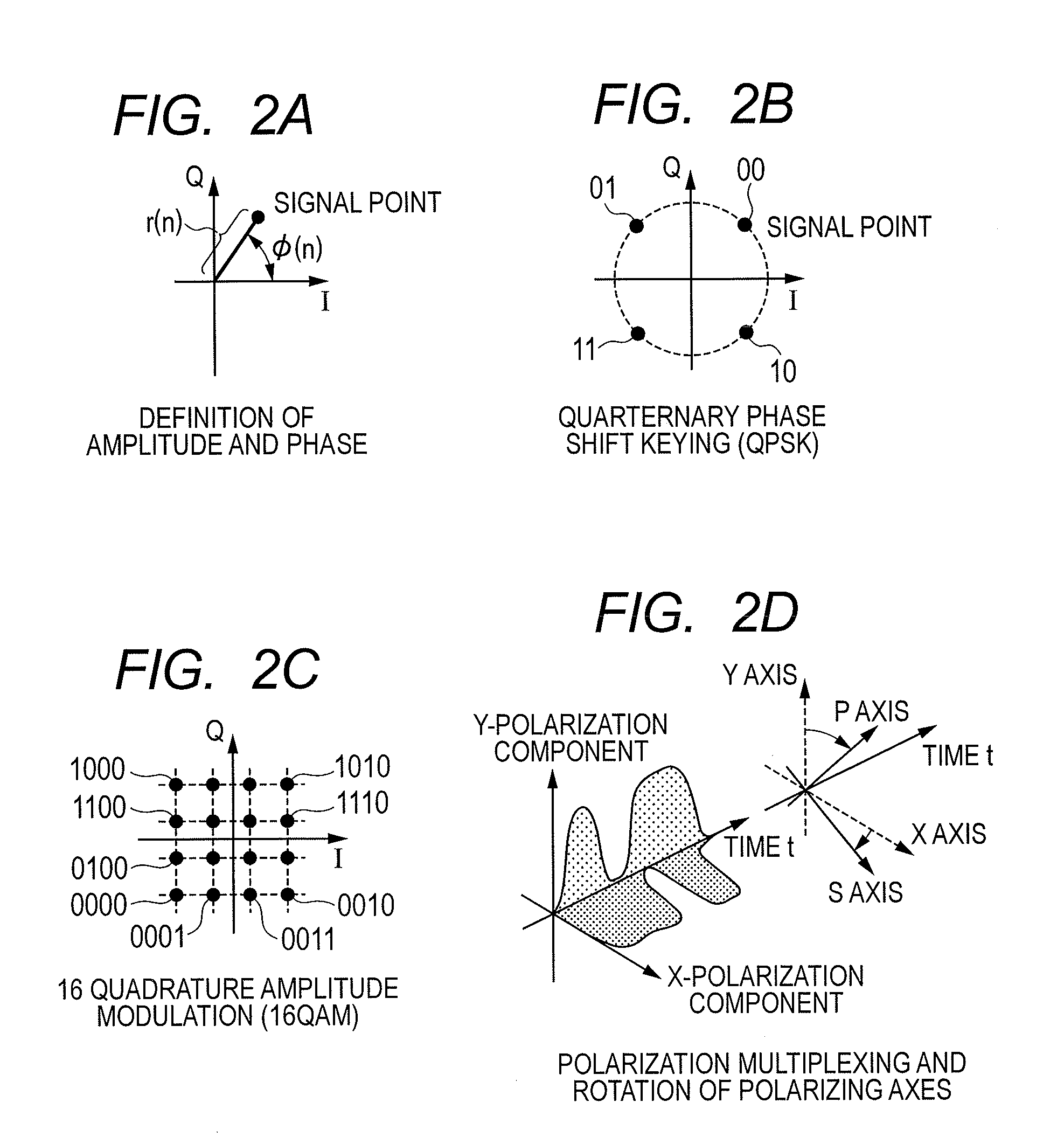
Patents
Literature
2699results about "Distortion/dispersion elimination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
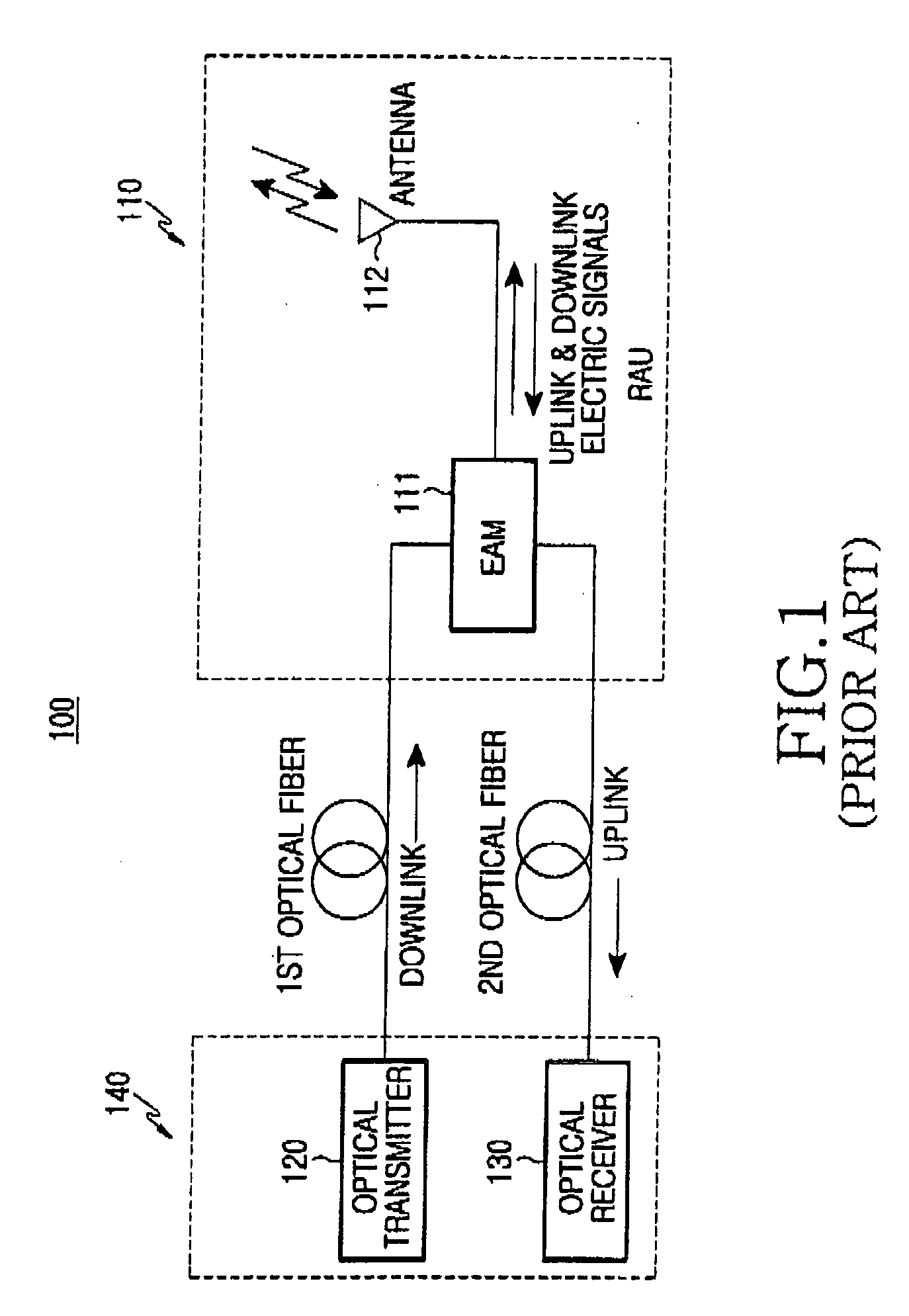
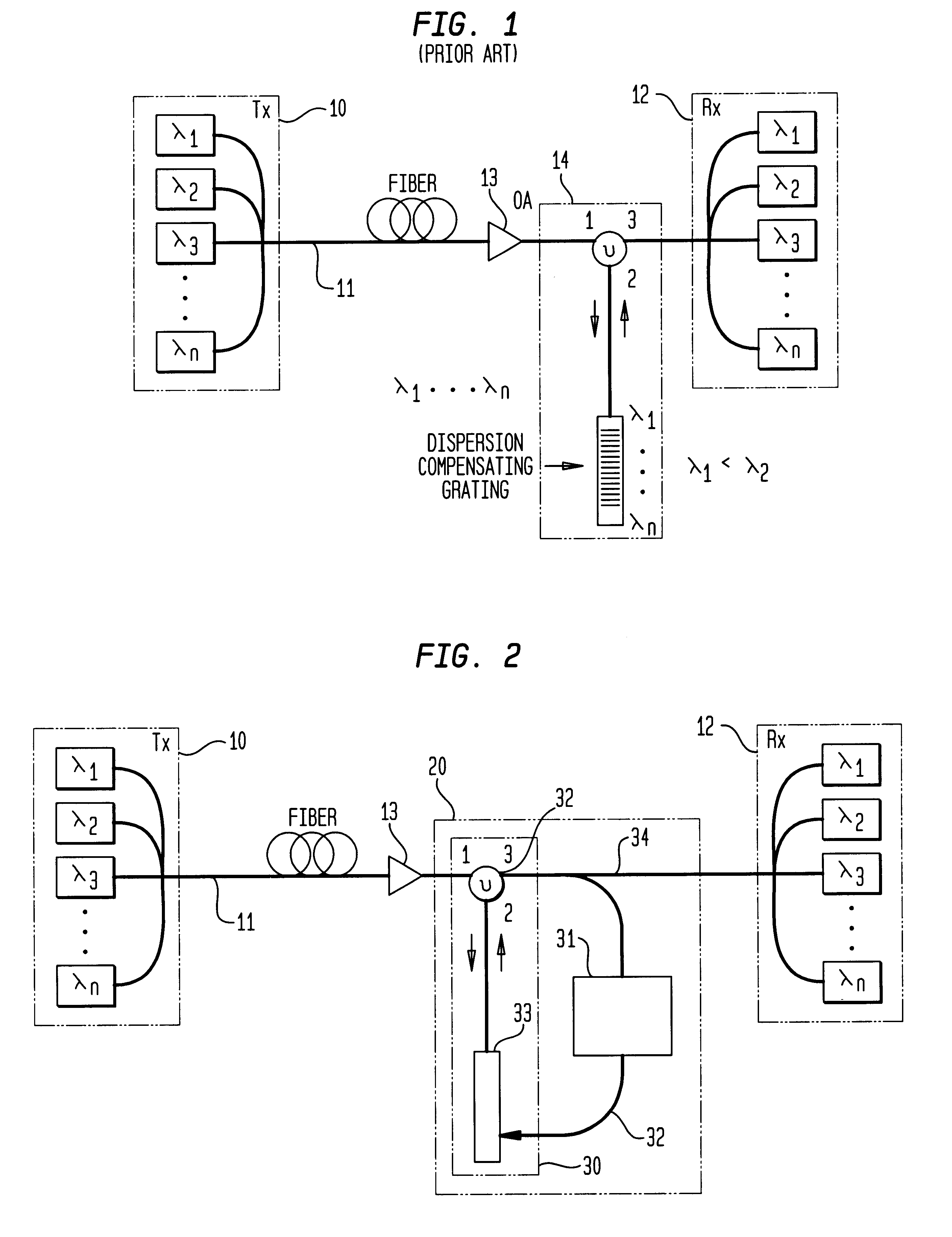
Electrically optimized hybird "last mile" telecommunications cable system
InactiveUS6091025AEqual performanceEquivalent signal performanceCoaxial cables/analogue cablesQuad constructionsElectrical conductorTelecommunications cable
A cable system is provided which can accomodate electrical and optical cabling. The conductors of the system employ a layer which is impedance-matched to space, decreasing their cross-section to electromagnetic interference. The conductors of the system also employ a layer which symmetrizes electromagnetic interference signals, reducing the effect of interference and crosstalk on the signals carried by the conductors. The system also includes a node interface device for connection to a global electrical and fiber network. The node interface device connects to a user interface device through the cable.
Owner:KHAMSIN TECH LLC
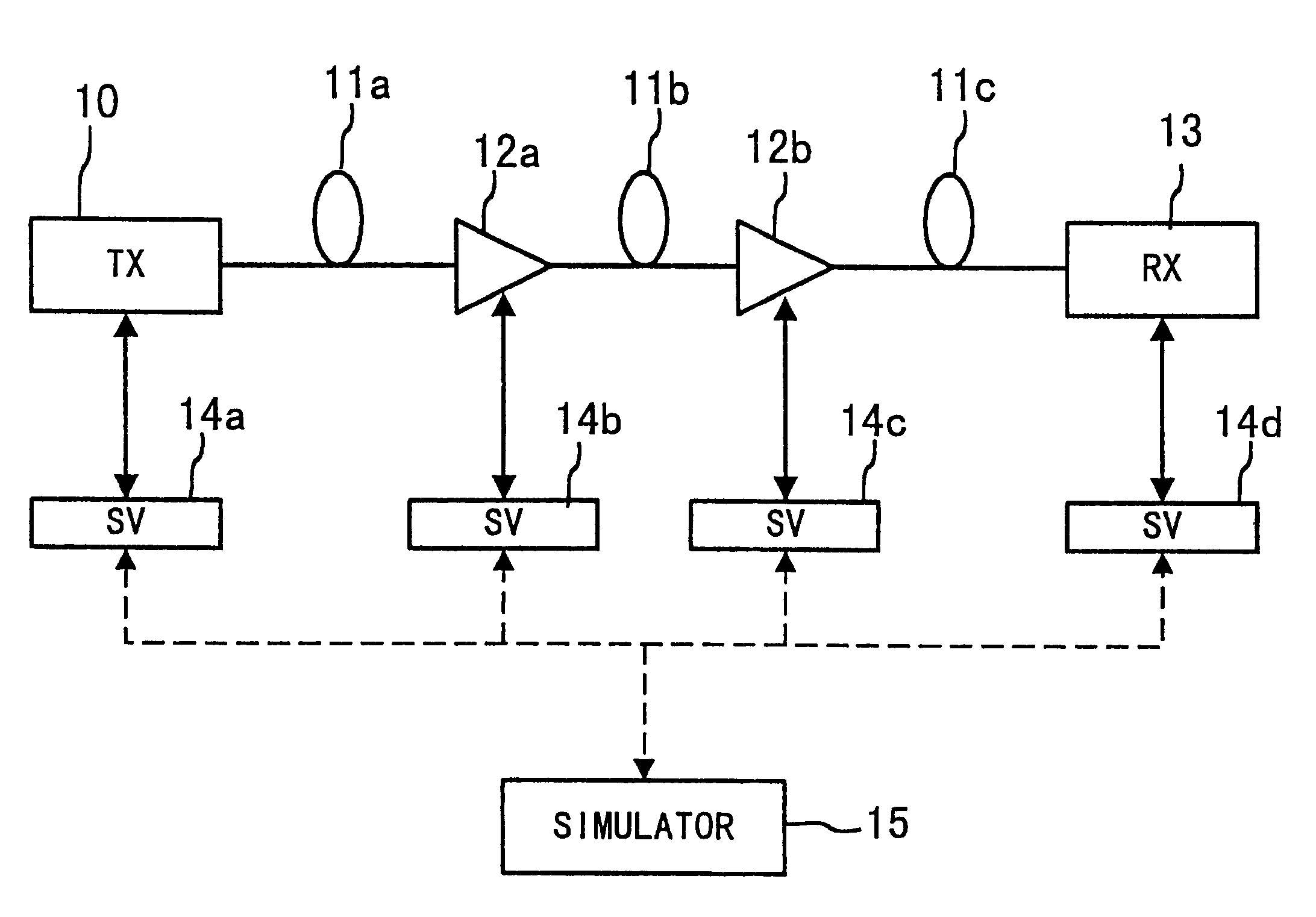
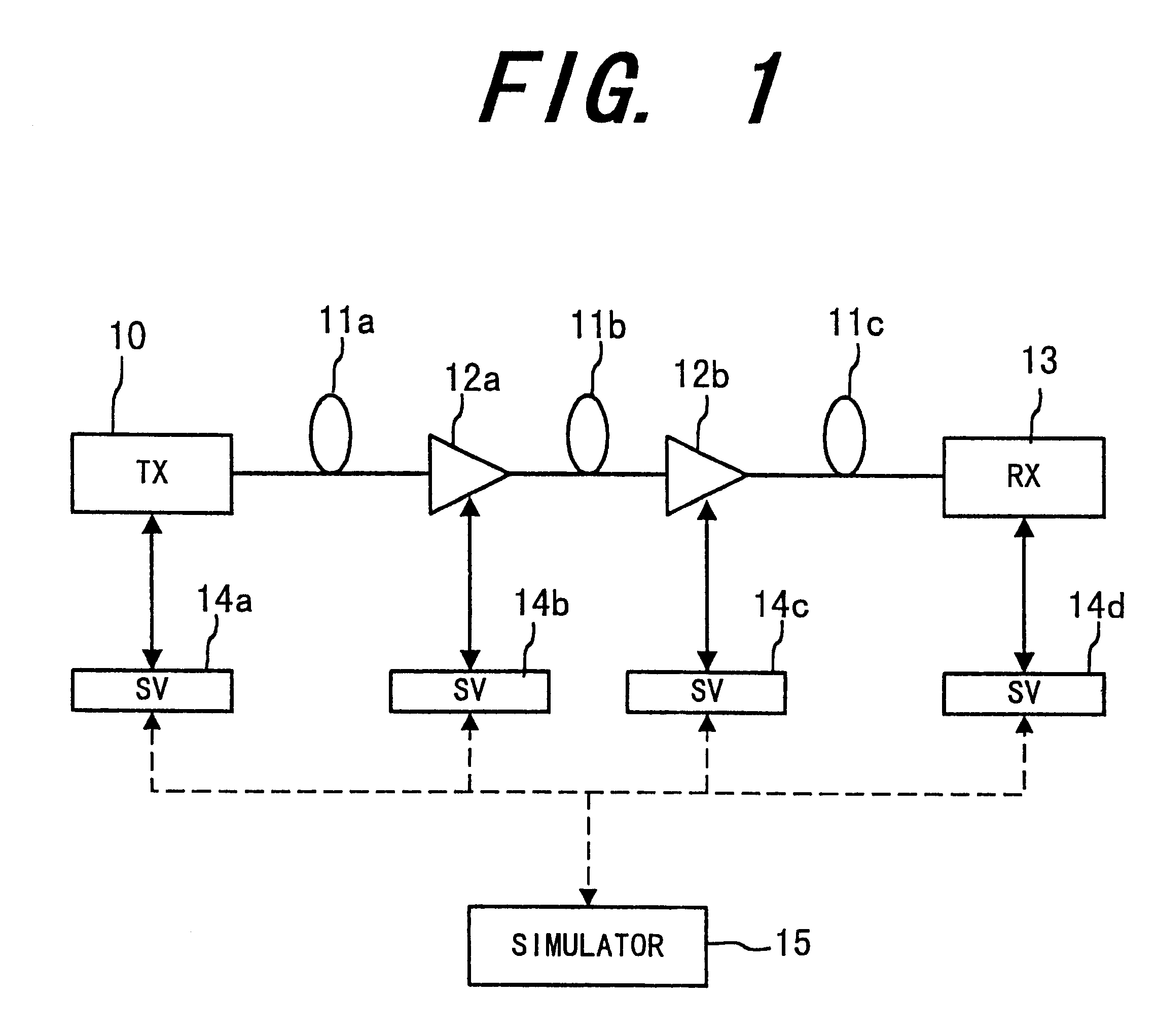
Signal transmission system and method for supervising the same
InactiveUS6229631B1Minimize bit-error rateMaximize Q-factorWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringEngineeringTransmission quality
A signal transmission system includes an interface unit that monitors the operating condition of each device. The signal transmission system also includes a simulator that simulates the transmission quality of the system in response to the operating condition of each device, and controls each device so as to optimize the transmission quality.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
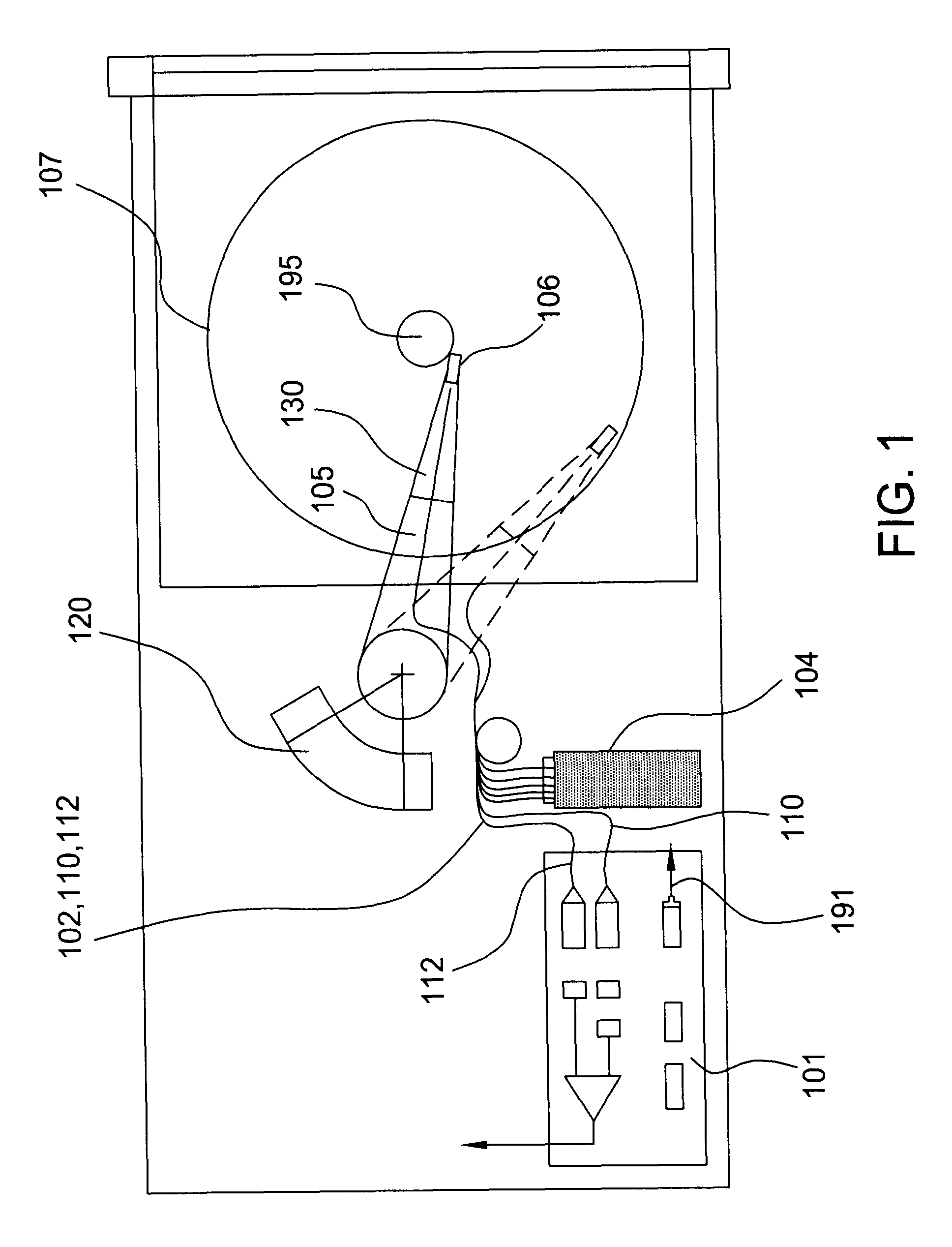
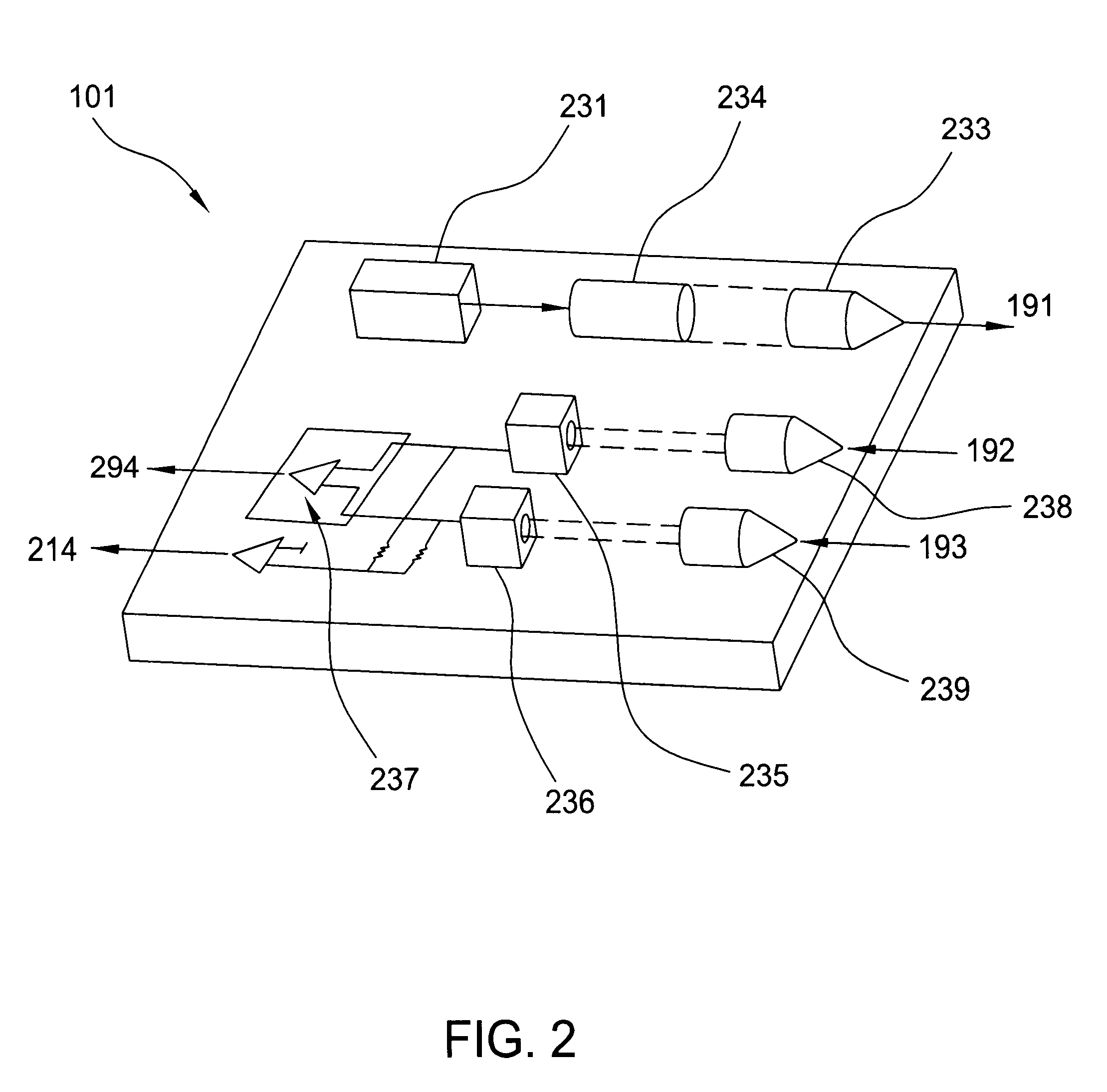
Data storage system having an optical processing flying head
InactiveUS6781927B1Low costOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesDigital dataData information
An optical data storage and retrieval system uses a flying head. The flying head is supported on a moving media having information stored in a plurality of stored data locations thereon. Information is stored in each of the plurality of media locations as physical structures capable of modulating the polarization state of incident light into one of two output polarization states. The flying head includes an optical processing assembly which directs an incident light beam having a source polarization state onto the moving media, accessing successive data locations. A reflected light beam having the source polarization state of the incident light beam modulated by a respective polarization modifying data location into one of the output polarization states is received by the flying head. The optical processing assembly optically transforms the modulated output polarization state of the reflected light beam into two return light beams having differentially modulated intensity related to the output polarization state of the reflected light beam. The two intensity modulated return light beams are optically coupled to a distal differential detector which outputs digital data representing the stored data information for the subject data location. A preferred embodiment includes optical fibers for coupling the incident and return light beams between the detector and the flying head. The optical assembly of a preferred embodiment includes an optical plate having pre-shaped and dimensioned recesses for automatically locating and aligning multiple optical components comprising the assembly. The flying head may also include a servo-controlled micro machined mirror for directing the incident and reflected light beams to and from the media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL (FREMONT LLC)
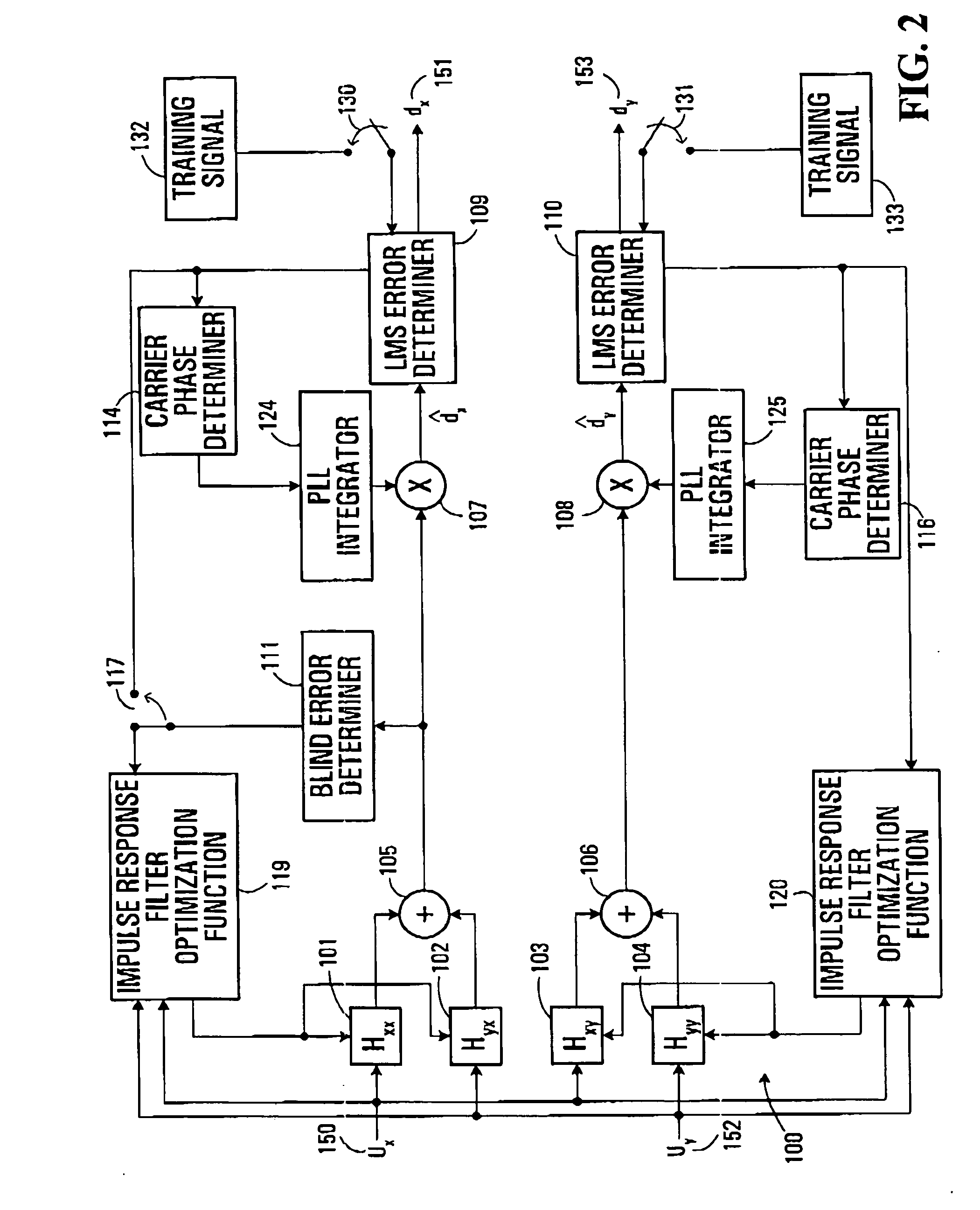
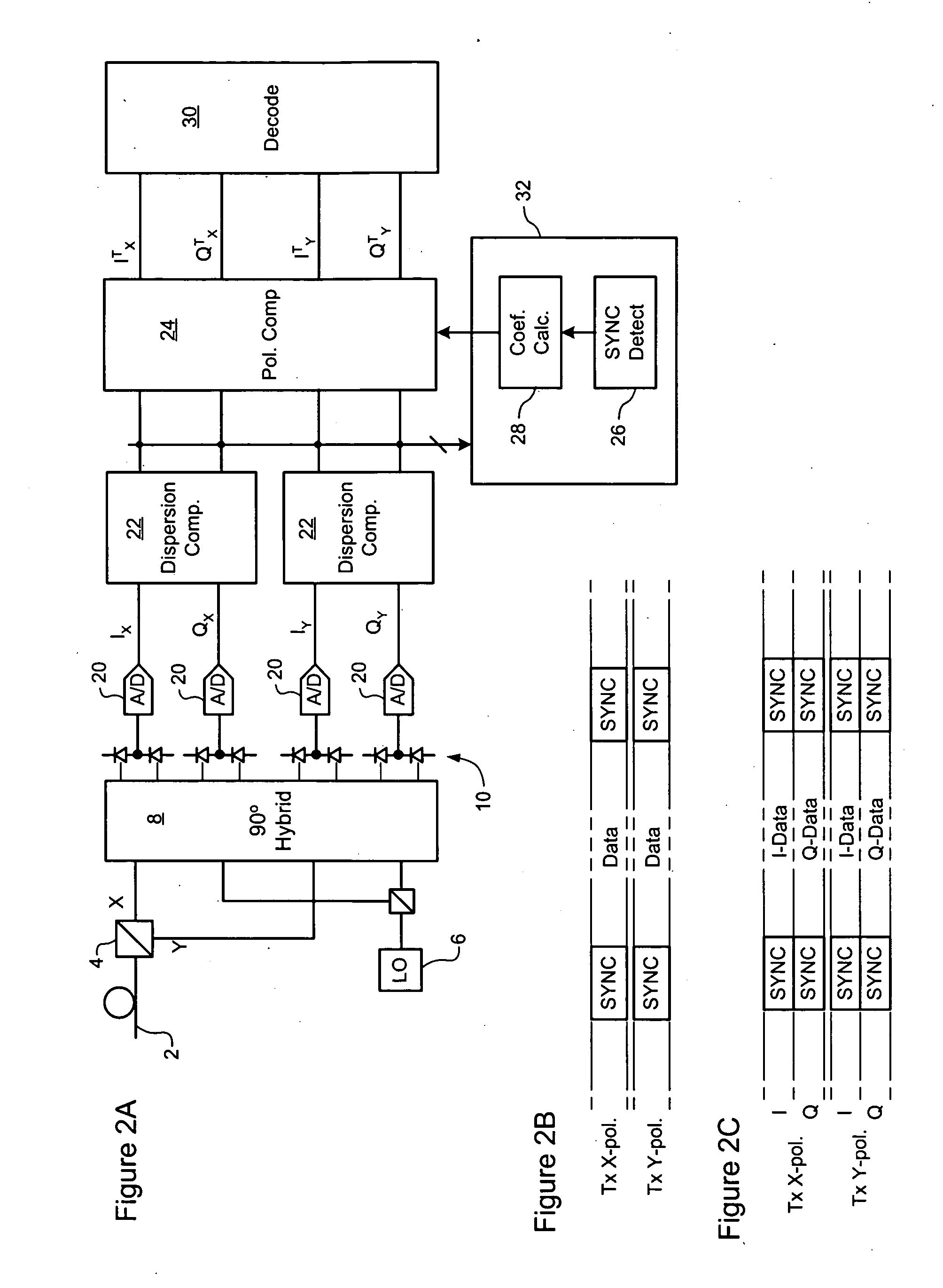
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
ActiveUS20050196176A1Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingSelf recovery
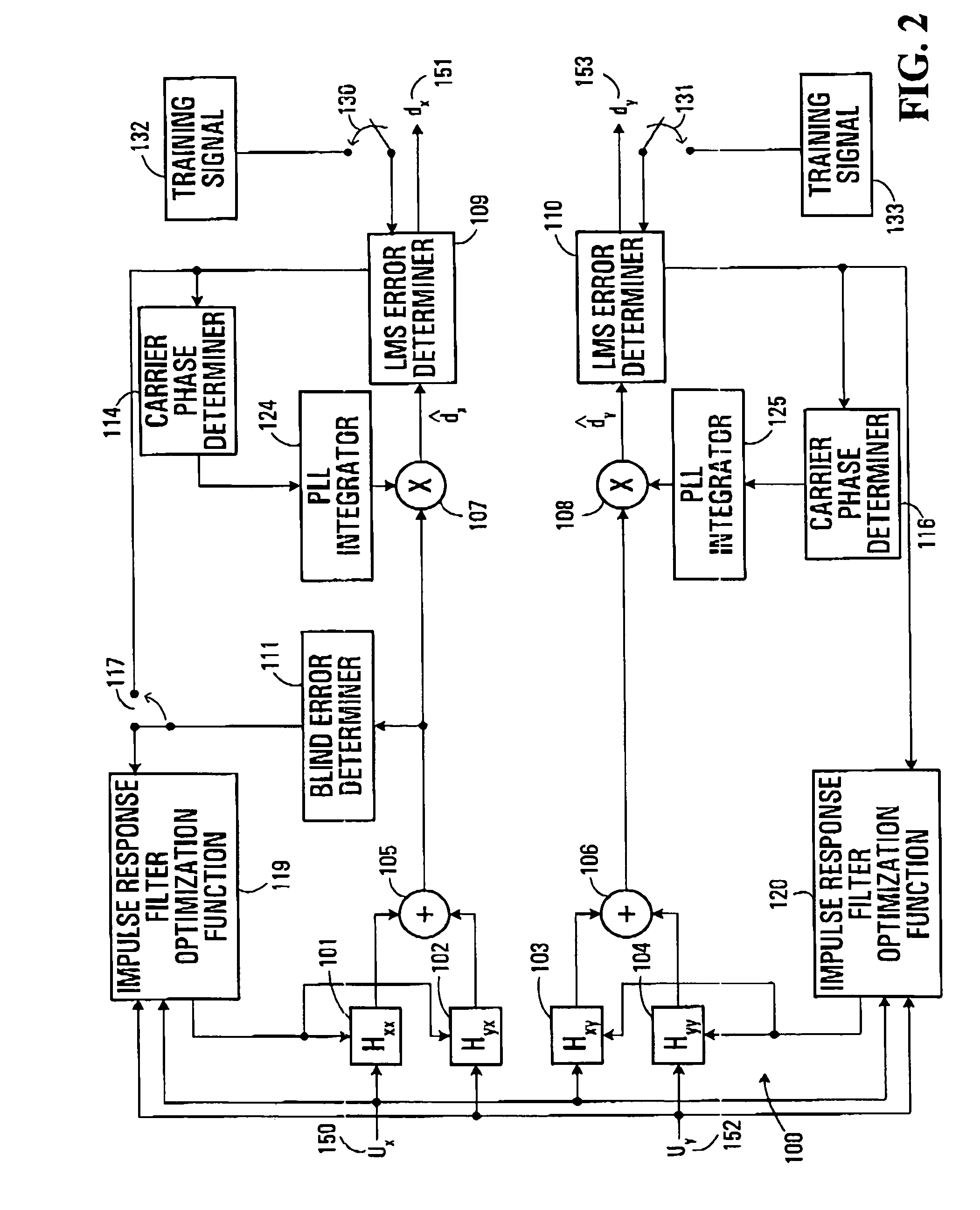
A method is provided for an equalization strategy for compensating channel distortions in a dual-polarization optical transport system wherein the received signal includes a complex signal of a first transmitted polarization component and a complex signal of a second transmitted polarization component. In a first step, a blind self-recovery mode used a blind adaptation algorithm in calculating and modifying multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of only the complex signal of the first transmitted polarization component. By recovering only a single polarization component in the first step the degenerate case of recovering only a single transmitted signal at both polarization component outputs of an equalizer is prevented. In a second step, equalization is performed in a training mode for calculating and modifying the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to enable recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. In a third step, equalization is performed in a data directed mode for continuing to calculate and modify the multiple complex equalizer transfer function coefficients to ensure continued recovery of the complex signals of the first and second transmitted polarization components. The method is suited for a digital signal processing implementation in a coherent receiver when a modulation scheme used on a transmitted signal is quadriphase-shift keying (QPSK). In other embodiments, the method can be used with modulation schemes such as binary PSK, M-ary PSK where M>4, or Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM).
