Patents
Literature
41330 results about "Carrier signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
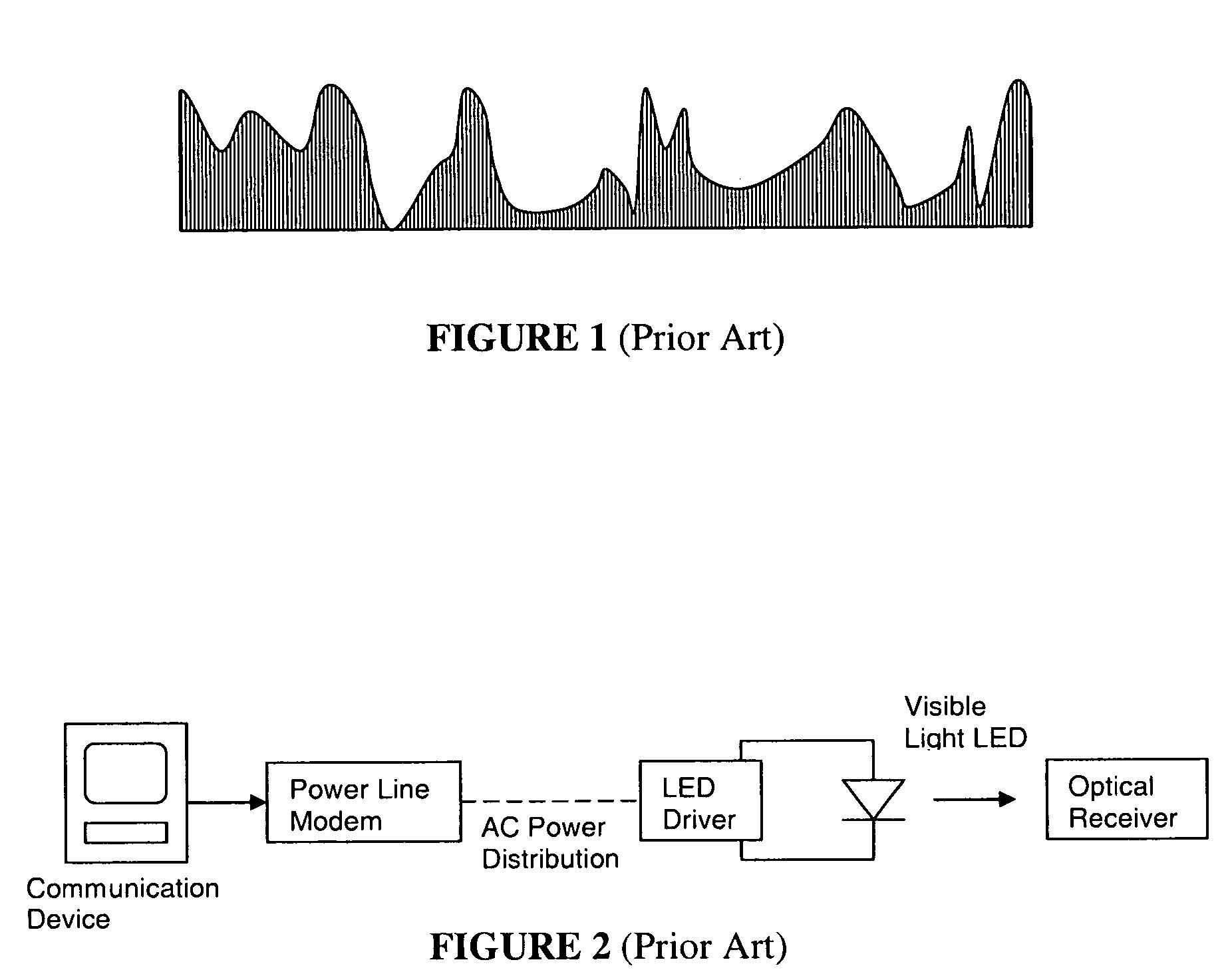
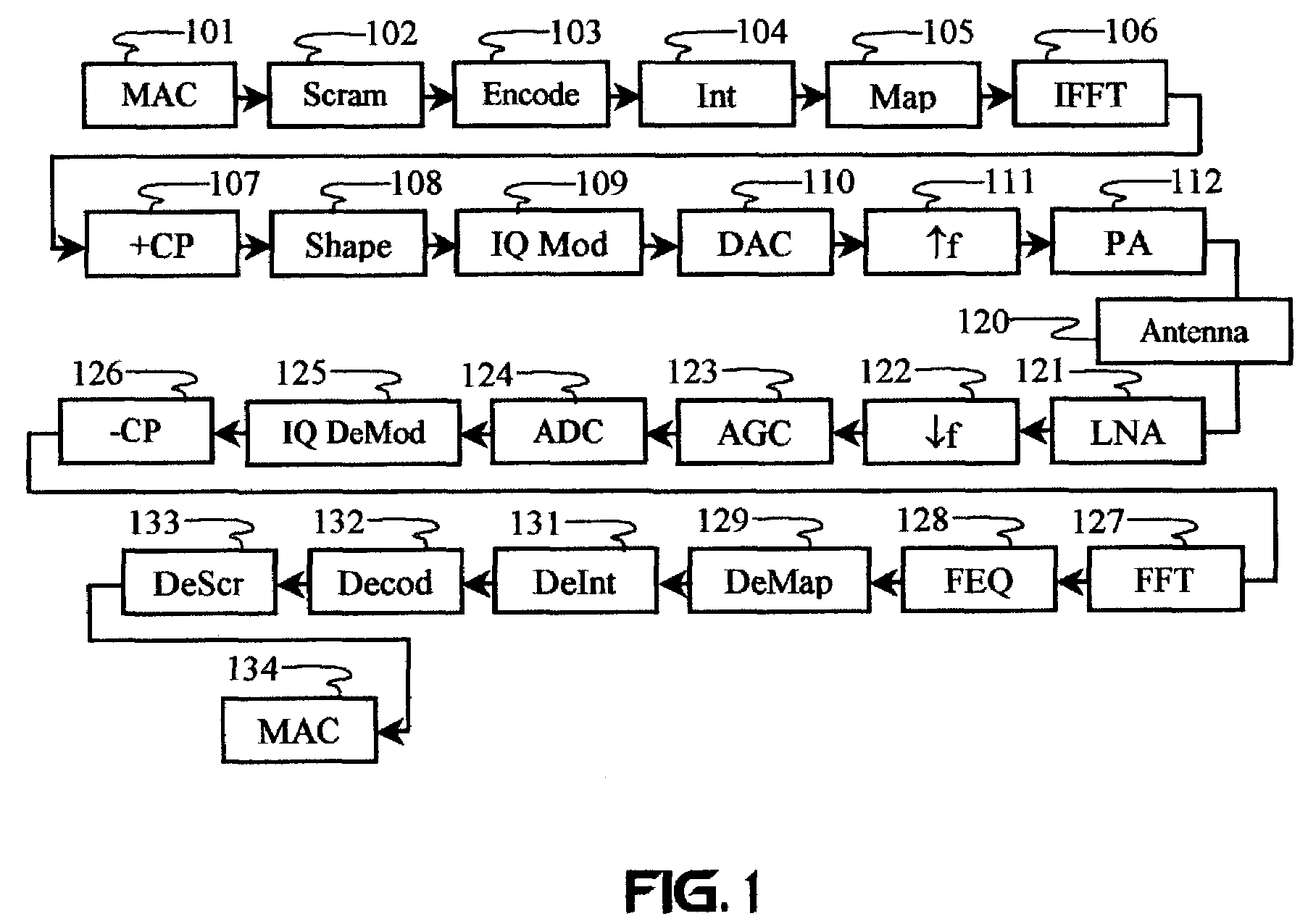
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a waveform (usually sinusoidal) that is modulated (modified) with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave usually has a much higher frequency than the input signal does. The purpose of the carrier is usually either to transmit the information through space as an electromagnetic wave (as in radio communication), or to allow several carriers at different frequencies to share a common physical transmission medium by frequency division multiplexing (as in a cable television system, for example). The term originated in radio communication, where the carrier wave is the radio wave which carries the information (modulation) through the air from the transmitter to the receiver. The term is also used for an unmodulated emission in the absence of any modulating signal.
Information input and output system, method, storage medium, and carrier wave
ActiveUS7015894B2Easy to operateEasy to distinguishInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsCarrier signalDisplay device
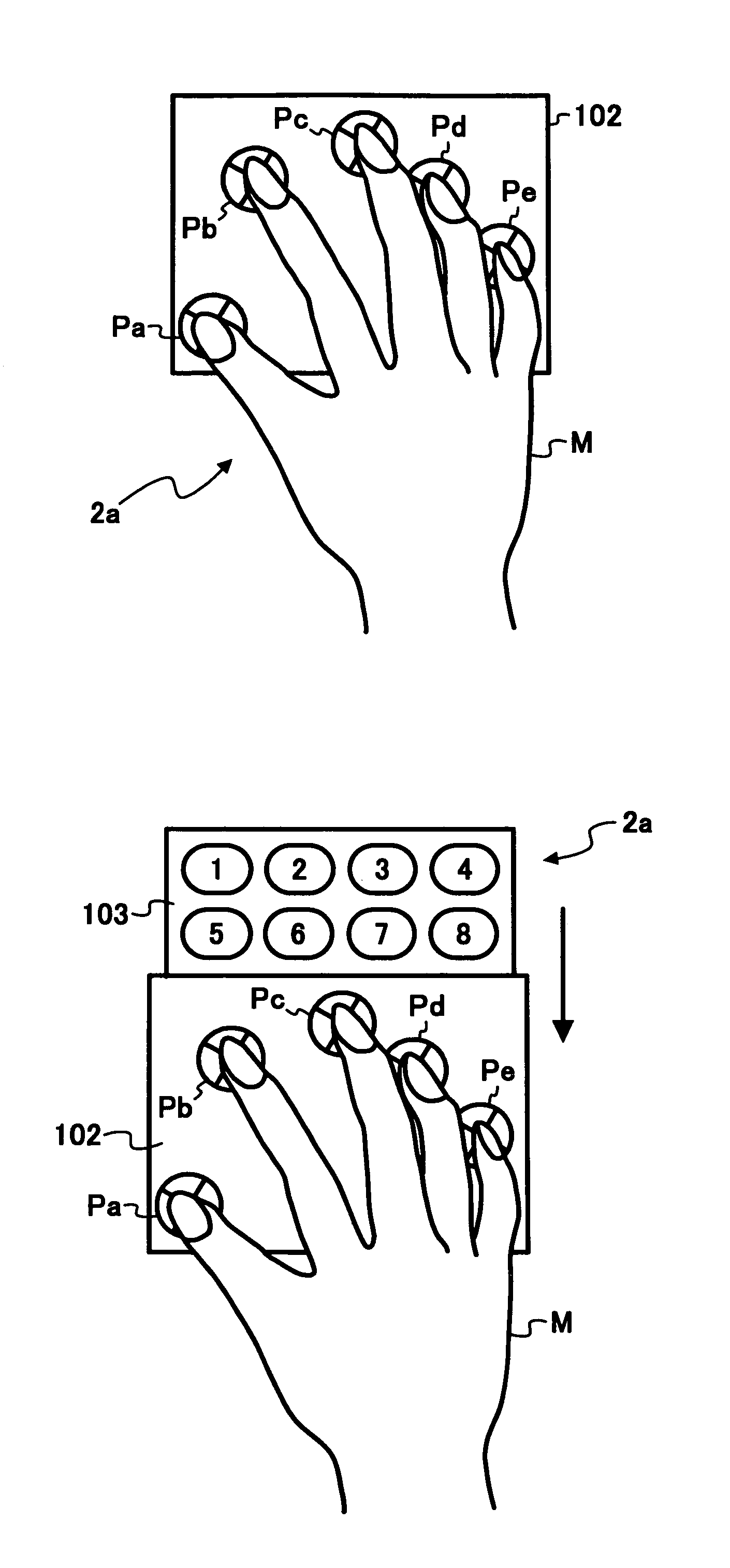
A coordinate input device detects coordinates of a position by indicating a screen of a display device with fingers of one hand, and transfers information of the detected coordinates to a computer through a controller. The computer receives an operation that complies with the detected coordinates, and executes the corresponding processing. For example, when it is detected that two points on the screen have been simultaneously indicated, an icon registered in advance is displayed close to the indicated position.
Owner:RICOH KK
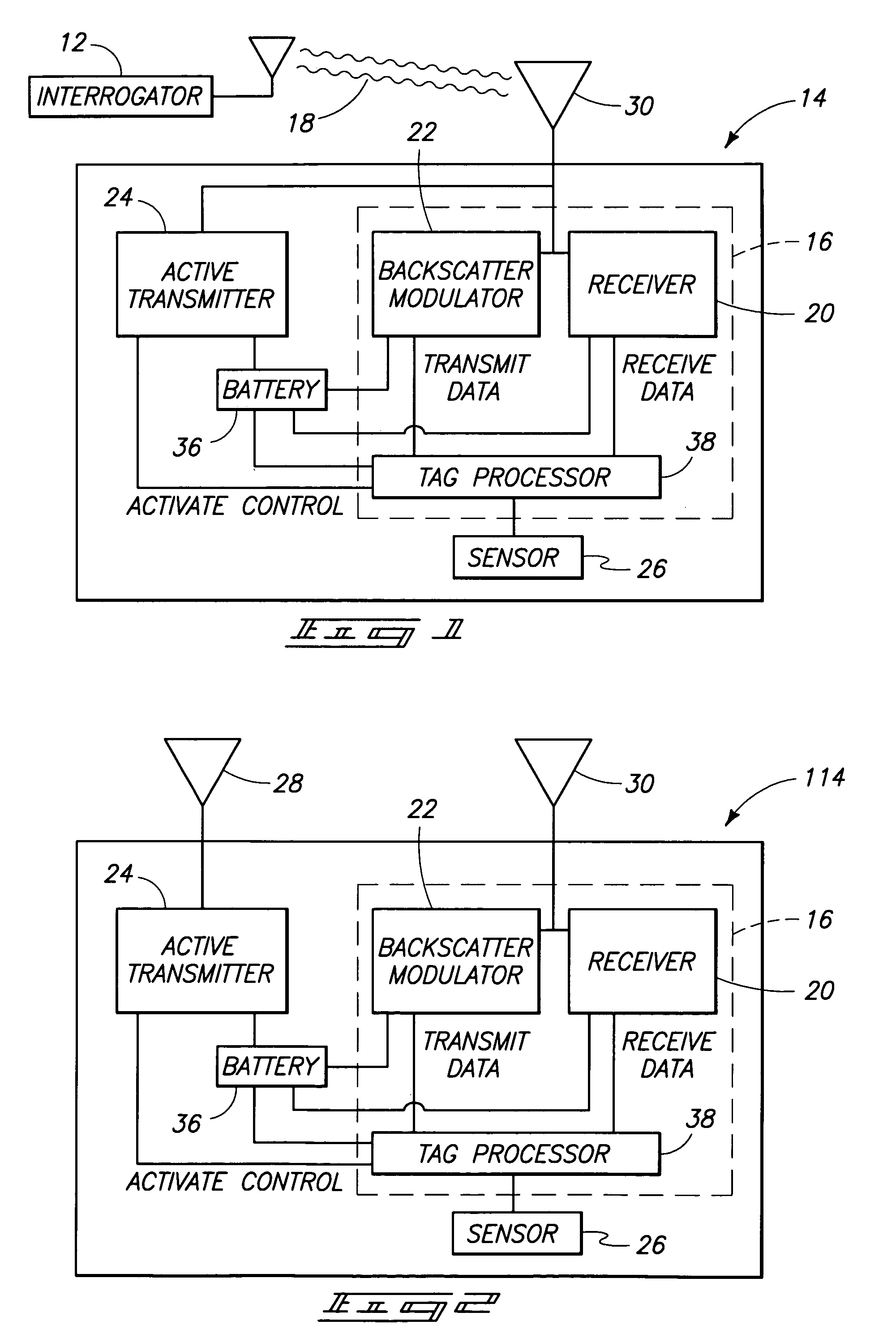
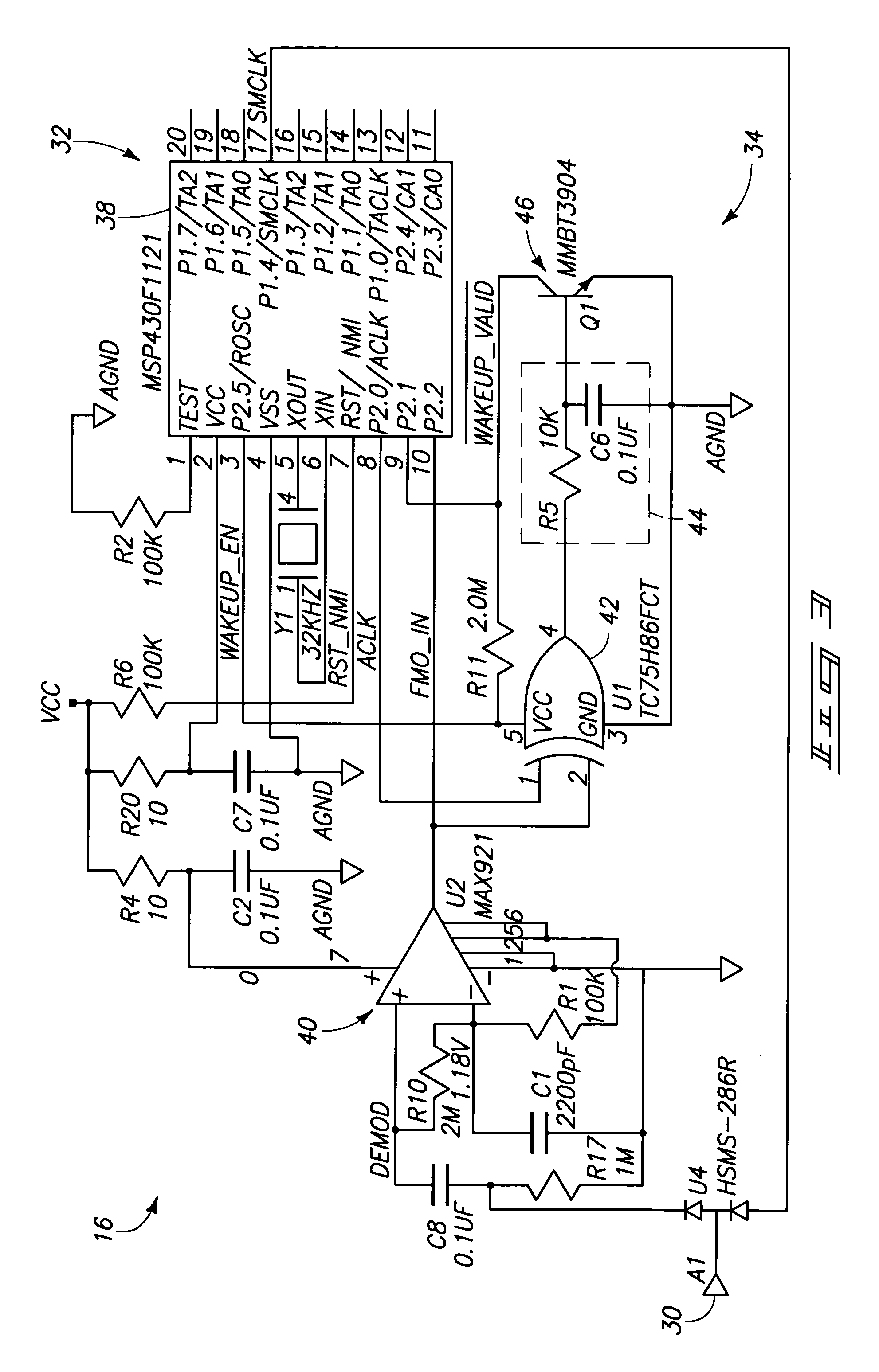
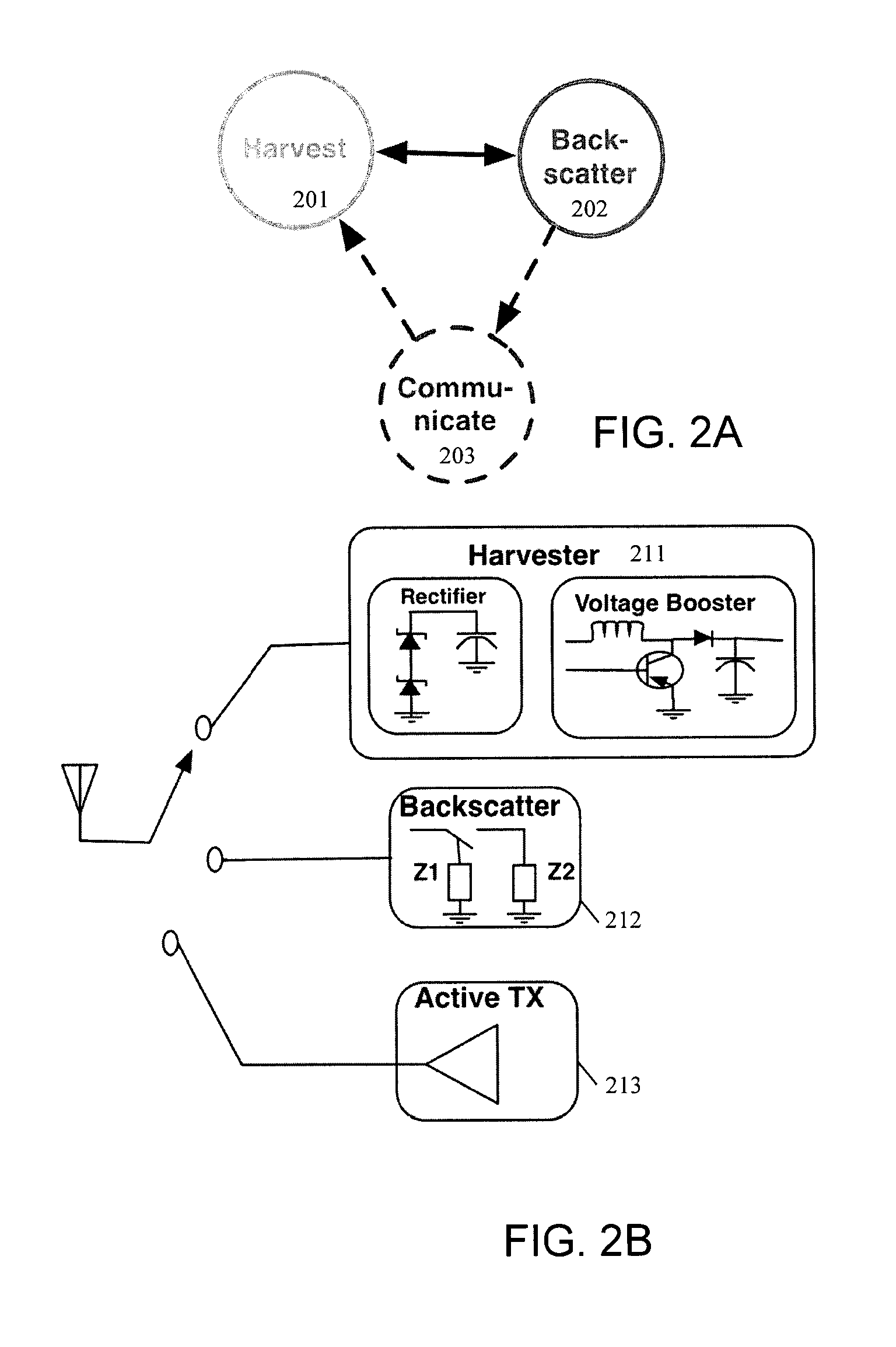
Semi-passive radio frequency identification (RFID) tag with active beacon
ActiveUS7348875B2Subscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesCarrier signalEngineering
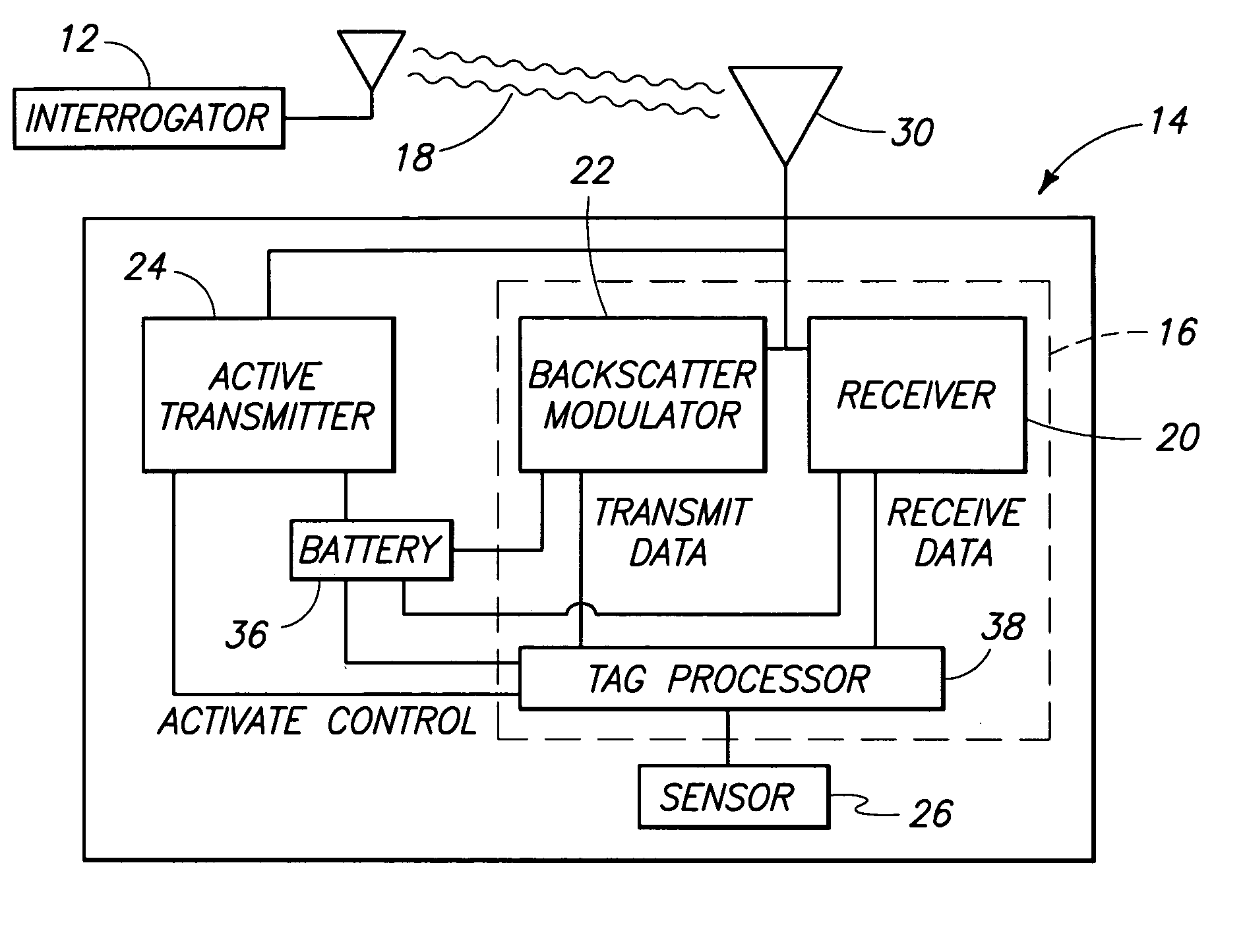
A radio frequency beacon device for use with a backscatter interrogator includes a processor; a receiver coupled to the processor; a backscatter modulator coupled to the processor; and an active transmitter coupled to the processor, the active transmitter being configured to transmit an RF signal, in response to a trigger signal, regardless of whether the interrogator is providing a carrier wave for backscatter modulation by the backscatter modulator. Other methods and apparatus are provided.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
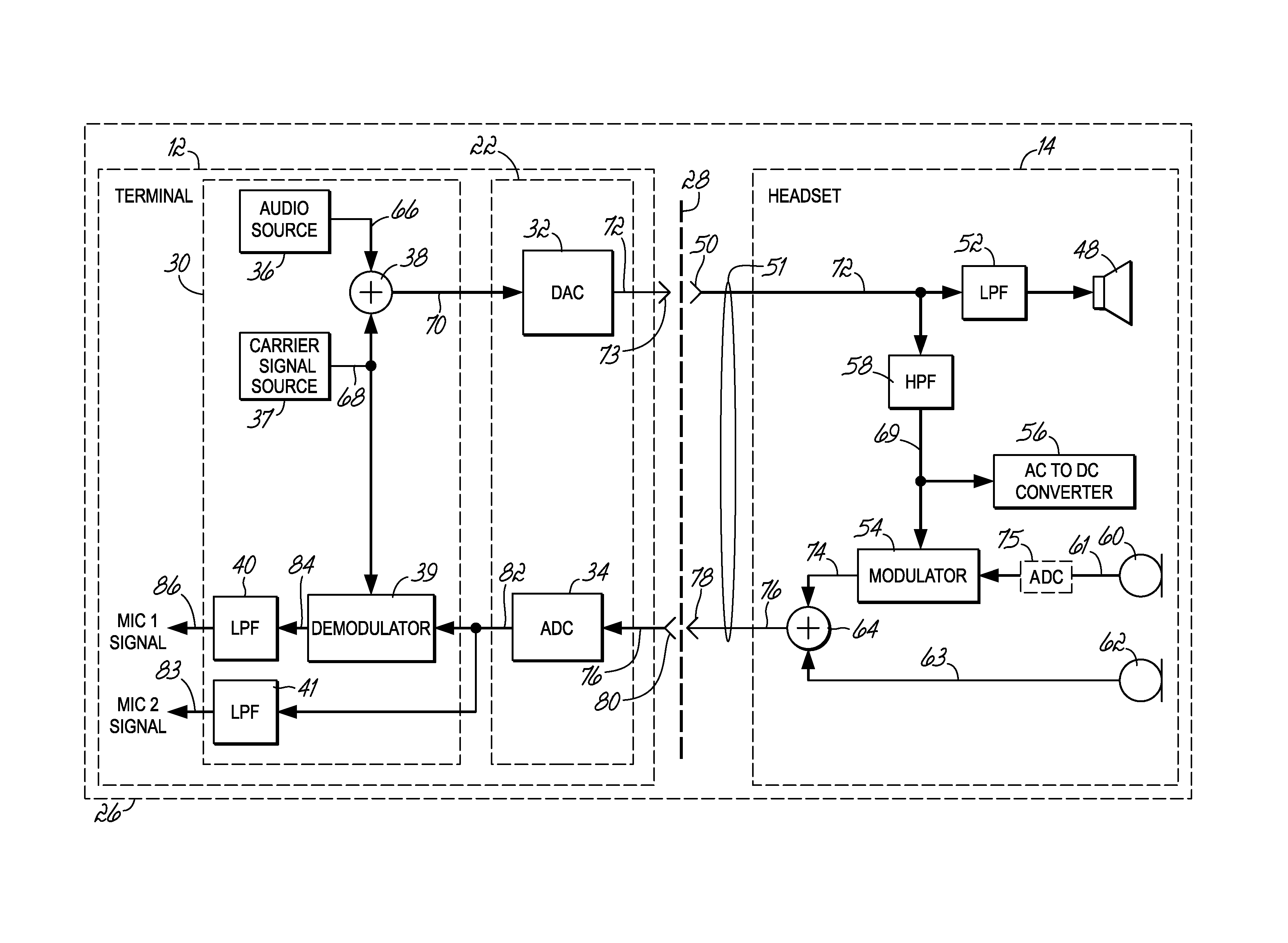
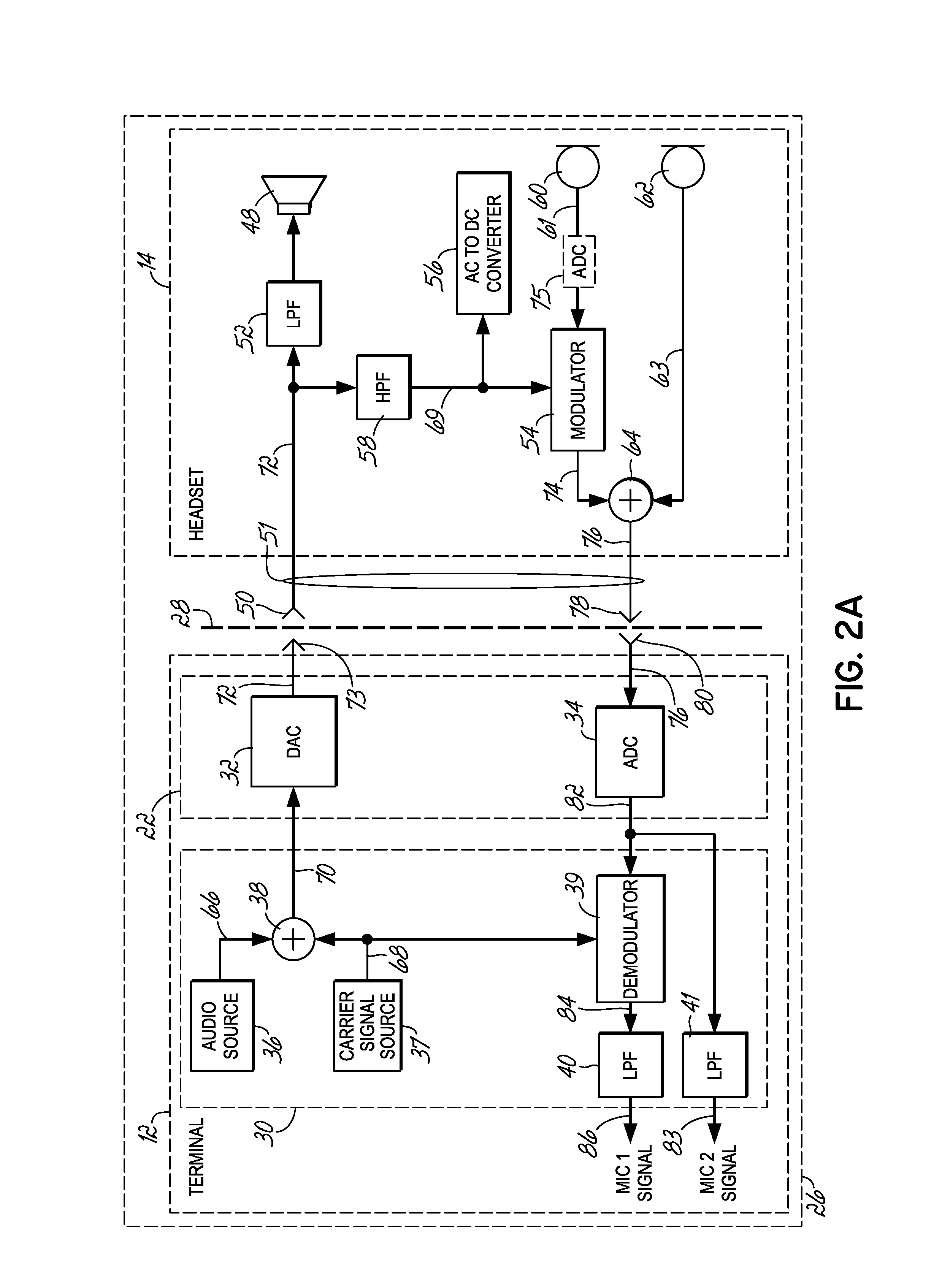
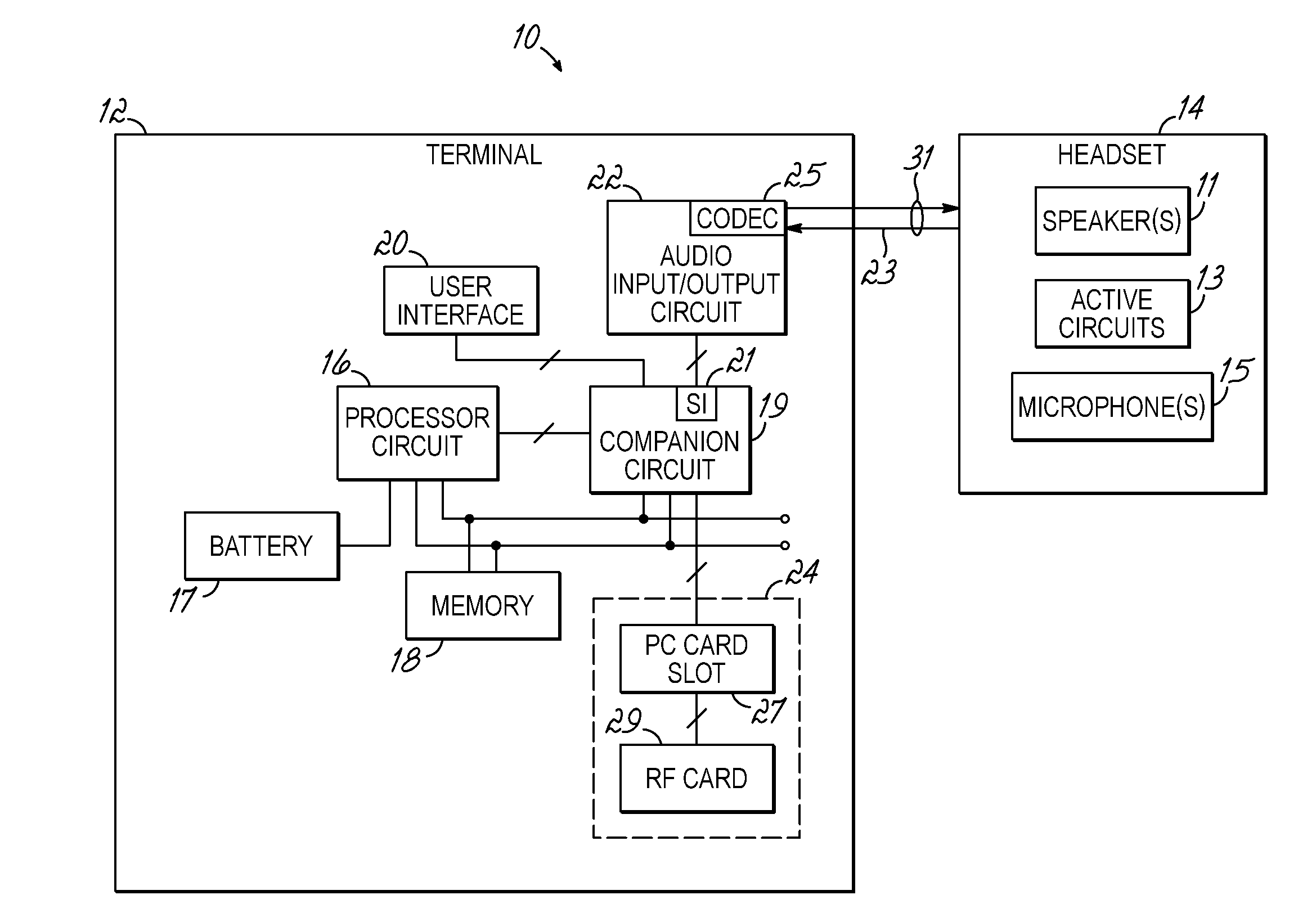
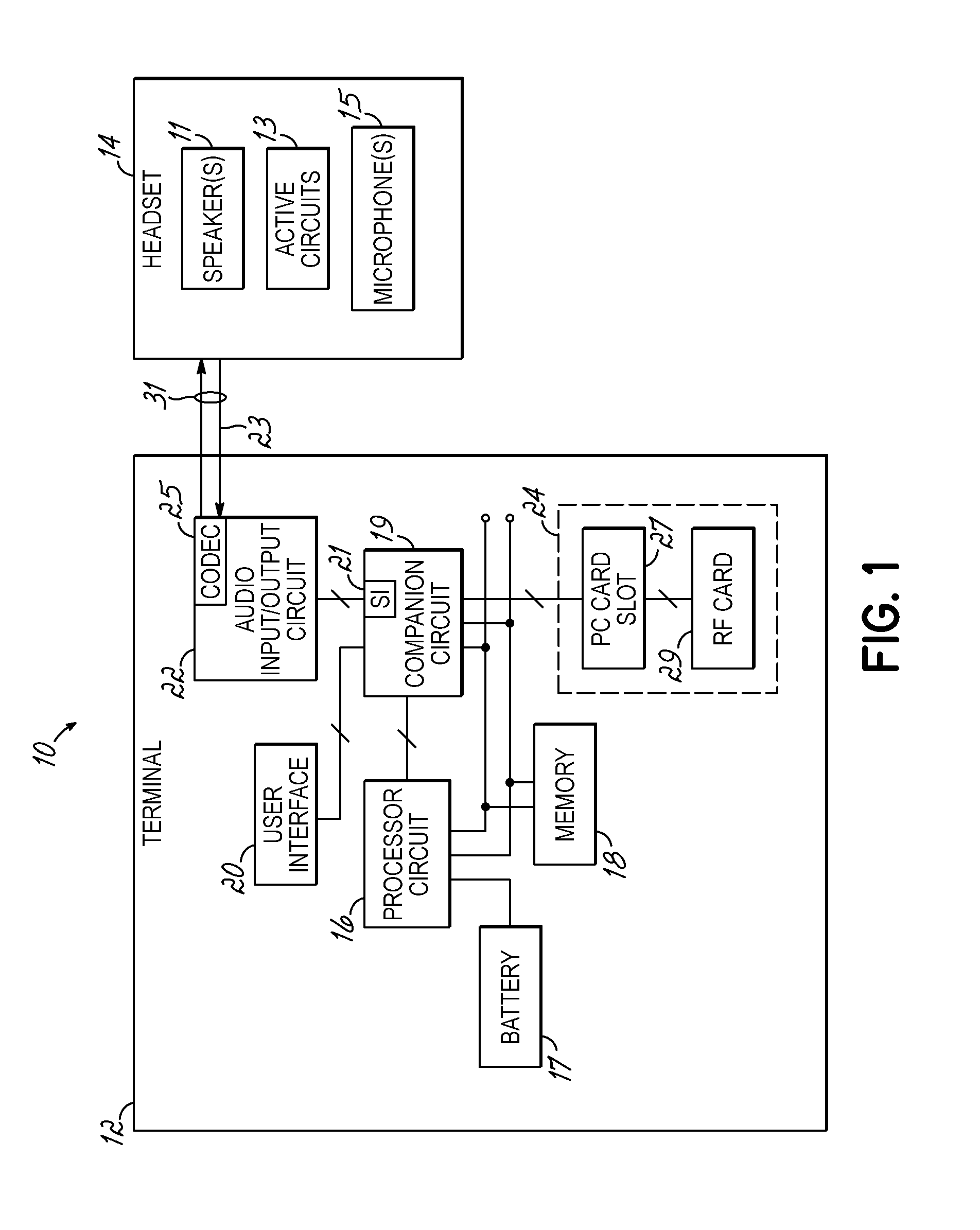
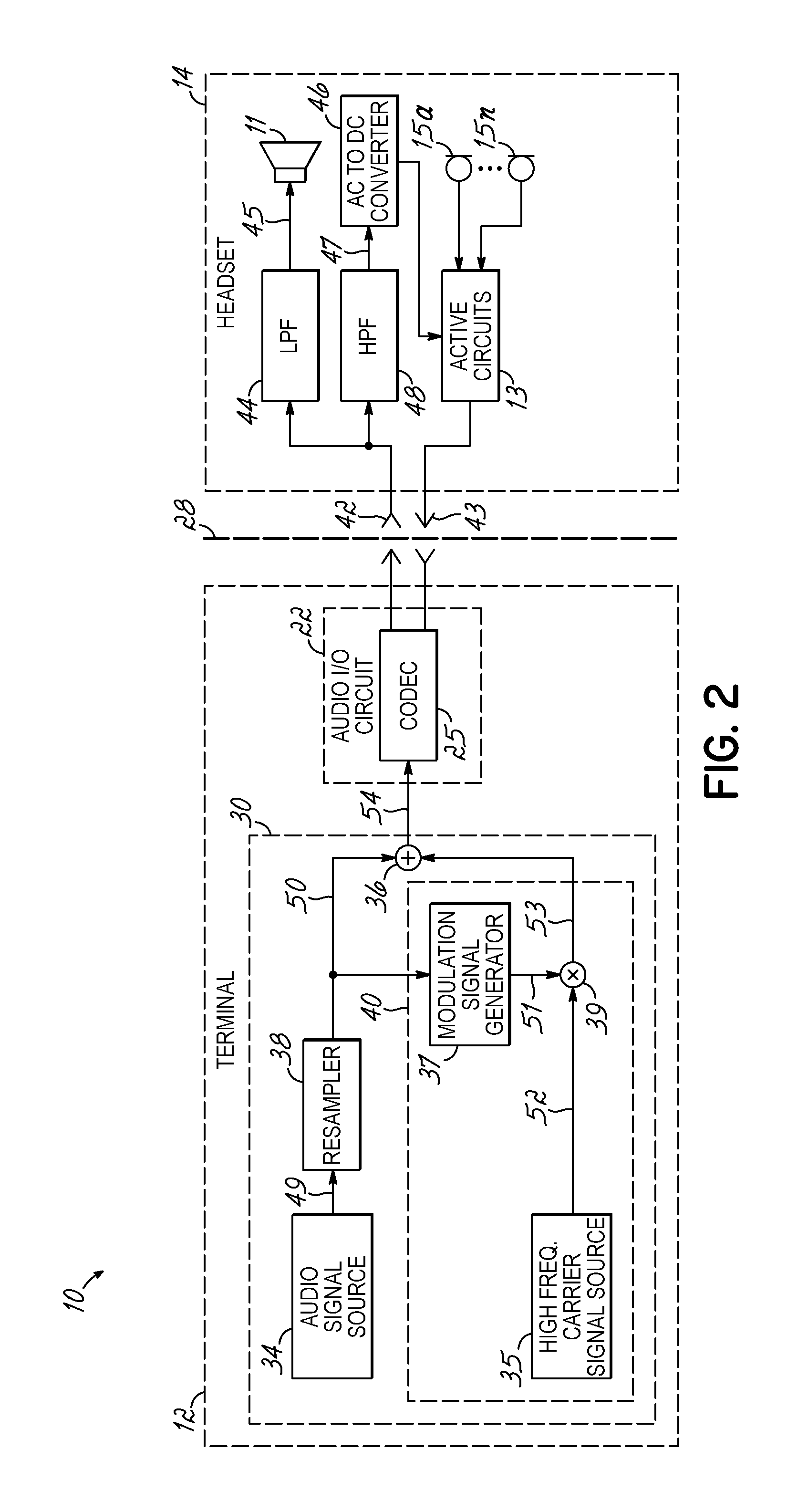
