Patents
Literature
727 results about "Protonation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the addition of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H⁺) to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming the conjugate acid. Protonation is a fundamental chemical reaction and is a step in many stoichiometric and catalytic processes. Some ions and molecules can undergo more than one protonation and are labeled polybasic, which is true of many biological macromolecules. Protonation and deprotonation (removal of a proton) occur in most acid–base reactions; they are the core of most acid–base reaction theories. A Brønsted–Lowry acid is defined as a chemical substance that protonates another substance. Upon protonating a substrate, the mass and the charge of the species each increase by one unit, making it an essential step in certain analytical procedures such as electrospray mass spectrometry. Protonating or deprotonating a molecule or ion can change many other chemical properties, not just the charge and mass, for example hydrophilicity, reduction potential, and optical properties can change.
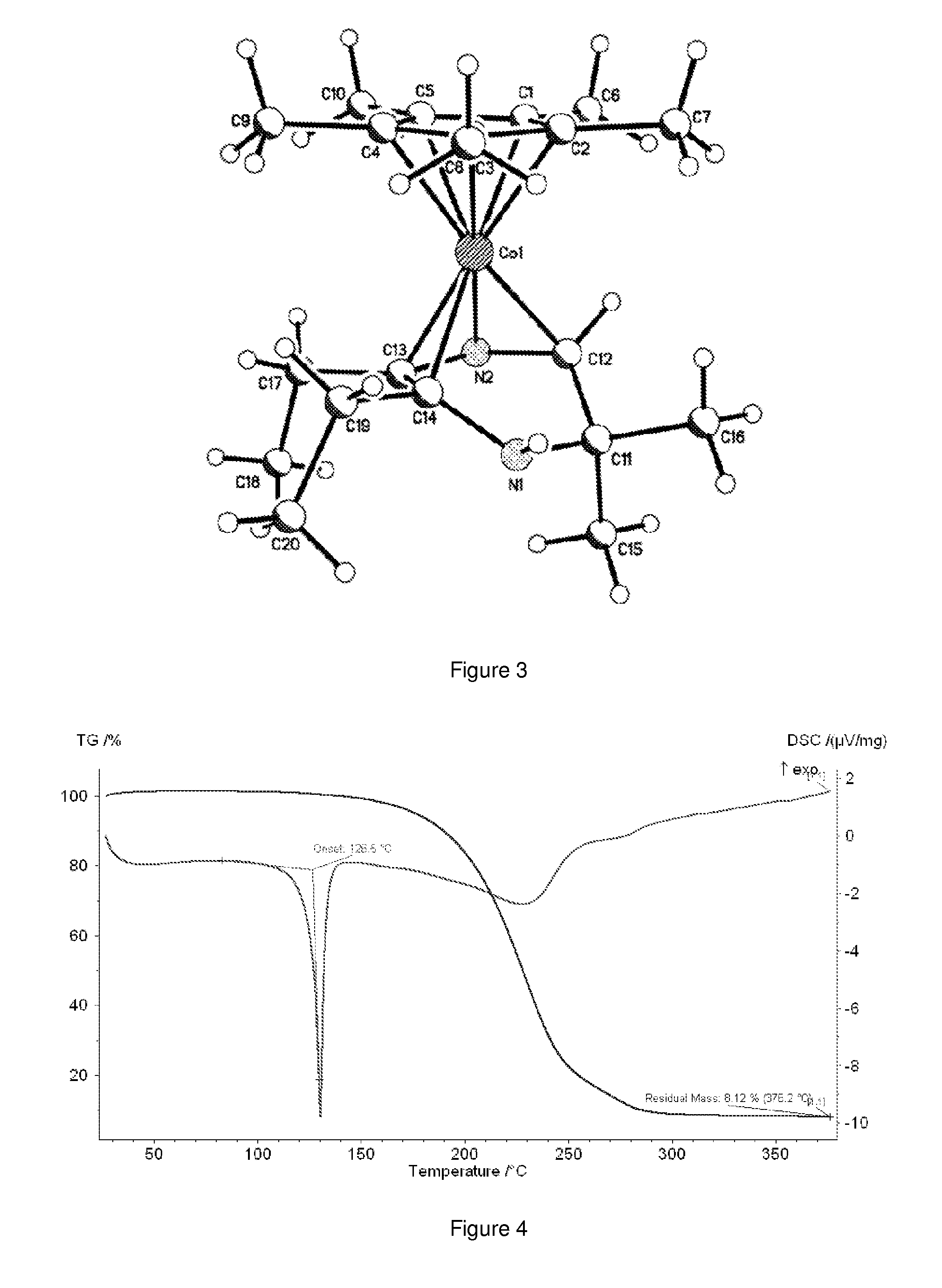
Volatile dihydropyrazinly and dihydropyrazine metal complexes
ActiveUS20150030782A1Improve responseHighly effectiveGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsVacuum evaporation coatingProtonationRuthenium
A composition comprising dihydropyrazinyl anions that can be coordinated as 6 electron ligands to a broad range of different metals to yield volatile metal complexes for ALD and CVD depositions are described herein. Also described herein are undeprotonated dihydropyrazines that can coordinate to metals as stabilizing neutral ligands. In one embodiment, the composition is used for the direct liquid injection delivery of the metal dihydropyrazinyl complex precursor to the chamber of an ALD or CVD chamber for the deposition of metal-containing thin films such as, for example, ruthenium or cobalt metal films.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
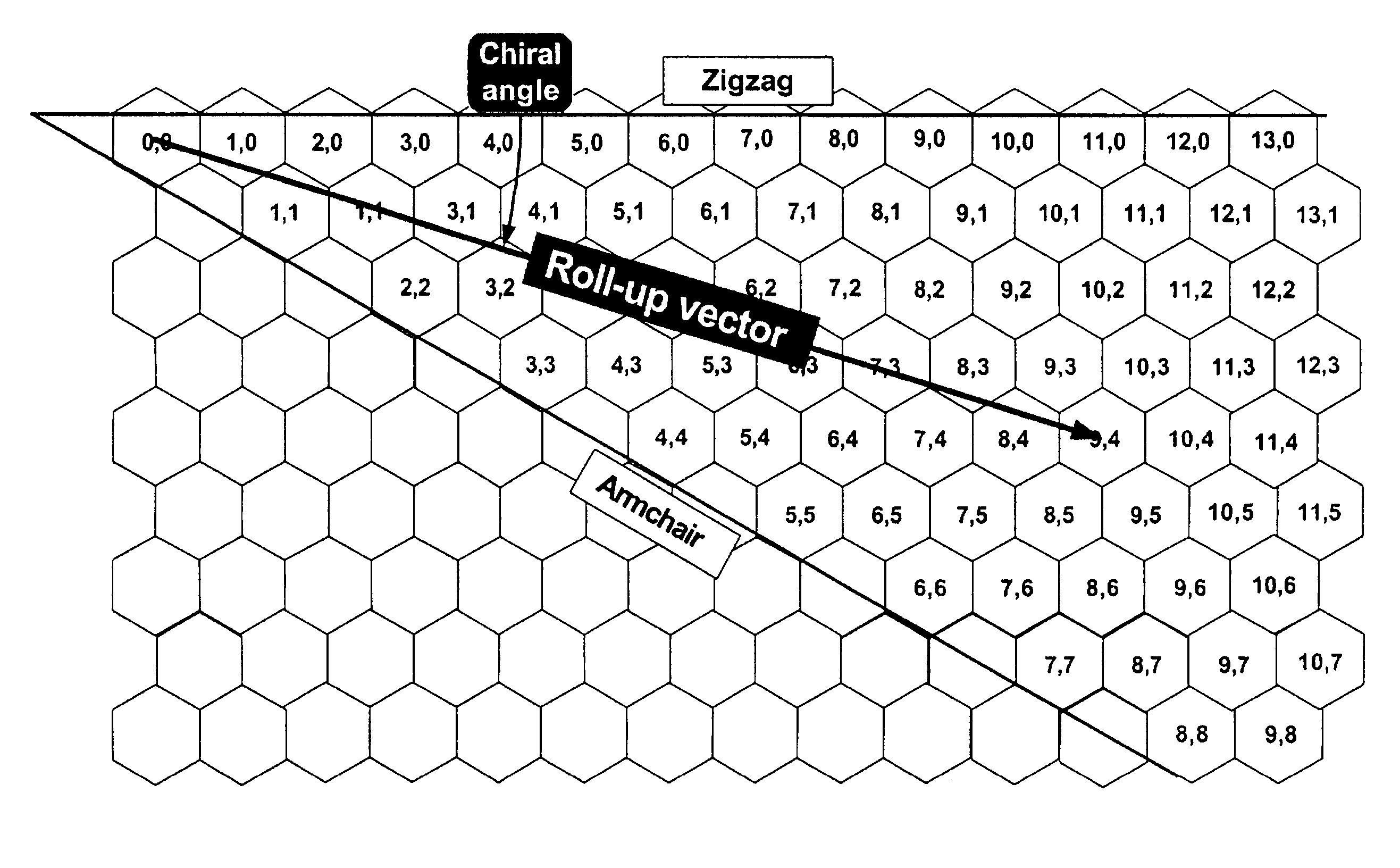
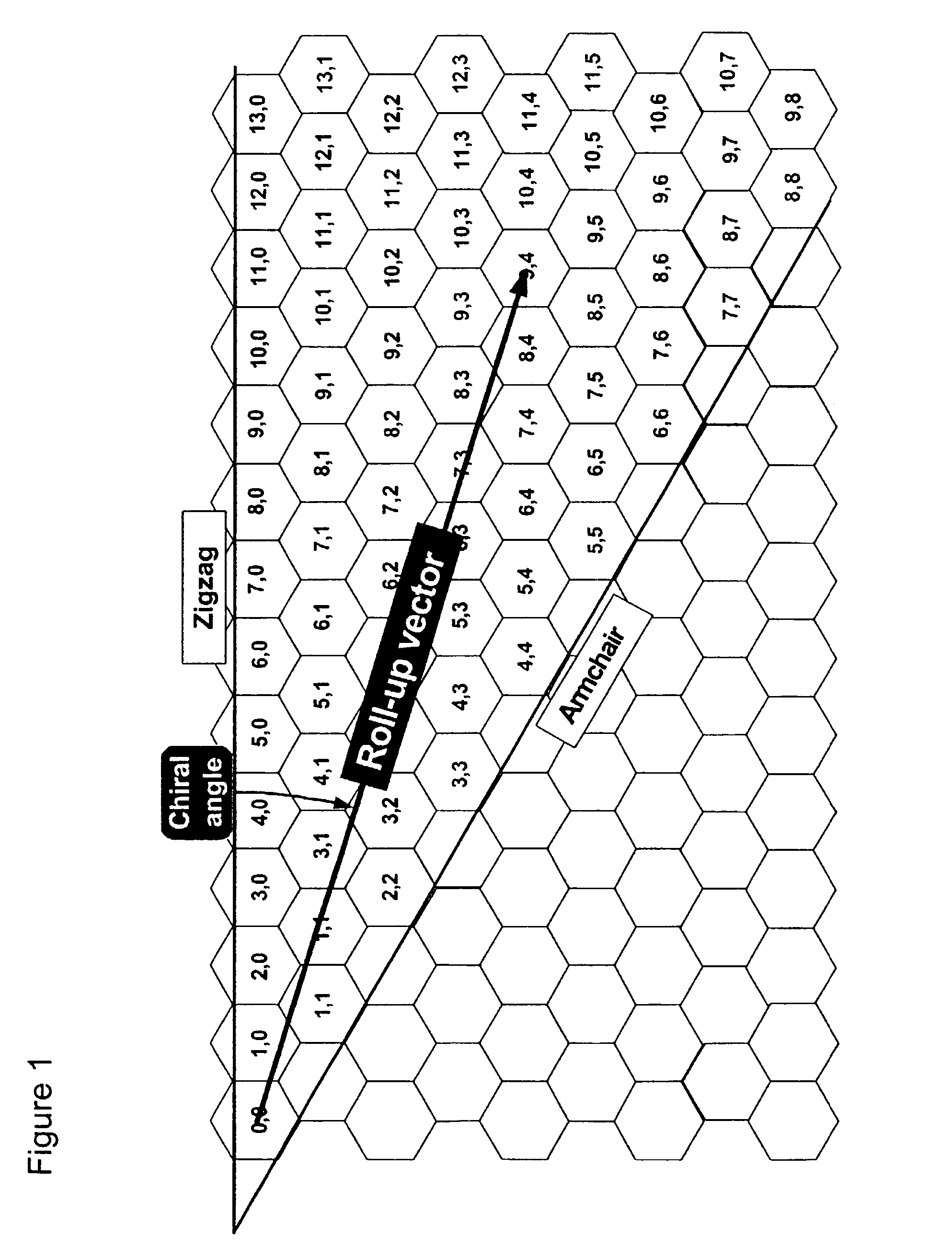
Method for separating single-wall carbon nanotubes and compositions thereof
The invention relates to a process for sorting and separating a mixture of (n, m) type single-wall carbon nanotubes according to (n, m) type. A mixture of (n, m) type single-wall carbon nanotubes is suspended such that the single-wall carbon nanotubes are individually dispersed. The nanotube suspension can be done in a surfactant-water solution and the surfactant surrounding the nanotubes keeps the nanotube isolated and from aggregating with other nanotubes. The nanotube suspension is acidified to protonate a fraction of the nanotubes. An electric field is applied and the protonated nanotubes migrate in the electric fields at different rates dependent on their (n, m) type. Fractions of nanotubes are collected at different fractionation times. The process of protonation, applying an electric field, and fractionation is repeated at increasingly higher pH to separated the (n, m) nanotube mixture into individual (n, m) nanotube fractions. The separation enables new electronic devices requiring selected (n, m) nanotube types.
