Patents
Literature
1413 results about "Electrostatic interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
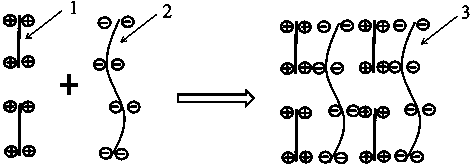
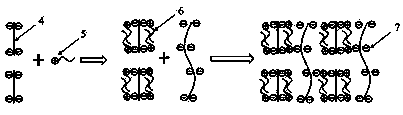
Electrostatic interaction (van der Waals interaction): The attractive or repulsive interaction between objects having electric charges.
Biodegradable mixed polymeric micelles for gene delivery
InactiveUS6210717B1Kind be easilySimple contentOrganic active ingredientsNanotechGene deliveryPolyester
A biodegradable, mixed polymeric micelle used to deliver a selected nucleic acid into a targeted host cell contains an amphiphilic polyester-polycation copolymer and an amphiphilic polyester-sugar copolymer. The polyester-polycation copolymer forms an electrostatic interaction with polyanionic nucleic acids, and the polyester-sugar copolymer directs the micelle-nucleic acid complex to cells in vivo. Additional copolymers with similar properties may also be included. The composition improves delivery efficiency by providing a particulate gene carrier for which particle size and charge density are easily controlled by multivariate means. Various kinds of ligands and other functional compounds may be also be introduced using the composition. The composition may be used in a method for transforming a targeted host cell with a selected nucleic acid.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
Supercharged proteins for cell penetration
InactiveUS20110112040A1Improved cell penetrationReduce biological activityMicrobiological testing/measurementSaccharide peptide ingredientsInfective disorderDisease cause
Compositions, systems and related methods for delivering a supercharged protein or a complex of a supercharged protein and therapeutic agent (e g, nucleic acid, peptide, small molecule) to cells are disclosed. Superpositively charged proteins may be associated with nucleic acids (which typically have a net negative charge) via electrostatic interactions. The systems and methods may involve altering the primary sequence of a protein in order to “supercharge” the protein (e g, to generate a superpositively-charged protein). The compositions may be used to treat proliferative diseases, infectious diseases, cardiovascular diseases, inborn errors in metabolism, genetic diseases, etc.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for preparing biomedical metal alloy material with multi-drug delivery system
InactiveUS20130164346A1Good biocompatibilityImprove adhesionInorganic non-active ingredientsSurgeryMetal alloyPharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system. A biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system according to the present invention is prepared by incorporating a therapeutic agent into a biodegradable material to prepare particles containing the therapeutic agent, treating the surface of the particles containing the therapeutic agent to have a charge opposite to the surface charge of a metal alloy material, and inducing an electrostatic interaction between the surface charges of the particles containing the therapeutic agent and the metal alloy material to immobilize the surface-treated particles containing the therapeutic agent on the surface of the metal alloy material.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Electrostatic levitation and attraction systems and methods
InactiveUS6841917B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageEngineeringElectrostatic interaction
An electrostatic interaction system includes a first structure having a first fixed electrostatic charge and a second structure having a second fixed electrostatic charge. The polarity of the first and second fixed electrostatic charges determines a positional relationship of the first structure to the second structure.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
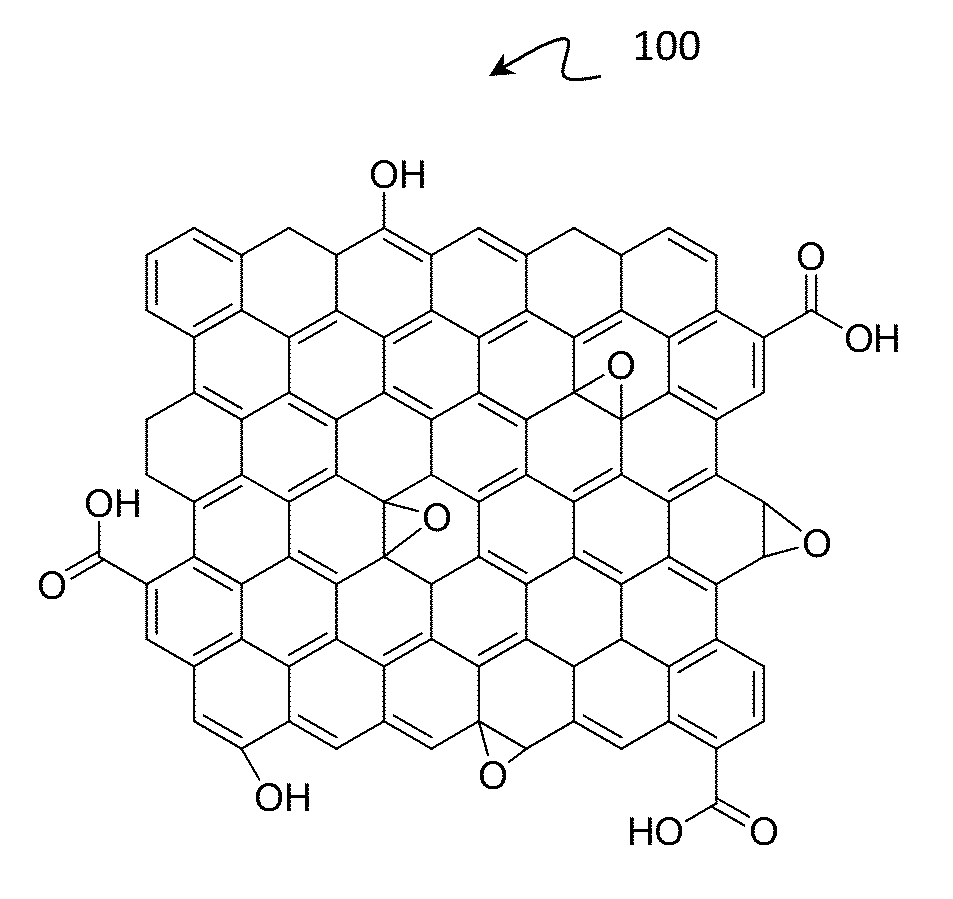
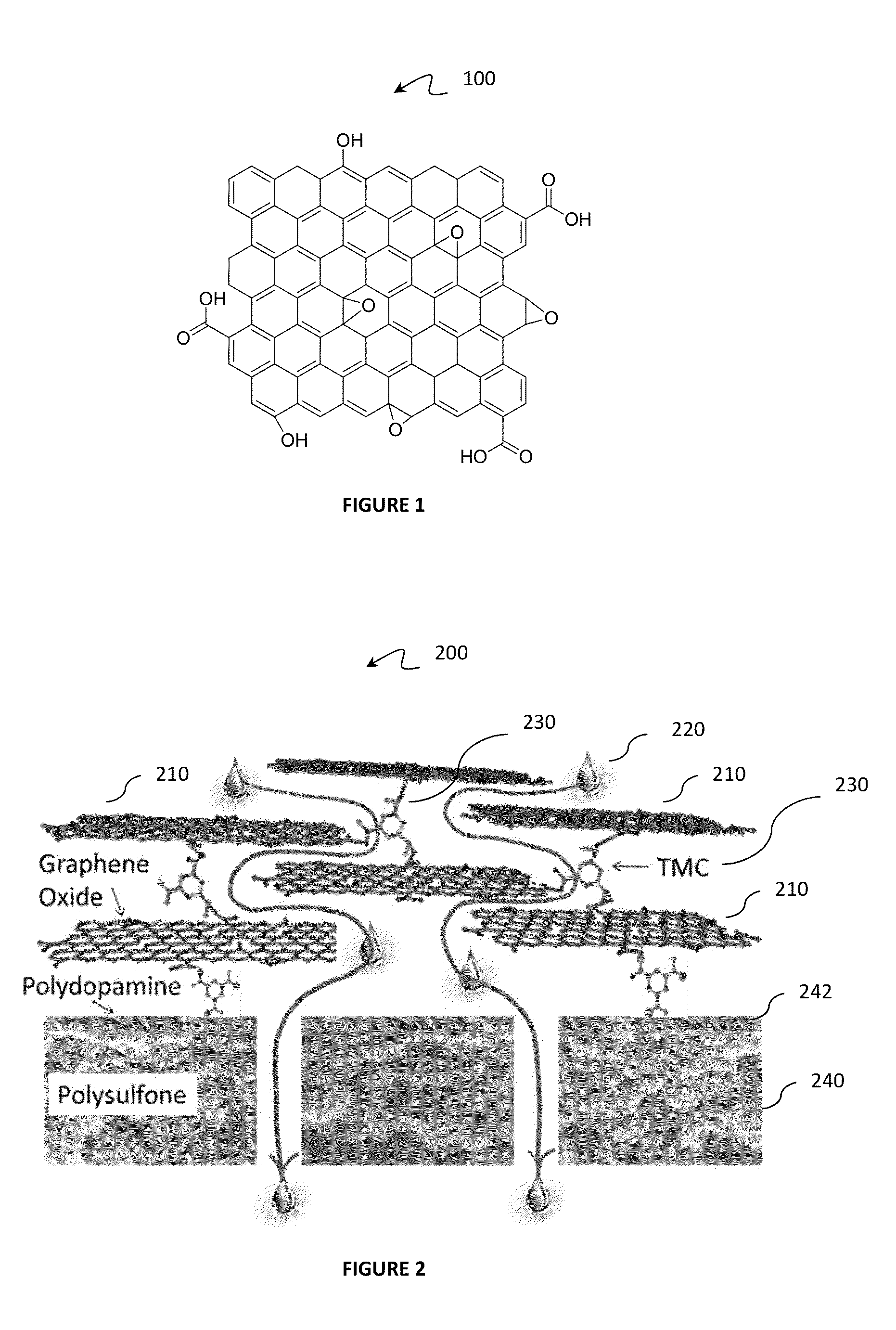
Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide membranes via electrostatic interaction and eludication of water and solute transport mechanisms
