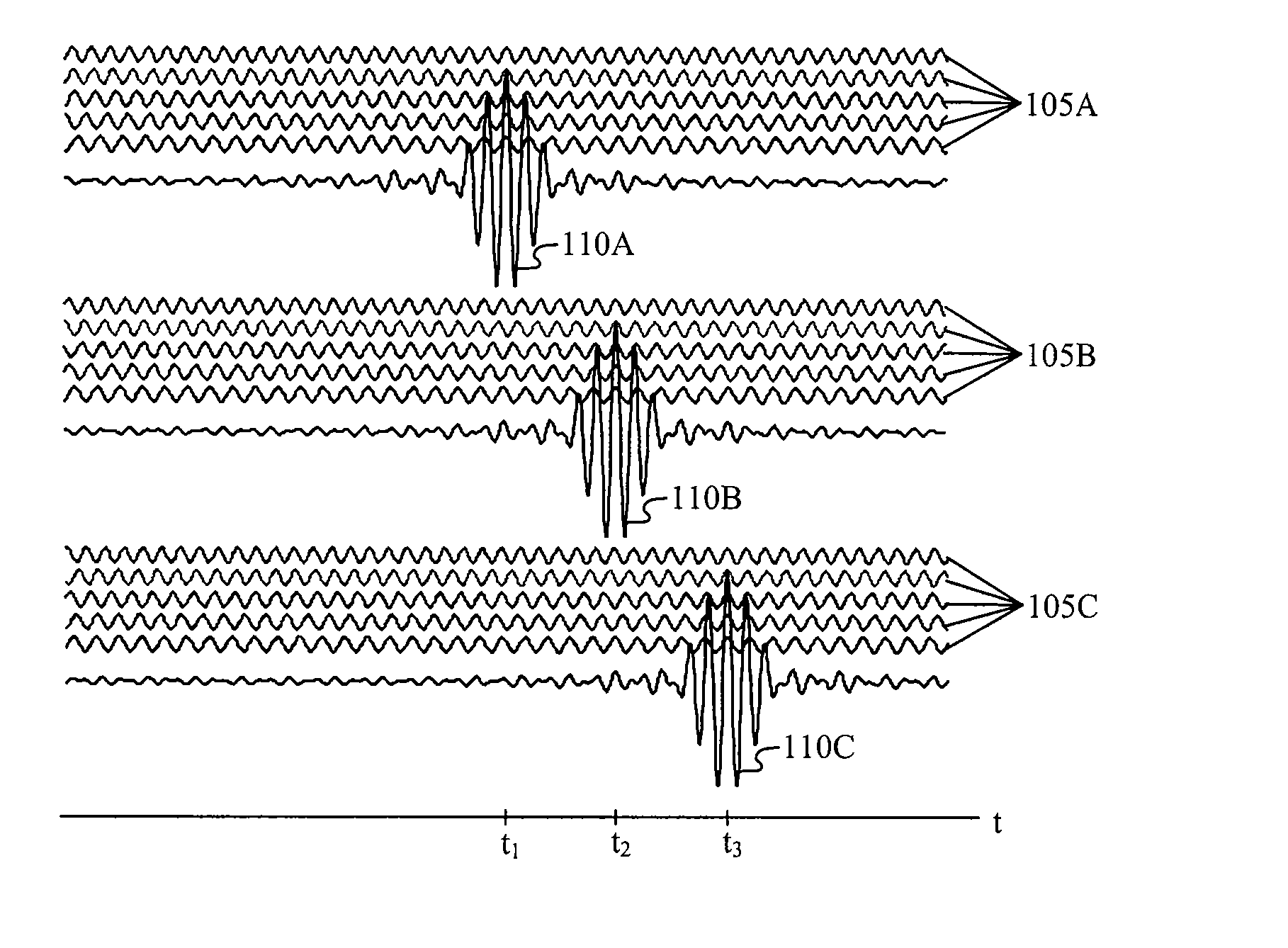
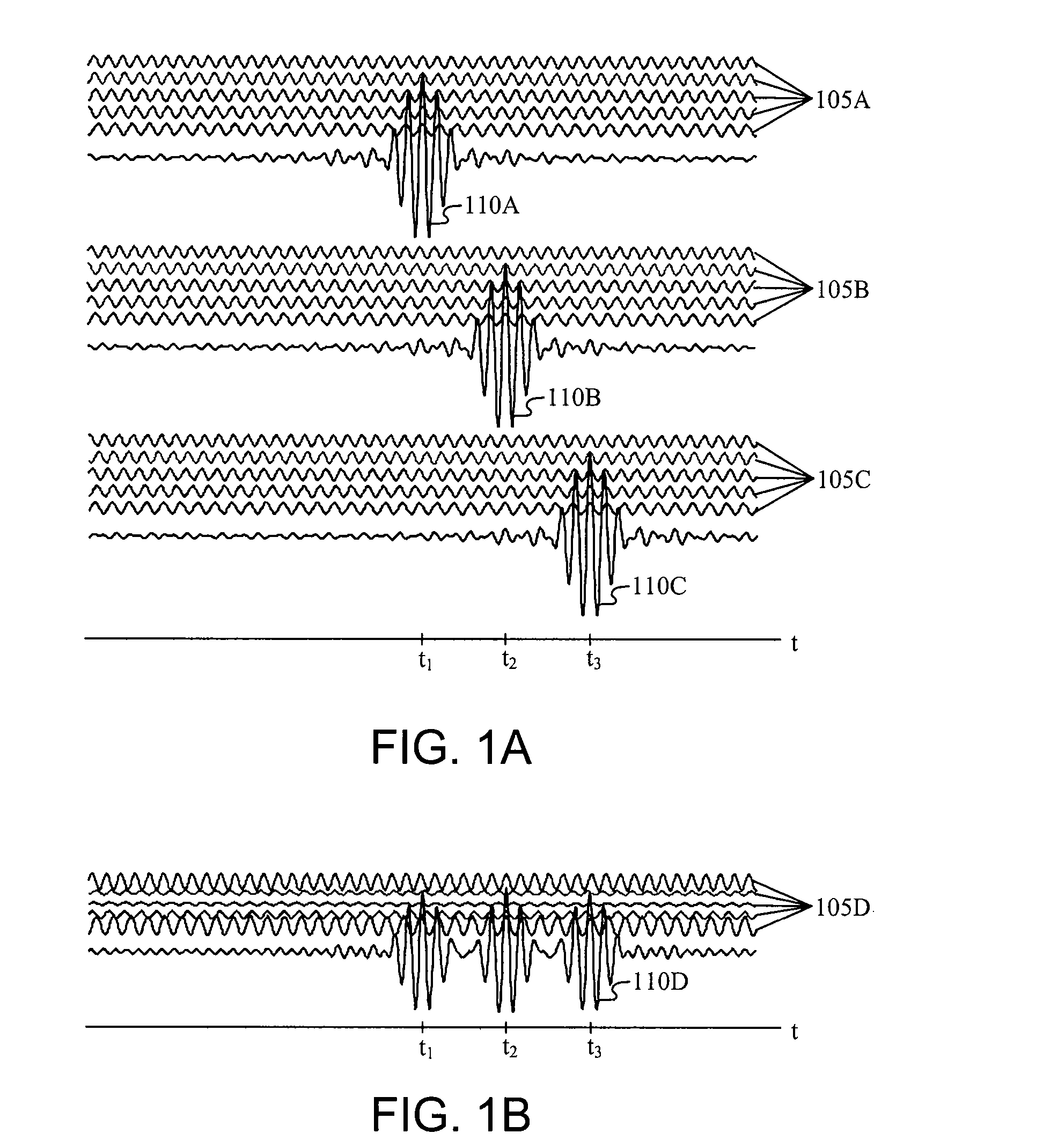
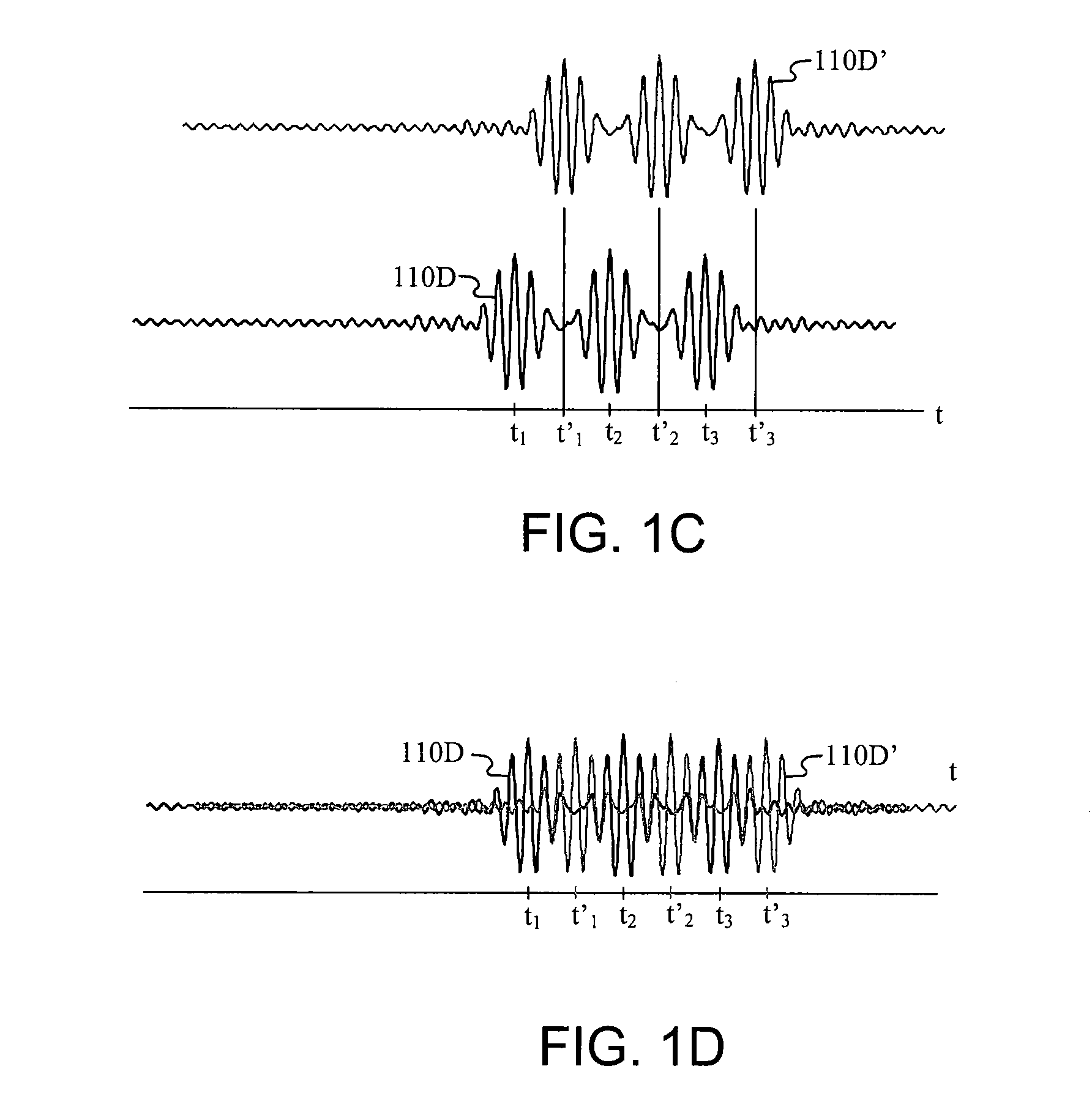
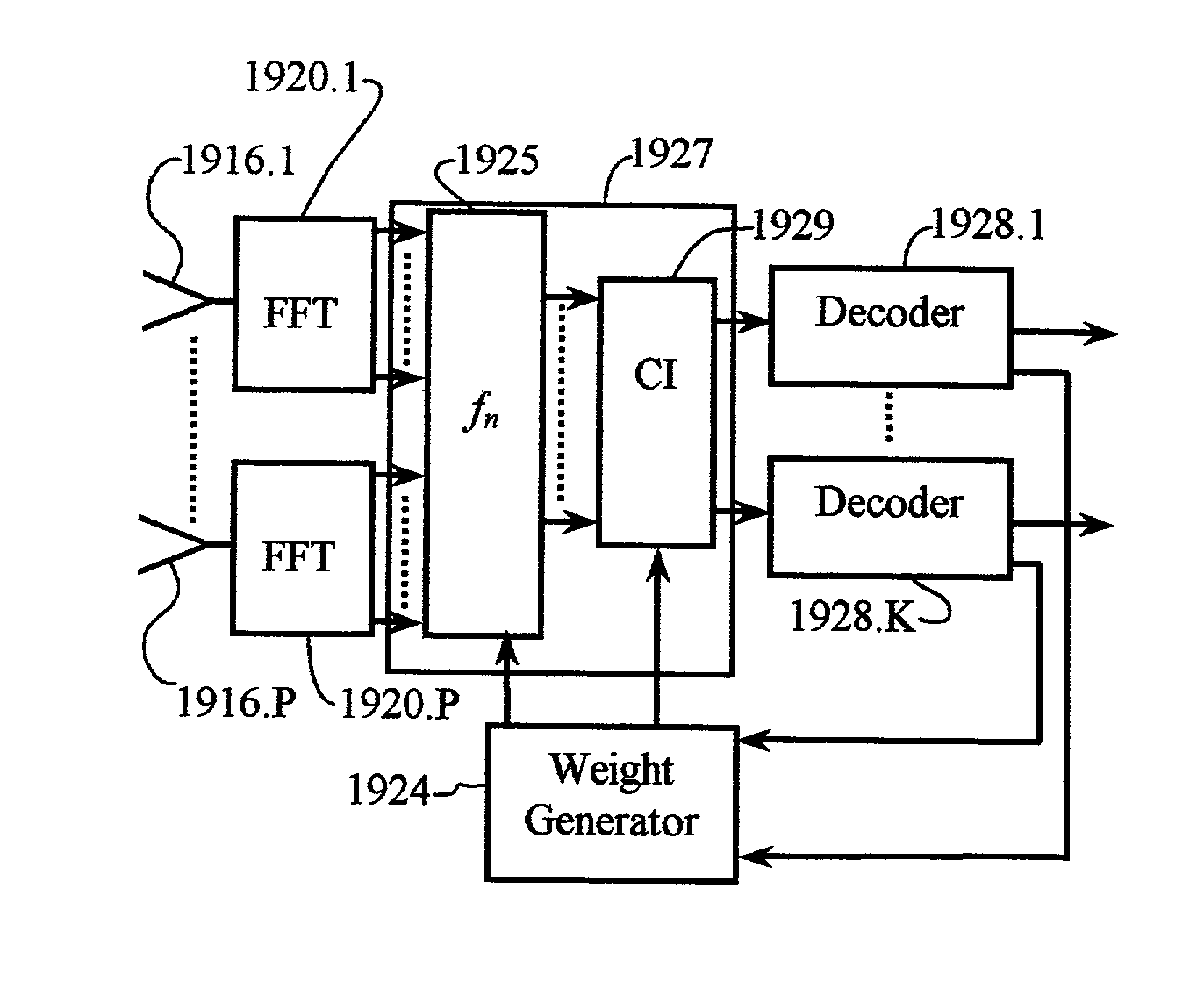
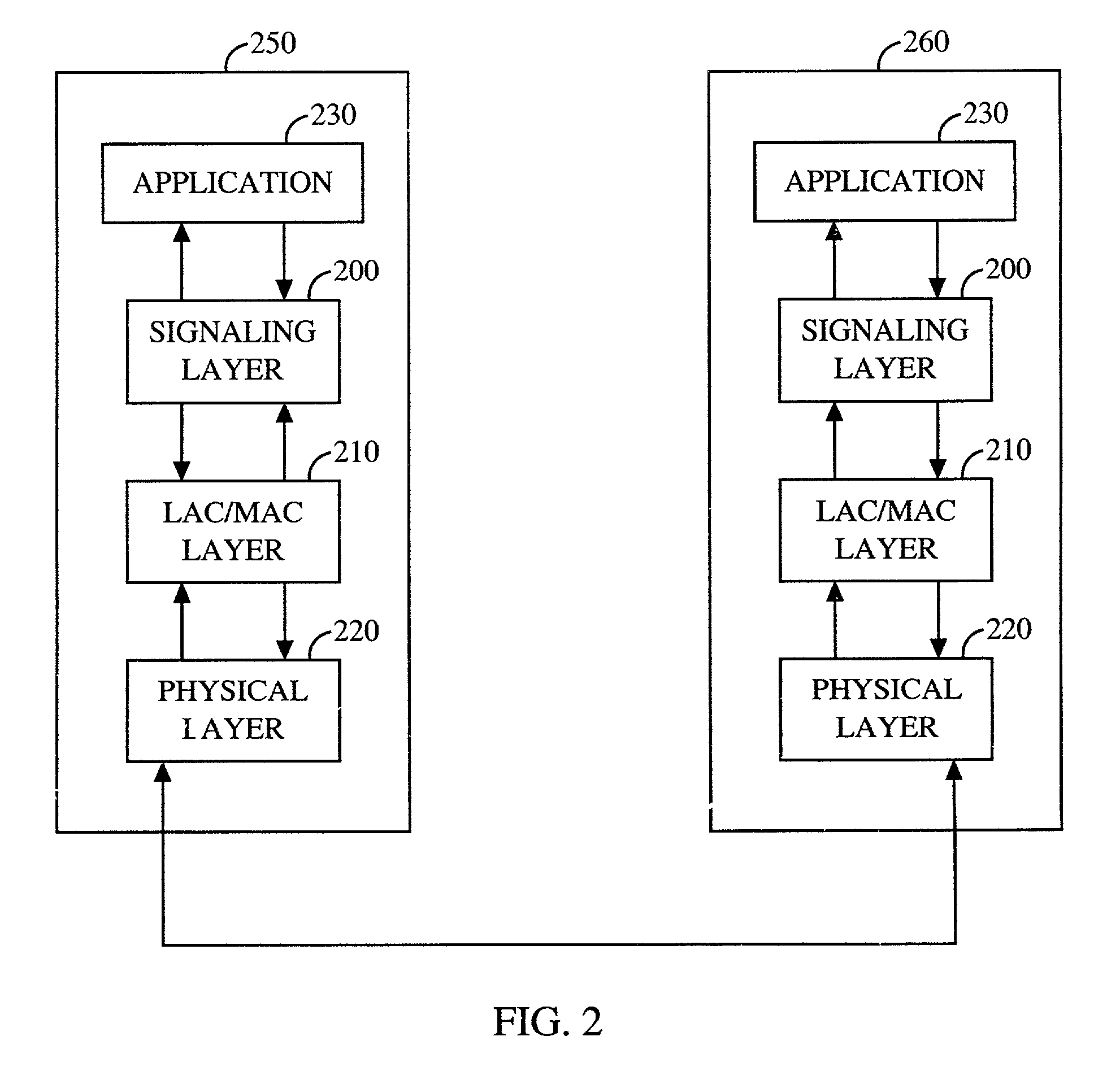
Patents
Literature
1383results about "Multiplex code generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
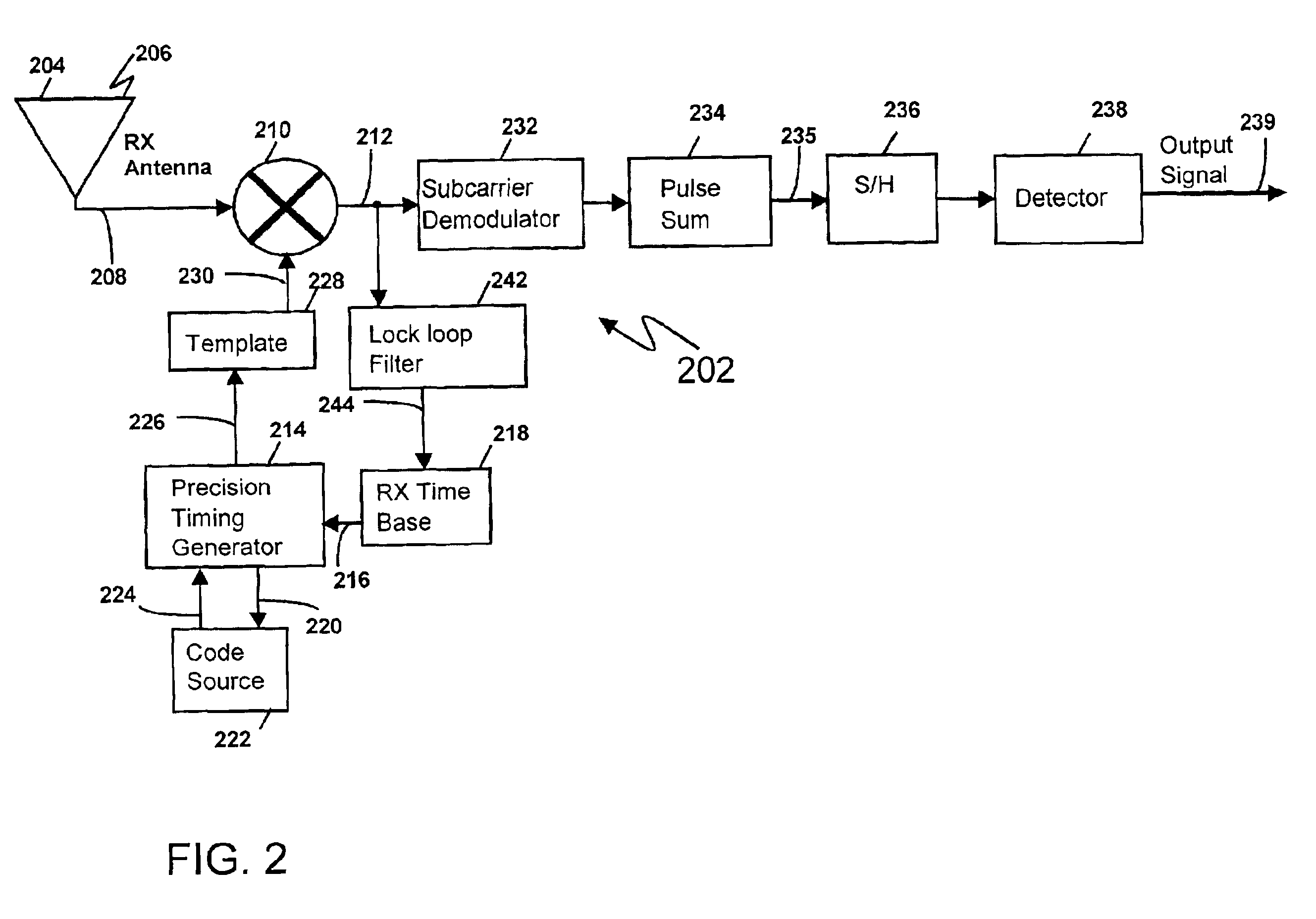
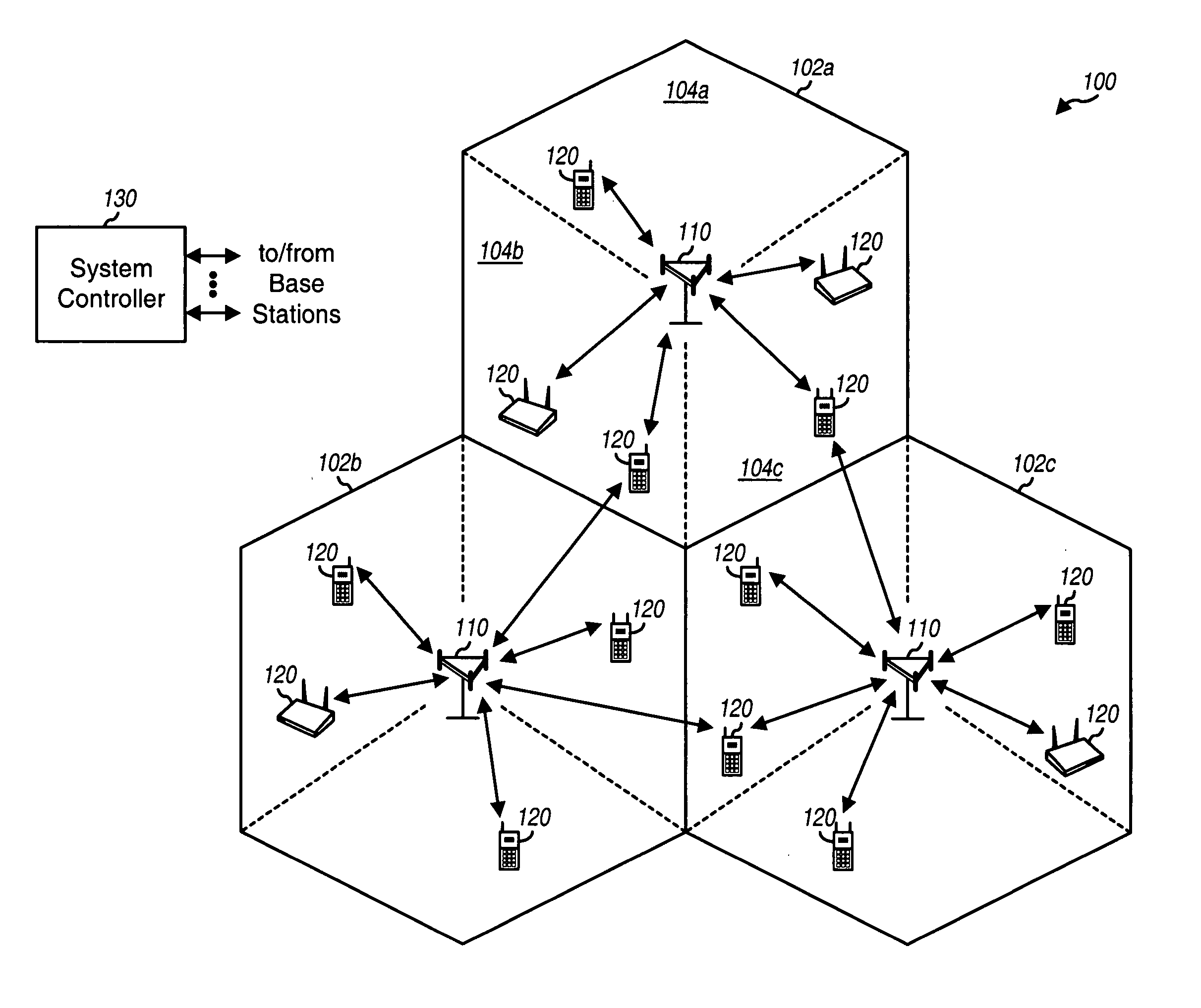
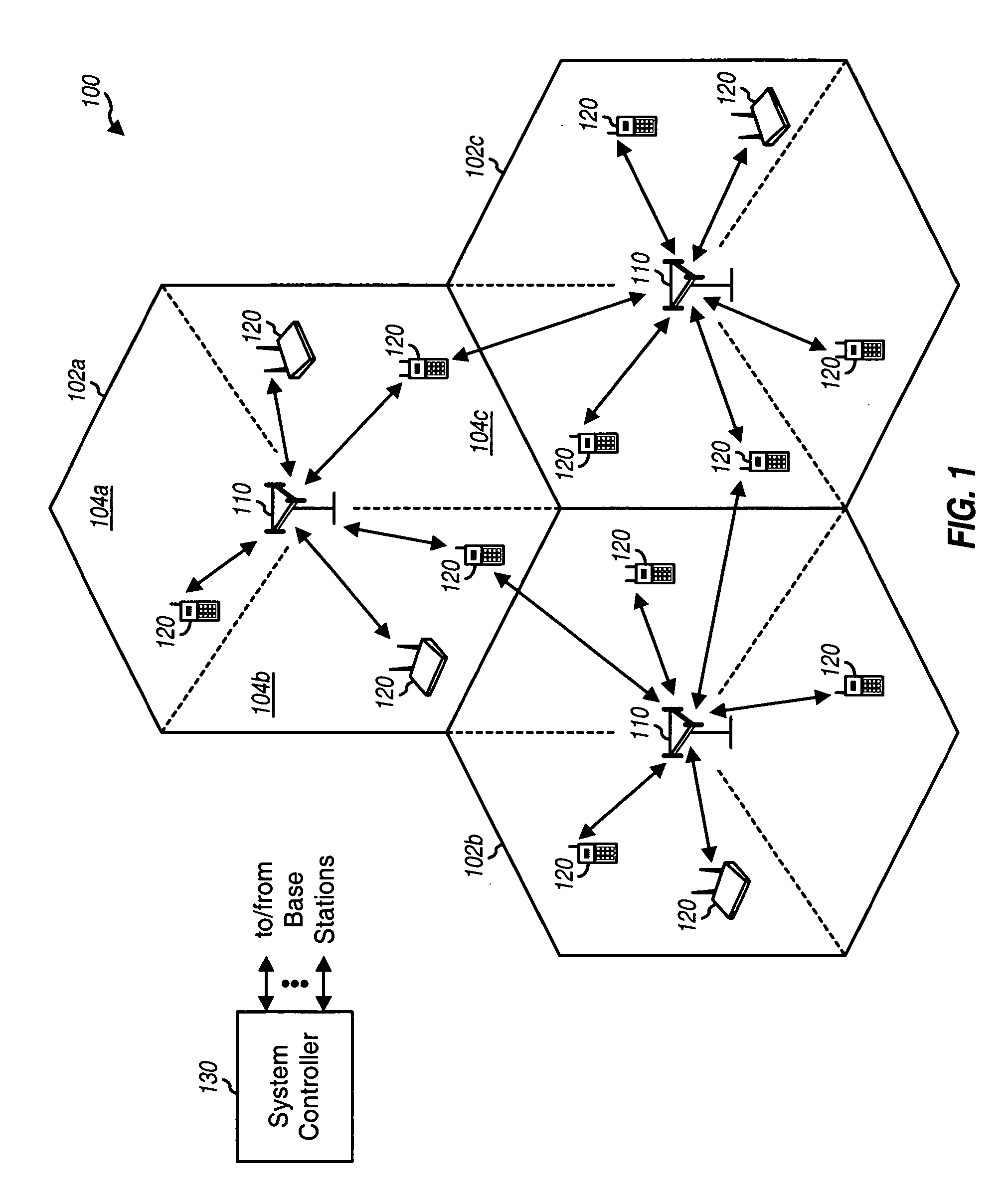
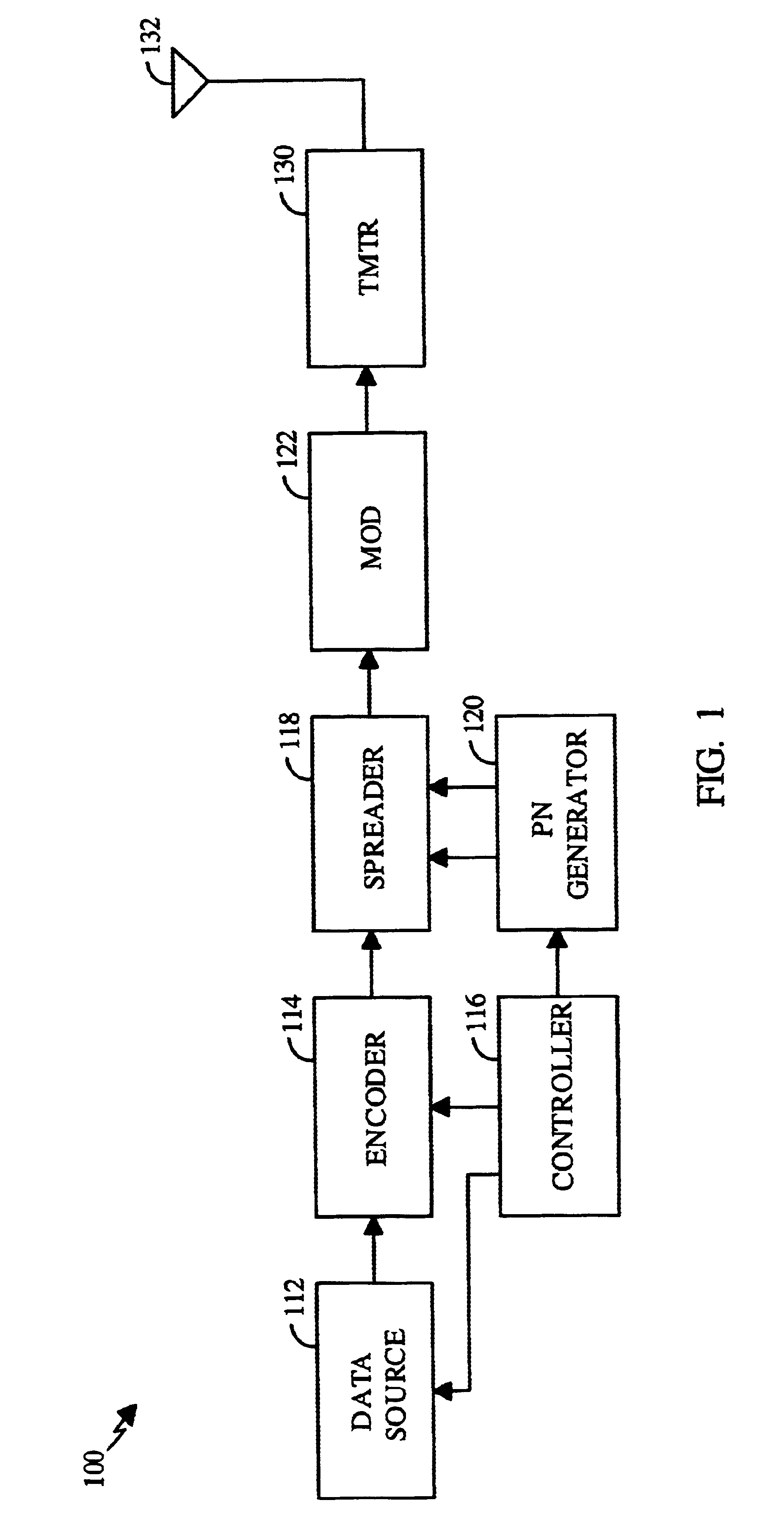
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
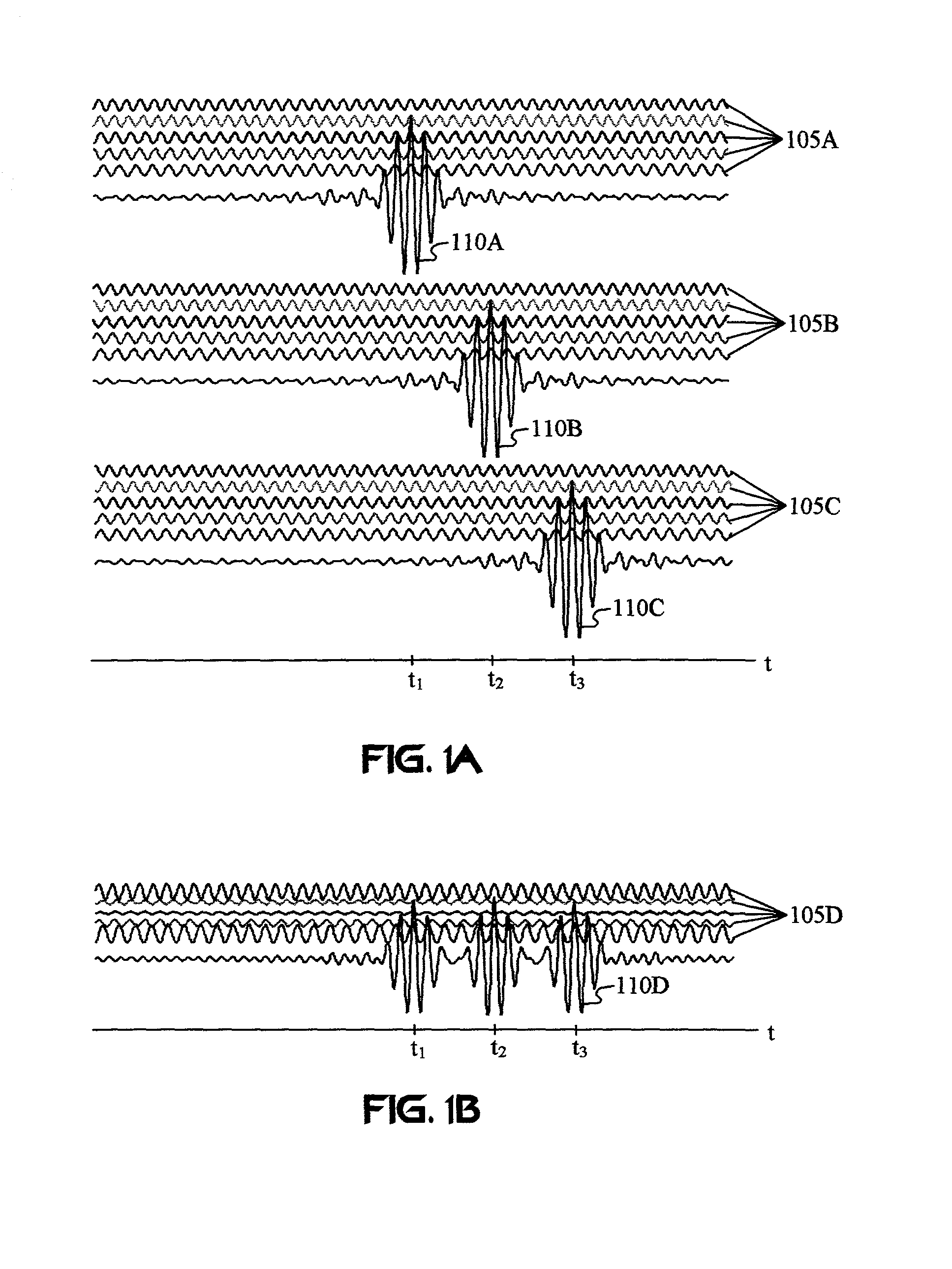
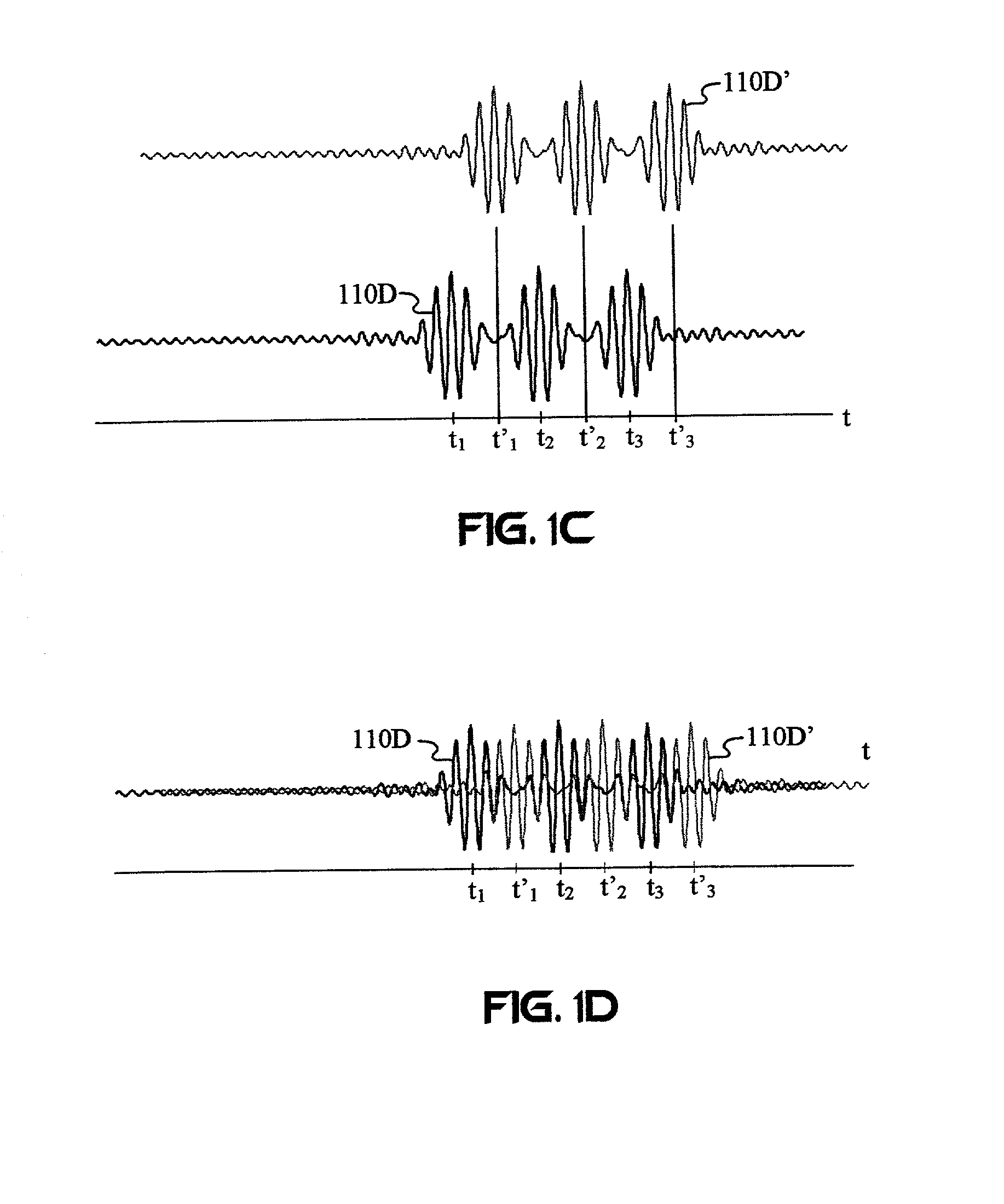
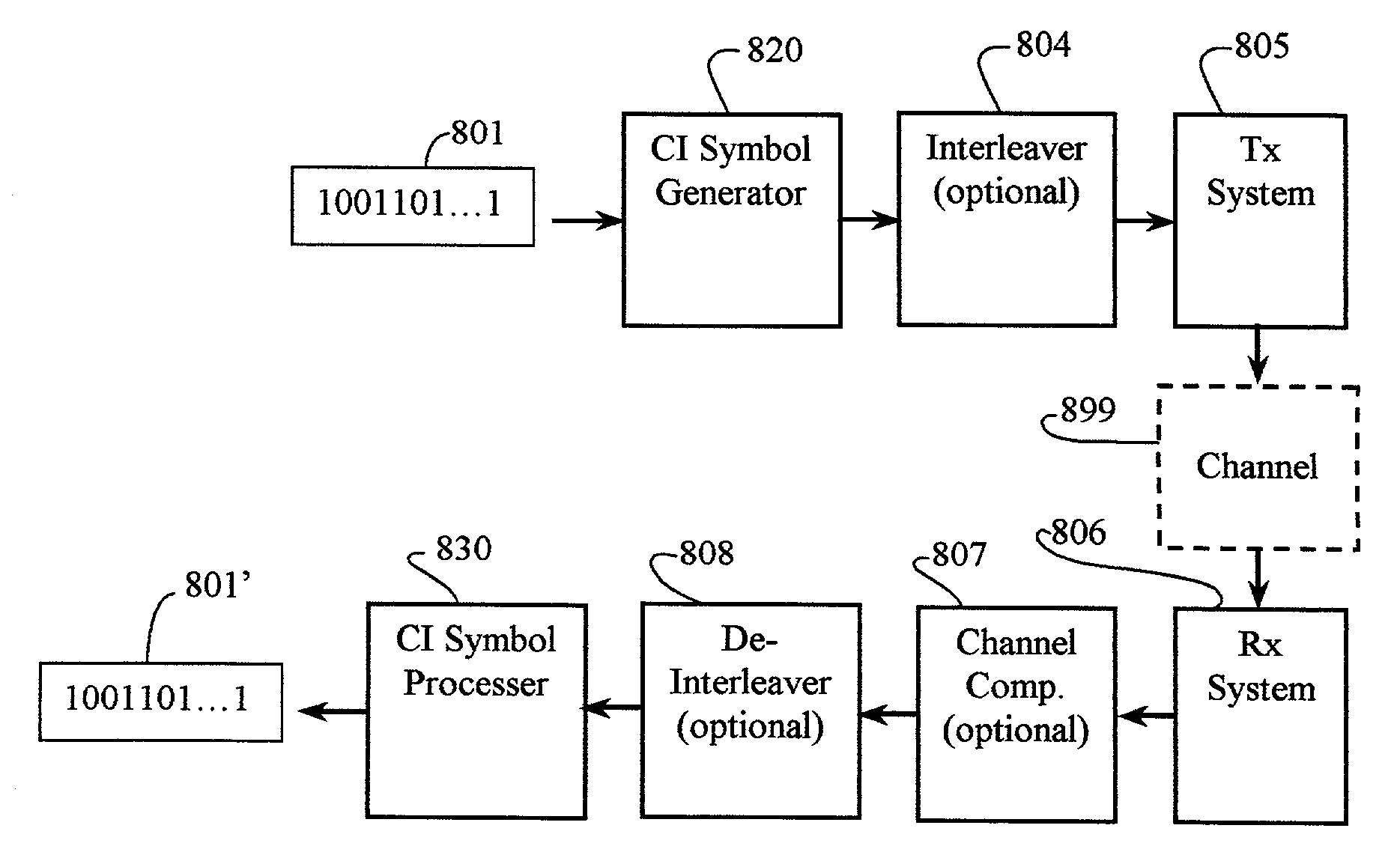
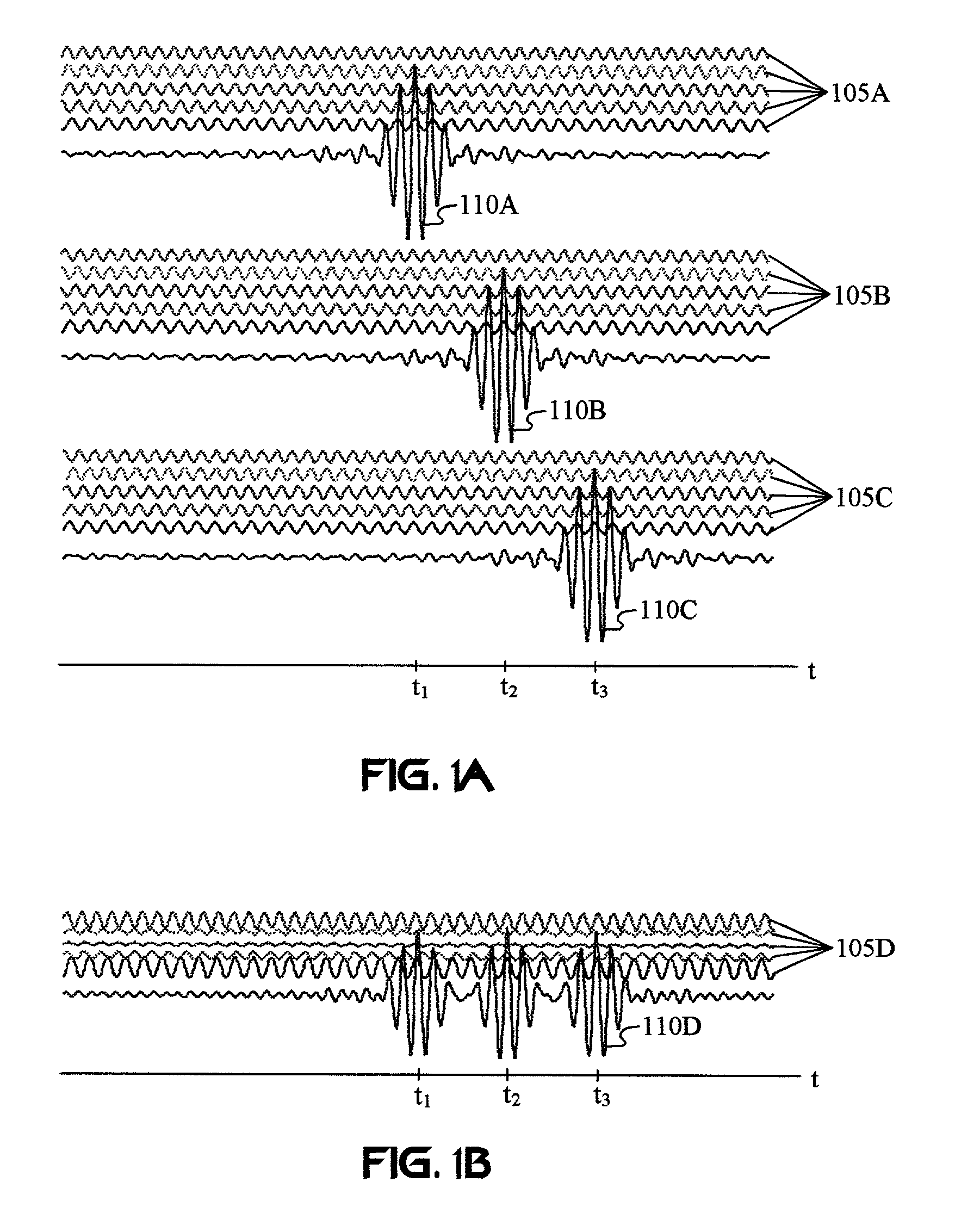
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Carrier interferometry networks
ActiveUS20080095121A1Improve throughputImprove bit error rateEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsWireless mesh networkTelecommunications link
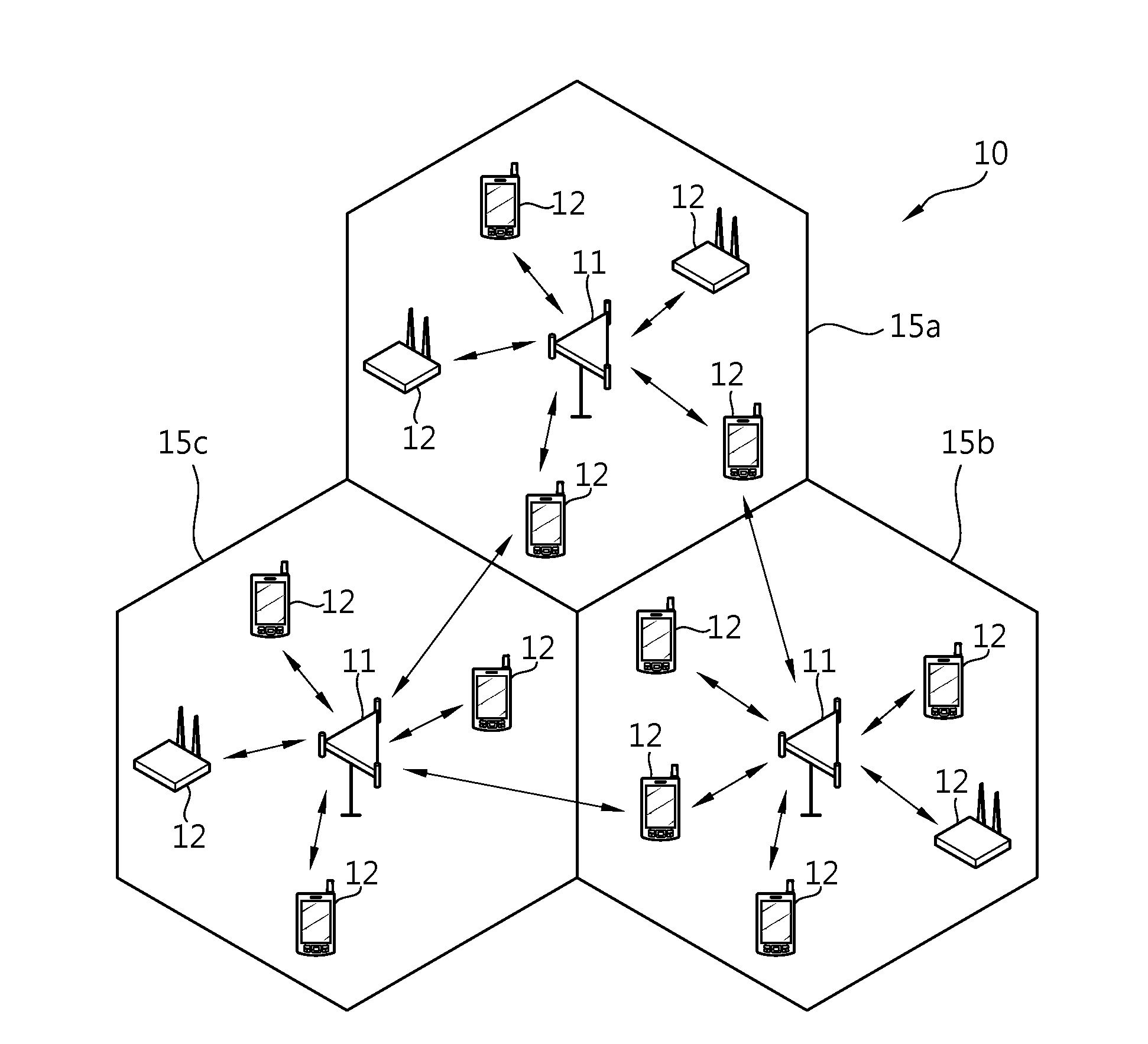
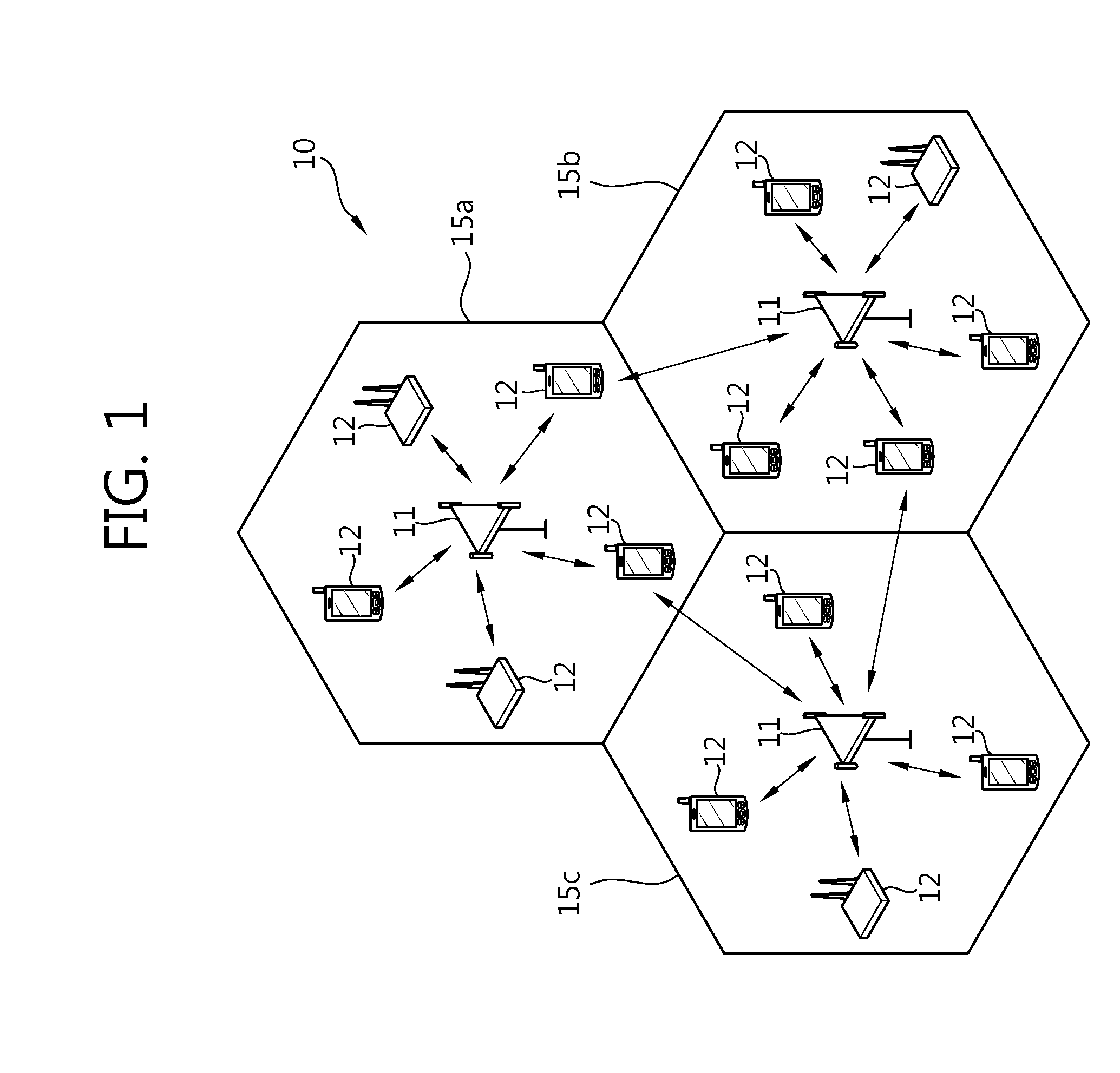
Applications of CI processing to ad-hoc and peer-to-peer networking significantly improve throughput, network capacity, range, power efficiency, and spectral efficiency. CI-based subscriber units perform network-control functions to optimize network performance relative to channel conditions, network loads, and subscriber services. CI codes are used to identify and address network transmissions. Channel characteristics of communication links are employed to encode, address, and authenticate network transmissions. CI transceivers used as relays and routers employ unique characteristics of transmission paths to code and decode network transmissions. A central processor is adapted to perform array processing with signals received from, and transmitted by, a plurality of subscriber units in a wireless network.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Array Antenna System and Spread Spectrum Beamformer Method
