Patents
Literature
38861results about "Color/spectral properties measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
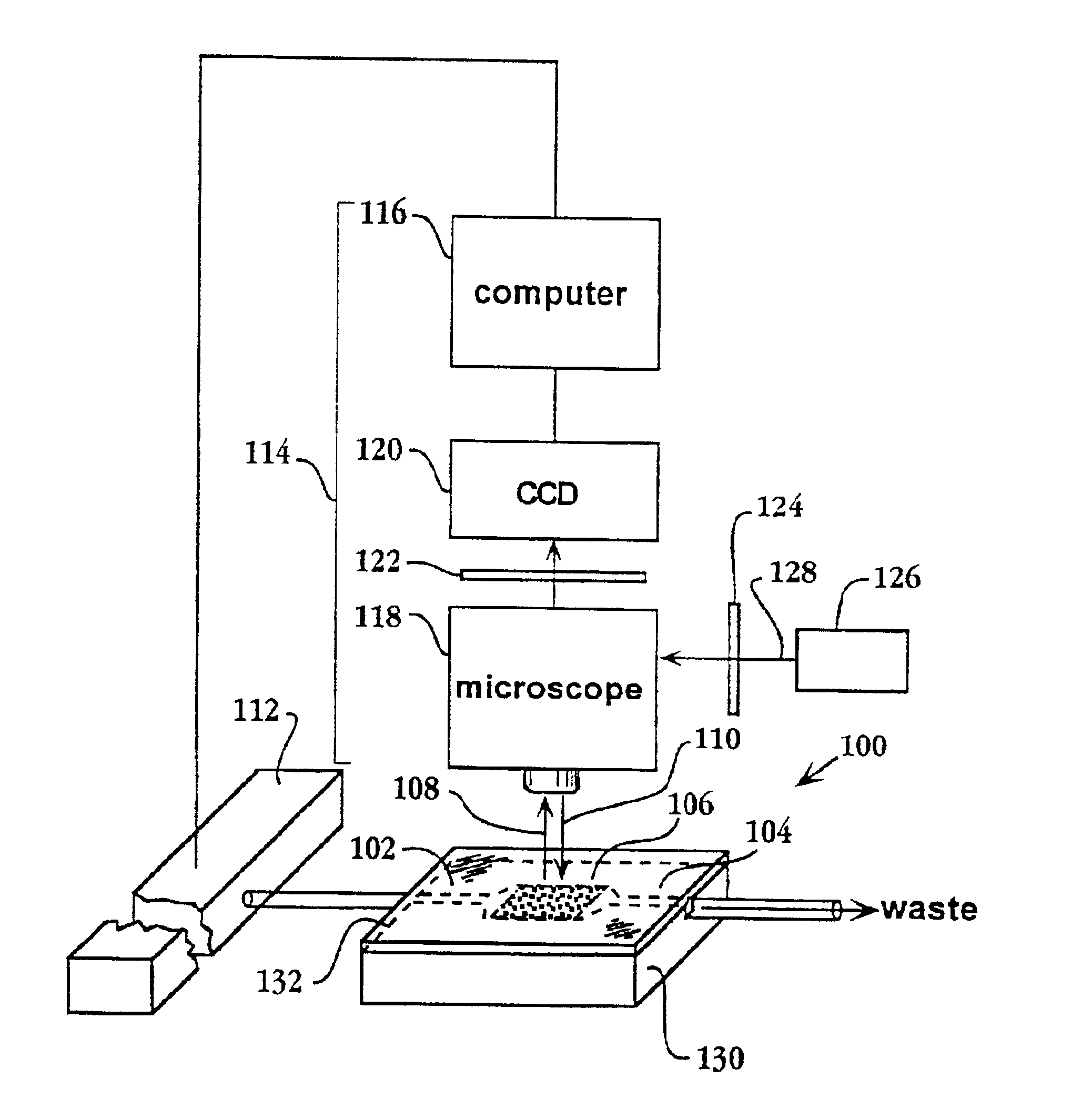
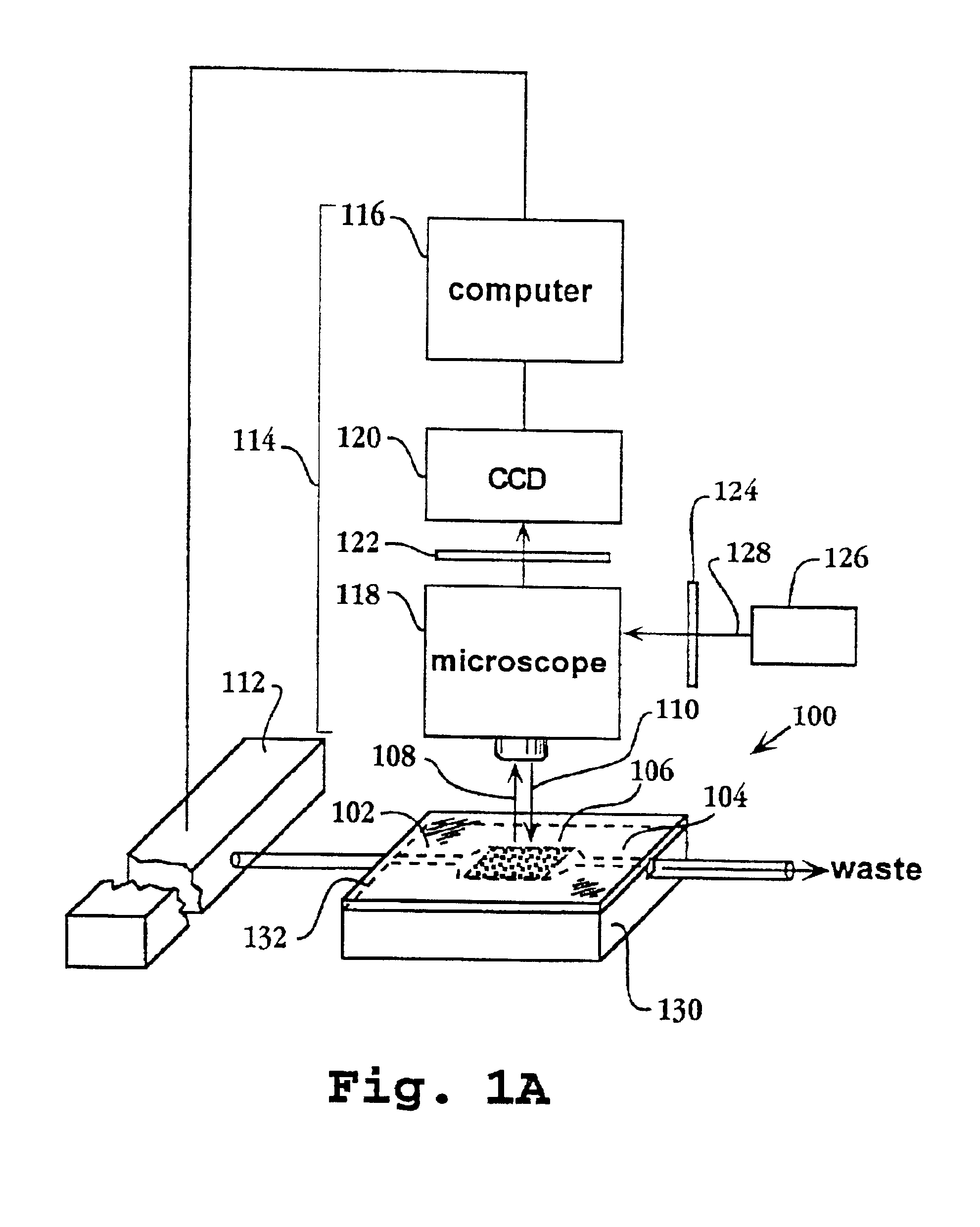
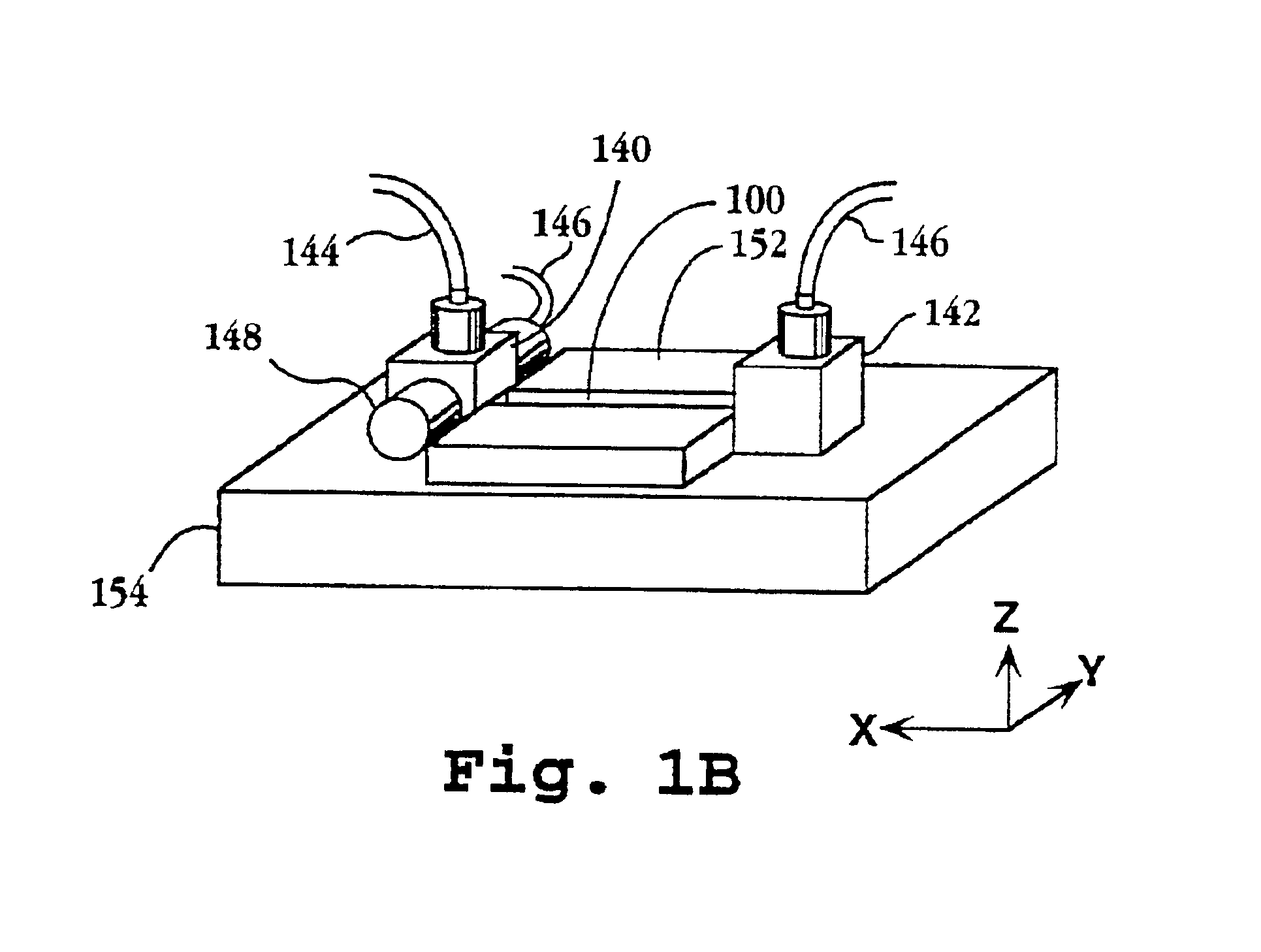
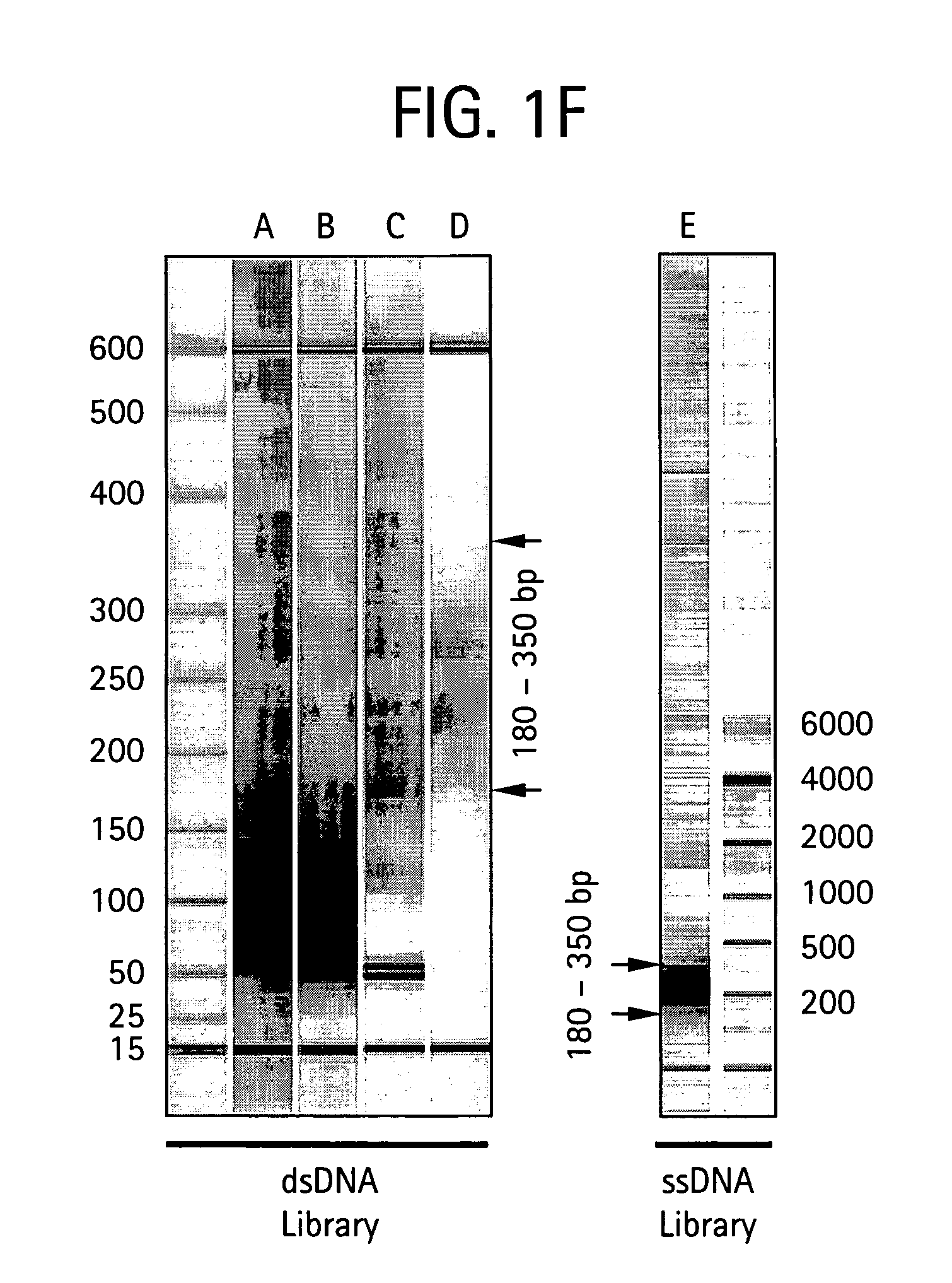
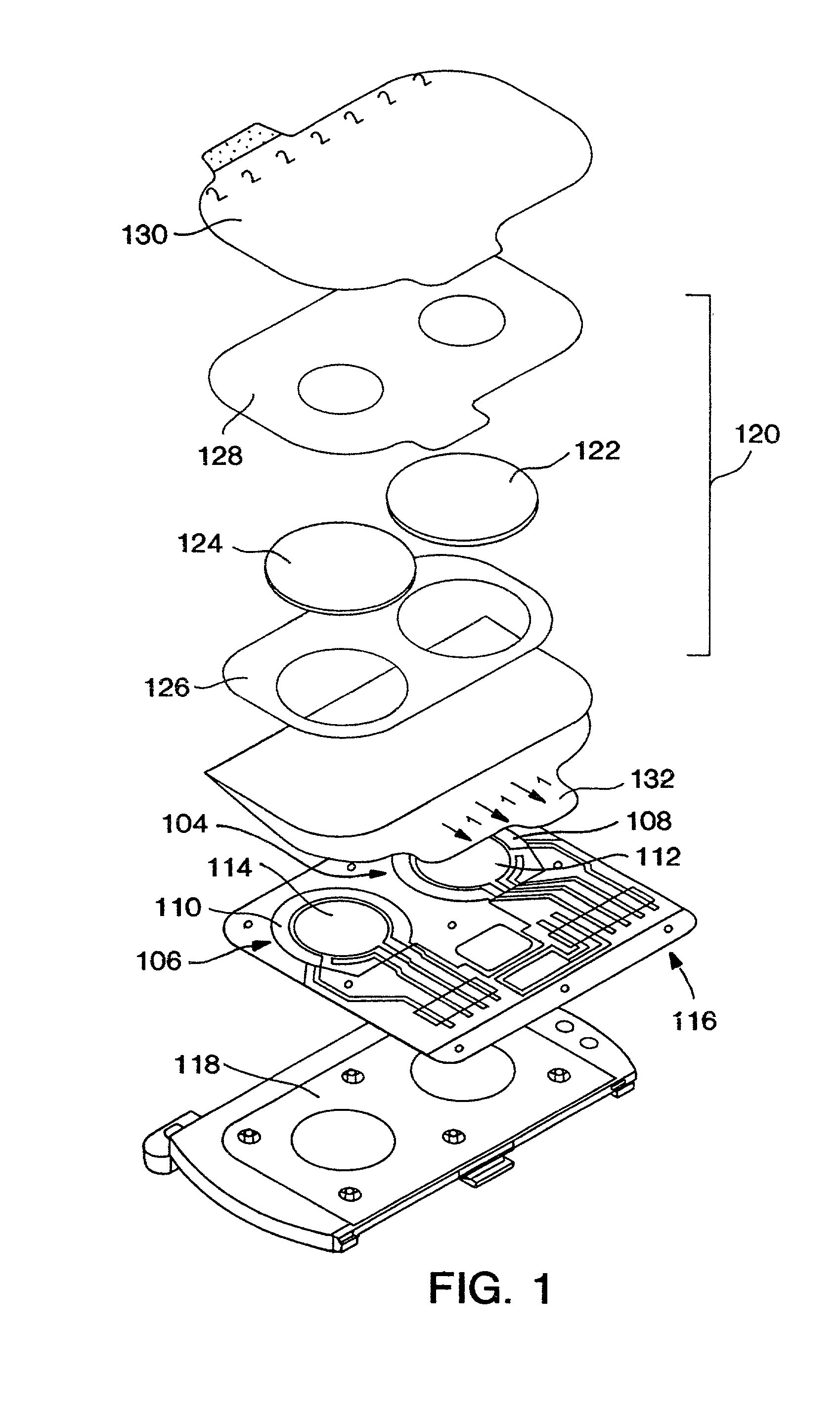
System and apparatus for sequential processing of analytes
InactiveUS6969488B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicroparticle
An apparatus and system are provided for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of analytes anchored to microparticles. Microparticles each having a uniform population of a single kind of analyte attached are disposed as a substantially immobilized planar array inside of a flow chamber where steps of an analytical process are carried out by delivering a sequence of processing reagents to the microparticles by a fluidic system under microprocessor control. In response to such process steps, an optical signal is generated at the surface of each microparticle which is characteristic of the interaction between the analyte carried by the microparticle and the delivered processing reagent. The plurality of analytes are simultaneously analyzed by collecting and recording images of the optical signals generated by all the microparticles in the planar array. A key feature of the invention is the correlation of the sequence of optical signals generated by each microparticle in the planar array during the analytical process.
Owner:SOLEXA
Flex circuit shielded optical sensor
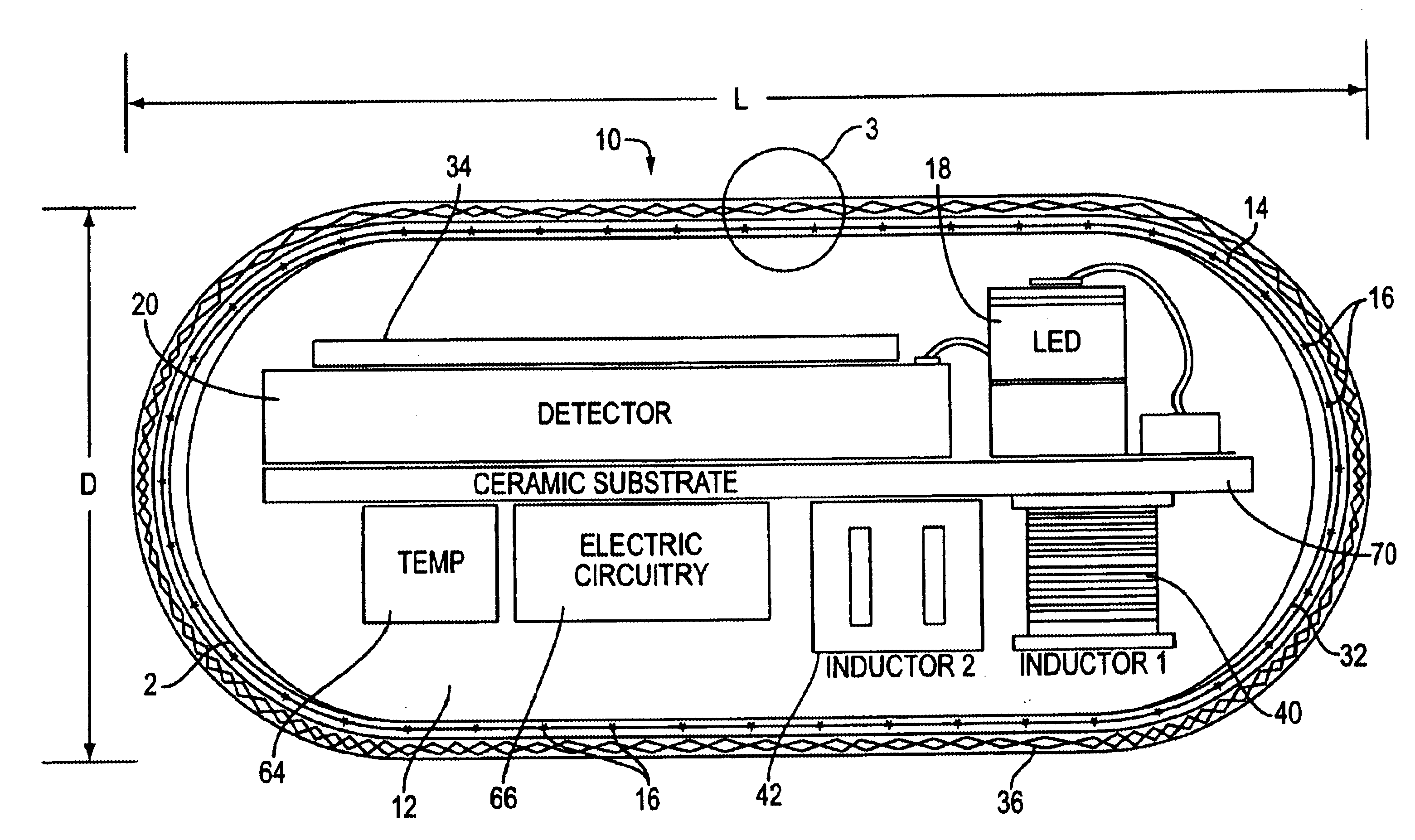
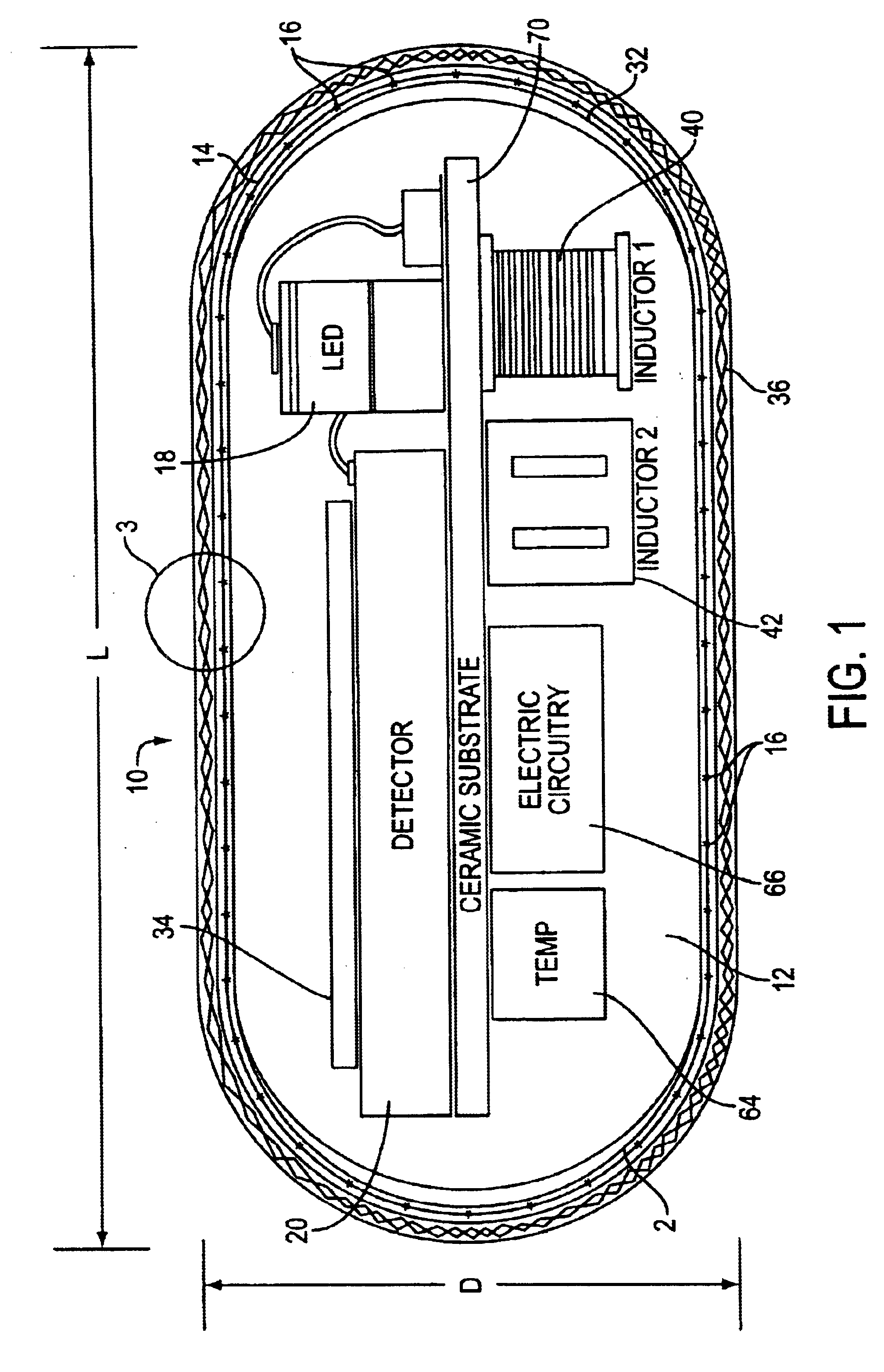
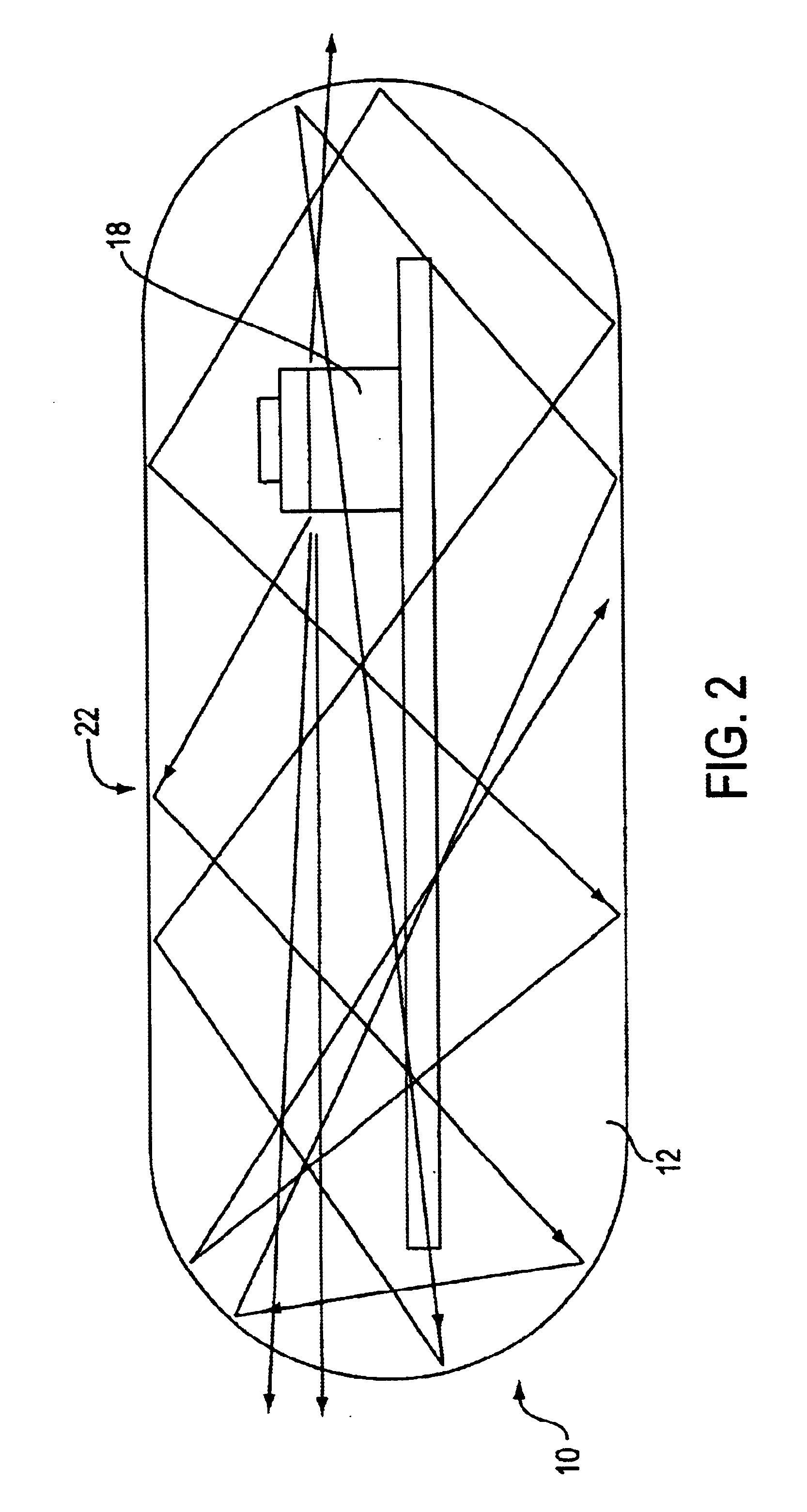
InactiveUS6985764B2Cross-talk/noise/interference reductionColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A flex circuit optical sensor has an integrated Faraday shield. A conductive trace layer disposed on a substrate is used to form a conductive grid which shields the face of a photodetector. A conductive ink layer is formed on a substrate side opposite the trace layer. The back and sides of the detector are shielded by flex circuit flaps that have the conductive ink layer but substantially exclude the trace layer so as to fold over and closely adhere to the detector body. The shielded substrate flaps advantageously eliminate a separate detector shield, which is typically fabricated with an etched copper part that must be attached to a flex circuit before mounting the detector.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
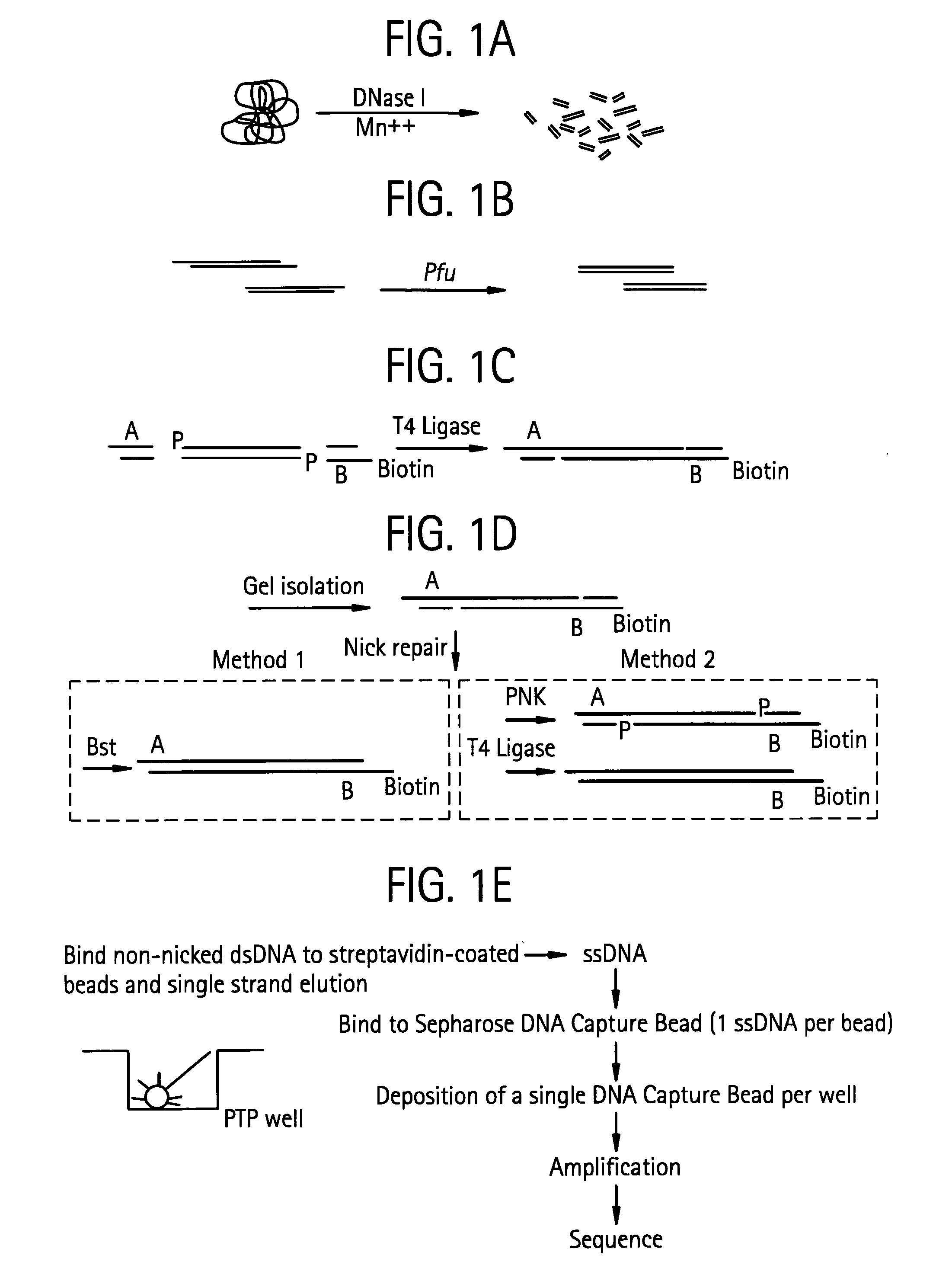
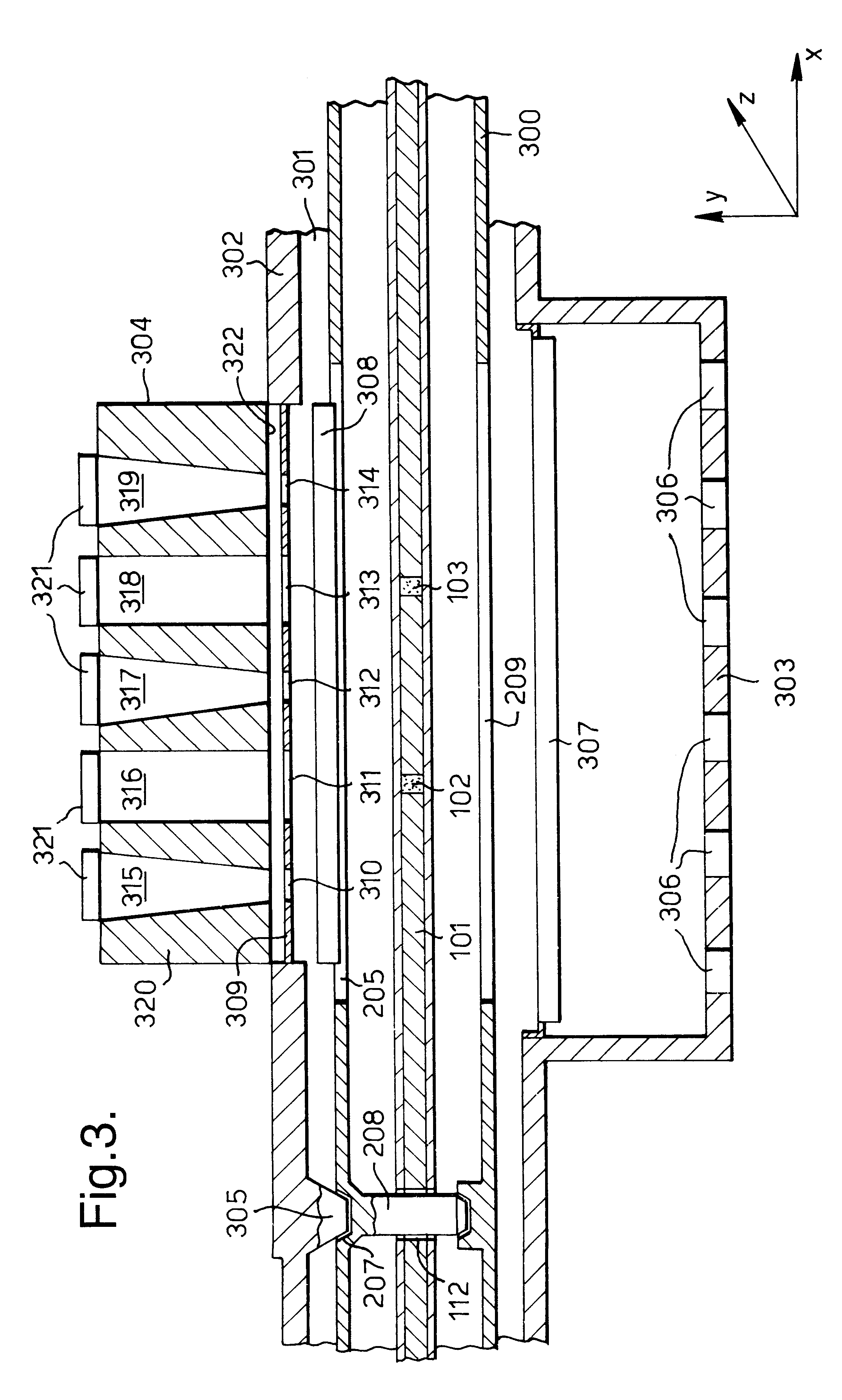
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Optical-based sensing devices
InactiveUS6330464B1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSurgeryAnalyteFluorescence
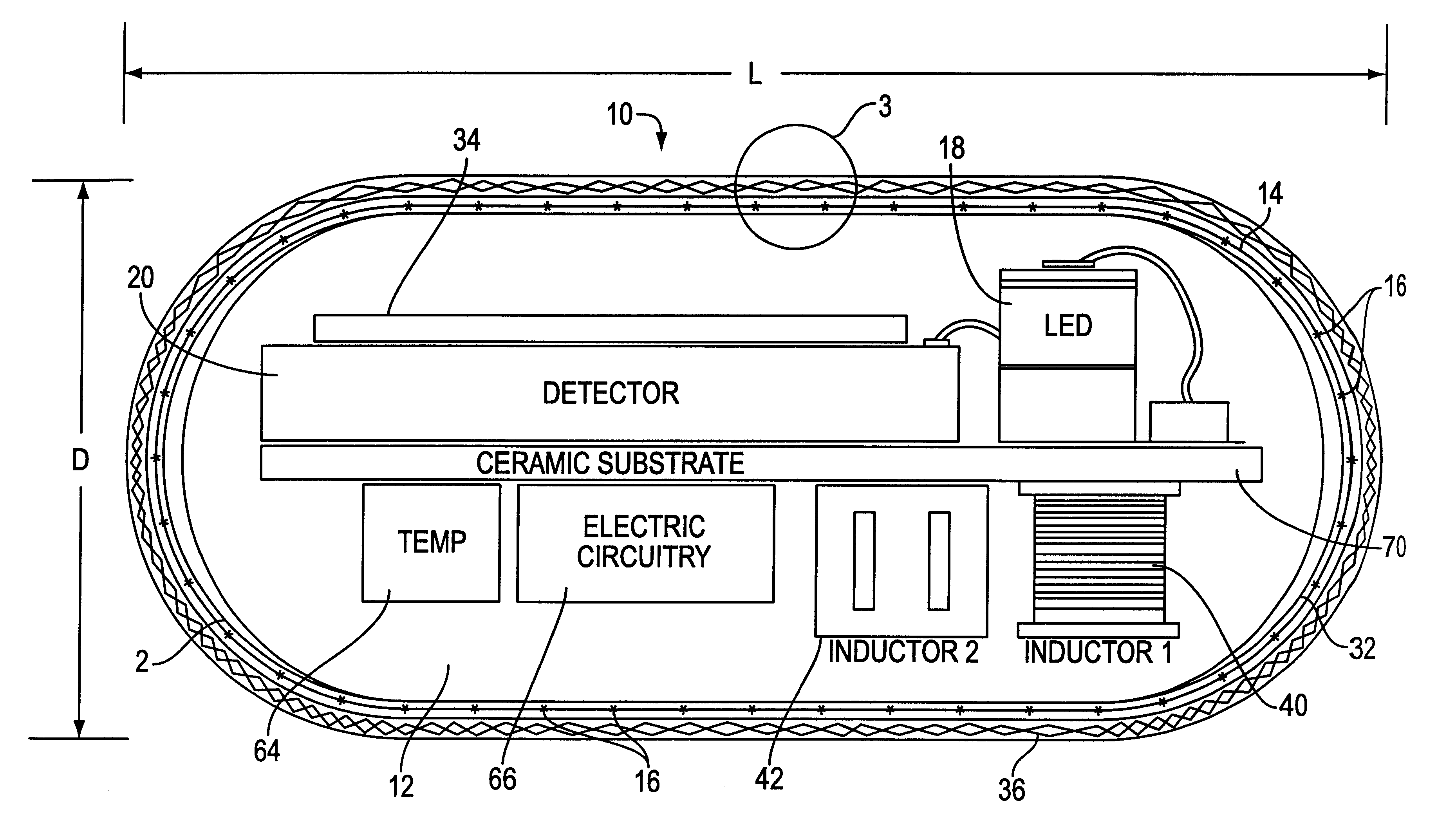
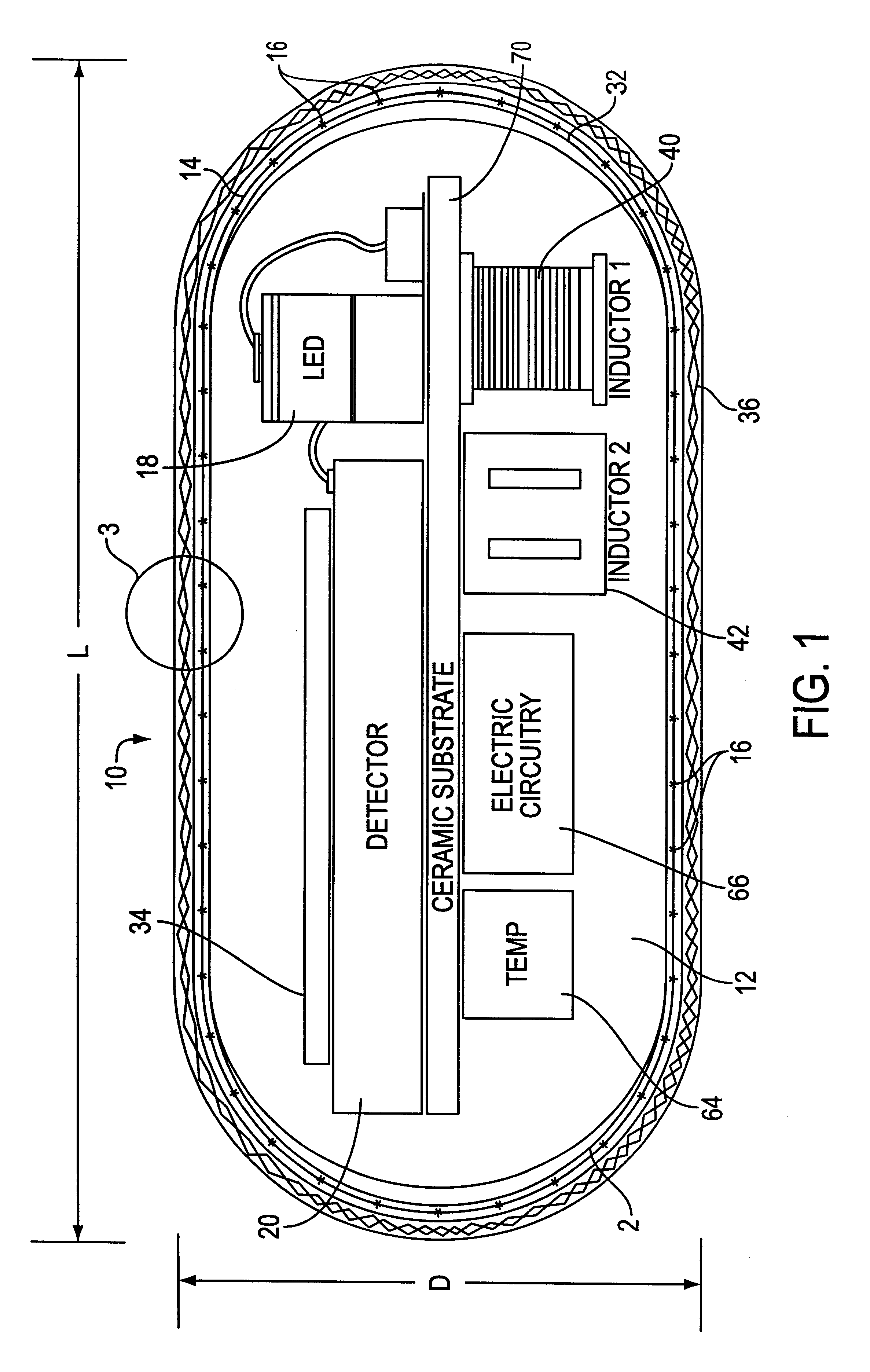
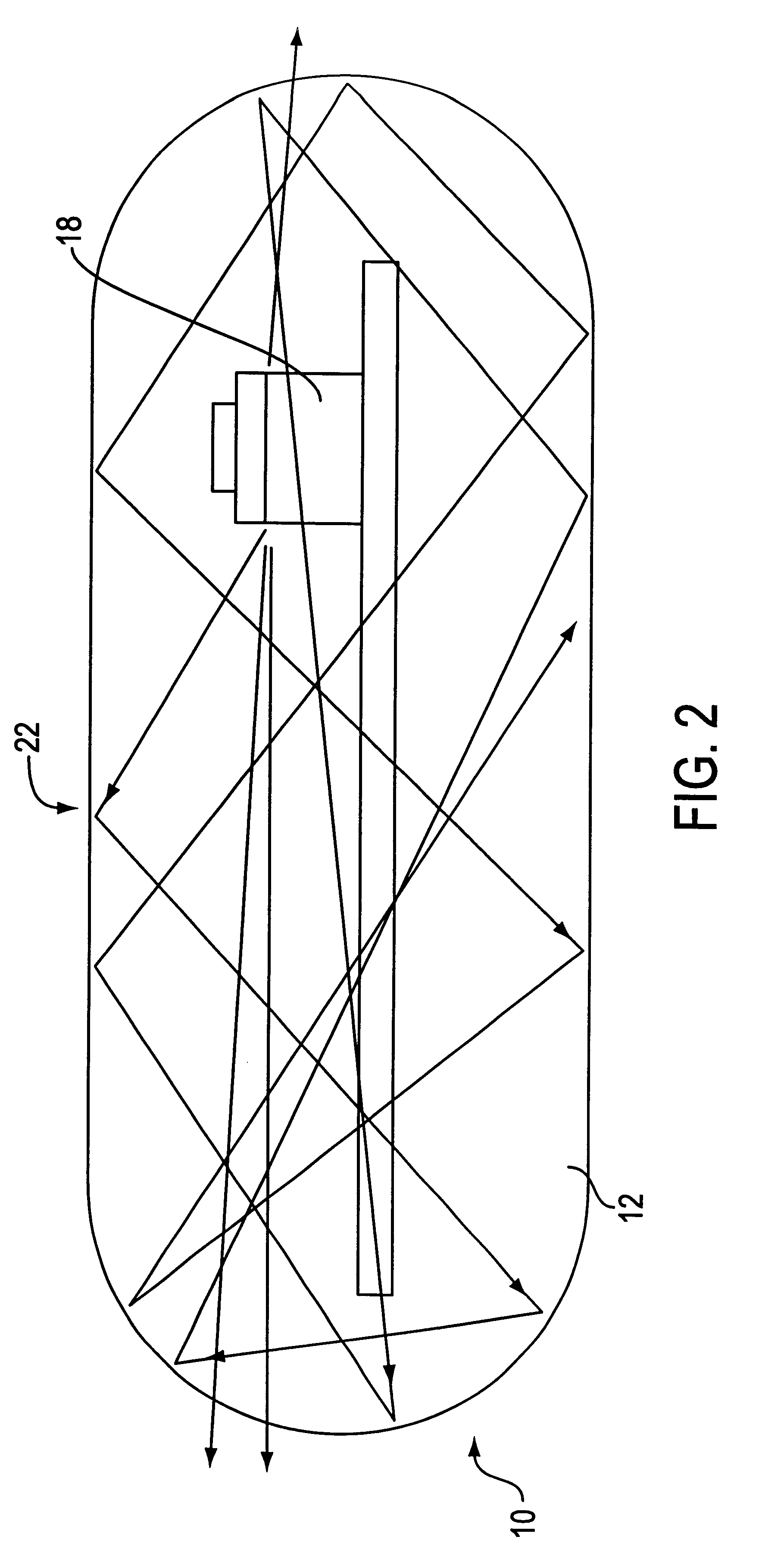
