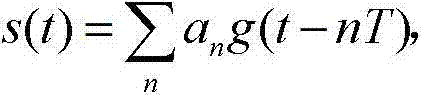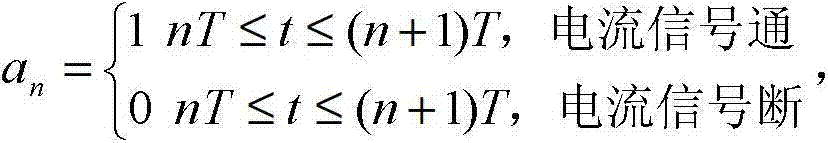Patents
Literature
156 results about "On-off keying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
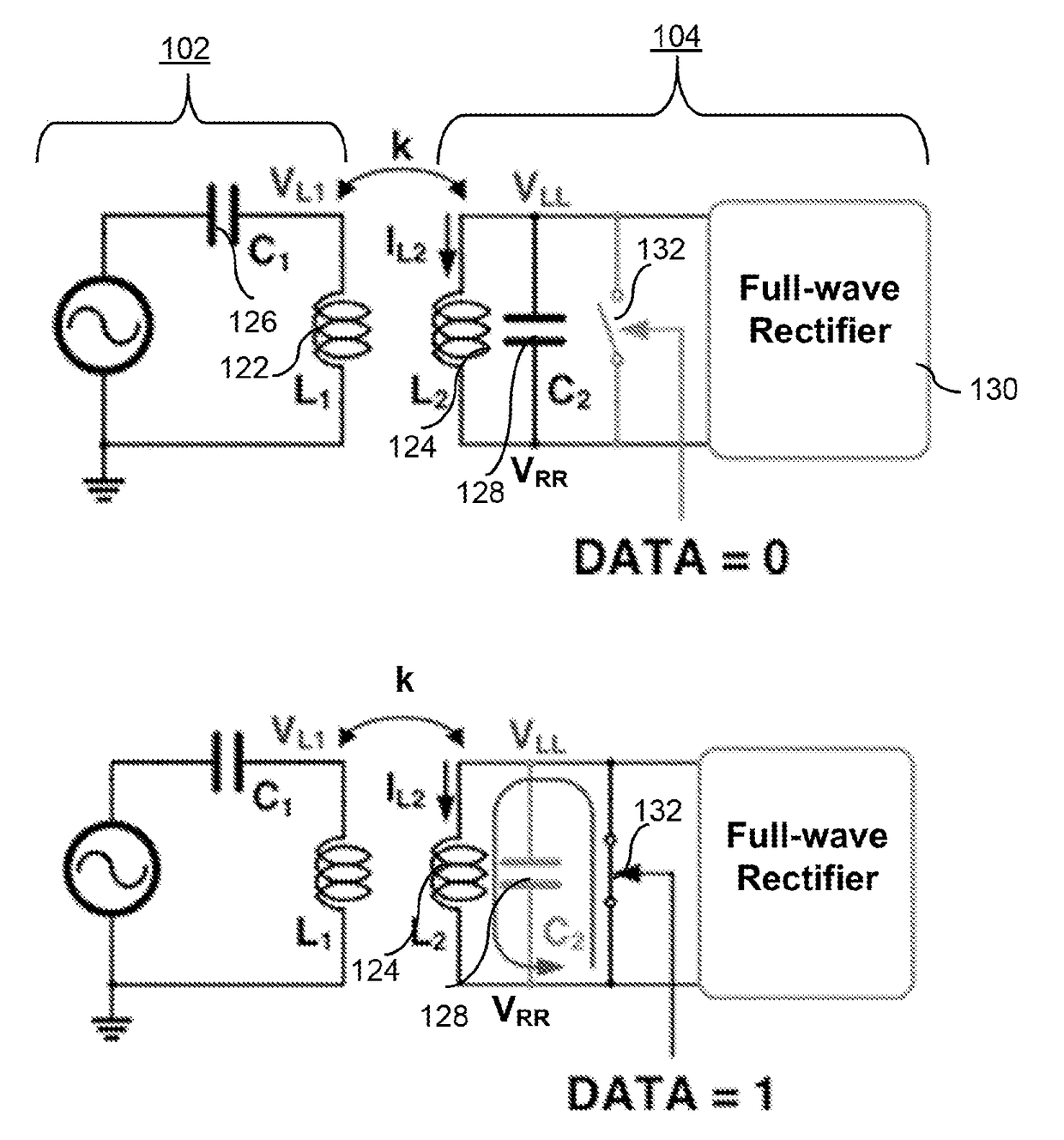
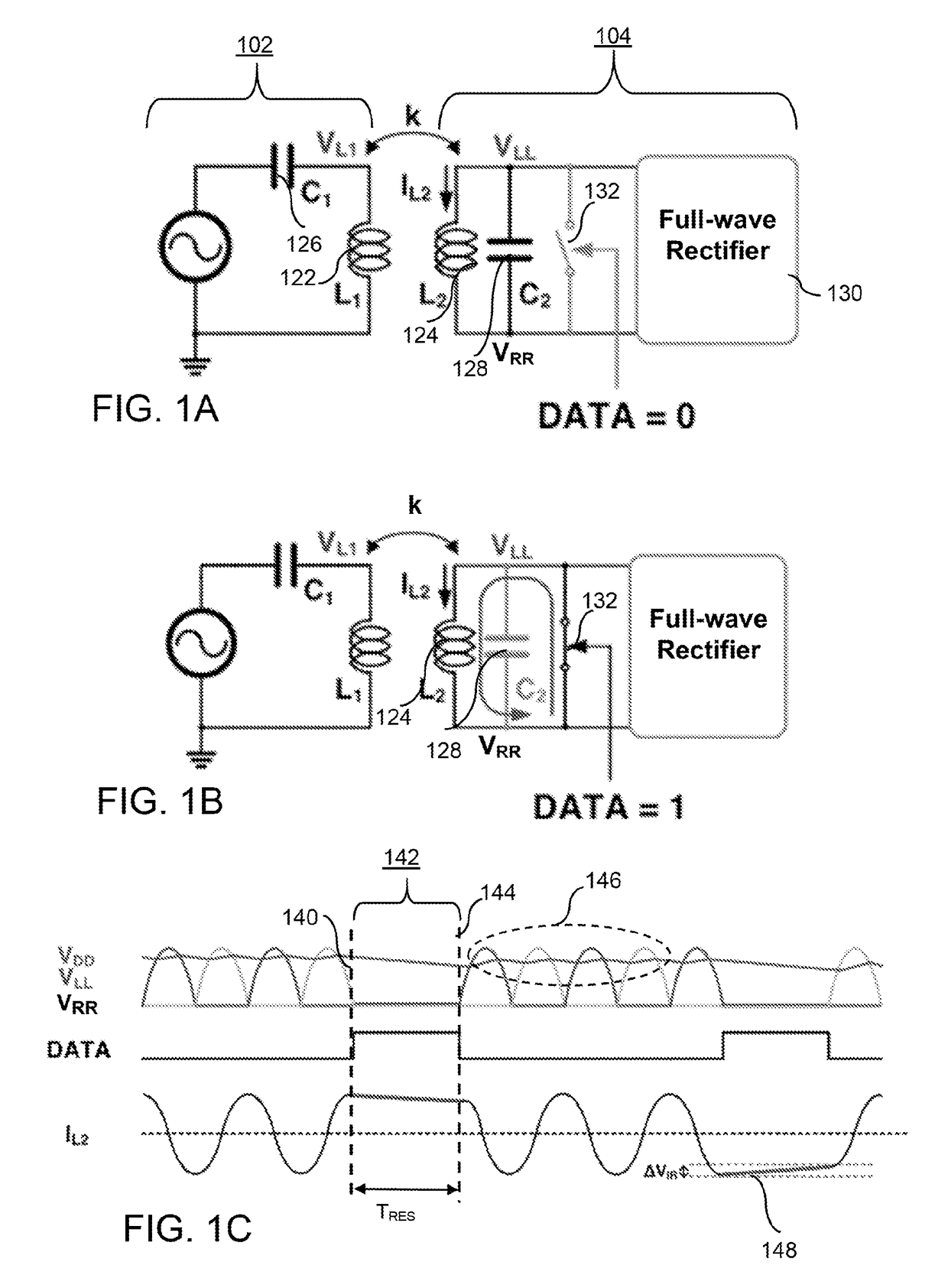
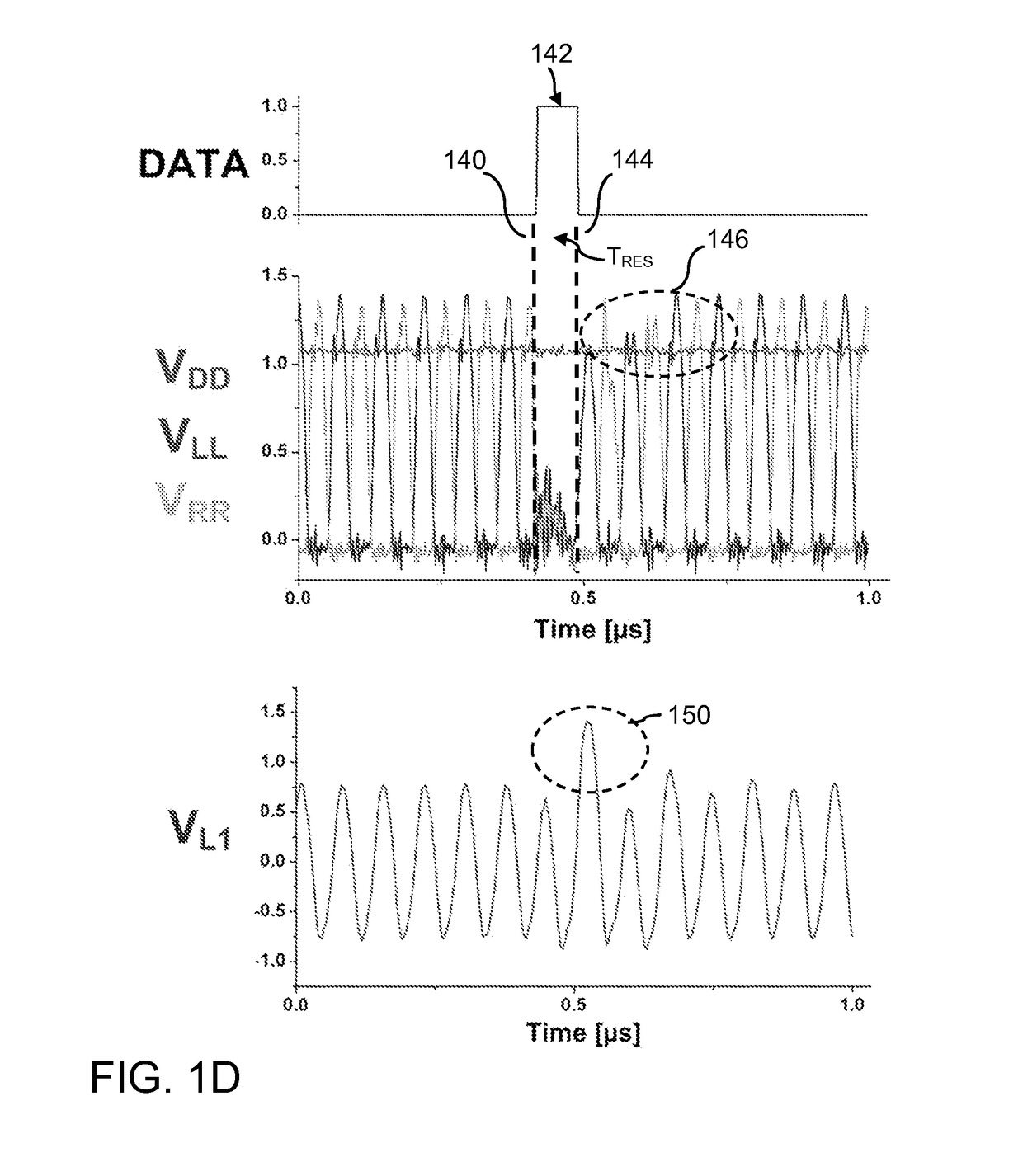
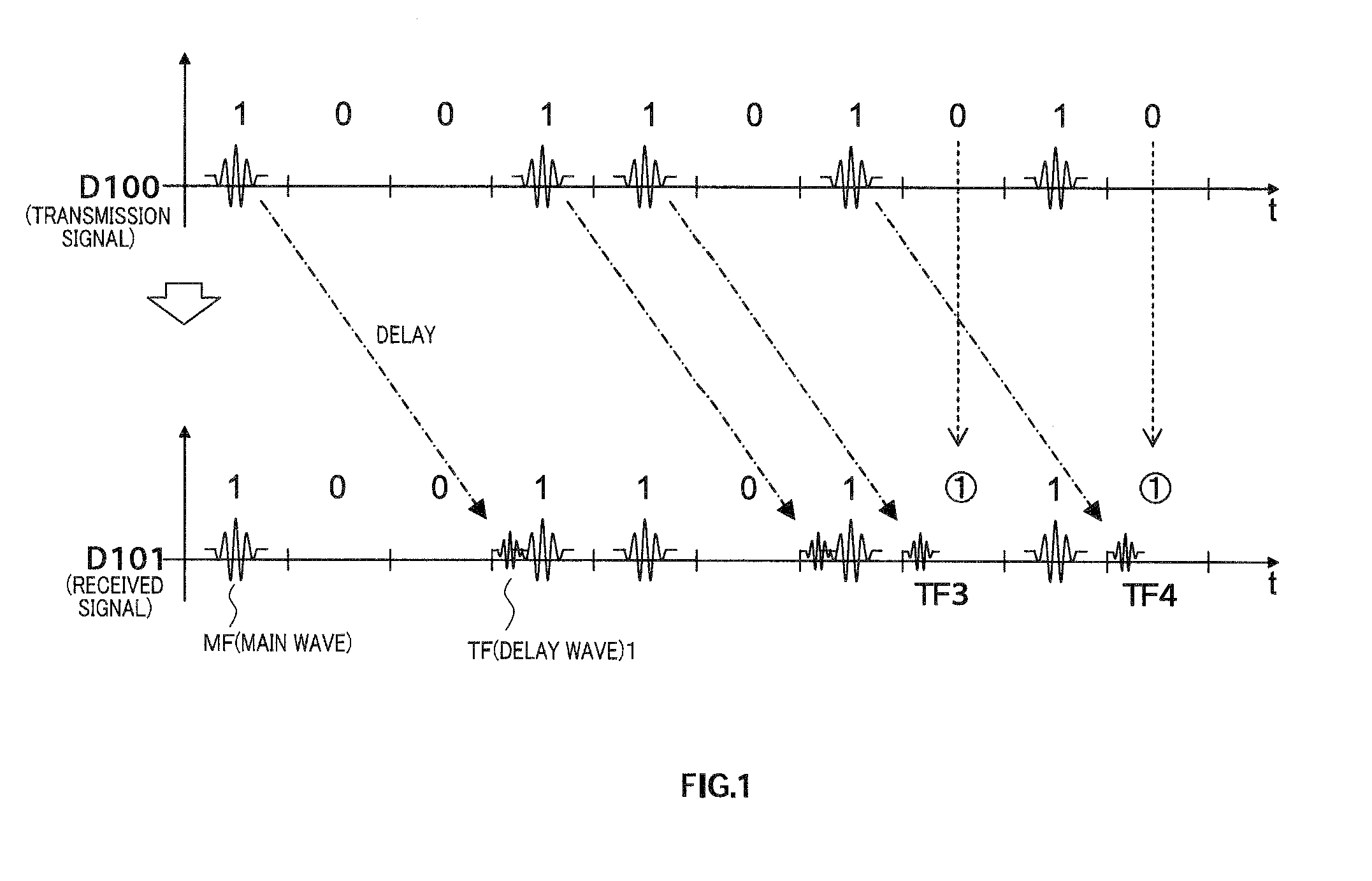
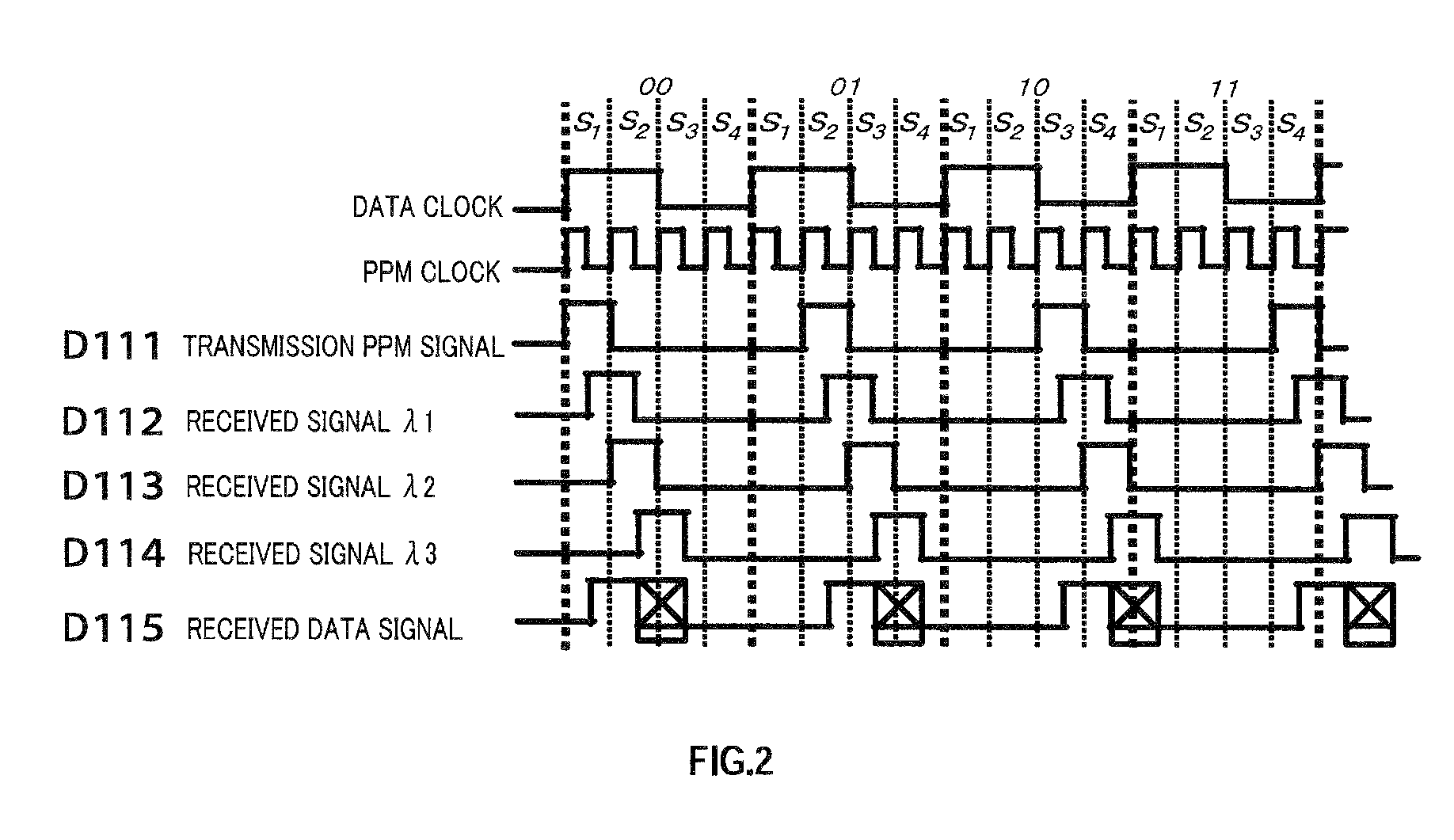
On-off keying (OOK) denotes the simplest form of amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation that represents digital data at the presence or absence of a carrier wave. In its simplest form, the presence of a carrier for a specific duration represents a binary one, while its absence for the same duration represents a binary zero. Some more sophisticated schemes vary these durations to convey additional information. It is analogous to unipolar encoding line code.
RFID transponder having active backscatter amplifier for re-transmitting a received signal
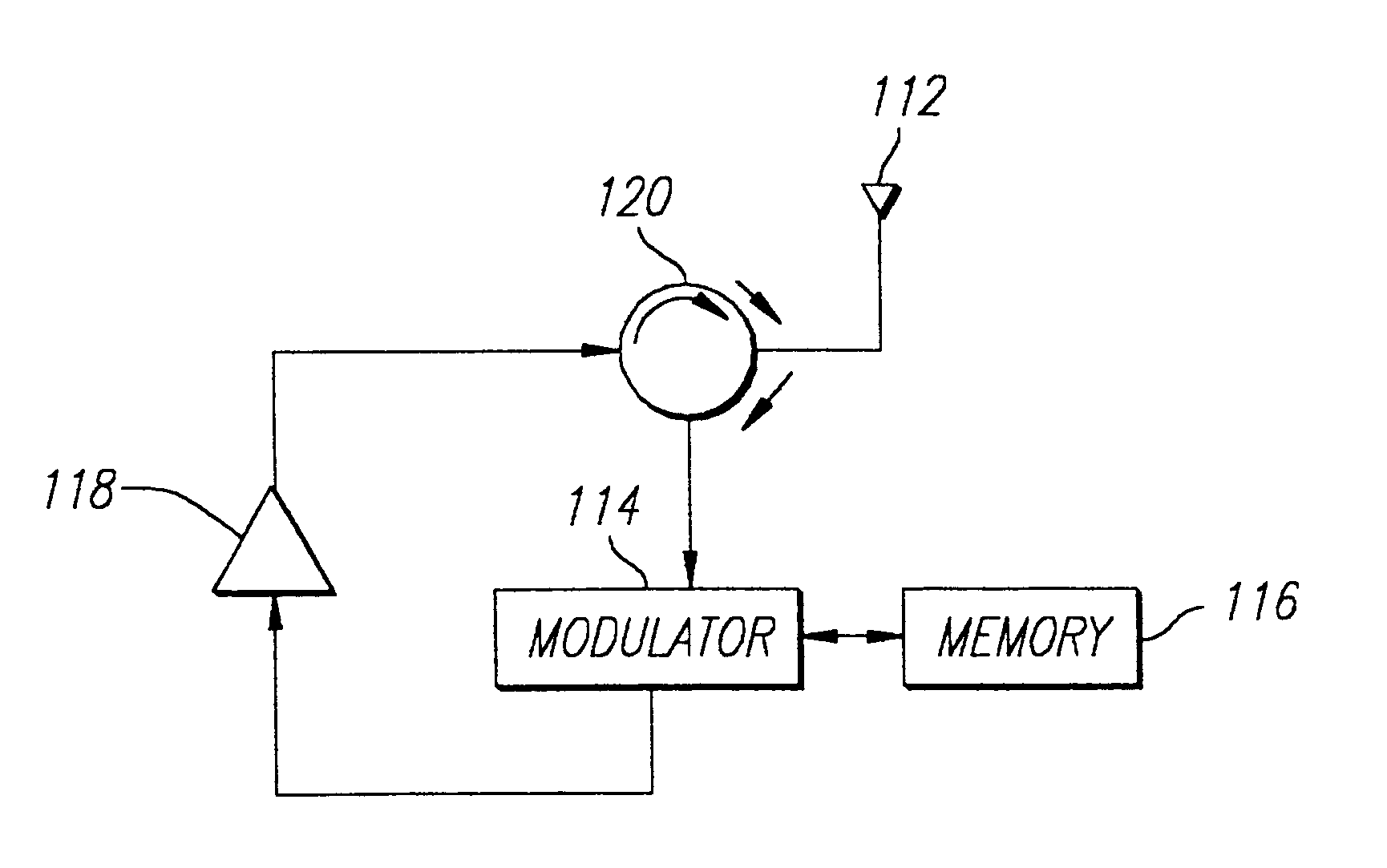
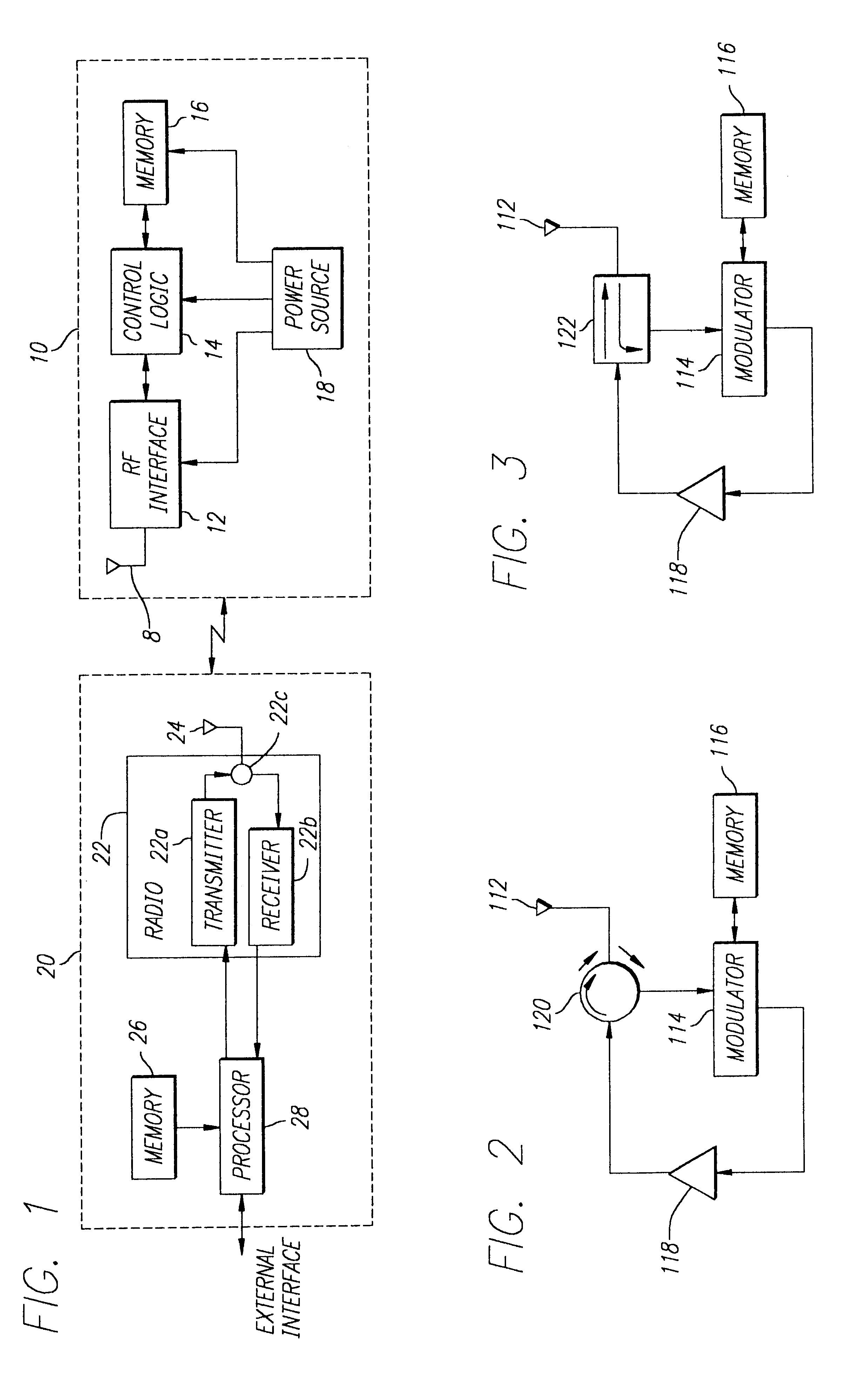
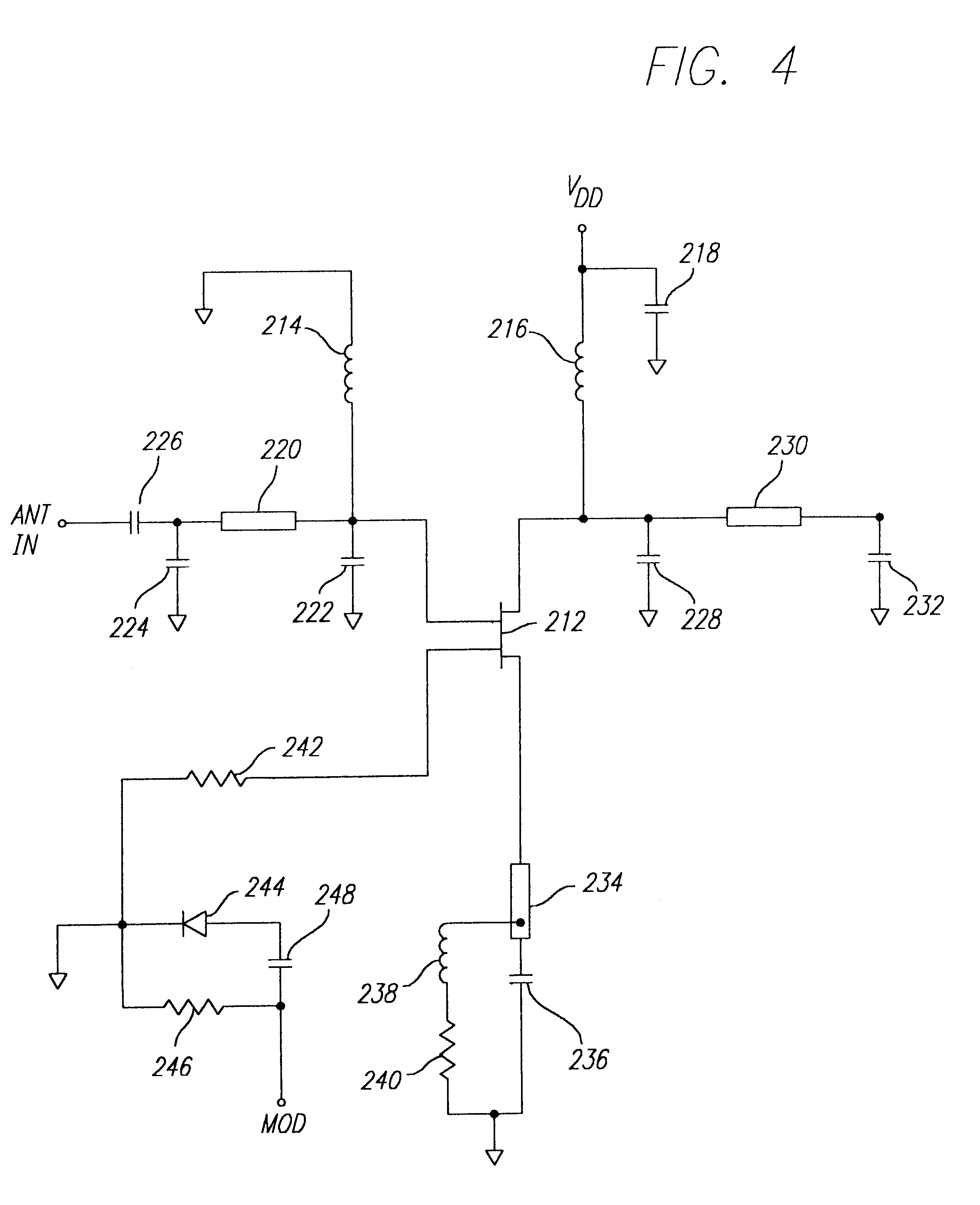
InactiveUS6838989B1Increase rangeEfficient separationRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalAudio power amplifierOn-off keying
An RFID transponder is provided with an active backscatter amplifier that amplifies and re-transmits a received signal. The RFID transponder comprises an antenna and a circulator having a first port connected to the antenna. A modulator is connected to a second port of the circulator. An amplifier is connected to a third port of the circulator, with the amplifier connected to the modulator. An RF signal impinging upon the antenna passes through the circulator, the amplifier, and the modulator, and returns to the antenna through the circulator. The modulator further comprises an input coupled to the second port of the circulator and an output coupled to an input of the amplifier. The amplifier has an output coupled to the third port of the circulator. The modulator is adapted to modulate the RF signal using on-off keying.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
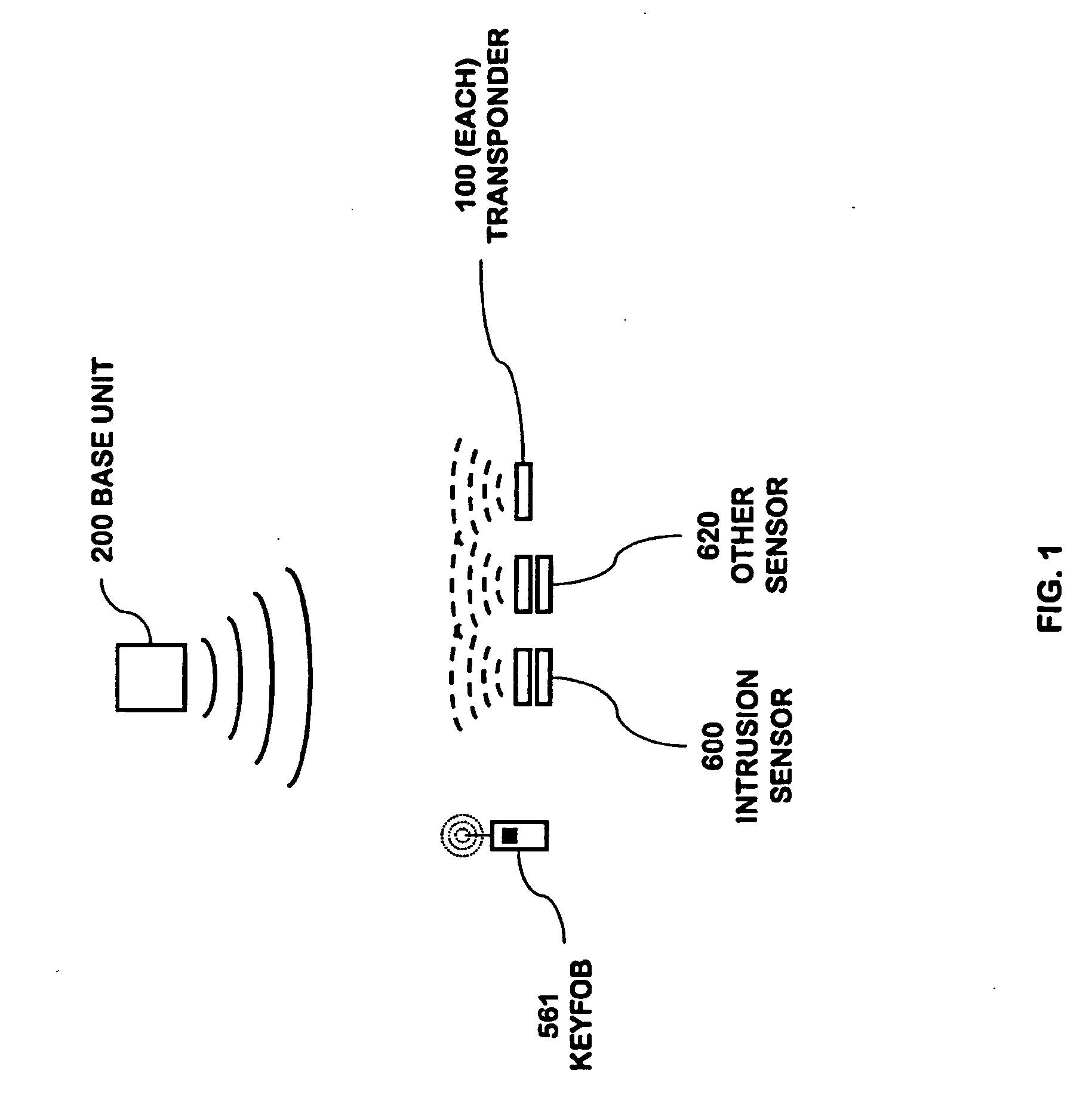
Power management of transponders and sensors in an RFID security network
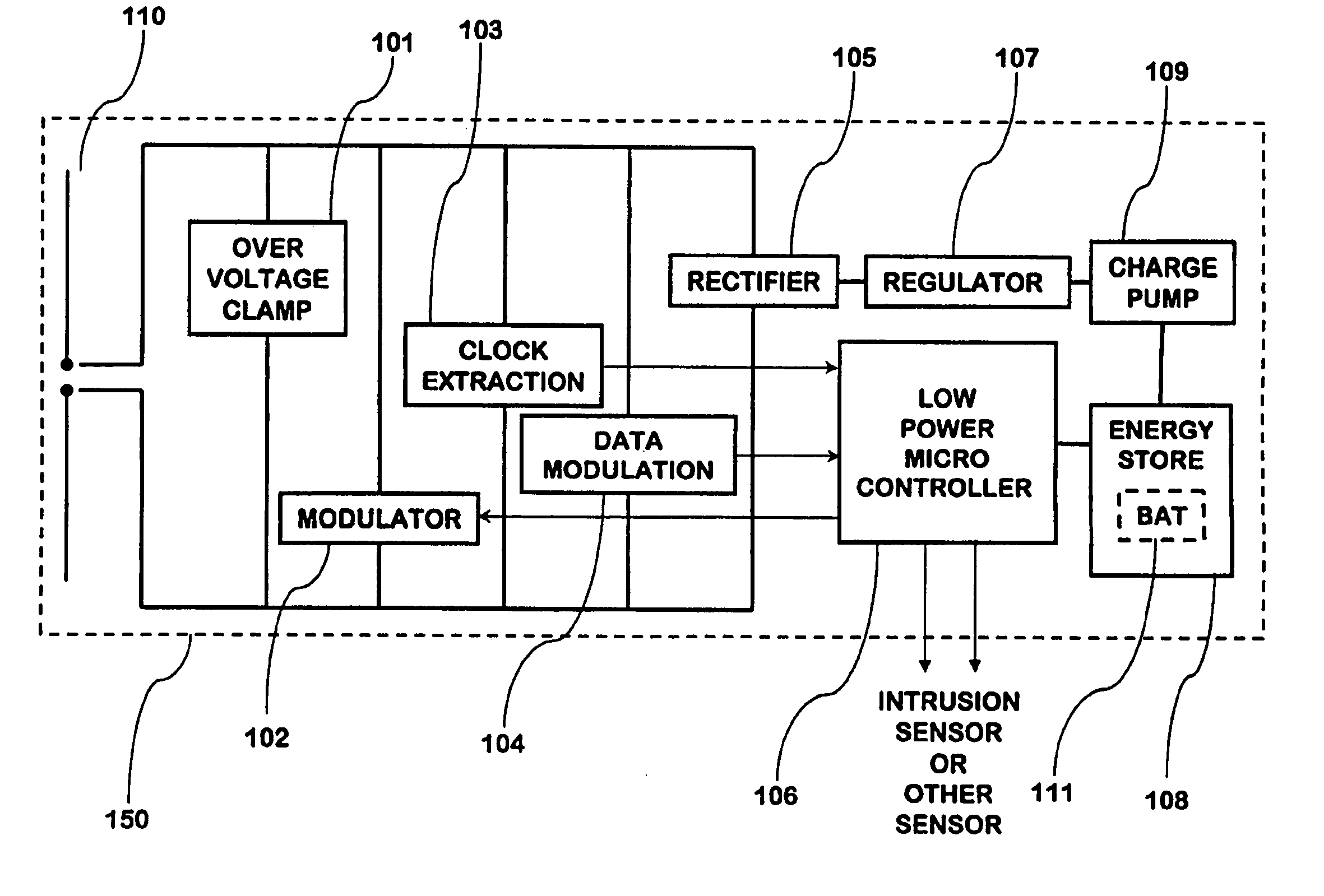
InactiveUS20060132302A1Improve reliabilityLow costElectric signal transmission systemsSafety arrangmentsAudio power amplifierOn-off keying
An RFID transponder with an associated sensor used in a security network including at least one RFID reader that transmits signals at a first frequency. The transponder has a processor controlling its other components. Transmitter circuitry coupled to a transmit antenna transmits signals to the reader at a second frequency. A receive antenna receives signals in a frequency band that includes the first frequency. One or more RF diodes obtain the signal from the receive antenna and output a power envelope signal representing the power level of the signal obtained from the receive antenna. An amplifier coupled to the output of the RF diode amplifies the power envelope signal received from the RF diode. The processor receives the amplified power envelope signal and decodes any data that have been encoded using an on-off keyed modulation scheme applied to the signal obtained from the receive antenna.
