Patents
Literature
99 results about "Flexible endoscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
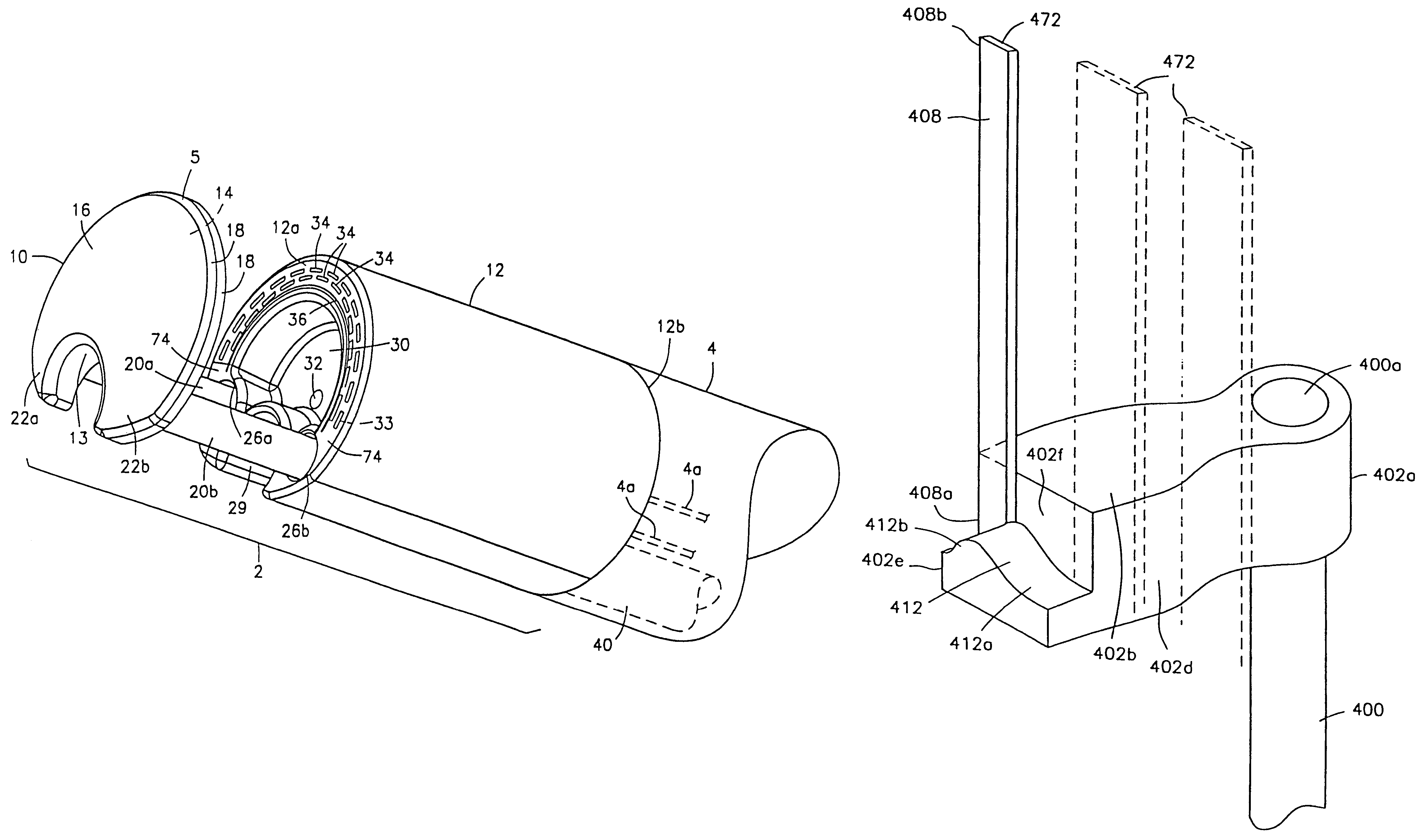
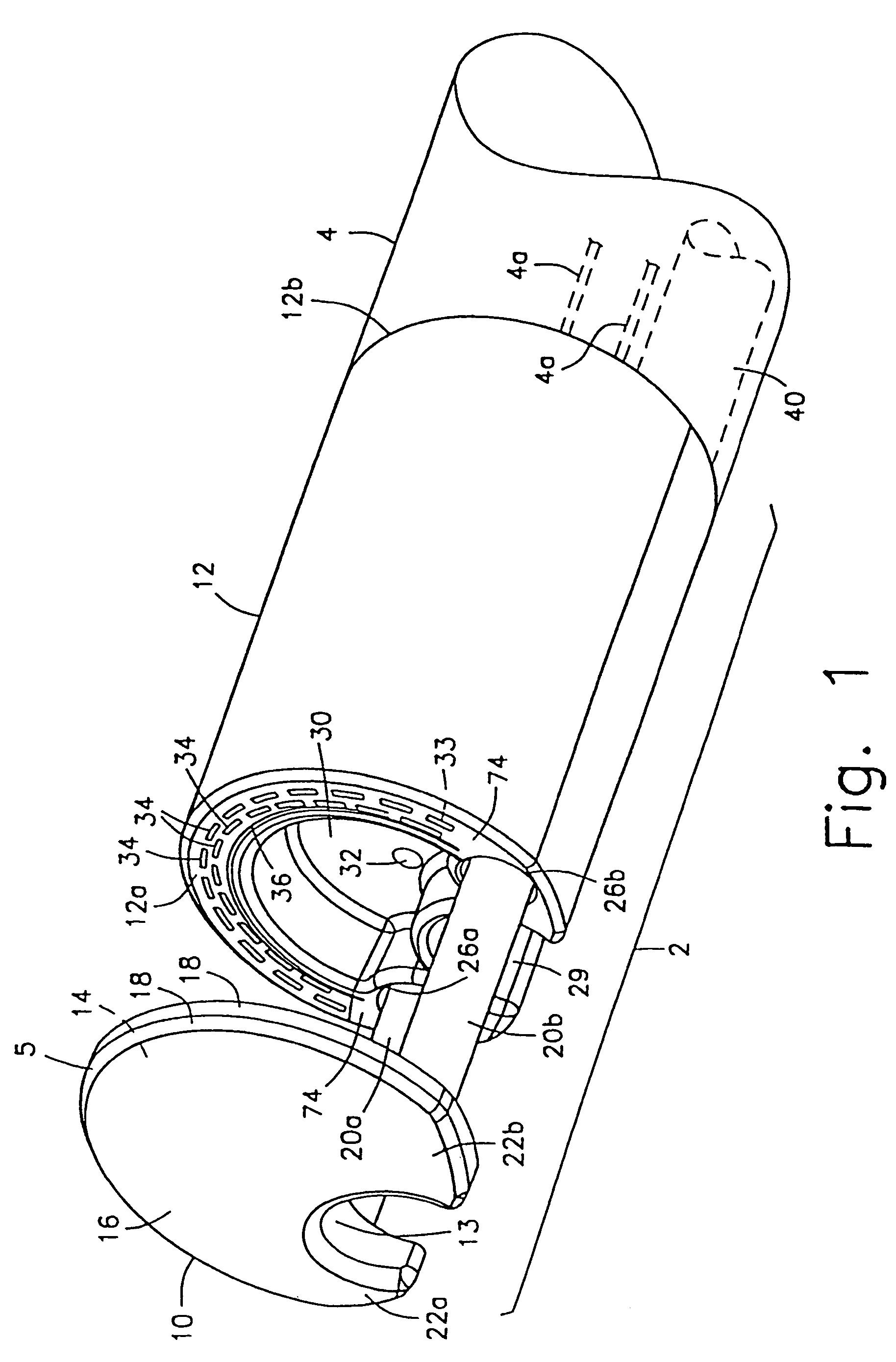
Method and device for full thickness resectioning of an organ
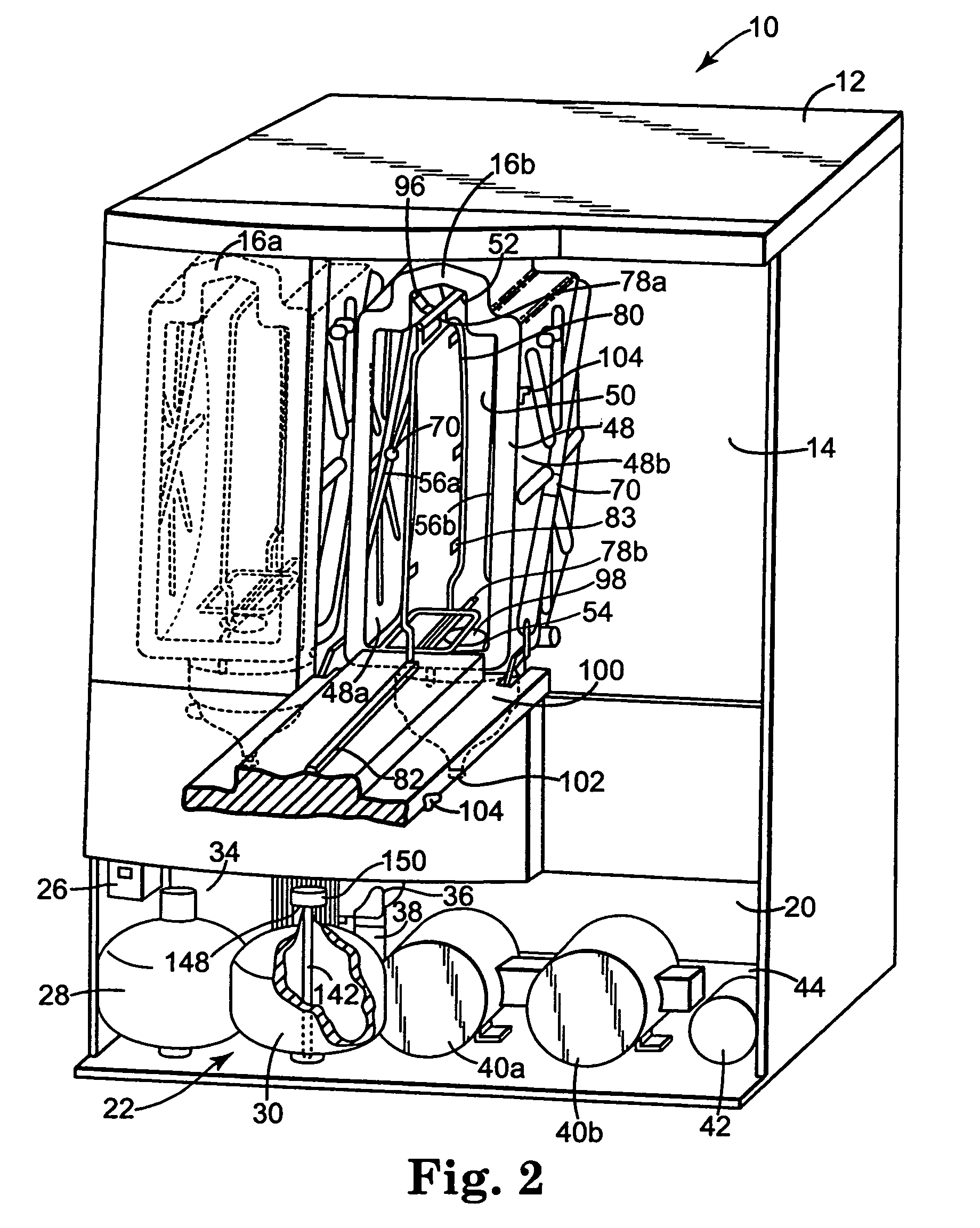
Described is a full-thickness resection system which includes a control unit coupled to a proximal end of a flexible endoscope. The control unit remains outside of a body when the stapling head is in an operative position within a body lumen. The control unit includes (i) an anvil actuator coupled to an anvil in the stapling head, actuation of the anvil actuator moves the anvil axially relative to a stapling mechanism in the stapling head to compress a folded full-thickness portion of lumenal tissue between the anvil and the stapling mechanism. In addition, the control unit includes (ii) a stapler actuator coupled to the stapling mechanism in the stapling head, actuation of the stapler actuator causing the stapling mechanism to drive staples through the folded lumenal tissue against the anvil. Also, the control unit includes (iii) a tissue cutter actuator coupled to a tissue cutter in the stapling head, actuation of the tissue cutter actuator causing the tissue cutter to resect portions of the folded lumenal tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and device for full thickness resectioning of an organ
A full-thickness resection system comprises a flexible endoscope and a stapling mechanism, wherein the endoscope is slidably received through at least a portion of the stapling mechanism. The stapling mechanism comprises an anvil and a stapling head mounted to the anvil so that the anvil and the stapling head are moveable with respect to one another between a tissue receiving position and a stapling position and wherein a gap formed between the stapling head and the anvil is larger in the tissue receiving position than it is in the stapling position. A position adjusting mechanism is provided for moving the anvil and the stapling head between the tissue receiving and stapling positions and a staple firing mechanism sequentially fires a plurality of staples from the stapling head across the gap against the anvil and through any tissue received in the gap and a knife cuts a portion of tissue received within the gap. A control unit which remains outside the body is coupled to the stapling mechanism for controlling operation of the position adjusting mechanism and the staple firing mechanism.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Circumferential full thickness resectioning device
