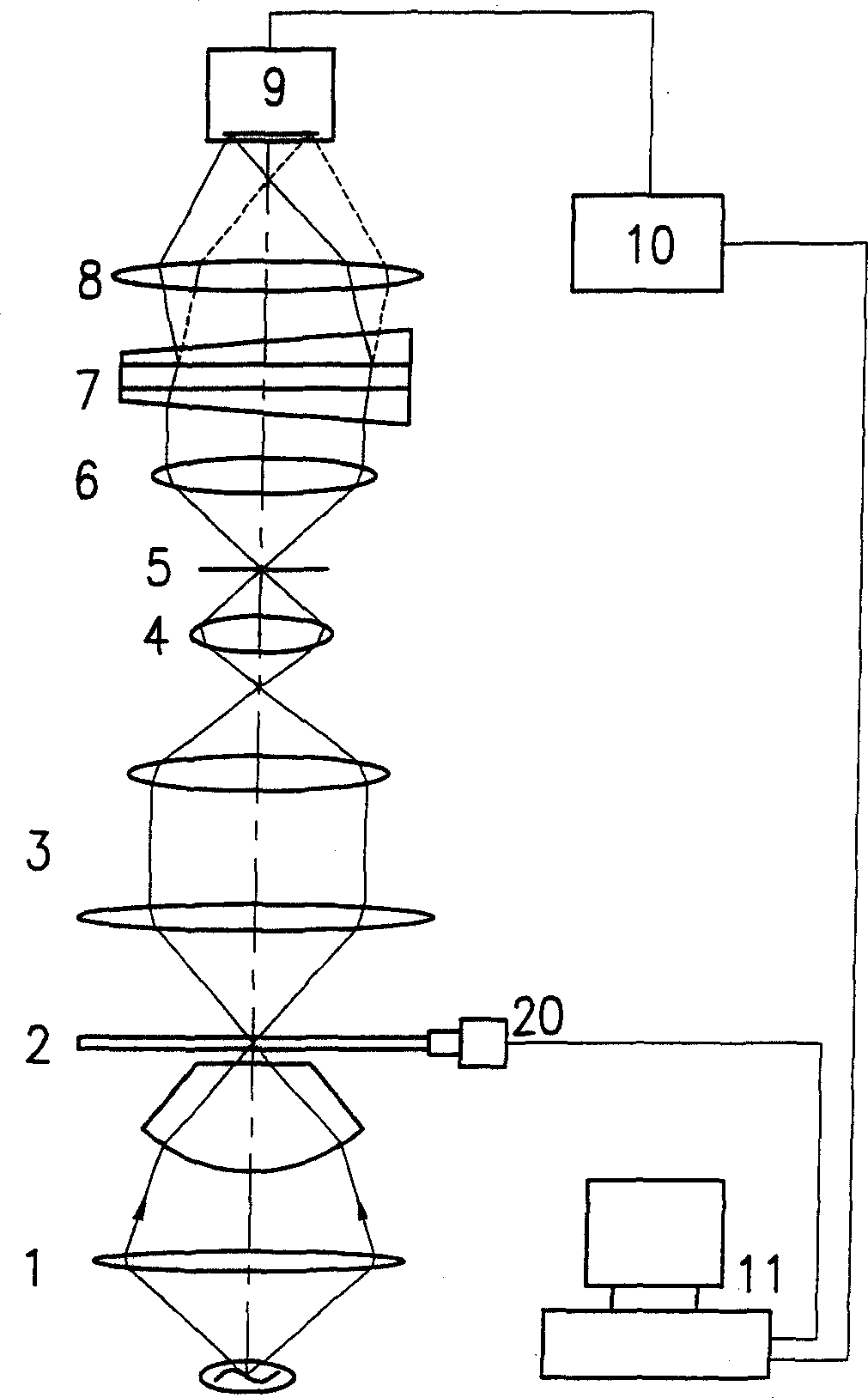
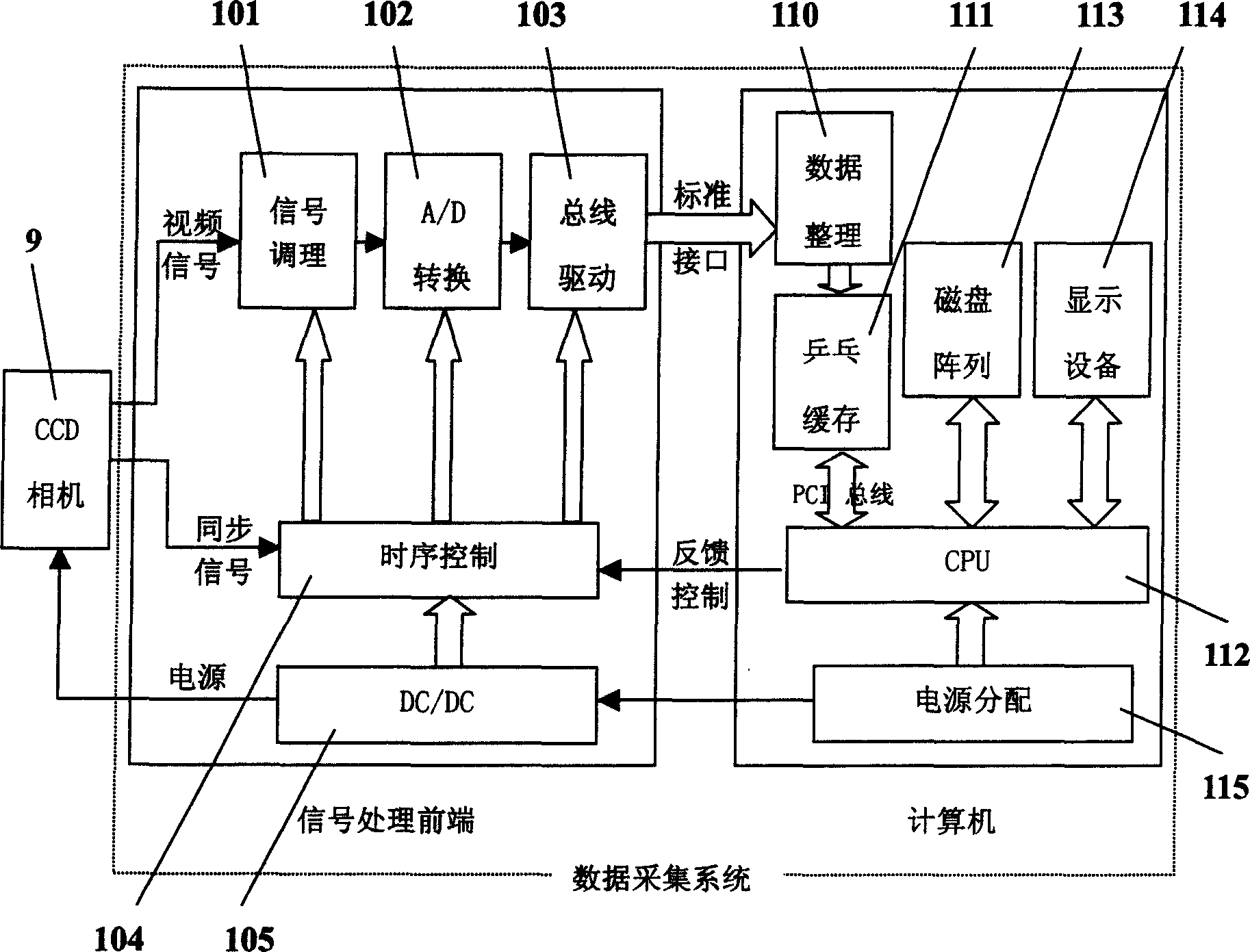
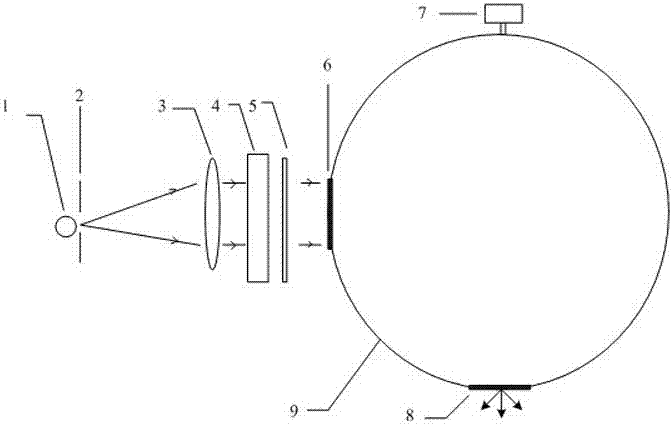
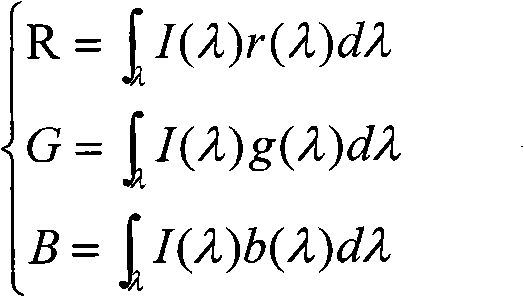Patents
Literature
551 results about "Spectrum imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
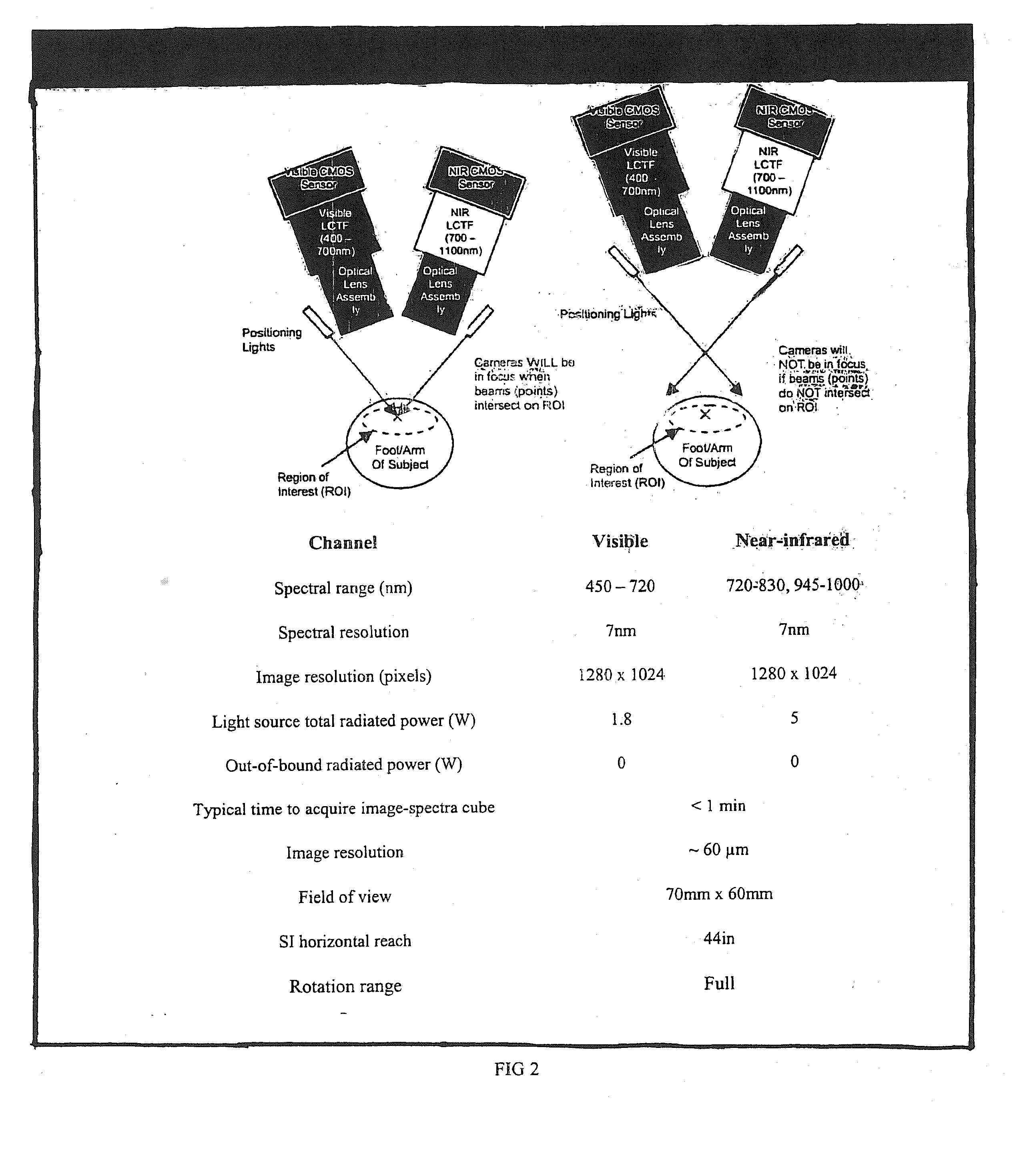
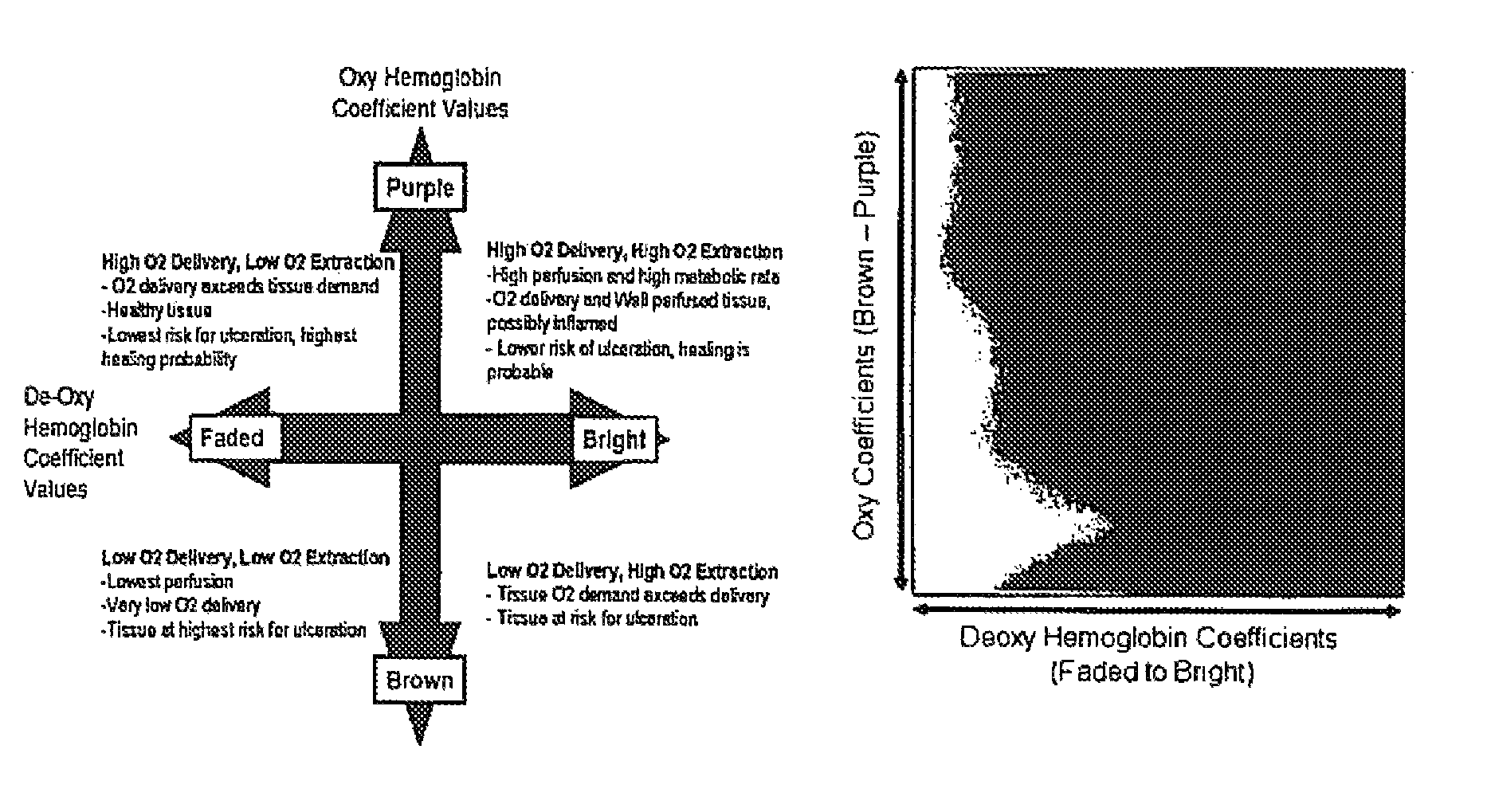
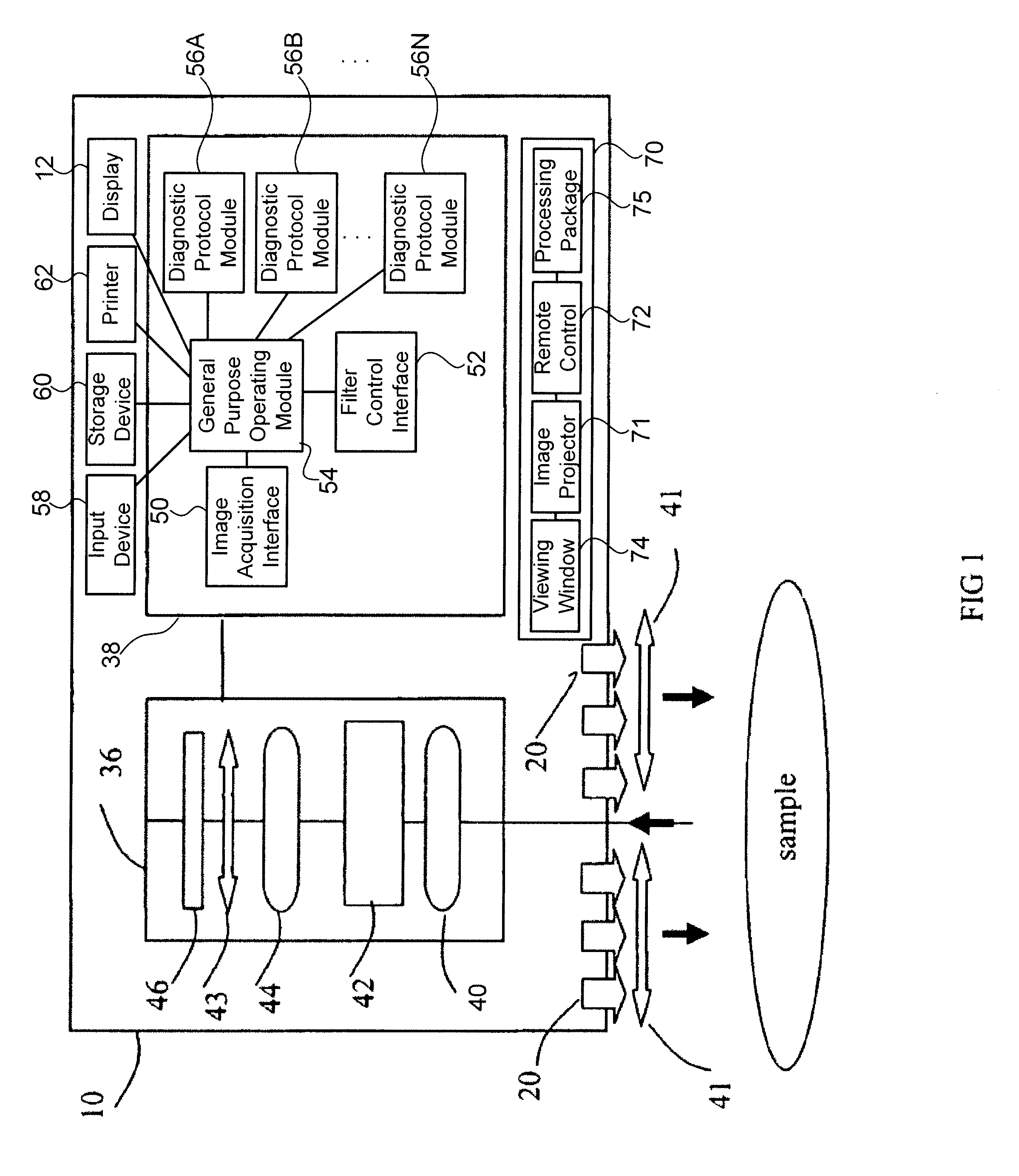
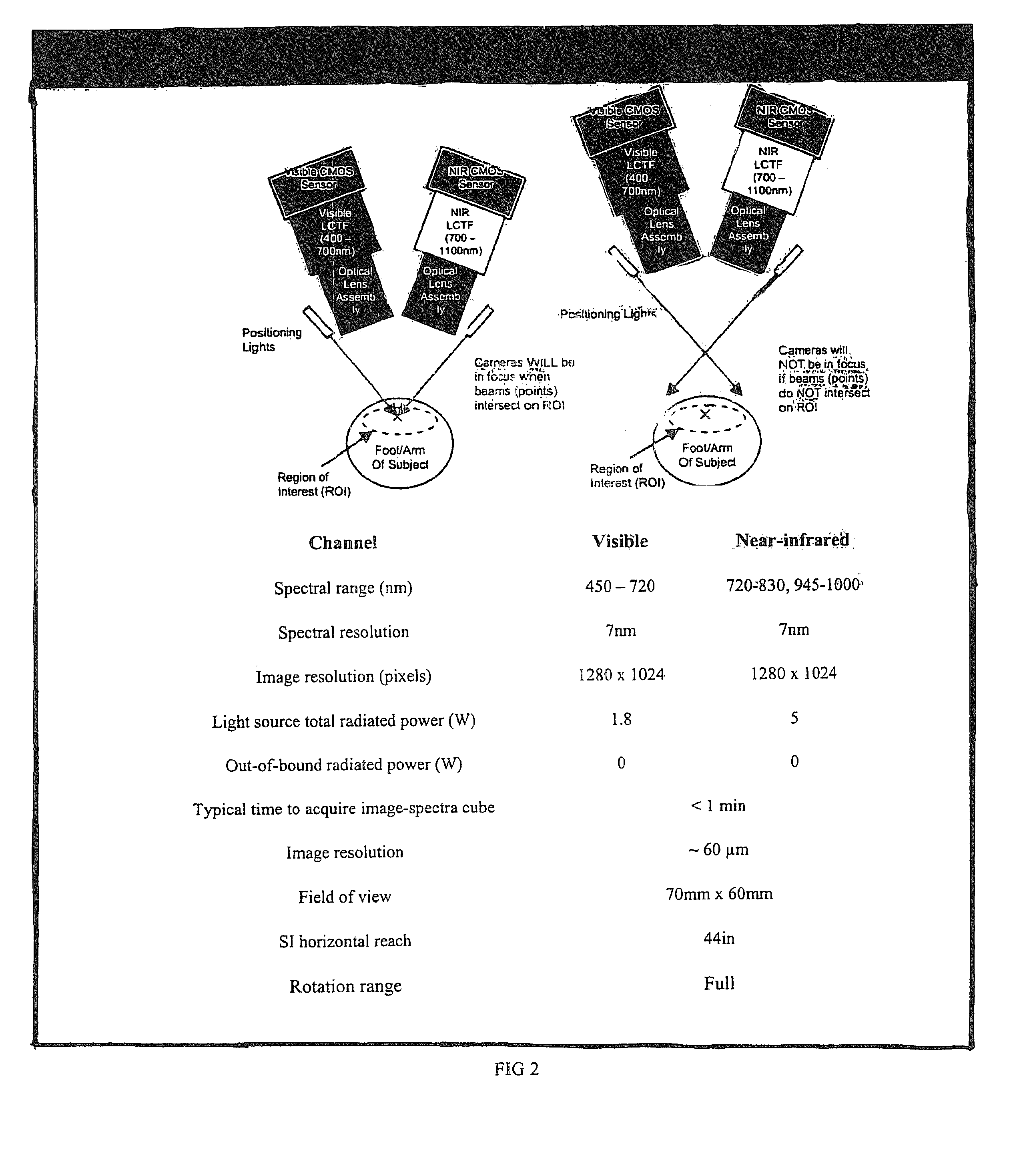
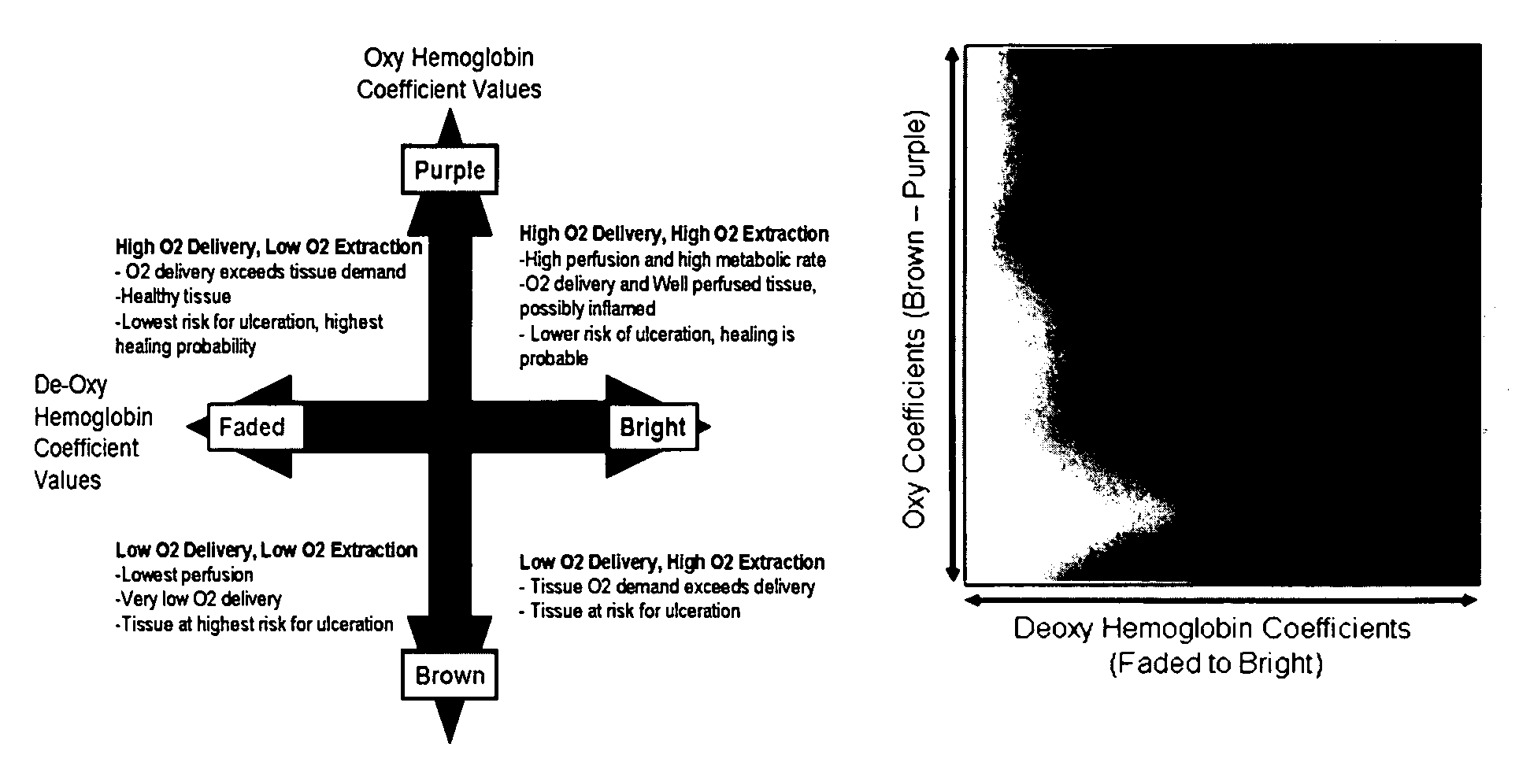
Hyperspectral imaging in diabetes and peripheral vascular disease
ActiveUS20070016079A1Reduce resolutionSmoothing imageImage analysisDiagnostics using lightDiseaseVascular disease
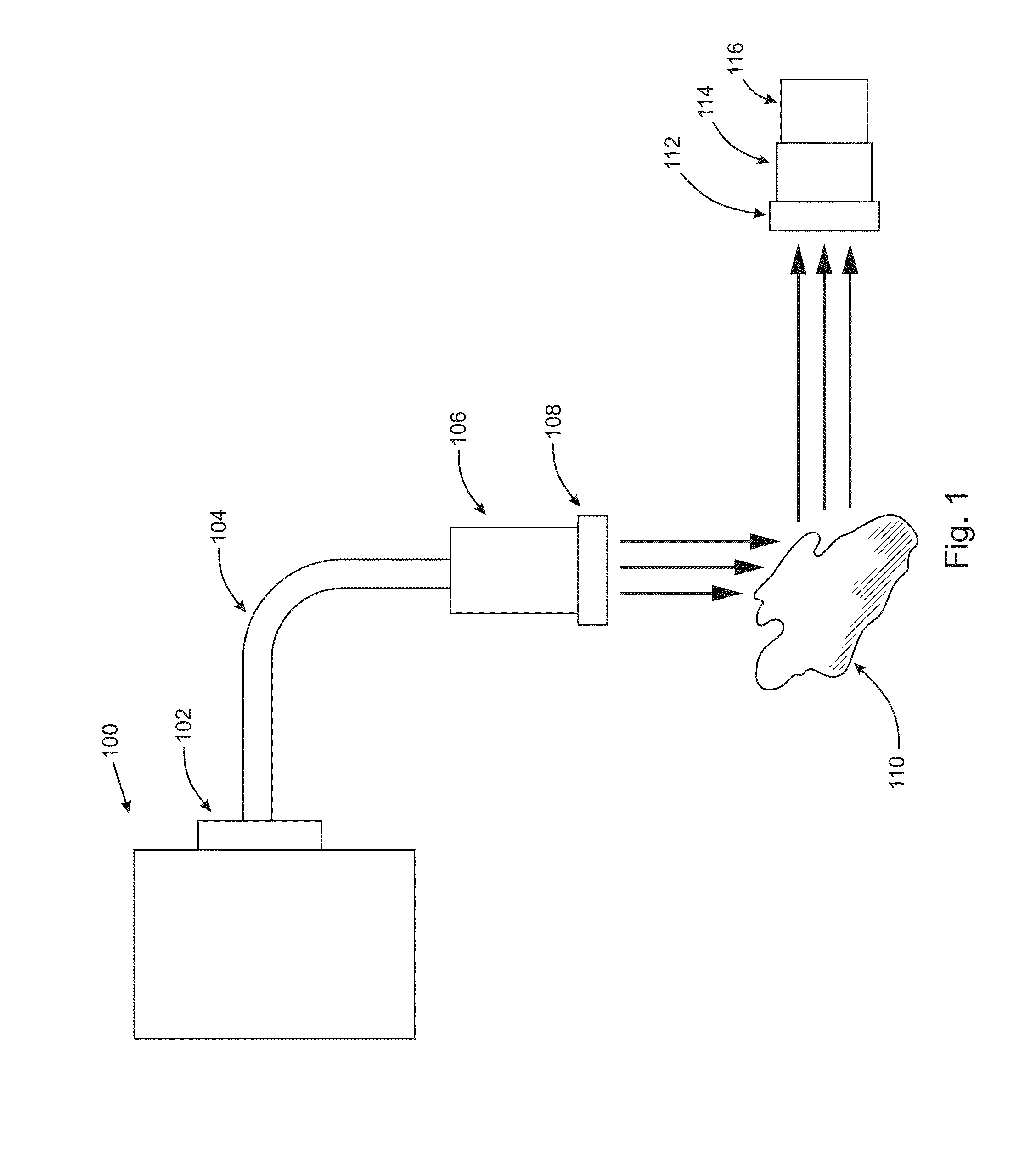
The invention is directed to methods and systems of hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of medical tissues. In particular, the invention is directed to new devices, tools and processes for the detection and evaluation of diseases and disorders such as, but not limited to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, that incorporate hyperspectral or multispectral imaging.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