InactiveUS20090103593A1Simple designEasy to processMultiplex code generationRadio transmissionMultiplexingTransceiver
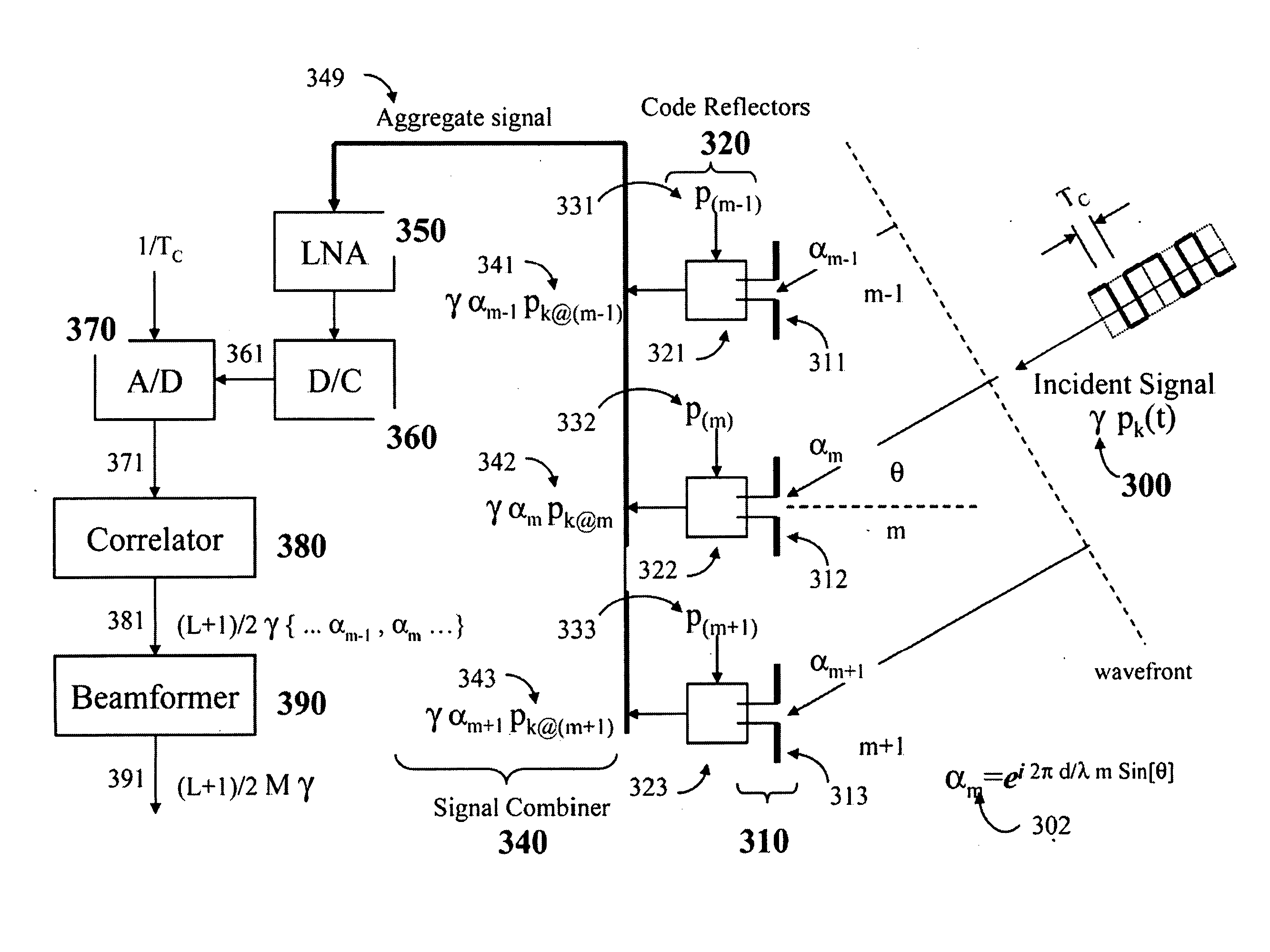
A method for transmitting digital beamformed signals in a transmit array antenna apparatus utilizing a single transceiver with one power amplifier, one up-frequency converter and one digital-to-analog converter for said array transmit antenna apparatus comprising the steps of: generating a first set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes; generating a plurality of weights, each weight being a beamforming amplitude and phase or delay for each element; generating a direct-sequence spread spectrum multiplexed signal containing such weights while using one of such first-set codes per element; converting such an multiplexed signal to a convenient radio frequency; amplifying and transmitting such a multiplexed radio frequency signal to the elements; generating a second set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes; extracting a radio frequency signal with direction-bearing weight information at each element while using a subset of codes from the second set; generating a third set of direct-sequence spread spectrum codes at each element; transmitting a signal with array gain beamformed towards a specific direction while using a transmit array apparatus composed of spaced elements, such a transmit beamformed signal being a radio frequency signal, a direct-sequence spread spectrum radio frequency signal containing a subset of codes from the third set, or a sequence of radio frequency pulses that have short duration and high power.
