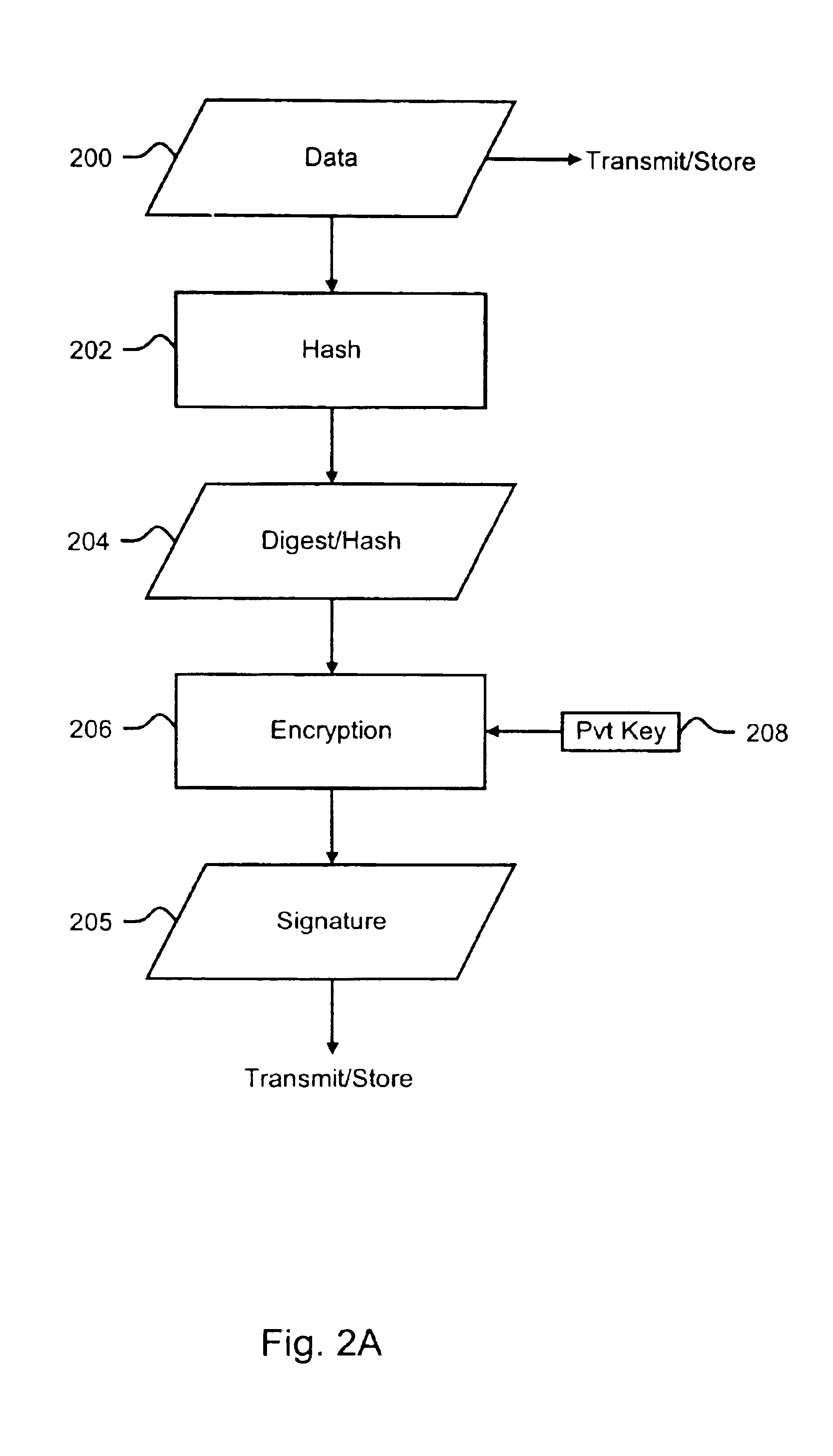
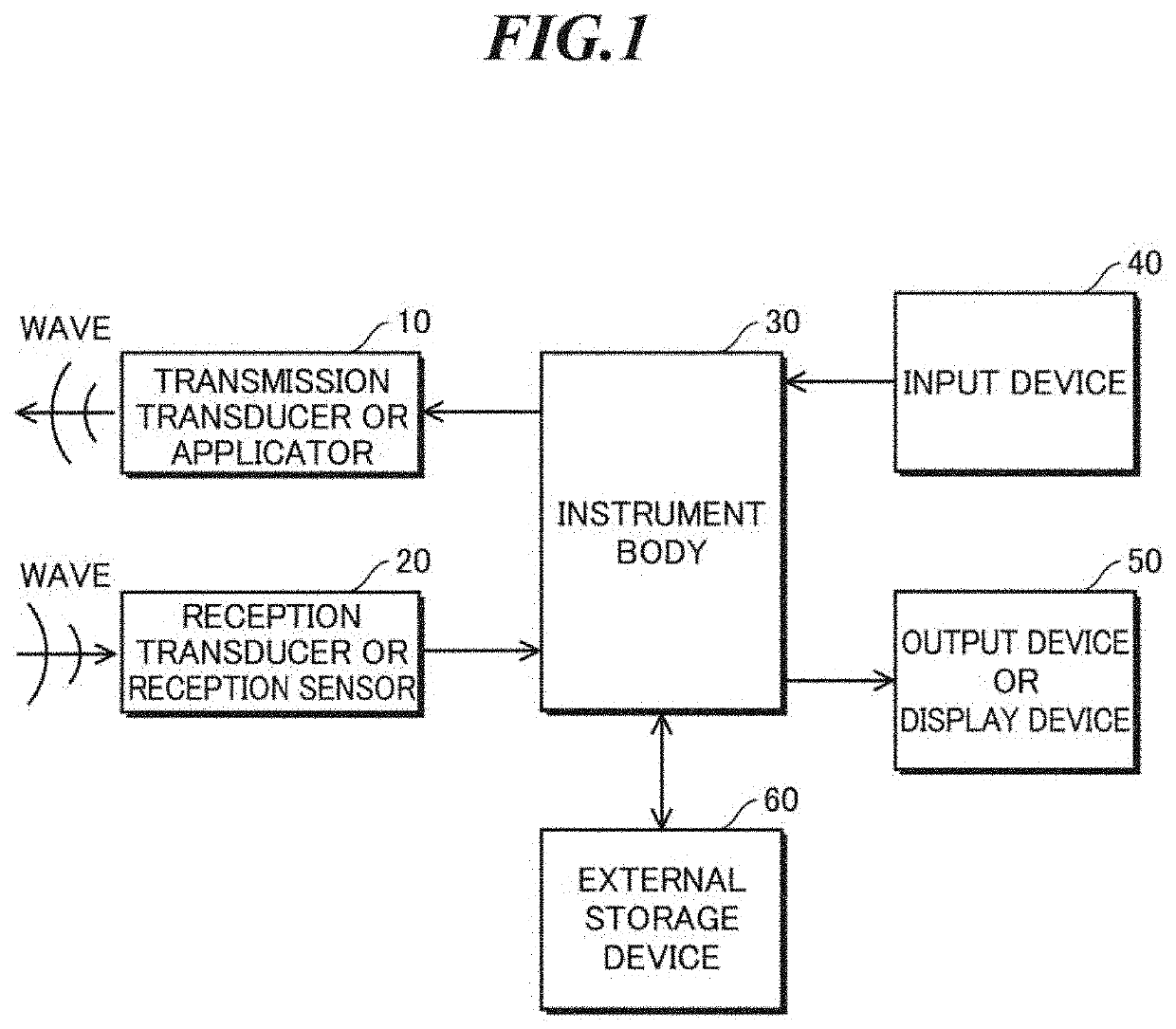
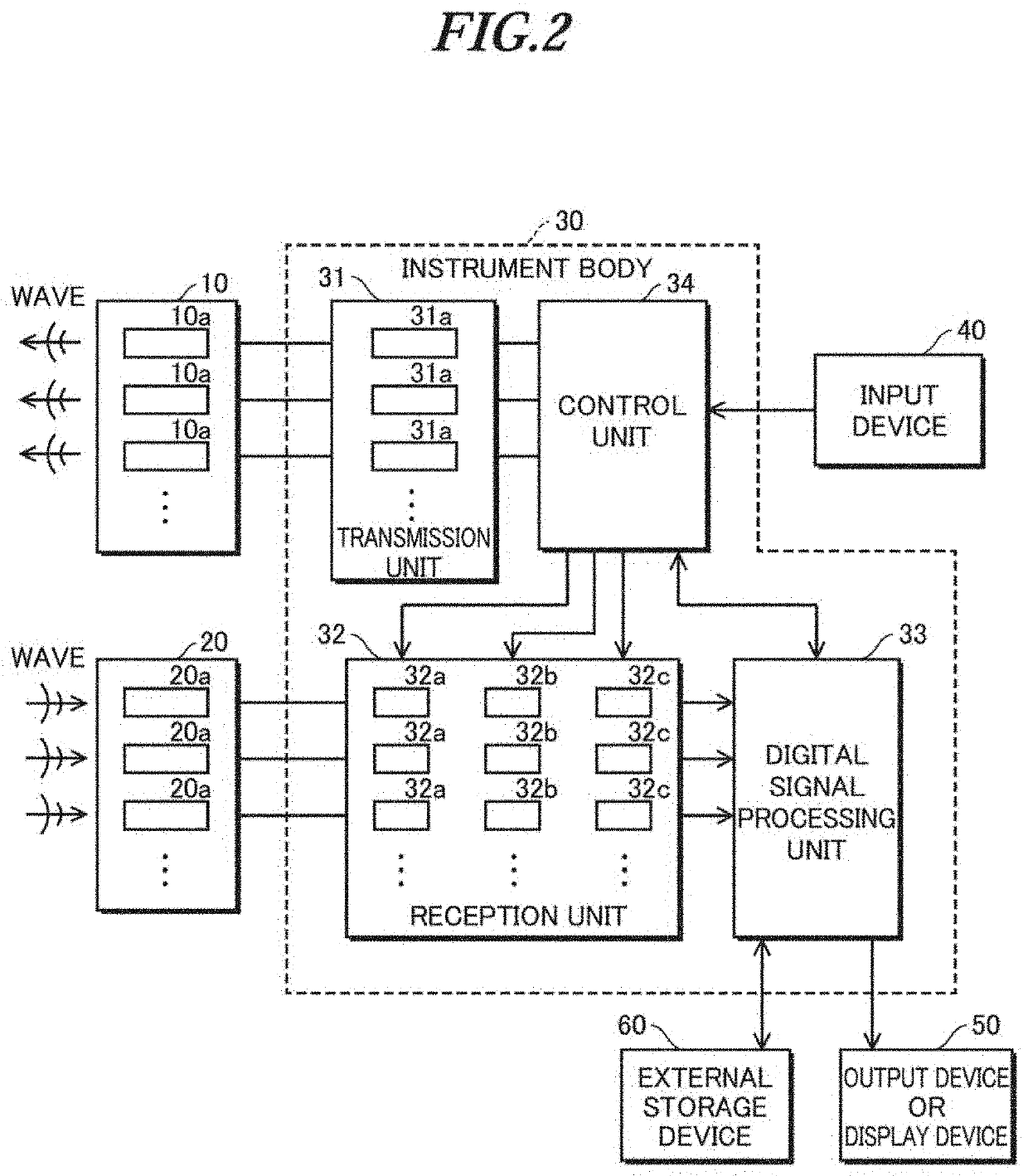
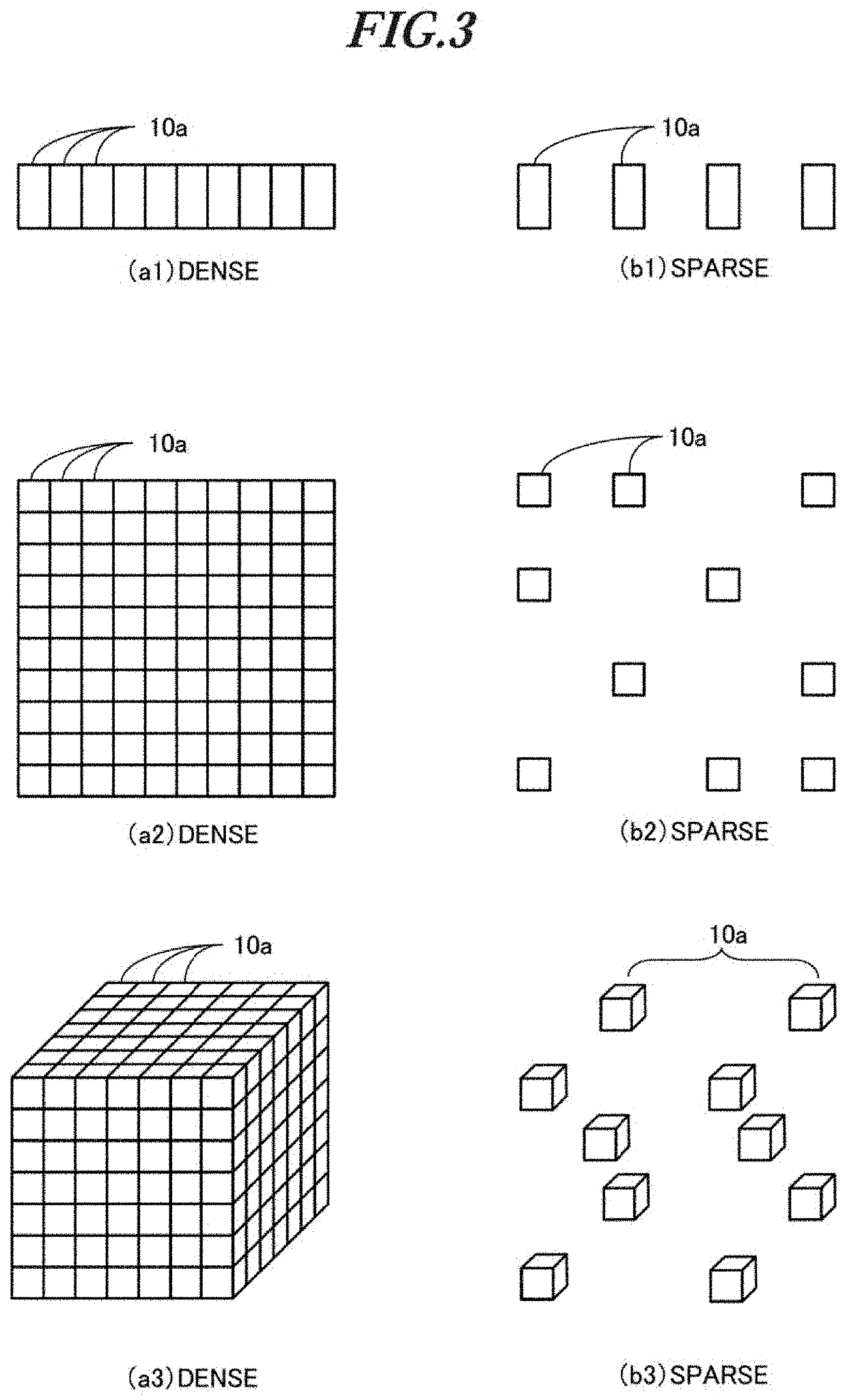
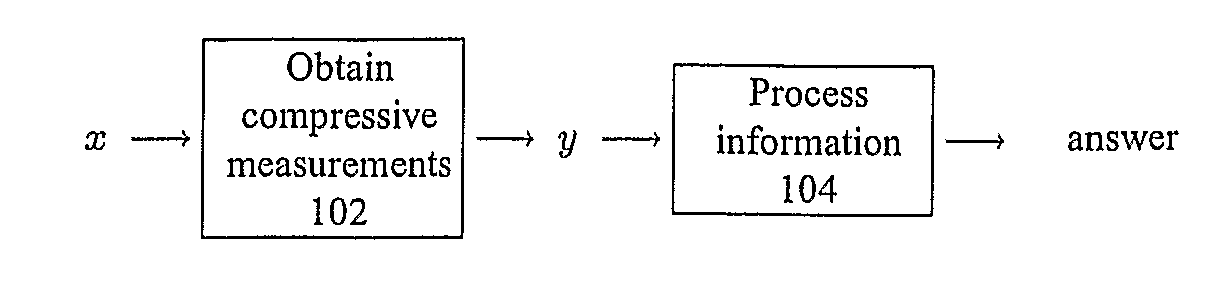Patents
Literature
9375 results about "Signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. In electronics and telecommunications, it refers to any time varying voltage, current or electromagnetic wave that carries information. A signal may also be defined as an observable change in a quantity.
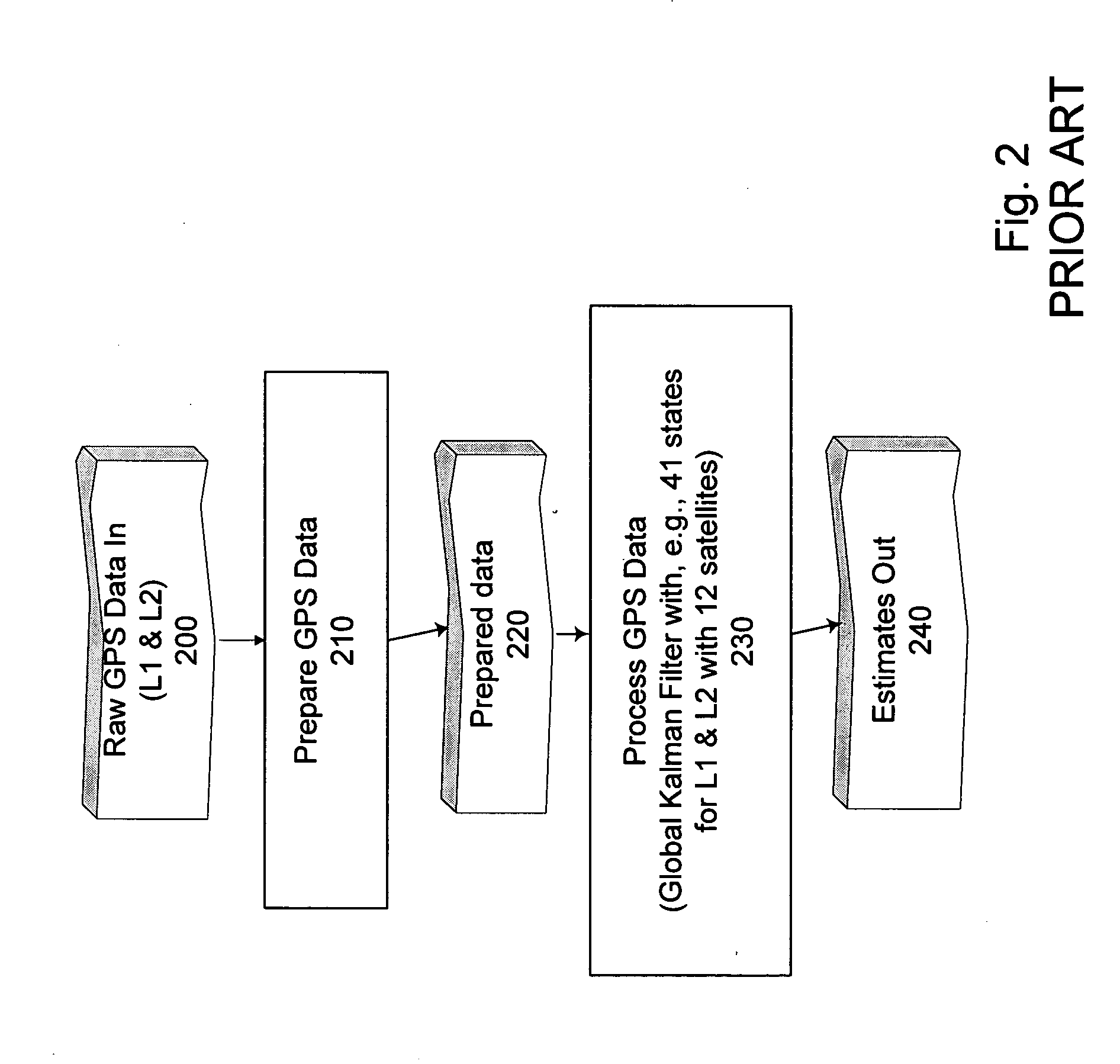
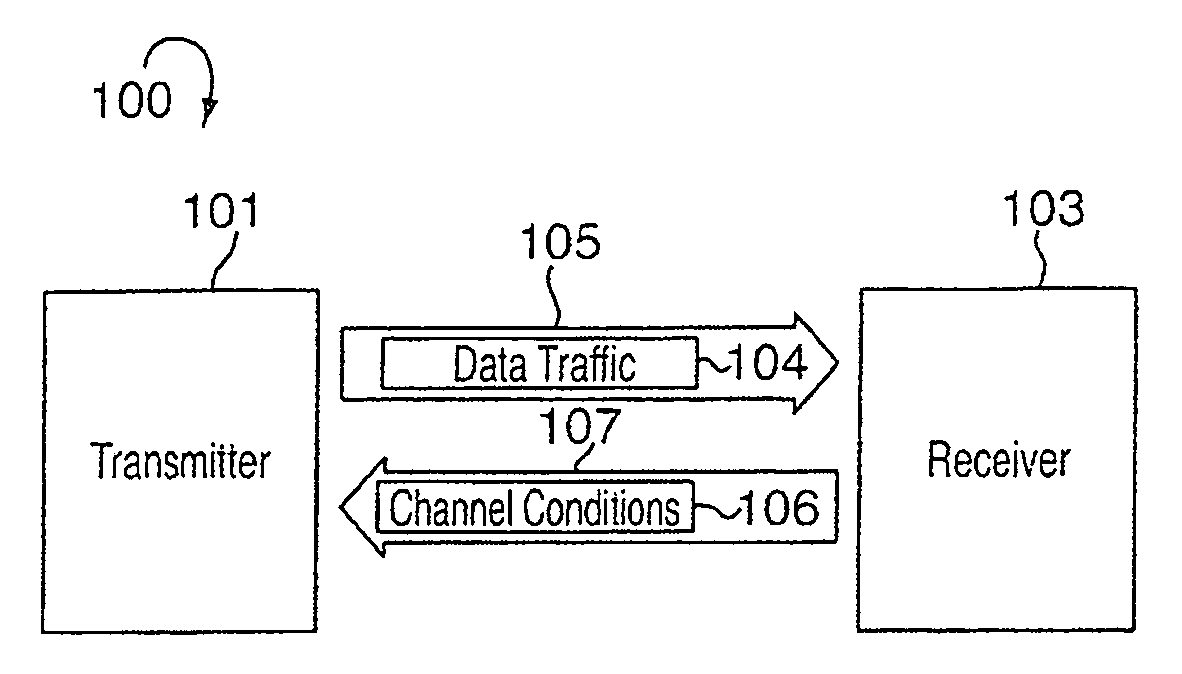
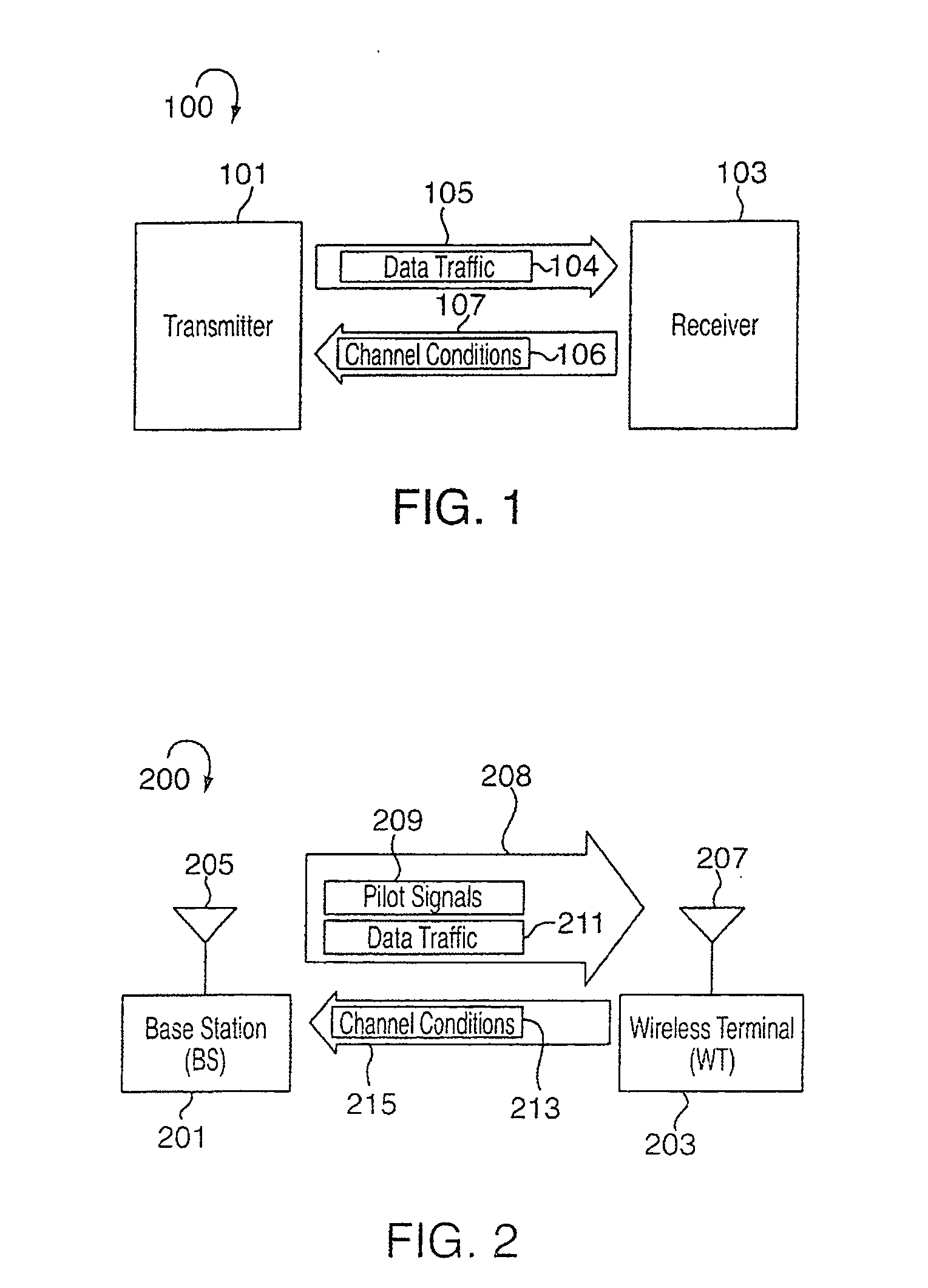
System and method for acquiring data
InactiveUS6839659B2Easy to carryImprove clarityAngiographyData acquisition and loggingData connectionHigh rate
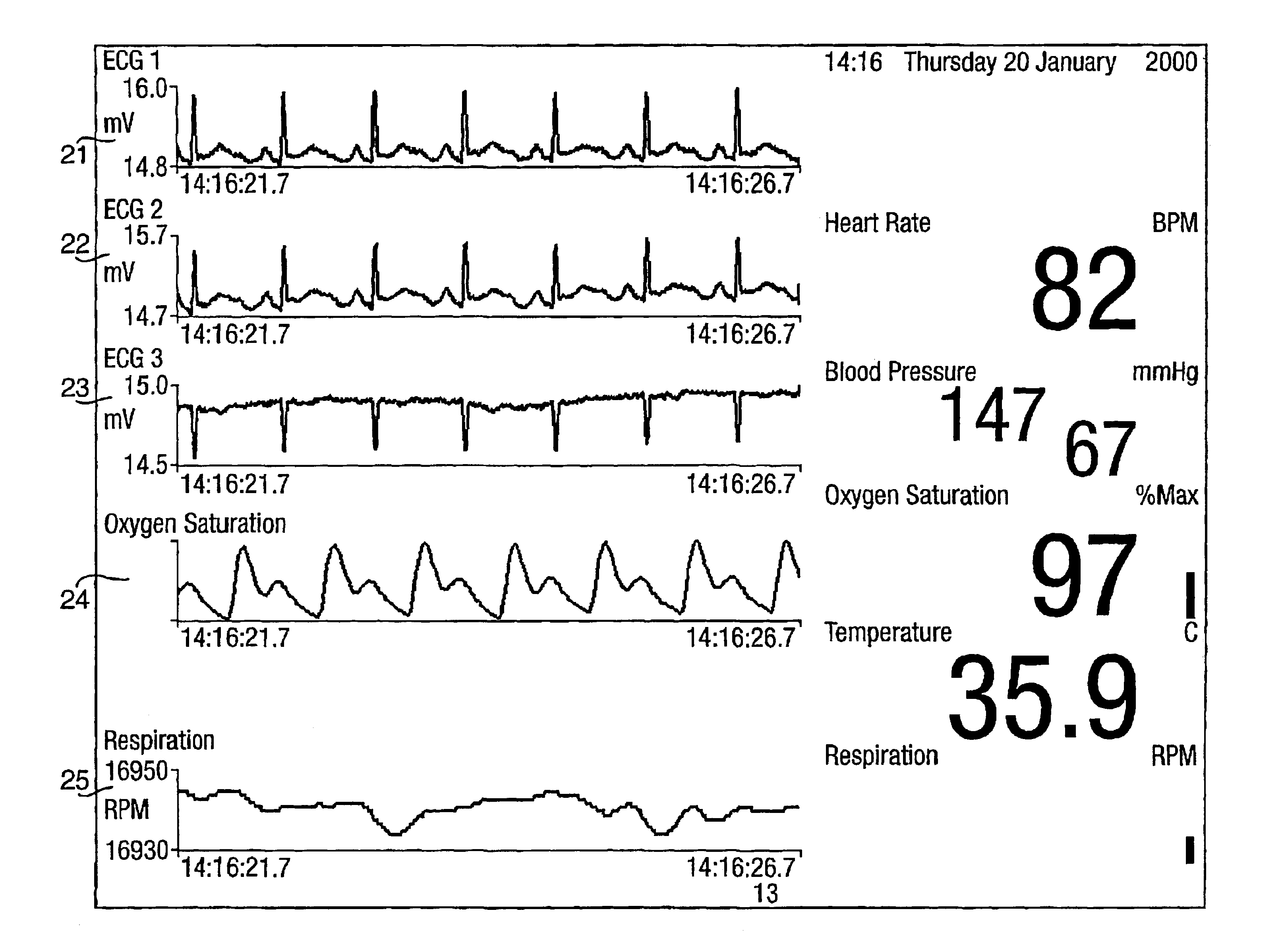
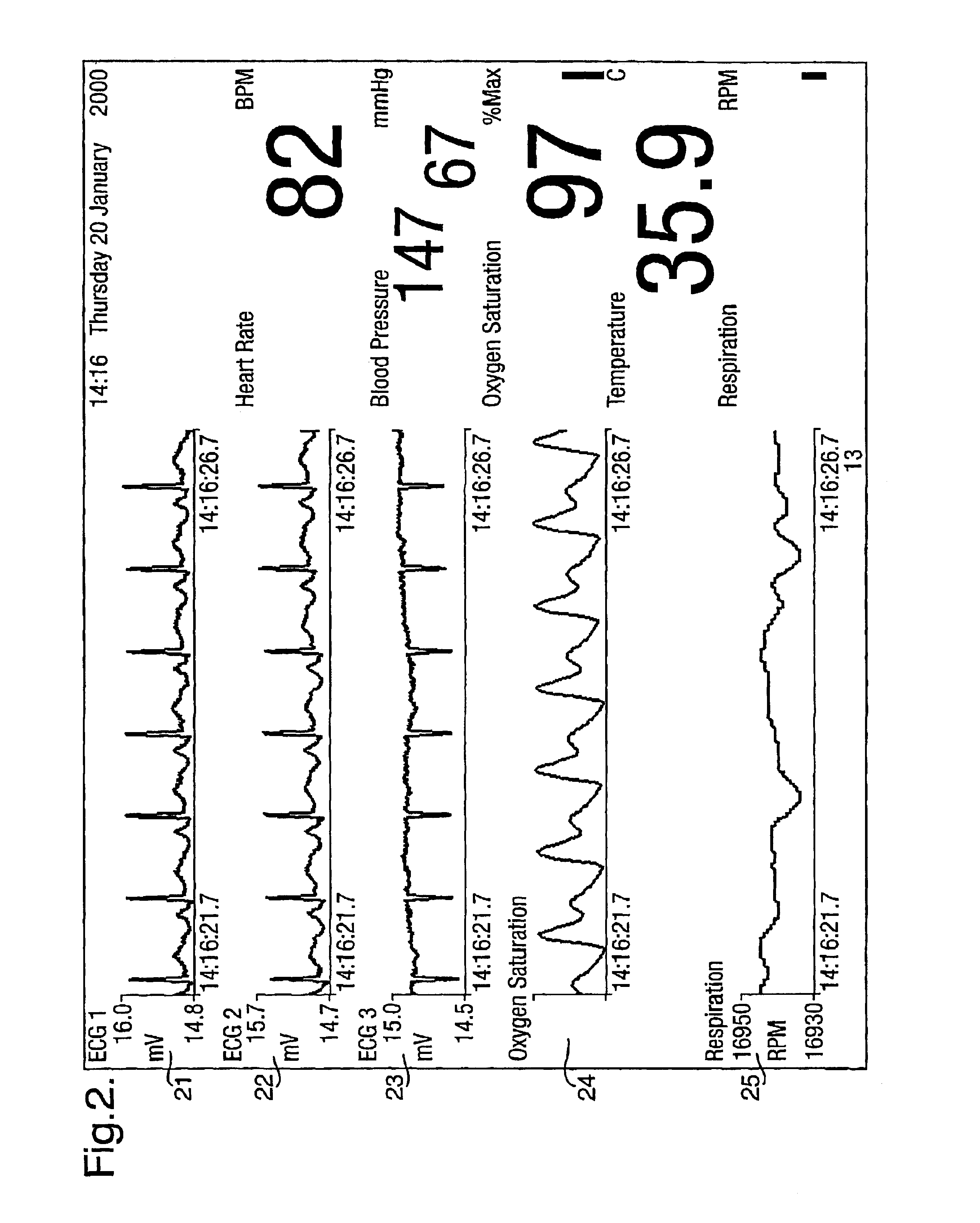
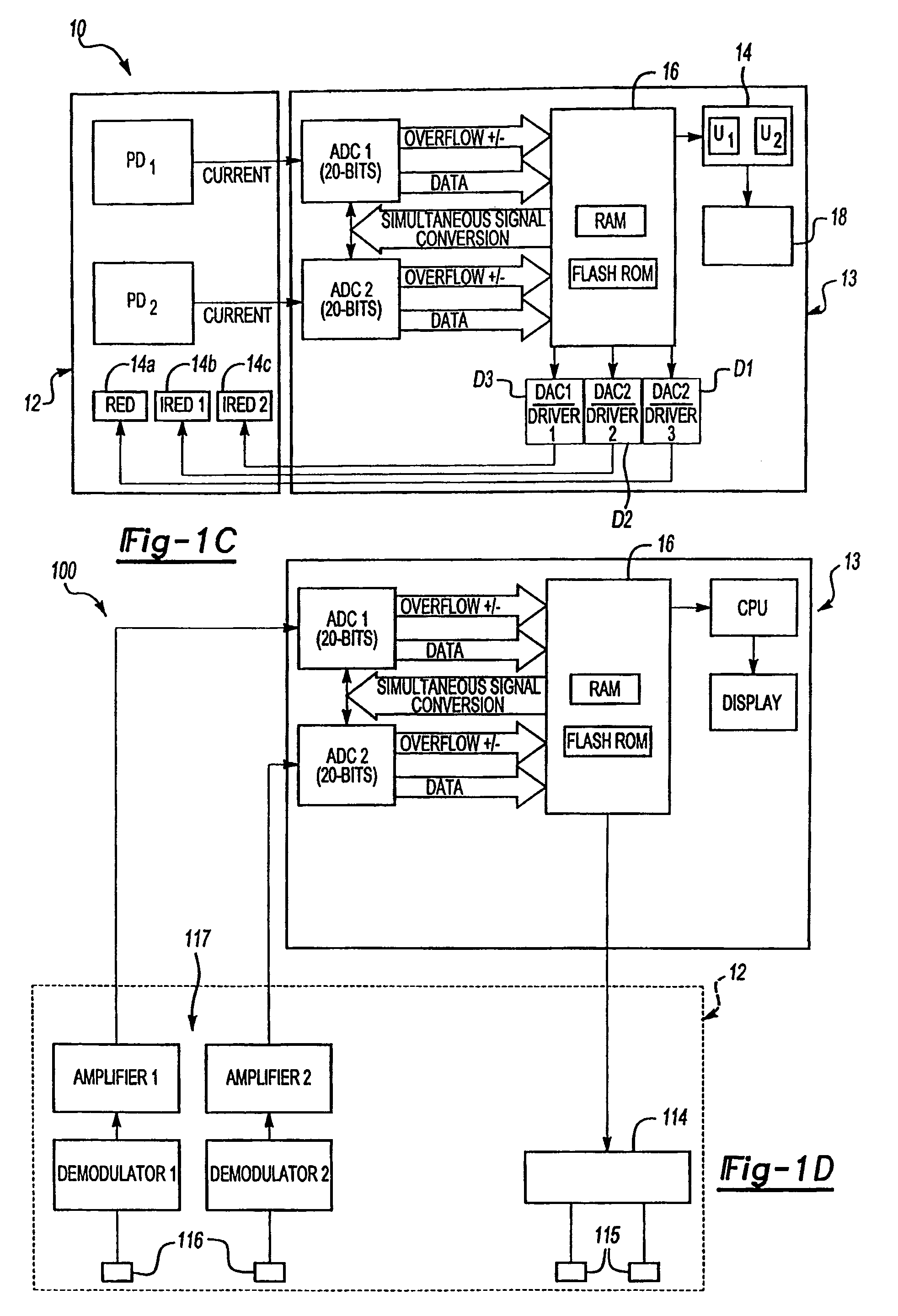
A system for acquiring, and displaying, data such as physiological data, from a plurality of data connection devices, each of which monitor one or more different parameters and output data at different sampling frequencies based on their own system clocks. The system receives the data signals at different sampling frequencies and associates each sample of each signal with a time stamp derived from a single master clock. Low rate and high rate data are treated differently. Low rate data is associated with the current value of the master clock, where as high rate data is time stamped by giving the first sample a time stamp equal to the current value of the current master clock, subsequent samples being given an estimated time stamp based on the expected interval between samples derived from the sampling frequency of the data collection device, and the timescale given to the first example. The estimated time stamp may be periodically corrected, and the estimation calculation can be improved by correcting the value used for the interval between samples. The different signals can be displayed together on a display aligned with respect to a time axis. The system can display, the data in two different timescales, one showing a few seconds of data and one showing a few hours of data. The data traces are scrolled across the time axis, new data being added to one end of the trace.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
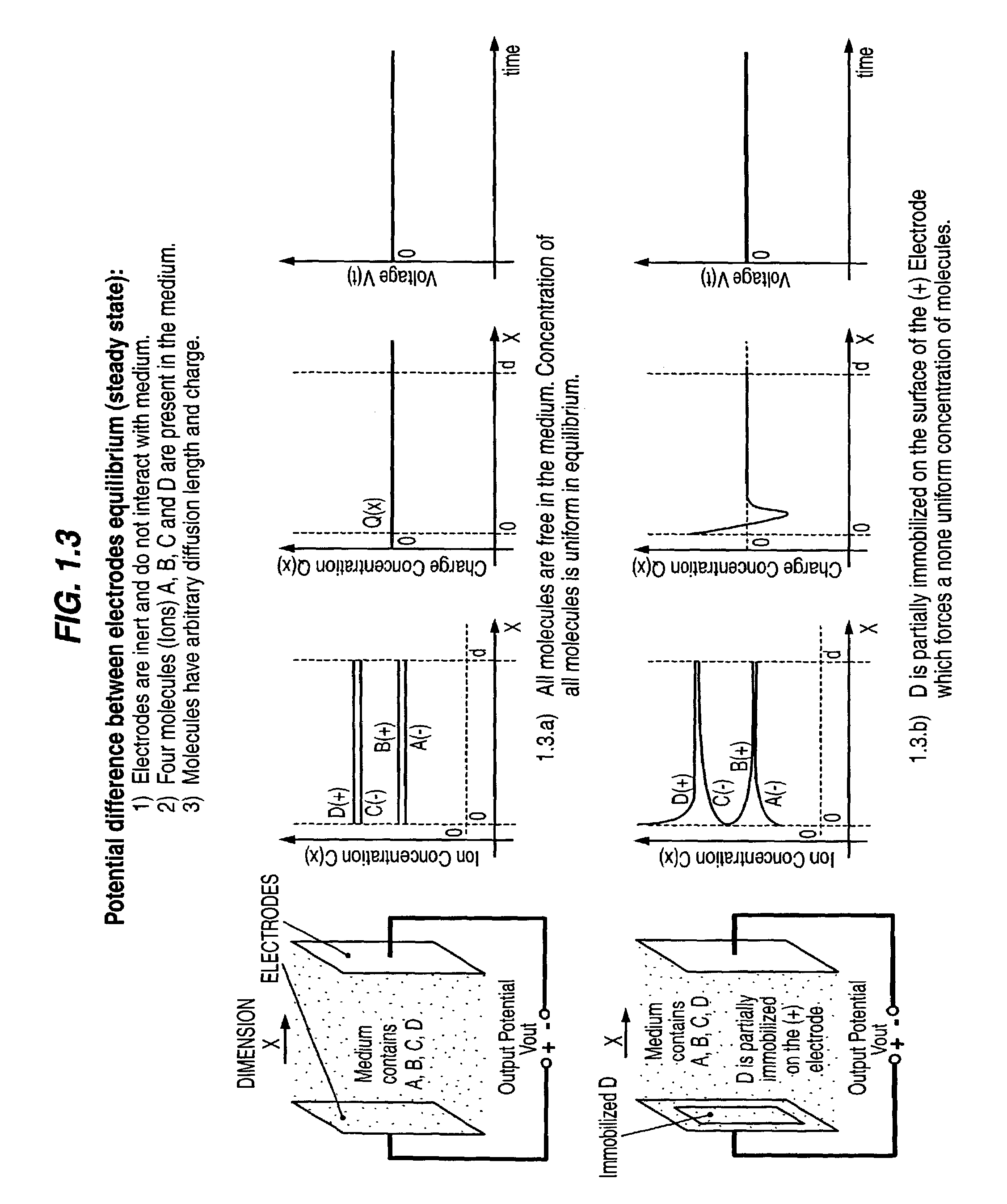
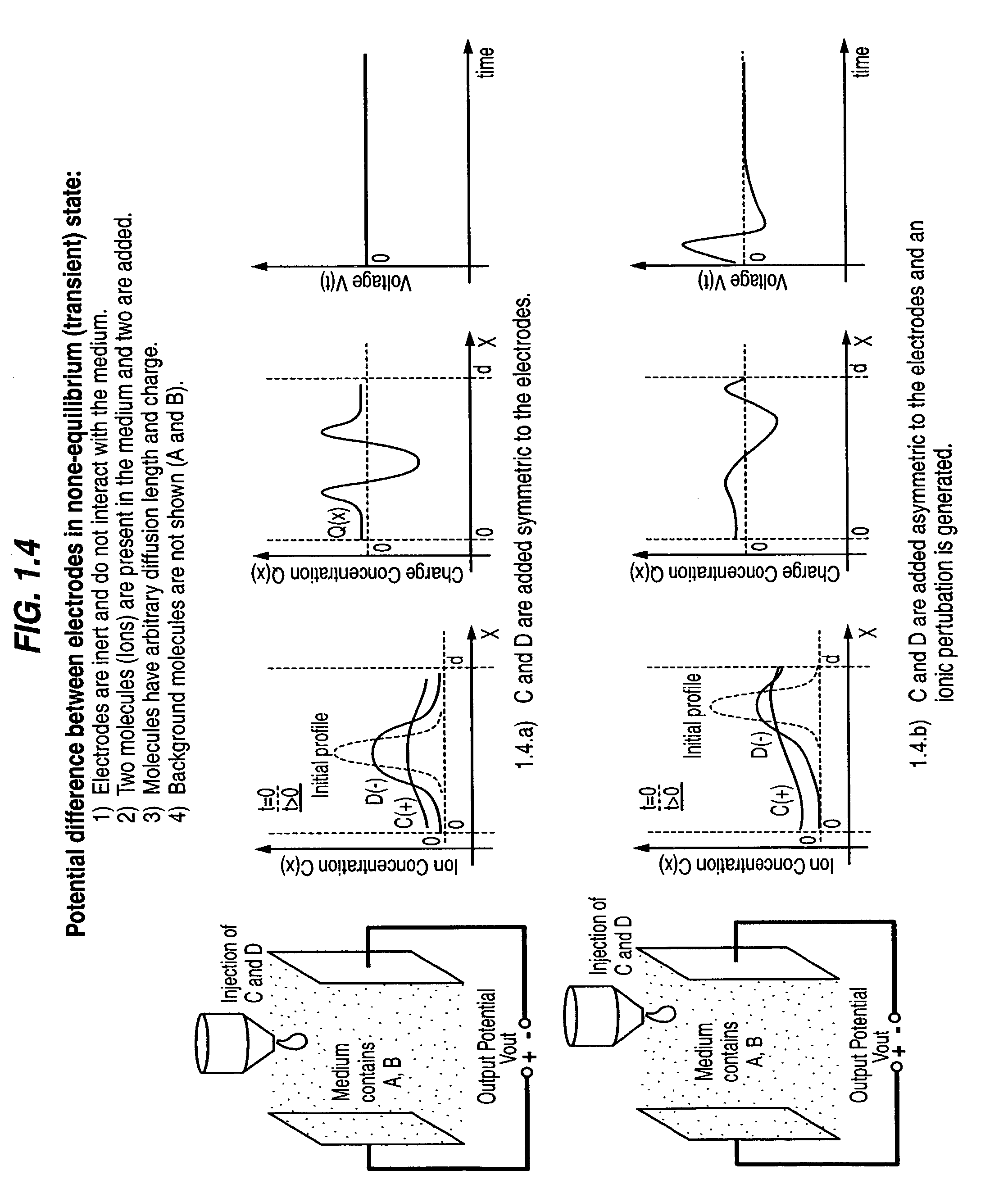
Transient electrical signal based methods and devices for characterizing molecular interaction and/or motion in a sample
InactiveUS7223540B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular entityElectric signal
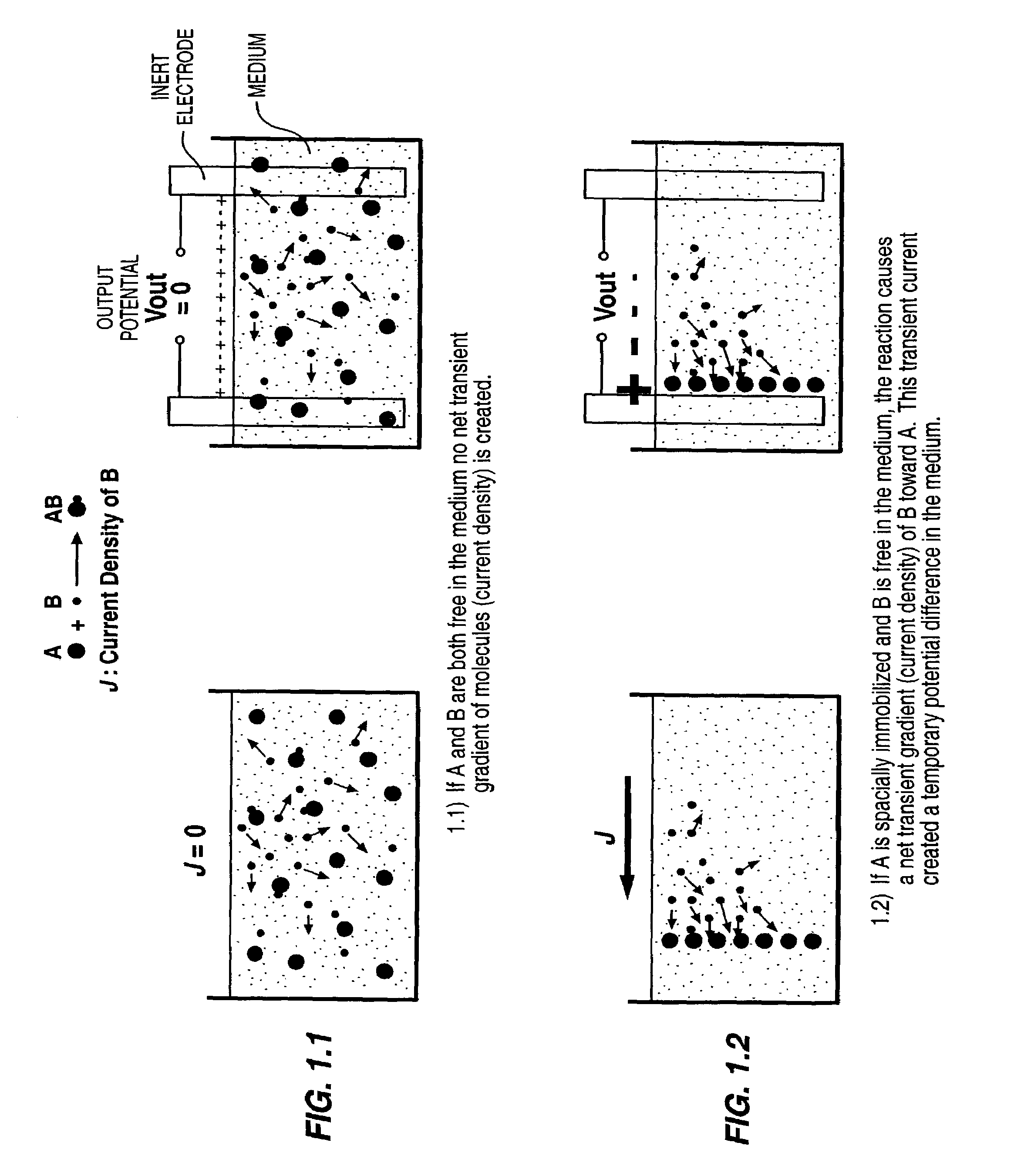
Devices for detecting a transient electrical signal in a sample are provided. Also provided are systems that include the subject devices. The subject devices and systems find use in a variety of applications, particularly in the characterization of a sample, and more particularly in the characterization of molecular entities in the sample.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
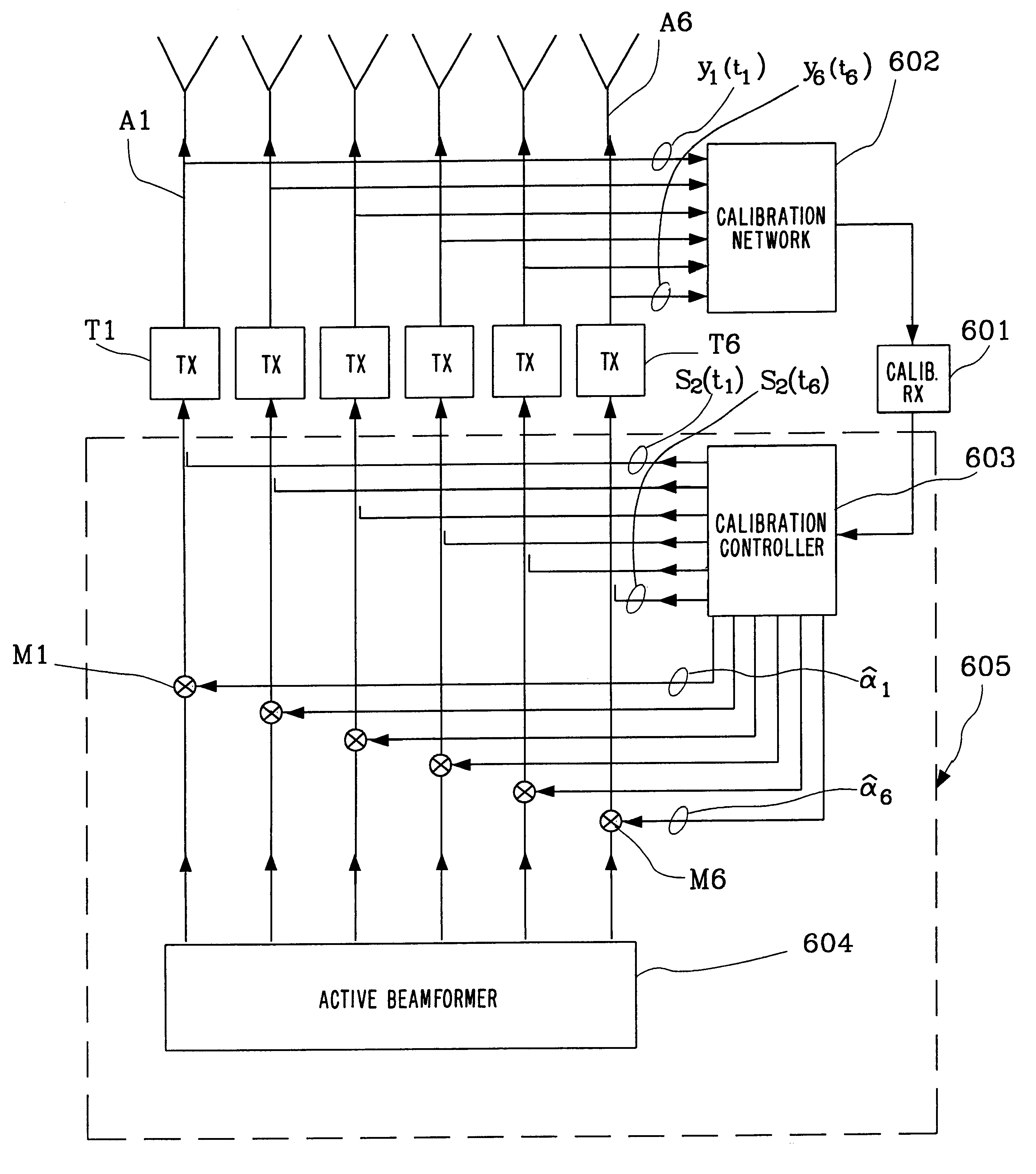
Antenna array calibration
InactiveUS6339399B1Improve performanceImprove accuracyWave based measurement systemsAntennasAmplitude distortionCellular communication systems
A method and a system for calibrating the reception and transmission of an antenna array for use in a cellular communication system is disclosed. The calibration of the reception of the antenna array is performed by injecting a single calibration signal into each of a number of receiving antenna sections, in parallel. The signals are collected after having passed receiving components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to received signals. The calibration of the transmission of the antenna array is preformed in a similar way. A single calibration signal is generated and injected into each of a number of transmitting antenna sections, one at a time. The signals are collected, one at a time, after having passed transmitting components that might have distorted the phase and amplitude. Correction factors are generated and applied to signals that are to be transmitted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for directional measurement of subsurface electrical properties
