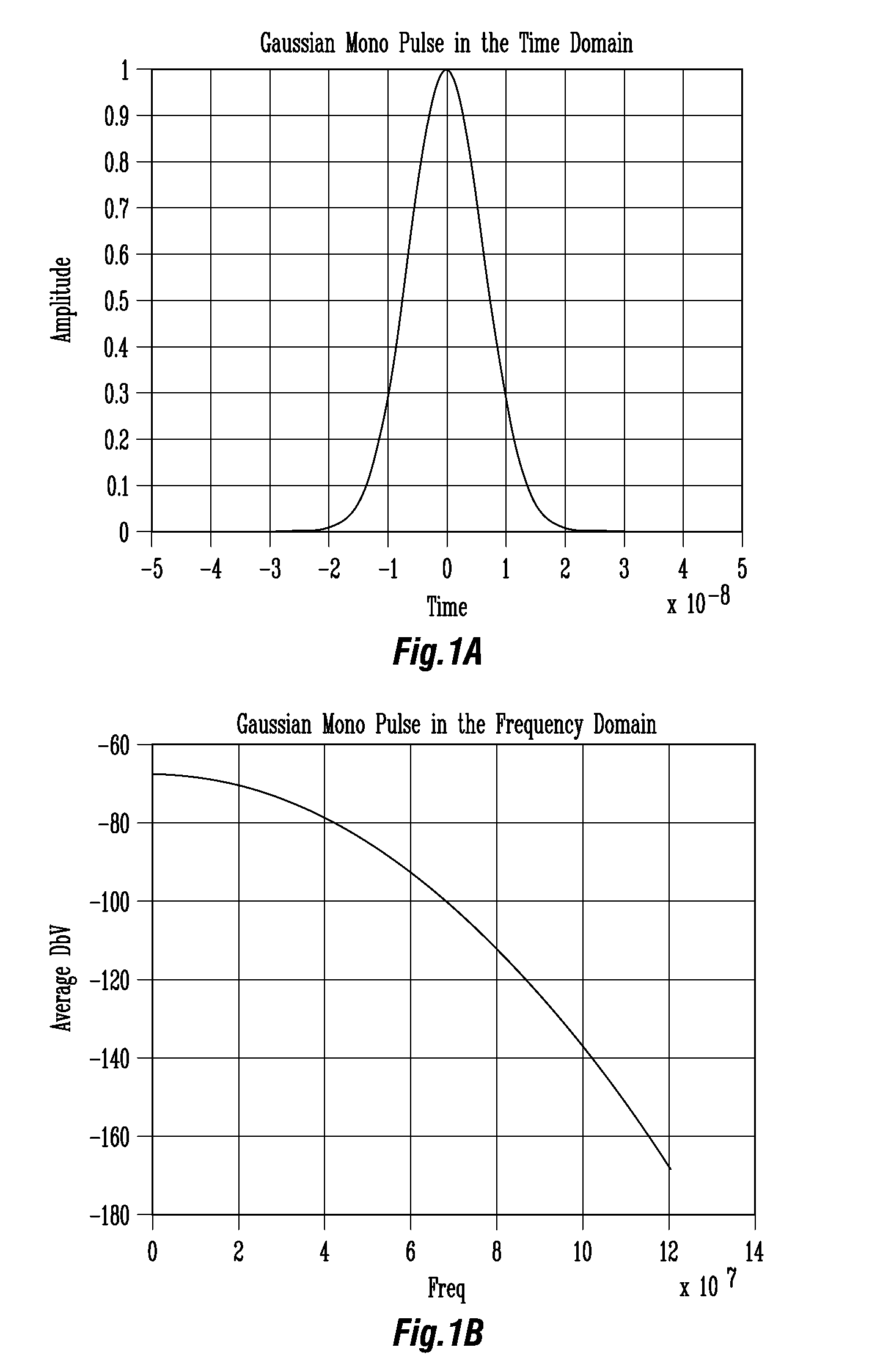
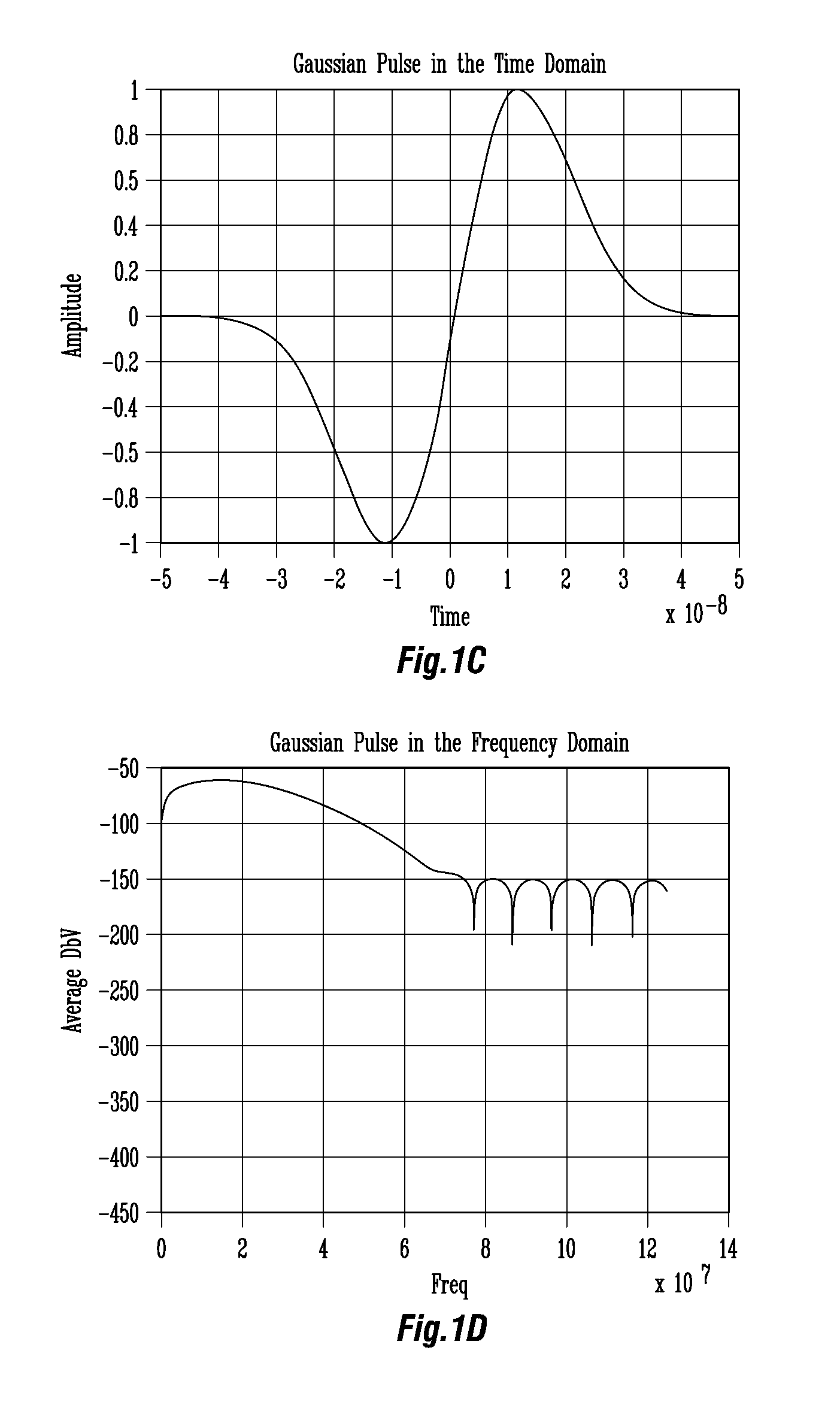
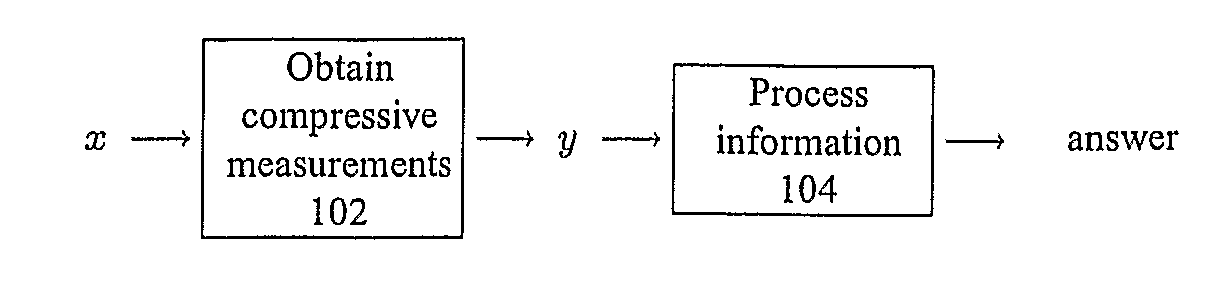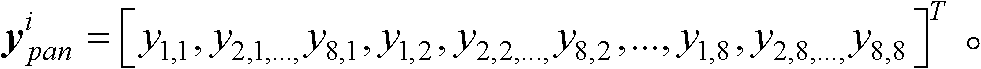Patents
Literature
675 results about "Signal recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
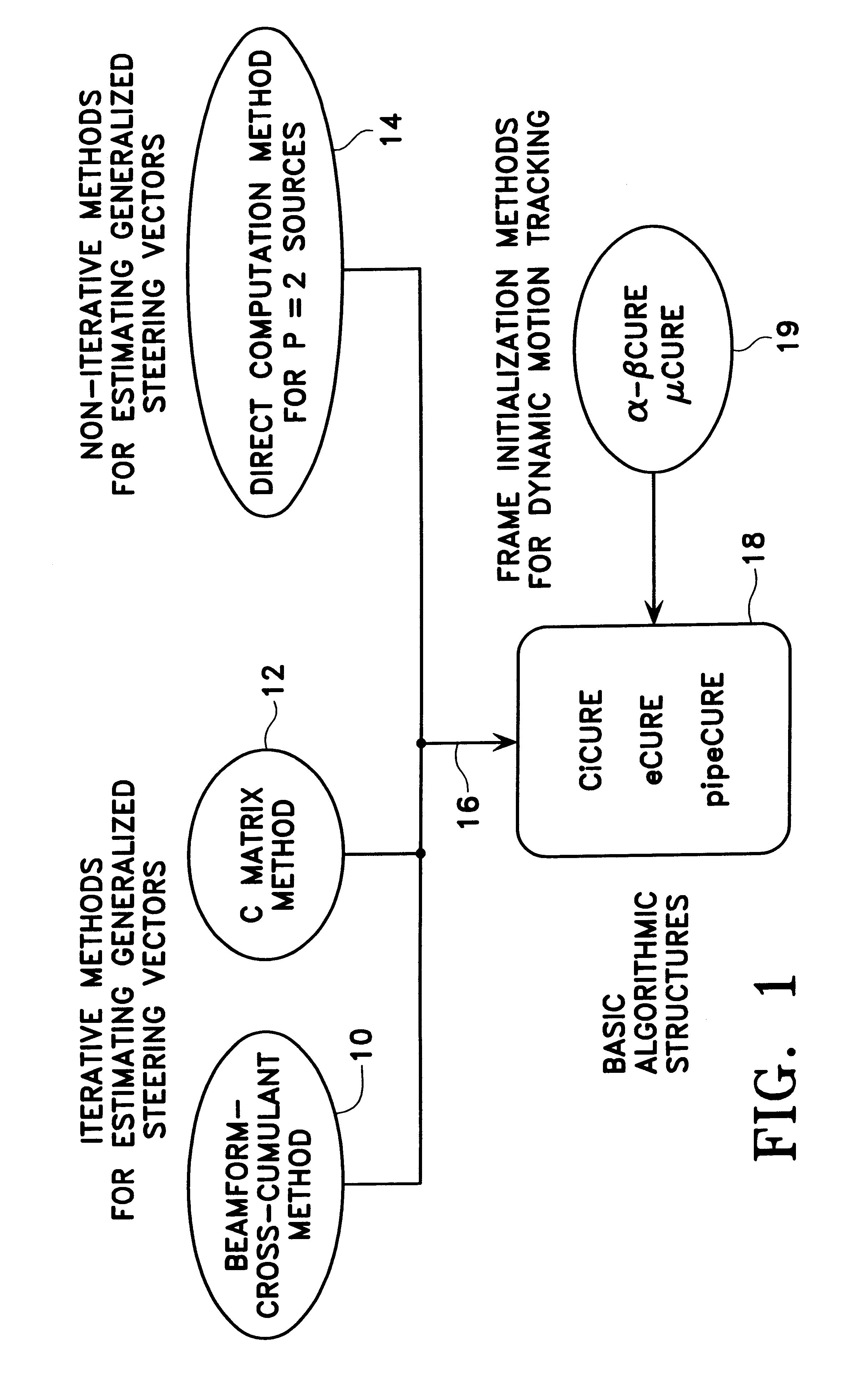
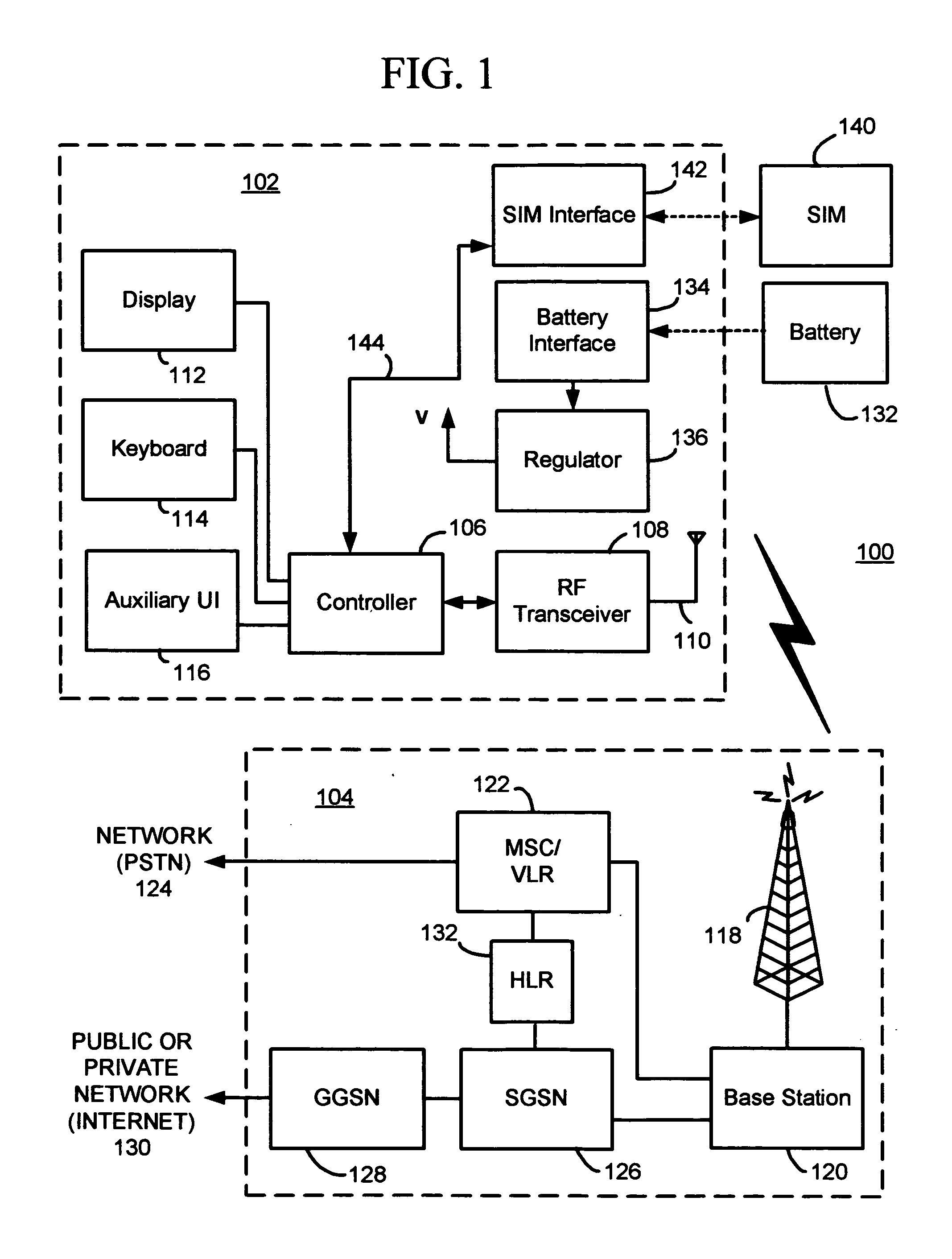
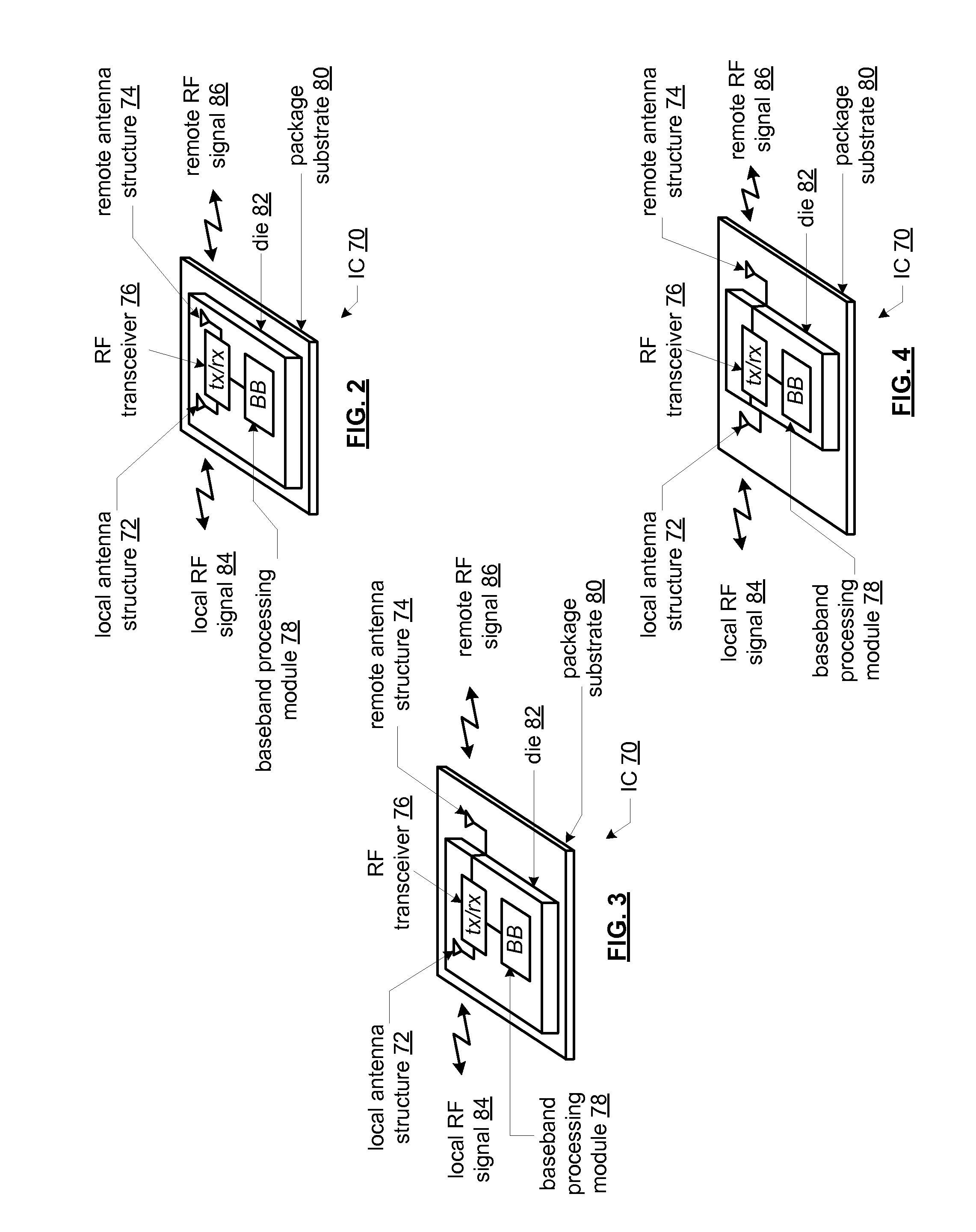
Active wafer for improved gigabit signal recovery, in a serial point-to-point architecture
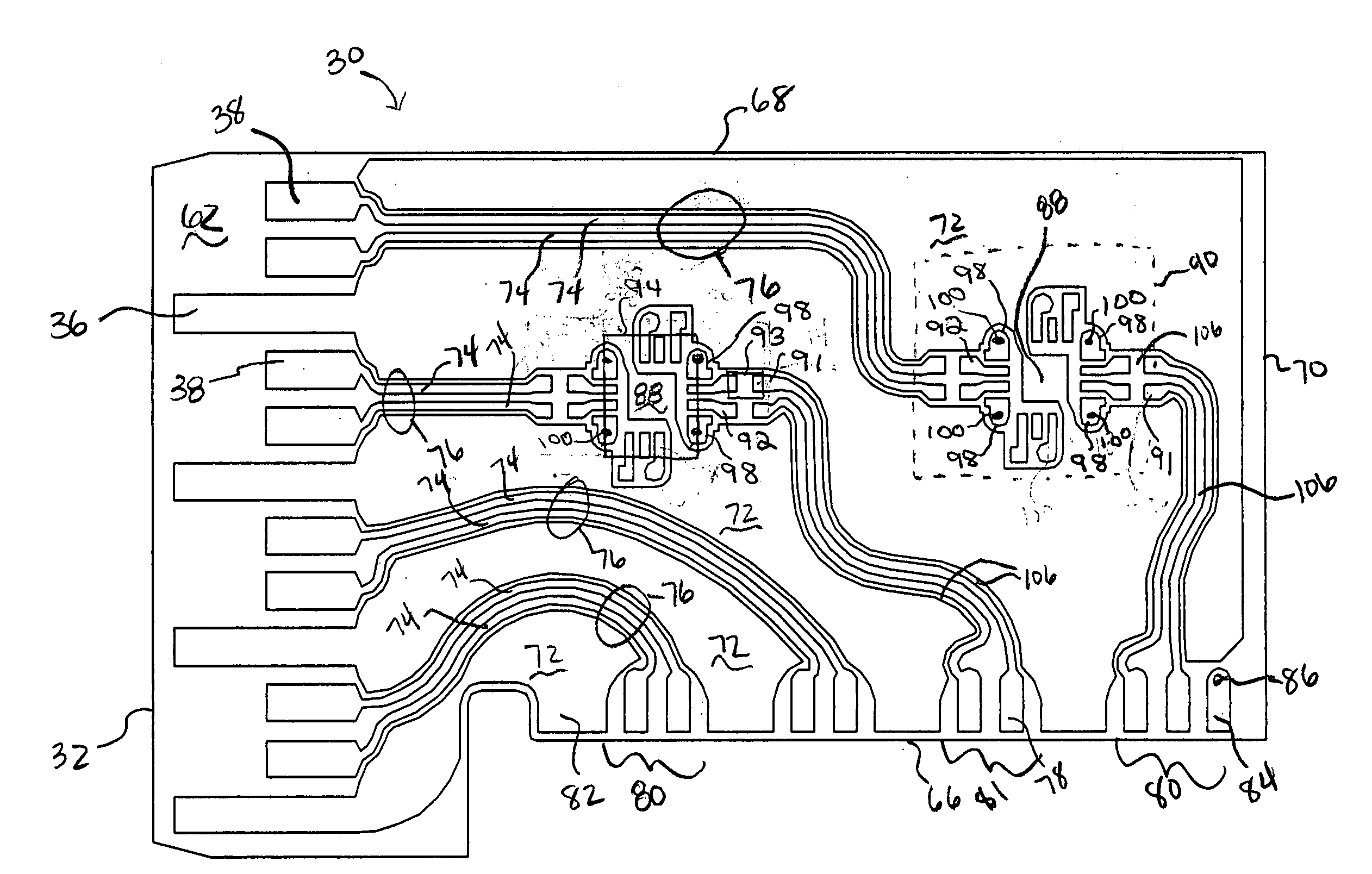
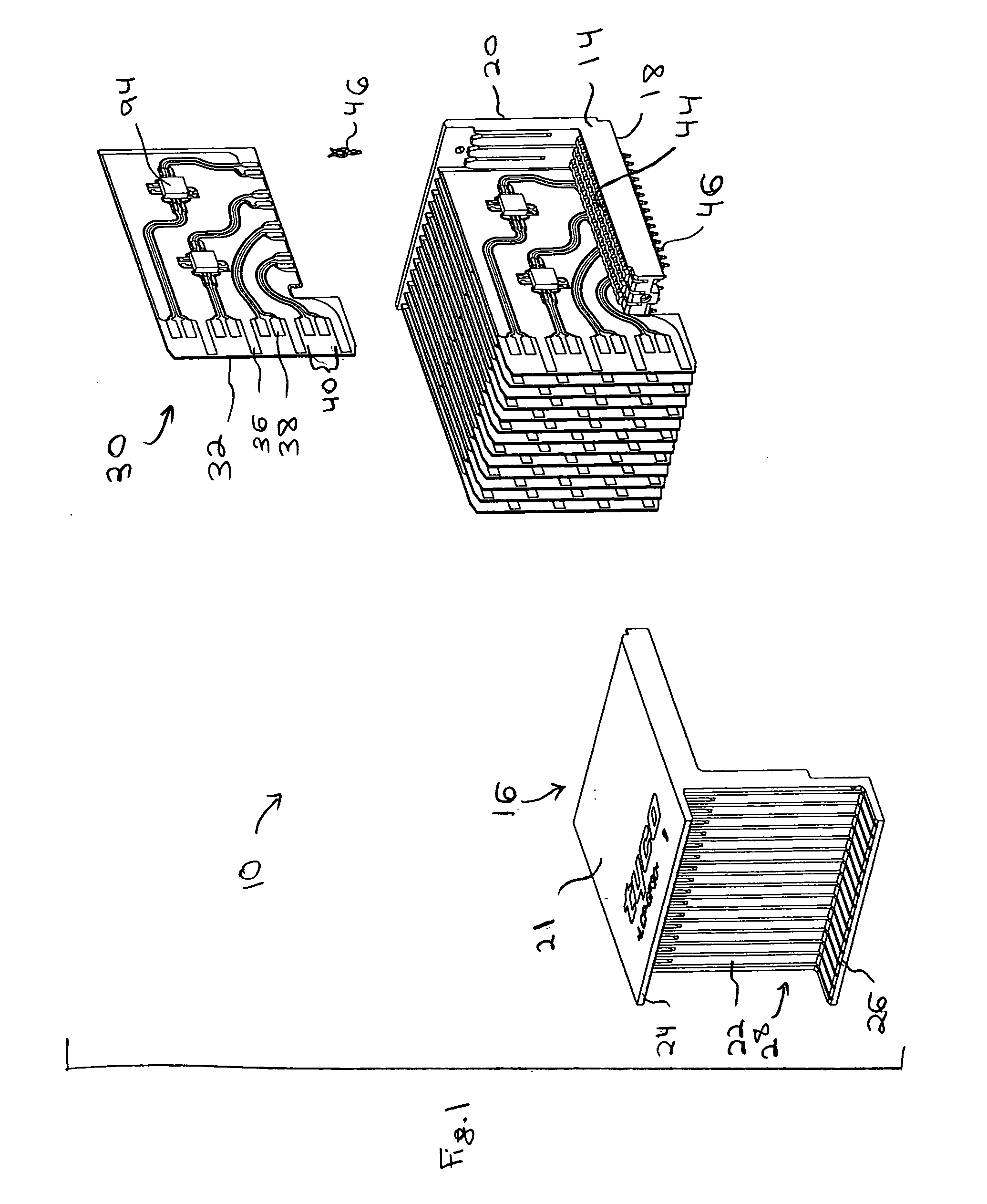
ActiveUS6932649B1Increase magnitudeCoupling device detailsPrinted circuitsContact padDifferential signaling
An electrical connector is provided for operation in a point-to-point application. The connector includes an insulated housing having first and second card interfaces configured to mate with associated first and second circuit cards. An electrical wafer is held in the housing and configured to operate in a point-to-point architecture. The signal traces end at signal contact pads located proximate to first and second edges, respectively. The signal contact pads receive a unidirectional signal. Each of the signal traces include a break section at an intermediate point along a length thereof to form a disconnect in the signal traces. The connector further includes an active compensation component bridging the break section in the signal traces. The active compensation component compensates the differential signal incoming from the input contact pads for signal degradation and transmits a compensated signal outward to the output contact pads. The active compensation component transmits the signal only in a single direction within the point-to-point architecture.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
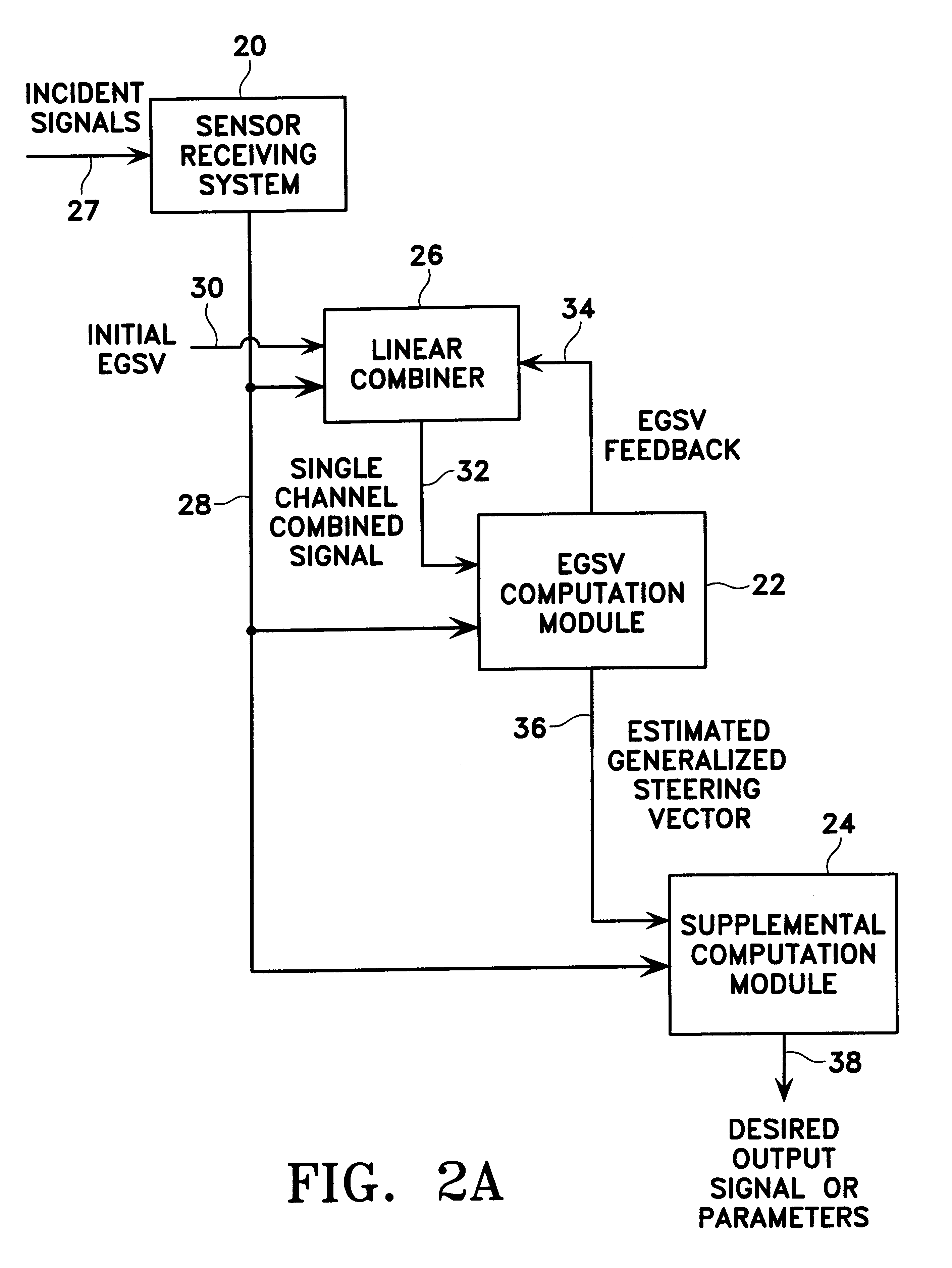
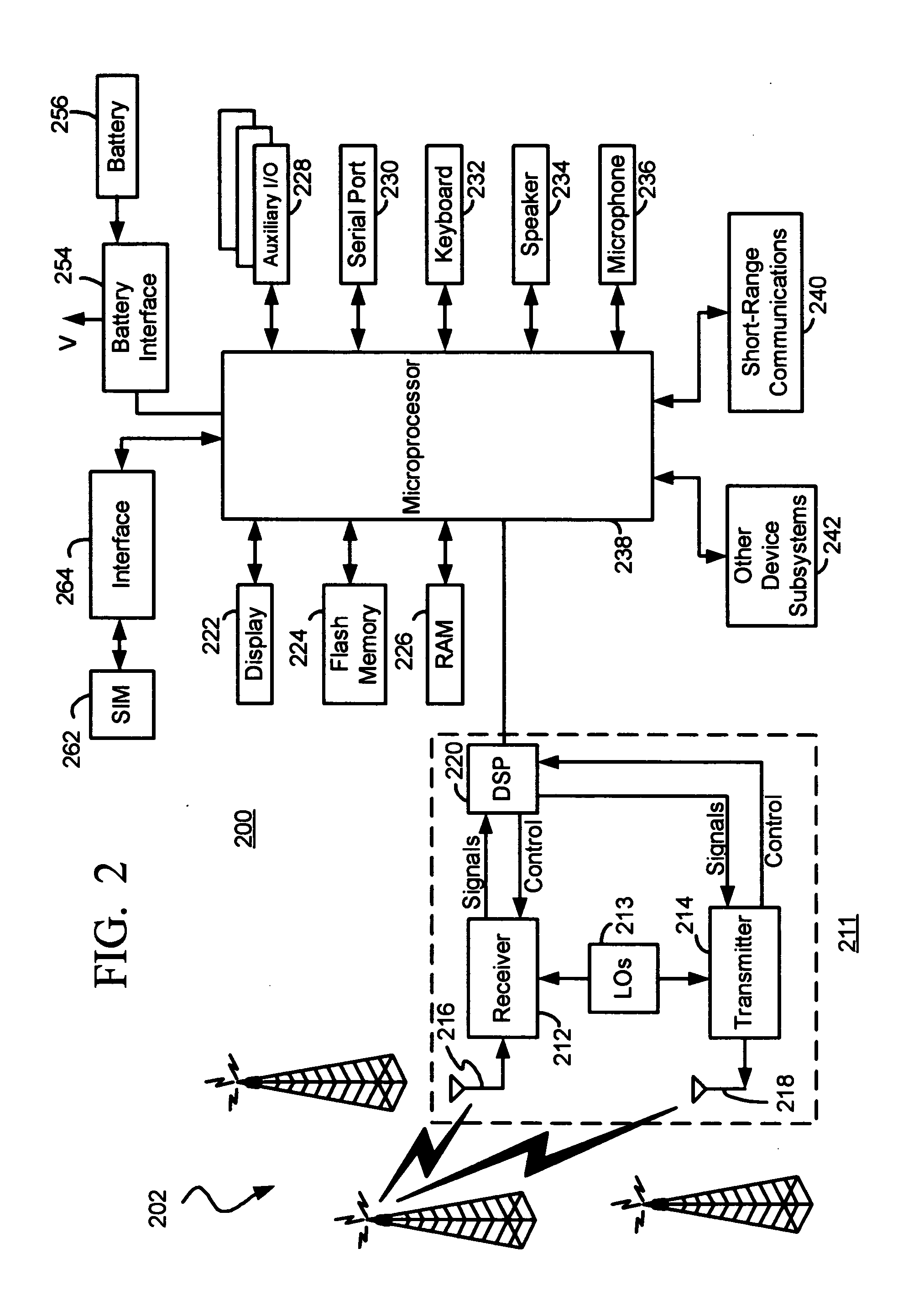
Method for processing radio signals that are subject to unwanted change during propagation
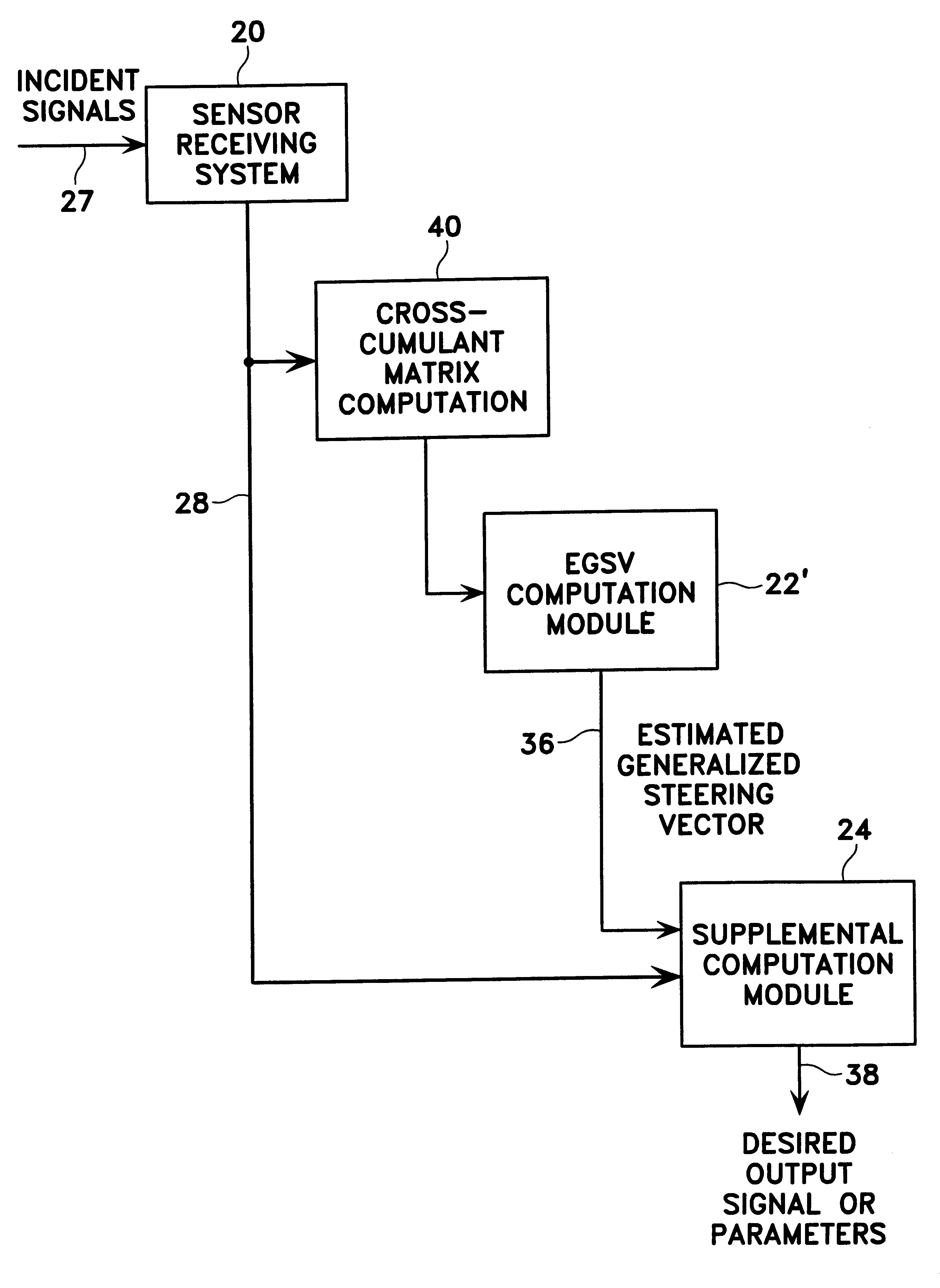
InactiveUS6208295B1Acquisition stableStable captureSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsRadio signalTransmitter
A method for processing received radio signals that are subject to unwanted change during propagation through the atmosphere, from a transmitter to a receiver array. The multiple signals are received as cochannel signals at the antenna array, and are processed to eliminate the effects of modification of the signals during propagation, wherein the processing step includes cumulant-based signal recovery without regard for the geometrical properties of the antenna array. In the invention as disclosed, two different information signals having two different polarization states are transmitted, and at least one of the transmitted signals is subjected to an unwanted change of its polarization state. The received signals are processed to separate and recover the two information signals without regard to their polarization states.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