Owner:APPLIED RADAR
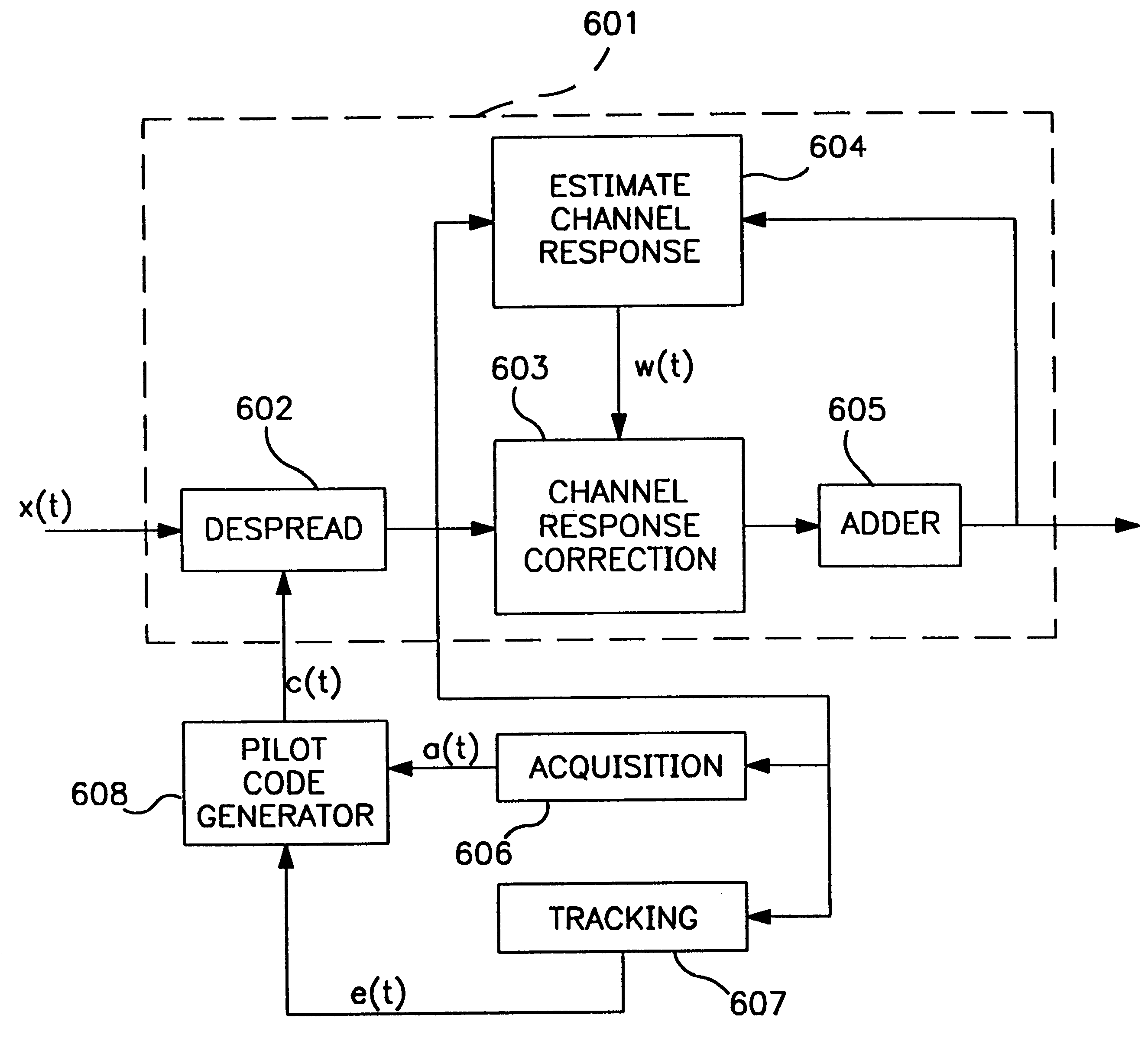
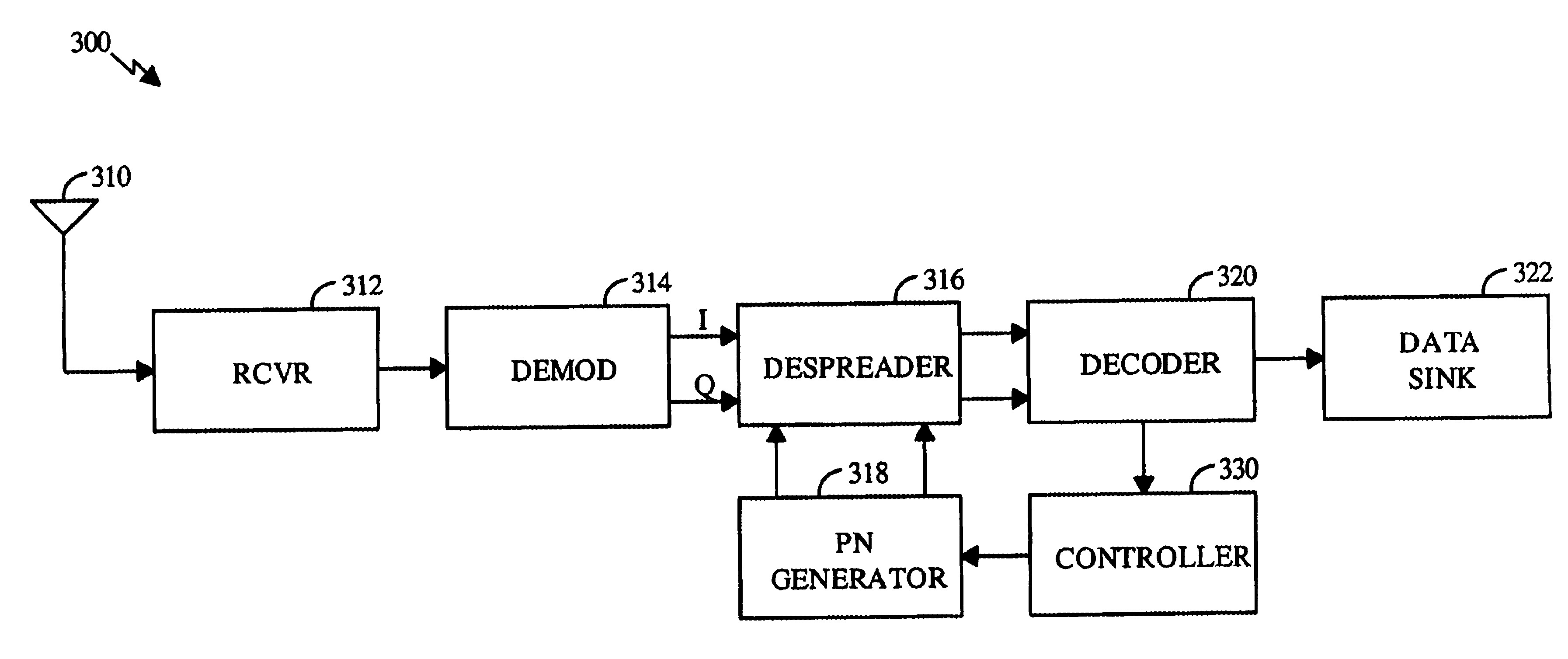
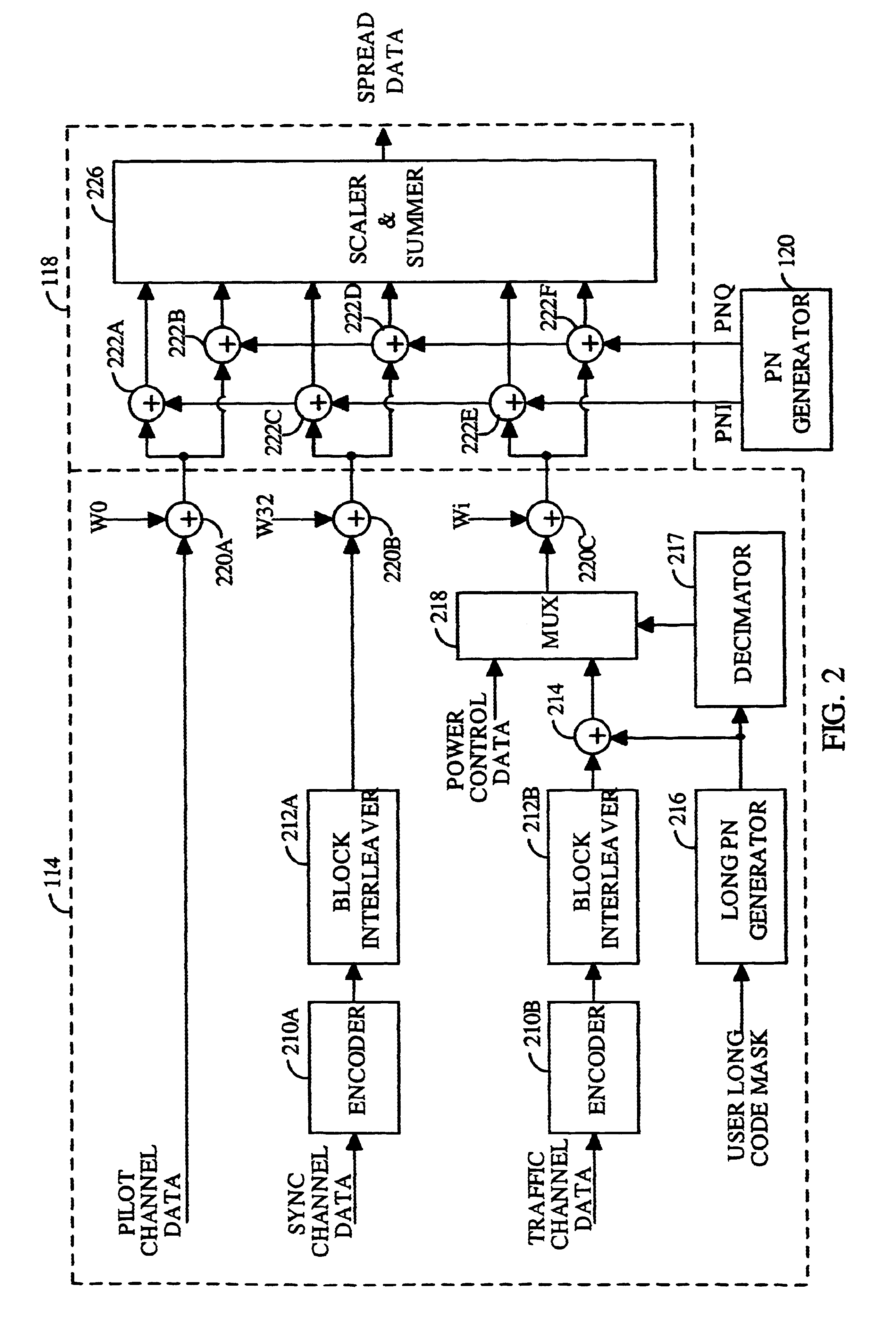
Code sequence generator in a CDMA modem
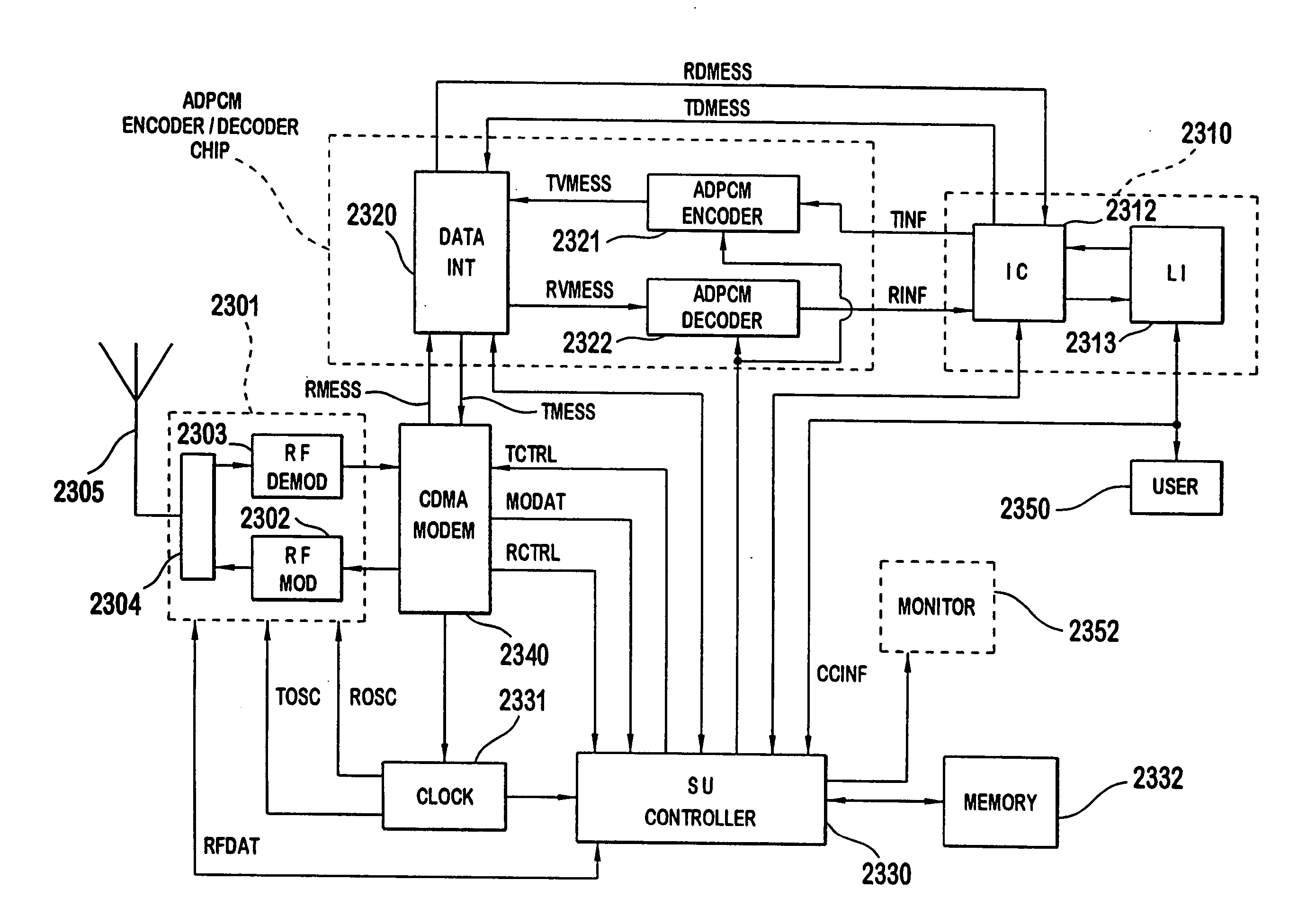
A CDMA modem includes a modem transmitter having: a code generator which provides an associated pilot code signal and which generates a plurality of message code signals: a spreading circuit which produces a spread-spectrum message signal by combining each of the information signals with a respective one of the message code signals; and a global pilot code generator that provides a global pilot code signal to which the message code signals are synchronized. The CDMA modem also includes a modem receiver having an associated pilot code generator and a group of associated pilot code correlators for correlating code-phase delayed versions of the associated pilot signal with a receive CDM signal to produce a despread associated pilot signal. The code phase of the associated pilot signal is changed responsive to an acquisition signal value until a pilot signal is received. The associated pilot code tracking logic adjusts the associated pilot code signal in phase responsive to the acquisition signal so that the signal power level of the despread associated pilot code signal is maximized. Finally, the CDMA modem receiver includes a group of message signal acquisition circuits, each including a plurality of receive message signal correlators which correlate respective local received message code signal to the CDM signal to produce a respective despread received message signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
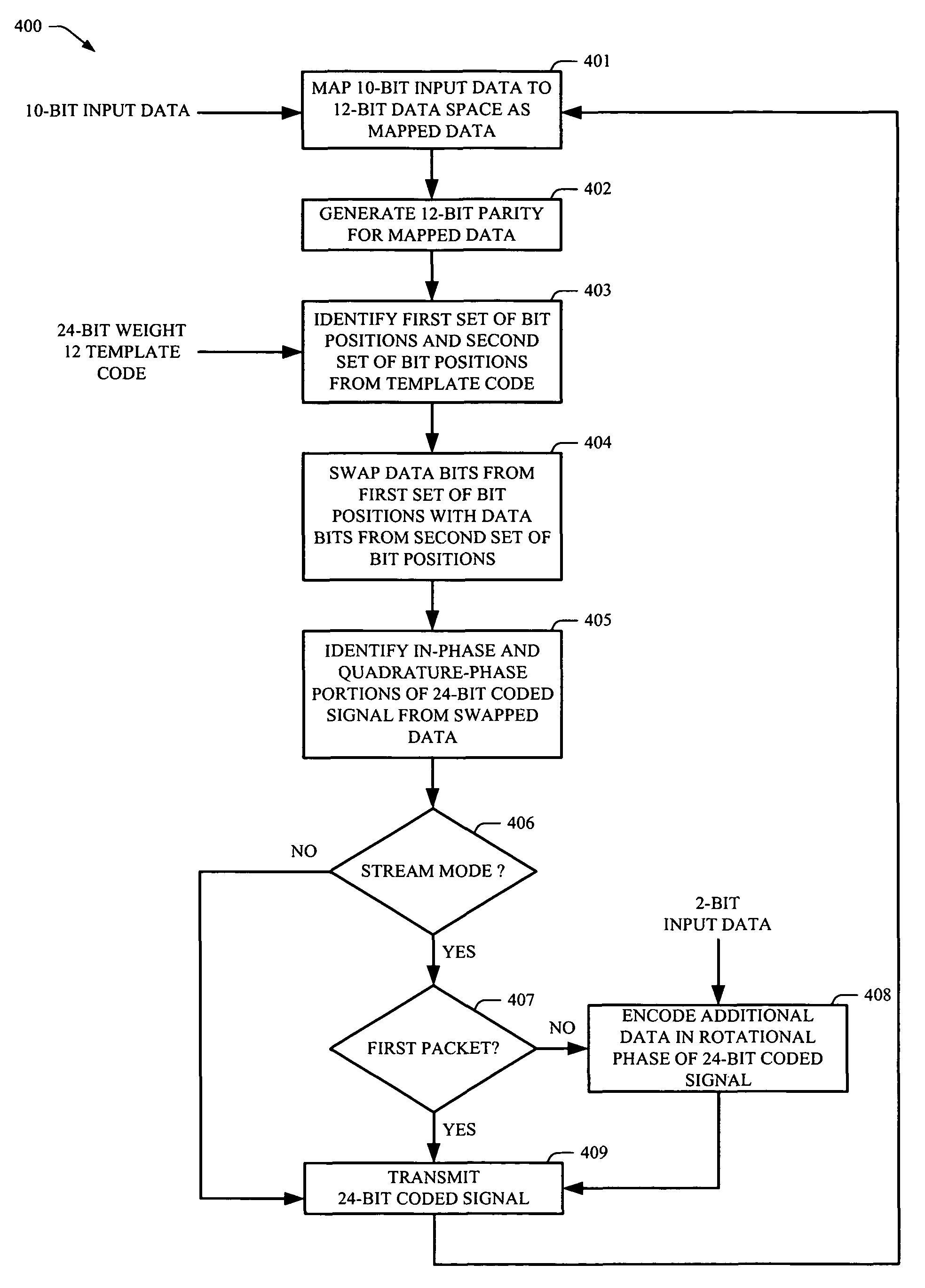
Rotationally invariant non-coherent burst coding
ActiveUS7779332B2Error correction/detection using block single space codingError preventionBit field24-bit
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
System and method for variable rate multiple access short message communications
ActiveUS20050259723A1Increase size of messageEasy to useModulated-carrier systemsMultiplex code generationComputer hardwareCommunications system
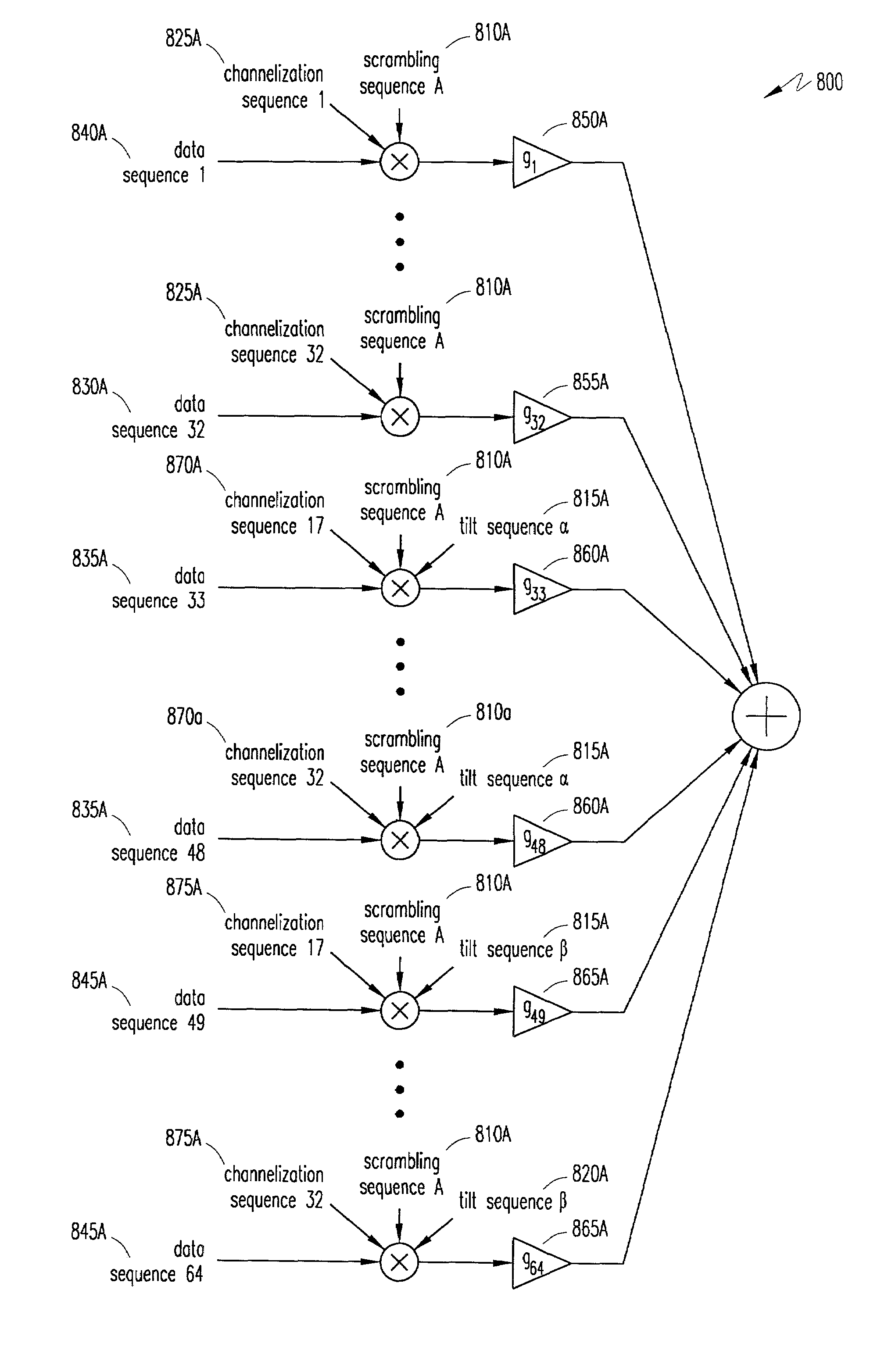