Owner:RICE UNIV
pH triggerable polymeric particles
A drug delivery system comprising pH triggerable particles is described. The pH triggerable particles comprise and agent(s) to be delivered, which is encapsulated in a matrix comprising a pH trigger agent and a polymer. Agents including nucleic acids may be delivered intracellularly using the inventive pH triggerable particles. Upon exposure to an acidic environment such as the endosome or phagosome of a cell, the particles dissolve or disrupt due to protonation or an increase in solubility of the pH triggering agent. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of preparing and administering these particles are also described. These particles may be particularly useful in genetic vaccination.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
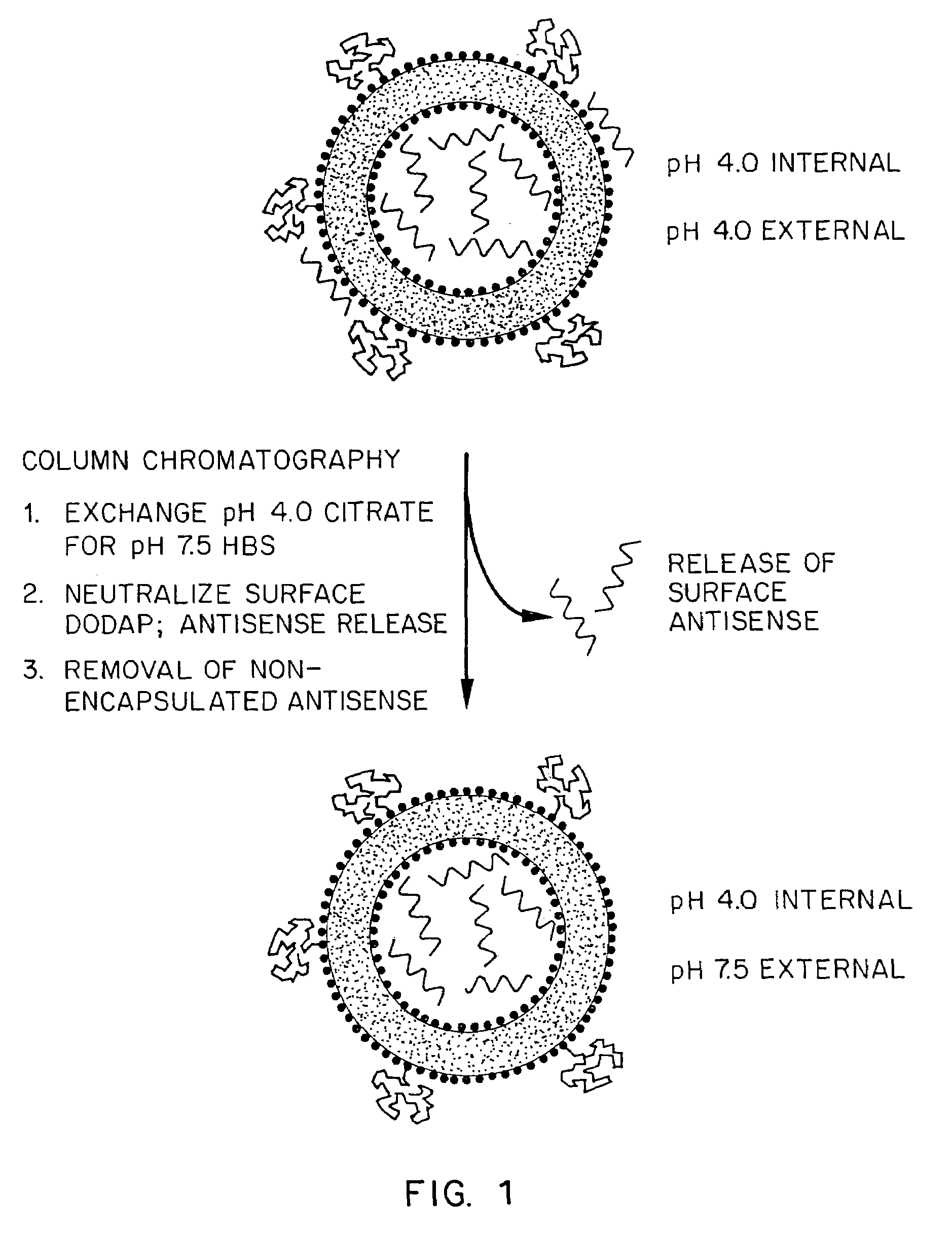
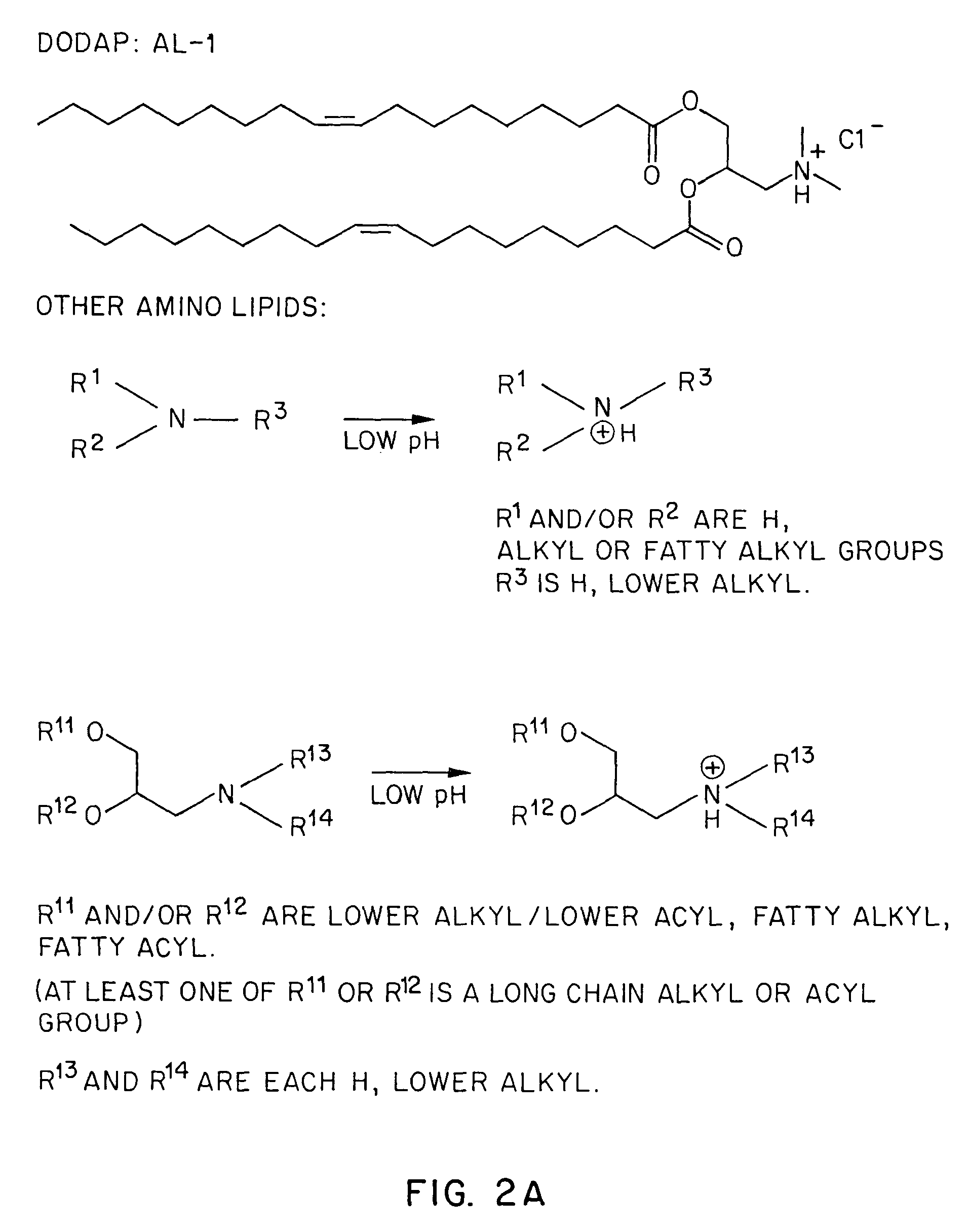
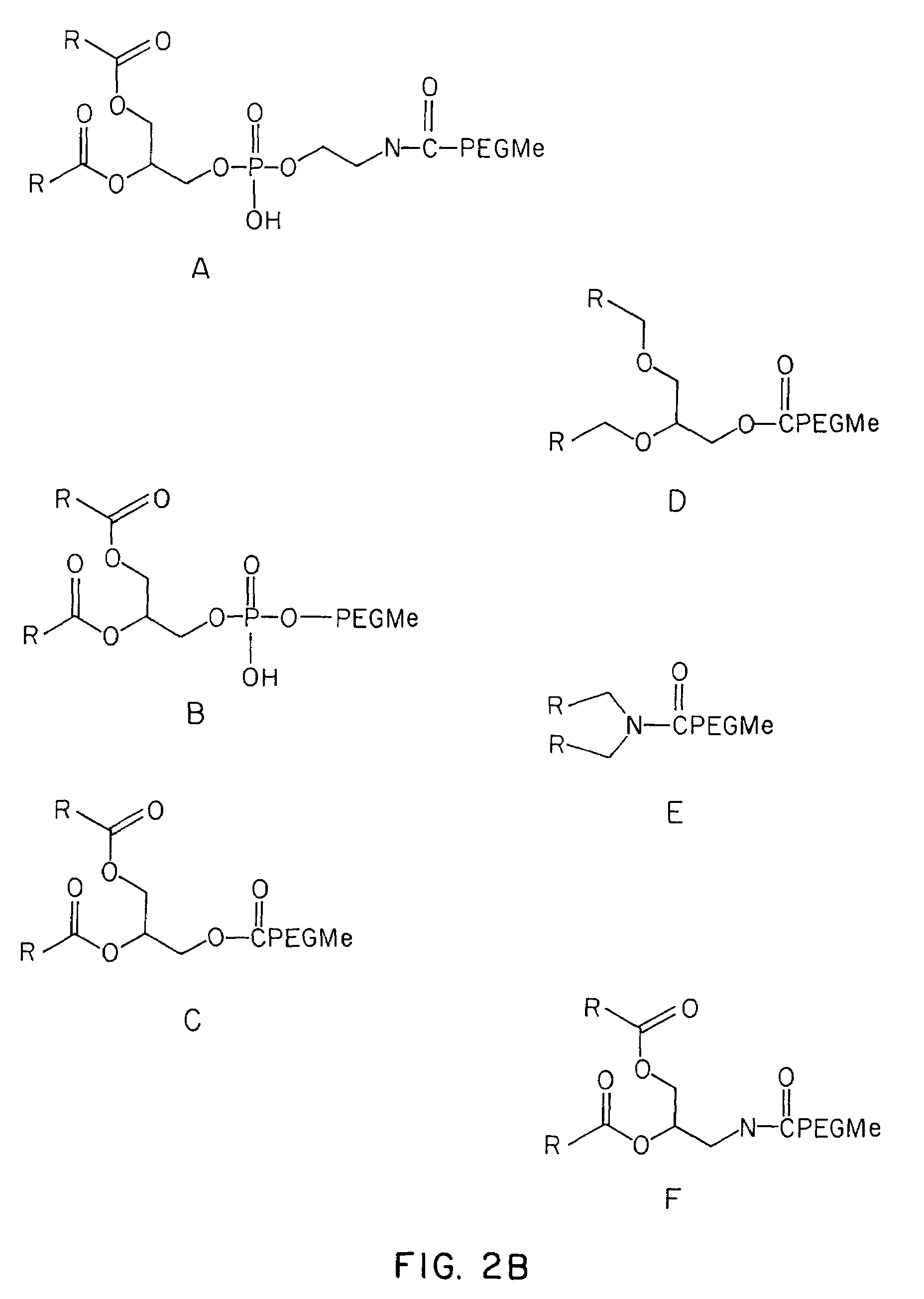
Lipid-encapsulated polyanionic nucleic acid
Methods for the preparation of a lipid-nucleic acid composition are provided. According to the methods, a mixture of lipids containing a protonatable or deprotonatable lipid, for example an amino lipid and a lipid such as a PEG- or Polyamide oligomer-modified lipid is combined with a buffered aqueous solution of a charged therapeutic agent, for example polyanionic nucleic acids, to produce particles in which the therapeutic agent is encapsulated in a lipid vesicle. Surface charges on the lipid particles are at least partially neutralized to provide surface-neutralized lipid-encapsulated compositions of the therapeutic agents. The method permits the preparation of compositions with high ratios of therapeutic agent to lipid and with encapsulation efficiencies in excess of 50%.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Pulmonary delivery of protonated/acidified nucleic acids
The present invention provides a method of treating bacterial respiratory infections by pulmonary administration of protonated / acidified nucleic acids. These modified nucleic acids are effective as bactericidal and / or bacteriostatic agents without regard to the class of bacteria, so are especially useful when diagnosis is difficult or when multiple infectious organisms are present. The antibiotic activity of nucleic acids of the invention is not dependent on either the specific sequence of the nucleic acid or the length of the nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
Shelf stable, reduced corrosion, ready to use peroxycarboxylic acid antimicrobial compositions
ActiveUS20090061017A1Advantageous sporicidal activityBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsSporeProtonation
The present invention relates to shelf stable and / or less corrosive peroxycarboxylic acid antimicrobial compositions, including ready-to-use compositions. Shelf stable compositions can include defined ratios of hydrogen peroxide to peroxycarboxylic acid and / or hydrogen peroxide to protonated carboxylic acid, but need not include strong acid. Reduced corrosion compositions can include carboxylic acid and corrosion inhibitor at acid pH. Compositions of the invention can have advantageous activity against spores.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Transdermal delivery system
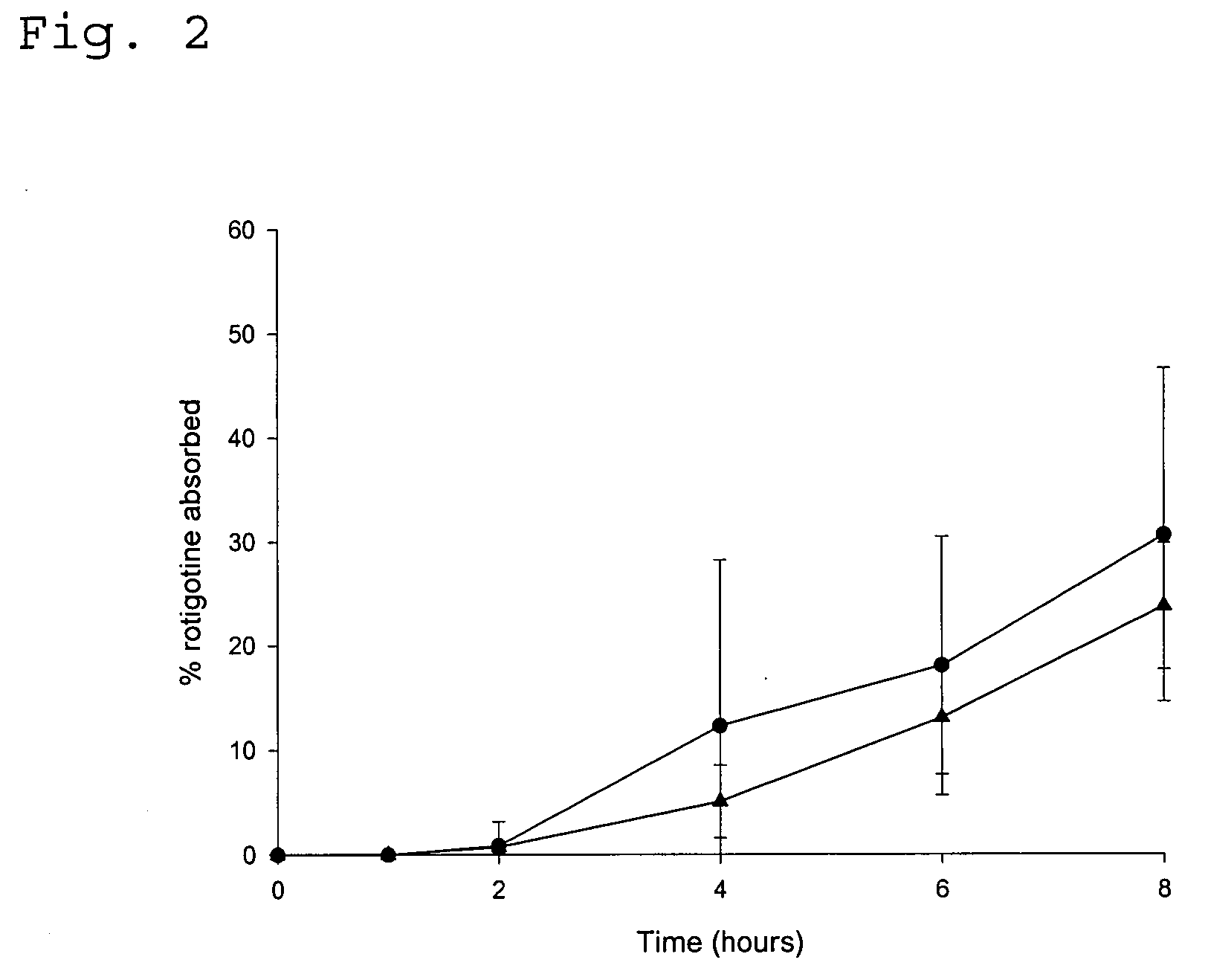
ActiveUS20040081683A1Facilitated releaseGood release effectPowder deliveryBiocideProtonationMedicine
An improved Transdermal Delivery System (TDS) comprising a backing layer inert to the components of the matrix, a selfadhesive matrix containing an amine-functional drug and a protective foil or sheet to be removed prior to use, characterized in that the self-adhesive matrix consists of a solid or semi-solid semi-permeable polymer (1) wherein an amine functional drug in its free base form has been incorporated, (2) which is saturated with the amine functional drug and contains said drug as a multitude of microreservoirs within the matrix, (3) which is highly permeable for the free base of the amine functional drug, (4) which is impermeable for the protonated form of the amine functional drug, (5) wherein the maximum diameter of the microreservoirs is less than the thickness of the matrix. is provided. Said TDS provides for enhanced flux of the amine functional drug across the TDS / skin interface.