Headset signal multiplexing system and method
Owner:VOCOLLECT
Method and system for power delivery to a headset
A power delivery method and system for powering a headset. A power signal is combined with an audio signal to form a composite signal that is communicated over a shared channel to the headset. The power signal is generated by modulating a carrier signal with a modulation signal. The modulation signal is derived from the amplitude of the audio signal so that the peak levels of the composite signal do not exceed the maximum allowable output of an audio I / O circuit driving the headset.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
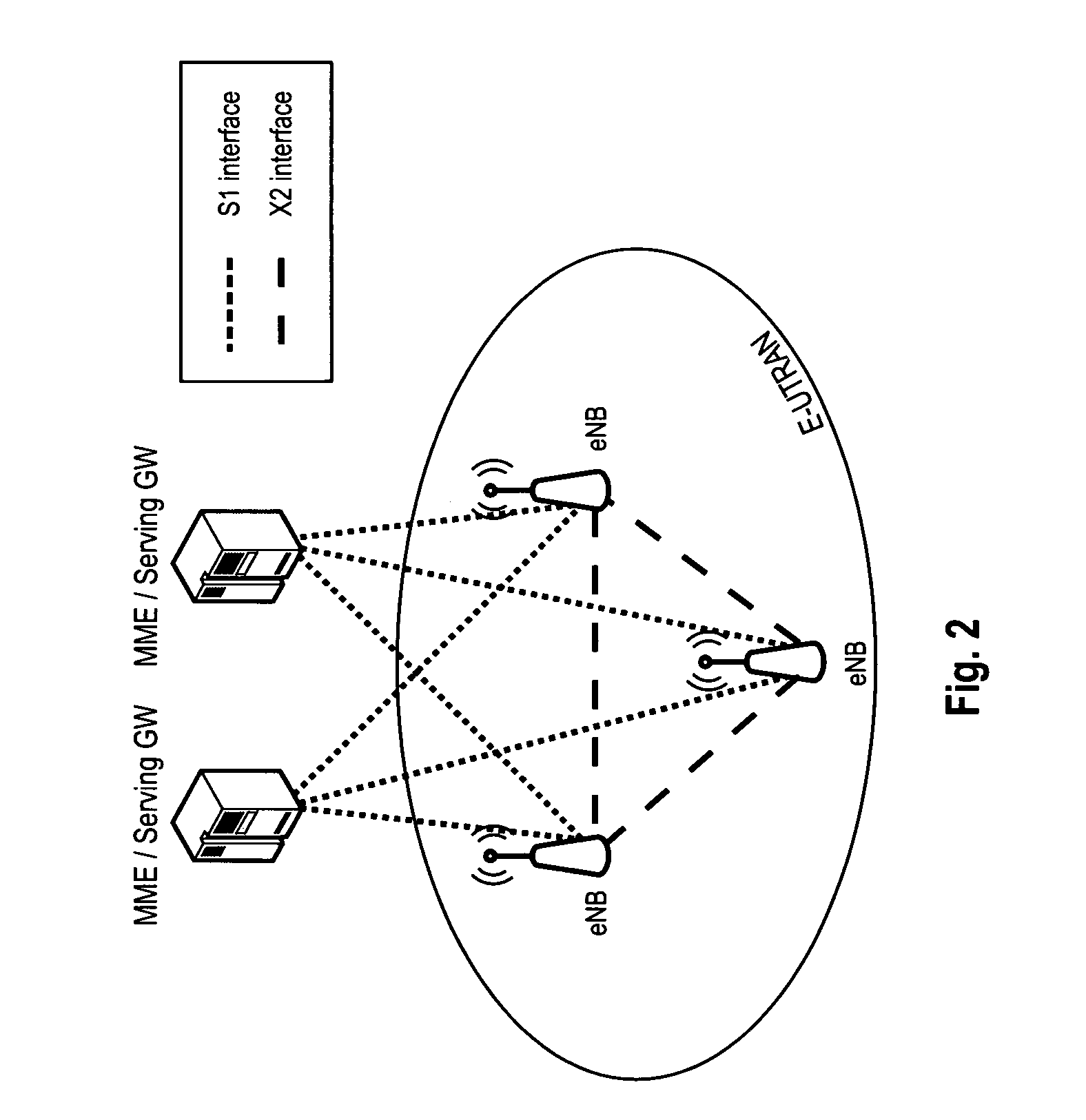
Radio communication system
InactiveUS7043271B1Reduce in quantityReduces constitutionTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityCarrier signalEngineering
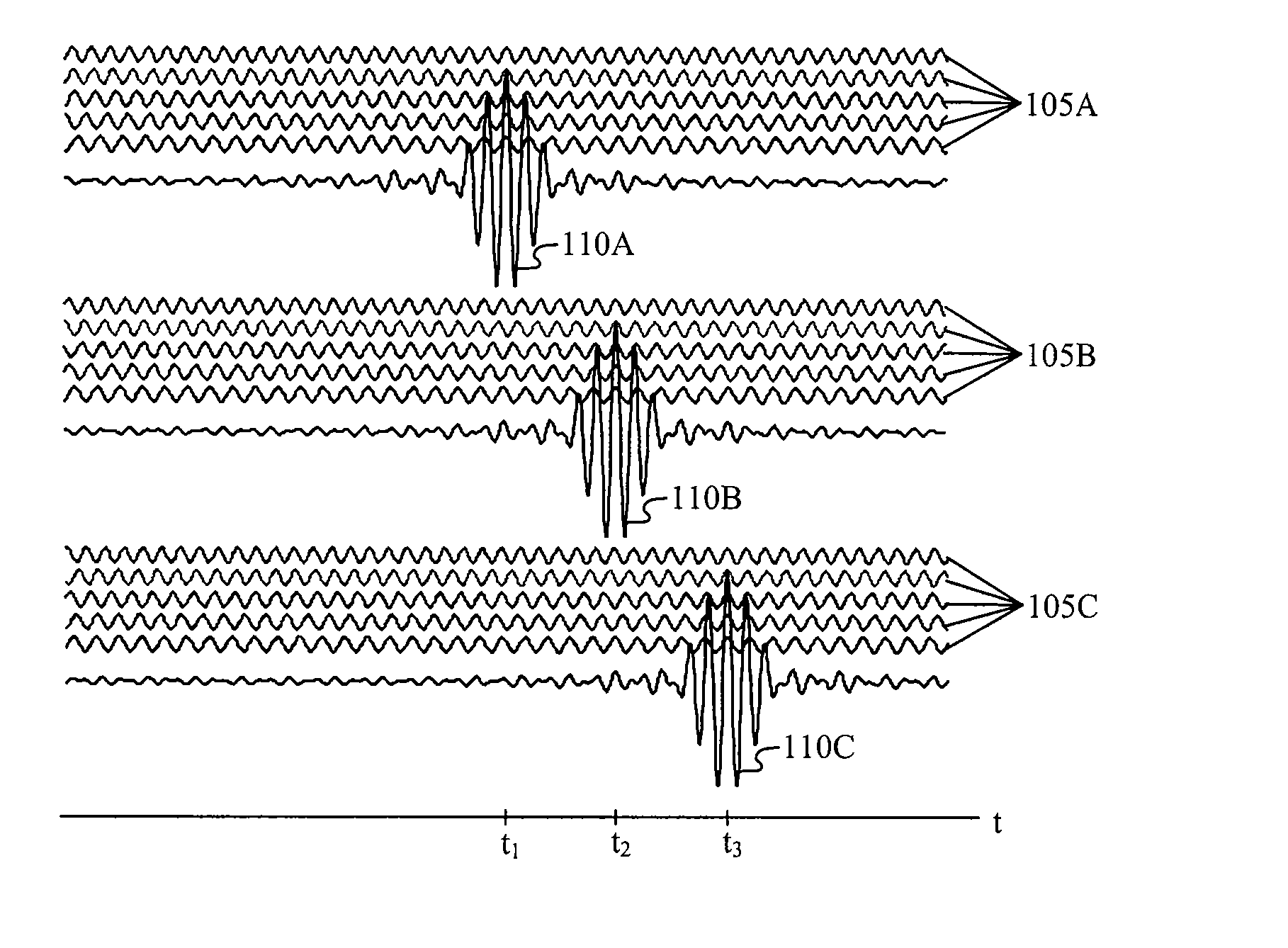
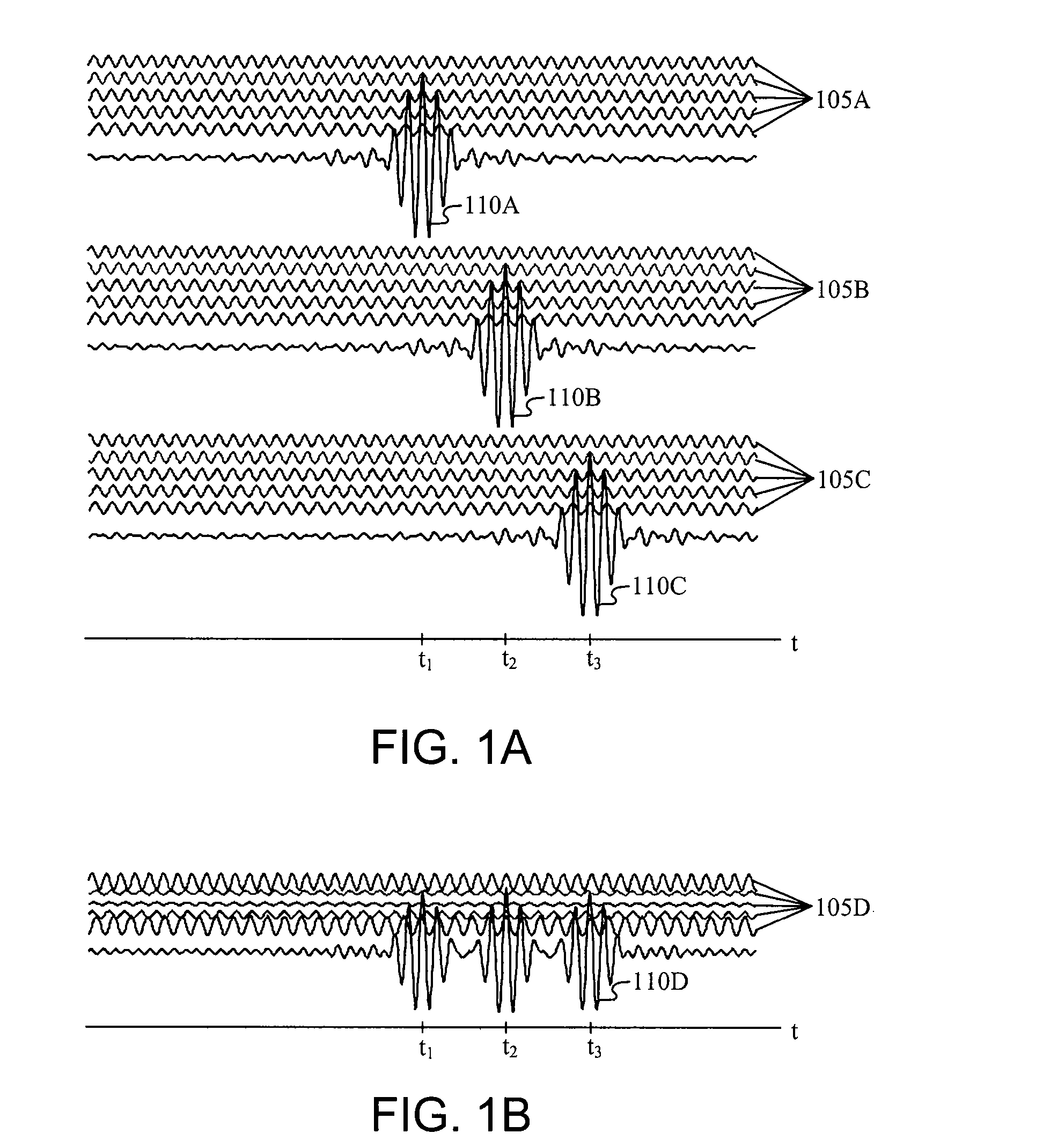
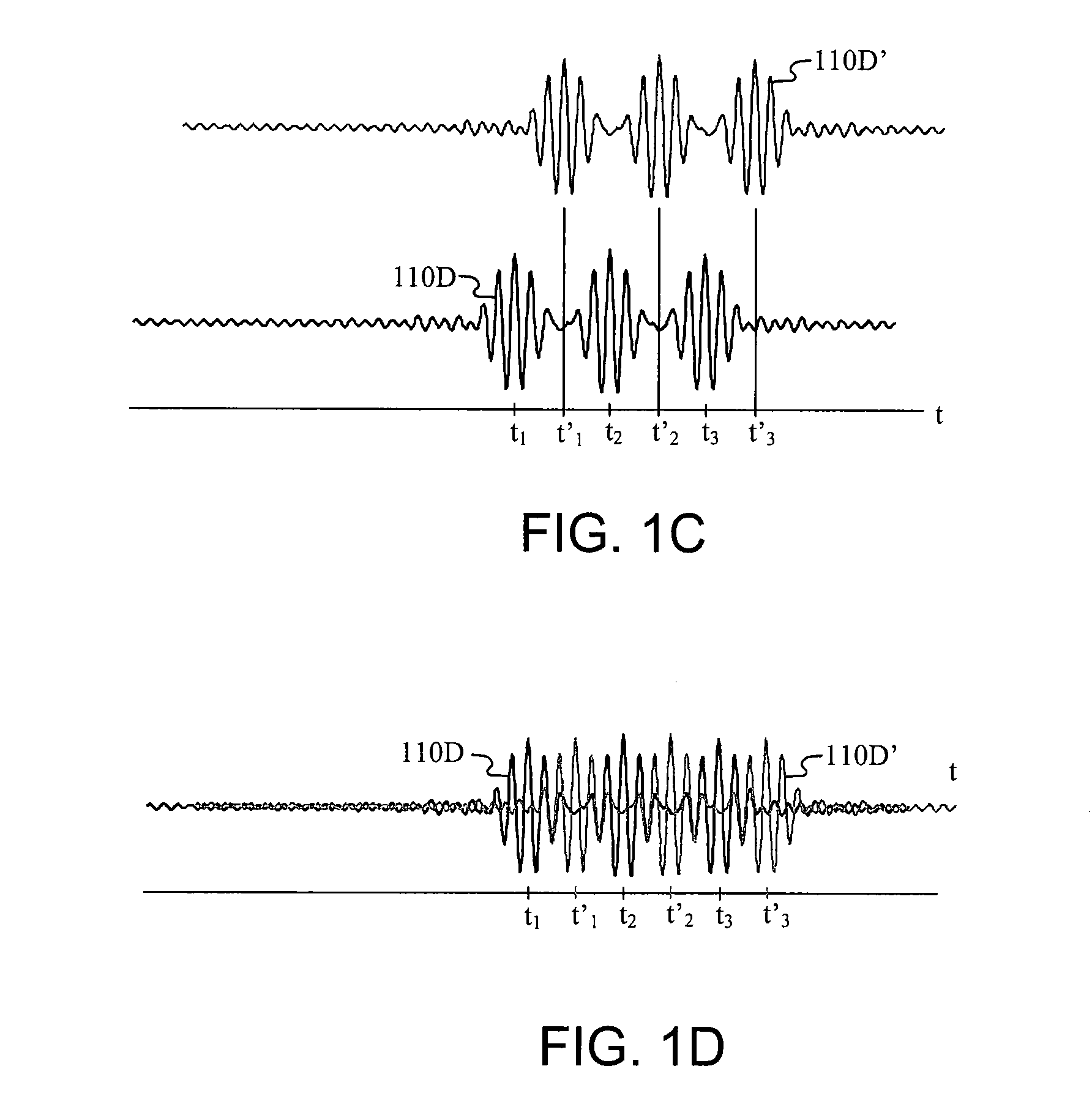
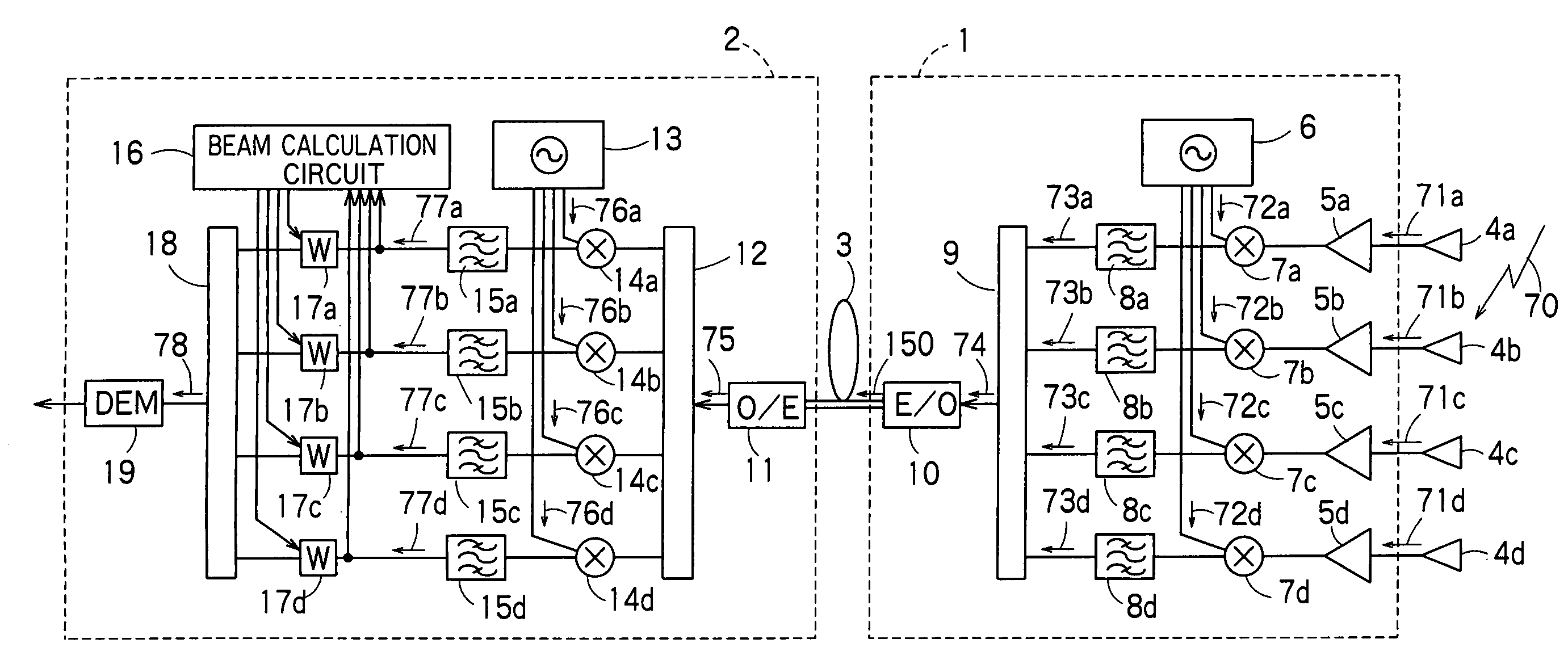
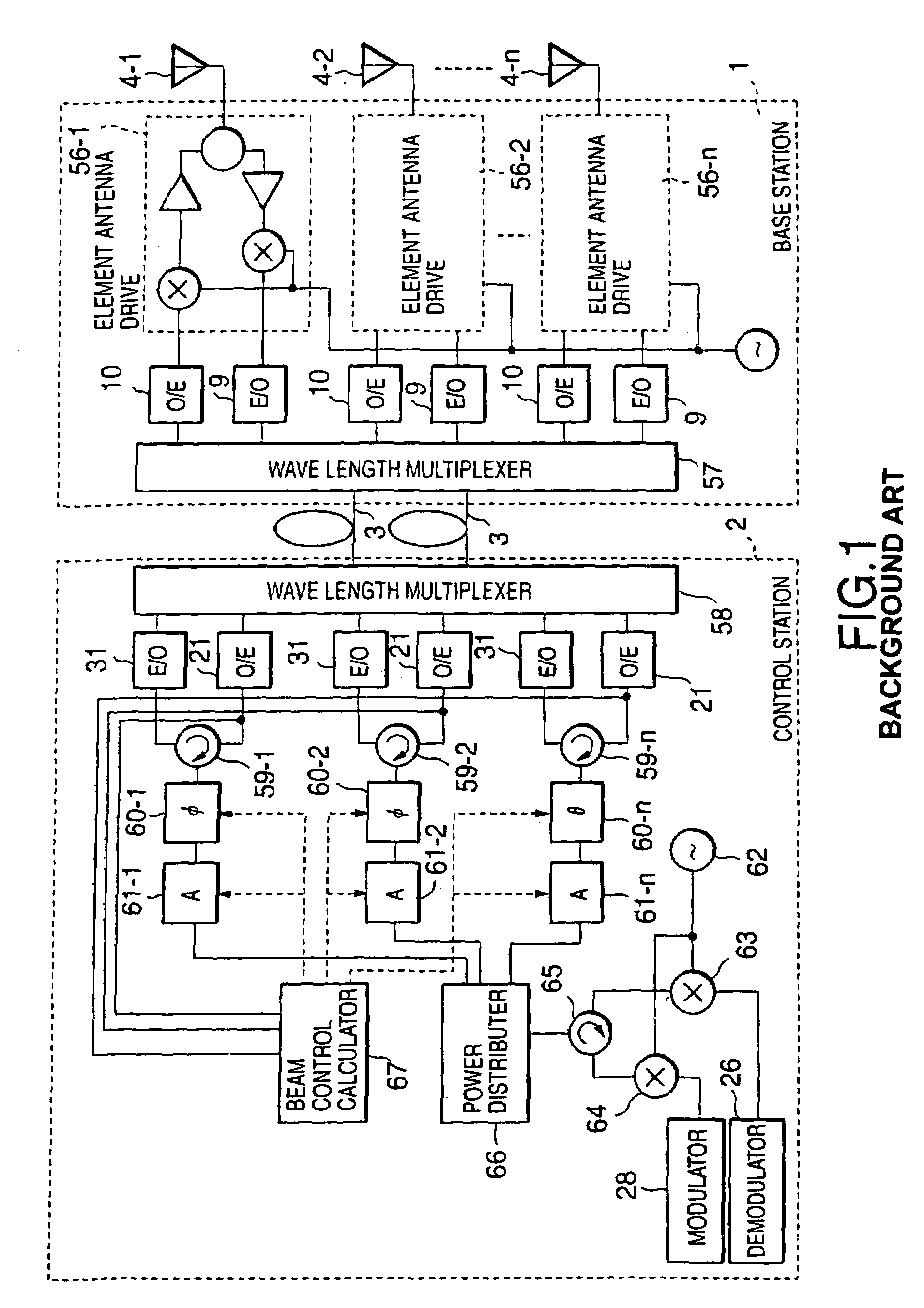
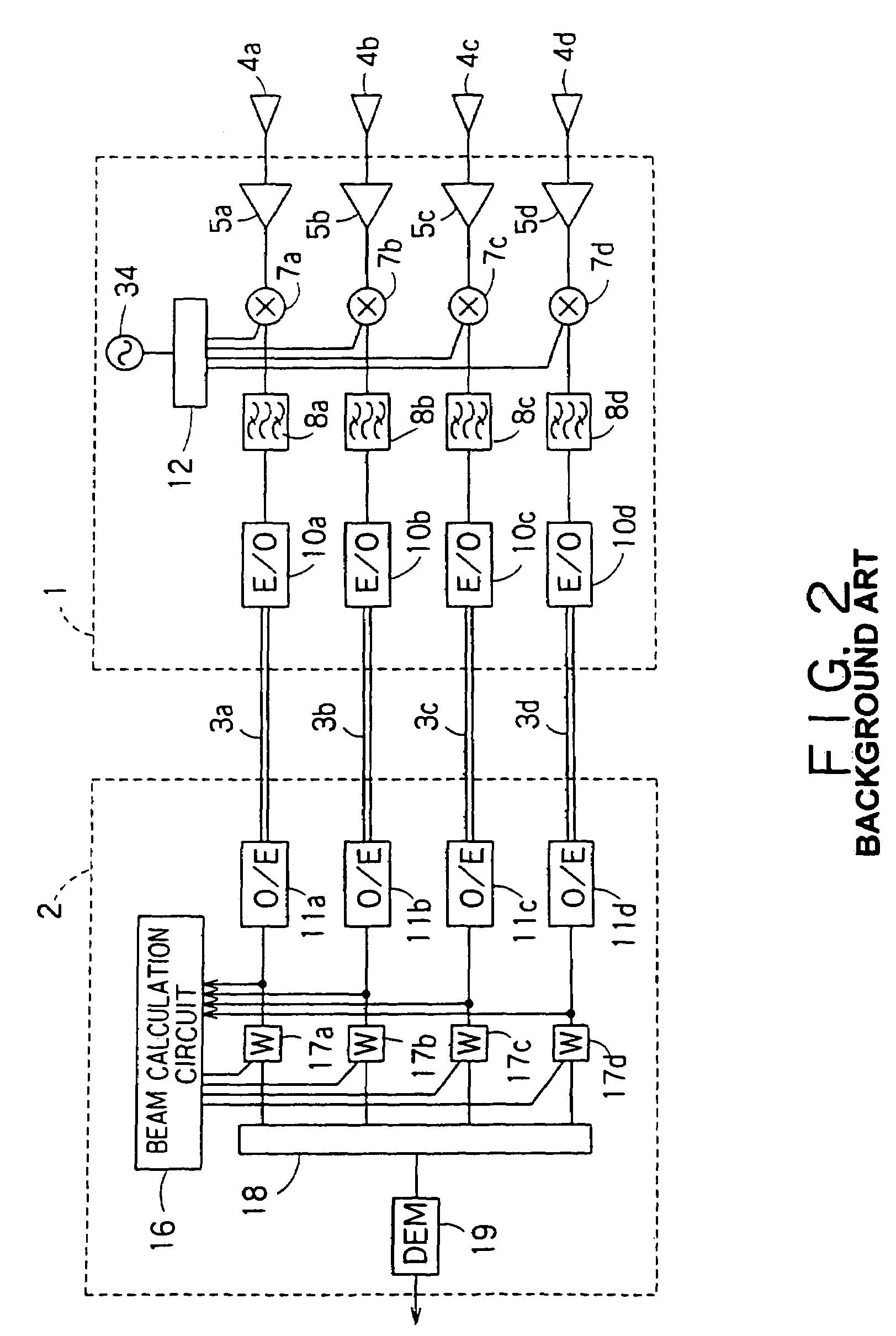
There is disclosed a radio communication system in which a constitution of a base station and further a control station can be simplified. A radio communication system according to the present invention converts a received signal received by a plurality of antenna elements in a base station to a signal of different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then the optical signal is transmitted to a control station via an optical fiber. Or the control station performs weighting to phase of the transmitted signal transmitted from a plurality of antennas of a base station, and then performs frequency conversion to different frequency band, and then conflates the converted signal in order to generate the sub-carrier wave multiplex signal. The signal is converted to an optical signal, and then an optical signal is transmitted to the base station side via the optical fiber. The control station and the base station divides the received sub-carrier wave multiplex signal by each frequency band, and then the frequency of the divided signals are converted to the same frequency band in order to generate the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. By such a constitution, it is possible to reduce constituent of the optical transmission components to the minimum and to simplify the constitution of the base station. Furthermore, it is possible to maintain the relative phase difference and the relative intensity of the transmitted / received signal of each antenna element. Because of this, it is possible to estimate an arrival direction of the received signal and to control radiation beam pattern of the transmitted signal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High efficiency high performance communications system employing multi-carrier modulation
