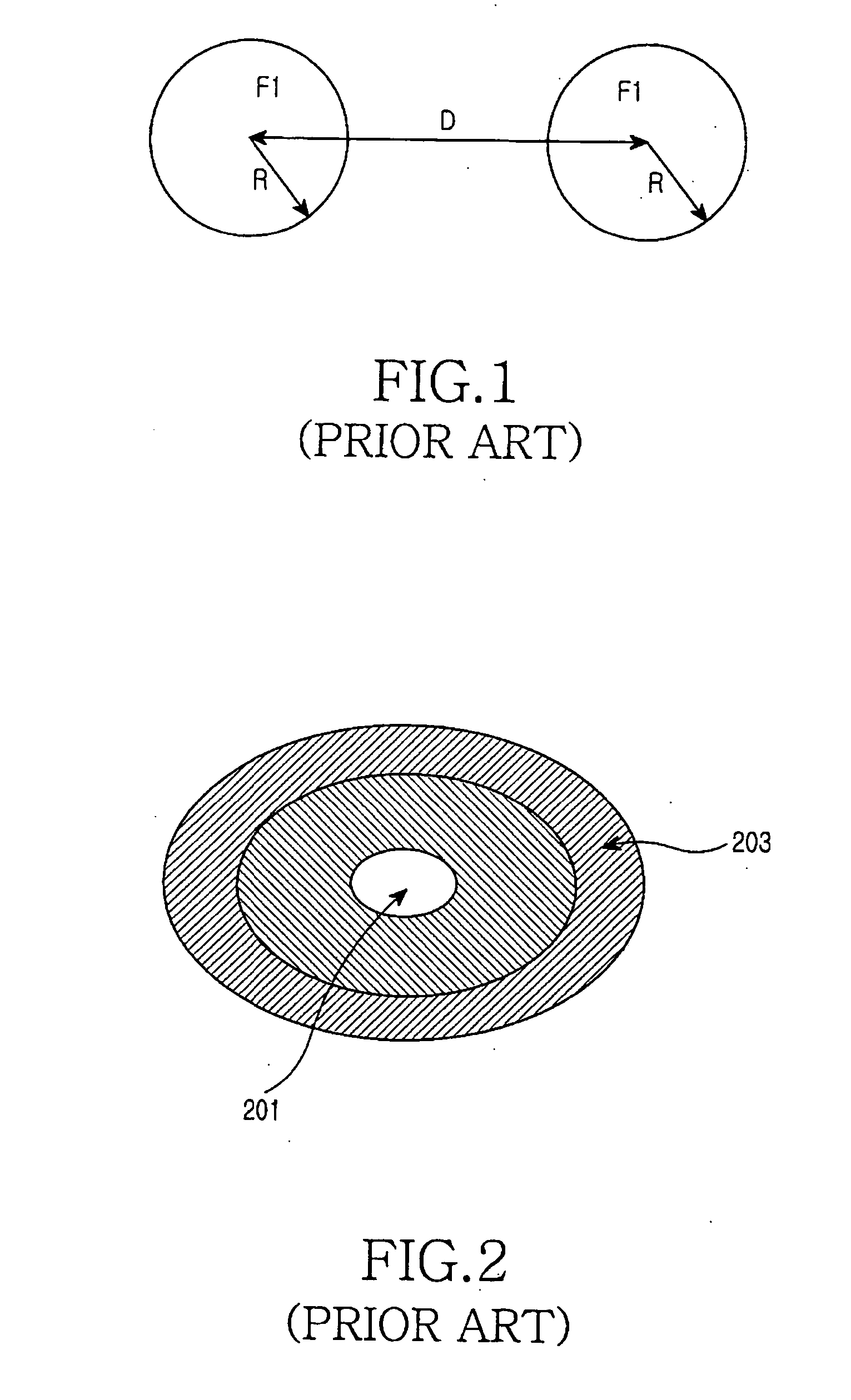
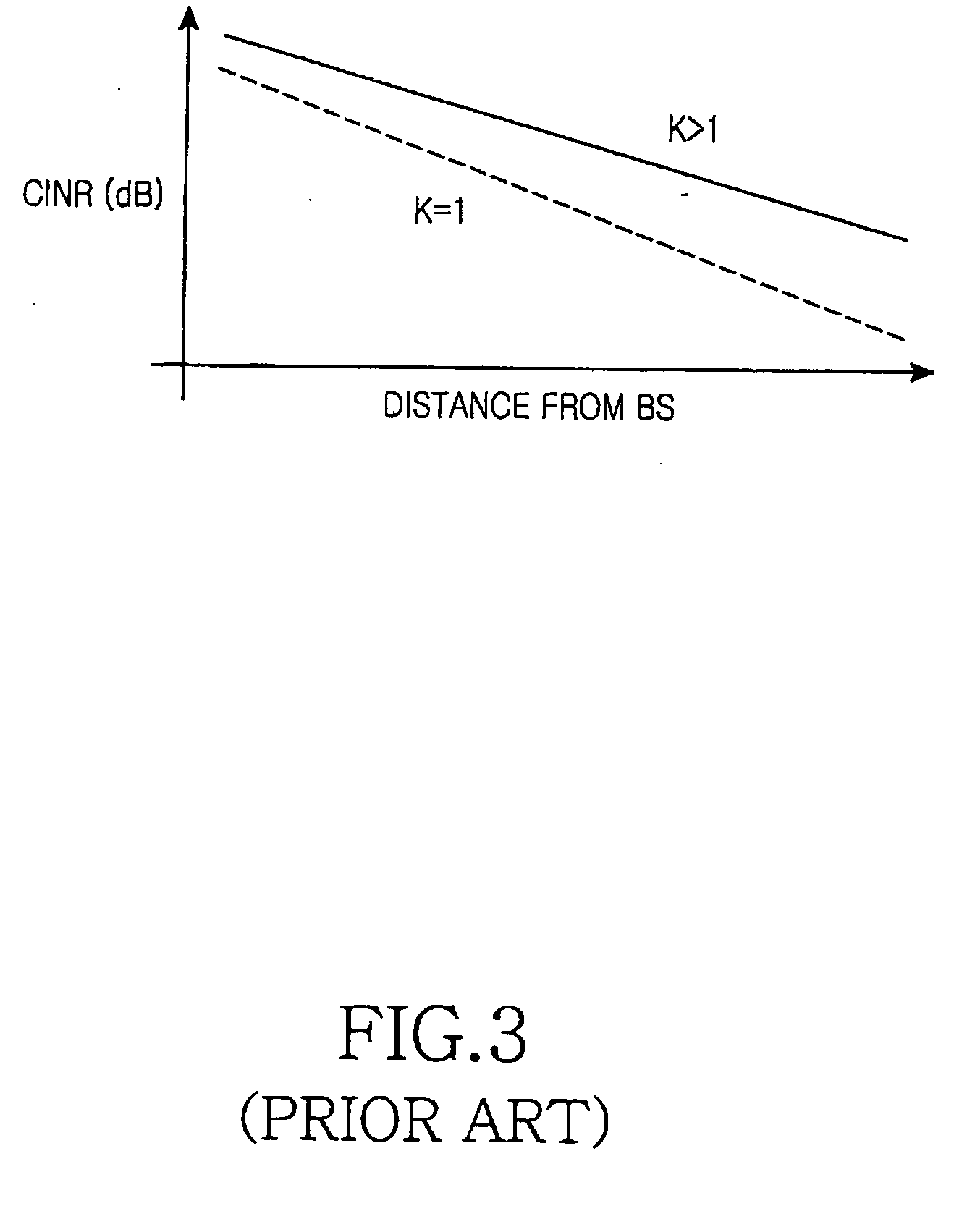
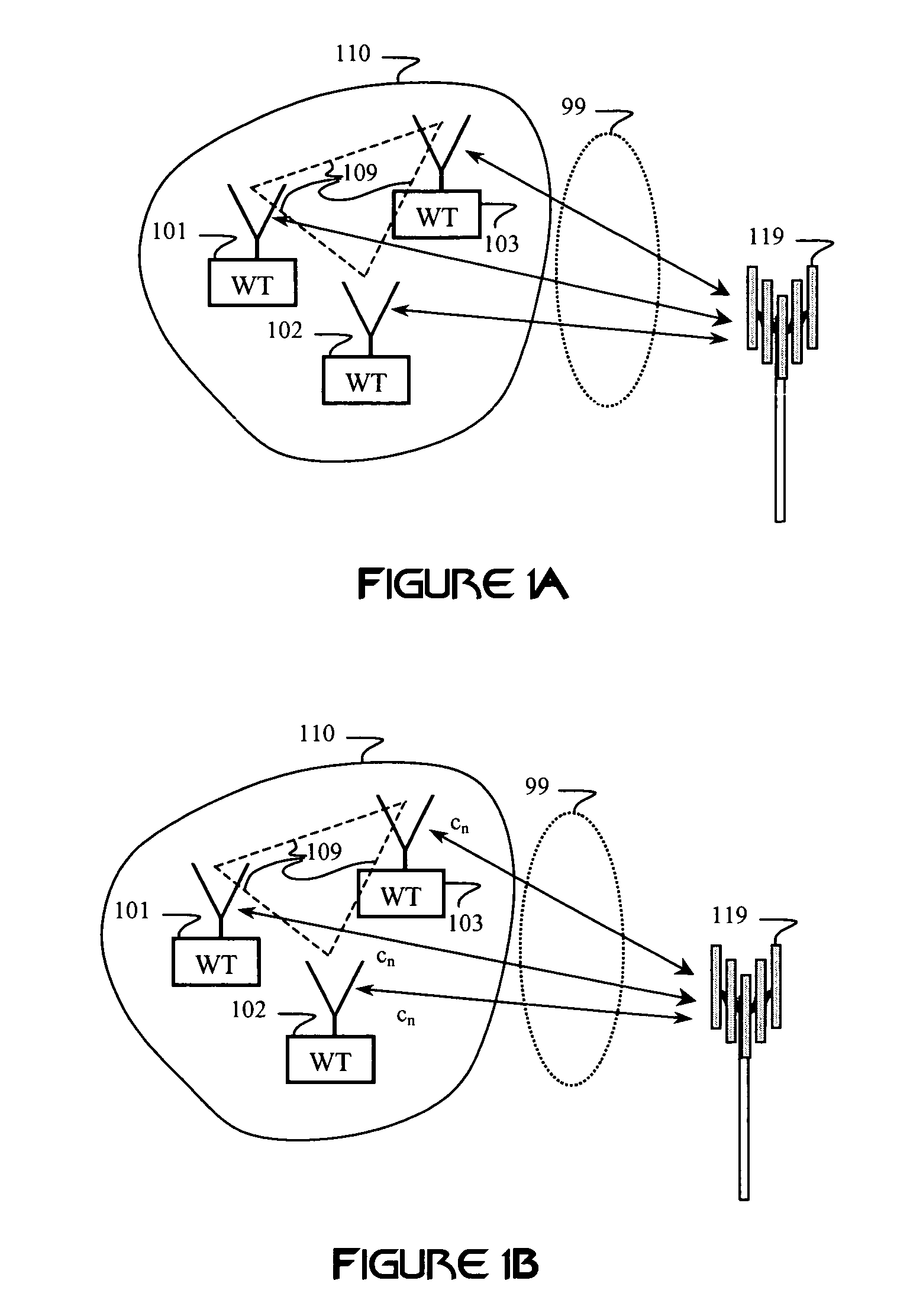