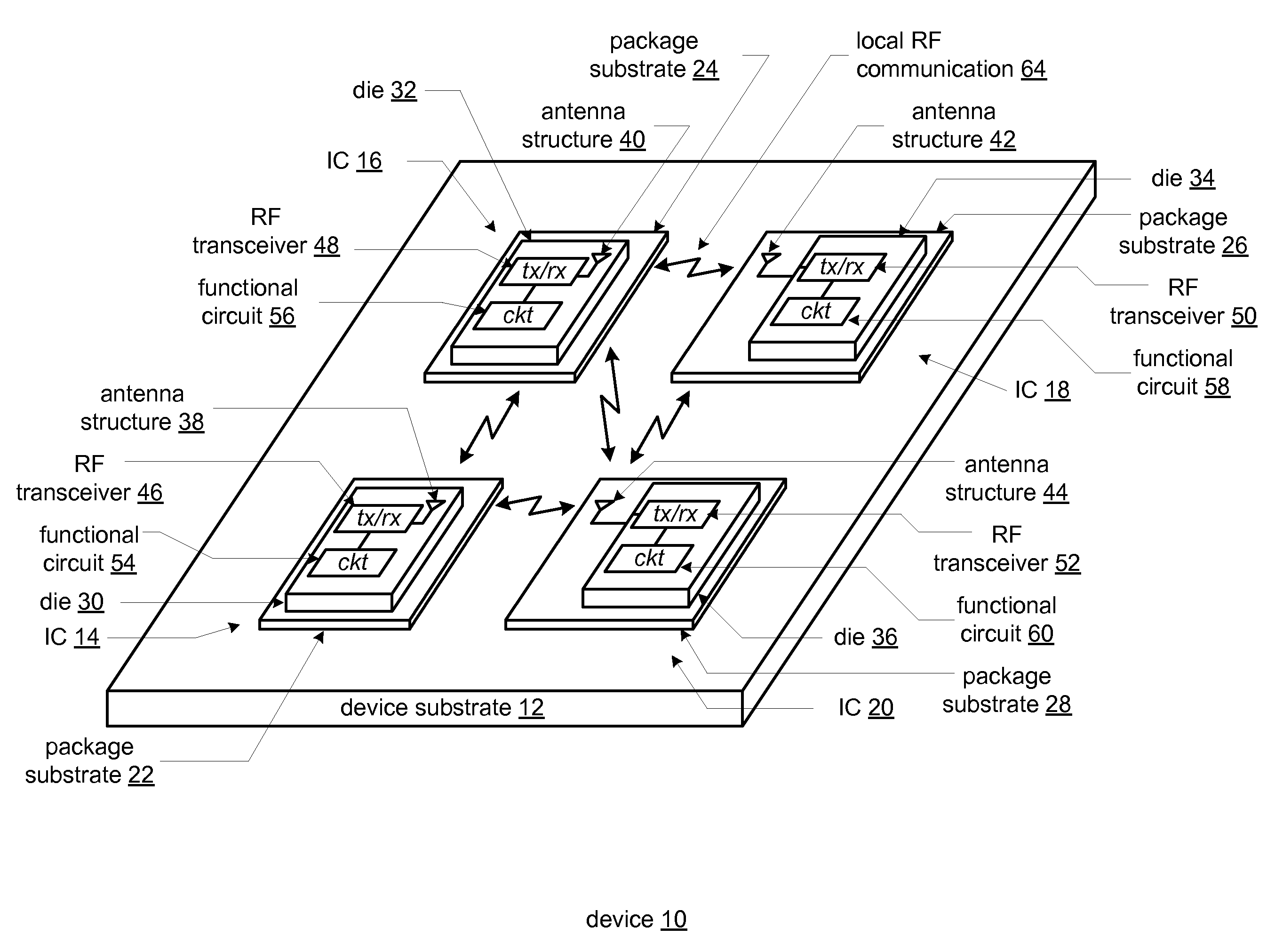
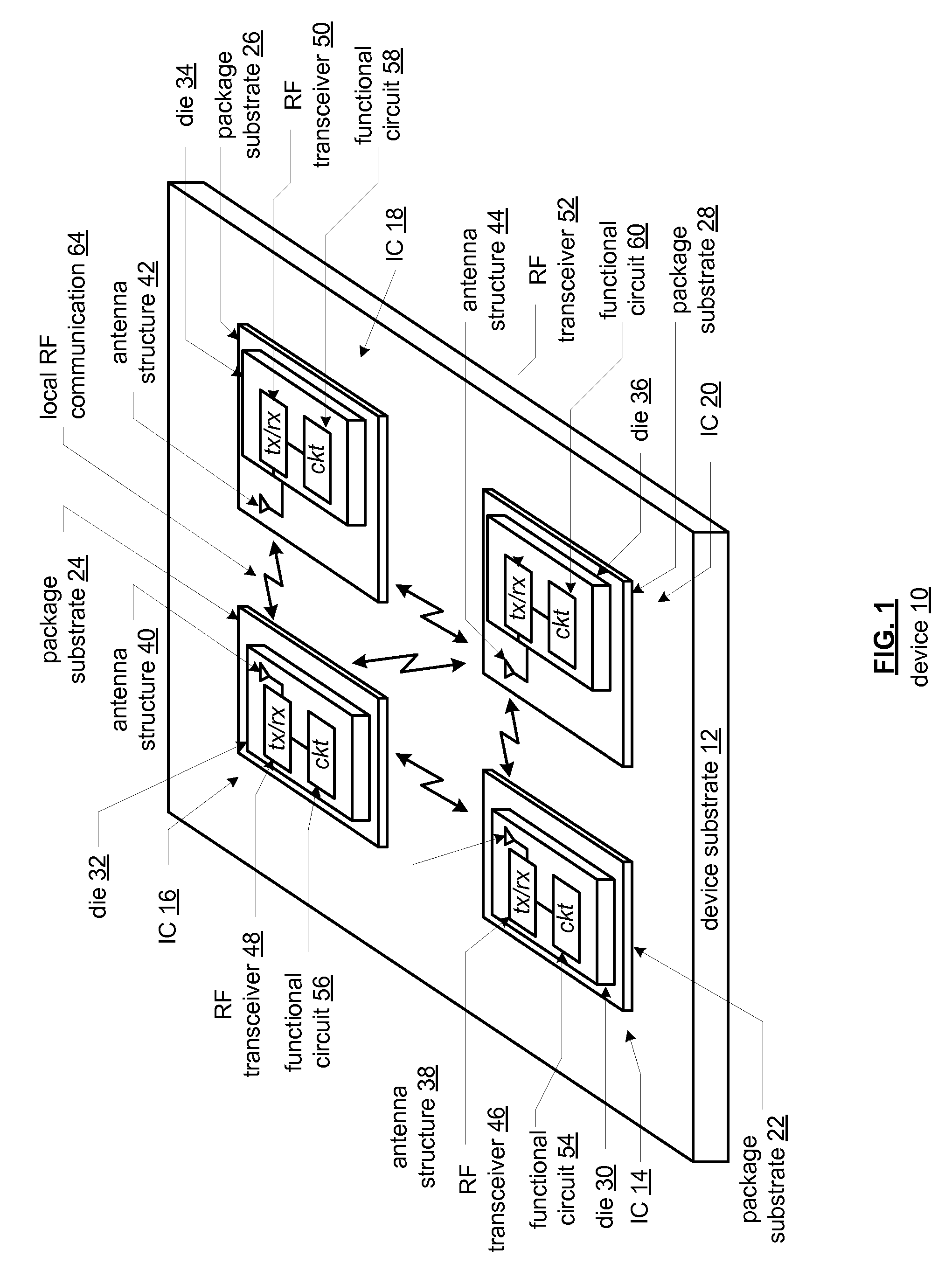
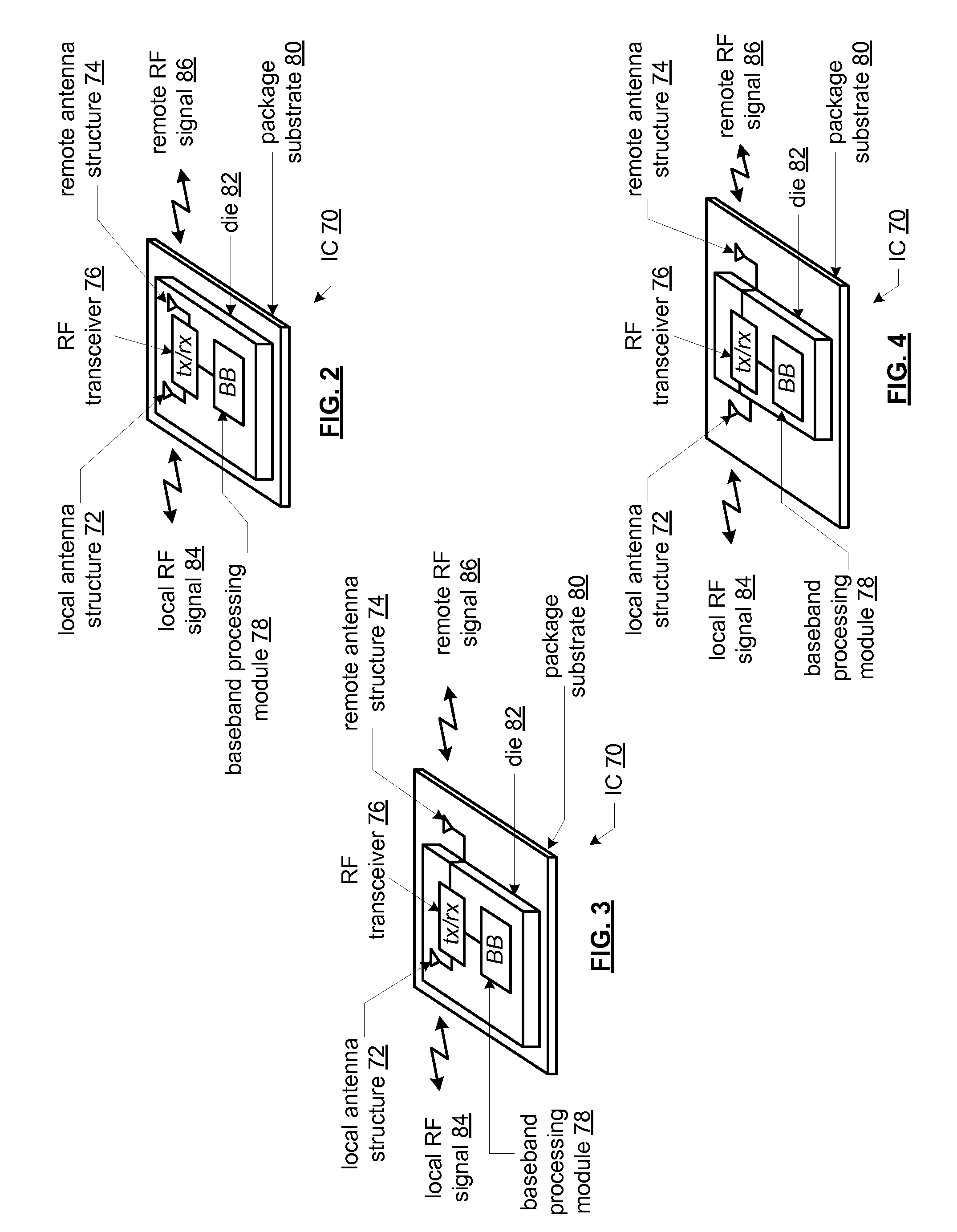
Reconfigurable MIMO transceiver and method for use therewith
ActiveUS20090010316A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesData streamWireless transceiver
A wireless transceiver includes a plurality of antennas. A plurality of signal recovery circuits generate a selected number of received signals from a first subset of the plurality of antennas, based on a control signal. A receiver section recovers an inbound data stream from the selected number of received signals. A plurality of transmitter sections generate a selected number of transmitted signals to a second subset of the plurality of antennas, based on the control signal, wherein the intersection between the first subset of the plurality of antennas and the second subset of the plurality of antennas is the null set for each value of the control signal.
Owner:NXP USA INC
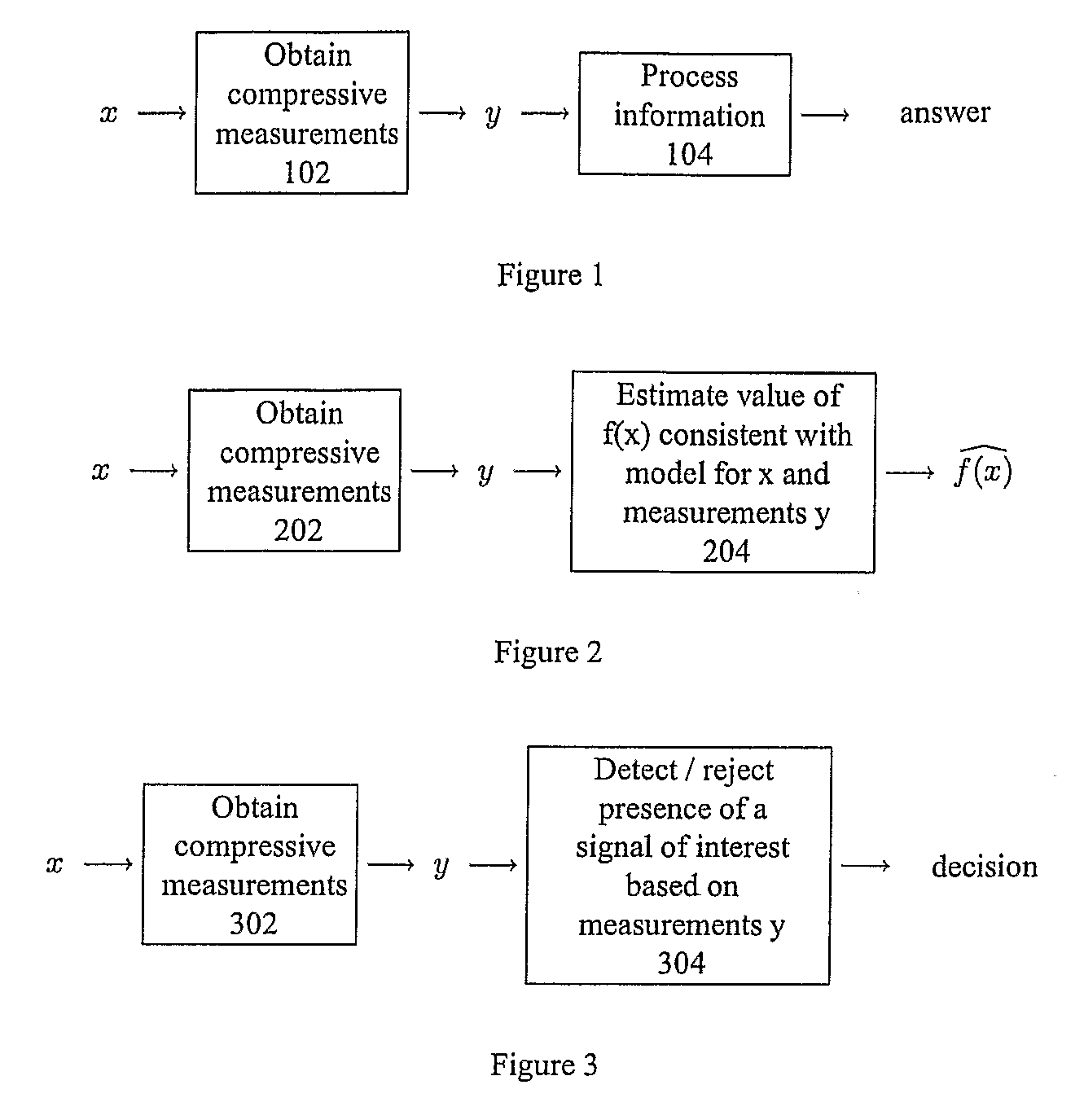
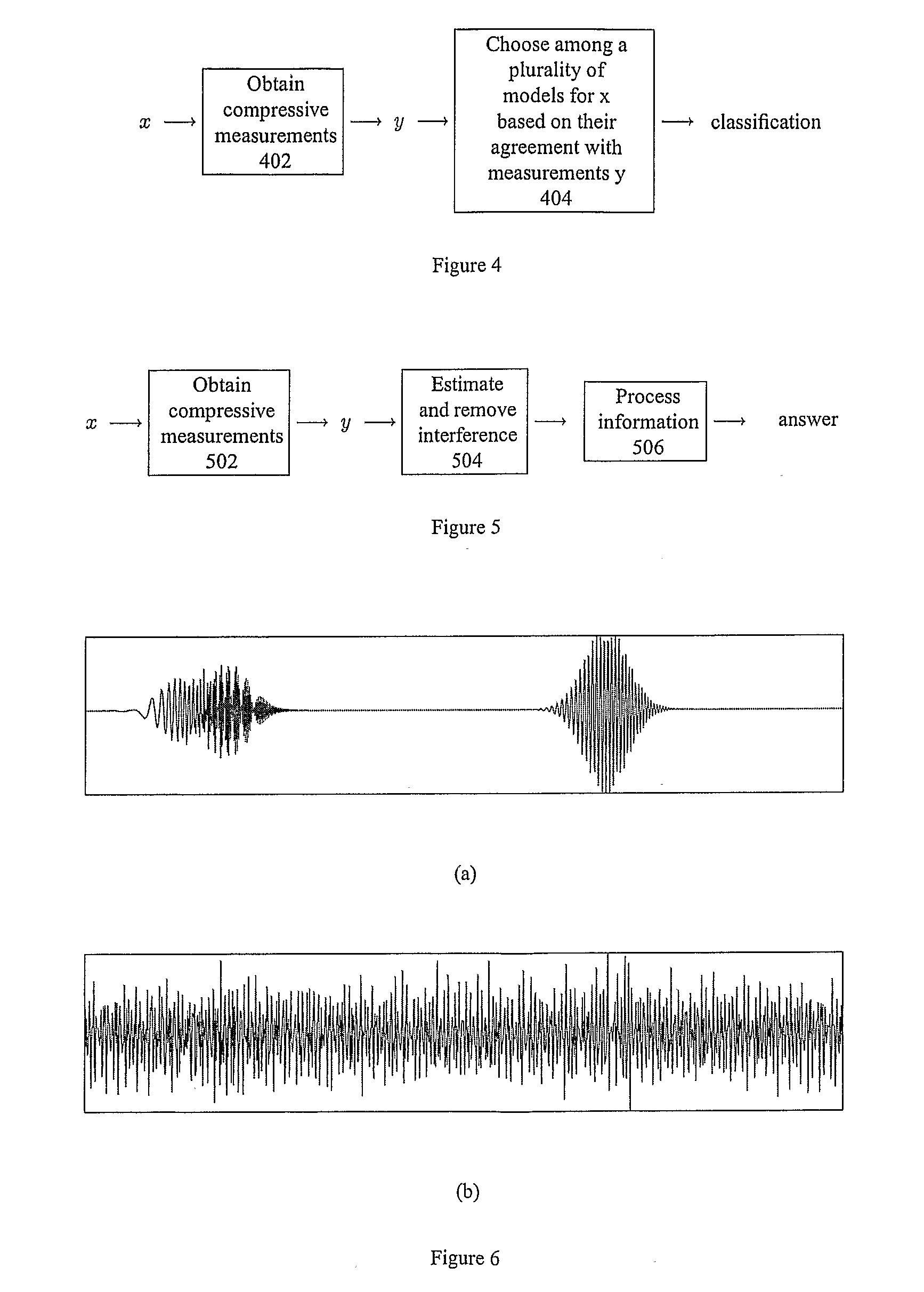
Method and Apparatus for Signal Detection, Classification and Estimation from Compressive Measurements
ActiveUS20080228446A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsDecision takingSignal restoration
The recently introduced theory of Compressive Sensing (CS) enables a new method for signal recovery from incomplete information (a reduced set of “compressive” linear measurements), based on the assumption that the signal is sparse in some dictionary. Such compressive measurement schemes are desirable in practice for reducing the costs of signal acquisition, storage, and processing. However, the current CS framework considers only a certain task (signal recovery) and only in a certain model setting (sparsity).We show that compressive measurements are in fact information scalable, allowing one to answer a broad spectrum of questions about a signal when provided only with a reduced set of compressive measurements. These questions range from complete signal recovery at one extreme down to a simple binary detection decision at the other. (Questions in between include, for example, estimation and classification.) We provide techniques such as a “compressive matched filter” for answering several of these questions given the available measurements, often without needing to first reconstruct the signal. In many cases, these techniques can succeed with far fewer measurements than would be required for full signal recovery, and such techniques can also be computationally more efficient. Based on additional mathematical insight, we discuss information scalable algorithms in several model settings, including sparsity (as in CS), but also in parametric or manifold-based settings and in model-free settings for generic statements of detection, classification, and estimation problems.