InactiveUS6100696AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationPhysicsInduction logging
A directional induction logging tool is provided for measurement while drilling. This tool is preferably placed in a side pocket of a drill collar, and it comprises transmitter and receiver coils and an electromagnetic reflector. The reflector, which may be a layer of highly conductive material placed between the coils and the body of the drill collar, serves to focus the electromagnetic fields generated and sensed by the tool in the direction away from the reflector, thus providing a directional response to formation conductivity with a relatively high depth of investigation. In preferred embodiments of the invention, magnetically permeable cores are placed within the coils to concentrate the magnetic fields that pass through them. Circuitry is described for balancing the mutual inductive coupling of the coils by injecting a direct current signal through one or more of the coils, which alters the magnetic permeability of the core material. The magnitude of the direct current required to achieve a balanced condition may be derived from the quadrature phase component of the return signal. Circuitry is also provided for generating a transmitted signal and for processing the return signals, including digital-to-analog conversion circuitry for providing digital data for transmission to the surface. This tool may be employed to provide real-time directional conductivity information that may be used to detect and follow bed boundaries in geosteering operations.
Owner:SINCLAIR PAUL L
Monitoring physiological condition and detecting abnormalities
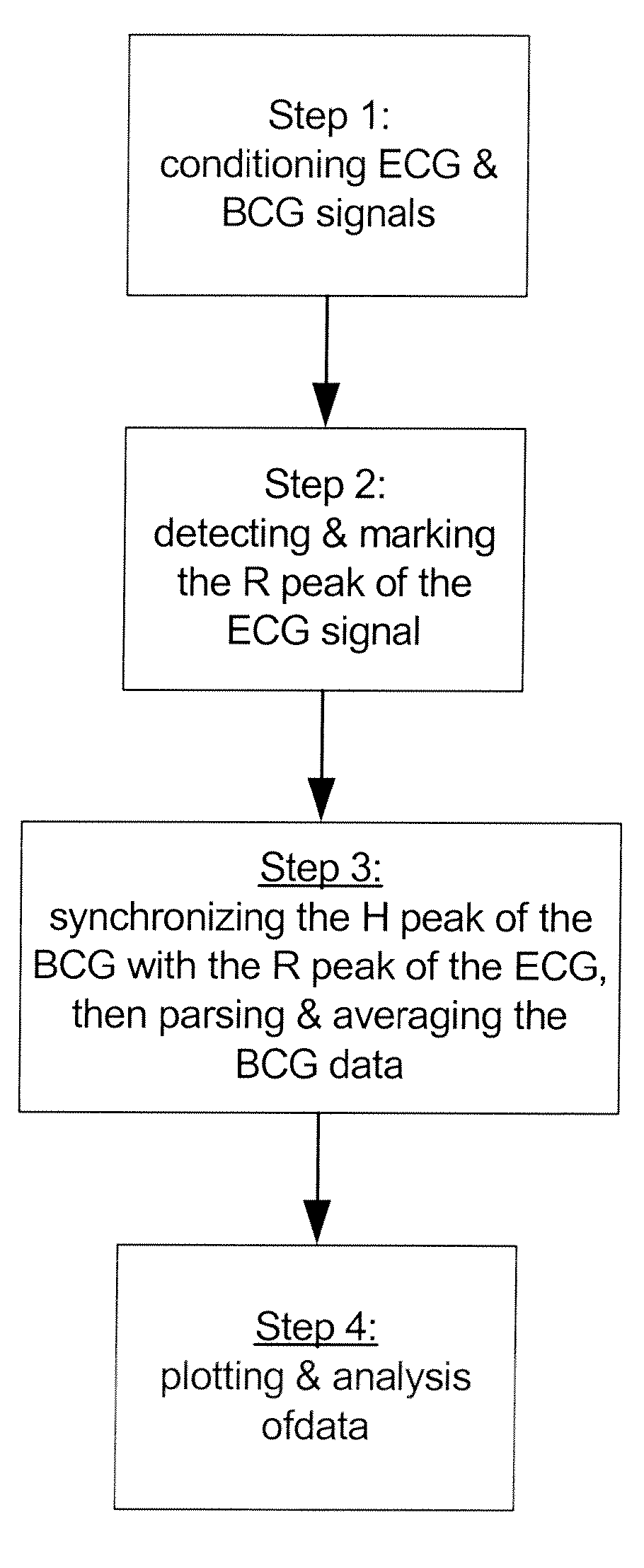
ActiveUS20080194975A1Monitoring usingElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsMedicineReference designator
A system for monitoring an individual's physiological condition and detecting abnormalities therein, comprising concurrently receiving at least a first signal and a second signal. The first and second signals are conditioned to minimize background extraneous noise after which, each signal is concurrently processed and analyzed to detect repeating cyclical patterns and further characterized to identify individual components of the repeating cycles. At least one individual component in one signal is selected as a reference marker for a selected component in the other signal. The two signals are then synchronized, outputs produced therefrom and stored in a database. The system is provided with a plurality of devices for acquiring, transmitting and conditioning at least two physiological signals, a software program cooperable with a microprocessor configured for receiving said transmitted signals and conditioned signals, and processing said signals to characterize and synchronize said signals and provide signal outputs derived therefrom, a database for storing said transmitted signals, conditioned signals, synchronized signals, and output signals derived therefrom. The output signals are useful for reporting and optionally for retransmission to the individual's body and providing physiologically stimulatory signals thereto.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL
Mitigating interference in a signal
InactiveUS7626542B2Improve performanceLower requirementAdaptive networkDigital technique networkEngineeringNon orthogonal
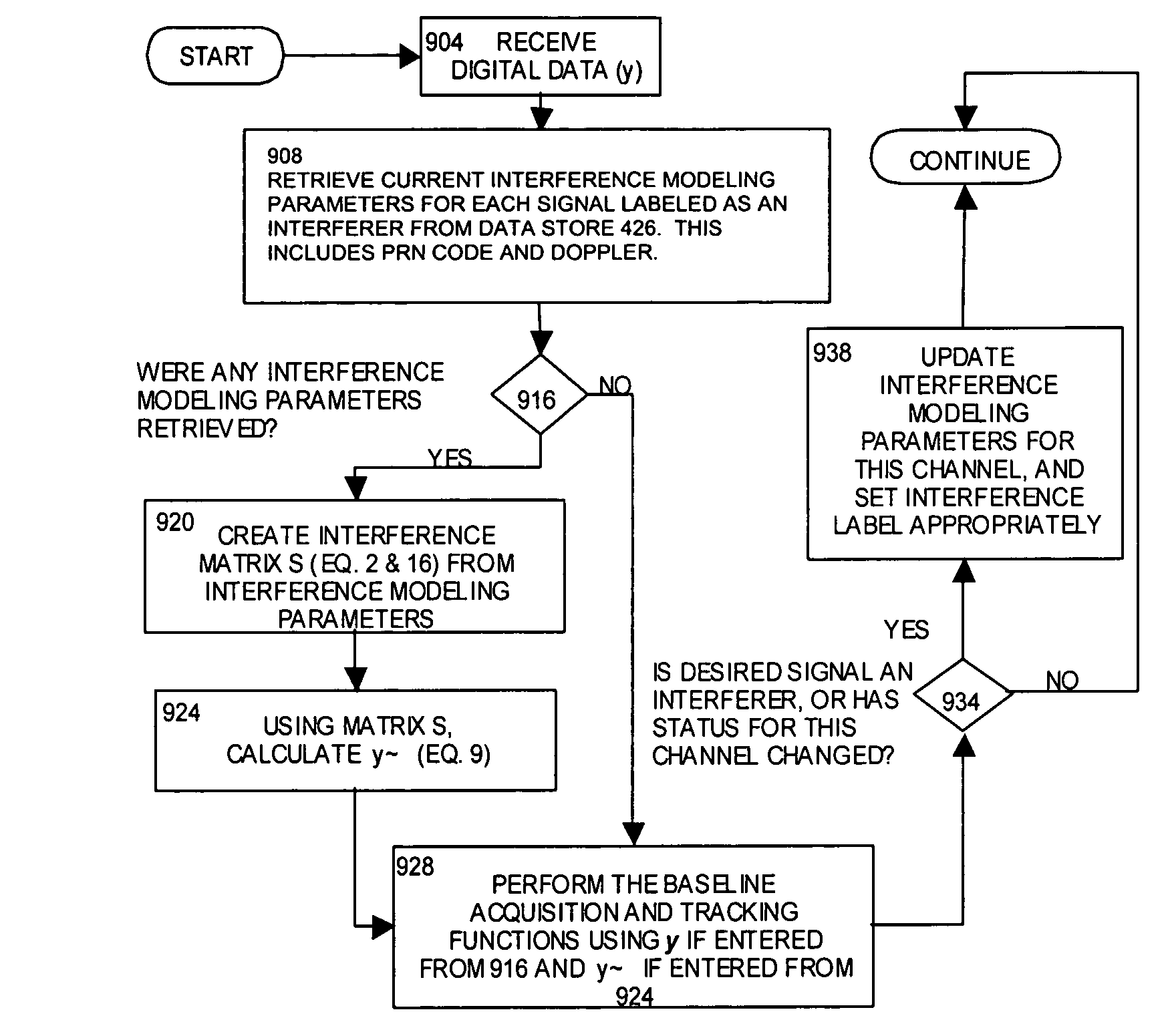
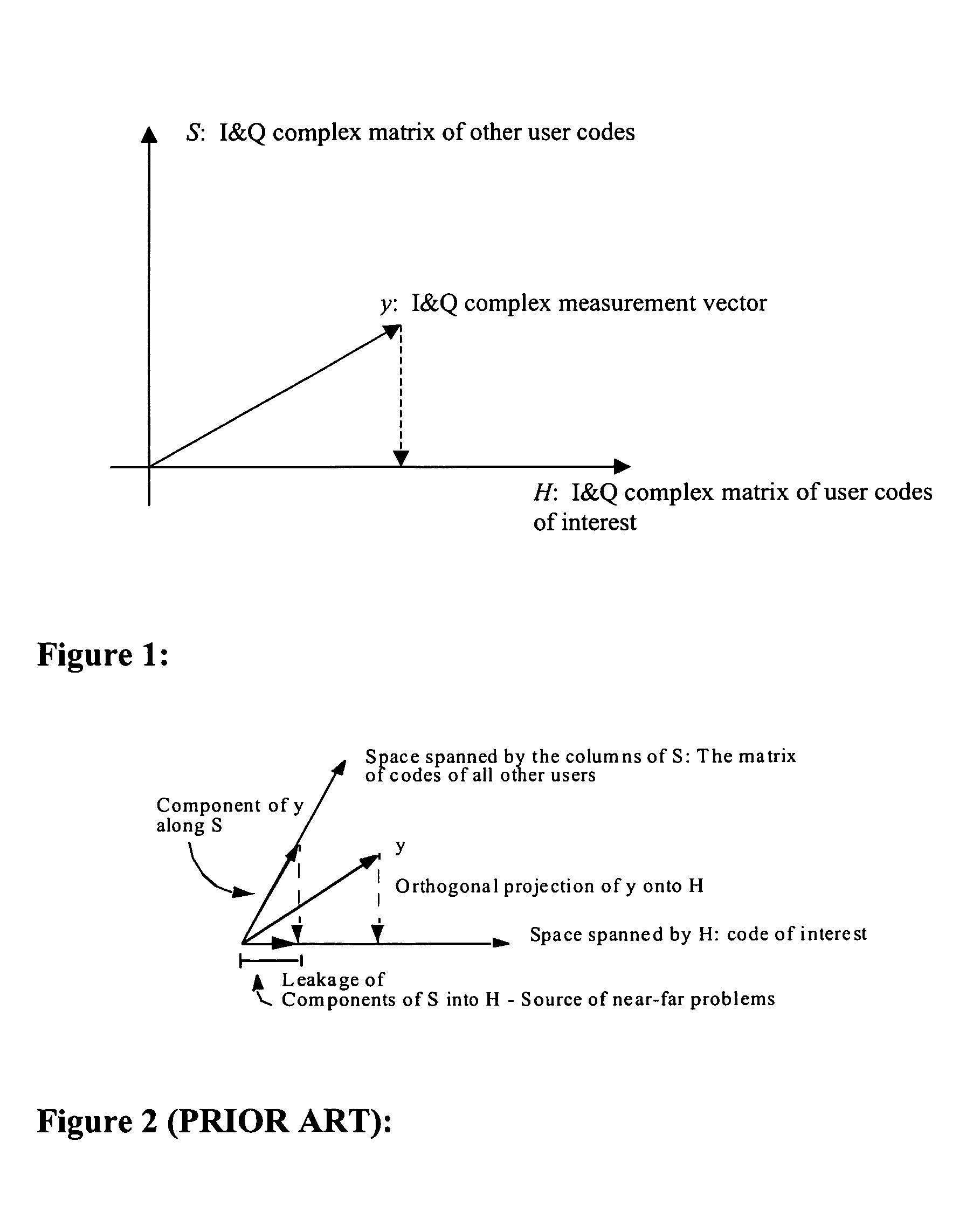
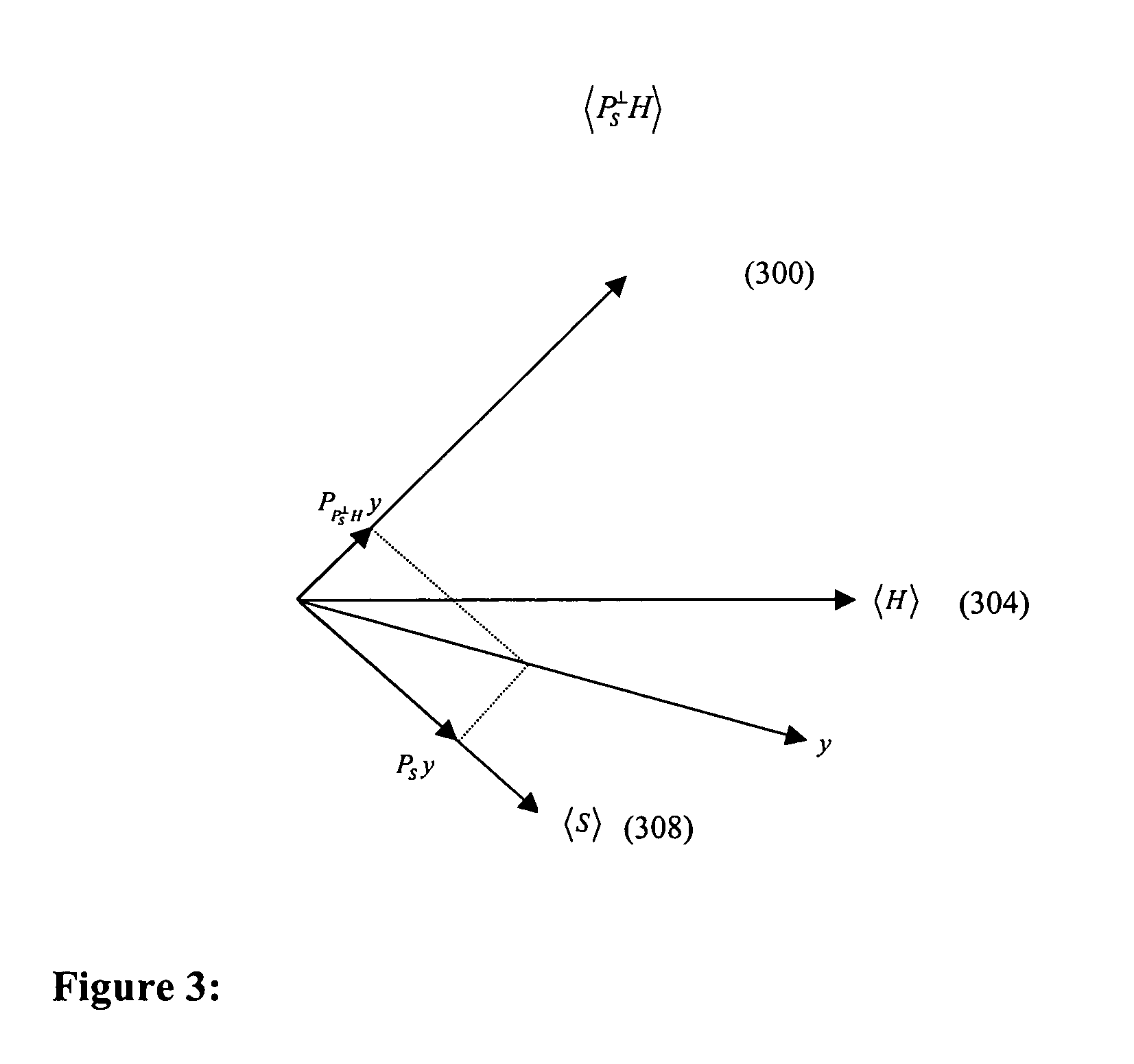
A method and receiver are disclosed for mitigating or substantially canceling signal interference between signals detected at the receiver. Once a presumed interfering signal(s) is acquired, parameters are determined that allow the interferer(s) to be modeled. The phase invariance of the process eliminates the need to acquire the interferer's phase. An orthogonal projection (for projecting onto a detection subspace which is orthogonal to a subspace spanned by the interferer(s)) is applied to the composite of all signals (y) for thereby projecting y onto the detection subspace. The interference subspace is non-orthogonal to a representation of desired (but interfered) signal of the composite signals. With the receiver properly equipped to perform this projection operation, interfering signals, multipath, multipath-like, and structured jamming signals can be effectively diminished.