Owner:UCB SA
Protonated/acidified nucleic acids and methods of use
The novel discovery that protonated nucleic acids inhibit bacterial growth is reported and methods for the preparation and therapeutic use of nuclease resistant and acid resistant protonated / acidified nucleic acids for administration to animals including man, to treat or prevent a bacterial infection are described.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
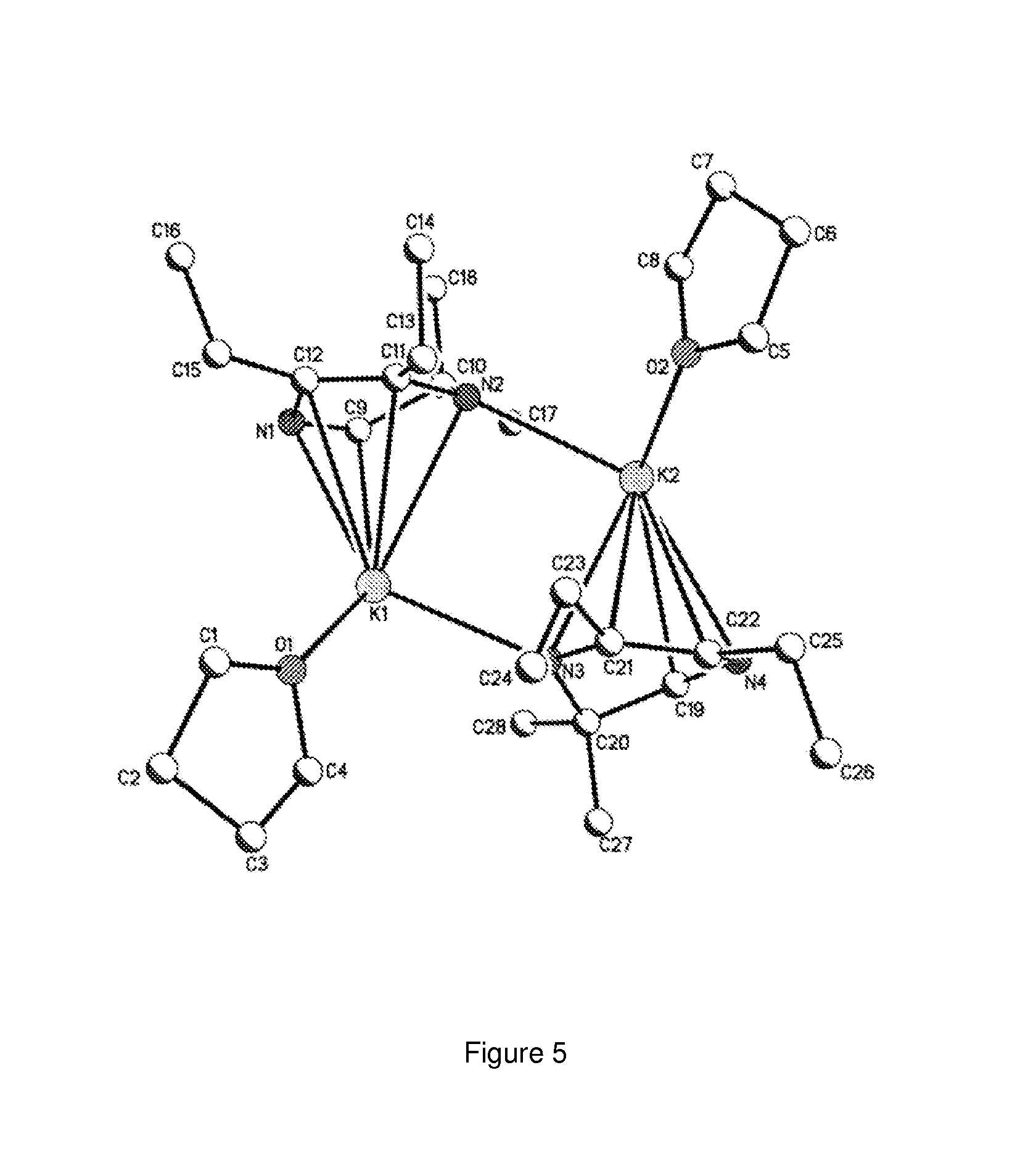
Mixed ionic liquid solution special for absorbing SO2 gas and preparation method thereof
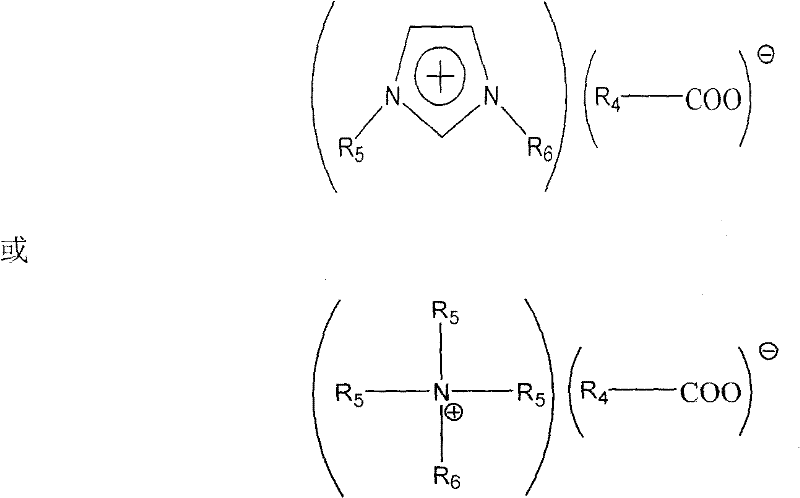
InactiveCN101745290AIncrease molar absorptionLow viscosityDispersed particle separationSulfur compoundsProtonationSulfolane
The invention relates to mixed ionic liquid formula solution, which consists of an ionic liquid A, an ionic liquid B and a mixed solvent C, wherein the positive ion of the ionic liquid A is the N,N-dialkyl imidazole positive ion or the N,N,N,N-tetra alkyl quaternary amine positive ion, while the negative ion thereof is the monobasic carboxylic negative ion; the positive ion of the ionic liquid B is the protonated alkylamine positive ion, while the negative ion thereof is the monobasic or binary or ternary carboxylic negative ion; and the mixed solvent C is aqueous solution of water, polyethylene glycol, polyglycol ether, propylene carbonate or tetramethylene sulfone. The mixed ionic liquid formula solution of the invention is strong base-weak acid and weak base-weak acid mixed salt solution, has wide pH buffering capacity, and can greenly efficiently absorb the SO2 gas in a reversible cycle mode. The mixed ionic liquid formula solution of the invention is adopted as a SO2 absorbent so that the requirement for the equipment required by SO2 absorption is simple, the operation condition of absorbing and desorbing SO2 is mild, the desulfurization efficiency is high, and the problems of waste solution and wastewater discharge and the like do not exist. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the mixed ionic liquid formula solution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Ruthenium(II) catalysts for use in stereoselective cyclopropanations
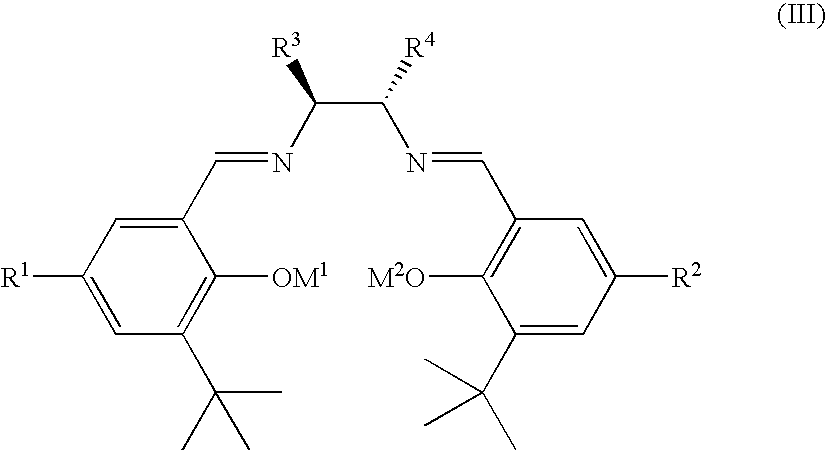
ActiveUS7754902B2High stereoselectivityHigh yieldRuthenium organic compoundsCobalt organic compoundsProtonationSalen ligand
Chiral ruthenium catalysts comprising salen and alkenyl ligands are provided for stereoselective cyclopropanation, and methods of cyclopropanation are provided. The chiral ruthenium catalyst is prepared in situ by combining an alkenyl ligand, a deprotonated chiral salen ligand, and a ruthenium (II) metal. A preferred catalyst is prepared in situ by combining 2,3-dihydro-4-venylbenzofuran, deprotonated 1,2-cyclohexanediamino-N,N′-bis(3,5-di-t-butyl-salicylidene) and RuCl2(p-cymene)]2.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto
ActiveUS6984734B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove hydrophobicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsProtonationCoupling
The present invention provides an oxidative coupling procedure that allows efficient synthesis of novel cyclo[n]pyrrole macrocycles. Therefore, the present invention provides cyclo[n]pyrroles where n is 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12, and derivatives, multimers, isomers, and ion and neutral molecule complexes thereof as new compositions of matter. A protonated form of cyclo[n]pyrrole displays a gap of up to 700 nm between strong Soret and Q-like absorption bands in the electronic spectrum, demonstrating no significant ground state absorption in the visible portion of the electronic spectrum. Uses of cyclo[n]pyrroles as separation media, nonlinear optical materials, information storage media and infrared filters are provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Preparation method of amphoteric ion exchange membrane
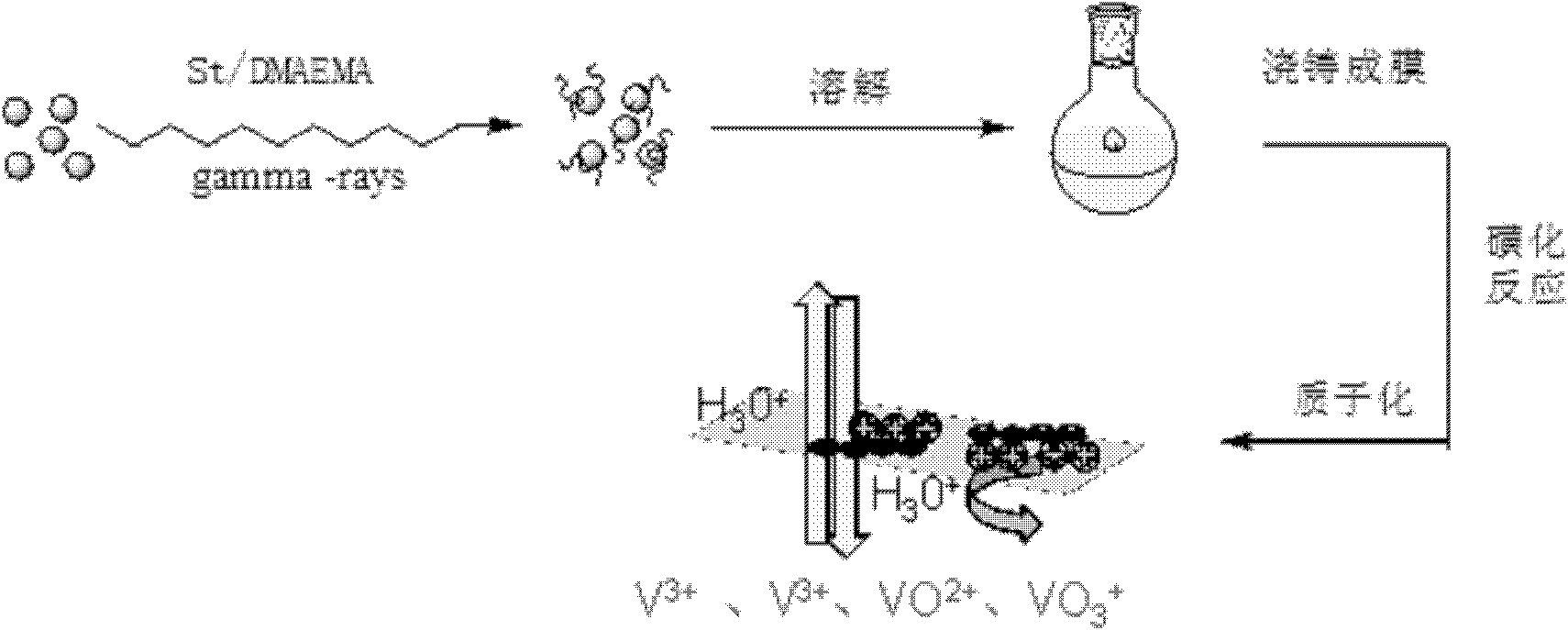
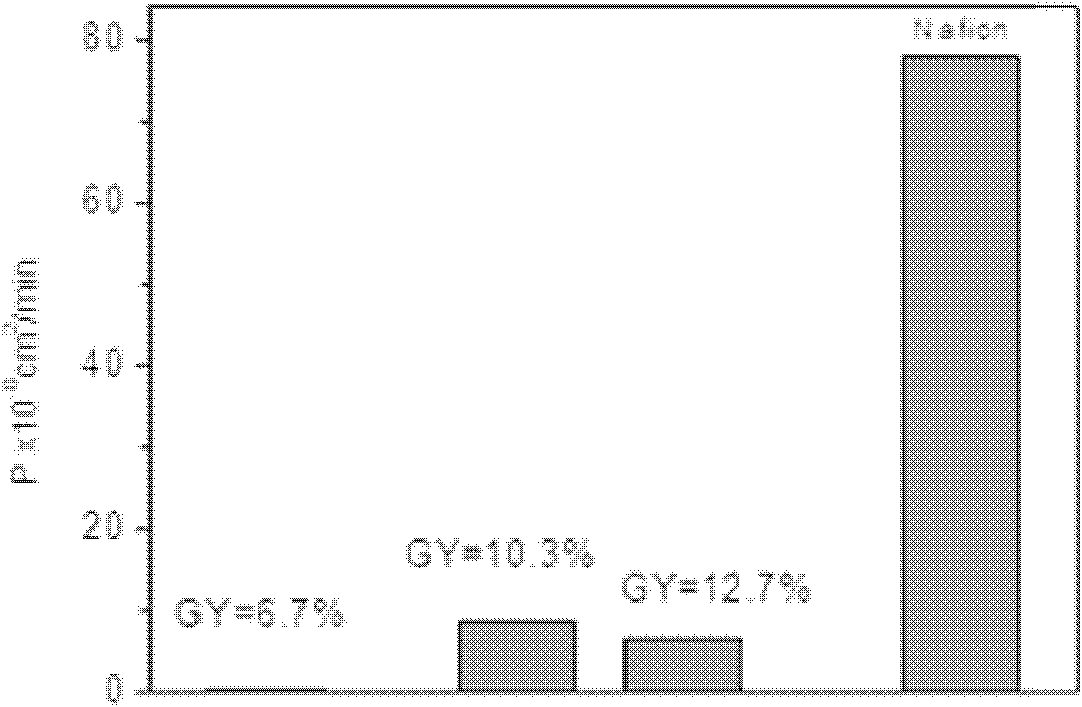
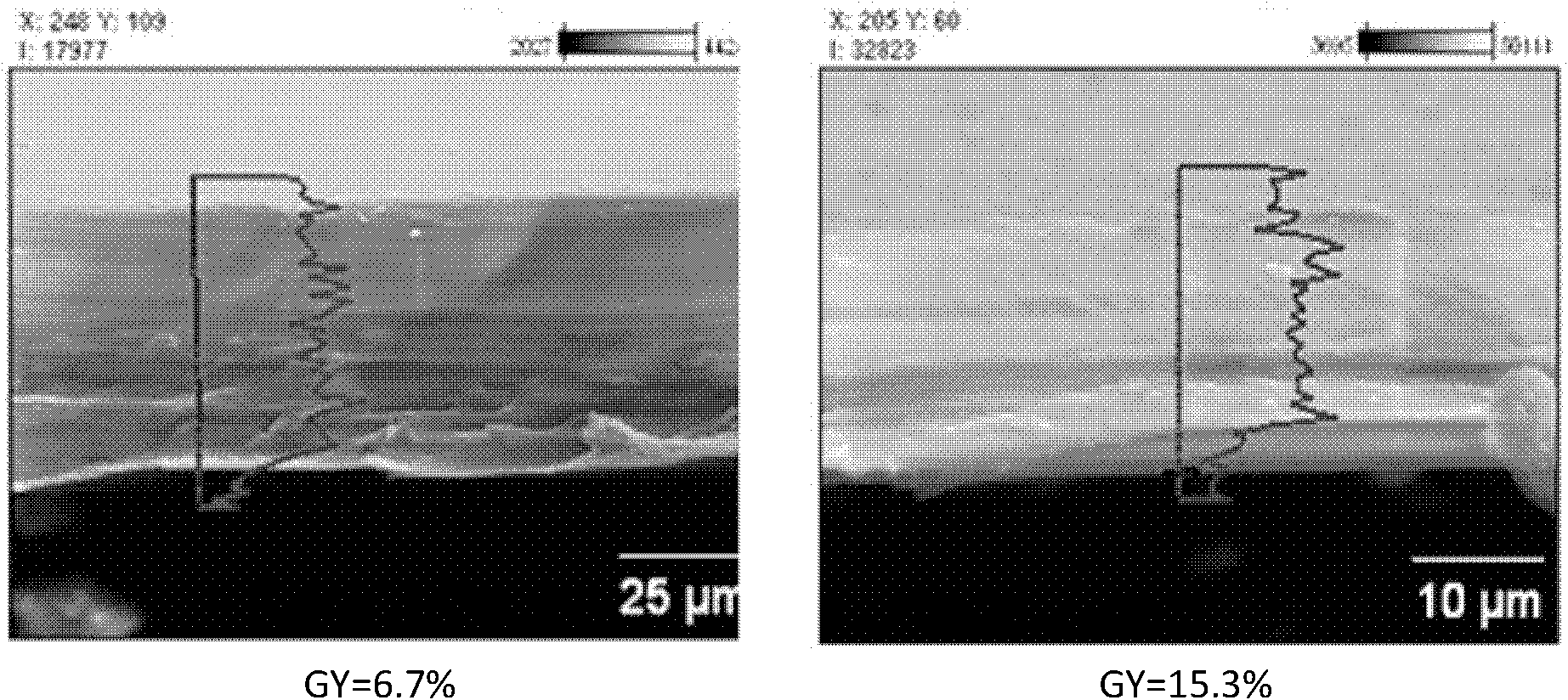
ActiveCN102181069AKeep hydrophilicEnsure normal conductionAmphoteric ion-exchangersCell component detailsProtonationBond energy