Owner:RICE UNIV
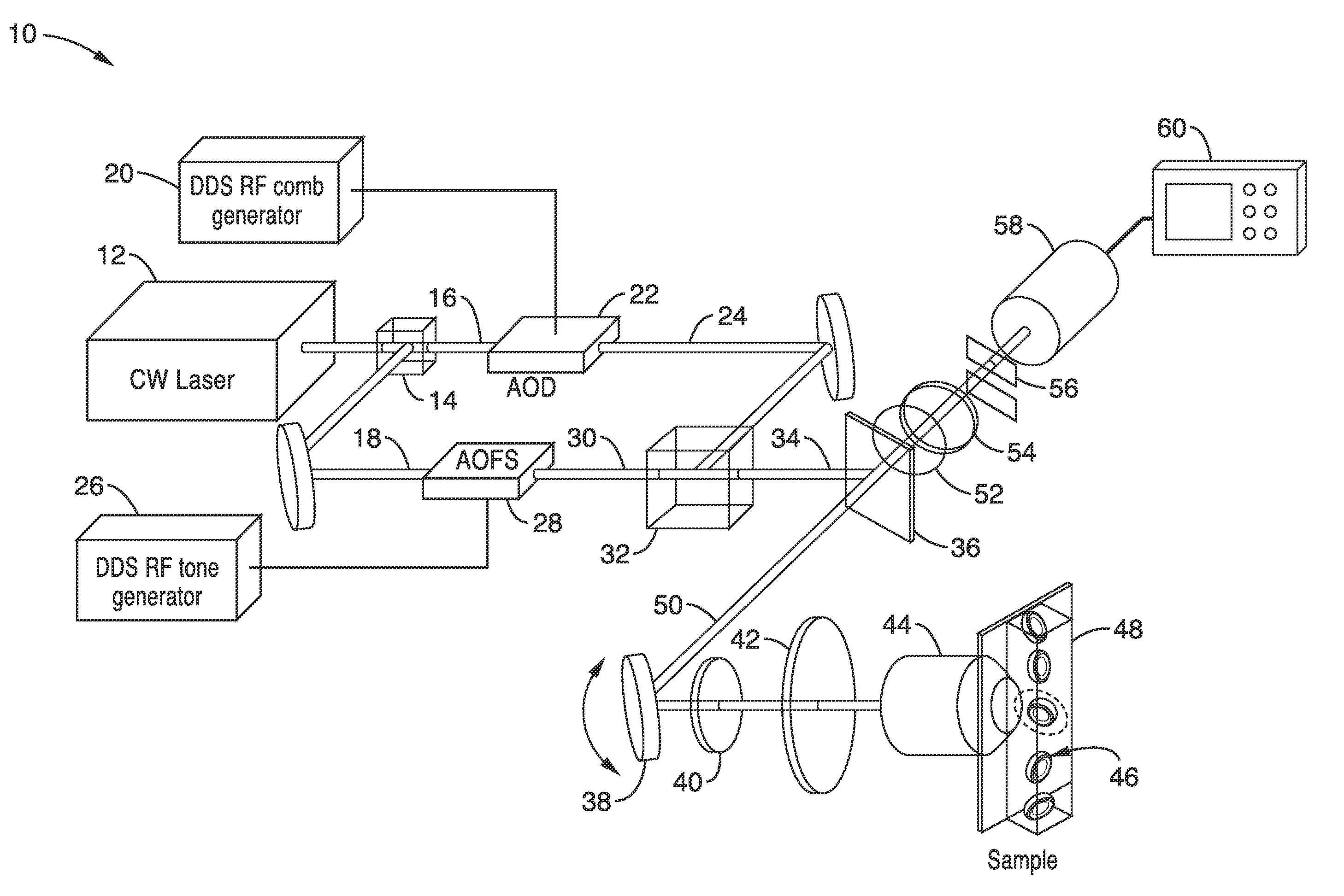
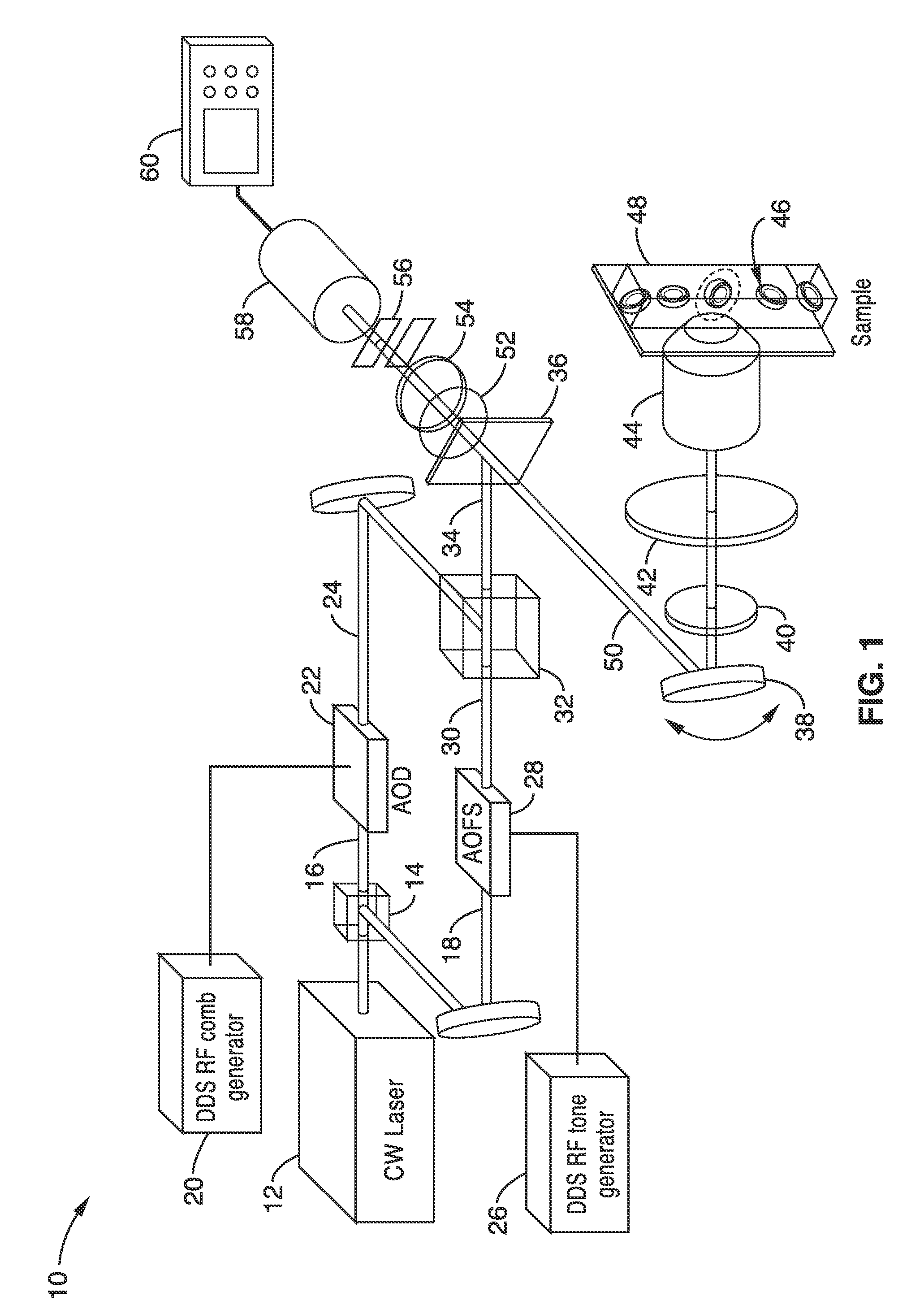
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
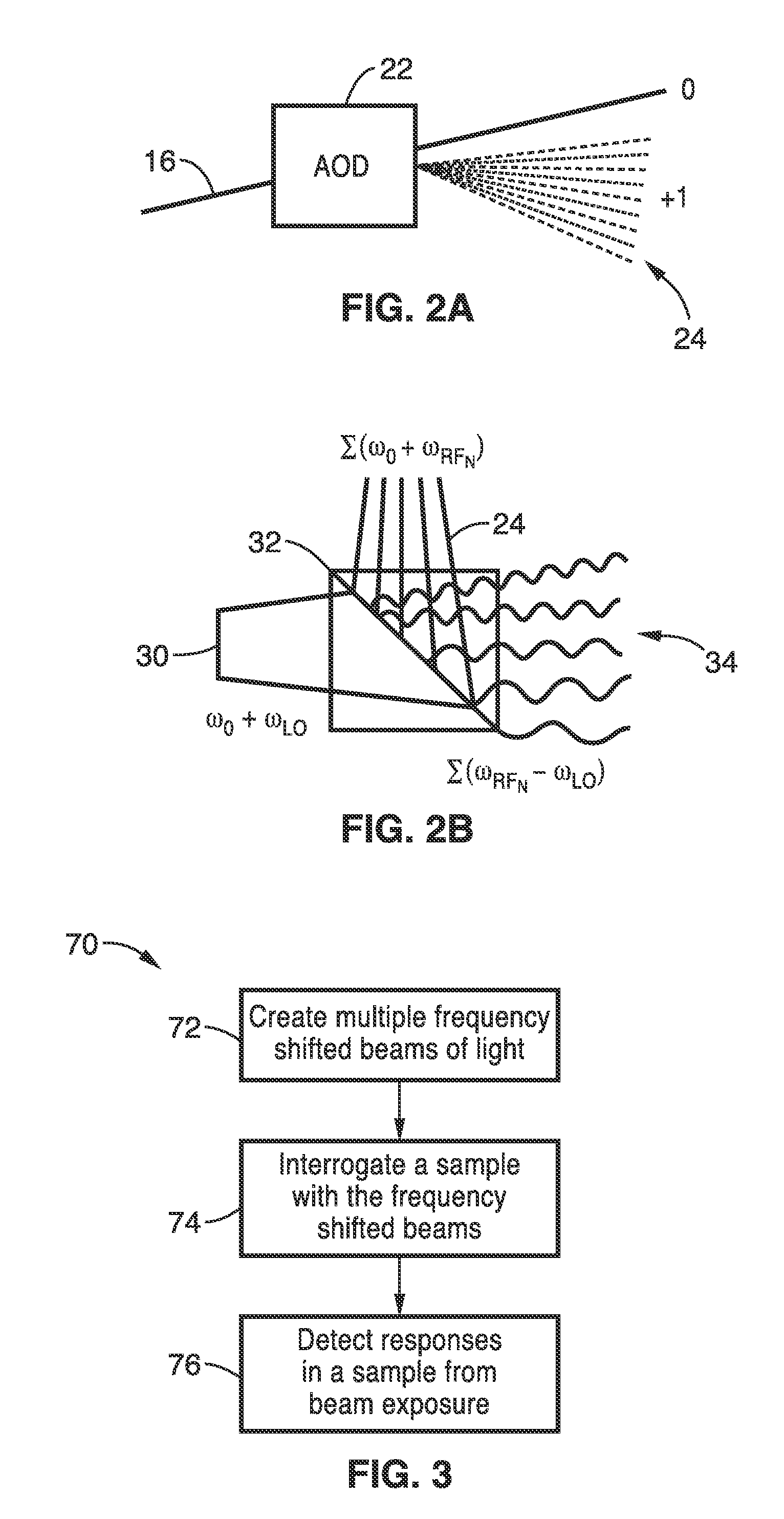
ActiveUS9423353B2Reduce image noiseScalable approachMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
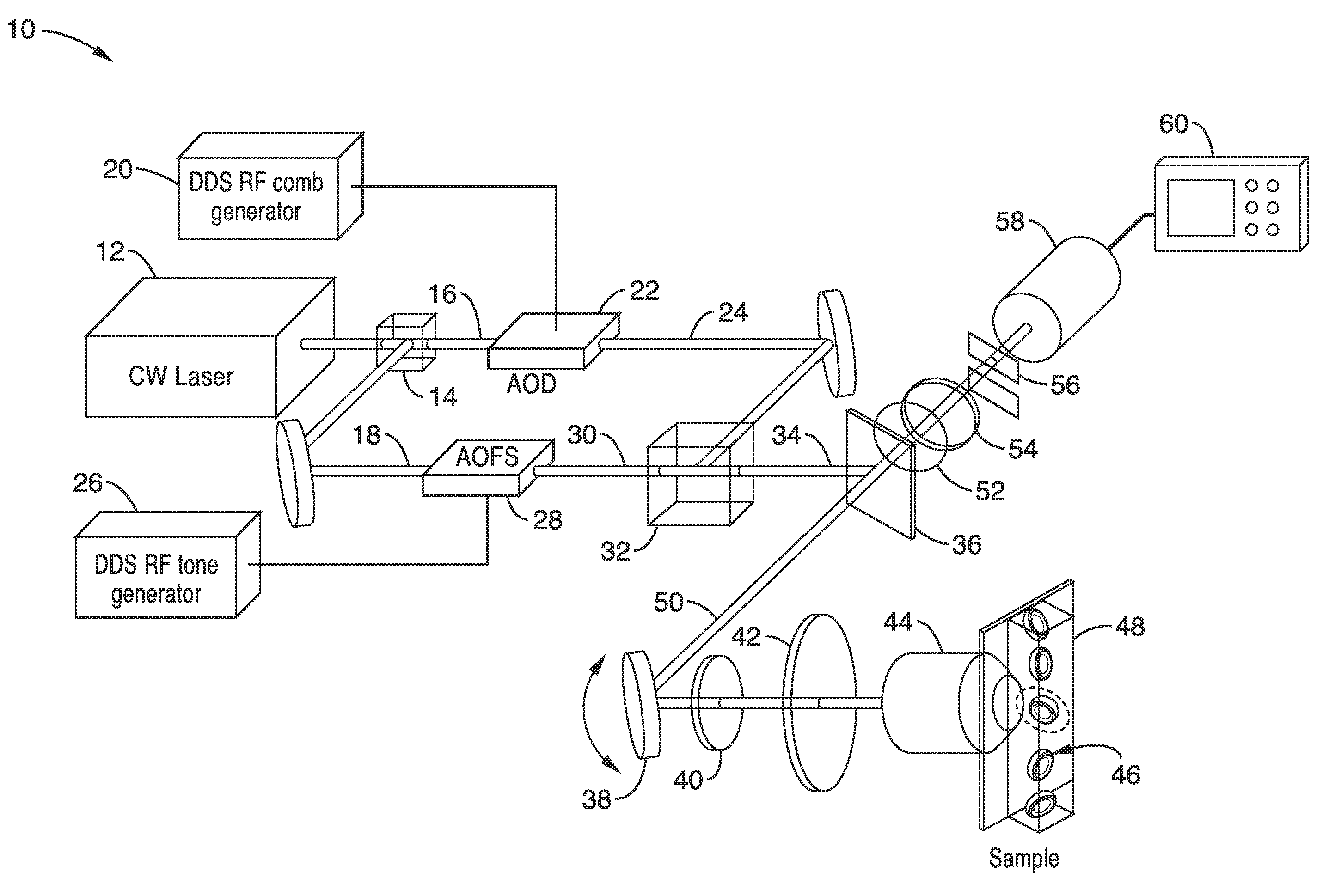
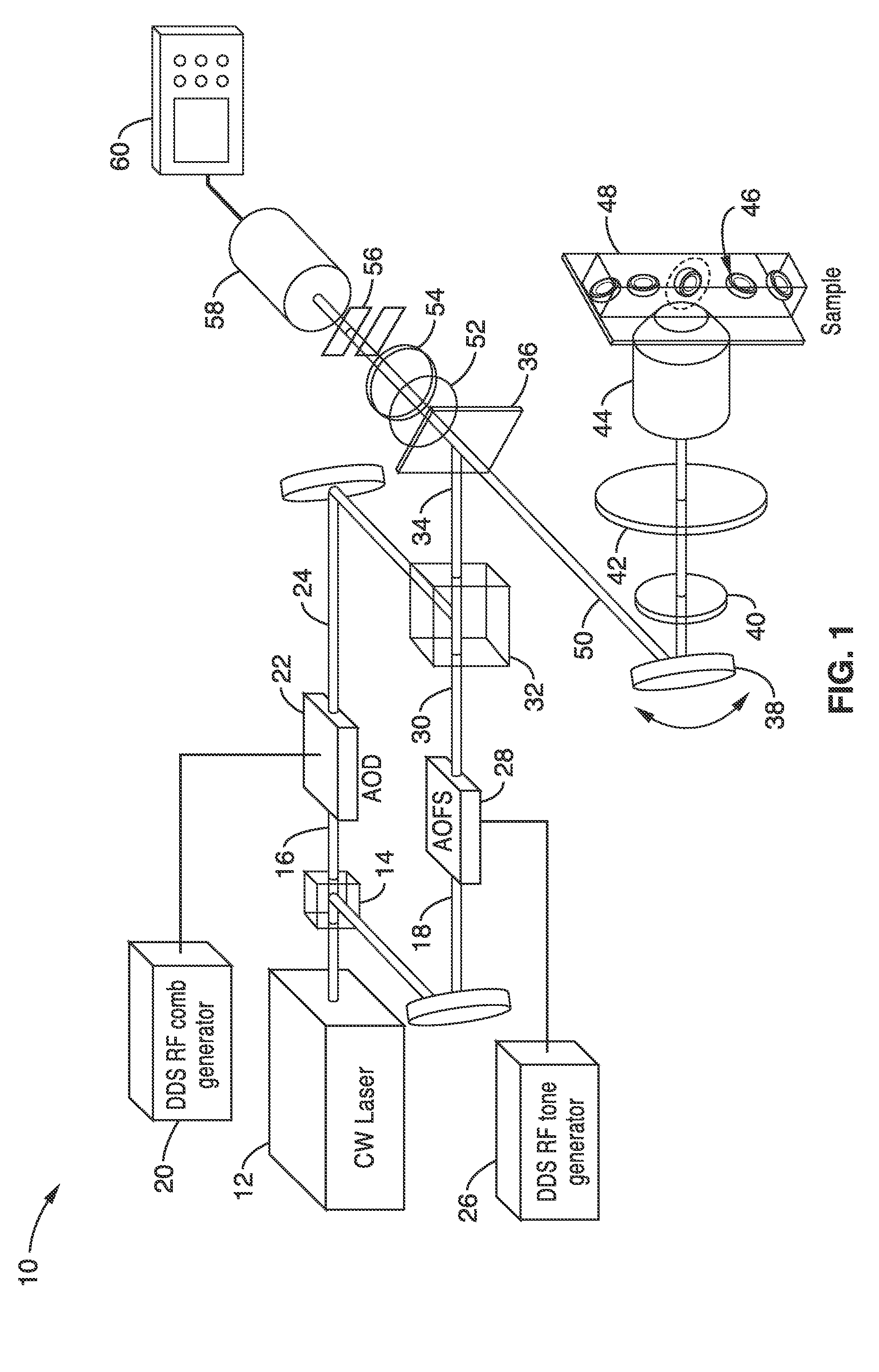
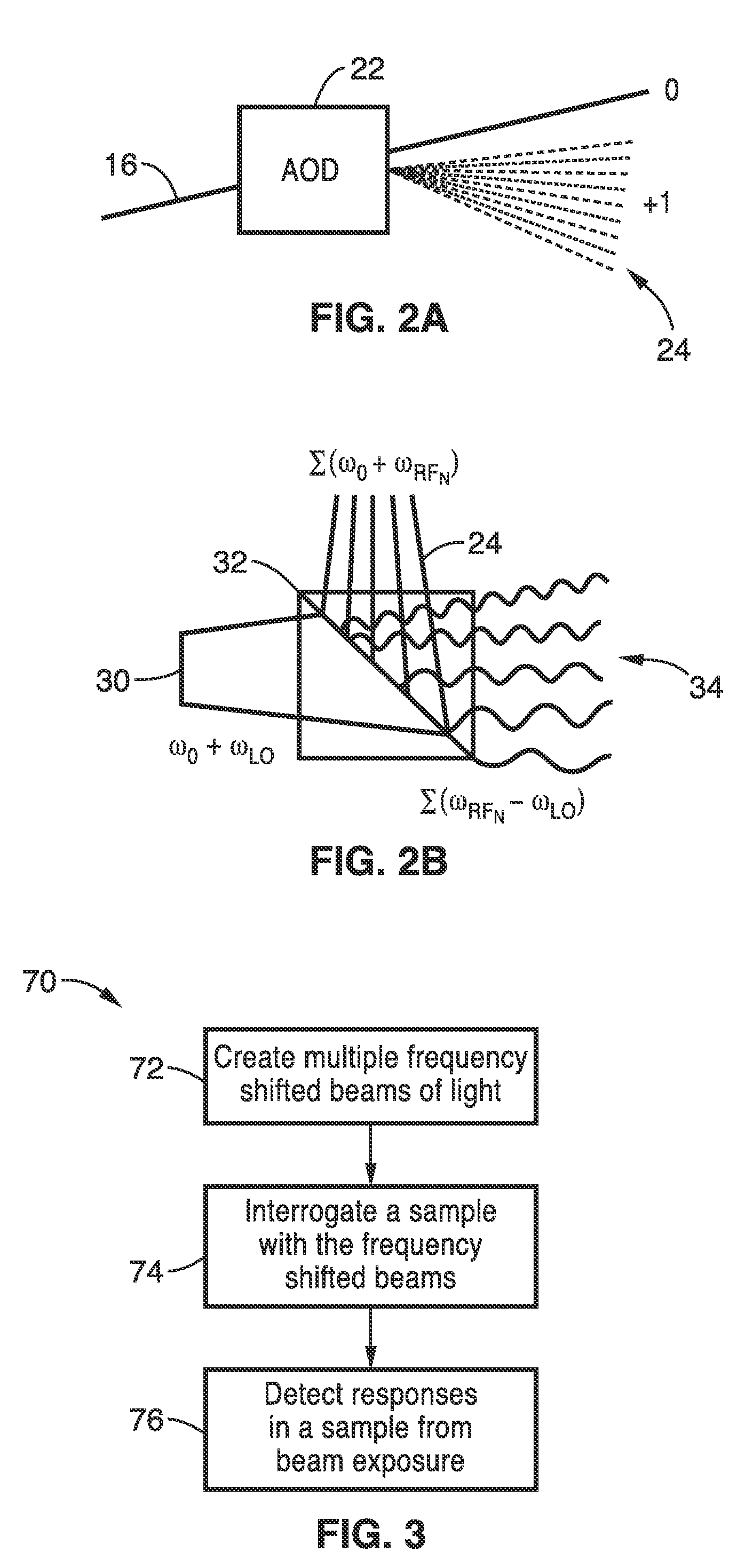
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Network selection methods and apparatus with home network prioritization after network signal recovery or power-on
ActiveUS20050107109A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsMobile station
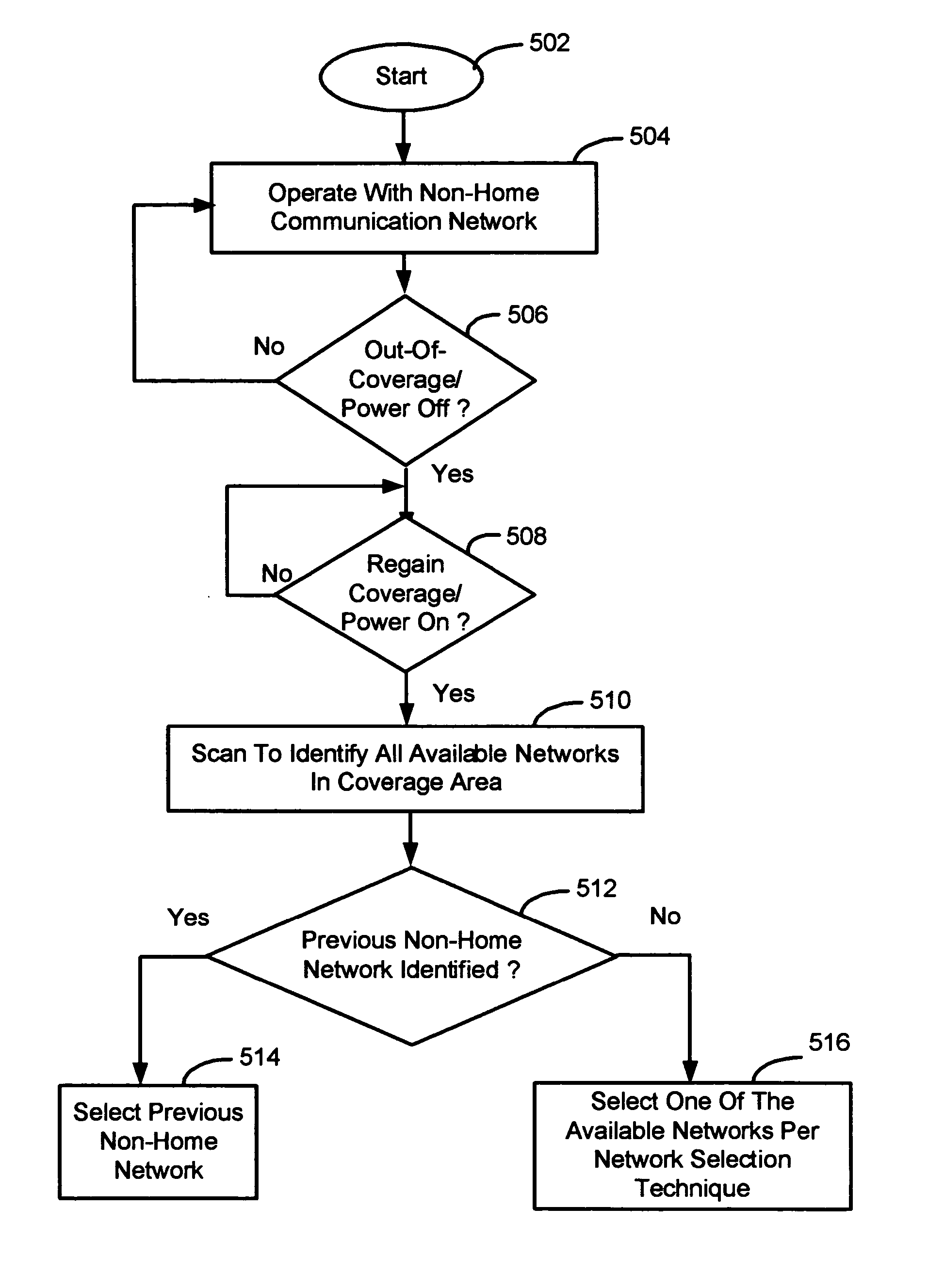
Network selection methods and apparatus with home network prioritization after network signal recovery and / or power-on are disclosed. In one illustrative example involving automatic network selection, a mobile station (200) selects and operates with a non-home communication network (406). The mobile station (200) then experiences an out-of-coverage condition (or a power down condition) but subsequently regains signal coverage (or is powered back on). In response, the mobile station (200) scans to identify a plurality of communication networks in its coverage area. If a home network (402) is identified as being available, the mobile station (200) selects and operates with the home network (402). Otherwise, if the previous non-home network (406) (e.g. the RPLMN) is identified as being available, the mobile station (200) continues operation with the previous non-home network (406).
