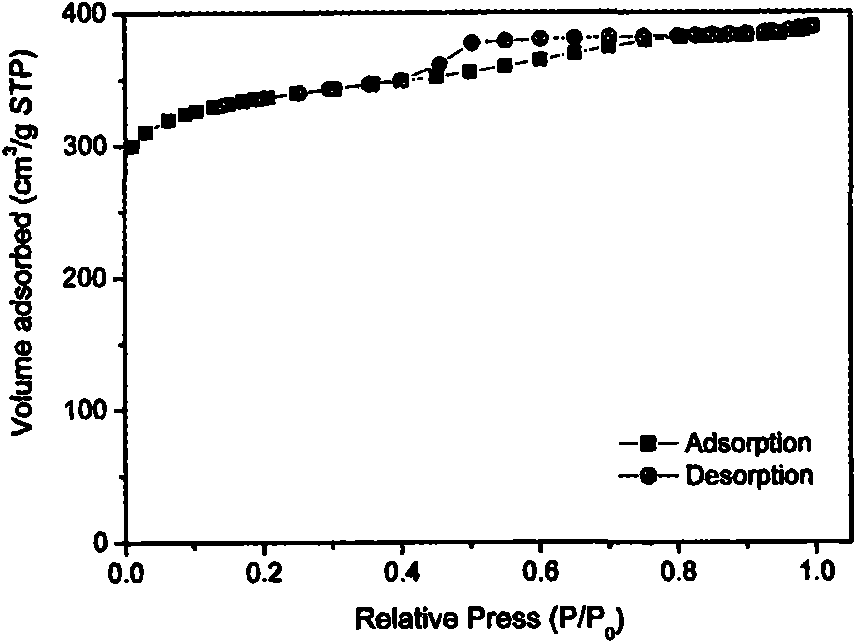
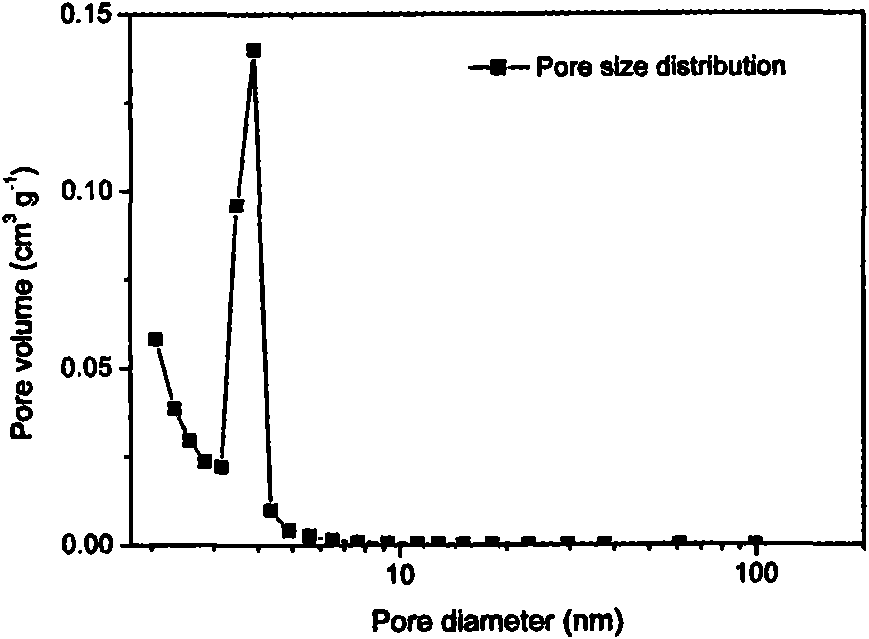
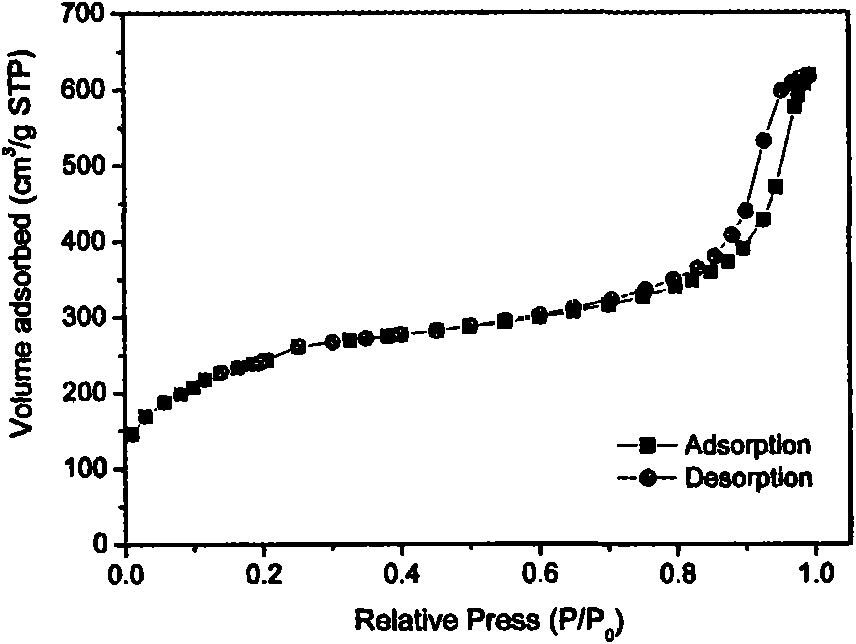
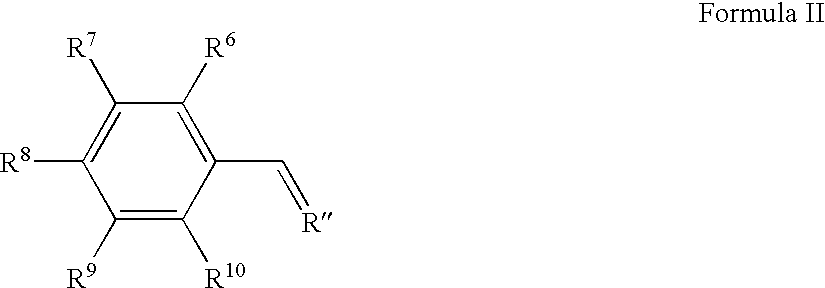Patents
Literature
1701results about "Copper organic compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20090291208A1Good step coverageImprove conductivityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diispropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates b the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diispropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Thermally stable volatile film precursors
ActiveUS20120058270A1Iron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCopper organic compoundsAtomic layer depositionPhotochemistry
A precursor for the deposition of a thin film by atomic layer deposition is provided. The compound has the formula MxLy where M is a metal and L is an amidrazone-derived ligand or an amidate-derived ligand. A process of forming a thin film using the precursors is also provided.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Volatile noble metal organometallic complexes
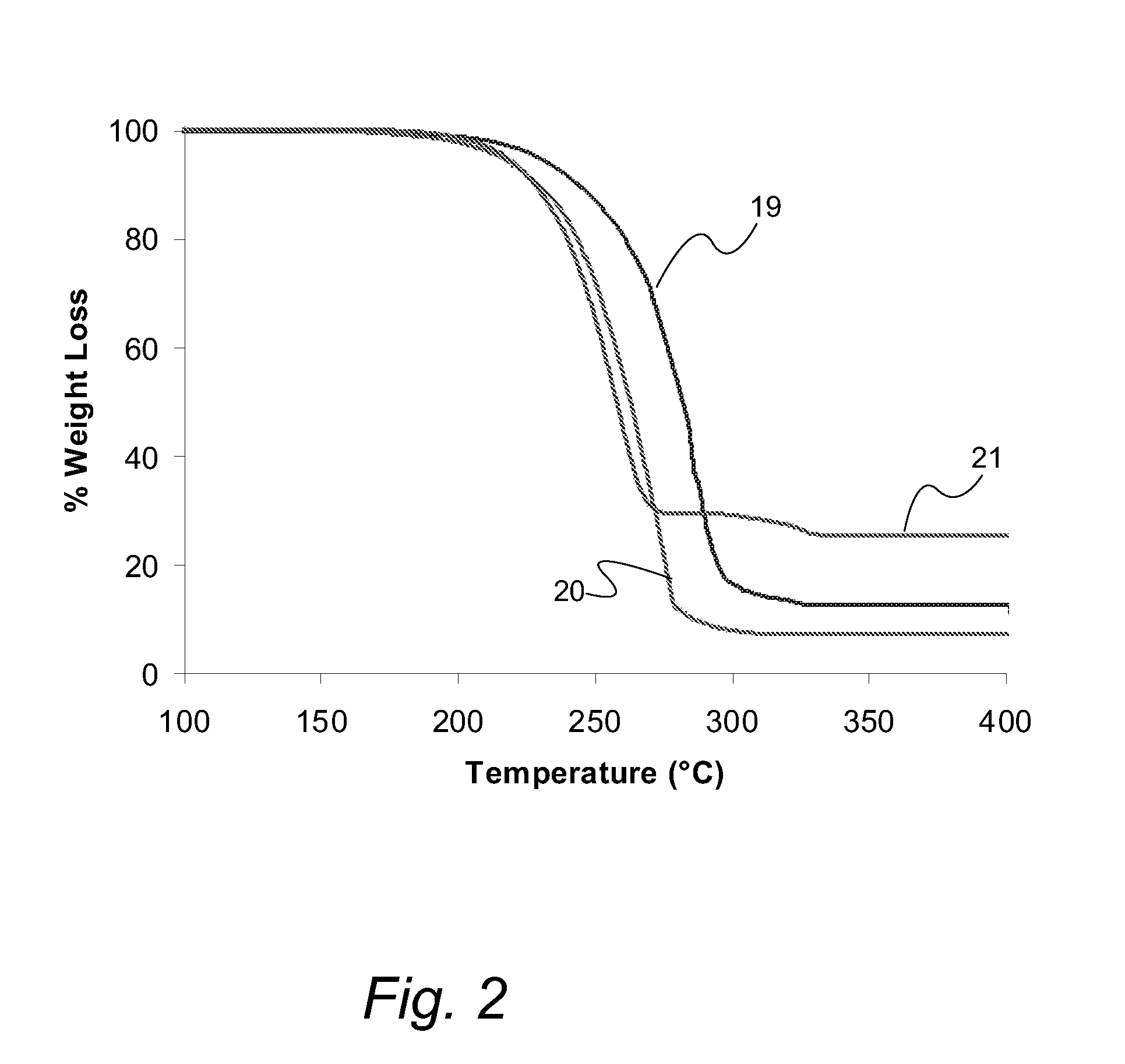
InactiveUS20050033075A1Reduce Van der Waals interactionBoiling and sublimation temperatureFurnaces without endless coreRuthenium organic compoundsIridiumIodide
A series of noble metal organometallic complexes of the general formula (I): MLaXb(FBC)c, wherein M is a noble metal such as iridium, ruthenium or osmium, and L is a neutral ligand such as carbonyl, alkene or diene; X is an anionic ligand such as chloride, bromide, iodide and trifluoroacetate group; and FBC is a fluorinated bidentate chelate ligand such as beta diketonate, beta-ketoiminate, amino-alcoholate and amino-alcoholate ligand, wherein a is an integer of from zero (0) to three (3), b is an integer of from zero (0) to one (1) and c is an 10 integer of from one (1) to three (3). The resulting noble metal complexes possess enhanced volatility and thermal stability characteristics, and are suitable for chemical vapor deposition(CVD) applications. The corresponding noble metal complex is formed by treatment of the FBC ligand with a less volatile metal halide. Also disclosed are CVD methods for using the noble metal complexes as source reagents for deposition of noble metal-containing films such as Ir, Ru and Os, or even metal oxide film materials IrO2, OsO2 and RuO2.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
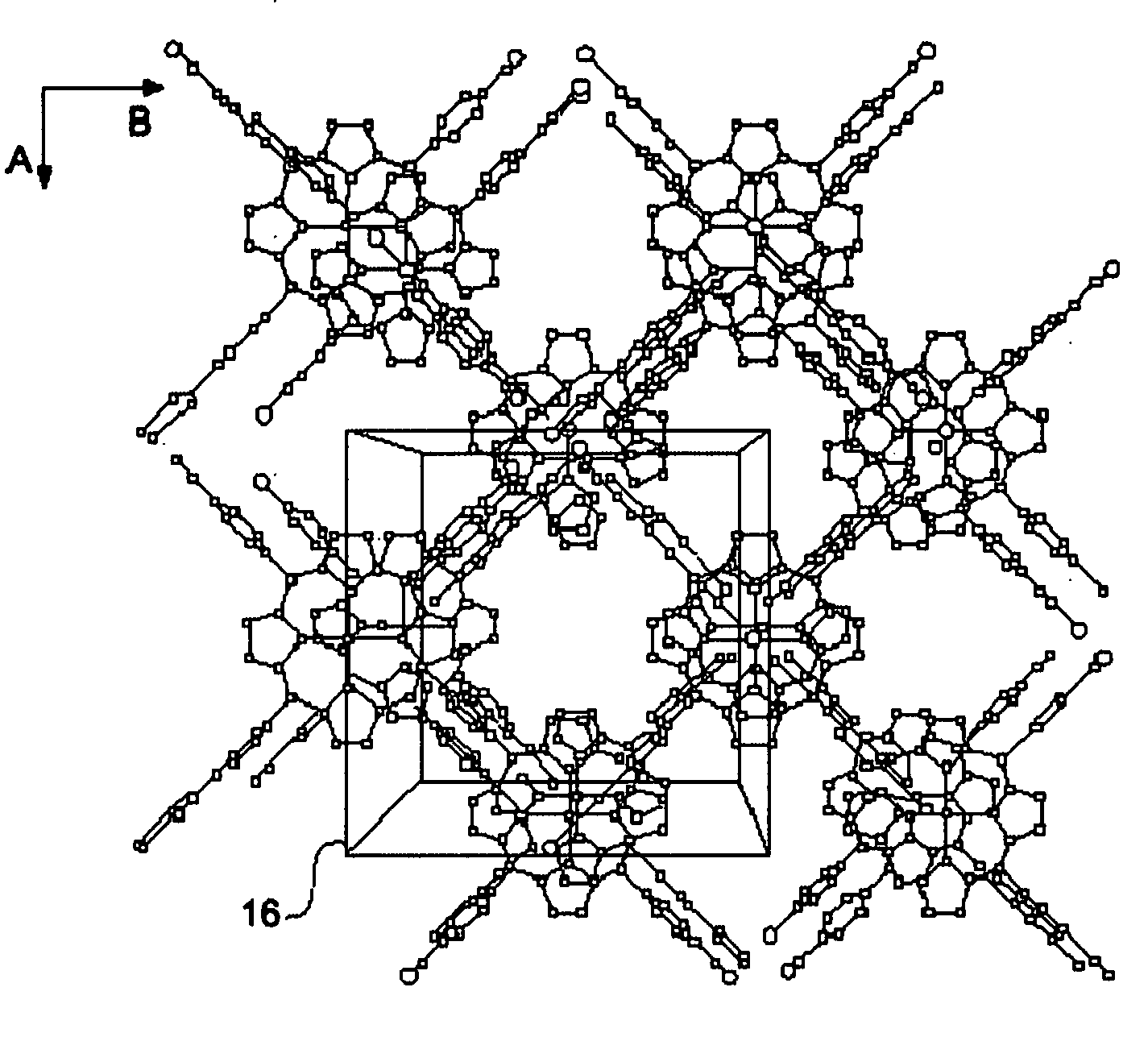
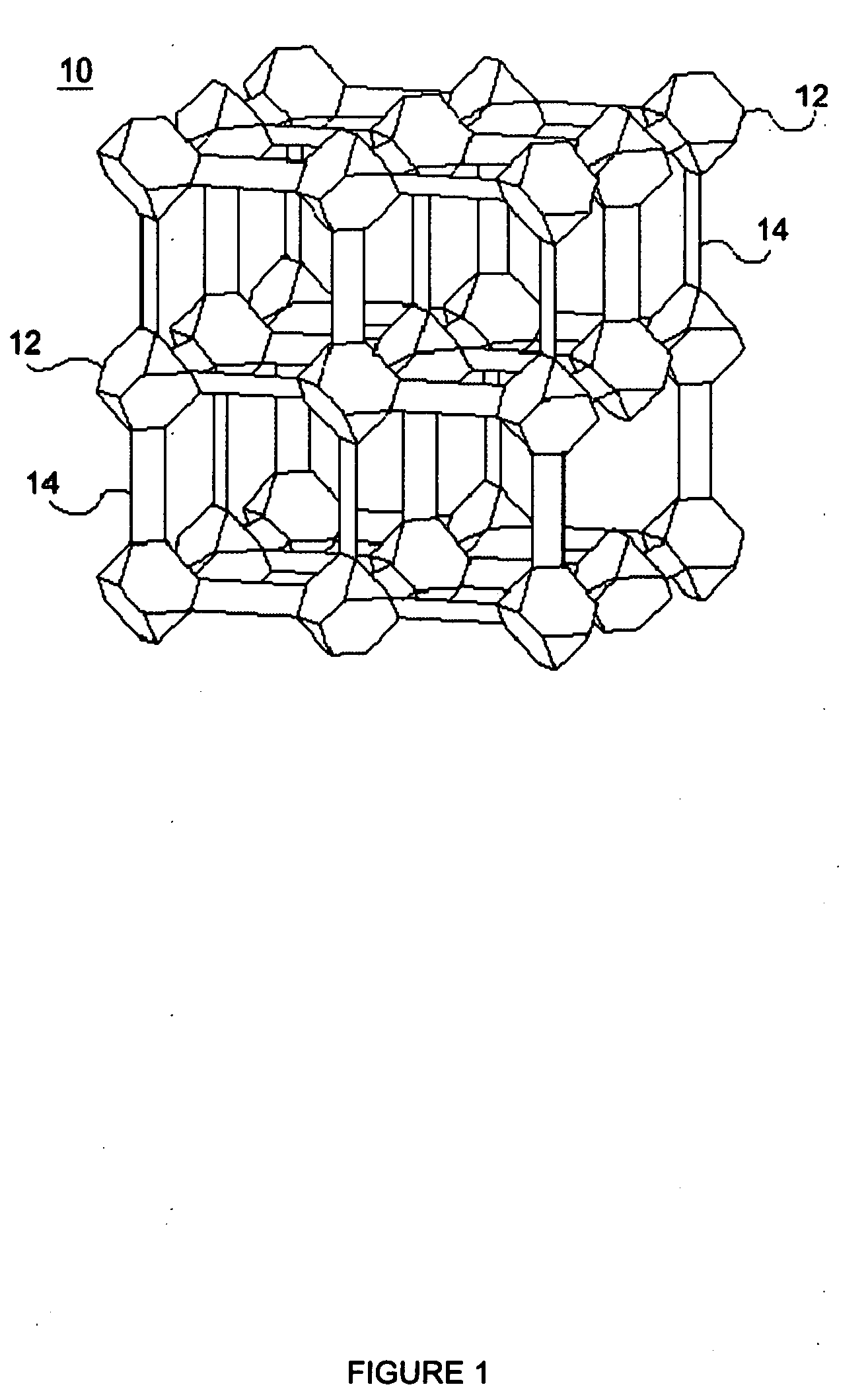
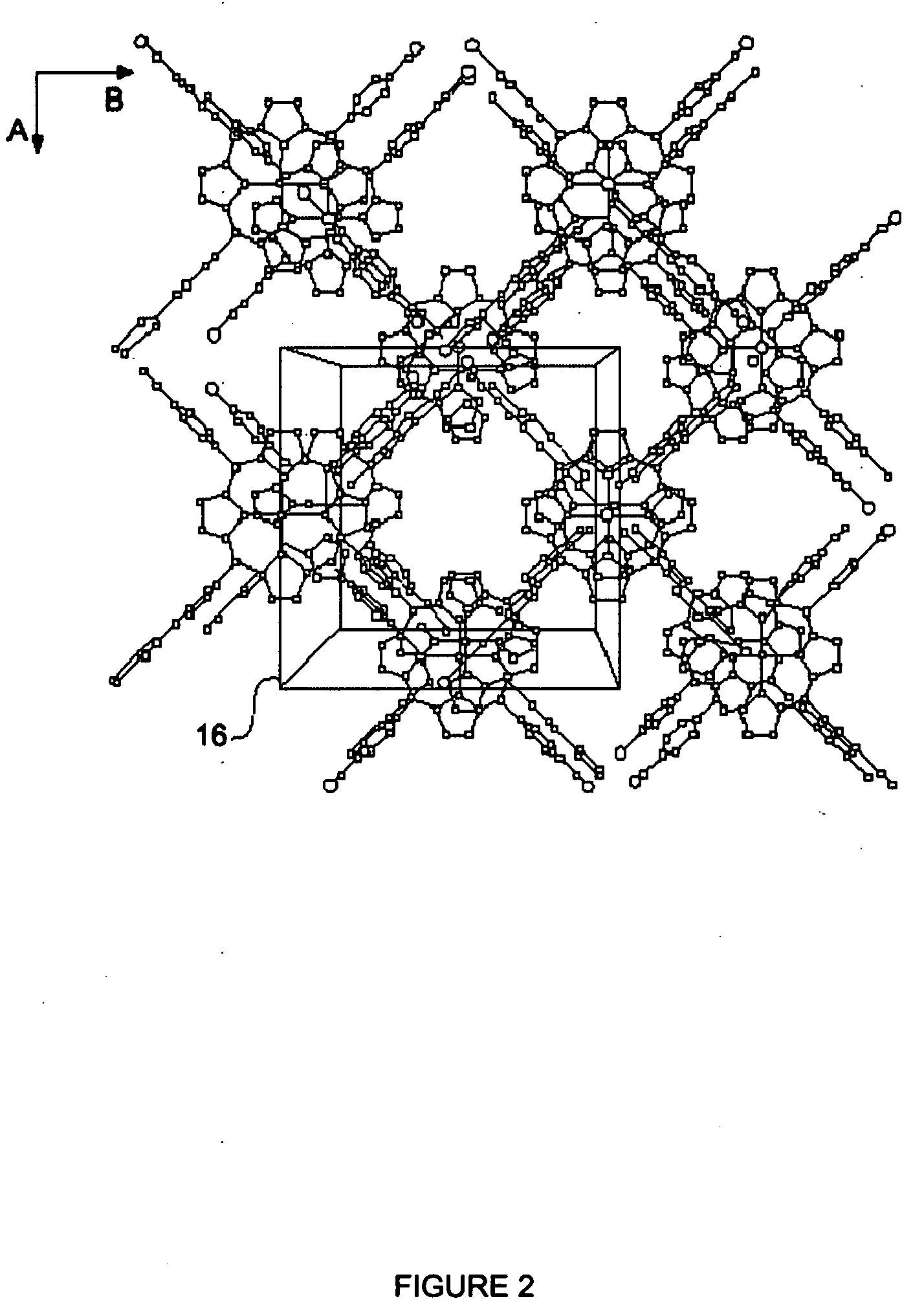
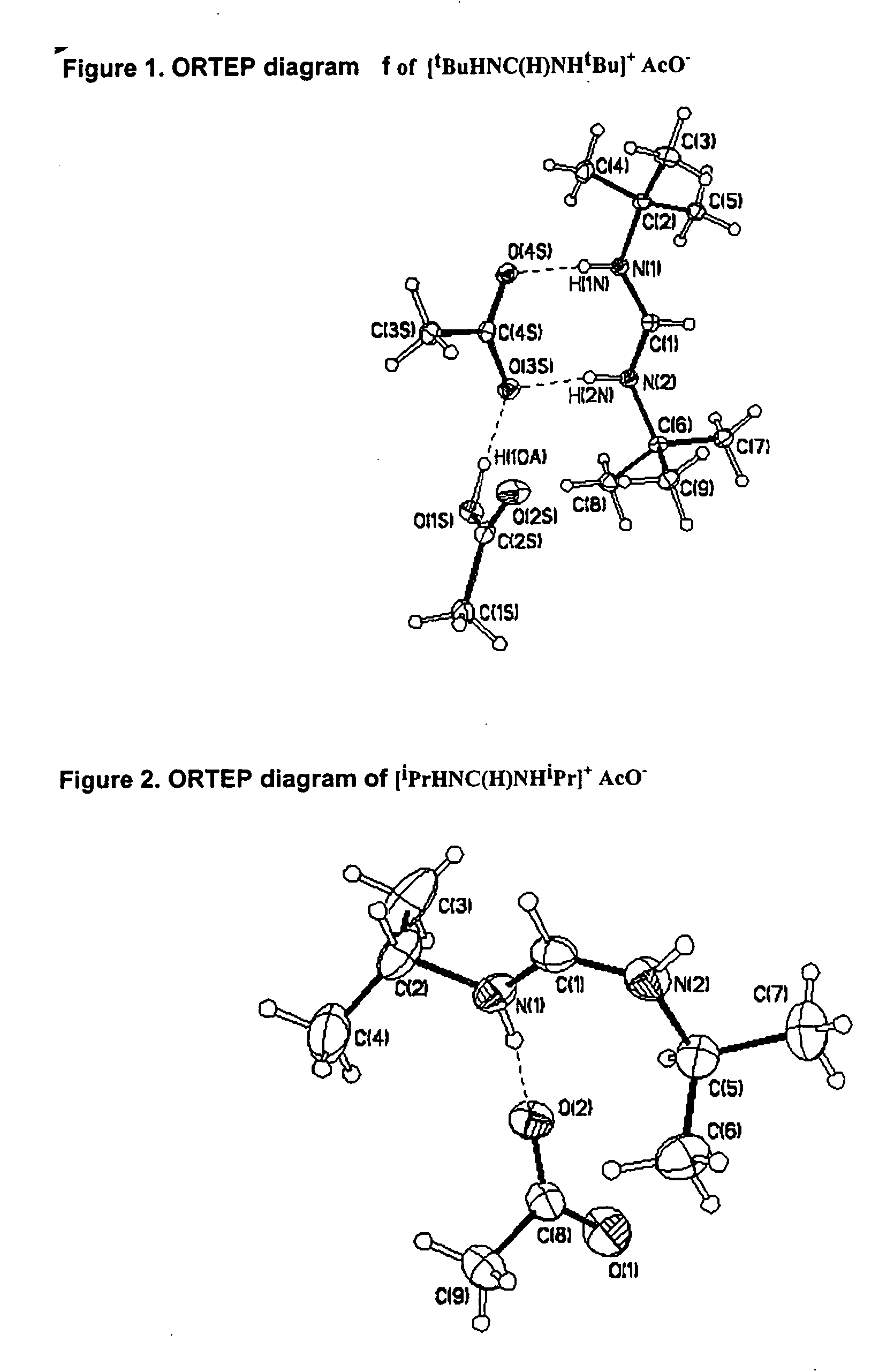
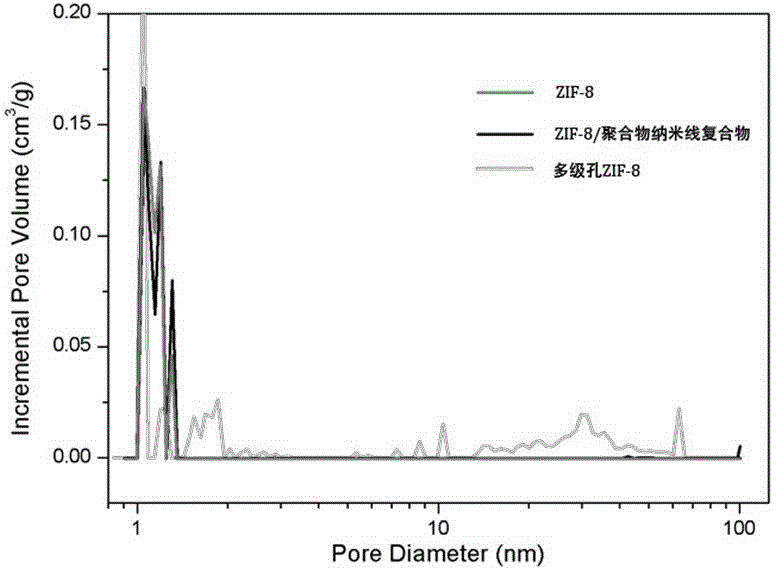
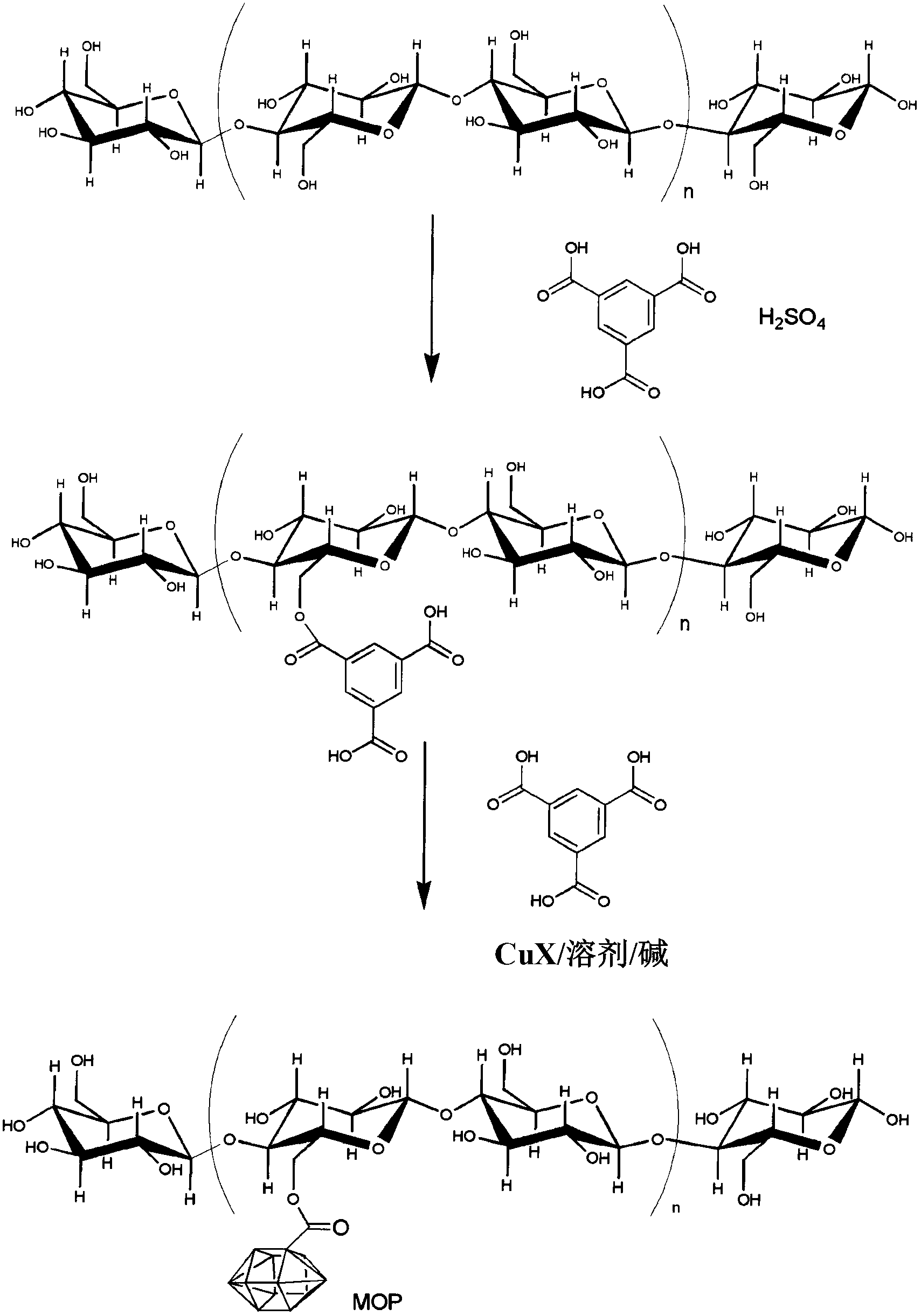
Nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in single-level or multilevel pore canal structure and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in a single-level or multilevel pore canal structure as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: at least one metal salt and at least one polyfunctional group organic ligand reacts with at least one template agent in at least one solvent under the condition that no hole aid agent exists or only one hole aid agent exist, and single-level or multilevel nanometer holes or channels with the size of 0.5-100 nm exist in at least one direction in the internal space of the obtained metal-organic frame solid. The nanometer hole metal-organic frame material with large hole size and the nanometer hole metal-organic frame material in the layered multilevel pore canal structure can be obtained without the synthesis of the large-size organic ligand and have wide applications.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