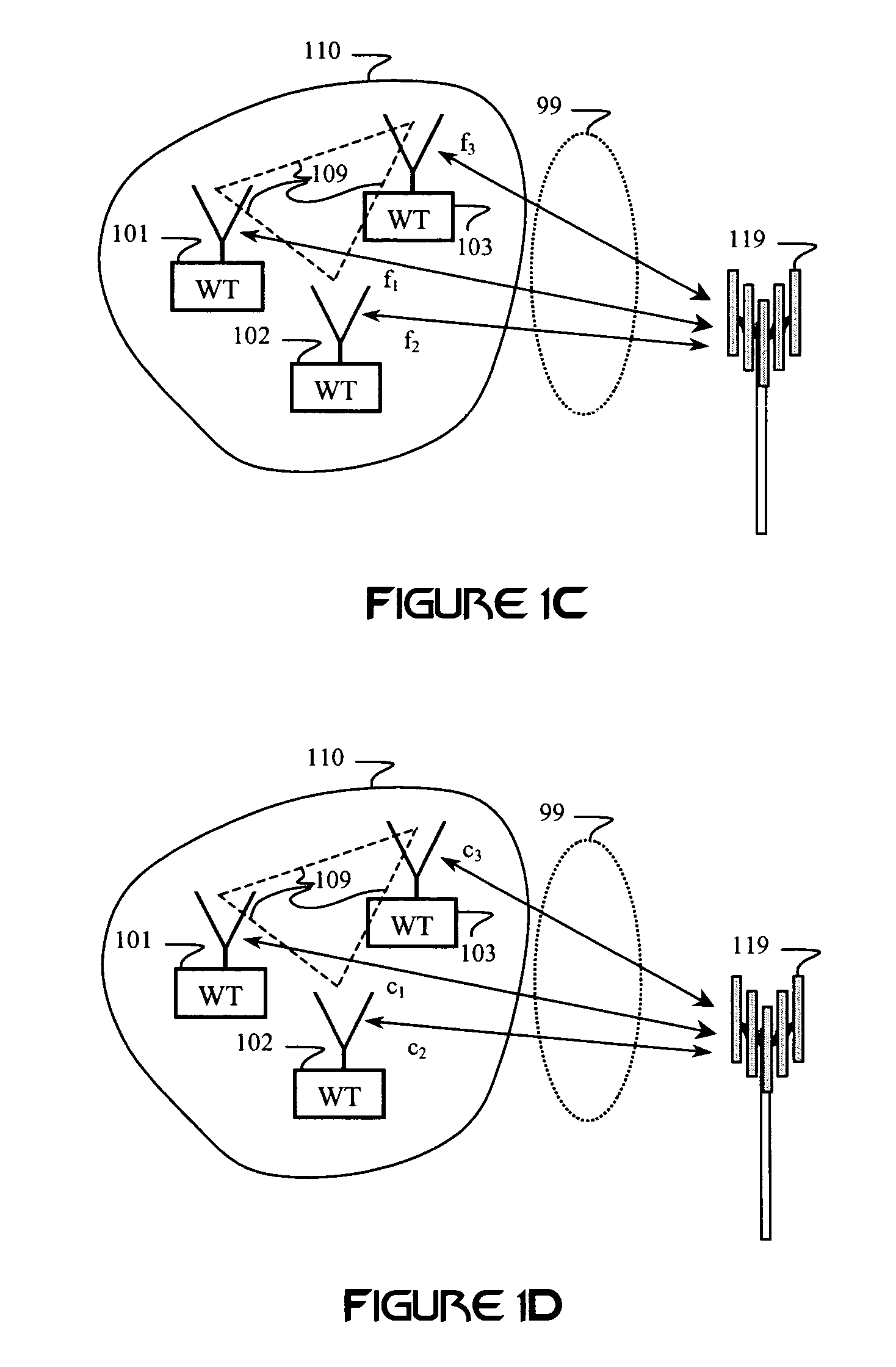
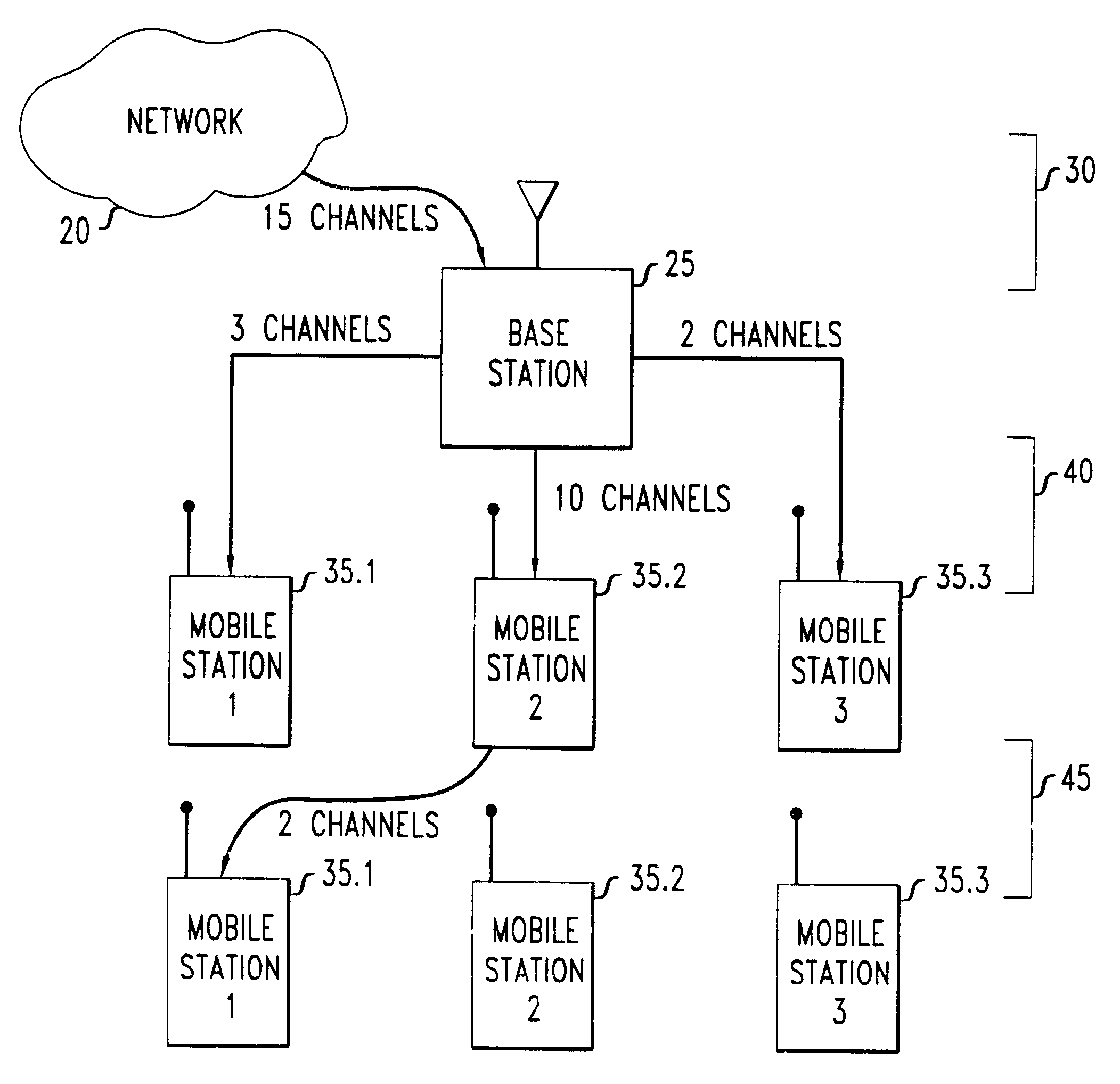
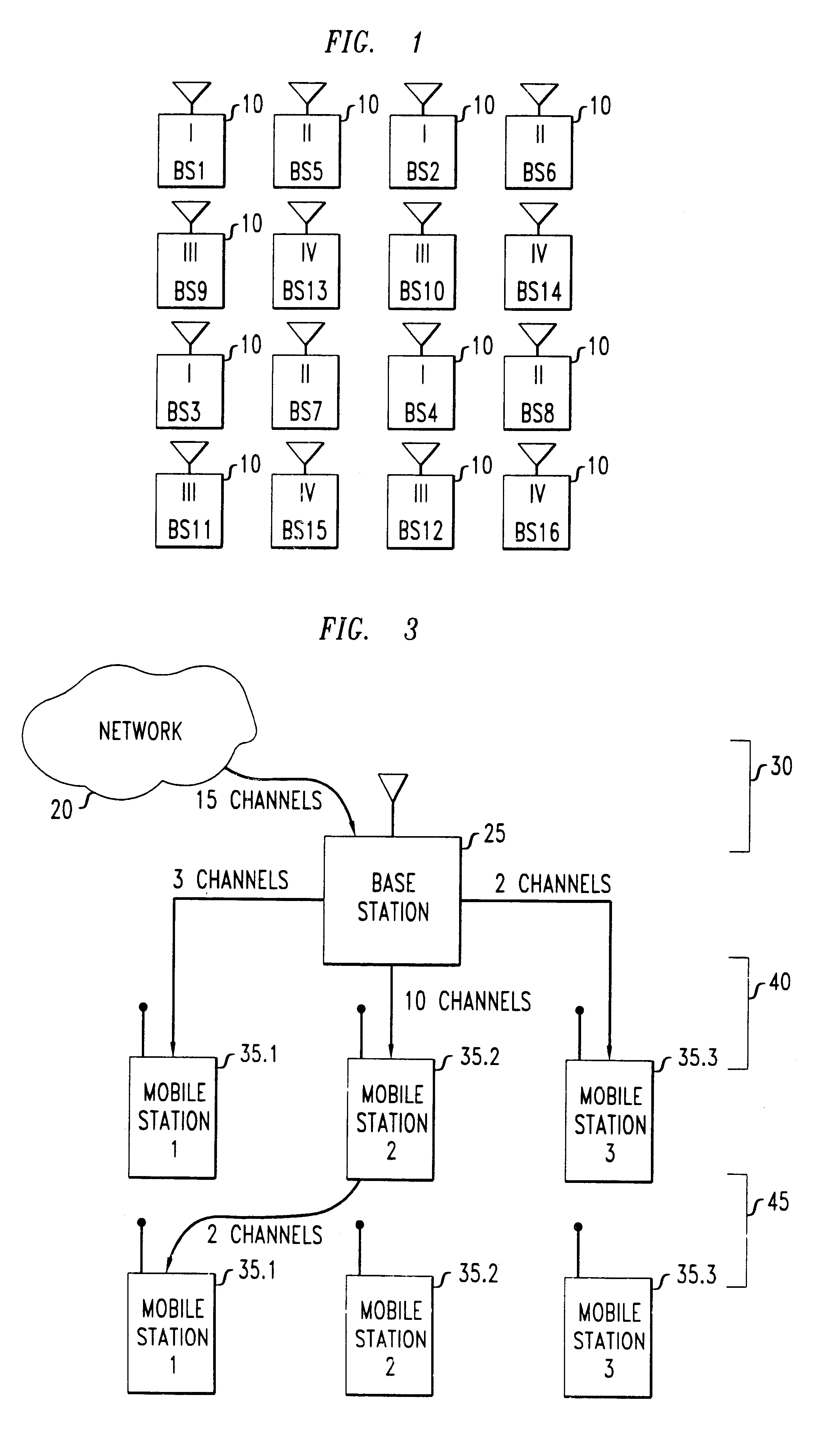