The invention discloses a preparation method of an amphoteric ion exchange membrane and relates to a preparation method of an amphoteric ion exchange membrane for an all-vanadium redox flow battery. According to the scheme, the preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing irradiation grafting on polymer powder poly(vinylidene fluoride); transforming the irradiation-grafted polymer powder into a membrane material; and sulfonating the membrane material, hydrolyzing, introducing a sulfonate radical group with a cationic exchange function, putting the membrane material into a hydrochloric acid aqueous solution for undergoing a protonation reaction and introducing basic nitril with an anion exchange function to obtain the amphoteric ion exchange membrane. In the method, commercial poly(vinylidene fluoride) resin with low price is taken as a raw material, so that the membrane making cost can be lowered; a C-F bond has large bond energy, so that the membrane can keep high chemical stability in a strong acid and high oxidizing electrochemical environment; and meanwhile, the problem of non-uniform distribution of grafted chains of the conventional heterogeneous irradiation-grafted membrane in the vertical direction of the membrane is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
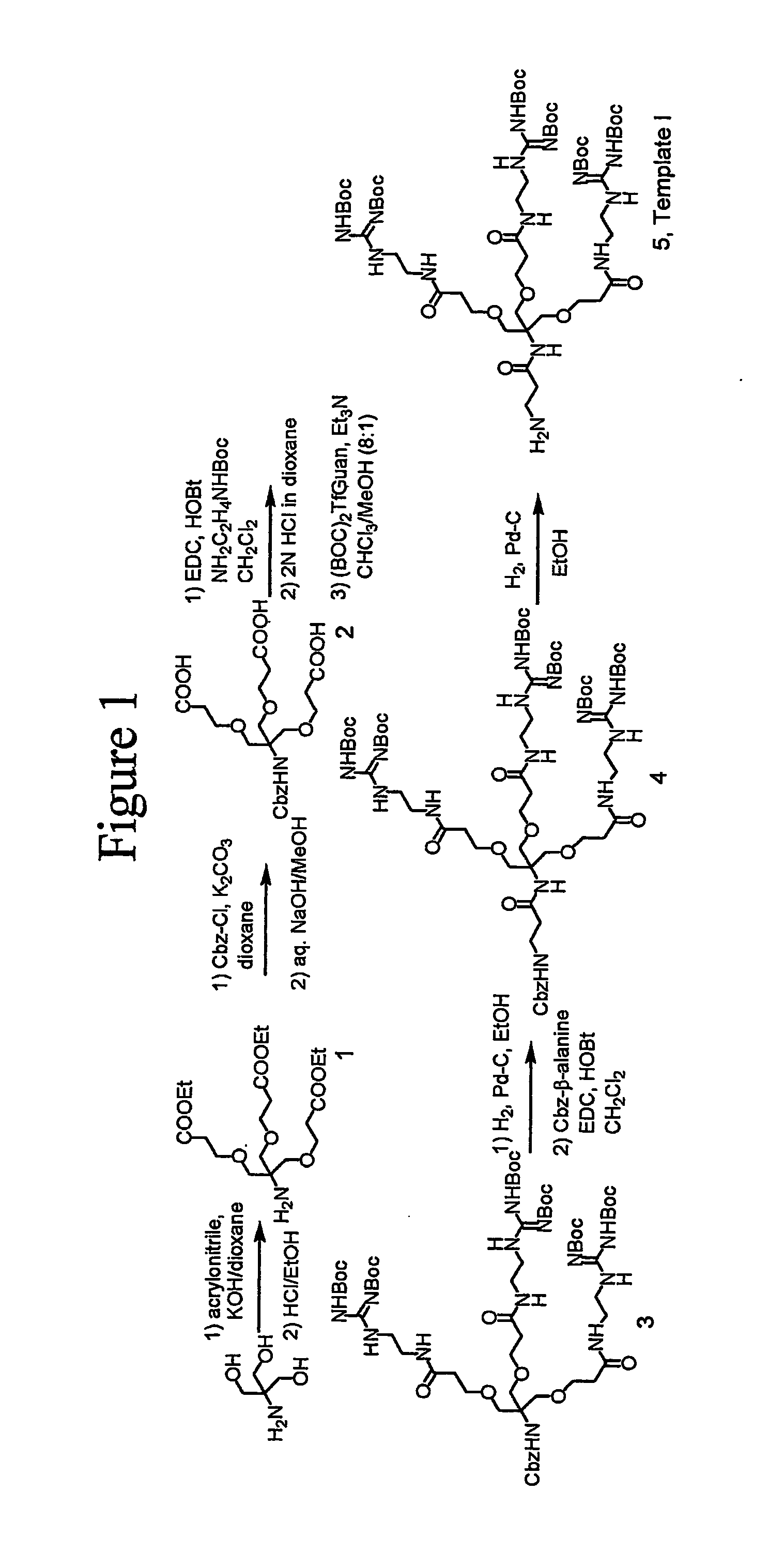
Dendrimers as molecular translocators
Transport molecules include a dendrimer and a biologically active molecule. The dendrimer of such transport molecules includes at least one guanidine group, at least one protonated guanidine group, at least one protected guanidine group, at least one amidine group, at least one protonated amidine group, at least one protected amidine group, at least one ureido group, at least one protonated ureido group, at least one protected ureido group, at least one thioureido group, at least one protonated thioureido group, or at least one protected thioureido group. The biologically active molecule is bonded to the dendrimer. A method of increasing the bioavailability of a drug includes bonding the drug to a dendrimer of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
High-quality graphene dispersion method and film preparation method
ActiveCN103449420AHigh dispersible concentrationNo dispersant residueGrapheneHigh concentrationProtonation
The invention relates to the field of graphene, particularly a high-quality graphene dispersion method and a method for preparing a film from a corresponding graphene dispersion solution or slurry. Graphene powder or aggregation-state slurry is added into a micromolecule amine compound solution to carry out dispersion treatment, so that the three amine micromolecule compounds are utilized to implement dispersion of the graphene; and in the dispersion solution, the molecules of the compounds are combined with the graphene under the pai-pai interaction, the amino group protonation is utilized to electrically charge the graphene, and the electrostatic repulsion action is utilized to prevent aggregation, thereby implementing the stable dispersion of the graphene. The dispersion solution or slurry can be subjected to spray coating, roller coating, scratch coating or any other conventional coating preparation method to obtain a graphene film on the substrate surface. The method can implement high-concentration efficient dispersion on high-quality graphene with the carbon / oxygen atom ratio of greater than 20 in multiple solvents; and after the film is formed and dried, no solvent or dispersant residue exists.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Biocompatible polymeric matrix and preparation thereof
InactiveUS20070077305A1Powder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProtonationControlled release
The invention discloses a biocompatible polymeric matrix which is functionalized through the reaction with a functionalizing agent including protonated carboxylic acid groups. There is also disclosed a method of preparation of the polymeric matrix and a pharmaceutical composition including the matrix as a carrier for controlled release of a bioactive agent. The pharmaceutical composition is suitable for immobilizing and protecting the bioactive agent from denaturing factors, and can take various forms such as tablets, spheres, films, hydrogels, and emulsions.