Owner:DATA FUSION CORP
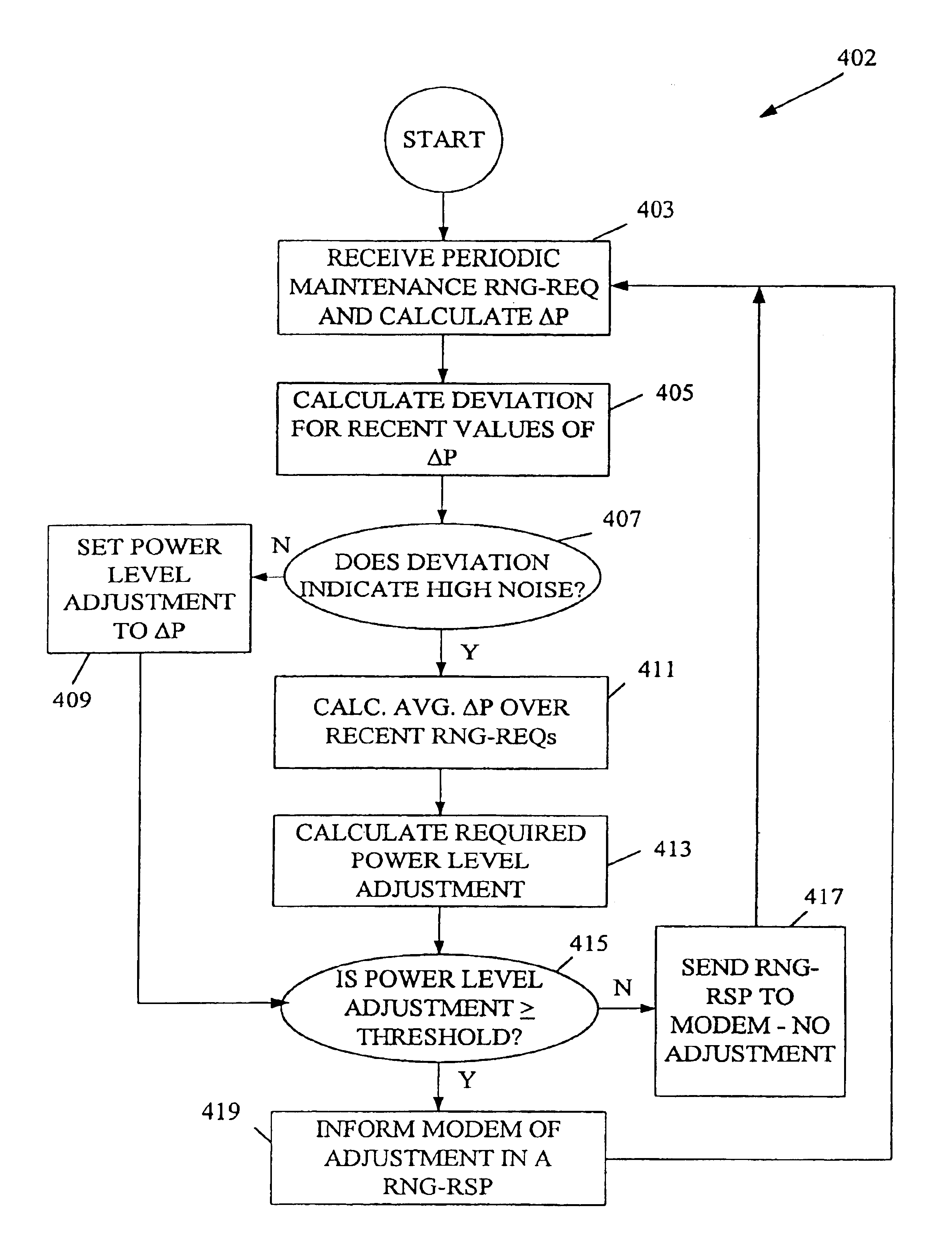
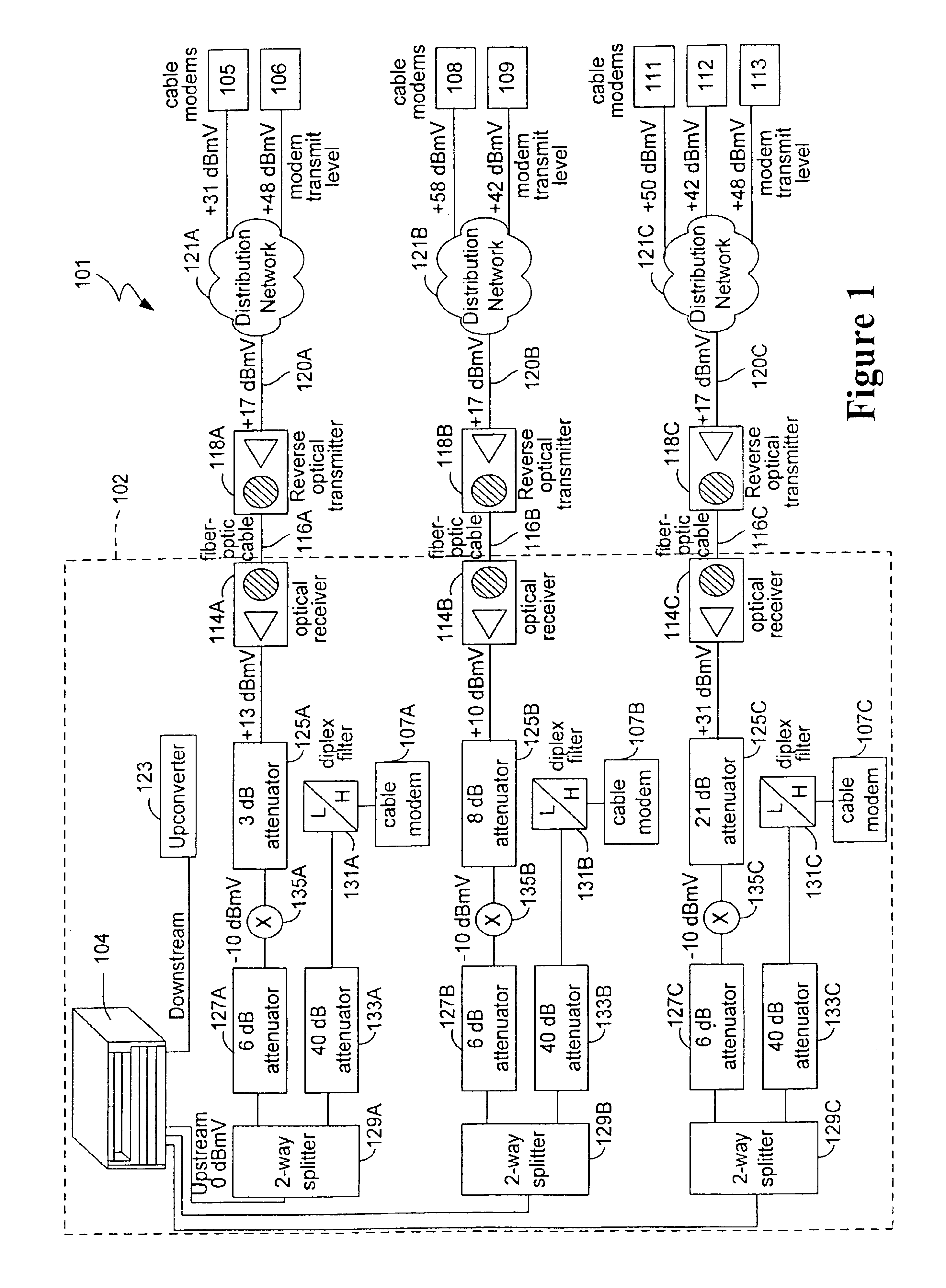
Intelligent power level adjustment for cable modems in presence of noise
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System, method and computer-readable medium for estimating direction of arrival of a signal incident on at least one antenna array
ActiveUS20160103199A1Simple and accurate procedureDirection findersAntennasSystems approachesAntenna array
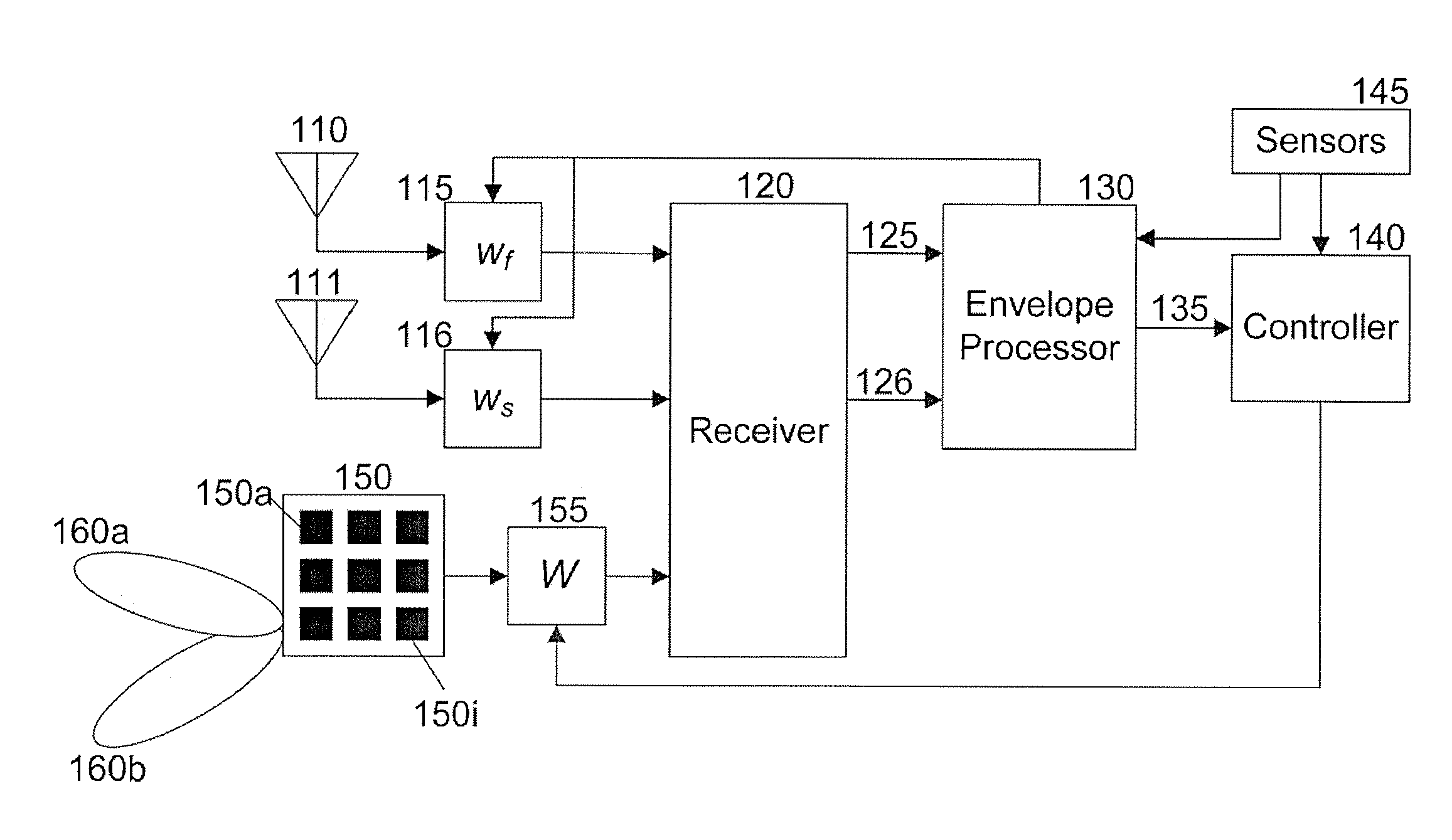
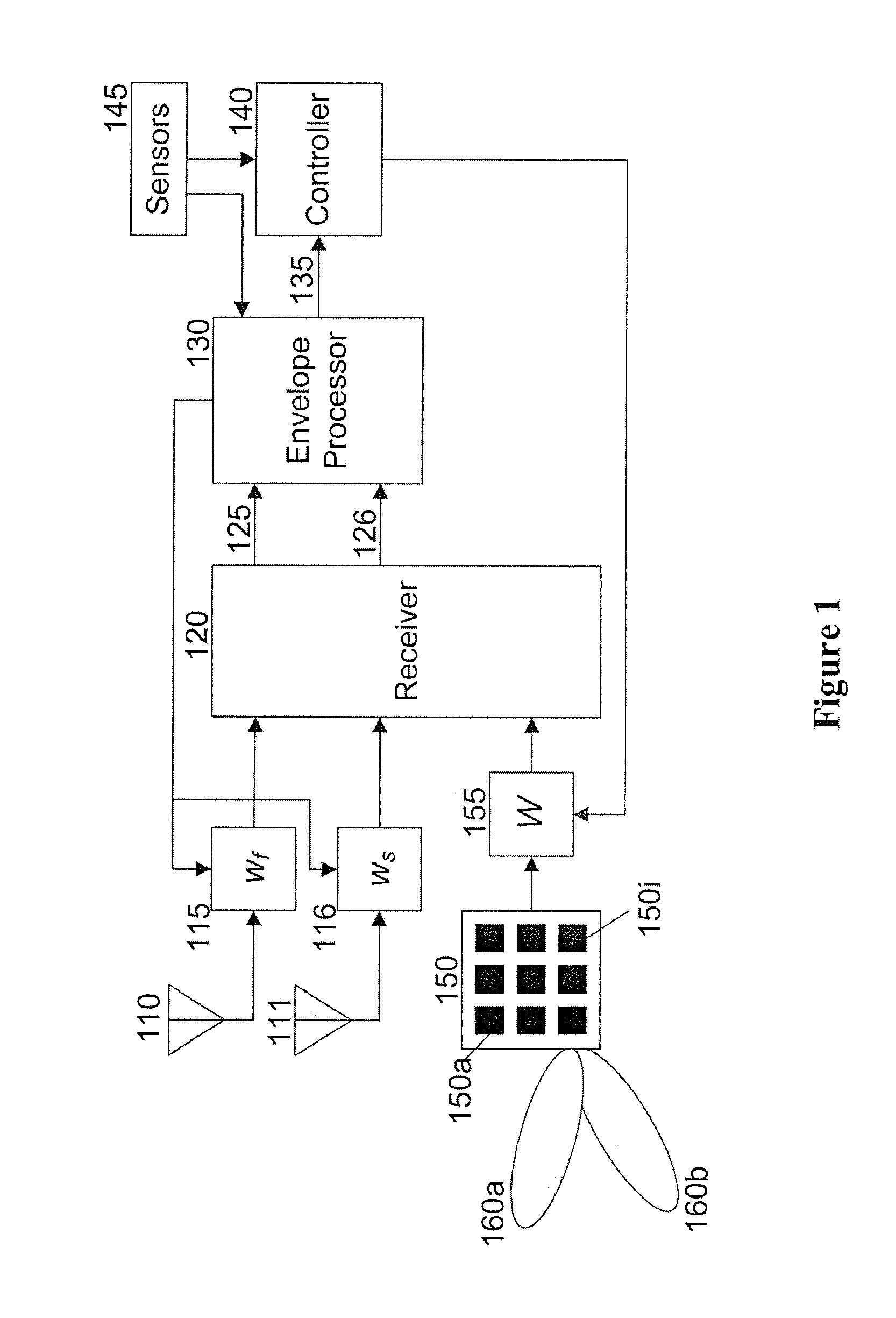
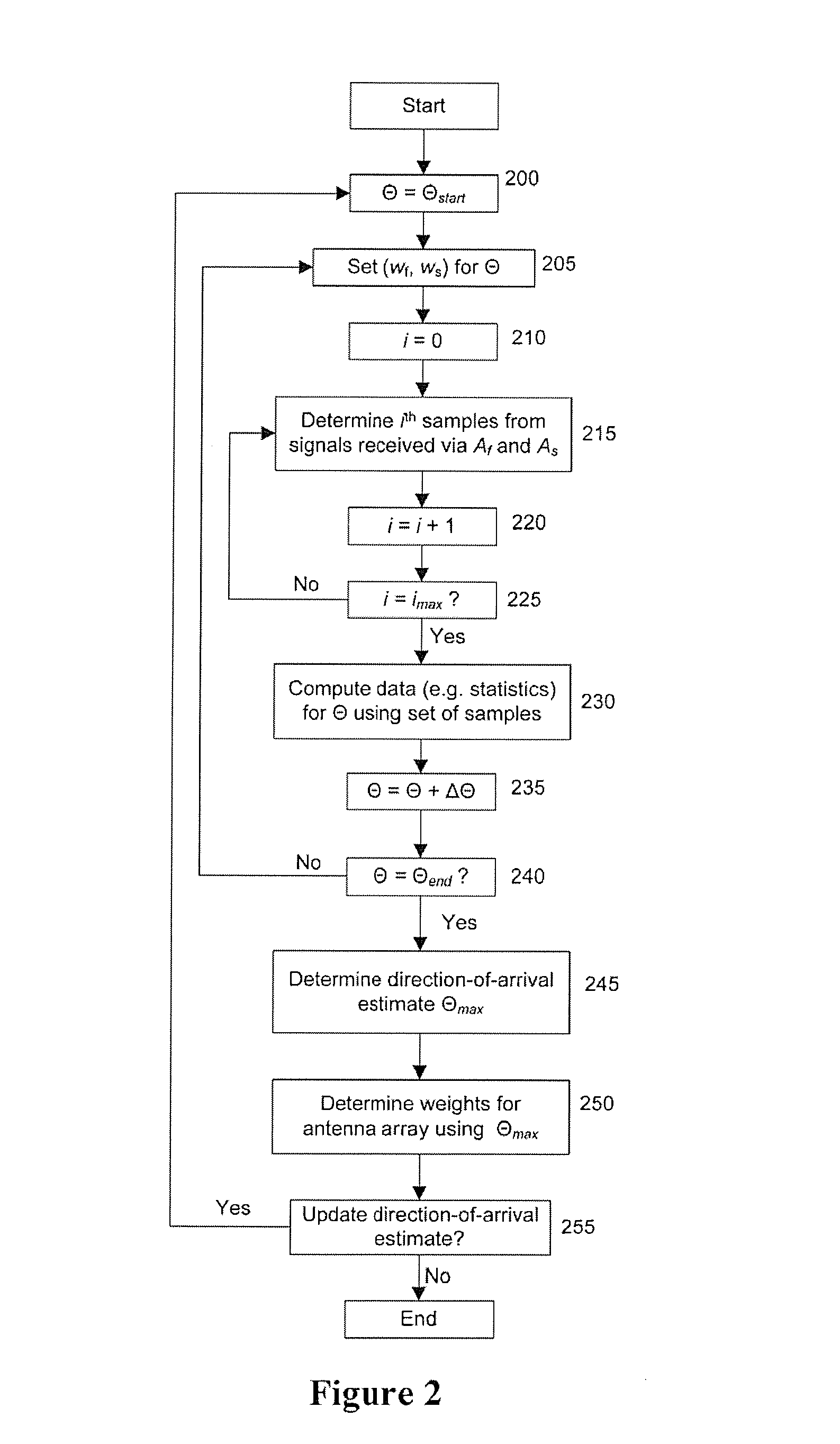
Exemplary embodiments include a computer-implemented method for configuring at least one antenna array comprising receiving a plurality of samples corresponding to signals incident on a plurality of antennas; using a computer arrangement, computing one or more data related to an envelope of the samples and estimating a direction of arrival of the signals incident on the antennas based on the one or more computed data; and configuring the at least one antenna array based on the estimated direction of arrival. The computing and estimating procedures can be performed for each of a plurality of direction-of-arrival candidates. The one or more data can be statistics corresponding to multipath shape factor parameters. The spatial selectivity of the at least one antenna array can be configured based on the estimated direction of arrival. Other exemplary embodiments include apparatus and computer-readable media embodying one or more of the exemplary computer-implemented methods and / or procedures.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
System and method for distributed input distributed output wireless communications
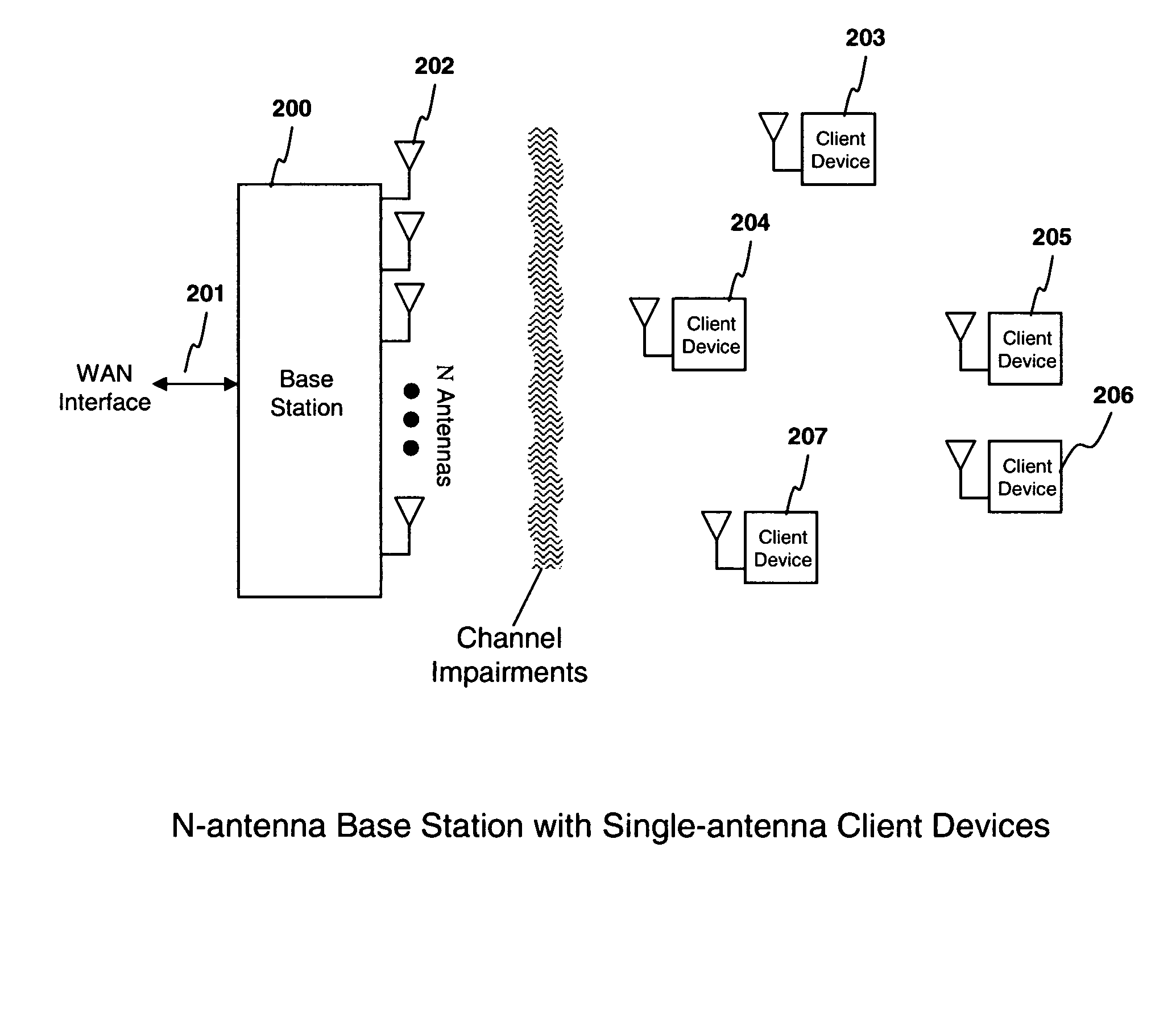
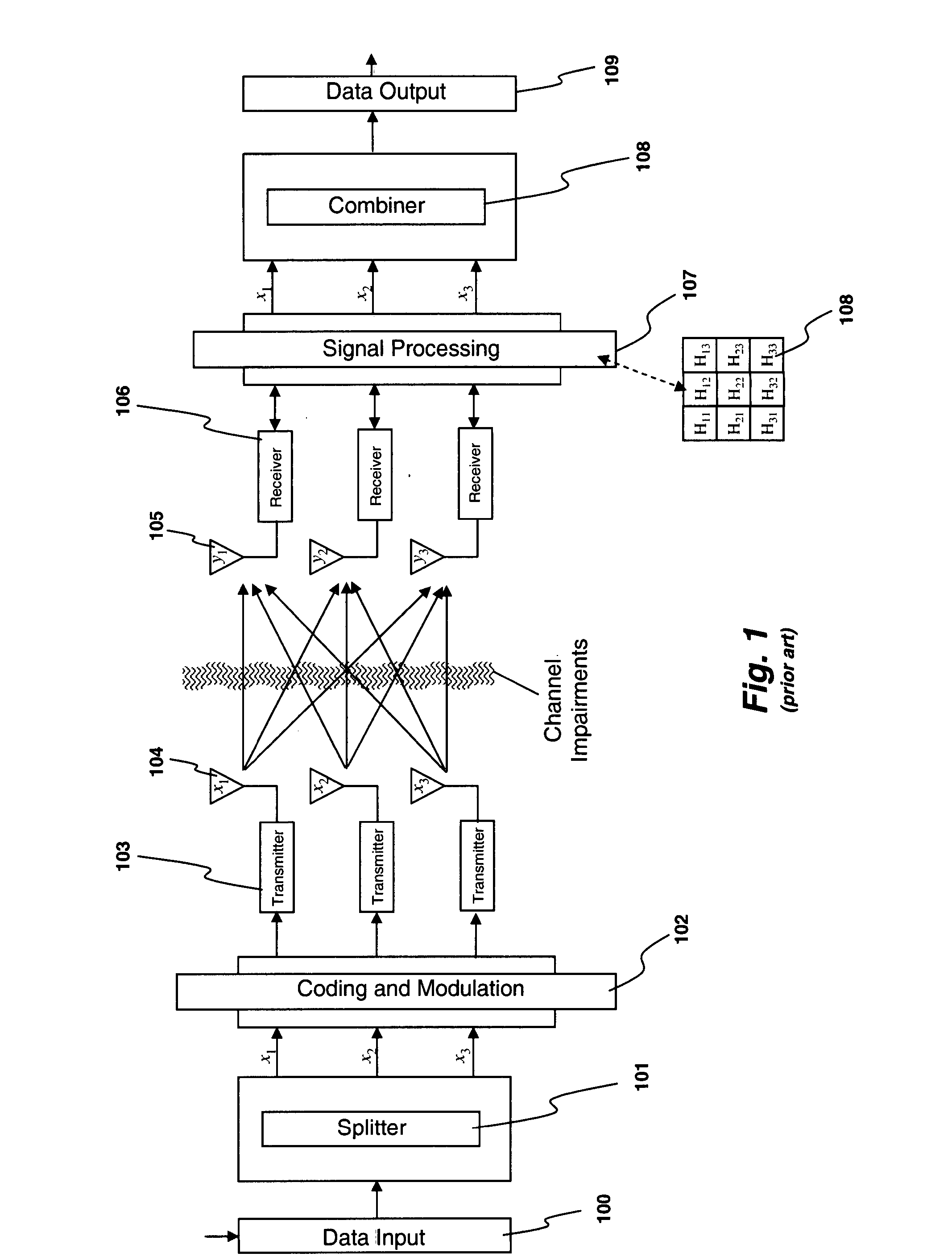
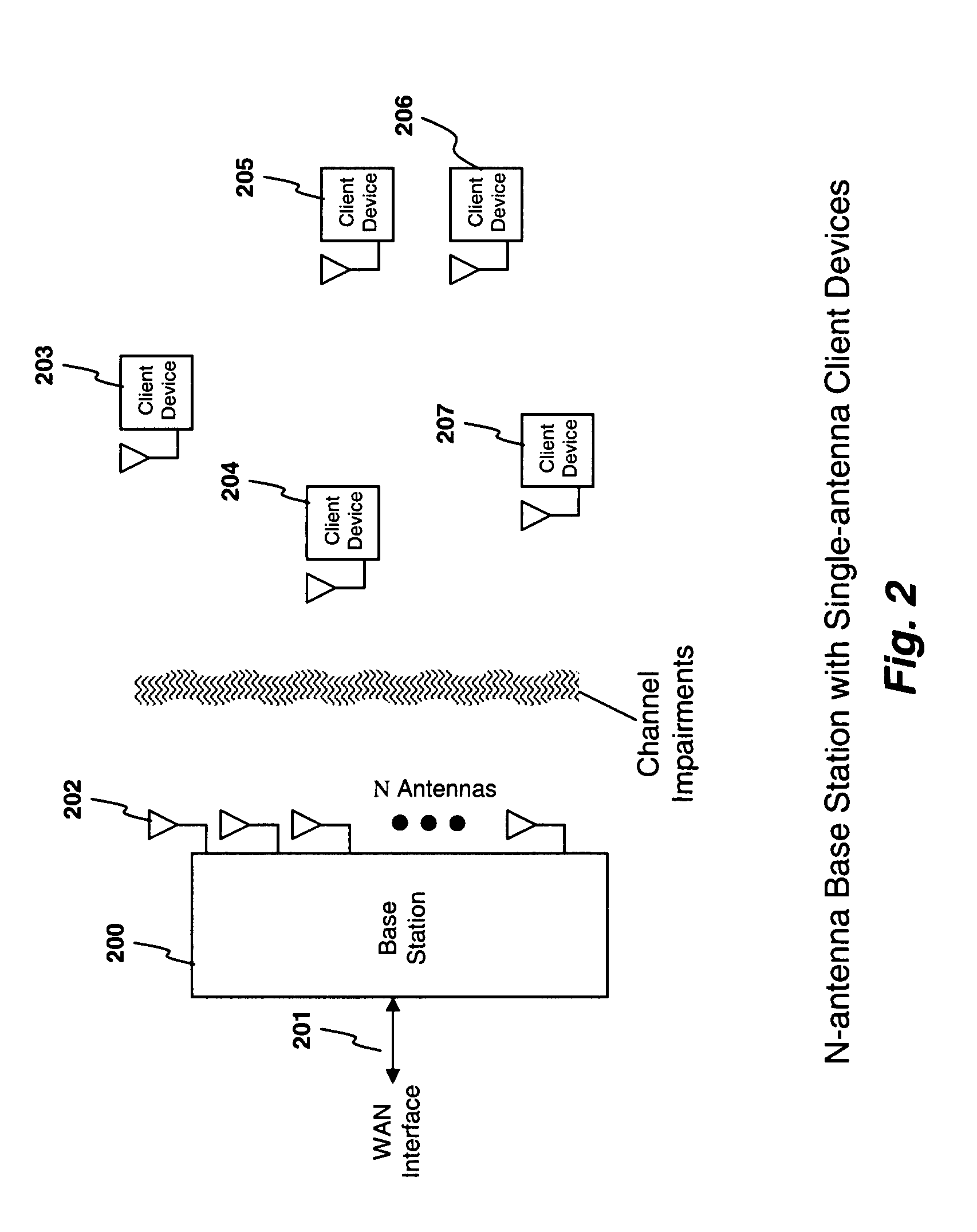
A system and method are described for compensating for frequency and phase offsets in a multiple antenna system (MAS) with multi-user (MU) transmissions (“MU-MAS”). For example, a method according to one embodiment of the invention comprises: transmitting a training signal from each antenna of a base station to one or each of a plurality of wireless client devices, one or each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate frequency offset compensation data, and receiving the frequency offset compensation data at the base station; computing MU-MAS precoder weights based on the frequency offset compensation data to pre-cancel the frequency offset at the transmitter; precoding training signal using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded training signals for each antenna of the base station; transmitting the precoded training signal from each antenna of a base station to each of a plurality of wireless client devices, each of the client devices analyzing each training signal to generate channel characterization data, and receiving the channel characterization data at the base station; computing a plurality of MU-MAS precoder weights based on the channel characterization data, the MU-MAS precoder weights calculated to pre-cancel frequency and phase offset and / or inter-user interference; precoding data using the MU-MAS precoder weights to generate precoded data signals for each antenna of the base station; and transmitting the precoded data signals through each antenna of the base station to each respective client device.