Owner:CIENA
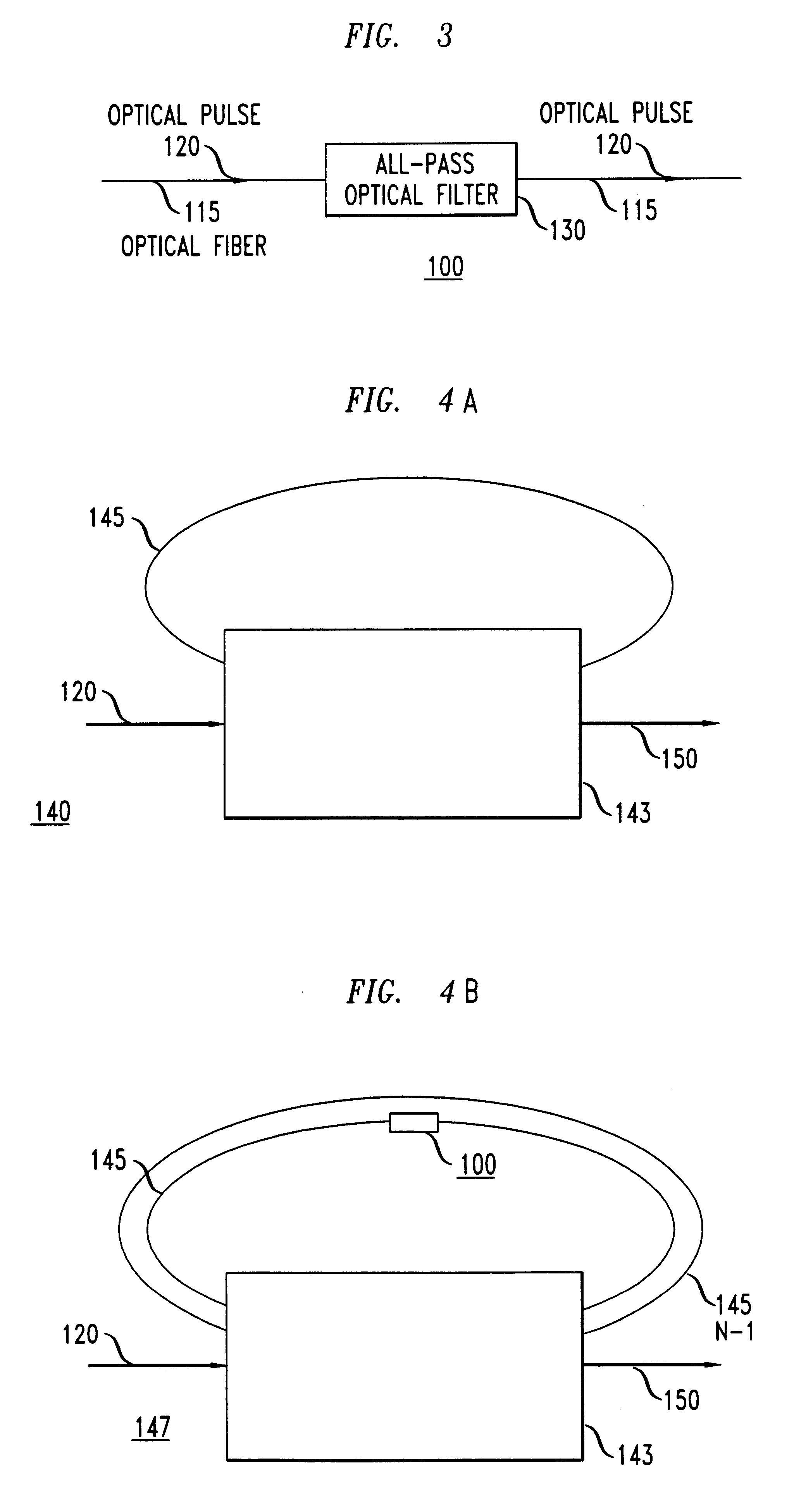
All-pass optical filters
An all-pass optical filter which reduces the dispersion of optical pulses transmitted therethrough is disclosed. The all-pass optical filter reduces the dispersion of optical pulses by applying a desired phase response to optical pulses transmitted therethrough. The all-pass optical filter also has a frequency independent amplitude response. The all-pass optical filter has a structure which includes at least one feedback path, a splitter / combiner, an input port, and an output port.
Owner:RPX CORP
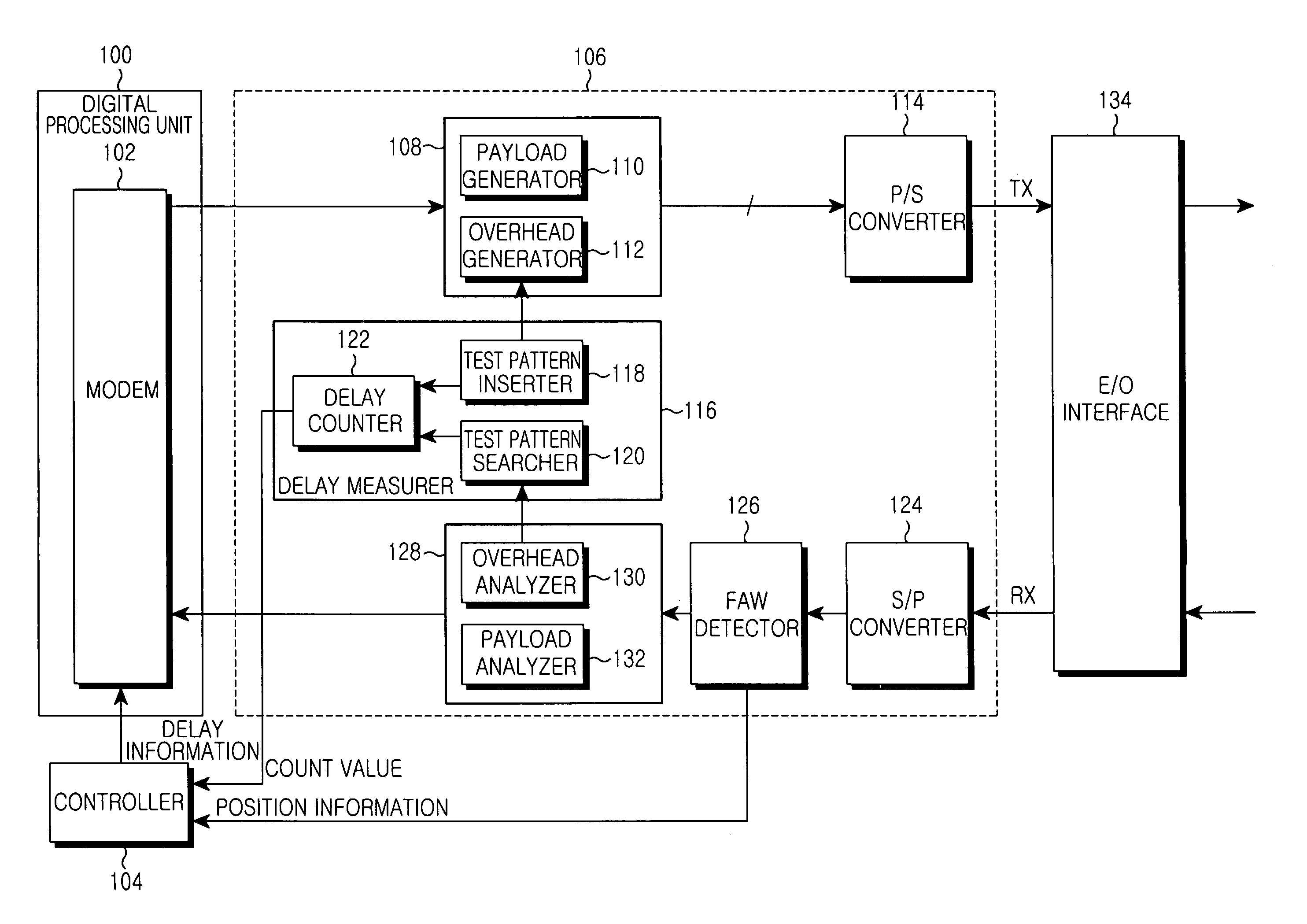
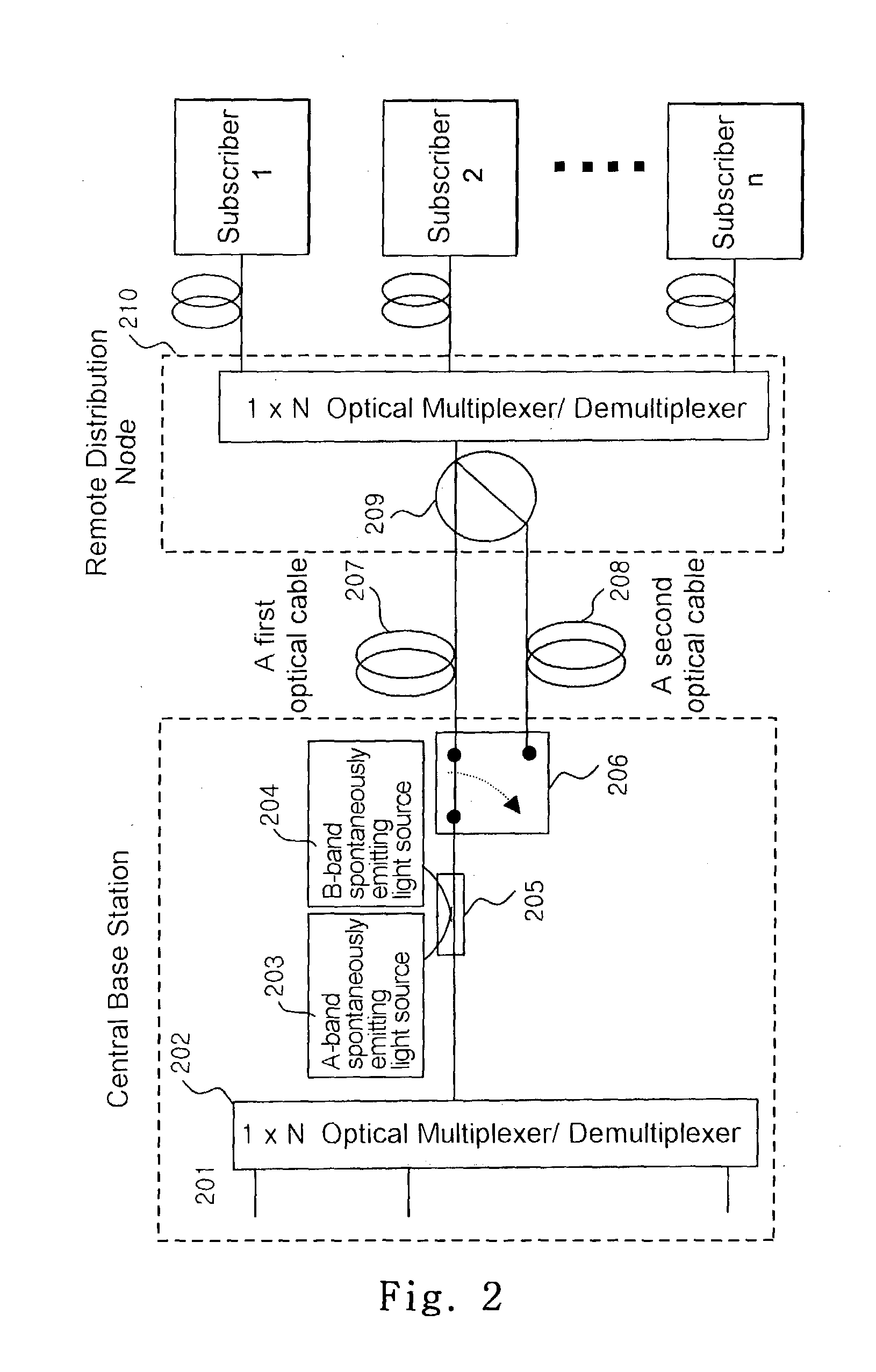
Apparatus and method for measuring and compensating delay between main base station and remote base station interconnected by an optical cable
InactiveUS7359408B2Time-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPropagation delayModem device
An apparatus and method for measuring and compensating for delay between a main base station and a remote base station interconnected by an optical cable. The main base station inserts a test pattern into an overhead part of an SDH frame to transmit the SDH frame to the remote base station, receives the SDH frame looped back by the remote base station to detect the test pattern, and measures propagation delay according to the test pattern. At least one frame alignment word (FAW) is detected at a predetermined position in the received SDH frame, and a delay error is calculated according to FAW detection information. The measured propagation delay with the delay error is compensated and produces propagation delay caused by the optical cable. A modulator / demodulator (MODEM) compensates for delay of a baseband signal to be transmitted to the remote base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System for transmitting optical data
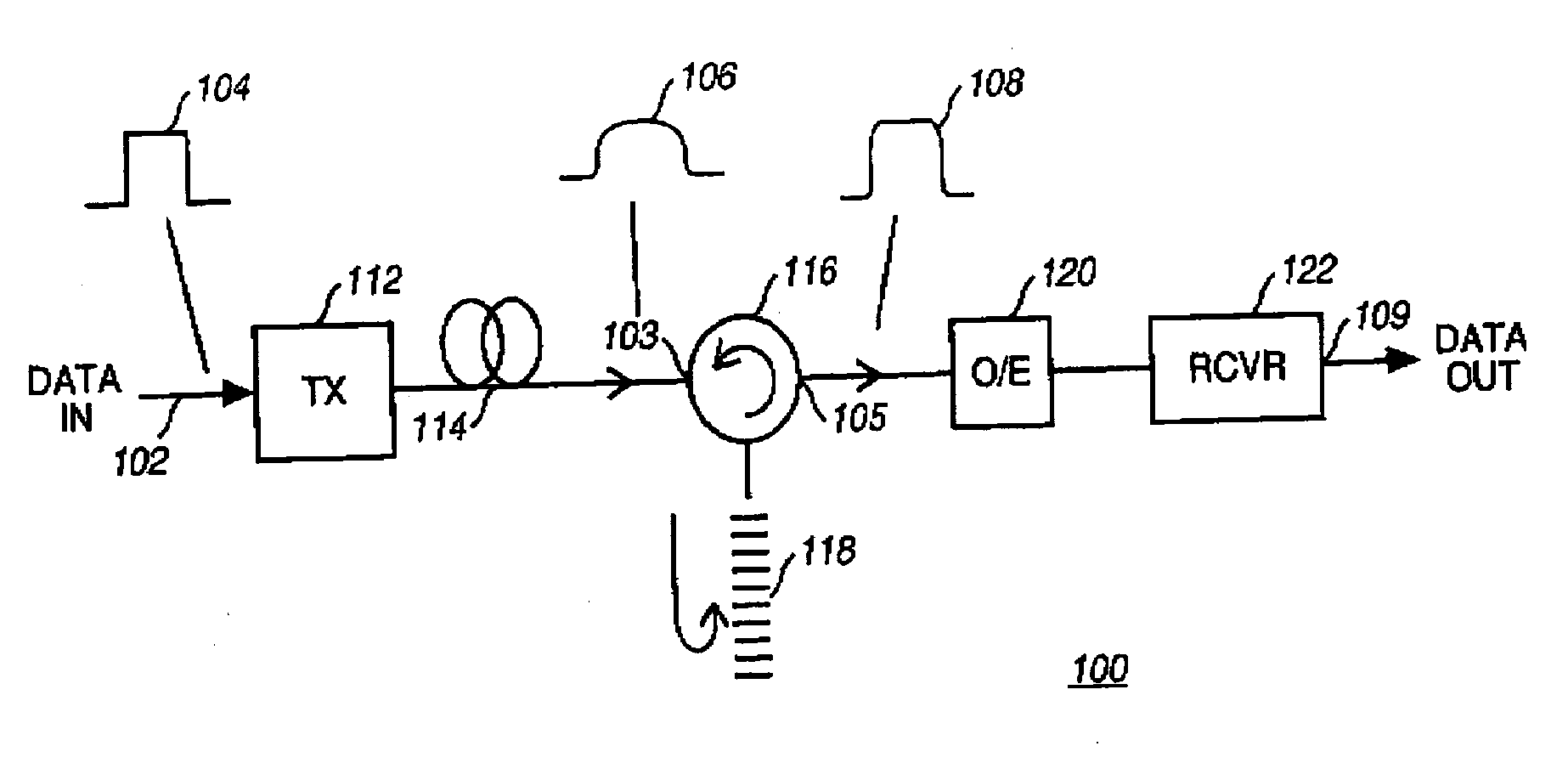
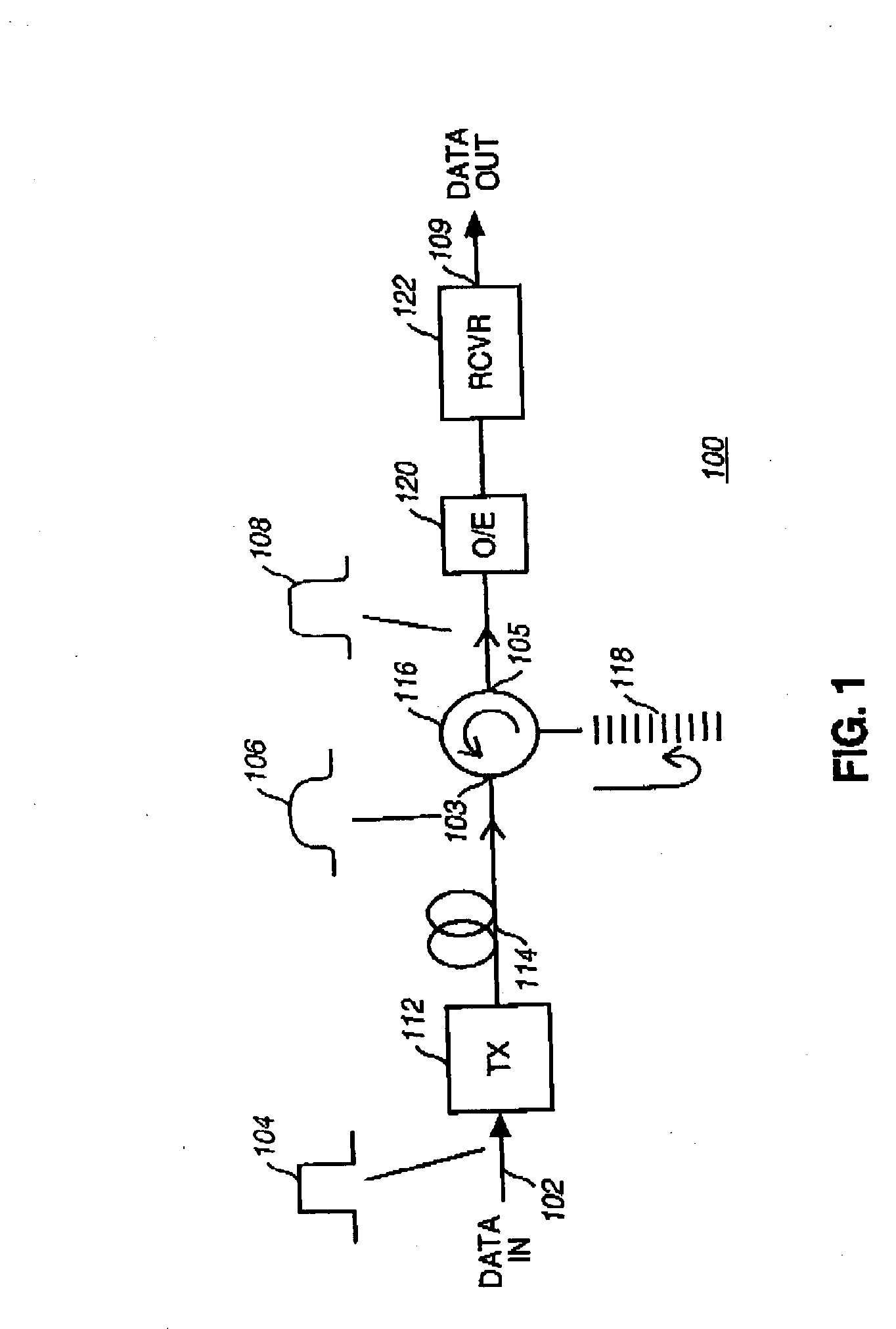
InactiveUS6563623B1Flexible useEasy to optimizeDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersPhase shiftedOptical power
The transmission system includes a first electro-optical modulator adapted to supply in response to an input electrical signal a controlled phase optical signal having an optical power modulated between low levels and high levels and a phase shift within each time cell that contains a low power level. To make it more flexible to use, the system includes a second electro-optical modulator controlled by the input signal and optically coupled to the first electro-optical modulator to apply to said controlled phase optical signal complementary power and / or phase modulation so as respectively to modify its extinction ratio and / or to apply a transient "chirp" to it.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Multimode Optical System
ActiveUS20100142969A1Signal-to-noise ratio is not degradedRaise the ratioDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersHigh bandwidthMulti-mode optical fiber
Disclosed is an optical system including a polychromatic optical source emitting multiple transverse modes, an optical link having at least one portion of multimode optical fiber, and an optical device positioned between the optical source and the input of the multimode optical fiber. The optical device can modify the distribution of the energy coupling of the transverse modes emitted by the source in the propagation modes of the multimode optical fiber.The optical system makes it possible to use low-cost transverse multimode optical sources for producing high-bandwidth Ethernet transmission networks having excellent performance.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