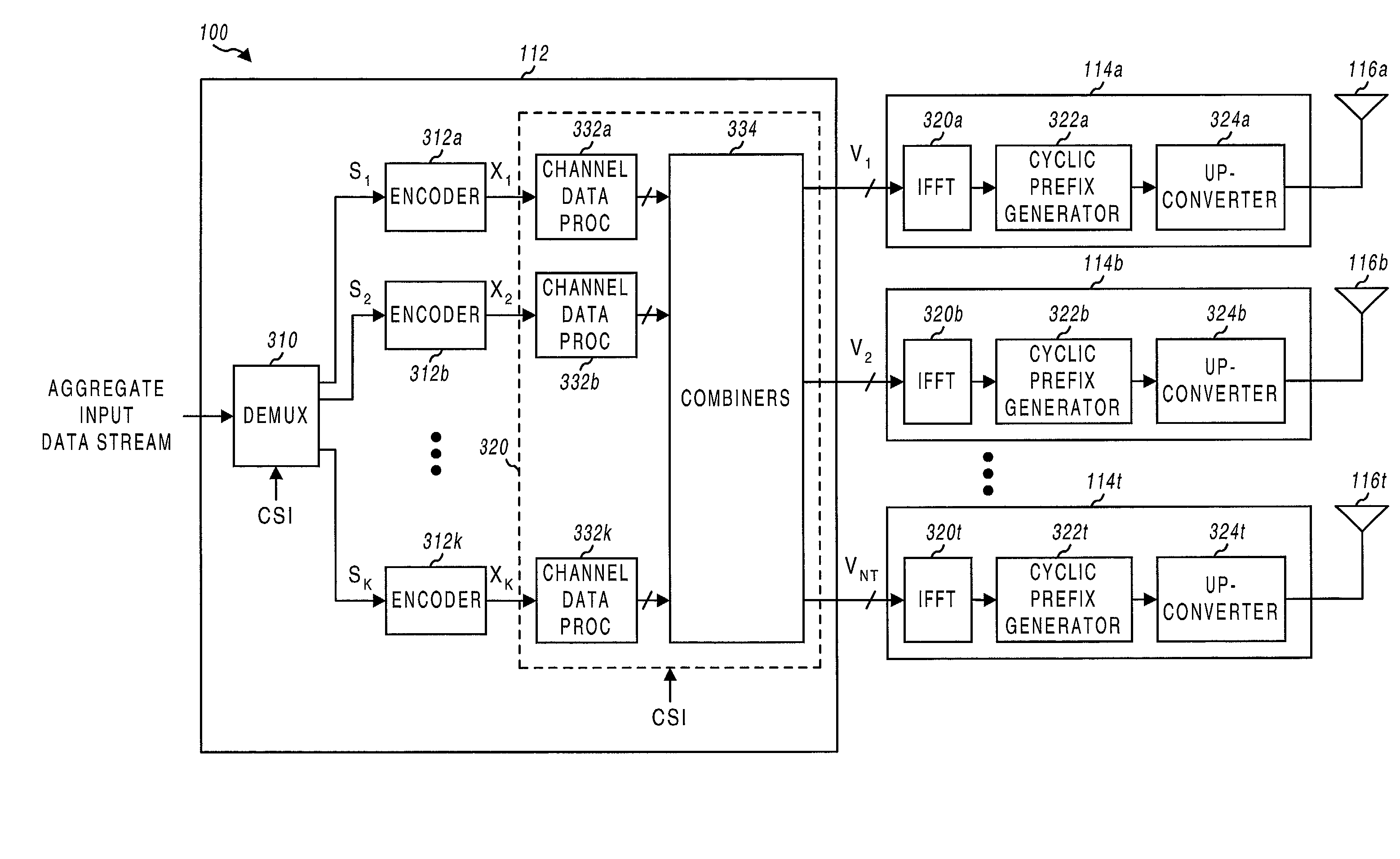
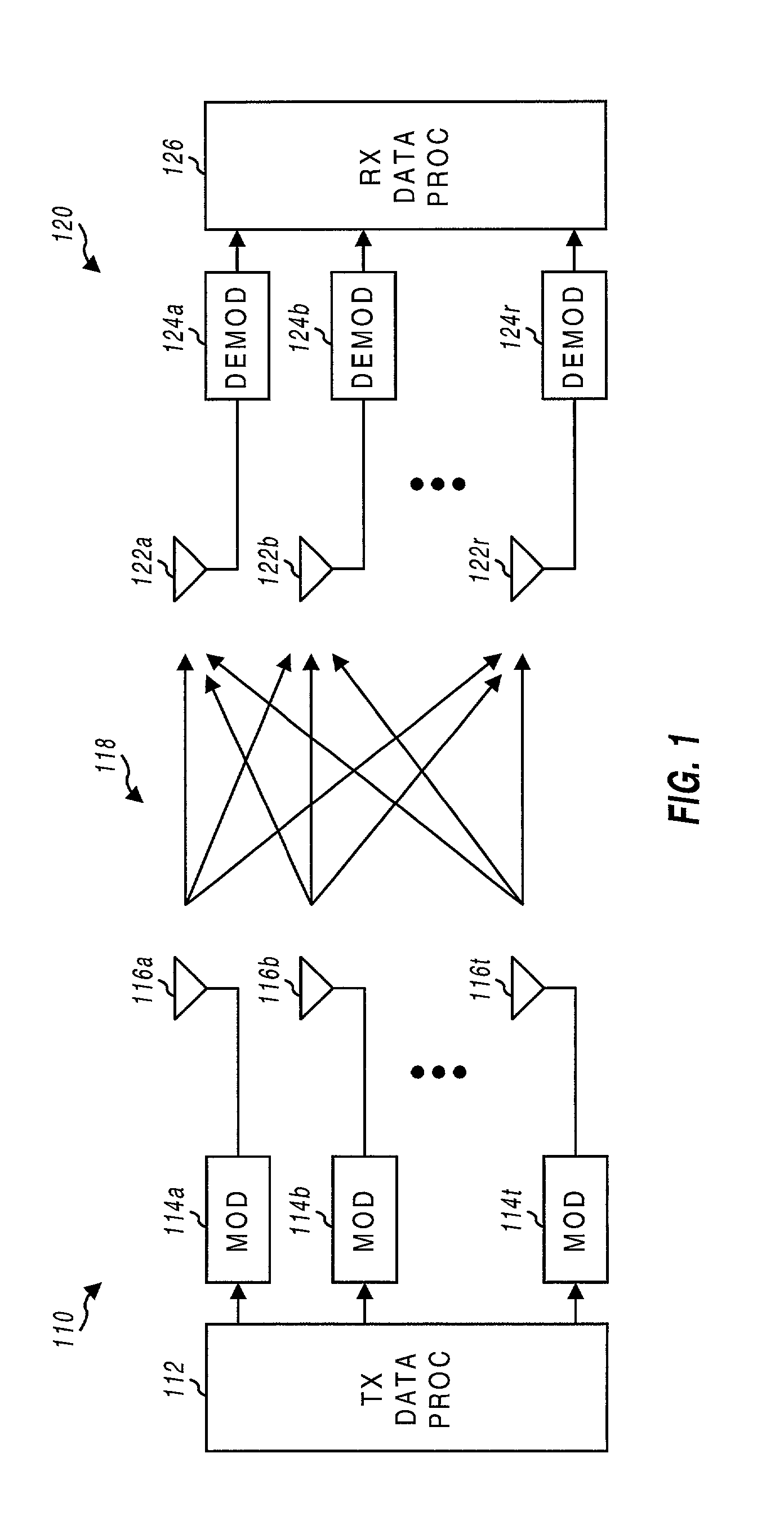
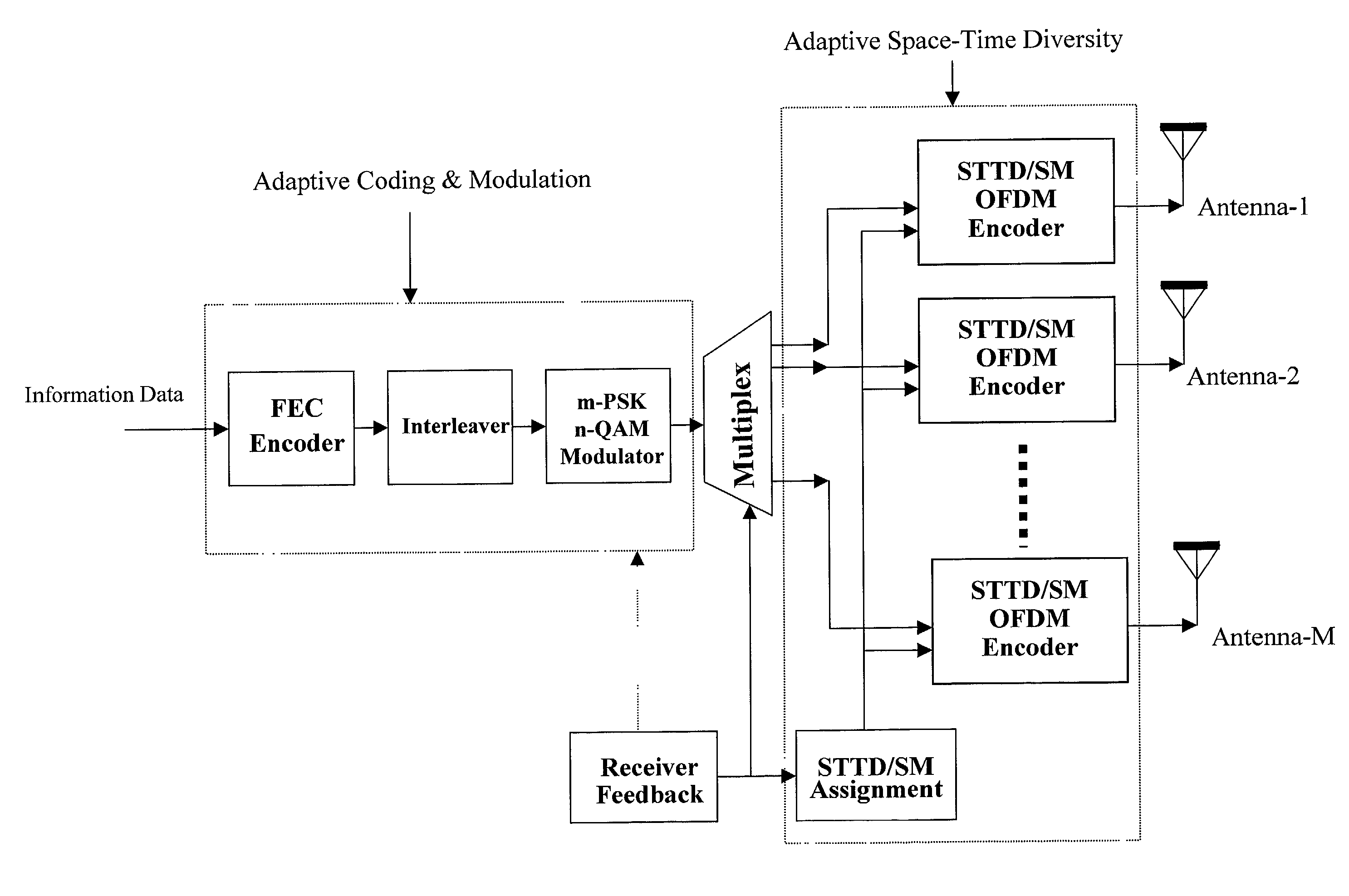
InactiveUS20020154705A1Increase diversityImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityFrequency diversityData streamHigh performance communication
Transmitter and receiver units for use in a communications system and configurable to provide antenna, frequency, or temporal diversity, or a combination thereof, for transmitted signals. The transmitter unit includes a system data processor, one or more modulators, and one or more antennas. The system data processor receives and partitions an input data stream into a number of channel data streams and further processes the channel data streams to generate one or more modulation symbol vector streams. Each modulation symbol vector stream includes a sequence of modulation symbol vectors representative of data in one or more channel data streams. Each modulator receives and modulates a respective modulation symbol vector stream to provide an RF modulated signal, and each antenna receives and transmits a respective RF modulated signal. Each modulator may include an inverse (fast) Fourier transform (IFFT) and a cyclic prefix generator. The IFFT generates time-domain representations of the modulation symbol vectors, and the cyclic prefix generator repeats a portion of the time-domain representation of each modulation symbol vector. The channel data streams are modulated using multi-carrier modulation, e.g., OFDM modulation. Time division multiplexing (TDM) may also be used to increase flexibility.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Dual mode tracking system
InactiveUS6353406B1Memory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsData warehouseDual mode
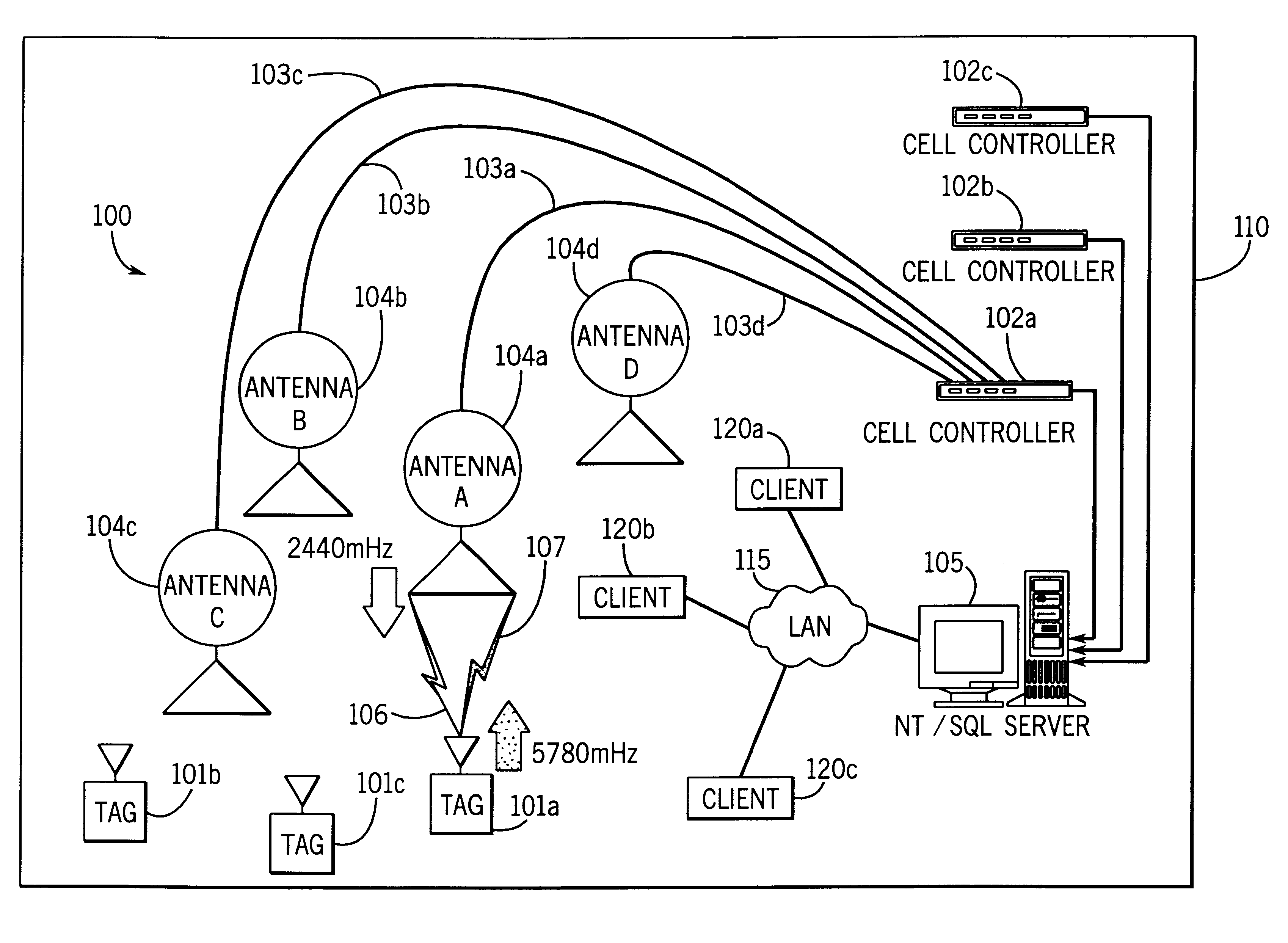
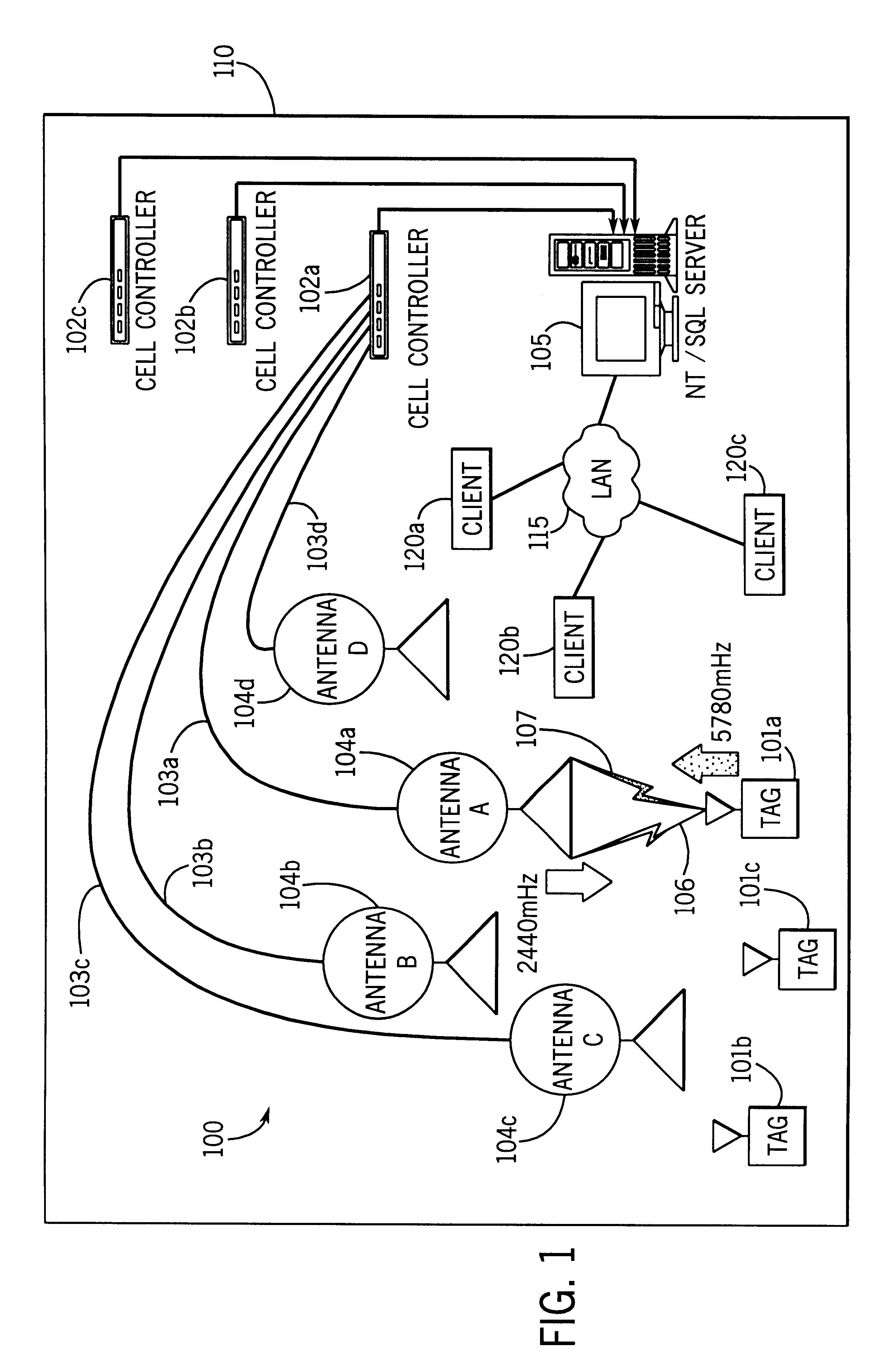
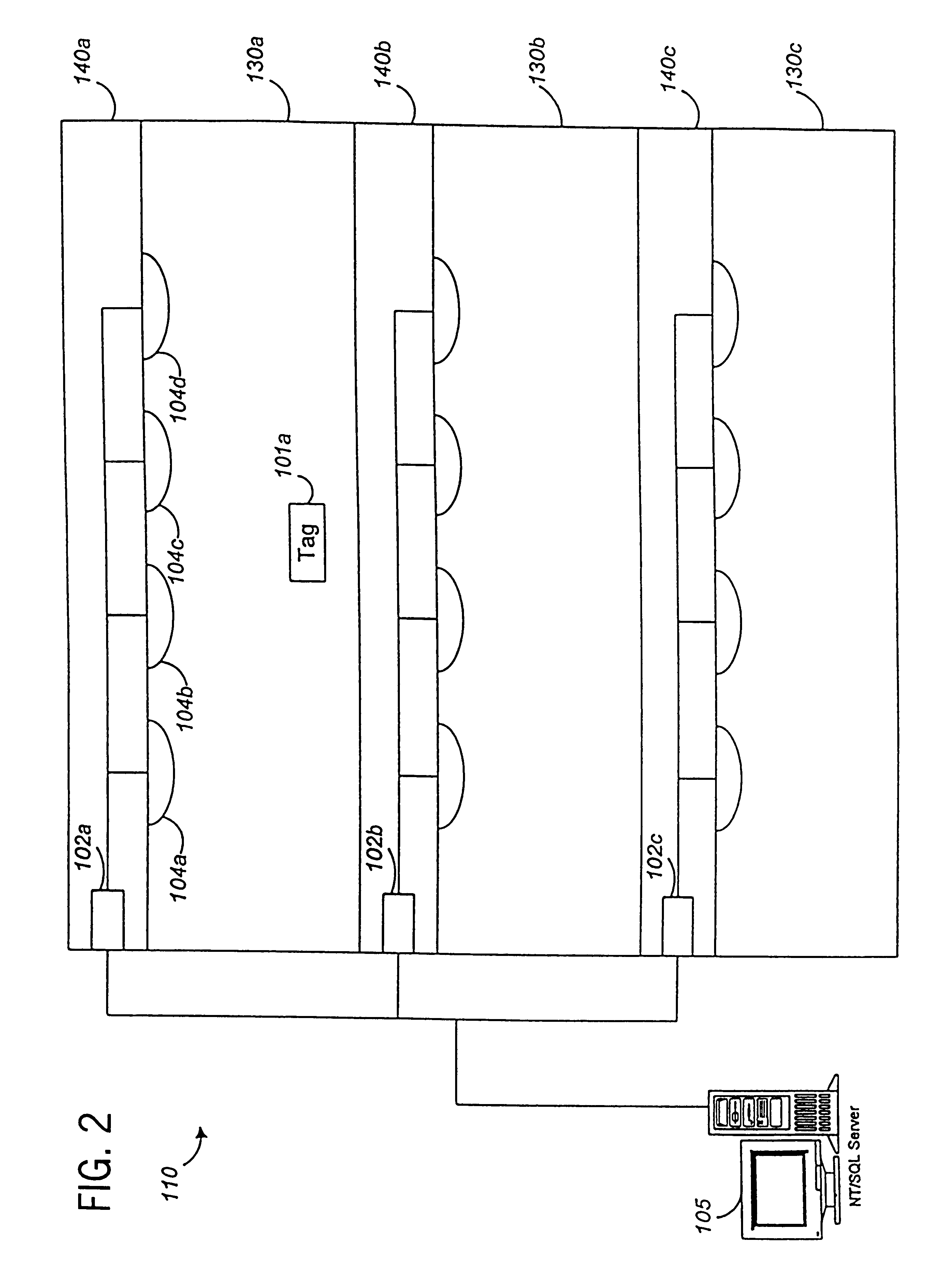
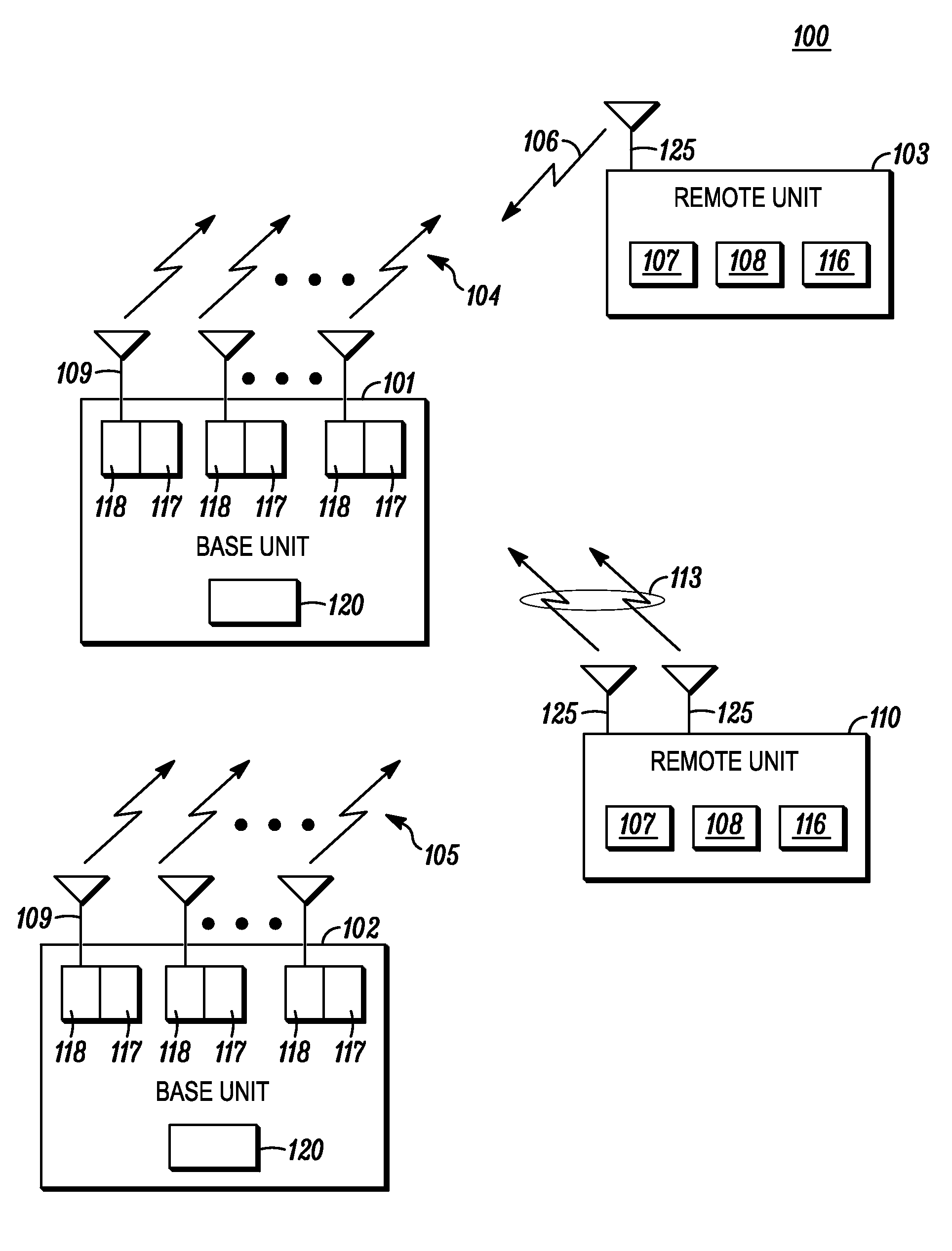
System for tracking mobile tags. Cell controllers with multiple antenna modules generate a carrier signal which is received by the tags. Tags shift the frequency of the carrier signal, modulate an identification code onto it, and transmit the resulting tag signal at randomized intervals. The antennas receive and process the response, and determine the presence of the tags by proximity and triangulation. The recursive-least squares (RLS) technique is used in filtering received signals. Distance of a tag from an antenna is calculated by measuring the round trip signal time. The cell controllers send data from the antenna to a host computer. The host computer collects the data and resolves them into positional estimates. Data are archived in a data warehouse, such as an SQL Server. Also disclosed is an article tracking system that supports both active and passive tags with a cell controller able to read both passive and active tag signals.