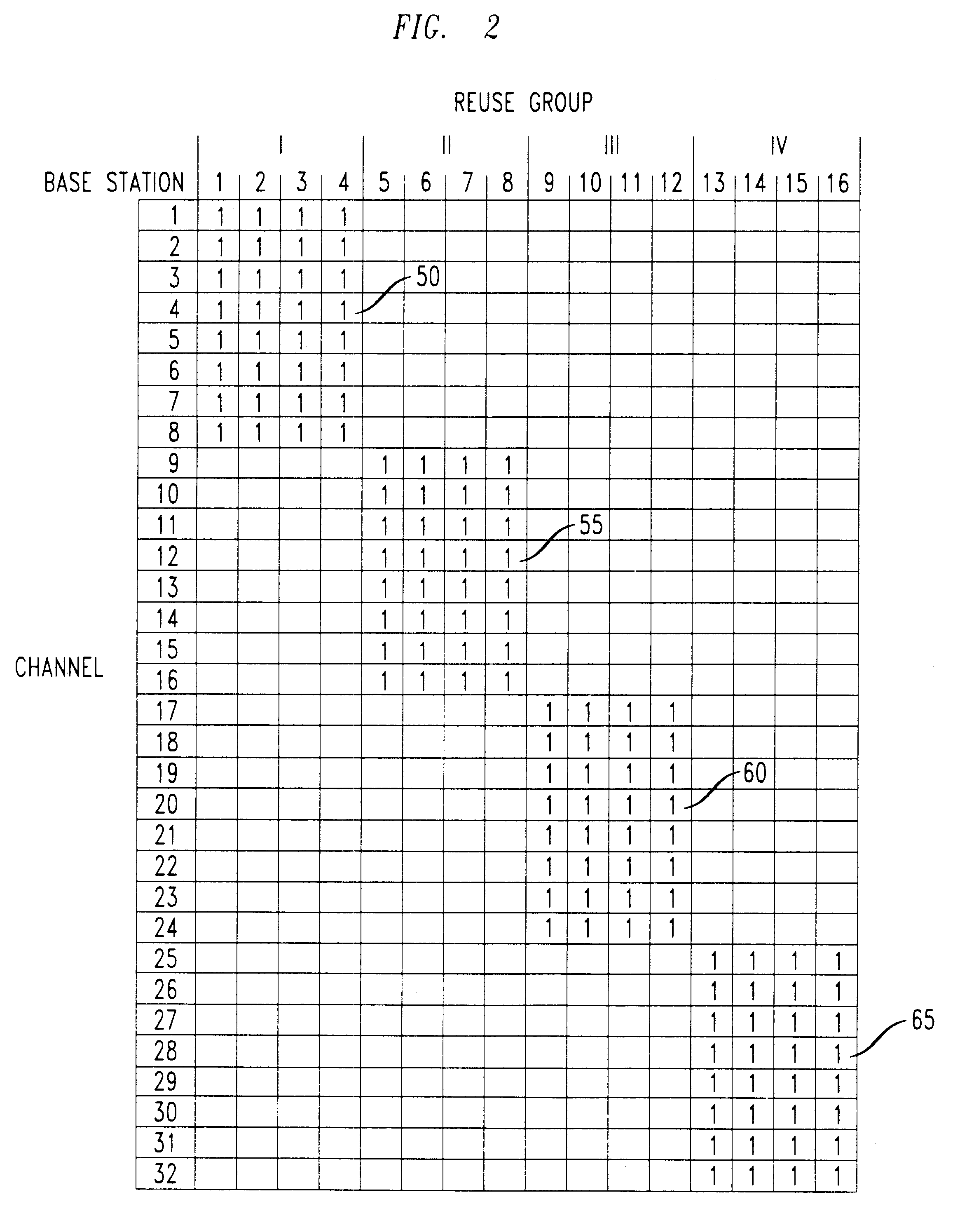
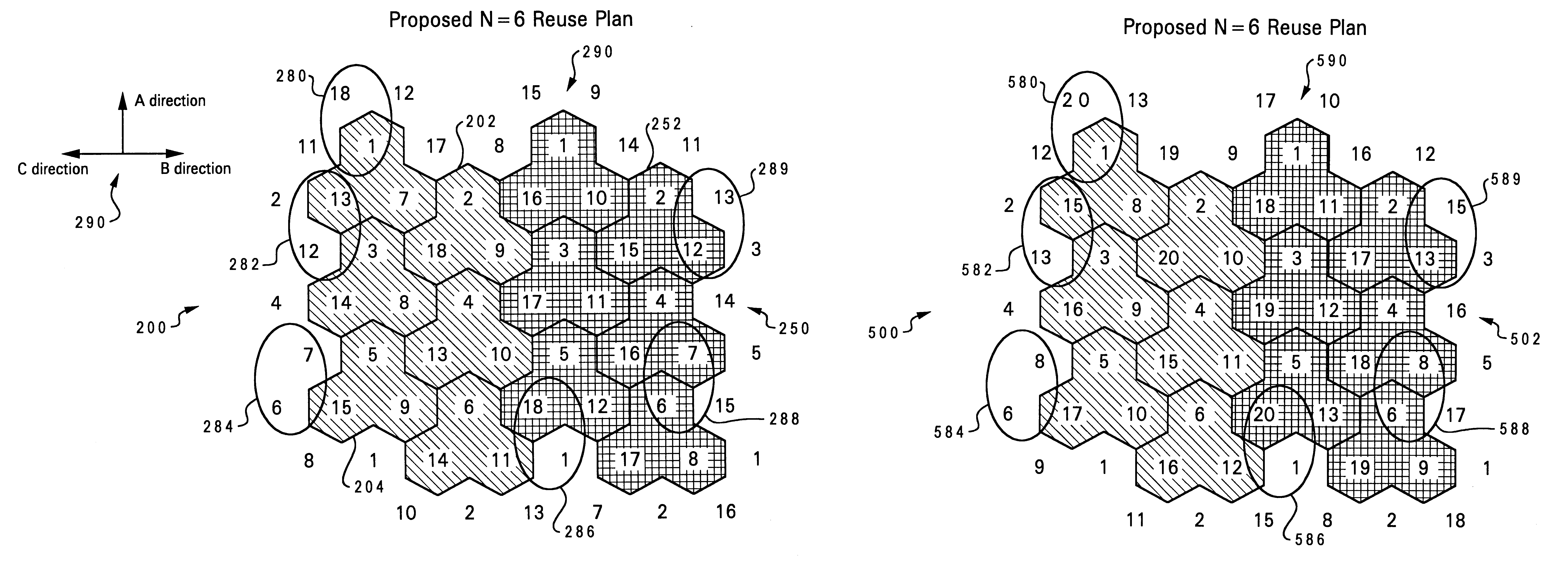
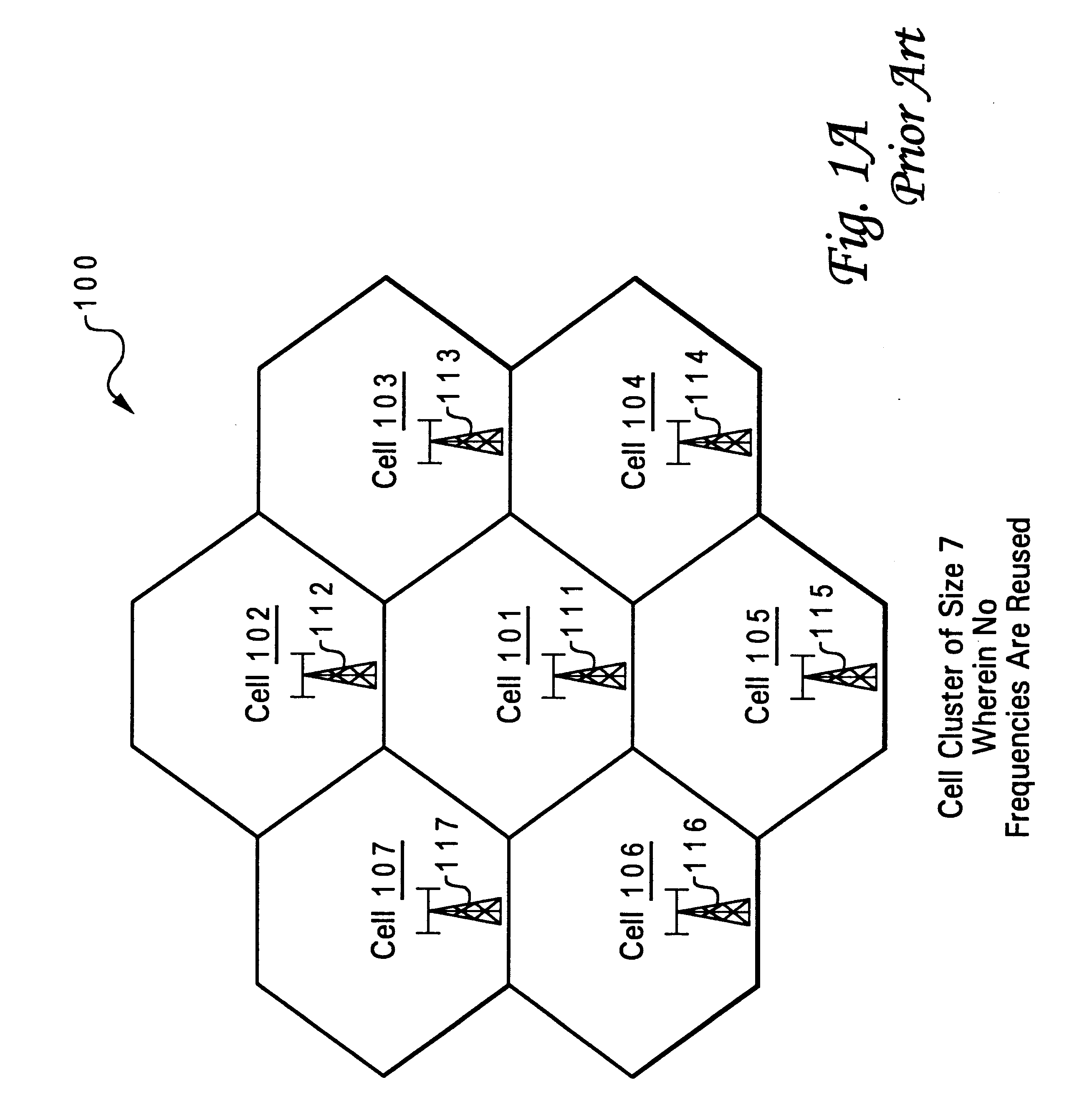