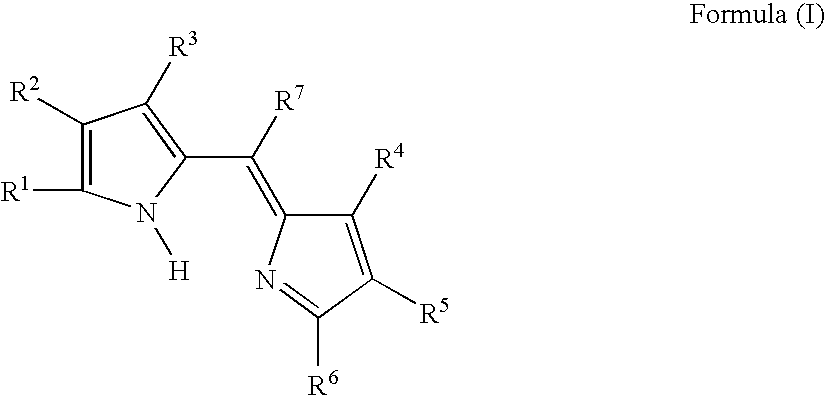
Compound or its tautomer, metal complex compound, colored photosensitive curing composition, color filter, and production
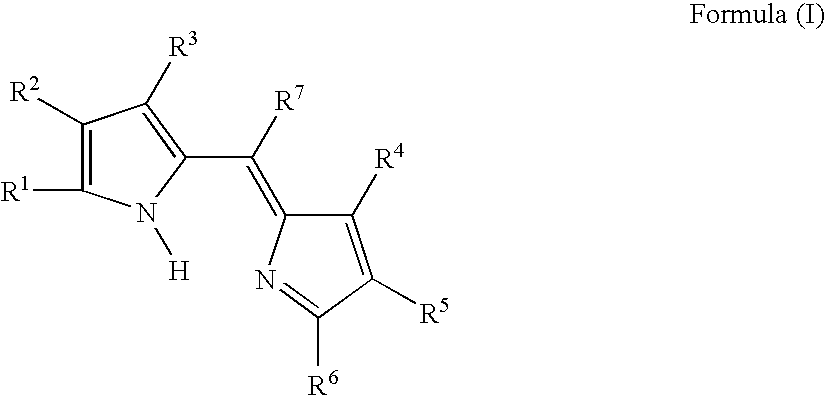
Provided is a colored photosensitive curing composition useful for color filters in primary colors, including blue, green, and red, having a high molar absorption coefficient and allowing a reduction in film thickness and superior color purity and fastness. A colored photosensitive curing composition, comprising, as its colorant, a dipyrromethene-based metal complex compound obtained from a metal or metal compound and a dipyrromethene-based compound represented by the following Formula (I): wherein in Formula (I), R1 to R6 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent group; and R7 represents a hydrogen or halogen atom, or an alkyl, aryl or heterocyclic group.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Preparation method and applications of porous metal organic skeleton material
ActiveCN104370820AGood application effectEasy to operateOther chemical processesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkSolvent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous metal organic skeleton material. The porous metal organic skeleton material comprises at least a metal ion and at least an organic compound that can be matched with the metal ion. The material can be prepared by dissolving metal compounds, organic ligand, and sustained-released alkali into a solvent and carrying out direct water (solvent) thermal synthesis at a certain temperature under a certain pressure so as to obtain the porous metal organic skeleton material. The operation of the provided preparation method is simple, the preparation method is suitable for massive industrial production and is suitable for the synthesis of porous metal organic skeleton membrane, and the provided porous metal organic skeleton material is used to absorb, separate, and store gas.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
metal complex
ActiveCN102282150AImprove overall lifespanImprove efficiencyIndium organic compoundsElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringOrganic electroluminescence
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20080241589A1Improve emission efficiencyIncreased durabilityIndium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSimple Organic CompoundsOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescent device is provided and includes: a pair of electrodes; and an organic compound layer between the pair of electrodes, the organic compound layer including a light-emitting layer. The at least one organic compound layer contains at least one of a compound represent by formula (I) and a compound represented by formula (II).
