Polymer microsphere containing inorganic nano microparticles, and its preparing method and use
An inorganic nano- and nano-particle technology, applied in biological testing, material inspection, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to control the morphology and crystallinity of the nano-particle surface structure, and the lack of strong enough interaction between the nano-particle and the polymer sphere. , to achieve the effect of convenient operation and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
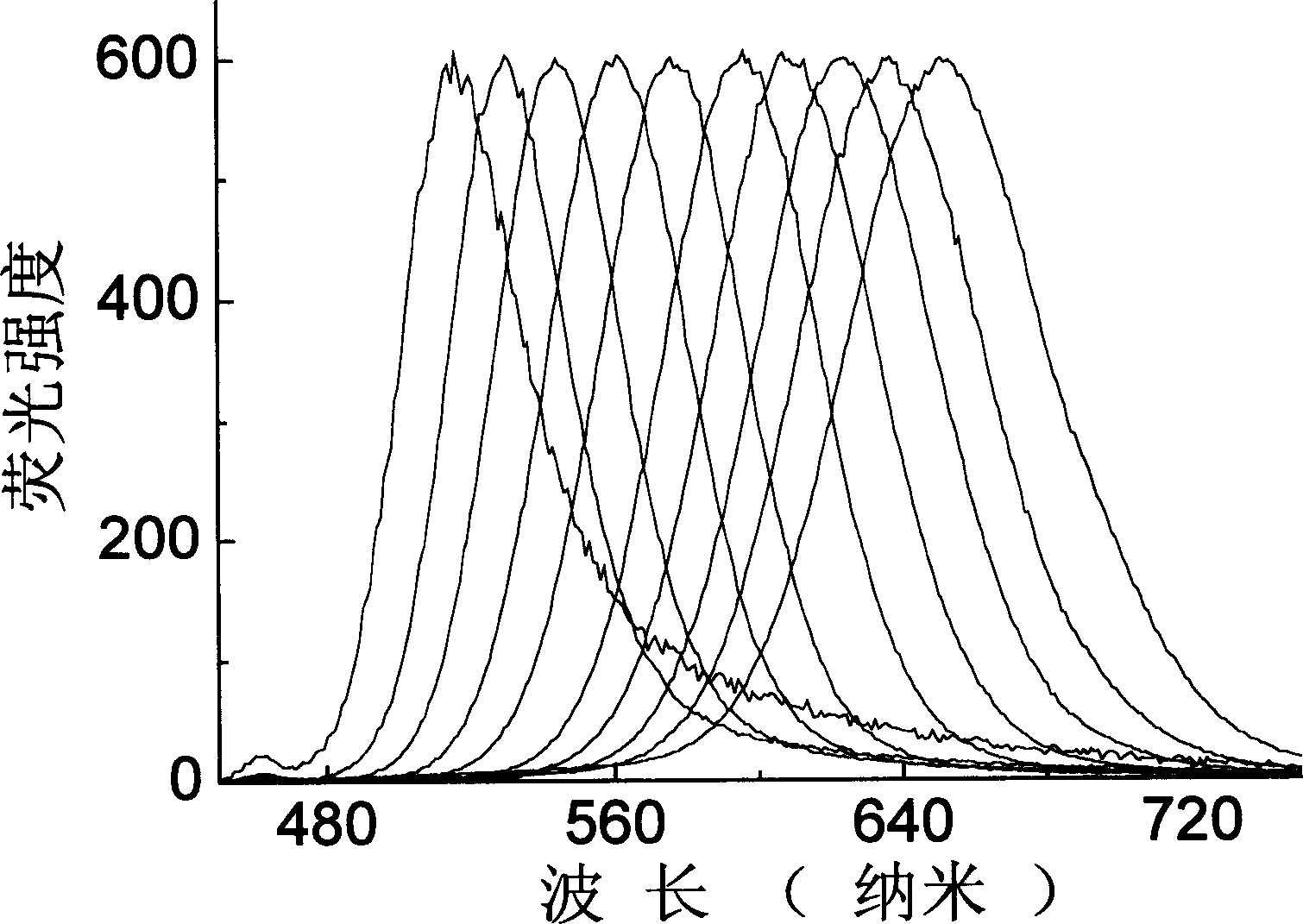
[0069] Weigh 1.315g cadmium perchlorate (Cd(ClO 4 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) Add to 150mL of deoxygenated secondary water, then add 0.55mL of thioglycolic acid as a modifier, adjust its pH value to 11.2 with 1M sodium hydroxide solution to form a solution containing mercapto compounds and cadmium ions. On the other hand, take 30mL of 0.5M sulfuric acid solution and inject it into a container containing 0.39g of aluminum telluride (Al 2 Te 3 ) in the flask, the generated H 2 Put all the Te into the cadmium ion solution, stir for 15 minutes, and then heat and reflux for 1 minute to 10 days to obtain an aqueous solution of cadmium telluride semiconductor nanoparticles with stable thioglycolic acid and a fluorescent emission center wavelength between 430 and 650 nanometers. Fluorescence spectrum see figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0071] Weigh 1.031g cadmium chloride (CdCl 2 2.5H 2 O) Add to 150mL deoxygenated secondary water, then add 0.55mL mercaptopropionic acid as a modifier, adjust its pH value to 11.2 with 1M sodium hydroxide solution to form a solution containing mercapto compounds and cadmium ions. The rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain an aqueous solution of cadmium telluride semiconductor nanoparticles with stable mercaptopropionic acid and a central wavelength of fluorescence emission between 430 and 650 nanometers.
Embodiment 3
[0073] Weigh 1.031g cadmium chloride (CdCl 2 2.5H 2 O) Add to 150mL deoxygenated secondary water, then add 0.65mL lipoic acid as a modifier, adjust its pH value to 11.2 with 1M sodium hydroxide solution to form a solution containing mercapto compounds and cadmium ions. The rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1 to obtain an aqueous solution of cadmium telluride semiconductor nanoparticles with stable lipoic acid and a center wavelength of fluorescence emission between 430 and 650 nanometers.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com