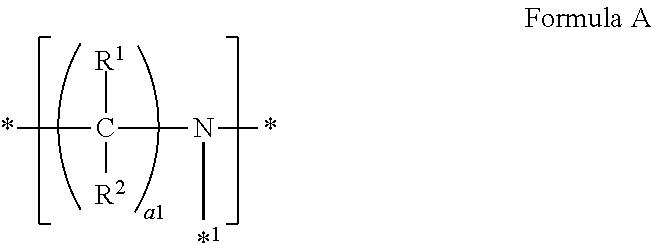
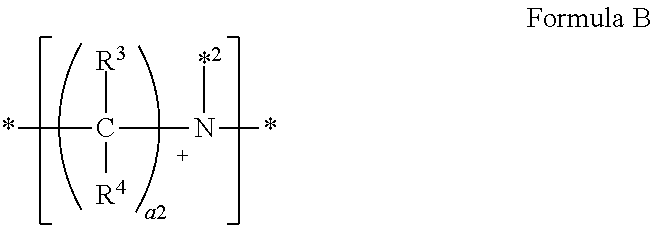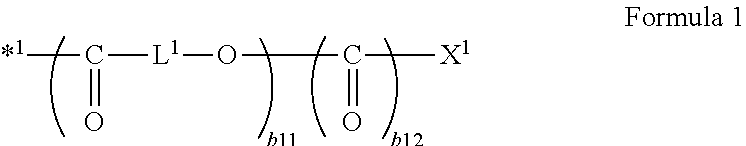Patents
Literature
220results about How to "High-density recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
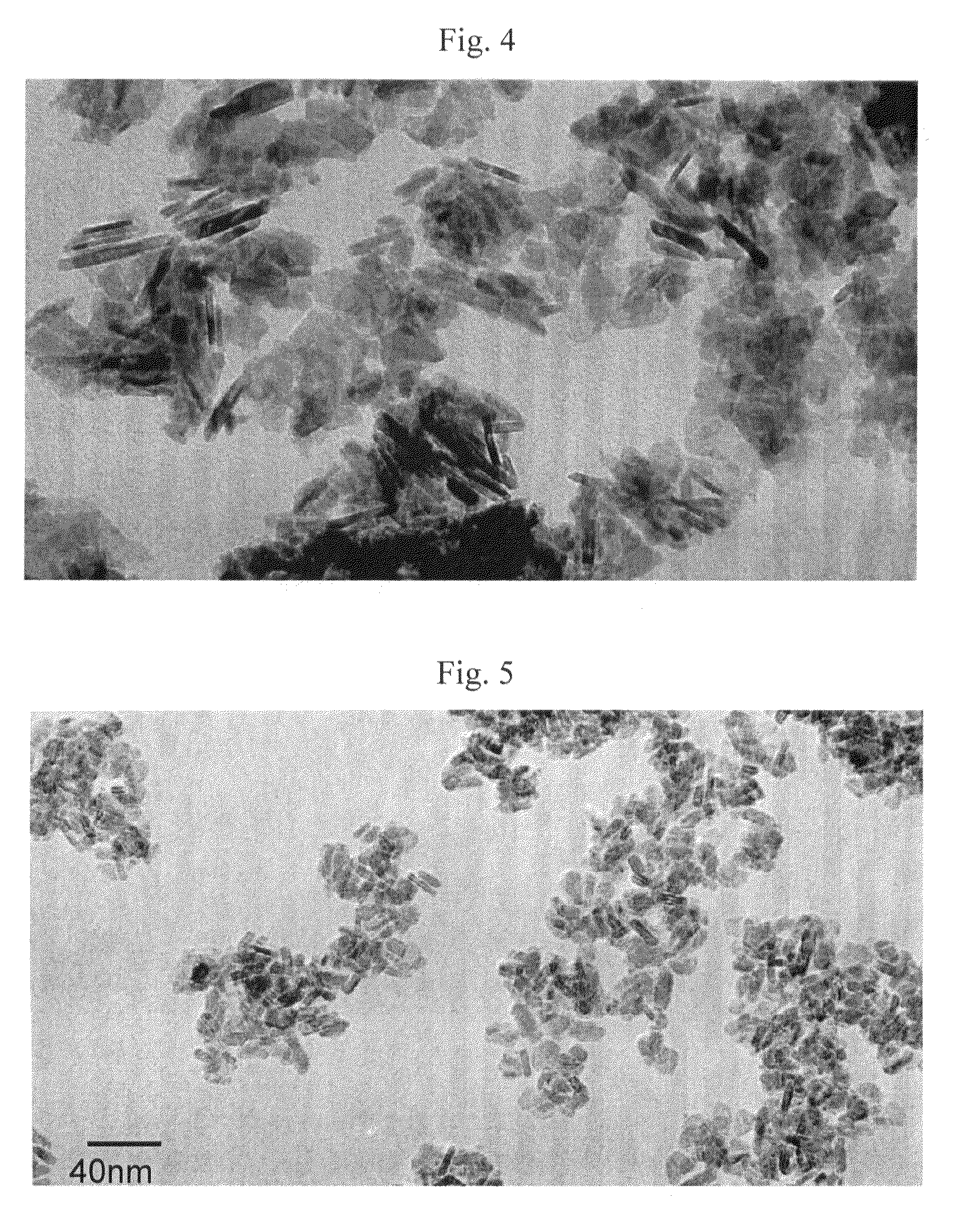
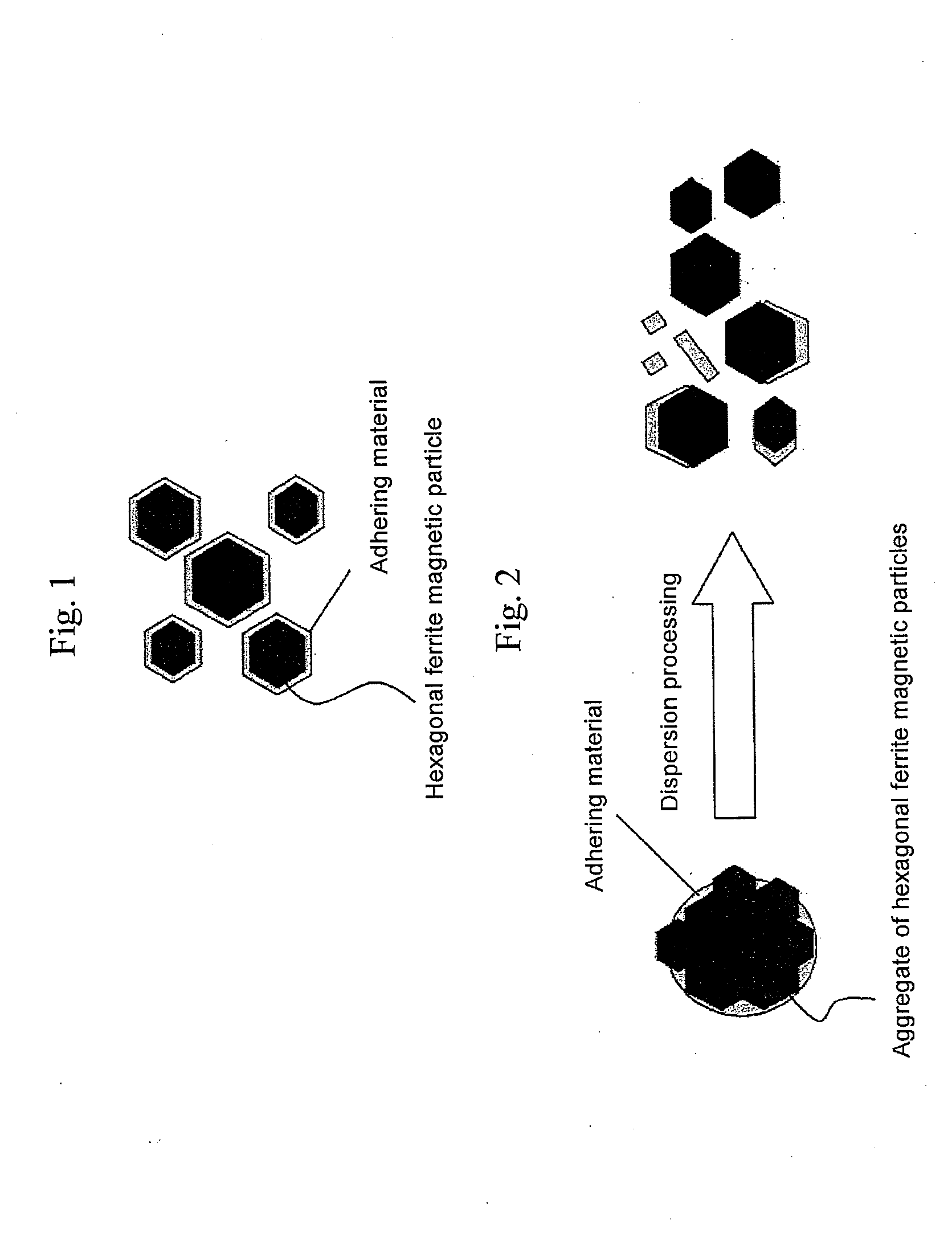
Hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20120177951A1Inhibit drop in thermal stabilityEnsure easeMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismBiological activationMaterials science
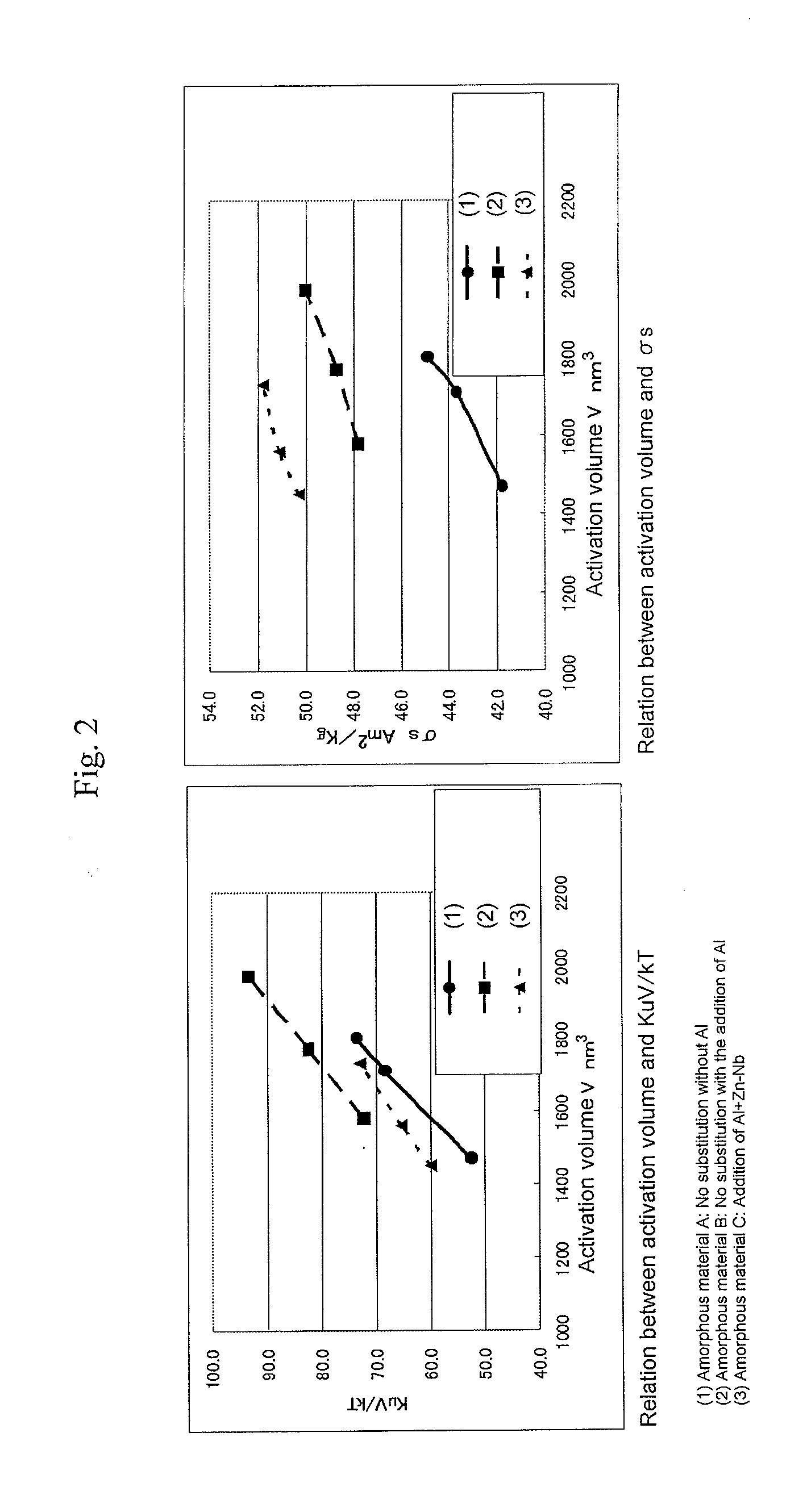
An aspect of the present invention relates to a hexagonal barium ferrite magnetic particle, wherein, relative to 100 atom percent of a Fe content, an Al content ranges from 1.5 to 15 atom percent, a combined content of a divalent element and a pentavalent element ranges from 1.0 to 10 atom percent, an atomic ratio of a content of the divalent element to a content of the pentavalent element is greater than 2.0 but less than 4.0, and an activation volume ranges from 1,300 to 1,800 nm3.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
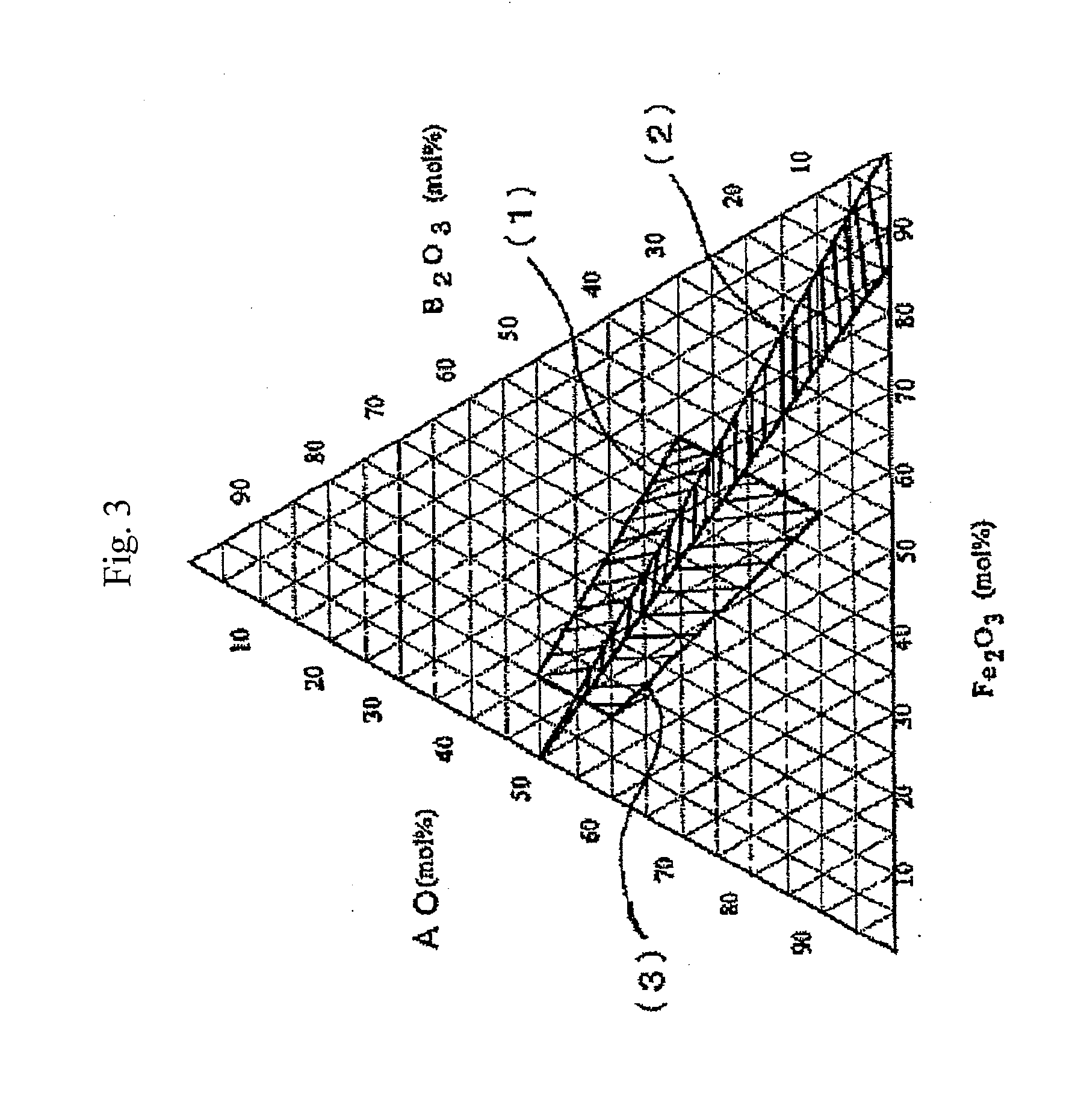
Hexagonal strontium ferrite magnetic powder and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130256584A1High-density recordingAdvances in high-density recordingInorganic material magnetismIron compoundsPhysicsChemistry
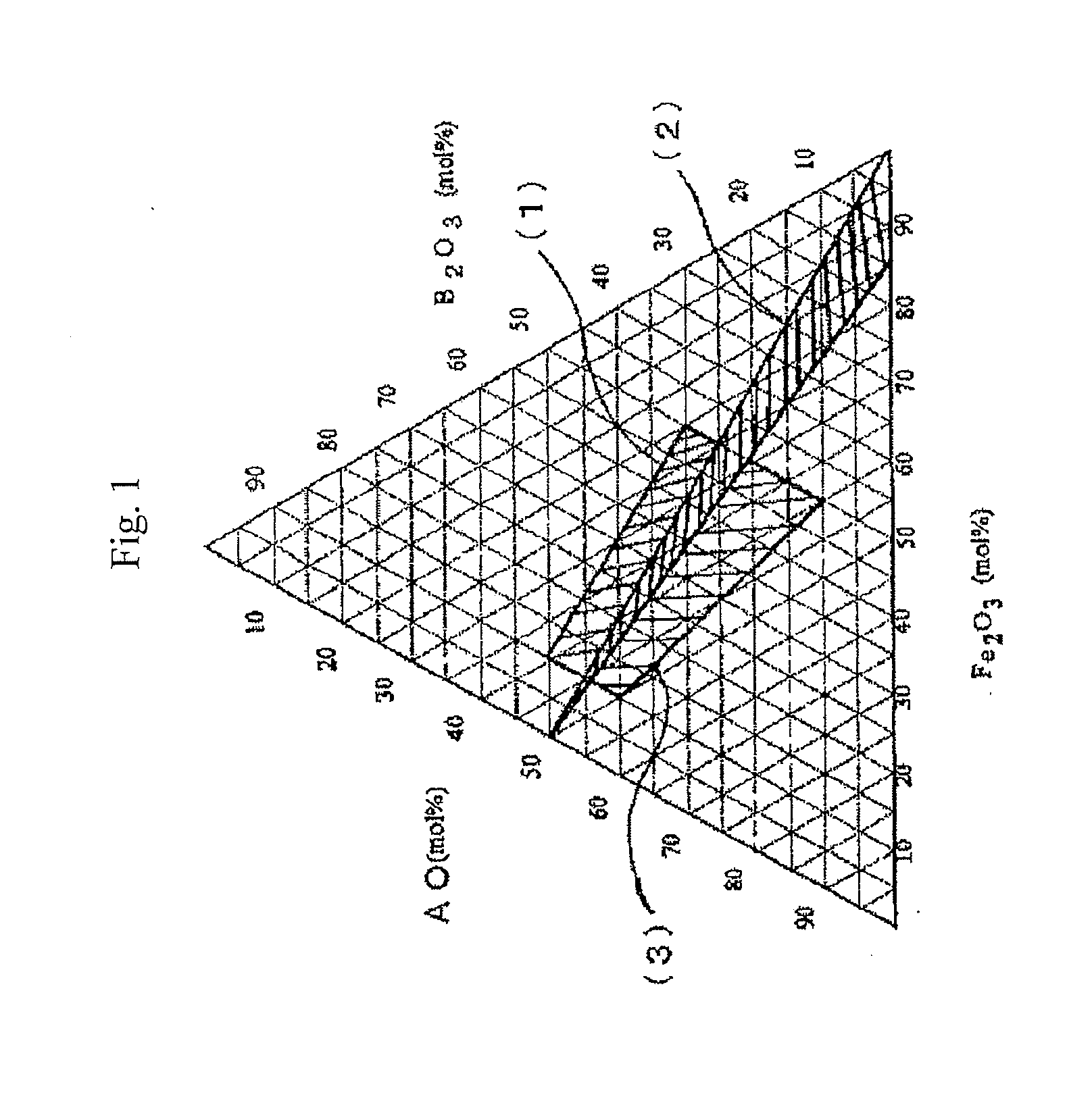
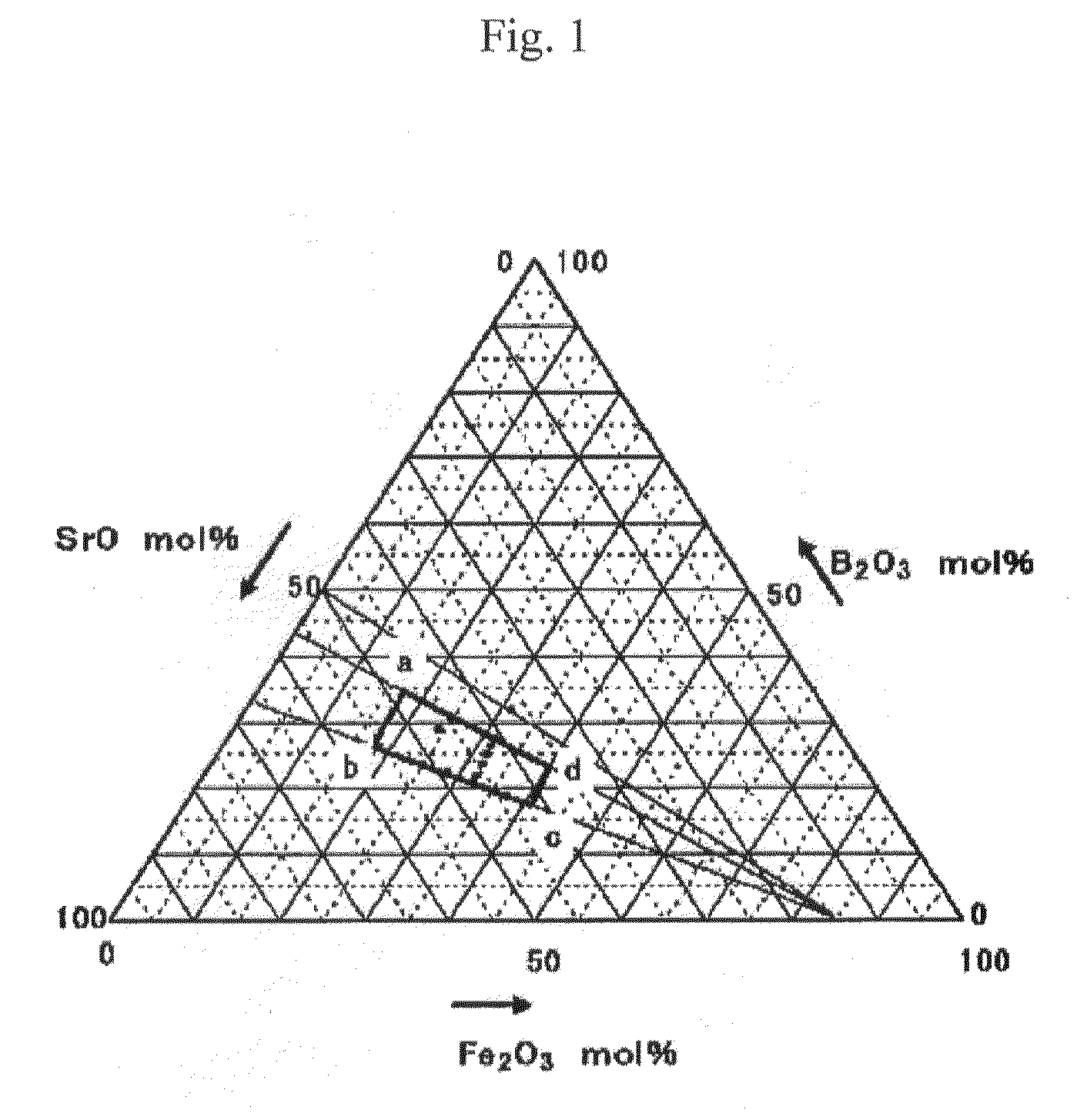
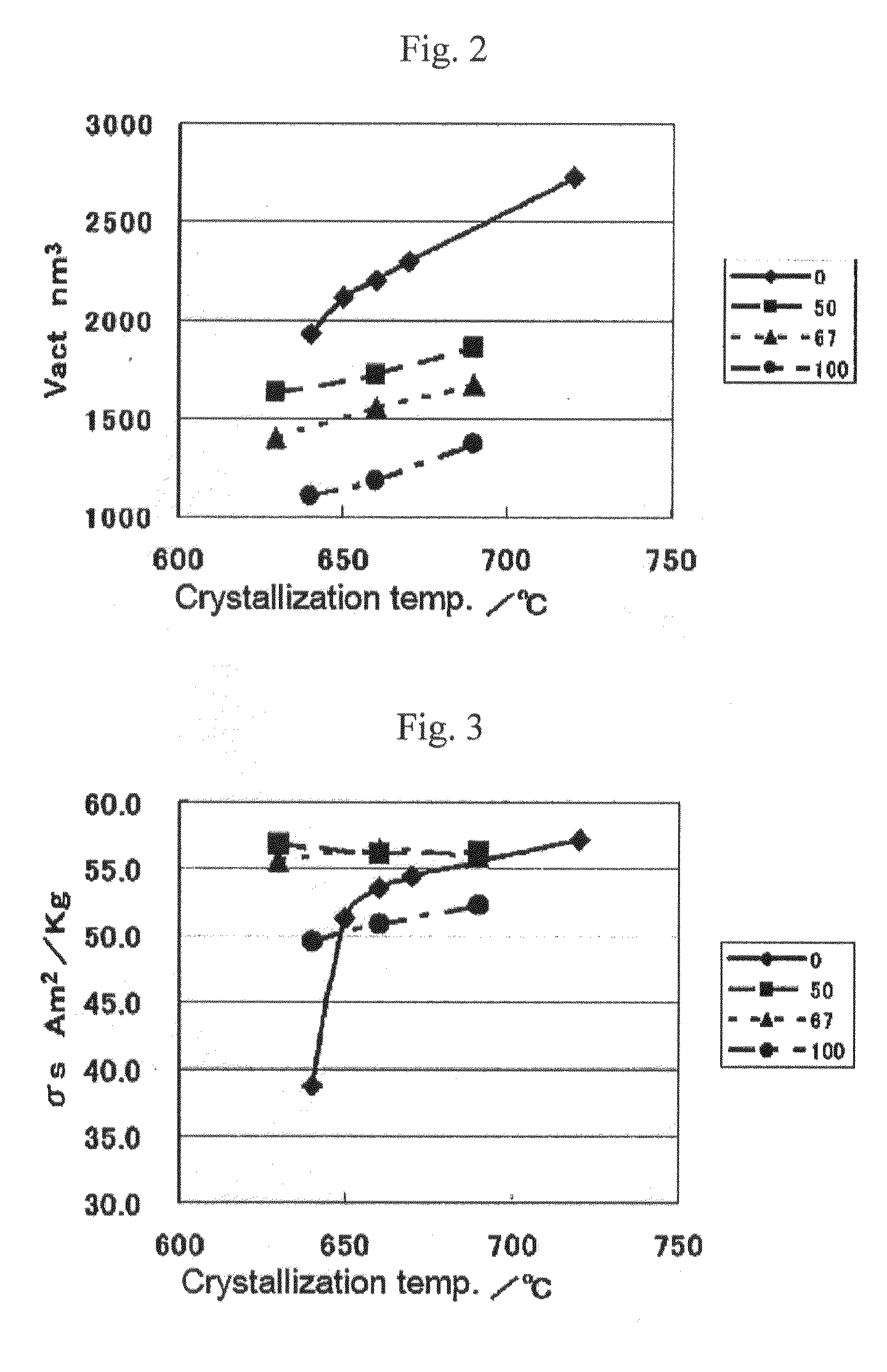