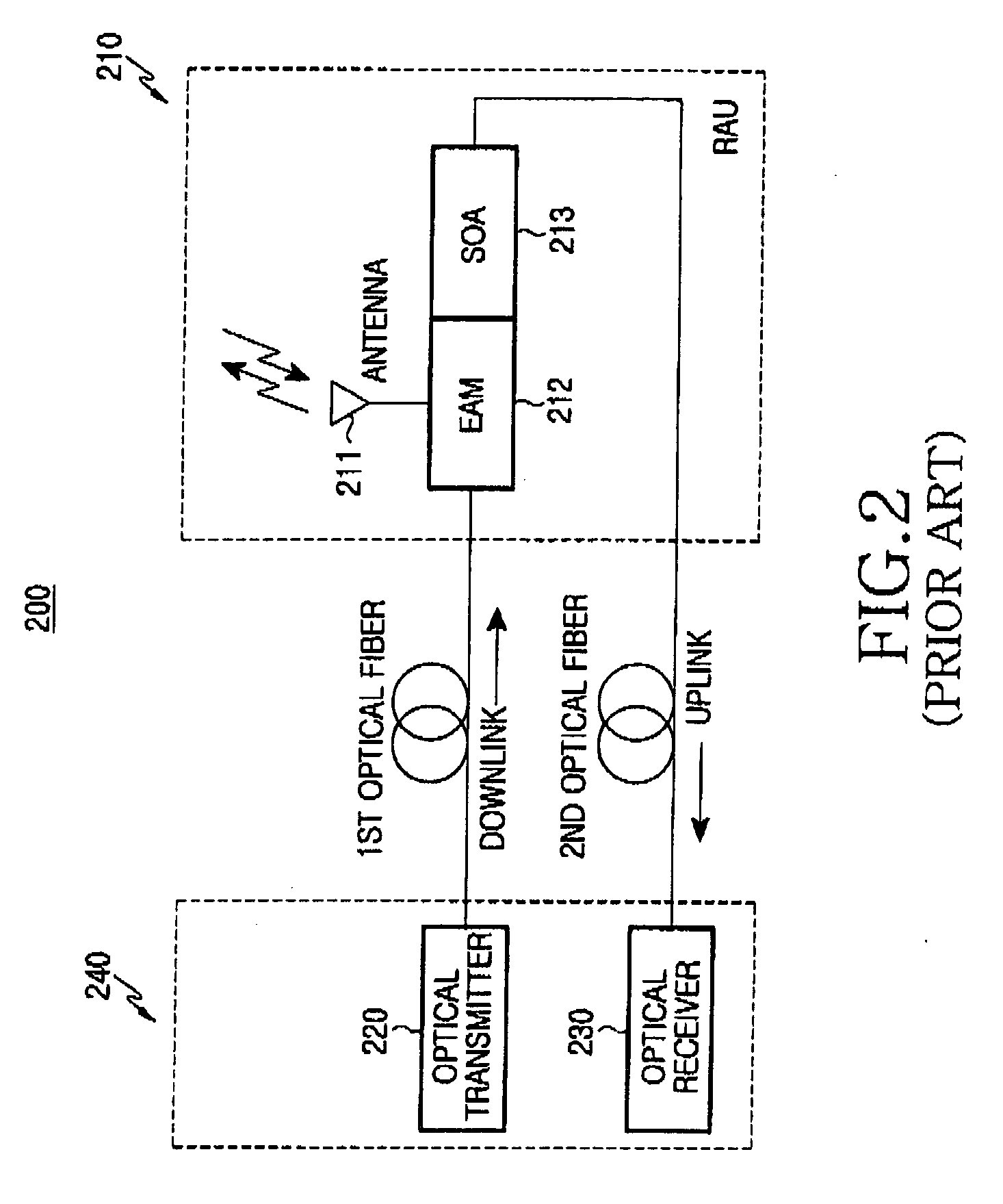
Optical fiber radio transmission system, transmission device, and reception device
InactiveUS20060239630A1Process stabilityExpand the radio rangeAmplifiers controlled by lightDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringLinearity
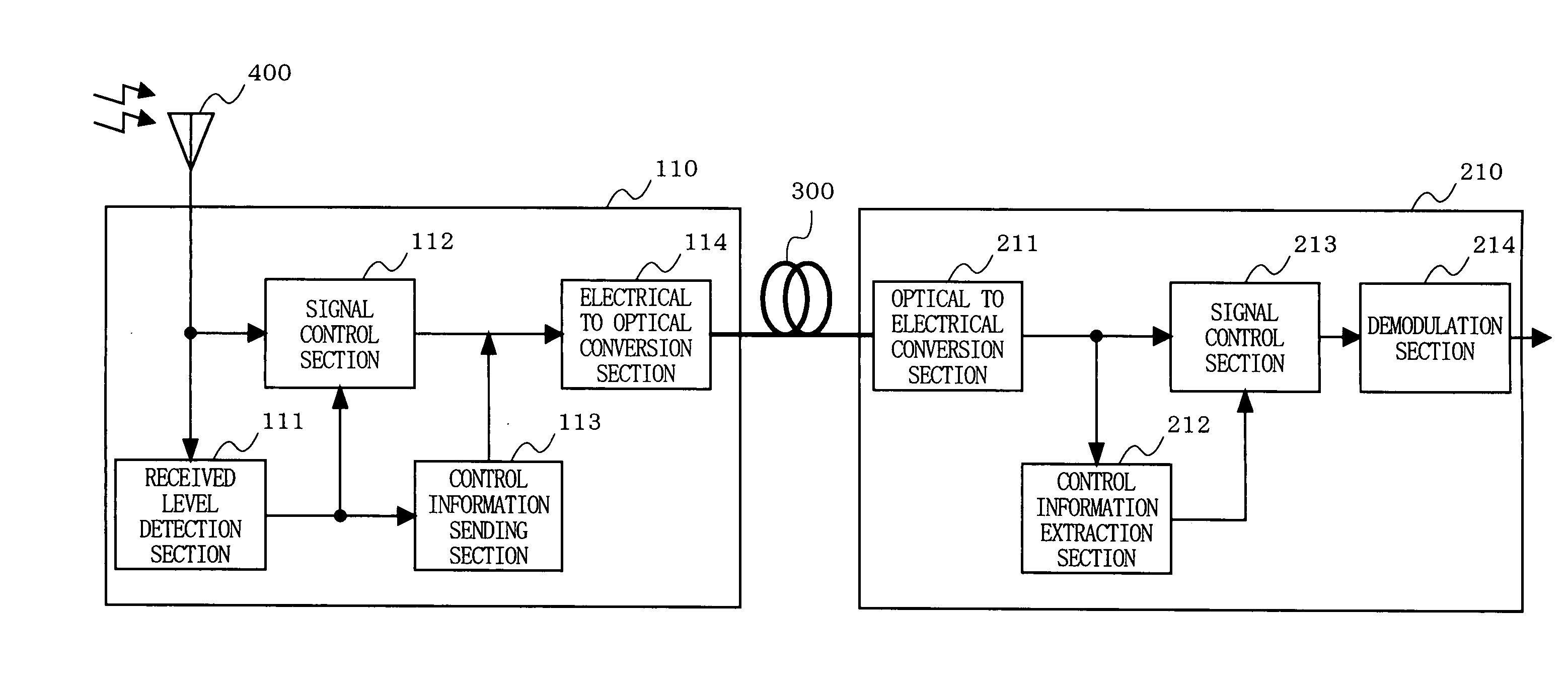
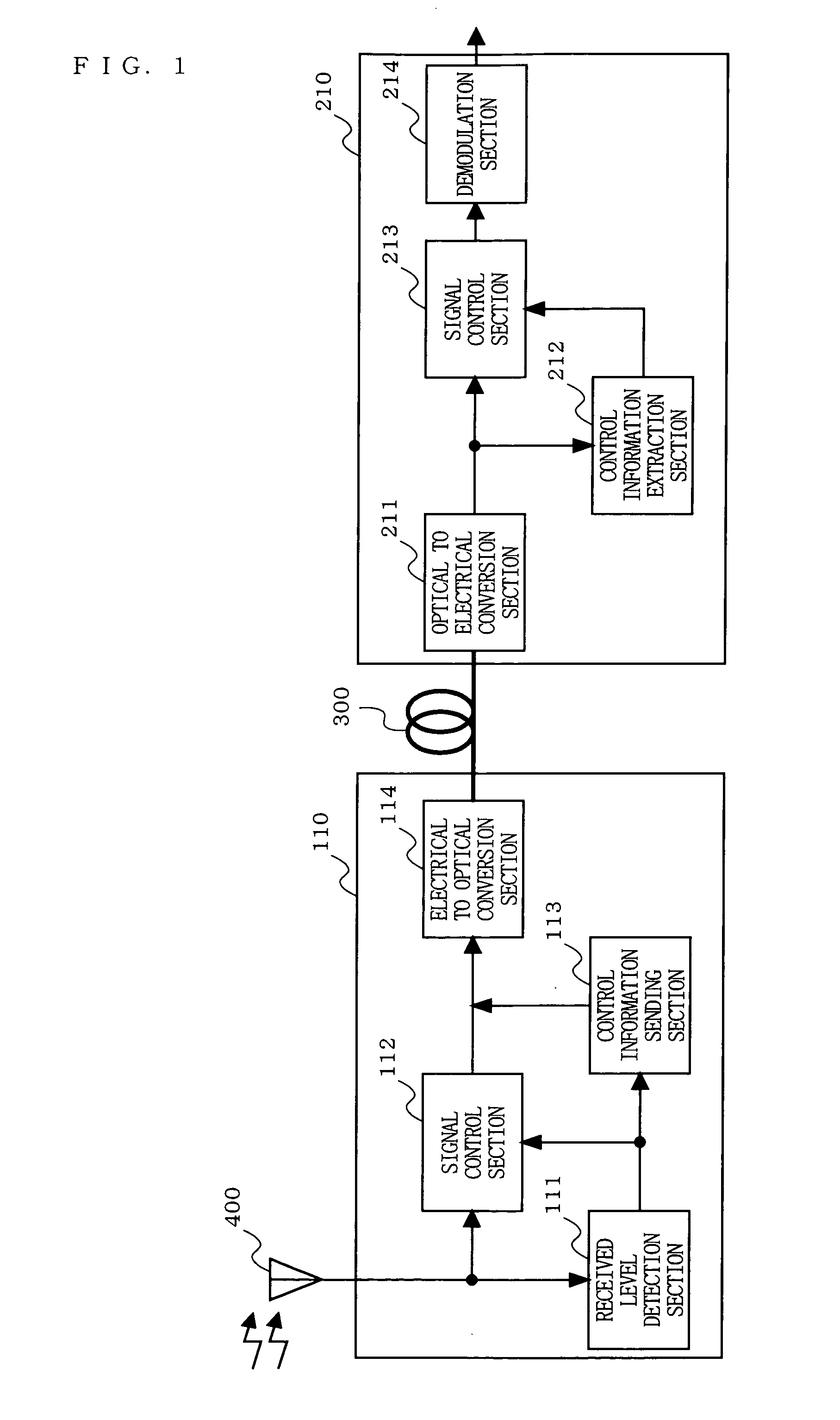
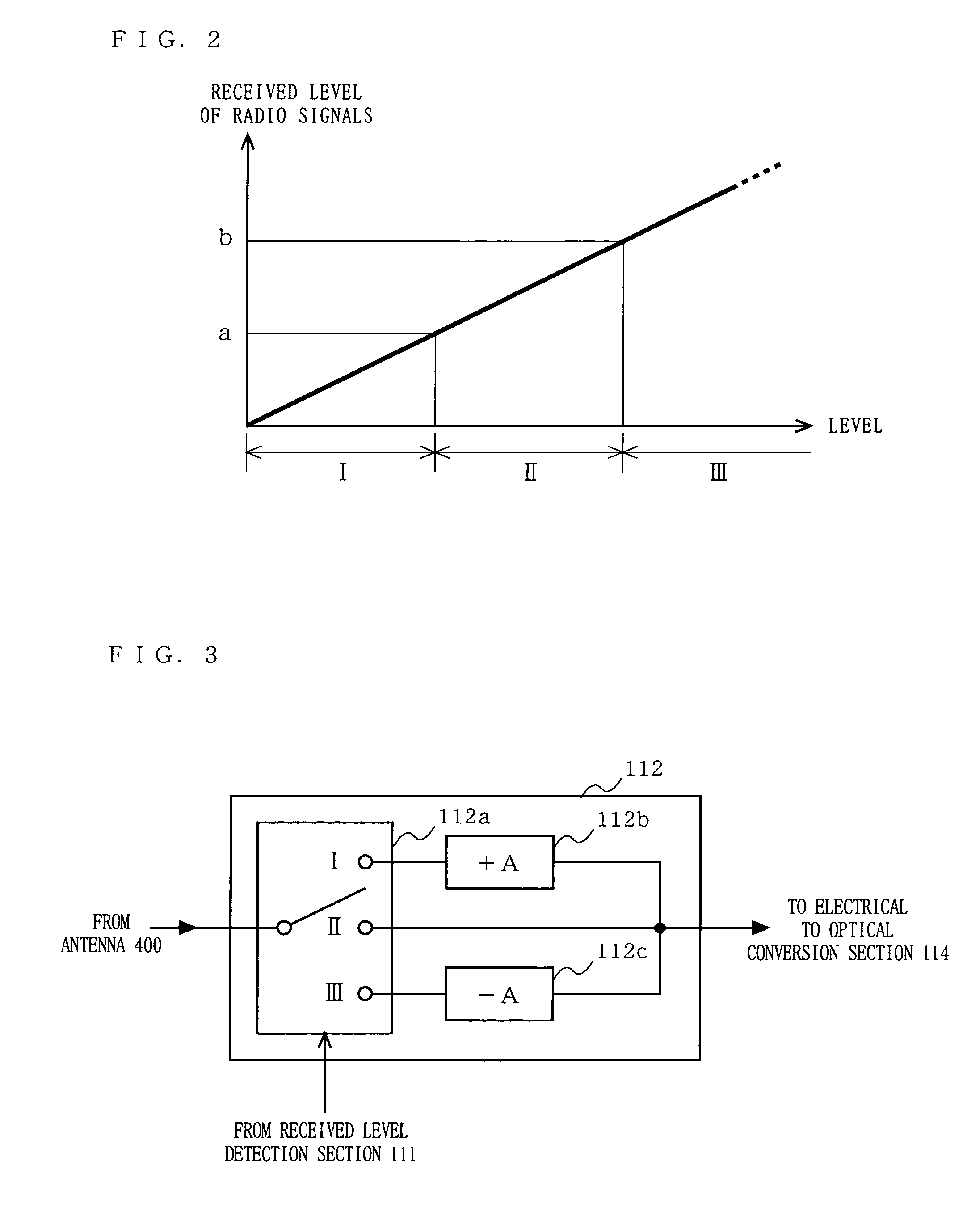
An optical fiber radio transmission system is provided which is capable of considerably improving the received dynamic range of radio signals and, in addition, is capable of optically transmitting radio signals while preventing the deterioration of transmission performance and the loss of linearity of an input signal more easily. A received level detection section 111 detects which one of predetermined levels, i.e., Level I, Level II, and Level III, the received level of a radio signal received by an antenna 400 falls under. A signal control section 112 performs an amplification / attenuation process on the radio signal in accordance with the detected level. A control information sending section 113 superimposes control information indicating the detected level on a primary signal obtained after the amplification / attenuation process. This signal is converted to an optical signal and transmitted. An optical to electrical conversion section 211 converts the optical signal received from a transmitting unit to an electrical signal. A control information extraction section 212 extracts the level from the control information, which has been superimposed on the primary signal. A signal control section 213 performs an amplification / attenuation process on the primary signal in accordance with the extracted level.
Owner:HASE KAZUTOSHI +2
Equalization, pulse shaping and regeneration of optical signals
InactiveUS6067180AImprove regenerative abilityLaser detailsTime-division optical multiplex systemsMach–Zehnder interferometerPulse shaping
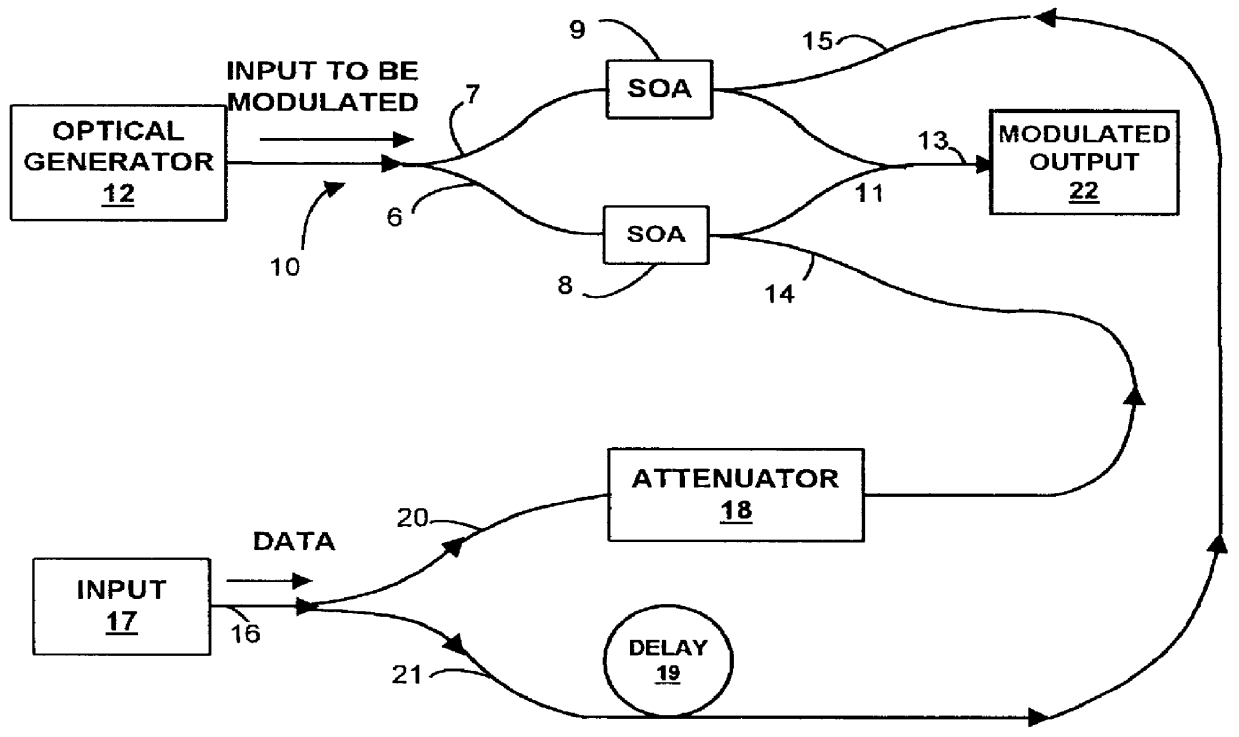
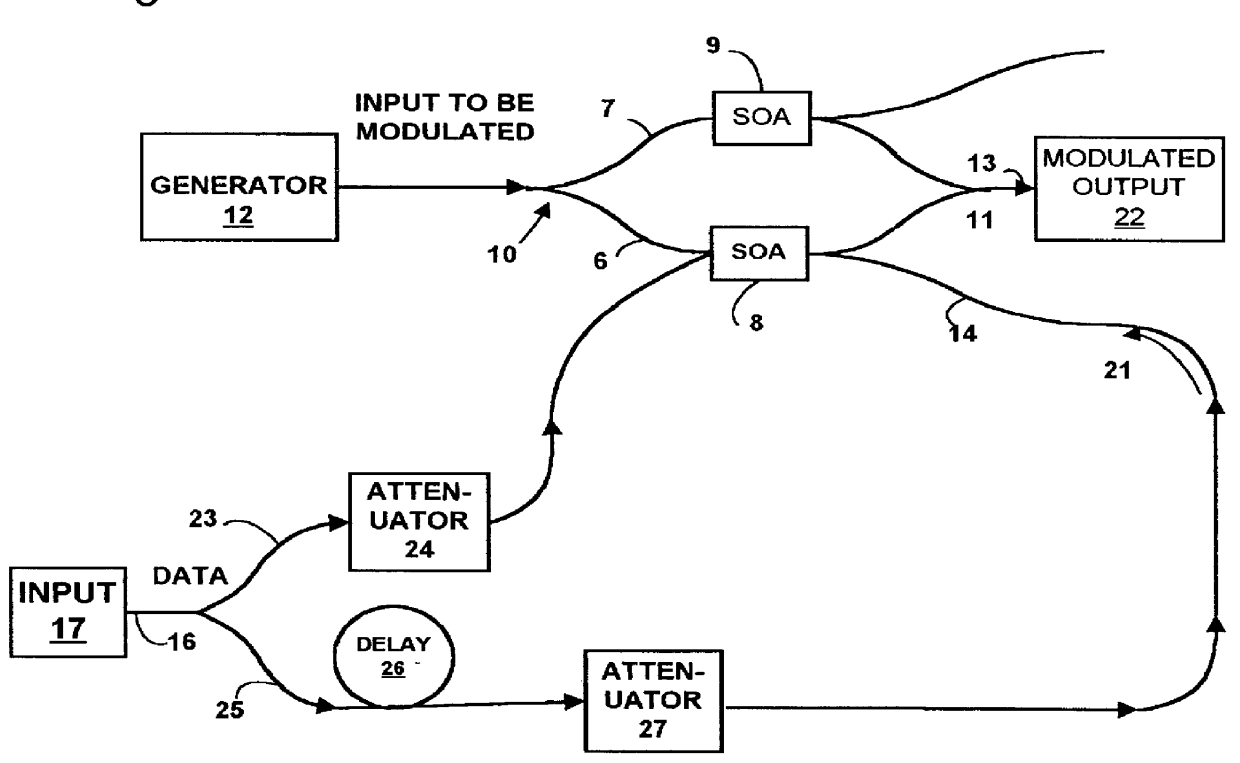
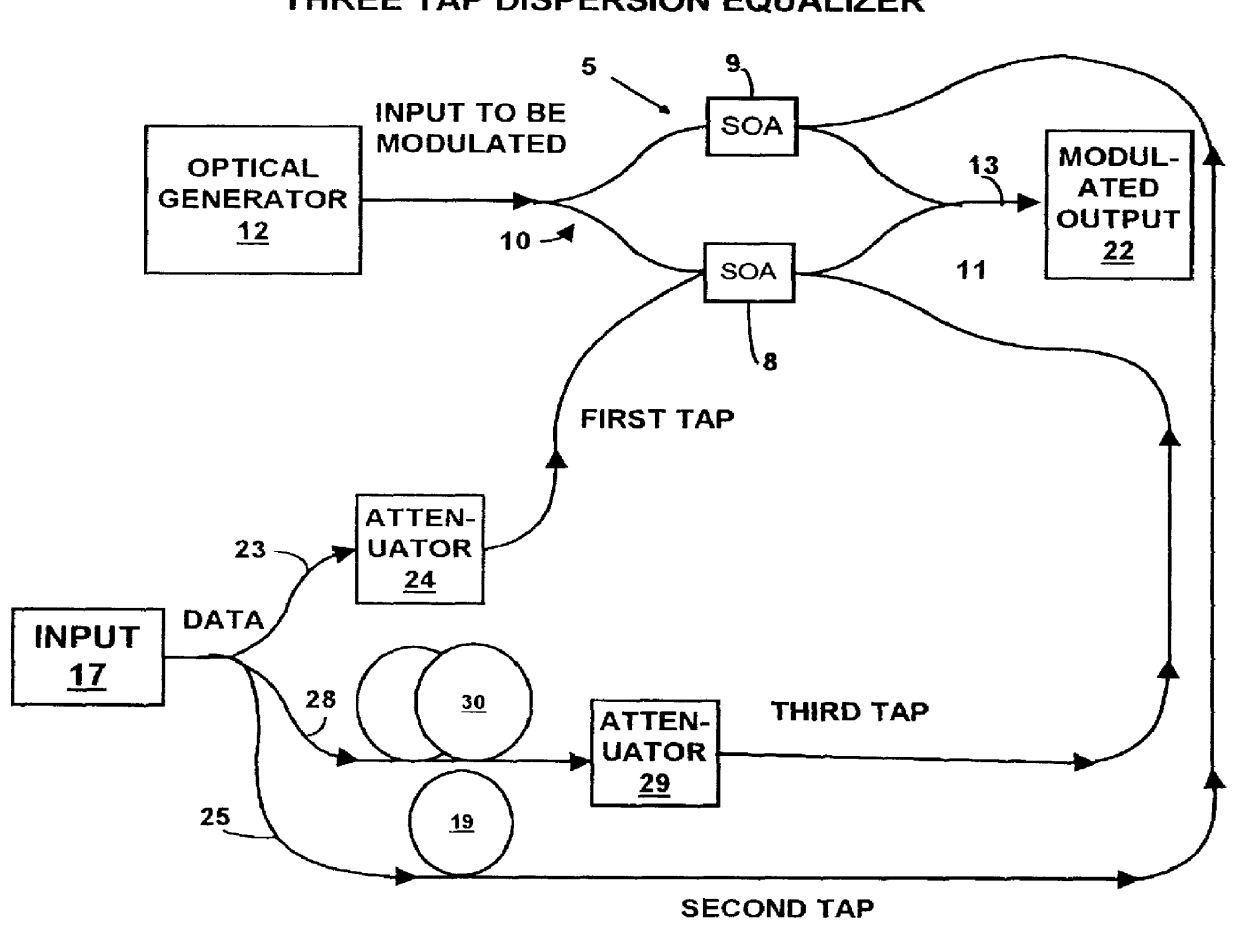
Data carrying optical signals are subjected to equalization or pulse shaping of the optical signal waveform. A plurality of optical tap signals derived from the optical signal are used to control a modulator operating on an input signal to provide an output signal having the desired waveform. A Mach-Zehnder interferometer having semiconductor optical amplifiers in each arm provides modulation by the effect of cross modulation induced by propagating the respective tap signals through a selected one of the semiconductor optical amplifiers. Various forms of transversal filter are provided by selecting the number of optical taps, assigning positive or negative weights and appropriate delays. The effects of dispersion in optical signals can be mitigated by utilizing optical taps with negative weights to subtract tail portions from the leading and trailing edges of a signal pulse. The invention has application to systems with high bit rates where equalization or pulse shaping in the electrical domain is difficult to implement.