An optical-based sensor for detecting the presence or amount of an analyte using both indicator and reference channels. The sensor has a sensor body with a source of radiation embedded therein. Radiation emitted by the source interacts with indicator membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. At least one optical characteristic of these indicator molecules varies with analyte concentration. For example, the level of fluorescence of fluorescent indicator molecules or the amount of light absorbed by light-absorbing indicator molecules can vary as a function of analyte concentration. In addition, radiation emitted by the source also interacts with reference membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. Radiation (e.g., light) emitted or reflected by these indicator molecules enters and is internally reflected in the sensor body. Photosensitive elements within the sensor body generate both indicator channel and reference channel signals to provide an accurate indication of the concentration of the analyte. Preferred embodiments are totally self-contained and are sized and shaped for use in vivo in a human being. Such embodiments preferably include a power source, e.g. an inductor, which powers the source of radiation using external means, as well as a transmitter, e.g. an inductor, to transmit to external pickup means the signal representing the level of analyte.
Owner:SENSEONICS INC
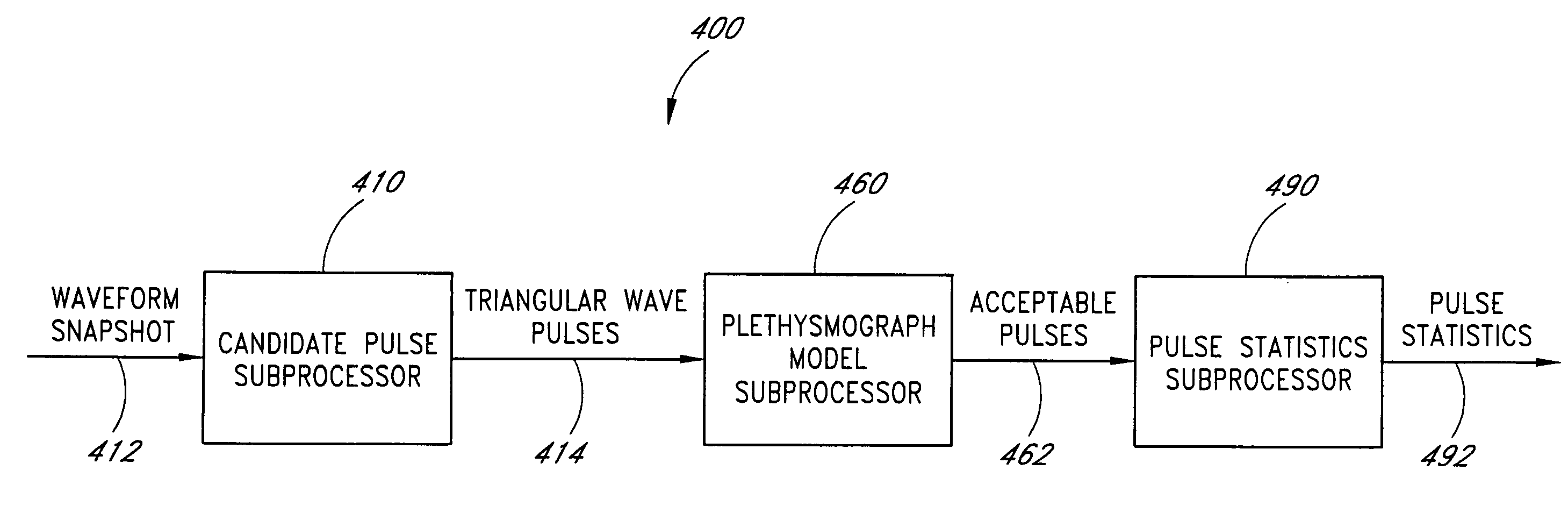
Plethysmograph pulse recognition processor
A time domain rule-based processor provides recognition of individual pulses in a pulse oximeter-derived photo-plethysmograph waveform.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
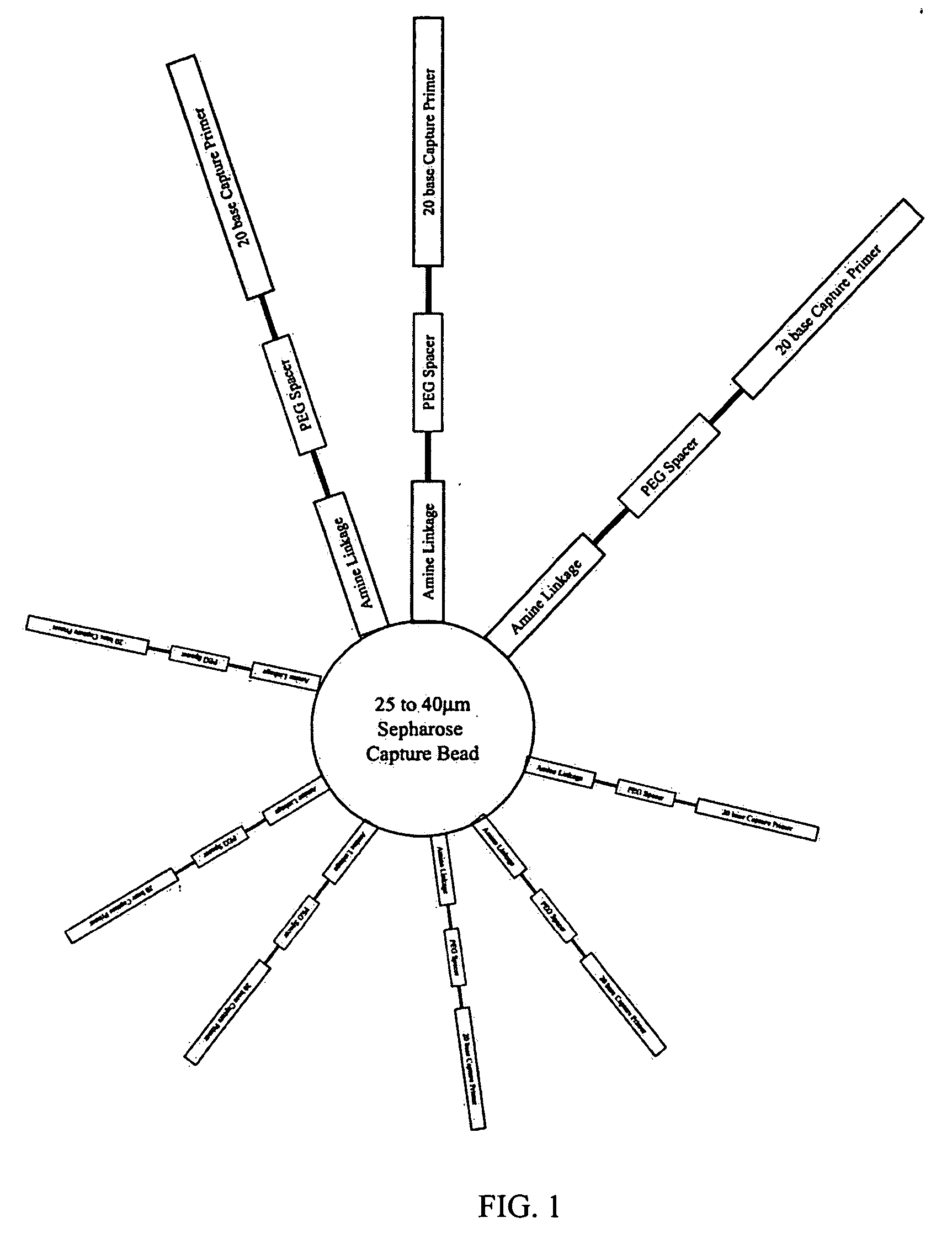
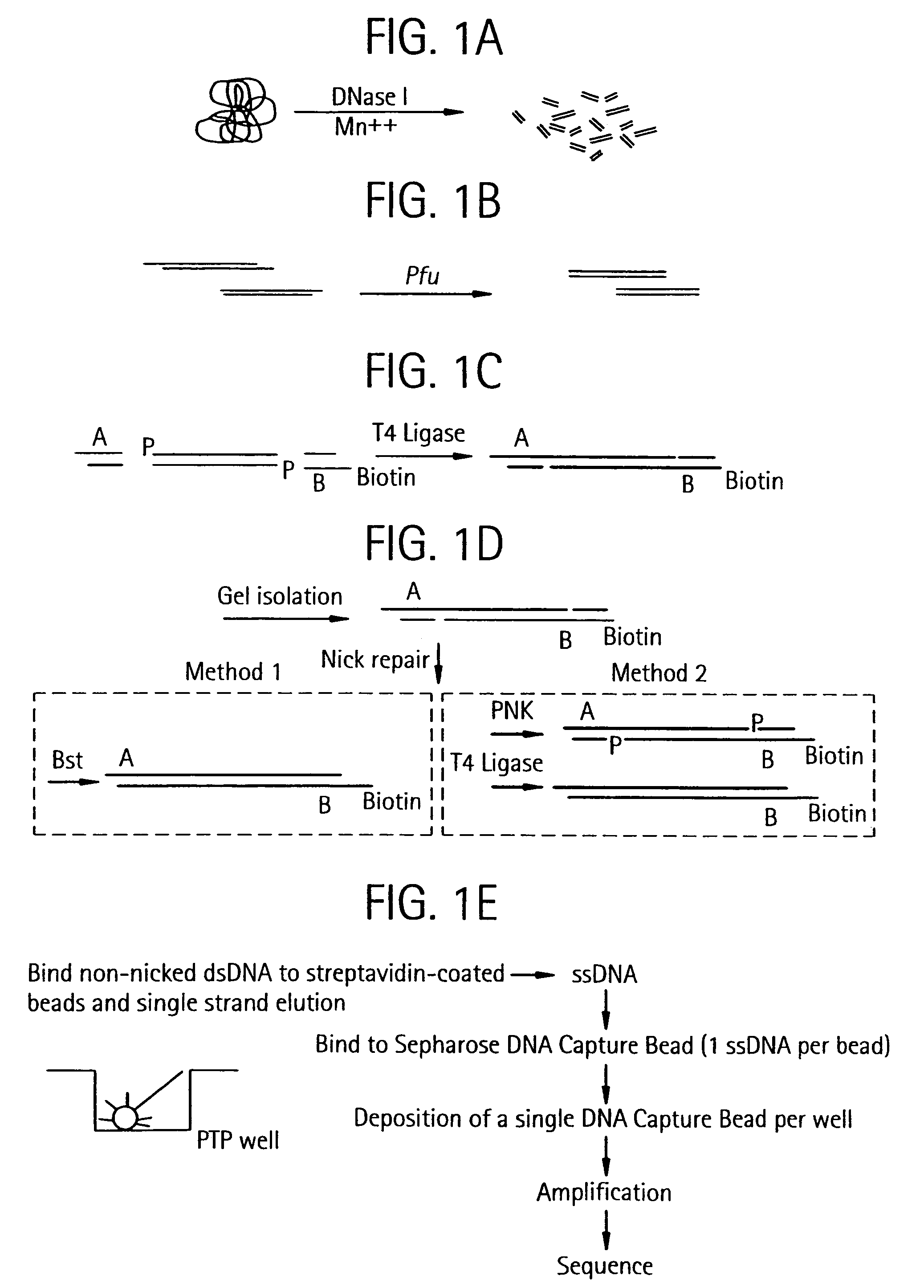
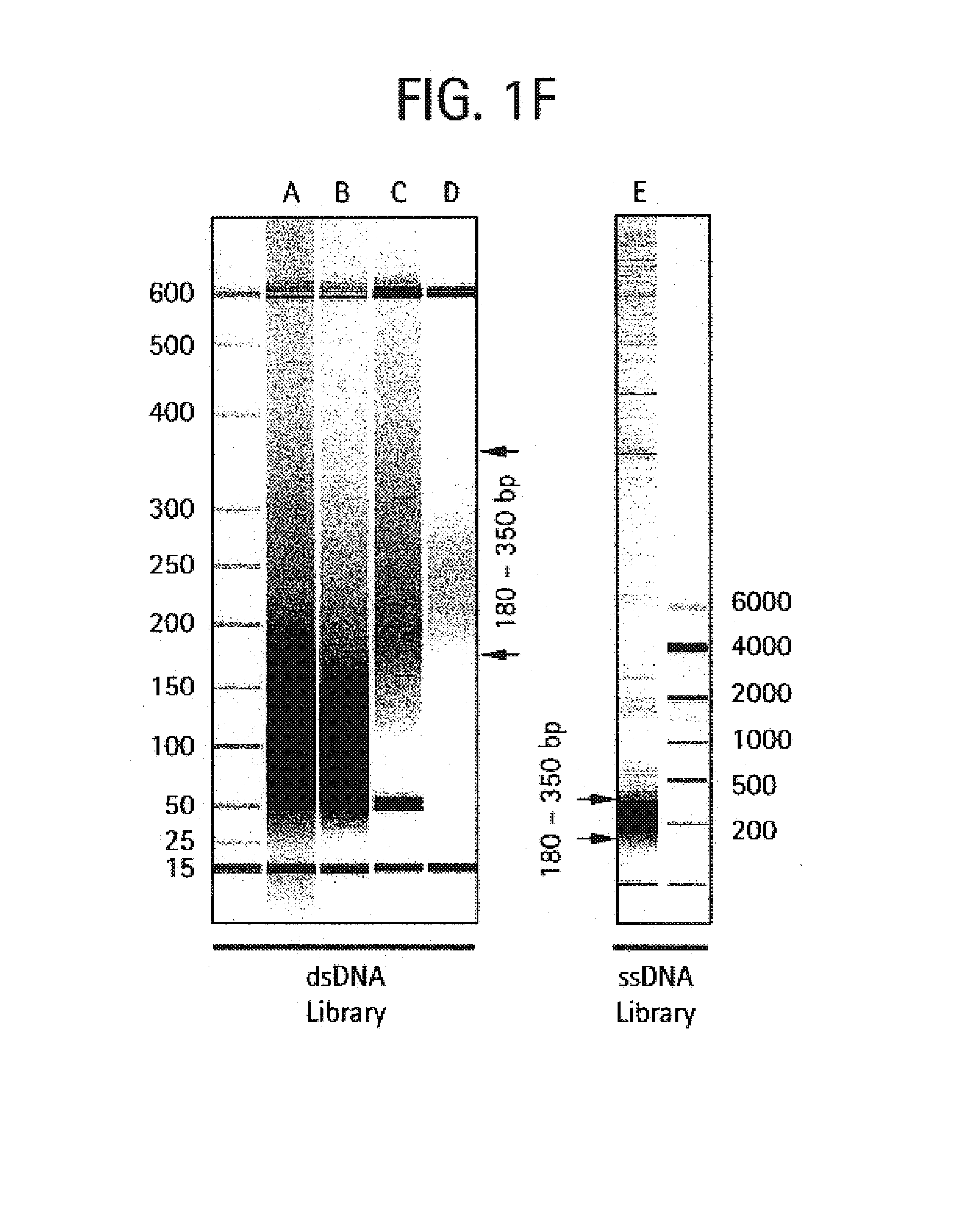
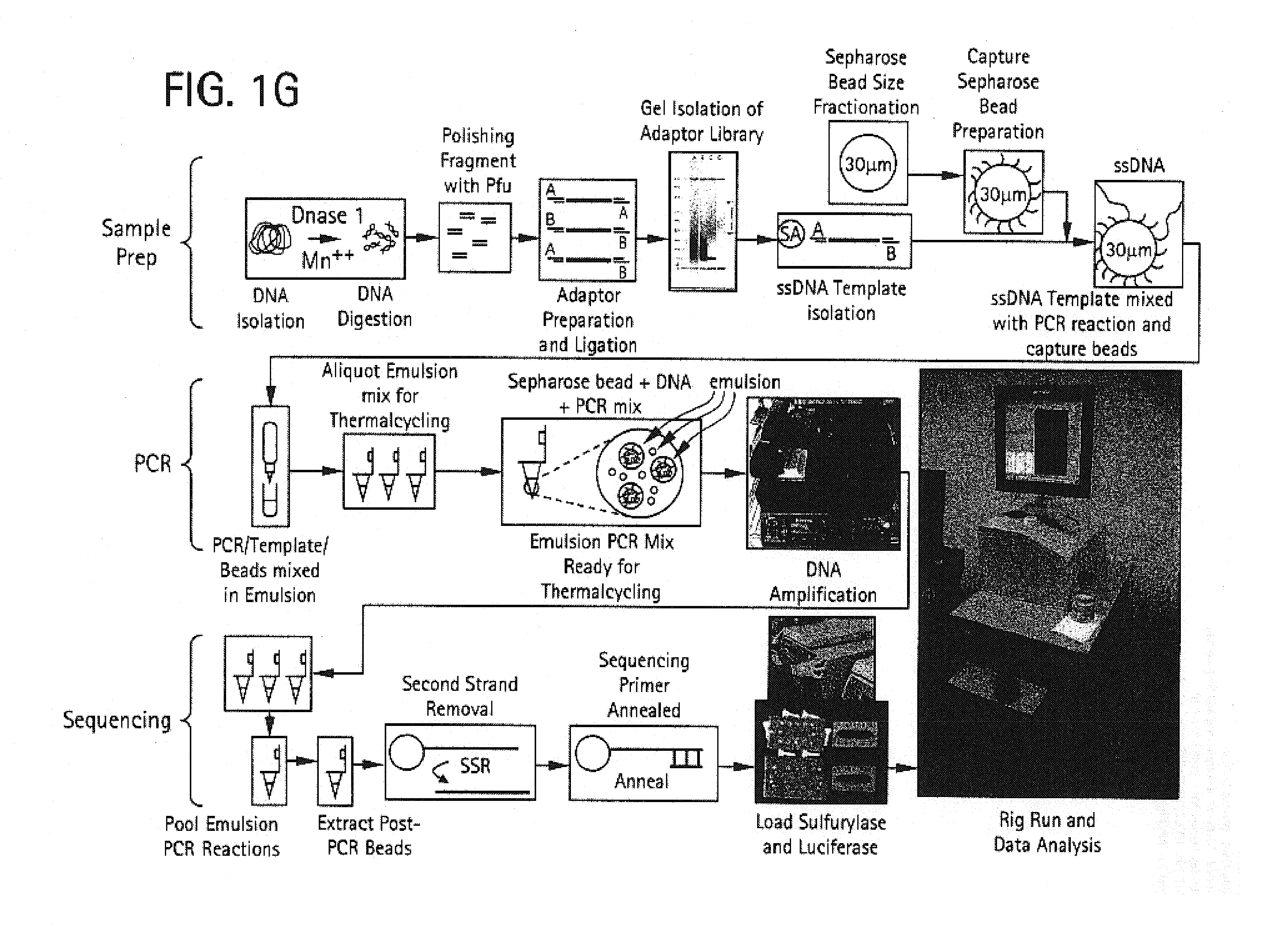
Bead emulsion nucleic acid amplification
Disclosed are methods for nucleic acid amplification wherein nucleic acid templates, beads, and amplification reaction solution are emulsified and the nucleic acid templates are amplified to provide clonal copies of the nucleic acid templates attached to the beads. Also disclosed are kits and apparatuses for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Method and devices for laser induced fluorescence attenuation spectroscopy
InactiveUSRE39672E1Large signal to noise ratioSurgeryScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationSpectroscopy
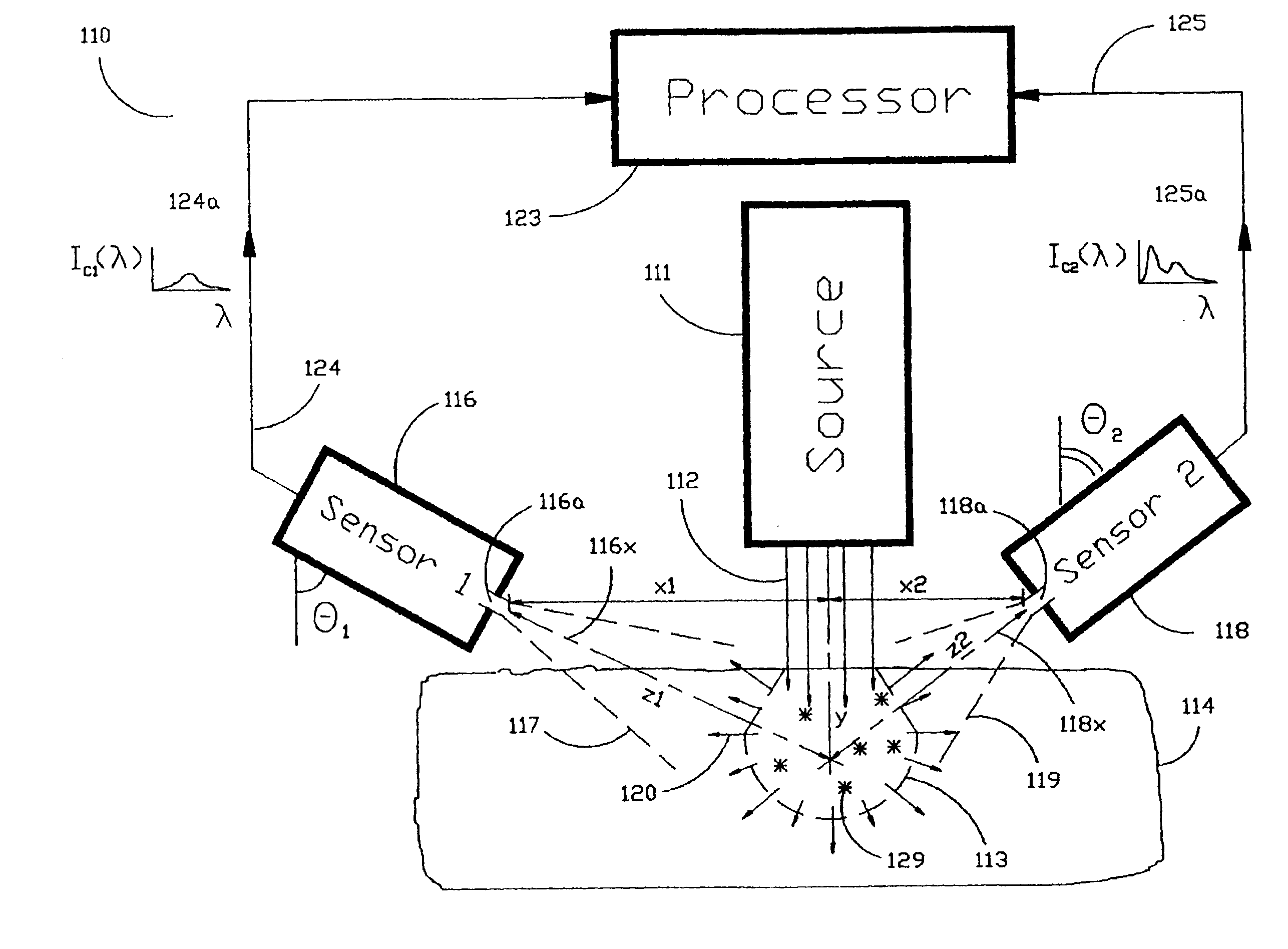
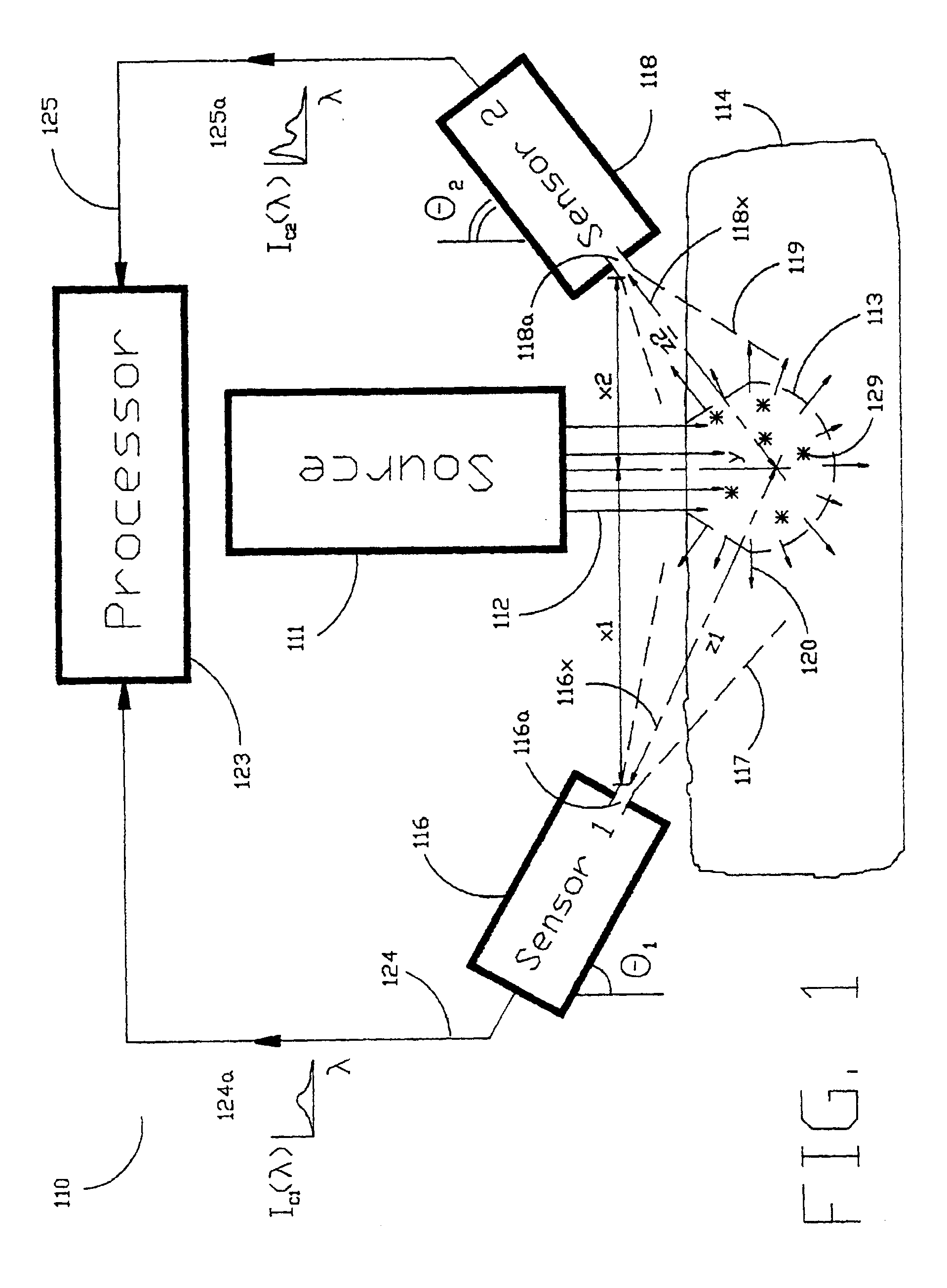
The Laser Induced Fluorescence Attenuation Spectroscopy (LIFAS) method and apparatus preferably include a source adapted to emit radiation that is directed at a sample volume in a sample to produce return light from the sample, such return light including modulated return light resulting from modulation by the sample, a first sensor, displaced by a first distance from the sample volume for monitoring the return light and generating a first signal indicative of the intensity of return light, a second sensor, displaced by a second distance from the sample volume, for monitoring the return light and generating a second signal indicative of the intensity of return light, and a processor associated with the first sensor and the second sensor and adapted to process the first and second signals so as to determine the modulation of the sample. The methods and devices of the inventions are particularly well-suited for determining the wavelength-dependent attenuation of a sample and using the attenuation to restore the intrinsic laser induced fluorescence of the sample. In turn, the attenuation and intrinsic laser induced fluorescence can be used to determined a characteristic of interest, such as the ischemic or hypoxic condition of biological tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Manual and automatic probe calibration
