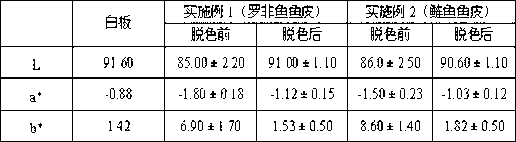
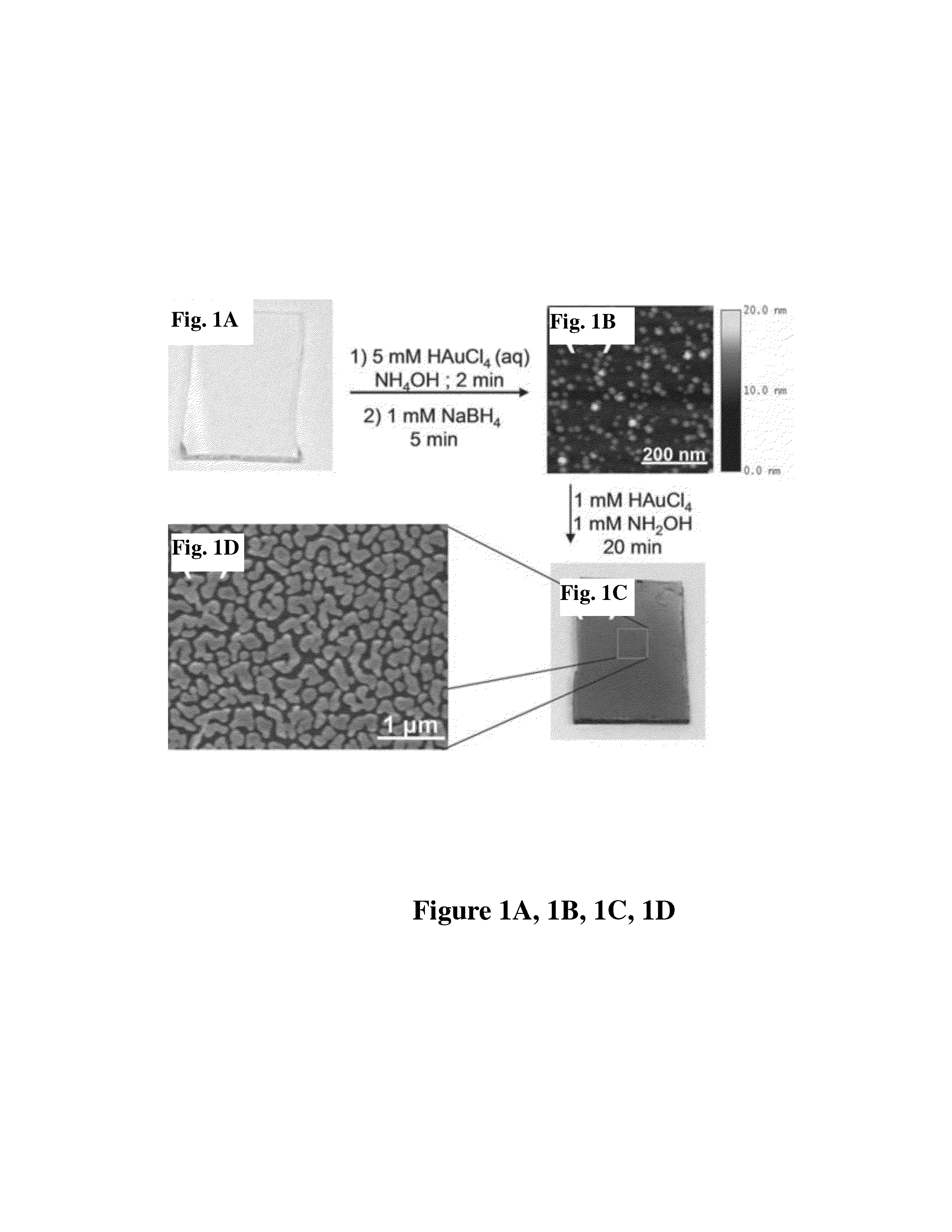
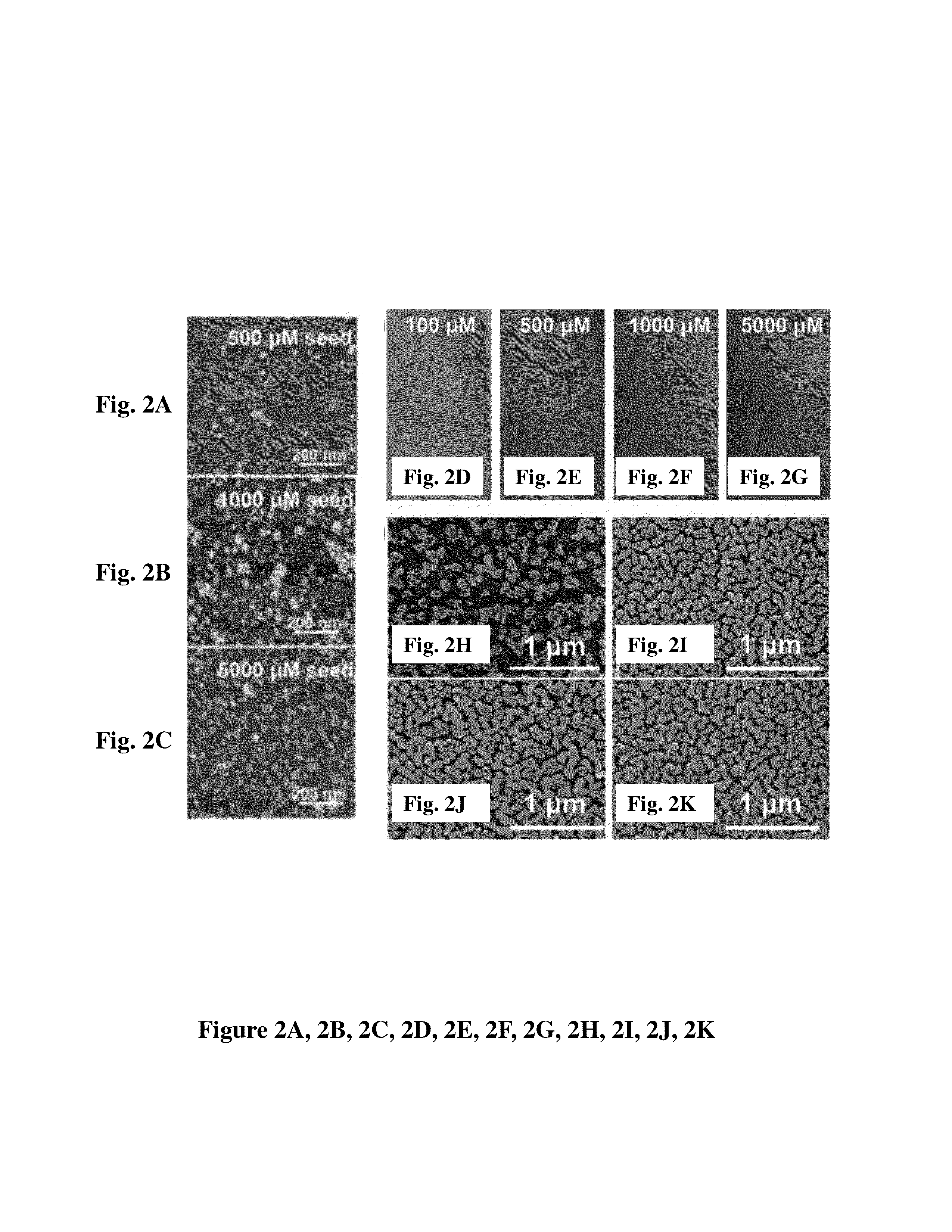
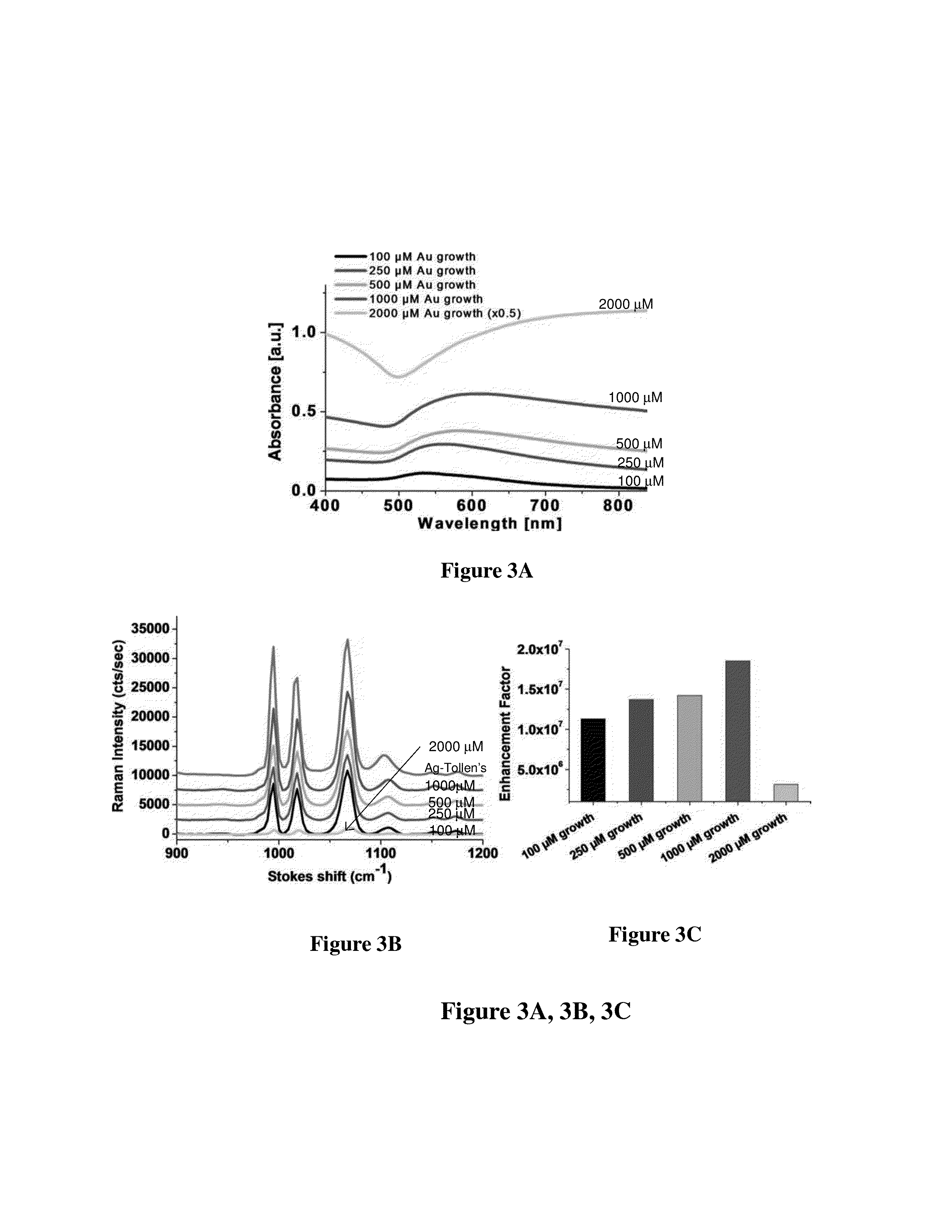
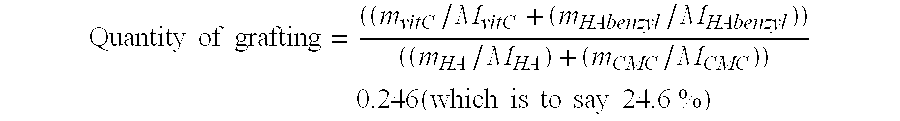Patents
Literature
5601 results about "Biomedicine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biomedicine (i.e. medical biology) is a branch of medical science that applies biological and physiological principles to clinical practice. The branch especially applies to biology and physiology. Biomedicine also can relate to many other categories in health and biological related fields. It has been the dominant health system for more than a century.