Owner:INGRID
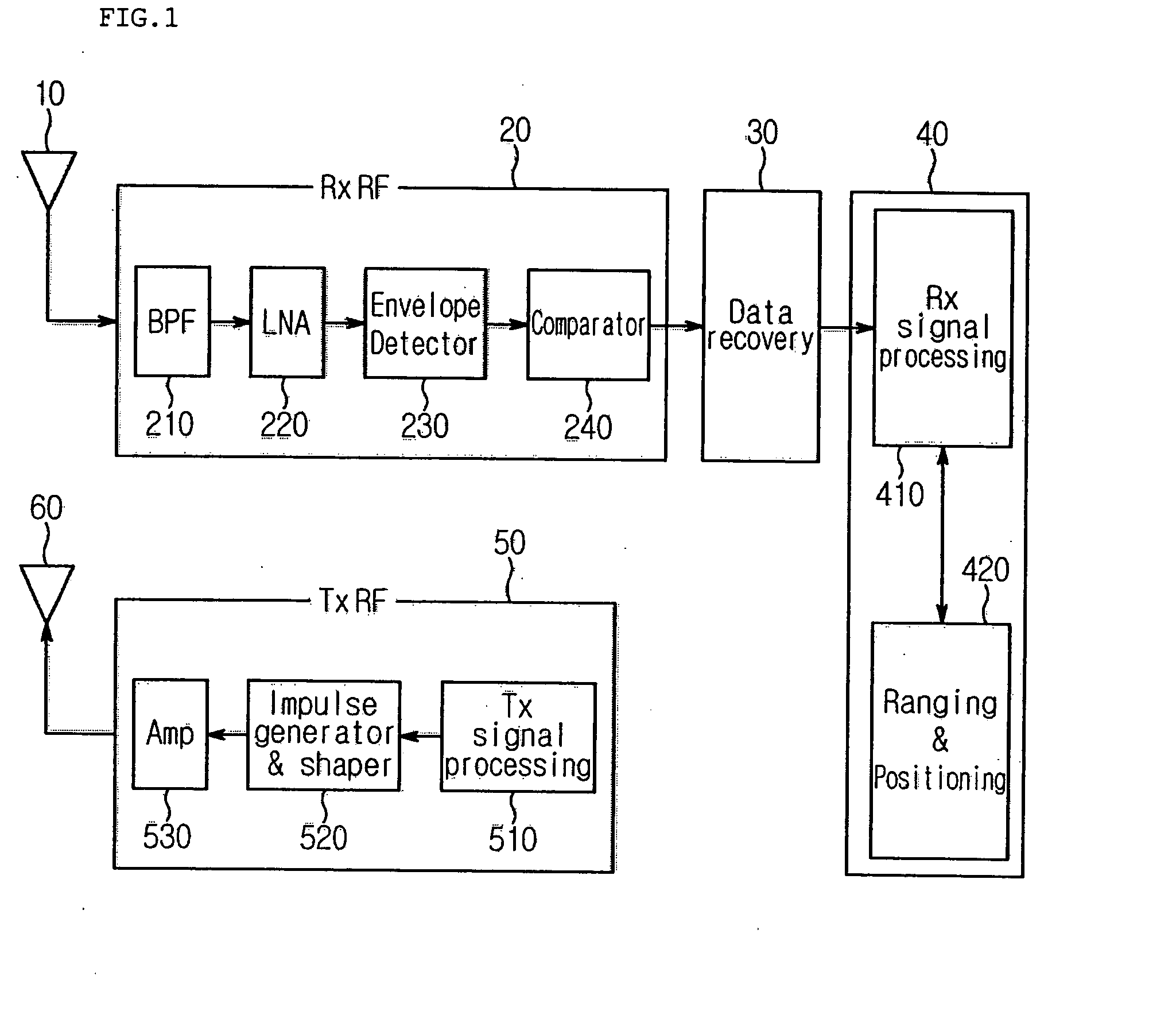
Impulse radio-based ultra wideband (IR-UWB) system using 1-bit digital sampler and bit decision window
ActiveUS20080056419A1Low costReduce power consumptionSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsOn-off keyingEngineering
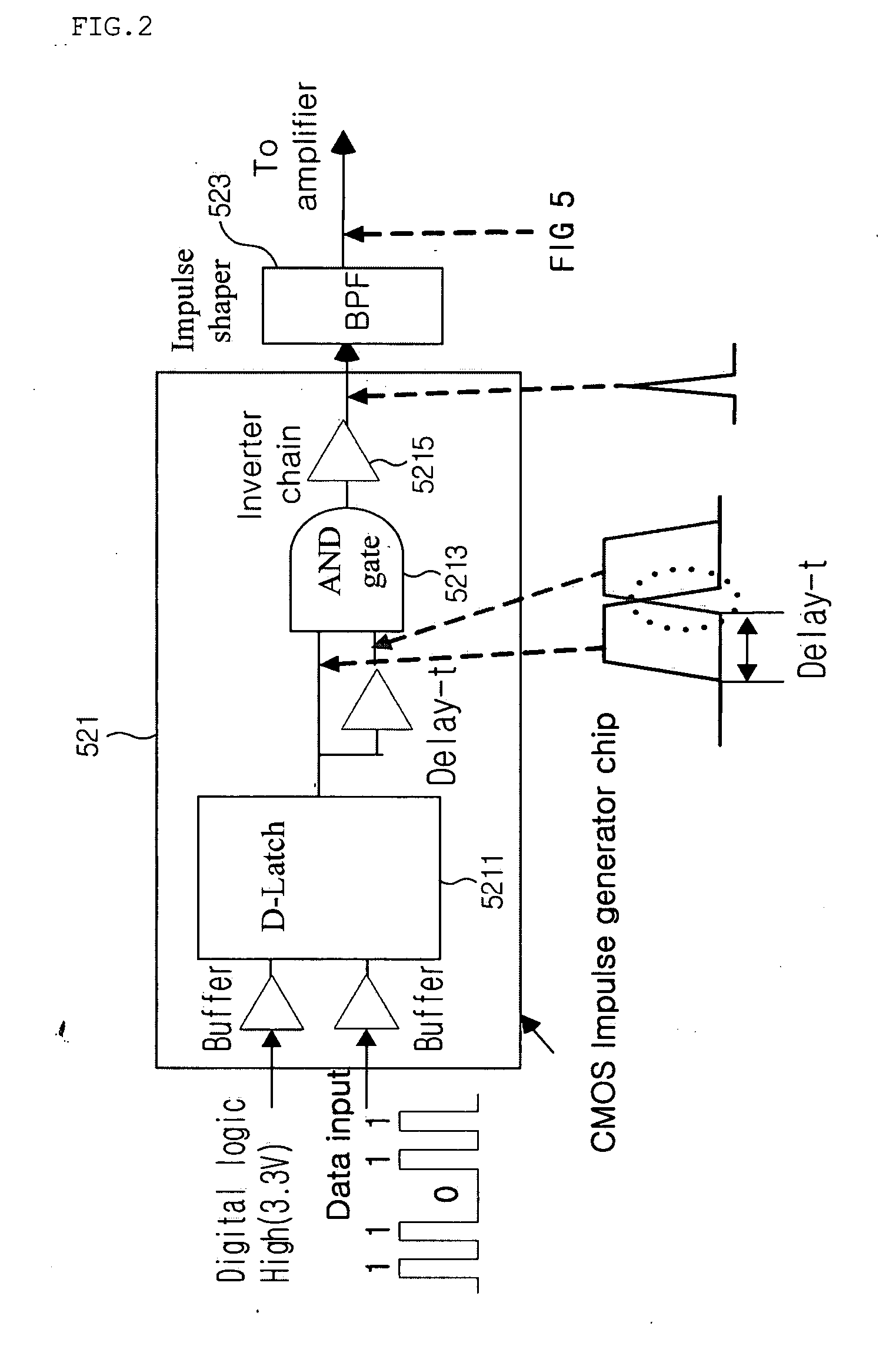
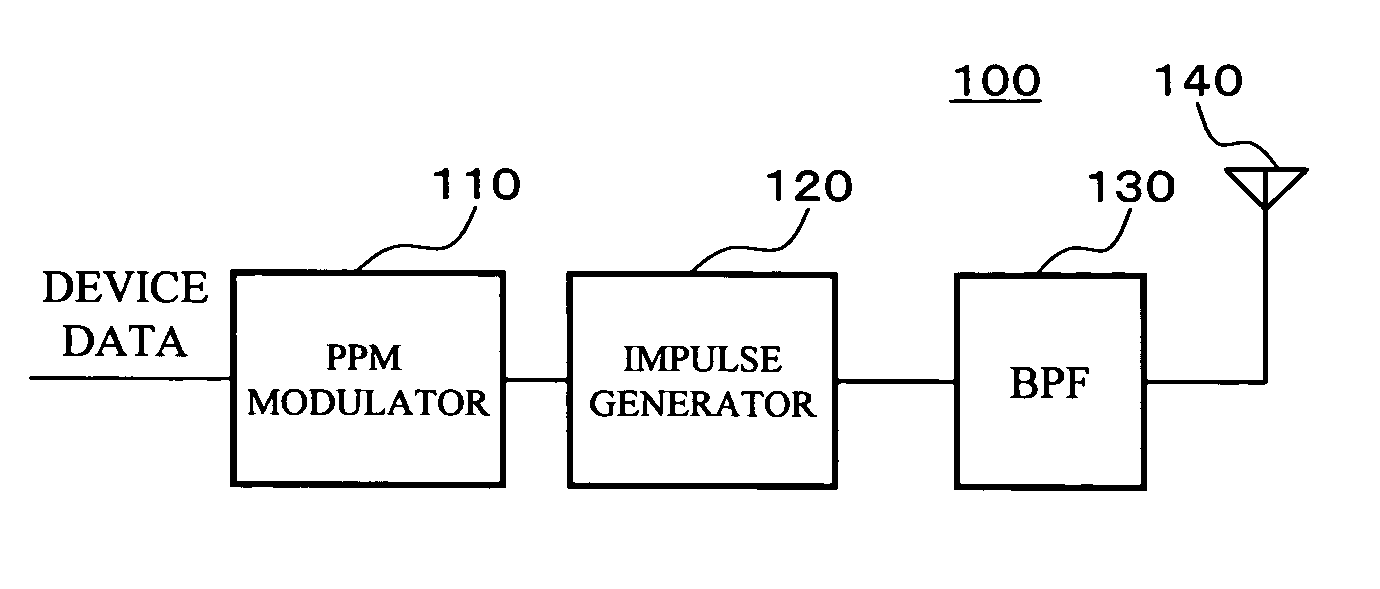
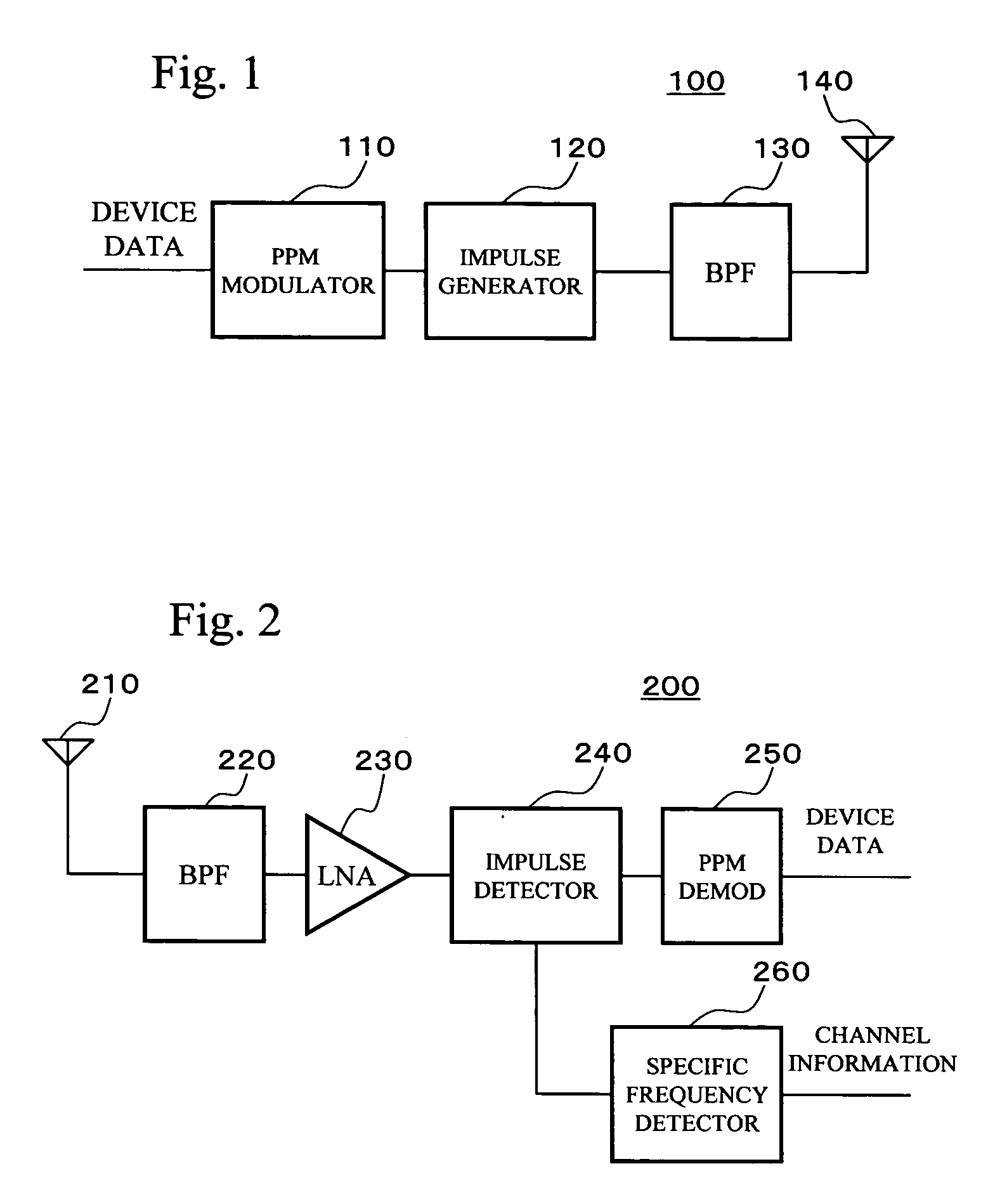
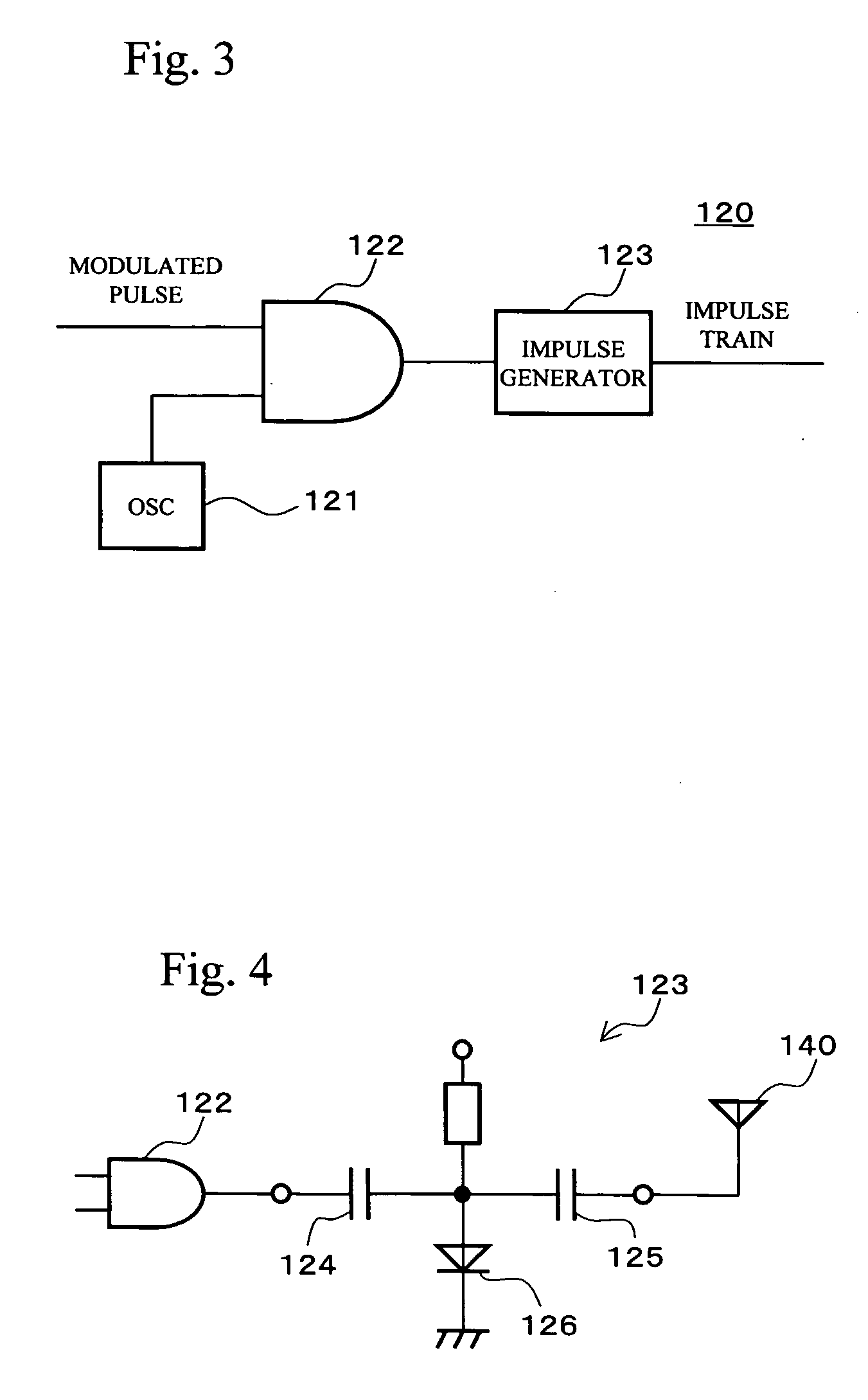
An impulse radio-based ultra wideband communication system, using an ultra wideband impulse and a 1-bit high-speed digital sampler, includes a transmitting RF module, a receiving RF module, a signal recovery unit, a transmitting signal processor, a receiving signal processor, and an ultra wideband antenna. The transmitting RF module includes an integrated impulse generator capable of implementing on-off-keying modulation and pulse position modulation, and an amplifier for amplifying output of the integrated impulse generator. The receiving RF module includes a two stage envelope detector for detecting a received signal and a comparator for converting the detected signal into a rectangular pulse. The signal recovery unit restores the signal from the receiving RF module to a digital signal using the 1-bit digital sampler. The signal processor includes a receiving signal processor for synchronizing the digital signal and decoding the detected signal. The ultra wideband antenna transmits and receives an ultra wideband signal.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
RF communications system utilizing digital modulation to transmit and receive data
InactiveUS7154938B2Reduce the impact of interferenceFacilitating spectrum sharingElectric signal transmission systemsAngle modulationOn-off keyingFrequency spectrum
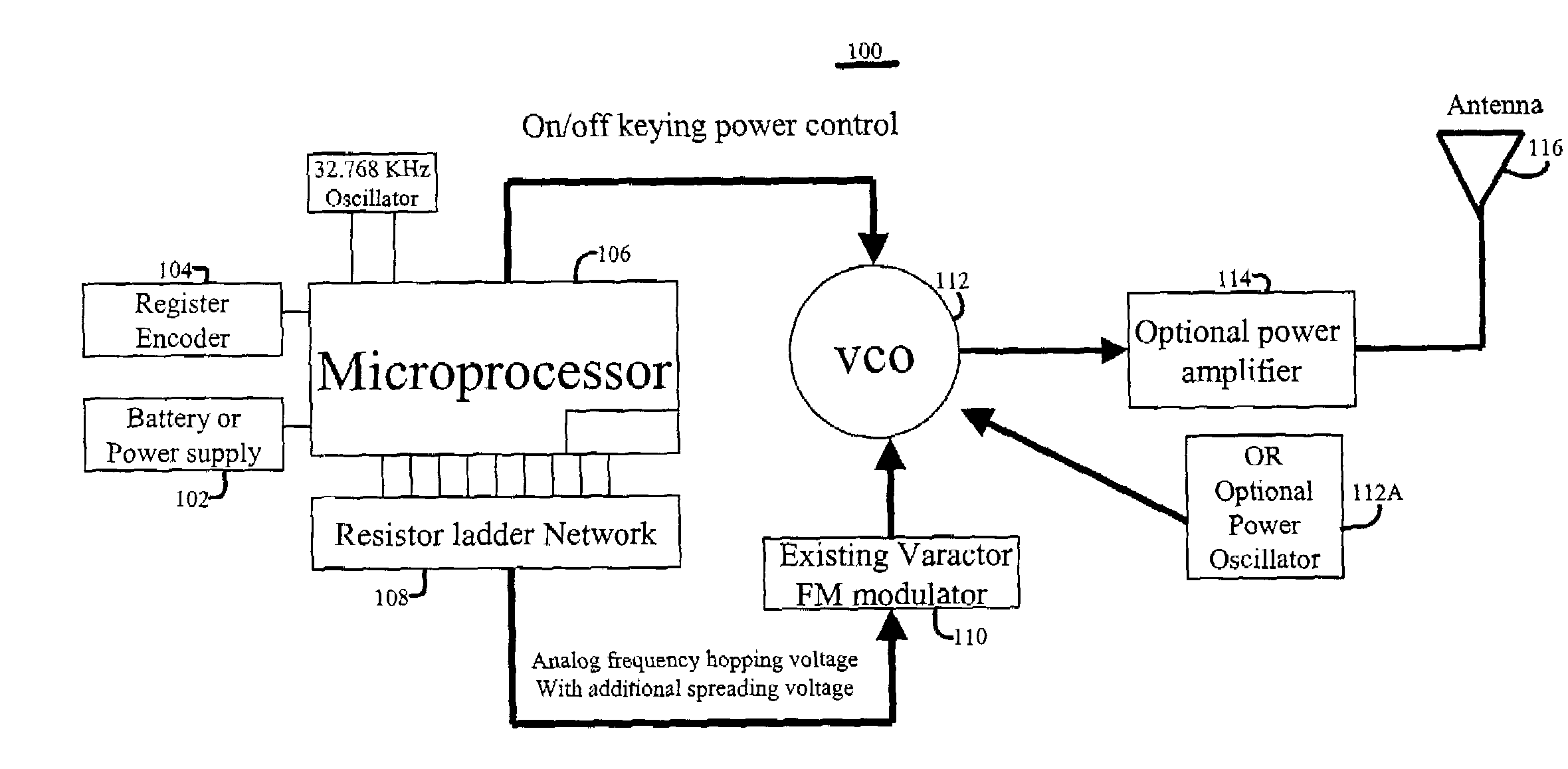
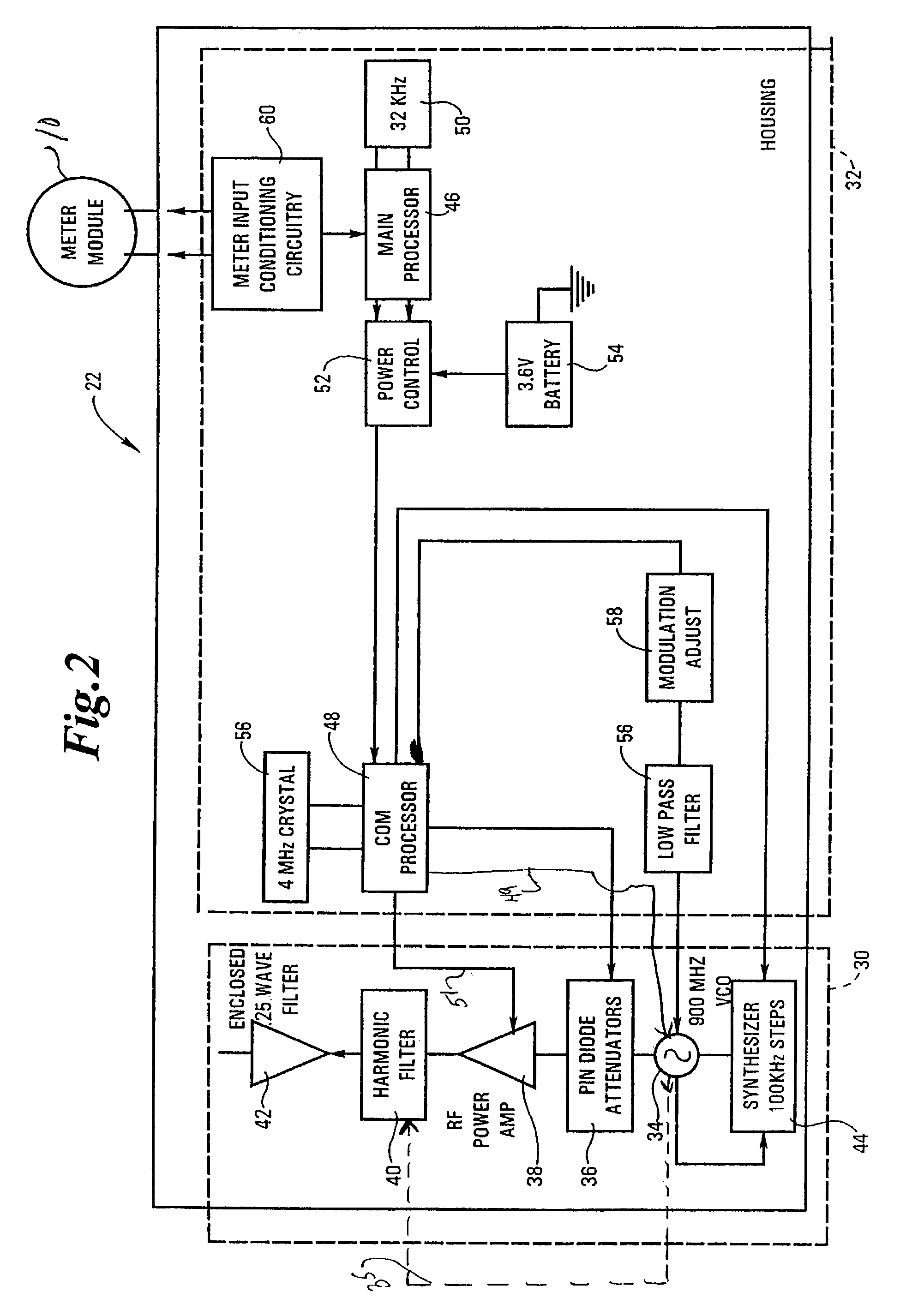
The RF communications system of the present invention wirelessly communicates data without encountering undue interference problems with other devices and complies with rules governing unlicensed, spectrum-sharing devices. In an example embodiment, a transmitter device includes a digital subsystem powered by a power supply that processes data from another device and a radio frequency (RF) sub-system that transmits the processed data using a frequency hopping scheme. The RF sub-system includes a microprocessor arrangement that ON-OFF keys a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) and provides a frequency-hopping scheme. The VCO is coupled to a signal frequency spreading arrangement that spreads the signal to a predetermined transmission bandwidth, wherein the frequency spreading occurs during an ON state of the ON-OFF keying and the transmission bandwidth exceeds a reception bandwidth at which the signal will be decoded.