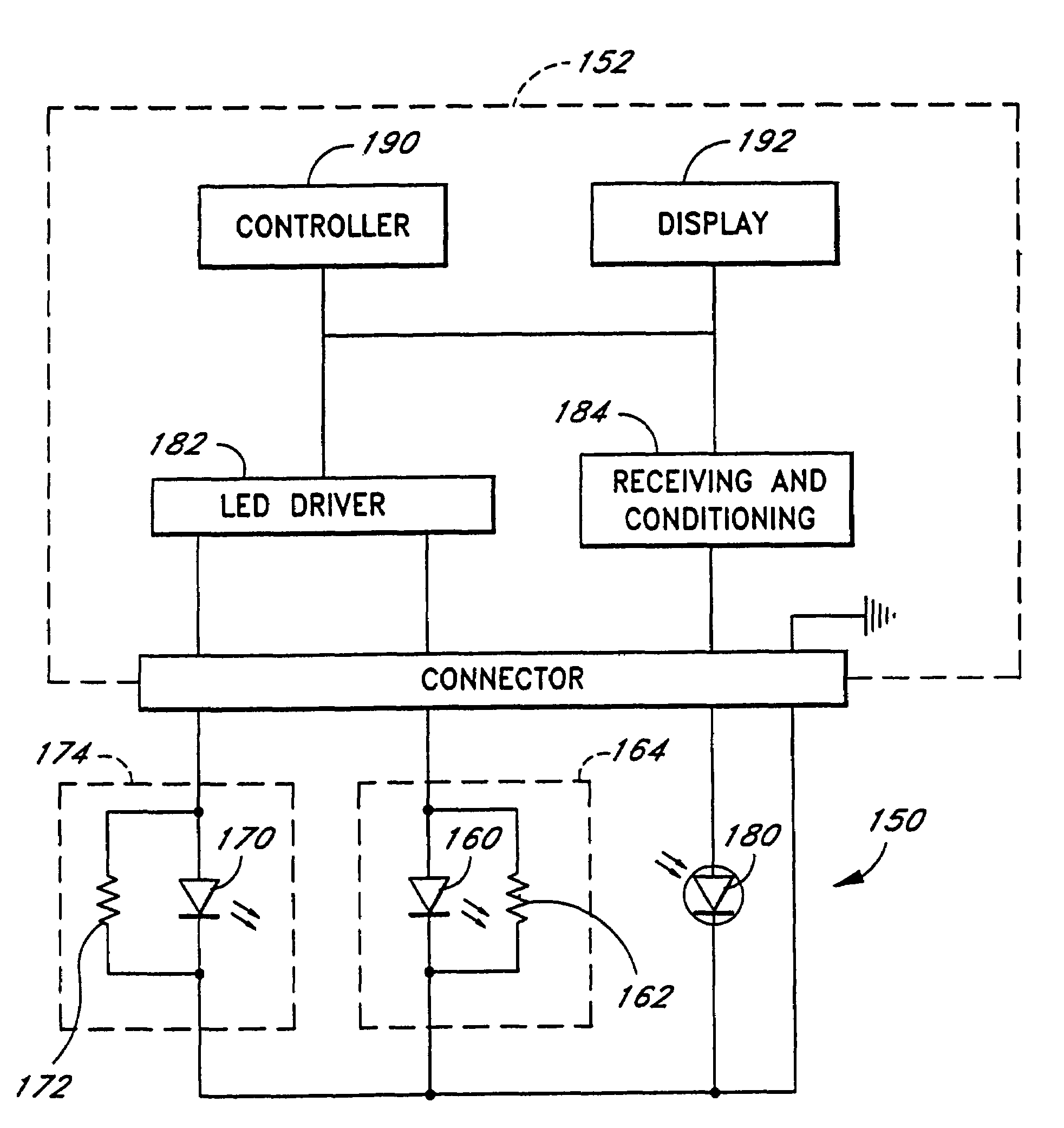
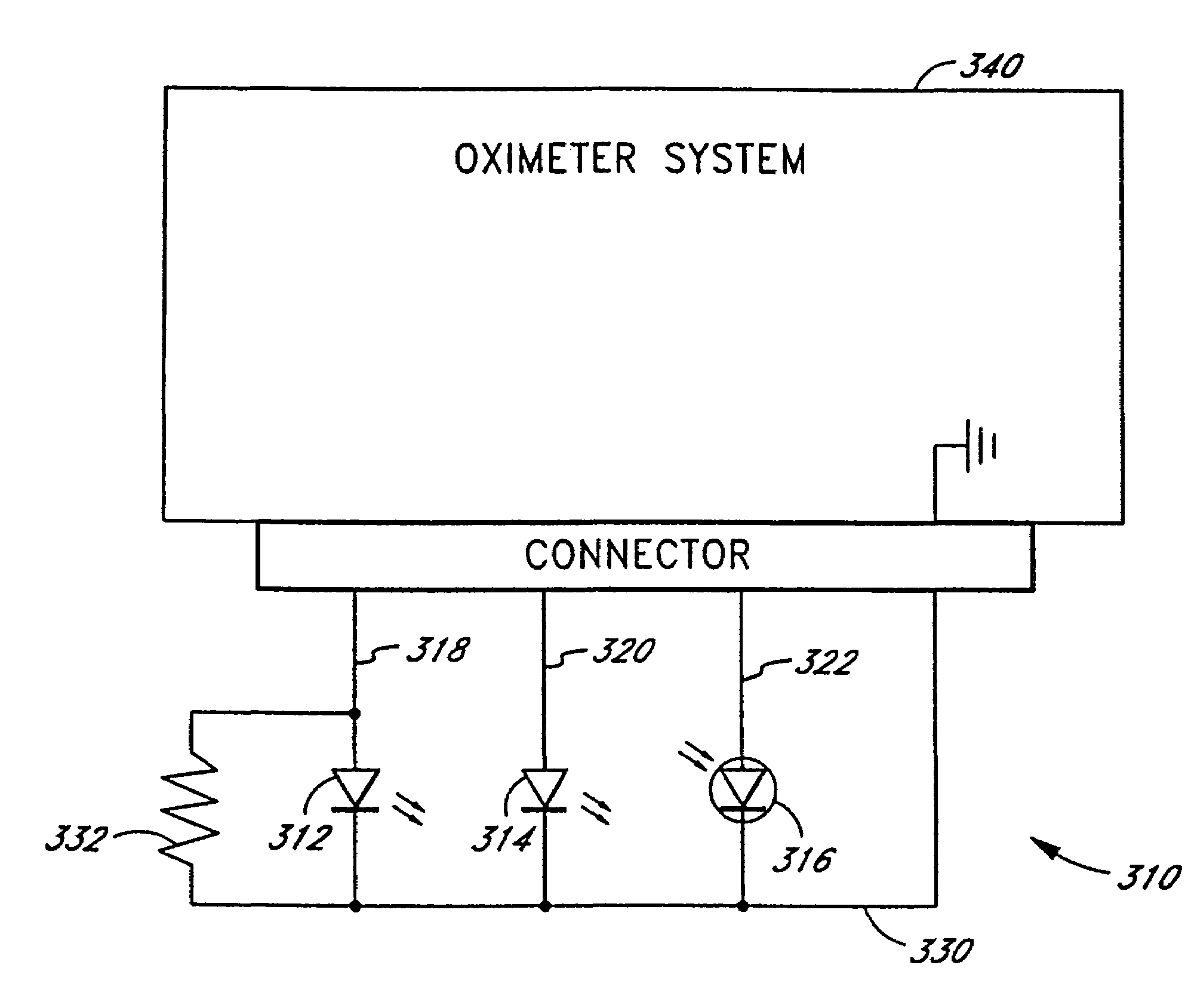
InactiveUS7496391B2Complicates designIncreased expenseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationElectronic componentProbe calibration
Embodiments of the present disclosure include an oximeter sensor system including a reusable portion including a substantially rigid connector connected to an end of a cable. The substantially rigid connector includes an electronic element housing at least one electronic component of a probe. The system also includes a disposable portion including a flexible wrap comprising a substantially rigid connection port shaped to receive the substantially rigid connector in a releasably securable manner.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Manual and automatic probe calibration
InactiveUS7526328B2Complicates designIncreased expenseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull Term NeonateEngineering
Embodiments of the present disclosure include an optical probe capable of communicating identification information to a patient monitor in addition to signals indicative of intensities of light after attenuation by body tissue. The identification information may indicate operating wavelengths of light sources, indicate a type of probe, such as, for example, that the probe is an adult probe, a pediatric probe, a neonatal probe, a disposable probe, a reusable probe, or the like. The information could also be utilized for security purposes, such as, for example, to ensure that the probe is configured properly for the oximeter, to indicate that the probe is from an authorized supplier, or the like. In one preferred embodiment, coding resistors could be provided across the light sources to allow additional information about the probe to be coded without added leads. However, any device could be used without it being used in parallel.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Methods and devices for prediction of hypoglycemic events
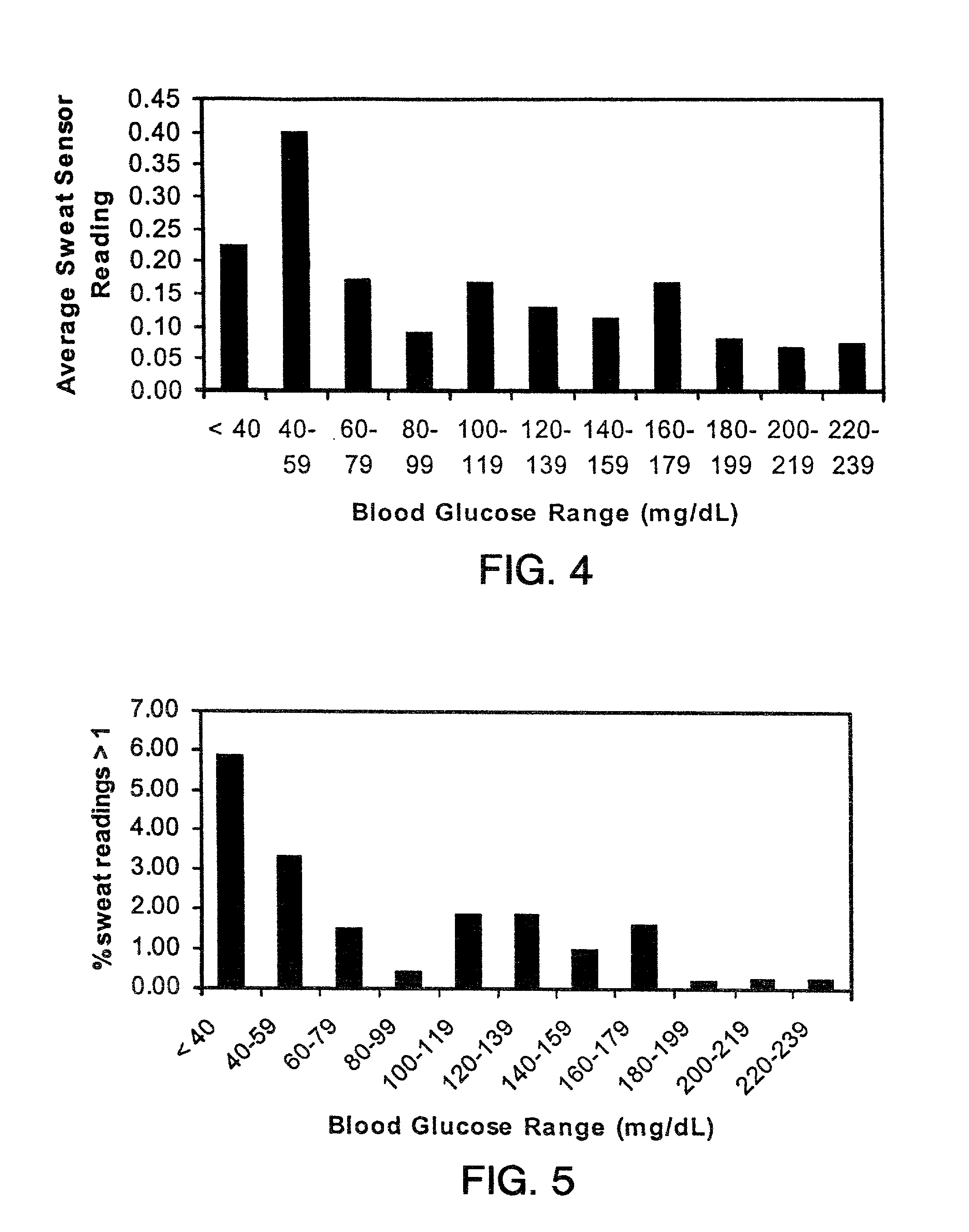
InactiveUS6882940B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData streamD-Glucose
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Methods and devices for prediction of hypoglycemic events
InactiveUS20020106709A1Avoid glucose level droppingMore time to respondMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData streamData mining
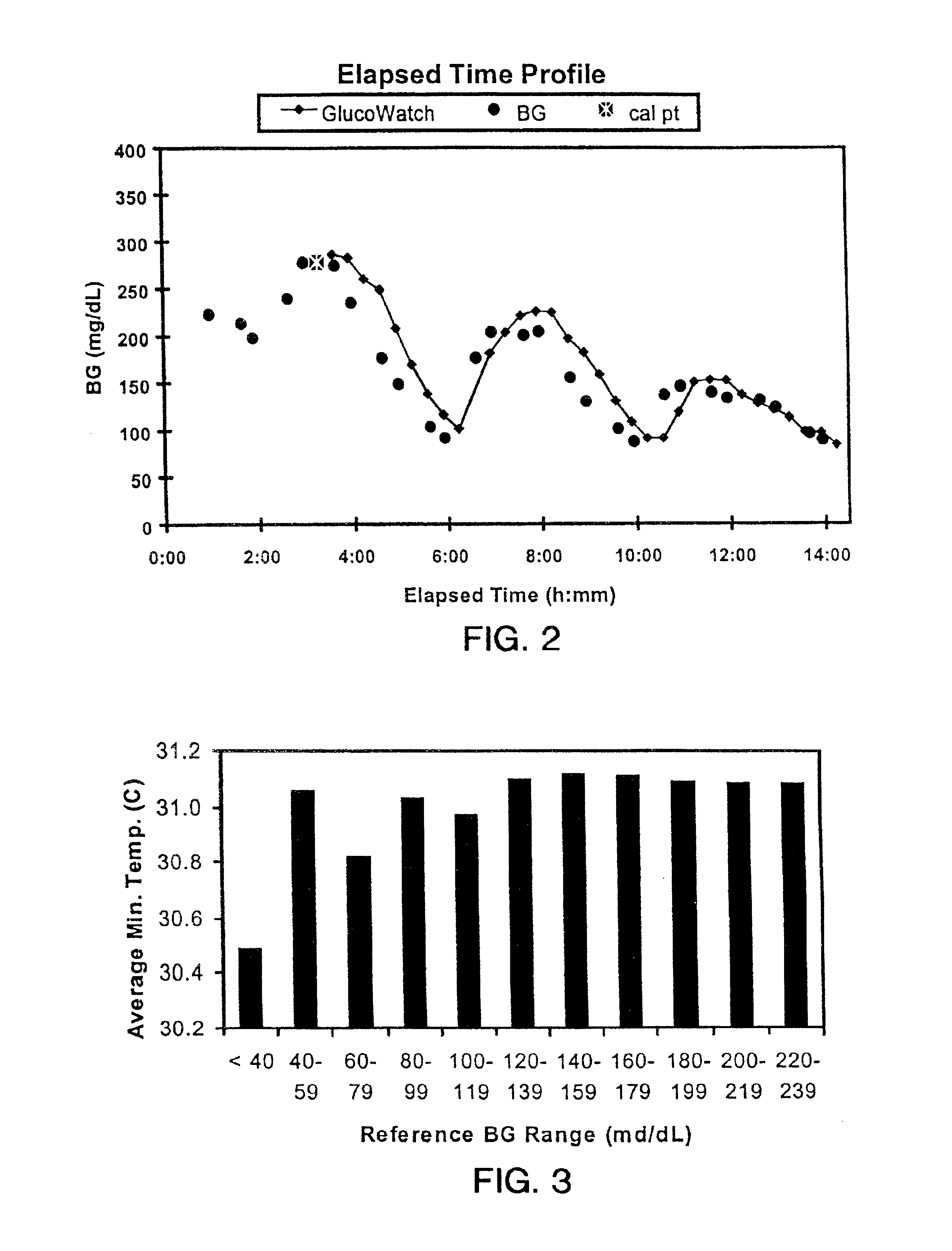
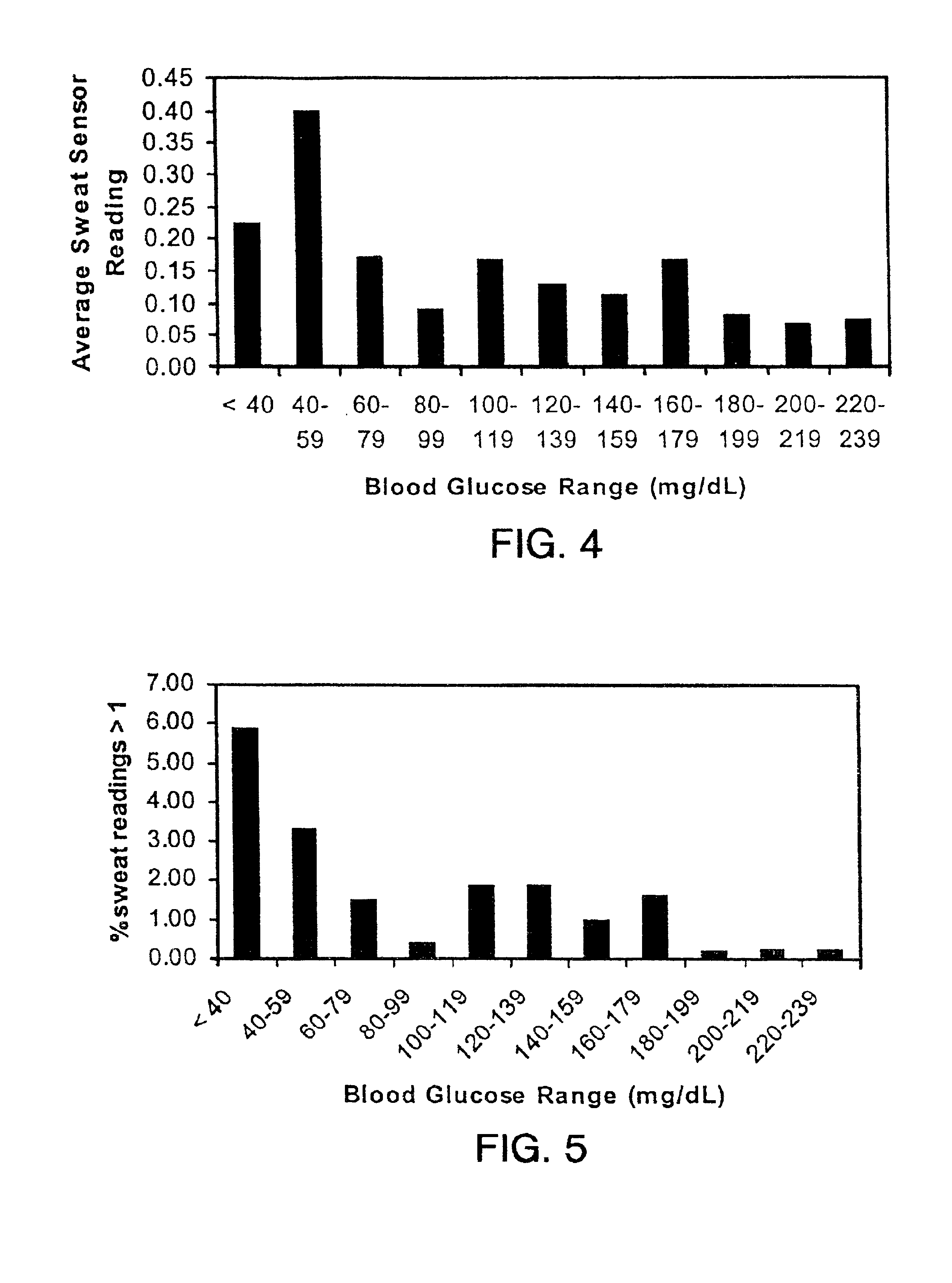
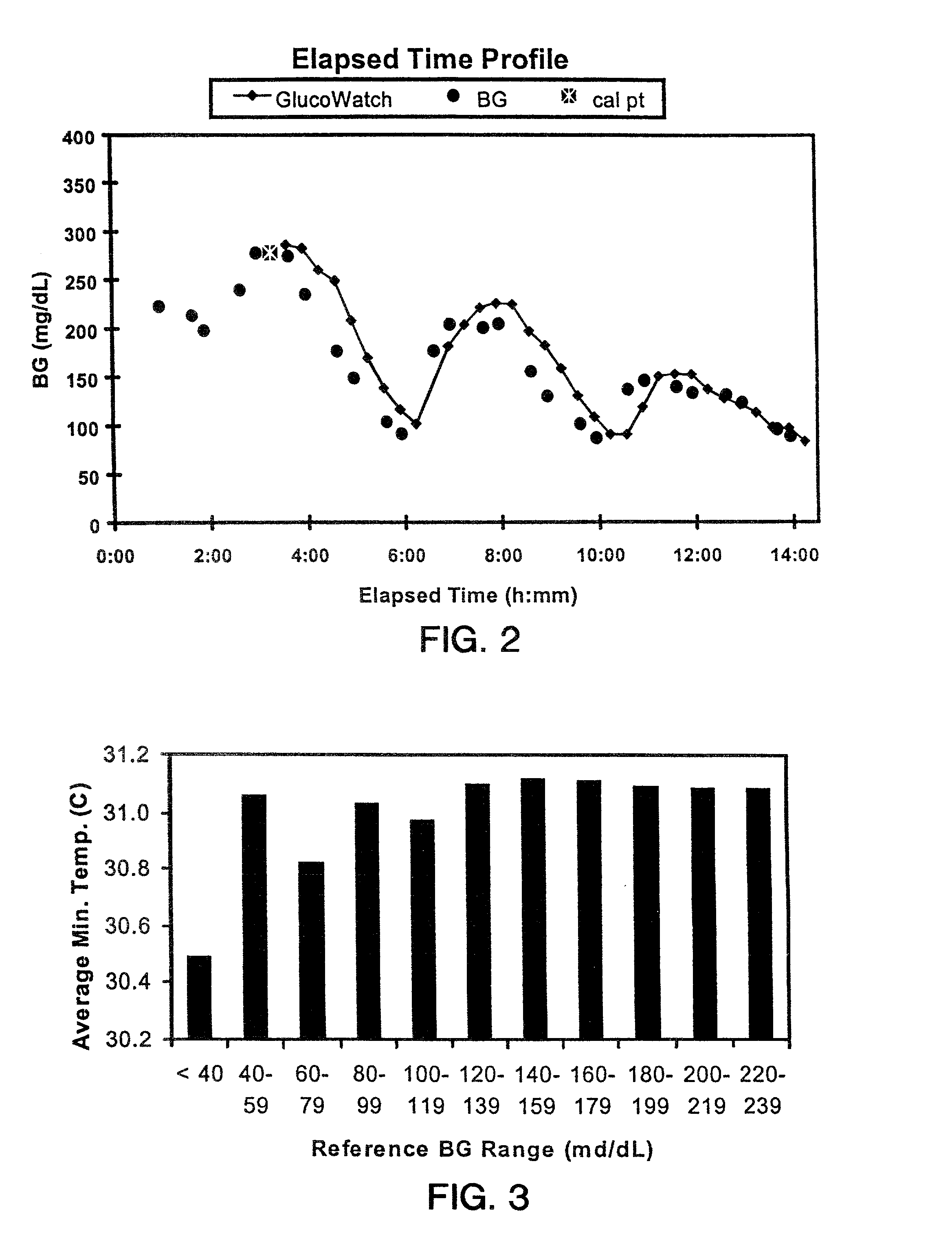
Described herein are methods, devices, and microprocessors useful for predicting a hypoglycemic event in a subject. The hypoglycemic predictive approach described herein utilizes information obtained from a data stream, e.g., frequently obtained glucose values (current and / or predicted), body temperature, and / or skin conductance, to predict incipient hypoglycemic events and to alert the user.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Pulse oximeter probe-off detector
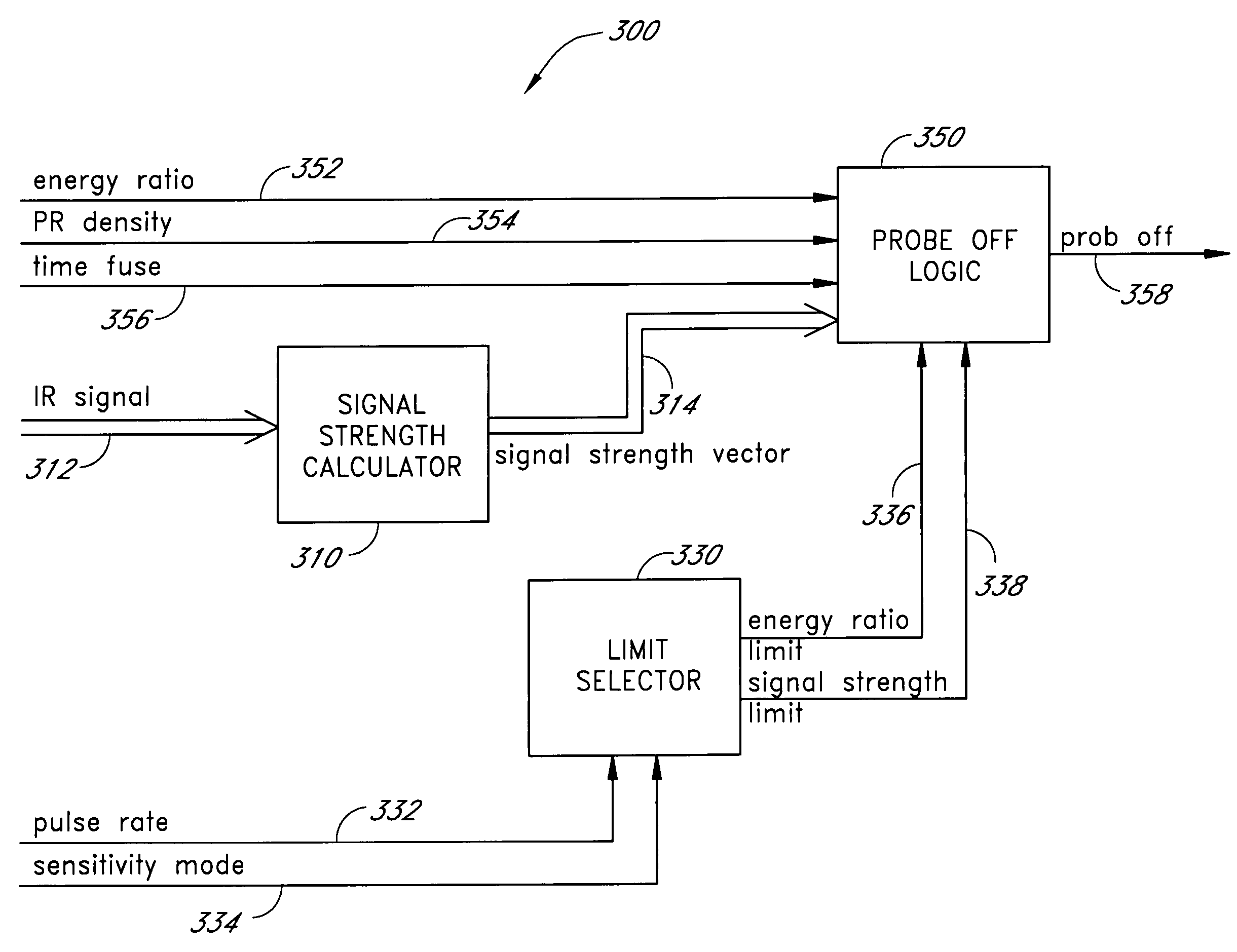
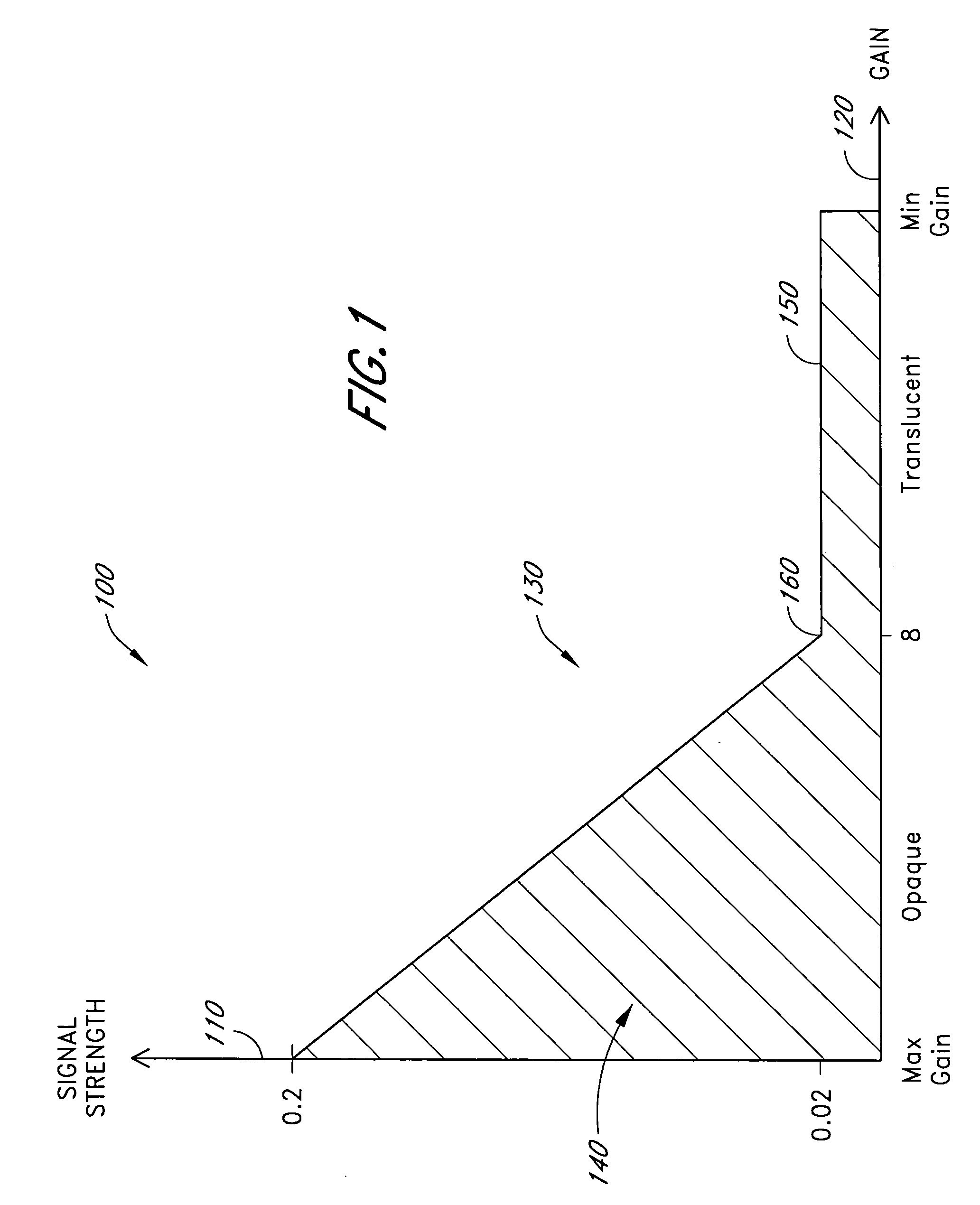
