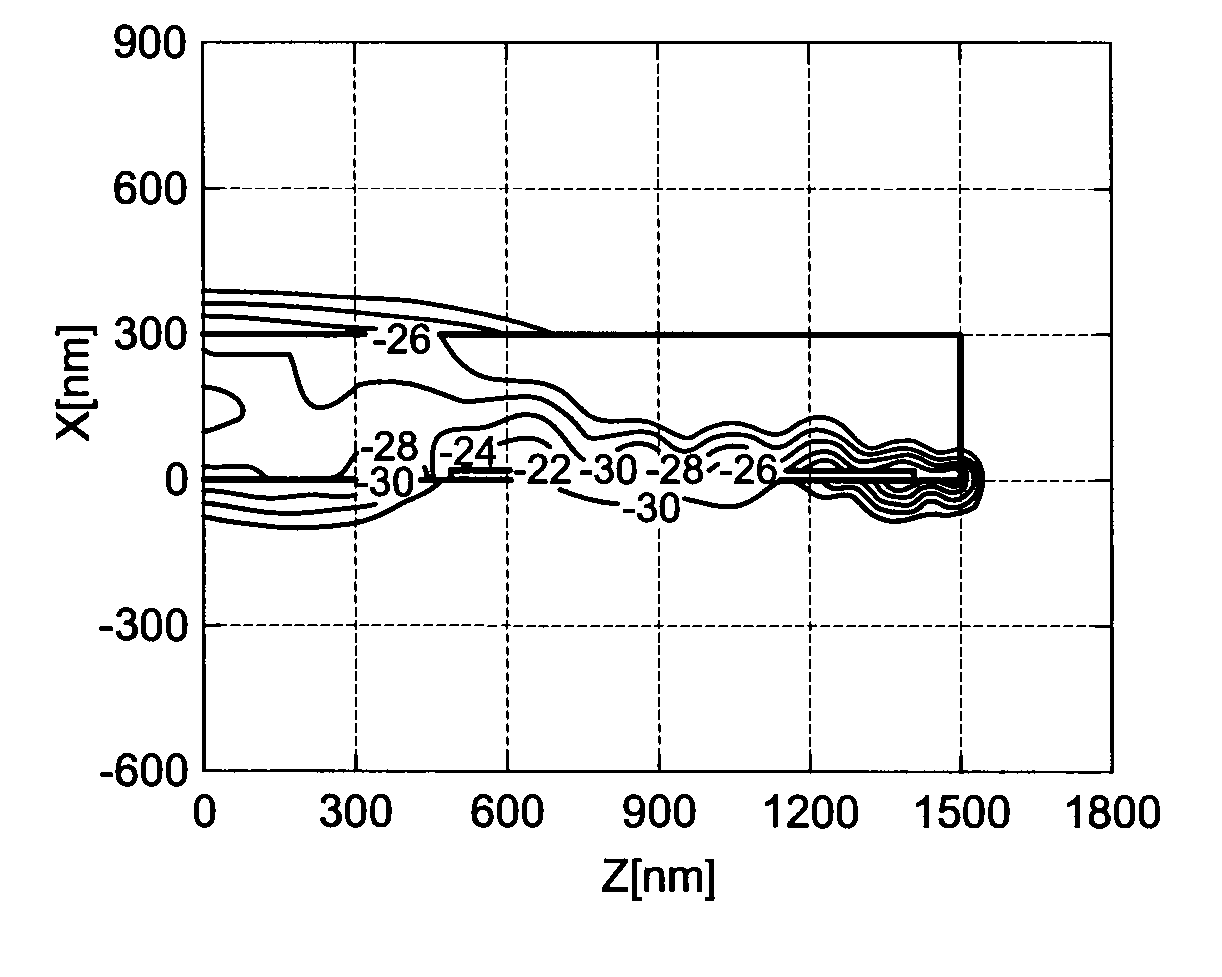
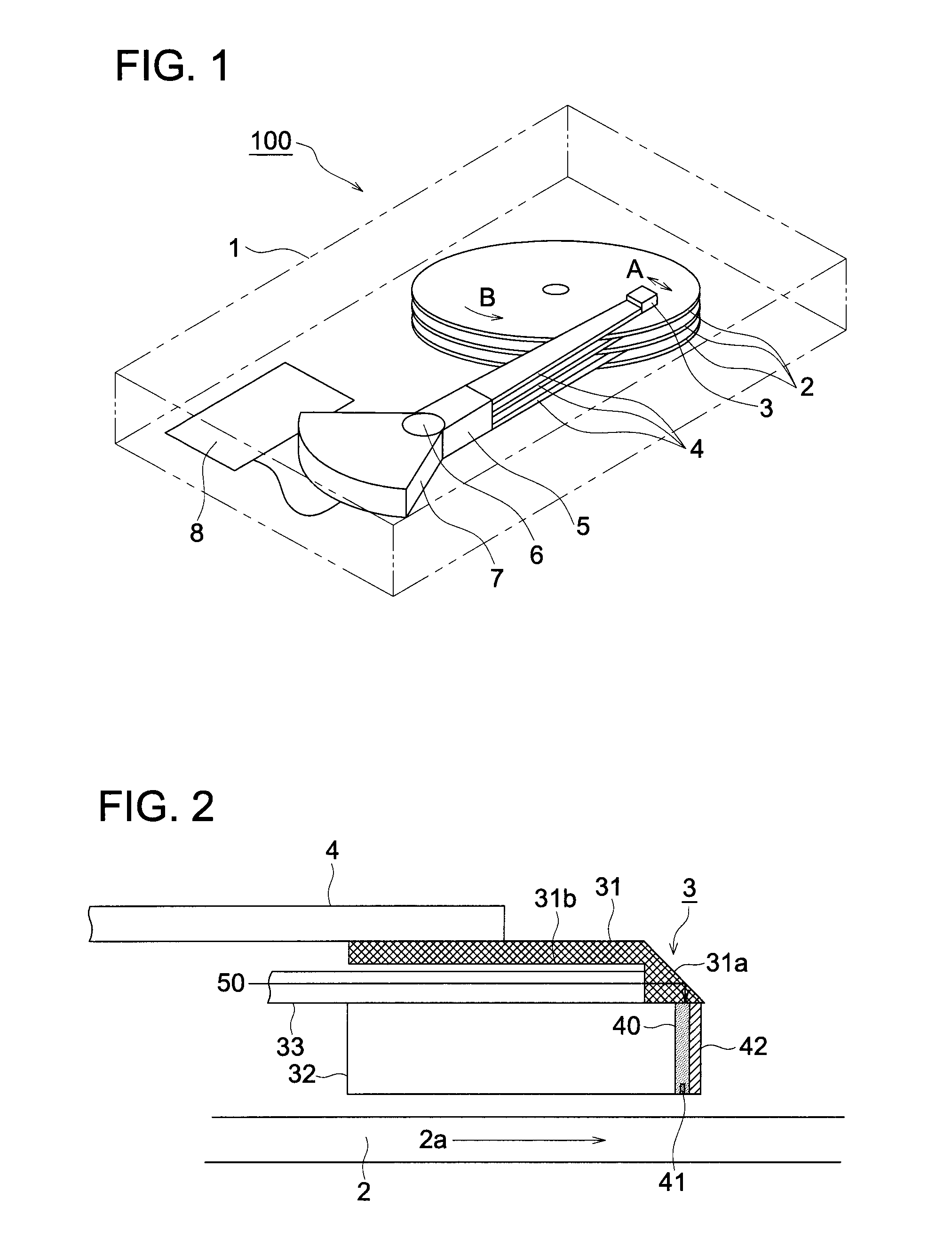
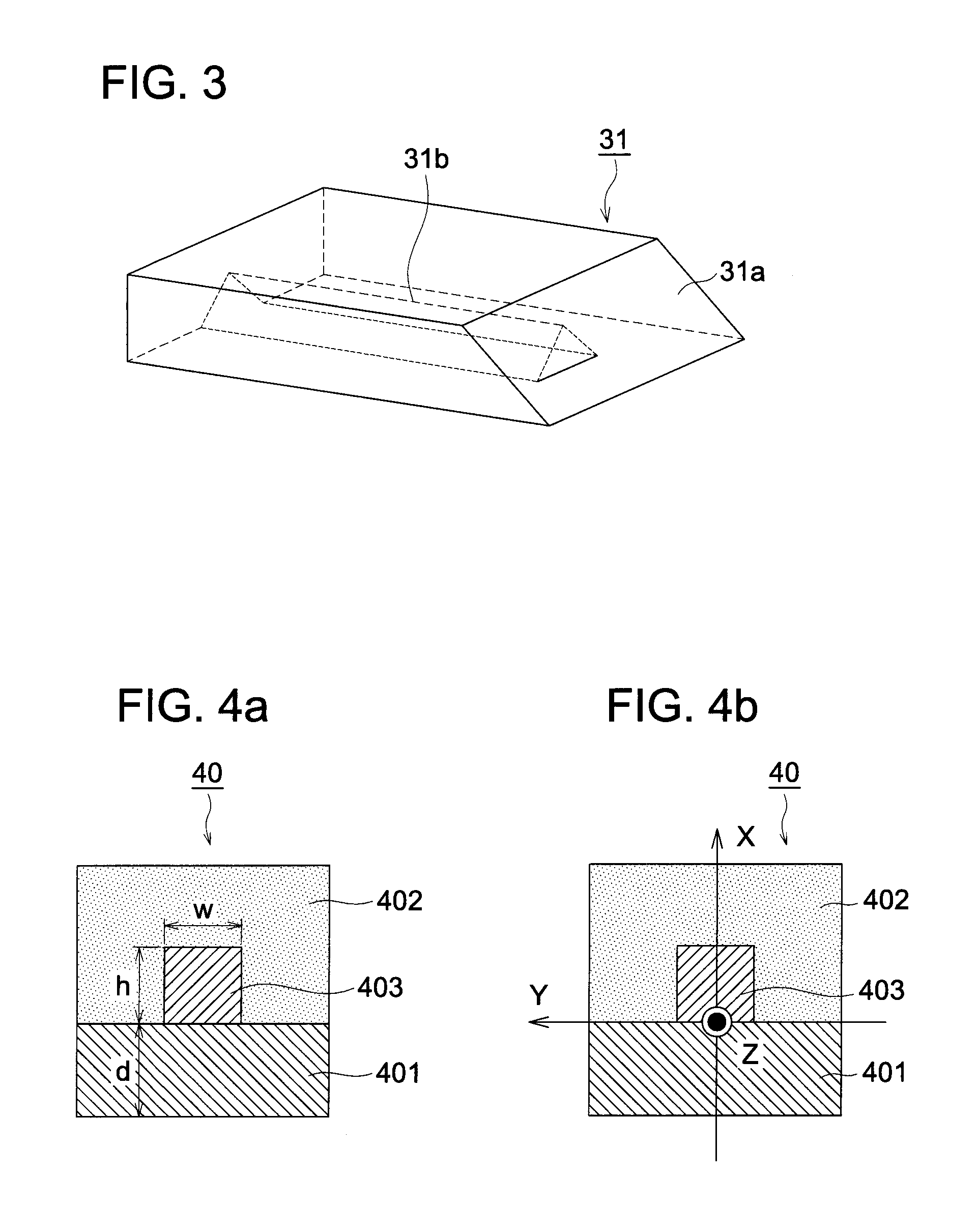
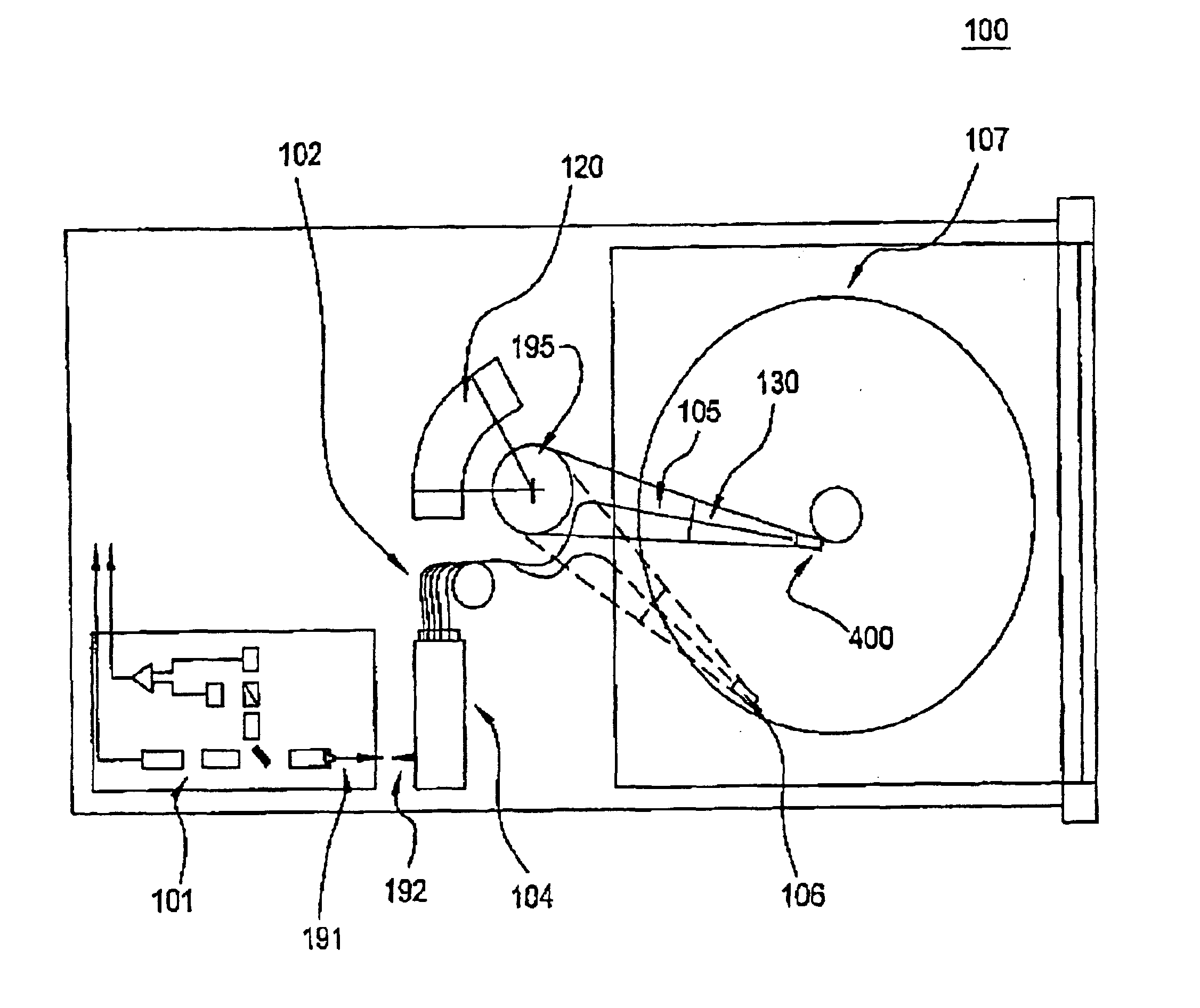
Patents
Literature
181results about "Optical flying-type heads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
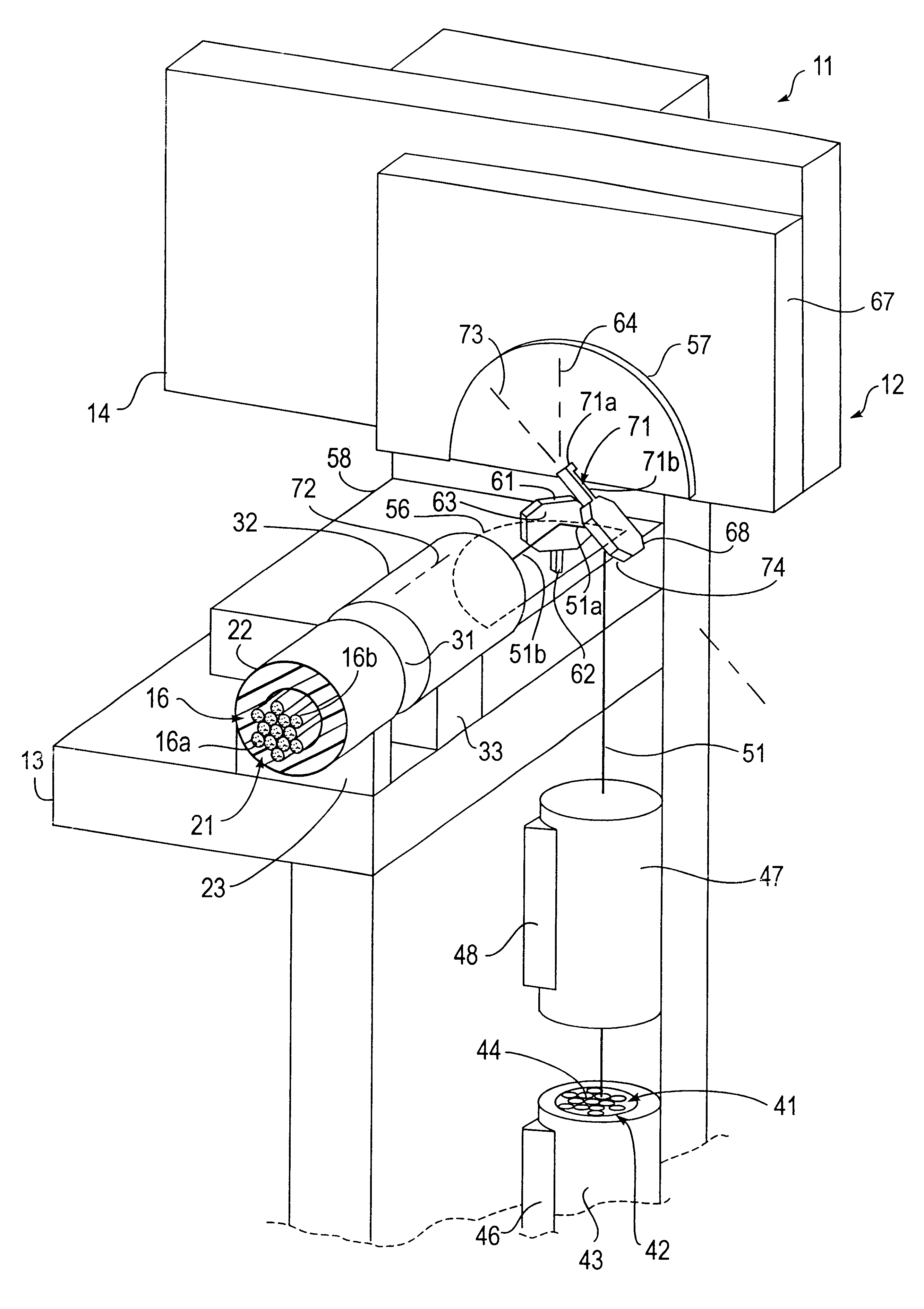
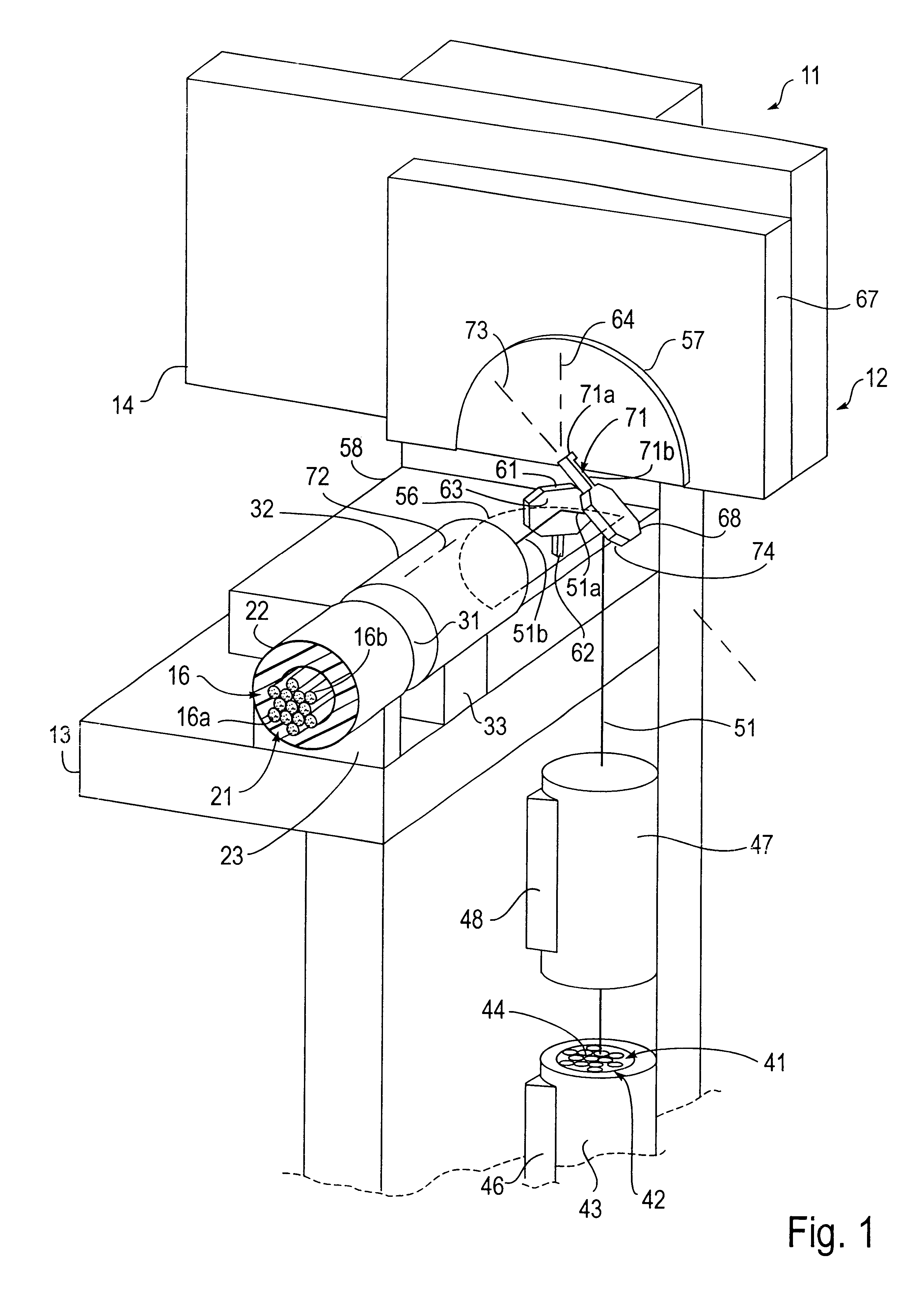
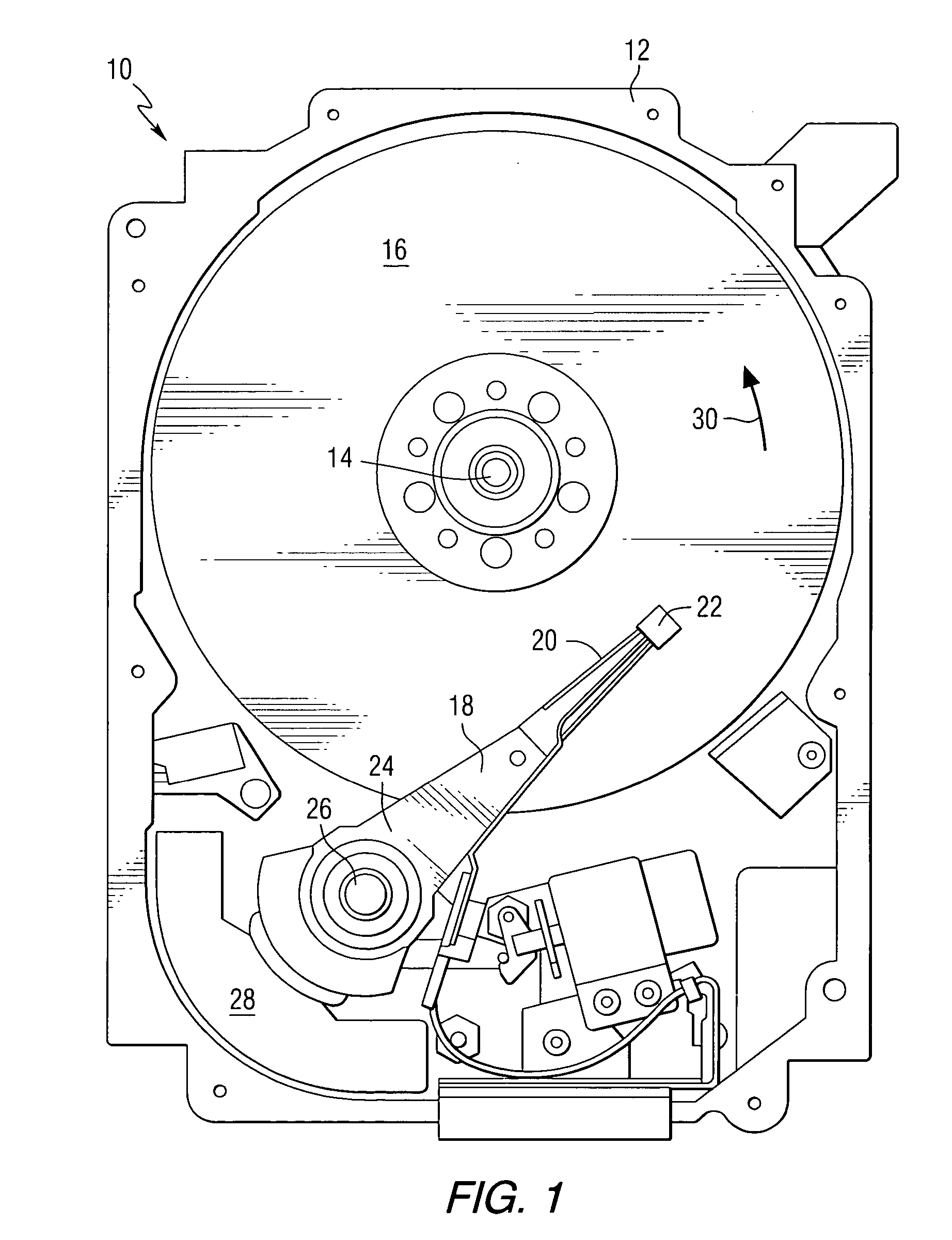
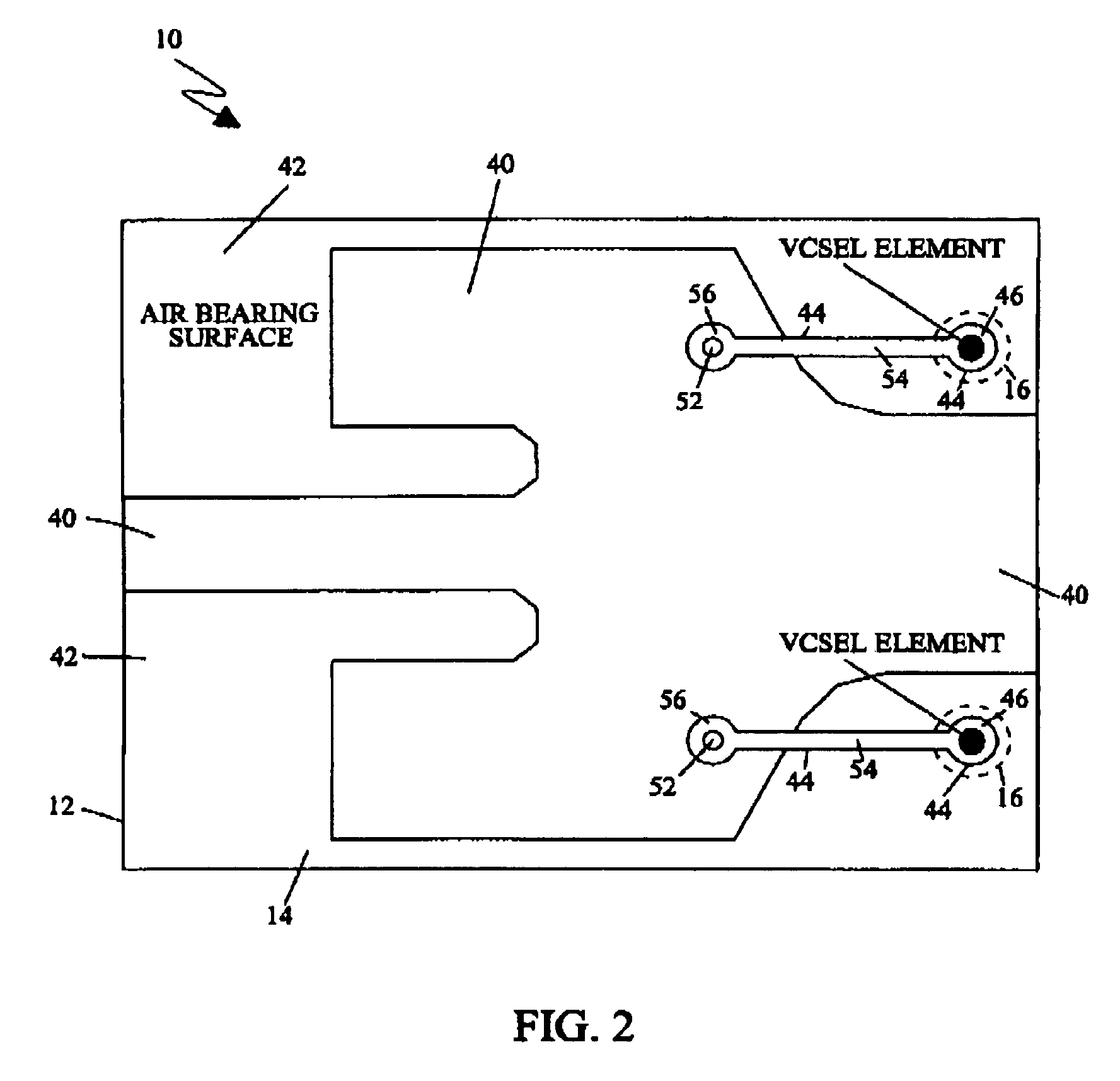
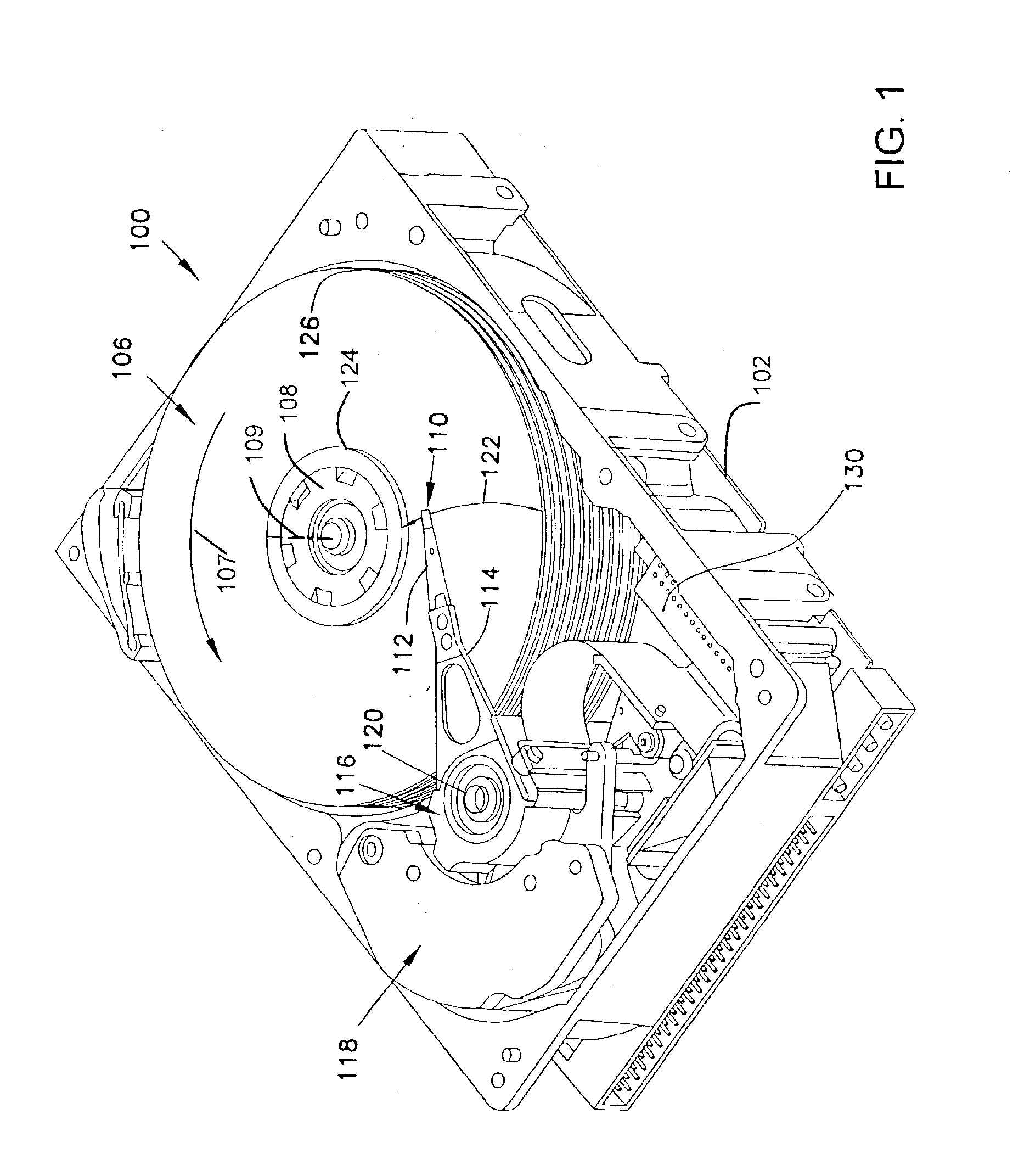
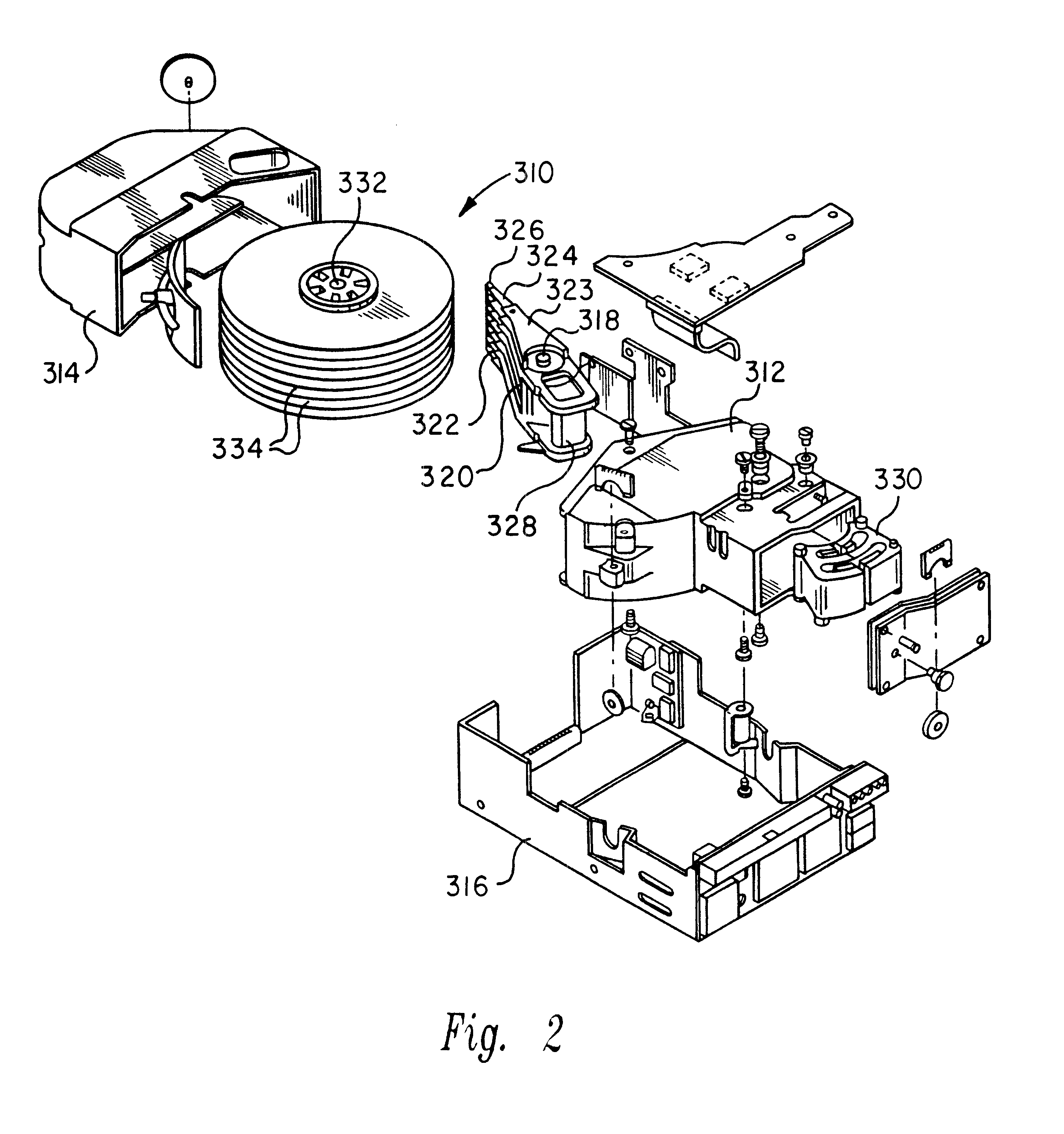
Data storage system having an optical processing flying head
InactiveUS6781927B1Low costOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesDigital dataData information
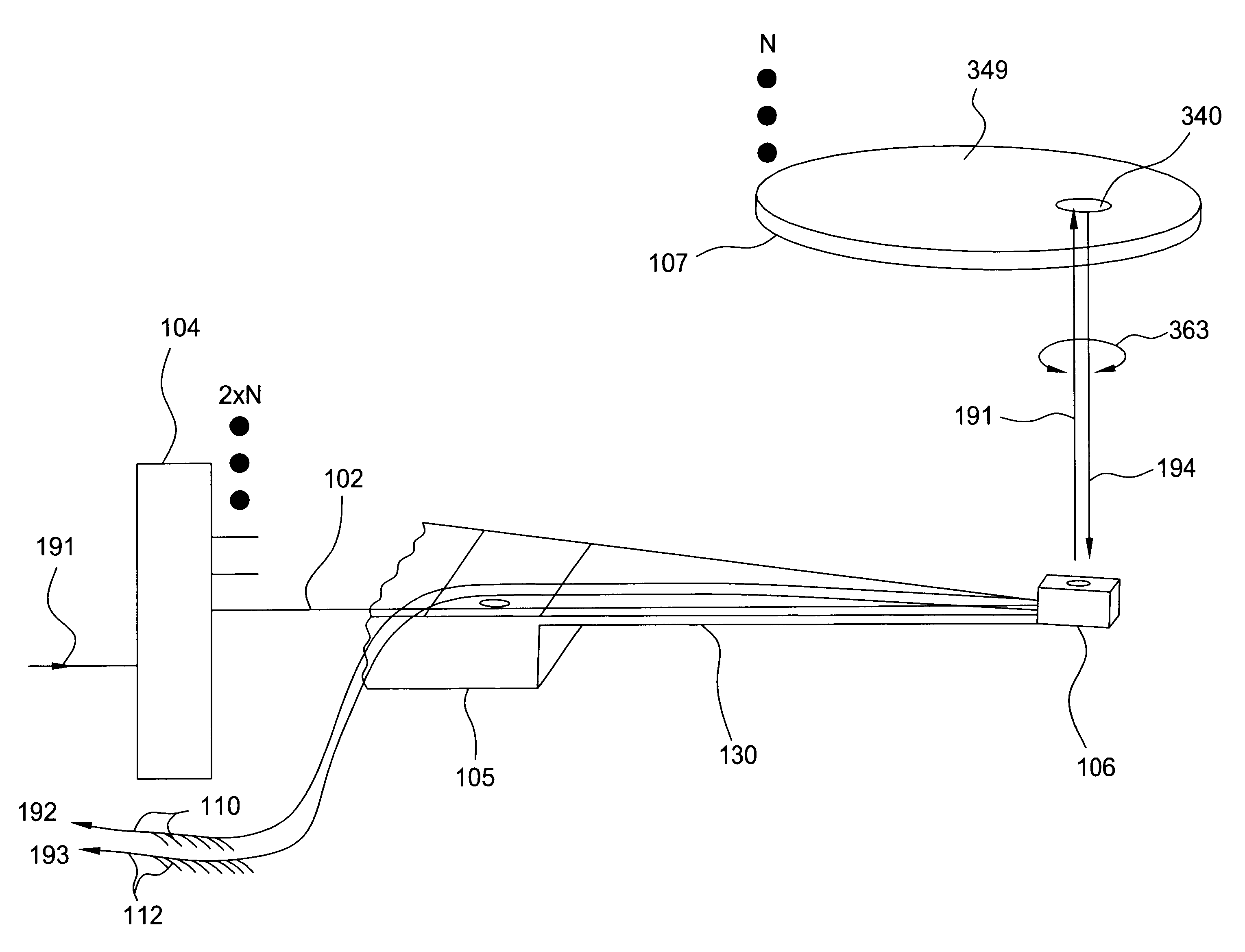
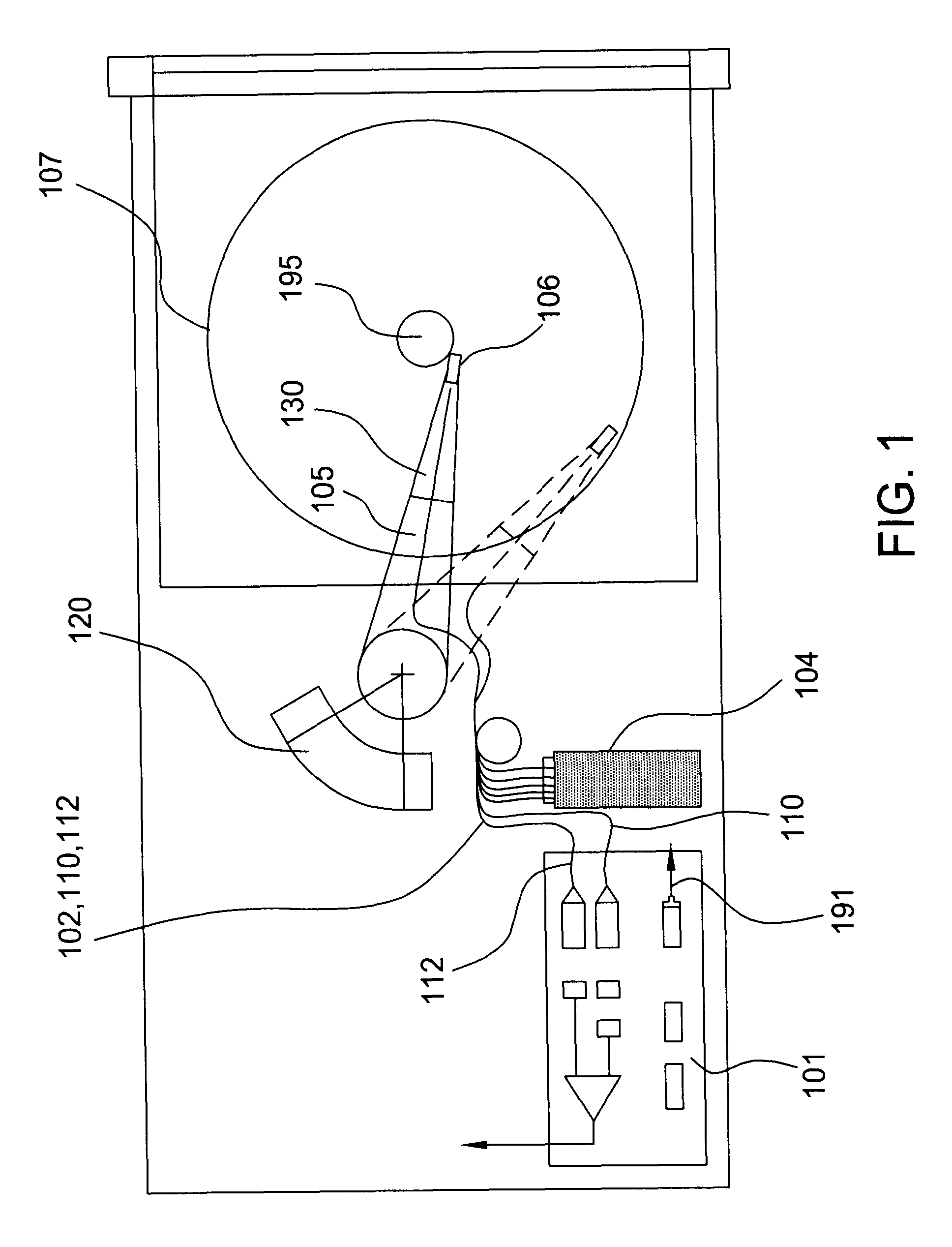
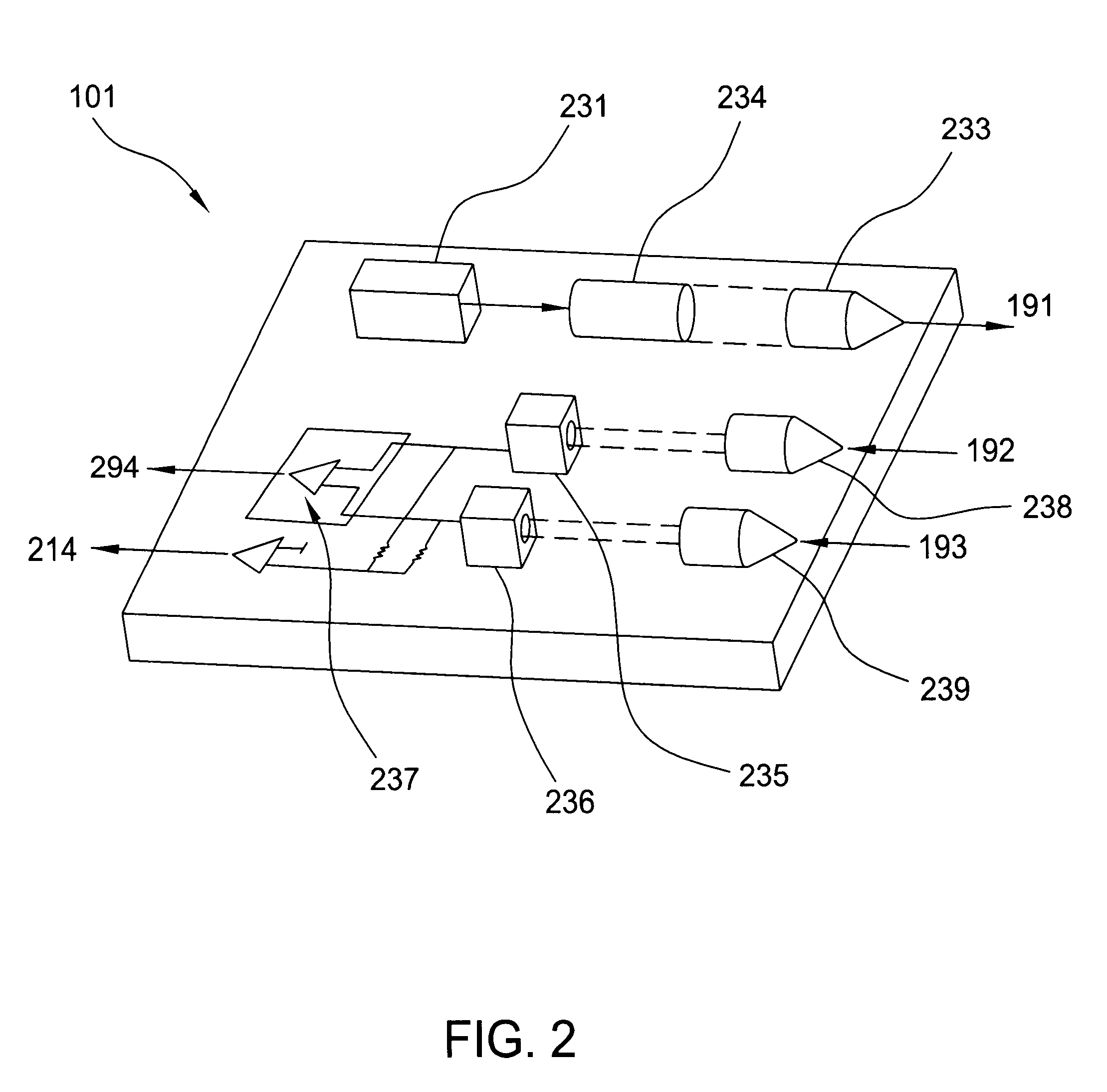
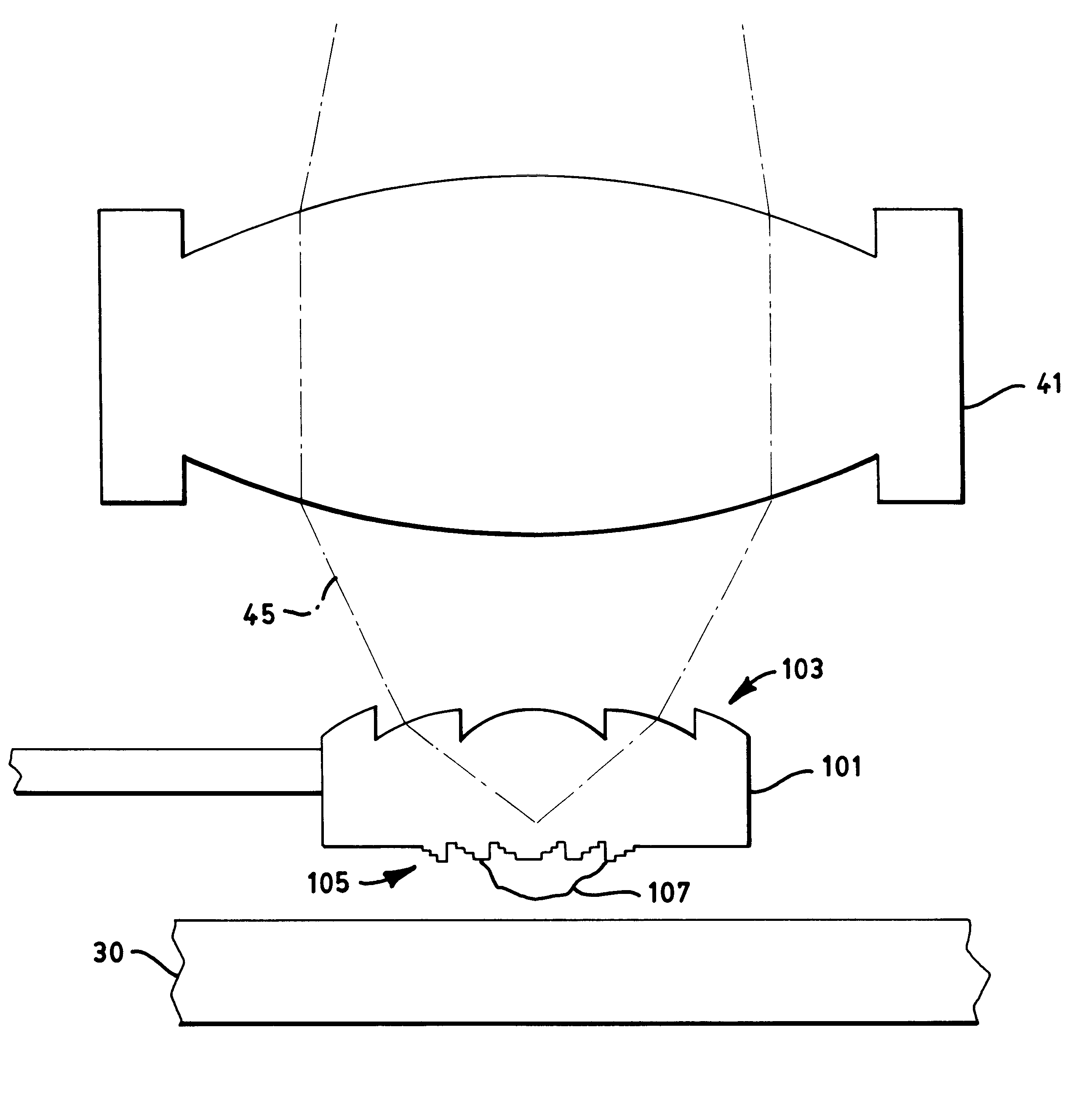
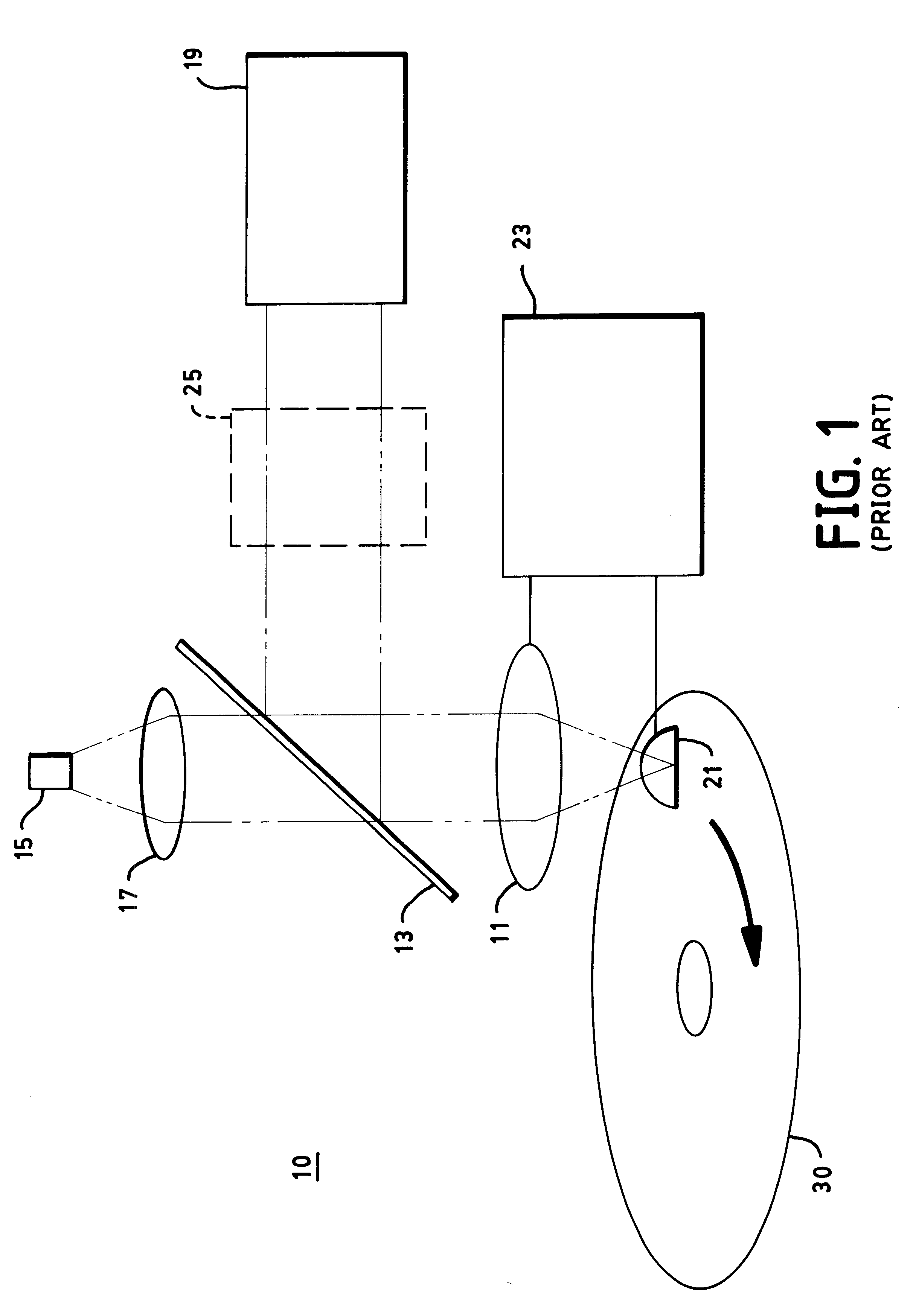
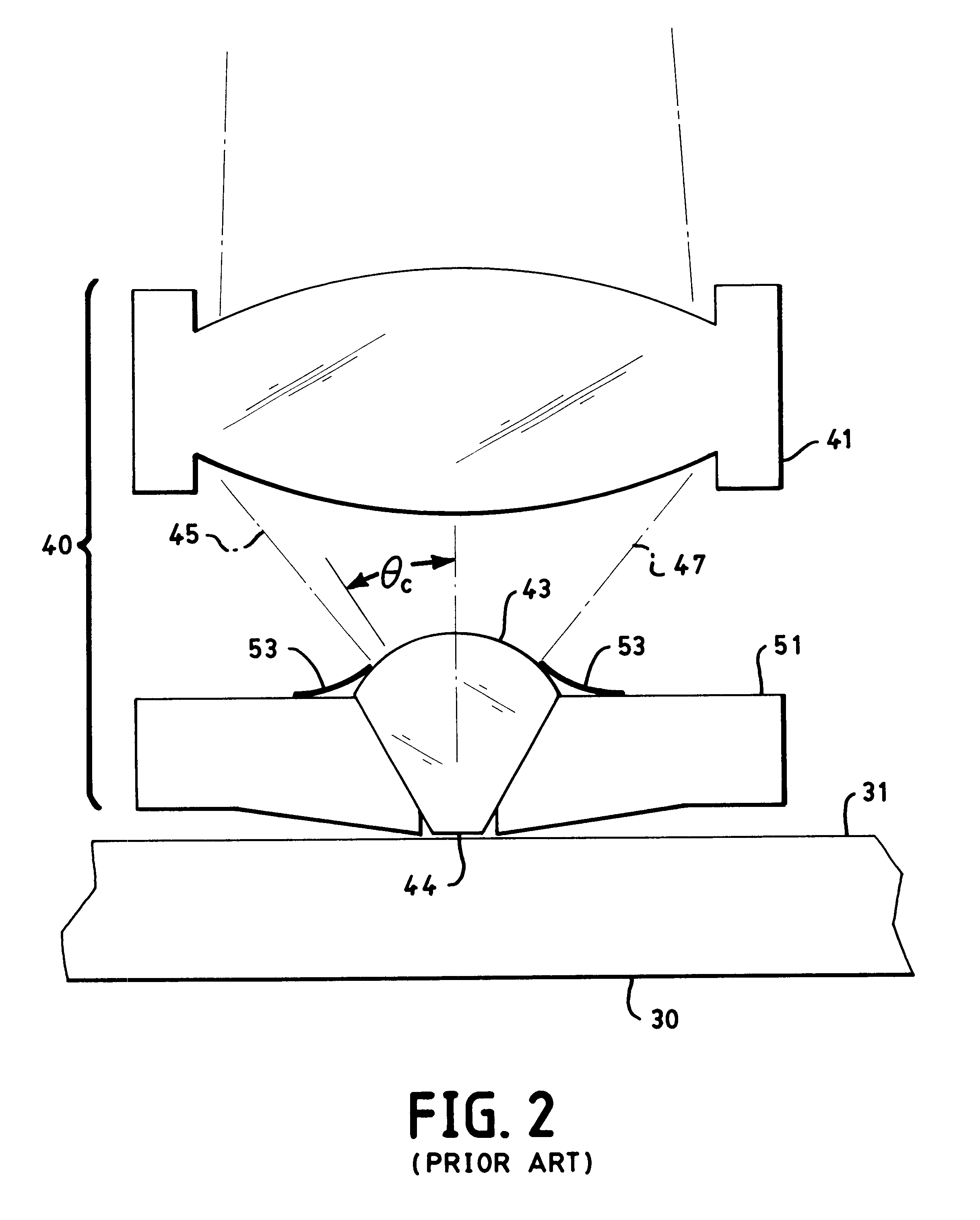
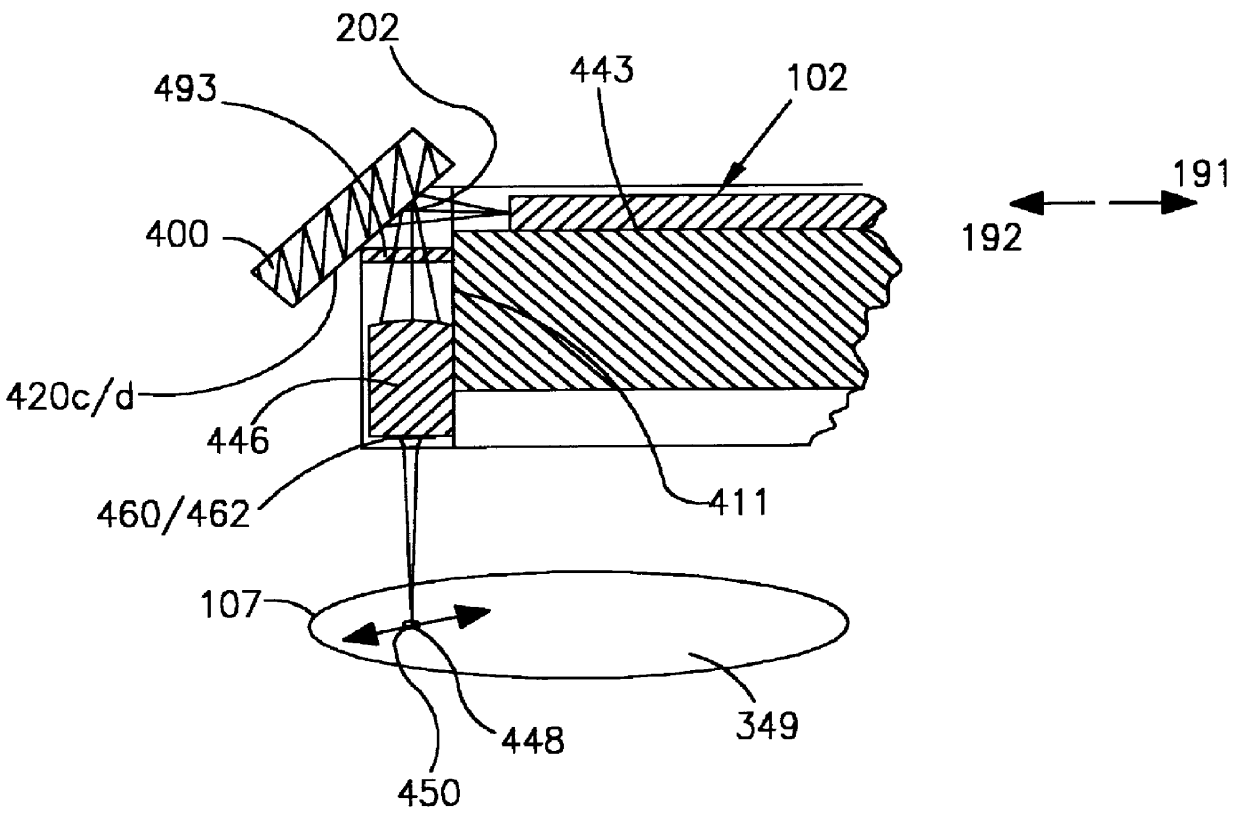
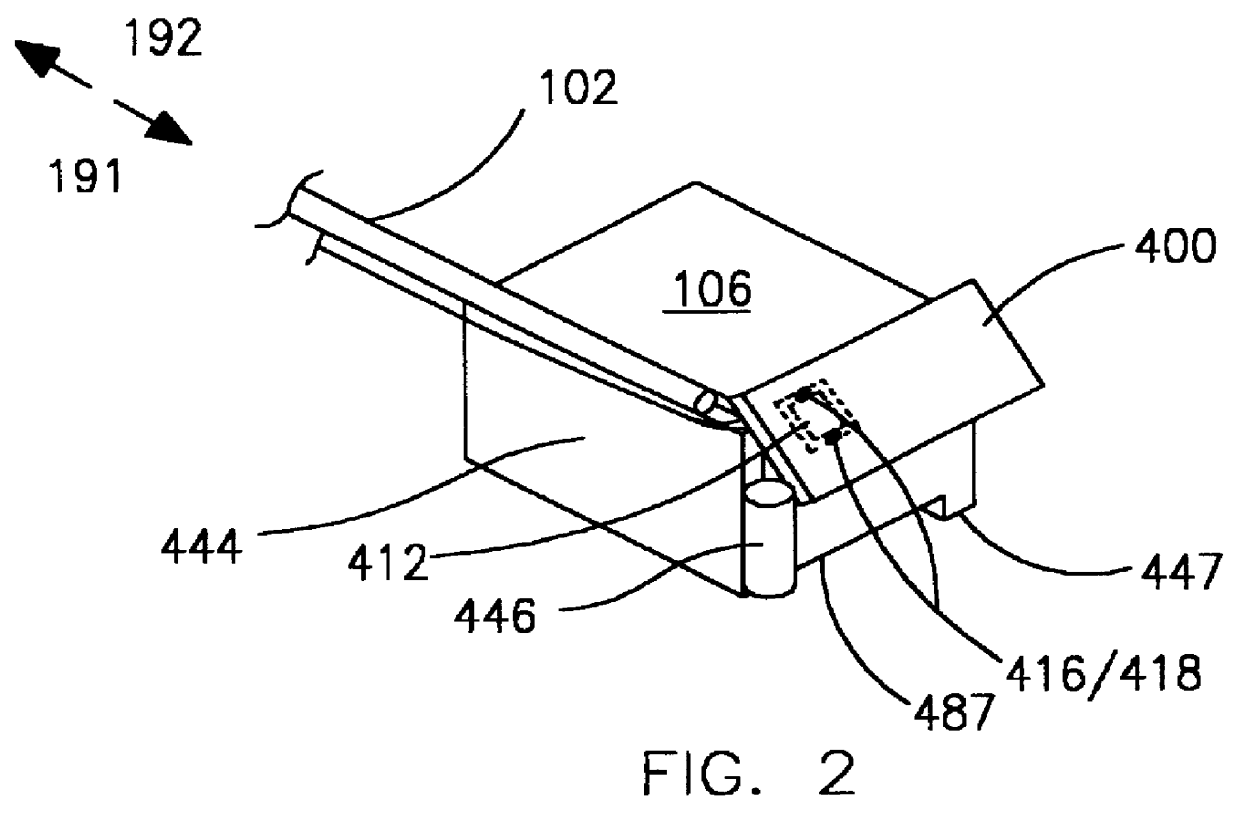
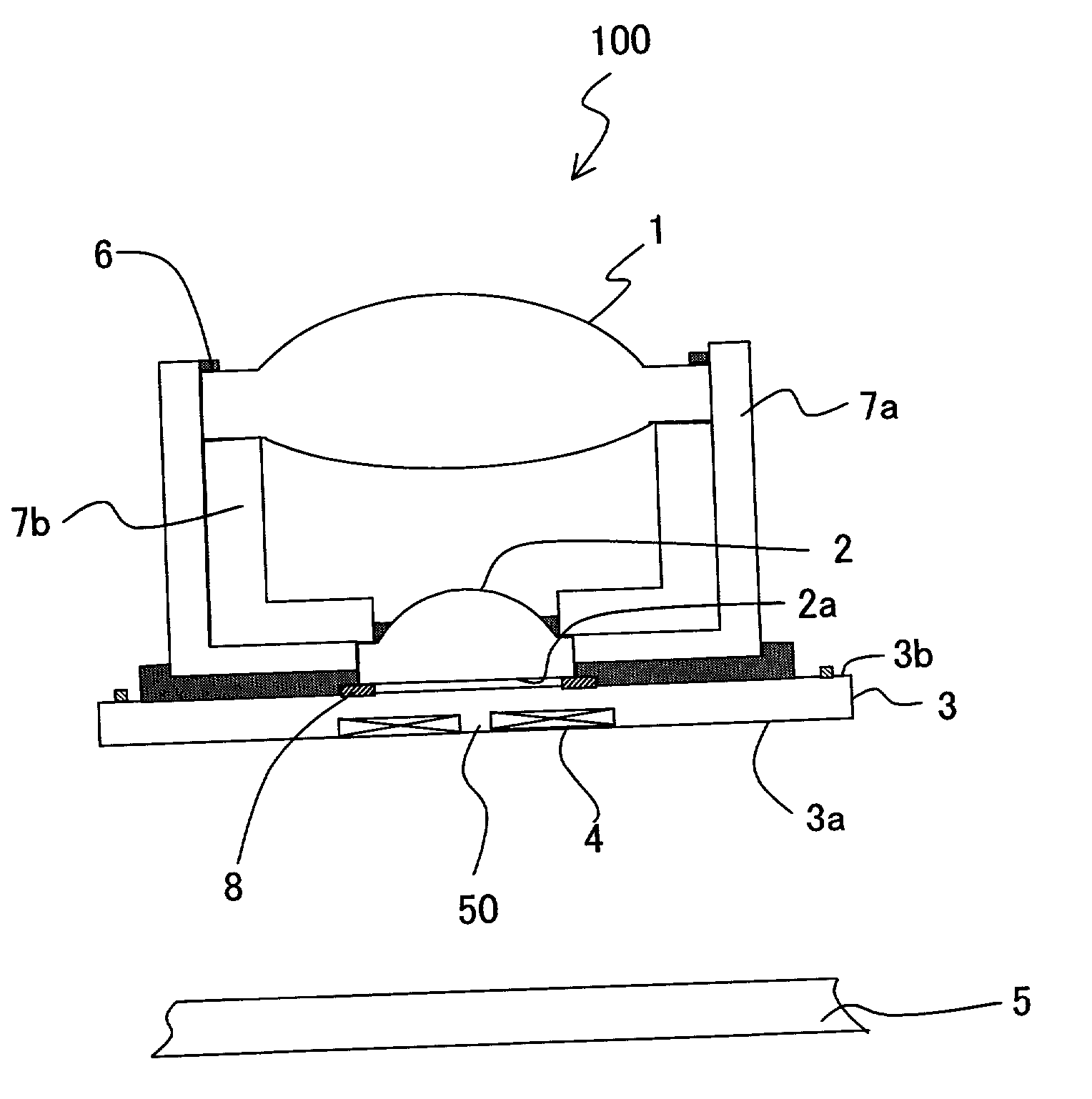
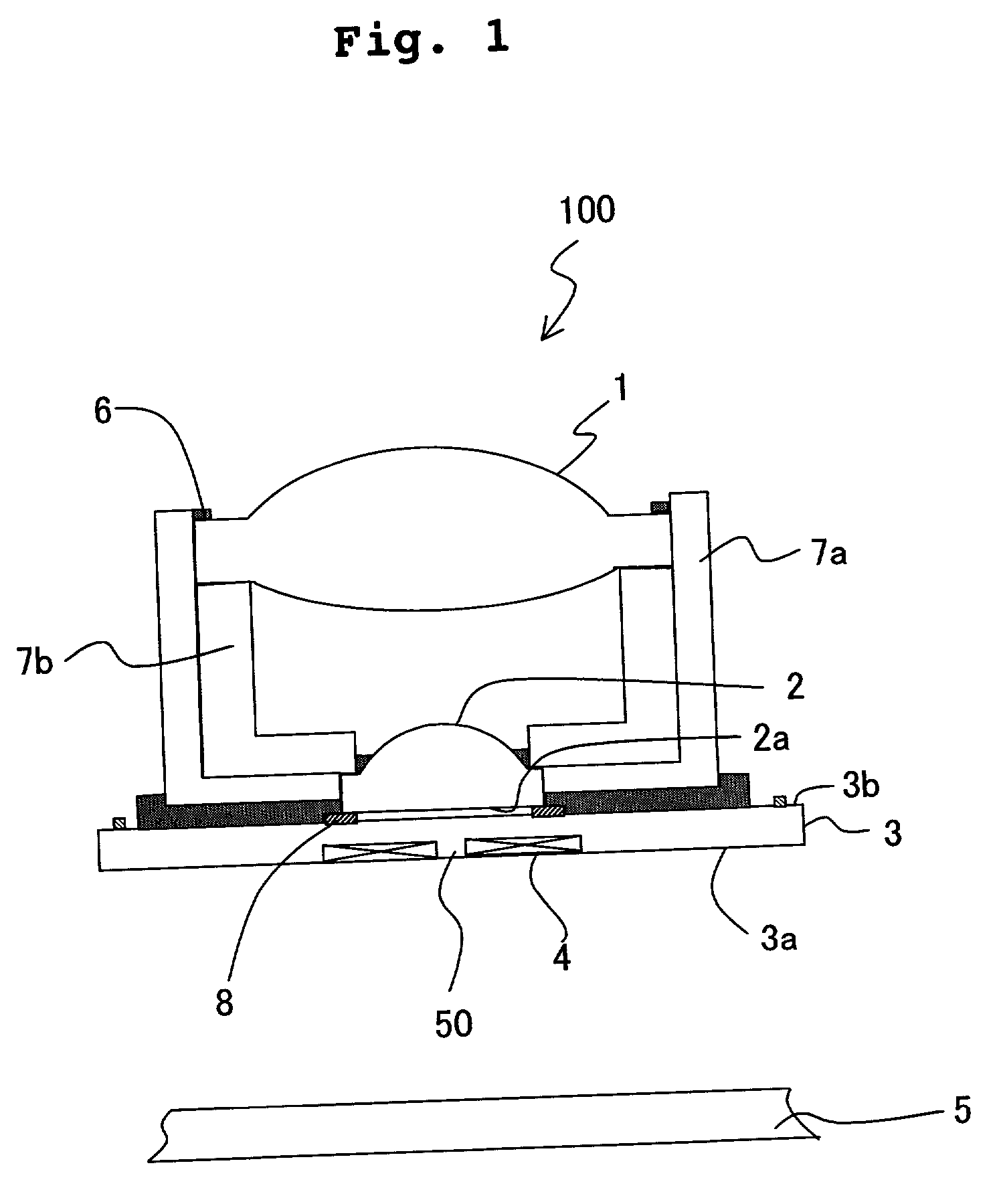
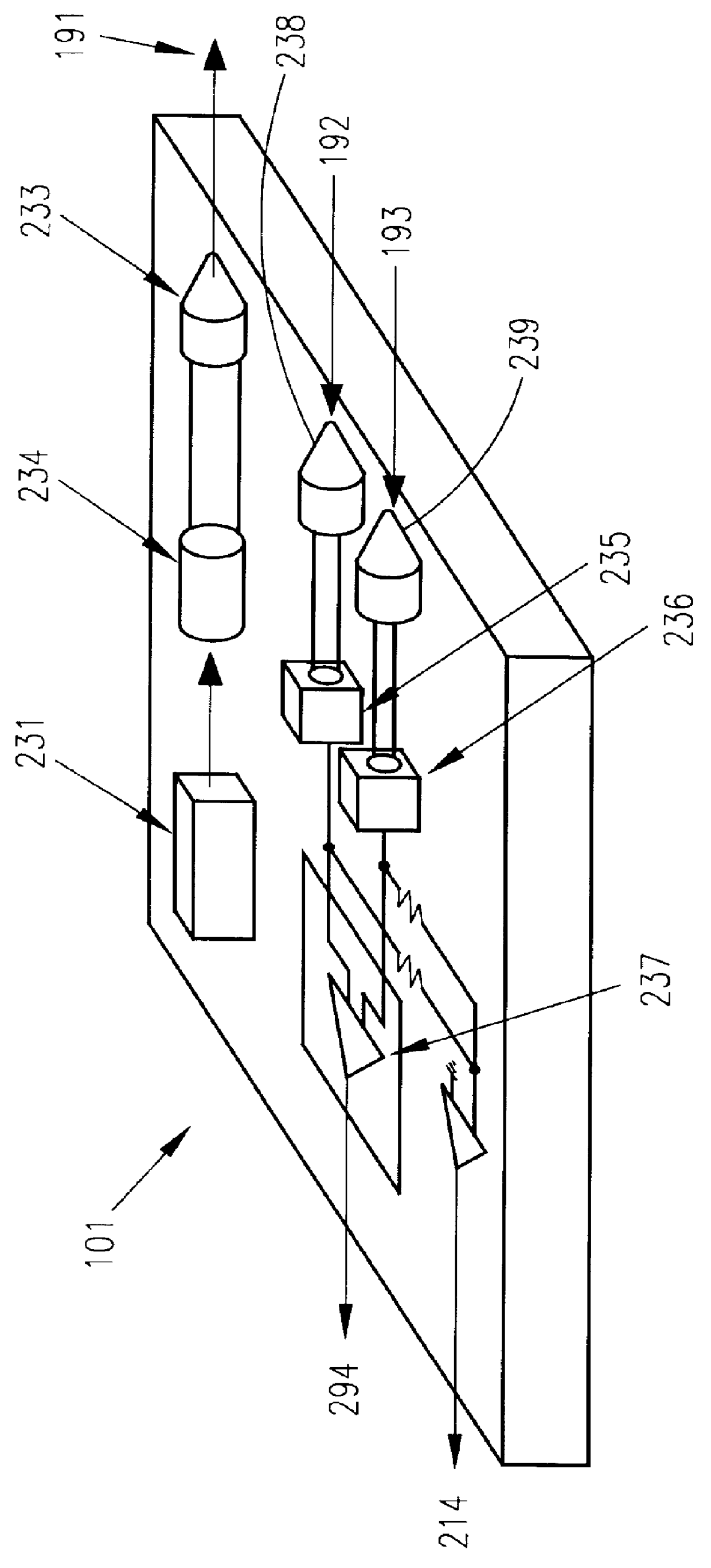
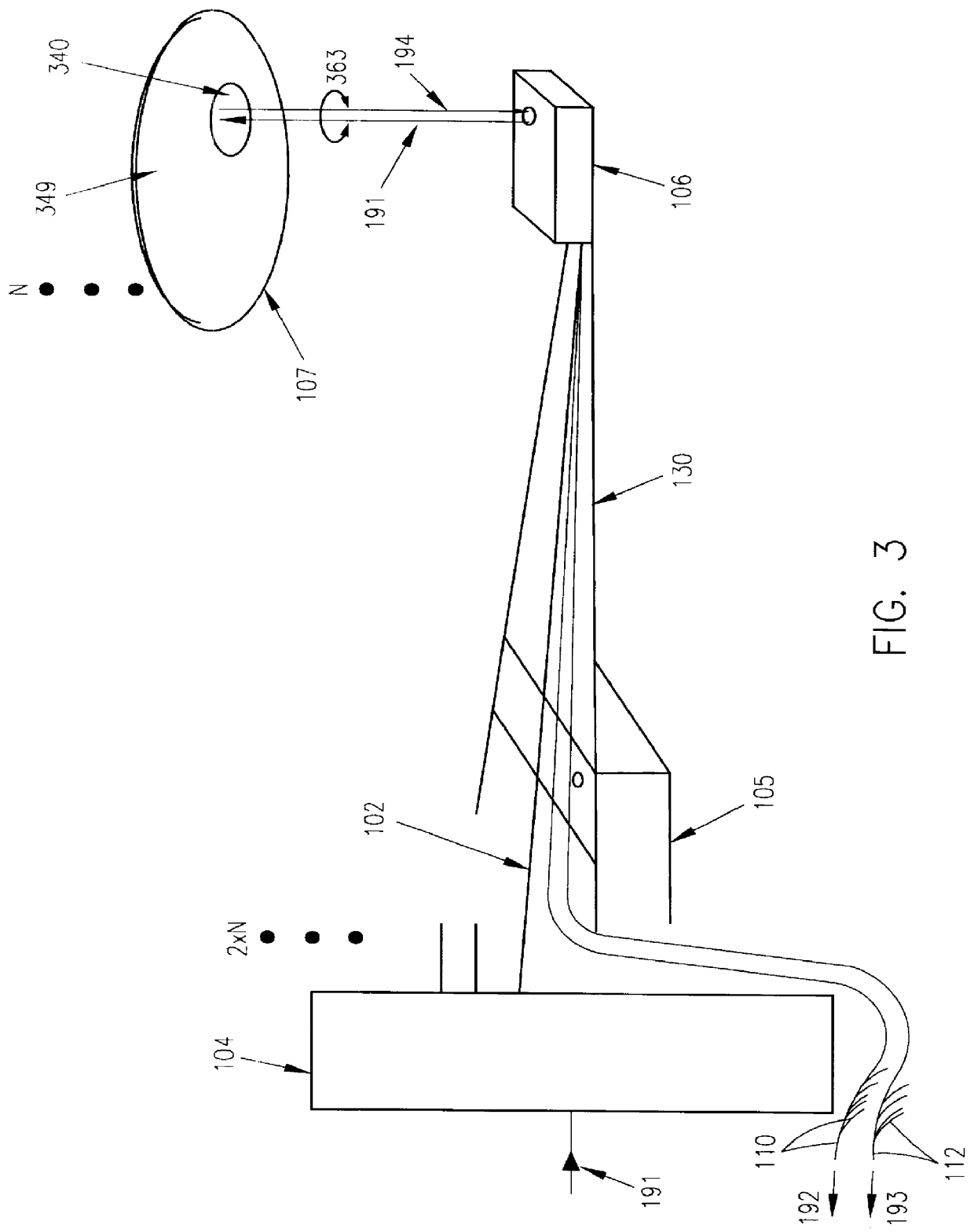
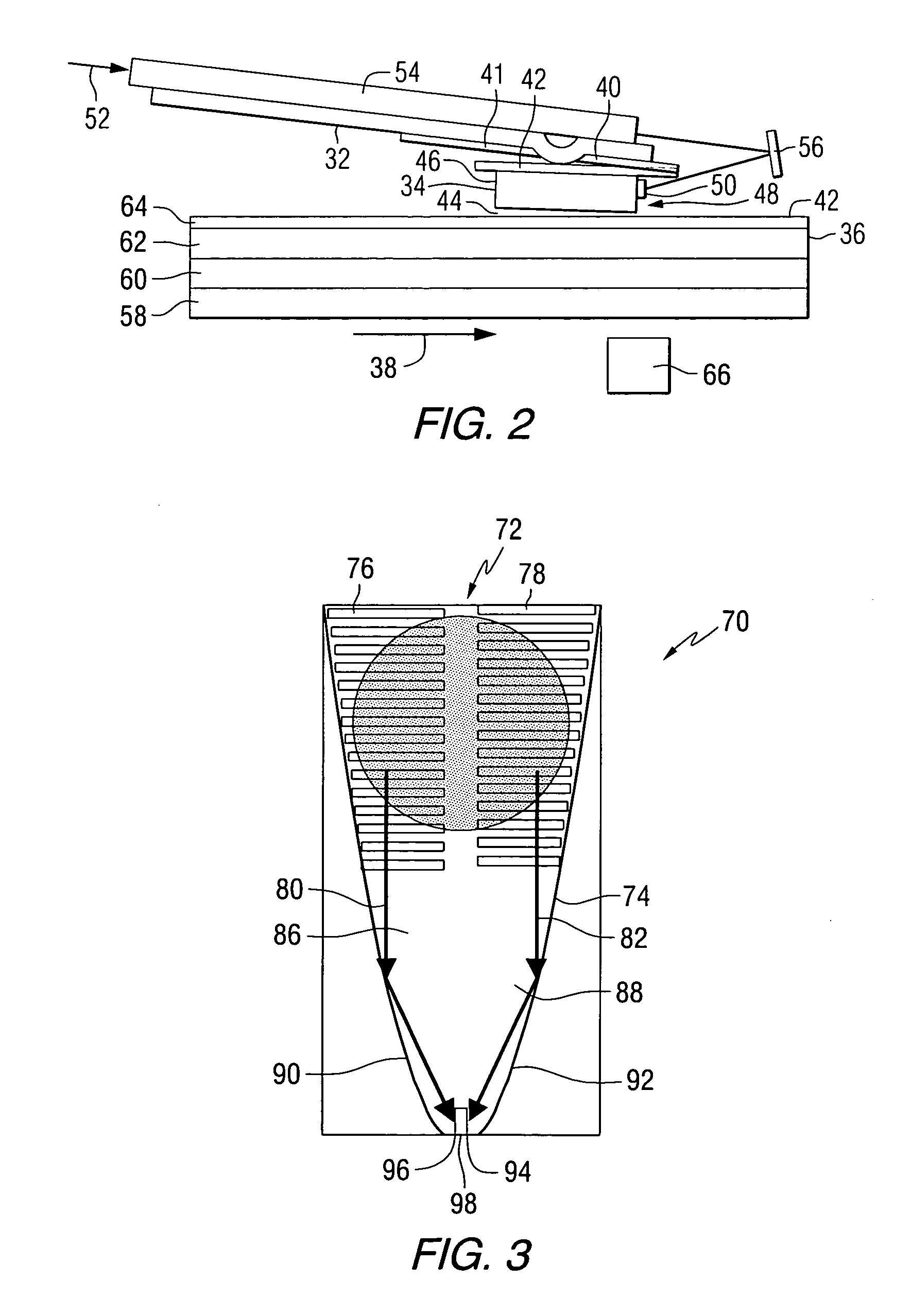
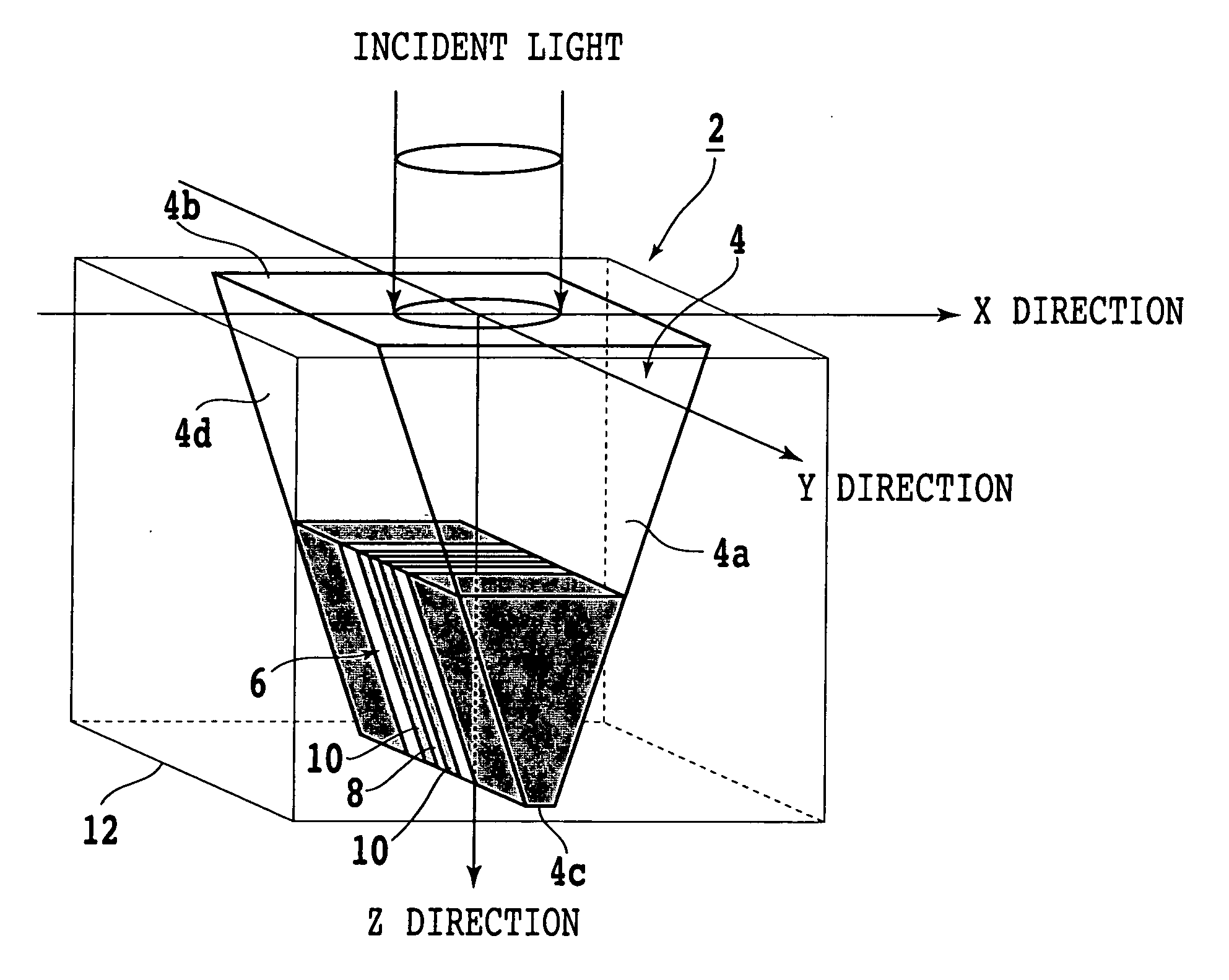
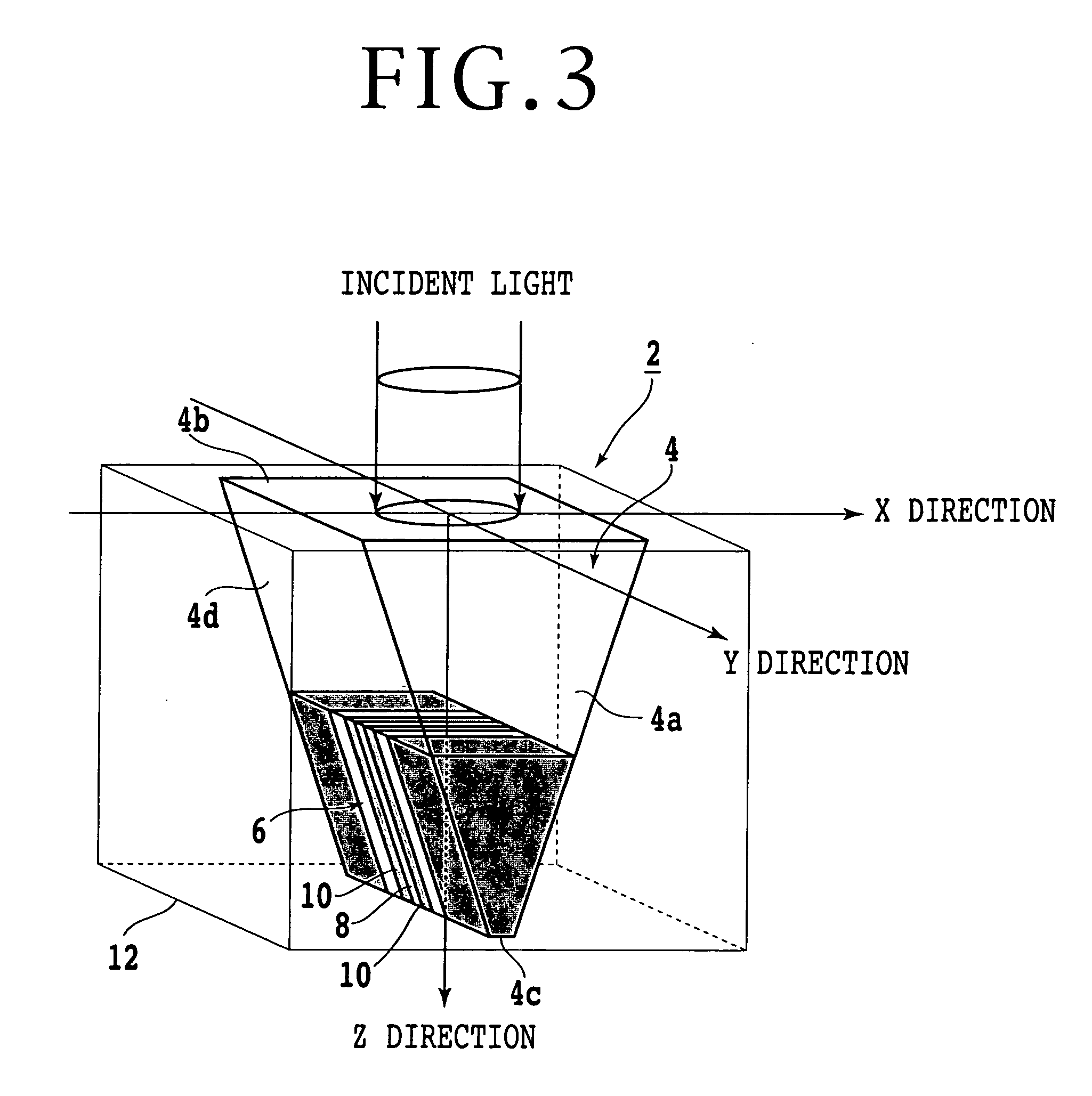
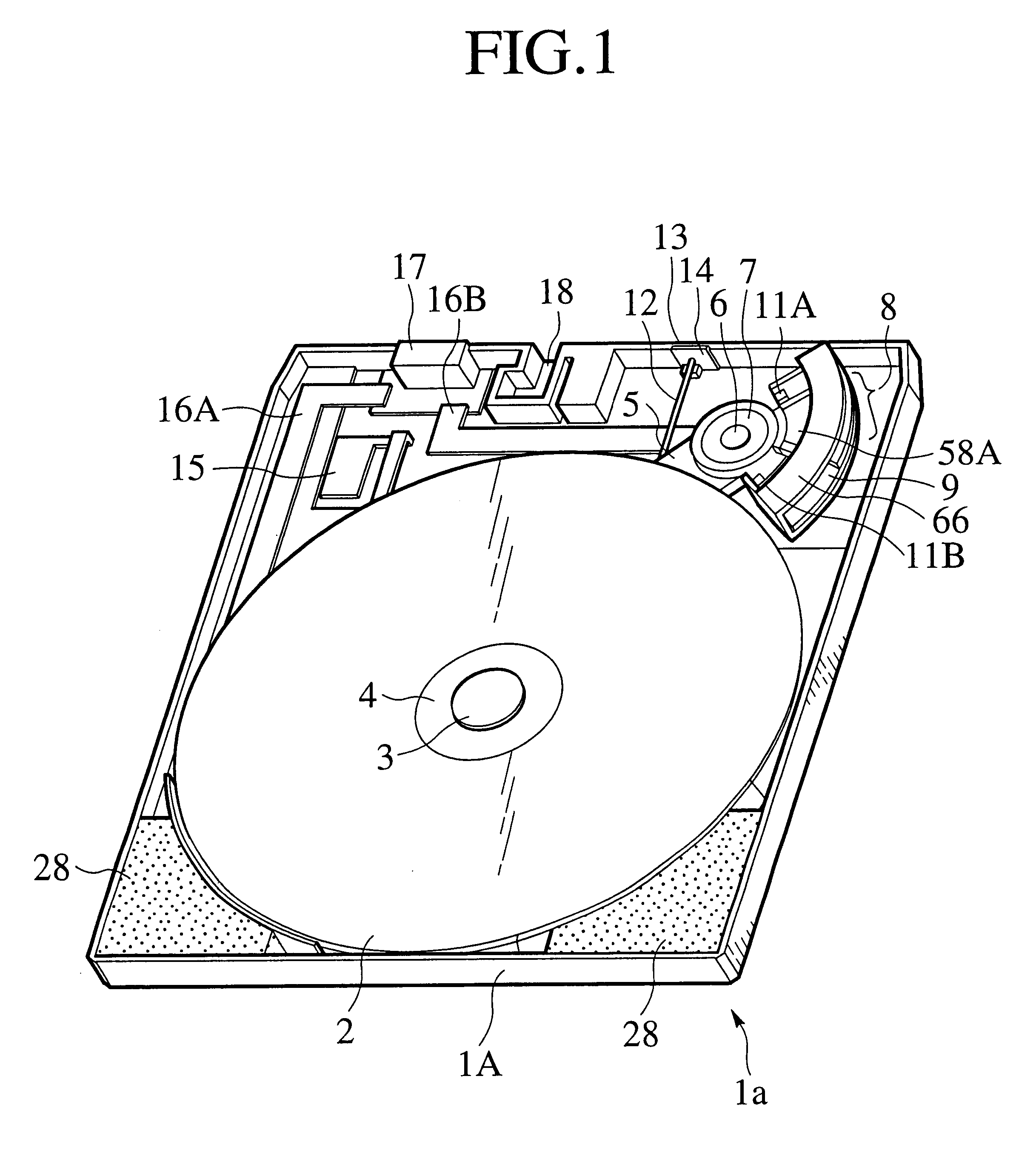
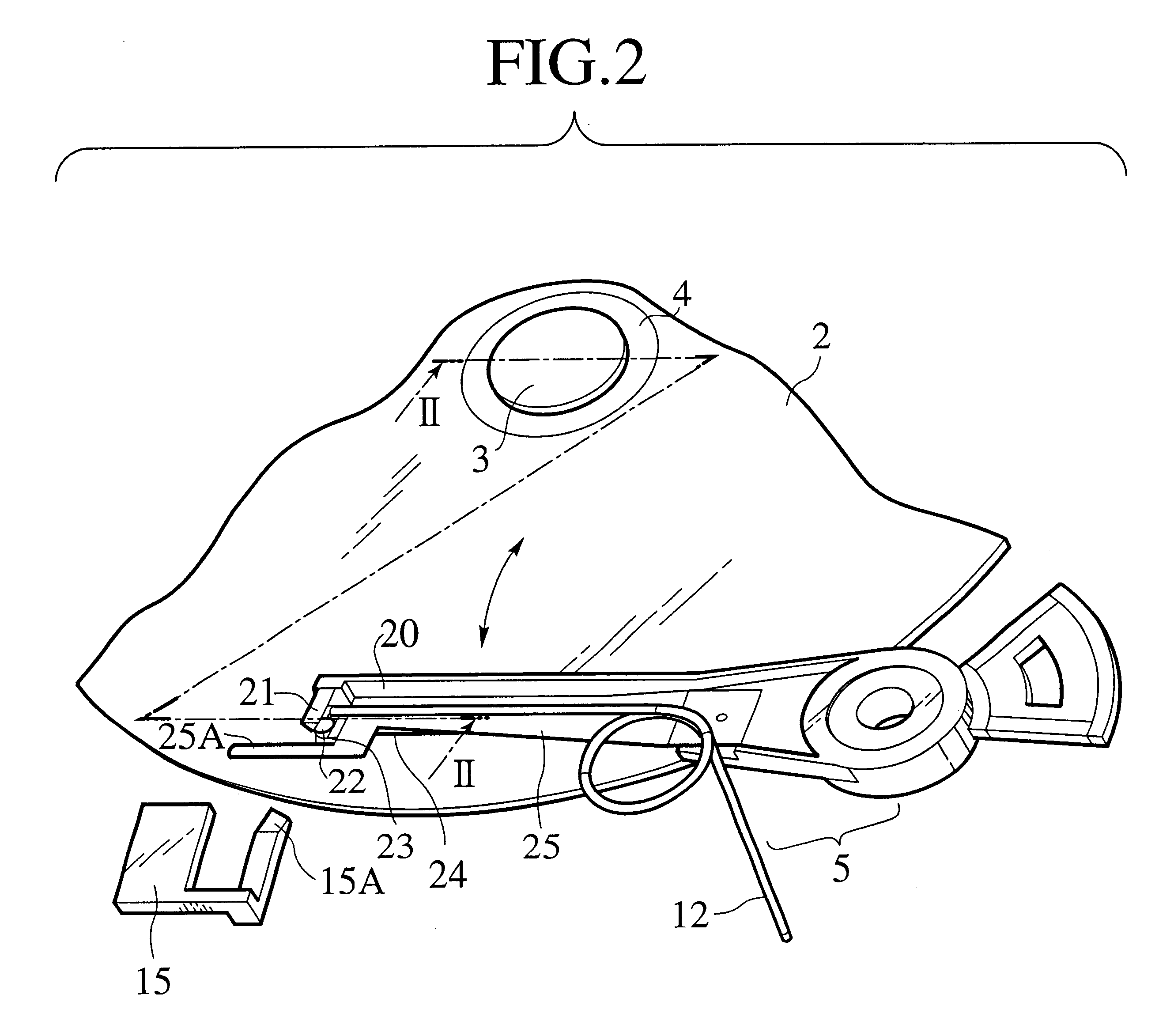
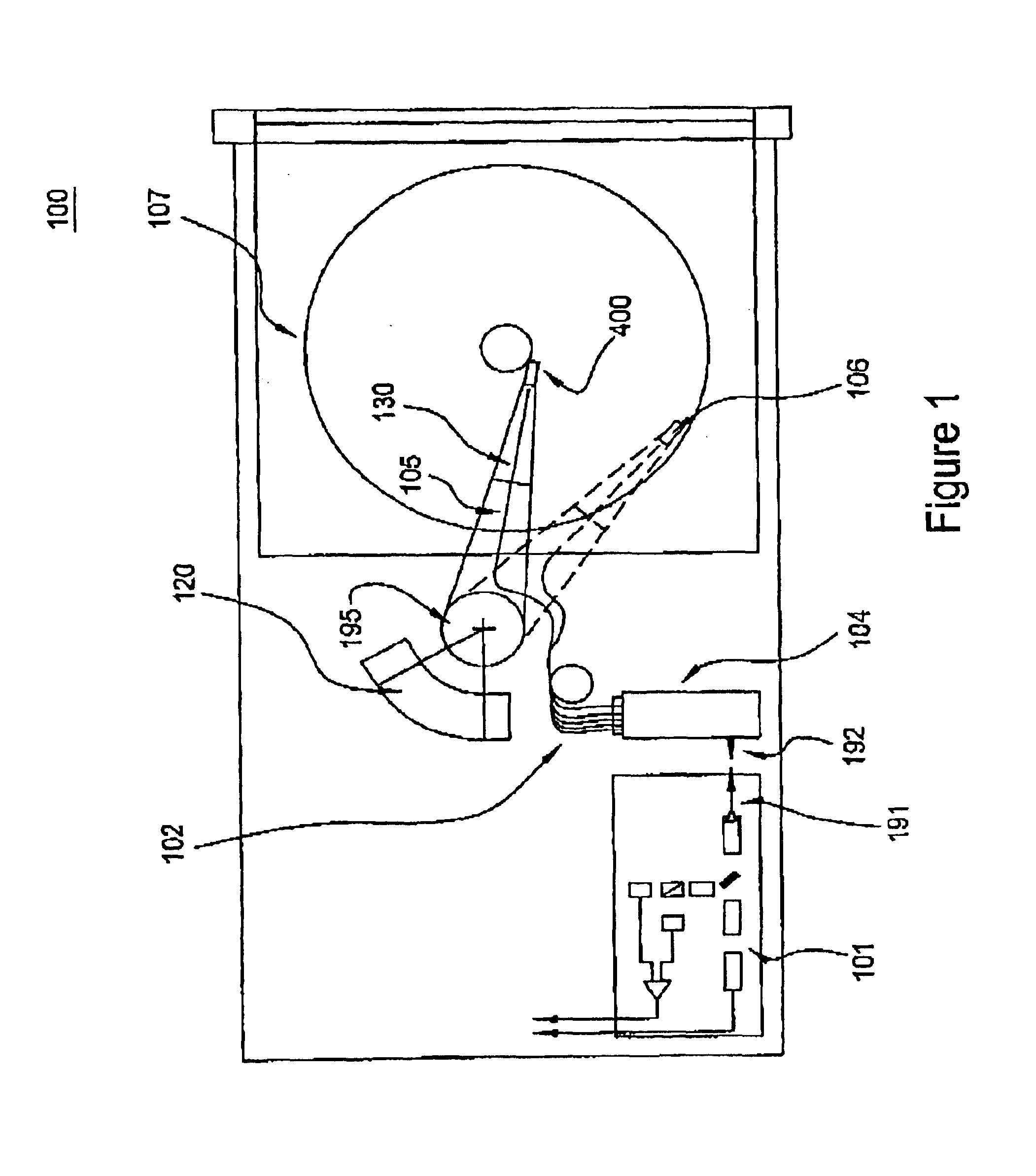
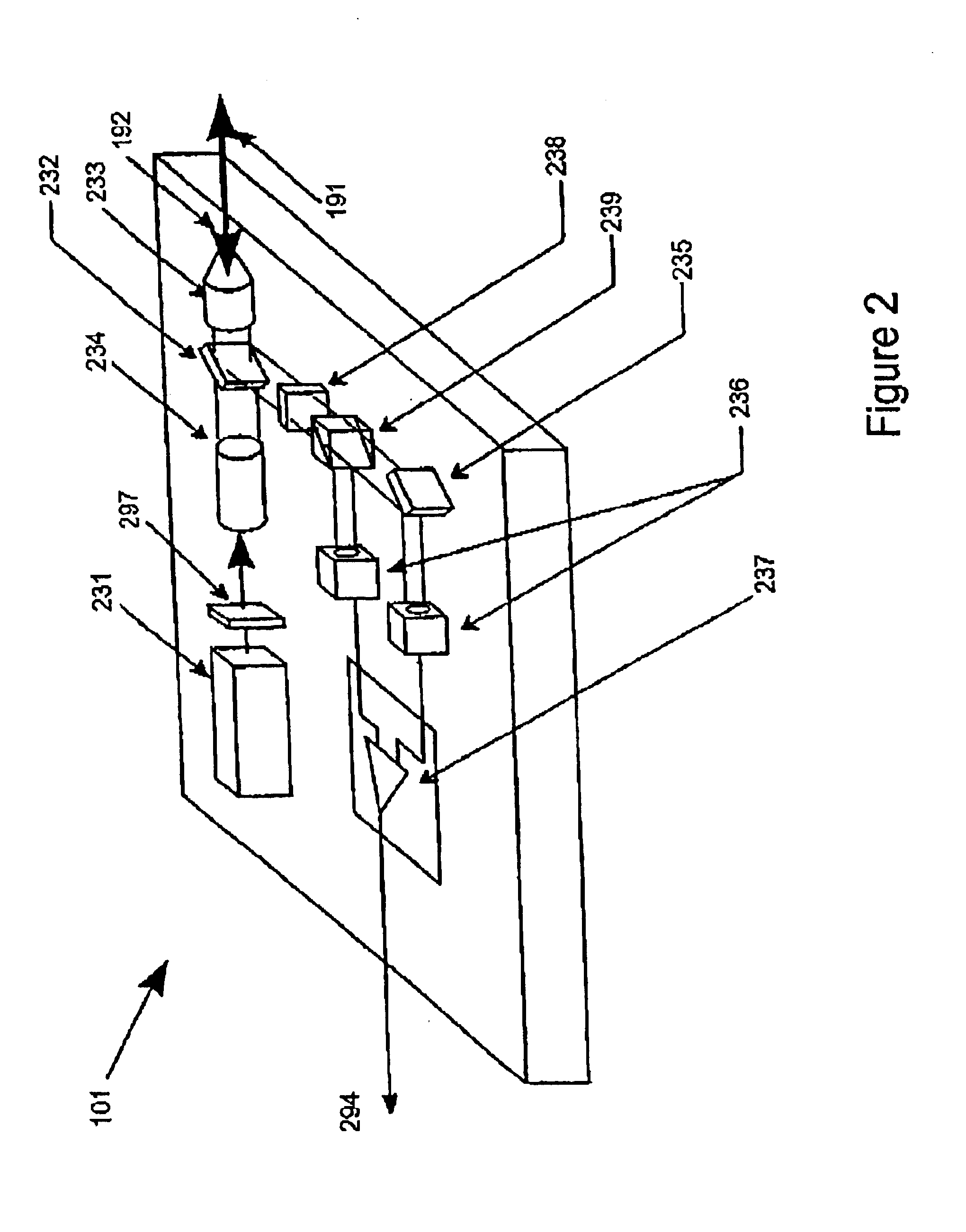
An optical data storage and retrieval system uses a flying head. The flying head is supported on a moving media having information stored in a plurality of stored data locations thereon. Information is stored in each of the plurality of media locations as physical structures capable of modulating the polarization state of incident light into one of two output polarization states. The flying head includes an optical processing assembly which directs an incident light beam having a source polarization state onto the moving media, accessing successive data locations. A reflected light beam having the source polarization state of the incident light beam modulated by a respective polarization modifying data location into one of the output polarization states is received by the flying head. The optical processing assembly optically transforms the modulated output polarization state of the reflected light beam into two return light beams having differentially modulated intensity related to the output polarization state of the reflected light beam. The two intensity modulated return light beams are optically coupled to a distal differential detector which outputs digital data representing the stored data information for the subject data location. A preferred embodiment includes optical fibers for coupling the incident and return light beams between the detector and the flying head. The optical assembly of a preferred embodiment includes an optical plate having pre-shaped and dimensioned recesses for automatically locating and aligning multiple optical components comprising the assembly. The flying head may also include a servo-controlled micro machined mirror for directing the incident and reflected light beams to and from the media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL (FREMONT LLC)
Data storage system and methods using diffractive near-field optics
InactiveUS6396789B1Minimize aberrationLow costOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsOptical pathOptical radiation