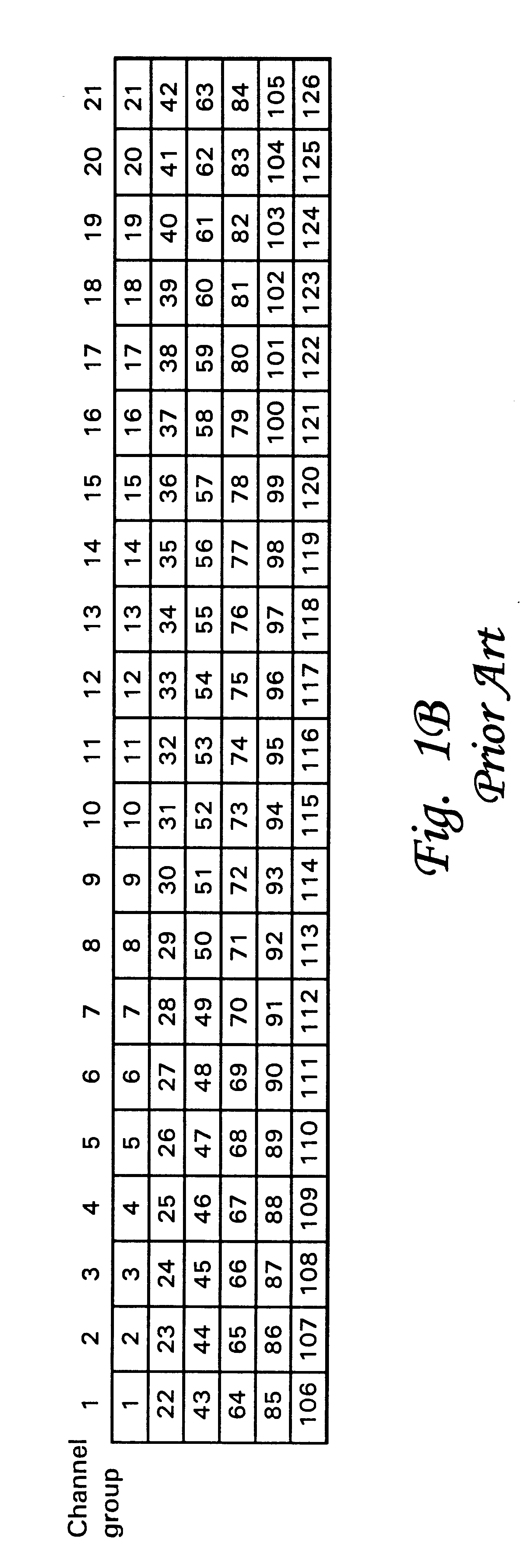
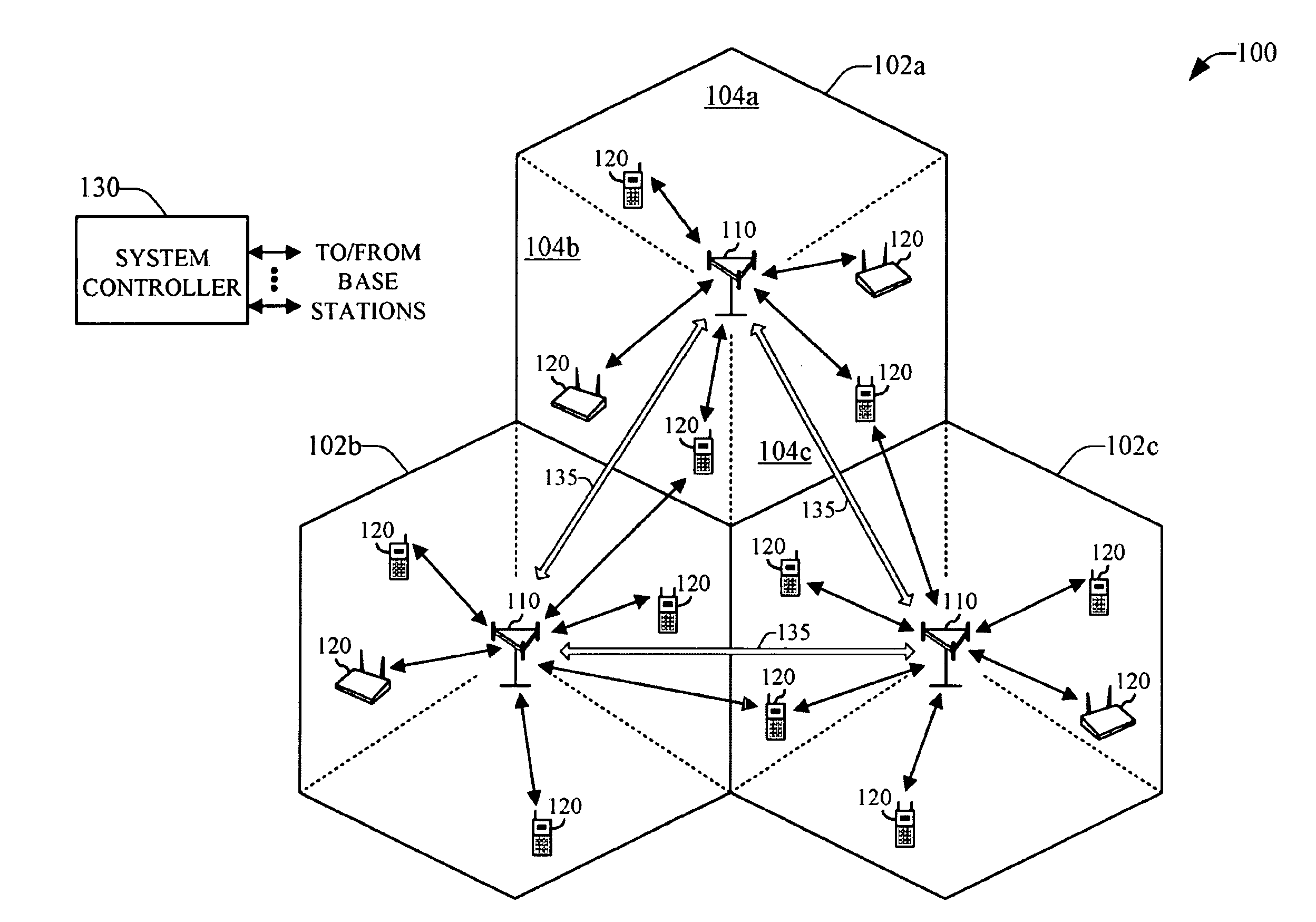
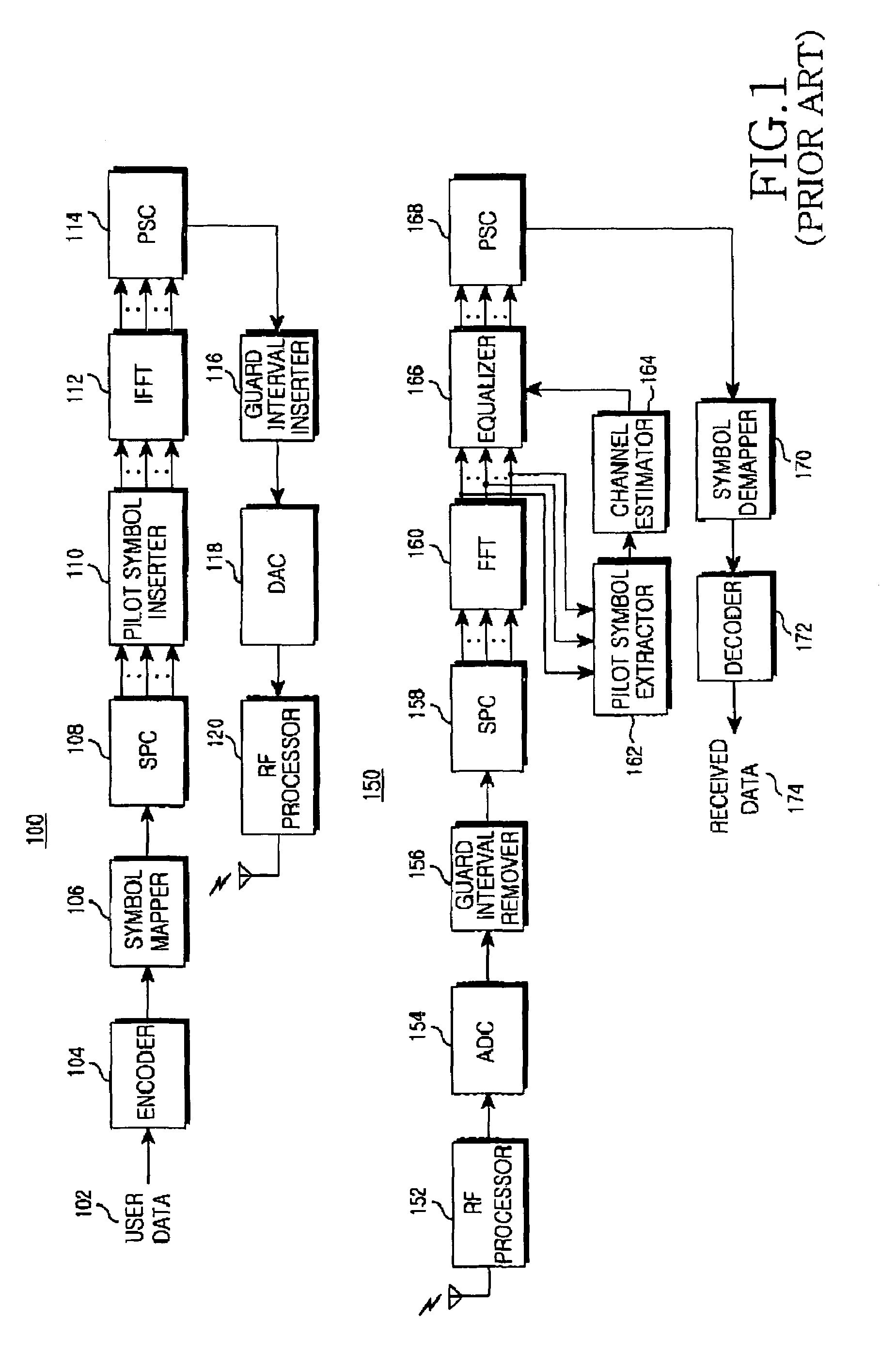