A method for synthesizing a water purification membrane is presented. The method includes stacking a plurality of graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets to create the water purification membrane, the stacking involving layer-by-layer assembly of the plurality of GO nanosheets and forming a plurality of nanochannels between the plurality of GO nanosheets for allowing the flow of a fluid and for rejecting the flow of contaminants. The method further includes cross-linking the plurality of GO nanosheets by 1,3,5-benzenetricarbonyl trichloride on a polydopamine coated polysulfone support.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Preparing method of nanometer particle carbon nanotube compound catalyst
InactiveCN101224434AEasy to operateGood catalyticOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsModified carbonElectrostatic interaction
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano particle carbon nanotube compound catalyst. The carbon nanotube with electric charges on surface is obtained from the materials which can generate non-covalent action with the carbon nanotube. Then nano particle with opposite electric charges on surface to that of the non-covalent modified carbon nanotube is added and completely mixed, and excess nano particle is removed to finally obtain the nano particle carbon nanotube catalyst compound. A plurality of nano particle carbon nanotube catalyst compounds can be prepared by the invention, all of which represent very good catalytic activities. The invention adopts the method of non-covalent modified carbon nanotube to obtain carbon nanotube with perfect surface. Meanwhile, the invention provides the nano particle, in particular, the morphology controllable nano particle on the load of carbon nanotube with an effective way by utilizing the electrostatic interaction of carbon nanotube and namo particle, thus extending the applications of morphology controllable nano particle in catalytic field.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of cobalt electro-catalysis oxygen reduction material wrapping nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube
ActiveCN105413730AOrderly arrangement and assemblyImprove performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesCooking & bakingOxygen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cobalt electro-catalysis oxygen reduction material wrapping a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube. The method includes the following steps of making melamine, cobalt nitrate hexahydrate and glucose react to obtain a self-assembled melamine precursor, and baking the self-assembled melamine precursor to obtain a cobalt nanoparticle hybrid material electro-catalysis oxygen reduction agent wrapping the nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube. In preparation of the precursor, a self-assembled body can be formed through the electrostatic interaction and the hydrogen-bond interaction by means of nitrate radicals and melamine under the acid condition, cobalt ions are adsorbed into the self-assembled body, ordered arrangement and assembly of materials in the high-temperature baking process are facilitated by the pre-assembled precursor, and therefore more catalysis active sites are exposed, and the improvement of the performance of a catalyst is facilitated.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Quantum dot/acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex, preparation method of quantum dot/acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex, and colored conversion coating
ActiveCN103772872AGood dispersionEvenly dispersedPhotomechanical coating apparatusPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPhotoluminescenceResin matrix
