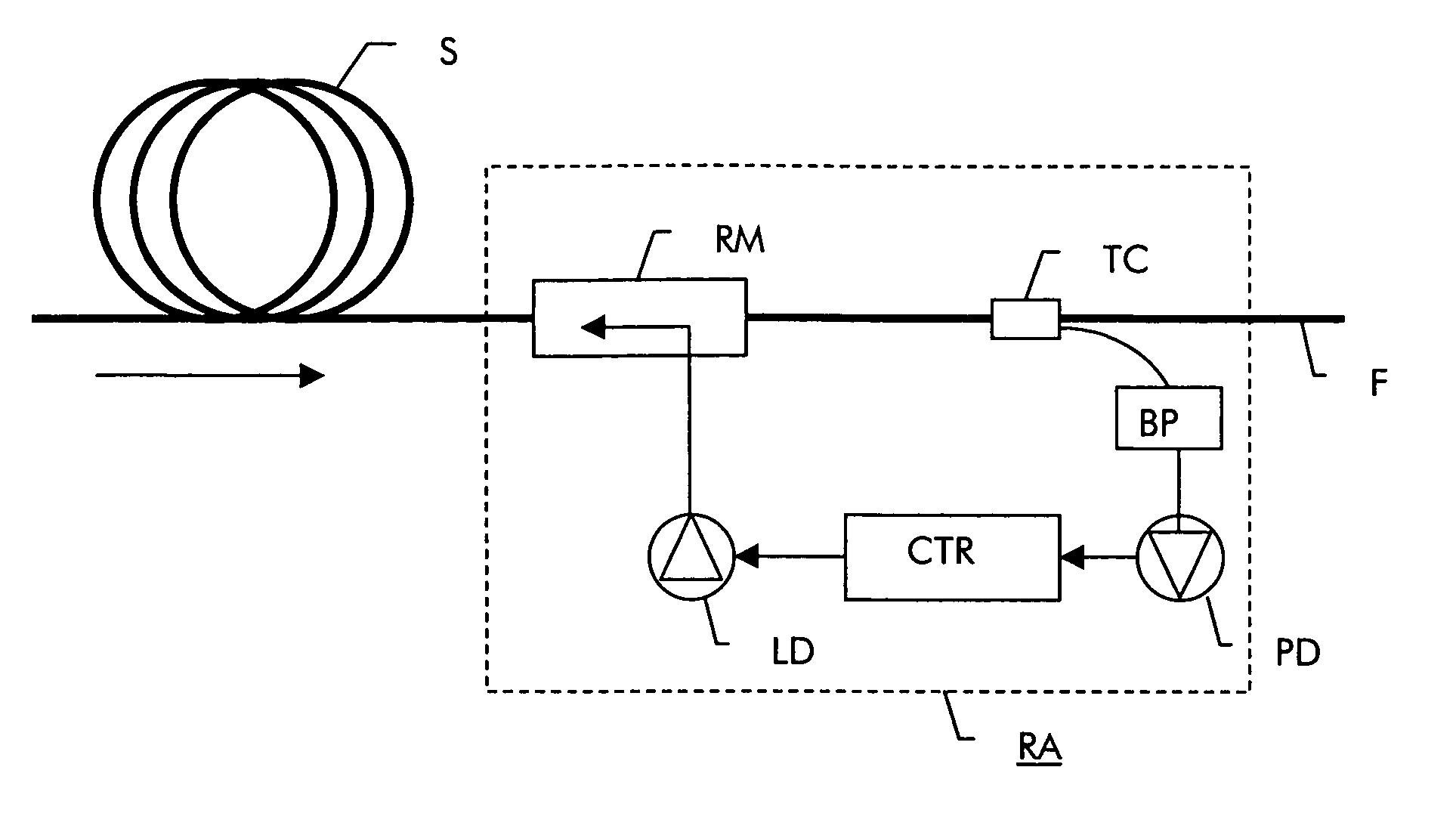
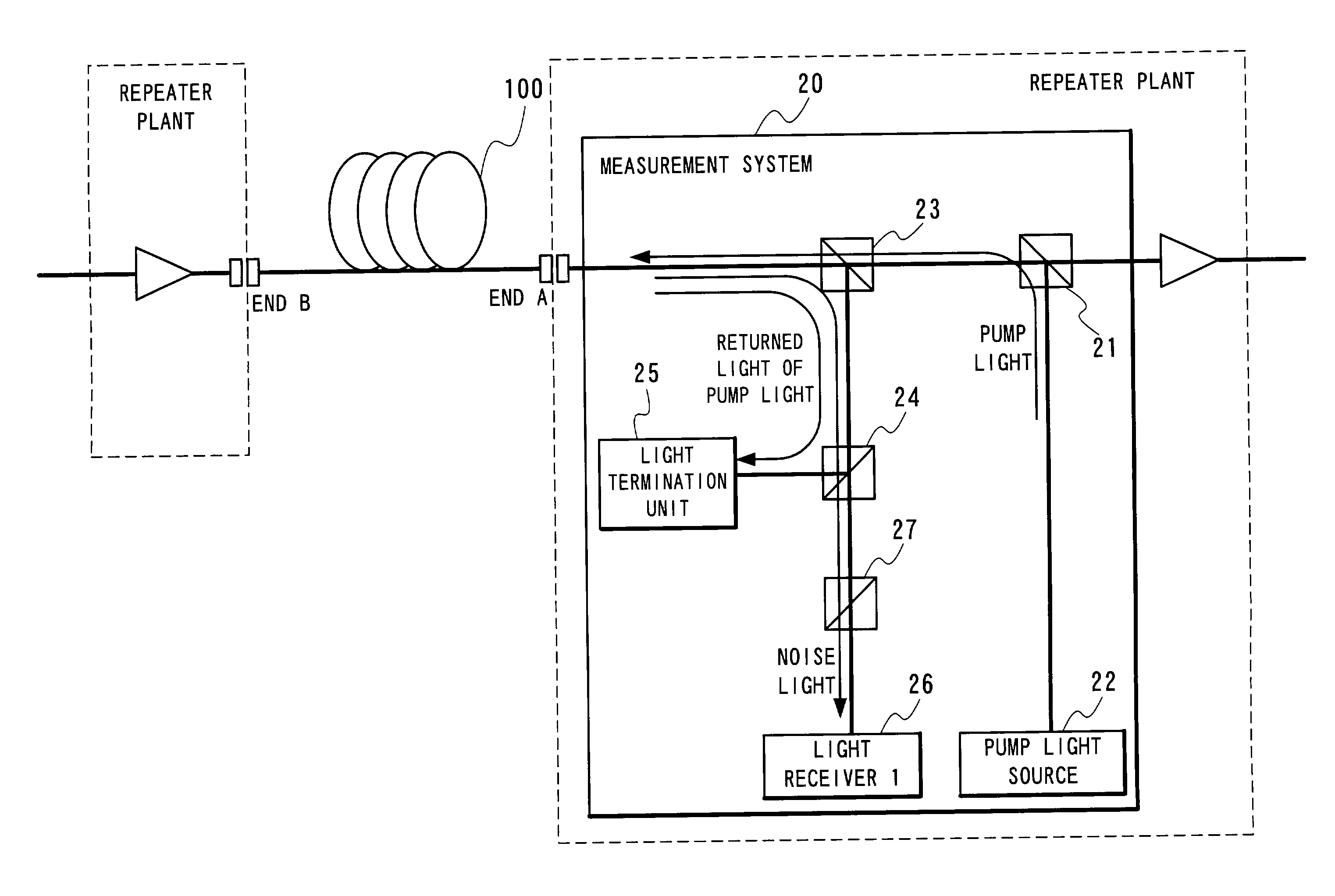
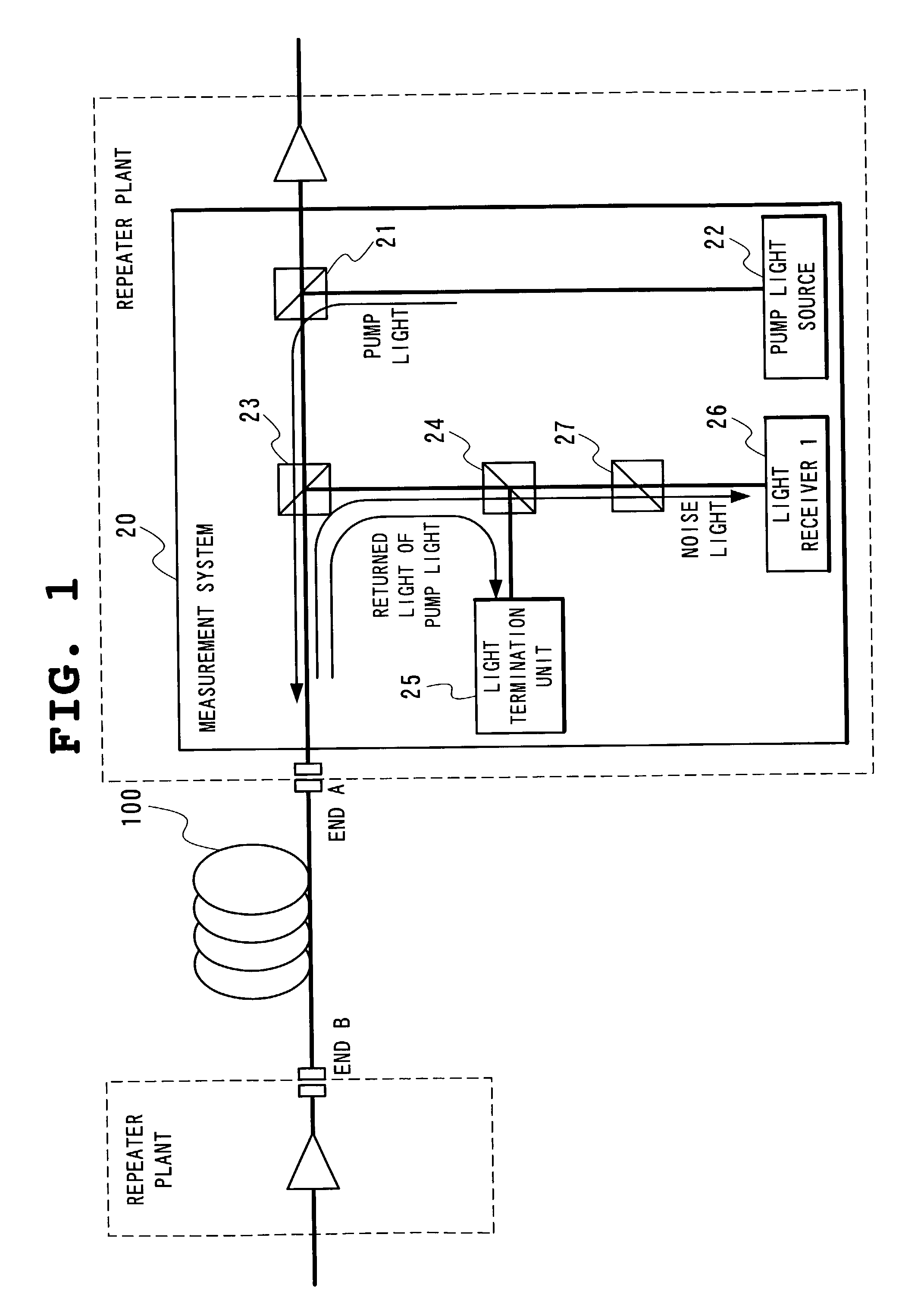
Method of determining the gain characteristic of a distributed Raman amplifier
InactiveUS20050105167A1Accurate and simple to determineLaser detailsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterFiberAudio power amplifier
A method of determining the gain characteristic of a Raman amplifier includes the steps of launching a pump light signal into a fiber; preliminary adjusting the power of the pump light signal to a value that lies in a range where the amplified spontaneous emission noise originating from the pump light signal is substantially proportional to the on / off gain provided by the power of the pump light signal; monitoring the power of the amplified spontaneous emission noise signal; varying the power of the pump light signal; measuring a variation in the power of the amplified spontaneous emission noise signal corresponding to the pump power variation; and determining the gain characteristic of the amplifier from the relative variation in pump power and the measured variation in noise power.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
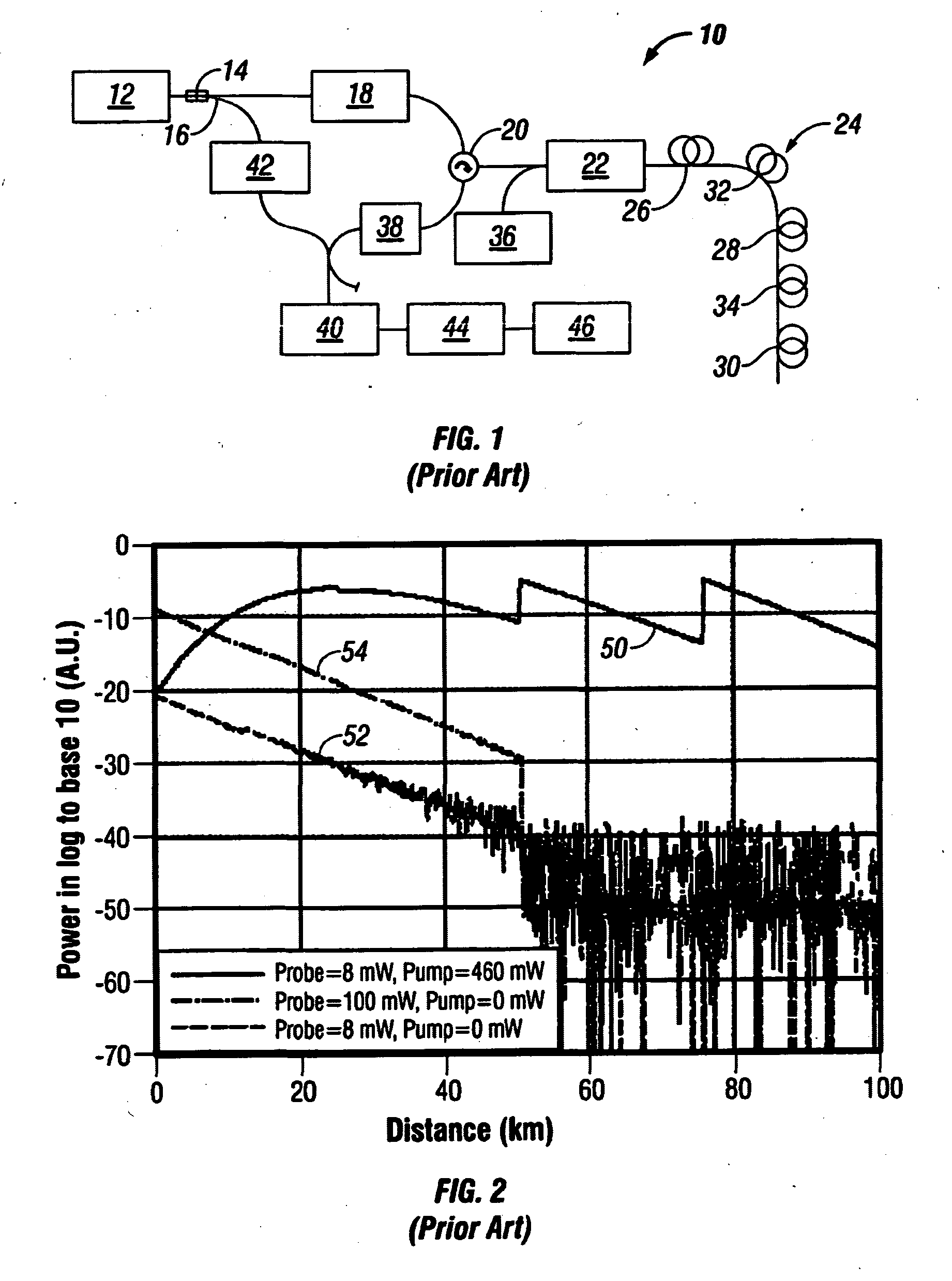
Raman amplifier system and method with integrated optical time domain reflectometer
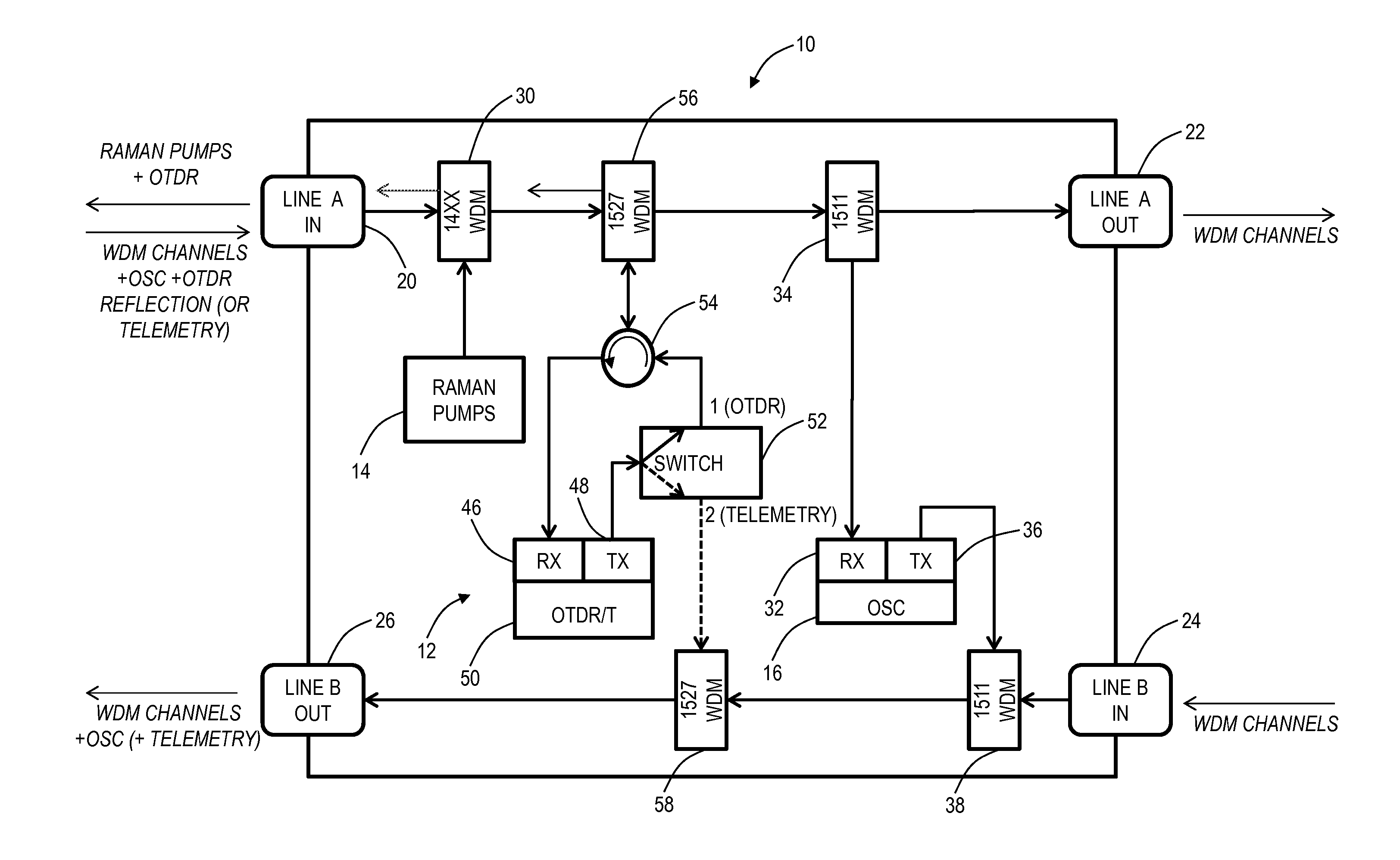
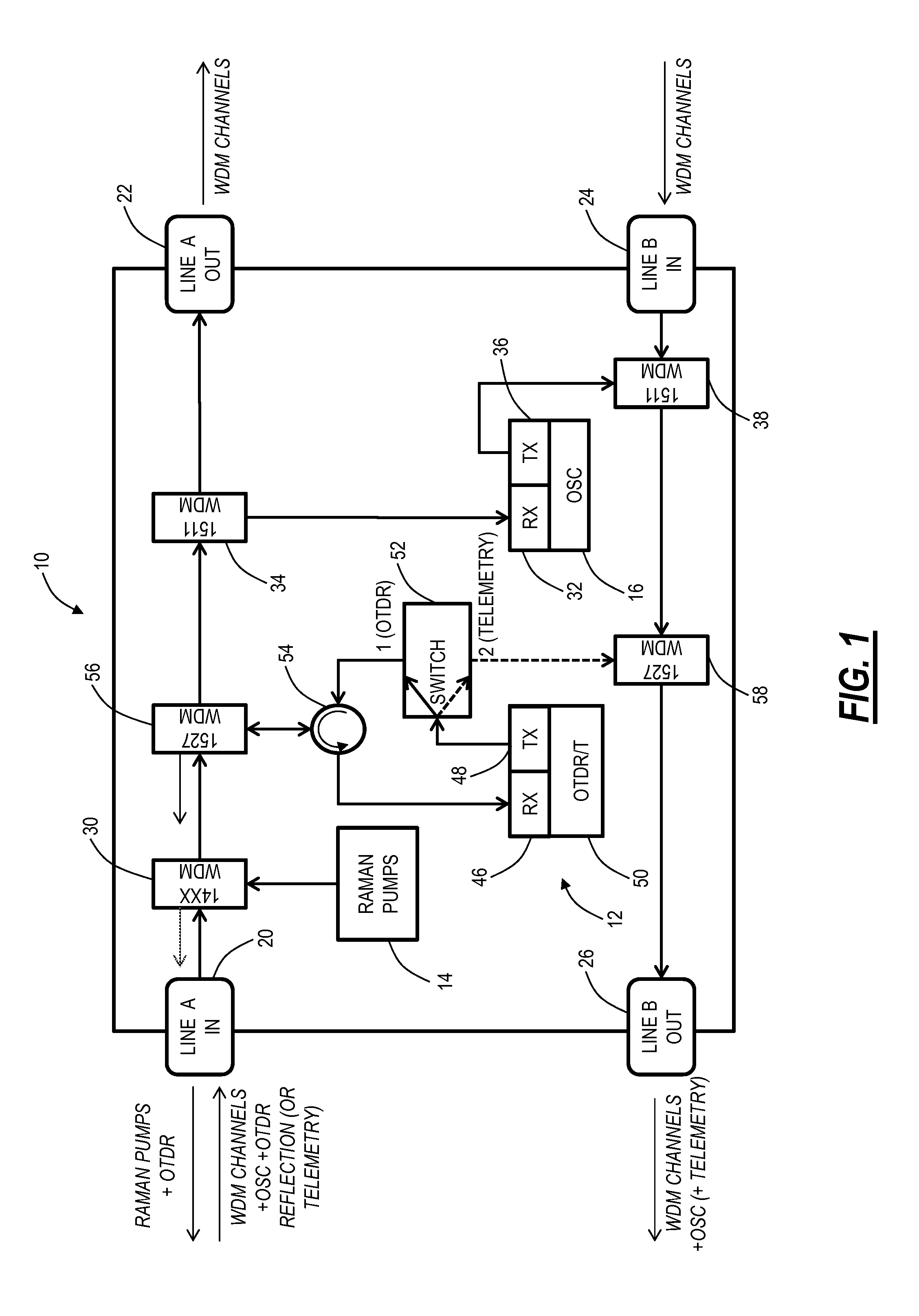
ActiveUS20140077971A1Security mechanismElectric signal transmission systemsLaser detailsFiberTime domain
Raman amplifier systems and methods with an integrated Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) for integrated testing functionality include an amplifier system, an OTDR and telemetry subsystem, and a method of operation. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem is configured to operate in an OTDR mode when coupled to a line in port and to operate in a telemetry mode when coupled to a line out port. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem enables on-demand fiber testing while also operating as a telemetry channel that is both a redundant optical service channel (OSC) and provides a mechanism to monitor Raman gain over time. The OTDR and telemetry subsystem minimizes cost and space by sharing major optical and electrical components between the integrated OTDR and other functions on the Raman amplifier.