Apparatus and method for bioelectric stimulation, healing acceleration, pain relief, or pathogen devitalization
ActiveUS7117034B2Minimal stressPromote healingElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEngineeringAnimal body
An method and method for generating an electrical signal for use in biomedical applications, including two timing-interval generators, each optionally driving a multistep sequencer; analog, digital or hybrid means for combining the resulting timed signals into a complex electrical signal; optional filtering means for blocking direct current, removing selected frequency components from the resulting signal, and / or providing voltage step-up if needed; and conductive means for coupling the resulting signal to a human or animal body, food, beverage or other liquid, cell or tissue culture, or pharmaceutical material, in order to relieve pain, stimulate healing or growth, enhance the production of specific biochemicals, or devitalize selected types of organisms.
Owner:HEALTHONICS INC
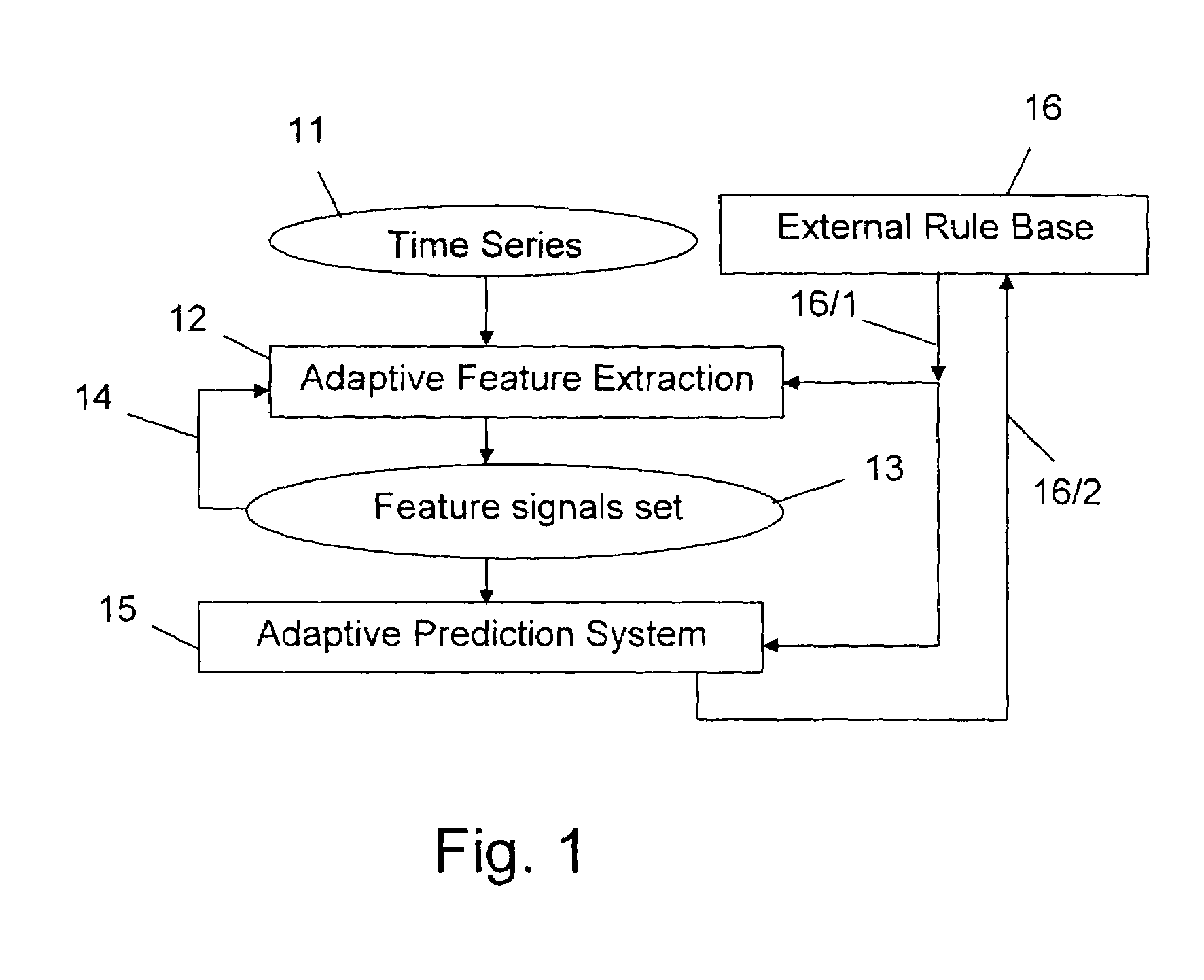
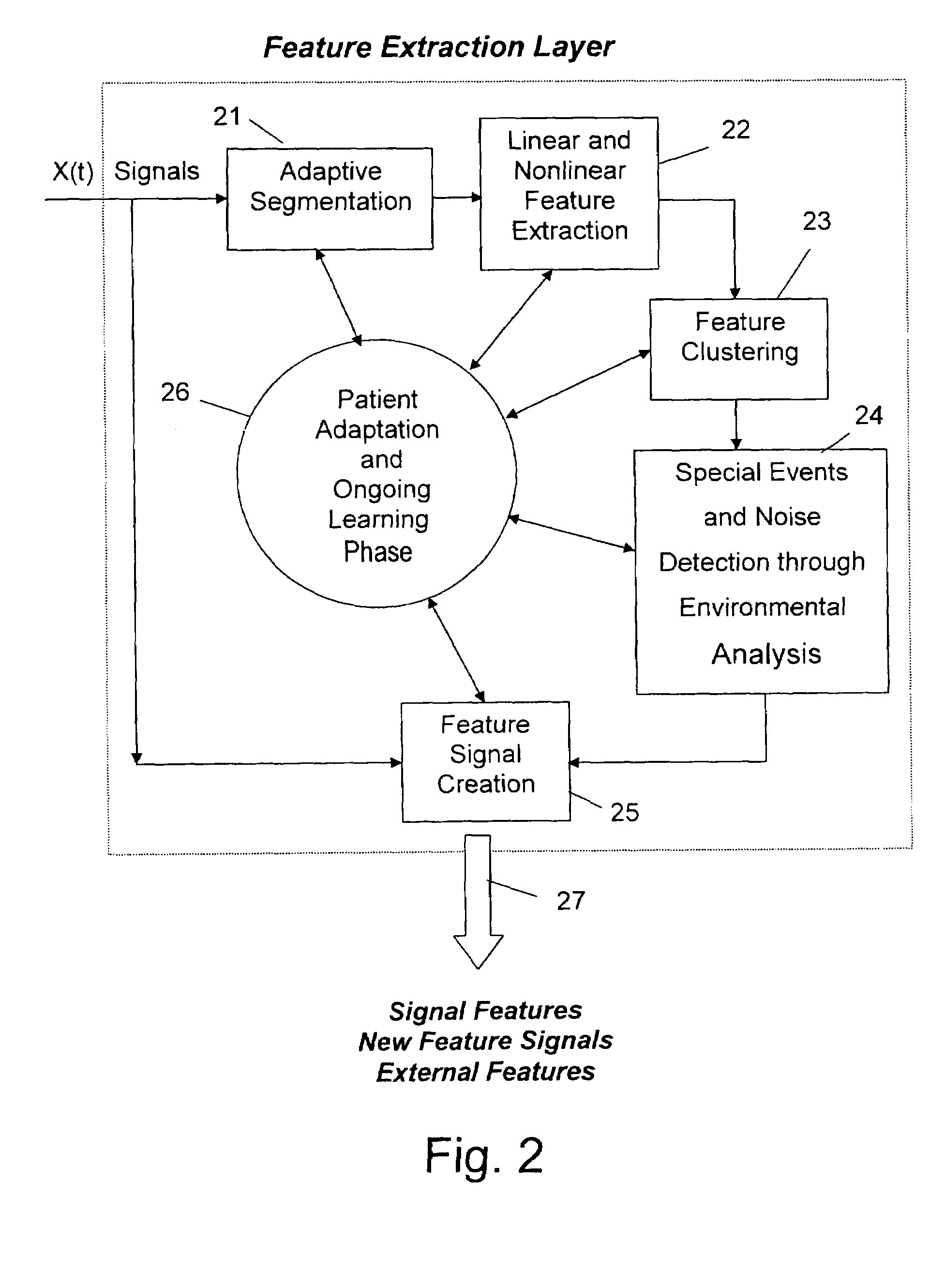
Adaptive prediction of changes of physiological/pathological states using processing of biomedical signals
A method and system predicts changes of physiological / pathological states in a patient, based on sampling, processing and analyzing a plurality of aggregated noisy biomedical signals. A reference database of raw data streams or features is generated by aggregating one or more raw data streams. The features are derived from the raw data streams and represent physiological / pathological states. Each feature consists of biomedical signals of a plurality of patients, wherein several patients have one or more of the physiological / pathological states. A path, which is an individual dynamics, between physiological / pathological states is obtained according to their order of appearance. Then, a prediction of being in physiological / pathological states, or transitions to physiological / pathological states in the patient, is obtained by comparing the individual dynamics with known dynamics, obtained from prior knowledge.