An apparatus for performing endoluminal anastomosis of an organ comprises an operative head including an endoscope receiving lumen for slidably receiving a flexible endoscope therein, the operative head including an annular tissue receiving space extending around a circumference of a distal end thereof and a stapling mechanism for firing staples around an entire circumference of the tissue receiving space and a tissue gripping mechanism for drawing into the tissue receiving space a portion of tissue extending around an entire circumference of the organ.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
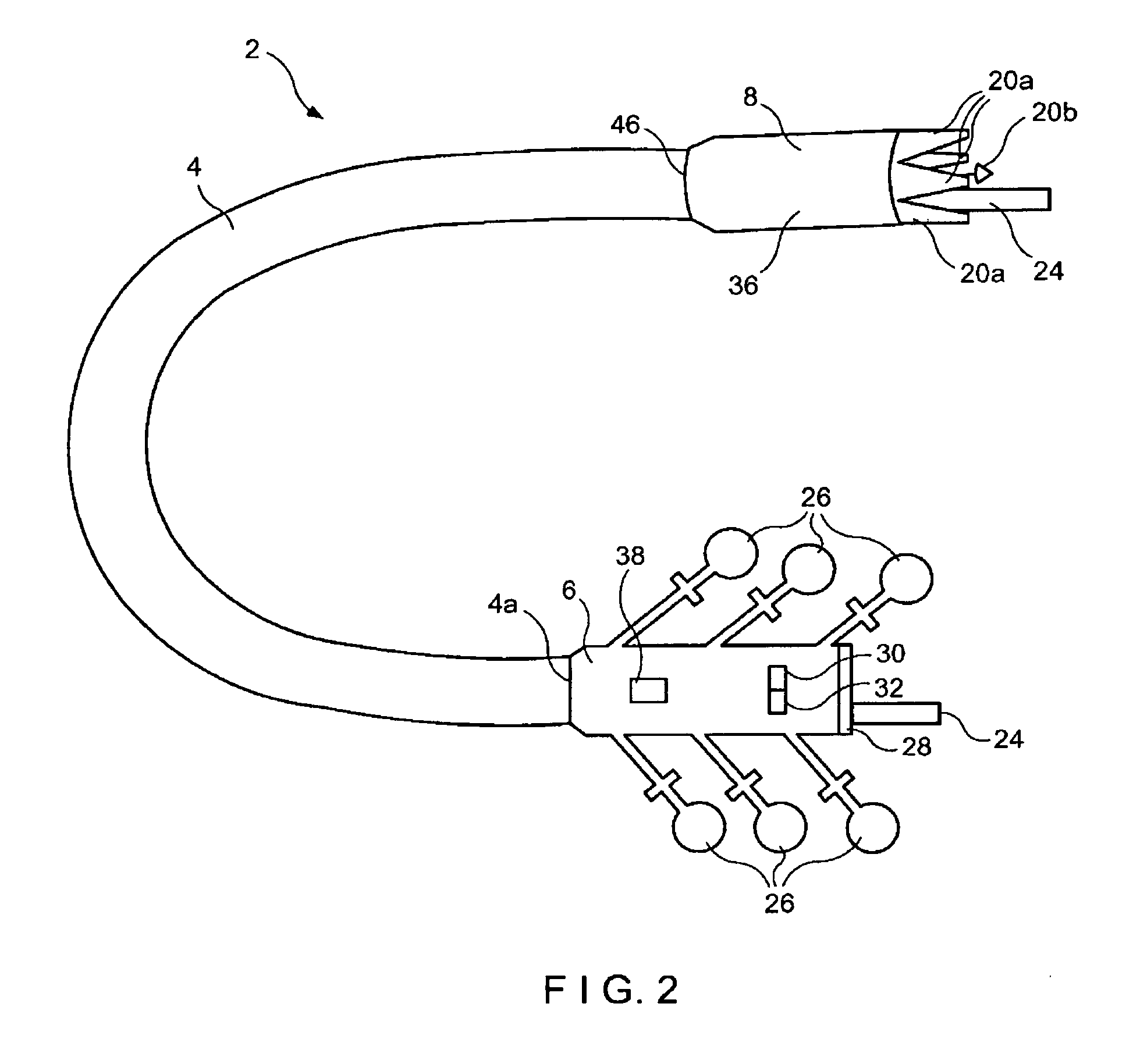
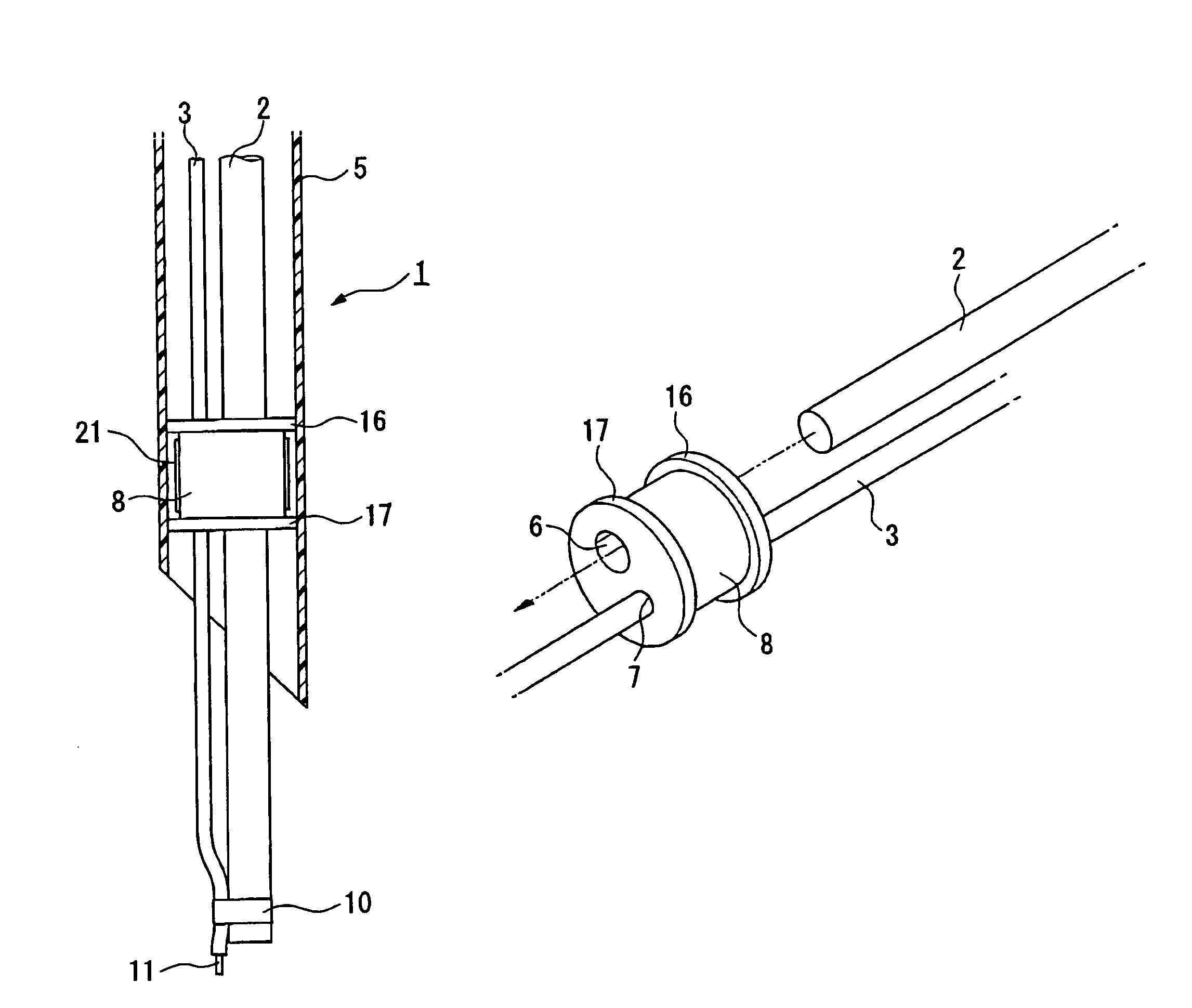
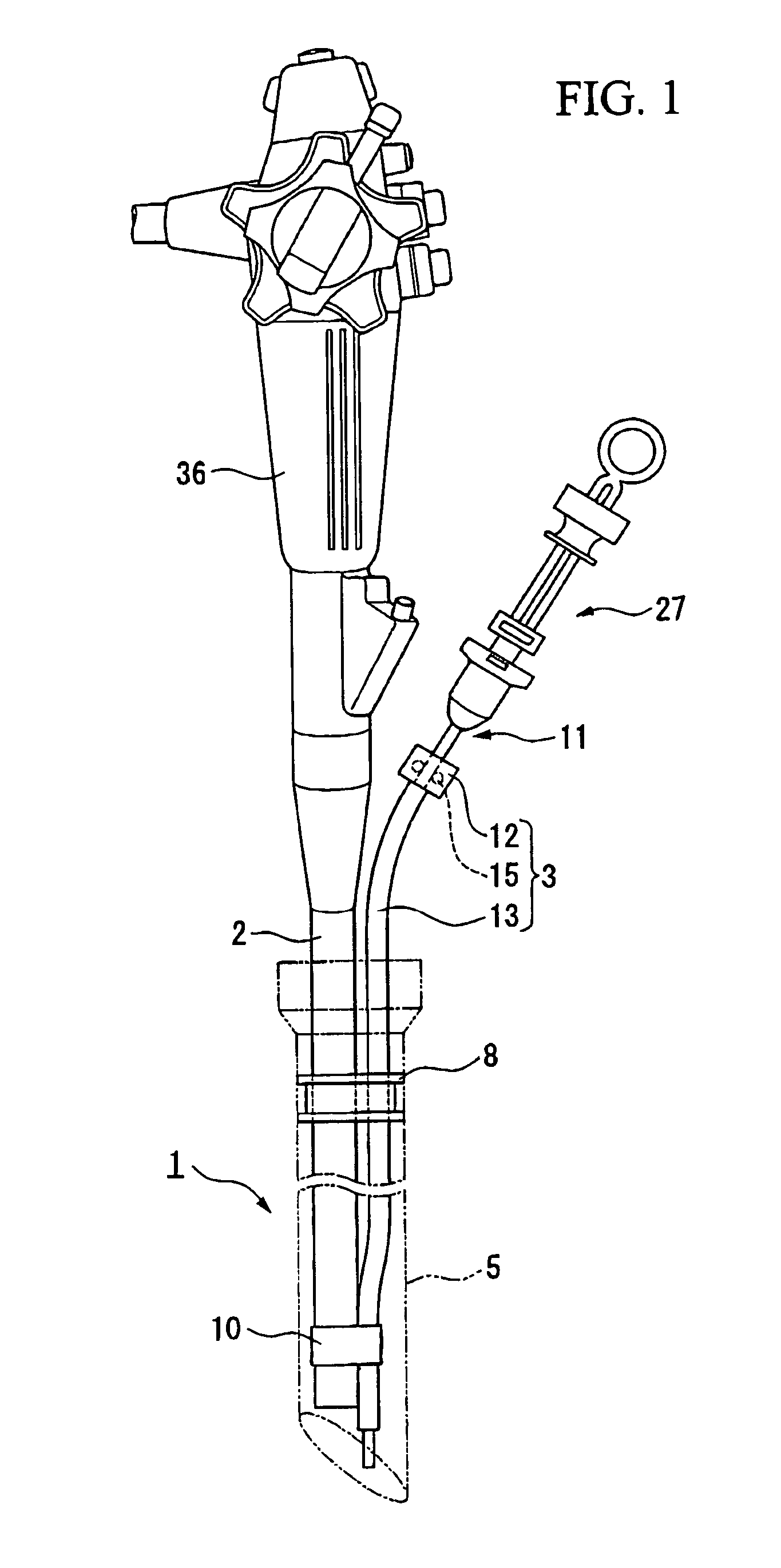
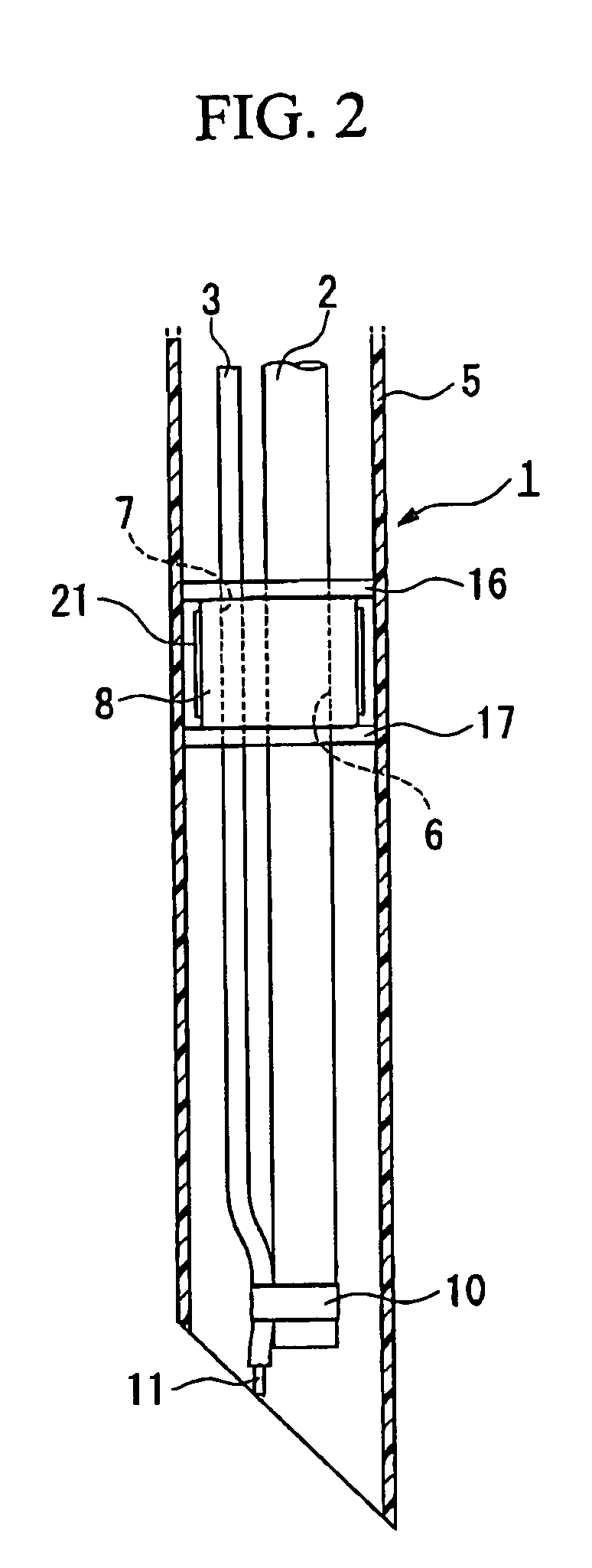
Insertion auxiliary implement
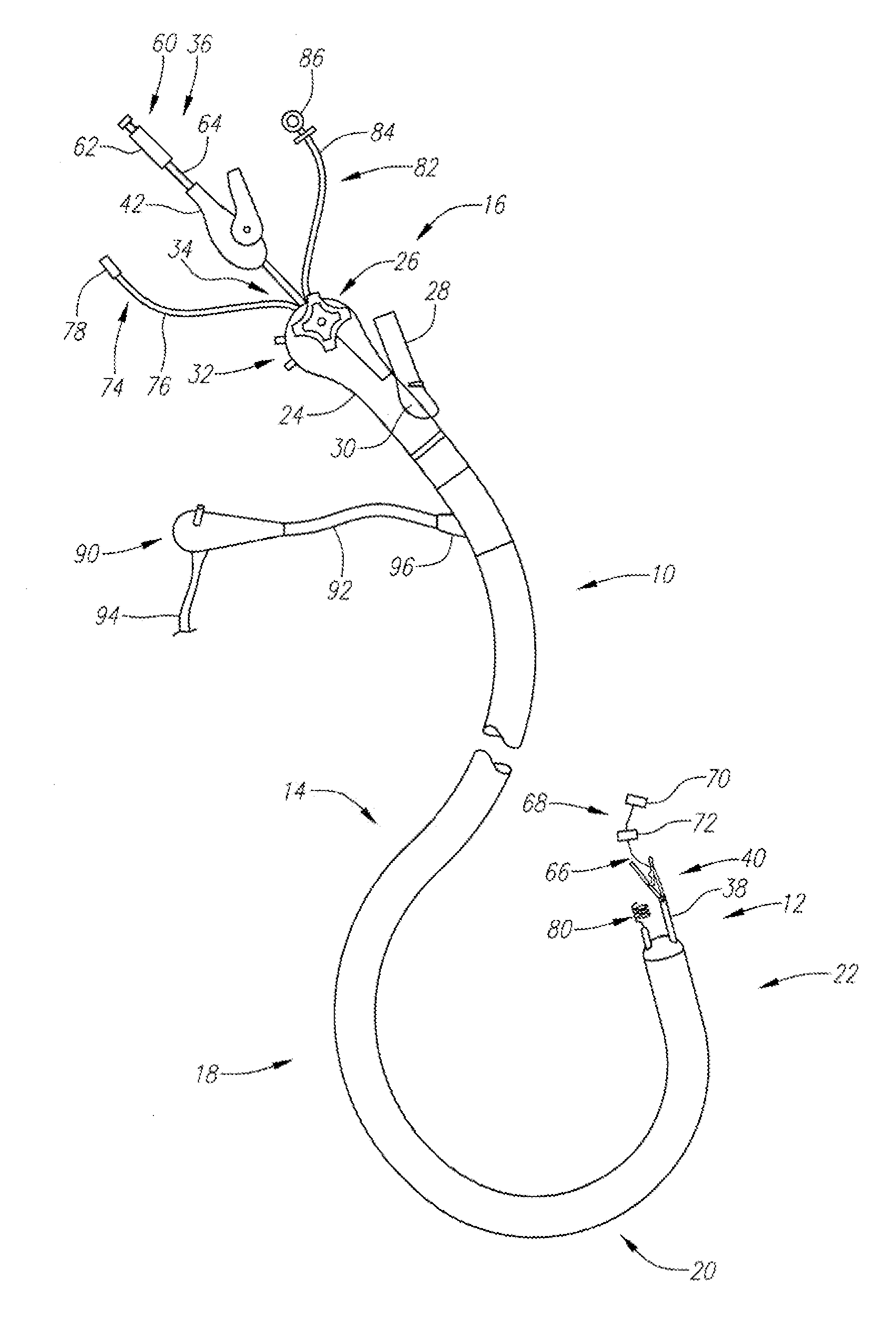
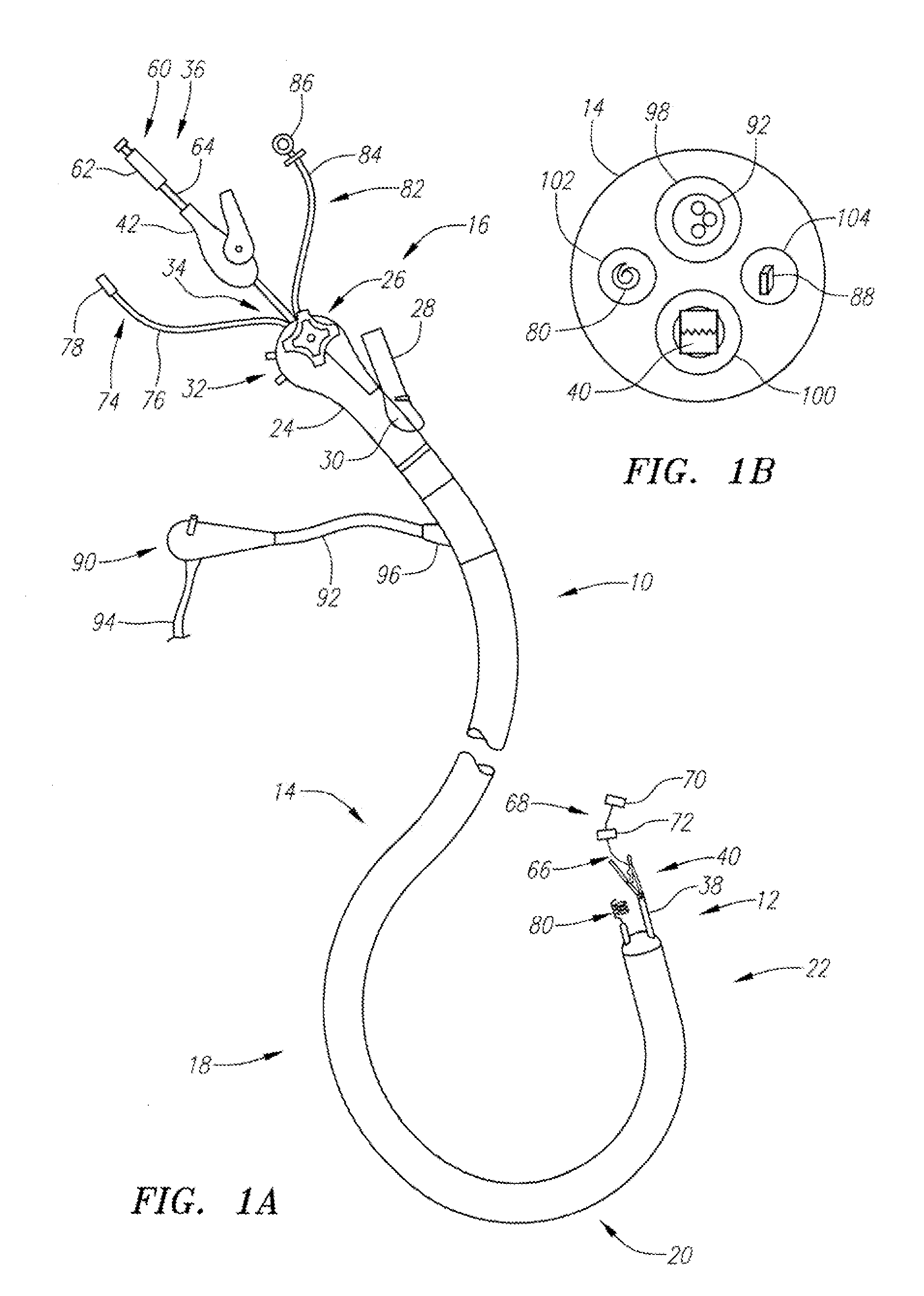
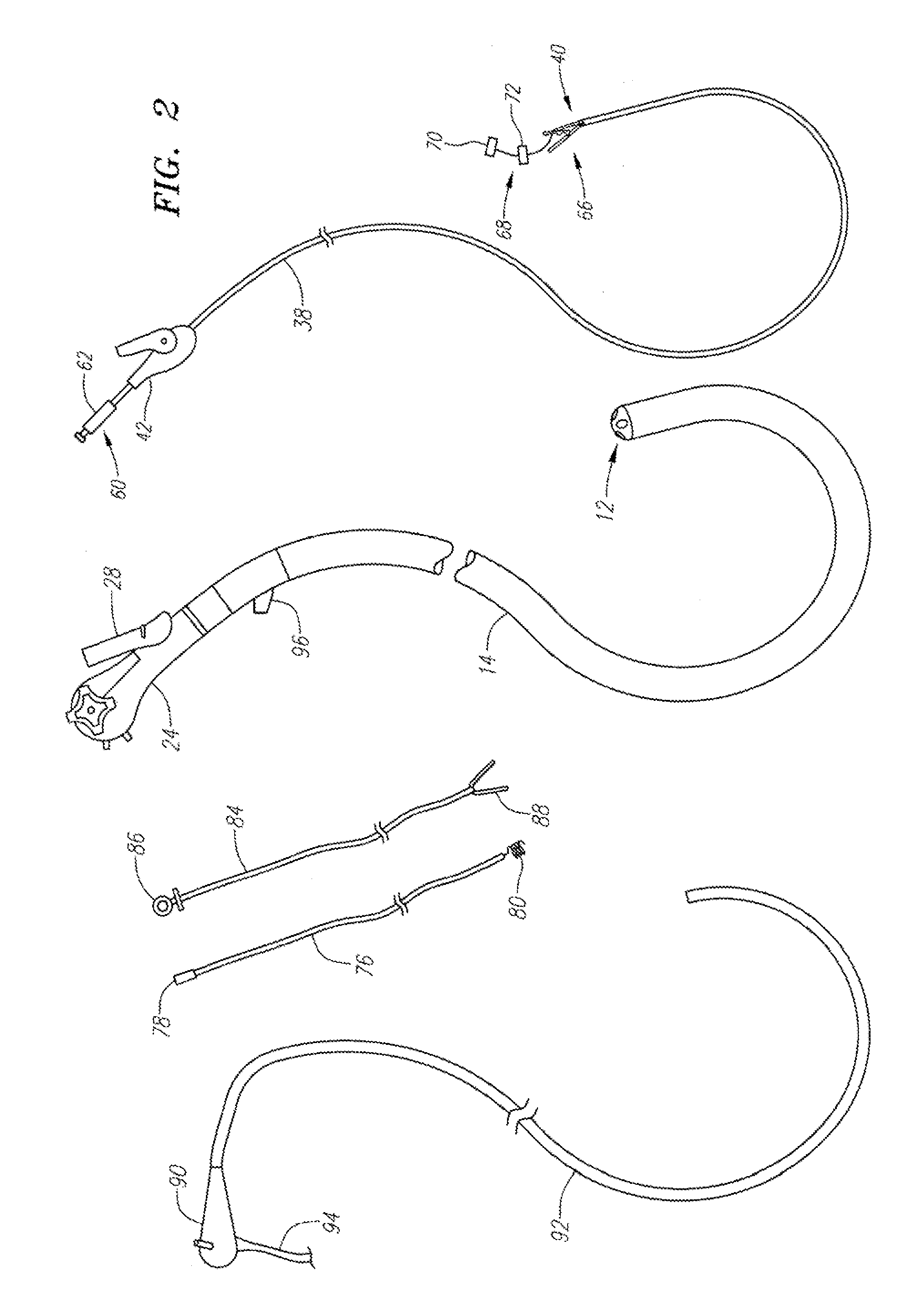
An insertion auxiliary implement of the present invention includes: a tubular part into which a flexible endoscope insertion part which is insertable into a body cavity, and one of a treatment tool and a channel into which the treatment tool is insertable, are insertable; and a sealing member which has through holes for supporting the endoscope insertion part and one of the treatment tool and the channel in the tubular part, and which airtightly and movably contacts each of a periphery of the endoscope insertion part, a periphery of the treatment tool or a periphery of the channel, and an inner surface of the tubular part, and thereby maintains airtightness between a distal end and a proximal end inside the tubular part.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Apparatus and method for steam reprocessing flexible endoscopes
A system for reprocessing flexible endoscopes having lumen therein. The reprocessing system deploys steam to disinfect and / or sterilize the endoscopes, and designs, components, and methods for reducing or balancing the reprocessing cycle time and the effects of thermal expansion and contraction on the endoscopes.
Owner:MEDIVATORS INC
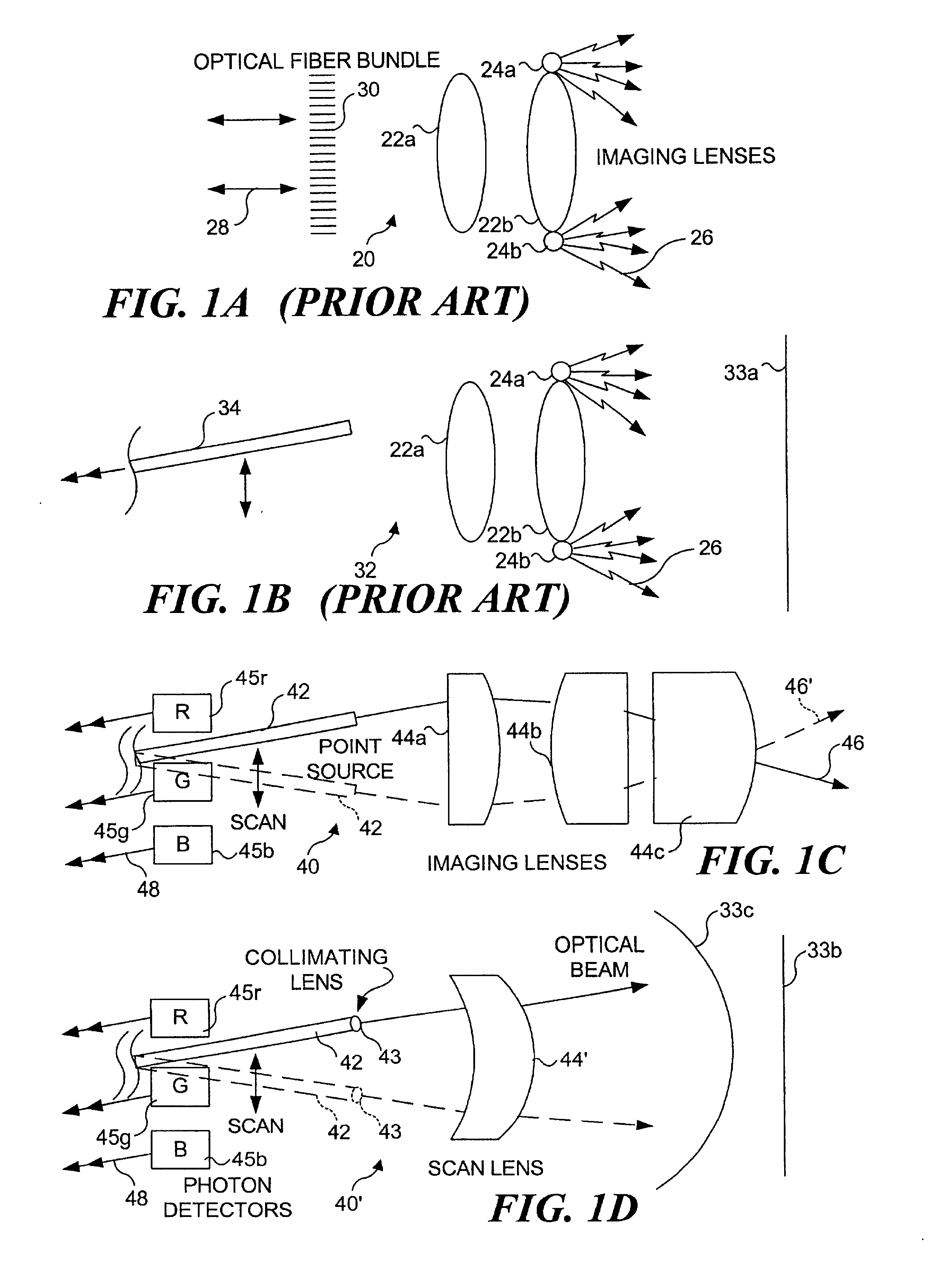
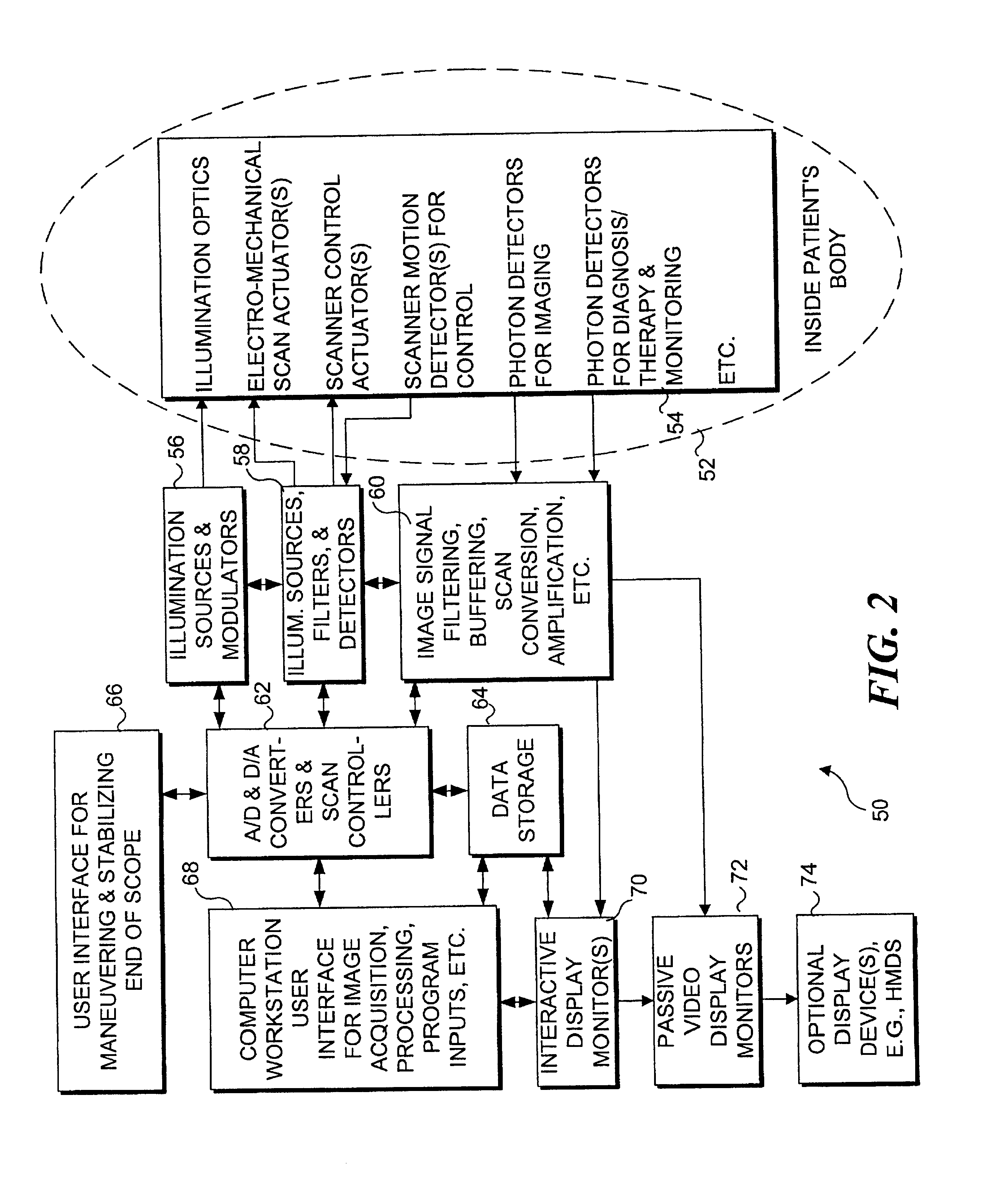
Medical imaging, diagnosis, and therapy using a scanning single optical fiber system
InactiveUS6975898B2High resolutionEasy to viewEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFlexible endoscopyHigh resolution imaging