Owner:CIENA
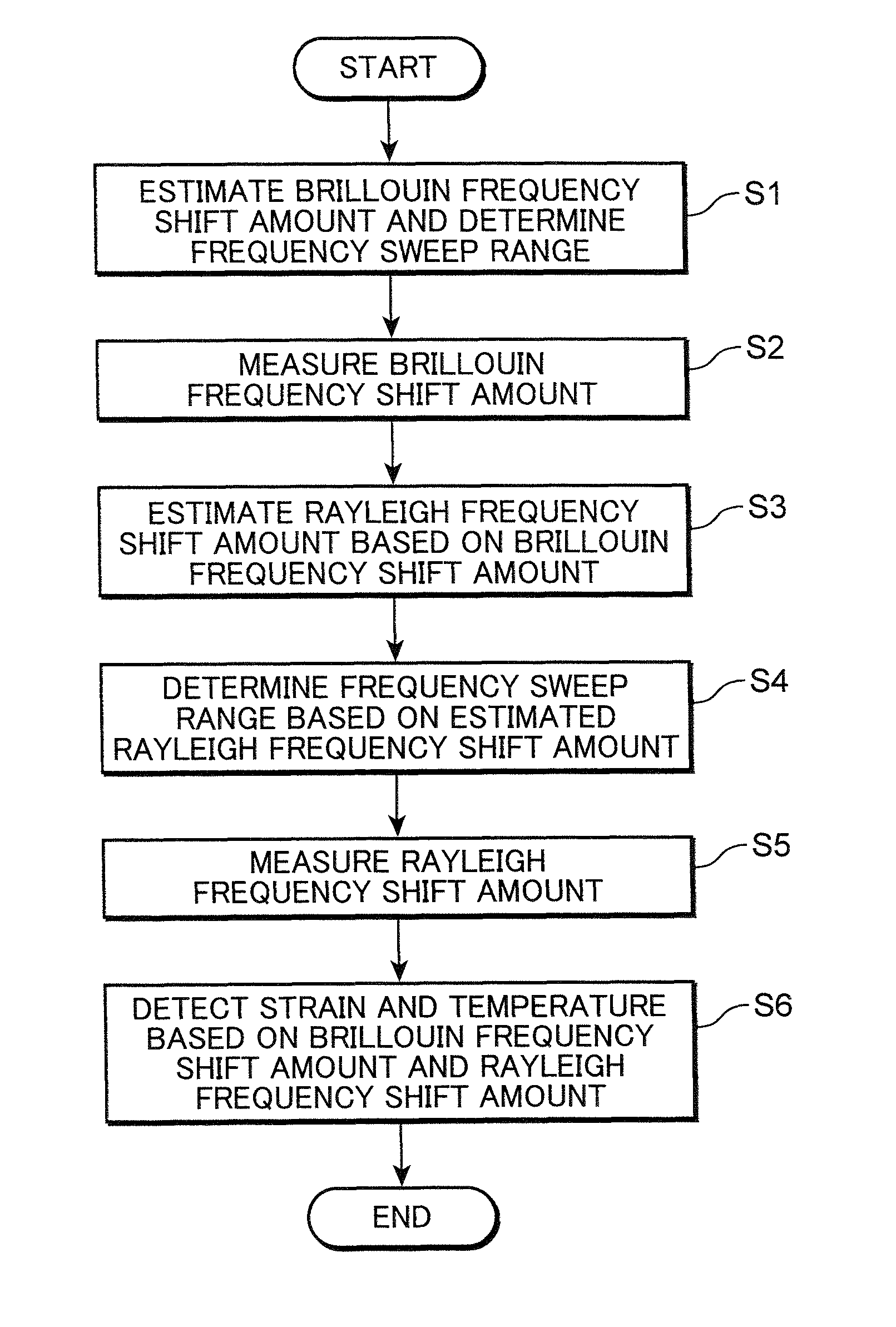
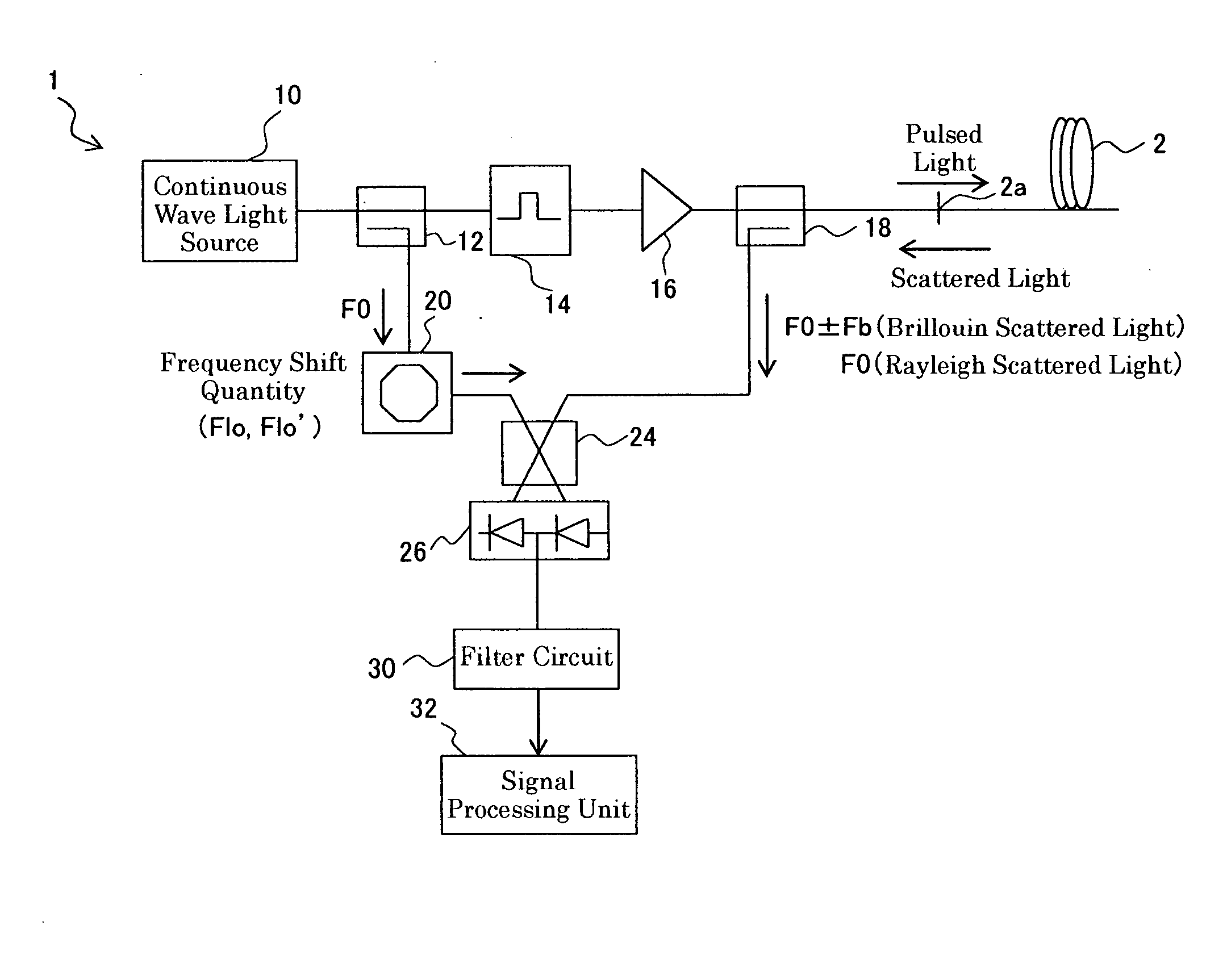
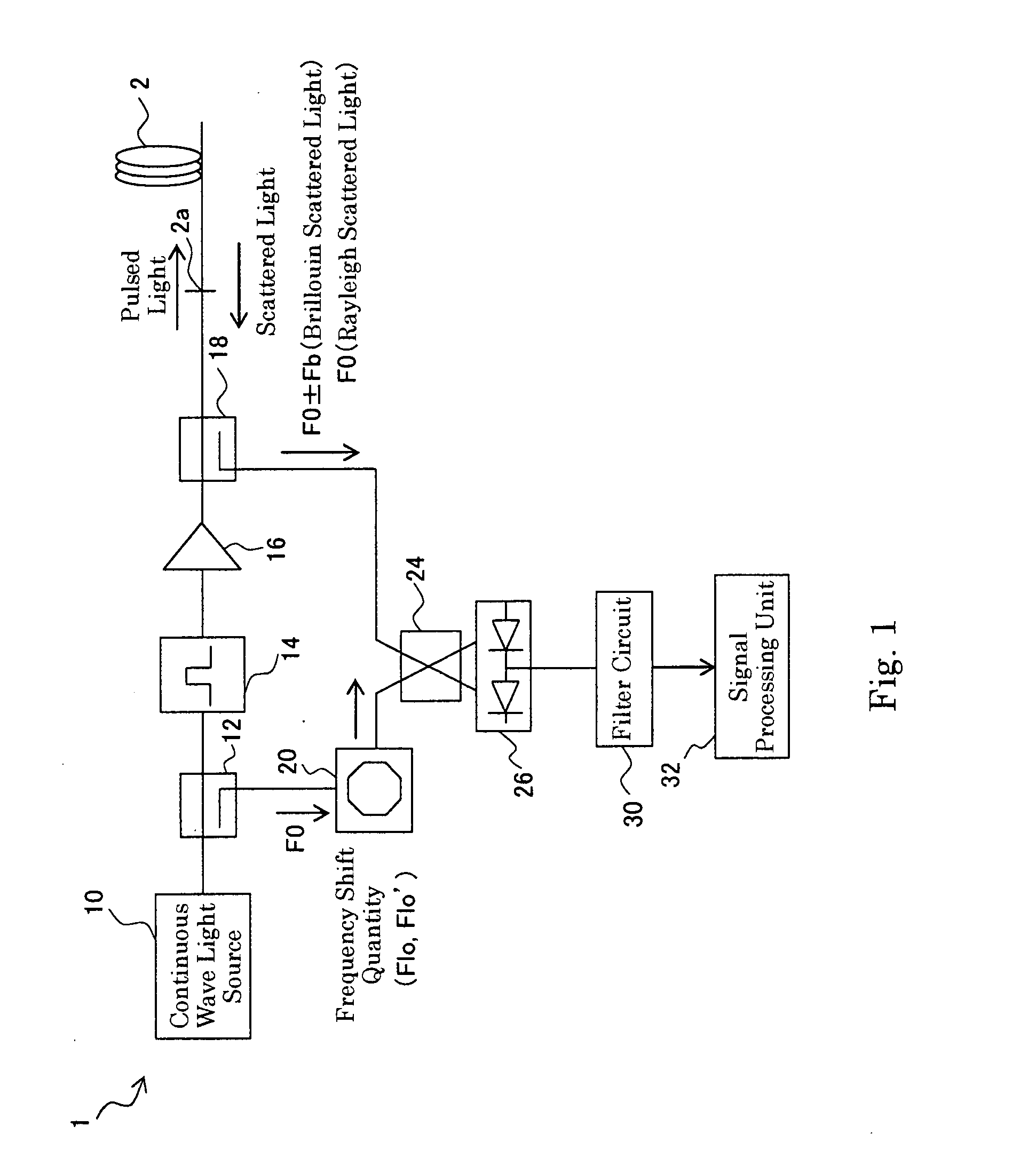
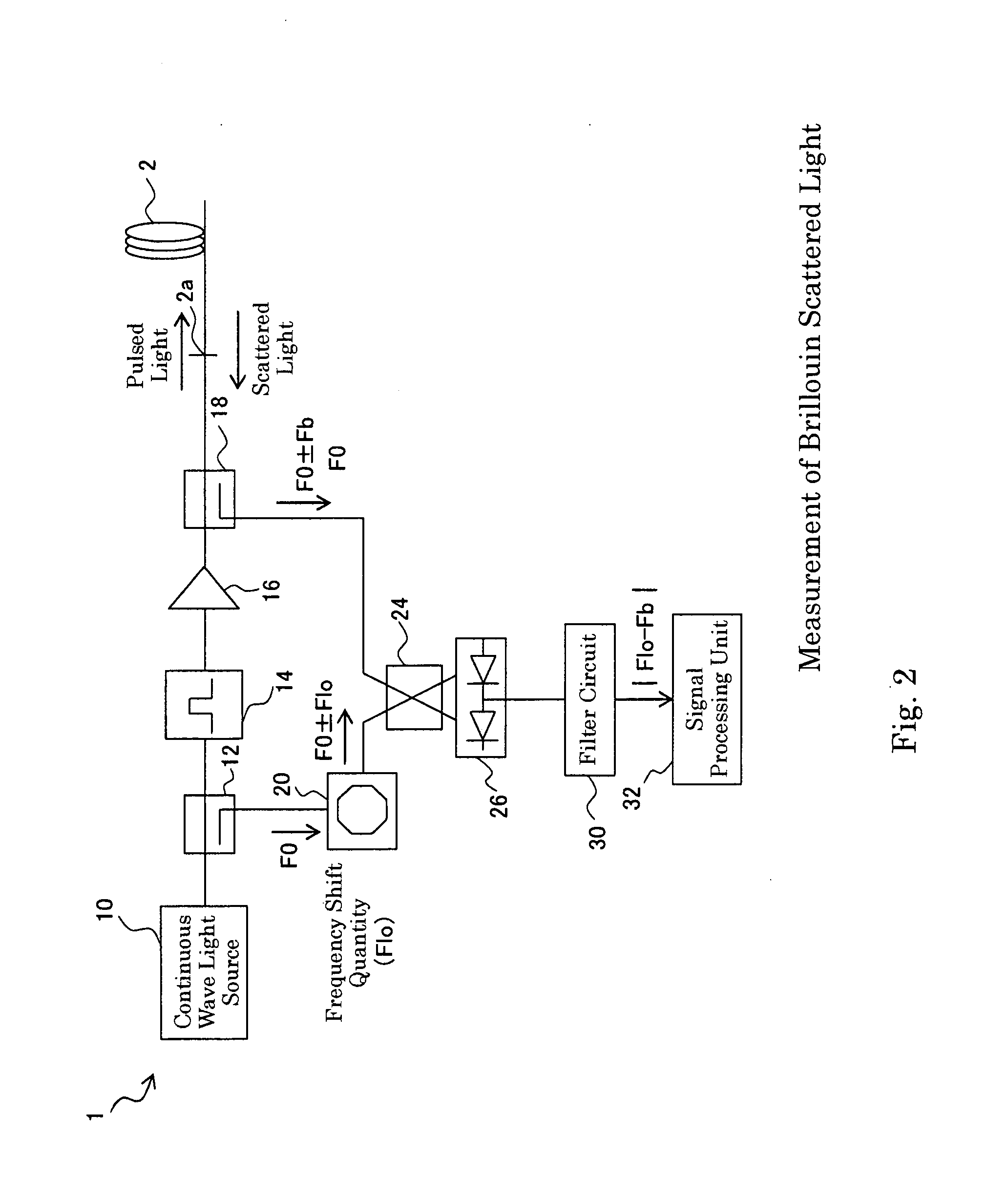
Measuring brillouin backscatter from an optical fibre using a tracking signal
ActiveUS20100002226A1Narrow down the frequency rangeReduce the amount requiredReflectometers using simulated back-scatterConstructionsFrequency measurementsFrequency shift
A method for measuring Brillouin backscattering from an optical fibre (18), comprises frequency mixing a first signal with a frequency f B (t) representative of the Brillouin frequency shift in backscattered light received from a deployed optical fibre with a second signal at a frequency f i (t) that varies in time in the same manner as a Brillouin shift previously measured from the fibre to produce a difference signal with a difference frequency iF(t) that has a nominally constant value corresponding to the situation where the received light has a Brillouin shift that matches the previously measured shift. The difference signal is acquired and processed to determine properties of the Brillouin shift and corresponding physical parameters producing the shift. The frequency mixing can be carried out. optically or electrically. Techniques for acquisition of the difference signal include the use of parallel frequency measurement channels and fast rate digital sampling.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
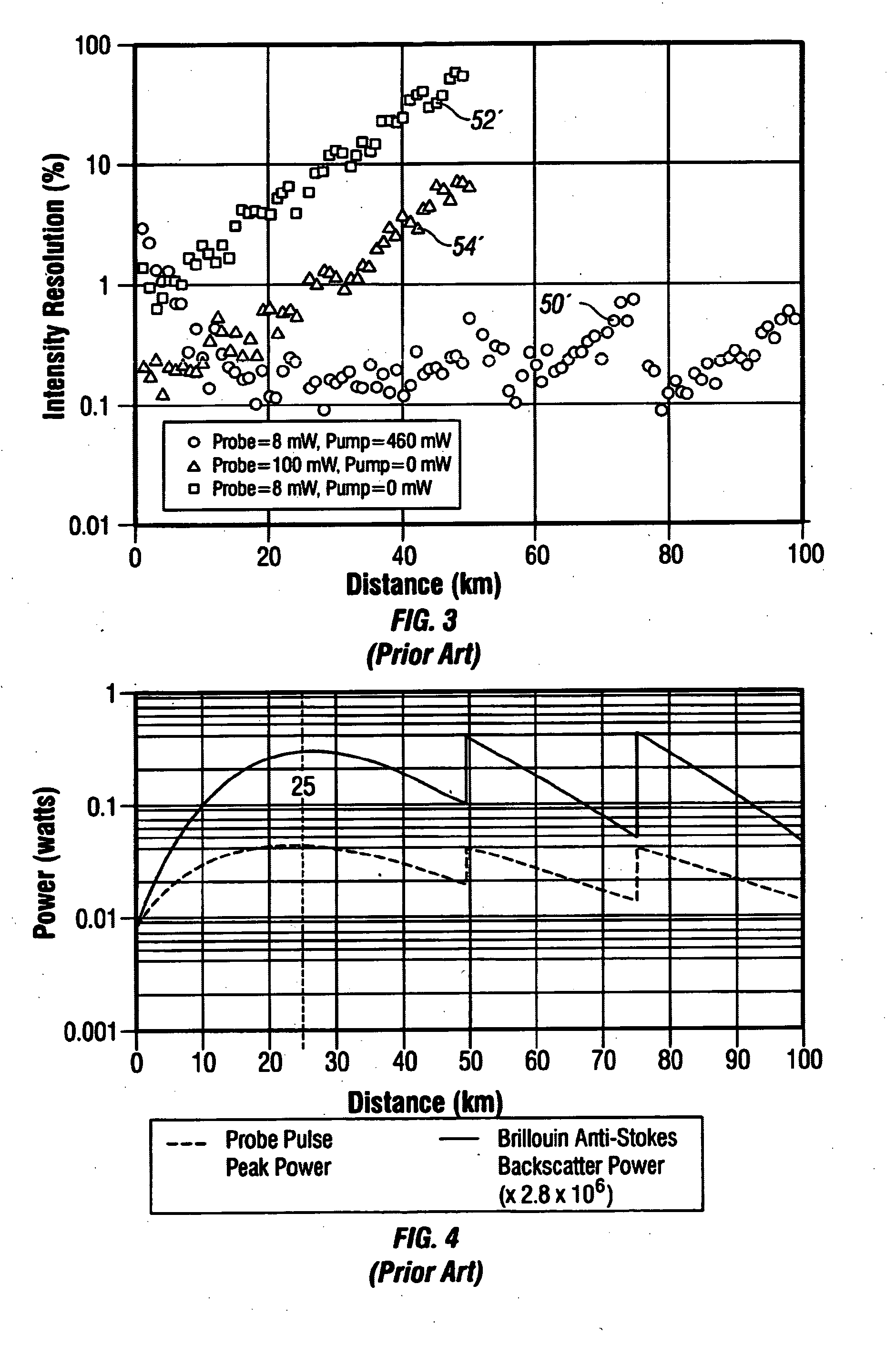
Raman amplification in distributed optical fiber sensing systems
InactiveUS20090263069A1Improve system performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioReflectometers using simulated back-scatterLaser using scattering effectsFiberLength wave
A method of providing Raman amplification in an optical fiber sensing system, comprises generating a probe pulse of light and launching the pulse into a sensing optical fiber, generating pump light at a shorter wavelength and modulating it to produce a time-varying intensity profile, and launching the pump light into the sensing fiber. such that the intensity of the launched pump light during launch of the probe pulse is different from the intensity at other times. Raman amplification of backscattered light produced by the probe pulse as it propagates along the fiber is achieved, as is amplification of the probe pulse if the pump power is non-zero during launch of the probe pulse.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
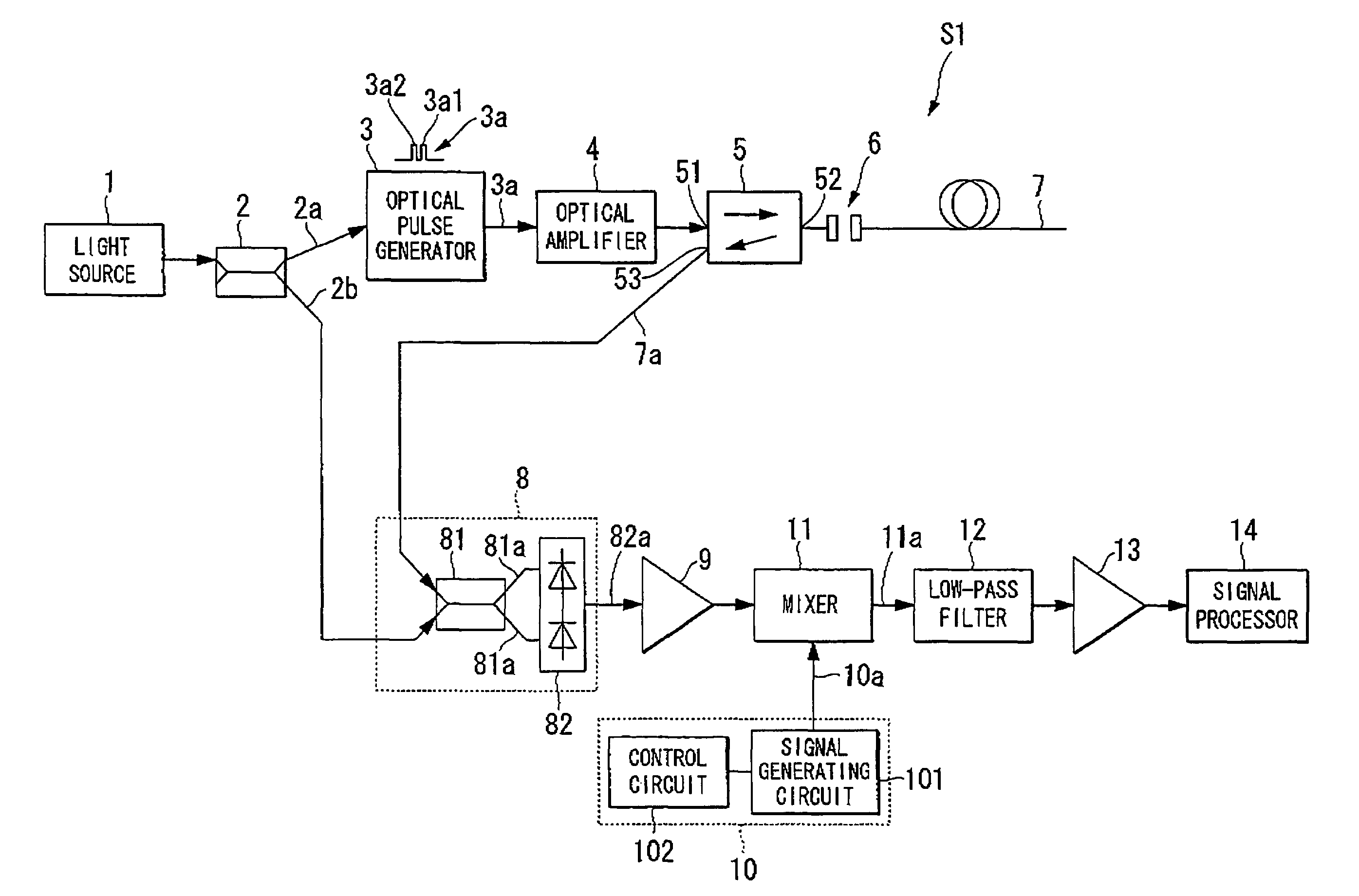
Apparatus for measuring the characteristics of an optical fiber
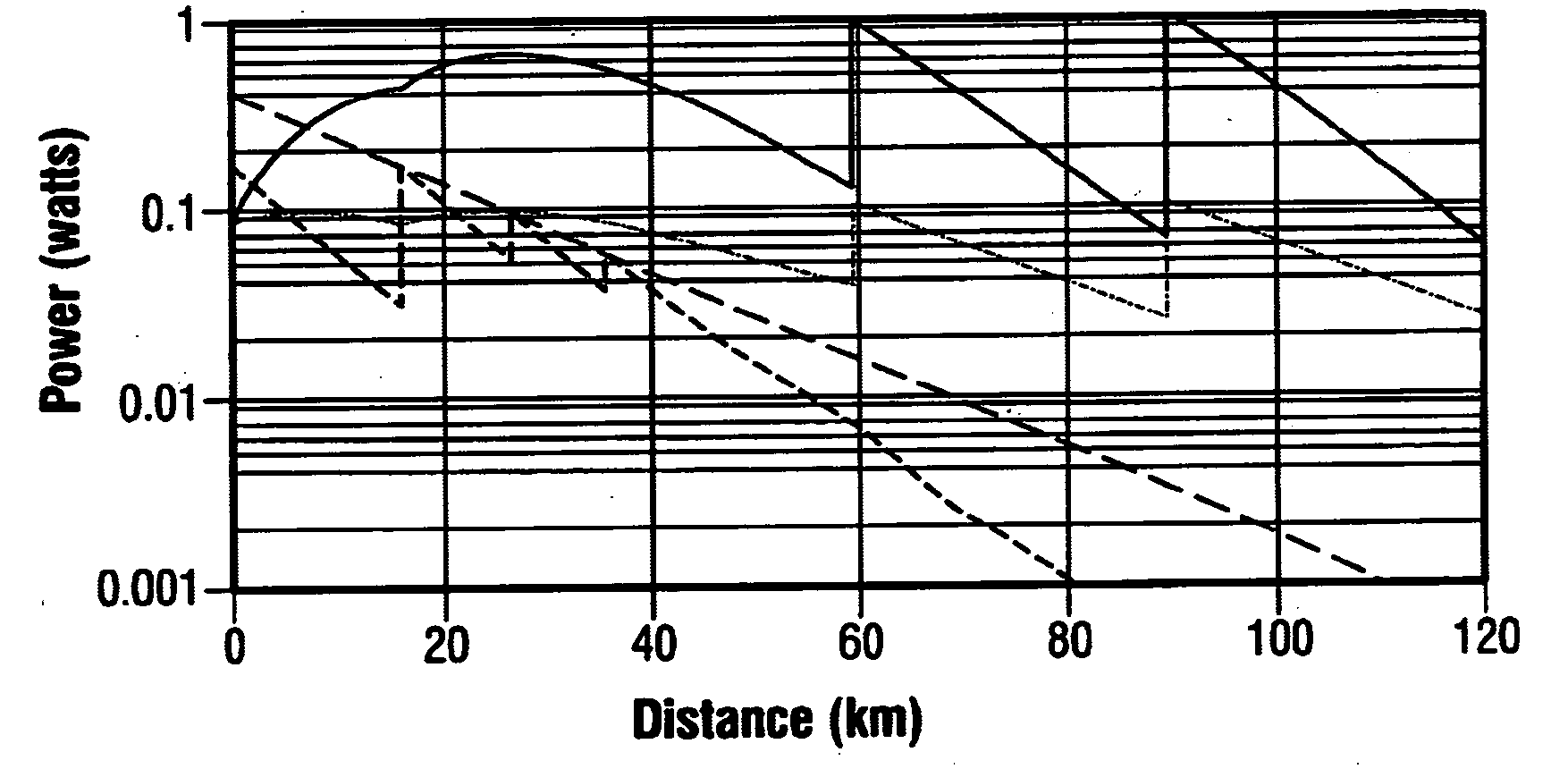
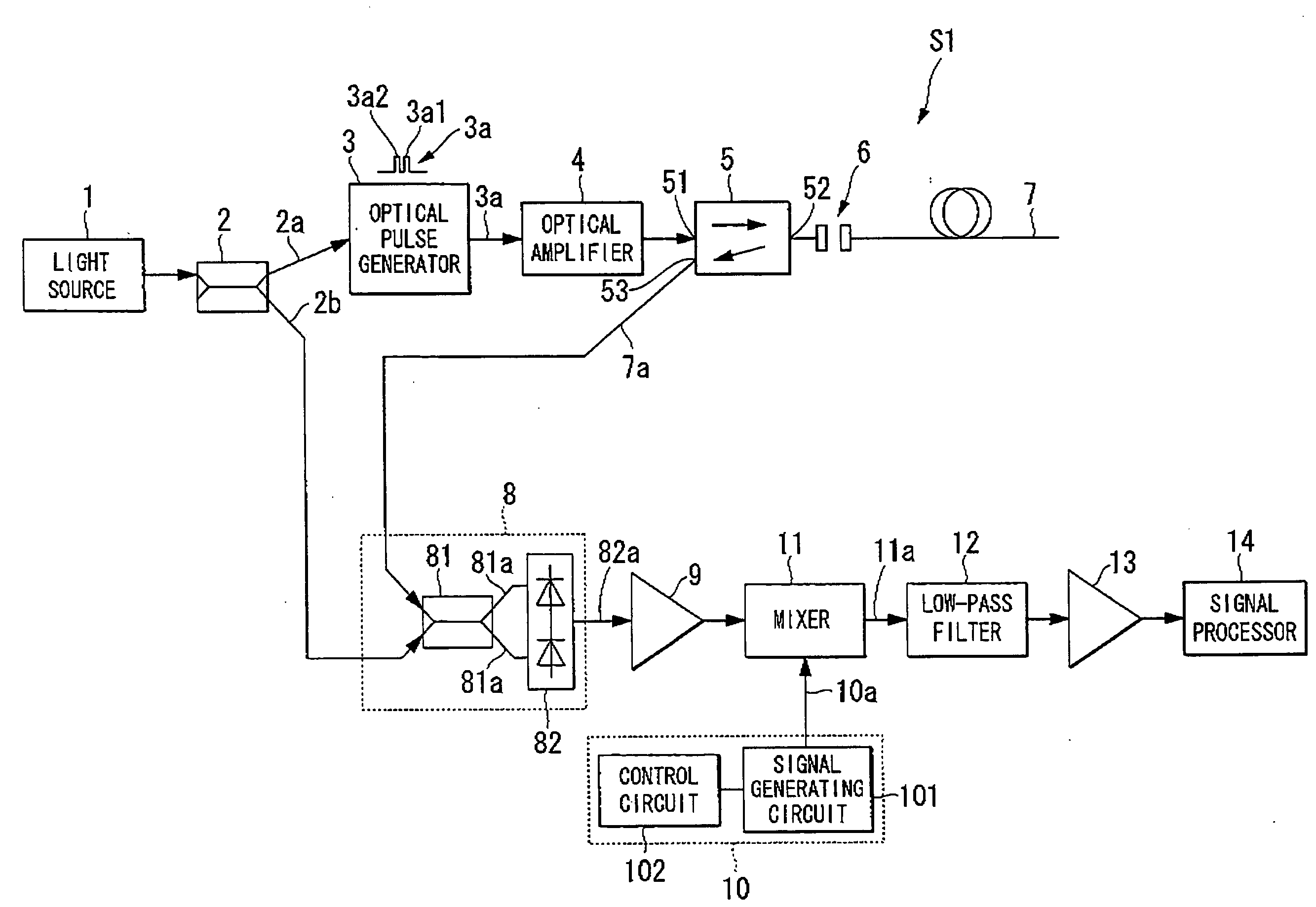
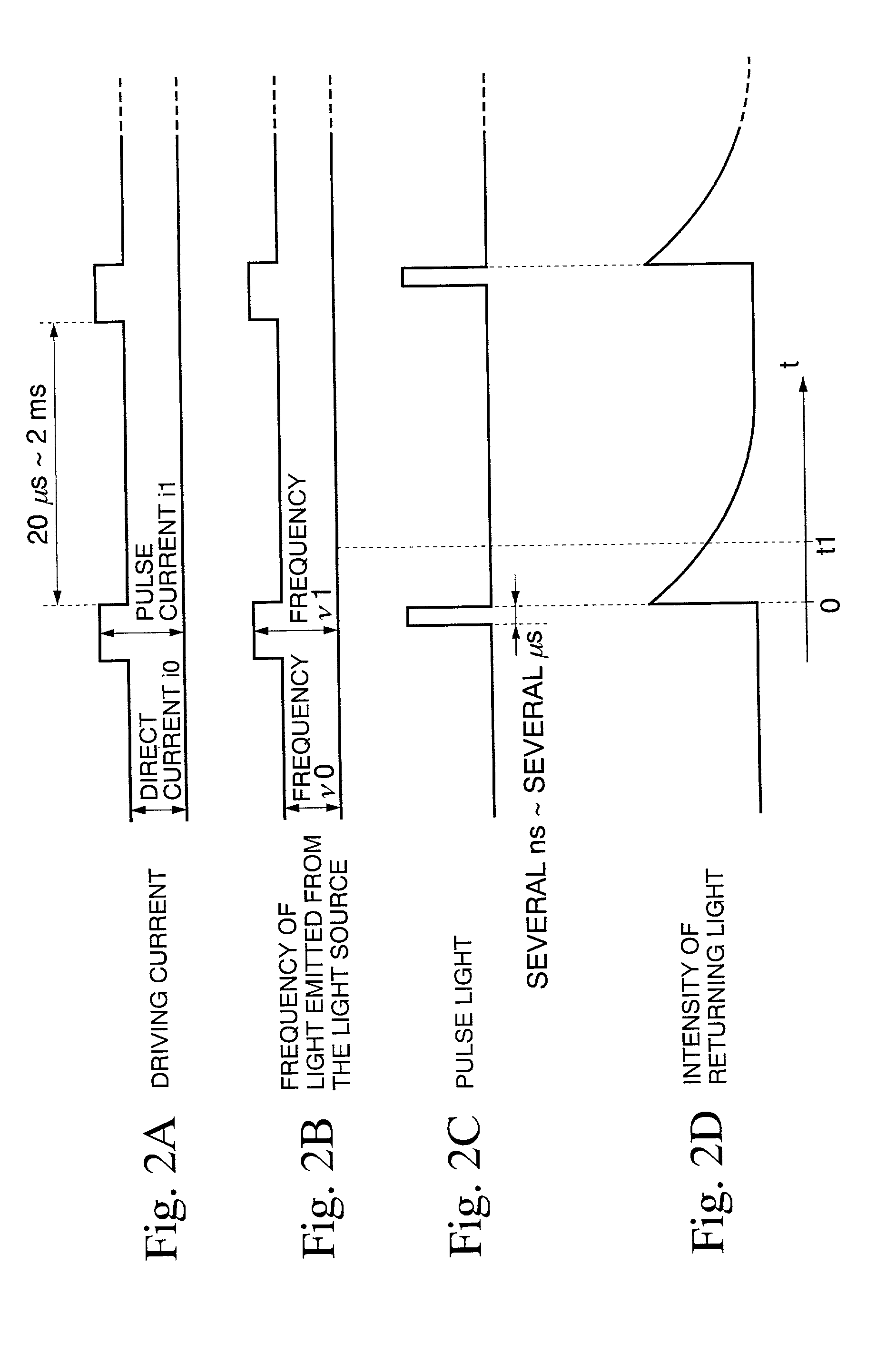
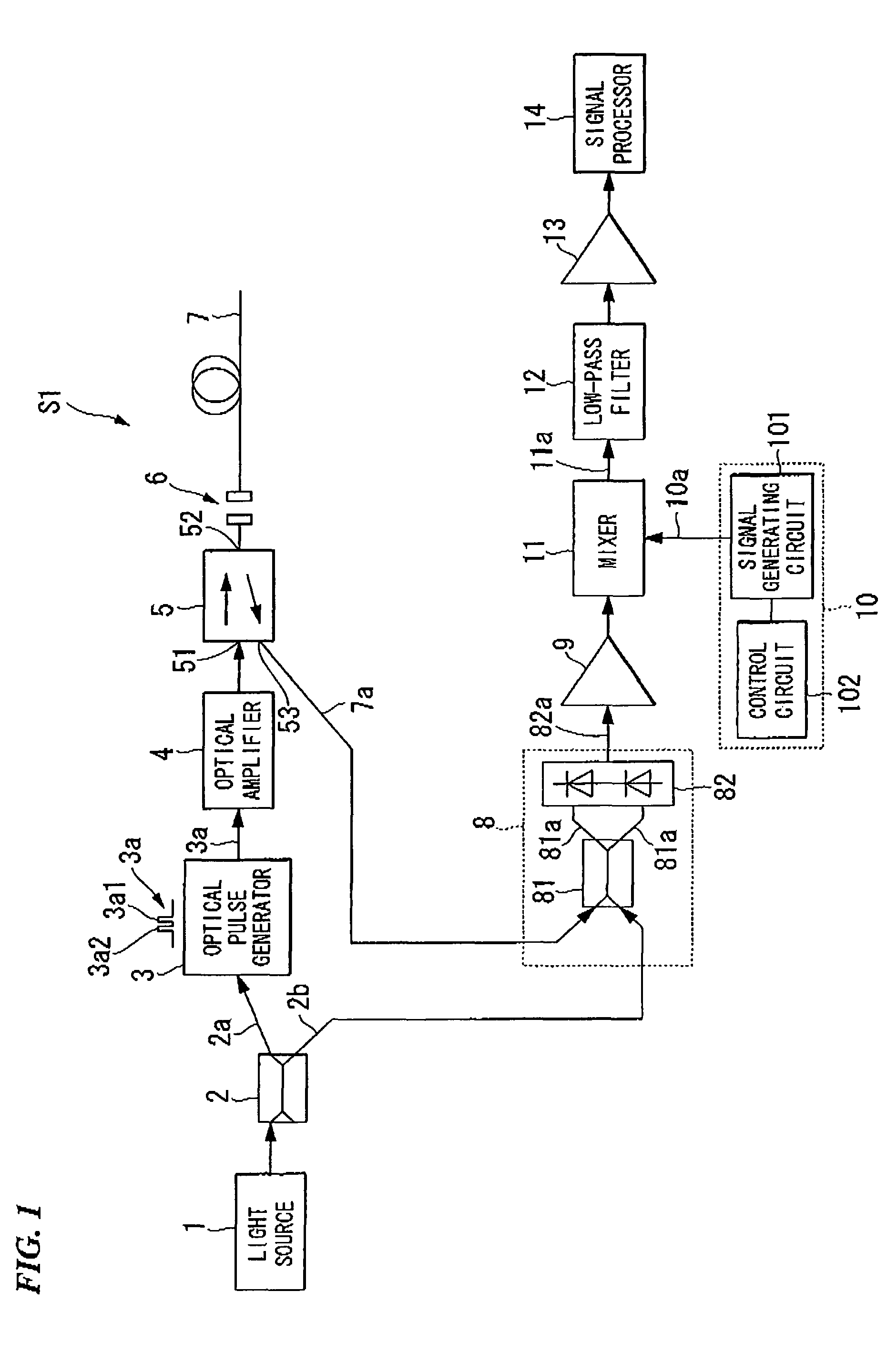
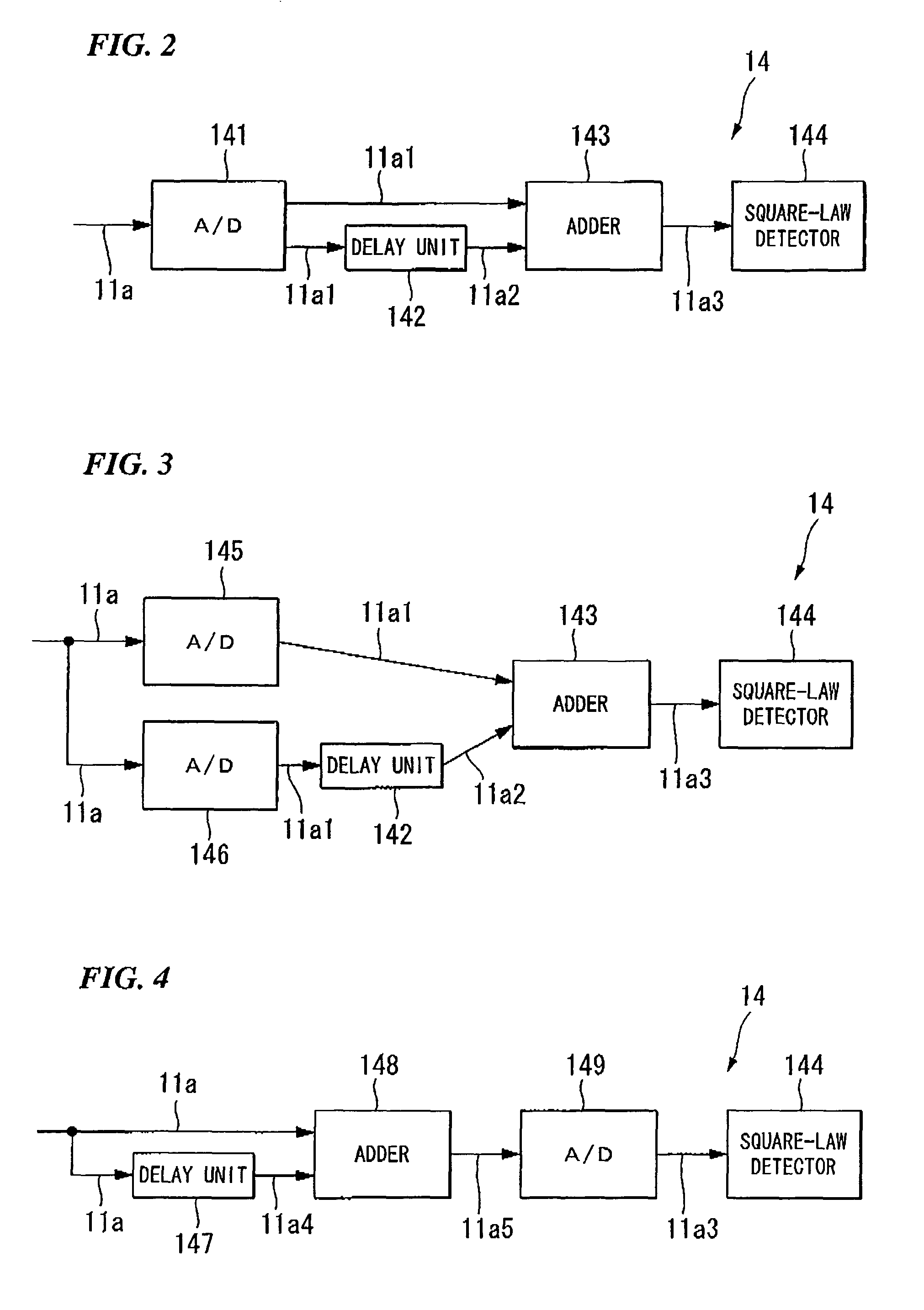
InactiveUS20080145049A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to detectRadiation pyrometryReflectometers using simulated back-scatterElectricityDelayed time
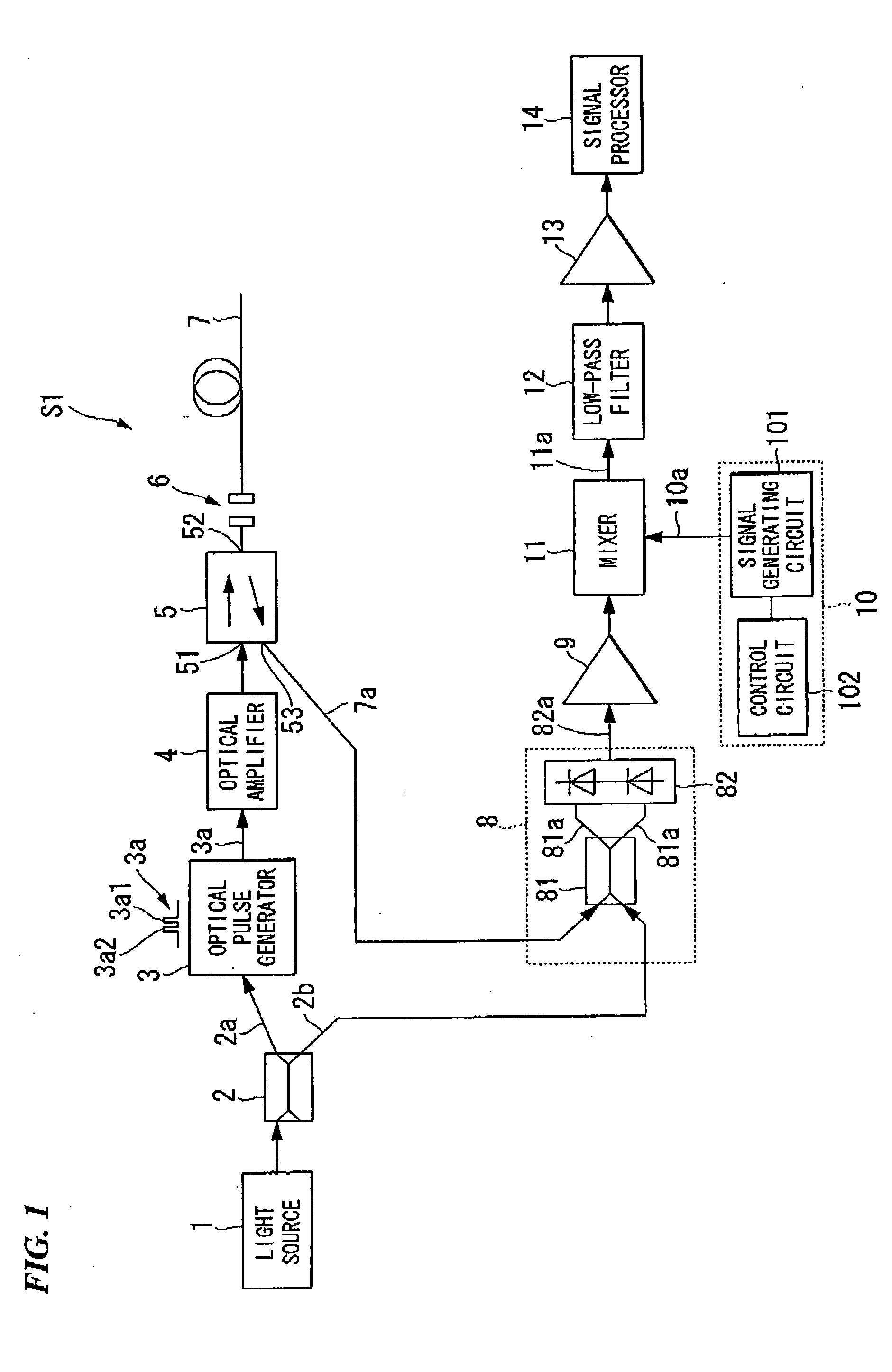
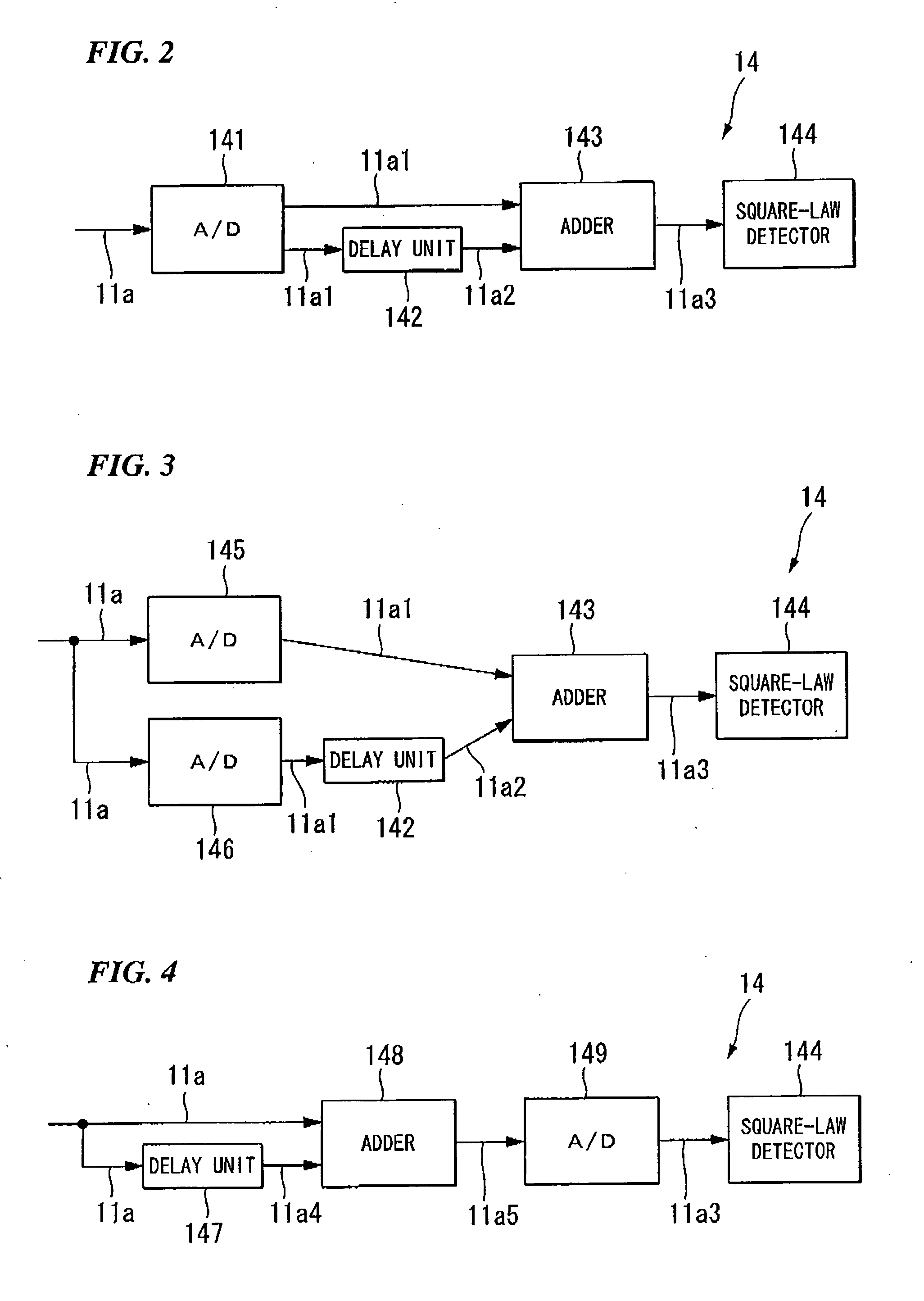
An apparatus for measuring the characteristics of an optical fiber is provided. An optical pulse generator generates, from a coherent light, first and second optical pulses having a time interval which is equal to or shorter tan a life time of an acoustic wave in the optical fiber. A detector couples the coherent light with a Brillouin backscattered light which includes first and second Brillouin backscattered lights belonging to the first and second optical pulses respectively, thereby generating an optical signal. The detector further converts the optical signal into an electrical signal. A signal processor takes the sum of the electrical signal and a delay electrical signal which is delayed from the electrical signal by a delay time corresponding to the time interval, thereby generating an interference signal, and finds the characteristics of the optical fiber based on the interference signal.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
Optical fiber characteristic measuring device
InactiveUS20020154291A1Low costSection be reducedReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement devicePhotoelectric conversion