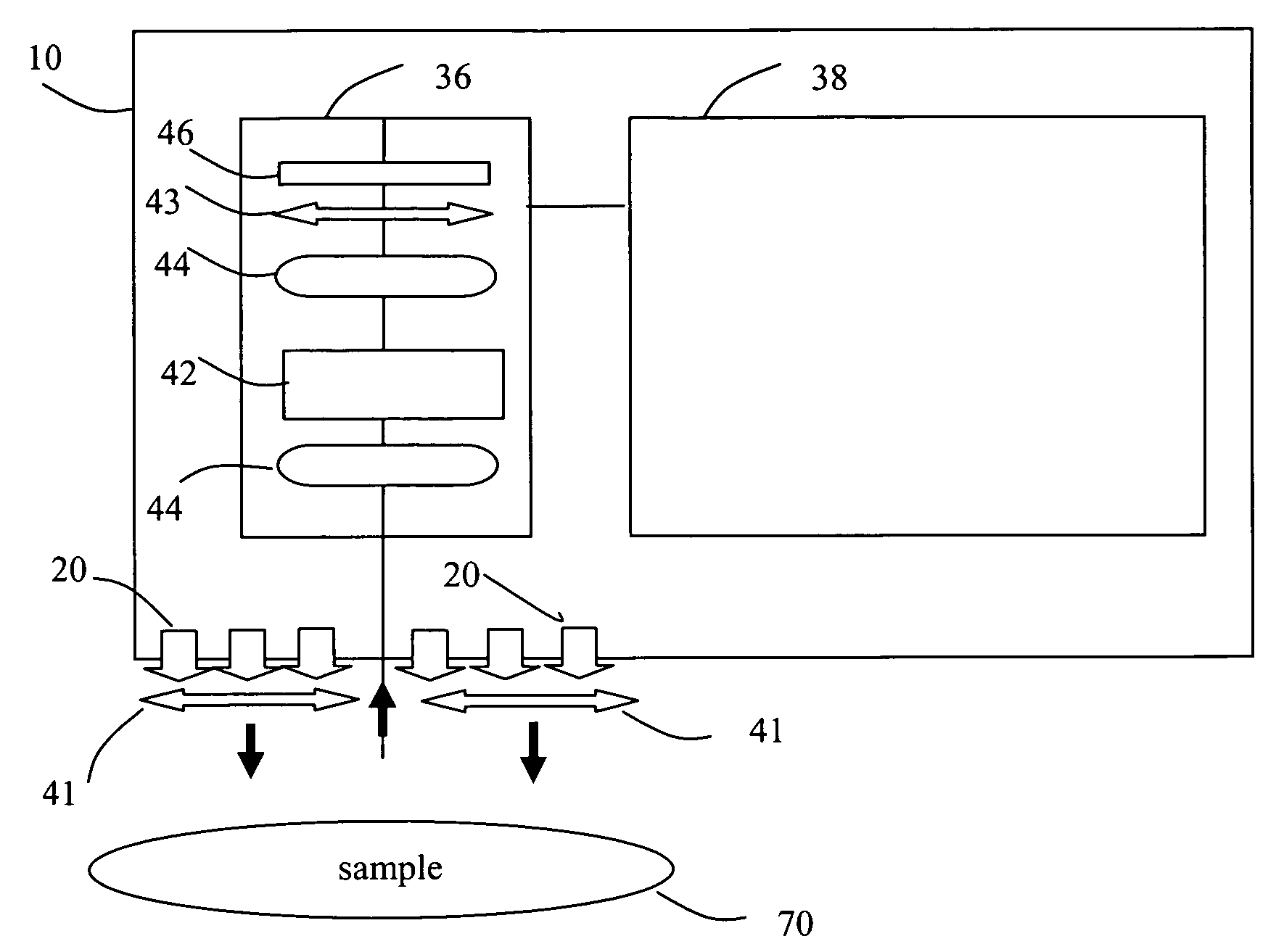
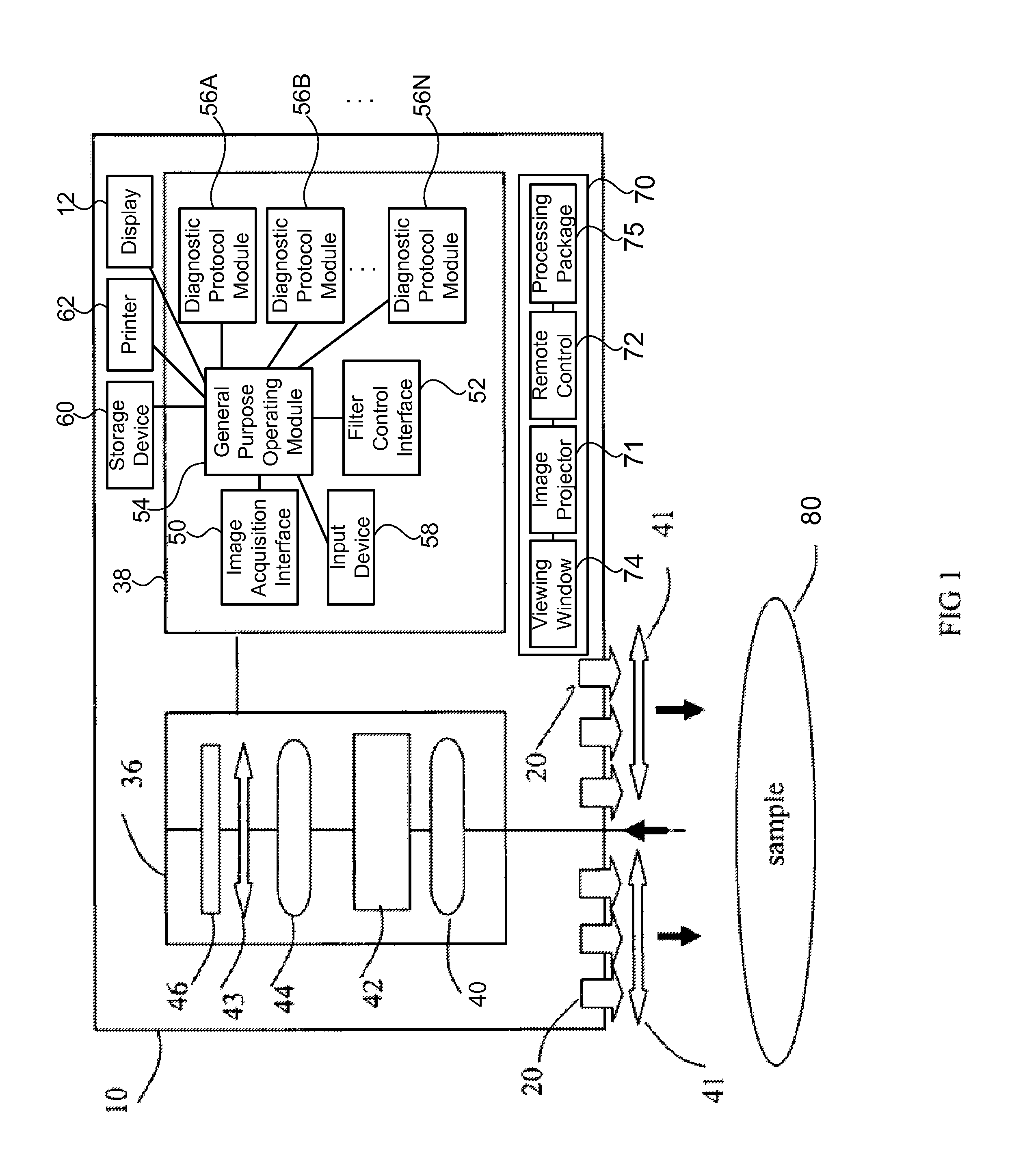
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
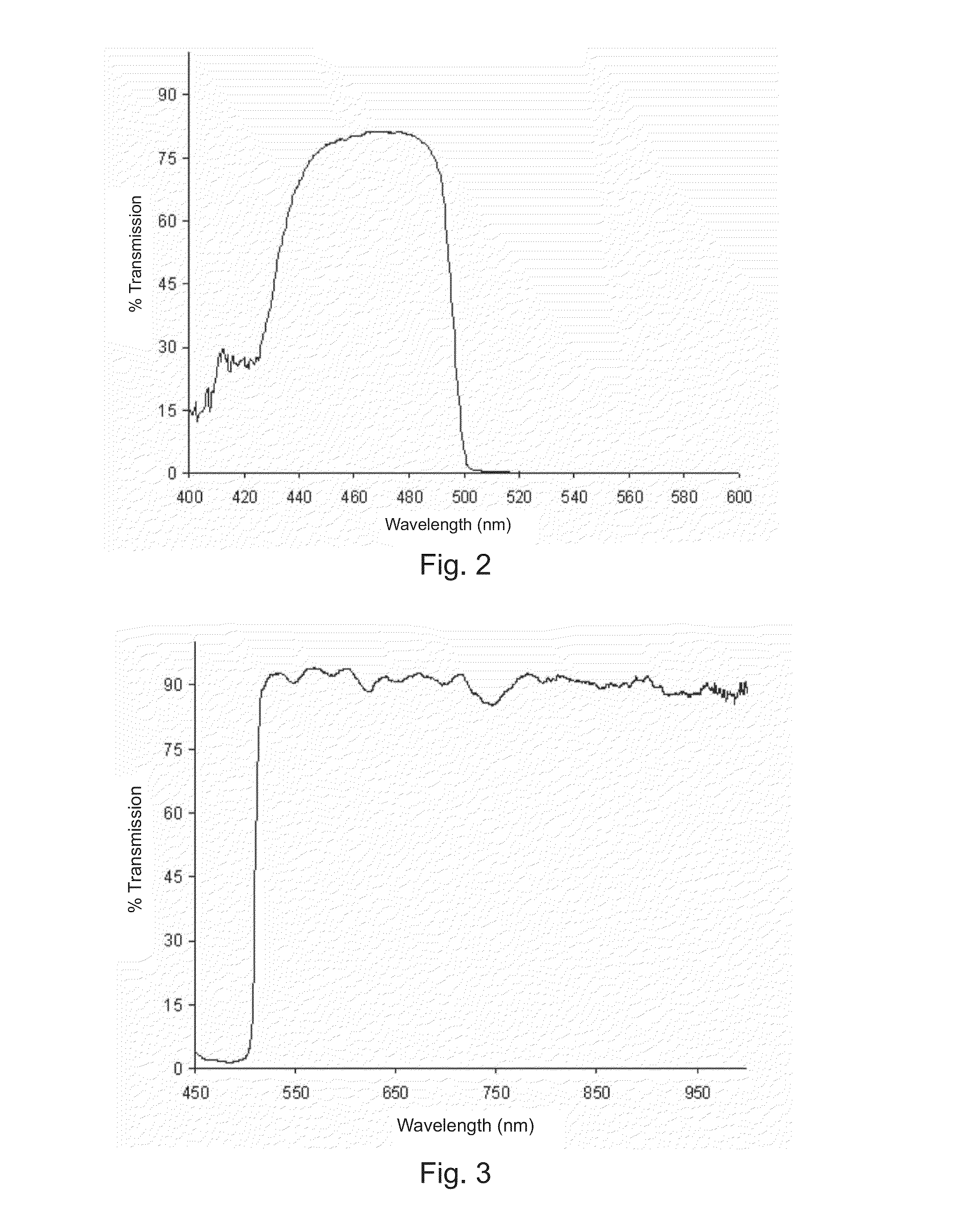
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
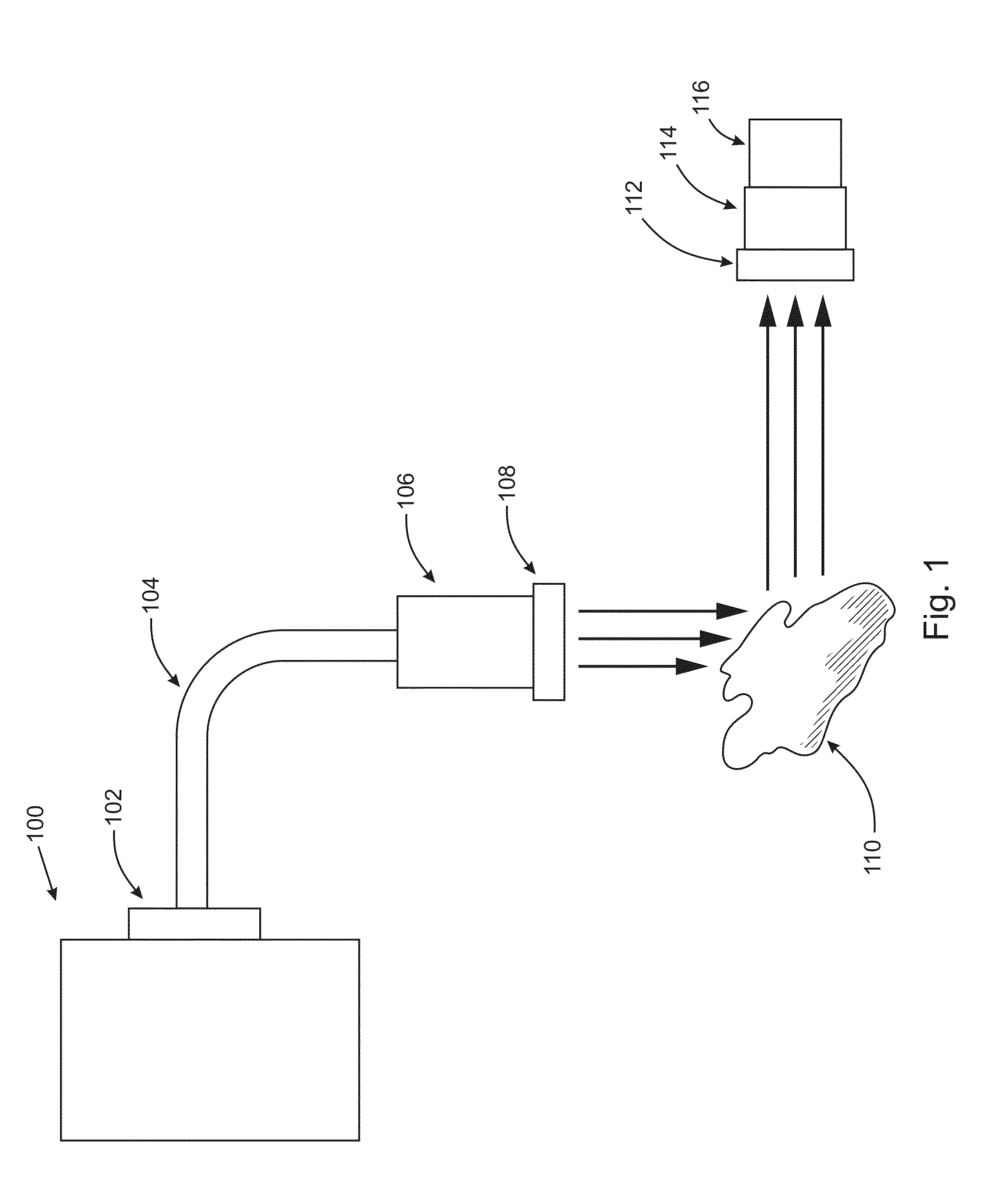
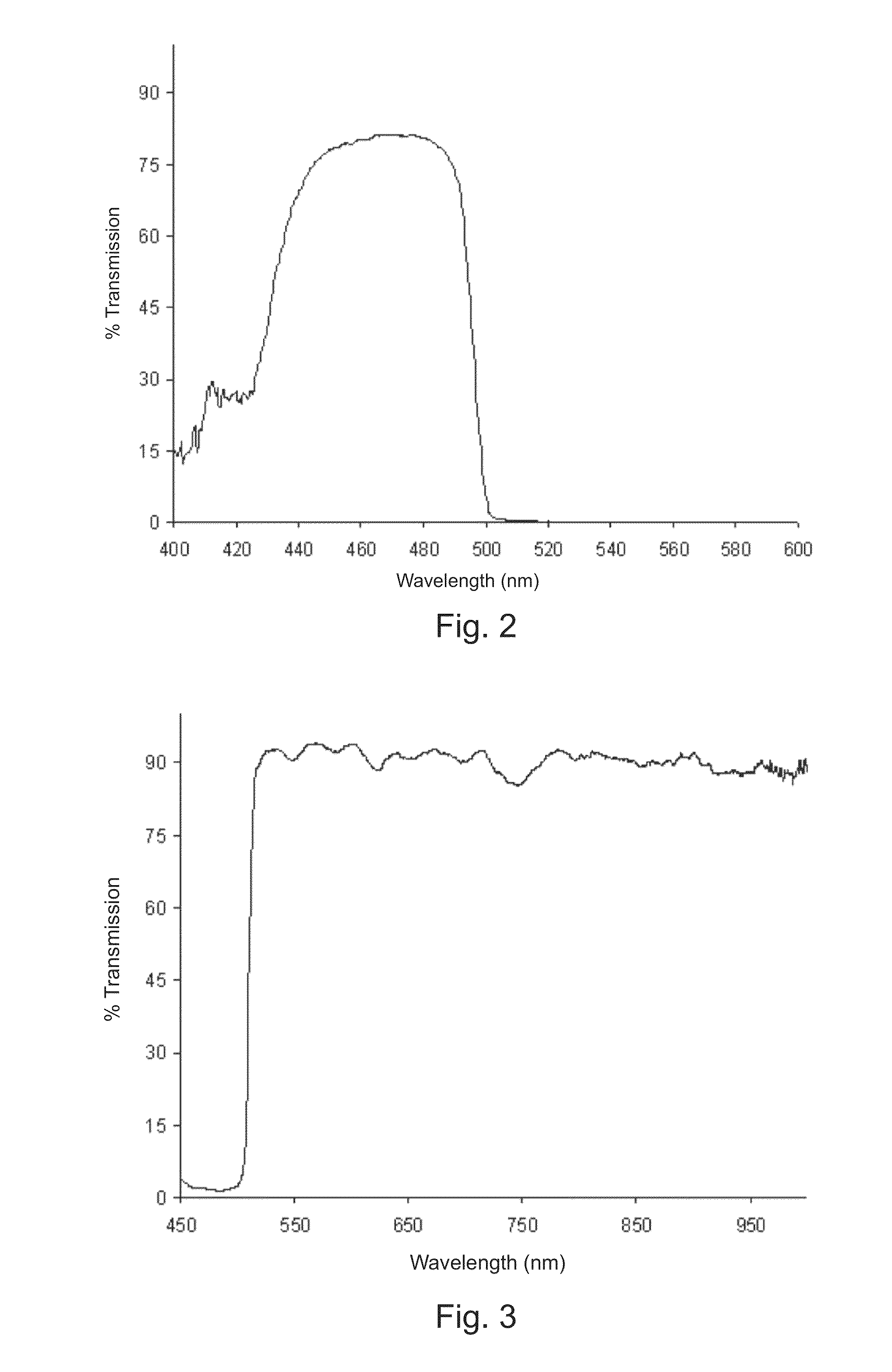
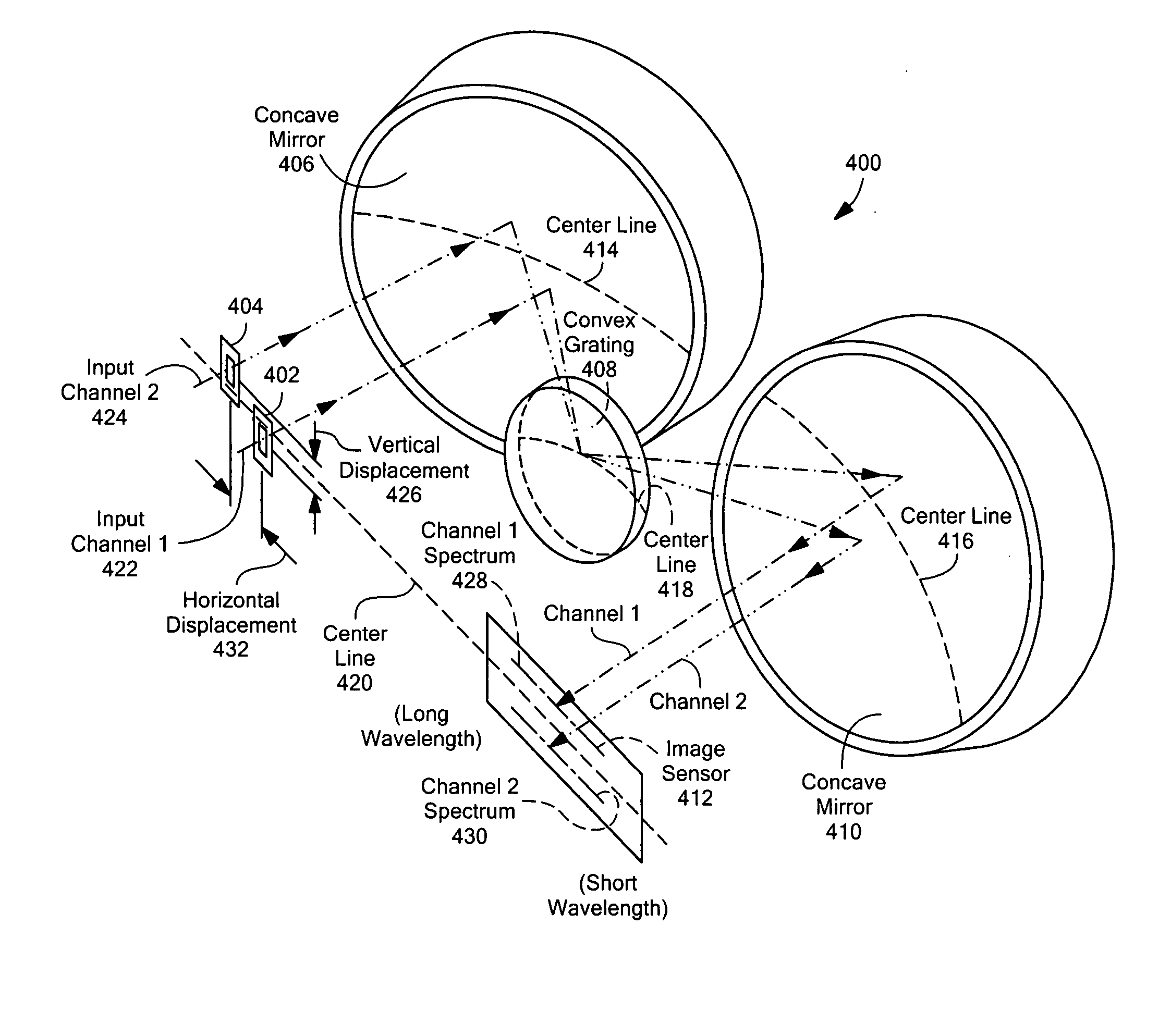
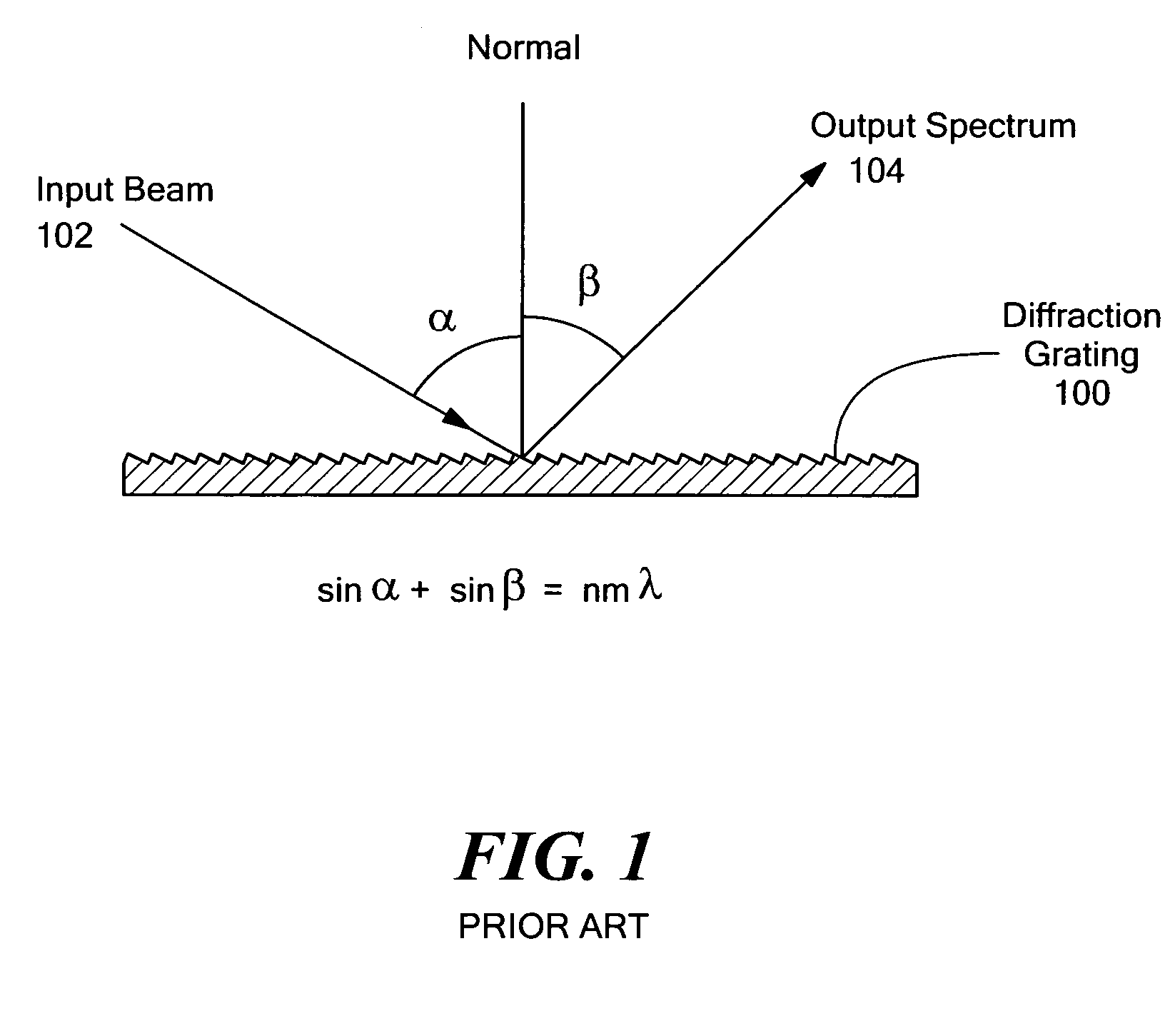
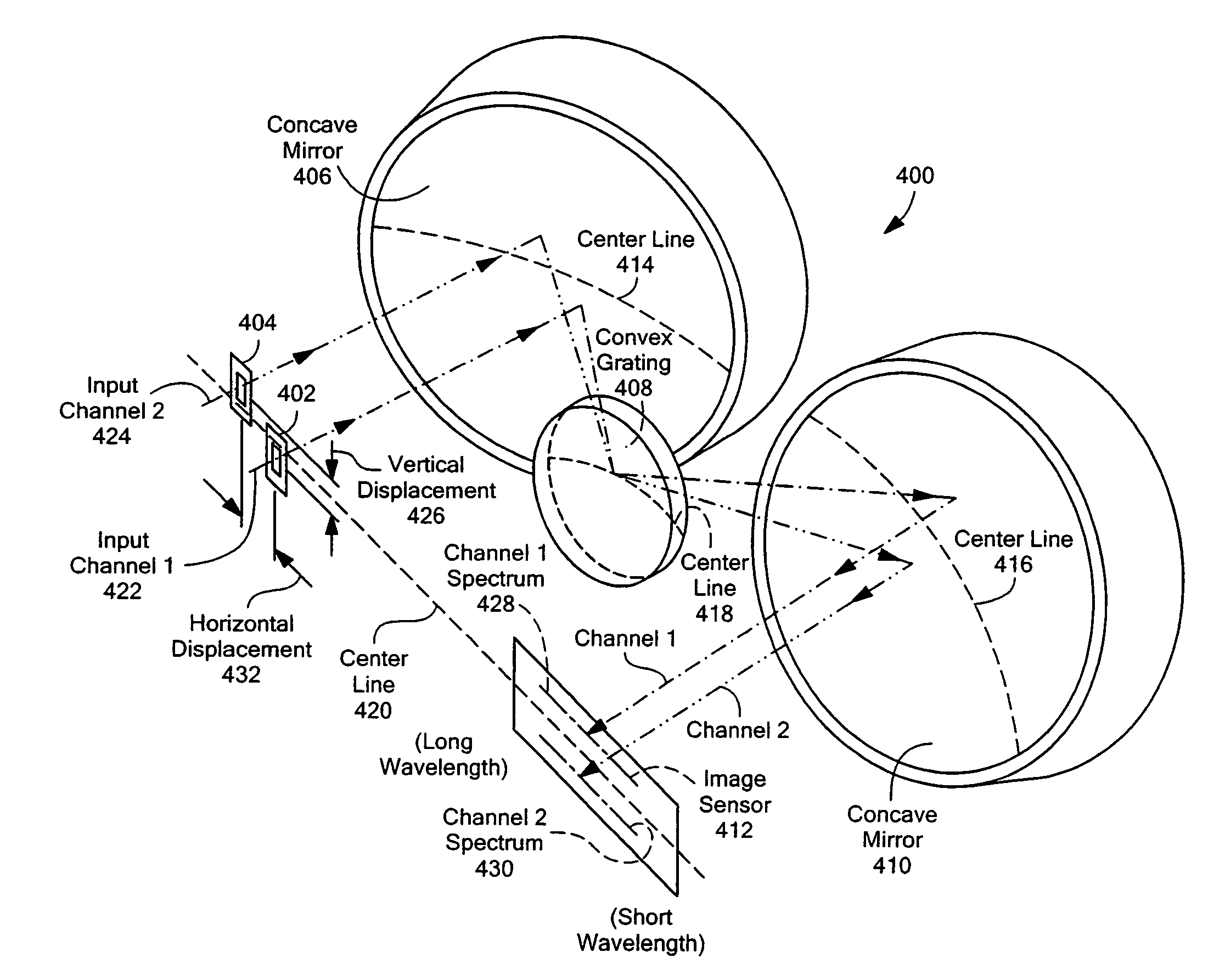
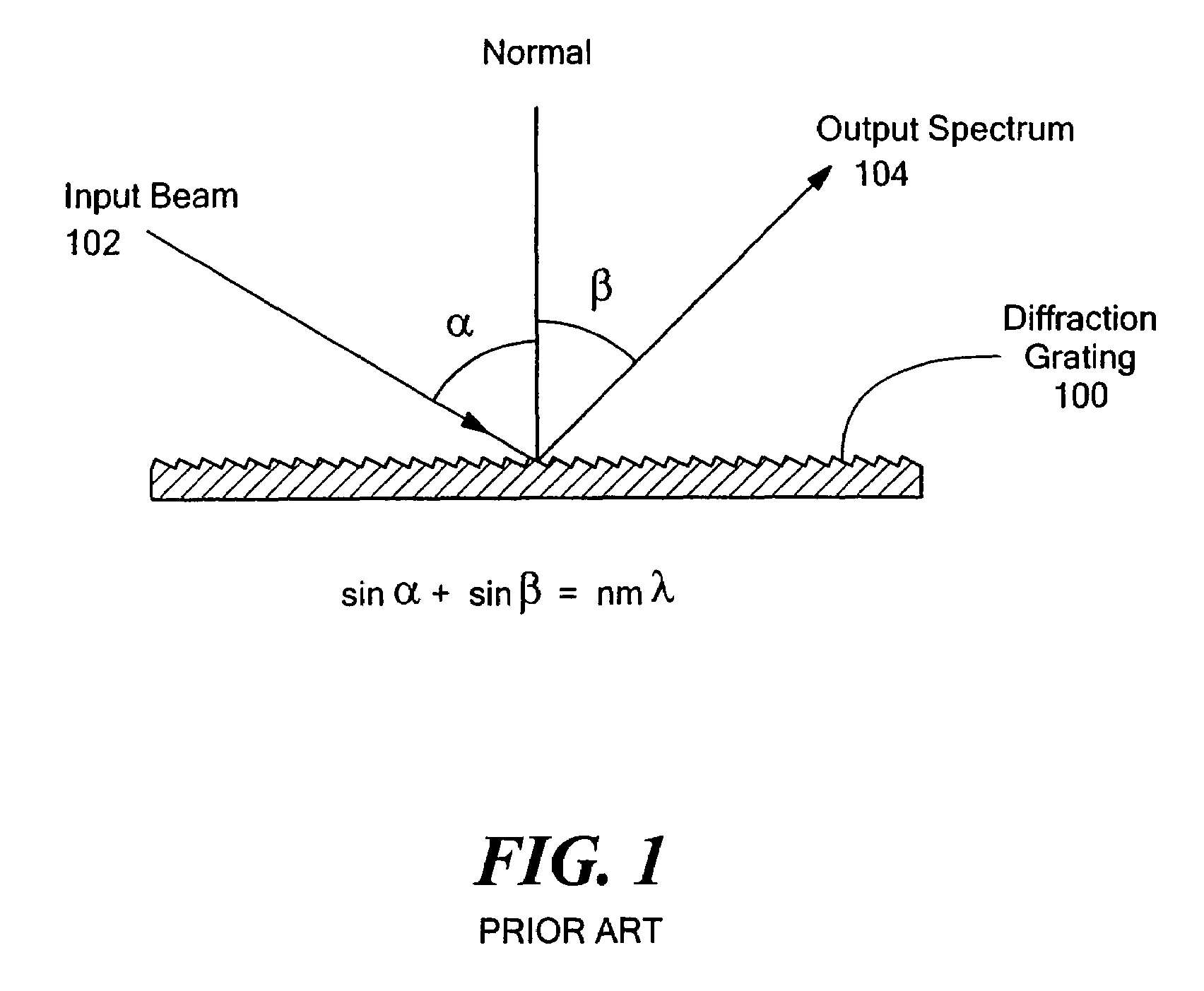
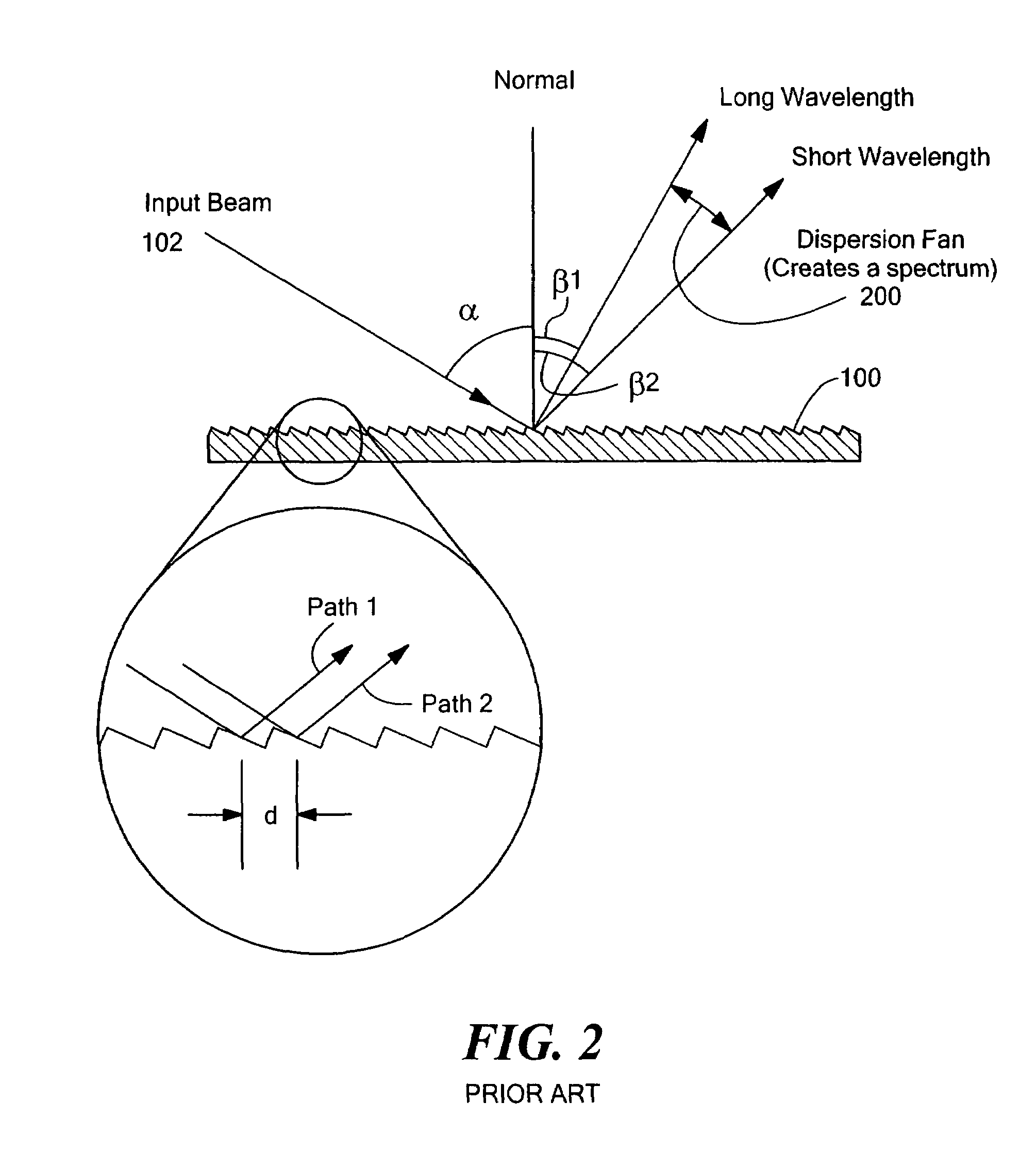
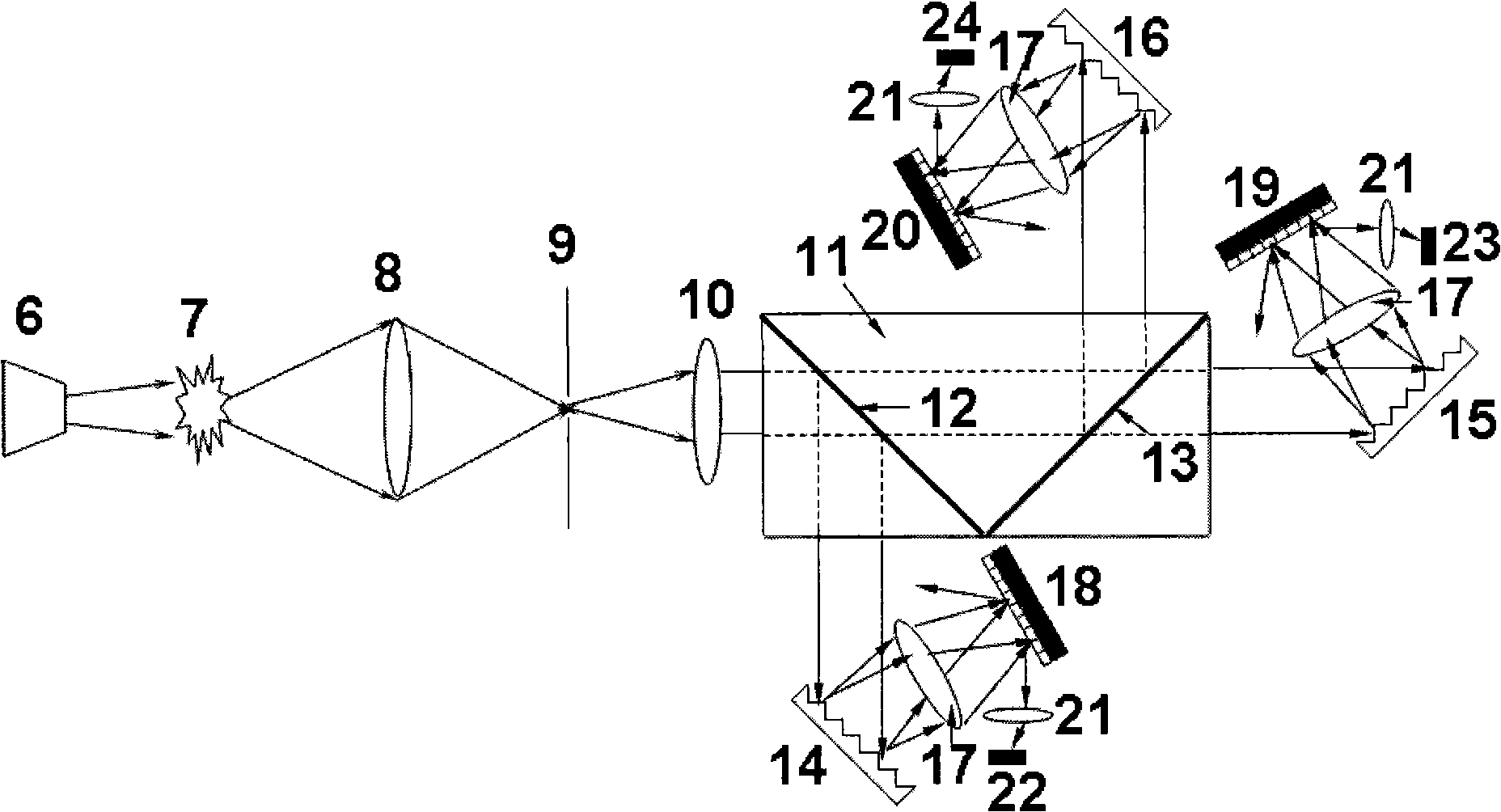
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
A multi-spectrum, multi-channel imaging spectrometer includes two or more input slits or other light input devices, one for each of two or more input channels. The input slits are vertically and horizontally displaced, with respect to each other. The vertical displacements cause spectra from the two channels to be vertically displaced, with respect to each other, on a single image sensor on a stationary image plane. The horizontal displacements cause incident light beams from the respective input channels to strike a convex grating at different respective incidence angles and produce separate spectra having different respective spectral ranges. A retroflective spectrometer includes a convex grating that, by diffraction, disperses wavelengths of light at different angles and orders approximately back along an incident light beam. A single concave mirror reflects both the input channel and the dispersed spectrum. A prism, set of mirrors, beam splitters or other optical element(s) folds the input channel(s) of a spectrometer to enable the input(s) to be moved away from the plane of the image sensor, thereby enabling a large camera or other device to be attached to the spectrometer without blocking the input(s). A mounting mechanism enables a curved optical element to be adjusted through lateral and transverse translations, without requiring a gimbal mount.