A communication system and receiver is provided that facilitates increased message size in a communication system that supports a large number of transmitters sharing a common frequency band. The communication system facilitates increased message size by incorporating a plurality of transmit bit sets in each burst of data. The additional transmit bit sets are incorporated into a plurality of transmit codes that are generated using at least one additional spreading code that is orthogonal to the base spreading code. The plurality of transmit codes are then combined into one composite message and the composite message is spread again using another scrambling sequence. The final composite spread message is transmitted to the receiver in the appropriate message time slot, resulting in CDM / TDMA burst signal that facilitates increased message size.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
System for using rapid acquisition spreading codes for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS20050265430A1Increase profitEnergy efficient ICTRadio transmission for post communicationCode division multiple accessCarrier signal
A system for rapidly acquiring a spreading code, used in a code division multiple access (CDMA) system, comprises a generator for generating a first long code and a second long code, with each long code having a length of N chips. The first long code is different from the second long code. A transmitter transmits the first long code and the second long code at a first phase angle and at a second phase angle, respectively, on a carrier signal over a communications channel using radio waves. The first long code and the second long code may be transmitted at an in-phase (I) angle and at a quadrature-phase (Q) angle, respectively, on the carrier signal. From the communications channel, an I acquisition circuit and a Q acquisition circuit may acquire, in parallel, the first long code and the second long code from the I angle and the Q angle, respectively, of the carrier signal by searching, in parallel, N / 2 chips of the first long code and the second long code.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
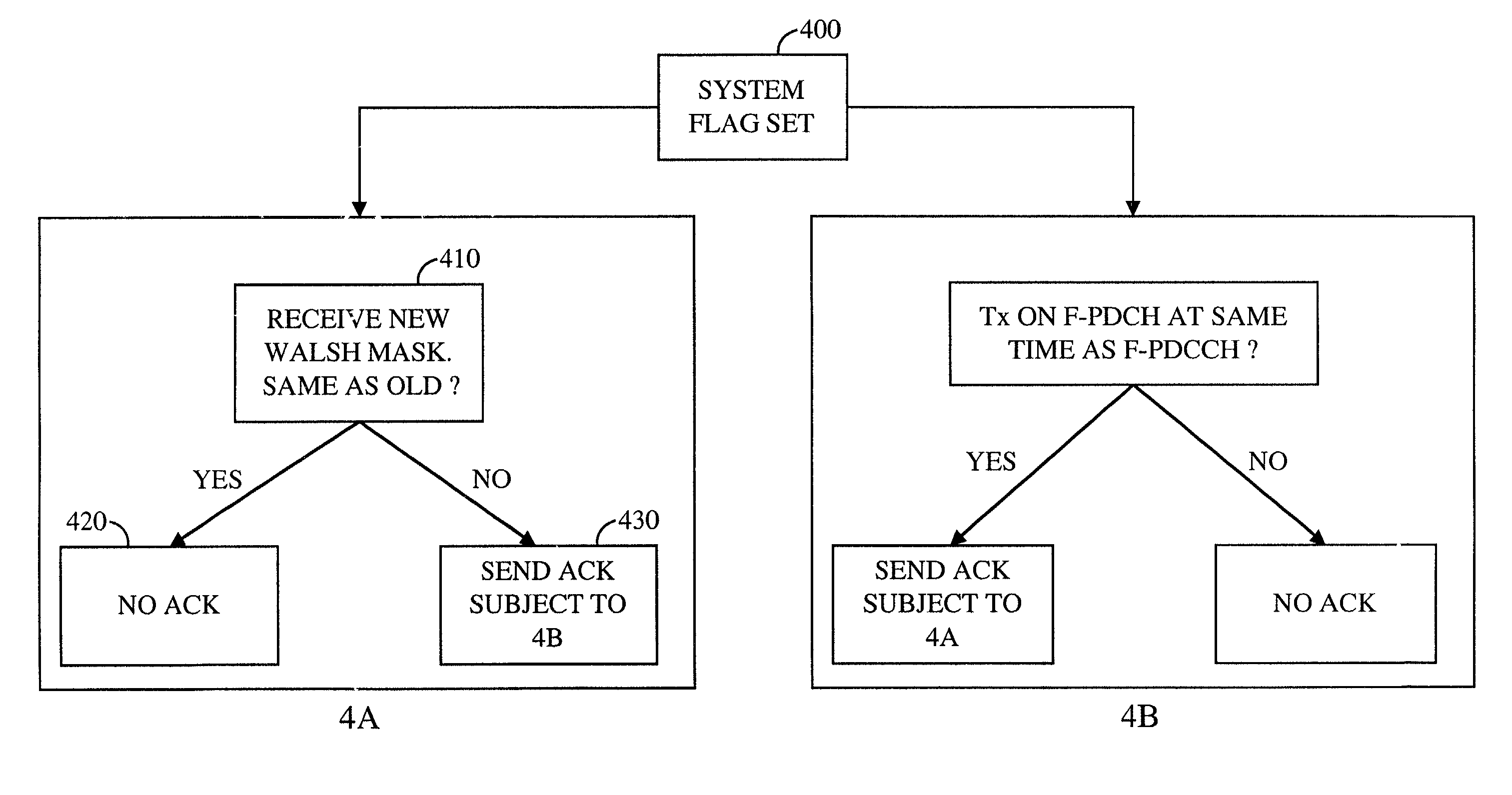
Method of transmitting control signal in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090290538A1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove system performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemResource block