optical fiber characteristic measuring device comprising a coherent light supply device, a light pulse generating device, a wave mixing device, a opto-electrical converting device, and a processing device, is provided such that parts have the frequency characteristic for corresponding to low frequency component for an opto-electrical converting device and a processing section so as to reduce the cost of the circuits.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Distributed optical fiber sensor
ActiveUS8699009B2Improve spatial resolutionReflectometers using simulated back-scatterPolarisation-affecting propertiesRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Owner:NEUBREX
Distributed and dynamical brillouin sensing in optical fibers
InactiveUS20130308682A1OptimizationReflectometers using simulated back-scatterForce measurementFiberOptical fiber cable
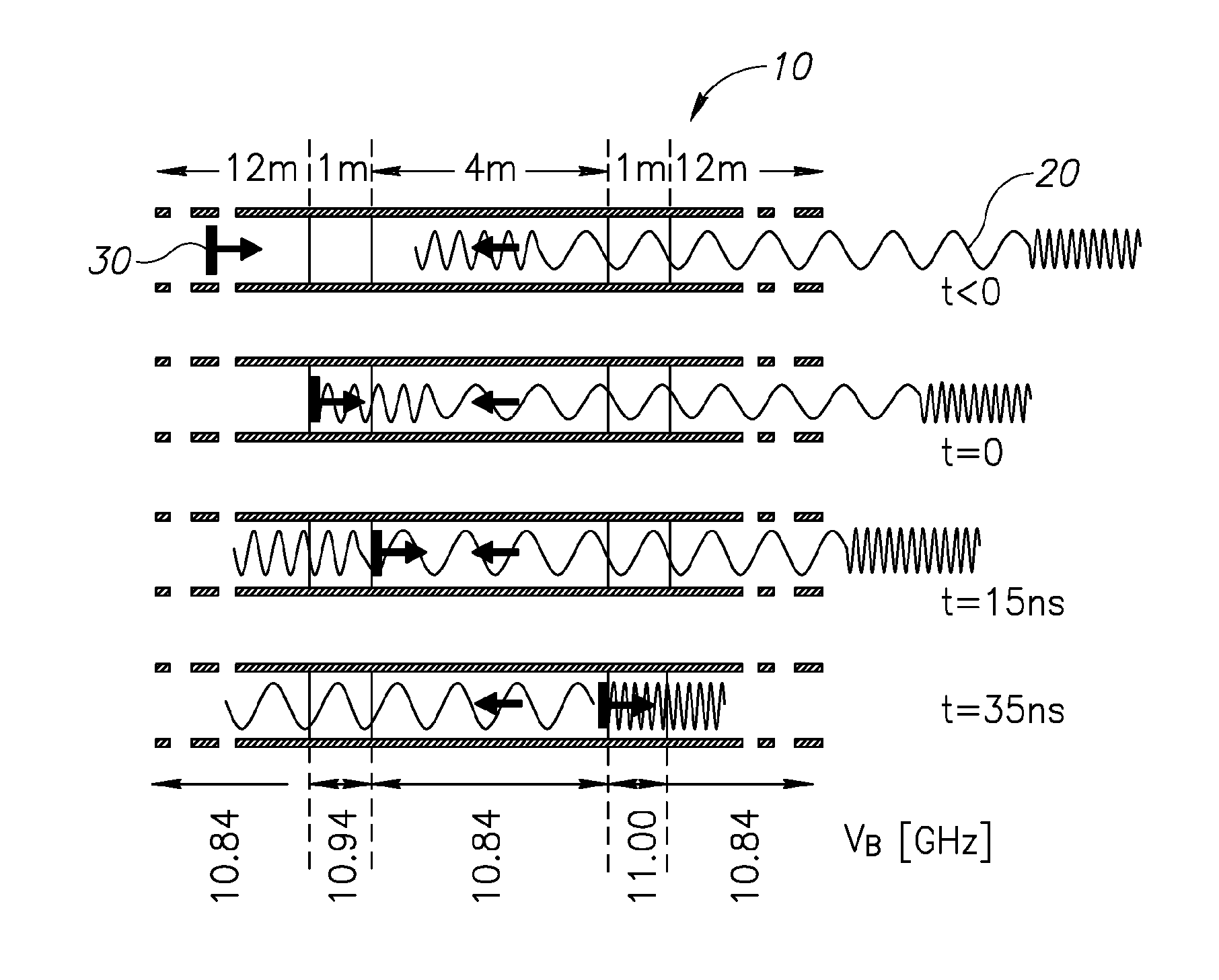
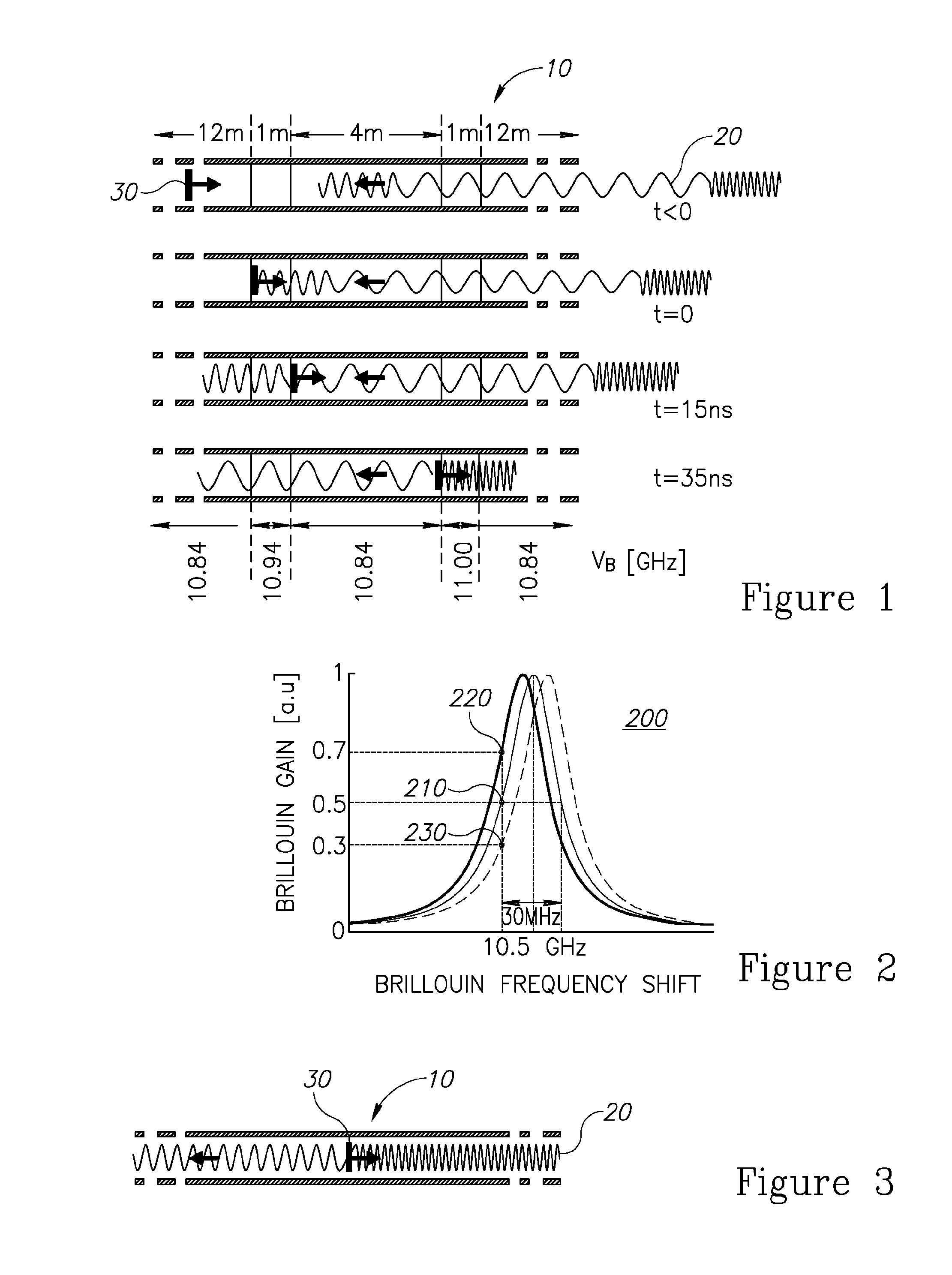
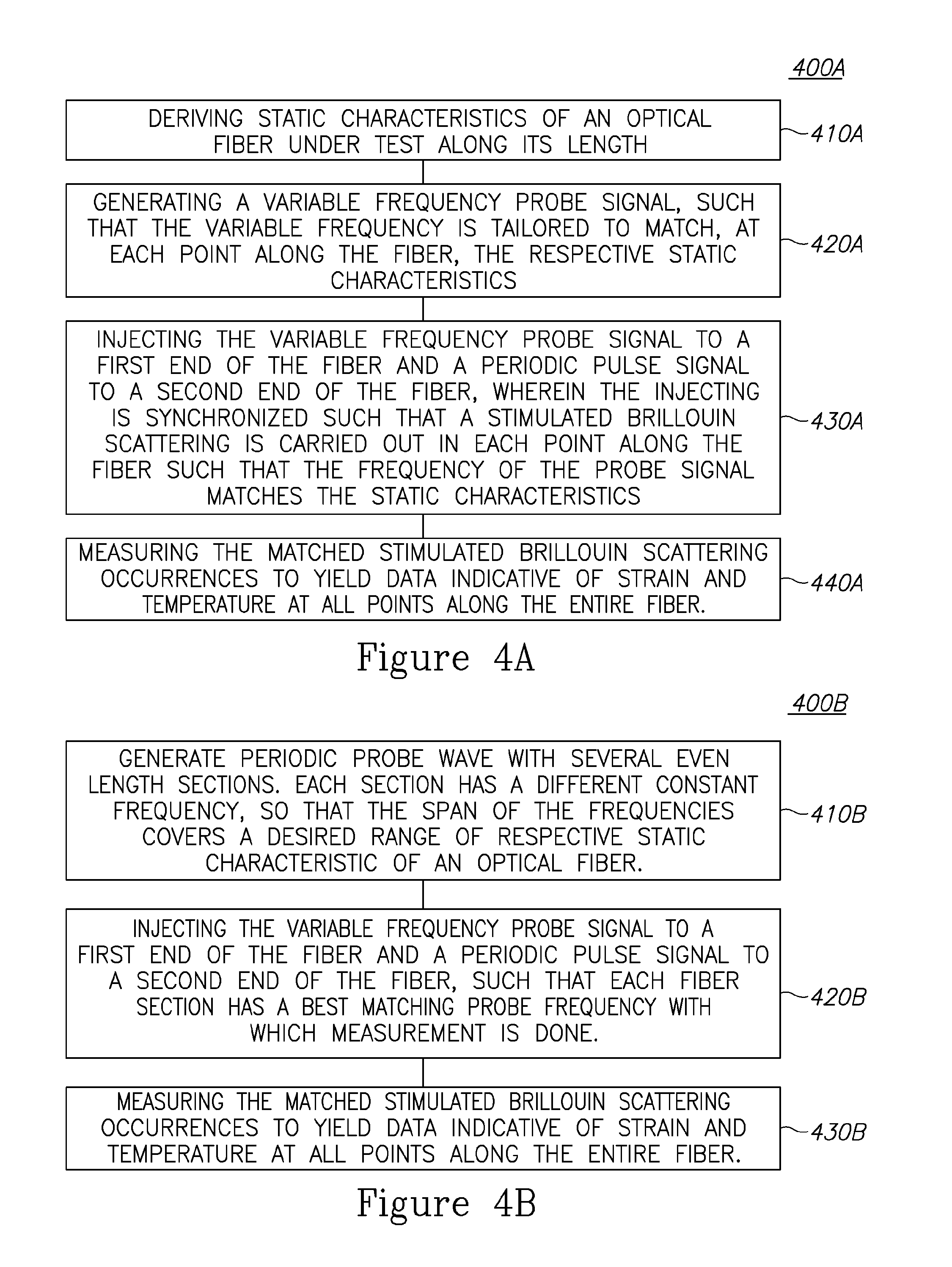
A method of distributed and dynamical Brillouin sensing in optical fibers is provided herein. The method includes the following stages: deriving average characteristics of an optical fiber along its length; generating a variable frequency probe signal, such that the variable frequency is tailored to match, at specified points along the fiber, the respective average characteristics; injecting the variable frequency probe signal to a first end of the optical fiber and a periodic pulse signal to a second end of the optical fiber, wherein the injecting is synchronized such that a stimulated Brillouin scattering is carried out at each one of the specified points along the optical fiber, such that a frequency difference between the probe signal and the pump signal matches the average characteristics of the fiber; and measuring occurrences of the stimulated Brillouin scattering, to yield data indicative of strain and temperature at all points along the optical fiber.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Brillouin optical time domain analyzer relevant to chaotic laser
InactiveCN102322806AWith ultra-broadband bandwidthImprove reliabilityReflectometers using simulated back-scatterThermometers using physical/chemical changesSignal lightSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a Brillouin optical time domain analyzer relevant to a chaotic laser, which is an optical fiber Brillouin optical time domain analyzer made according to the chaotic laser relevant principle, the coherent amplification Brillouin scattered light, the temperature effect and the optical time domain reflection principle. In the analyzer, the same chaotic laser device serves as the local reference light source and the pump signal light source of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer. According to the chaotic laser relevant principle, the chaotic laser has an ultra-wide frequency width; signal light and local light are relevantly processed to obtain a high spatial resolution, so that the reliability of the sensor can be effectively improved, the spatial resolution can reach the centimeter level, the number of pump photons entering the sensing optical fiber is increased, the signal to noise ratio of the sensor system is 10dB, and the measurement length of the sensor can reach 50km; and the same chaotic laser device is adopted to serve as the local reference light source and the pump signal light source of the Brillouin optical time domain analyzer, thereby solving the problem of locking a narrow-band detection laser and a narrow-band pump laser, and improving system stability.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
Method for measuring nonlinear optical properties, and optical amplifier and optical transmission system using same
InactiveUS20080013162A1InhibitionIncrease powerReflectometers using simulated back-scatterDistortion/dispersion eliminationAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
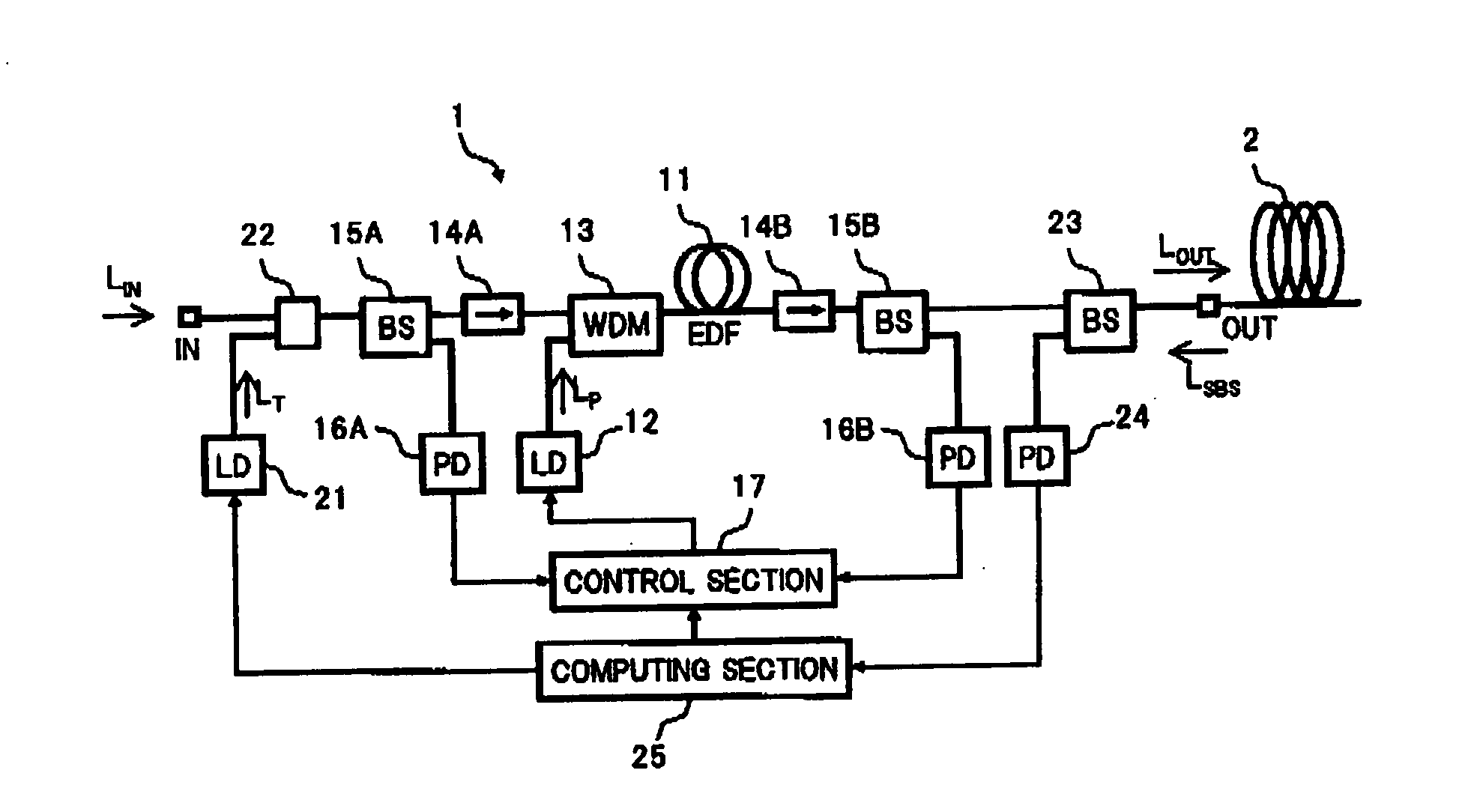
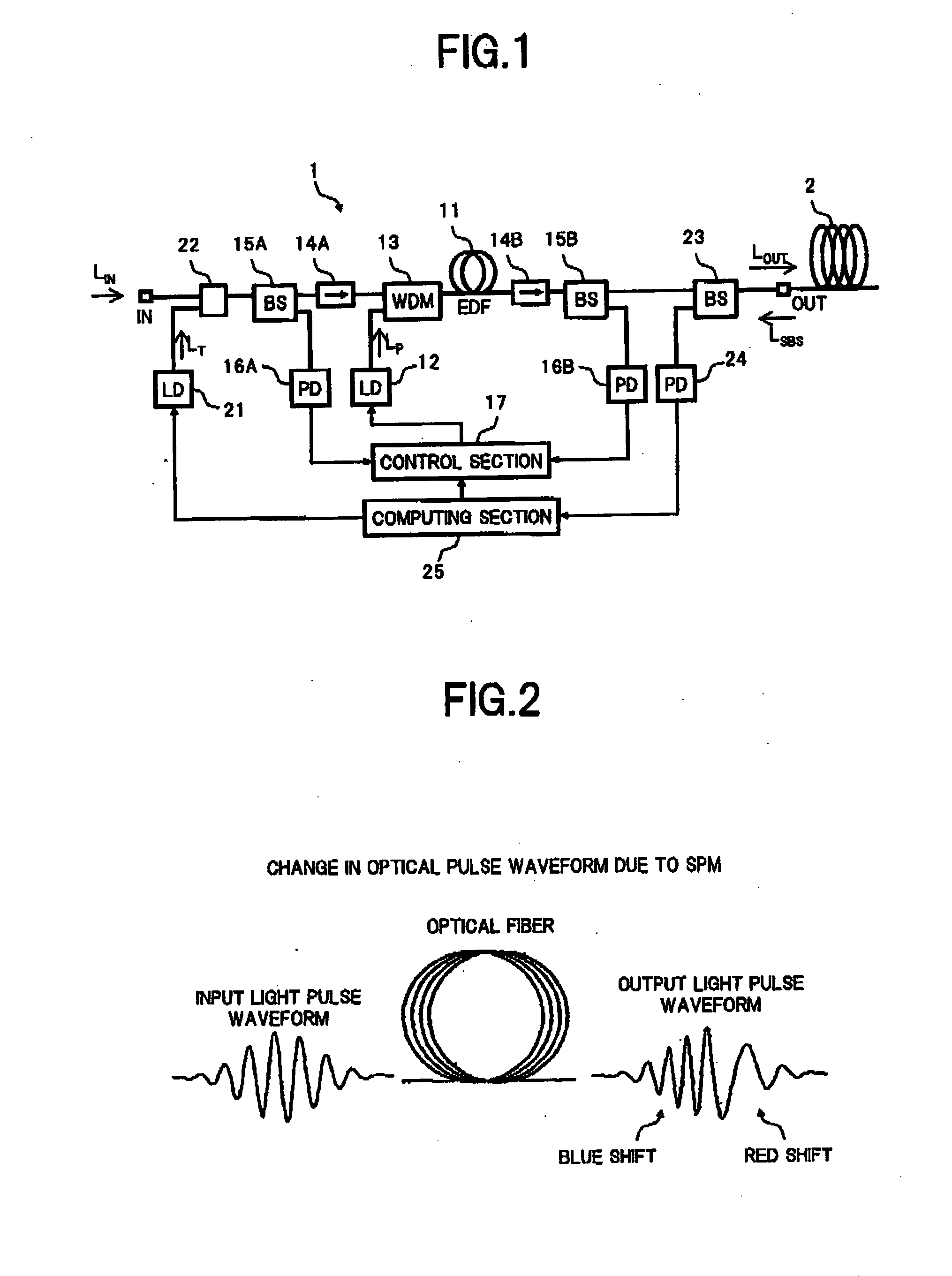
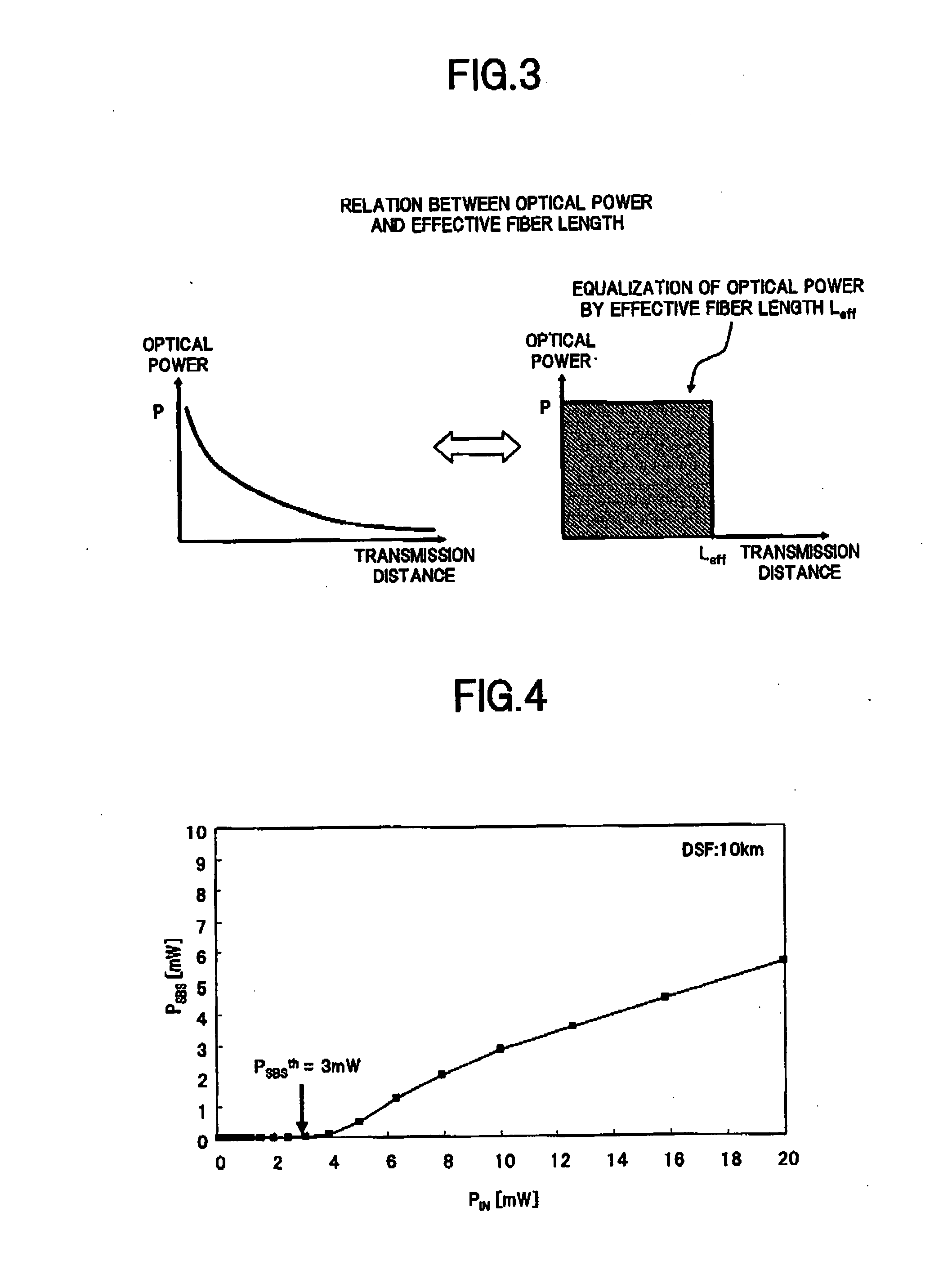