An integrated endoscopic image acquisition and therapeutic delivery system for use in minimally invasive medical procedures (MIMPs). The system uses directed and scanned optical illumination provided by a scanning optical fiber or light waveguide that is driven by a piezoelectric or other electromechanical actuator included at a distal end of an integrated imaging and diagnostic / therapeutic instrument. The directed illumination provides high resolution imaging, at a wide field of view (FOV), and in full color that matches or excels the images produced by conventional flexible endoscopes. When using scanned optical illumination, the size and number of the photon detectors do not limit the resolution and number of pixels of the resulting image. Additional features include enhancement of topographical features, stereoscopic viewing, and accurate measurement of feature sizes of a region of interest in a patient's body that facilitate providing diagnosis, monitoring, and / or therapy with the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Methods and devices for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity
A novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity is described. More specifically, a technique for accessing the peritoneal cavity via the wall of the digestive tract is provided so that examination of and / or a surgical procedure in the peritoneal cavity can be conducted via the wall of the digestive tract with the use of a flexible endoscope. As presently proposed, the technique is particularly adapted to transgastric peritoneoscopy. However, access in addition or in the alternative through the intestinal wall is contemplated and described as well. Transgastric and / or transintestinal peritoneoscopy will have an excellent cosmetic result as there are no incisions in the abdominal wall and no potential for visible post-surgical scars or hernias.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
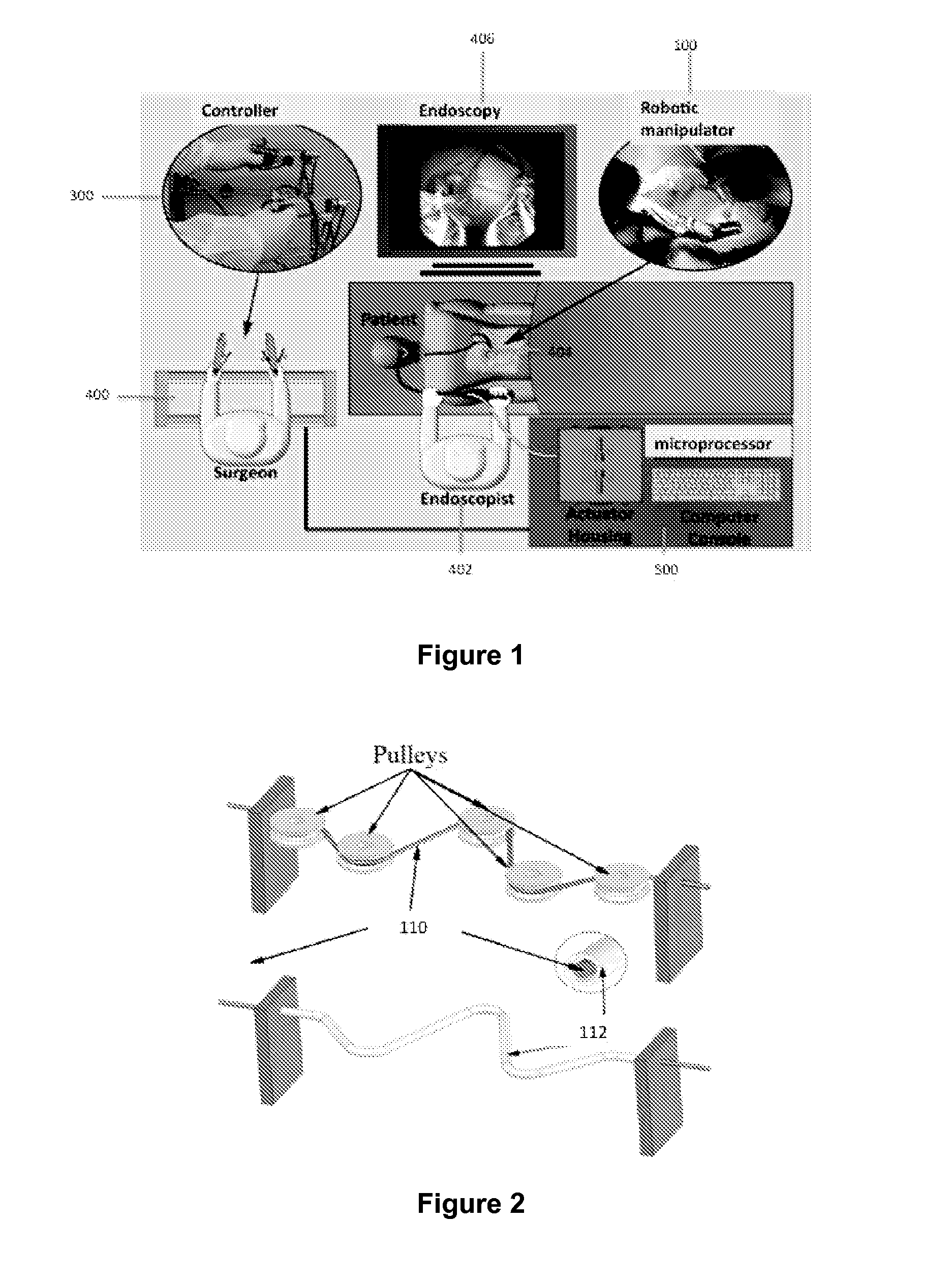
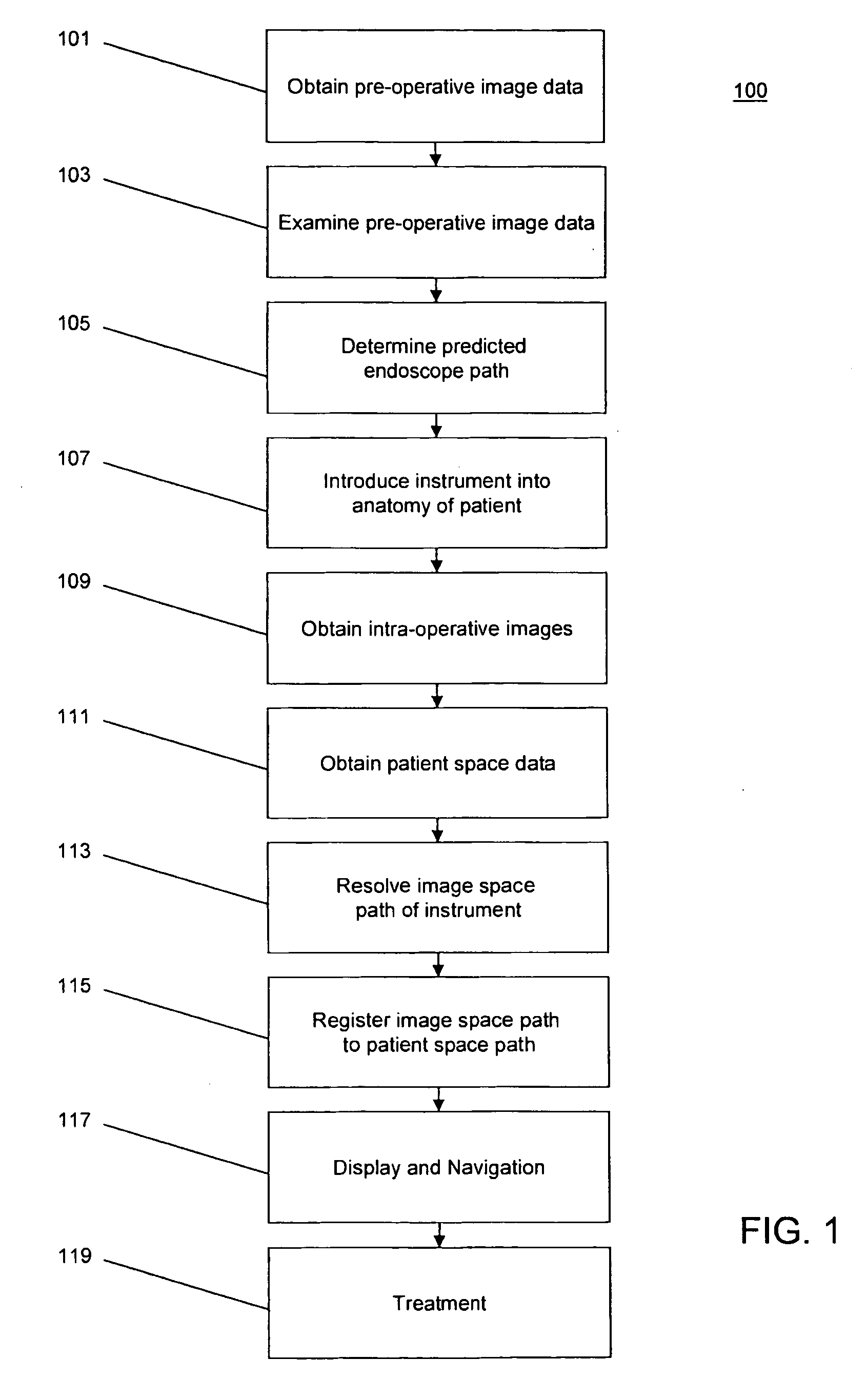
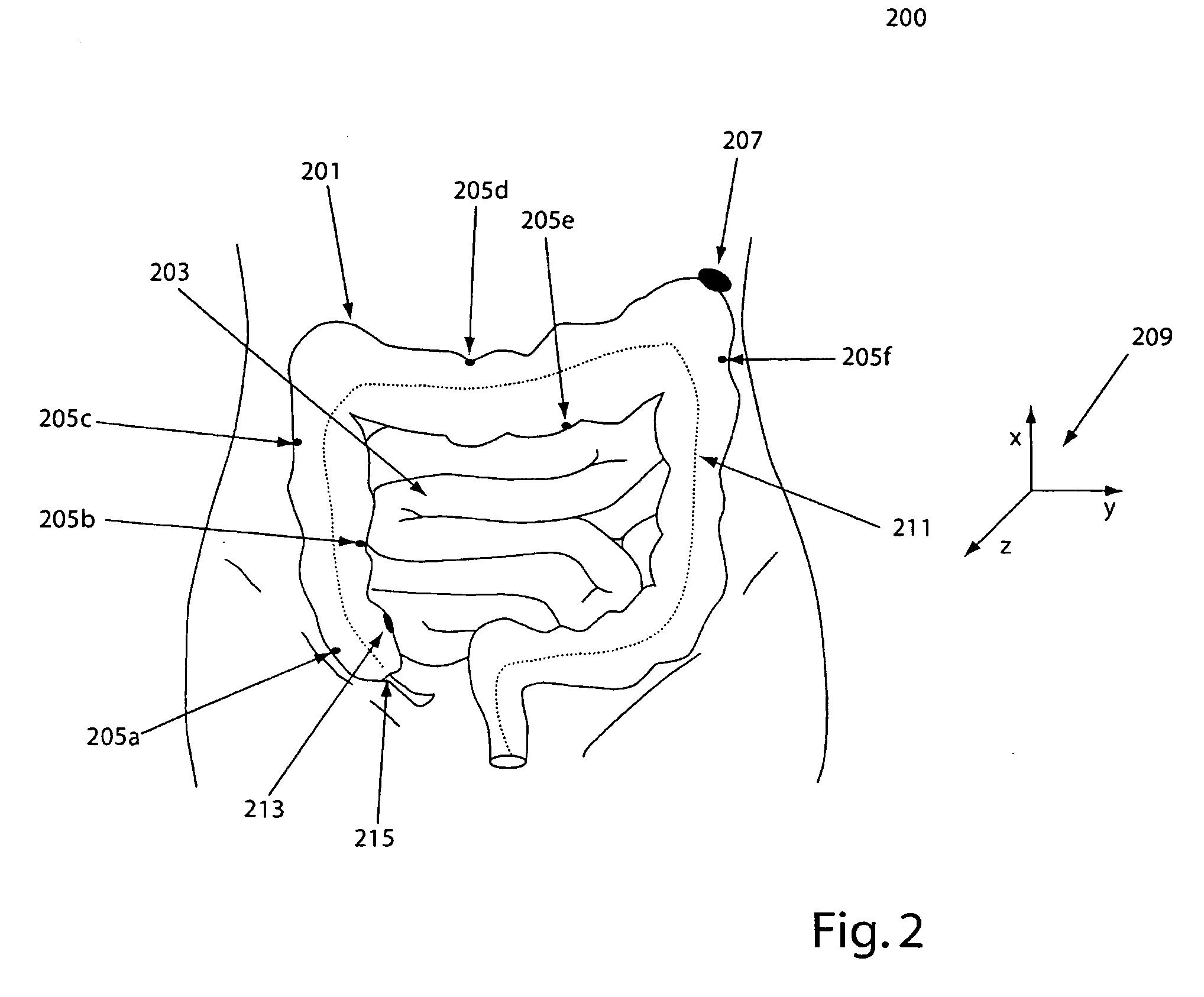
System, method and devices for navigated flexible endoscopy
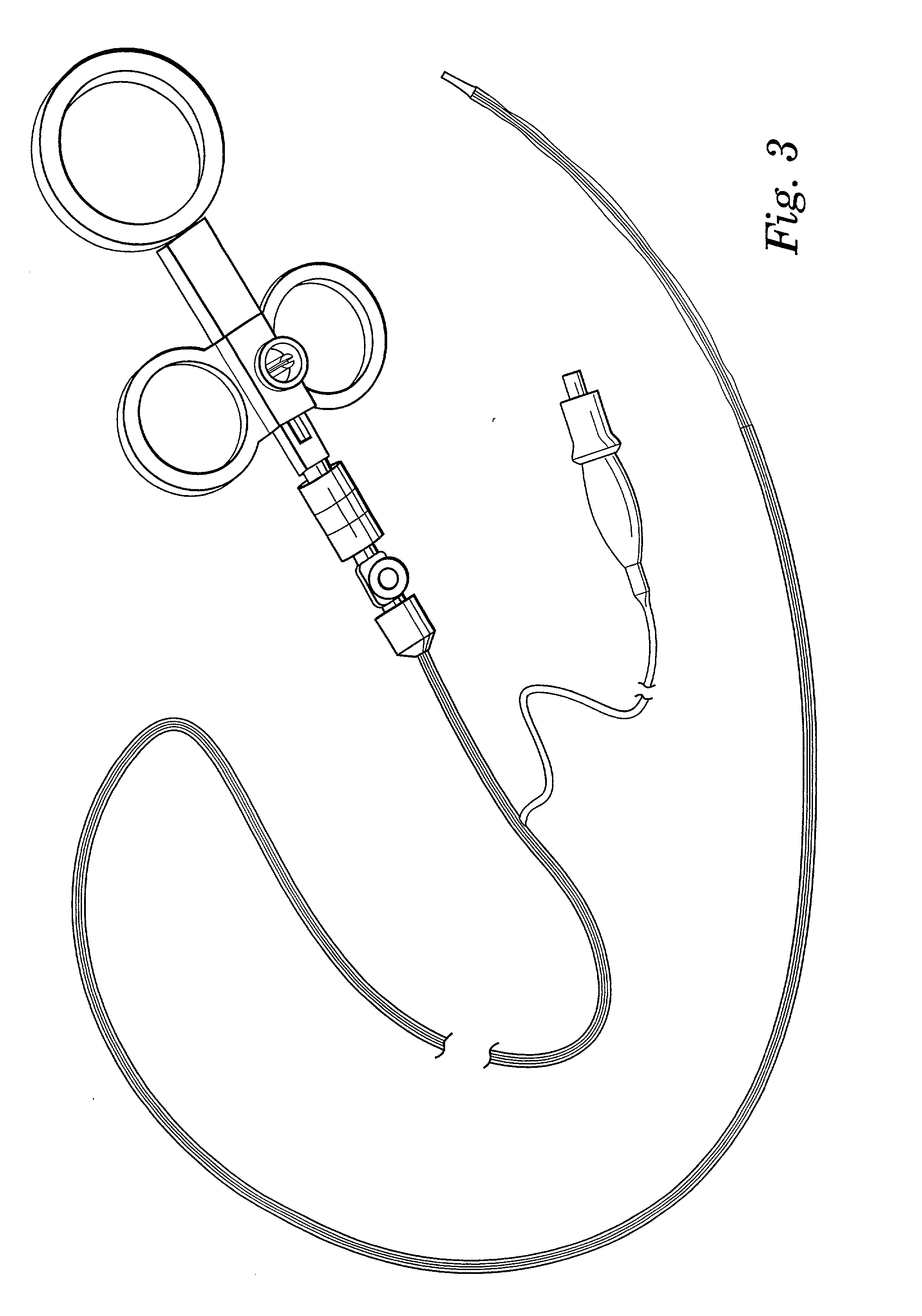
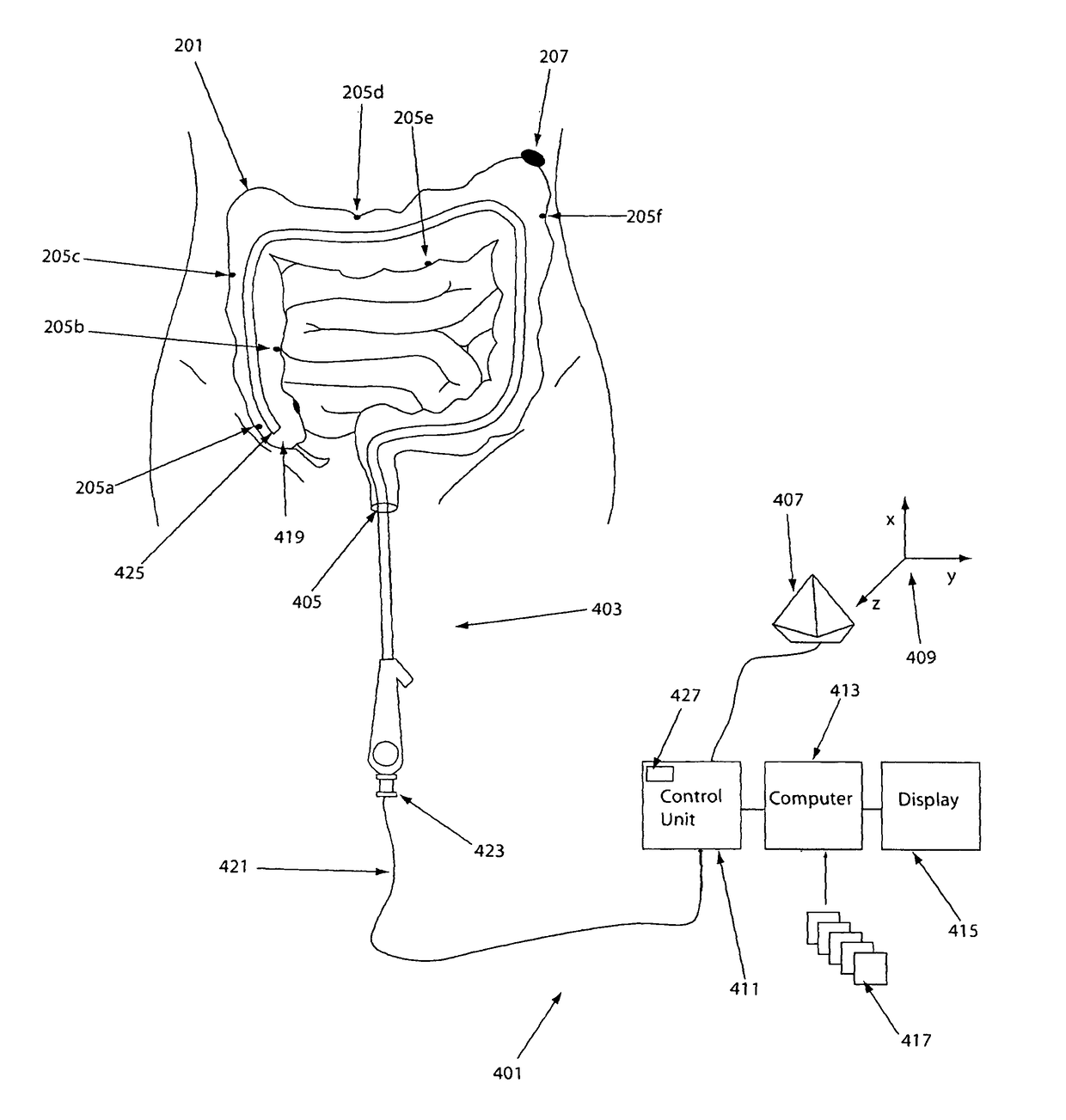
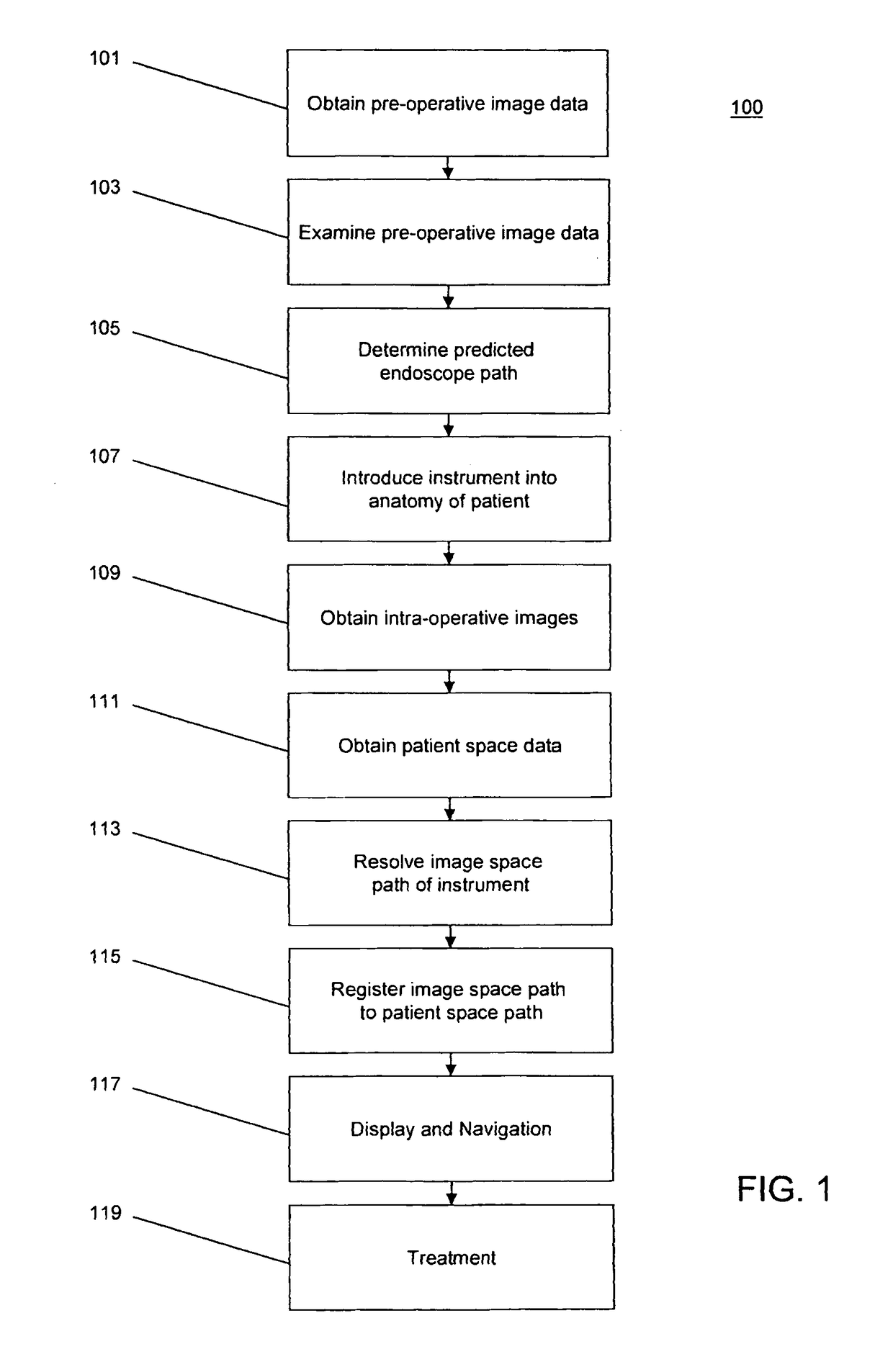
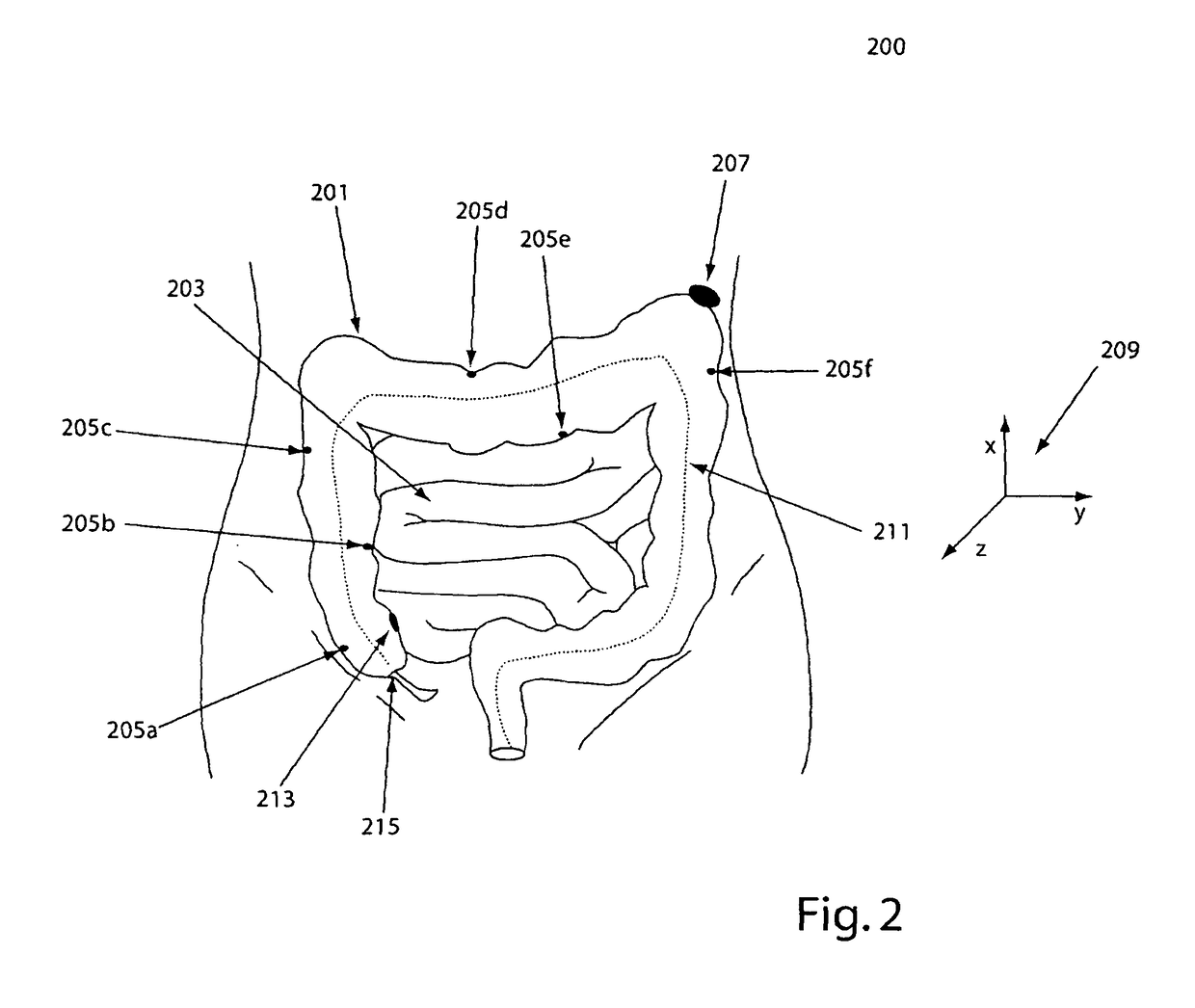
The invention provides a method and system for performing an image-guided endoscopic medical procedure. The invention may include registering image-space coordinates of a path of a medical instrument within the anatomy of a patient to patient-space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In some embodiments, the image space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument may be predicted coordinates such as, for example, a calculated centerline through a conduit-like organ, or a calculated “most likely path” of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In other embodiments, the path of the medical instrument may be an actual path determined using intra-operative images of the patient's anatomy with the medical instrument inserted therein. The registered instrument may then be navigated to one or more items of interest for performance of the endoscopic medical procedure.