Owner:RF TECH +1
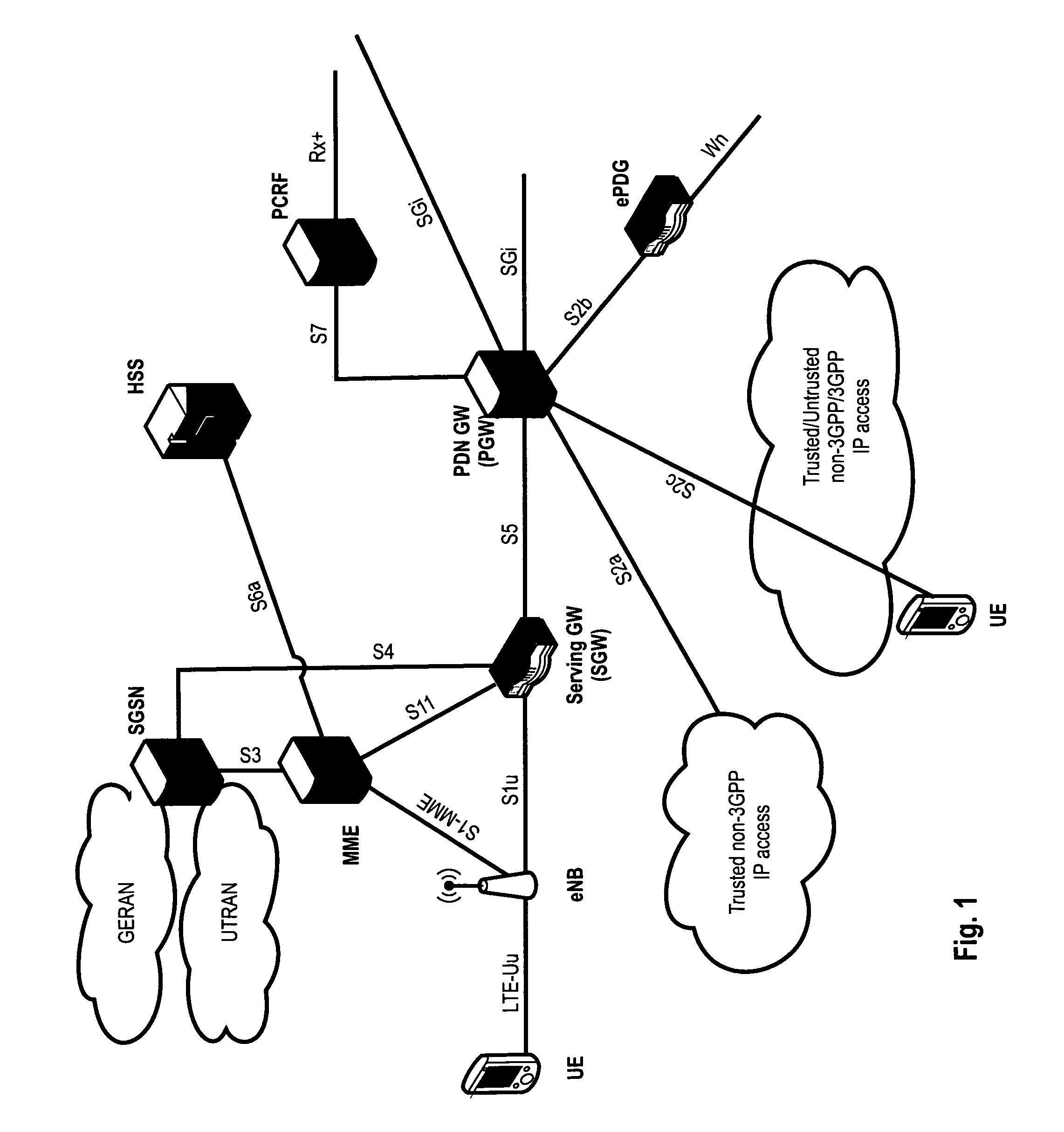
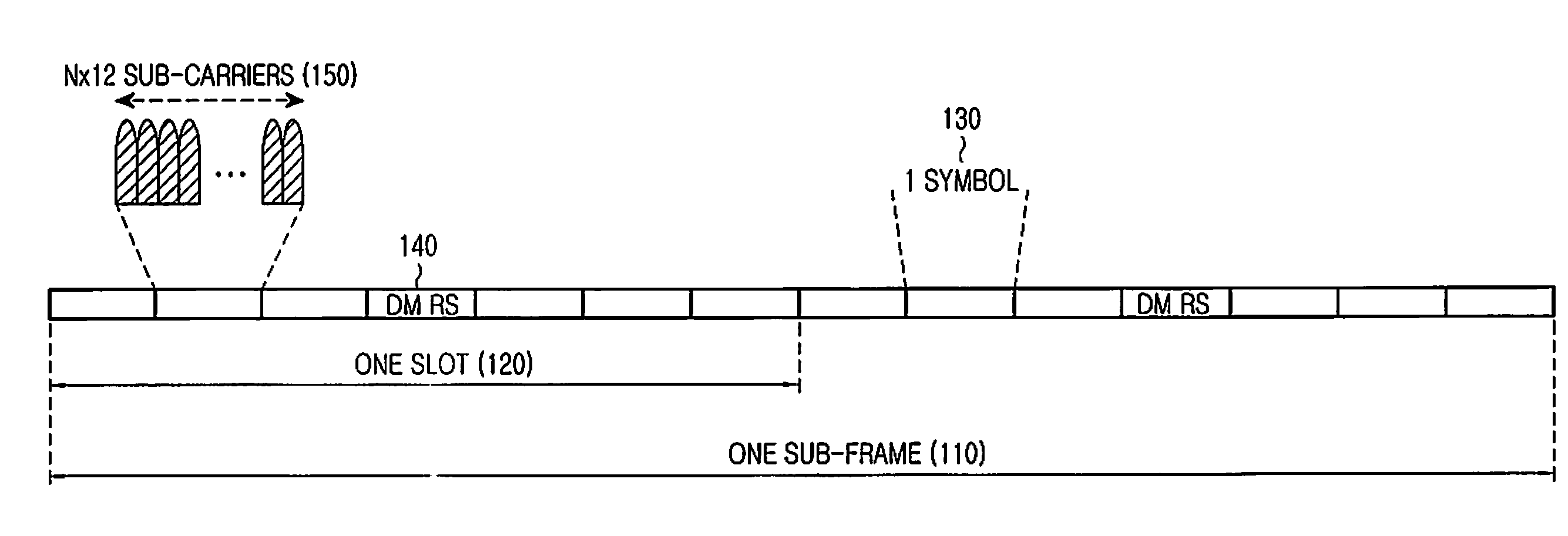
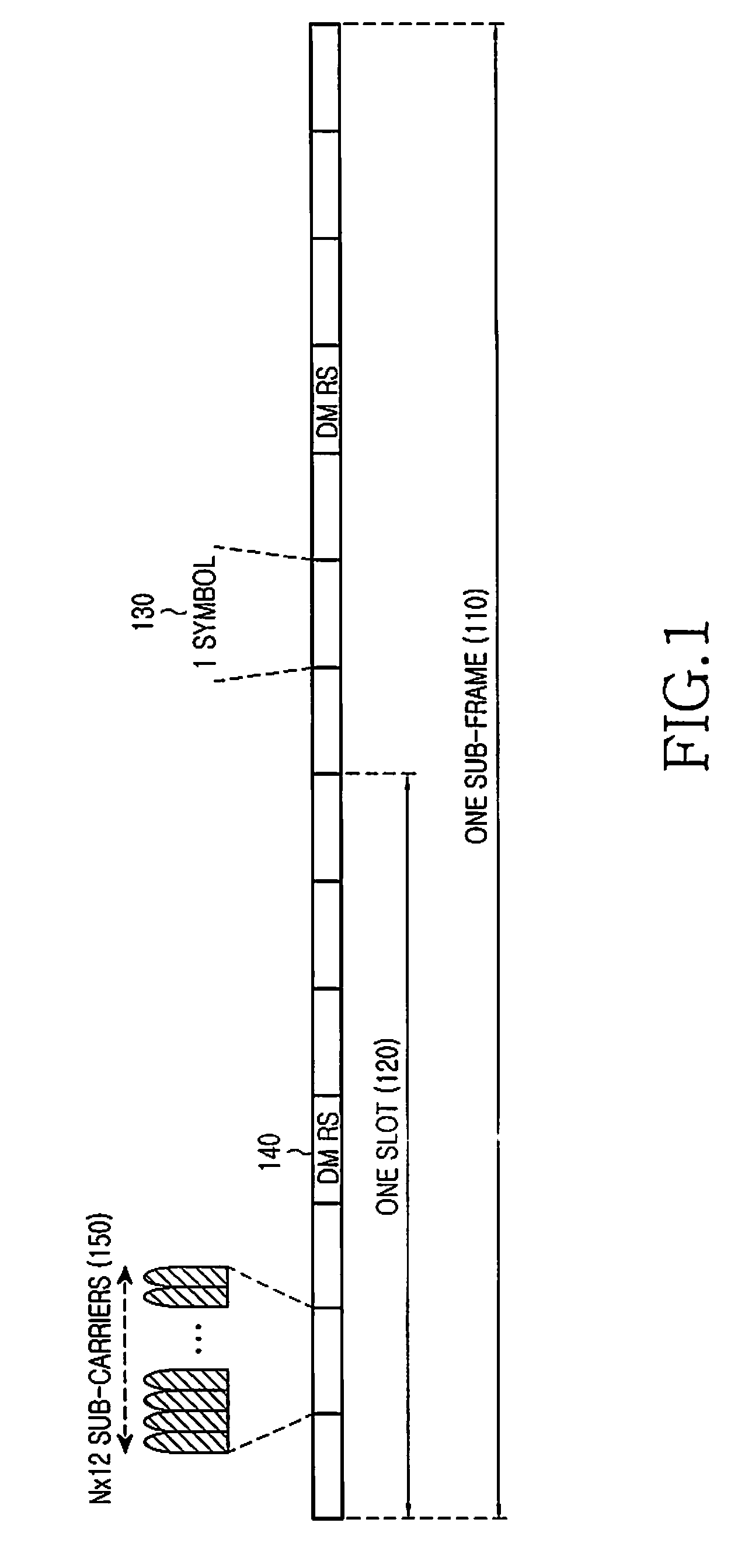
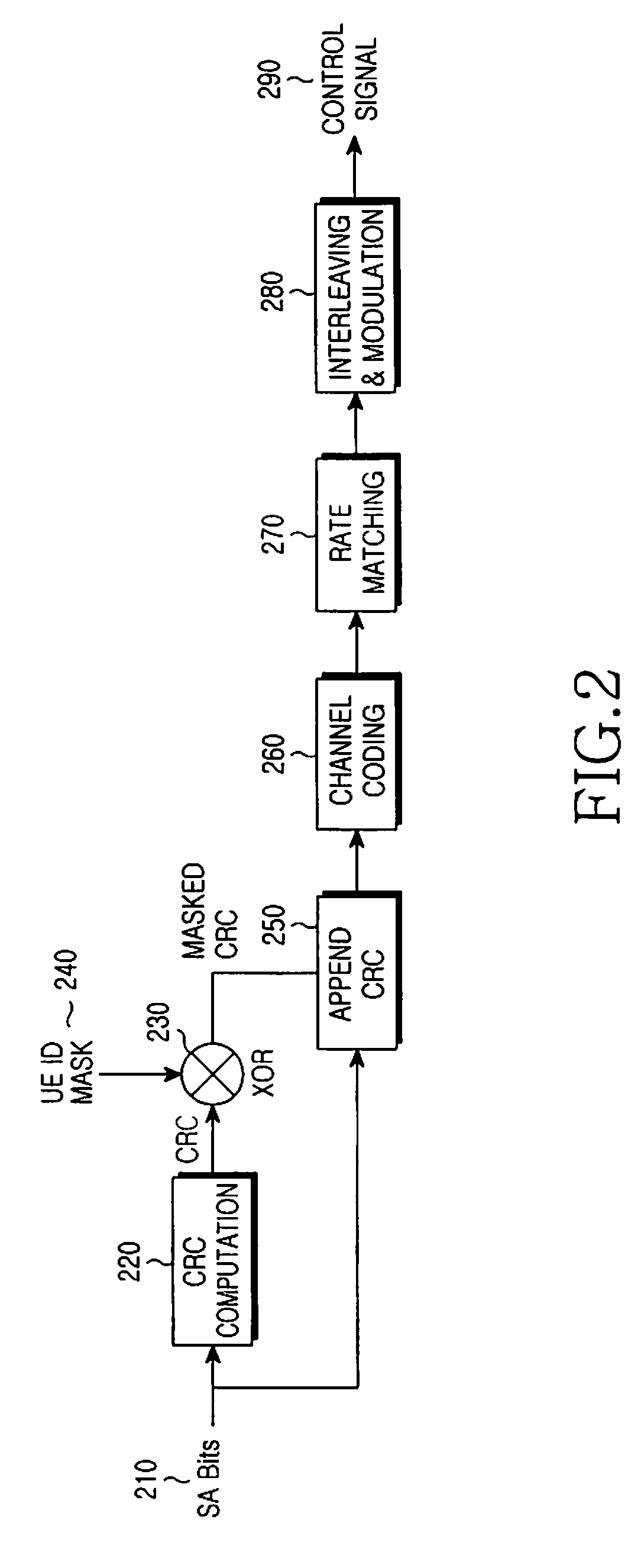
Control Channel Provisioning and Signaling
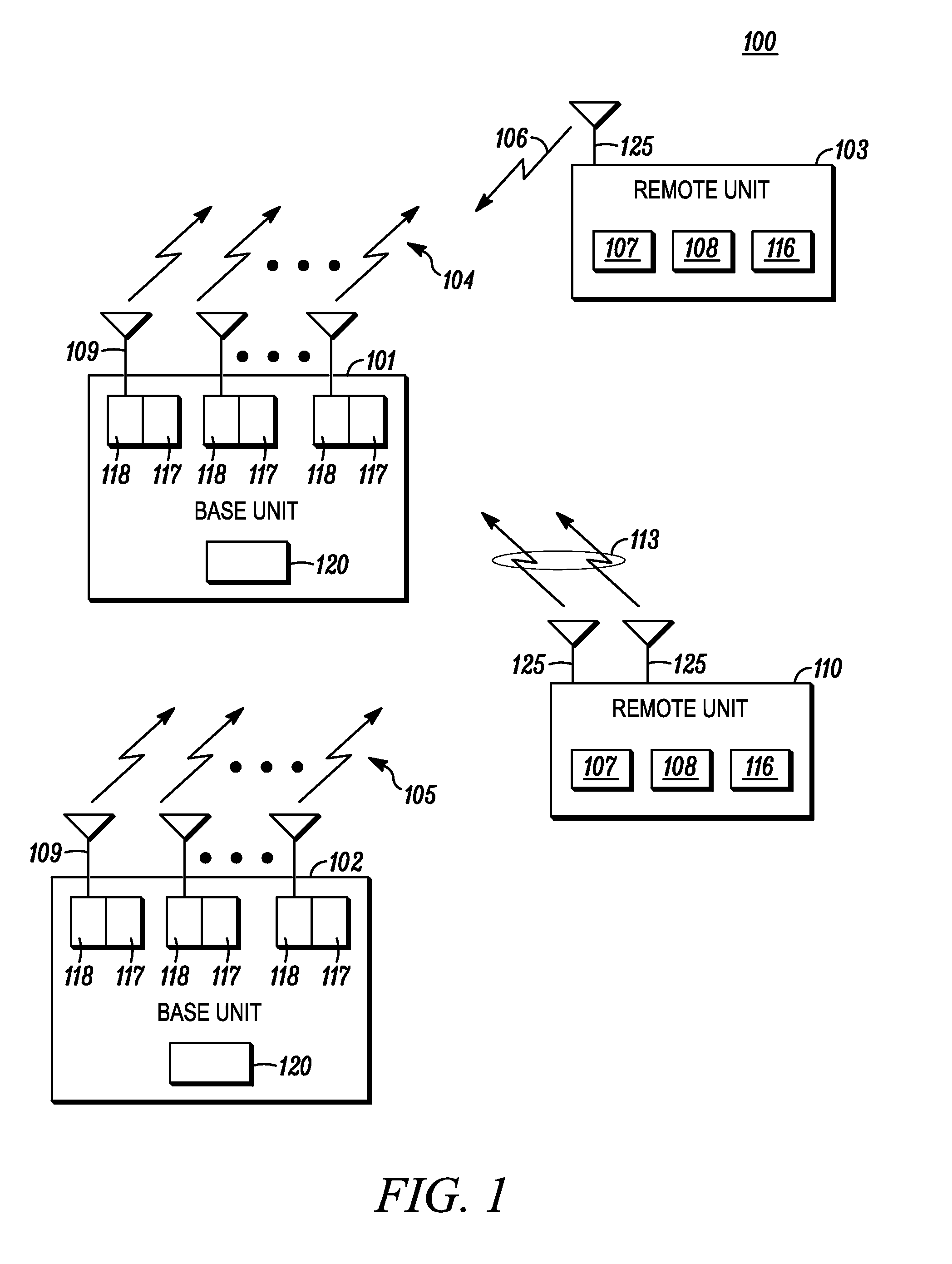
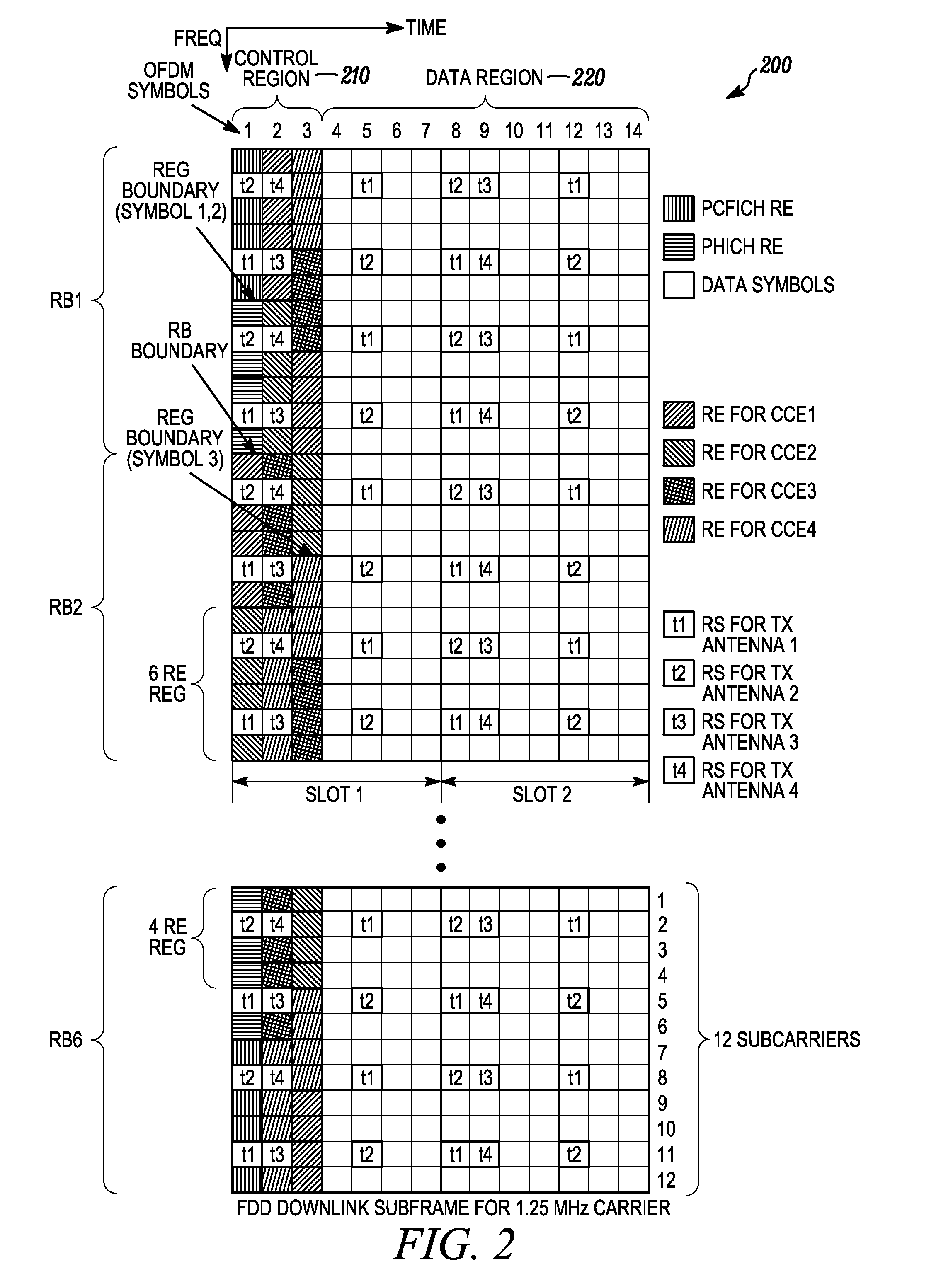
There is provided a communication device and a base unit, and methods thereof, for determining control information. The communication device receives a control channel message associated with the communication device in a control region on a first carrier from a base unit. The communication device also determines a set of resources in a search space within the control region, attempts to decode the set of resources in the search space for the control channel message, and determines control information from the decoded control channel message. The base unit generates a control channel message comprising control information associated with the communication device, determines a set of resources in a search space within a control region, selects a subset of resources within the determined set of resources for transmitting the control channel message, and transmits the control channel message on the selected resources in the control region on a first carrier.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
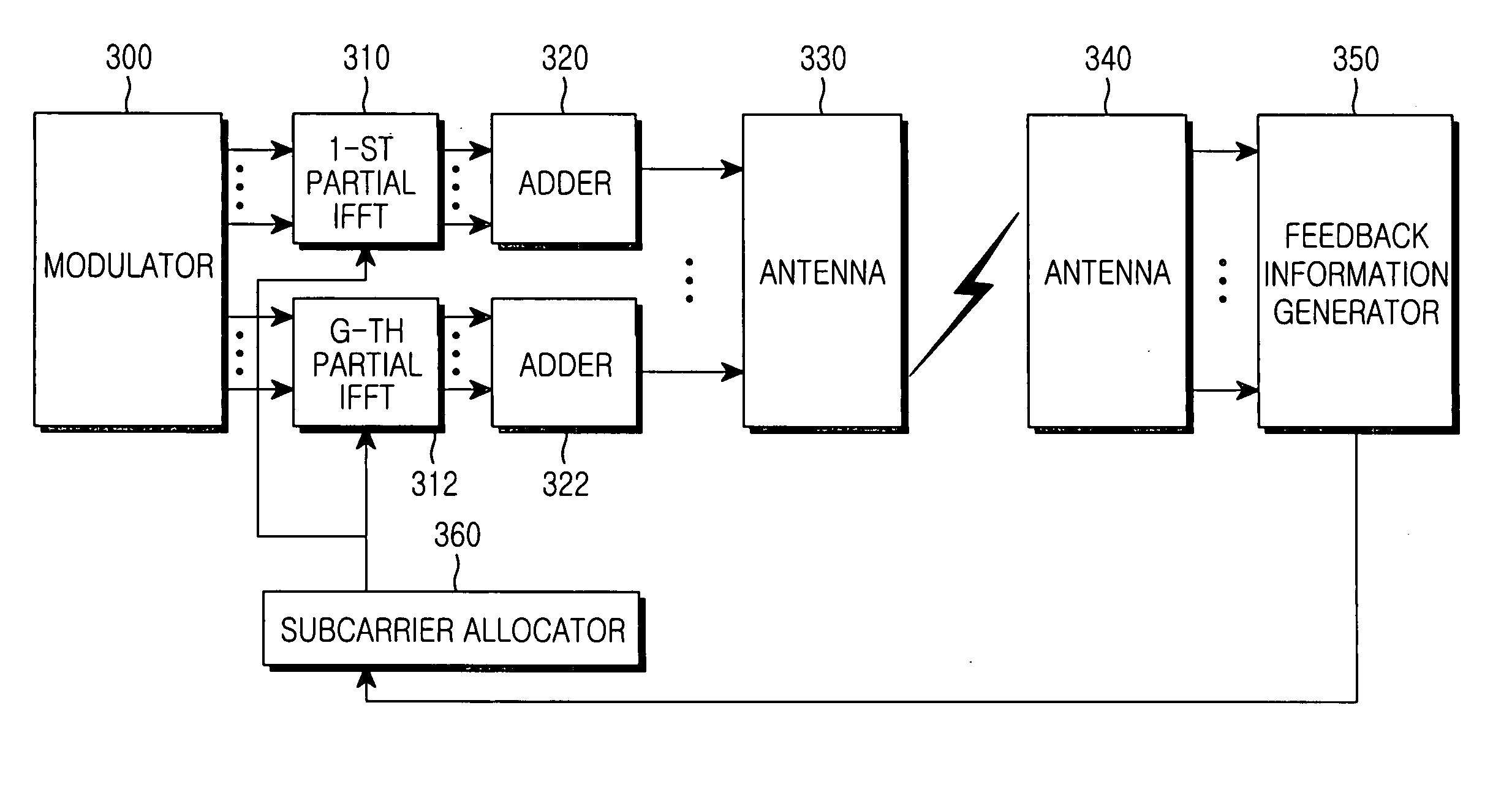
Method and apparatus for performing effective feedback in wireless communication system supporting multiple antennas
ActiveUS20120076028A1Easy to operateModulated-carrier systemsTransmission systemsChannel state informationCommunications system
A method for transmitting channel status information (CSI) of downlink multi-carrier transmission includes generating the CSI including at least one of a rank indicator (RI), a first precoding matrix index (PMI), a second PMI and a channel quality indicator (CQI) for one or more downlink carriers, the CQI being calculated based on precoding information determined by a combination of the first and second PMIs, determining, when two or more CSIs collide with one another in one uplink subframe of one uplink carrier, a CSI to be transmitted on the basis of priority, and transmitting the determined CSI over a uplink channel. If a CSI including an RI or a wideband first PMI collides with a CSI including a wideband CQI or a subband CQI, the CSI including a wideband CQI or a subband CQI has low priority and is dropped.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information for carrier aggregated spectrums
InactiveUS20100271970A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
Methods and apparatus for transmitting uplink control information (UCI) in carrier aggregated spectrums are disclosed. UCI may include, but is not limited to, Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI), Rank Indication (RI), Channel Quality Indicator (CQI), Acknowledge / Not Acknowledge (ACK / NACK) and Scheduling Request (SR). For symmetric carrier aggregation, uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) component carriers may be paired and use physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) in each UL component carrier to send UCI for the corresponding DL component carrier. For asymmetric carrier aggregation, methods are provided for UCI transmission and resource allocation depending on component carrier configuration or assignment. Methods are provided for multiple and single component carrier configurations that may further provide backward compatibility.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
Power supply system
InactiveUS20050068019A1Save spaceDc network circuit arrangementsCircuit monitoring/indicationElectric forceElectricity
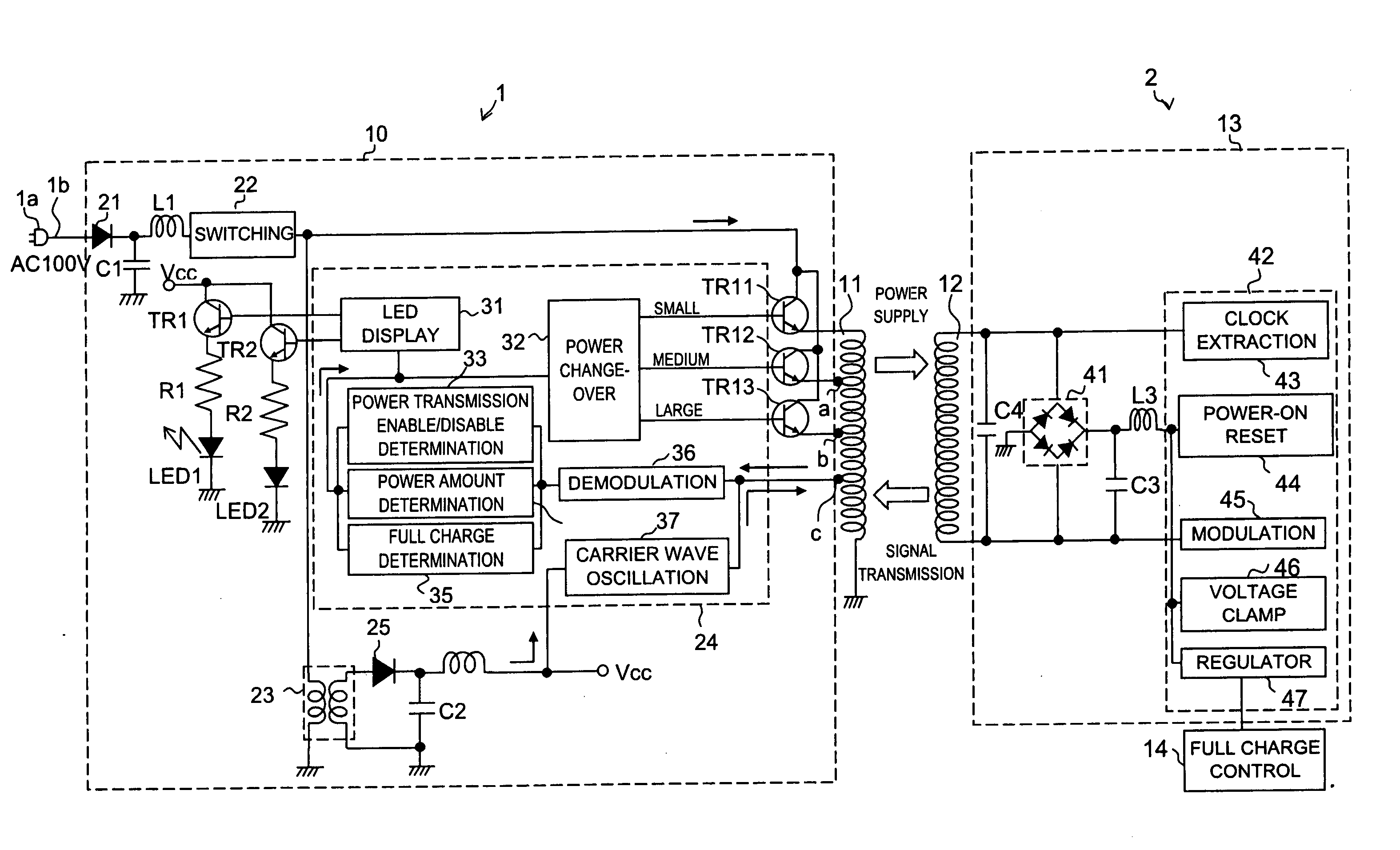
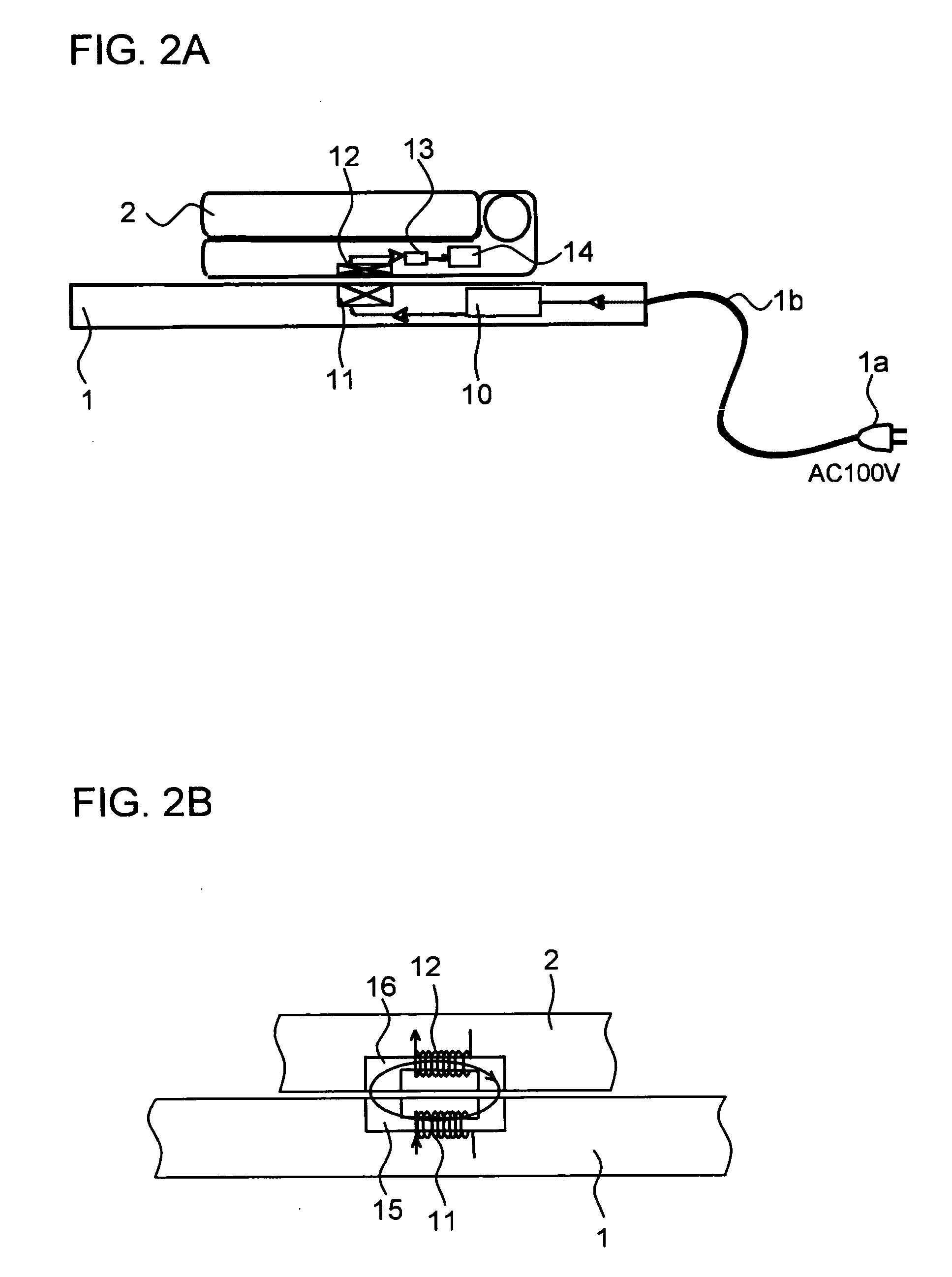
A power supply system according to the present invention comprises: a primary side coil; a power transmission apparatus having a primary side circuit for feeding a pulse voltage resulted from switching a DC voltage which is obtained by rectifying and smoothing a commercial power supply to the primary side coil; a secondary side coil magnetically coupled to the primary side coil; and power reception equipment having a secondary side circuit for rectifying and smoothing voltage induced across the secondary side coil, wherein there is provided a power adjusting section for adjusting a level of power to be transmitted according to power required by the power reception equipment. The power adjusting section has, in the primary side circuit, a carrier wave oscillation circuit for supplying a carrier wave to the primary side coil, a demodulation circuit for demodulating a modulated signal transmitted from the secondary circuit and received by the primary side coil, and a power change-over section for selecting a level of power to be transmitted according to an information signal from the power reception equipment and demodulated by the demodulation circuit. The power adjusting section has, in the secondary side circuit, a modulation circuit for modulating the carrier wave fed from the carrier wave oscillation circuit and received by the secondary side coil with the information signal from the power reception equipment and transmitting the modulated signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