The invention discloses a quantum dot / acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex, a preparation method of the quantum dot / acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex, and a colored conversion coating, wherein the quantum dot / acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex is prepared by virtue of electrostatic interaction between an annion acrylate polymer and quantum dots with opposite charges. According to the invention, the quantum dots are pre-dispersed into the acrylate polymer, so as to prepare quantum dot / acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex. By virtue of similar composition of an acrylate polymer protection layer and acrylics as well as an acrylics modified photoresist resin matrix, the quantum dots can be easily dispersed into photoresist, are not easy to separate and are uniformly dispersed without aggregation, and thus the photoluminescent characteristic of the quantum dots is ensured. After the colored conversion coating prepared from the quantum dot / acrylate polymer nanocrystal complex is applied to a display, the colors of sub-pixel units of R / G / B colors corresponding to the colored conversion coating are relatively pure and have the relatively high saturability, energy of a backlight is sufficiently utilized, and the luminous efficiency is relatively high.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Pharmaceutical composition containing surface-coated microparticles
InactiveUS20110189299A1Increase capacityImprove efficiencyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMedicineMicroparticle
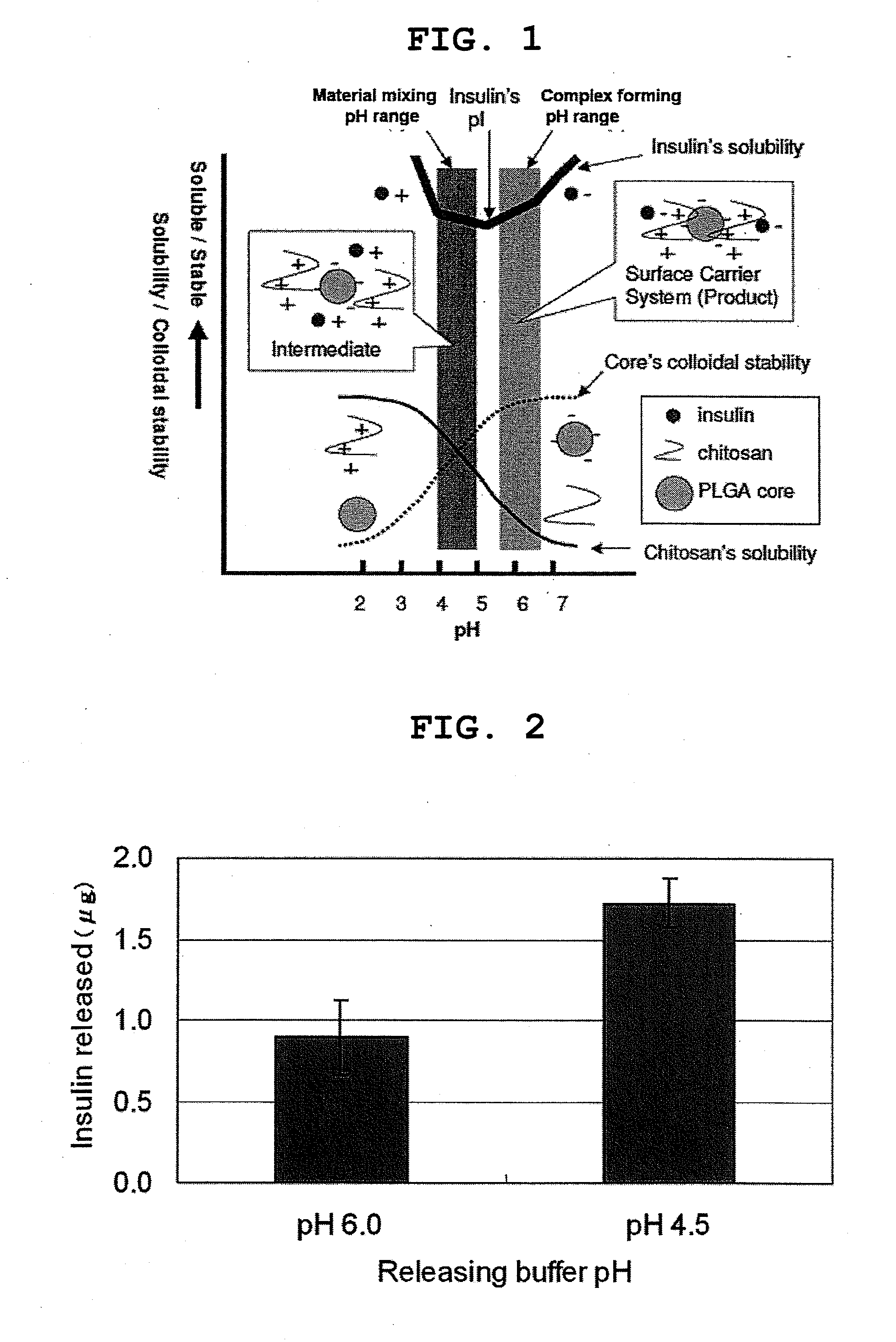
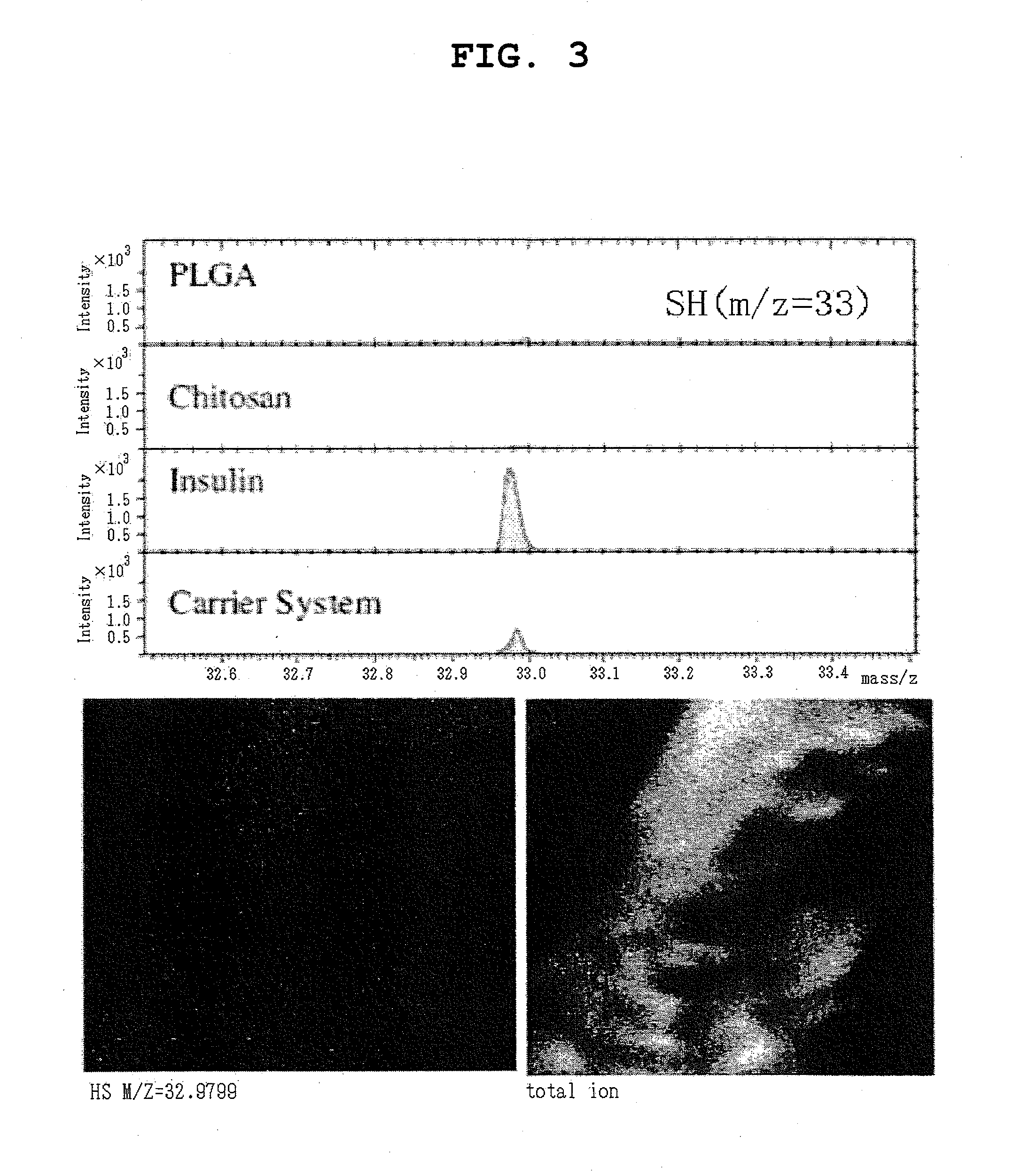
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition that can be used for efficient administration of low-molecular weight drugs and polymeric compounds such as peptides and proteins by methods other than injection, as well as a method for producing the composition. The pharmaceutical composition is for transmucosal administration and comprises (a) a drug having a positive or negative charge at a predetermined pH, (b) a pharmaceutically acceptable small particle and (c) a pharmaceutically acceptable surface-coating polymer capable of being electrically charged at the pH, wherein the surface of the small particle is coated by the surface-coating polymer, the drug is immobilized on the surface of the small particle via the surface-coating polymer, and a complex is formed by a noncovalent interaction between the small particle and the surface-coating polymer and a concurrent electrostatic interaction between the surface-coating polymer and the drug.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
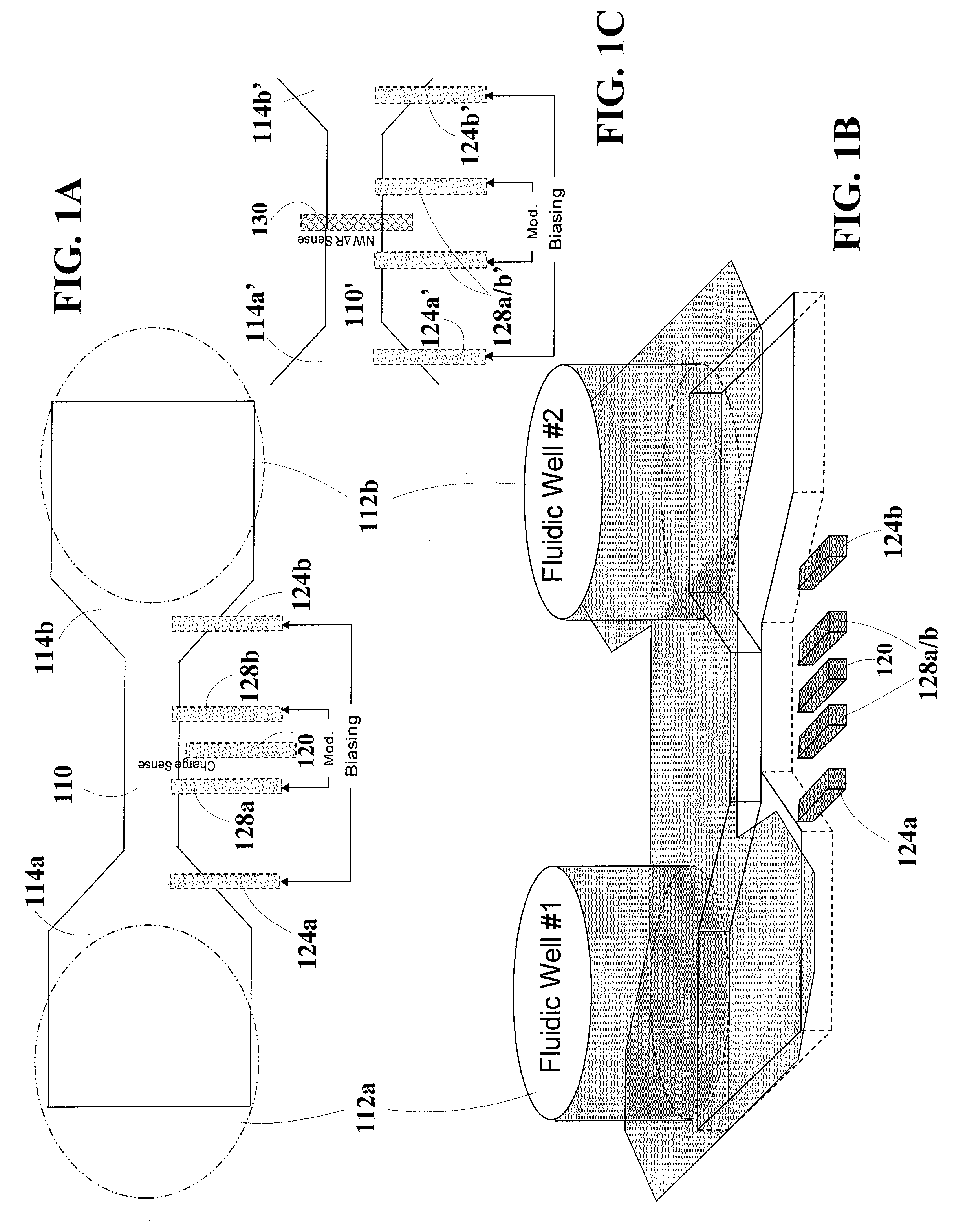
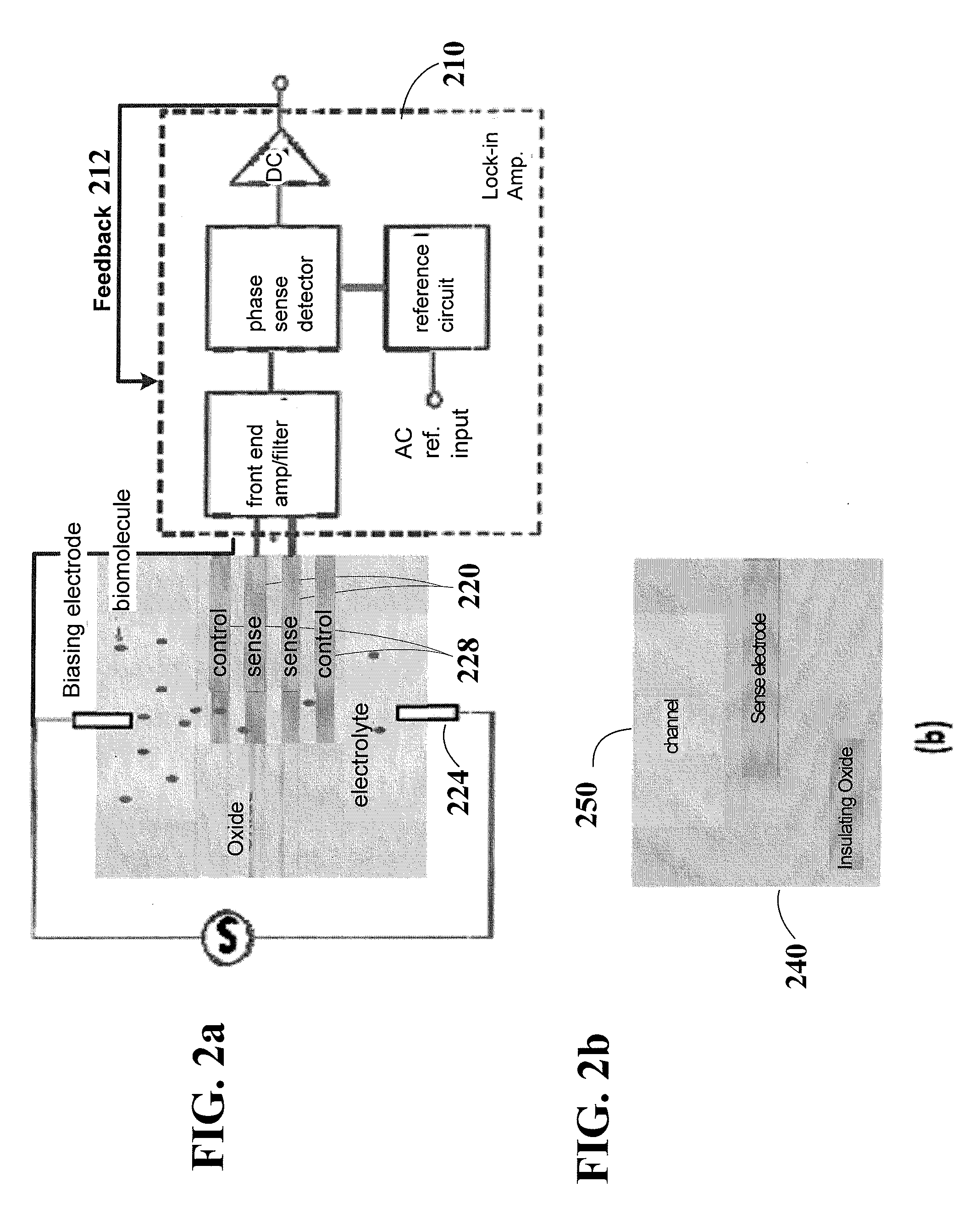
Electro-diffusion enhanced bio-molecule charge detection using electrostatic interaction
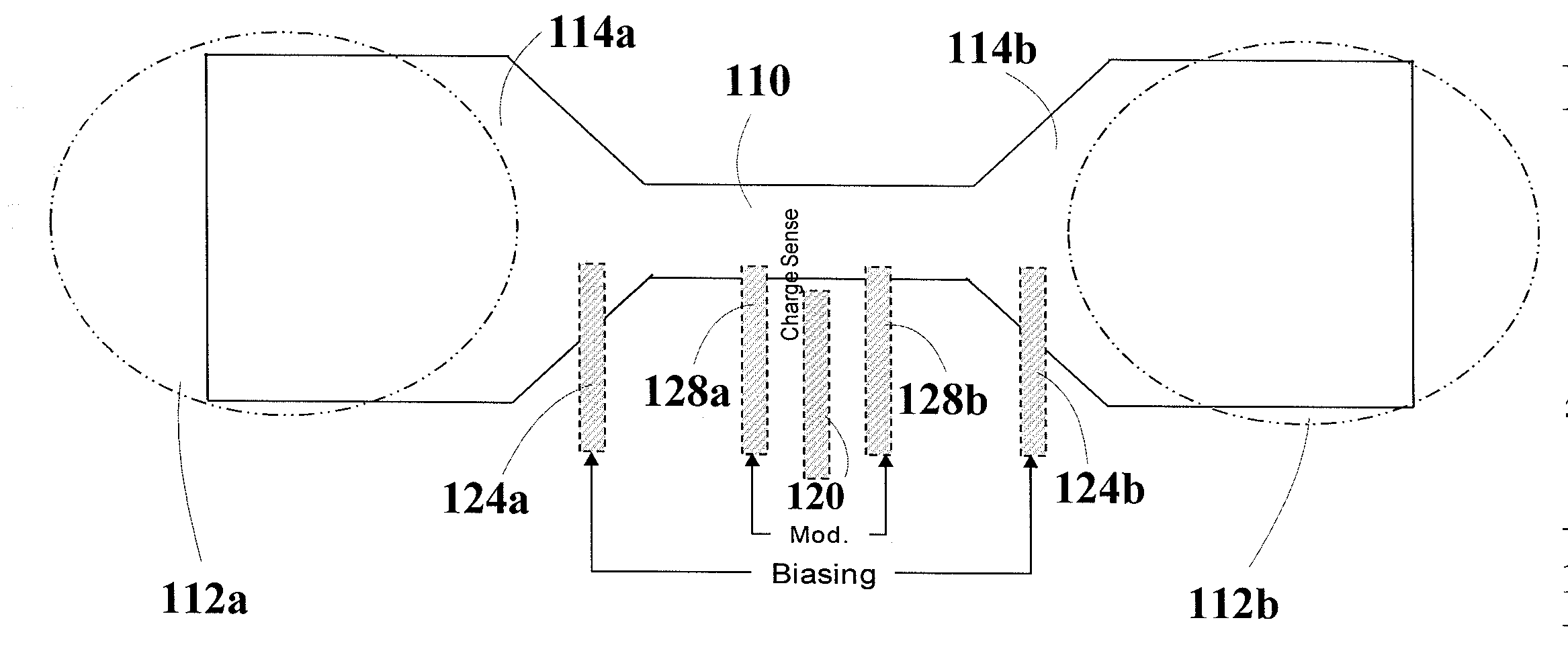
According to one aspect, the disclosure is directed to an example embodiment in which a circuit-based arrangement includes a circuit-based substrate securing a channel, with an effective width that is not limited by the Debye screening length, along a surface of the substrate. A pair of reservoirs are included in or on the substrate and configured for containing and presenting a sample having bio-molecules for delivery in the channel. A pair of electrodes electrically couple a charge in the sample to enhance ionic current flow therein (e.g., to overcome the electrolyte screening), and a sense electrode is located along the channel for sensing a characteristic of the biological sample by using the electrostatic interaction between the enhanced ionic current flow of the sample and the sense electrode. Actual detection occurs by using a charge-signal processing circuit to process the sensed charge signal and, therefrom, provide an output indicative of a signature for the bio-molecules delivered in the channel.