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing hexagonal strontium ferrite magnetic powder, which comprises melting a starting material mixture which has a composition, as a composition converted into an oxide, lying within a region enclosed by the following four points:(a) SrO=48.0 mol %, Fe2O3=17.2 mol %, B2O3=34.8 mol %;(b) SrO=55.9 mol %, Fe2O3=17.7 mol %, B2O3=26.4 mol %;(c) SrO=41.7 mol %, Fe2O3=40.9 mol %, B2O3=17.4 mol %;(d) SrO=36.7 mol %, Fe2O3=40.1 mol %, B2O3=23.2 mol %;in a ternary diagram with SrO, Fe2O3, which may include an Fe substitution element, and B2O3 as apexes, to provide a melt, and quenching the melt to obtain a solidified product; and heat treating the solidified product to precipitate hexagonal strontium ferrite magnetic particles within the solidified product.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20110244272A1Improve coercive forceReduce particlesMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic materials for record carriersHeat treatedMaterials science
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle comprising melting an Al-containing starting material mixture to prepare a melt and quenching the melt to obtain an amorphous material; subjecting the amorphous material to heat treatment to cause a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle to precipitate in a product obtained by the heat treatment; collecting a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle by subjecting the product to treatment with an acid and washing, wherein the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle collected has a particle size ranging from 15 to 30 nm, comprises 0.6 to 8.0 weight percent of Al, based on Al2O3 conversion, relative to a total weight of the particle, and Al adheres to a surface of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160093323A1High density recordingAdequate running durabilityBase layers for recording layersTape carriersFatty acid compositionMagnetic layer