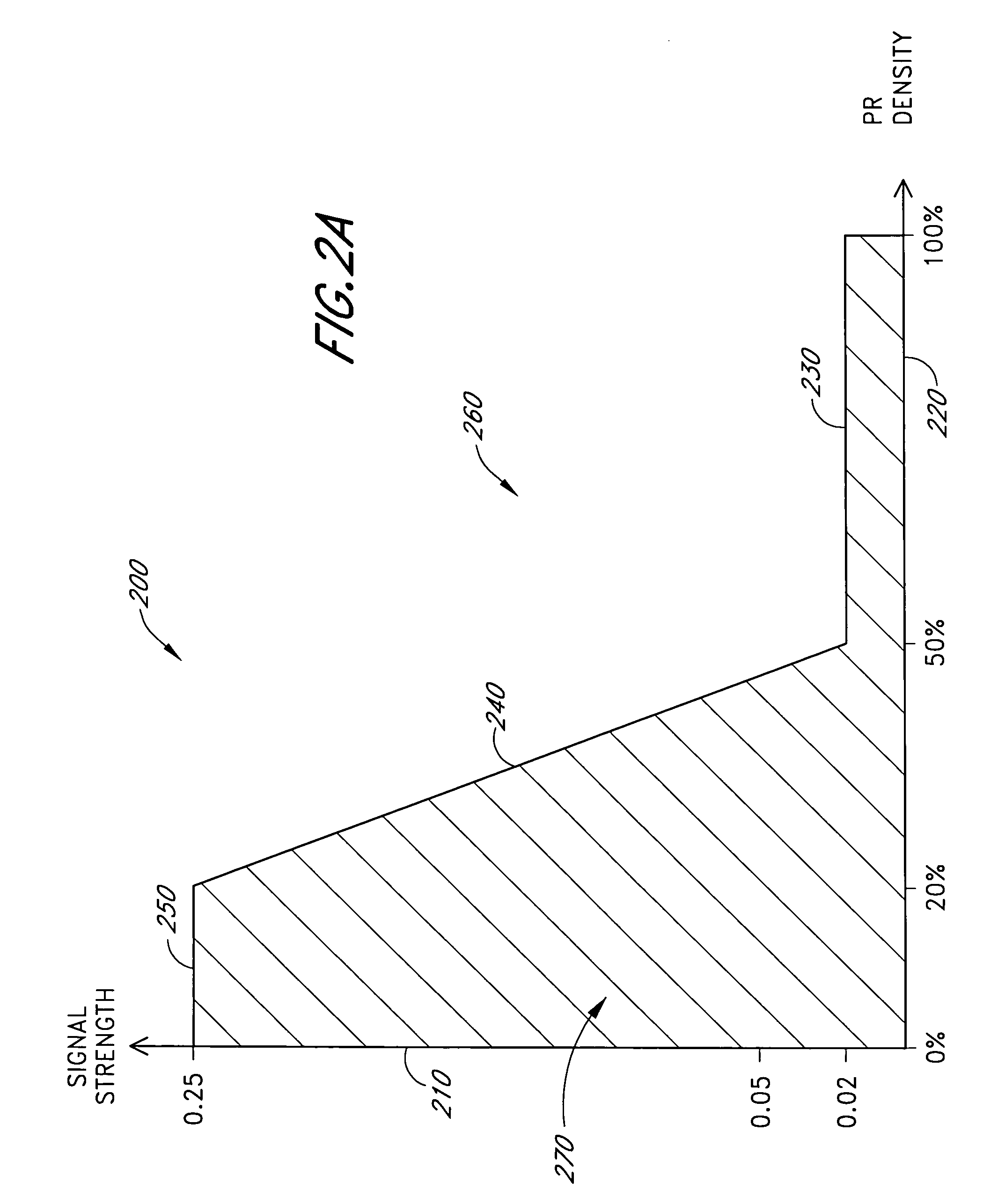
InactiveUS7471969B2Reduce probe off errorLimited abilitySensorsColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh signal intensitySignal quality
A processor provides signal quality based limits to a signal strength operating region of a pulse oximeter. These limits are superimposed on the typical gain dependent signal strength limits. If a sensor signal appears physiologically generated, the pulse oximeter is allowed to operate with minimal signal strength, maximizing low perfusion performance. If a sensor signal is potentially due to a signal induced by a dislodged sensor, signal strength requirements are raised. Thus, signal quality limitations enhance probe off detection without significantly impacting low perfusion performance. One signal quality measure used is pulse rate density, which defines the percentage of time physiologically acceptable pulses are occurring. If the detected signal contains a significant percentage of unacceptable pulses, the minimum required signal strength is raised proportionately. Another signal quality measure used in conjunction with pulse rate density is energy ratio, computed as the percentage of total energy contained in the pulse rate fundamental and associated harmonics.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Medical imaging, diagnosis, and therapy using a scanning single optical fiber system
InactiveUS6975898B2High resolutionEasy to viewEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFlexible endoscopyHigh resolution imaging
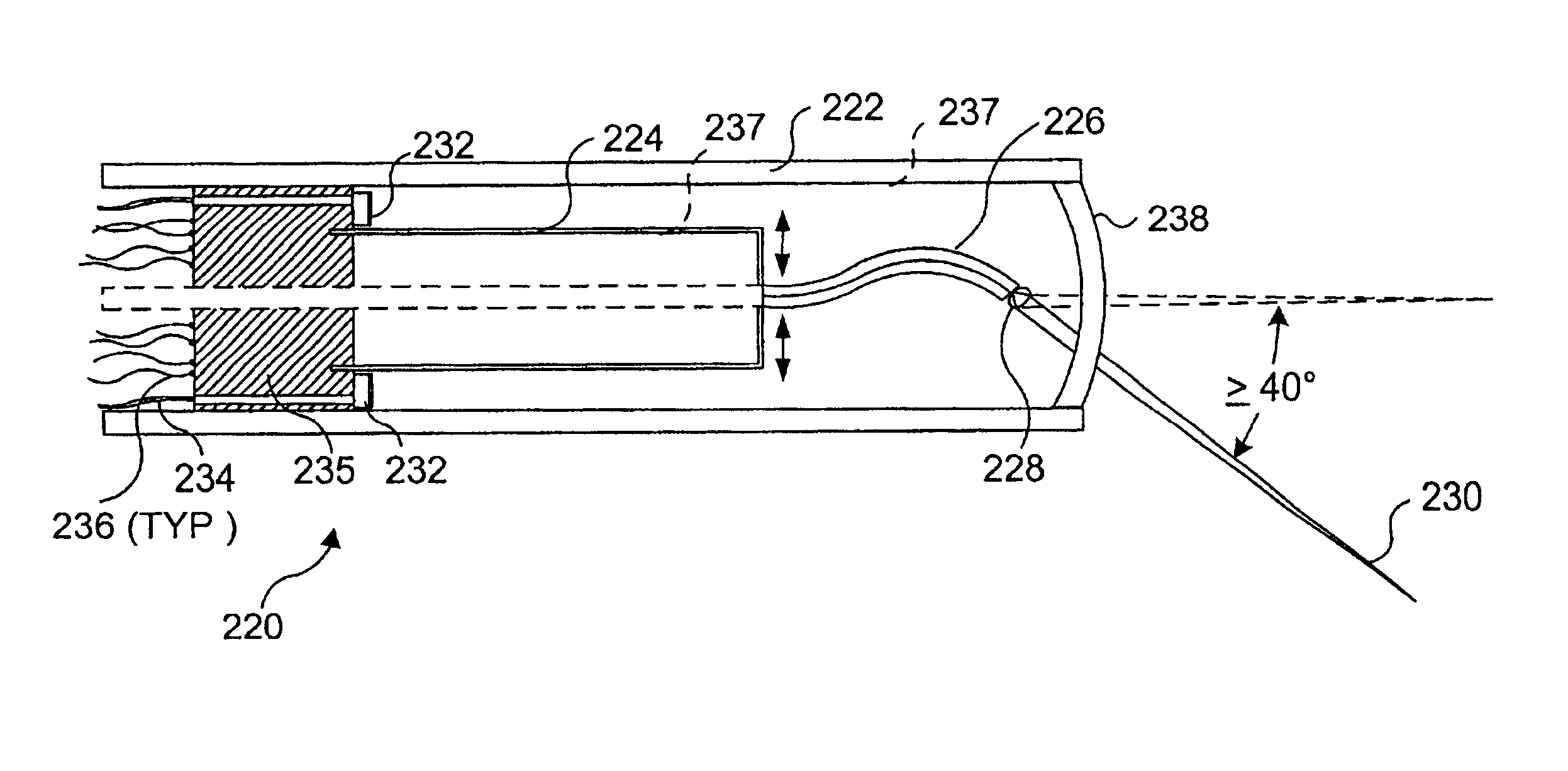
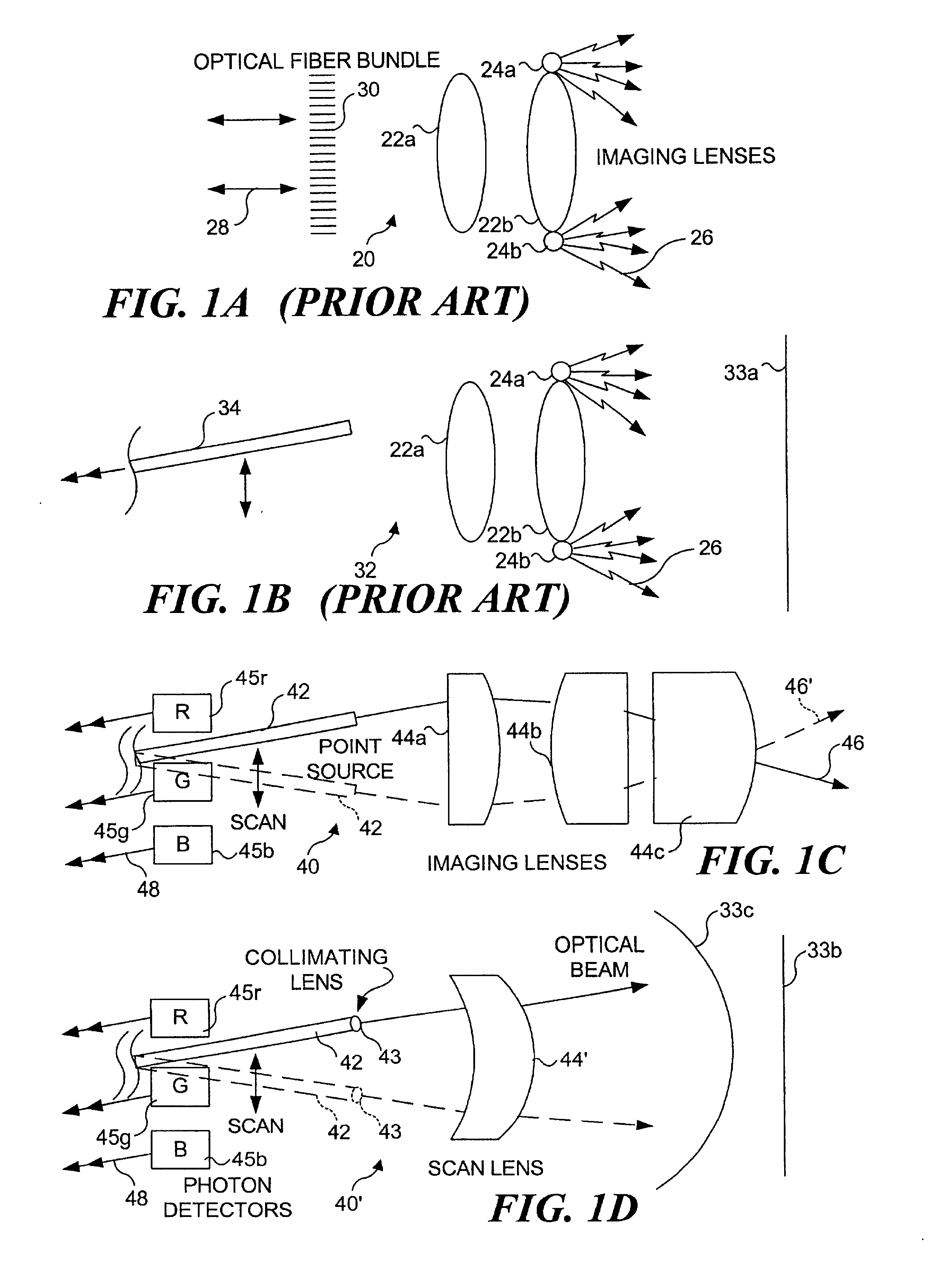
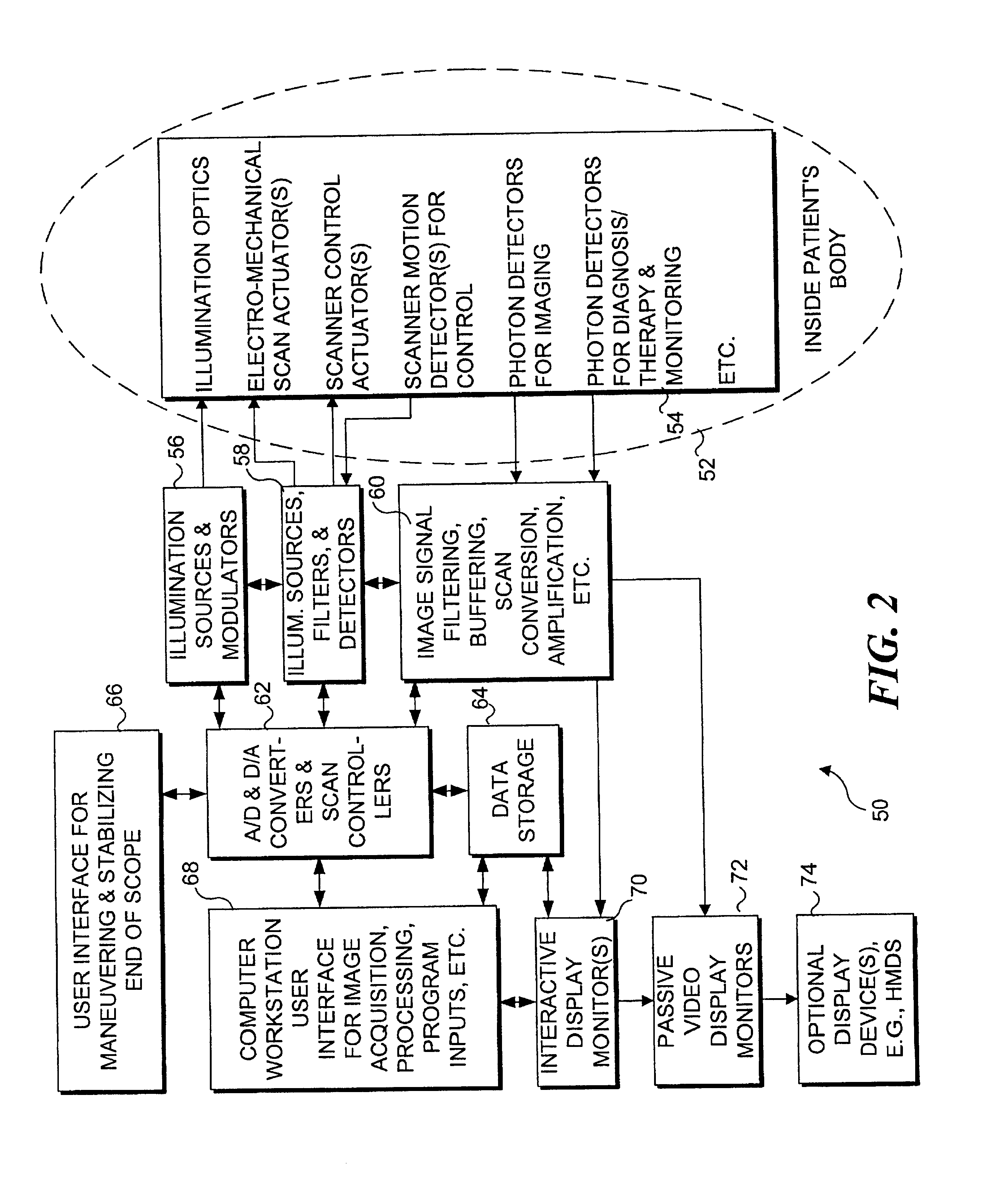
An integrated endoscopic image acquisition and therapeutic delivery system for use in minimally invasive medical procedures (MIMPs). The system uses directed and scanned optical illumination provided by a scanning optical fiber or light waveguide that is driven by a piezoelectric or other electromechanical actuator included at a distal end of an integrated imaging and diagnostic / therapeutic instrument. The directed illumination provides high resolution imaging, at a wide field of view (FOV), and in full color that matches or excels the images produced by conventional flexible endoscopes. When using scanned optical illumination, the size and number of the photon detectors do not limit the resolution and number of pixels of the resulting image. Additional features include enhancement of topographical features, stereoscopic viewing, and accurate measurement of feature sizes of a region of interest in a patient's body that facilitate providing diagnosis, monitoring, and / or therapy with the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Microfluidic system with integrated permeable membrane
InactiveUS20050266582A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical reactionCompound (substance)
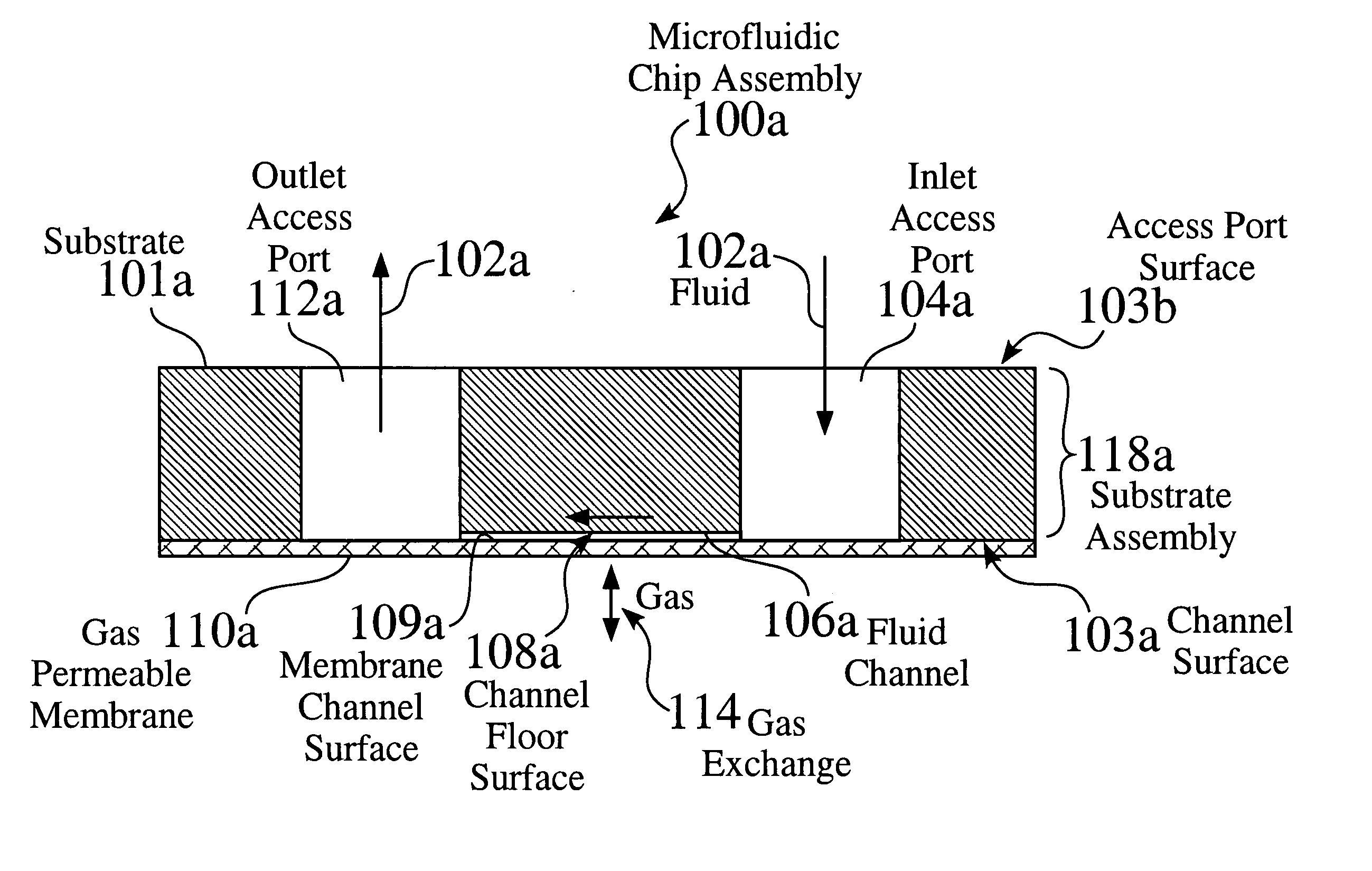
A microfluidic system for performing chemical reactions or biochemical, biological, or chemical assays utilizing a microfabricated device or “chip.” The system may include, among others, an integrated membrane fabricated from a chemically inert material whose permeability for gases, liquids, cells, and specific molecules, etc. can be selected for optimum results in a desired application.