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
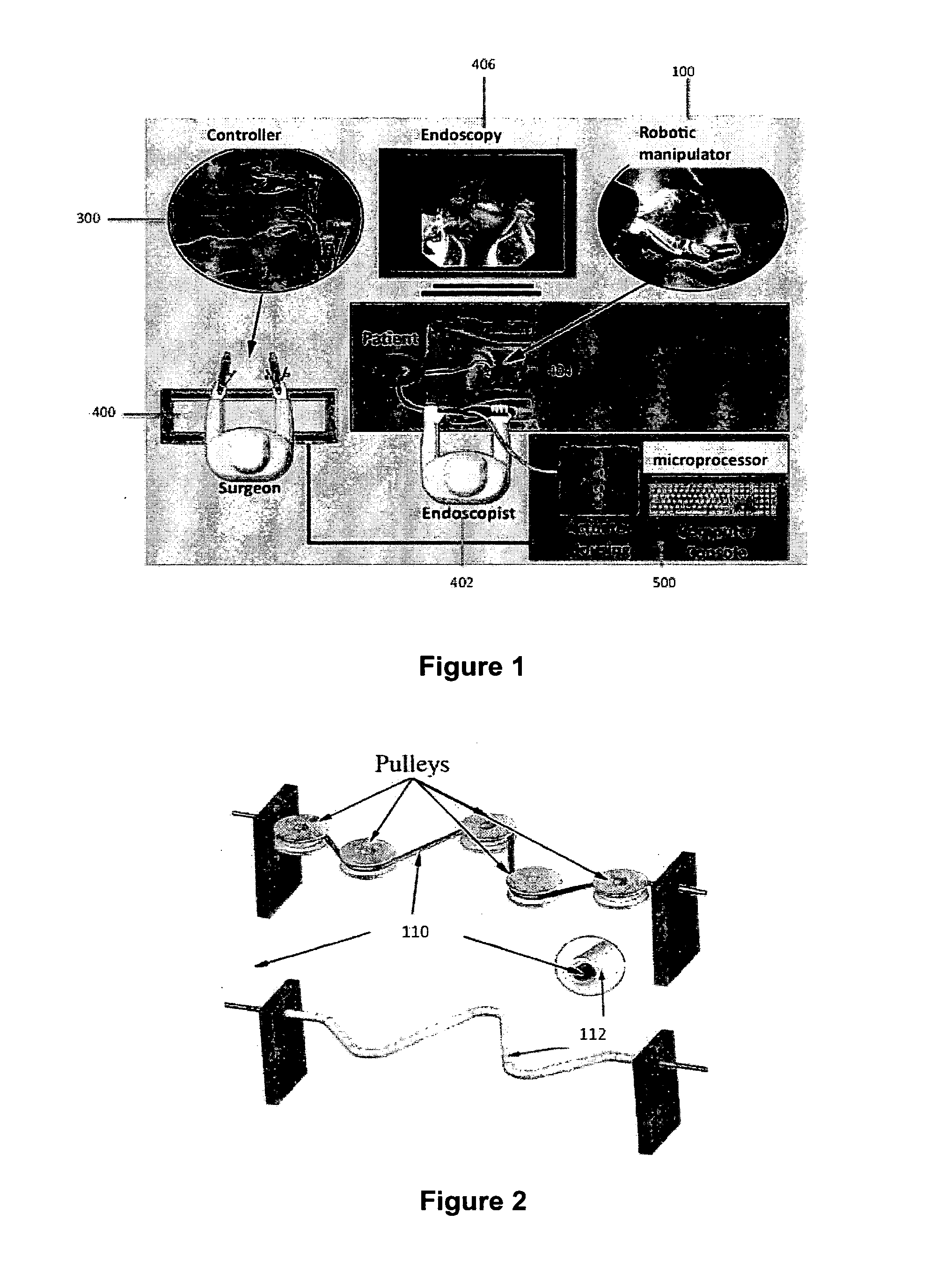
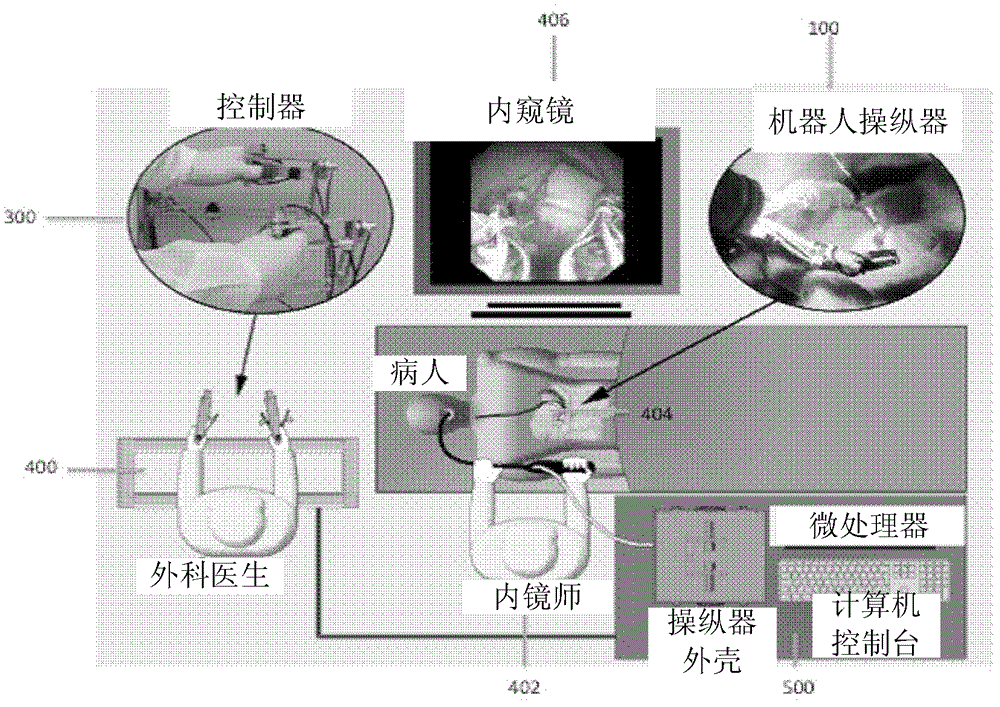
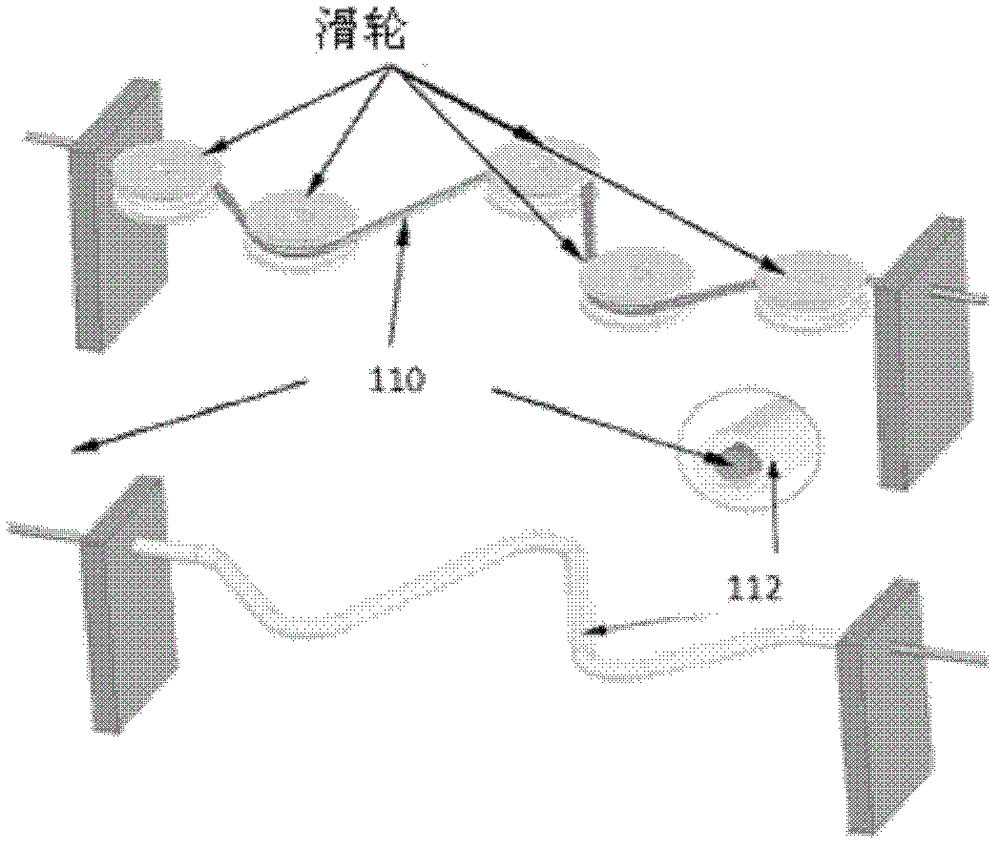
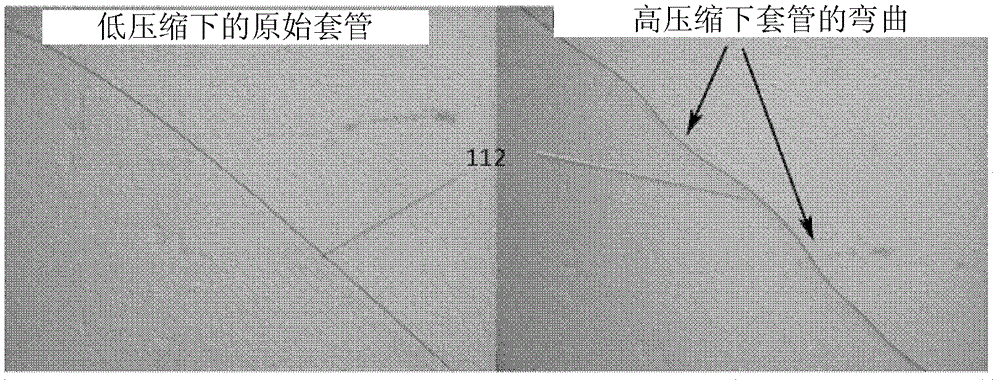
Robotic system for flexible endoscopy
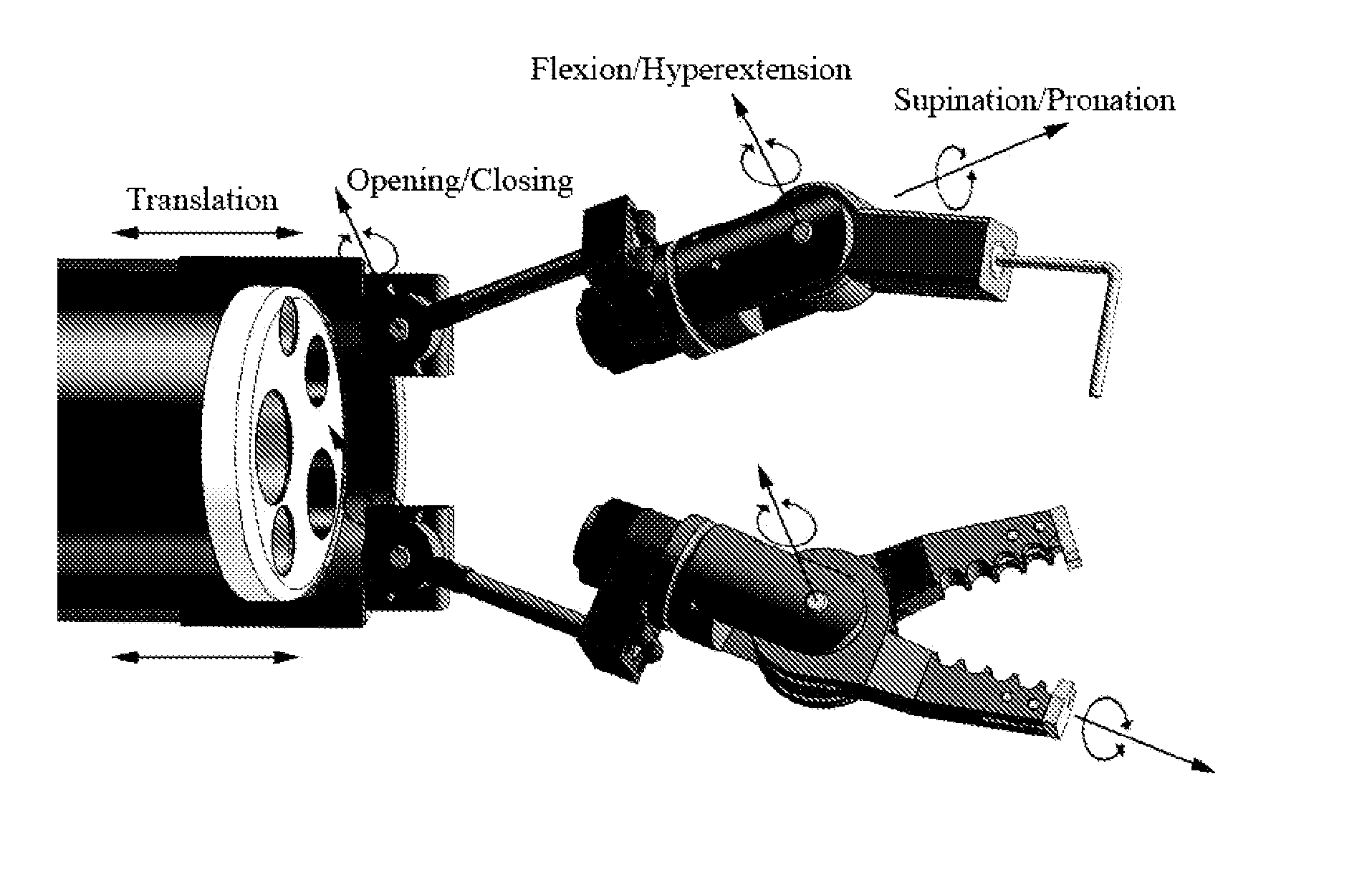
InactiveUS8882660B2Intricate and precise surgical interventionRemove scarsEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingFlexible endoscopyRobotic systems
A robotic manipulator controller and system for use in flexible endoscopy, the manipulator comprising a flexible member configured to be coupled to an endoscope, and an arm connected to and movable by the flexible member, wherein the flexible member has a first end connected to the arm and a second end connectable to the controller to allow a physical movement of the arm to be controllable by a physical movement of the controller.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
System, method and devices for navigated flexible endoscopy
The invention provides a method and system for performing an image-guided endoscopic medical procedure. The invention may include registering image-space coordinates of a path of a medical instrument within the anatomy of a patient to patient-space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In some embodiments, the image space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument may be predicted coordinates such as, for example, a calculated centerline through a conduit-like organ, or a calculated “most likely path” of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In other embodiments, the path of the medical instrument may be an actual path determined using intra-operative images of the patient's anatomy with the medical instrument inserted therein. The registered instrument may then be navigated to one or more items of interest for performance of the endoscopic medical procedure.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
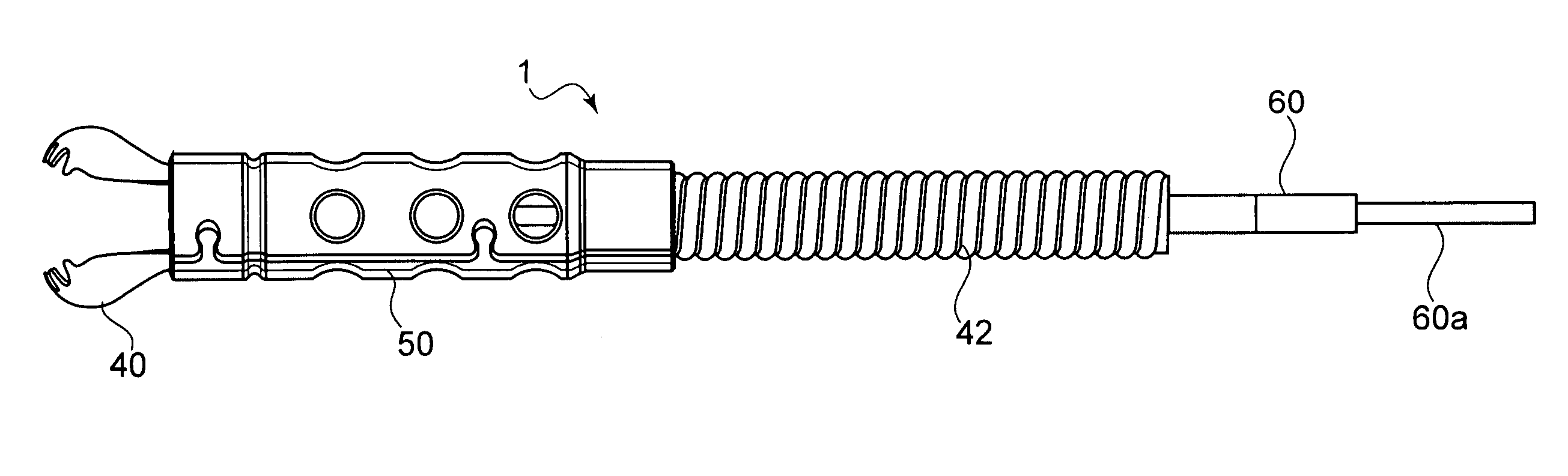
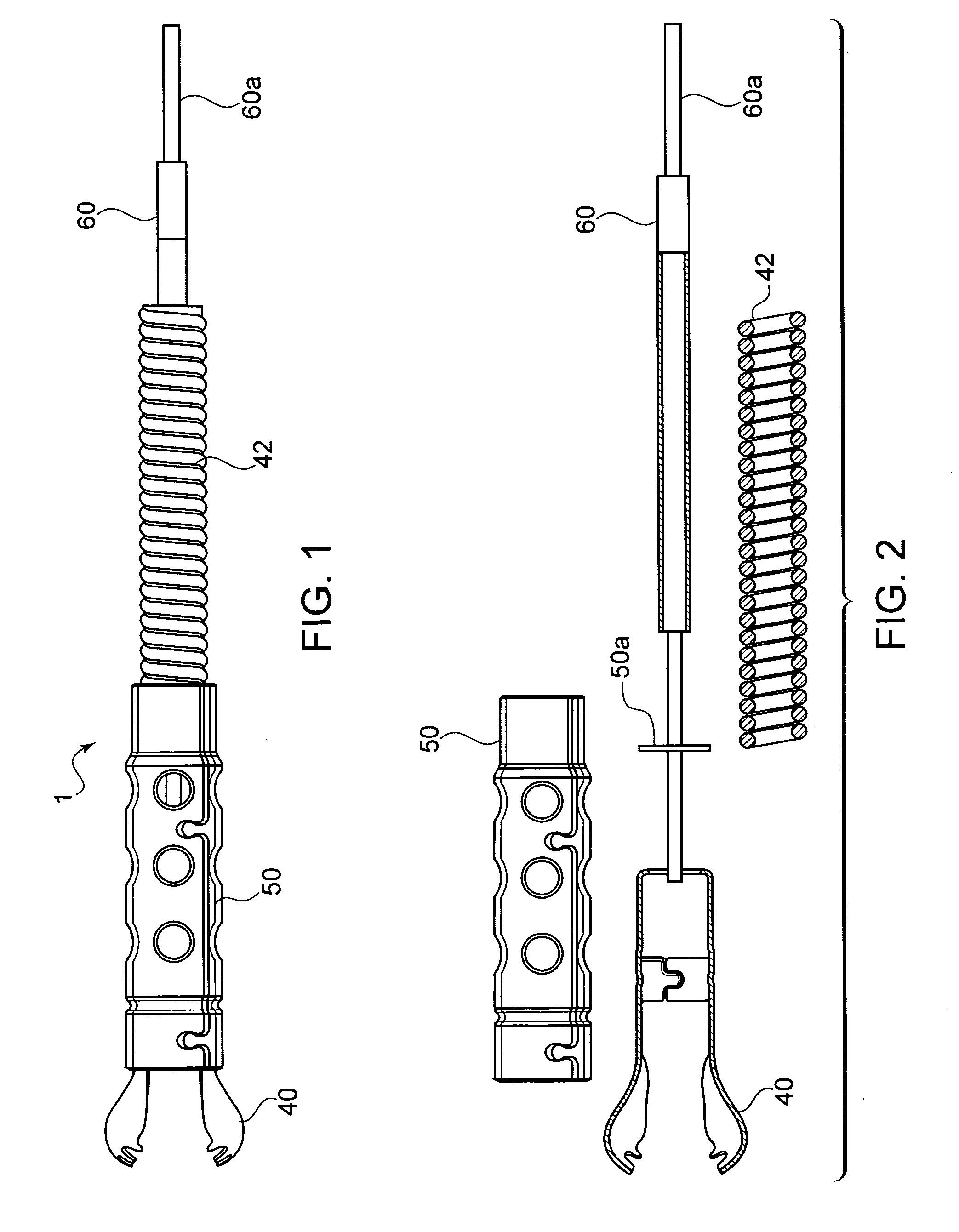
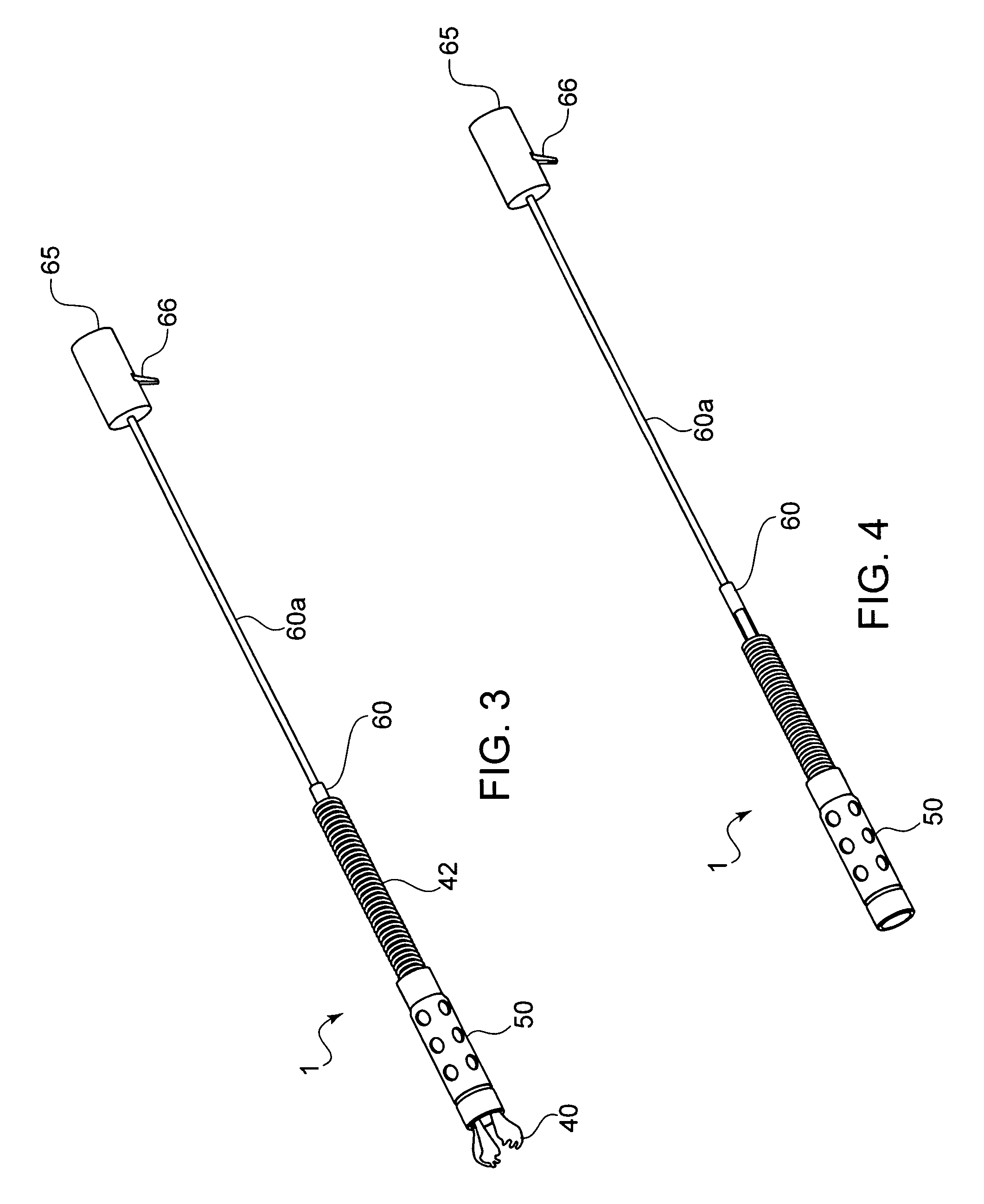
Detachable shaft flexible endoscope
ActiveUS9107573B2Good adhesionEasy detachmentSurgeryEndoscopesElectric power transmissionFlexible endoscopy