Owner:WIDEMED
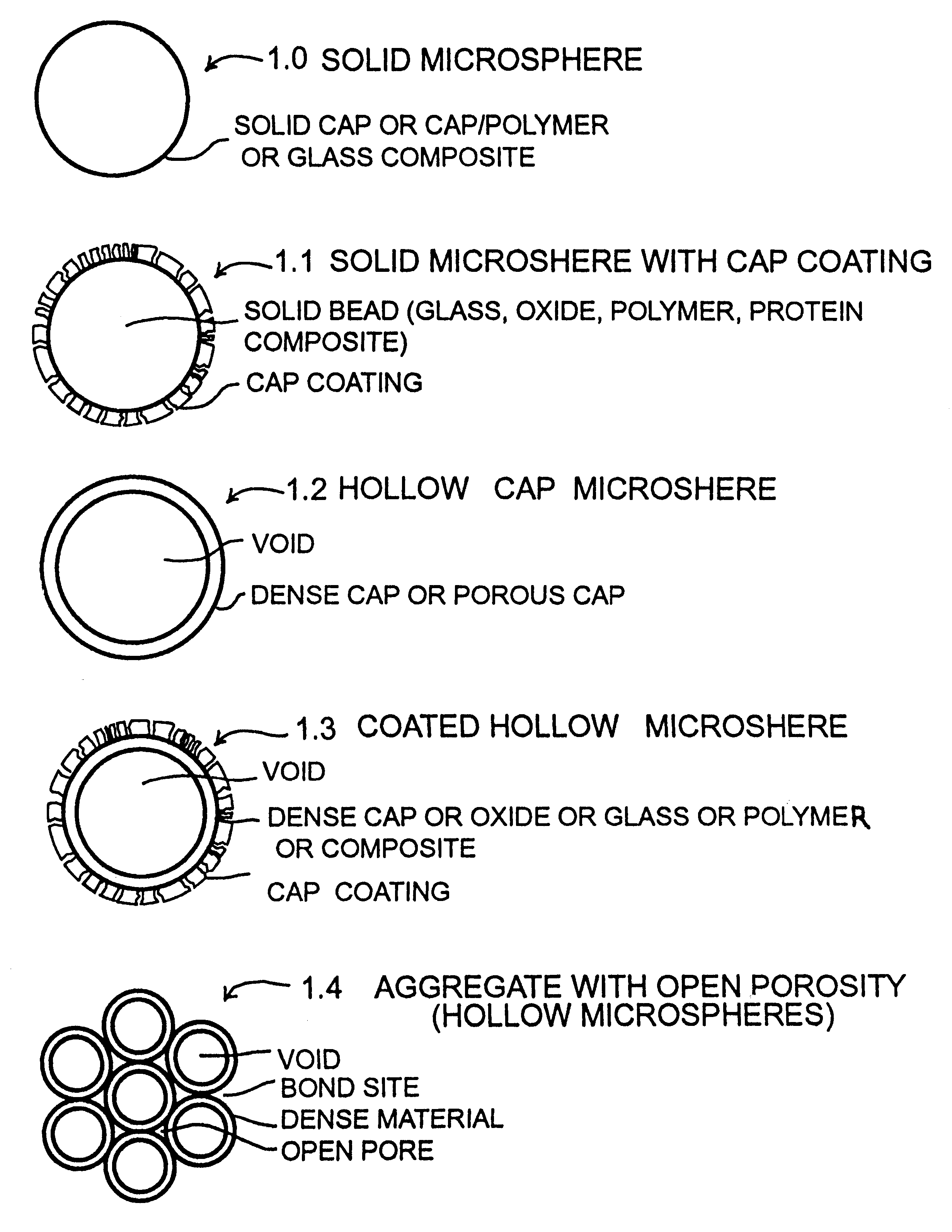
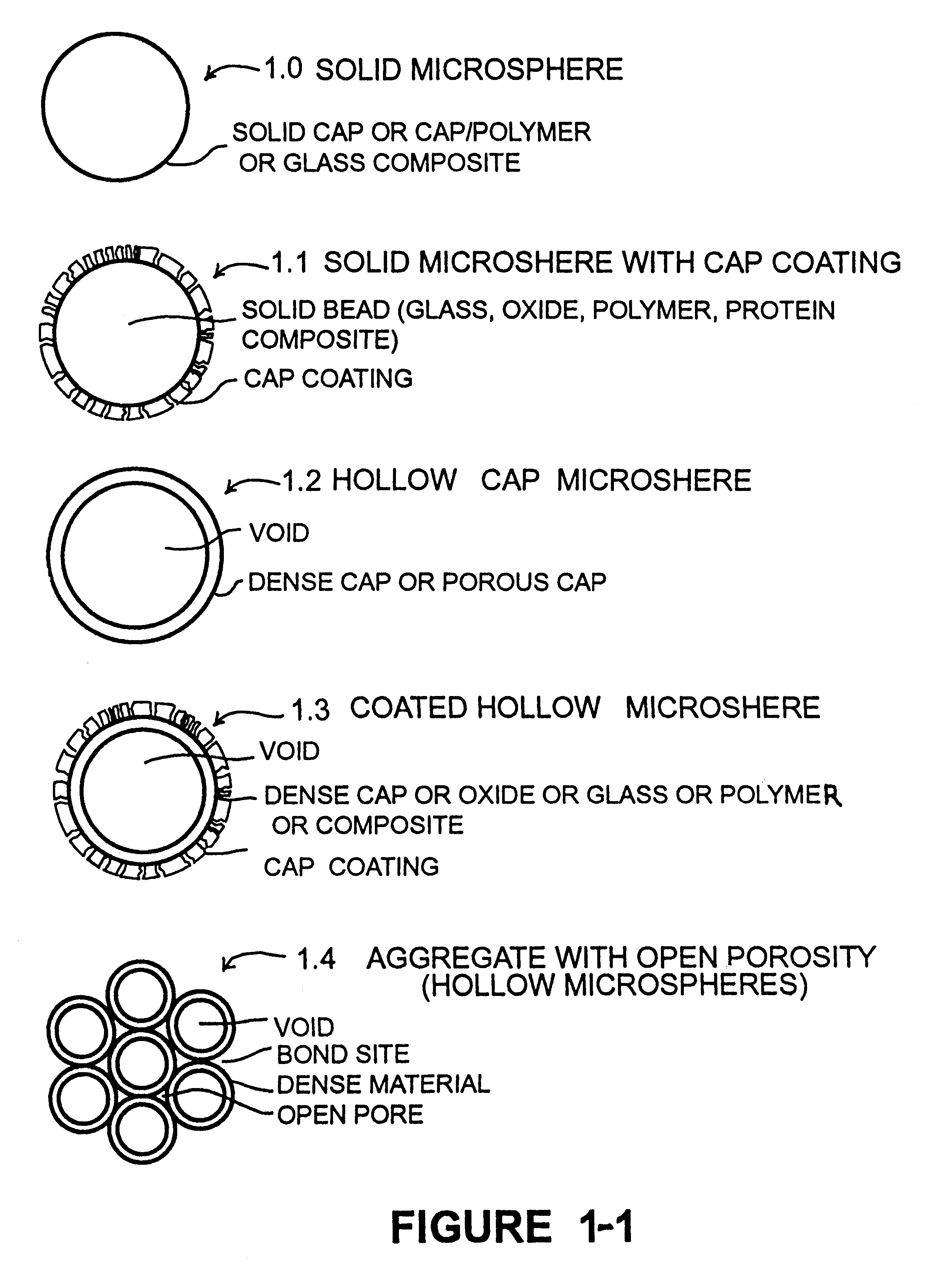
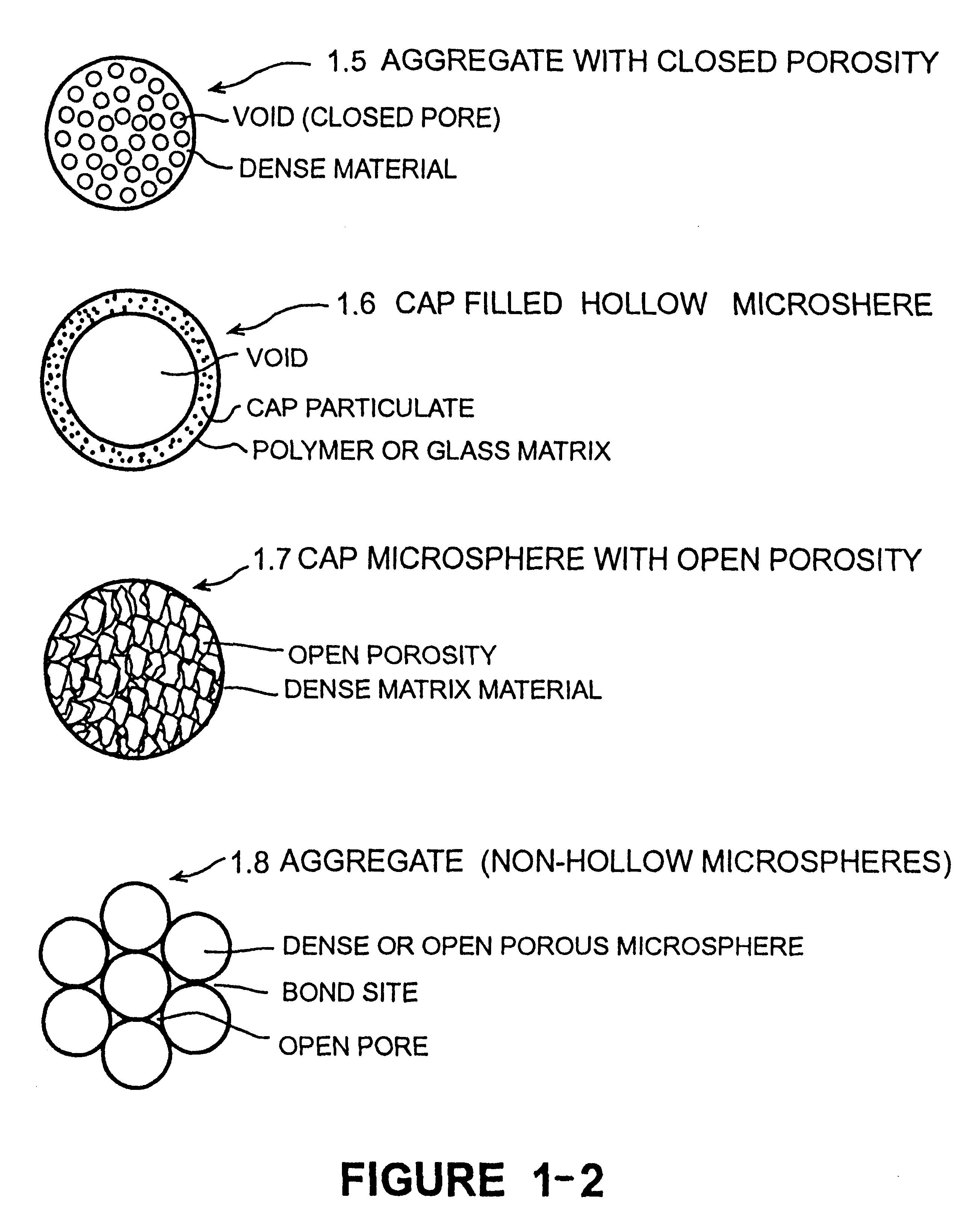
Calcium phosphate microcarriers and microspheres
InactiveUS6210715B1Increase resorbabilityCompressive strengthPowder deliveryBiocideChemistryCalcium biphosphate
The present invention provides calcium phosphate-based (CAP) microcarriers and microspheres and their use in cell culturing systems, chromatography and implantable biomedical materials.