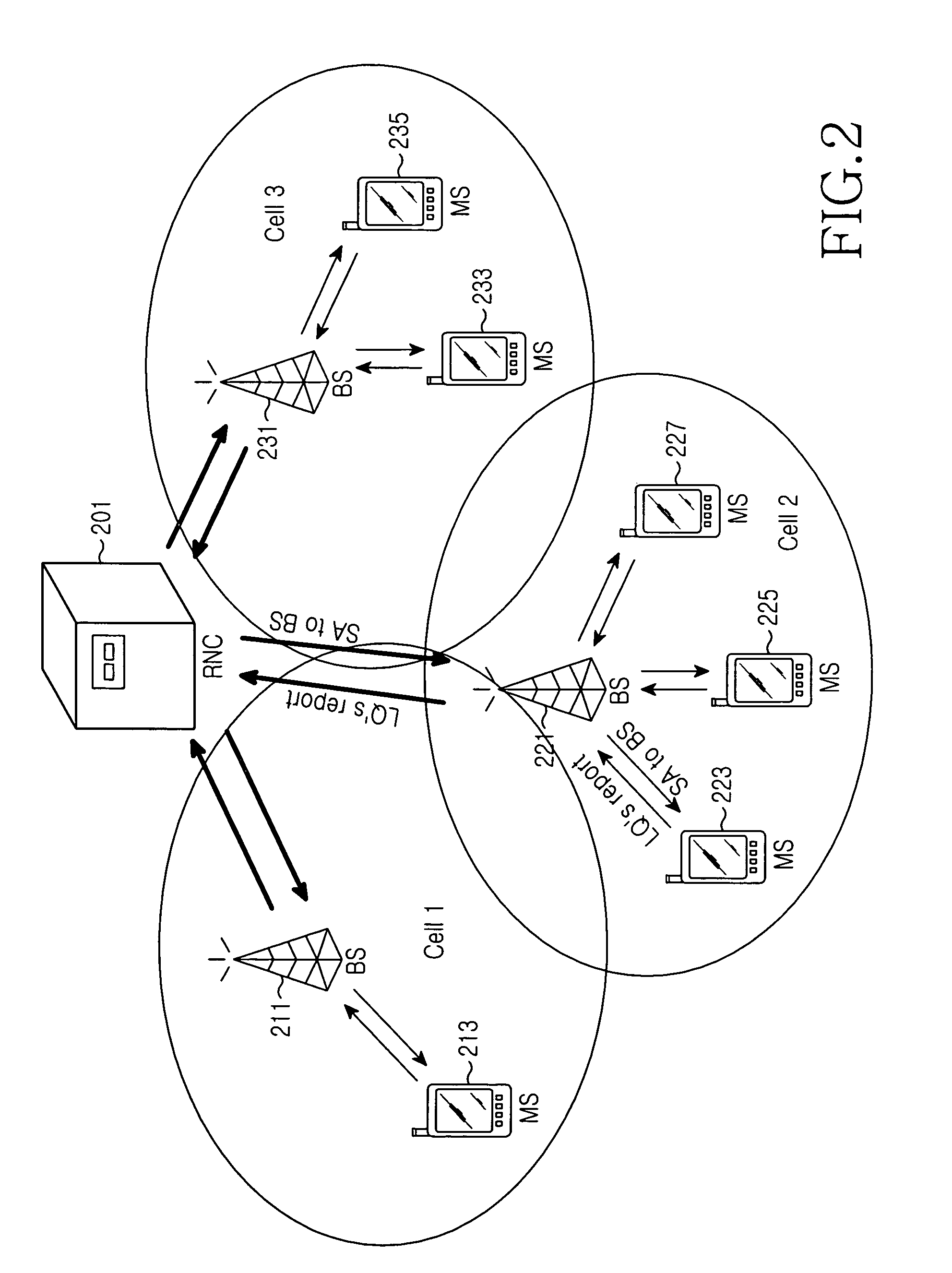
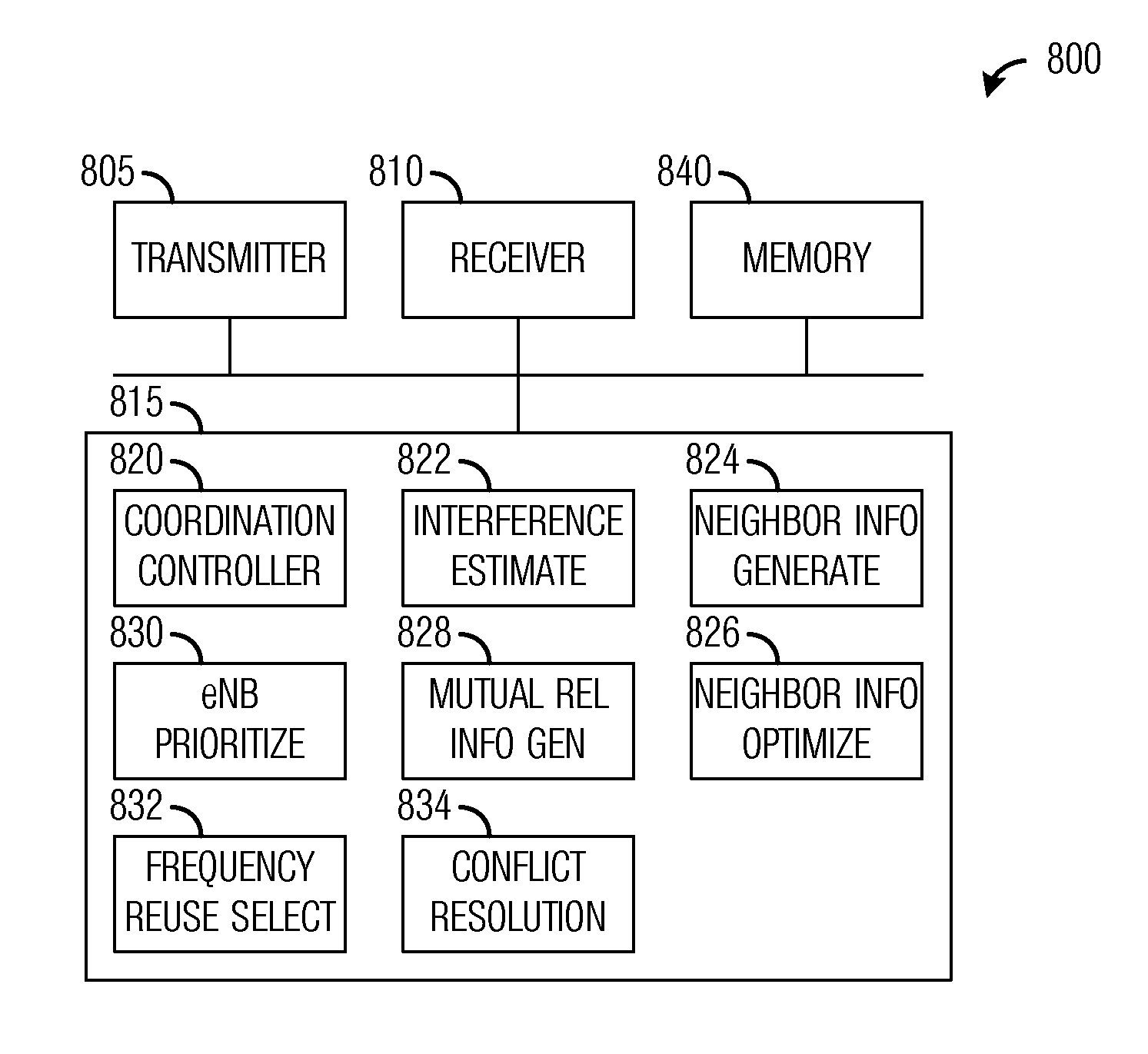
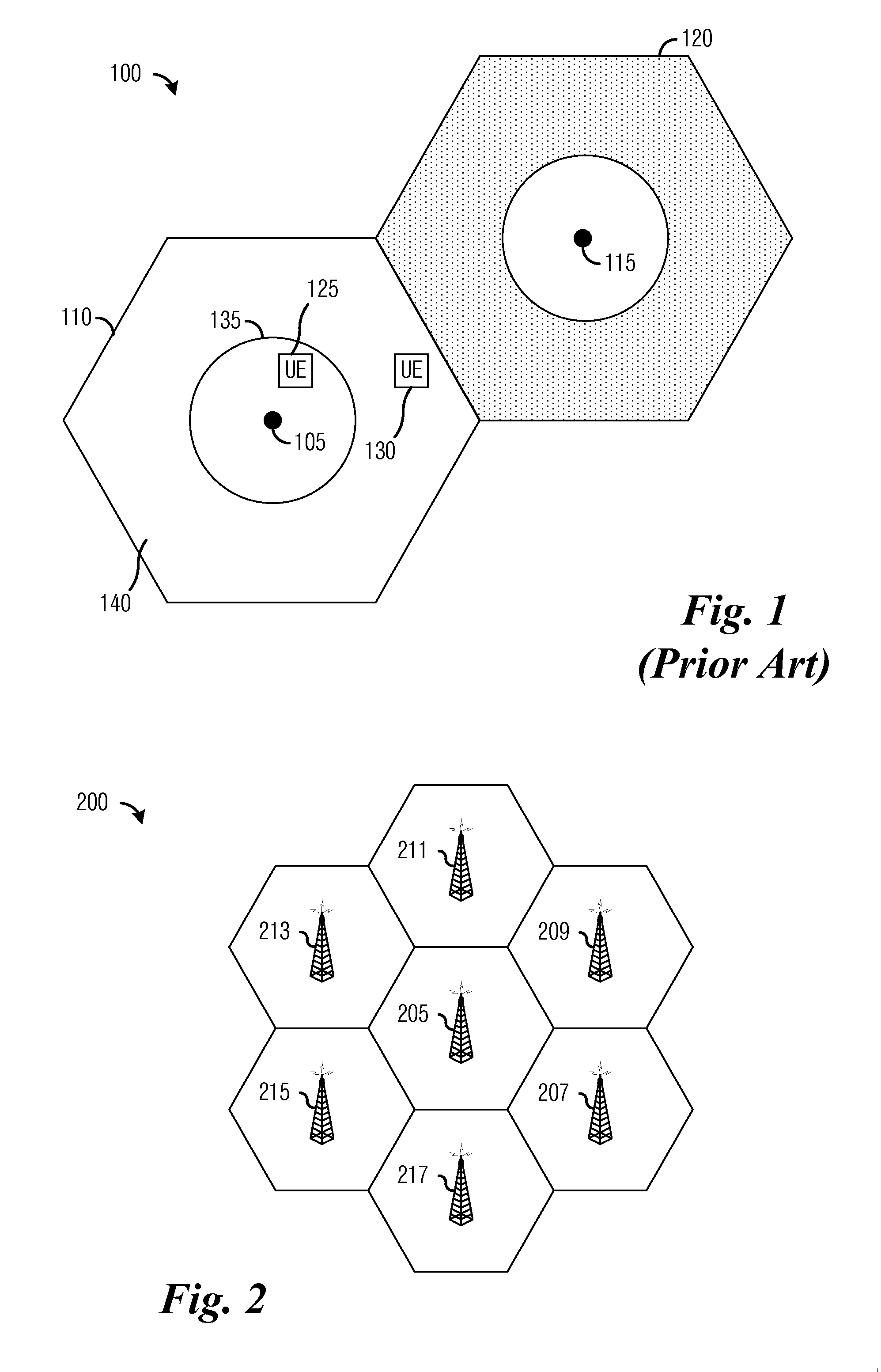