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biogastrone acid-polyethyleneglycol /chitosan liver target composite drug administration system and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101254308AThe method is novel and simpleMild conditions for pelletingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCancer cellPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a novel liver target drug carrier-glycyrrhetinic acid-polyethylene glycol / chitosan or chitosan derivative liver target compound drug delivery system. During the preparation of the nano-drug delivery system, the liver target small-molecule glycyrrhetinic acid is firstly used for modifying amino polyethylene glycol by the different sites, then a water soluble big-molecule liver target compound is prepared and is mixed with a solution containing chitosan or chitosan derivative by a certain proportion, an ion cross-linking agent is added under the stirring condition, and a target group is introduced at the same time of the spontaneous formation of nanoparticles by physical winding and electrostatic interaction. The method of introducing the target group of the invention is novel, the formation of spheres is simple, the conditions are moderate, and the content of the target group is high (the weight percentage of glycyrrhetinic acid is 5 to 30 percent). The drug delivery system has strong killing capacity to the cancer cells, the in vitro experiments show that the drug delivery system has very strong binding capacity with the liver cells, and the high content of the target group can improve the liver target capacity of the drug delivery system, realize the target positioning of the liver and open a new way for the treatment of liver cancer.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
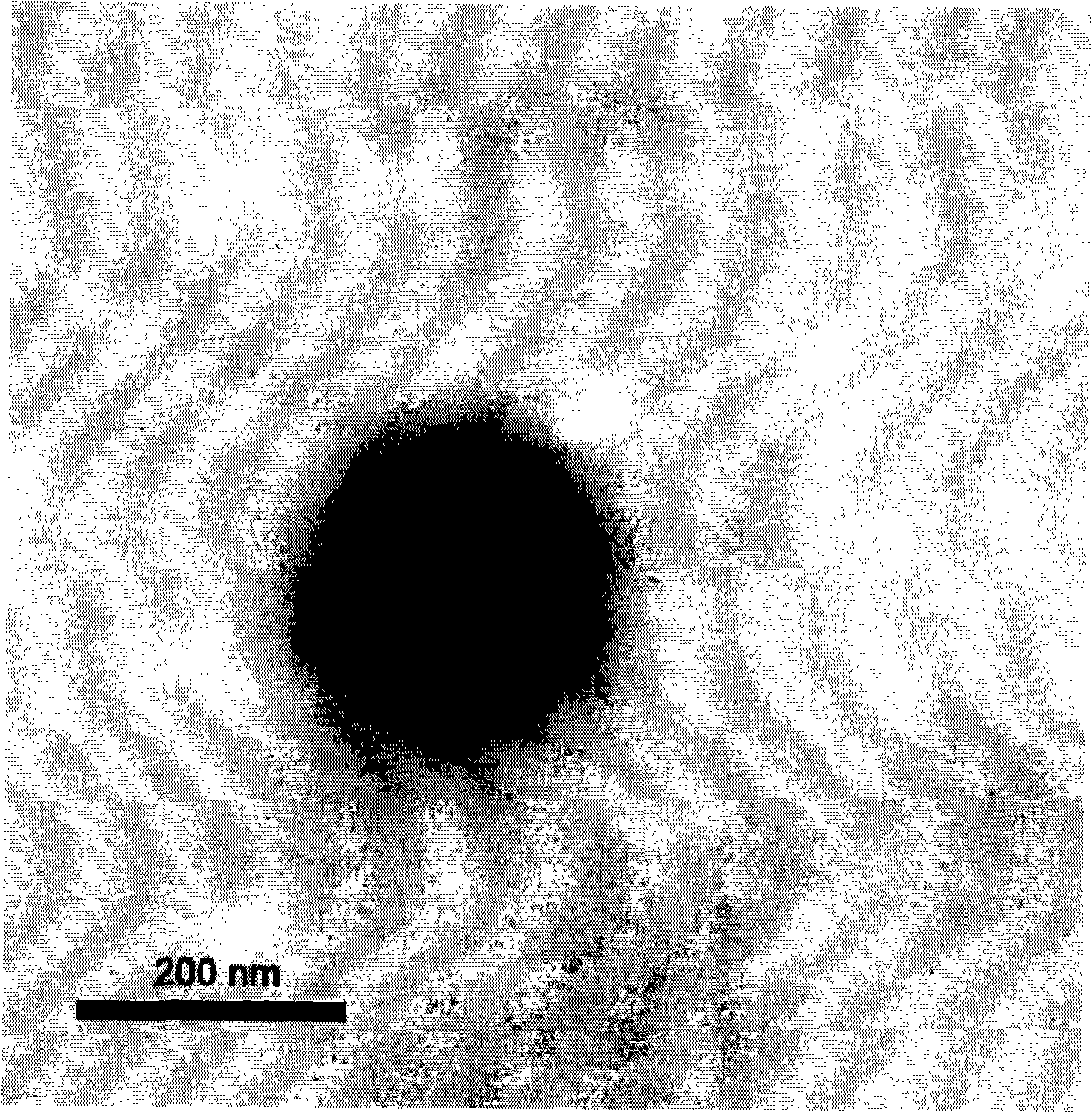
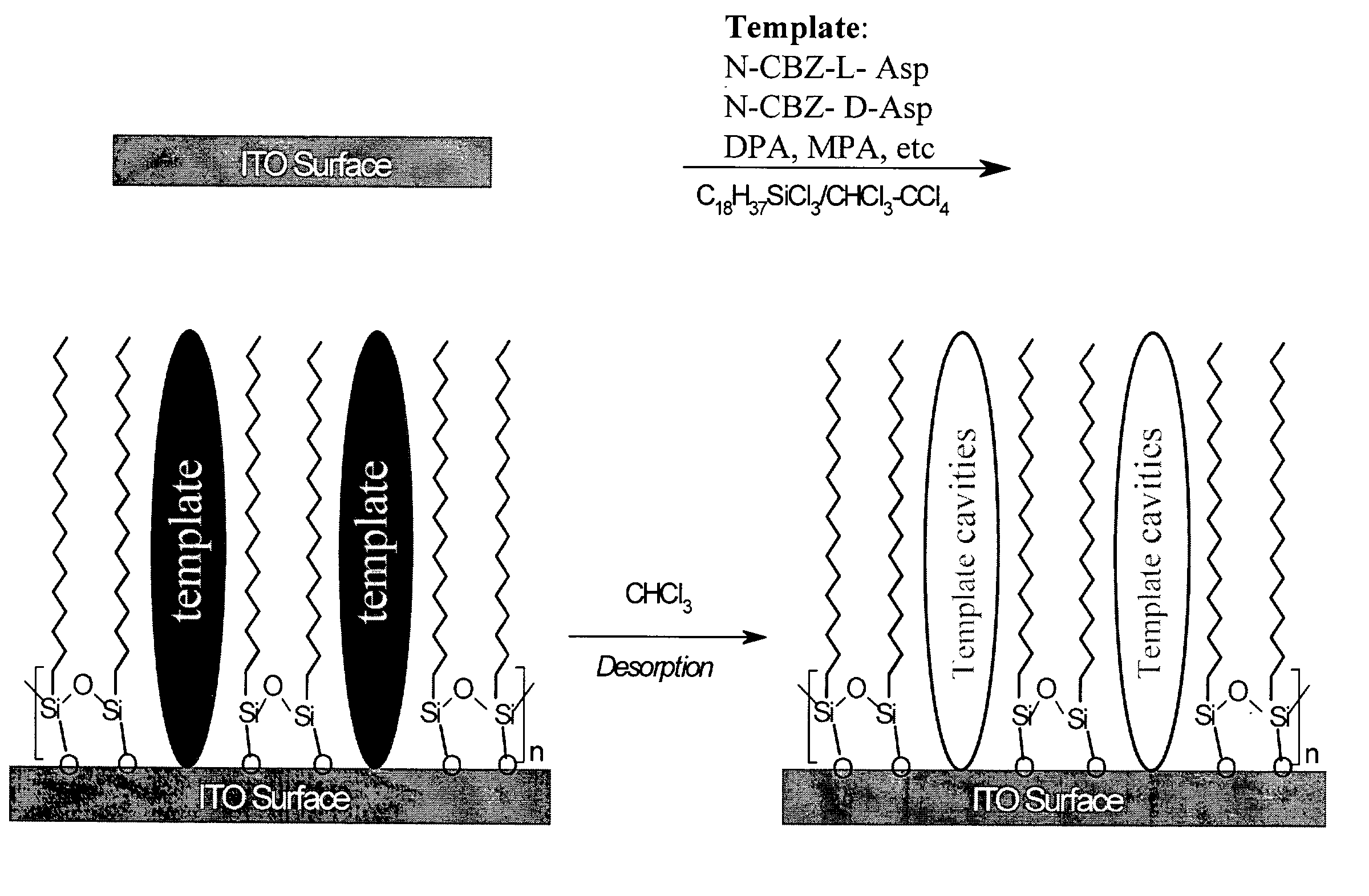
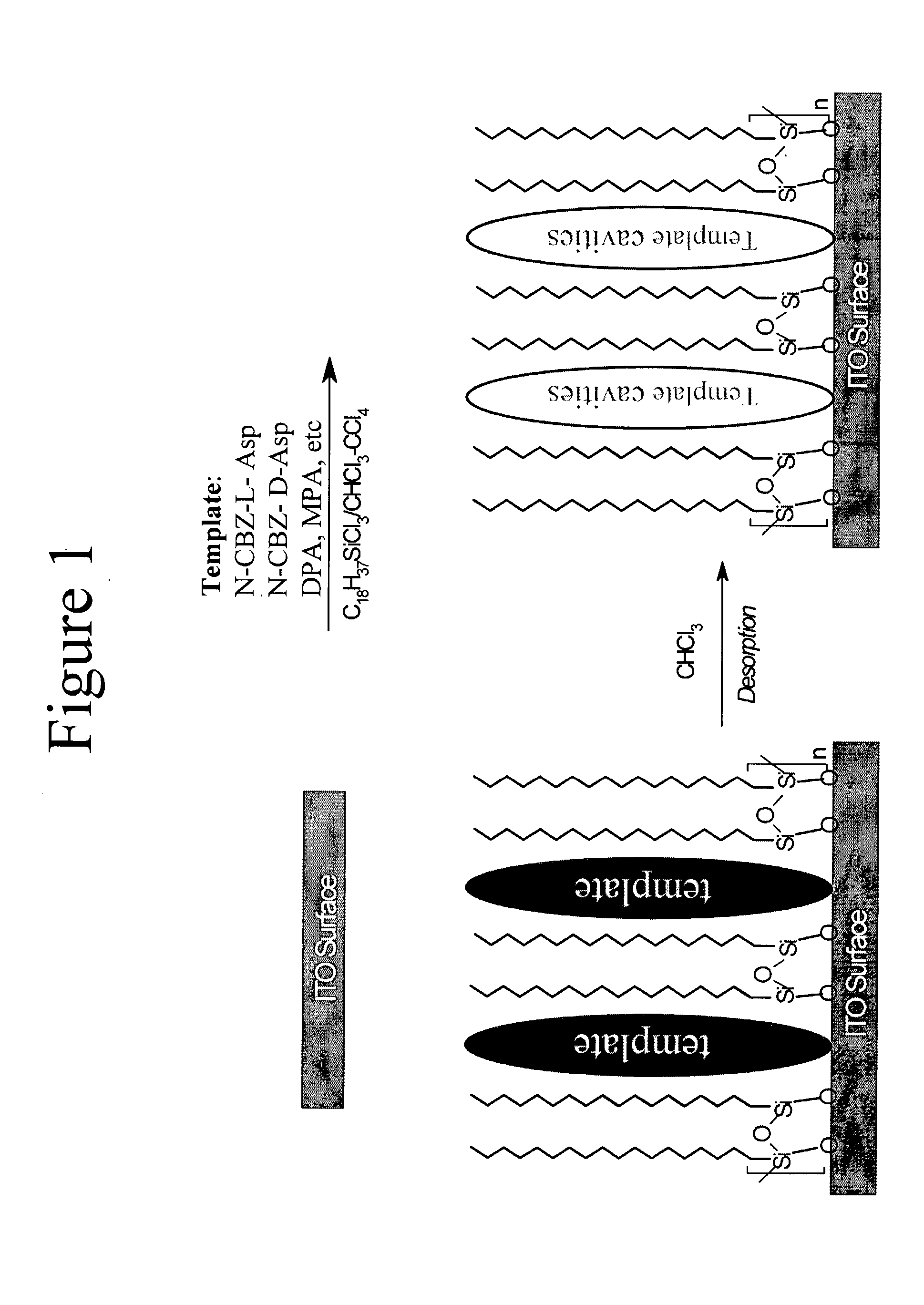
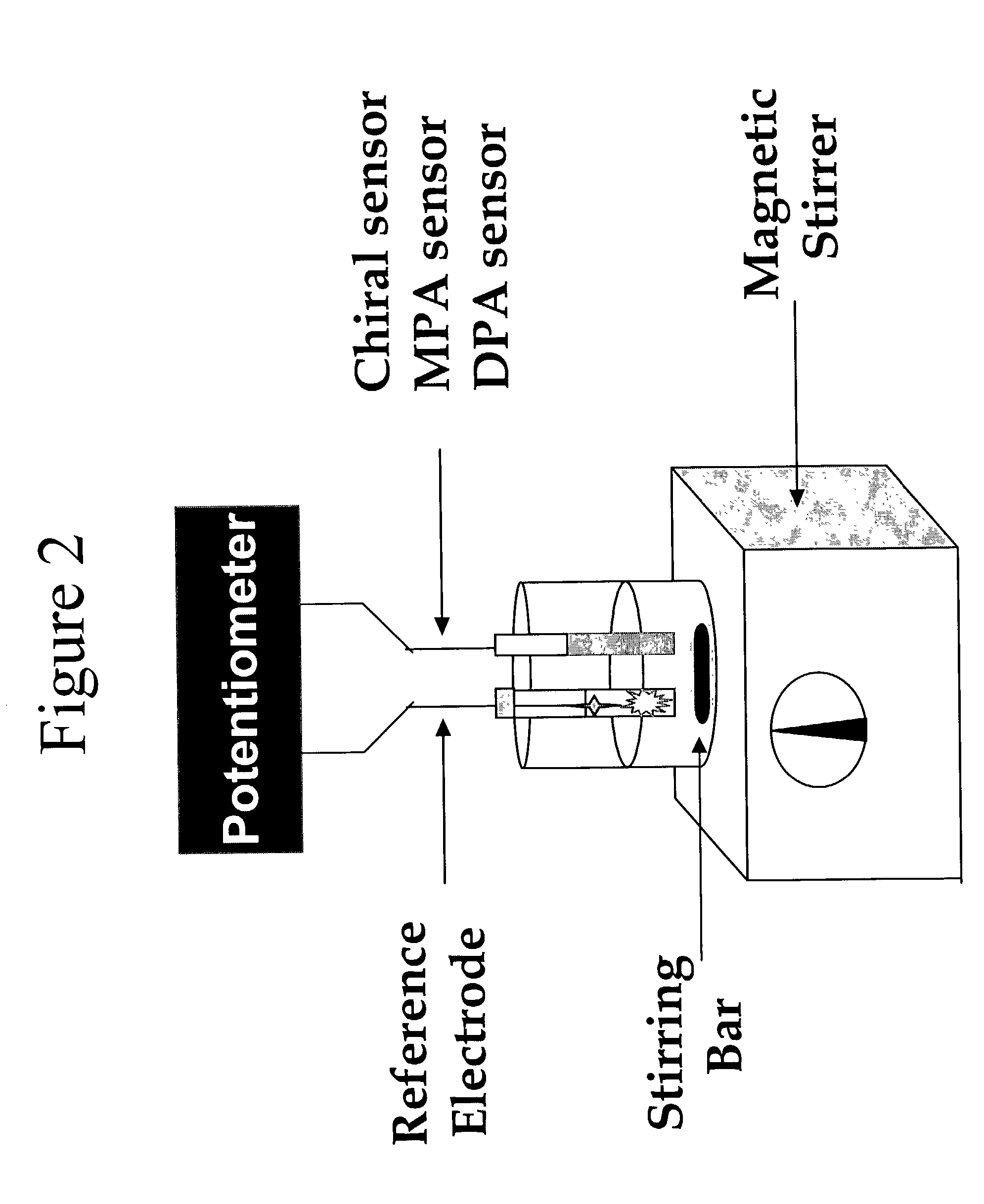
Surface imprinting: integration of molecular recognition and transduction
InactiveUS20040058380A1High sensitivityEnhanced signalBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCouplingElectrostatic interaction
Surface-molecularly imprinted sensors were fabricated for detecting ionic molecules. Target molecules are recognized by the combination of a hydrophobic interaction with the imprinted polymer layer to provide specificity and an electrostatic interaction to provide sensitivity Coupling surface imprinting techniques with an electrochemical detection method, such as potentiometry, allows specific recognition of target molecules and translation of the recognition event into an output signal by the sensor.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Cellulose-based magnetic aerogel material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104479174AHigh activityHigh specific surface propertiesOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismCelluloseFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a cellulose-based magnetic aerogel material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out chemical modification, thereby obtaining high-activity amphoteric cellulose; firmly combining the amphoteric cellulose and a graphene oxide through electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding forces and the like to build a framework of the aerogel material. Disperse loading of a magnetic nano ferroferric oxide can be achieved by virtue of the advantages of high surface activity and super-large specific surface area; the structure uniformity and the stability of the magnetic aerogel of the amphoteric cellulose are ensured through the steps of cross-linking, freeze-drying and the like; the characteristics of high specific surface properties, good affinity, biodegradability and the like of the cellulose are kept by the magnetic aerogel; and the magnetic aerogel obtains high surface activity and superparamagnetic property, has the advantages of low cost, high strength, amphoteric characteristic, biocompatibility and the like, has the characteristics of high specific surface area, high loading capacity, high surface activity, intelligent positioning and the like, and has significant adsorption capacity on pollutants such as heavy metal ions and organic molecules.