Owner:CAP BIOTECH
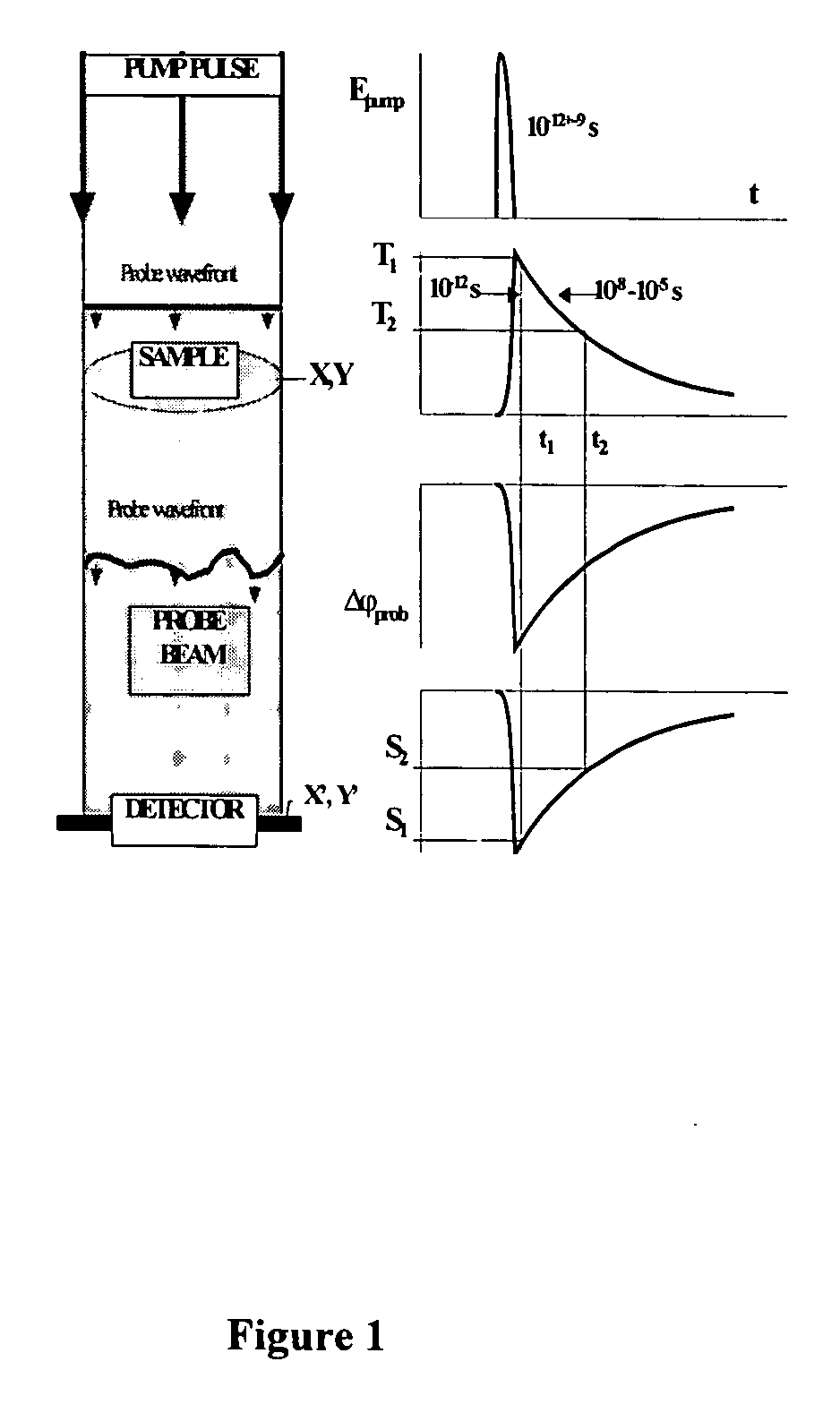
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
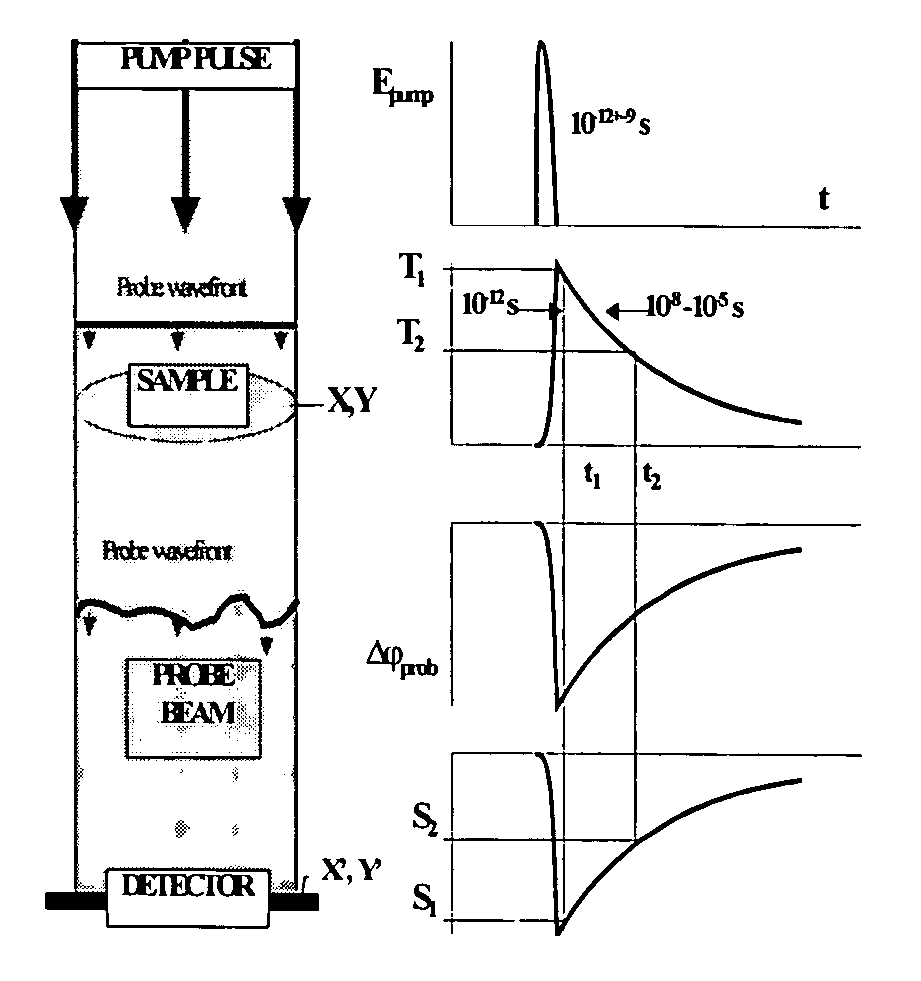
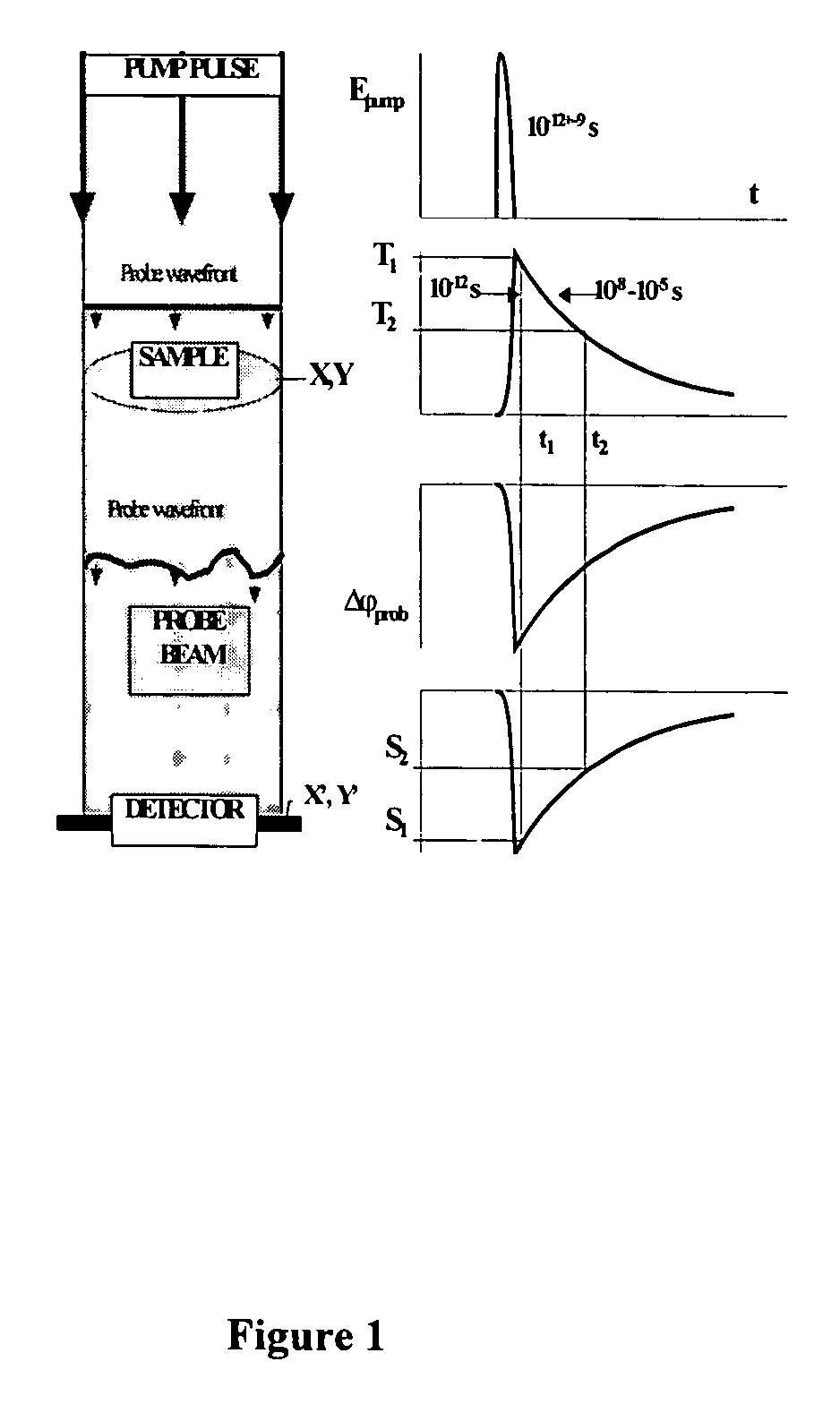
InactiveUS20040085540A1Increase sensitivity and resolutionImprove resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsRefractive index
The invention relates to optical microscopy, in particular to methods for photothermal examination of absorbent microinhomogeneities using laser radiation sources and can be widely used in laser engineering, industry and biomedicine for examining relatively transparent objects containing submicron impurities, including the detection of local inclusions and defects in ultrapure optical and semiconductor materials and the non-destructive diagnosis of biological samples on a cellular and subcellular level. The aim of the invention is to increase the sensitivity, spatial resolution and informativity of examination of local absorbent microinhomogeinities in transparent objects and to measure said microinhomogeinities even when they are less than the used emission wavelength. The inventive method consists in radiating a sample with a pumping laser beam. The duration of the radiation is equal to or less than a representative time for cooling the examined microinhomogeinity. The relatively large surface of the sample is radiated, the shape thereof being greater than the wavelength of the used pumping laser. Thermal variations of the refractive index occurring in the sample as a result of absorption produced with the aid of the pumping beam are recorded by measuring parameters of a test laser beam. The diameter of the test beam is chosen in such a way that it is equal to or greater than the diameter of the pumping beam. A diffraction-limited phase distribution along the cross-section of the testing laser beam is transformed into an amplitude image, the microinhomogeinity properties being determined by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
Method for designing polypeptides for the nanofabrication of thin films, coatings, and microcapsules by electrostatic layer-by-layer self assembly
ActiveUS20050069950A1Great control over mechanical stability and diffusive propertyIncrease profitPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesThin membraneNanomanufacturing
A method for designing polypeptides for the nanofabrication of thin films, coatings, and microcapsules by ELBL for applications in biomedicine and other fields.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND
Methods and systems for applications for Z-numbers
ActiveUS8311973B1Reliable informationNatural language translationImage analysisDecision takingDependability
Generally, decisions are based on information. To be useful, information must be reliable. Basically, the concept of a Z-number relates to the issue of reliability of information. A Z-number, Z, has two components, Z=(A,B). The first component, A, is a restriction (constraint) on the values which a real-valued uncertain variable, X, is allowed to take. The second component, B, is a measure of reliability (certainty) of the first component. Typically, A and B are described in a natural language, for example: (about 45 minutes, very sure). Z-number has many applications, especially in the realms of economics, decision analysis, risk assessment, prediction, anticipation, rule-based characterization of imprecise functions and relations, and biomedicine. Different methods, applications, and systems are discussed. Other Fuzzy concepts are also discussed.