A method of transmitting a control signal in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes acquiring a resource index, the number of cyclic shifts (CSs) and a CS interval, wherein the number of CSs is an integer multiple of the CS interval, determining a CS index based on the number of CSs and the CS interval, generating a cyclically shifted sequence by cyclically shifting a base sequence by a CS amount obtained from the CS index, generating a modulated sequence based on the cyclically shifted sequence and a symbol for a control signal and transmitting the modulated sequence after mapping the modulated sequence to a resource block obtained from the resource index.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
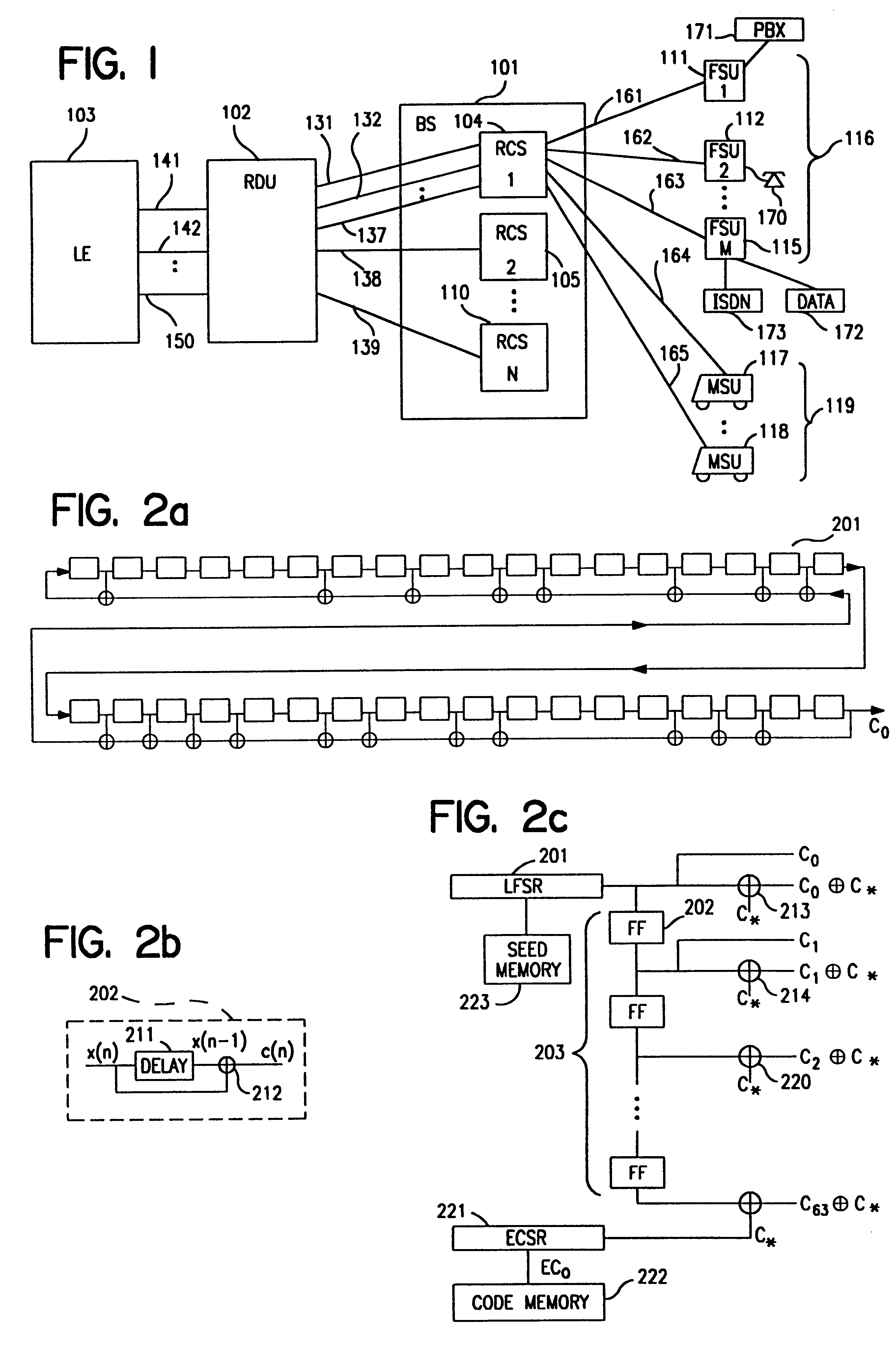
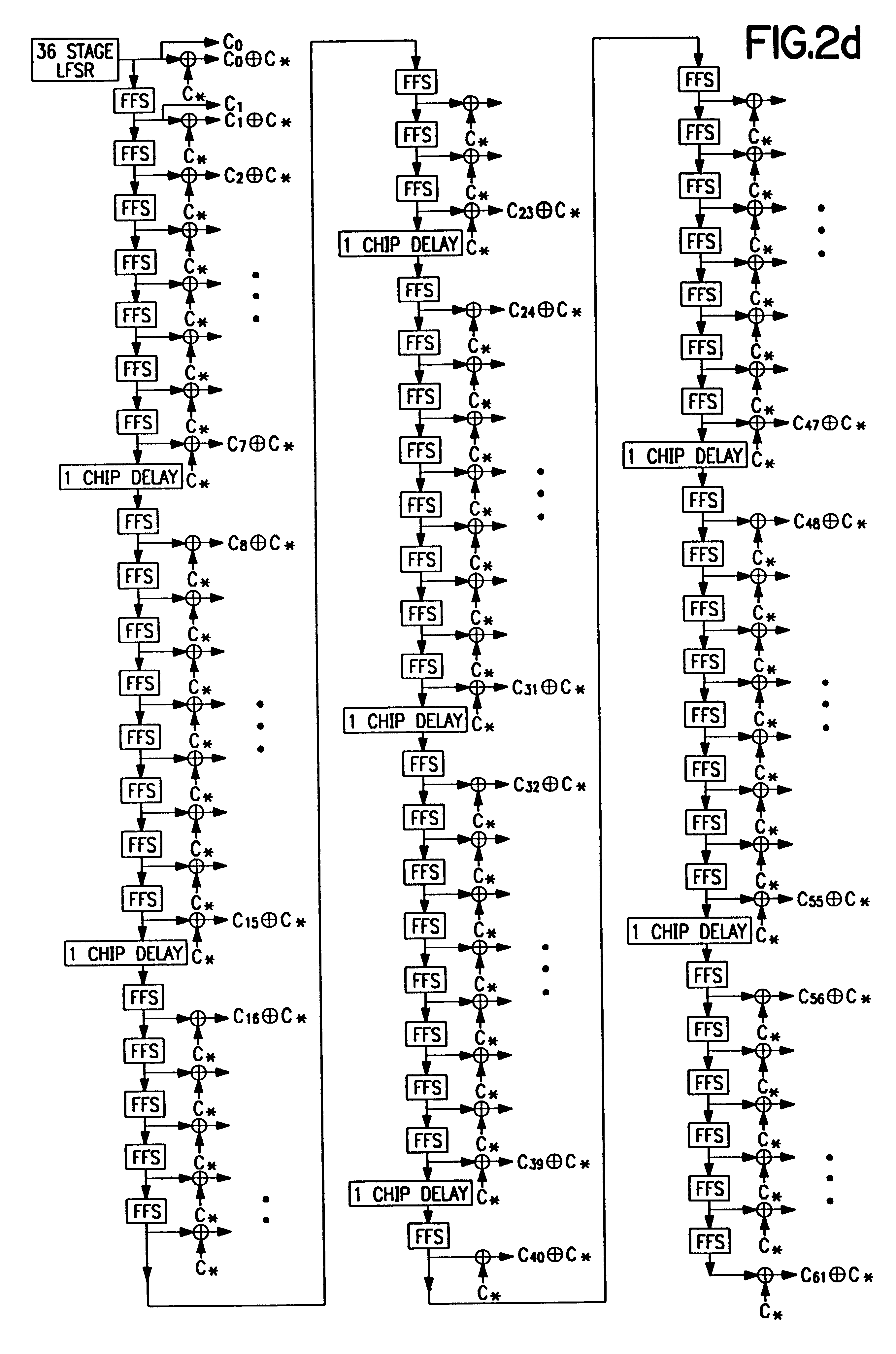
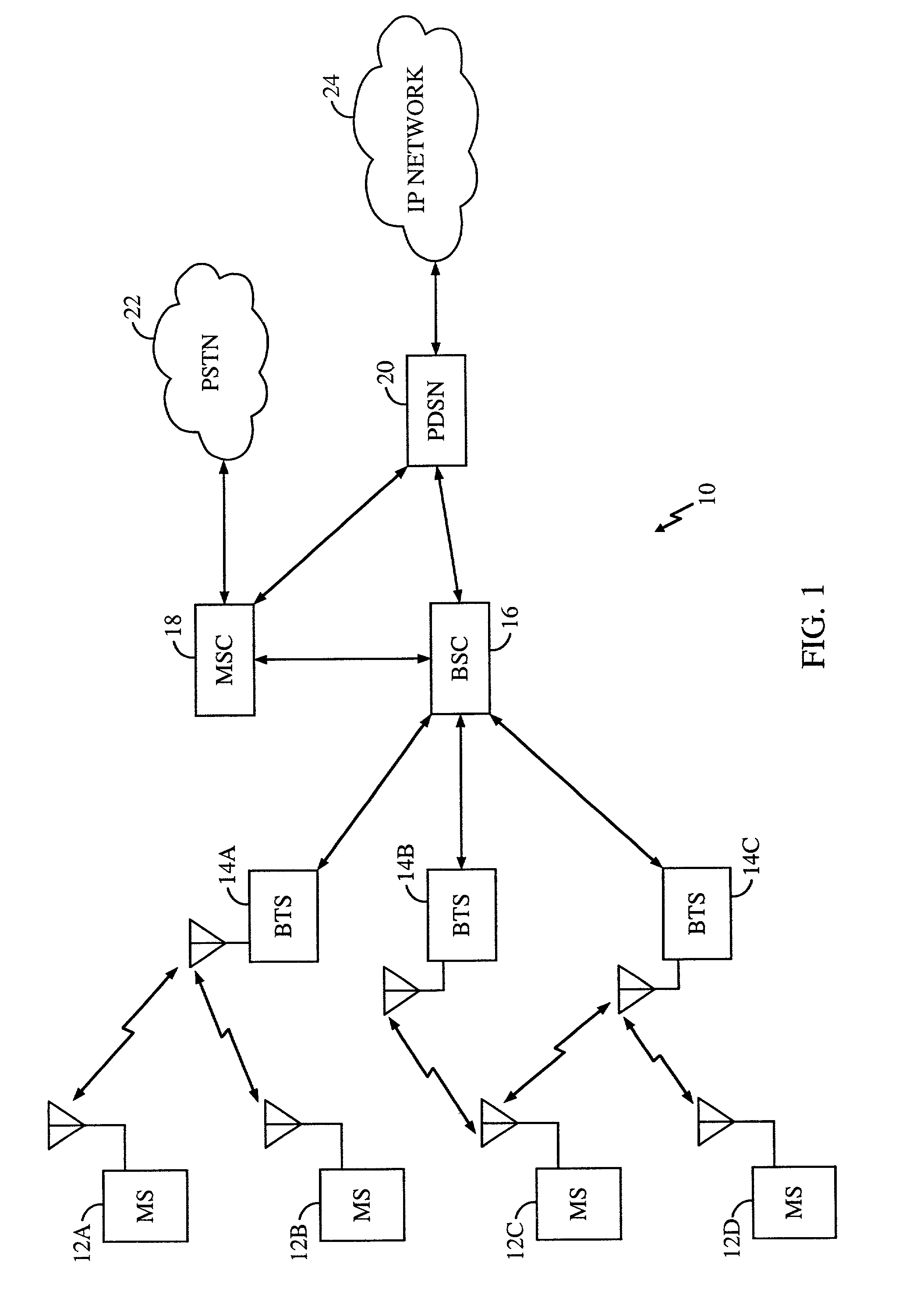
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
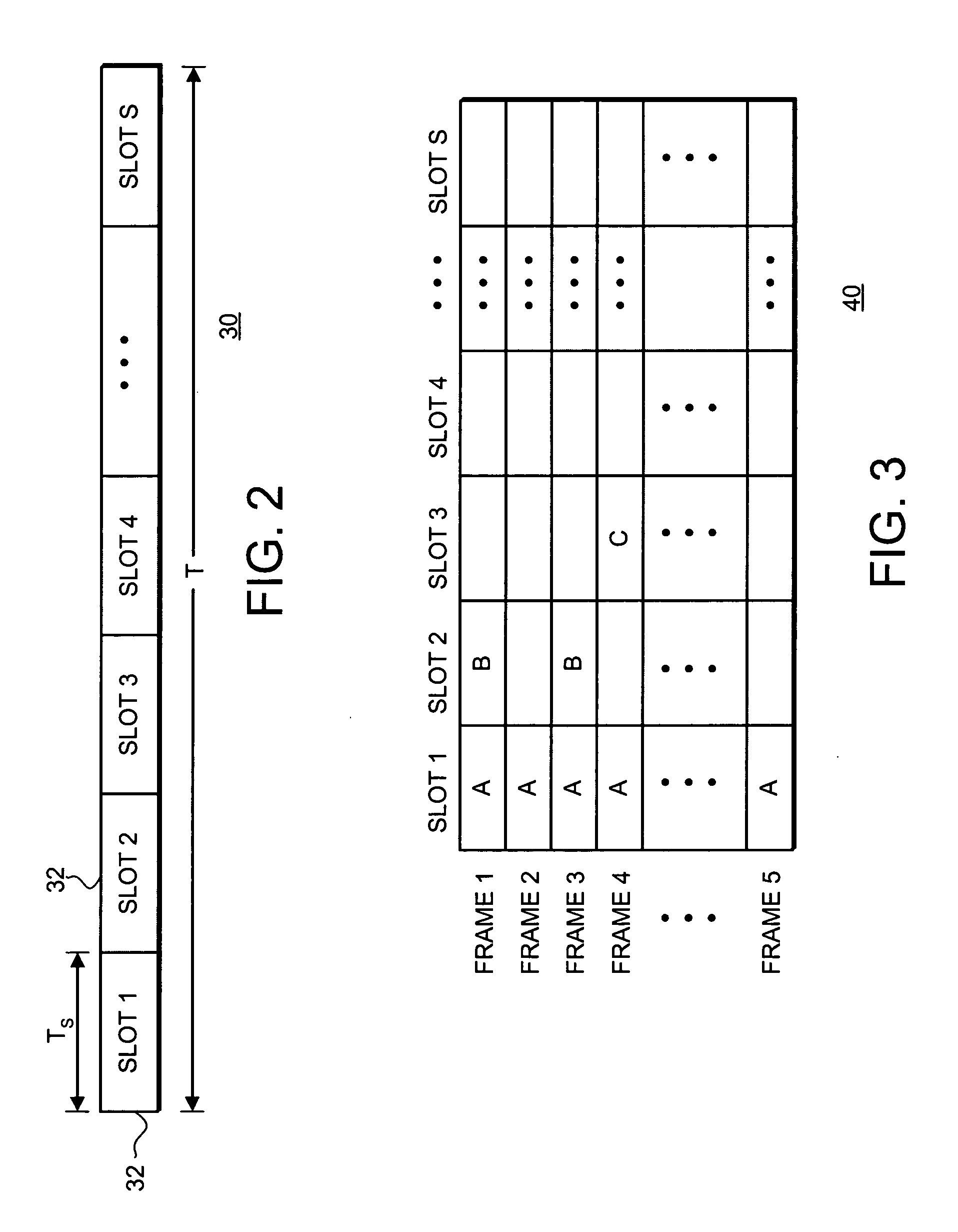
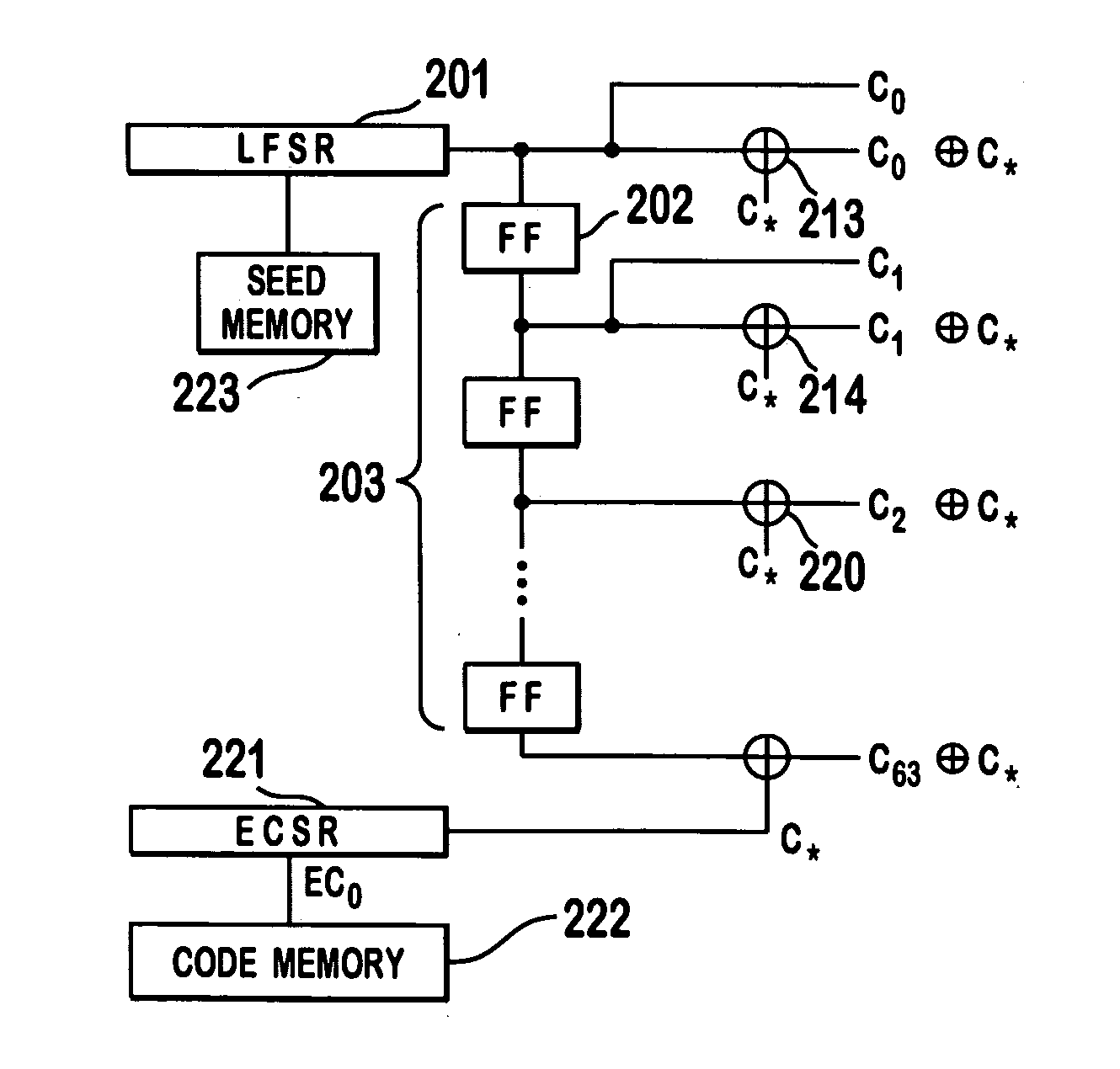
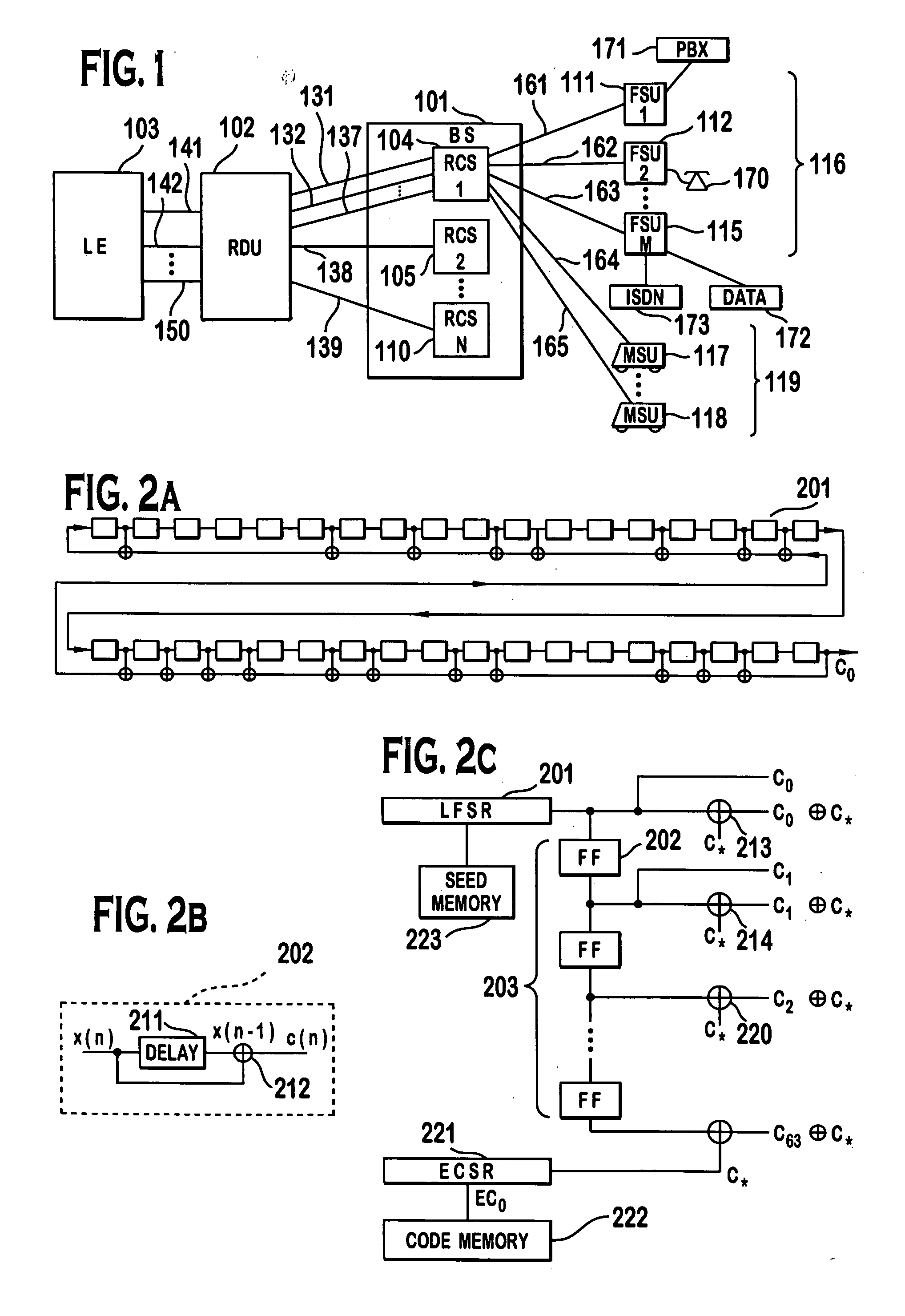
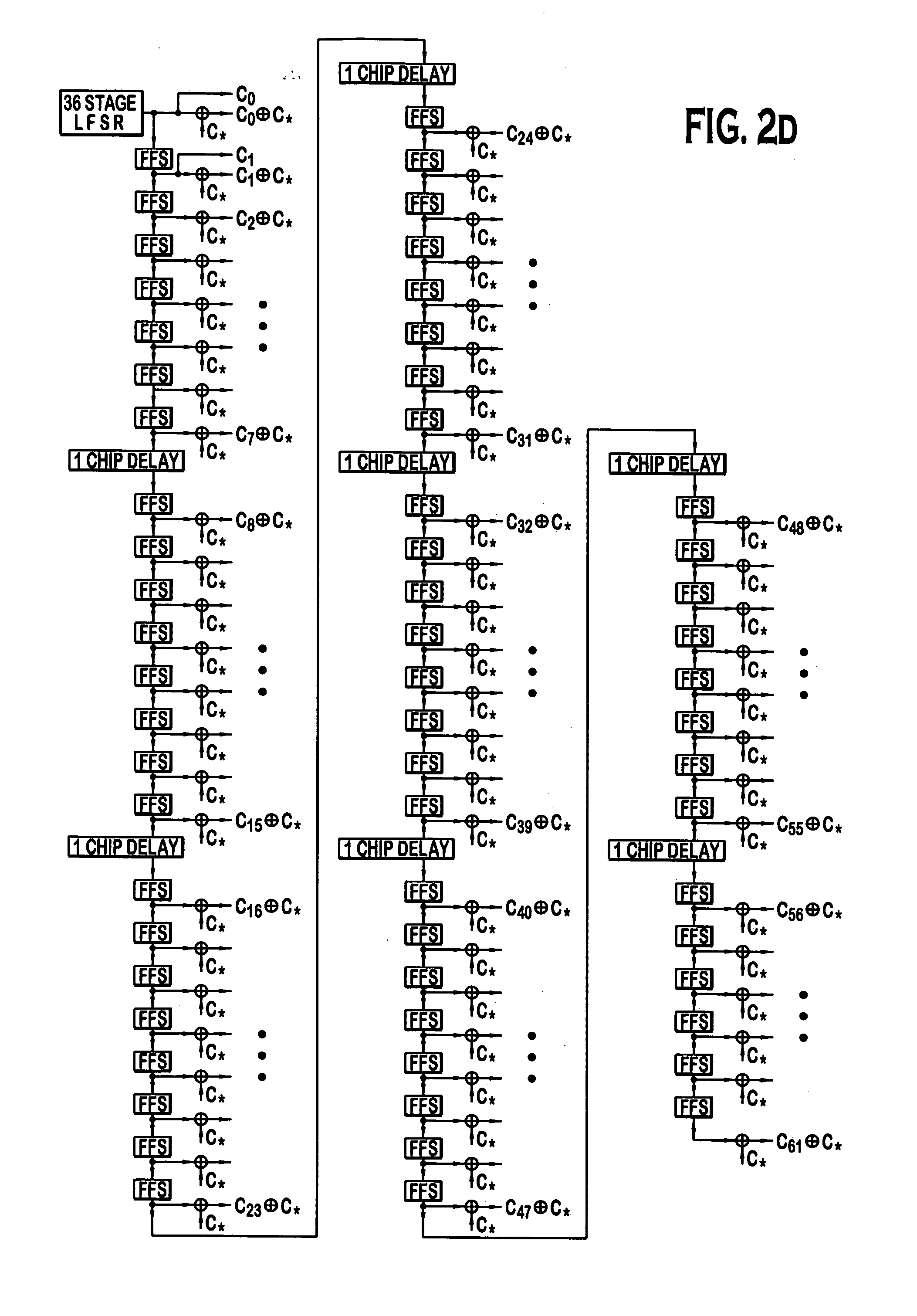
InactiveUS6885652B1Increase profitPower managementBaseband system detailsModem deviceSystem capacity
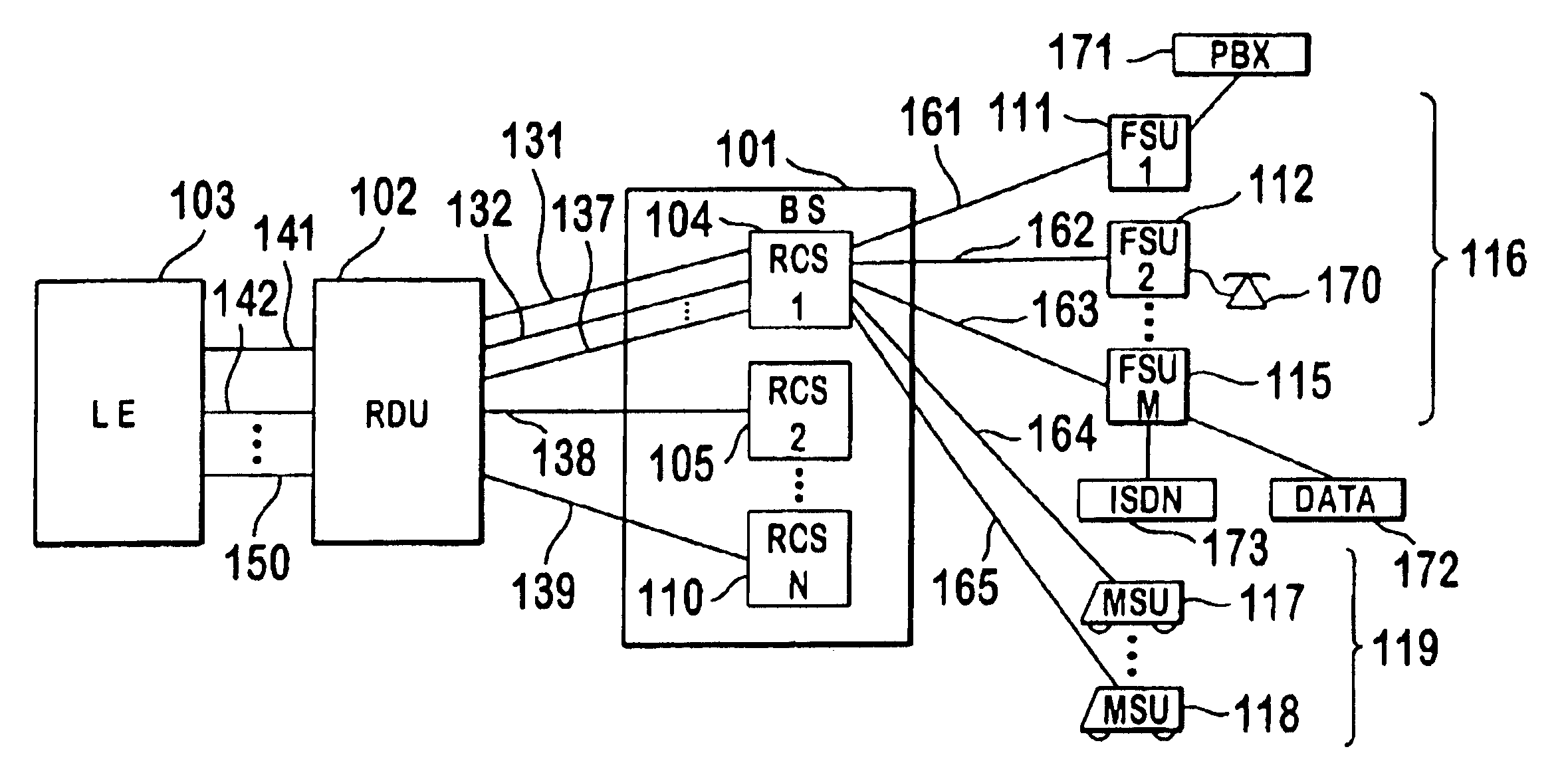
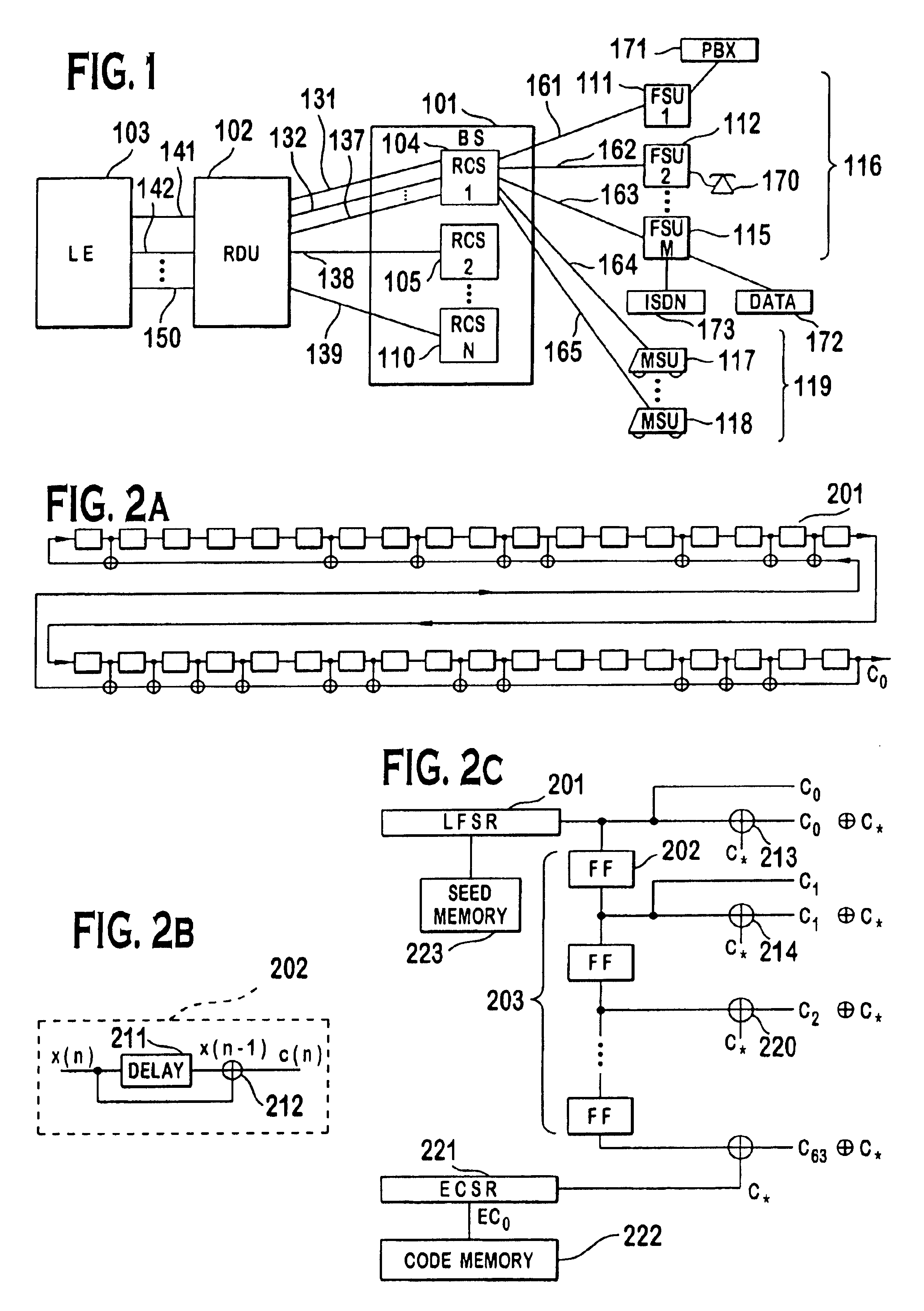
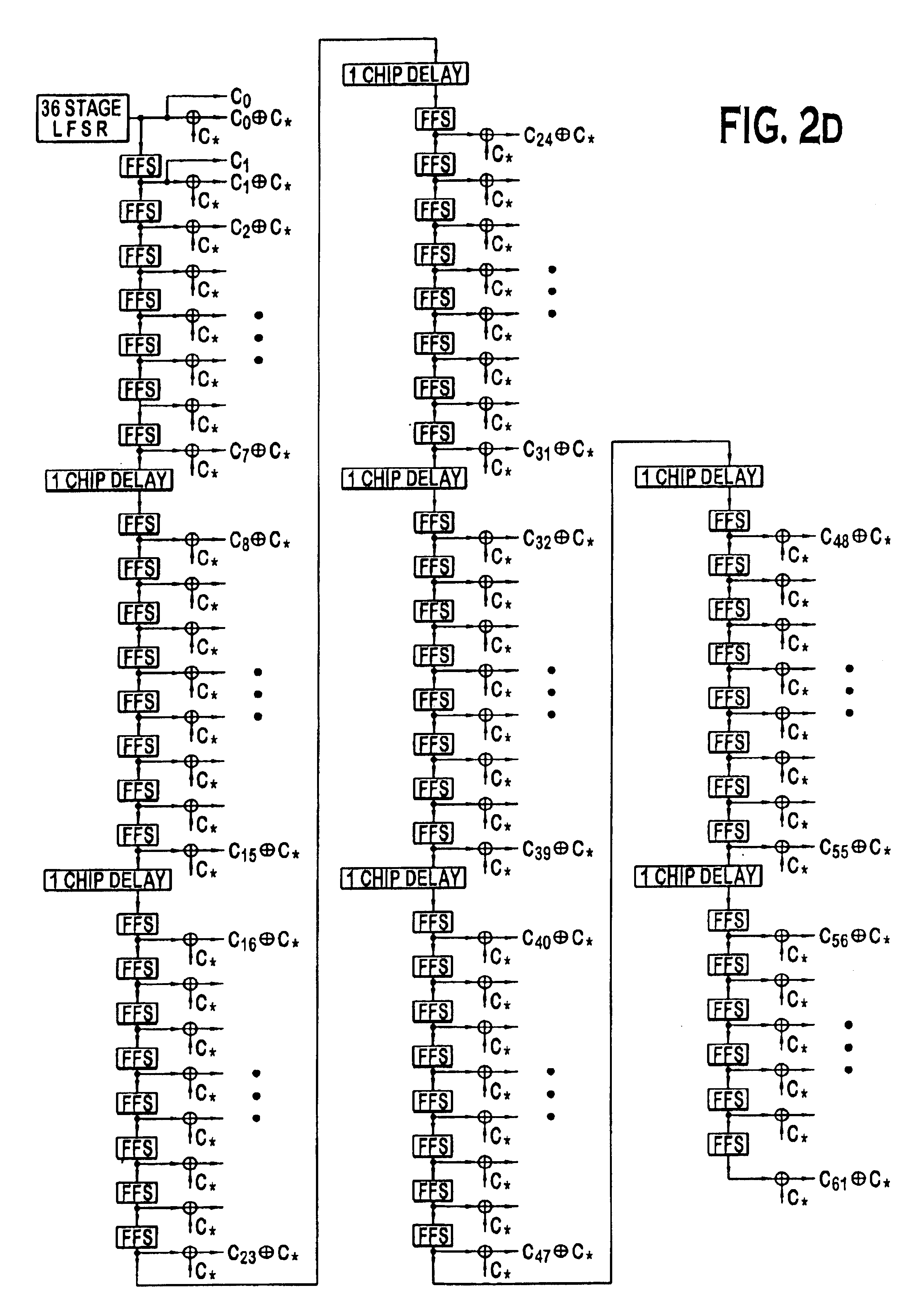
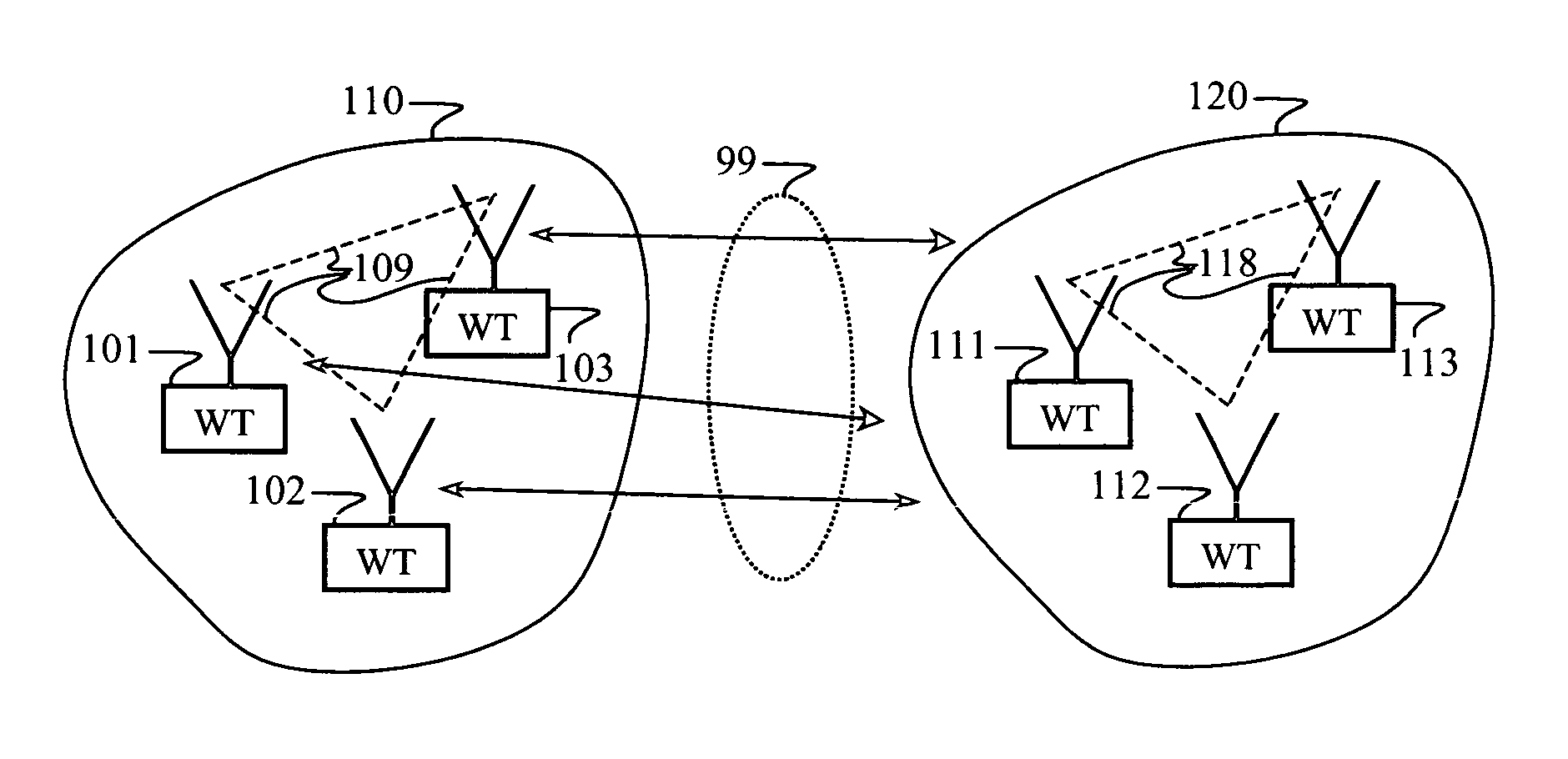
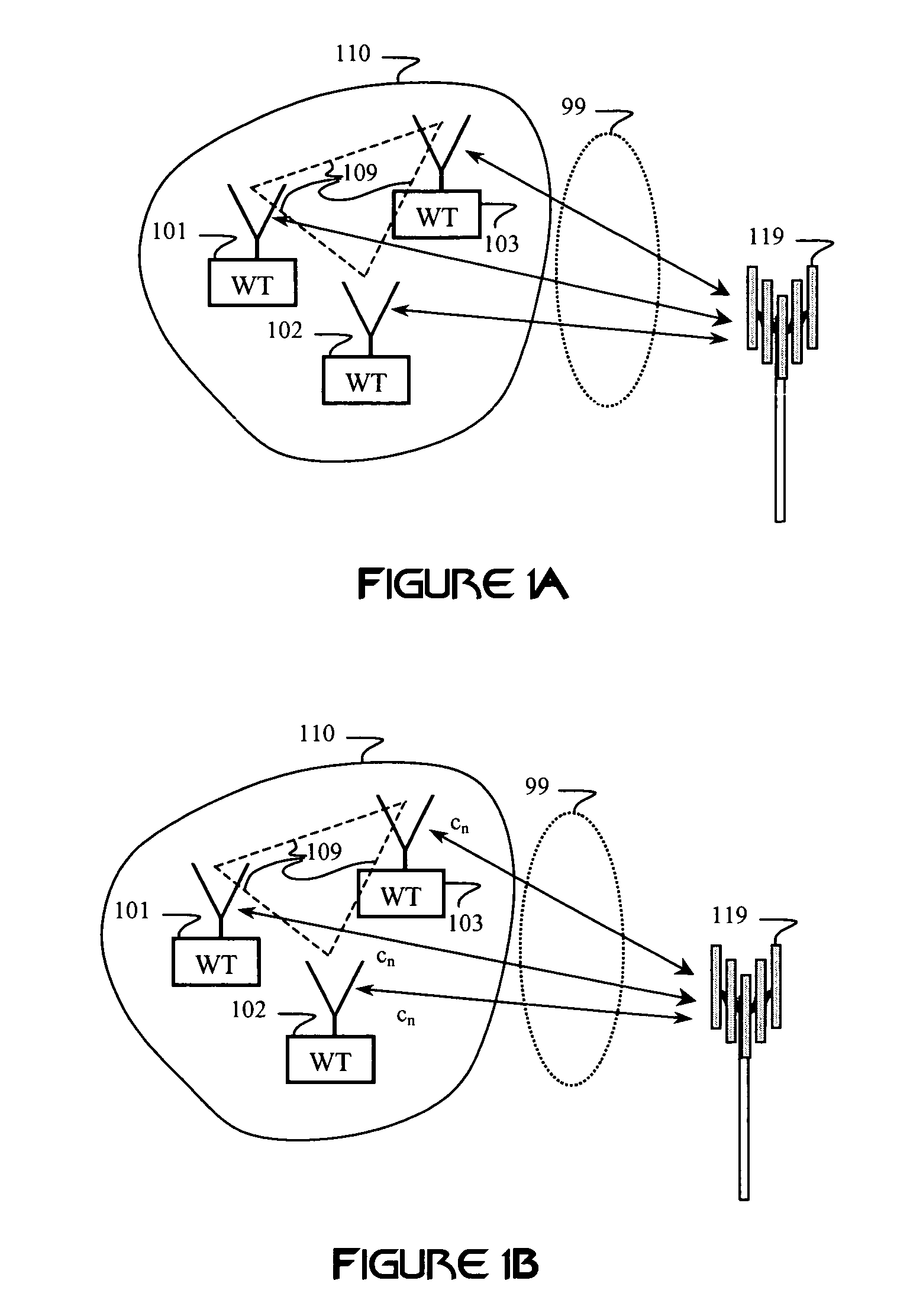
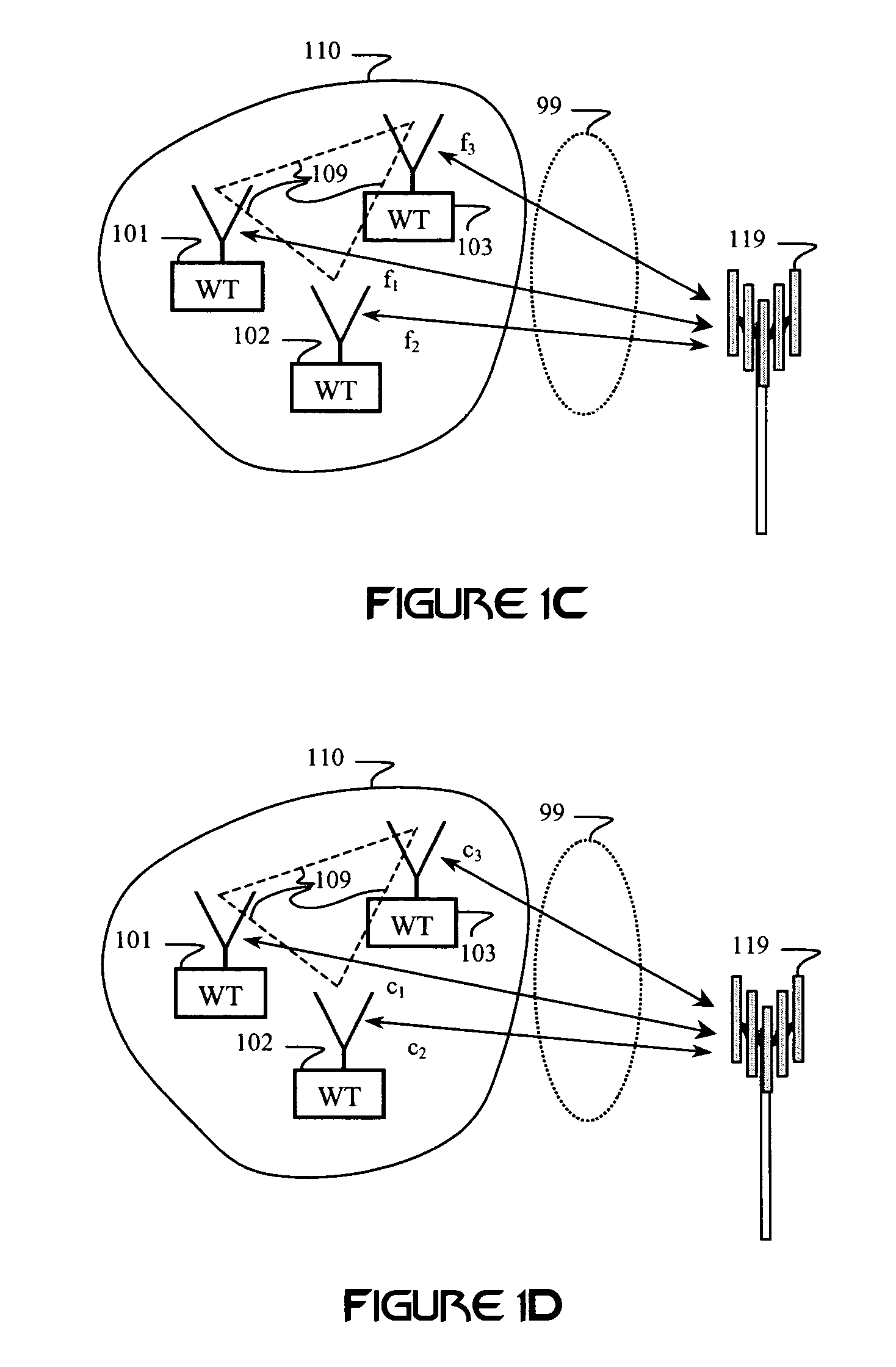
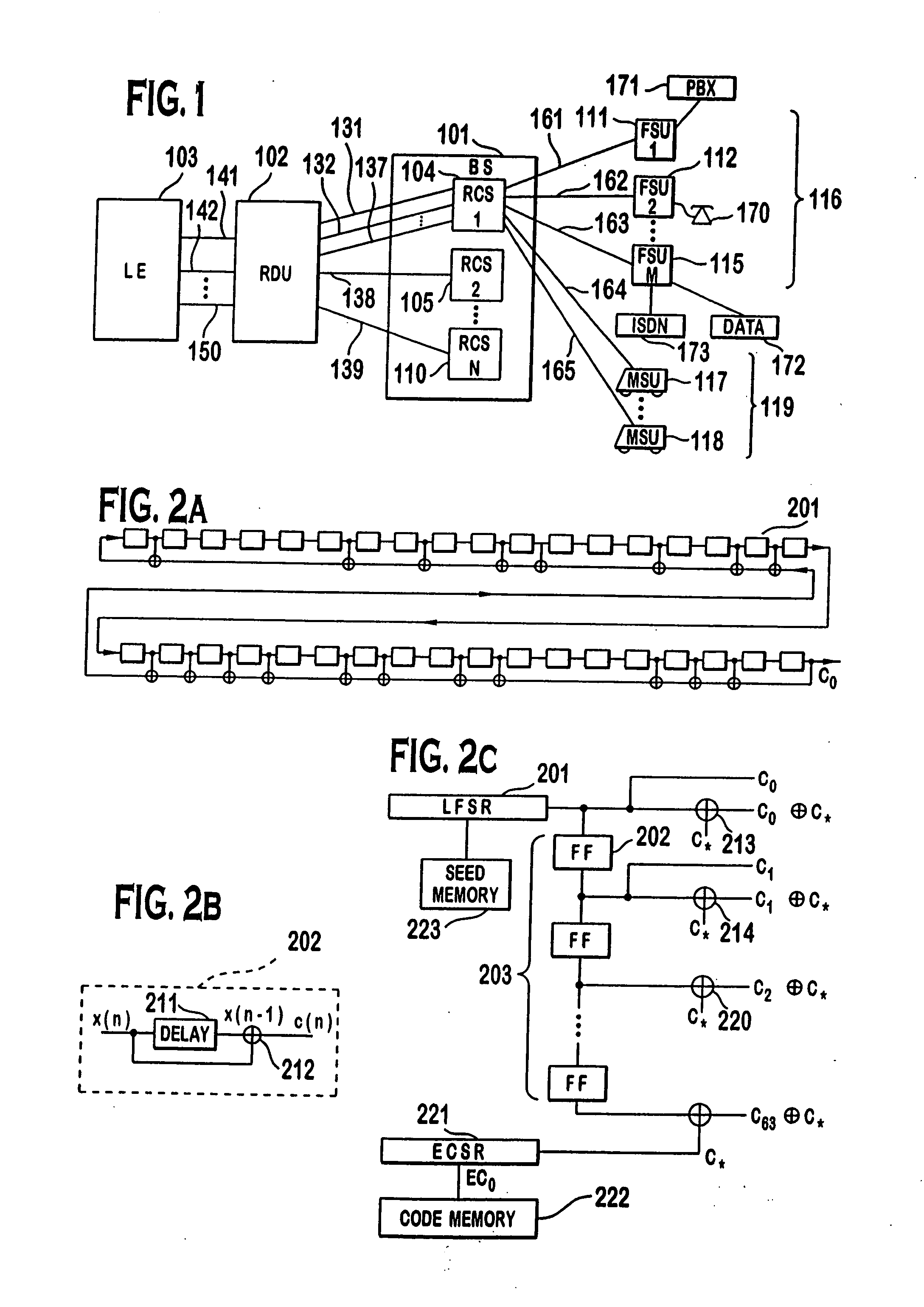
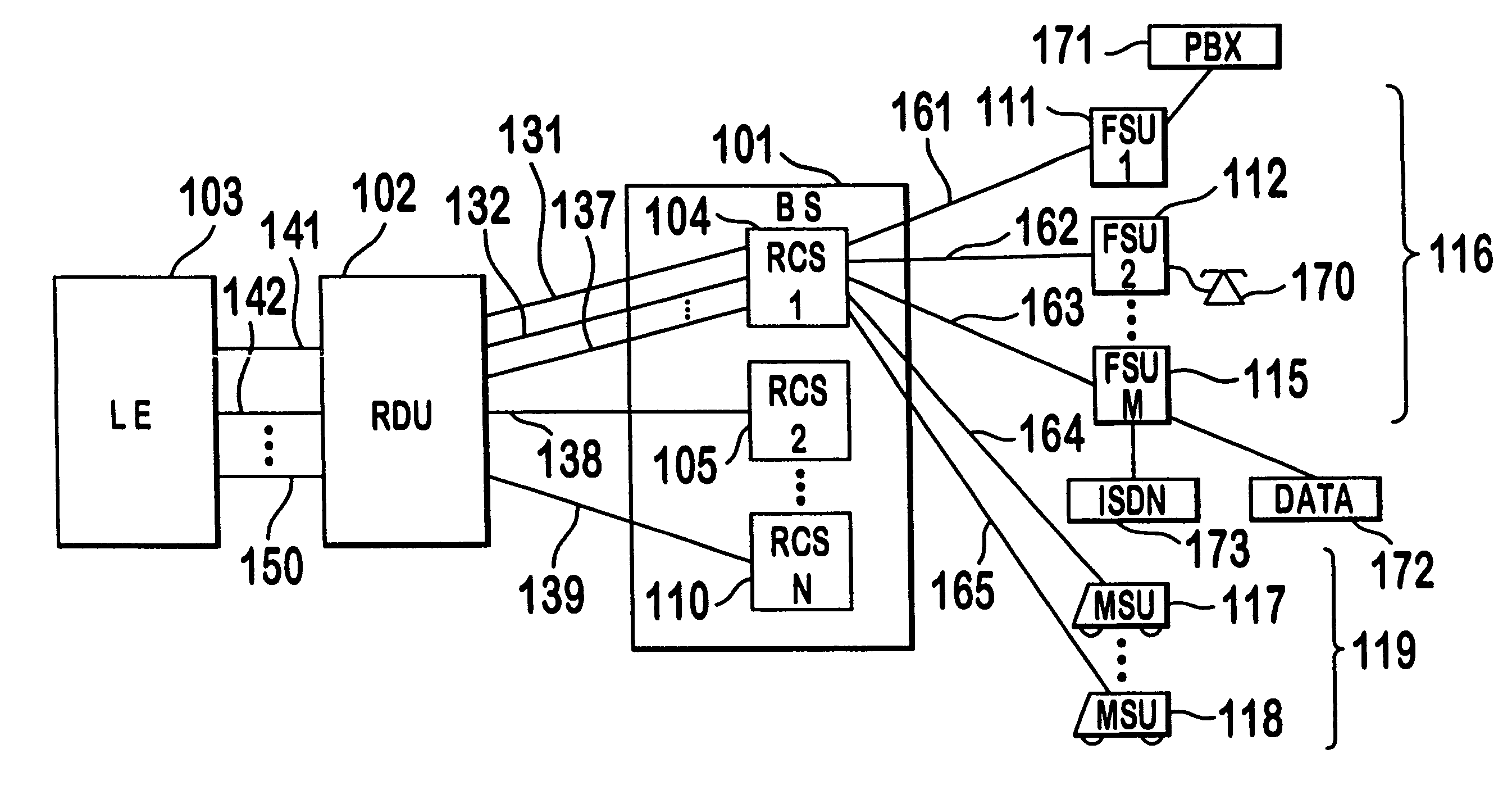
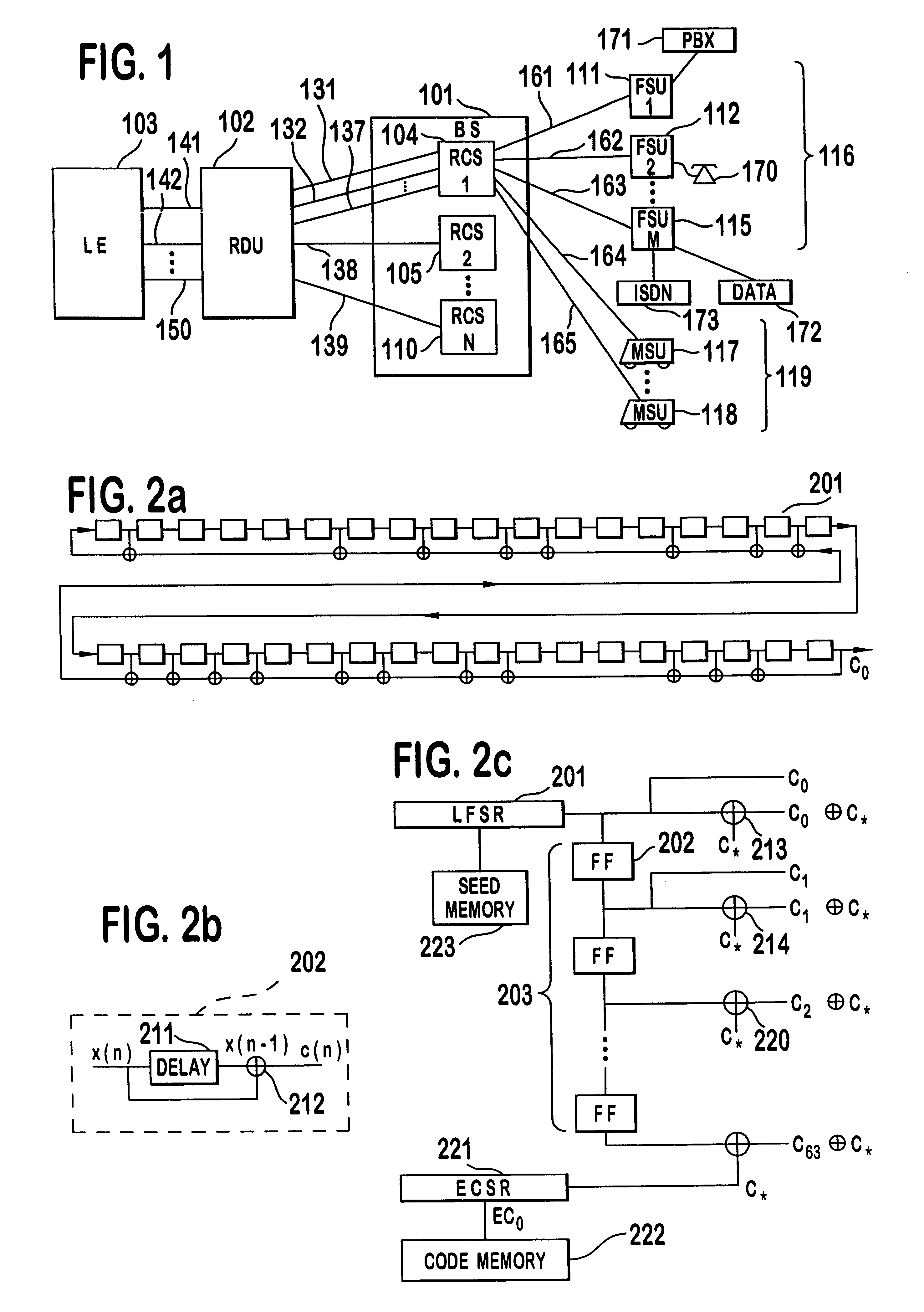
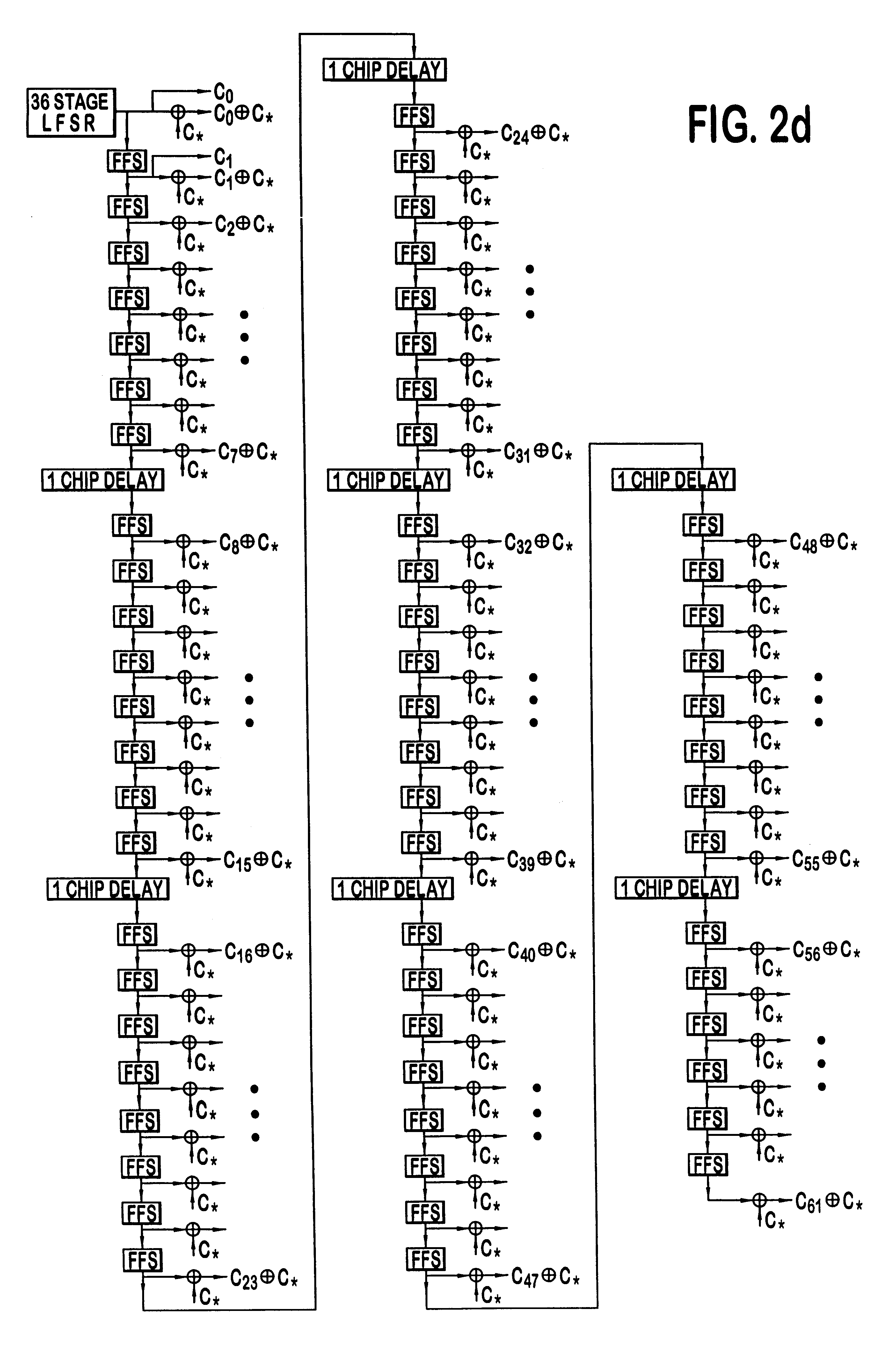
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for generating a large number of codes having desirable correlation properties
InactiveUS6912240B2Desirable propertyMultiplex code generationTransmissionPhase differenceSelf correlation
The present invention relates to a method for generating and apparatus for employing code families having desirable correlation properties. Regardless of code length, maximum autocorrelation of the codes is 4 for any nonzero offset and maximum cross-correlation of any two codes from a code family is 4 for any offset. The codes can be used in impulse radio systems and non-impulse radio systems including CDMA, TDMA, FDMA, OFDM and various other frequency hopping and direct sequence systems. The codes can be used to specify various impulse radio and non-impulse radio signal characteristics including pulse position in time, amplitude, width, type, phase, phase difference, frequency, spreading code, etc. The codes have the unique property that they can specify as many as two components in which a signal is not present. A method of code compression is provided.