Owner:UDC IRELAND
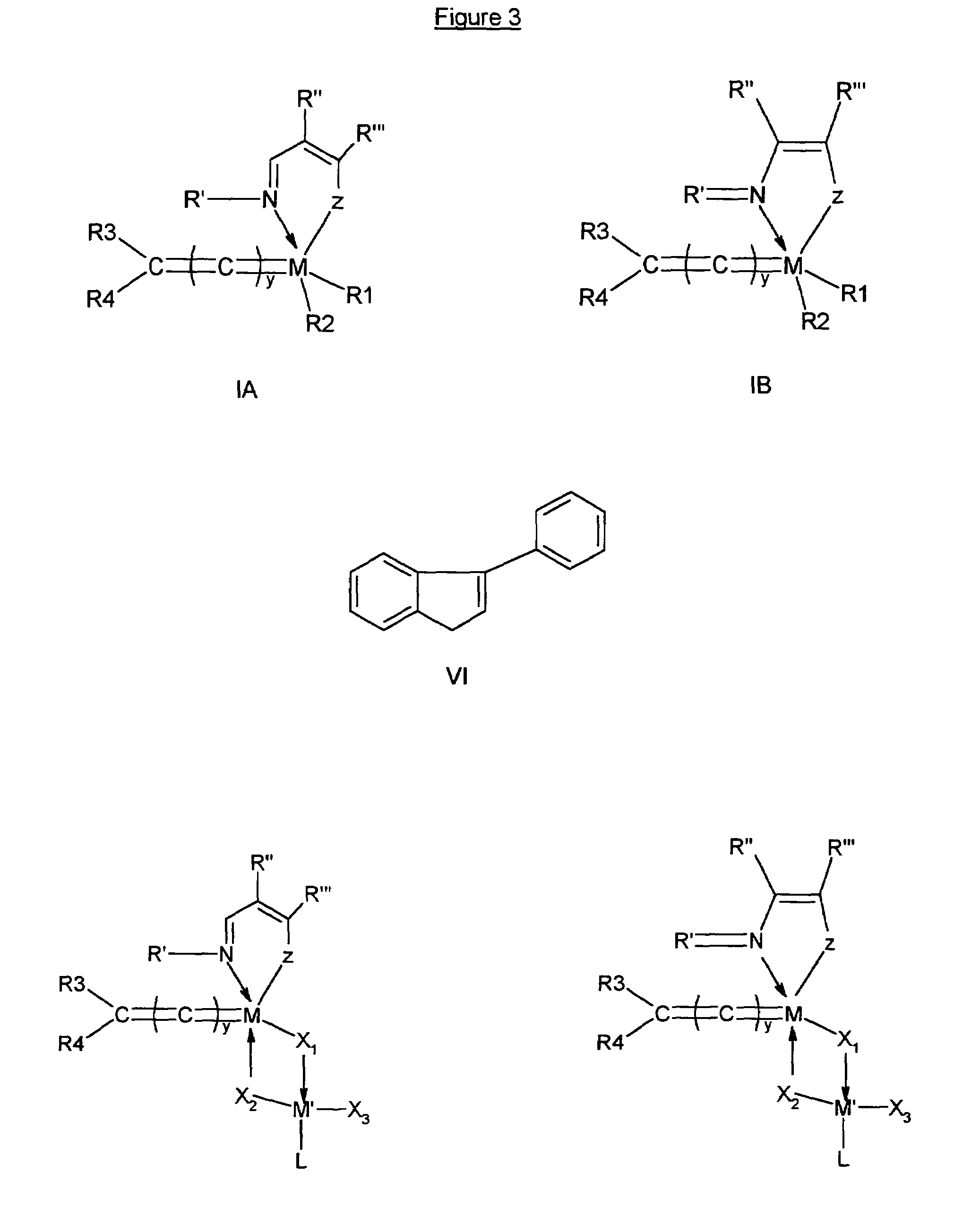
Metal complexes for use in olefin metathesis and atom group transfer reactions
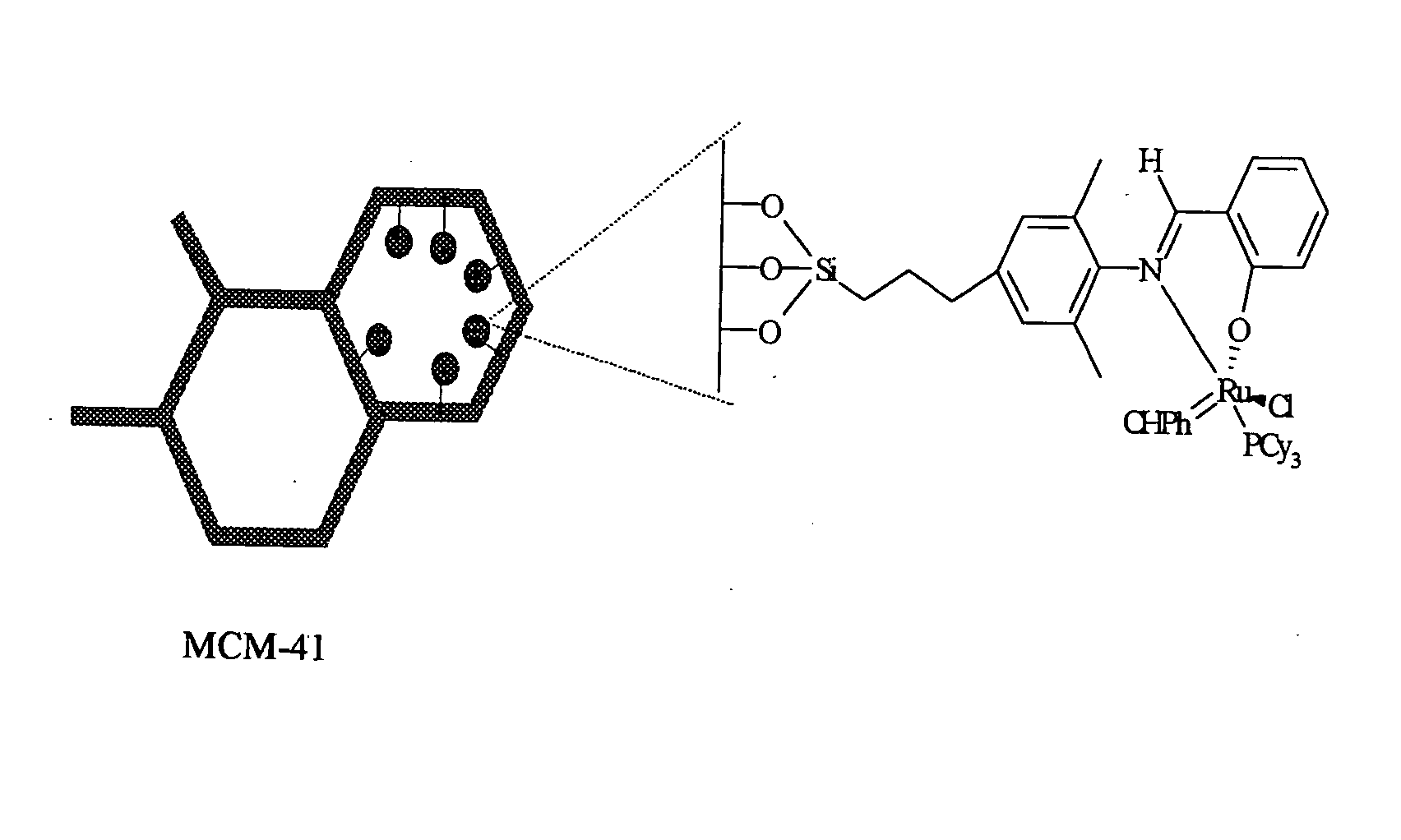
InactiveUS20070185343A1Promote catalysisRuthenium organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsOrganic synthesisAlkene
Improved catalysts useful in a number of organic synthesis reactions such as olefin metathesis and atom or group transfer reactions are made by bringing into contact a multi-coordinated metal complex comprising a multidentate Schiff base ligand, and one or more other ligands, with an acid under conditions such that said acid is able to at least partly cleave a bond between the metal and the multidentate Schiff base ligand of said metal complex, optionally through intermediate protonation of said Schiff base ligand.
Owner:TELENE SAS
Compositions comprising and methods for forming functionalized carbon-based nanostructures
InactiveUS20120116094A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsNanostructureMaterials science
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Cytoprotective compounds, pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations, and methods
InactiveUS20030073712A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicineCongestive heart failure chf
Cytoprotective compounds, many of which are phenolic derivatives characterized by a substituted phenol having certain conjugated bonds, are useful in the treatment of certain ischemic or inflammatory conditions, including but not limited to stroke, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, and skin disorders characterized by inflammation or oxidative damage. They are also useful in the manufacture of pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
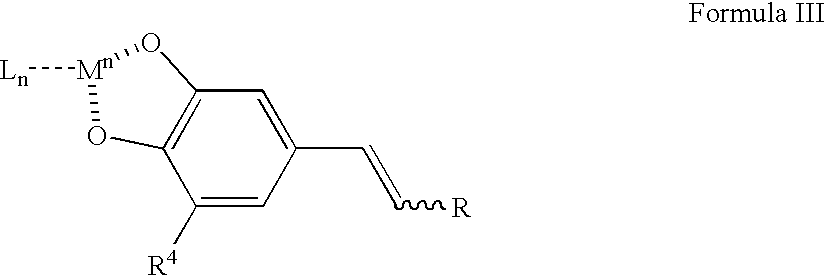
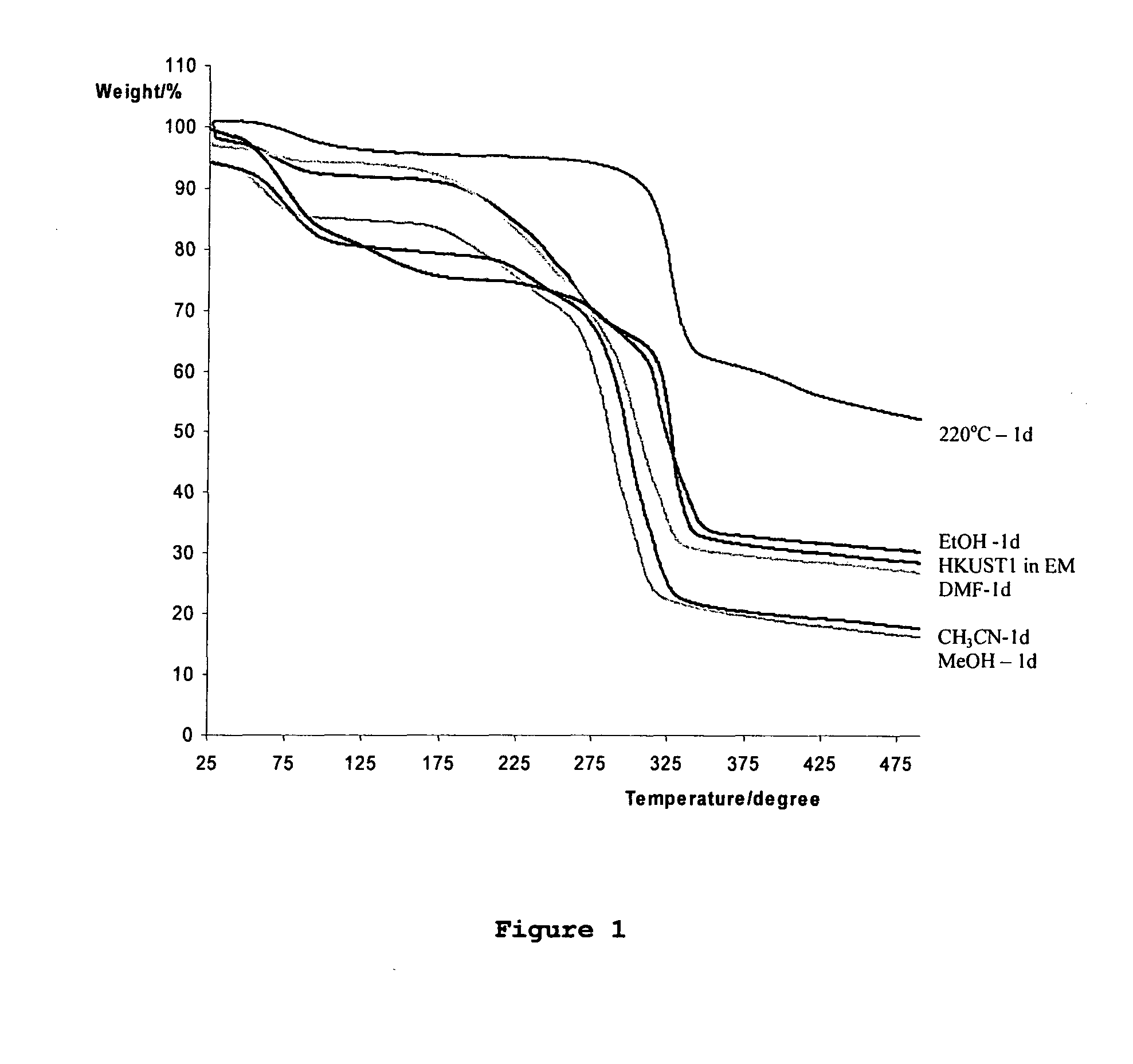
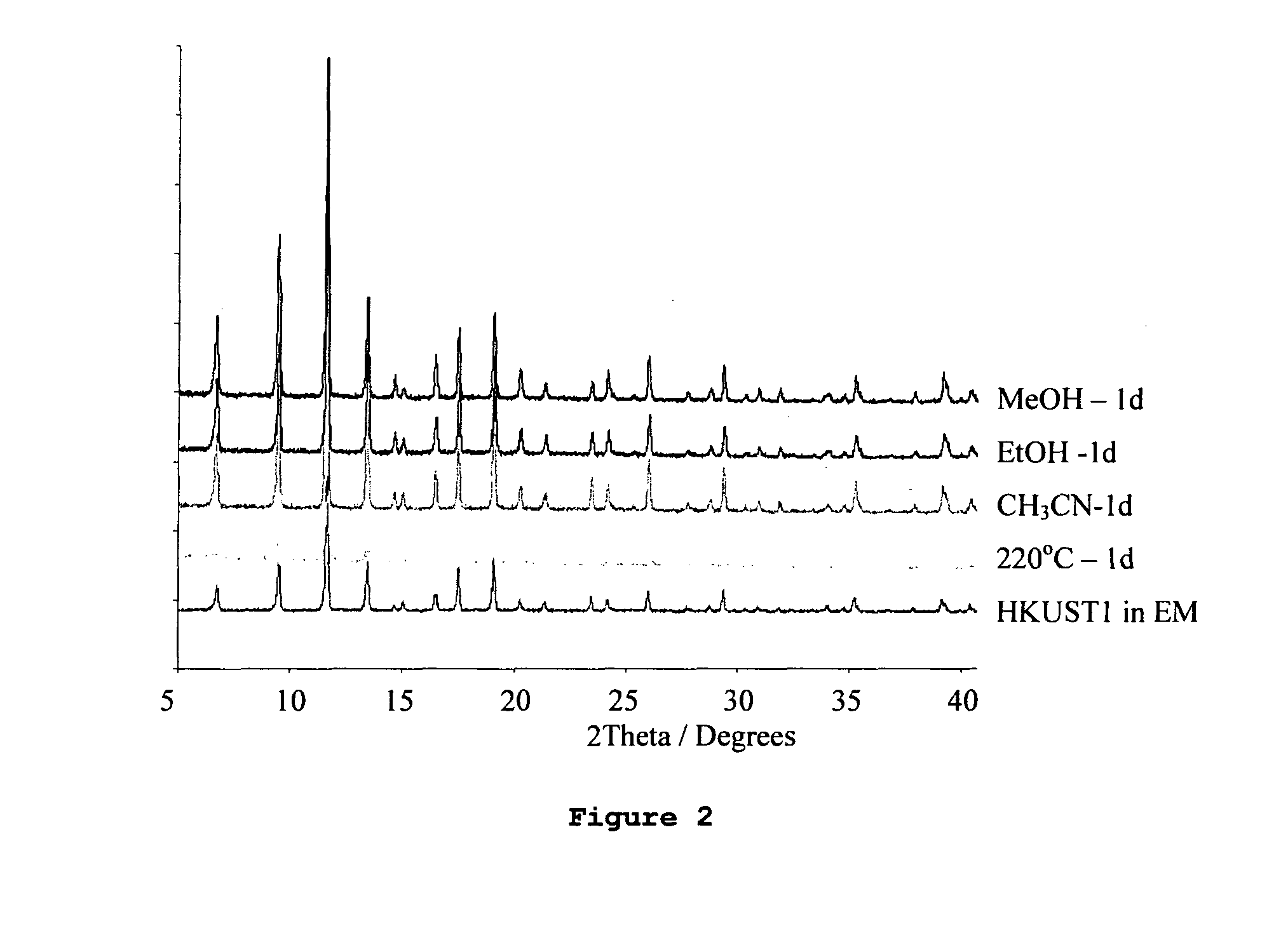
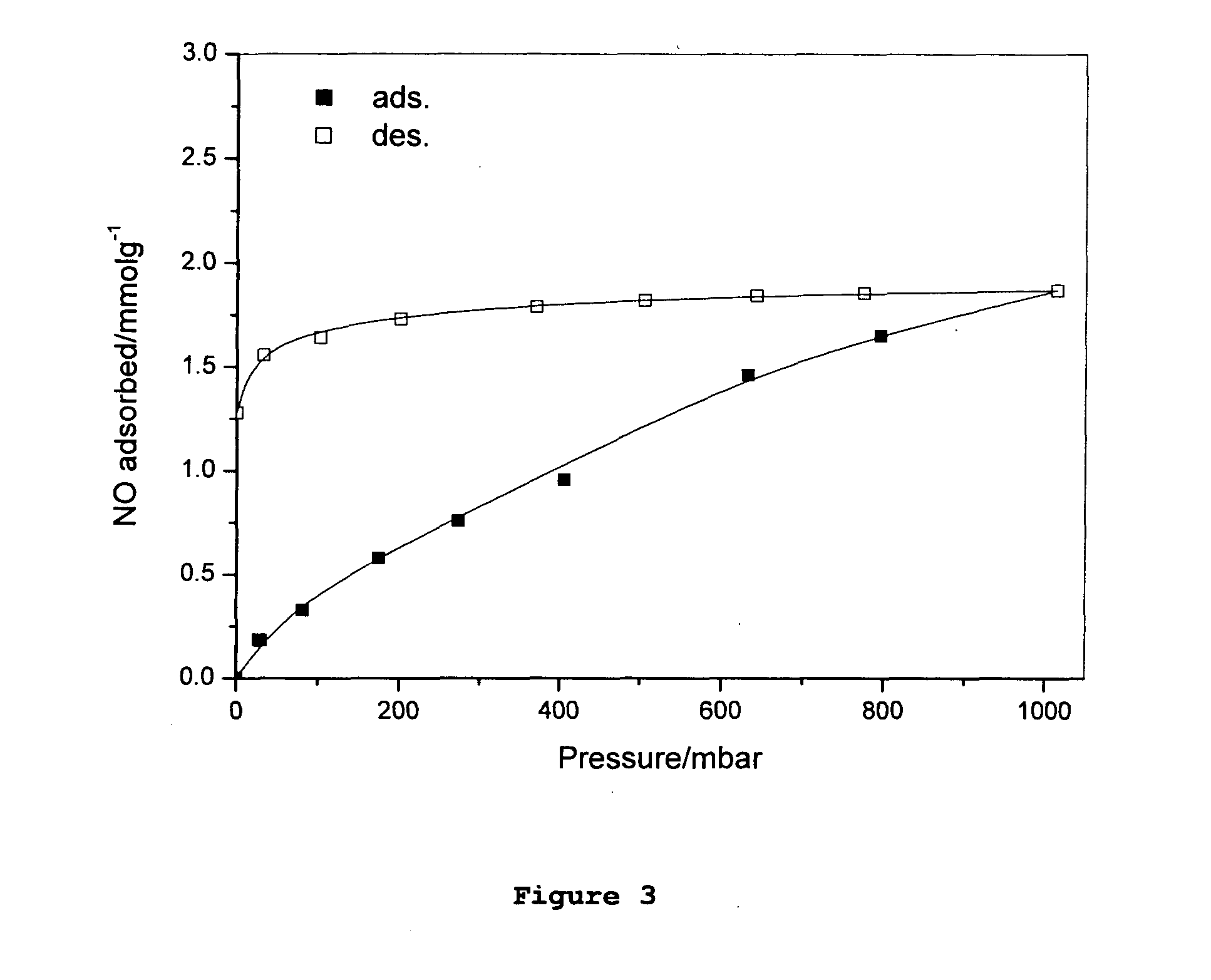
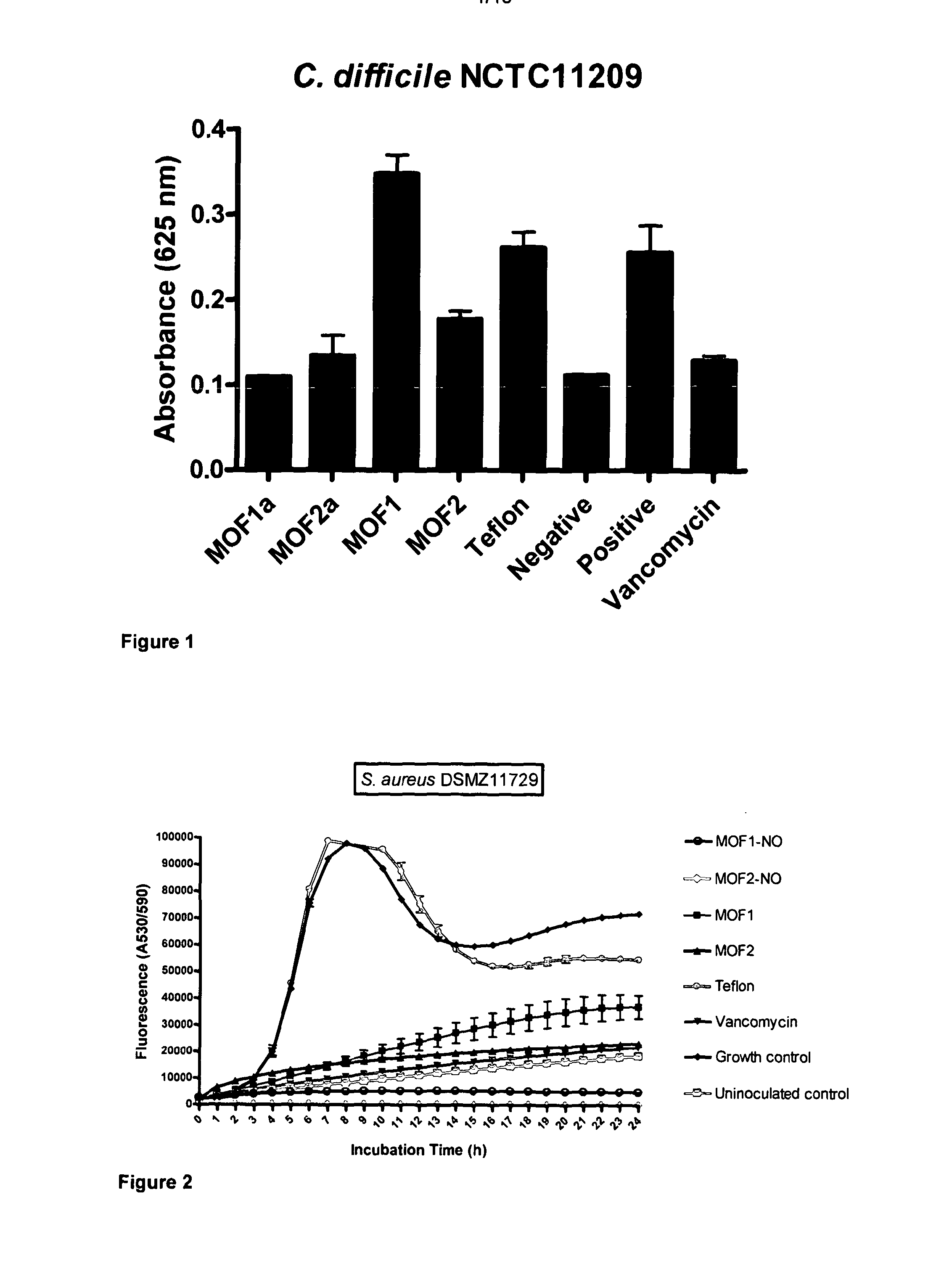
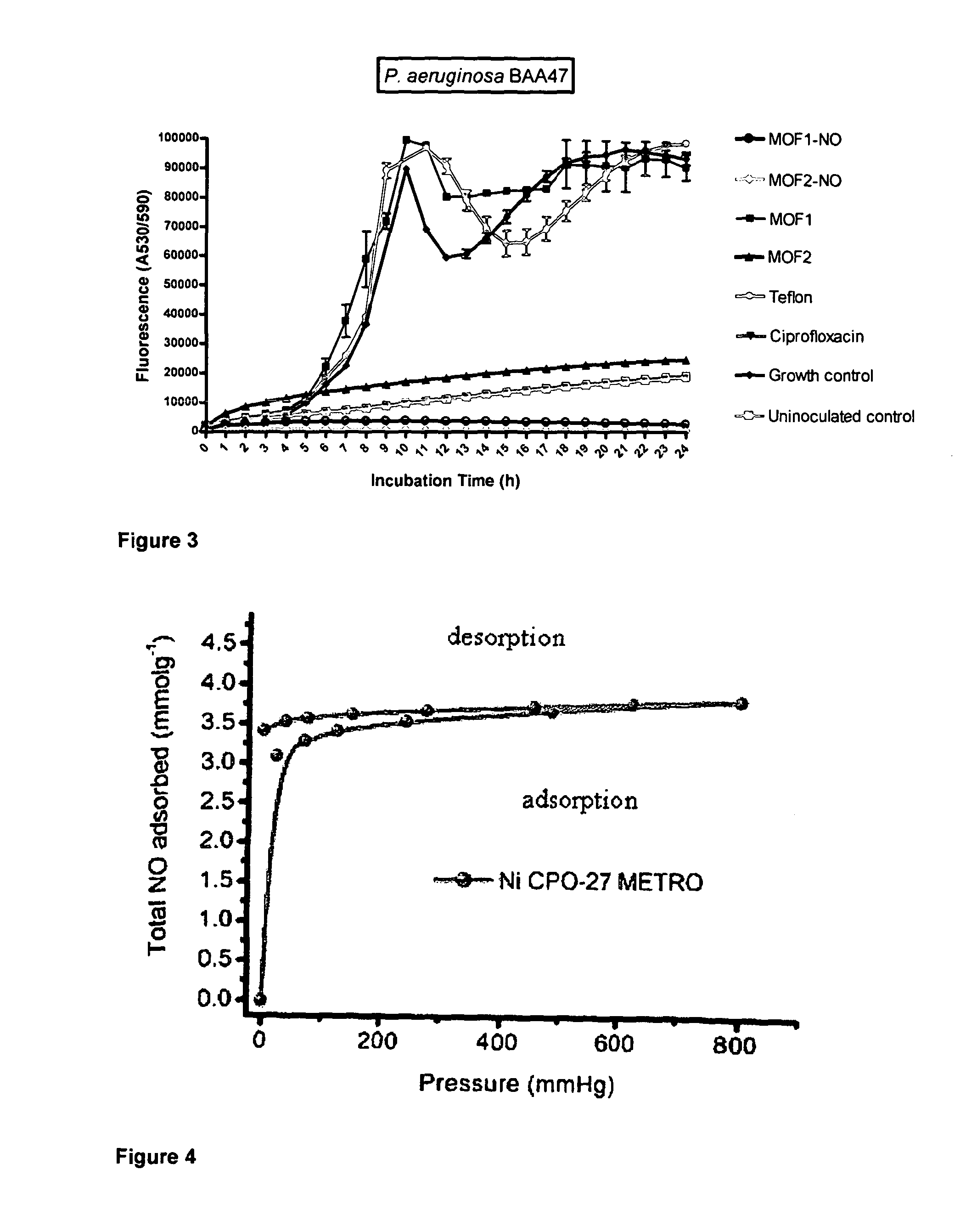
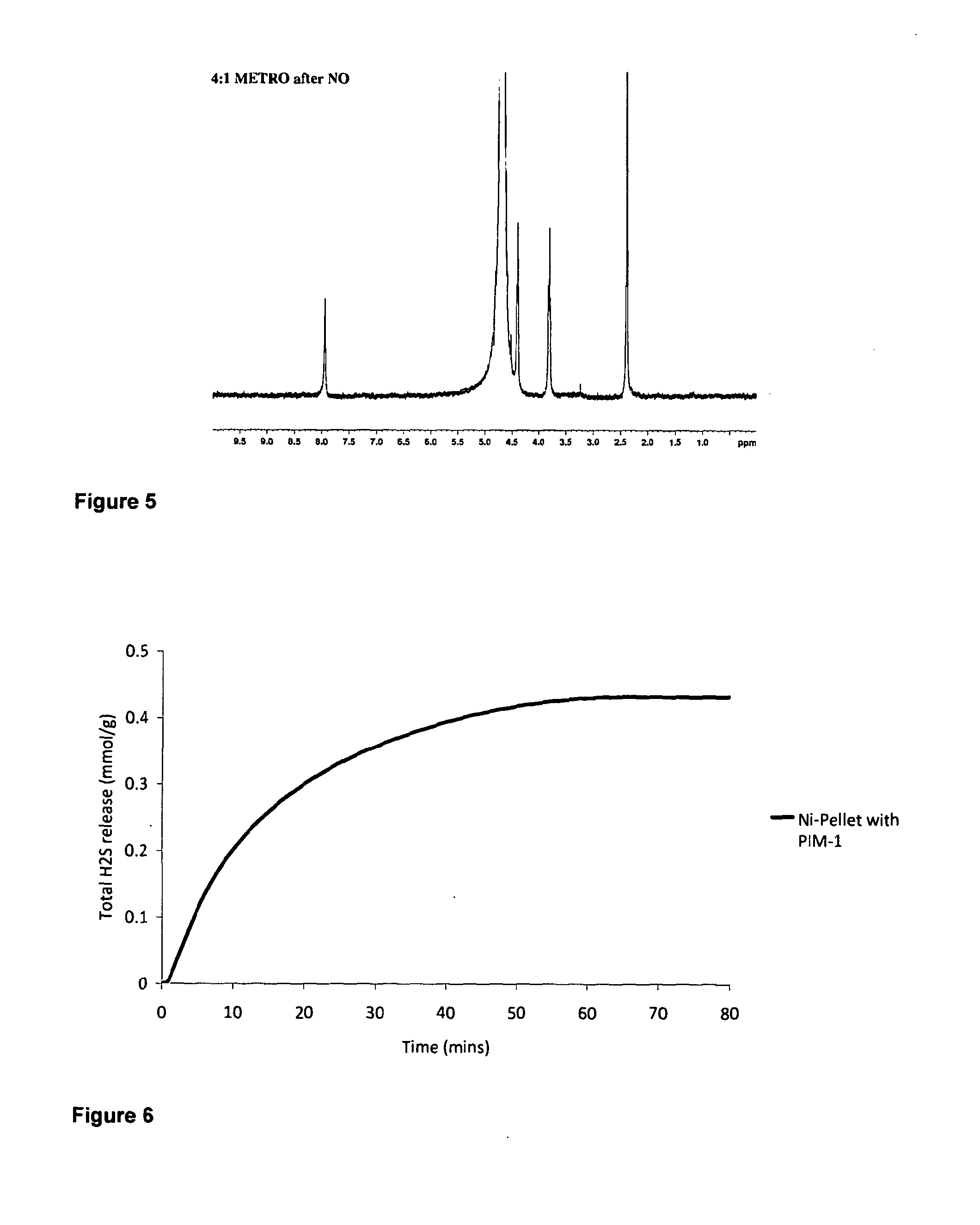
Adsorption and release of nitric oxide in metal organic frameworks
ActiveUS20100239512A1Reduce restenosisImprove adsorption capacityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMetal-organic frameworkNitric oxide
Disclosed are metal organic frameworks that adsorb nitric oxide, NO-loaded metal organic frameworks, methods of preparing the NO-loaded metal organic frameworks, methods of releasing the nitric oxide into a solution or into air, and uses of the metal organic frameworks.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