Owner:WIRELESS INNOVATIONS LLC
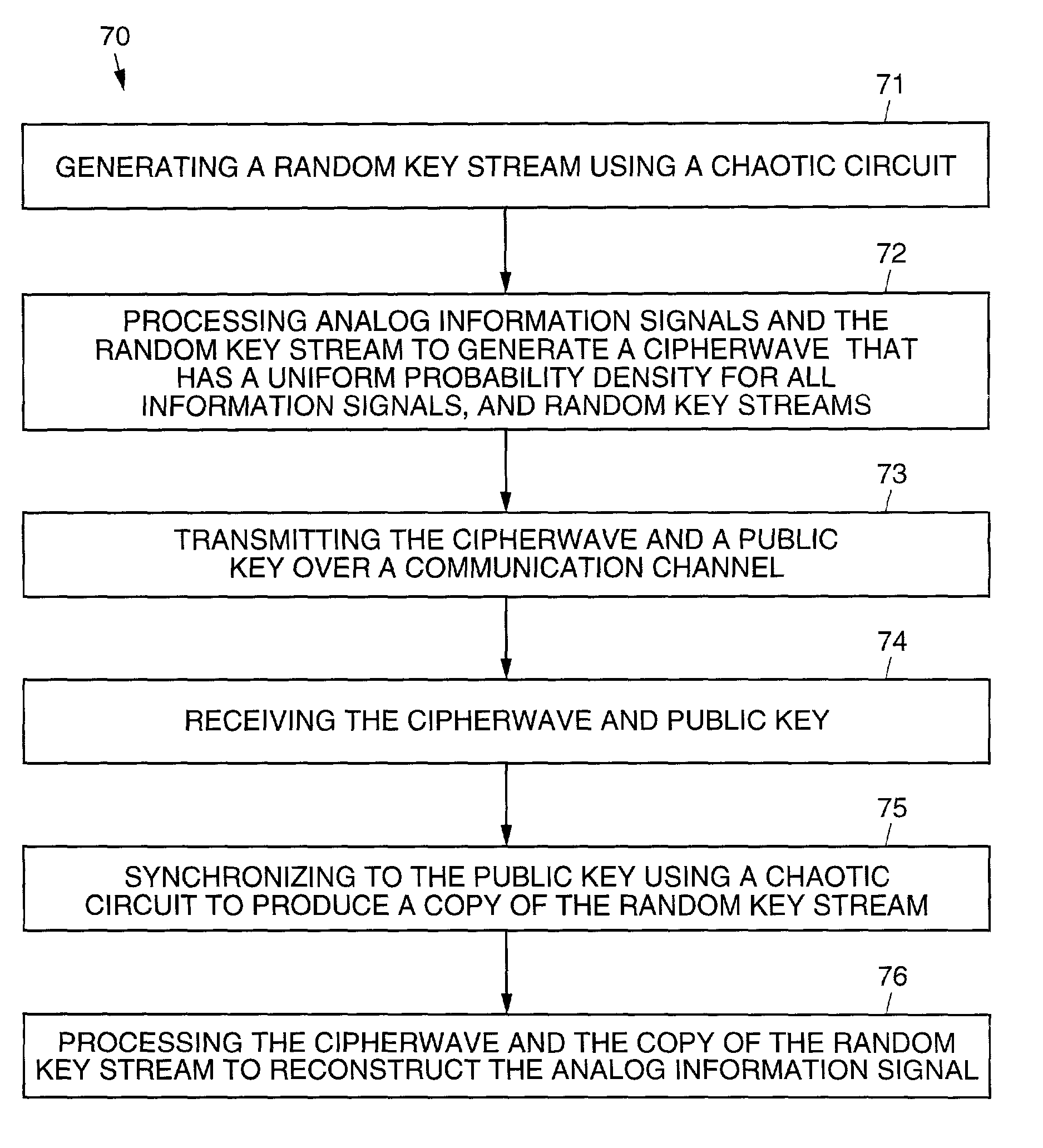
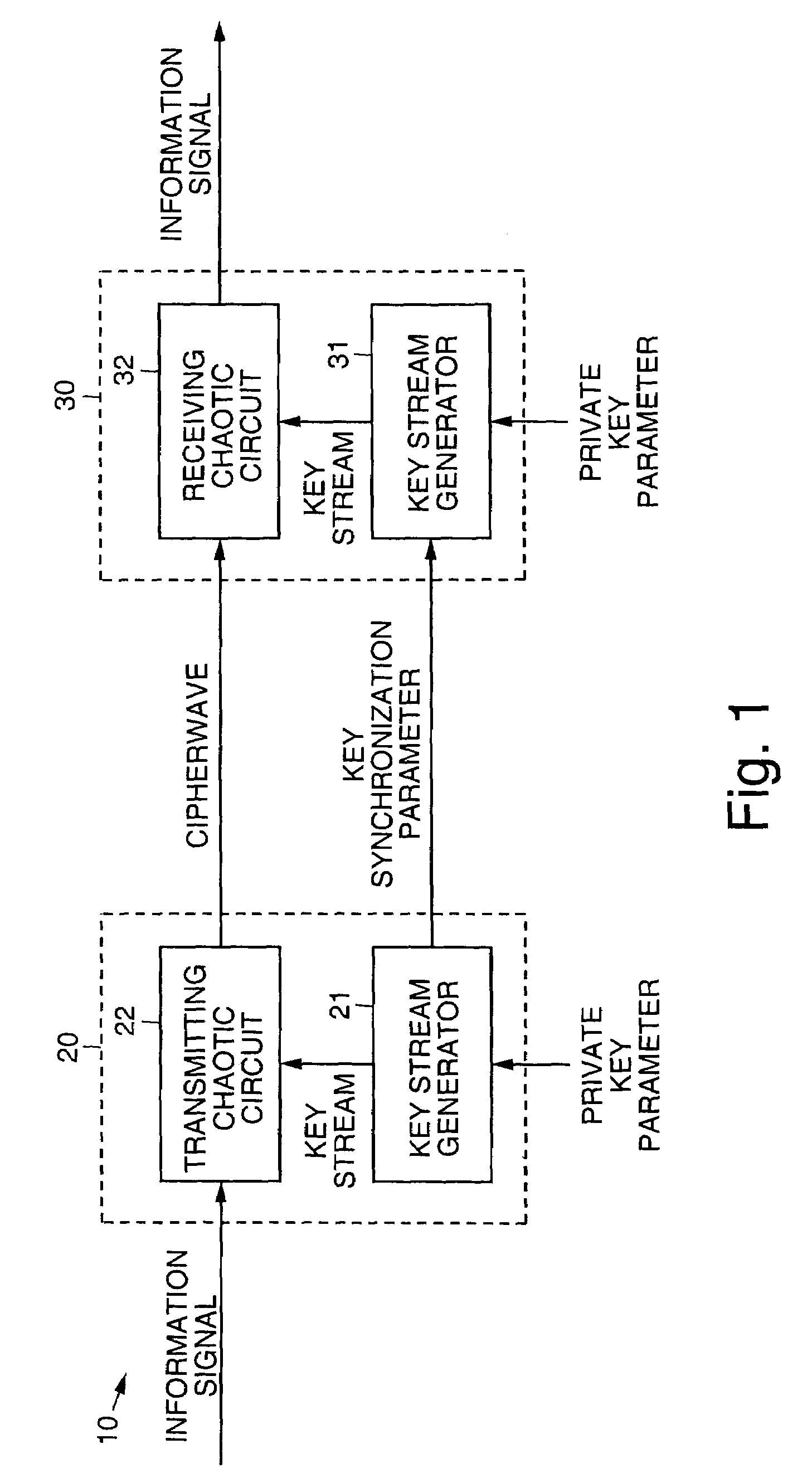
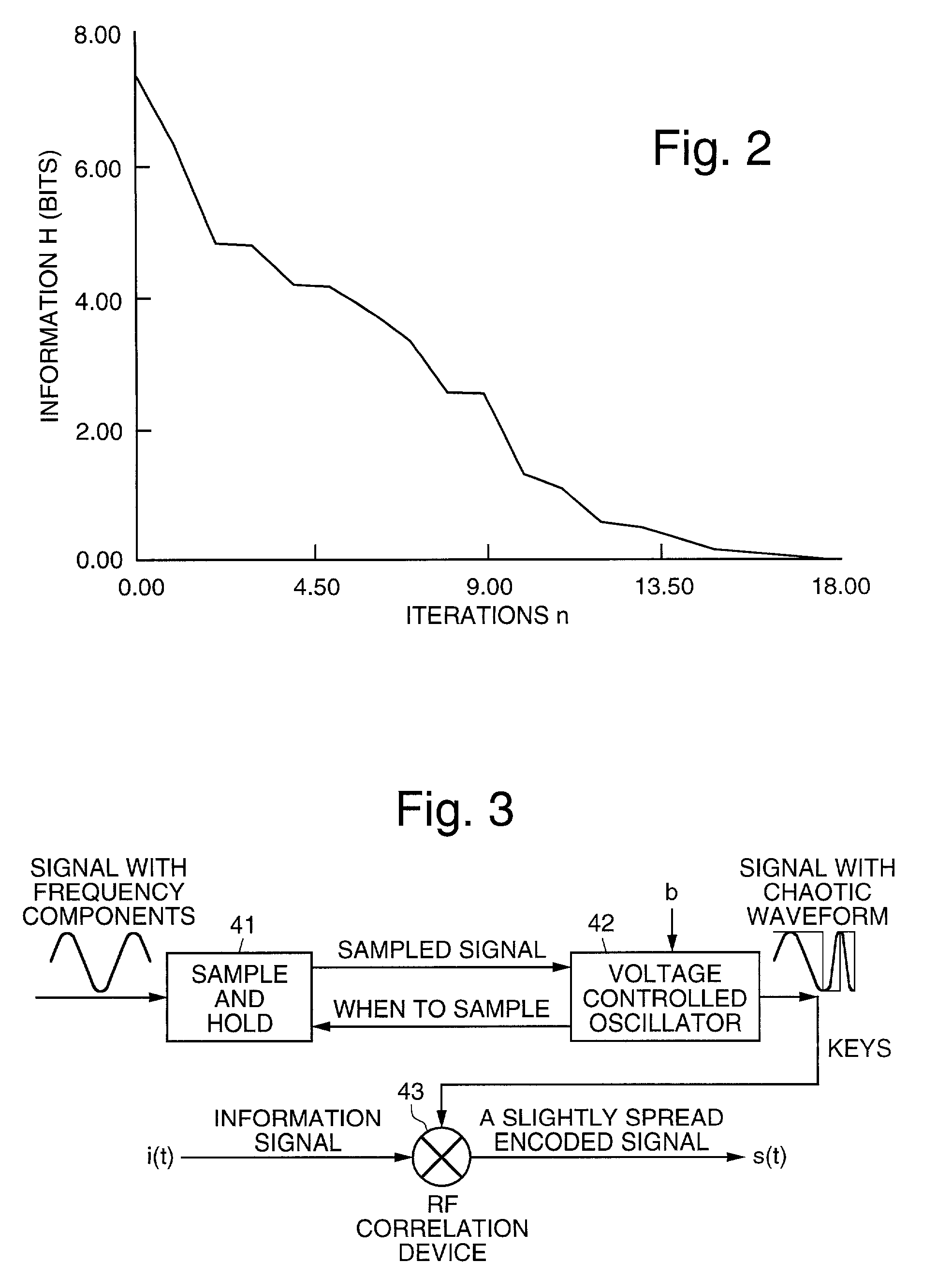
Chaotic privacy system and method
InactiveUS7076065B2Multiple keys/algorithms usageSecuring communication by chaotic signalsComputer scienceTransmitter
Systems and methods for protecting privacy in transmitting an analog information signal. The present invention combines the information signal with an analog random signal generated by a chaotic circuit and transmits the signal. The received signal is synchronized using a receiving chaotic circuit. The received signal is demodulated using a synchronized replica of the analog random signal. The information signal is recovered since the product of the random signals generated in the transmitter and in the receiver, is unity. Techniques used in the present invention for generating chaos, synchronization, and signal recovery are also disclosed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Methods and systems for sending side-channel data during data inactive period
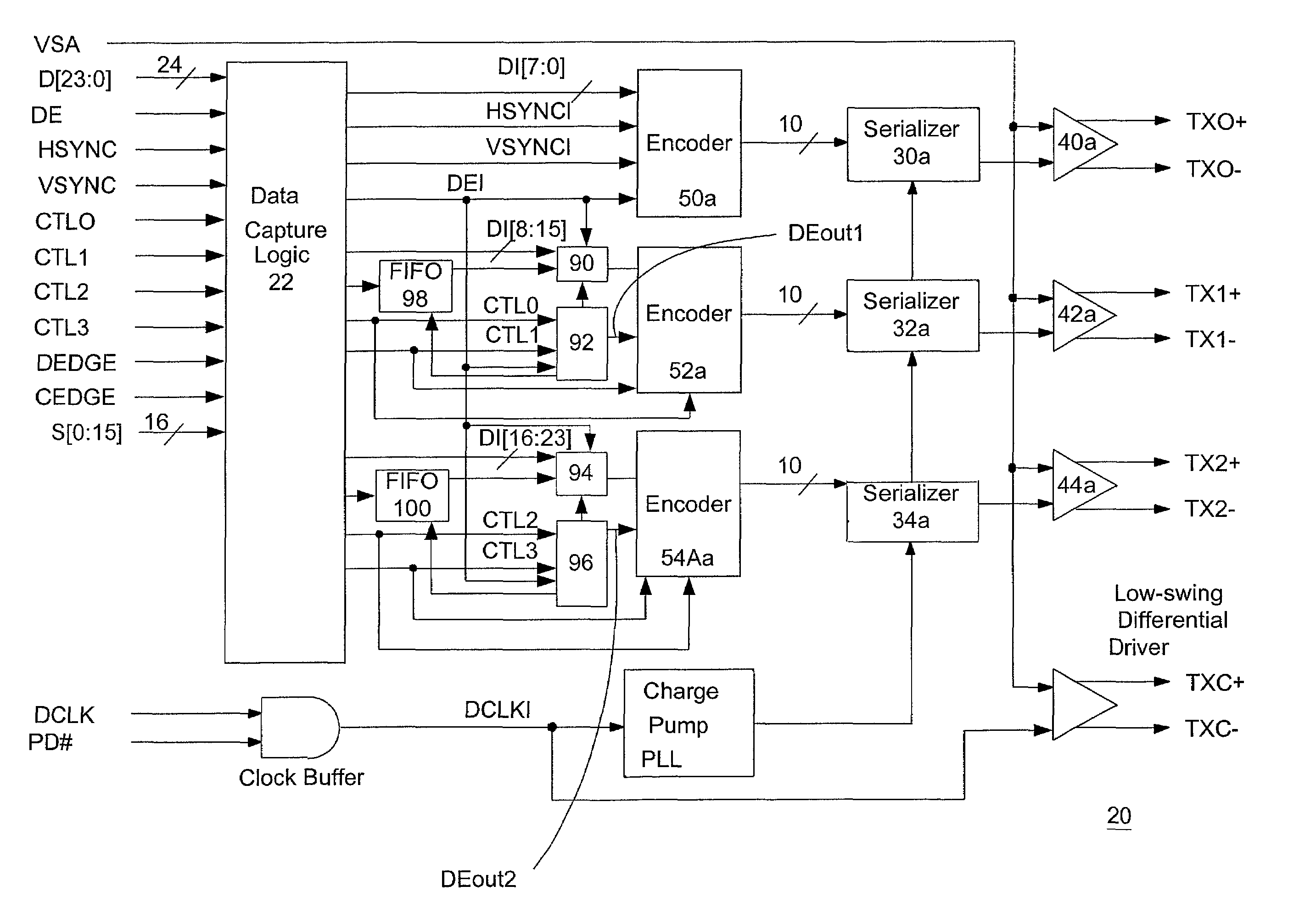
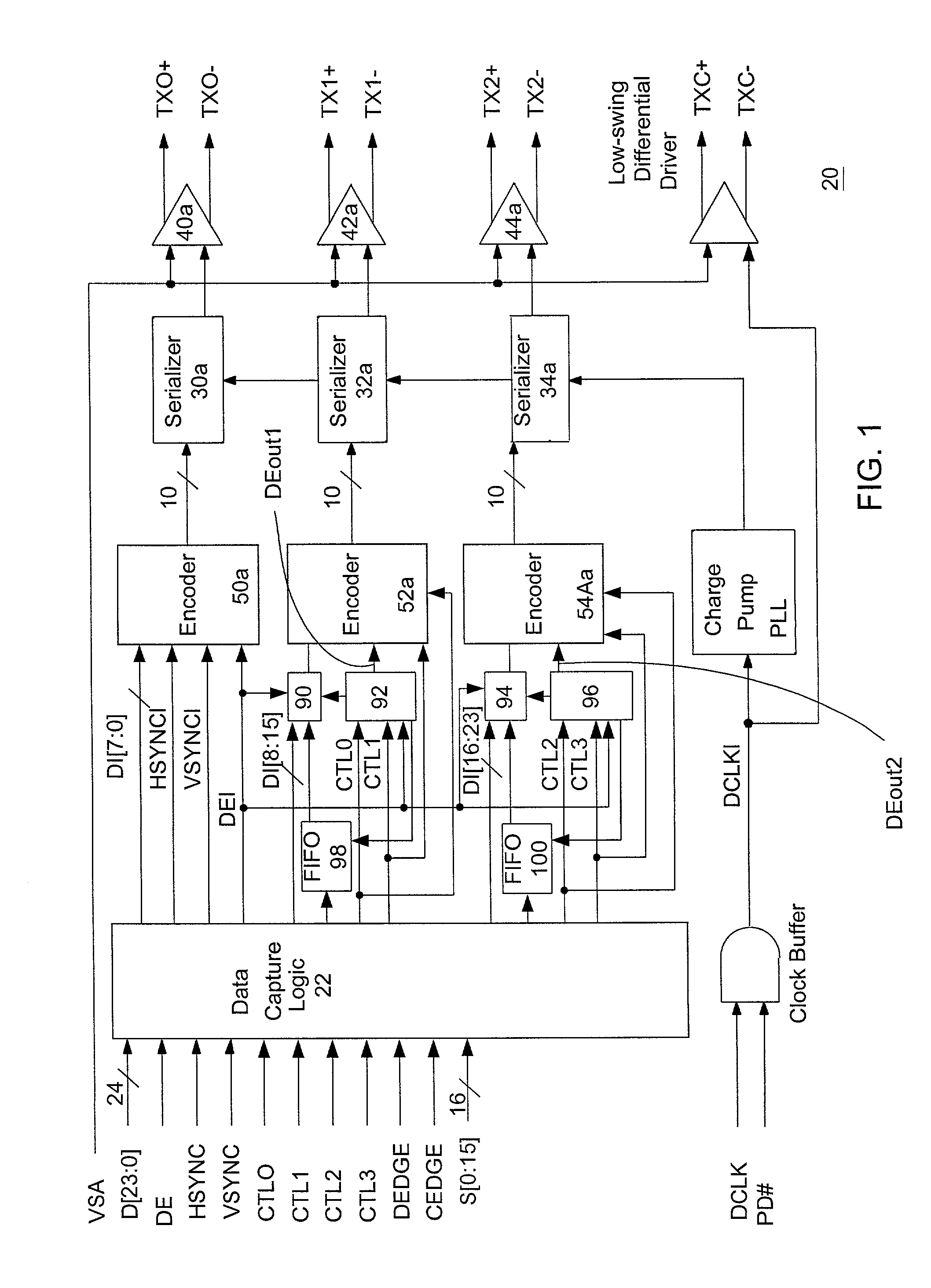
ActiveUS6954491B1Easy transferTransmission control/equalisingTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkControl signal
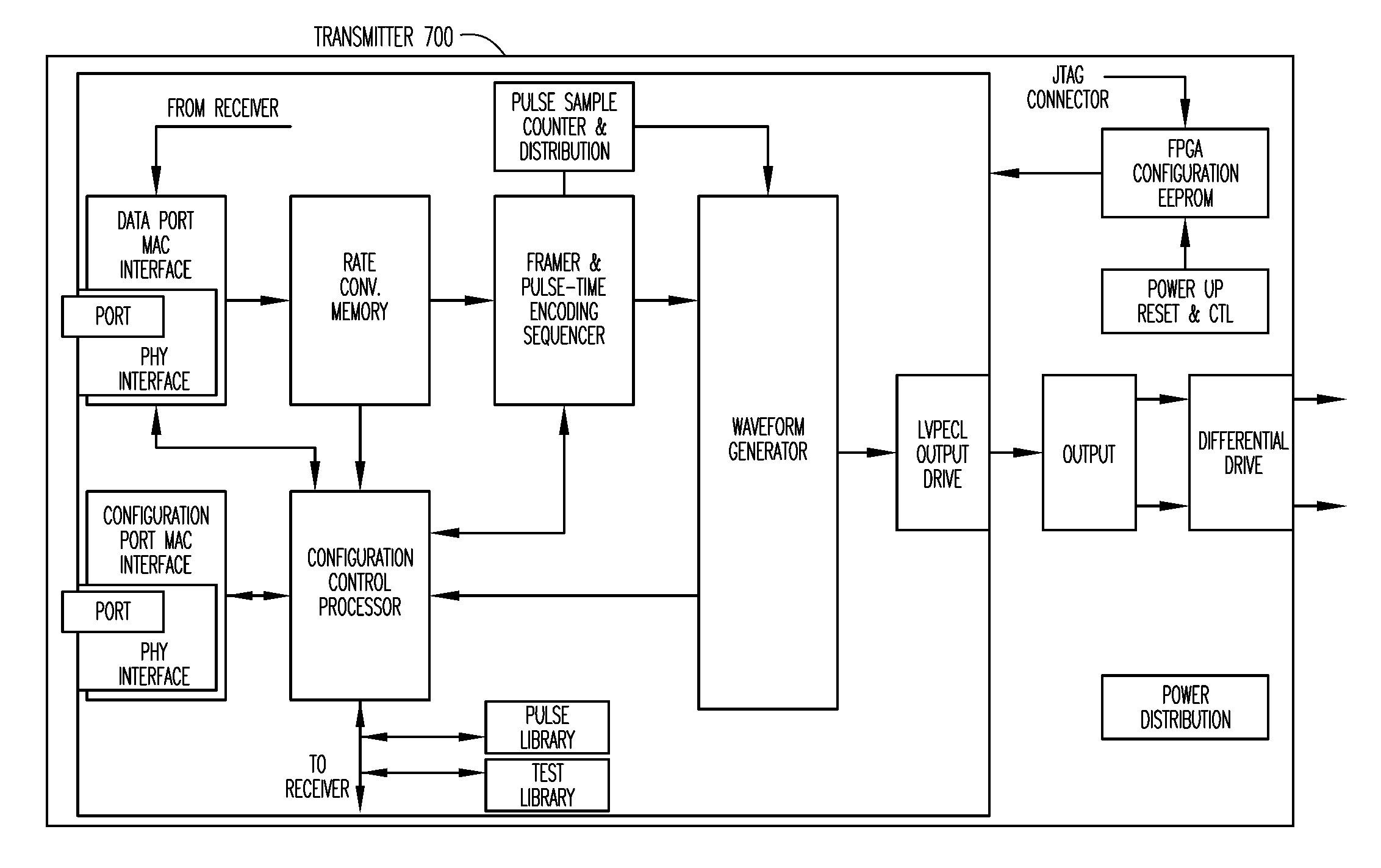
The present invention relates to a serial interface transmission system with more than one data line, in which the transmitted data has in-band and out-of-band characters. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods and systems for sending side channel data over a high-speed digital communications link, e.g., a video link. One embodiment of the invention provides a high-speed digital transmitter capable of sending side channel data. The transmitter includes a channel zero encoder, a multiplexer, data enable out (DEout) control logic, and a channel one encoder. The channel one encoder receives input from the channel one multiplexer and the channel one DEout control logic. Another embodiment of the invention provides a high-speed digital receiver capable of receiving side channel data. The receiver includes a channel zero decoder, a channel one decoder, DEI signal and FIFO control signal recovery logic, and a channel one de-multiplexer. The DEI signal and FIFO control signal recovery logic receives input from the channel one decoder. Similarly, the channel one demultiplexer receives input from the channel one decoder.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Circuits, Architectures, Apparatuses, Systems, and Methods for Merging of Management and Data Signals, and for Recovery of a Management Signal
ActiveUS20120170927A1Low costEasy to manageTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsManagement unitTransceiver
An optical and / or optoelectrical transceiver and system are disclosed that enable parallel transmission of data and management signals via an optical fiber without affecting data signal transmissions transmitted on the optical fiber. Furthermore, the present transceiver and system provide a fault diagnosis function for an optical fiber link. The transceiver and system generally comprise an interface, an intersecting transmission management unit, a driver, a management signal driving unit, an optical transmitter, an optical receiver, an amplifier, a management signal recovery unit, a management unit, and optionally, a power supply unit.
Owner:MAGNOLIA SOURCE CAYMAN
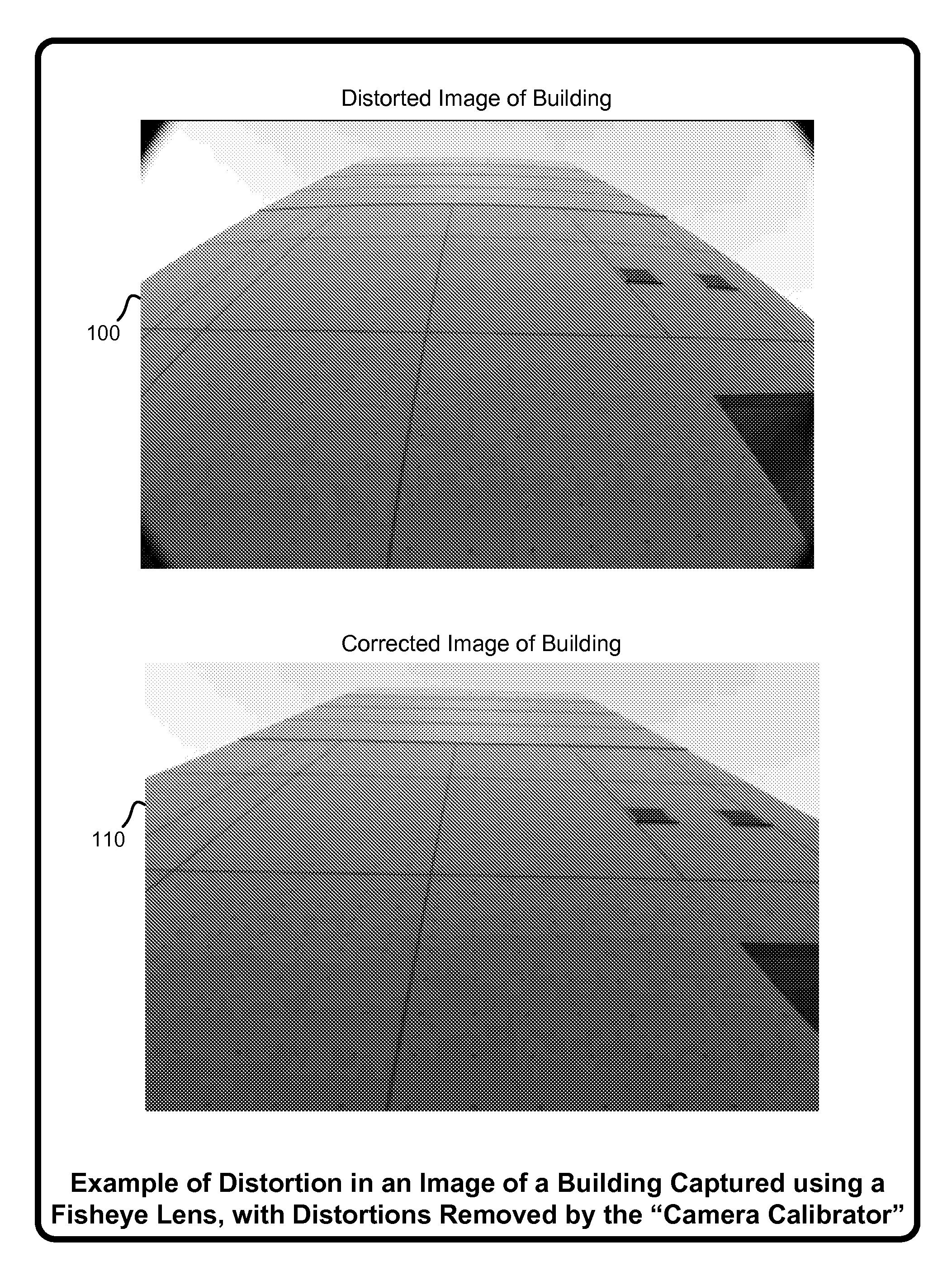
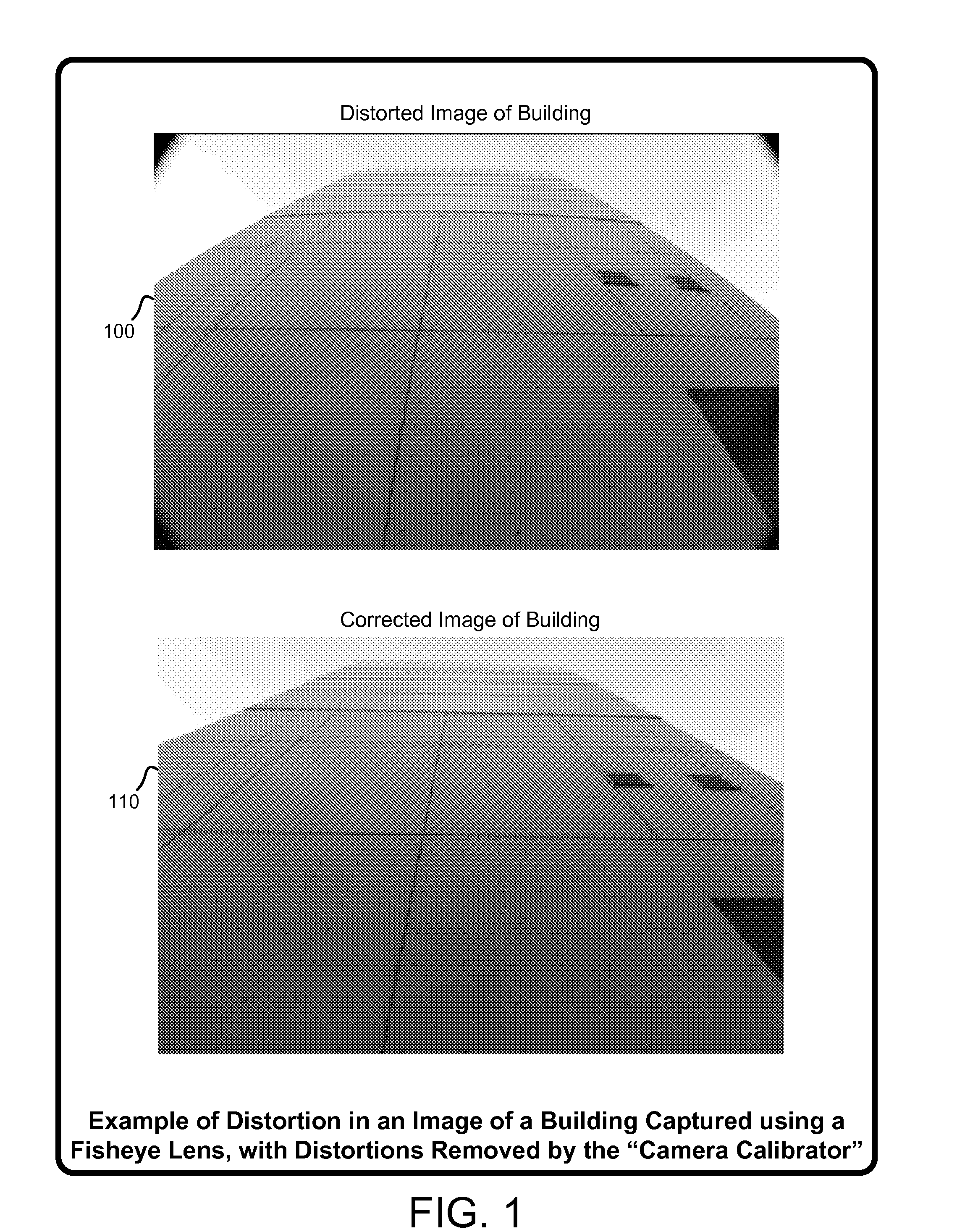
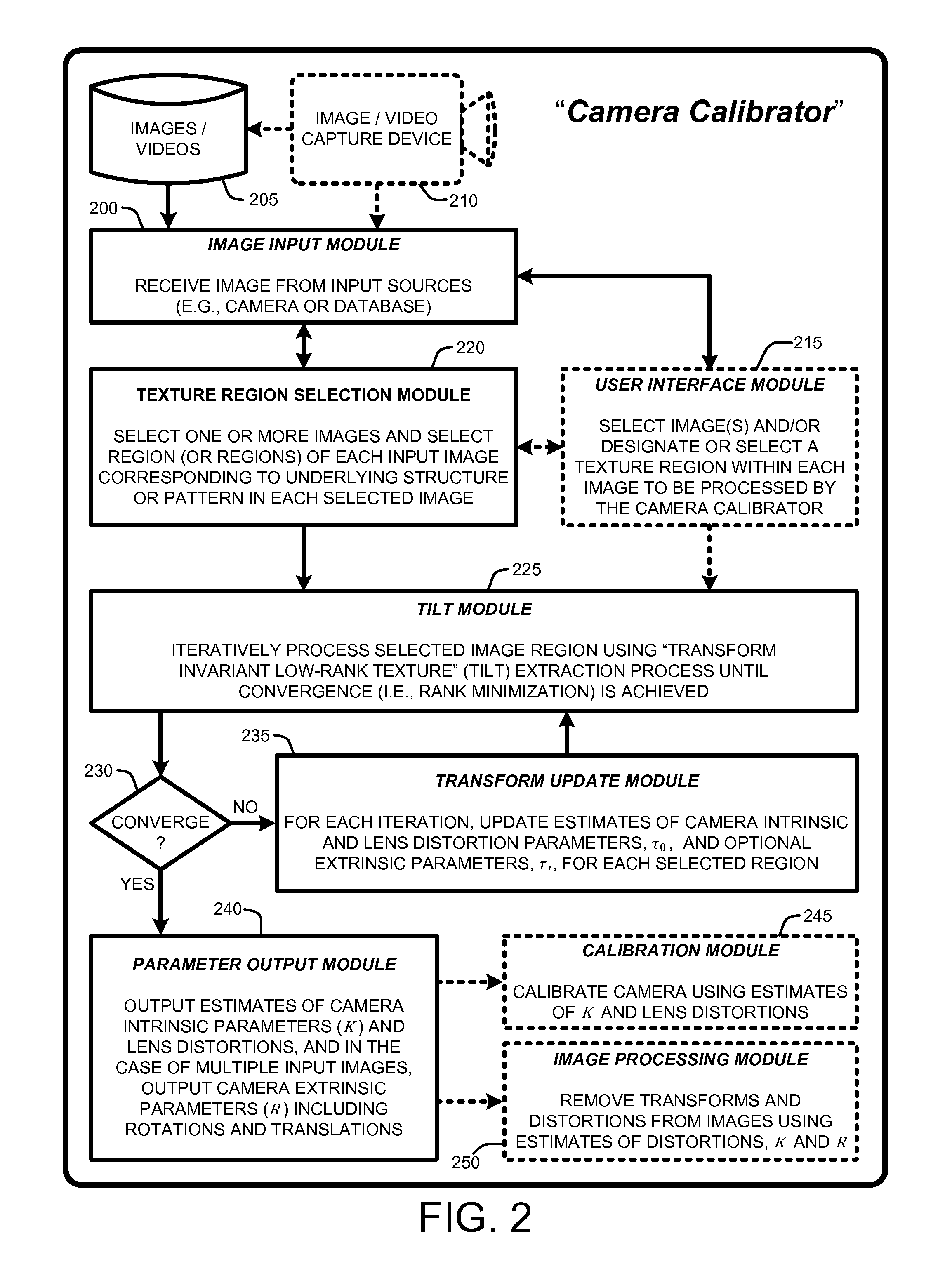
Camera calibration with lens distortion from low-rank textures
InactiveUS20120133780A1Simple and accurate and flexibleEfficiently and effectively extractingImage enhancementImage analysisCamera lensImage extraction
A “Camera Calibrator” provides various techniques for recovering intrinsic camera parameters and distortion characteristics by processing a set of one or more input images. These techniques are based on extracting “Transform Invariant Low-Rank Textures” (TILT) from input images using high-dimensional convex optimization tools for matrix rank minimization and sparse signal recovery. The Camera Calibrator provides a simple, accurate, and flexible method to calibrate intrinsic parameters of a camera even with significant lens distortion, noise, errors, partial occlusions, illumination and viewpoint change, etc. Distortions caused by the camera can then be automatically corrected or removed from images. Calibration is achieved under a wide range of practical scenarios, including using multiple images of a known pattern, multiple images of an unknown pattern, single or multiple images of multiple patterns, etc. Significantly, calibration is achieved without extracting or manually identifying low-level features such as corners or edges from the calibration images.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
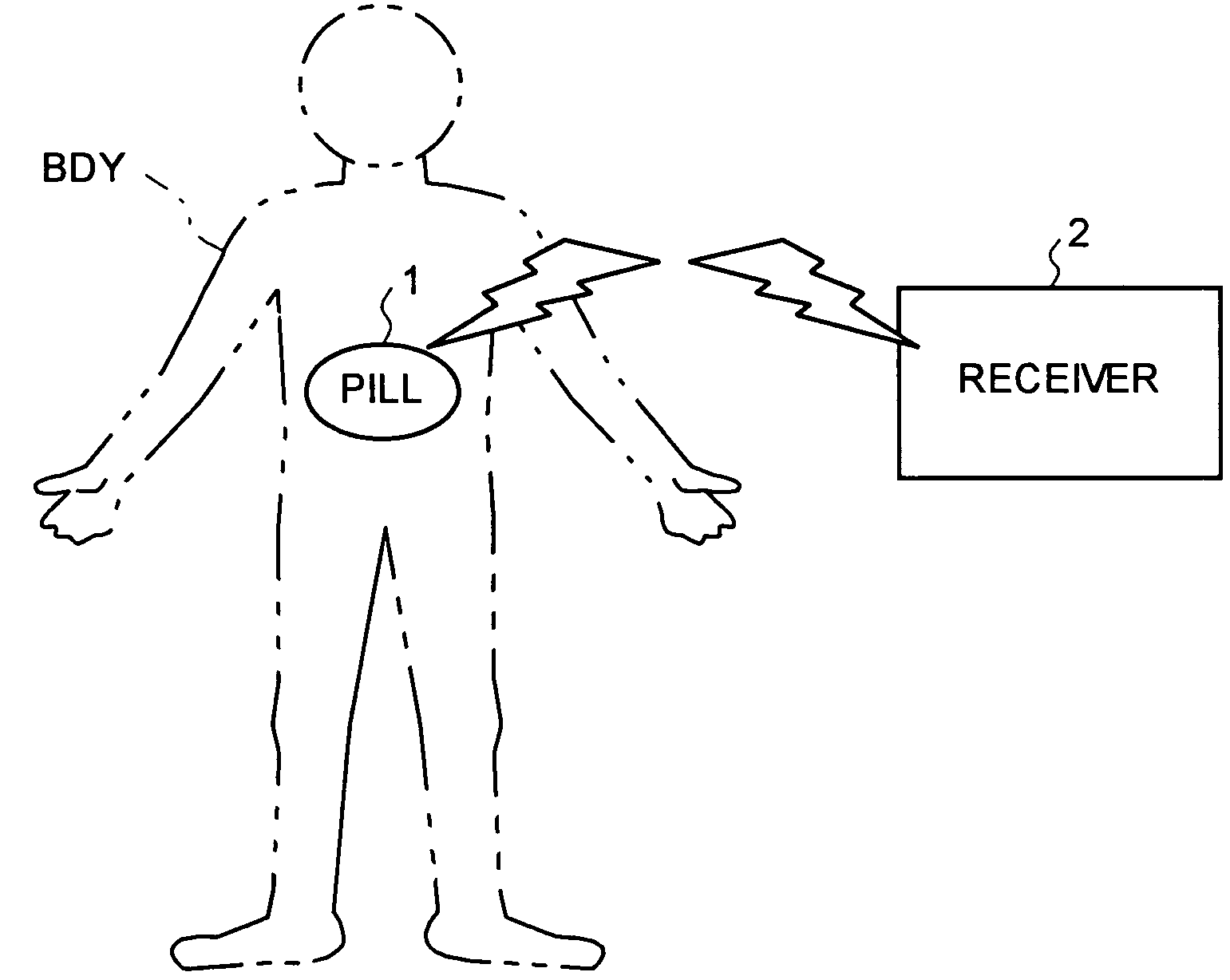
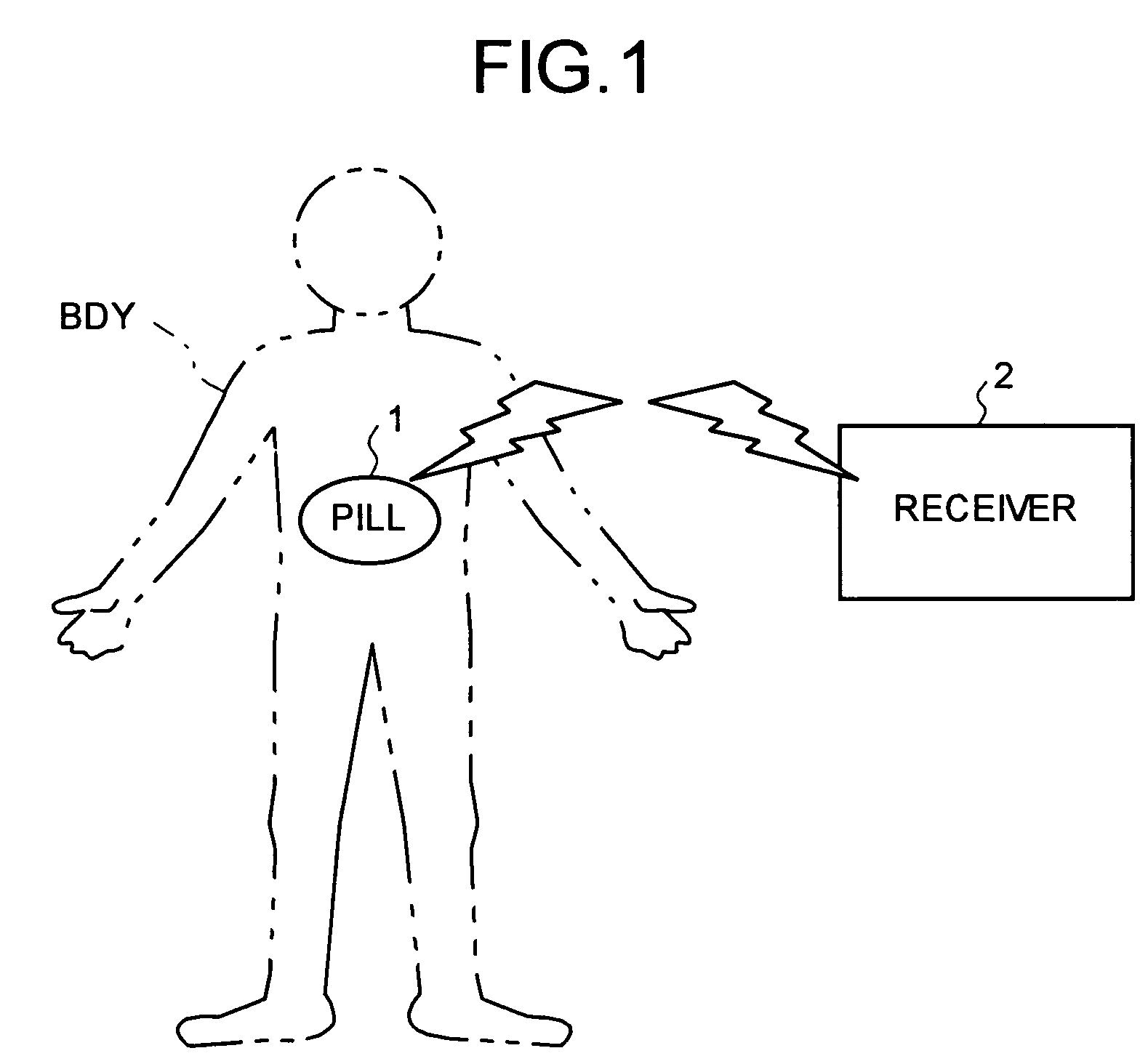
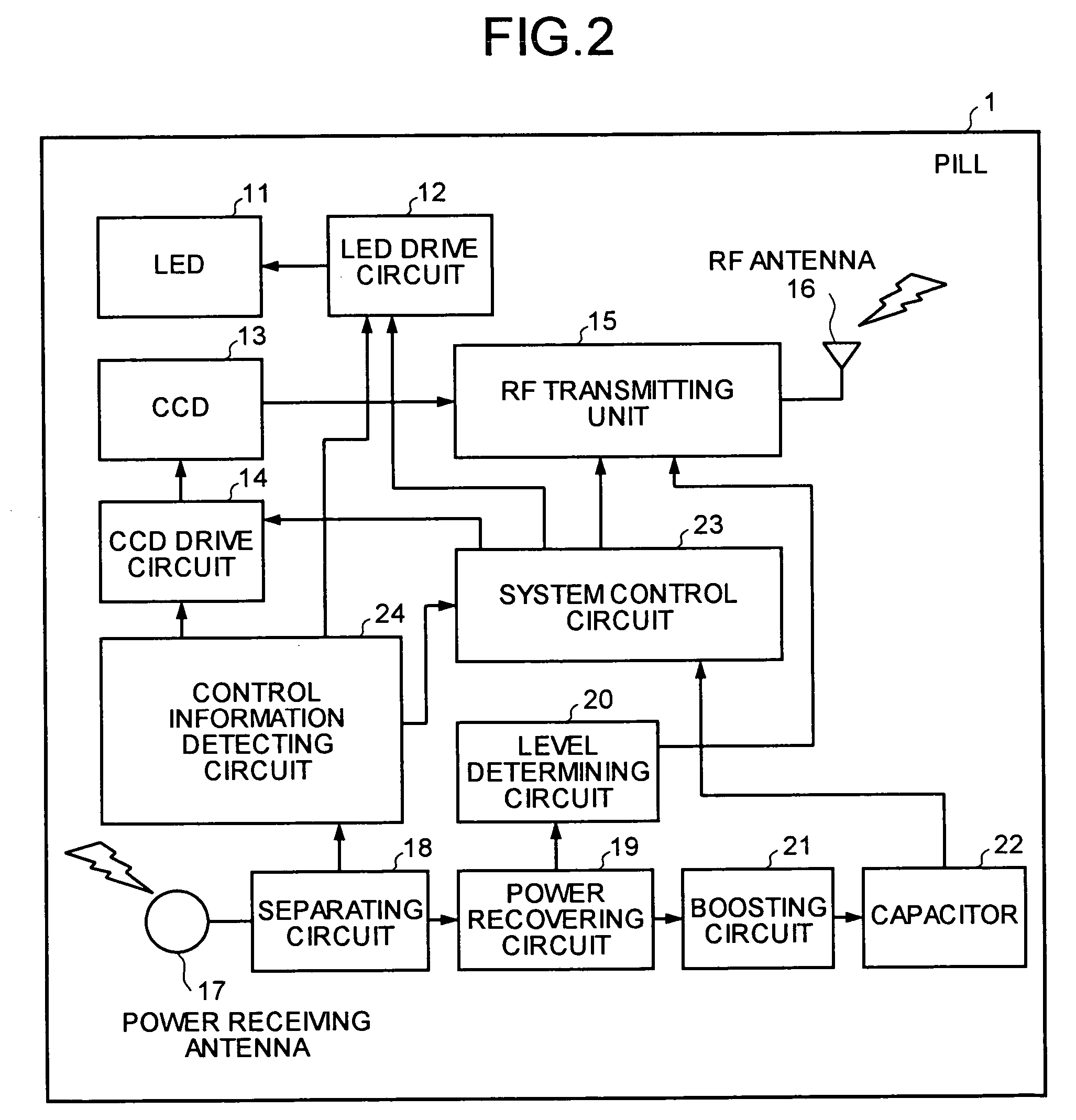
Wireless in-vivo information acquiring system and body-insertable device
A pill inserted into a body of a patient acquires in-vivo information on the body of the patient. The in-vivo information on the body of the patient is input to a receiver from the pill through a receiving antenna. The pill receives a power-supply signal from the receiver through a power receiving antenna, and a power recovering circuit recovers power from the power-supply signal. A level determining circuit compares the power recovered with a predetermined value to determine the strength of the power-supply signal, and wirelessly transmits the determination result signal to the receiver.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
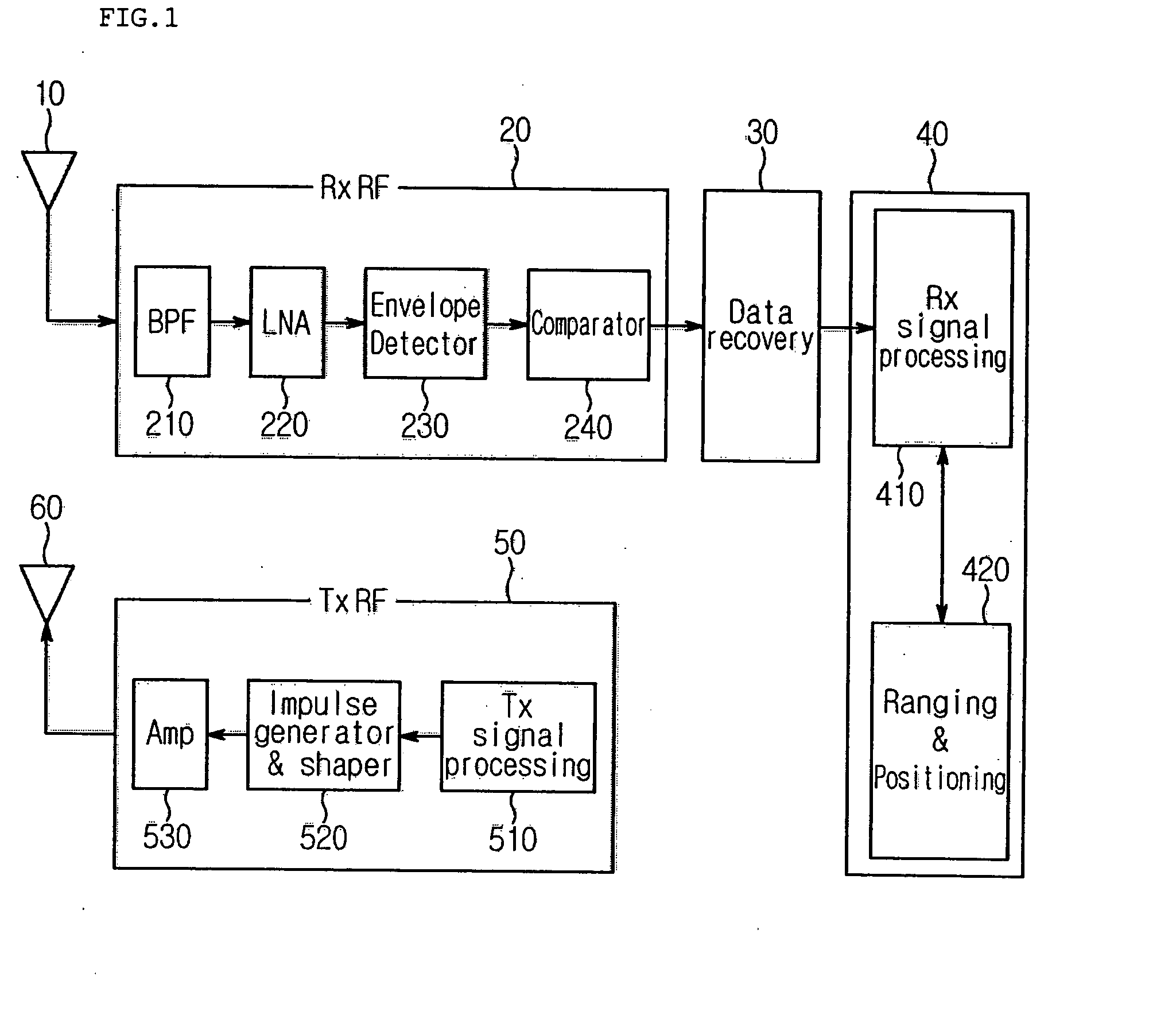
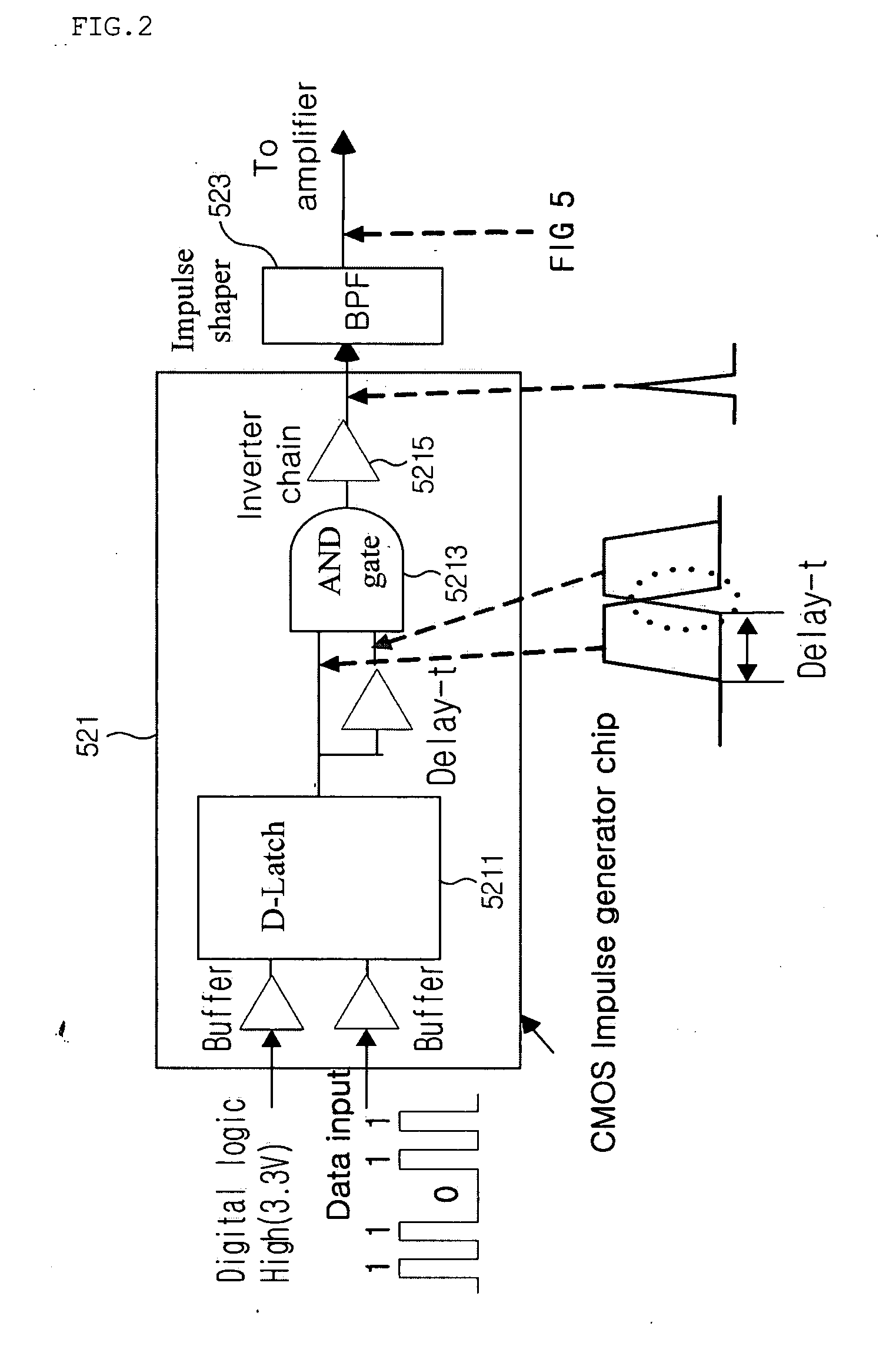
Impulse radio-based ultra wideband (IR-UWB) system using 1-bit digital sampler and bit decision window