In an optical amplifier of the present invention, an input light is supplied to one end of an optical fiber connected to an output port, and the power of a light In an opposite direction which is input to the output port from the one end of the optical fiber, is measured, thereby obtaining a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) occurrence threshold in the optical fiber based on the measurement result. Then, using the SBS occurrence threshold, a relation been the input light power and an occurrence amount of the self phase modulation (SPM) or the like in the optical fiber is obtained to be reflected on a control of the optical amplifier, so that an occurrence of the SPM or the like in the optical fiber is suppressed. As a result, It becomes possible to accurately measure, with a simple configuration, the nonlinear optical properties of the optical fiber actually connected to the output port of the optical amplifier, so that the optical S / N ratio degradation due to a nonlinear optical effect can be effectively suppressed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High-power fiber amplifier
InactiveUS20090231682A1Laser detailsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterOptoelectronicsAmplifier
Fiber light amplifiers adapted for high power application are provided. In embodiments of the invention, the light signal to be amplified is coupled to a cladding mode of an active waveguide region which is cladding doped. The amplified light is coupled to an output fiber have waveguiding properties matching those of the active cladding of the active waveguide region. In other embodiments, two or more amplifying stages are provided coupled by a wavelength selective loss element which couples the Stokes wave co-propagating with the signal to be amplified out of the signal guiding mode prior to the onset of SRS.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
Long-distance polarization and phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry based on random laser amplification
ActiveUS20140183360A1Avoid large noiseSimple structureReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansRandom laserPhase sensitive
A long-distance polarization and phase-sensitive reflectometry based on random laser amplification for extending a sensing distance includes a long-distance polarization and phase-sensitive reflectometry of a distributed Raman amplification based on optical fiber random lasers generated by unilateral pumps, a long-distance polarization and phase-sensitive reflectometry of a distributed Raman amplification based on optical fiber random lasers generated by bilateral pumps, and a long-distance polarization and phase-sensitive reflectometry of a Raman amplification based on a combination of optical fiber random lasers generated by unilateral pumps and a common Raman pump source, which are applied in optical fiber perturbation sensing and have a capability of greatly improving a working distance of a sensing system and a high practicability.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
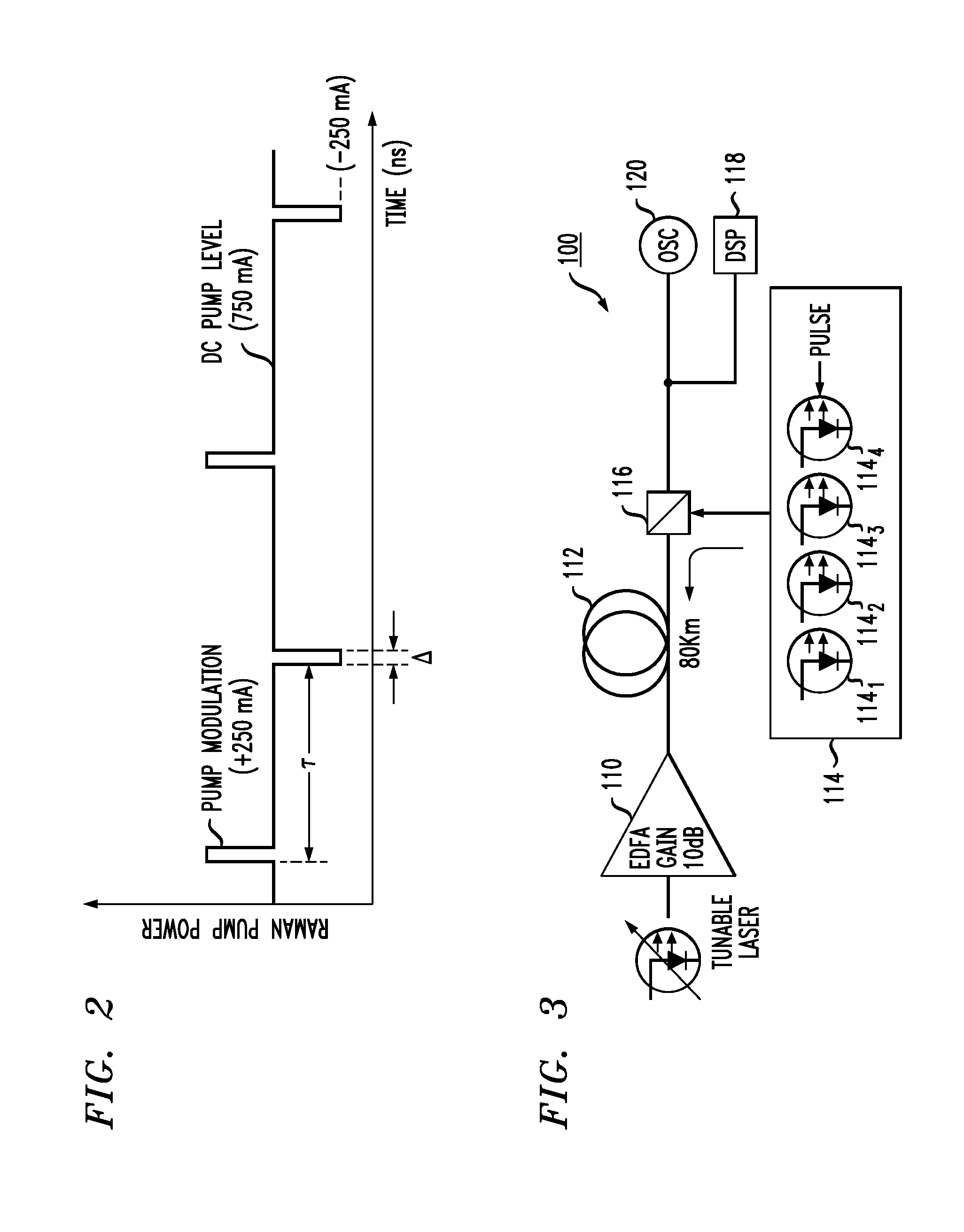
In-Service Optical Time Domain Reflectometry Utilizing Raman Pump Source
ActiveUS20150253217A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterLaser using scattering effectsTime domainCommunications system
An arrangement for providing real-time, in-service OTDR measurements in an optical communication system utilizing distributed Raman amplification. One or more of the laser diodes used to provide the pump light necessary to create optical gain is modified to also generate short duration pulses that ride above or below the conventional pump light. These short duration pulses (which co-exist with the pump light within the optical fiber) are used in performing OTDR measurements, with a conventional processing system used to evaluate reflected pulses and create the actual OTDR measurements.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method for mapping of dispersion and other optical properties of optical waveguides
ActiveUS20090079967A1Correction for dispersionHighly fashionReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical propertyWaveguide