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
Hyperspectral Imaging of Angiogenesis
ActiveUS20070249913A1Reduce resolutionSmoothing imageDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiseaseBlood vessel
The invention is directed to methods and systems of hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of medical tissues. In particular, the invention is directed to new devices, tools and processes for the detection and evaluation of diseases and disorders such as, but not limited to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease and cancer, that incorporate hyperspectral or multispectral imaging.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
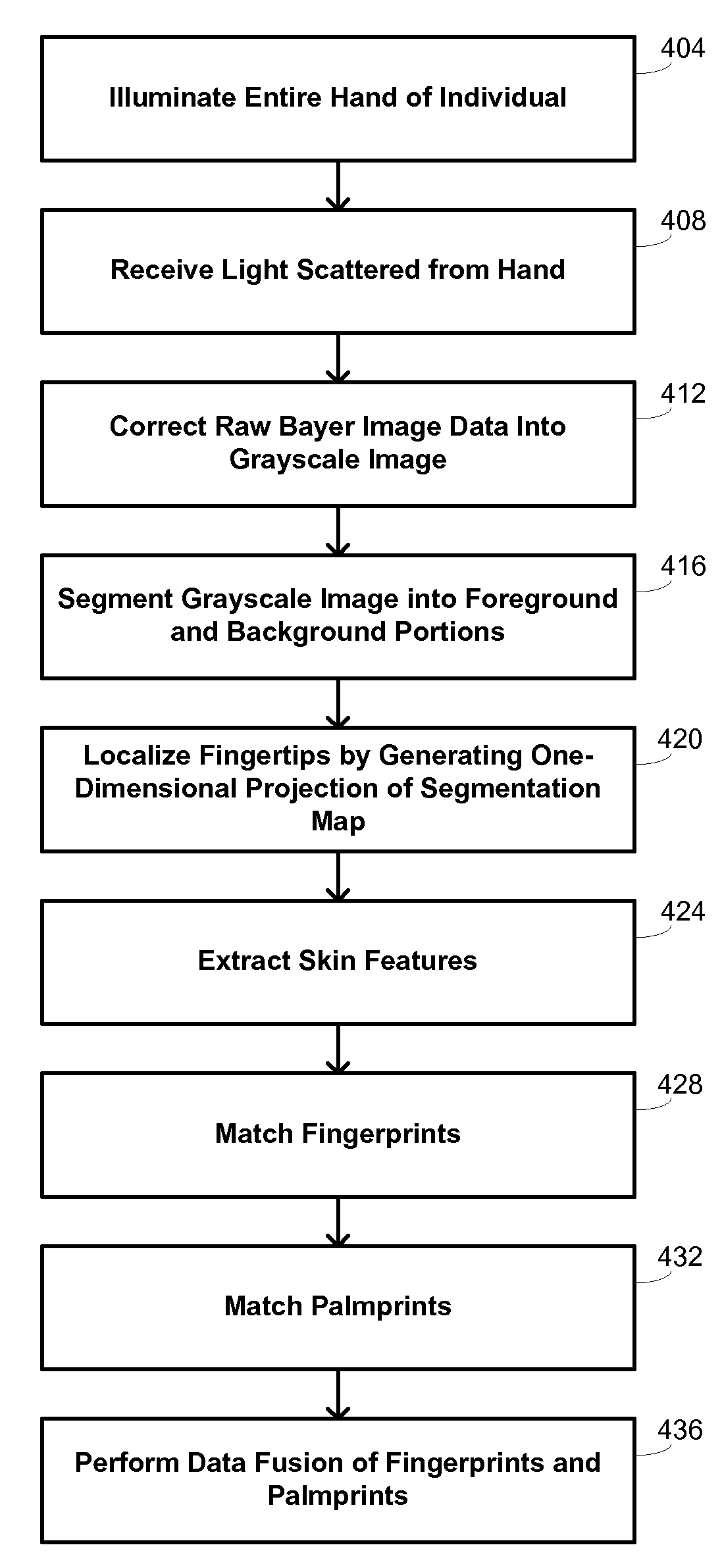
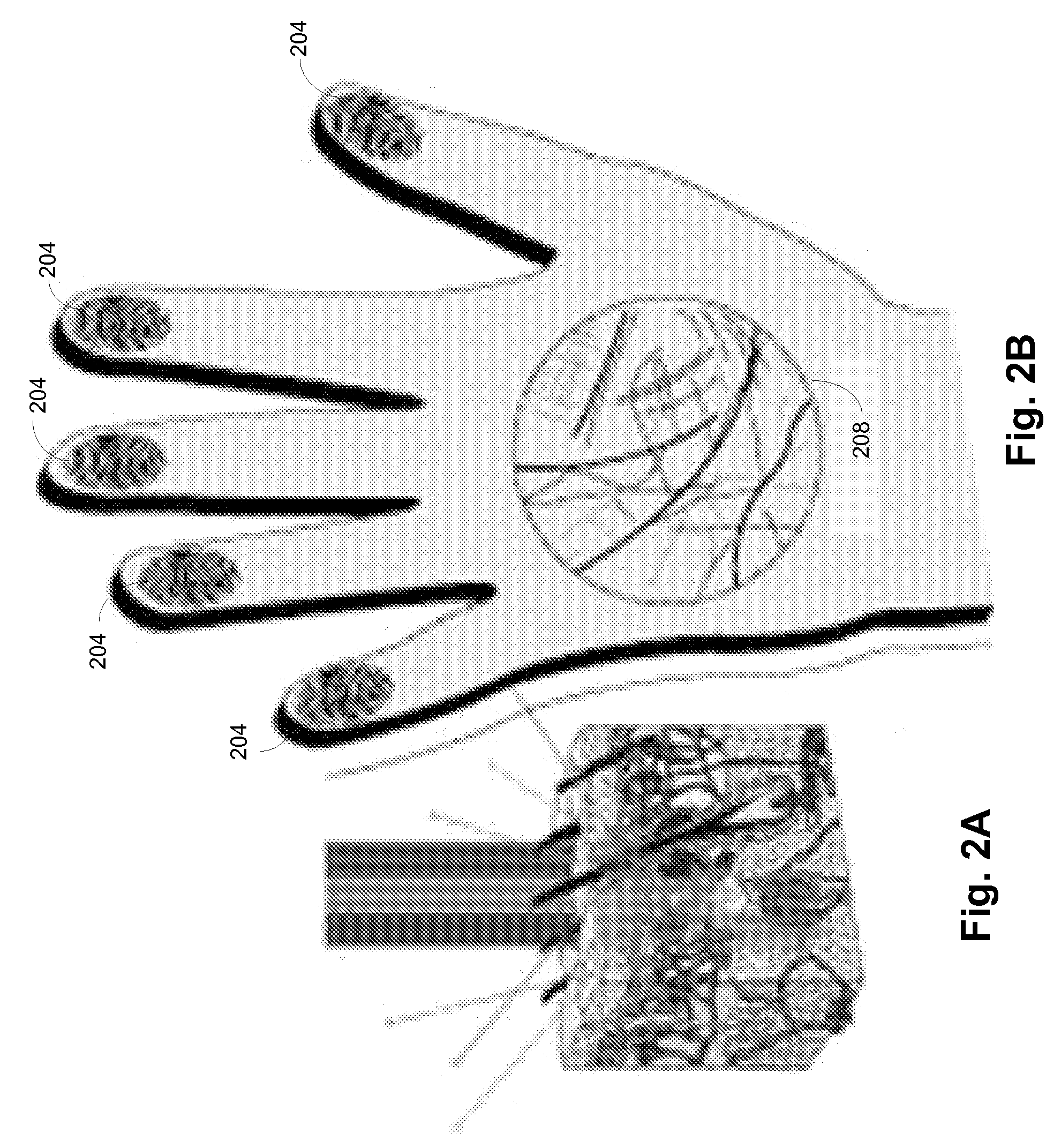
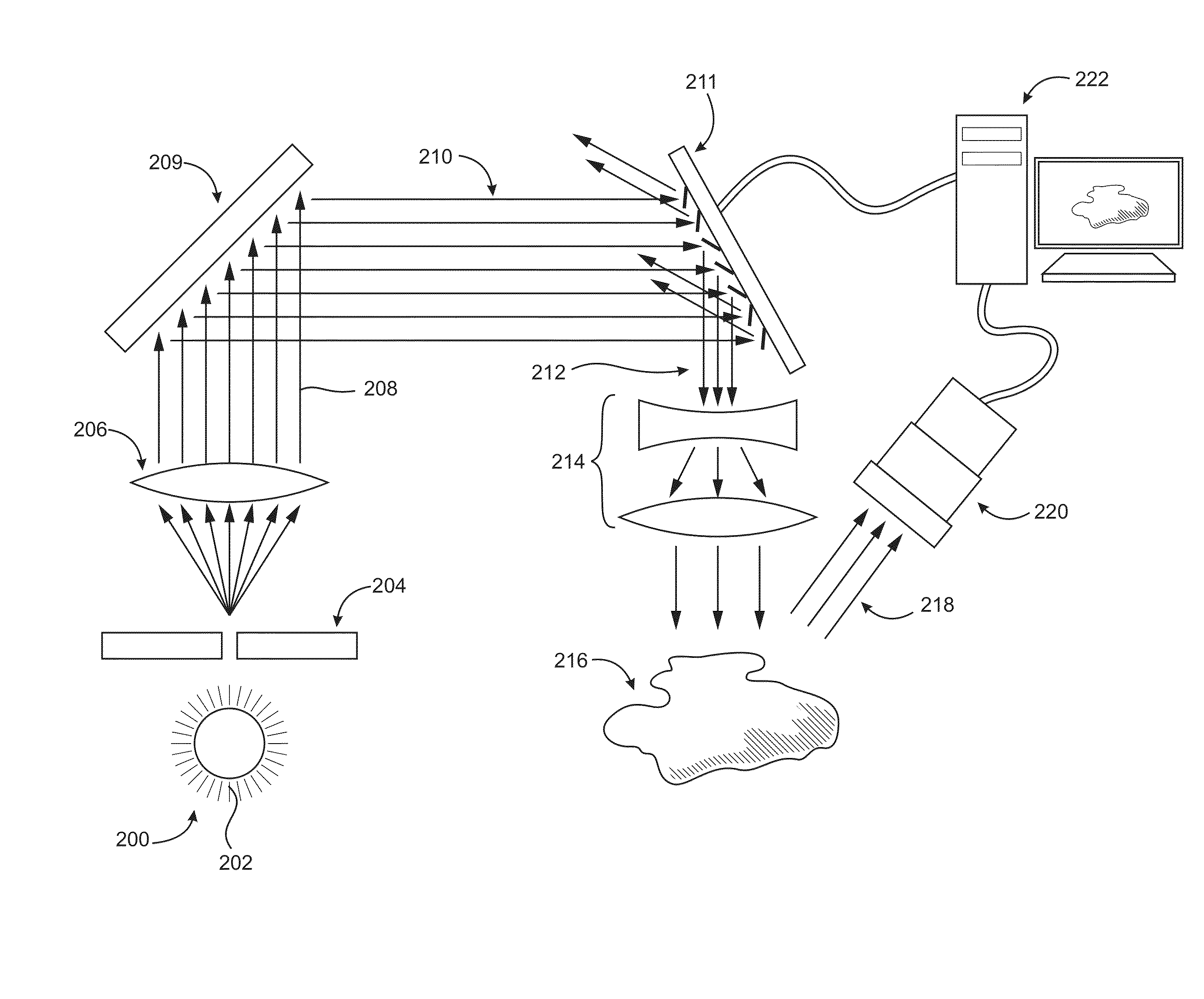
Multibiometric multispectral imager
InactiveUS20080192988A1Digital data authenticationPrint image acquisitionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMedicine
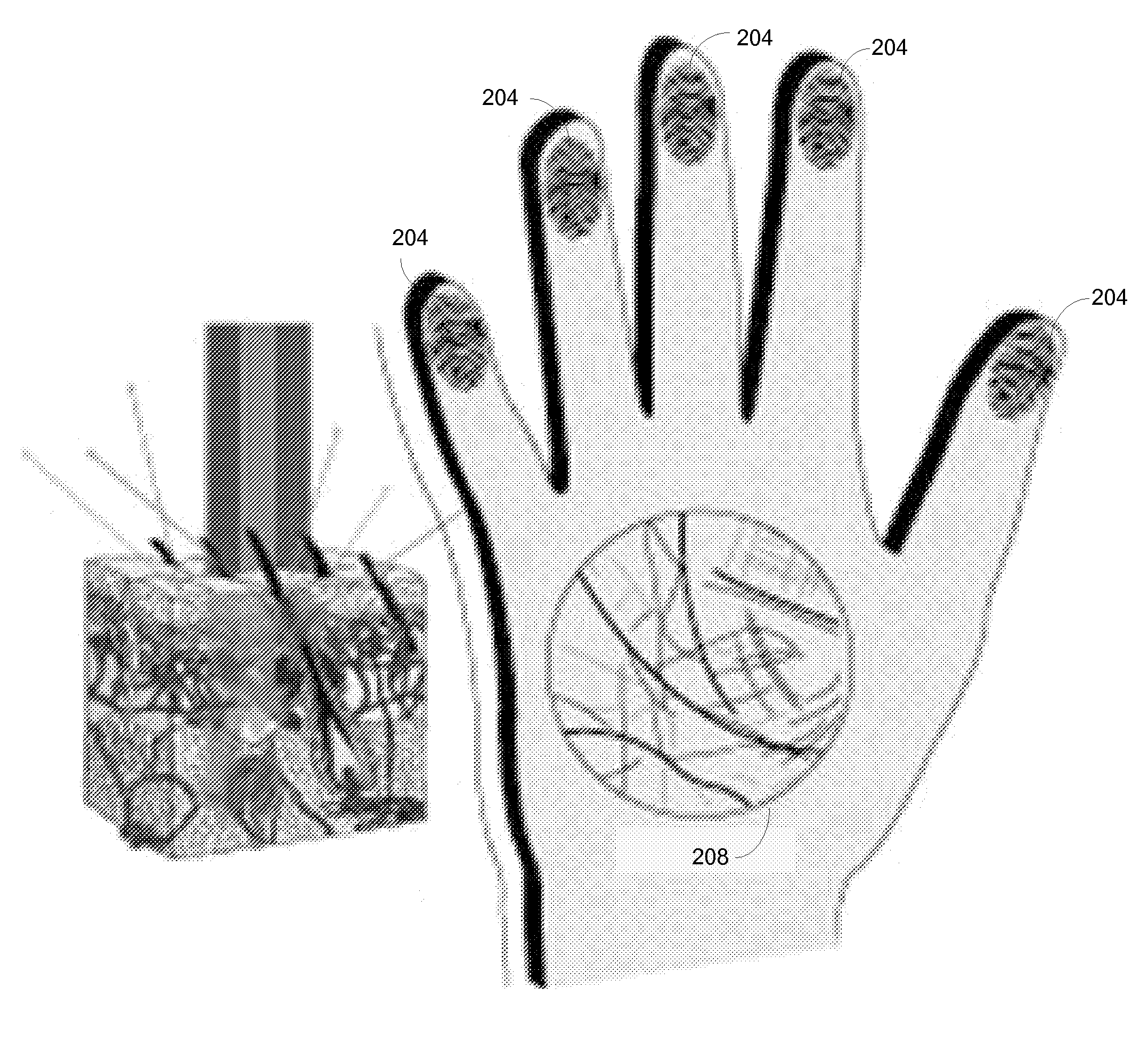
A skin site of an individual is illuminated and light scattered from the skin site under multispectral conditions is received. The light includes light scattered from tissue beneath a surface of the skin site. Multiple biometric modalities are derived from the received light. The biometric modalities are fused into a combined biometric modality that is analyzed to perform a biometric function.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
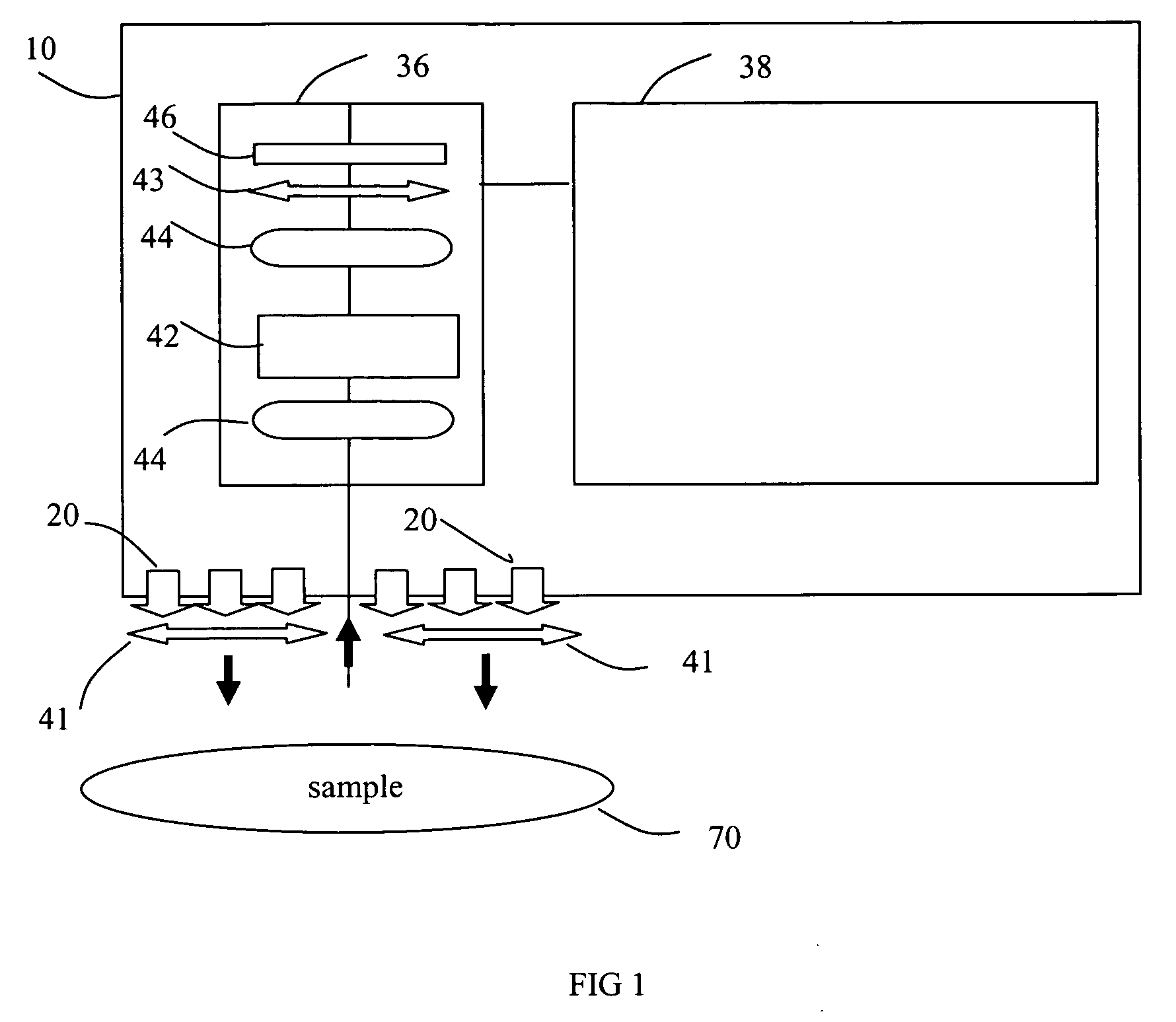
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20130296710A1Maintain body temperatureImage enhancementImage analysisLight beamLength wave
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:ZUZAK KAREL J +4
Multibiometric multispectral imager
InactiveUS7899217B2Electric signal transmission systemsImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMedicine
A skin site of an individual is illuminated and light scattered from the skin site under multispectral conditions is received. The light includes light scattered from tissue beneath a surface of the skin site. Multiple biometric modalities are derived from the received light. The biometric modalities are fused into a combined biometric modality that is analyzed to perform a biometric function.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
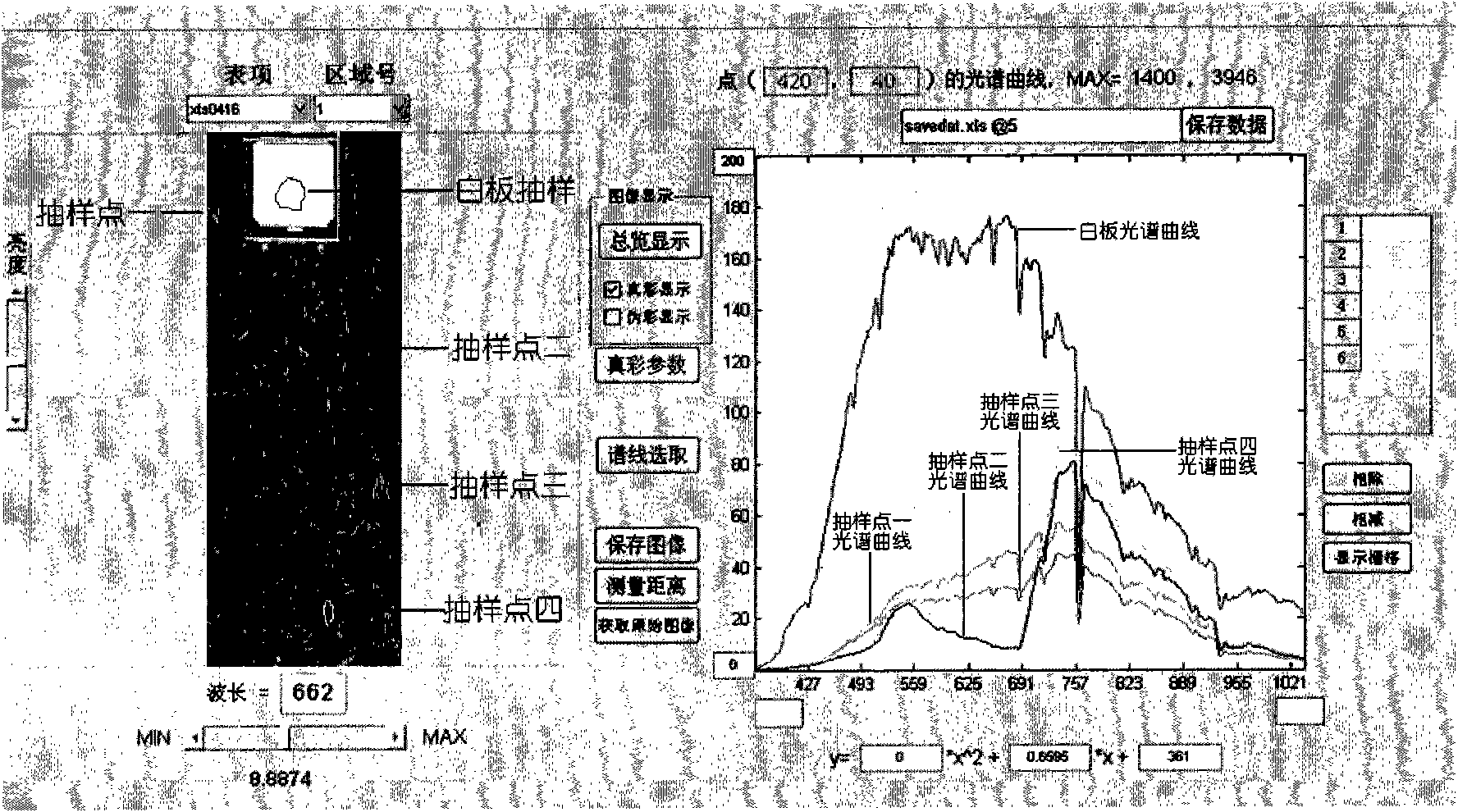
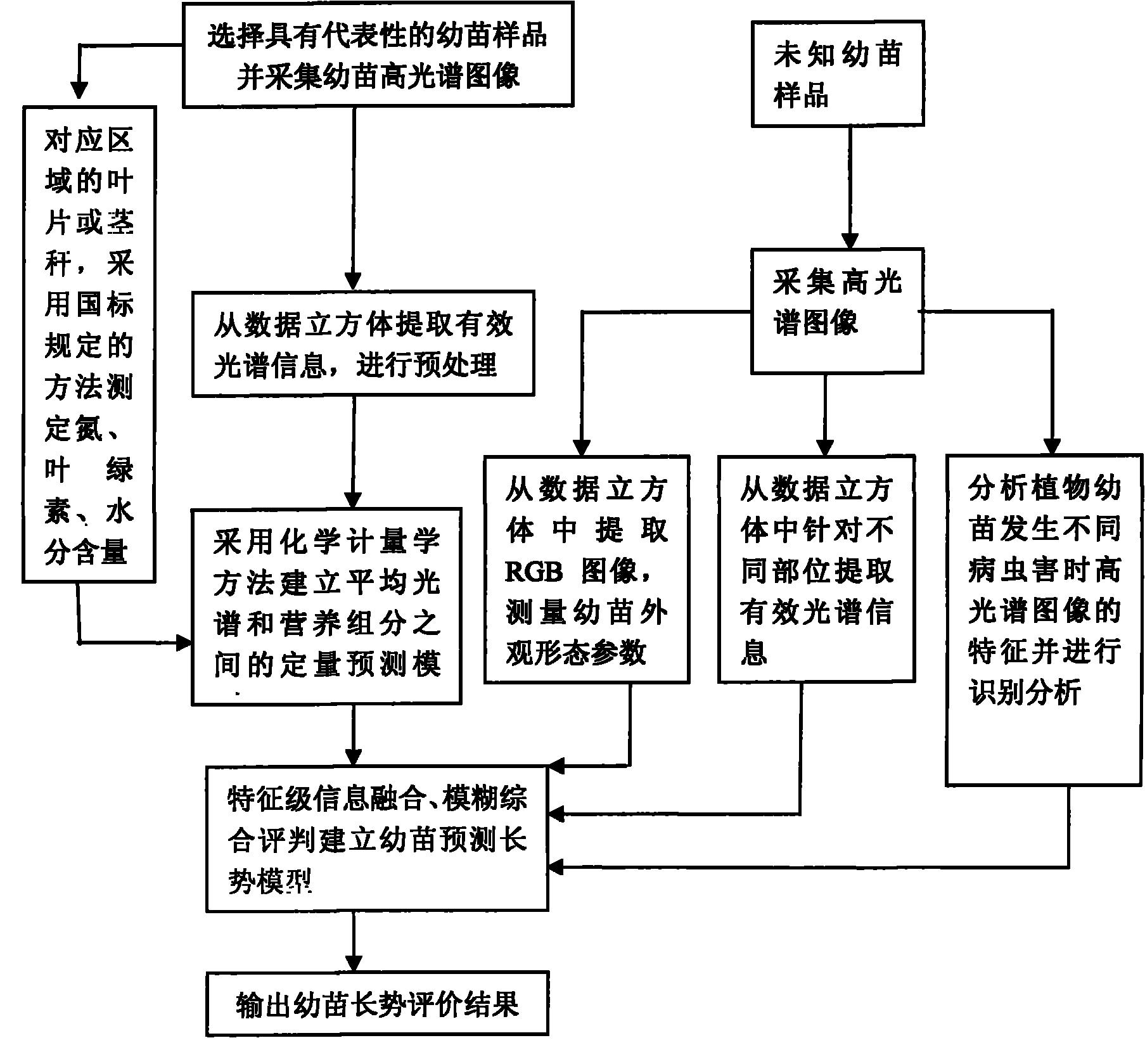
Nondestructive detection method for comprehensive character living bodies of plant seedlings
ActiveCN101881726ARealize evaluationAvoid errorsColor/spectral properties measurementsDiseaseContent distribution
The invention relates to a nondestructive detection method for comprehensive character living bodies of plant seedlings, which comprises the following steps of: performing high-spectrum imaging on the plant seedlings, extracting RGB images and a spectrum of a specific area from a high-spectrum data cube, and acquiring morphological parameter, component content distribution and disease and insect pest information of the seedlings by image processing and spectrum analysis; and establishing a growth prediction model of the plant seedlings by adopting a character-level information fusion method and a fuzzy comprehensive judgment method. The method can realize comprehensive judgment on characters of appearance, nutritional component and disease and insect pest information of the seedlings, and overcome the error caused by un-uniformity during component measurement.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
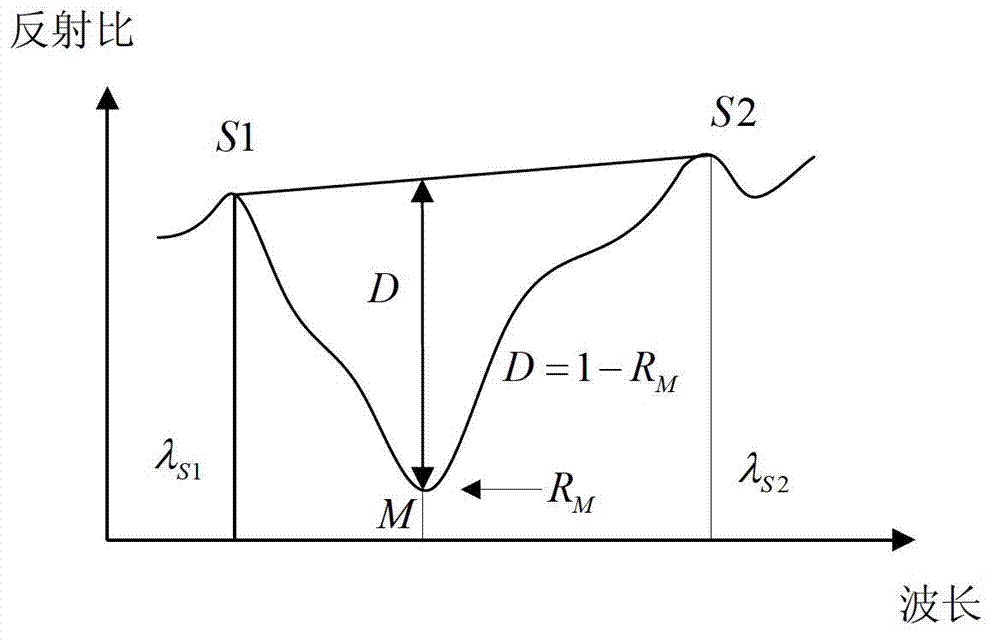
Near-infrared spectrum imaging system and near-infrared spectrum imaging method for diagnosis of depth and area of burn skin necrosis
ActiveCN103815875AFavorable guidanceAvoid painDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical sensorsTissue proteinBurned skin
The invention provides a near-infrared spectrum imaging system for diagnosis of depth and area of burn skin necrosis. The near-infrared spectrum imaging system comprises a spectrum imager and a computer-control system. The spectrum imager acquires 1100-2500nm waveband spectral signals of burn skin necrosis tissue of a target area, the spectral signals are subjected to image analyzing and processing through the computer-control system, the depth and area of burn of the target area can be acquired through spectral matching recognition upon a spectral reflectance curve corresponding to each image element in spectral images and a standard spectral reflectance curve in a burn skin necrosis spectral database in a data module and are synthesized into three-dimensional image display of the target area. By the near-infrared spectrum imaging system, the spatial structure of skin changed due to tissue protein denaturation before and after the skin burn can be specified, so that micron-level information about boundaries of normal skin tissue and necrotic tissue and the depth of burn skin necrosis can be provided visually, and clinical diagnosis, treatment and prognosis judgment can be supportively facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DEPUSI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