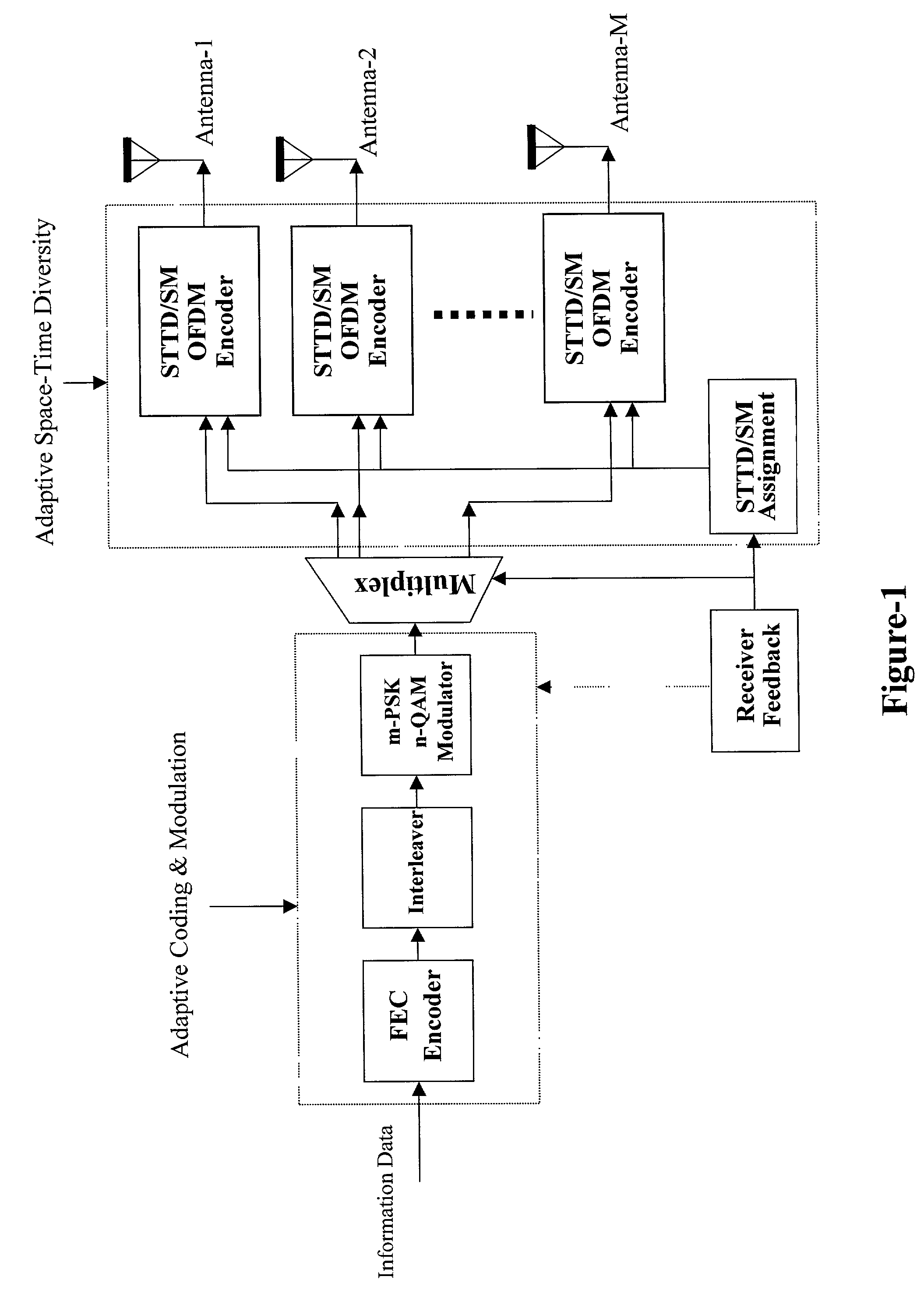
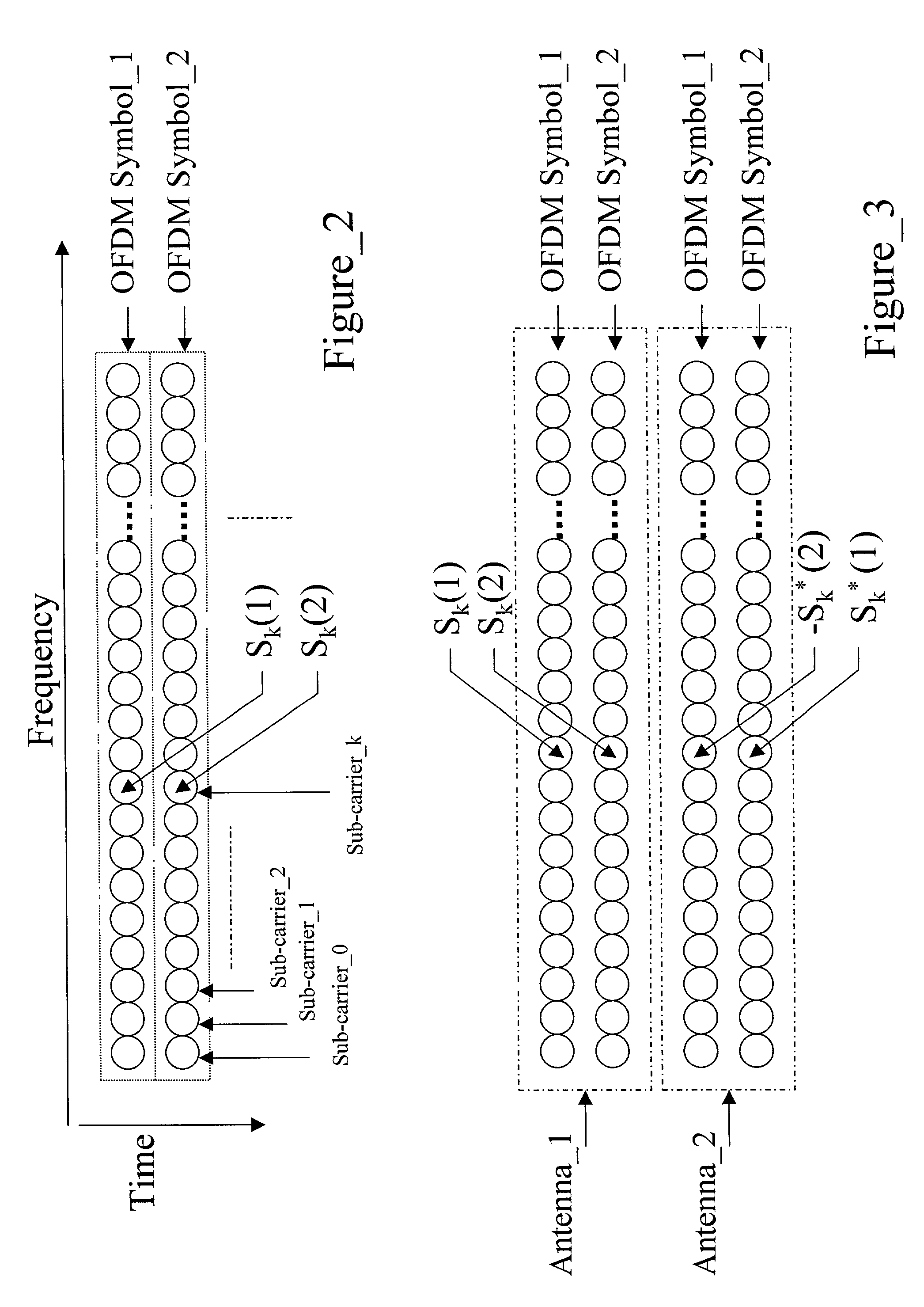
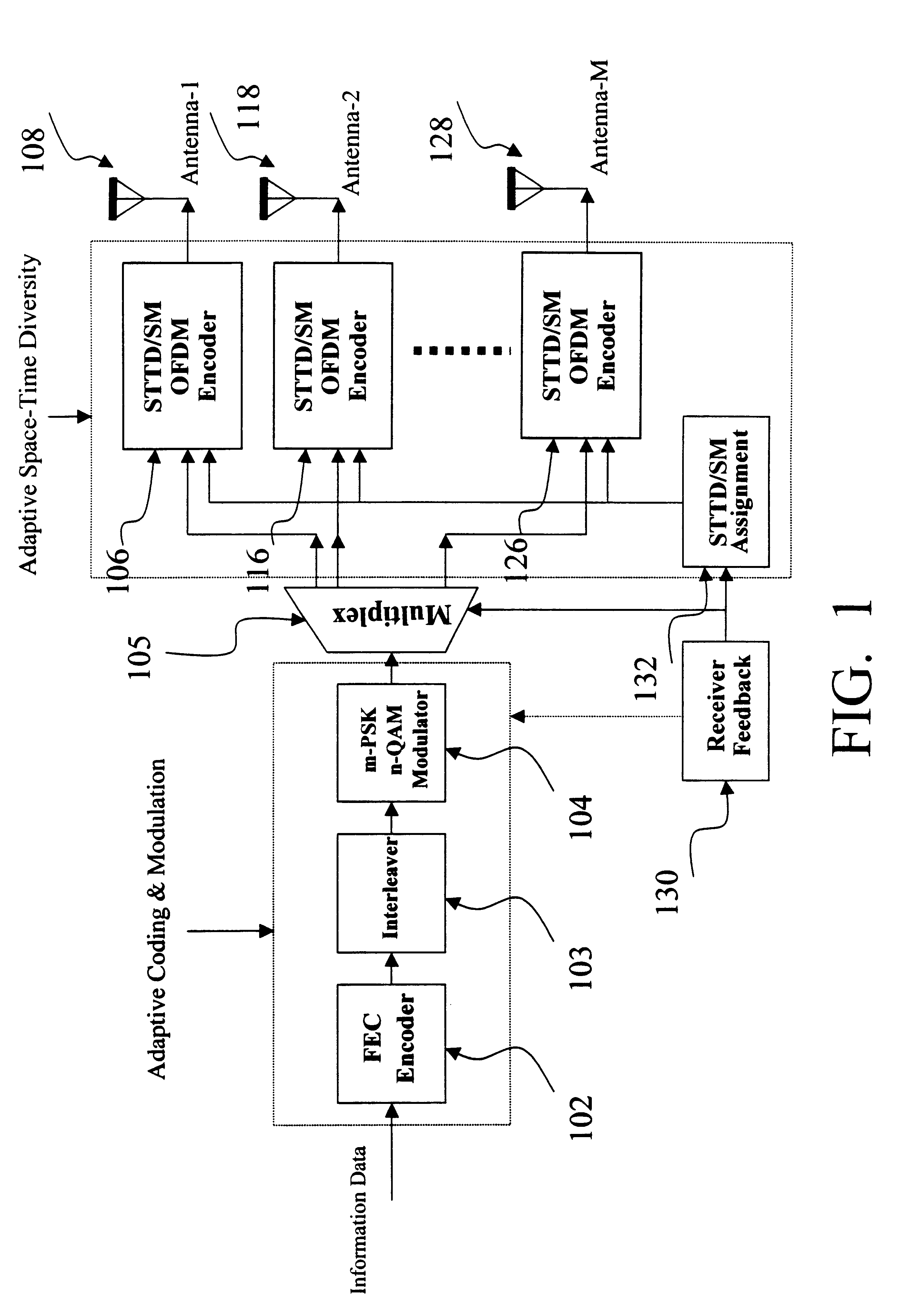
Adaptive time diversity and spatial diversity for OFDM
InactiveUS6985434B2Gain is assured with time diversityReduce signalingSpatial transmit diversityMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsCarrier signalData rate
An adaptable orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing system (OFDM) that uses a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) to having OFDM signals transmitted either in accordance with time diversity to reducing signal fading or in accordance with spatial diversity to increase the data rate. Sub-carriers are classified for spatial diversity transmission or for time diversity transmission based on the result of a comparison between threshold values and at least one of three criteria. The criteria includes a calculation of a smallest eigen value of a frequency channel response matrix and a smallest element of a diagonal of the matrix and a ratio of the largest and smallest eigen values of the matrix.
Owner:APPLE INC
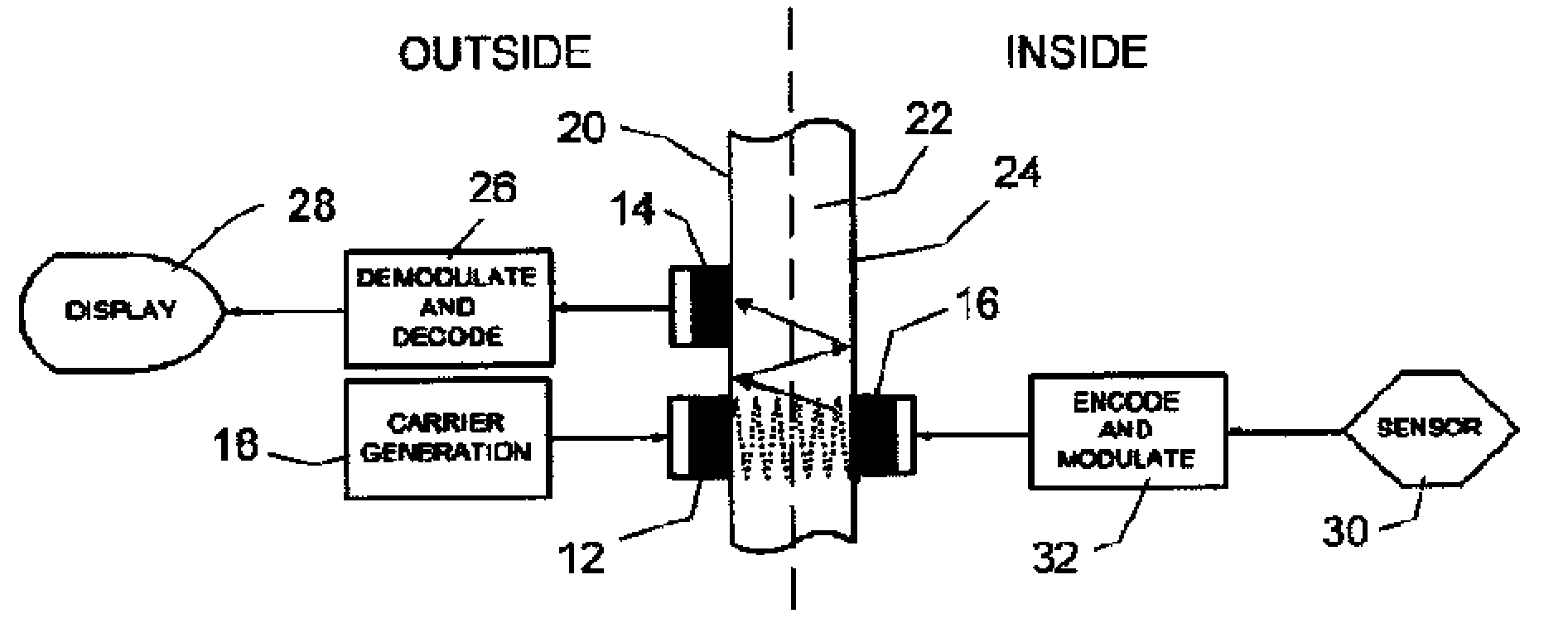
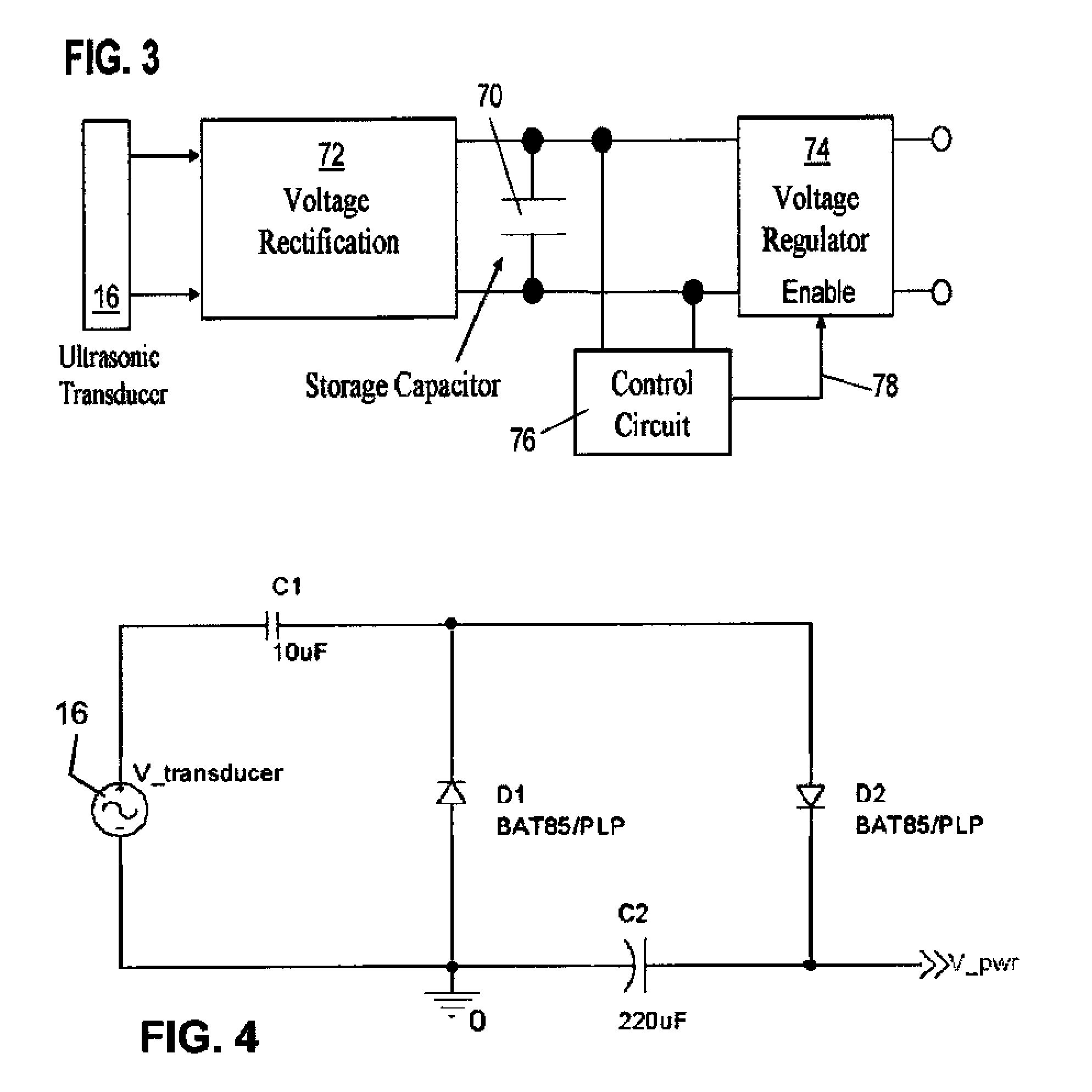
Ultrasonic Through-Wall Communication (UTWC) System
InactiveUS20100027379A1Reduced Power RequirementsMinimal complexityNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Apparatus for communicating information across a solid wall has one or two outside ultrasonic transducers coupled to an outside surface of the wall and connected to a carrier generator for sending an ultrasonic carrier signal into the wall and for receiving an output information signal from the wall. One or two inside ultrasonic transducers are coupled to an inside surface of the wall and one of them introduces the output information signal into the wall. When there are two inside transducers inside the wall, one receives the carrier signal and the second transmits the carrier after it is modulated by the output information from the sensor. When there is one inside transducer, the output information from the sensor is transmitted by changing the reflected or returned signal from the inside transducer. A power harvesting circuit inside the wall harvests power from the carrier signal and uses it to power the sensor.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY +1
Transmit power control for physical random access channels
ActiveUS20130058315A1Increase the likelihood of successAvoid low successPower managementSynchronisation arrangementUplink transmissionTransmitted power
The invention relates to methods for adjusting the transmit power utilized by a mobile terminal for uplink transmissions, and to methods for adjusting the transmit power used by a mobile terminal for one or more RACH procedures. The invention is also providing apparatus and system for performing these methods, and computer readable media the instructions of which cause the apparatus and system to perform the methods described herein. In order to allow for adjusting the transmit power of uplink transmissions on uplink component carriers, the invention suggests introducing a power scaling for uplink PRACH transmissions performing RACH procedures on an uplink component carrier. The power scaling is proposed on the basis of a prioritization among multiple uplink transmissions or on the basis of the uplink component carriers on which RACH procedures are performed.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Adaptive multicarrier wireless communication system, apparatus and associated methods
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive carrier allocation and power control in multi-carrier communication systems
InactiveUS6751444B1Power managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemCarrier signal
An apparatus and process for allocating carriers in a multi-carrier system is described. In one embodiment, the process comprises determining a location of a subscriber with respect to a base station, selecting carriers from a band of carriers to allocate to the subscriber according to the location of the subscriber with respect to the base station, and allocating selected carriers to the subscriber.