A method is provided for measurement of dispersion or other optical and mechanical properties within a waveguide by inducing four-photon mixing at different locations within the waveguide by timing a pump signal to counter-collide with and abruptly amplify or attenuate one or both of a probe pulse and a signal pulse at each location. The measurement of the components of the resulting mixing signal created by each collision is used to calculate dispersion defined by the location at which the collision occurred. By combining the measurements from all of the locations, a spatial map of dispersion or other optical or mechanical properties within the waveguide can be generated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
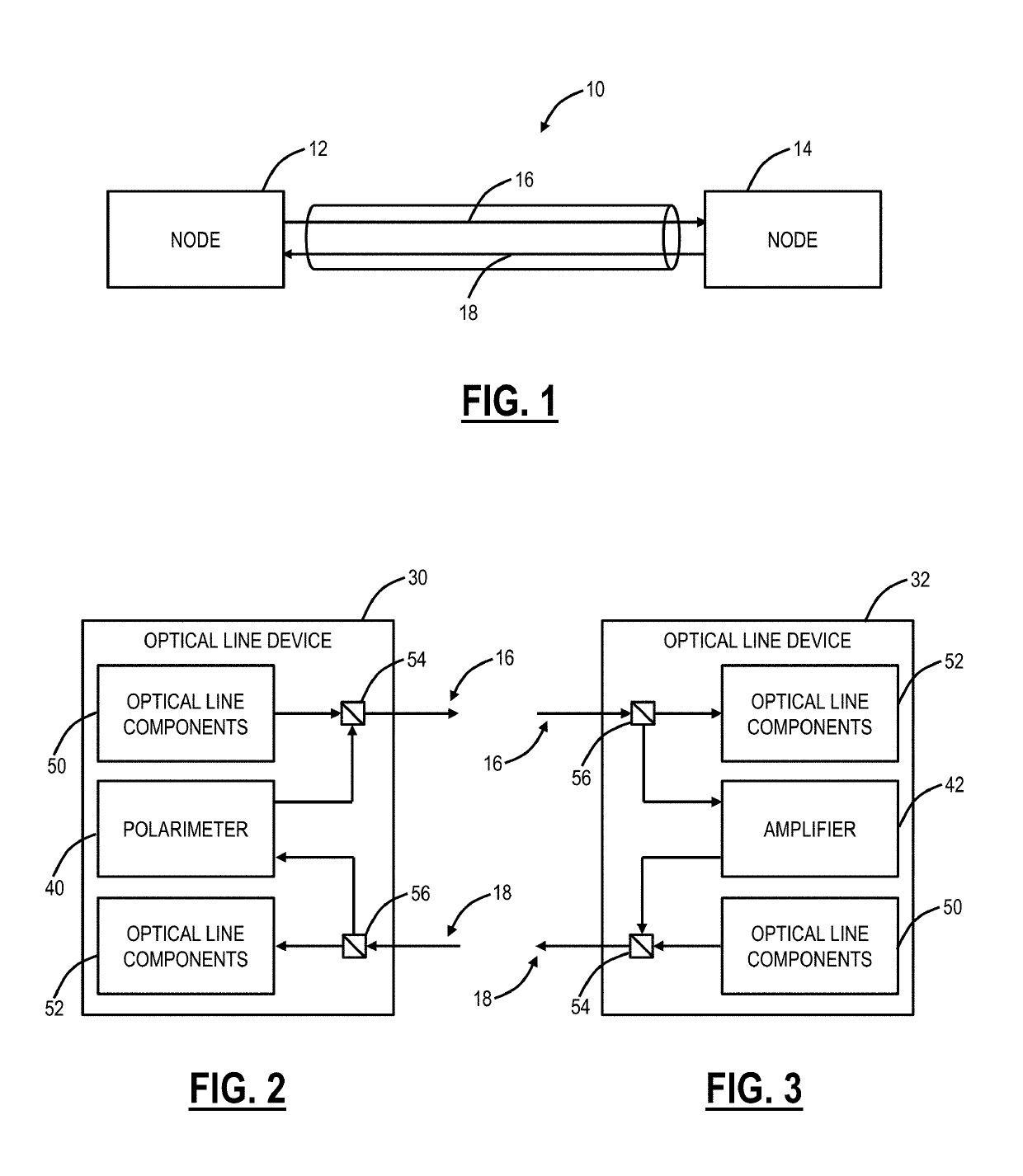
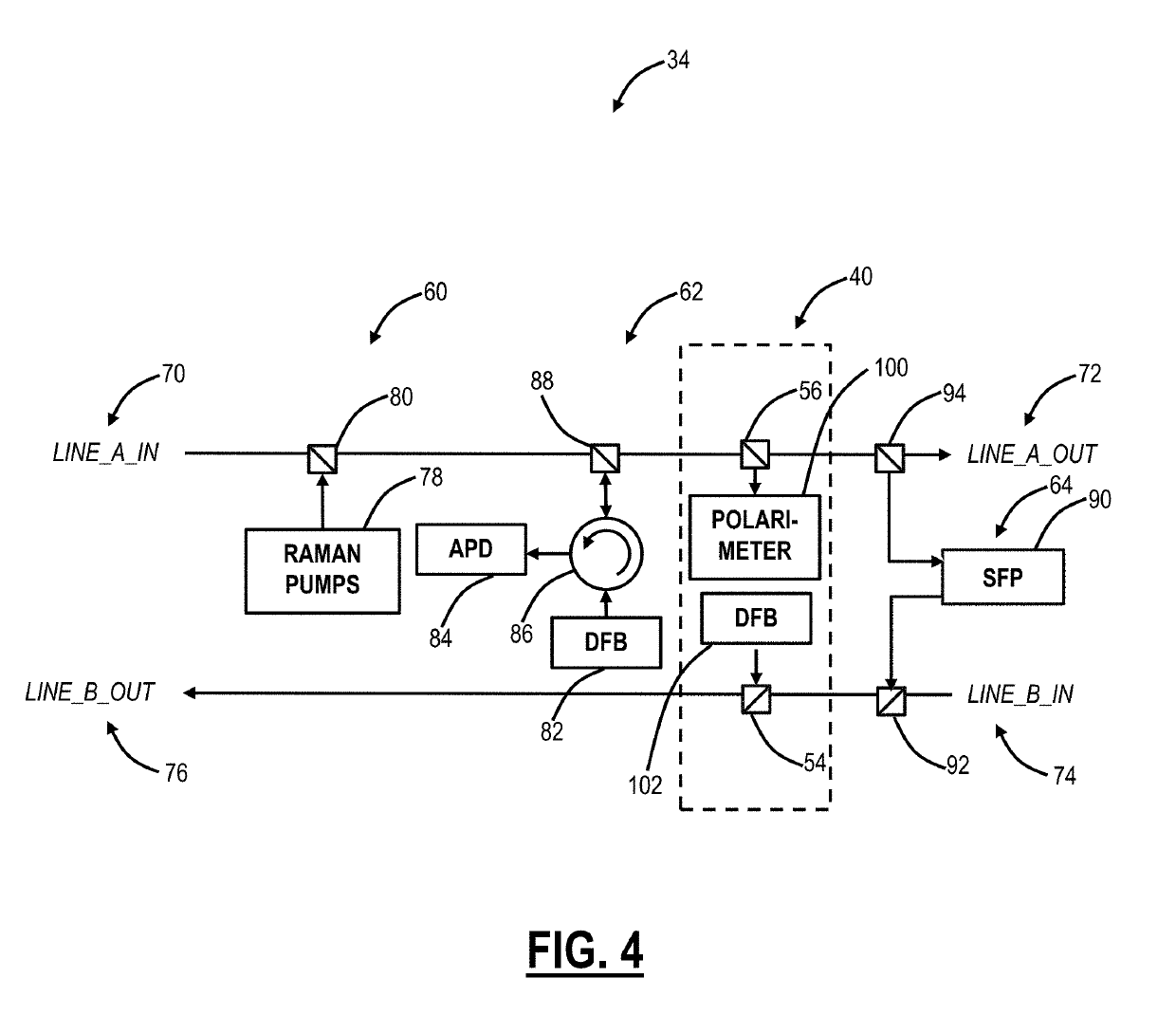
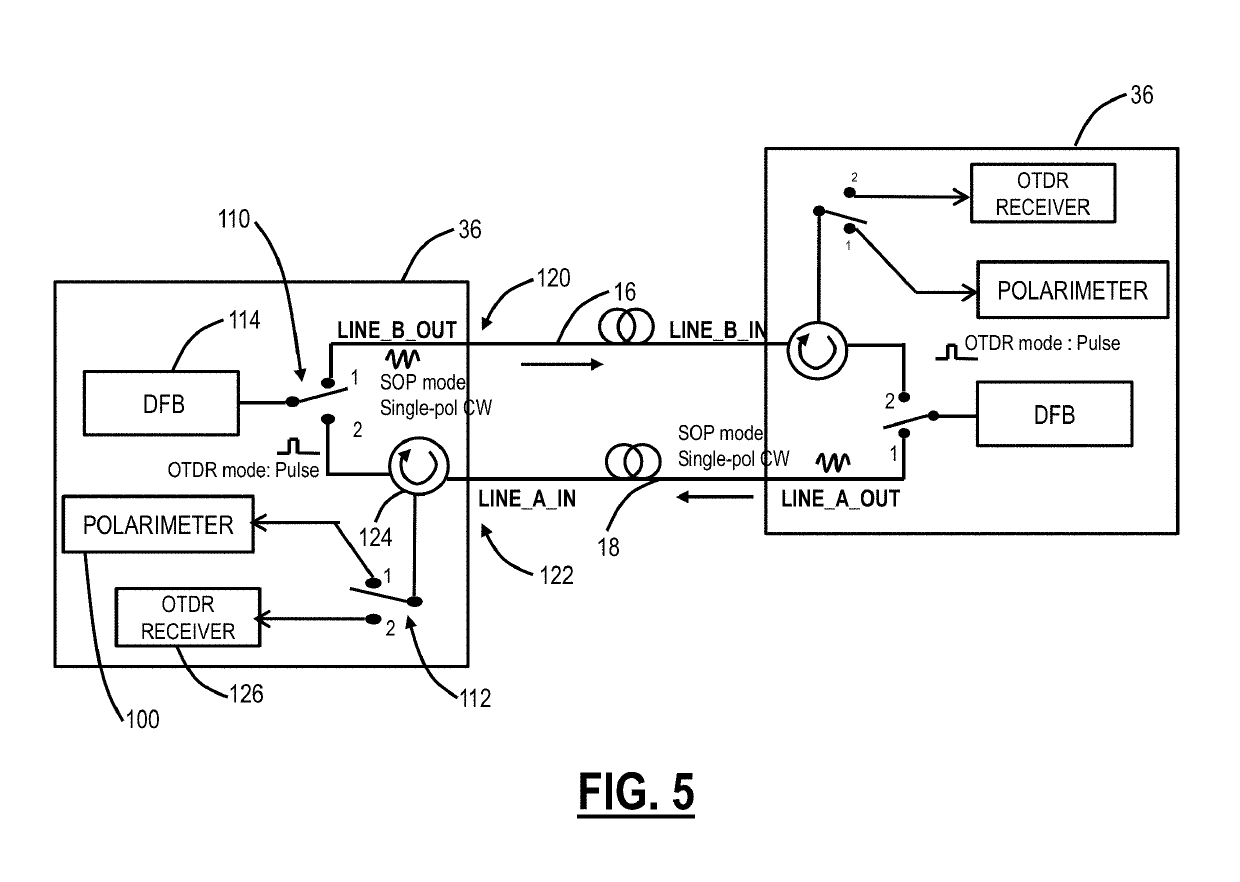
Optical fiber characterization measurement systems and methods
ActiveUS10411796B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterOptical amplifierElectrical and Electronics engineering
Systems and methods for characterizing an optical fiber performed in part by an optical node in an optical line system include performing one or more measurements to characterize the optical fiber with one or more components at the optical node, wherein the one or more components perform functions during operation of the optical node and are reconfigured to perform the one or measurements independent of the functions; and configuring the optical node for communication over the optical fiber based on the one or more measurements. The one or more components can include any of an Optical Service Channel (OSC), an Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR), and an optical amplifier. The configuring can include setting a launch power into the optical fiber based on the one or more measurements.
Owner:CIENA
Apparatus for measuring the characteristics of an optical fiber
InactiveUS7873273B2Improve spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometryReflectometers using simulated back-scatterElectricityDelayed time
An apparatus for measuring the characteristics of an optical fiber is provided. An optical pulse generator generates, from a coherent light, first and second optical pulses having a time interval which is equal to or shorter tan a life time of an acoustic wave in the optical fiber. A detector couples the coherent light with a Brillouin backscattered light which includes first and second Brillouin backscattered lights belonging to the first and second optical pulses respectively, thereby generating an optical signal. The detector further converts the optical signal into an electrical signal. A signal processor takes the sum of the electrical signal and a delay electrical signal which is delayed from the electrical signal by a delay time corresponding to the time interval, thereby generating an interference signal, and finds the characteristics of the optical fiber based on the interference signal.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
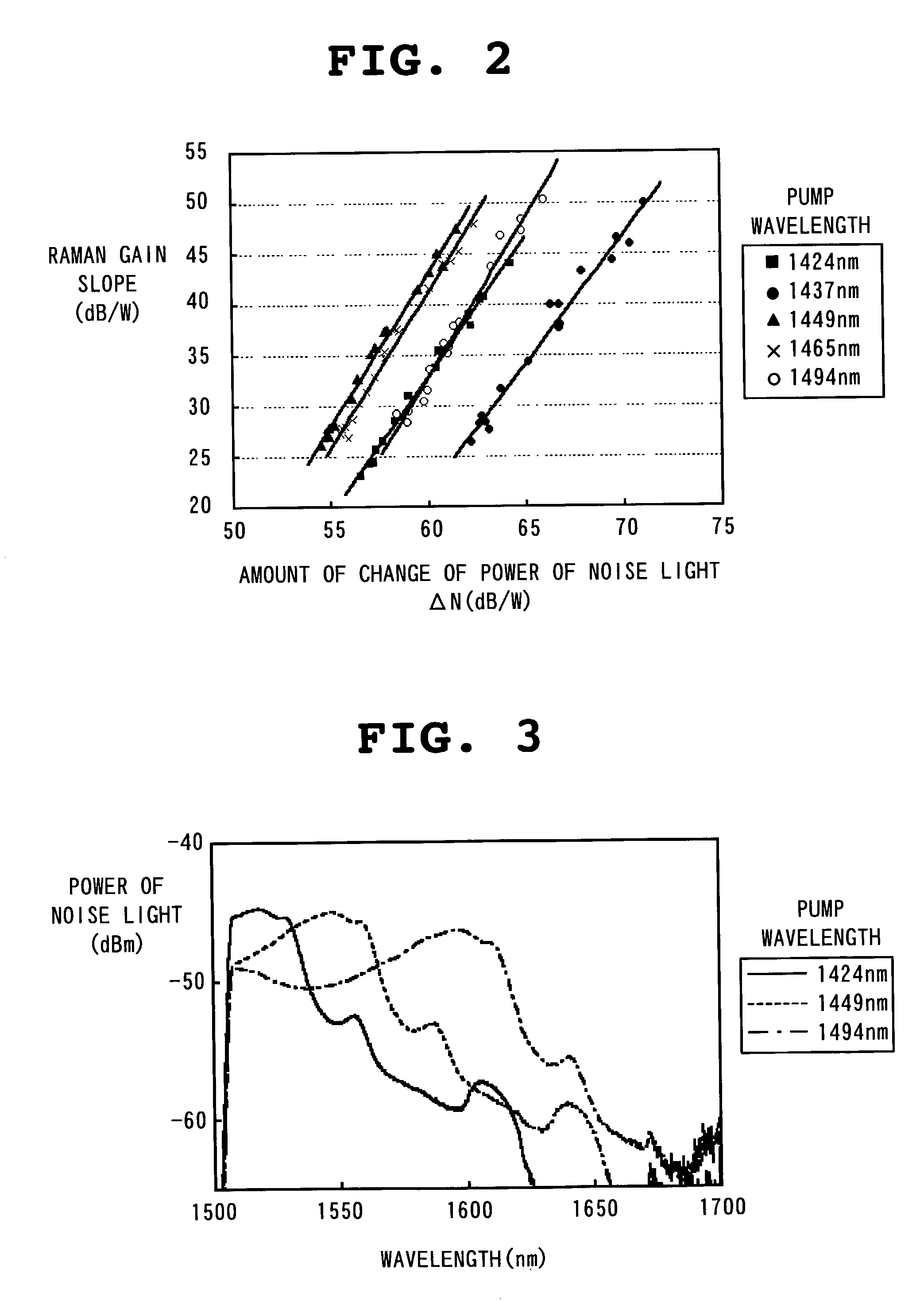
Optical fiber transmission system, raman gain slope measuring device and raman gain slope measuring method
InactiveUS7061665B2High cost performanceImprove workabilityLaser using scattering effectsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMeasurement deviceOptical power
In Raman gain slope measurement method and device measures Raman gain slope which is a value obtained by normalizing a gain generated by Raman amplification caused by pump light incident on an optical fiber by optical power of the pump light in question. The method and device measures the power of noise light and operates based on a relationship between the optical power of pump light incident on an optical fiber and the optical power of the measured noise light generated by the application of the pump light, Raman gain slope of the optical fiber in question is thus calculated.
Owner:NEC CORP
Real-time fiber optic interferometry controller
ActiveUS9772238B2Improve Utilization and FlexibilityIncrease utility and flexibilityReflectometers using simulated back-scatterSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMultiplexingFiber