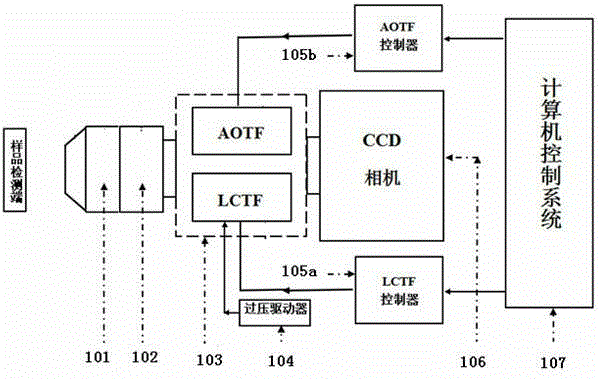
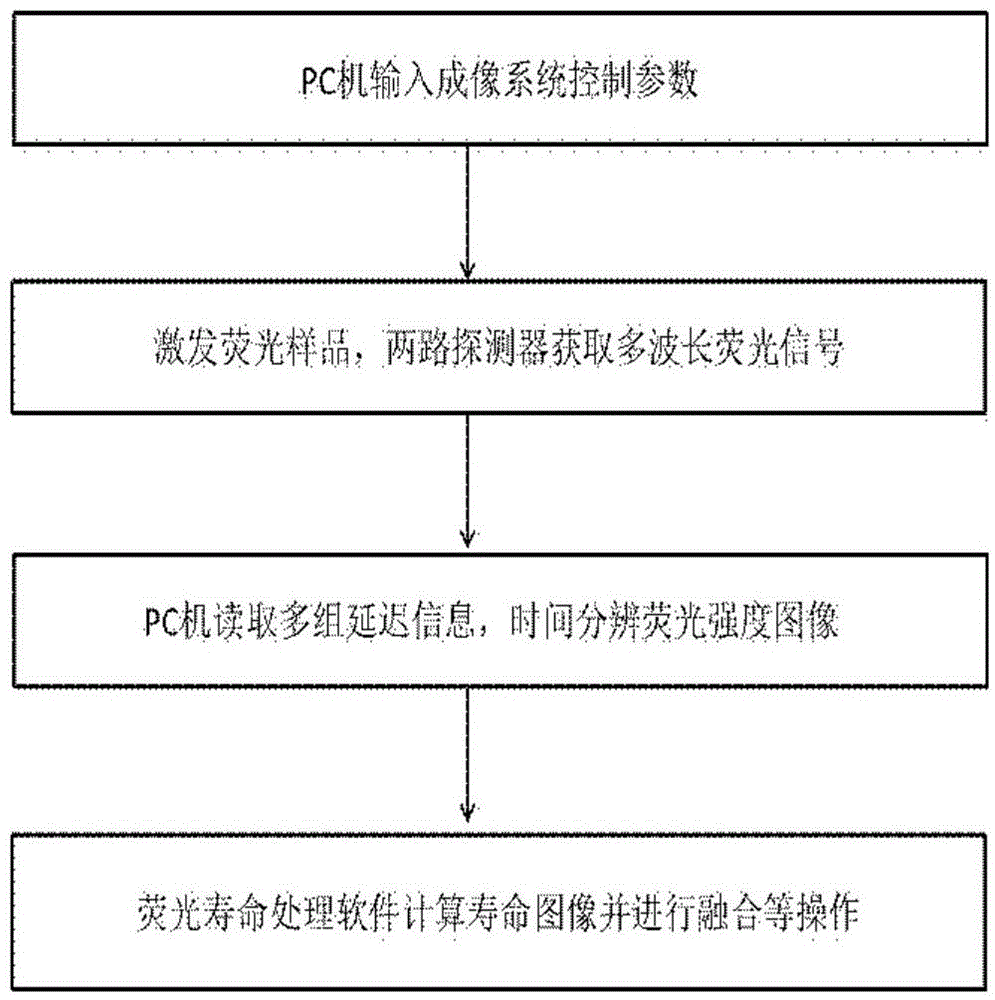
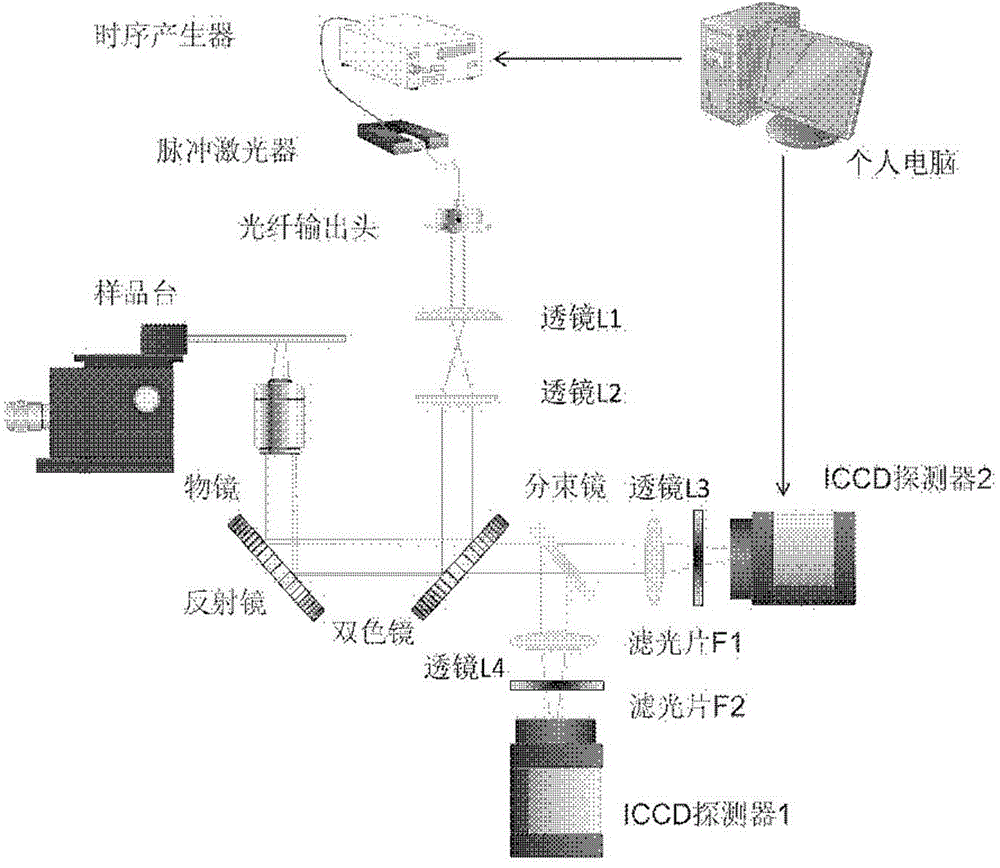
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-channel, multi-spectrum imaging spectrometer
Owner:HEADWALL PHOTONICS
Spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device
ActiveCN103439254AImproving the Detection Capability of Micro-area Raman SpectroscopyHigh detection sensitivityRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging, and relates to a spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device, wherein a confocal microscopic technology and a Raman spectrum detecting technology are combined. A spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by using rayleigh scattering light discarded in confocal Raman spectrum detection, high-resolution imaging and detection of a three-dimensional geometric position of a sample are realized; and a spectrum detection system is controlled by using an extreme point of the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system to be capable of accurately capturing Raman spectrum information excited by a focusing point of an objective lens, and further spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum high-space-resolution imaging and detection of image and spectrum integration are realized. The spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device provide a new technical approach for high-space-resolution detection of the three-dimensional geometrical position and spectrum in a microcell, can be widely applied to the fields such as physics, chemistry, biomedicine, material science, environmental sciences, petrochemical engineering, geology, medicines, foods, criminal investigation and jewelry verification, and are capable of carrying out nondestructive identification and deep spectrum analysis of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multi-channel multi-target ultra-optical spectrum imaging method and system based on digital micro lens device
InactiveCN101303291AReduce dataAccurate identificationColor/spectral properties measurementsGratingData acquisition
The invention discloses a multichannel multiobjective hyper-spectral imaging method based on numerical microscopes, characterized in that, an object is imaged on a slit plane, an emergent light is collimate into a parallel light, split into ultraviolet light, infrared light and visible light, which are diffracted into the dispersion through the respective split grating diffraction, then is focused on the corresponding numerical microscope; the turning state of the numerical microscope is controlled by the computer, and the emergent light of the on-state is projected on the detector, used for image and post-treatment through the data acquisition treatment. The device is arranged with a multi-agglutination prism of the dichroism filter, and the dispersion of the ultraviolet light, the infrared light and the visible light is realized. The method realizes the image information acquisition of the triband of infrared light, visible light and ultraviolet light, solves the problems that the spectrum imaging data are too large without affecting the spectrographic detection quality of the target area, and is in favor of realizing the multiobjective identification and the real-time track.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Hyperspectral Imaging in Diabetes and Peripheral Vascular Disease
ActiveUS20070232930A1Reduce resolutionSmoothing imageDiagnostics using lightSensorsDiabetes mellitusVascular disease
The invention is directed to methods and systems of hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of medical tissues. In particular, the invention is directed to new devices, tools and processes for the detection and evaluation of diseases and disorders such as, but not limited to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, that incorporate hyperspectral or multispectral imaging.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
Hyperspectral imaging in diabetes and peripheral vascular disease
The invention is directed to methods and systems of hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of medical tissues. In particular, the invention is directed to new devices, tools and processes for the detection and evaluation of diseases and disorders such as, but not limited to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, that incorporate hyperspectral or multispectral imaging.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
Hyperspectral imaging in diabetes and peripheral vascular disease
The invention is directed to methods and systems of hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of medical tissues. In particular, the invention is directed to new devices, tools and processes for the detection and evaluation of diseases and disorders such as, but not limited to diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, that incorporate hyperspectral or multispectral imaging.