Owner:REARDEN
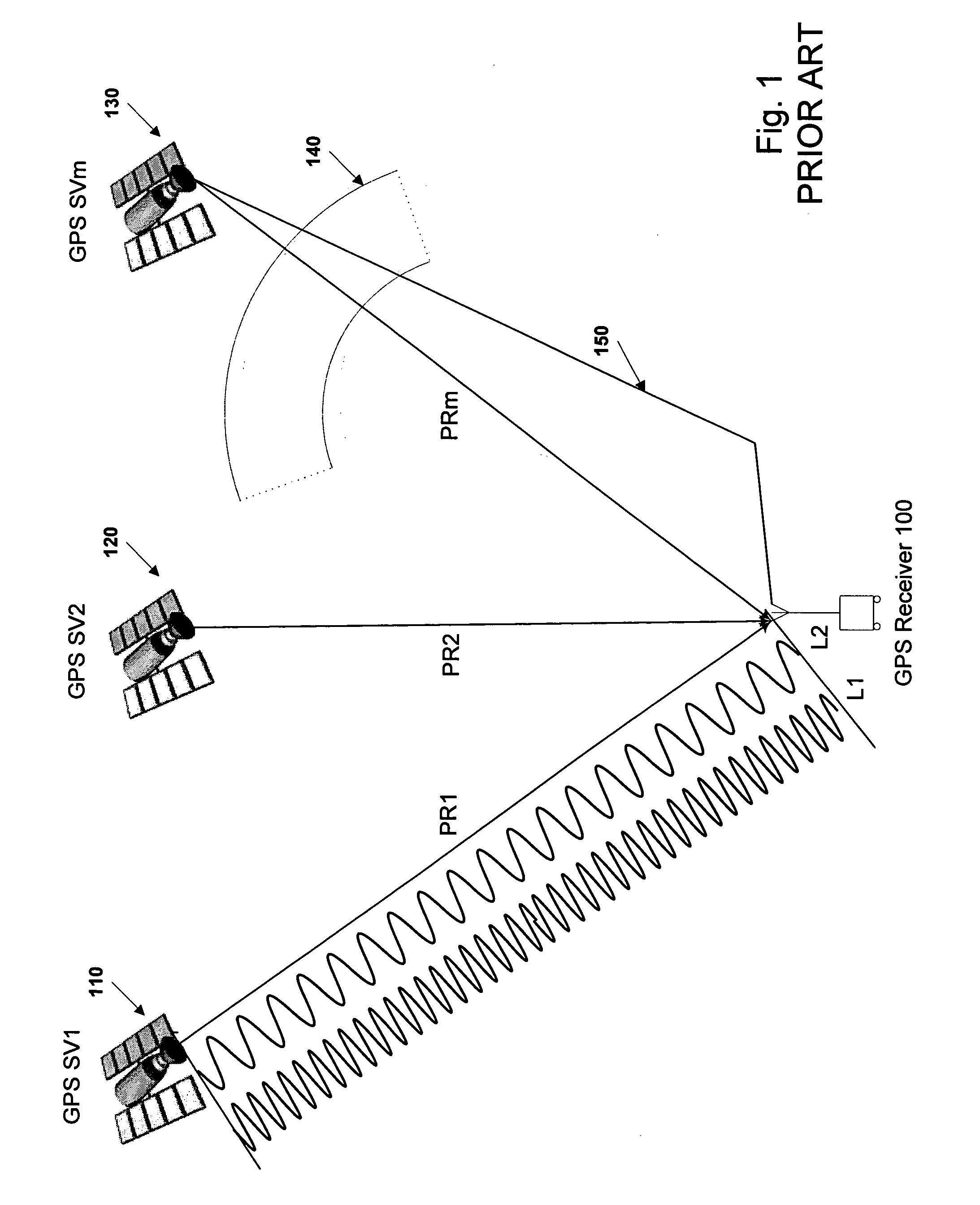
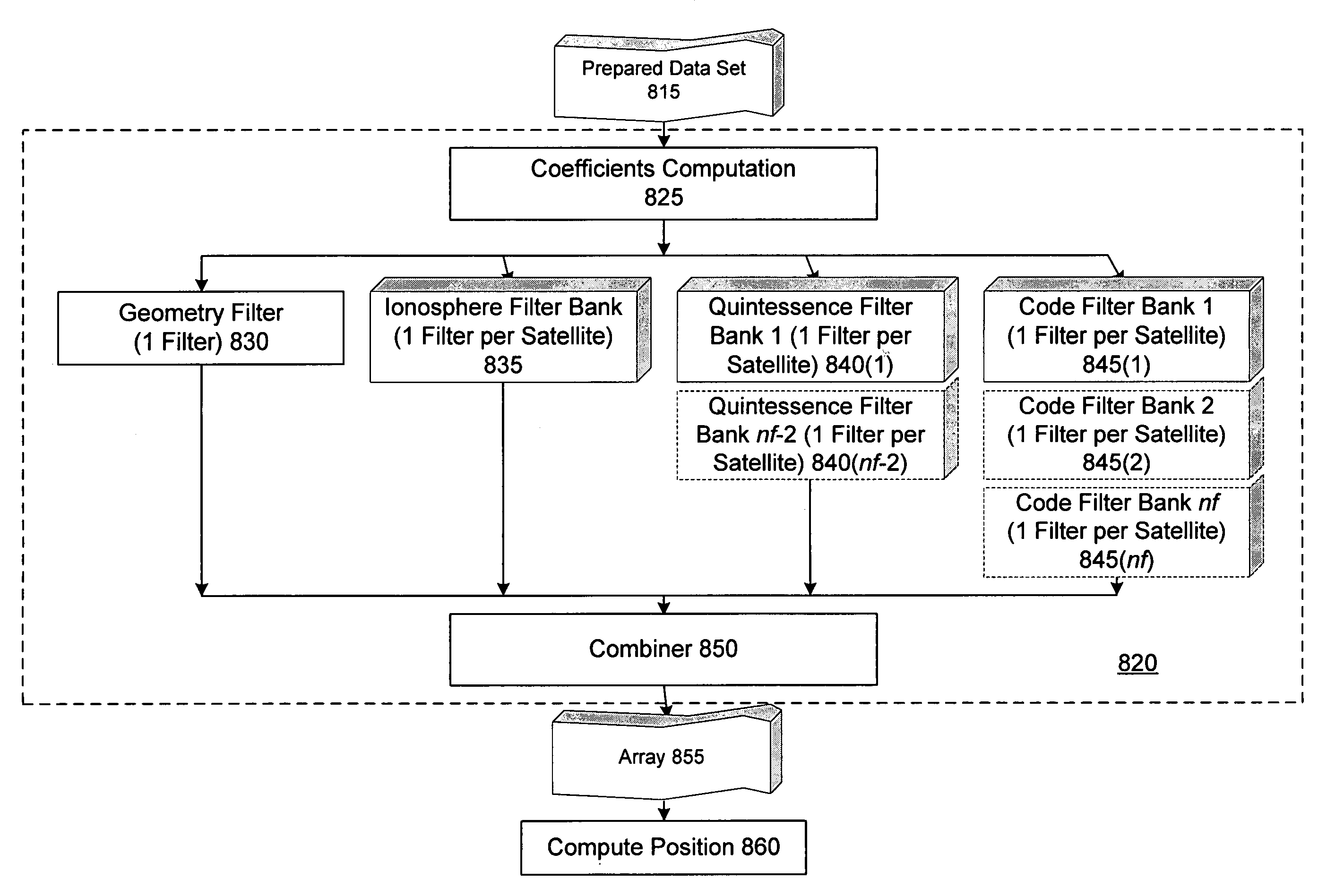
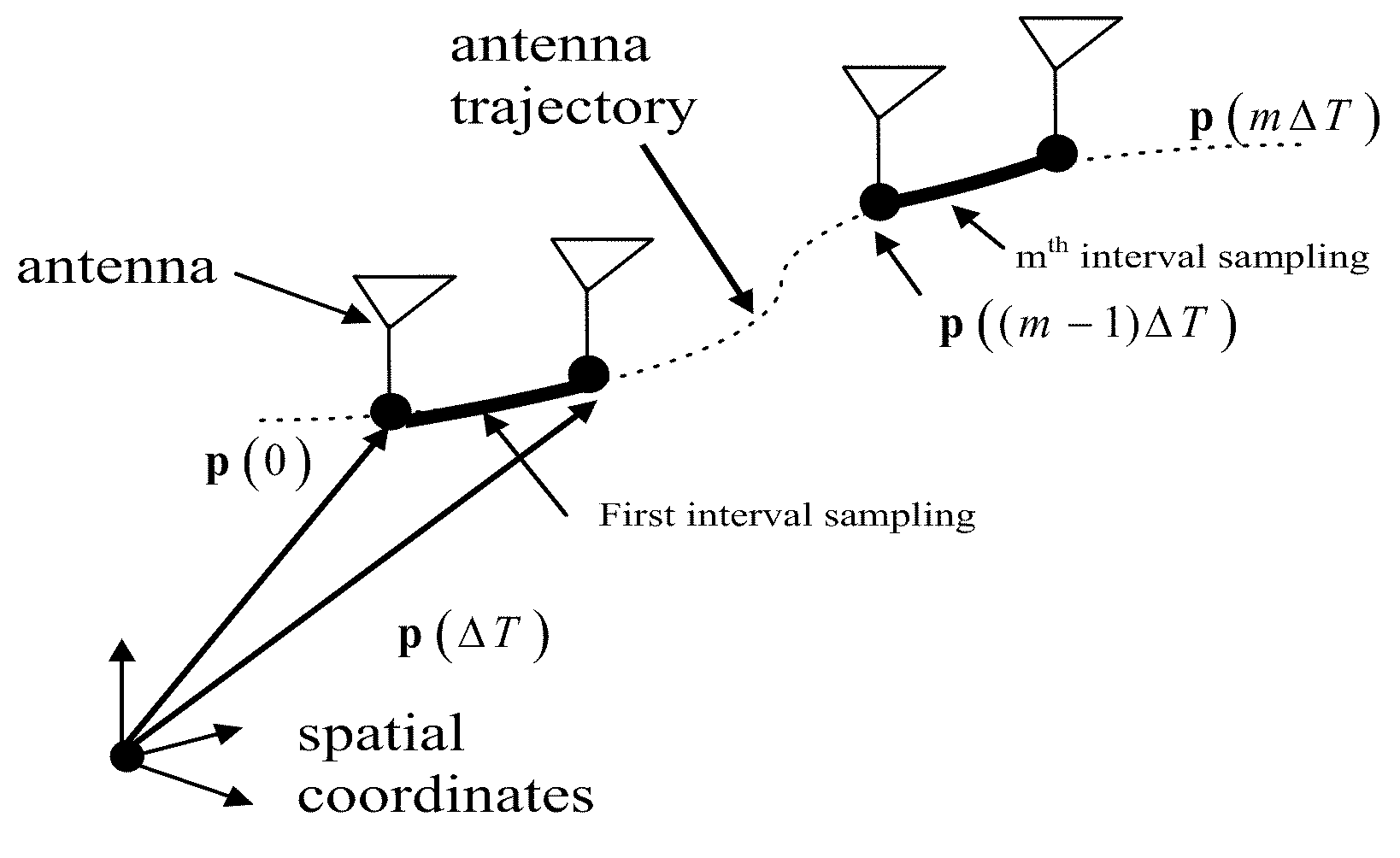
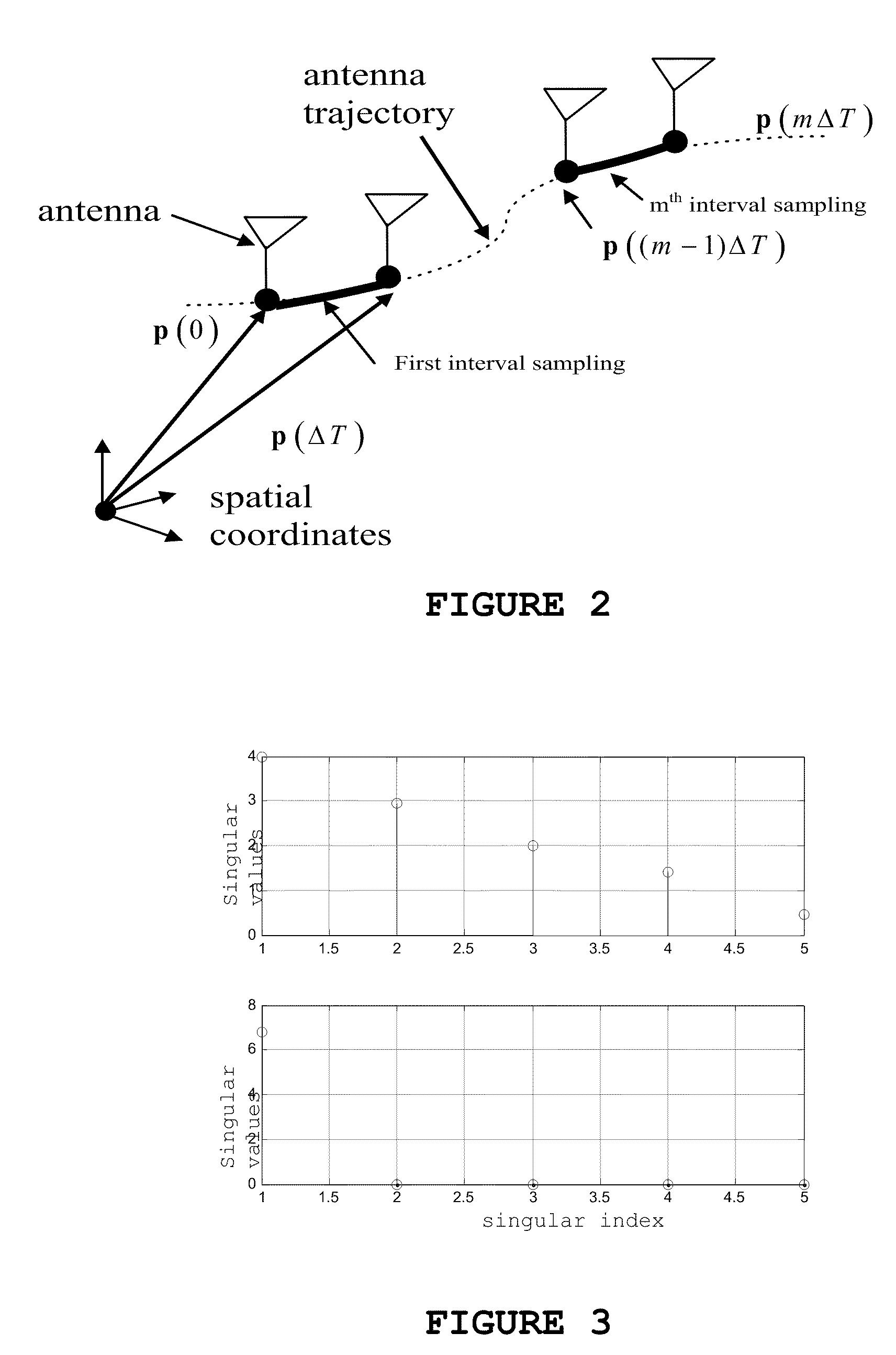
Ambiguity estimation of GNSS signals for three or more carriers
ActiveUS20050101248A1Reduce effortValidation is greatly reducedPosition fixationRadio transmissionCarrier signalComputer science
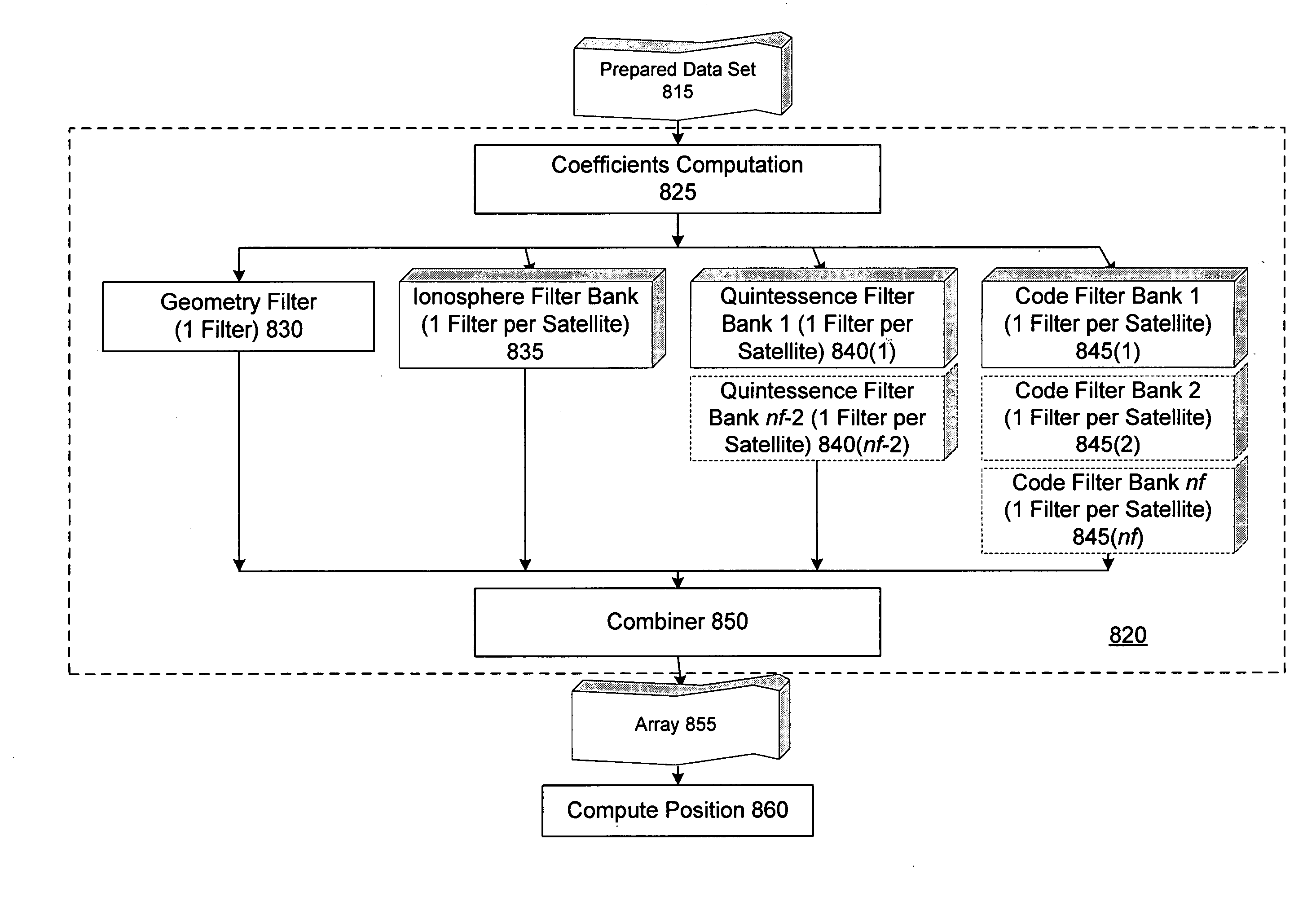
Methods and apparatus are provided for factorized processing of a set of GNSS signal data derived from signals having at least three carriers. A geometry filter is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the geometry carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. A bank of ionosphere filters is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry-free ionosphere carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the ionosphere carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. At least one bank of Quintessence filters is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a geometry-free and ionosphere-free carrier-phase combination to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the geometry-free and ionosphere-free carrier-phase combination and associated statistical information. At least one code filter is applied to the set of GNSS signal data using a plurality of geometry-free and ionosphere-free code-carrier combinations to obtain an array of ambiguity estimates for the code-carrier combinations and associated statistical information. The resulting arrays are combined to obtain a combined array of ambiguity estimates for all carrier phase observations and associated statistical information.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
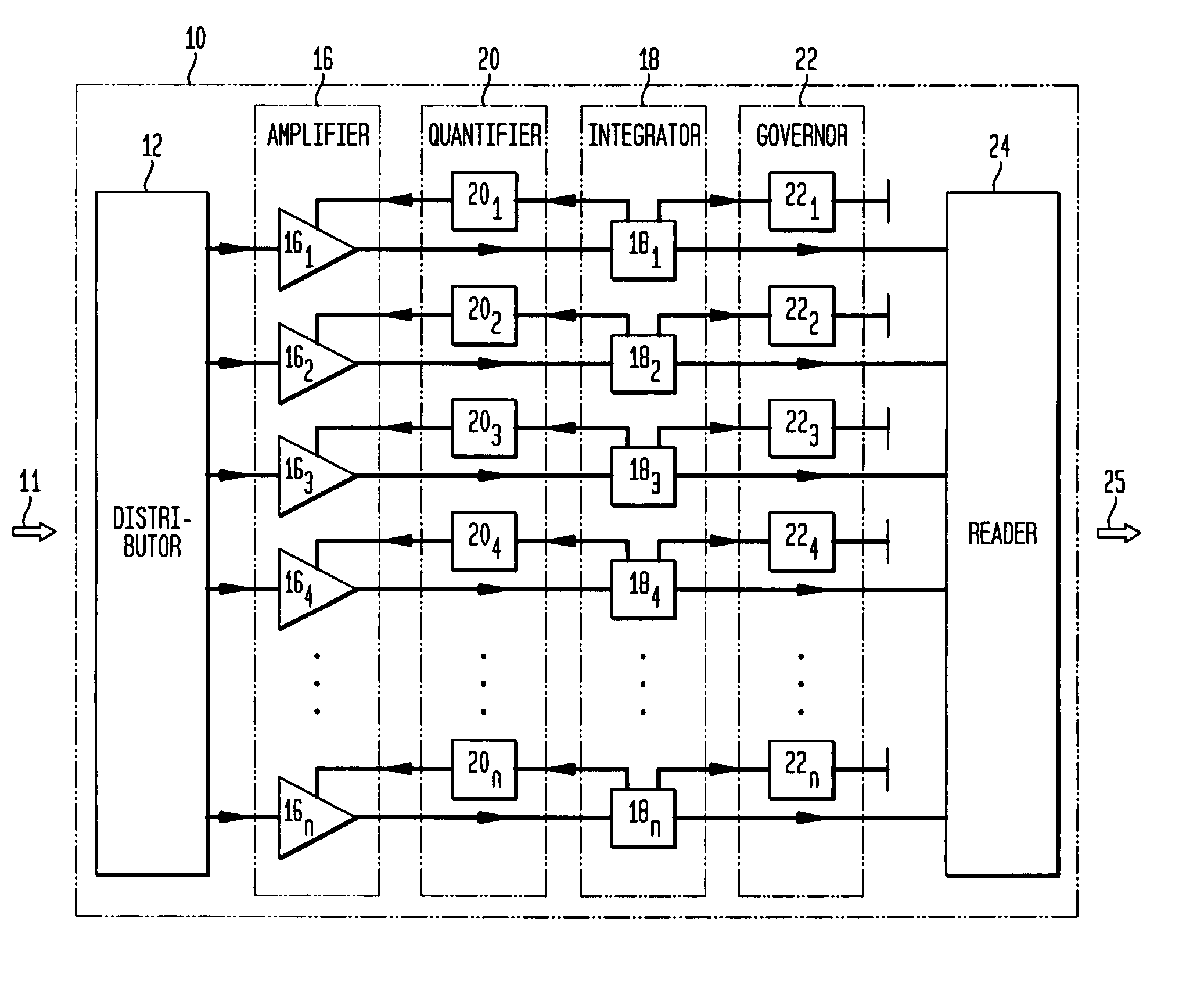
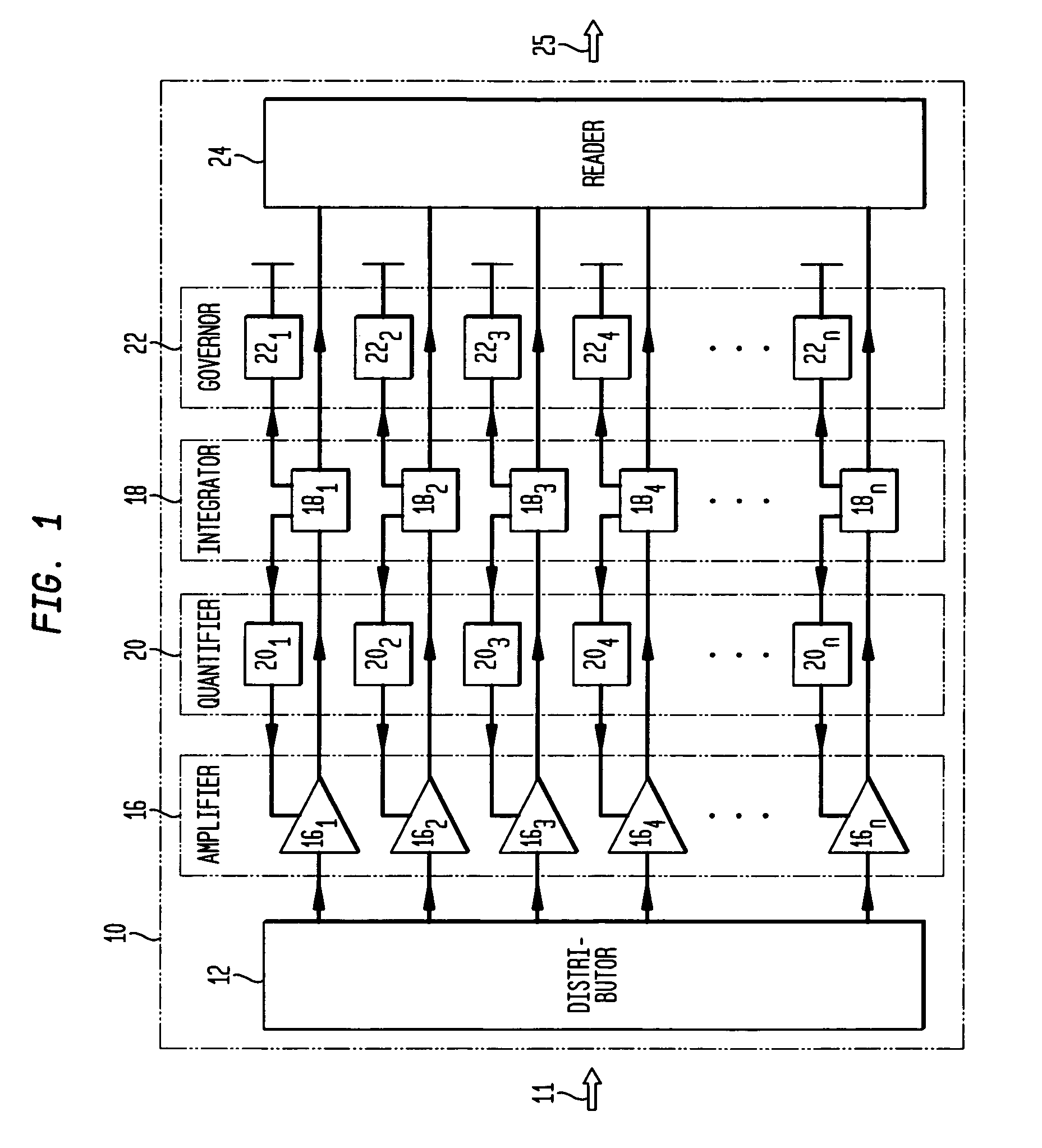
High sensitivity, high resolution detection of signals
A system and method providing for the detection of an input signal by distributing the input signal into independent signal components that are independently amplified. Detection of an input signal comprises generating from the input signal a plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components, each having a respective known number of elementary charges, the number of the plurality of spatially separate elementary charge components being a known monotonic function of the magnitude of said input signal; and independently amplifying each of the plurality of spatially divided elementary charge components to provide a respective plurality of signal charge packets, each signal charge packet having a second number of elementary charges greater than the respective known number by a respective amplification factor.