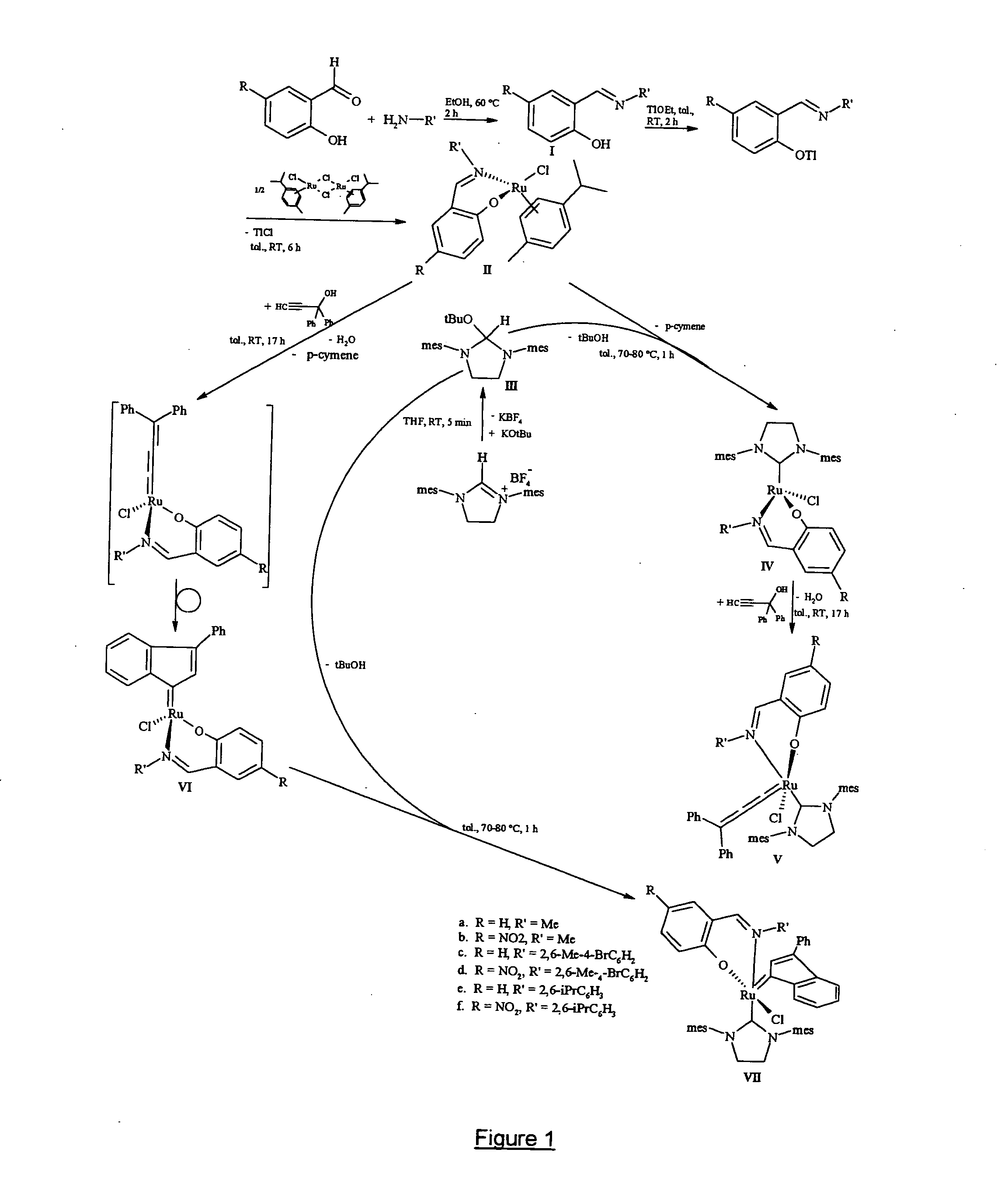
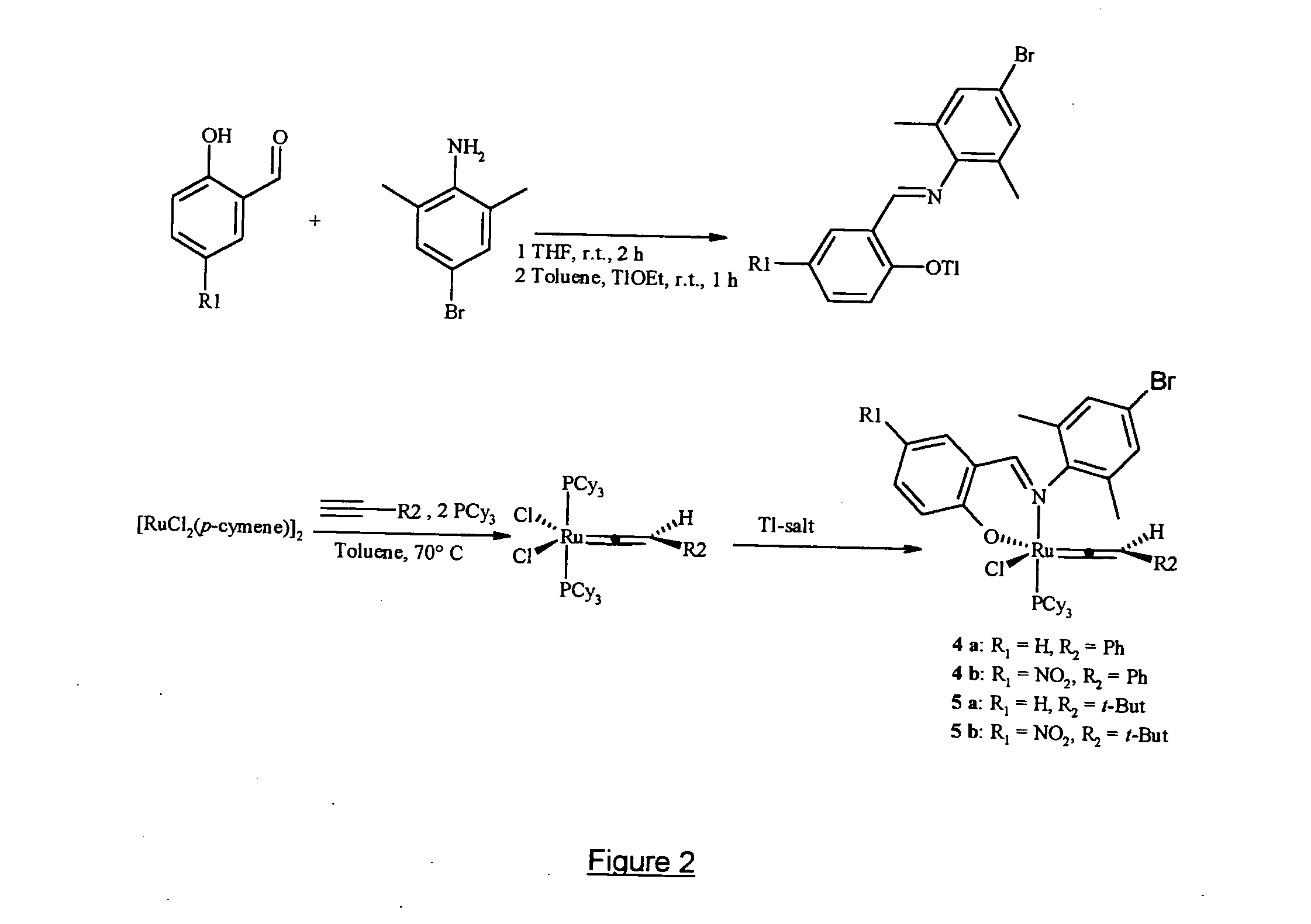
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
InactiveUS20050043541A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic chemistry methodsFuranHigh activity
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Metal complexes, methods, and uses thereof
Metal complexes that exhibit multiple radiative decay mechanisms, together with methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Organometal complex and light-emitting element using the same
ActiveUS7238806B2Reduce power consumptionImprove heat resistanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsArylHydrogen
An organometallic complex according to the present invention comprises a structure represented by the following general formula (1). In the formula, R1 to R5 are any one selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, a halogen element, an acyl group, an alkyl group, an alkoxyl group, an aryl group, a cyano group, and a heterocyclic group, Ar is an aryl group having an electron-withdrawing group or a heterocyclic group having electron-drawing group, and M is an element of Group 9 or an element of Group 10.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
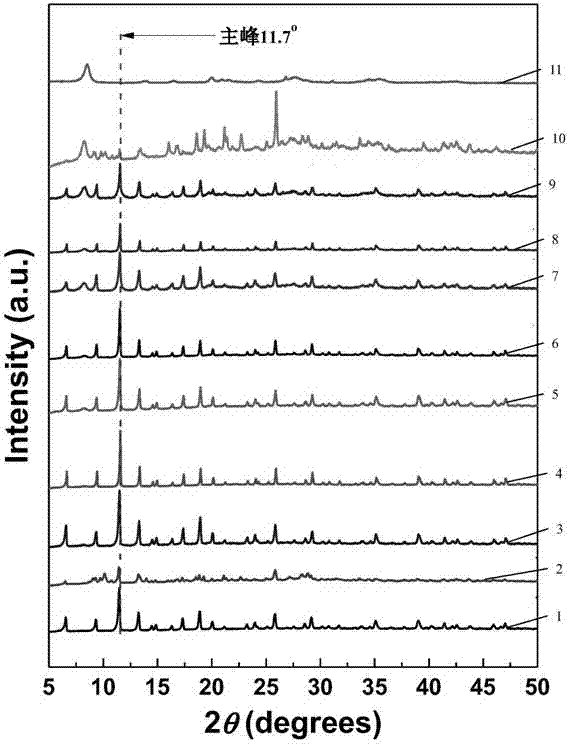
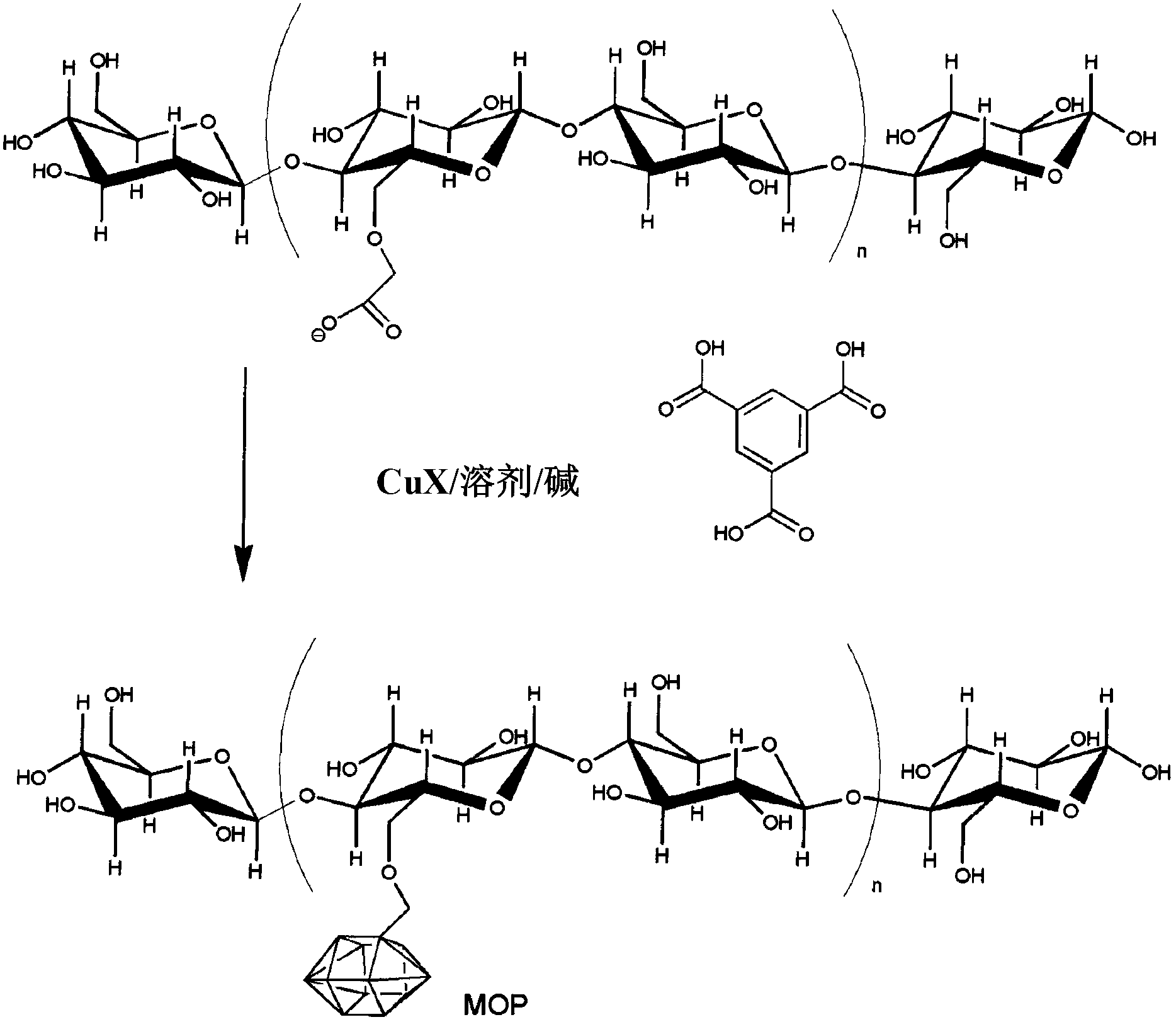
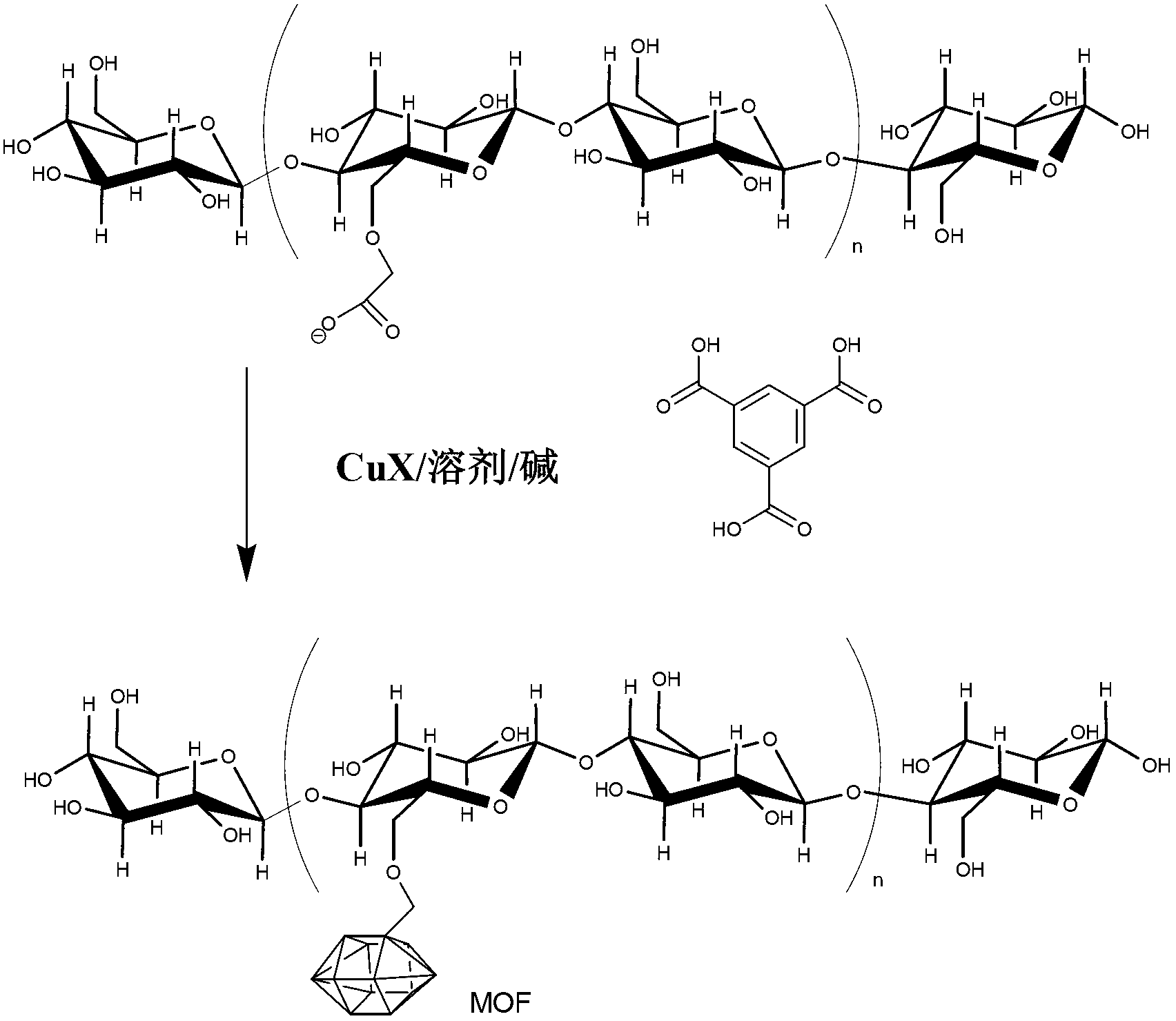
Rapid metal organic framework molecule synthesis method
InactiveUS20090131643A1Rapidly synthesizing MOF moleculesSynthesis fastGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsSynthesis methodsMetal-organic framework
A rapid, simple and versatile metal organic framework molecule (MOF) synthesis method particularly adapted to make non-linear MOFs includes heating MOF precursors, such as a metal or metal oxide and an organic ligand, in a microwave oven for a period sufficient to achieve crystallization. Microwave-assisted MOF synthesis yields high quality MOF crystals in a reaction time ranging from about 5 seconds to about 2.5 minutes, compared to hours and days required in conventional solvothermal and hydrothermal methods. In addition, microwave assisted methods provide MOF materials with uniform crystal size and well-defined shape. Further, microwave synthesis of MOFs allows the size and shape of MOF crystals to be tailored for use in a wide range applications by manipulating reaction conditions. Secondary growth processes may also be employed to grow larger crystals using seeds obtained from microwave-assisted synthesis methods.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Class of volatile compounds for the deposition of thin films of metals and metal compounds