Owner:HYPERMED IMAGING
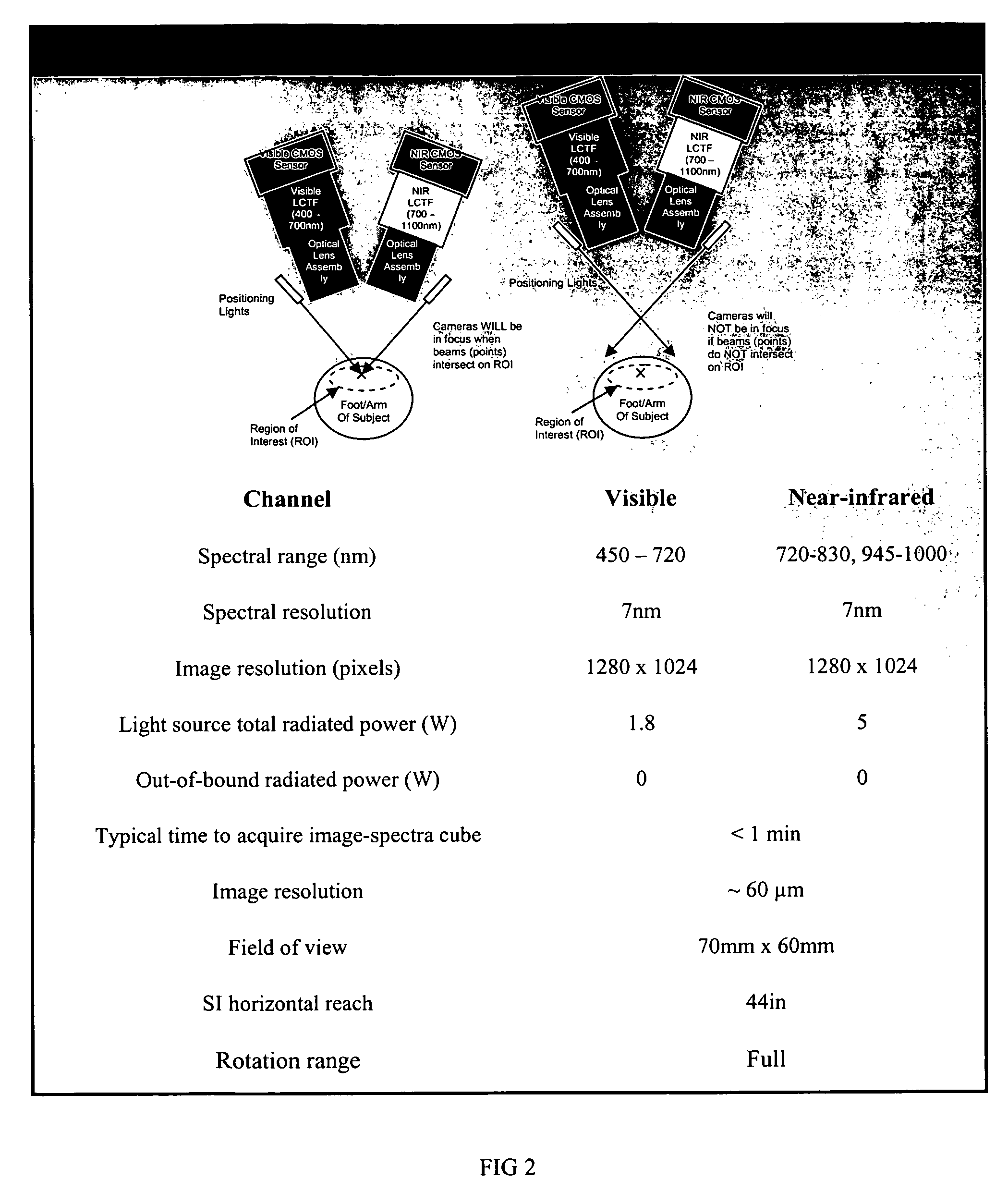
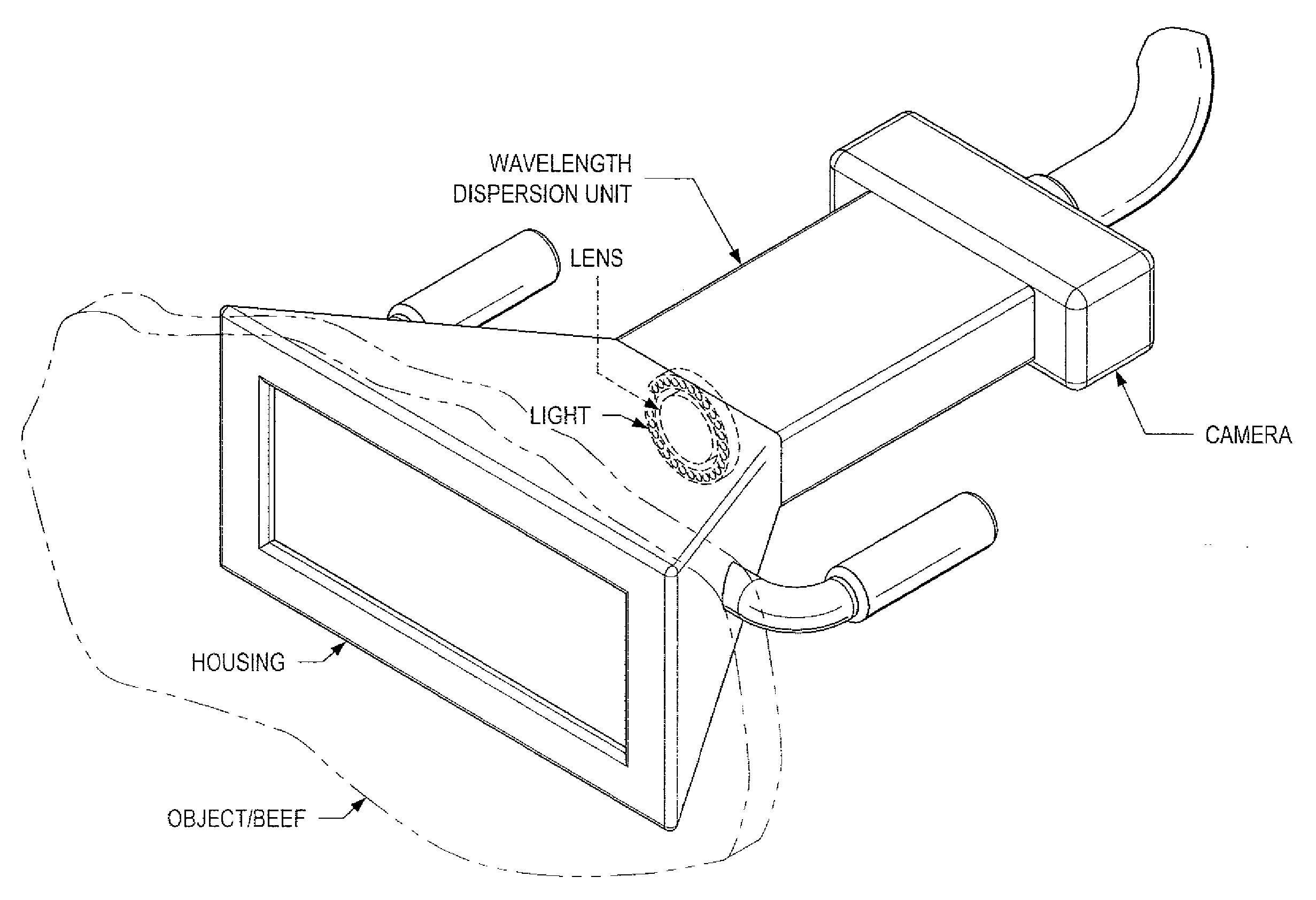
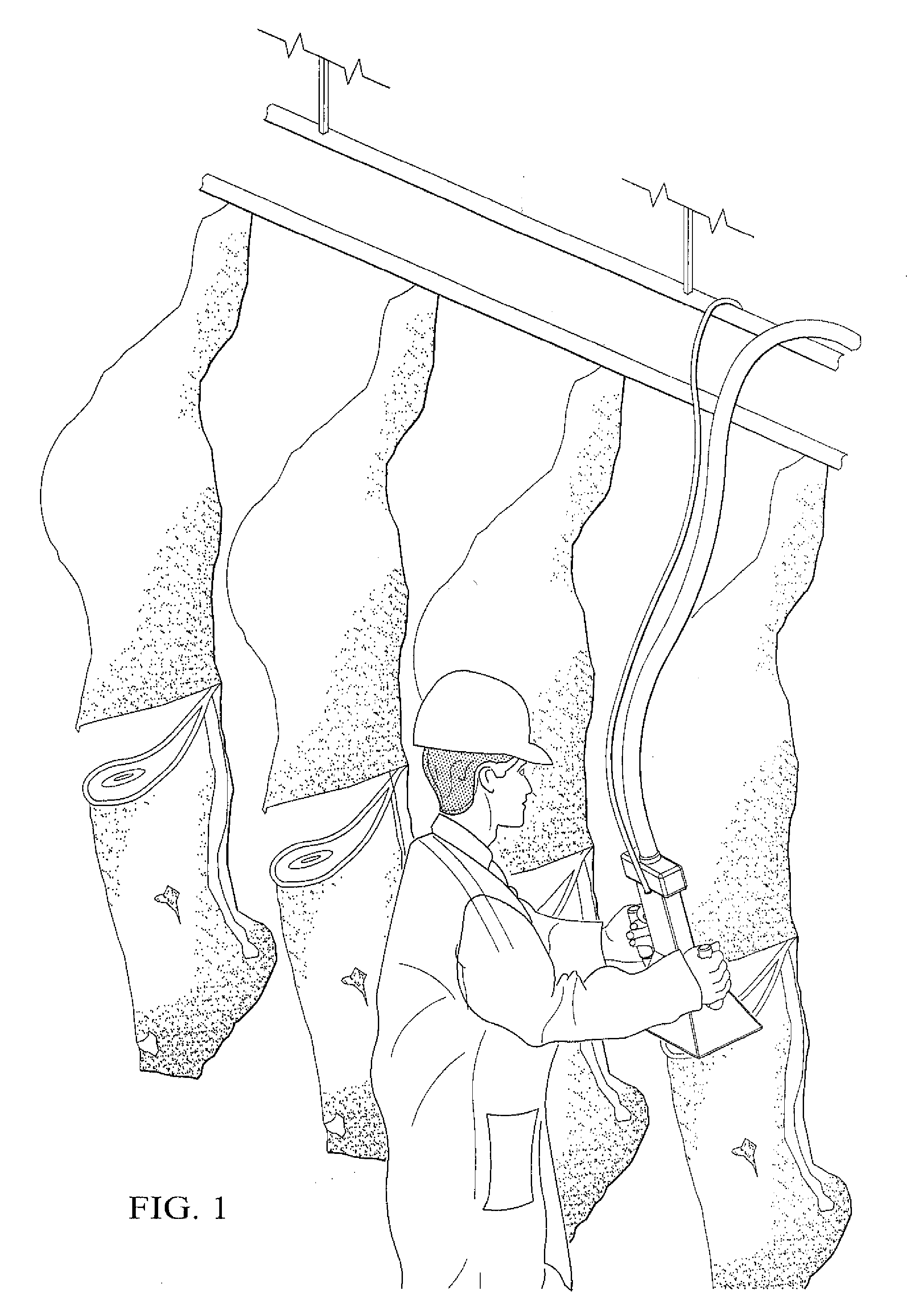
System and Method for Analyzing Properties of Meat Using Multispectral Imaging
ActiveUS20110273558A1Eliminates lag and delayRapid and objective determinationImage enhancementImage analysisMeat tendernessIndustrial setting
A system and method for obtaining multispectral images of fresh meat at predetermined wavelength bands at a first time, subjecting the images to analysis in an image analysis system comprising a computer programmed to perform such analysis, and outputting a forecast of meat tenderness at a later point in time. Predetermined key wavelength bands are precorrelated with a high degree of prediction of meat tenderness and / or other properties of meat and are used in the multispectral system and method. A system and method for determining the key wavelengths is also disclosed. The multispectral imaging system and method is suitable for use in an industrial setting, such as a meat processing plant. The system and method is useful in a method for determining quality and yield grades at or near the time of imaging in lieu of visual inspection with the unaided human eye, increasing efficiency and objectivity.
Owner:CARNE TENDER LLC
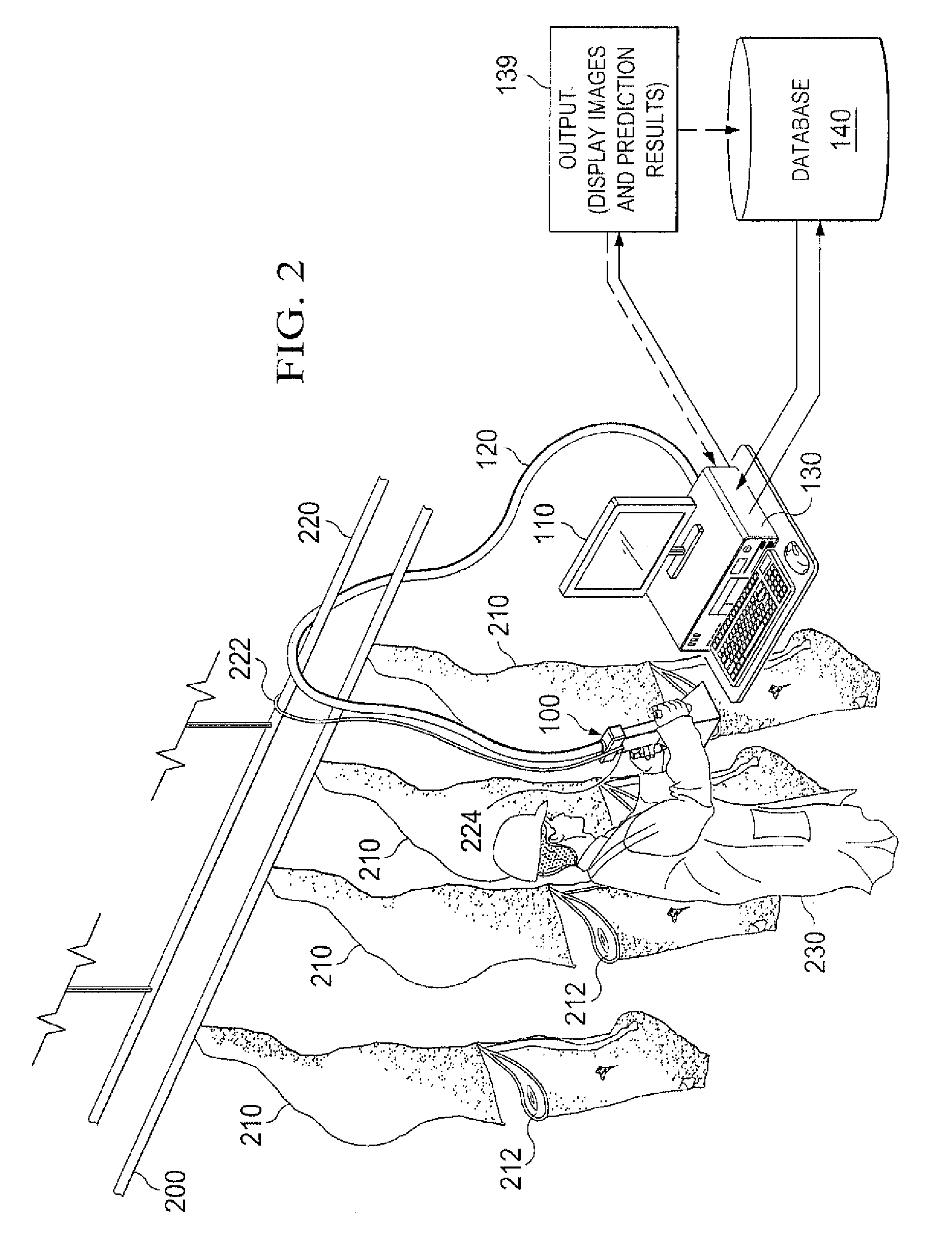
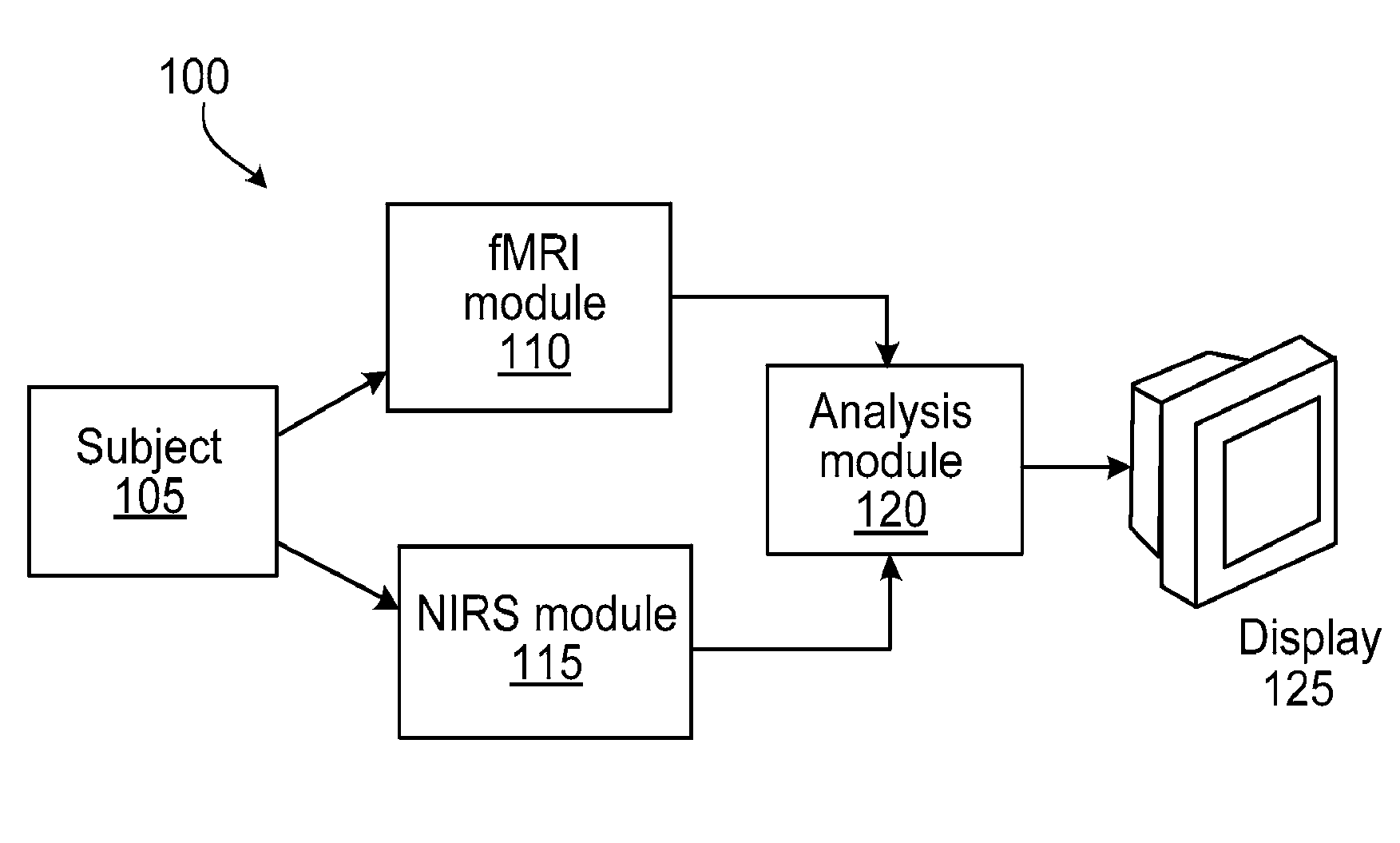
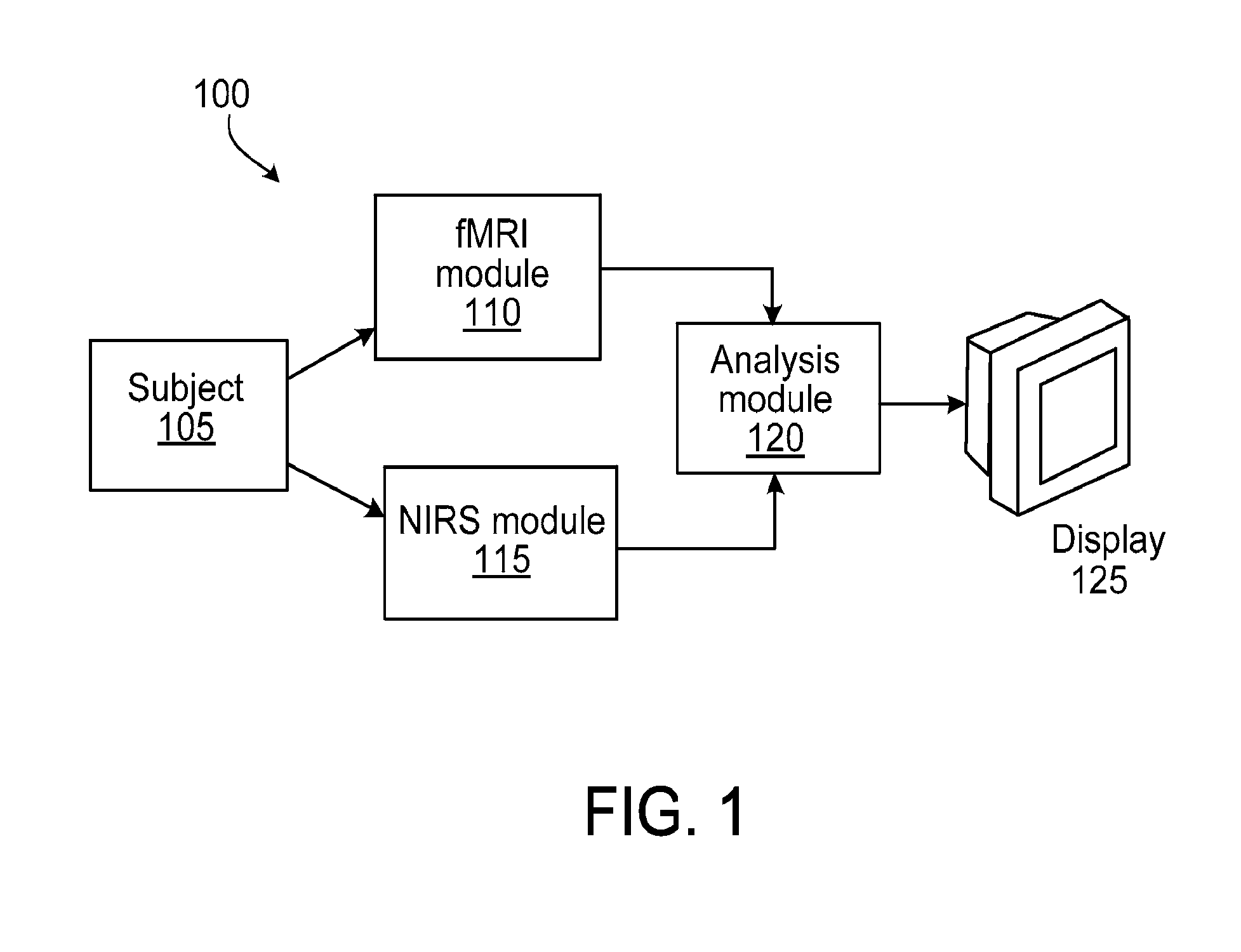
Multi-modal imaging of blood flow
ActiveUS20130144140A1Improved and non-invasive measurement of blood flow and blood volumeLow costDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterData setImaging data
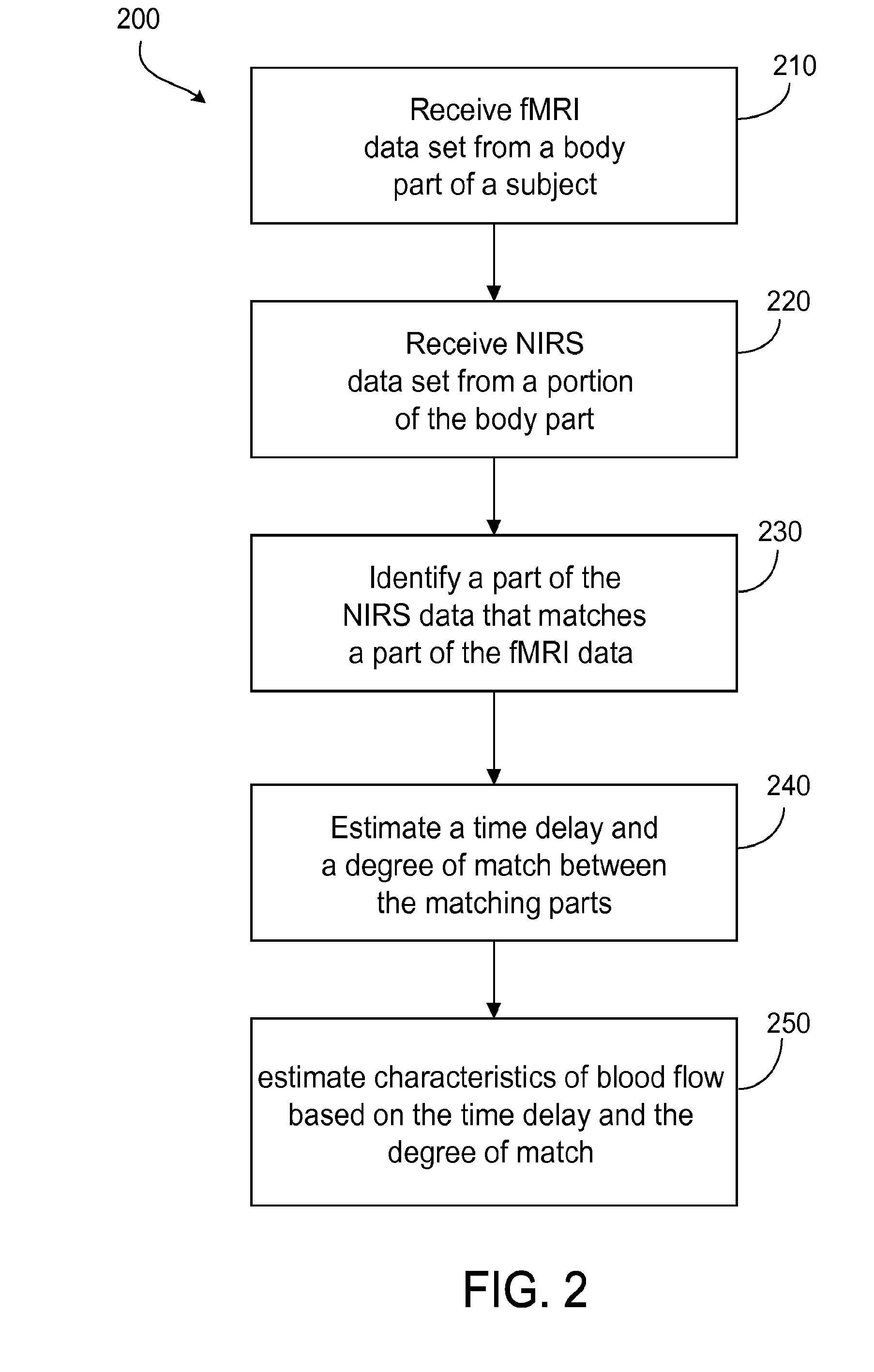
The application features methods, devices, and systems for measuring blood flow in a subject. The computer-implemented methods include receiving functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data that provides information on at least one of volume or oxygenation of blood at one or more locations in a body over a first predetermined length of time. The methods also include receiving near-infrared spectroscopic (NIRS) imaging or measurement data representing at least one of blood concentration or oxygenation at a first portion of the body over a second predetermined length of time. The methods further include deriving, from the fMRI data corresponding to a second portion of the body, a time varying data set representing changes in blood oxygenation or volume or both blood oxygenation and volume at the second portion over the first predetermined length of time and determining, by a computing device, a time delay and a value of a similarity metric corresponding to a part of the spectroscopic imaging data that most closely matches the time varying data set. The time delay represents a difference between a first time in which blood flows from a third portion in the body to the first portion and a second time in which blood flows to the second portion from the third portion. The value of the similarity metric represents an amount of blood at the second portion. An estimate of a characteristic of at least one of blood flow or blood volume in the second portion at a given time is determined based on the time delay and the value of the similarity metric.
