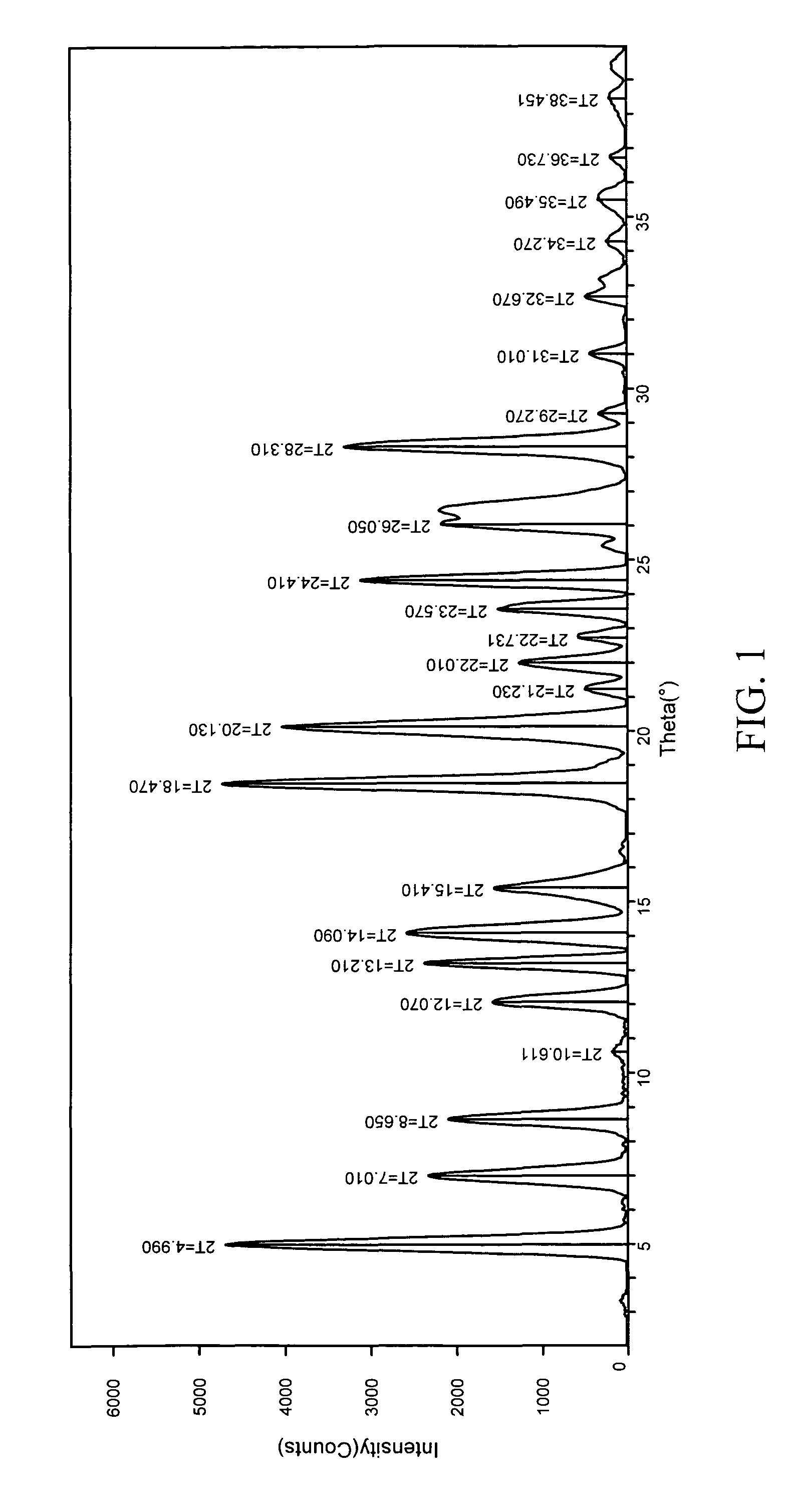
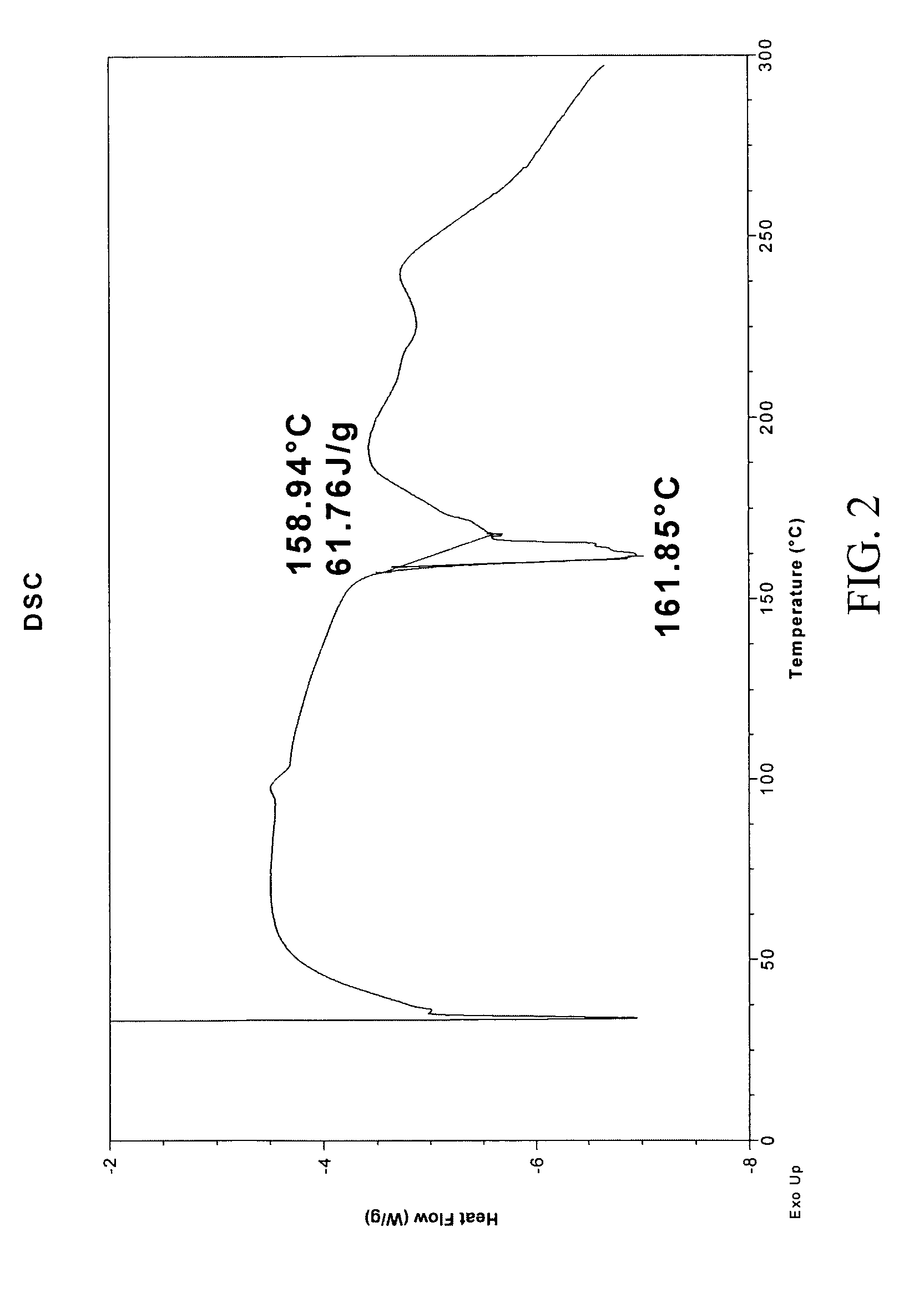
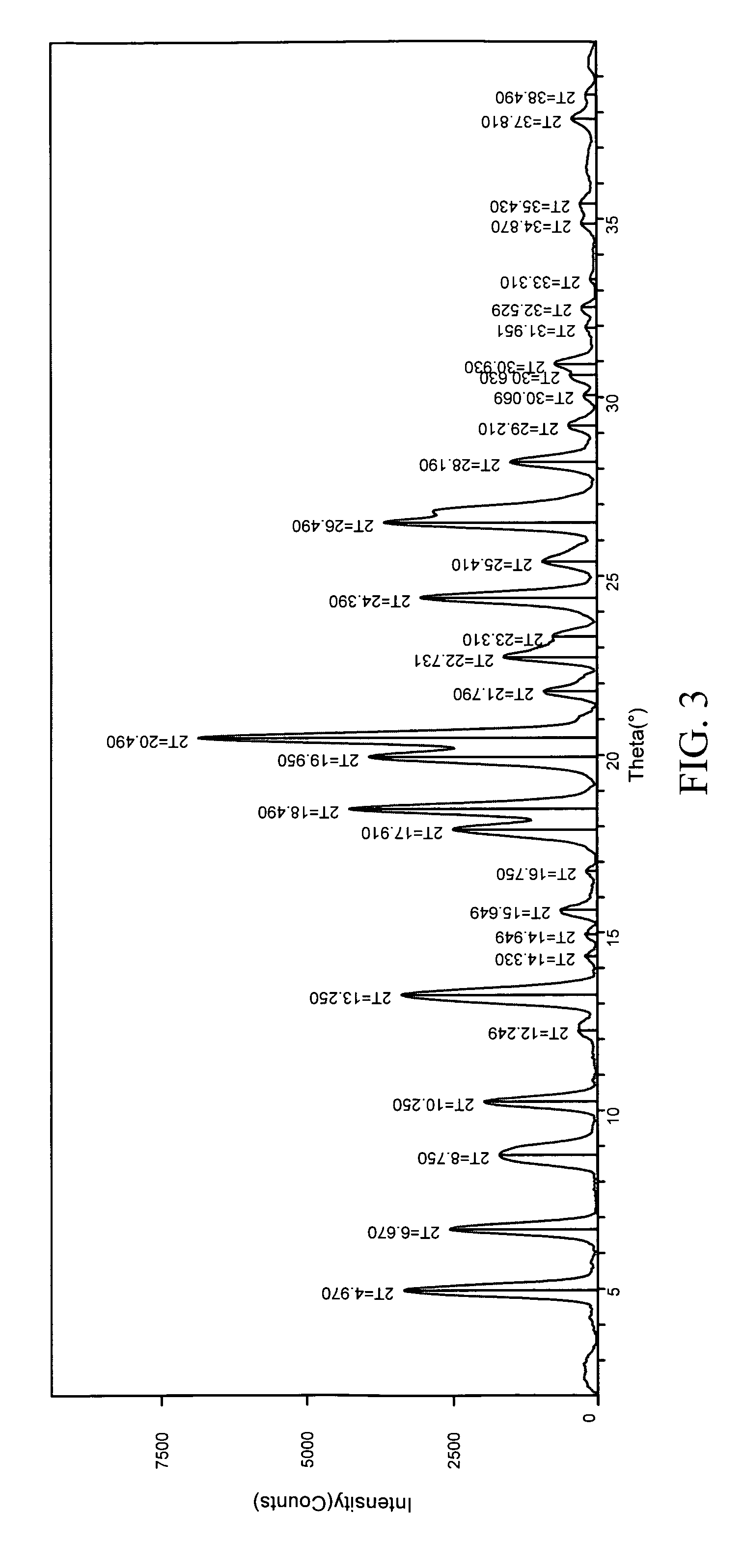
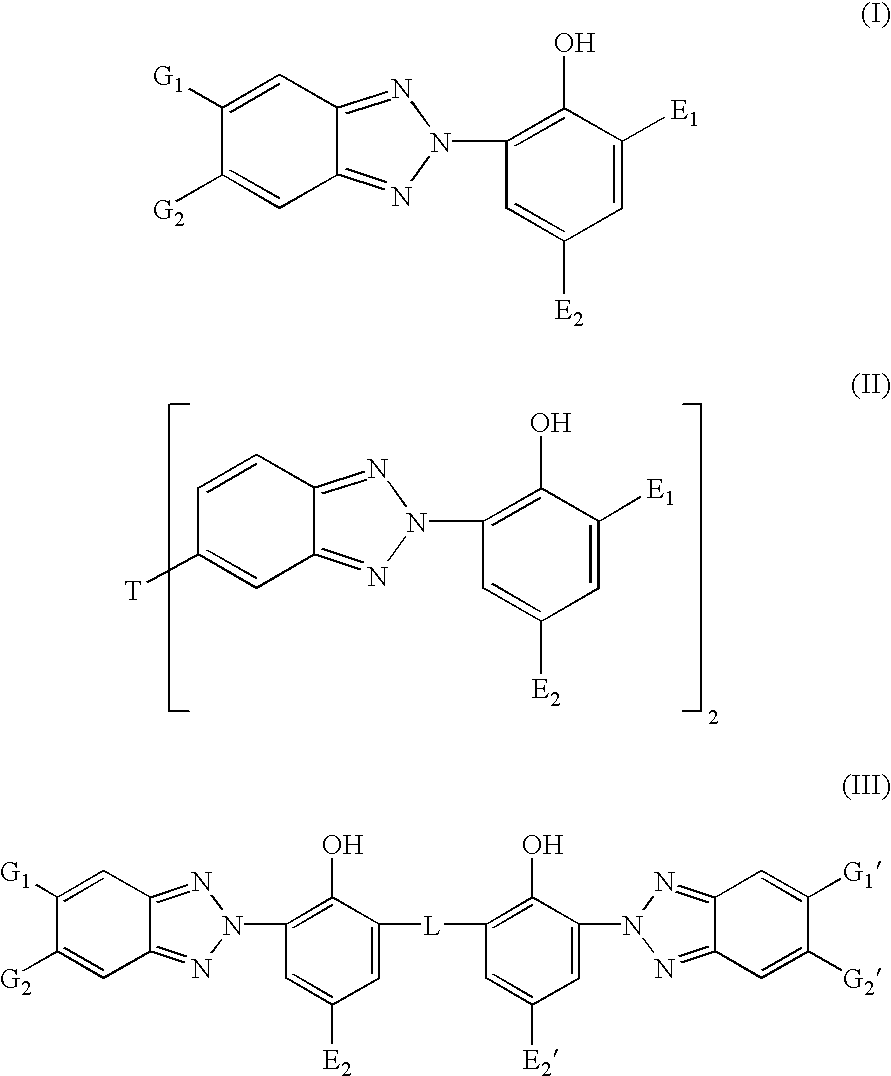
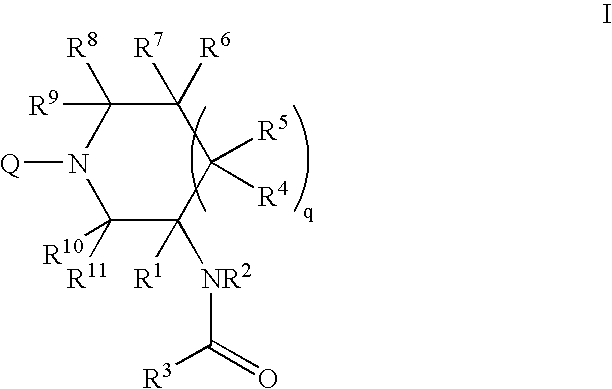
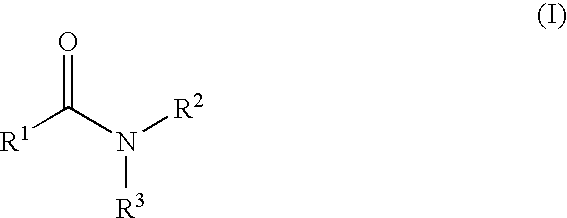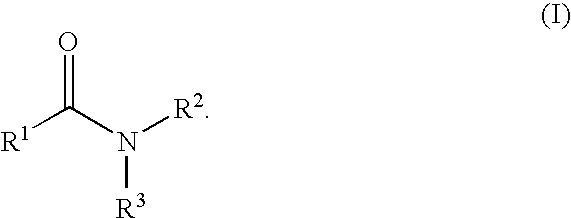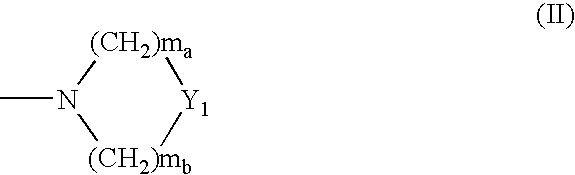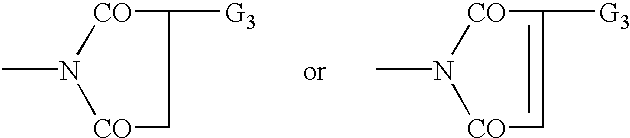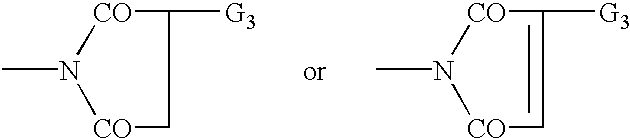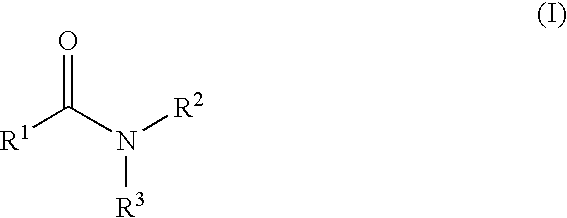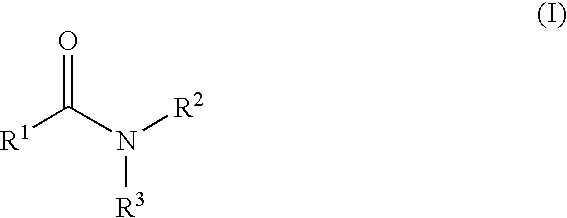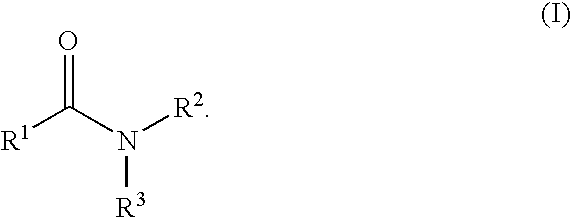Patents
Literature
30254 results about "Amide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
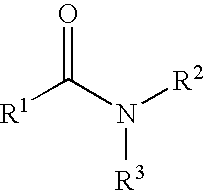
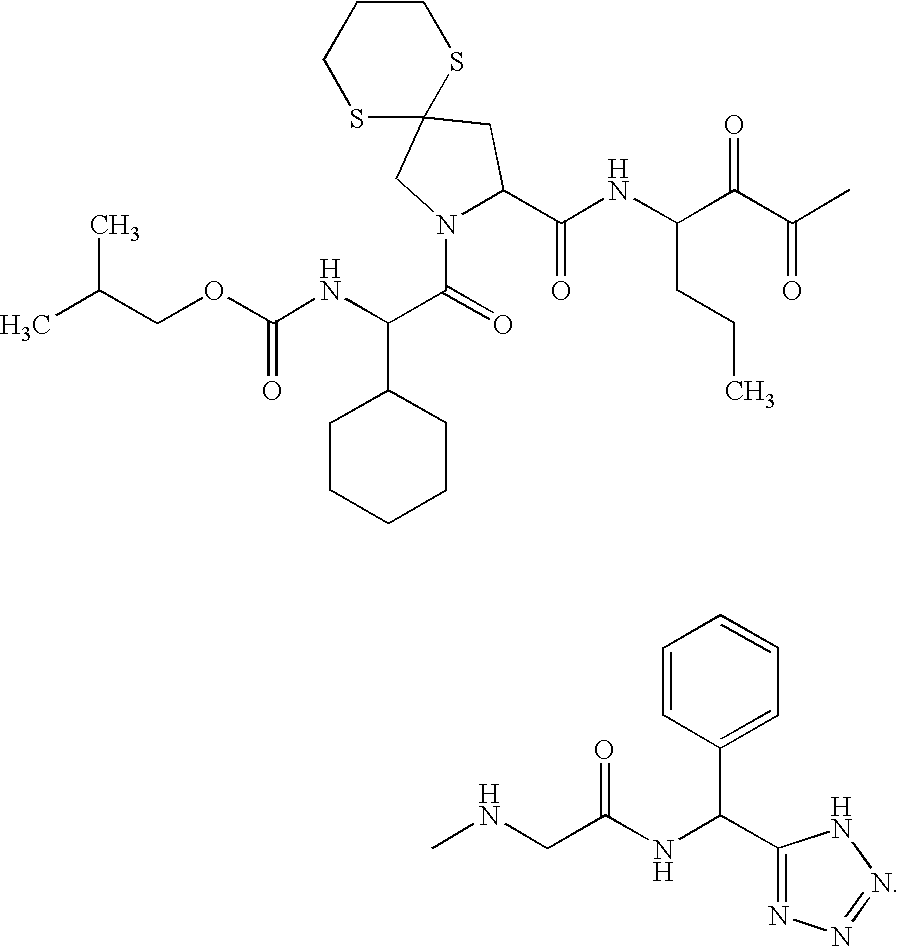
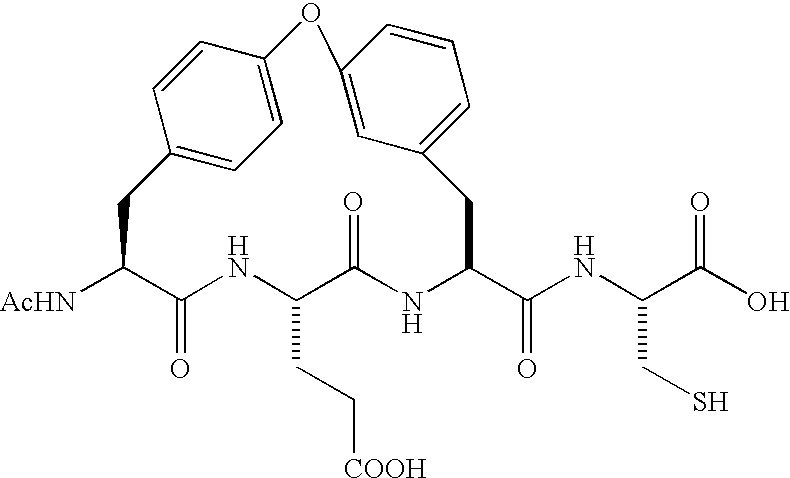
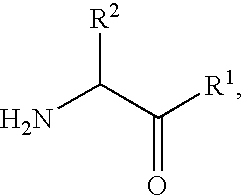