The magnetic tape comprises a nonmagnetic layer comprising nonmagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, and comprises a magnetic layer comprising ferromagnetic powder and binder on the nonmagnetic layer, wherein a fatty acid ester, a fatty acid amide, and a fatty acid are contained in either one or both of the magnetic layer and the nonmagnetic layer, with the magnetic layer and nonmagnetic layer each comprising at least one selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid ester, a fatty acid amide, and a fatty acid, a quantity of fatty acid ester per unit area of the magnetic layer in extraction components extracted from a surface of the magnetic layer with n-hexane falls within a range of 1.00 mg / m2 to 10.00 mg / m2, and a weight ratio of the quantity of fatty acid ester per unit area of the magnetic layer to a combined total of a quantity of fatty acid amide and a quantity of fatty acid, quantity of fatty acid ester / (quantity of fatty acid amide+quantity of fatty acid), per unit area of the magnetic layer falls within a range of 1.00 to 3.00 in the extraction components.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Thermally assisted magnetic head
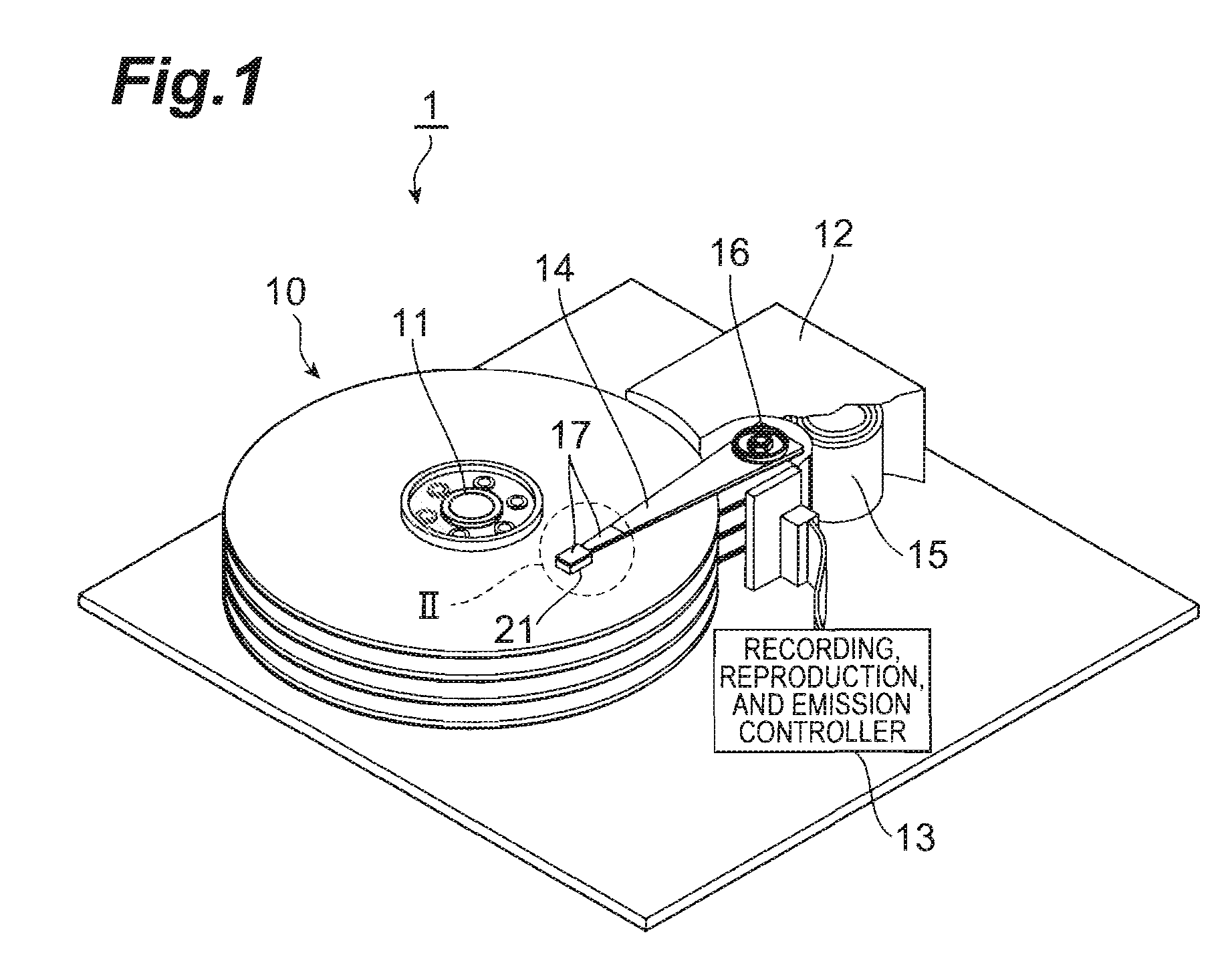
ActiveUS20080043360A1Increase productionSimple structureCombination recordingRecord information storageEngineeringWaveguide