Owner:THE MCLEAN HOSPITAL CORP
Differential confocal Raman spectra test method
InactiveCN101290293AImproved microspectral detection capabilitiesImprove detection performanceRaman scatteringLight beamAbsolute measurement
The invention belongs to the micro-spectrum imaging technical field and relates to a differential confocal raman spectral test method. The method integrates the technical characteristics of the differential confocal detection method and the raman spectral detection method, forms a test method capable of realizing sample microarea spectral detection, precisely catches focus positions of excitation light beams through the differential confocal technology, detects raman spectra of corresponding positions, simultaneously adopts a designed pupil filter, sharpens Airy disc major lobes of a differential confocal raman spectral system, improves the microarea raman spectral detectability and precisely acquires microarea space spectrum information which comprises spectral information and position information of microarea samples. The method obviously improves the microarea spectral detectability of a confocal raman spectromicroscope, has absolute tracking zero points and bipolar tracking characteristics, realizes absolute measurement of physical dimension, can be widely applied in the technical fields such as biomedicine, life sciences, biophysics, biochemistry, industrial precision detection and so on to perform high-precision detection of geometric positions and spectral characteristics of microareas, and has very important application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
High microspectrum imaging system
InactiveCN1563947AMain indicators are highMature technologyColor/spectral properties measurementsMicro imagingData acquisition
Disclosed system as an integrated system integrates micro imaging system with high spectrum imaging system, including optical microscope, spectroscope, area array CCD camera and dedicated software of data acquisition and treatment. The disclosed system provides microcosmic spectrogram combining image with spectrum, applicable to clinical medicine, biology, materials science and microelectronics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spectrum scaling apparatus used for spectrum imager
InactiveCN102353447ARadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsBirefringent crystalEngineering
The invention discloses a spectrum scaling apparatus used for a spectrum imager. The apparatus is characterized in that: a light beam which is emitted by a broadband light source (1) goes through a diaphragm (2) and a collimating lens (3) and irradiates a wavelength tuning optical filter (4), a plurality of narrowband optical signals which are distributed in a comb-shaped mode and have different wavelengths are outputted, after light intensity adjusting by a broadband bandpass optical filter (5), the signals enter into an integrating sphere (9) from an integrating sphere incident light hole (6) for depolarization and space uniformity processing, and an integrating sphere light extraction hole (8) outputs a surface light source. A spectrum imager to be measured is placed on the light extraction hole (8) for spectrum scaling. According to the apparatus, a birefringence crystal is utilized to carry out light transmission rate modulation, a passband peak value position and a bandwidth size can be adjusted, a plurality of narrowband light intensity signals changing with a wavelength are provided in a broadband range, wavelength scanning is not needed when carrying out spectrum scaling on the spectrum imager, wavelength scaling with one-time imaging is realized, and the apparatus is suitable for scaling a large field of view and large caliber spectrum imager.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
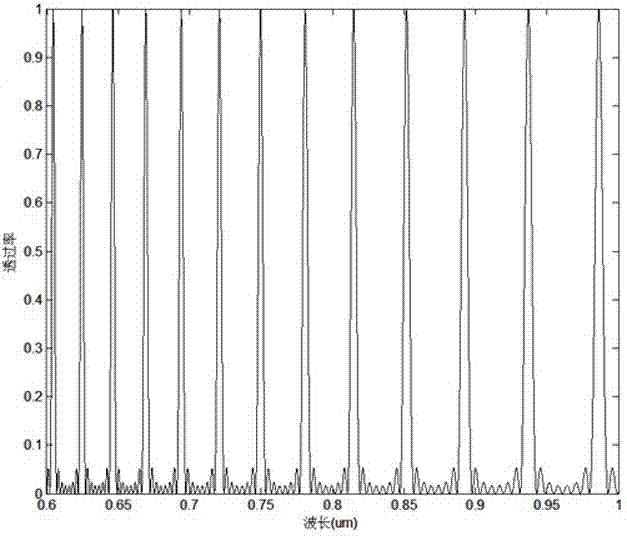
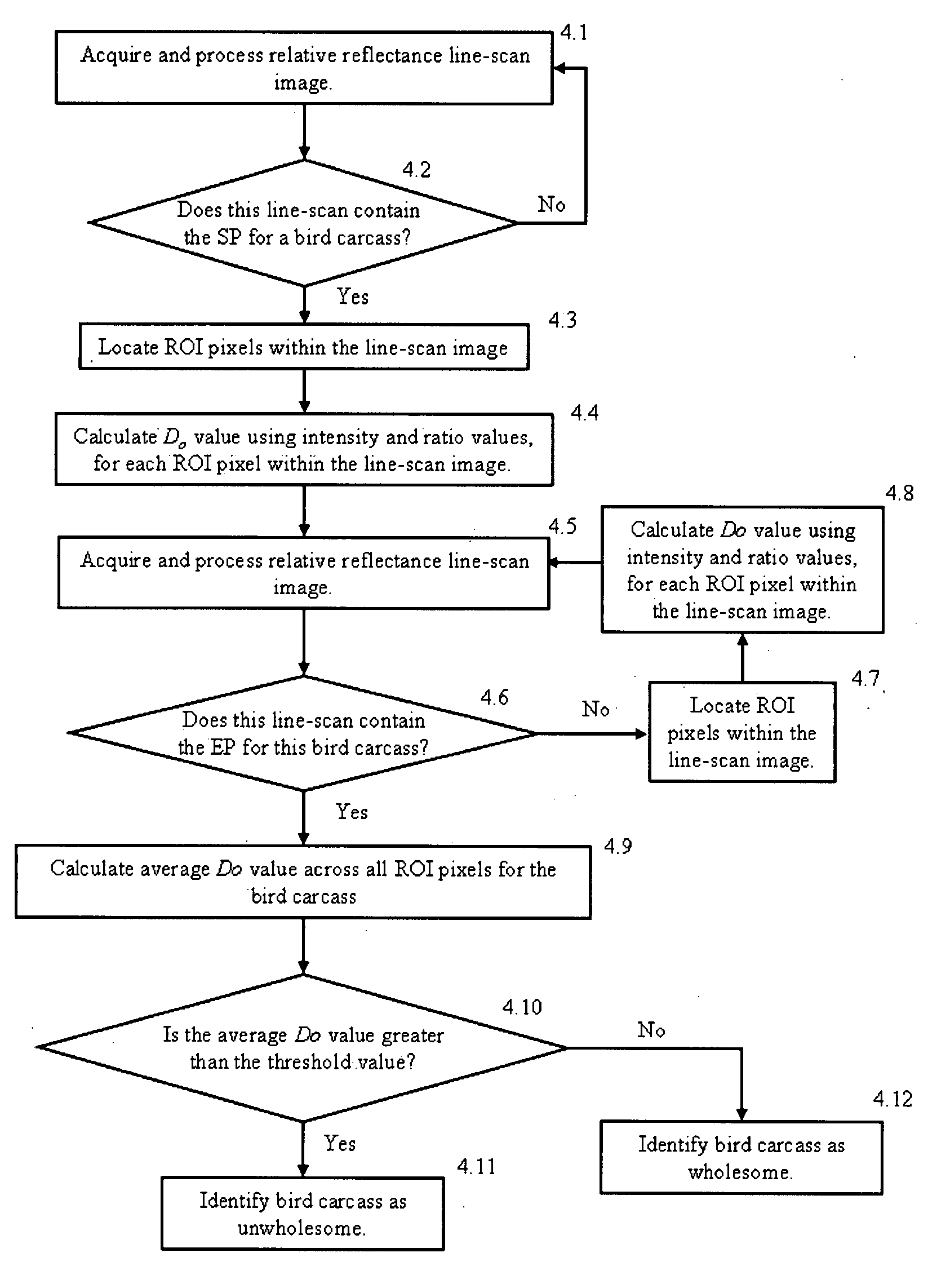
Method and system for wholesomeness inspection of freshly slaughtered chickens on a processing line
ActiveUS20090087033A1Quick and accurate identificationImage analysisCarcasses classification/gradingImaging algorithmSpectrograph
An imaging system containing an electron-multiplying charge-coupled device detector and line-scan spectrograph is used for identifying wholesome and unwholesome freshly slaughtered chicken carcasses on high-speed commercial chicken processing lines. Multispectral imaging algorithms allow for real-time online identification of wholesome and unwholesome chicken carcasses.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
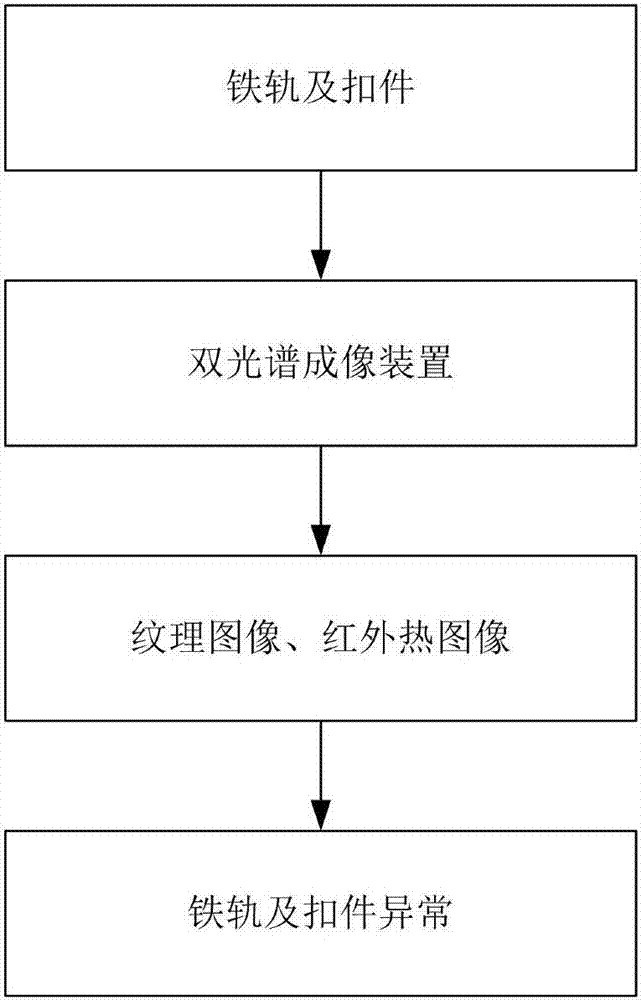
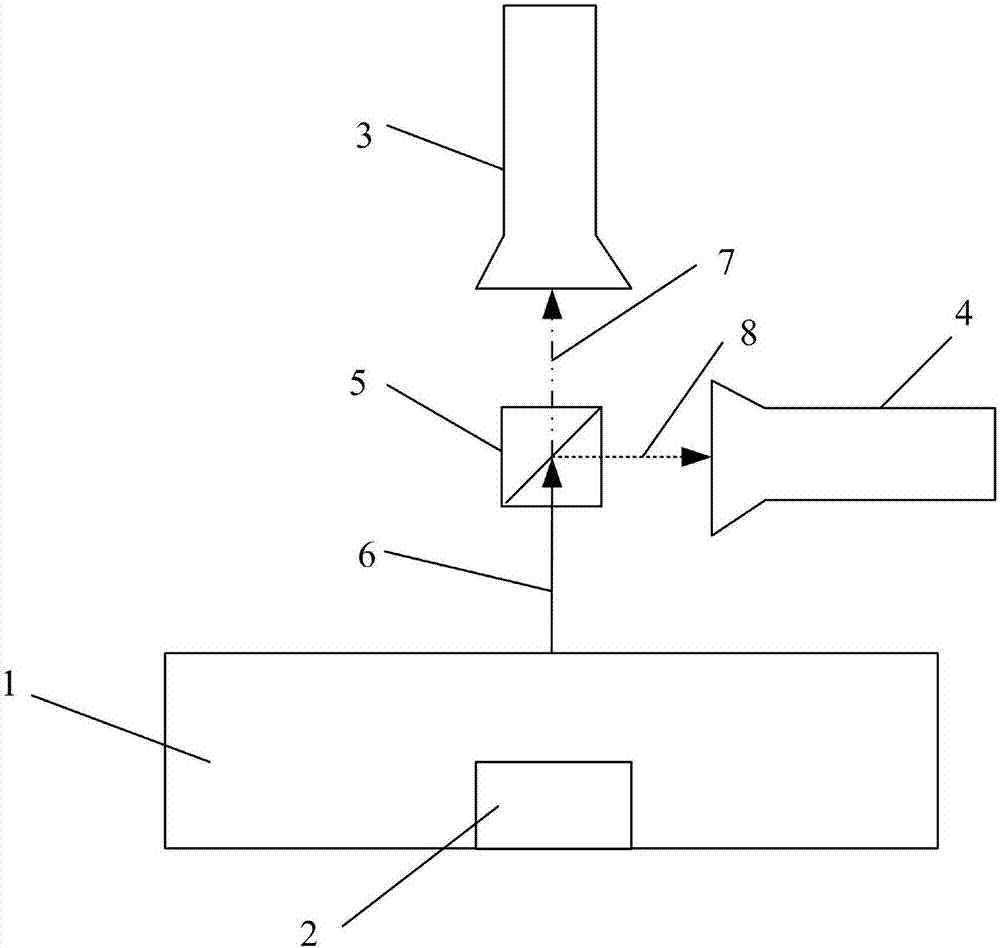
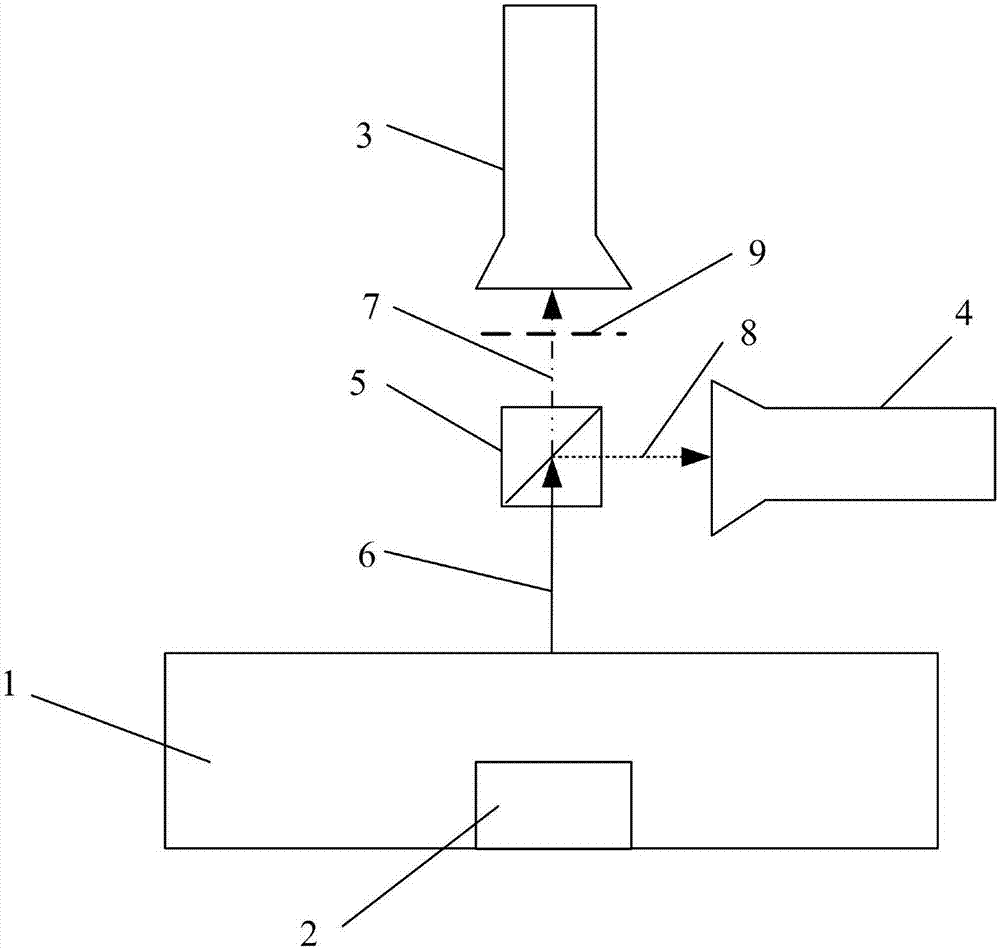
Method for detecting abnormal conditions of rails and fasteners through double-spectrum imaging
PendingCN107576666AImprove damage detection capabilitiesRefined comparative analysisOptically investigating flaws/contaminationRailway auxillary equipmentPattern recognitionRail transit
The invention discloses a method for detecting abnormal conditions of rails and fasteners through double-spectrum imaging, which belongs to the technical field of rail transport safety detection, andis used for solving the problem of difficulty in detecting the abnormal conditions of rails and fasteners in the prior art. According to the method, a visible light camera and an infrared camera forma double-spectrum imaging device for performing double-spectrum imaging on the rail and fastener areas and respectively acquiring the texture images and infrared thermal images of the rails and the fasteners; the texture images are adopted for positioning the rails and fasteners in the infrared thermal images; the background model comparison is adopted for detecting the abnormal conditions of missing, loosening and breaking of the fasteners; the texture images and the infrared thermal images are jointly used for detecting the rail peeling, scratching, corrugation and cracks. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the abnormal detection efficiency for the rails and the fasteners is effectively promoted and the rail transit safety is guaranteed.