Owner:LE TIEN CANH +2
Fluid system having controllable reversible viscosity
ActiveUS7119050B2Improve solubilityPreventing potential phase separationFluid removalFlushingProtonationBetaine
This Invention relates to methods of treating a subterranean hydrocarbons reservoir comprising contacting the formation with a treating fluid comprising an aqueous solution, an acid, a surfactant acting as gelling agent essentially consisting of erucylamidopropyl betaine (or a protonated / deprotonated homolog or salt thereof). The treating fluid may further comprise a lower n-alcohol for improved temperature stability.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Organic lithium salt electrolytes having enhanced safety for rechargeable batteries and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060068295A1Improve propertiesImprove thermal stabilityAlkaline accumulatorsOrganic electrolyte cellsProtonationCarboxylic salt
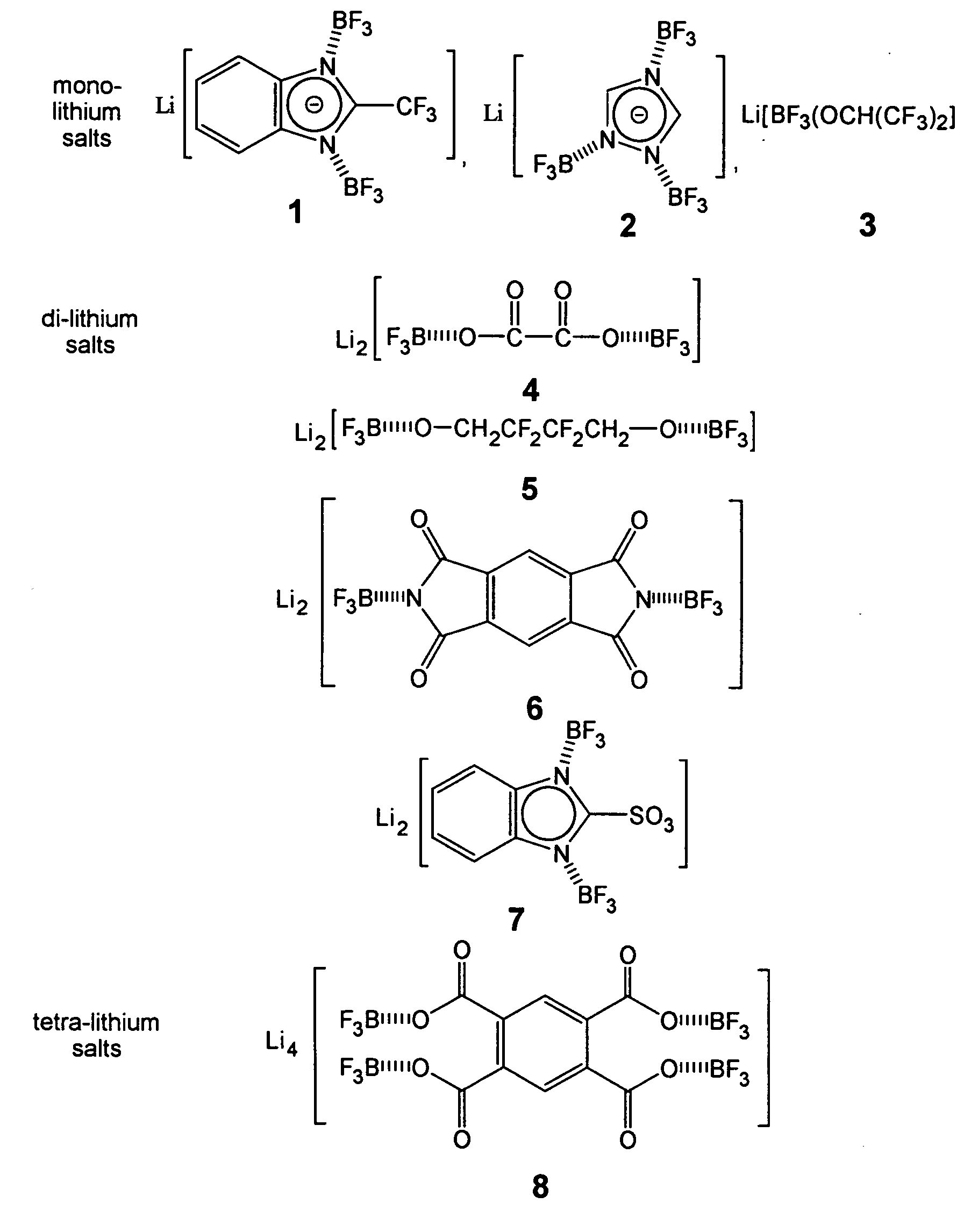
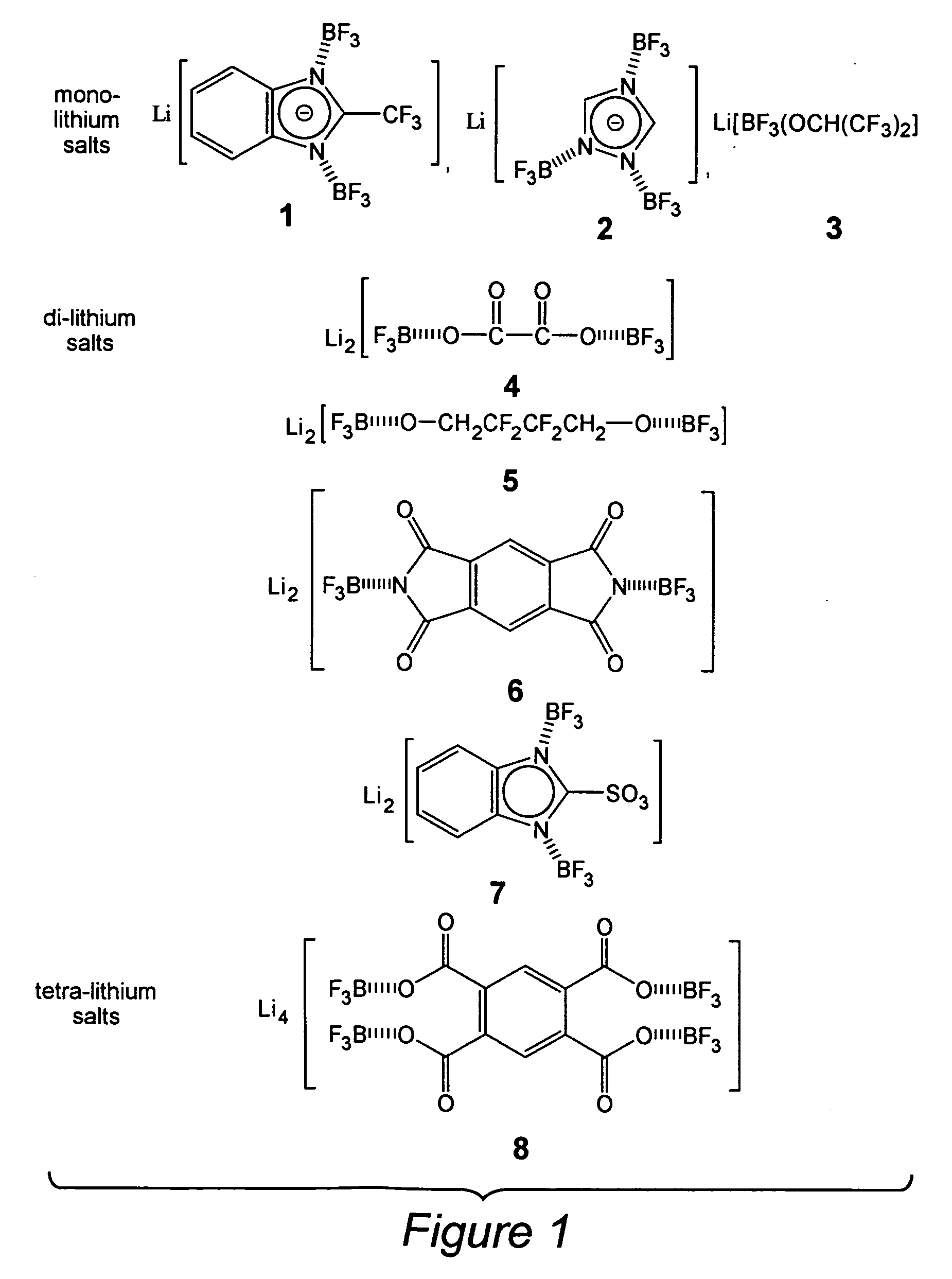
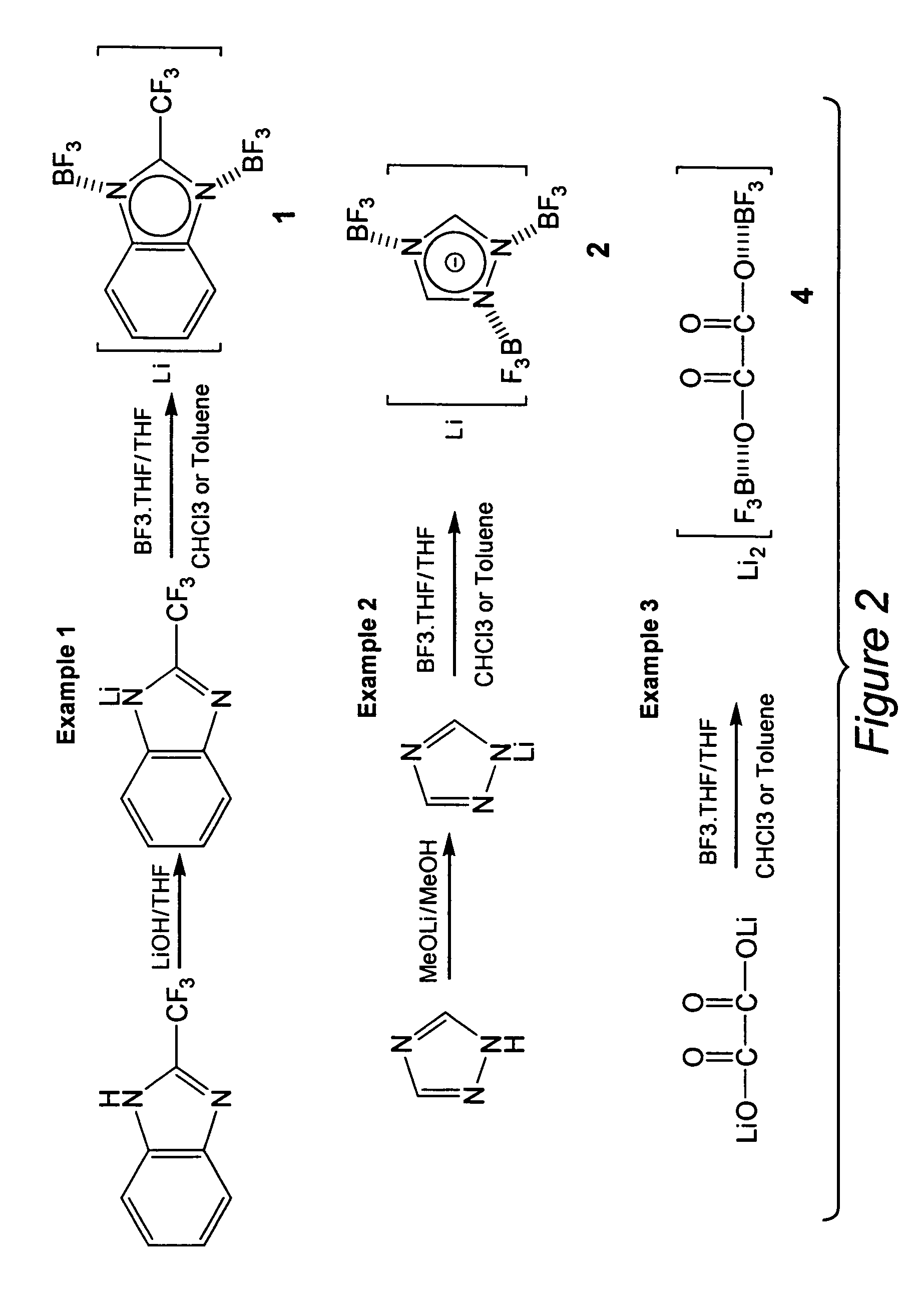
Organic lithium salts suitable for use in electrolytes for primary or secondary rechargeable batteries include de-localized bulky anions over Lewis acid fragments, typically BF3, and organic moieties. The organic moieties may be, for example, anions derived from fused nitrogen heterocycles (e.g. benzeneimidate, benzitriazolate and the like); multi carboxylates (e.g. oxalate, 1,2,4,5-benzenetetracarboxylate and the like), and pyromellitic diimidate. The organic lithium salts of the invention have the general formula: Liq[Org(MXn)m], in which Org represents the organic moieties and MXn represents an organic or inorganic boron, aluminum or phosphorous containing Lewis acid. The organic lithium salts are conveniently prepared by reacting an organic compound having at least one de-protonation group selected from NH, OH, SH or COOH with an inorganic or organic lithium compound to generate an organic lithium processor salt, and thereafter bringing the organic lithium processor salt into contact with an inorganic or organic Lewis acid to obtain the organic lithium product salt.