An optical assembly suitable for use with an optical medium for the storage and retrieval of data, the optical assembly comprising: a source of illumination for providing a beam of optical radiation, an objective lens disposed in the optical path of the beam for redirecting the beam to the optical medium, and a diffractive optical element disposed between the redirected beam of radiation and the optical medium such that at least a portion of the redirected beam of radiation passes through a surface of the diffractive optical element and is reflected to the objective lens.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Near-field optical head having tapered hole for guiding light beam
InactiveUS7599277B1High strengthHigh mechanical strengthOptical flying-type headsIntegrated optical head arrangementsPlanar substrateLight reflection
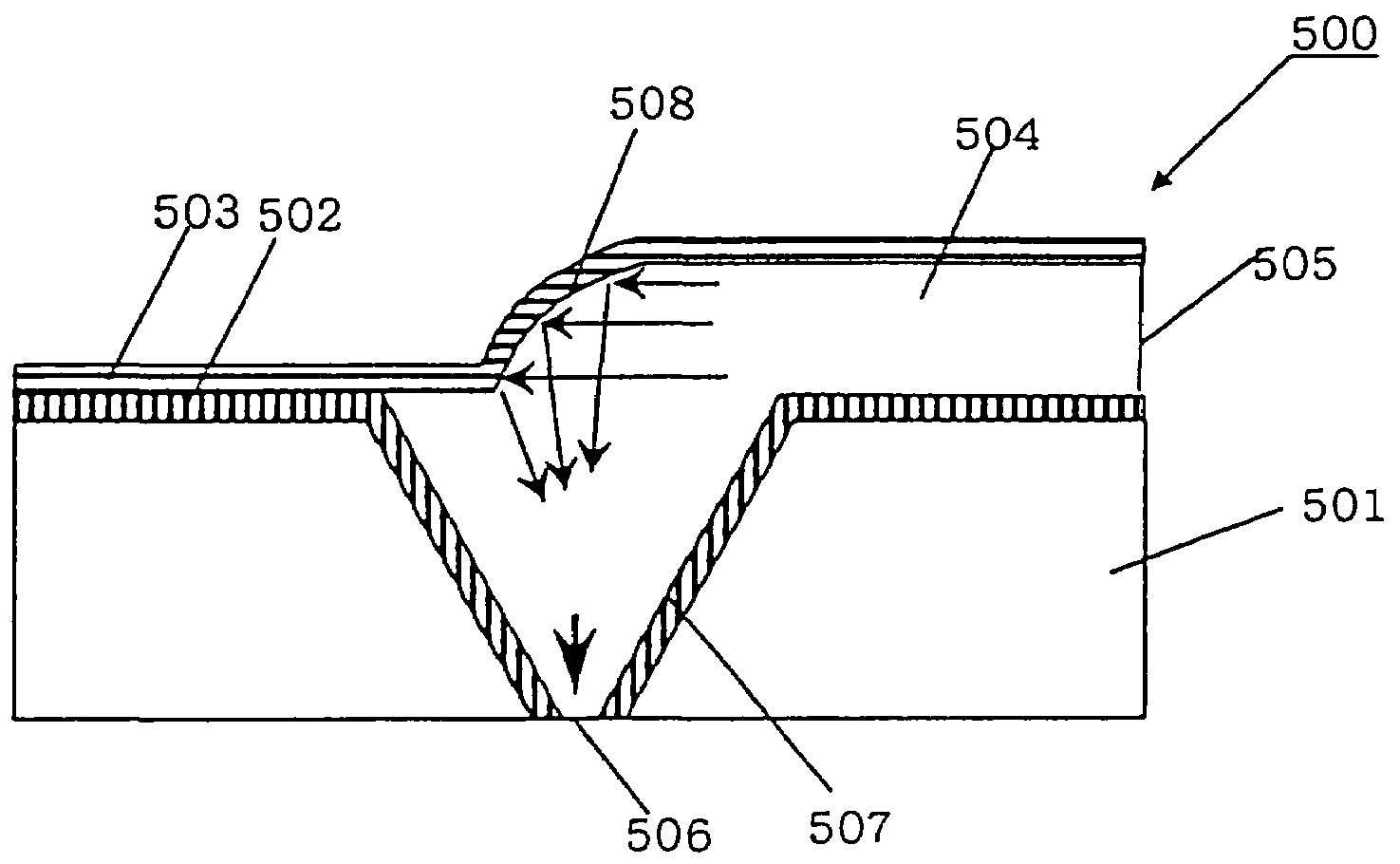
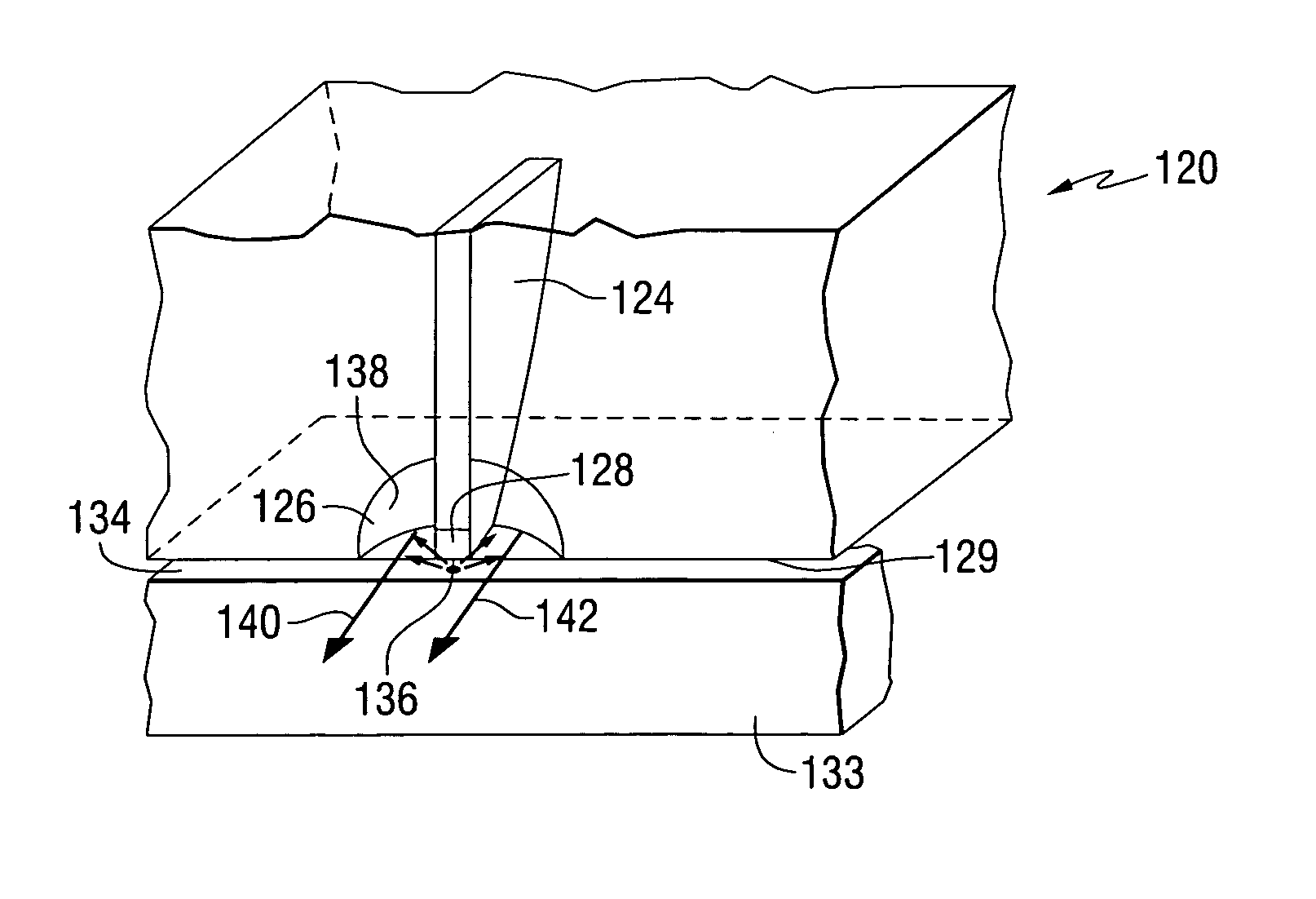
A near-field optical head has a planar substrate having a first surface, a second surface disposed opposite to the first surface, and an inverted conical or pyramidal hole extending through the first and second surfaces. The conical or pyramidal hole has at least one fine aperture formed at an apex thereof and is disposed on the first surface of the planar substrate. An optical waveguide is disposed on the second surface of the planar substrate for propagating light. A light reflection film is disposed in the optical waveguide for reflecting in the direction of the fine aperture light propagated through the optical waveguide.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Information recording medium, information recording method, and information reproducing method
InactiveUS20040028869A1High density recordingImprove recording densityMaterial nanotechnologyOptical flying-type headsElectricityHigh density
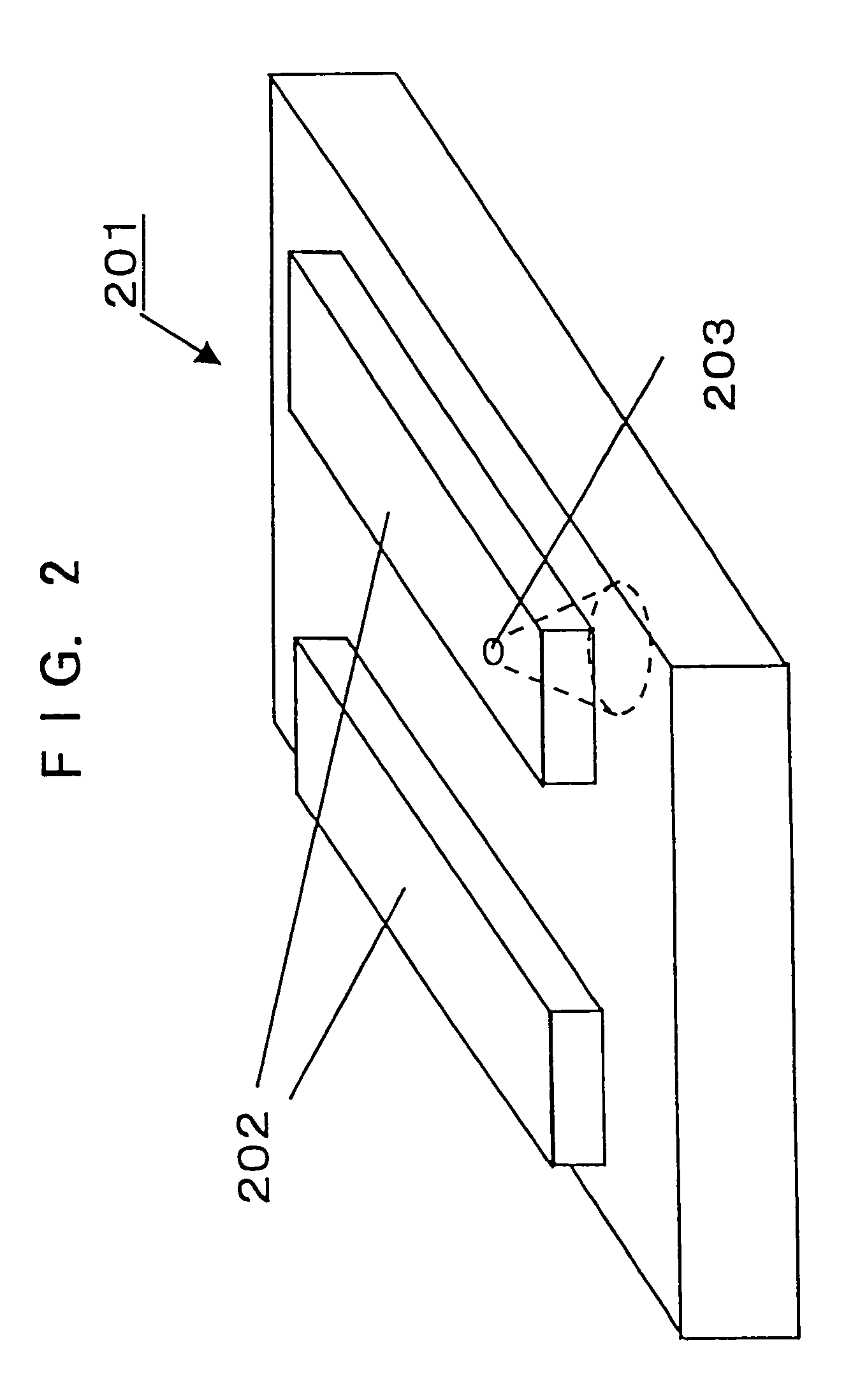
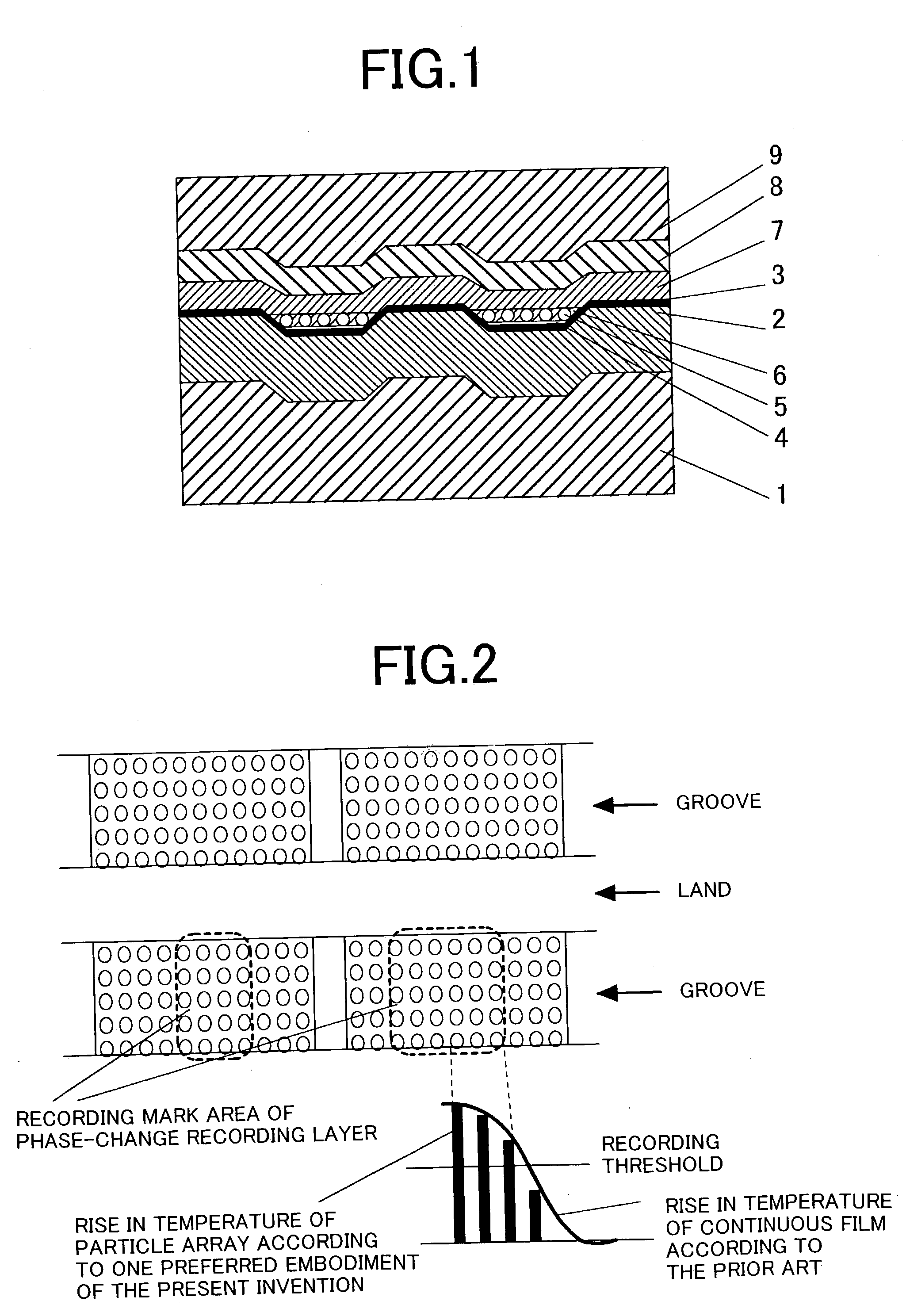
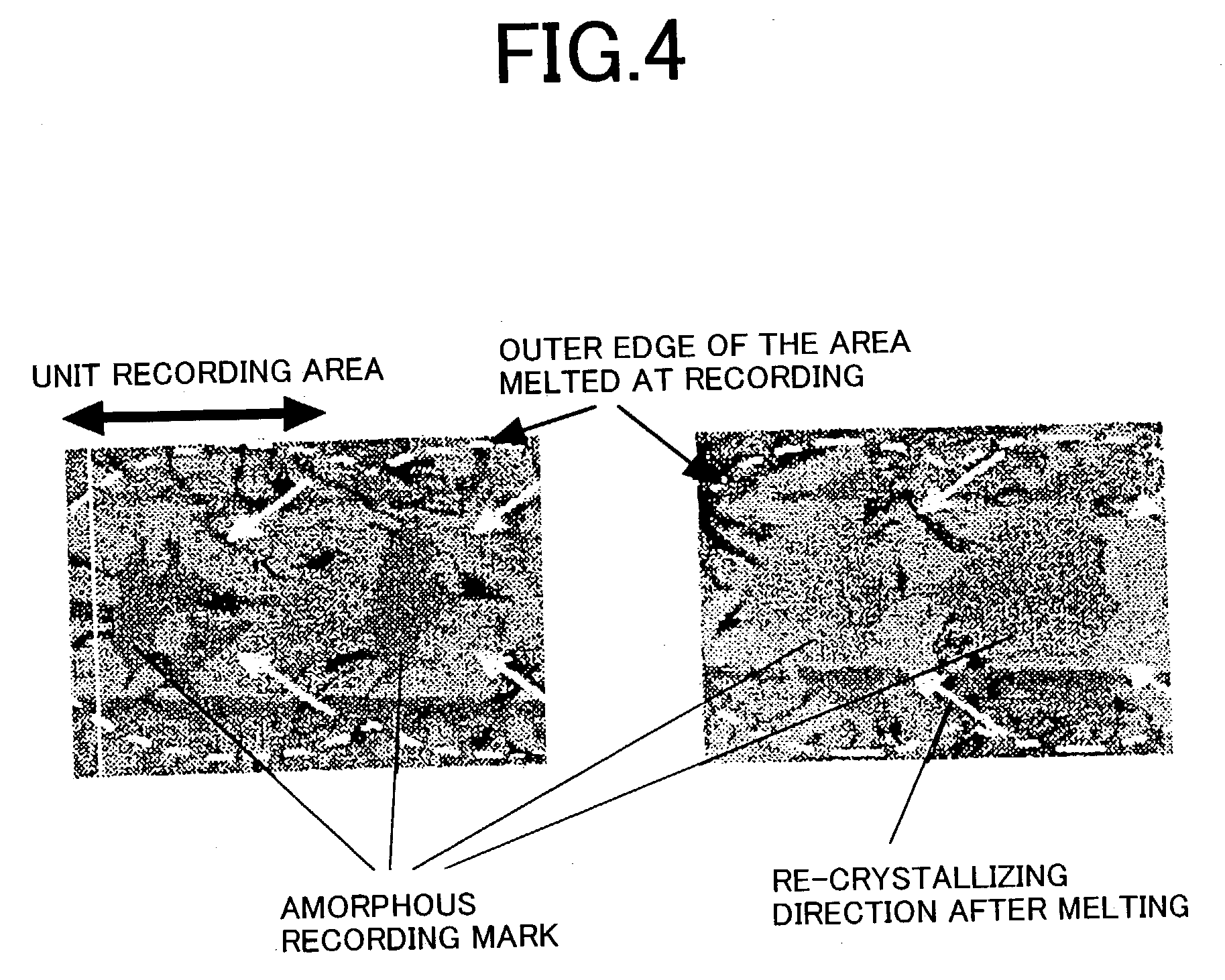
The information recording medium accosting to the preferred embodiment of the present invention achieves high-speed, high-density recording. The layer, in which ultra-particles made from an optical absorption metal, dielectric, or recording material are formed into regular arrays, is deposited. Resonant Plasmon excitation and resonance absorption of ultra-particles enable the edges of the recorded marks to be identified clearly and intense absorption to occur only in the given layer depending on the wavelength in the case of the multi-layer medium, achieving high-density, large-capacity recording.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
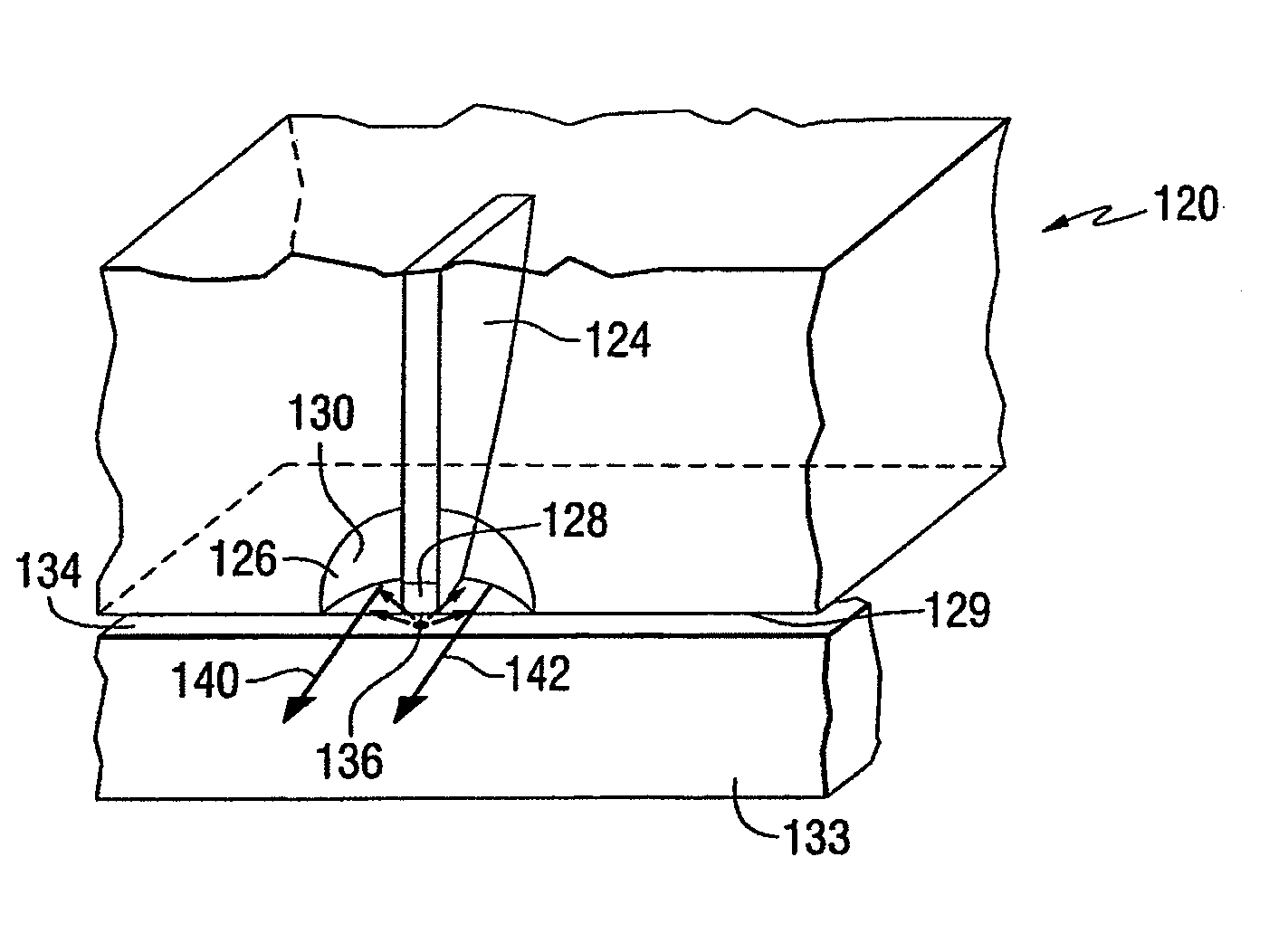
Optical near-field generator and recording apparatus using the optical near-field generator
InactiveUS7529158B2Reduce the impactReduce impactNanomagnetismOptical flying-type headsPenetration depth
A near-field optical probe and optical near-field generator are provided. A problem of a probe having a scatterer in which optical near-field noises are generated at the parts other than for a point at which an intense optical near-field is generated, is solved. In one example of the probe, a surface of the parts except for a vertex of the scatterer at which the intense optical near-field is generated is etched so that an etching depth becomes not less than a penetration depth of the optical near-field. The probe facilitates control of noises when a sample is observed or recording marks are reproduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Data storage system having an improved surface micro-machined mirror
InactiveUS6061323AImproved stiffness/mass ratioReduced operating requirementsOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesEngineeringData storage system