Owner:AMPLIFICATION TECH INC
Device and method for extracting information from characteristic signals
ActiveUS20130271591A1Improve accuracySignal to noise ratio is smallColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsData streamElectromagnetic radiation
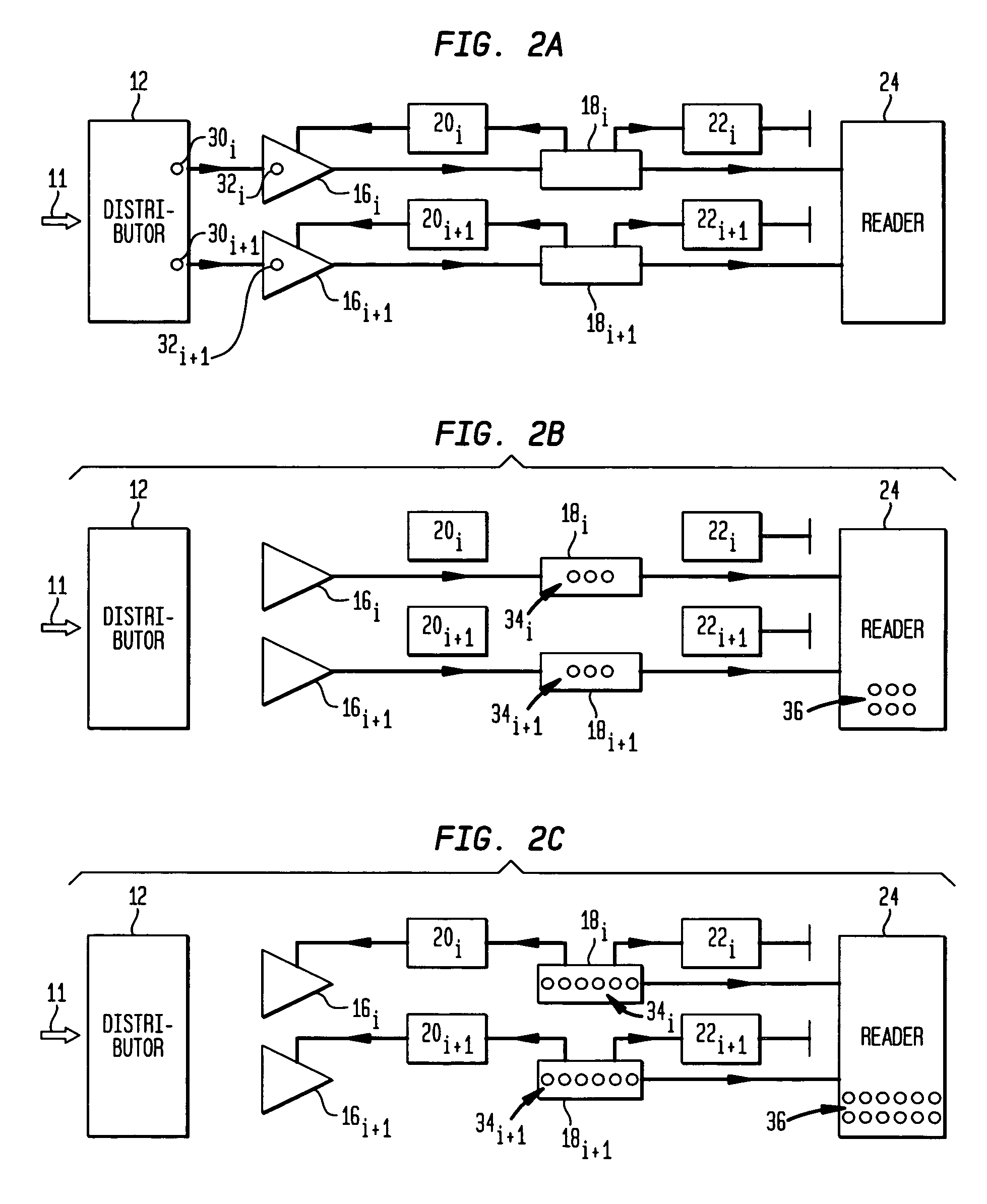
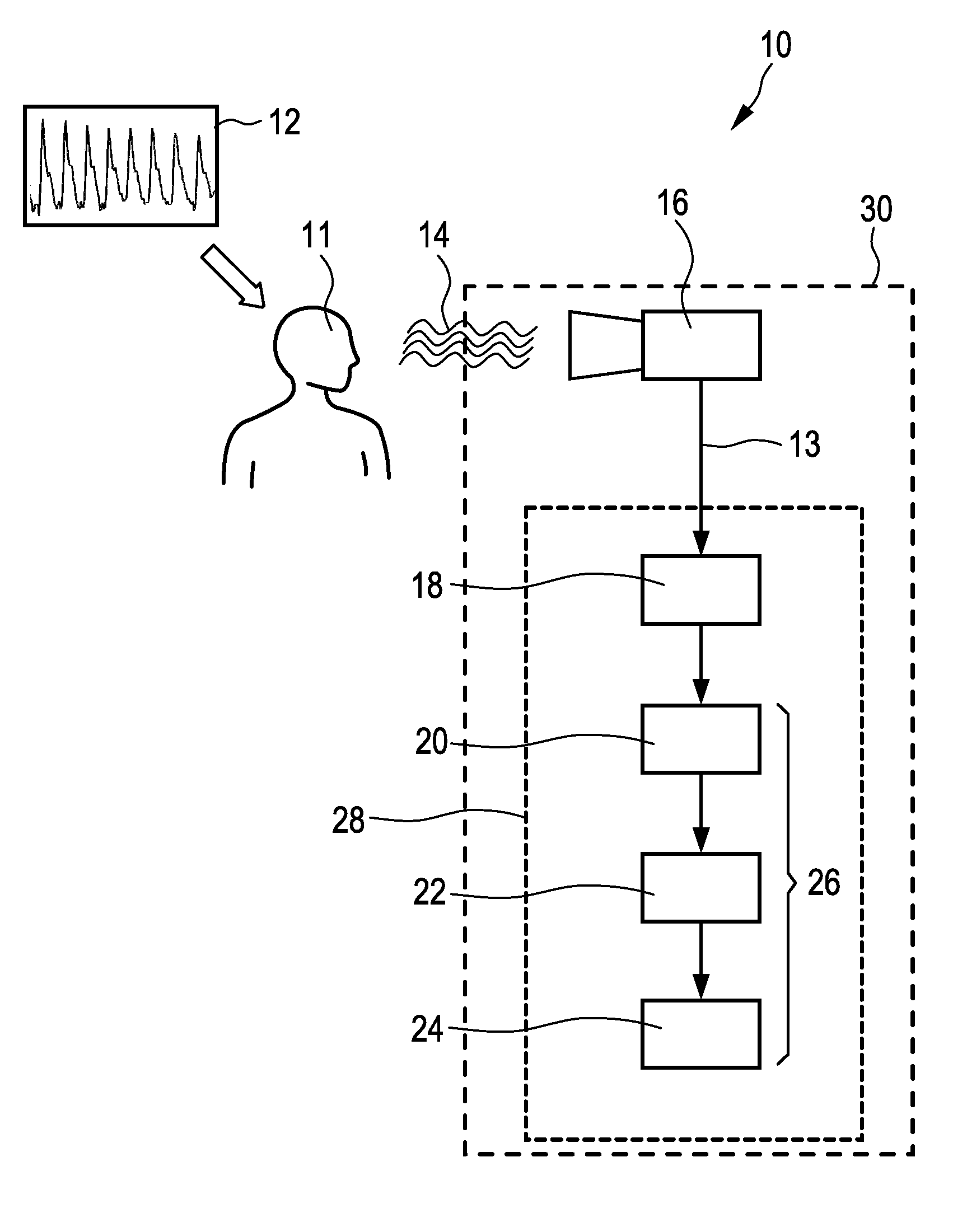
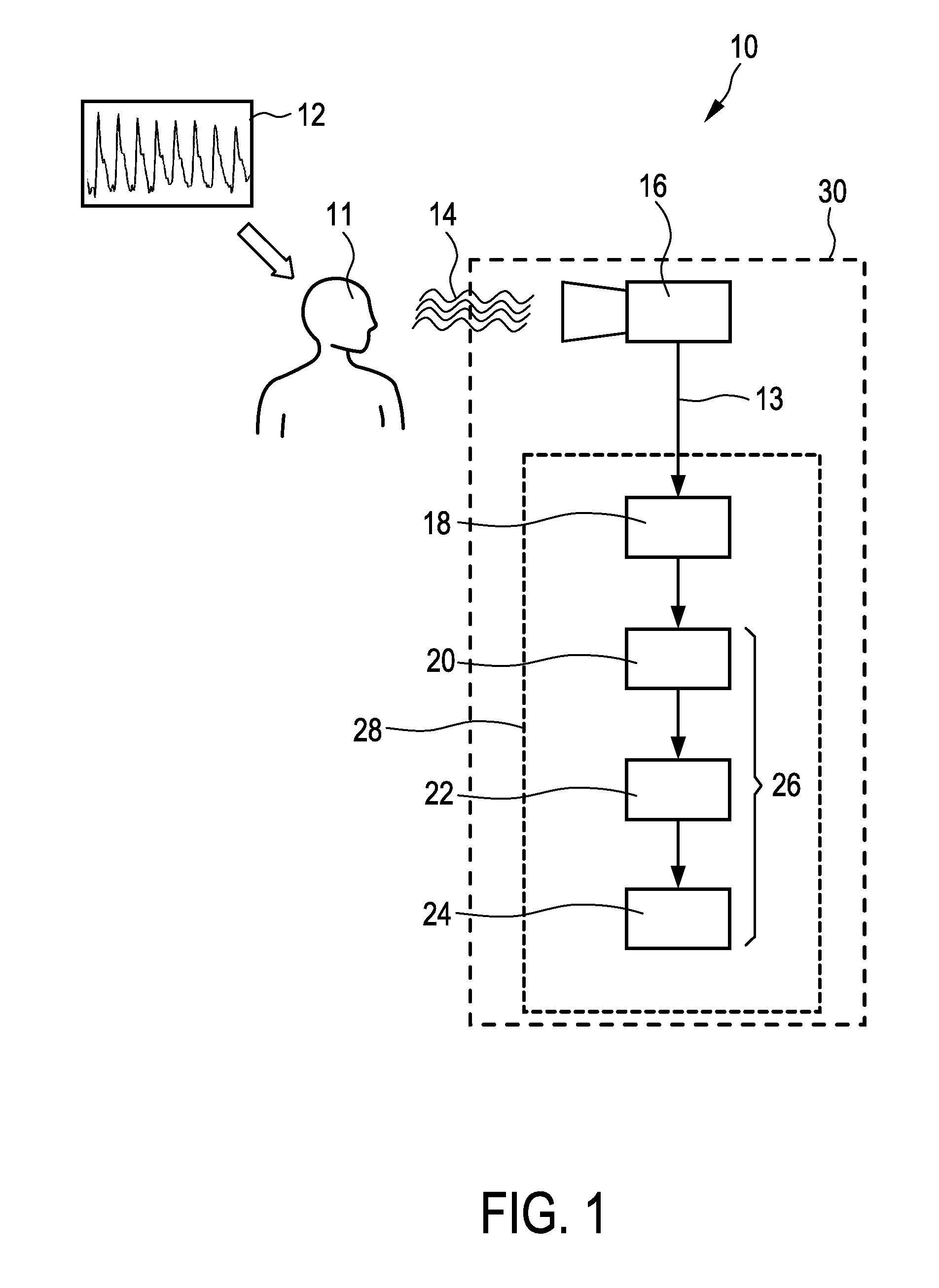
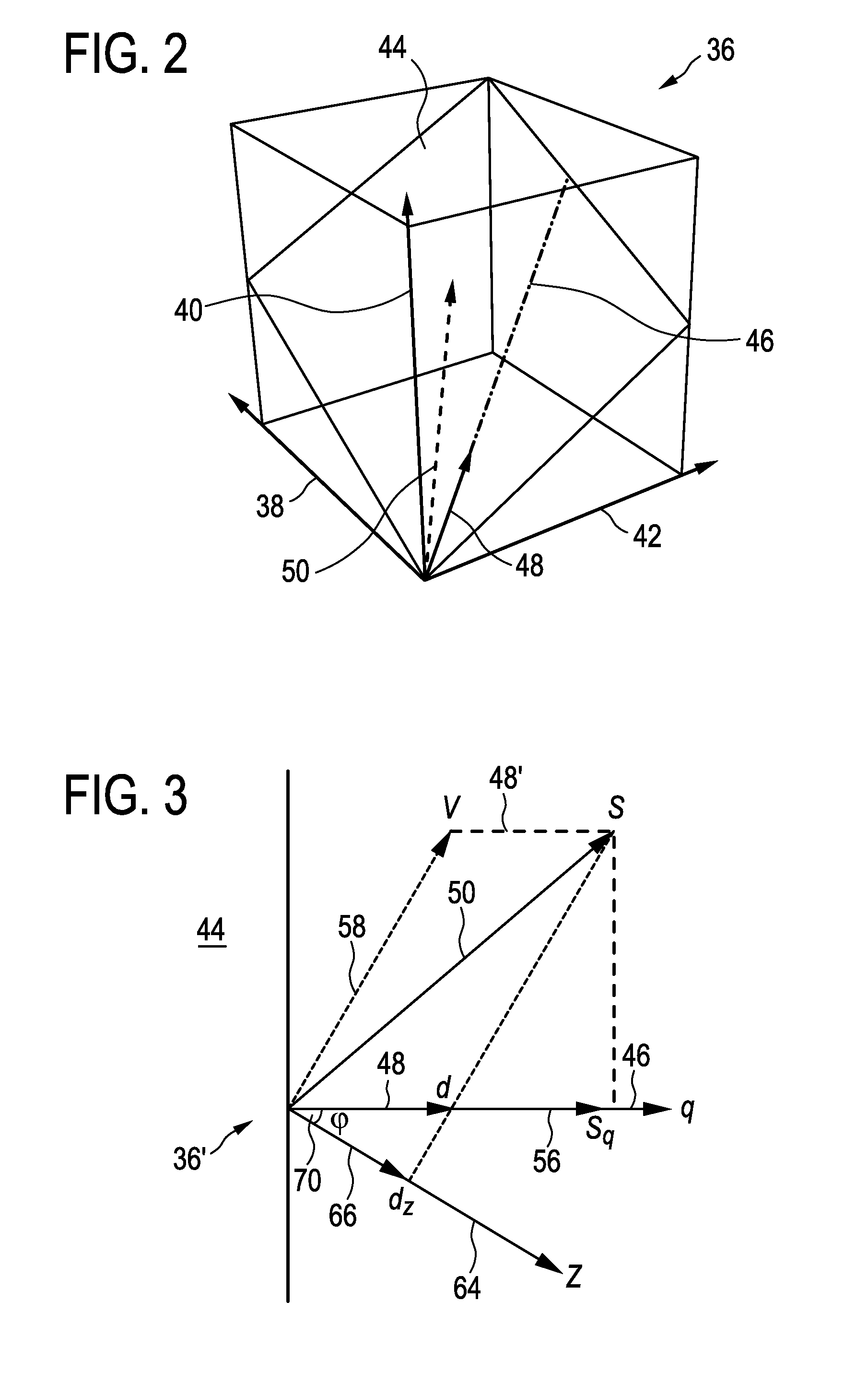
The present invention relates to a device and a method for extracting information from detected characteristic signals. A data stream (76, 78, 80, 82) derivable from electromagnetic radiation (14) emitted or reflected by an object (11) is received and a plurality of characteristic index elements (50) varying over time can be extracted therefrom. The index elements (50) comprise physiological information (48) indicative of at least one at least partially periodic vital signal (12), and a disturbing signal component (58). For eliminating the disturbing signal component (58) to a great extent, the characteristic index elements (50) can be projected to a disturbance-reduced index element (64) having a distinct orientation in relation to a presumed orientation of the disturbing signal component (58). The disturbance-reduced index element (64) is chosen so as to reflect a dominant main orientation and length of the disturbing signal component (58) over time. Consequently, the mainly genuine physiological information (48) extracted from the data stream (76, 78, 80, 82) in this way can be utilized for determining the at least one at least partially periodic vital signal (12).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods and apparatus for mitigating known interference
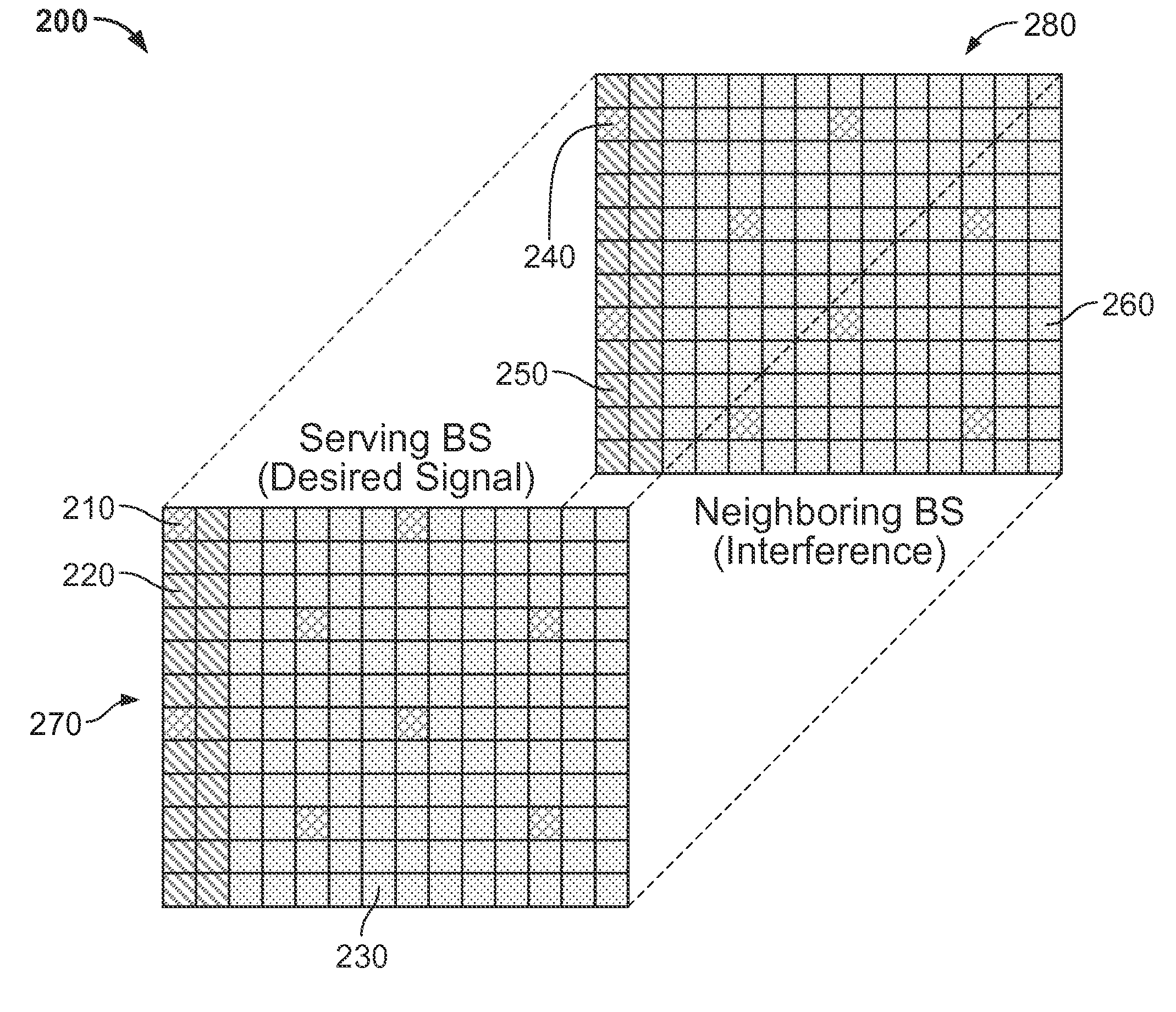
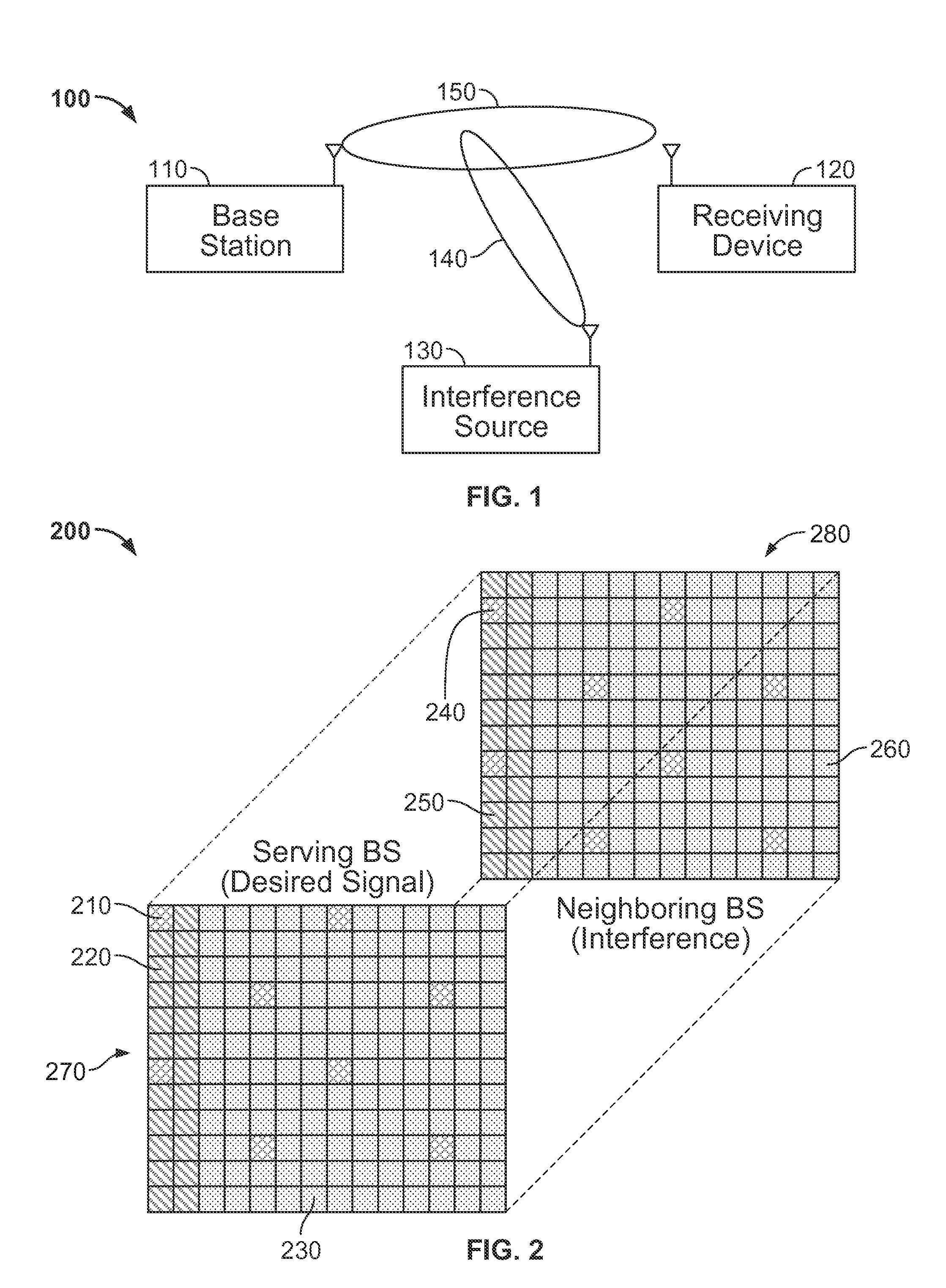
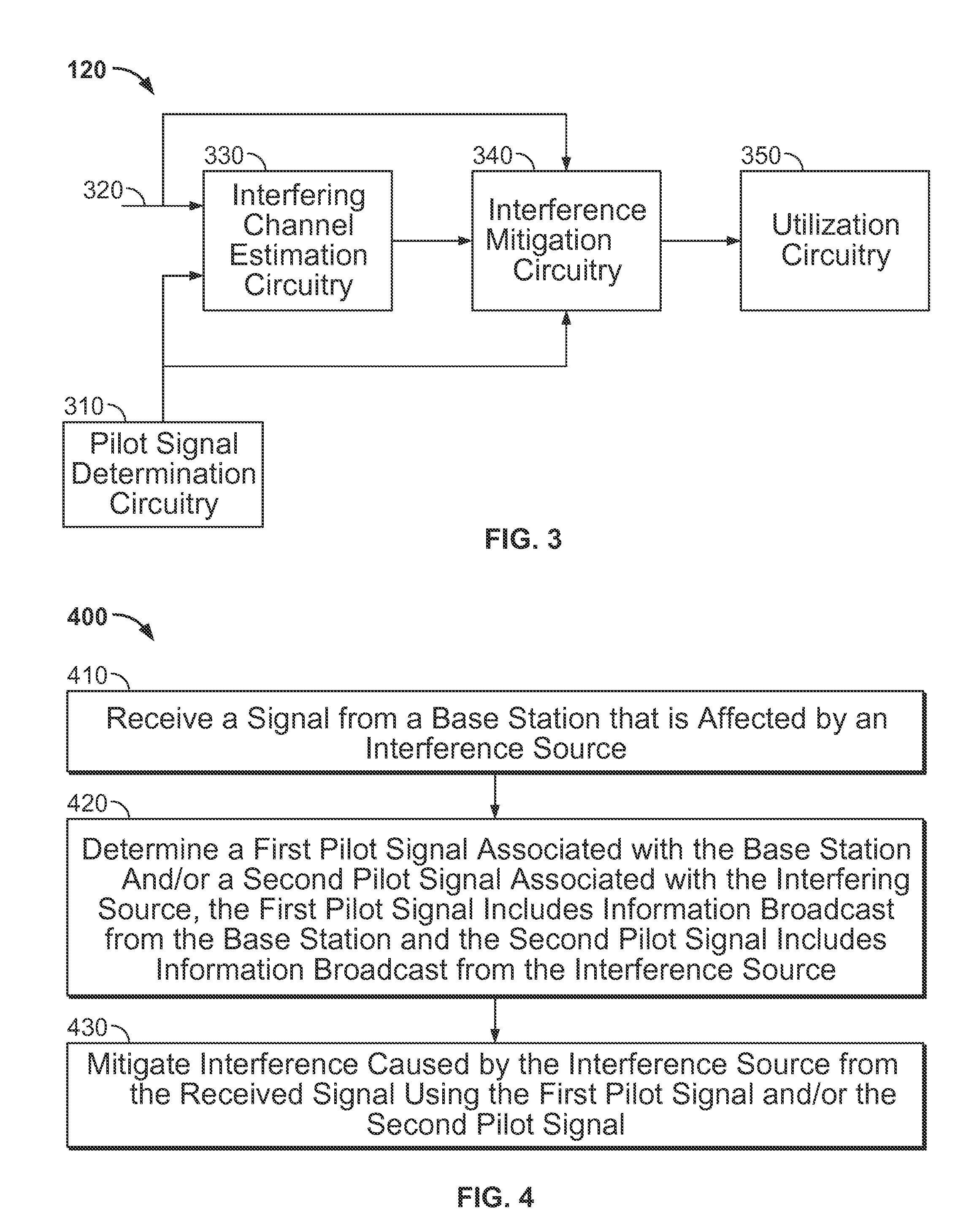
ActiveUS20130115988A1Reduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsPilot signalSystems engineering
Systems and methods for mitigating known interference at a receiving device are provided. A signal from a transmission source is received by a receiving device that is affected by an interference source. At least one of a first pilot signal associated with the transmission source and a second pilot signal associated with the interfering source is determined. The first pilot signal includes information broadcast from the transmission source and the second pilot signal includes information broadcast from the interference source. Interference caused by the interference source is mitigated from the received signal using at least one of the first pilot signal and the second pilot signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
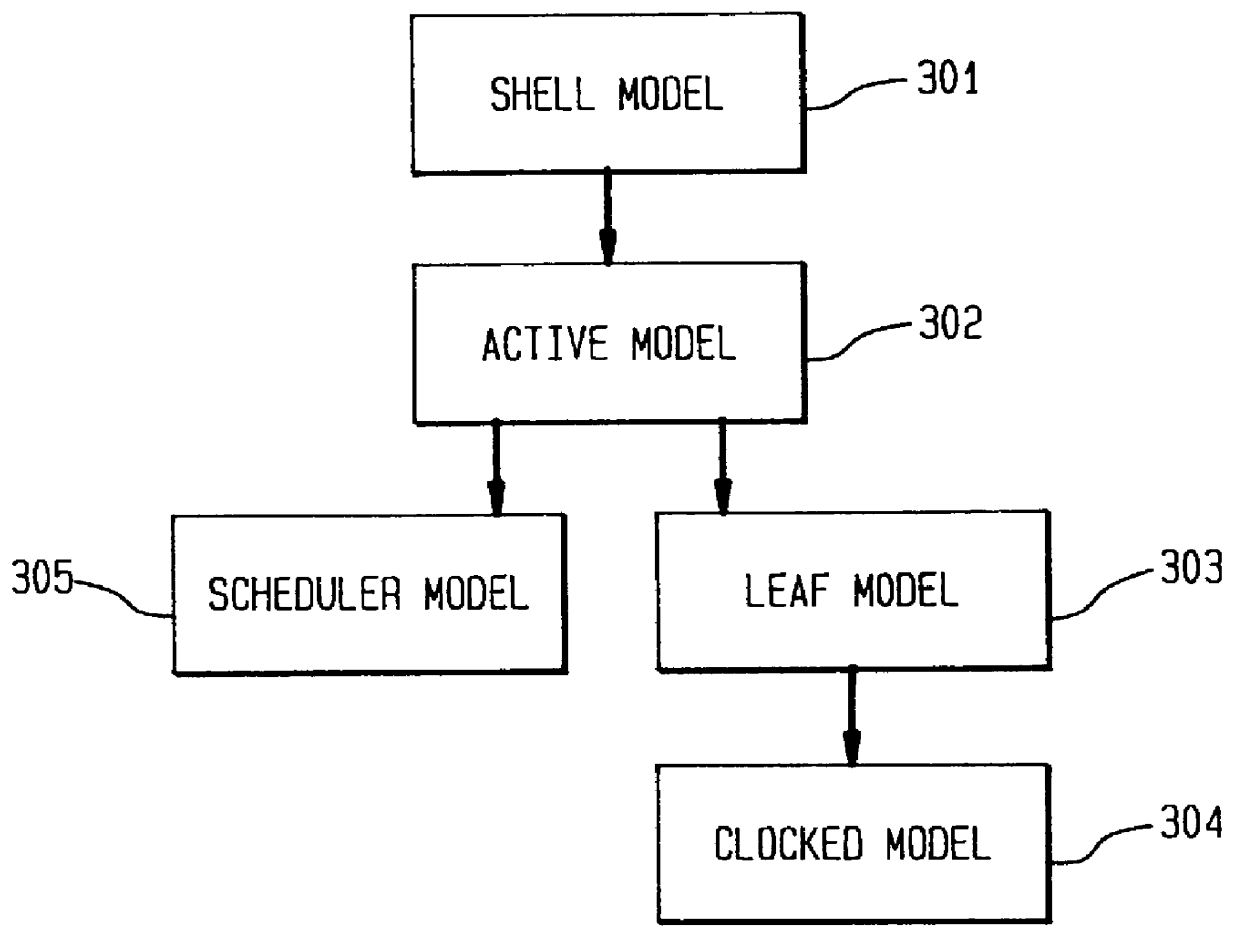
Simulation model using object-oriented programming
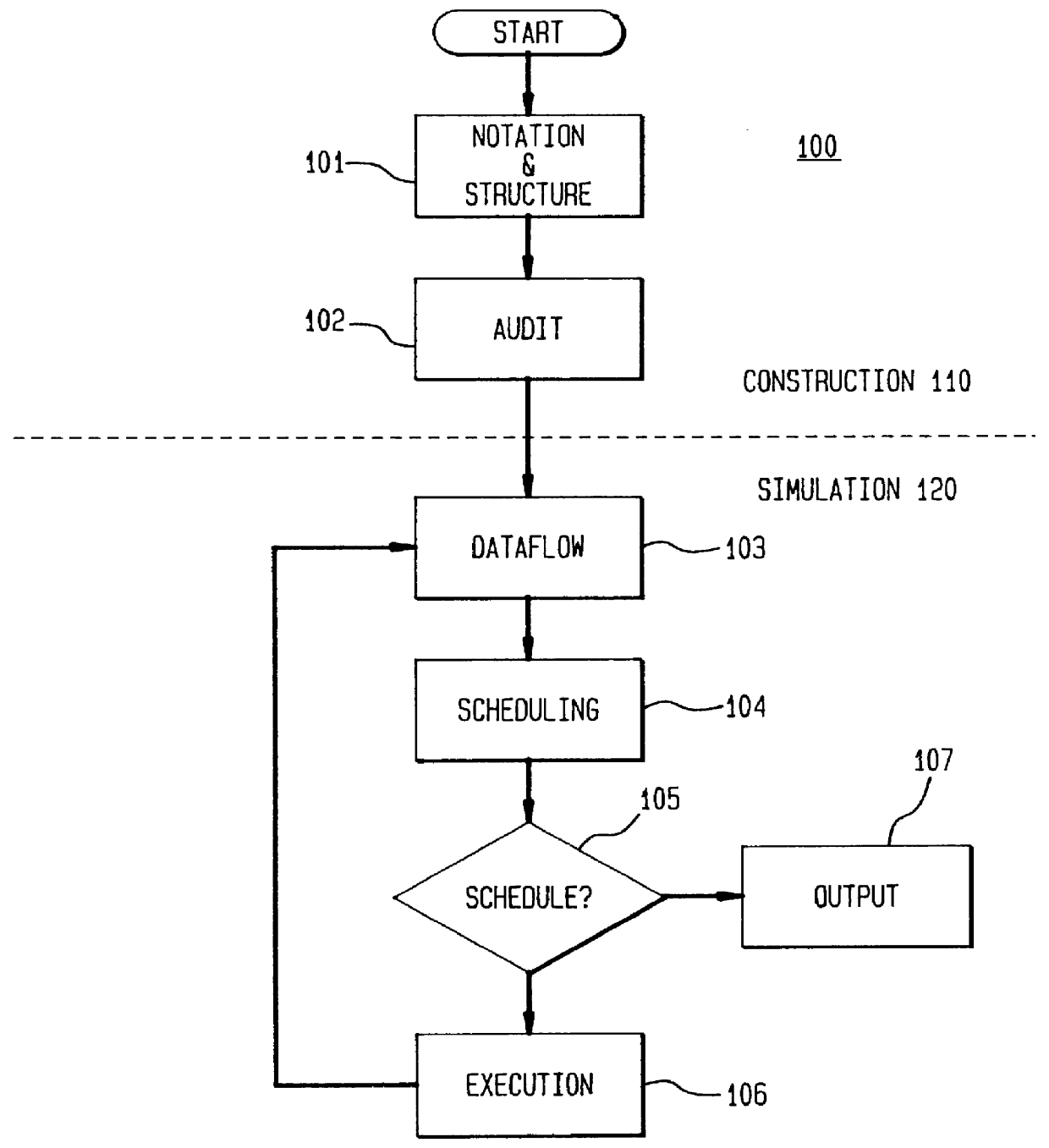
InactiveUS6053947AIncrease execution speedEfficiency and flexibilityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designComputer basedPriority scheduling
A method, apparatus and system for simulating the operation of a circuit using a computer-based simulator comprising: (a) distributing at least one signal upon to one or more simulation model subcircuit functions, which use the signal, upon a change in the signal; (b) scheduling one or more subcircuit functions that use the signal for execution according to a priority assigned to each subcircuit function; and (c) providing an output value to the simulator when no subcircuit functions are scheduled, otherwise, executing one or more subcircuit functions with the highest priority and returning to step (a) to repeat the process.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
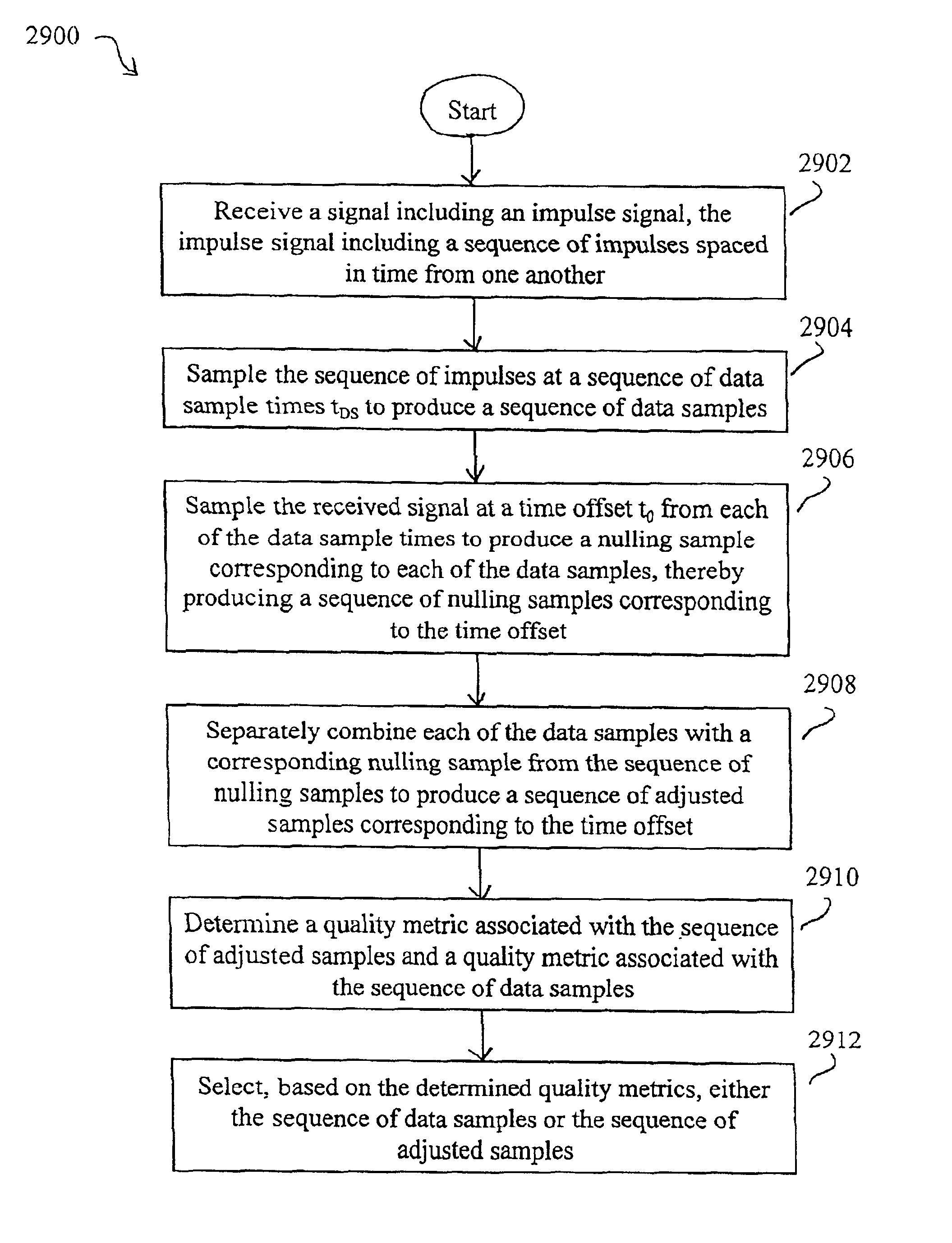
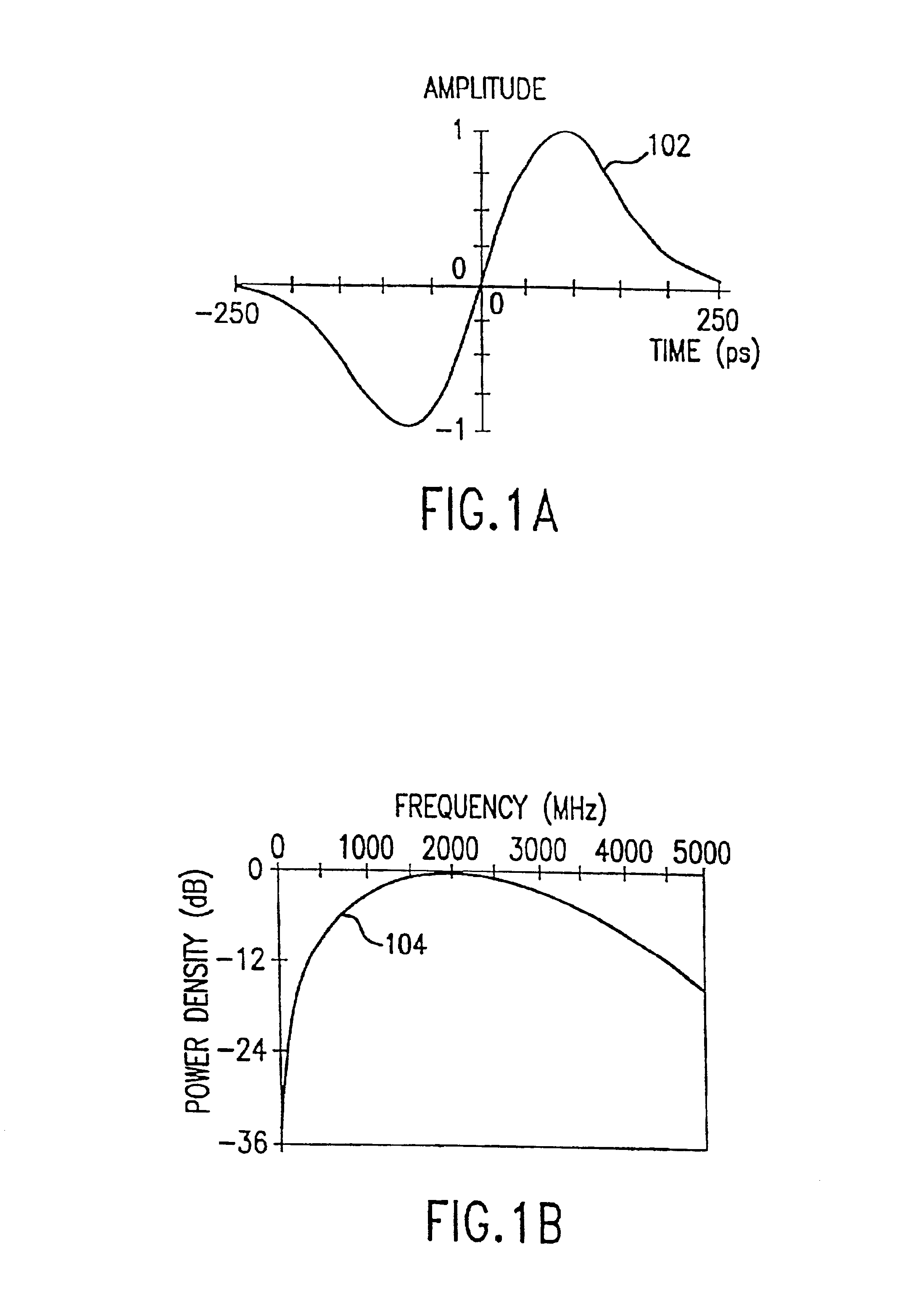
Method and system for reducing potential interference in an impulse radio
InactiveUS6914949B2Reduce distractionsReduce broadband noiseError preventionTransmission systemsInterference ratioRadio reception
Potential interference is reduced in an impulse radio. A signal including an impulse signal and potential interference is received by the impulse radio. The impulse signal includes a sequence of impulses. The sequence of impulses of the received signal is sampled at a sequence of data sample times to produce a sequence of data samples. The received signal is also sampled at a plurality of time offsets from each of the data sample times to produce a plurality of nulling samples corresponding to each of the data samples. A separate sequence of nulling samples for each of the time offsets is thereby produced. Each of the data samples is then separately combined with a corresponding nulling sample from each of the separate sequences of nulling samples to produce a separate sequence of adjusted samples corresponding to each of the time offsets. A separate quality metric, representative of a signal-to-interference level, is then determined for each of the separate sequences of adjusted samples. A preferred sequence of samples is selected for further signal processing based on the determined quality metrics. Alternatively or additionally, one of the plurality of time offsets is selected as the preferred time offset based on the determined quality metrics.