Owner:ROCKSTAR CONSORTIUM INC
Optical network for bi-directional wireless communication
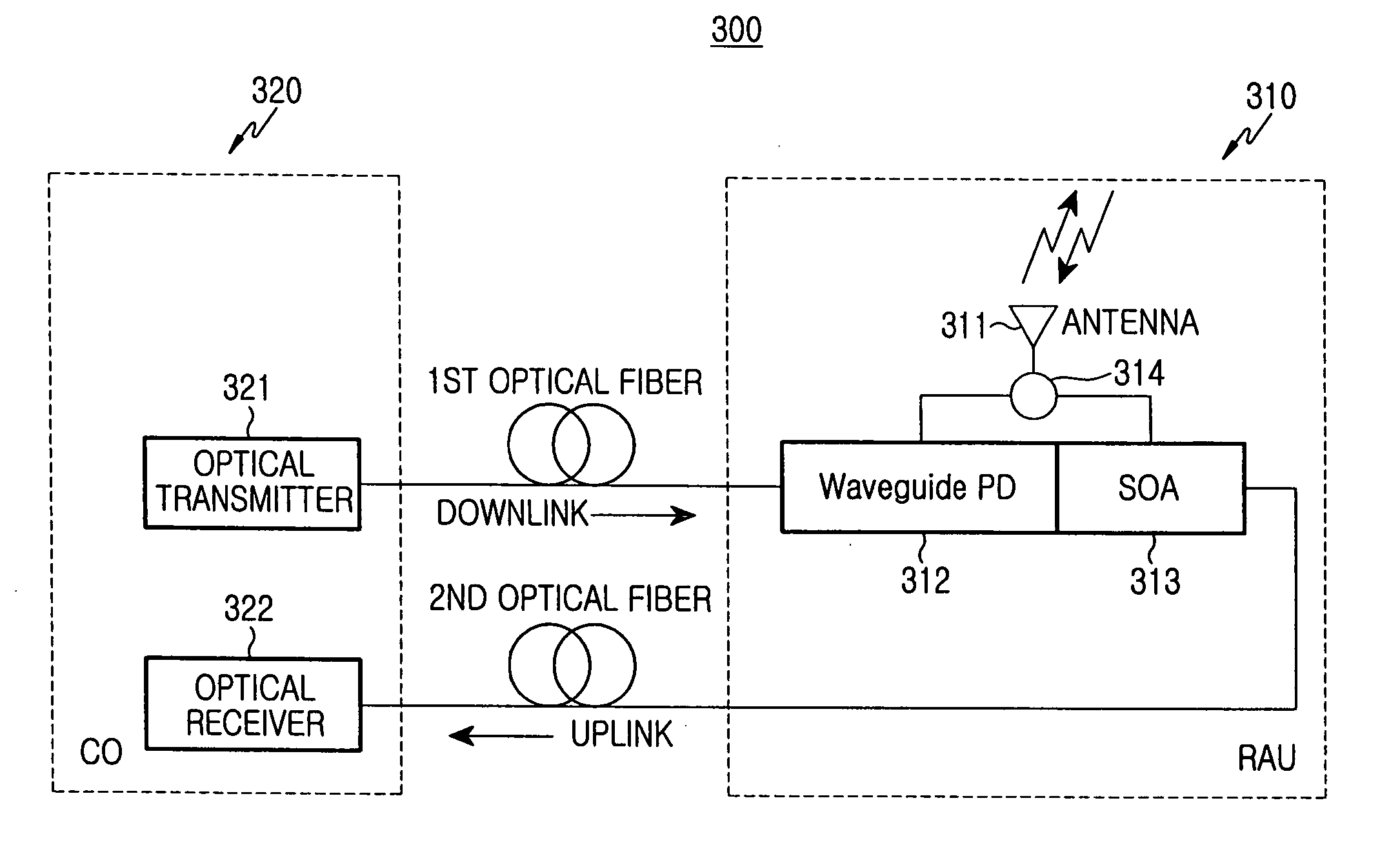
InactiveUS20060104643A1Sufficient power marginReduce power lossRadio transmissionDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
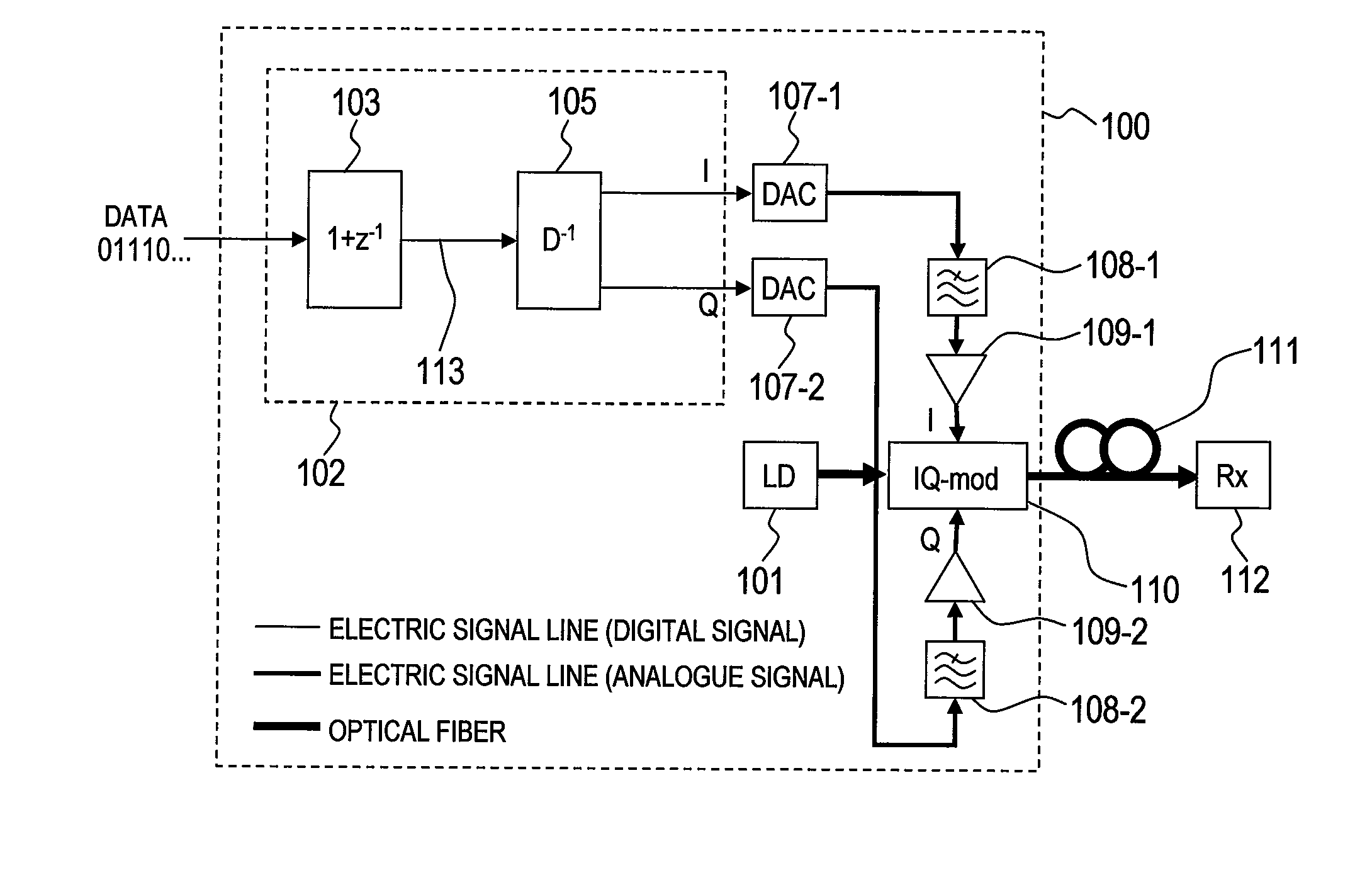
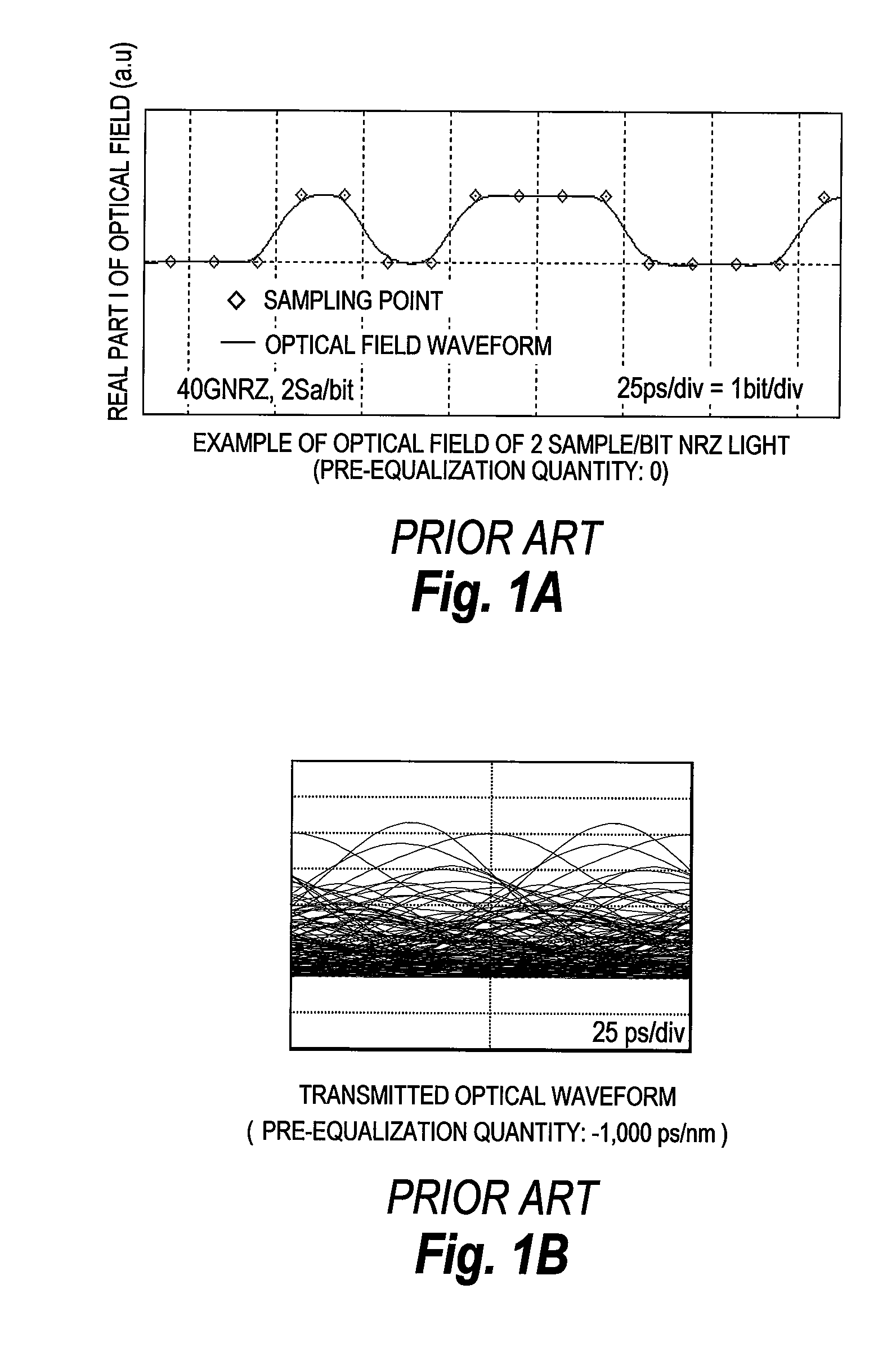
Pre-equalized optical transmitter and pre-equalized optical transmission system
InactiveUS20090238580A1Reduced Tolerance RequirementsReduce consumptionDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersEngineeringAnalog signal
Provided is a pre-equalized optical transmitter, comprises: a laser source; a duo-binary pre-coder circuit; a pre-equalization circuit for applying an inverse function of chromatic dispersion; at least two D / A converters; and an optical field modulator comprising at least two input terminals for an electric signal. The pre-equalized optical transmitter: converts, by the duo-binary pre-coder circuit, a digital information signal of a predetermined symbol time to be transmitted into a digital complex signal including one sampling point per symbol; equalizes, by the pre-equalization circuit, degradation in transmission of the digital complex signal; converts, by the D / A converters, the equalized digital complex signal into an analogue signal; suppresses an analogue signal leaking outside a Nyquist bandwidth by at least 23 dB; modulates, by the optical field modulator, light output from the laser source with the analogue signal to generate a modulated optical field signal; and transmits the modulated optical field signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method, optical device, and system for optical fiber transmission
InactiveUS6847758B1Increase input powerImprove transmission distanceLaser detailsCladded optical fibreWaveform shapingChirp
The present invention relates to a method for optical fiber transmission which can increase a transmission distance. A first optical fiber having dispersion is first provided. An optical signal is next supplied to the first optical fiber so that the optical signal is compressed on the time axis as propagating in the first optical fiber. In the case that the dispersion is normal dispersion, for example, prechirping is performed so that the optical signal has down-chirp. A compressed optical signal output from the first optical fiber is supplied to an optical device having a saturated gain. According to this method, the transmission distance can be increased by the effective combination of compression of the optical signal and waveform shaping by the optical device.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
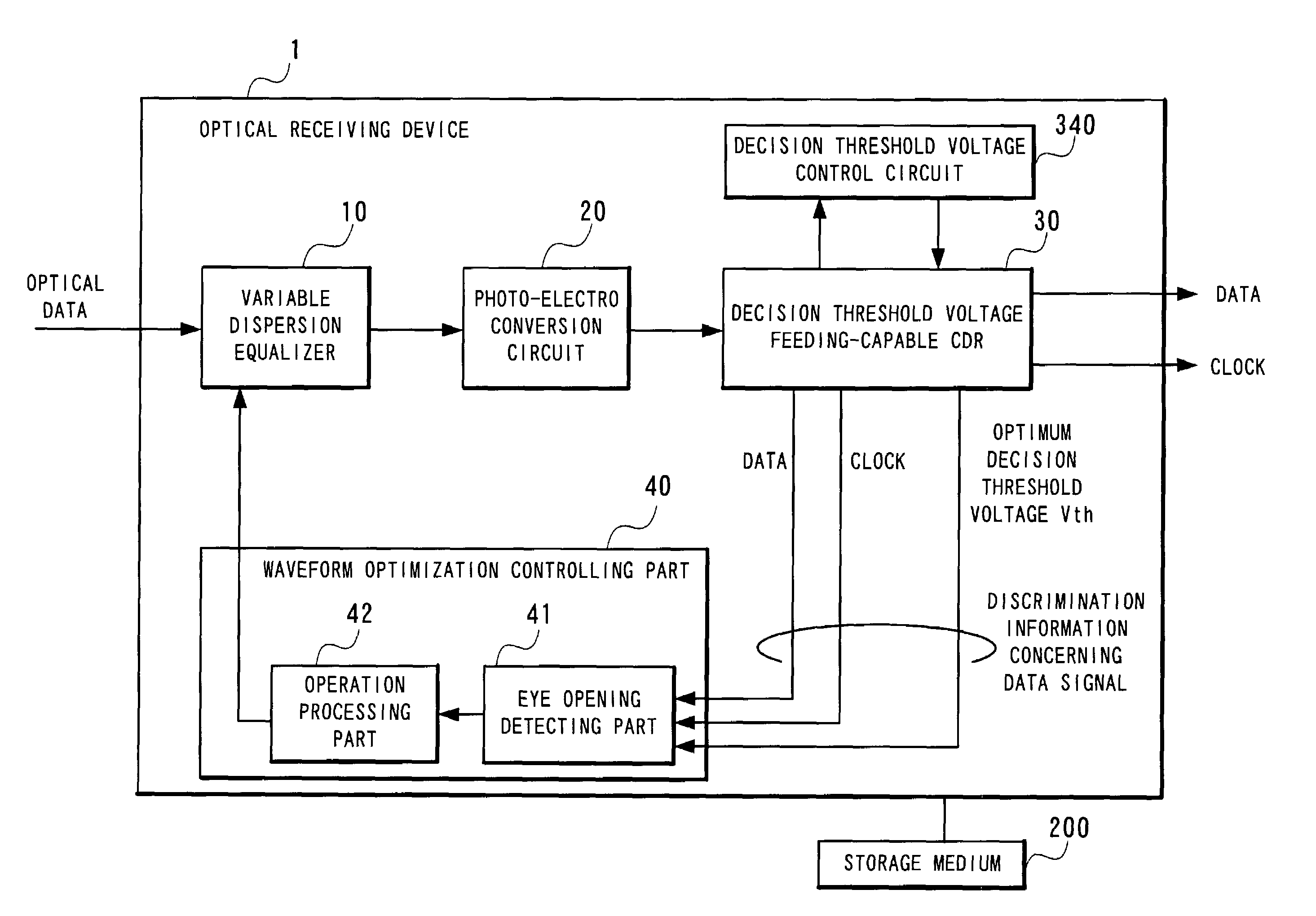
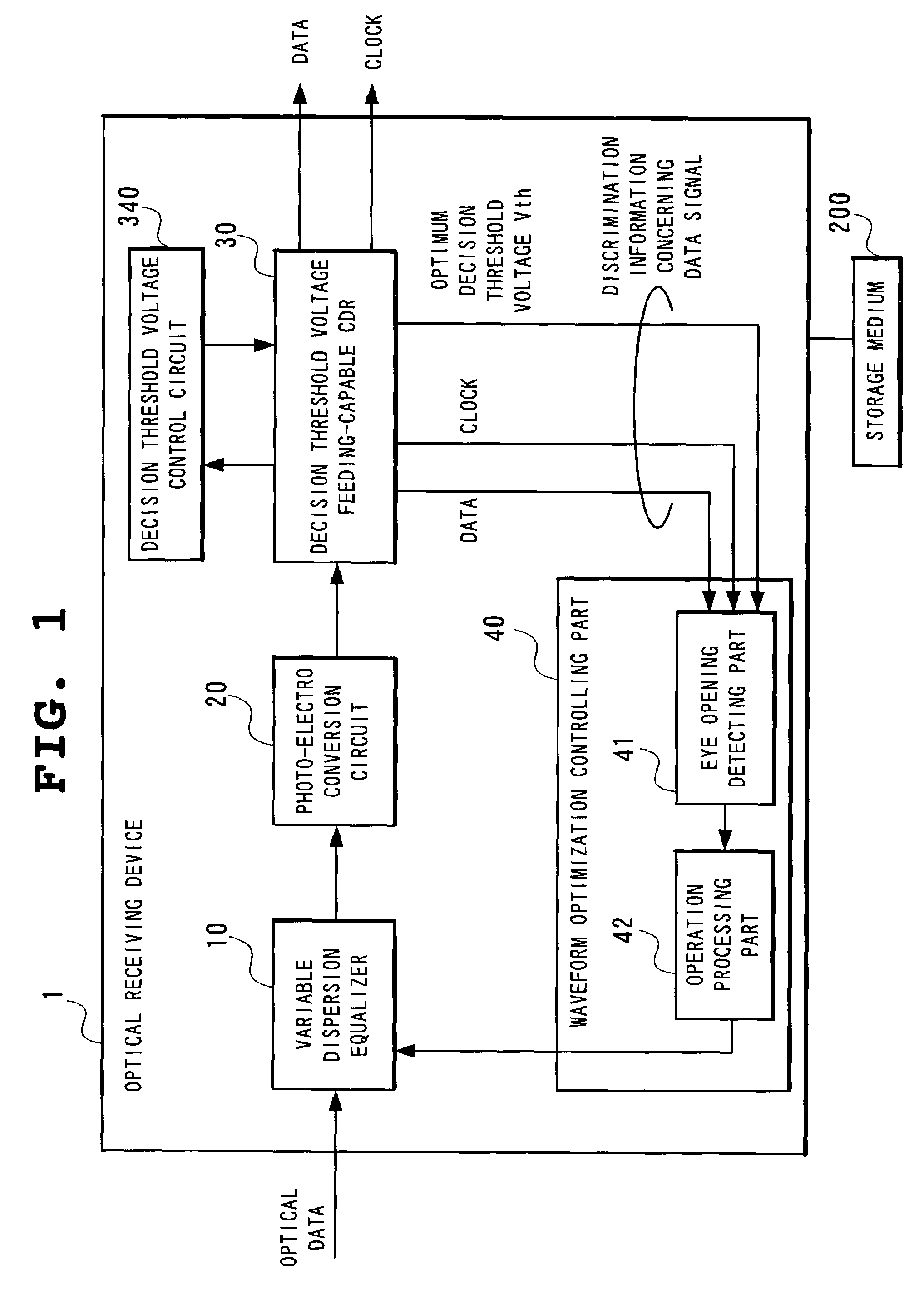
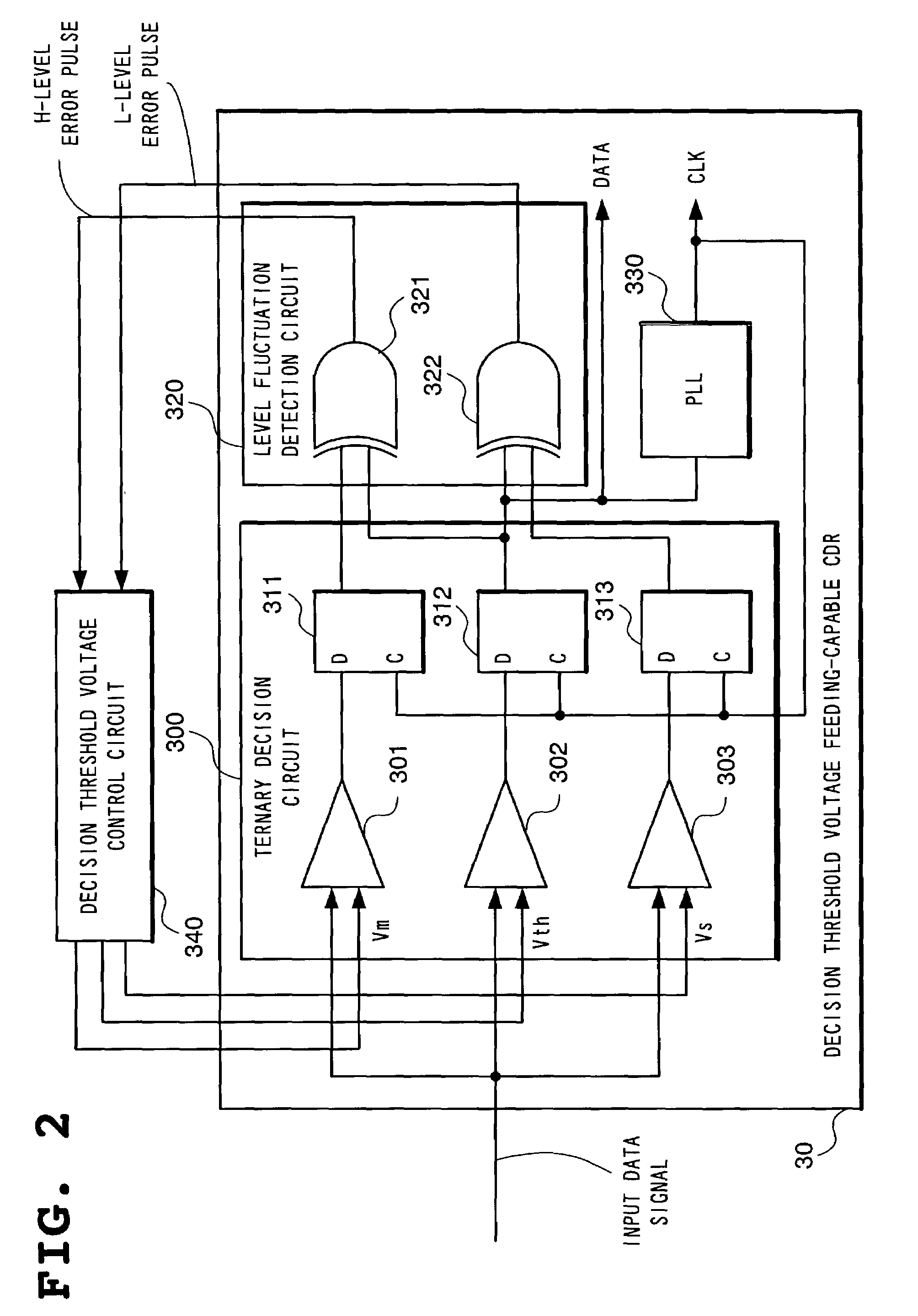
Optical receiving device, waveform optimization method for optical data signals, and waveform optimization program for optical data signals
InactiveUS7123846B2Improve waveformOptimize optical waveformTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersData signalControl data
This optical receiving device for discriminating and recovering a data signal, which results from converting an optical signal input through a dispersion equalizer into an electrical signal and amplifying it to a pre-determined amplitude, by using a clock and data recovery circuit for discriminating a data signal at the decision point controlled to achieve the optimum position controls the dispersion characteristics of a dispersion equalizer so that the error count in the recovered data signal by using a clock and data recovery circuit will be minimized by controlling the eye pattern of the data signal which has been amplified to a pre-determined amplitude.
Owner:NEC CORP
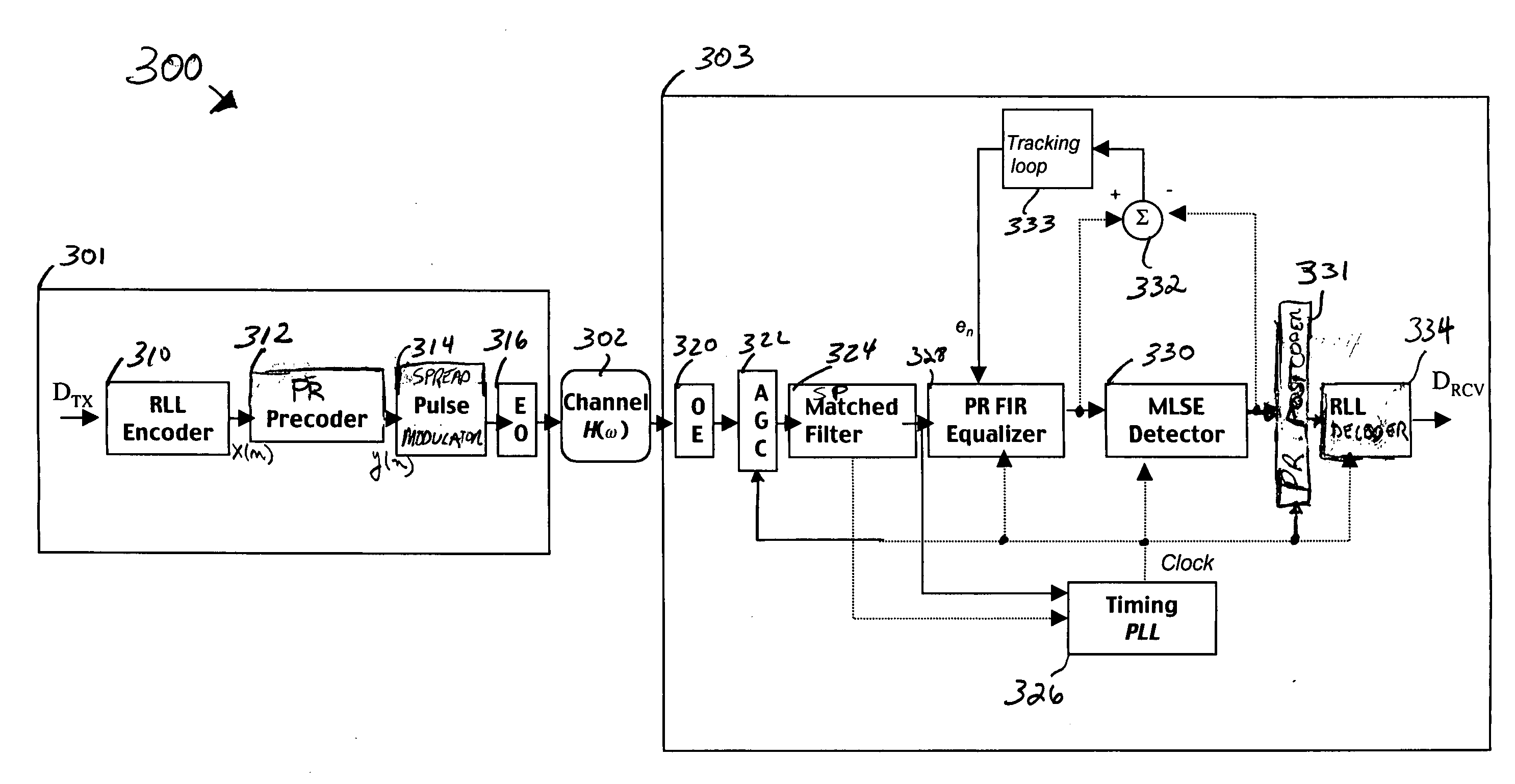
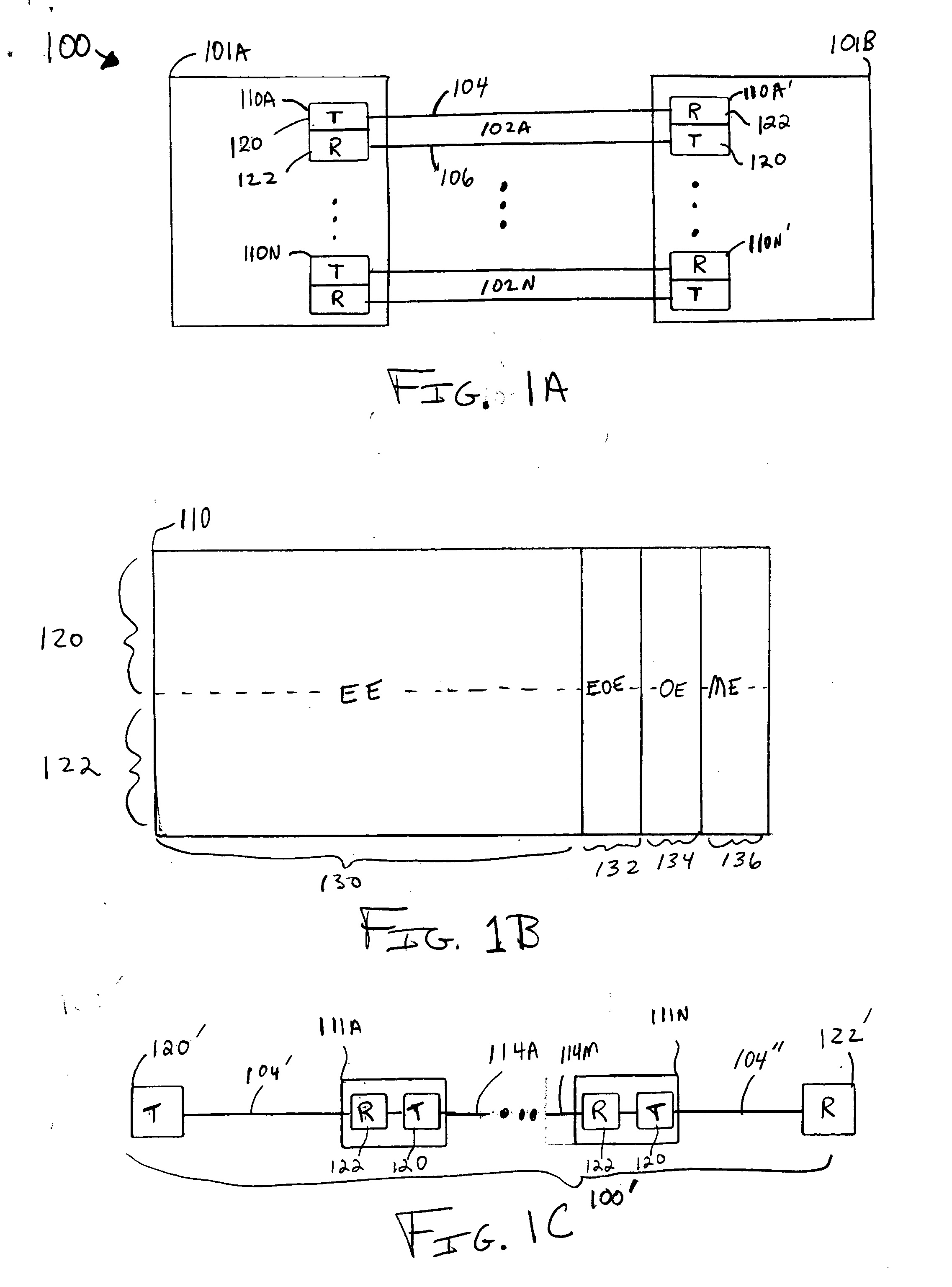
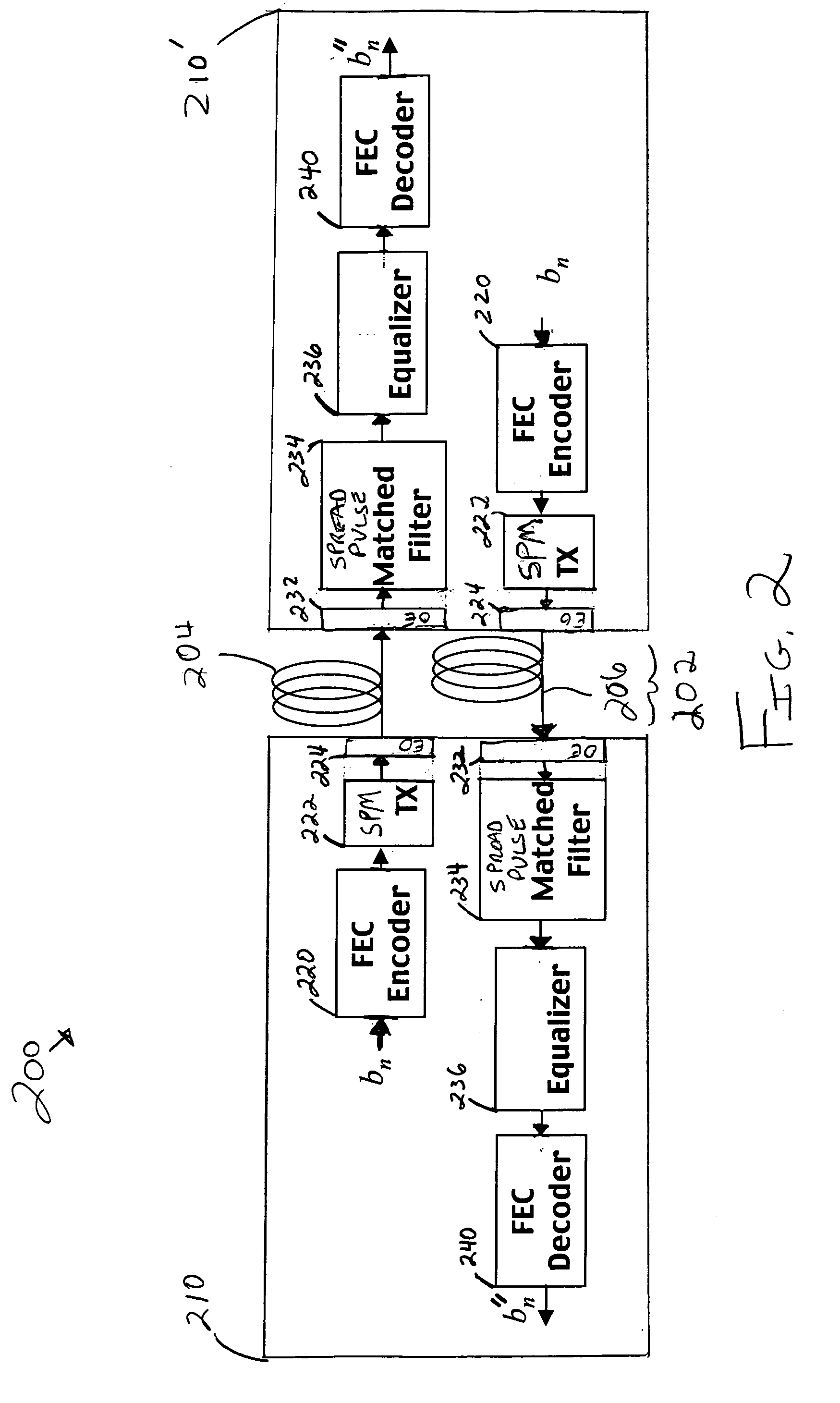
Methods of spread-pulse modulation and nonlinear time domain equalization for fiber optic communication channels