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
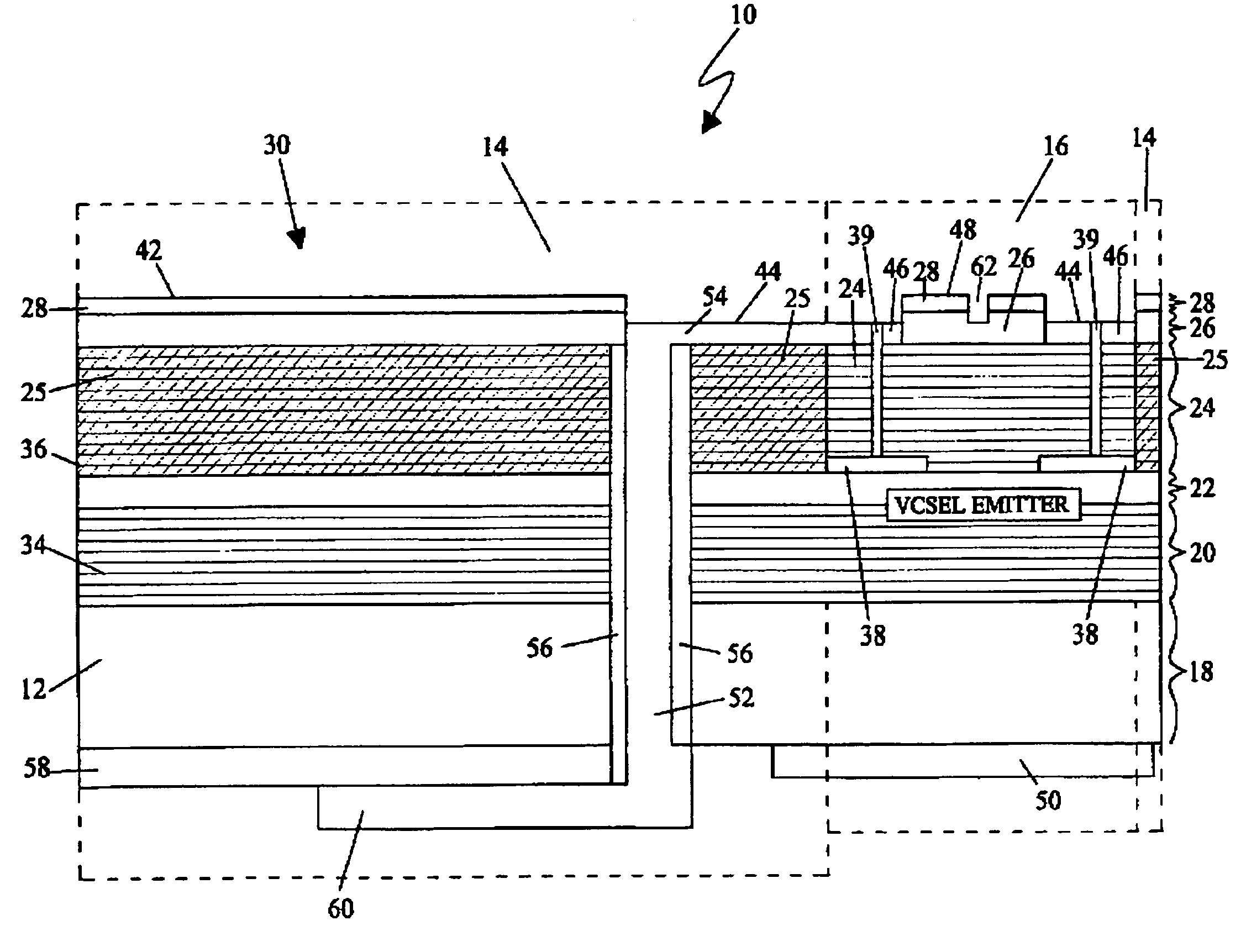
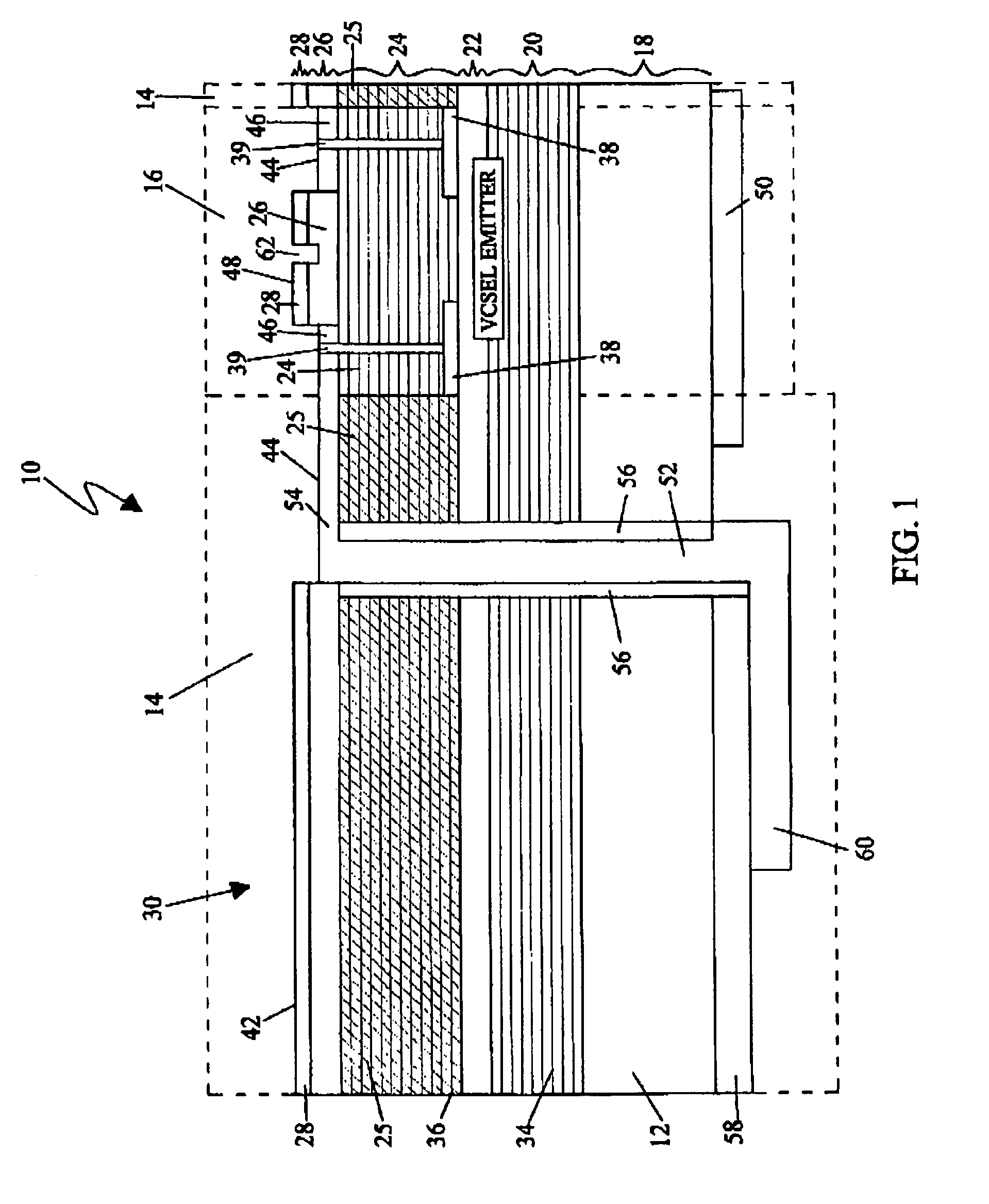
Light delivery technique for heat assisted magnetic recording head
InactiveUS7345840B2Optical flying-type headsFluid-dynamic spacing of headsFiberHeat-assisted magnetic recording
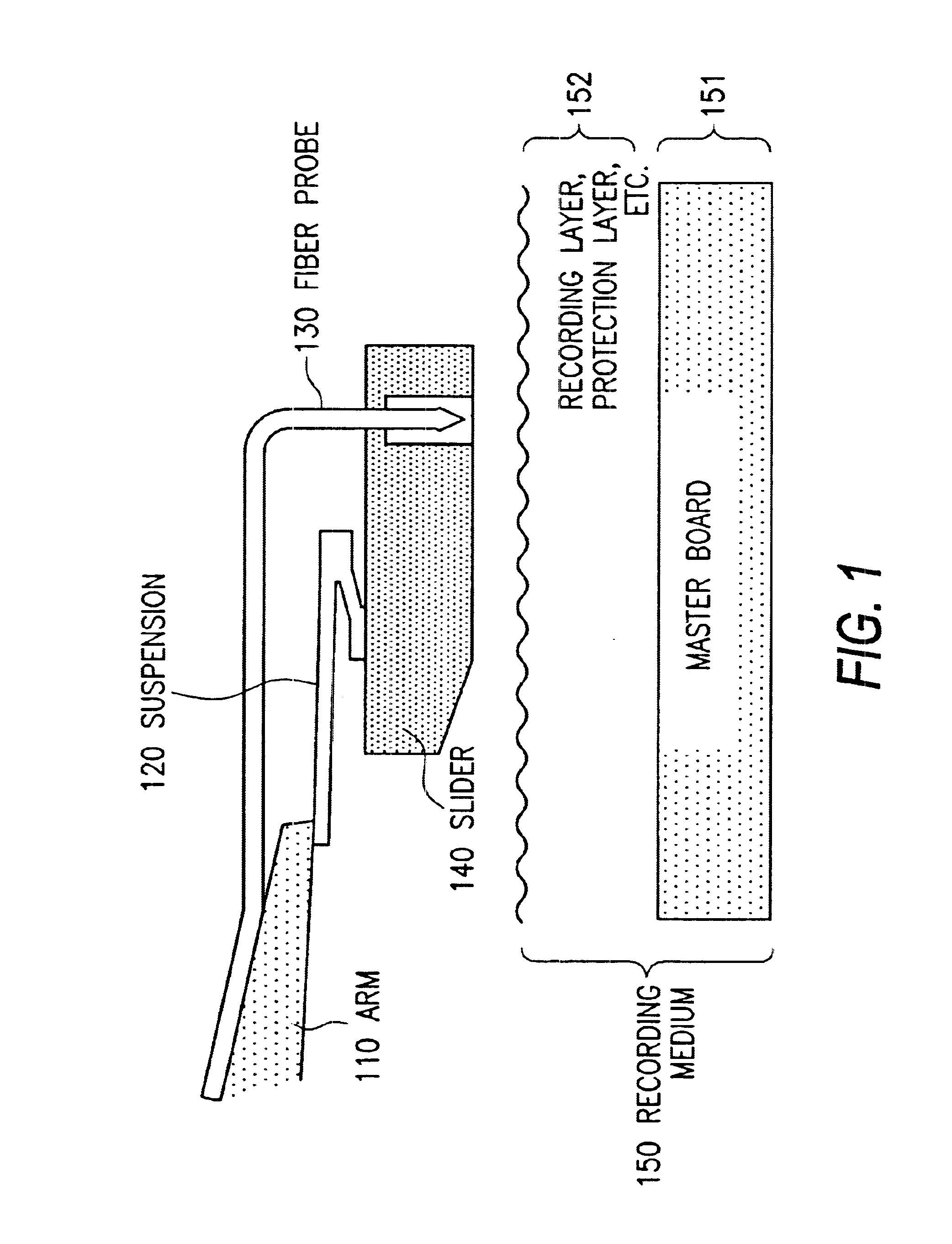
A suspension arm for an optical transducer comprises a load beam, a slider coupled to the load beam by a gimbal assembly and including an optical transducer positioned adjacent to an end of the slider facing a pivot point of the suspension arm, and an optical fiber for transmitting light toward the transducer, wherein an end of the optical fiber is positioned adjacent to the transducer such that light emitted from the fiber passes directly to the transducer. Disc drives that include the suspension arm, and a method of transmitting light to an optical transducer, are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS7596072B2Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingPhase changeElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magneto-optical head and magneto-optical recording apparatus including same
InactiveUS20020097639A1Avoid thermal expansionAppropriately maintain optical characteristicOptical head protectionOptical flying-type headsOptical propertyEngineering
A magneto-optical recording head comprises a magnetic coil formed on a lower surface of a transparent substrate opposed to a magneto-optical disk. A heat sink layer is provided at the outside of the magnetic coil on the lower surface. An objective lens is supported on an upper surface of the transparent substrate. The heat, which is generated by the magnetic coil, is released via the heat sink layer to the space between the magneto-optical disk and the substrate. The release of the heat is facilitated by the air stream which is generated by the rotation of the magneto-optical disk. The heat can be effectively released from the magnetic coil without inhibiting optical characteristics of the objective lens.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
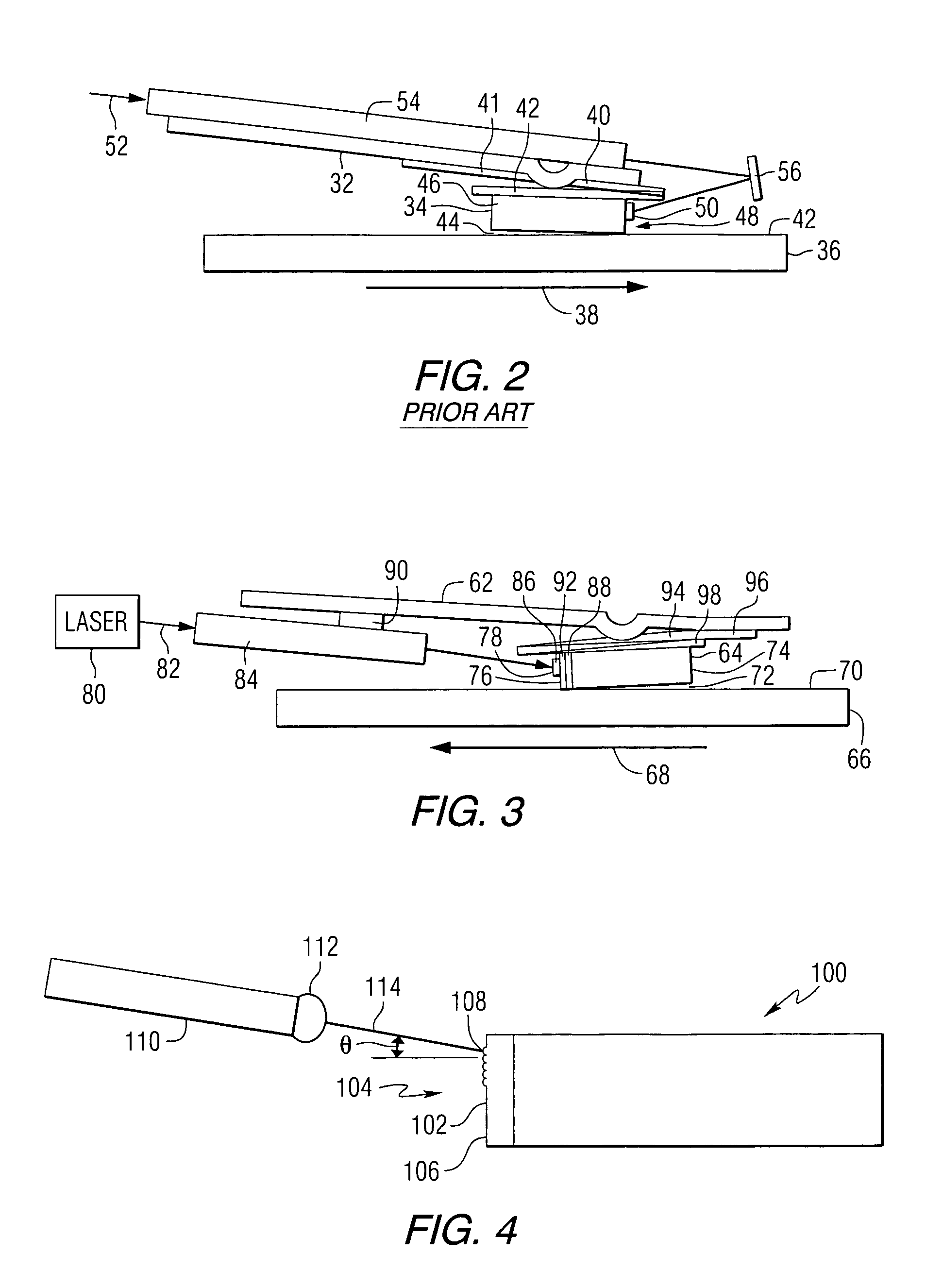
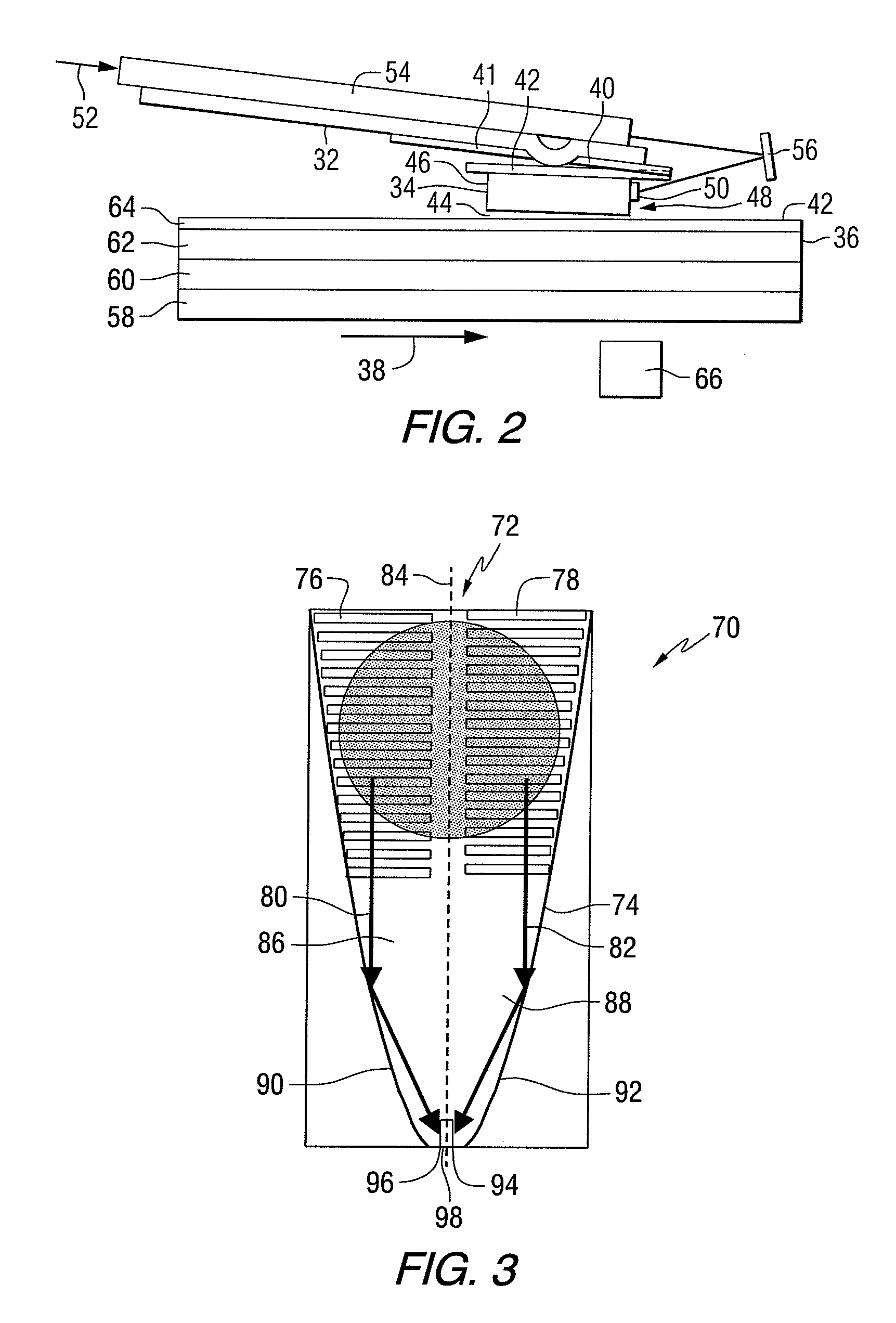
Data storage system having an optical processing flying head
An optical data storage and retrieval system uses a flying head. The flying head is supported on a moving media having information stored in a plurality of stored data locations thereon. Information is stored in each of the plurality of media locations as physical structures capable of modulating the polarization state of incident light into one of two output polarization states. The flying head includes an optical processing assembly which directs an incident light beam having a source polarization state onto the moving media, accessing successive data locations. A reflected light beam having the source polarization state of the incident light beam modulated by a respective polarization modifying data location into one of the output polarization states is received by the flying head. The optical processing assembly optically transforms the modulated output polarization state of the reflected light beam into two return light beams having differentially modulated intensity related to the output polarization state of the reflected light beam. The two intensity modulated return light beams are optically coupled to a distal differential detector which outputs digital data representing the stored data information for the subject data location. A preferred embodiment includes optical fibers for coupling the incident and return light beams between the detector and the flying head. The optical assembly of a preferred embodiment includes an optical plate having pre-shaped and dimensioned recesses for automatically locating and aligning multiple optical components comprising the assembly. The flying head may also include a servo-controlled micro machined mirror for directing the incident and reflected light beams to and from the media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