Owner:HAIMEN ZHUOWEI TEXTILE CO LTD
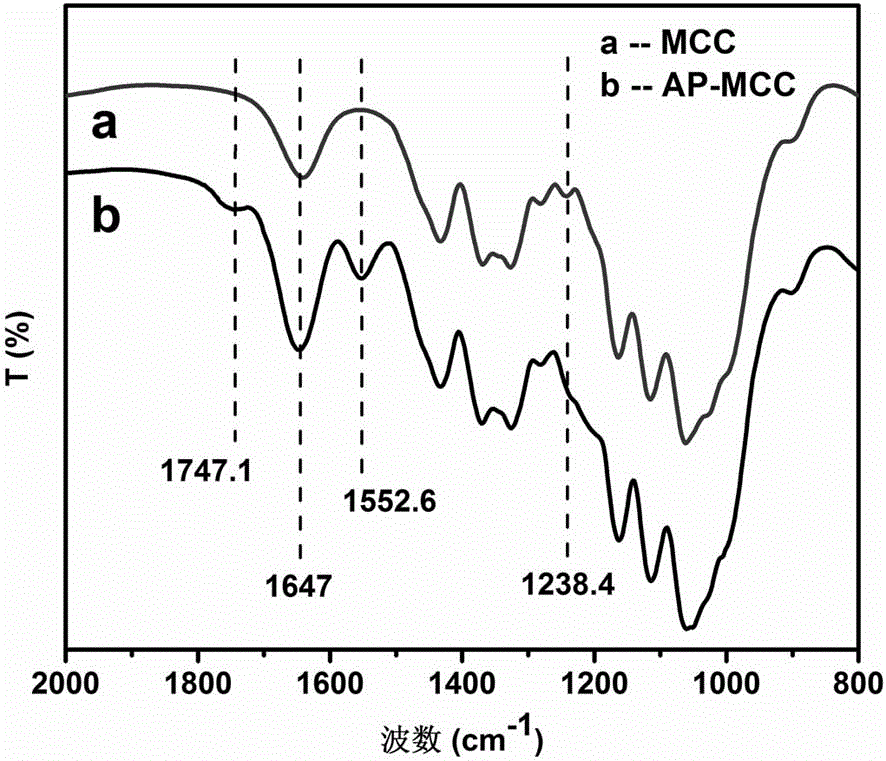
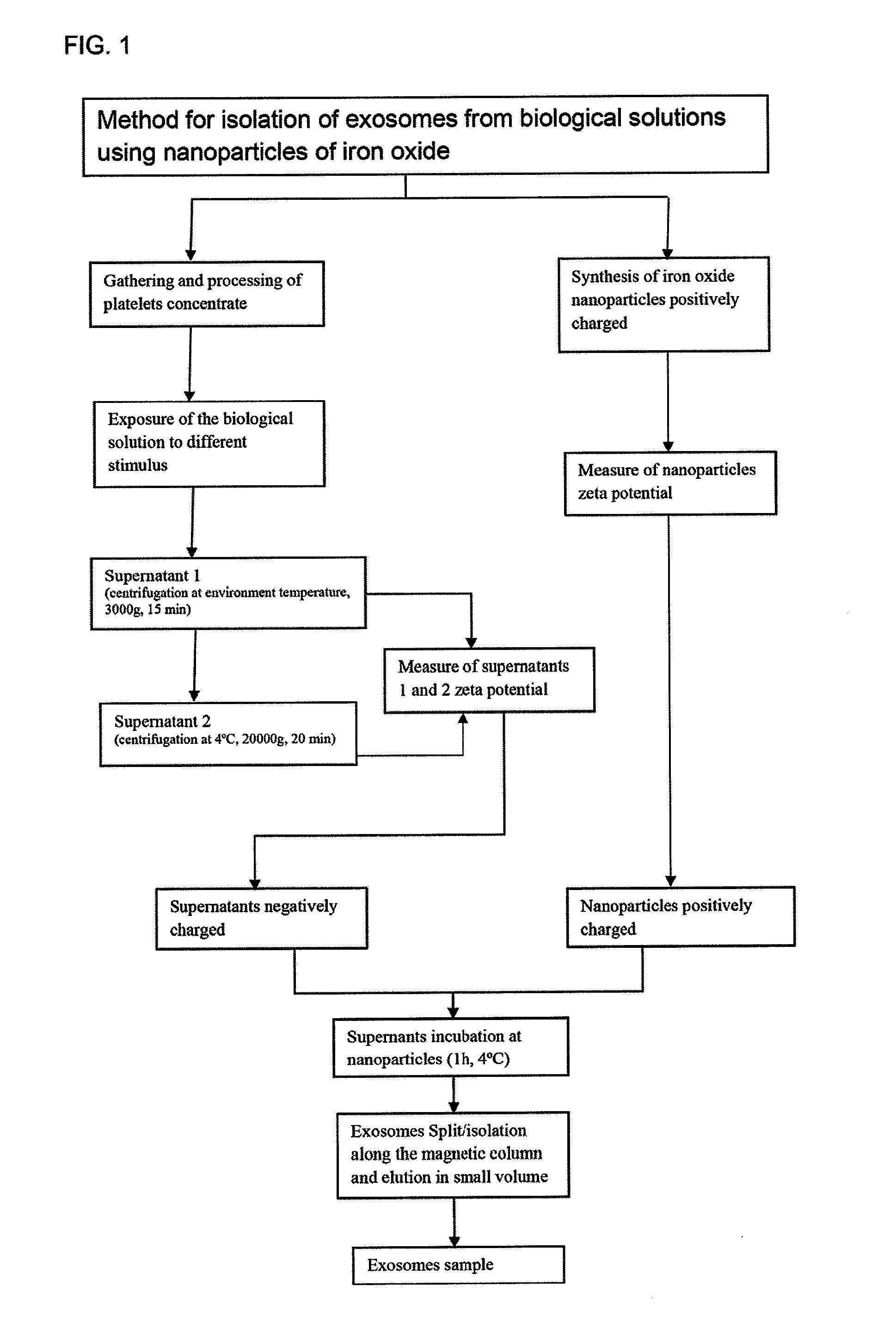
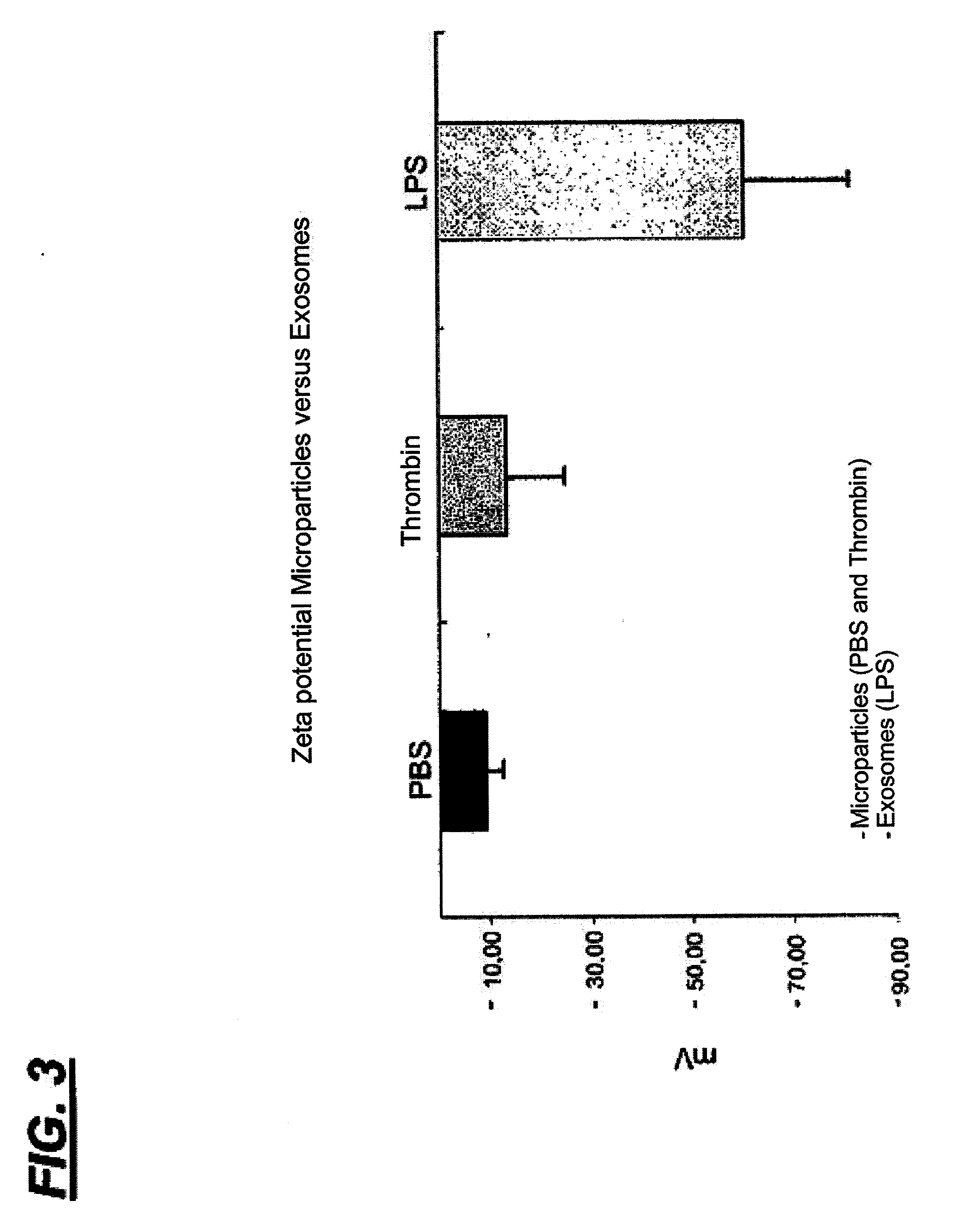
Method for isolating exosomes from biological solutions using iron oxide nanoparticles
InactiveUS20120070858A1Electrostatic separationMicrobiological testing/measurementZeta potentialMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for isolating exosomes from blood platelets using superparamagnetic nanoparticles of iron oxide (Fe3O4), by means of a charge attraction mechanism based on the predetermined Zeta potential of the exosomes. The method involves the use of iron oxide nanoparticles that are previously synthesised with a predetermined positive charge, and that bond to the negatively charged exosomes contained in the biological sample. During incubation, the cationic magnetic nanoparticles are absorbed by the surface of the membrane of the exosomes owing to electrostatic interaction. Exposure of the material to a magnetic field makes it possible to separate the exosomes bonded to the nanoparticles. The success of this technique has been confirmed by characterisation of the exosomes by flow citometry. The method has been shown to be suitable for this purpose, since it allows exosomes to be isolated and purified, without undergoing alterations of their original morphological and structural characteristics.
Owner:SOC BENEF ISRAELITA BRAS HOSPITAL ALBERT EINSTEIN
Coated particles for lithium battery cathodes
Particles of cathodic materials are coated with polymer to prevent direct contact between the particles and the surrounding electrolyte. The polymers are held in place either by a) growing the polymers from initiators covalently bound to the particle, b) attachment of the already-formed polymers by covalently linking to functional groups attached to the particle, or c) electrostatic interactions resulting from incorporation of cationic or anionic groups in the polymer chain. Carbon or ceramic coatings may first be formed on the surfaces of the particles before the particles are coated with polymer. The polymer coating is both electronically and ionically conductive.
Owner:SEEO
Method for preparing stealthy fabric with double functions of radar stealth and infrared stealth
ActiveCN104060474AImprove bonding fastnessExcellent infrared stealth effectPhysical treatmentMulti bandPolyurethane adhesive
The invention belongs to the field of absorbing material research, and particularly relates to a method for preparing stealthy fabric with double functions of radar stealth and infrared stealth. According to the method, the binding strength of a radar stealth layer and textile is improved by using electrostatic interaction between plasma grafting-introduced carboxyl and polyaniline absorbing materials and the surface etching effect of low-temperature plasma; the binding strength of the radar and the infrared stealth layers and the textile is improved by using the reactivity between a binary aldehyde crosslinking agent and amino on a polyaniline polymer and a microcapsule wall material and a polyurethane adhesive; the obtained stealth coating is not only good in binding strength with the textile, but also light in quality and good in durability, and has multi-band stealth effects of radar, infrared light and visible light.
Owner:江苏华宏昌明科技有限公司
Polymer microsphere containing inorganic nano microparticles, and its preparing method and use
The invention relates to a method for connecting nanoparticles and polymer spheres with chemical bonding in the polymer microspheres and its preparation and biomedical applications, which recombines the water-soluble inorganic nano-particles into hydrophobic polymers with reactive surfactant through emulsion polymerization. In this way, the multi-functional polymer microspheres can be obtained through the recombination of different types of nanoparticles on the same microspheres. The positive charge on the microsphere surface can couple the biological molecules onto it by the electrostatic interaction to get a microsphere fluorescent probe used in immunodetection, chromosome analysis of multiple genes, protein array, DNA sequencing and simultaneous detection in different regions of gene chips and cell or biological tissues.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gas-filled microvesicle assembly for contrast imaging
ActiveUS20070071685A1Extreme flexibilityImprove stress resistanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsMicrosphereEngineering
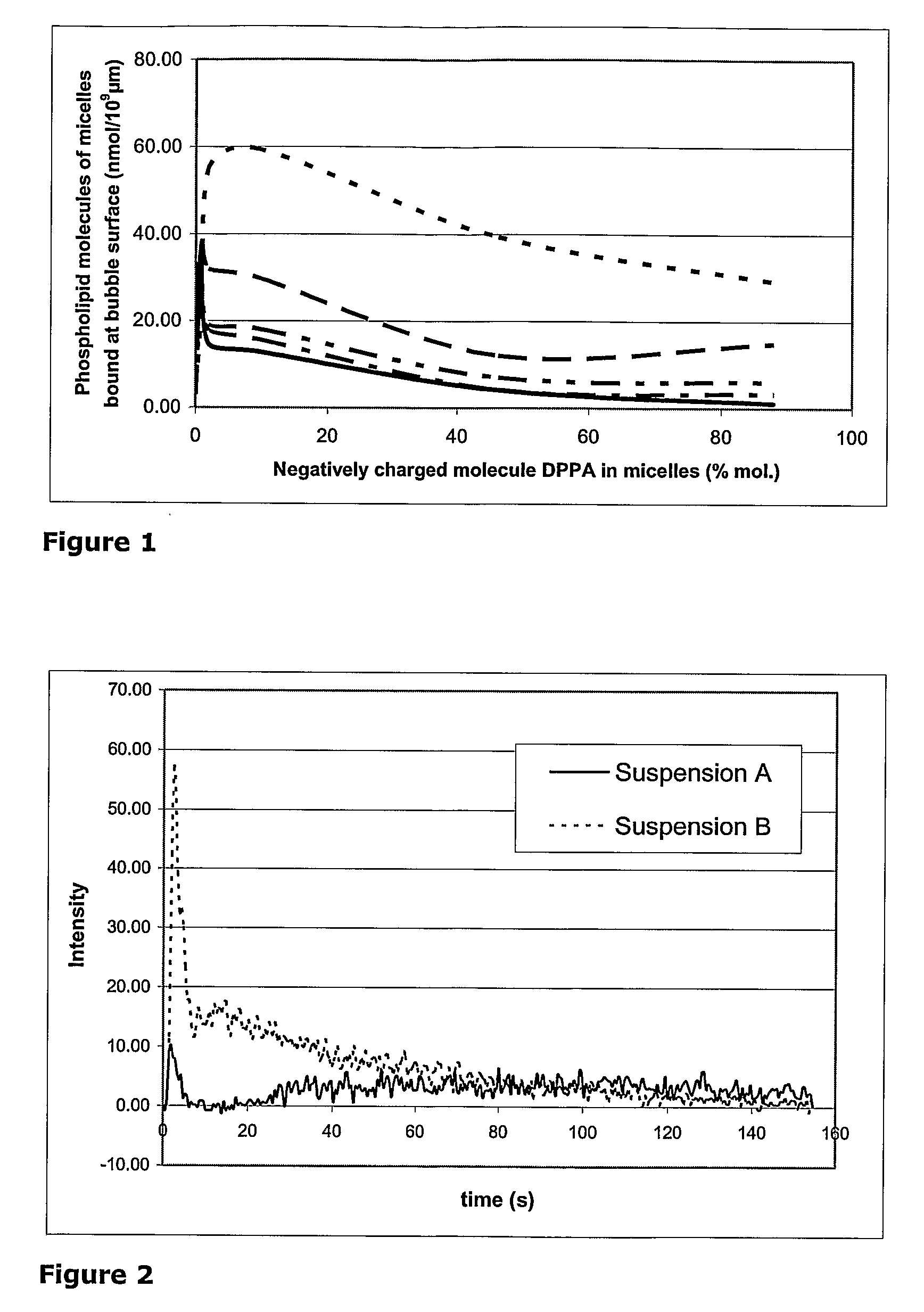
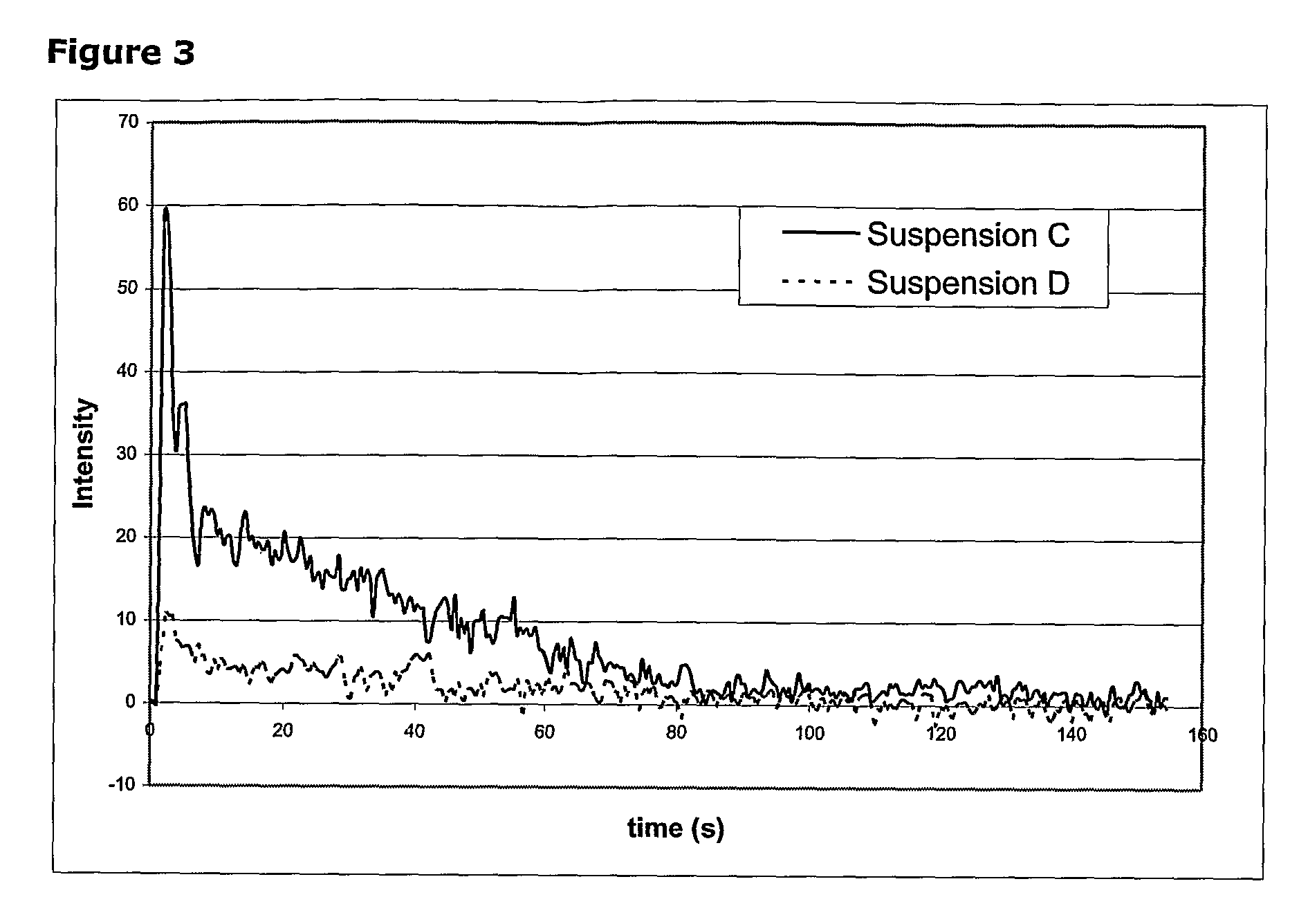
Assembly comprising a gas-filled microvesicle and a structural entity which is capable to associate through an electrostatic interaction to the outer surface of said microvesicle (microvesicle associated component—MAC), thereby modifying the physico-chemical properties thereof. Said MAC may optionally comprise a targeting ligand, a bioactive agent, a diagnostic agent or any combination thereof. The assembly of the invention can be formed from gasfilled microbubbles or microballoons and a MAC having a diameter of less than 100 pm, in particular a micelle and is used as an active component in diagnostically and / or therapeutically active formulations, in particular for enhancing the imaging in the field of ultrasound contrast imaging, including targeted ultrasound imaging, ultrasound-mediated drug delivery and other imaging techniques such as molecular resonance imaging (MRI) or nuclear imaging.