Methods, apparatus, and systems for an optical communication channel. A data signal is preconditioned prior to transmission over a fiber optic cable to minimize signal distortion and transmitted over a fiber optic cable. Preconditioning may include none, one or more, or all of the following: encoding the data signal using a run length limited code, correlating bits of the data signal, and spreading out the pulses in the time-domain in the data signal. The pulse spreading function can be implemented either in the electrical domain prior to the electrical-to-optical conversion; in the optical domain during and / or after the electrical-to-optical conversion; or a combination of both. During reception, the data signal and clock are recovered. Recovery may include maintaining an amplitude in an electrical signal, filtering the electrical signal, shaping the electrical signal, and removing distortions and intersymbol interference (ISI) from the received electrical signal.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
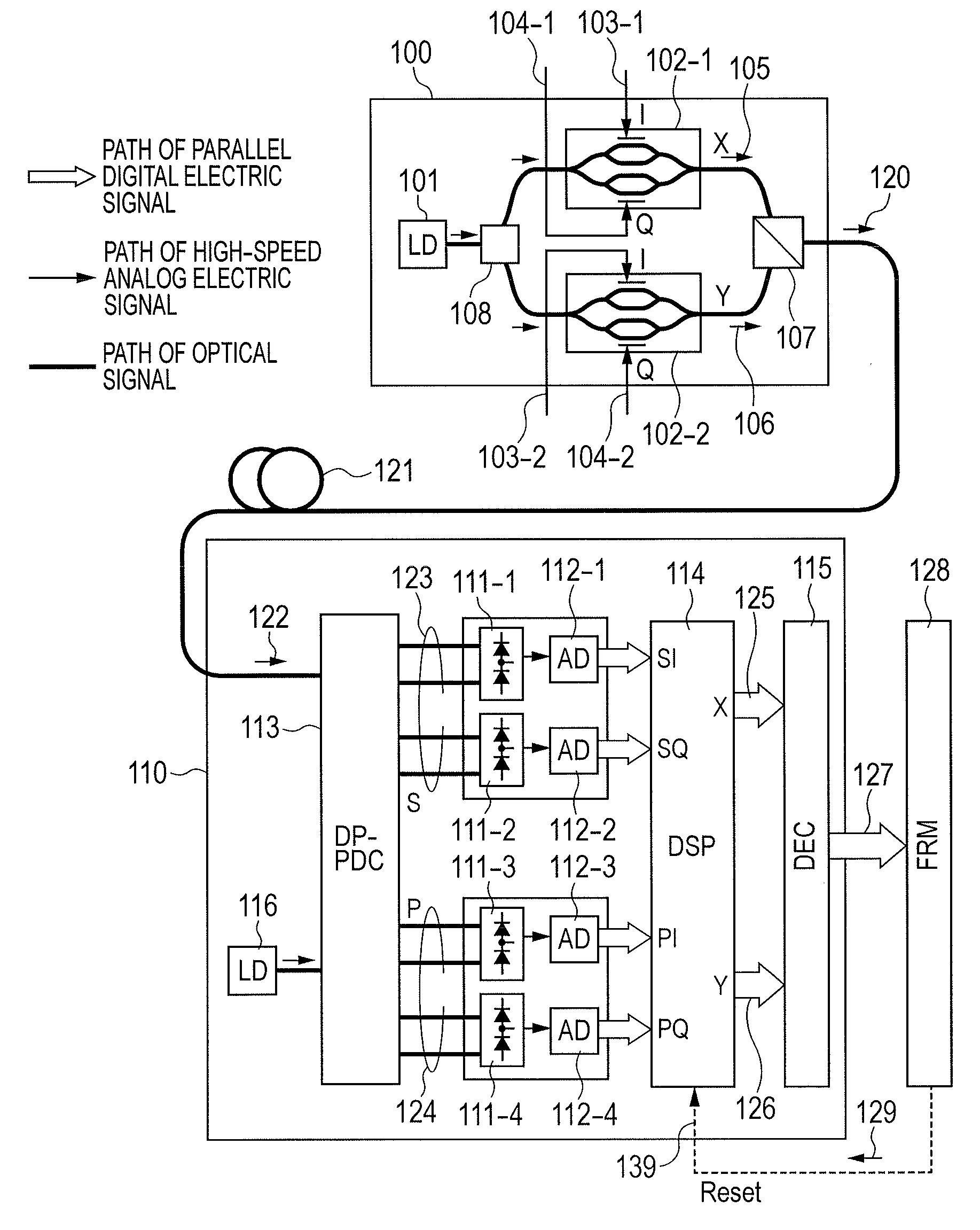
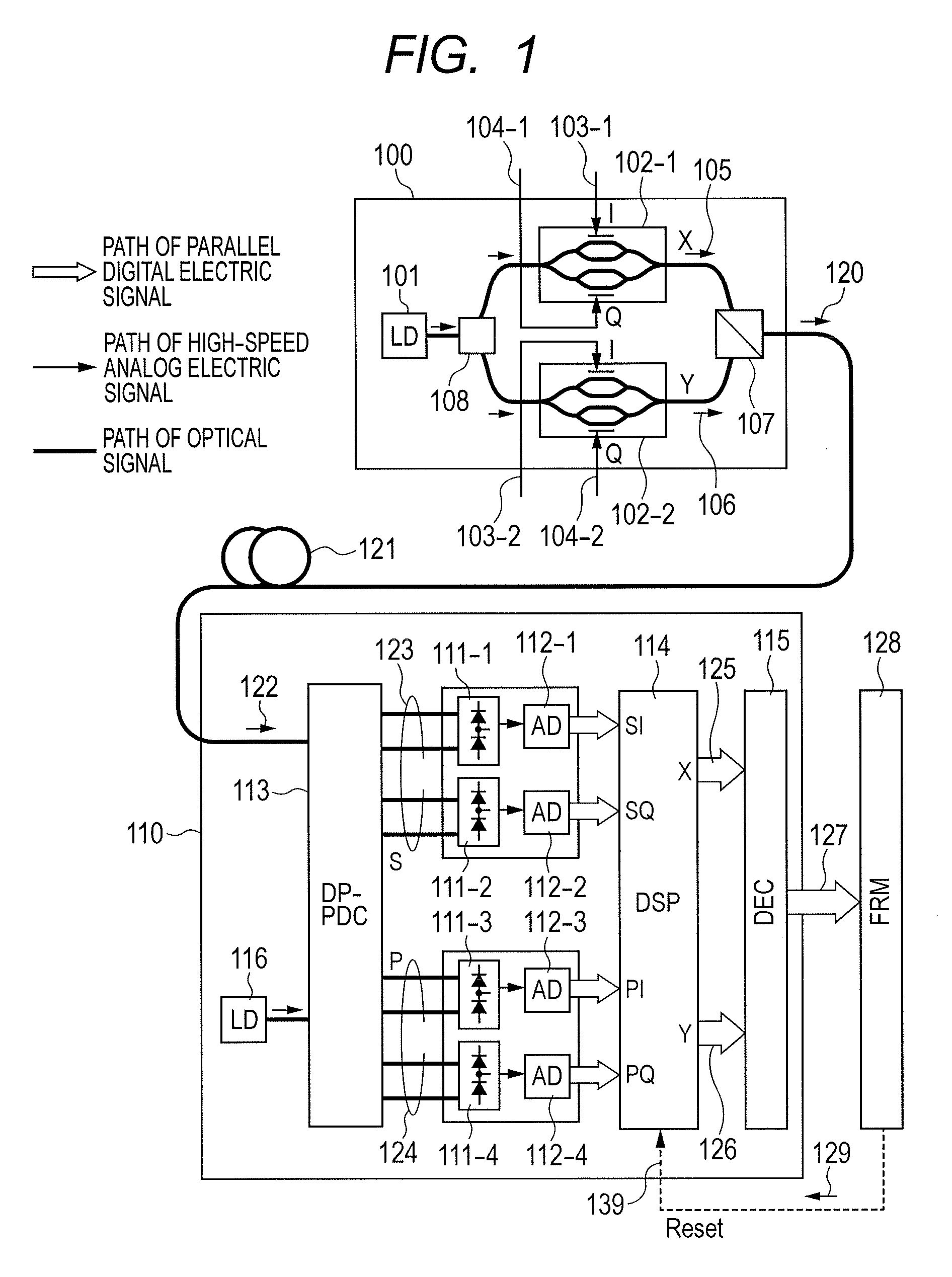
Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmission System, Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmitter, and Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Receiver
InactiveUS20120134676A1Preventing signal quality degradationReliable polarizationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsDigital signal processingPolarization diversity
There is a need to prevent two receivers from converging on a state of receiving the same polarization state, fast start receivers, and ensure highly reliable operations. A polarization-multiplexed transmitter previously applies frequency shifts of frequencies +Δf and −Δf to X-polarization and Y-polarization digital information signals to be transmitted. Optical field modulators modulate and polarization-multiplex the signals. As a result, a frequency difference of 2Δf is supplied to X-polarization and Y-polarization components. A polarization diversity coherent optical receiver 215 receives the signal. A frequency estimation portion in a digital signal processing circuit detects a frequency difference signal in both polarization components. This signal is used to a polarization splitting circuit in the digital signal processing circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical transmitter
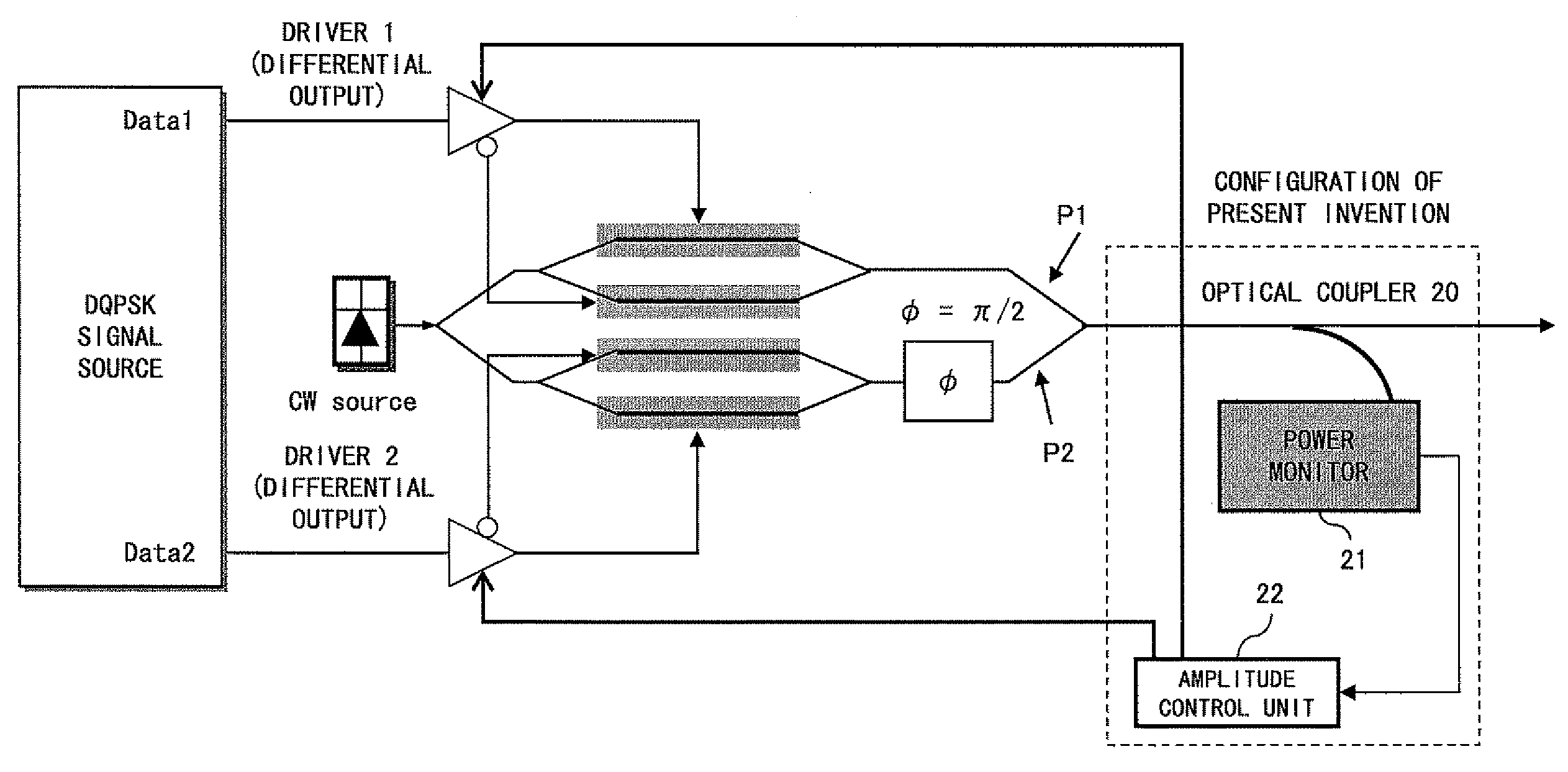
InactiveUS20080080872A1Avoid signal attenuationDegradation of the quality of a transmission signal can be suppressedPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringAmplitude controlOptical coupler
A signal Data1 and Data2 are output from a DQPSK signal source. The output signal is input to the modulator drivers 1 and 2 of the differential output. A drive signal is applied from the drivers 1 and 2 to a modulator, and modulated light is output. An optical coupler 20 branches modulator output, and a power monitor 21 detects the power of the branched light. A detection result is transmitted to an amplitude control unit 22. The amplitude control unit 22 adjusts the amplitude of the drivers 1 and 2 such that the detection result of the power monitor 21 can be the maximum.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
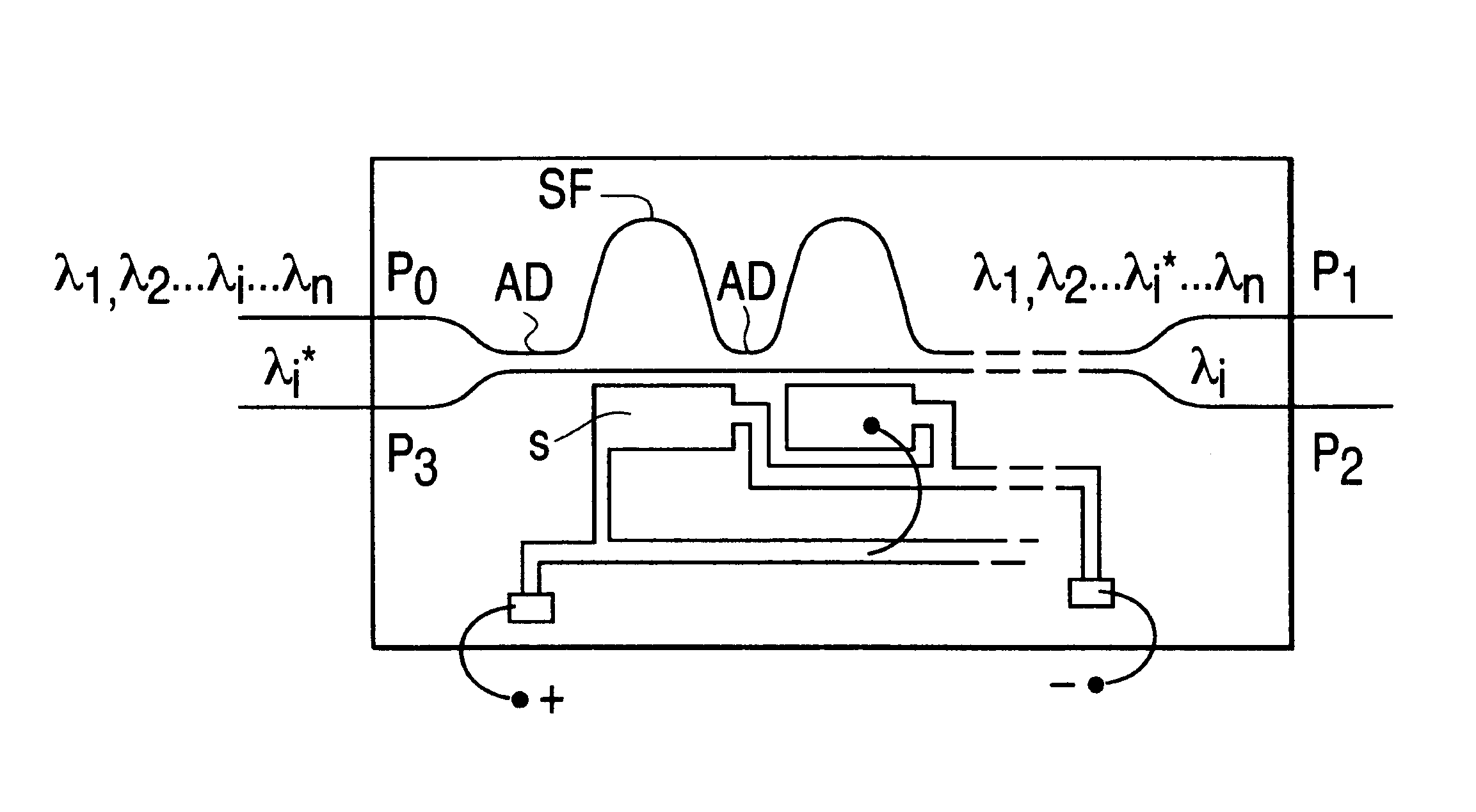
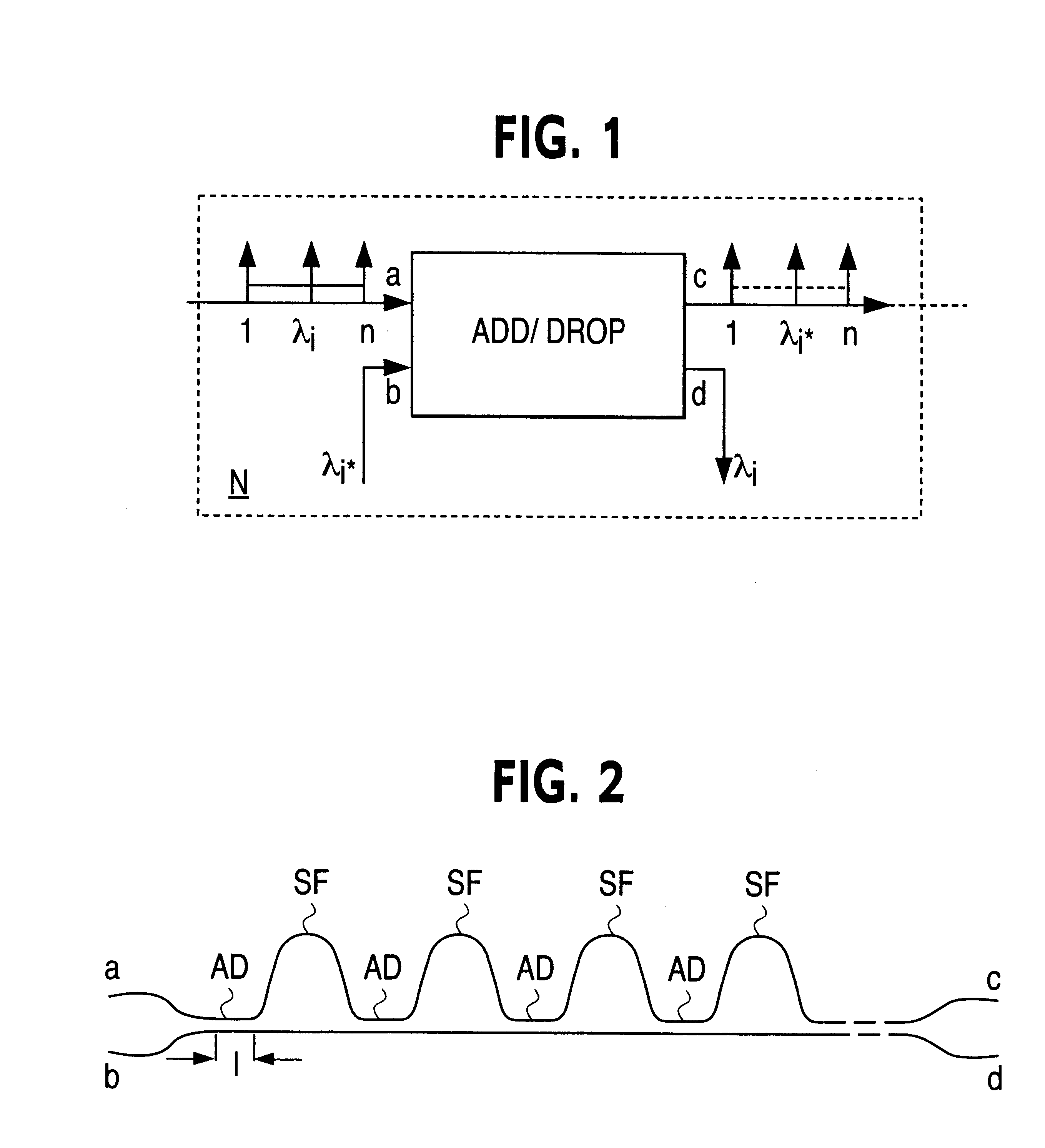
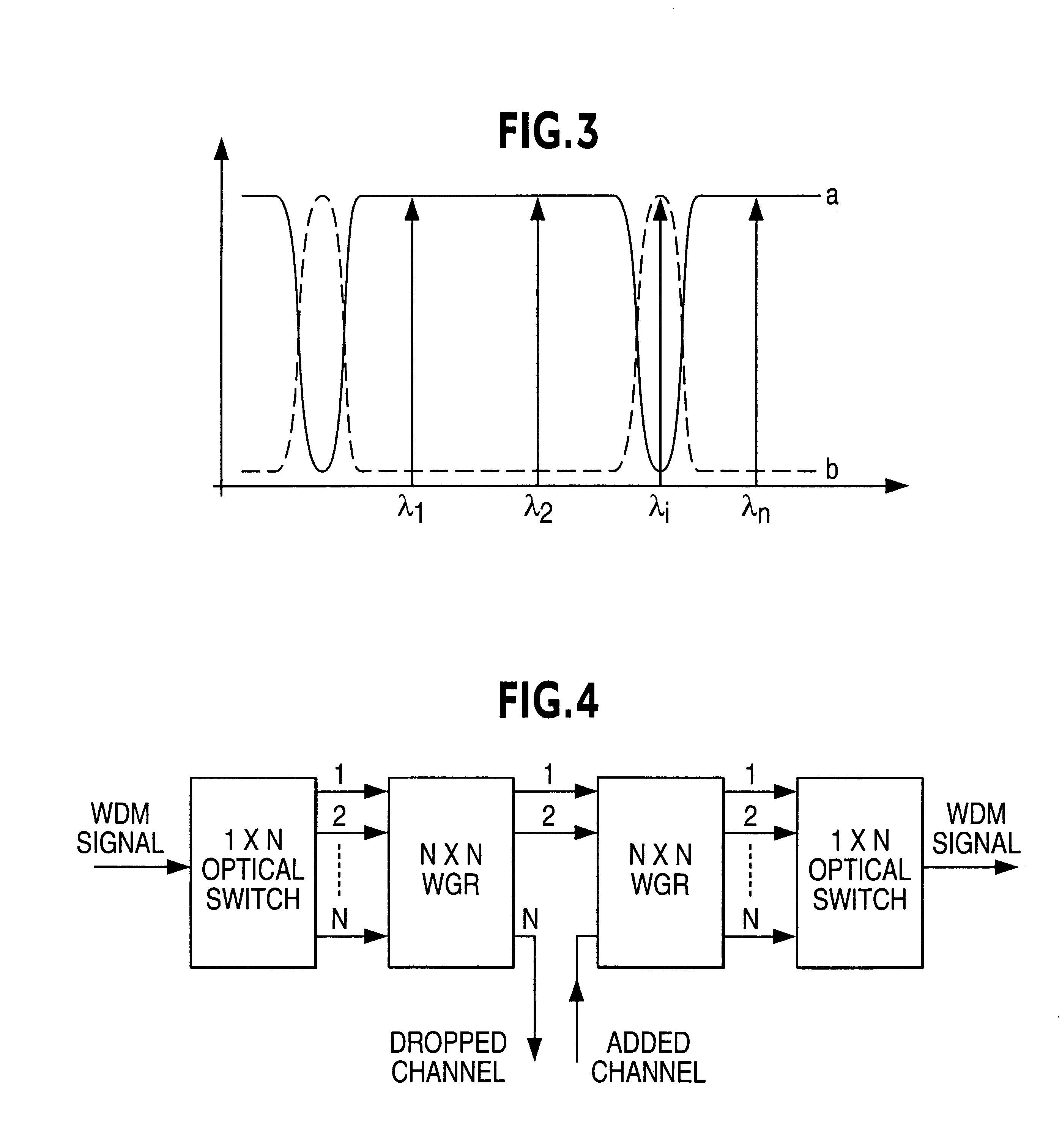
Tunable add/drop optical device
InactiveUS6285810B1Reduce complexityLow costCoupling light guidesTransmission monitoringRefractive indexCarrier signal
Tunable add / drop optical device for injecting or extracting (add / drop) at least a selected optical channel or carrier wavelength in or from a set of multiplexed channels or carriers of different wavelengths comprising a plurality of directional couplers (AD1 . . . AD6) and a plurality of phase-shift stages (SF1 . . . SF5) alternately connected in cascade, wherein each phase-shift stage defines a certain optical path length difference (DELTAL1 . . . DELTAL5) between two distinct optical paths of the stage. The tuning is performed modifying the refraction index of one path of said phase shift stages by means of Joule effect heating strips (L1 . . . L5) or by means of metallic field plates adapted to receive a signal suitable to modify the electric field intensity. The first two phase-shift stages of said plurality of phase-shift stages have differences of length of optical paths different from each other and in a preestablished ratio while the remaining phase-shift stages have differences of length of optical paths identical. It is thus possible to provide a device having an exceptionally flat cross response characteristic, substantially free of ripple due to an inevitable truncation of the Fourier expansion series.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