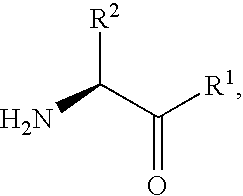
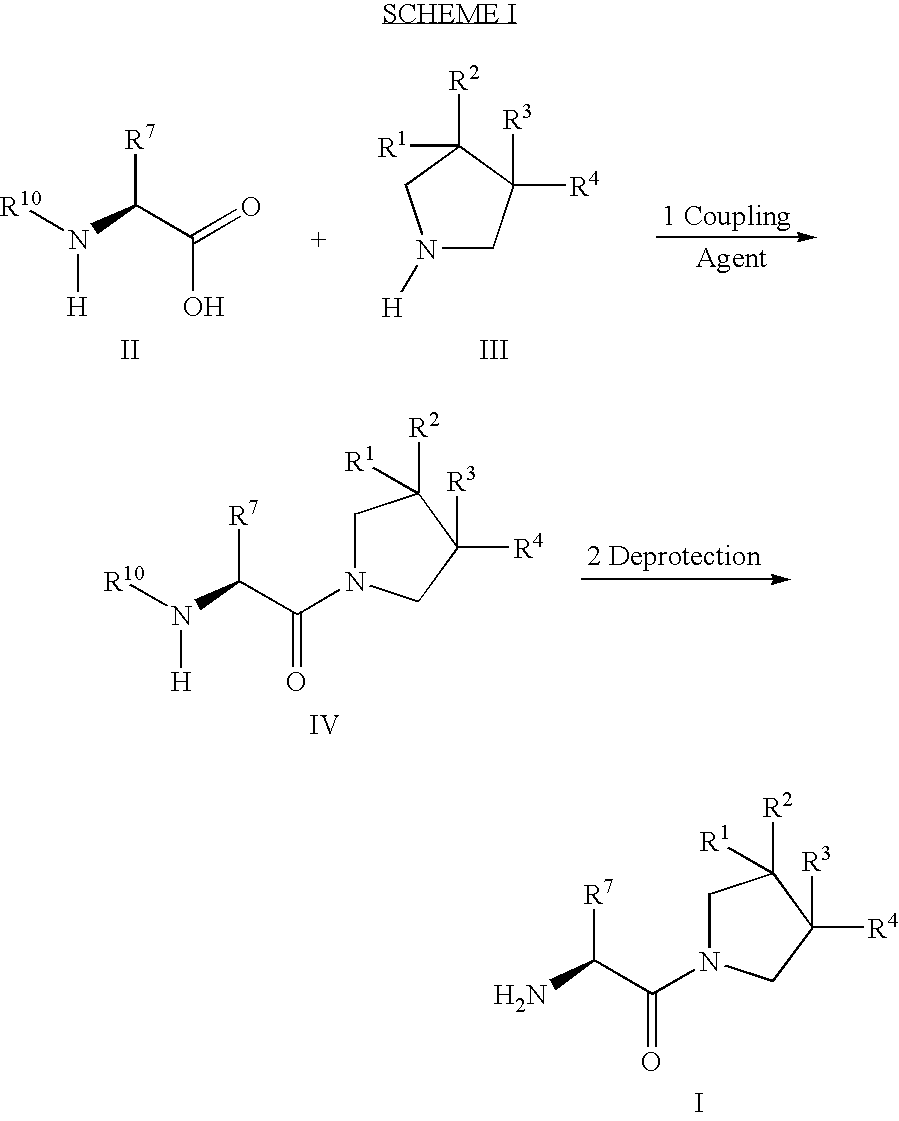
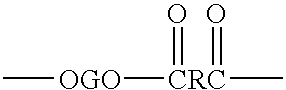
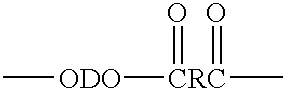
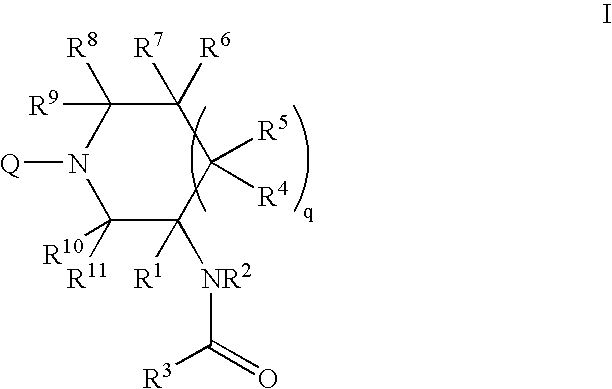
An amide (/ˈæmaɪd/ or /ˈæmɪd/ or /ˈeɪmaɪd/), also known as an acid amide, is a compound with the functional group RₙE(O)ₓNR′₂ (R and R′ refer to H or organic groups). Most common are carboxamides (organic amides) (n = 1, E = C, x = 1), but many other important types of amides are known, including phosphoramides (n = 2, E = P, x = 1 and many related formulas) and sulfonamides (E = S, x = 2). The term amide refers both to classes of compounds and to the functional group (RₙE(O)ₓNR′₂) within those compounds.
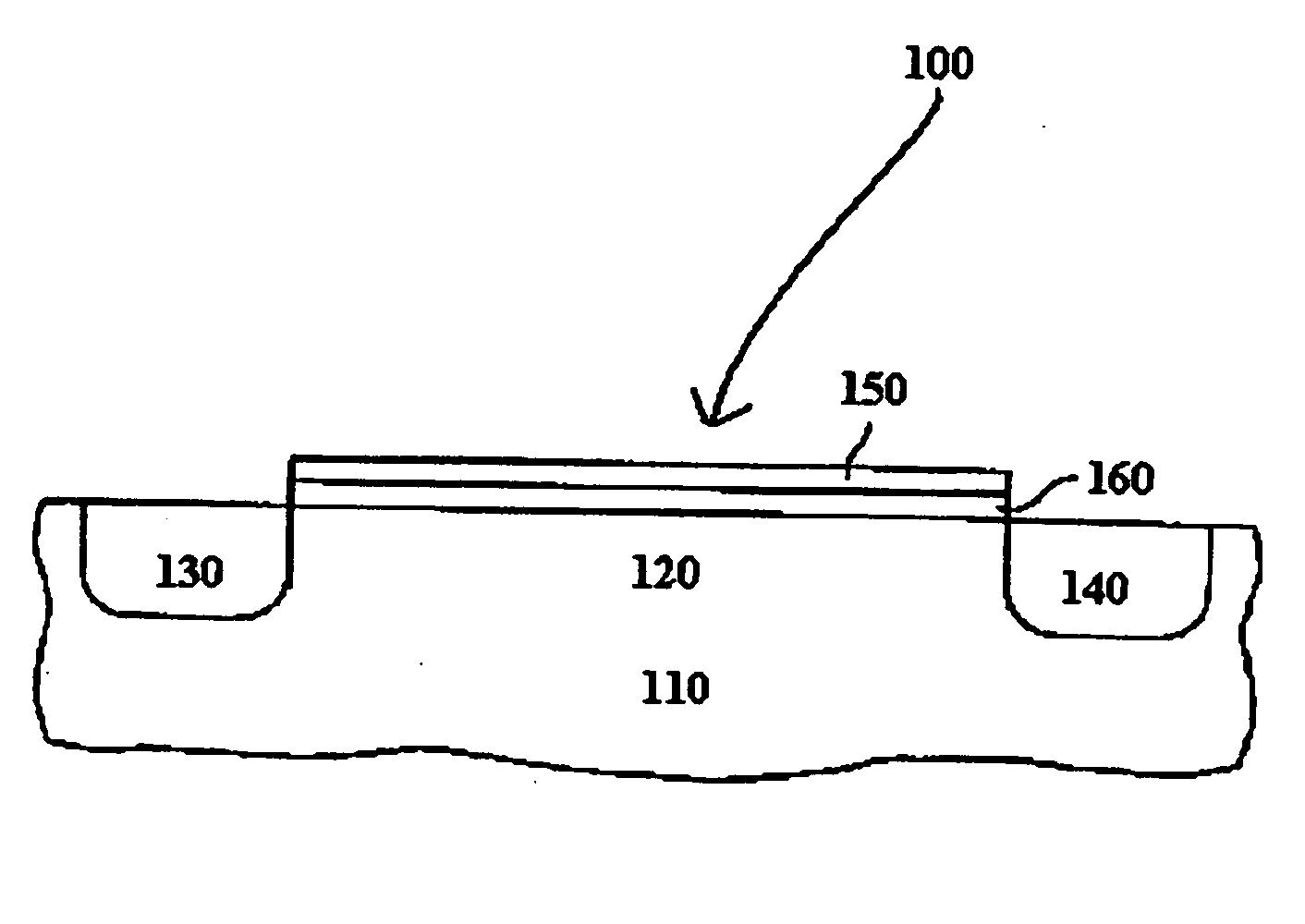
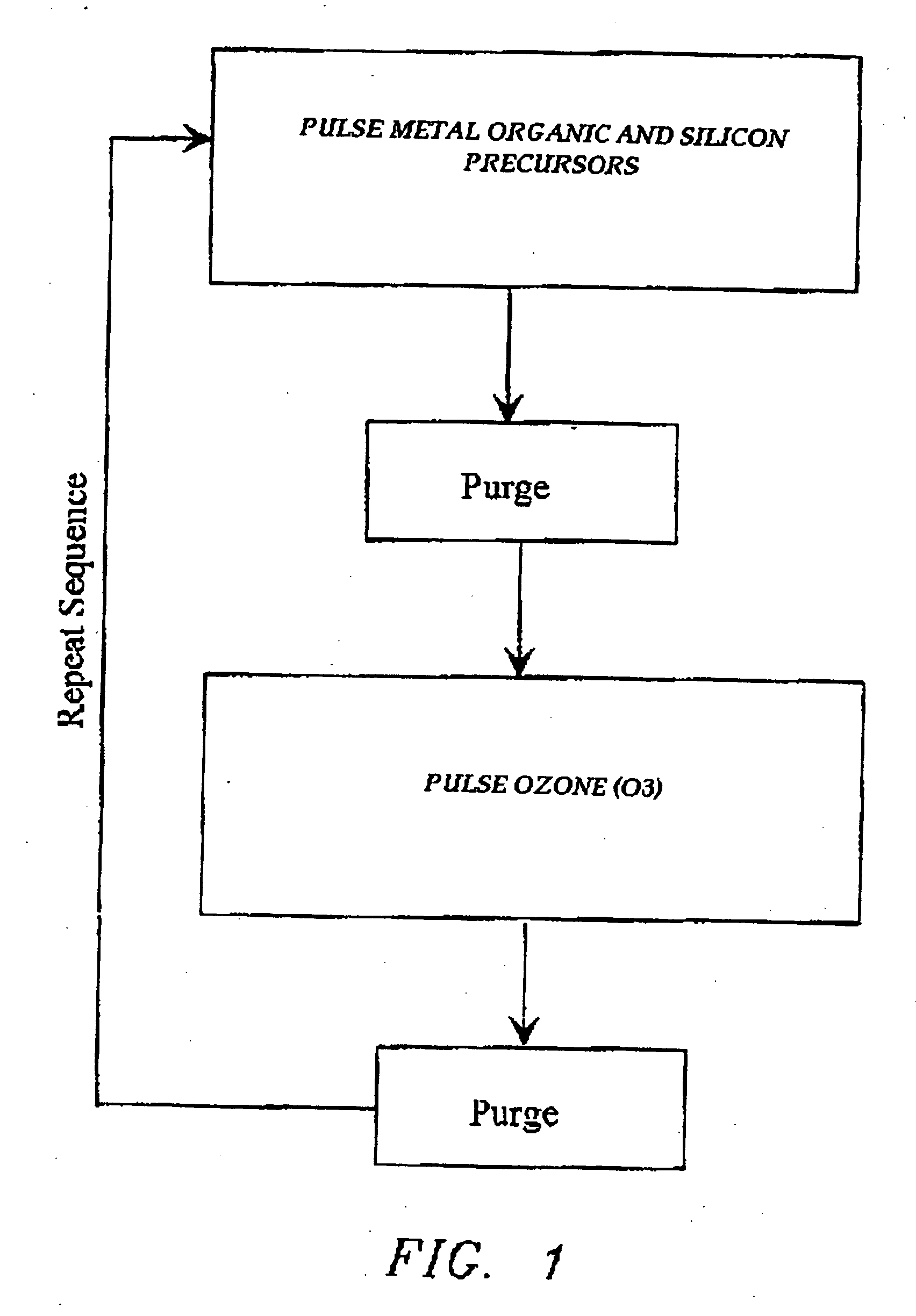