ActiveUS20080056419A1Low costReduce power consumptionSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsOn-off keyingEngineering
An impulse radio-based ultra wideband communication system, using an ultra wideband impulse and a 1-bit high-speed digital sampler, includes a transmitting RF module, a receiving RF module, a signal recovery unit, a transmitting signal processor, a receiving signal processor, and an ultra wideband antenna. The transmitting RF module includes an integrated impulse generator capable of implementing on-off-keying modulation and pulse position modulation, and an amplifier for amplifying output of the integrated impulse generator. The receiving RF module includes a two stage envelope detector for detecting a received signal and a comparator for converting the detected signal into a rectangular pulse. The signal recovery unit restores the signal from the receiving RF module to a digital signal using the 1-bit digital sampler. The signal processor includes a receiving signal processor for synchronizing the digital signal and decoding the detected signal. The ultra wideband antenna transmits and receives an ultra wideband signal.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
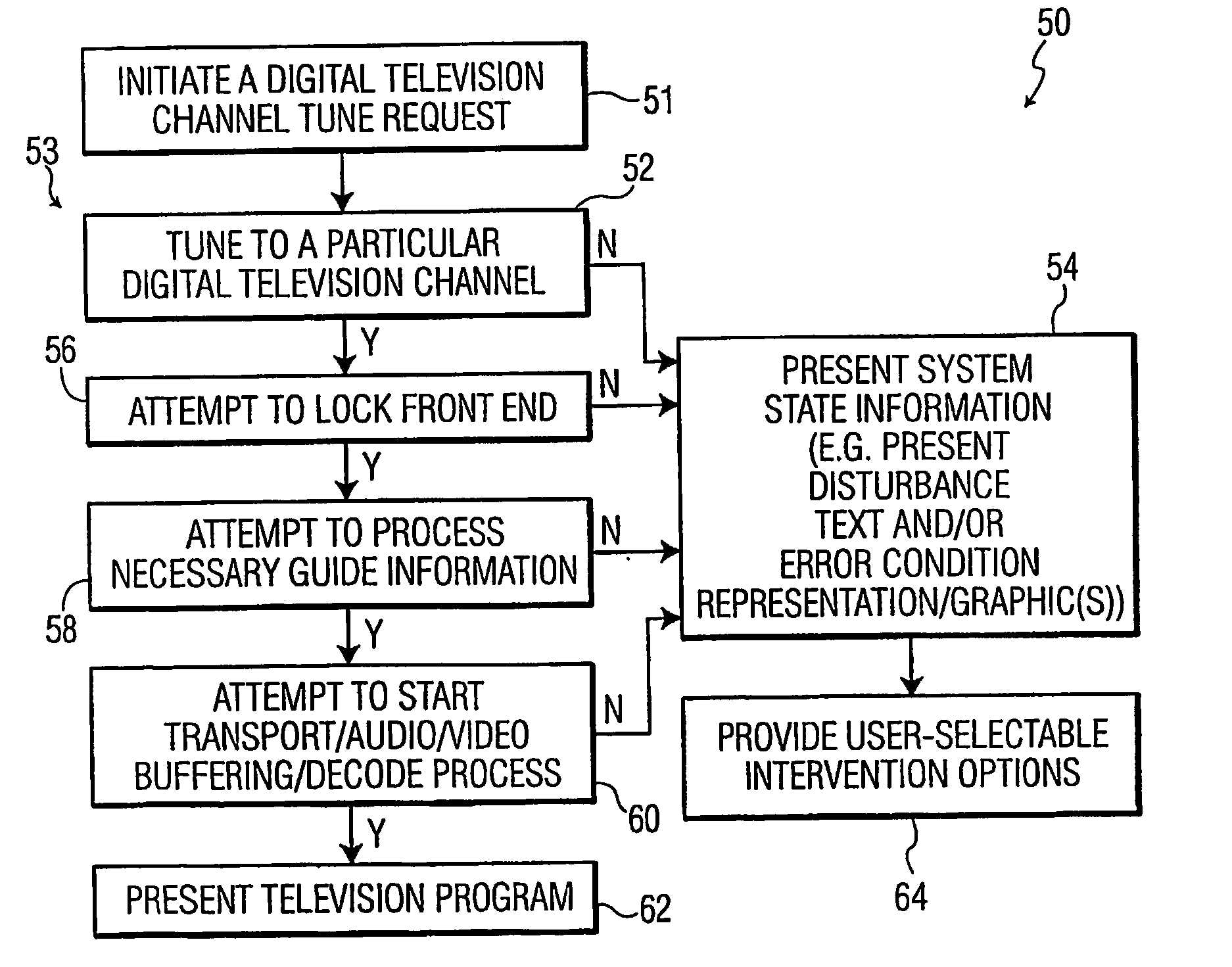
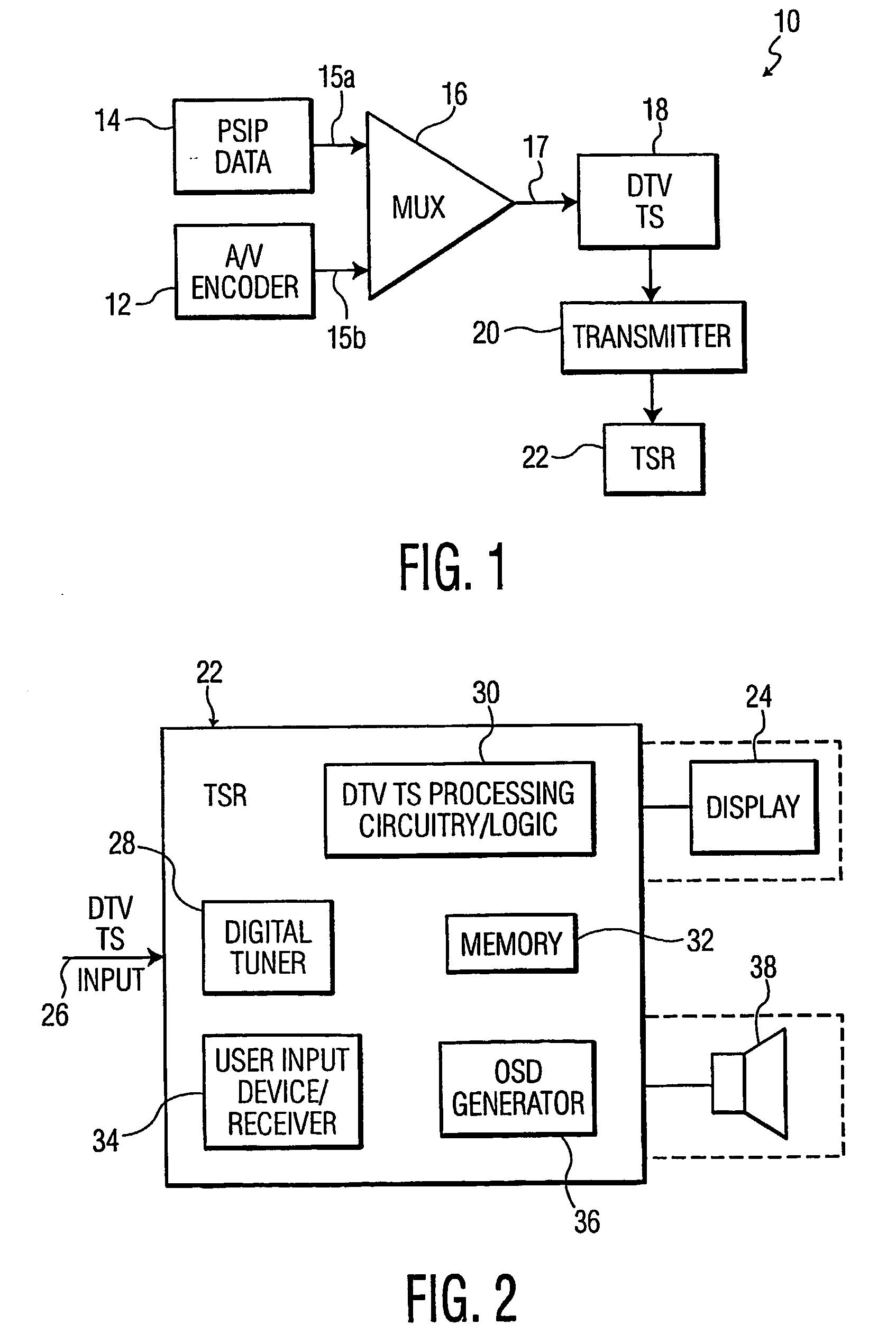
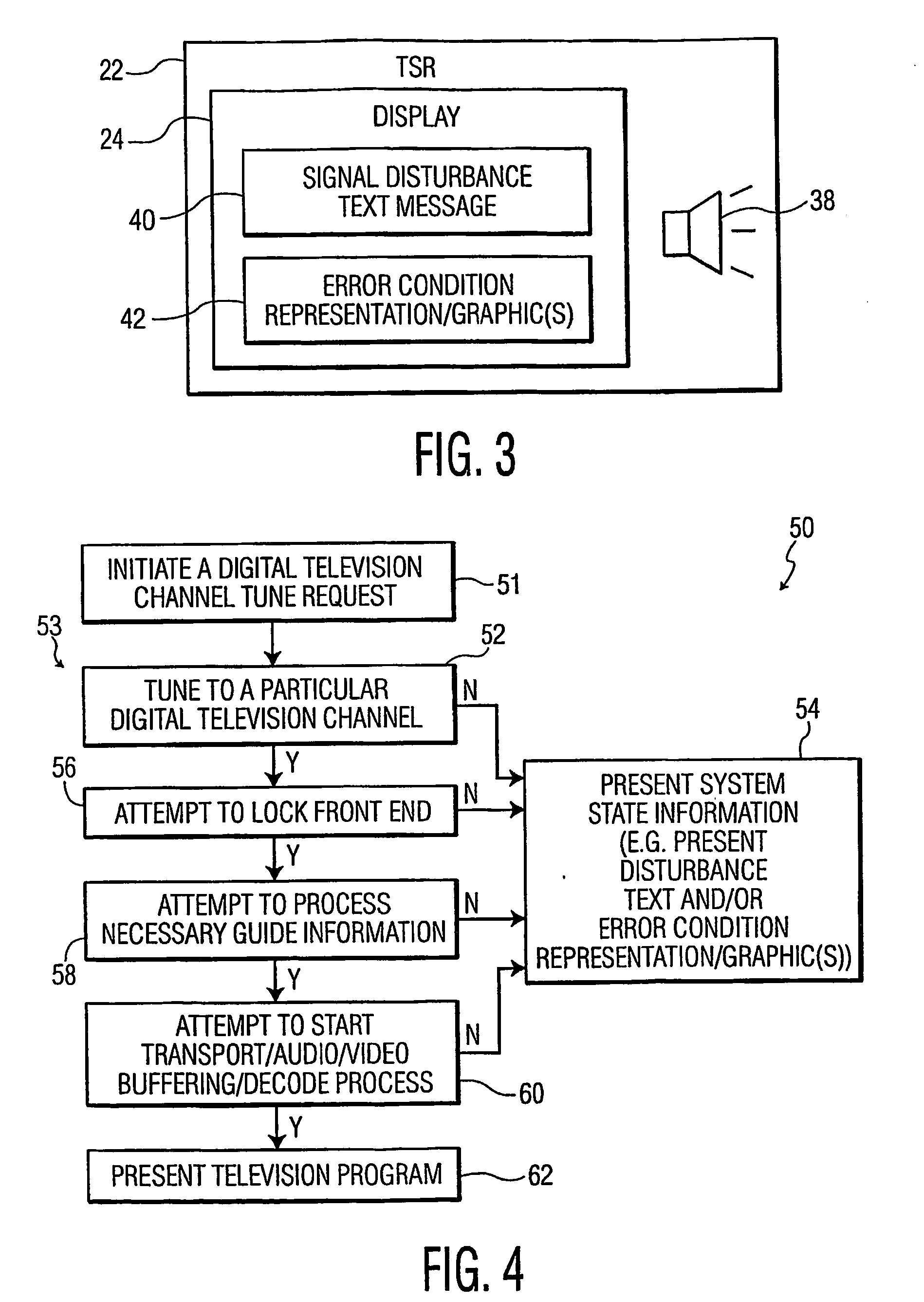
Automatic signal error display and user guided signal recovery in a digital television signal receiver
In a digital television signal receiver, upon a signal disturbance of a digital television signal, system state information, with regard to the nature of the signal disturbance of the particular digital television channel is preferably automatically provided to a user as on-screen display representation or graphic thereof. The digital television signal receiver may further provide intervention options for user-guided recovery of the digital television signal that are preferably automatically provided as on-screen menu options.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
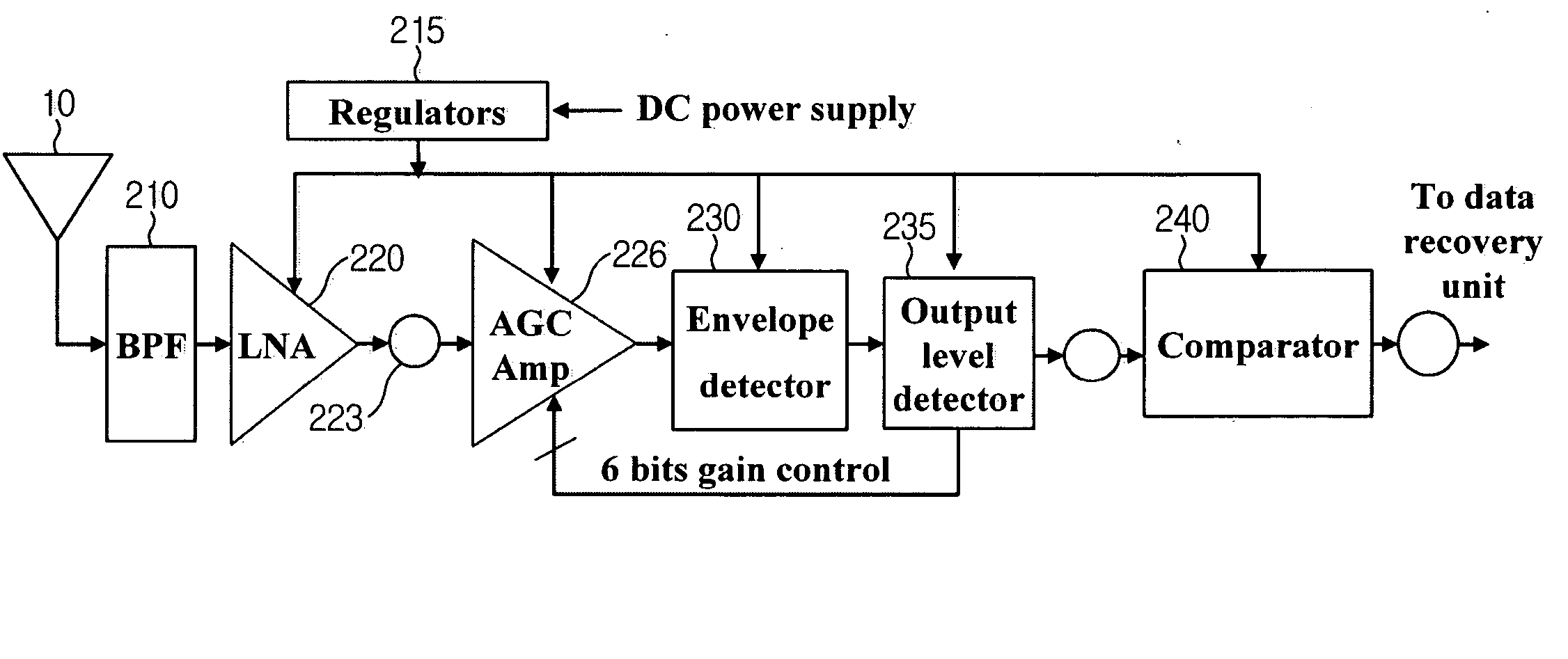
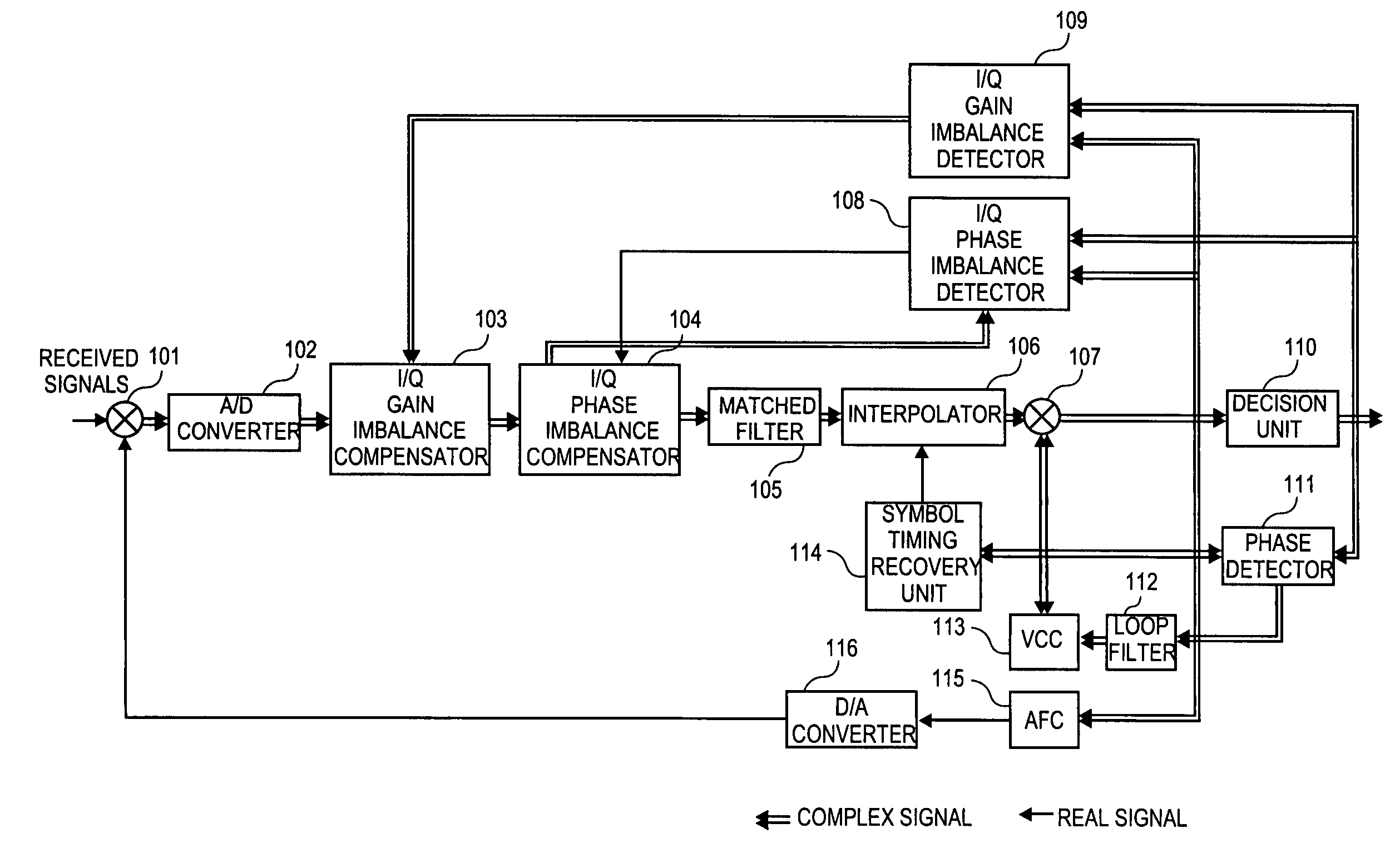
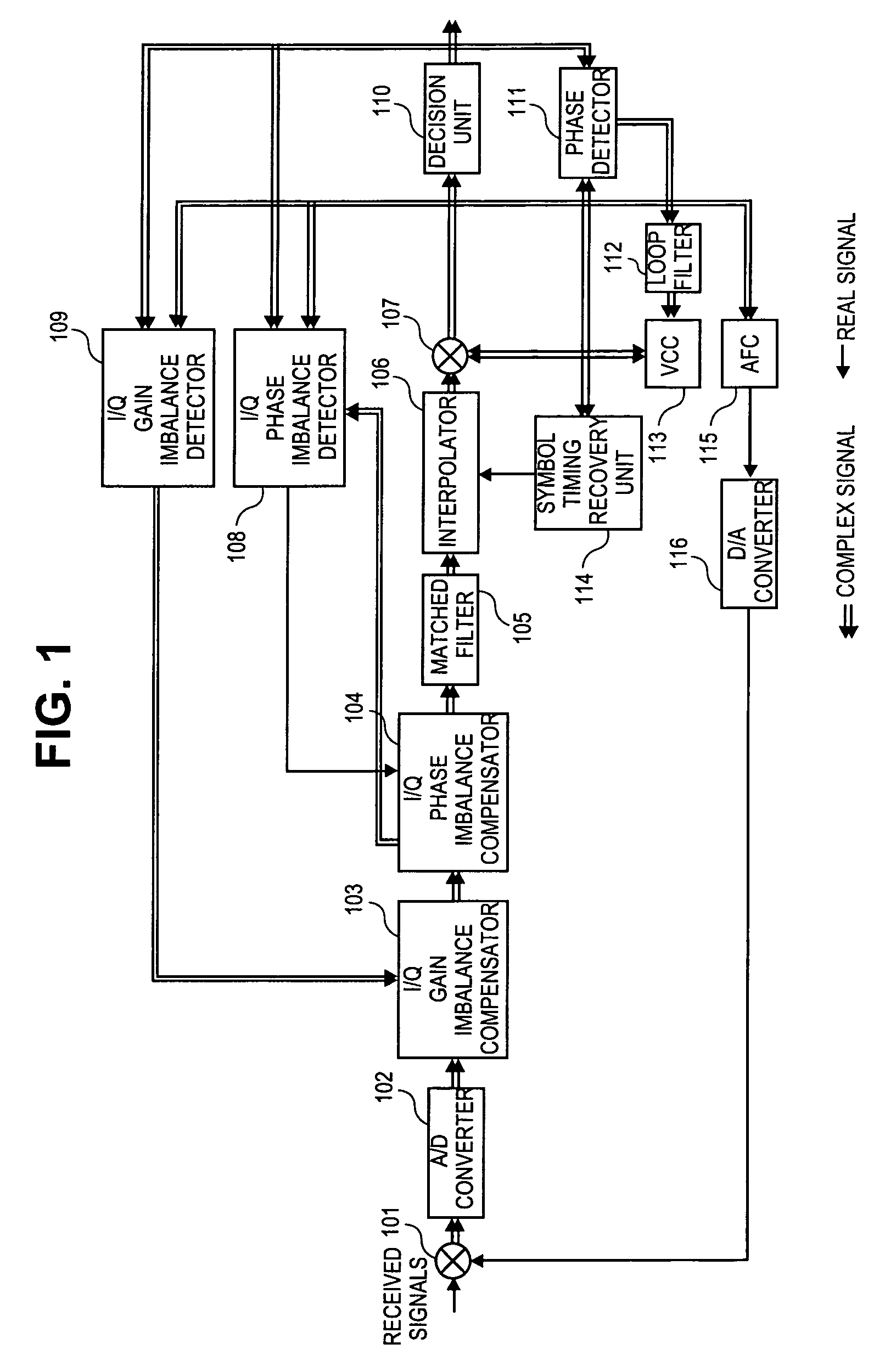
Quadrature demodulator for compensating for gain and phase imbalances between in-phase and quadrature-phase components
InactiveUS7010059B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsQuadrature modulationPhase imbalance
Disclosed is a quadrature demodulator for high-speed wireless communication, which comprises: an A / D converter for converting received signals into digital signals; a signal recovery unit for recovering carriers and symbol timing from the signals converted by the A / D converter; a decision unit for detecting recovered signals output by the signal recovery unit, and performing a decision process on them; an I / Q gain imbalance detector for detecting gain imbalances of the I and Q-phase components from the recovered signals, and outputting an I / Q gain compensation value for compensating for the gain imbalances; and an I / Q gain compensator, provided between the A / D converter and the signal recovery unit, for reflecting the I / Q gain compensation value output by the I / Q gain imbalance detector to the received signals.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency-multiplexed excitation
ActiveUS20160003741A1Reduce image noiseScalable approachPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersBeam splitterLaser scanning microscope
Apparatus and methods for fluorescence imaging using radiofrequency multiplexed excitation. One apparatus splits an excitation laser beam into two arms of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer. The light in the first beam is frequency shifted by an acousto-optic deflector, which is driven by a phase-engineered radiofrequency comb designed to minimize peak-to-average power ratio. This RF comb generates multiple deflected optical beams possessing a range of output angles and frequency shifts. The second beam is shifted in frequency using an acousto-optic frequency shifter. After combining at a second beam splitter, the two beams are focused to a line on the sample using a conventional laser scanning microscope lens system. The acousto-optic deflectors frequency-encode the simultaneous excitation of an entire row of pixels, which enables detection and de-multiplexing of fluorescence images using a single photomultiplier tube and digital phase-coherent signal recovery techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for data transmission and recovery
InactiveUS20070279408A1Reliable high speed transmissionCathode-ray tube indicatorsData switching by path configurationDigital dataMultiplexing
Multiple data streams are distributed using conventional data cables and multiplexing circuits by taking advantage of a technique that allows reliable high speed transmission of digital data. In one example, a number of parallel data streams (e.g., video data streams) are serialized to allow them to be economically and reliably transmitted over conventional data cables (e.g., category 5 or category 6 twisted pair cables, and automotive data transmission cables) over long distance. The parallel data streams are recovered by deserializing from the transmitted signal using a data recovery technique that recovers a clocking signal from the transmitted signal. In another example, multiple data streams from multiple asynchronous sources are multiplexed to provide an input data stream to a display device. The multiple data stream may be provided through, for example, conventional connection cables (e.g., DVI, LEONI, CATS or CAT6 cables).
Owner:INTERSIL CORP
Radar signal recovery method based on in-depth study under complex noise environment
ActiveCN108226892AAchieve recoveryImplement Adaptive RecoveryWave based measurement systemsRecovery methodData set