Owner:ITRON
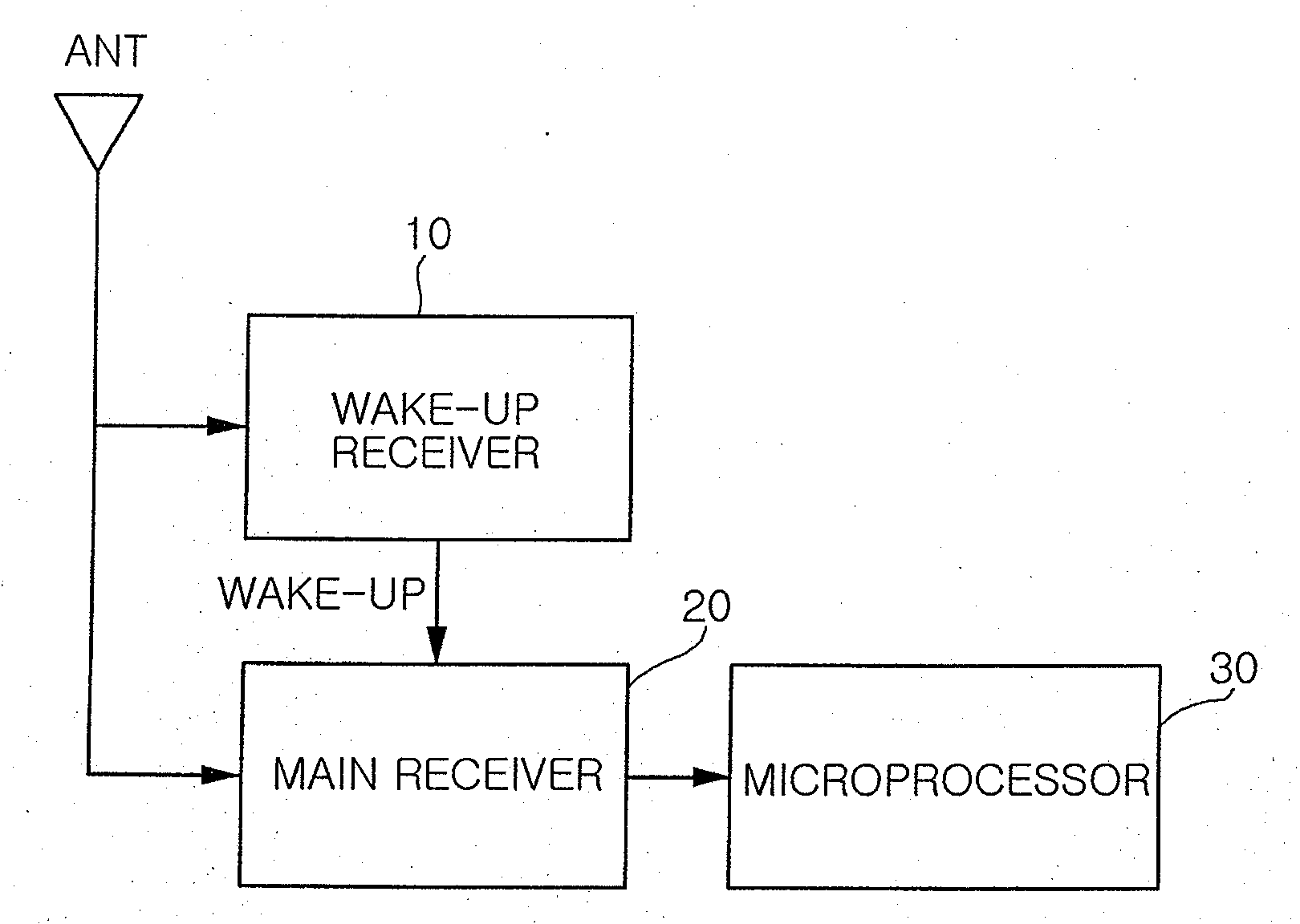
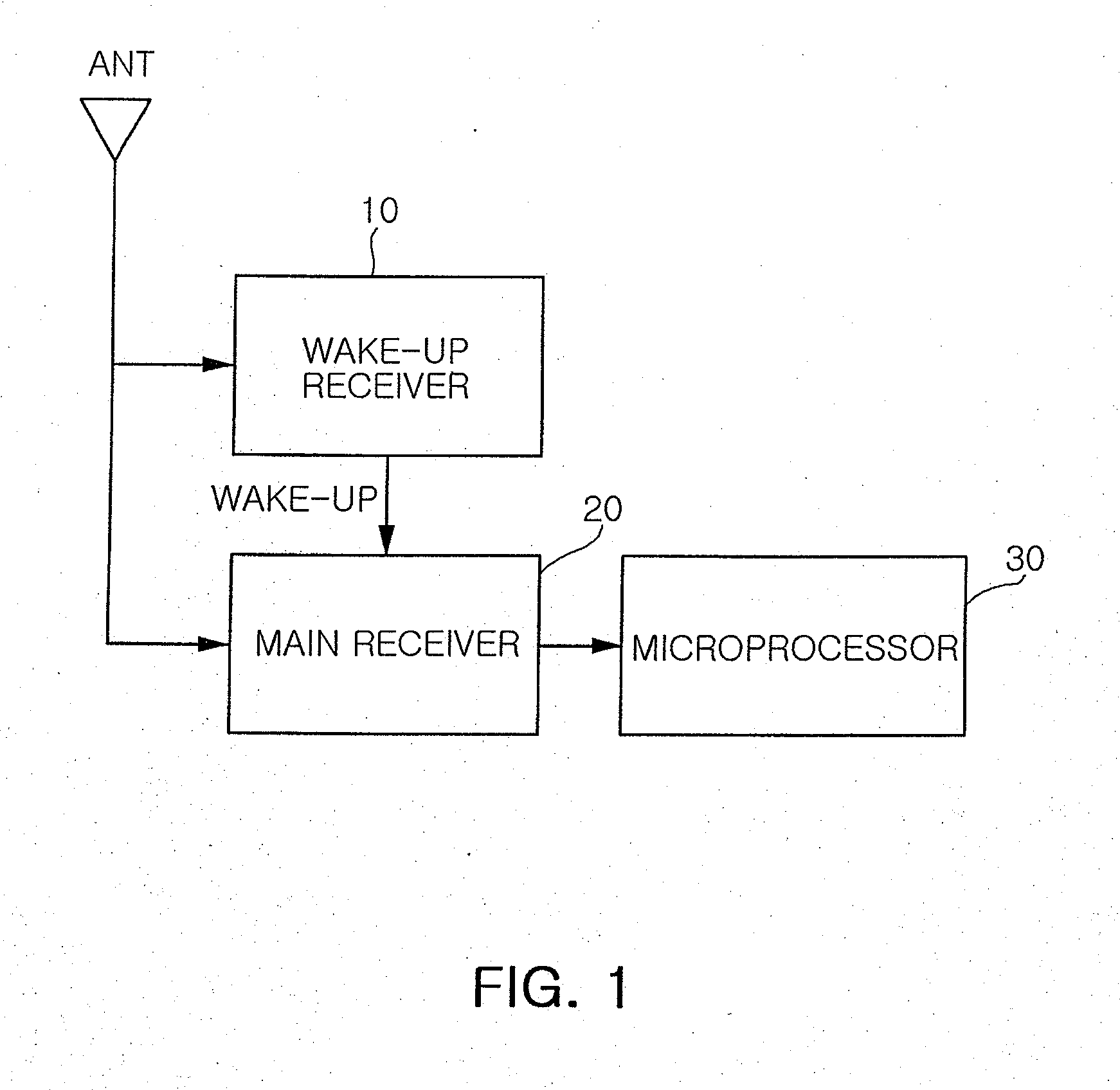
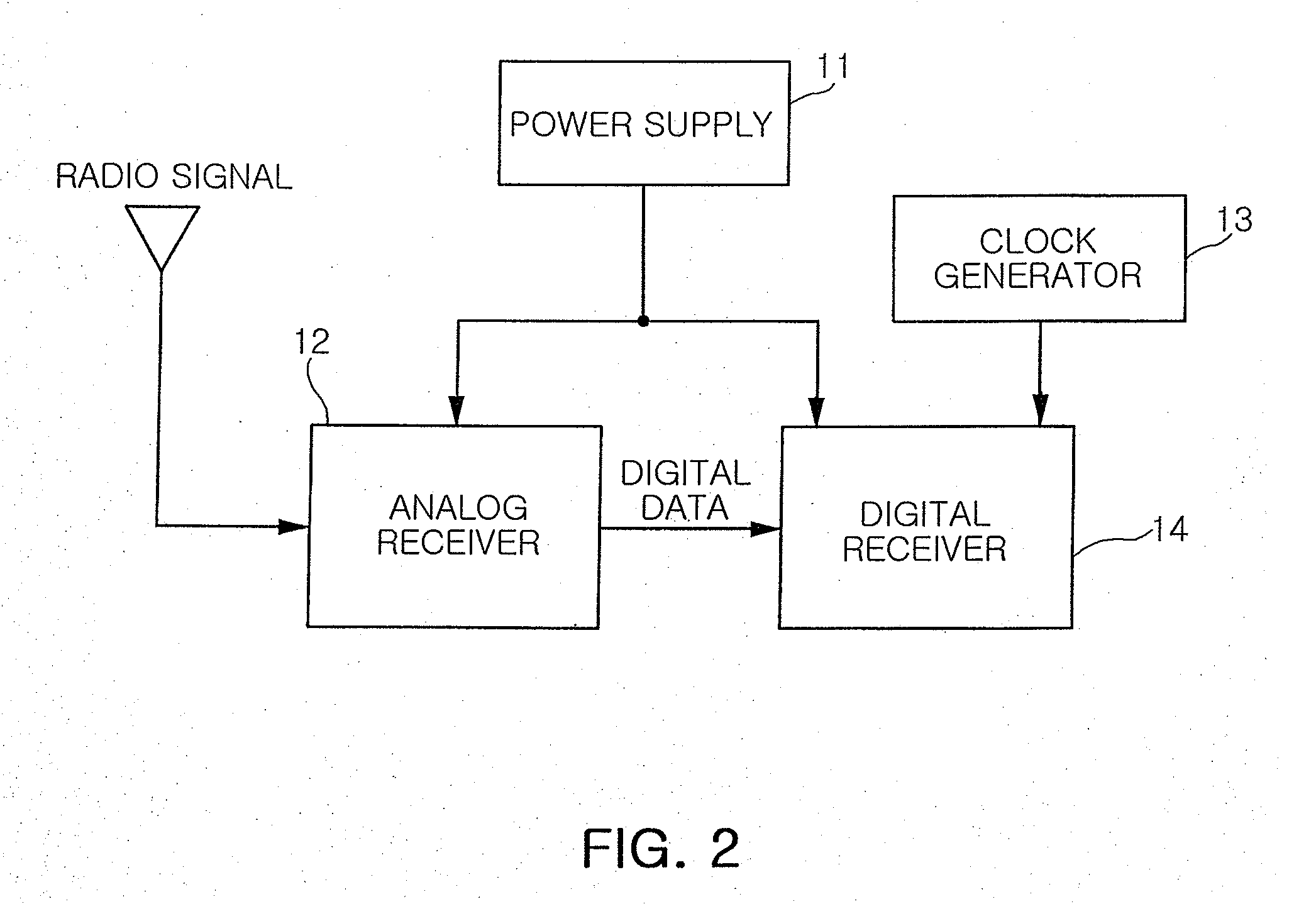
Ultra low-power wake-up receiver
InactiveUS20080108318A1Reduce power consumptionShorten operation timeEnergy efficient ICTPower managementOn-off keyingRadio reception
Provided is an ultra low-power wake-up receiver capable of reducing an operating time of an analog receiver by controlling operation on / off of the analog receiver according to a clock signal from a digital receiver in an amplitude-shift keying (ASK) or on-off keying (OOK) radio receiver. The ultra low-power wake-up receiver includes: a clock generator generating a clock signal having a predetermined frequency; an operation controller controlling analog operation-on for a predetermined time according to the clock signal from the clock generator; an analog receiver maintaining an operation-on state for a predetermined time according to the analog operation-on control performed by the operation controller, and being operated off after the predetermined time; and a digital receiver being operated on while the analog receiver maintains the operation-on state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
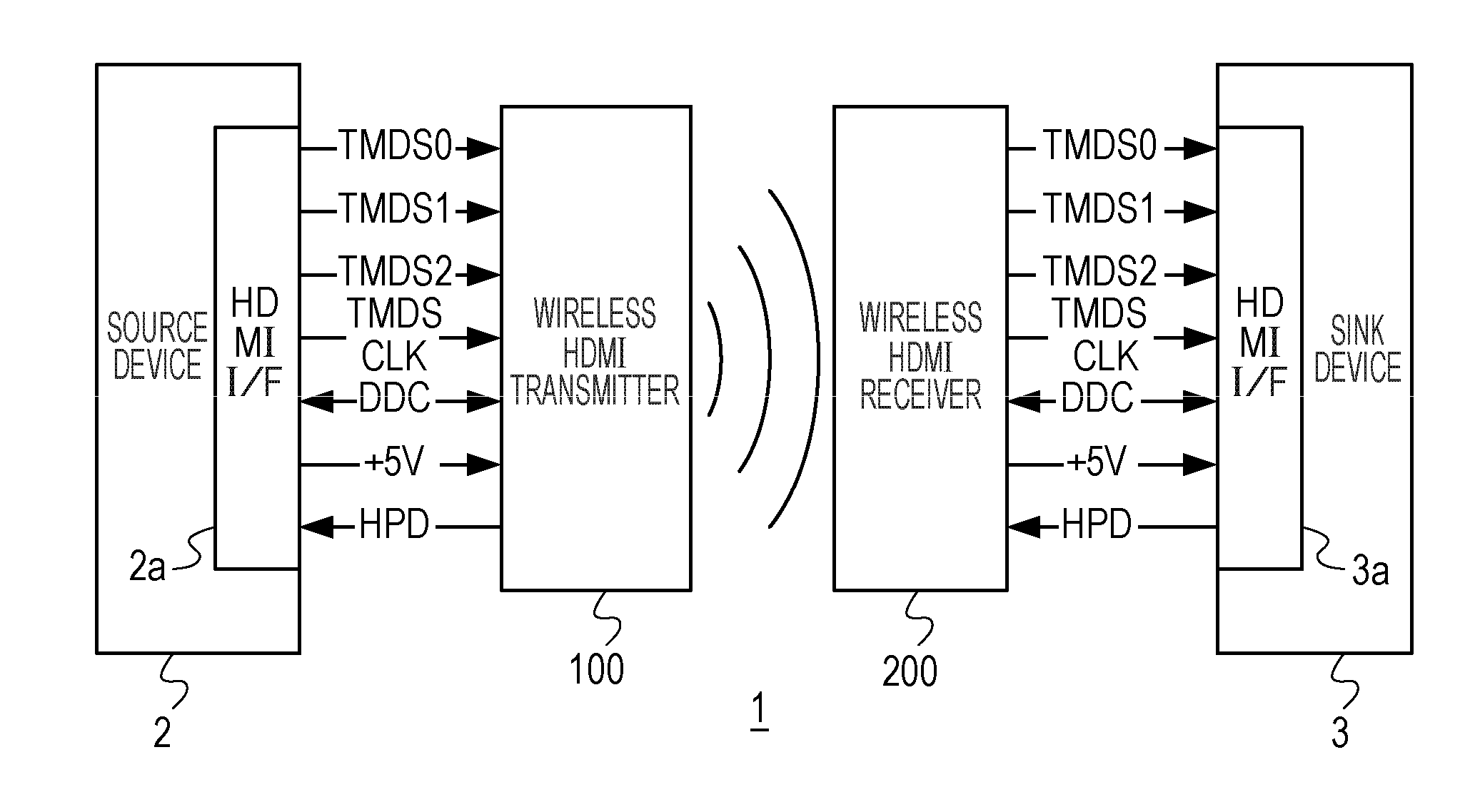
Wireless transmission system and wireless transmitter, wireless receiver, wireless transmission method wireless reception method and wireless communication method used with same
InactiveUS20130010849A1Low priceEliminate needAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsModulation with suppressed carrierOn-off keyingWireless transmission
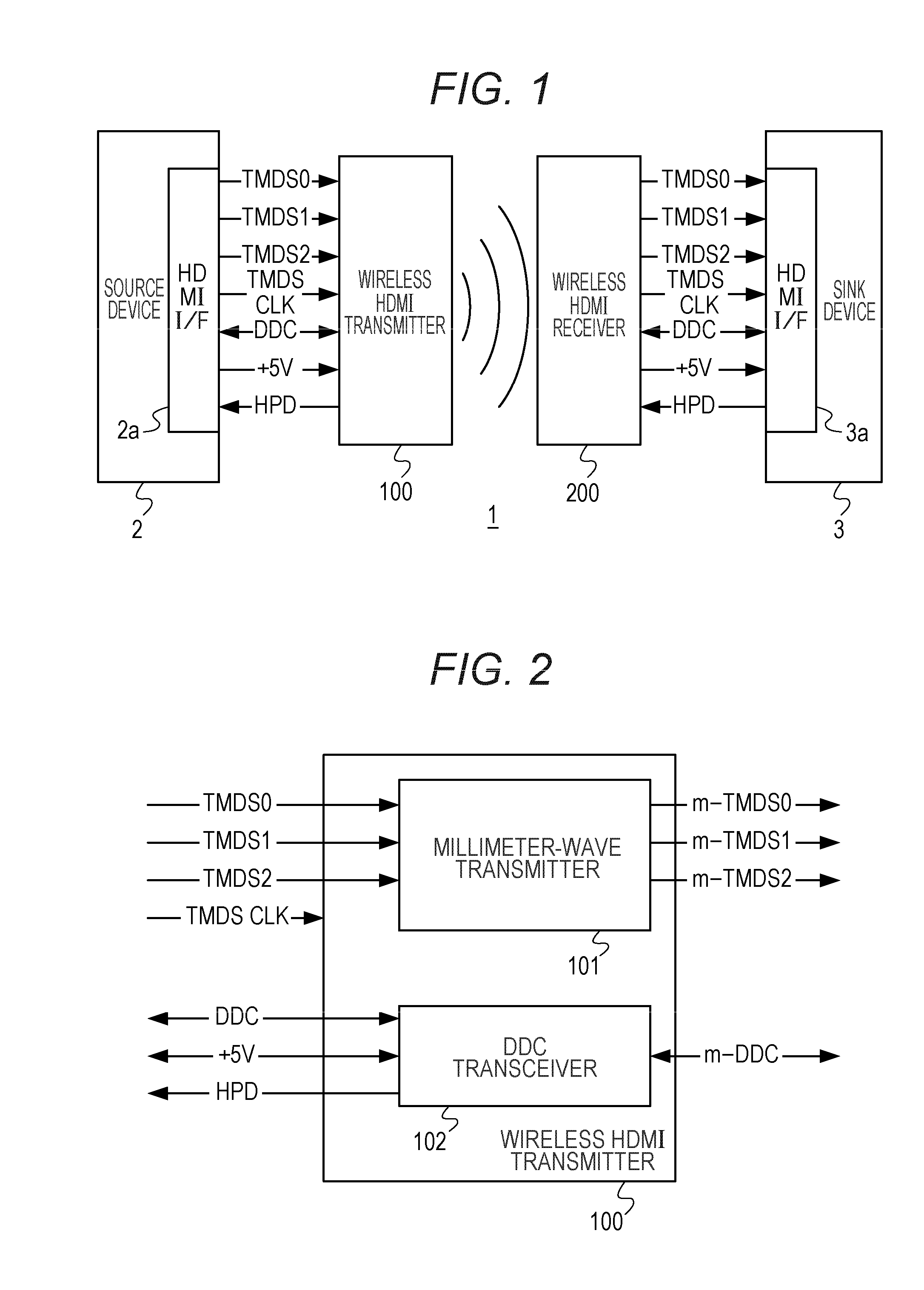
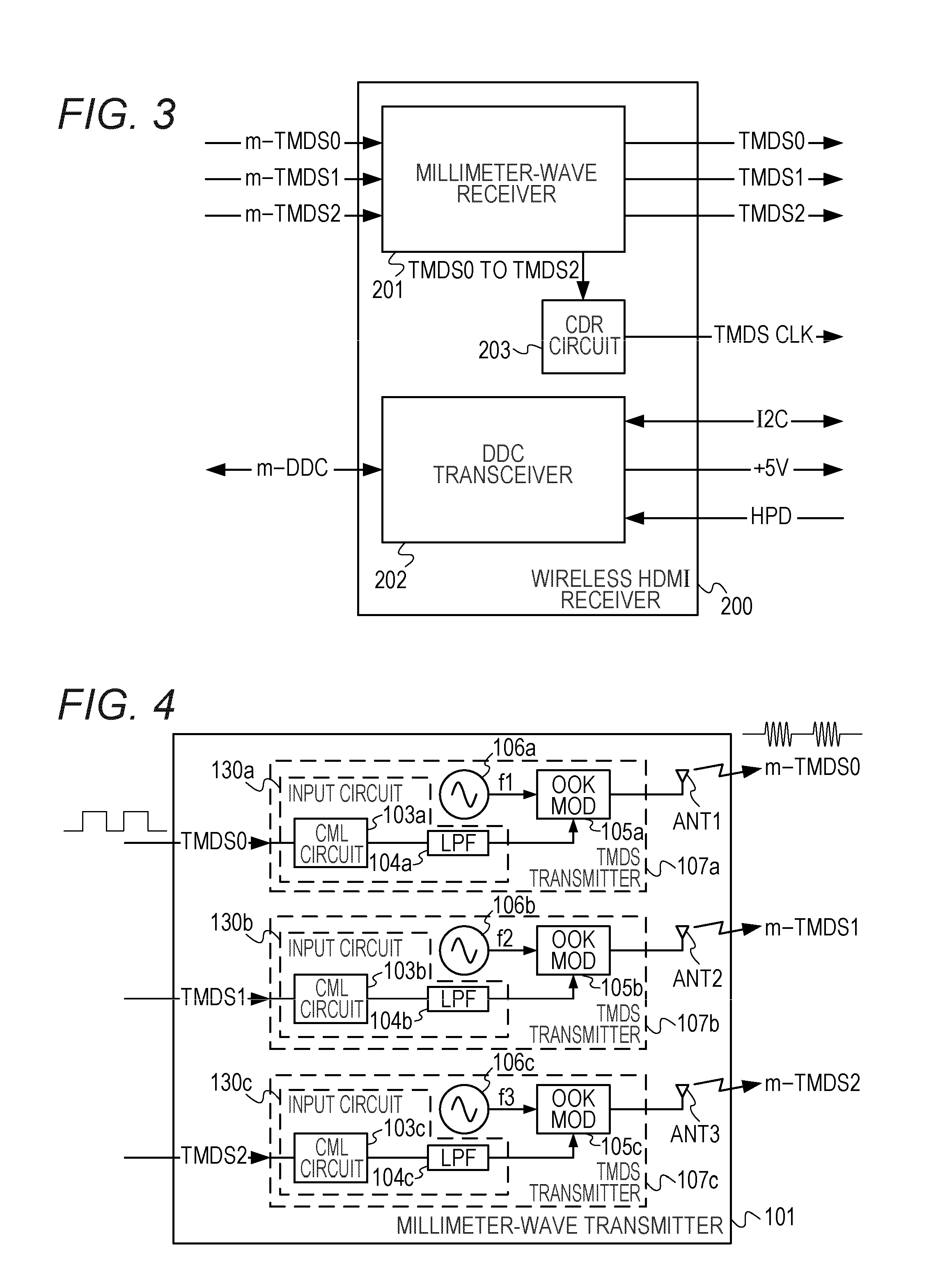
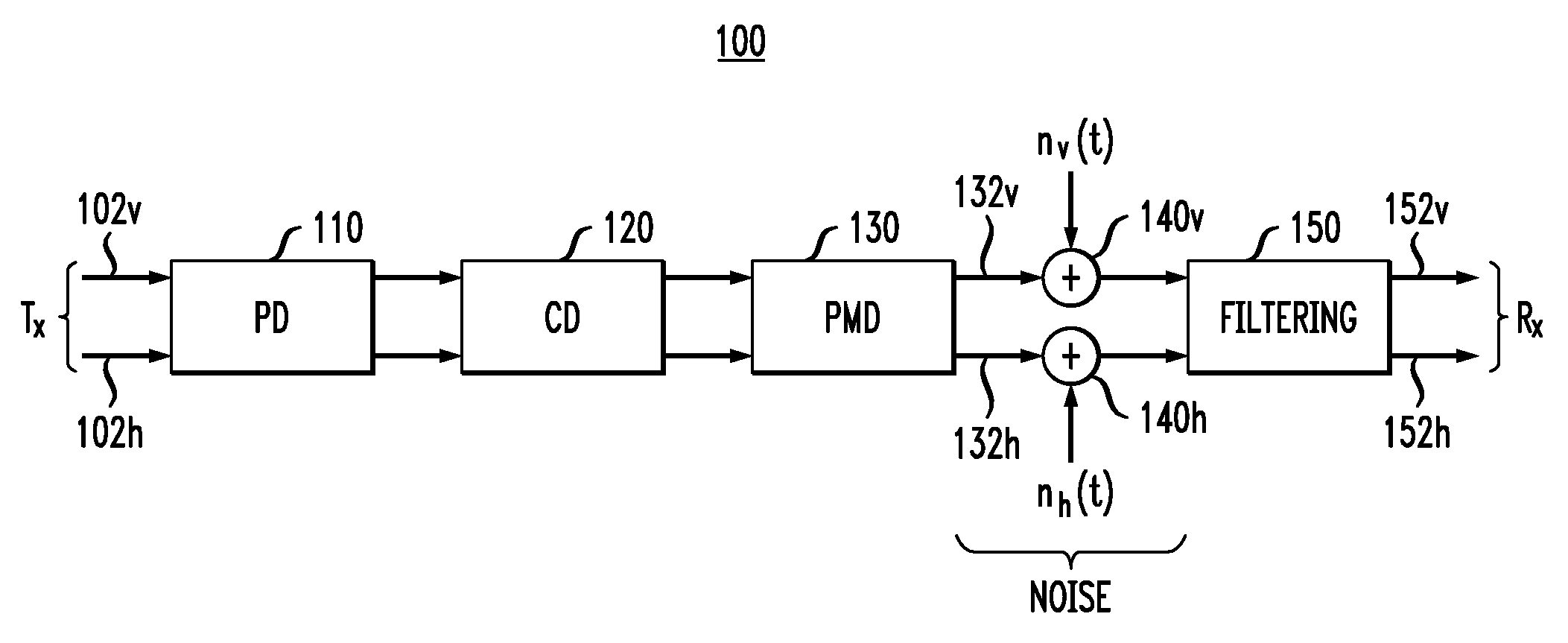
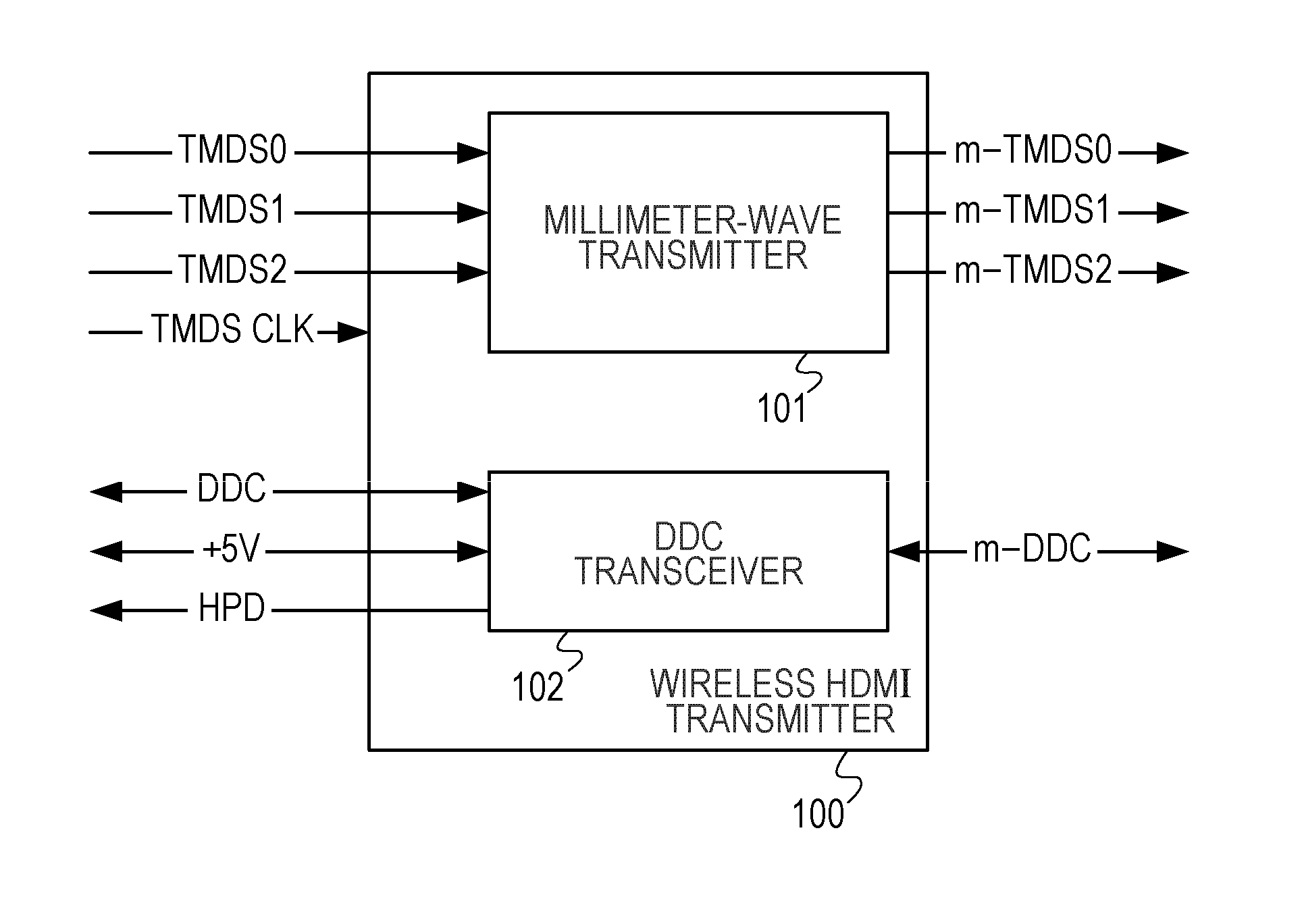
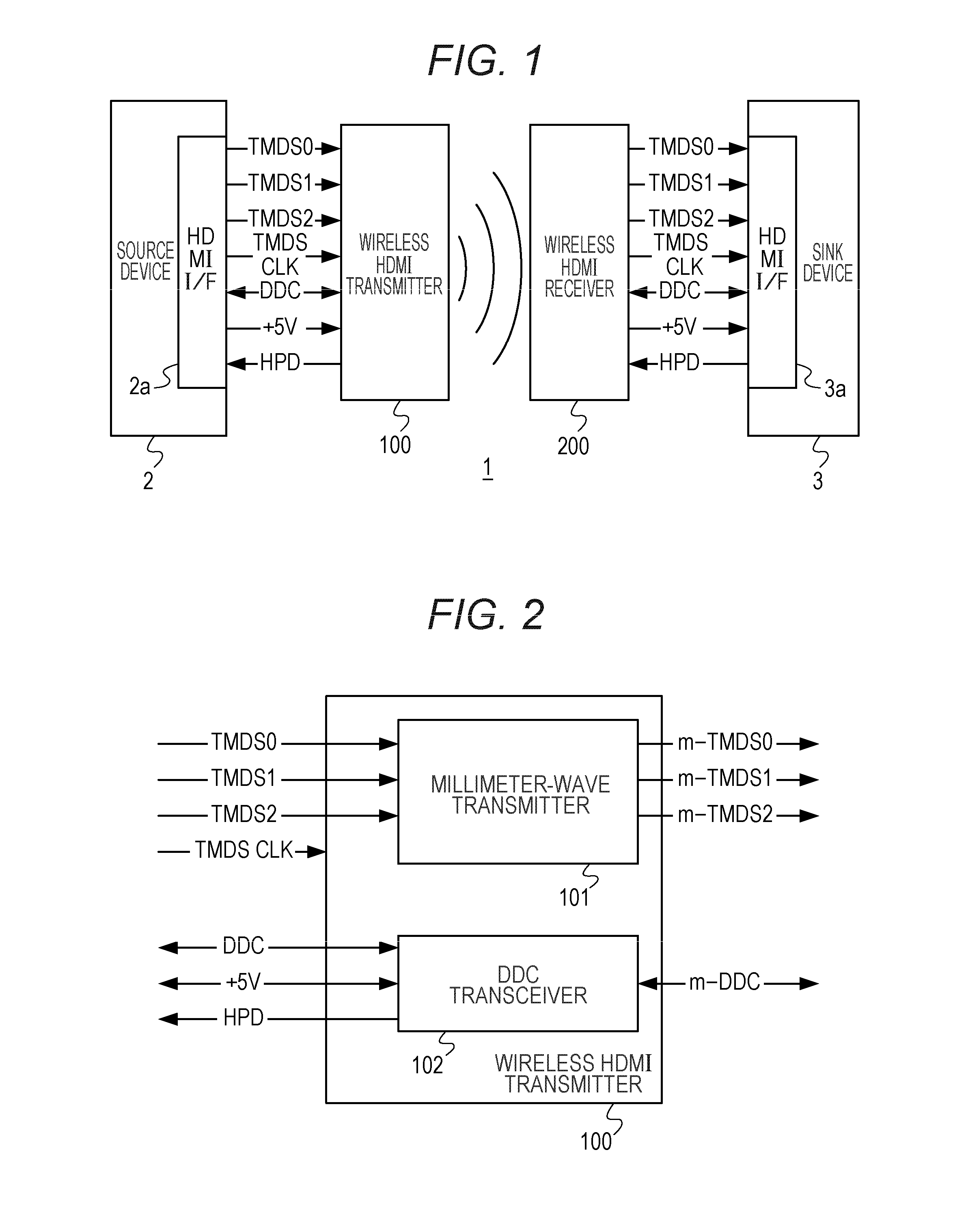
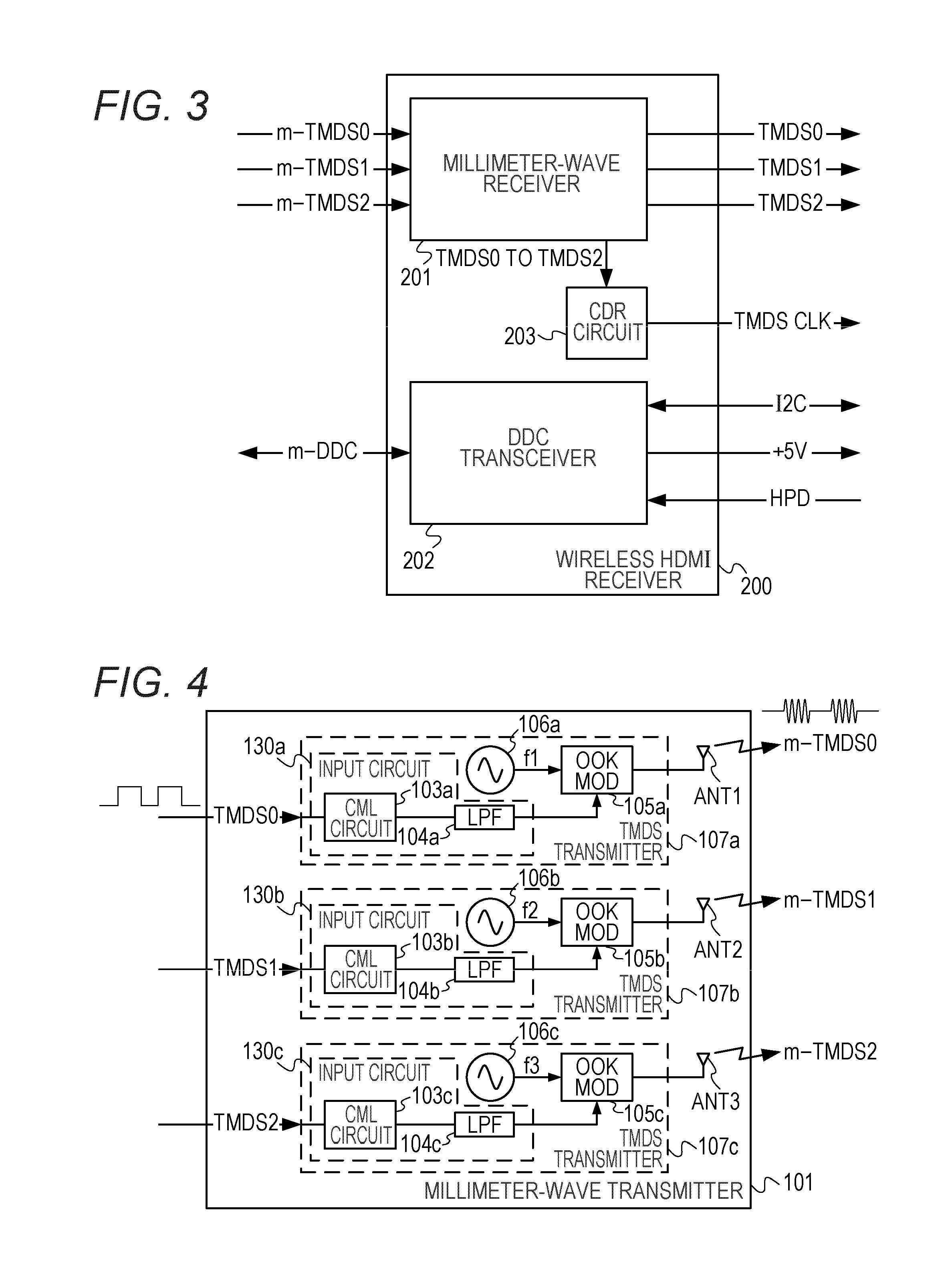
A wireless transmission system includes a wireless HDMI transmitter and a wireless HDMI receiver. The wireless HDMI transmitter includes a carrier oscillator provided for each channel of an HDMI transmission path to output a carrier signal in a millimeter band, an OOK modulator provided for each carrier oscillator to perform on-off keying modulation on a carrier signal outputted by its corresponding carrier oscillator, and an input circuit provided for each channel of the HDMI transmission path to input a digital signal outputted by a source device to the OOK modulator. Radio signals have different planes of polarization from their adjacent channels.