Owner:Z ADVANCED COMPUTING
Multiple purpose, portable apparatus for measurement, analysis and diagnosis
InactiveUS20050203353A1Satisfies needAccurately detecting colorBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData displayPoint of care
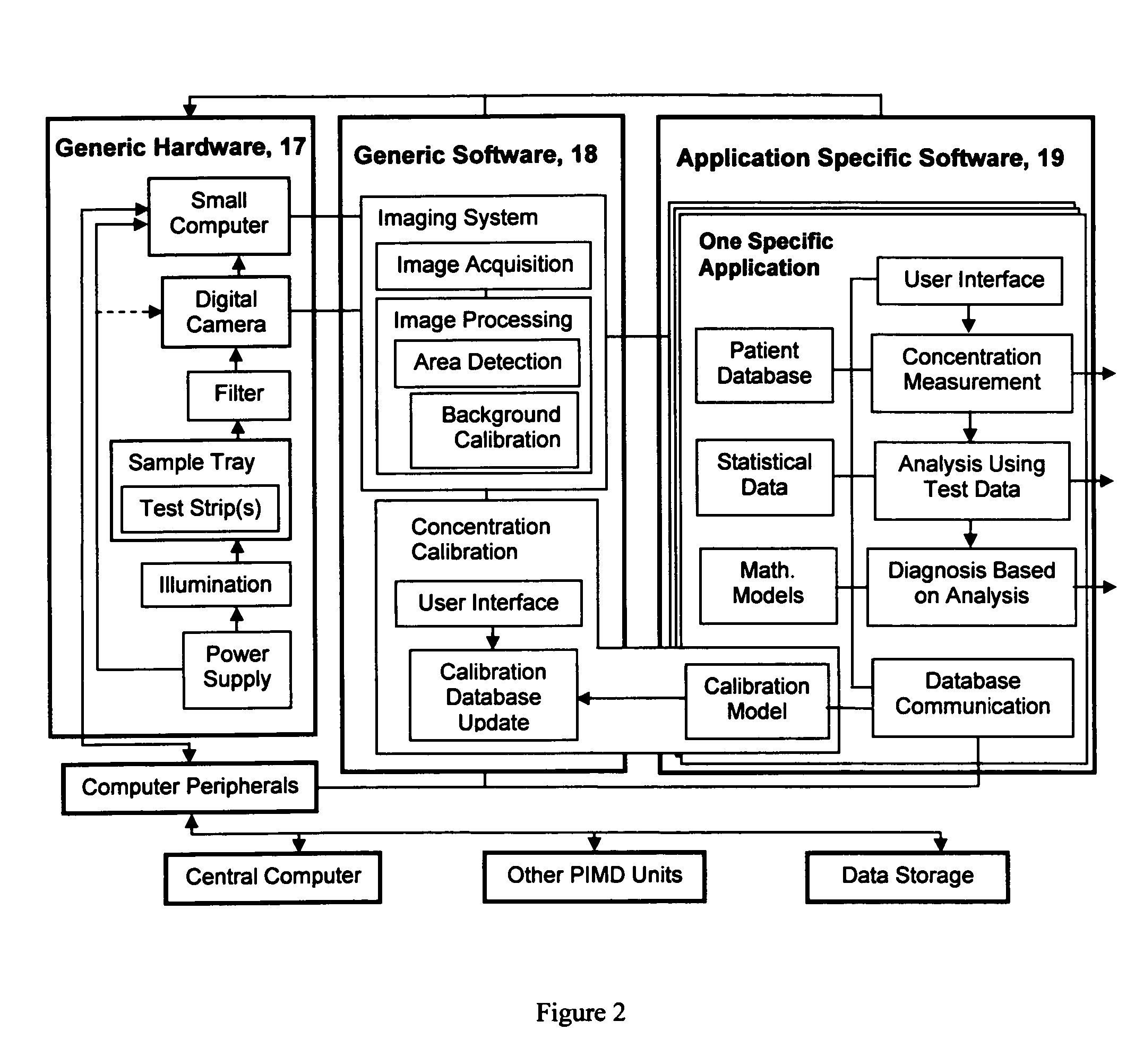
The present invention pertains to a portable apparatus for quantitatively measuring the concentration of specific substances in test samples of a lateral flow or microplate assay in medical, biomedical and chemical applications, and for making subsequent analysis and diagnosis. The portable apparatus includes a sample tray for carrying and aligning the test sample in the apparatus; a enclosure that may also serves as the frame of the apparatus; a digital image acquisition system that is used to obtain the digital image of the test sample on the sample tray; and a data display, processing, and analysis unit that is a general purpose or dedicated computer, such as a handheld computer (HHC), a pocket personal computer (PPC), a personal digital assistant (PDA), a palm-top computer, a laptop computer, or a dedicated microprocessor and associated hardware, for measuring the concentration of specific substances in the test sample, and making subsequent analysis and diagnosis, based on the measurement, statistical data, prior knowledge and mathematical model. The stated enclosure and frame, the digital image acquisition system, and the data display, processing and analysis unit are integrated to form the portable apparatus for various applications. The integrated apparatus of this invention, with a possible name—Portable Intelligent Multi-Diagnoser (PIMD), thus forms a portable and multiple-purpose tool for measuring the concentration of specific substances in test samples, and making subsequent analysis and diagnosis in a variety of settings, such as a mobile site, point of care or near patient care, and small laboratories.
Owner:MA JIE +1
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS20110098572A1High resolution imagingEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
An imaging probe for a biological sample includes an OCT probe and an ultrasound probe combined with the OCT probe in an integral probe package capable of providing by a single scanning operation images from the OCT probe and ultrasound probe to simultaneously provide integrated optical coherence tomography (OCT) and ultrasound imaging of the same biological sample. A method to provide high resolution imaging of biomedical tissue includes the steps of finding an area of interest using the guidance of ultrasound imaging, and obtaining an OCT image and once the area of interest is identified where the combination of the two imaging modalities yields high resolution OCT and deep penetration depth ultrasound imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biomedical devices containing internal wetting agents
InactiveUS20050154080A1Improve wettabilitySurgeryTissue regenerationPolymer scienceHydrophilic polymers
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Complex matrix for biomedical use
InactiveUS20060246137A1Easy to useEnhance lipPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkComplex matrix
A complex matrix is constituted by at least one biocompatible polymer of natural origin, cross linked and to which are grafted small chains of a molecular weight less than 50,000 Da with an amount of grafting of 10 to 40%, as well as a process for preparation of a biocompatible matrix that is partly degradable, constituted by at least one polymer of natural origin, consisting: on the one hand, grafting small chains of molecular weight less than 10,000 Da, with a grafting amount of 10 to 40%, on the other hand, cross linking the principal polymer chains to create a homogeneous matrix.
Owner:ANTEIS SA
Method and device for photothermal examination of microinhomogeneities
InactiveUS7230708B2Improve resolutionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansRefractive indexLaser beams
The invention relates to optical microscopy, and more particularly to the methods for photothermal examination of absorbing microheterogeneities using laser radiation. The invention can be widely used in laser technique, industry, and biomedicine to examine transparent objects with absorbing submicron fragments, including detection of local impurities and defects in super-pure optical and semiconducting materials and non-destructive diagnostics of biological samples on cellular and subcellular levels.The object of the present invention is to increase sensitivity, spatial resolution and informative worth when examining local absorbing heterogeneities in transparent objects, as well as to detect the size of said heterogeneities even if said size is smaller than the radiation wavelength used.Said object is achieved by the pump beam irradiation of a sample, the duration of said irradiation not being longer than the characteristic time of cooling of the microheterogeneity observed. A relatively vast surface of the sample is irradiated at once, the size of said surface not being larger than the wavelength of the pump laser used. The refraction index thermal variations, induced by the pump beam in the sample and being the result of absorption, are registered by the parameter change of the probe laser beam. A chosen probe beam diameter should not be smaller than the pump beam diameter. The diffraction-limited phase distribution over the probe laser beam cross-section is transformed to an amplitude image using a phase contrast method. The properties of microheterogeneities are estimated by measuring said amplitude image.
Owner:LAPOTKO TATIANA MS
Ester derivatives of hyaluronic acid for the preparation of hydrogel materials by photocuring