Owner:TIME DOMAIN
Orthogonal Differential Vector Signaling Codes with Embedded Clock
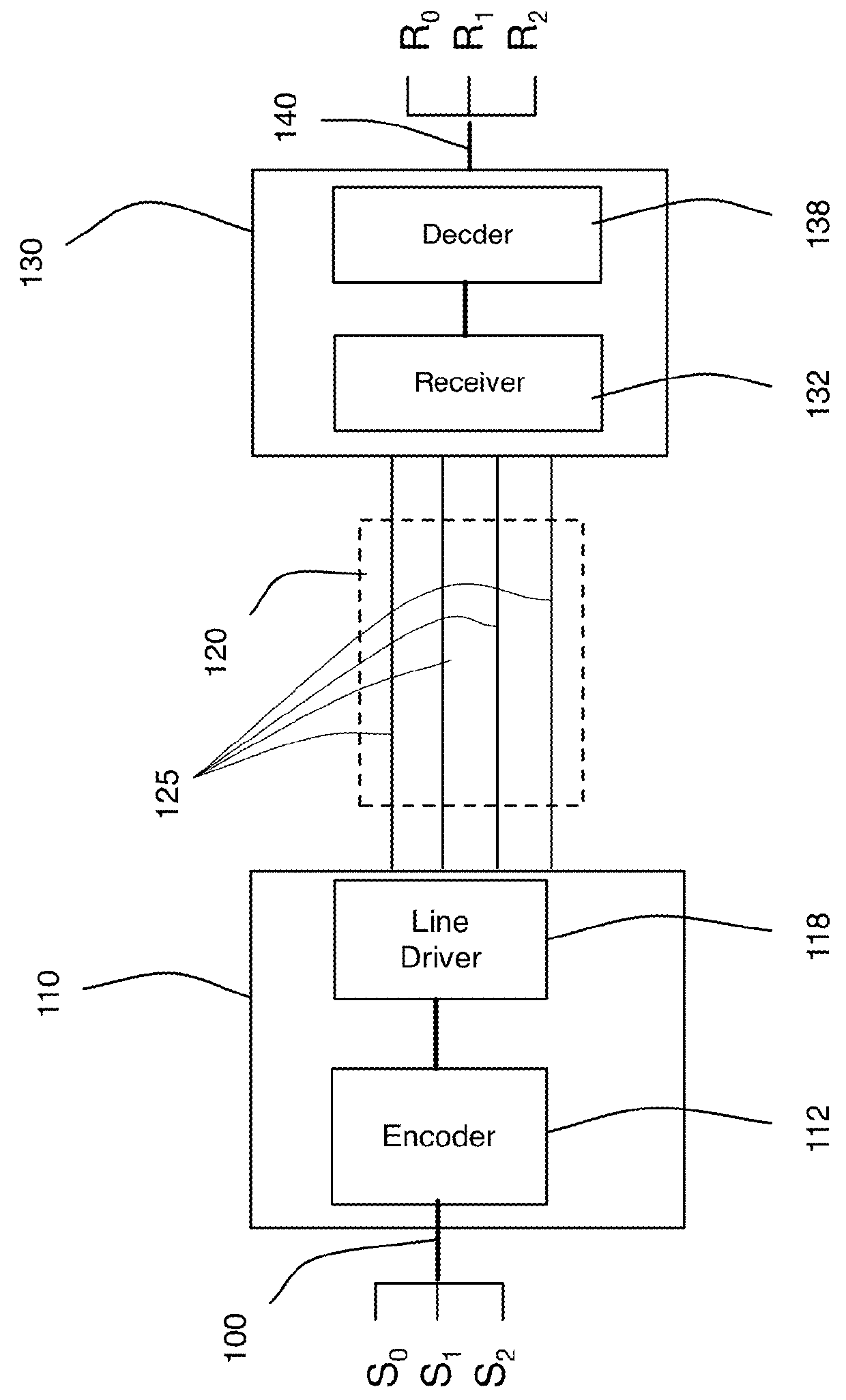
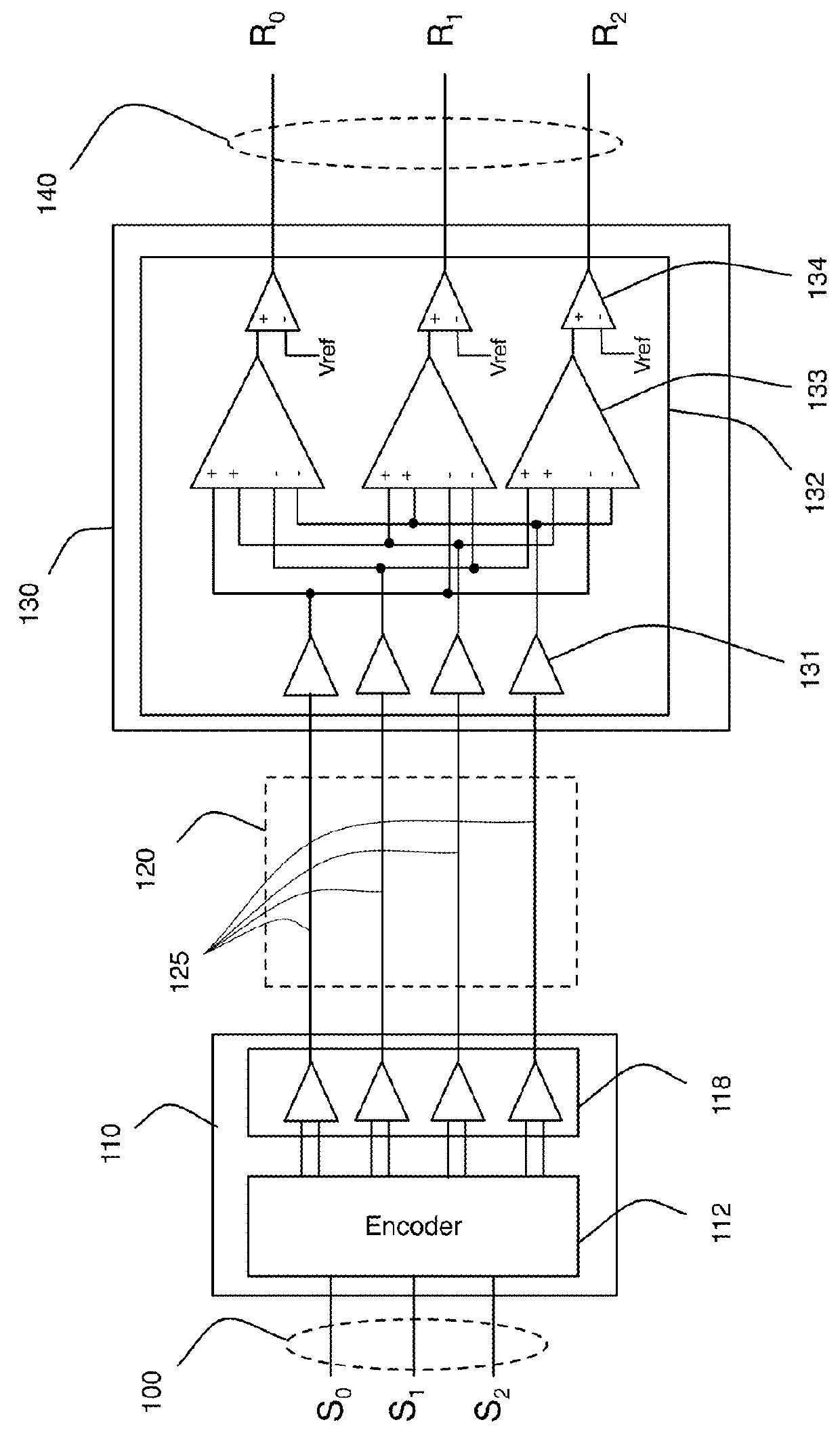
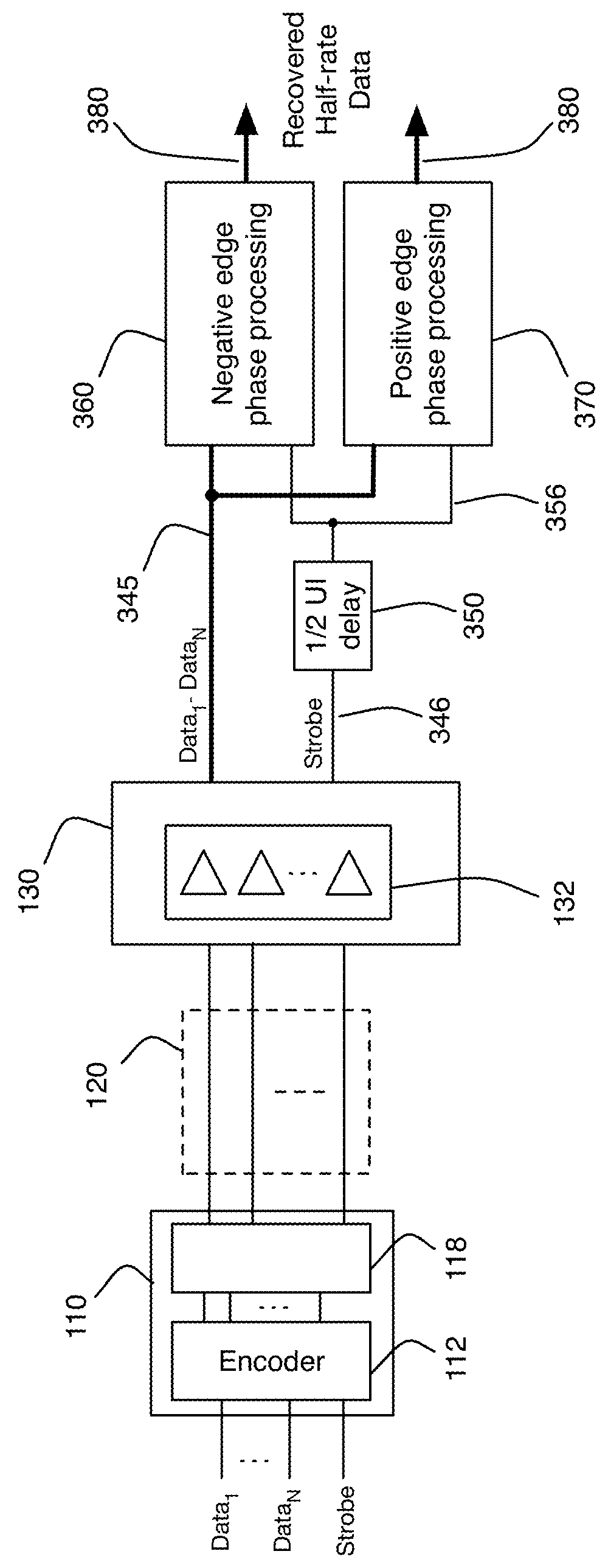
Orthogonal differential vector signaling codes are described which support encoded sub-channels allowing transport of distinct but temporally aligned data and clocking signals over the same transport medium. Embodiments providing enhanced LPDDR interfaces are described which are suitable for implementation in both conventional high-speed CMOS and DRAM integrated circuit processes.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
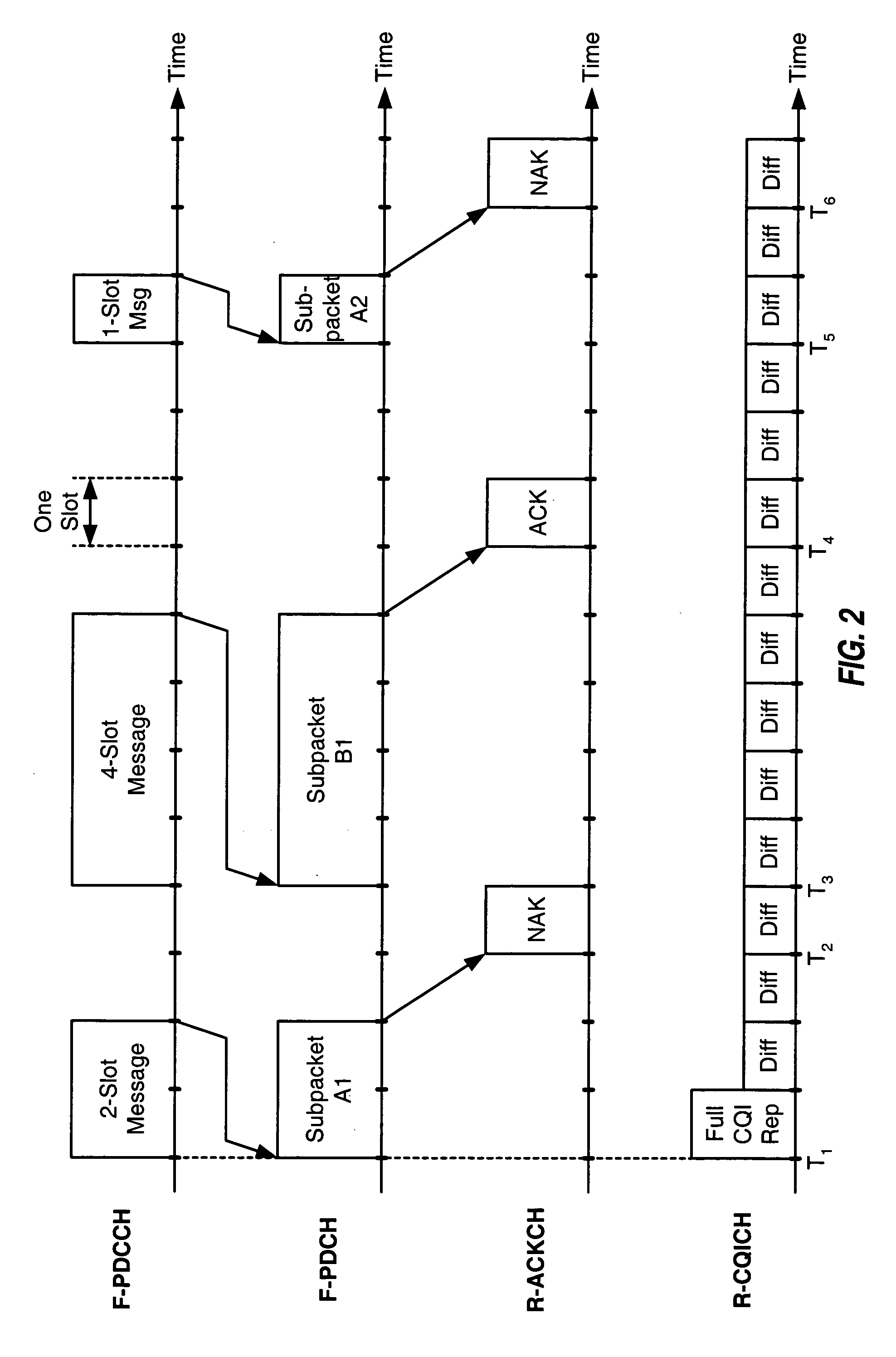
Method and apparatus for high rate data transmission in wireless communication
ActiveUS20060221883A1Improve transmission performanceFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionHigh rateCarrier signal
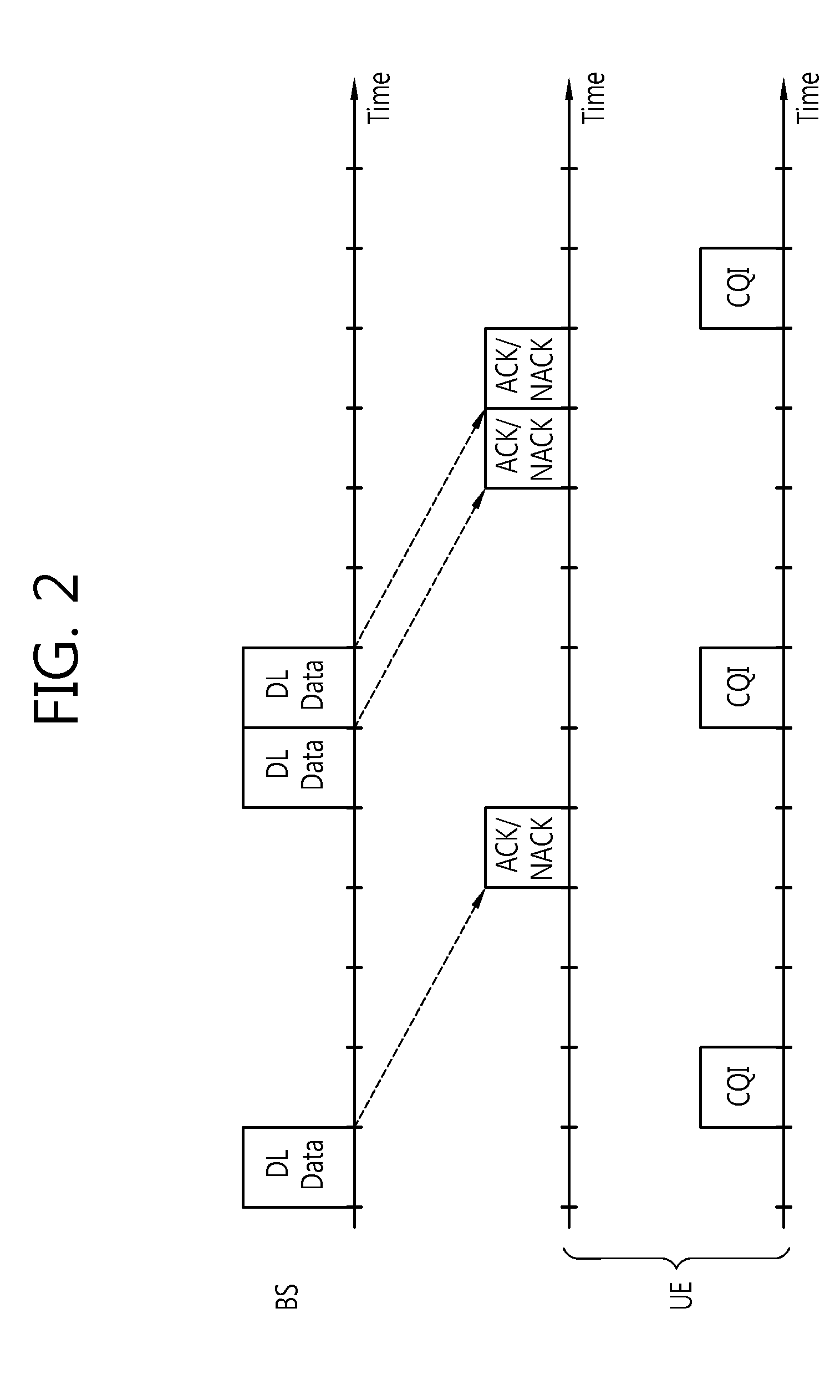
Techniques for utilizing multiple carriers to substantially improve transmission capacity are described. For multi-carrier operation, a terminal receives an assignment of multiple forward link (FL) carriers and at least one reverse link (RL) carrier. The carriers may be arranged in at least one group, with each group including at least one FL carrier and one RL carrier. The terminal may receive packets on the FL carrier(s) in each group and may send acknowledgements for the received packets via the RL carrier in that group. The terminal may send channel quality indication (CQI) reports for the FL carrier(s) in each group via the RL carrier in that group. The terminal may also transmit data on the RL carrier(s). The terminal may send designated RL signaling (e.g., to originate a call) on a primary RL carrier and may receive designated FL signaling (e.g., for call setup) on a primary FL carrier.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
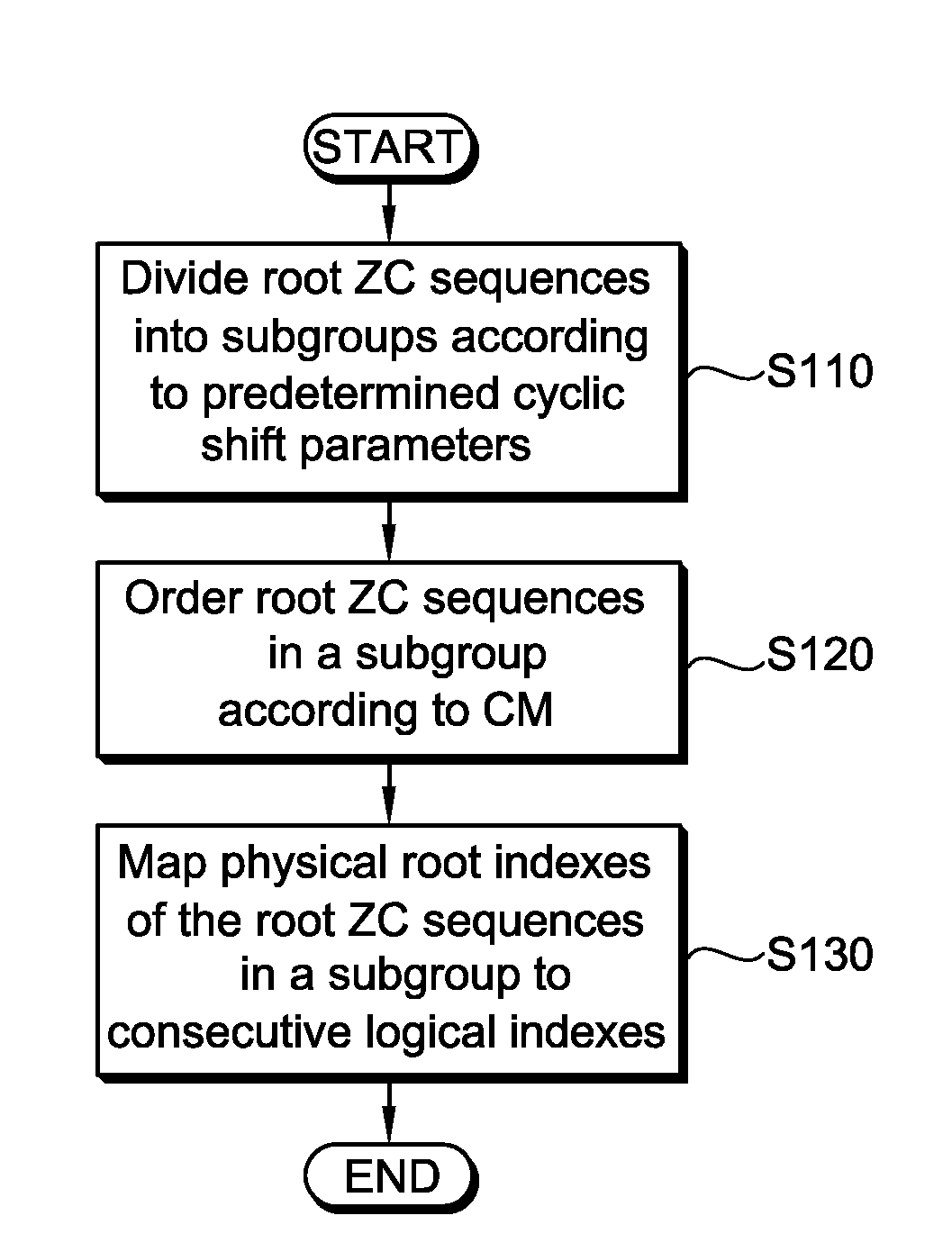
Method of generating random access preambles in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080235314A1Modulated-carrier systemsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
A method of generating random access preambles includes receiving information on a source logical index and generating random access preambles in the order of increasing cyclic shift from root ZC sequences with the consecutive logical indexes from the beginning of the source logical index until a predetermined number of the random access preambles are found, wherein the consecutive logical indexes are mapped to root indexes of the root ZC sequences.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Information content distribution based on privacy and/or personal information
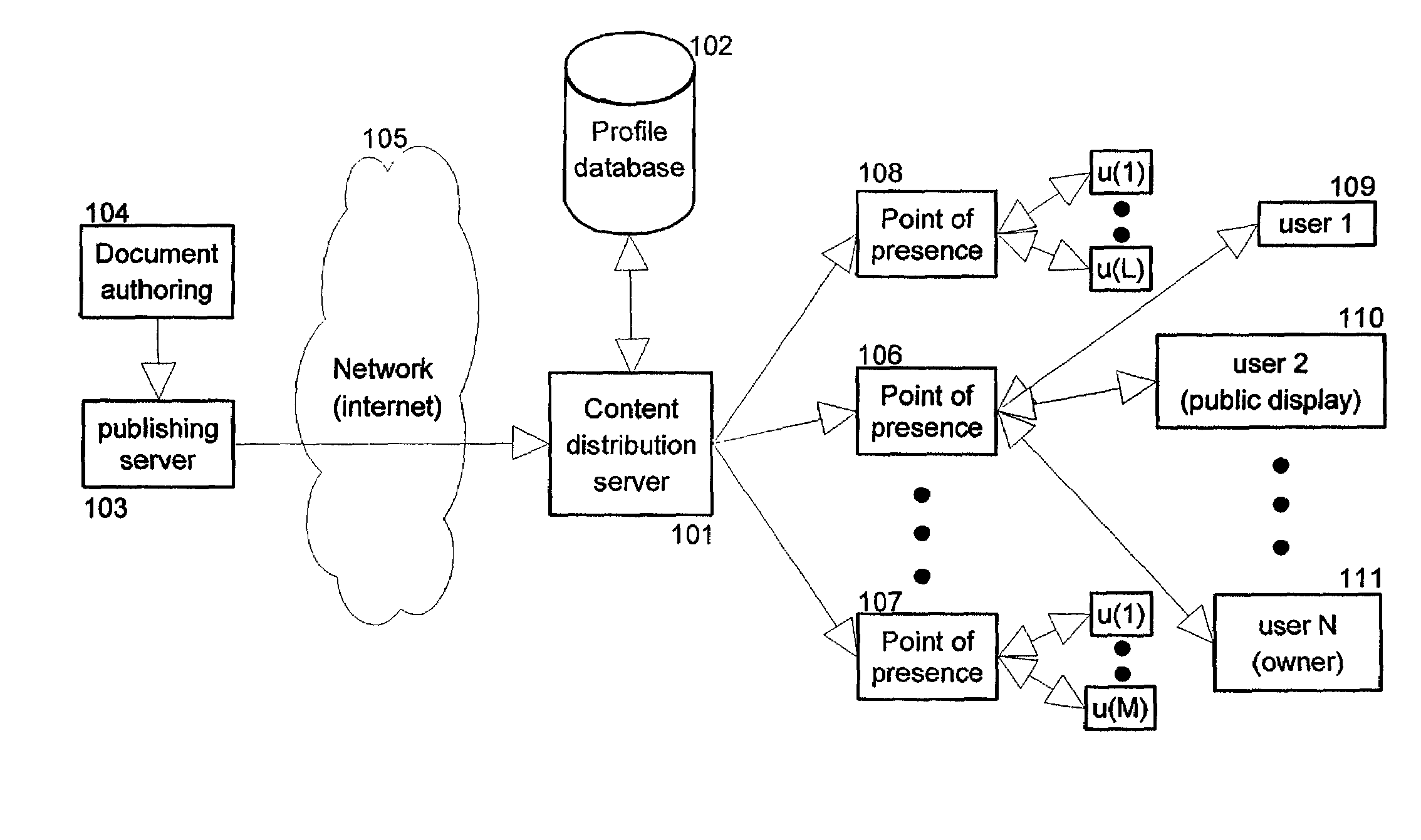
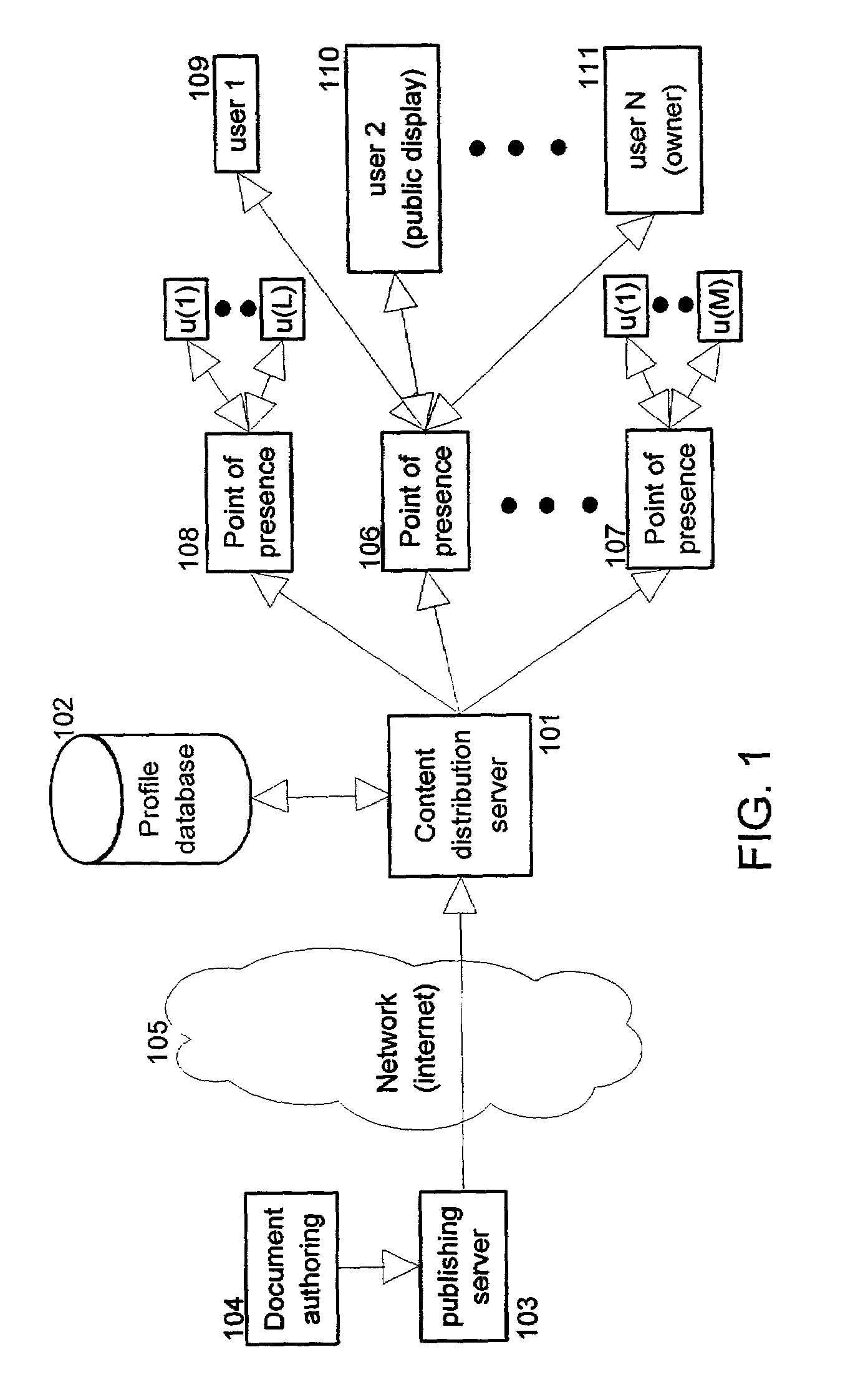
InactiveUS7162451B2Protect user privacyData representation error detection/correctionError preventionContent distributionPublic place
The present invention provides methods and apparatus to protect user privacy while accessing information in public places, using both public and personal devices. This is achieved by employing a mechanism that prevents private information from being displayed on public devices. Instead, this type of information is made available only to a user's personal device(s) that the user carries and / or trusts. An example embodiment of the invention shows relevant parts of the information content, referred to also as information documents or simply documents, to multiple devices based on privacy level and user preferences. Embodiments of the present invention also provide personalized services based on privacy levels defined by users. These users can for example be customers of a retail store. The service provided is sometimes also based on user history of accessing information documents. It permits personalized information to be sent to a customer's personal device.