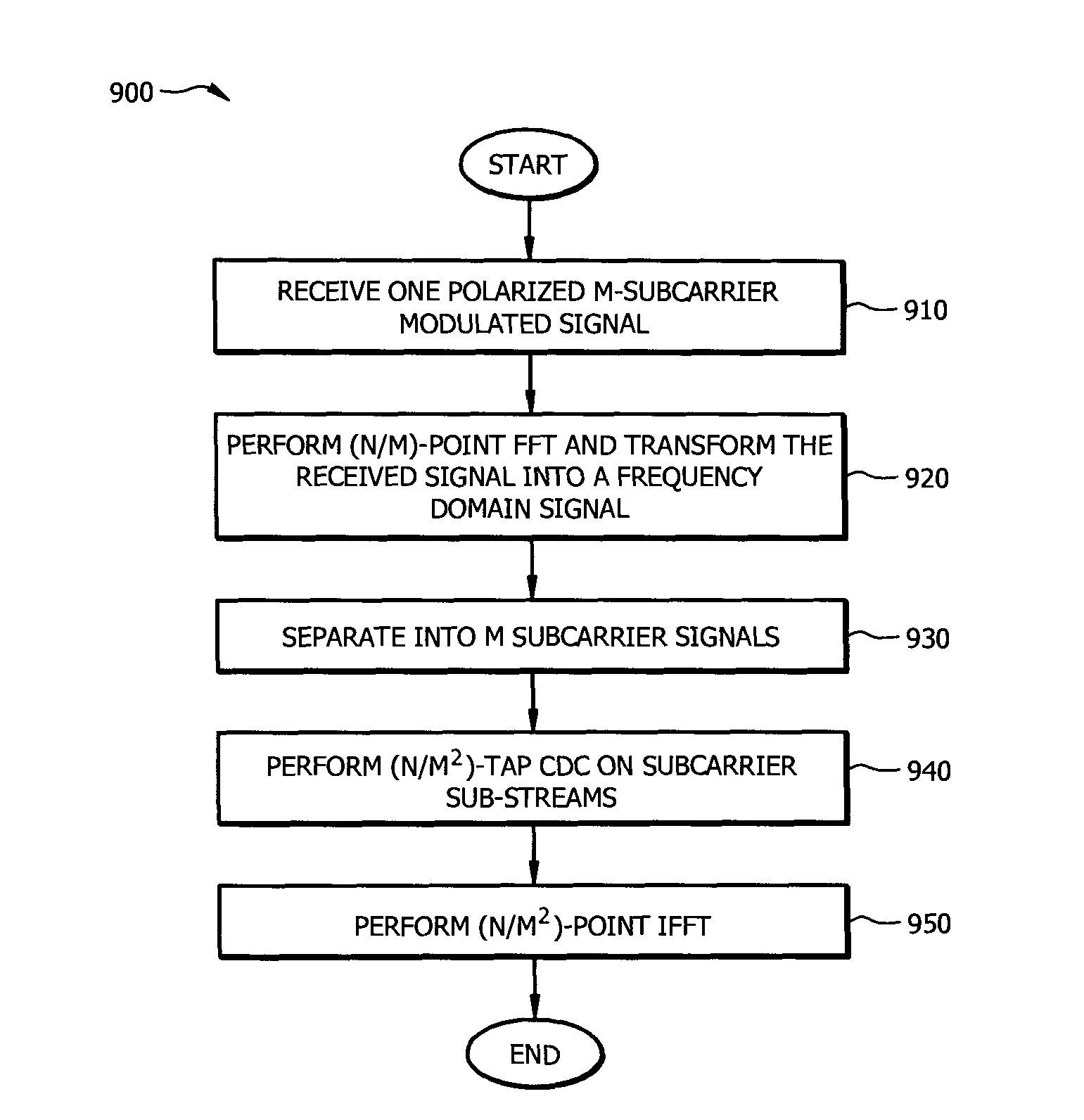
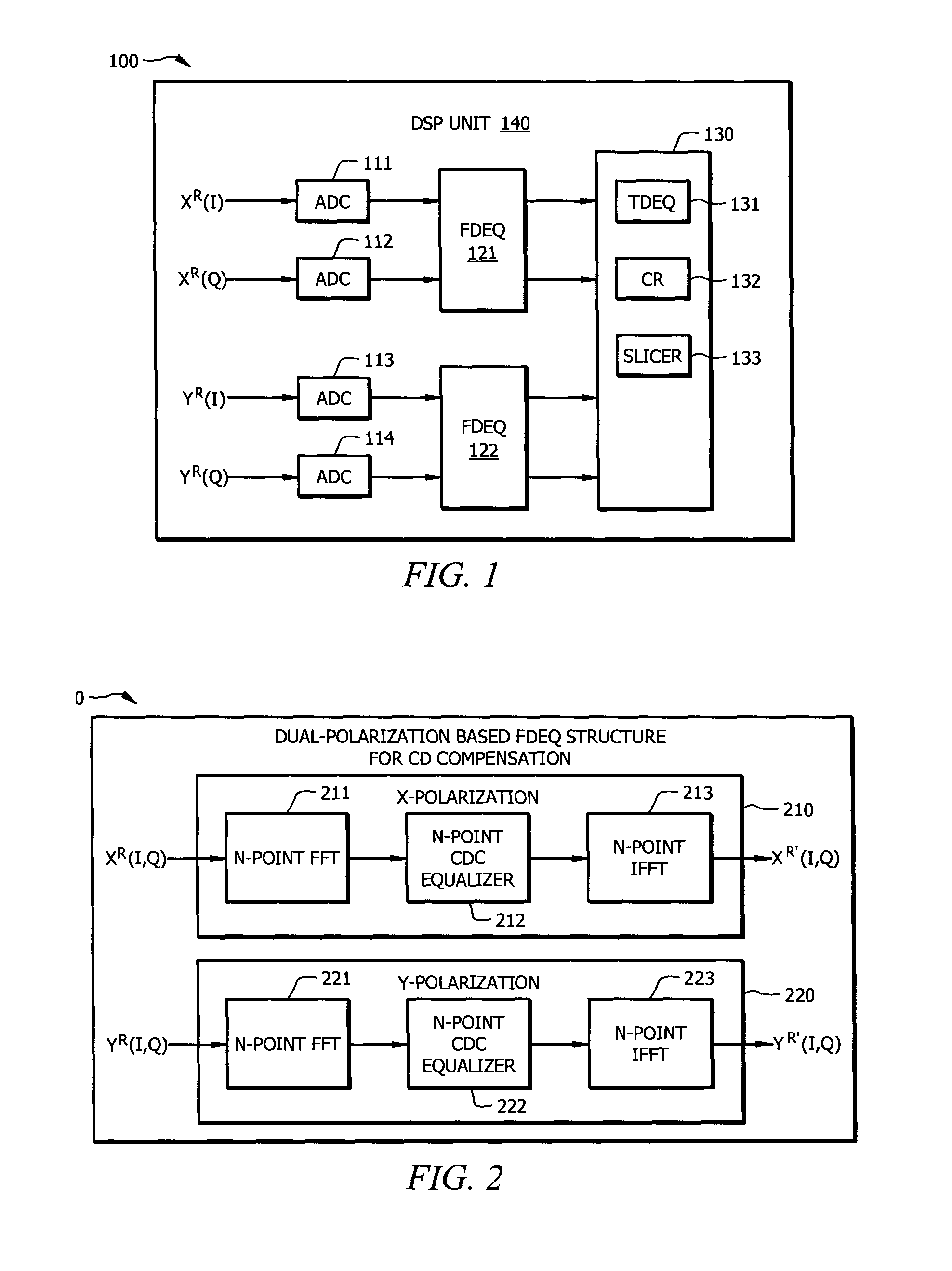
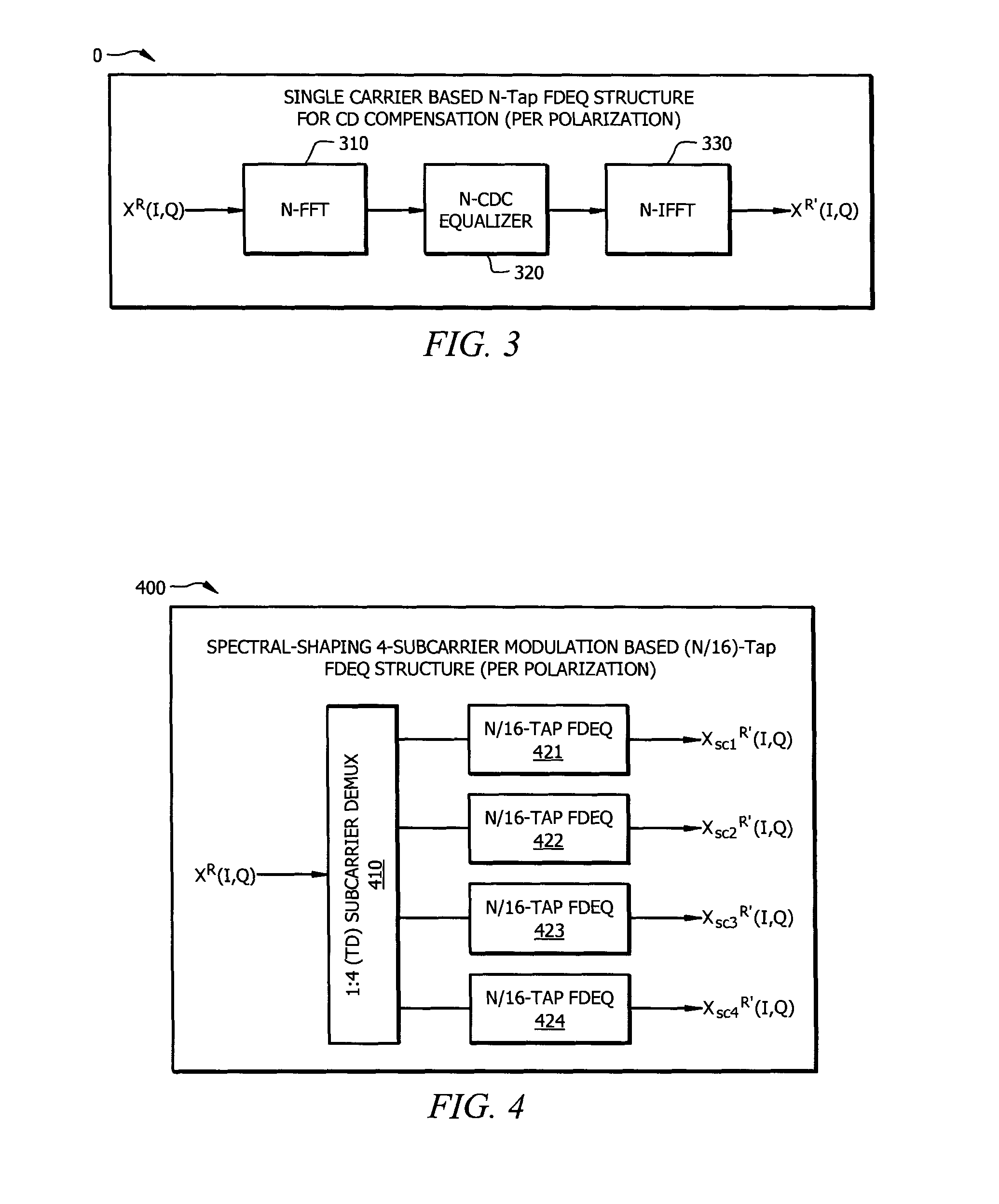
Resource-Efficient Digital Chromatic Dispersioin Compensation in Fiber Optical Communication Using Spectral-Shaping Subcarrier Modulation
ActiveUS20140099116A1Polarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberFrequency spectrum
An optical receiver comprising a frontend configured to receive an optical signal and convert the optical signal into a plurality of digital electrical signals comprising a plurality of spectrally shaped subcarrier signals carrying symbol mapped data information, and a digital signal processor (DSP) unit coupled to the frontend and configured to receive the digital signals from the frontend, demulitplex the digital signals into the subcarrier signals, and compensate chromatic dispersion (CD) for each of the subcarrier signals by applying an equalizer, wherein each of the subcarrier signals is associated with a unique tone frequency and a unique spectral shape. Also disclosed is an optical transmitter comprising a digital signal processor (DSP) unit configured to map data symbols onto a plurality of electrical subcarrier signals that are non-overlapping and spectrally shaped in a frequency domain.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
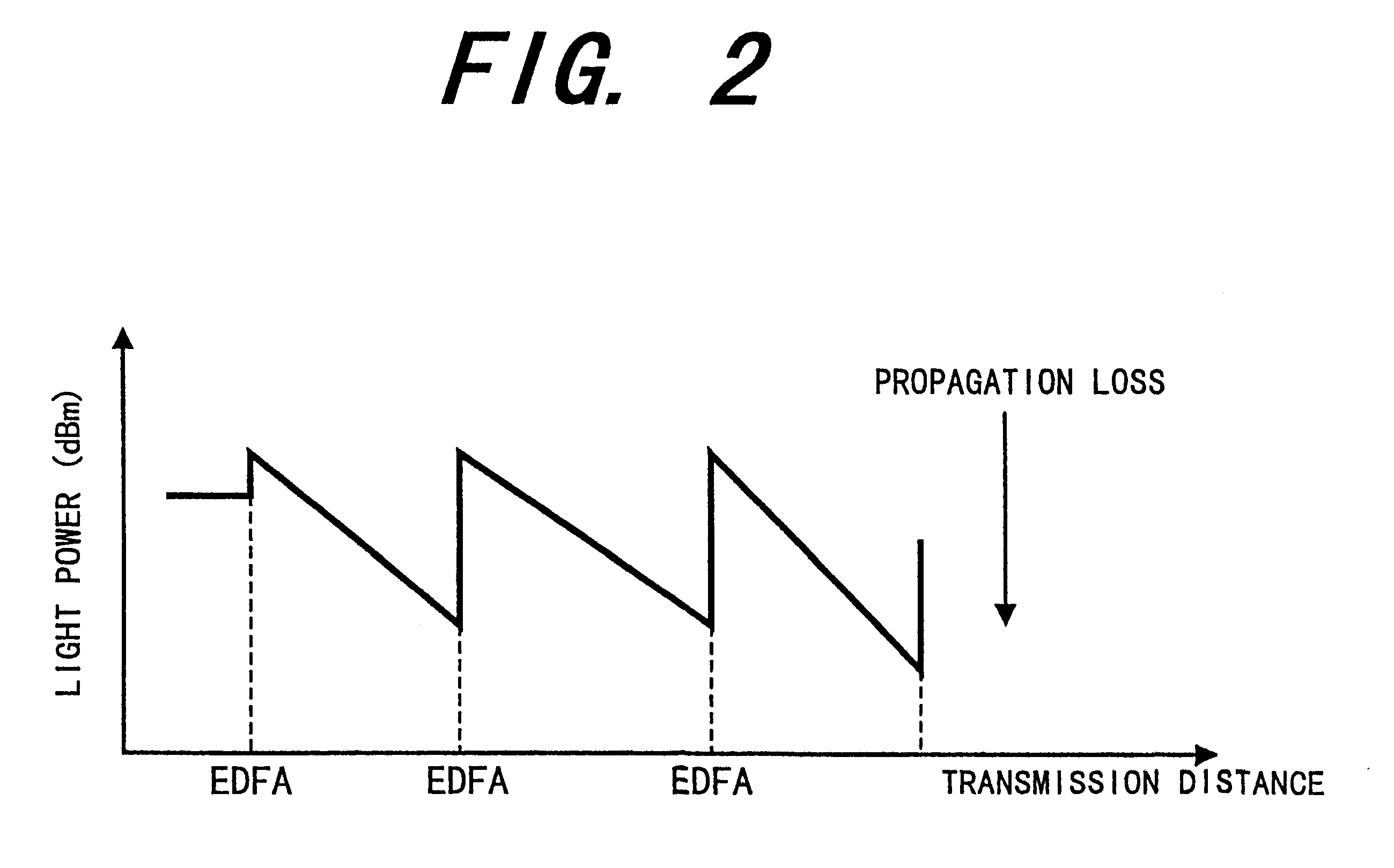
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20030142978A1Decreasing and compensating optical lossLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
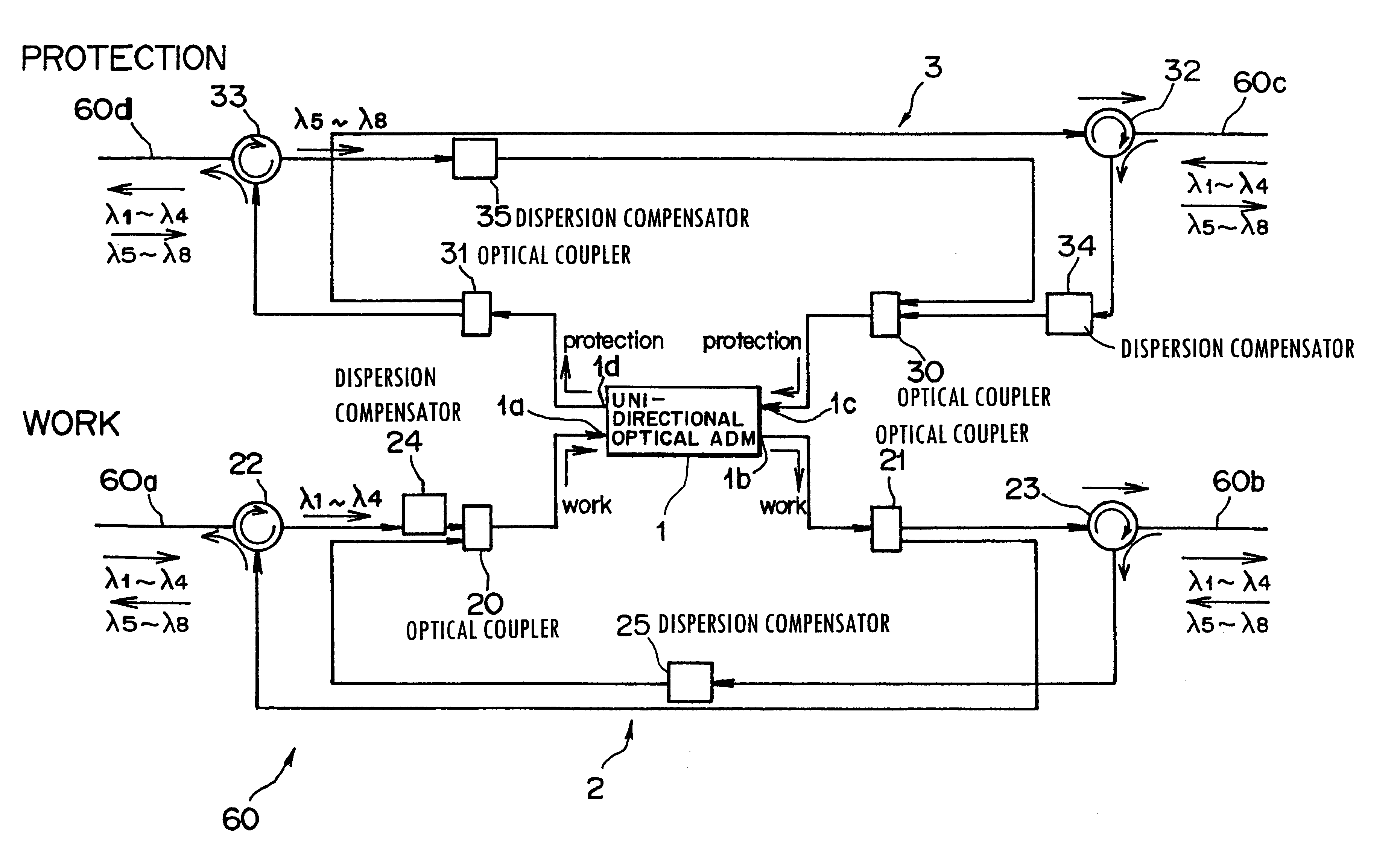
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance. A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path. In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
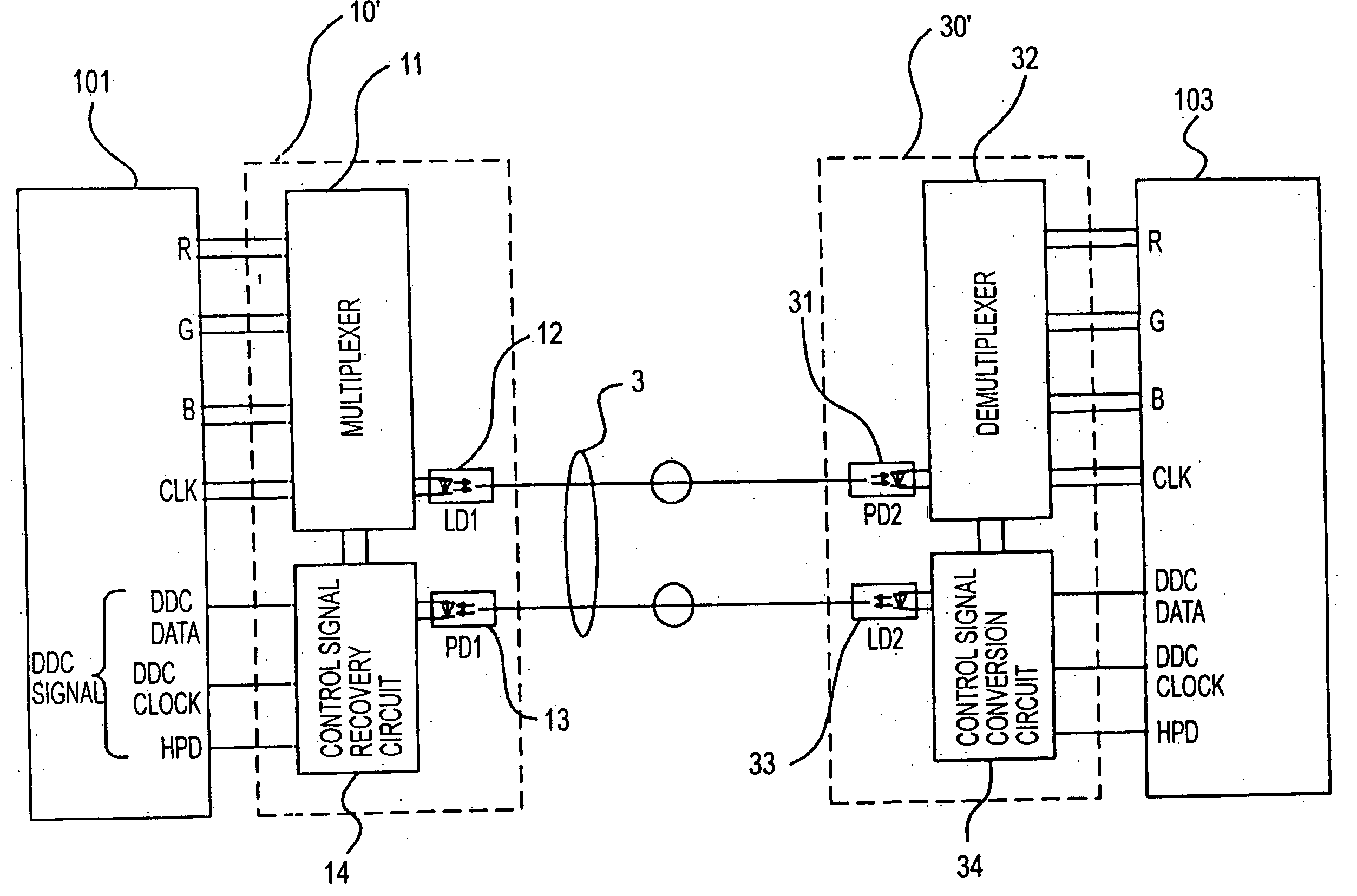
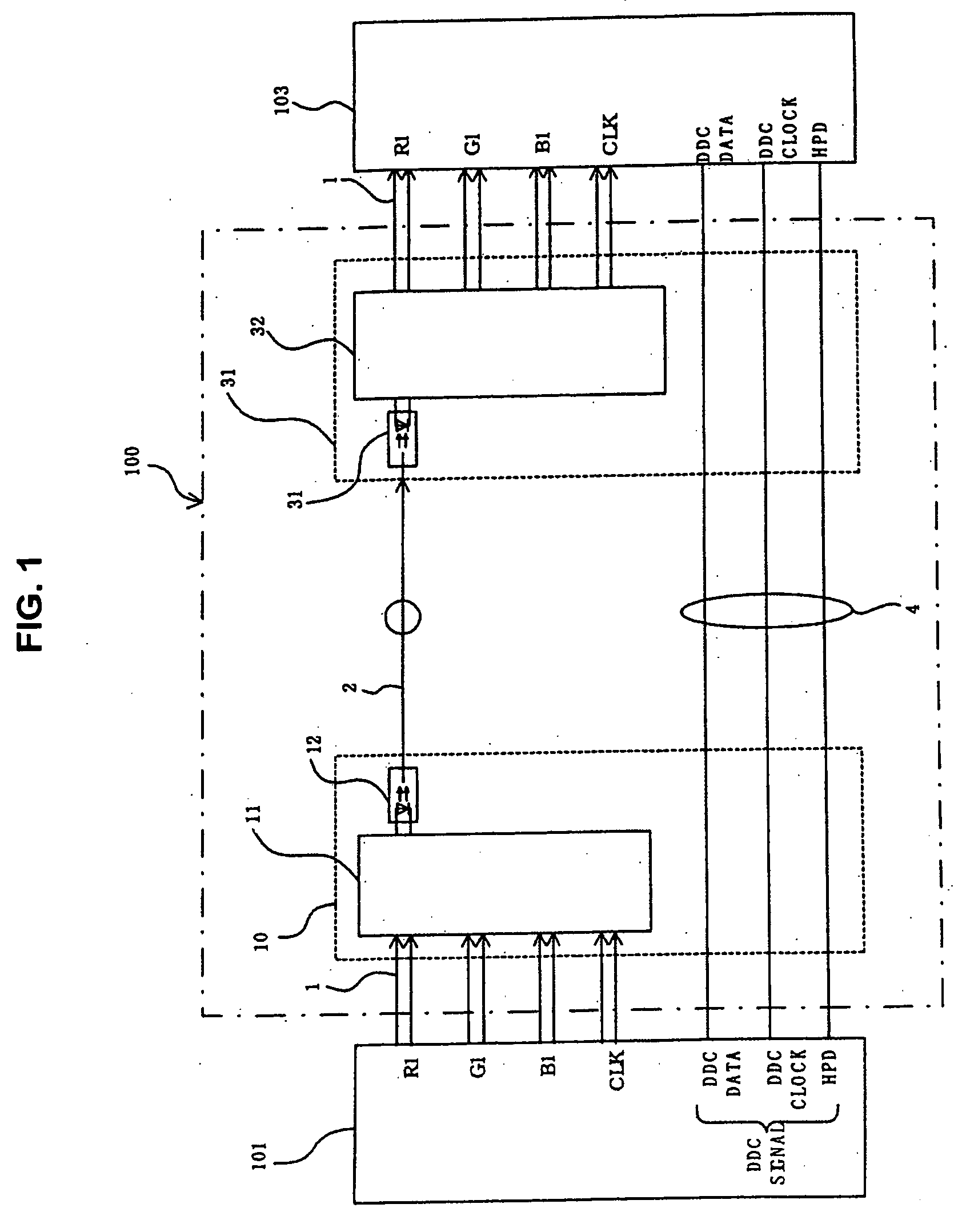
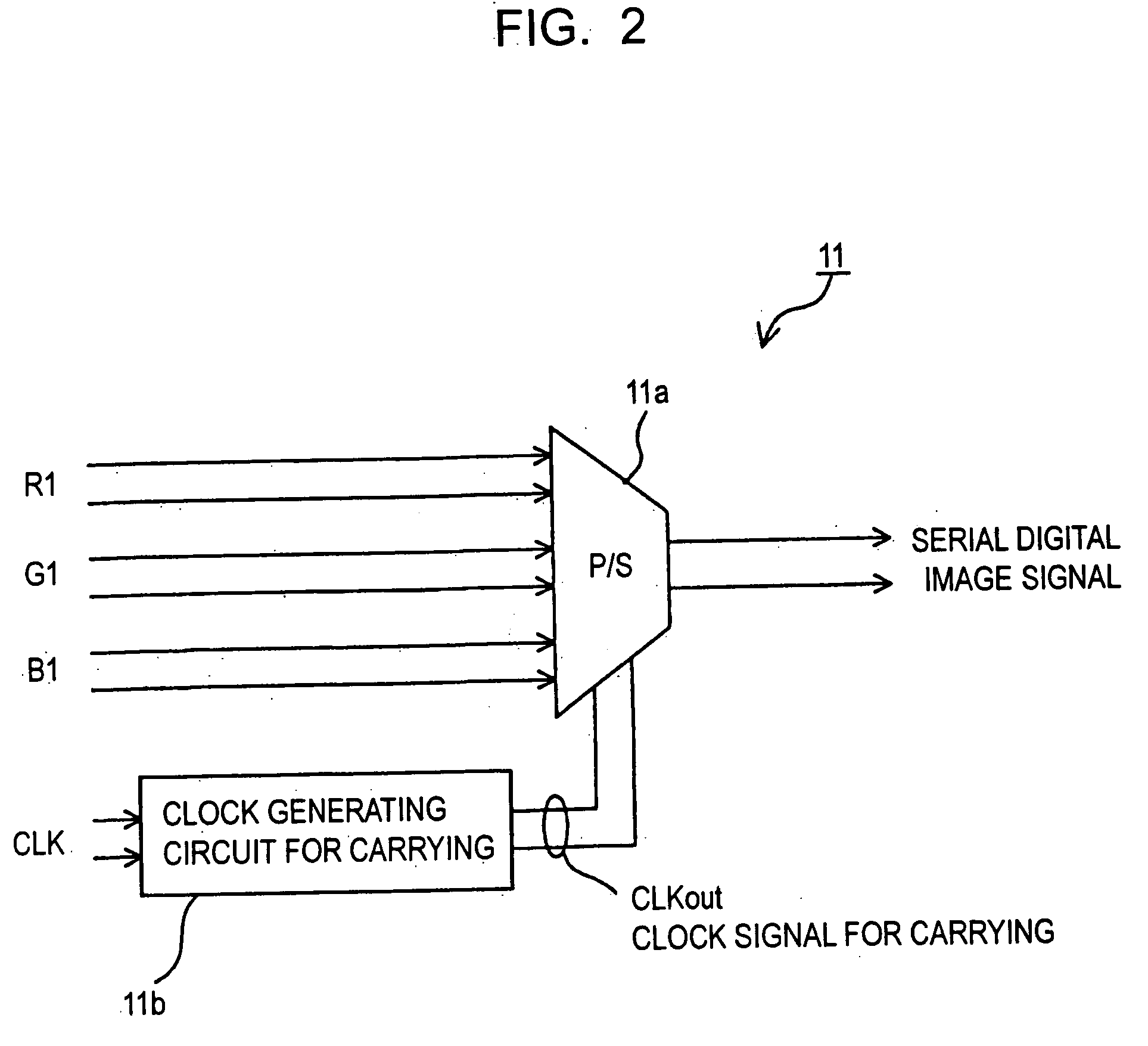
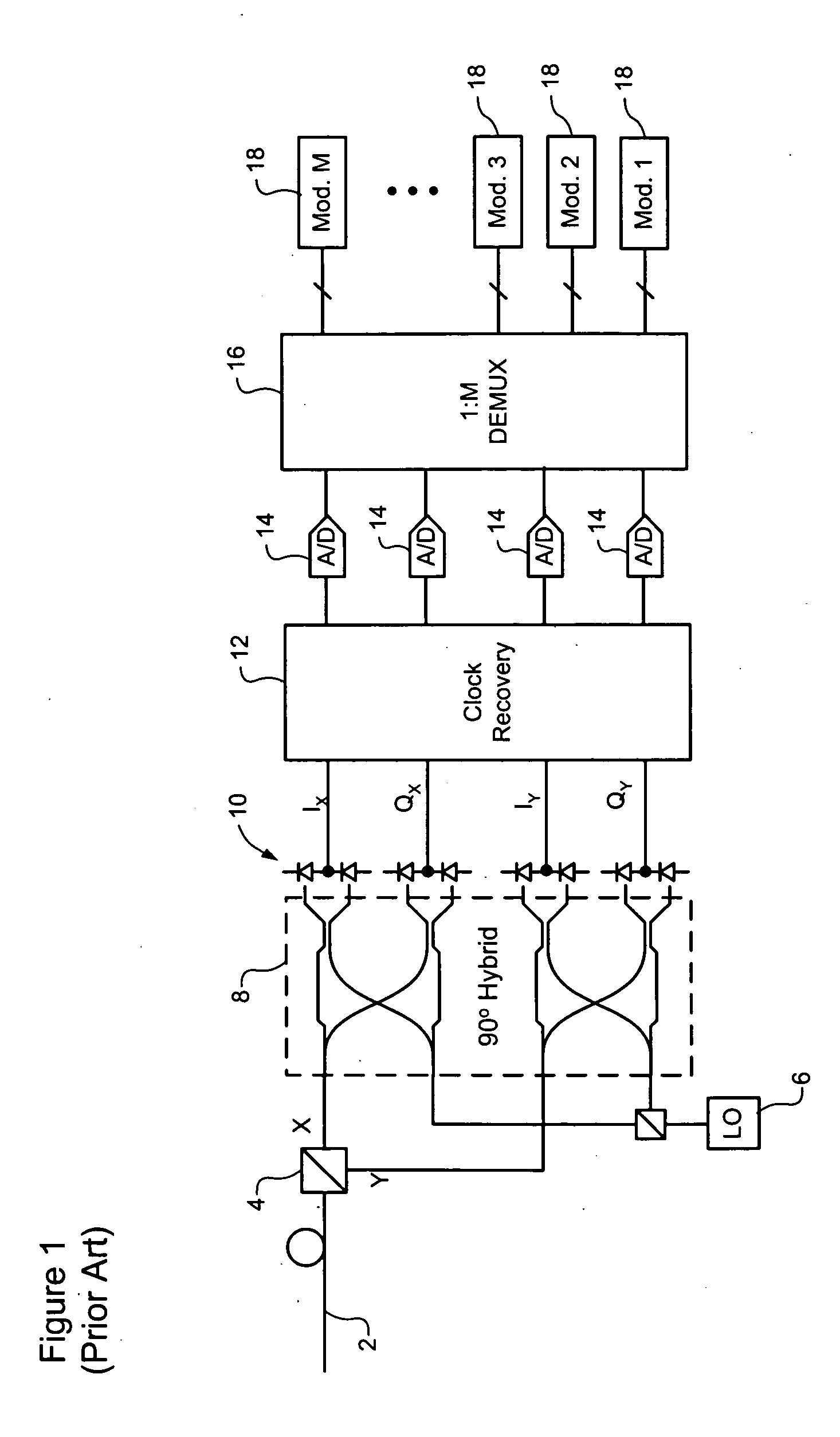
Method for transmitting digital image signal, digital image transmitting device, digital image sending device and digital image receiver
InactiveUS20050063707A1Quality improvementIncrease costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexerSignal on
A multiplexer of a transmission section generates a clock signal by multiplying a reference clock signal of a digital image signal by a predetermined number ‘K’. A parallel digital image signal is converted into a serial digital signal on the basis of the clock signal, and the serial digital signal is converted into an optical signal in an optical transmission section for transmitting. A demultiplexer extracts a reception clock signal from a serial digital reception signal which is converted into an electric signal in an optical reception section of a reception section, the serial digital reception signal is converted into a parallel signal and a signal corresponding to the parallel digital image signal on the basis of the reception clock signal, and a clock signal corresponding to the reference clock signal is recovered by multiplying the reception clock signal by ‘1 / K’.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Apparatus and method of compensating for compact digital domain chromatic dispersion
InactiveUS20090238578A1Reduce in quantitySave computing resourcesDistortion/dispersion eliminationFinite impulse responseDigital signal processing
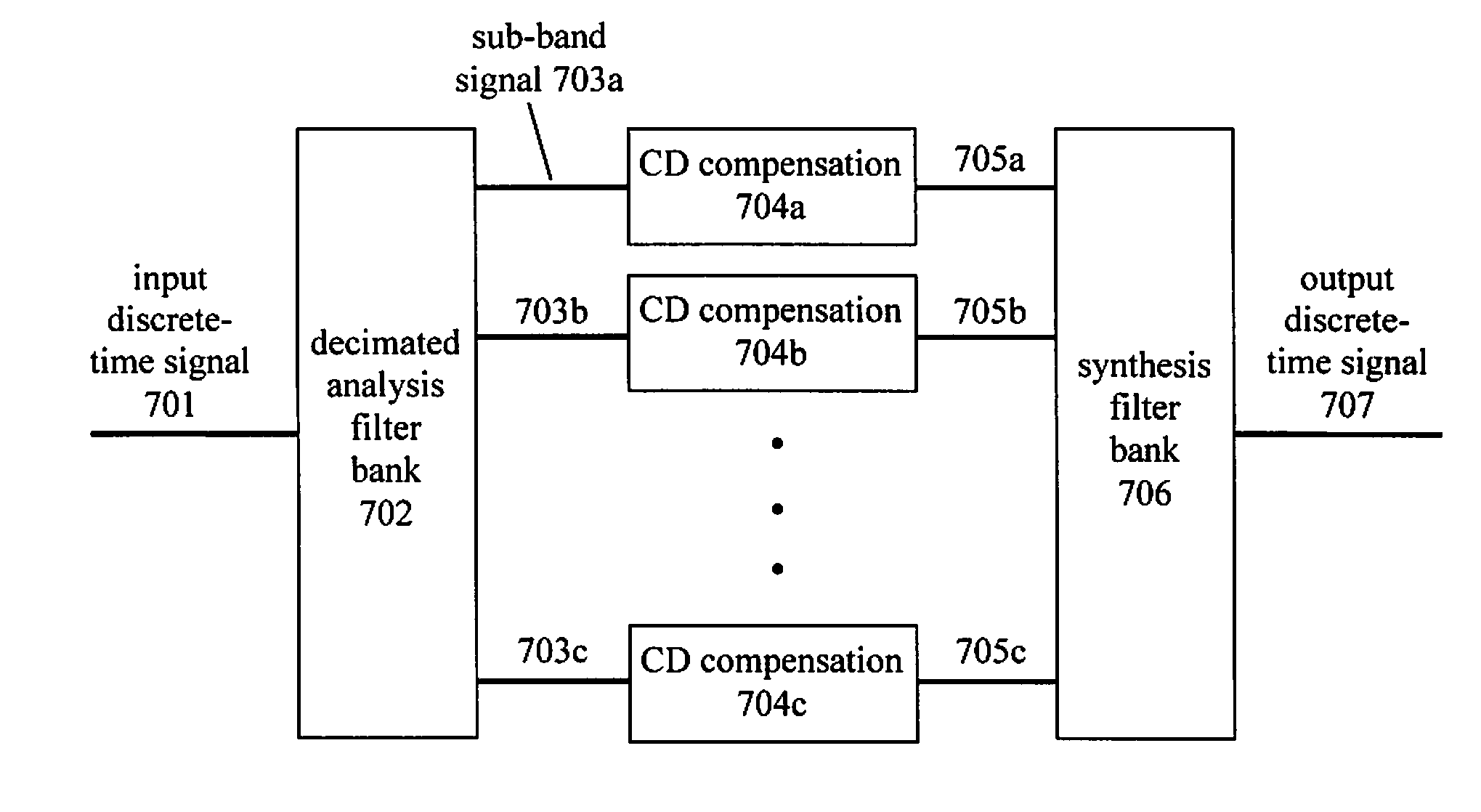