The present invention relates to hyaluronic acid ester derivatives, whose carboxylic groups are partially esterified with hydroxy groups of propiophenone derivatives, to the hydrogel materials consisting of the said hyaluronic acid ester derivatives, to their preparation process by photocuring of the hyaluronic acid ester derivatives, and their use in the biomedical, sanitary and surgical fields, and in the medical field as controlled release systems for drugs.
Owner:FIDIA FARM SPA
Dual microcontroller-based liquid infusion system
Owner:AMRITA VISHWA VIDYAPEETHAM
In situ-forming hydrogel for tissue adhesives and biomedical use thereof
ActiveUS20120156164A1Excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strengthExcellent tissue adhesivenessAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDrugTissue adhesives
Disclosed herein are an in situ-forming, bioadhesive hydrogel and the medical uses thereof. Being formed by in situ crosslinking through an enzymatic reaction, the hydrogel has an advantage over conventional bioadhesive hydrogels in terms of biocompatibility. In addition, the in situ-forming bioadhesive hydrogel has excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength and has excellent tissue adhesiveness thanks to modification with / without dopa derivatives. The hydrogel finds a variety of applications in the biomedical field, including bioadhesives or hemostats, implant substances for tissue regeneration and augmentation, carriers for delivering biologically active materials or drugs, etc.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Preparation method of novel three-dimensional nitrogen doped graphene composite material system
ActiveCN105000548AEfficient preparationThe preparation process is easy to controlHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesNitrogen doped grapheneBiomedicine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel three-dimensional nitrogen doped graphene composite material system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, uniformly dispersing graphene oxide in a solvent at room temperature, adding a selected material and a nitrogen-containing compound, and uniformly mixing to form a mixed solution; 2, reacting the mixed solution at a temperature from room temperature to 150DEG C for 0-8h; and 3, cooling the above obtained product to room temperature, centrifuging, collecting the obtained product, washing, and drying to obtain the nitrogen doped graphene composite material. The three-dimensional nitrogen doped graphene composite material system with the nitrogen content of 8-19% can be efficiently and controllably prepared through the method, and the nitrogen content of the system can be controlled by changing the kind and the amount of the added nitrogen-containing compound, the reaction temperature and the reaction time; and the method is simple, is easy to enforce, allows the yield to be greater than 98.9%, and can be widely used in fields of water treatment, biomedicines, energy generation, conversion and storage devices, electrostatic prevention, heat management, heat conduction and dissipation, sensors, electromagnetic shielding, wave absorption and catalysis.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing biomedical metal alloy material with multi-drug delivery system
InactiveUS20130164346A1Good biocompatibilityImprove adhesionInorganic non-active ingredientsSurgeryMetal alloyPharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides a method for preparing a biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system. A biomedical metal alloy material with a multi-drug delivery system according to the present invention is prepared by incorporating a therapeutic agent into a biodegradable material to prepare particles containing the therapeutic agent, treating the surface of the particles containing the therapeutic agent to have a charge opposite to the surface charge of a metal alloy material, and inducing an electrostatic interaction between the surface charges of the particles containing the therapeutic agent and the metal alloy material to immobilize the surface-treated particles containing the therapeutic agent on the surface of the metal alloy material.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Superparamagnetic colloidal nanocrystal structures
ActiveUS20100224823A1High magnetizationGood water dispersibilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentMagnetitePhotonics
Monodisperse colloidal nanocrystal clusters of magnetite (Fe3O4) with tunable sizes from about thirty to about three hundred nanometers have been synthesized using a high-temperature hydrolysis process. The colloidal nanocrystal clusters are capped with polyelectrolytes, and highly water soluble. Each cluster is composed of many single magnetite crystallites, thus retaining the superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature. The combination of superparamagnetic property, high magnetization, and high water dispersibility makes the colloidal nanocrystal clusters ideal candidates for various important biomedical applications such as drug delivery and bioseparation. The present invention is further directed to methods for forming colloidal photonic crystals from both aqueous and nonaqueous solutions of the superparamagnetic colloidal nanocrystal clusters with an external magnetic field applied thereto. The diffraction of the photonic crystals can be tuned from near infrared to visible and further ultraviolet spectral region by varying the external magnetic field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
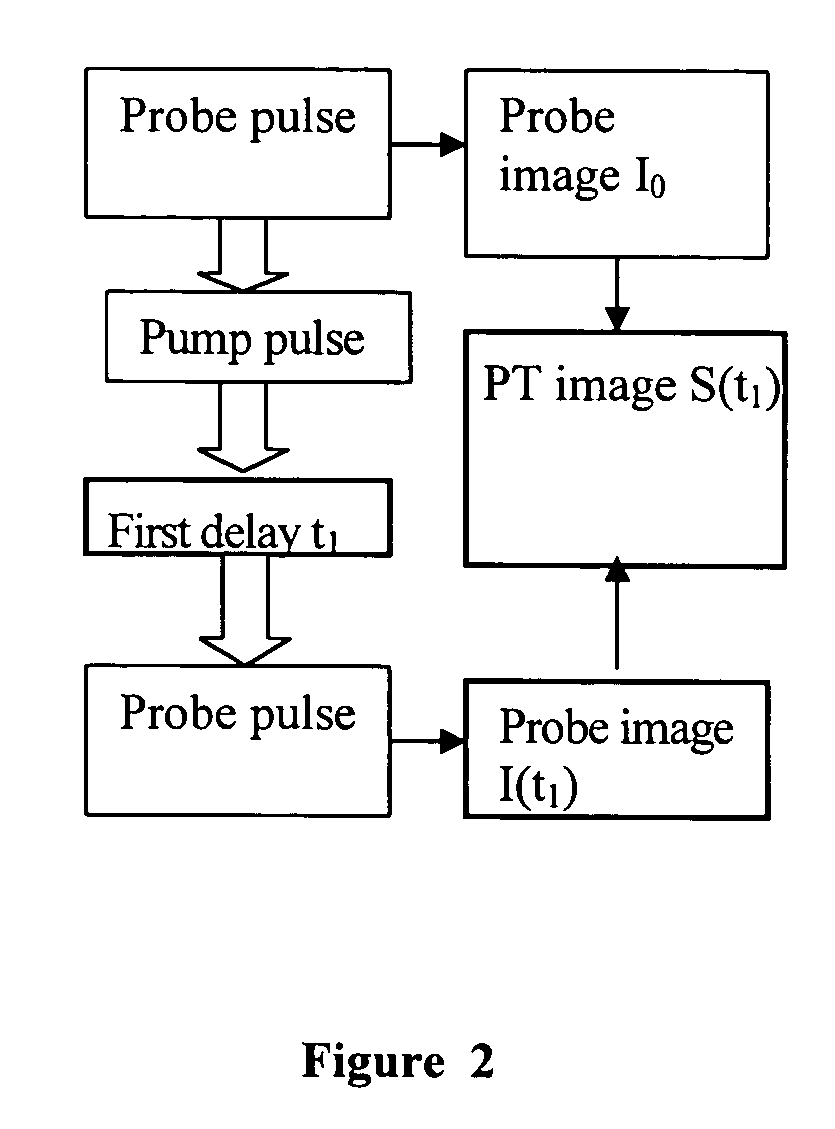
Systems and methods for thermophotonic dynamic imaging
Owner:MANDELIS ANDREAS +2
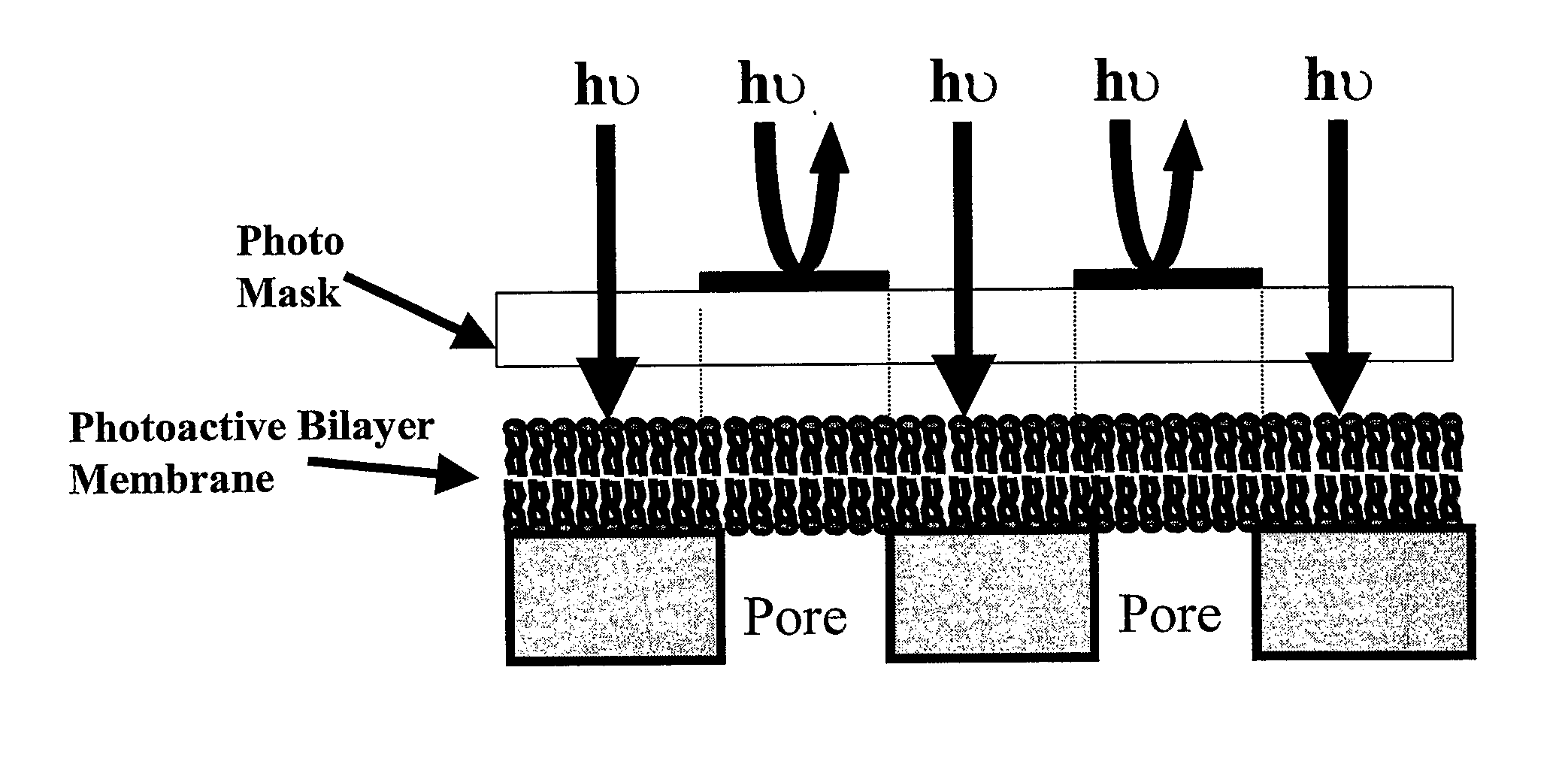
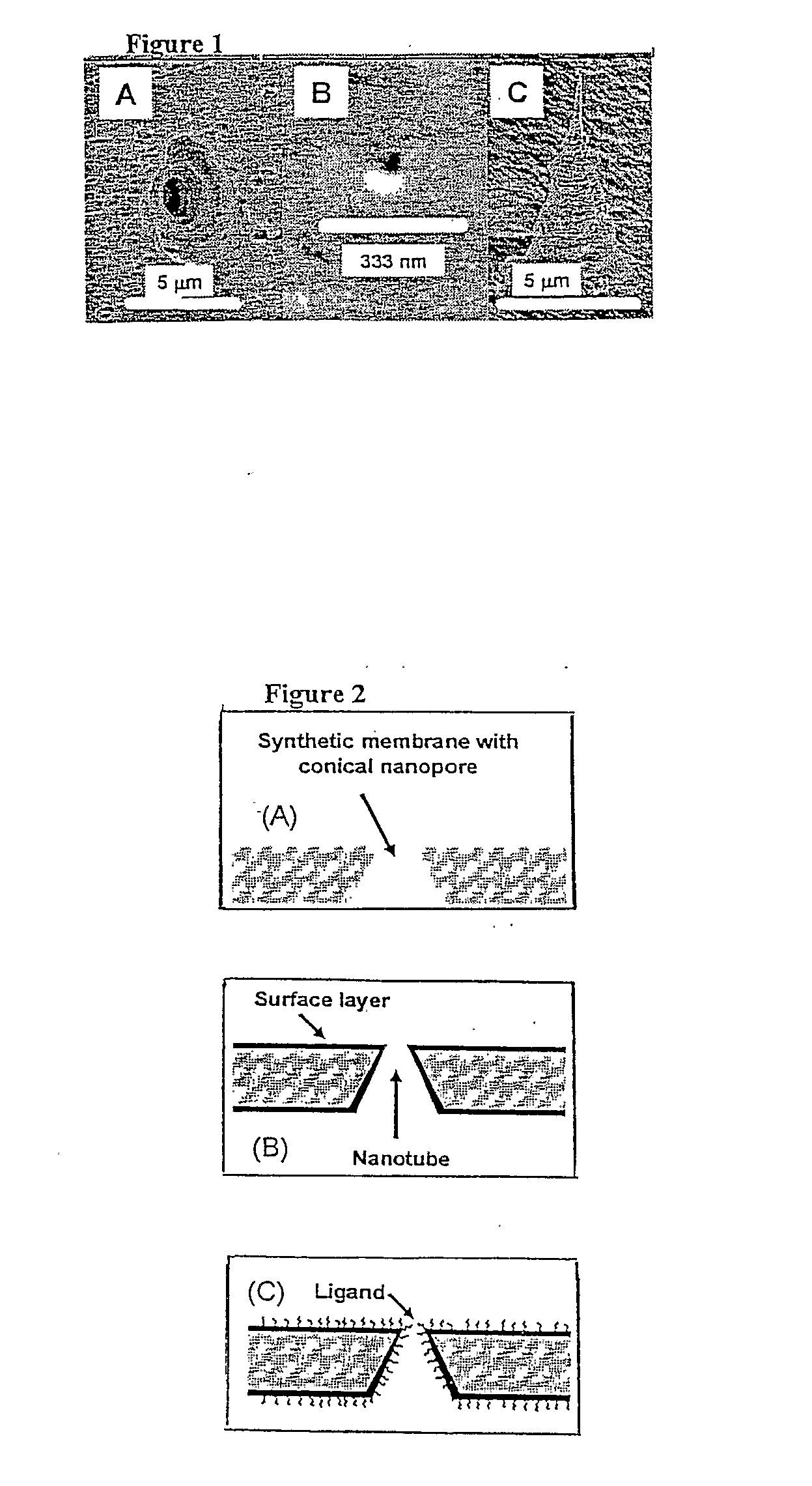
Chemical, Particle, and Biosensing with Nanotechnology
InactiveUS20080025875A1Reduce manufacturing costEase and flexibility of preparationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological macromoleculeMolecular recognition