A thermally assisted magnetic head has a slider having a medium-facing surface, and a light source unit having a light source support substrate, and a light source disposed on the light source support substrate. The slider has a slider substrate and a magnetic head portion disposed on a side of the medium-facing surface in the slider substrate; the magnetic head portion includes a magnetic recording element for generating a magnetic field, and a waveguide for receiving light through an end face opposite to the medium-facing surface, and guiding the light to the medium-facing surface; the light source support substrate is fixed to a surface opposite to the medium-facing surface in the slider substrate so that light emitted from the light source can enter the end face of the waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording medium
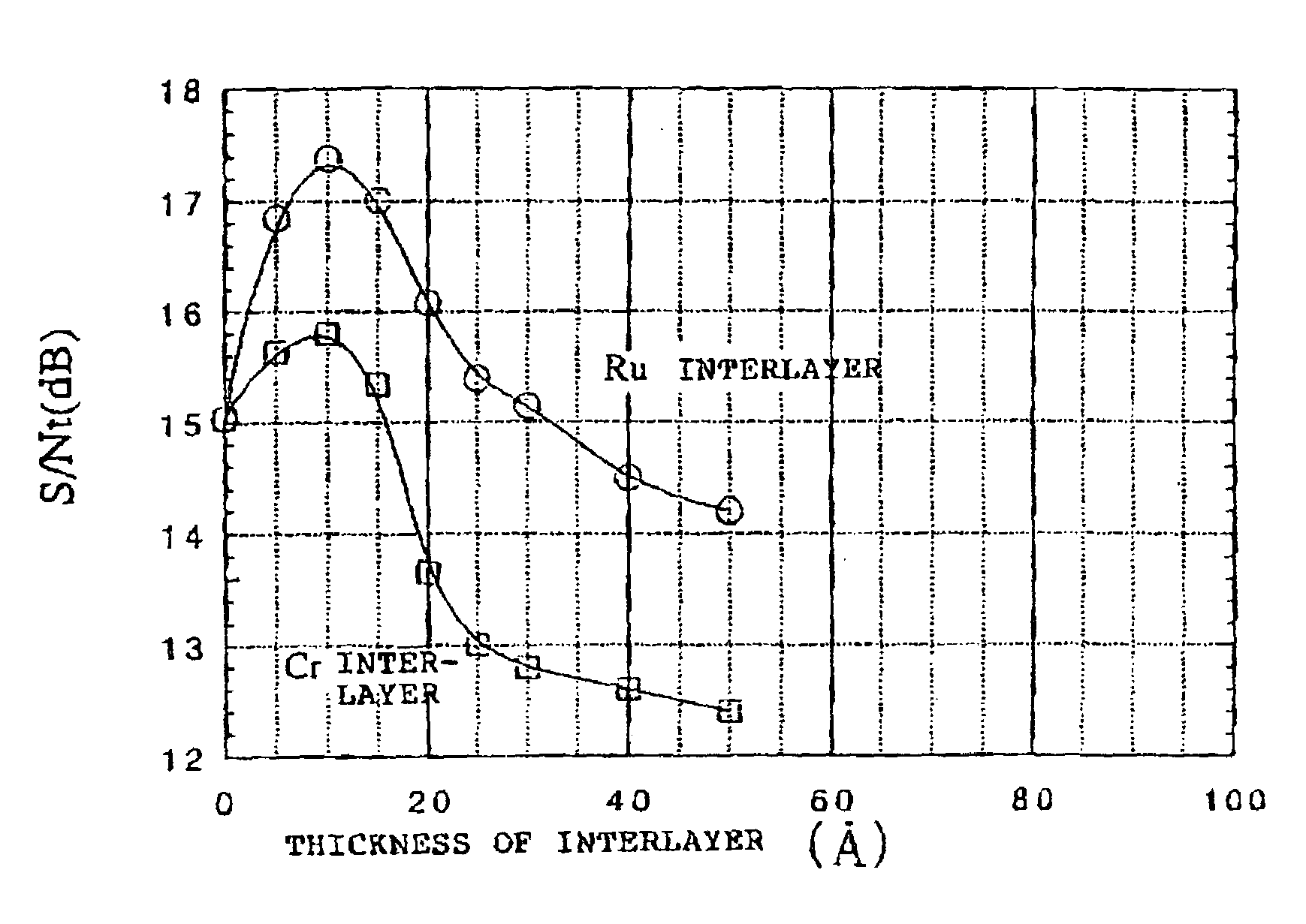
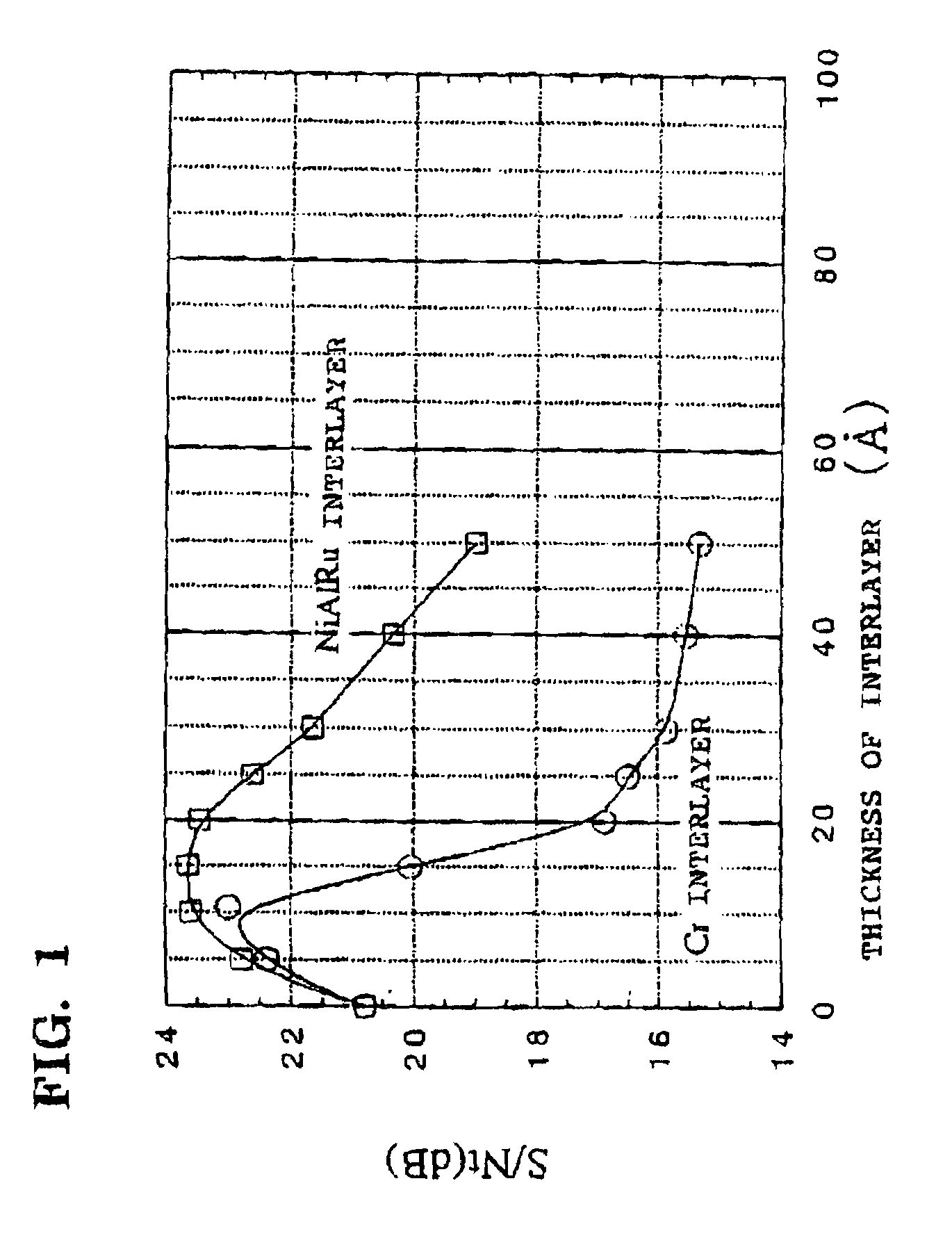
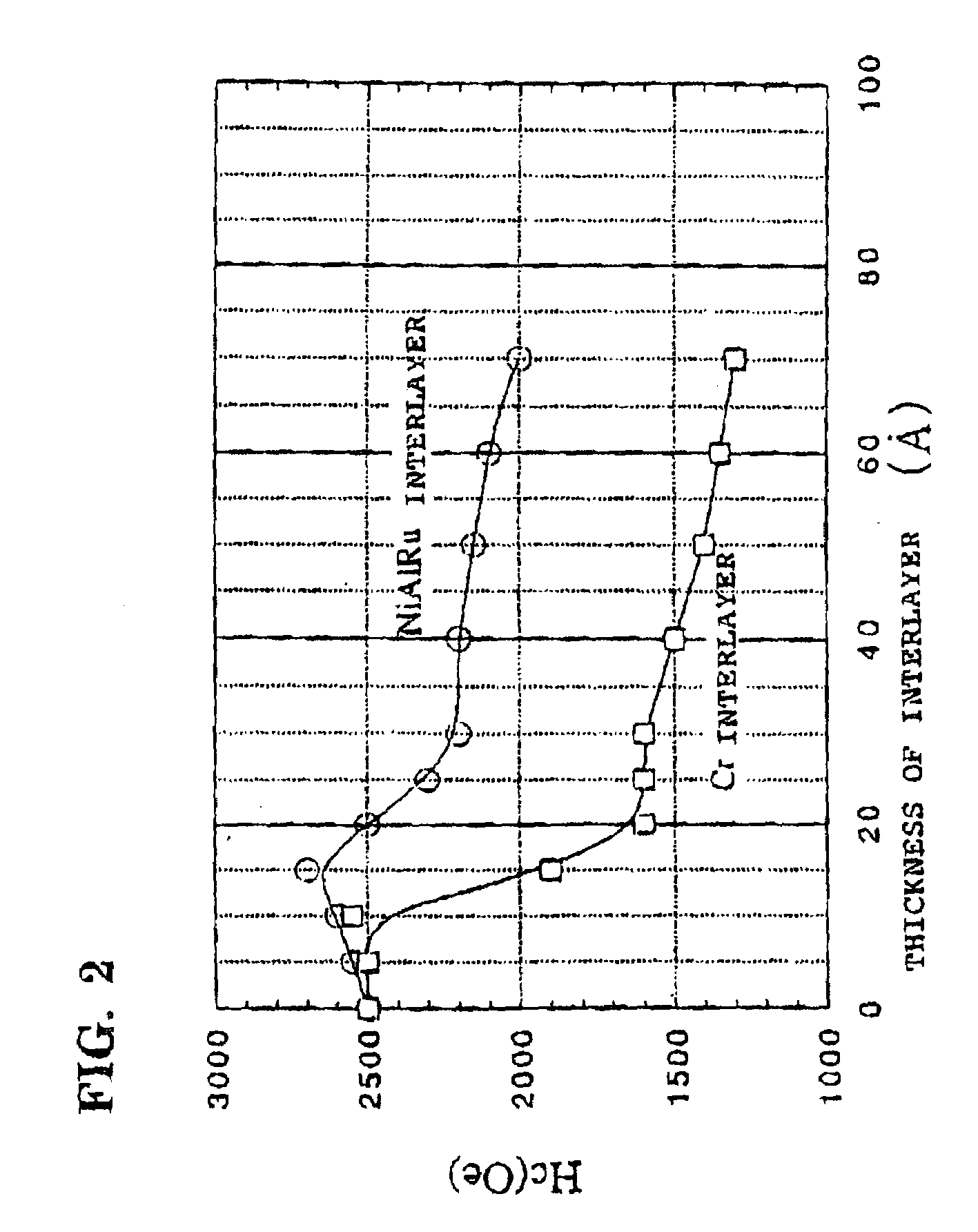
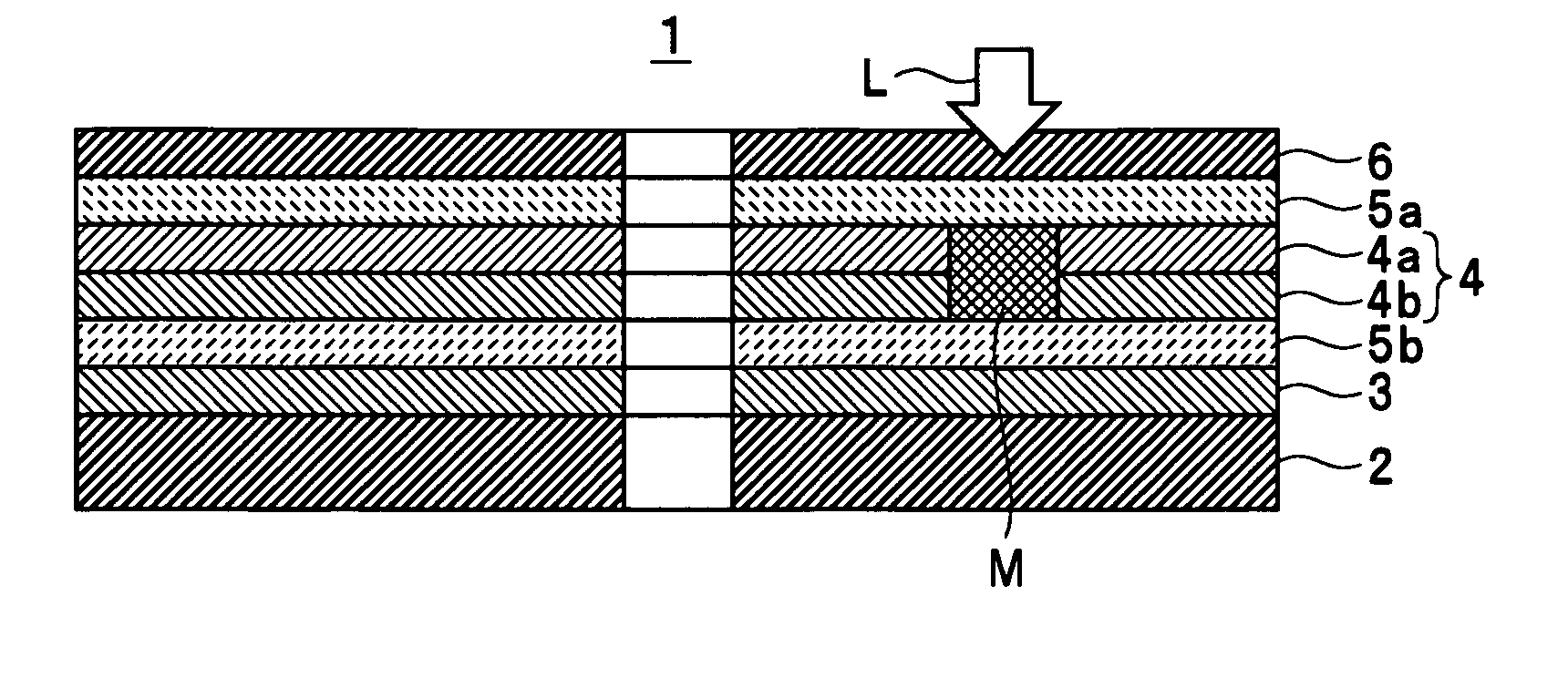
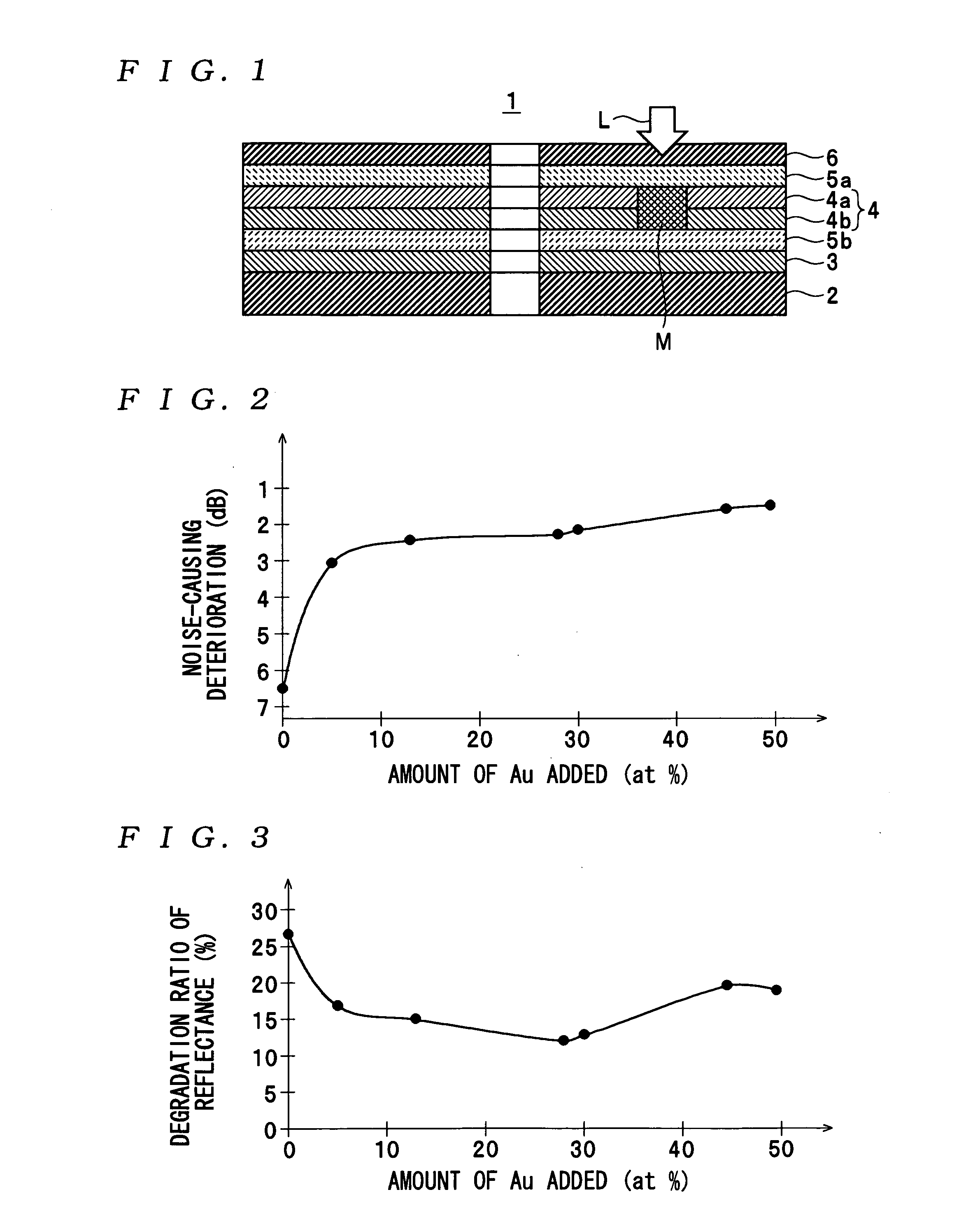
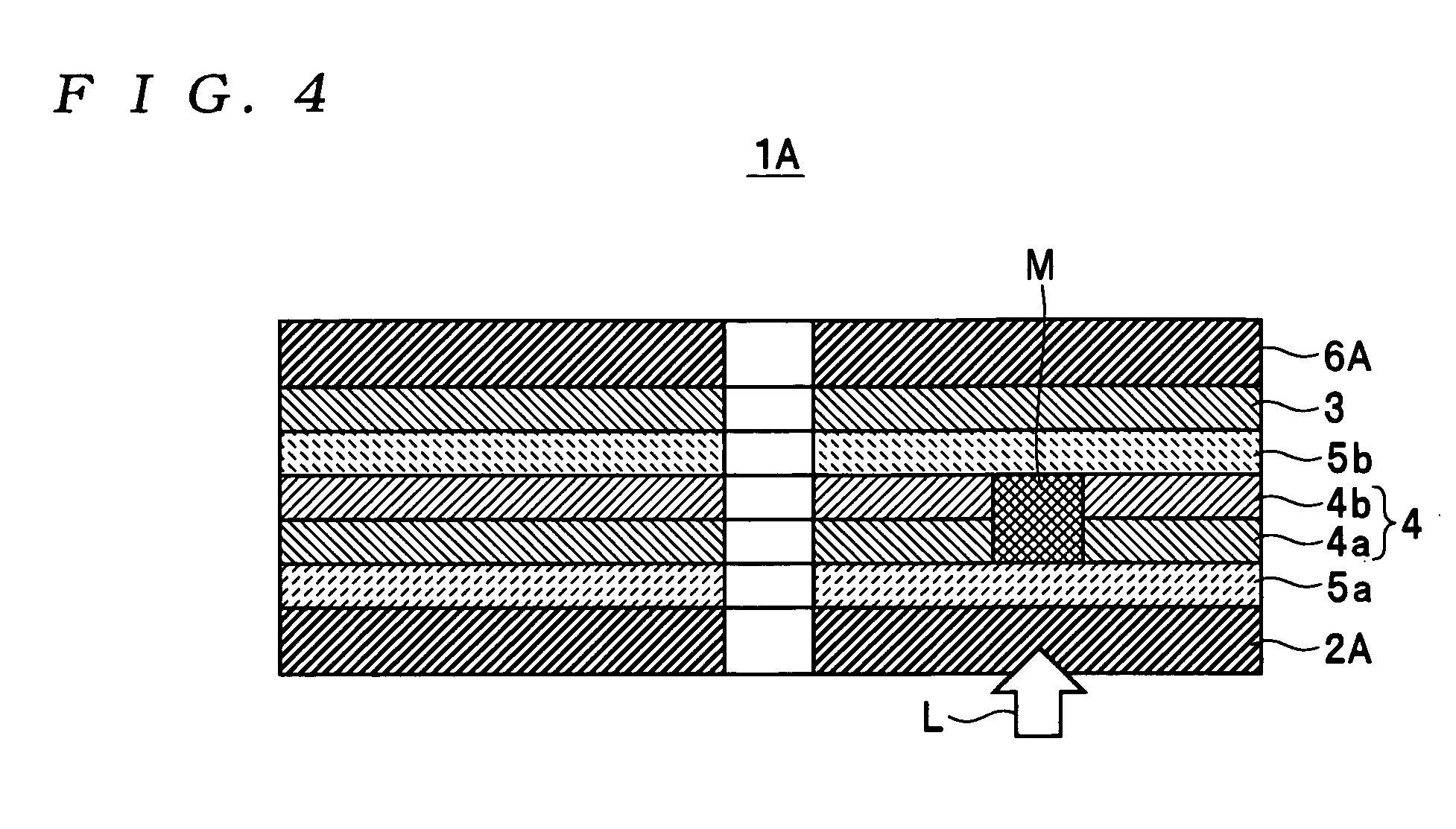
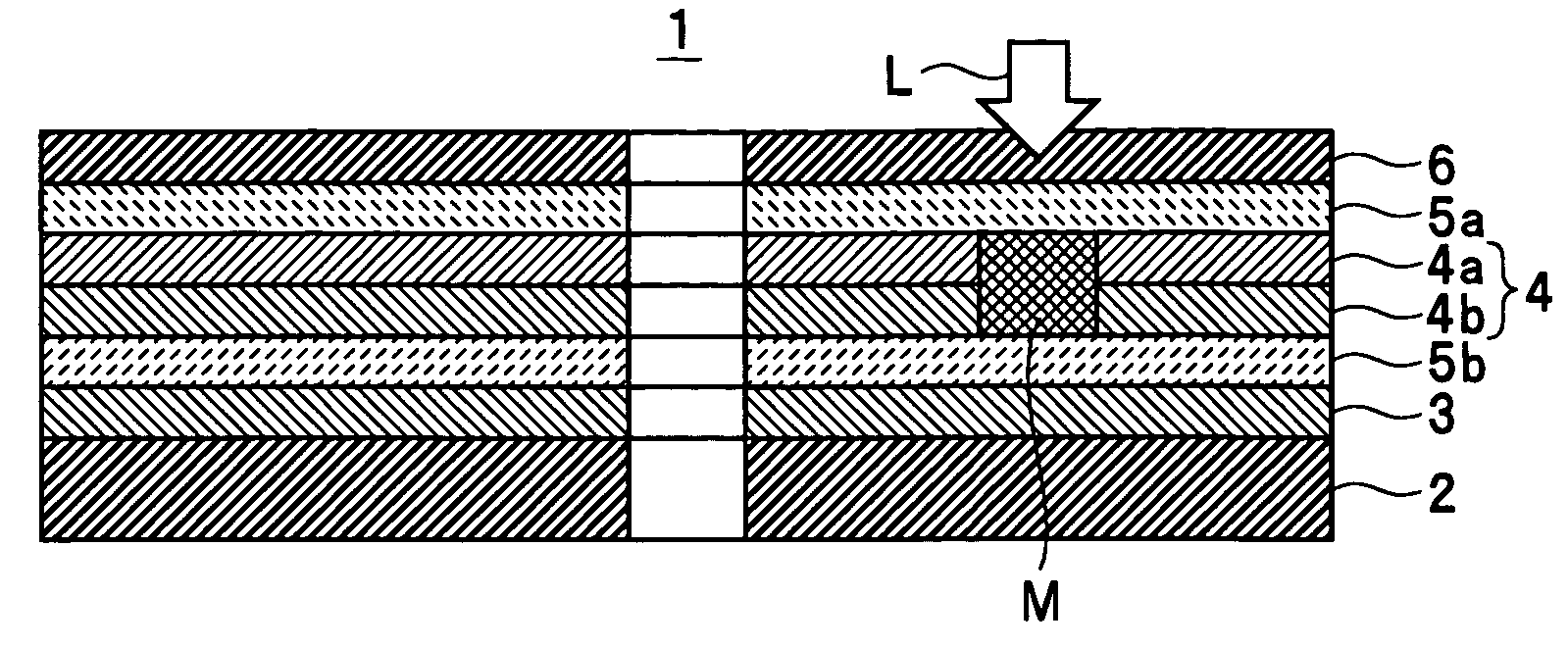
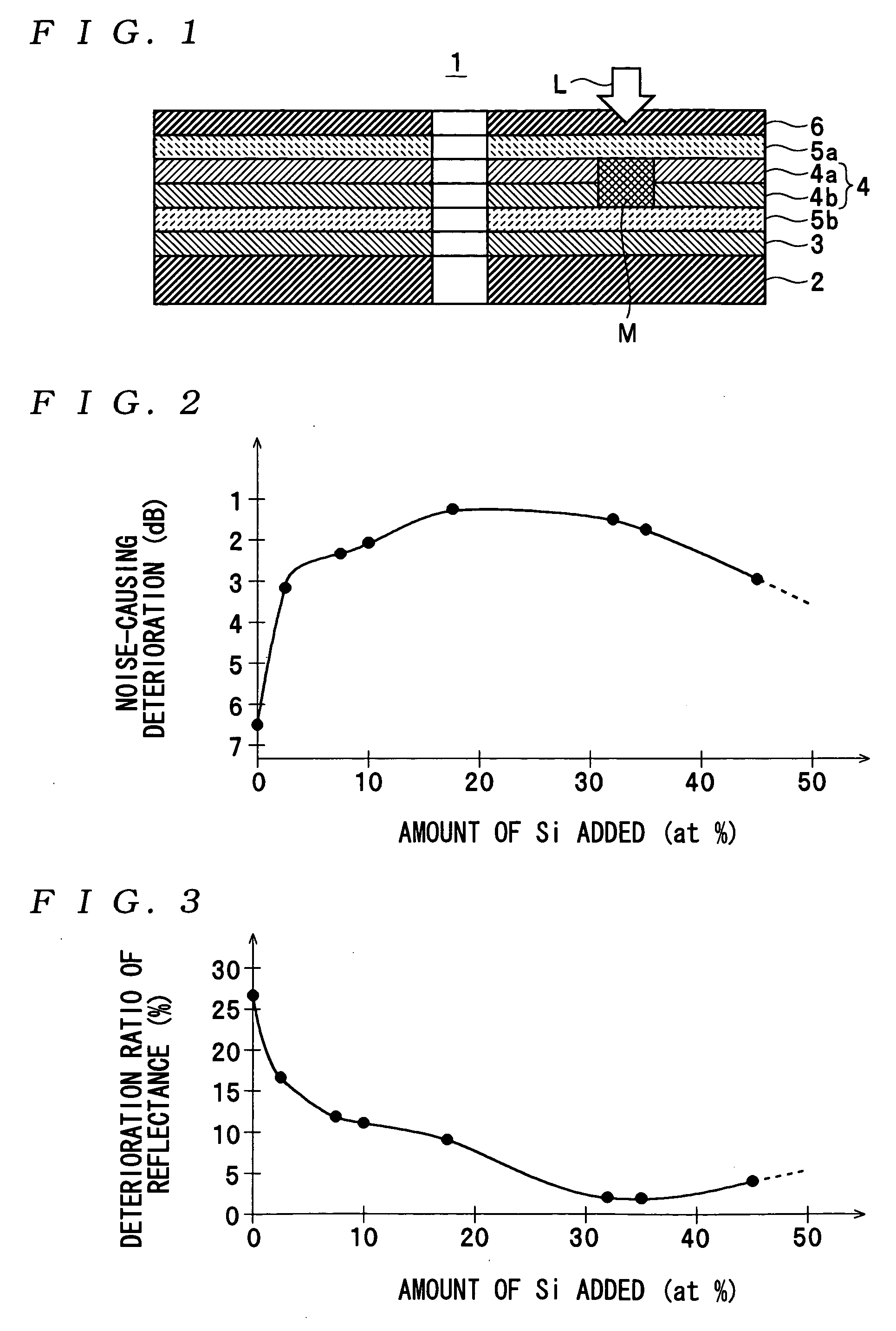
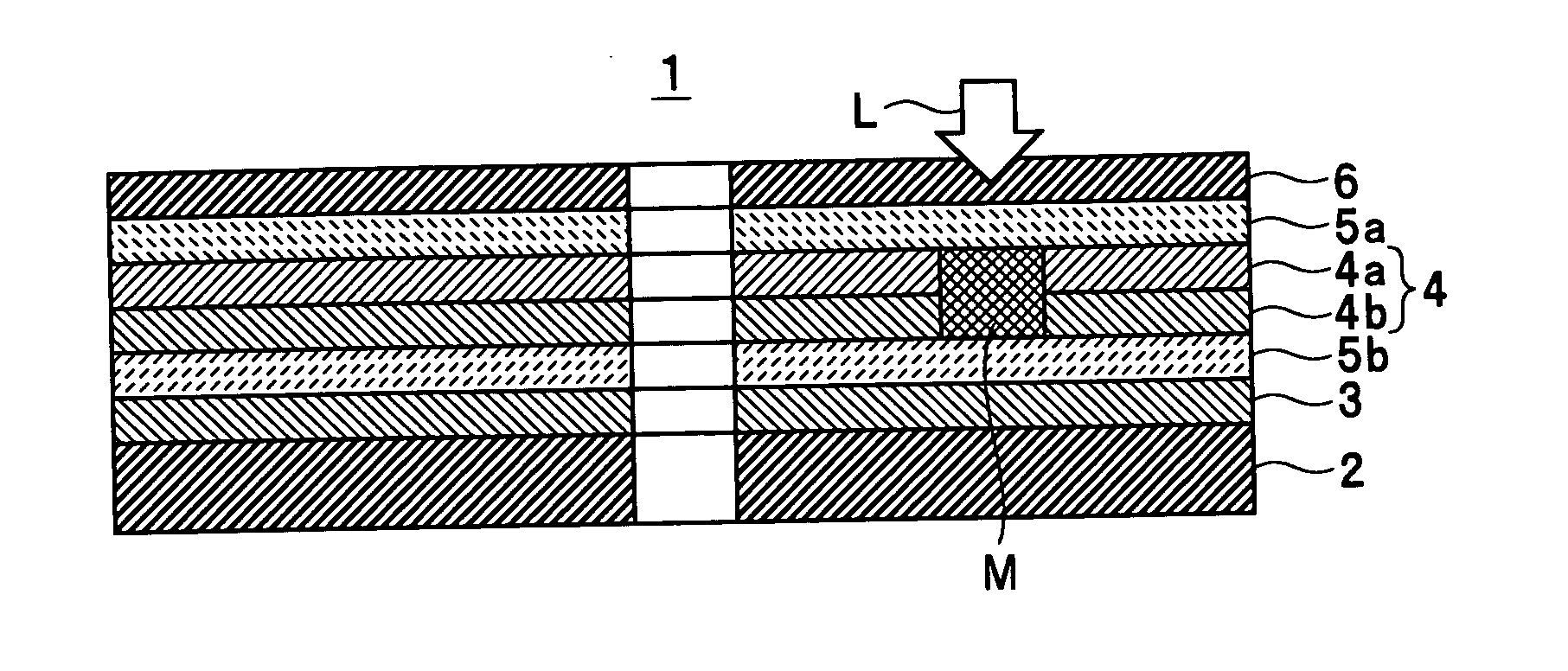
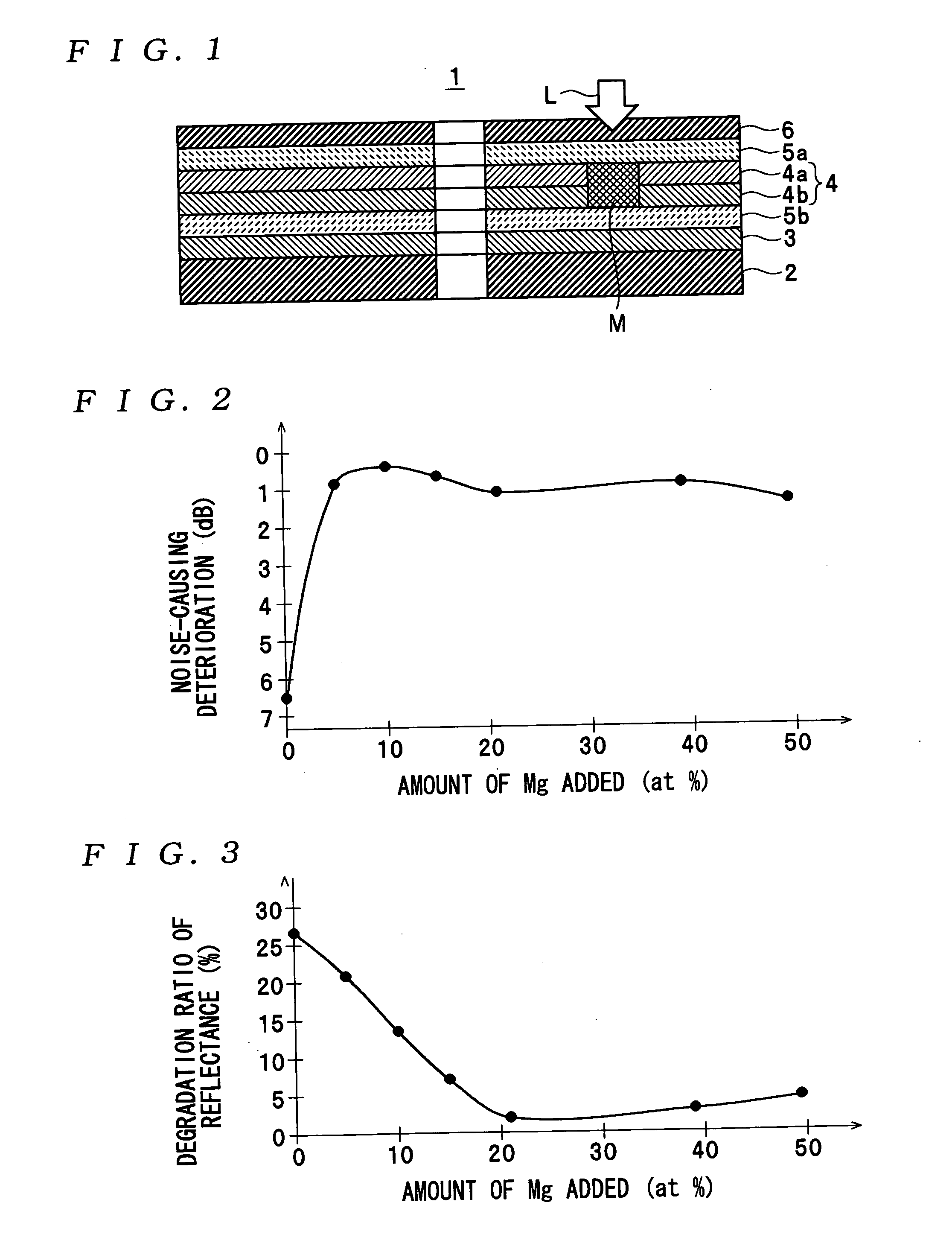
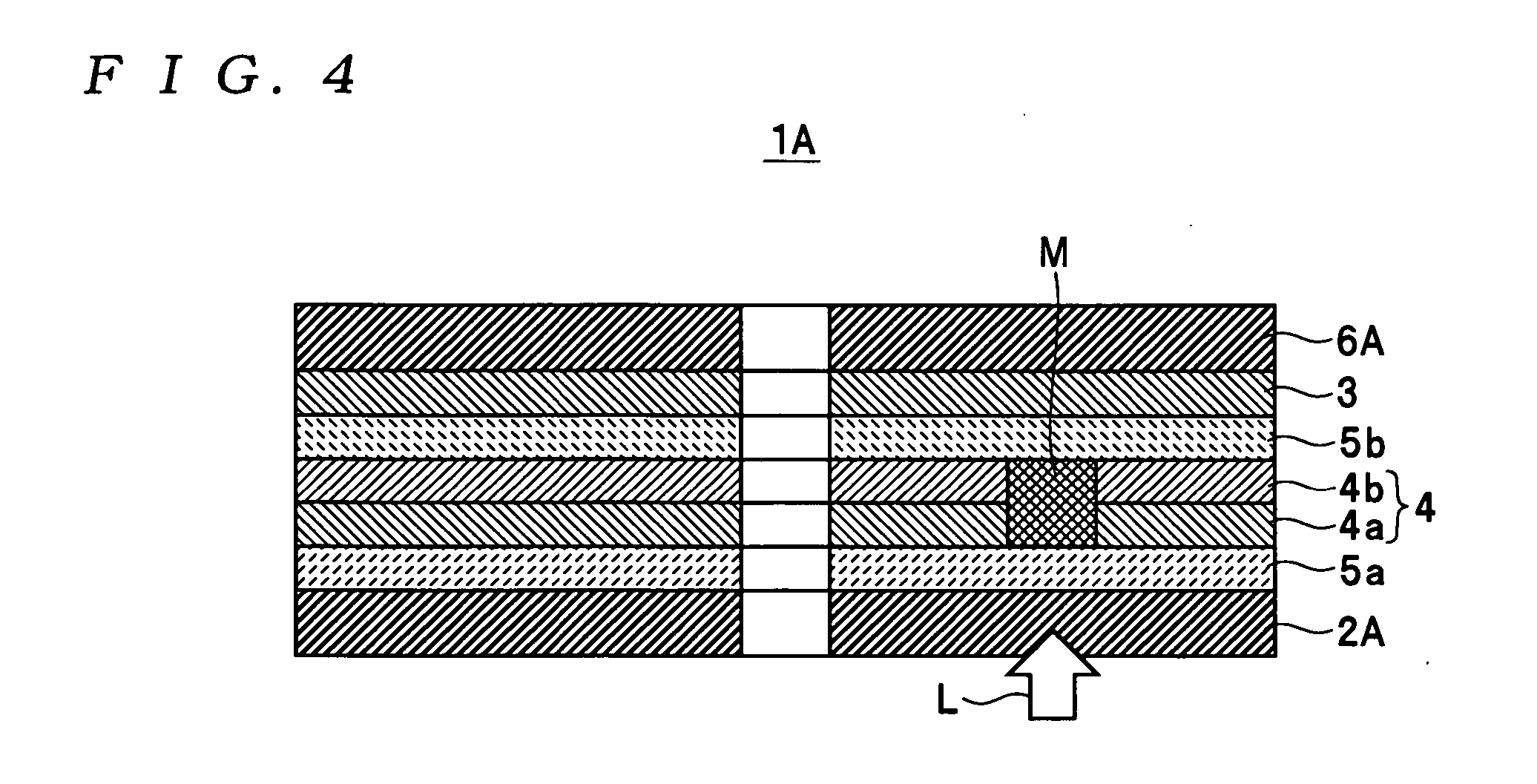
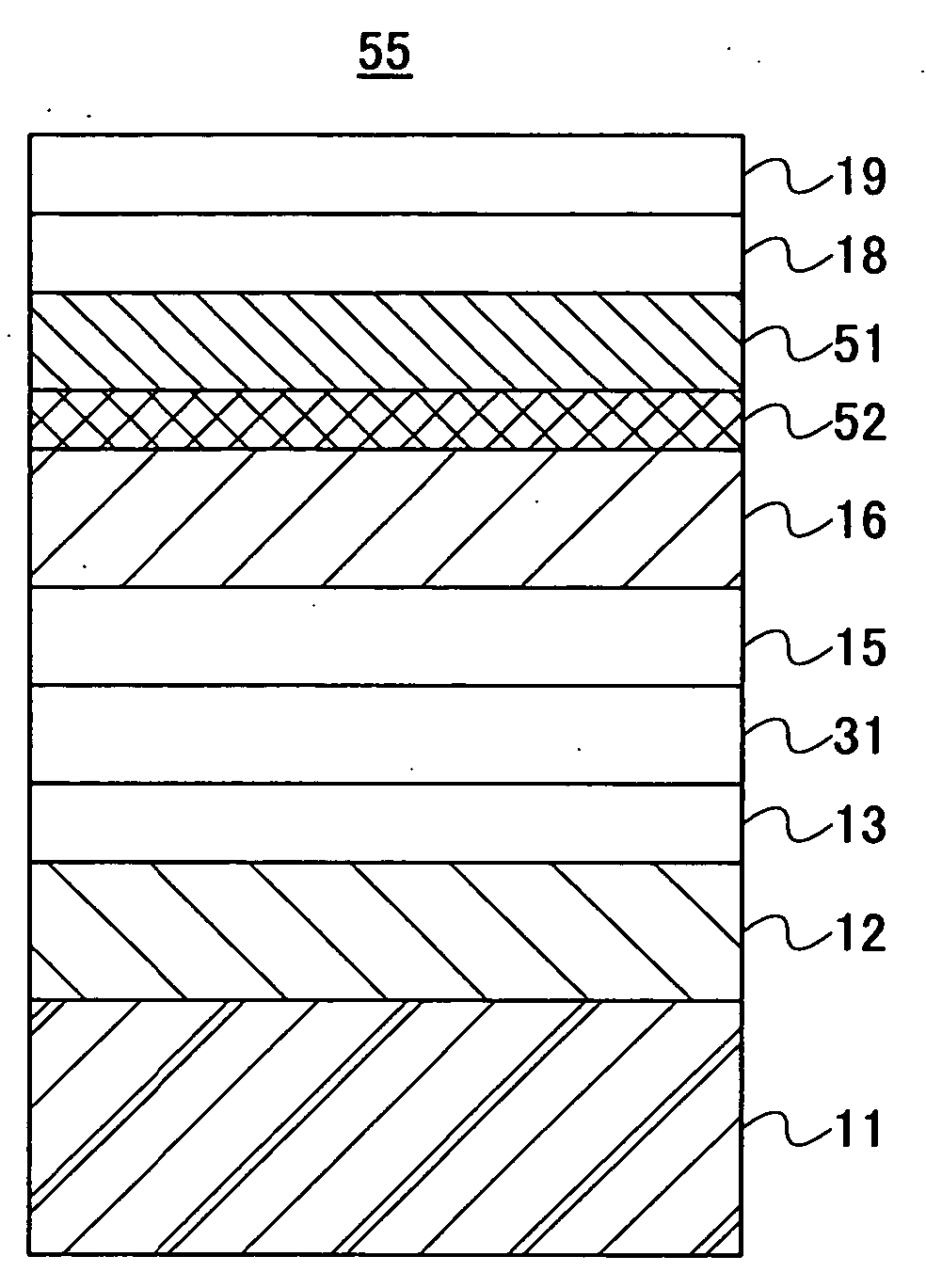
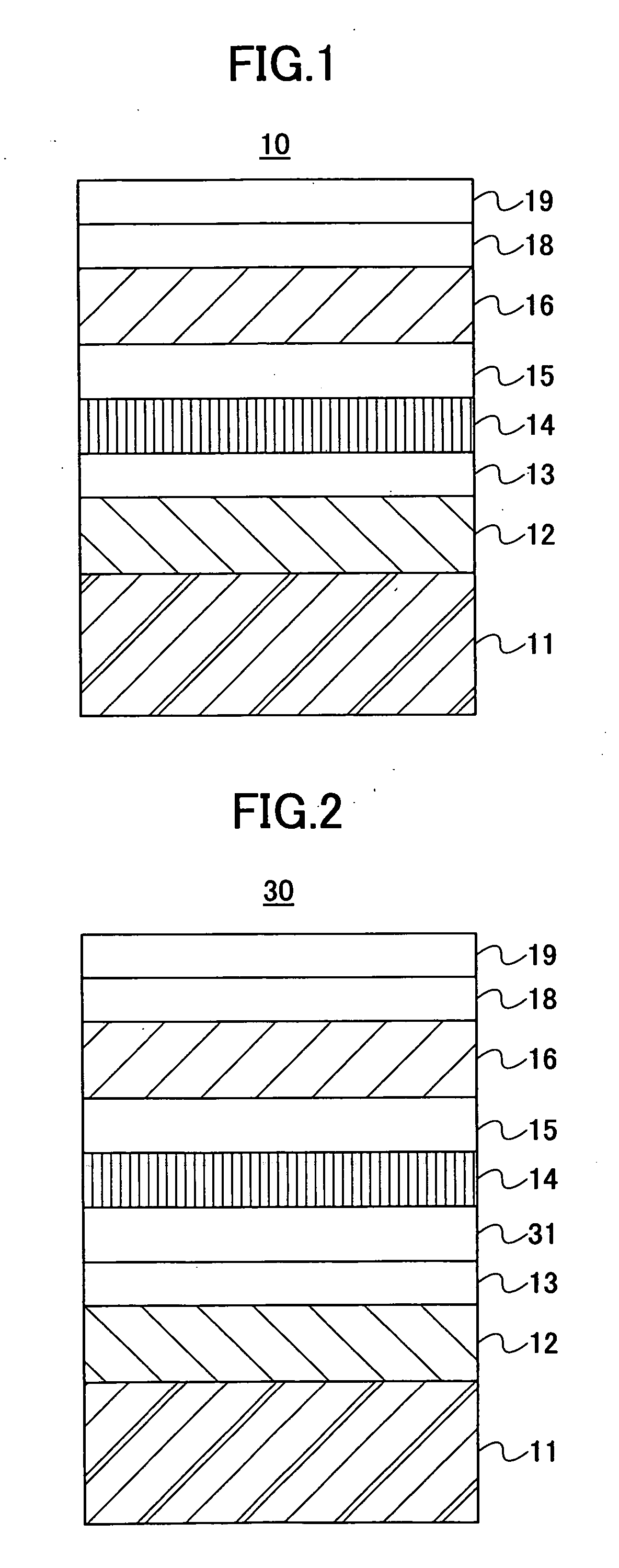
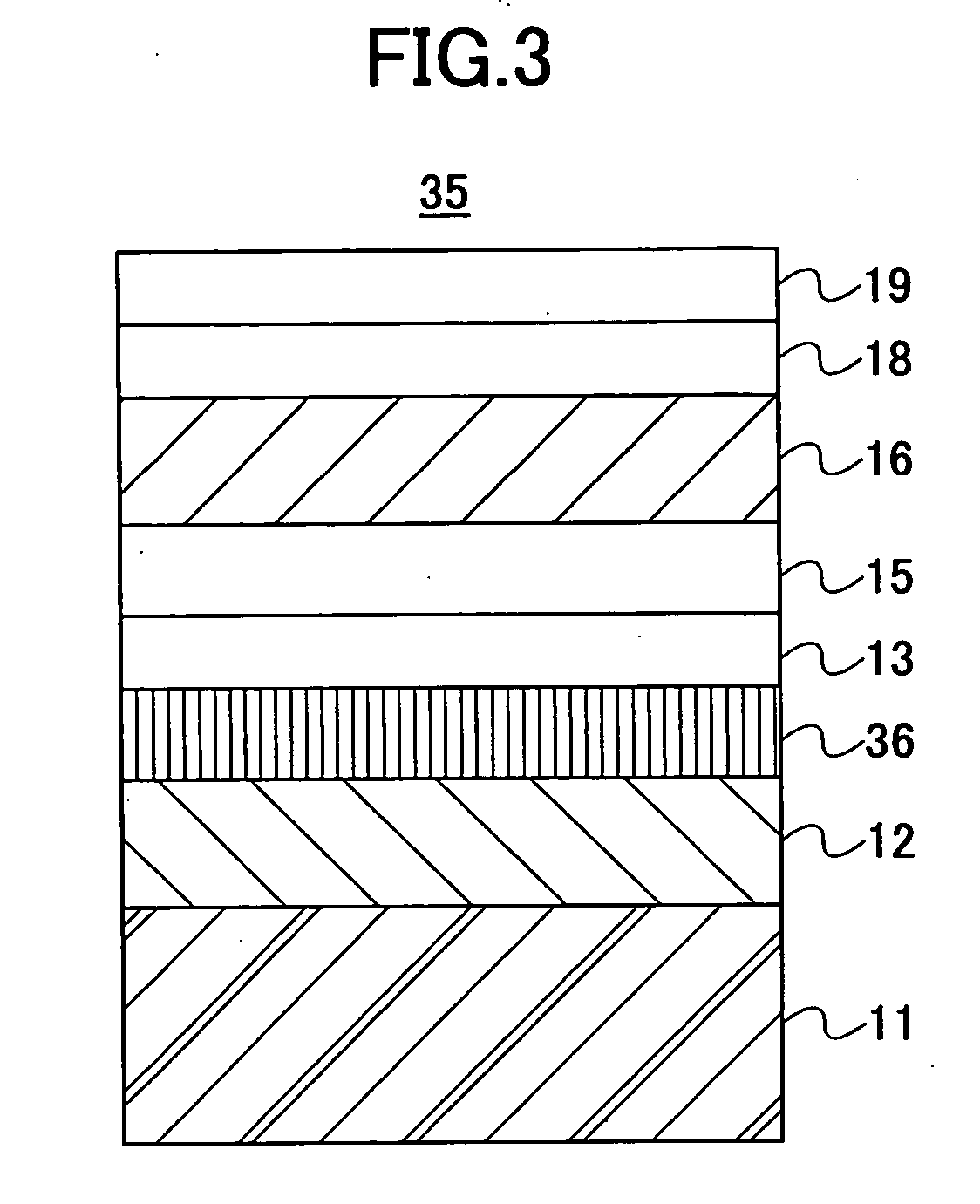
InactiveUS7166374B2High-density recordingReduce noiseRecord information storageMagnetic recordingInter layerCrystal structure
A magnetic recording medium comprising a non-ferromagnetic substrate and a magnetic recording film formed on the substrate with an underlayer interposed therebetween, wherein the magnetic recording film comprises a plurality of magnetic layers and an interlayer made of a material having a B2 crystal structure or an interlayer made of Ru, disposed between the adjacent magnetic layers.