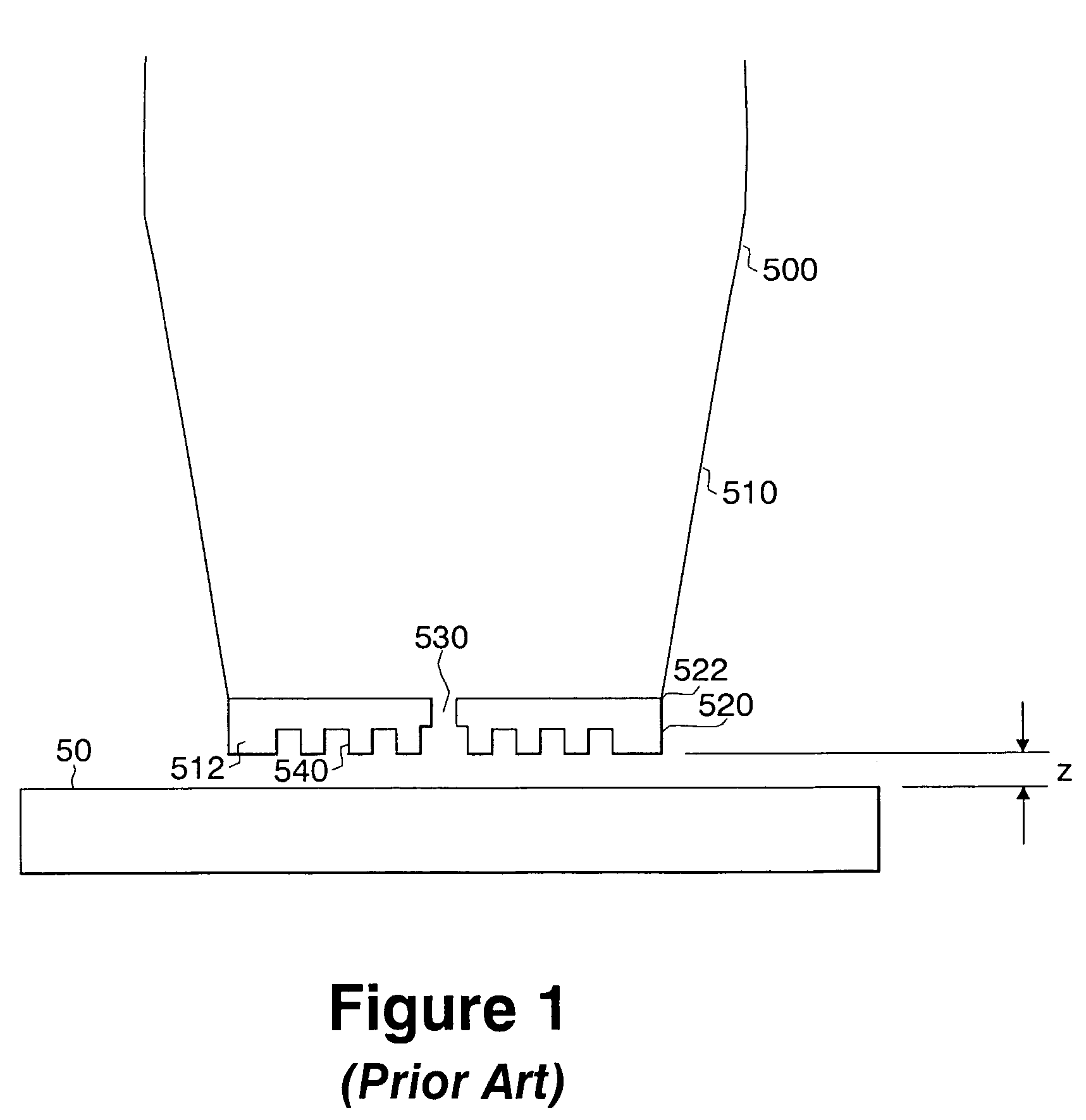
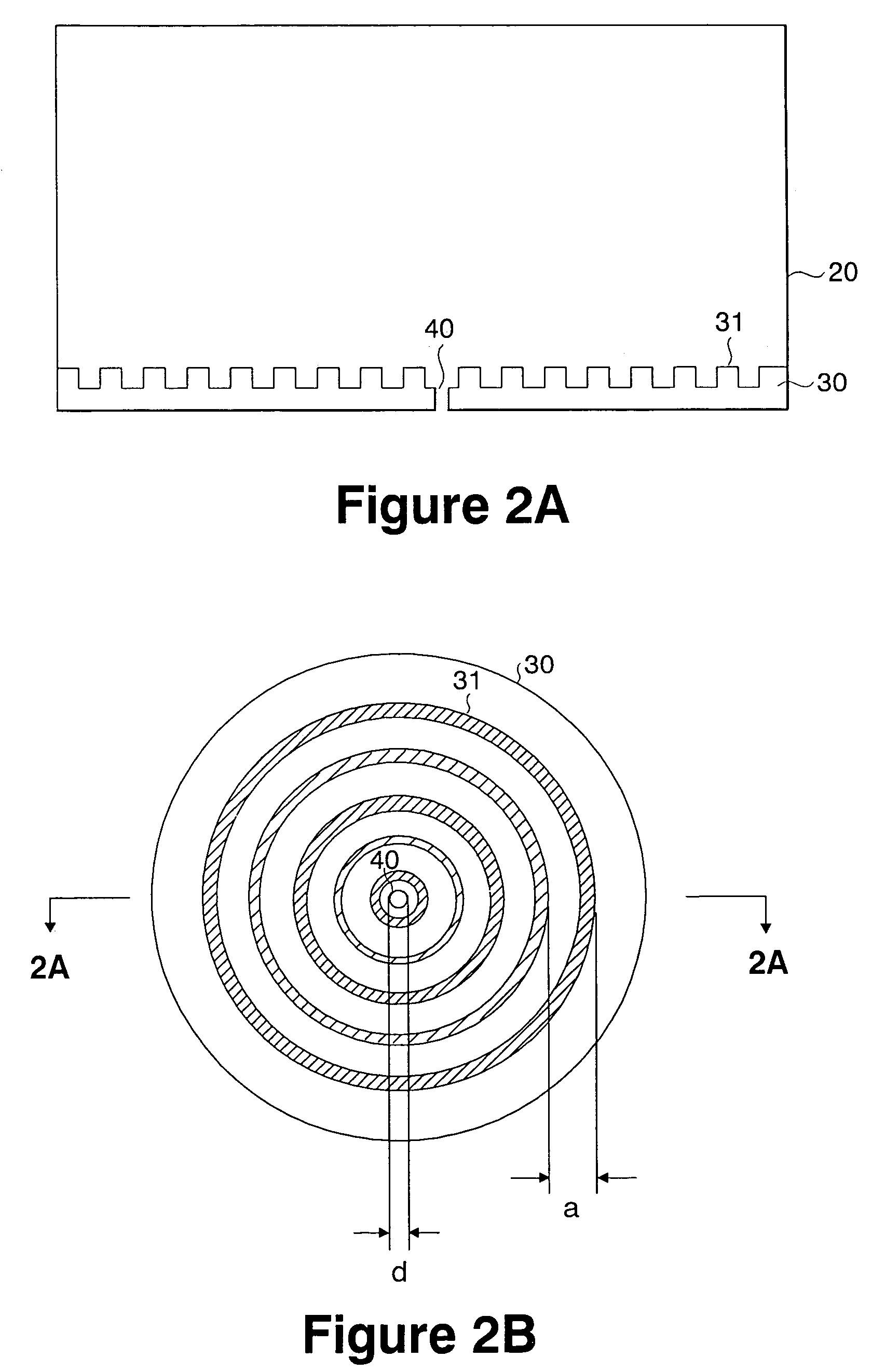
Disc head slider designs to reduce particle sensitivity
A head slider is provided that includes a slider body having leading and trailing slider edges and first and second side edges. The body further includes an air bearing surface generally disposed within a bearing surface plane. A raised portion is positioned on the bearing surface plane and spaced apart from the leading edge. Also, a comb structure is provided having a plurality of raised protrusions positioned proximate and substantially parallel to the leading edge of the slider, wherein the plurality of raised protrusions form gaps throughout the leading edge.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Optical microswitch with rotary electrostatic microactuator
InactiveUS6301403B1Reduce transmission lossFast switching timeOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesFiberIn plane
An optical microswitch comprising a support body and first and second output fibers carried by the body. A rotary electrostatic microactuator is carried by the body and extends in plane. A micromirror is disposed out of the plane. The microactuator has a mirror holder coupled to the micromirror and at least one comb drive assembly coupled to the mirror holder for driving the micromirror about an axis of rotation extending perpendicular to the plane between a first position for reflecting a laser beam to the first output fiber and a second position for reflecting the laser beam to the second output fiber.
Owner:COHERENT INC
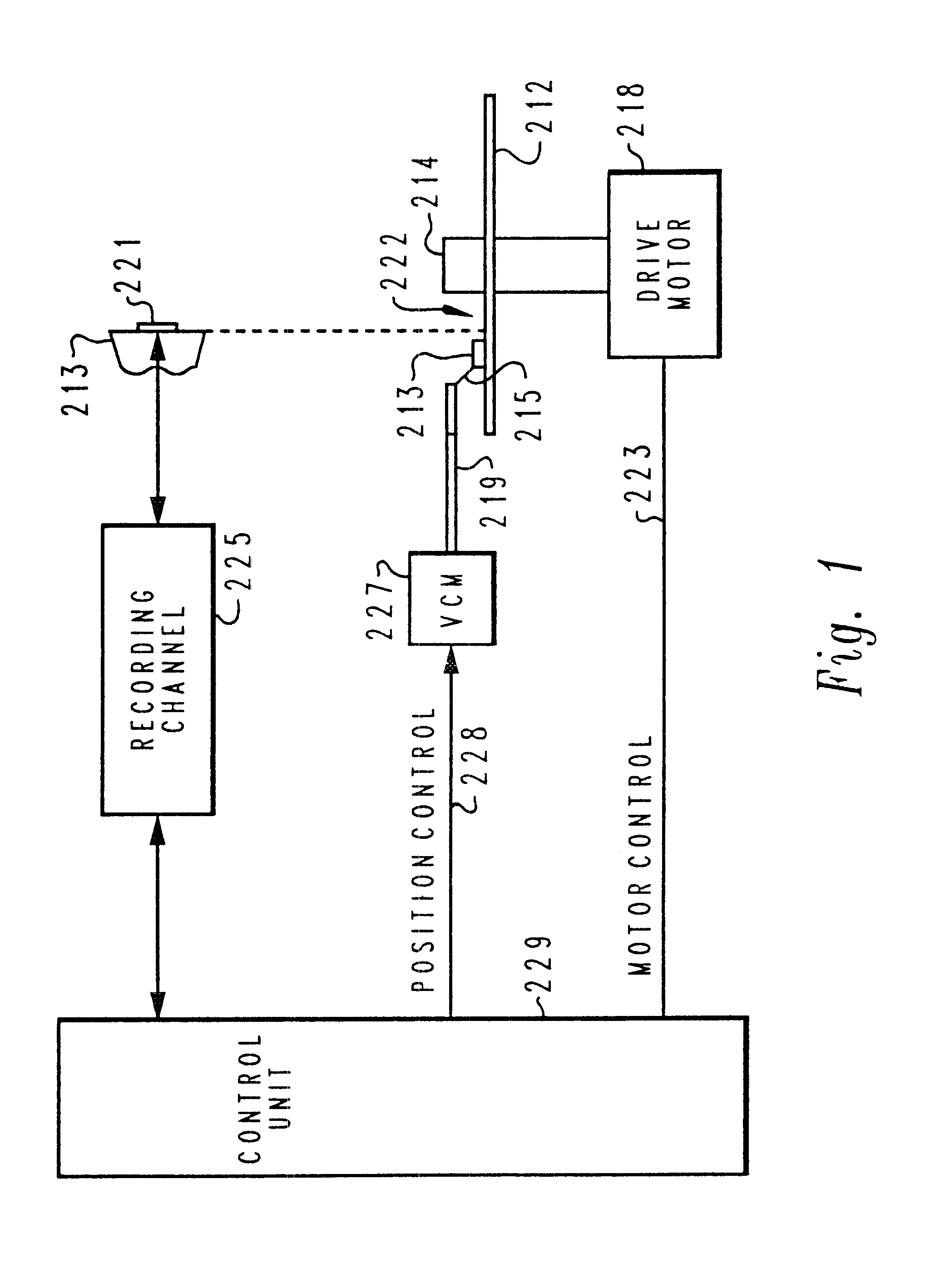
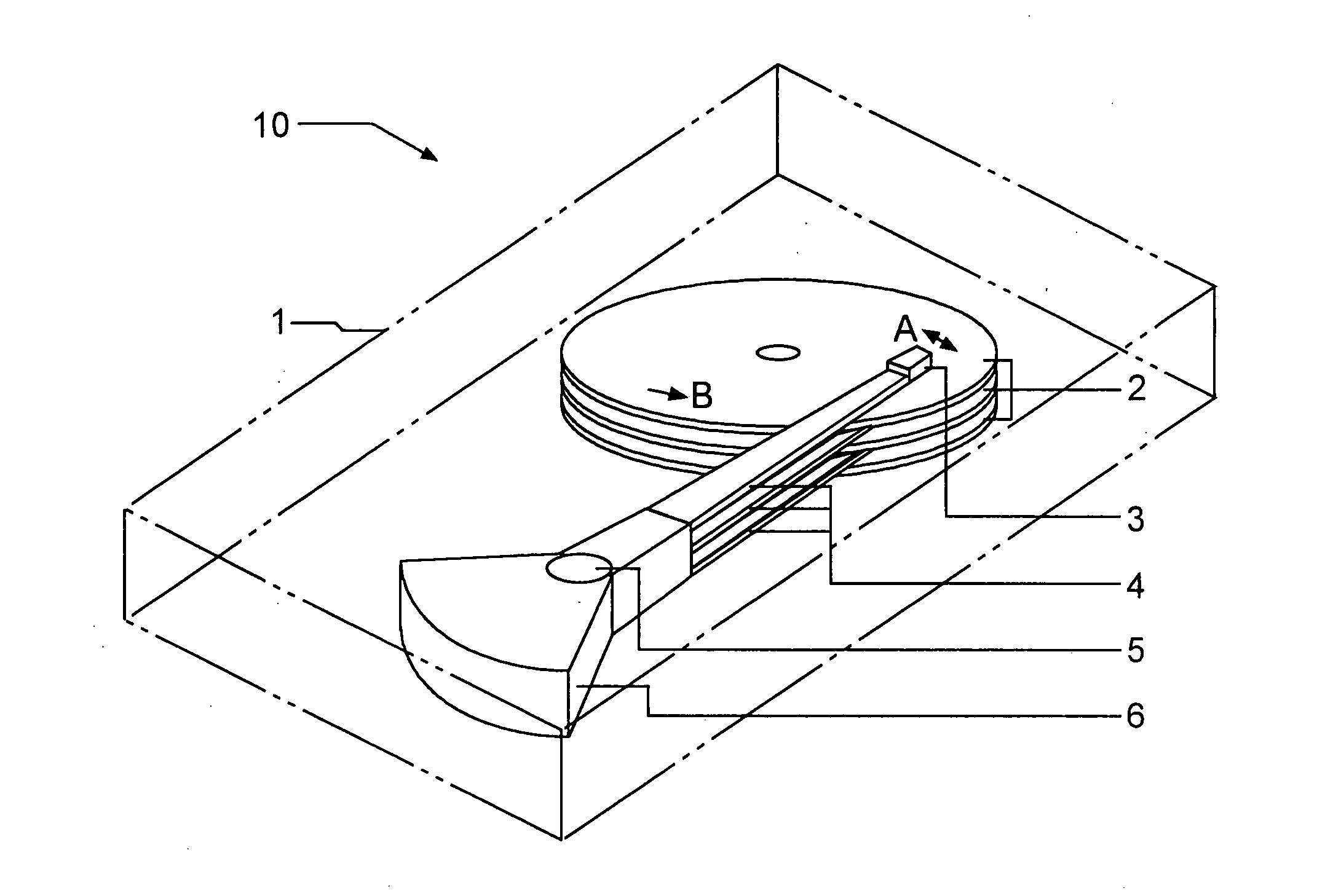
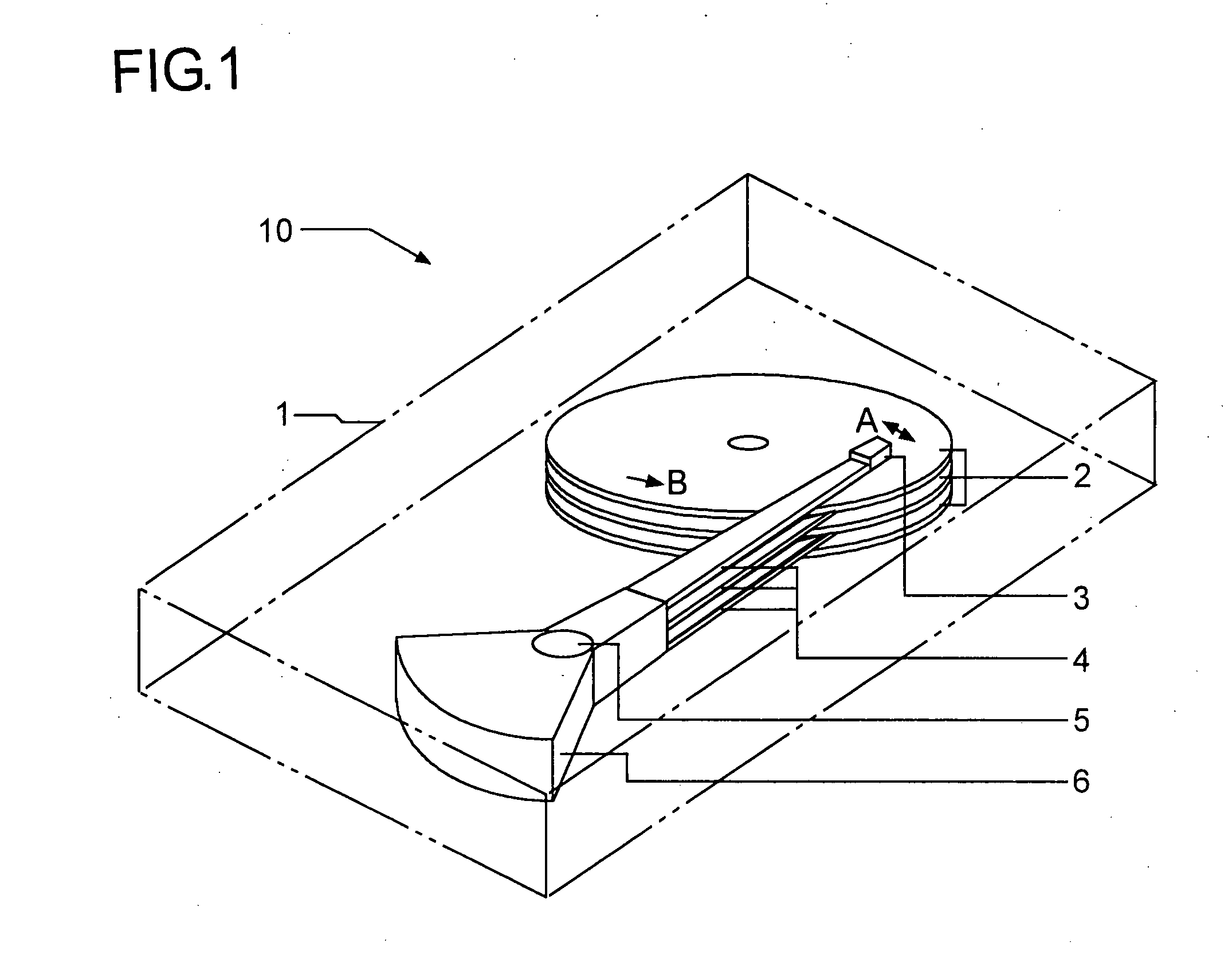
Optical information recording and reproducing apparatus
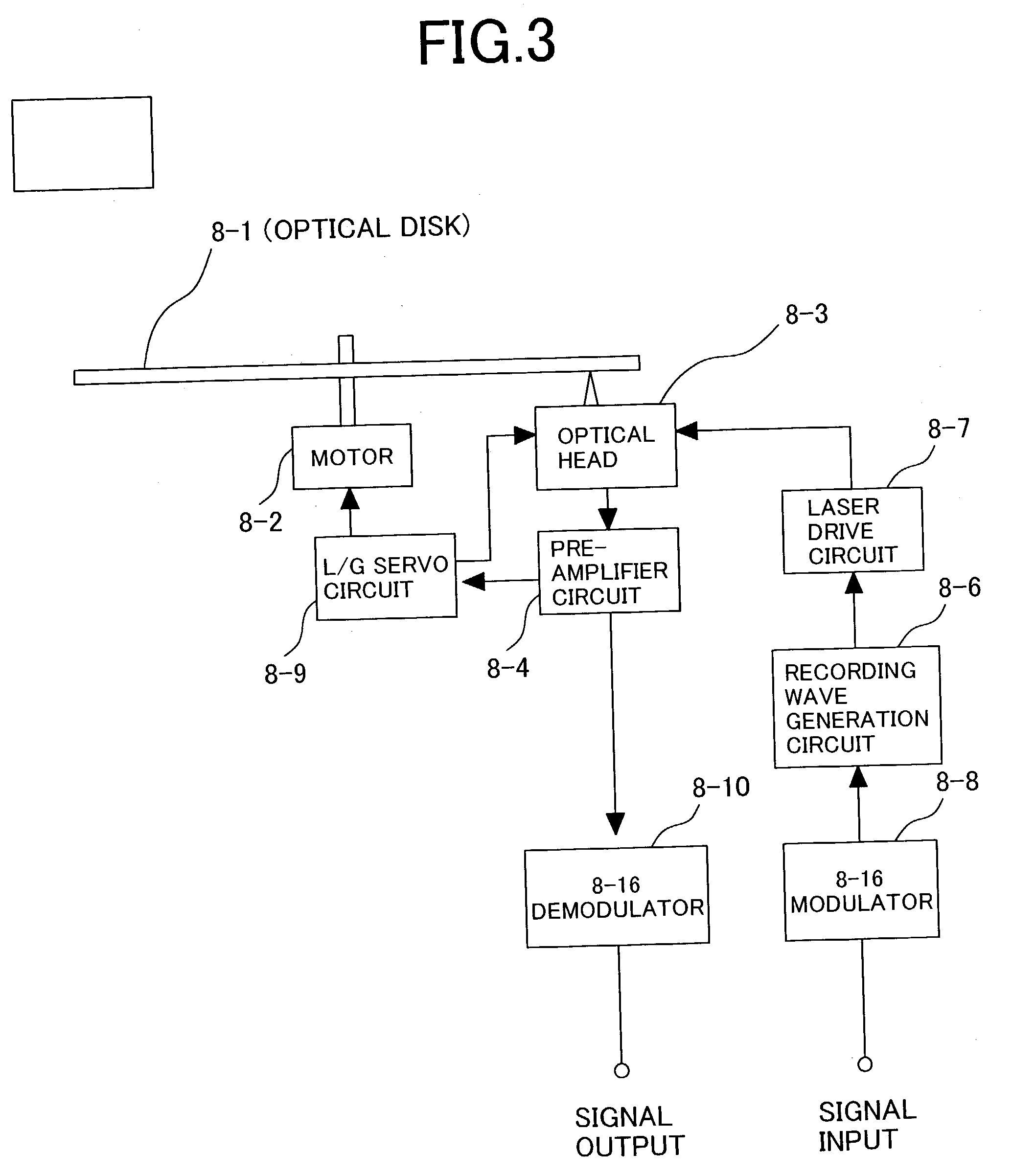
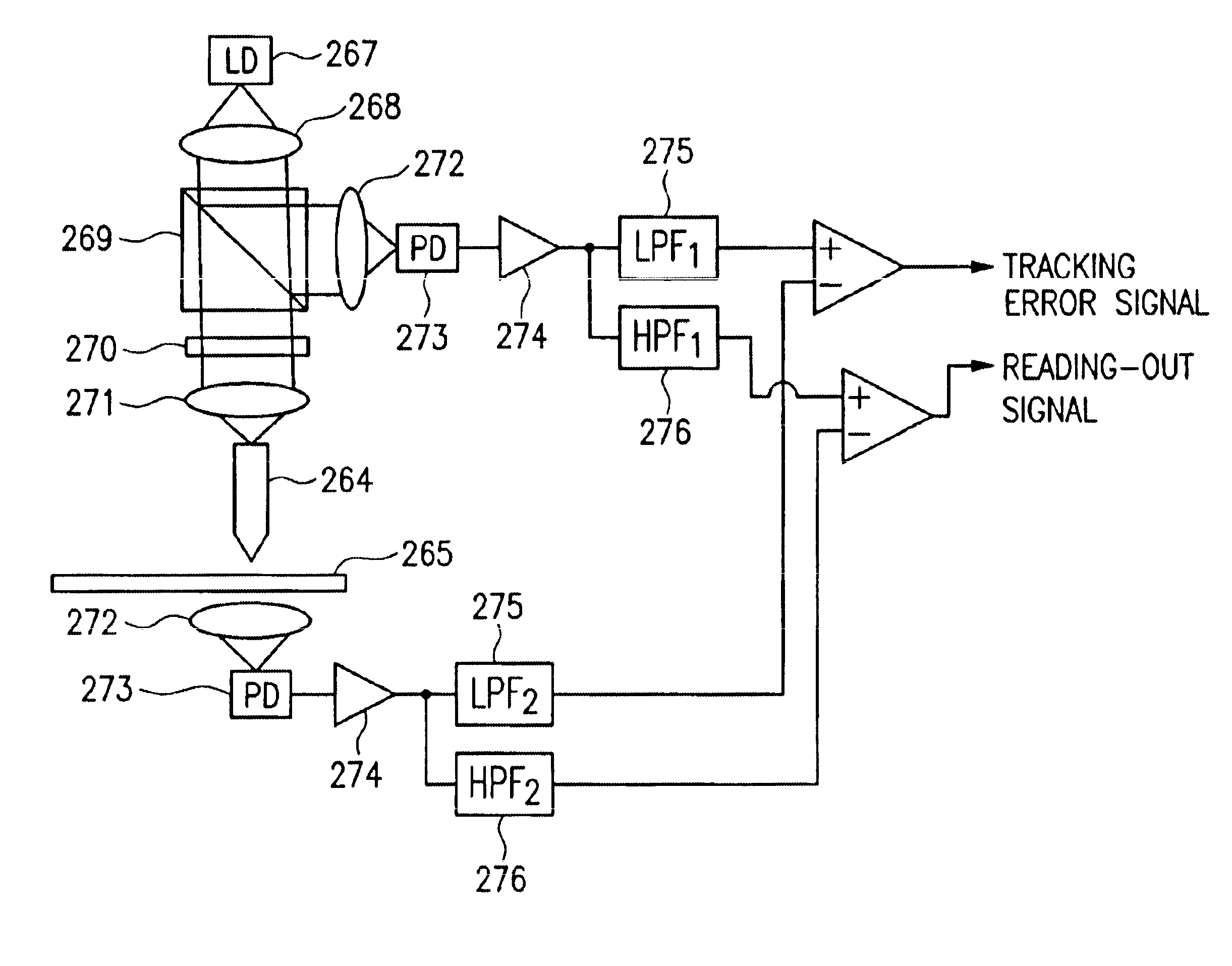
An optical information recording / reproducing apparatus enabling fine actuation of almost several nm order for performing the tracking correction includes a pair of fixed electrodes so as to put a probe therebetween in a direction perpendicular to the direction of data row arrangement on a recording medium and a voltage applying medium for applying the voltage between the respective fixed electrodes and the probe. The position of the tip end of the probe is controlled by the action of electrostatic attractive force between the fixed electrodes and the probe caused by applying the voltage thereacross. The probe is constructed with center core clad therearound. The base part is fixed and the sharpened tip end is free, as a so-called cantilever structure. The apparatus further enables to obtain the tracking error. Laser light is emitted from the tip end and radiated onto the information recording medium. The light reflected on the recording medium is converted optoelectrically. The average value of the electric signal is outputted as the tracking error signal. An information recording / reproducing apparatus capable of improving the stability of the control voltage for tracking the probe includes control voltages and bias voltage applying members respectively independent from each other.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS20060133230A1Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingElectromagnetic radiationOptical recording