Owner:BRACCO SUISSE SA
Antibacterial hydrogel composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105268015AImprove water absorptionHigh broad-spectrum antimicrobial propertiesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWound dressingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides an antibacterial hydrogel composite material and a preparation method thereof. The antibacterial trauma repair material is hydrogel formed by chitosan and gamma-polyglutamic acid according to a mass ratio of 1 / 0.5-2 through electrostatic interaction, and nano silver is synthesized and loaded in situ on the hydrogel by taking PVP as a dispersant. the preparation method is simple, convenient and quick, and the trauma repair material is high in practicability. The composite hydrogel trauma repair material integrates bactericidal and immune activity, high biocompatibility and hemostatic activity that chitosan has, high water absorbency that gamma-polyglutamic and broad-spectrum antibacterial property and freeness of drug resistance that nano silver has, and composite hydrogel nano silver is small in grain diameter, uniform in distribution and less prone to aggregation, thereby having high antibacterial performance; when the material is used for wound dressing, wound infection can be avoided effectively, and wound healing can be accelerated.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
An MOF-precious metal composite SERS substrate and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN107478635AImprove adsorption capacityQuick checkMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingPorosityComposite substrate
The invention relates to the field of MOF-precious metal nanocomposites, and particularly relates to an MOF-precious metal composite SERS substrate and a preparing method thereof. In an alcohol solution, CTAB modified positive-charged precious metal nanoparticles are loaded onto the surface of an MOF material through electrostatic functions to form the MOF-precious metal composite SERS substrate. Compared with in-situ growth methods, the precious metal nanoparticles are loaded onto the surface of the MOF material through electrostatic functions in the method, a high porosity, a high specific surface area and excellent adsorption capability of the MOF material are maintained, morphology, the size and density of the metal nanoparticles on the surface of the MOF can be accurately controlled, and a large amount of Raman active sites are prepared, thus further effectively improving properties of the composite substrate SERS. The MOF-AuNPs composite SERS substrate prepared by the method has double functions including adsorption enrichment and Raman enhancement, does not need surface modification and can achieve direct and highly sensitive detection of molecules such as fluoranthene.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
MEMS closed chamber heat engine and electric generator
A heat engine, preferably combined with an electric generator, and advantageously implemented using micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) technologies as an array of one or more individual heat engine / generators. The heat engine is based on a closed chamber containing a motive medium, preferably a gas; means for alternately enabling and disabling transfer of thermal energy from a heat source to the motive medium; and at least one movable side of the chamber that moves in response to thermally-induced expansion and contraction of the motive medium, thereby converting thermal energy to oscillating movement. The electrical generator is combined with the heat engine to utilize movement of the movable side to convert mechanical work to electrical energy, preferably using electrostatic interaction in a generator capacitor. Preferably at least one heat transfer side of the chamber is placed alternately into and out of contact with the heat source by a motion capacitor, thereby alternately enabling and disabling conductive transfer of heat to the motive medium.
Owner:NASA UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR
Preparation method of two-dimensional inorganic layered compound/graphene composite material
InactiveCN104183830ALow equipment requirementsEasy to operateHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesElectronic transmissionChemical compound
The invention discloses a preparation method of a two-dimensional inorganic layered compound / graphene composite material. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps: preparing layered compound dispersion liquid with positive charges on the surface and oxidized graphene dispersion liquid with negative charges; mixing the two kinds of solution to perform self-assembling under an electrostatic interaction to obtain the ordered two-dimensional inorganic layered compound / graphene composite material assembled alternatively layer by layer; and carrying out reduction reaction on the composite material under certain conditions to obtain the two-dimensional inorganic layered compound / graphene composite material. According to the two-dimensional inorganic layered compound / graphene composite material, the two-dimensional inorganic layered compound and the graphene are assembled alternatively layer by layer under the electrostatic interaction; the required equipment has low requirement and is easy to operate; the graphene can provide a good electronic transmission channel for the inorganic layered material, so as to enhance the electrical conductivity of the inorganic layered material, prevent agglomeration, and achieve an important effect on the material structure stability. The two-dimensional inorganic layered compound / graphene composite material can be widely applied to the fields of catalytic and electrochemical energy storage fields.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing anti-pollution polysulfone porous membrane by self-assembling immobilization of metal ions