Owner:WD MEDIA +1
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050069732A1High-density recordingIncreased durabilityProtective coatings for layersLayered productsCarbon filmHigh density
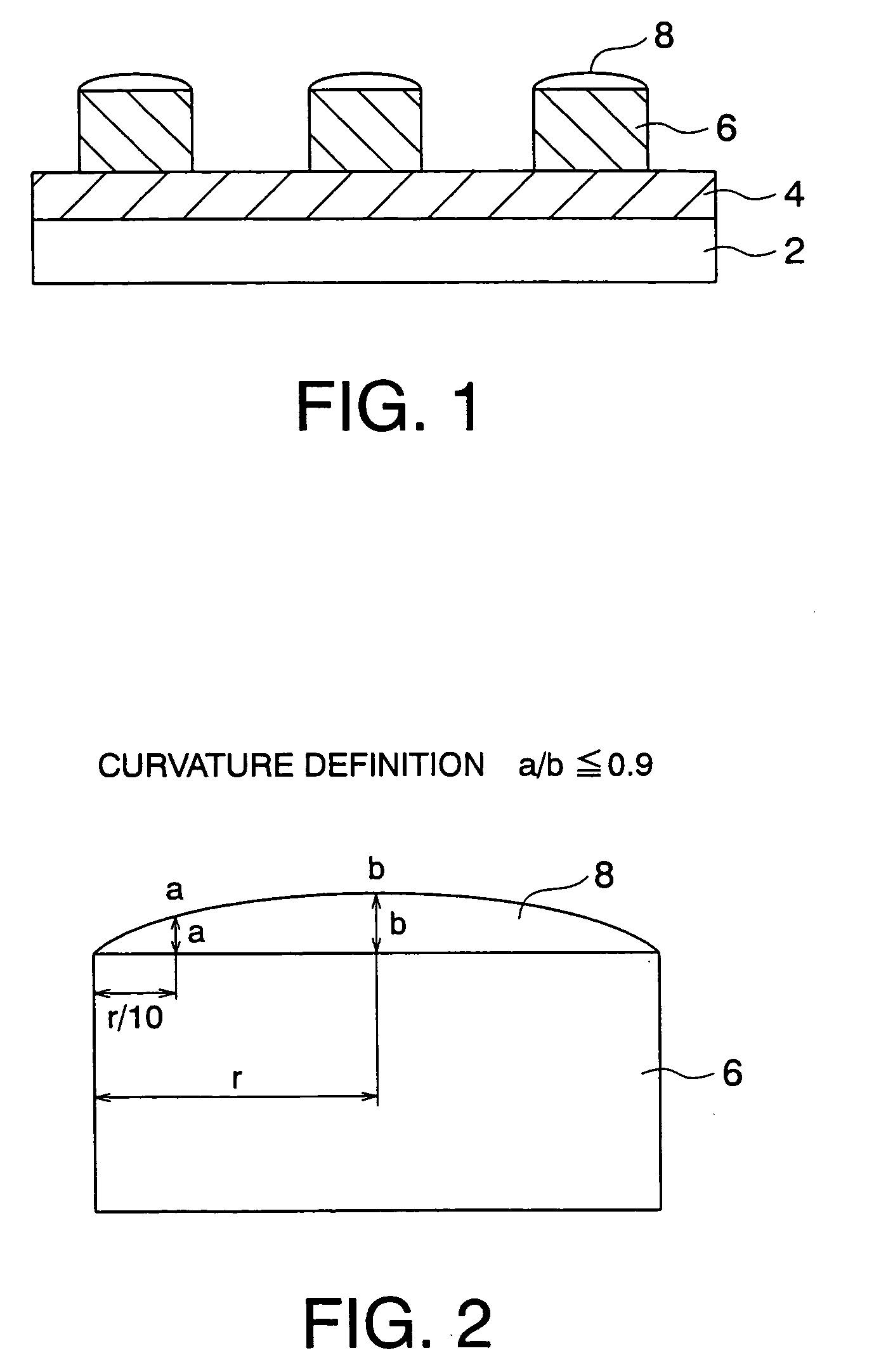
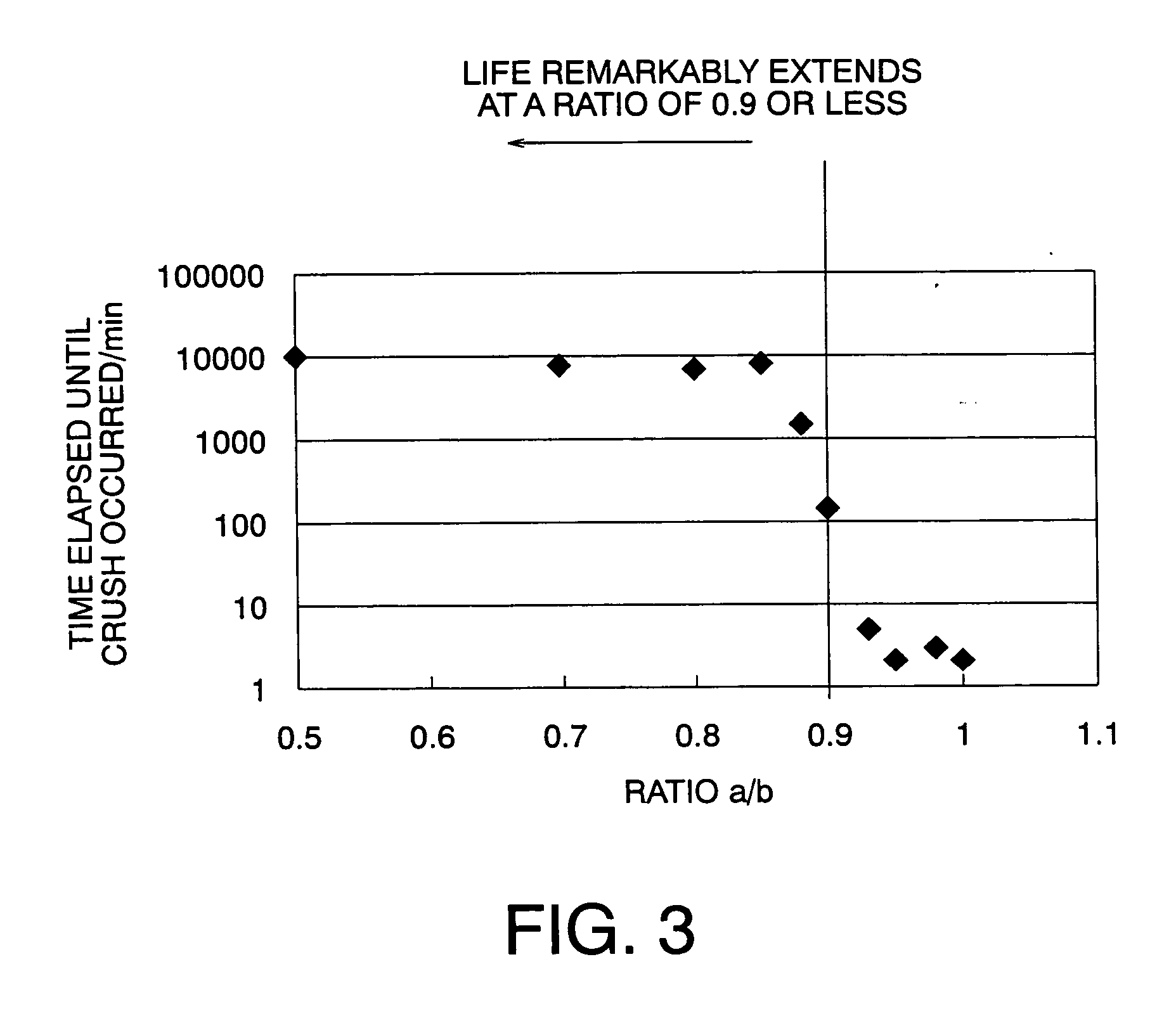
A magnetic recording medium which allows high density recording and has excellent durability can be obtained. A magnetic recording medium includes: a plurality of ferromagnetic material dots arranged on a soft magnetic layer formed on a non-magnetic substrate so as to be separated from one another; and carbon films which are formed on the respective ferromagnetic material dots, each carbon film having a smooth film face shape in a section passing through the center of each ferromagnetic material dot and a film thickness gradually decreasing from the center of the ferromagnetic material dot toward an outer edge thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS20050047306A1High-density recordingCombination recordingMechanical record carriersHigh densityRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which is capable of performing high-density recording of record data, and storing the recorded data for a long time period such that the recorded data can be normally reproduced during the long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Cu as the main component and having Au added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS20050018591A1High-density recordingCombination recordingLayered productsLaser beamsHigh density
An optical information recording medium which is capable of performing high-density recording of record data, and storing the recorded data for a long time period such that the recorded data can be normally reproduced during the long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Cu as the main component and having Si added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Glass substrate for an information recording medium and information recording medium employing it
InactiveUS20050096210A1Improve yieldIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersEdge surfaceRecording layer
A chemically strengthened glass substrate for use as the substrate of an information recording medium such as a magnetic disk, magneto-optical disk, DVD, or MD, wherein a strengthened layer formed by chemical strengthening exists on the outer edge surface and on the inner edge surface but substantially not on a surface on which an information recording layer is formed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
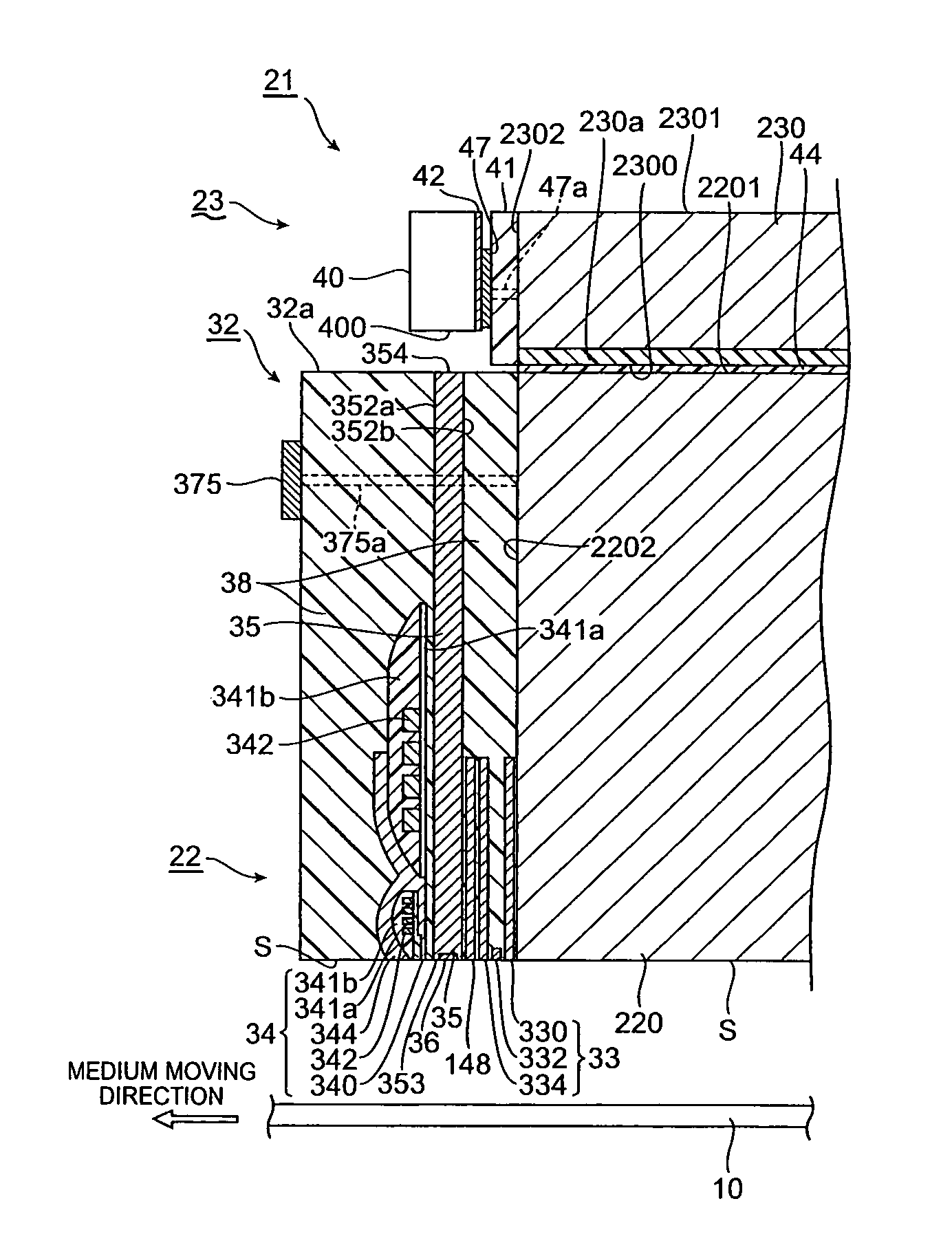
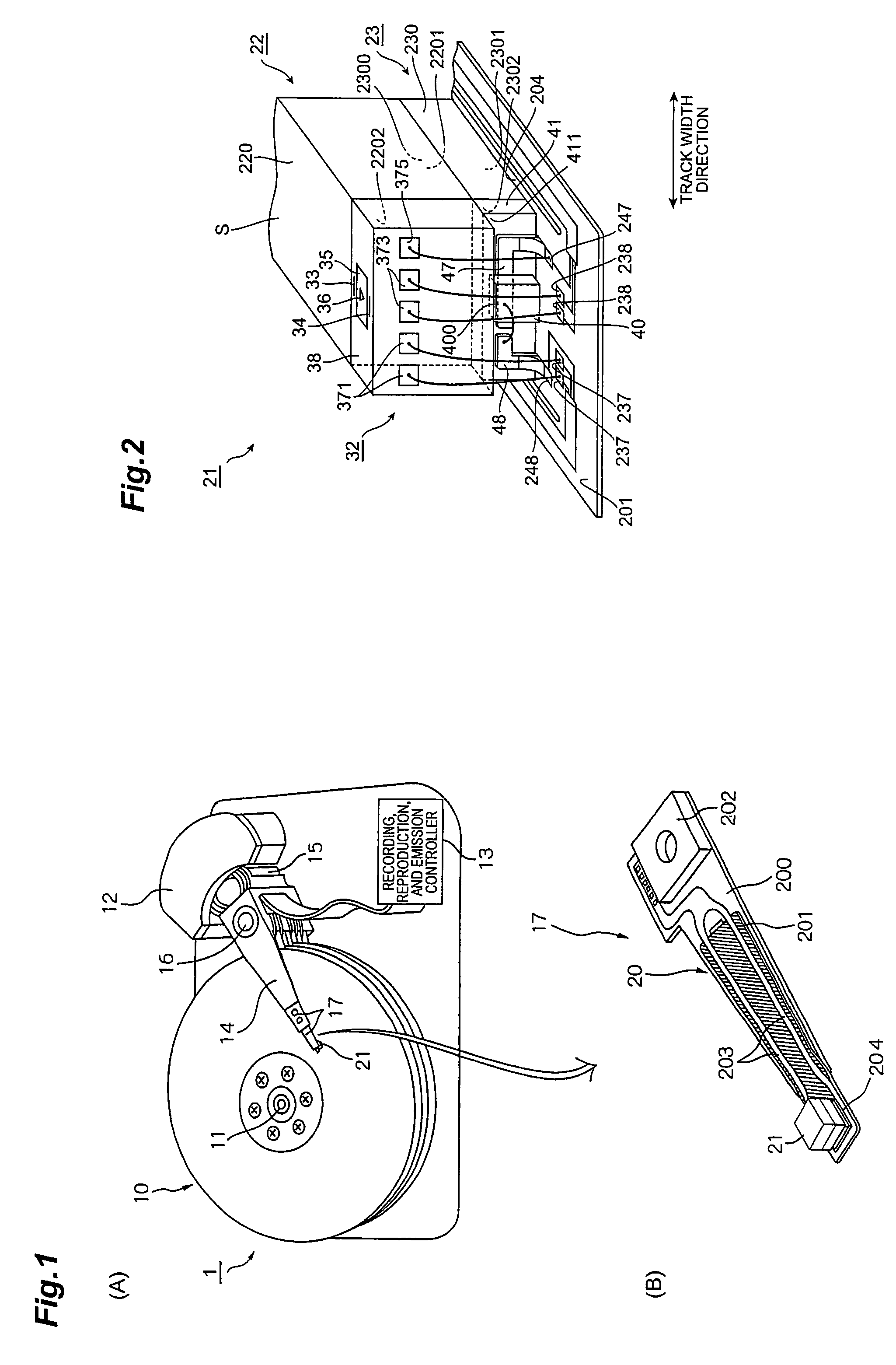
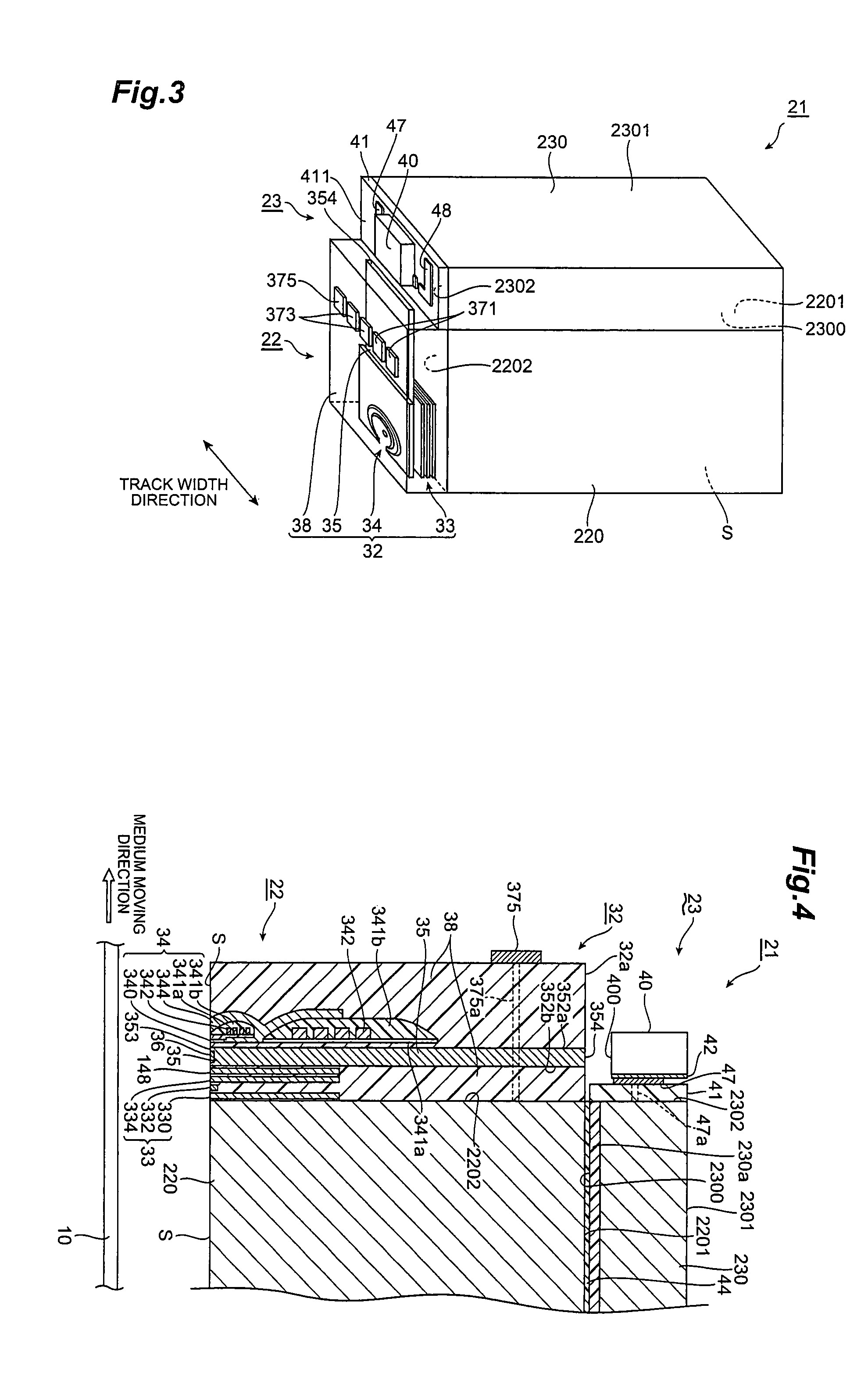
Near-field light generator plate, thermally assisted magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive
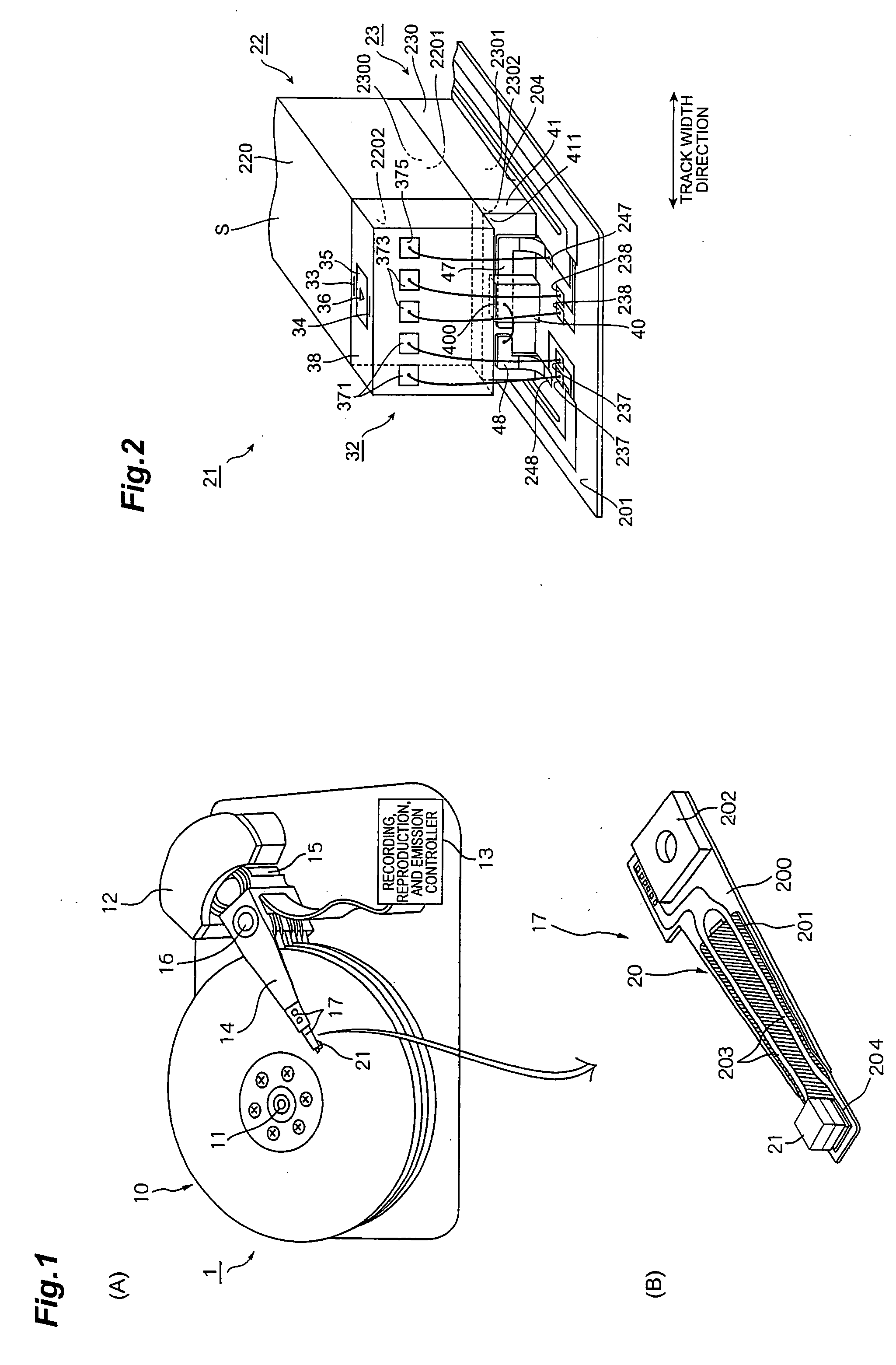
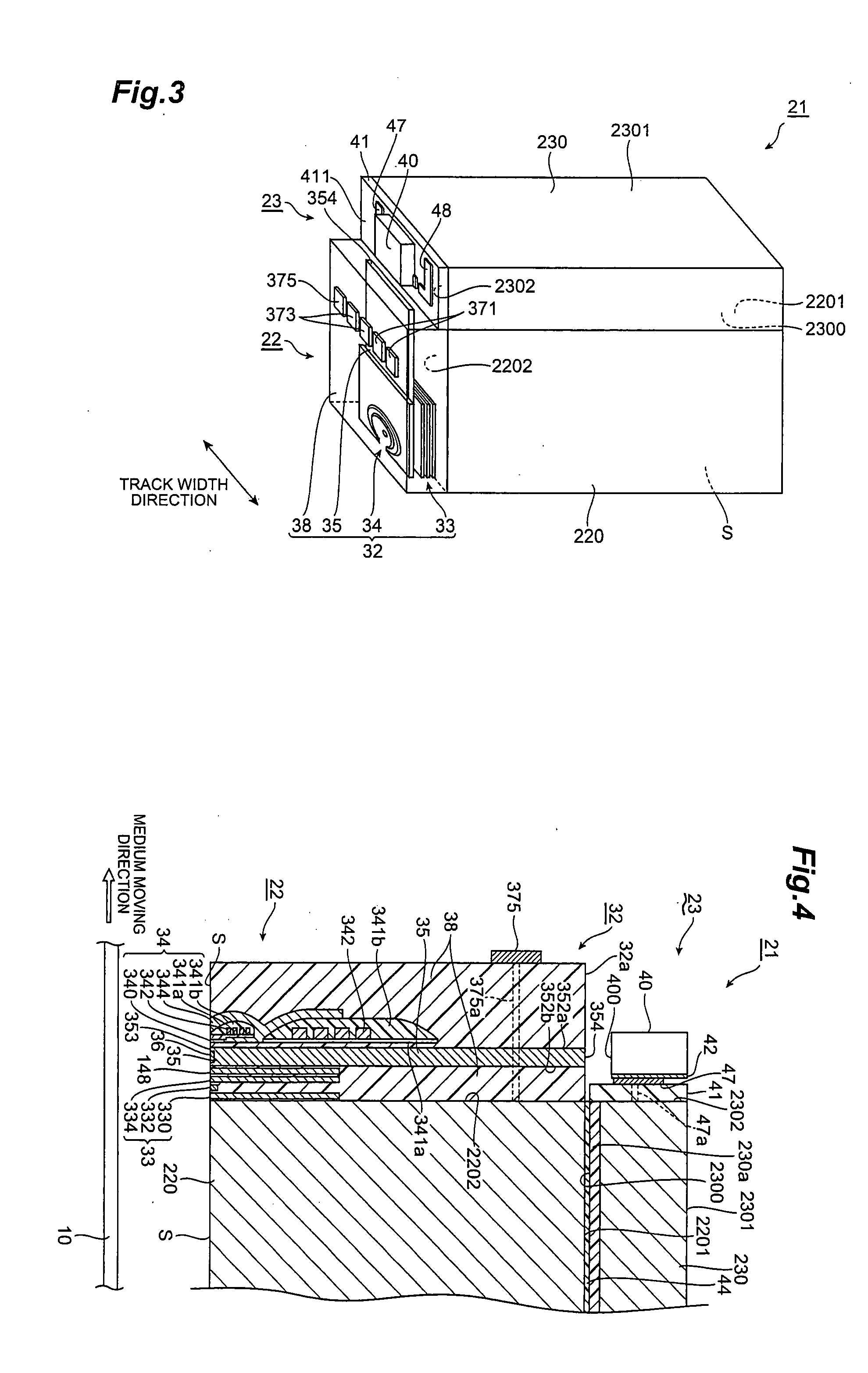
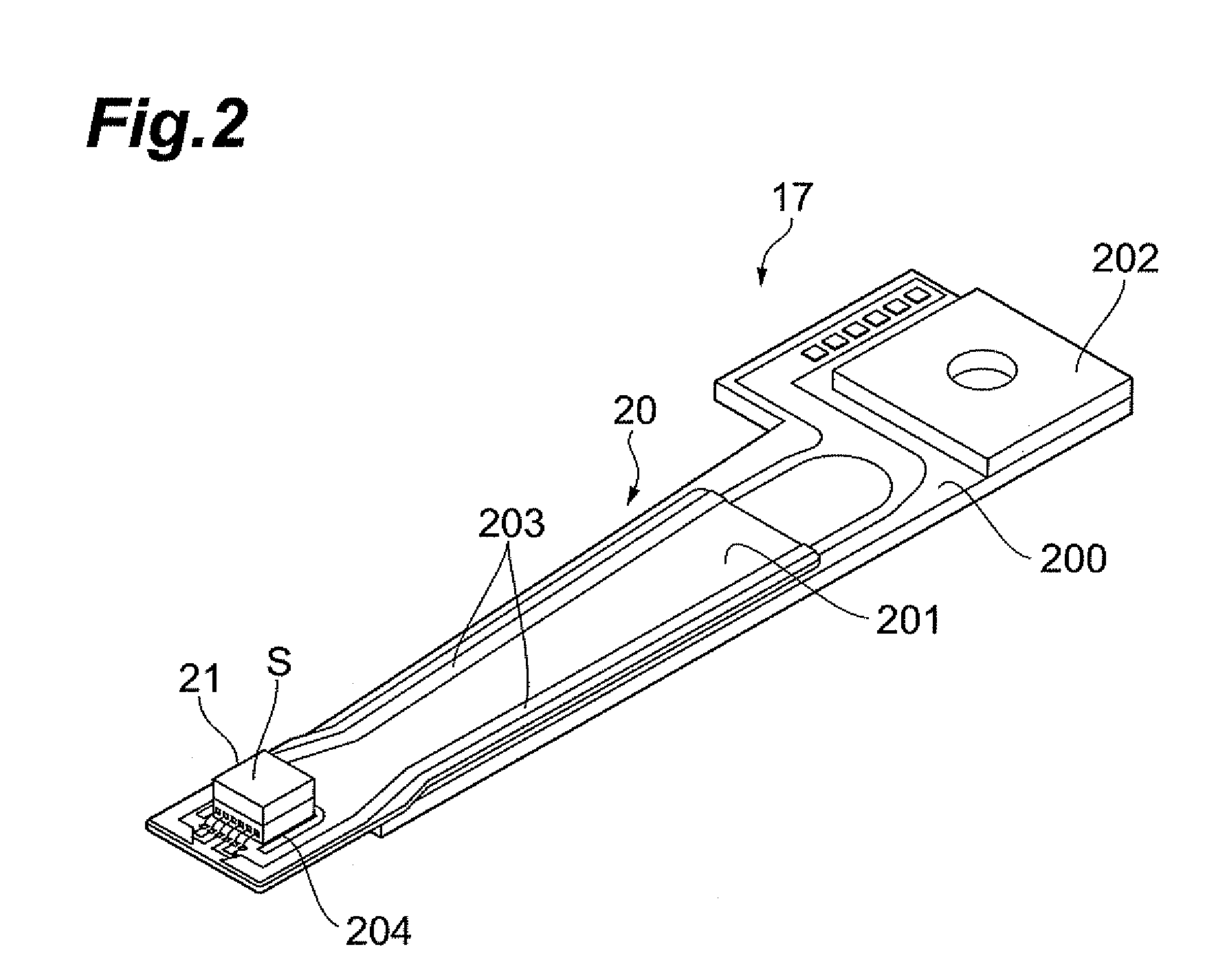
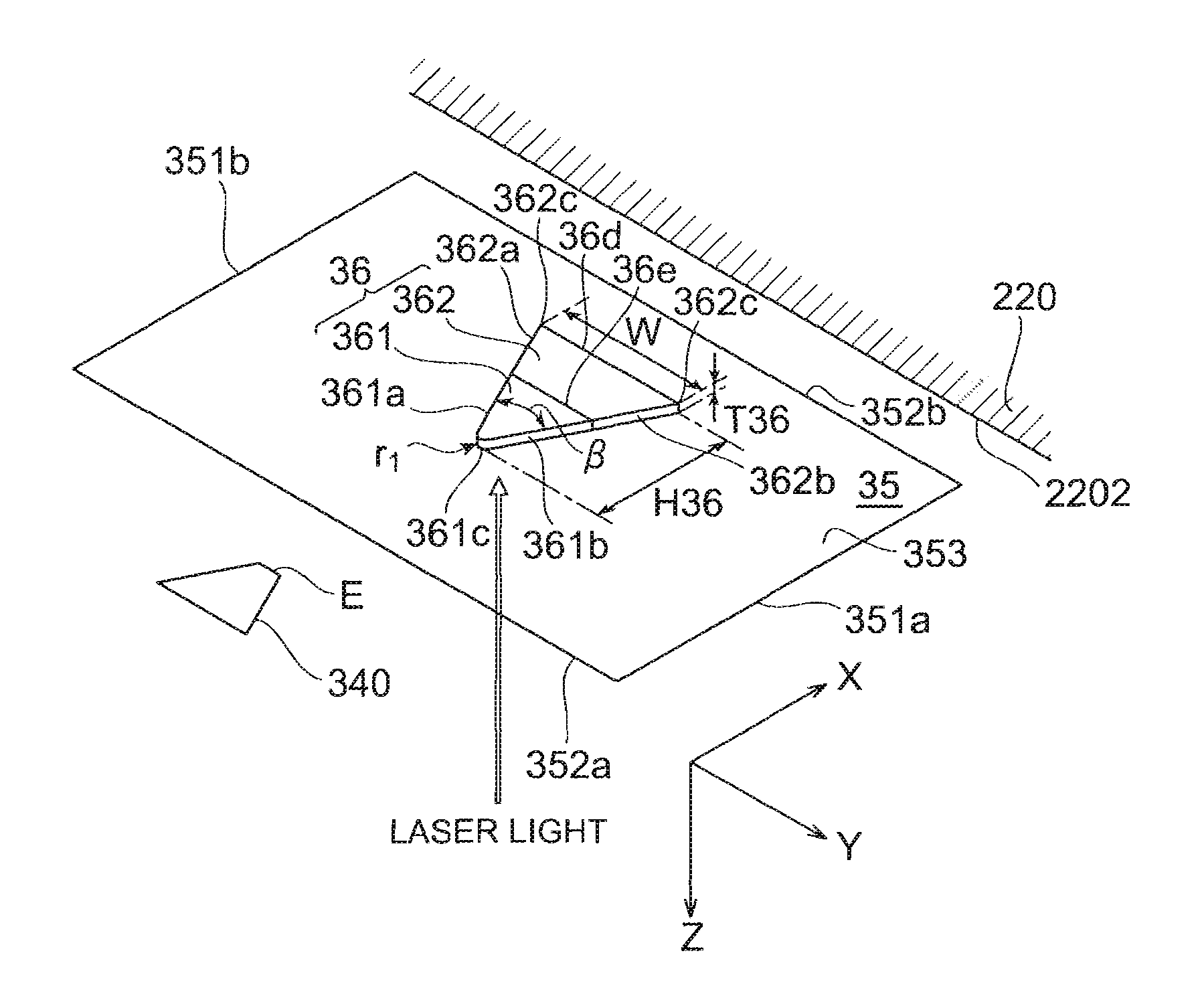
ActiveUS20080198496A1Easily projectedSmall spot sizeRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHard disc driveConductive materials
A near-field light generator plate 36 of the present invention is arranged to face a medium 10, and one portion 36b and other portion 36a in a medium-facing surface S thereof are made of their respective electroconductive materials different from each other. Since the one portion and the other portion in the medium-facing surface are made of the electroconductive materials different from each other, this medium-facing surface is formed by a surface removing step such as polishing or etching from the medium-facing surface side so that a difference between heights of the one portion and the other portion is readily made based on the difference of the materials.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS20050047301A1High-density recordingCombination recordingMechanical record carriersHigh densityRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which is capable of performing high-density recording of record data, and storing the recorded data for a long time period such that the recorded data can be normally reproduced during the long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Cu as the main component and having Mg added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
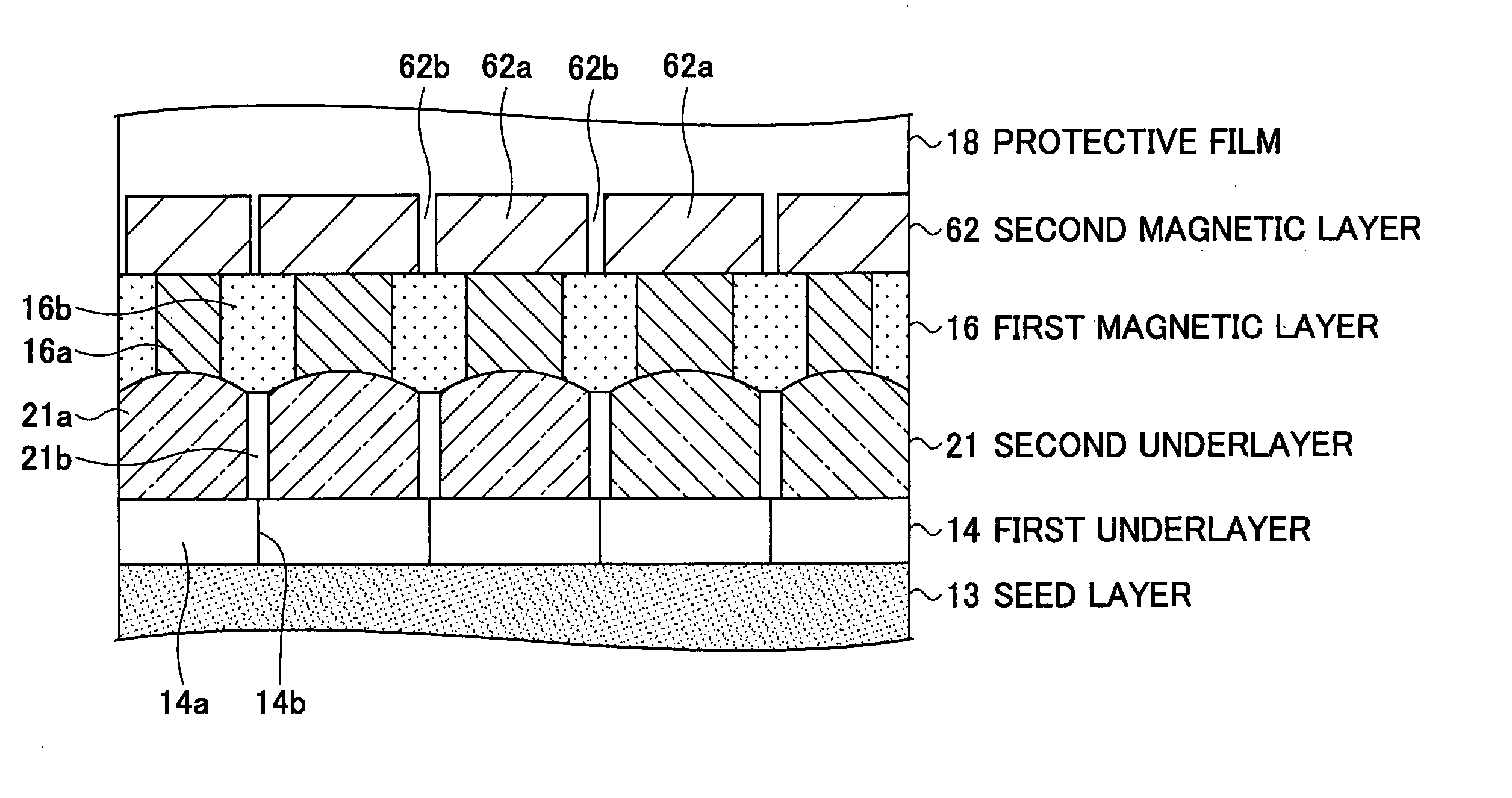
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic storage device
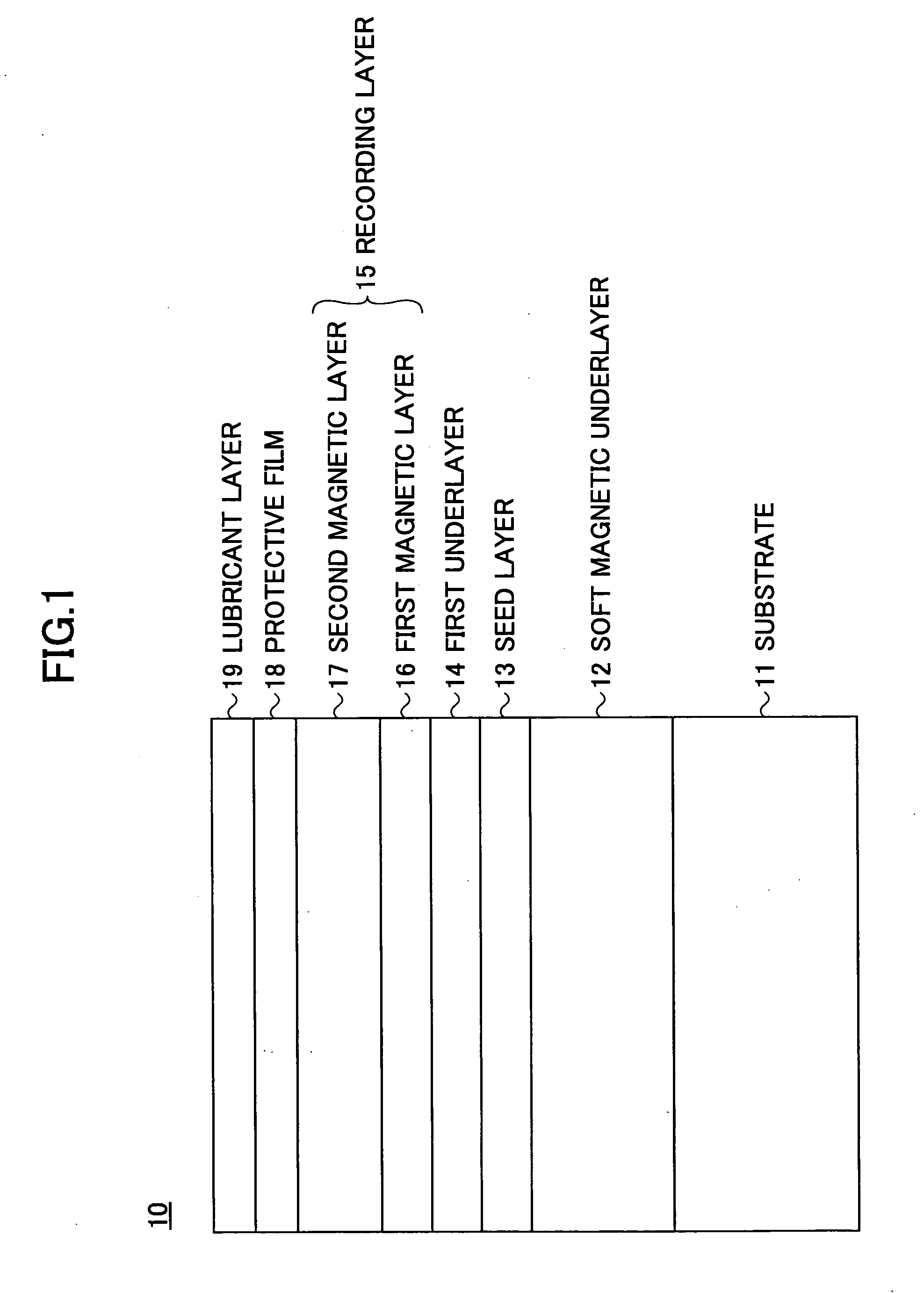
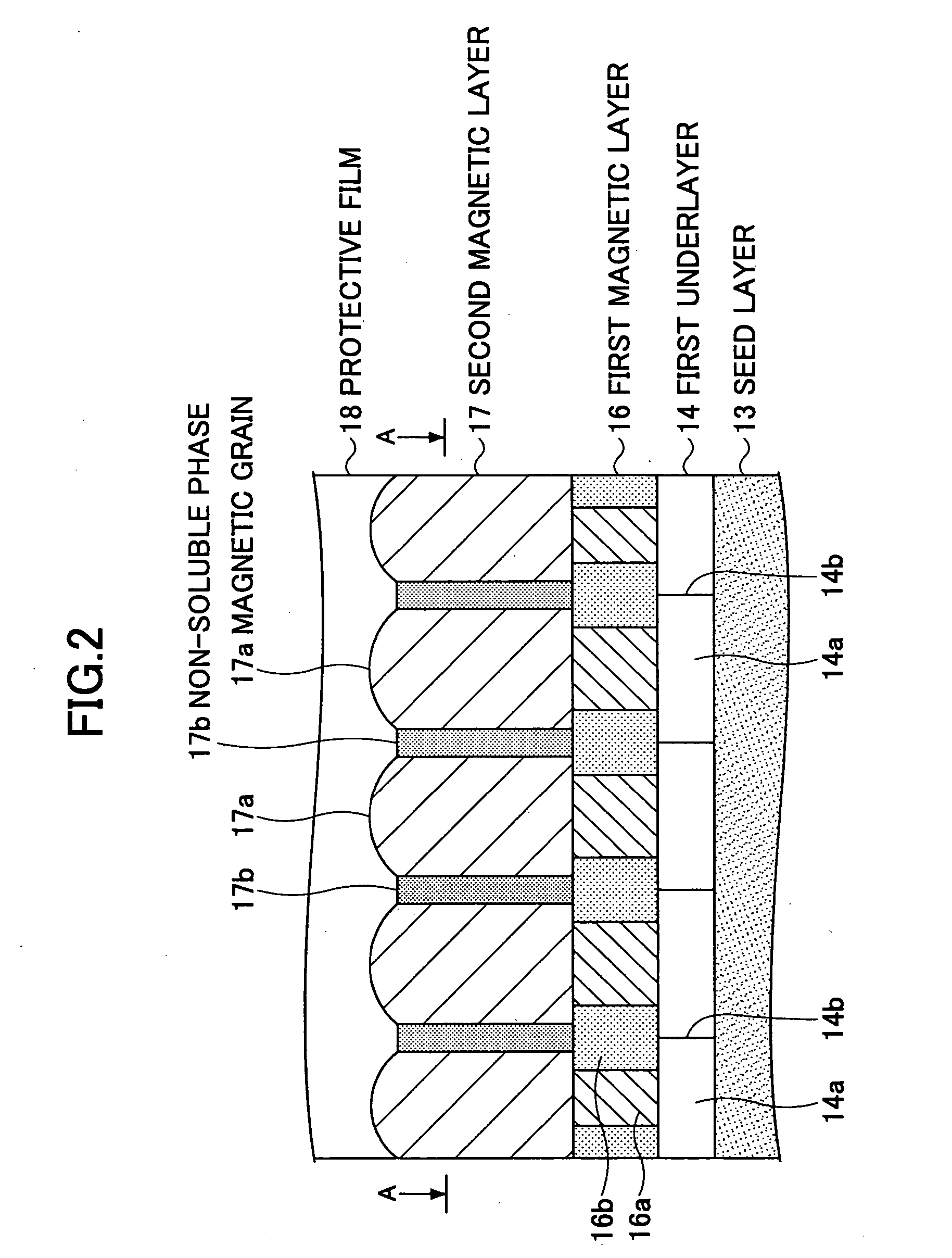
InactiveUS20060222902A1Medium noise is reducedImprove signal-to-noise ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh densityMagnetic storage
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium for enabling high density recording is disclosed. The perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate on which a soft magnetic underlayer, a seed layer made of a non-crystalline material, an underlayer made of Ru or an Ru alloy including Ru as a main component, and a recording layer including a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer. The first and second magnetic layers include a plurality of magnetic grains having easy magnetization axes in a substantially perpendicular direction with respect to the substrate surface, and first and second nonmagnetic non-soluble phases segregating the magnetic grains of the first and second magnetic layers, respectively. The first magnetic layer includes the first non-soluble phase at a first atomic concentration that is higher than a second atomic concentration of the second non-soluble phase in the second magnetic layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Glass composition, glass substrate employing it for an information recording medium, and information recording medium employing it