Owner:KAON SYST +1
Wafer plate and mask arrangement for substrate fabrication
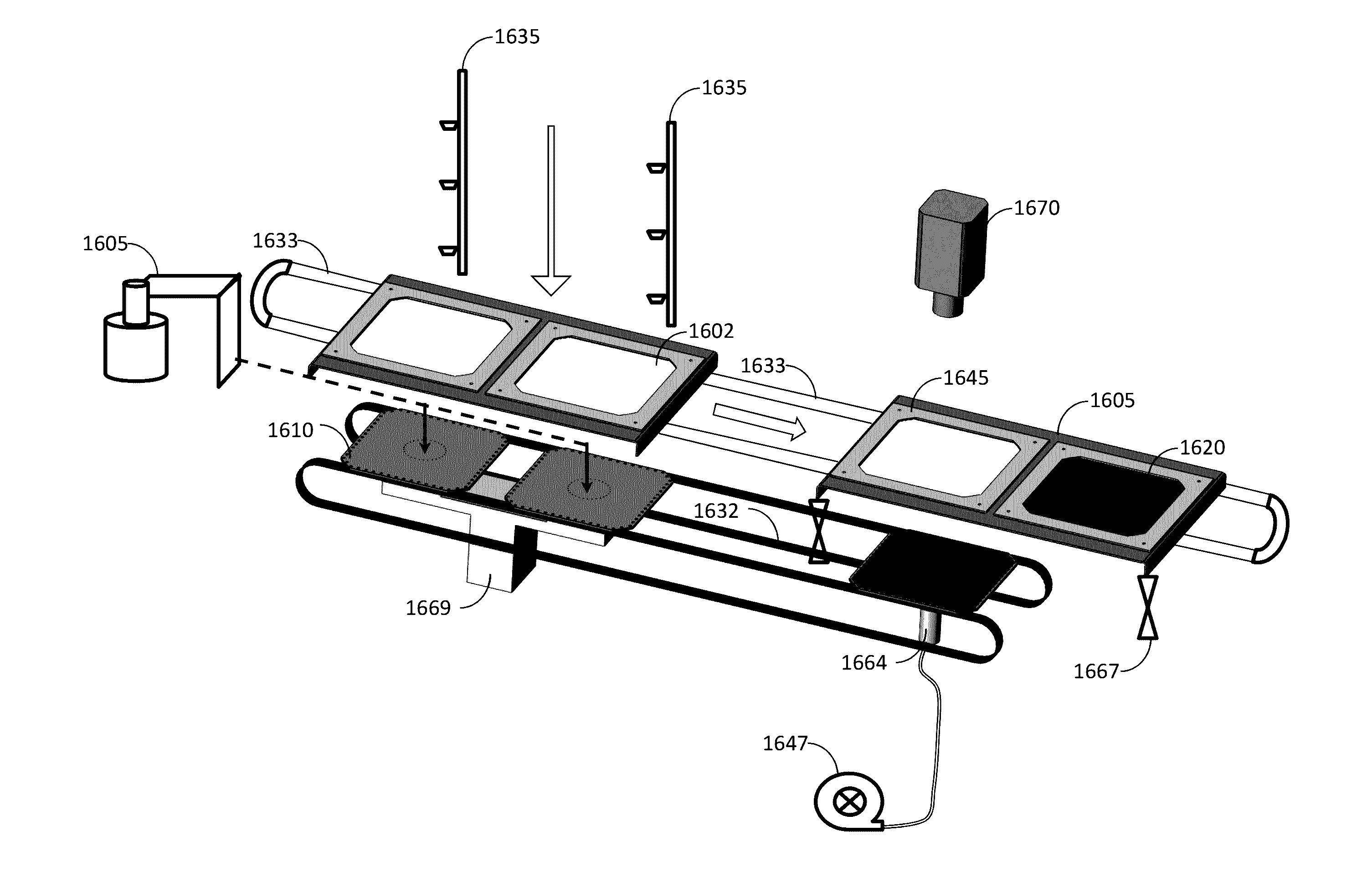
ActiveUS20170062258A1Improve cooling effectAvoid accidental movementVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarrier signalMechanical engineering
A system for processing wafers in a vacuum processing chamber. Carrier comprising a frame having a plurality of openings, each opening configured to accommodate one wafer. A transport mechanism configured to transport the plurality of carriers throughout the system. A plurality of wafer plates configured for supporting wafers. An attachment mechanism for attaching a plurality of wafer plates to each of the carriers, wherein each of the wafer plates is attached to a corresponding position at an underside of a corresponding carrier, such that each of the wafers positioned on one of the wafer carriers is positioned within one of the plurality of opening in the carrier. Mask attached over front side of one of the plurality of opening in the carrier. Alignment stage supports wafer plate under the opening in the carrier. A camera positioned to simultaneously image the mask and the wafer.
Owner:INTEVAC
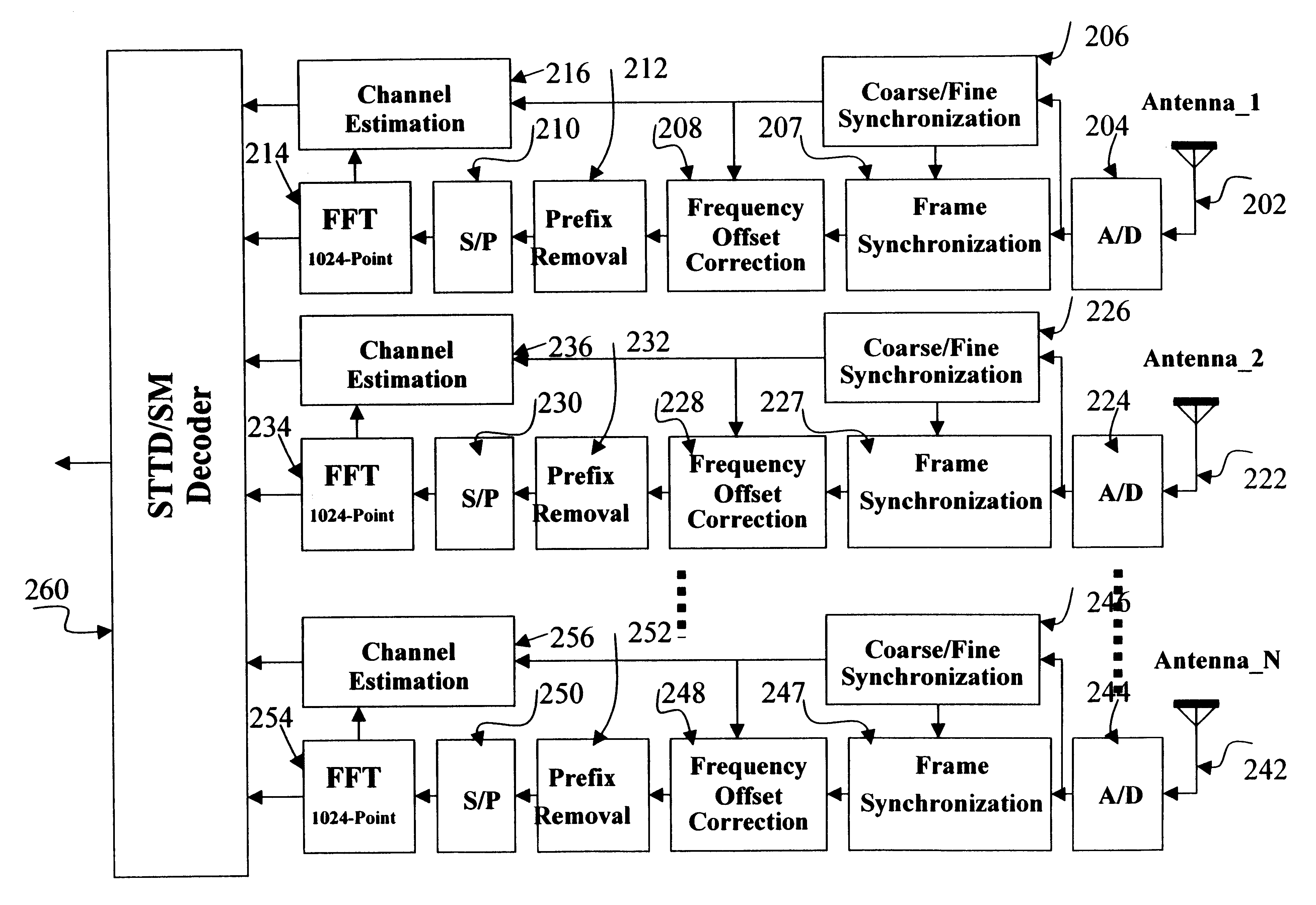
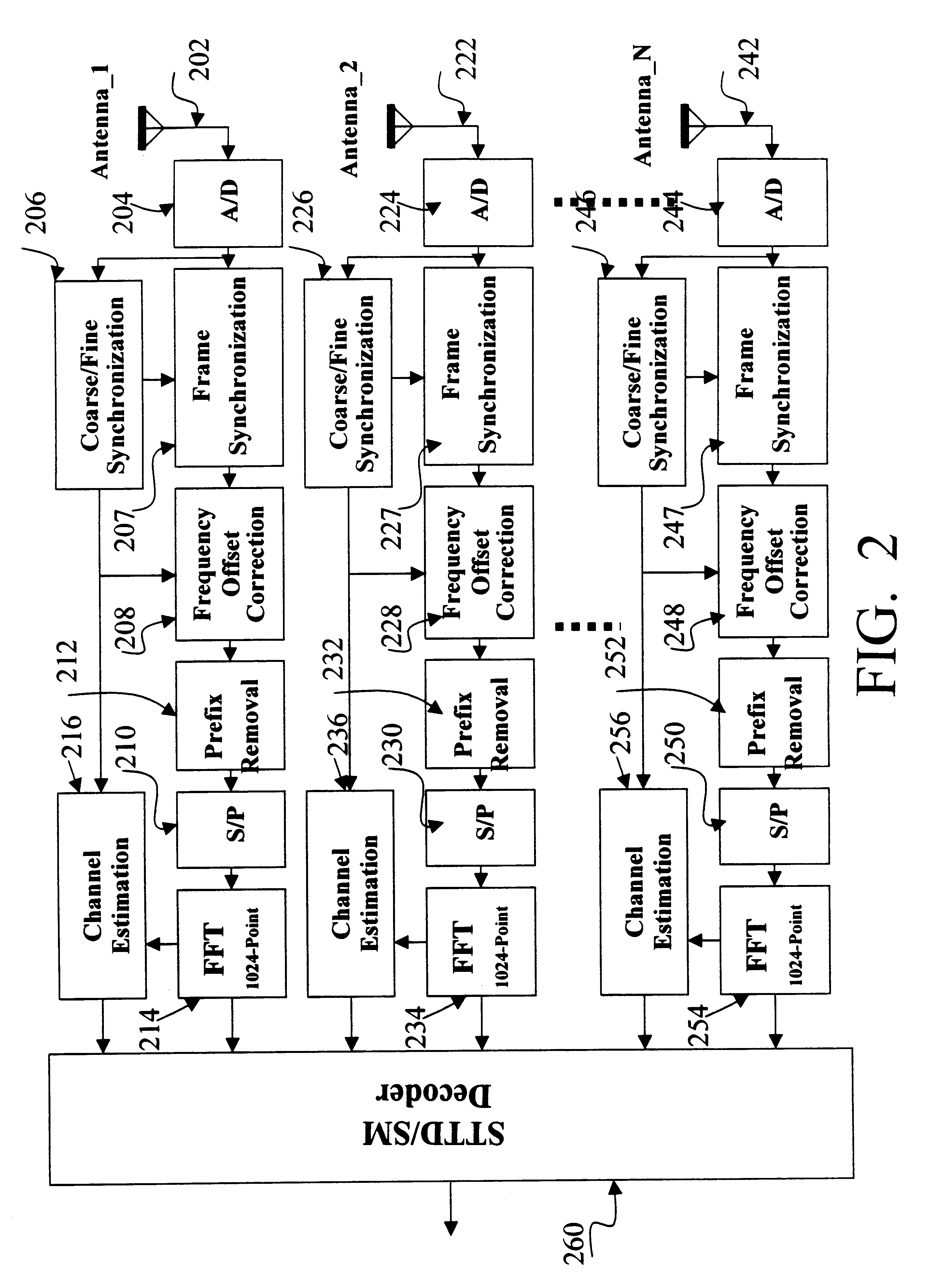
Channels estimation for multiple input-multiple output, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system
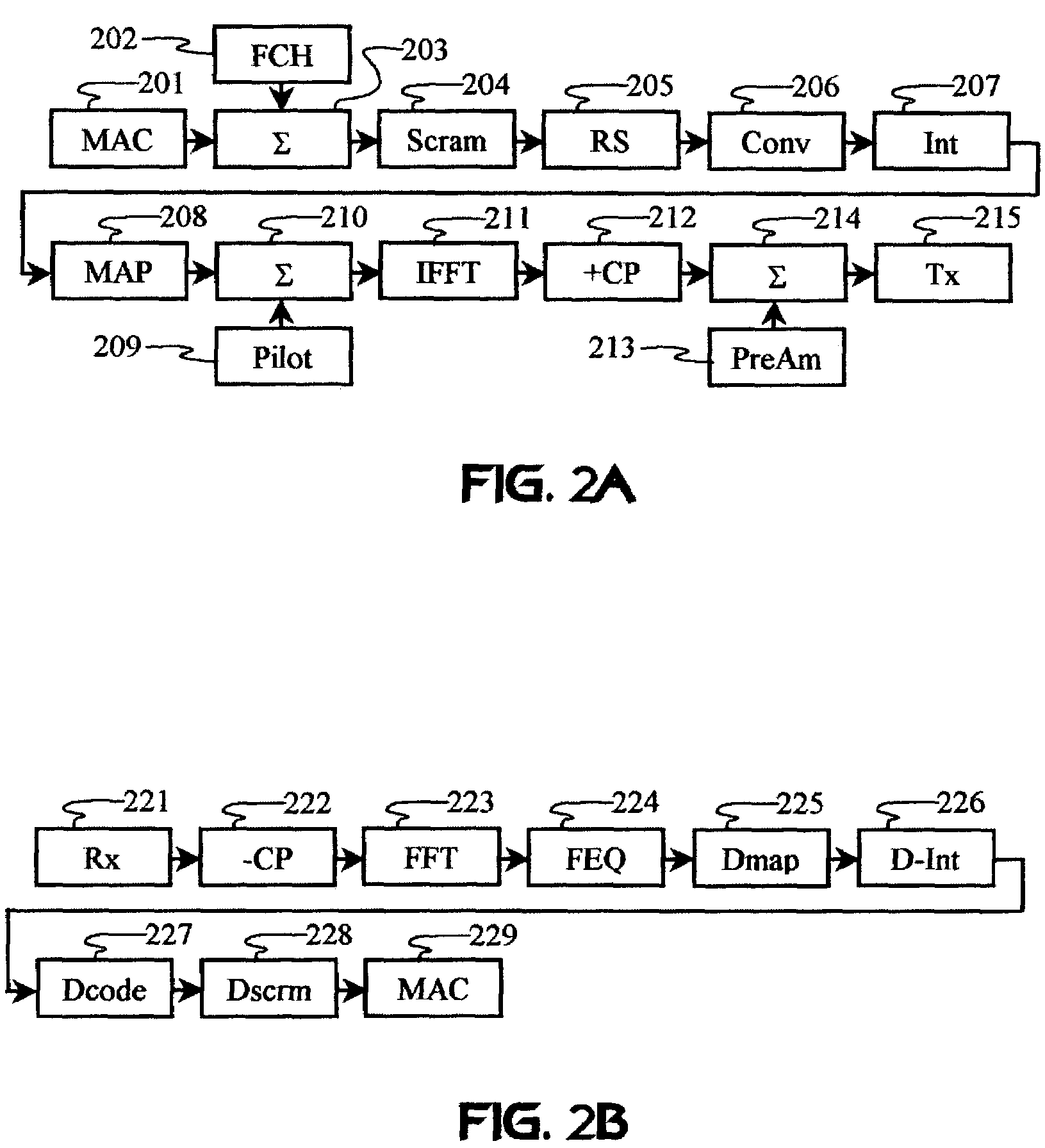
The distortion in the sub-carrier signals is determined by transmitting known values that are incorporated into the preamble portion of the frame and / or are incorporated into pilot symbols that are inserted into the data portion of the frame. The receiver typically receives these known values in a distorted form and then processes the distorted values together with the original known values to obtain a channel response. The channel response is then used to estimate the frequencies at which the channels are received.
Owner:APPLE INC
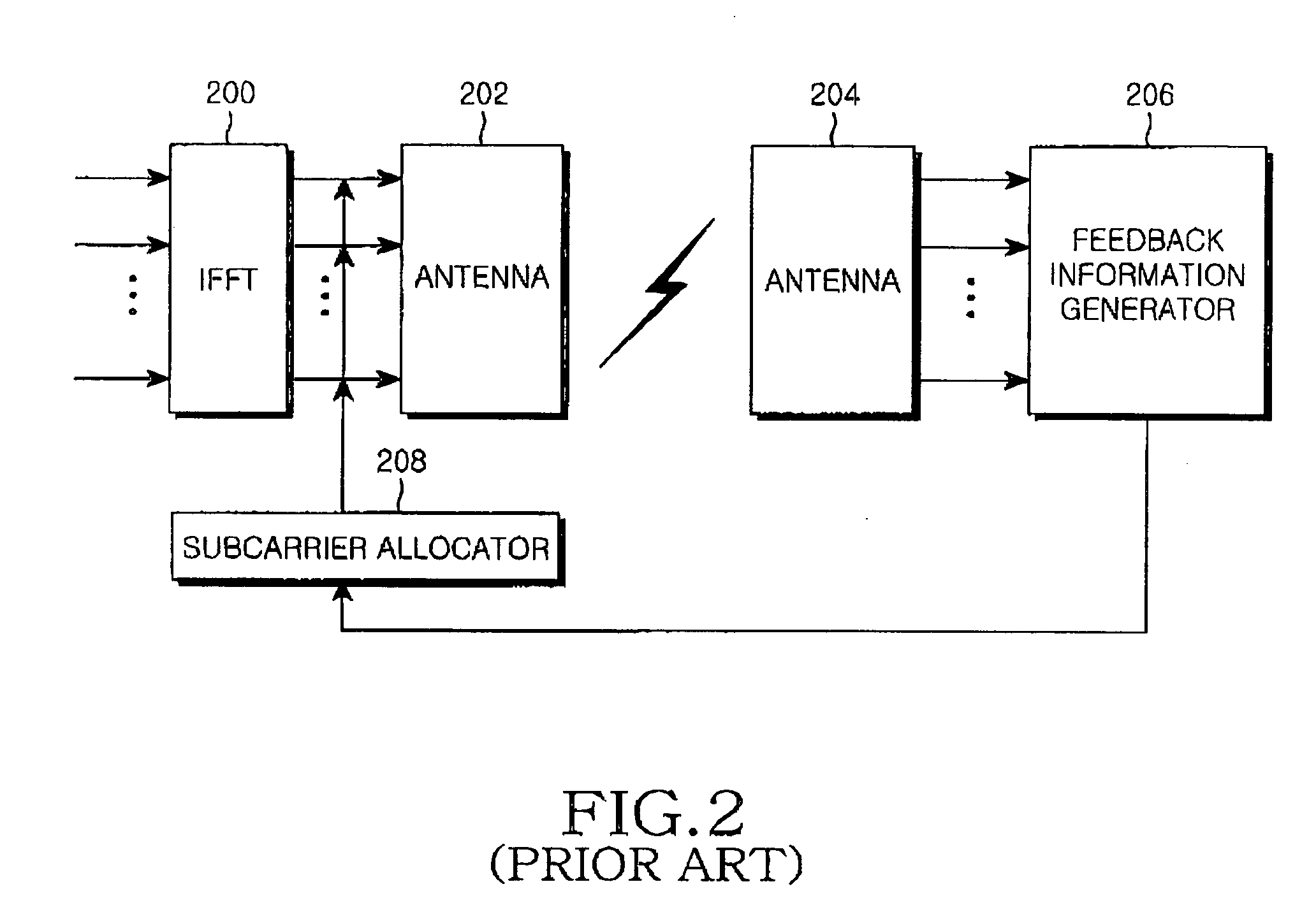
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving channel quality information of subcarriers in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
InactiveUS20050128993A1Reducing uplink feedback informationError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
A method of transmitting / receiving channel quality information (CQI) of subcarriers in an OFDM system where data is transmitted on the subcarriers via one or more transmit antennas. The subcarriers are grouped into subcarrier groups each having at least one subcarrier and further grouped into subgroups each having one or more subgroups. A user equipment generates CQIs for one or more allocated subcarrier groups and the transmit antennas or CQIs for the allocated subcarrier groups, the subgroups of the subcarrier groups, and the transmit antennas. The group CQIs and the subgroup CQIs are transmitted to a Node B in one or more physical channel frames.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for illumination and communication
InactiveUS20060239689A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageCarrier signalData signal
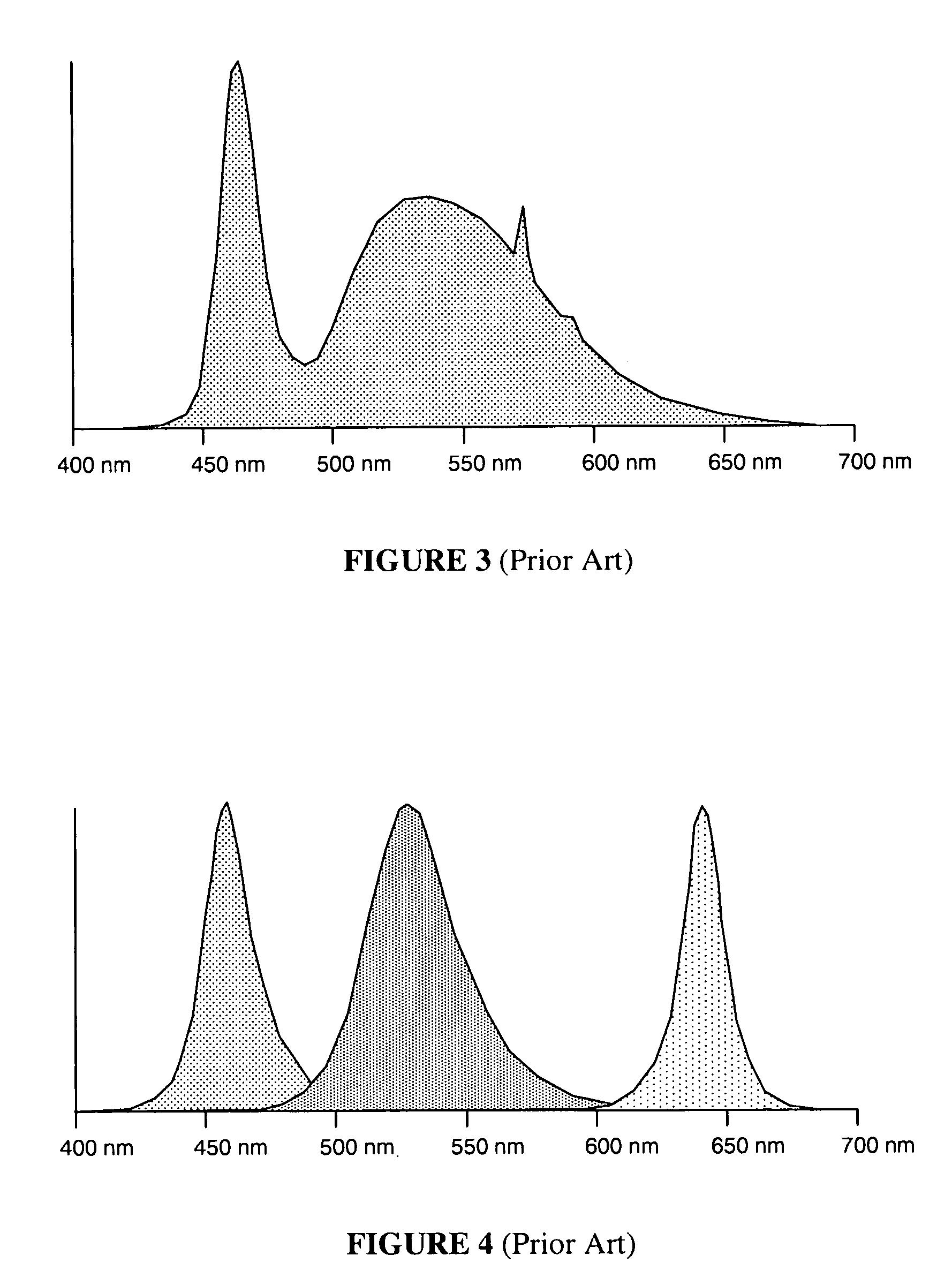
The present invention provides a method and apparatus of using light-emitting elements for illumination as well as communication of data, wherein potential flicker due to sub-fusion frequency data correlations can be reduced compared to prior art techniques, while reducing redundancy in the data transmission. The intensity of the illumination from the light-emitting elements is controlled by a dimming signal such as a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal or a pulse code modulation (PCM) signal, for example. An amplitude-modulated data signal is then superimposed on the dimming signal for communication of data. The dimming signal thus acts as a carrier signal for the data signal. A sensing means is then used to receive the data signal by detecting all or part of the illumination from the light-emitting elements. The data signal can subsequently be extracted from the detected illumination.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
On-demand data system
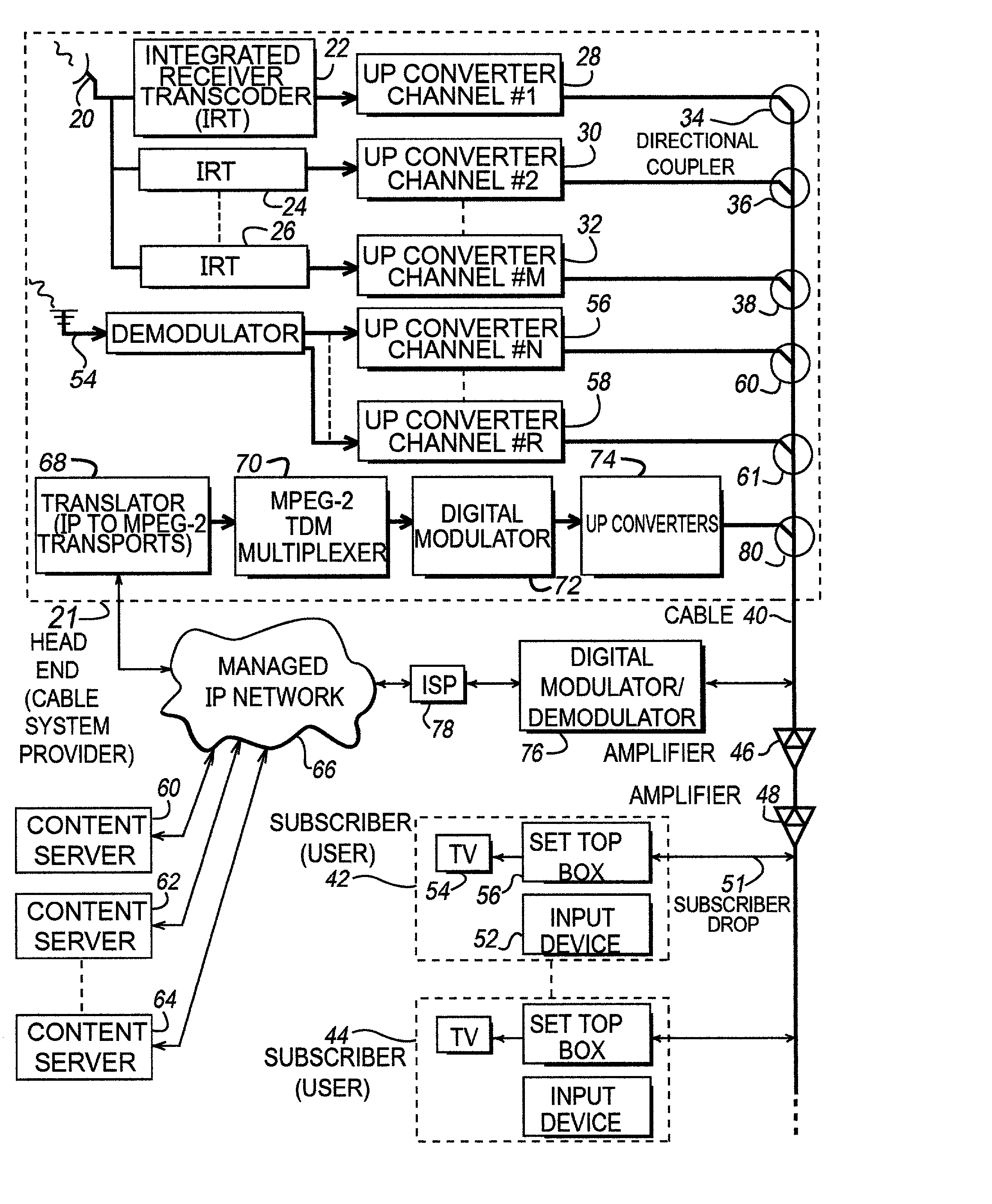
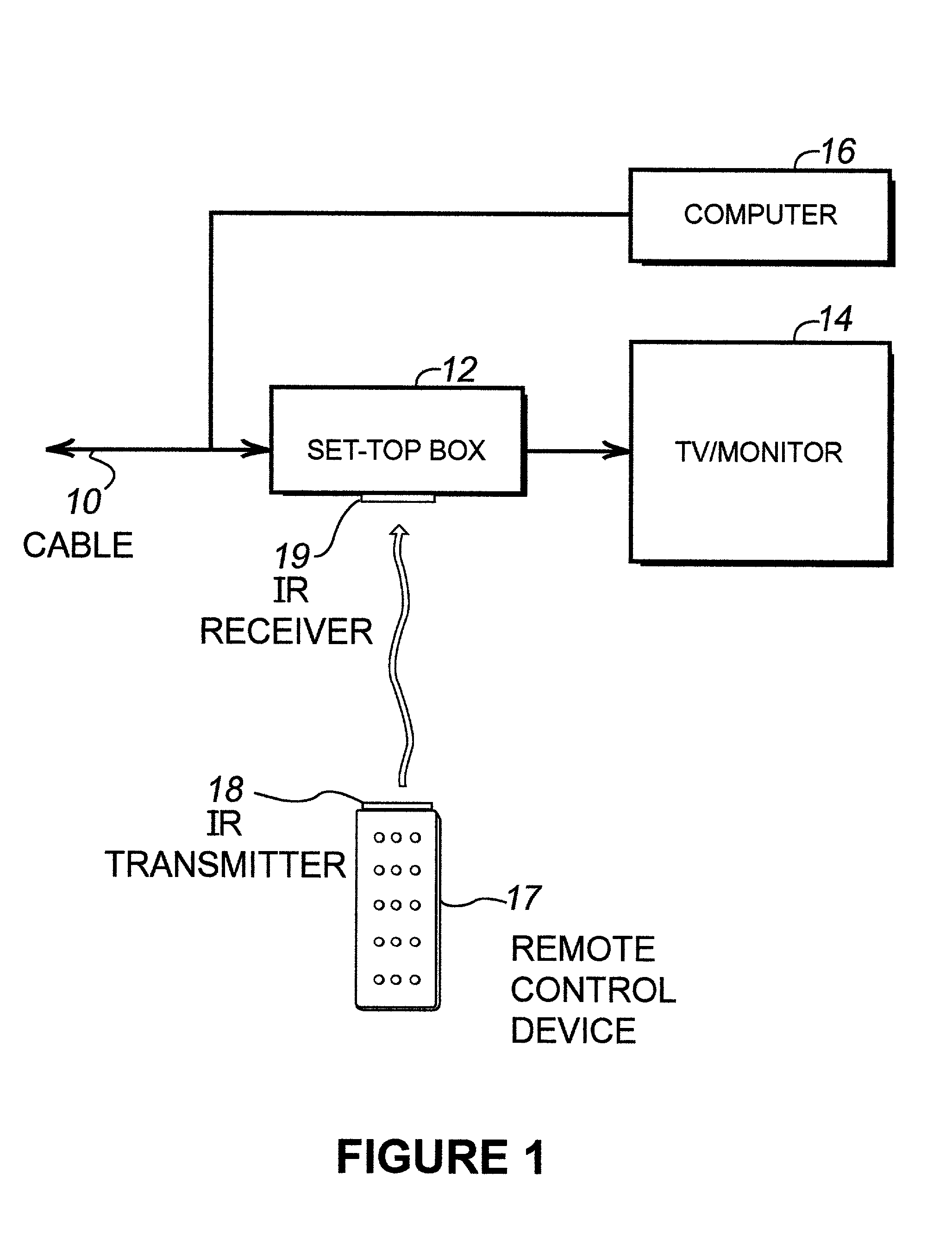
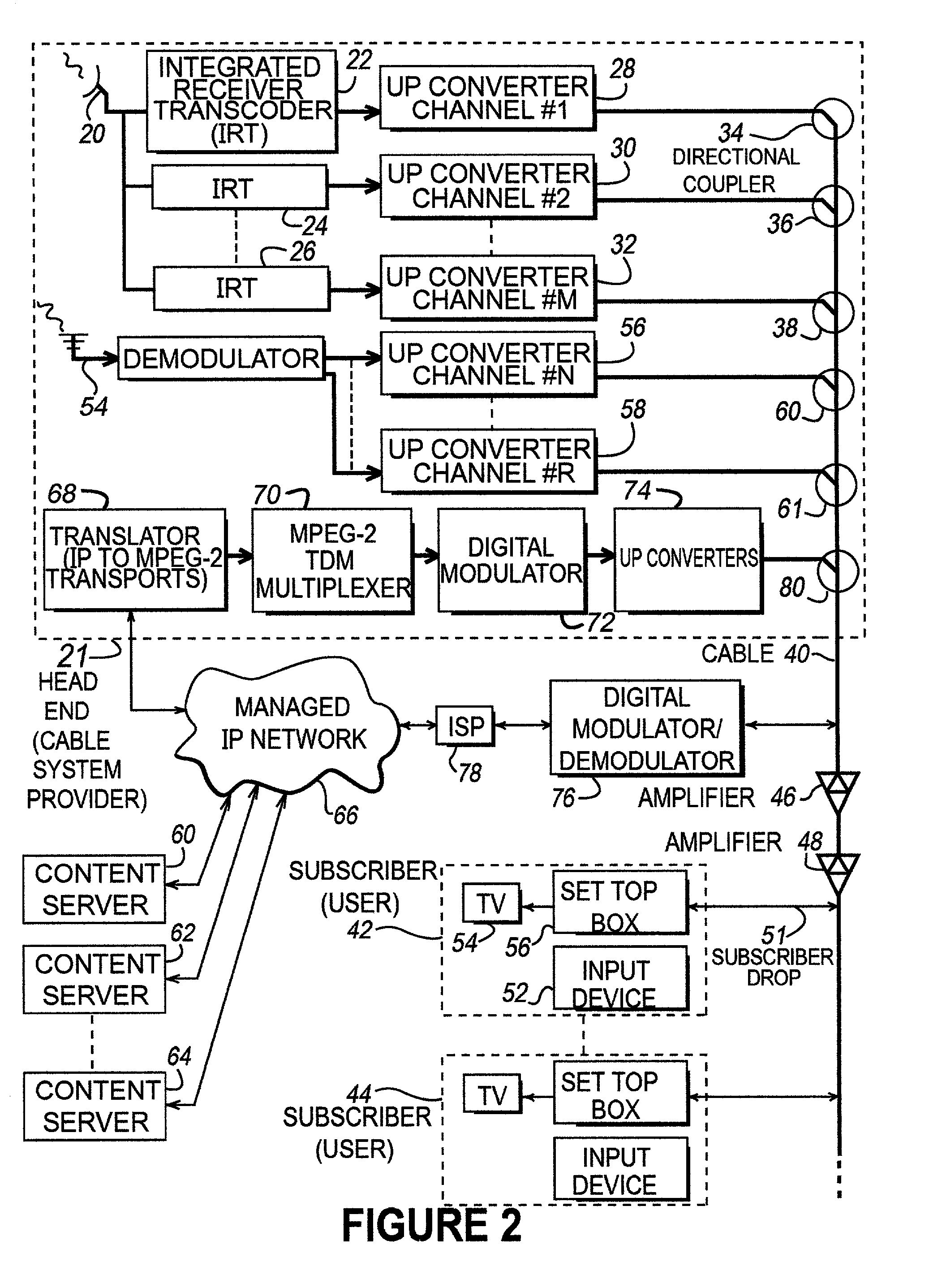
InactiveUS20020046406A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesQuality of serviceTransport system
Disclosed is a system for allowing on-demand delivery of data, such as MPEG-2 compressed video data, to a subscriber from a content server. The system utilizes a managed IP network that is coupled to the one or more content servers that allows the content servers to deliver data such as video, audio, and textual data with a guaranteed quality of service that is at least as good as broadcast quality service. The managed IP network is connected to a head end or other local cable service provider where video is delivered locally to subscribers. The IP transport data is translated to MPEG transport data, multiplexed onto an MPEG transport system, digitally modulated onto an rf carrier and up-converted to a specific frequency channel. The signal is then applied to the cable for delivery to the subscriber. Upstream signaling occurs through a set top box or computer that is connected to the cable and subsequently to a digital modulator / demodulator and ISP to a managed IP network 66. Low band signals can also be transmitted from the content servers back to the set top box or computer indicating confirmation of an order. Also, control signals such as stop, rewind, fast-forward, and slow can be transmitted back to the content server to control the transmission of data from the content server to the subscriber.