Owner:ALEREON
Signal processing method and device for signal-to-noise improvement
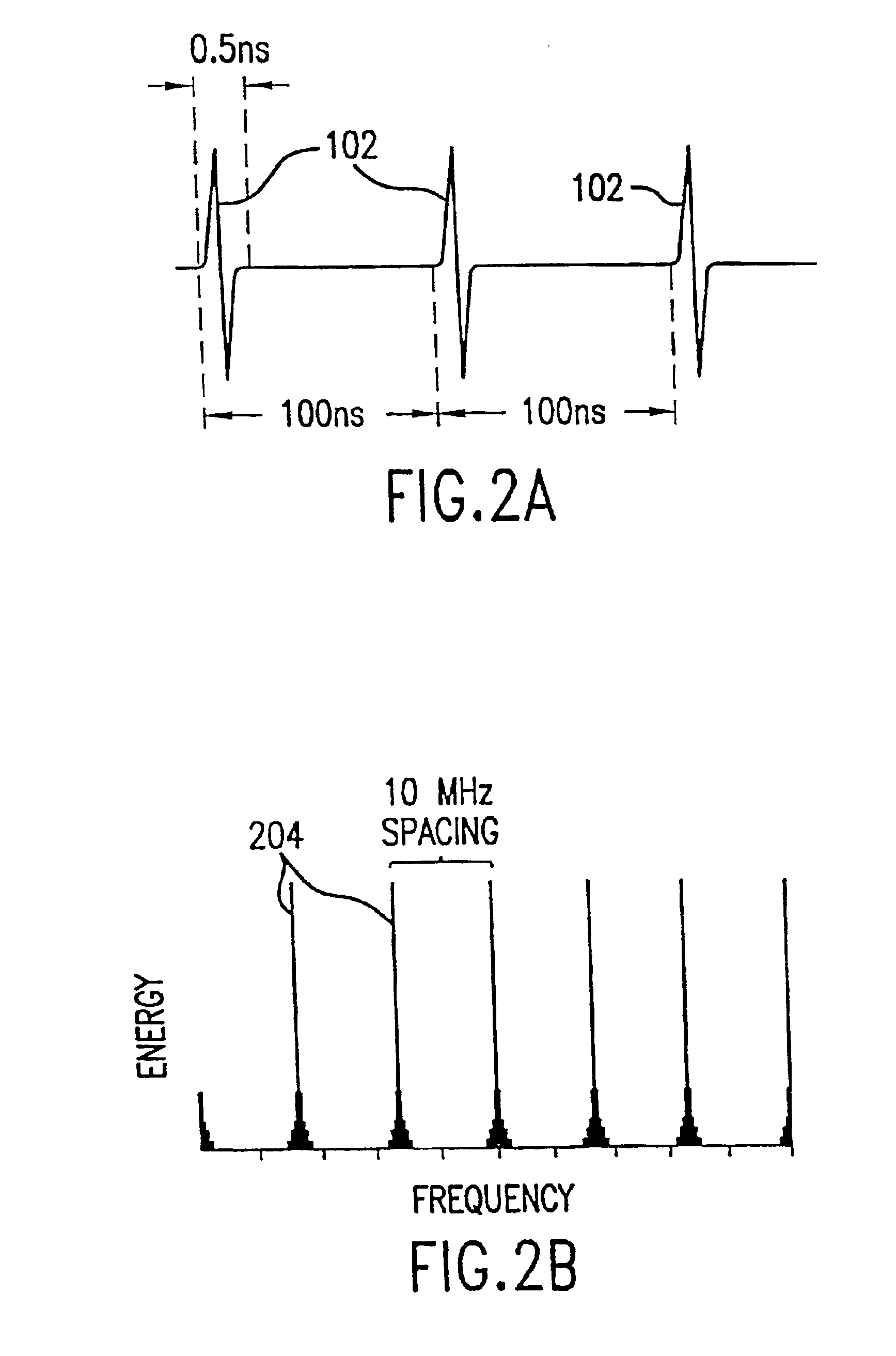
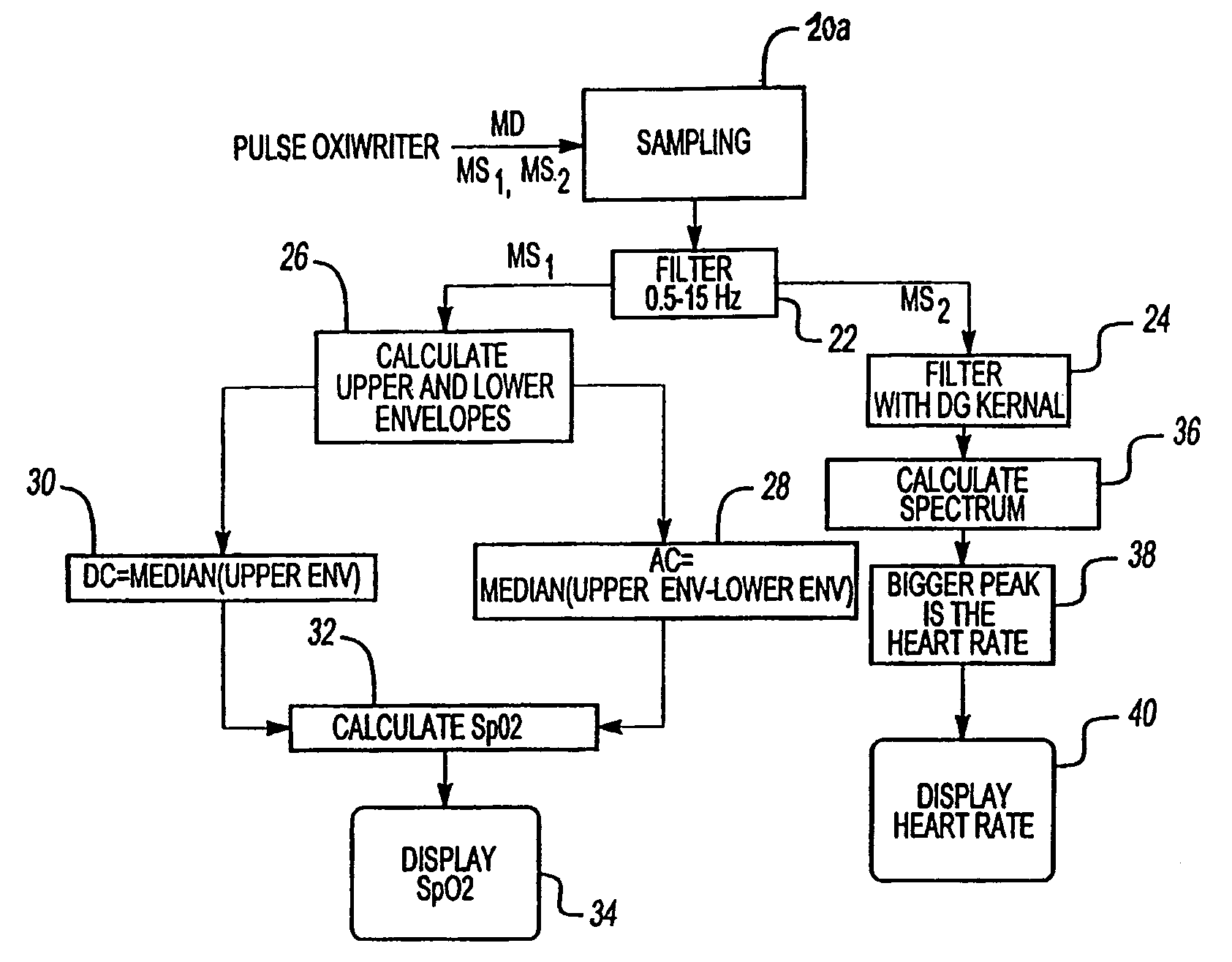
InactiveUS7027850B2Increase heightAdditional componentCatheterSensorsEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and apparatus extract a signal component of a measured signal using one of two methods. If the signal component in the measured signal is a periodic signal with a certain well-defined peak-to-peak intensity value, upper and lower envelopes of the measured signal are determined and analyzed to extract said signal component of the measured signal. This signal component can further be used to calculate a desired parameter of the sample. The DC component of the signal is determined as the median value of the upper envelope, and the AC component is determined as the median value of the difference between the upper and lower envelopes. If the signal component of the measured signal is a periodic signal characterized by a specific asymmetric shape, a specific adaptive filtering is applied to the measured signal, resulting in the enhancement of the signal component relative to a noise component. This adaptive filtering is based on a derivative of the Gaussian Kernel having specific parameters matching the characteristics of the signal component.
Owner:CONMED CORP
Ambiguity estimation of GNSS signals for three or more carriers
ActiveUS7432853B2Reduce effortValidation is greatly reducedPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalComputer science
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
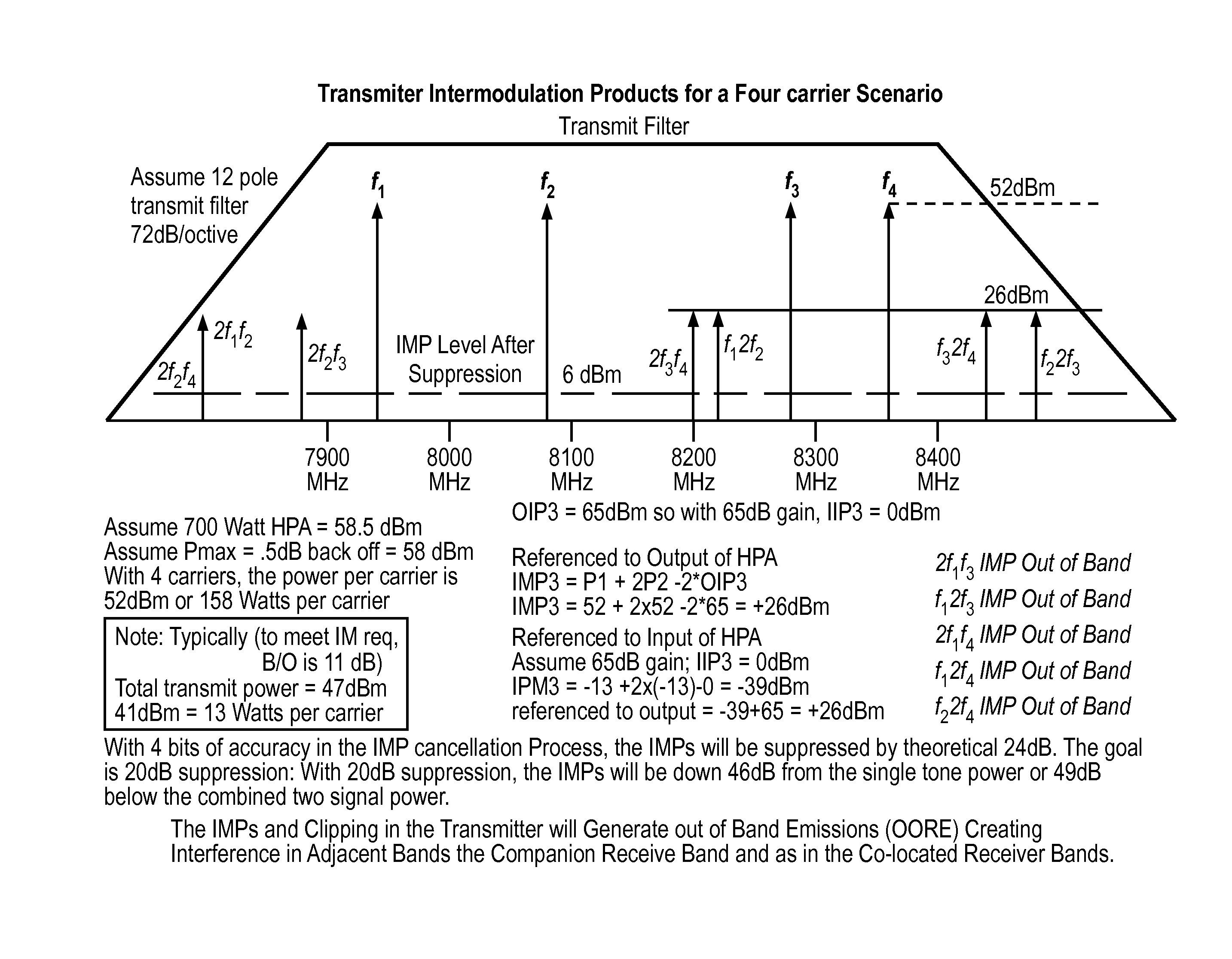
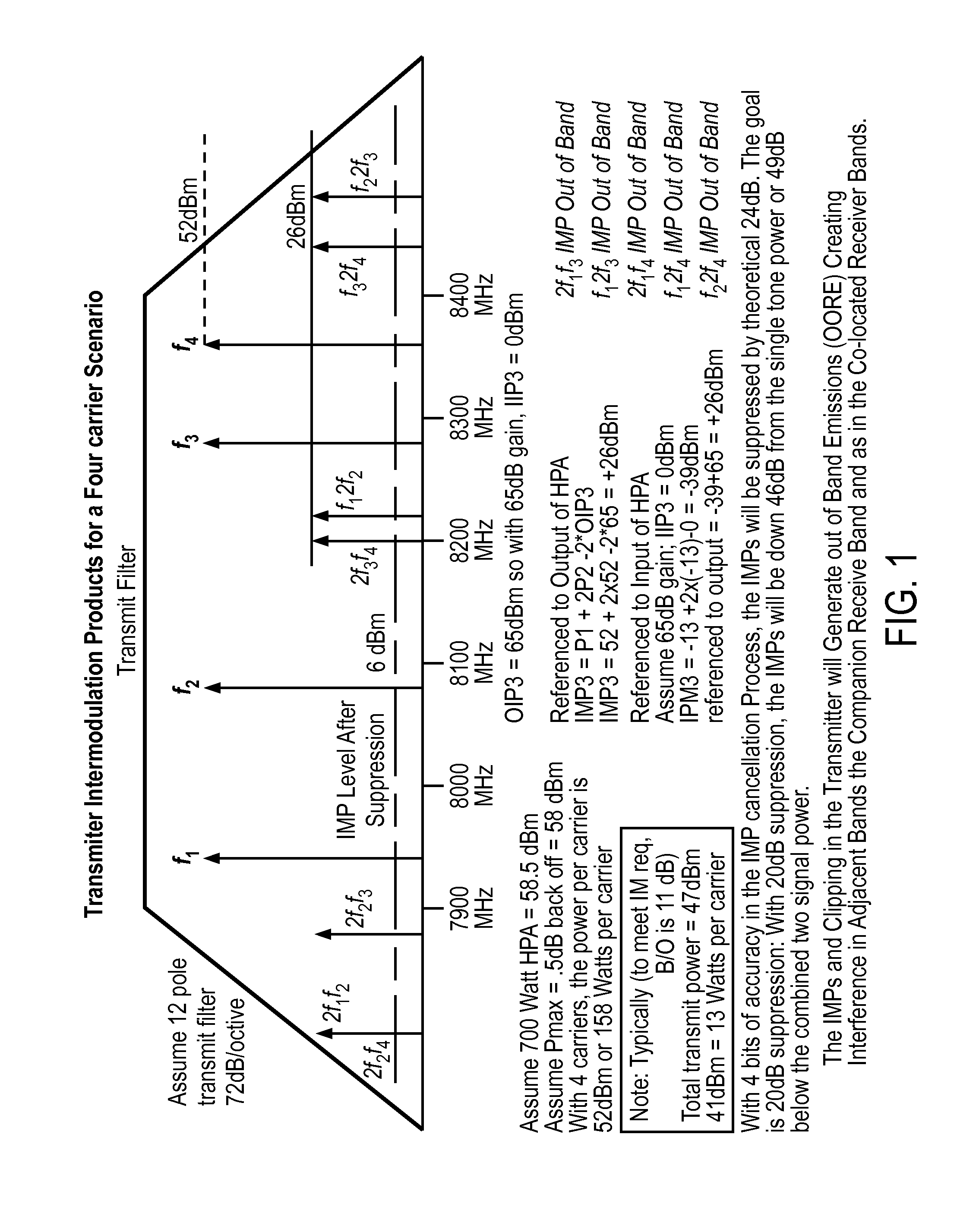
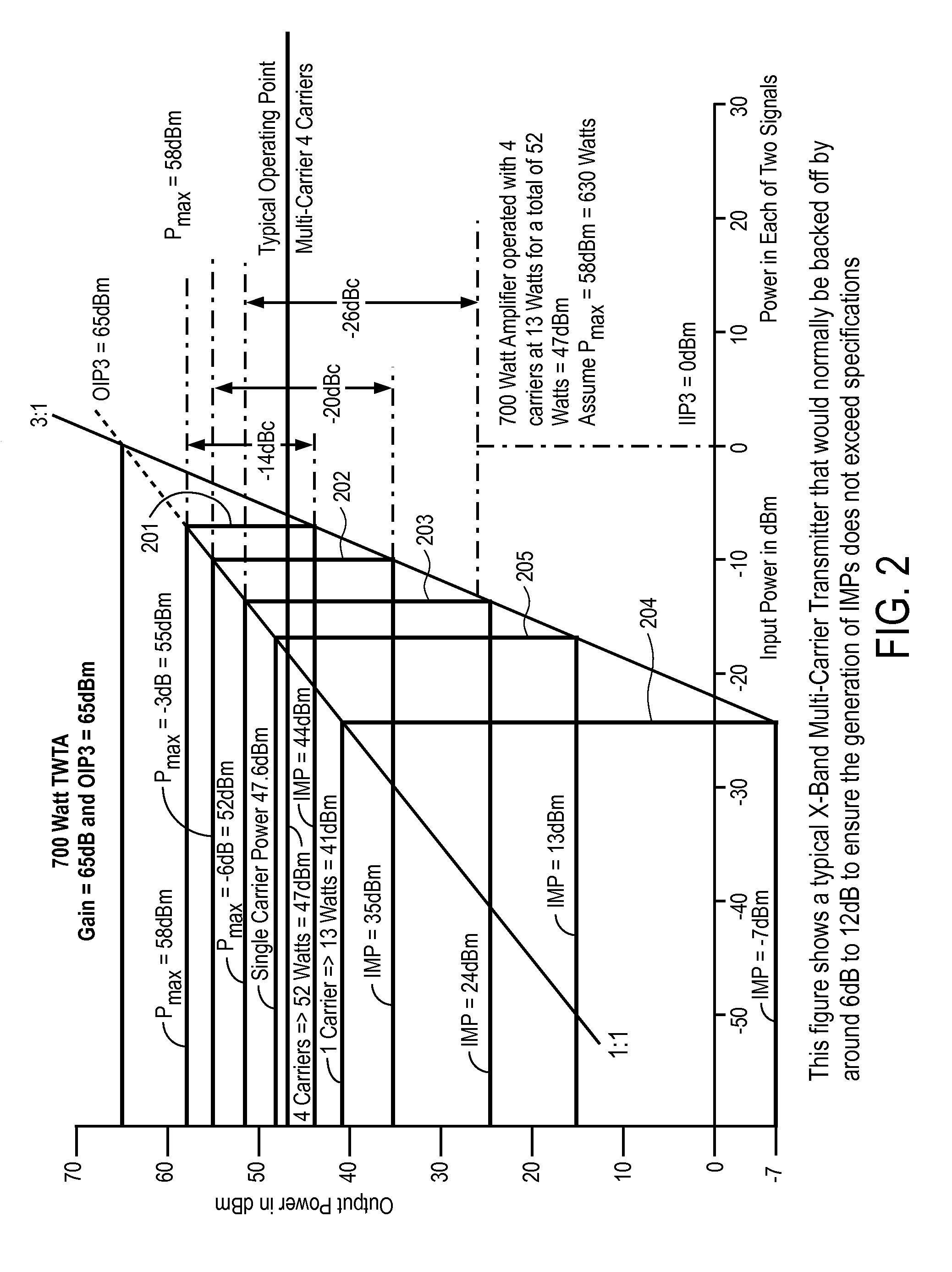
Mitigation of transmitter passive and active intermodulation products in real and continuous time in the transmitter and co-located receiver
ActiveUS20110075754A1Secret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksLinear componentEngineering
A transmitter channel interference mitigation processing method for cancellation of intermodulation products are described. In one embodiment, a method comprising generating continuous and real time IMP cancellation signals (ICS) in the baseband digital signal set of the transmitter based on a transmitter signal set, combining digital IMP cancellation signals with a digital baseband transmitter signal set such that the digital cancellation signals, when converted to analog signals and transmitted as part of an analog transmitter signal set, are cancelled by and so cancel the IMPs generated by the non-linear components in the analog transmitter hardware, including digitally generating the IMP cancellation signals using a process based on a power series description of a non-linear process generating the IMPs, generating 3rd order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three signals of the transmitter signal set to create 3rd order IMP cancellation signals, generating 5th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five signals of the transmitter signal set to create 5th order IMP cancellation signals, generating 7th order IMP cancellation signals by digitally multiplying two or three or five or seven signals of the transmitter signal set to create 7th order IMP cancellation signal, generating odd order IMP cancellation signals (ICS) by digitally multiplying an odd number of digital signals and combining multiplied digital signals with the transmitter baseband digital signals, creating IMP cancellation signals in the receiver, and cancelling one or both of active and passive IMPs generated in a transmitter path that fall within a receiver passband.