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
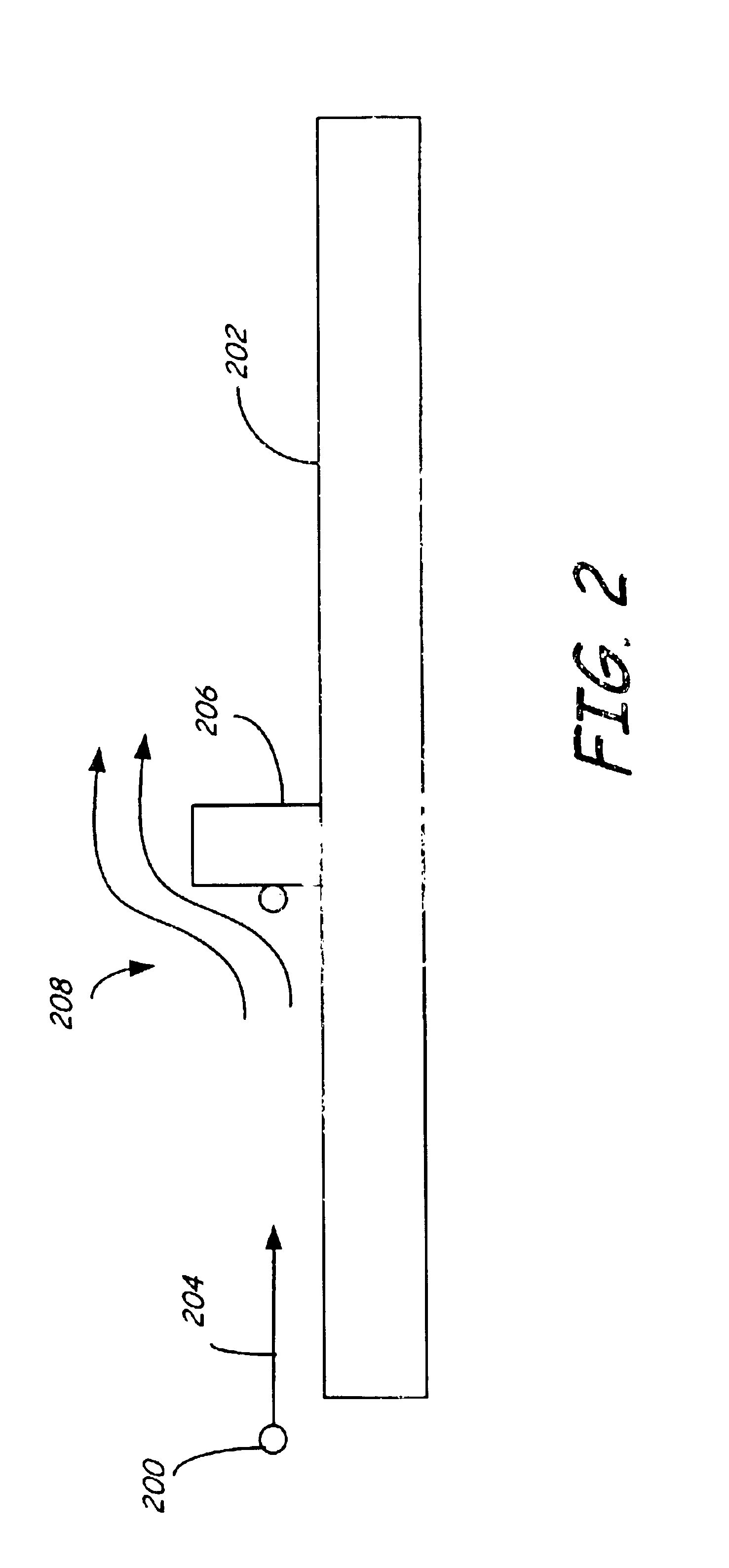
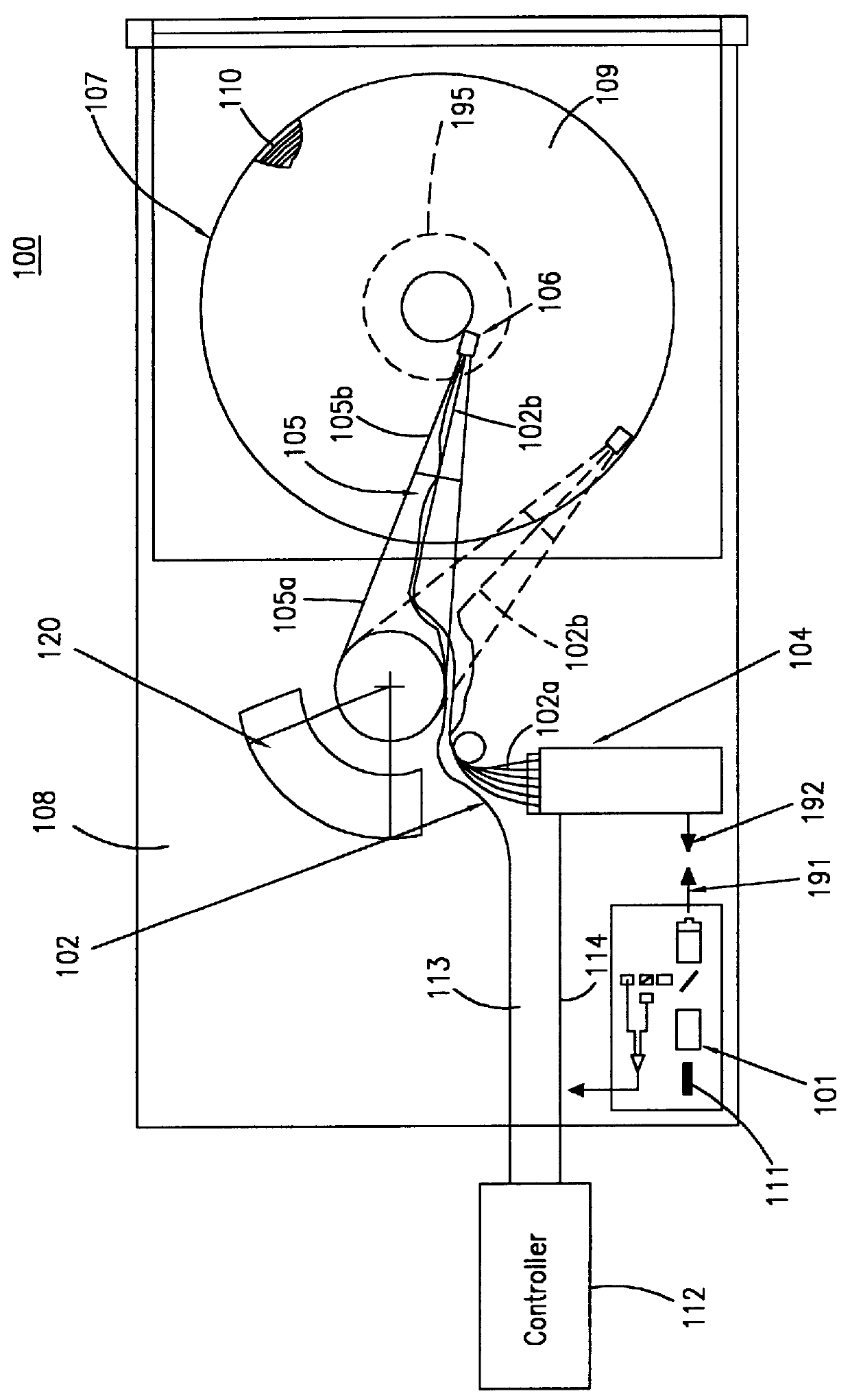
Method for manufacturing magneto-optical data storage system
InactiveUS6076256AImproved stiffness/mass ratioReduced operating requirementsMaterial nanotechnologyLine/current collector detailsLight beamOptical storage
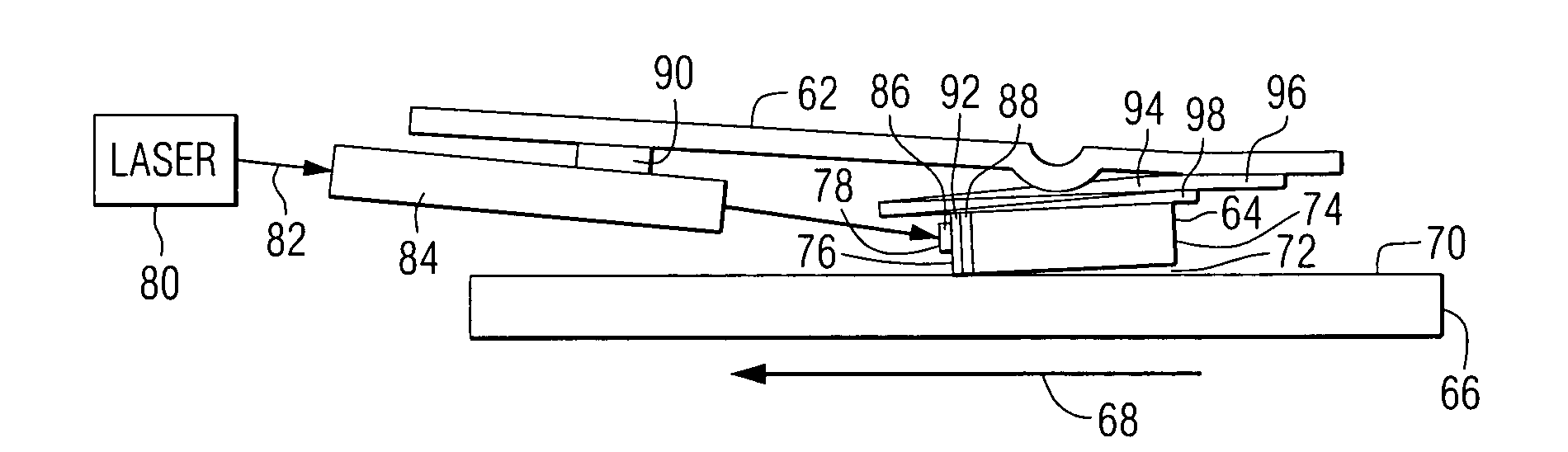
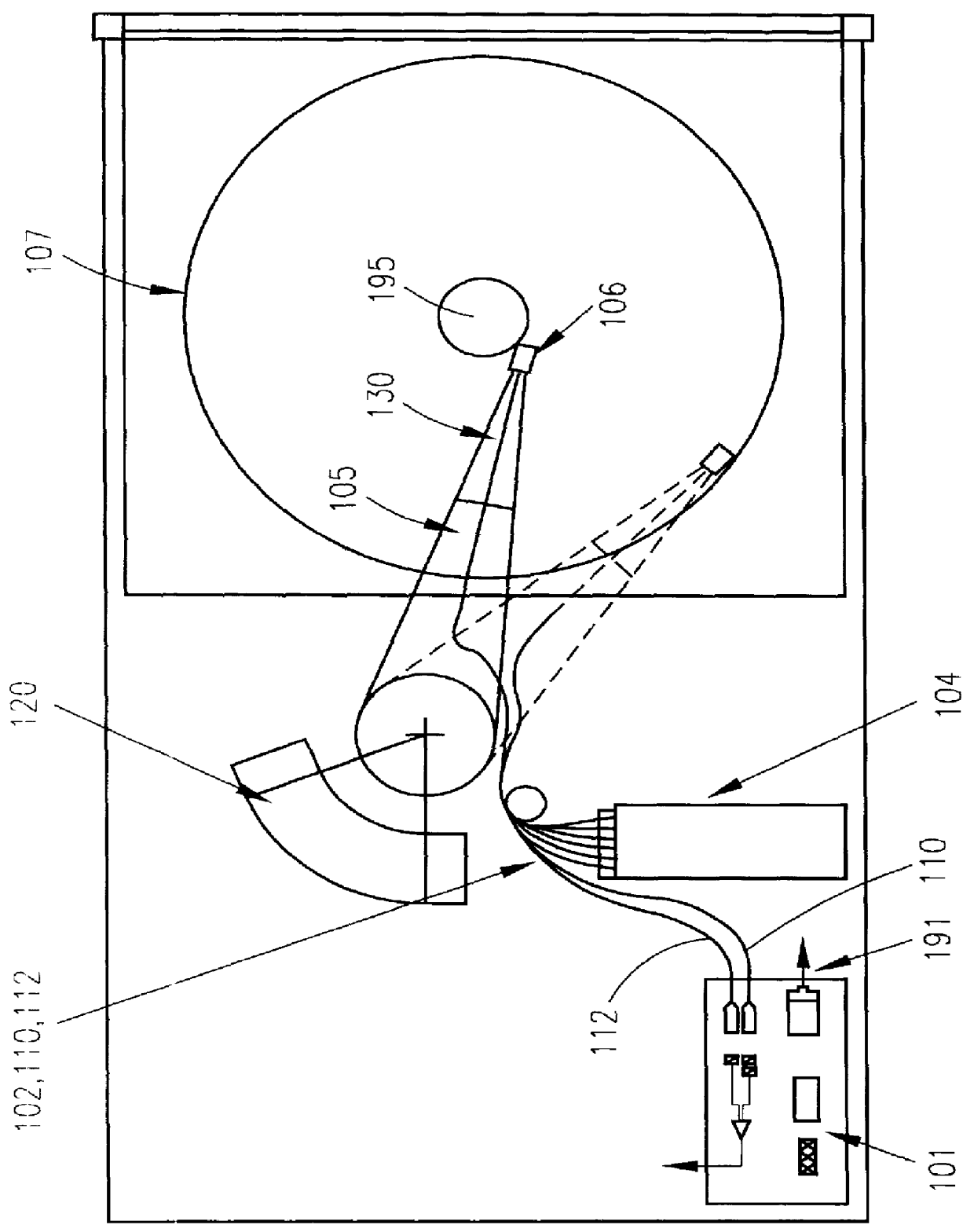
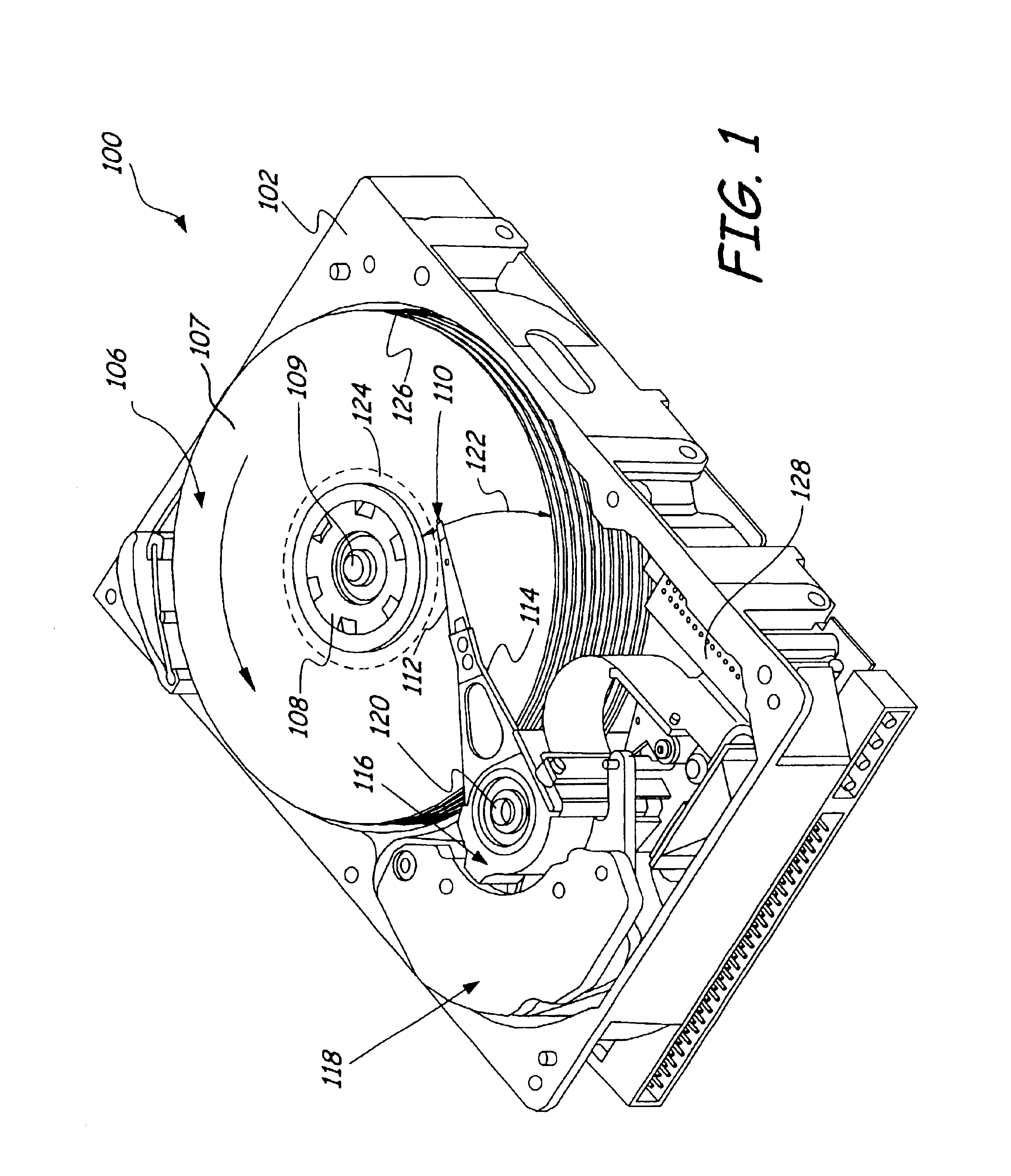
A method for manufacturing a magneto-optical data storage system. The method includes the steps of providing a support surface and rotatably mounting a magneto-optical disk having a planar storage surface with a plurality of concentrically disposed data tracks onto the support surface. A proximal extremity of an arm is pivotably mounted on the support surface so that a distal extremity of the arm pivots between first and second positions relative to the storage surface. An optical light emitter and receiver emitting a laser beam is carried by the distal extremity of the arm. A flying magneto-optical head is mounted on the distal extremity of the arm. A mirror assembly is attached to the head. The mirror of the mirror assembly can be rocked between first and second positions for reflecting the laser beam between the optical light emitter and receiver and the storage surface of the magneto-optical disk so as to permit the optical recording and / or reading of information on the storage surface.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Optical near-field generator and recording apparatus using the optical near-field generator
InactiveUS20090207703A1Reduce impactReduce componentsNanomagnetismOptical flying-type headsPenetration depth
A near-field optical probe and optical near-field generator are provided. A problem of a probe having a scatterer in which optical near-field noises are generated at the parts other than for a point at which an intense optical near-field is generated, is solved. In one example of the probe, a surface of the parts except for a vertex of the scatterer at which the intense optical near-field is generated is etched so that an etching depth becomes not less than a penetration depth of the optical near-field. The probe facilitates control of noises when a sample is observed or recording marks are reproduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical head and information storage device
InactiveUS20050157393A1Improve light utilization efficiencyHigh speed scanOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsRefractive indexComputational physics
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Disk cartridge, optical disk drive, optical library and optical storage system
InactiveUS6614751B1Simple structureLow costCarrier constructional parts dispositionApparatus for flat record carriersDisk enclosureLocking mechanism
At least an optical disk, a spindle motor, an optical head assembly and a seeking mechanism are mounted in a disk cartridge to accordingly establish a hermetically sealed structure. On the other hand, a disk cartridge guide member, an optical assembly, a disk cartridge lock mechanism, an optical path switching mechanism and the like are mounted in an optical disk drive. This enables the structure of improving the dust immunity of the disk cartridge and the low cost. Moreover, the optical disk drive can accommodate a plurality of disk cartridges. Thus, a disk cartridge implements a memory corresponding to various services. Or, an optical library