Owner:SILICON LIBRARY
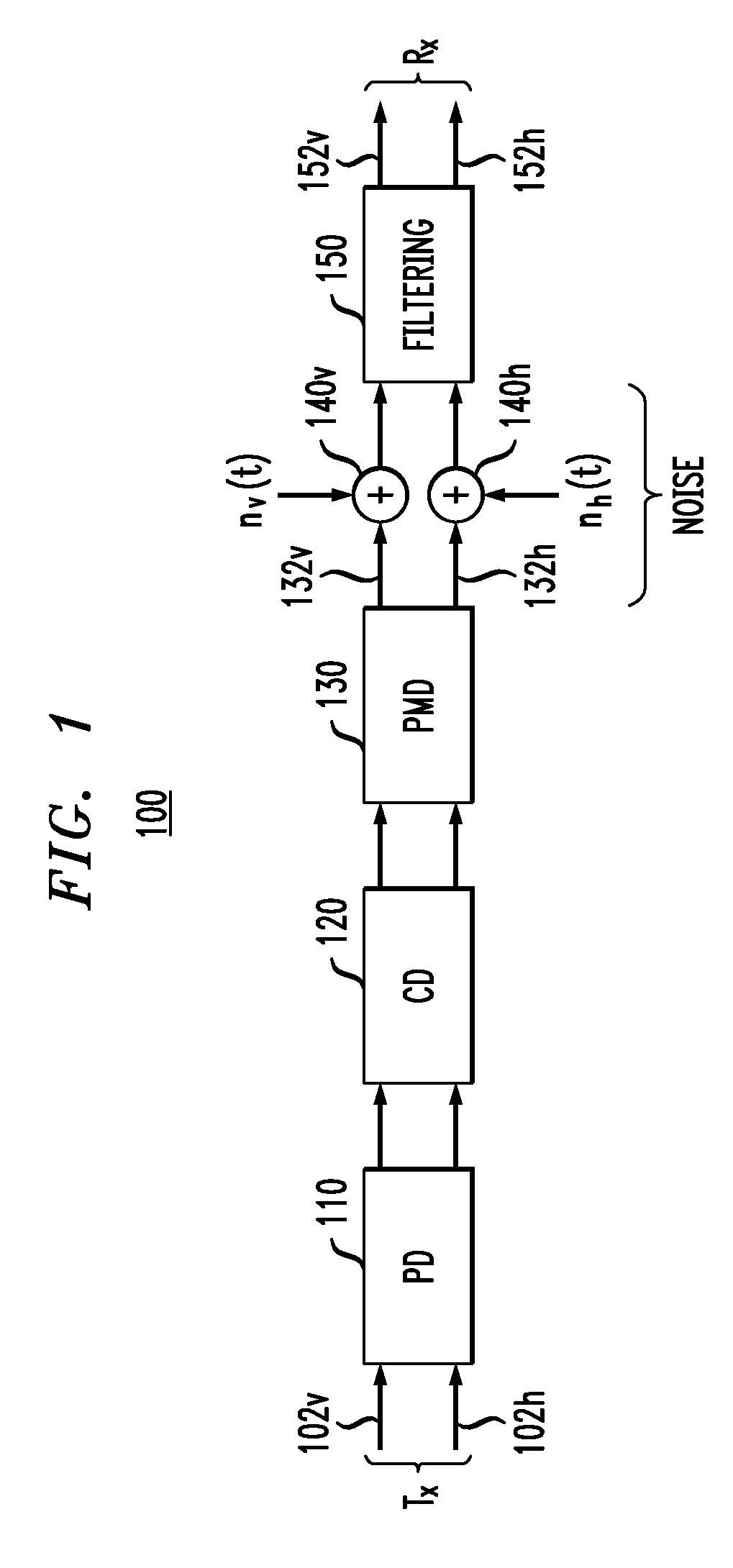
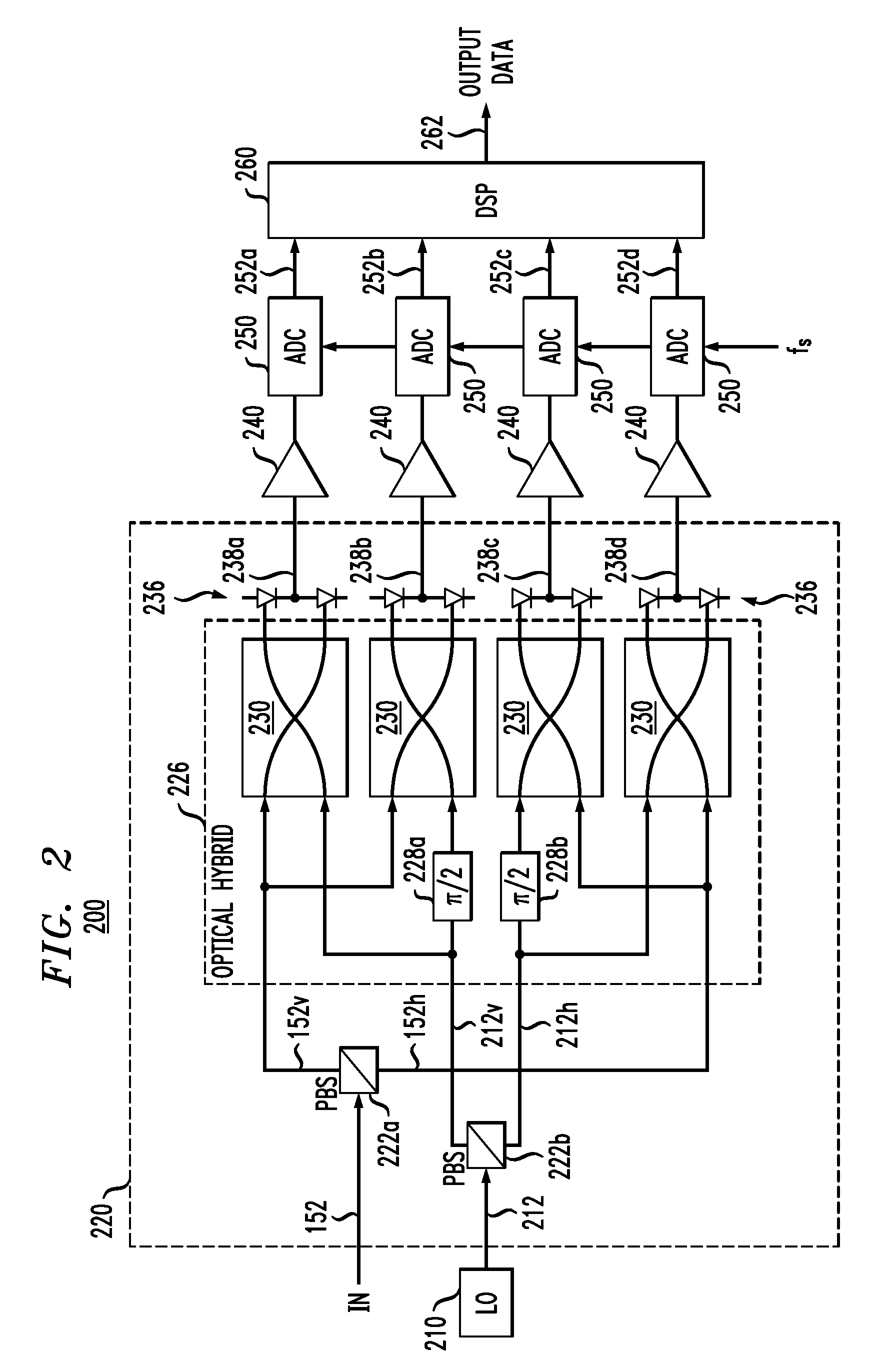
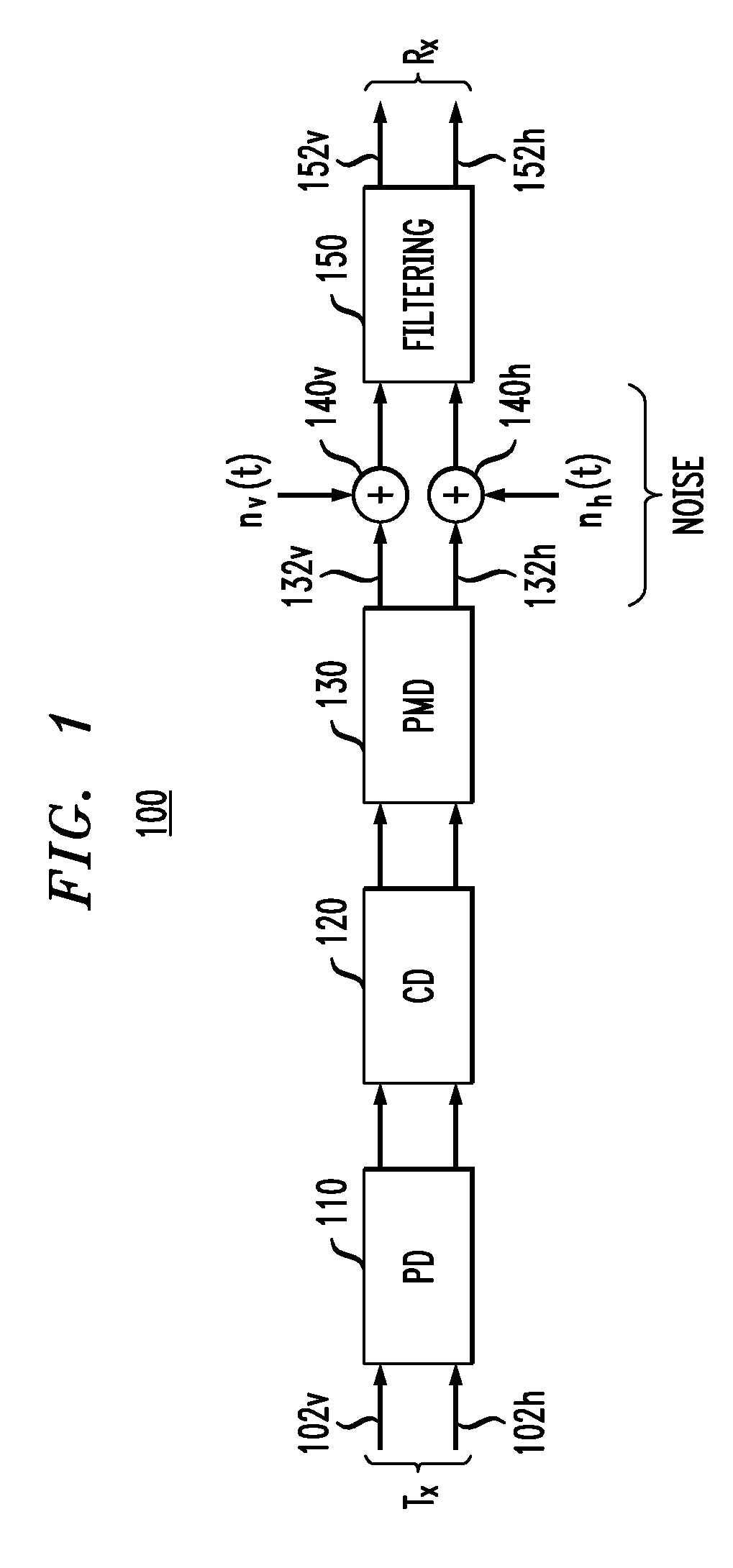
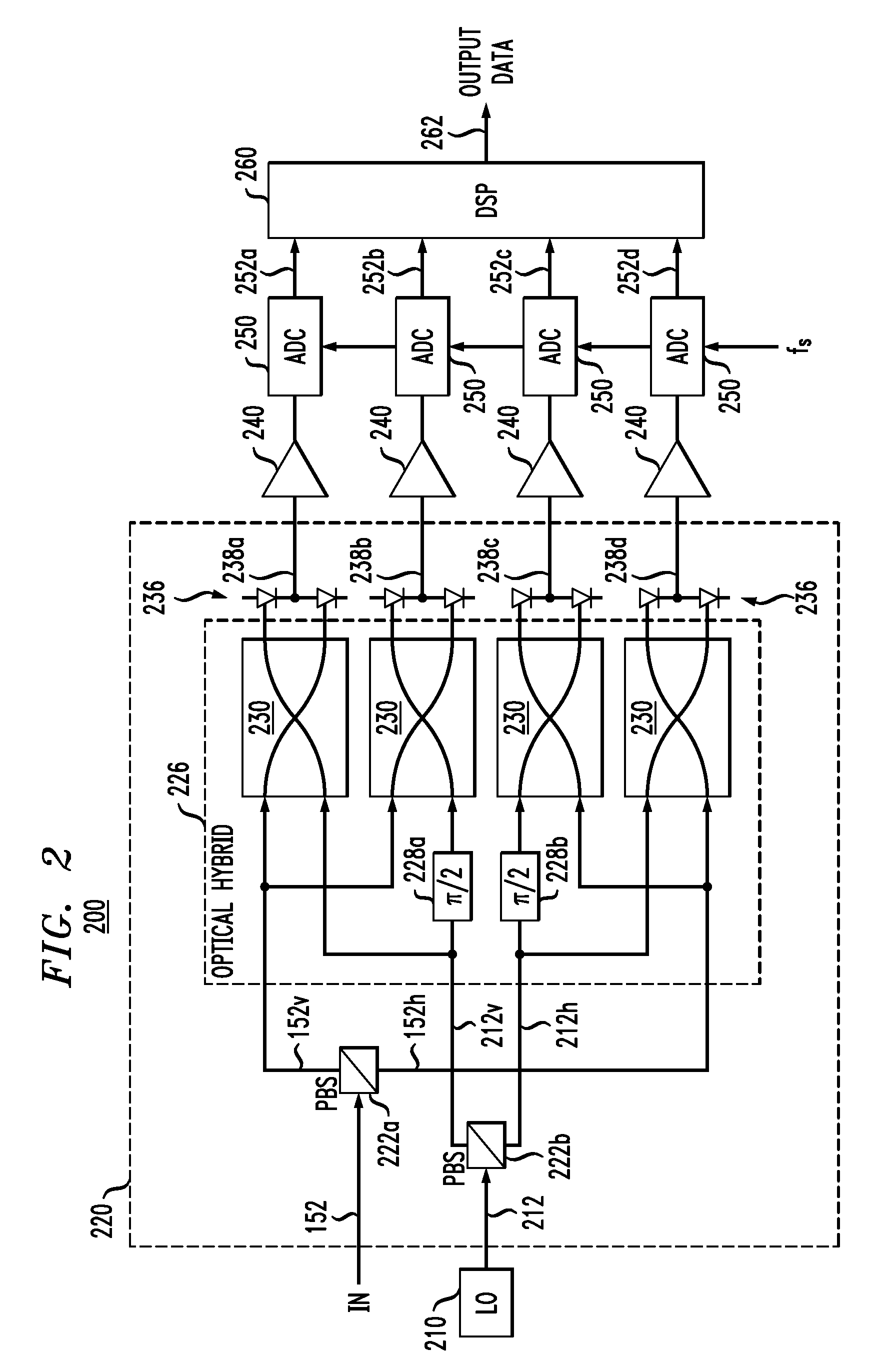
Polarization tracking and signal equalization for optical receivers configured for on-off keying or pulse amplitude modulation signaling
According to one embodiment, an optical receiver adapted to recover OOK or PAM data carried by a modulated optical carrier has an optical detector adapted to produce a sequence of vector pairs having first and second digital vectors indicative of complex values of first and second polarization components, respectively, of the modulated optical carrier at a corresponding sampling time. The optical receiver also has a digital processor that is connected to receive the sequence and is adapted to perform a rotation on each pair in a manner that tends to compensate for polarization rotation produced by transmitting the modulated optical carrier from an optical transmitter thereof to the optical receiver. The digital processor is further adapted to estimate values of the OOK or PAM data encoded onto each of the first and second polarization components based on the vectors produced by the rotation in a manner responsive to values of energy errors in the estimated values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Transmitter and transmitting method of code division multiplexing wireless communication system using on-off keying modulation scheme
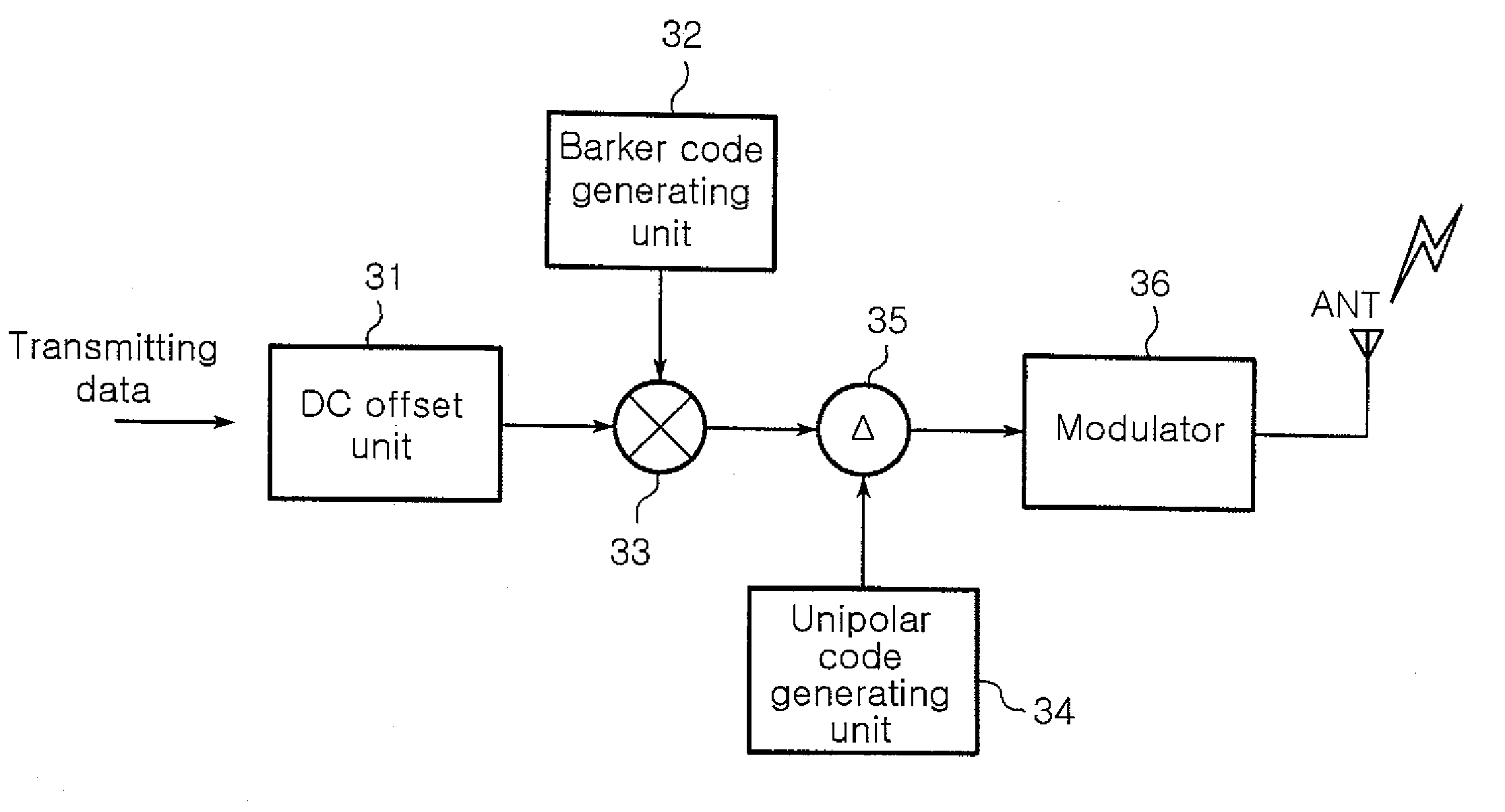
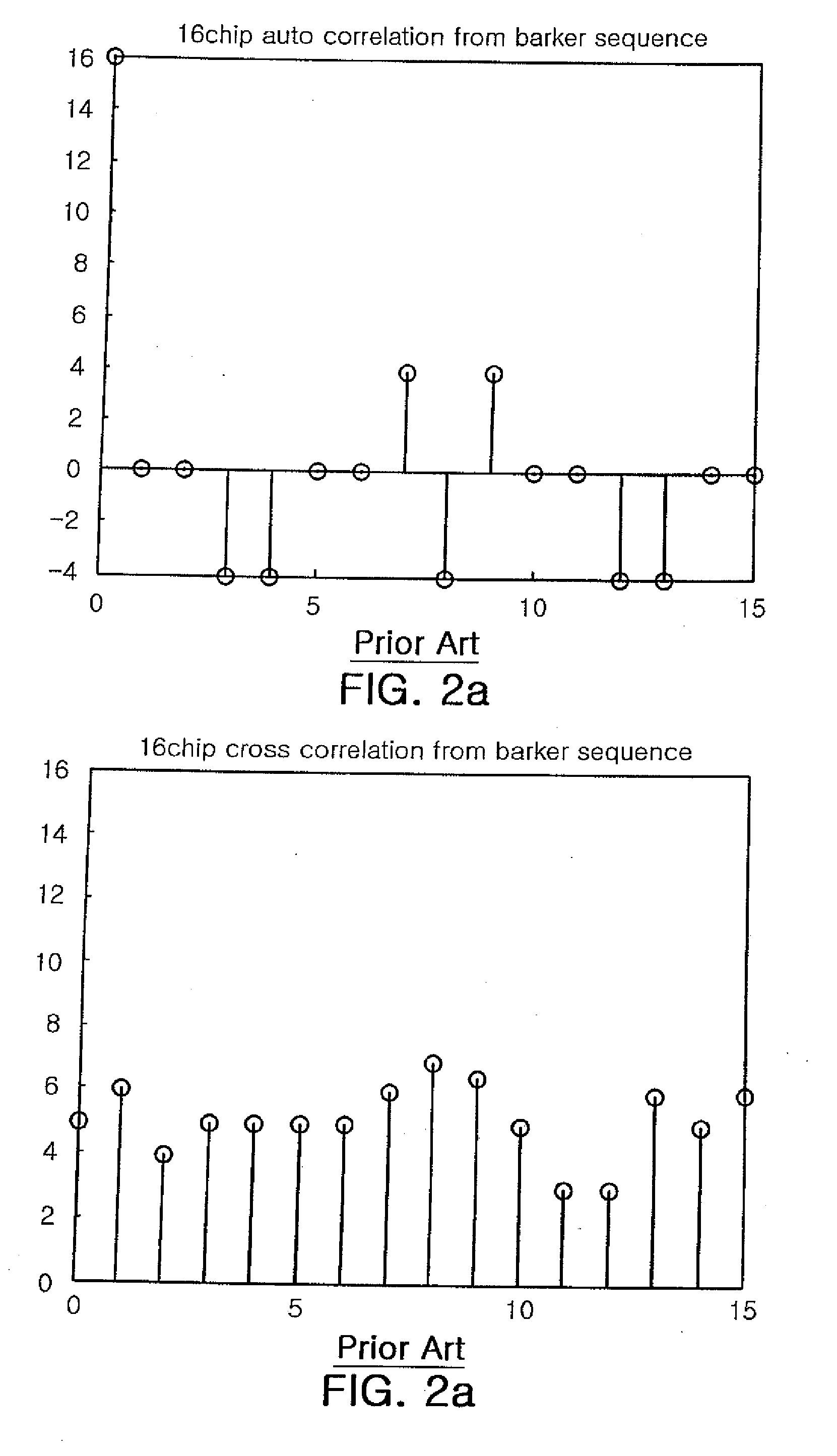
InactiveUS20070133495A1Improving auto correlation characteristicImproving correlation characteristic crossError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplexingOn-off keying
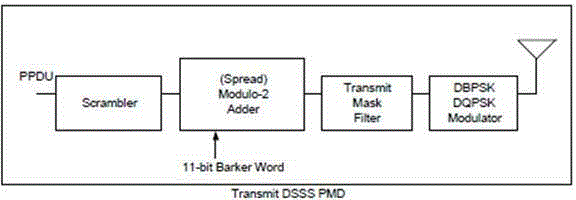
A transmitter and a transmitting method in a code division multiplexing (CDM) wireless communication system are provided. The transmitter includes a DC offset unit, a Barker code generating unit, a multiplier, a unipolar code generating unit, a Kronecker product unit, and a modulator. The DC offset unit transforms digital transmitting data to bipolar data, and the Barker code generating unit generates a Barker code. The multiplier multiplies the bipolar data with the Barker code and outputting the multiplying result, and the unipolar code generating unit generates a predetermined unipolar code. The Kronecker product unit multiplies the multiplying result from the multiplier and the unipolar code based on the Kronecker product, and outputs the result thereof, and the modulator modulates the output of the Kronecker produce unit through the On-Off keying modulation scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
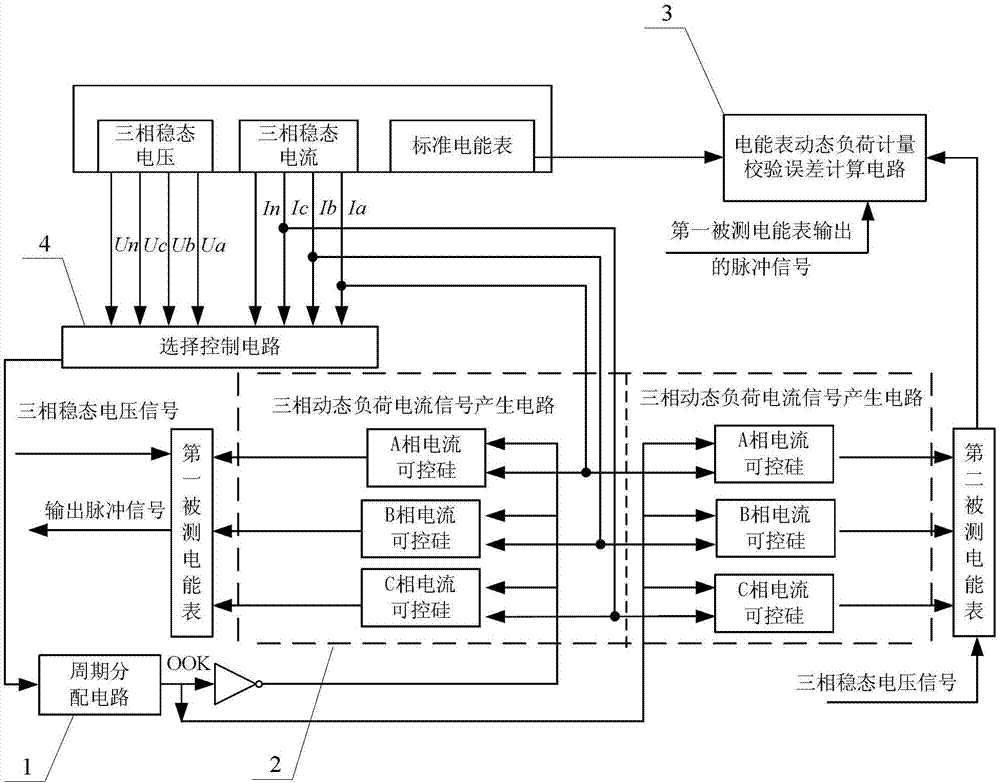
Electric energy meter dynamic measurement cycle power sequence proportional allocation calibration method
The electric energy meter dynamic measurement cycle power sequence proportional allocation calibration method belongs to the technical field of electric energy meter dynamic performance measurement. The electric energy meter dynamic measurement cycle power sequence proportional allocation calibration method solves the problem that a power signal source is adopted to produce dynamic load electric energy signals, and therefore measurement tracing error can not be given out in the existing dynamic performance measurement test of an electric energy meter. The electric energy meter dynamic measurement cycle power sequence proportional allocation calibration method adopts synchronous on-off keying (OOK) cycle on-off control signals generated from three-phase steady-state voltages or three-phase steady-state current signals to dynamically distribute the three-phase steady-state current signals, by using a power electronic component, such as controllable silicon, transient state, short time and long time three kinds of periodically-changed dynamic load current signals are controlled to be produced, and dynamic load power is input into the electric energy meter under test in a discrete electric energy sequence mode. Dynamic load measurement validation error of the electric energy meter under the test is calculated by collecting output impulse of a standard electric energy meter and the electric energy meter under the test, and dynamic load measurement test tracing of the electric energy meter under the test can be achieved. The electric energy meter dynamic measurement cycle power sequence proportional allocation calibration method is suitable for validation of electric energy meters.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Wireless transmission system and wireless transmitter, wireless receiver, wireless transmission method, wireless reception method and wireless communication method used with same
ActiveUS20130010848A1Low priceQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsOn-off keyingWireless transmission
A wireless transmission system includes a wireless HDMI transmitter and a wireless HDMI receiver. The wireless HDMI transmitter includes a carrier oscillator provided for each channel of an HDMI transmission path to output a carrier signal in a millimeter band, an OOK modulator provided for each carrier oscillator to perform on-off keying modulation on a carrier signal outputted by its corresponding carrier oscillator, and an input circuit provided for each channel of the HDMI transmission path to input a digital signal outputted by a source device to the OOK modulator.
Owner:SILICON LIBRARY +1
Bidirectional optical communications having quick data recovery without first establishing timing and phase lock
InactiveUS20060002489A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsOn-off keyingManchester code
A method of transmitting and rapidly recovering a burst of data without first having to establish a timing or phase lock. The signals are transmitted as modified Manchester coded signals having pulse transitions at a clocking pulse rate which is a multiple of the clocking pulse rate at which the signals are originally generated, and wherein the MOOSE coded signal is modified by ON-OFF keying.
Owner:TELLABS BEDFORD
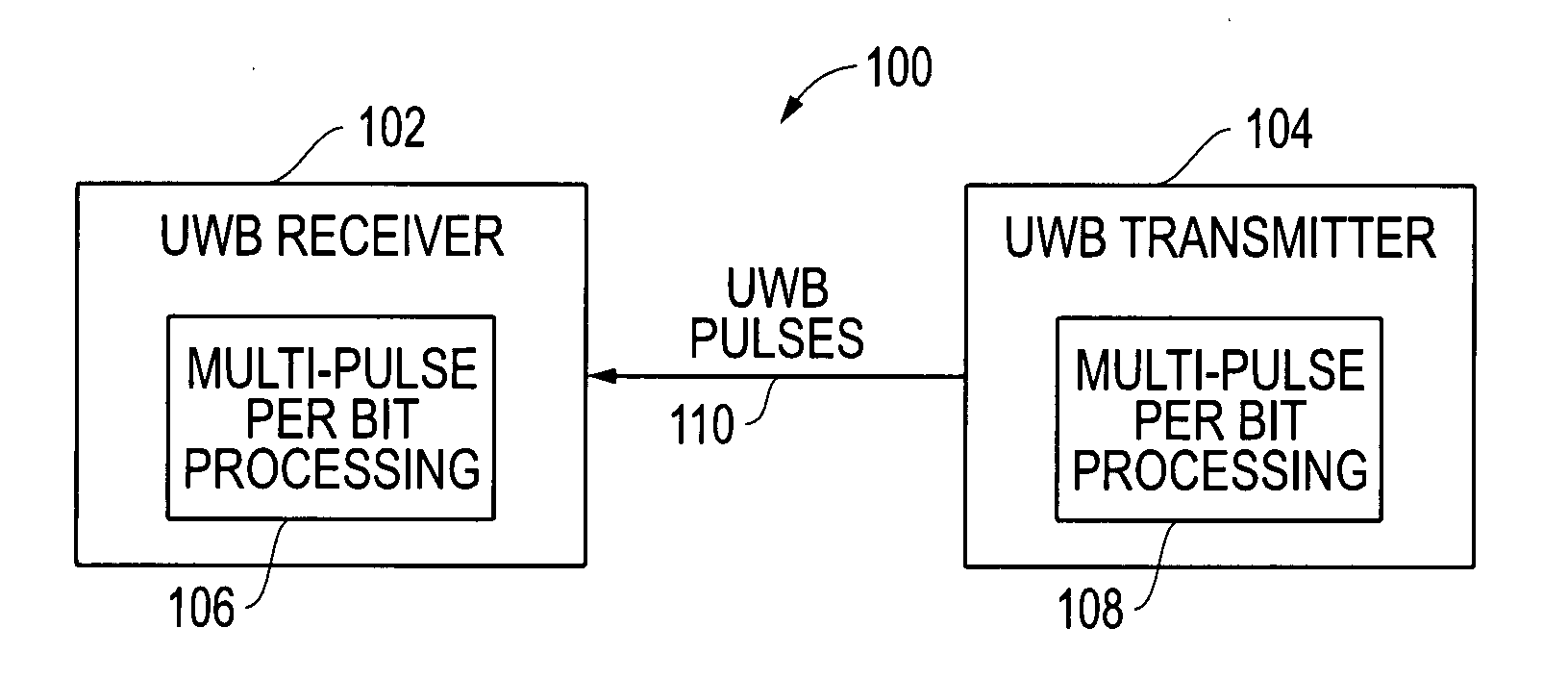
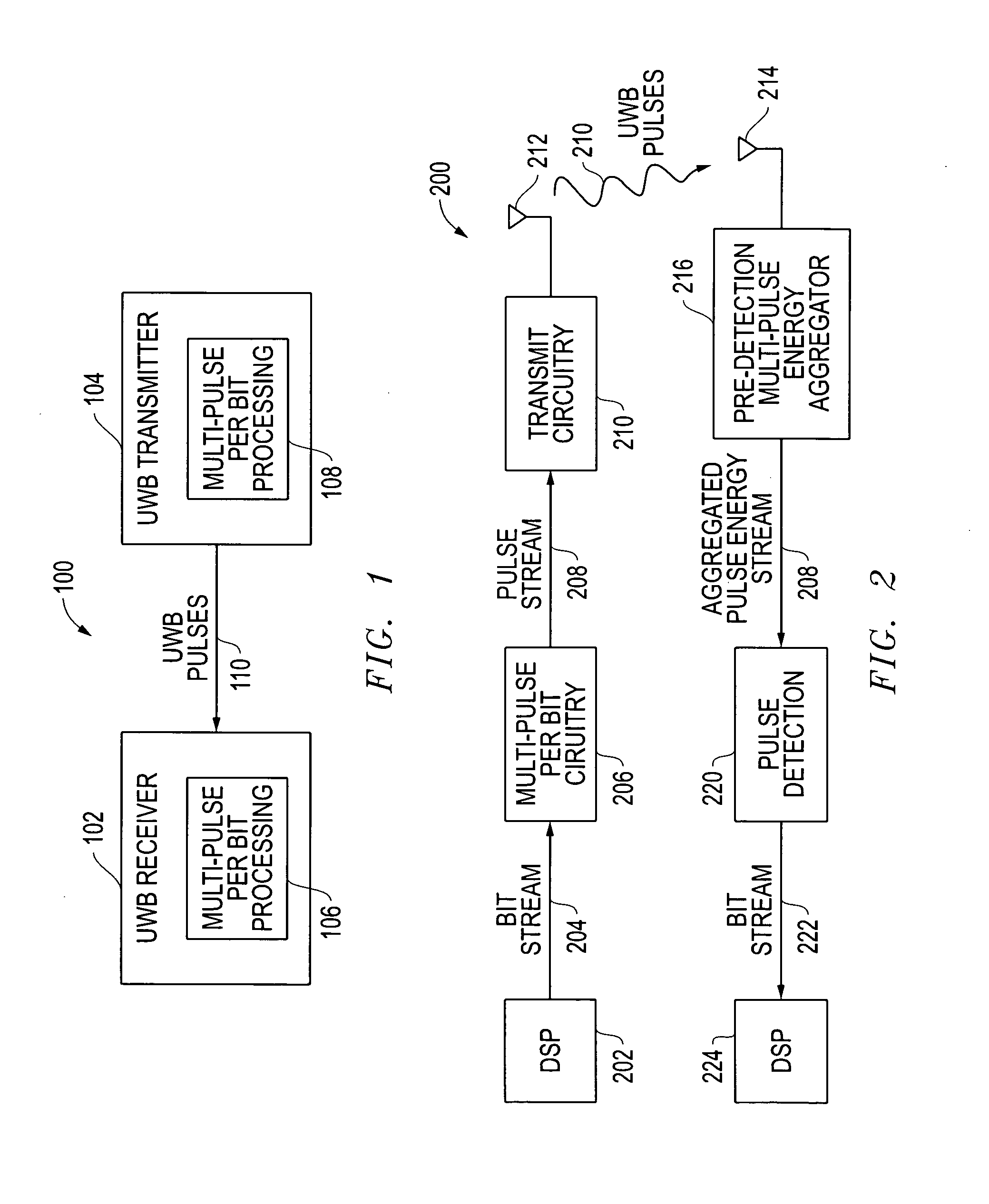
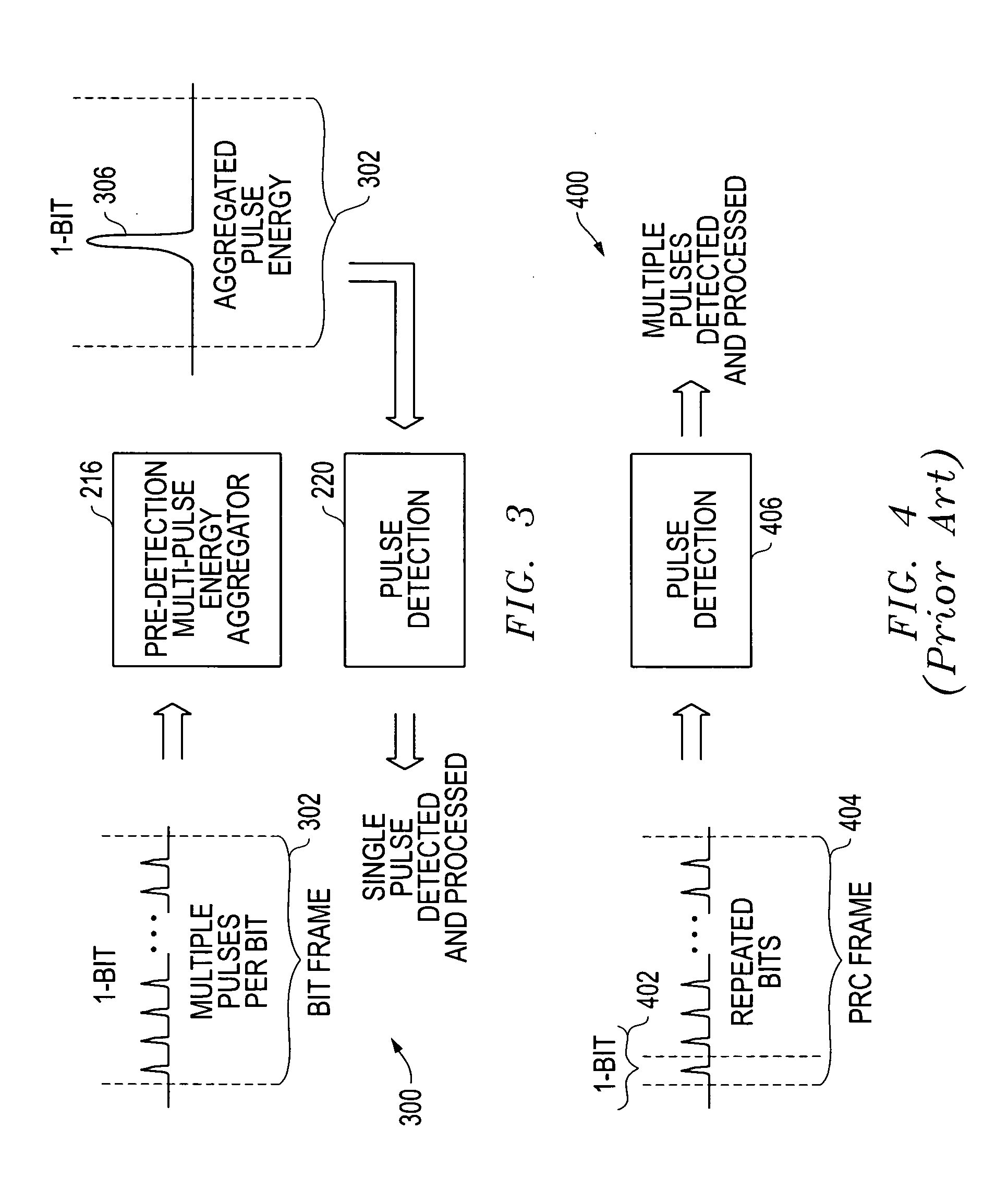
Pulse-level interleaving for UWB systems
Systems and methods are disclosed that provide pulse-level interleaving for multi-pulse-per-bit ultra wideband (UWB) transmit and receive processing techniques to provide significantly improved multi-access for UWB systems and, more particularly, for long range UWB systems. A bit stream is processed such that each bit in a bit stream is represented by a plurality of bits in a bit frame and then transmitted using a plurality of UWB pulses for each bit frame. Where on-off-keying (OOK) modulation is used, each logic “1” is sent out as a plurality of pulses, and each logic “0” is sent out as a plurality of non-pulses. Pulse-level interleaving (PLI) of the pulses across multiple bit frames prior to transmission is provided to allow for improved multi-access (MA) by a plurality of UWB transmitters operating at the same time. Rather than attempt to detect each pulse as it arrives at the receiver, the receiver instead first de-interleaves the pulses and then aggregates the energy from the multiple pulses within each bit frame. The aggregated pulse energy is then processed by a pulse detector to detect a pulse. Where OOK modulation is used, this pulse detection detects the existence of a pulse or the lack of a pulse within the bit frame.