A modular fiber optic interferometry control system and method for extracting information from superimposed waves is disclosed. The system comprises a first module for converting a radio frequency input to a multiplexed binary data stream, a second module for correlating a pseudo random number (PRN) reference with a received PRN code modulated backscattered signal, and a third module comprising control logic. In some embodiments the system further comprises one or more of a fourth module for generating a power stream, a fifth module for event interrogation, and a sixth module for noise reduction.
Owner:ADELOS INC
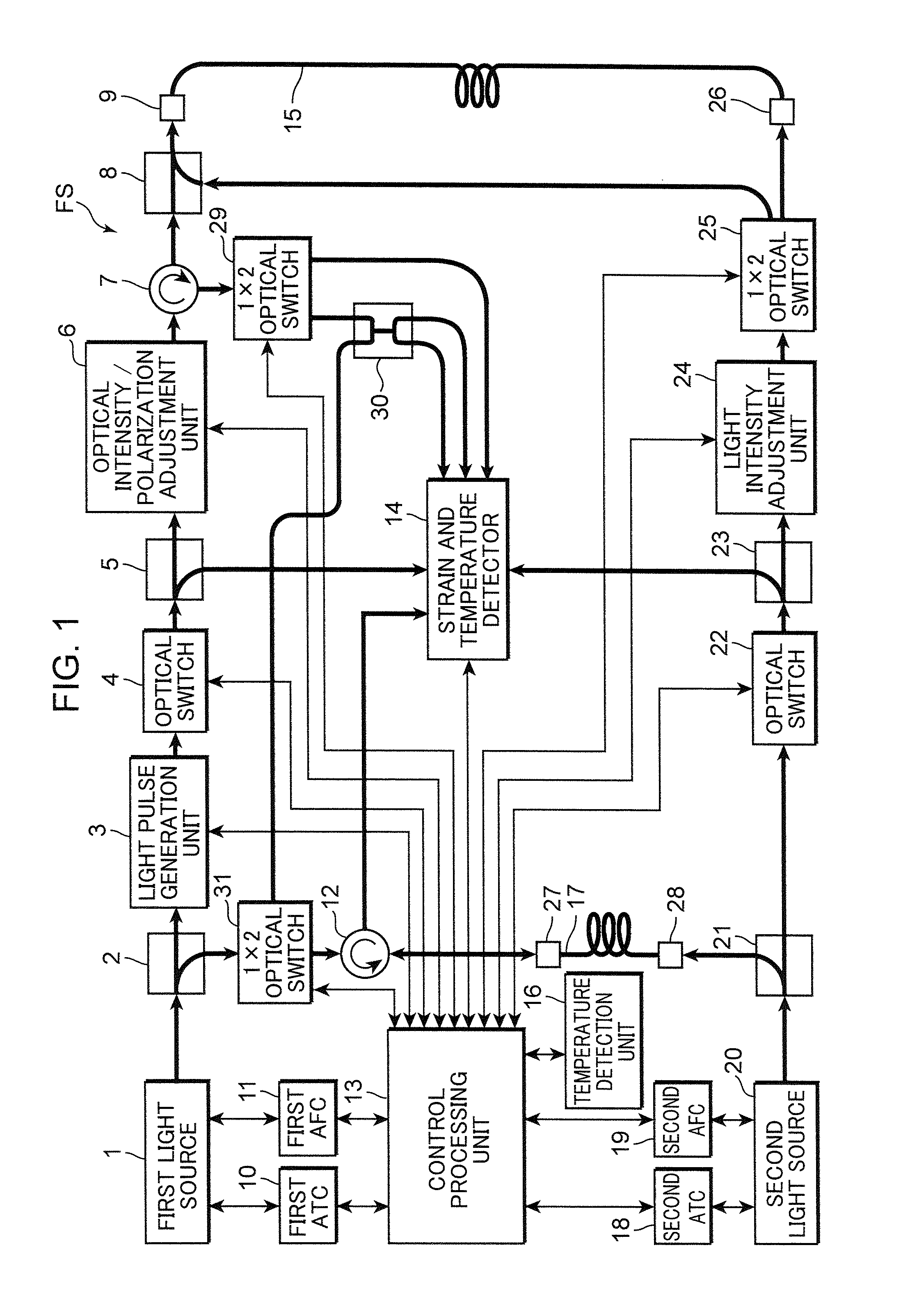
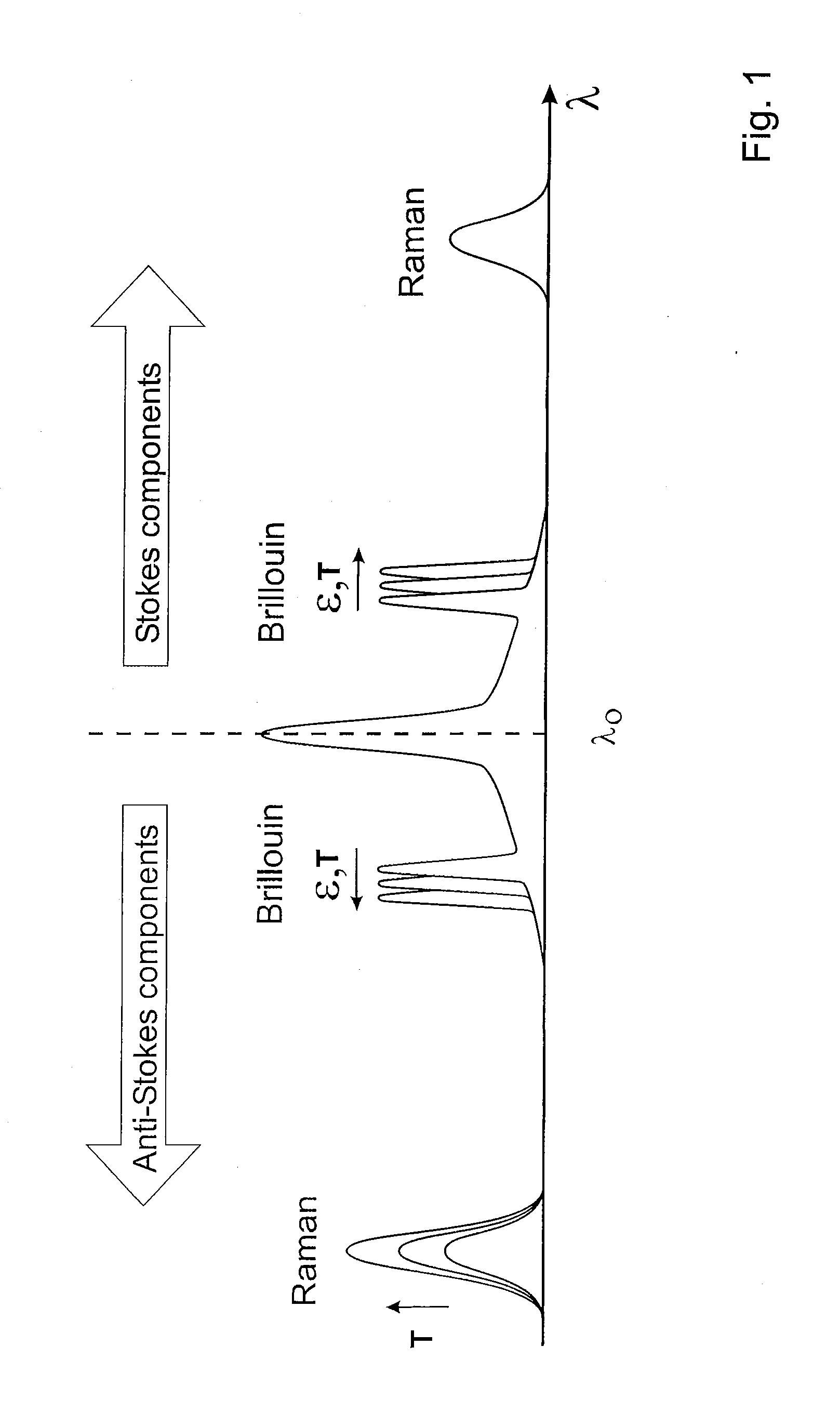
Spectral measurement apparatus and measurement method utilizing brillouin scattering
InactiveUS20080193126A1Ensure correct executionReliable judgmentReflectometers using simulated back-scatterForce measurementFiberLine width
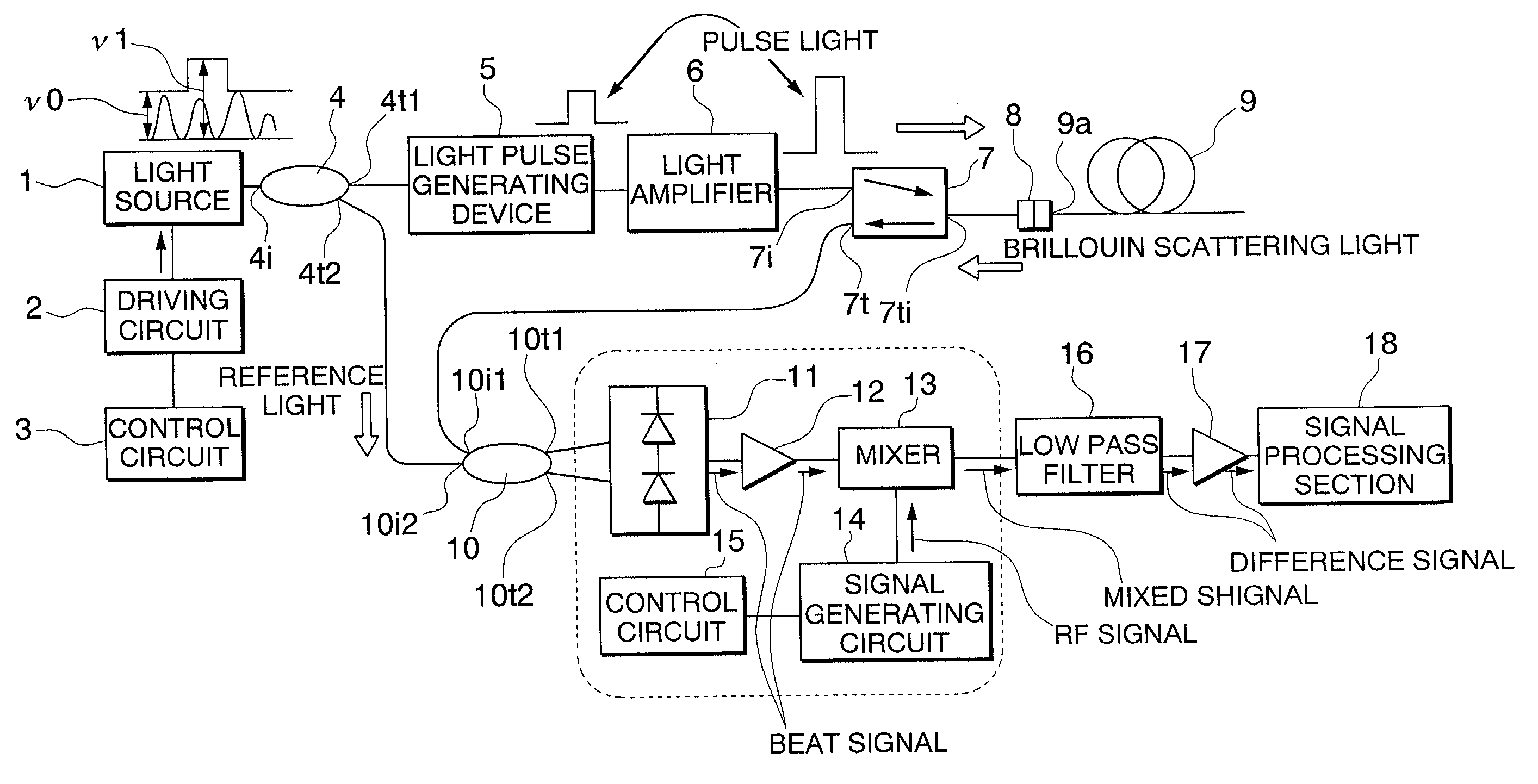
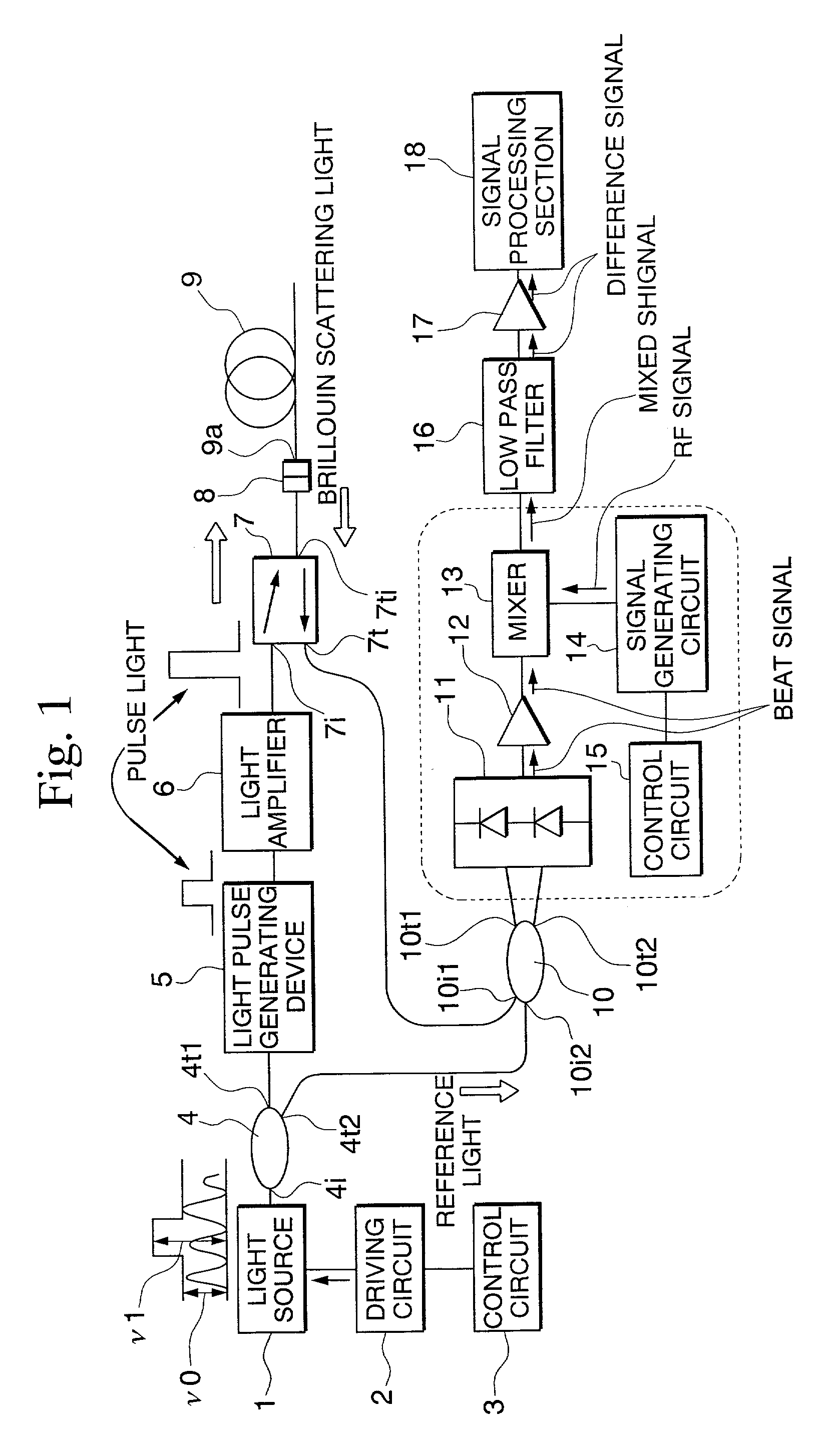
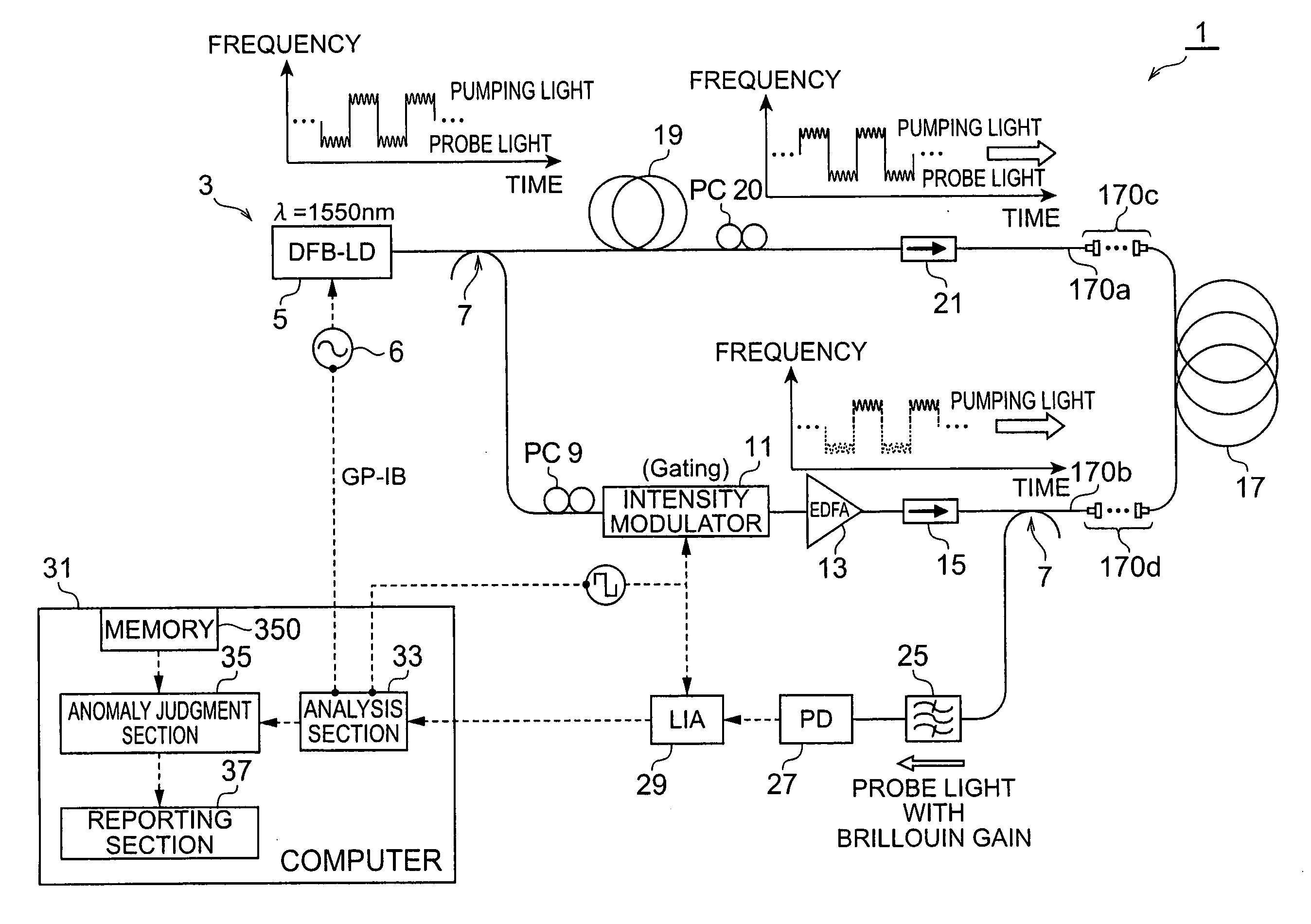
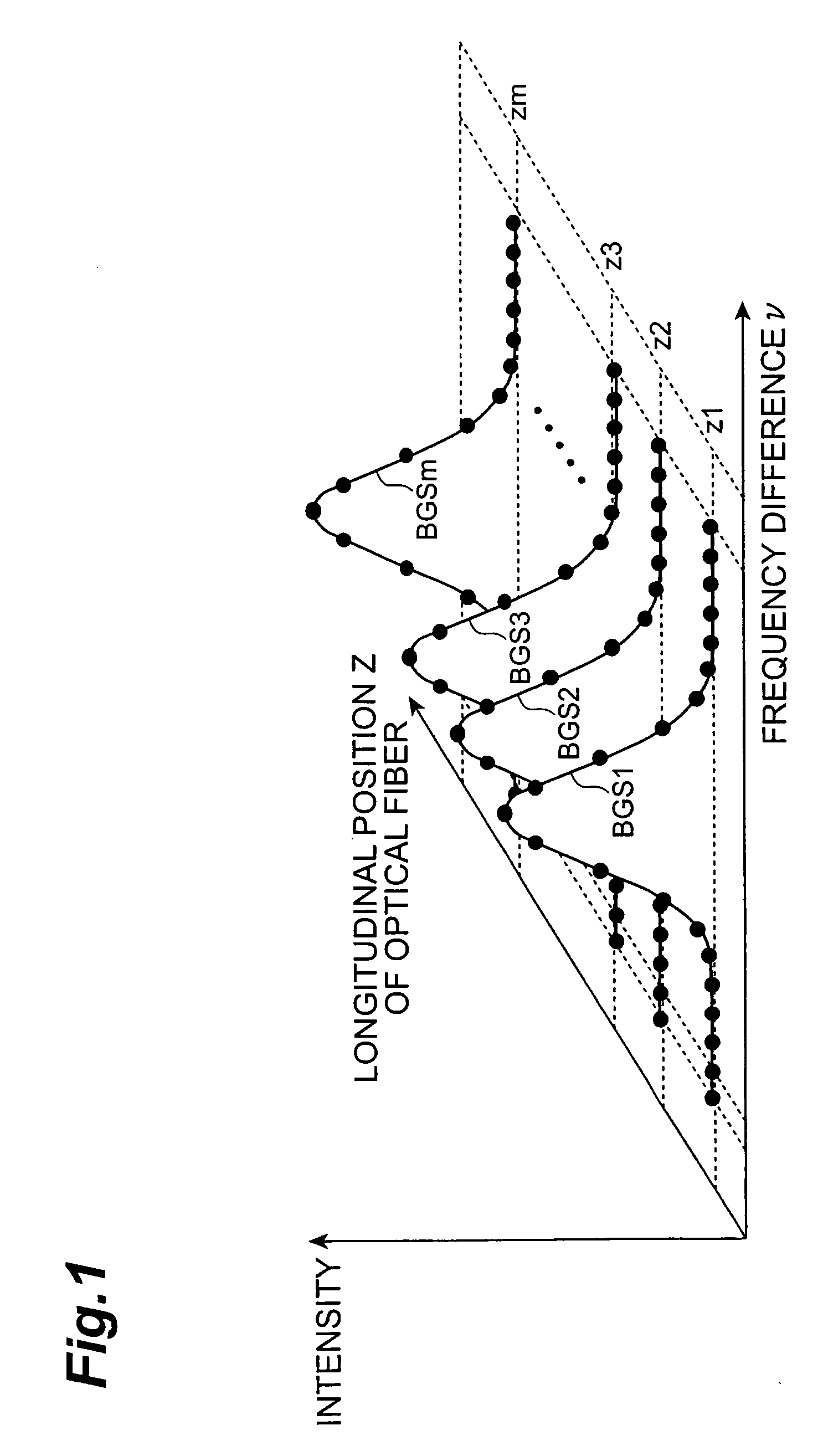
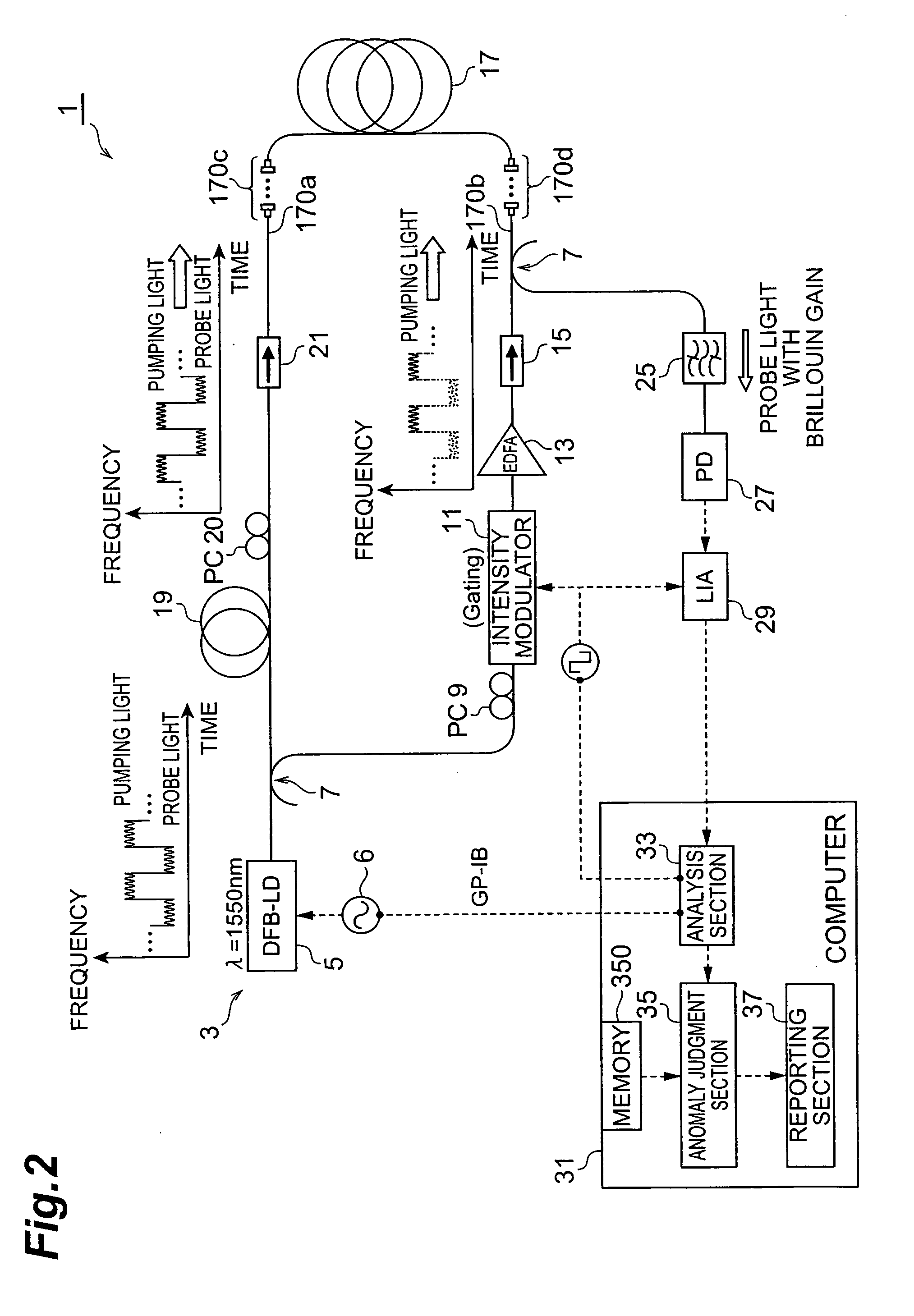
The present invention relates to a spectral measurement apparatus and measurement method utilizing Brillouin scattering, which judge the state of the temperature or strain of an optical fiber more quickly. The spectral measurement apparatus comprises a light source, an analysis section, and an anomaly judgment section. The light source outputs pumping light and probe light. The pumping light and probe light thus output are caused to enter in opposite directions to the sensing fiber. The analysis section analyzes the gain received by the probe light as a result of the Brillouin scattering. The anomaly judgment section judges the state relating to the temperature or strain of the sensing fiber on the basis of the analysis result of the analysis section. The frequency difference υ between the pumping light and probe light is set within a predetermined frequency difference setting range. The frequency difference setting range is a range which includes the frequency difference at which the peak value of the reference gain spectrum of the gain received by the probe light is obtained when the temperature or strain of the sensing fiber is in the reference state and is set at or below the line width of the reference gain spectrum
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
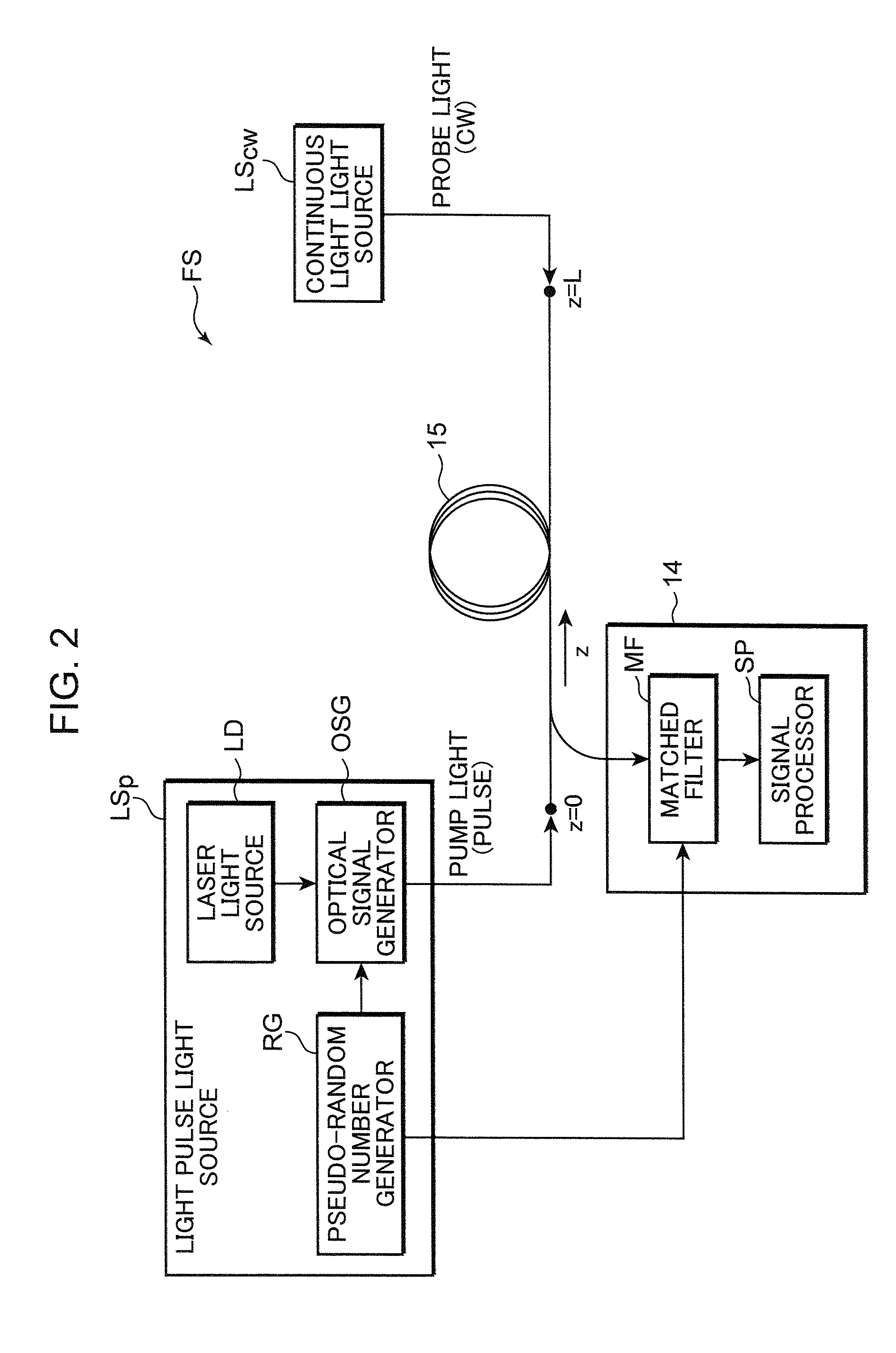
Method and system for measuring the wavelength dispersion and nonlinear coefficient of an optical fiber, method of manufacturing optical fibers, method of measuring wavelength-dispersion distribution, method of compensating for measurement errors, and method of specifying conditions of measurement
ActiveUS20050058417A1Reflectometers dealing with polarizationReflectometers using simulated back-scatterLength waveAstigmatism
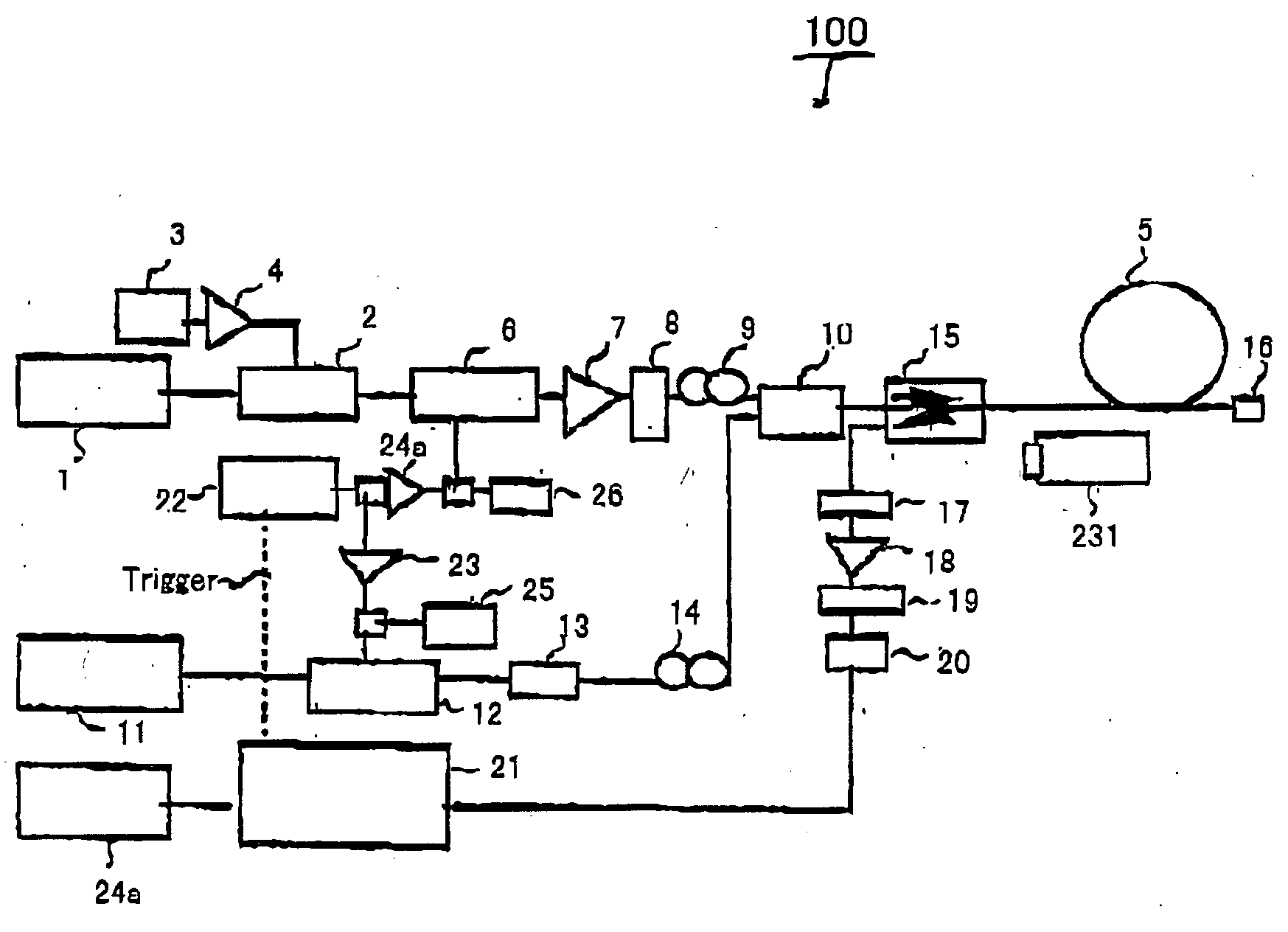
A method of simultaneously specifying the wavelength dispersion and nonlinear coefficient of an optical fiber. Pulsed probe light and pulsed pump light are first caused to enter an optical fiber to be measured. Then, the power oscillation of the back-scattered light of the probe light or idler light generated within the optical fiber is measured. Next, the instantaneous frequency of the measured power oscillation is obtained, and the dependency of the instantaneous frequency relative to the power oscillation of the pump light in a longitudinal direction of the optical fiber is obtained. Thereafter, a rate of change in the longitudinal direction between phase-mismatching conditions and nonlinear coefficient of the optical fiber is obtained from the dependency of the instantaneous frequency. And based on the rate of change, the longitudinal wavelength-dispersion distribution and longitudinal nonlinear-coefficient distribution of thee optical fiber are simultaneously specified.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sensor and method of sensing
ActiveUS20140152982A1Increase motivationAccurate of propertyRadiation pyrometryReflectometers using simulated back-scatterOptical propagation