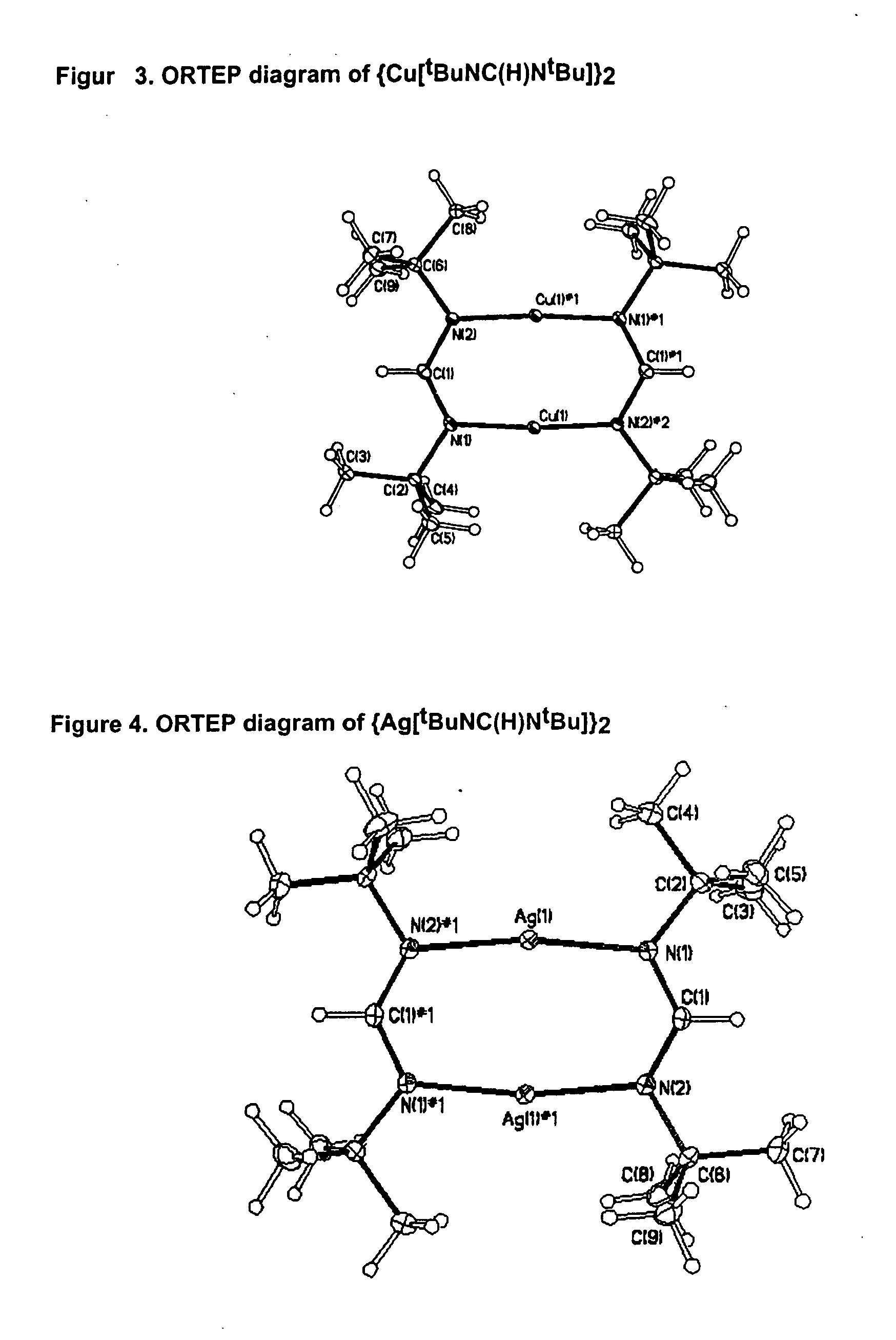
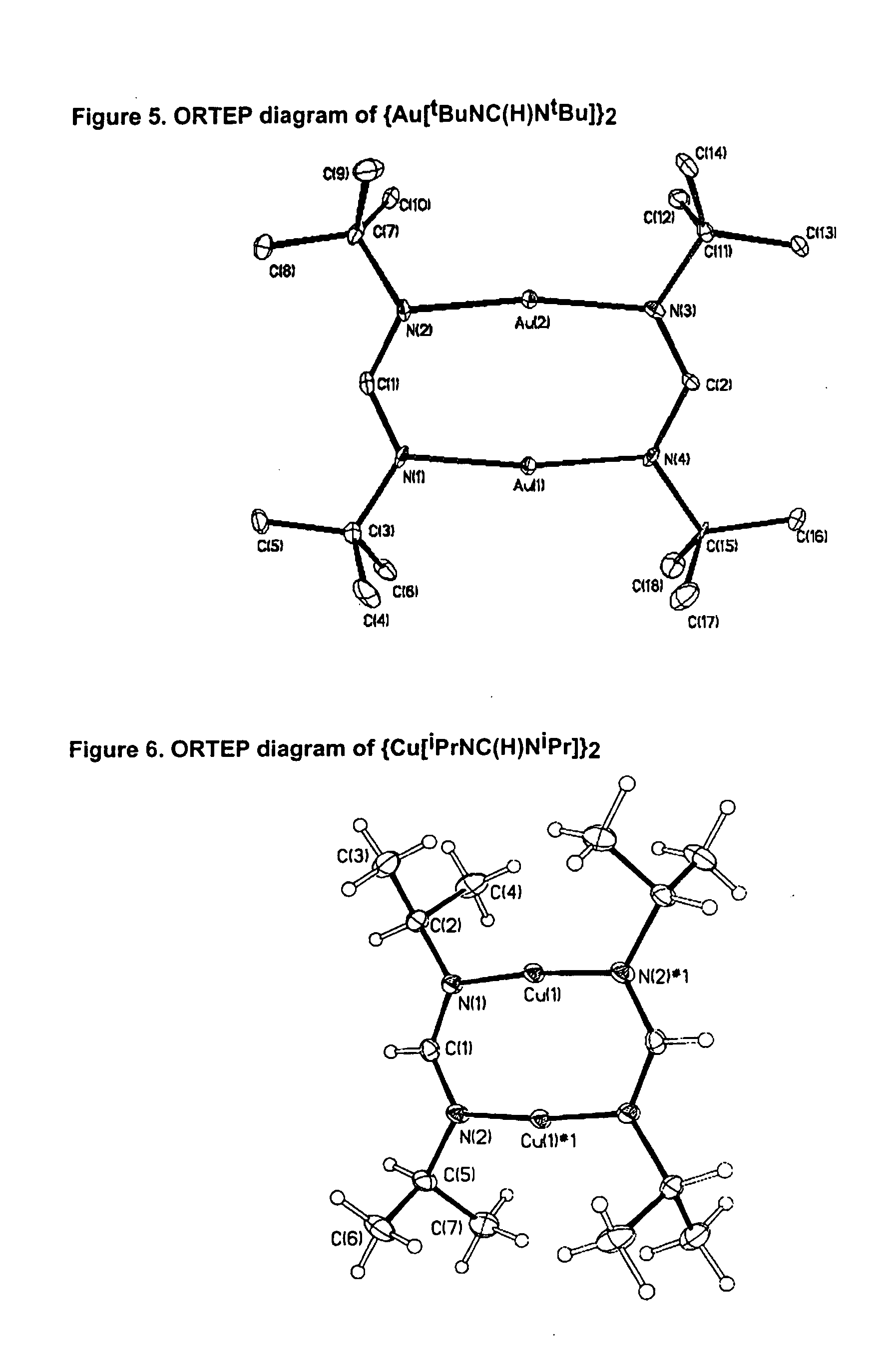
The invention provides an organometallic complex, containing oxygen free organic ligands, for the deposition of a metal, preferably copper, silver or gold, and preferably by way of chemical vapor deposition. The organometallic complex having the formula [(Do)nMLx]k where M is a metal preferably selected from the group consisting of Cu, Ag and Au; Do is selected from the group comprising ethers, phosphines, olefins, sulfides, pyridines, carbonyl, hydroxyl, cyclopentadiene, benzene derivatives, allyls, alkyls, amines, polyamines, aniline derivatives, cyclooctadiene and combinations thereof; n is an integer having a value from 0 to 4; k is an integer having a value from 1 to 4; x is an integer having a value from 1 to 4; and L is an amidinate ligand of the formula R1—NC(R2)N—R3 where R1, R2 and R3 are selected from the group consisting of alkyls, allyls, aryls, heteroaryls, hydrogen, non-metals and metalloids; and where R1, R2 and R3 are different or the same.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Preparation method of metal-organic framework compound with hierarchical pore structure
InactiveCN104151336AGuaranteed stabilityMaintain crystal shapeCopper organic compoundsZinc organic compoundsSolventIon
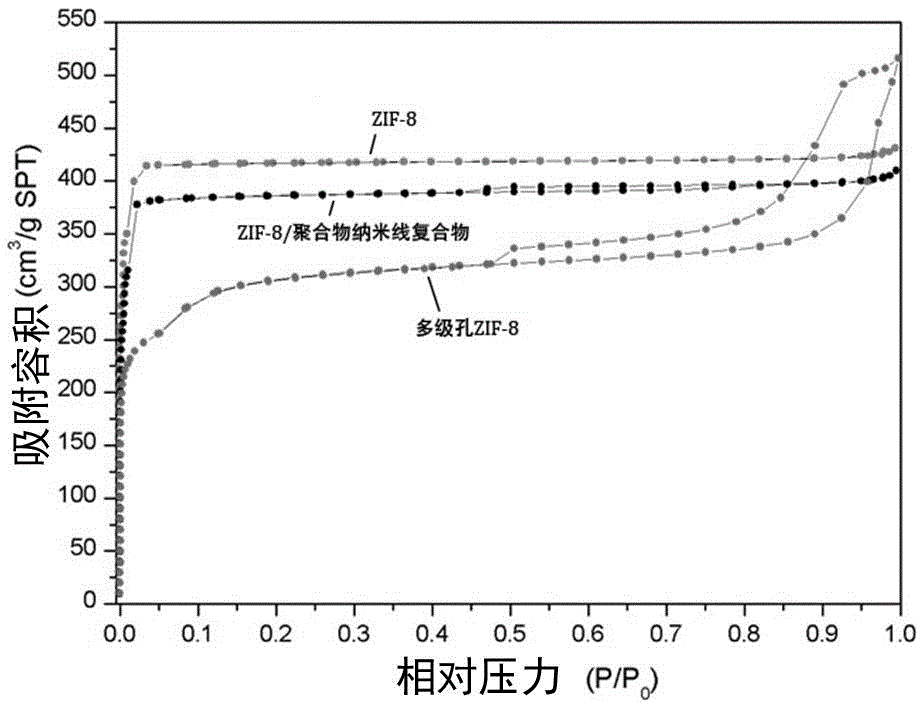
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanocomposite materials and in particular relates to a preparation method of a metal-organic framework compound with a hierarchical pore structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, self-assembling a diblock copolymer in a solvent to form a flexible polymer nanowire with a core-shell structure, and cross-linking cores to obtain a polymer nanowire with a stable solvent; adding metal ions and organic ligands into a nanowire solution to form a mixed solution; crystallizing at the room temperature to obtain a metal-organic framework / core-shell structure polymer nanowire compound; calcining to remove the polymer nanowire to obtain a hierarchical pore material with MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) micropores, small mesopores formed after calcination of a shell layer of the polymer nanowire and large mesopores formed after calcinations