of the present invention has mechanisms for mounting and detaching the optical disk cartridge and accordingly accommodating a large number of disk cartridges in a limited space. Moreover, it is possible to provide an extremely small type of an optical disk drive to thereby design a memory unit applicable to various services including a portable apparatus. This is a media convertible storage system, which is superior in dust immunity and rapid access of a fixed magnetic disk and can record large-scale information and can satisfy various requests from miscellaneous application fields.
Owner:KATAO HISASHI
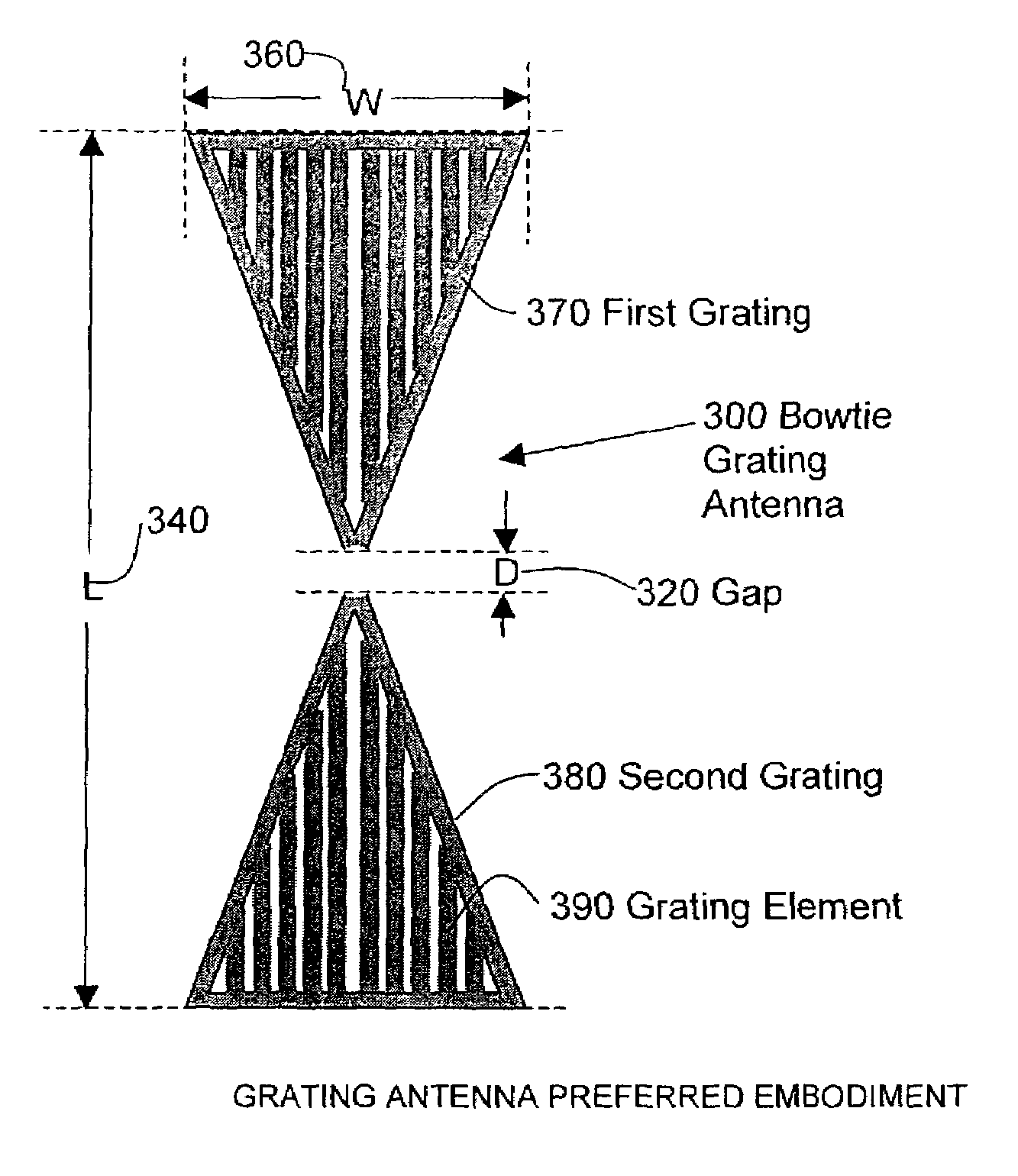
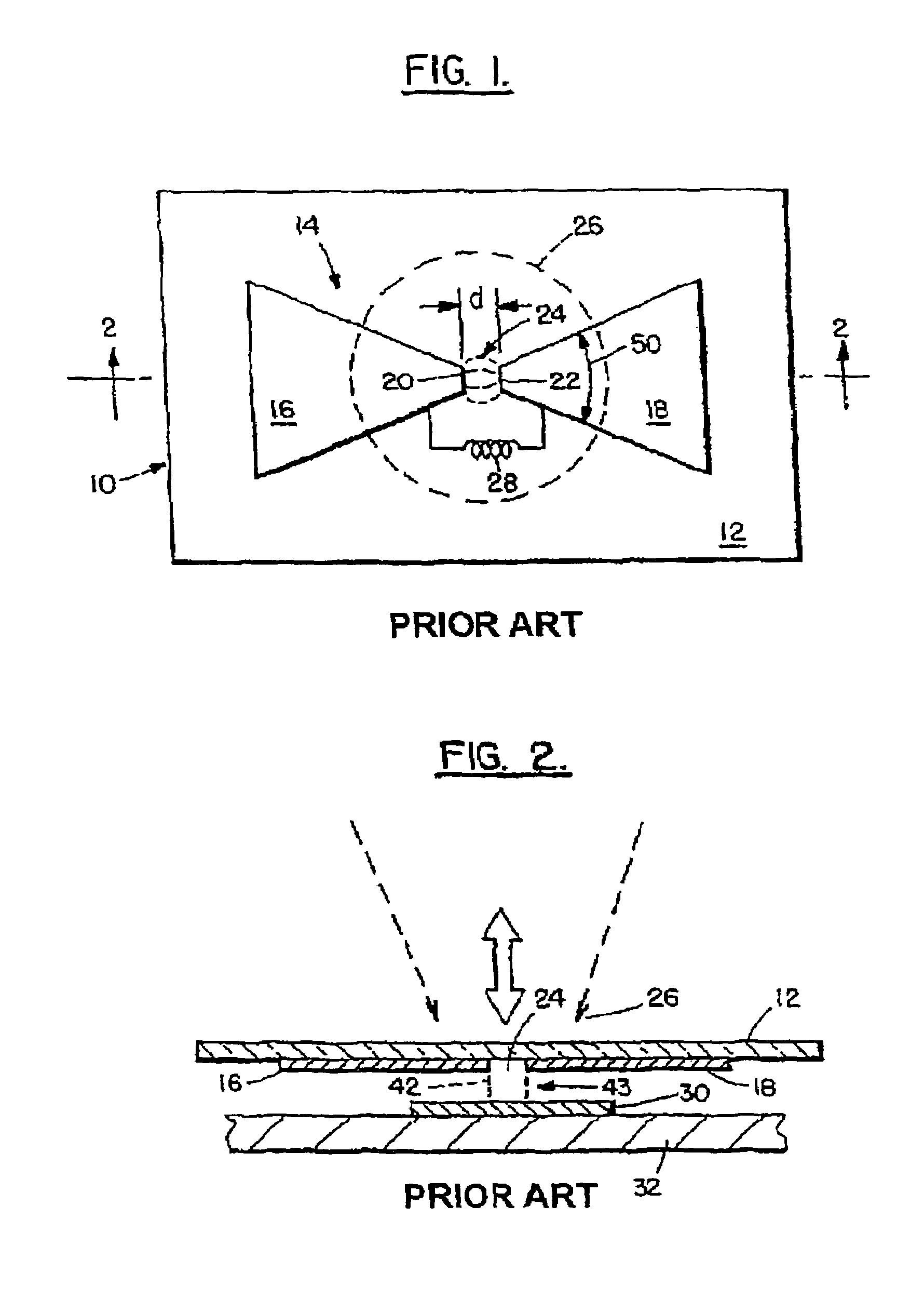
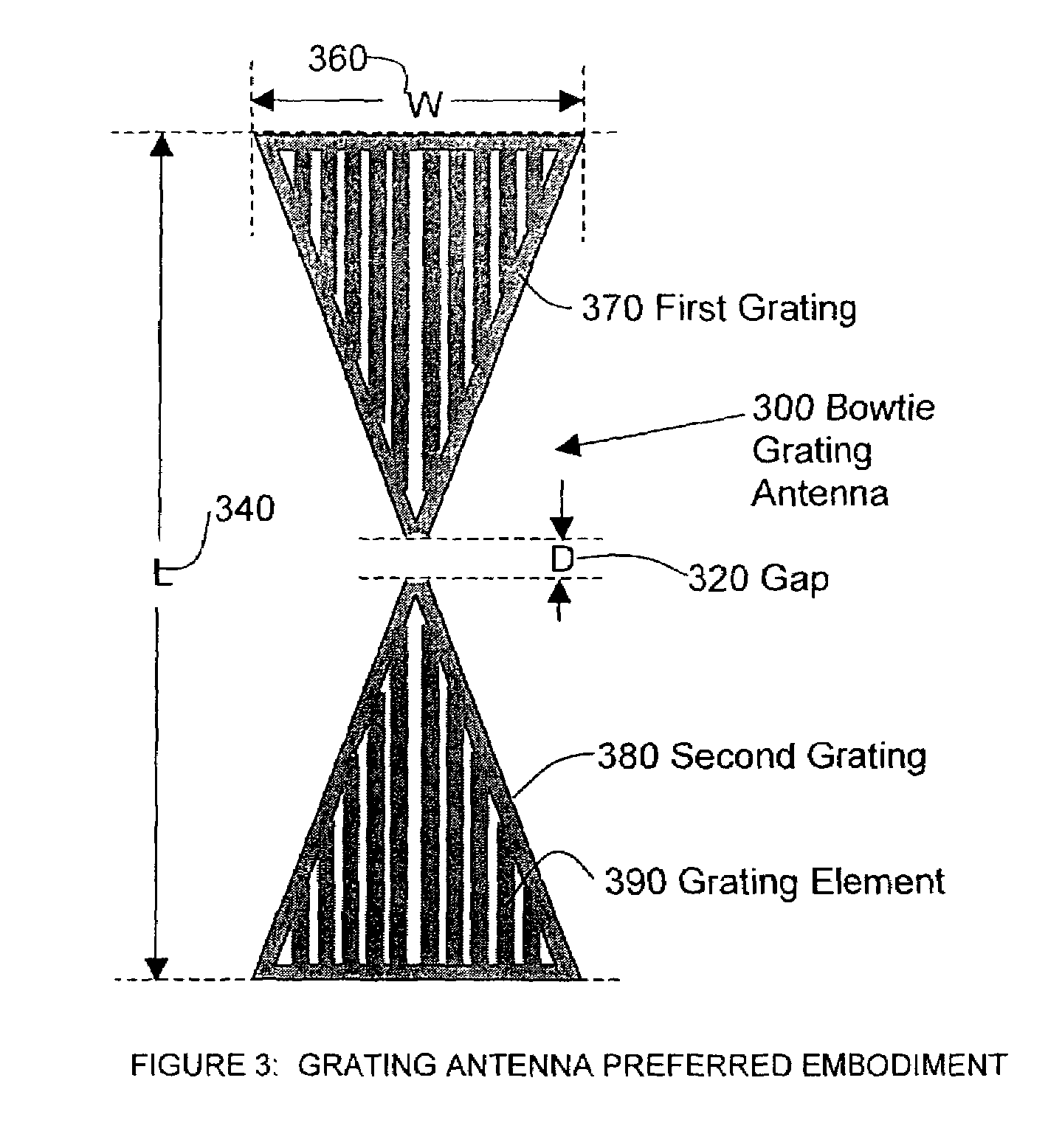
Optical disc head including a bowtie grating antenna and slider for optical focusing, and method for making
InactiveUS7177236B2Maintain positionReduce manufacturing costCombination recordingOptical flying-type headsGratingAudio power amplifier
A slider system have been developed to aid in the spacing between read / write heads and the storage medium, and a grating antenna amplifier has been developed to improve illumination spot size and polarization characteristics. The grating antenna can be attached to a grayscale slider to obtain a distance between the illumination spot and antenna that lies in the near field region.
Owner:MEMS OPTICAL
Optical head and information storage device
InactiveUS7106664B2Improve light utilization efficiencyHigh speed scanOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsRefractive indexDielectric layer
An optical head including a first dielectric layer having a first refractive index, a pair of second dielectric layers located adjacent to the first dielectric layer on both sides thereof, each of the second dielectric layers having a second refractive index larger than the first refractive index, a pair of third dielectric layers located adjacent to the second dielectric layers, and a pair of fourth dielectric layers located adjacent to the third dielectric layers, each of the fourth dielectric layers having a third refractive index larger than the first refractive index. Light is incident on the optical head in a direction orthogonal to a layering direction of the first to fourth dielectric layers. The first dielectric layer and each of the third dielectric layers have different refractive indices or different thicknesses.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical information recording-reproduction apparatus
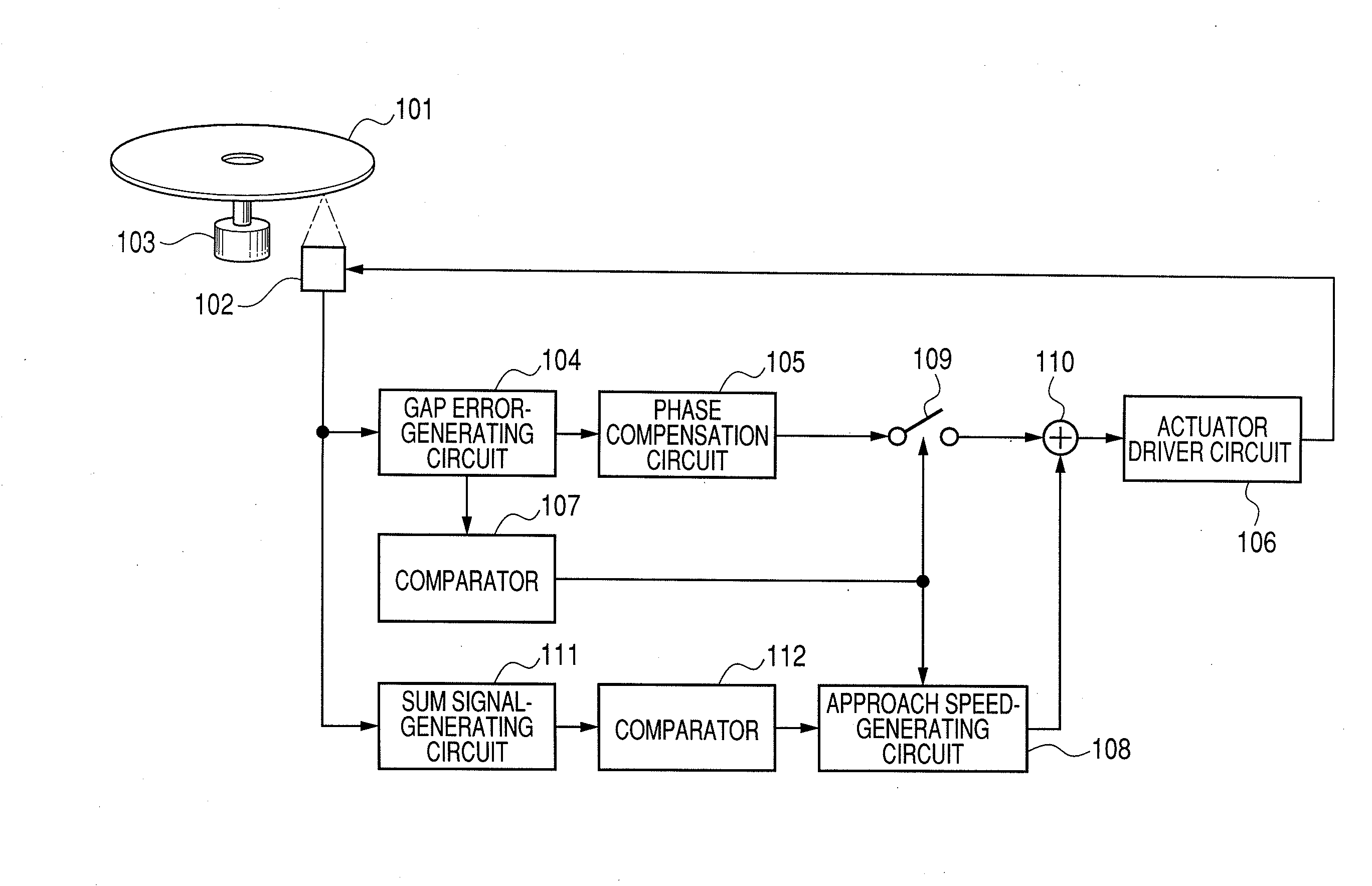
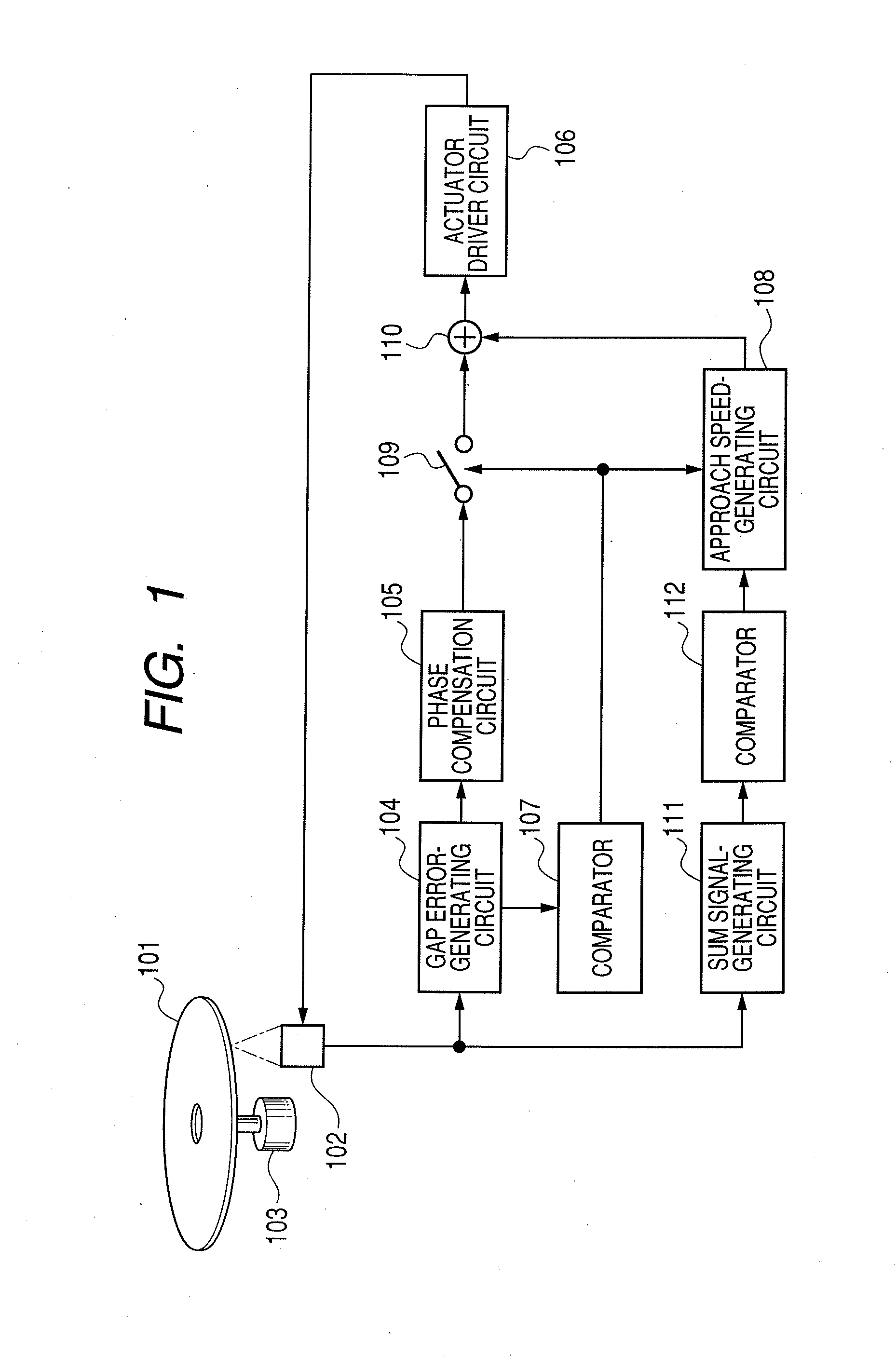
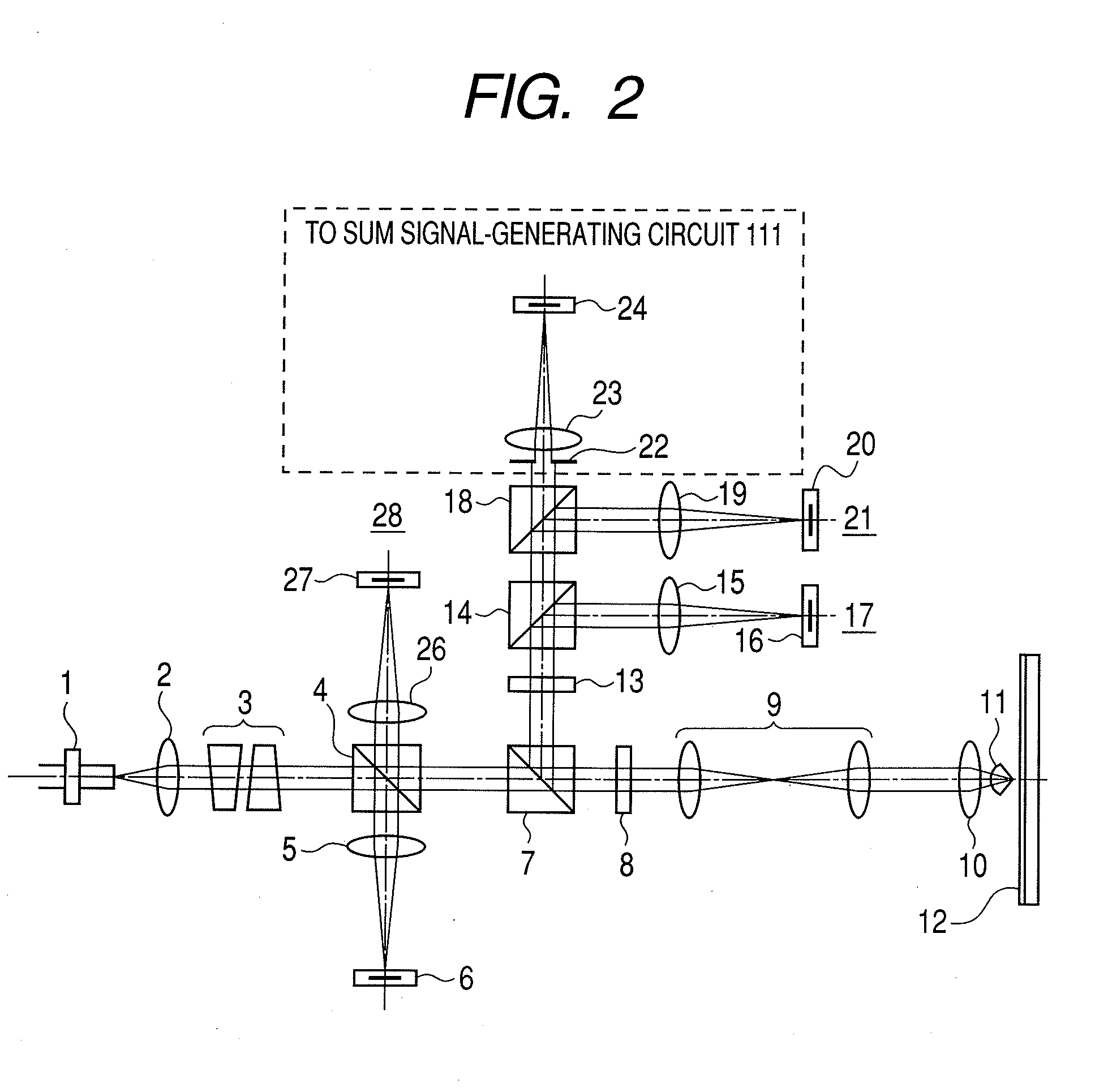
InactiveUS20080198728A1High speed approachStable servo-controlOptical head protectionOptical flying-type headsDriver circuitLight beam
An optical information recording-reproduction apparatus comprises: a light source; an objective lens and a SIL (solid immersion lens) for focusing a light beam from the light source on an optical recording medium; an aperture element for collecting a part of the light beam reflected by an optical recording medium, corresponding to the effective aperture number of the objective lens and SIL of less than 1; a detecting element for detecting the part of the light beam from the aperture element corresponding to the effective aperture number of less than 1; a speed-generating circuit for reducing the speed of approach of the SIL to the recording medium in accordance with the level of the signal detected by the detecting element; and a driver circuit for driving the objective lens and the SIL in accordance with output from the speed-generating circuit.