A flexible endoscope includes a handle, a flexible shaft having a distal end and a proximal end, a coupling mechanism releasably attaching the handle to the distal end of the flexible shaft, an illumination unit disposed in the flexible shaft, the illumination unit providing light to an area in front of the distal end of the flexible shaft, and an imaging unit disposed in the flexible shaft, the imaging unit generating image data of the area in front of the distal end of the flexible shaft, wherein the coupling mechanism includes an electrical channel for transmitting electrical power to the illumination unit and the imaging unit, and a data channel for transmitting the image data from the imaging unit.
Owner:KARL STORZ ENDOVISION INC
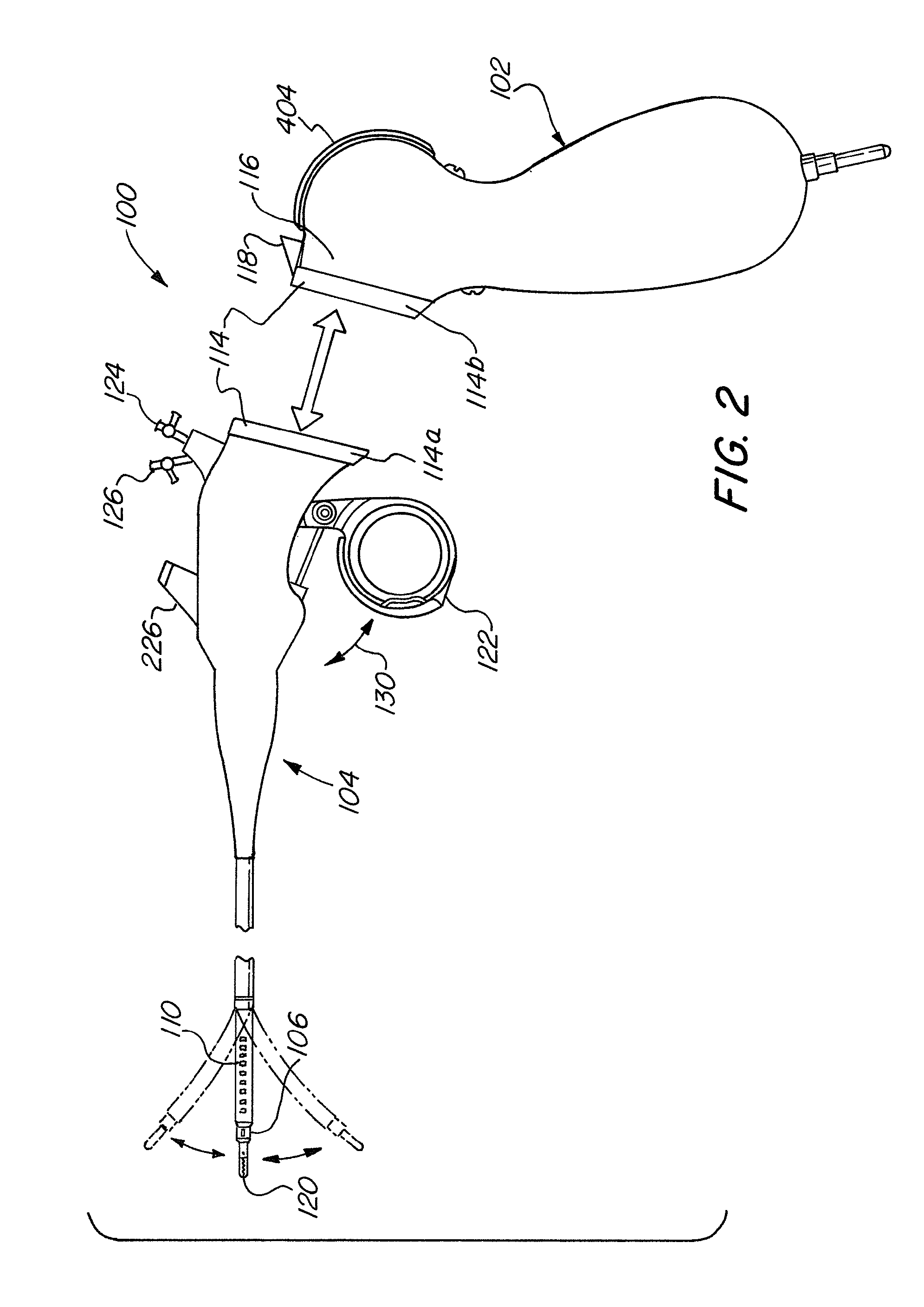
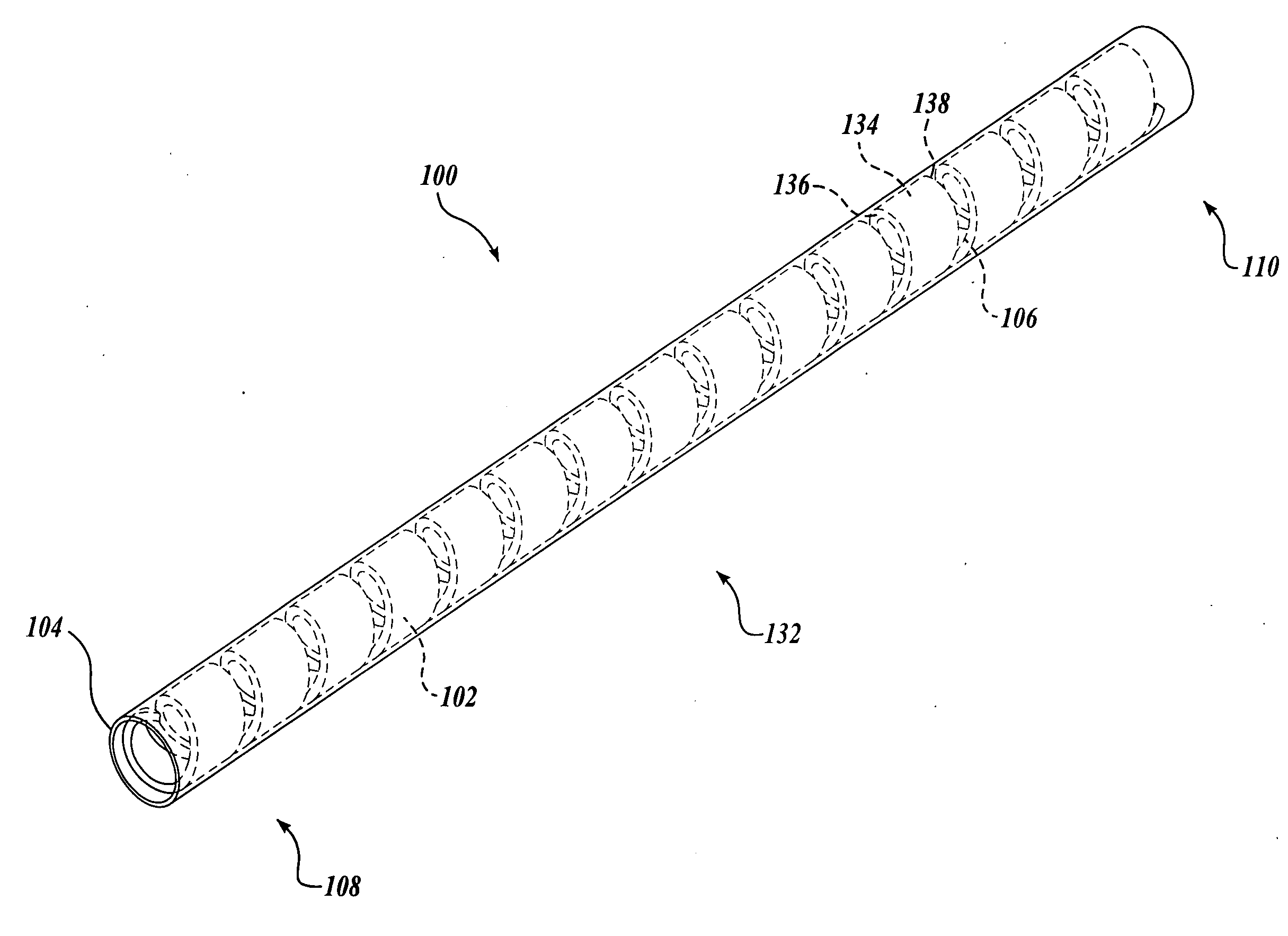
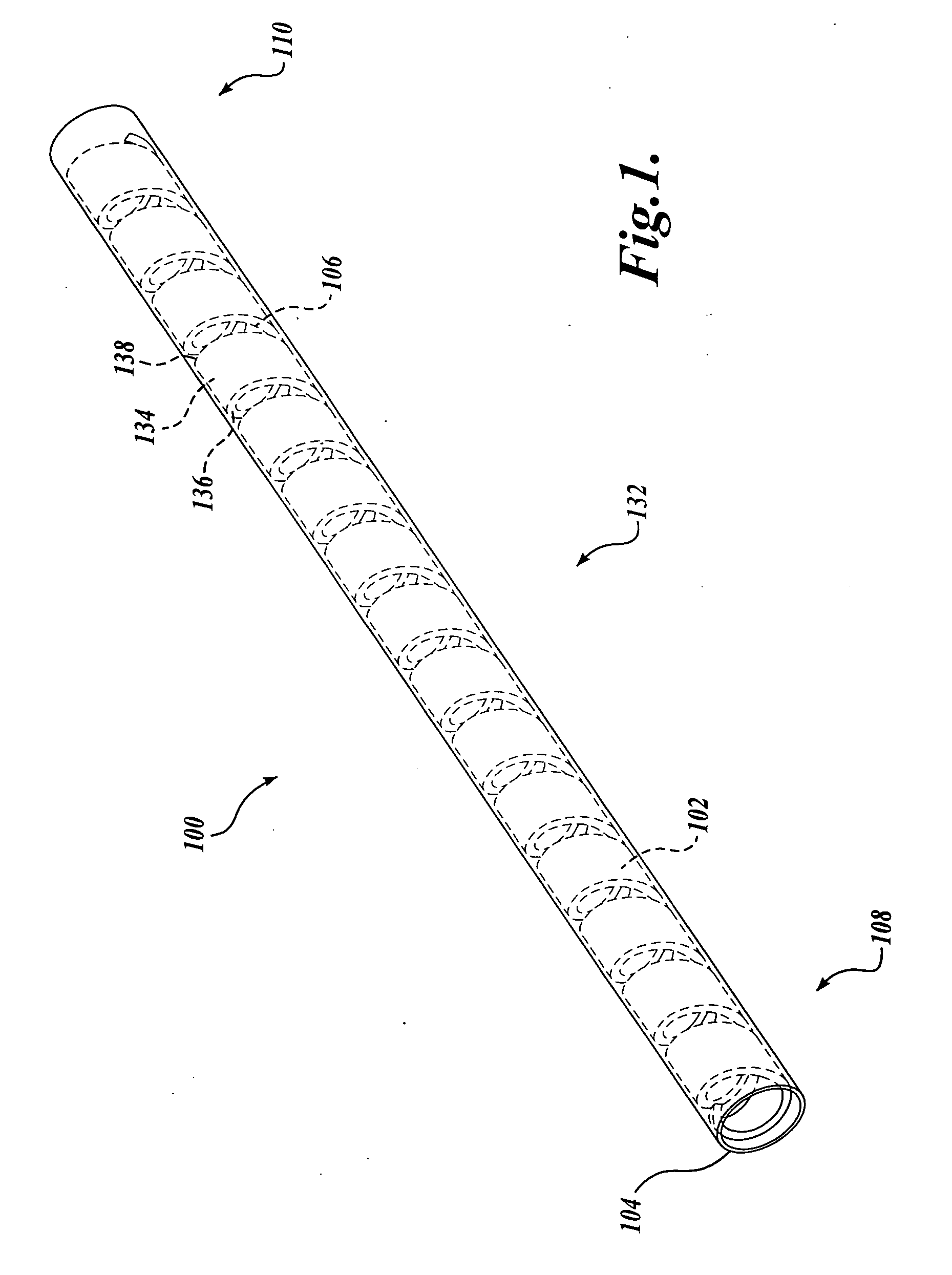
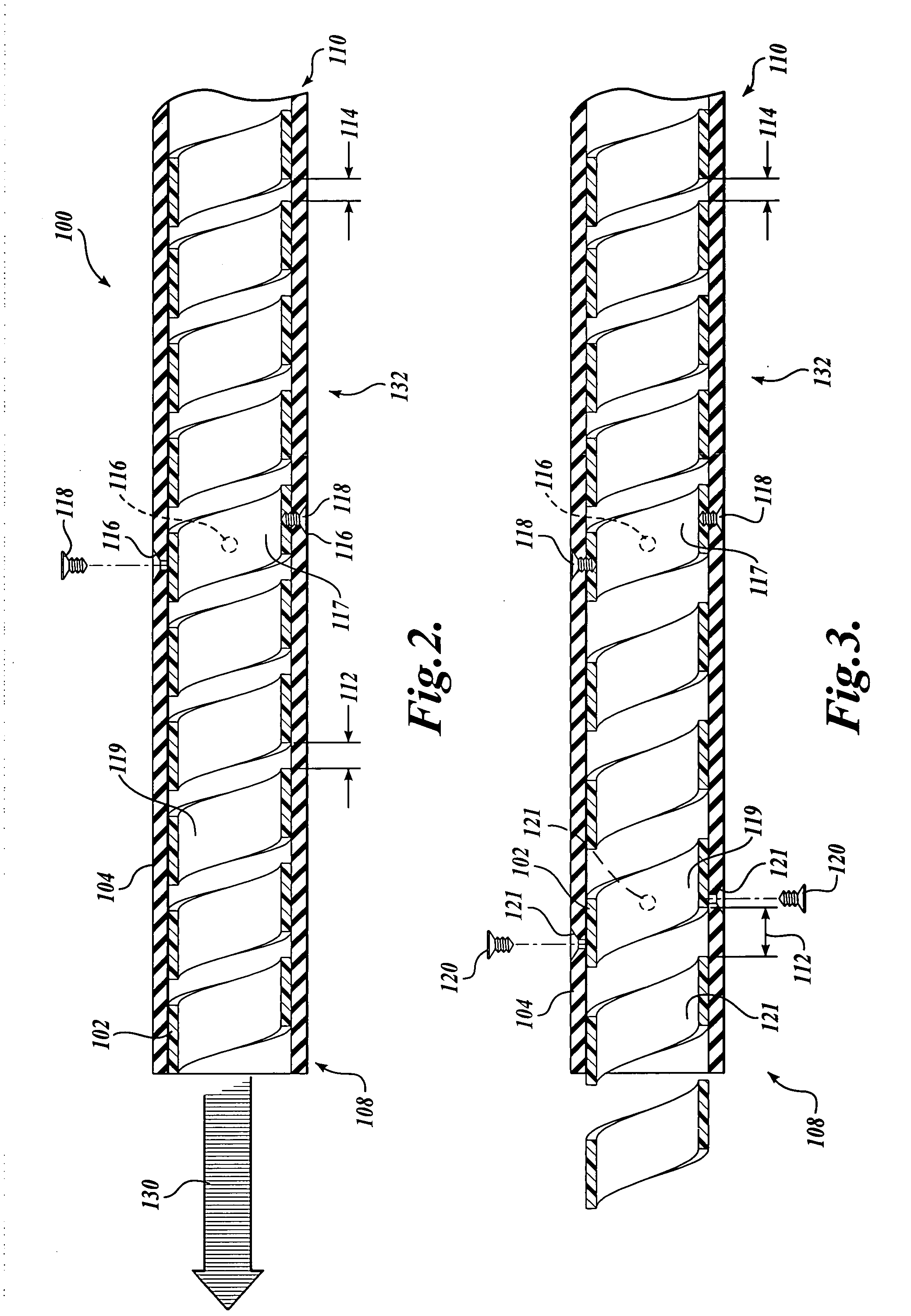
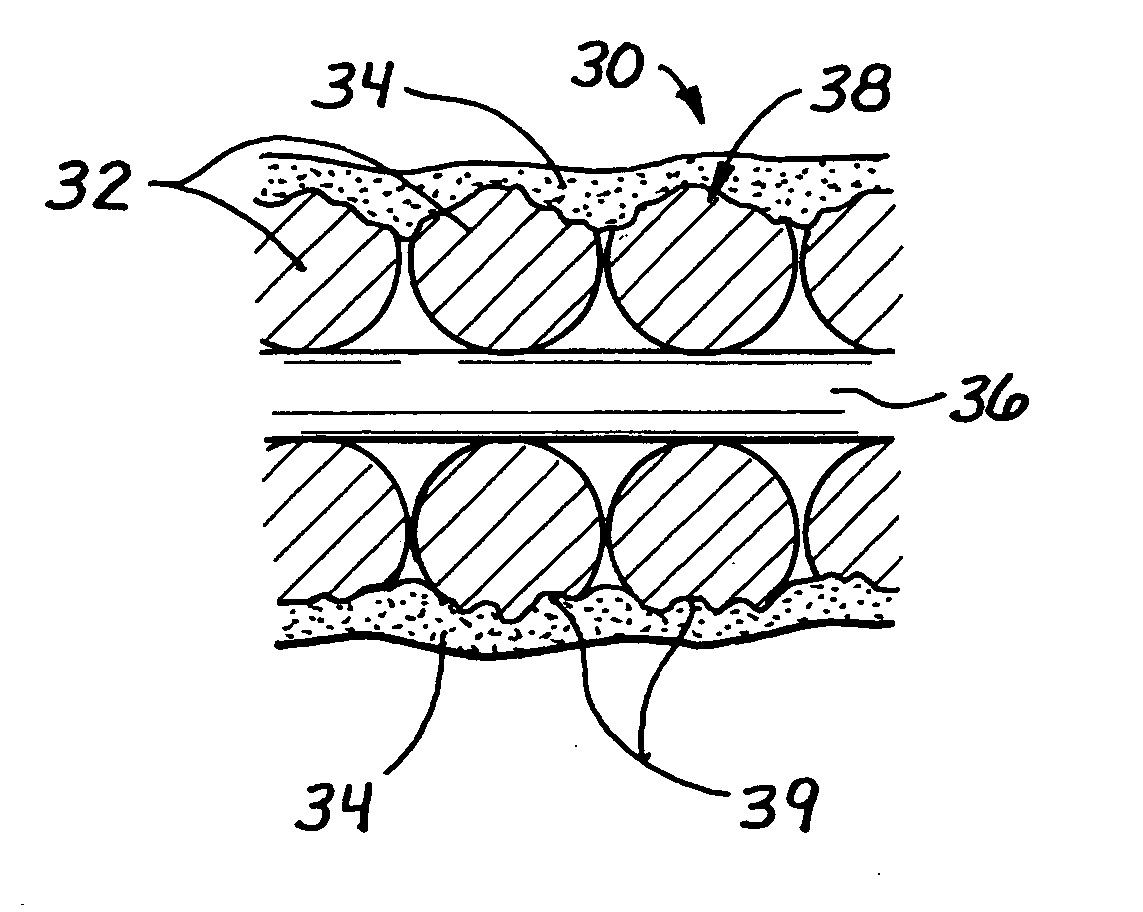
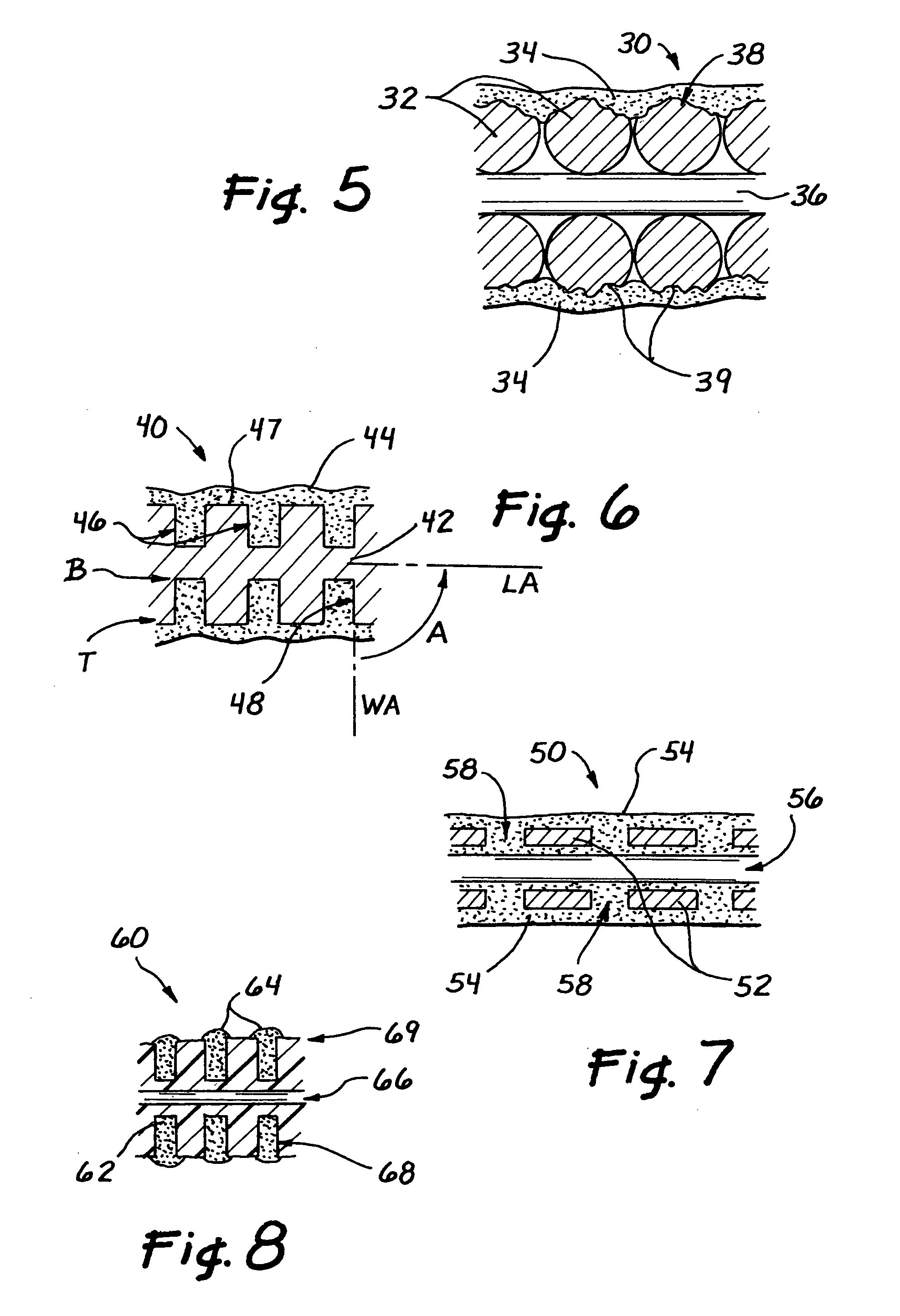
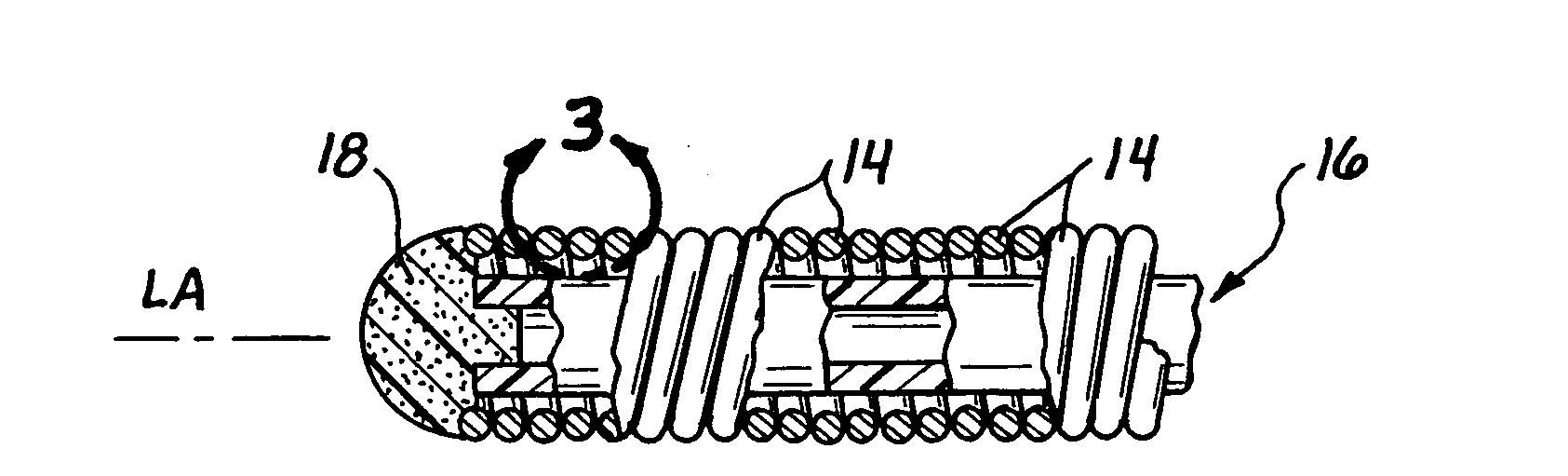
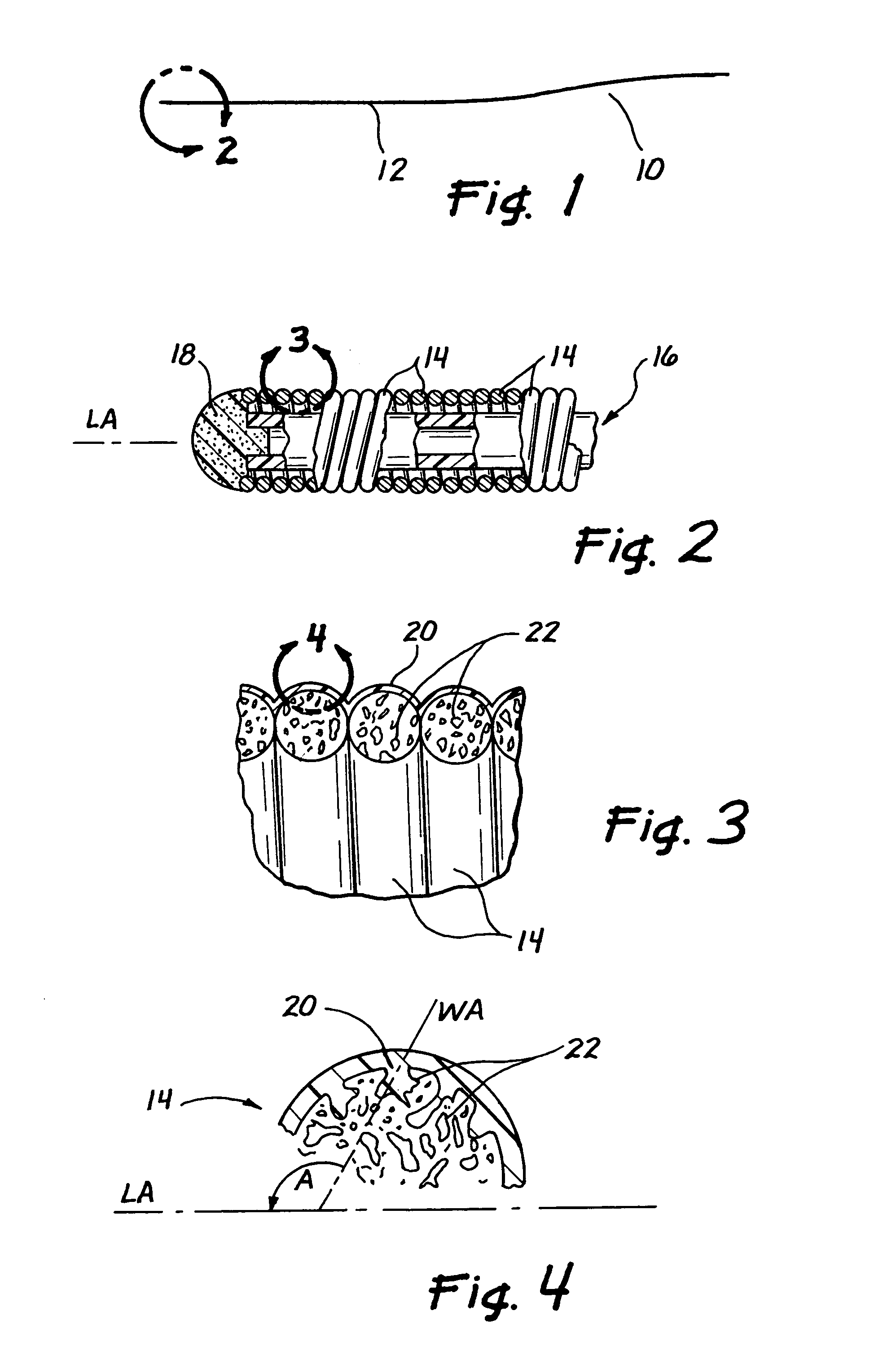
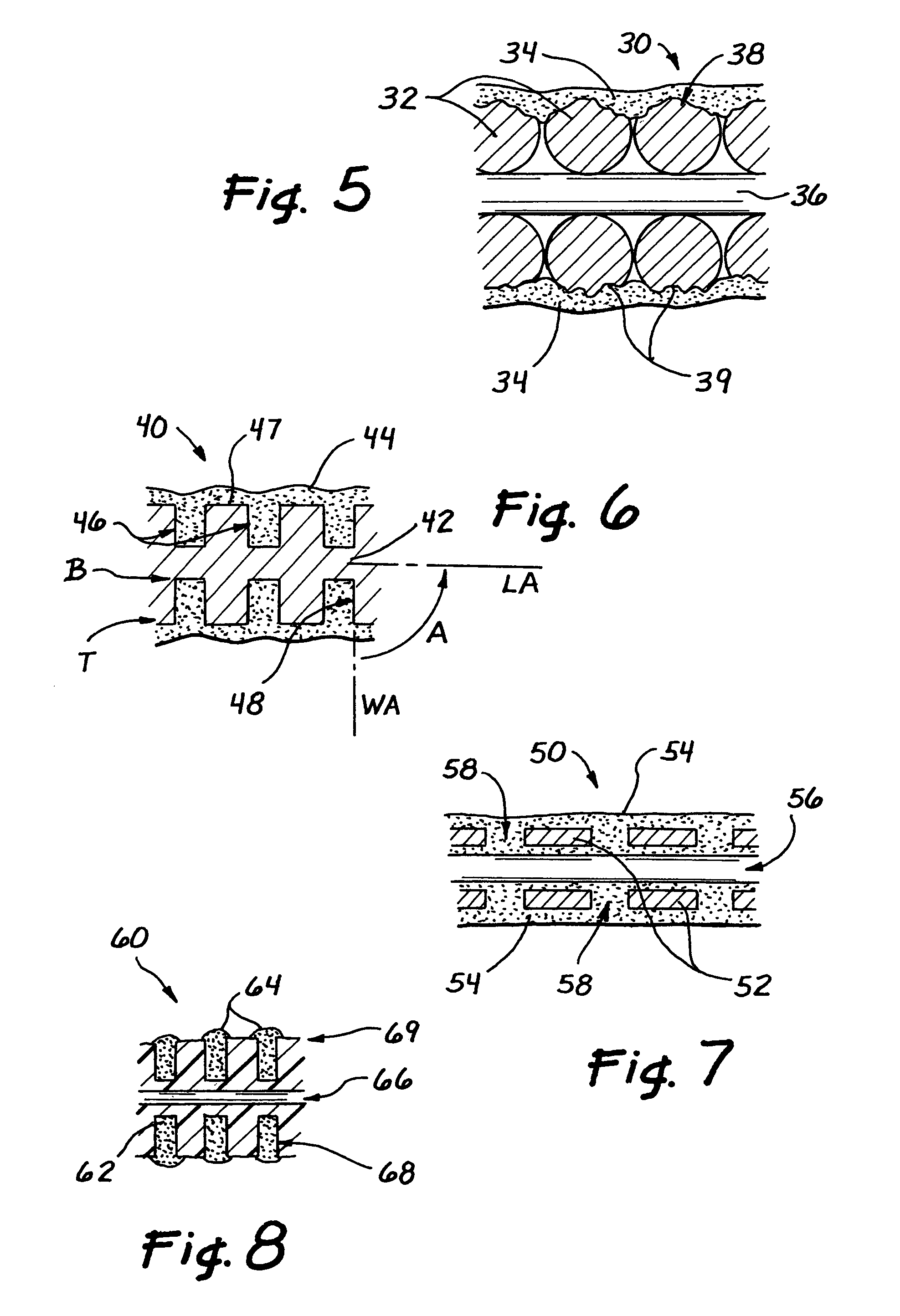
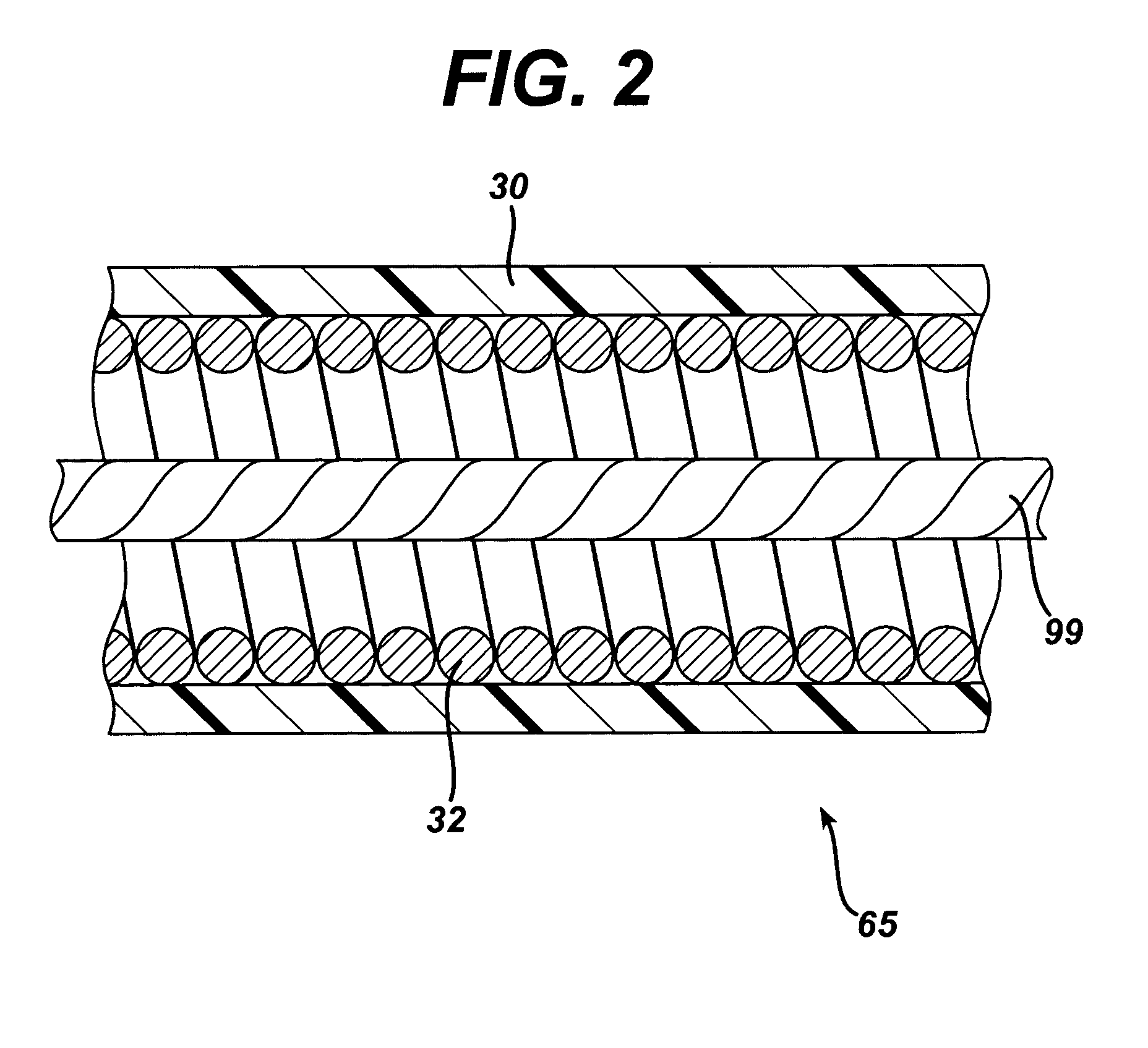
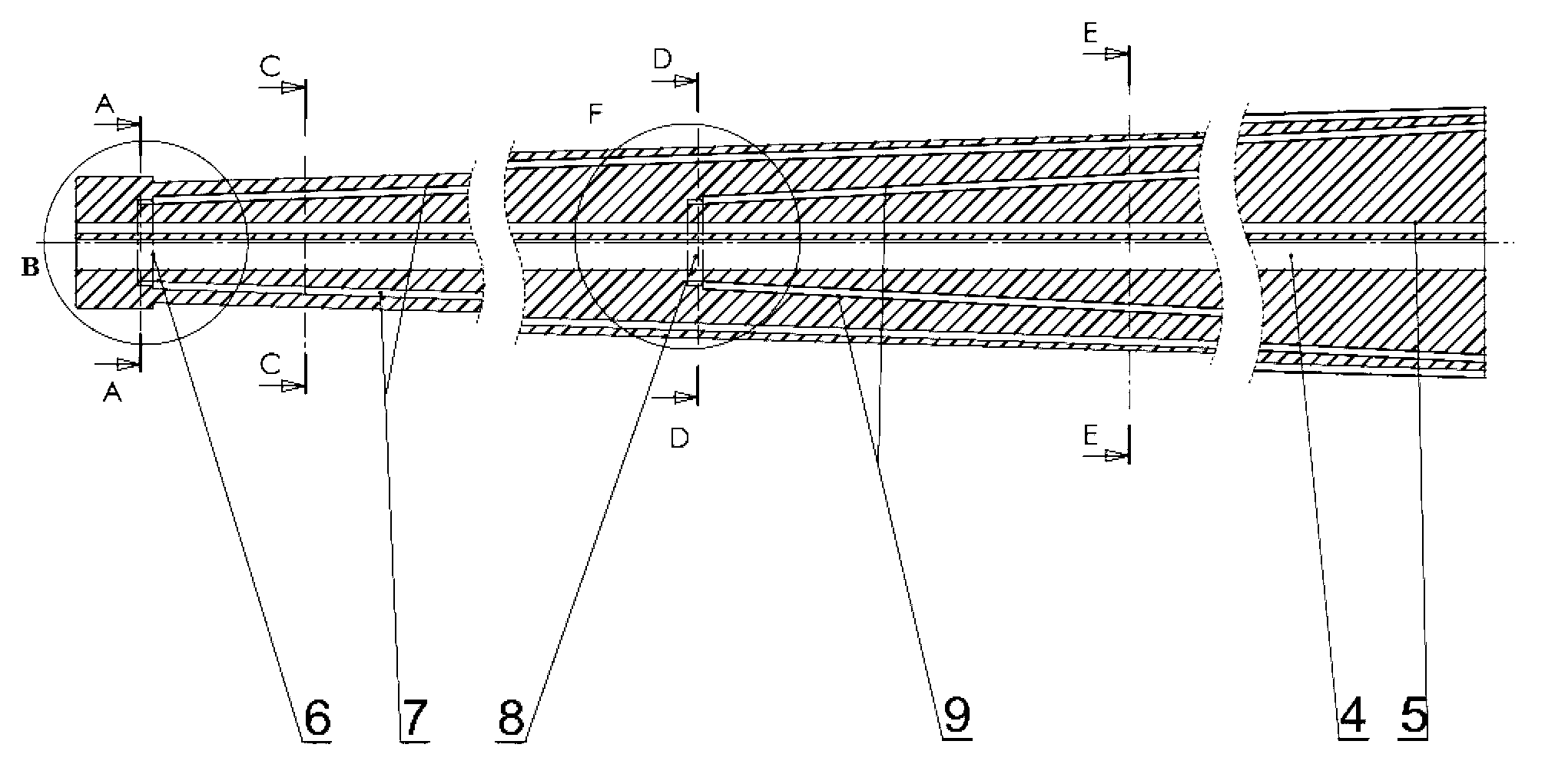
Flexible endoscope with variable stiffness shaft
A shaft for a medical device includes an outer sheath and a flexible spiral wrap therein. The flexibility of the spiral wrap is modified by changing the width of the wraps of a spiral, the thickness of the wraps of a spiral, or the gap spacing of the spiral. The spacing between wraps is maintained by attaching the spiral wrap to the cover sheath that surrounds the spiral wrap at two or more locations.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medical devices having full or partial polymer coatings and their methods of manufacture
Medical devices for insertion into the body of human or veterinary patients, wherein the device comprises a) a working element (e.g. a wire, a guidewire, a tube, a catheter, a cannula, a scope (e.g., rigid or flexible endoscope, laparoscope, sigmoidoscope, cystoscope, etc.) a probe, an apparatus for collecting information from a location within the body (e.g., an electrode, sensor, camera, scope, sample withdrawal apparatus, biopsy or tissue sampling device, etc.) which has an outer surface and b) a continuous or non-continuous coating on the outer surface of the working element. The outer surface of the working element is prepared to create a surface topography which promotes mechanical or frictional engagement of the coating to the working element. In some embodiments the coating is a lubricious coating, such as a fluorocarbon coating or a hydrogel that becomes lubricious when contacted by a liquid. In some embodiments, the coating may expand as swell. Also disclosed as methods for manufacturing such devices.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Robotic system for flexible endoscopy