ActiveUS20050215414A1Excellent specific elastic modulusLow alkali elutionBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageRecording mediaChemistry
A glass substrate used as a substrate of an information recording medium such as a magnetic disk, magneto-optical disk, DVD, or MD, and a glass composition used to make such a glass substrate, contains the following glass ingredients: 40 to 70% by weight of SiO2; 1 to 20% by weight of Al2O3; 0 to 10% by weight, zero inclusive, of B2O3; SiO2+Al2O3+B2O3 accounting for 60 to 90% by weight; a total of 3.0 to 15% by weight of R2O compounds, where R═Li, Na, and K; a total of 2.0 to 15% by weight of R′O compounds, where R═Mg, and Zn; and a total of 1.0 to 20% by weight of MOx (TiO2+ZrO2+LnxOy), where LnxOy represents at least one compound selected from the group consisting of lanthanoid metal oxides, Y2O3, Nb2O5, and Ta2O5. Here, the following condition is fulfilled: 0.070<(total content of R′O compounds) / (SiO2+Al2O3+B2O3)<0.200.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Thermally assisted magnetic head and manufacturing method of same
ActiveUS20090168220A1High-density recordingPrecise positioningDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageHigh densityMagnetic poles
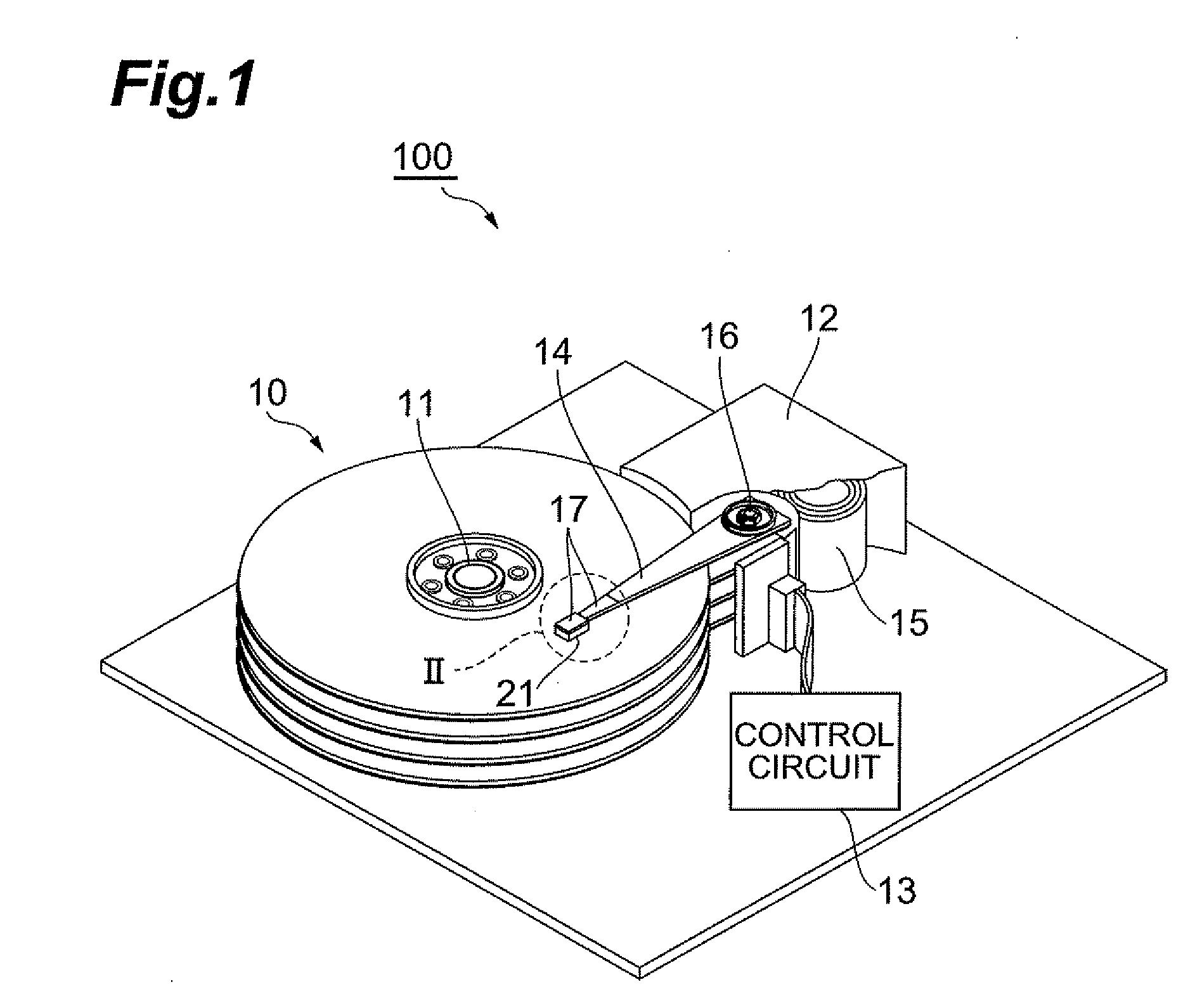
When first and second near-field light-generating portions are irradiated with laser light or other energy rays, near-field light is generated at the tips of both the near-field light-generating portions. By means of the near-field light thus generated, a magnetic recording medium opposing the medium-opposing surface is heated, and the coercivity of the magnetic recording medium is lowered. Since at least a portion of the main magnetic pole is positioned within the spot region including the region between the first and second near-field light-generating portions, the tips of both the near-field light-generating portions and the main magnetic pole can be brought extremely close together, and high-density recording can be performed.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thermally assisted magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive
ActiveUS8077556B2Low coercivityHigh-density recordingRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHard disc drivePhoto irradiation
A thermally assisted magnetic head has a medium-facing surface facing a magnetic recording medium; a near-field light generator disposed on a light exit face in the medium-facing surface; a magnetic recording element located adjacent to the near-field light generator; and a light emitting element disposed so that emitted light thereof reaches the near-field light generator; the near-field light generator is comprised of a cusp portion and a base portion; when λin represents a wavelength of the emitted light from the light emitting element immediately before the emitted light reaches the near-field light generator, an intensity of near-field light generated when the material forming the cusp portion is irradiated with the light of the wavelength λin is stronger than an intensity of near-field light generated when the material forming the base portion is irradiated with the light of the wavelength λin.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thermally assisted magnetic head having main pole arranged between near-field light-generating portions and manufacturing method of same
ActiveUS8116034B2High-density recordingPrecise positioningDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageHigh densityMagnetic poles
When first and second near-field light-generating portions are irradiated with laser light or other energy rays, near-field light is generated at the tips of both the near-field light-generating portions. By means of the near-field light thus generated, a magnetic recording medium opposing the medium-opposing surface is heated, and the coercivity of the magnetic recording medium is lowered. Since at least a portion of the main magnetic pole is positioned within the spot region including the region between the first and second near-field light-generating portions, the tips of both the near-field light-generating portions and the main magnetic pole can be brought extremely close together, and high-density recording can be performed.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Glass composition, glass susbstrate employing it for an information recording medium, and information recording medium employing it
ActiveUS7687419B2Excellent specific elastic modulusLow alkali elutionMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersRecording mediaChemistry
A glass substrate used as a substrate of an information recording medium such as a magnetic disk, magneto-optical disk, DVD, or MD, and a glass composition used to make such a glass substrate, contains the following glass ingredients: 40 to 70% by weight of SiO2; 1 to 20% by weight of Al2O3; 0 to 10% by weight, zero inclusive, of B2O3; SiO2+Al2O3+B2O3 accounting for 60 to 90% by weight; a total of 3.0 to 15% by weight of R2O compounds, where R=Li, Na, and K; a total of 2.0 to 15% by weight of R′O compounds, where R=Mg, and Zn; and a total of 1.0 to 20% by weight of MOx (TiO2+ZrO2+LnxOy), where LnxOy represents at least one compound selected from the group consisting of lanthanoid metal oxides, Y2O3, Nb2O5, and Ta2O5. Here, the following condition is fulfilled:0.070<(total content of R′O compounds) / (SiO2+Al2O3+B2O3)<0.200.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS7157128B2High-density recordingCombination recordingLayered productsHigh densityRecording layer