Owner:CYTODISCOVERY
Method for determining concentration of an analyte in a test strip
InactiveUS6541266B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTarget analysisAnalyte
The present invention provides a method of measuring an analyte, such as glucose in a fluid sample, such as whole blood, by a reflectance reading device. The method includes making periodic intermediate calculations of analyte level and dynamically ascertaining when an analytical reaction has reached an end point. Once stable, the process stops making periodic calculations and reports the final, actual glucose concentration. According to an exemplary embodiment, the method is performed by a reflectance photometer using an analytical test strip containing reagents that react with an analyte of interest in the test fluid. The end point is determined by calculating an intermediate analyte level of the testing element at predetermined intervals and calculating a ratio value corresponding to the (n)th measurement to an (n-5)th measurement. When two consecutive ratio values are less than or equal to a predetermined value, the end point is deemed reached and the final analyte level ascertained.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
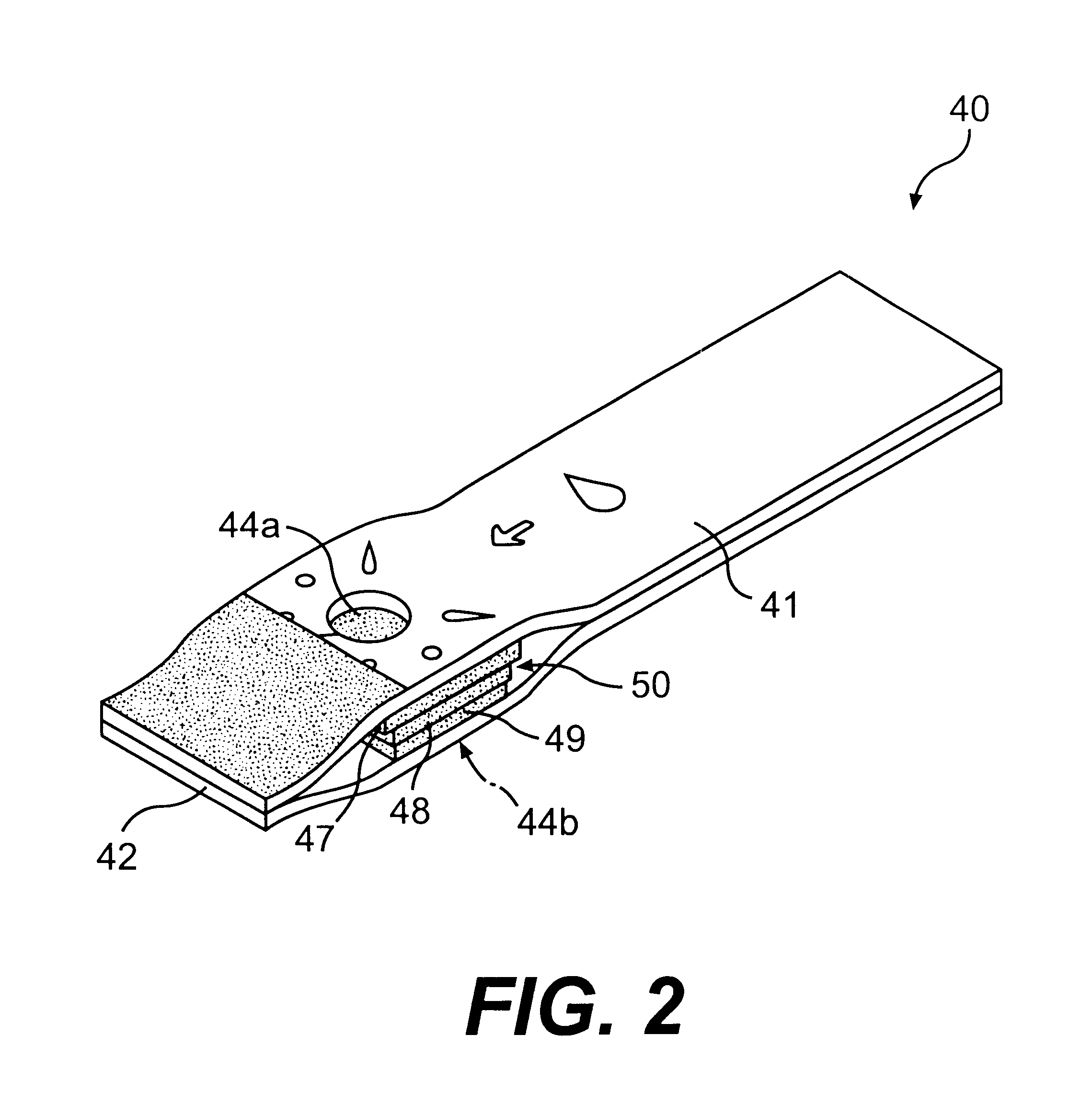
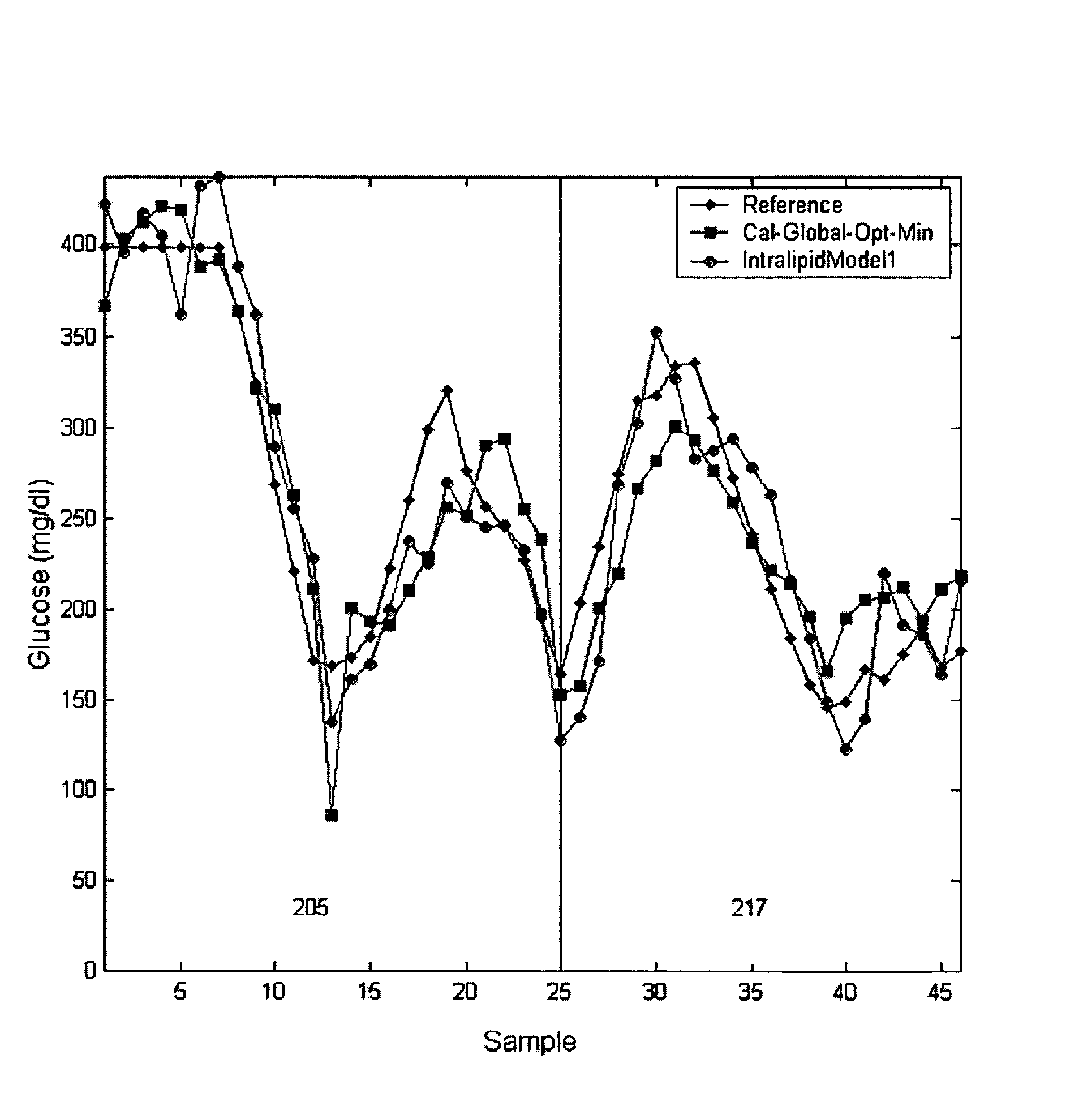
Method of adapting in-vitro models to aid in noninvasive glucose determination
InactiveUS7317938B2Easy to controlStrict controlDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsConcentrations glucoseNon invasive
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
InactiveUS6989891B2Withdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSpectral bandsCell wall
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Apparatus and method for treating a substrate with UV radiation using primary and secondary reflectors
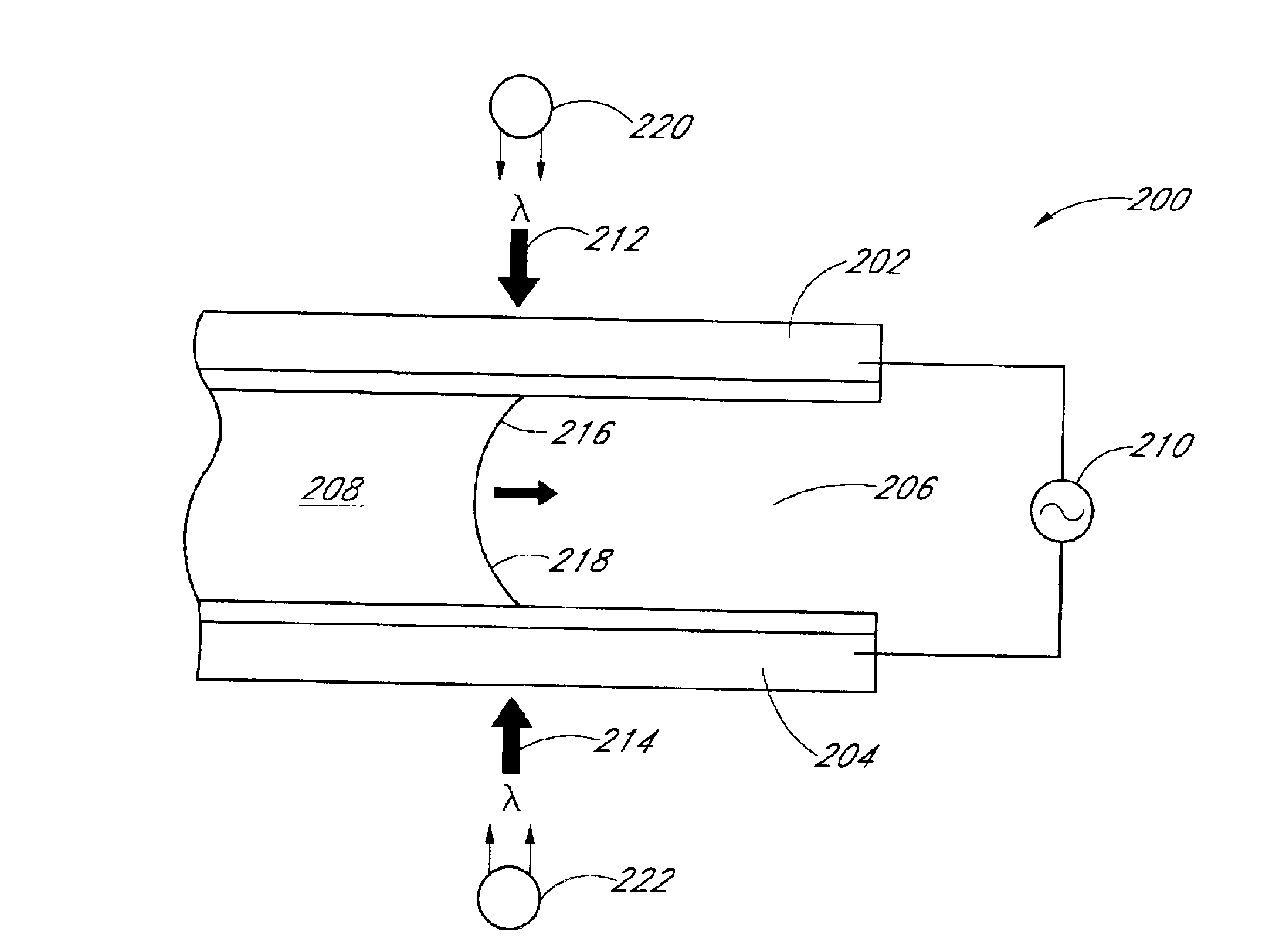
ActiveUS7566891B2Reduce light lossRadiation pyrometryPretreated surfacesProcess regionUltraviolet radiation
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to an ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber for curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and to methods of curing dielectric materials using UV radiation. A substrate processing tool according to one embodiment comprises a body defining a substrate processing region; a substrate support adapted to support a substrate within the substrate processing region; an ultraviolet radiation lamp spaced apart from the substrate support, the lamp configured to transmit ultraviolet radiation to a substrate positioned on the substrate support; and a motor operatively coupled to rotate at least one of the ultraviolet radiation lamp or substrate support at least 180 degrees relative to each other. The substrate processing tool may further comprise one or more reflectors adapted to generate a flood pattern of ultraviolet radiation over the substrate that has complementary high and low intensity areas which combine to generate a substantially uniform irradiance pattern if rotated. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Reading devices and assay devices for use therewith
InactiveUS6235241B1Accurate placementFacilitate and control formationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCombined useEngineering
An assay result reader, for use in conjunction with an assay device comprising a porous liquid-permeable carrier in the form of a strip or sheet through the thickness of which electromagnetic radiation is transmissible, the carrier including a detection zone in which an assay result is revealed by specific binding of a detectable material directly or indirectly to a binding agent immobilized in the detection zone, detection of the detectable material being effected by determining the extent to which electromagnetic radiation transmitted through the thickness of said carrier is attenuated by the presence of the detectable material bound in the detection zone.
Owner:INVERNESS SWITZERLAND GMBH
Methods of amplifying and sequencing nucleic acids
An apparatus and method for performing rapid DNA sequencing, such as genomic sequencing, is provided herein. The method includes the steps of preparing a sample DNA for genomic sequencing, amplifying the prepared DNA in a representative manner, and performing multiple sequencing reaction on the amplified DNA with only one primer hybridization step.
Owner:454 LIFE SCIENCES CORP
Optical-based sensing devices
InactiveUS6711423B2Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSurgeryAnalyteFluorescence
An optical-based sensor for detecting the presence or amount of an analyte using both indicator and reference channels. The sensor has a sensor body with a source of radiation embedded therein. Radiation emitted by the source interacts with indicator membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. At least one optical characteristic of these indicator molecules varies with analyte concentration. For example, the level of fluorescence of fluorescent indicator molecules or the amount of light absorbed by light-absorbing indicator molecules can vary as a function of analyte concentration. In addition, radiation emitted by the source also interacts with reference membrane indicator molecules proximate the surface of the body. Radiation (e.g., light) emitted or reflected by these indicator molecules enters and is internally reflected in the sensor body. Photosensitive elements within the sensor body generate both indicator channel and reference channel signals to provide an accurate indication of the concentration of the analyte. Preferred embodiments are totally self-contained and are sized and shaped for use in vivo in a human being. Such embodiments preferably include a power source, e.g. an inductor, which powers the source of radiation using external means, as well as a transmitter, e.g. an inductor, to transmit to external pickup means the signal representing the level of analyte.