Owner:IBM CORP
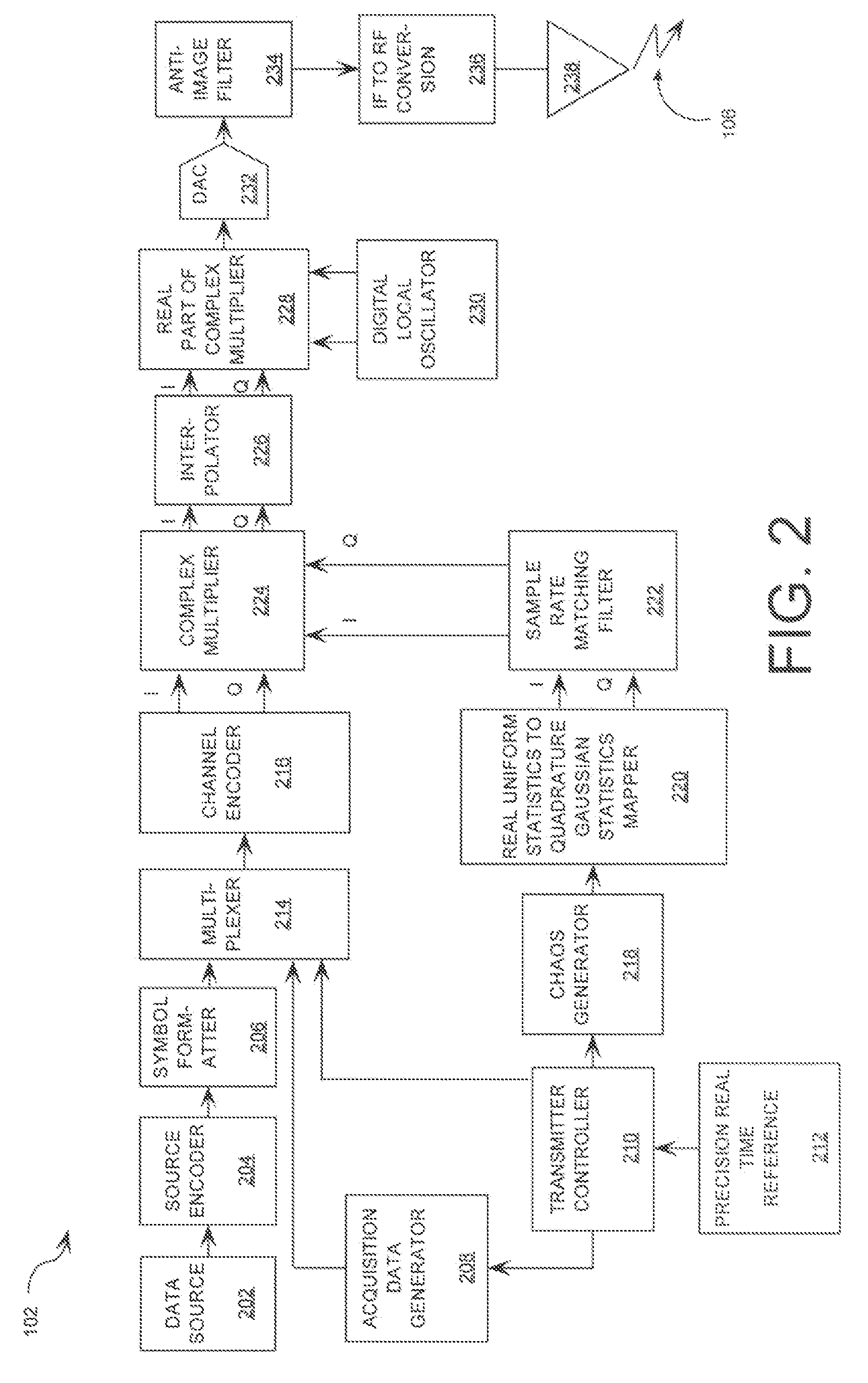
Featureless coherent chaotic amplitude modulation
ActiveUS20090310650A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsConstant powerPulse-code modulation
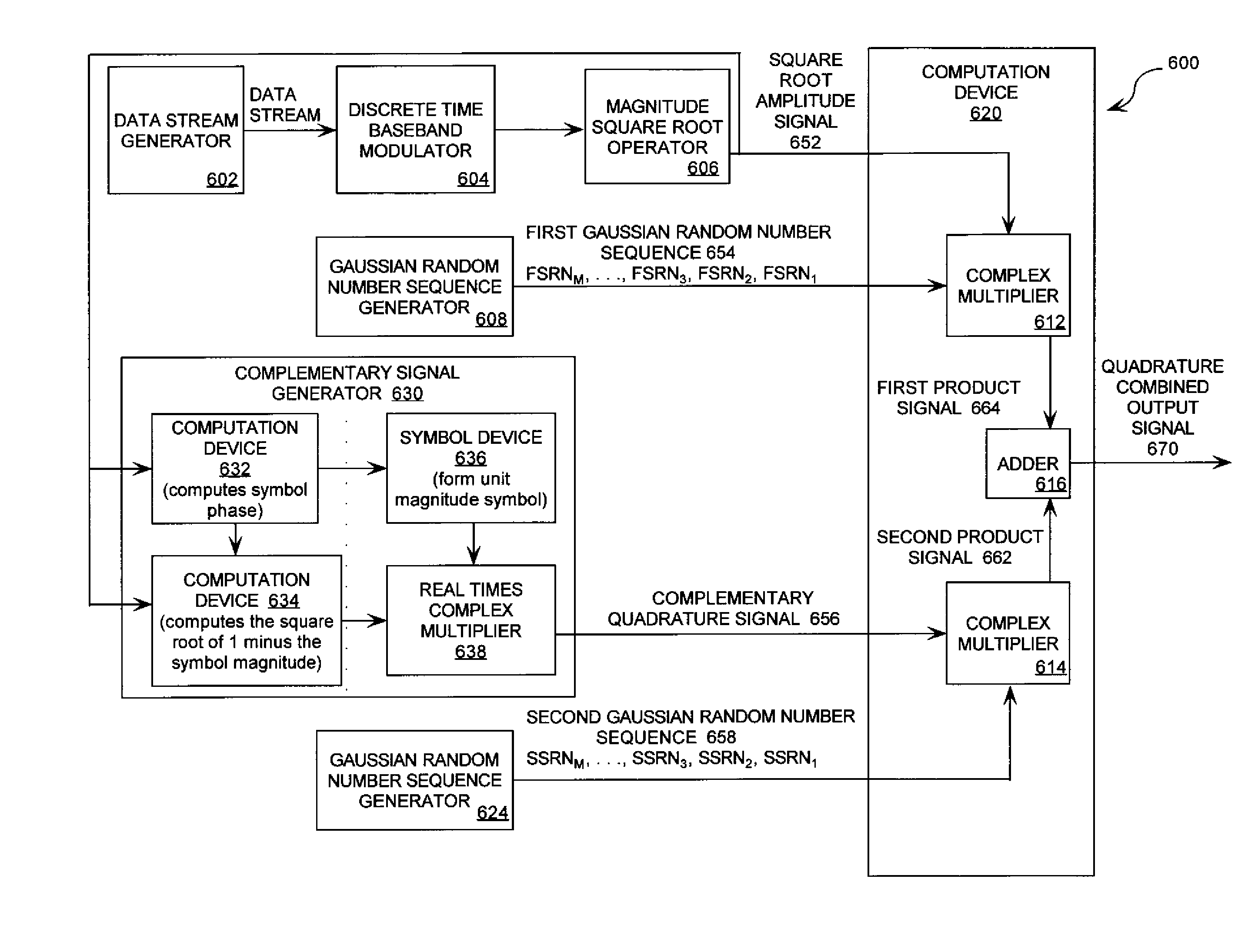
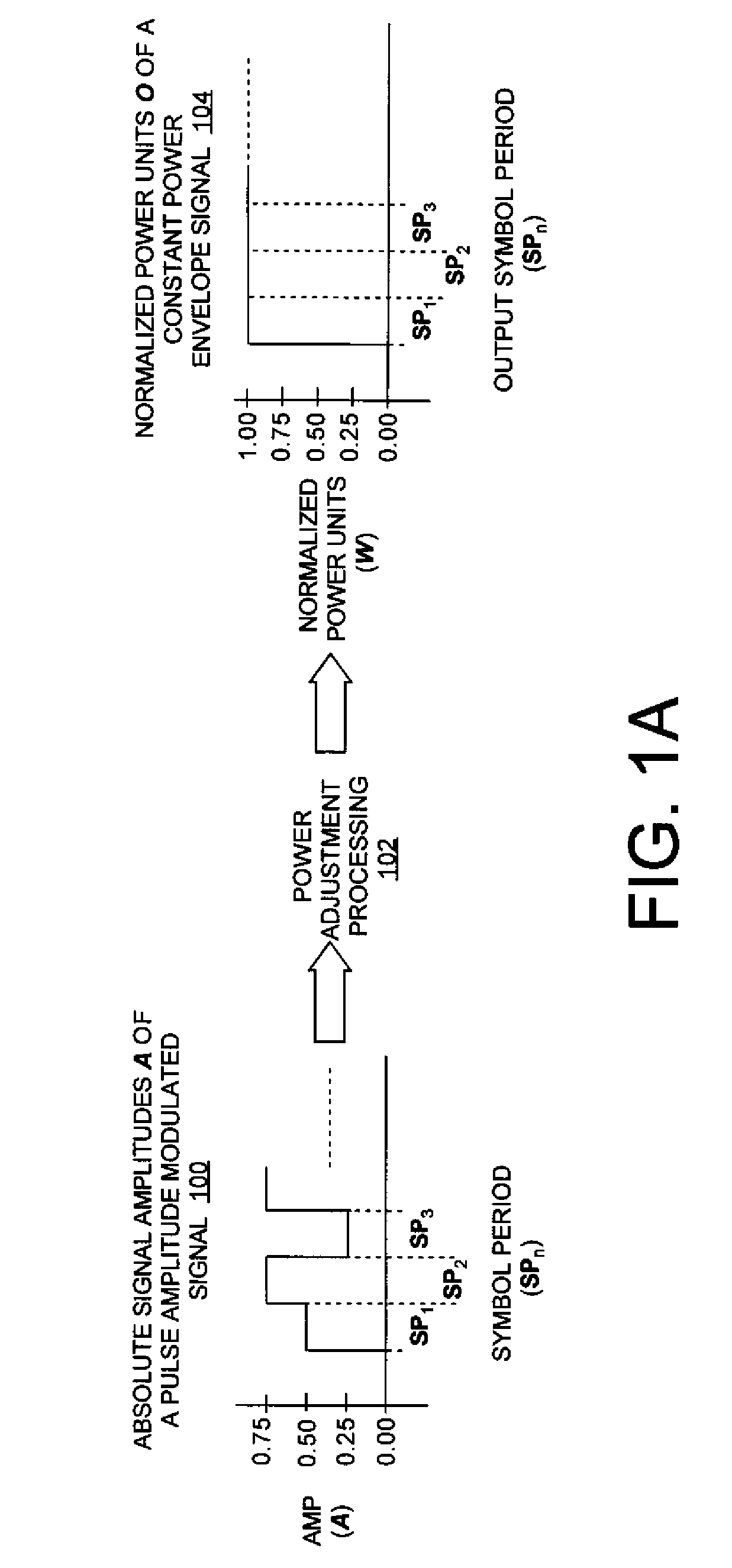
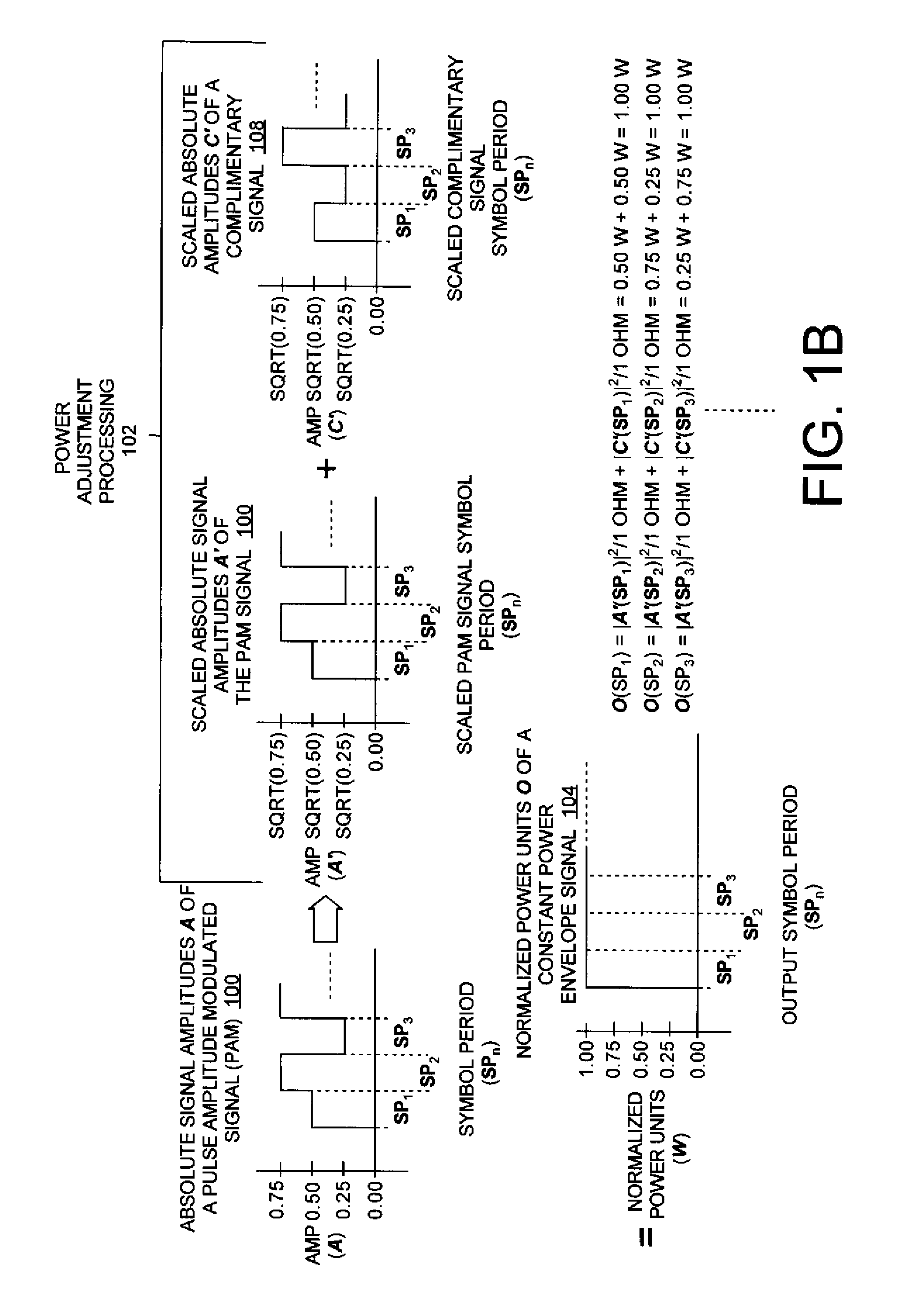
Systems (400, 500, 600) and methods (300) for generating a chaotic amplitude modulated signal absent of cyclostationary features by preserving a constant variance. The methods involve: generating a PAM signal including pulse amplitude modulation having a periodically changing amplitude; generating a first part of a constant power envelope signal (FPCPES) by dividing the PAM signal by a square root of a magnitude of the PAM signal; generating a second part of the constant power envelope signal (SPCPES) having a magnitude equal to a square root of one minus the magnitude of the PAM signal; and generating first and second spreading sequences (FSS and SSS). The methods also involve combining the FPCPES with the FSS to generate a first product signal (FPS) and combining the SPCPES with the SSS to generate a second product signal (SPS). A constant power envelope signal is generated using the FPS and SPS.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Cooperative beam-forming in wireless networks
ActiveUS8670390B2Site diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseWireless mesh network
A beam-forming system comprises a cooperative array of wireless terminals coupled to at least one wireless wide area network (WWAN) and communicatively coupled to a wireless local area network (WLAN) configured to provide information exchanges between the wireless terminals. A cooperative beam-forming system employing the WLAN provides antenna-array processing benefits (such as frequency reuse, interference rejection, array-processing gain, antenna-switching diversity) to the individual wireless terminals. A network access operator facilitates network control functionality between the WWAN and the cooperative array of wireless terminals.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
InactiveUS20040252668A1Easy to liftMaximize signal to noisePower managementBaseband system detailsSystem capacityCode division multiple access
A subscriber unit for use in a multiple access spread-spectrum communication system includes a spread spectrum radio interface, responsive to a rate function signal from a base station, and first and second despreaders. The base station assigns the rate function spread-spectrum message channels and the first despreader recovers and modifies an information signal one of the spread spectrum message channels. The information channel mode is then modified for processing by the second despreader, with the second despreader supporting a different information signal rate. The subscriber unit has a capability of communicating with a dynamically changing a transmission rate of an information signal which includes multiple spread spectrum message channels. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for a radio carrier station and the subscriber units, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active subscriber units for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Sending transmission format information on dedicated channels
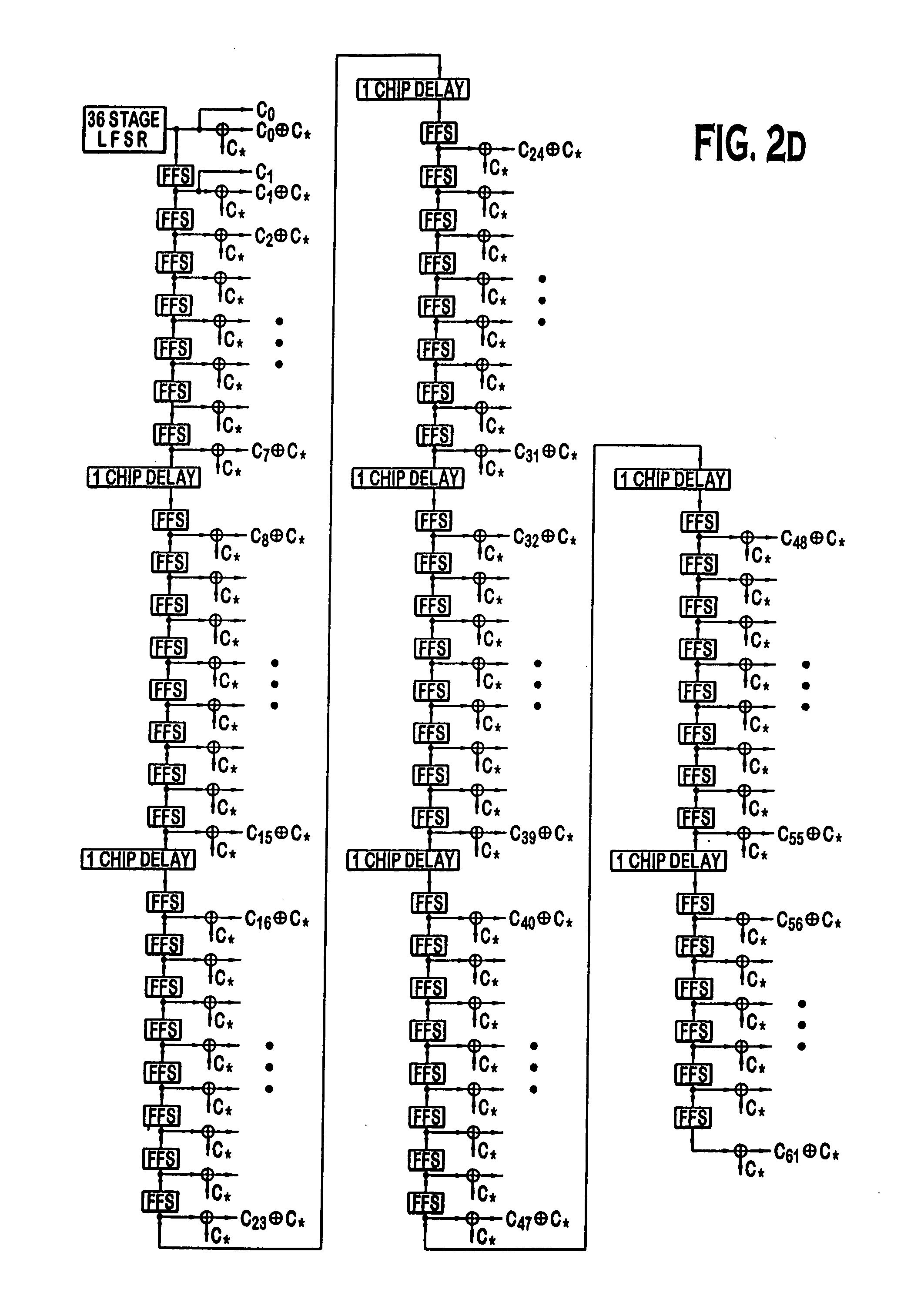
InactiveUS7161971B2Information transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplex code generationBroadcast channelsRadio channel
Transmissions on the dedicated channel are encoded using a set of paramaters that are picked from a large selection of potential parameters. If the remote station does not know the particular set of parameters that were used by a base station, then the remote station would have to attempt to decode the transmission using every set of parameters, until the transmission is decoded correctly. This is an inefficient methodology. Hence, transmission format information is typically transmitted on a broadcast channel so that a remote station could receive the transmission format information. However, the broadcast channel has reliability problems. New methods and apparatus are presented to allow a base station to determine an overlapping set of Walsh code sequences that can be used to send the transmission format information on the dedicated channel, rather than a broadcast channel. Using the overlapping set allows the remote station to decode the information.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Cooperative Wireless Networks
A wireless local area network (WLAN) communicatively couples together a group of mobile wireless terminals configured to operate in a wireless wide area network (WWAN). A network-management operator processes WWAN-control messages used by the mobile wireless terminals and the WWAN. One or more of the mobile wireless terminals may function as the network-management operator.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Method and apparatus for spreading sequence hopping in code-multiplexed control channels
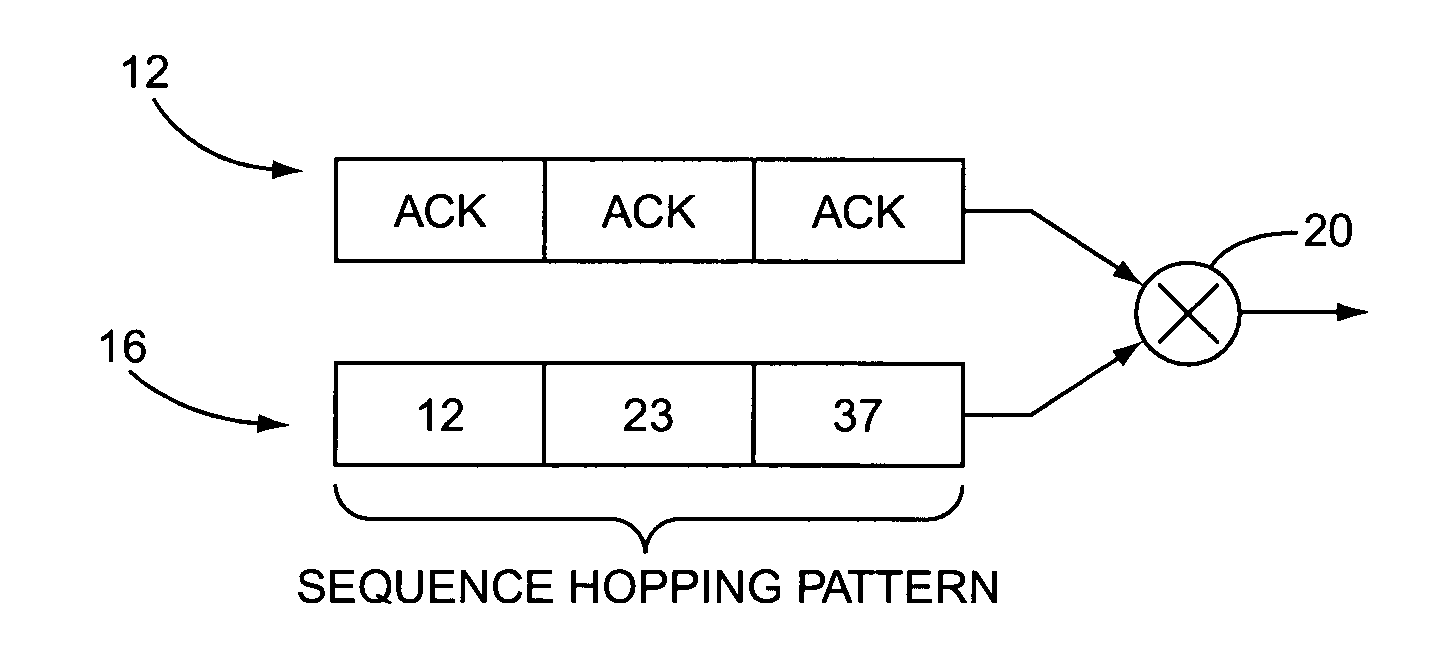
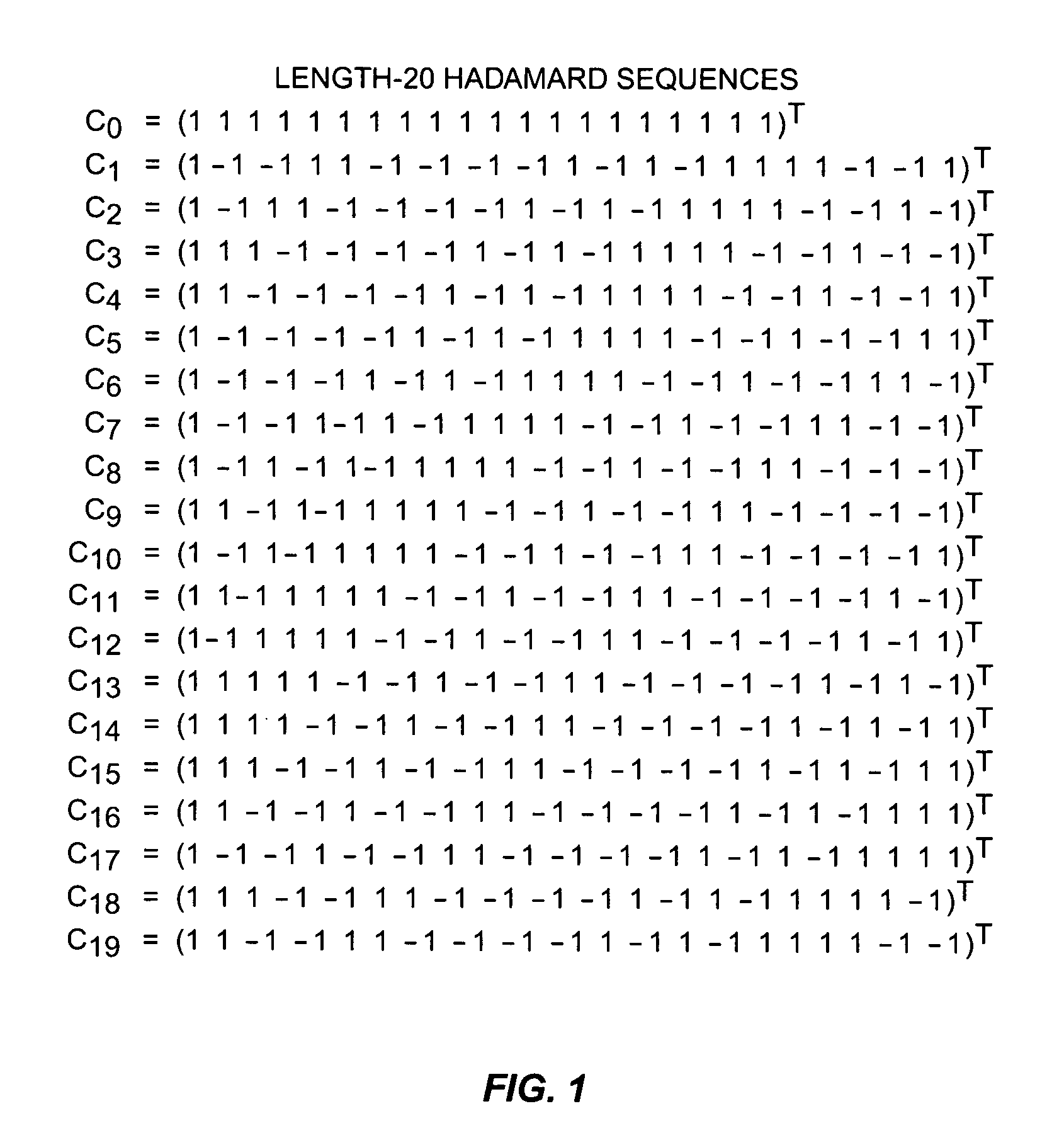
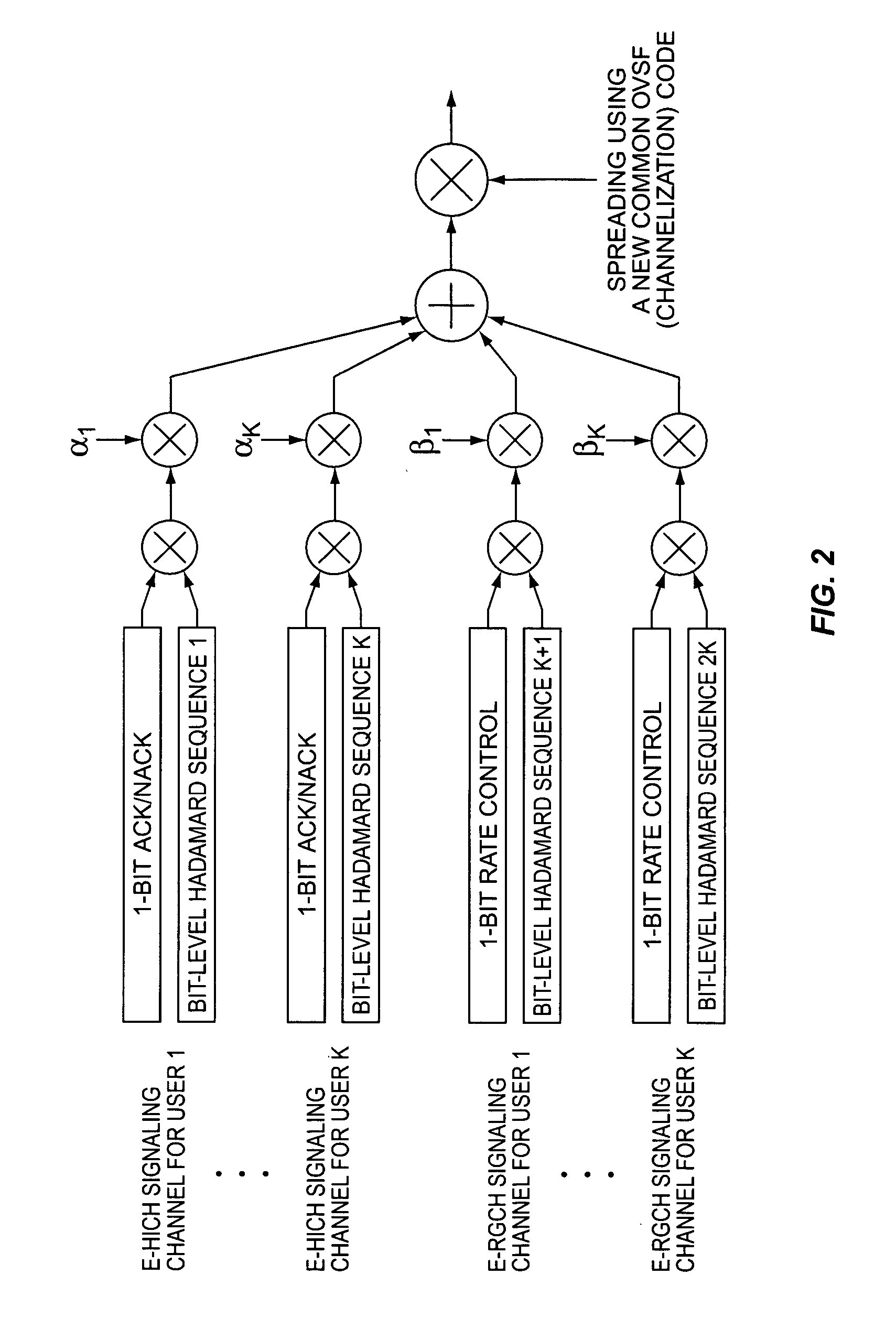
ActiveUS20060056360A1Reduce impactMultiplex code generationRadio transmissionMultiplexingControl signal
A method and apparatus for code multiplexing one or more control signals onto a shared control channel. According to the present invention, a control signal for transmission from a base station to a mobile station terminal is repeated in each slot of a predetermined time interval. The control signal in each slot is spread using a bit-level spreading sequence, where the bit-level spreading sequence varies from slot to slot according to a predefined sequence-hopping pattern. The spread control signals generated for transmission to each mobile station terminal are then combined and spread using a common channelization code.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
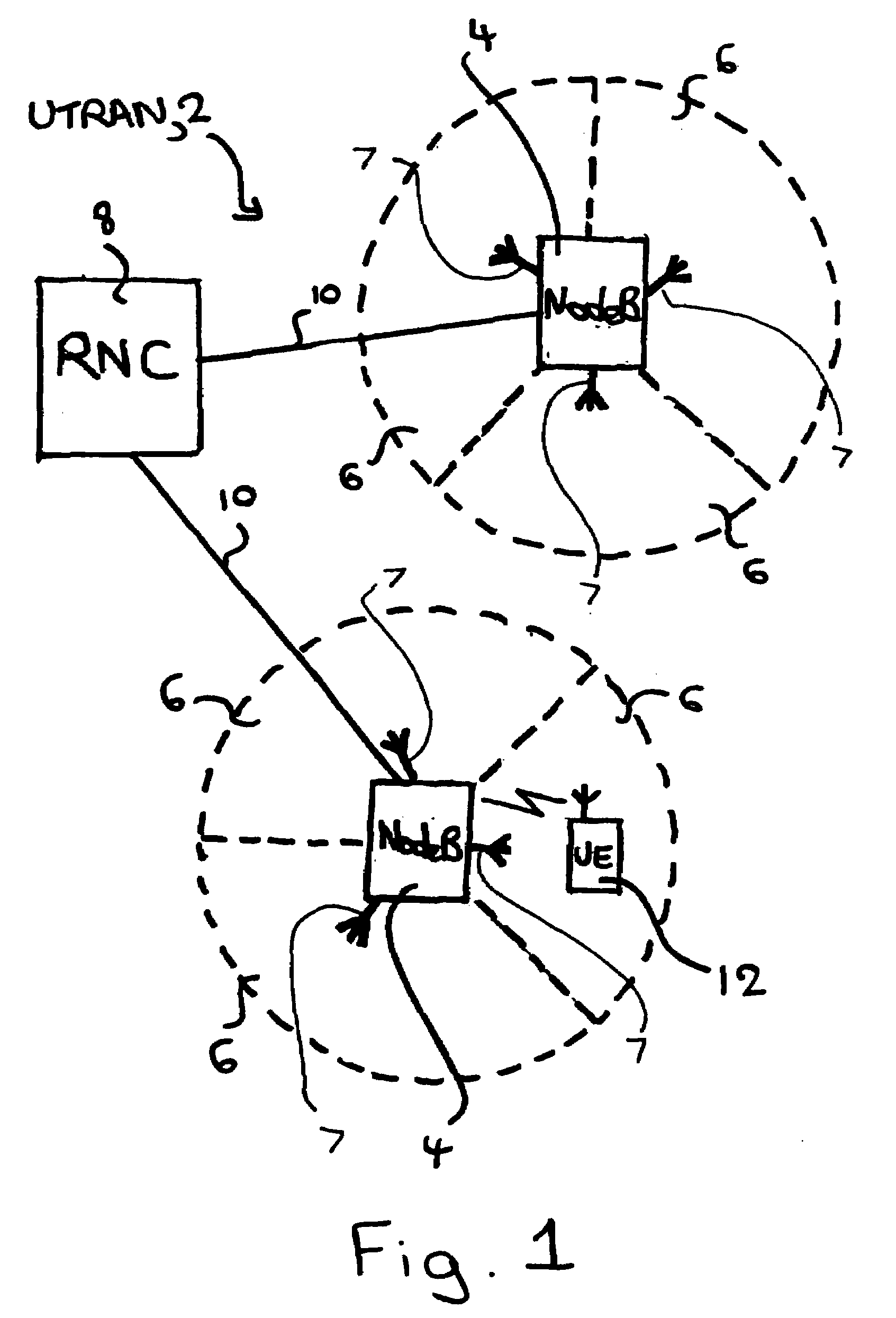
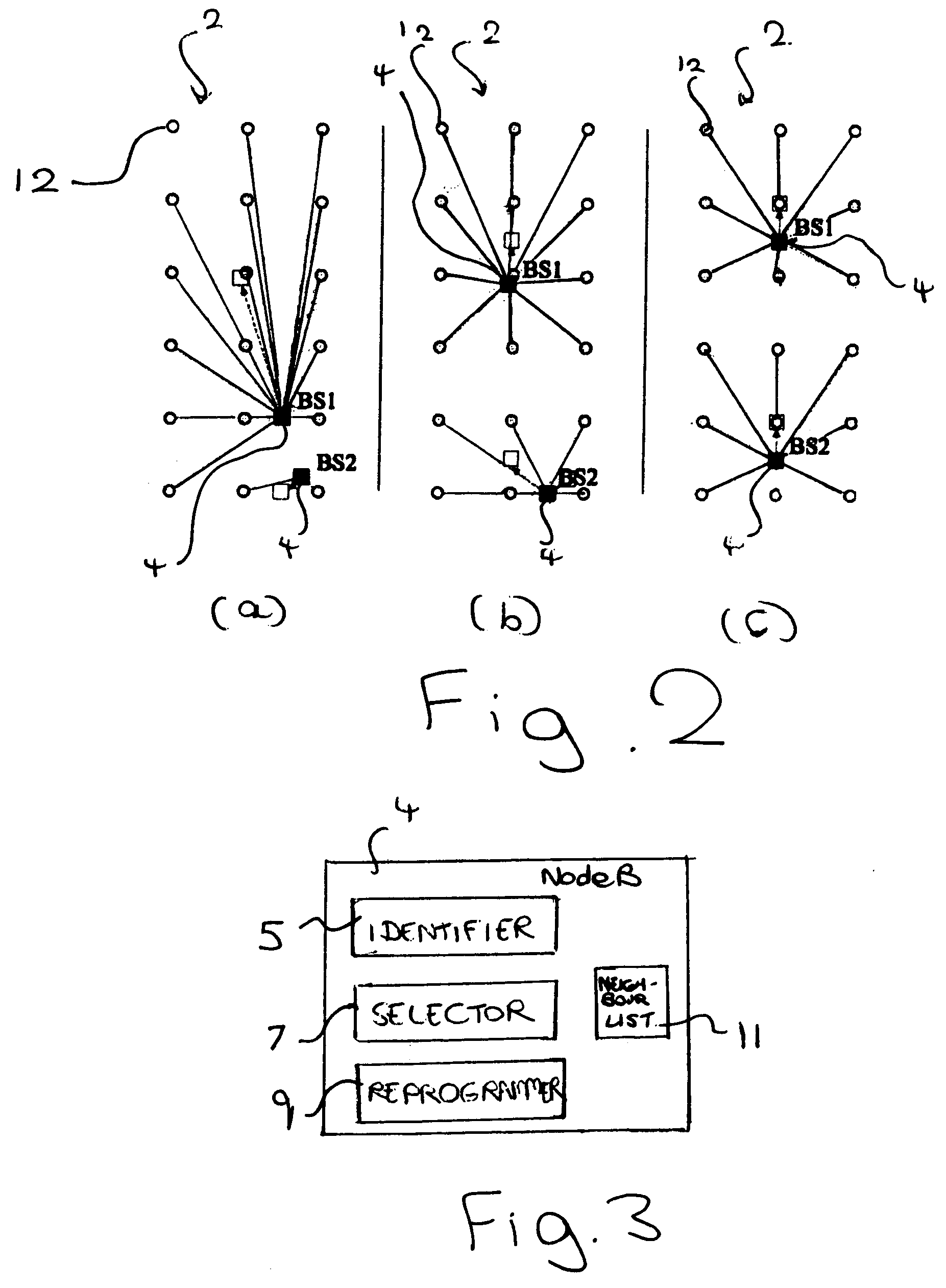
Changing the scrambling code of a base station for wireless telecommunications
A method is provided of a base station for wireless telecommunications changing scrambling code to be applied to pilot signals for transmission. The method comprises automatically:identifying a need to change scrambling code,selecting a new scrambling code for use,reprogramming the base station to use the scrambling code, andusing the new scrambling code for subsequent pilot signal transmissions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
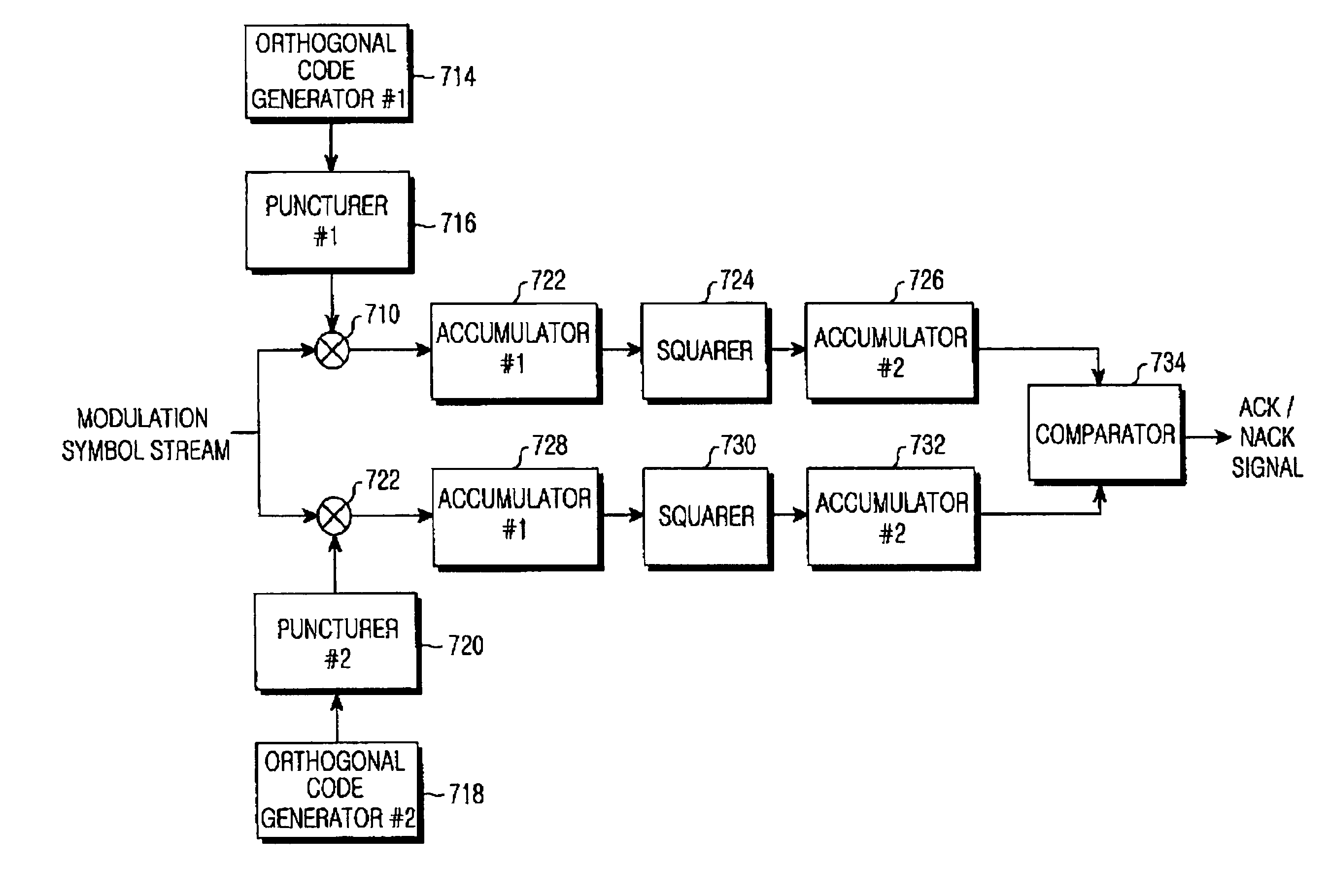
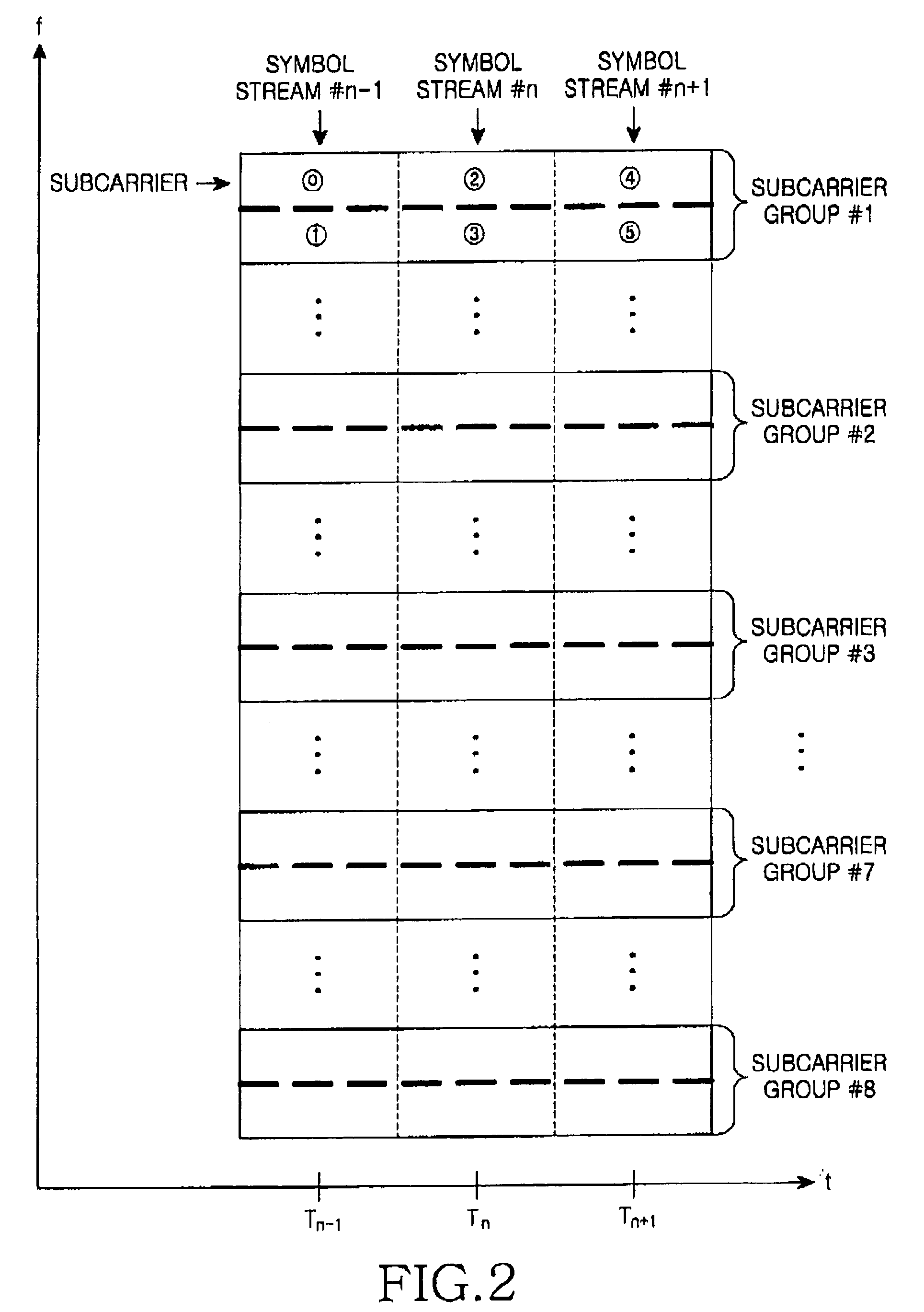
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a data frame processing result in an OFDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS20050195732A1Reduce waste of resourcesShow cabinetsError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemMobile communication systems
An apparatus and method for transmitting a processing result on a received data frame in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) mobile communication system. The method includes selecting an orthogonal codeword corresponding to the processing result among predetermined orthogonal codewords, and transmitting the selected orthogonal codeword through at least one subcarrier group assigned for transmitting the processing result. A length of the orthogonal codeword is determined according to a number of symbol units included in the subcarrier group, and the predetermined orthogonal codewords are orthogonal with each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
PN generators for spread spectrum communications systems