Owner:CABLE TELEVISION LAB
Multiple access method and system
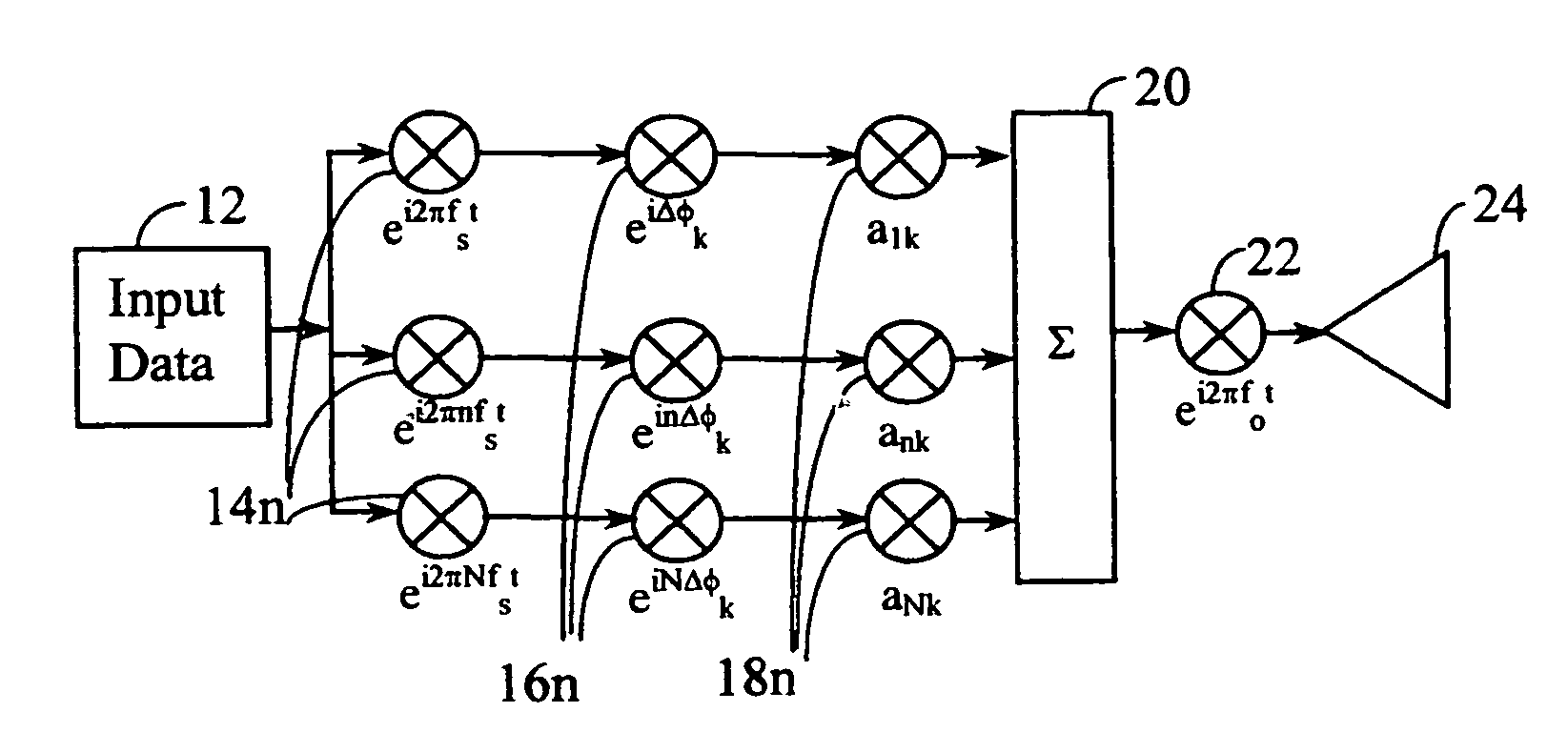
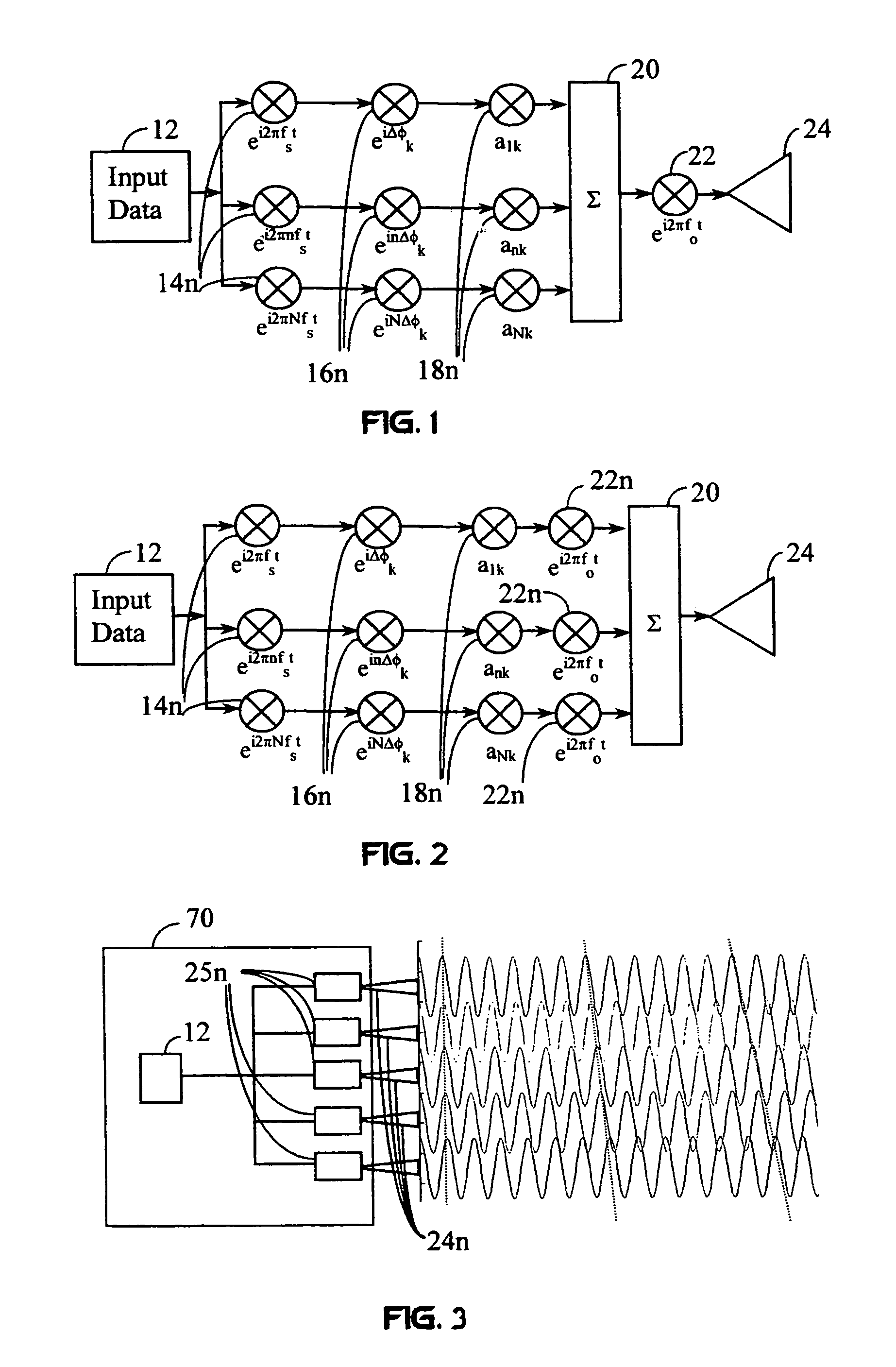
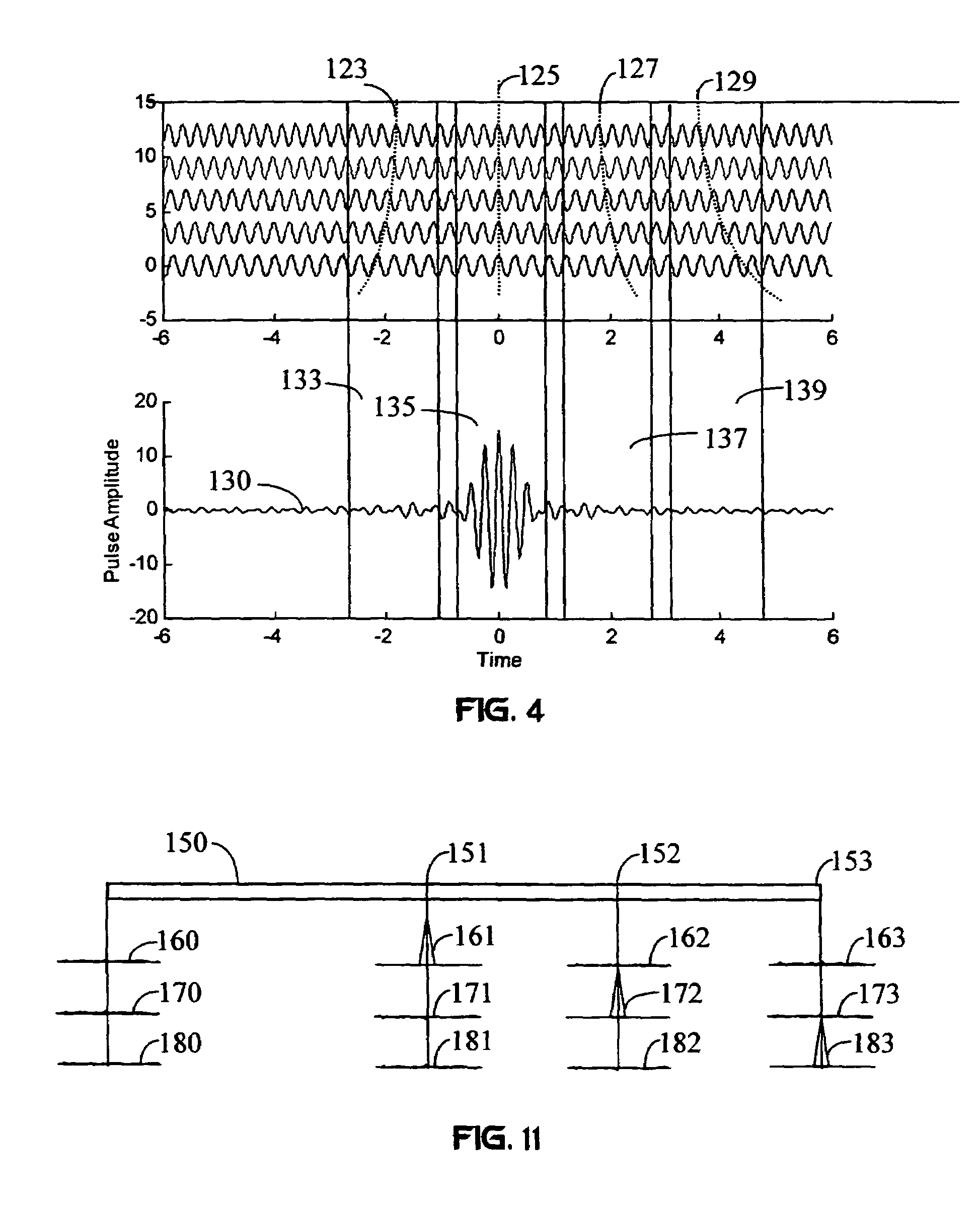
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
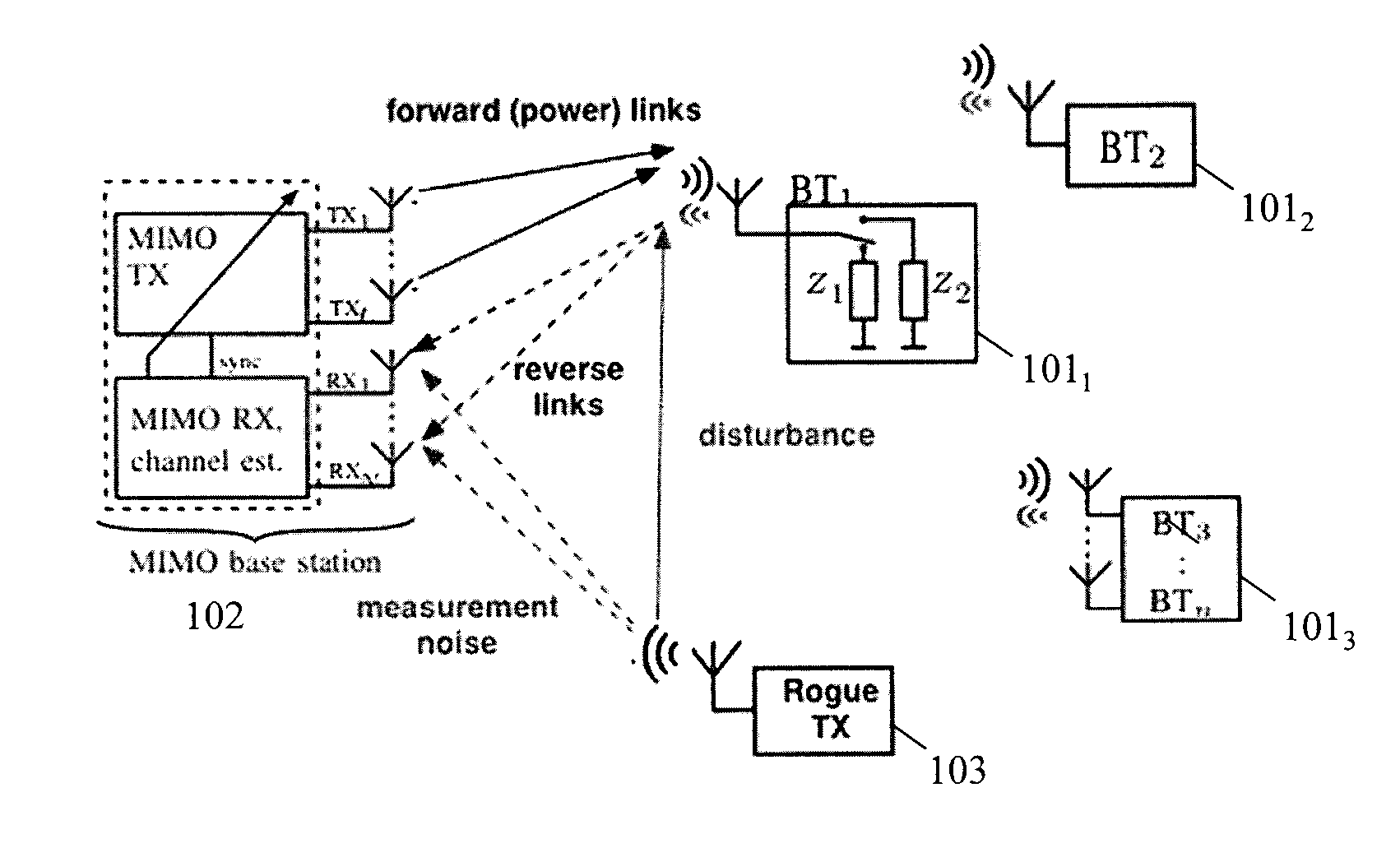
Real-time wireless power transfer control for passive backscattering devices
ActiveUS20150091706A1Electromagnetic wave systemCircuit arrangementsClosed loop feedbackCarrier signal
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for real-time wireless power transfer control. In one embodiment, a system comprises: an RF-energy harvesting sensor tag operable to generate a first backscatter signal and at least one base station operable to deliver RF power to the sensor tag by emitting a first waveform comprising a plurality of subcarriers, wherein the first backscatter signal is generated by the sensor tag by modulated scattering of the first waveform as incident upon the sensor tag, and further wherein the at least one base station subsequently emits a second waveform determined at least in part by a closed-loop feedback control algorithm responsive to measurements of the first backscatter signal.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
Orthogonal superposition coding for direct-sequence communications
ActiveUS7317750B2Efficient processingImprove signal to noise ratioTransmission path divisionInter user/terminal allocationFrequency spectrumSuperposition coding
An adaptation to Carrier Interferometry synthesis and analysis provides for complex coding and decoding in a sliding window transform. Coding and decoding functionality can be extended to spatial processing in systems employing multiple transceiver elements. Poly-amplitude codes permit successive interference cancellation in spatial and frequency-domain processing. Handoffs in cellular systems are facilitated by selecting spectral / base station combinations that optimize link performance.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
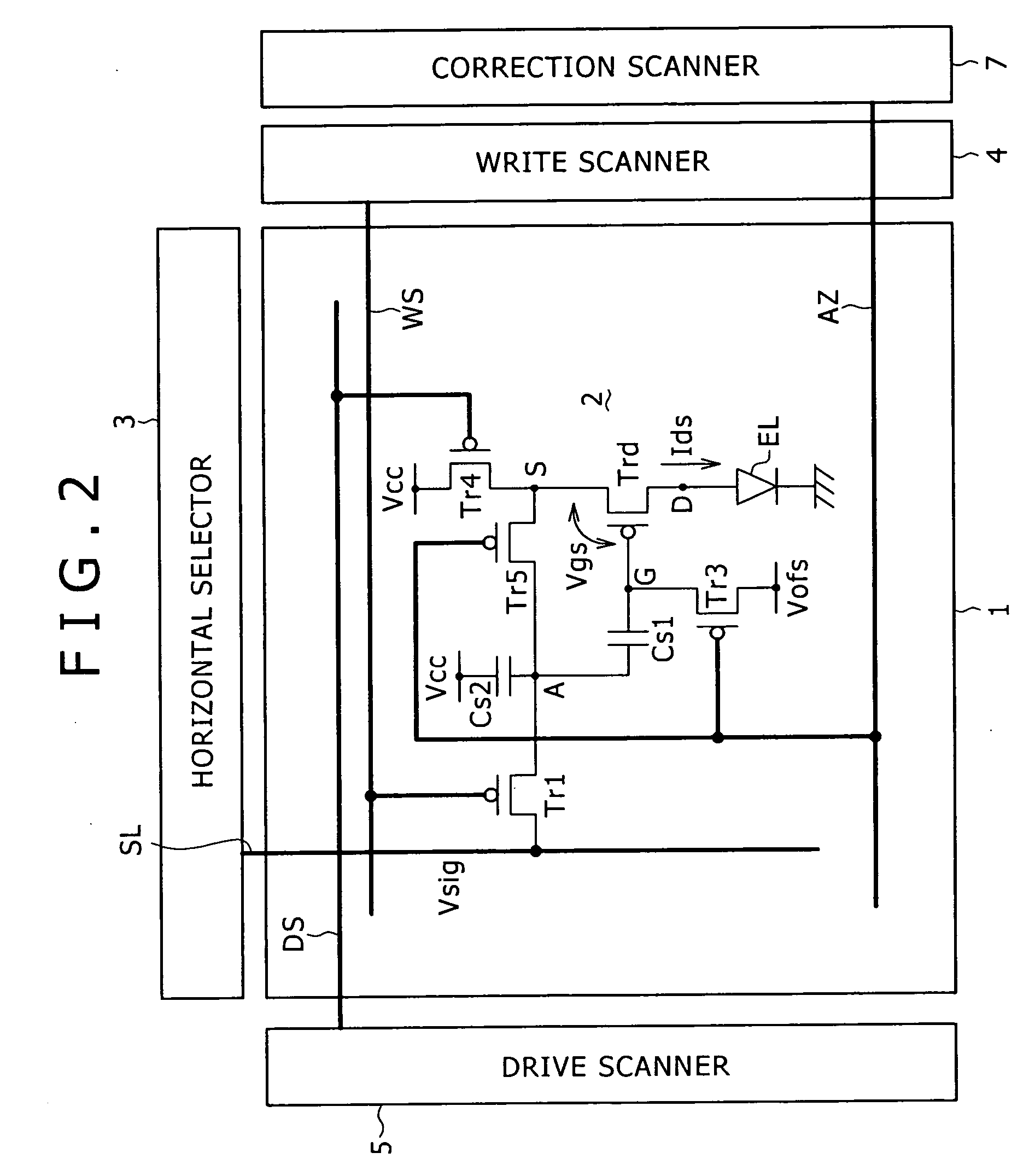
Pixel circuit, display and driving method thereof
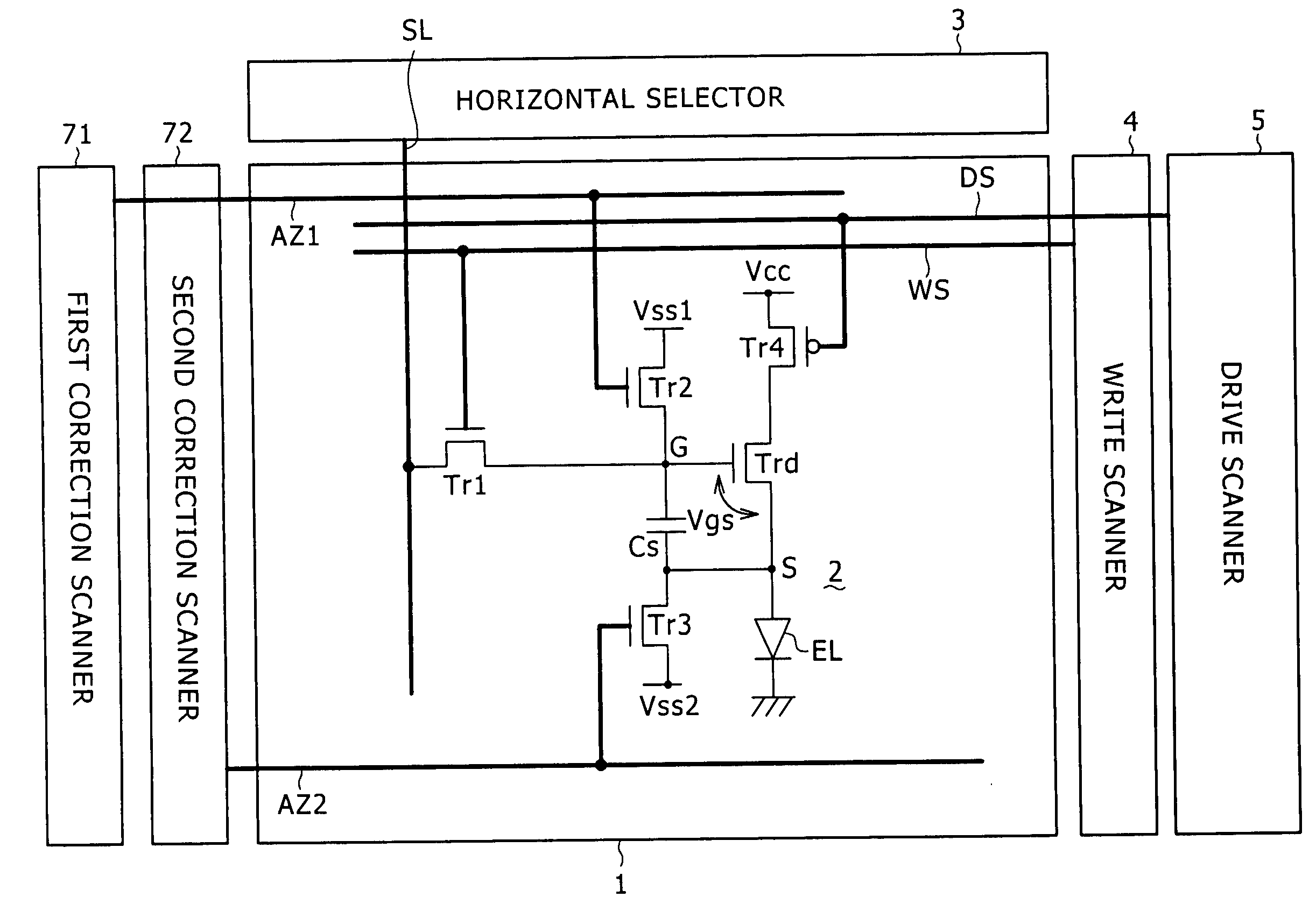
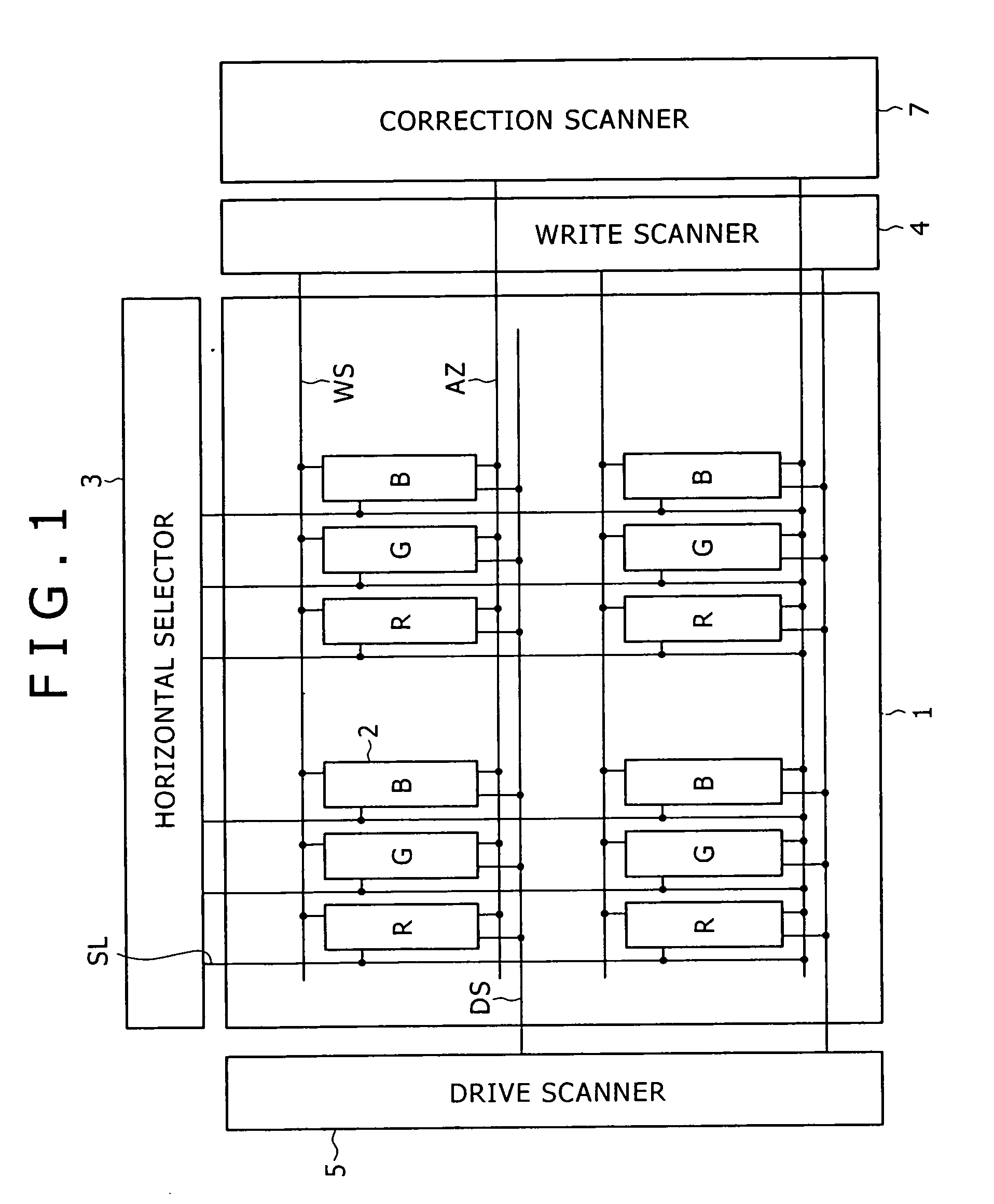
InactiveUS20060170628A1Eliminate dependenciesImprove mobilityElectroluminescent light sourcesHeater elementsCapacitanceScan line
The invention provides a pixel circuit that can cancel the influence of the mobility of a drive transistor. A drive transistor supplies to a light-emitting element, an output current dependent upon an input voltage during a certain emission period. The light-emitting element emits light with a luminance dependent upon a video signal in response to the output current supplied from the drive transistor. The pixel circuit includes a correction unit that corrects the input voltage held by a capacitive part before the emission period or at the beginning of the emission period, in order to cancel the dependence of the output current on the carrier mobility. The correction unit operates during part of a sampling period in response to control signals supplied from scan lines. Specifically, the correction unit extracts the output current from the drive transistor while the video signal is sampled, and negatively feeds back the output current to the capacitive part to thereby correct the input voltage.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus and method for supporting transmission of sounding reference signals from multiple antennas