Owner:CANON KK
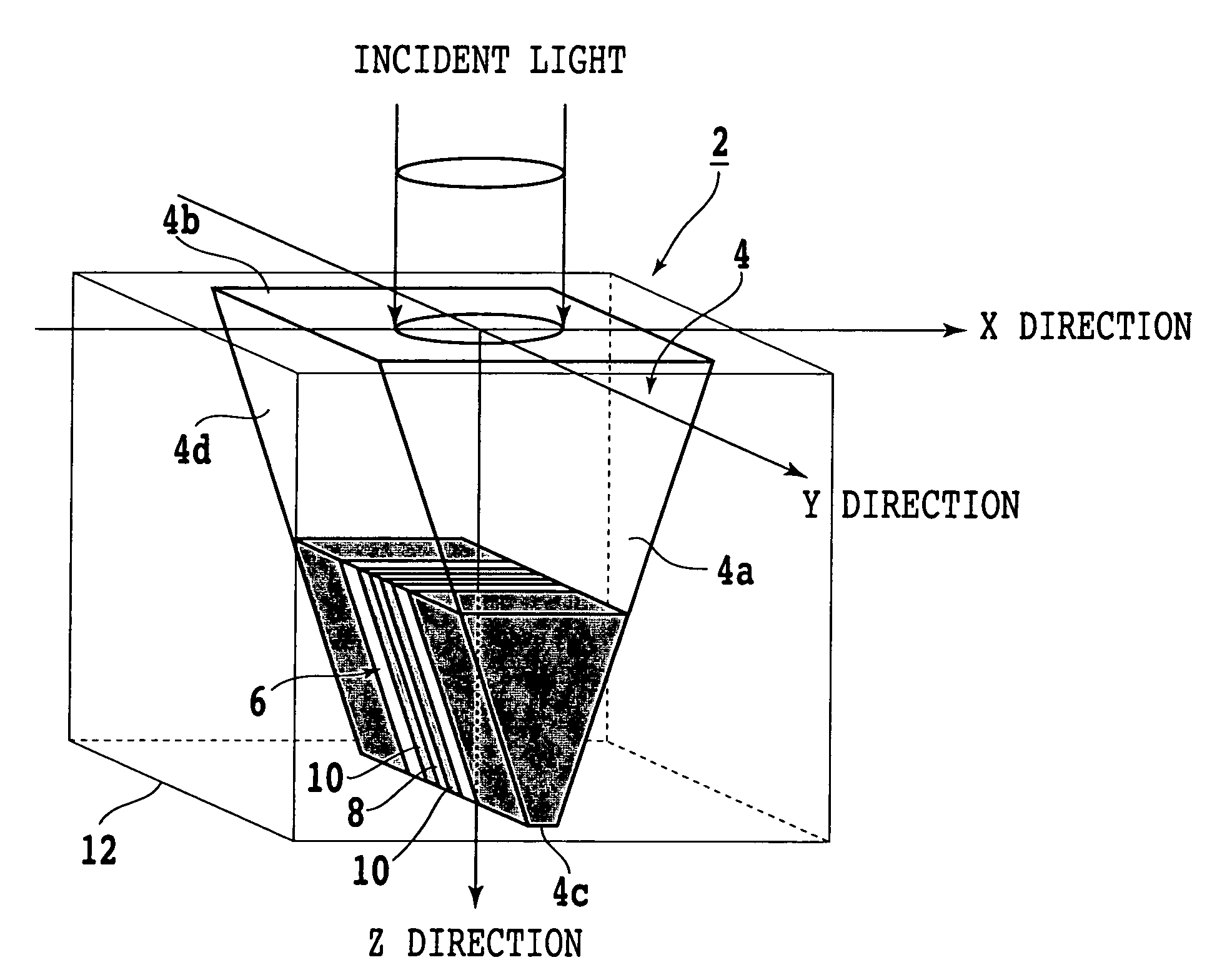
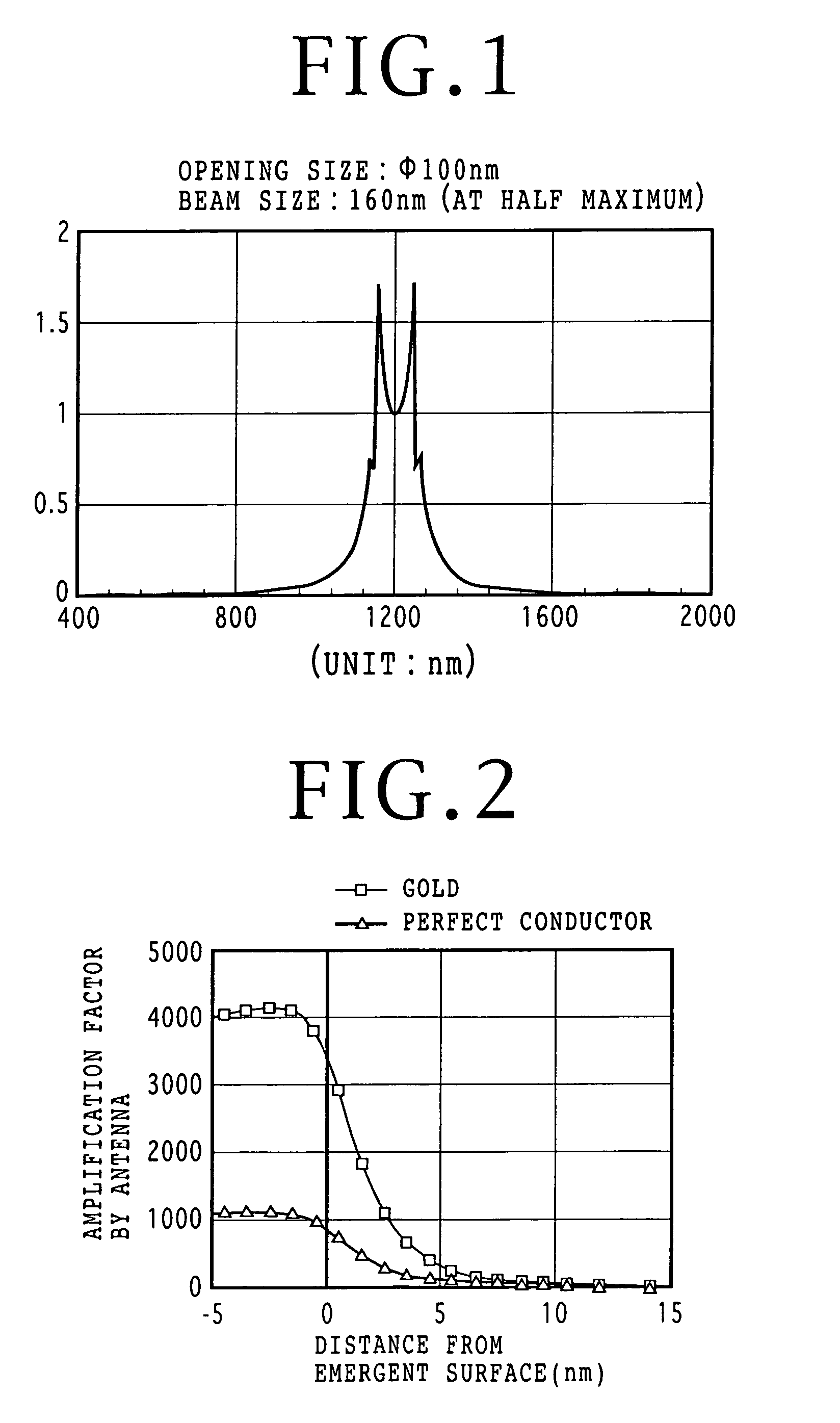
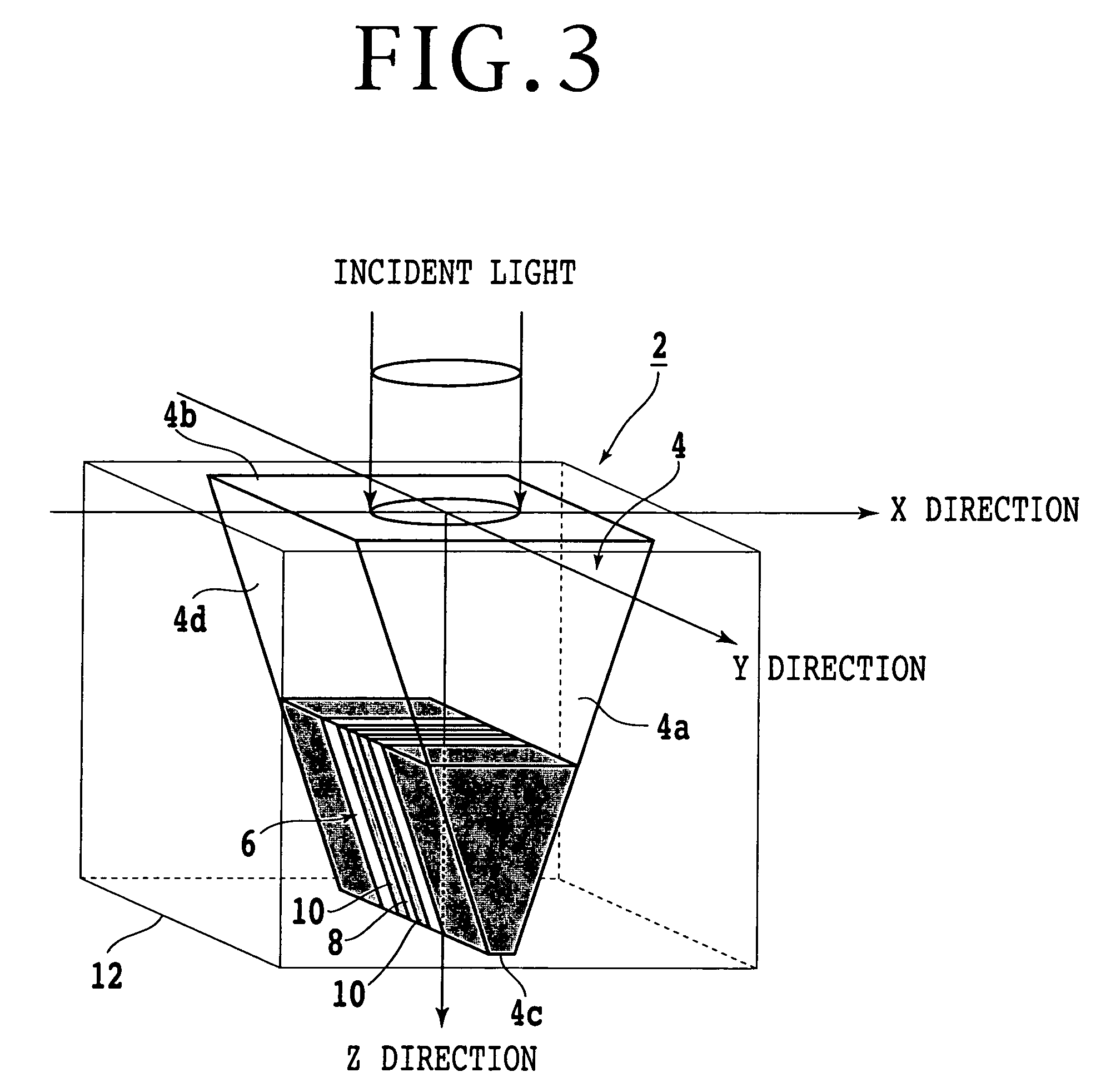
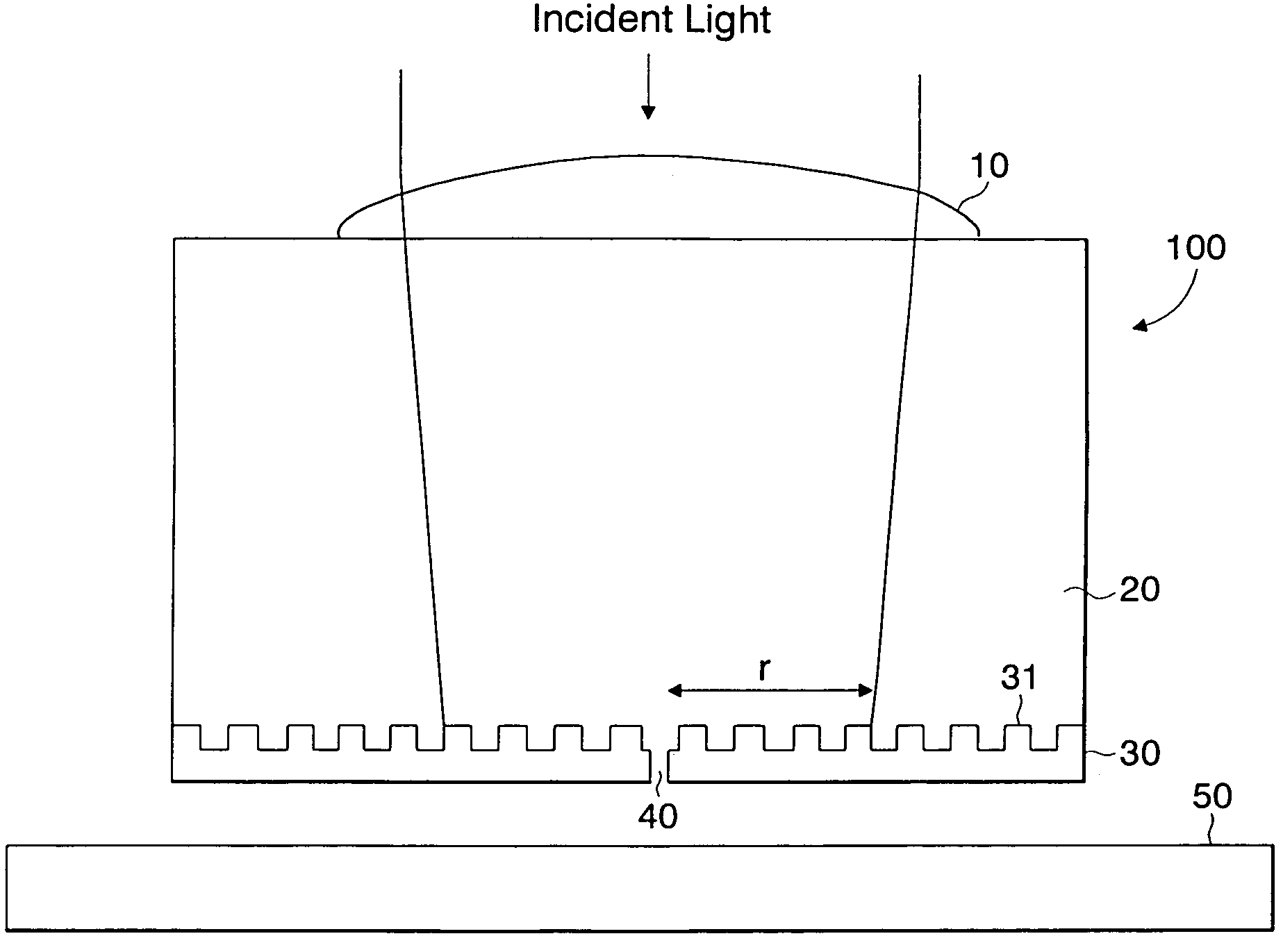
Optical element for enhanced transmission of light and suppressed increase in temperature
InactiveUS7154820B2Improve power densityAvoid temperature riseBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptical flying-type headsLight beamWavelength
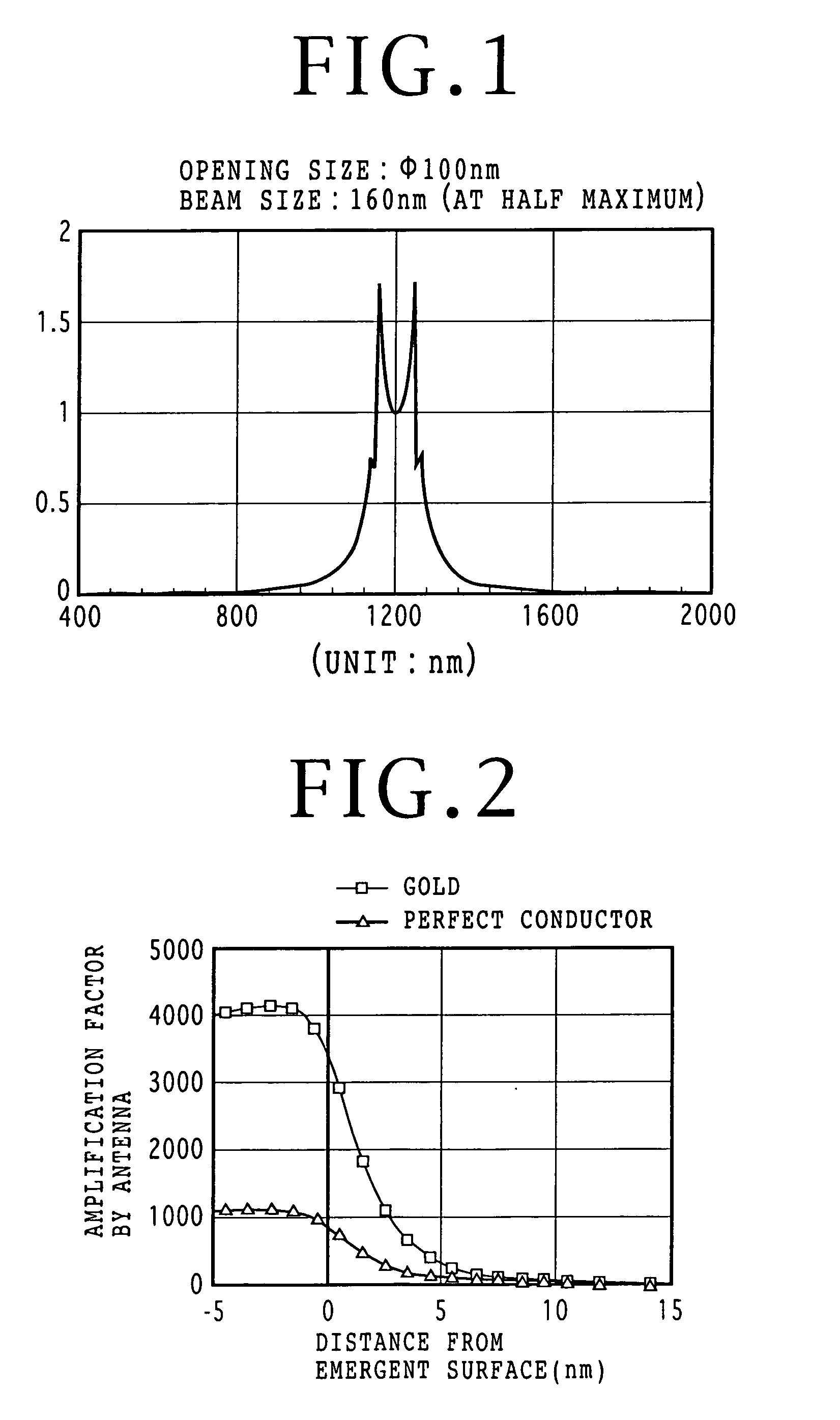
An optical element structure allowing an increased power density of aperture-transmitted light while suppressing increase in temperature is disclosed. A conductive film has a sub-wavelength aperture formed therein and a periodic surface topography formed thereon. A lens focuses light onto the periodic surface topography with a predetermined diameter. The predetermined diameter of incident light on the conductive film and a period of the periodic surface topography are determined so that a power ratio of aperture-transmitted light to the light beam is greater than that of aperture-transmitted light which would be obtained if no periodic surface topography is provided in the conductive film.
Owner:NEC CORP
Near-field optical head system with integrated slider and laser
InactiveUS6963530B1Quickly and easily attachedComplex and time-consuming and attachmentCombination recordingOptical flying-type headsSemiconductor materialsAir bearing
A near-field optical apparatus having one or more solid state lasers and an aerodynamically shaped slider which comprise a single integrated, monolithic device fabricated from the same base semiconductor material. The monolithic optical head can be quickly and easily attached to the read arm of an optical read / write device without requiring attachment of separate laser elements, and without micropositioning or use of optical microscopy for positioning the lasers. The optical head comprising a single semiconductor substrate including a first region which defines a slider having an air bearing surface, and at least one second, laser region which defines a diode laser, with the diode laser having an emission face which is substantially co-planar with the air bearing surface. The semiconductor substrate preferably includes an active layer, a p-clad layer or reflective layer adjacent a first side of the active region, an n-clad layer or reflective layer adjacent a second side of the active layer, and an n-semiconductor layer adjacent the n-clad layer. A slider region of the semiconductor substrate includes an air bearing surface, adjacent the p-clad layer, which is aerodynamically structured and configured to define a slider. The integral lasers include a p-electrical contact adjacent to the p-clad layer and proximate to the laser emission face, and an n-electrical contact adjacent to the n-clad layer or an n-semiconductor layer. The laser mode is defined by oxidized or ion-diffusion regions associated with the p-clad layer or n-clad layer of the laser. A conductive via through the substrate allows electrical connection with the p-side contact to be achieved from the n-side of the substrate. The optical head is used in a near-field optical system with an optical medium having a phase change layer.
Owner:RES INVESTMENT NETWORK
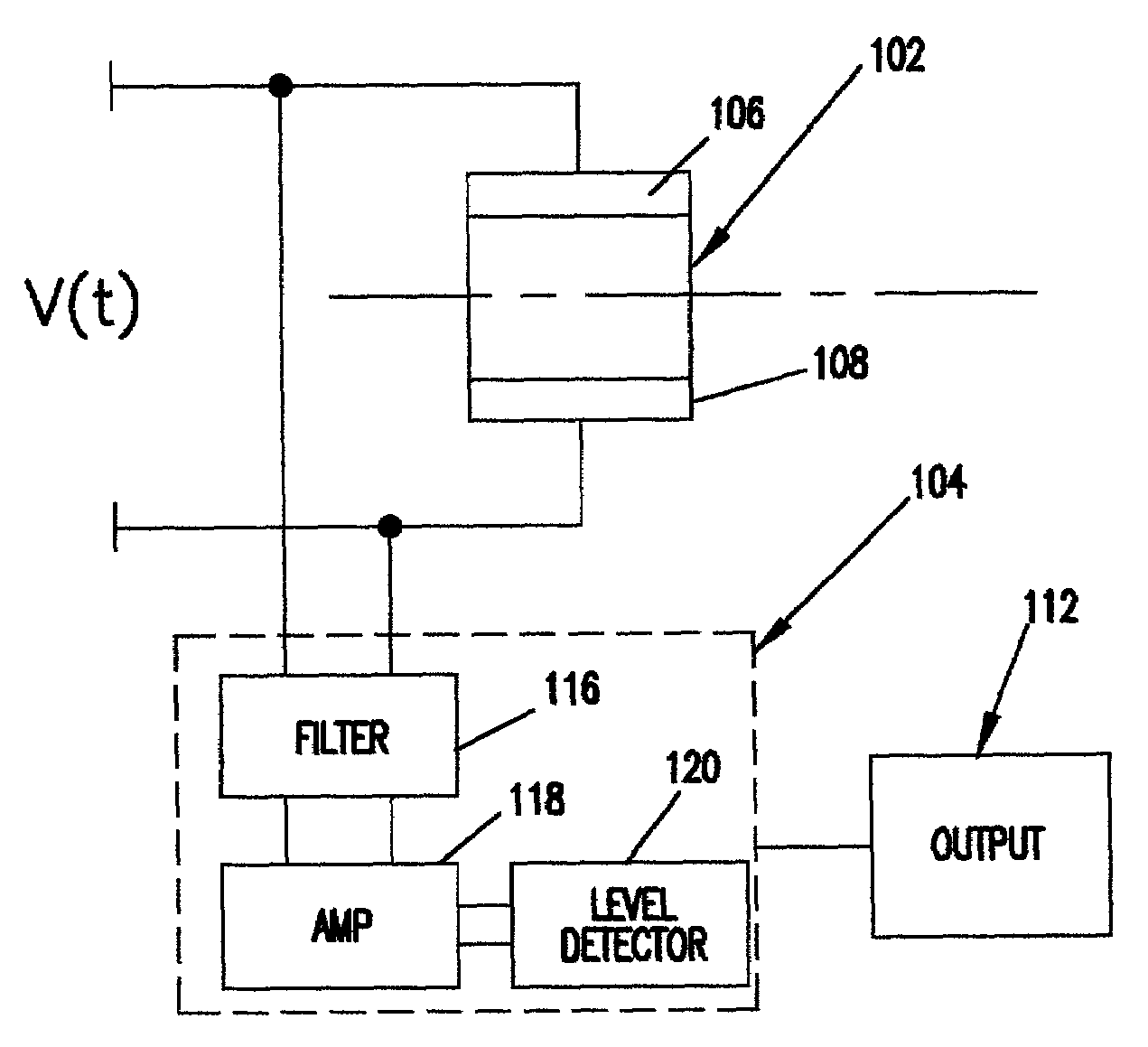
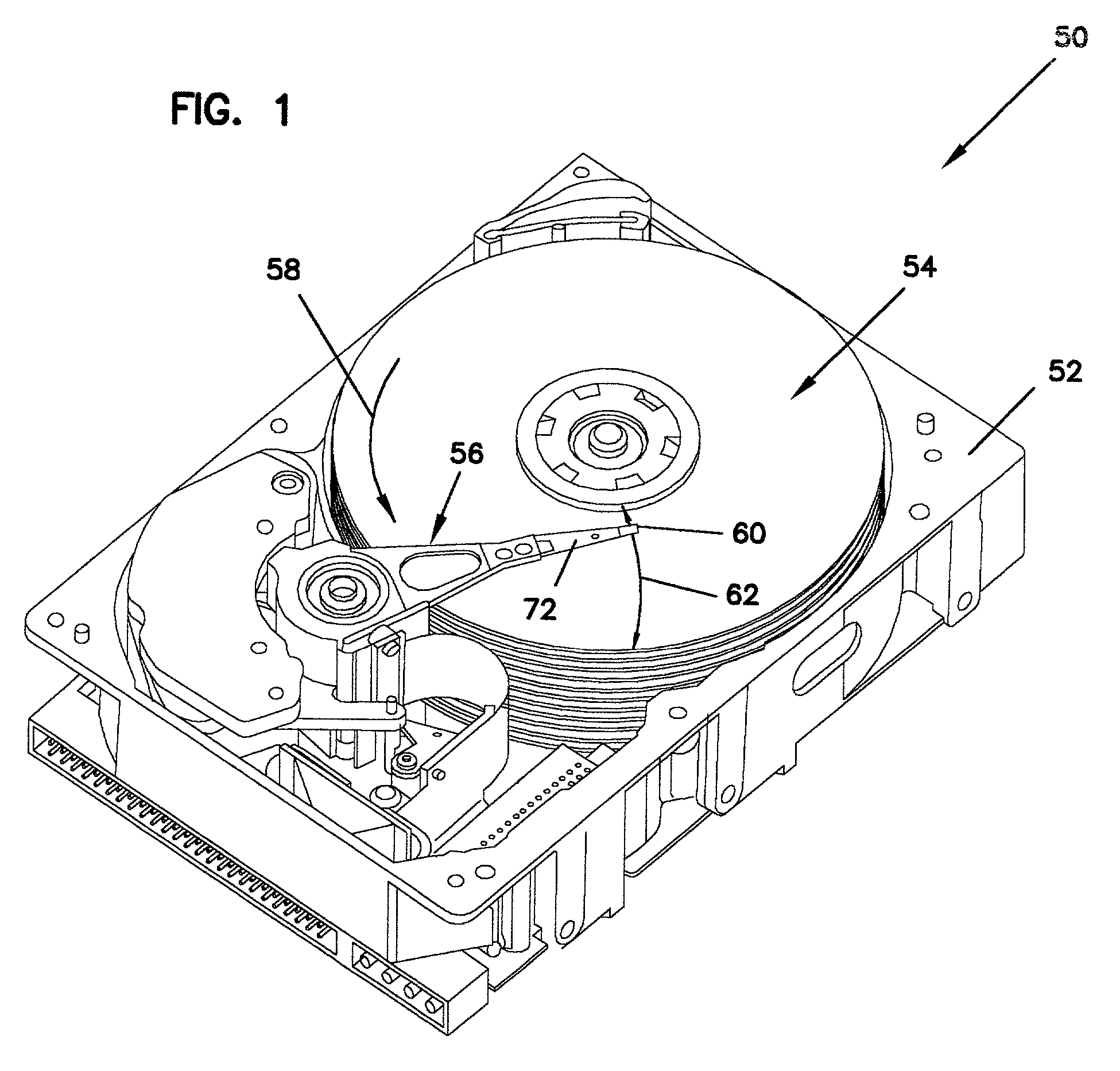
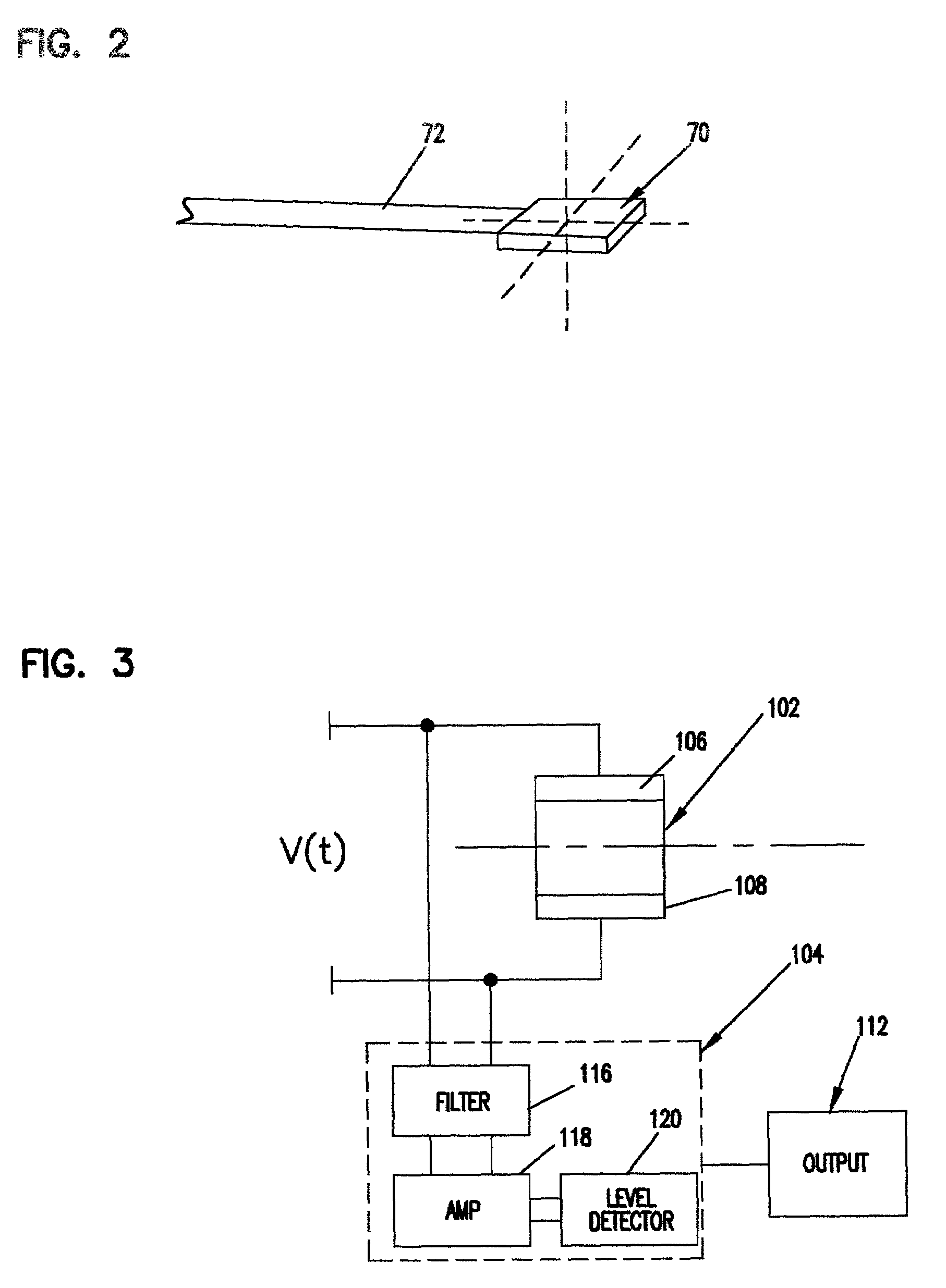
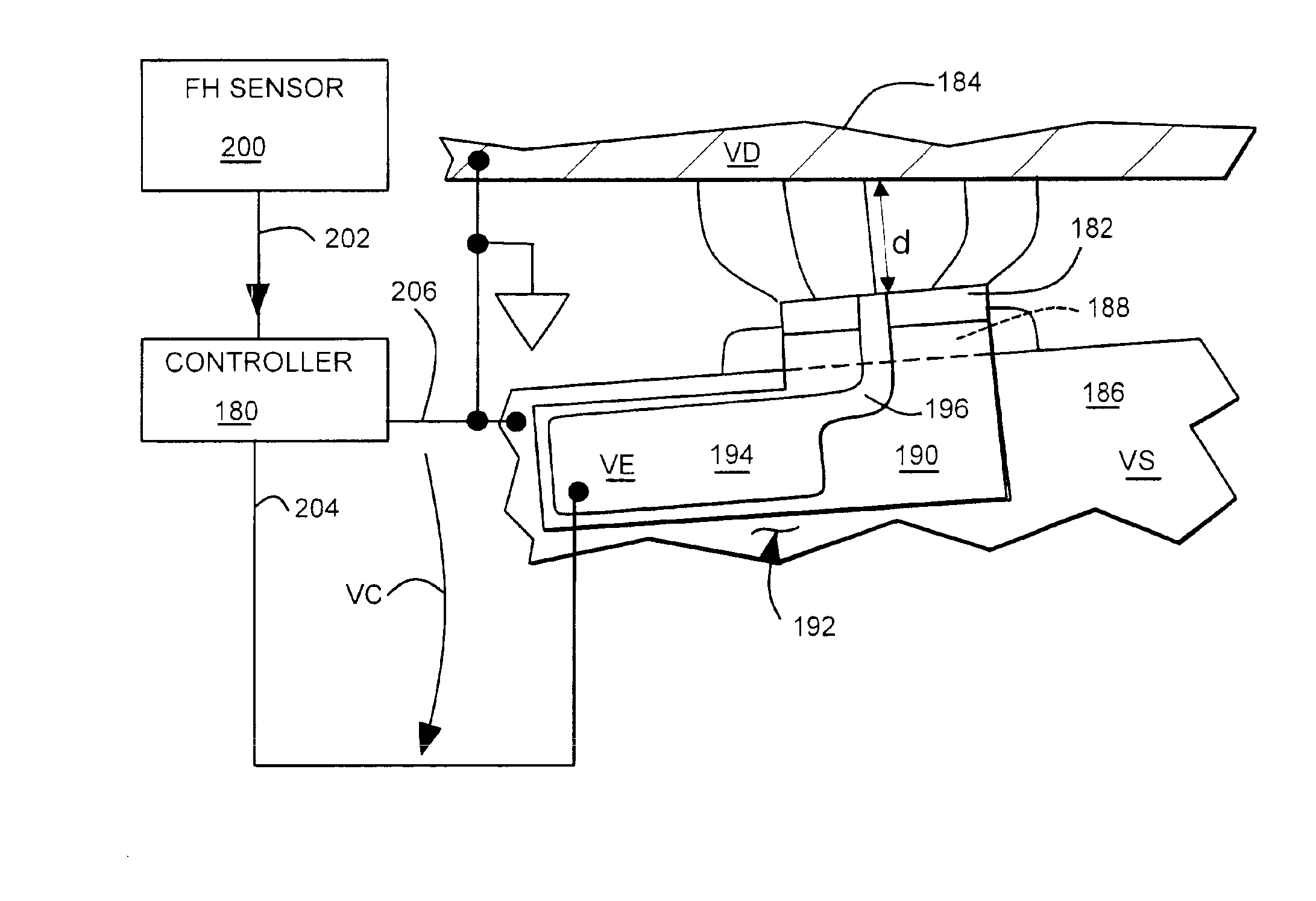
Head vibration detection device and method
A disc drive including a transducer supported on the head suspension assembly to induce a transducer signal in response to head vibration. The transducer signal is level detected to output a level detected signal indicative of head vibration. A method for detecting head vibration via a transducer on a head suspension assembly. The transducer on the head suspension assembly operating between a detection mode and an actuator mode for selectively detecting vibration and actuating the head.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
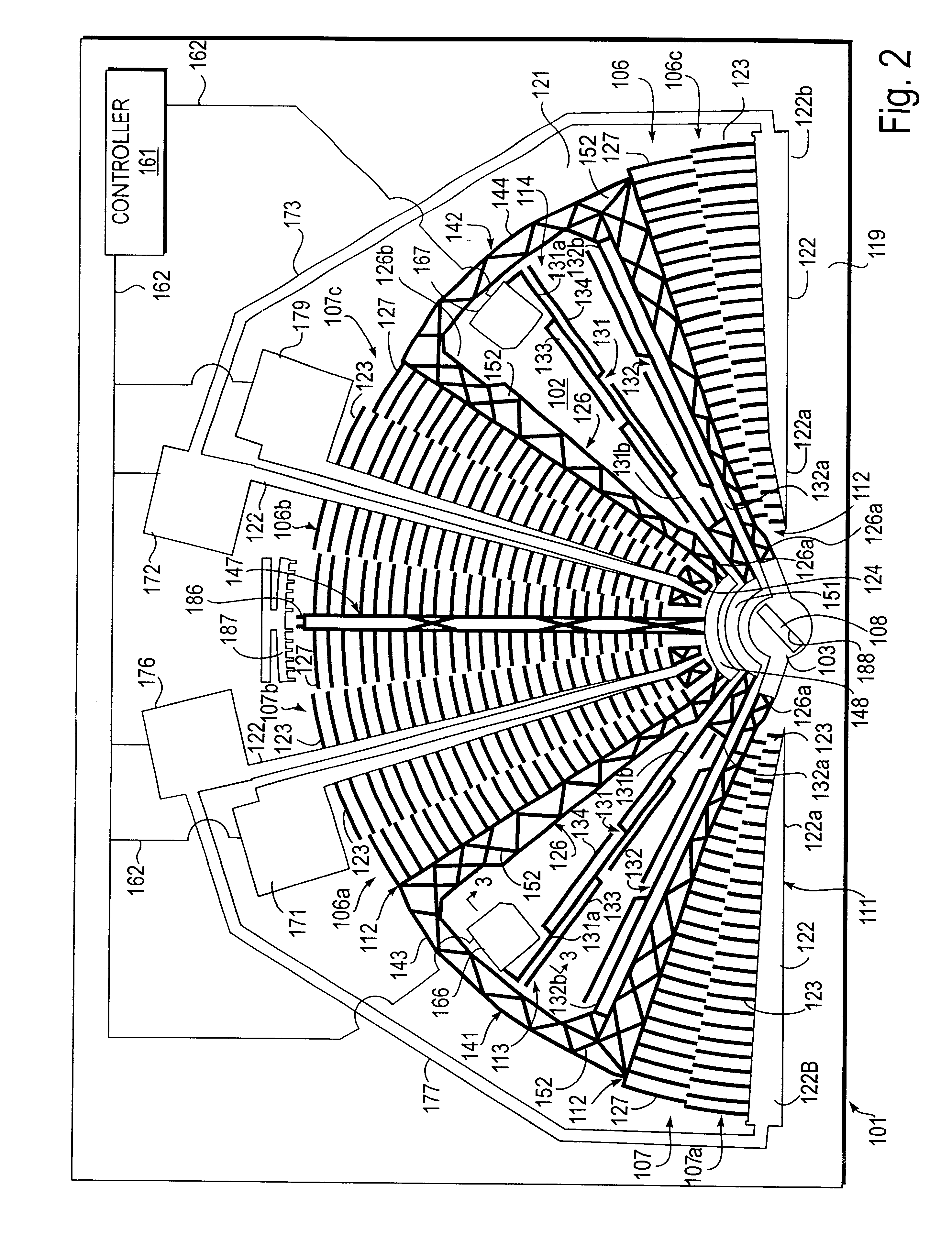
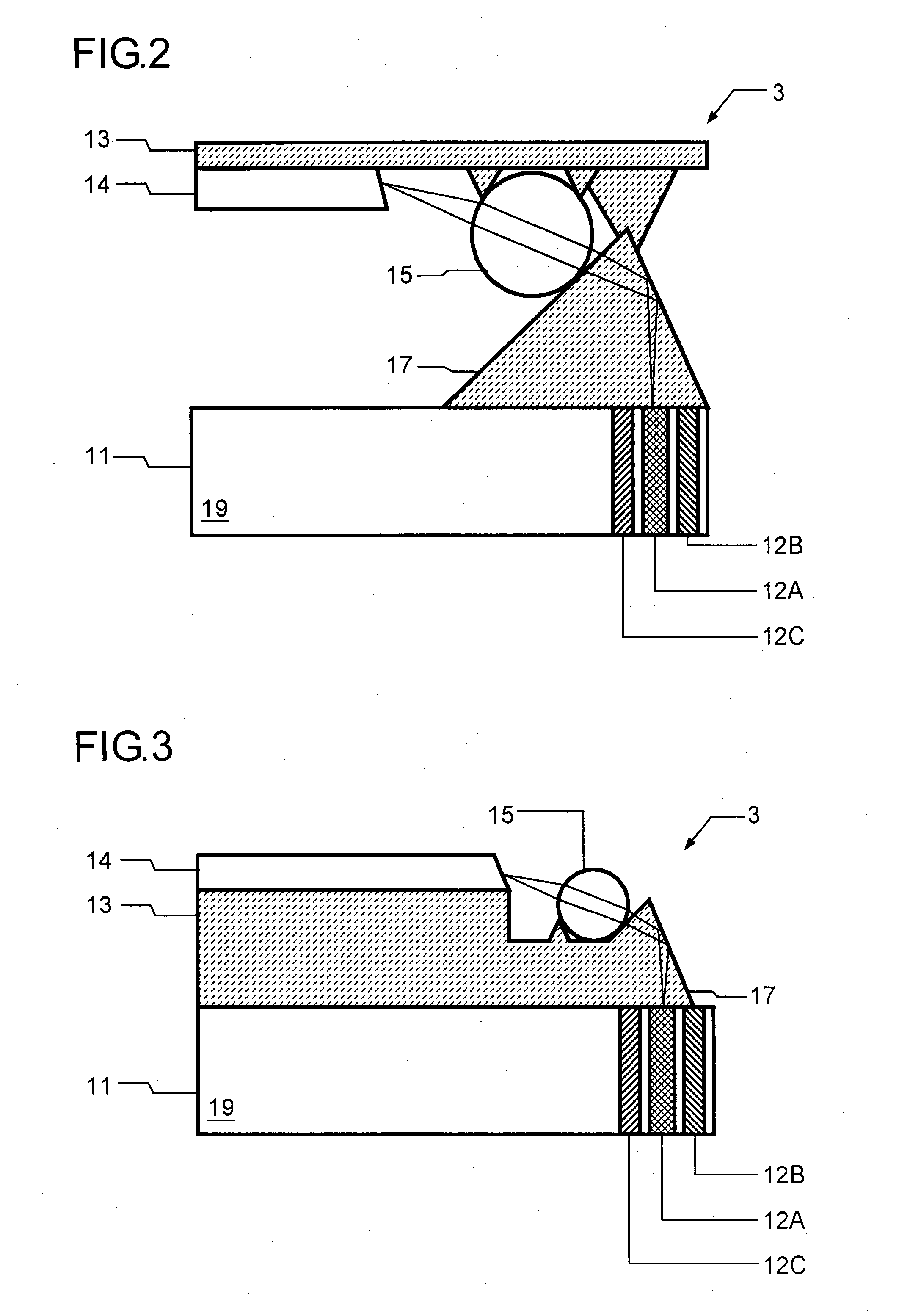
Information recording/reading head, and information recording/reproducing device
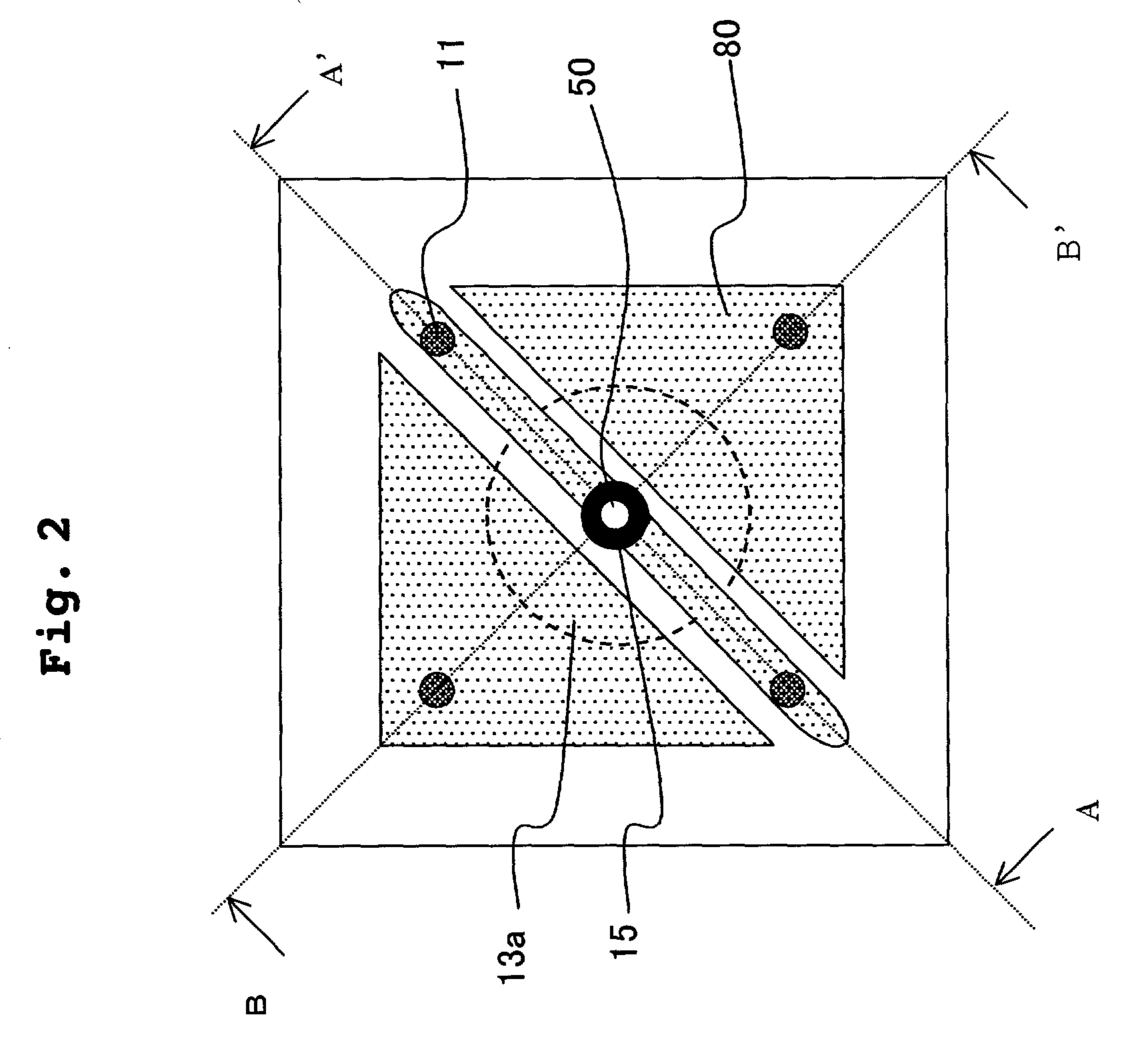
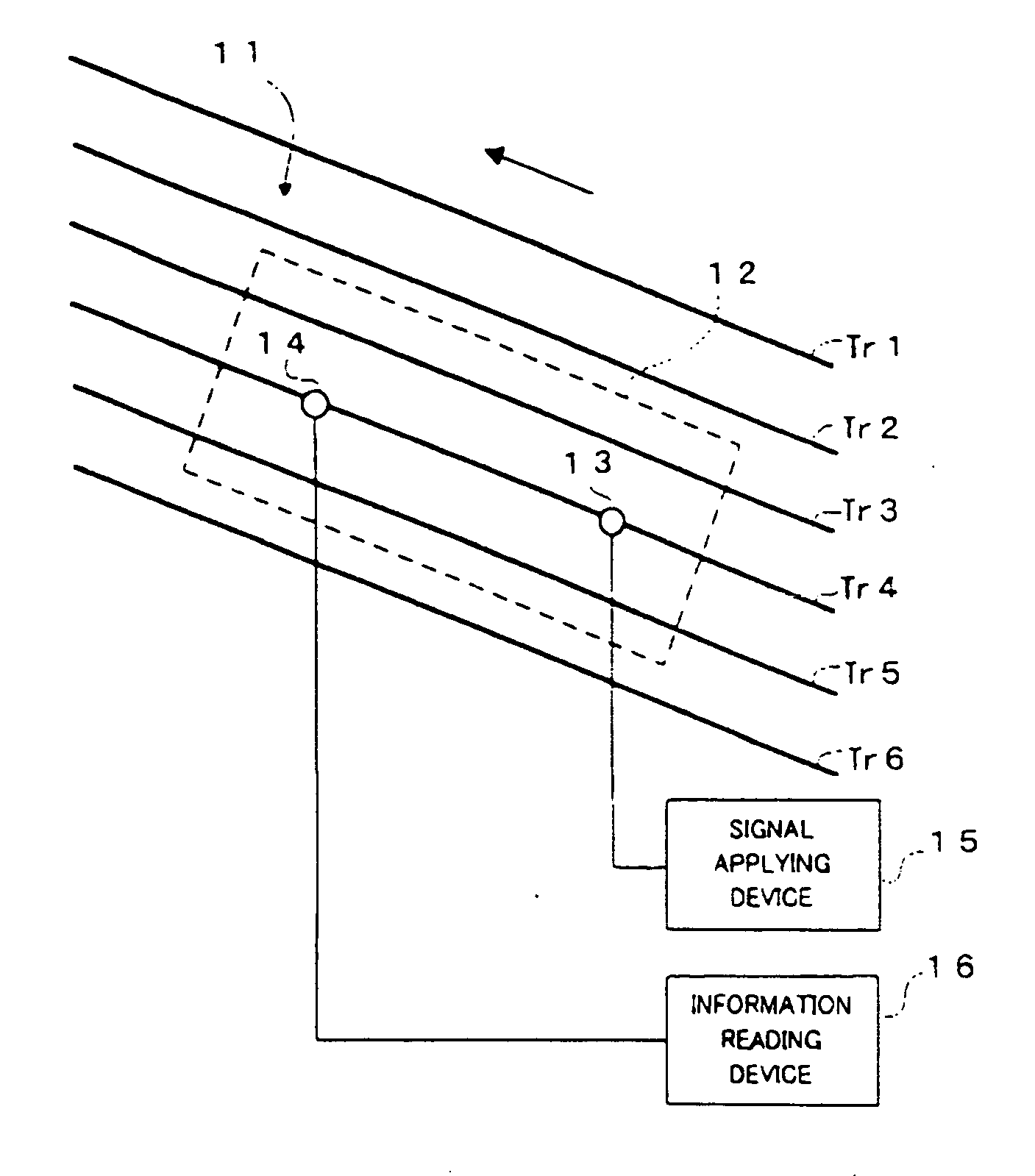
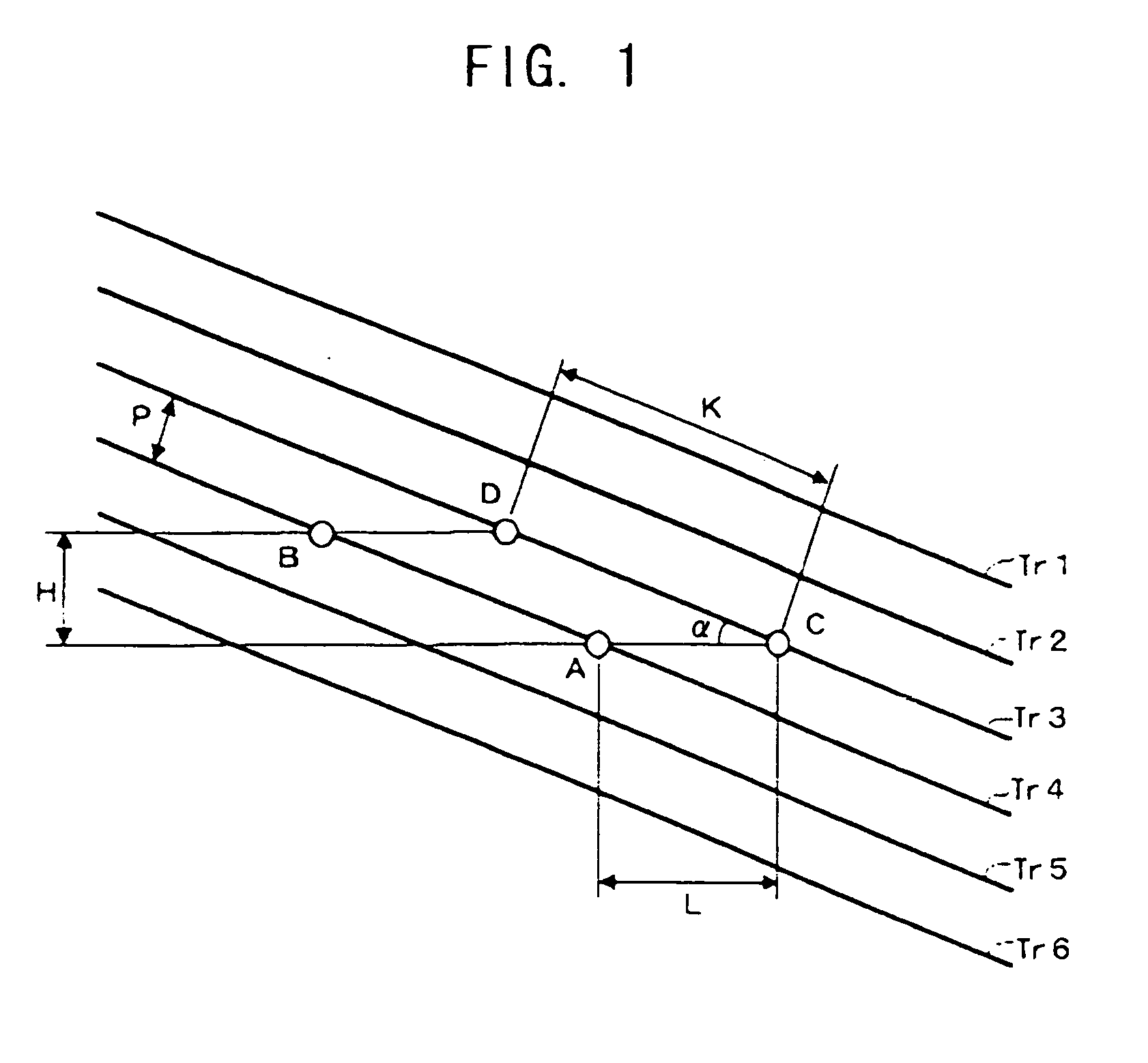
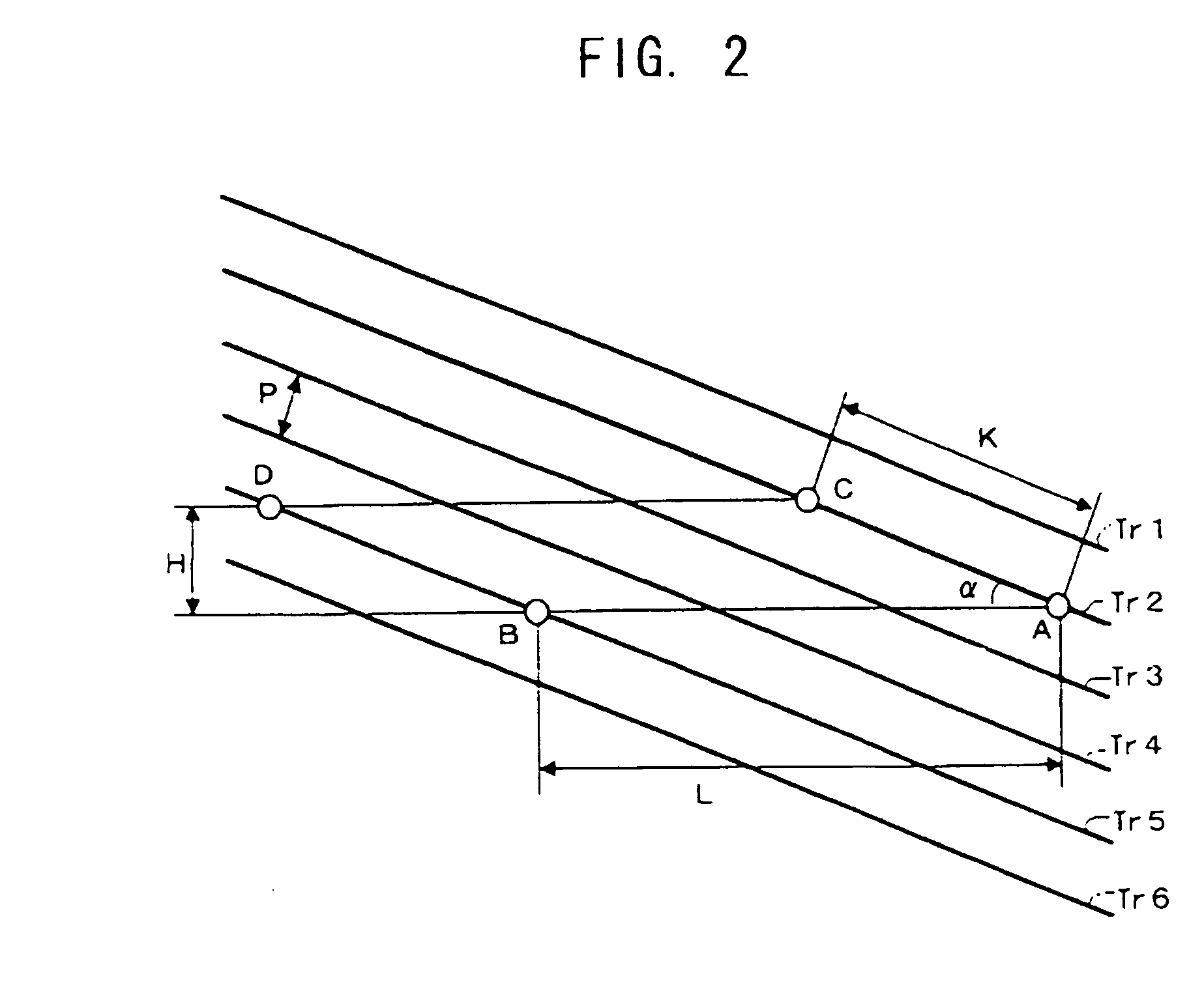
InactiveUS20060245312A1Increase productionEnhanced informationOptical flying-type headsNanoinformaticsLine segmentParallelogram