Owner:SKC POWER TECH
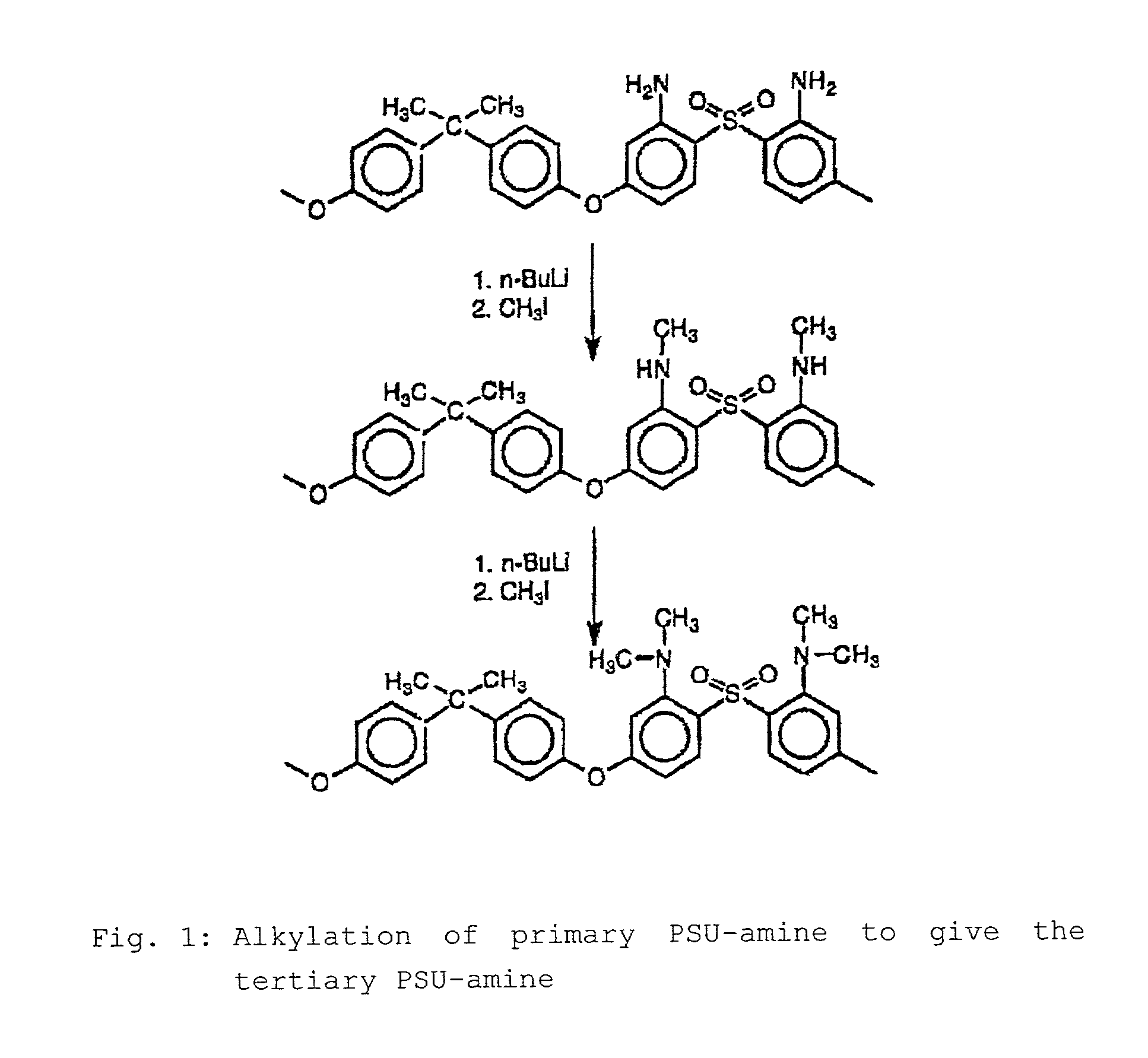
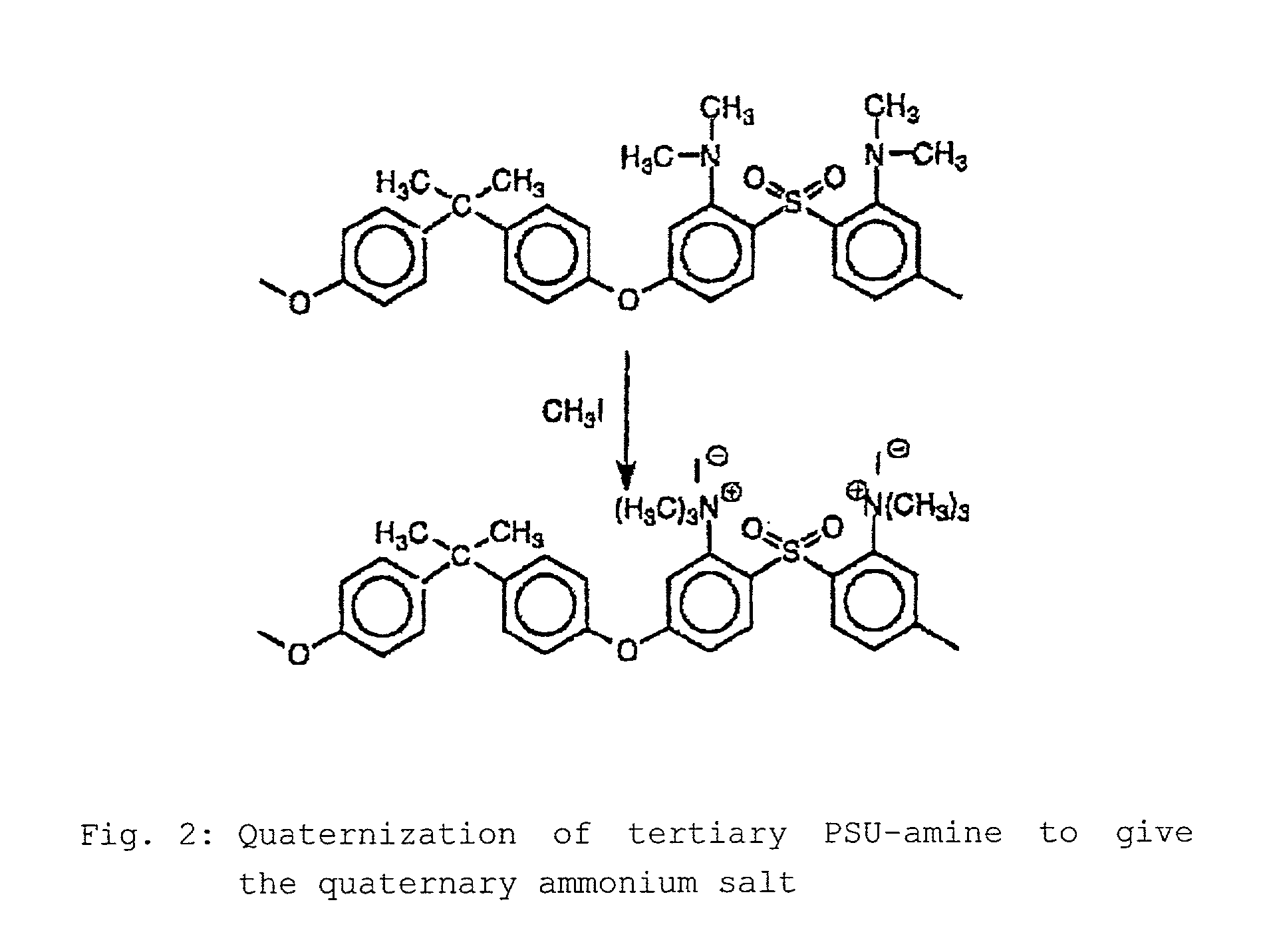
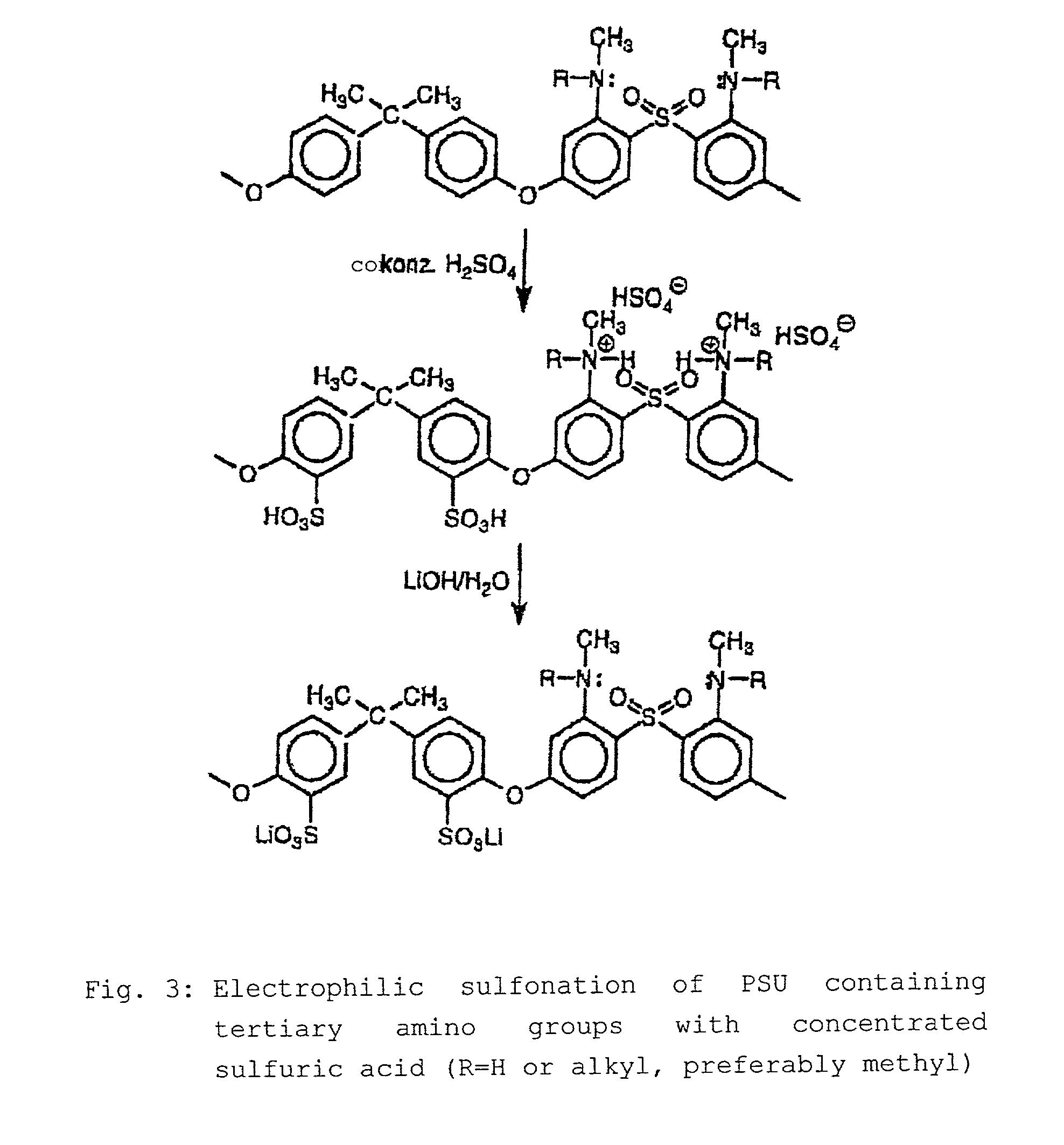
Step-by-step alkylation of polymeric amines
InactiveUS7132496B2Ion-exchange process apparatusNon-metal conductorsHydrophilic polymersOrganic base
The invention relates to the following: a method for step-by-step alkylation of primary polymeric amines by step-by-step deprotonation with a metallo-organic base and a subsequent reaction with an alkyl halide; a method for modifying tertiary polymeric amines with other functional groups; polymers with secondary / tertiary amino groups and with quaternary ammonium groups; polymers with secondary / tertiary amino groups and other functional groups, especially cation exchanger groupings; membranes consisting of the above polymers, either non-crosslinked or ionically or covalently cross-linked; acid-base-blends / membranes, and a method for producing same, consisting of basic polymers with polymers containing sulphonic acid, phosphonic acid or carboxyl groups; the use of ion exchanger polymers as membranes in membrane processes, e.g., polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, direct methanol fuel cells, redox batteries, or electrodialysis; the use of the inventive hydrophilic polymers as membranes in dialysis and reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, diffusion dialysis, gas permeation, pervaporation and perstraction.
Owner:HARING THOMAS
Charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability
A charged mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN)-based drug delivery system for controlled release and enhanced bioavailability is disclosed. The system comprises a positively charged MSN, which has a silica matrix and an array of pores and / or nanochannels in the matrix. The entire substance of the matrix, all the surfaces and the pores and / or nanochannels comprise a plurality of silanol (Si—OH) and quaternary ammonium functional groups. The bioavailability of a negatively charged bioactive compound can be increased by loading it into the pores and / or nanochannels. The silanol (Si—OH) functional groups on the surfaces lining the walls of the pores and / or nanochannels are free to deprotonate in a fluid having pH above the pI of the positively charged MSN and lead to a sustained release of the negatively charged drug from the pores and / or nanochannels, and thereby enhance the bioavailability of the drug.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Absorbent articles comprising super absorbent polymer having a substantially non-convalently bonded surface coating
The present invention relates to absorbent articles comprising superabsorbent polymer particles. The superabsorbent polymer particles are coated with cationic polymers having 1 to 25 mol / kg, referring to the total weight of the cationic polymers, of cationic groups, which can be protonated. The cationic polymers are not substantially covalently bound to the superabsorbent polymer particles. Furthermore, the superabsorbent polymer particles are not substantially covalently surface cross-linked.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Cleaning compositions with alkoxylated polyalkanolamines
ActiveUS20090124529A1Improved anti-redepostion benefit benefitImproved benefit grease cleaning benefitOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsProtonationLaundry detergent
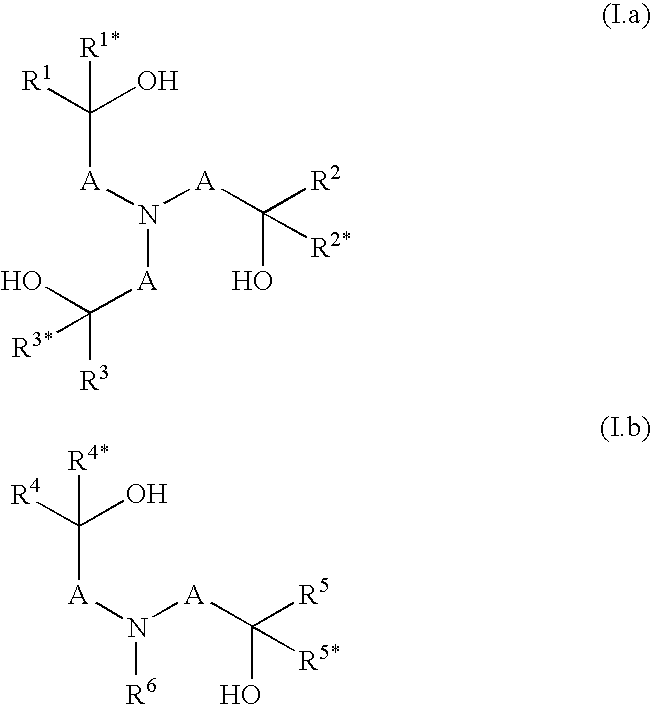
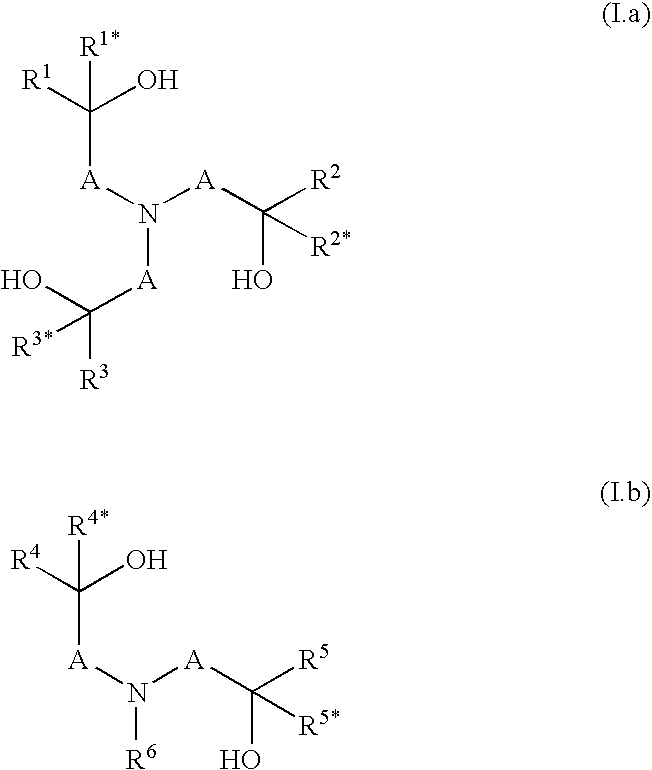
Laundry detergent and cleaning compositions comprising alkoxylated polyalkanolamine polymers obtainable by condensation of N-(hydroxyalkyl)amines and reacting the remaining hydroxy and / or secondary amino groups of the condensation product with alkylene oxides and / or derivatives obtainable by quaternization, protonation, sulphation and / or phosphation of said polymers.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Methods for using reversible phase oil-based drilling fluid
Invert emulsion compositions including an oleaginous, a non-oleaginous and an amine surfactant that are useful in the oil and gas well drilling art are disclosed. The amine surfactant is selected so that the invert emulsion can be converted form a water-in-oil type emulsion to a oil-in-water type emulsion upon the protonation of the amine surfactant. Deprotonation of the amine surfactant reverses the conversion. This solution also permits the conversion of oil-wet solids in the fluid into water-wet solids.