Methods and apparatuses, through the use of a Downlink Control Indication (DCI) format or through higher layer signaling, for dynamic activation and deactivation of Sounding Reference Signal (SRS) transmissions from User Equipments (UEs) in an UL Component Carrier (CC) with configured SRS transmissions, the dynamic configuration of SRS transmissions parameters, the dynamic activation and configuration of SRS transmissions in an UL CC without previously configured SRS transmissions for a reference UE, and the configuration of SRS transmissions from multiple UE transmitter antennas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
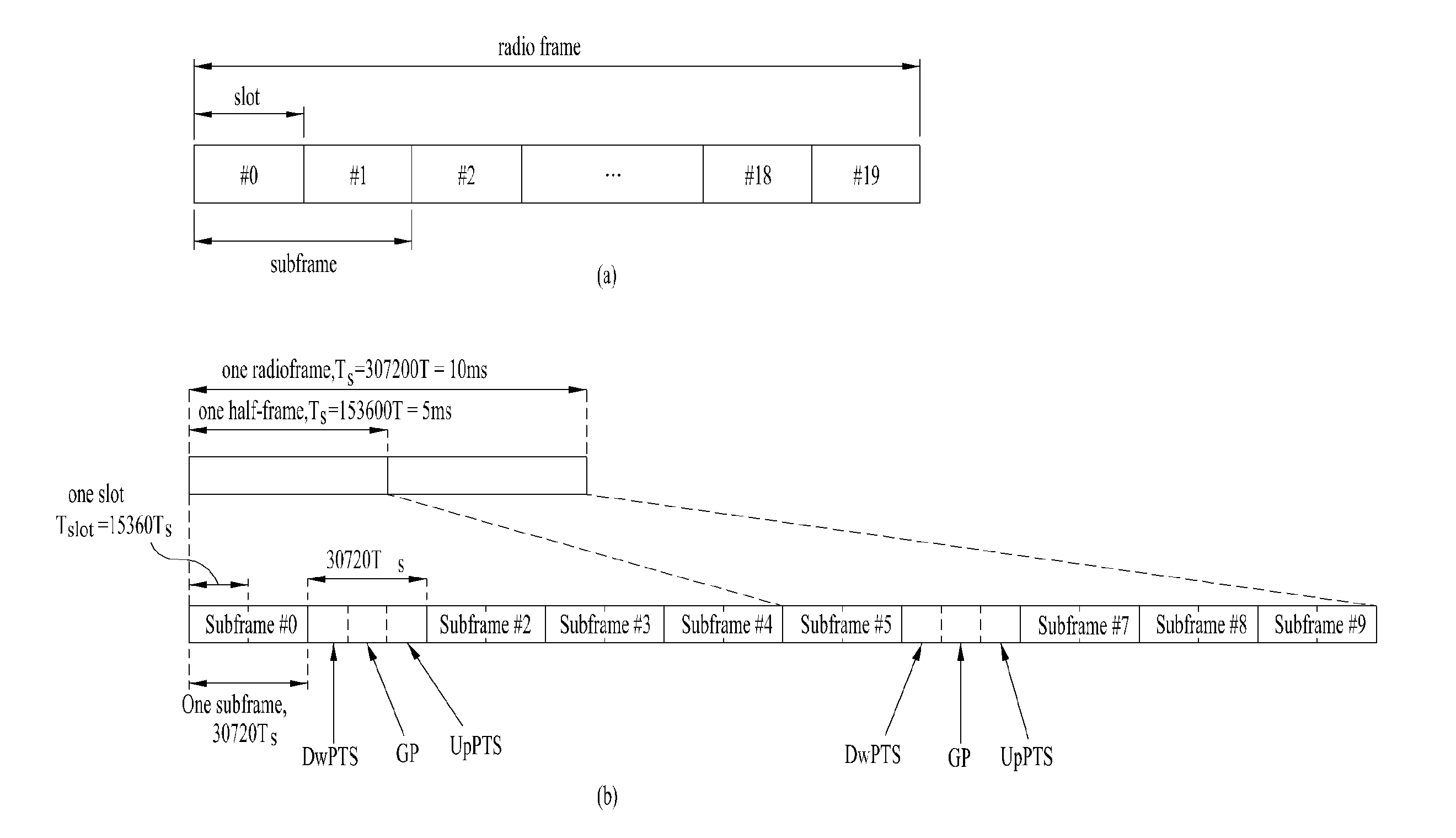
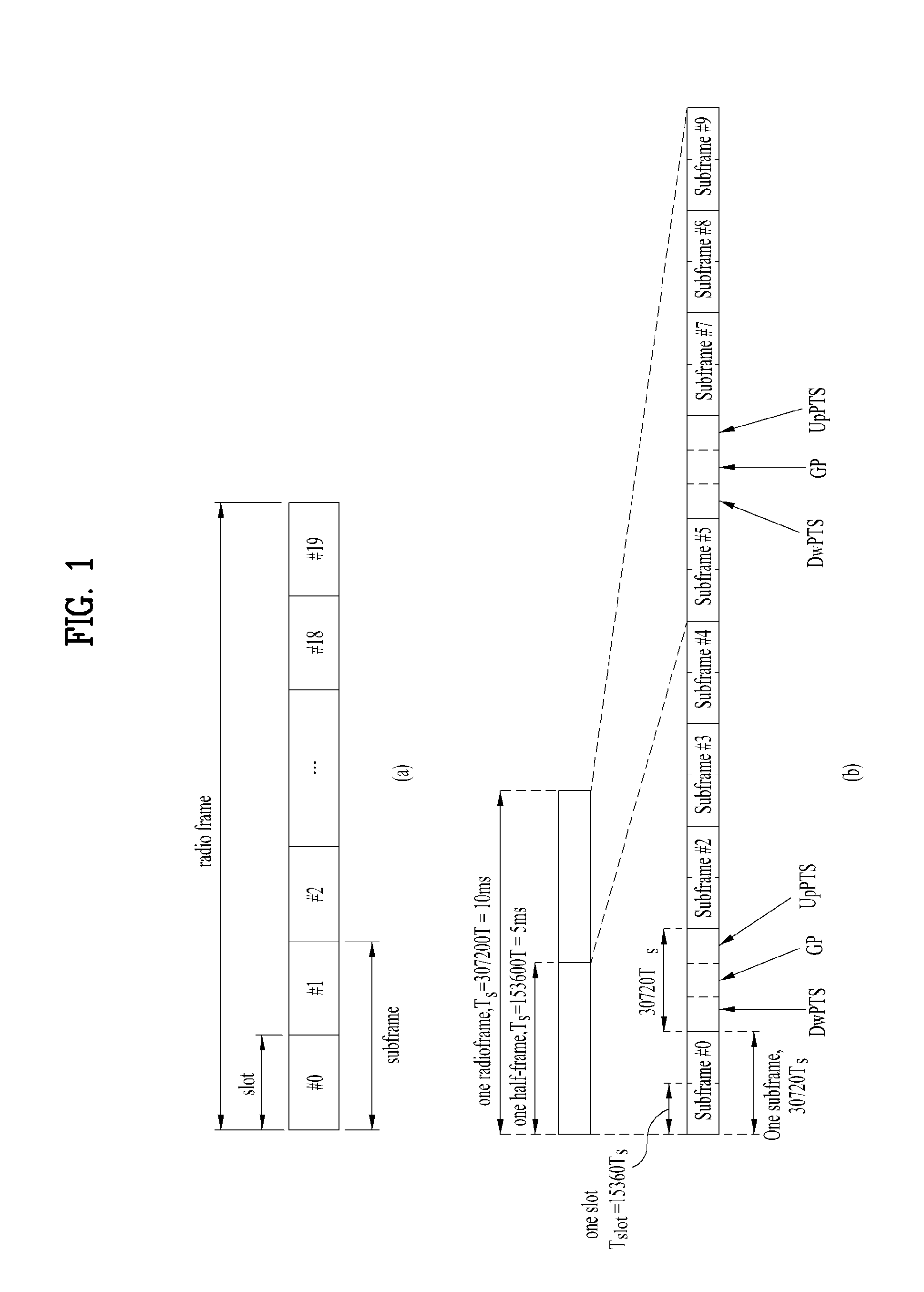
Propagation delay difference reporting for multiple component carriers
The invention relates to methods for reporting on downlink timings by a mobile terminal in a mobile communication system. In order to allow for an aggregation access point to obtain information on propagation delay differences of downlink transmissions on aggregated serving cells, the invention suggests the mobile terminal to report timing information based on reception time difference information for a the target / reference cell. The mobile terminal performs measurements relating to transmission and / or reception time differences on the target / reference cell, and reports same to the eNodeB. The eNodeB compares the measurement result to a predefined maximum propagation delay time difference. Alternatively, the mobile terminal performs the measurements, compares same to the predefined maximum propagation delay time difference and then report the comparison result to the eNodeB.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
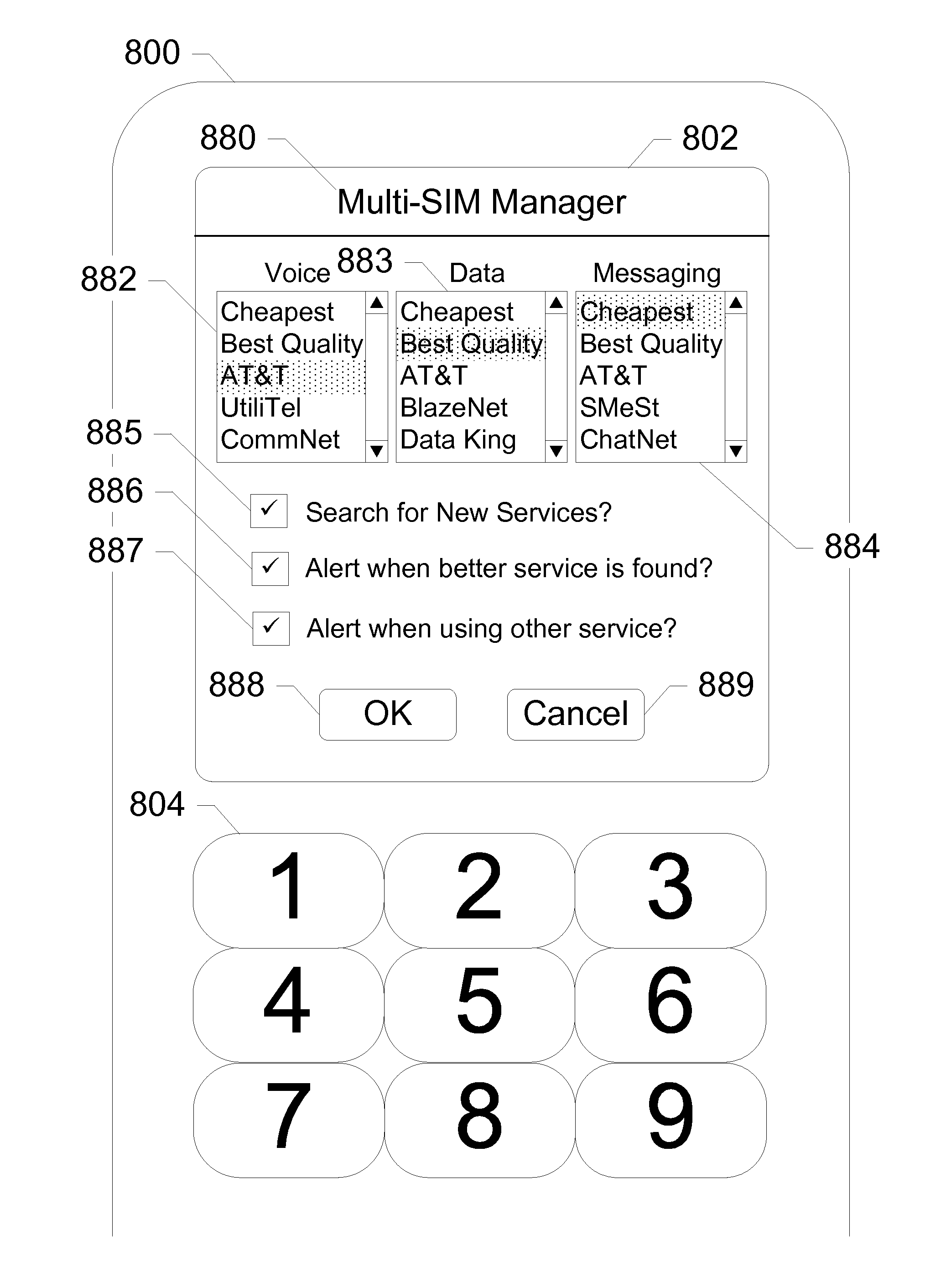
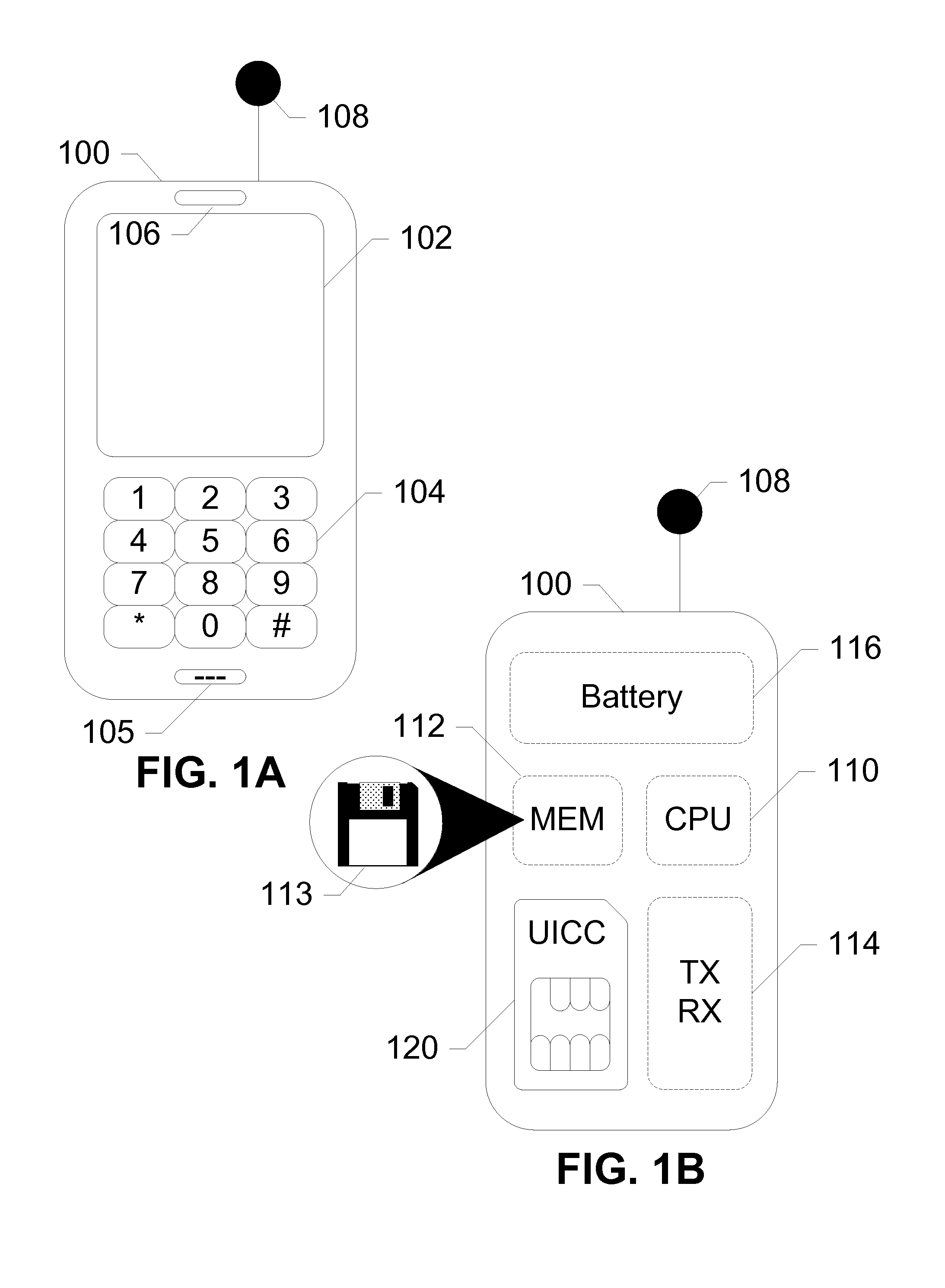
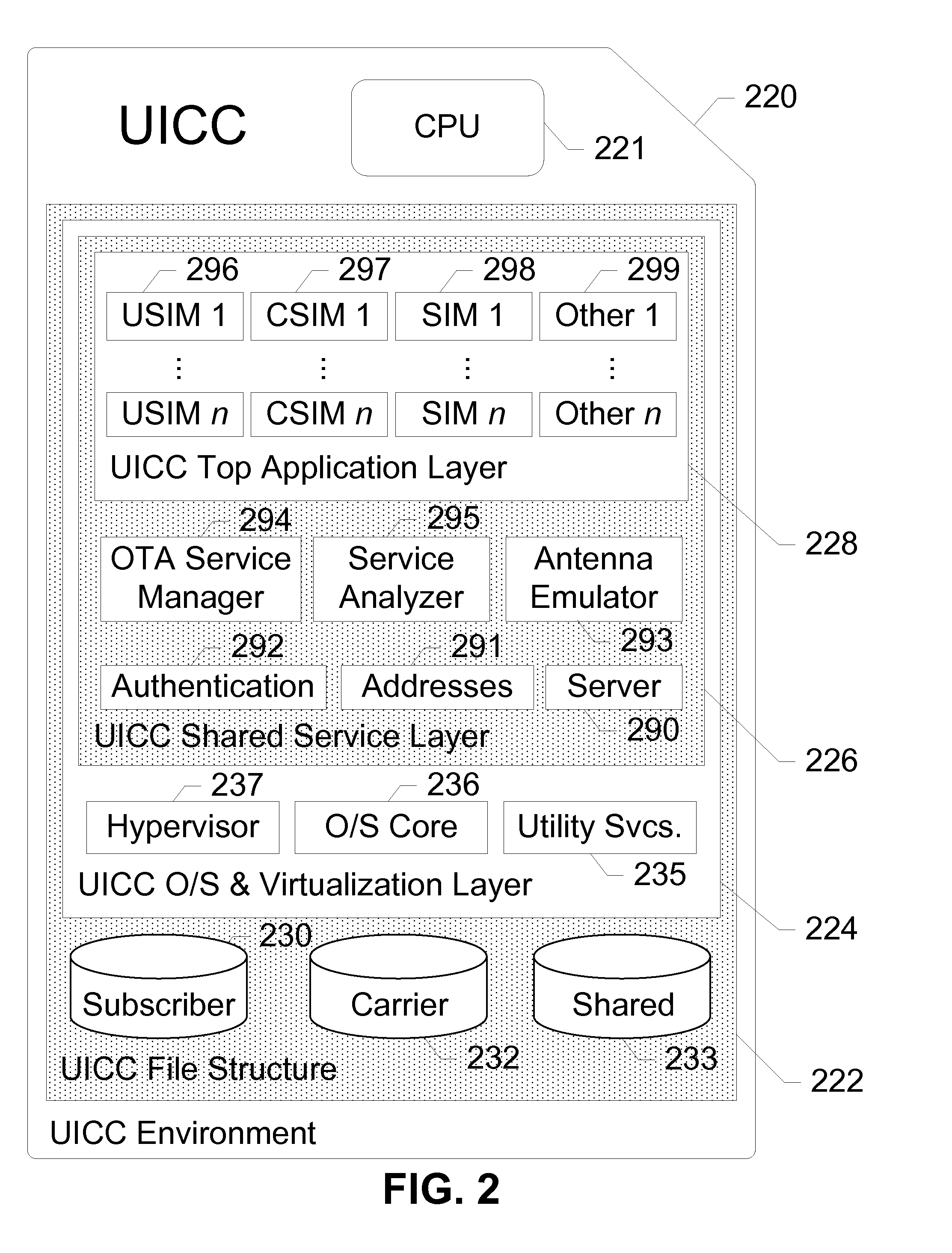
UICC Carrier Switching Via Over-The-Air Technology
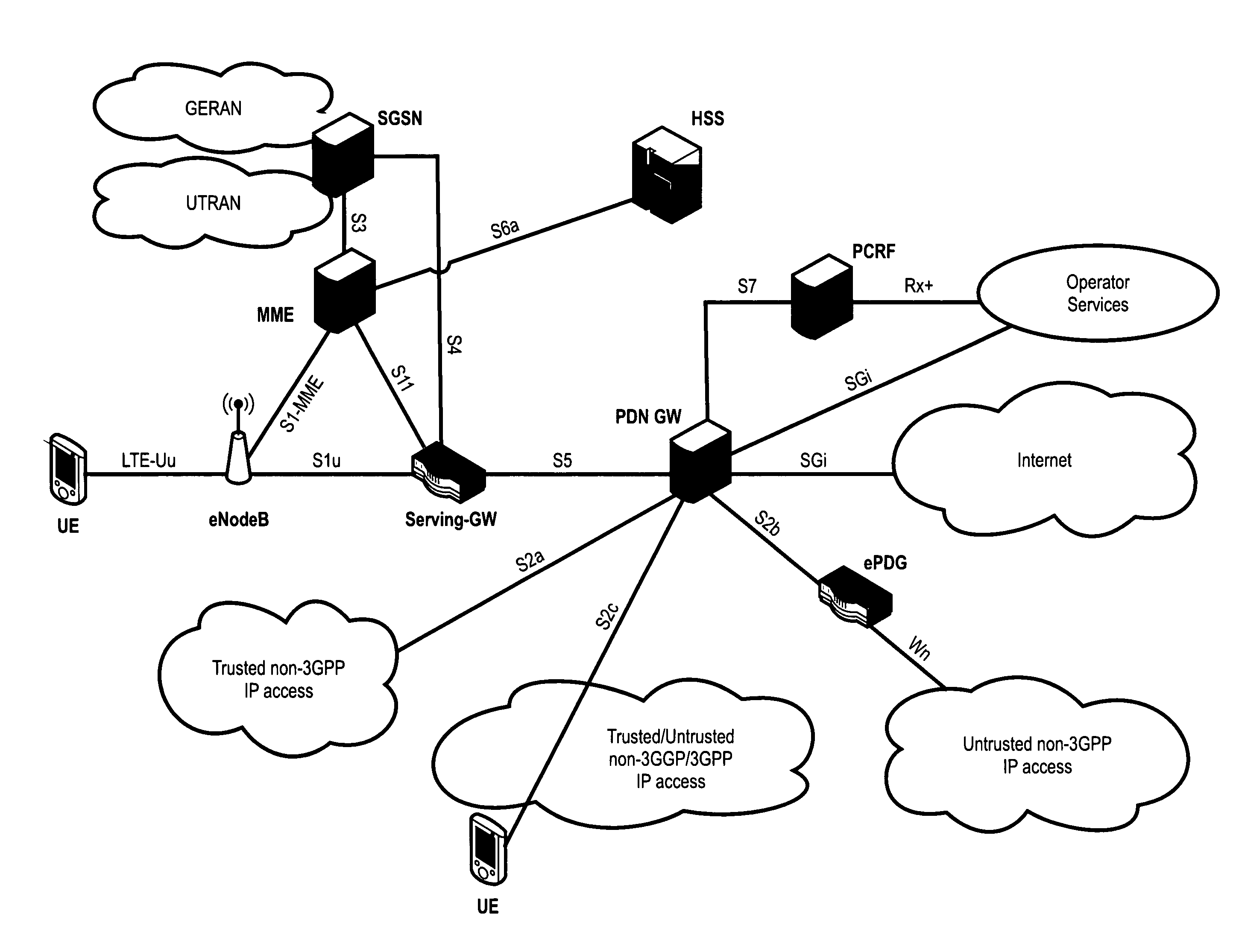
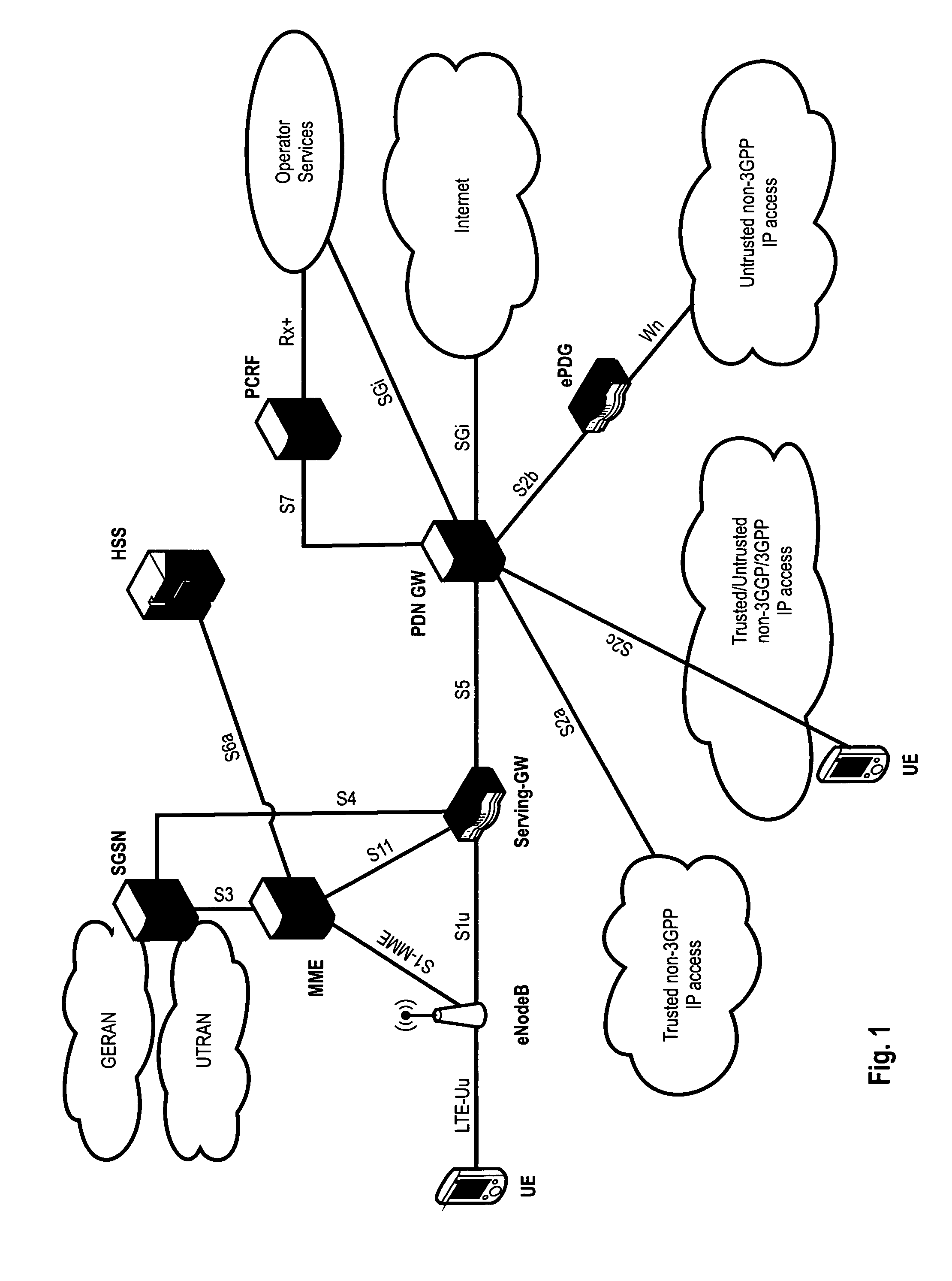
ActiveUS20130023235A1Eliminate needService provisioningUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionVirtual userCarrier signal
Devices, systems, and methods are disclosed which relate to provisioning a universal integrated circuit card (UICC) with multiple services. The UICC enables a wireless communication device to communicate through multiple carriers by using a unique virtual subscriber identity module (SIM) to register with each carrier. The unique virtual SIM is one of a plurality of virtual SIMs stored on and managed by the UICC. A carrier network includes a server for provisioning a new virtual SIM on a UICC over-the-air (OTA) when a new customer requests a service such as voice, data, or other type of service. These UICCs may also include logic to automatically select the best carrier for a voice call depending on the user settings.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com