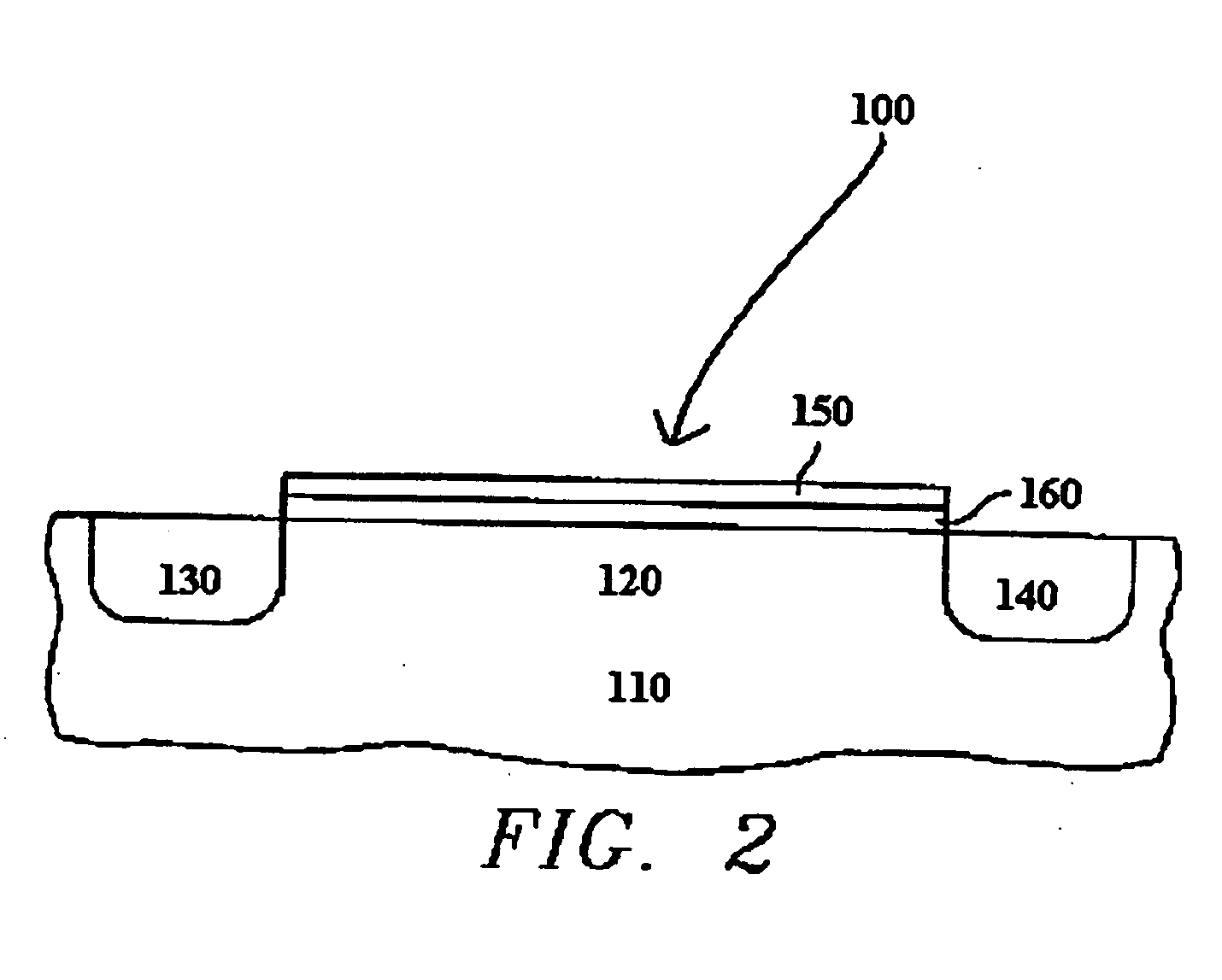
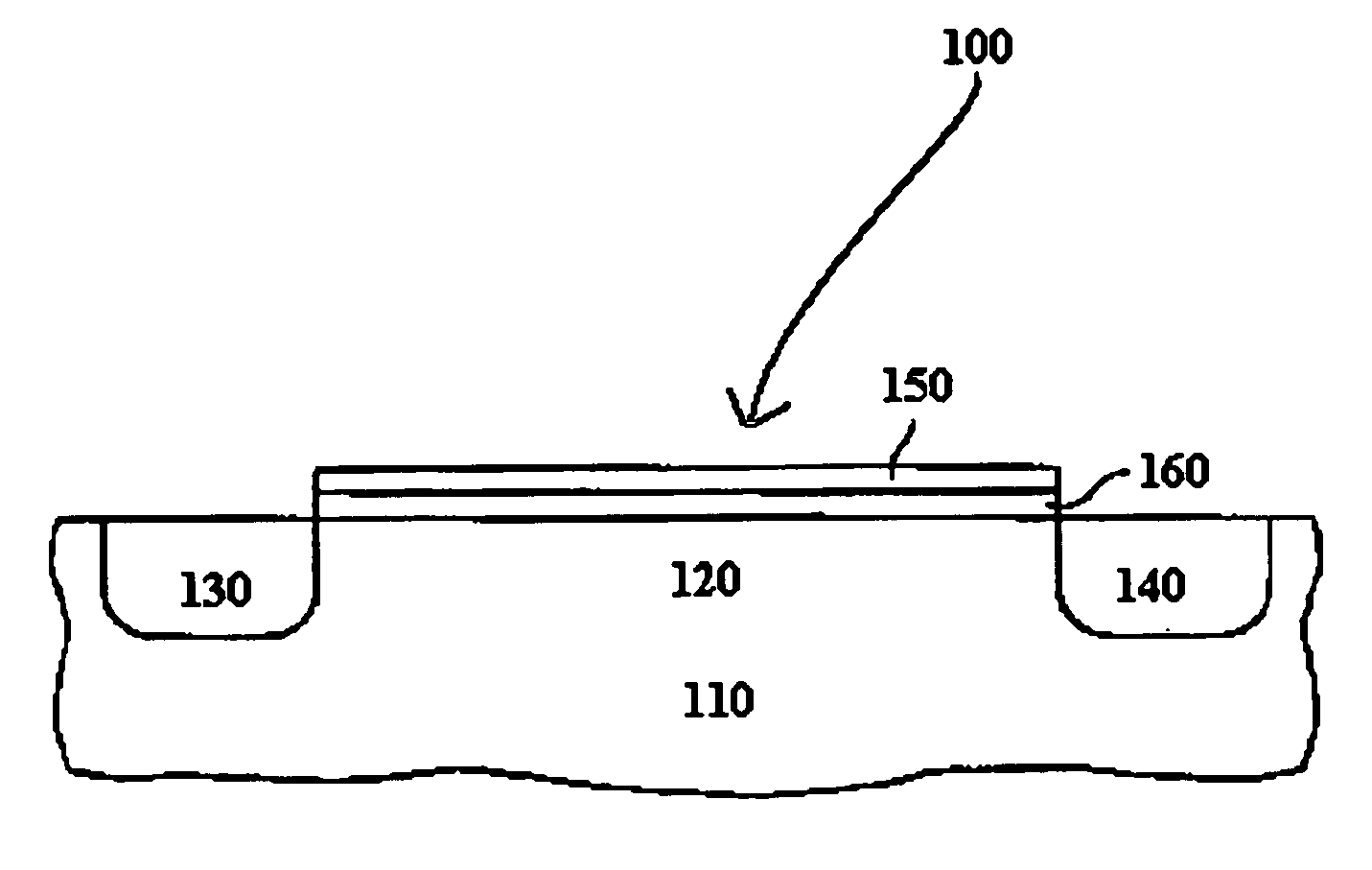
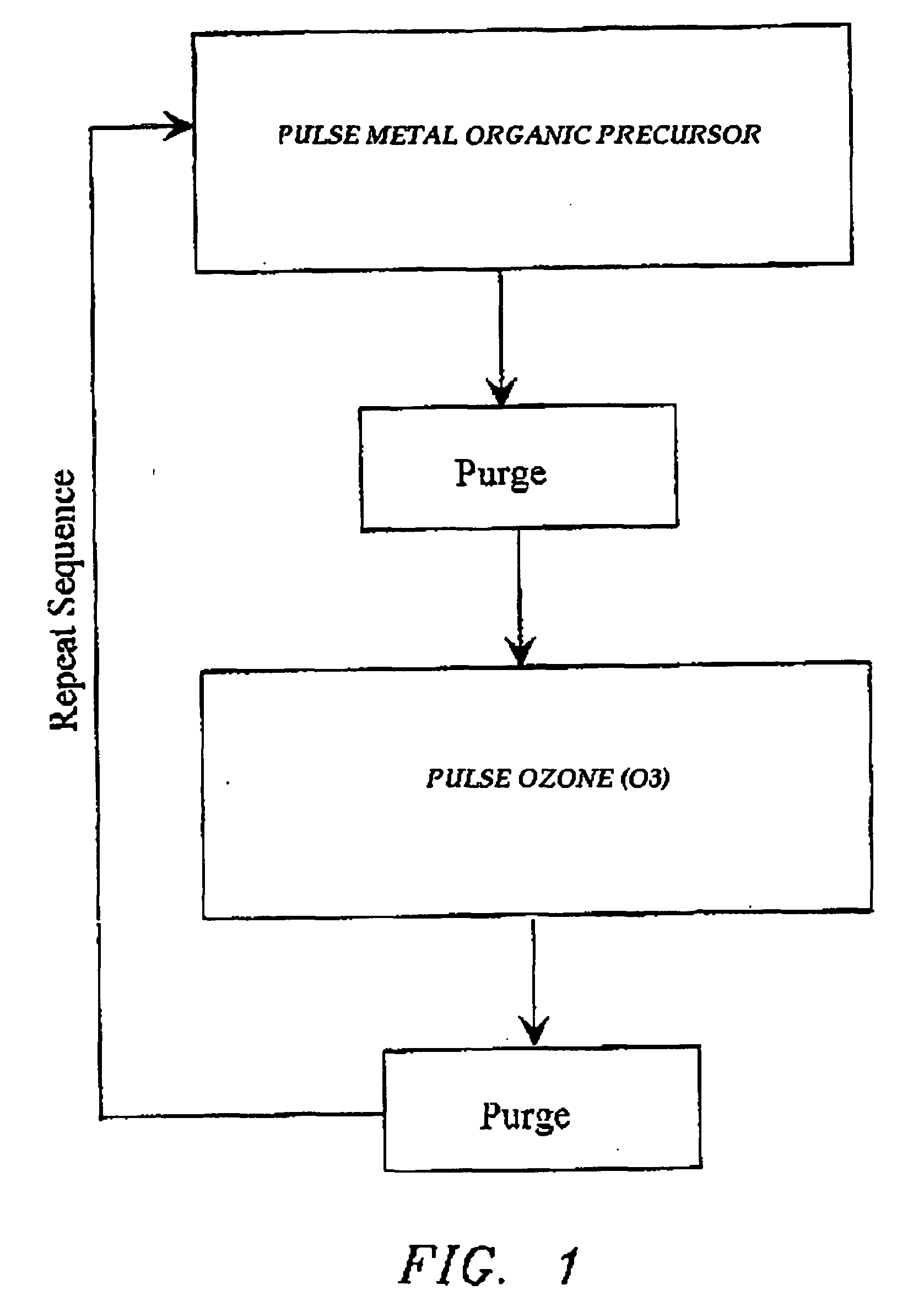
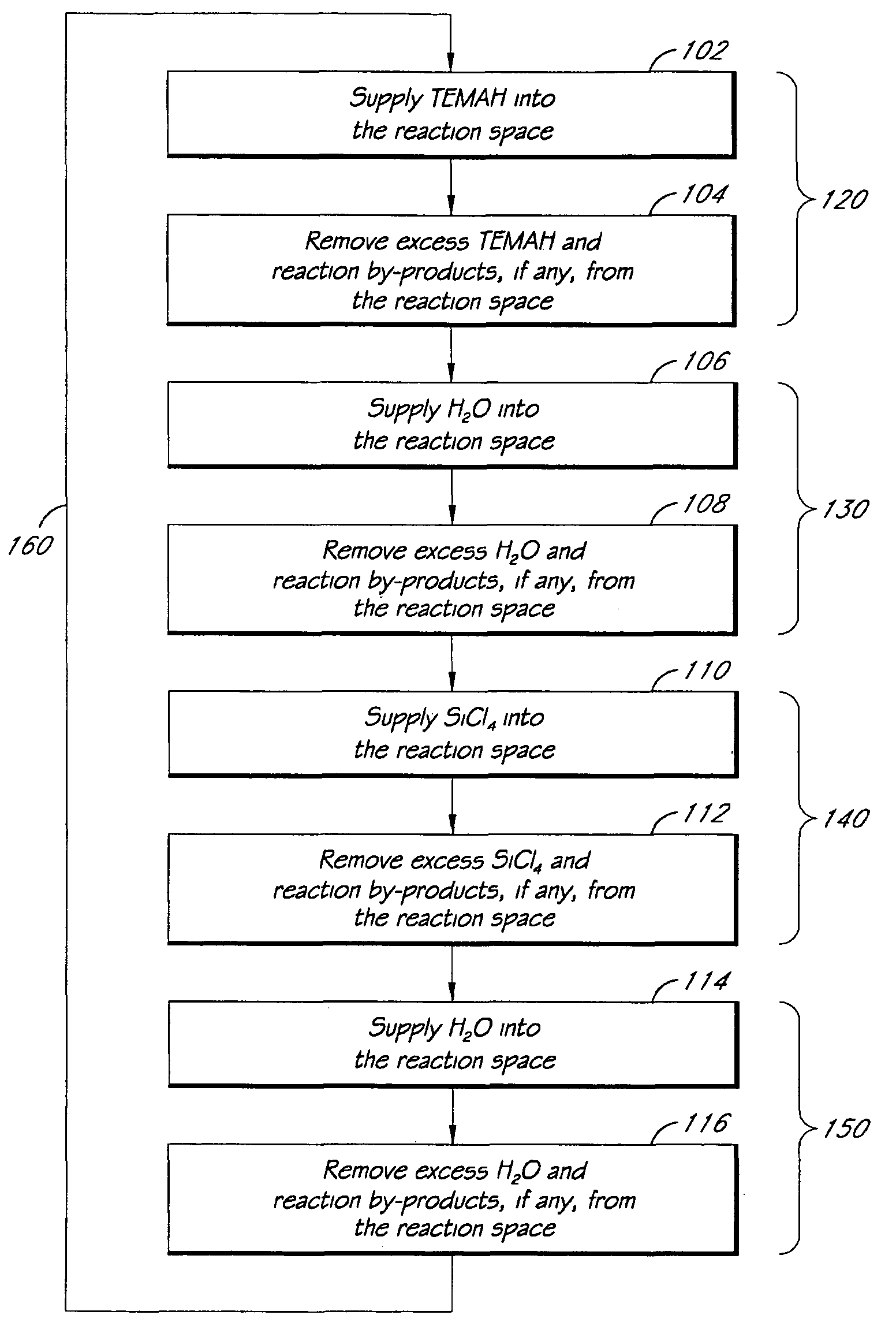
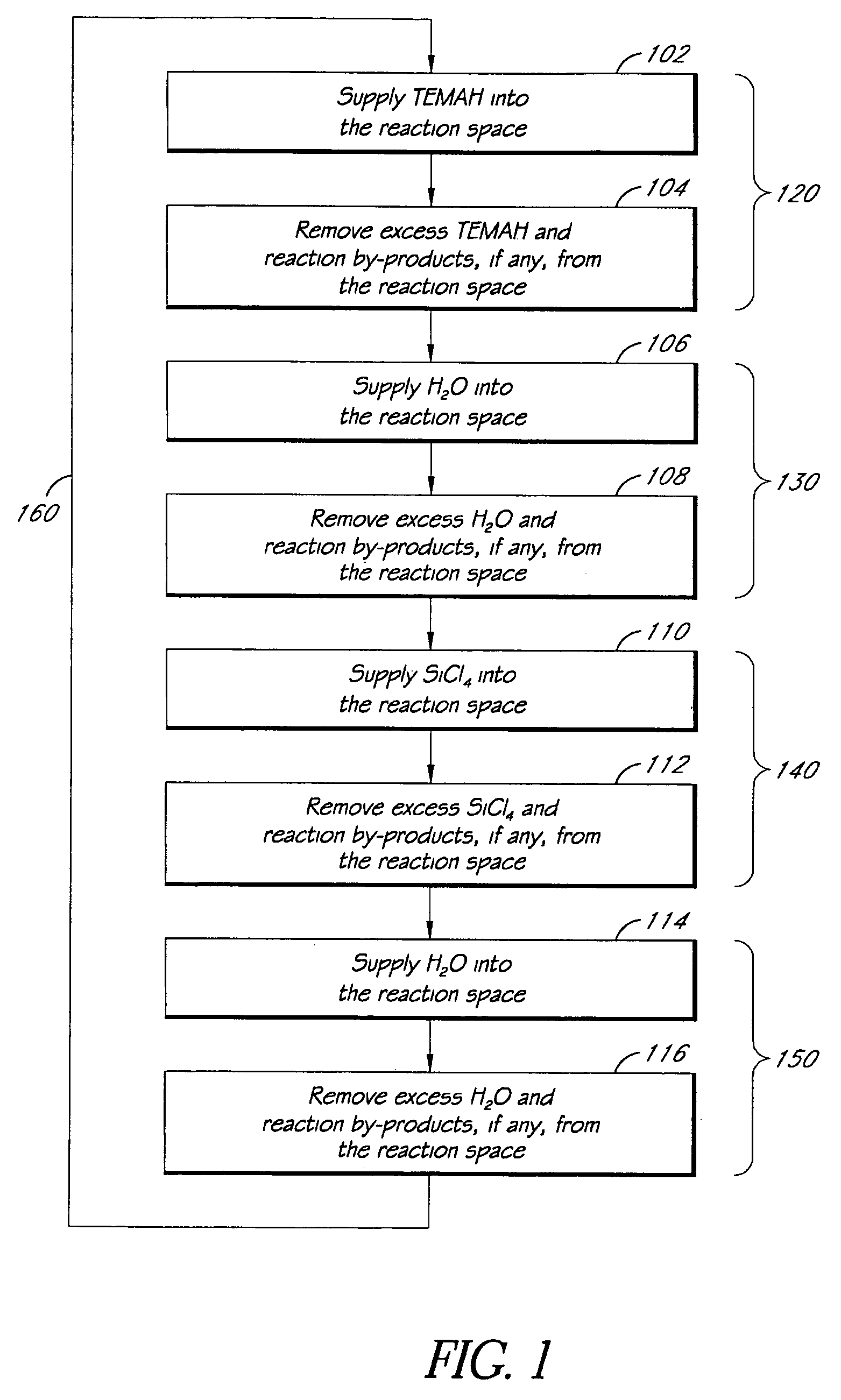
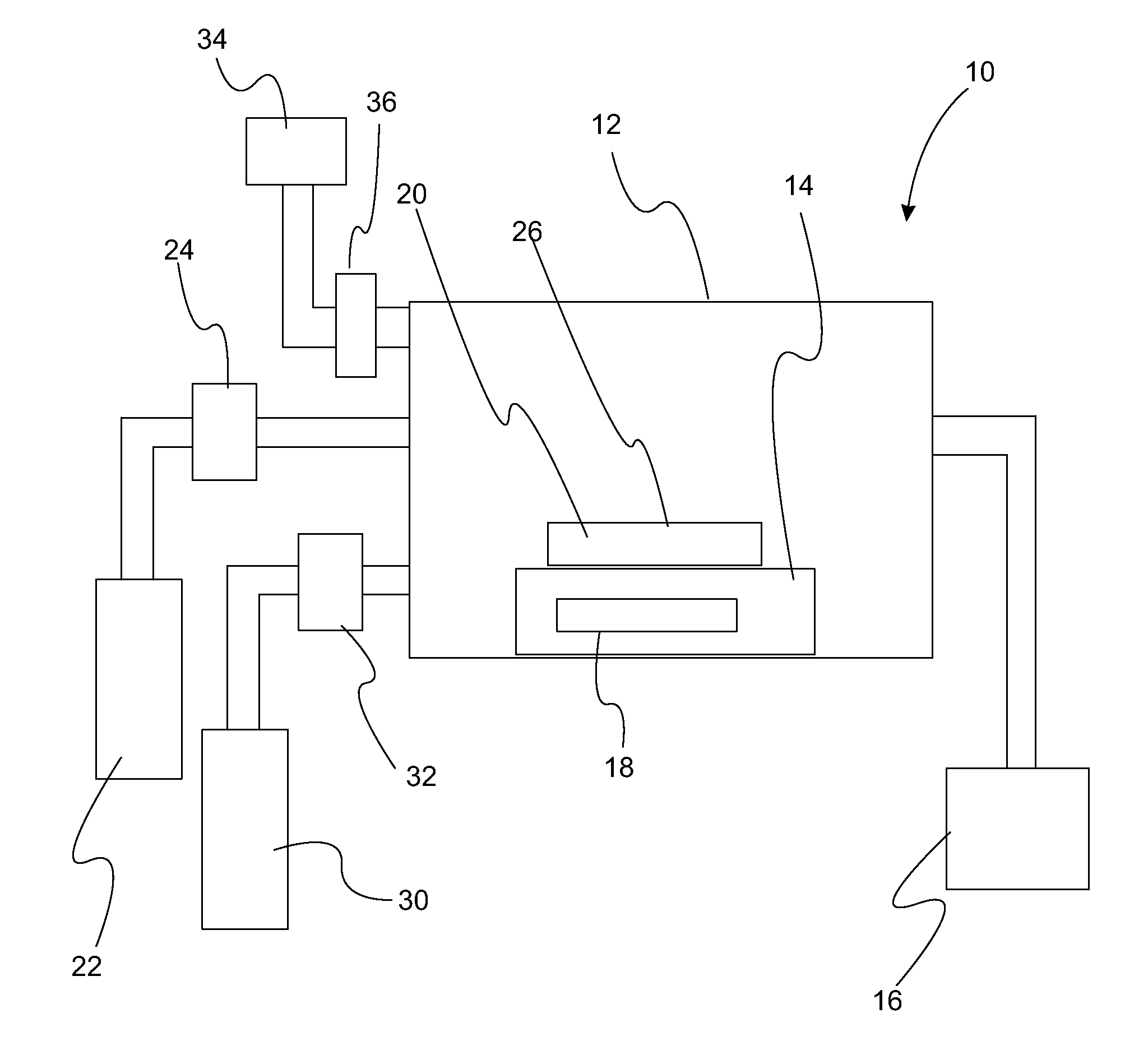
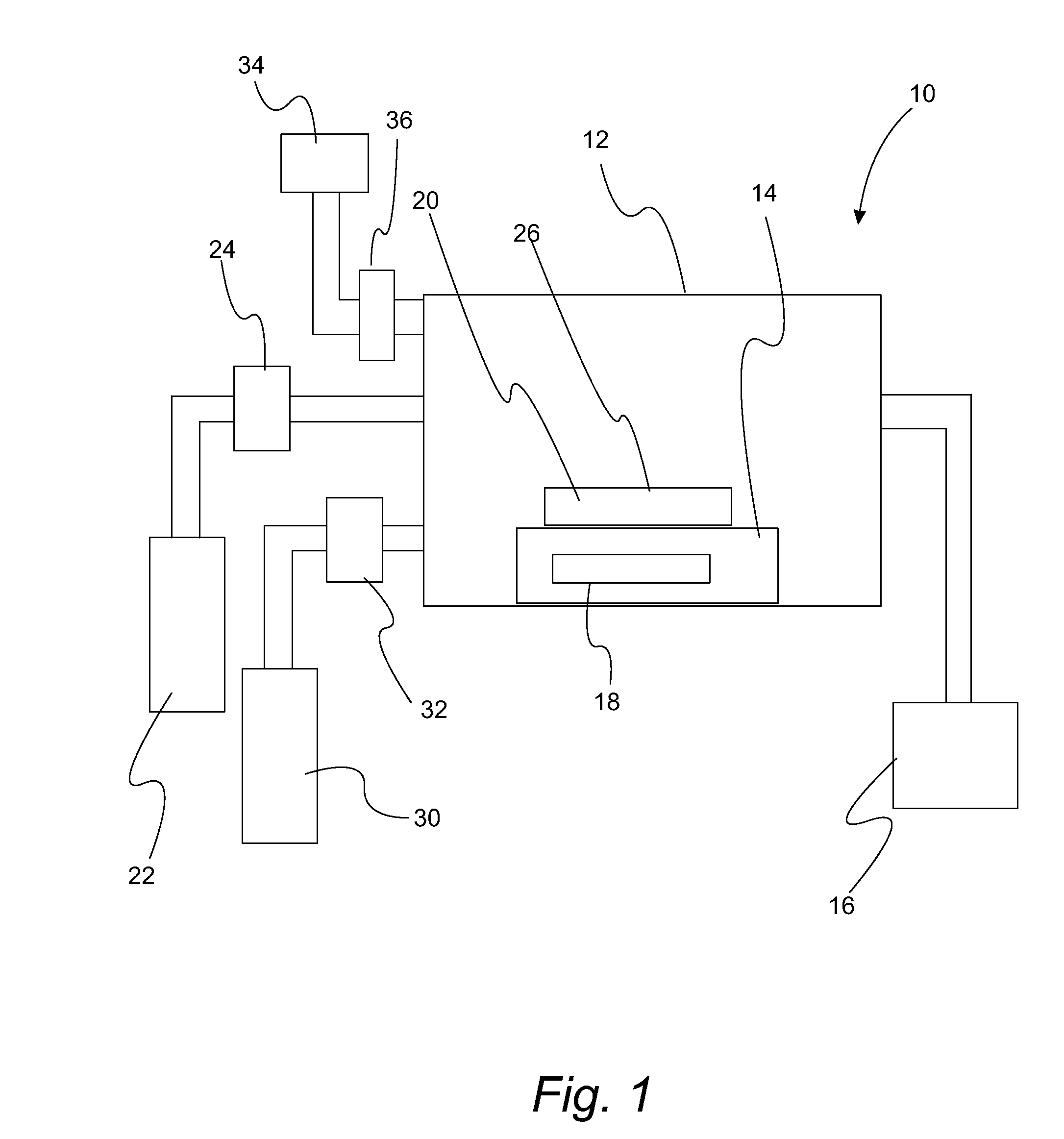
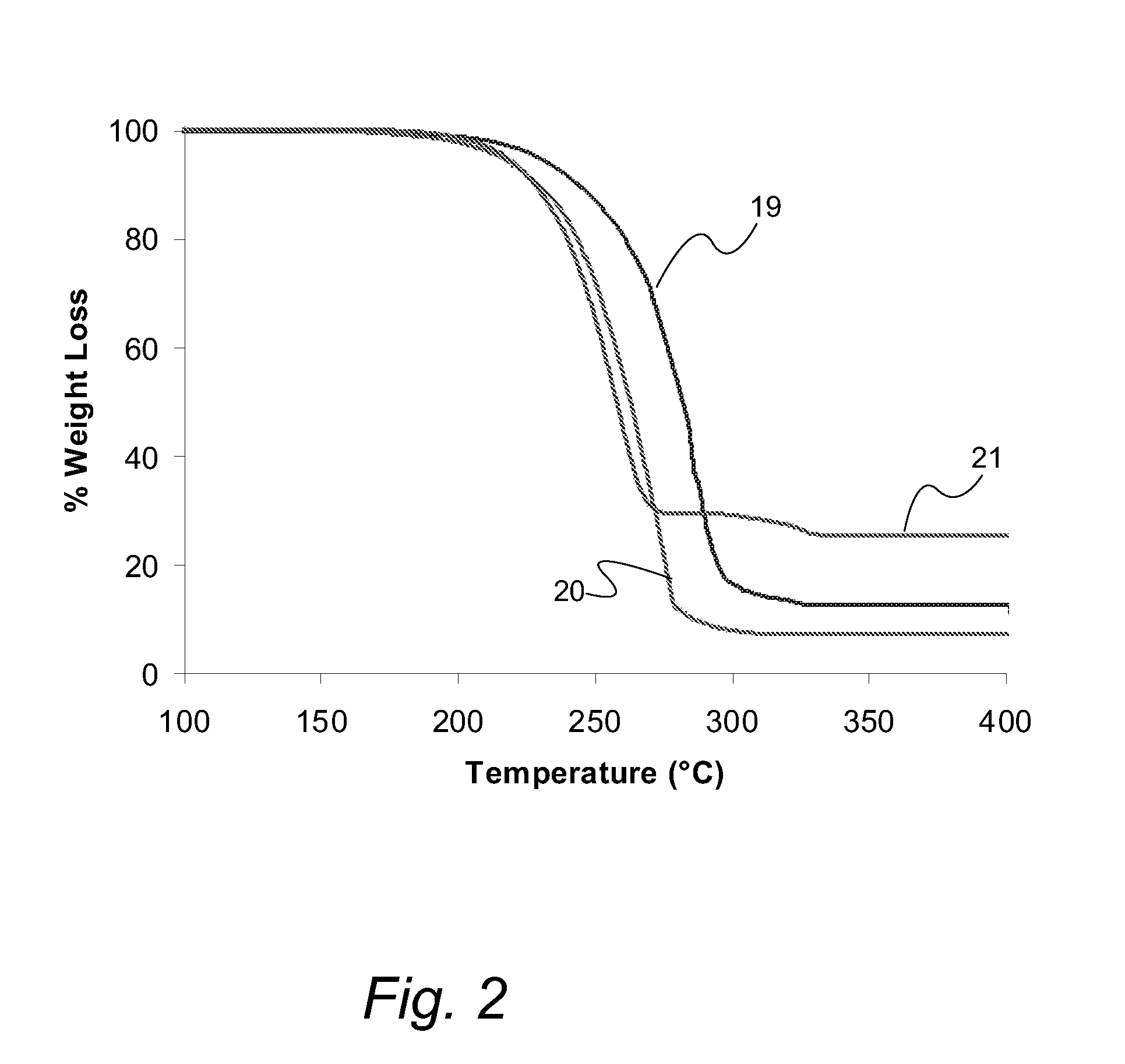
Atomic layer deposition of high k metal silicates
InactiveUS20060228888A1Reduce carbon pollutionReduce stepsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHafniumAtomic layer deposition
The present invention relates to the atomic layer deposition (“ALD”) of high k dielectric layers of metal silicates, including hafnium silicate. More particularly, the present invention relates to the ALD formation of metal silicates using metal organic precursors, silicon organic precursors and ozone. Preferably, the metal organic precursor is a metal alkyl amide and the silicon organic precursor is a silicon alkyl amide.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC +1
Atomic layer deposition of high-k metal oxides
InactiveUS20060258078A1Improve thermal stabilityLess growthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric layerTitanium oxide
The present invention relates to the atomic layer deposition (“ALD”) of high k dielectric layers of metal oxides containing Group 4 metals, including hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, and titanium oxide. More particularly, the present invention relates to the ALD formation of Group 4 metal oxide films using an metal alkyl amide as a metal organic precursor and ozone as a co-reactant.