Owner:L 3 COMM INTEGRATED SYST
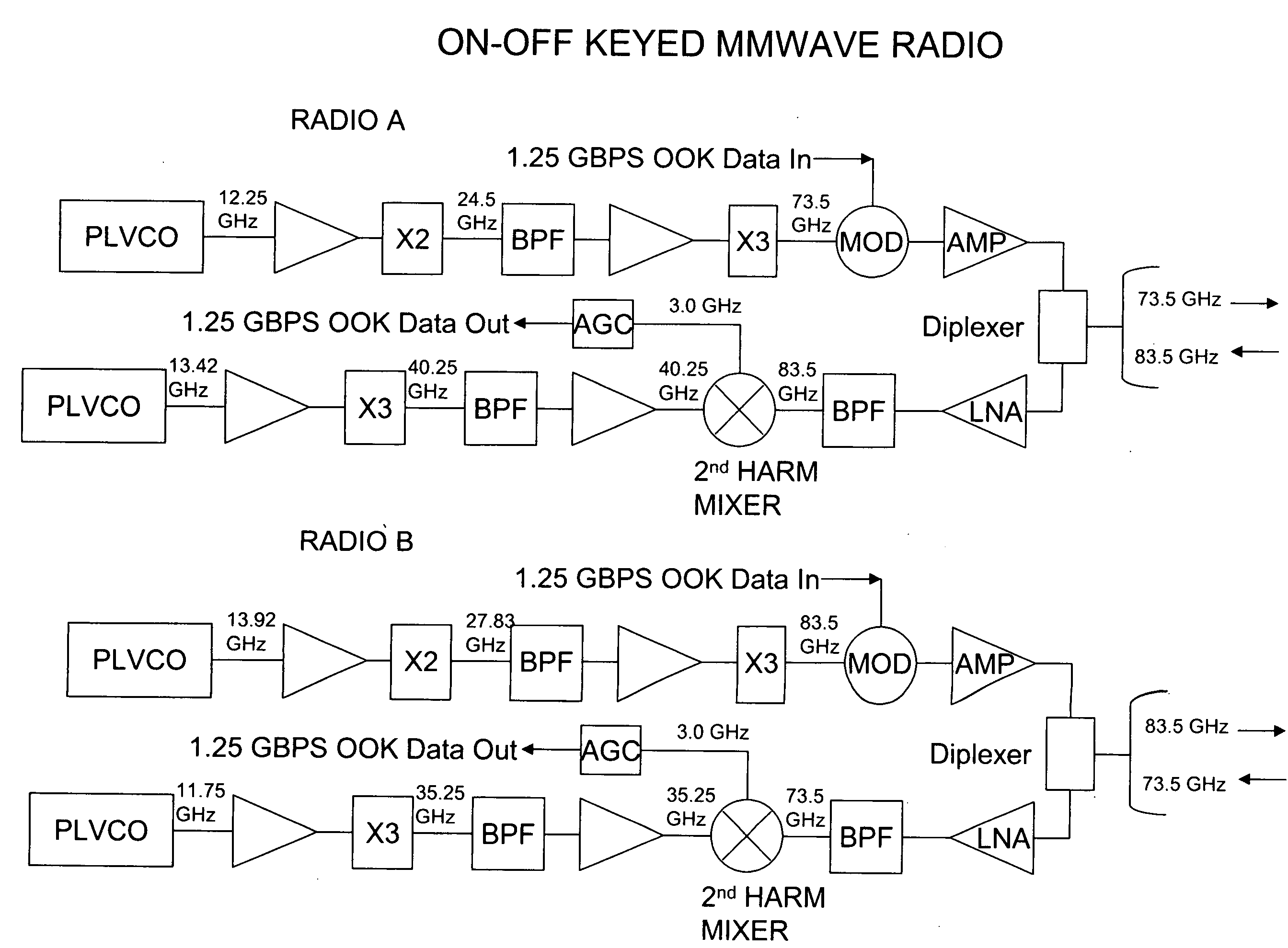
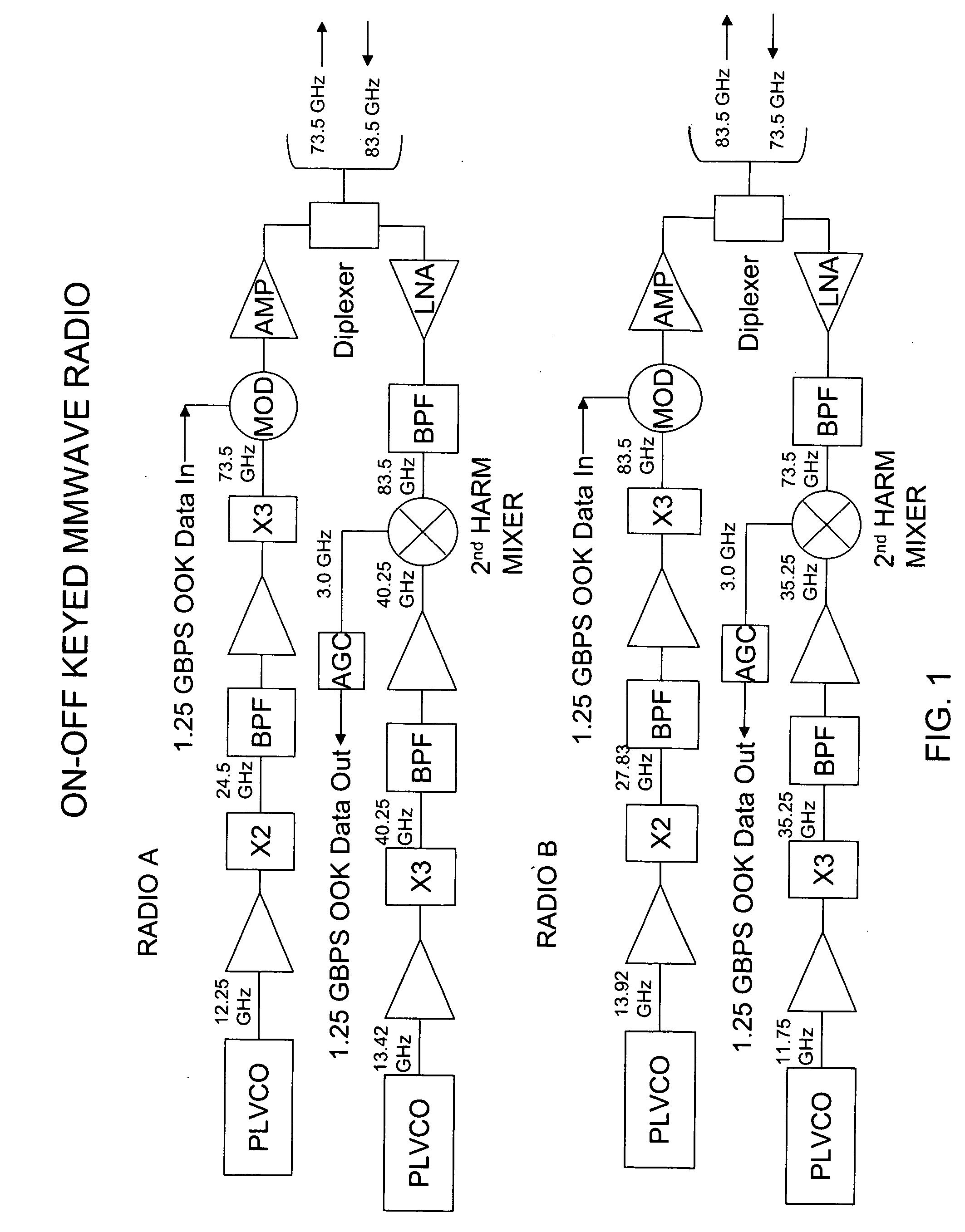
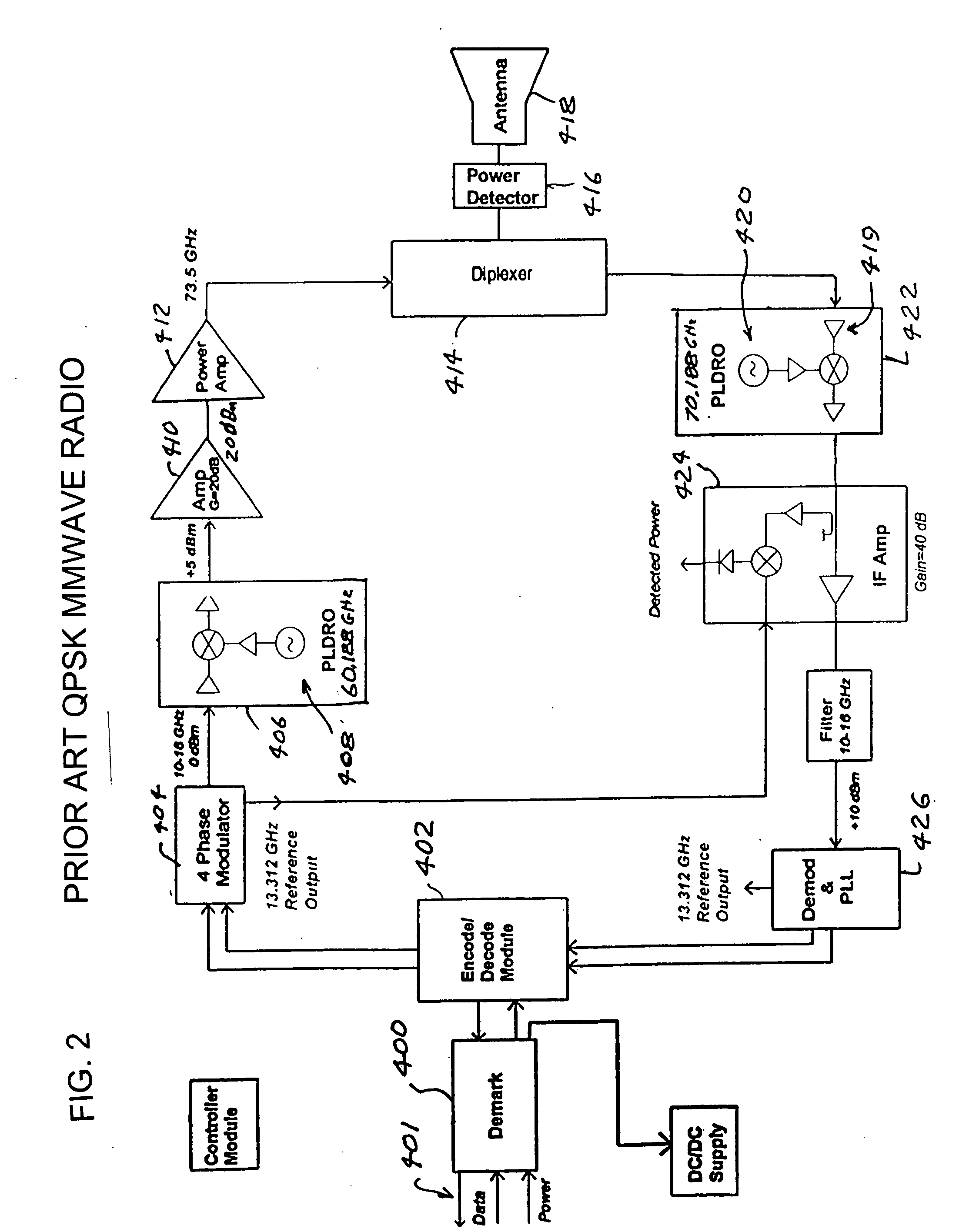
Millimeter wave radio with phase modulation
InactiveUS20100034316A1More reliabilityIncrease data ratePhase-modulated carrier systemsTwo bandCarrier signal
Millimeter wave radio with phase modulation. In preferred embodiments each of the two radios in a link uses a single aperture to transmit radiation in one of the two bands, and receive radiation in the other of the bands. The counterpart radio used to form a link preferably is almost identical, except for the interchange of the transmit and receive frequencies. Preferred embodiments utilize a modulation scheme in which the radios each receive on-off keyed data and transmit the on-off keyed data encoded in a millimeter wave carrier wave with binary phase shift keying.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
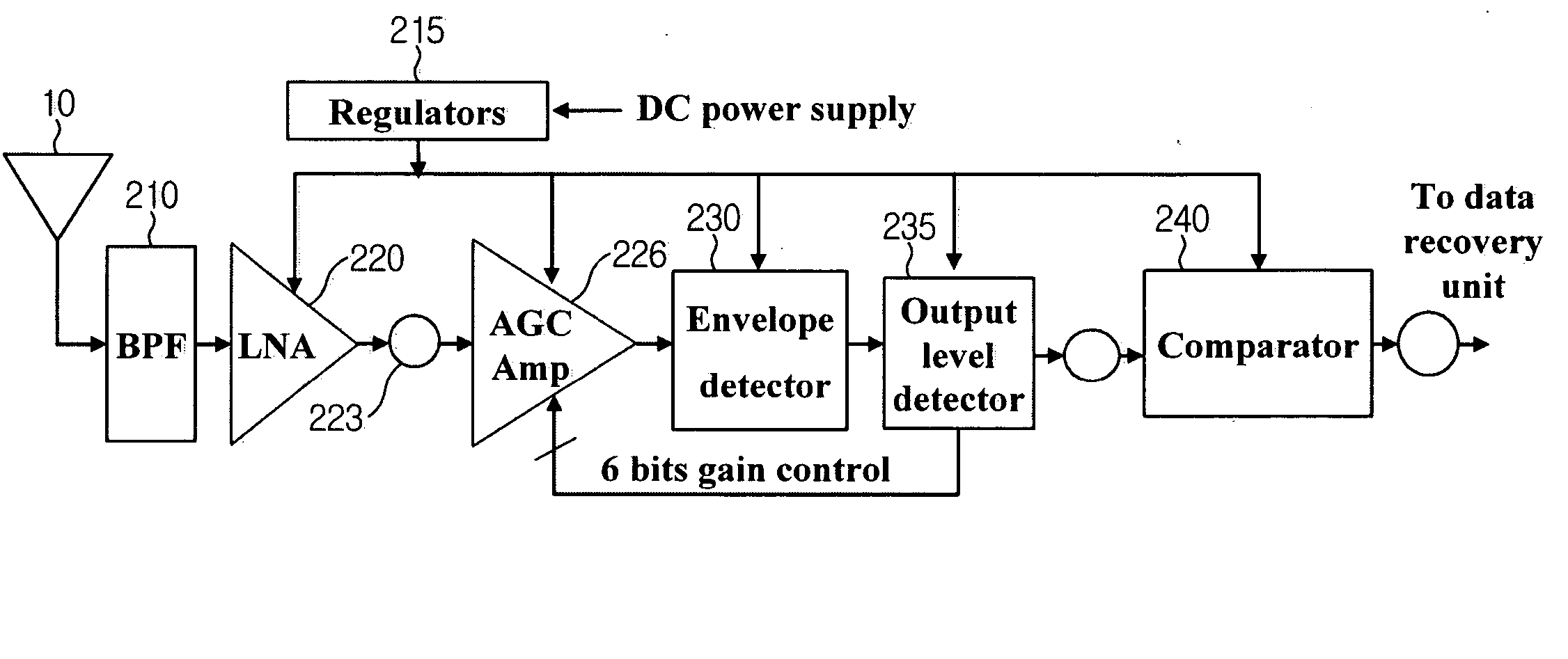
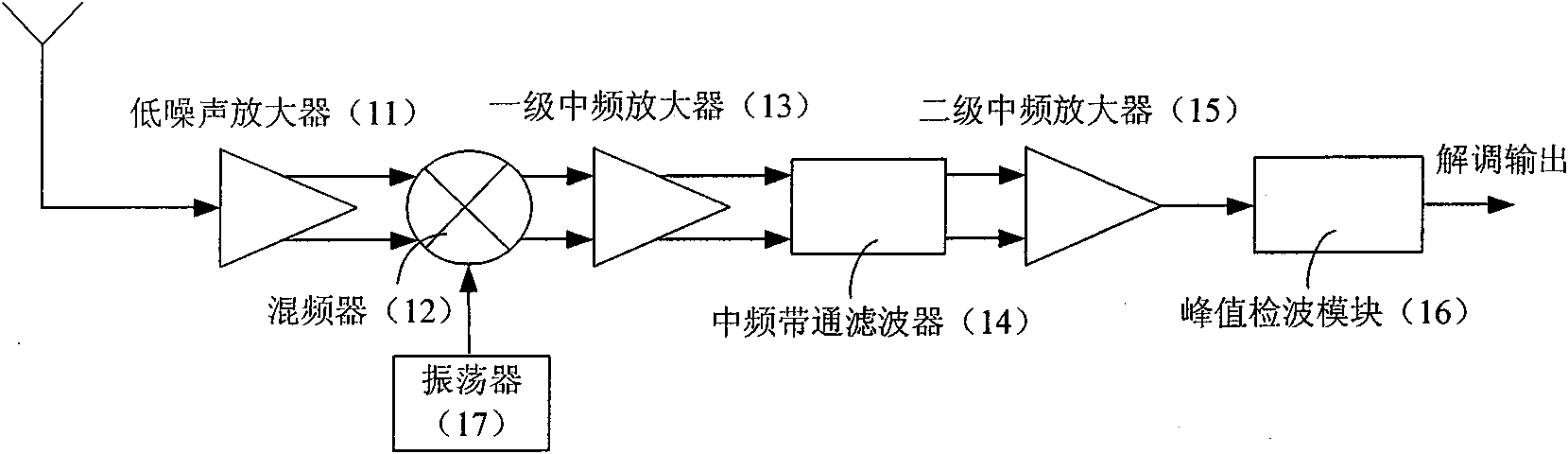
Amplitude shift keying (ASK)/on-off keying (OOK) radio frequency (RF) receiving circuit
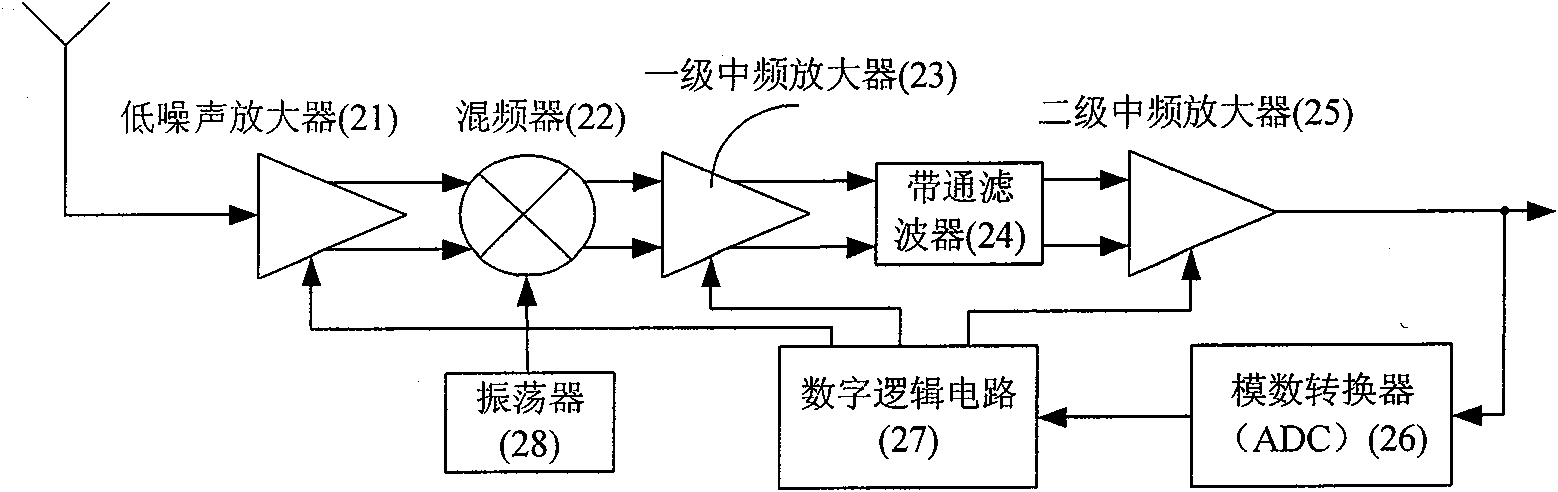
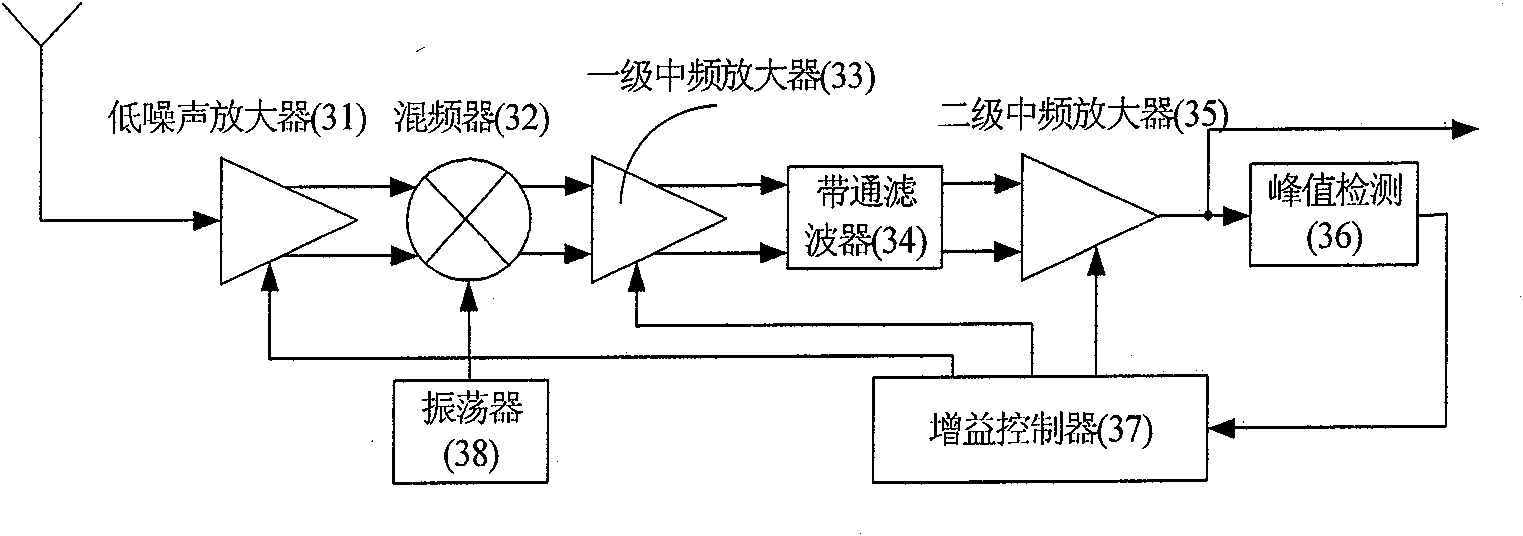
InactiveCN102064841AImprove dynamic rangeImprove anti-interference abilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringCapacitance
The invention provides an amplitude shift keying (ASK) / on-off keying (OOK) radio frequency (RF) receiving circuit. The receiving circuit is characterized in that after a low noise amplifier amplifies the received signal, the amplified received signal and local oscillation generated by an oscillator are jointly input into a mixer; the mixer reduces the frequency output by the low noise amplifier to intermediate frequency; the intermediate frequency signal output by the mixer is demodulated and output by a peak detection module after being amplified by a primary intermediate frequency amplifier, filtered by an intermediate frequency bandpass filter and amplified by a secondary intermediate frequency amplifier; a charge pump is driven after the peak detection output potential is compared with the fourth reference potential Vref4; the charge pump charges and discharges a capacitor to obtain gain control signals; the gain control signals are fed back to the low noise amplifier, the primary intermediate frequency amplifier and the secondary intermediate frequency amplifier to form an automatic gain control loop; and the low noise amplifier, the primary intermediate frequency amplifier and the secondary intermediate frequency amplifier respectively input the first, second and third reference potentials. The receiving circuit solves the problem of blocking during close range remote control, and meanwhile, the antijamming capability of the receiving circuit is improved and the cost is saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
Physical layer architecture for terahertz wireless network
ActiveCN104901777ASimple designAvoid Digital Signal ProcessingForward error control useDigital signal processingTransceiver
The invention discloses physical layer architecture for the terahertz wireless network. The architecture comprises a transmitting end and a receiving end. The transmitting end comprises a scrambler module, a framer module, a forward error correction (FEC) encoder module, a preamble module, a high-speed transceiver module, an on-off keying (OOK) modulation module and a terahertz oscillator; and the reception end comprises a reception processing module corresponding to the transmitting end, as well as a direct detector, a high-speed transceiver and CDR module, a frame synchronizer module, an FEC decoder module, a de-framer module and a descrambler module. The physical layer architecture can be used to directly process bit data flow, complex digital signal processing is avoided, the architecture can be applied to single-channel terahertz high-speed wireless network as high as 100Gbps magnitude, the structure is simpler, convenience is provided for design of special processors, and the power consumption and size are easy to control; and the physical layer architecture can be completely parallel in technical feasibility, can be realized on the basis of a present horizontal FPGA device, and requirement for hardware performance is lower than that of present architecture.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Method and apparatus for acoustic downhole telemetry and power delivery system using transverse or torsional waves
ActiveUS20160265349A1Improve linking efficiencyInterference minimizationSurveySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionOn-off keyingTransmitted power
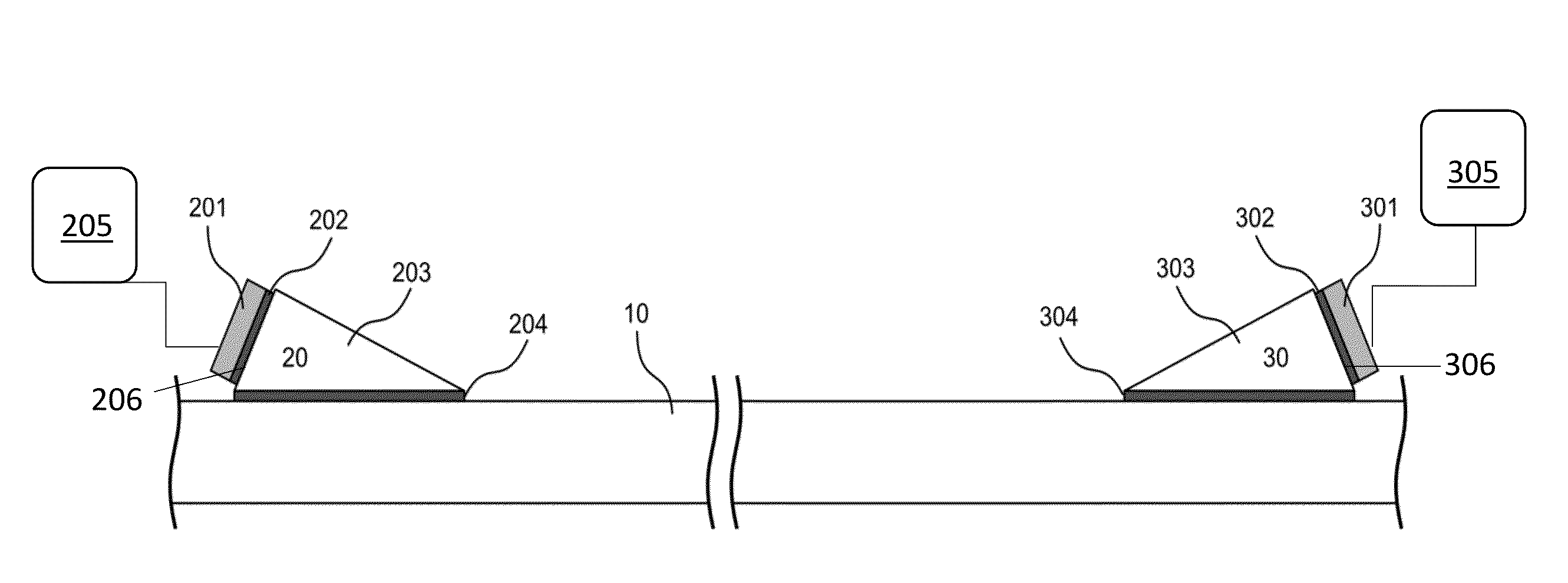
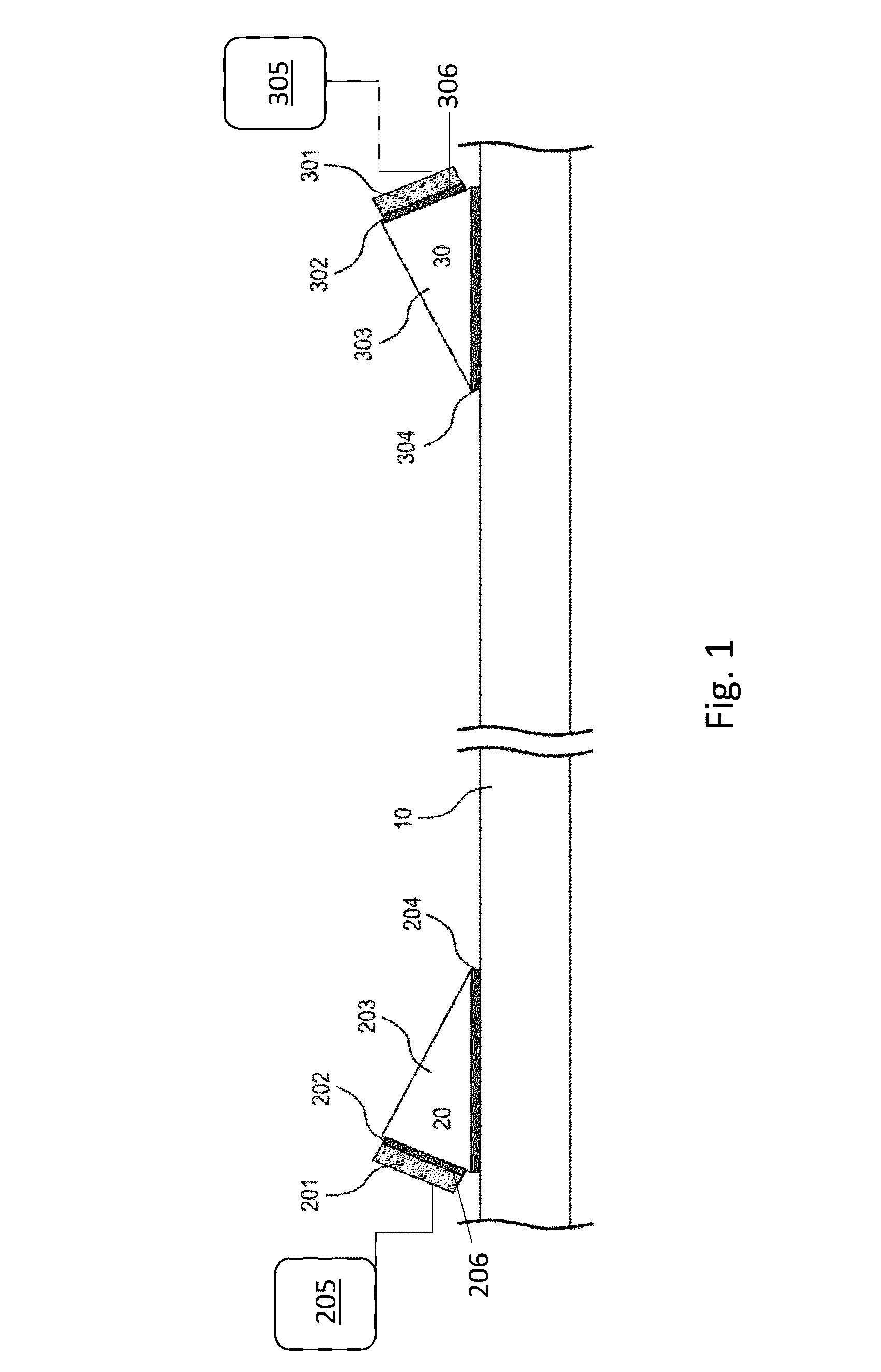
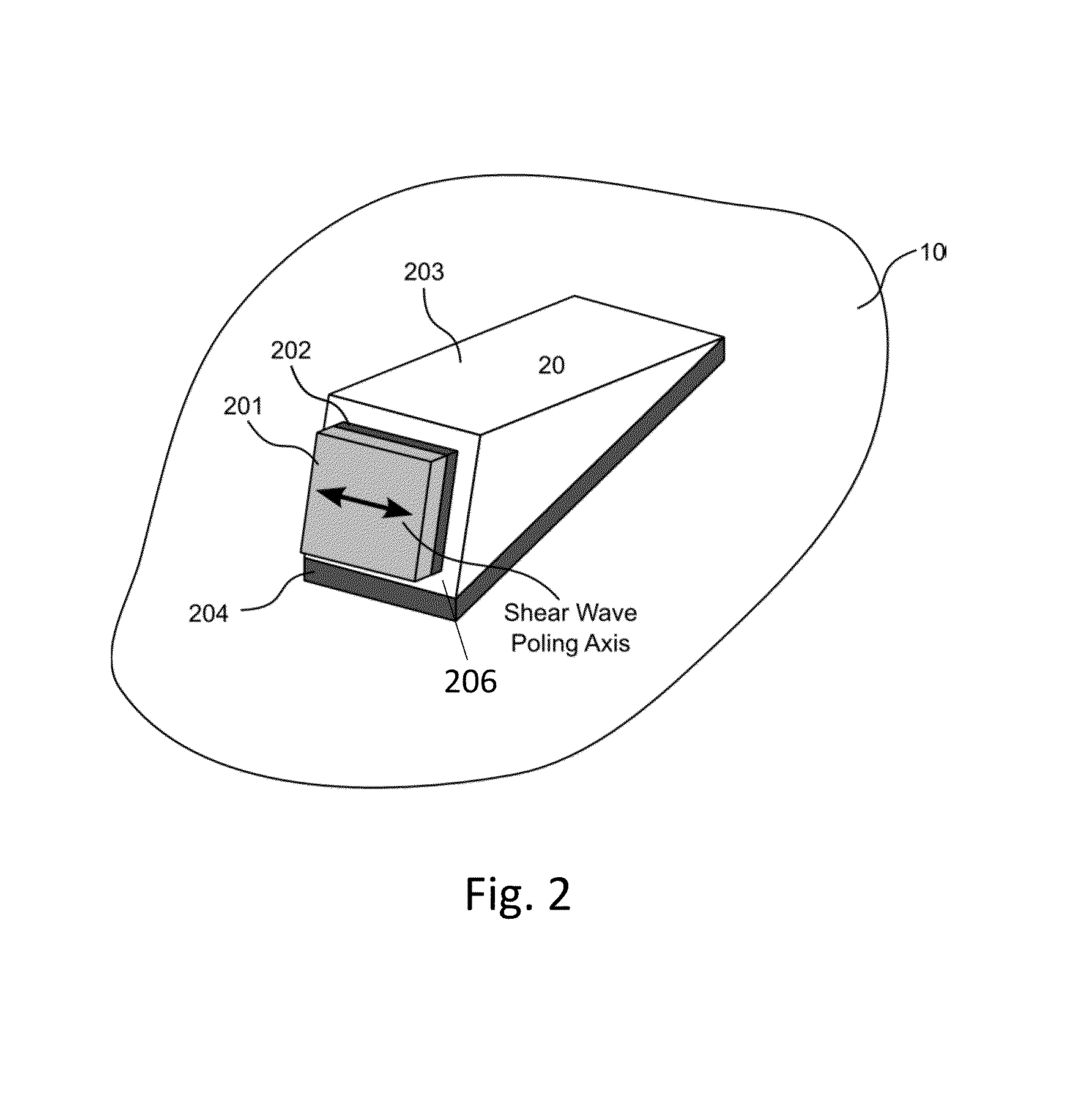
Methods and apparatus for transmitting power and data along a metal pipe using wideband acoustic waves. Arrangements use shear-horizontal waves, transmitting narrowband signals for power applications and wideband signals for communications having a bandwidth greater than the coherence bandwidth of the acoustic-electric channel. Chirp wave signals, direct sequence spread signals, and on-off keying are used. Acoustic-electric channels include wedges fixed to a pipe or other substrate, transducers fixed to the wedges, and electronics linked to each transducer for sending and receiving power and signals. Matching networks, rectification circuits, and non-coherent signal reception methods may be used.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Wireless data and power transfer over an inductive telemetry link