The invention relates to a radar signal recovery method based on in-depth study under a complex noise environment, which includes steps of structuring of a radar simulation data set; structuring of anetwork model: recovering a self-adaptive radar signal under the noise environment by a generated confronting network in the in-depth study, and the generated confronting network is composed of a judger and a generator; the judger and the generator are formed by using a thick connection convolution neutral network; training of the generated confronting network: mixing five groups of simulation radar time sequence images under five signal-to-noise ratio environments, generating the training data and training the generated confronting network; recovering the signal of the tested radar image by the generated confronting network.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and implementation device
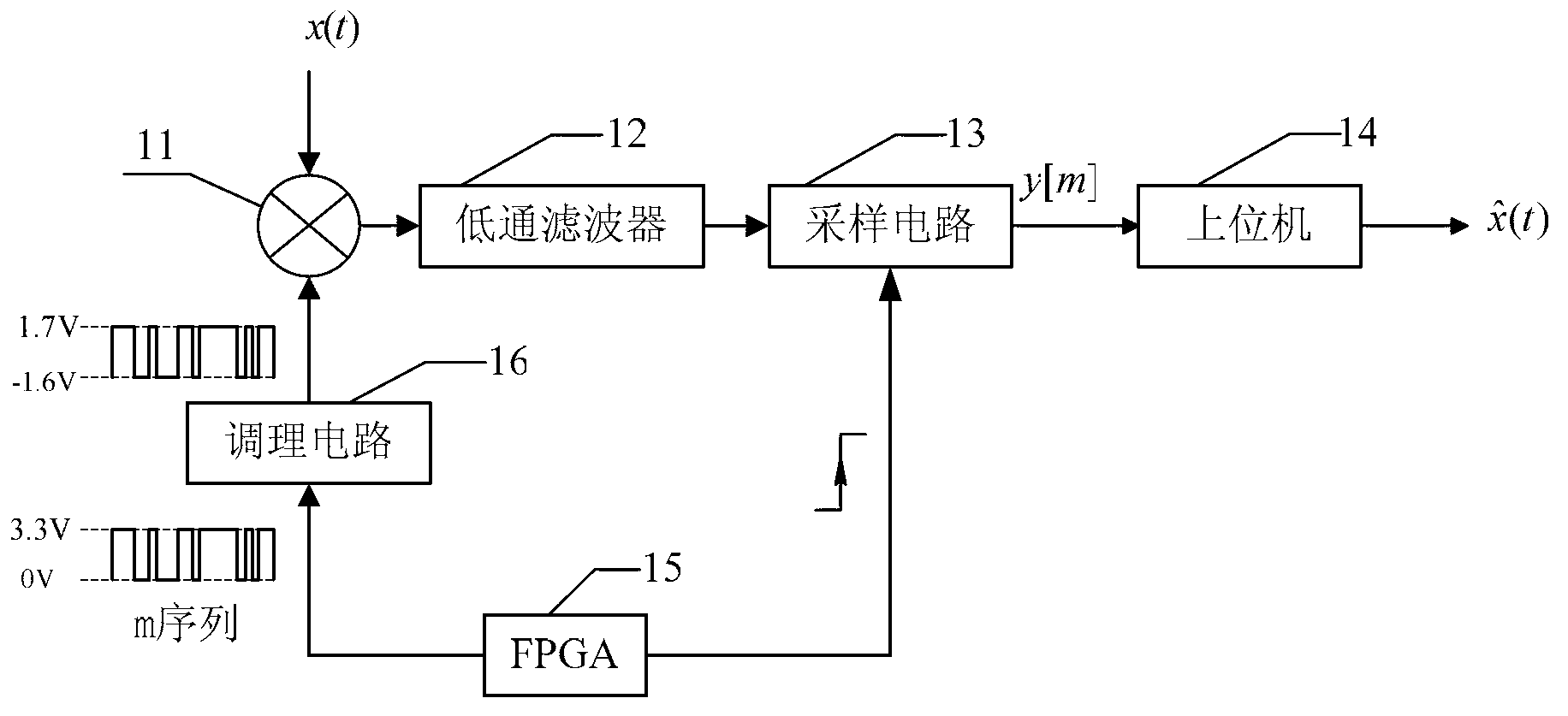
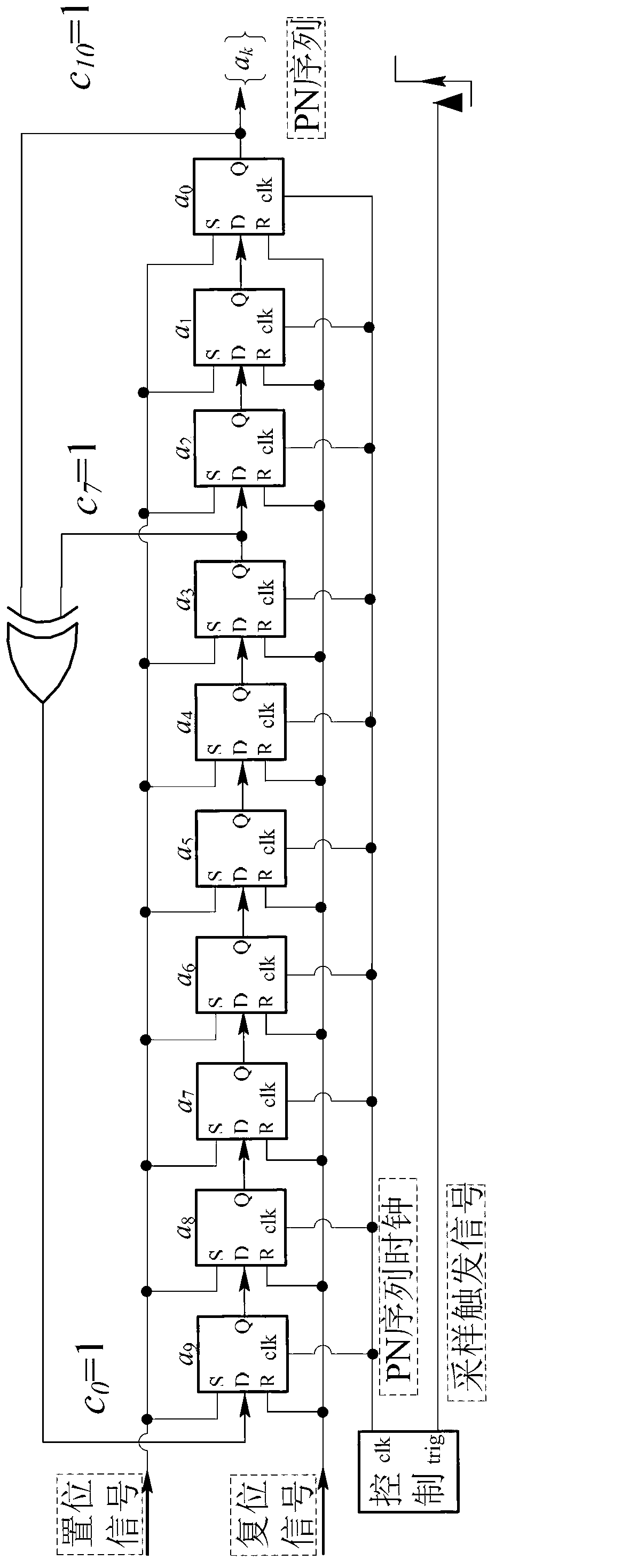
ActiveCN103178853ADownsamplingReduced rate requirementsAnalogue-digital convertersLow-pass filterSignal on
The invention relates to a compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and an implementation device, which are used for lowering a sampling rate of frequency-domain sparse signals on the premise of guaranteeing the restoration effect of the signals. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a trigger signal and an m sequence by an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), carrying out frequency mixing on the m sequence and the measured sparse signal after the m sequence is modulated, and carrying out filtering by a low pass filter; sampling the filtered signal and storing sampled data by a data sampling module after the data sampling module detects the triggering signal; and calculating a transfer function of a system and the m sequence corresponding to the sampled data when the signal is reconstructed, and then restoring the original signal by an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) signal reconstructing algorithm. The compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and the implement device are suitable for the under-sampling of frequency-domain sparse analogue signals.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Multimode transceiver for use with multiple antennas and method for use therewith
InactiveUS20090130990A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesData streamTransceiver
A wireless transceiver includes a plurality of antennas. A plurality of signal recovery circuits generate a selected number of received signals from a first subset of the plurality of antennas, based on a control signal. A receiver section recovers an inbound data stream from the selected number of received signals. A transmitter module generates a transmit signal to a selected one of the plurality of antennas, based on the control signal. The intersection between the first subset of the plurality of antennas and the selected one of the plurality of antennas is the null set for each value of the control signal. The control signals can be generated in multiple different operational modes including, for instance, a cyclic modes and a fixed mode of operation.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
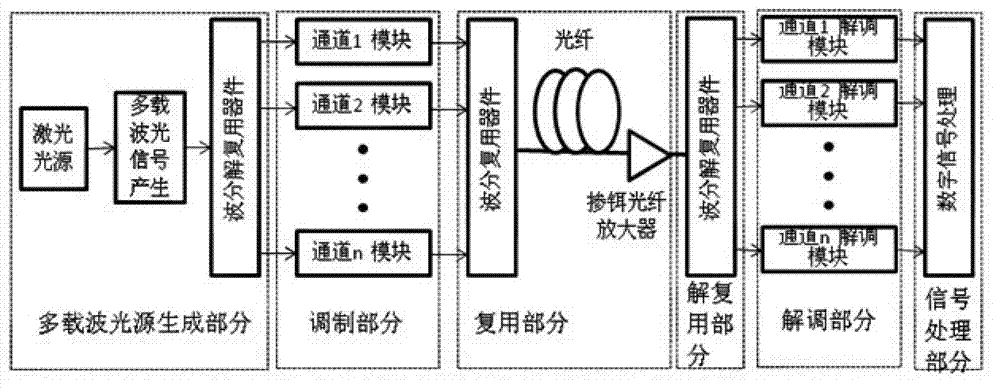
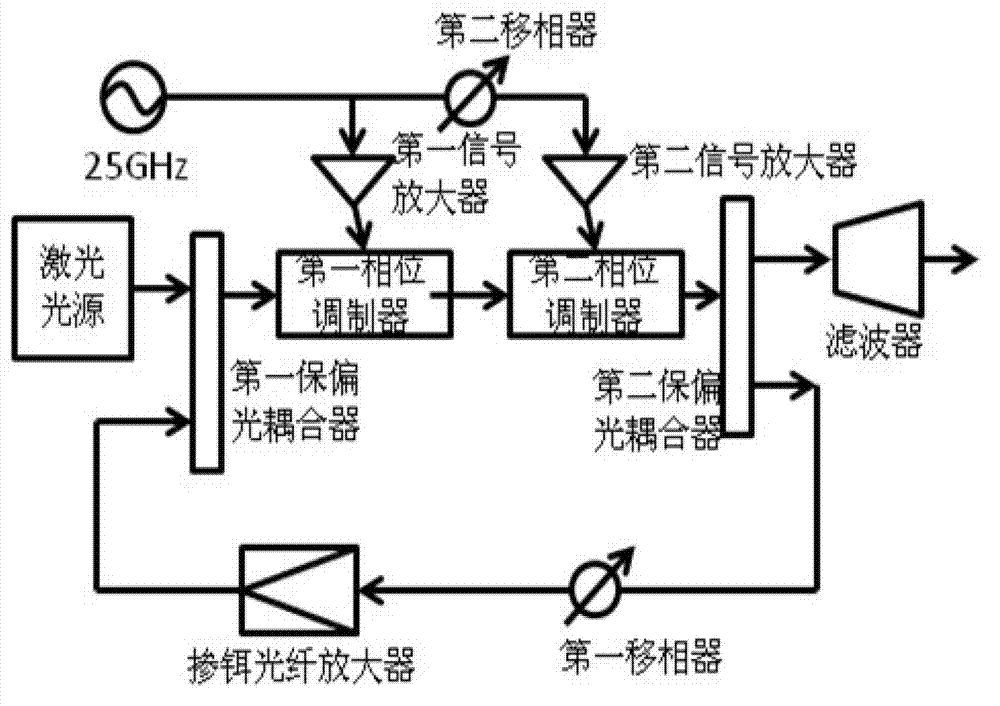
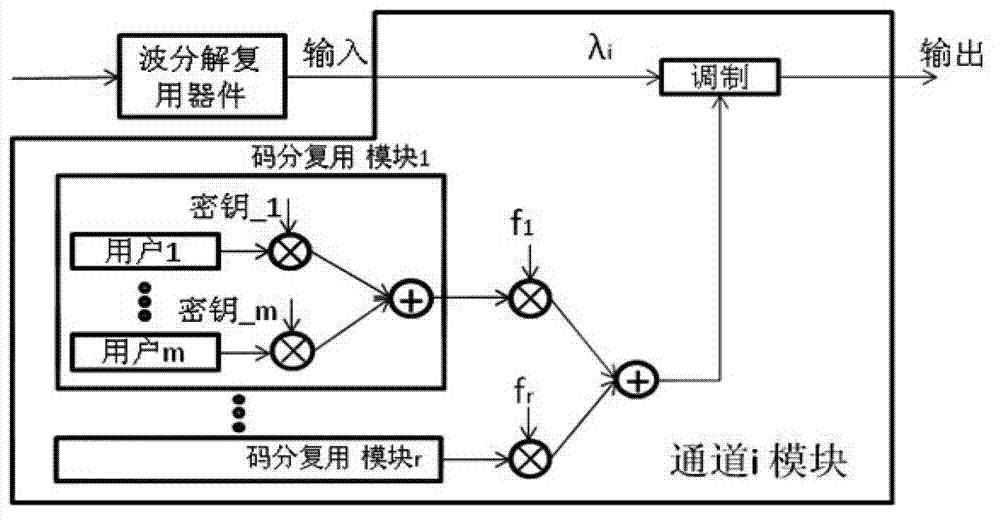
Multi-carrier code division multiplexing light transmission system and method based on ultra dense wavelength division multiplexing
InactiveCN102932089AImprove communication capacityMake the most of your bandwidthWavelength-division multiplex systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMulti carrierTransmission system
The invention discloses a multi-carrier code division multiplexing light transmission system and a multi-carrier code division multiplexing light transmission method based on ultra dense wavelength division multiplexing. The system comprises a multi-carrier light source generating part, a modulating part, a multiplexing part, a demultiplexing part, a demodulating part and a signal processing part which are sequentially connected. Firstly, a multi-carrier light source is generated by a single-frequency light source; then the modulating part modulates each branch electric signal onto a corresponding optical carrier; the multiplexing part is used for multiplexing each modulated optical carrier into an optical fiber channel; the demultiplexing part is used for separating each optical carrier in the signals to conduct signal recovery; the demodulating part is used for demodulating each branch signal; and the signal processing part is used for carrying out compensation on the demodulated signals. The method disclosed by the invention is fused with a code division multiplexing technology, a subcarrier modulating and demodulating technology, a wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing technology, a subcarrier demodulating technology based on coherent demodulation and the like. The multi-carrier code division multiplexing light transmission system and the multi-carrier code division multiplexing light transmission method based on ultra dense wavelength division multiplexing improve the message capacity of a network system and have the advantages of simpleness for capacity expansion, reliable performance and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
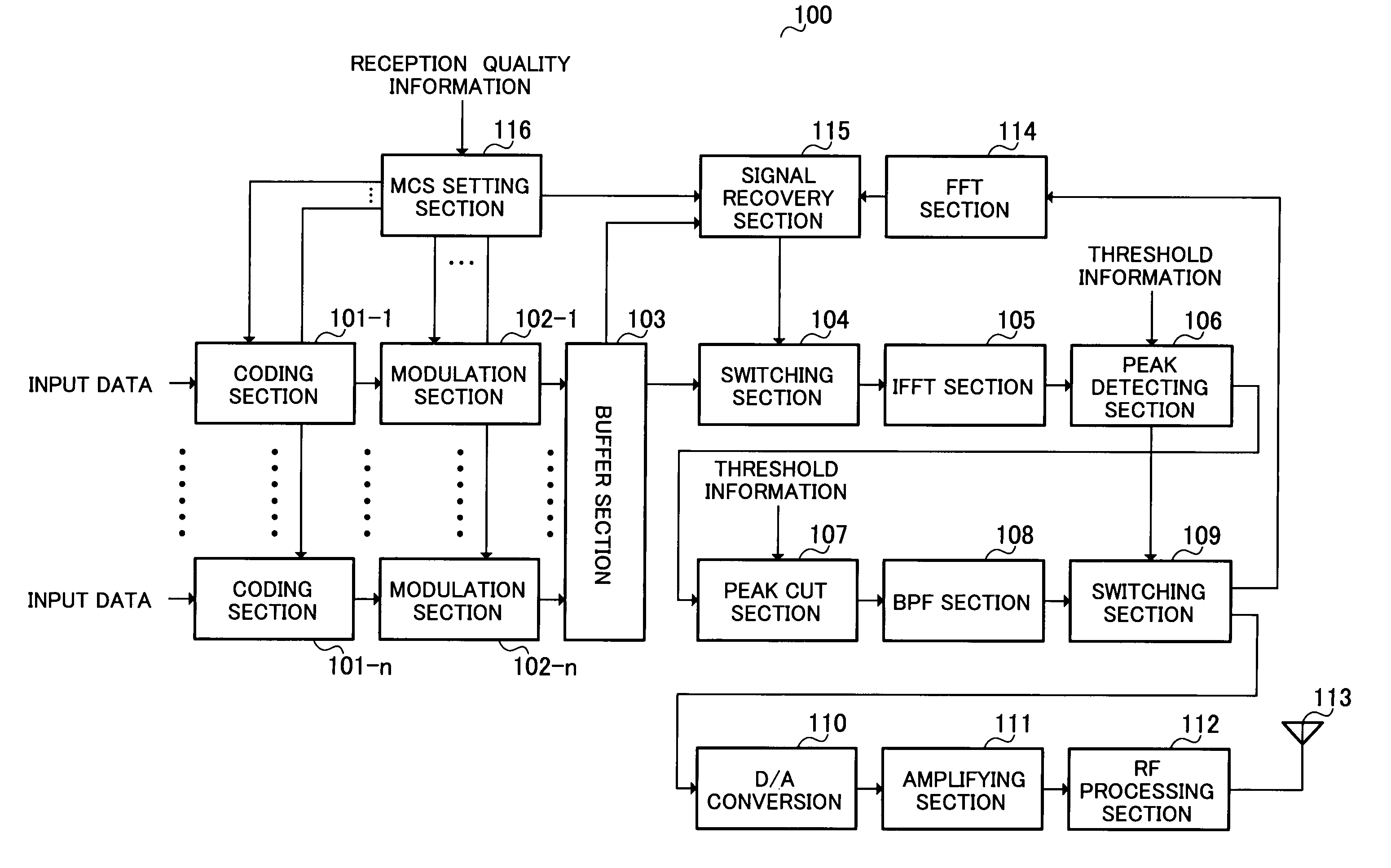
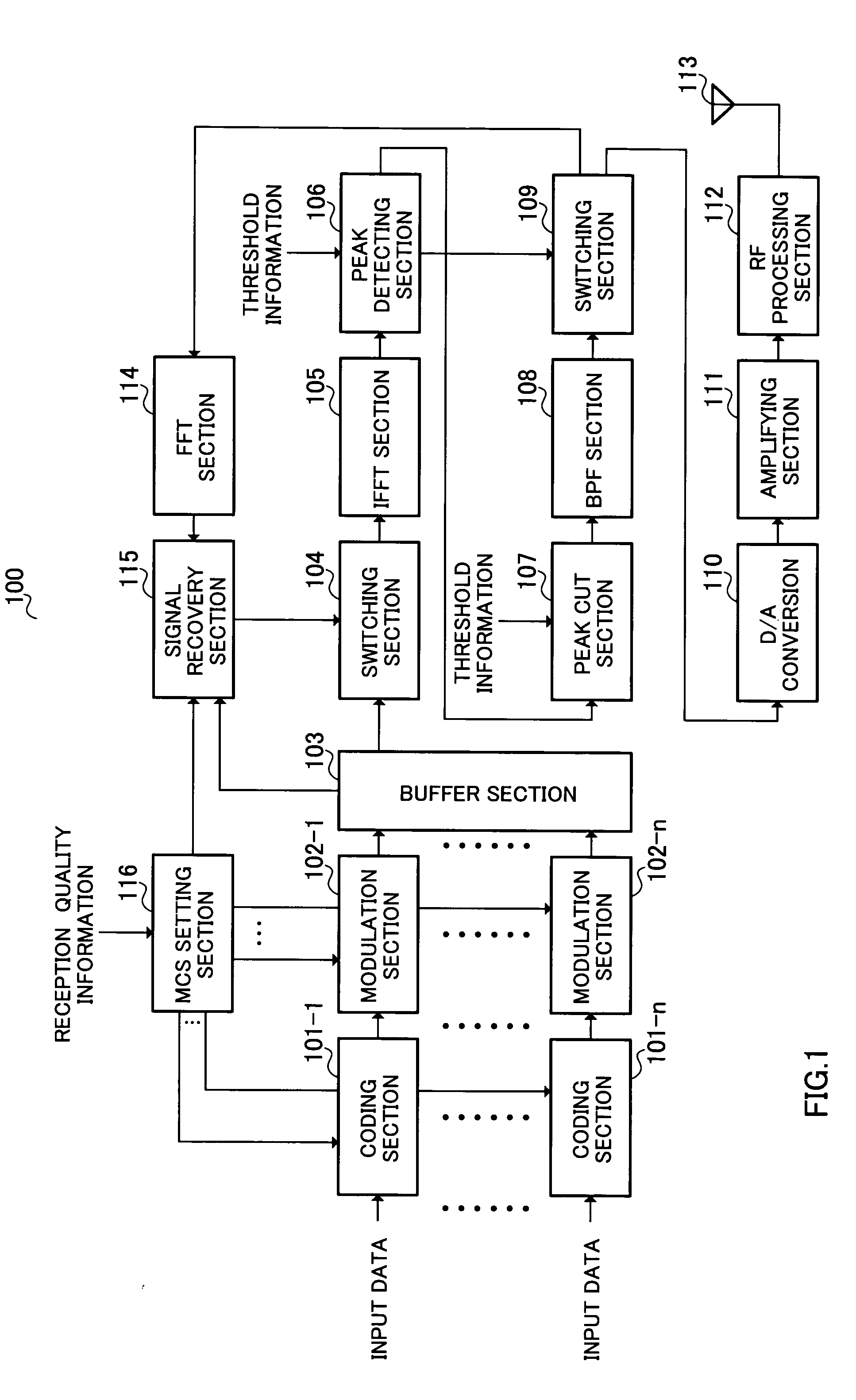
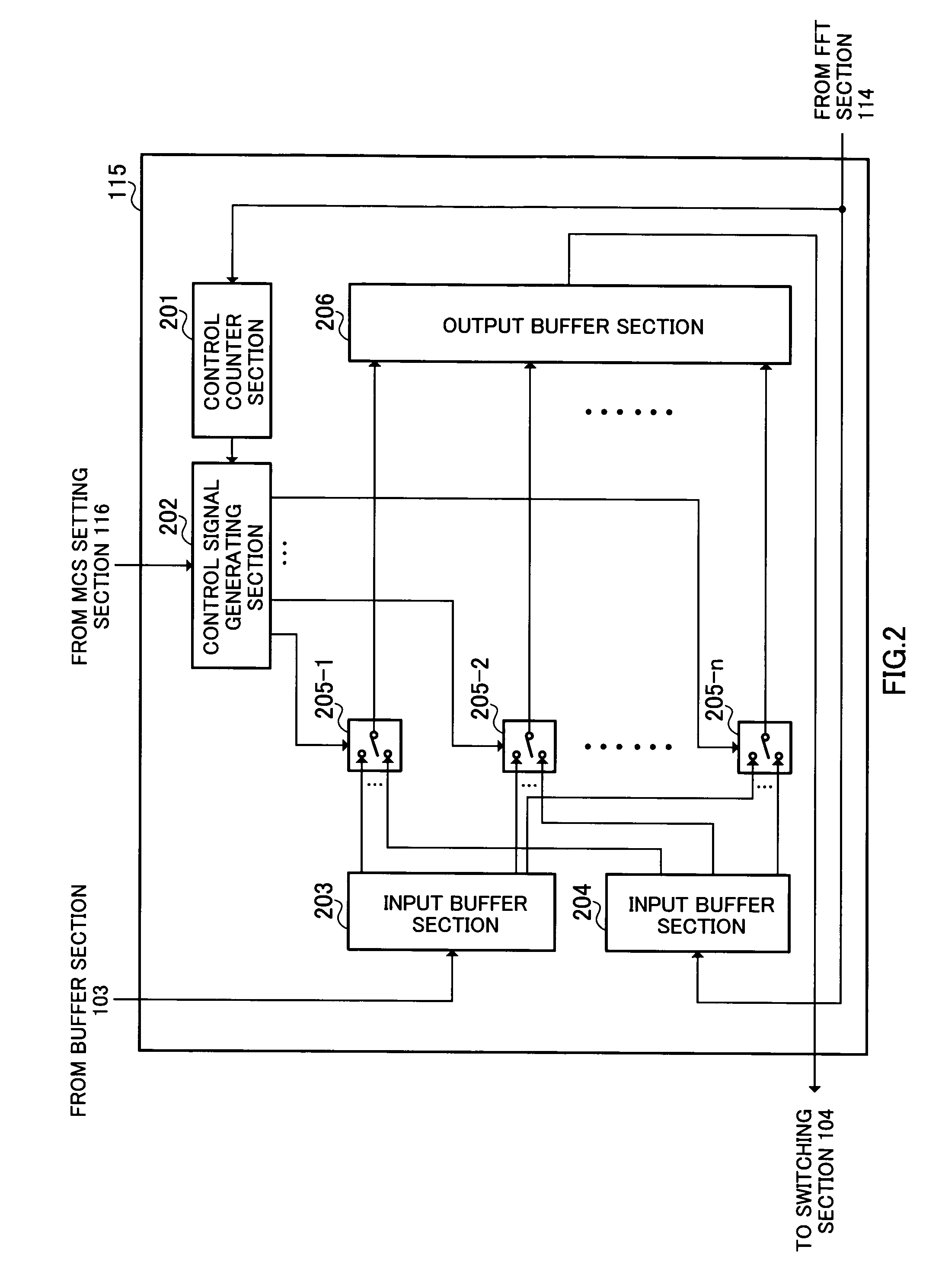
Radio Communication Apparatus and Peak Suppression Method
InactiveUS20080233901A1Improve efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTSubstation equipmentPeak valueEngineering