The probes of an information recording / reading head (110) are arranged such that if the positions of their tip portions are A, B, C, and D, a parallelogram is formed in which a line segment AB is parallel to a line segment CD, and a line segment AC is parallel to a line segment BD, and that if a ratio of the length of the line segment AB to the length of the line segment AC is η and the height of the parallelogram is H when the line segment AC is regarded as a base, the following relationship is satisfied: H=η·P.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
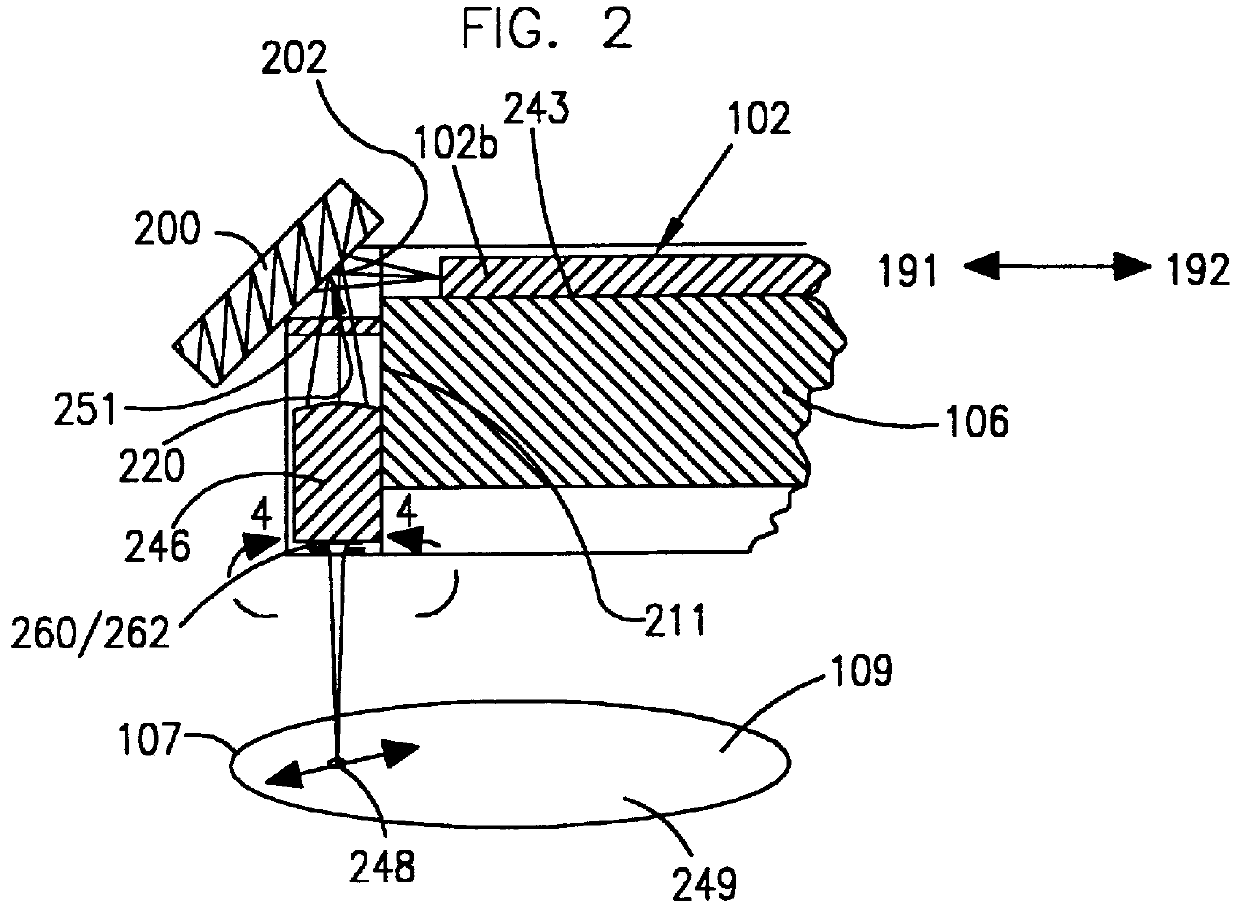
Disc drive slider with protruding electrostatic actuator electrode
A device for accessing data stored on a medium includes a substrate that has a transducer on a back side, a bottom side facing the disc, and a surface that protrudes from the bottom side. An insulation layer is placed on top of the surface. An electrostatic actuator electrode is placed on top of the insulation layer. The electrostatic actuator electrode faces the medium across an electrostatically charged portion of an air layer. The electrostatic actuator electrode protrudes above the surface into the electrostatically charged portion of the air layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
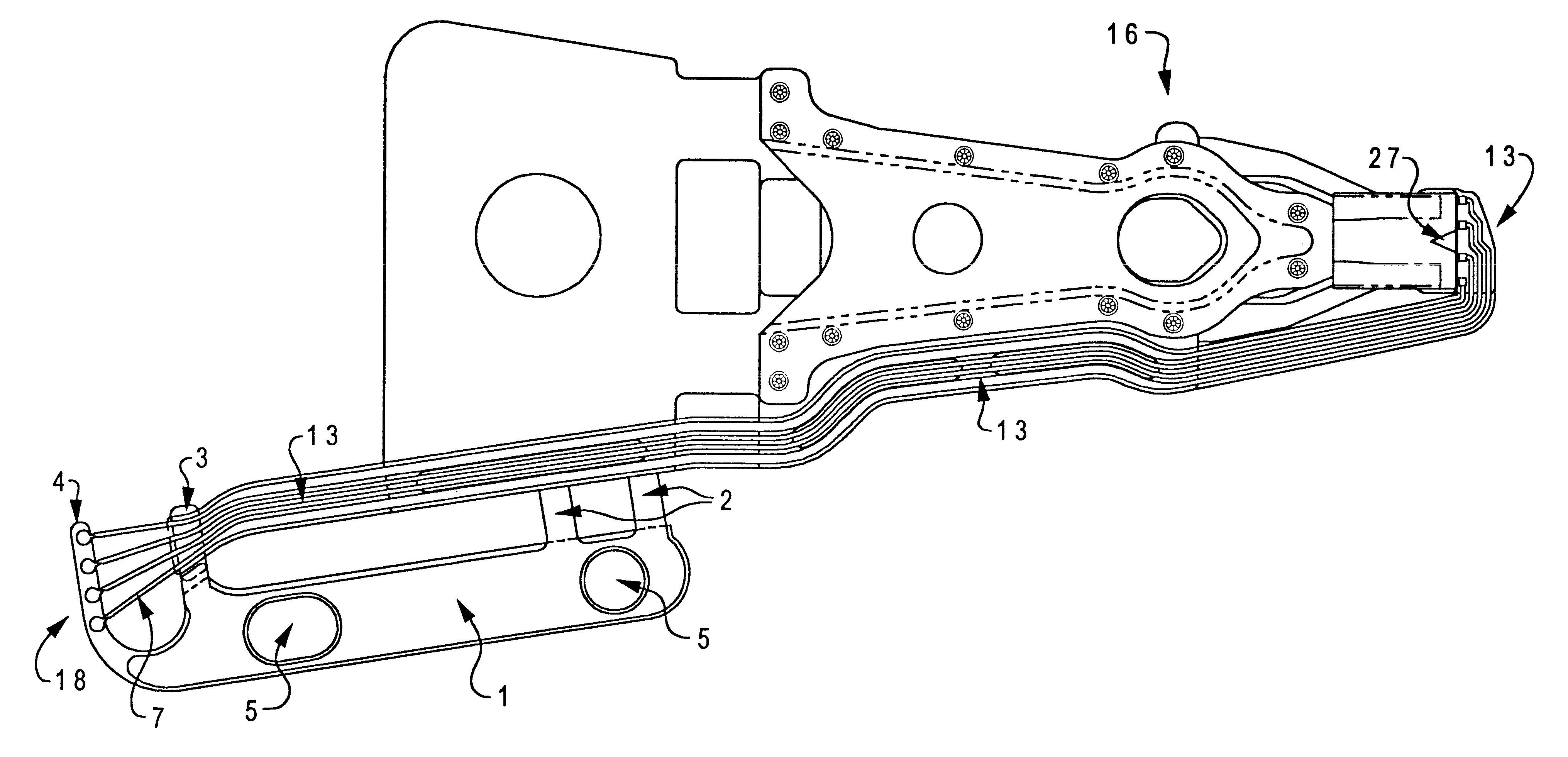
Multilayered suspension with conductive lead structure extending beyond base layer
InactiveUS6477014B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsCarrier constructional parts dispositionTransducerEngineering
A multilayered suspension having a slider end and a termination end, the suspension being suitable for use in an information storage system slider-suspension assembly is provided. The suspension comprises a conductive lead structure having at least one conductor line contained in a patterned conductive layer formed over one or more layers. The conductive lead structure is suitable on the slider end for connection to transducer leads of a slider, and on the termination end for connection to arm-electronics termination pads. The suspension further comprises a fixture, formed from one or more layers, being substantially in the same plane as the termination end of the conductive lead structure and having one or more anchor tabs laminated to a layer of the conductive lead structure. The fixture is suitable for aligning the conductor lines to the termination pads by rotating the termination end of the conductive lead structure in the plane of the termination end.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Recording head and recorder
A recorder has a recording head which uses light for information recording to a recording medium. The recording head has a slider and an optical waveguide. The slider moves relative to the recording medium while floating thereon. The optical waveguide is provided in the slider and has a refractive index difference of 20% or more between a core and a cladding.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Near-field light emitting device, optical recording head and optical recorder
InactiveUS20110292774A1Simple structureEfficiently emitsCombination recordingOptical flying-type headsOptical recordingWaveguide
Provided is a near-field light emitting device which emits near-field light efficiently by simple structure. A near-field light emitting device comprises a waveguide which is equipped with a core and a clad touching the core and is coupled with light having an electric field component in the direction perpendicular to the boundary surface of the core and clad, and a planar metal structure which is arranged along the above-mentioned boundary surface where the electric field component is in the perpendicular direction. The metal structure has a tip adjoining the light exit surface of the core, and a side projecting to the clad where the width of the metal structure in the direction perpendicular to the propagation direction of the light coupled with the waveguide is wider than the width of the core.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Single frequency laser source for optical data storage system
InactiveUS6850475B1Increase the number ofExpand accessOptical flying-type headsOptical beam sourcesPolarization-maintaining optical fiberOptical fiber cable
An optical data storage system utilizes optical fibers for transfer of information to and from storage media. The storage media includes magneto-optical storage disks. The optical fibers are single-mode polarization maintaining optical fibers. A single frequency laser diode provides a source of polarized light. Accordingly, a polarization state conveyed by the polarization maintaining optical fiber is accurately reproduced with reduced noise, as compared to use of a Fabry-Perot laser diode.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com