InactiveCN104548969AHas hydrophilic antibacterial propertiesStrong anti-pollutionSemi-permeable membranesAntibacterial activityIndustrial scale
The invention relates to a method for preparing an anti-pollution polysulfone porous membrane by self-assembling immobilization of metal ions. According to surface electrical load properties of a membrane prepared from a polysulfone material, an amino-containing compound with high positive charge density and hydrophily is used as a modification material, the modification material is adsorbed by the surface of the polysulfone porous membrane under electrostatic interaction, through a large amount of amino groups of the modification material, the modification material and Cu<2+>, Zn<2+> or Ag<+> of an inorganic antibacterial agent undergo a coordinated complexation reaction, and the inorganic antibacterial agent is immobilized on the modification material molecule by complexation action so that the polysulfone porous membrane with good hydrophily and antibacterial activity is obtained. The prepared polysulfone porous membrane has hydrophily, antibacterial property and pollution resistance. The method has simple processes, does not need complex equipment and is suitable for industrial scale application. The porous membrane can be widely used in water treatment in the field of environment, chemical engineering, foods and medicine.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of double-emission carbon-based nano probe and product of preparation method
ActiveCN108913132AEasy to prepareLow costNanoopticsThermometers using physical/chemical changesBiological imagingColor changes
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-emission carbon-based nano probe prepared based on an electrostatic interaction induced self-assembling method and application of a product ofthe preparation method to in-vivo and in-vitro temperature detection of organisms, and belongs to the technical field of colorimetric fluorescence detection. The preparation method comprises synthesisof blue fluorescence carbon dots (B-CDs) which have no temperature sensitivity and negative charges on surfaces, preparation of red fluorescence carbon dots (R-CDs) which have temperature sensitivityand positive charges on surfaces and preparation of the double-emission carbon-based nano probe. According to the double-emission carbon-based nano probe obtained by the preparation method, the double-emission carbon-based nano probe has different responsiveness aiming at different temperature and has different compound temperature color changes; the double-fluorescence emission nano probe can beused for colorimetrically detecting in-vivo and in-vitro temperature of the organisms by naked eyes, and has high sensitivity (0.93 percent / DEG C) and operation repeatability, so that the double-fluorescence emission nano probe provides convenience for biological imaging, temperature sensing, environment monitoring, food safety and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Waterborne acrylate resin emulsion and synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN101565484AImprove performanceGood film formingFibre treatmentEster polymer adhesivesIsooctyl acrylateEmulsion
The invention pertains to the technical field of polymer materials and particularly relates to a waterborne resin emulsion for car cleaning cloth or common cleaning cloth and a textile finishing adhesive agent, a synthetic method and application of the waterborne resin emulsion. The resin emulsion consists of a waterborne resin polymer, an emulsifier, an evocating agent, a pH value modulator and water; the waterborne resin polymer is obtained by polymerization of 3-5 monomers such as butyl acrylate, ethyl hexyl acrylate and methyl methacrylate and the like. The synthesis comprises two steps of monomer pre-emulsion and polymerization by the evocating agent. The product of the invention has stable performance and good film formation performance, as well as soft hand feeling, good moisture permeability, long-term moisture and environment protection by absorbing fine dusts when used as cleaning cloth, and when used as a textile adhesive agent, the product can not only realize the characteristics and requirements above, but also decrease electrostatic interaction of the textile, thus having good and wide application in the textile field.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Composite janus microspheres based oil-water micro-emulsion separation method
ActiveCN108311067AEfficient separationEasy to separateFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater treatment compoundsChemical compositionMicrosphere
The invention discloses a composite janus microspheres based oil-water micro-emulsion separation method. With the polymers Janus microspheres with different structures and different chemical compositions as a base material, the method comprises the following steps: adsorbing magnetic nano particles on the surfaces of the microspheres through electrostatic interaction, to obtain composite Janus microspheres with magnetic responsiveness; mixing and stirring the composite Janus microspheres and an oil-water emulsion; realizing demulsification and layering of the oil-water emulsion; after the layering, applying a magnetic field to realize efficient and quick oil-water separation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the composite Janus microspheres serve as a particle surfactanton the oil-water interface to realize the demulsification and layering of the oil-water emulsion; by applying the magnetic field, efficient and quick separation of oil and water can be realized. Theoil-water micro-emulsion separation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, quick process and easiness in condition control, and is applicable to efficient separation of oil water formed by different types of large-area oil.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