ActiveUS20170118543A1Transmit power can be effectivelyIncrease data rateNear-field transmissionSub-station arrangementsFull cycleElectric power transmission
A telemetry device includes a resonant inductive link with a primary LC tank and secondary LC tank configured to resonate at a carrier frequency. A modulator assembly in communication with the secondary LC tank implements data-synchronized cyclic on-off keying modulation (COOK) to periodically create a short across the secondary LC tank in response to a pulse from a phase selector and phase-locked loop. During the full cycle-length of the short, data can be transmitted across the inductive link while the charge across the secondary LC tank is preserved. Power may be transferred across the link during non-shorted cycles.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
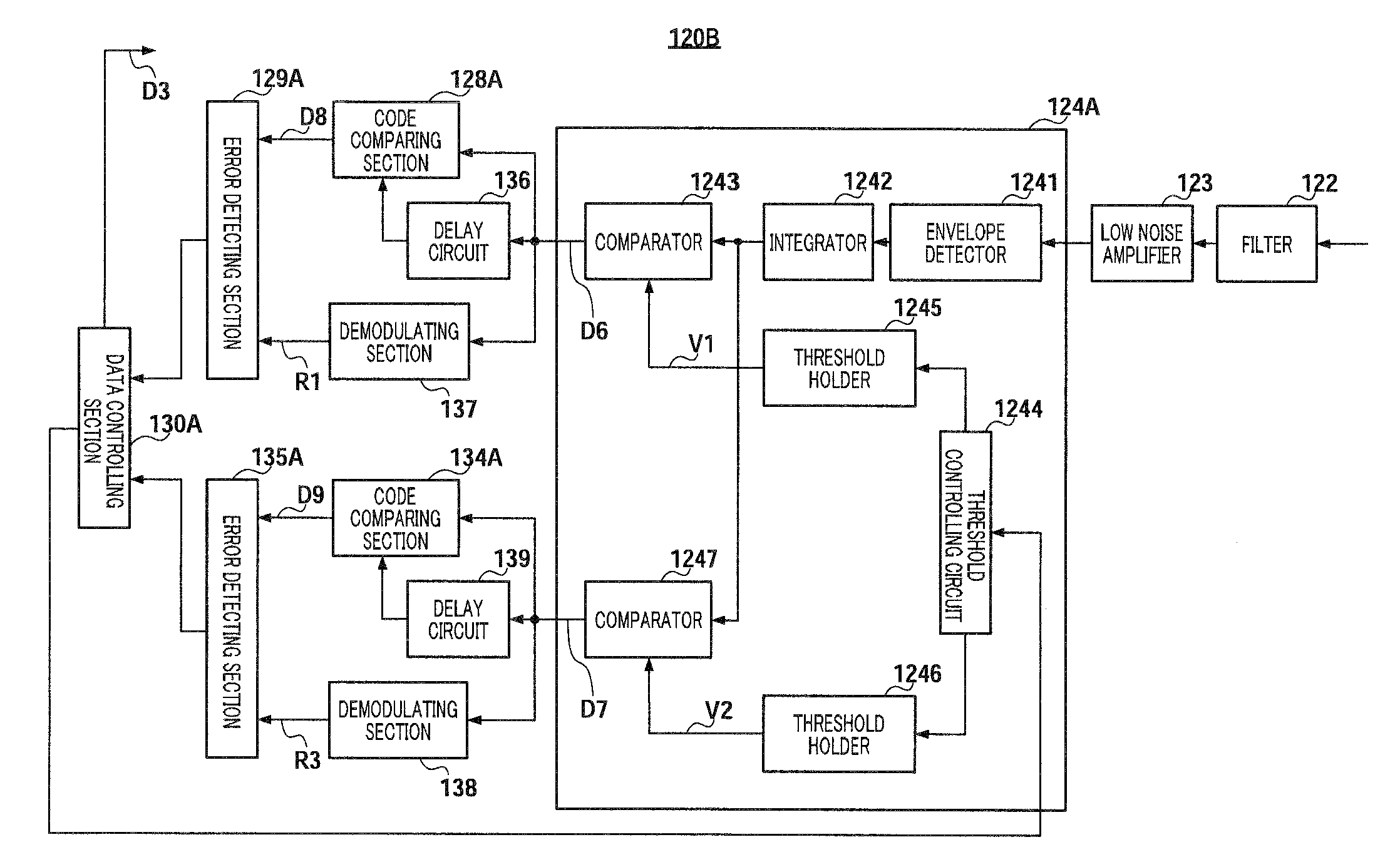
Code error detecting device, wireless system and code error detecting method
InactiveUS20090177954A1Accurate detectionCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer hardwareOn-off keying
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
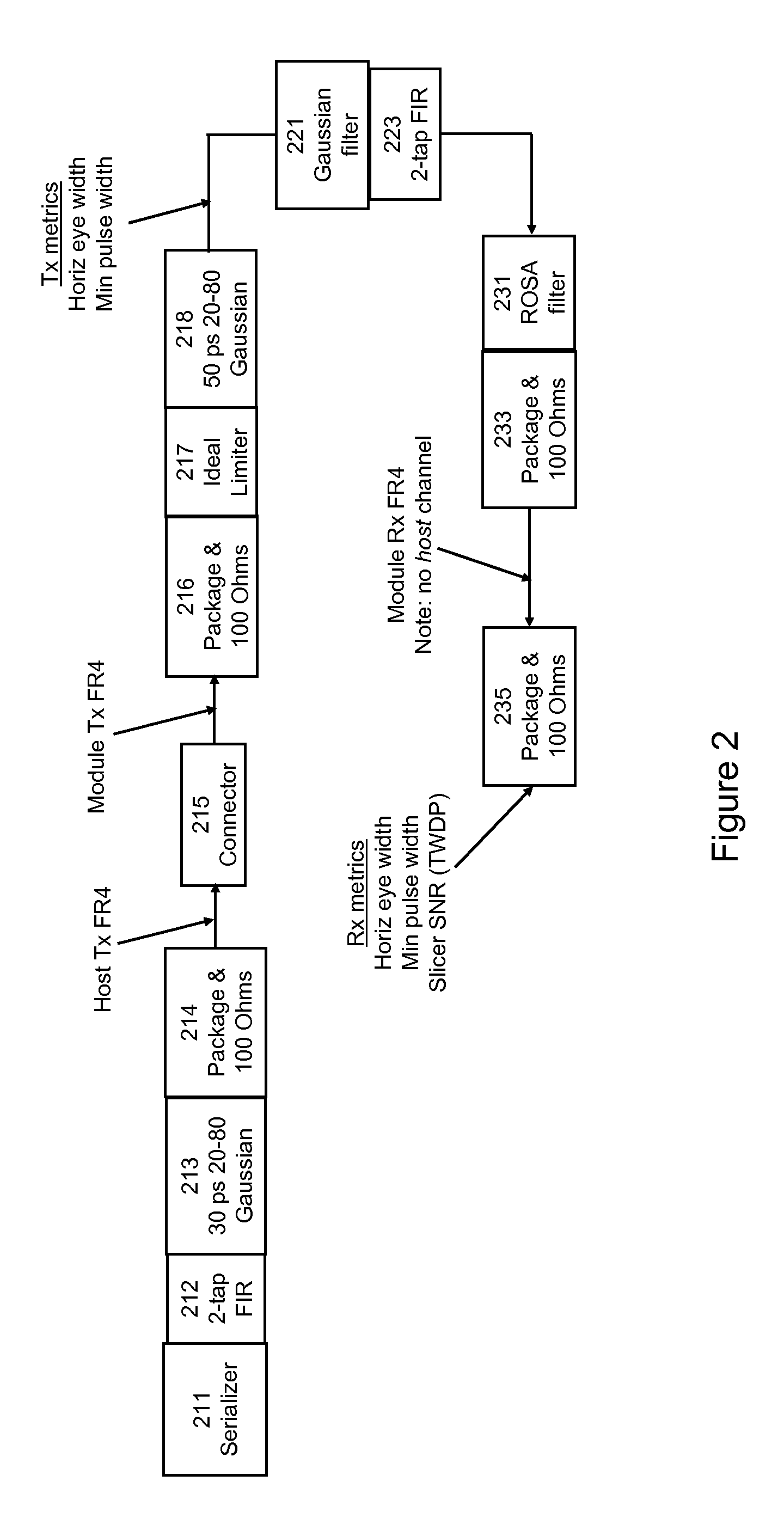
Reducing pulse narrowing in the transmitter signal that drives a limiting E/O converter for optical fiber channels
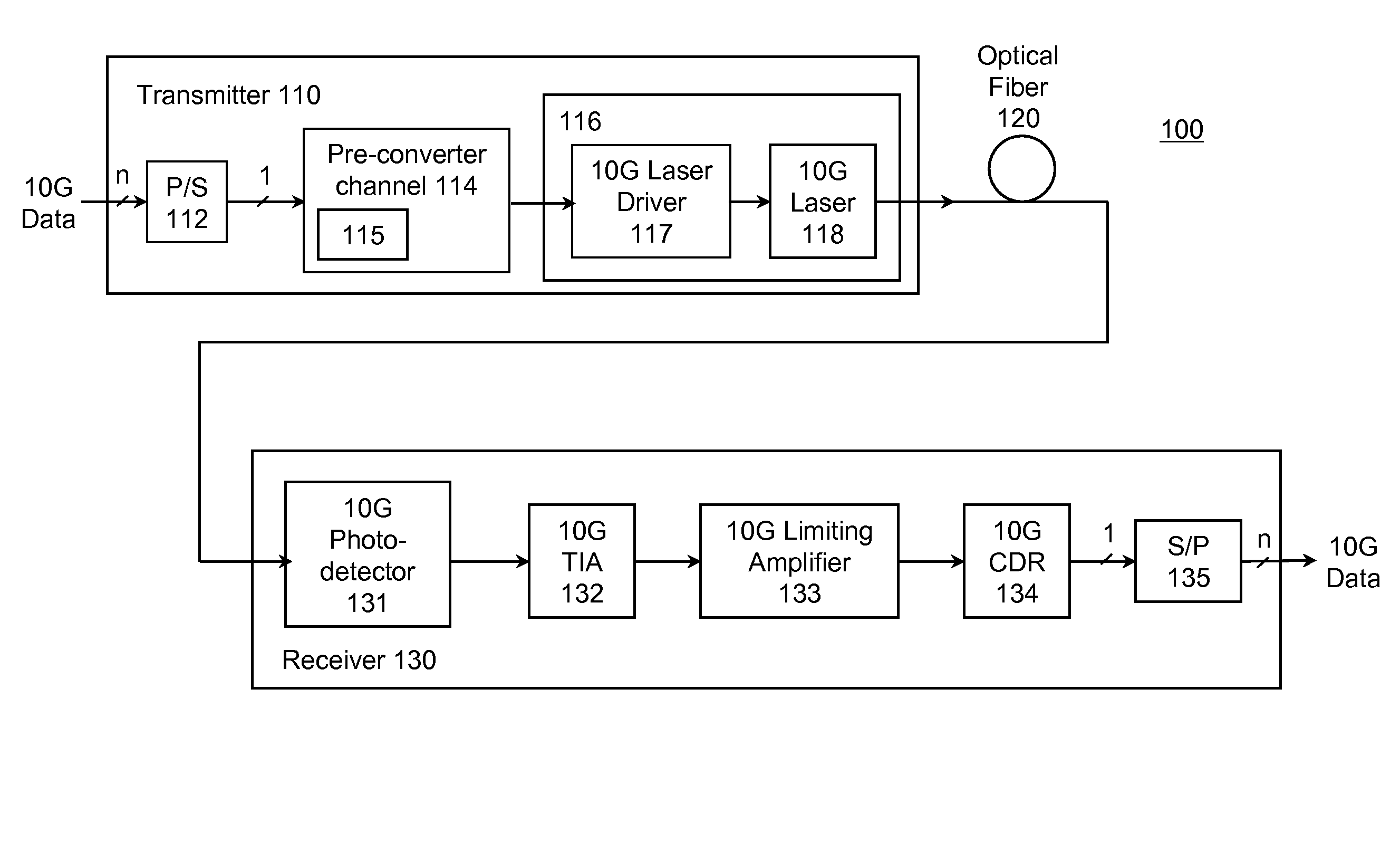
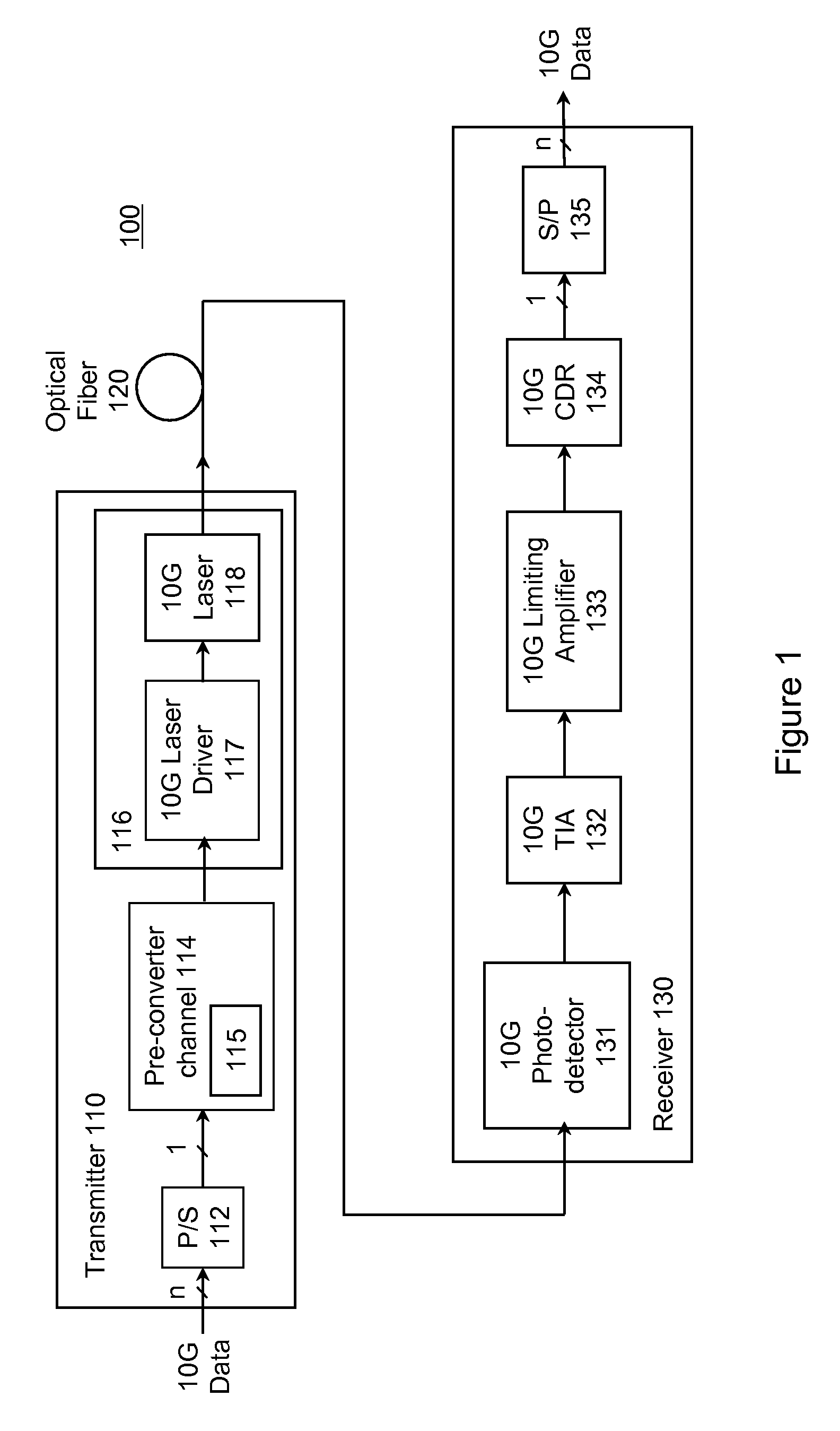
ActiveUS8229303B1Reduce and minimize pulse narrowingMinimize pulse widthElectromagnetic transmittersOn-off keyingBuck converter
A transmitter reduces or minimizes pulse narrowing. In one approach, an optical transmitter is designed to transmit data over an optical fiber at a specified data rate using on-off keying. The transmitter includes a pre-converter electrical channel and a limiting E / O converter. The pre-converter electrical channel produces a pre-converter signal that drives the limiting E / O converter. The pre-converter electrical channel is designed to reduce pulse narrowing in the pre-converter signal. In one implementation, the pre-converter electrical channel includes a pre-emphasis filter that is designed to minimize pulse width shrinkage.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
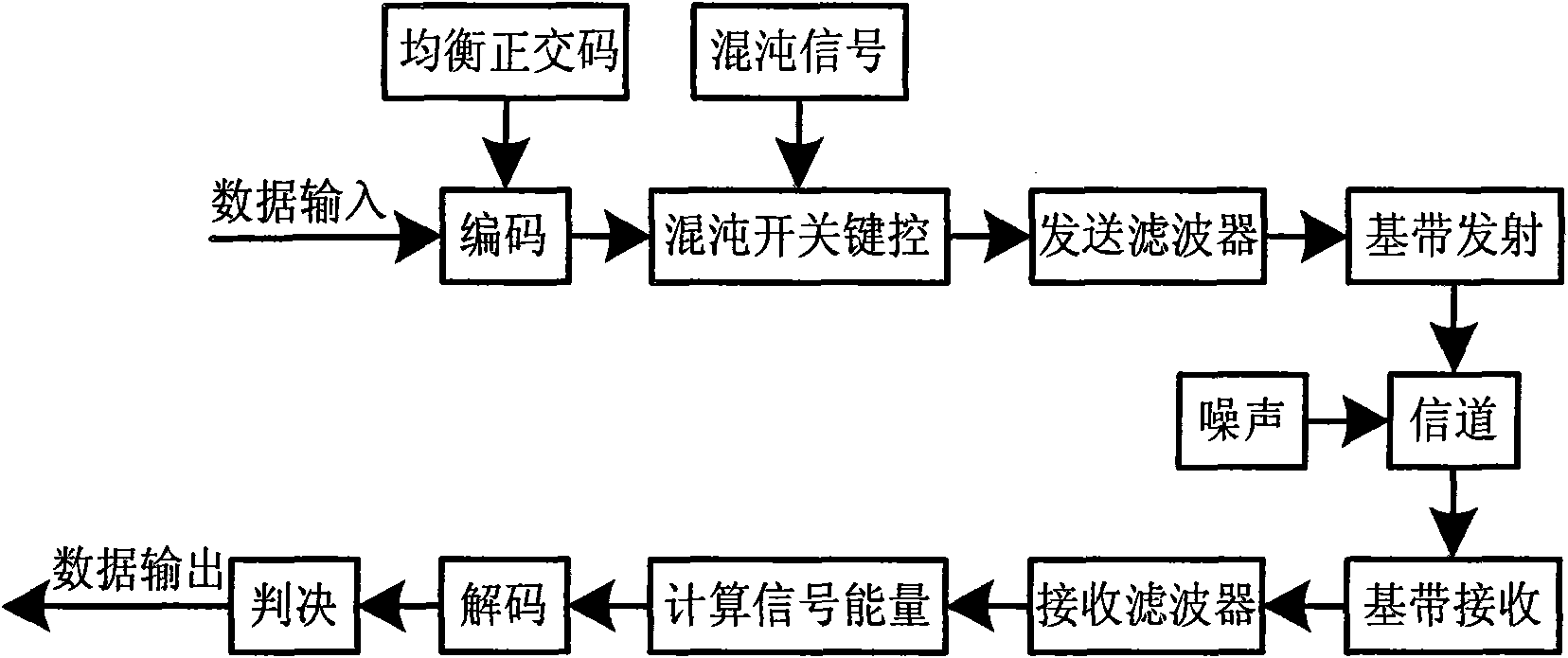
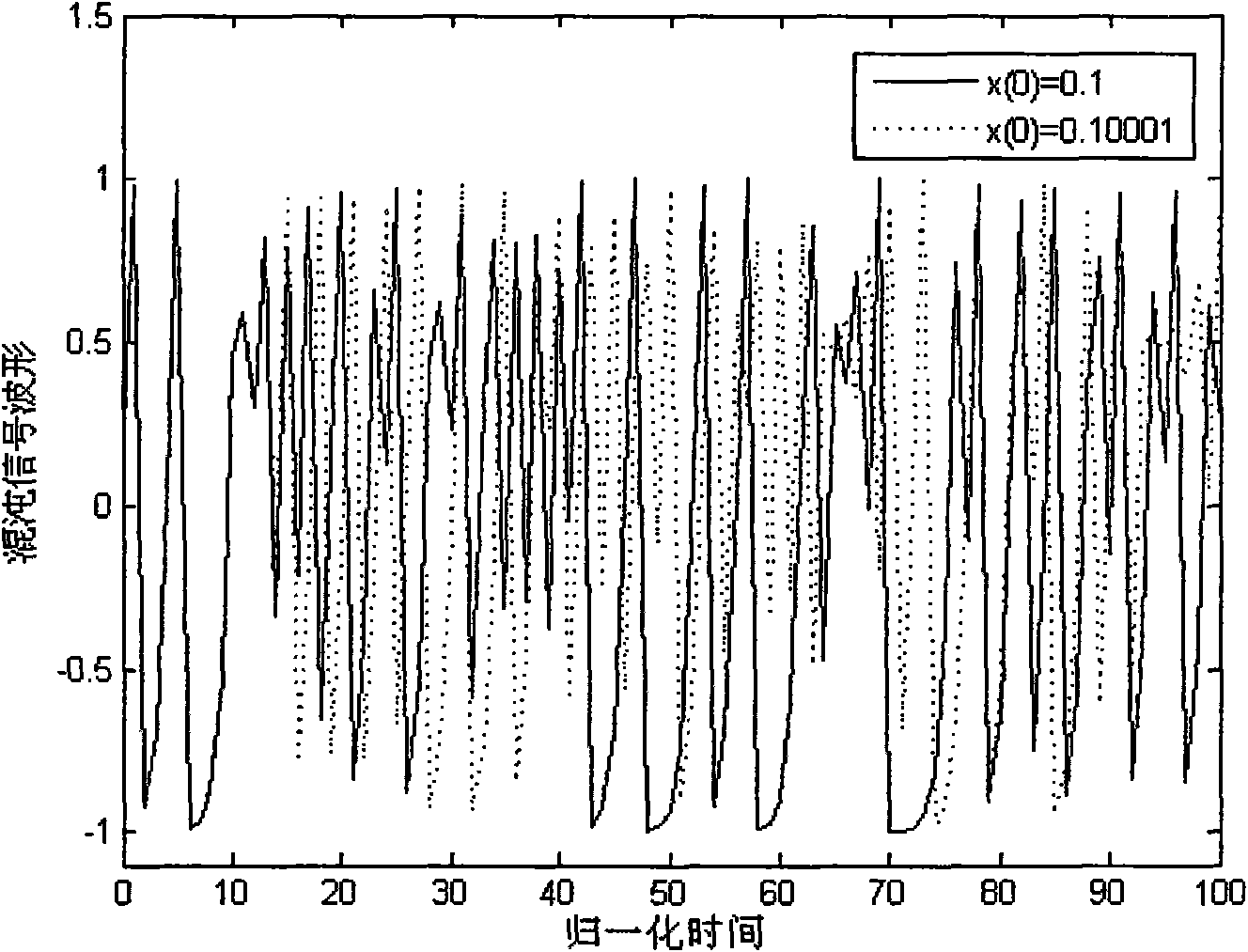
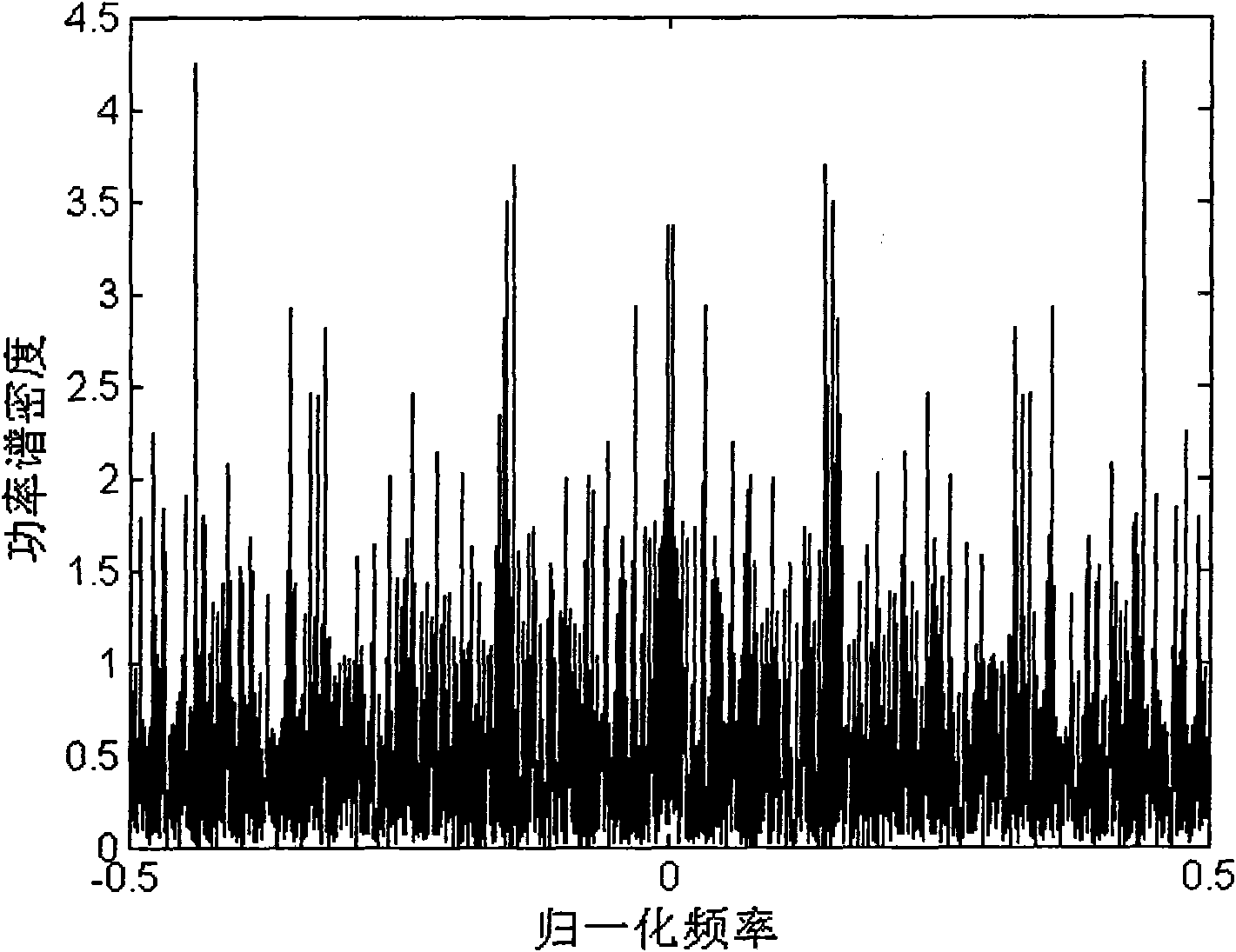
Ultra wide band chaotic communication method
InactiveCN101605112AAvoid disadvantagesReduce difficultyEqualisersTransmitter/receiver shaping networksOn-off keyingFiltration
The invention discloses an ultra wide band chaotic communication method, comprising the following steps: balanced orthographic coding is carried out on the data which are to be sent; the balanced orthographic coding has two code words b0 and b1, each code word has identical number of code element '0' or '1', and b0 and b1 are orthographic with each other; after chaotic on-off keying modulation is carried out on the data which are to be sent and filtration and wave form moulding treatment are carried out on the signal s(t) which is to be transmitted, the signal s(t) is sent to a receiving terminal; and filtered after the receiving terminal receives the signal sent by a transmitting terminal, and signal energy is calculated and decoded; decoding is carried out by adopting the orthogonality and symmetry of balanced orthographic coding; and finally data are judged and output according to the size relation between the output value of coding units and zero. The communication system receiver terminal in the invention avoids the process of estimating and searching the optimal nonzero threshold value, overcomes the defect of the current chaotic on-off keying modulation ultra wide band communication system, and thus reducing the difficulty of system realization.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Communication apparatus
InactiveUS20060045177A1Simplified structure and sequenceFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationOn-off keyingEngineering
Owner:FUJITSU COMPONENENT LTD
All-optical methods and systems
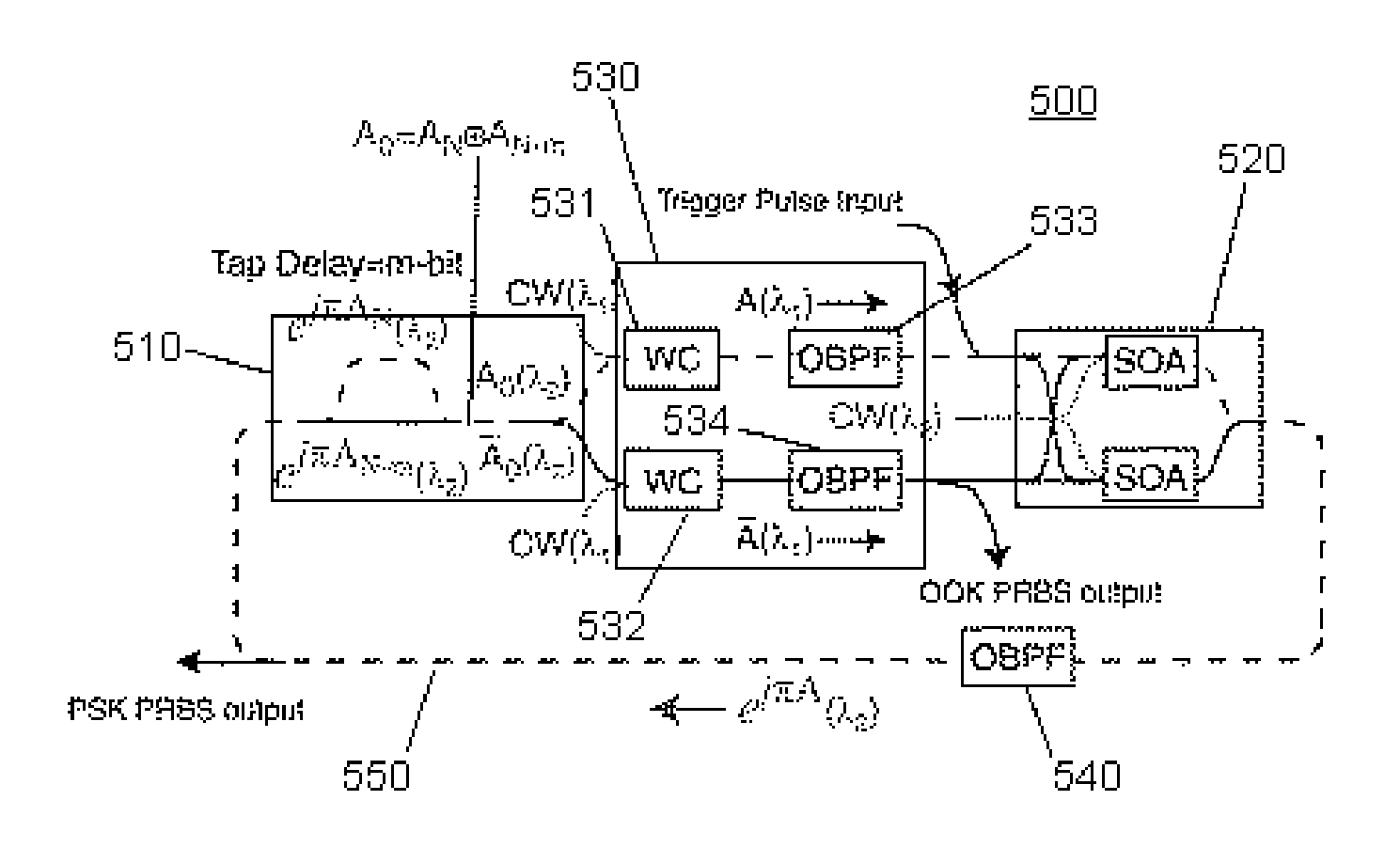
InactiveUS20070071449A1Reduced pattern dependenceGood suitElectromagnetic repeatersInstrumentsShift registerOn-off keying
An all-optical modulation format converter for converting optical data signals modulated in an on-off-keying (OOK) format to a phase-shift-keying (PSK) format. The OOK-to-PSK converter can be coupled to a delay-line interferometer to provide an all-optical wavelength converter for differential PSK (DPSK). The OOK-to-PSK converter can also be used in all-optical implementations of various functions, including, for example, exclusive-OR (XOR) logic, shift registers, and pseudo-random binary sequence (PRBS) generators.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
High-bit-rate long-haul fiber optic communication system techniques and arrangements
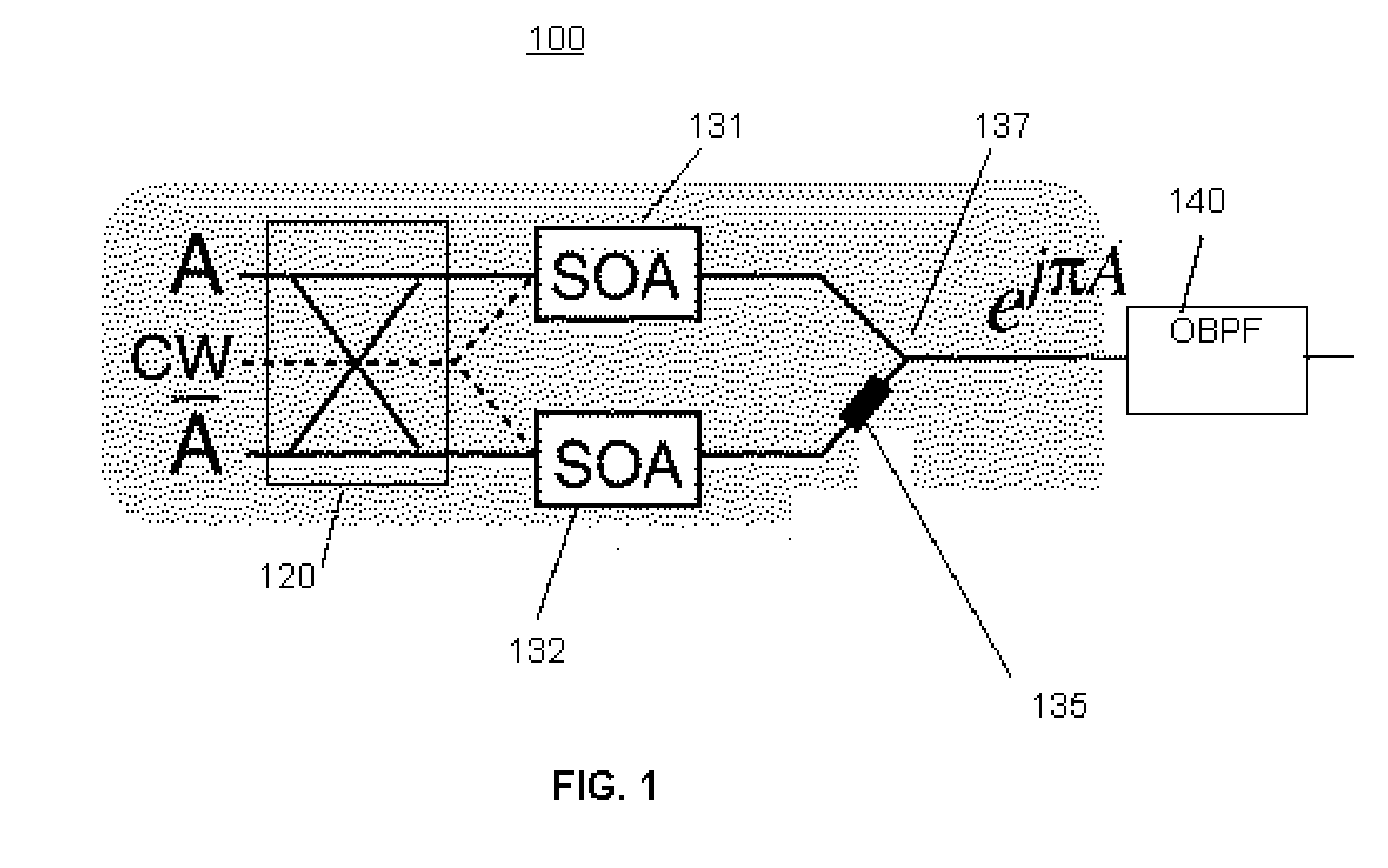
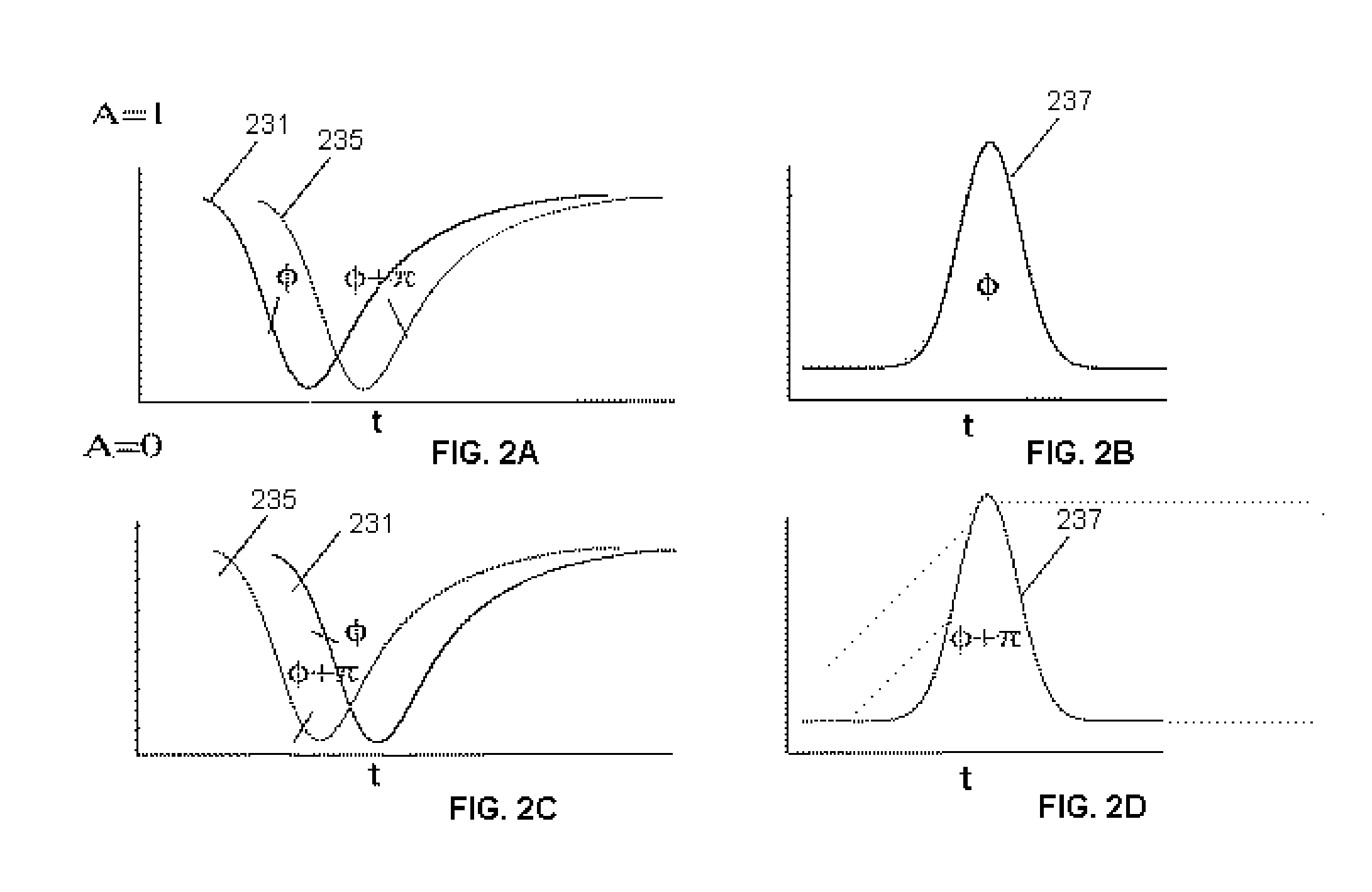