Owner:AVIZA TECHNOLOGY INC +1
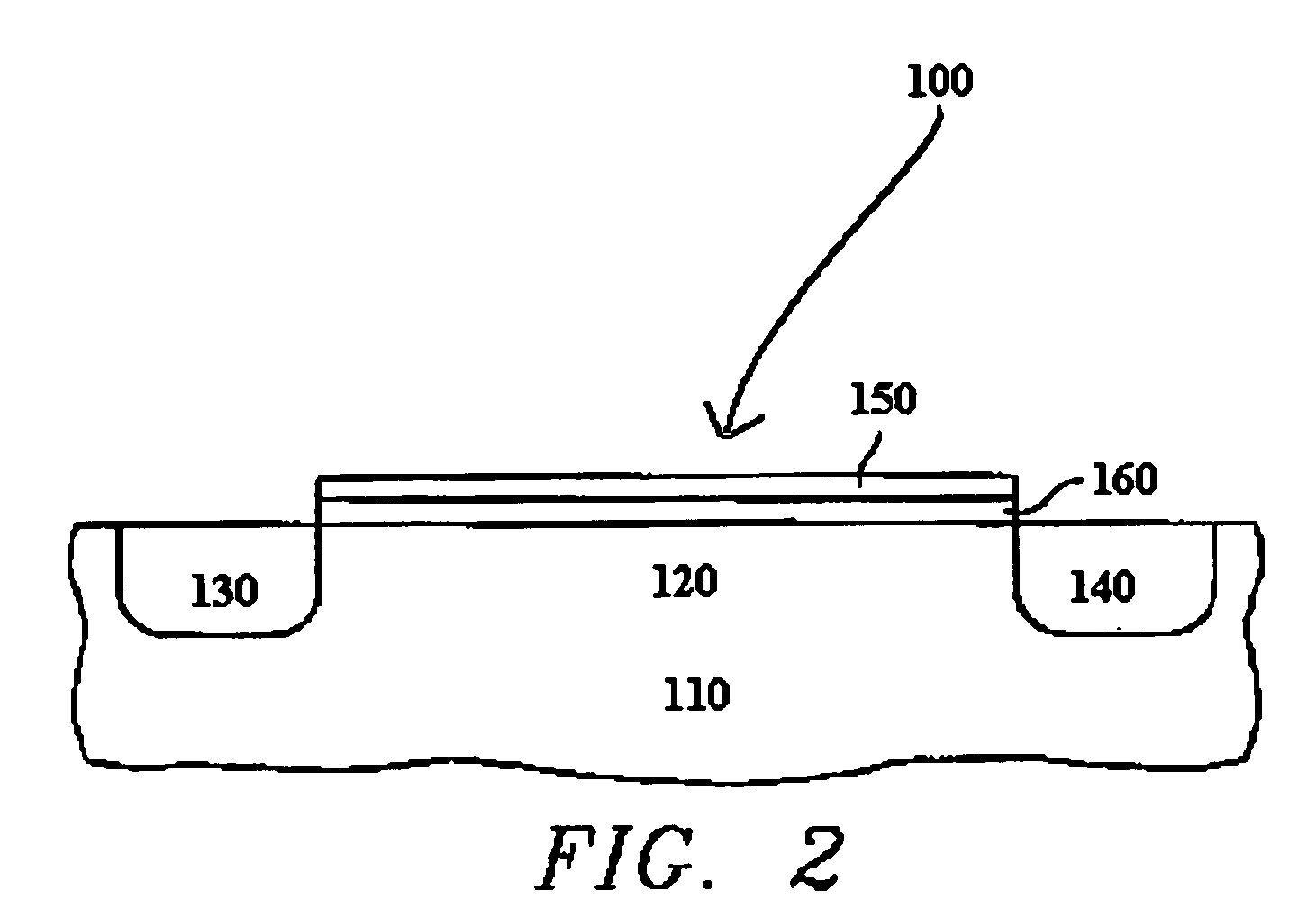
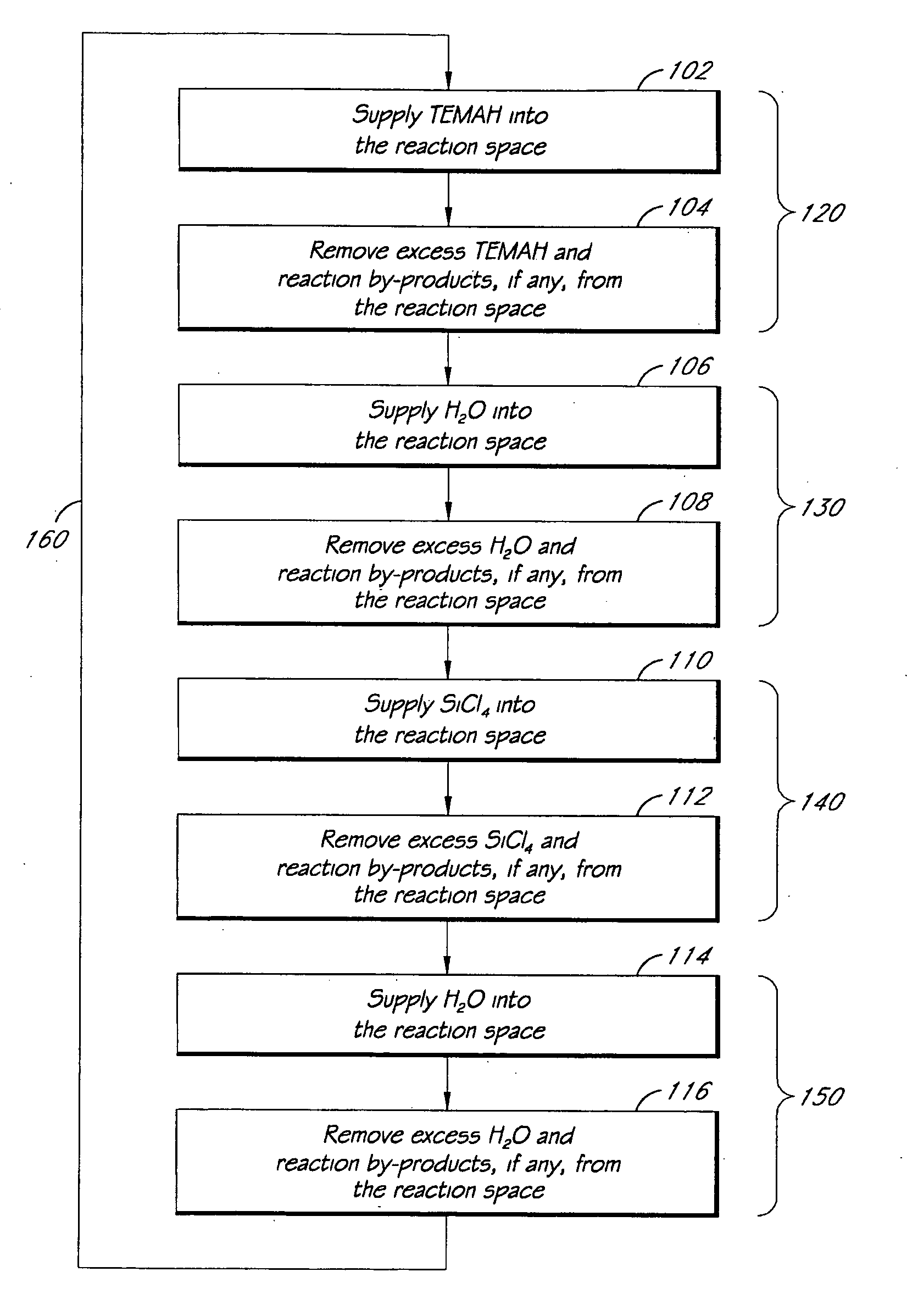
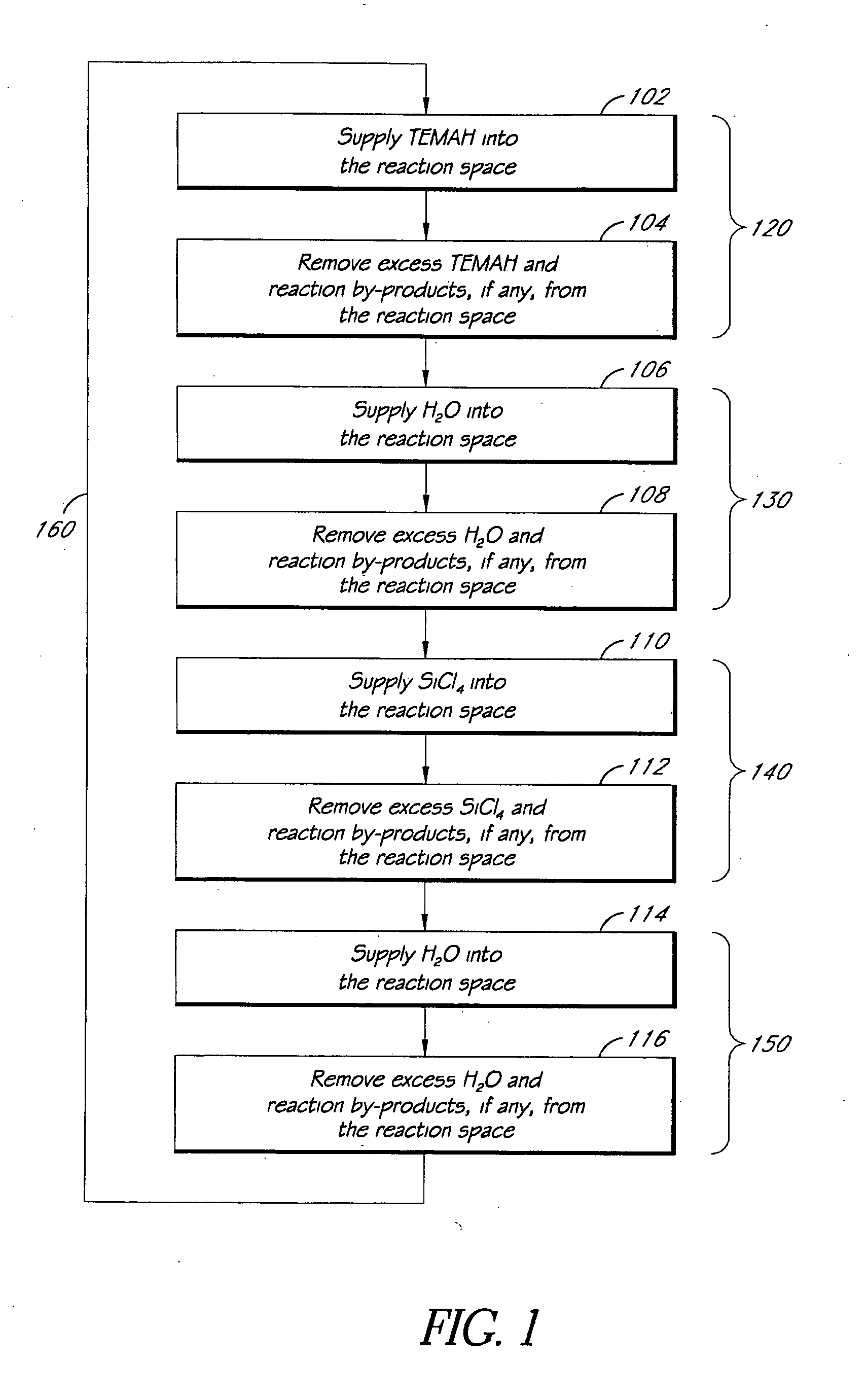
ALD of metal silicate films
ActiveUS20080020593A1Readily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseHafnium
Methods for forming metal silicate films are provided. The methods comprise contacting a substrate with alternating and sequential vapor phase pulses of a metal source chemical, a silicon source chemical and an oxidizing agent. In preferred embodiments, an alkyl amide metal compound and a silicon halide compound are used. Methods according to preferred embodiments can be used to form hafnium silicate and zirconium silicate films with substantially uniform film coverages on substrate surfaces comprising high aspect ratio features (e.g., vias and / or trenches).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
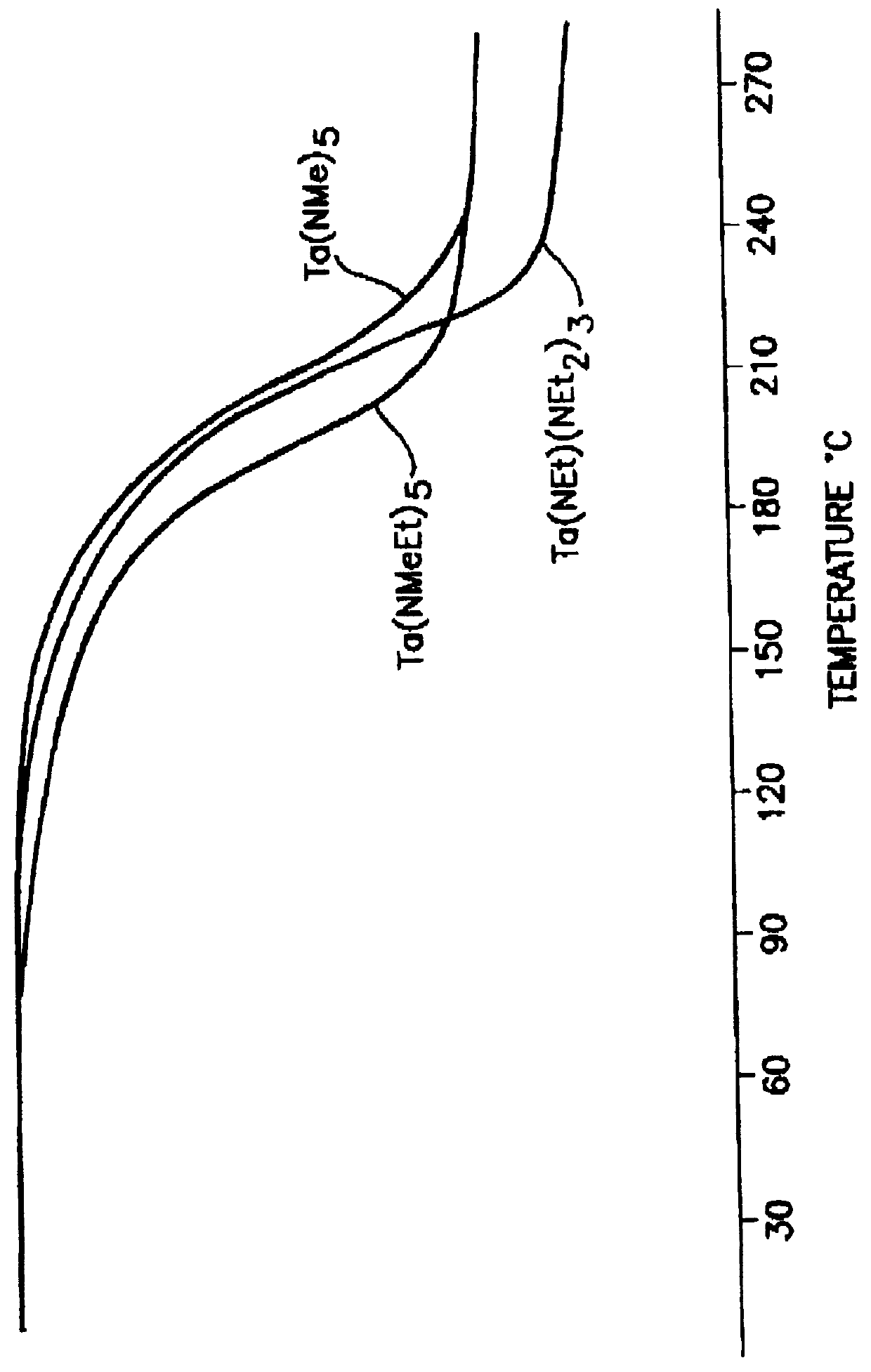
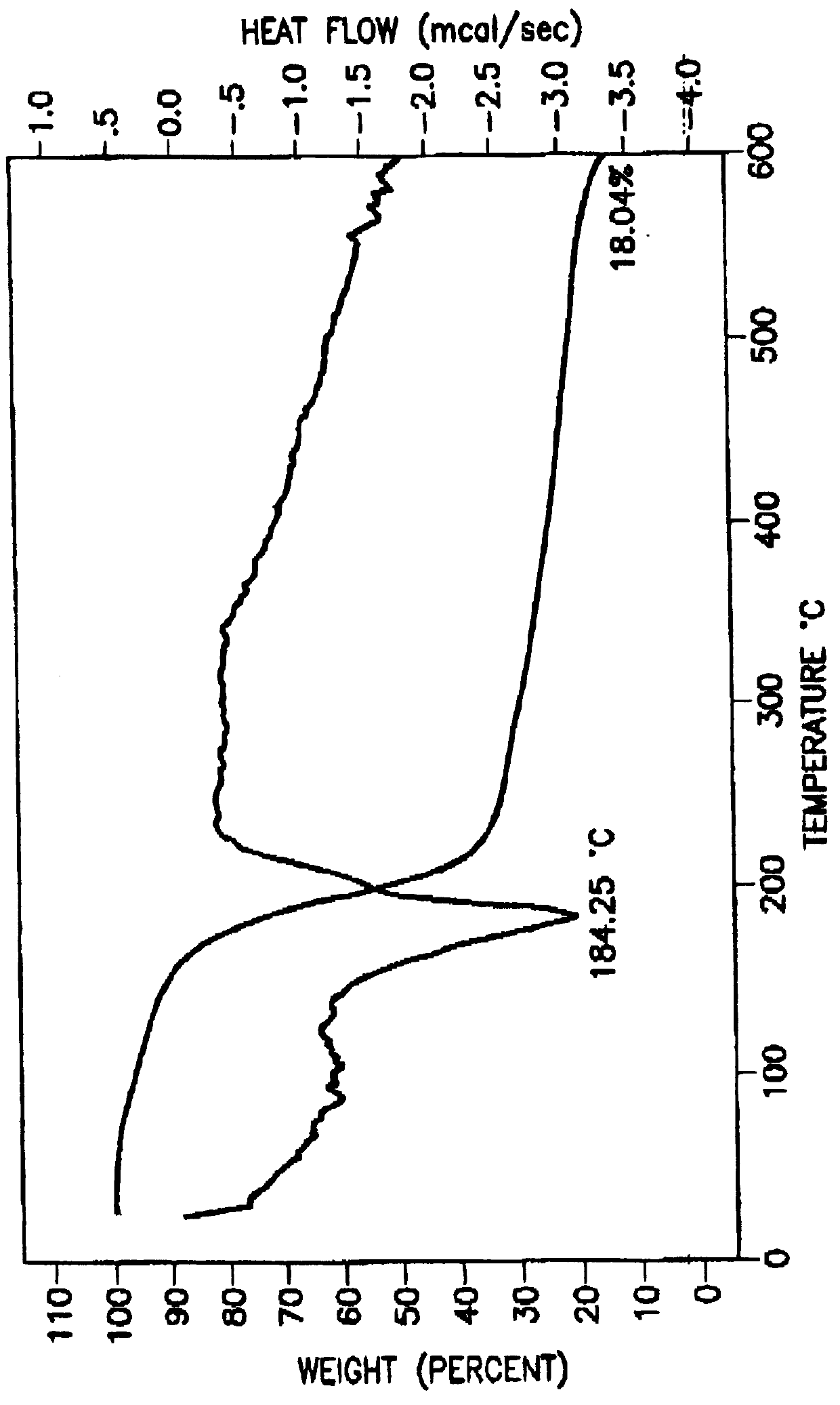
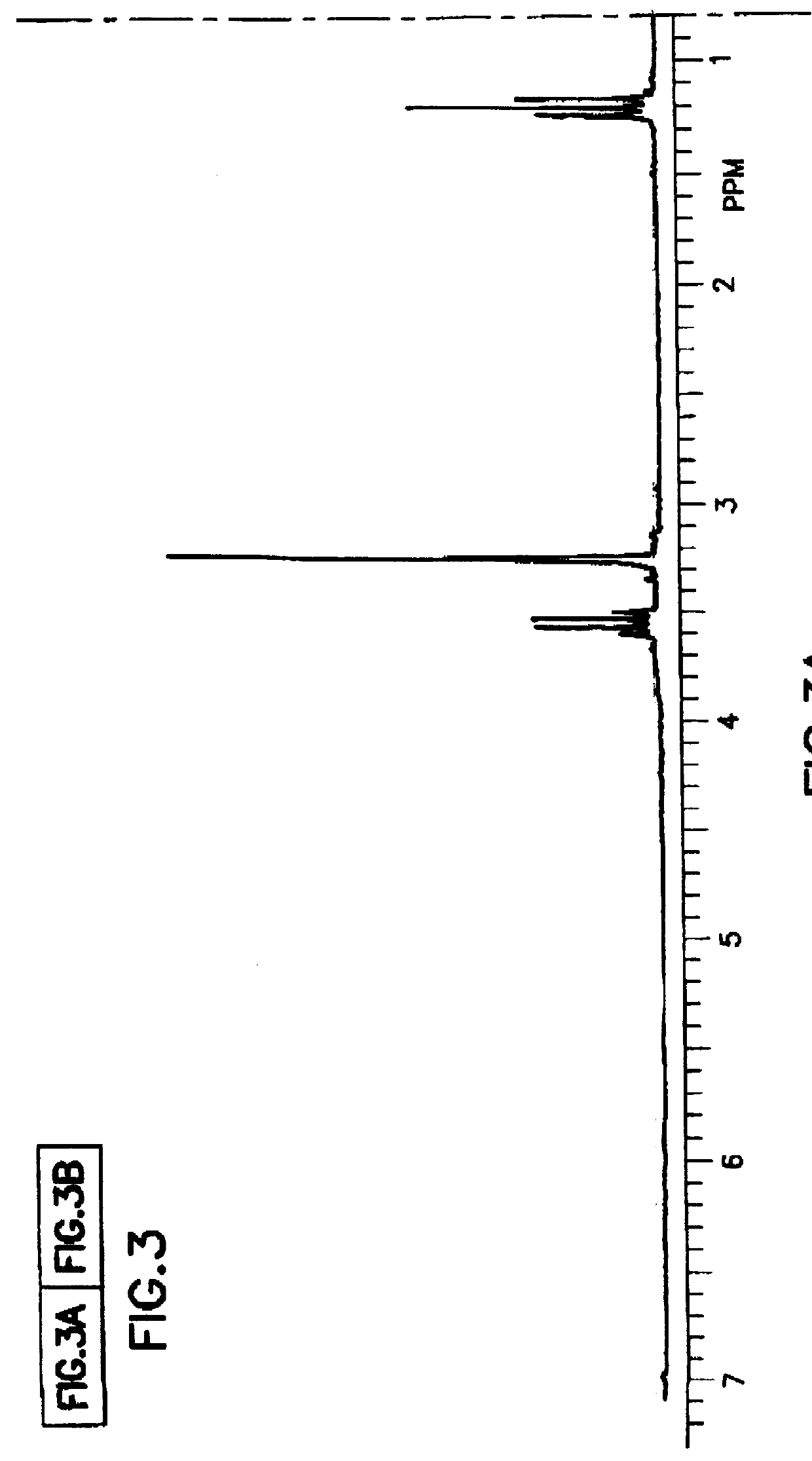
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6015917ARapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microlectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
ALD of metal silicate films
ActiveUS7795160B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseHafnium
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Thermally stable volatile film precursors
ActiveUS20120058270A1Iron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCopper organic compoundsAtomic layer depositionPhotochemistry
A precursor for the deposition of a thin film by atomic layer deposition is provided. The compound has the formula MxLy where M is a metal and L is an amidrazone-derived ligand or an amidate-derived ligand. A process of forming a thin film using the precursors is also provided.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Novel flavors, flavor modifiers, tastants, taste enhancers, umami or sweet tastants, and/or enhancers and use thereof
ActiveUS20050084506A1Enhancing savory tasteIncrease sweet tasteBiocideCosmetic preparationsMonosodium glutamateSalty taste
The present invention relates to the discovery that certain non-naturally occurring, non-peptide amide compounds and amide derivatives, such as oxalamides, ureas, and acrylamides, are useful flavor or taste modifiers, such as a flavoring or flavoring agents and flavor or taste enhancer, more particularly, savory (the “umami” taste of monosodium glutamate) or sweet taste modifiers,—savory or sweet flavoring agents and savory or sweet flavor enhancers, for food, beverages, and other comestible or orally administered medicinal products or compositions.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Heteroaryl sulfonamides and CCR2
Compounds are provided that act as potent antagonists of the CCR2 receptor. Animal testing demonstrates that these compounds are useful for treating inflammation, a hallmark disease for CCR2. The compounds are generally aryl sulfonamide derivatives and are useful in pharmaceutical compositions, methods for the treatment of CCR2-mediated diseases, and as controls in assays for the identification of CCR2 antagonists.