Owner:MI
Preparation process of composite proton exchanging member based on hydrophilic porous poly tetrafluoro ethylene matrix
InactiveCN1861668AGood resin fillingImprove proton conductivityFuel cellsTetrafluoroethyleneProtonation
A composite proton exchange membrane base on hydrophilic porous polytetrafluoroethene and used for fuel battery is prepared through hydrophilic treating to porous polytetrafluoroethene, filling proton conducting resin, heat treating and protonating. It has high proton conductivity, mechanical strength and gas permeability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
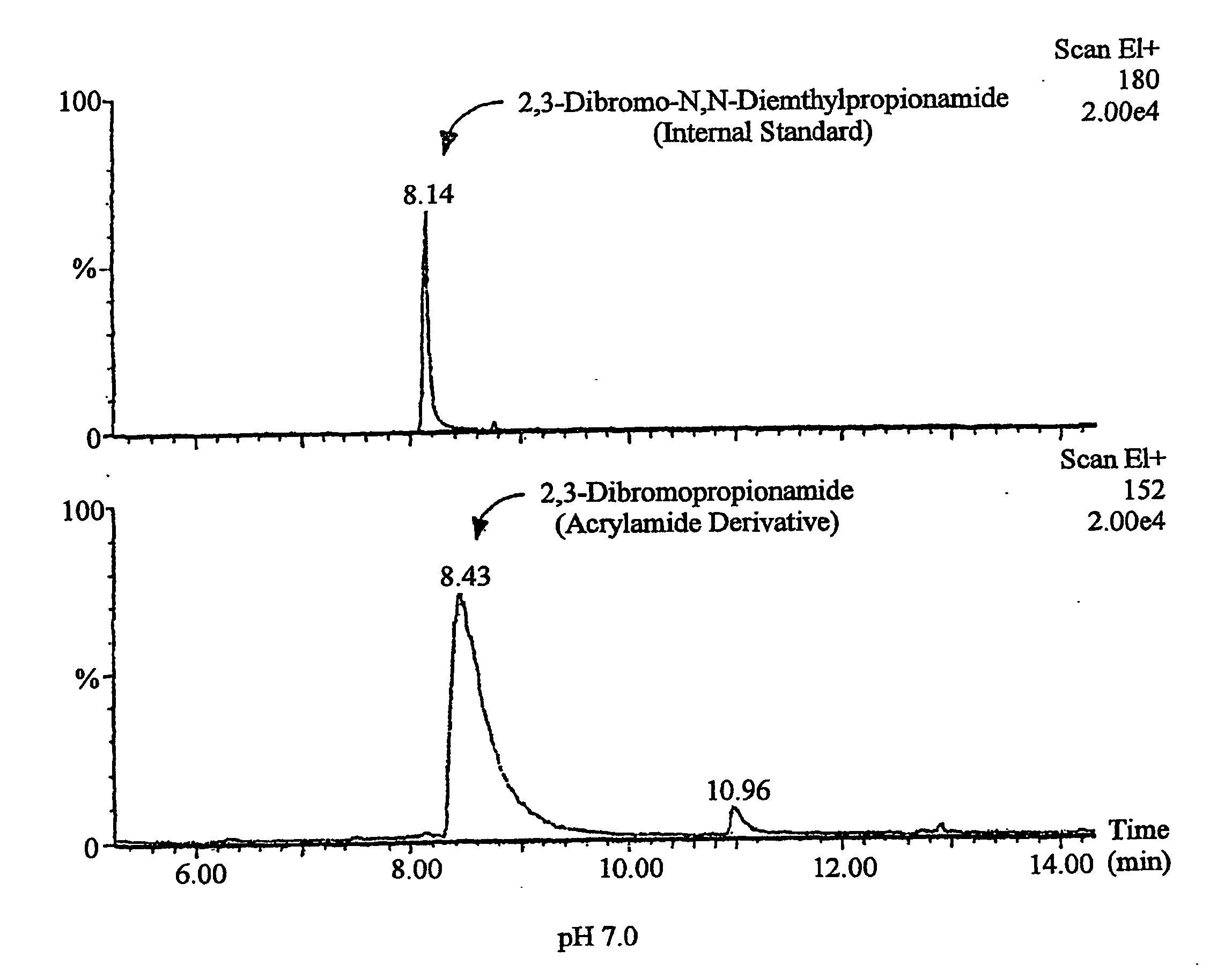
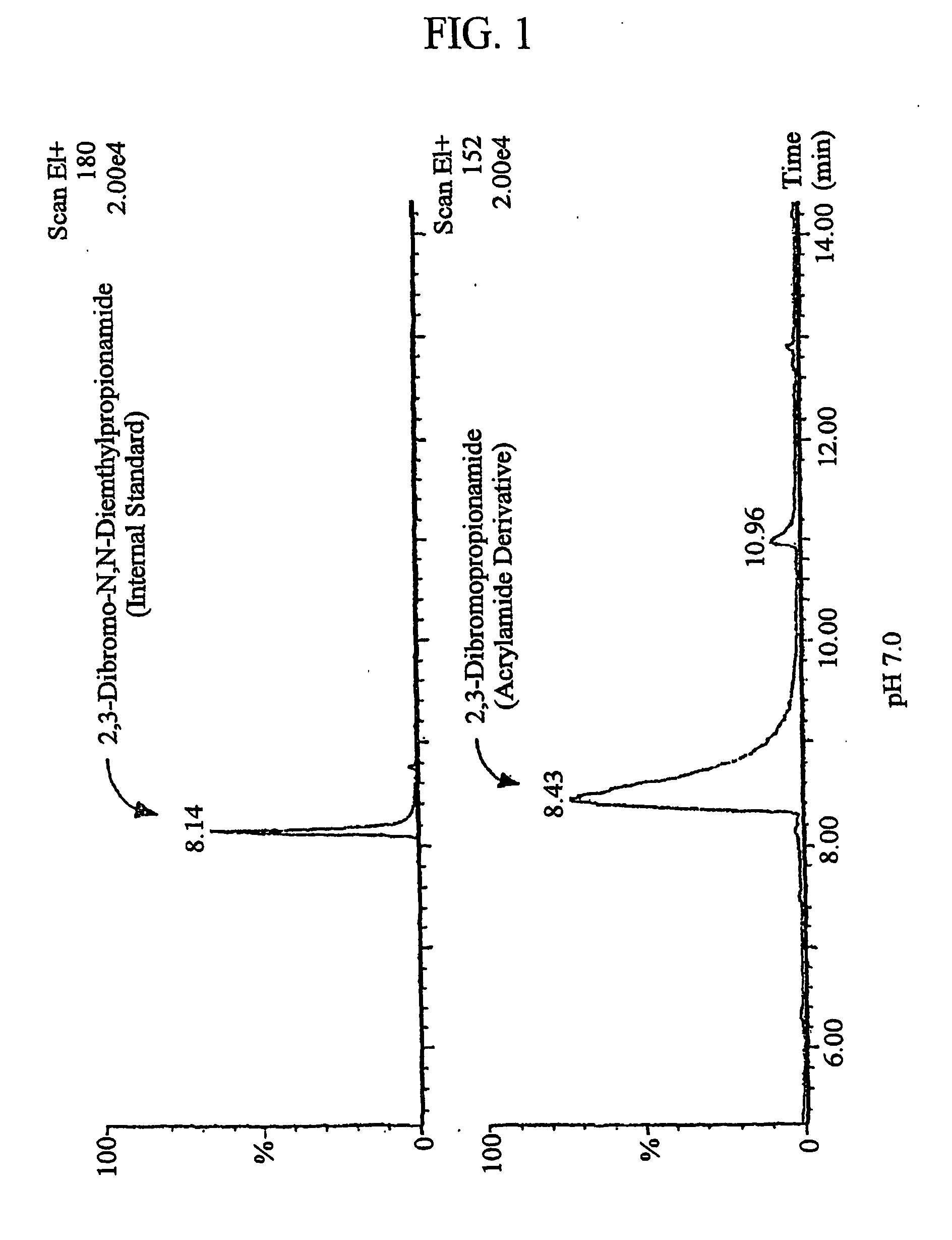
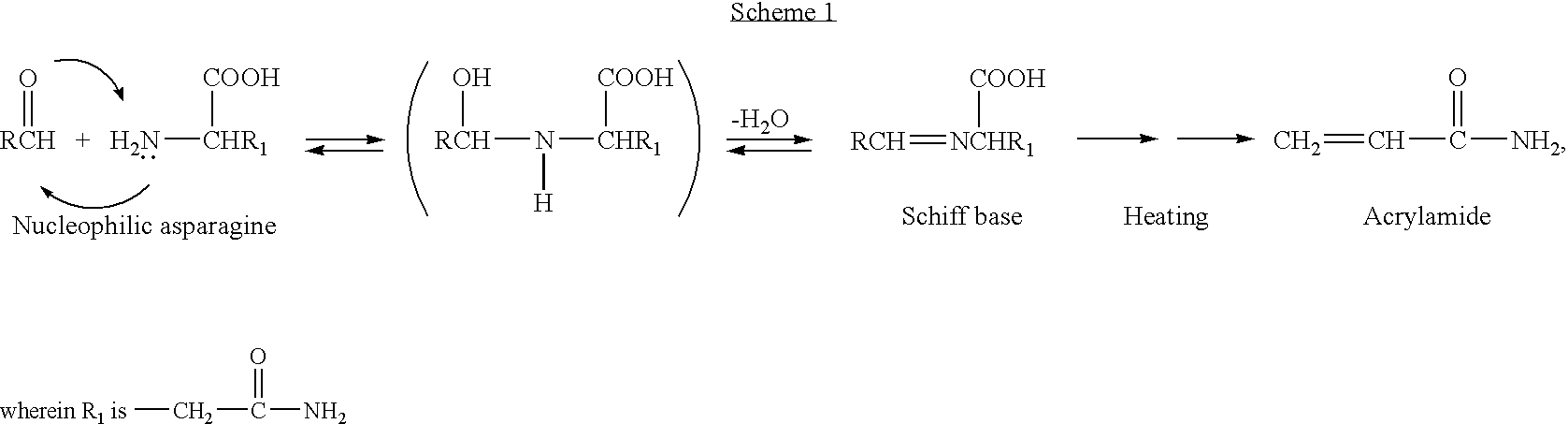
Method for the reduction of acrylamide formation
InactiveUS20060240174A1Reduce acrylamide formationReduce formationConfectionerySweetmeatsProtonationAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a method for the reduction of acrylamide formation, in which a nucleophilic a-amino group (—NH2) is protonated and converted into a non-nucleophilic amine (—NH3+). The inventive method has the effect of allowing the formation of acrylamide to be highly reduced by simple treatment with a pH-lowering agent. Particularly, when applied to foods or foods ingredients, the inventive method has the effect of allowing the formation of acrylamide to be highly reduced without affecting the flavor and color of the foods or foods ingredients.
Owner:JUNG MUN YHUNG
Method of surface cross-linking highly neutralized superabsorbent polymer particles using bronsted acids
A method of surface cross-linking superabsorbent polymer particles having a relatively high degree of neutralization is provided. Brønsted acids are selectively applied onto the surface of the superabsorbent polymer particles to selectively facilitate a relatively high number of protonated carboxyl groups at the surface of the superabsorbent polymer particles while the relatively high degree of neutralization in the core of the superabsorbent polymer particles remains substantially unaffected.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
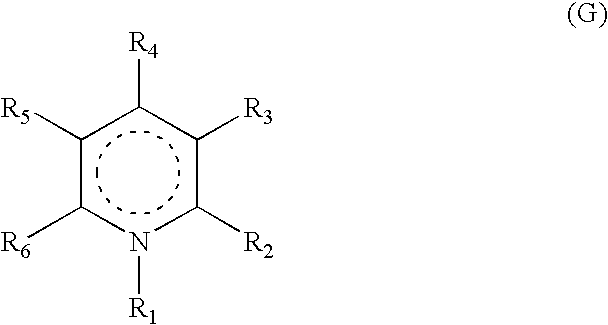
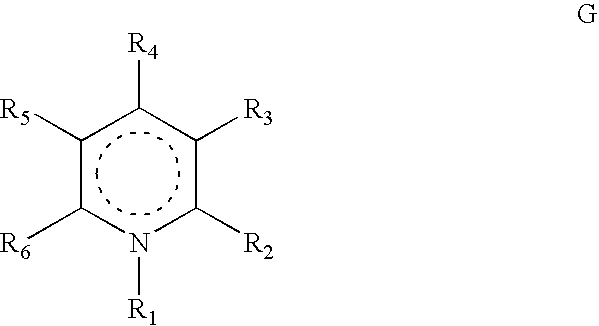
Heterocyclic compounds, their preparation and their use as medicaments, in particular as Anti-alzheimer agents
The invention is related to compound which comprises at least one radical C═Y, Y being O or S, and an oxidable and non protonable nitrogen atom N wherein the distance (d) between the at least one carbon atom of the radical group C═Y and the nitrogen atom, when oxidized, is comprised between 0.3 and 0.8 nanometers. The invention is related to new heterocyclic compounds defined by formula G, their preparation, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising them and to their use as therapeutic agents, particularly in the treatment of neurodegenerative or Alzheimer disease.