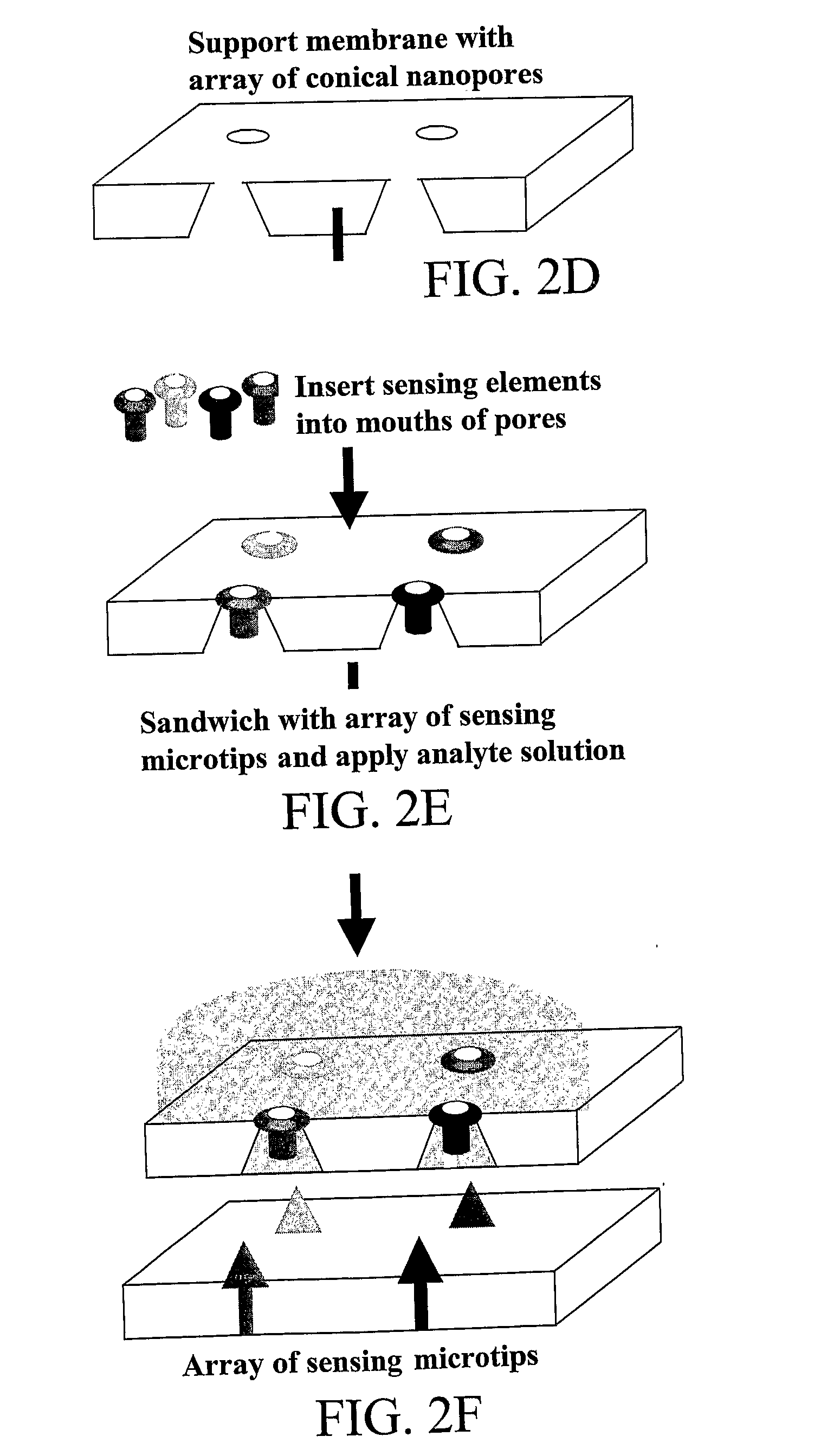
The subject invention provides novel and efficacious systems and methods for particle, chemical, and / or biocompound sensing. In one embodiment, the system of the invention comprises a sensing device that includes a membrane containing at least one nanochannel that spans all or substantially all of the thickness of the membrane. The nanochannel(s) of the invention can be functionalized to enhance target analyte detection and quantification. In one embodiment, the nanochannel is conically shaped and includes a molecular recognition agent for a target analyte. In certain operations, the sensing systems of the invention quantitatively and qualitatively detect biochemical / biomedical species and biomacromolecules, such as proteins, DNA, cells, spores and viruses, with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Structurally modified acellular tissue engineering scaffolds and methods of production
ActiveUS20070248638A1Seed efficiency be facilitateImprove seeding efficiencyCell culture supports/coatingUnknown materialsBiomedical implantFreeze dry
Methods are provided for producing a bioscaffold from natural tissues by oxidizing a decellularized tissue to produce a bioscaffold having pores therein. The pore size and porosity is increased to better accommodate intact cells so that live cells can better infiltrate and inhabit the bioscaffold. The bioscaffold may be freeze-dried or lyophilized, sterilized and (optionally) aseptically packaged for subsequent use. A further aspect of the present invention is a bioscaffold produced by the processes described herein. Methods of treatment using the bioscaffold as a graft or as a biomedical implant for implantation are also provided. Also provided are methods of seeding a bioscaffold with mammalian cells, wherein the seeding carried out either in vitro or in vivo, and wherein a bioscaffold produced as described herein is utilized for said seeding.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
Modified chitosan having catechol group and biomedical material prepared from modified chitosan
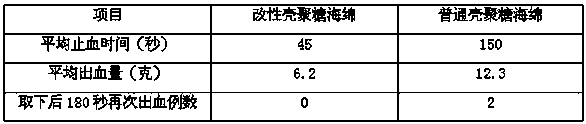
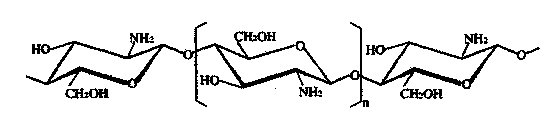
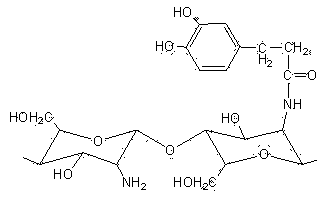
The invention discloses a biomedical material and a product thereof. The biomedical material has main characteristic that a compound having a catechol group structure is grafted on chitosan to form a chitosan biomedical material having the catechol group structure; or the grafted chitosan is cross-linked to prepare a novel macromolecular biomedical material. The catechol has cell adhesion, so that tissue adhesiveness of the chitosan can be changed, and blood cells can be adsorbed on the material surface to achieve better bleeding-steeping effect. By virtue of the mediation, performance of the chitosan is improved, and tissue affinity is improved. The material is prepared into a novel bleeding-stopping sponge by freeze-drying, and prepared into novel dressing by spinning or prepared into powder dressing by reverse flocculating.
Owner:HAINAN JIANKE PHARMA
Method for preparing micro/nano porous ceramic fibers by low-temperature electrostatic spinning
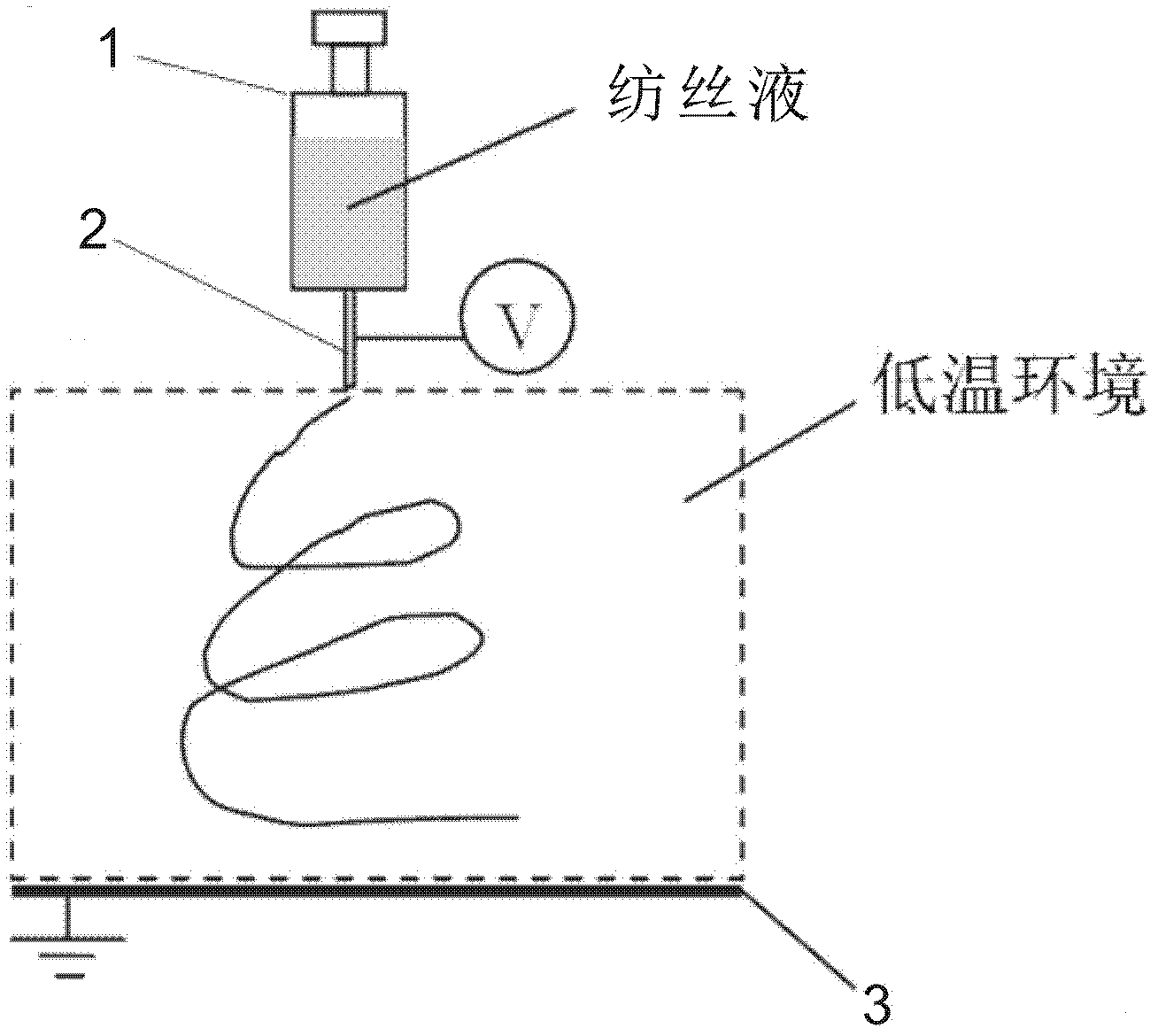
The invention relates to a method for preparing micro / nano porous ceramic fibers by low-temperature electrostatic spinning. With combining electrostatic spinning technology and freeze-drying technology, the micro / nano porous ceramic fibers are prepared by freeze-drying and sintering after electrostatic spinning at a low temperature; and the method comprises four steps of preparing a spinning solution, electrostatic spinning at a low temperature, freeze-drying and sintering. The method for preparing micro / nano porous ceramic fibers by low-temperature electrostatic spinning can obtain an extremely high specific surface area, and is beneficial to improving performances of contacting, catalyzing, separating and sensing of ceramic fibers, and has wide application prospects in fields of biomedicine, filter materials, catalyst carriers, fuel cells, electronic element appliances and the like.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
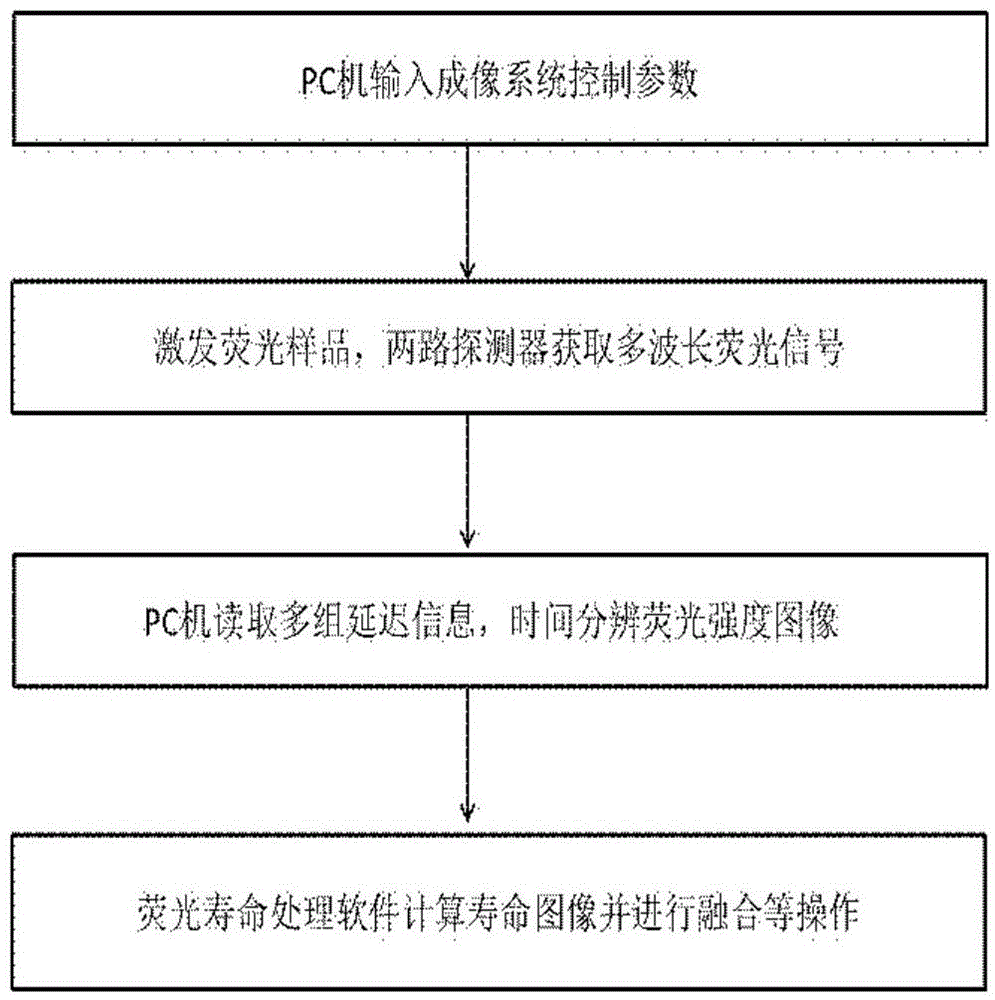
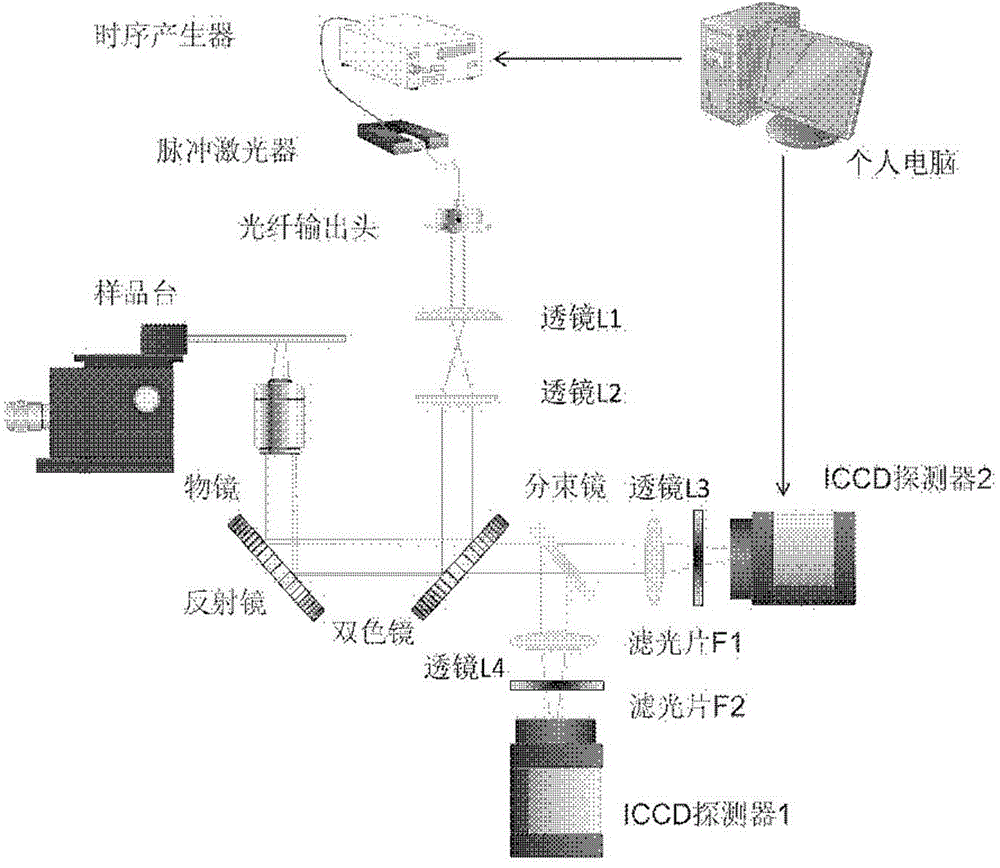
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extraction and preparation method for micromolecule fishskin collagen peptide
The invention discloses an extraction and preparation method for micromolecule fishskin collagen peptide, which comprises the following technical steps of: taking the fishskin of freshwater fish as raw material; removing non-collagenous protein; carrying out steps of degreasing, deodorizing, smashing and the like; under the acidic condition, carrying out heating hydrolysis processing to collagenous protein; controlling the degradation degree of the collagenous protein with an enzymolysis method; obtaining a target micromolecule collagen peptide with a membrane separation method; recycling protease, and then carrying out nanofiltration desalting; and after activated carbon binding resin is decolored and deodorized, carrying out spray drying to obtain the colorless and tasteless micromolecule fishskin collagen peptide. The extraction and preparation method disclosed by the invention has a simple technology, the protease is recycled by membrane separation, and therefore the cost is saved. The prepared micromolecule collagen peptide is colorless and tasteless and can be widely applied to industries relevant to the health of the human body, such as health care food, biomedicine, and cosmetics.
Owner:NINGDE XIAWEI FOOD
Fluorescence enhancing plasmonic nanoscopic gold films and assays based thereon
ActiveUS20130172207A1Enhance plasmonic near-infrared fluorescenceEnhanced fluorescence emissionPeptide librariesNucleotide librariesAssayGold film