Owner:CHEMOCENTRYX INC
Tantalum amide precursors for deposition of tantalum nitride on a substrate
InactiveUS6379748B1Rapid heat treatmentSilicon organic compoundsPolycrystalline material growthFerroelectric thin filmsChemical vapor deposition
Tantalum and titanium source reagents are described, including tantalum amide and tantalum silicon nitride precursors for the deposition of tantalum nitride material on a substrate by processes such as chemical vapor deposition, assisted chemical vapor deposition, ion implantation, molecular beam epitaxy and rapid thermal processing. The precursors may be employed to form diffusion barrier layers on microelectronic device structures enabling the use of copper metallization and ferroelectric thin films in device construction.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Breathable composite sheet structure and absorbent articles utilizing same
A breathable composite sheet material, a method for making such a sheet material, and an absorbent article utilizing the sheet material are provided. The composite sheet material is comprised of a thermoplastic film adhered directly to a fibrous substrate. The thermoplastic film comprises at least 50% by weight of a polymer material from the group of block copolyether esters, block copolyether amides and polyurethanes. The substrate comprises a fibrous web of at least 50% by weight of polyolefin polymer synthetic fibers. The composite sheet exhibits a peel strength of at least 0.1 N / cm, a dynamic fluid transmission of less than about 0.75 g / m2 when subjected to an impact energy of about 2400 joules / m2, and a moisture vapor transmission rate, according to the desiccant method, of at least 1500 g / m2 / 24 hr. The absorbent article comprises (a) a topsheet; (b) a backsheet; and (c) an absorbent core located between the topsheet and the backsheet; wherein the backsheet comprises the non-porous, substantially fluid impermeable, moisture vapor permeable composite sheet material described above. The composite sheet material is oriented such that the film layer of the composite sheet material faces toward the absorbent core. The absorbent article may comprise a disposable diaper.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
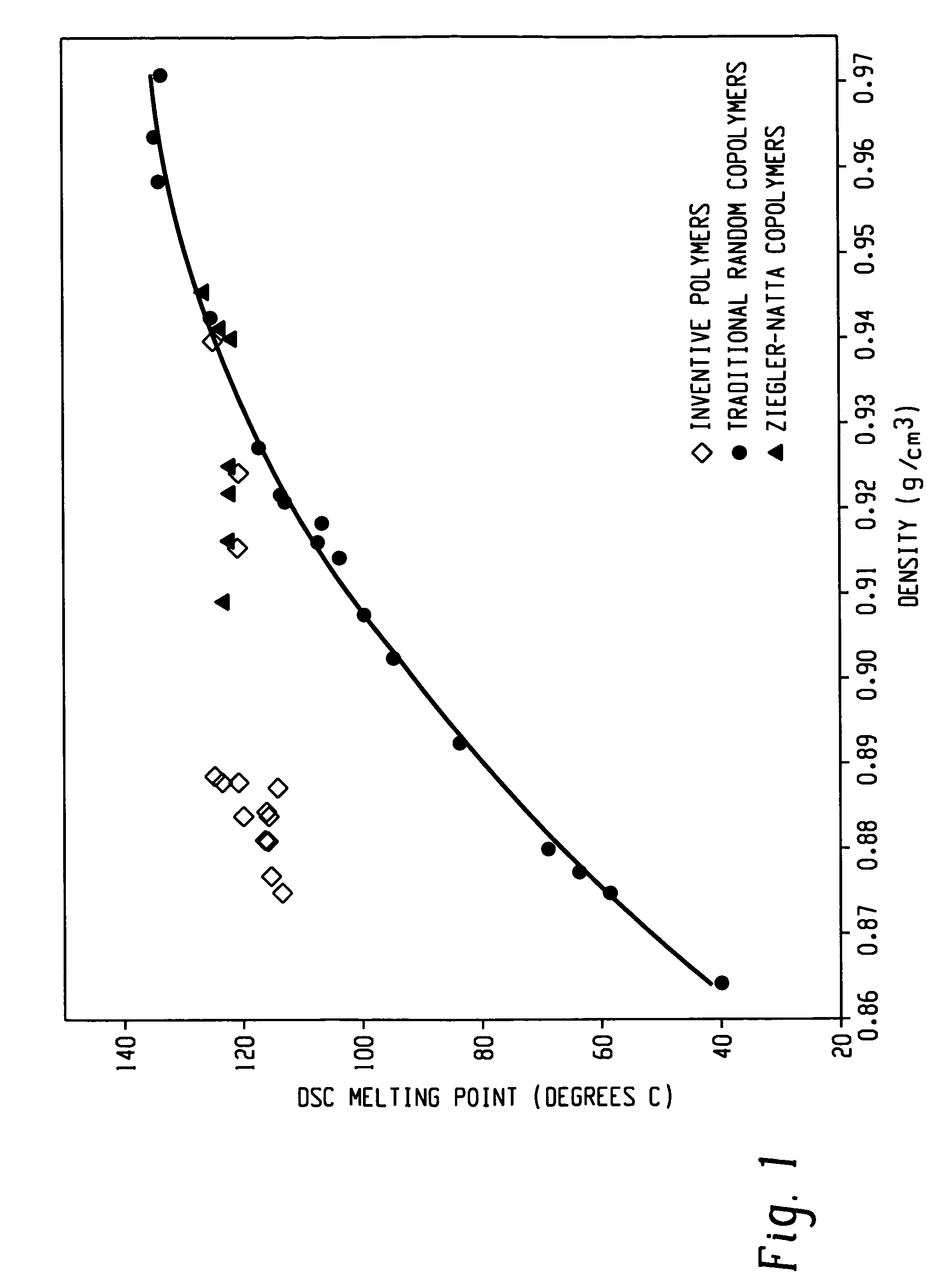
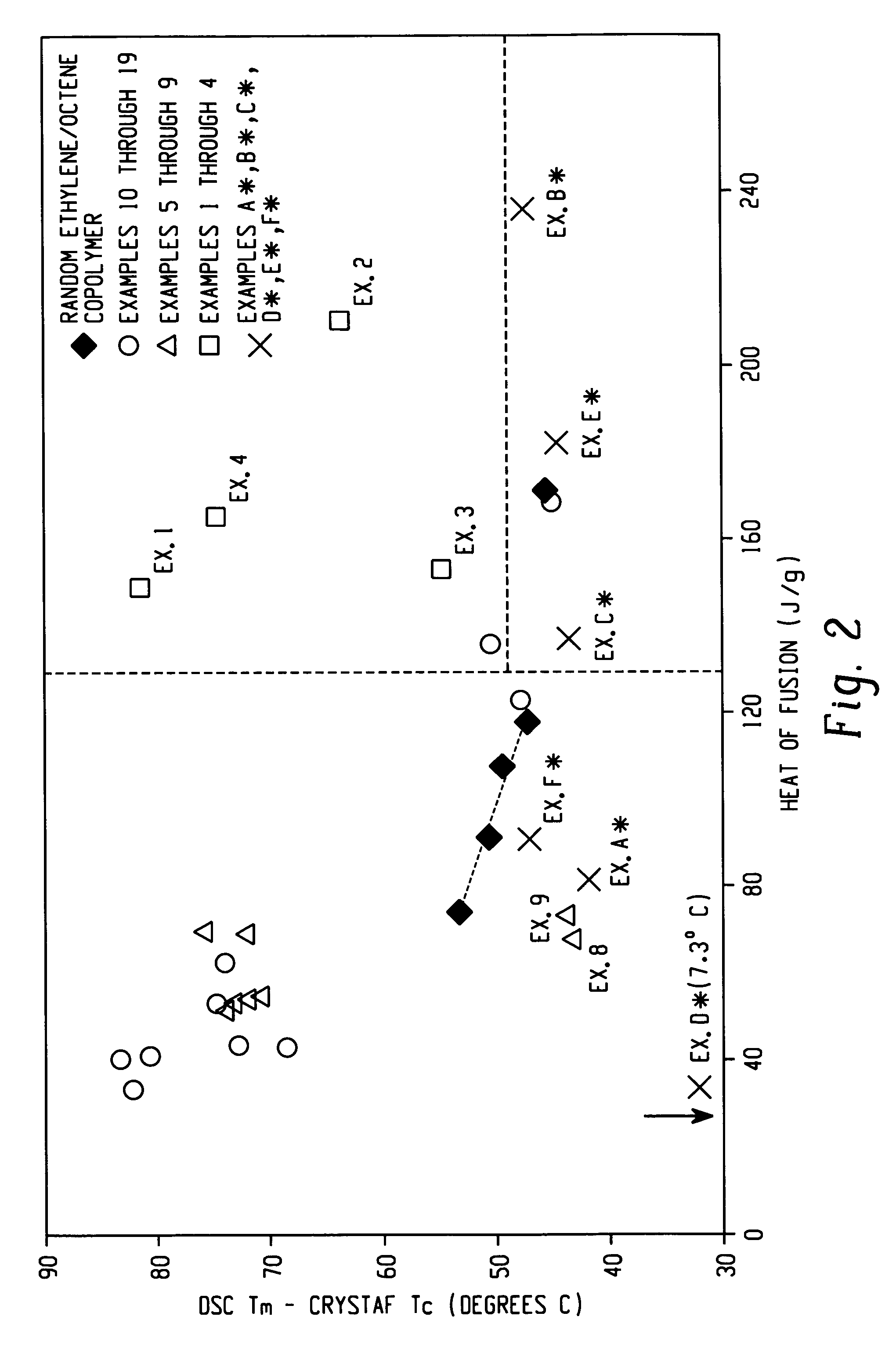
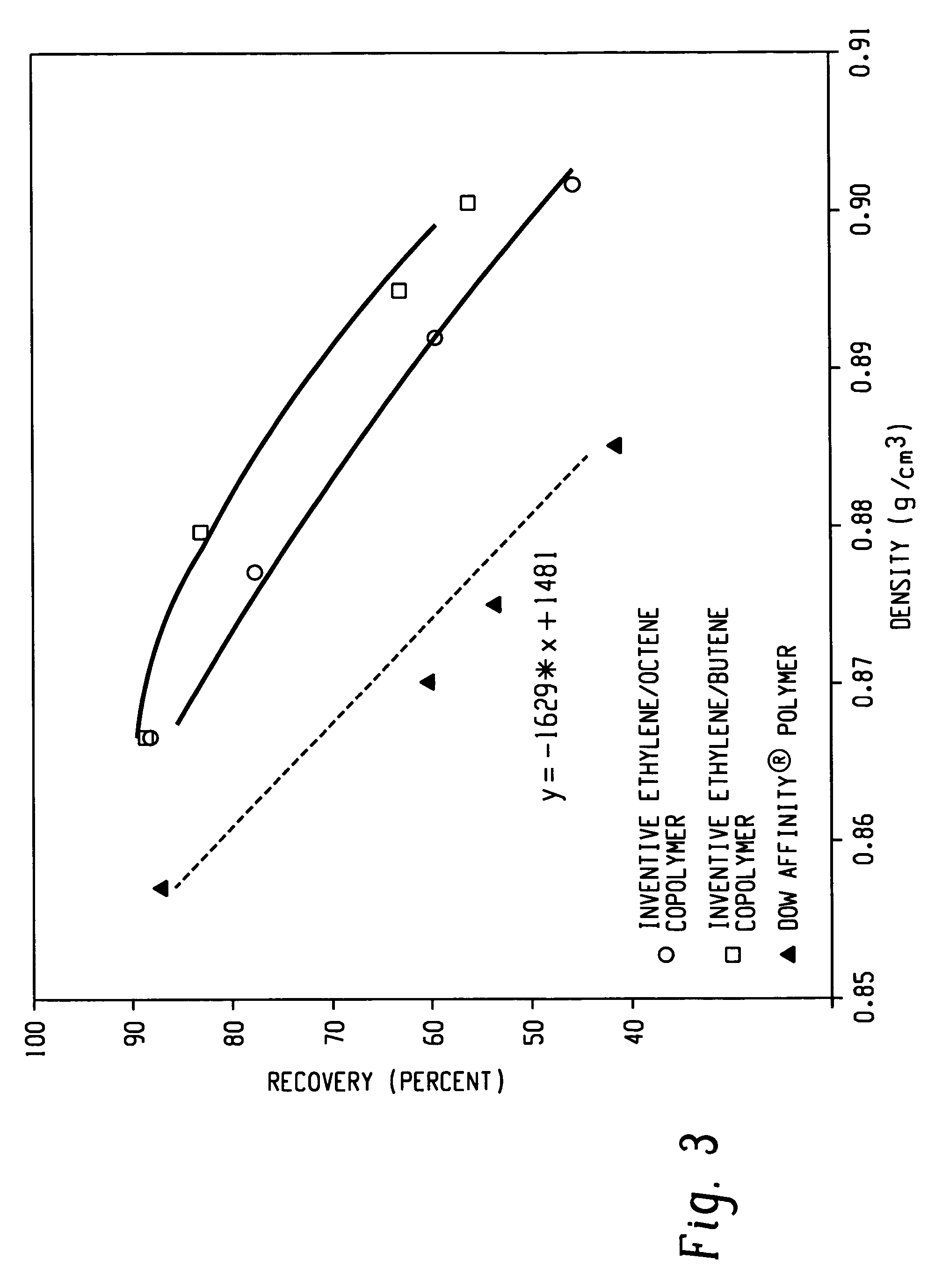
Anti-blocking compositions comprising interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
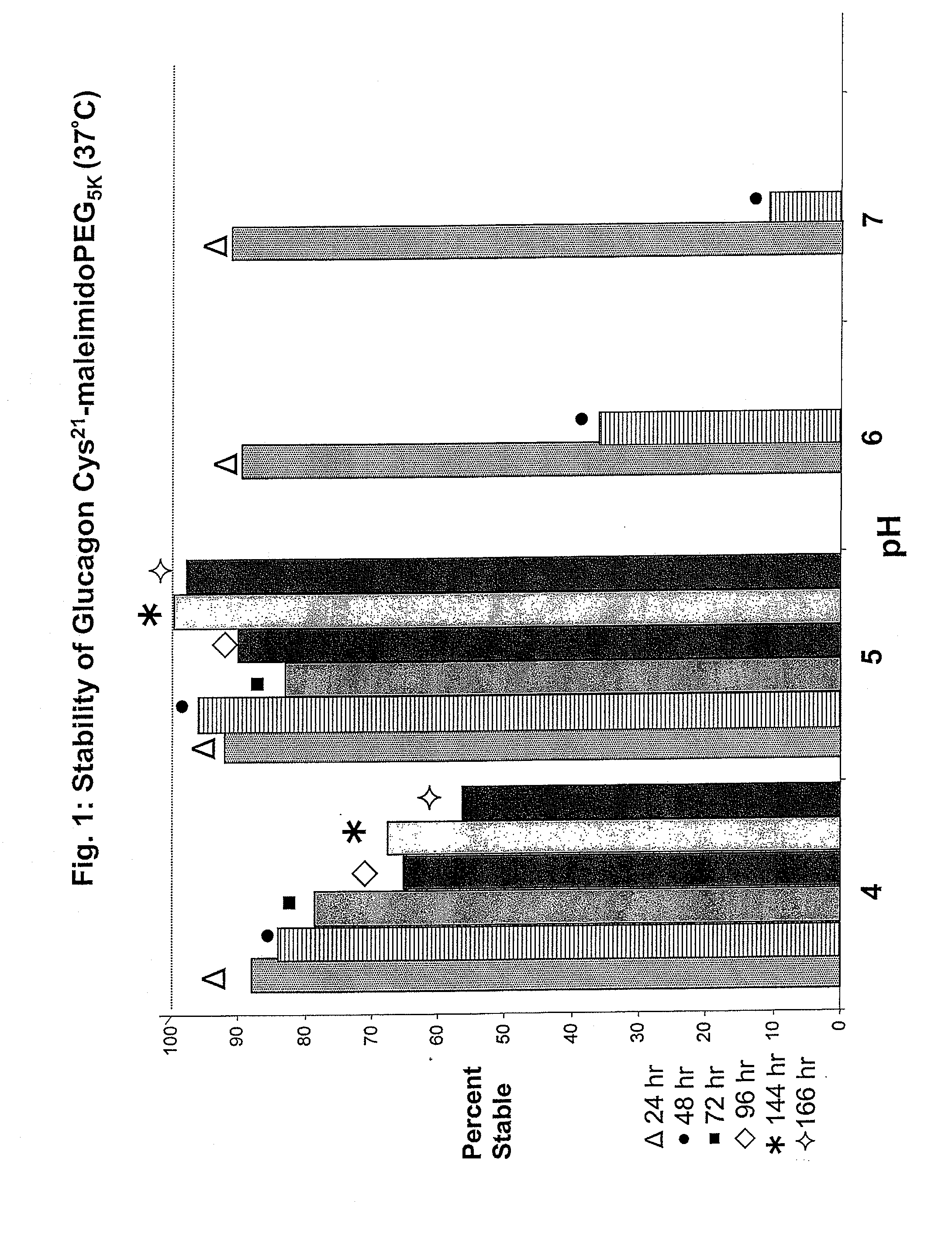
Glucagon/glp-1 receptor co-agonists
InactiveUS20100190701A1High activityEnhanced biophysical stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCarboxylic acid
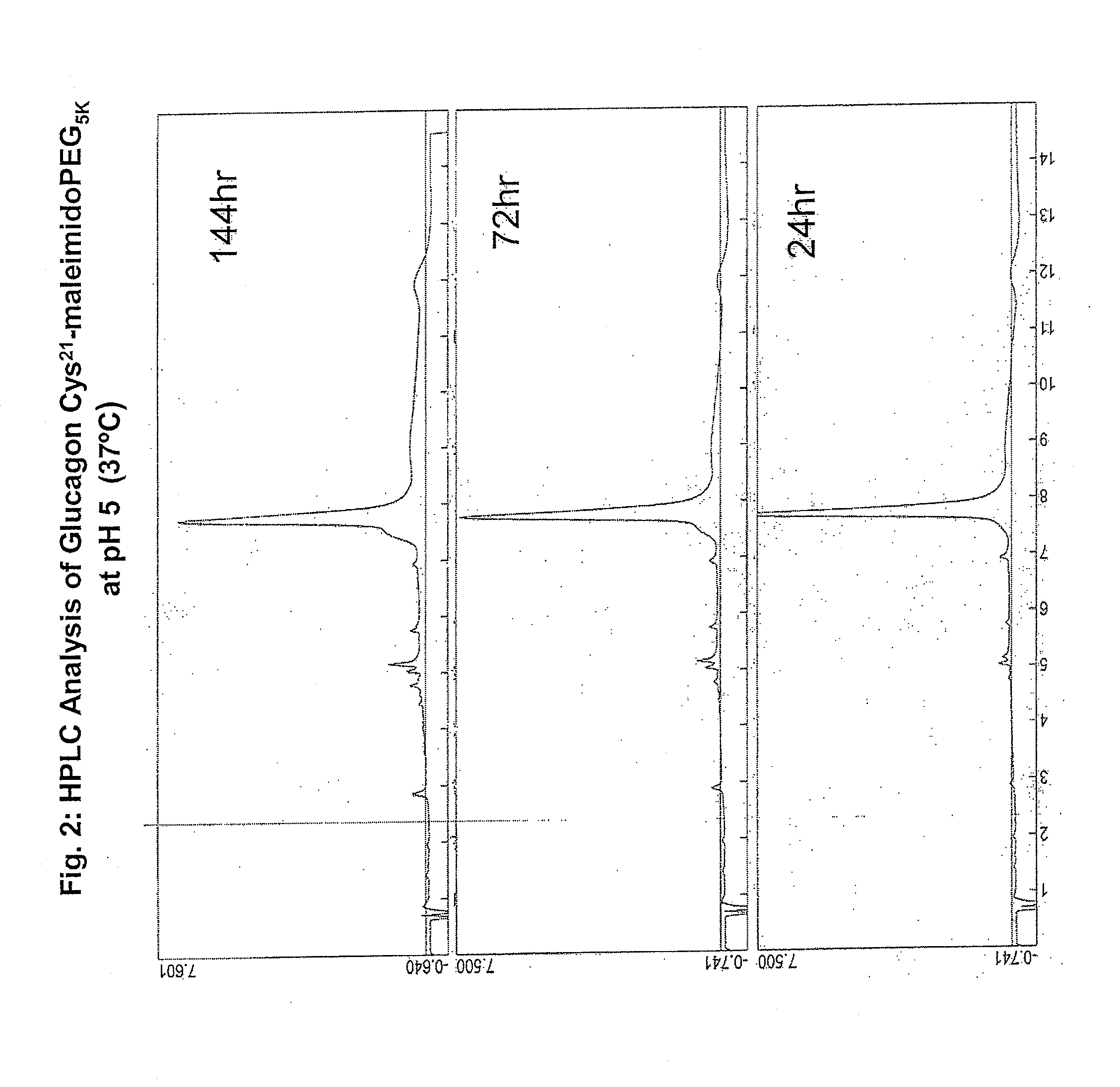
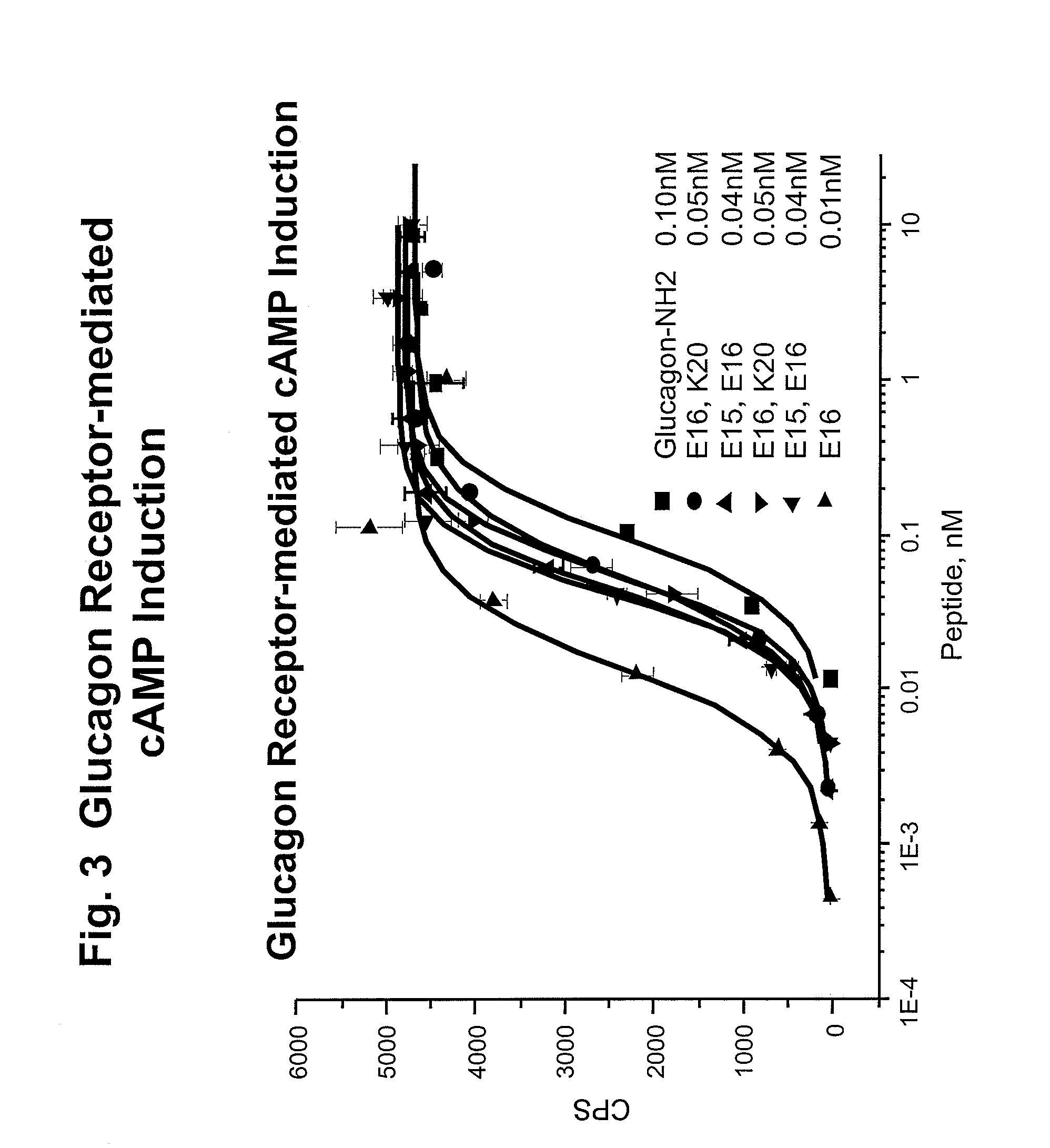
Modified glucagon peptides are disclosed having enhanced potency at the glucagon receptor relative to native glucagon. Further modification of the glucagon peptides by forming lactam bridges or the substitution of the terminal carboxylic acid with an amide group produces peptides exhibiting glucagon / GLP-1 receptor co-agonist activity. The solubility and stability of these high potency glucagon analogs can be further improved by modification of the polypeptides by pegylation, substitution of carboxy terminal amino acids, or the addition of a carboxy terminal peptide selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 26 (GPSSGAPPPS), SEQ ID NO: 27 (K-RNRNNIA) and SEQ ID NO: 28 (KRNR).
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Wound healing polymer compositions and methods for use thereof
The present invention provides bioactive polymer compositions that can be formulated to release a wound healing agent at a controlled rate by adjusting the various components of the composition. The composition can be used in an external wound dressing, as a polymer implant for delivery of the wound healing agent to an internal body site, or as a coating on the surface of an implantable surgical device to deliver wound healing agents that are covalently attached to a biocompatible, biodegradable polymer and / or embedded within a hydrogel. Methods of using the invention bioactive polymer compositions to promote natural healing of wounds, especially chronic wounds, are also provided. Examples of biodegradable copolymer polyesters useful in forming the blood-compatible, hydrophilic layer or coating include copolyester amides, copolyester urethanes, glycolide-lactide copolymers, glycolide-caprolactone copolymers, poly-3-hydroxy butyrate-valerate copolymers, and copolymers of the cyclic diester monomer, 3-(S)[(alkyloxycarbonyl)methyl]-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione, with L-lactide. The glycolide-lactide copolymers include poly(glycolide-L-lactide) copolymers formed utilizing a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 5:95 to 95:5 and preferably a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 45:65 to 95:5. The glycolide-caprolactone copolymers include glycolide and ε-caprolactone block copolymer, e.g., Monocryl or Poliglecaprone.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Topologically segregated, encoded solid phase libraries comprising linkers having an enzymatically susceptible bond