InactiveUS20120078053A1Reduce inertiaExtreme environmental conditionEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingFlexible endoscopyRobotic systems
A robotic manipulator controller and system for use in flexible endoscopy, the manipulator comprising a flexible member configured to be coupled to an endoscope, and an arm connected to and movable by the flexible member, wherein the flexible member has a first end connected to the arm and a second end connectable to the controller to allow a physical movement of the arm to be controllable by a physical movement of the controller.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
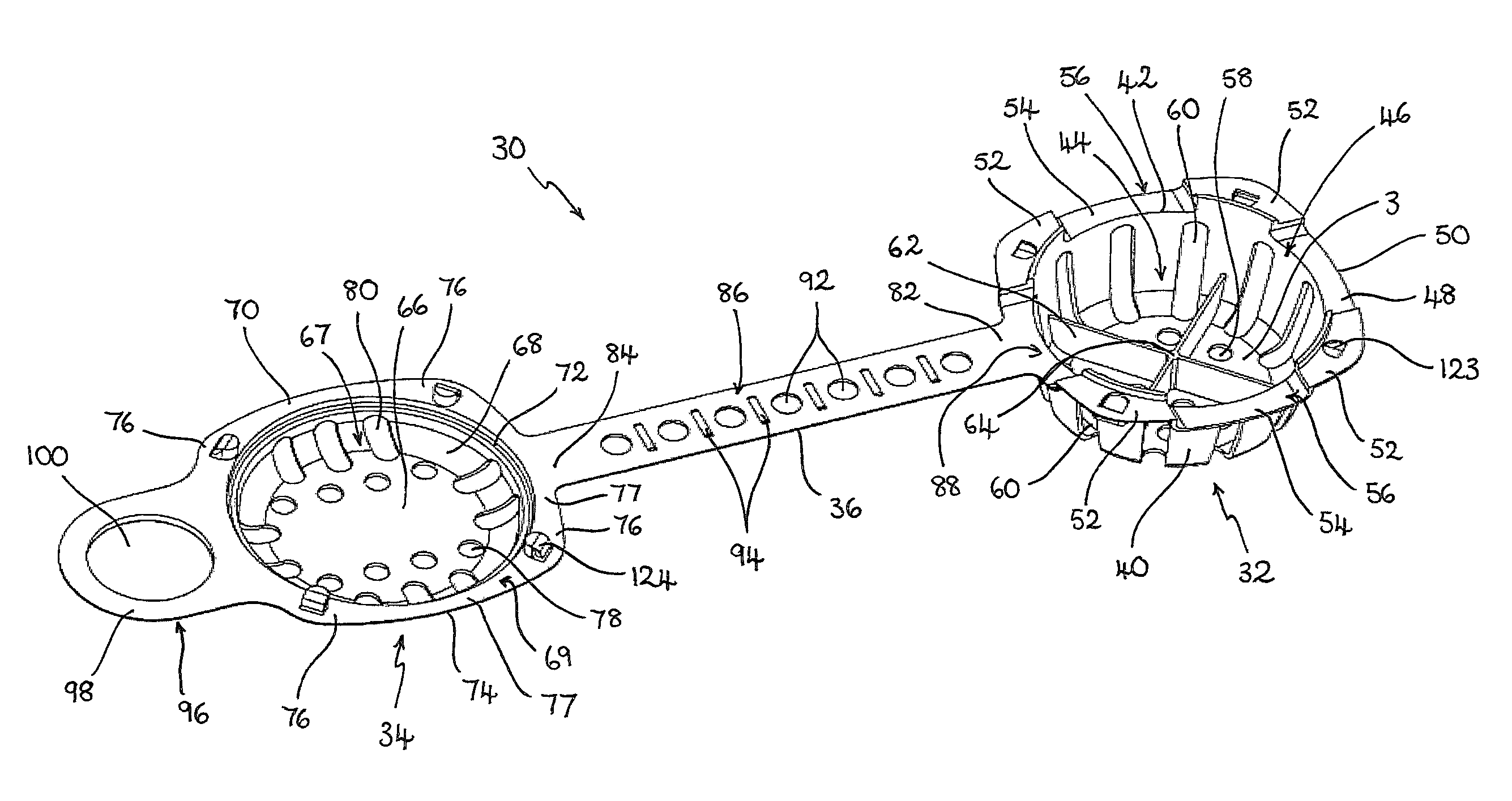
Tissue approximation system
InactiveUS20080234703A1Easy to watchEffective movementSurgical staplesWound clampsFlexible endoscopyEndoscope
Methods and devices for approximating tissue are disclosed. The methods and devices utilize a device for applying an implantable tissue fastener and a variety of implantable tissue fasteners. The tissue-fastening device can be delivered endoscopically and can be adapted to function along side or in conjunction with a flexible endoscope. In general, the device can include a flexible shaft having an implantable tissue fastener applier disposed at a distal end thereof and a handle for operating the implantable tissue fastener applier disposed at a proximal end thereof. A variety of self-deploying implantable tissue fasteners can be used with the tissue fastener applier device.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
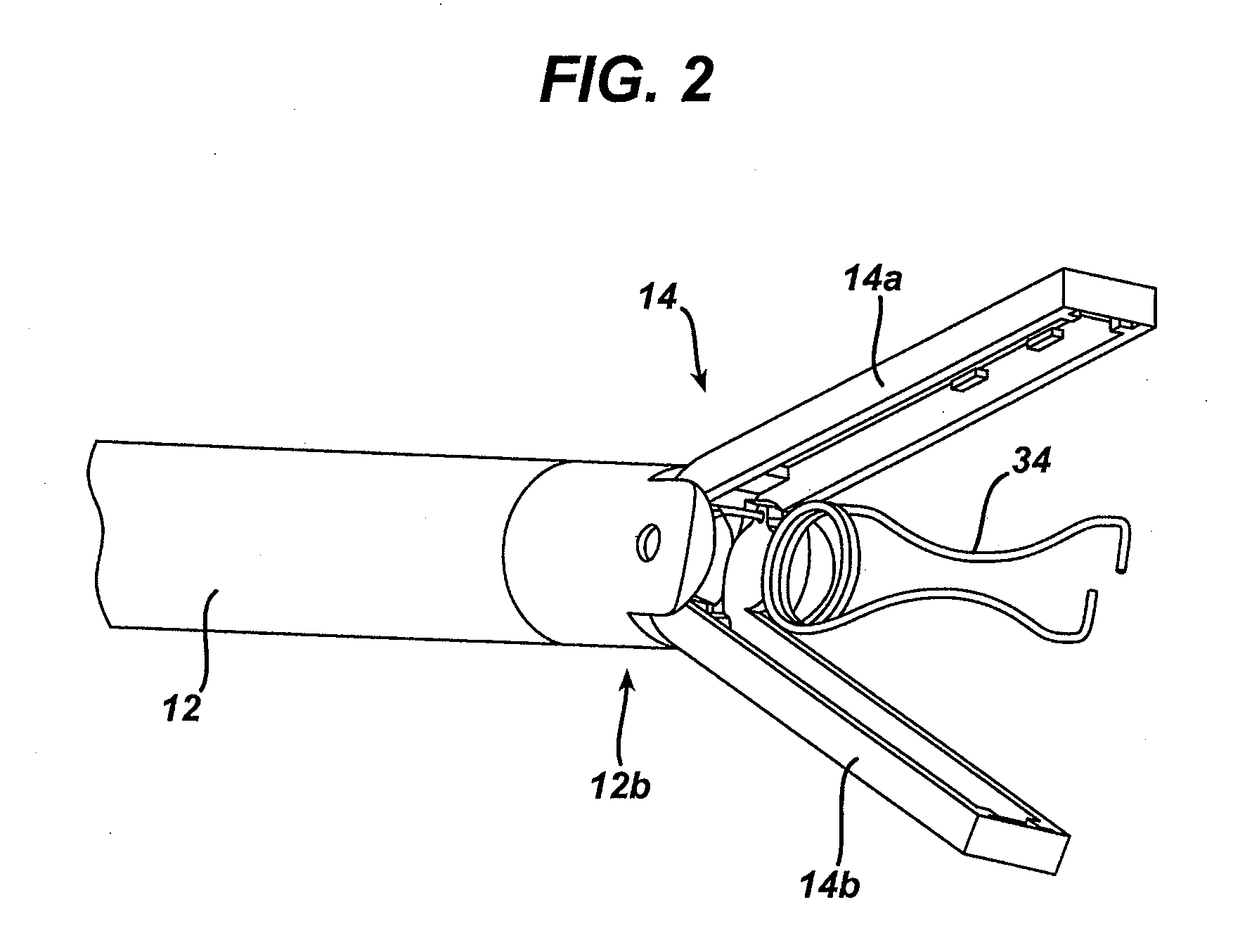
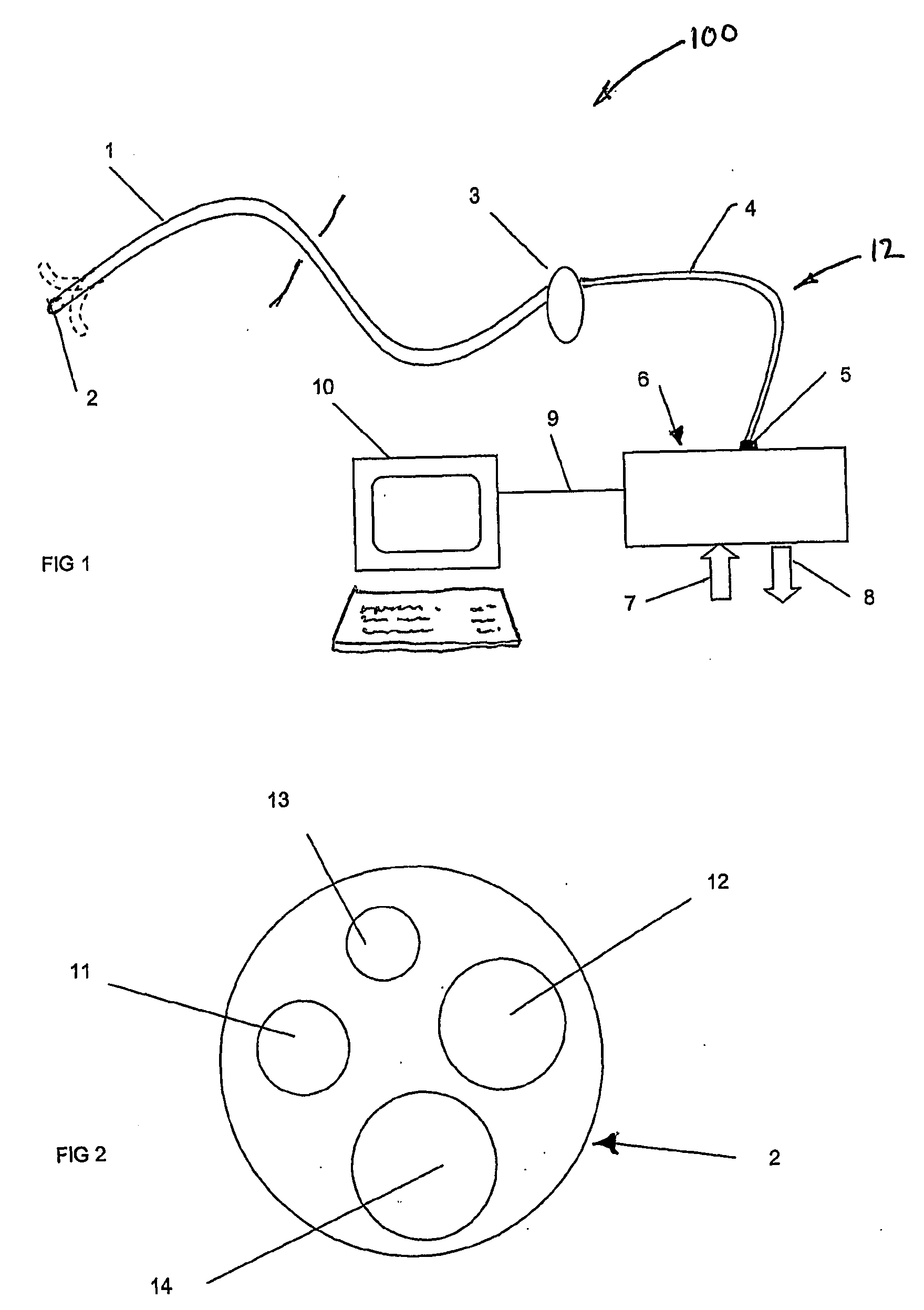
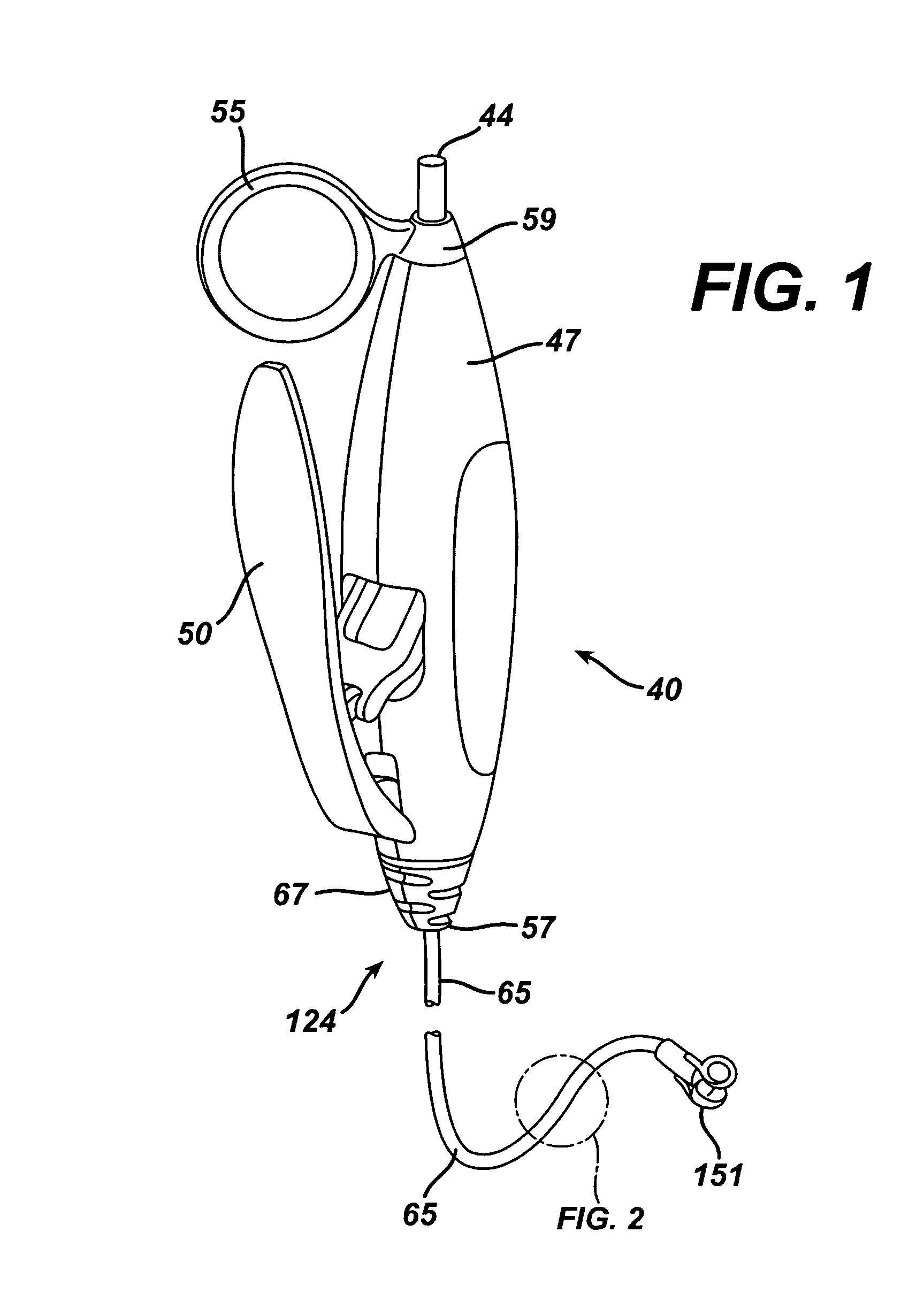
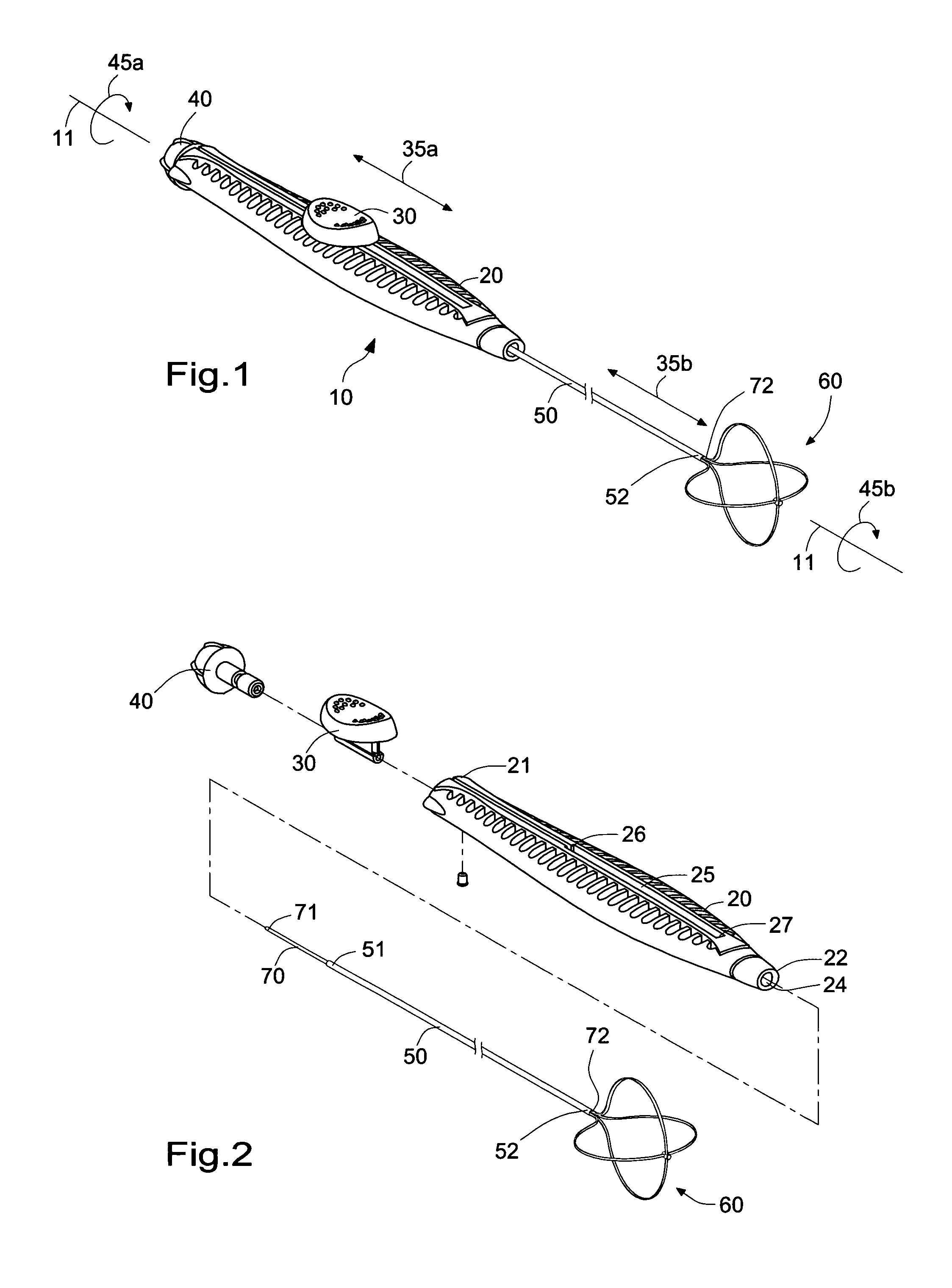
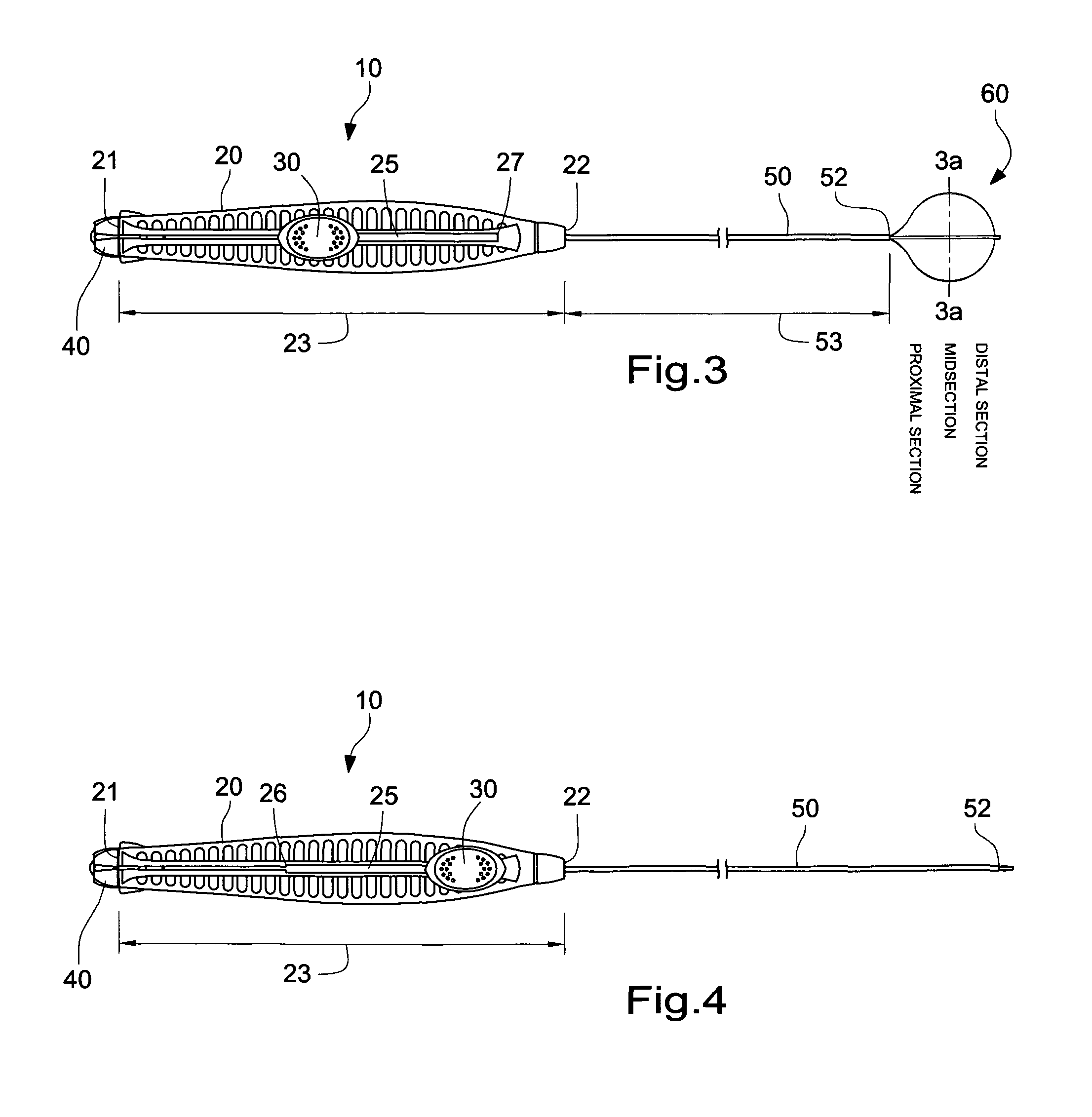
Disposable flexible endoscope
A disposable endoscope system (100) connects to a reusable control and monitor unit 6,10 and comprises a flexible insertion section (1) connected to an operating handle (3) that connects to an umbilical cord (4). The end interface (5) of the umbilical is the final component of the disposable endoscope. The flexible insertion section (2) has a video camera (12), an illumination source (11) and an actively steered section that is controlled from the operating handle. The endoscope provides PC mouse functionality, enabling image and procedure logging and controls and integration with other patient management systems.