InactiveUS6661833B1Random number generatorsMultiplex code generationCommunications systemMobile station
Techniques to improve the acquisition process in a spread spectrum environment. The signals from different CDMA systems are spread with different sets of PN sequences, with the PN sequences in each set being uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the other sets. By using uncorrelated PN sequences, the likelihood of detecting a pilot signal from an undesired system is reduced or minimized, and the mean time to acquisition of the pilot signal from the desired system is improved. The mobile station can attempt to acquire the pilot signal by processing the received signal with a first set of PN sequences corresponding to a first hypothesis of the particular signal being acquired. If acquisition of the pilot signal fails, a second set of PN sequences corresponding to a second hypothesis is selected and used to process the received signal. The PN sequences in the second set are uncorrelated to the PN sequences in the first set. The PN sequences for the first set can be generated based on the characteristic polynomials defined by IS-95-A, and the PN sequences for the second set can be the reverse of the PN sequences for the first set.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Error control coding for orthogonal differential vector signaling
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving a pilot signal for distinguishing a base station in a communication system using an OFDM scheme
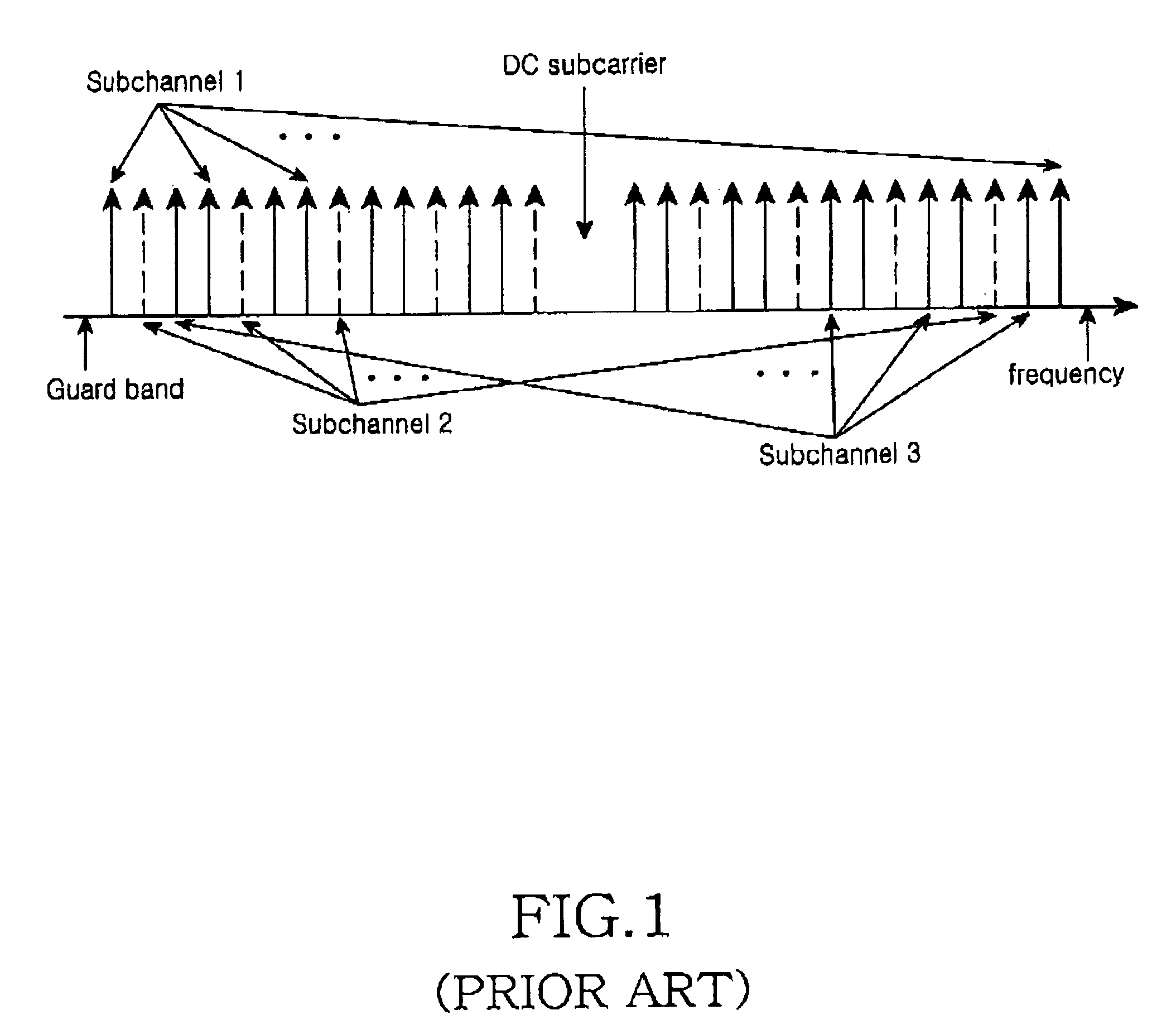
InactiveUS7369531B2Transmission path divisionFrequency-division multiplexCommunications systemData signal
A method for transmitting reference signals in a radio communication system in which a frequency band is divided into a plurality of sub-frequency bands. The reference signals are transmitted through at least one of the plurality of sub-frequency bands, and data signals are transmitted through the plurality of sub-frequency bands except for the at least one of the plurality of sub-frequency bands. The method includes the steps of: determining a reference signal pattern representing positions of the at least one of the plurality of sub-frequency bands through which the reference signals are transmitted in consideration of a preset time and a preset bandwidth; generating the reference signals using a PN code and a Walsh code; and transmitting the reference signals through the sub-frequency bands corresponding to the reference signal pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
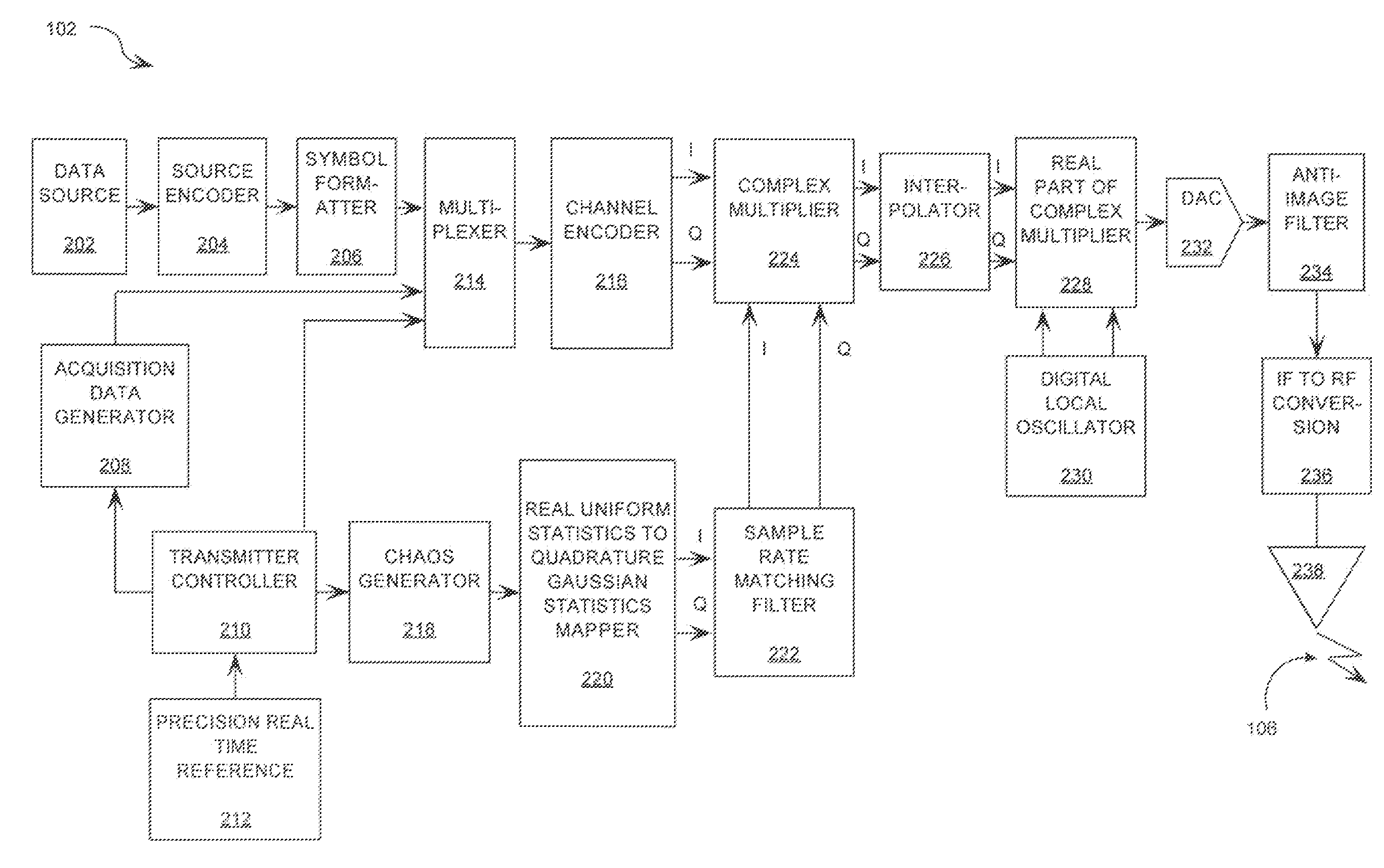
Spread Spectrum Communications System and Method Utilizing Chaotic Sequence
ActiveUS20080304666A1Minimize timing difference uncertaintyMinimize the differenceMultiplex code generationSecuring communicationCommunications systemNumbering system
A method is provided for generating a coherent chaotic sequence spread spectrum communications system. The method includes phase modulating a carrier with information symbols. The method also includes generating a string of discrete time chaotic samples. The method further includes modulating the carrier in a chaotic manner using the string of discrete time chaotic samples. Each of the discrete time chaotic samples has a shorter sample time interval than the duration of the information symbols. The generating step includes selecting a plurality of polynomial equations. The generating step also includes using residue number system (RNS) arithmetic operations to respectively determine solutions for the polynomial equations. The solutions are iteratively computed and expressed as RNS residue values. The generating step further includes determining a series of digits in the weighted number system based on the RNS residue values. The method further includes synchronizing the chaos generated at the receiver with that generated at the transmitter without periodic transfer of state update information.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Network equipment and message transferring method based on multiple-core processor
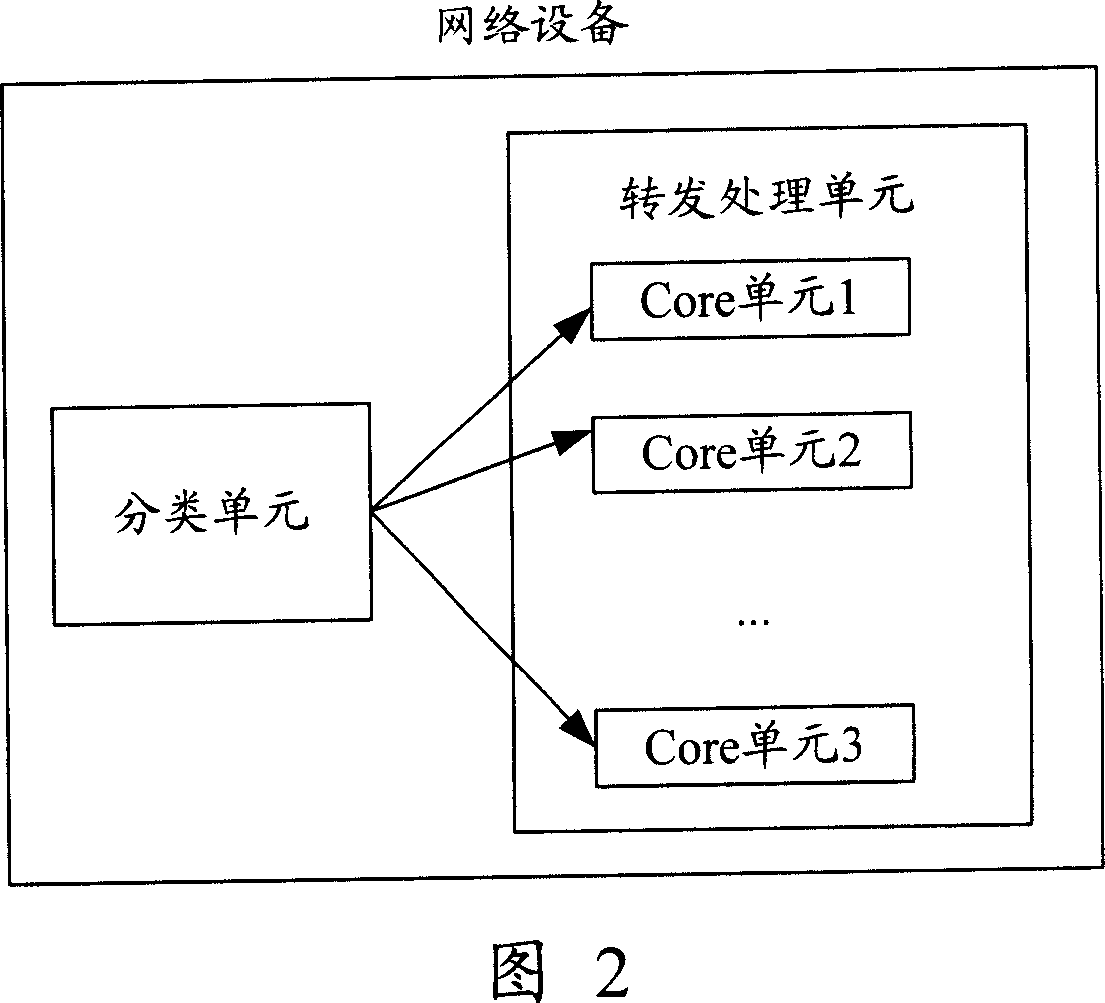
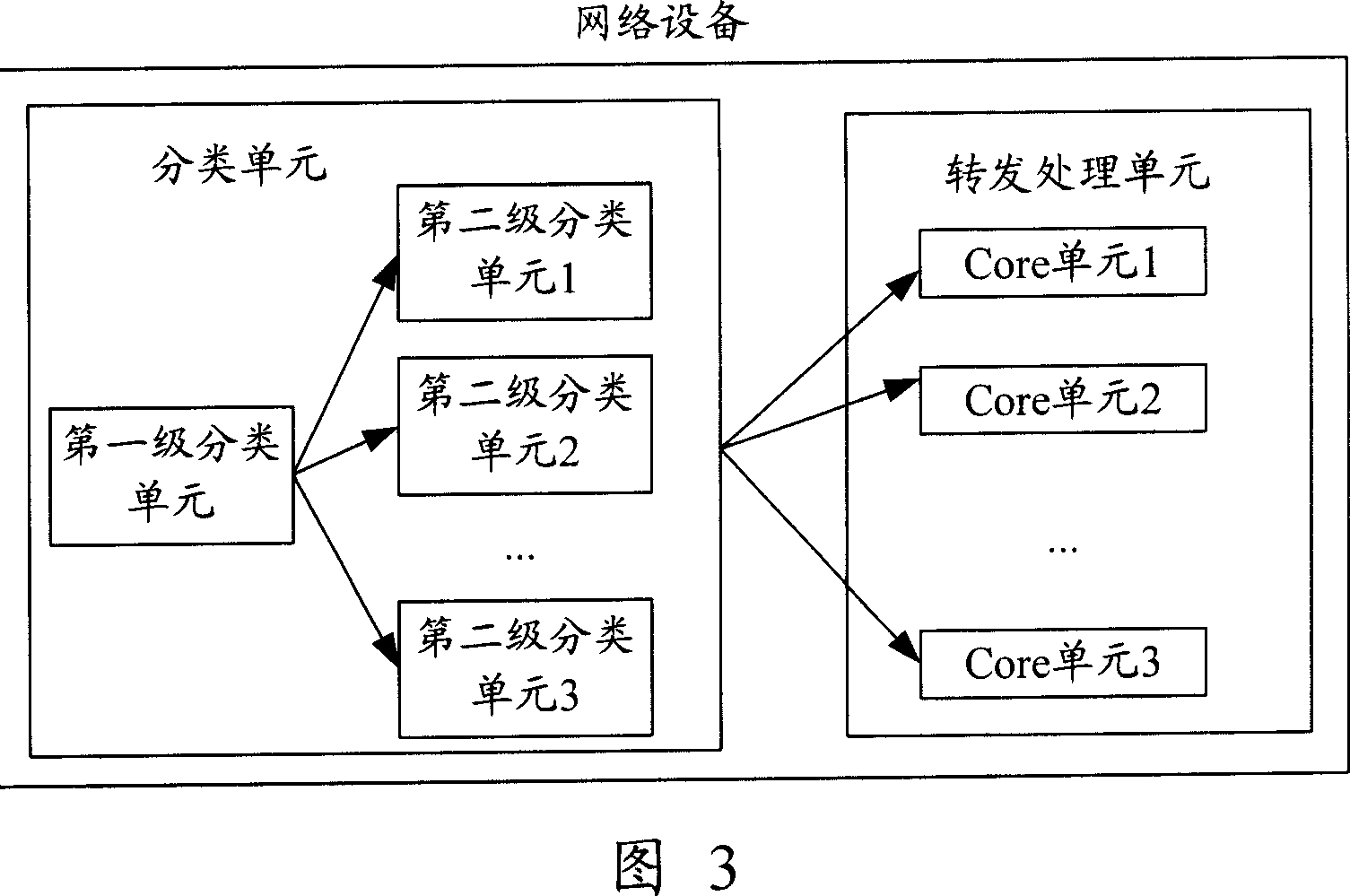
ActiveCN1921457AForwarding Processing GuaranteesImprove packet forwarding and processing capabilitiesPulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionMulti-core processorTransfer Ability
The invention relates to a network device, and a report transfer method based on multi-core processor. Wherein, said network device comprises: classifying unit and transfer processor with multi-core unit; the classifying unit receives report at any port of network device, selects core unit from the transfer processor, and sends received report to selected core unit; one core unit of transfer processor transfers report when receives report. The invention can use classifying unit to select core unit to balance the load between core units, to make them parallel transfer reports, to improve the report transfer ability of network device.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Capacity management method for a code division multiple access (CDMA) communication system
A multiple access, spread-spectrum communication system processes a plurality of information signals received by a Radio Carrier Station (RCS) over telecommunication lines for simultaneous transmission over a radio frequency (RF) channel as a code-division-multiplexed (CDM) signal to a group of Subscriber Units (SUs). The RCS receives a call request signal that corresponds to a telecommunication line information signal, and a user identification signal that identifies a user to receive the call. The RCS includes a plurality of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) modems, one of which provides a global pilot code signal. The modems provide message code signals synchronized to the global pilot signal. Each modem combines an information signal with a message code signal to provide a CDM processed signal. The RCS includes a system channel controller is coupled to receive a remote call. An RF transmitter is connected to all of the modems to combine the CDM processed signals with the global pilot code signal to generate a CDM signal. The RF transmitter also modulates a carrier signal with the CDM signal and transmits the modulated carrier signal through an RF communication channel to the SUs. Each SU includes a CDMA modem which is also synchronized to the global pilot signal. The CDMA modem despreads the CDM signal and provides a despread information signal to the user. The system includes a closed loop power control system for maintaining a minimum system transmit power level for the RCS and the SUs, and system capacity management for maintaining a maximum number of active SUs for improved system performance.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Partly orthogonal multiple code trees
A method, system and apparatus for spreading physical channels using partly orthogonal multiple code trees. A portion of a first code tree is used to spread the physical channels. This first code tree is a combination of a channelization code sequence and a first scrambling code sequence. A portion of a second code tree is used to spread the physical channels that are remaining and were not spread using the first code tree. This second code tree is a combination of the channelization code sequence and a second scrambling code formed by modifying the first scrambling code. The portion of the second code tree used to spread the channels is orthogonal to the portion of the first code tree used. A plurality of other code trees could be formed using scrambling codes based on the modification of the first scrambling code.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com