An optical information recording medium which is capable of performing high-density recording of record data, and storing the recorded data for a long time period such that the recorded data can be normally reproduced during the long time period. An optical information recording medium has a recording layer formed on a substrate, for having a laser beam irradiated thereto for recording and reproduction of record data. The recording layer includes a first sub-recording film and a second sub-recording film. The first sub-recording film is formed of a first material containing Si as the main component. The second sub-recording film is formed of a second material containing Cu as the main component and having Si added thereto, and disposed in the vicinity of the first recording film.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
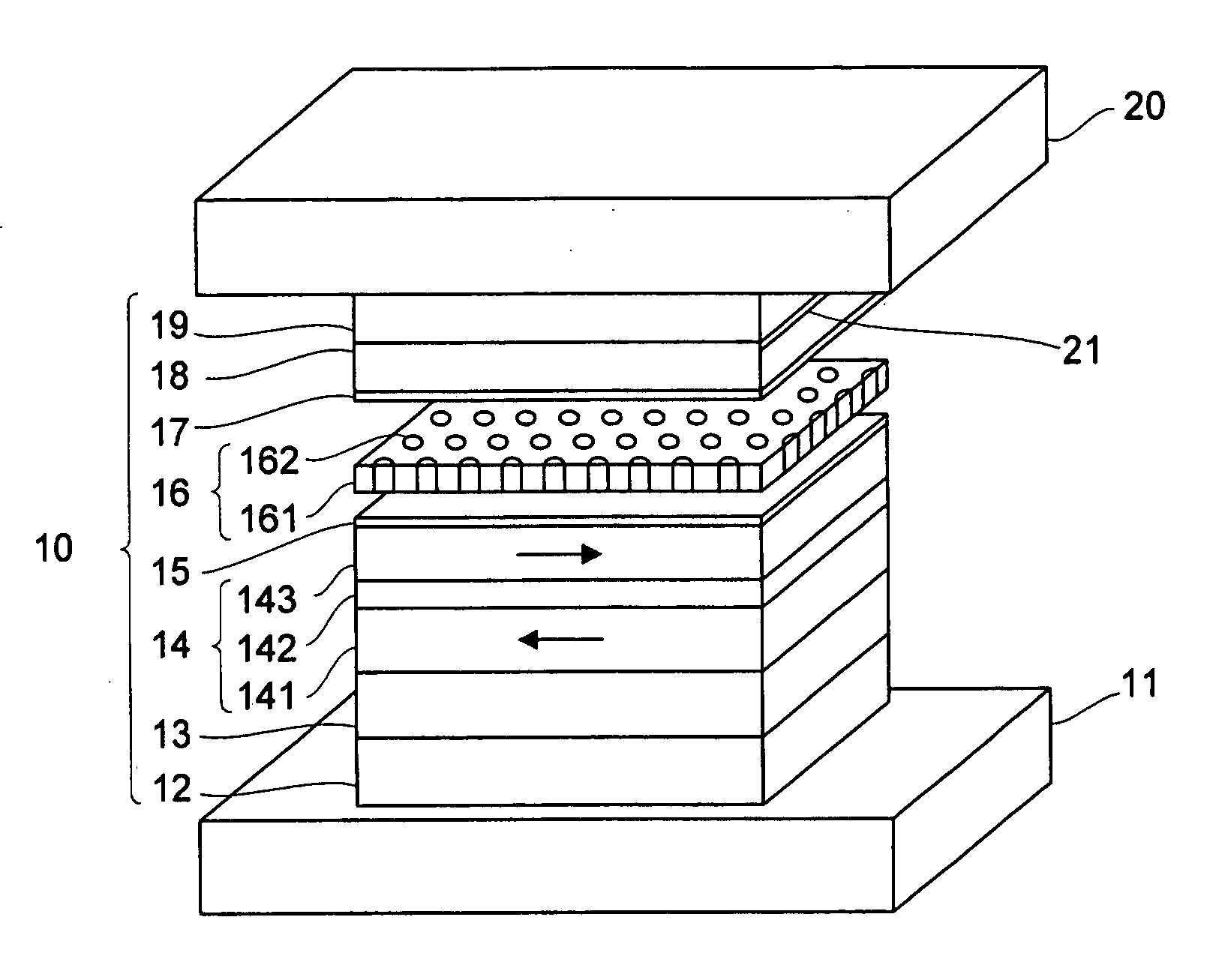
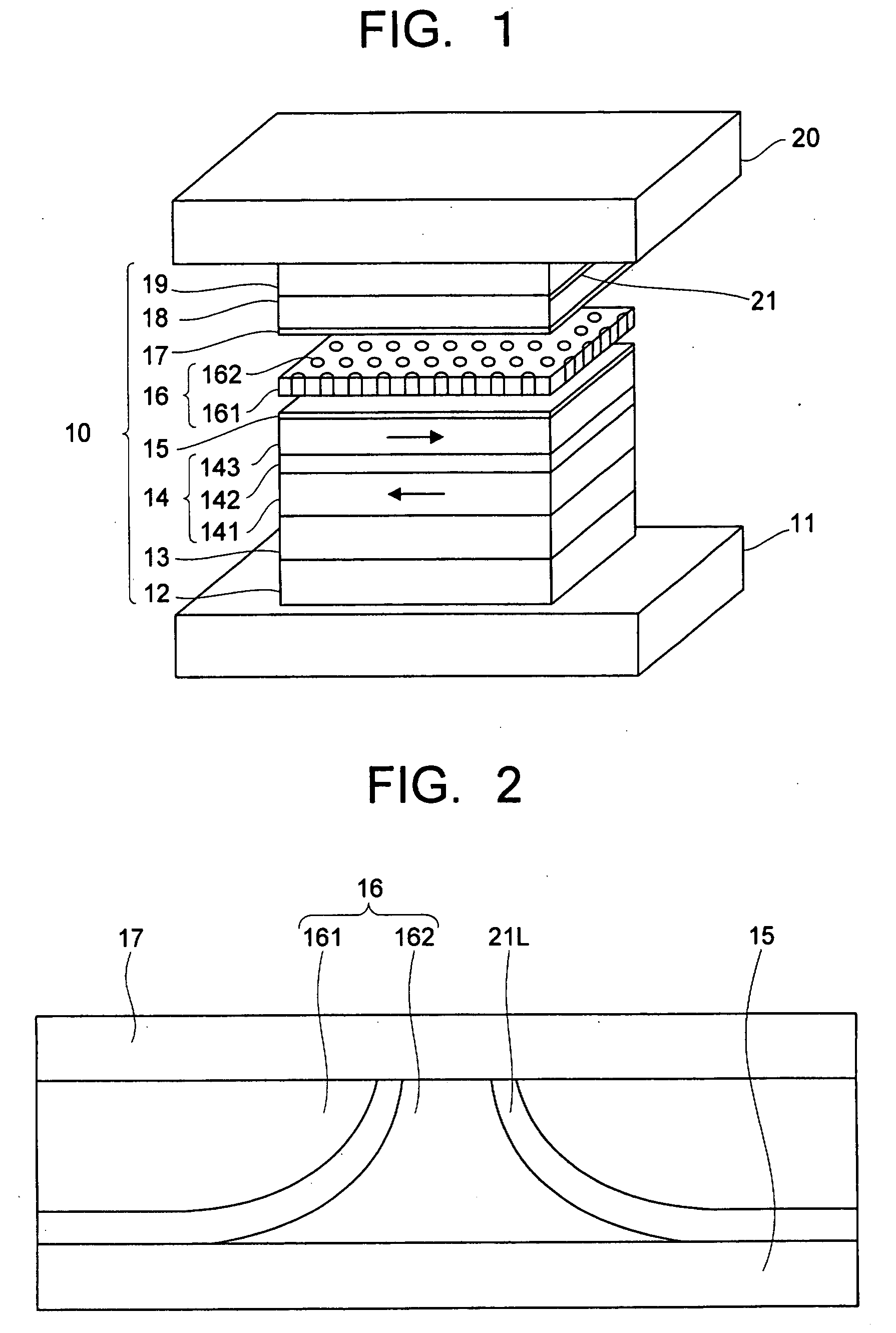
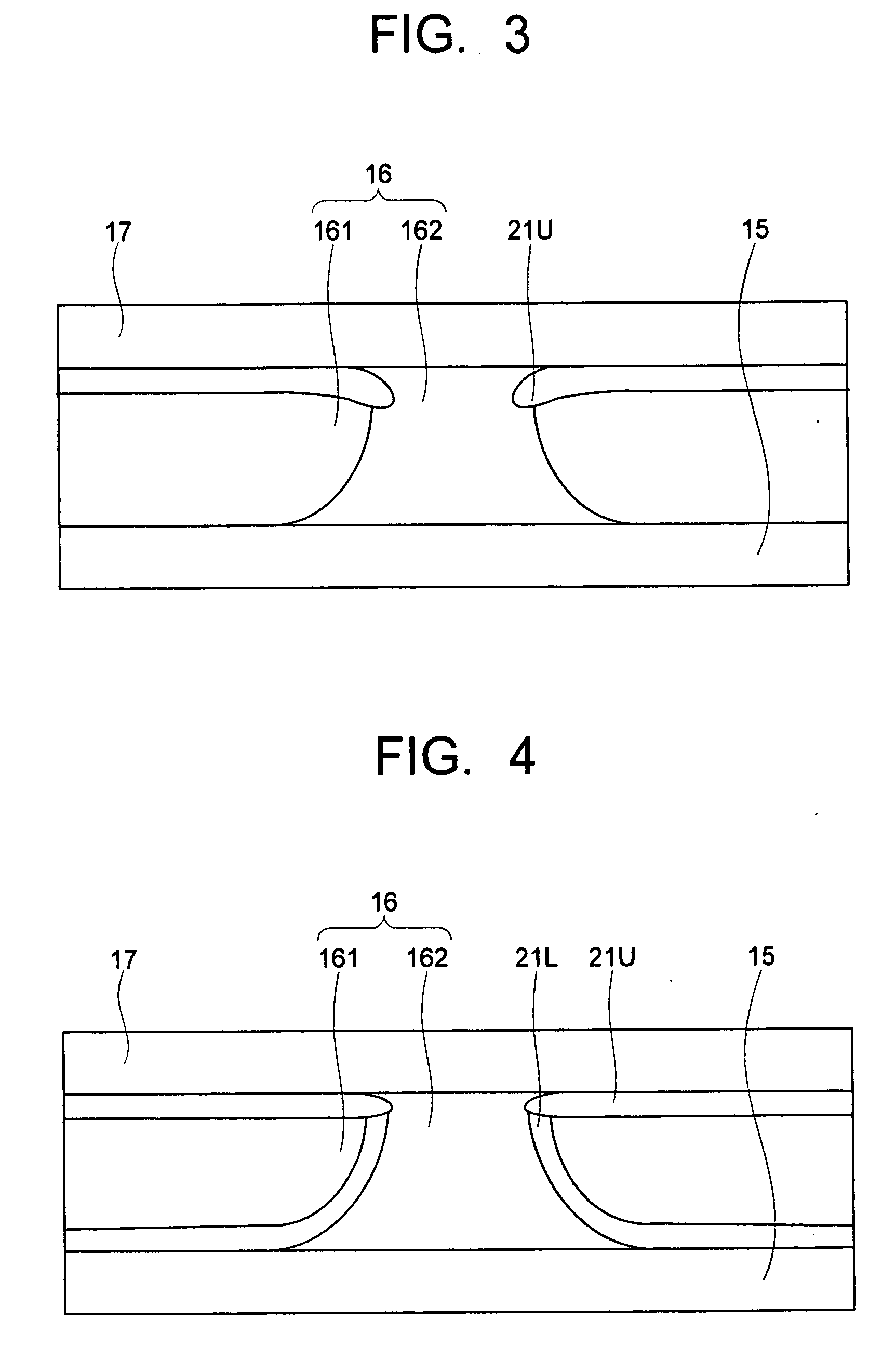
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic storage apparatus and recording method
InactiveUS20050053803A1Improve write performanceHigh-density recordingDifferent record carrier formsMechanical record carriersNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic storage
A magnetic recording medium is provided with a first magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic coupling layer provided on the first magnetic layer, and a second magnetic layer provided on the nonmagnetic coupling layer. The first and second magnetic layers are exchange-coupled, and have magnetization directions which are mutually parallel in a state where no external magnetic field is applied thereto, and the first magnetic layer switches the magnetization direction thereof before the second magnetic layer in response to a recording magnetic field which switches the magnetization directions of the first and second magnetic layers.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Ultra-high-density magnetic recording media and methods for making the same
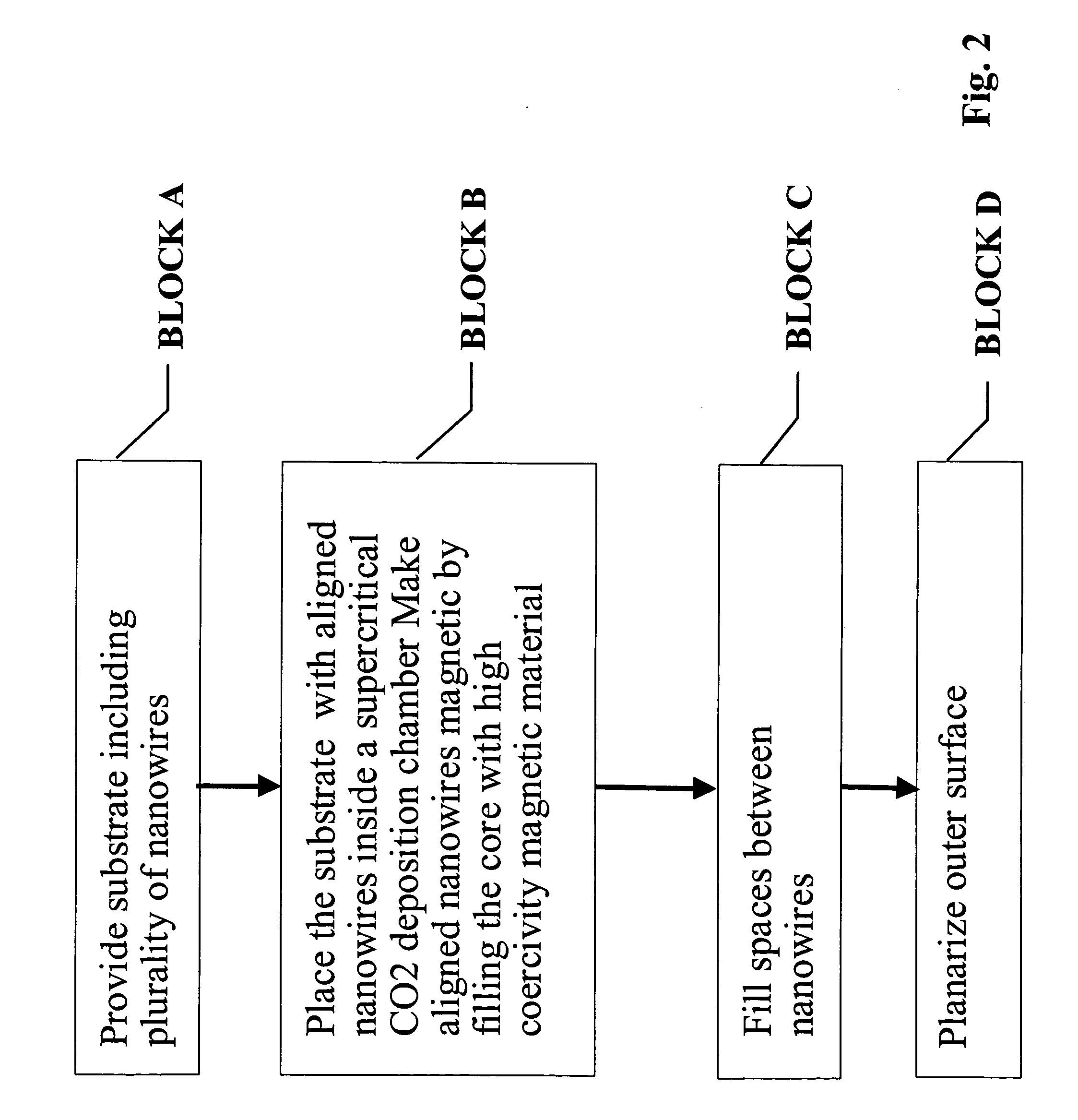
InactiveUS20050079282A1High density recordingImprove coercive forceNanoinformaticsRecord information storageNanowireHigh density
In accordance with the invention, a high density recording medium is fabricated by novel methods. The medium comprises an array of nanomagnets disposed within a matrix or on the surface of substrate material. The nanomagnets are advantageously substantially perpendicular to a planar surface. The nanomagnets are preferably nanowires of high coercivity magnetic material inside a porous matrix or an array of vertically aligned nanotubes, or on the surface of flat substrate. Such media can provide ultra-high density recording with bit size less than 50 nm and even less than 20 nm. A variety of techniques are described for making such media.
Owner:JIN SUNGHO
Method for manufacturing a magneto-resistance effect element, and magneto-resistance effect element
InactiveUS20080008909A1High-density recordingNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsCurrent limitingElectrical conductor
A method for manufacturing a magneto-resistance effect element includes: forming a first magnetic layer; forming a first metallic layer, on the first magnetic layer, mainly containing an element selected from the group consisting of Cu, Au, Ag; forming a functional layer, on the first metallic layer, mainly containing an element selected from the group consisting of Si, Hf, Ti, Mo, W, Nb, Mg, Cr and Zr; forming a second metallic layer, on the functional layer, mainly containing Al; treating the second metallic layer by means of oxidizing, nitriding or oxynitiriding so as to form a current confined layer including an insulating layer and a current path with a conductor passing a current through the insulating layer; and forming, on the current confined layer, a second magnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and magnetic storage apparatus
InactiveUS20060199043A1High track densityNarrow widthBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic storageNon magnetic
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate and has a construction to stack consecutively on the substrate, a soft-magnetic backing layer, a seed layer, a magnetic flux slit layer, a non-magnetic intermediate layer, a recording layer, a protective layer, and a lubricating layer, wherein the magnetic flux slit layer 13 includes soft-magnetic particles of generally columnar structure having a boundary part of a non-magnetic part and constricts the magnetic flux from the recording head only to the part where the soft-magnetic particle is provided and suppresses thereby spreading of the magnetic flux. Further, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium carrying a magnetic flux slit layer over the recording layer is disposed.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Carbon nanotube composite material, magnetic material and production thereof
InactiveUS20050255313A1Magnetic homogeneityImprove fill rateCarbon compoundsNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeChemical modification
A carbon nanotube composite material contains a carbon nanotube and a continuous layer of a metal covering the inner surface of the carbon nanotube. It is produced by forming a metallic matrix layer and treating the metallic matrix layer to form plural nanoholes in the metallic matrix layer to thereby form a nanohole structure, the nanoholes extending in a direction substantially perpendicular to the plane of the metallic matrix layer; forming carbon nanotubes inside the nanoholes; and covering inner surfaces of the carbon nanotubes with a continous layer of a metal. It has a well controlled small size, has excellent and uniform physical properties, is resistant to oxidation of the metal with time, is highly chemically stable, has good durability enabling repetitive use, has good coatability, high wettability and dispersibility with other materials, is easily chemically modified, is easily handled and is useful in various fields.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic storage device, and fabricating method thereof