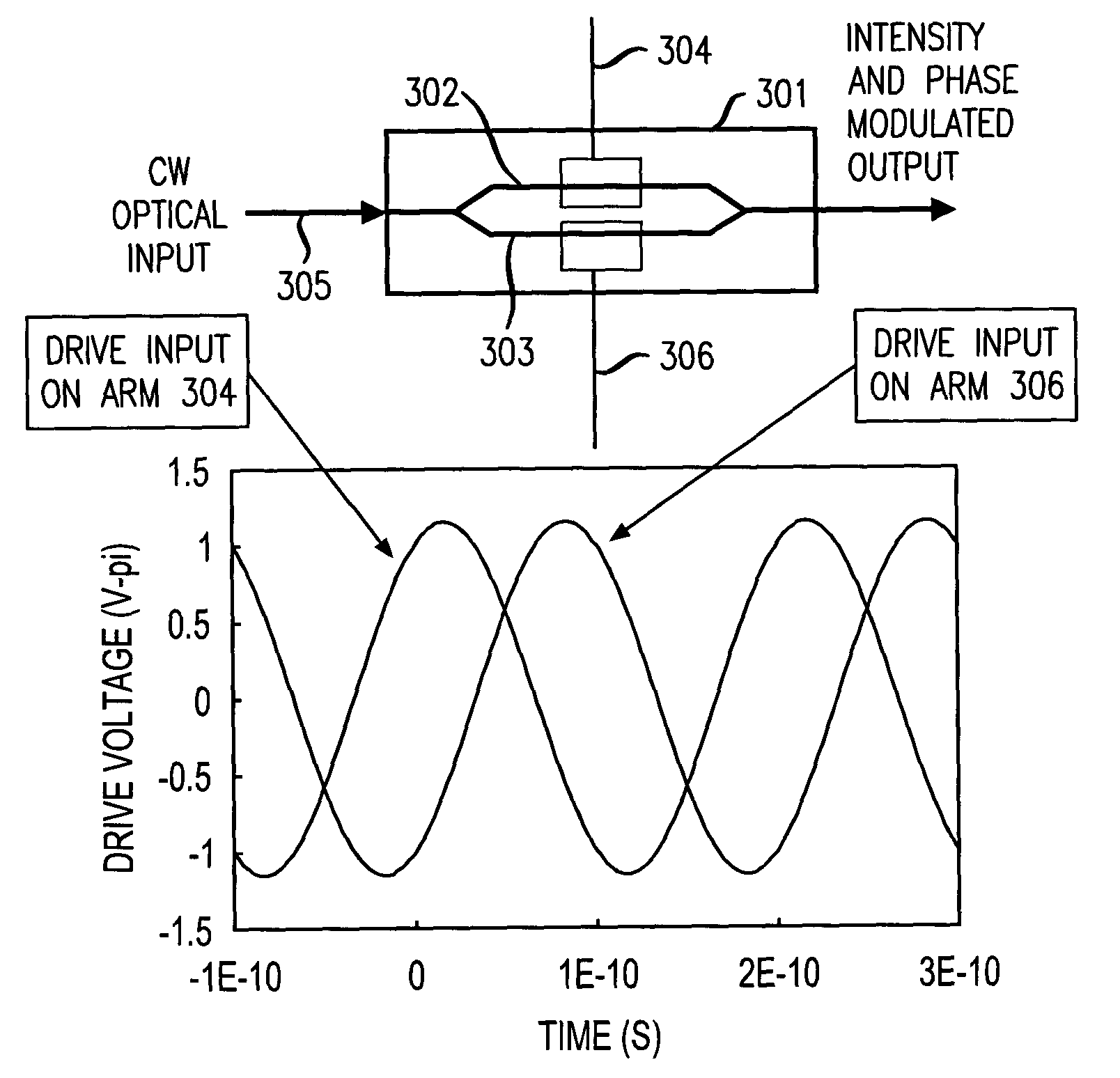
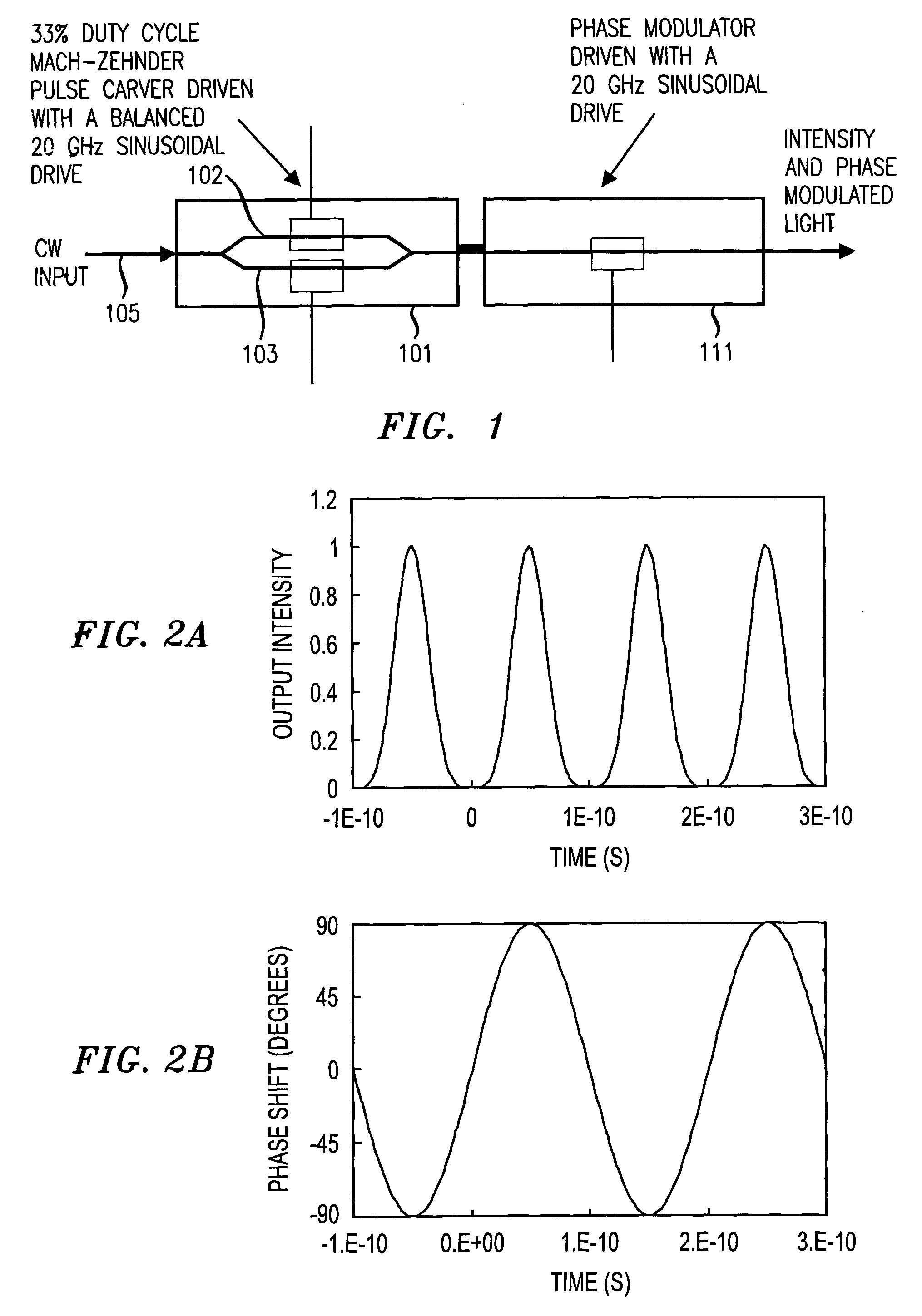
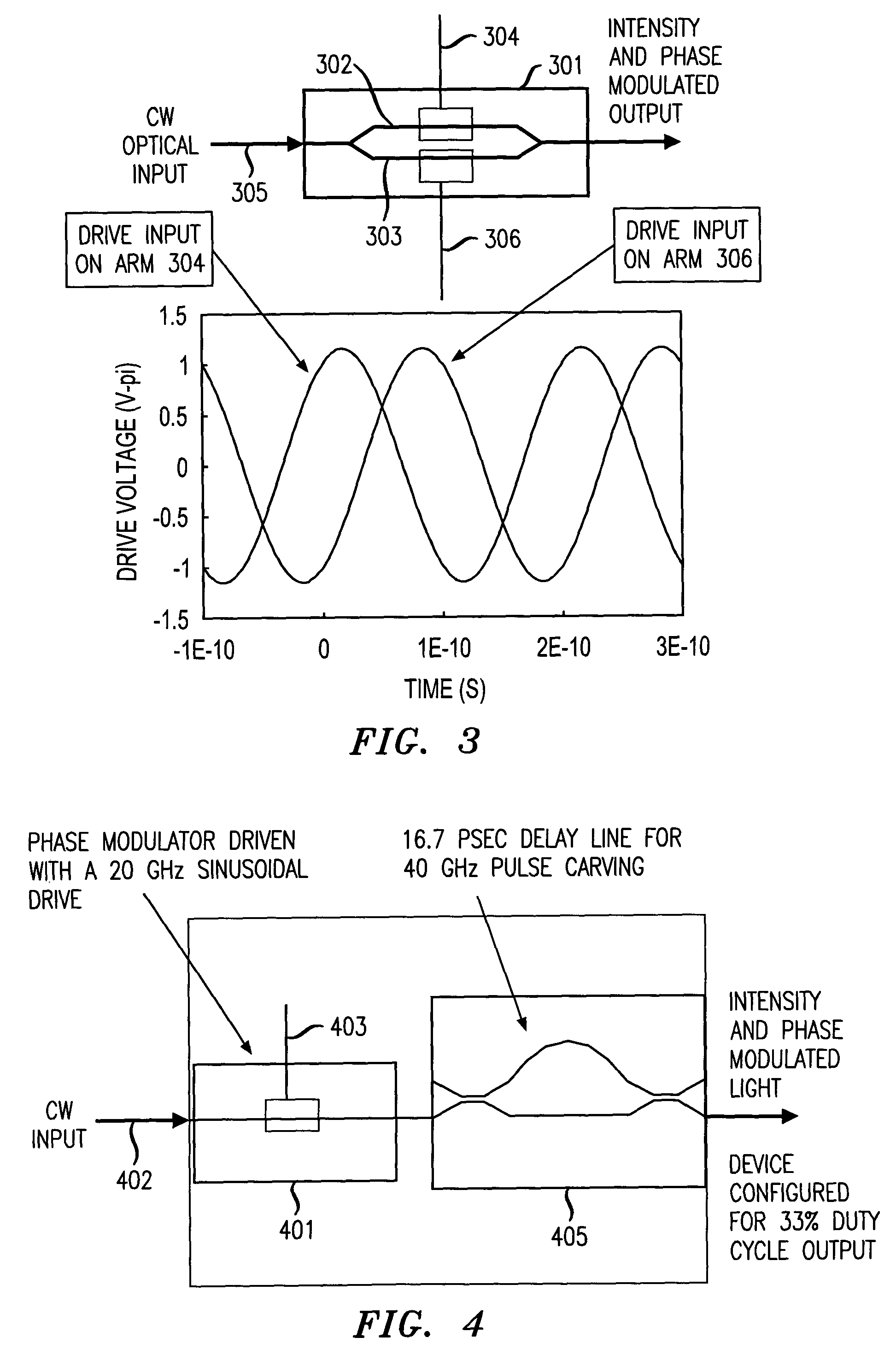
A 90 degree Alternate-Phase (AP) on-off keying (OOK) transmission format for high bit rate, long-haul optical transmission systems employing a chirped or a chirp-free pulse stream generated by a pulse generator (e.g., Mach Zehnder modulator) driven by mixing two electrical signals—one for intensity modulation and another for pulse modulation. These electrical signals may be two properly skewed sinusoidal electrical signals at half the desired data rate thereby generating a pulse stream in which the maximum optical phase modulation occurs at the intensity peak of each pulse and is 90 degrees out of phase with its nearest neighbors.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
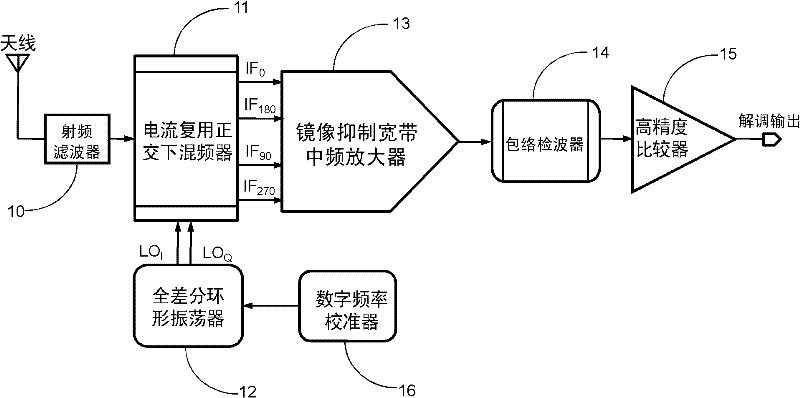
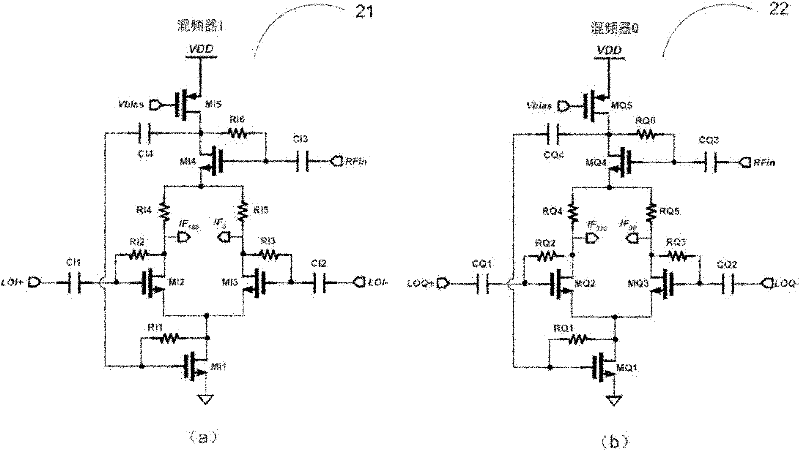
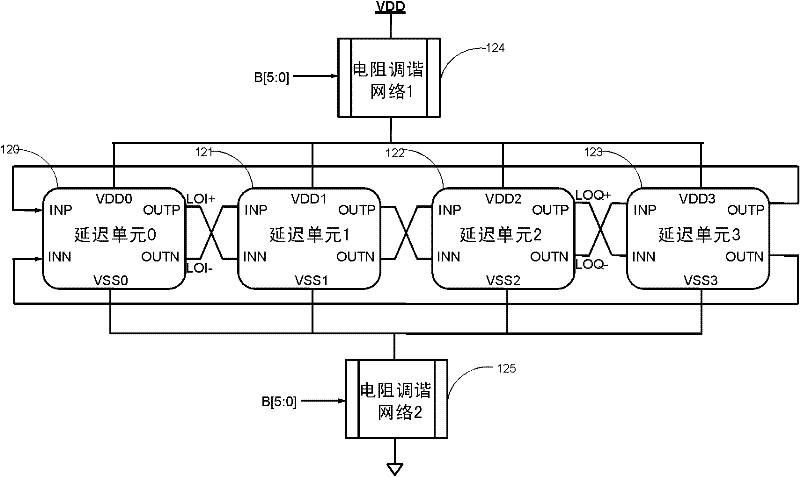
OOK (on-off keying) receiving device with low power consumption
ActiveCN102163982AMake up for deficienciesSimple structureAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMultiplexingOn-off keying
The invention discloses an OOK (on-off keying) receiving device with low power consumption, which comprises a radio-frequency filter, a lower current multiplexing quadrature mixer, a fully-differential annular oscillator, an image rejection broadband intermediate frequency amplifier, an envelope detector, a high-precision comparator and a digital frequency calibrator, wherein the input end of the radio-frequency filter is connected with an antenna; the input end of the lower current multiplexing quadrature mixer is connected with the output end of the radio-frequency filter; the output end of the fully-differential annular oscillator is connected with the input end of the lower current multiplexing quadrature mixer; the input end of the image rejection broadband intermediate frequency amplifier is connected with the output end of the lower current multiplexing quadrature mixer; the input end of the envelope detector is connected with the output end of the image rejection broadband intermediate frequency amplifier; the input end of the high-precision comparator is connected with the output end of the envelope detector; and the output end of the digital frequency calibrator is connected with the input end of the fully-differential annular oscillator, and the digital frequency calibrator is used for carrying out digital calibration on the output frequency of the fully-differential annular oscillator.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
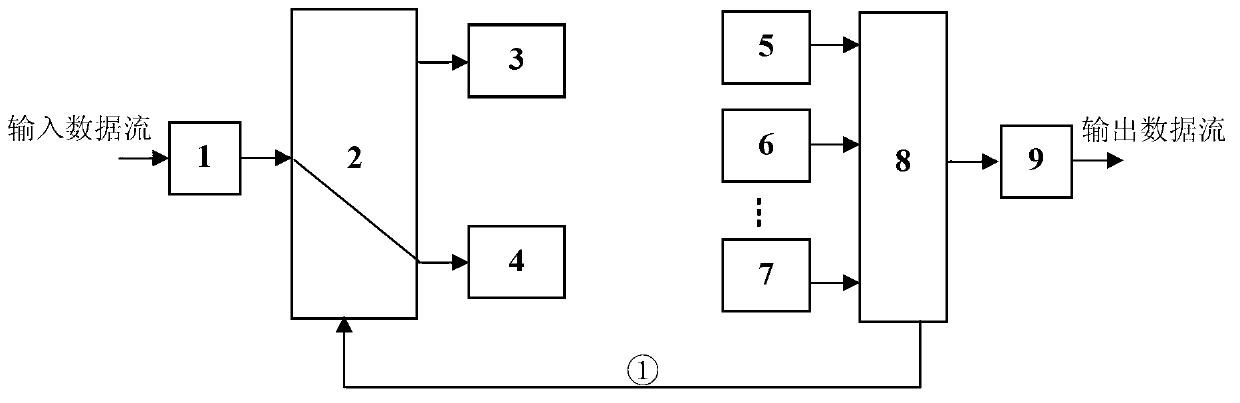
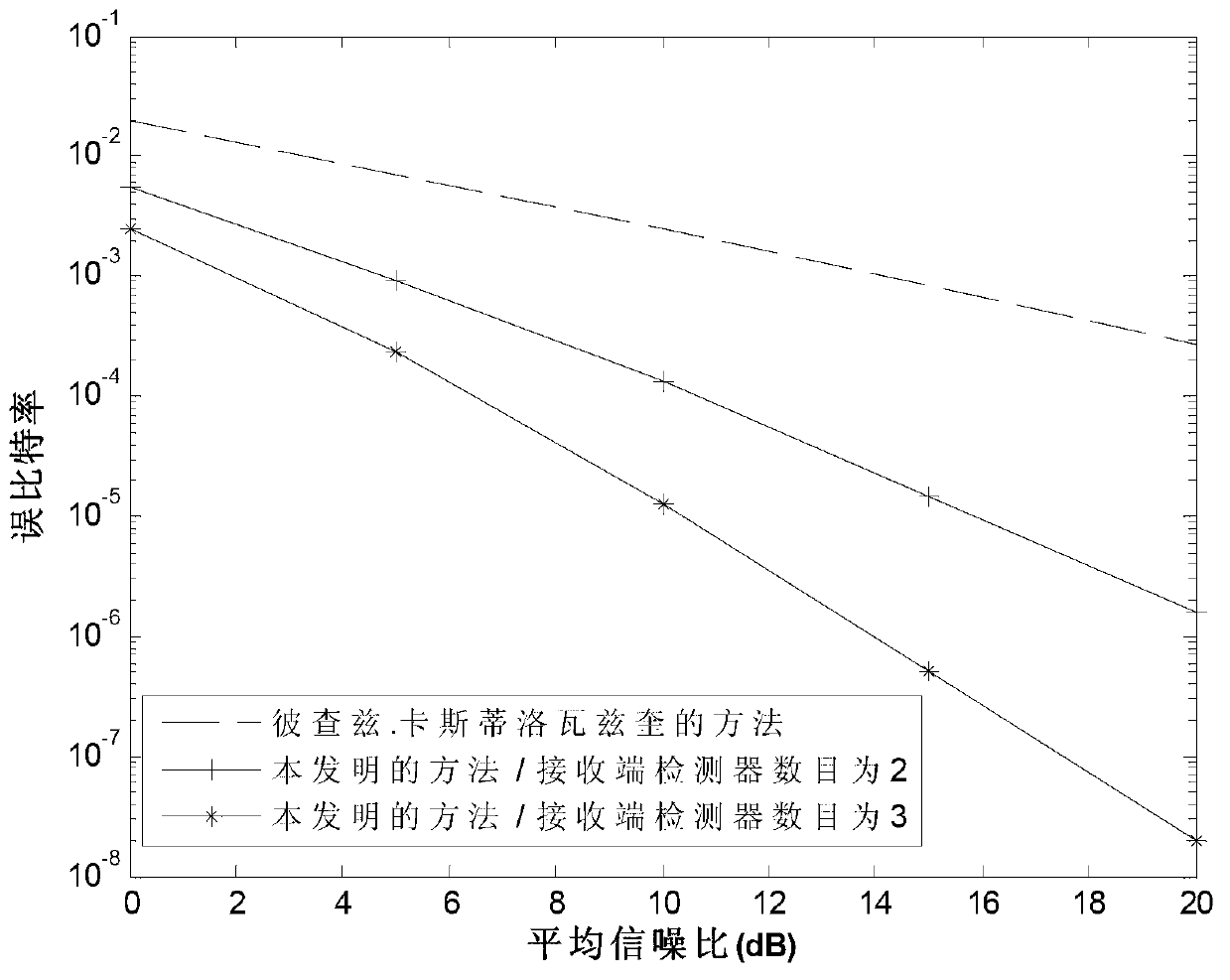
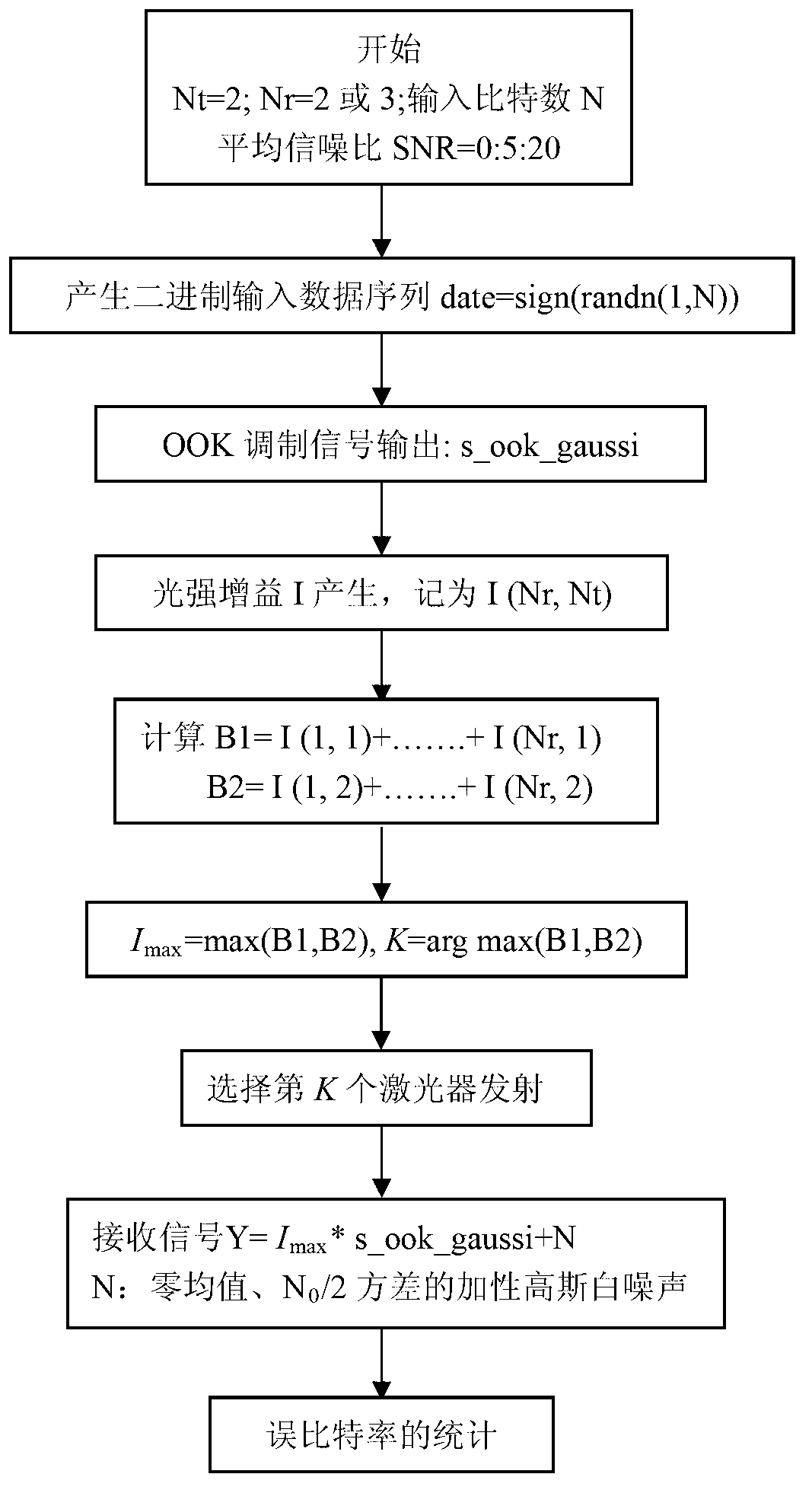
Transmitting light path selecting method for combined diversity reception in MIMO (Multiple-input and Multiple-Output)free space optical communication
ActiveCN102820923AImprove system performanceReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityElectromagnetic transmissionOn-off keyingOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a transmitting light path selecting method for combined diversity reception in MIMO (Multiple-input and Multiple-Output)free space optical communication, and belongs to the technical field of MIMO free space optical communication. The transmitting light path selecting method comprises the following steps of: carrying out comparison on the light intensity gain after the gains from each laser to Nr detectors and the like are combined to obtain a serial number of the laser with maximum light intensity gain value, and then feedbacking the serial number of the laser to a light path selector at a transmitting end by a low-speed feedback channel so as to enable the transmitting end to select and activate the optimal laser for transmitting light signals. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the system performances of the MIMO free space optical communication modulated on basis of OOK (On-Off Keying) are obviously improved, and compared with maximal-ratio combining reception, the complexity for realizing the method of united equal-gain combining reception, adopted by the invention, on hardware can be reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Polarization tracking and signal equalization for optical receivers configured for on-off keying or pulse amplitude modulation signaling
According to one embodiment, an optical receiver adapted to recover OOK or PAM data carried by a modulated optical carrier has an optical detector adapted to produce a sequence of vector pairs having first and second digital vectors indicative of complex values of first and second polarization components, respectively, of the modulated optical carrier at a corresponding sampling time. The optical receiver also has a digital processor that is connected to receive the sequence and is adapted to perform a rotation on each pair in a manner that tends to compensate for polarization rotation produced by transmitting the modulated optical carrier from an optical transmitter thereof to the optical receiver. The digital processor is further adapted to estimate values of the OOK or PAM data encoded onto each of the first and second polarization components based on the vectors produced by the rotation in a manner responsive to values of energy errors in the estimated values.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