Patents
Literature
563 results about "Frequency reuse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
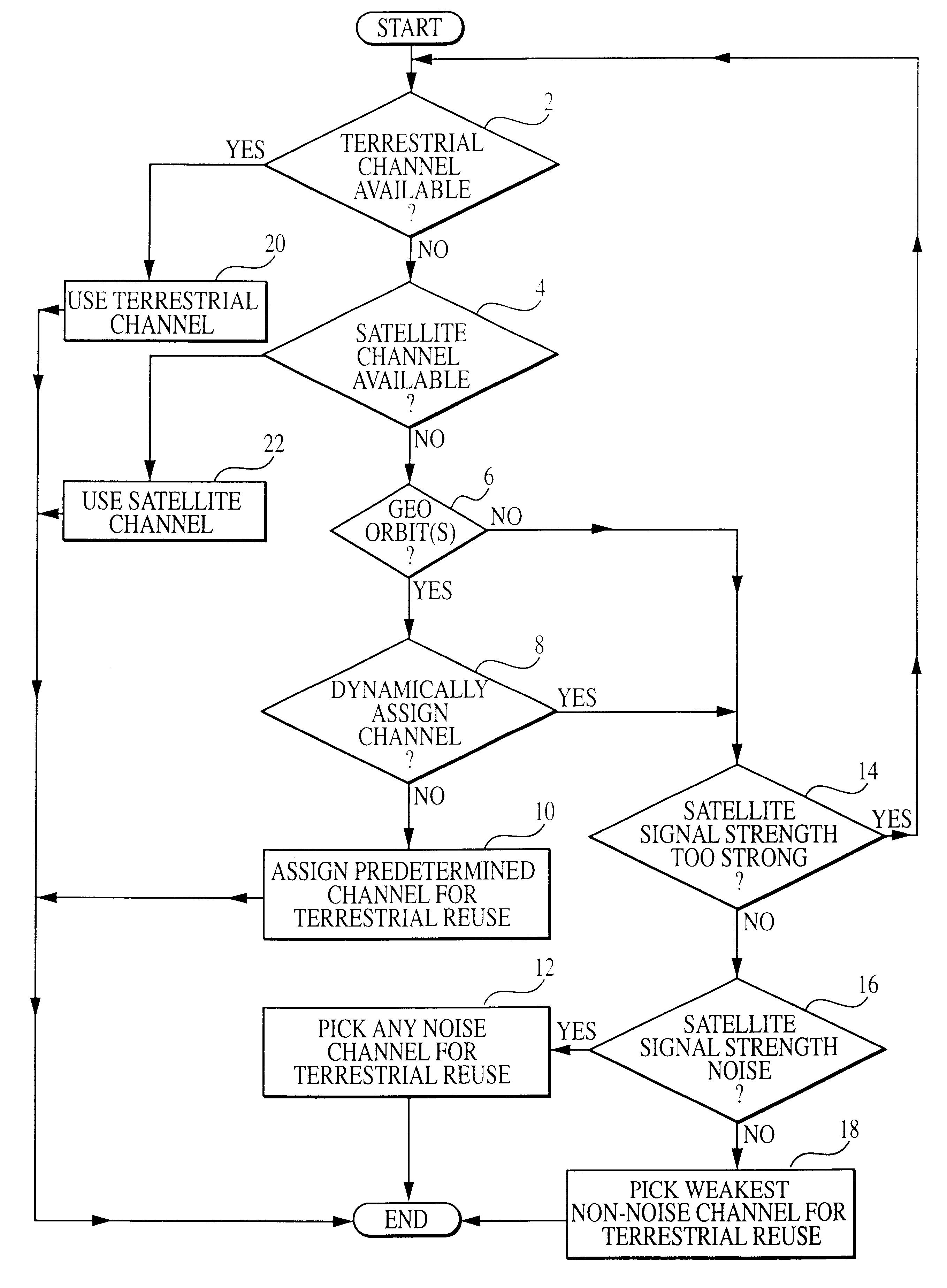
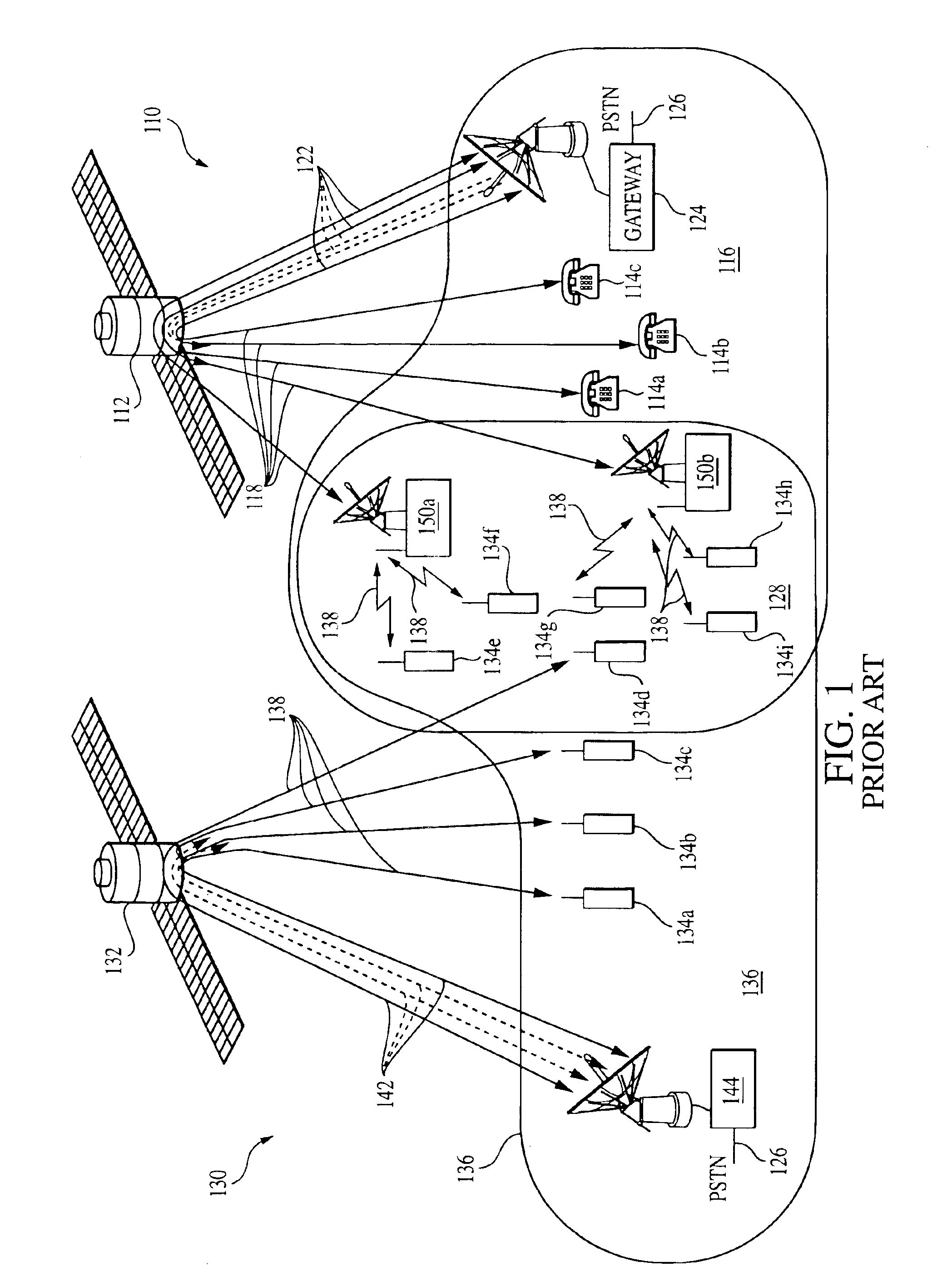
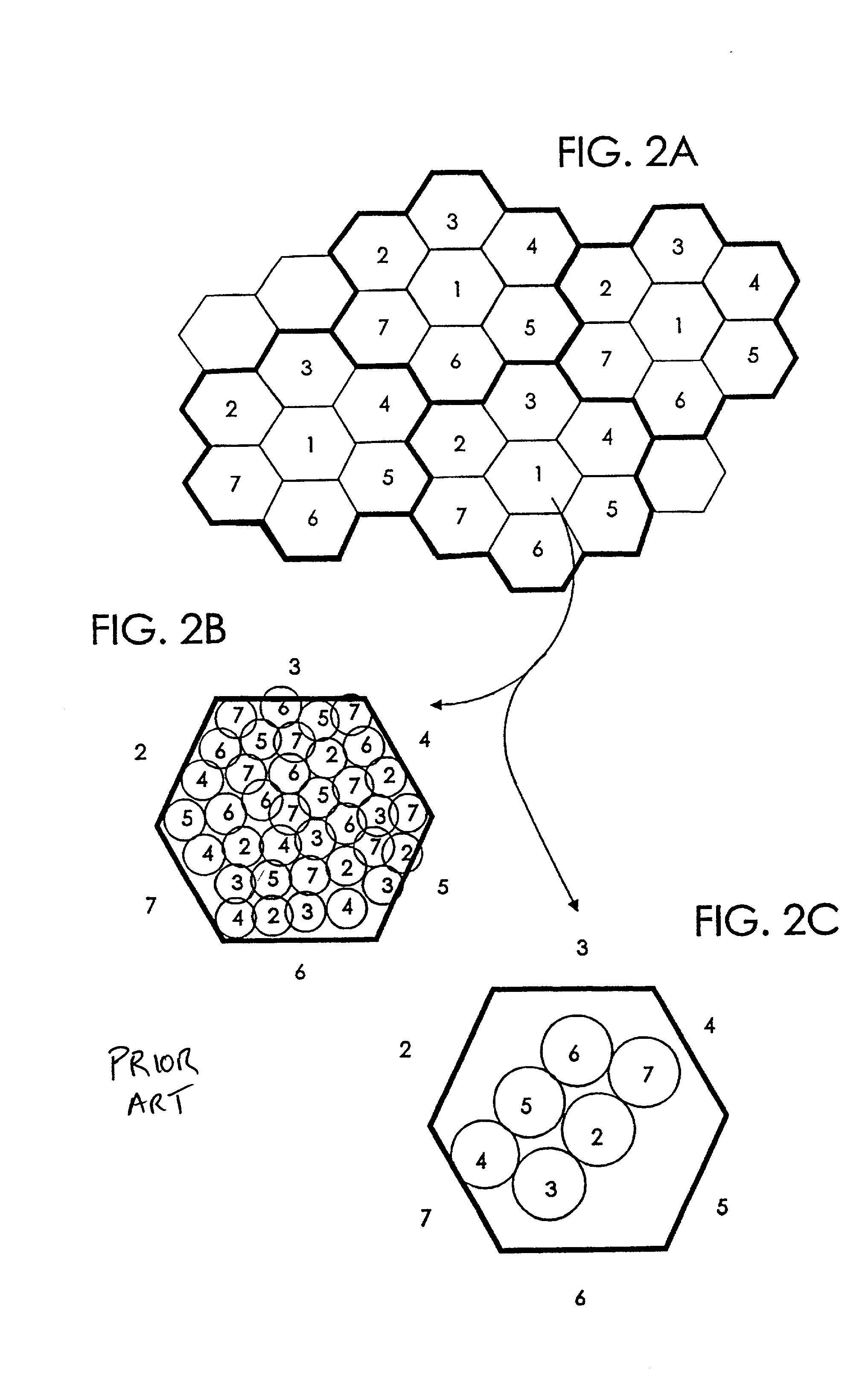