InactiveUS20060061900A1High-density magnetic recording operationReduce widthNanoinformaticsFilamentary/web record carriersMagnetic storageMagnetic dots
A magnetic recording medium has a recording layer (42) formed over the substrate. The recording layer is structured by a nonmagnetic base, and a plurality of magnetic dots formed in the nonmagnetic base. The magnetic dots are aligned in a prescribed direction in each track or each group of adjacent tracks of the magnetic recording medium. In a preferred example, the magnetic dots align in a direction tilting at a prescribed angle with respect to the width of the track.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical information recording medium
InactiveUS6661770B2Increased durabilityImprove noiseInformation arrangementLayered productsHigh densityLaser light
An optical recording medium that is excellent in both C / N and reproducing durability and is capable of carrying out high density recording with excellent sensitivity and reflectivity. The optical recording medium comprises a substrate having grooves with specified dimensions, and a recording layer comprising an organic substance having at least one maximum absorption peak in each of a range from 600 to 800 nm and a range from 300 to 400 nm. In another aspect, the optical information recording medium includes a recording layer comprising a certain organic substance and capable of recording information by irradiation with laser light having a wavelength of from 380 to 500 nm through a lens having an aperture (NA) of 0.7 or more, and a substrate having grooves with specified dimensions.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Thermally assisted magnetic head
ActiveUS7804655B2Reduce yieldEasy to implementCombination recordingRecord information storageEngineeringWaveguide
A thermally assisted magnetic head has a slider having a medium-facing surface, and a light source unit having a light source support substrate, and a light source disposed on the light source support substrate. The slider has a slider substrate and a magnetic head portion disposed on a side of the medium-facing surface in the slider substrate; the magnetic head portion includes a magnetic recording element for generating a magnetic field, and a waveguide for receiving light through an end face opposite to the medium-facing surface, and guiding the light to the medium-facing surface; the light source support substrate is fixed to a surface opposite to the medium-facing surface in the slider substrate so that light emitted from the light source can enter the end face of the waveguide.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Resin film
ActiveUS20190180781A1High-density recordingAdjustmentDisposition/mounting of recording headsBase layers for recording layersYoung's modulusEngineering
To provide a resin film, of which dimensional stability required of an ultra-high density recording medium can be controlled easily by drive tension, and which has processability at high temperature in a processing step of the resin film into a magnetic recording medium. A resin film having a Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction of 1 GPa or more and a film thickness of 1 μm or more, wherein the product of the Young's modulus in the longitudinal direction and the thickness is 5 GPa·μm or more and 20 GPa·μm or less and wherein a dimensional change in the film longitudinal direction is −2% or more and +2% or less when the film is heated at a rate of 5° C. / min under a load of 2 kg / mm2 applied in the longitudinal direction and the temperature has reached 110° C., the resin film satisfying at least either of the following (1) or (2): (1) the Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction is 6 GPa or less and the film thickness is 4.5 μm or less; and (2) the Young's modulus in the film longitudinal direction is 4 GPa or less and the film thickness is 6 μm or less.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording/reproducing apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20090195924A1Easy to controlHigh-density recordingRecord information storageMagnetic recordingInter layerHigh density
Embodiments of the present invention help allow accurate control of the magnetization reversal in a magnetic recording layer in small reversal units, whereby high-density recording can be achieved. According to one embodiment, by forming an intermediate layer having a granular structure similar to that of the magnetic recording layer below the magnetic recording layer, a continuous crystal grain boundary is formed at the interface between the magnetic recording layer and the intermediate layer, thereby preventing incomplete formation of the crystal grain boundary found in the initial growth layer of the magnetic recording layer. The intermediate layer comprises a non-magnetic alloy comprising Co and Cr as its main components and an oxide such as Al, Cr, Hf. Mg, Nb, Si, Ta, Ti and Zr. Further, the average content of the oxygen element in the intermediate layer is in the range from 6 at % to 20 at %.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording/reproduction apparatus
ActiveUS20080182131A1Reduce grain sizeHigh-density recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageMagnetic layerMaterials science
According to one embodiment, a soft magnetic layer, a first nonmagnetic underlayer having a fine crystal structure and made of Pd or a Pd alloy, a second nonmagnetic underlayer made of Ru or an Ru alloy, and a perpendicular magnetic recording layer are stacked on a nonmagnetic substrate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com