A method and apparatus of compensating for compact digital domain chromatic dispersion. The distortion of an optical signal due to chromatic dispersion is compensated by a digital signal processing in the electrical domain, either prior to the optical transmitter or following the receiver. The circular coefficient approximation and sub-band processing reduce the amount of computations to execute a given level of chromatic dispersion compensation compared to a direct finite impulse response filter implementation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical transmission device for bi-directional optical communication
InactiveUS6278536B1Low costWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringOptical communication
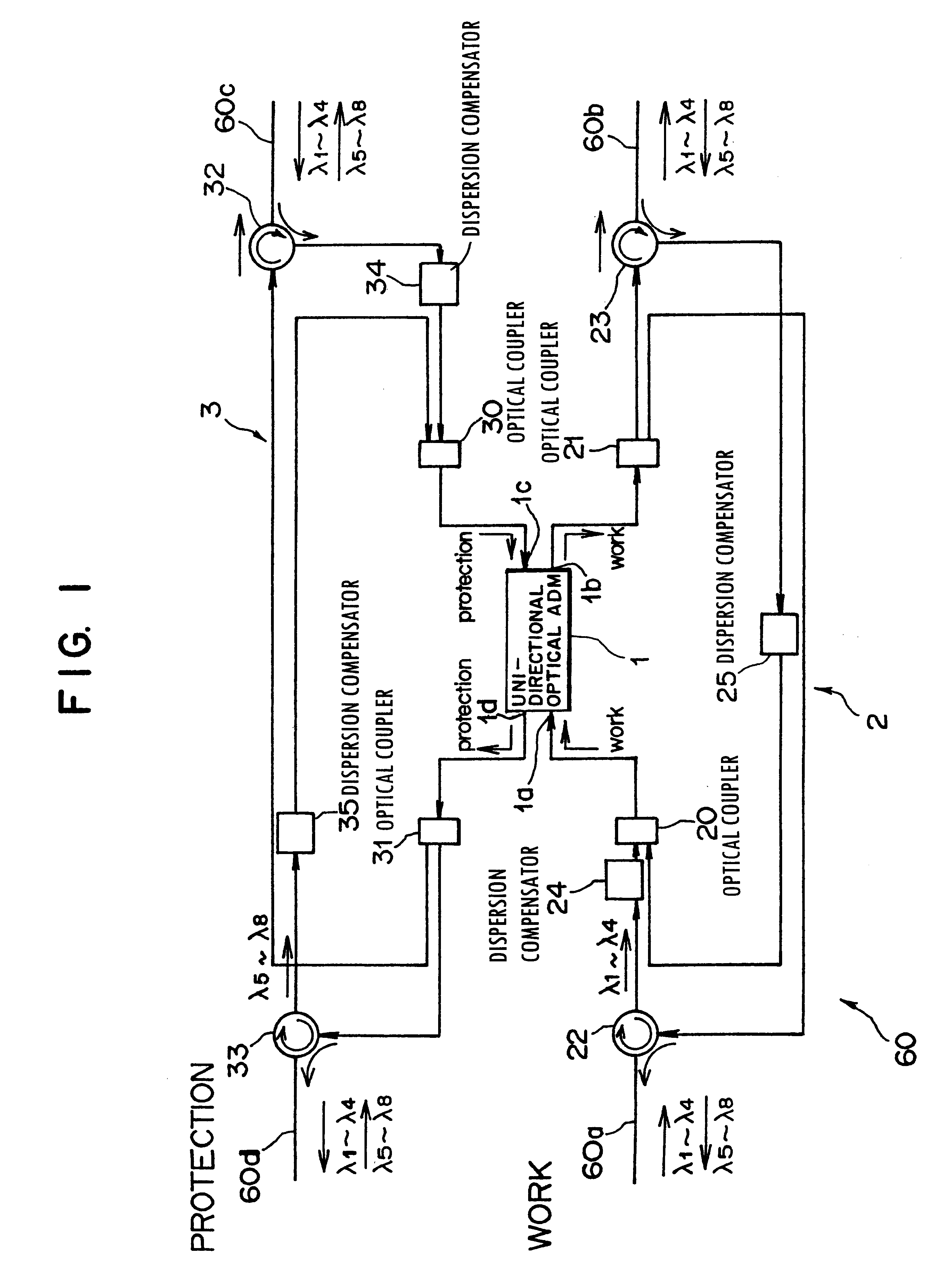
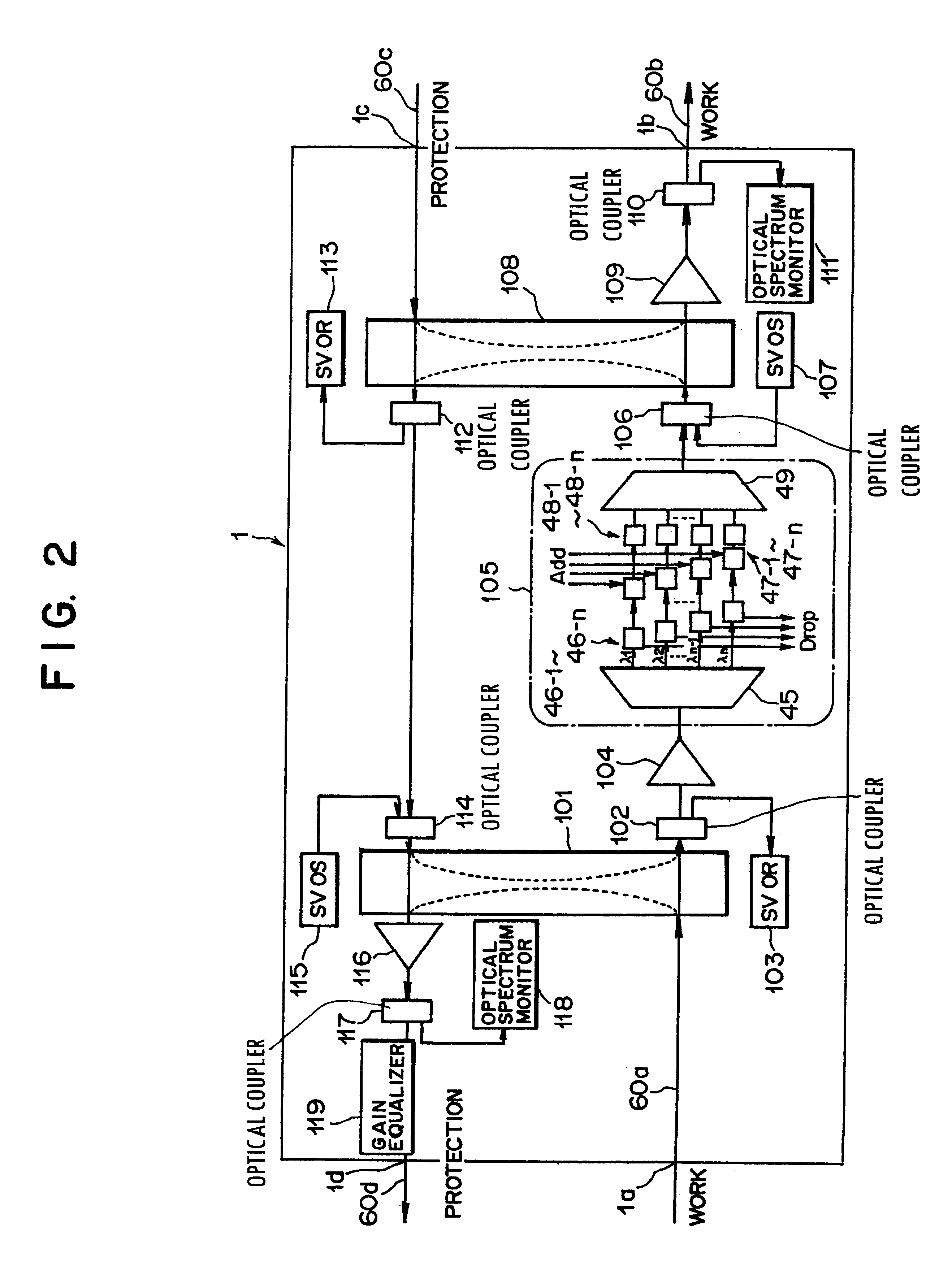
This invention discloses an optical transmission device used for bi-directional optical communications. The optical transmission device comprises a uni-directional optical signal processing unit for performing specified optical signal processing for optical signals transmitted in a single direction and a uni-direction / bi-direction changing unit for unifying the flows of clockwise and counterclockwise optical signals in a single direction, inputting these flow-unified optical signals to the uni-directional optical signal processing unit and dividing the flow of optical signals from the uni-directional optical signal processing unit between clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Bi-directional wavelength-division multiplexing optical communications can be performed by unifying the transmission routes (flows) of optical signals transmitted in two ways in a single direction and using the existing optical transmission device for uni-directional optical communications.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Equalization strategy for dual-polarization optical transport system
ActiveUS7315575B2Avoid convergencePrevent degradationMultiple-port networksError preventionDigital signal processingTransport system
Owner:CIENA
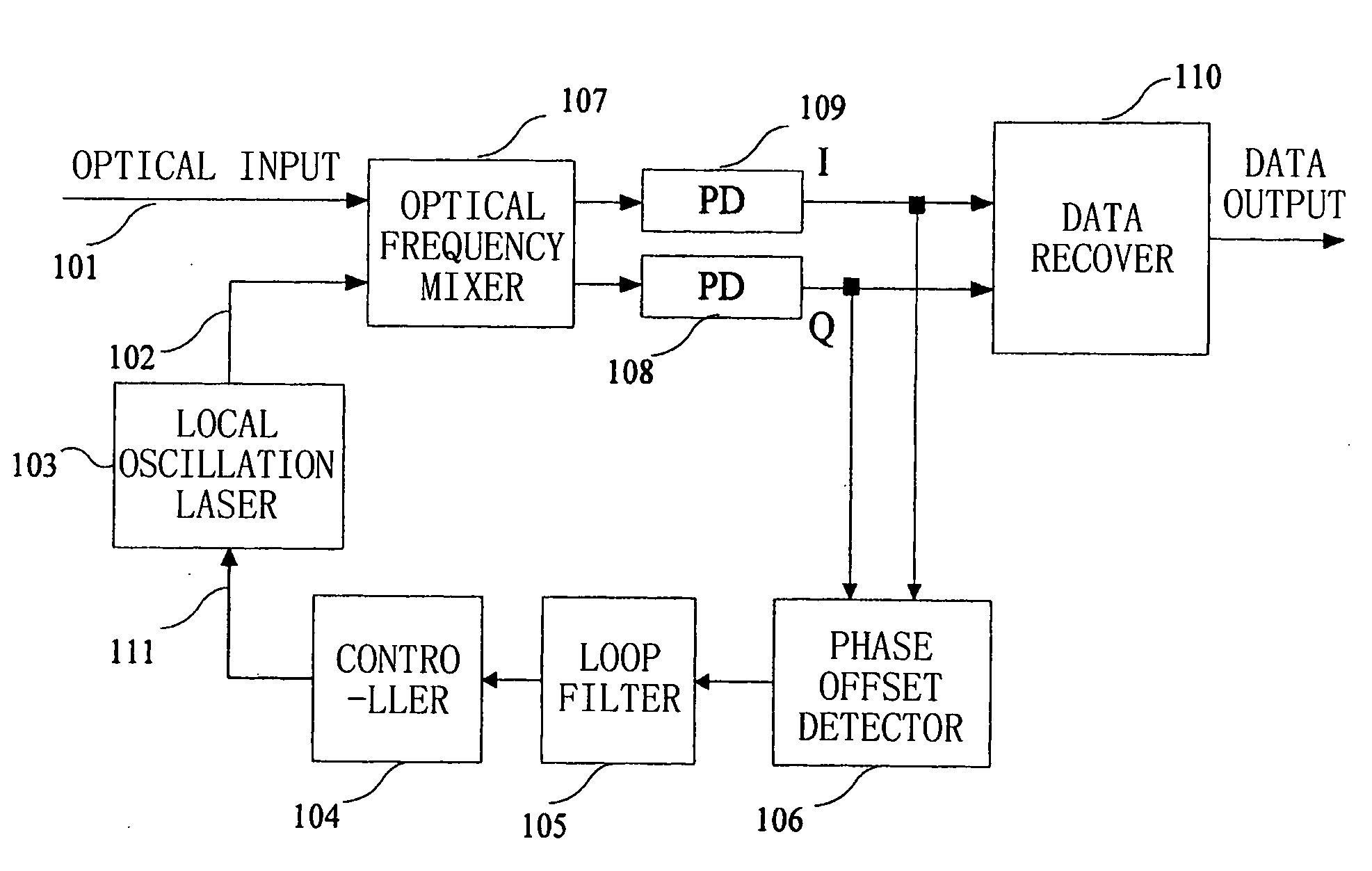
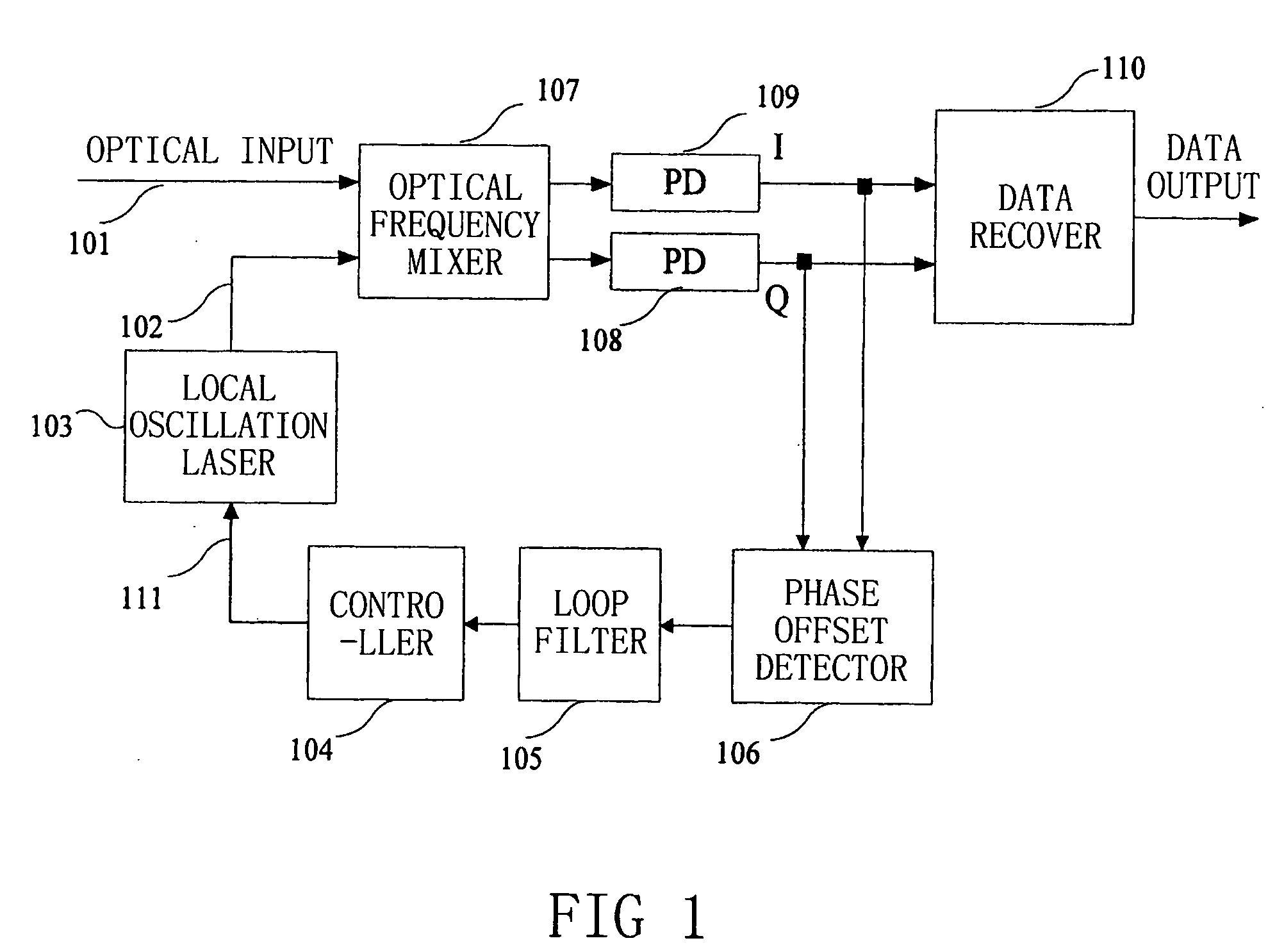
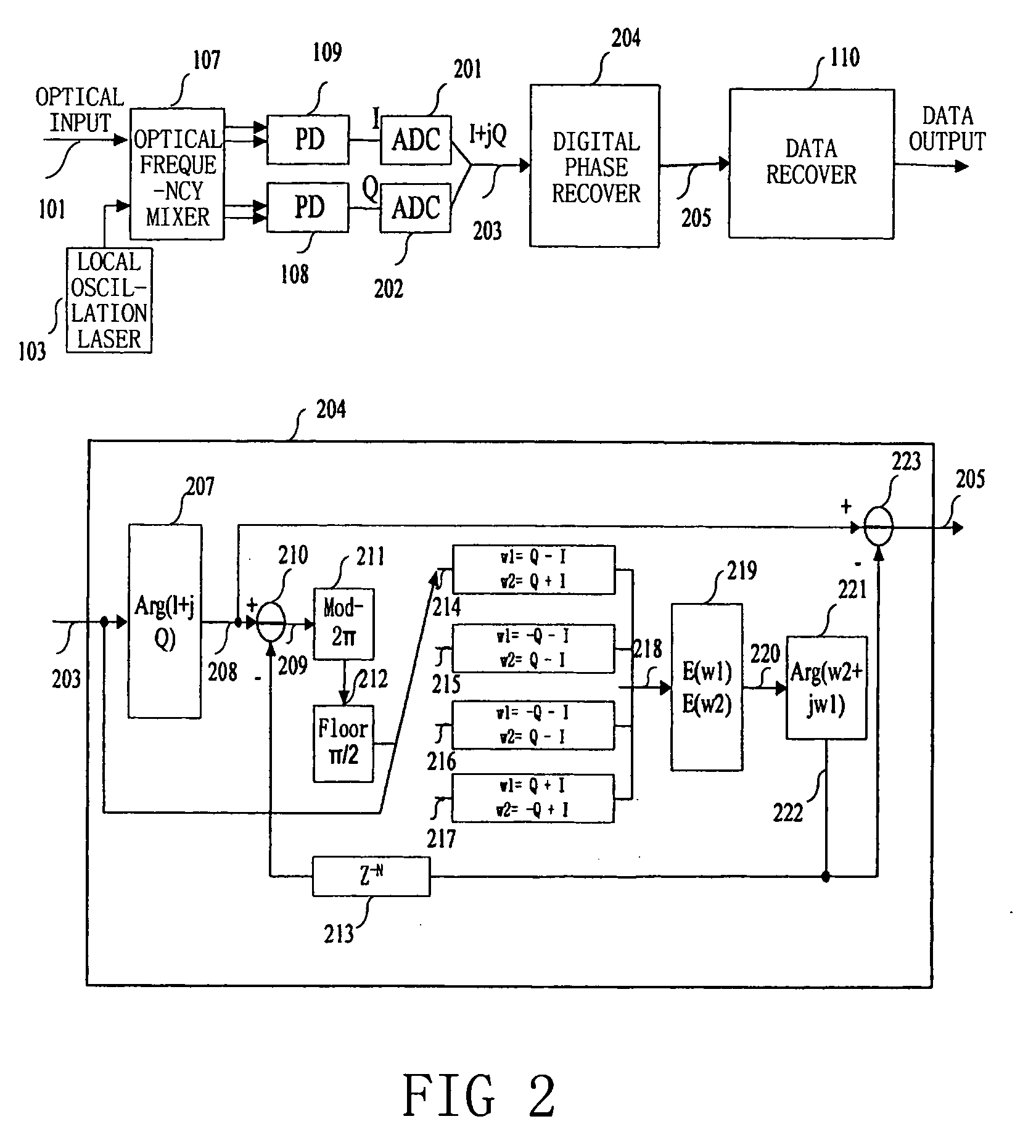
Frequency offset compensating apparatus and method, and optical coherent receiver
The present invention relates to a frequency offset compensating apparatus and method, and an optical coherent receiver. The optical coherent receiver includes a front end processor and a frequency offset estimator, of which said front end processor converts an inputted optical signal into a base band digital electric signal, and said frequency offset estimator estimates a phase offset change introduced by a frequency offset in said base band digital electric signal; said frequency offset compensating apparatus comprises an M output integrator, for integrating the phase offset change introduced by the frequency offset to acquire M inverse numbers of the phase offset introduced by the frequency offset, where M is an integer greater than 1; a series-parallel converting device, for dividing said base band digital electric signal into M sub base band digital electric signals; M complex multipliers, for constructing the corresponding inverse numbers in the M inverse numbers to be complex numbers, and multiplying them with the corresponding sub base band digital electric signals in the M sub base band digital electric signals; and a parallel-series converting device, for converting the M sub base band digital electric signals multiplied by said complex multipliers into a base band electric signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Characterization and control of optical dispersion compensating element
ActiveUS20050147415A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationEngineeringOptical communication
An apparatus and method are applied to characterizing an dispersion-affecting element for use in controlling chromatic dispersion in an optical communications link. Information regarding the behavior of the dispersion-affecting element is recorded and stored in a medium that is provided for deployment with the dispersion-affecting element to enable improved management and active control of the dispersion-affecting element. The suitability of the dispersion-affecting element for operating under different conditions may also be characterized.