Owner:SENSEONICS INC
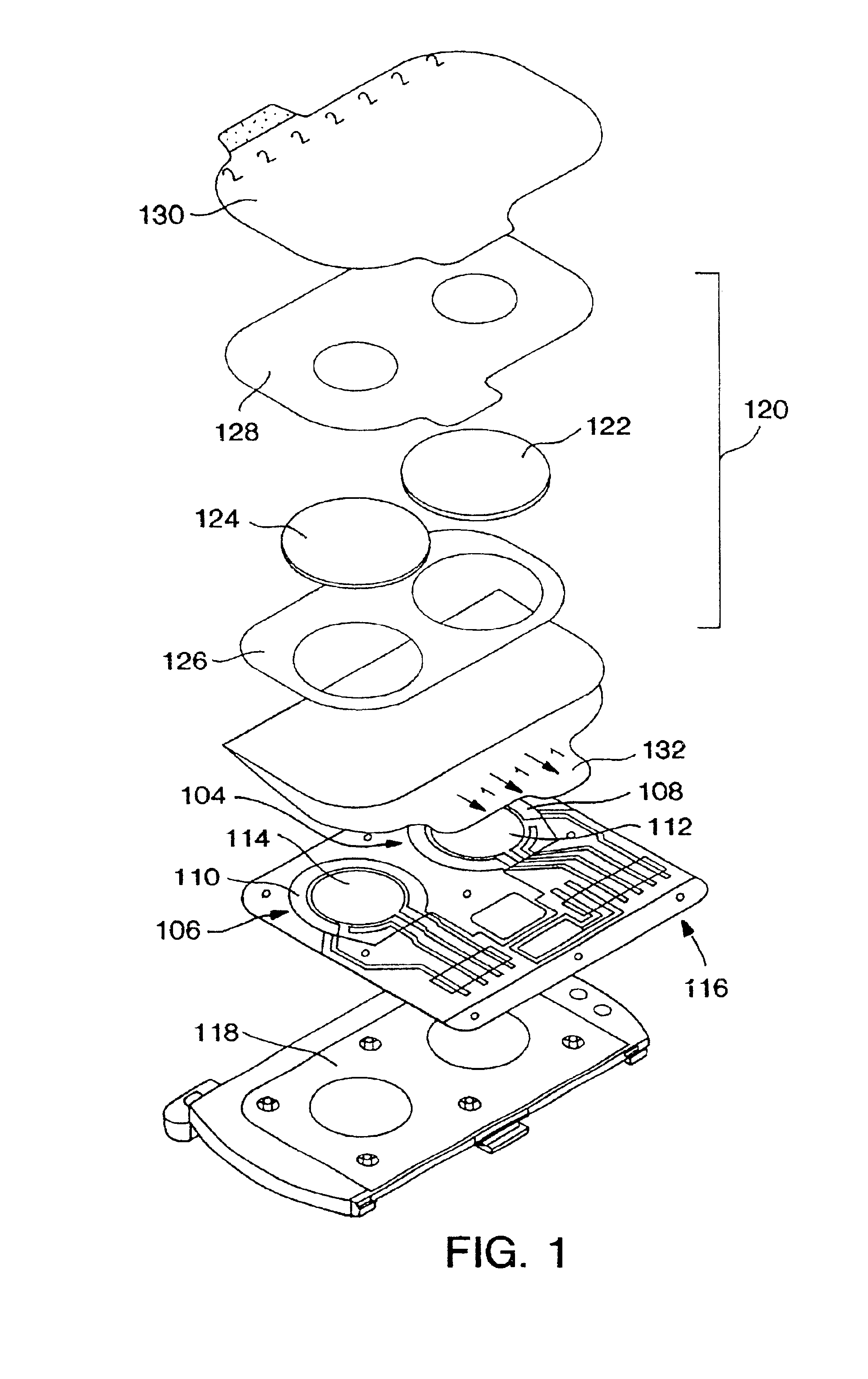
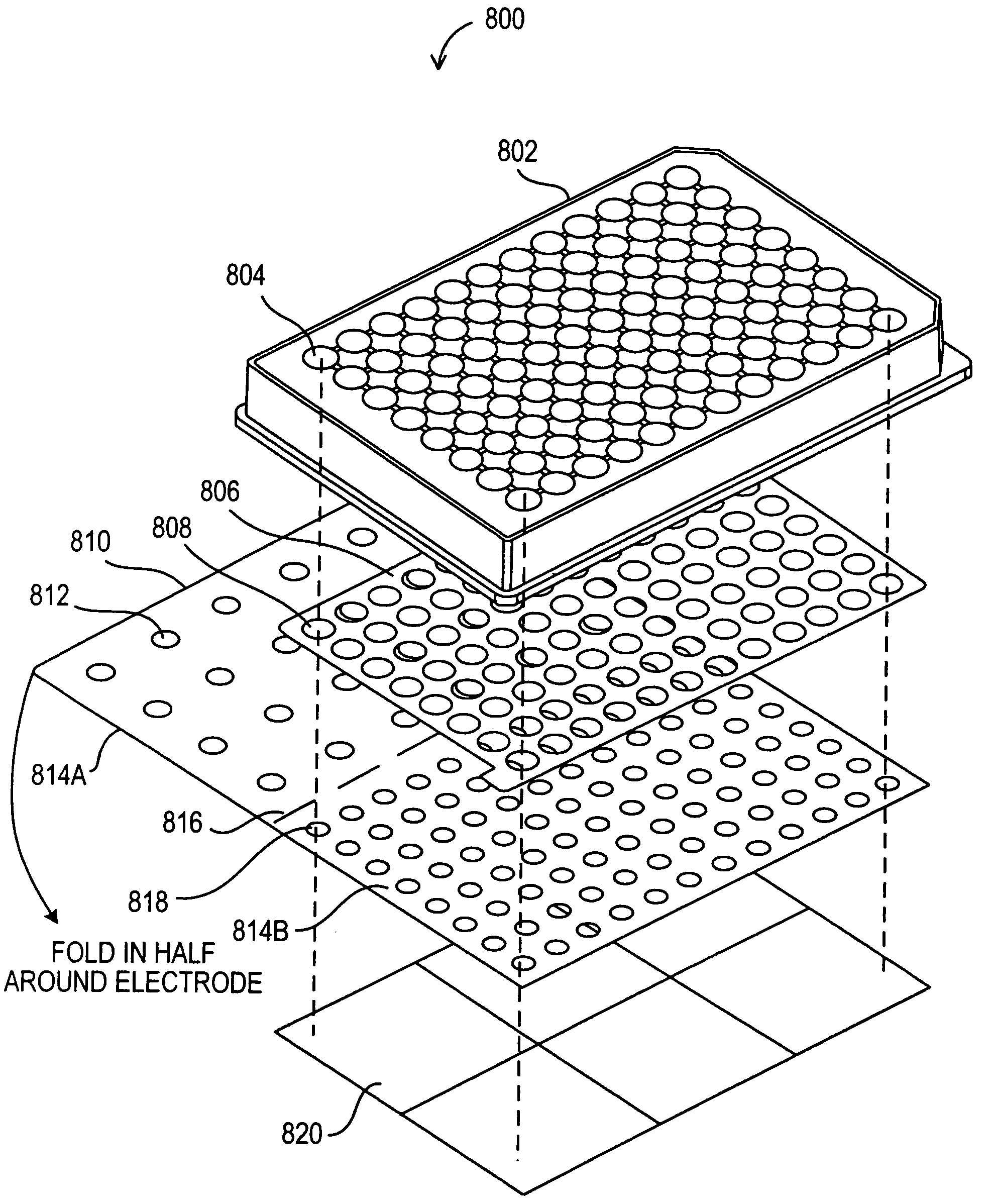
Modular assay plates, reader systems and methods for test measurements
ActiveUS20050142033A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease assayAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
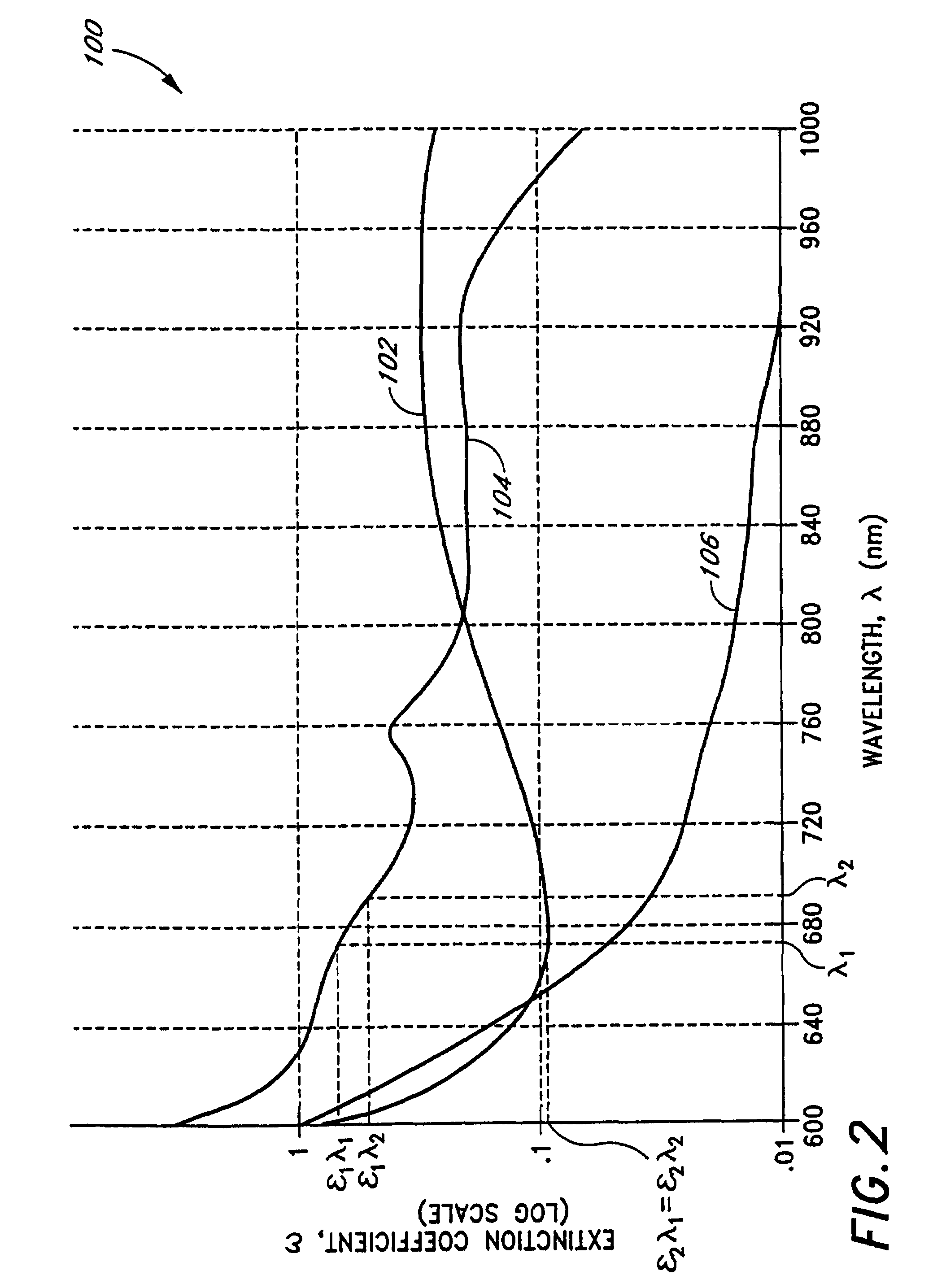
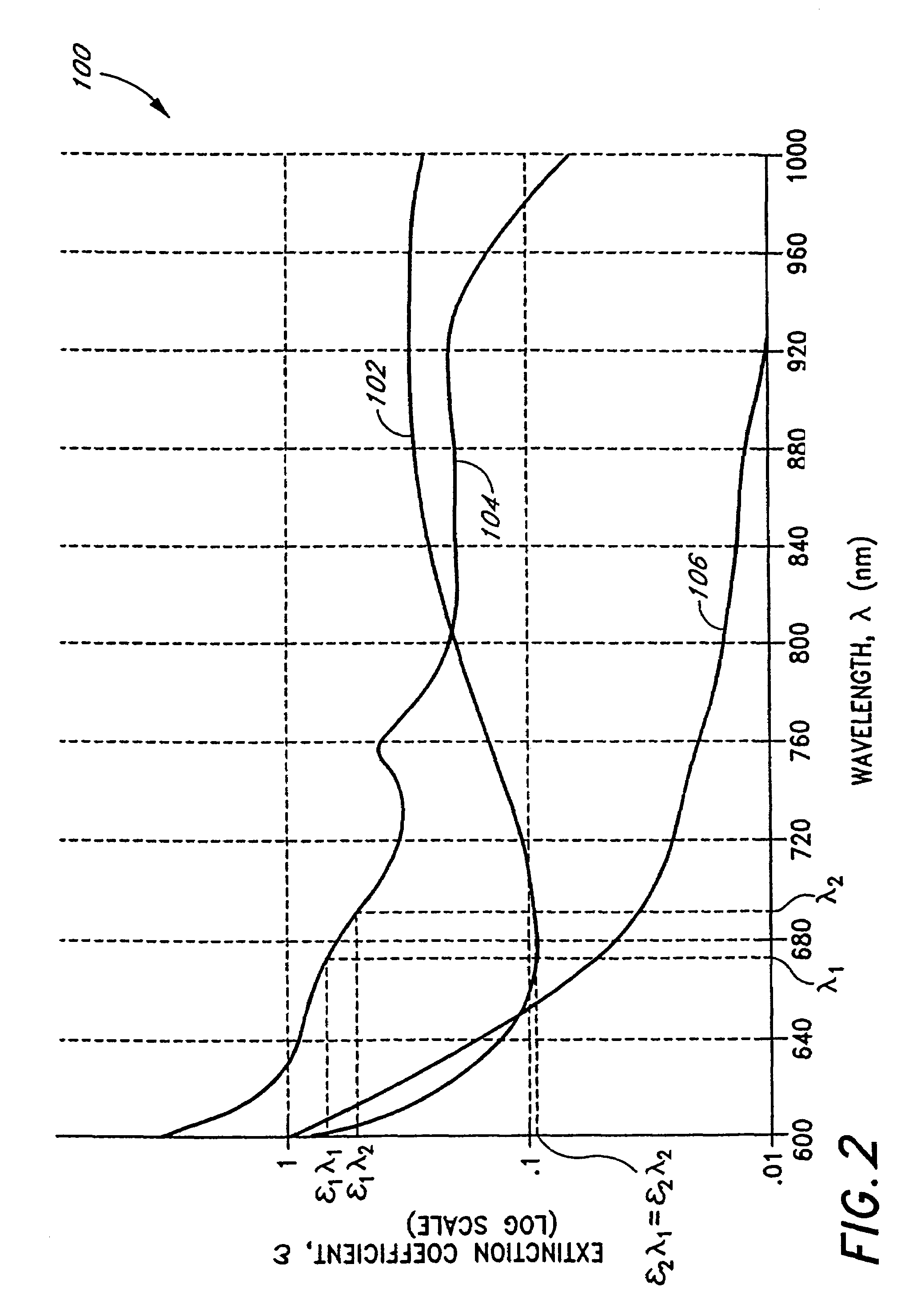
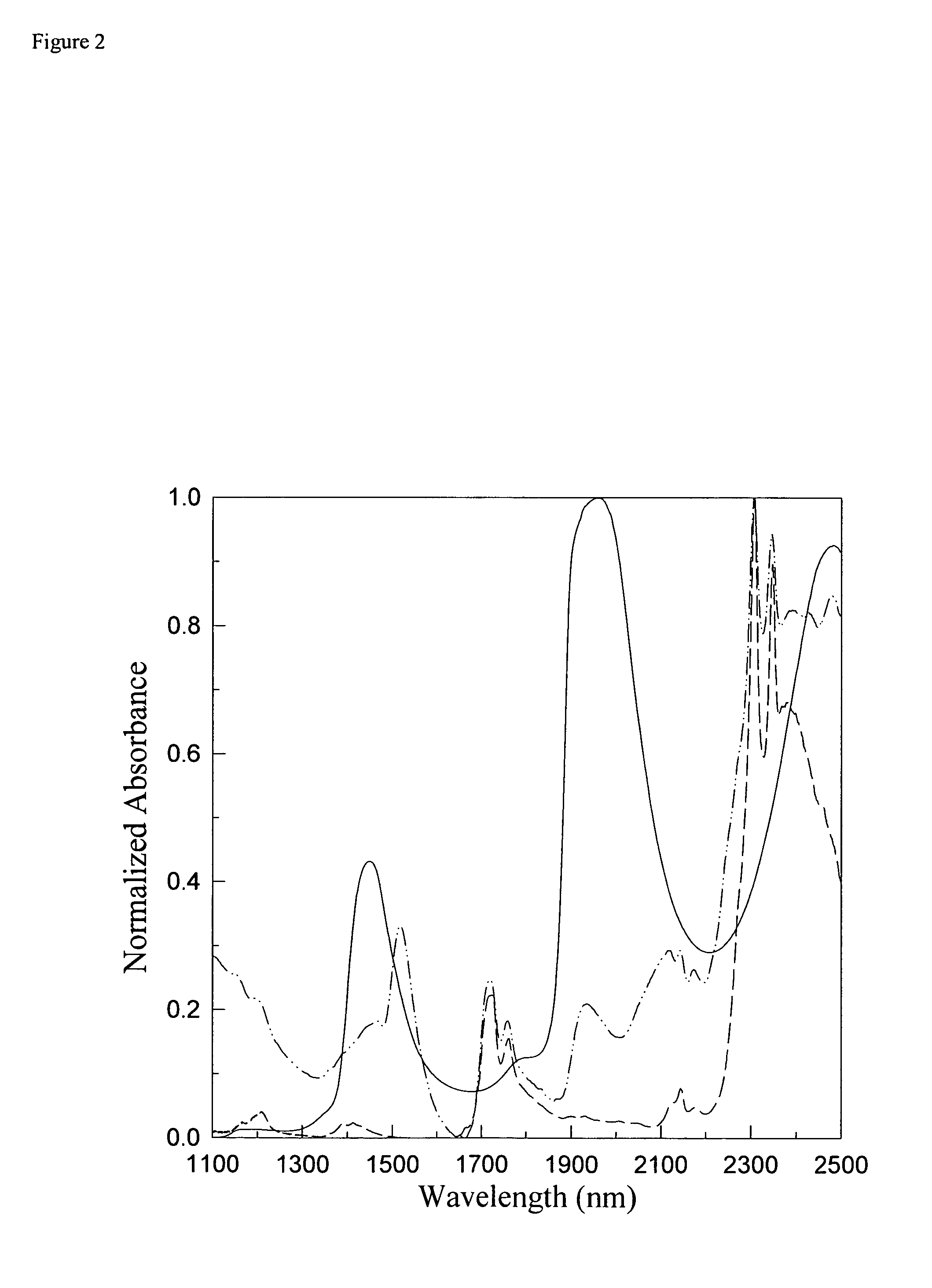
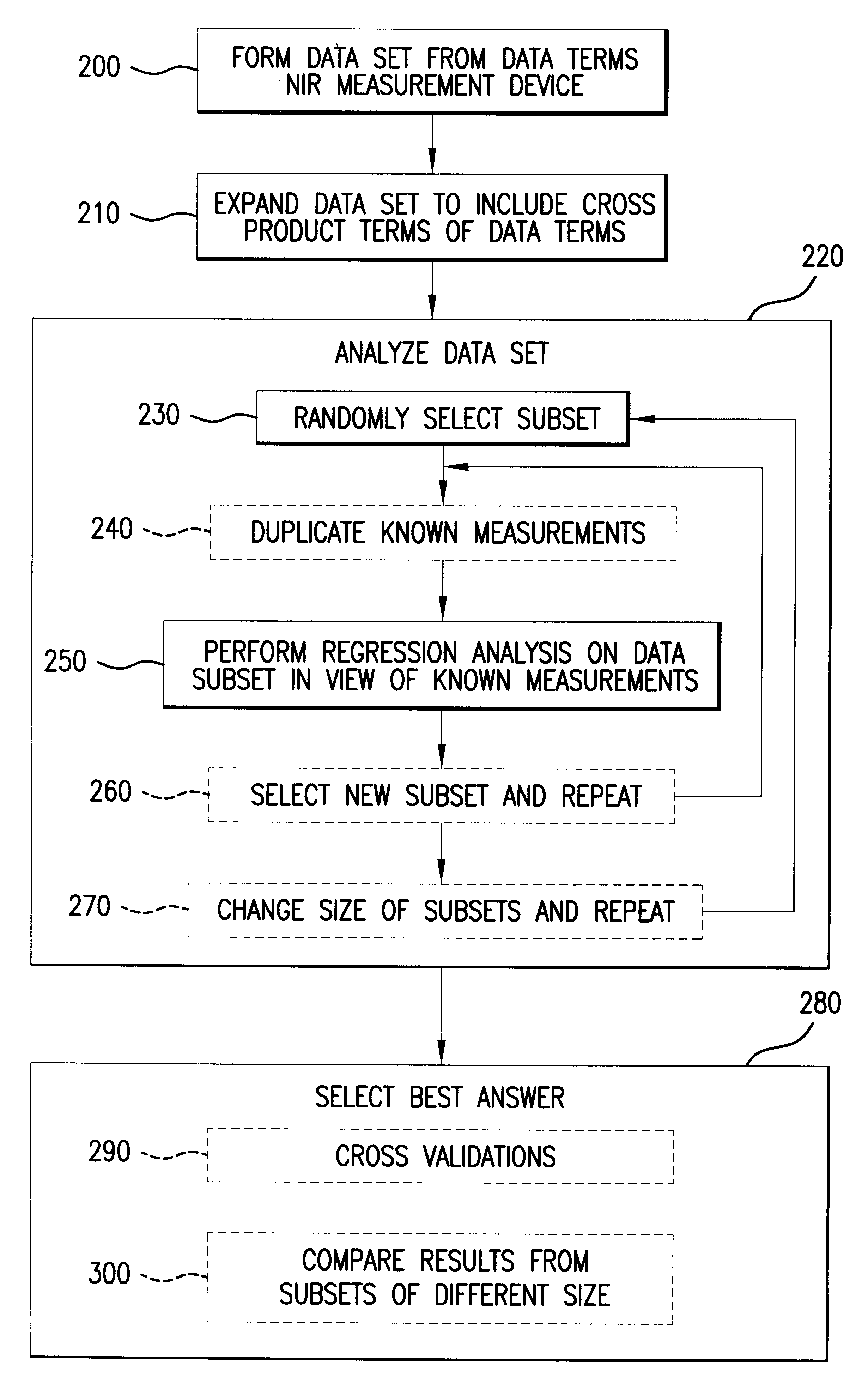
Calibration of near infrared quantitative measurement device using optical measurement cross-products
In a method to improve the calibration of a non-invasive, near infrared (NIR) measurement device, a plurality of data terms is formed for the NIR measurement device. Then the codependence of the data terms is evaluated by forming cross-products terms using the data terms. Next, sets of prespecified sizes are randomly formed from the data terms and the cross-product terms. Each of these sets of terms is evaluated by testing the ability of the set to predict a set of accurate measurements using regression analysis. The method then selects one of the sets based on preselected criteria and uses the selected set to calibrate the NIR measurement device.
Owner:FUTREX
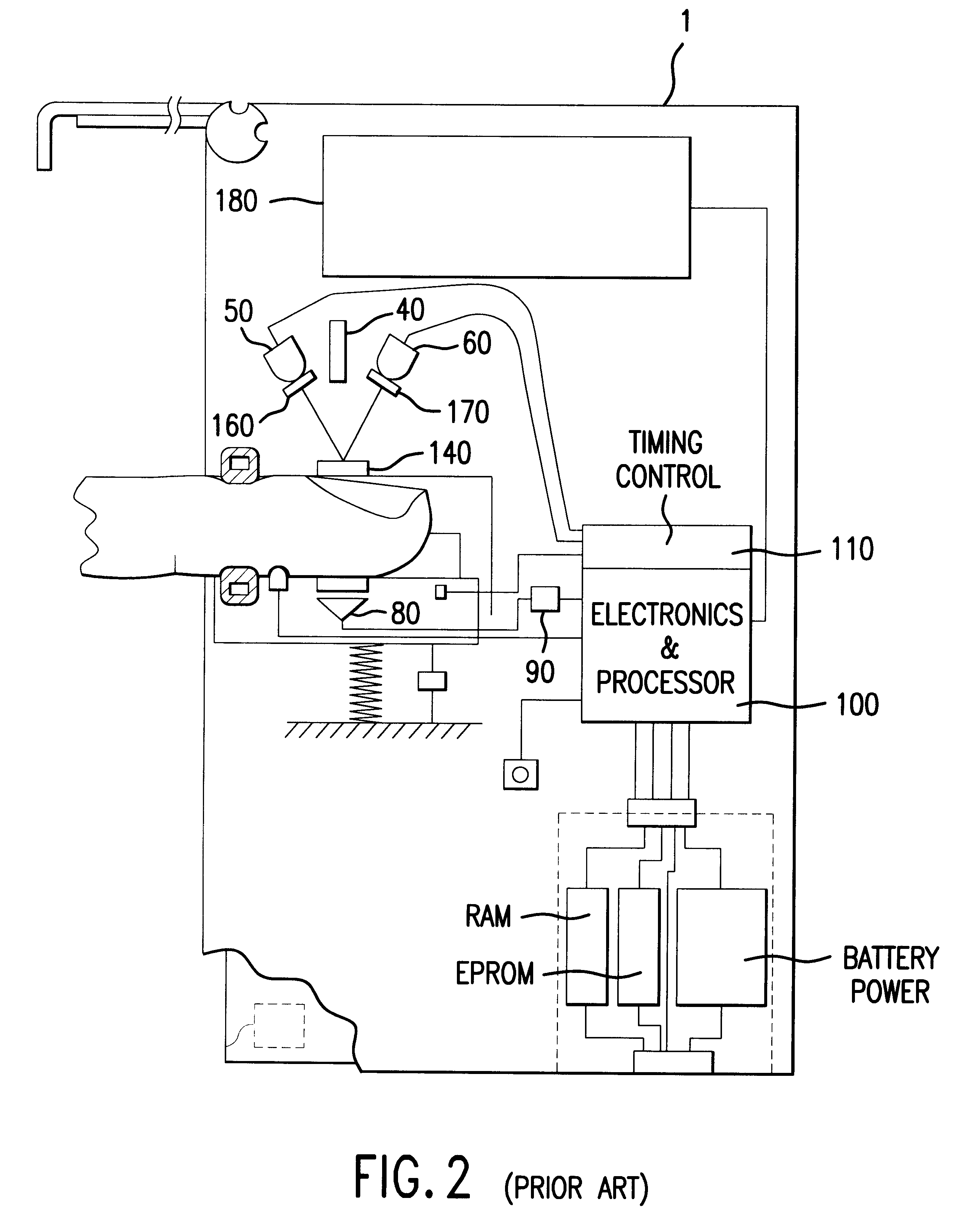
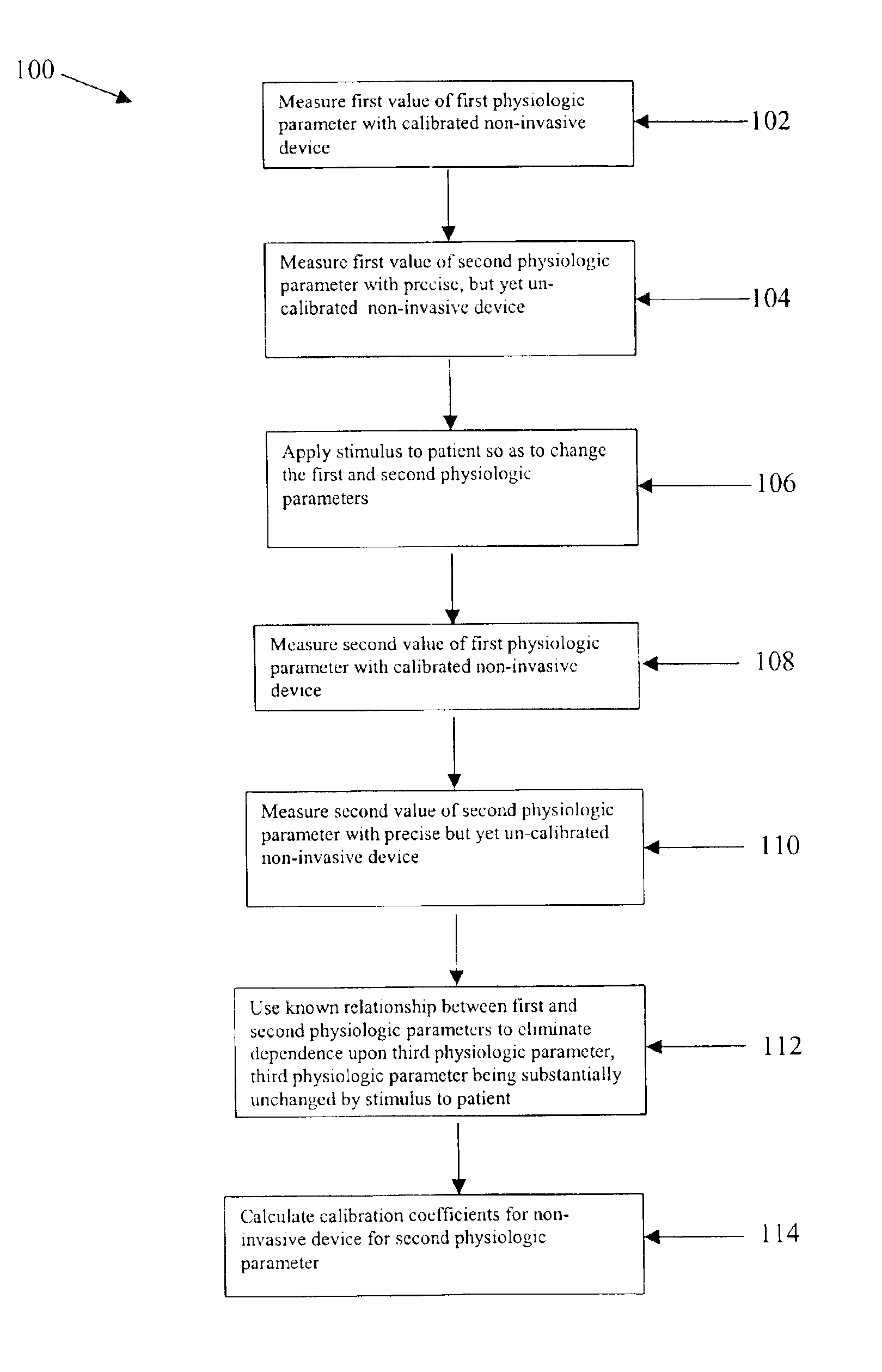
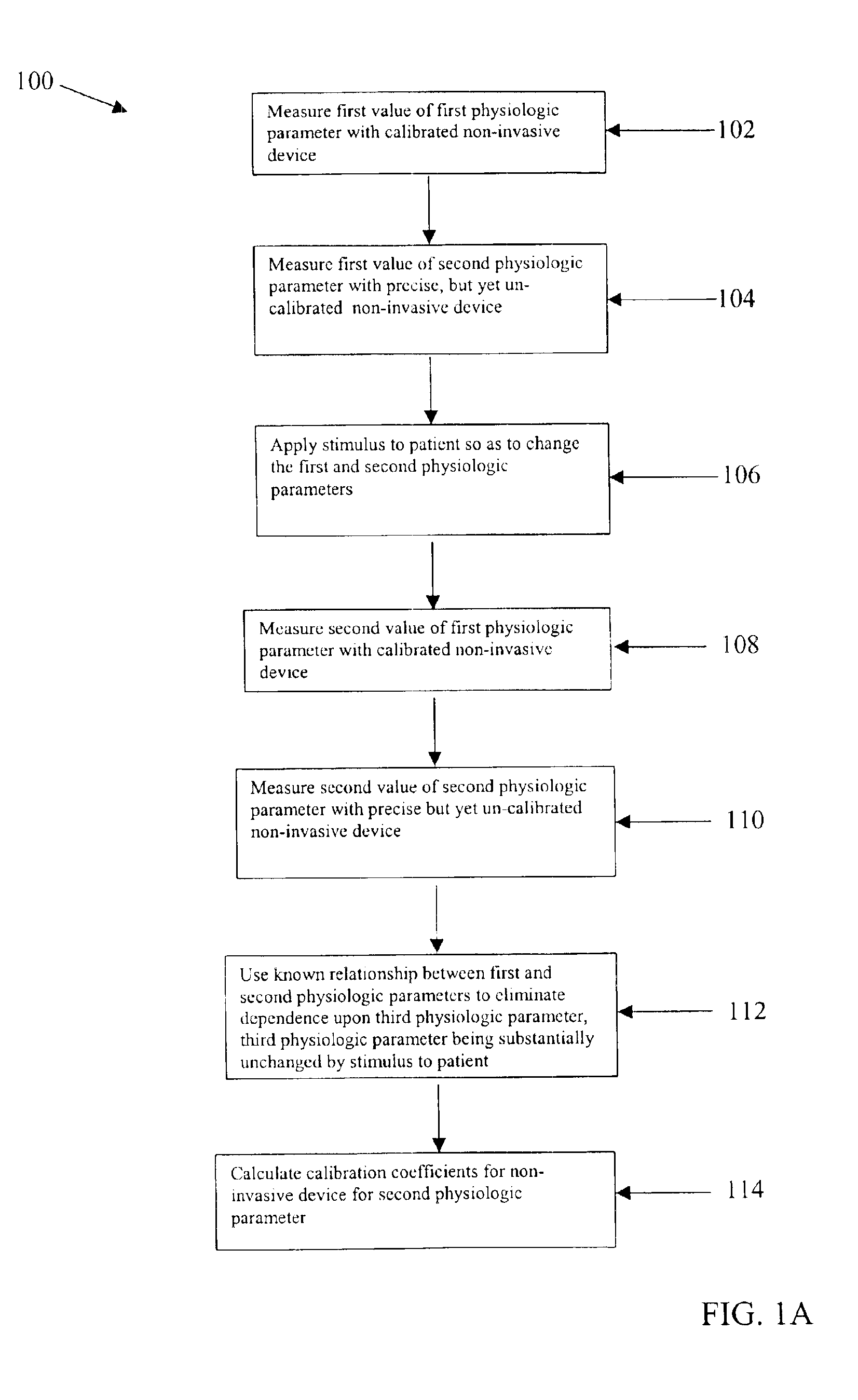
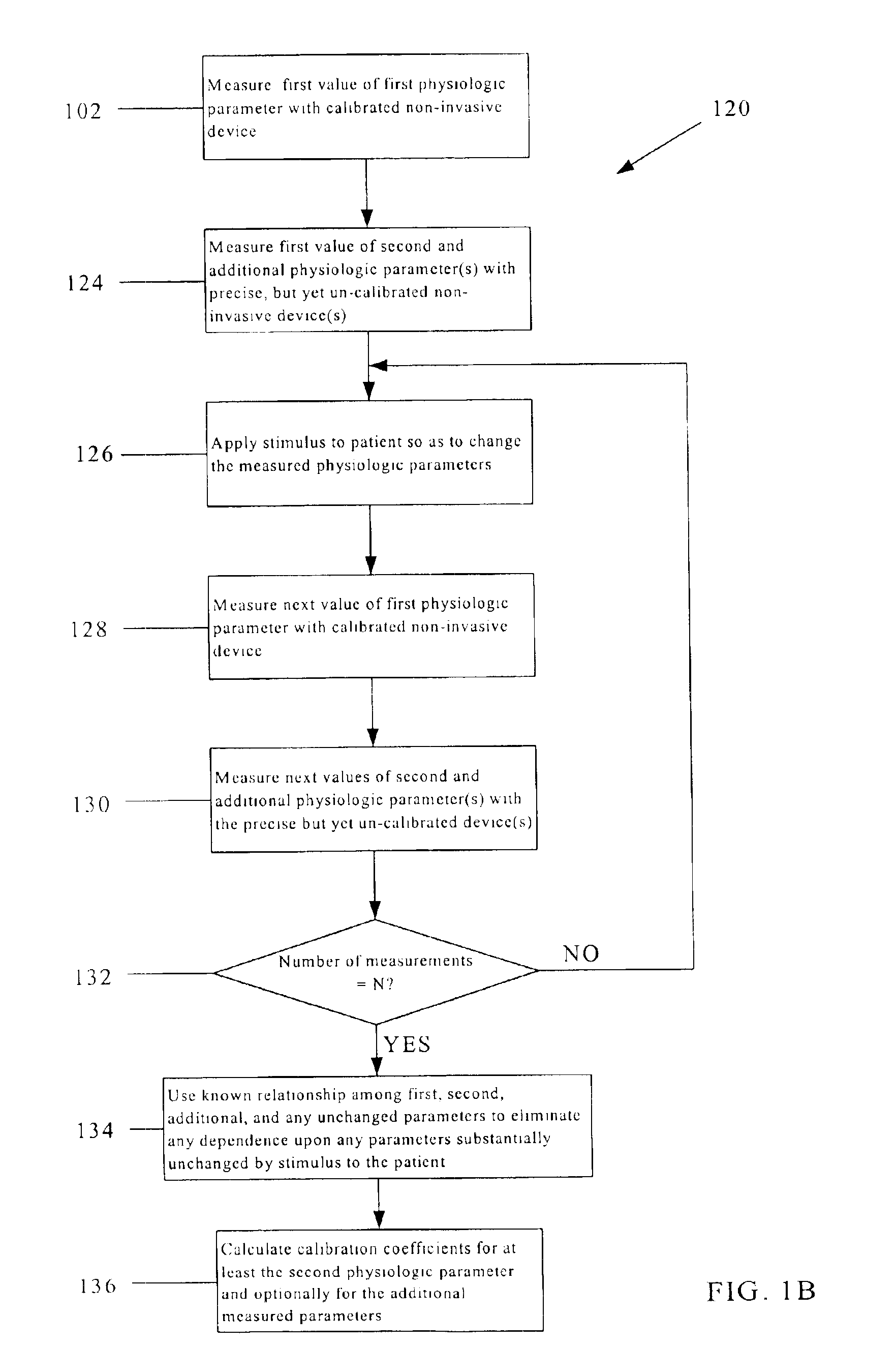
Calibration technique for non-invasive medical devices
There is a need for a non-invasive method of calibrating medical devices at the point of care, where the calibration is performed without the removal of blood or bodily fluids. The invention is directed to an approach for calibrating a first non-invasive sensor in which the tissue being measured is modulated in some way so as to after the value of the parameter being measured by the first optical sensor. A second sensor detects another parameter that also changes with the modulation. The second sensor is absolutely calibrated. Where there is a known relationship between the first and second parameters, a calibration may be derived for the first sensor. Such a technique is applicable to calibrating non-invasive sensors for monitoring a wide variety of physiologic parameters including, inter alia, glucose, blood gases, blood electrolytes and blood pH.