Owner:FINESSE WIRELESS LLC
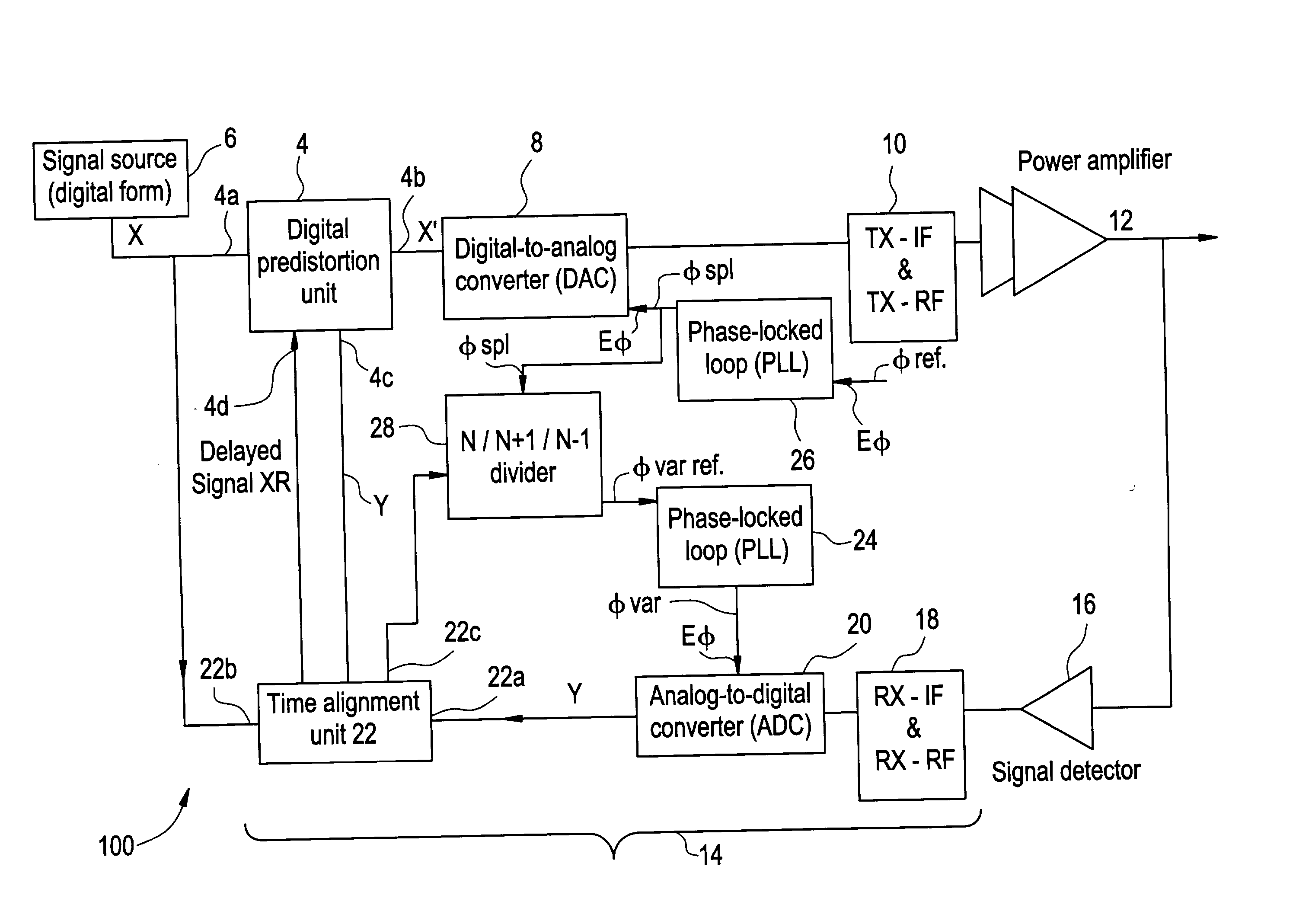
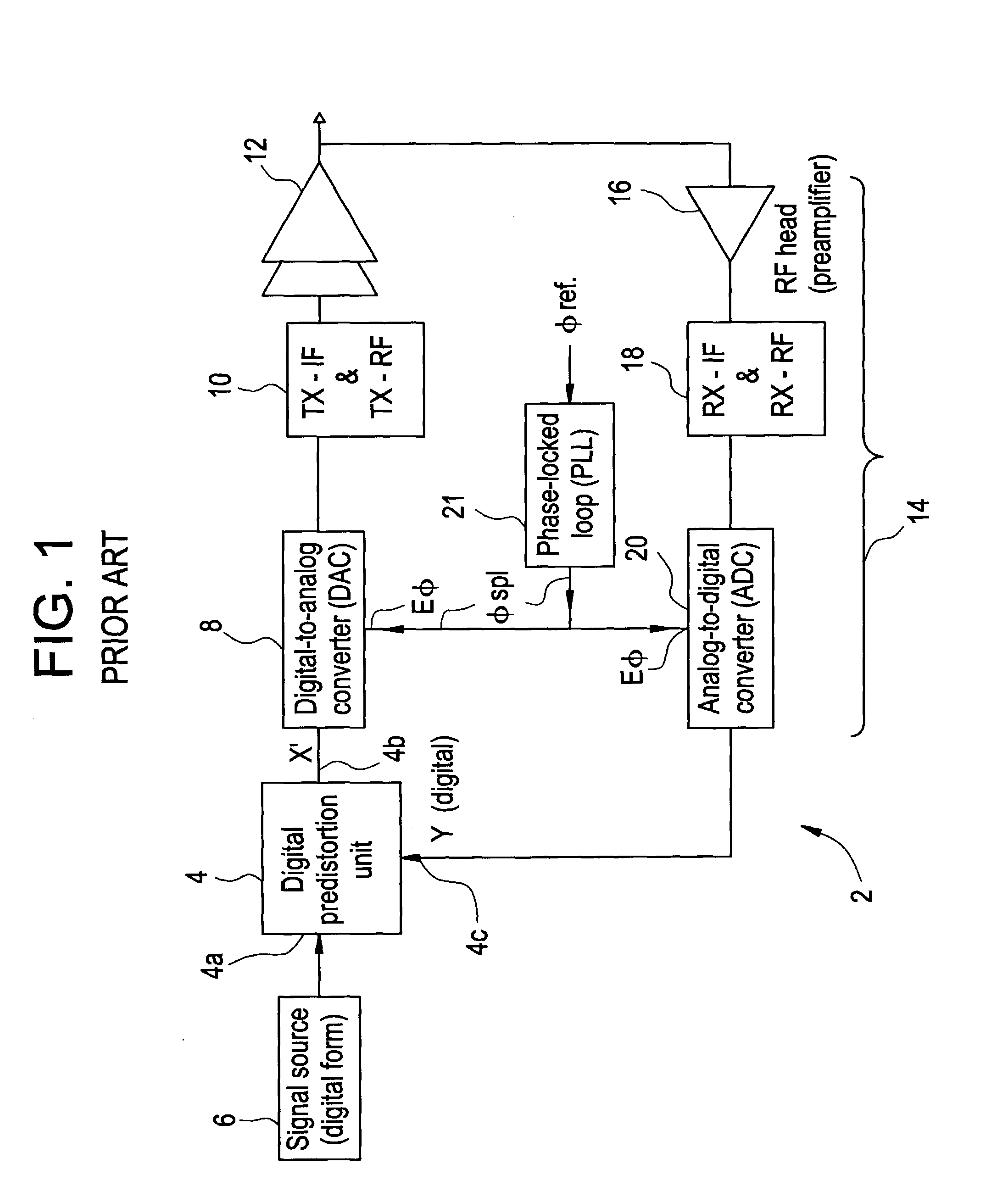
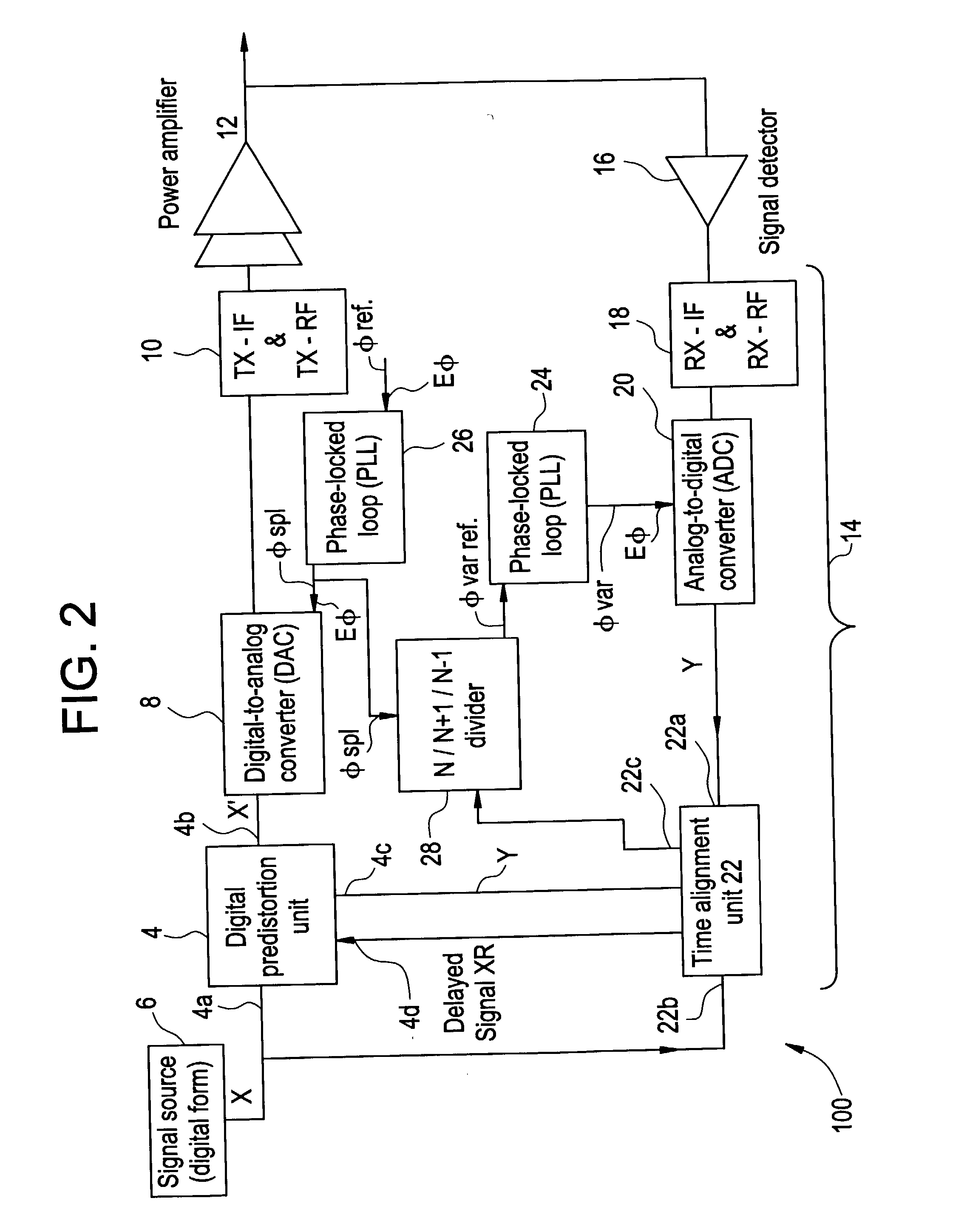
Method and apparatus for preparing signals to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier
InactiveUS20030156658A1Improve electricity efficiencyImprove performance efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierUnit of time
The invention relates to a method of preparing signals (X and Y) to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier (12), the signals comprising a signal (X) before amplification and a signal (Y) after amplification by said amplifier. Preparation includes time aligning (22) the signal before amplification (X) with the signal after amplification (Y) before using them to establish said predistortion. The invention preferably operates in two stages, namely a stage of coarse time alignment, in which the signal before amplification (X) is subjected to a time delay comprising an integer number of first time units, and a stage of fine time alignment, in which a delay or advance value of a fraction of the first time unit is determined.
Owner:EVOLIUM
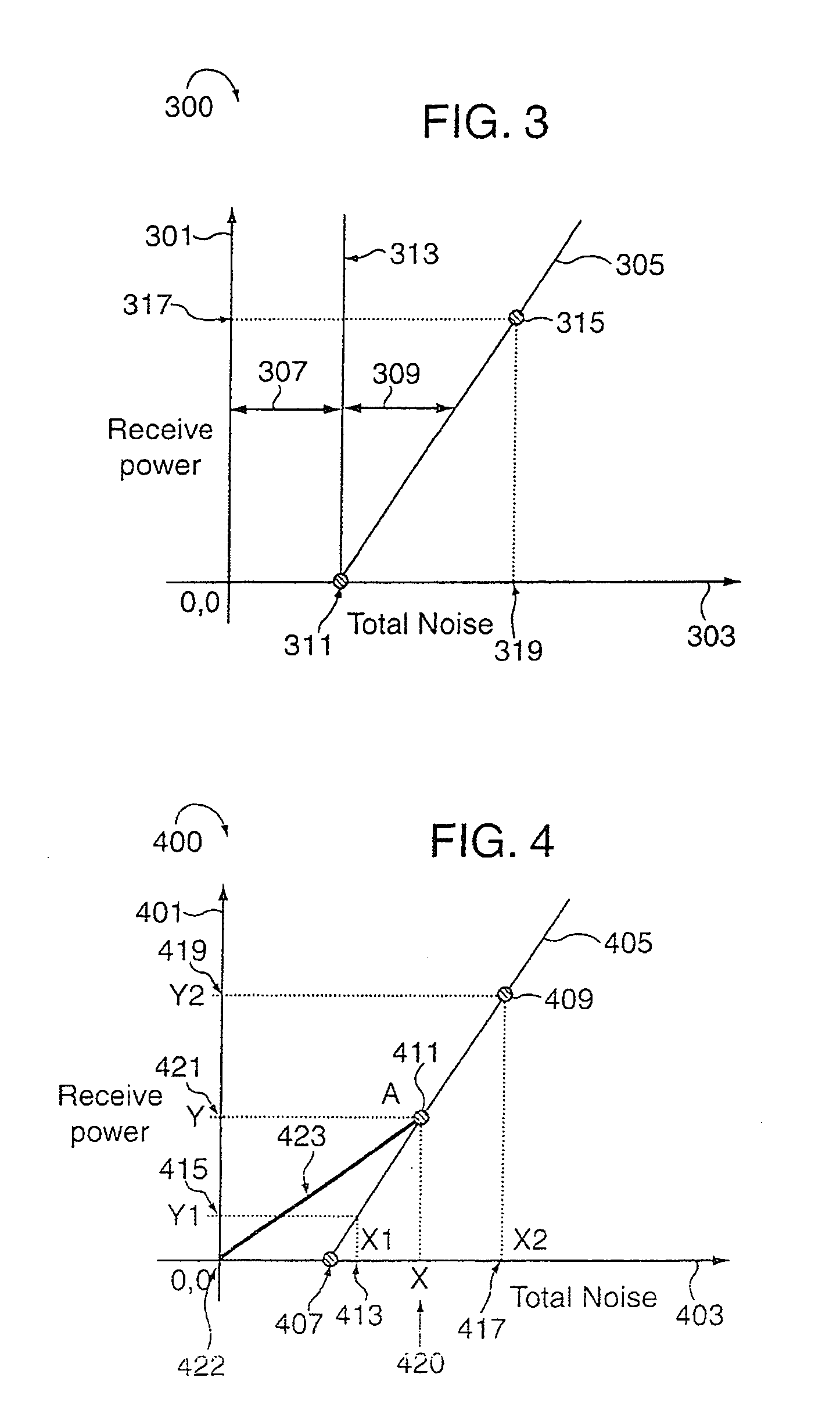
Methods and apparatus for characterizing noise in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20080013500A1Reduce distractionsPower managementTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSignal on
Improved pilot signal sequences which facilitate multiple channel quality measurements, e.g., through the use of different signal pilot transmission power levels, are described. In various implementations the transmitted pilot sequences facilitate determining the contribution of interference from other sectors of a cell using the same tones, e.g., in a synchronized manner, as the sector in which the pilot signal measurements are being made. To measure noise contributions from neighboring sectors a sector NULL pilot, e.g., a pilot with zero power, is transmitted in an adjacent sector at the same time a pilot signal with a pre-selected, and therefore known, non-zero power is transmitted in the sector where the received pilot signal measurement is made. To facilitate background noise measurements, a cell NULL is supported in some embodiments. In the case of a cell NULL, all sectors of a cell transmit a Null pilot, on a tone that is used to measure background noise. Since no power is transmitted in the cell on the tone during the measurement, any measured signal on the tone is attributable to noise, e.g., background noise which may include inter-cell interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Detection of Low-Amplitude Echoes in a Received Communication Signal
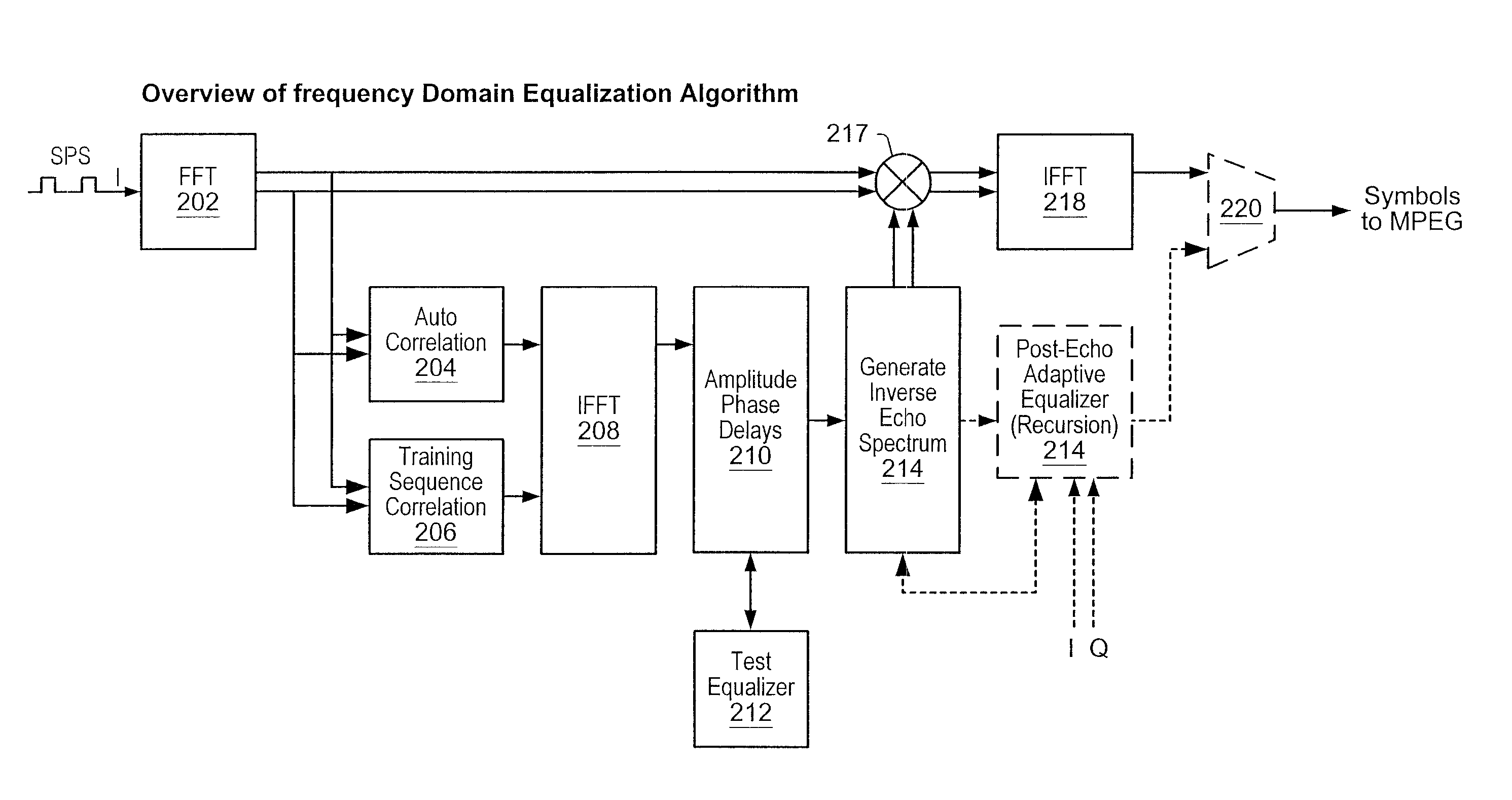
ActiveUS20110007789A1Great time separationFast convergenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTime domainFrequency spectrum analysis
A system and method for identifying minor echoes present in an input signal in the situation where a set of major echoes has already been identified from the input signal. The method includes: computing a spectrum F corresponding to a sum of the major echoes; computing a weighted power spectrum SM of the spectrum F; subtracting the weighted power spectrum SM from a weighted power spectrum PIN of the input signal to obtain a difference spectrum; performing a stabilized division of the difference spectrum by a conjugate of the spectrum F to obtain an intermediate spectrum; computing an inverse transform of the intermediate spectrum to obtain a time-domain signal; and estimating parameters one or more of the minor echoes from the time-domain signal. The echo parameters are usable to remove at least of portion of the one or more estimated minor echoes from the input signal.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
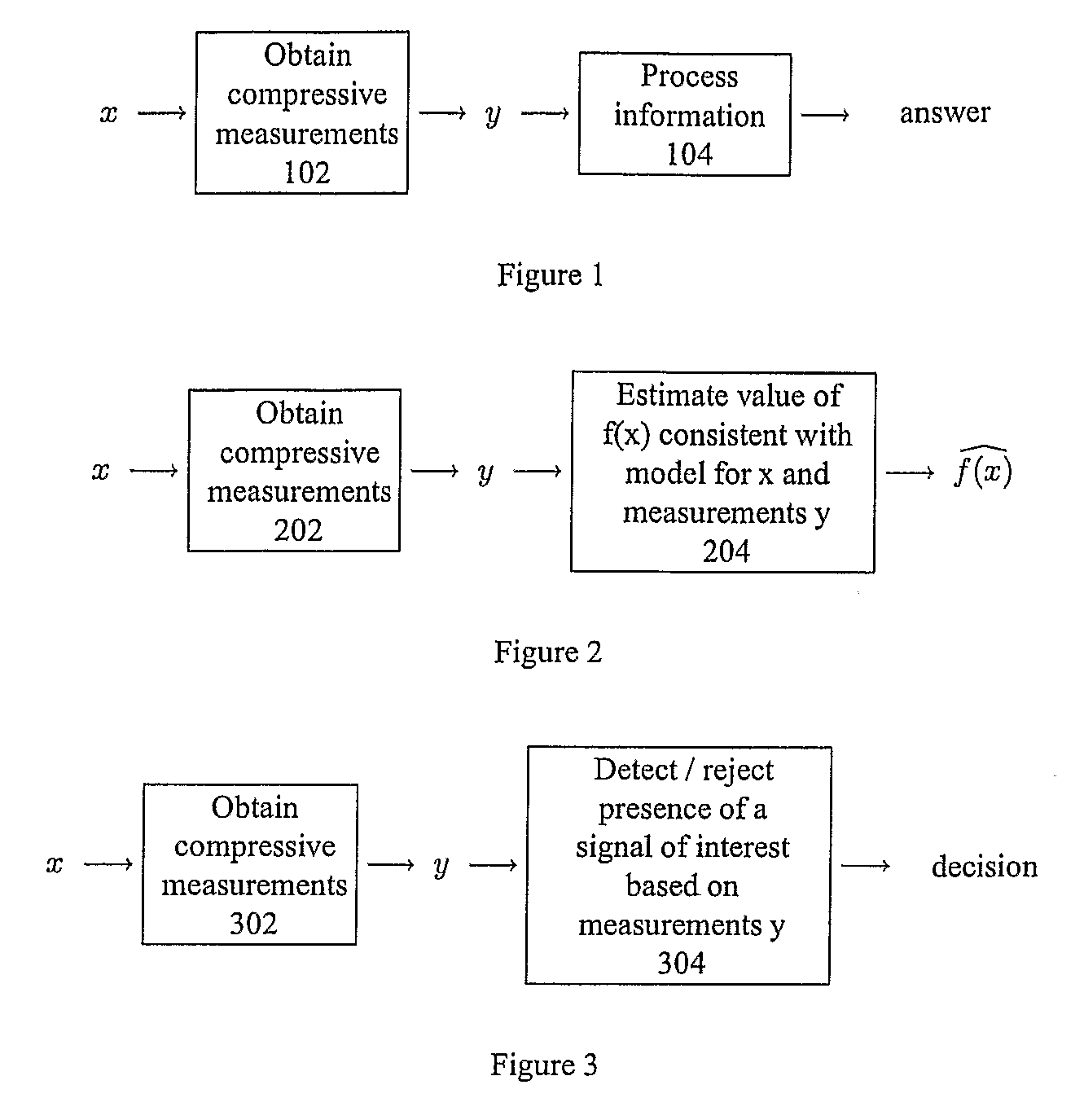
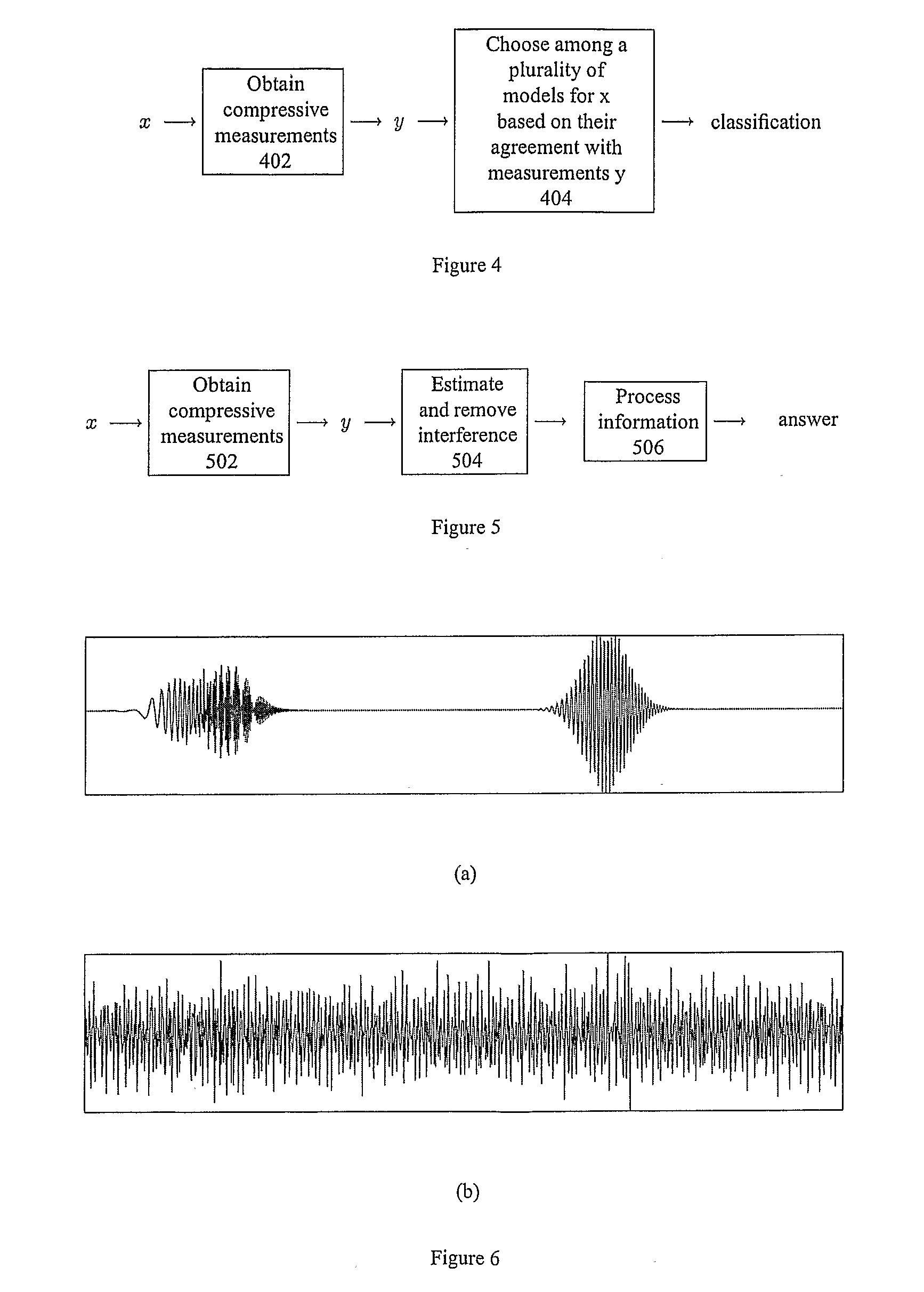
Method and Apparatus for Signal Detection, Classification and Estimation from Compressive Measurements
ActiveUS20080228446A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDecision takingSignal restoration
The recently introduced theory of Compressive Sensing (CS) enables a new method for signal recovery from incomplete information (a reduced set of “compressive” linear measurements), based on the assumption that the signal is sparse in some dictionary. Such compressive measurement schemes are desirable in practice for reducing the costs of signal acquisition, storage, and processing. However, the current CS framework considers only a certain task (signal recovery) and only in a certain model setting (sparsity).We show that compressive measurements are in fact information scalable, allowing one to answer a broad spectrum of questions about a signal when provided only with a reduced set of compressive measurements. These questions range from complete signal recovery at one extreme down to a simple binary detection decision at the other. (Questions in between include, for example, estimation and classification.) We provide techniques such as a “compressive matched filter” for answering several of these questions given the available measurements, often without needing to first reconstruct the signal. In many cases, these techniques can succeed with far fewer measurements than would be required for full signal recovery, and such techniques can also be computationally more efficient. Based on additional mathematical insight, we discuss information scalable algorithms in several model settings, including sparsity (as in CS), but also in parametric or manifold-based settings and in model-free settings for generic statements of detection, classification, and estimation problems.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Methods and systems for encoding and protecting data using digital signature and watermarking techniques
InactiveUS6961854B2Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsCompact discDigital signature
Systems and methods are provided for protecting and managing electronic data signals that are registered in accordance with a predefined encoding scheme, while allowing access to unregistered data signals. In one embodiment a relatively hard-to-remove, easy-to-detect, strong watermark is inserted in a data signal. The data signal is divided into a sequence of blocks, and a digital signature for each block is embedded in the signal via a watermark. The data signal is then stored and distributed on, e.g., a compact disc, a DVD, or the like. When a user attempts to access or use a portion of the data signal, the signal is checked for the presence of a watermark containing the digital signature for the desired portion of the signal. If the watermark is found, the digital signature is extracted and used to verify the authenticity of the desired portion of the signal. If the signature-containing watermark is not found, the signal is checked for the presence of the strong watermark. If the strong watermark is found, further use of the signal is inhibited, as the presence of the strong watermark, in combination with the absence or corruption of the signature-containing watermark, provides evidence that the signal has been improperly modified. If, on the other hand, the strong mark is not found, further use of the data signal can be allowed, as the absence of the strong mark indicates that the data signal was never registered with the signature-containing watermark.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
Beamforming method, measurement and imaging instruments, and communication instruments
ActiveUS10624612B2Increase speedImprove accuracyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrgan movement/changes detectionCarrier signalS transform