Owner:SINGLE USE SURGICAL
Medical devices having full or partial polymer coatings and their methods of manufacture
Medical devices for insertion into the body of human or veterinary patients, wherein the device comprises a) a working element (e.g. a wire, a guidewire, a tube, a catheter, a cannula, a scope (e.g., rigid or flexible endoscope, laparoscope, sigmoidoscope, cystoscope, etc.) a probe, an apparatus for collecting information from a location within the body (e.g., an electrode, sensor, camera, scope, sample withdrawal apparatus, biopsy or tissue sampling device, etc.) which has an outer surface and b) a continuous or non-continuous coating on the outer surface of the working element. The outer surface of the working element is prepared to create a surface topography which promotes mechanical or frictional engagement of the coating to the working element. In some embodiments the coating is a lubricious coating, such as a fluorocarbon coating or a hydrogel that becomes lubricious when contacted by a liquid. In some embodiments, the coating may expand as swell. Also disclosed as methods for manufacturing such devices.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
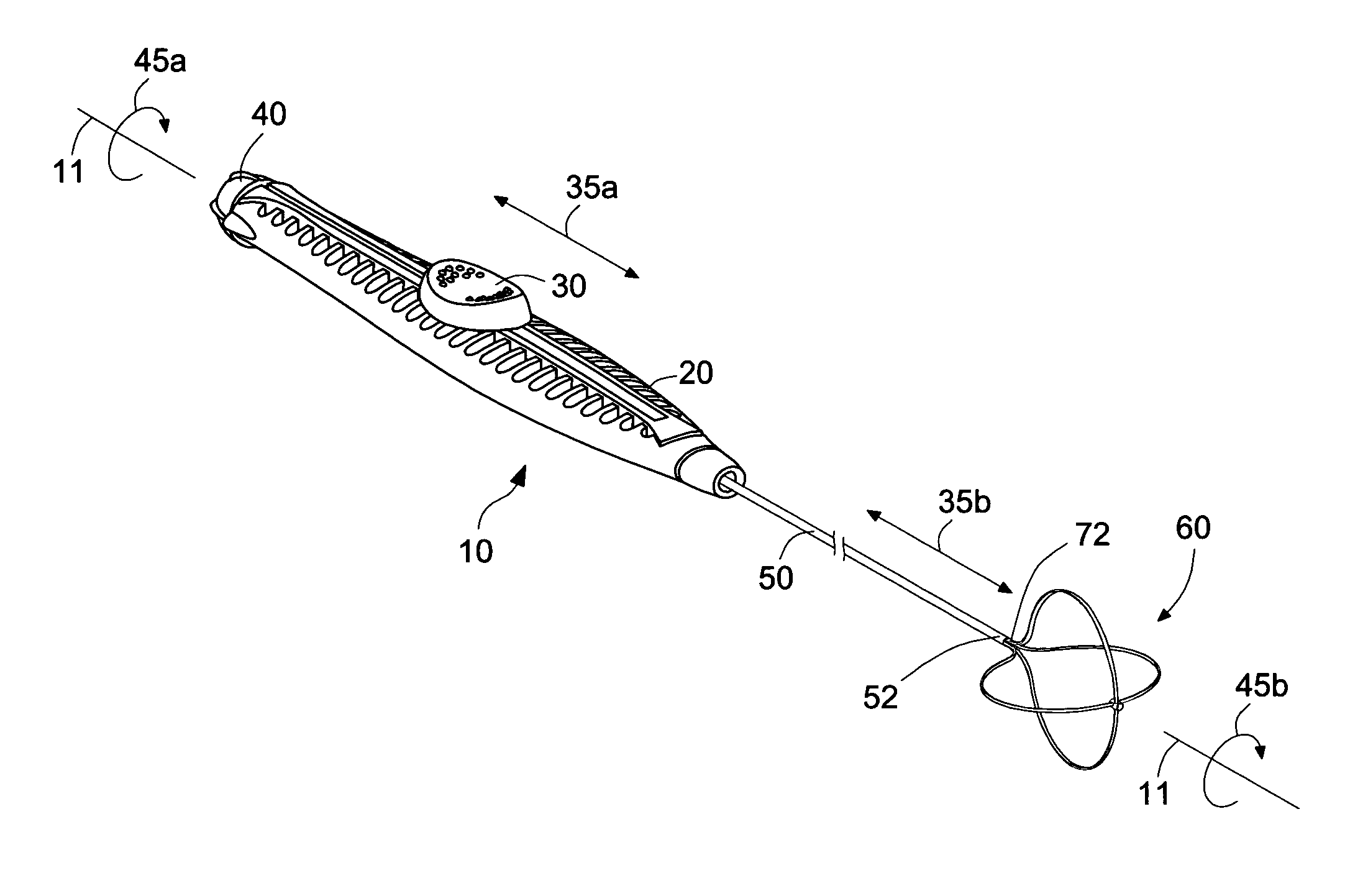
Actuation mechanism for flexible endoscopic device
InactiveUS7708756B2Minimize the potential for miscommunicationsAvoid insufficient lengthSurgical needlesSurgical scissorsFlexible endoscopyActuator
An endoscopic accessory medical device is provided. The device can include a handle, a flexible shaft, and an end effector. The handle can include an actuator for operating the end effector through a wire or cable pulling member that extends through the flexible shaft. The handle and actuator can be operable with a single hand, such that the operation of the end effector can be accomplished with the same hand that is used to hold the handle and advance the end effector through an endoscope. The handle can include an actuation mechanism that is decoupled from operation of the end effector when the actuator is in a first open position, which becomes operatively coupled to the end effector when the actuator is moved to a second position, such as by squeezing the actuator, and which operates the end effector when the actuator is moved further to a third position.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Apparatus and method for steam reprocessing flexible endoscopes
A system for reprocessing flexible endoscopes having lumen therein. The reprocessing system deploys steam to disinfect and / or sterilize the endoscopes, and designs, components and methods for reducing or balancing the reprocessing cycle time and the effects of thermal expansion and contraction on the endoscopes.
Owner:MEDIVATORS INC
Endoscopic instrument management system
InactiveUS20100137681A1Easy to manageImproved force transmissionEndoscopesSurgical forcepsFlexible endoscopyEngineering
Endoscopic instrument management systems are described herein which allow one or more operators to manage multiple different instruments utilized in endoscopic procedures. In one aspect, responsibility for instrumentation management between one or more operators may be configured such that a first set of instruments is controlled by a primary operator and a second set of instruments is controlled by a secondary operator. The division of instrumentation may be facilitated by the use of separated instrumentation platforms or a single platform which separates each instrument for use by the primary operator. Such platforms may be configured as trays, instrument support arms, multi-instrument channels, as well as rigidized portions of instruments to facilitate its handling, among others. In another aspect, one or more plastically deformable instrument manifolds are provided to guide flexible endoscopic instruments into and through an endoscopic access device.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Automated actuator for spring based multiple purpose medical instruments
InactiveUS20110124961A1EndoscopesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsFlexible endoscopeElectrical connection
An automated actuator for the spring-based end effector of a medical instrument to be used by a single operator without assistance for biopsy, clipping, clamping, grasping, snaring, cutting, dissecting or other operative functions with electrical connections for cautery or hot biopsy used independently or combined with a rigid or flexible endoscope of any size. The control mechanism may be a spring(s), gear(s), electrical solenoid or motor, air or hydraulic pressure activated piston or a combination thereof. Automated action may be initiated by voice, hand or foot controls. The actuating mechanism may be disposable, attached to or separable from the end effector instrument or permanently attached to be reusable. The automated instrument may be combined with an endoscope.
Owner:ZIMMON DAVID
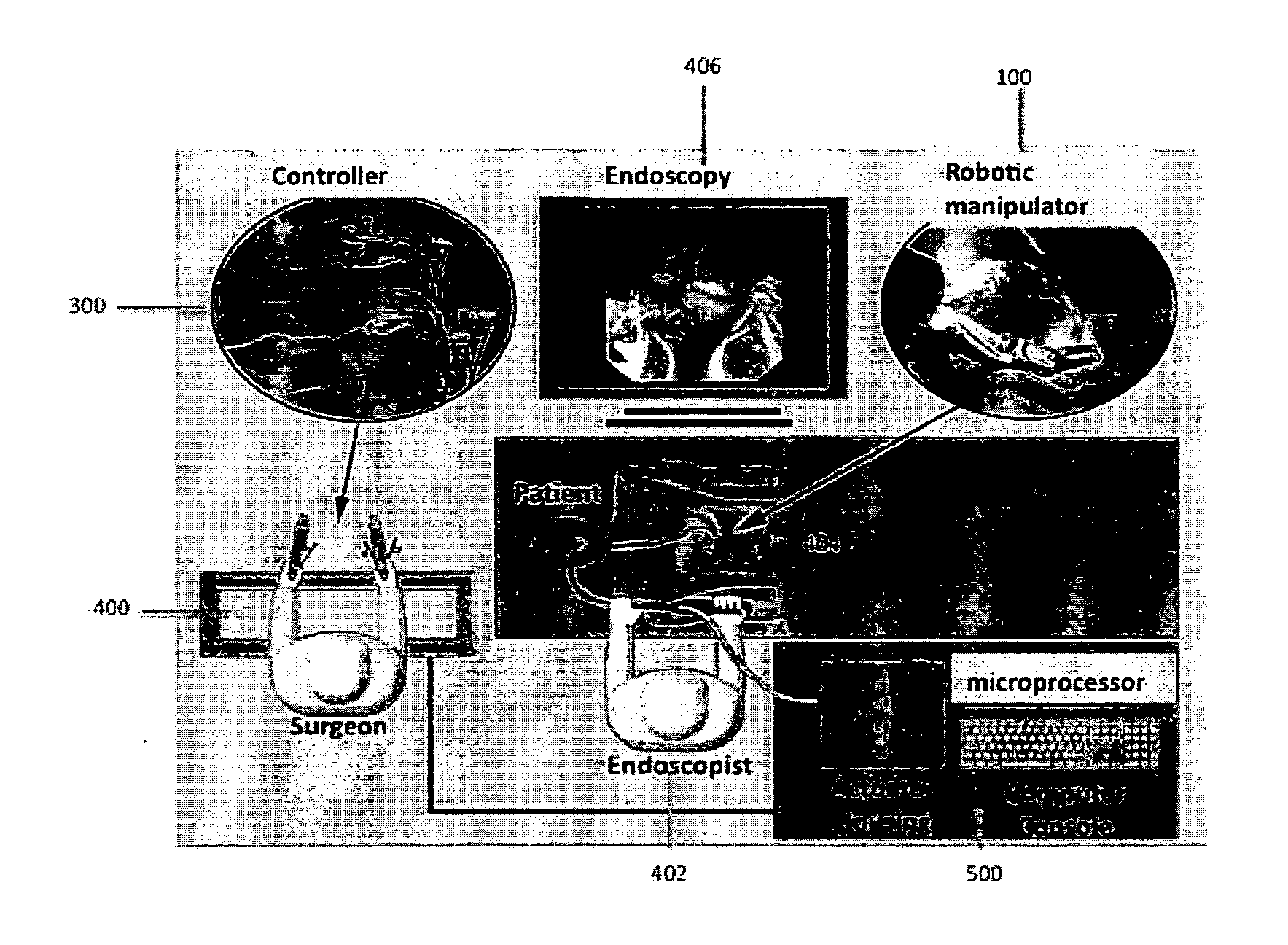
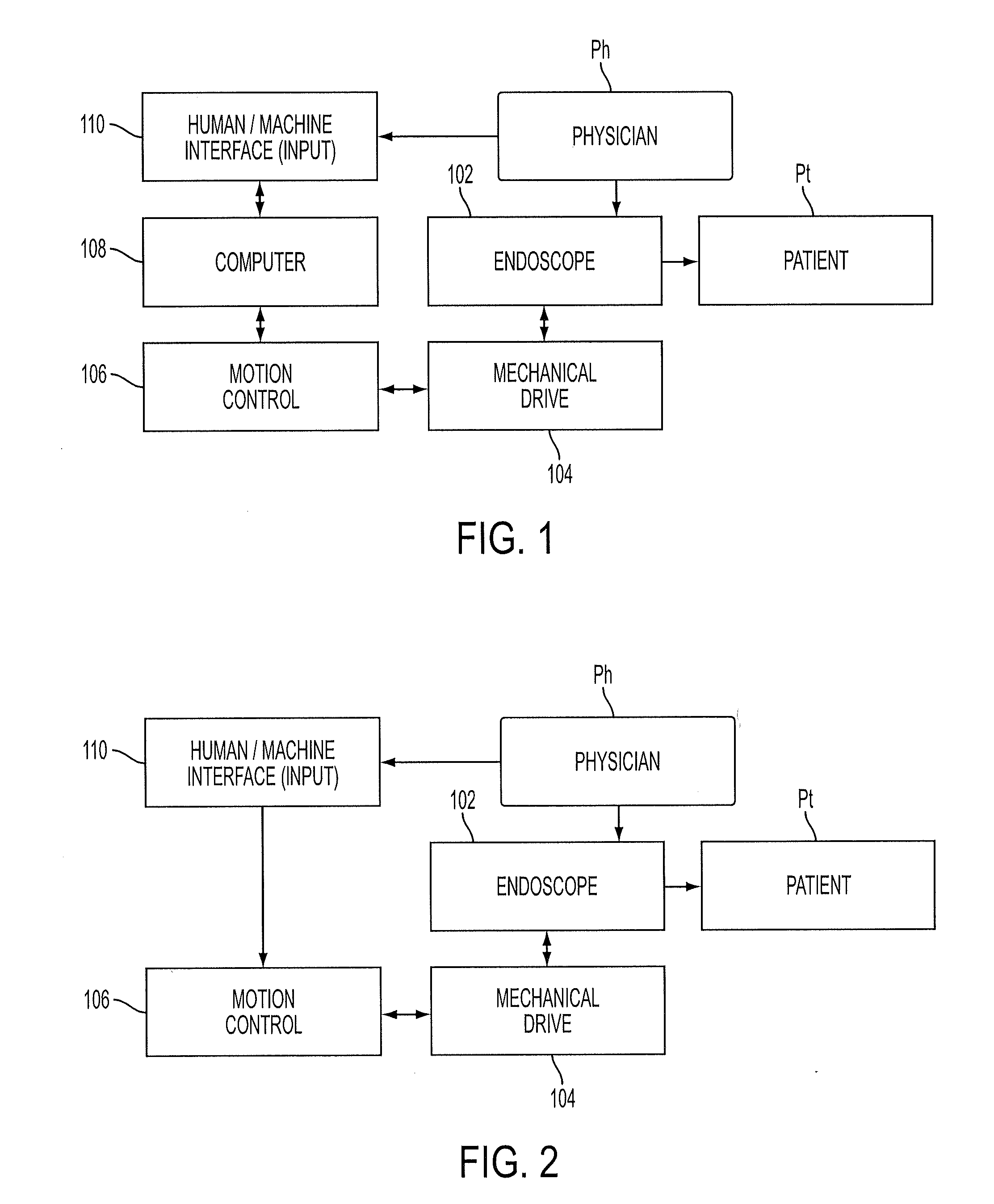
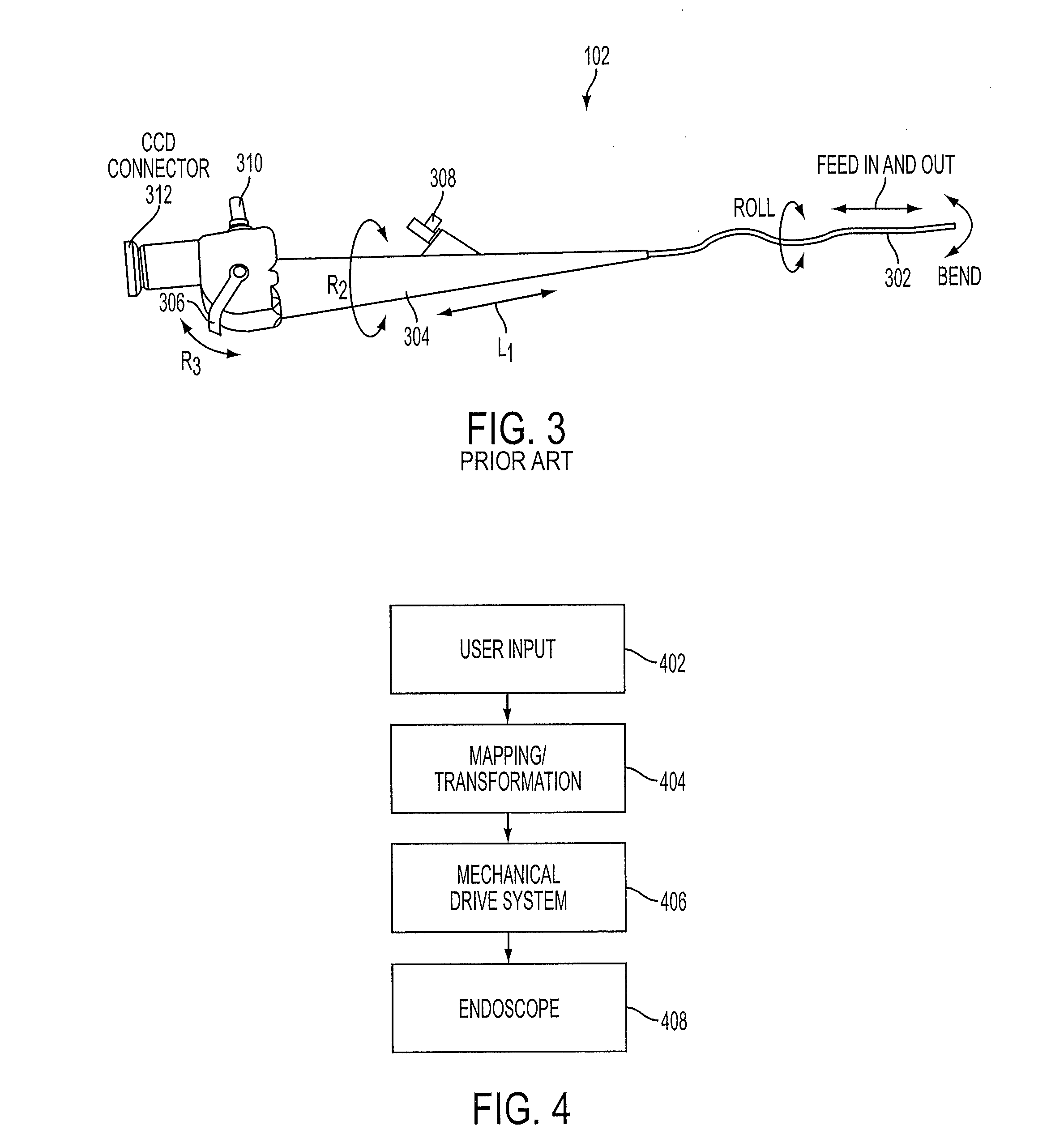
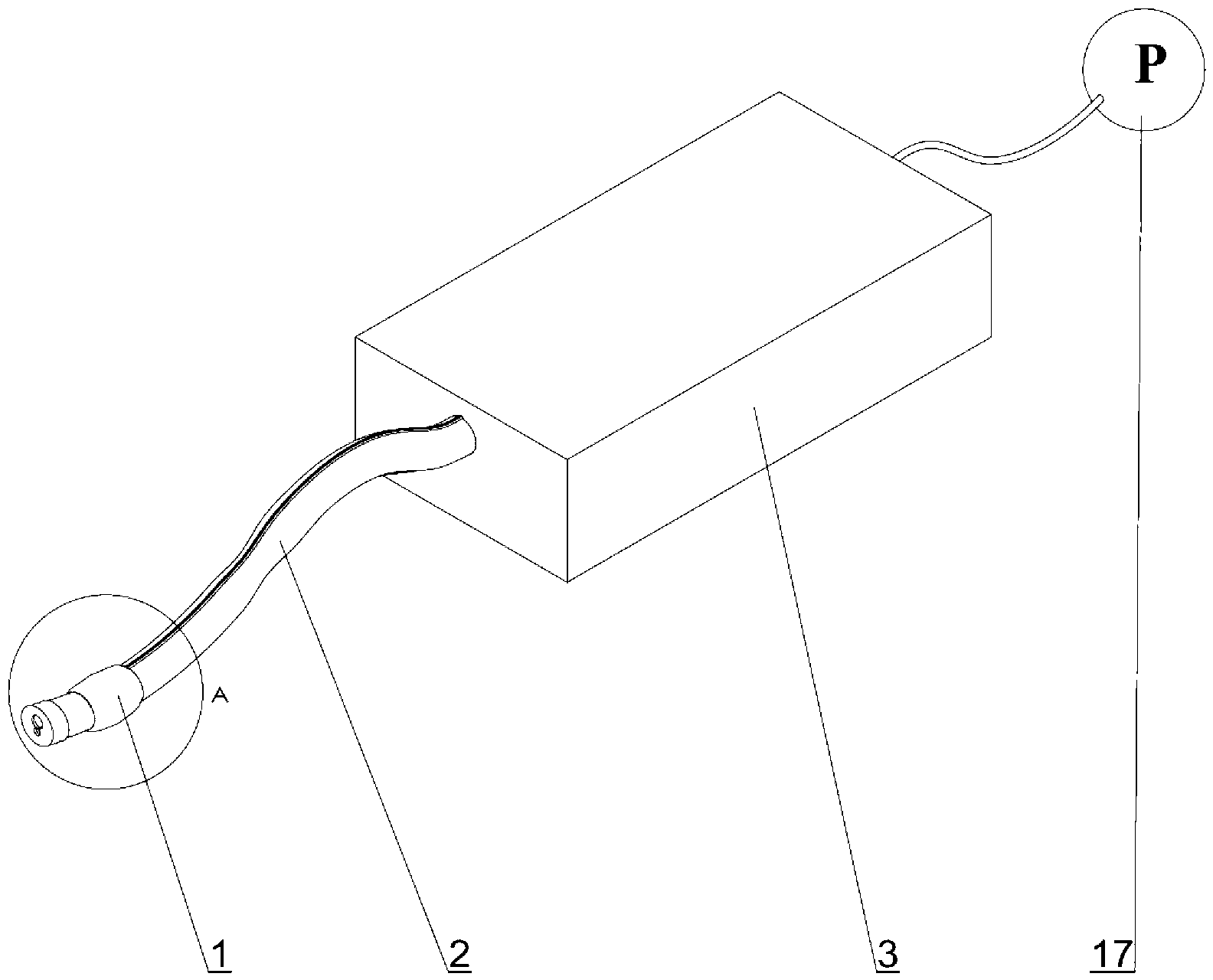
Enhanced control of flexible endoscopes through human-machine interface
ActiveUS20130123580A1Smooth and precise controlEndoscopesMedical devicesFlexible endoscopyHuman–machine interface
An electromechanical drive system with drop-in capability allows manipulation of the majority of existing endoscopes. The invention does not require retrofitting of existing endoscopes and maintains the current clinical workflow. The drive system can be controlled through a human / machine interface, which could consist of a variety of different input devices, including a joystick, keyboard, or game controller.
Owner:CHILDRENS NAT MEDICAL CENT
Flexible endoscope robot with variable rigidity
The invention discloses a flexible endoscope robot with the variable rigidity. One end of a conduit component is connected with a driving component; a ball bag component is arranged on the end part of the free end of the conduit component; a fluid supply component is connected with the ball bag component via a fluid pipe; the conduit component is made of soft silica gel; the inside of the conduit component is provided with a plurality of embedded rope yarns and a hard fixed knot; the first end of each embedded rope yarn is connected with the hard fixed knot; the second end of each embedded rope yarn is fixedly connected with the driving component; the dragging of the embedded rope yarns and the propelling movement of the conduit are controlled by the driving component; the ball bag component is detachably installed on the conduit component and can move along the peripheral surface of the conduit component within a large range; and the fluid supply component is used for discharging fluid to the ball bag component via the fluid conduit to control the expansion and the contraction of the ball bag component. According to the flexible endoscope robot with the variable rigidity, on one hand, the conduit rigidity can be controllably changed, action between the conduit and the human body tissue is reduced, and the discomfort of a patient is lowered. On the other hand, the tail end position of the conduit can be more precisely controlled, and the working intensity of an operator is lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Storage device
ActiveUS8939287B2Unique setMinimize contactSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusFlexible endoscopyEndoscope
The present invention relates to a device for storage of medical equipment. In particular, the present invention relates to a single-use storage device for components of a piece of medical equipment that retains the components with the piece of medical equipment. More particularly the storage device may be used to store endoscope valves, with the parent flexible endoscope. A single-use storage device for medical equipment comprises a container portion, for holding one or more pieces of medical equipment, a closure portion, designed to engage with the container portion to form an enclosure around said medical equipment, a plurality of apertures permitting fluid flow through the storage device, and securing means to secure the closure portion to the container portion, the securing means arranged such that once the closure portion has been secured to the container portion using the securing means the closure portion and container portion cannot be separated without permanently disabling the securing means.
Owner:STERIS SOLUTIONS LTD
Robotic system for flexible endoscopy
ActiveCN102802551ASmall inertiaEndoscopesSurgical instruments for heatingFlexible endoscopyRobotic systems
A robotic manipulator (100), controller (300) and system for use in flexible endoscopy, the manipulator (100) comprising a flexible member configured to be coupled to an endoscope, and an arm connected to and movable by the flexible member, wherein the flexible member has a first end connected to the arm and a second end connectable to the controller (300) to allow a physical movement of the arm to be controllable by a physical movement of the controller (300).
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
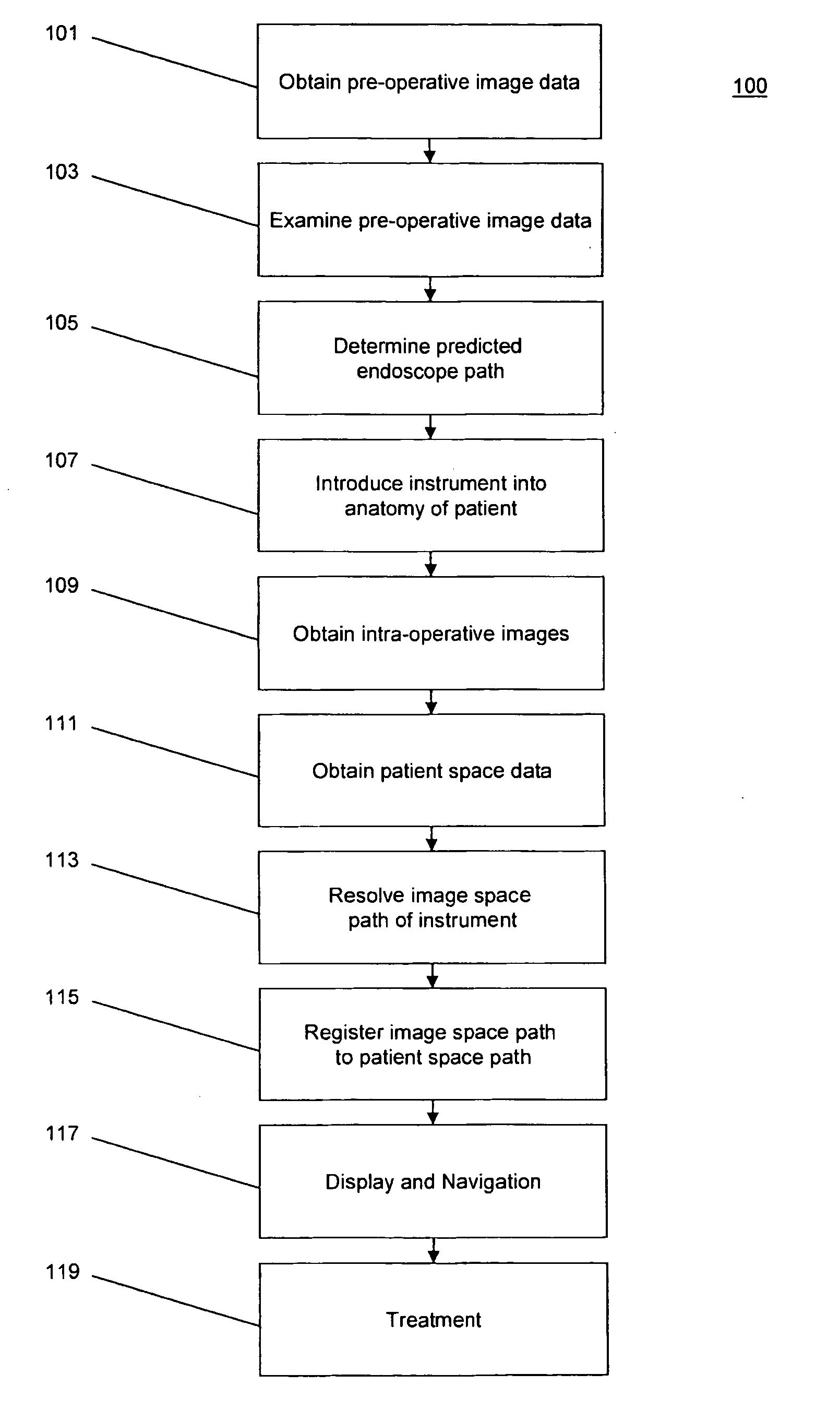
Stone retriever for flexible endoscopes having small diameter working channels
A medical retrieval device and method used in endoscopic procedures to retrieve stones has a shaft comprising a sheath with a lumen and a drive wire slidably disposed within the lumen for operating a stone entrapping mechanism on the distal end of the retrieval device. The shaft has an average outside diameter of less than 1.9 Fr. The shaft, sheath and drive wire each have proximal, intermediate and distal portions, and each of the corresponding portions are in generally similar locations along the longitudinal length of the device. The proximal portions of the shaft and the drive wire are preferably stiffer than the corresponding intermediate portions of the shaft and drive wire. The proximal and intermediate portions of the sheath have generally similar stiffnesses. The shaft reduces flow resistance within the working channel of an endoscope, increasing the flow of irrigation fluid in order to improve procedural visibility. The shaft varies in flexibility to match the requirements of a flexible endoscope and facilitate deflection of the endoscope.