of a core layer. According to the MOFs material with the hierarchical pore structure, the advantages of the micropores and the micropores are combined, the mass transfer speed of the MOFs material is improved, relatively large molecules can conveniently enter the MOFs material, and the application potential of the MOFs material in the field of catalysis, adsorption and the like is improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
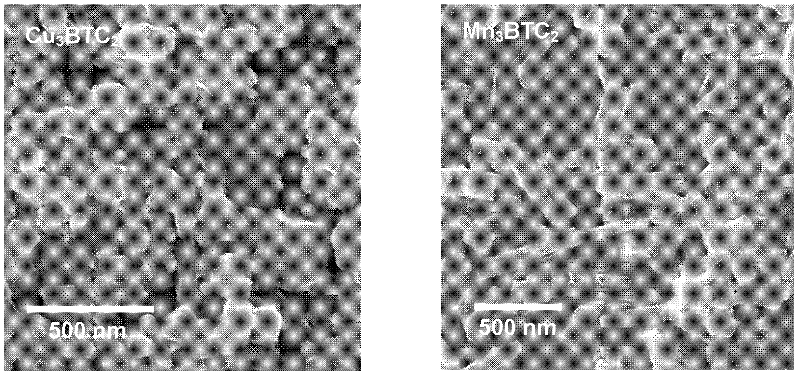
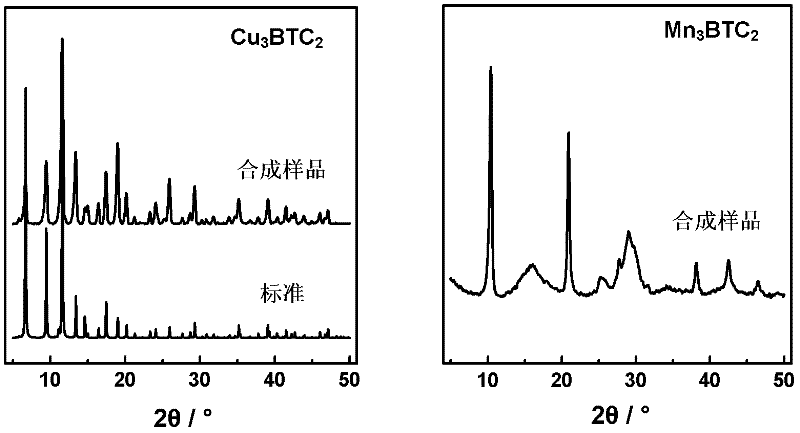
Method for synthesizing BTC (1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid)-based nanoscale organometallic framework material
InactiveCN102336774AAvoid pollutionAvoid wastingCopper organic compoundsNickel organic compoundsMetal-organic frameworkNano devices
The invention discloses a method for rapidly synthesizing a BTC (1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid)-based nanoscale organometallic framework material at room temperature. The nanomaterial is prepared by the following steps: mixing metal acetate aqueous solution with BTC solution at room temperature, and reacting to obtain BTC-based organometallic framework nanoparticles. The method is rapid, simple and energy-saving; the yield is high; the used raw materials and solvents are inexpensive and easily available; the safety problem of commonly used nitrate is not caused; the method is favorable to the industrial production and has wide application prospects in the fields of catalysis, adsorption, drug carriers, building of nano devices and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-stability metal organic skeleton hybrid material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103694260AHigh hydrothermal stabilitySimple methodOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCopper organic compoundsMass ratioHybrid material
The invention discloses a high-stability metal organic skeleton hybrid material. The metal organic skeleton hybrid material has high hydrothermal stability, and comprises metal organic skeleton and attapulgite, wherein the mass ratio of the attapulgite to the metal organic skeleton is (0.005-0.7):1.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Coordination polymer material with multistage pore passage structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102161671ALarge hole sizeEasy to prepareCopper organic compoundsNickel organic compoundsSelf-assemblyChemical engineering