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Local Causal and Markov Blanket Induction Method for Causal Discovery and Feature Selection from Data
In many areas, recent developments have generated very large datasets from which it is desired to extract meaningful relationships between the dataset elements. However, to date, the finding of such relationships using prior art methods has proved extremely difficult especially in the biomedical arts. Methods for local causal learning and Markov blanket discovery are important recent developments in pattern recognition and applied statistics, primarily because they offer a principled solution to the variable / feature selection problem and give insight about local causal structure. The present invention provides a generative method for learning local causal structure around target variables of interest in the form of direct causes / effects and Markov blankets applicable to very large datasets and relatively small samples. The method is readily applicable to real-world data, and the selected feature sets can be used for causal discovery and classification. The generative method GLL-PC can be instantiated in many ways, giving rise to novel method variants. In general, the inventive method transforms a dataset with many variables into either a minimal reduced dataset where all variables are needed for optimal prediction of the response variable or a dataset where all variables are direct causes and direct effects of the response variable. The power of the invention and significant advantages over the prior art were empirically demonstrated with datasets from a diversity of application domains (biology, medicine, economics, ecology, digit recognition, text categorization, and computational biology) and data generated by Bayesian networks.
Owner:ALIFERIS KONSTANTINOS CONSTANTIN F +1
Material for bone tissue engineering scaffold and making method thereof
InactiveCN101032632AImprove mechanical propertiesGood biocompatibilityBone implantBiocompatibility TestingBiological materials
The present invention relates to biological material technology, and is especially porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used as high strength biomedicine rack material for human body hard tissue defection and its preparation process. The porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material used in bone tissue engineering rack has porosity of 5-99 % and pore diameter of 50-900 microns. Owing to easy degradation and absorption of magnesium inside body, the bone tissue engineering rack of porous magnesium, magnesium alloy and composite magnesium material has excellent mechanical performance and excellent biocompatibility and can provide 3D space for cell to grow.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gradient coating for biomedical applications
ActiveUS20110014258A1Reduce infectionReduce riskBiocideNervous disorderBiomedical engineeringAnti-Microbial Agents
The present invention provides a coating comprising a bioactive material and an antimicrobial agent, wherein the concentration of said antimicrobial agent varies throughout the thickness of the coating.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Preparation method and application of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with shell-core structure
ActiveCN102500291AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyExcitation spectral bandwidthMagnetic materialsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with a shell-core structure. Firstly, a silica magnetic microsphere with a shell-core structure is prepared by using one or more than one of nanoparticles of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, MeFe2O4 (Me=Co, Mn, Ni), metal Ni, Co, Fe, and alloy Fe-Co, Ni-Fe as the inner core, and coating a silica shell, and then a fluorescent material (a chelate of Eu3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Tb3+ and the like) is absorbed on the silica shell. Then, a layer of silica is coated on the surface to improve the stability of the fluorescent magnetic microsphere, and to prevent agglomeration and fluorescent material leakage. A lot of rare earth fluorescent materials are wrapped in the shell layer, so the fluorescence intensity signal of a prepared sample is greatly increased. The nanoparticle has dual functions of enrichment and marking, and has wider application prospects in the biomedical field.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOEASY BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
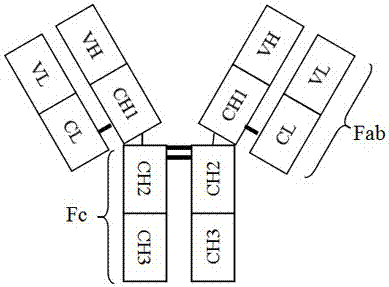
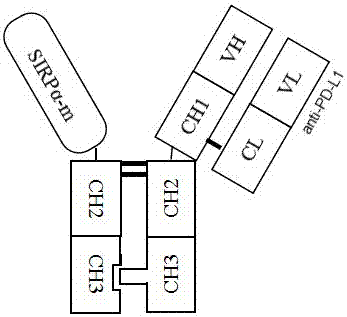
CD47 and PD-L1 targeting bifunctional fusion protein
ActiveCN107459578AImprove targetingHigh activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDisulfide bondingBlood safety
The invention relates to a CD47 and PD-L1 targeting bifunctional fusion protein, belongs to the field of biomedicine, and solves the problems that anti-PD-1 / PD-L1 treatment is poor in a low-immunogenicity tumor treatment effect and anti-CD47 treatment is poor in a targeting ability. The fusion protein is composed of a CD47 binding part and a PD-L1 binding part which are linked by a disulfide bond, can block the binding of CD47 and SIRPalpha, can block the binding of PD-L1 and PD-1, can achieve the effects of activating macrophages to phagocytize tumor cells and promoting antigen presentation in natural immunity, can achieve an effect of promoting the activation of tumor specific T cells in acquired immunity, and has lower blood toxicity; and as compared with the single use of anti-PD-L1 or anti-CD47 for treatment, the fusion protein has better antitumor curative effects and blood safety.
Owner:TAIZHOU MABTECH PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com