Owner:ANNEX MEDICAL
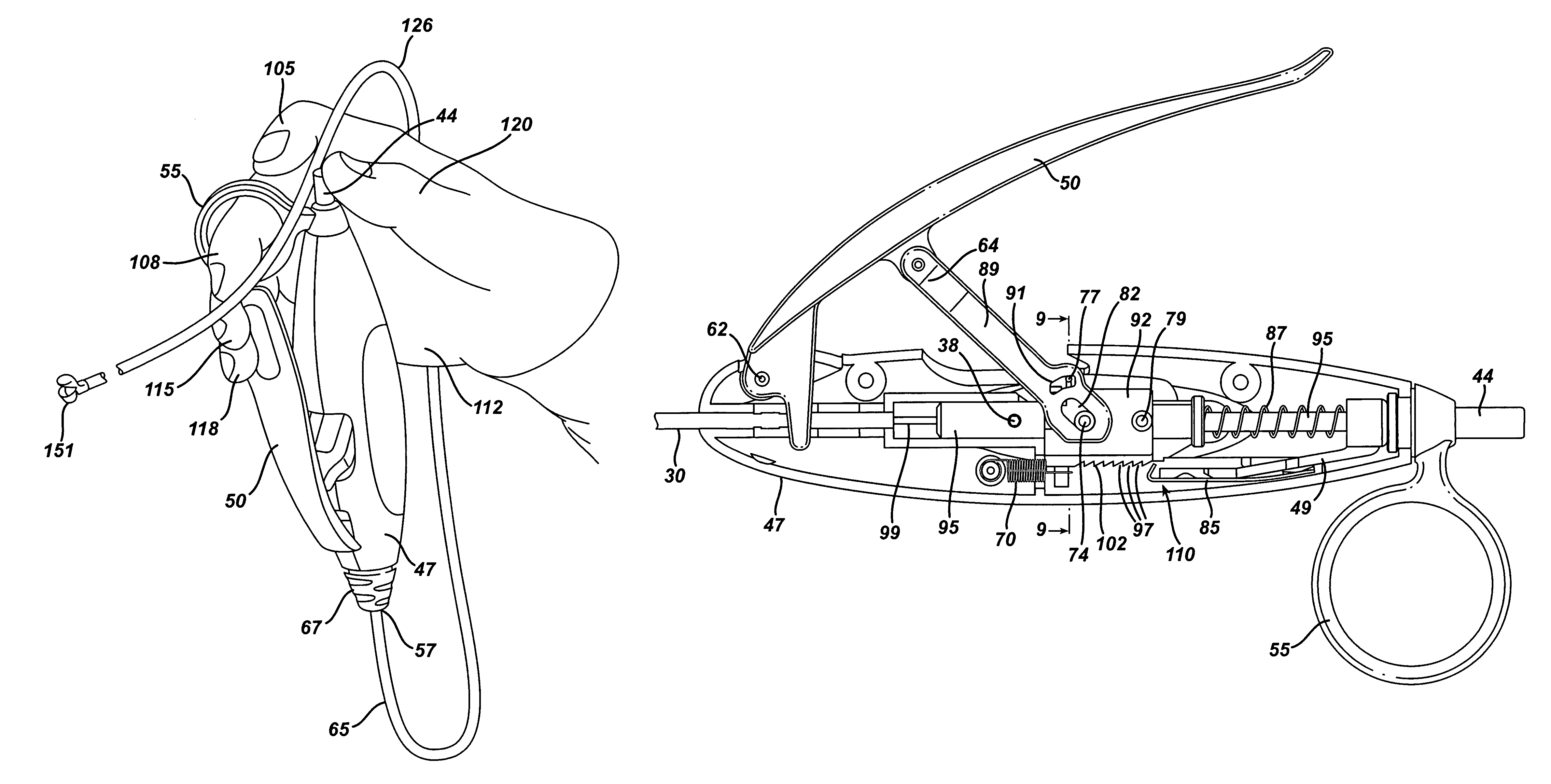
METHOD FOR SECURING MEDICAL DEVICES TO TREAT OBESITY, GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) AND IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME (iBS) REVERSIBLY
InactiveUS20100234886A1Avoid a back jump of the flexible endoscope while firingGive stiffness to the endoscope when firing the stapleSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsFlexible endoscopyArm folding
Owner:GODIN NORMAN
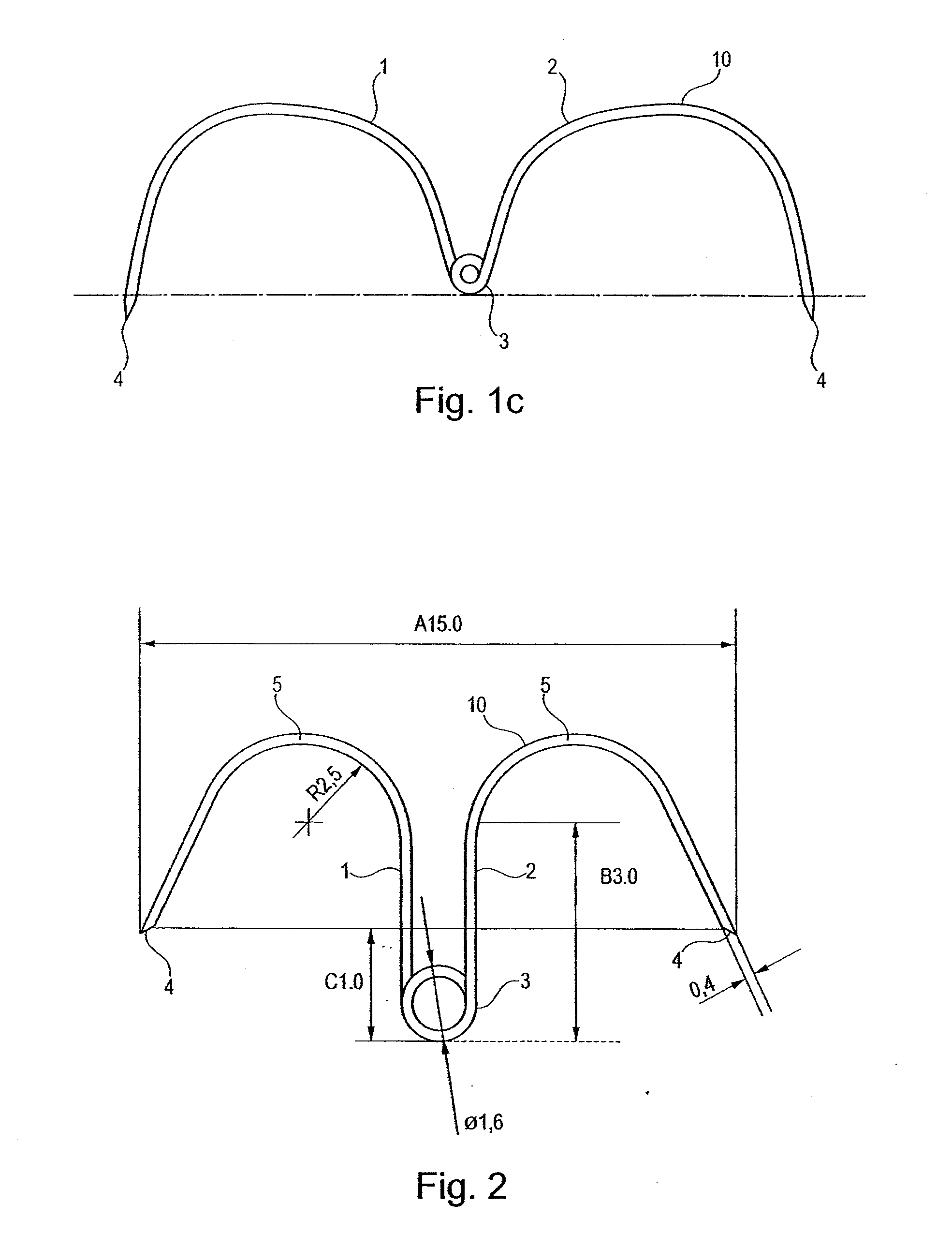
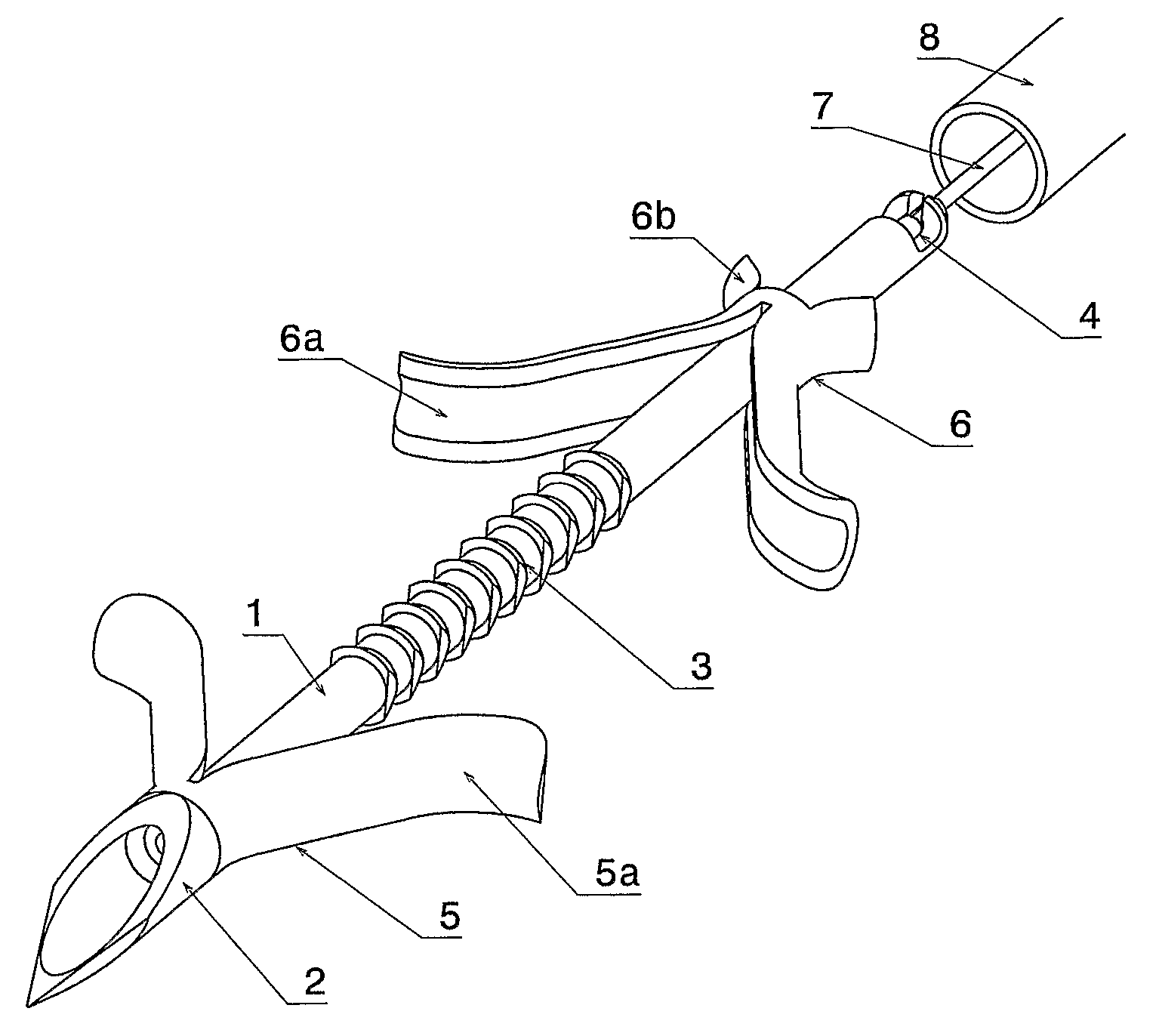
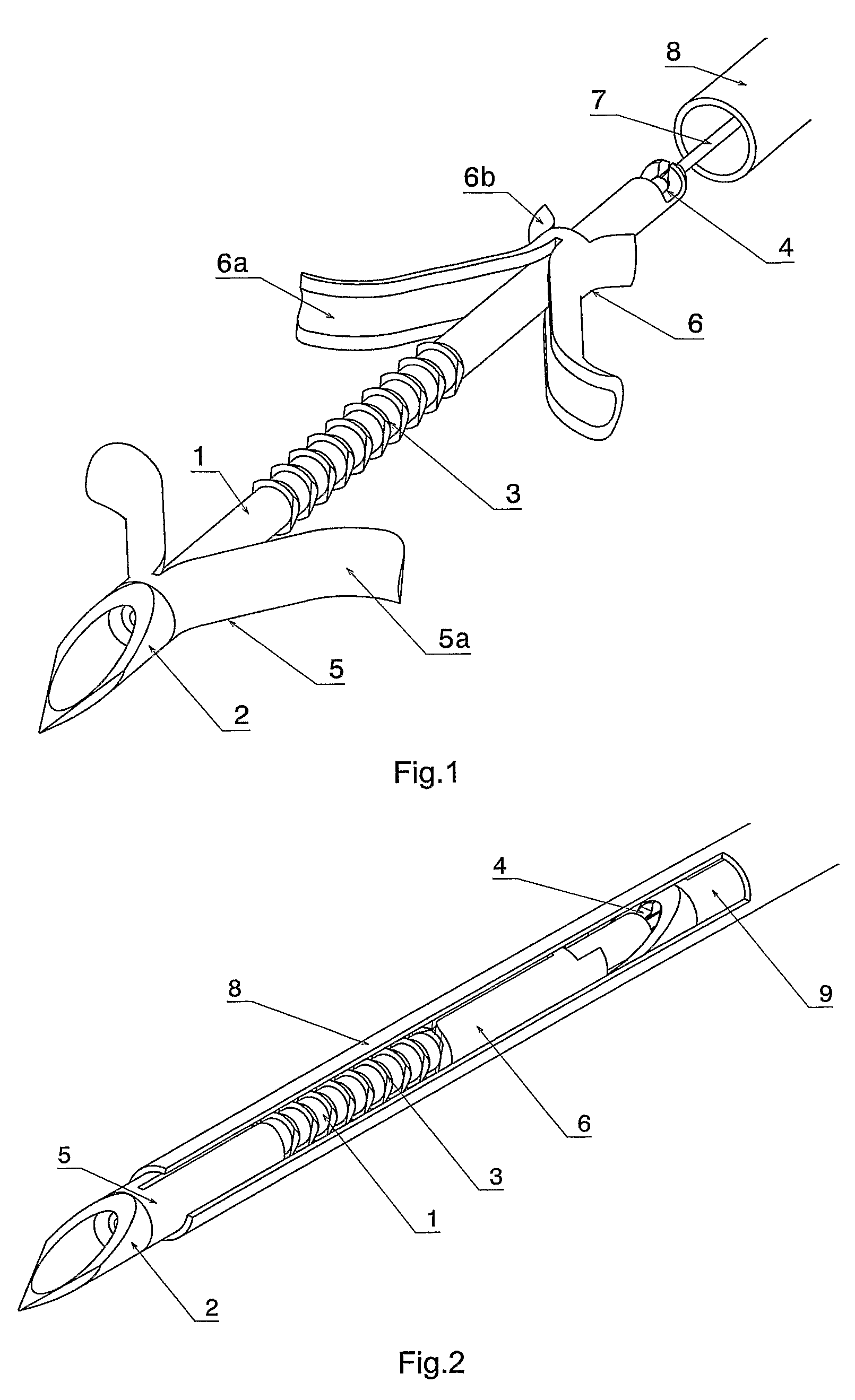
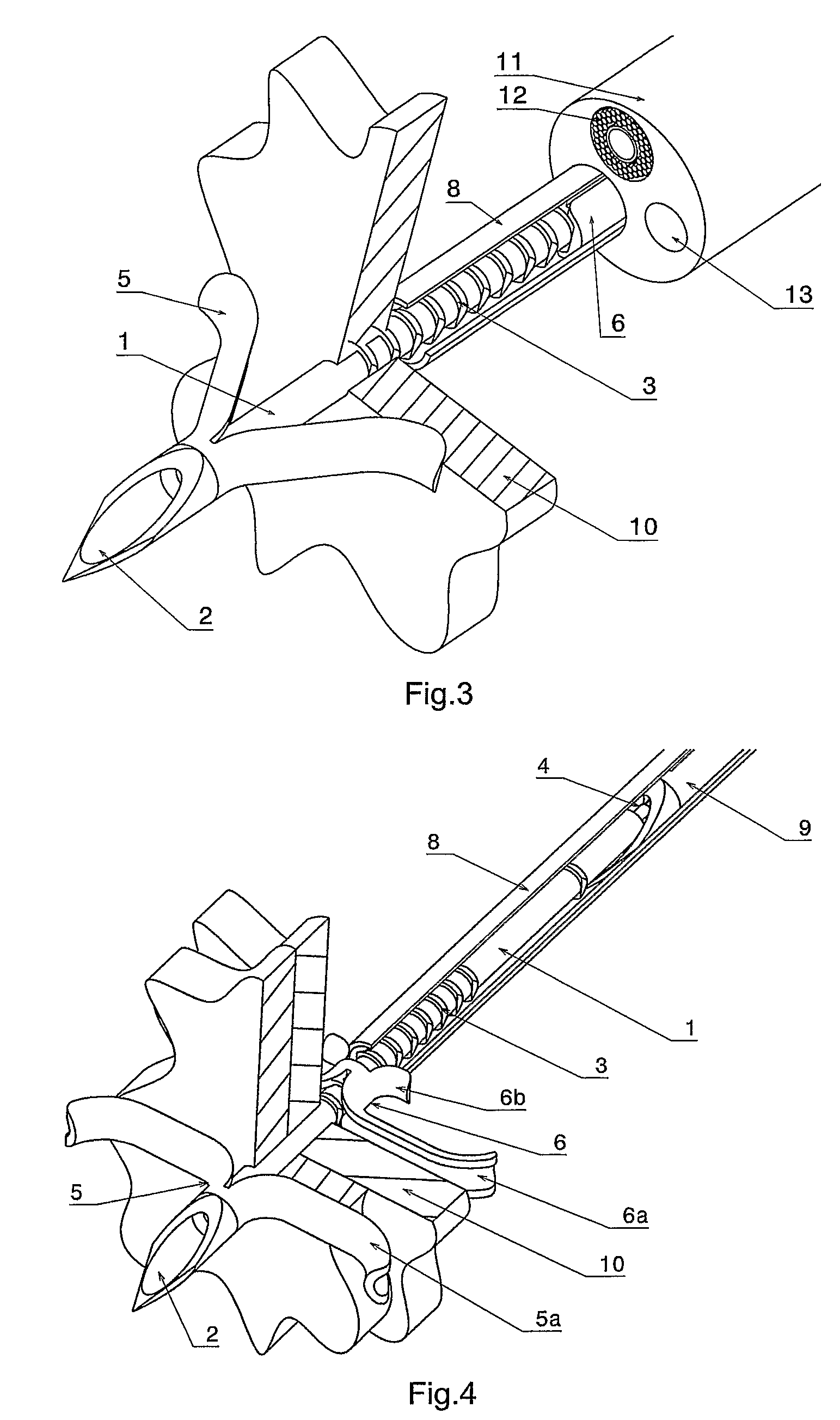
Blind rivet for adapting biological tissue and device for setting the same, in particular through the instrument channel of an endoscope
InactiveUS8663254B2Avoid disadvantagesSuitable for useSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisFlexible endoscopyContact force
A self-piercing blind rivet is provided for apposing biological tissue together with a device for setting the same, especially through the instrumental channel of a flexible endoscope. Without the help of further instruments, it is possible to fix, approximate and appose tissue layers, the contact force while connecting the tissue layers being adjustable. The rivets are stored in the setting device, so that they can be applied in order. The rivet and setting device enable the surgeon to combine tissue discontinuities conveniently by means of an endoscope. The surgical procedure is simplified further because the rivets can remain in the body.
Owner:TECH UNIV MUNCHEN
Storage device
ActiveUS20130220855A1Prevent disengagementUnique setSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusFlexible endoscopyEndoscope
The present invention relates to a device for storage of medical equipment. In particular, the present invention relates to a single-use storage device for components of a piece of medical equipment that retains the components with the piece of medical equipment. More particularly the storage device may be used to store endoscope valves, with the parent flexible endoscope. A single-use storage device for medical equipment comprises a container portion, for holding one or more pieces of medical equipment, a closure portion, designed to engage with the container portion to form an enclosure around said medical equipment, a plurality of apertures permitting fluid flow through the storage device, and securing means to secure the closure portion to the container portion, the securing means arranged such that once the closure portion has been secured to the container portion using the securing means the closure portion and container portion cannot be separated without permanently disabling the securing means.
Owner:CANTEL UK LTD
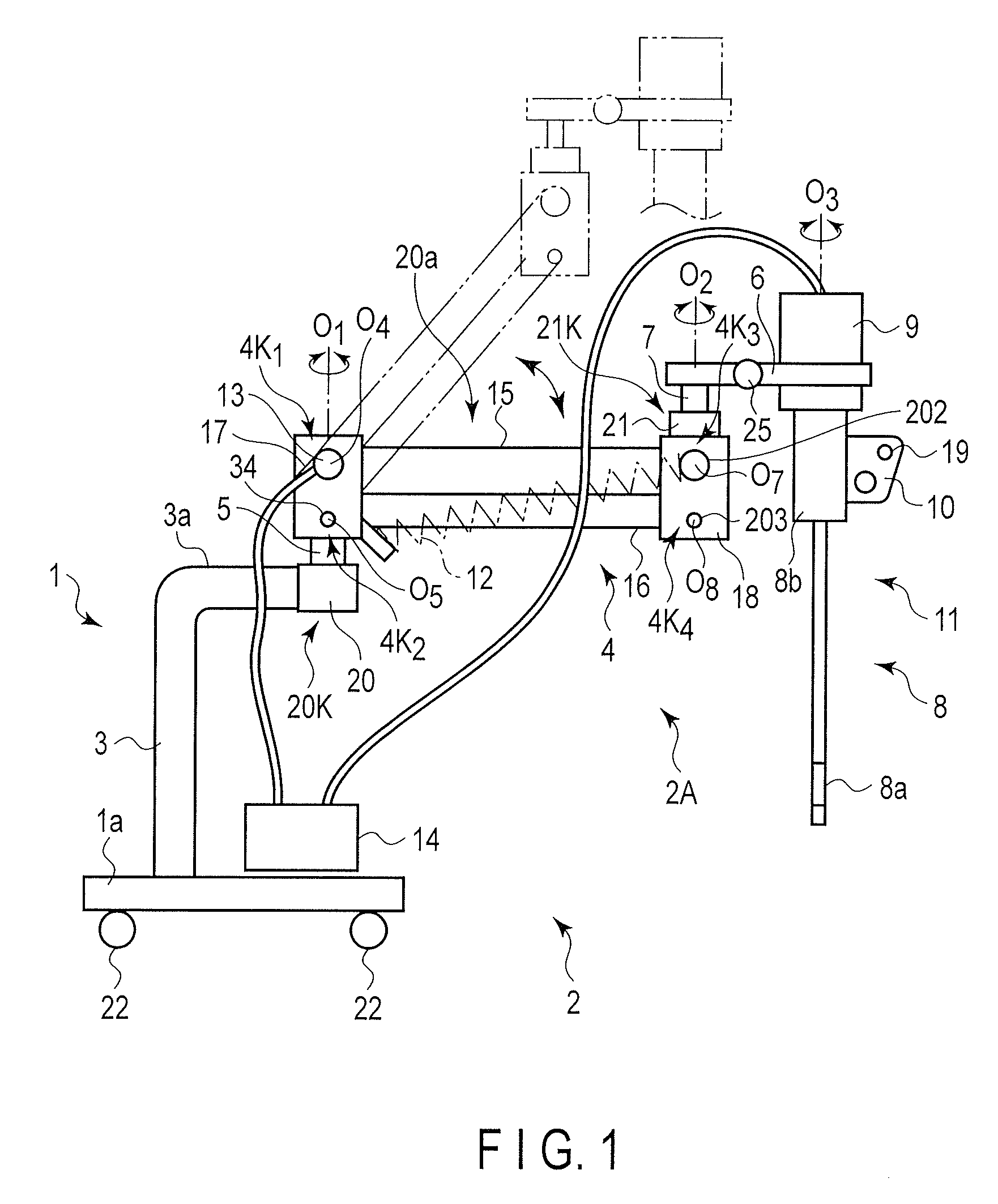
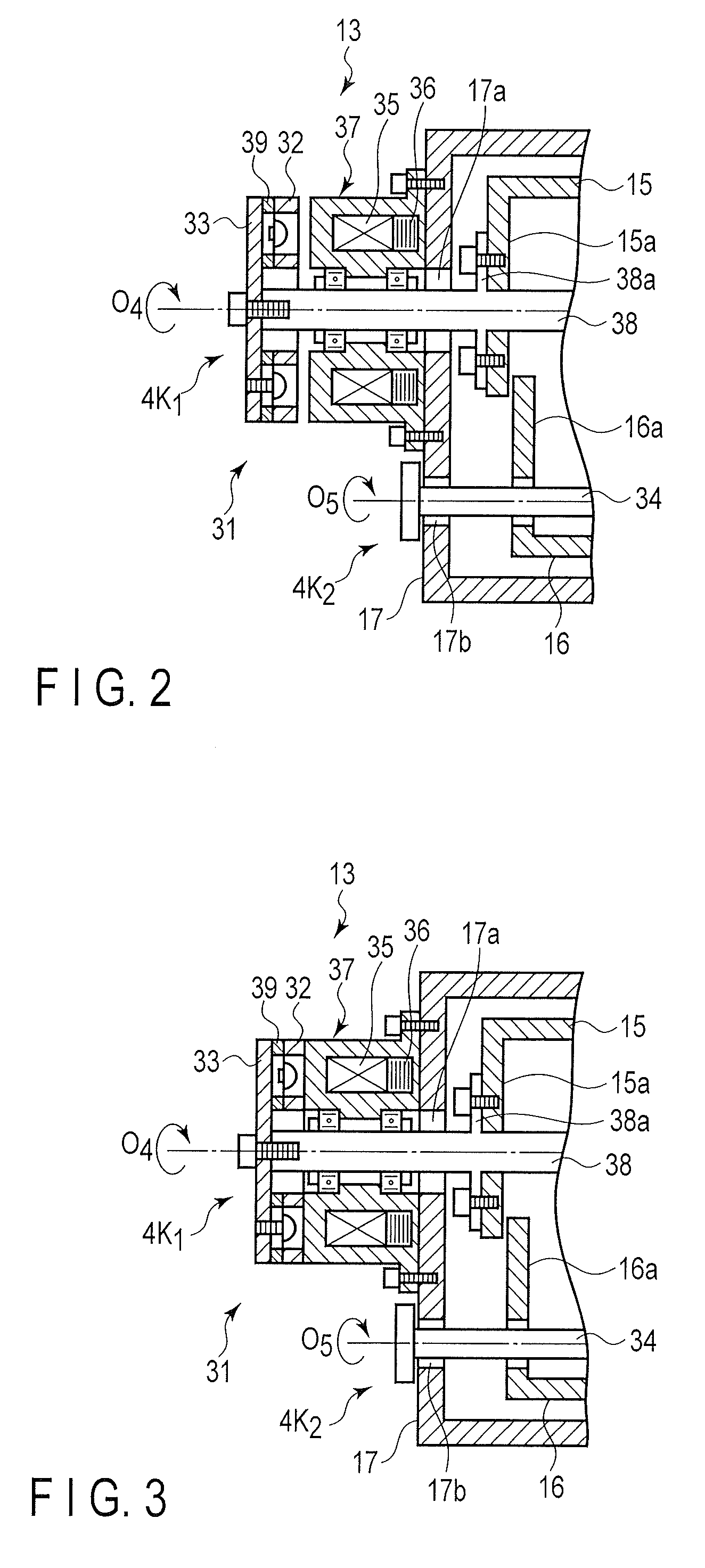
Supporting apparatus for medical device
A supporting apparatus for medical device comprises a balance mechanism which movably and tiltably maintains a flexible endoscope and balances a weight of the flexible endoscope and a link mechanism section. Further, the supporting section of the flexible endoscope comprises a transparent photo interrupter which detects attachment / detachment of the flexible endoscope, and the supporting apparatus for medical device is provided with a controller which outputs a control signal to switch lock sections to a fixed state, based on a detection signal from the photo interrupter, when the flexible endoscope is detected to be detached from the supporting section by the photo interrupter.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com