Owner:成都精工华耀科技有限公司
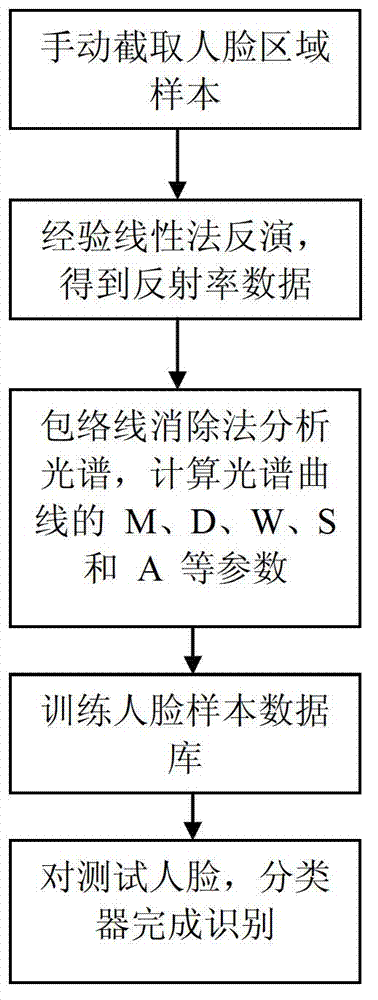
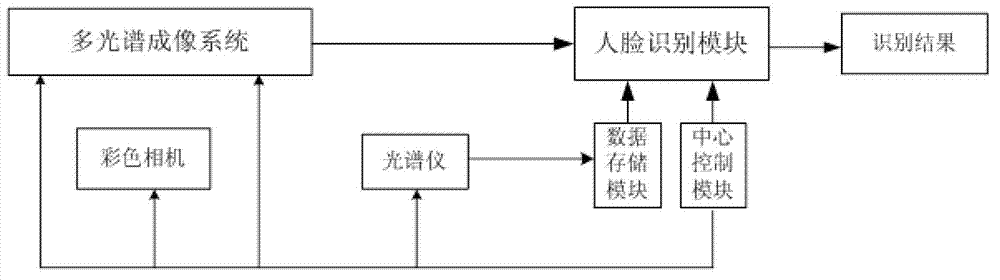
Multispectral face identification method, and system thereof
InactiveCN102831400AImprove separabilityEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionCamera lens
The invention relates to a multispectral face identification method, and a system thereof. The system is characterized by comprising a multispectral imaging system, a color camera, a face identification module, a data storage module, a central control module, and a spectrometer. The multispectral imaging system outputs filmed face image data to the face identification module. The face identification module identifies the face image data according to information in a standard face database in the data storage module, and then outputs an identification result. The central control module controls image filming of the multispectral imaging system and identification of the face identification module. The multispectral imaging system comprises an objective lens, a liquid crystal adjustable optical filter, and a CCD camera. The liquid crystal adjustable optical filter is disposed in front of a CCD camera lens of the CCD camera, and the objective lens is disposed on a front end of the liquid crystal adjustable optical filter. In the method, a plurality of characteristics of the face image is extracted, thereby making a between-class distance in an identification process more obvious and separability of identification algorithm better which help to improve identification effects.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
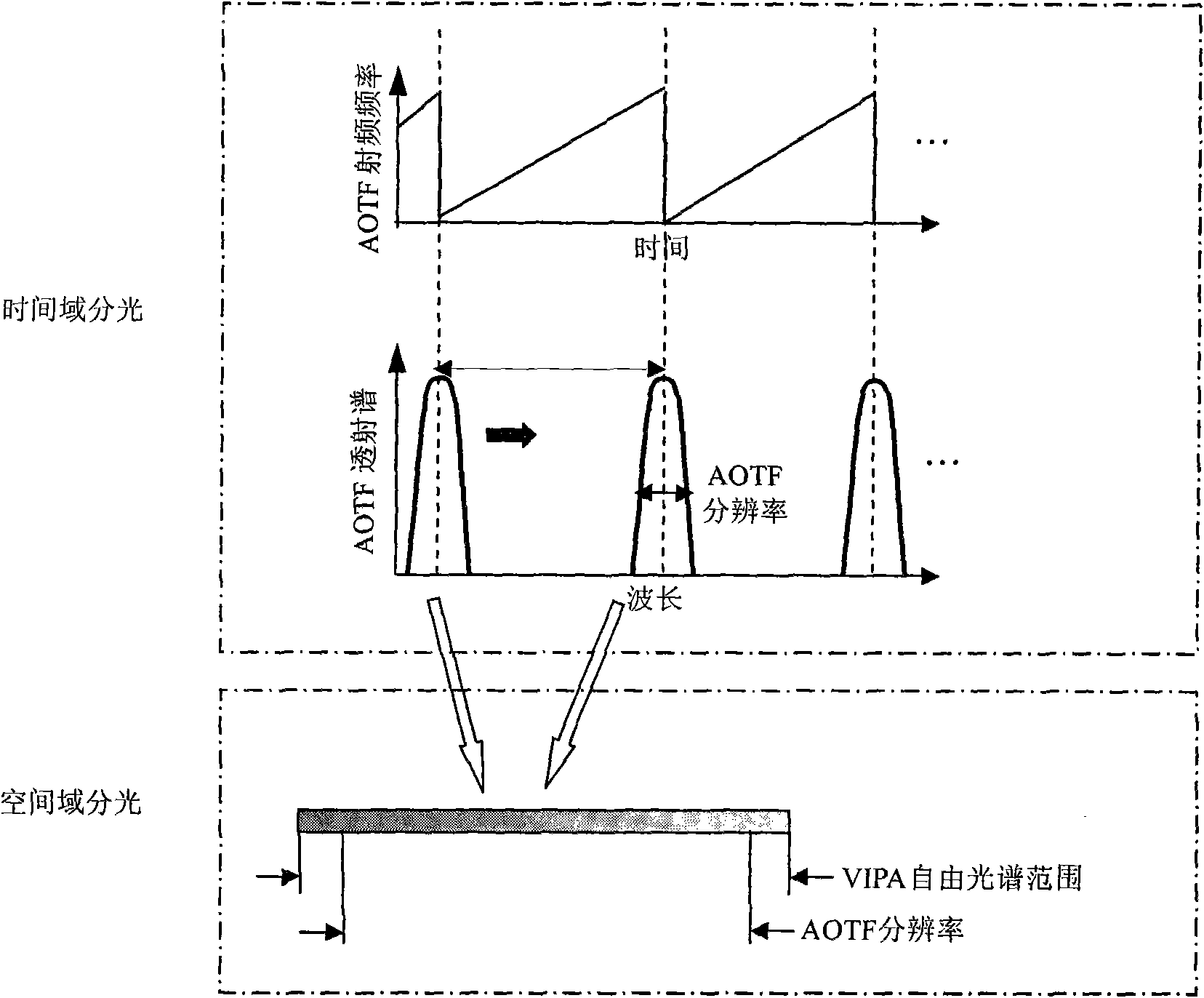
Method and system for wide-spectrum and high-resolution detection based on space-time light splitting in OCT
InactiveCN101617935AHigh resolutionSmall field of viewPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSample imageOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a method and a system for wide-spectrum and high-resolution detection based on space-time light splitting in OCT. Low-coherence lights emitted from a broadband light source enter a broadband optical fiber coupler through an optical isolator, and respectively enter a scanning probe and a reference arm after light splitting by the coupler. The returned lights generate interference in the broadband optical fiber coupler, a detection arm detects interference signals after the interference signals are decomposed into different spectral components, and then the interference signals are sent to a computer so as to reconstruct a sample image. In the detection arm, interference spectral signals firstly pass through a time domain light splitting device with low resolution and wide free spectrum range, then pass through a space domain light splitting device with high resolution and narrow free spectrum range, and then are detected by a spectrum imaging system. On the premise of satisfying the requirement of high spectrum resolution, the invention can reduce a visual field of the spectrum imaging system, and solves the problems of field curvature, spectrum interference and the like existing during large visual field spectrum imaging, thereby spectral domain OCT imaging with high signal-to-noise ratio and high resolution is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Real-time monitoring method for growth characters of tea trees in intensive cultivation
ActiveCN103439265AAchieve high quality and high yieldImprove qualityUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansColor/spectral properties measurementsBudTea leaf
The invention discloses a real-time monitoring method for growth characters of tea trees in intensive cultivation. The method comprises the following steps: performing real-time data acquisition by a tea tree living body growth character data acquisition device based on online location, transmitting the acquired data to an artificial comprehensive management center through a wireless communication way to process, wherein the acquired data comprises current location data acquired by a locating mechanism, fresh tea leaves spectrum data acquired by a high spectrum imaging sensor, and average growth height of fresh tea leaves measured by an ultrasonic wave sensor, and judging the best fresh tea leaf picking time based on that the data and a picking judgment model established off line are combined by the artificial comprehensive management center. The picking judgment model comprises a bud size growth measurement model based on average growth height, a yield correlation model and a quality correlation model based on the high spectrum image data. The real-time monitoring method for the growth characters of the tea trees in intensive cultivation is beneficial to realizing of intensive cultivation and automation in planting of the tea trees.
Owner:湖南星索尔航空科技有限公司
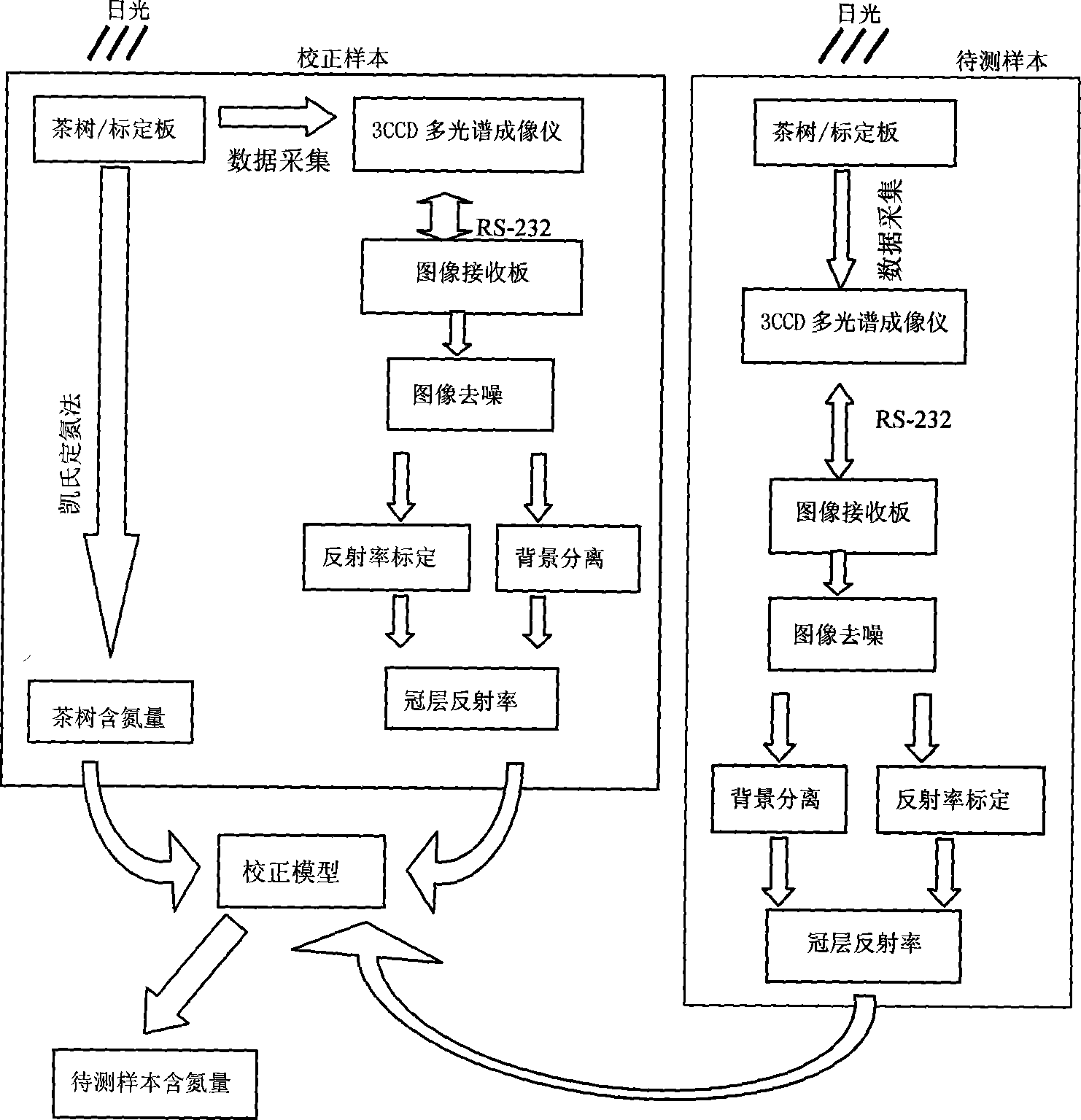
Method for quickly non-destructive measurement for nitrogen content of tea using multiple spectrum imaging technology
InactiveCN101059427ARapid determinationAccurate measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsResearch ObjectObject based
The invention discloses a method for quickly non-damage measuring the nitrogen content of tea tree, via multi-spectrum image technique, comprising that first using a 3CCD multi-spectrum image device to collect the multi-spectrum image information of correct sample, while the nitrogen content of sample (tea tree) is measured by international standard method. The obtained image is processed by silent algorism to improve image quality, and by background separation to obtain the image of object, then obtains the reflective index (character parameter) of object based on a standard reflective plate and a nominal reflective curvature. The invention uses multi-element correct algorism to build the quantitative relationship between the character parameter of tea-tree multi-spectrum image and tea-tree nitrogen content, to build a correct model, and then inputs the character parameter of multi-spectrum image of the sample into the correct model, to be tested and obtain the nitrogen content of the tea tree. The 3CCD multi-spectrum image device via a RS-232 interface is connected with an image receiving plate mounted on a computer. The invention can measure nitrogen content of tea tree quickly, accurately, non-damage and online.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
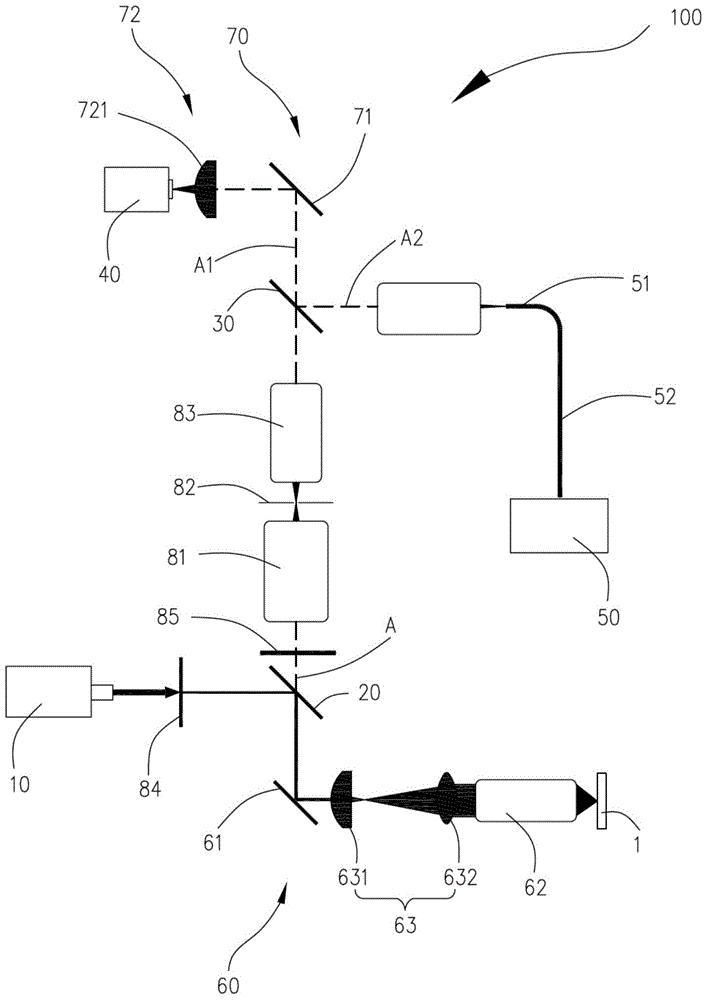
Living body fluorescent endoscopic spectrum imaging device
ActiveCN101904737AHigh spectral resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBand-pass filterMolecular level
The invention relates to a live body fluorescent endoscopic spectrum imaging device, comprising a light source unit, a light split unit, a scanning light guide unit, a fiber bundle endoscopic unit, an electrooptical signal detection and acquisition unit and a computer, wherein the light source unit consists of a collimating unit and a band filter. The imaging device is characterized in that the light of the collimating unit passes through the band filter and then enters the light split unit, the light split unit is provided with two paths of interfaces, one path of the interfaces of the light split unit is connected with the scanning light guide unit, the scanning light guide unit is connected with the fiber bundle endoscopic unit, and the other path of the interfaces of the light split unit is connected with the electrooptical signal detection and acquisition unit which is connected with the computer. The imaging device has the characteristics that: 1, a Fourier transform spectrometer is used to detect a sample excitation spectrum, and has the advantages of high spectral resolution (1nm), adjustable spectral resolution and the like; and 2, the fluorescent live body endoscopic spectrum imaging system can provide not only imaging diagnosis at tissue level but also spectrum diagnosis at molecular level.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Physiological signal remote monitoring system based on multimodal imaging technique and application thereof
ActiveCN106580294AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsMonitoring systemData acquisition
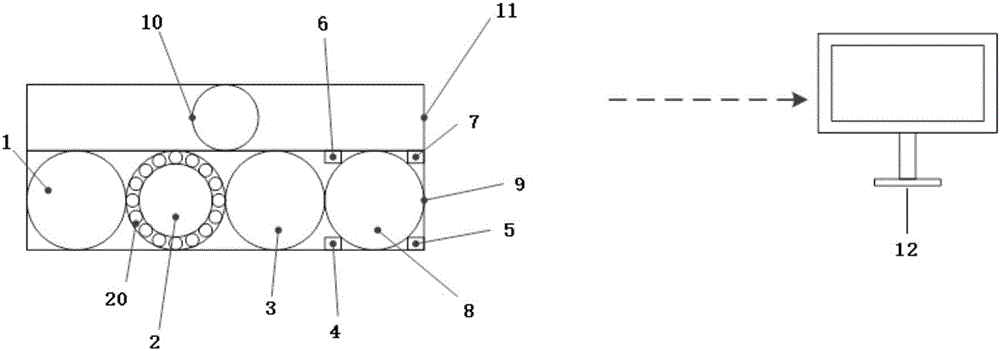
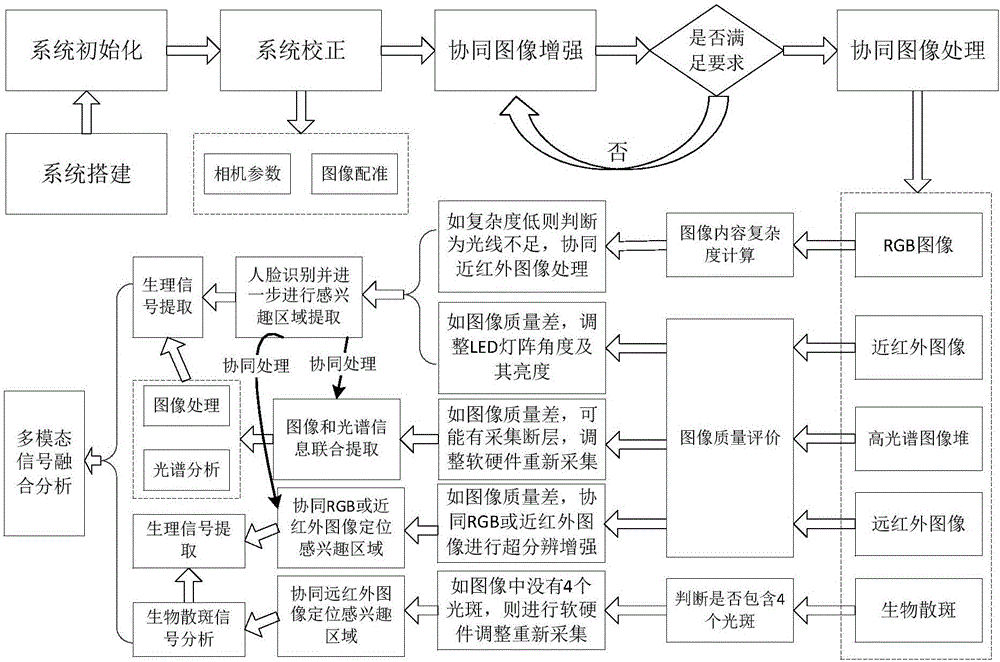
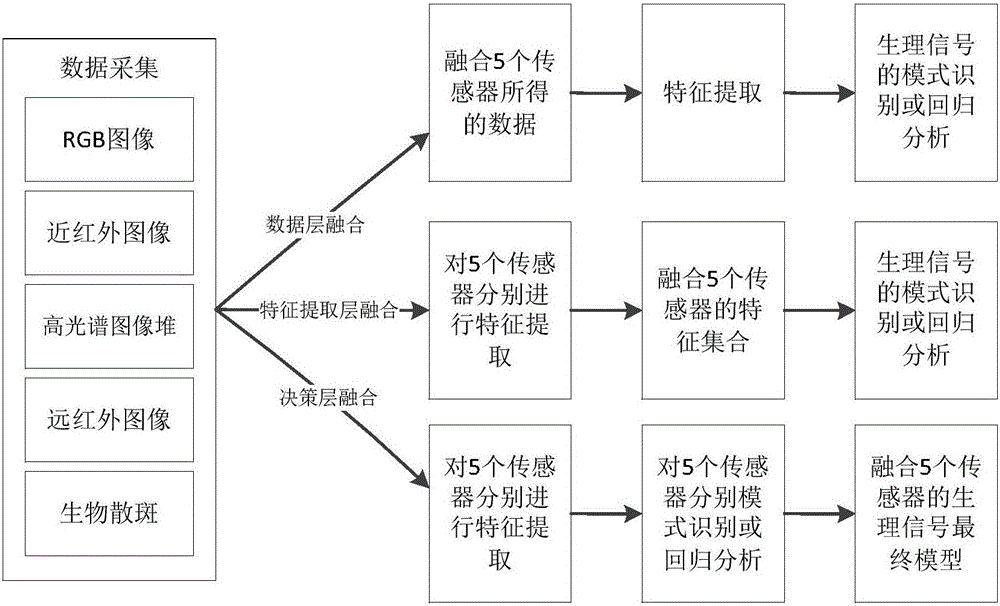
The invention provides a physiological signal remote monitoring system based on multimodal imaging technique and application thereof; the physiological signal remote monitoring system comprises an integrated imaging module, a hyperspectral imaging module and a control terminal; the hyperspectral imaging module is disposed above the integrated imaging module, and the integrated imaging module and the hyperspectral imaging module are respectively in communication connection with the control terminal. The physiological signal remote monitoring system integrating the 5 imaging modes of hyperspectral mode, visible light mode, near-infrared mode, far-infrared mode and laser bio-speckle mode can provide high-precision extraction and analysis for physiological signals; meanwhile, the physiological signal remote monitoring system allows coordinated data acquisition among multimodal devices and coordinated processing and analysis among data, such that the different application needs such as sleep monitoring and diseased pig screening are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Super-resolution fluorescence spectrum imaging microscope
ActiveCN104597590AImprove imaging effectImaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser transmitterFluorescence spectrometry
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence spectrum imaging microscope. The super-resolution fluorescence spectrum imaging microscope comprises a laser emitter, a dichroic mirror, a spectroscope, an image controller and a spectrograph, the laser emitter stimulates fluorophores of a sample to emit fluorescence, the spectroscope divides the fluorescence into a first beam of light path and a second beam of light path, both the first beam of light path and second beam of light path have fluorescence signals of the fluorescence and spurious signals of exciting light, the first beam of light path is emitted to the image controller to gather the intensity information of the fluorescence, the second beam of light path is emitted to the spectrograph to analyze the spectrum information of the fluorescence and distinguish fluorescence signals from different fluorophores in the fluorescence according to the spectrum information, and the spectrum information gathered by the spectrograph is used for distinguishing the fluorescence signals of the fluorescence and spurious signals of the exciting light so as to distinguish the exciting light from the fluorescence signals through the spectrograph and improve the imaging effect of the super-resolution fluorescence spectrum imaging microscope.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com