The invention provides a coordination polymer material with a multistage pore passage structure and a preparation method thereof. The coordination polymer material with a multistage pore passage structure is internally provided with the multistage pore passage structure, the multistage pore passage structure is a microporous and / or mesoporous and / or macroporous multistage pore passage structure which is formed by the self assembly between the metal ion and the organic ligand, the apertures of the micropores are less than or equal to 2nm, the apertures of the mesopores are from 2nm to 50nm, and the apertures of the macropores are more than 50nm. The coordination polymer material with a multistage pore passage structure is large in specific surface, the large-size organic ligand does not need to be synthesized, and the coordination polymer material with larger porous sizes can be obtained without the template agent and the pore assisting agent, so that the invention is simple in preparation method, and low in cost.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Display, and Electronic Device
InactiveUS20110315968A1Easy injectionReduce the driving voltageCopper organic compoundsSolid-state devicesAlkaline earth metalConcentration gradient
In the light-emitting element in which a plurality of EL layers is separated from each other by a charge generation layer, provided are an electron relay layer in contact with an anode side of the charge generation region and an electron transport layer in contact with the electron relay layer. The electron transport layer contains an alkaline earth metal. A concentration gradient of the alkaline earth metal contained in the electron transport layer is such that the concentration of the alkaline earth metal becomes lower from an interface between the electron transport layer and the electron relay layer to the anode.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
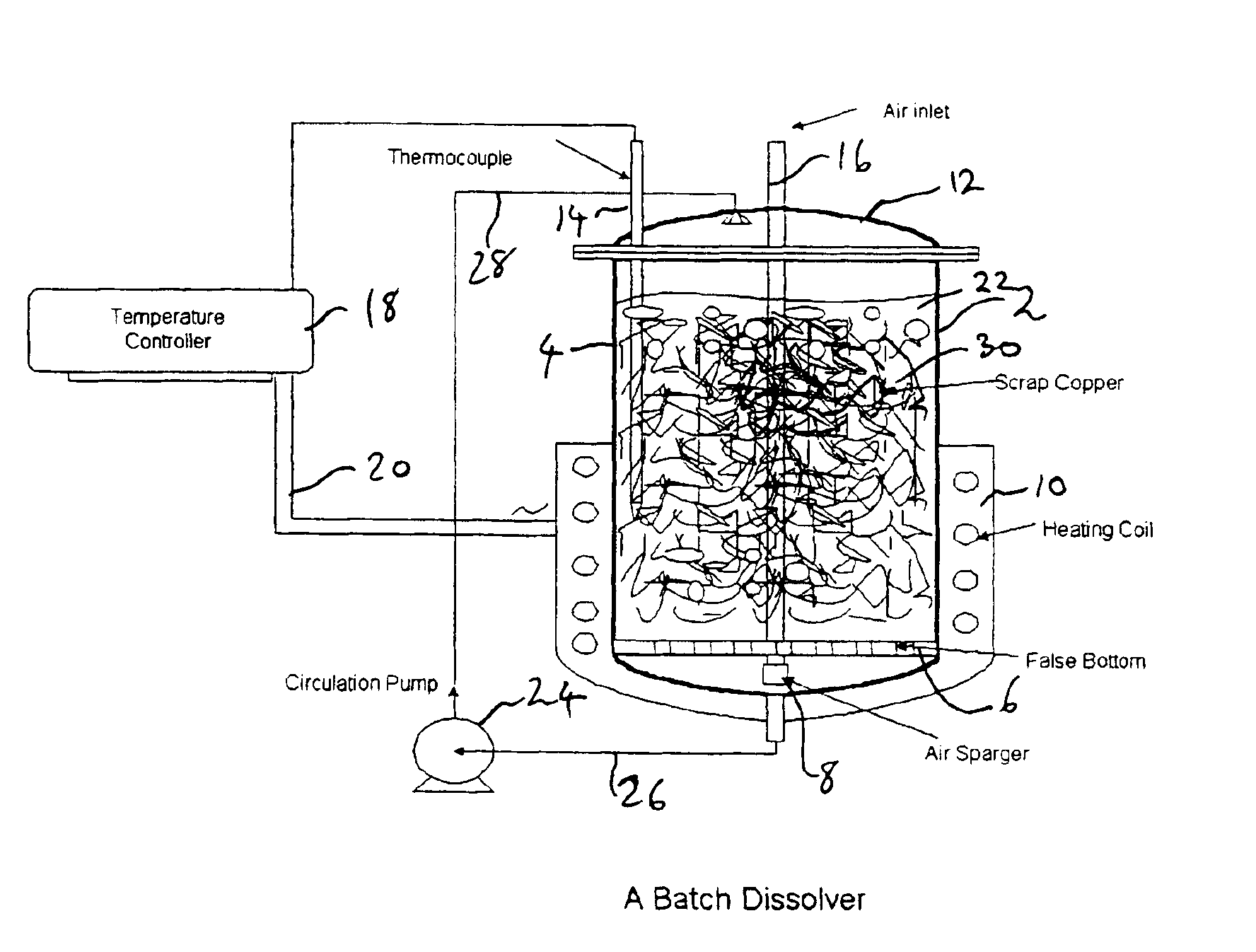
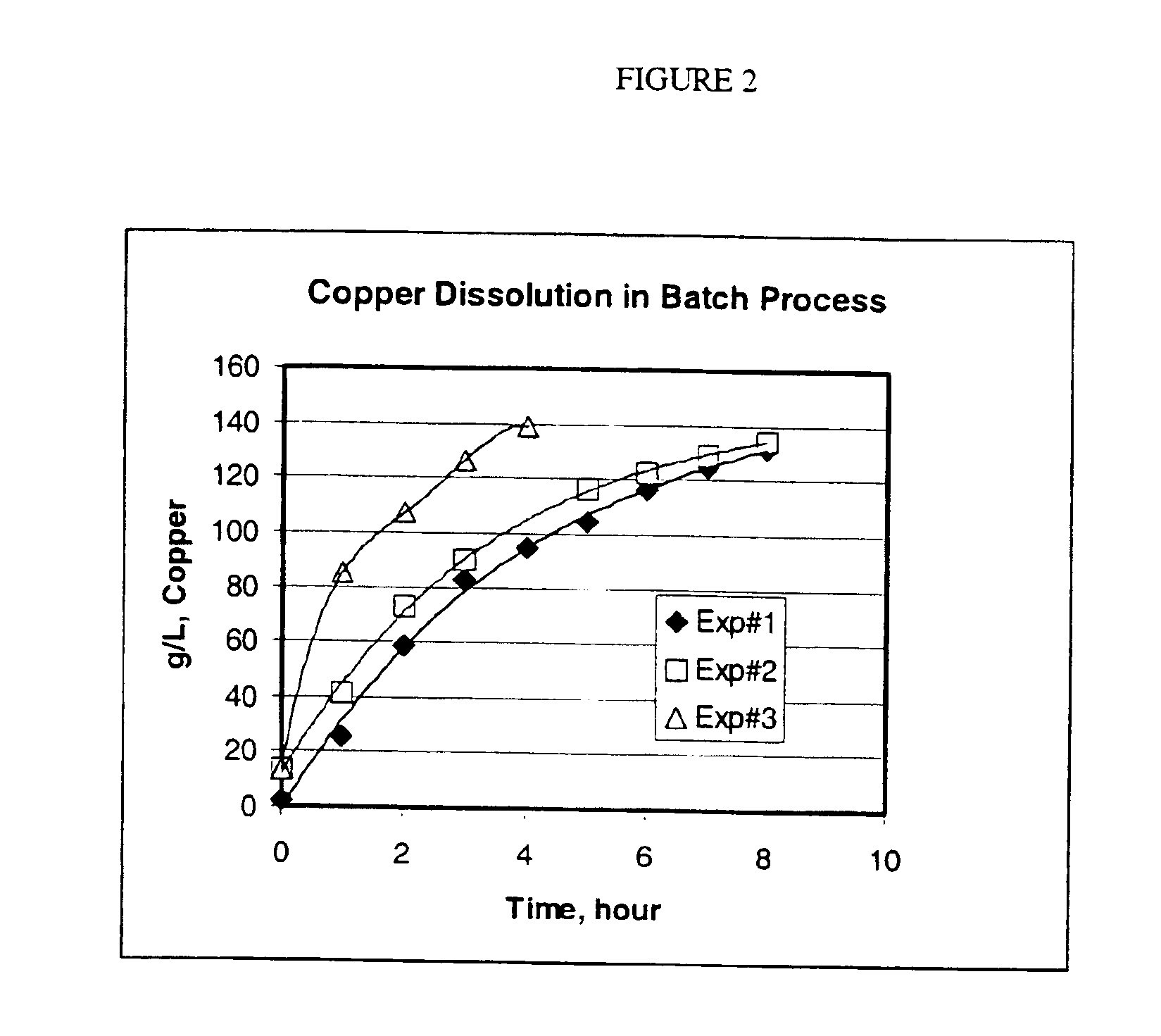
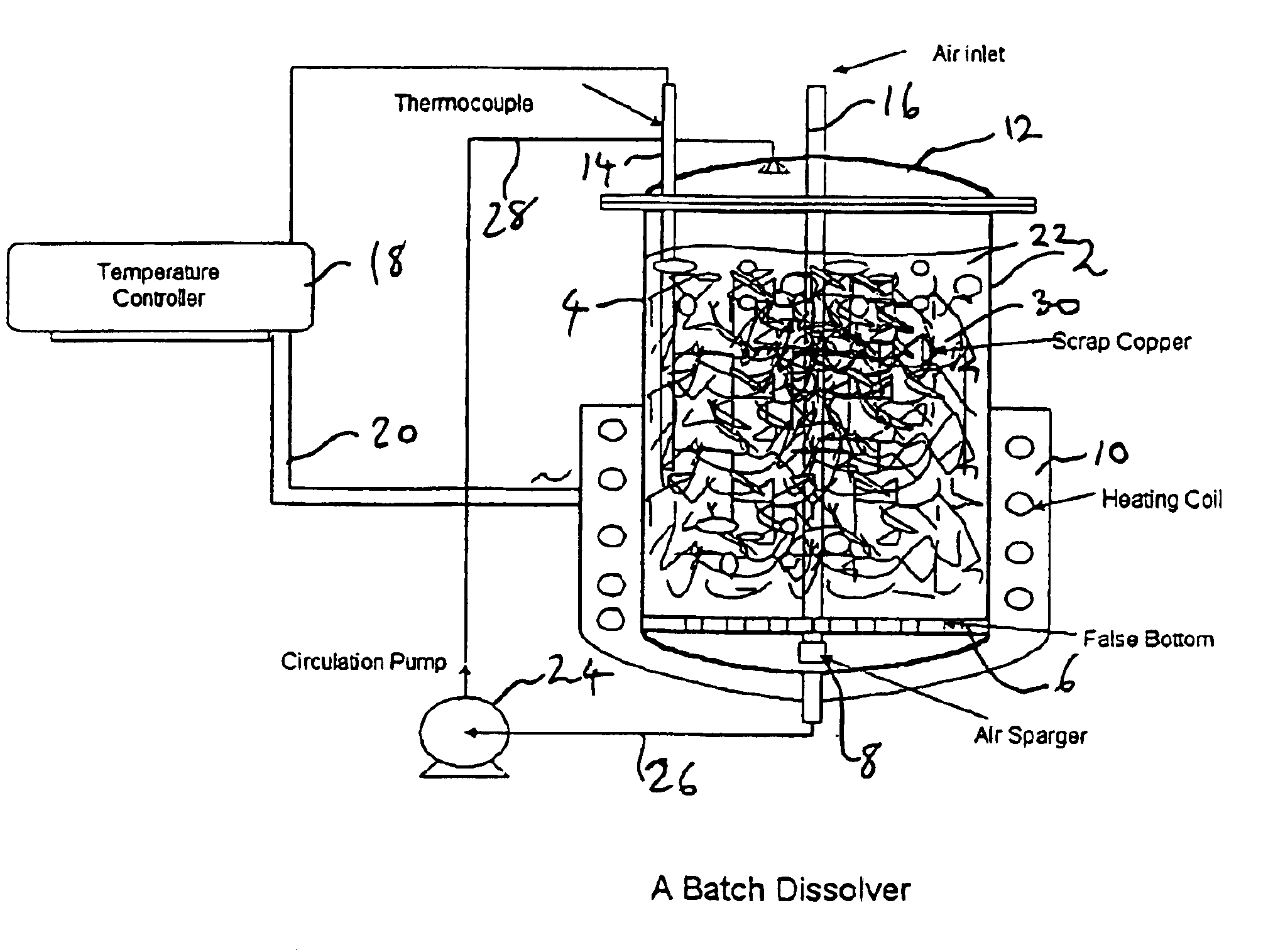
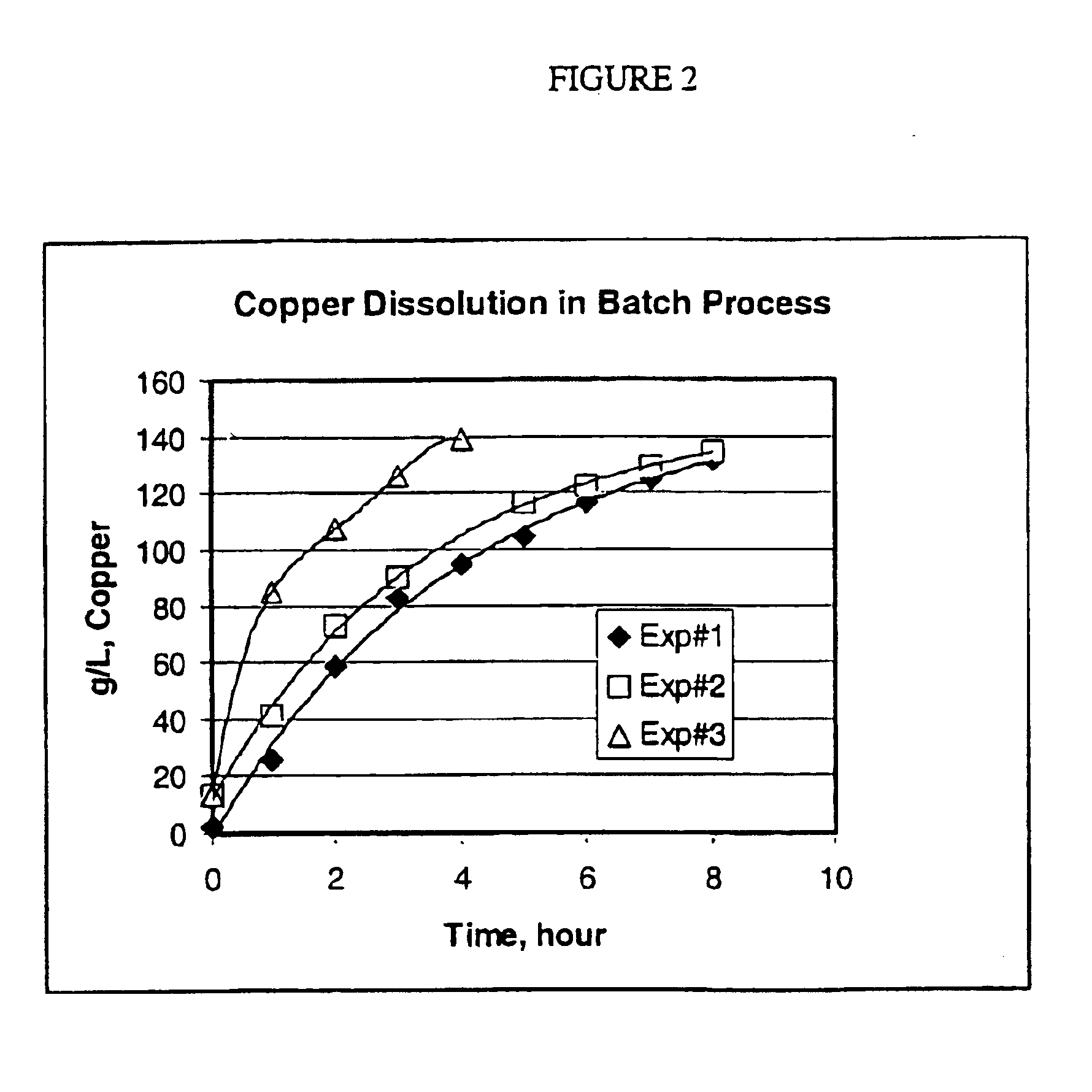
Process for the dissolution of copper metal
InactiveUS6905531B2Efficient productionCopper organic compoundsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processPregnant leach solutionDissolution
Process for producing a copper-containing aqueous solution, in which a copper mass is dissolved in the presence of an oxidant in an aqueous leach liquor containing monoethanolamine and (HMEA)2CO3. The leach liquor is produced by partially carbonating the monoethanolamine.