Owner:CIENA
Optical communication system incorporating automatic dispersion compensation modules
InactiveUS6370300B1Improve system performanceWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesGratingData integrity
In accordance with the invention, an optical communication system is provided with one or more automatic dispersion compensation modules. Each module has an adjustable dispersion element, a data integrity monitor and a feedback network whereby the monitor adjusts the dispersion element to optimize system performance. In a preferred embodiment the dispersion compensating modules comprise chirped fiber Bragg gratings in which the chirp is induced in the grating by passing a current along distributed thin film heaters deposited along the length of the fiber. The magnitude of the applied current determines the dispersion of the grating. A data integrity monitor is configured to sense the integrity of transmitted data and to provide electrical feedback for controlling the current applied to the grating.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
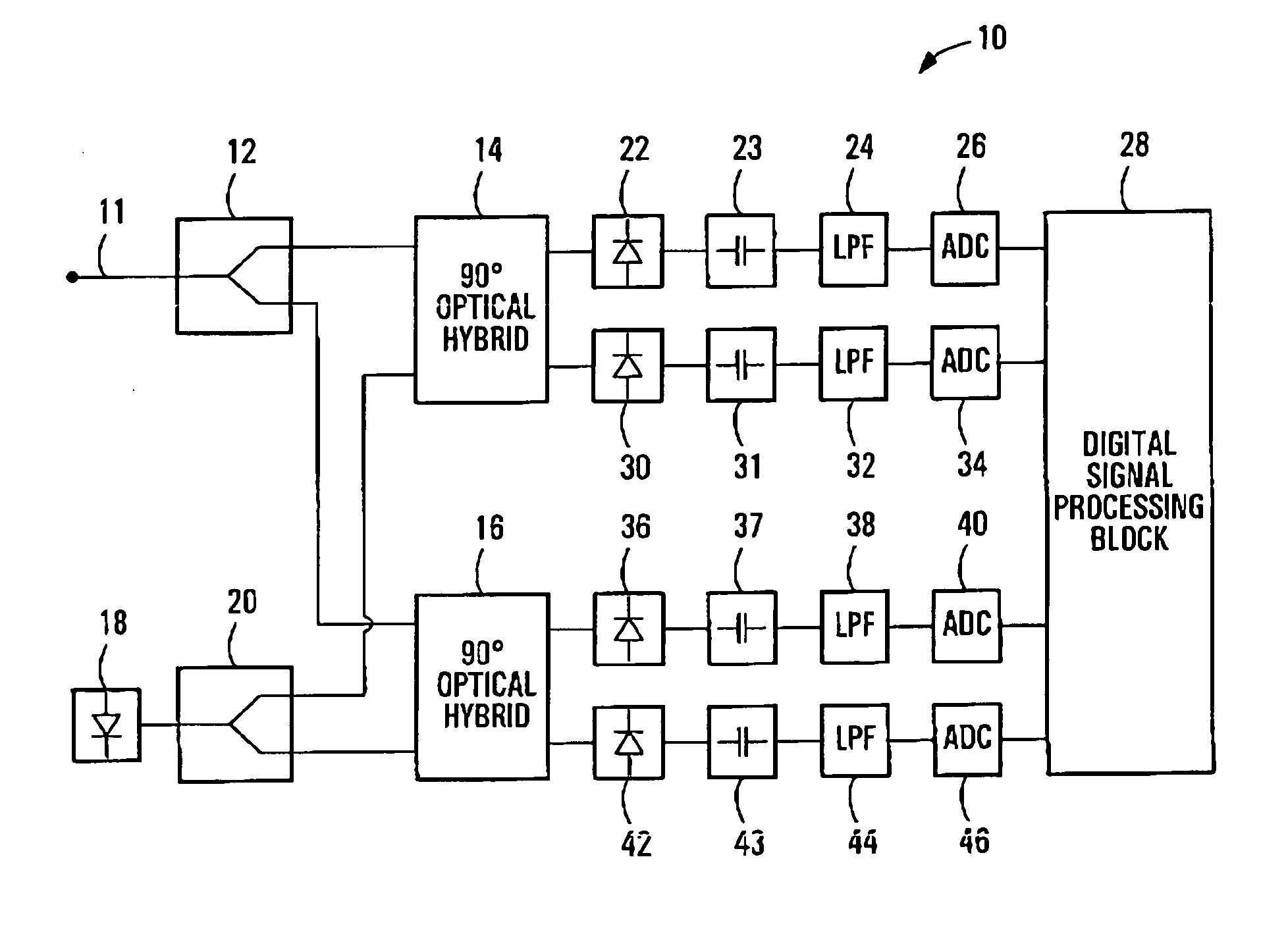
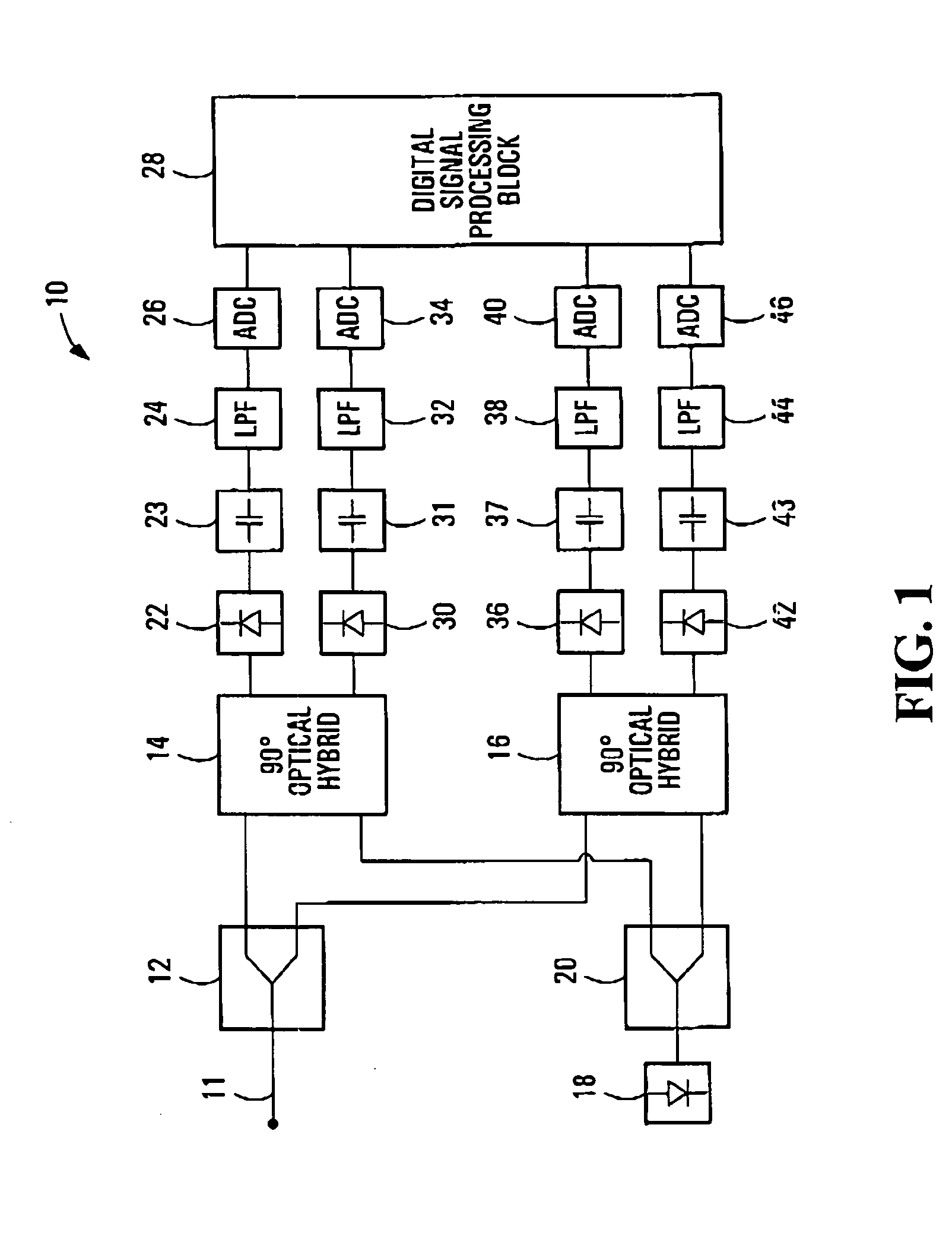
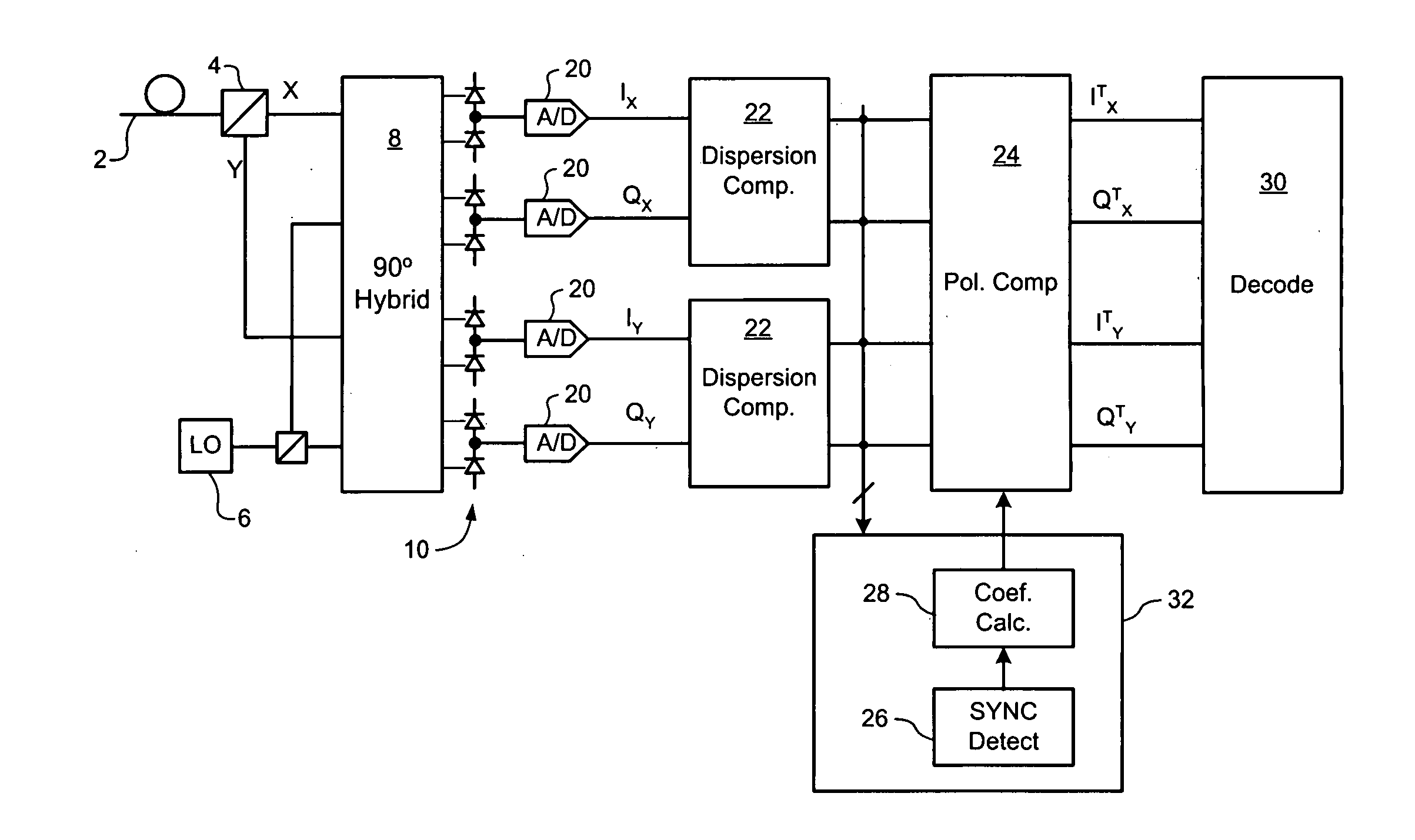
Polarization compensation in a coherent optical receiver
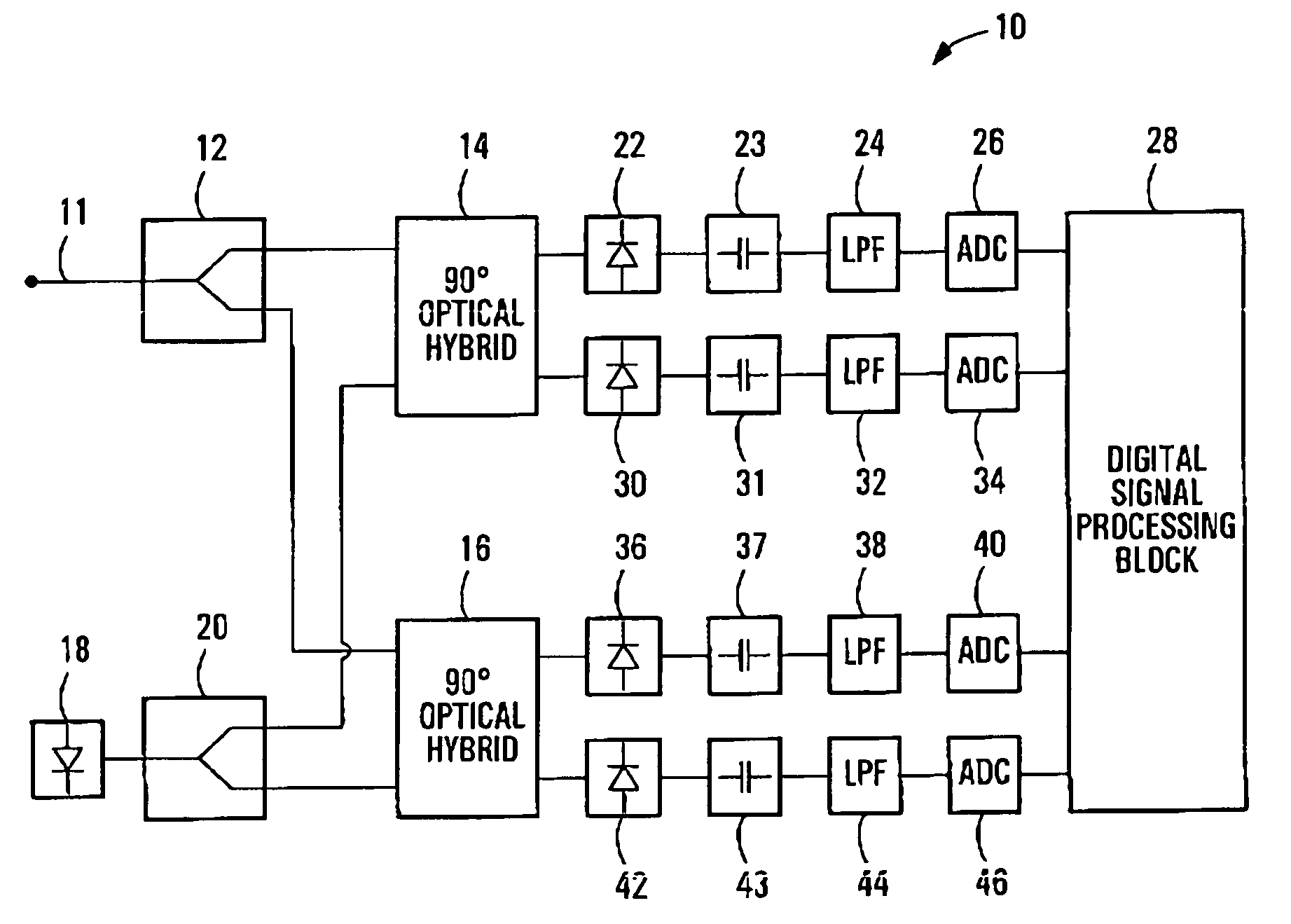
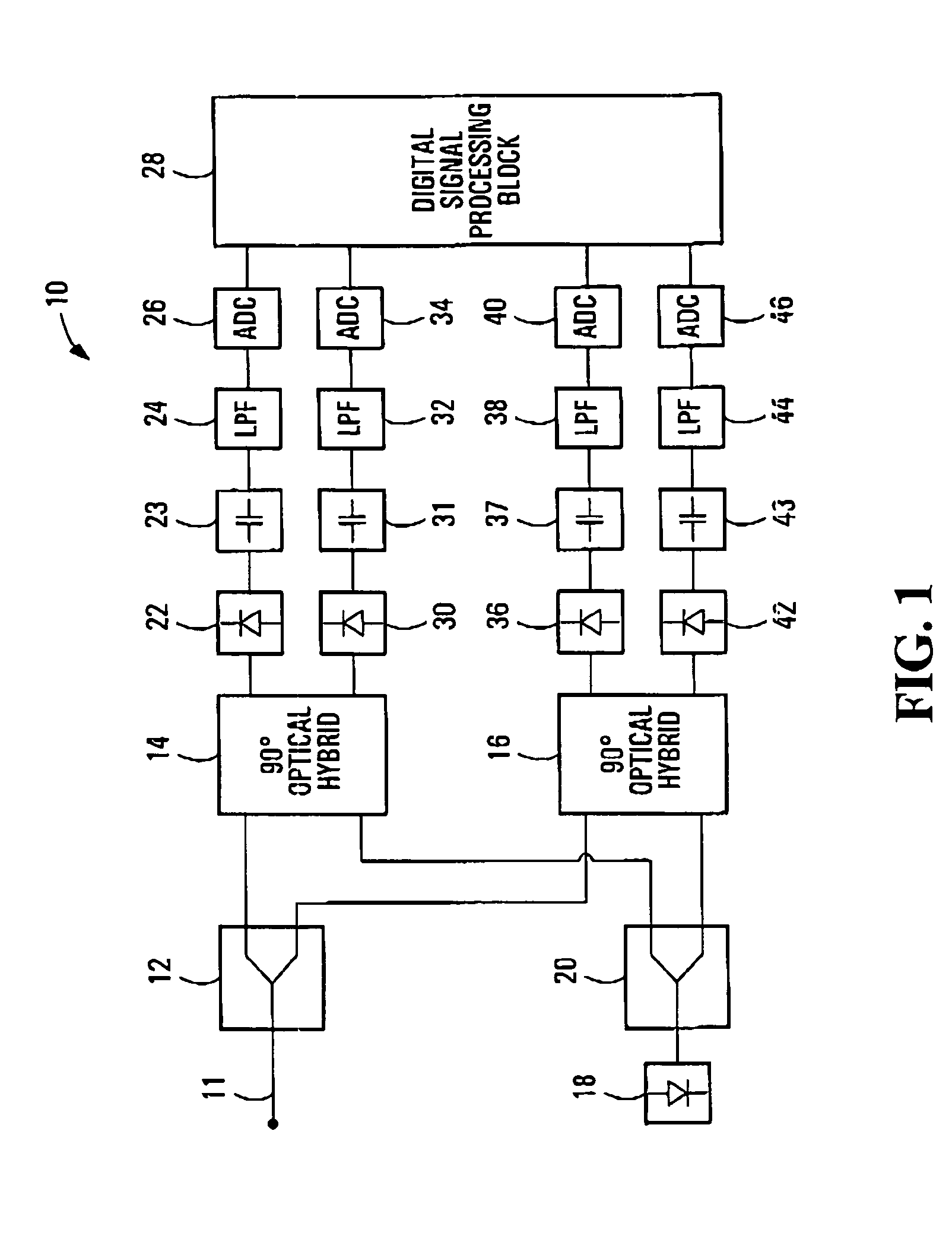
ActiveUS20070092259A1Polarisation multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationPolarization dependentOptical receivers
A method of processing a stream of digital samples of an optical signal received by a coherent optical receiver. The digital sample stream is processed to generate a dispersion compensated sample stream. The dispersion compensated sample stream is then processed to compensate polarization dependent impairments of the optical signal.
Owner:CIENA
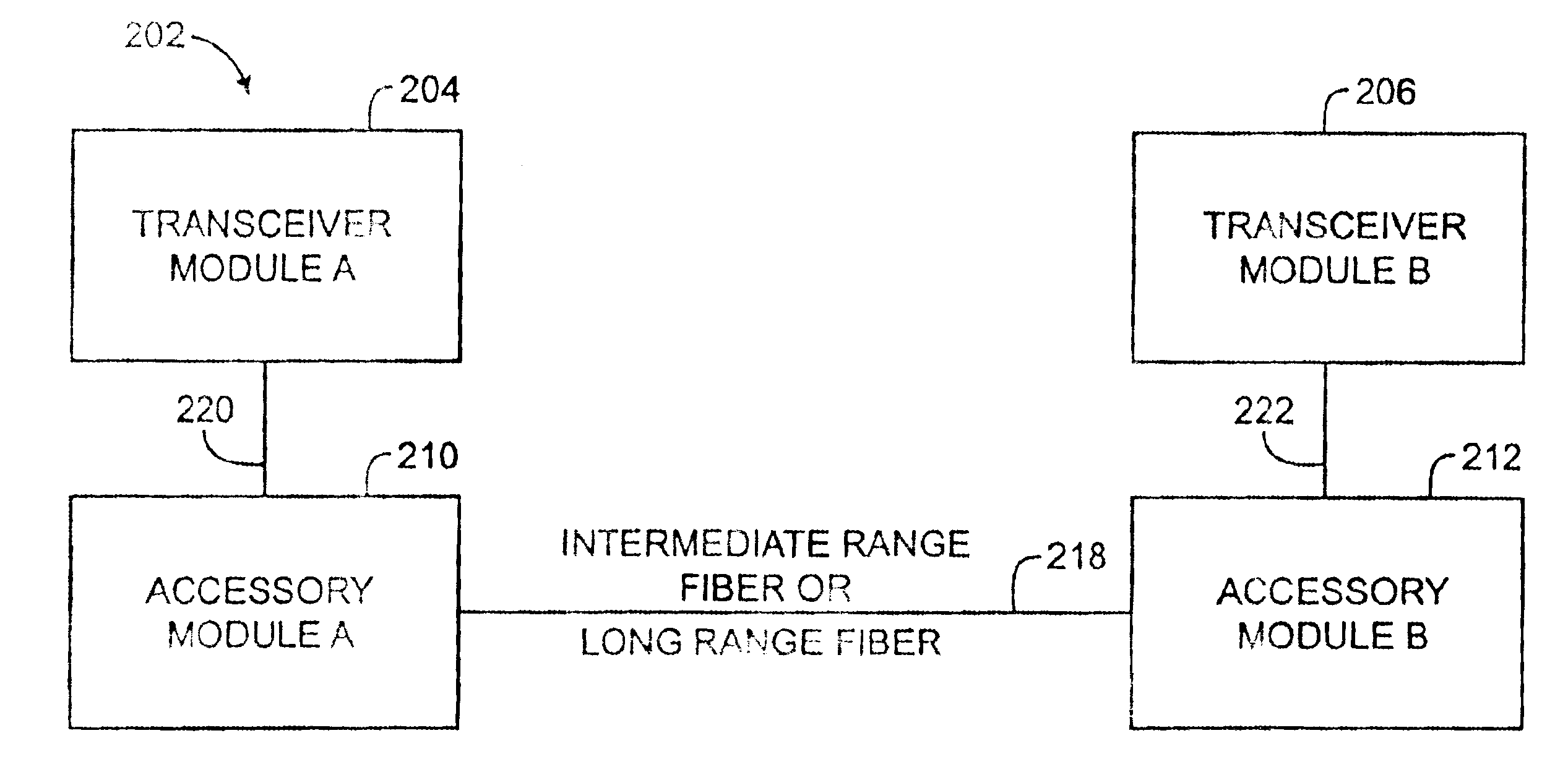
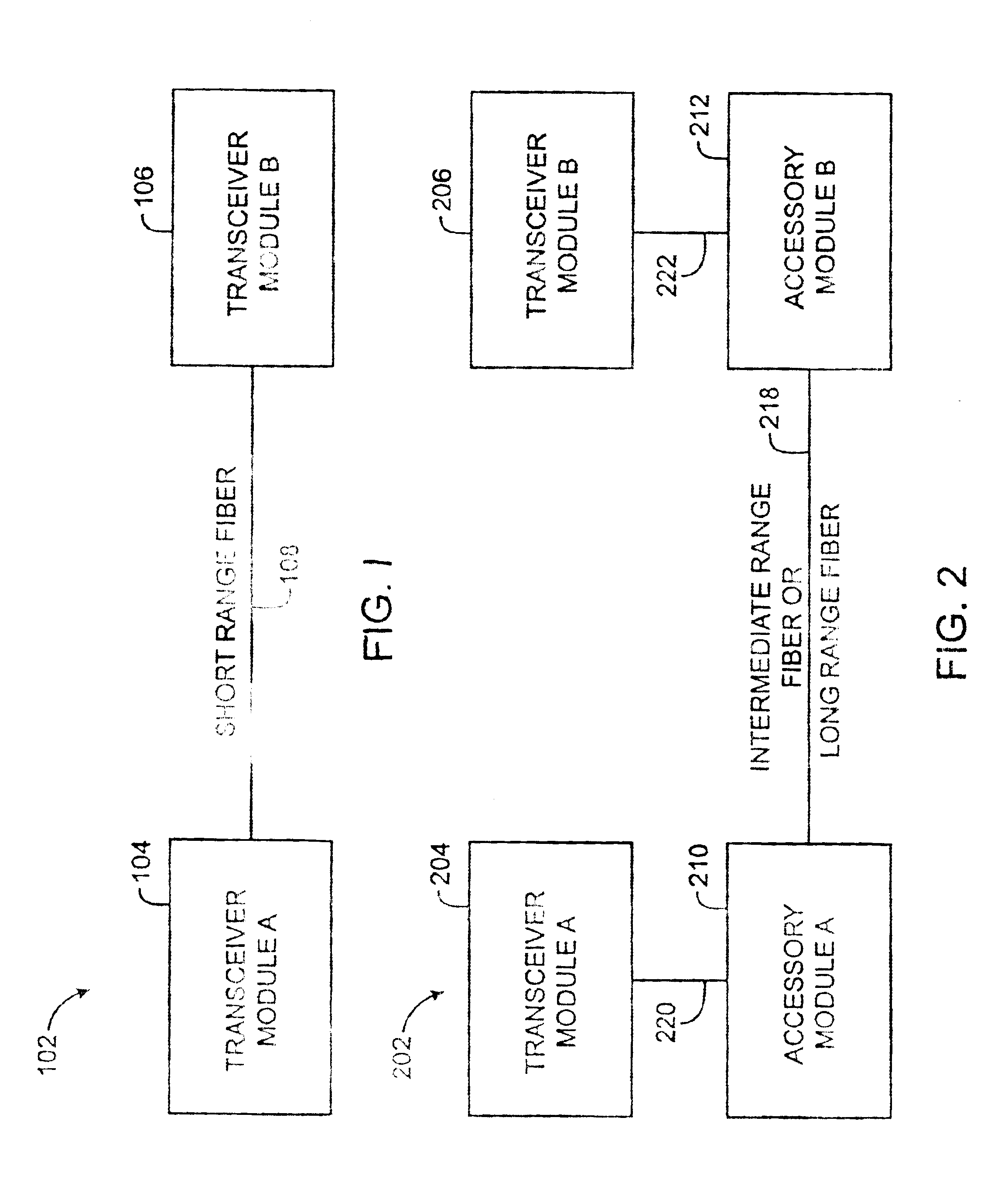
Modular transceiver and accessory system for use in an optical network
A modularized network component system that includes a transceiver module and a separate accessory module, and enables the transmissions range of the transceiver module to be augmented by the accessory module, is disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an optical network includes a fiber, a first device, and a second device. The first and second devices are coupled to the fiber such that the second device is in communication with the first device through the fiber. The second device includes a first modular subsystem that is arranged both to transmit data and to receive data through the fiber. The first modular subsystem is substantially physically decoupleable from the second device and from the fiber such that the first modular subsystem may be readily replaced within the second device by another modular subsystem.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
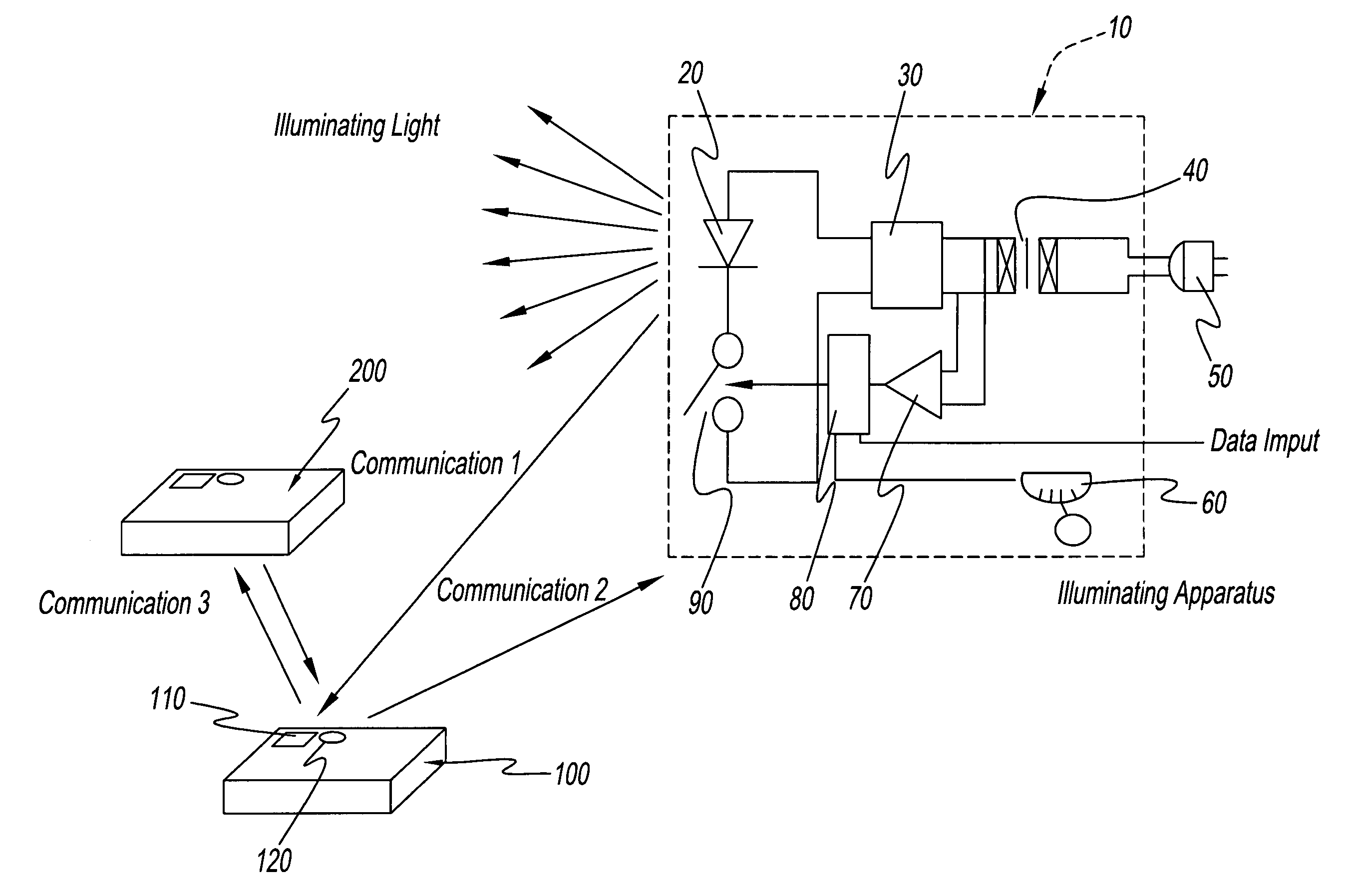
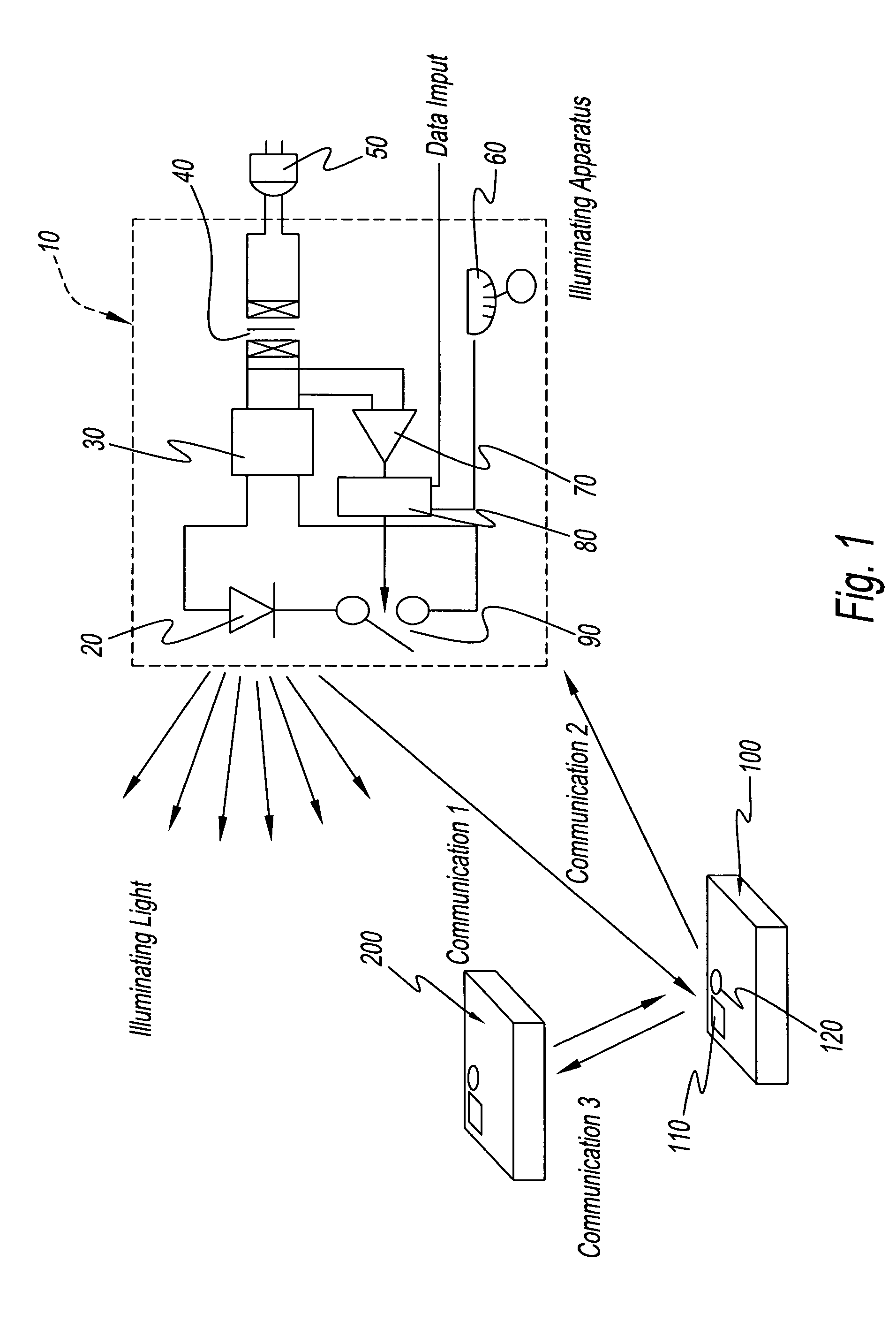
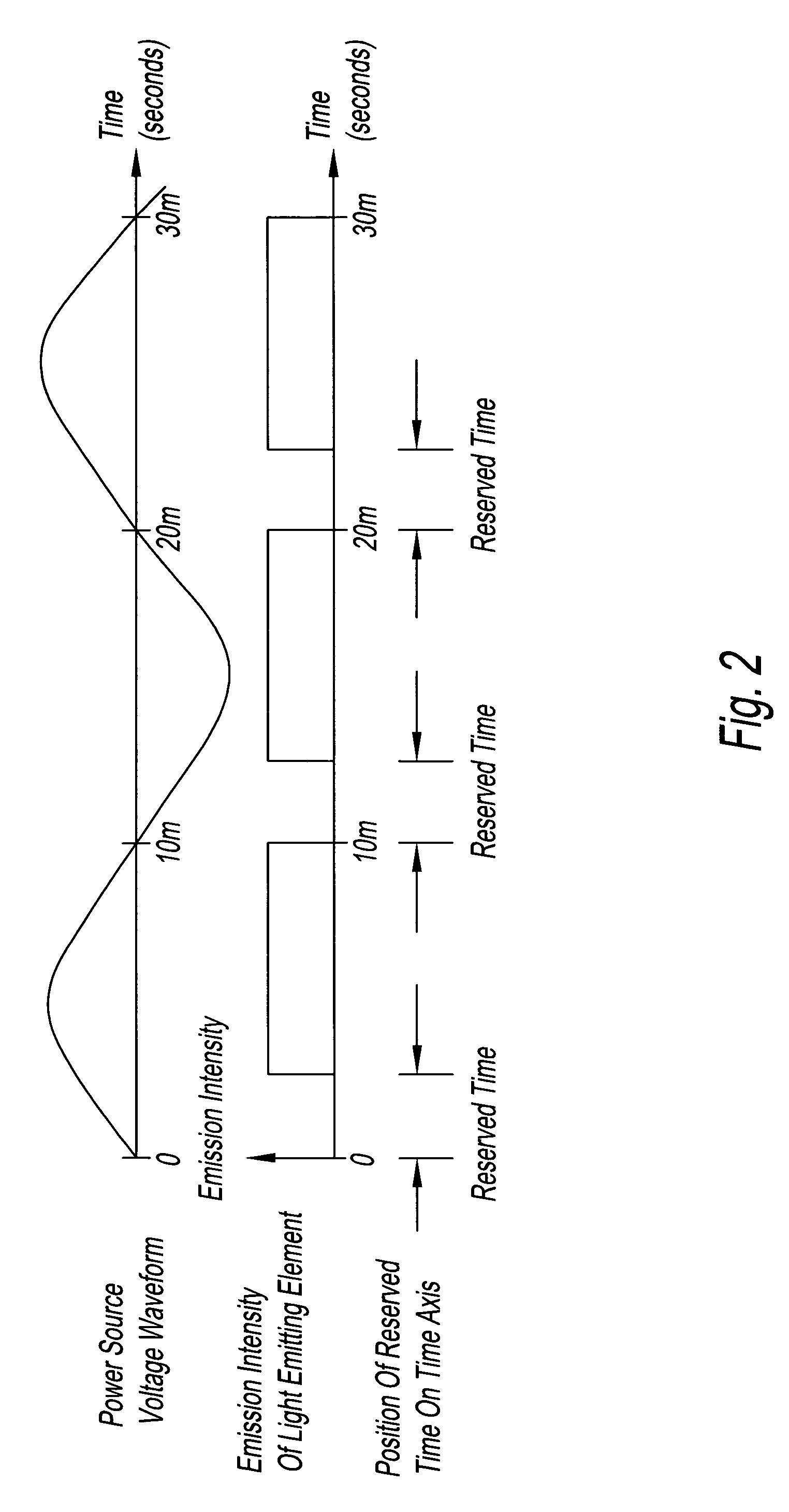
Light communication system and illumination apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7548698B2Light communication of lightLight type of lightTime-division optical multiplex systemsPower distribution line transmissionElectricityCommunications system
An illumination apparatus is used in the light communication system. The apparatus receives electricity from a commercial alternating-current power source and a light-emitting element in the apparatus emits light. The zero passage time of commercial alternating-current power source is detected and signals are transmitted from illumination apparatus, or intercommunications between terminals of communication equipment take place, during a specific reserved time that is in synchronization with this zero passage time.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com