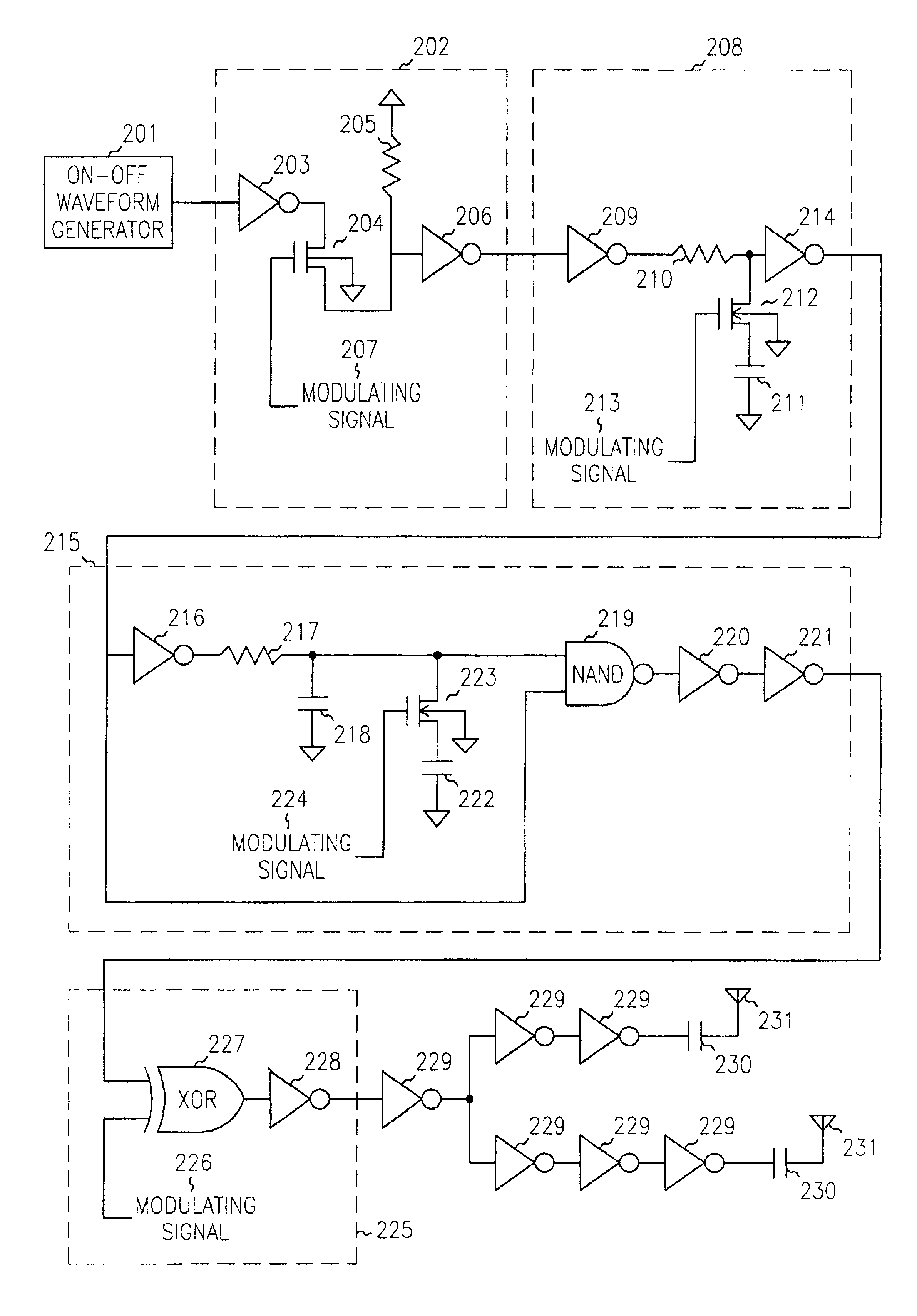
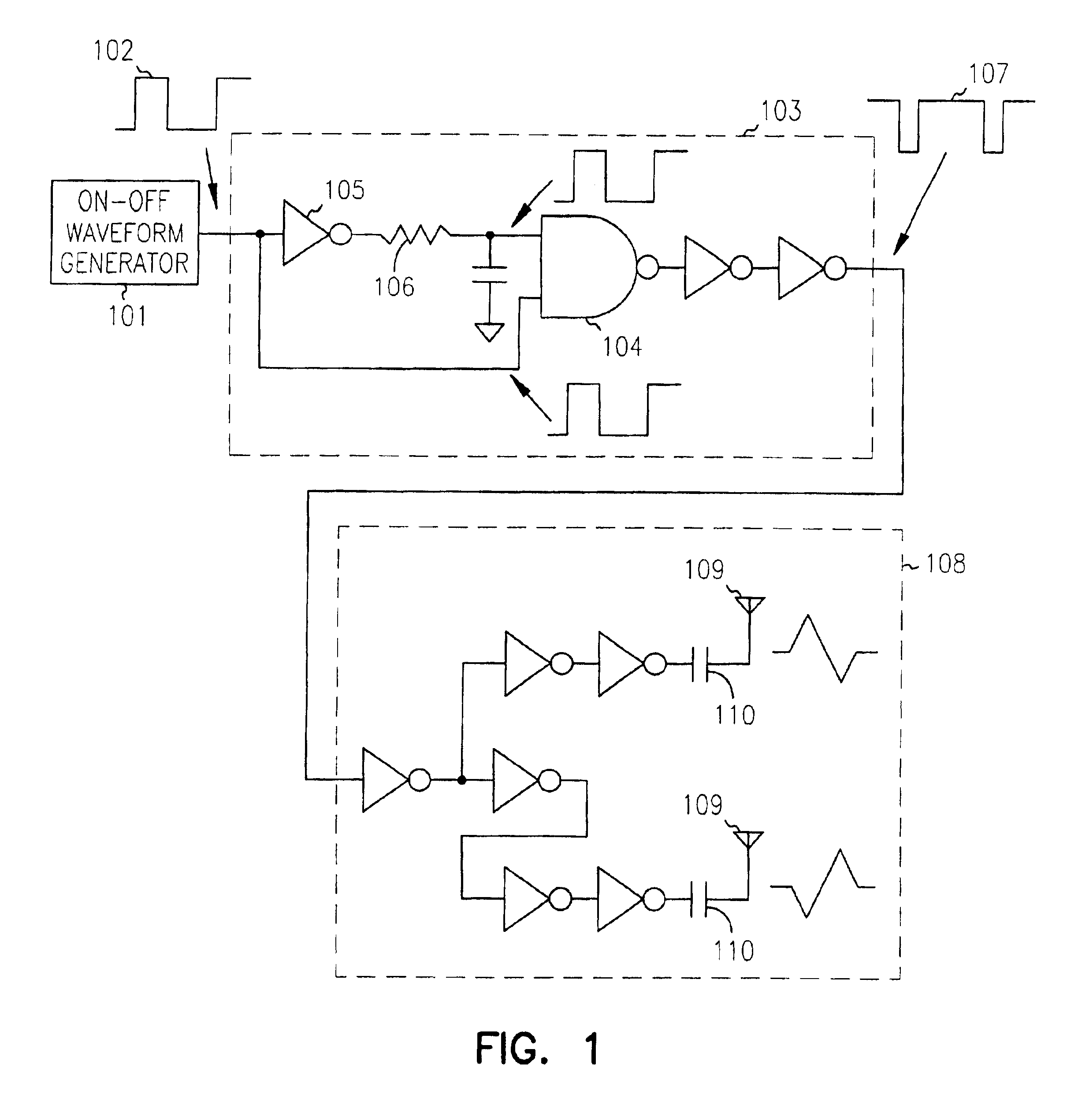
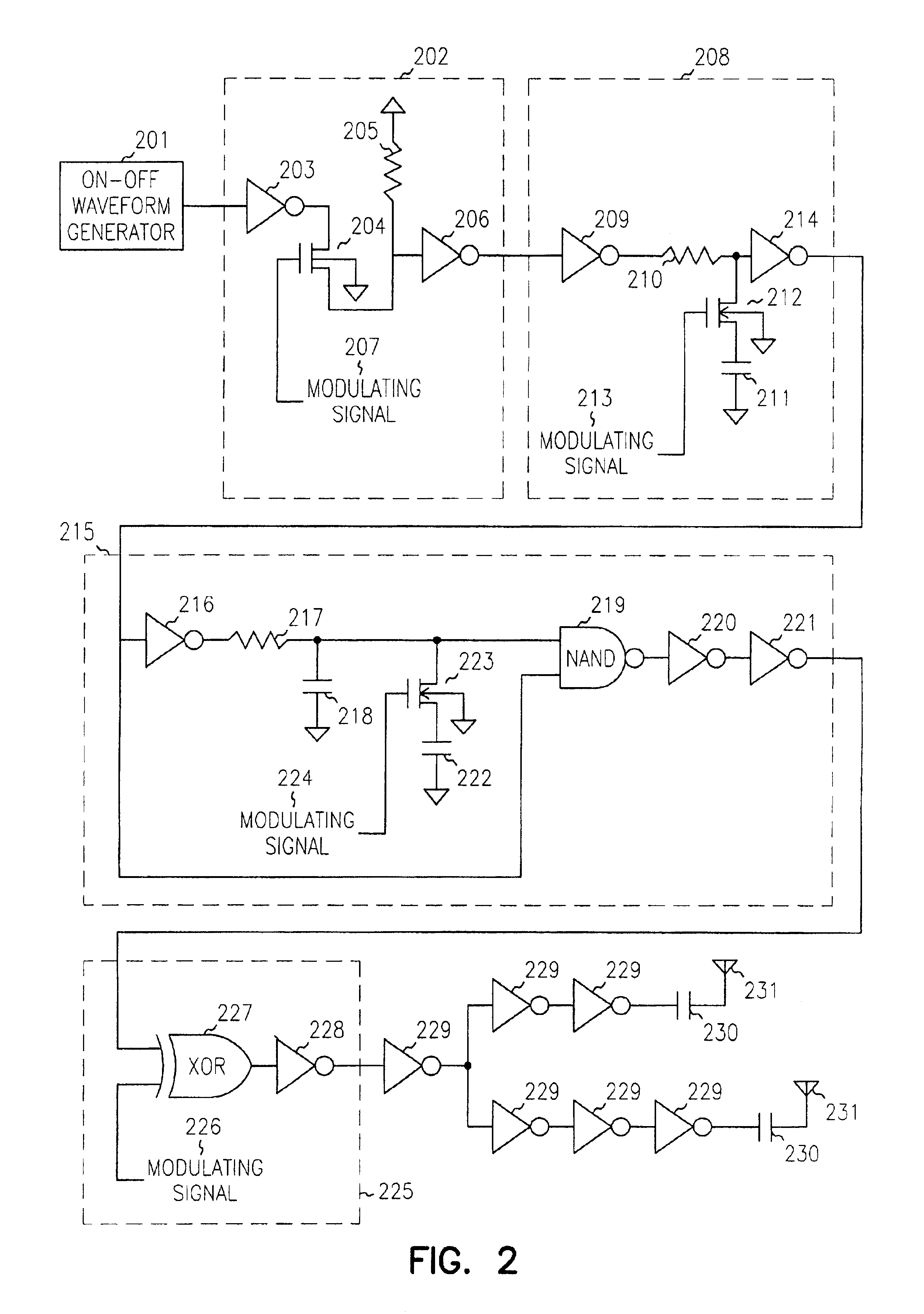
Ultra-wideband impulse generation and modulation circuit
InactiveUS6911874B2Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationPosition-modulated pulse demodulationUltra-widebandOn-off keying
A modulated ultra wideband pulse generation system is provided. The system comprises a pulse waveform generator circuit operable to generate an on-off pulse waveform, and a modulating circuit operable to receive a modulating signal and to modulate the on-off pulse waveform in response to the modulating signal. Further embodiments of the invention comprise a variable bandwidth circuit operable to alter the bandwidth of the pulses comprising the on-off pulse waveform. Various embodiments of the invention comprise on-off keying modulation, pulse position modulation, and pulse phase modulation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
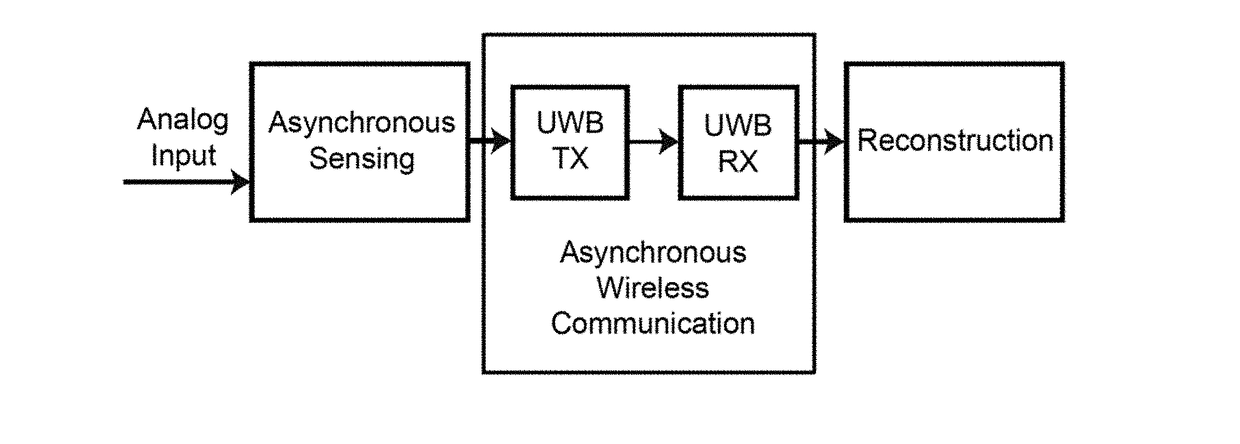
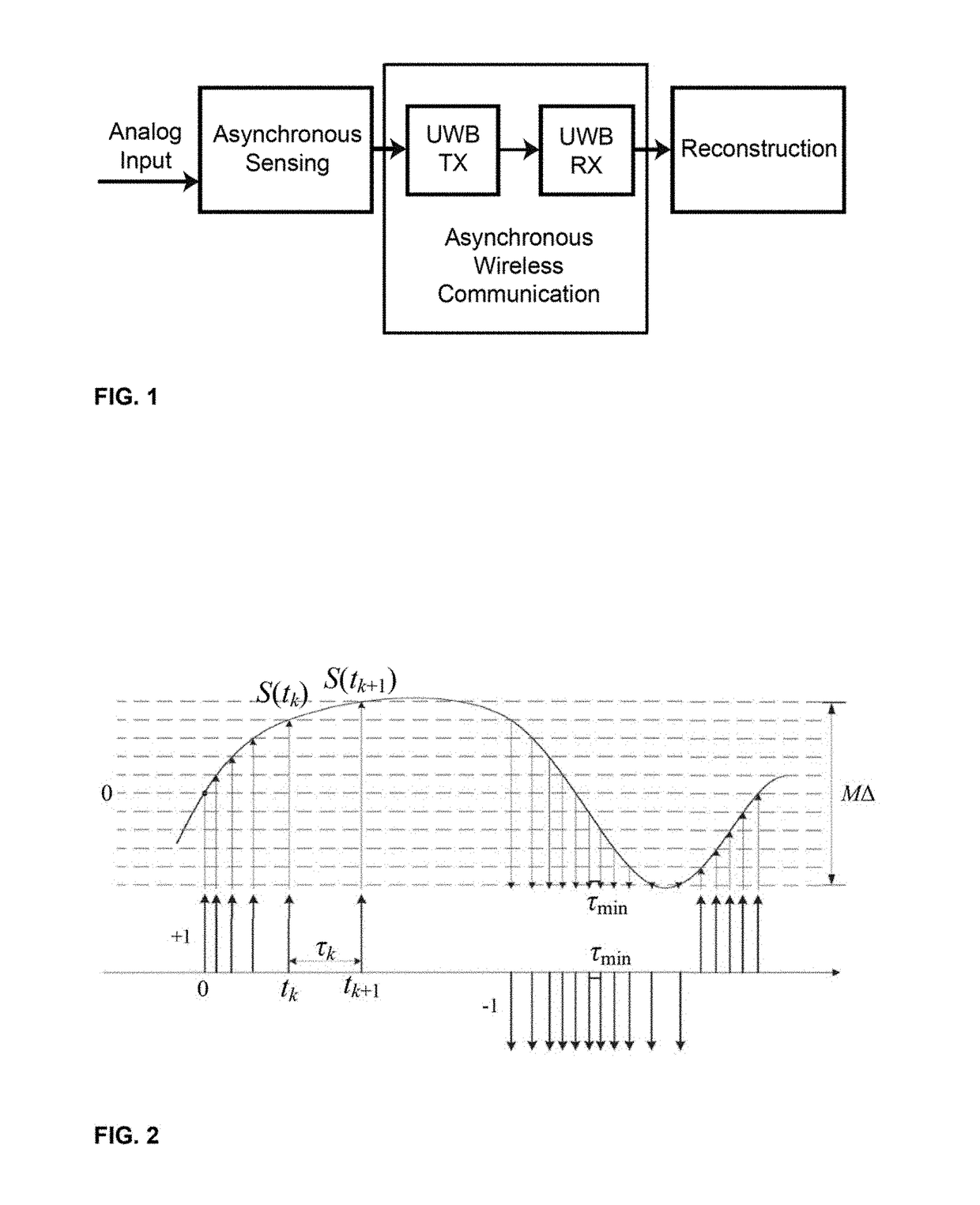
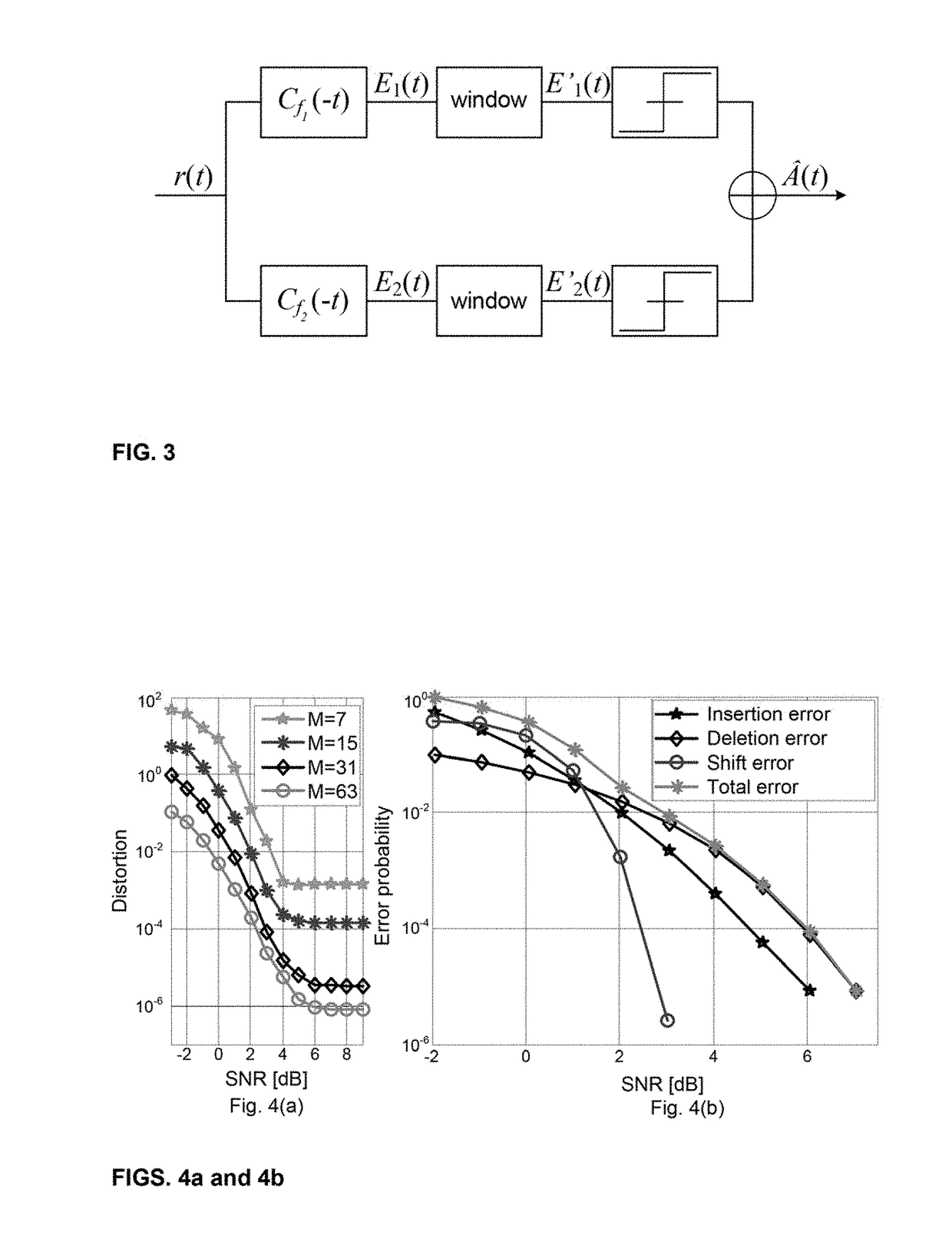
Asynchronous wireless sensing
ActiveUS20180019862A1Reliable communicationReduce peak power consumptionSynchronisation information channelsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTime informationAsynchronous serial communication
Low-complexity asynchronous wireless sensing and communication architecture is disclosed for low power wireless sensors. Schemes are based on asynchronous digital communications and Ultra-Wideband impulse radios. In asynchronous radio, combination of frequency-shift-keying (FSK) and on-off-keying (OOK) to remove clock synchronization is applied. Improved asynchronous non-coherent transmitters and receivers achieve both low power and low complexity while seamlessly combined with asynchronous level-crossing modulation. Both uncoded and coded asynchronous communication may be utilized. Coded asynchronous communication may use error correction. Forward error correction schemes for asynchronous sensor communication are utilized where dominant errors consist of pulse deletions and insertions, and where instantaneous encoding takes place. Forward error correction is also accomplished where a continuous-time sparse waveform signal is asynchronously sampled and communicated over a noisy channel via Q-ary frequency-shift keying. Concatenated code employs outer systematic convolutional codes and inner embedded marker codes that preserve timing information and protect against symbol insertions and deletions.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT NEW MEXICO STATE UNIV +1
Demodulation method in molecular communication
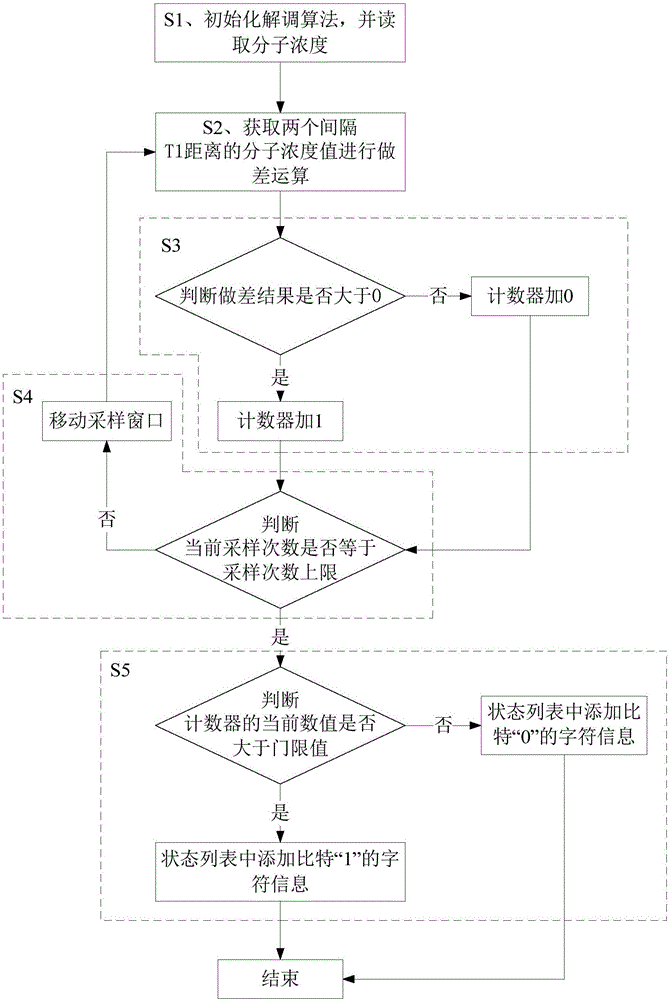
InactiveCN106301600ALighten the computational burdenImprove reliabilityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDiffusionMolecular communication
The invention discloses a demodulation method in molecular communication. The demodulation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: assuming that an originating party adopts a time-slot on-off keying (OOK) method to represent a digital signal, judging whether a molecular concentration received in a time slot has an obvious rising process or not during the demodulation process, if the molecular concentration has the obvious rising process, demodulating the molecular concentration to be information bit '1', and otherwise demodulating to be information bit '0'. By adopting the demodulation method, the defect of unreliability caused by demodulation by virtue of detection of the molecular concentration can be overcome; and moreover, the molecular concentration only needs to be sampled in a period of time after the beginning of each time slot rather than in the whole time slot, so that the calculation burden of the demodulation algorithm is alleviated. Meanwhile, the technical scheme is realized according to a variation rate of the molecular concentration, so that the influence of the intersymbol interference caused by a molecular aggregation problem on a demodulation result can be effectively alleviated, the reliability of the demodulation algorithm is improved, and the demodulation method is generally suitable for demodulating information in the molecular communication based on a diffusion way.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
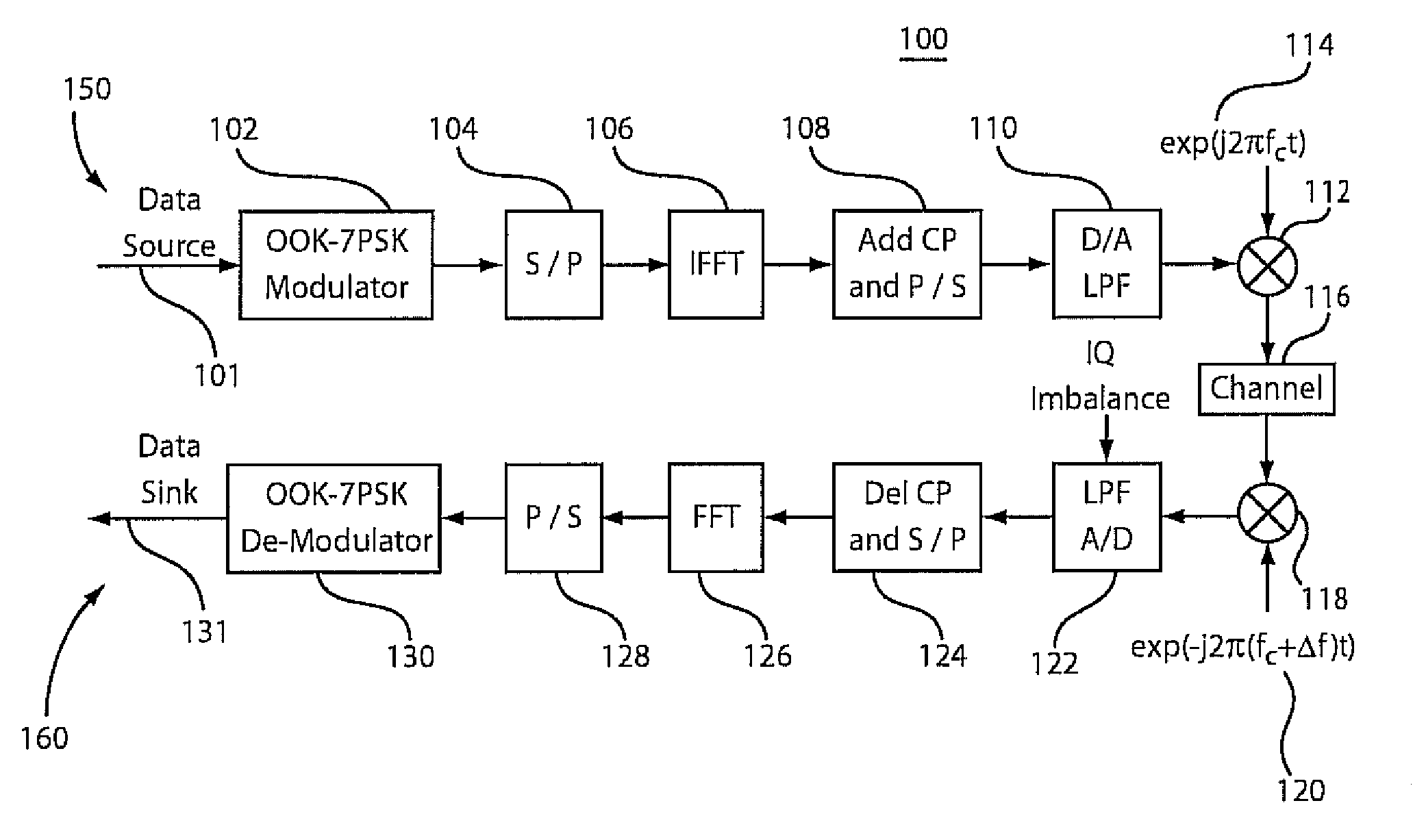
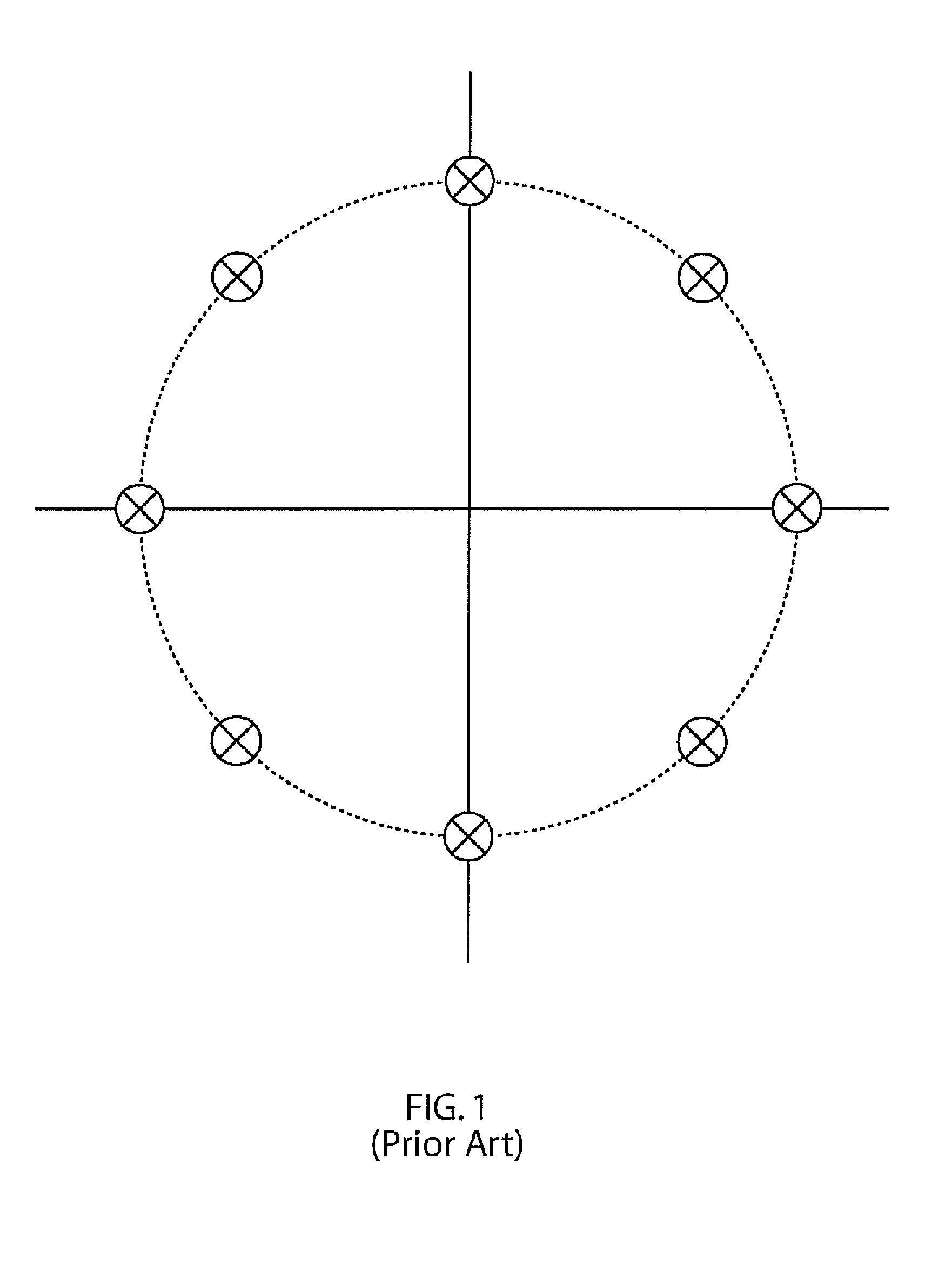
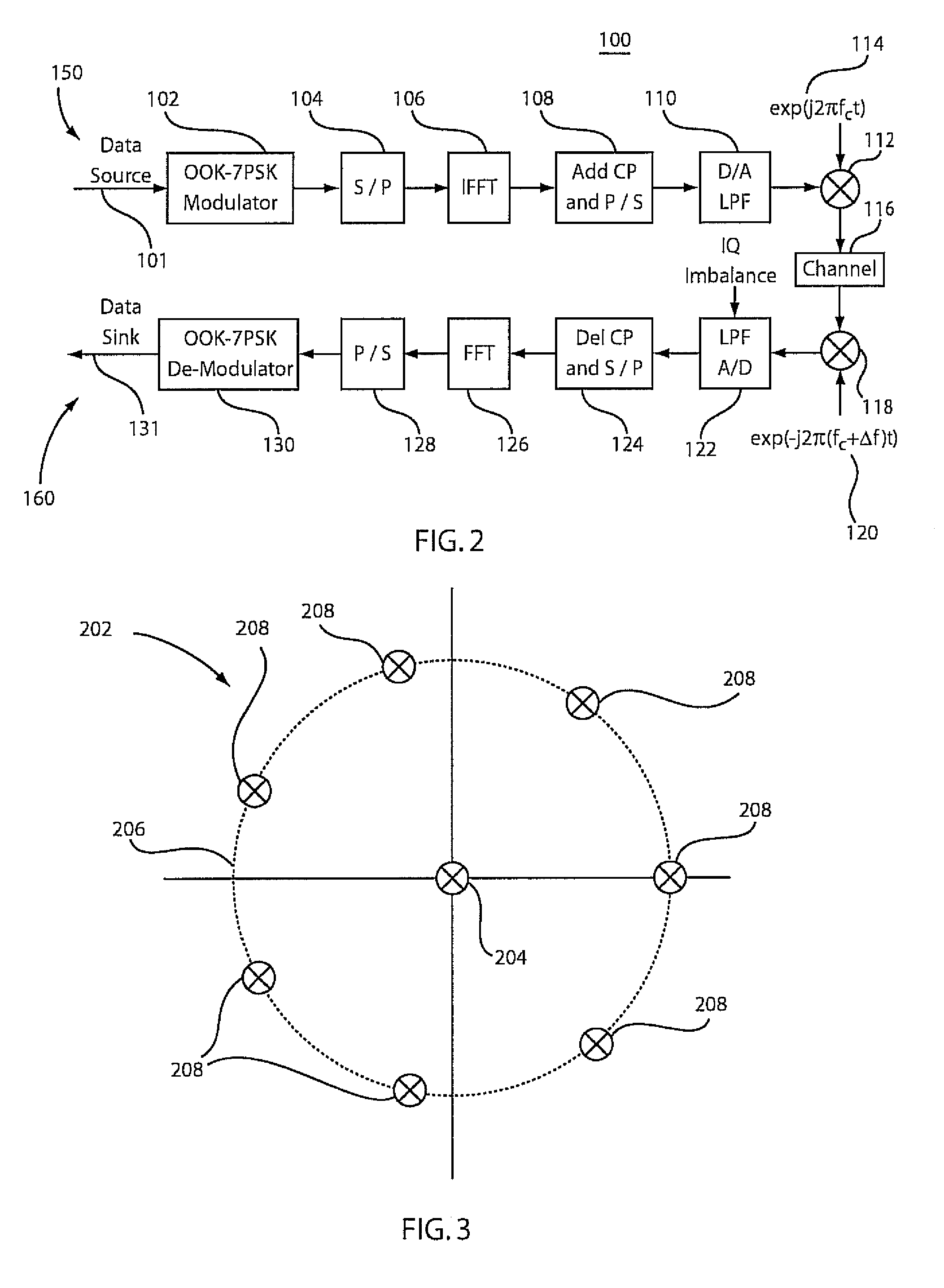
On-off keying - 7-phase shift keying modulation system and method for fiber communication
A modulation system includes a modulator configured to employ a modulation mechanism on data. The mechanism includes a signal constellation configured to map sub-carriers which include a signal to be modulated. The signal constellation has a plurality of points asymmetrically disposed on a circle about an origin and a point at the origin wherein a number of sub-carriers becomes variable over different symbol intervals. Corresponding demodulators and corresponding methods are also disclosed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com