The invention relates to libraries of synthetic test compound attached to separate phase synthesis supports. In particular, the invention relates to libraries of synthetic test compound attached to separate phase synthesis supports that also contain coding molecules that encode the structure of the synthetic test compound. The molecules may be polymers or multiple nonpolymeric molecules. Each of the solid phase synthesis support beads contains a single type of synthetic test compound. The synthetic test compound can have backbone structures with linkages such as amide, urea, carbamate (i.e., urethane), ester, amino, sulfide, disulfide, or carbon-carbon, such as alkane and alkene, or any combination thereof. Examples of subunits suited for the different linkage chemistries are provided. The synthetic test compound can also be molecular scaffolds, such as derivatives of monocyclic of bicyclic carbohydrates, steroids, sugars, heterocyclic structures, polyaromatic structures, or other structures capable of acting as a scaffolding. Examples of suitable molecular scaffolds are provided. The invention also relates to methods of synthesizing such libraries and the use of such libraries to identify and characterize molecules of interest from among the library of synthetic test compound.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
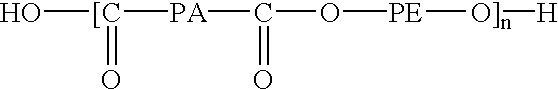
Design of poly(ester amides) for the control of agent-release from polymeric compositions
The present invention generally encompasses a medical article, such as a medical device or coating comprising an agent or combination of agents, wherein the agent is distributed throughout a polymeric matrix. The polymeric matrix comprises an agent and a poly(ester amide) having a design that was preselected to provide a predetermined release rate of the combination of agents from the medical article.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Acylsulfonamide compounds as inhibitors of hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease
ActiveUS20060046956A1Modulate activityInhibit HCVBiocideDipeptide ingredientsDiseaseHcv hepatitis c virus
The present invention discloses novel compounds which have HCV protease inhibitory activity as well as methods for preparing such compounds. In another embodiment, the invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds as well as methods of using them to treat disorders associated with the HCV protease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Toughened epoxy adhesive composition
ActiveUS20060276601A1Improved lap shear and impact peel strengthGood storage stabilityPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsElastomerEnd-group
The invention is an epoxy resin based adhesive composition comprising an epoxy resin and a compound comprising an elastomeric prepolymer residue selected from the group of a polyurethane, a polyurea and a polyurea polyurethane having isocyanate end groups, the isocyanate end groups of said prepolymer residue being capped by a capping compound selected from the group consisting of a primary aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, heteroaromatic and araliphatic amine, a secondary aliphatic, cycloaliphatic, aromatic, heteroaromatic and araliphatic amine, a thiol and an alkyl amide, said capping compound being bound to the end of the polymer chain of the elastomeric prepolymer in a manner such that the end to which it is bonded no longer has a reactive group. In addition to the capping compound defined above above, a capping compound selected from the group consisting of a phenol and a polyphenol can be used for capping the isocyanate end groups of the prepolymer residue
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
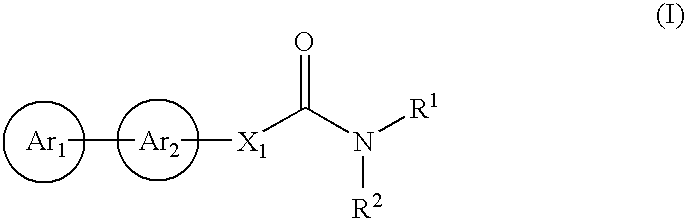
Cinnamide compound
The present invention relates to a compound represented by Formula (I): (wherein Ar1 represents an imidazolyl group which may be substituted with 1 to 3 substituents; Ar2 represents a pyridinyl group, a pyrimidinyl group, or a phenyl group which may be substituted with 1 to 3 substituents; X1 represents (1) —C≡C— or (2) a double bond etc. which may be substituted; R1 and R2 represent, for example, a C1-6 alkyl group or C3-8 cycloalkyl group which may be substituted) or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof and to the use thereof as pharmaceutical agents. The object of the present invention is to find a therapeutic or preventive agent for diseases caused by Aβ. According to the present invention, a therapeutic or preventive agents for diseases caused by Aβ can be provided.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Fluorinated cyclic amides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors
InactiveUS6710040B1Easy to prepareEase of detectabilityBiocideOrganic chemistryAcute coronary syndromeDisease progression
The invention relates to new therapeutically active and selective inhibitors of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and the use of such compounds for treating diseases that are associated with proteins that are subject to processing by DPP-IV, such as Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance, metabolic syndrome (Syndrome X or insulin resistance syndrome), glucosuria, metabolic acidosis, cataracts, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic cardiomyopathy, Type 1 diabetes, obesity, conditions exacerbated by obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, osteopenia, frailty, bone loss, bone fracture, acute coronary syndrome, infertility due to polycystic ovary syndrome, short bowel syndrome, anxiety, depression, insomnia, chronic fatigue, epilepsy, eating disorders, chronic pain, alcohol addiction, diseases associated with intestinal motility, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel syndrome and to prevent disease progression in Type 2 diabetes. The invention also relates to a method of identifying an insulin secretagogue agent for diabetes.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials
InactiveUS6107427AAvoid problemsReverse twist can beLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryActive polymerAryl
The invention is concerned with novel cross-linkable, photoactive polymer materials with 3-aryl-acrylic acid esters and amides as well as their use as orienting layers for liquid crystals and for the production of non-structured or structured optical elements and multi-layer systems.