A radio communication apparatus enabling reduction in peak-to-average power ratio without decreasing the transmission efficiency. In this apparatus, buffer section 103 temporarily stores input data prior to peak suppression. Peak detecting section 106 detects a peak with an amplitude level not less than a threshold. Peak cut section 107 reduces the detected peak to the threshold. Switching section 109 is switched so that the peak suppressed signal is output to FFT section 114 when the peak is detected, while the peak suppressed signal is subjected to transmission processing when the peak is not detected. Based on MCS information, signal recovering section 115 eliminates a signal assigned to a subcarrier set for MCS of a high level, and as a substitute, assigns the signal prior to peak suppression stored in buffer section 103. MCS setting section 116 selects MCS based on reception quality information of a communicating party.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for Bayes compressed sensing signal recovery based on self-adaptive measurement matrix
ActiveCN103840838AShort calculation timeImprove recovery accuracyCode conversionBayesian compressive sensingSelf adaptive
The invention provides a method for Bayes compressed sensing signal recovery based on a self-adaptive measurement matrix and relates to the field of the information and communication technology. The method aims at solving the problem that an existing compressed sensing signal recovery method is low in accuracy. Based on the design of the self-adaptive measurement matrix in compressed sensing and combined with the Bayes compressed sensing algorithm, a design scheme of the compressed sensing method is obtained. The method is characterized in that the designed measurement matrix can be generated in a self-adaptive mode according to different signals, the purposes of determinacy and storage of the matrix are both achieved, and combined with the Bayes compressed sensing recovery algorithm of a relevant vector machine, the priority of a layered structure is introduced. The design scheme passes simulation verification, it is confirmed that the good signal recovery effect can be obtained, and the error range of recovered signals can be evaluated. The method is suitable for wireless signal transmission occasions in the information and communication technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
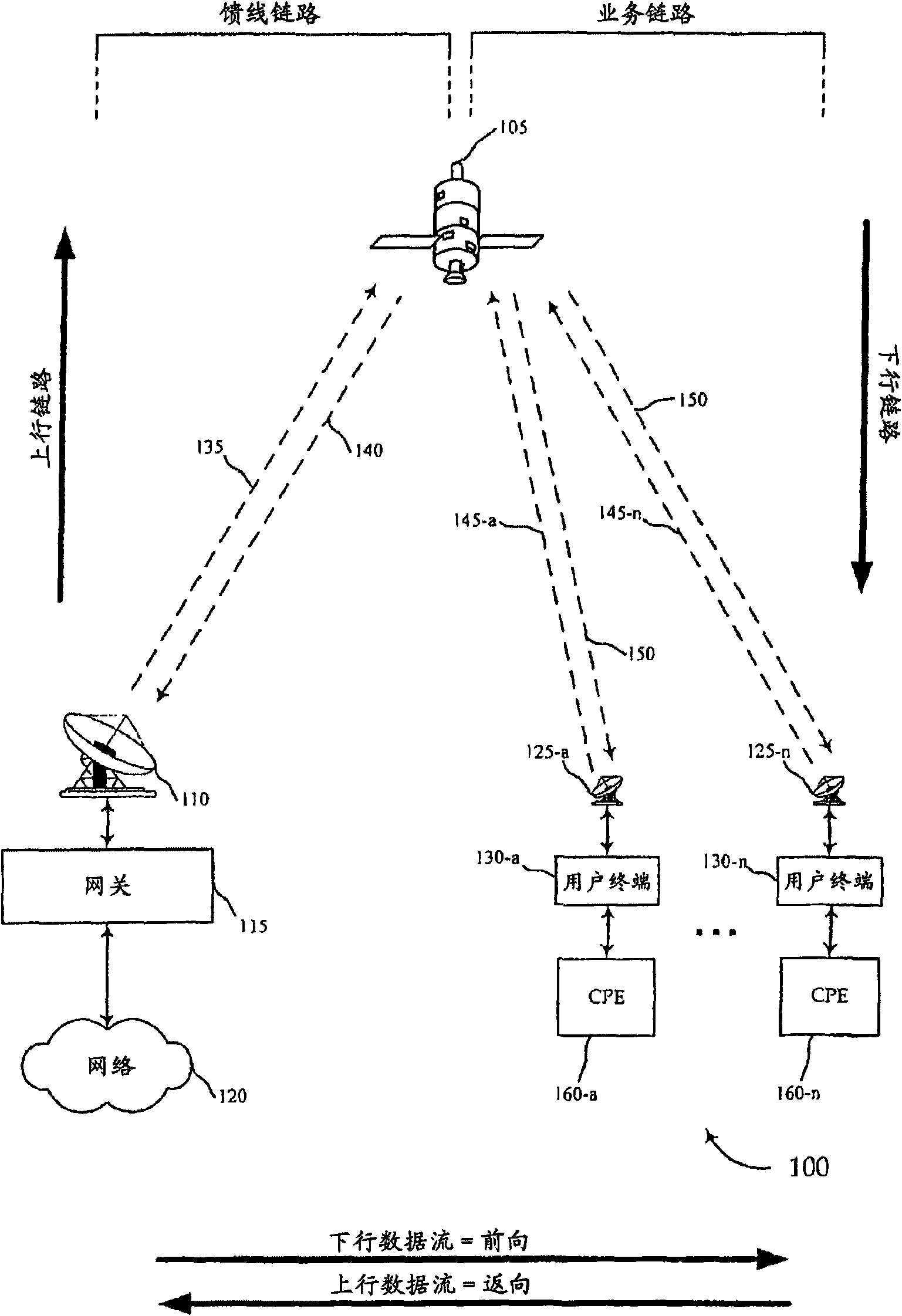
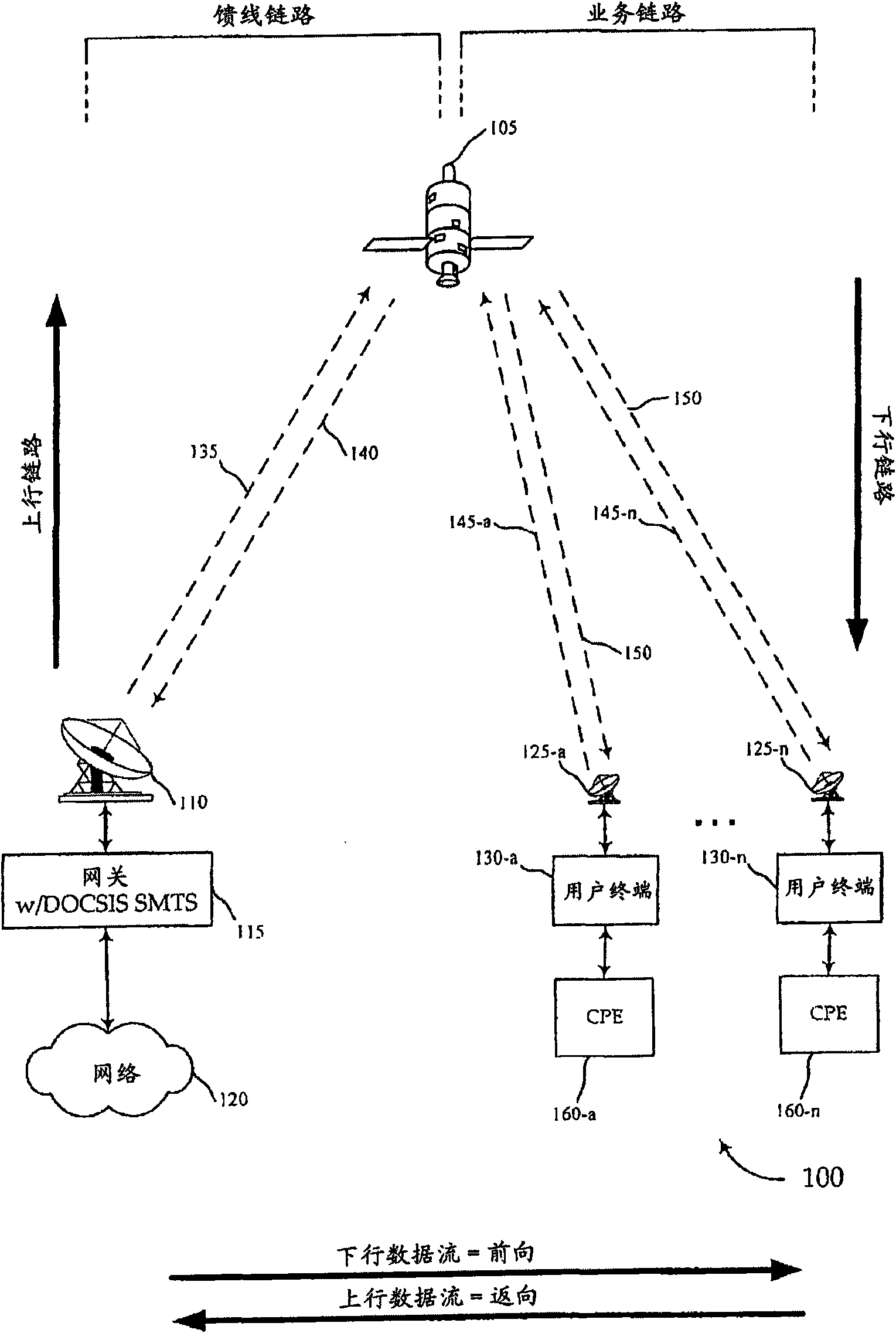
Improved spot beam satellite systems
A method is presented for transmitting data in a satellite system having multiple spot beams comprising (1) sending a broadband signal in a forward direction from a gateway terminal to a communications satellite for relay to at least one subscriber terminal, (2) receiving the broadband signal at the communications satellite, wherein the communications satellite comprises a bent pipe repeater having a plurality of satellite-based transmission amplifiers, (3) using one of the plurality of satellite-based transmission amplifiers to amplify the broadband signal and no other broadband signal from the gateway terminal, to produce an amplified broadband signal, (4) sending the amplified broadband signal as one of a plurality of service spot beams to the at least one subscriber terminal, and (5) receiving and retrieving data from the amplified broadband signal at the at least one subscriber terminal.
Owner:VIASAT INC
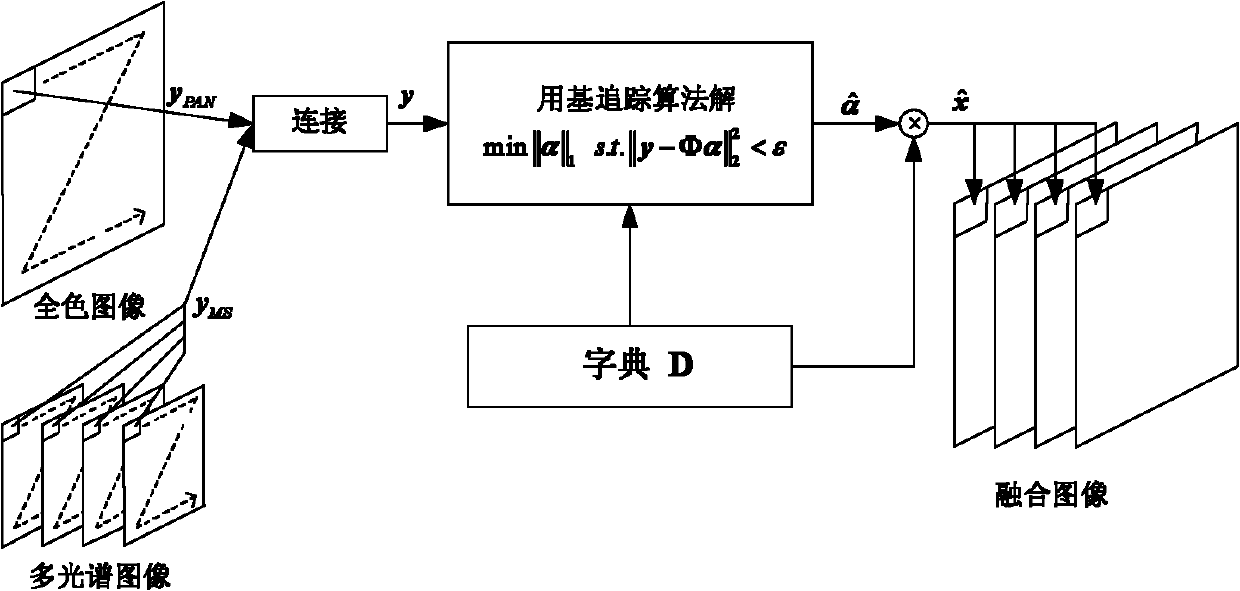
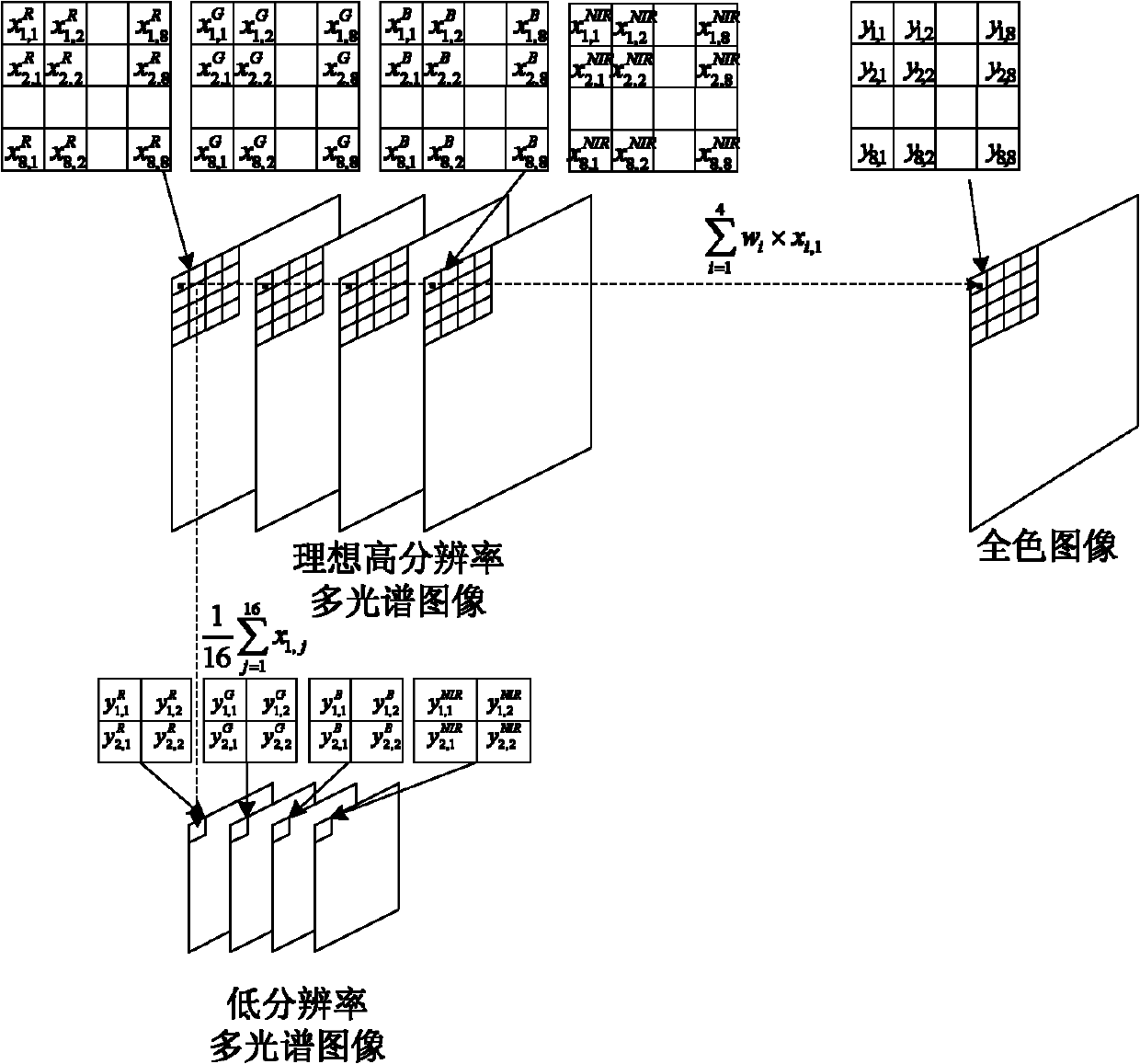
Compressive sensing theory-based satellite remote sensing image fusion method
InactiveCN101996396AConform to visual characteristicsAvoid complexityImage enhancementColor imageRemote sensing image fusion
The invention discloses a compressive sensing theory-based satellite remote sensing image fusion method. The method comprises the following steps of: vectoring a full-color image with high spatial resolution and a multi-spectral image with low spatial resolution; constructing a sparsely represented over-complete atom library of an image block with high spatial resolution; establishing a model from the multi-spectral image with high spatial resolution to the full-color image with high spatial resolution and the multi-spectral image with low spatial resolution according to an imaging principle of each land observation satellite; solving a compressive sensing problem of sparse signal recovery by using a base tracking algorithm to obtain sparse representation of the multi-spectral color image with high spatial resolution in an over-complete dictionary; and multiplying the sparse representation by the preset over-complete dictionary to obtain the vector representation of the multi-spectral color image block with high spatial resolution and converting the vector representation into the image block to obtain a fusion result. By introducing the compressive sensing theory into the image fusion technology, the image quality after fusion can be obviously improved, and ideal fusion effect is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
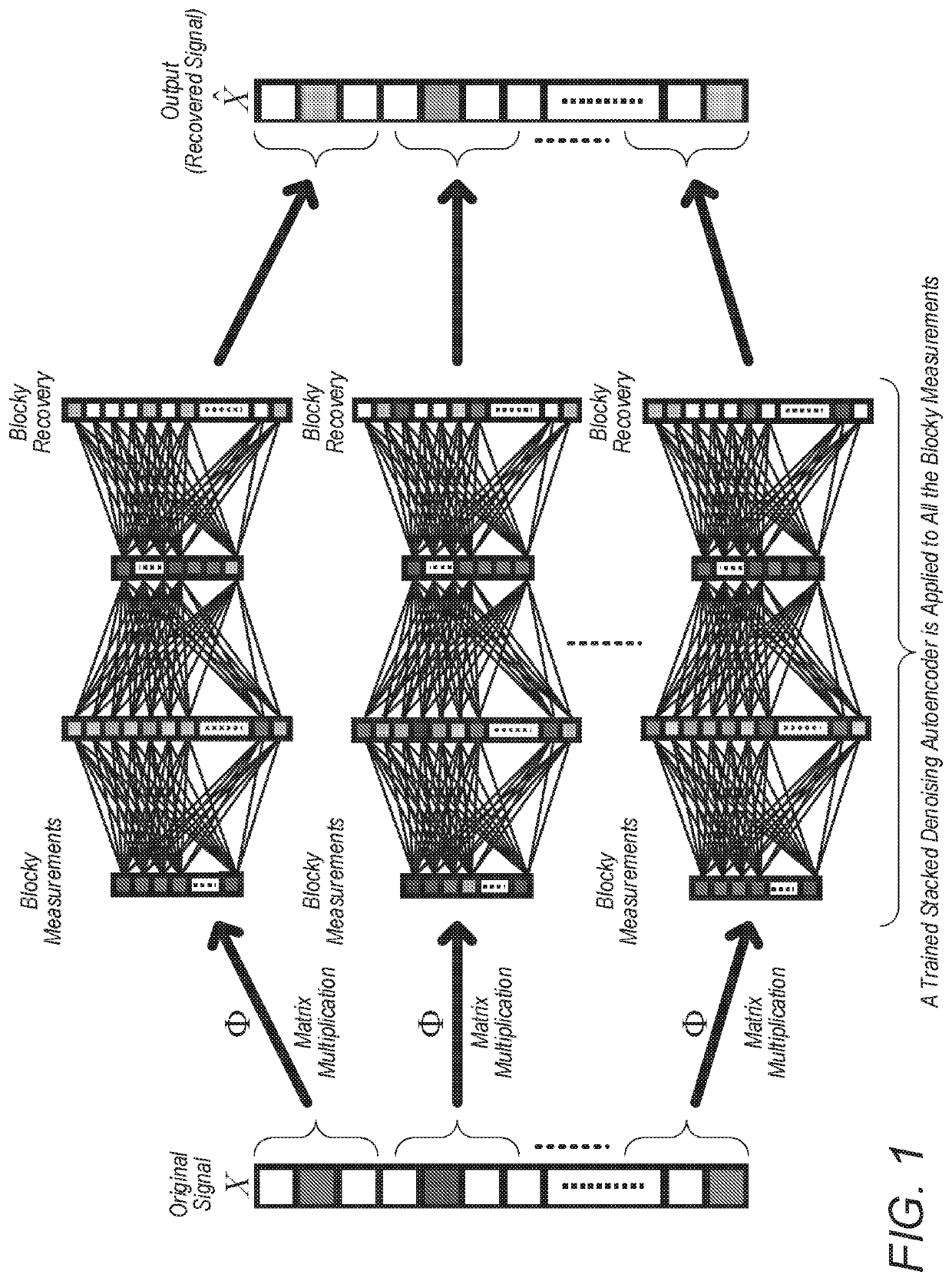
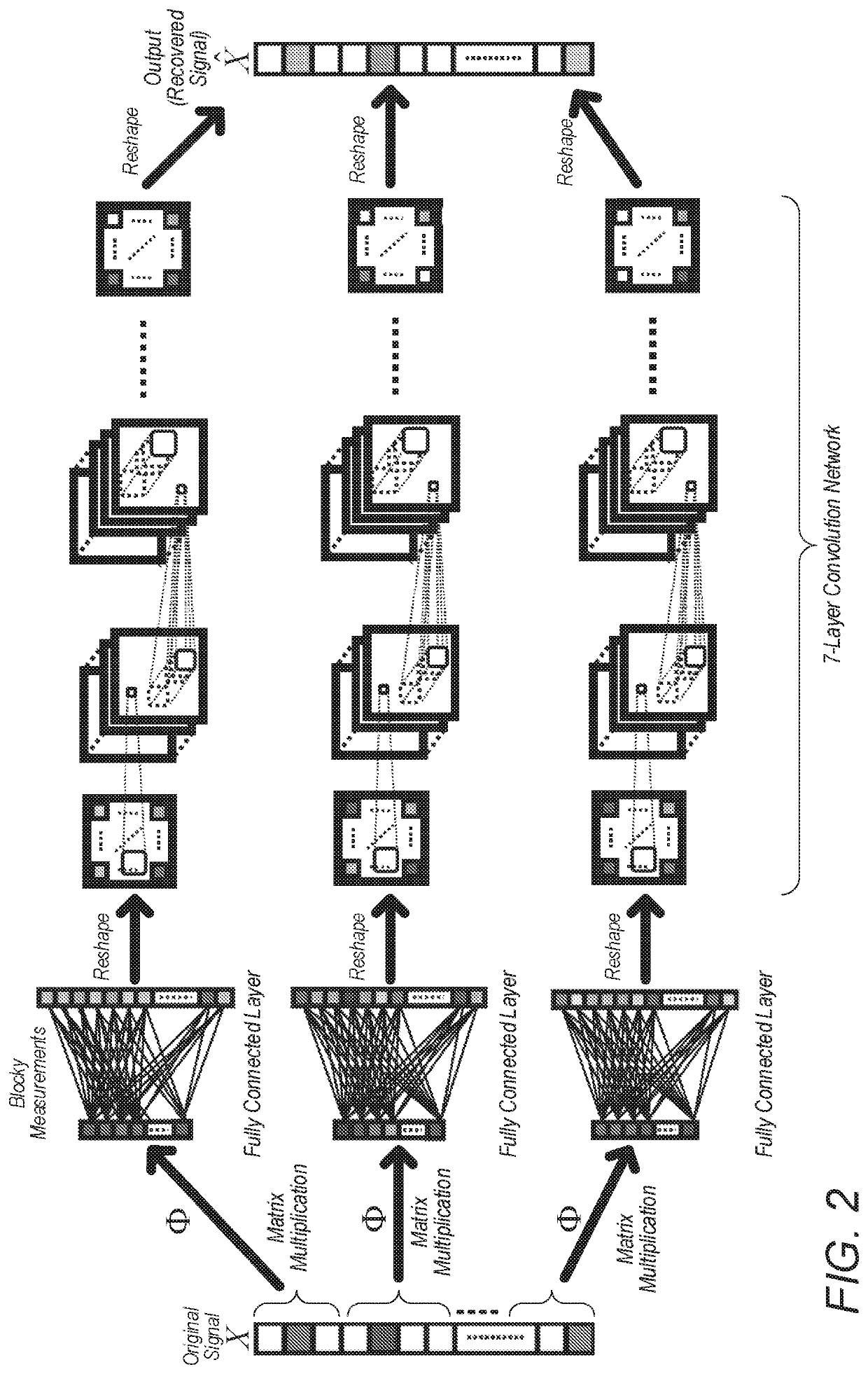
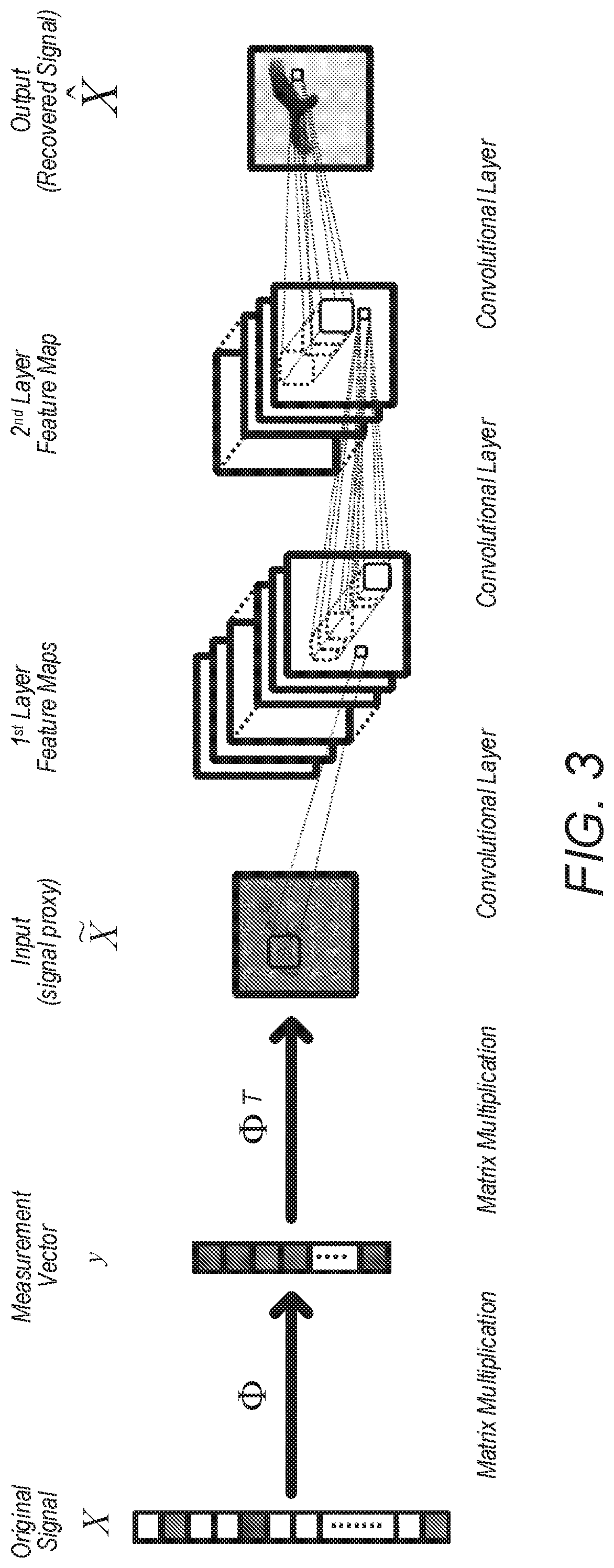
Signal Recovery Via Deep Convolutional Networks
ActiveUS20190340497A1Promote recoverySparse connectivityReconstruction from projectionCode conversionNon real timePerformance recovery
Real-world data may not be sparse in a fixed basis, and current high-performance recovery algorithms are slow to converge, which limits compressive sensing (CS) to either non-real-time applications or scenarios where massive back-end computing is available. Presented herein are embodiments for improving CS by developing a new signal recovery framework that uses a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) to learn the inverse transformation from measurement signals. When trained on a set of representative images, the network learns both a representation for the signals and an inverse map approximating a greedy or convex recovery algorithm. Implementations on real data indicate that some embodiments closely approximate the solution produced by state-of-the-art CS recovery algorithms, yet are hundreds of times faster in run time.