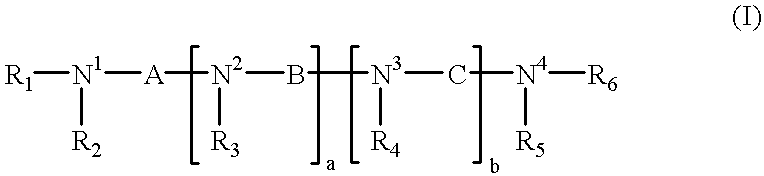
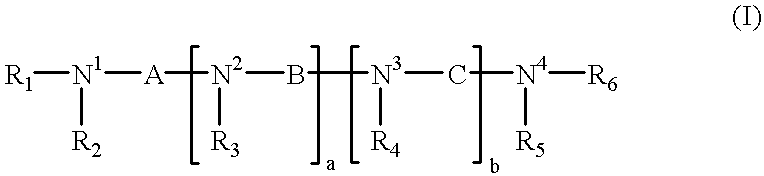
Analogs of biologically active, naturally occurring polyamines, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment
Polyamines having the formula:or a salt thereof with a pharmaceutically acceptable acid wherein: R1-R6 may be the same or different and are alkyl, aryl, aryl alkyl, cycloalkyl, optionally having an alkyl chain interrupted by at least one etheric oxygen atom, or hydrogen;N1, N2, N3 and N4 are nitrogen atoms capable of protonation at physiological pH's;a and b may be the same or different and are integers from 1 to 4;A, B and C may be the same or different and are bridging groups which effectively maintain the distance between the nitrogen atoms such that the polyamines:(i) are capable of uptake by a target cell upon administration thereof to a human or non-human animal; and(ii) upon uptake by the target cell, competitively bind via an electrostatic interaction between the positively charged nitrogen atoms to substantially the same biological counter-anions as the intracellular natural polyamines in the target cell;the polyamines, upon binding to the biological counter-anion in the cell, function in a manner biologically different than the intracellular polyamines, the polyamines not occurring in nature; as well as pharmaceutical compositions embodying the polyamines and methods of treating patients requiring anti-neoplastic therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
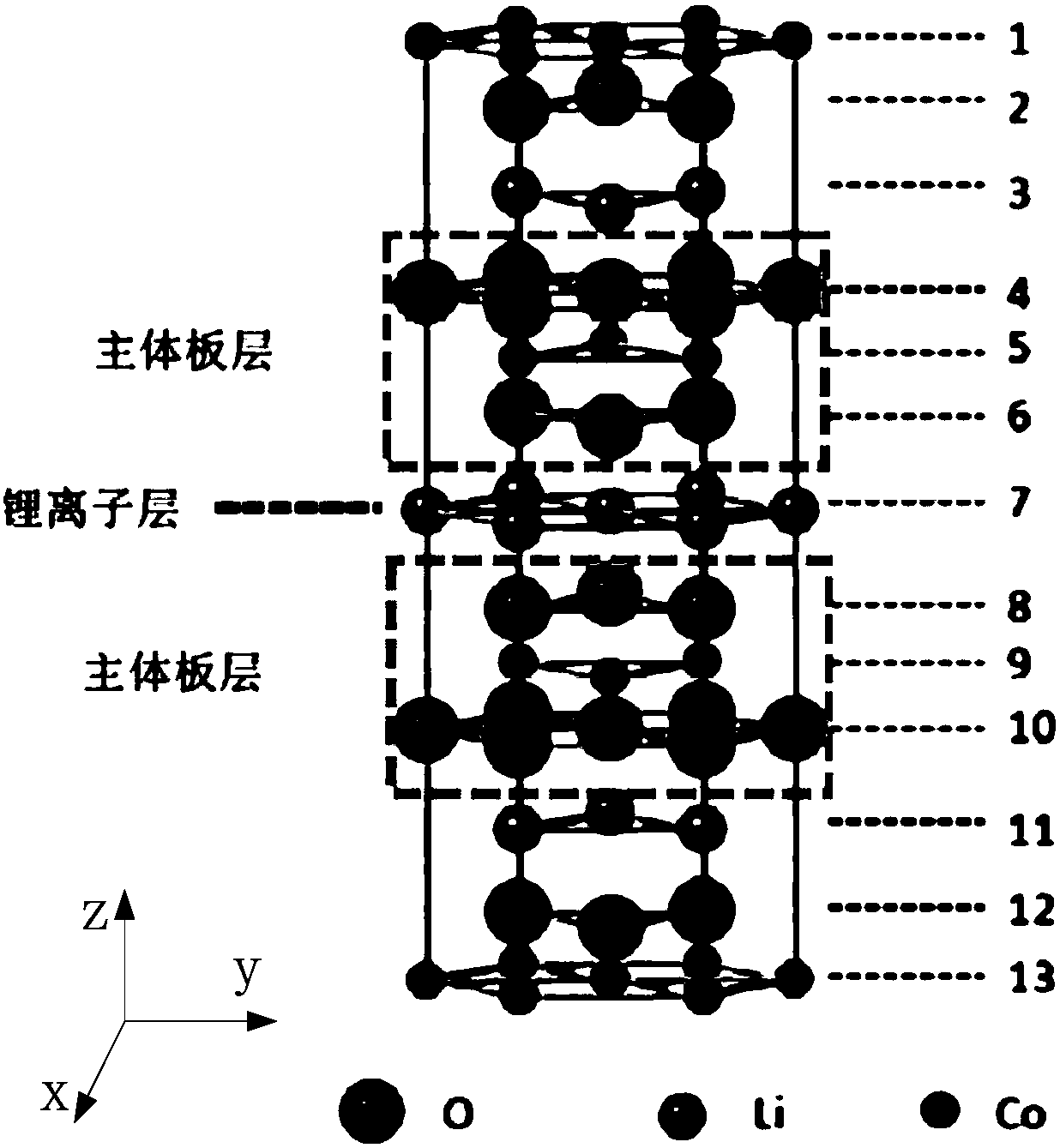
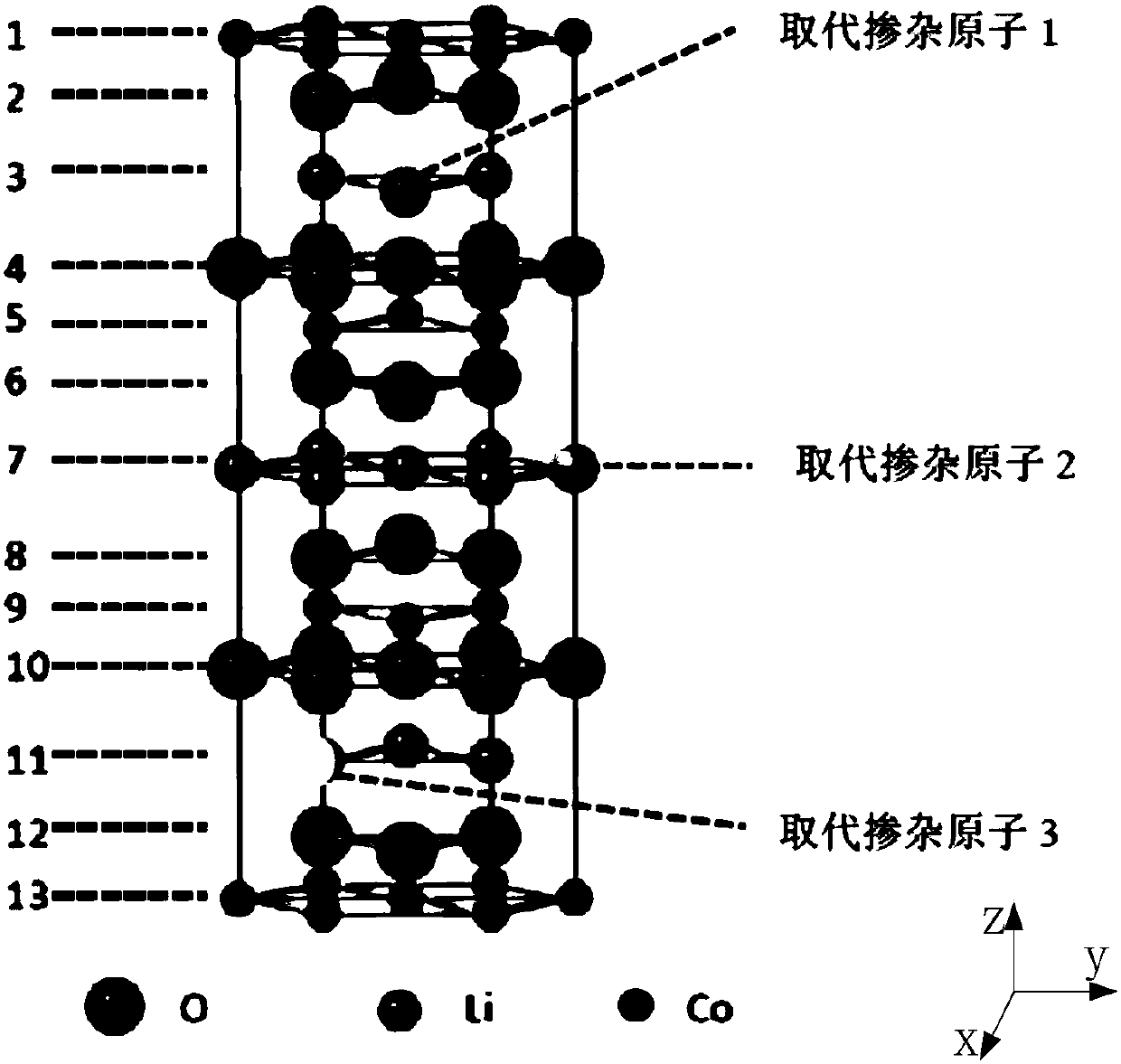
High-voltage lithium cobaltate positive electrode material and preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN109786738AImprove cycle stabilityAlleviate volume changesCell electrodesSecondary cellsDissolutionLithium-ion battery
Embodiments of the present invention provide a high voltage lithium cobaltate positive cathode material, including a lithium cobaltate substituted and doped at lithium positions. The lithium cobaltatesubstituted and doped at lithium positions has a general formula of Li1-xMaxCoO2, where x is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.05, Ma is a doping element, Ma is selected from one or more ofelements having an ionic radius ranging from 68 pm to 90 pm and an ion valence state greater than or equal to 1. The high-voltage lithium cobaltate positive electrode material is formed by substituting and doping lithium cobaltate at lithium positions, and the electrostatic interaction and cobalt dissolution of lithium cobaltate caused by lithium de-intercalation at a high voltage is alleviated, so that the structure and cycle stability of the material is improved, and the material has a high capacity and good cycle stability at the high voltage. Embodiments of the present invention further provide a high-voltage lithium cobaltate positive electrode material preparation method and a lithium ion battery.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
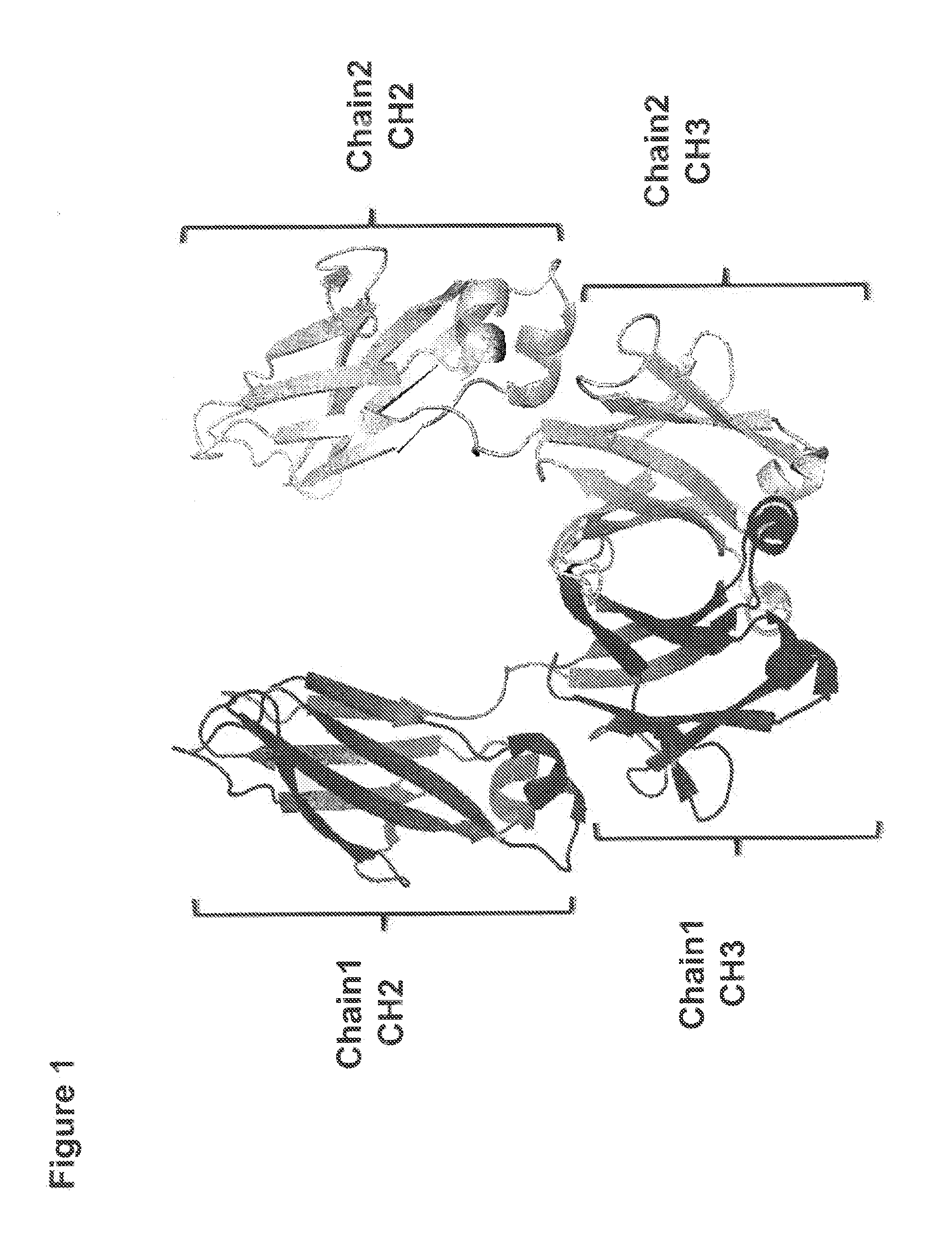
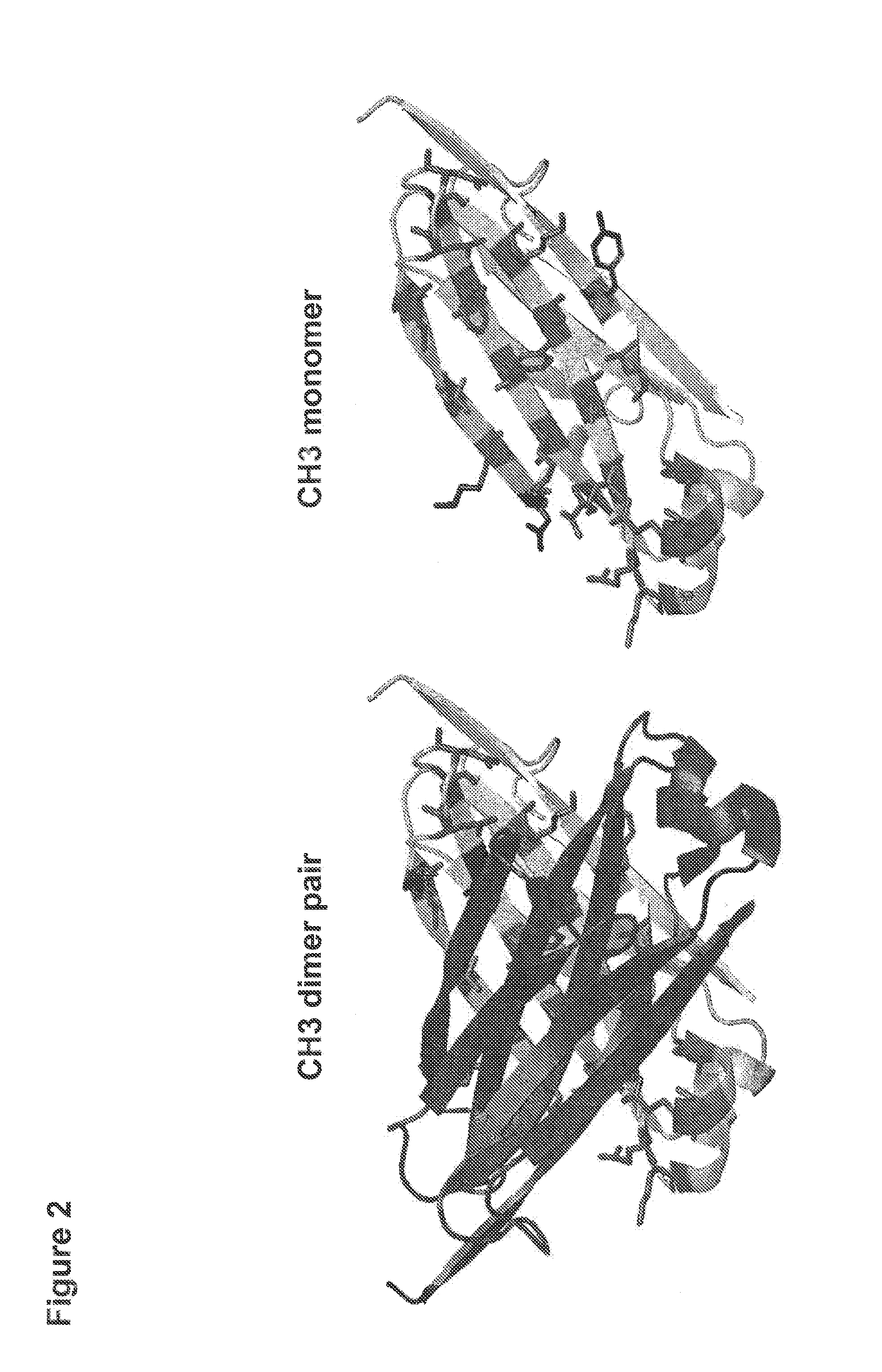
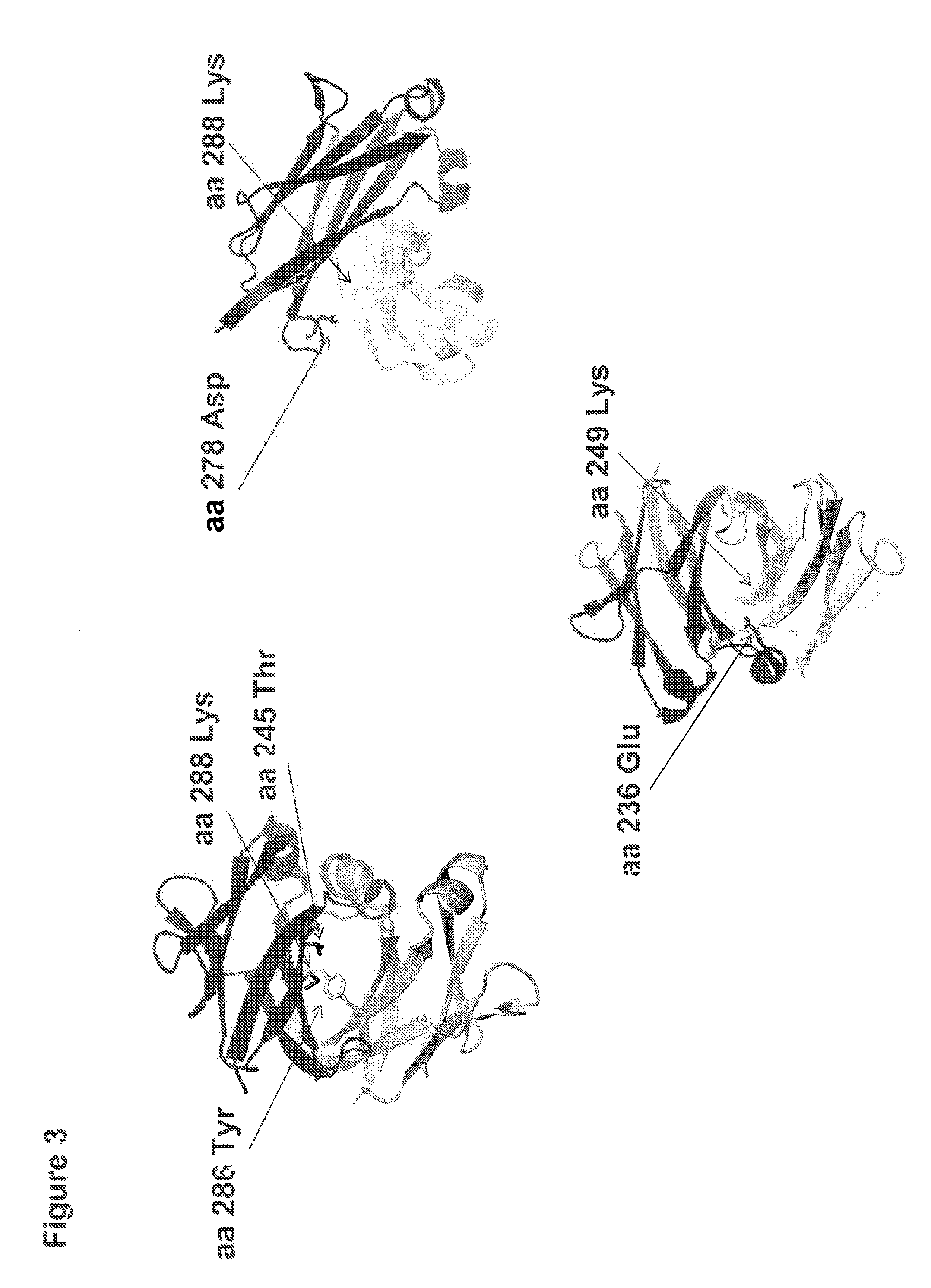
Method for Making Heteromultimeric Molecules
ActiveUS20130253172A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsBispecific antibodyElectrostatic interaction
Owner:MEREO BIOPHARMA 5 INC
In-situ cross-linked polymer binding agent for lithium ion battery and electrode prepared from same
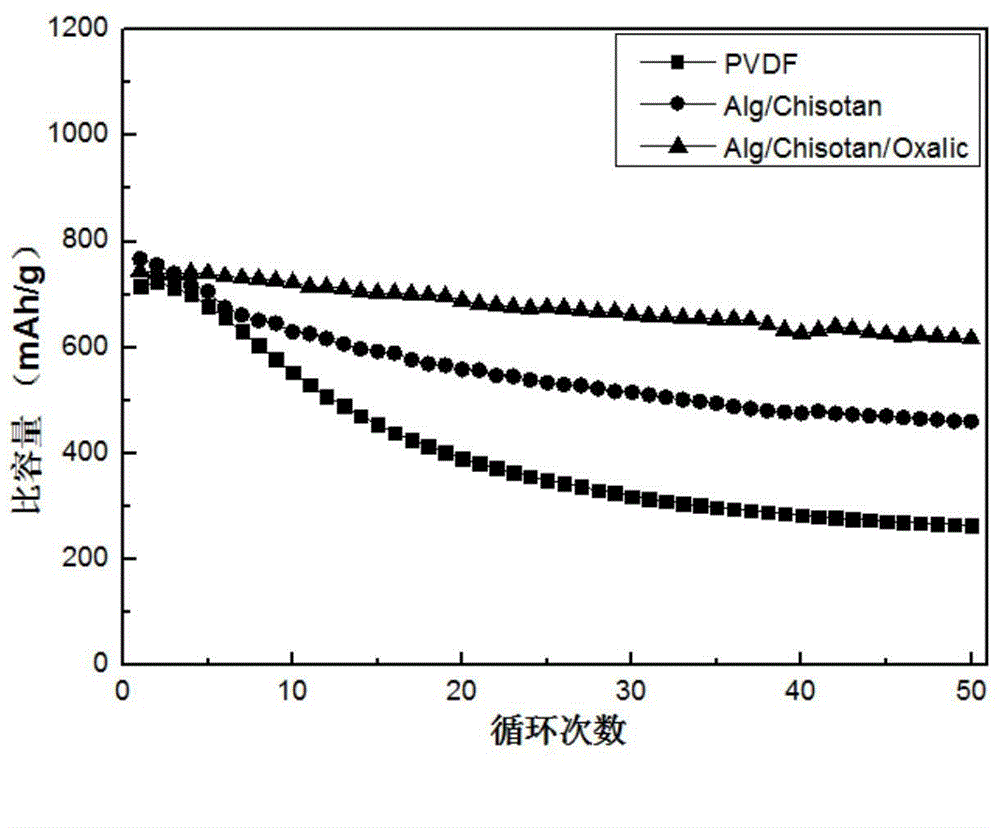
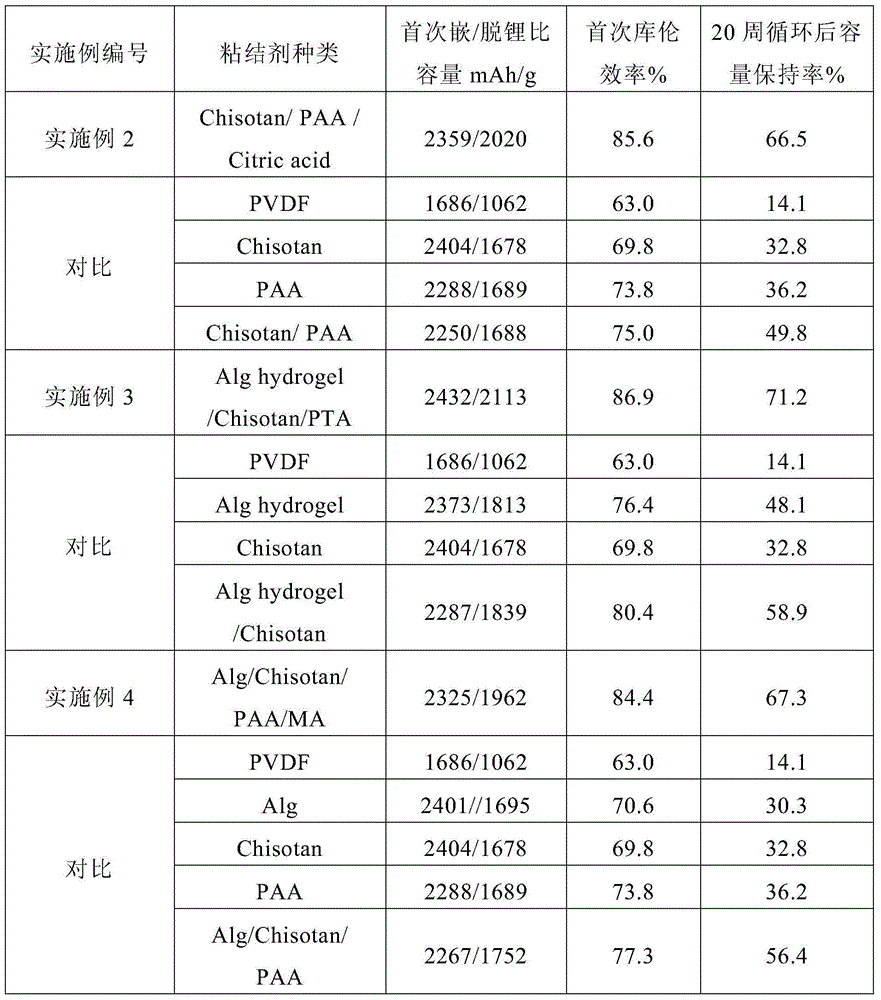
ActiveCN106159271AAvoid reunionImprove dispersion uniformitySecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesCyclic processCross-link
The invention discloses an in-situ cross-linked polymer binding agent for a lithium ion battery and an electrode prepared from the in-situ cross-linked polymer binding agent. The polymer binding agent is of a three-dimensional network structure and is formed through in-situ polymerization of chitosan, at least one of polymers containing a carboxyl group or a carboxylate group, and at least one of micromolecule polybasic carboxylic acid and micromolecule polybasic carboxylate. An amidogen group on a chitosan molecular chain and a carboxyl group of the other polymer form a three-dimensional network structure in situ through electrostatic interaction at the room temperature, and dispersion uniformity of active materials in the electrode is improved. When the polymer binding agent is in use, a pole piece is subjected to further heat treatment, the cross-linking effect of the polymer chains is enhanced, and the stability of the electrode structure in the cycle process is improved. The electrochemical performance of the electrode of the lithium ion battery can be improved when the in-situ cross-linked polymer binding agent is used for preparing the electrode in situ, and particularly a more obvious improving effect is achieved on high specific capacity positive pole lithium-rich materials, a negative pole silicon substrate, tin-based materials and Li-S-based materials.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com