Owner:INST NAT DES SCI APPLIQUEES DE ROUEN INSA +2
Preparation method of protonized ionic liquid modified rubber/inorganic filler composite material
InactiveCN101831093AThe synthesis process is simpleEnvironmentally friendly and pollution-freeProtonationVulcanization
The invention relates to a preparation method of a protonized ionic liquid modified rubber / inorganic filler composite material, which comprises the steps of: 1, preparing a structure of a functional protonized ionic liquid; and 2, ensuring that the functional protonized ionic liquid is used for an in situ modified inorganic filler reinforced rubber composite material. The invention can effectively lower the agglomeration among strong-polarity inorganic fillers, improves the diffusion of the fillers in a rubber base body, and is beneficial to improving the processing property, the vulcanization characteristic, the mechanical property, the abrasive resistance and the like of the rubber / inorganic filler composite material. The method has the characteristics of popularization and low cost, and can be widely applied to preparing various high-property rubber / inorganic filler composite materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Analogs of biologically active, naturally occurring polyamines, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment
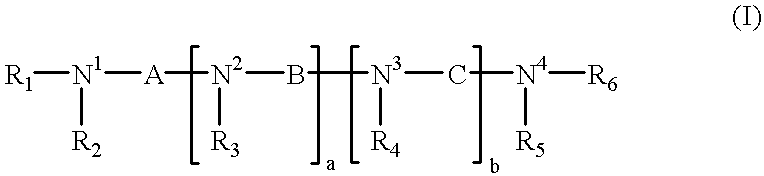
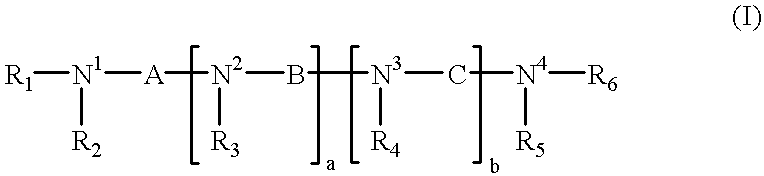
Polyamines having the formula:or a salt thereof with a pharmaceutically acceptable acid wherein: R1-R6 may be the same or different and are alkyl, aryl, aryl alkyl, cycloalkyl, optionally having an alkyl chain interrupted by at least one etheric oxygen atom, or hydrogen;N1, N2, N3 and N4 are nitrogen atoms capable of protonation at physiological pH's;a and b may be the same or different and are integers from 1 to 4;A, B and C may be the same or different and are bridging groups which effectively maintain the distance between the nitrogen atoms such that the polyamines:(i) are capable of uptake by a target cell upon administration thereof to a human or non-human animal; and(ii) upon uptake by the target cell, competitively bind via an electrostatic interaction between the positively charged nitrogen atoms to substantially the same biological counter-anions as the intracellular natural polyamines in the target cell;the polyamines, upon binding to the biological counter-anion in the cell, function in a manner biologically different than the intracellular polyamines, the polyamines not occurring in nature; as well as pharmaceutical compositions embodying the polyamines and methods of treating patients requiring anti-neoplastic therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Stable Aqueous Systems Comprising Proteins
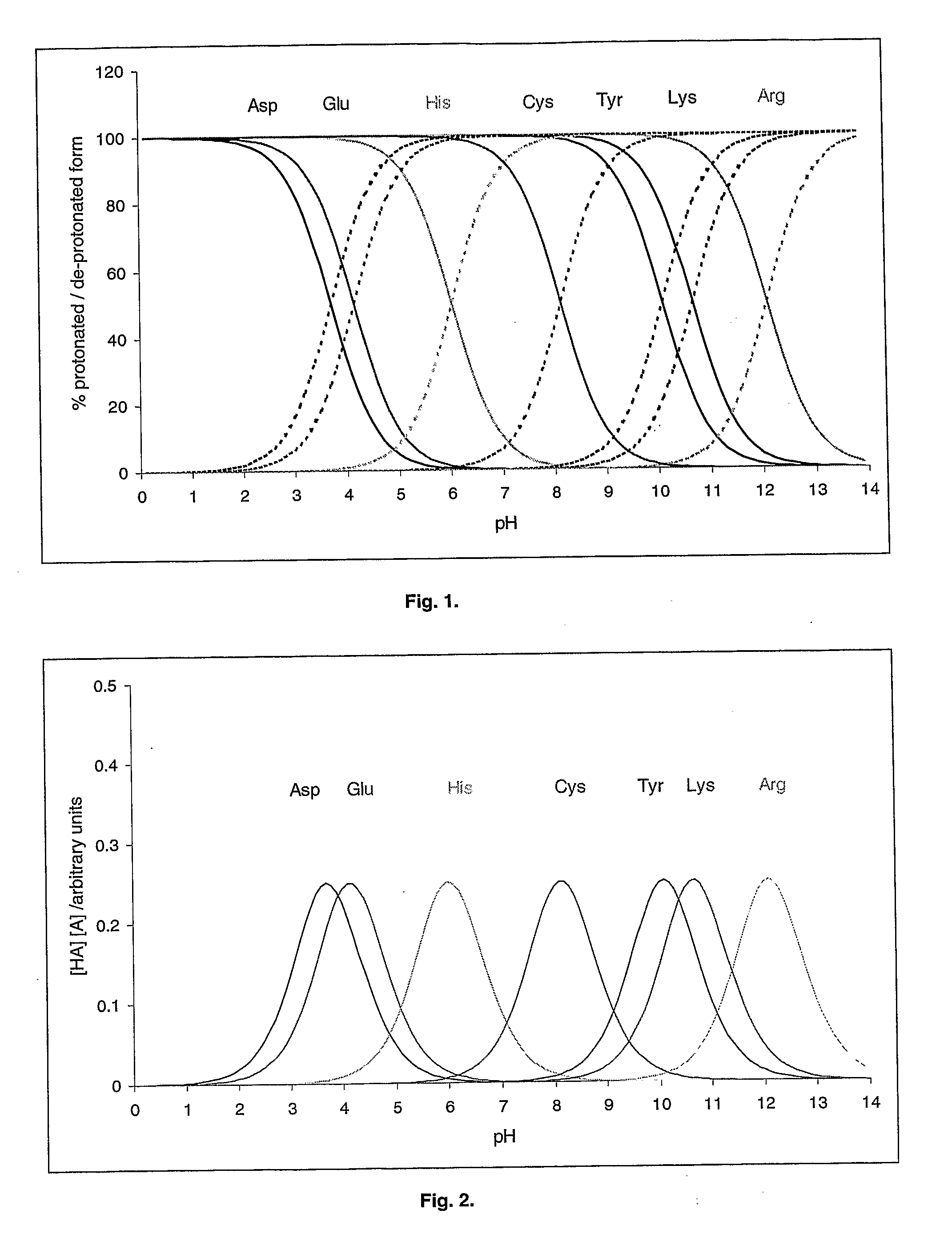
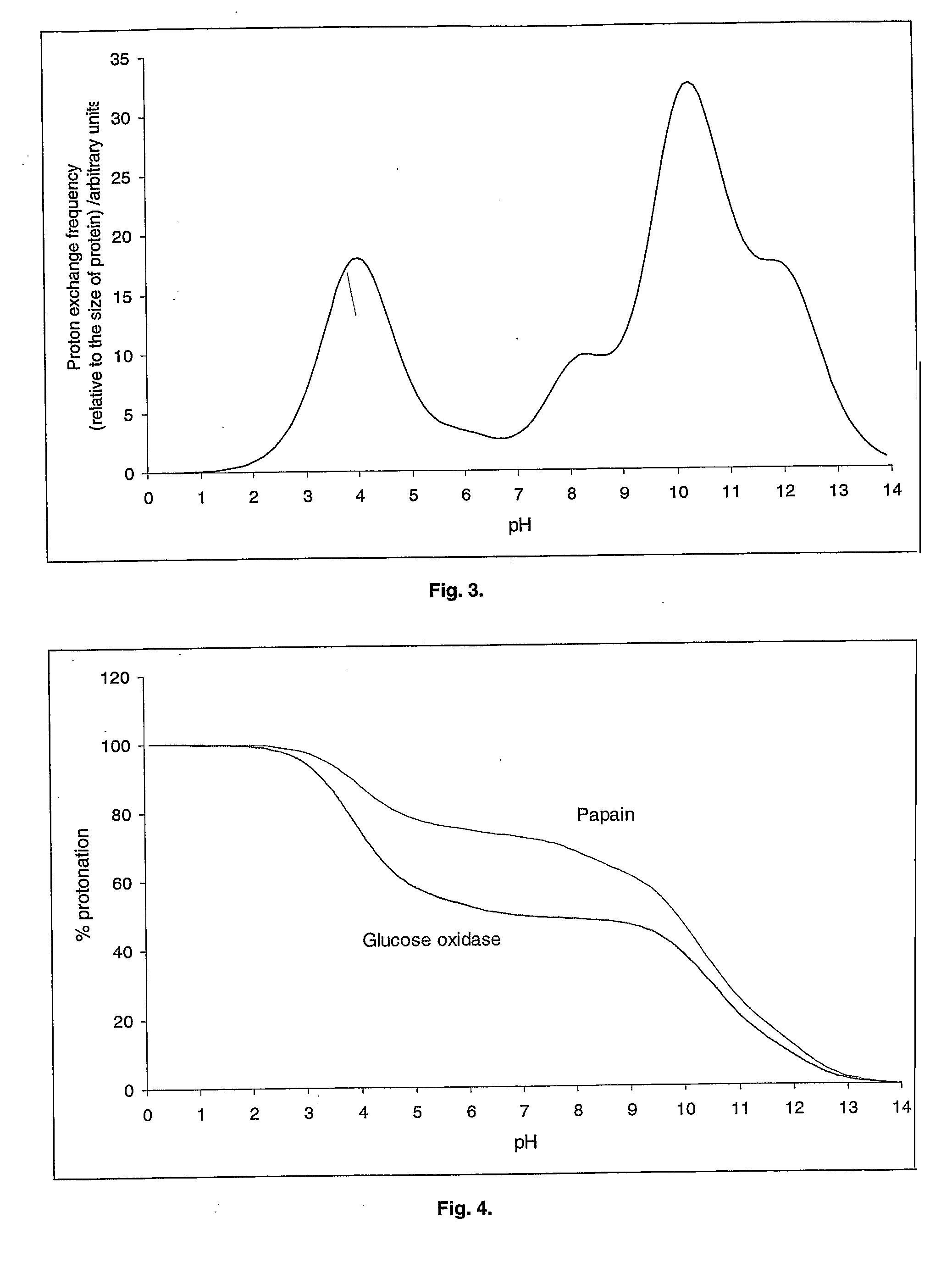
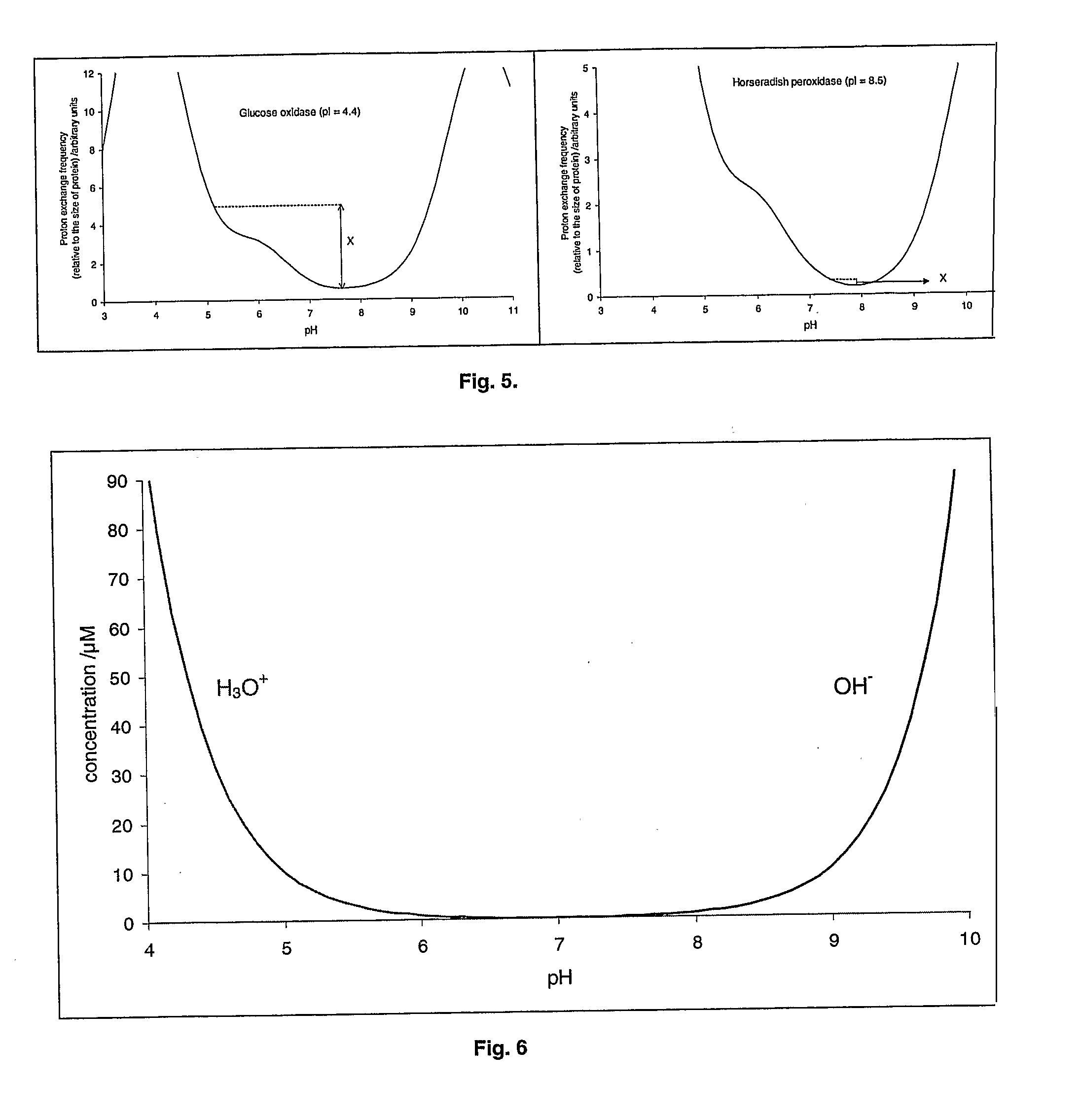
An aqueous system comprises a protein and one or more stabilising agents, characterised in that (i) the one or more stabilising agents have ionisable groups capable of exchanging protons with the protein and with the ionised products of water dissociation; (ii) the ionisable groups include first groups that are positively charged when protonated and uncharged when deprotonated, and second groups that are uncharged when protonated and negatively charged when deprotonated; and (v) the pH of the composition is within a range of protein stability that is at least 50% of the maximum stability of the protein with respect to pH.
Owner:ARECOR LTD
Dispersions containing organopolysiloxane/polyurea copolymers
Aqueous dispersions containing organopolysiloxane / polyurea copolymers prepared by reacting aminoalkyl-functional organopolysiloxanes with a diisocyanate in water in the presence of a protonating acid, and optionally one or more surfactants and / or protective colloids. The organopolysiloxane / polyurea polymers may be prepared without the presence of ionic groups if desired.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
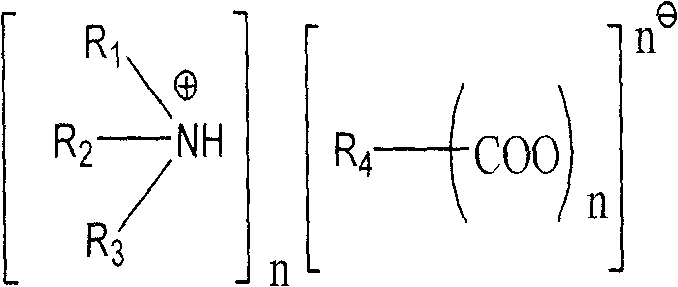
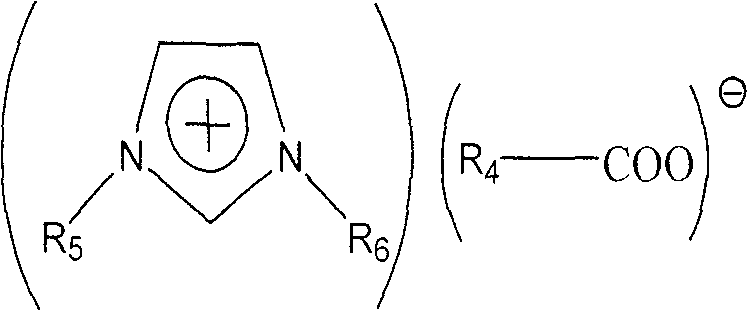


![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00001.png)
![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00002.png)
![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00003.png)