Owner:ROLIC AG
Pharmaceutical co-crystal compositions
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a co-crystal of an API and a co-crystal former; wherein the API has at least one functional group selected from ether, thioether, alcohol, thiol, aldehyde, ketone, thioketone, nitrate ester, phosphate ester, thiophosphate ester, ester, thioester, sulfate ester, carboxylic acid, phosphonic acid, phosphinic acid, sulfonic acid, amide, primary amine, secondary amine, ammonia, tertiary amine, sp2 amine, thiocyanate, cyanamide, oxime, nitrile diazo, organohalide, nitro, s-heterocyclic ring, thiophene, n-heterocyclic ring, pyrrole, o-heterocyclic ring, furan, epoxide, peroxide, hydroxamic acid, imidazole, pyridine and the co-crystal former has at least one functional group selected from amine, amide, pyridine, imidazole, indole, pyrrolidine, carbonyl, carboxyl, hydroxyl, phenol, sulfone, sulfonyl, mercapto and methyl thio, such that the API and co-crystal former are capable of co-crystallizing from a solution phase under crystallization conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES +2
Highly-resilient thermoplastic elastomer compositions
A thermoplastic composition of (a) an acid copolymer, (b) a salt of a high molecular weight, monomeric organic acid; (c) a thermoplastic polymer selected from copolyetheresters, elastomeric polyolefins, styrene diene block copolymers, elastomeric polyolefins thermoplastic polyurethanes and copolyetheramides; (d) cation source; and (d) optionally a filler. Also included is use of such compositions in components of one-, two- and three-piece golf balls or multi-layered golf balls made therefrom.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Silicone hydrogels comprising n-vinyl amides and hydroxyalkyl (meth)acrylates or (meth)acrylamides
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Hepatitis C inhibitor tri-peptides
ActiveUS7091184B2Better pharmacokinetic profileNot significant inhibitory activityBiocideDipeptide ingredientsHcv ns3 proteaseHepatitis C
Compounds of formula (I):wherein R1 is hydroxyl or sulfonamide derivative; R2 is t-butyl or —CH2—C(CH3)3 or —CH2-cyclopentyl; R3 is t-butyl or cyclohexyl and R4 is cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl or cyclohexyl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, are described as useful as inhibitor of the HCV NS3 protease.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Bloom-resistant benzotriazole UV absorbers and compositions stabilized therewith
Benzotriazole UV absorbers substituted with a ultra long ester or amide moiety wherein the ester or amide group is a hydrocarbyl group of 25 to 100 carbon atoms or is a group of alkyl of 25 to 100 carbon atoms interrupted by 5 to 39 oxygen atoms and terminated with an omega-OH or an omega-OR group exhibit excellent stabilization efficacy while they concomitantly do not bloom when incorporated into polyolefin films. These benzotriazole UV absorbers also provide excellent protection to white, dyed, dipped, unscented and / or scented candle wax from discoloration and degradation.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM CORP
Amido compounds and their use as pharmaceuticals
The present invention relates to inhibitors of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1, antagonists of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR), and pharmaceutical compositions thereof. The compounds of the invention can be useful in the treatment of various diseases associated with expression or activity of 11-β hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase type 1 and / or diseases associated with aldosterone excess.
Owner:INCYTE CORP
Aromatic amides and ureas and their uses as sweet and/or umami flavor modifiers, tastants and taste enhancers
InactiveUS20060045953A1Improve responseInduce savory taste perceptionFood preparationMonosodium glutamateSalty taste
The inventions disclosed herein relate to non-naturally occurring amide compounds that are capable, when contacted with comestible food or drinks or pharmaceutical compositions at concentrations preferably on the order of about 100 ppm or lower, of serving as savory (“umami”) or sweet taste modifiers, savory or sweet flavoring agents and savory or sweet flavor enhancers, for use in foods, beverages, and other comestible or orally administered medicinal products or compositions, optionally in the presence of or in mixtures with conventional flavoring agents such as monosodium glutamate or known natural and artificial sweeteners.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Polymer particles for delivery of macromolecules and methods of use
InactiveUS20070134332A1Slow down rate of bio-degradationImprove stabilityPowder deliveryNervous disorderPolyesterBound water
The present invention provides biodegradable polymer particle delivery compositions for delivery of macromolecular biologics, for example in crystal form, based on polymers, such as polyester amide (PEA), polyester urethane (PEUR), and polyester urea (PEU) polymers, which contain amino acids in the polymer. The polymer particle delivery compositions can be formulated either as a liquid dispersion or a lyophilized powder of polymer particles containing bound water molecules with the macromolecular biologics, for example insulin, dispersed in the particles. Bioactive agents, such as drugs, polypeptides, and polynucleotides can also be delivered by using particles sized for local, oral, mucosal or circulatory delivery. Methods of delivering a macromolecular biologic with substantial native activity to a subject, for example orally, are also included.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Liquid crystalline thermosets from ester, ester-imide, and ester-amide oligomers
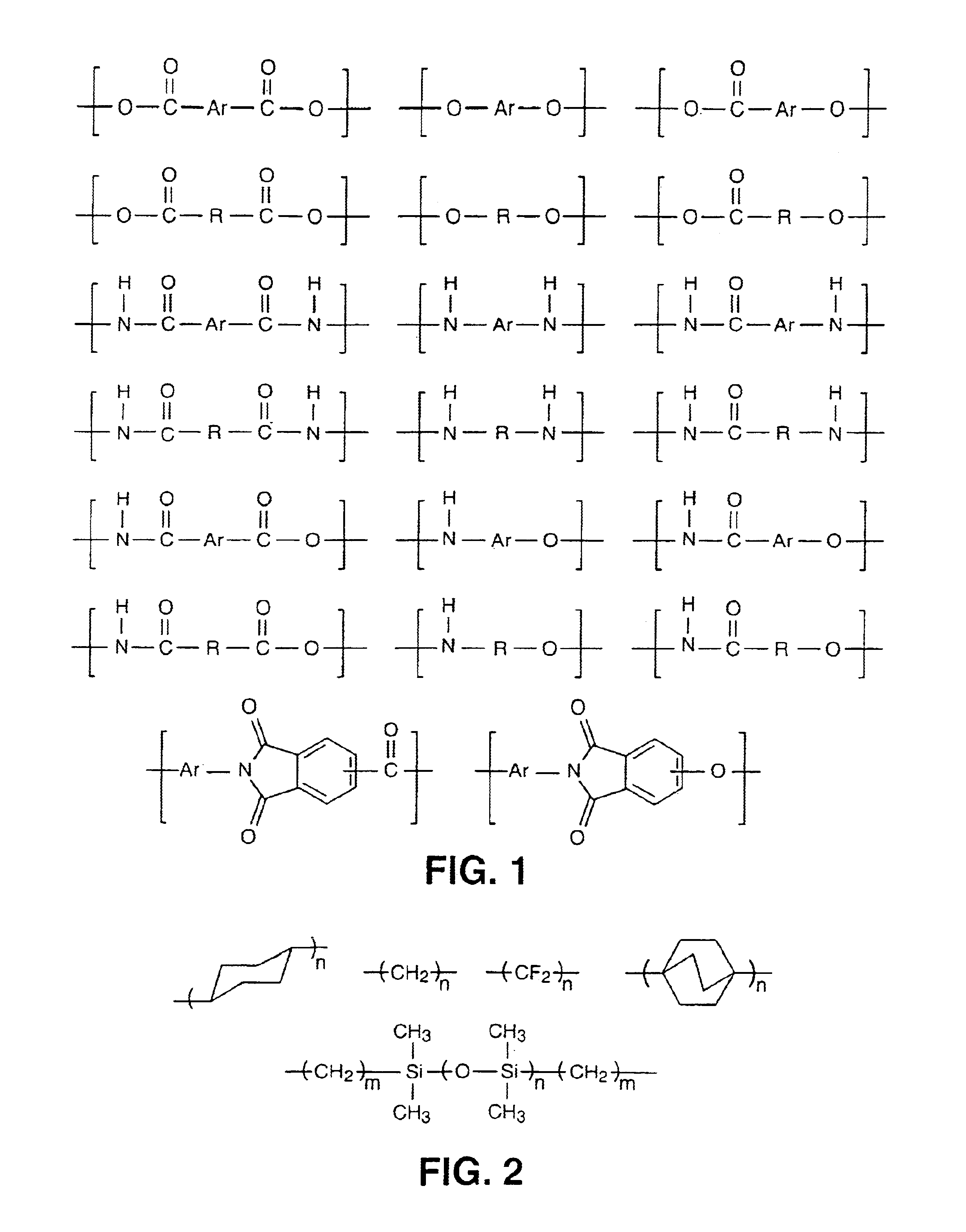
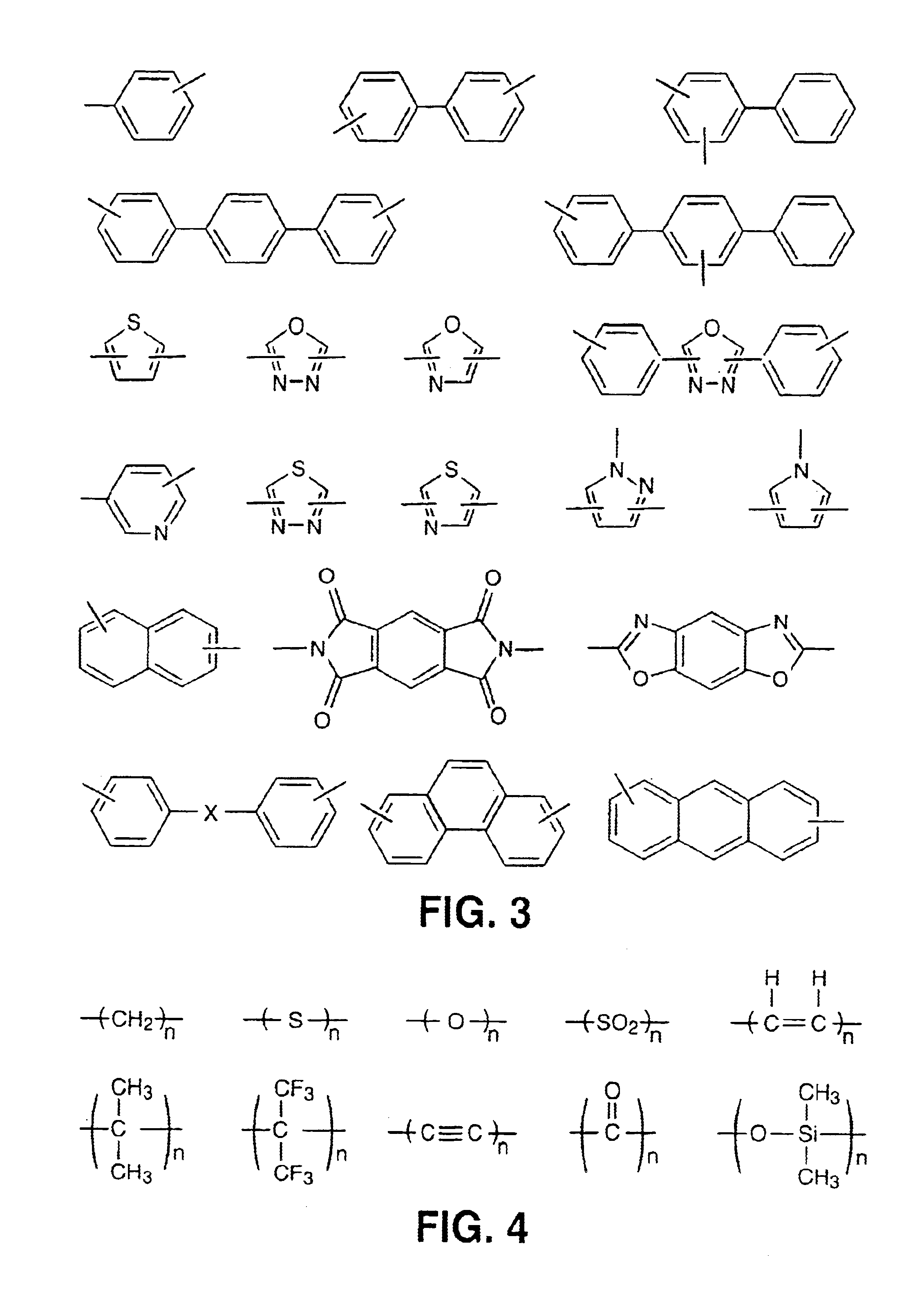
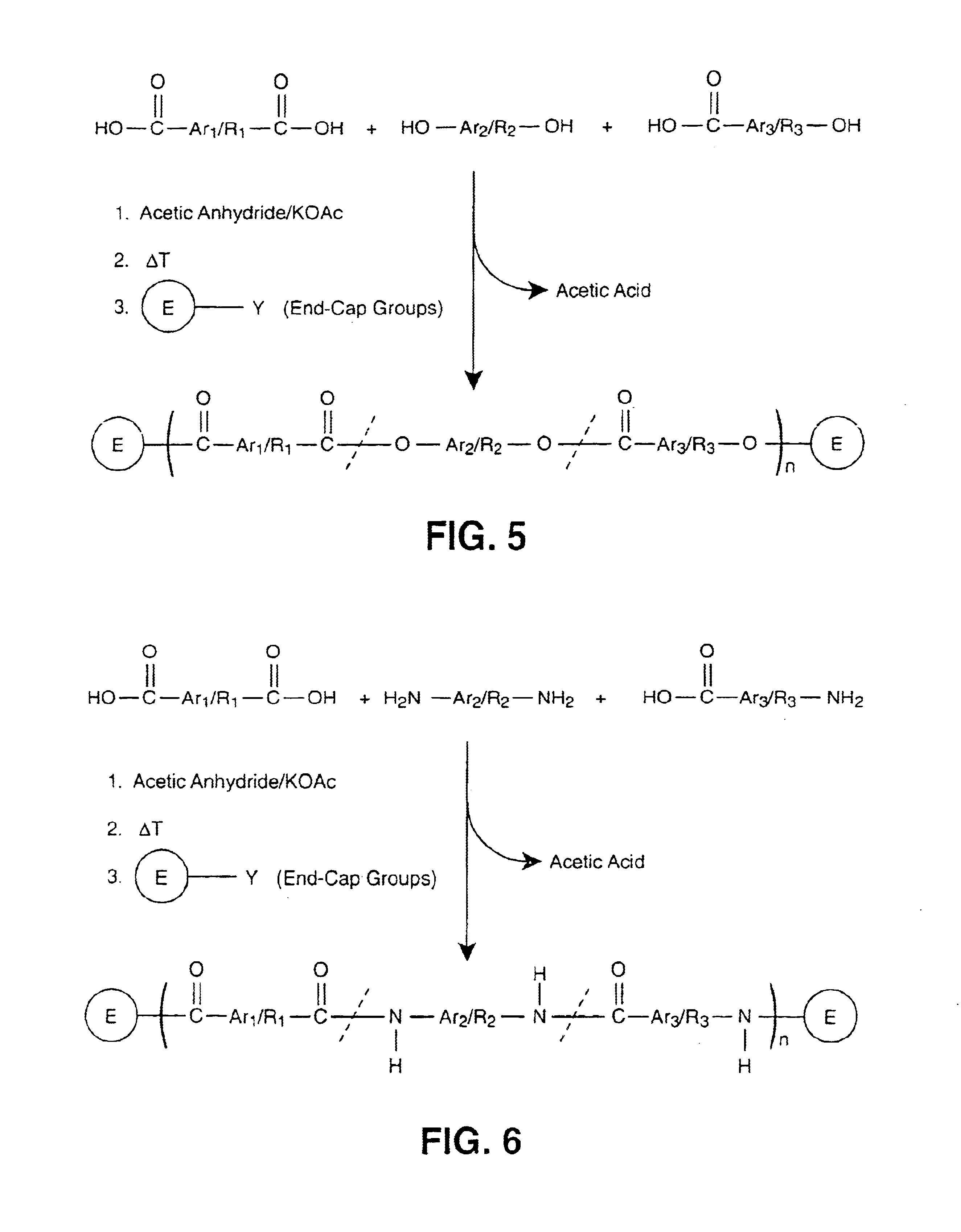
InactiveUS6939940B2Low viscosityLow dielectric constantLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid crystallineEnd-group
Main chain thermotropic liquid crystal esters, ester-imides, and ester-amides were prepared from AA, BB, and AB type monomeric materials and were end-capped with phenylacetylene, phenylmaleimide, or nadimide reactive end-groups. The resulting reactive end-capped liquid crystal oligomers exhibit a variety of improved and preferred physical properties. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are thermotropic and have, preferably, molecular weights in the range of approximately 1000-15,000 grams per mole. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers have broad liquid crystalline melting ranges and exhibit high melt stability and very low melt viscosities at accessible temperatures. The end-capped liquid crystal oligomers are stable for up to an hour in the melt phase. These properties make the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers highly processable by a variety of melt process shape forming and blending techniques including film extrusion, fiber spinning, reactive injection molding (RIM), resin transfer molding (RTM), resin film injection (RFI), powder molding, pultrusion, injection molding, blow molding, plasma spraying and thermo-forming. Once processed and shaped, the end-capped liquid crystal oligomers were heated to further polymerize and form liquid crystalline thermosets (LCT). The fully cured products are rubbers above their glass transition temperatures. The resulting thermosets display many properties that are superior to their non-end-capped high molecular weight analogs.
Owner:NASA
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com