According to the invention, these aims are achieved by means of a sensor, suitable for sensing one or more properties of one or more structures, the sensor comprising, a first optical propagation path which is configurable to cooperate with a structure whose properties are to be sensed; a second optical propagation path which is configurable to cooperate with a structure whose properties are to be sensed; a third optical propagation path; a means for amplifying a signal which propagates in the third optical propagation path, so that the signal is amplified before it begins propagation along the second optical propagation path, and a means to prevent the propagation of signals from the second optical propagation path to the third optical propagation path. There is further provided a corresponding method of sensing.
Owner:OMNISENS
Noise management for optical time delay interferometry
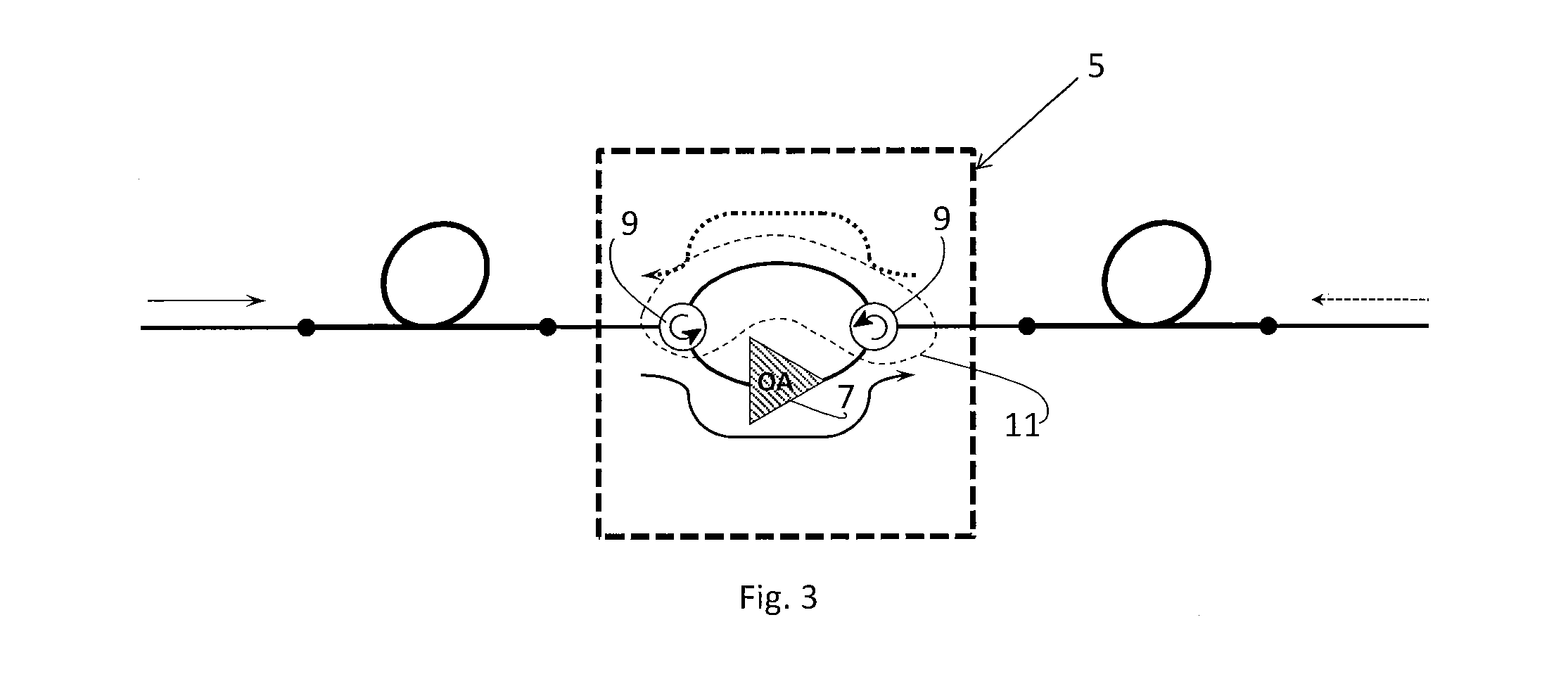
ActiveUS20160187223A1Reduce acoustic noiseReduce the noise floorReflectometers using simulated back-scatterSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration attenuationTime delays
An integrated fiber interferometry interrogator for generating superimposed waves is disclosed. The system is optimized for efficiency and vibration attenuation. The system comprises an optical light source for generating a first signal, a first signal splitter which splits the first signal into a reference signal and an interrogation signal, optical modulators for modulating the signals, a fiber coupler connected to a fiber under test, an isolator, a circulator with a plurality of connections for directing the signals, a signal mixer for mixing the signals into superimposed waves, and photo diodes for receiving the superimposed waves.
Owner:ADELOS LLC
Distortion measuring apparatus, method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20070171401A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
A distortion of a device under test (such as an optical fiber) can be precisely measured. There is provided a distortion measuring device including a signal processing unit 32 having a Brillouin scattered light spectrum recording unit 322a which records a spectrum of Brillouin scattered light generated in an optical fiber as a result of supplying incident light, a Rayleigh scattered light spectrum recording unit 322b which records a spectrum of Rayleigh scattered light generated in the optical fiber as a result of supplying the incident light, a deconvolution unit 324 which derives a Brillouin gain spectrum of the optical fiber based on the recorded spectrum of the Brillouin scattered light and the recorded spectrum of the incident light, a peak frequency deriving unit 326 which derives a peak frequency at which the derived Brillouin gain spectrum takes the maximum value, and a distortion deriving unit 328 which derives a distortion of the optical fiber based on the derived peak frequency.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Method and system for adjusting the sensitivity of optical sensors
InactiveUS20070280582A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterThermometers using physical/chemical changesLight beamPhysics
A method and a system for adjusting the sensitivity of an optical sensor are provided. A first beam of light in an optical fiber is separated into first and second portions propagating therethrough at a first speed. A second beam of light is directed into the optical fiber to interact with the first beam of light such that the first and second portions propagate through the optical fiber at a second speed. The propagation speed in turn influences the sensitivity of the optical sensor.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Detection method and device for high-dynamic-range optical time domain reflection
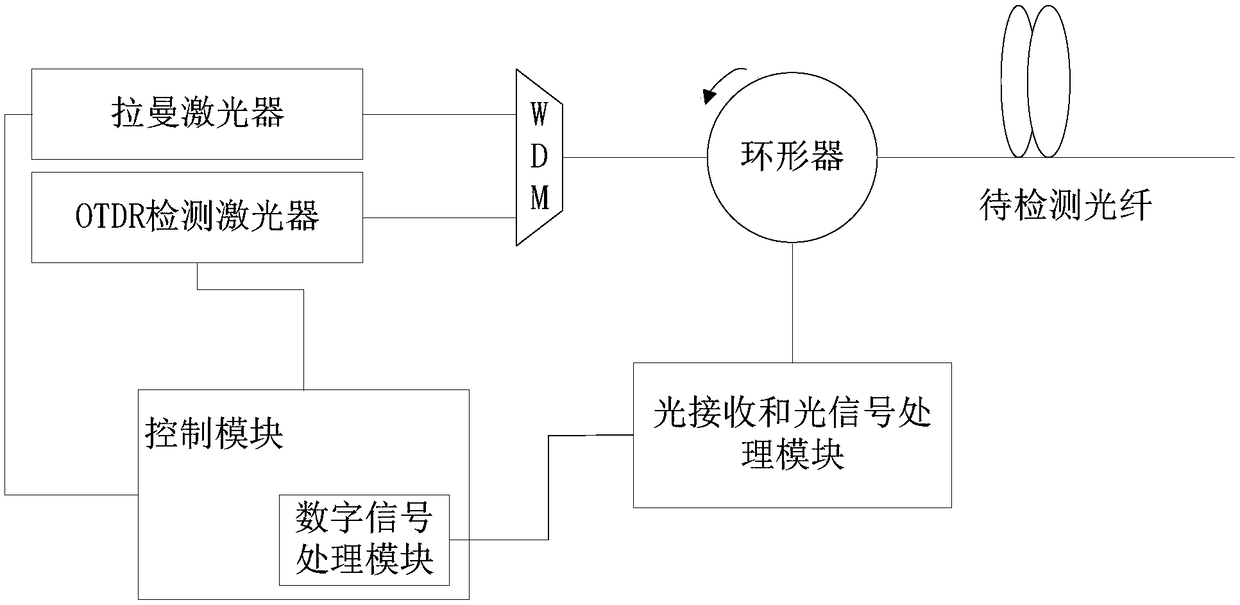
ActiveCN108199767AMeasurement GuaranteeSolve Distortion Issues with Shorter SlopesReflectometers using simulated back-scatterElectromagnetic transmissionRayleigh scatteringTime-domain reflectometer
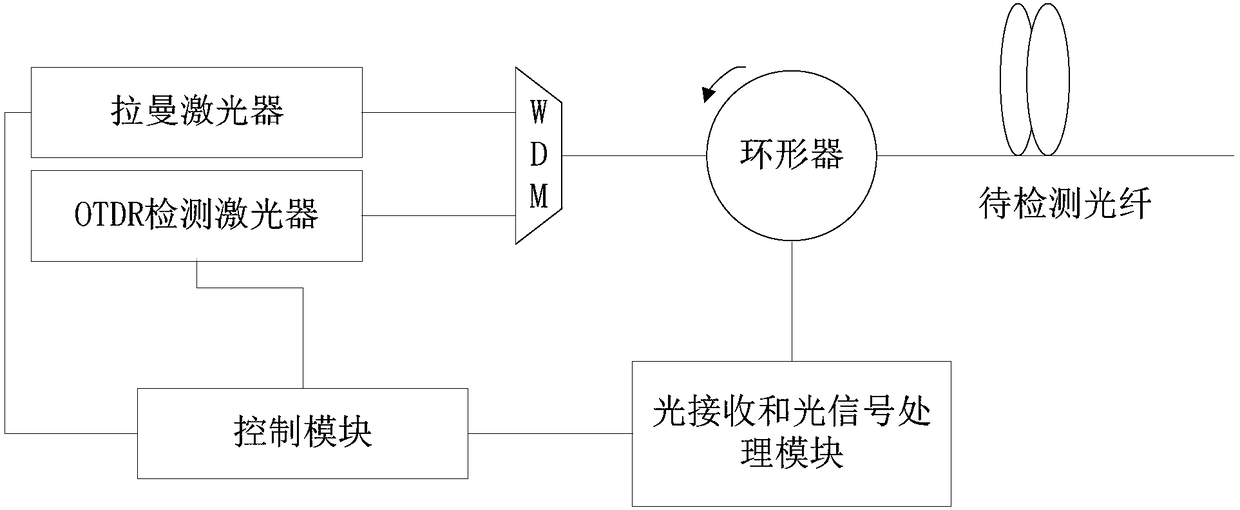
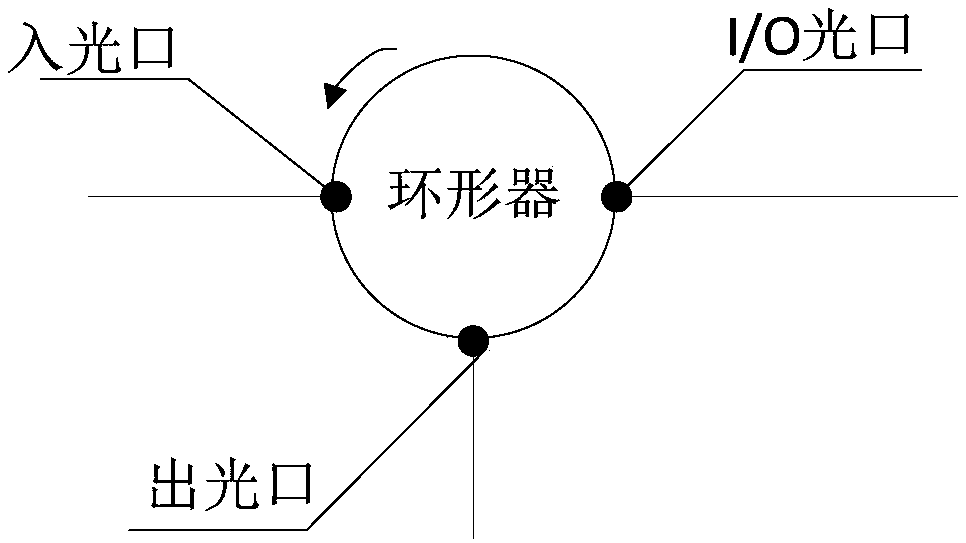