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
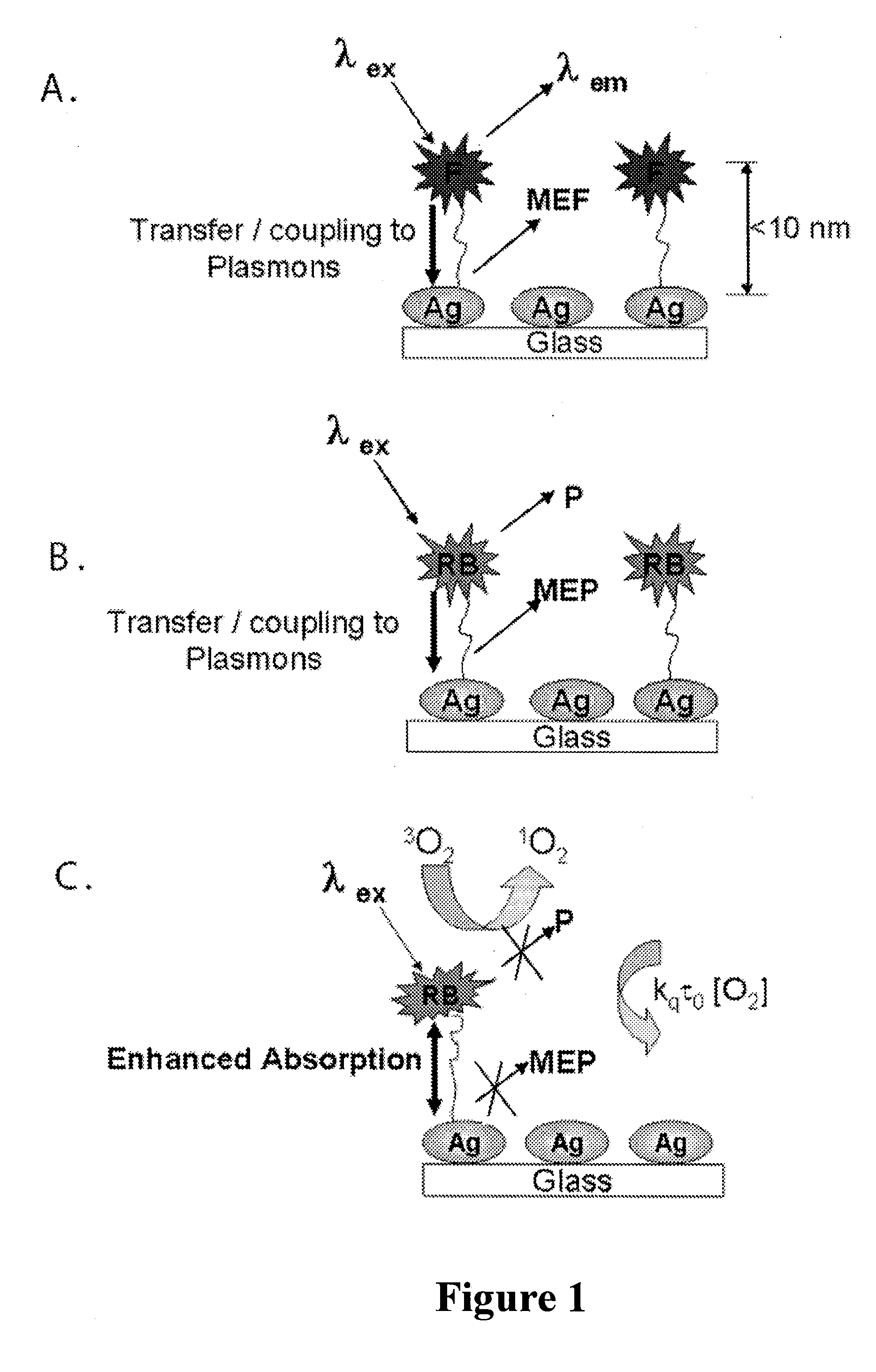
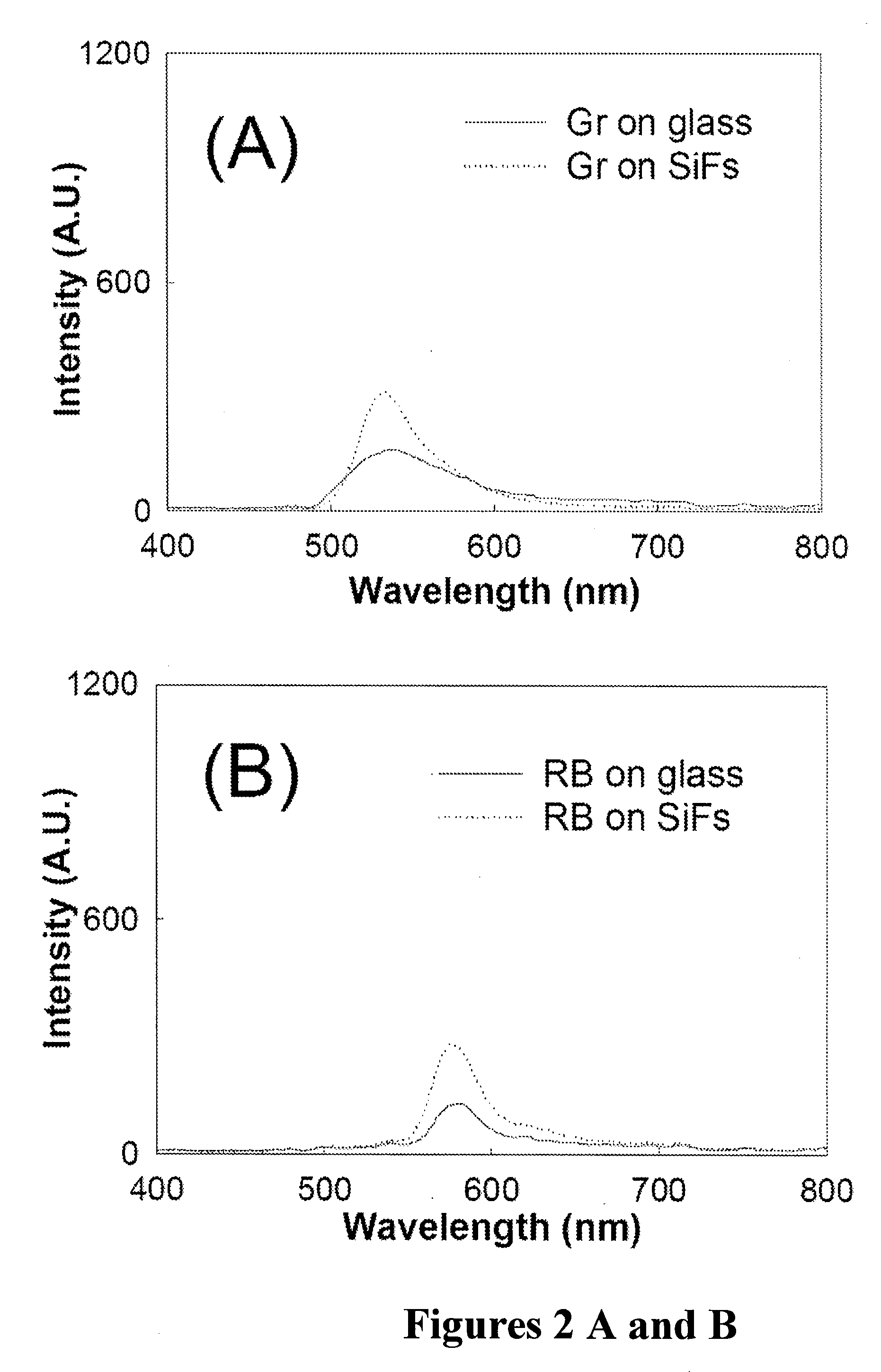
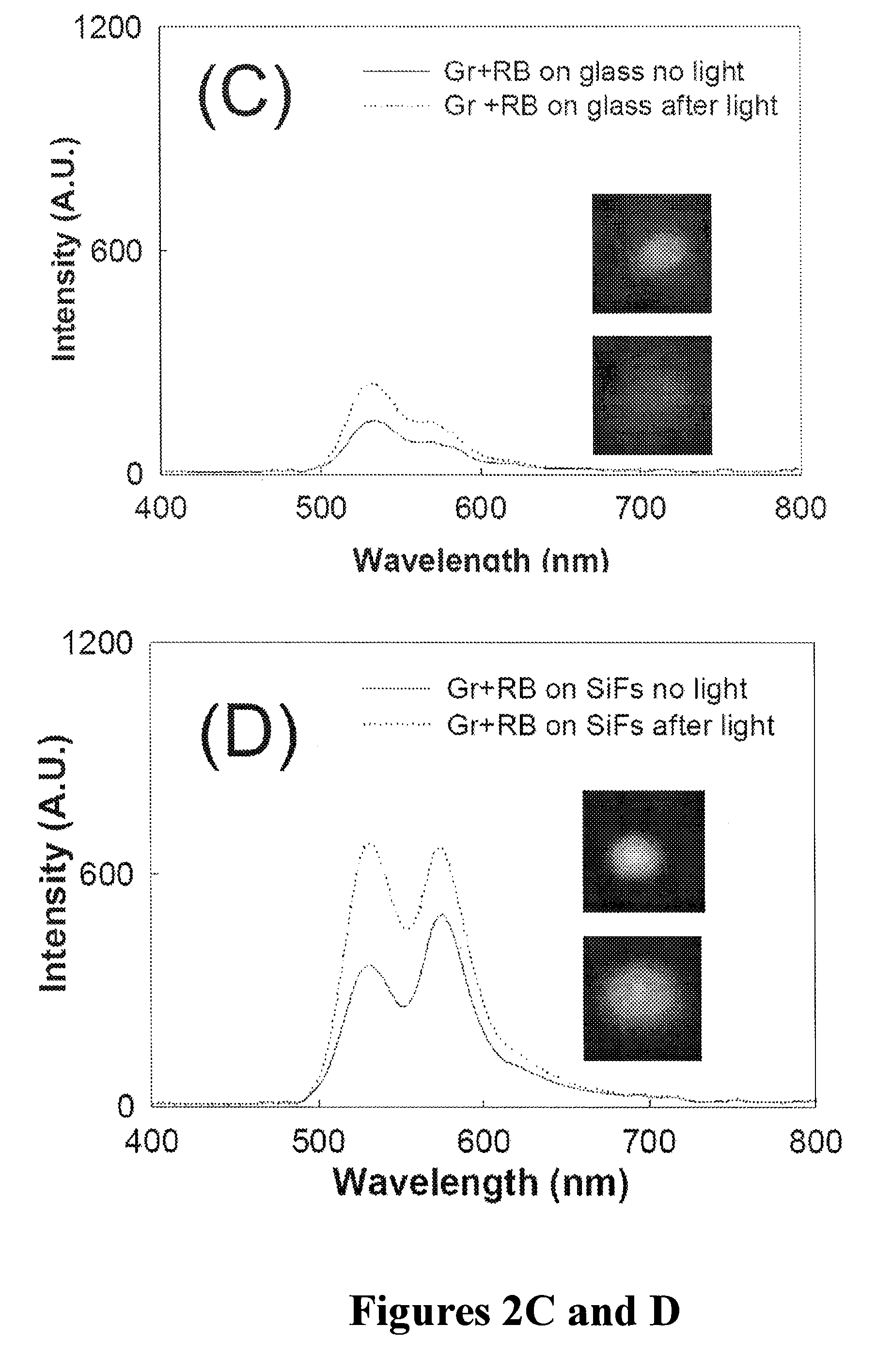
Plasmonic engineering of singlet oxygen and/or superoxide generation
ActiveUS20080215122A1Increase triplet yieldIncreased oxygen generationBiocideGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsEnergy absorptionSuperoxide
The present invention provides for a method to increase the triplet yield of a photosensitizer by the coupling to metal surface plasmons which leads to increased singlet oxygen generation by electric field enhancement or enhanced energy absorption of the photosensitizer. The extent of singlet oxygen enhancement can be tuned for applications in singlet oxygen based clinical therapy by modifying plasmon coupling parameters, such as metallic nanoparticle size and shape, photosensitizer / metallic nanoparticle distance, and the excitation wavelength of the coupling photosensitizer.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Metal Complexes, Methods, and Uses Thereof
Metal complexes that exhibit multiple radiative decay mechanisms, together with methods for the preparation and use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Labeled macrophage scavenger receptor antagonists for imaging atherosclerosis and vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS20020127181A1Copper organic compoundsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismArtery diseasesCholesterol
Detectably labeled macrophage scavenger receptor antagonists useful for the diagnosis and monitoring of various cardiovascular diseases including but not limited to atherosclerosis, vulnerable plaque, coronary artery disease, renal disease, thrombosis, transient ischemia due to clotting, stroke, myocardial infarction, organ transplant, organ failure and hypercholesterolemia.
Owner:LANTHEUS MEDICAL IMAGING INC
Metal organic framework modified materials, methods of making and methods of using same
InactiveCN103338858AGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesProductsFiberMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a MOF (metal organic framework)-modified materials and methods of making and methods of using same. The MOFs are covalently bound to the materials. Examples of suitable materials include fibers and thin films. The MOF-modified materials can be made by forming MOFs in situ such that they are covalently bound to the materials. The MOF-modified materials can be used in methods where gases and / or toxic chemicals are absorbed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
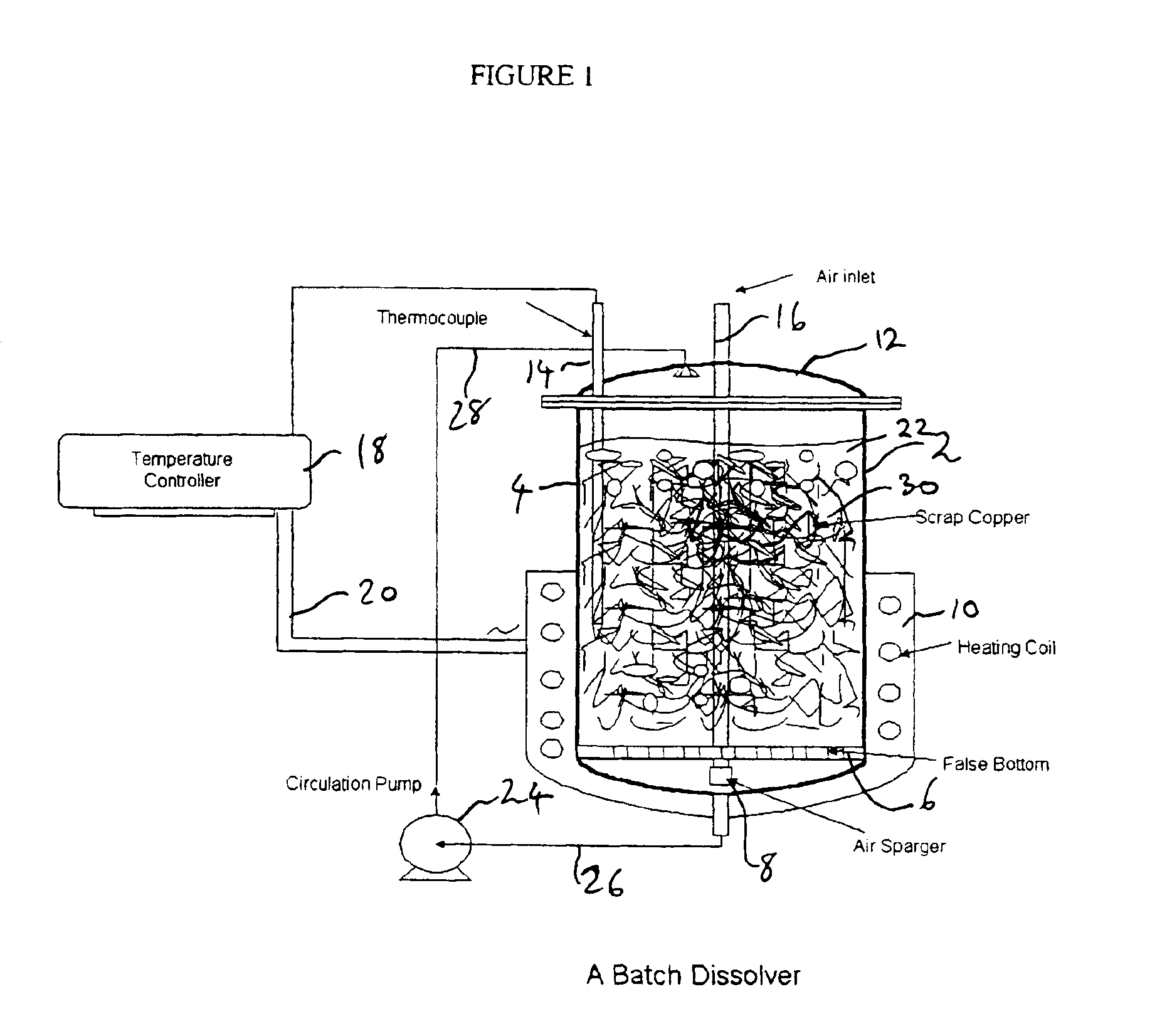
Process for the dissolution of copper metal
InactiveUS6905532B2Efficient productionCopper organic compoundsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processPregnant leach solutionDissolution
Owner:KOPPERS PERFORMANCE CHEM
Anti-microbial metal organic framework
InactiveUS20130171228A1More cost-effectivelyQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismMetal-organic framework
The present invention relates to metal organic framework materials which possess anti-microbial properties. The present invention also provides methods of preparing such metal organic framework materials and uses of the metal organic framework materials to prevent or treat microbial infections, or provide surfaces which limit contamination by micro-organisms.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com