Owner:CHIKAYOSHI SUMI
Methods and apparatus for transmitting signals through network elements for classification
InactiveUS20060112035A1Highly efficient establishmentDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionNetwork elementArtificial intelligence
The present invention provides techniques for transmitting at least one signal through an element of a classification system. One or more input signals are received at the element. One or more functional components are extracted from the one or more input signals, and one or more membership components are extracted from the one or more input signals. An output signal is generated from the element comprising a functional component and a membership component that correspond to one or more functional components and membership components from one or more input signals.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
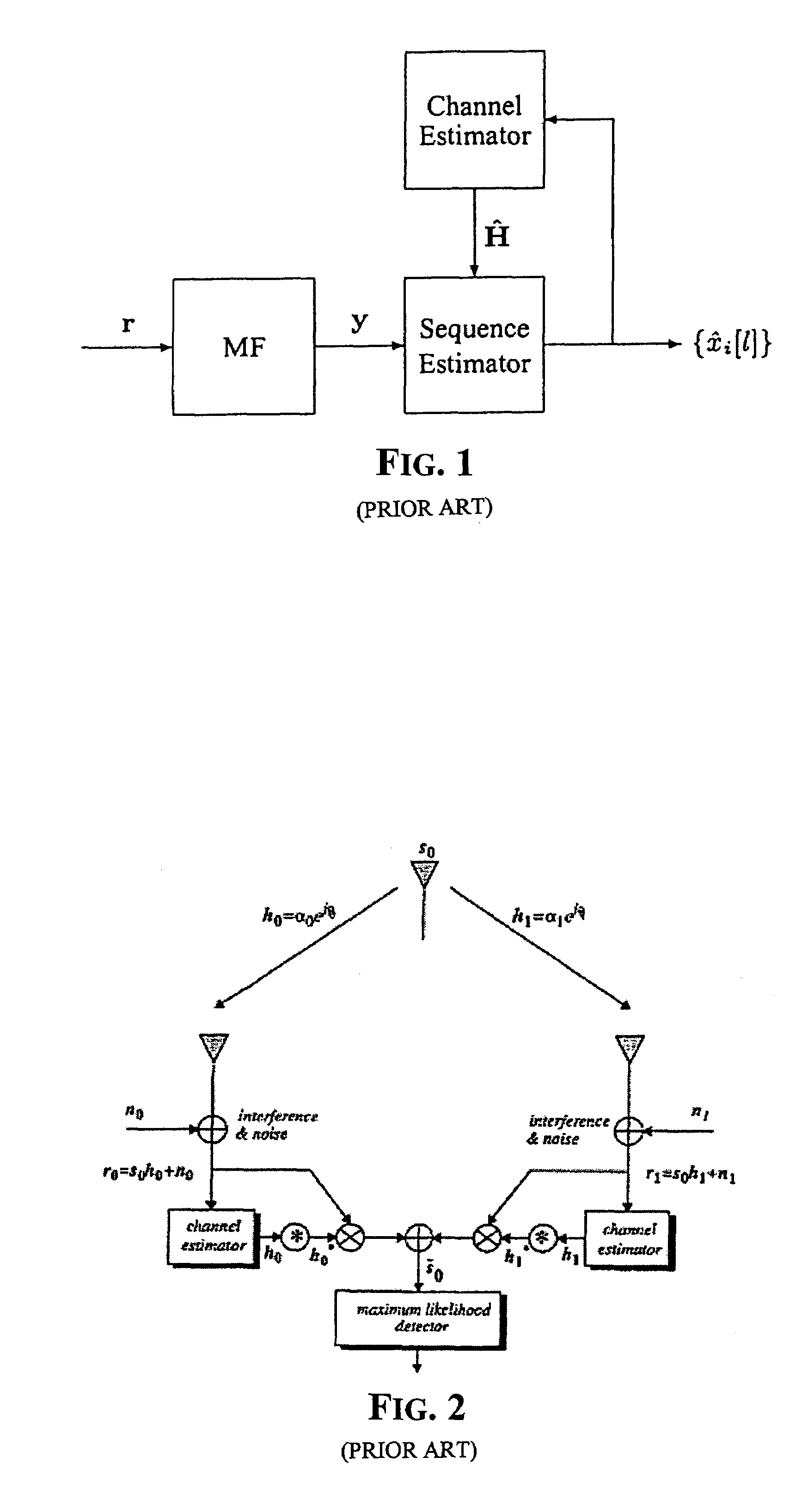
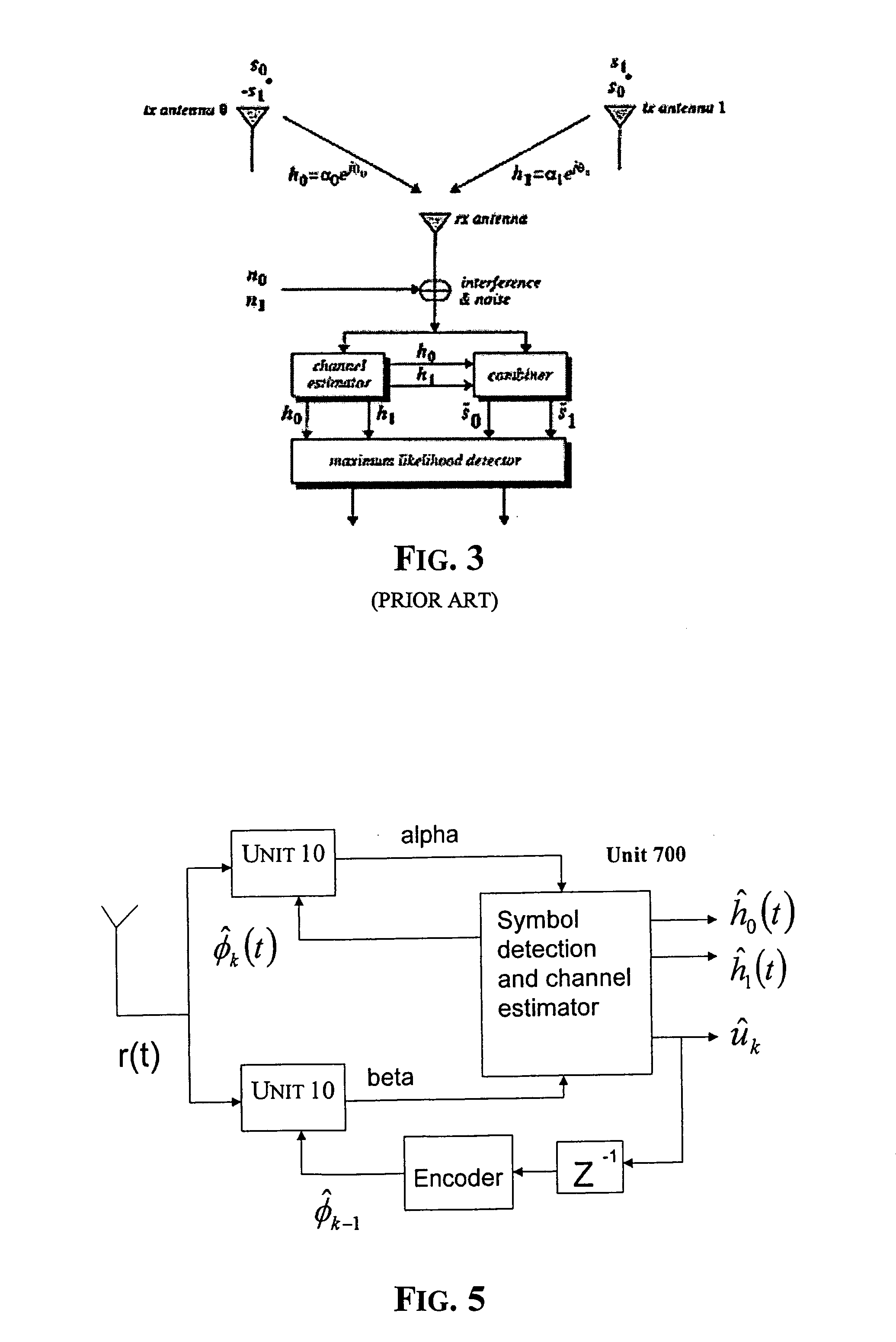
Method of estimating fading coefficients of channels and of receiving symbols and related single or multi-antenna receiver and transmitter
The method is for estimating the fading coefficients of a plurality of transmission channels on which signals to be sent, generated as a function of a sequence of symbols, are transmitted according to a particular modulation, e.g. AM-PSK modulation. The fading coefficients are estimated by using estimations of the transmitted symbols obtained in advance, thus obtaining DC components of the received signal by coherent demodulation locked to the phases of the transmitted AM-PSK signals, and processing these DC components. The method may not require the choice of a stochastic distribution model of the channel fading, thus it remains efficient even when the channel characteristics vary significantly. Moreover, the method works correctly even if the received stream is disturbed by inter-symbolic interference (ISI) and / or by multi-path fading.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
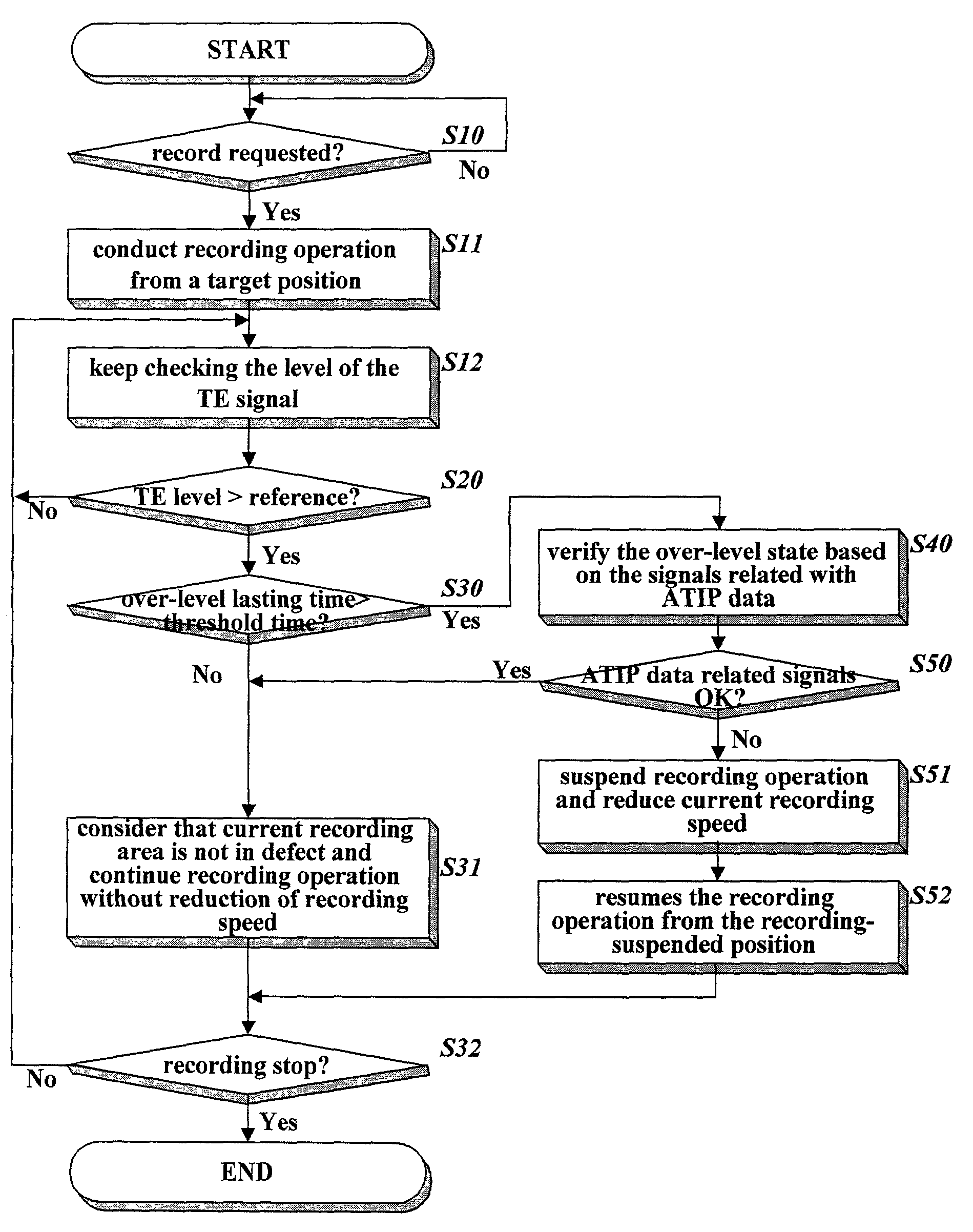
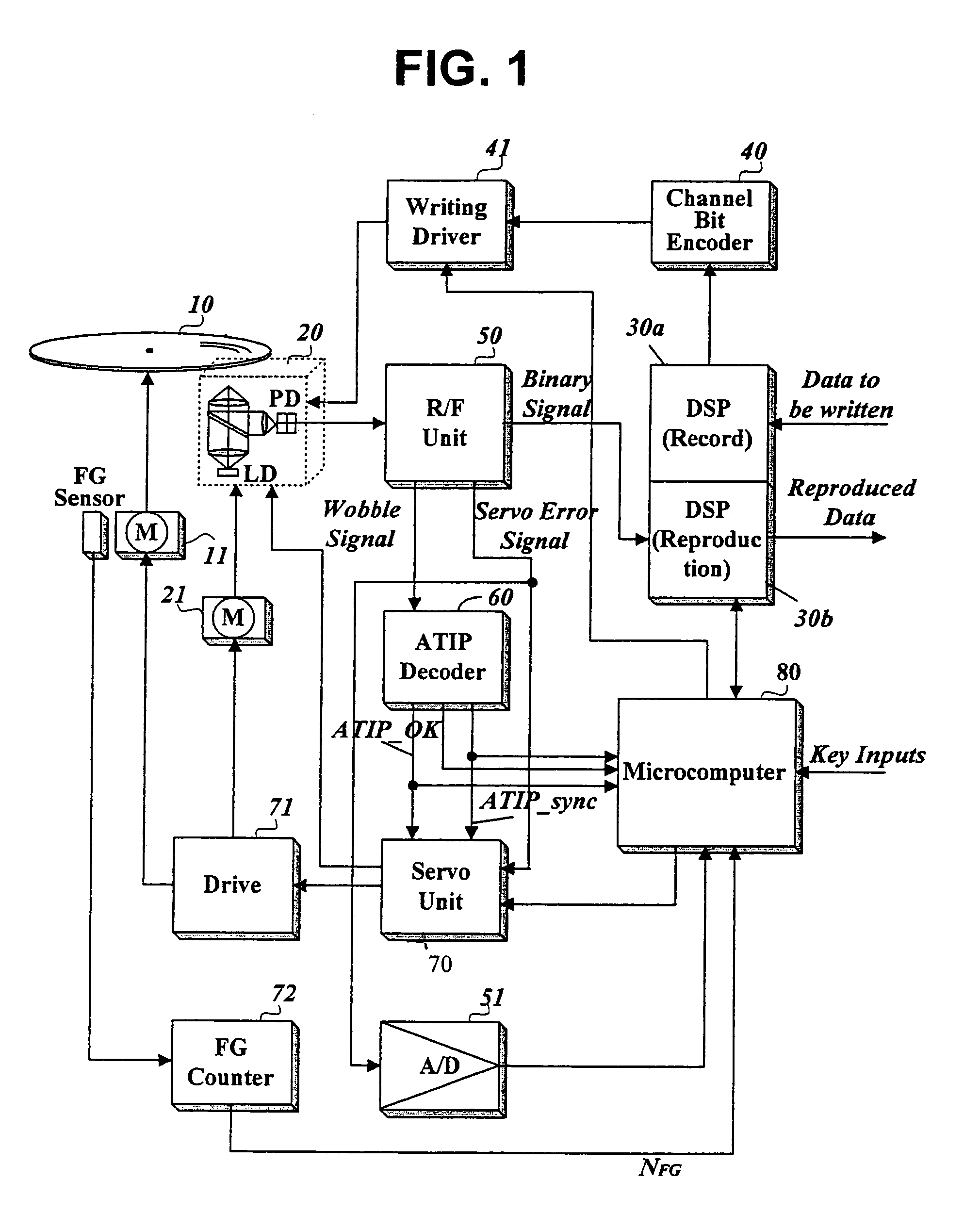
Method of detecting a defect area of a disk
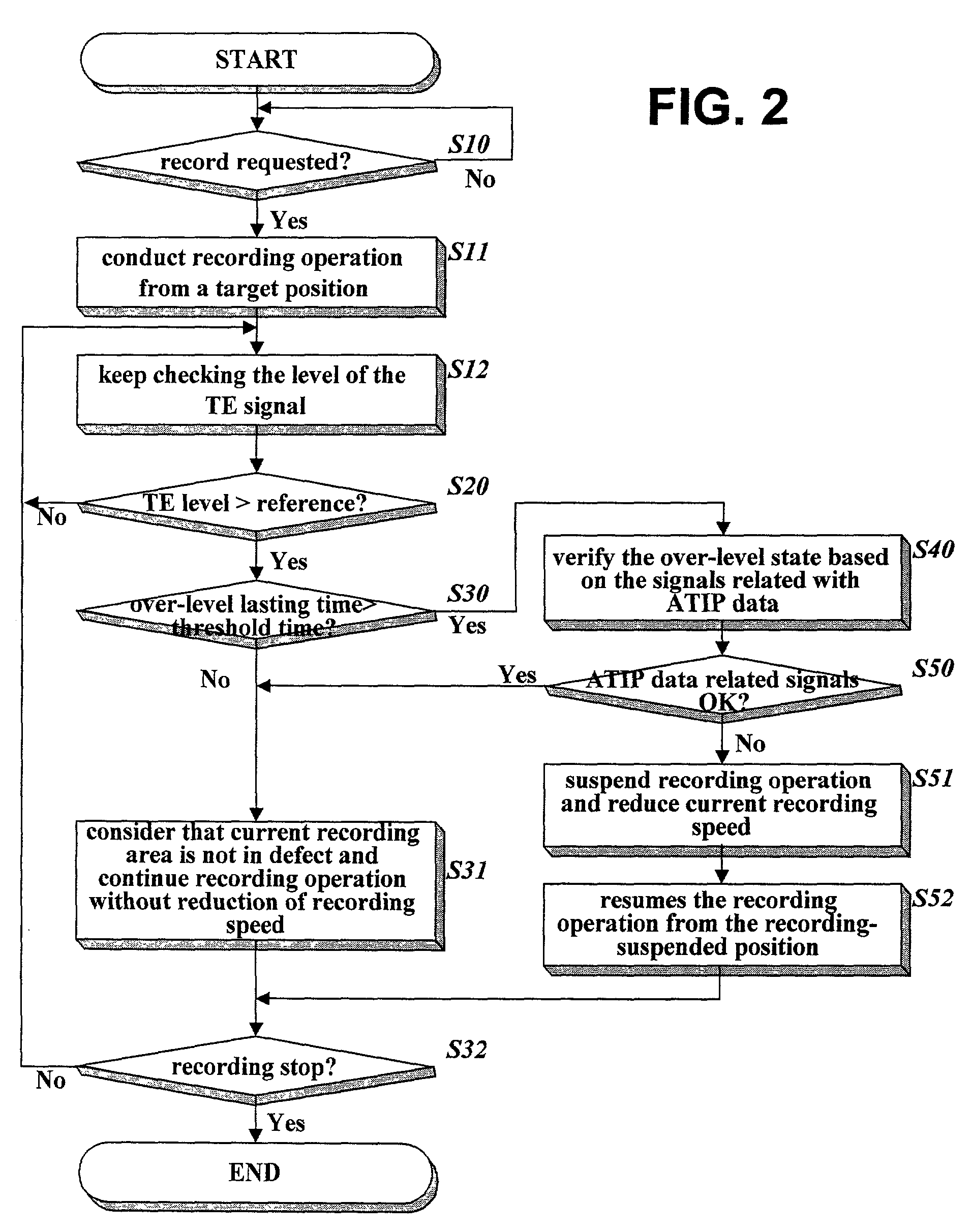
InactiveUS7092334B2Combination recordingProduction of permanent recordsData recordingComputer science
The present invention relates to a method of detecting a defect area without any mistake during data recording on a writable disk. This method detects a level of a servo error signal produced during a recording operation, checks whether the servo error signal is in an abnormal state based on the detected level, detects a periodic wobble signal or periodicity of the abnormal state occurrences of the servo error signal produced during the recording operation, and determines whether a recording area is in defect based on successful decoding of the detected periodic wobble signal or the periodicity of the abnormal state occurrences if the servo error signal is in an abnormal state. This method ensures exact detection of a defect area, whereby unnecessary speed reduction can be eliminated and successful data writing can be also guaranteed even in a defect area.
Owner:HITACHI LG DATA STORAGE KOREA
Method and device for feeding back channel state information reports
ActiveCN103516464AIncrease flexibilityOvercoming costly problemsError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel state informationCarrier signal
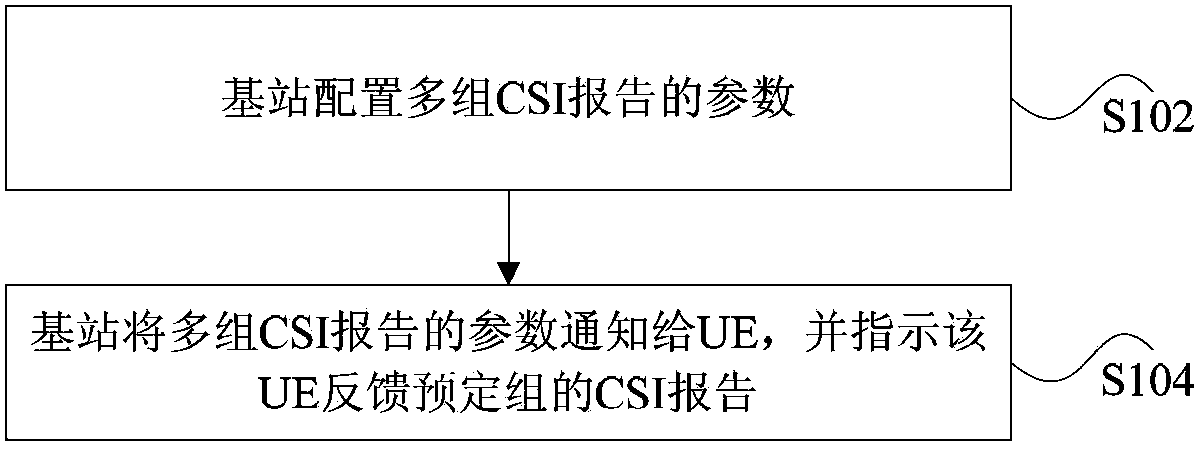
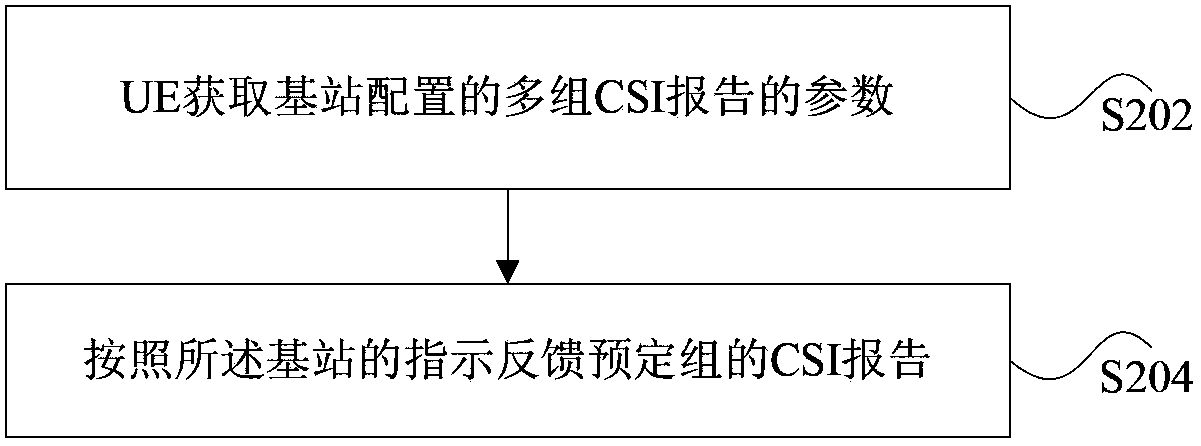
The invention discloses a method and a device for feeding back channel state information reports. The method includes the following steps that: a base station configures parameters of a plurality of groups of channel state information (CSI) reports; and the base station informs UE about the parameters of the plurality of groups of channel state information (CSI) reports and instructs the UE to feed back the channel state information (CSI) reports of a predetermined group. The parameters of each group of channel state information (CSI) reports in the plurality of groups of channel state information (CSI) reports comprise a resource allocation parameter of one or a plurality of channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources which are used for channel measurement. The parameters of each group of channel state information (CSI) reports in the plurality of groups of channel state information (CSI) reports further comprise one of the following parameters: distribution information of one or a plurality of interference measurement resources corresponding to each channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resource in one or the plurality of channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources; a parameter which is used for indicating the corresponding relationship between one or the plurality of channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources and the interference measurement resources; a parameter which is used for indicating the corresponding relationship between the channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources and channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources used for interfering calculation; and / or a parameter used for indicating the corresponding relationship between one or a plurality of channel state information reference signal (CSI-RS) resources and component carriers in carrier aggregation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
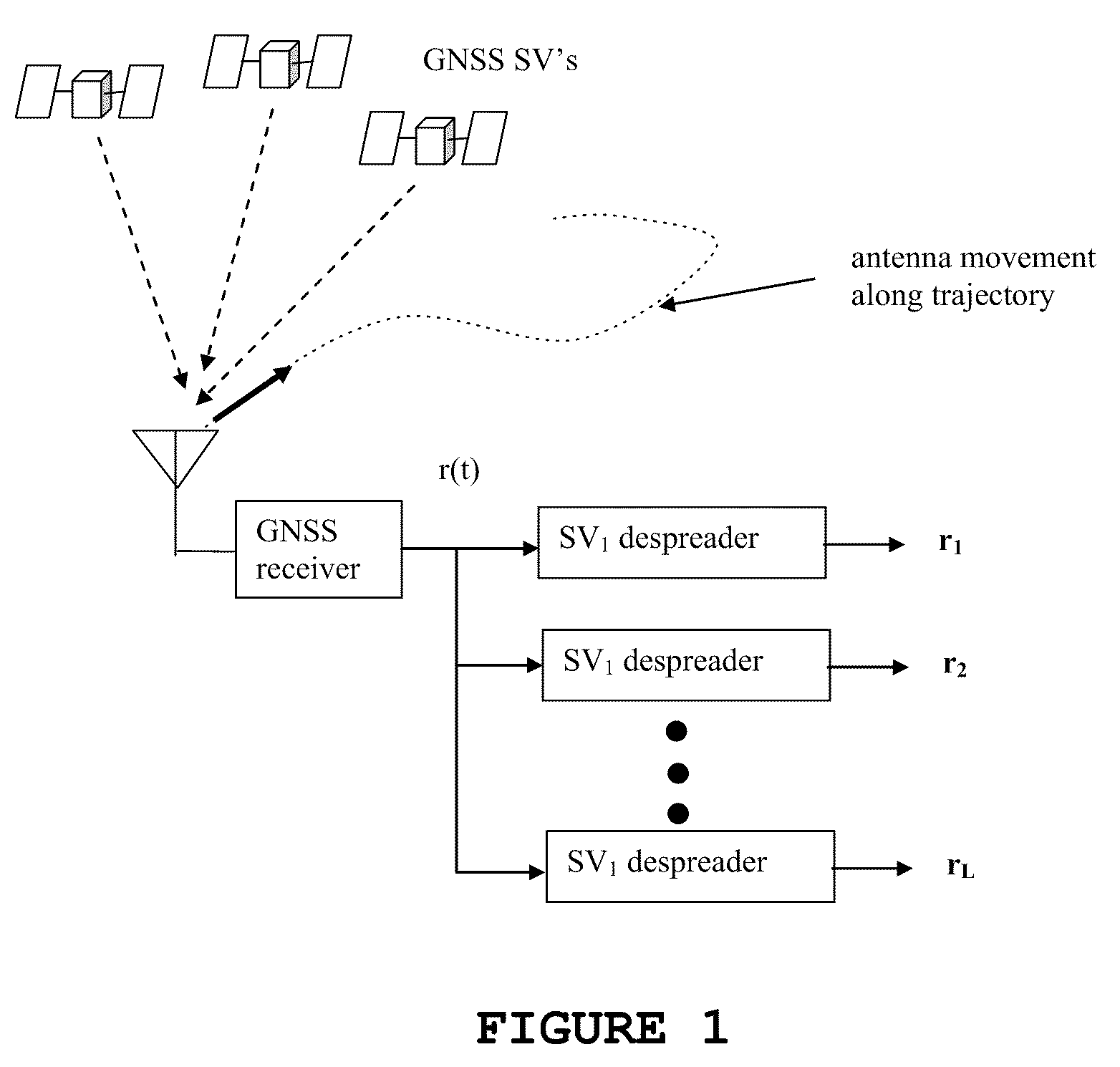
Method and system for detecting GNSS spoofing signals
ActiveUS7952519B1Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsSatellite radio beaconingSpatial correlationEnvironmental geology
Methods and systems for detecting GNSS signals originating from an inauthentic source. A synthetic array using a receiver antenna which is randomly spatially translated may be used to gather alleged GNSS signals. The signals are then processed to determine the spatial correlation between them. A high spatial correlation between the signals indicates a probable inauthentic source for the GNSS signals.
Owner:UTI LLP
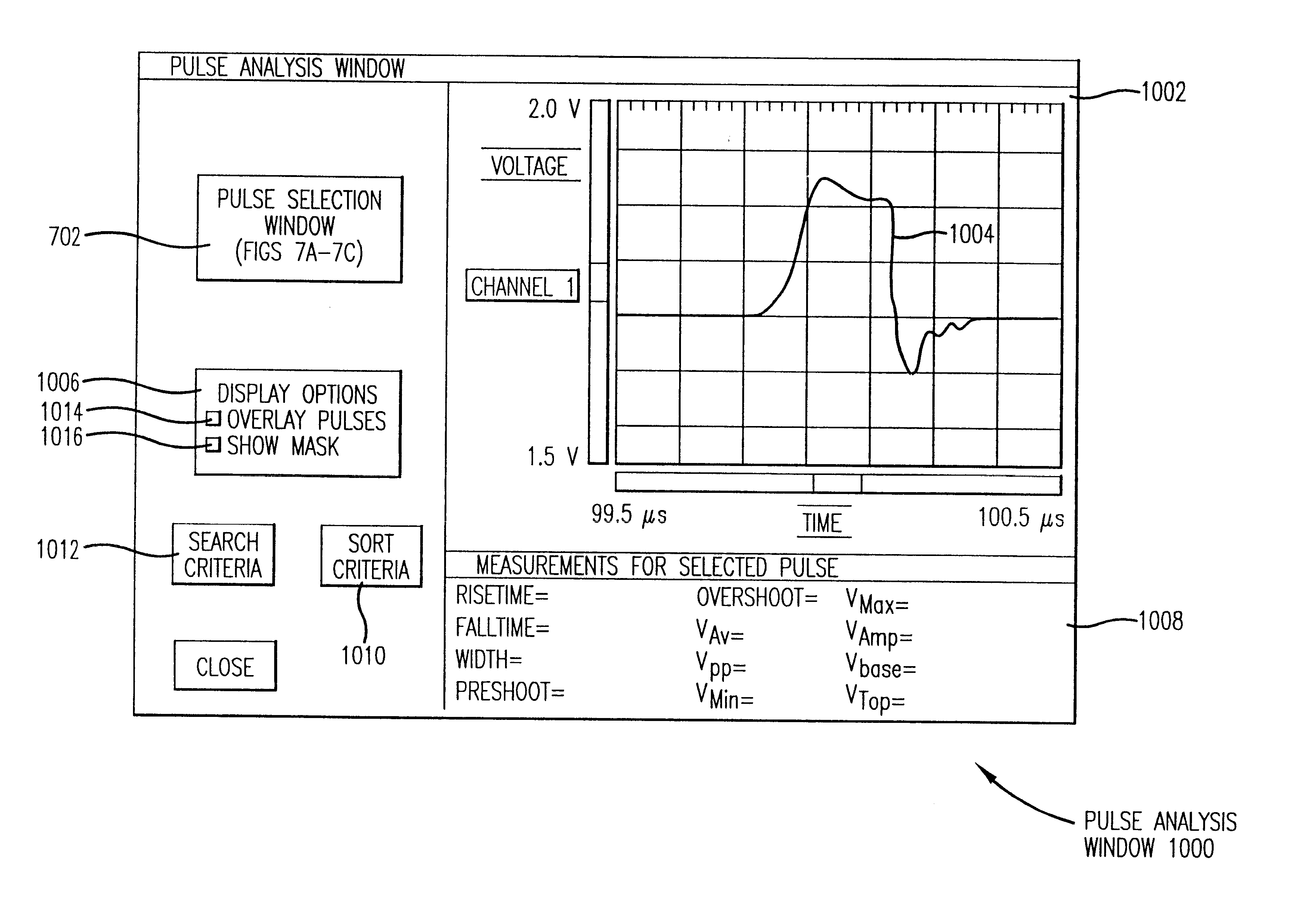
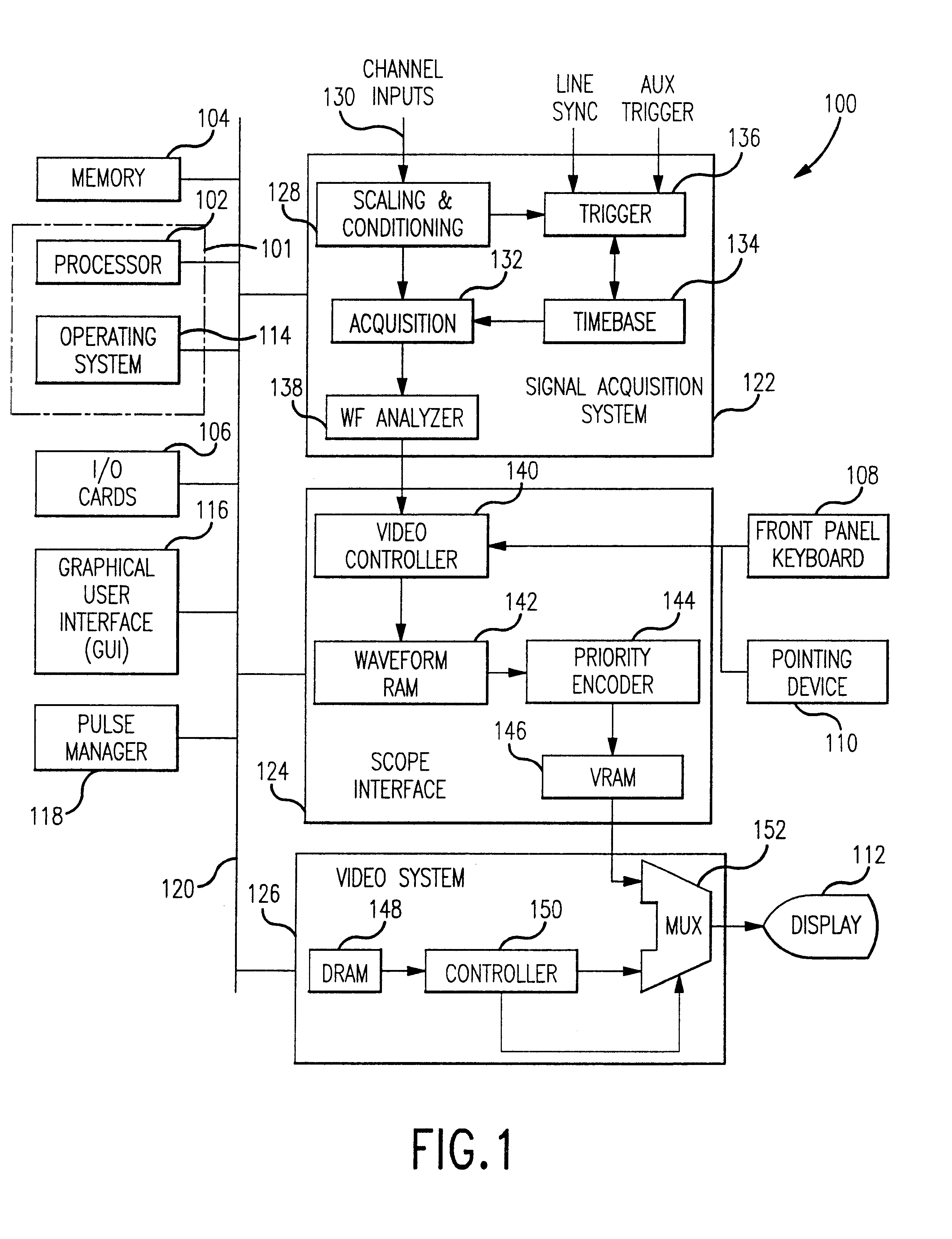
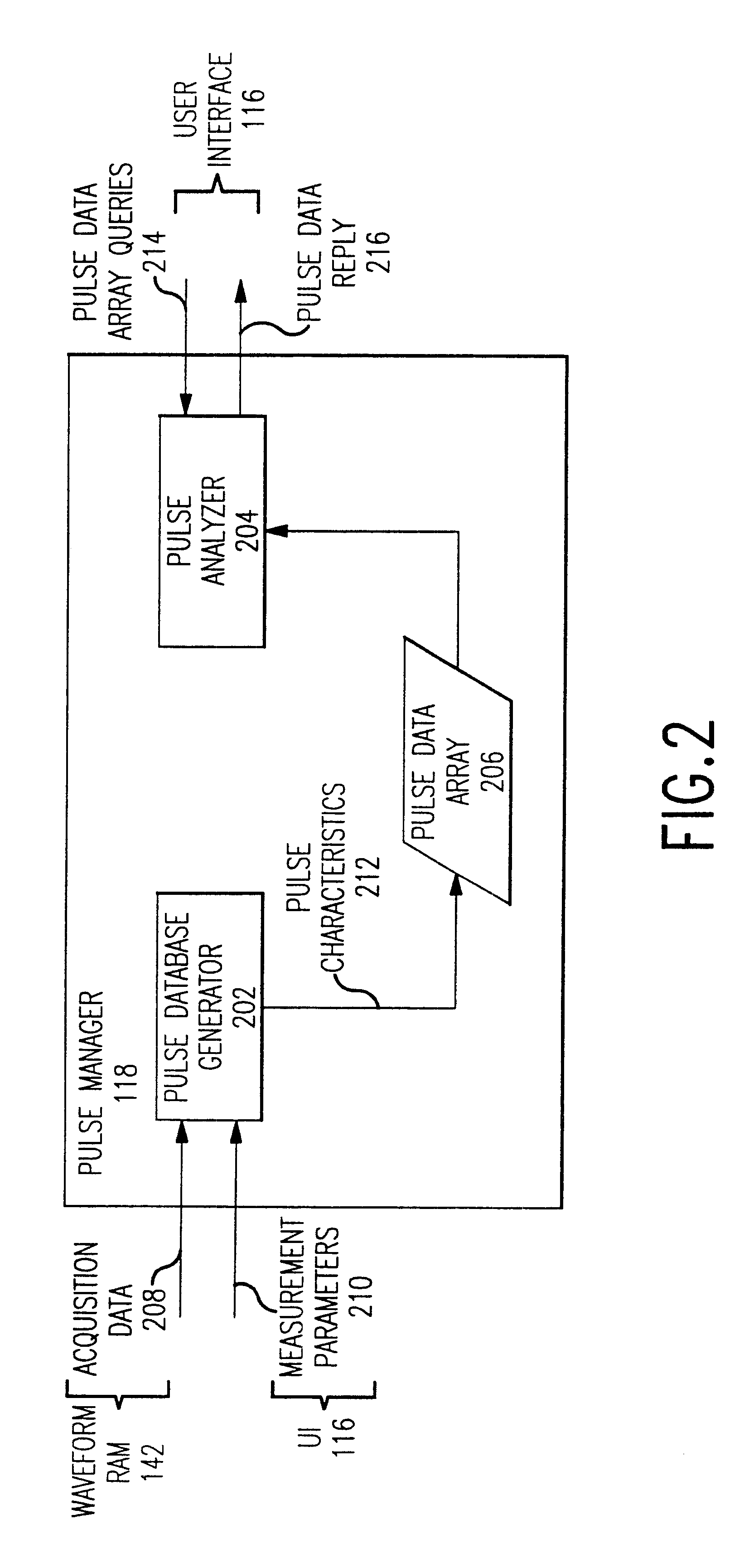
System and method for enabling an operator to analyze a database of acquired signal pulse characteristics
A pulse management system configured to perform a plurality of pulse measurements on each of a plurality of pulses of an acquired signal and to store results of the pulse measurements in an accessible data structure. The pulse management system includes a pulse analyzer that searches the data structure for pulses of the acquired signal that satisfy operator-provided search criteria. Similarly, the pulse analyzer can sort the selected subset of pulses based on sort criteria provided, for example, by an operator. The pulse analyzer can provide the operator with a user interface environment in which the operator specifies the search and sort criteria and in which the pulse analyzer displays the selected pulses with their associated pulse measurement results. The operator can advance through the selected pulses in any manner desired to display different pulses together or separately. The pulse analyzer thereby provides an operator with the capability to gain insights into a large number of acquired pulses through the selection of individual pulses meeting desired characteristics or relative time of occurrence, through the filtering or selection of pulses meeting specified criteria, and through the arrangement of those pulses according to the same or different criteria.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com