The invention relates to the technical field of optical time domain reflectometer, and provides a detection method and device for high-dynamic-range optical time domain reflection. The device comprises a Raman laser and an OTDR detection laser, which are respectively connected to a WDM, wherein a light outlet of the WDM is connected to a light inlet of a circulator; a light receiving and light signal processing module is connected to a light outlet of the circulator; the light receiving and light signal processing module is further connected to a control module; the control module is used forcontrolling a driving pin of the Raman laser, and controlling the Raman laser to emit at least two light pulses with a time interval in a detection time period according to the relevant information ofreflection light. According to a multi-pulse solution, the light pulses can be amplified and detected through forward Raman light pulses, the Raman light pulses can be continuously sent through the Raman laser after the OTDR detection laser is closed in order to directly amplify and detect back Rayleigh scattering light signals or Fresnel reflection light signals generated by the light pulses.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Optical time domain reflectometry
InactiveUS20080030739A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterScattering properties measurementsOptical radiationUltrasound attenuation
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optical fiber line characteristic analysis apparatus and analysis method thereof
ActiveUS20140098362A1Inexpensive analysisReflectometers using simulated back-scatterMaterial analysis by optical meansTarget fibersVIT signals
A test pulse is generated from a first and a second test light beam pulse with different wavelengths, with a predetermined time difference applied between the first and the second test light beam pulse. A circulator inputs the test pulse to a trunk fiber of a measurement target fiber line. A reflected light is extracted which is output from an input end of the trunk fiber. A filter extracts stimulated Brillouin backscattered light. A receiver receives and converts the scattered light into an electrical signal. A processing device carries out the signal to determine in which of N branched fibers the stimulated Brillouin scattered light is generated, while varying a time difference between the first and the second test pulse.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method and system for an ultimately fast frequency-scanning brillouin optical time domain analyzer
ActiveUS20160273998A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainComputational physics
A method and a system for ultimately fast frequency-scanning Brillouin optical time domain analysis are provided herein. The method may include: simultaneously launching two pairs each having a pulsed pump wave and a counter-propagating constant wave (CW) probe wave, into an optical fiber, wherein the pulsed pumps have orthogonal States of Polarization (SOPs), and wherein the two CW probe waves have a same SOP; scanning common pump-probe frequency difference, over a frequency range that encompasses a respective Brillouin Gain Spectrum (BGS) and current and expected spectral shifts of the BGS along the optical fiber; deriving, a local Brillouin Frequency Shift (BFS), in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, which is defined as the pump-probe frequency difference which maximizes the Brillouin gain on the BGS; and determining strain and / or temperature in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, based on the respective local BFS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Measuring Brillouin backscatter from an optical fibre using a tracking signal
ActiveUS8134696B2Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeReflectometers using simulated back-scatterConstructionsFiberTemporal change
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Popular searches
Using optical means Transmission monitoring Radio-over-fibre Using wave/particle radiation means Transmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systems Converting sensor output Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangements Non-electrical signal transmission systems Optical multiplex Converting sensor output optically
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com