Owner:OPTICAL SENSORS
Device and method for in vitro determination of analyte concentrations within body fluids
A reagentless whole-blood analyte detection system that is capable of being deployed near a patient has a source capable of emitting a beam of radiation that includes a spectral band. The whole-blood system also has a detector in an optical path of the beam. The whole-blood system also has a housing that is configured to house the source and the detector. The whole-blood system also has a sample element that is situated in the optical path of the beam. The sample element has a sample cell and a sample cell wall that does not eliminate transmittance of the beam of radiation in the spectral band.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
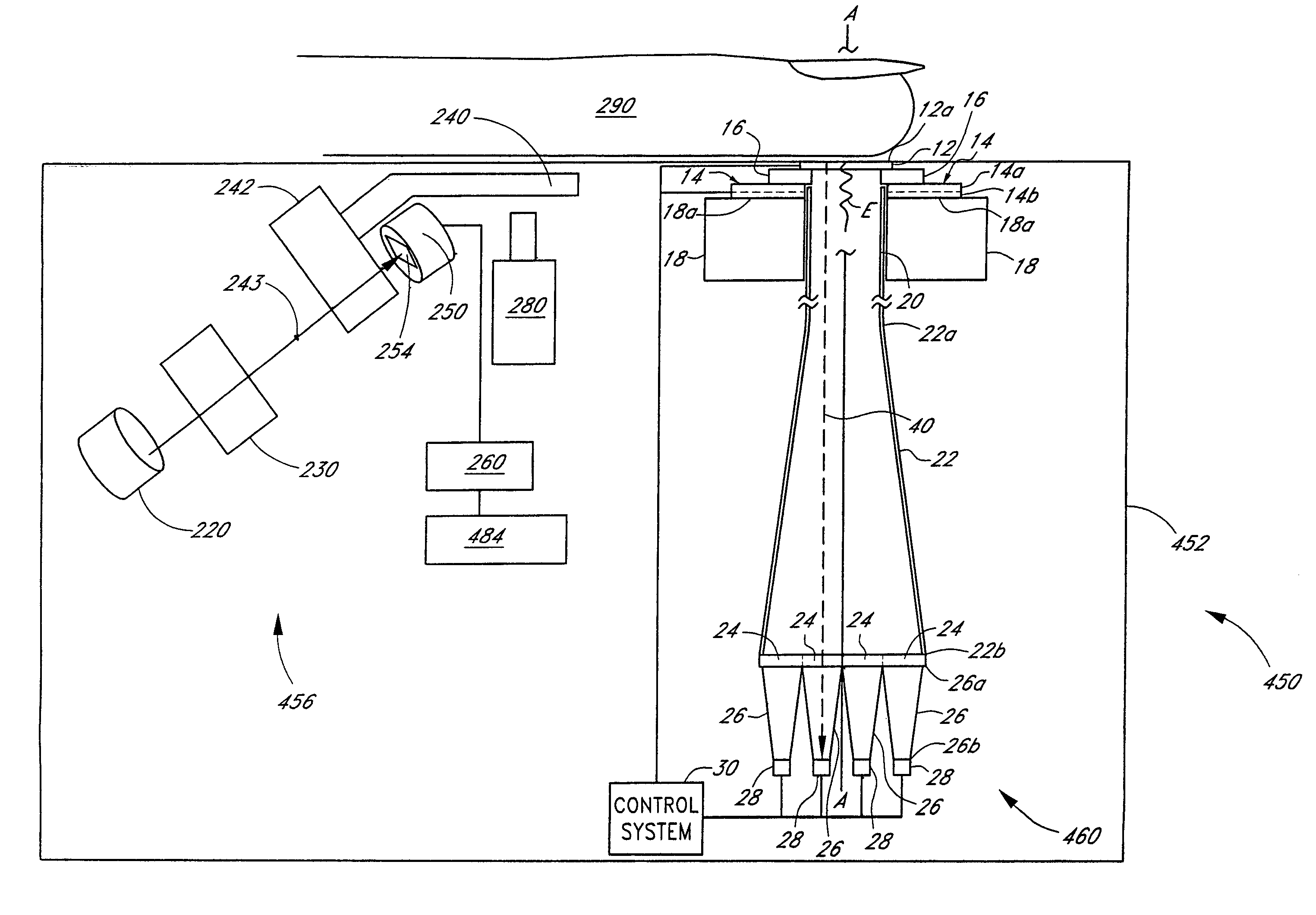
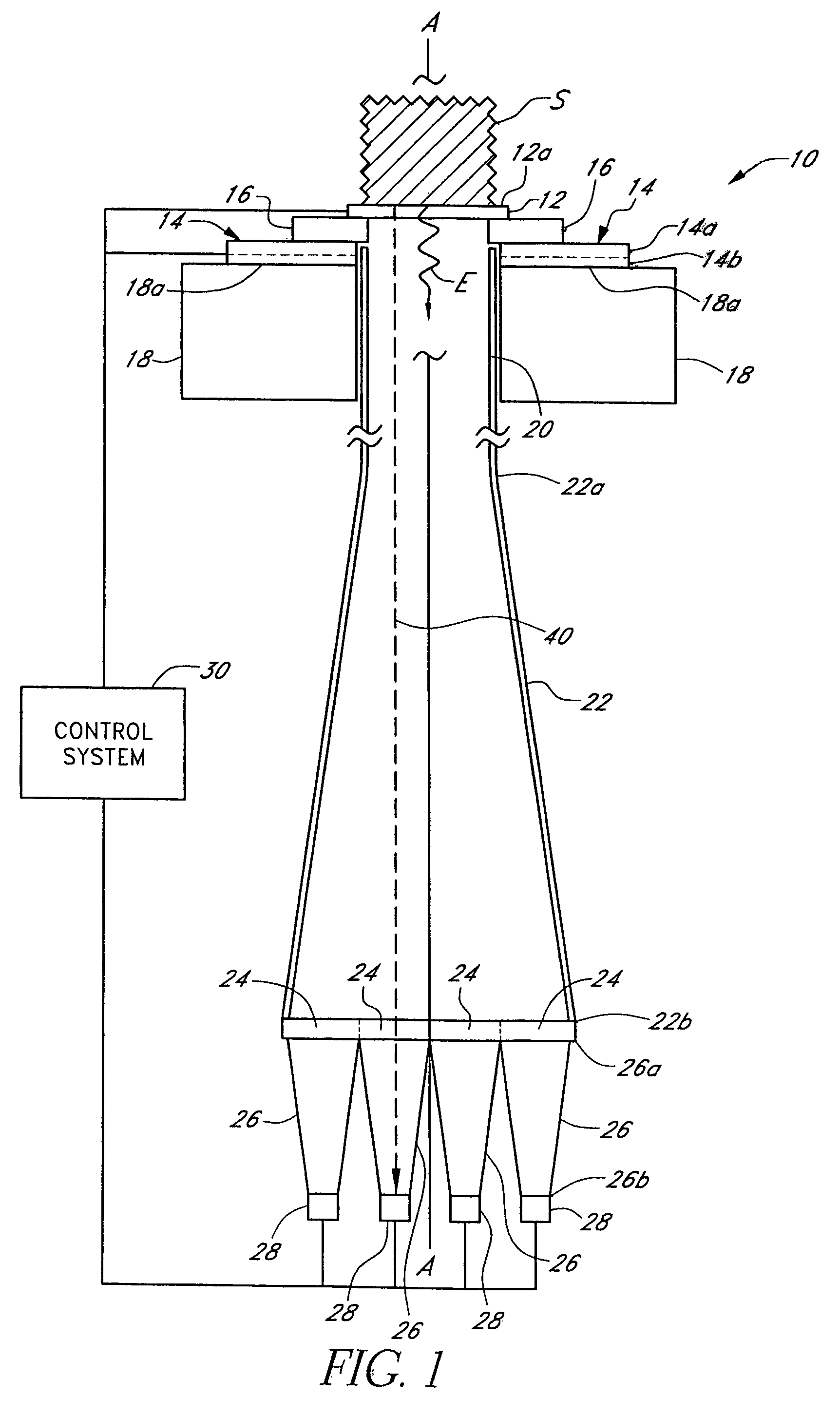
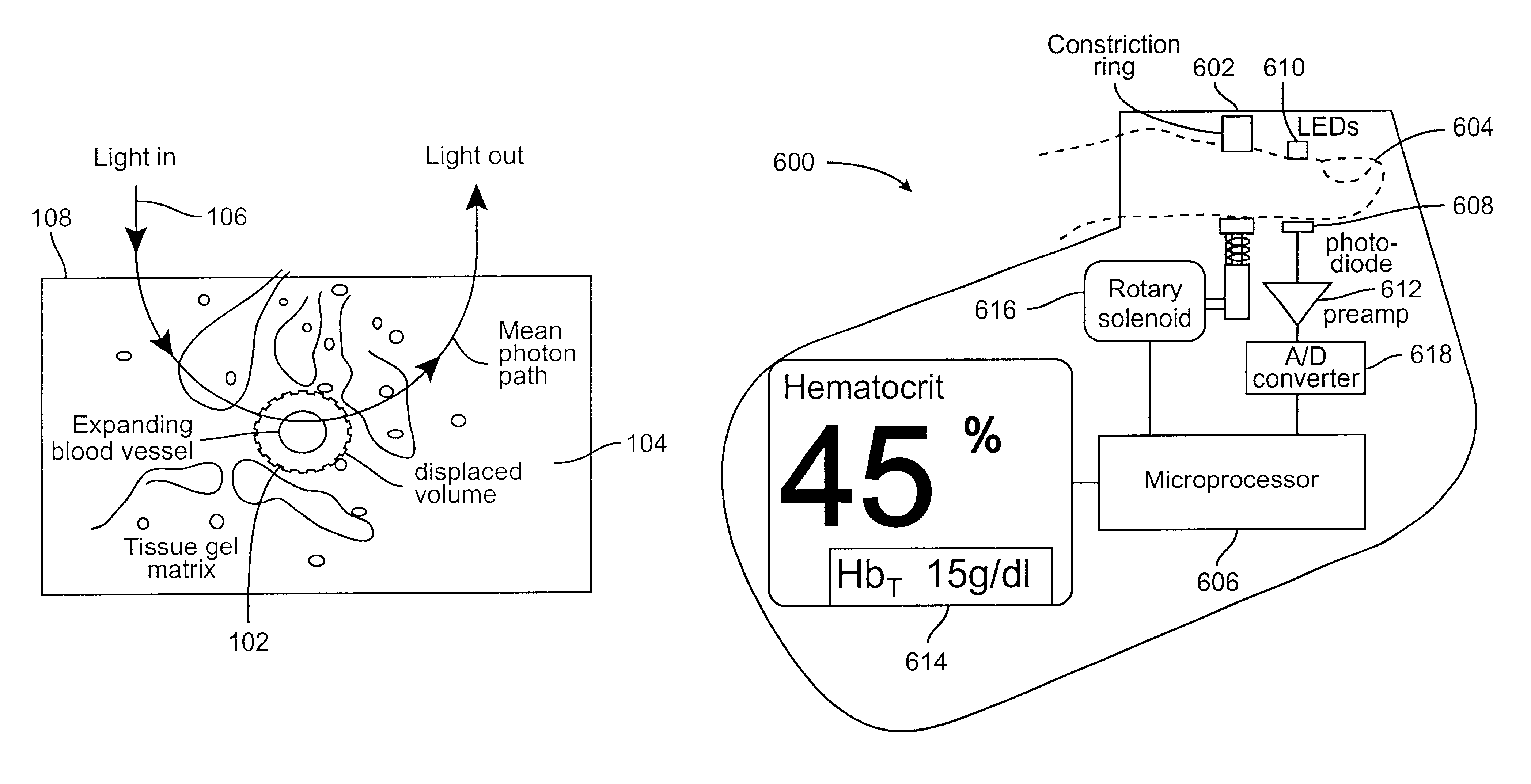
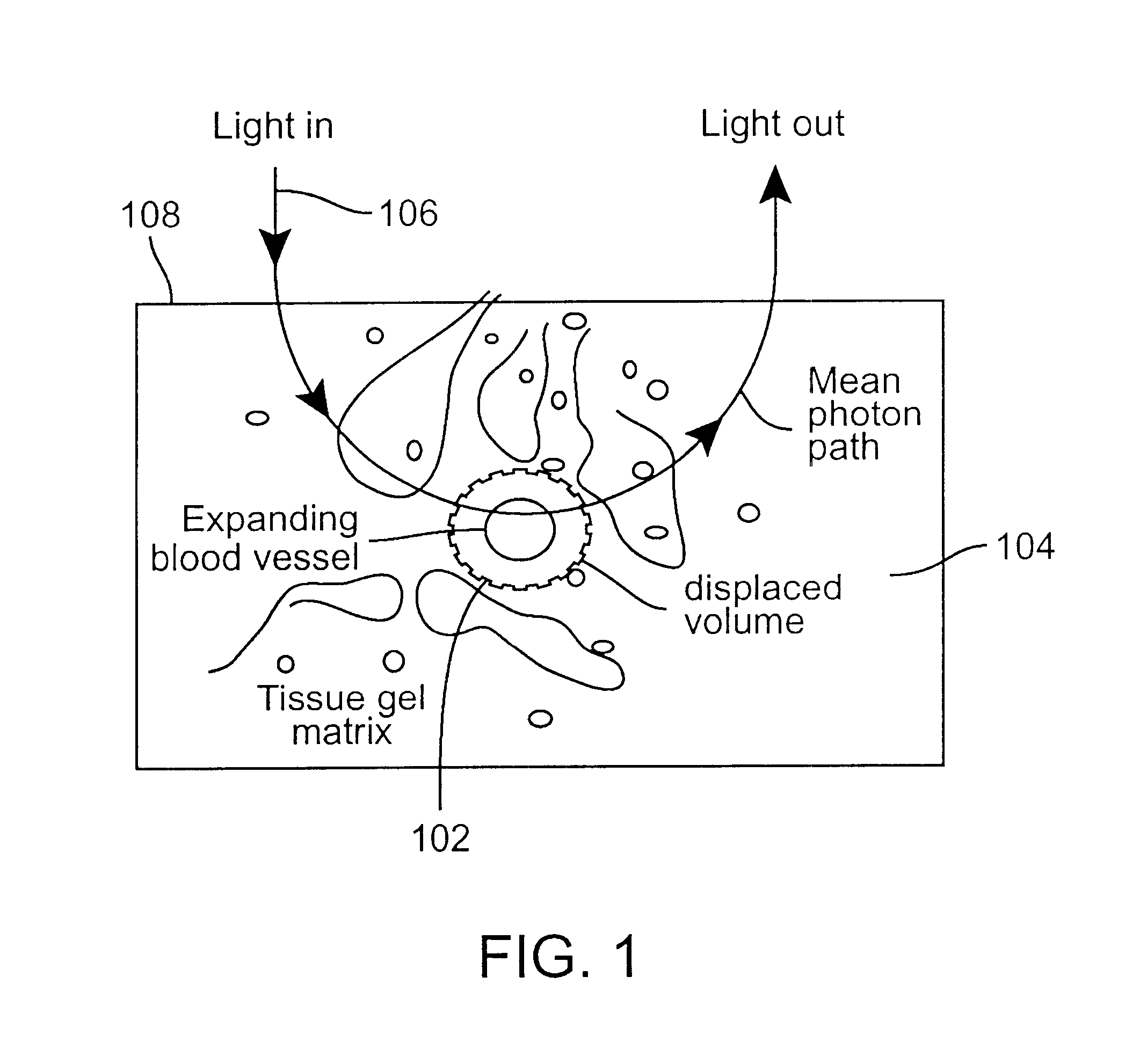
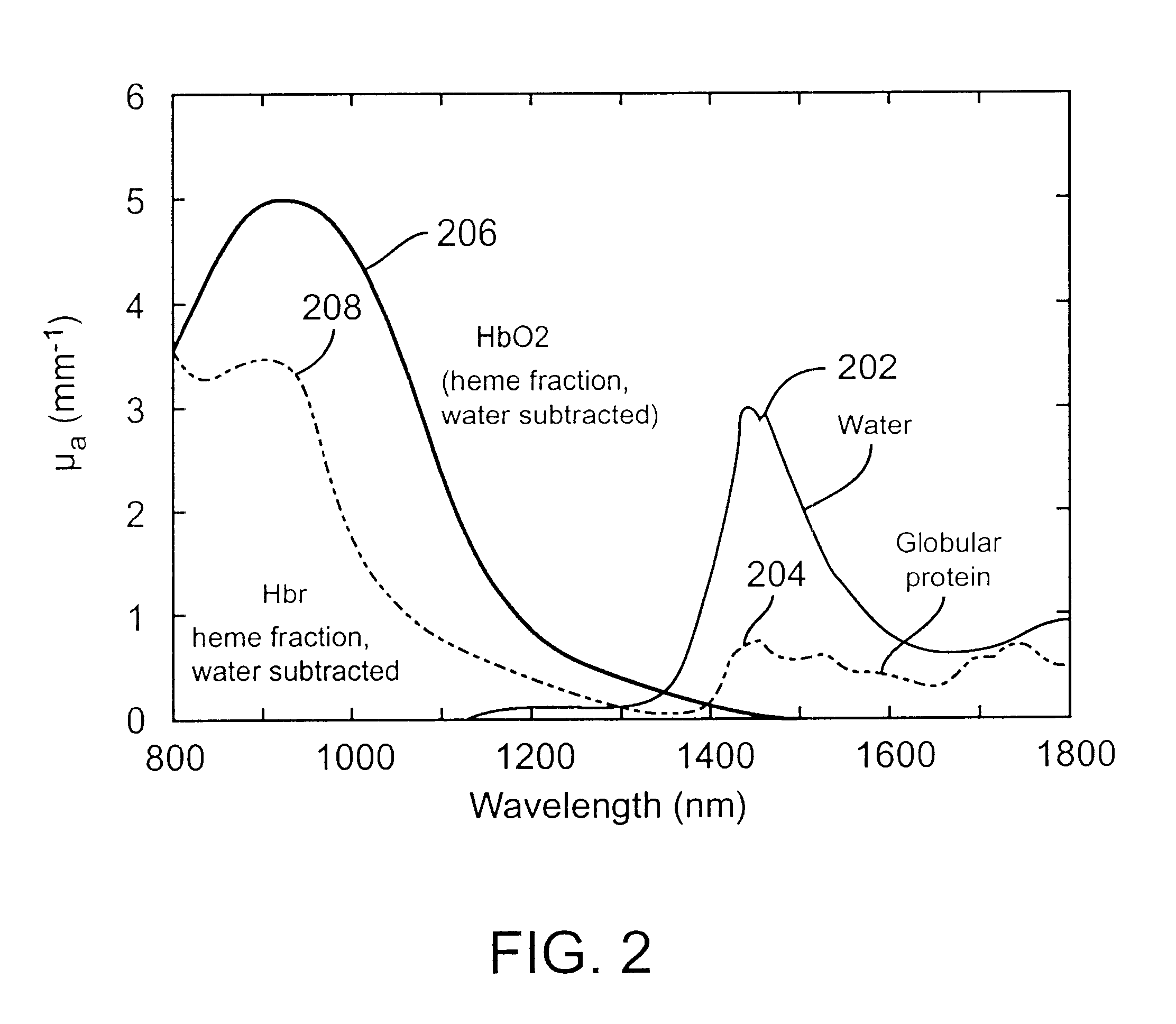
Method and apparatus for improving the accuracy of noninvasive hematocrit measurements
A device and a method to provide a more reliable and accurate measurement of hematocrit (Hct) by noninvasive means. The changes in the intensities of light of multiple wavelengths transmitted through or reflected light from the tissue location are recorded immediately before and after occluding the flow of venous blood from the tissue location with an occlusion device positioned near the tissue location. As the venous return stops and the incoming arterial blood expands the blood vessels, the light intensities measured within a particular band of near-infrared wavelengths decrease in proportion to the volume of hemoglobin in the tissue location; those intensities measured within a separate band of wavelengths in which water absorbs respond to the difference between the water fractions within the blood and the displaced tissue volume. A mathematical algorithm applied to the time-varying intensities yields a quantitative estimate of the absolute concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. To compensate for the effect of the unknown fraction of water in the extravascular tissue on the Hct measurement, the tissue water fraction is determined before the occlusion cycle begins by measuring the diffuse transmittance or reflectance spectra of the tissue at selected wavelengths.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
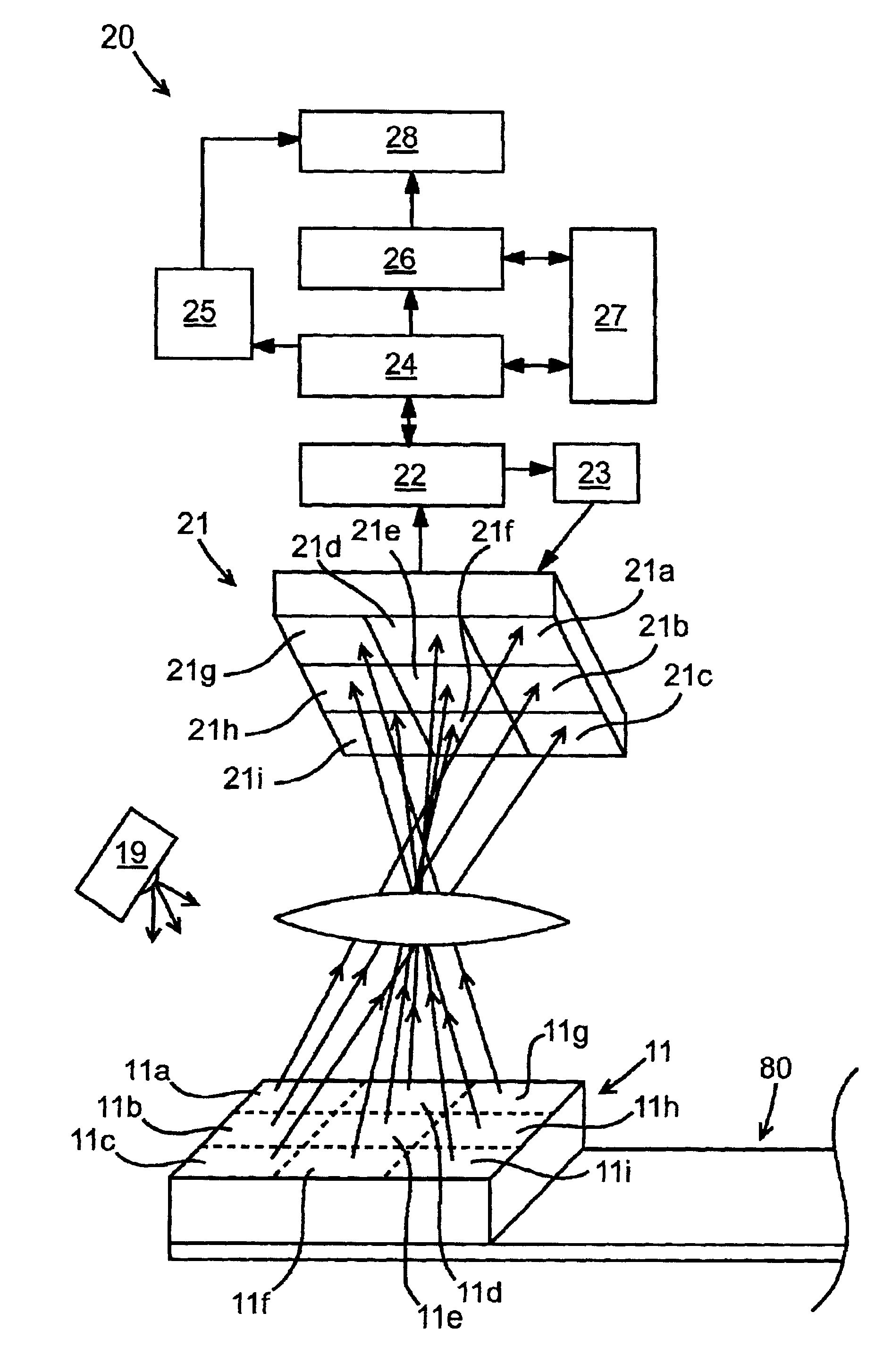
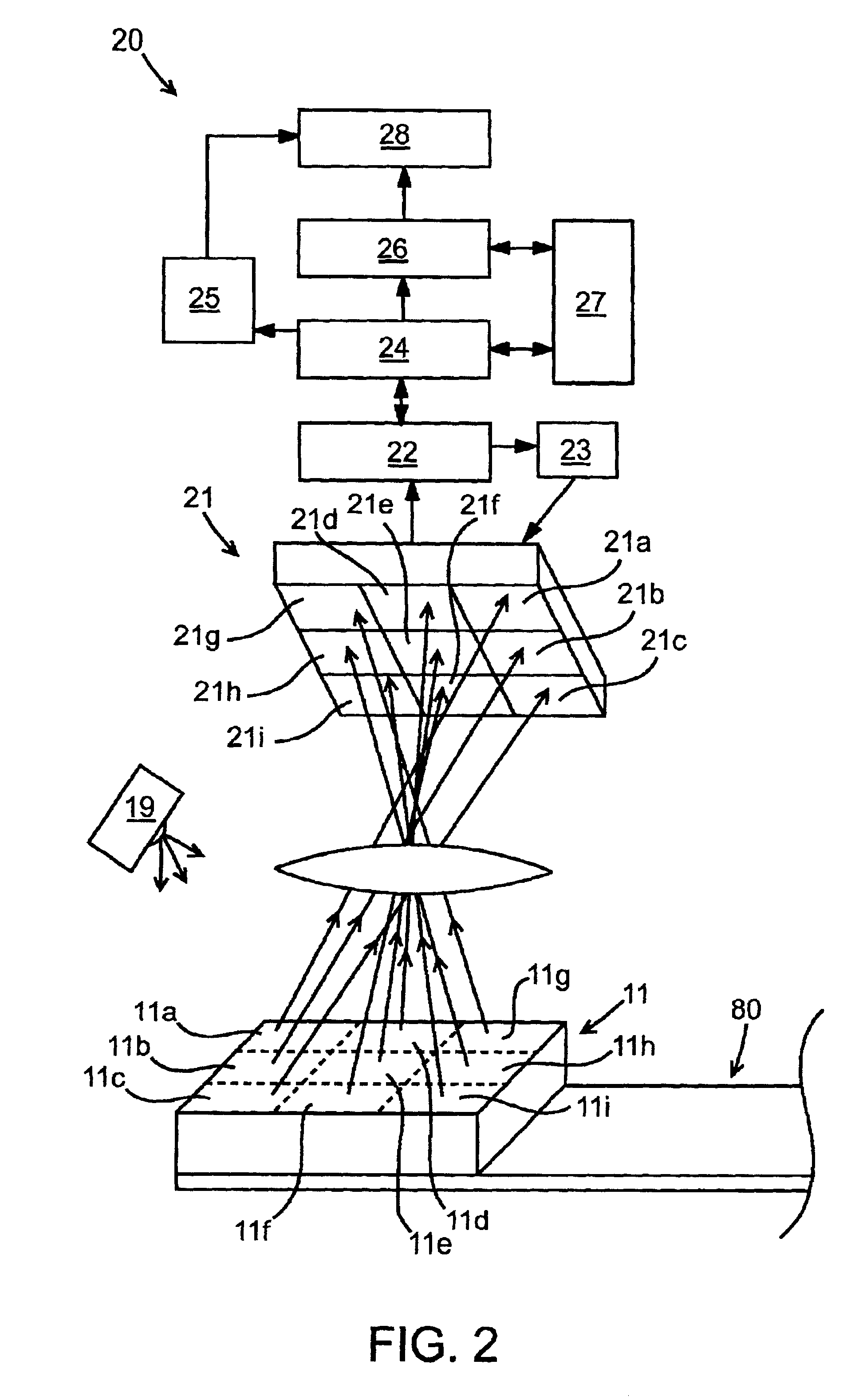
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Apparatuses and methods for analyte concentration determination
InactiveUS6847451B2Investigating moving sheetsColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteInsufficient Sample