Owner:RICE UNIV
High bandwidth data transport system
InactiveUS7961705B2Increase chanceTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationUltra-widebandTransport system
Owner:LIGHTWAVES SYST
High-speed underwater communication system based on blue-green light source
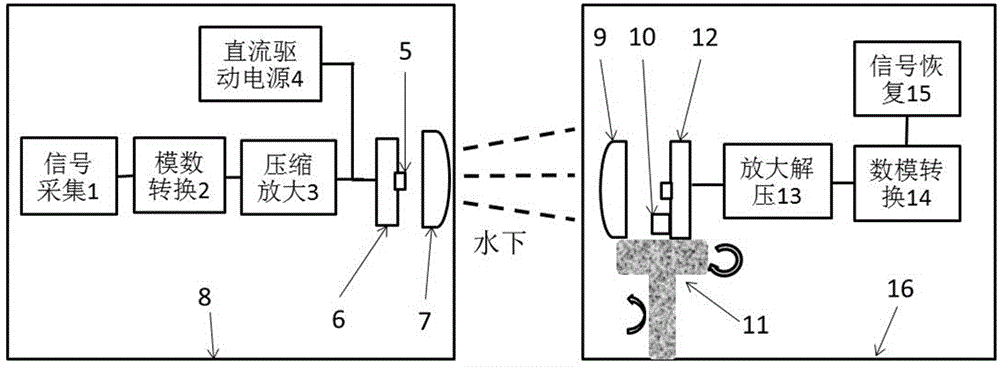
InactiveCN106452585AHigh bandwidthIncrease data transfer rateClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic receiversTime delaysShortest distance
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and specifically discloses a high-speed underwater communication system based on a blue-green light source. An efficient gallium nitride-based LED (Light Emitting Diode) or a laser light source which is 450nm or about 520nm in light emitting wavelength is used; an emitter comprises a signal acquiring module, an analog-to-digital conversion module, a compressing and amplifying module, a direct-current driving power supply, a blue-green light source, a corresponding heat-dissipation packaging device, an emitting antenna and a waterproof device; and a receiver comprises a signal receiving antenna, an automatic aligning module, a detector, a signal amplifying and decompressing module, a digital-to-analog conversion module, a signal recovering module and a waterproof module. In the high-speed underwater communication system, a receiving end automatic aligning module is added, so that short-distance and long-distance high-speed underwater communication can be realized. The high-speed underwater communication system has the advantages of large bandwidth, high data transmission rate, high confidentiality, low energy consumption and short time delay.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method of performing structure-based bayesian sparse signal reconstruction
InactiveUS8861655B1Reduce complexityEasy to measureError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexitySignal reconstruction
The method of performing structure-based Bayesian sparse signal reconstruction is a Bayesian approach to sparse signal recovery that has relatively low complexity and makes a collective use of: a priori statistical properties of the signal and noise; sparsity information; and the rich structure of the sensing matrix Ψ. The method is used with both Gaussian and non-Gaussian (or unknown) priors, and performance measures of the ultimate estimate outputs are easily calculated.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
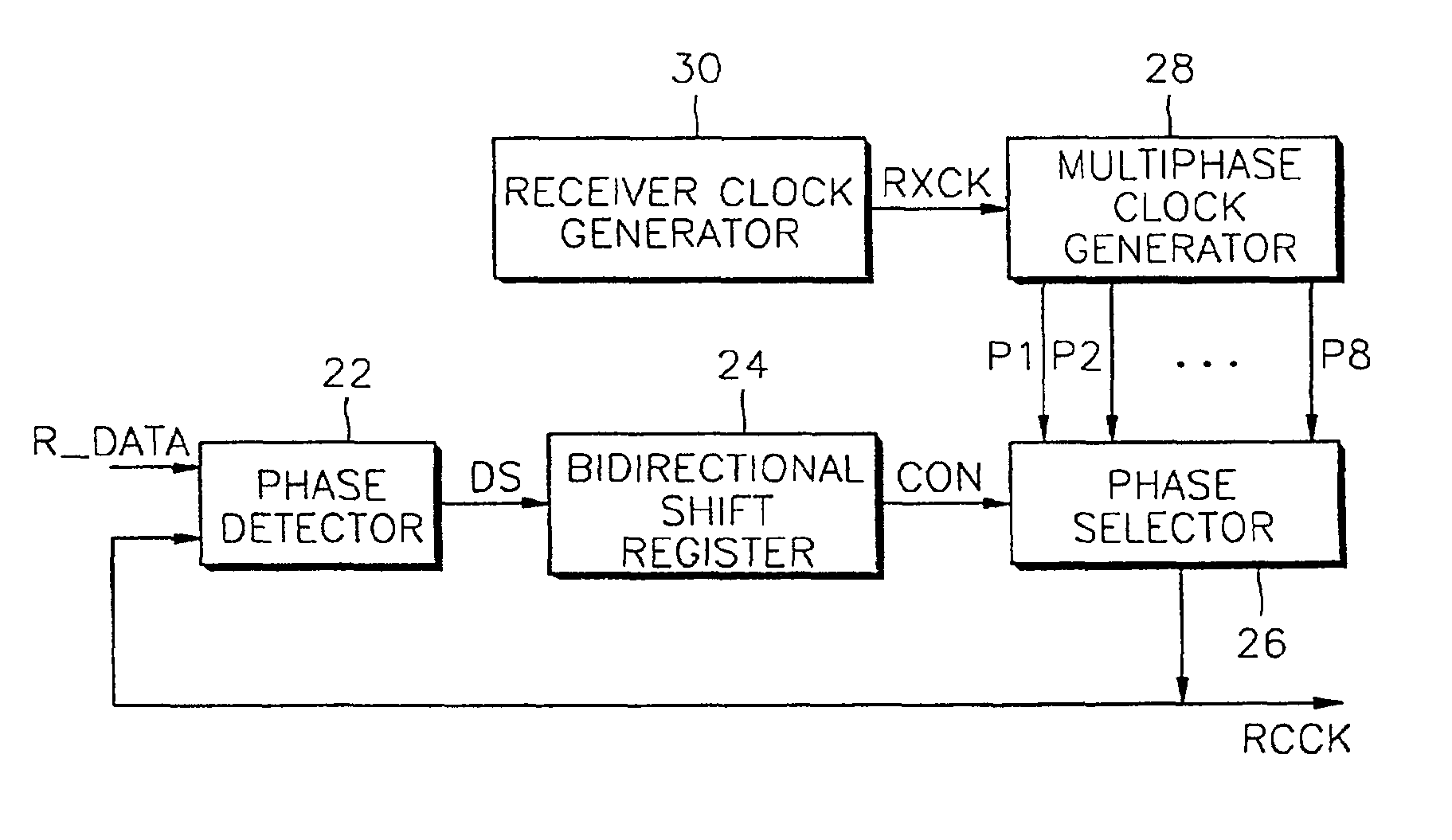
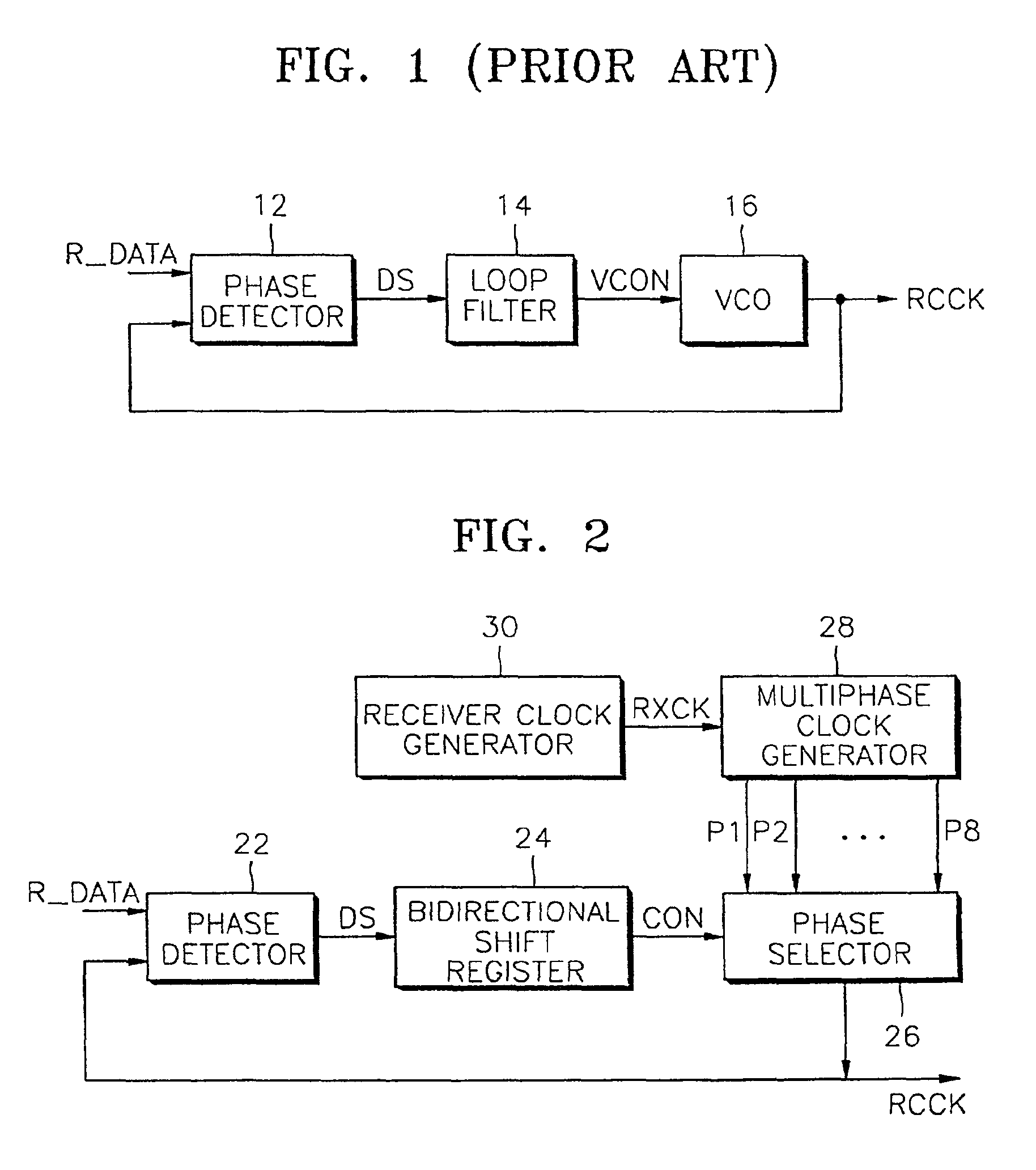
Clock signal recovery circuit used in receiver of universal serial bus and method of recovering clock signal
InactiveUS6954506B2Energy efficient ICTAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsPhase detectorShift register
A clock signal recovery circuit that is implemented in a receiver of a universal serial bus (USB) and a method for recovering a clock signal. The clock signal recovery circuit comprises a phase detector, a bidirectional shift register, a multiphase clock signal generator, and a phase selector. The phase detector detects a difference in phases between received data and a predetermined recovery clock signal and generates a first control signal indicative of the detected phase difference. The shift register is shifted in response to the detected signal and outputs a second control signal. The multiphase clock signal generator receives a receiver clock signal having the same frequency as that of a clock signal used in a USB transmitter (from which the data is transmitted) and generates a plurality of phase clock signals, preferably, first through N-th phase clock signals having the same frequencies as that of the receiver clock signal and having differences of about (360 / N)*I degree (°) (where N is an integer, and I is an integer equal to or greater than 0 and equal to or less than N−1) from a phase of the receiver clock signal, respectively. The phase selector selects one of the first through N-th phase clock signals in response to the second control signal and outputs the selected phase clock signal as the recovery clock signal. Preferably, N is an integer equal to or greater than 2 and equal to or less than 8.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
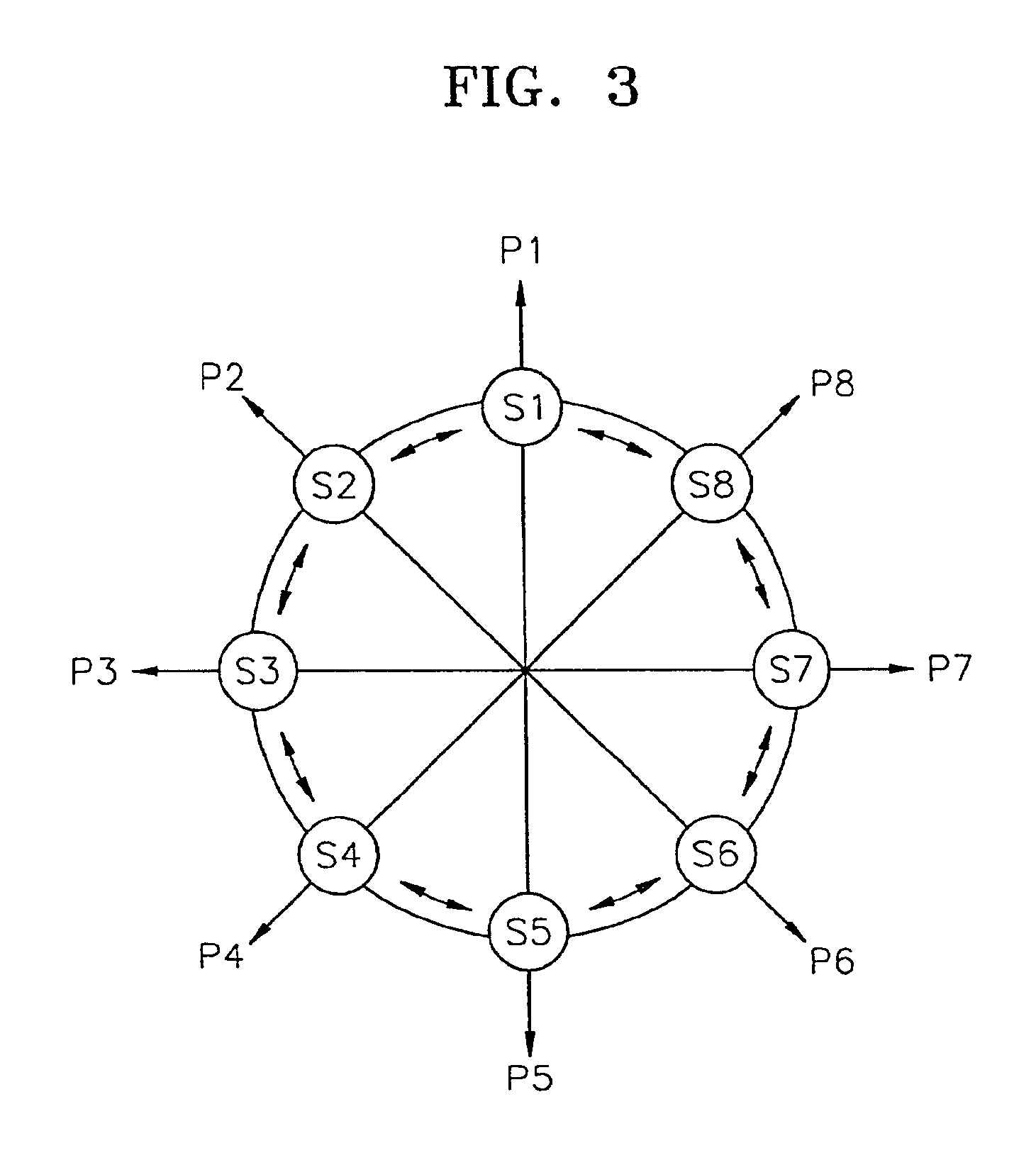
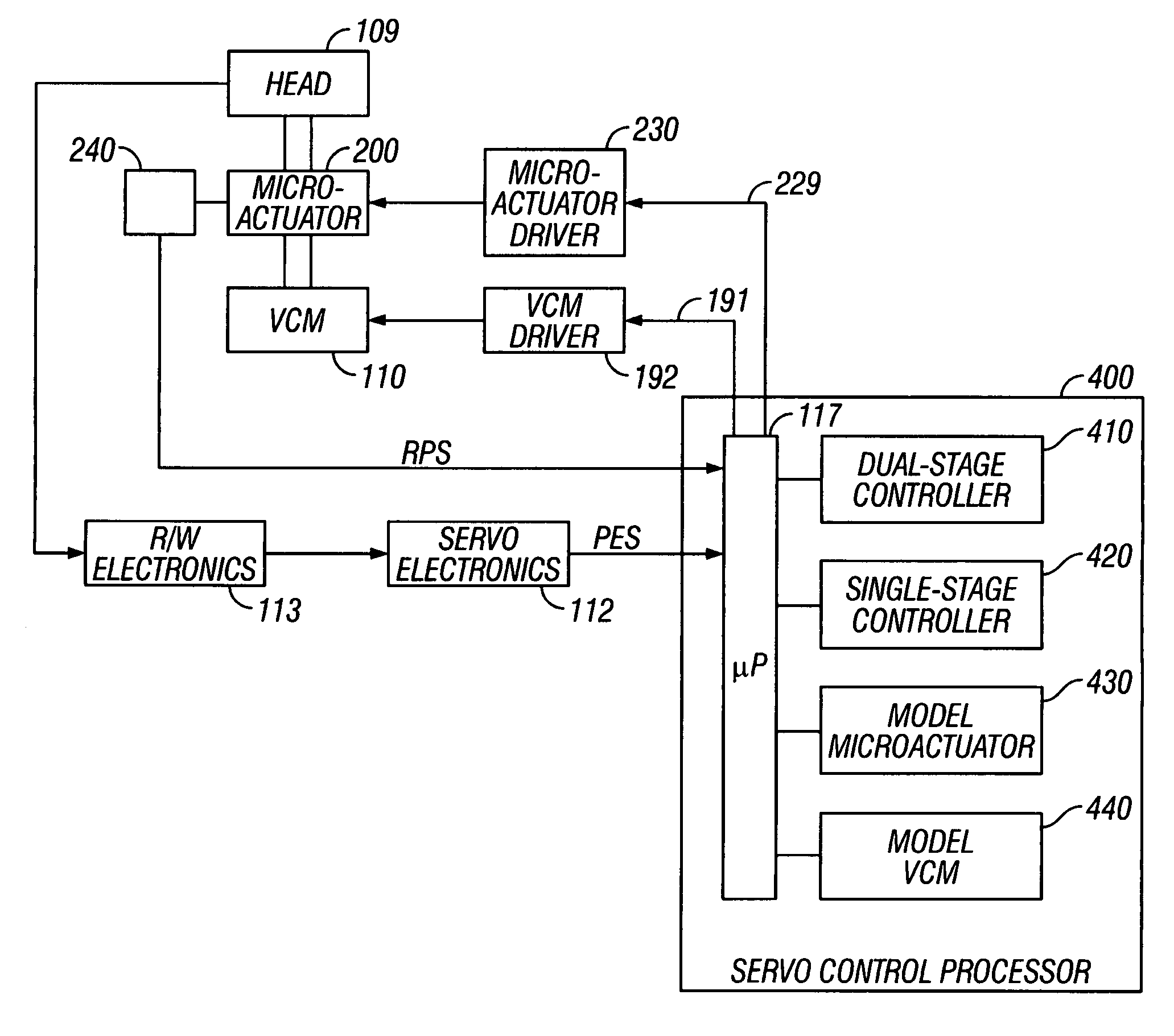
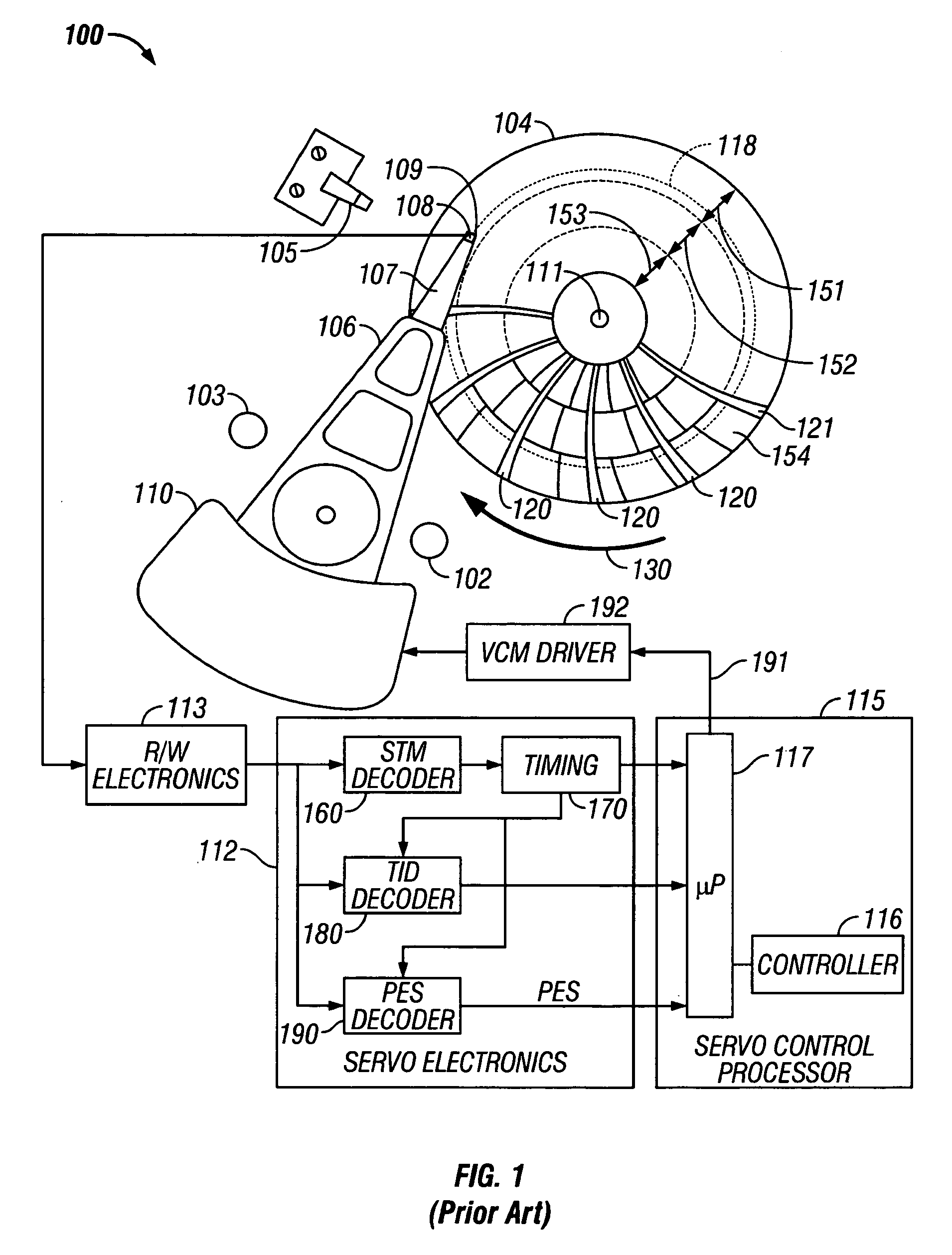
Dual-stage actuator disk drive with secondary actuator failure detection and recovery using relative-position signal
InactiveUS7072134B1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsDual stageActuator fault detection
A dual-stage actuator disk drive uses a secondary-actuator failure-detection and calibration test run by the servo control processor and a relative-position sensor for measuring the position of the secondary actuator relative to its neutral position in response to the calibration test. The secondary-actuator failure detection and calibration test can be performed on a regular schedule or at selected times, such as at disk drive start-up. With the primary actuator biased at a test location, such as a crash stop or a load / unload ramp, the servo control processor generates a test signal to the secondary actuator and receives a relative-position signal (RPS) from the relative-position sensor in response to the test signal. The test comprises two measurements: a measurement of the secondary actuator static characteristics, and a measurement of the secondary actuator dynamic characteristics.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com