Apparatuses and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. The subject apparatuses include at least one light source, a detector array, means for determining whether a sufficient amount of sample is present on each of the plurality of different areas, and means for determining the concentration of the analyte based on the reflected light detected from those areas determined to have sufficient sample, where areas having insufficient sample are not used in analyte concentration determination. The subject methods include illuminating each area of a test strip, obtaining reflectance from each of the different areas, determining which areas have sufficient sample based on detected light therefrom and deriving analyte concentration from the areas determined to have sufficient sample, where areas determined not to have sufficient sample are not used in the derivation. Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
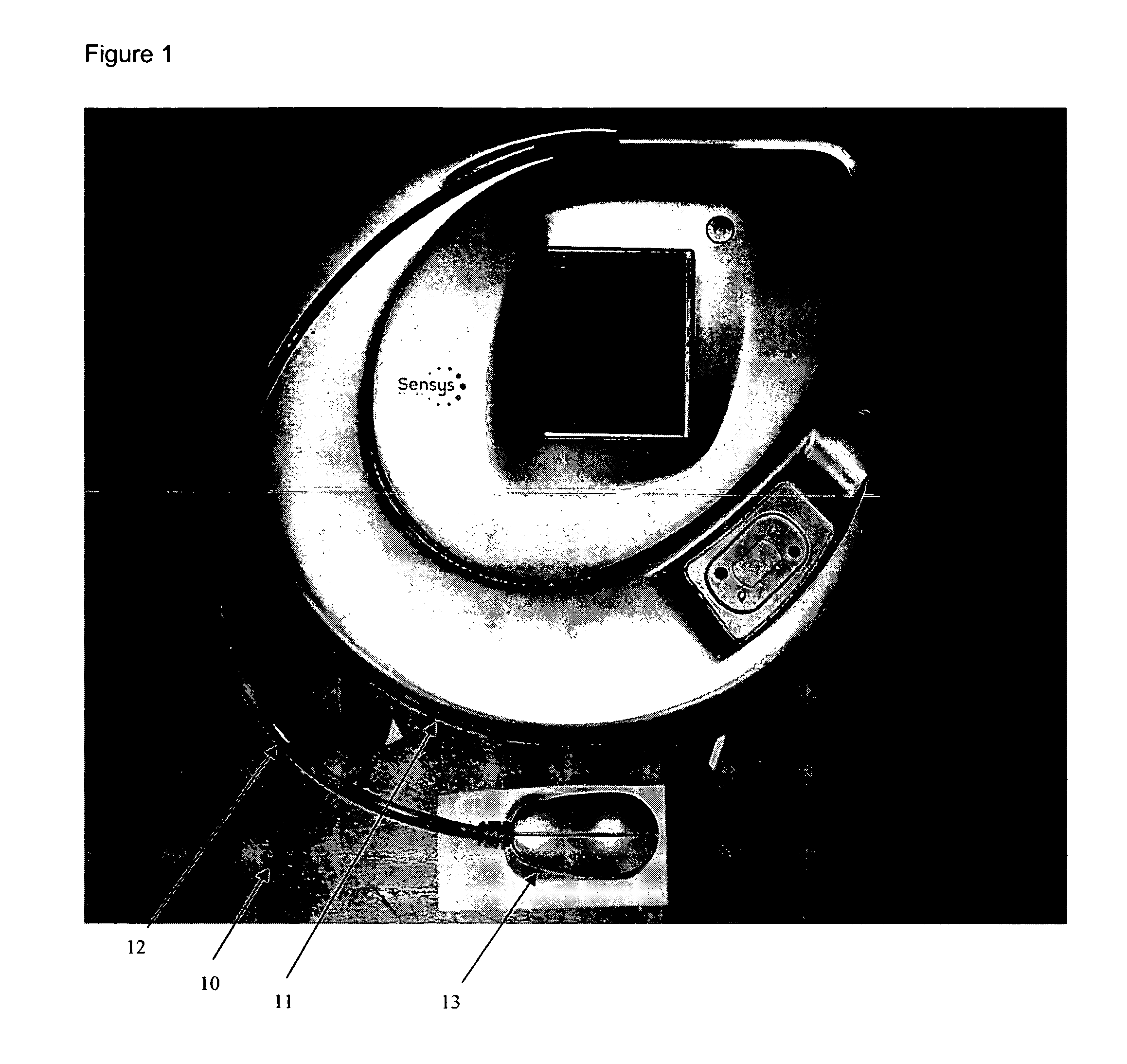
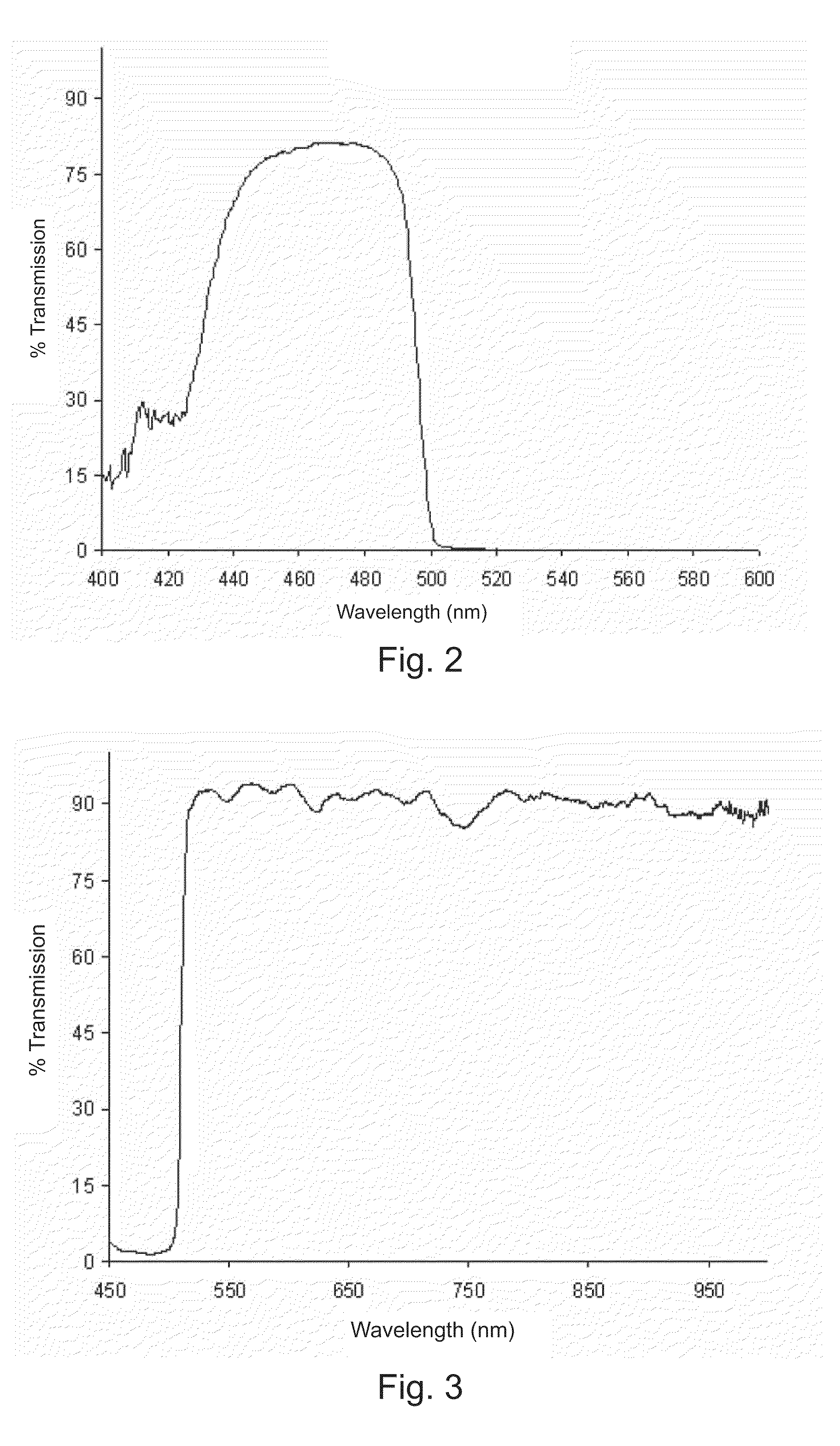
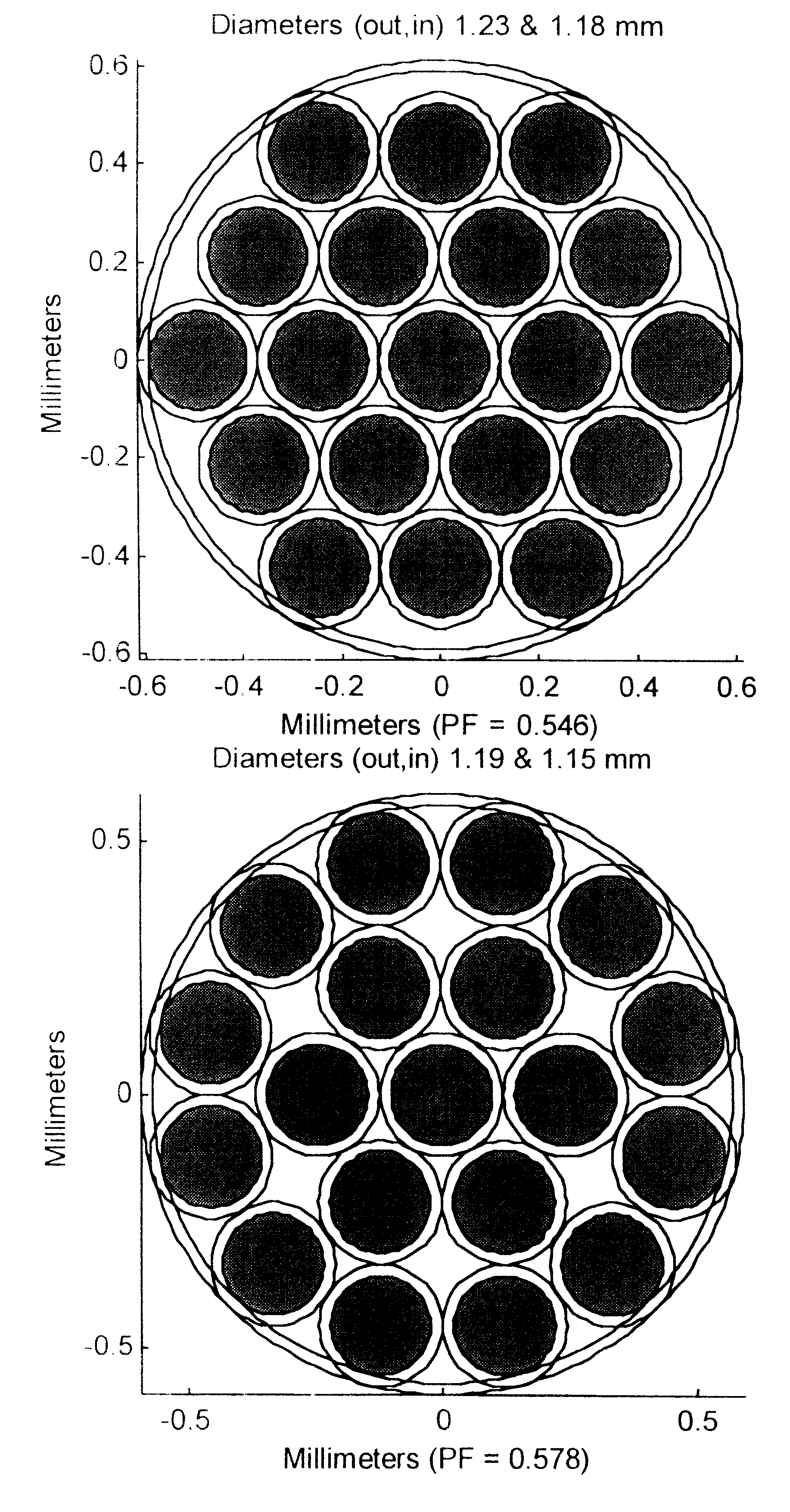
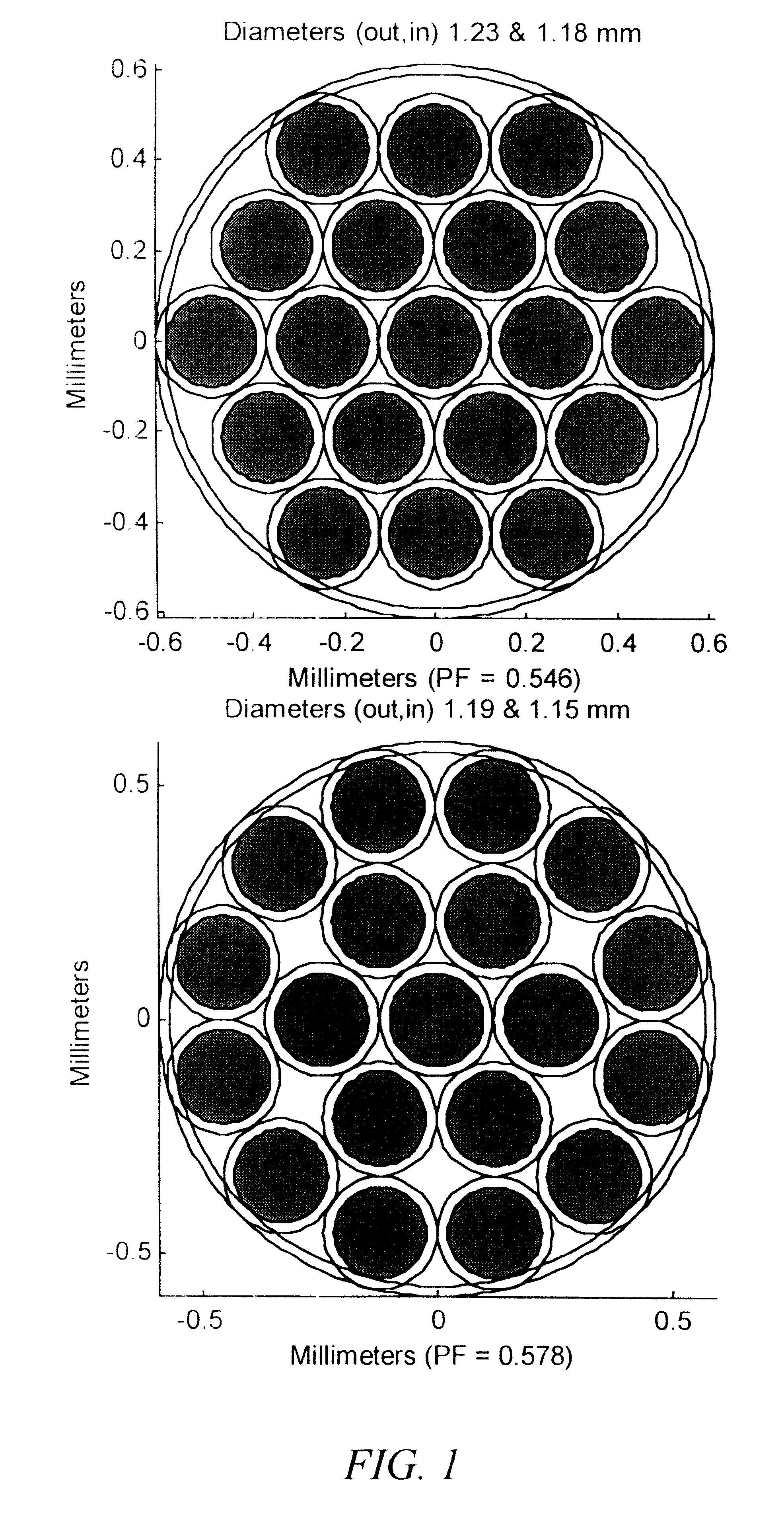
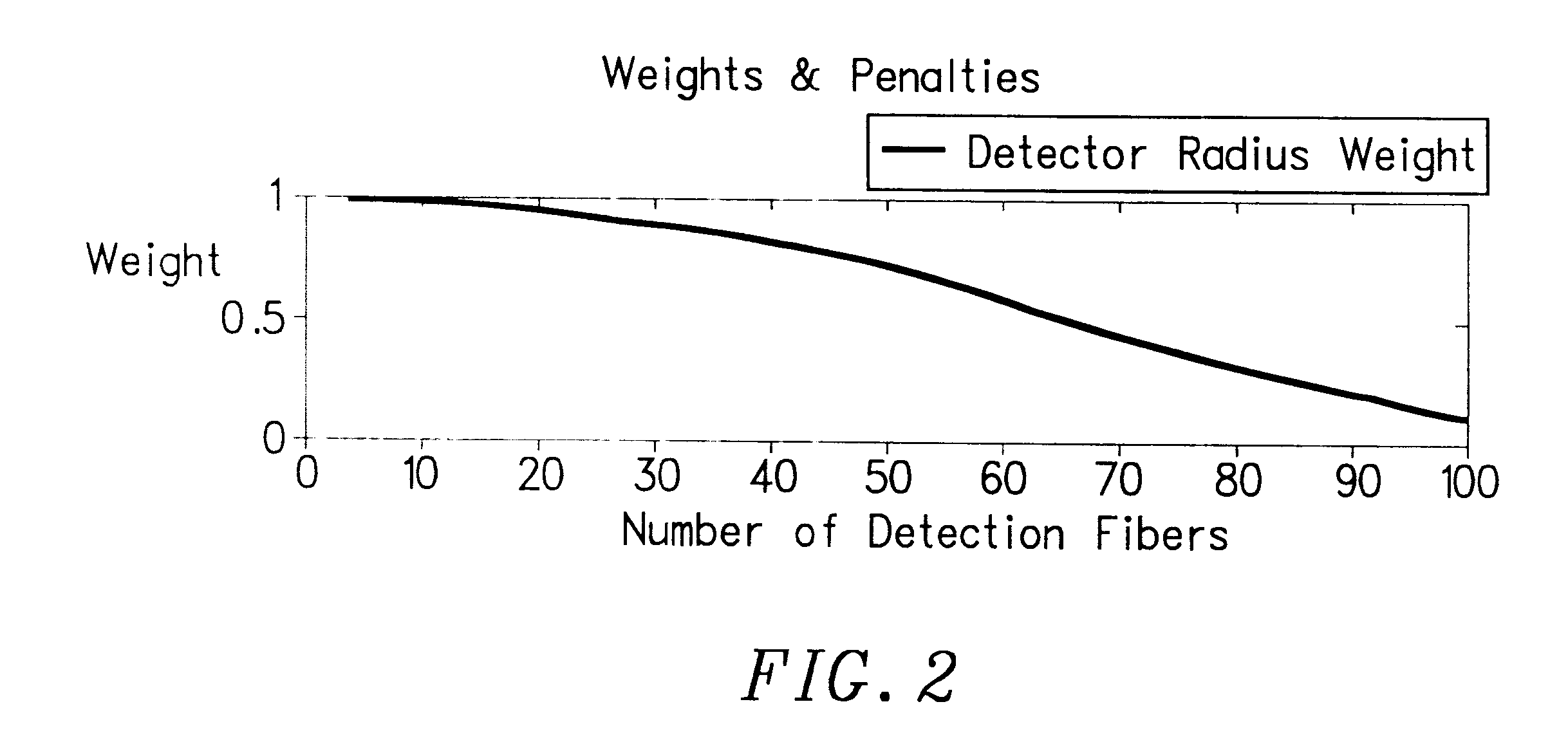
Fiber optic illumination and detection patterns, shapes, and locations for use in spectroscopic analysis
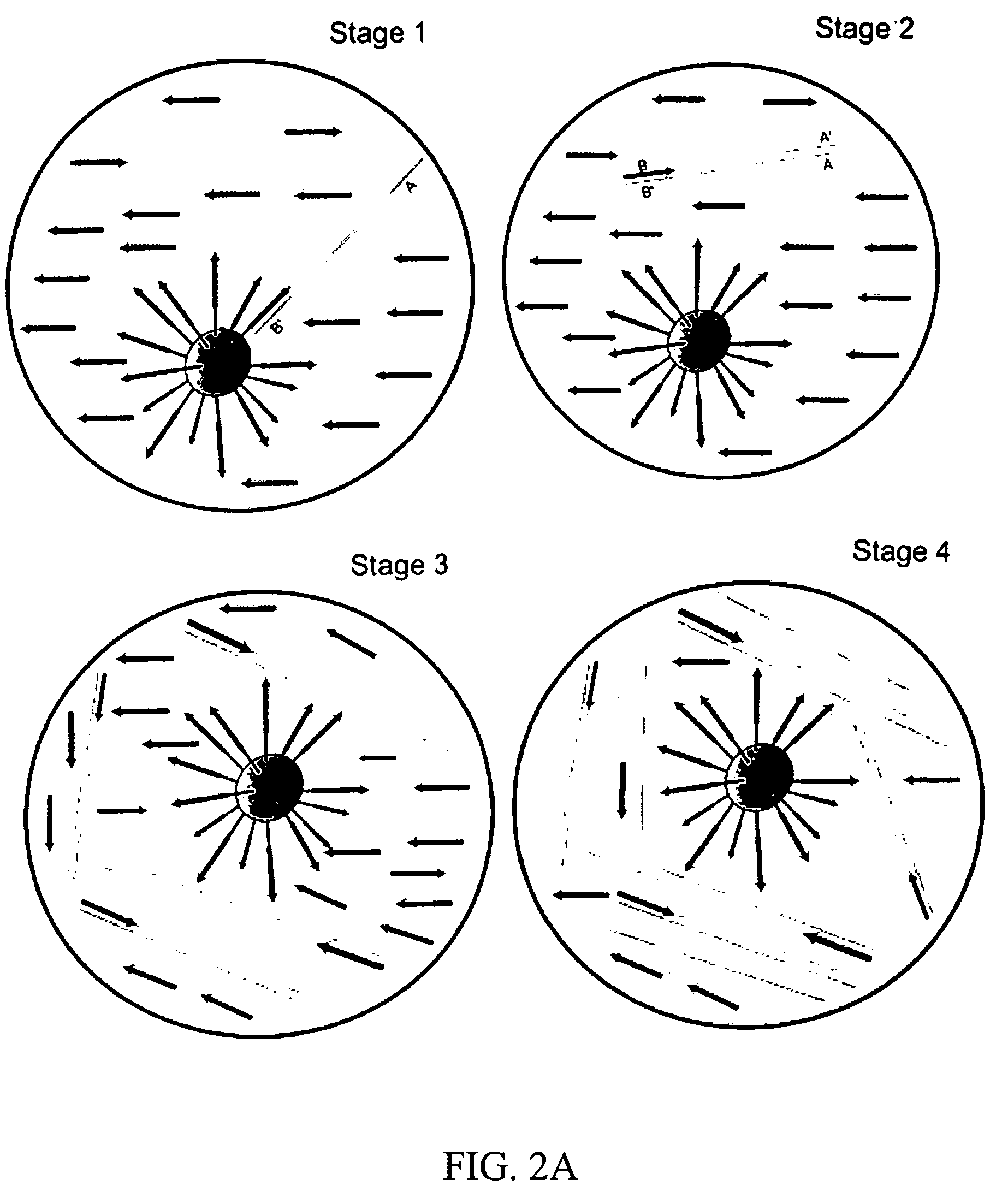
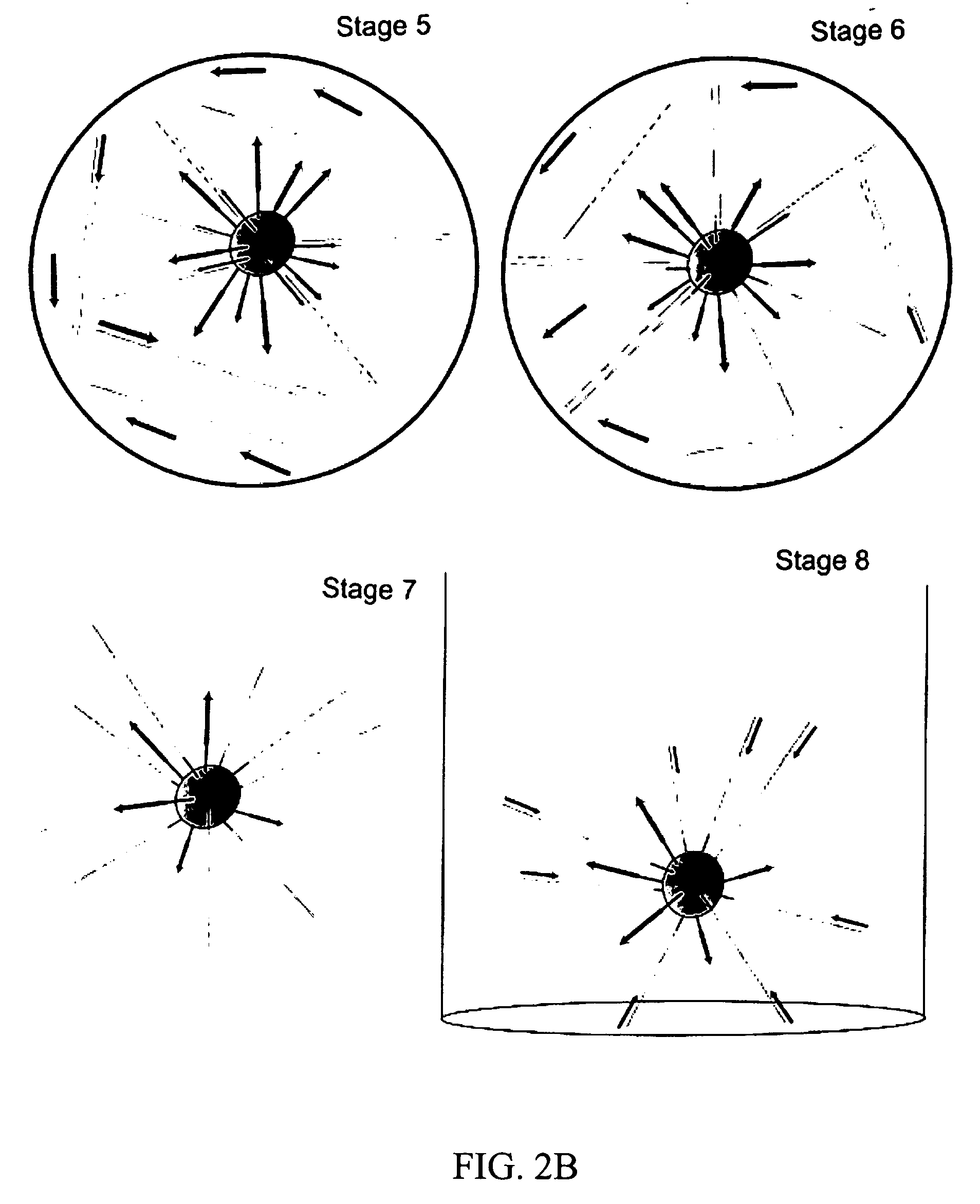
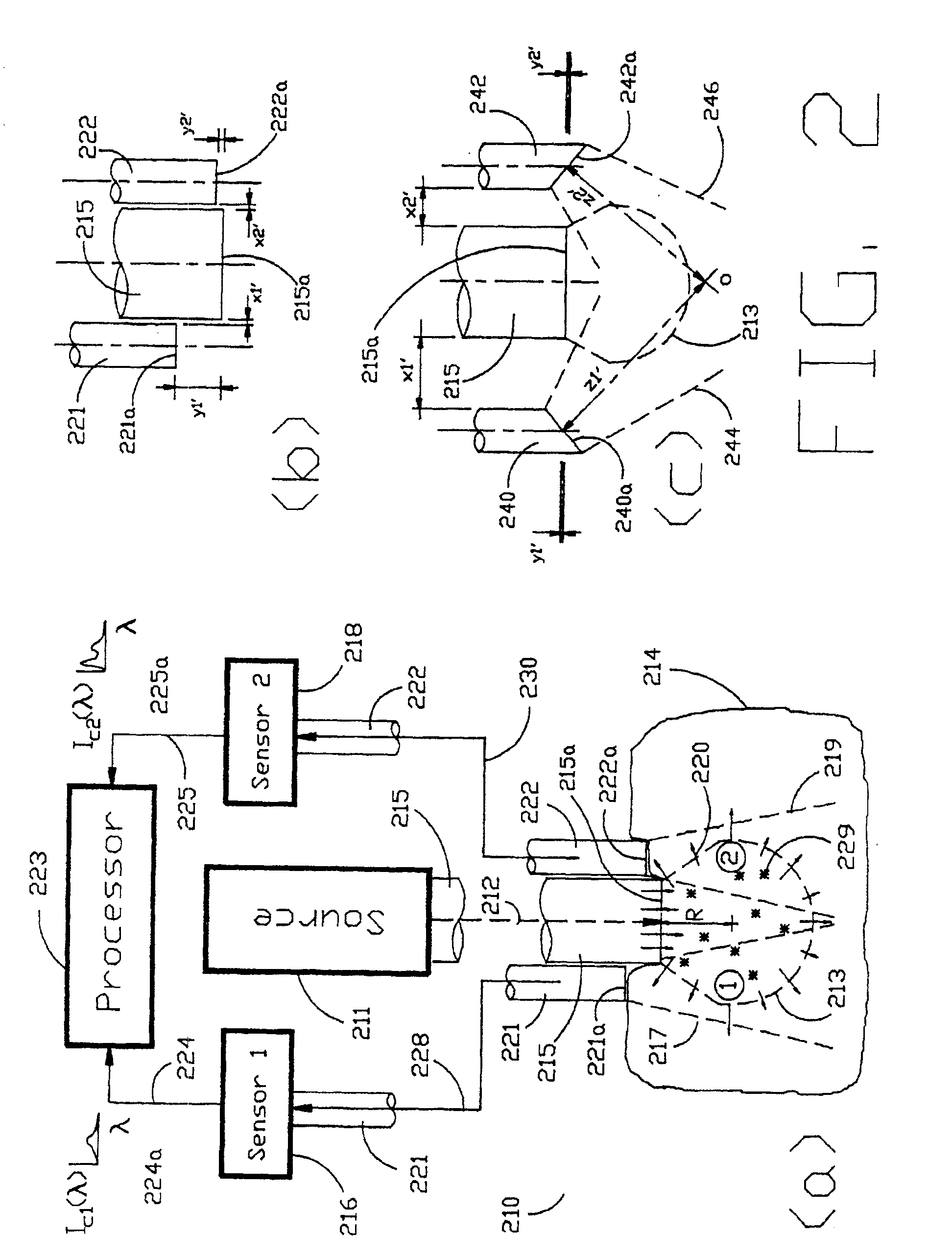
InactiveUS6411373B1Scattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberMonochromator
The invention provides a design process that is used in the determination of the pattern of detector and illumination optical fibers at the sampling area of a subject. Information about the system, specifically a monochromator (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at an output slit) and the bundle termination at a detector optics stack (e.g. to determine the optimal number of fibers at the bundle termination), is of critical importance to this design. It is those numbers that determine the ratio and number of illumination to detection fibers, significantly limiting and constraining the solution space. Additional information about the estimated signal and noise in the skin is necessary to maximize the signal-to-noise ratio in the wavelength range of interest. Constraining the fibers to a hexagonal perimeter and prescribing a hex-packed pattern, such that alternating columns contain illumination and detection fibers, yields optimal results. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, two detectors share the totality of the detection fibers at the sampling interface. A third group of detection fibers is used for classification purposes.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com