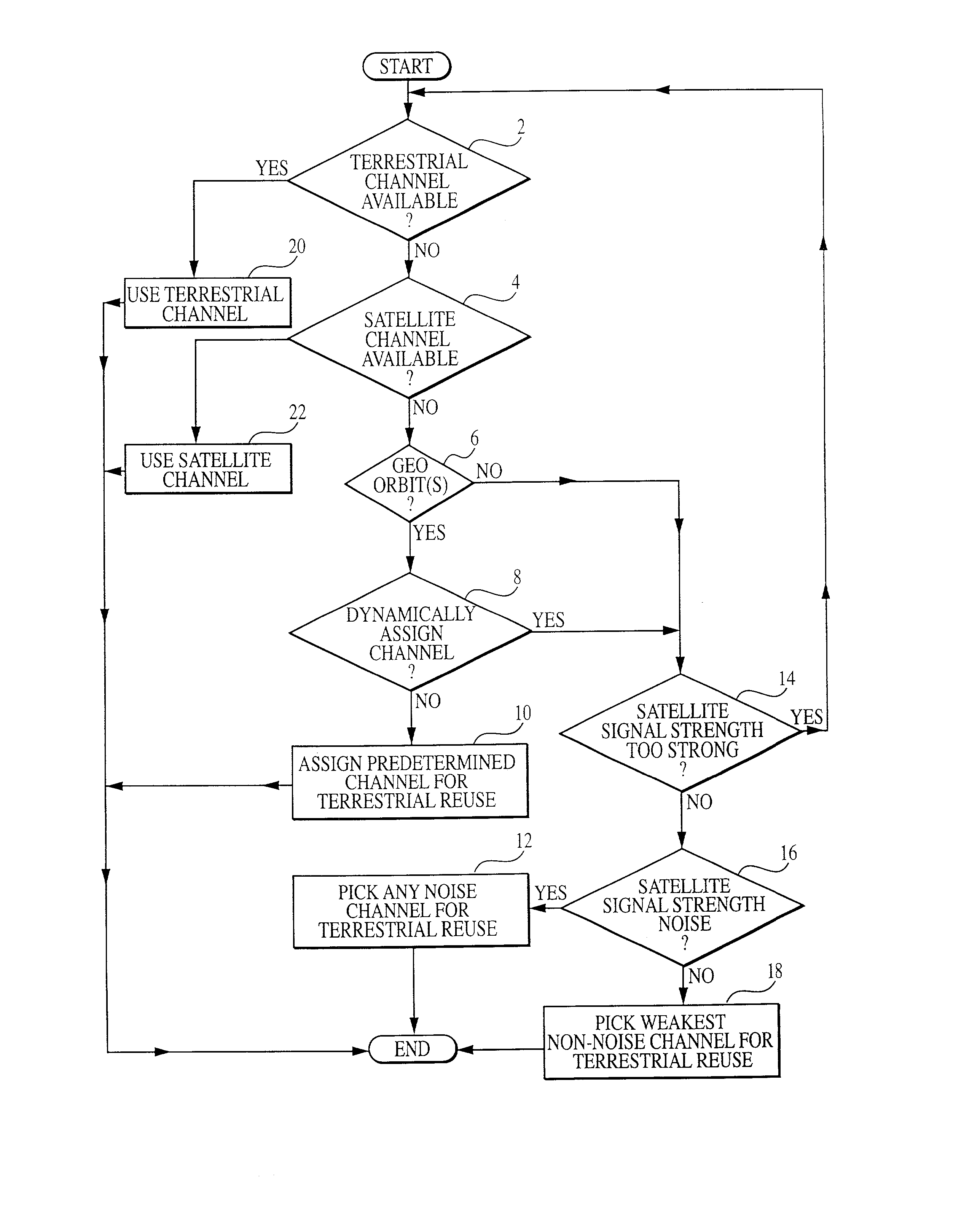
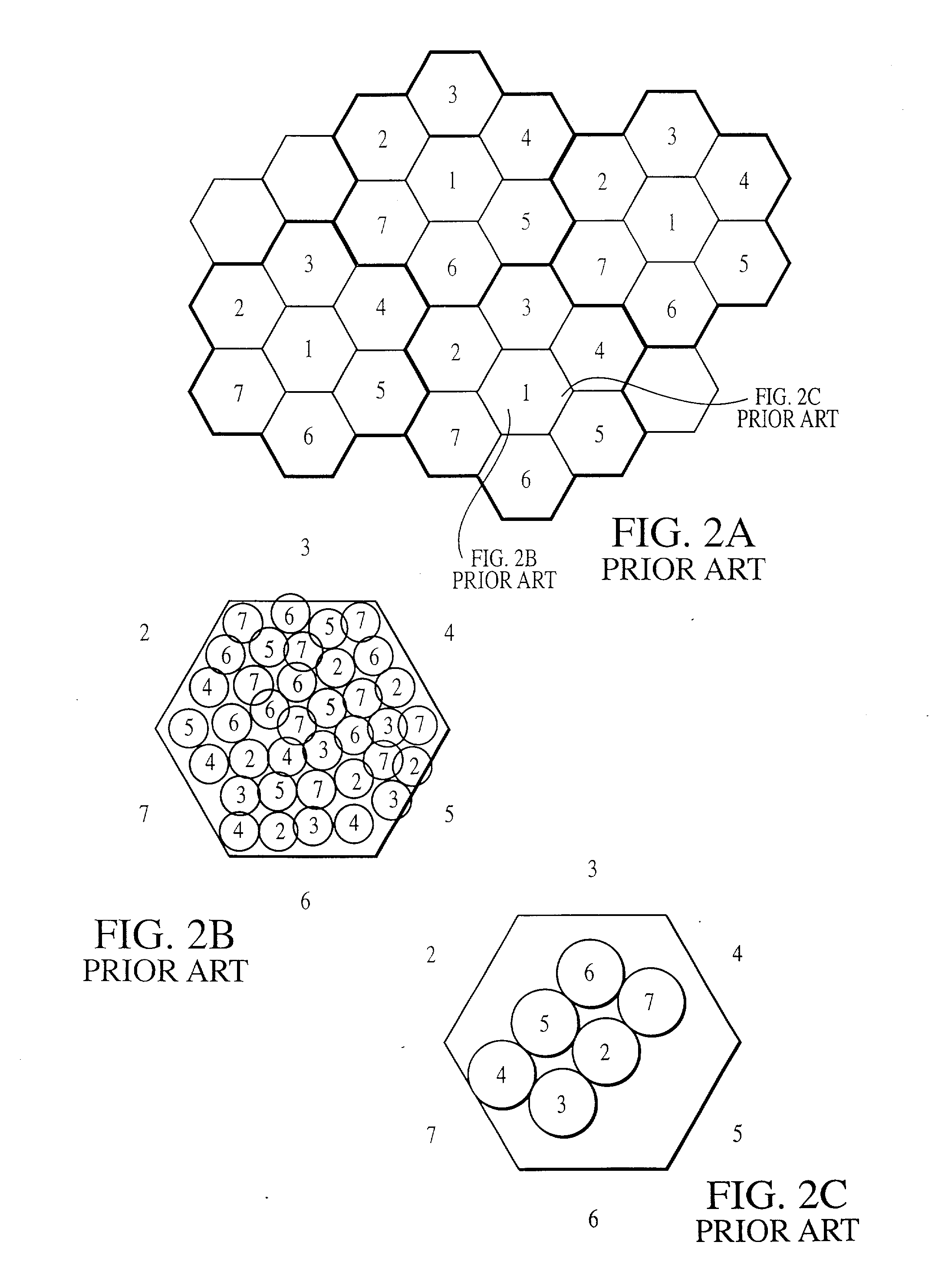
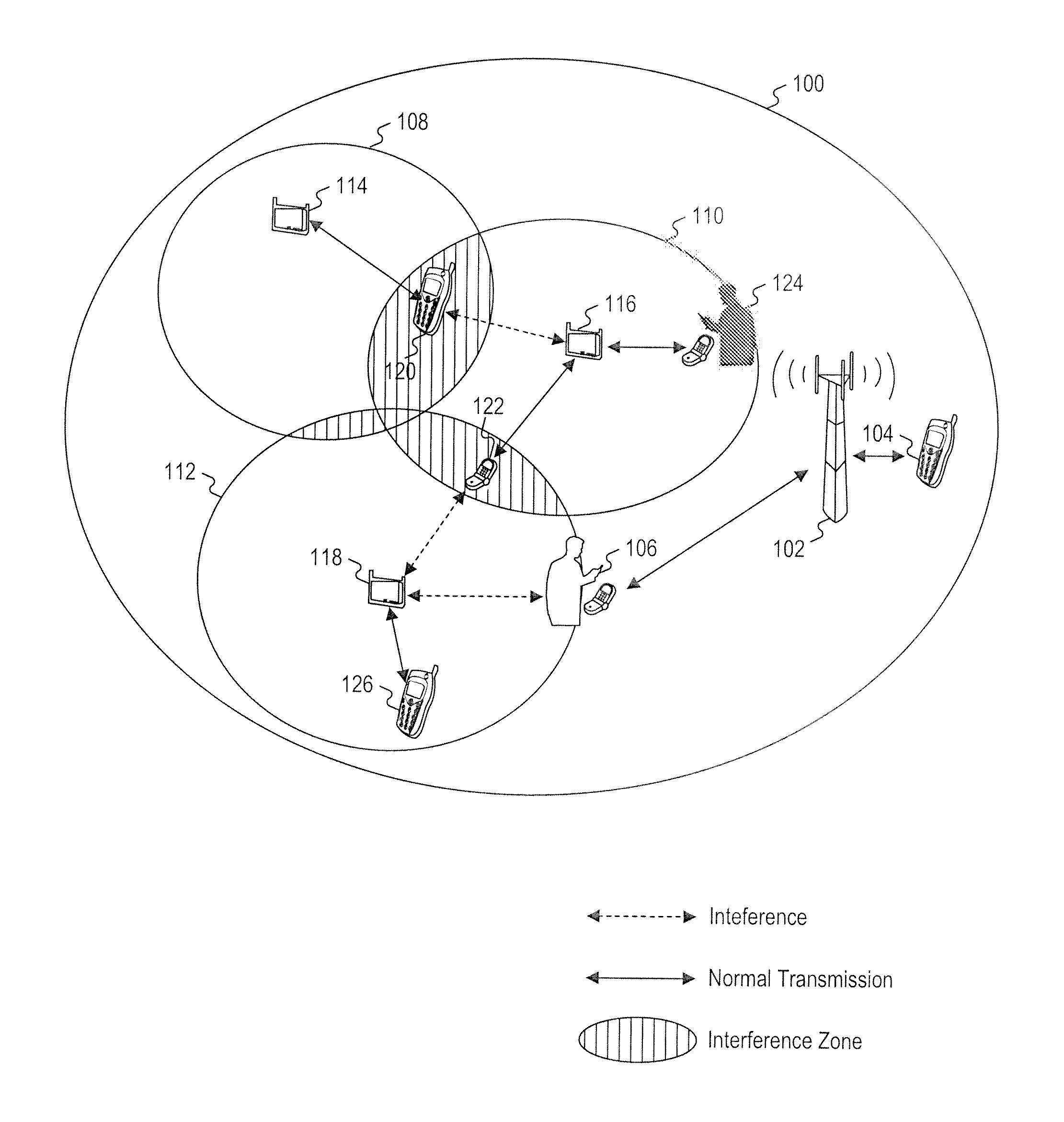
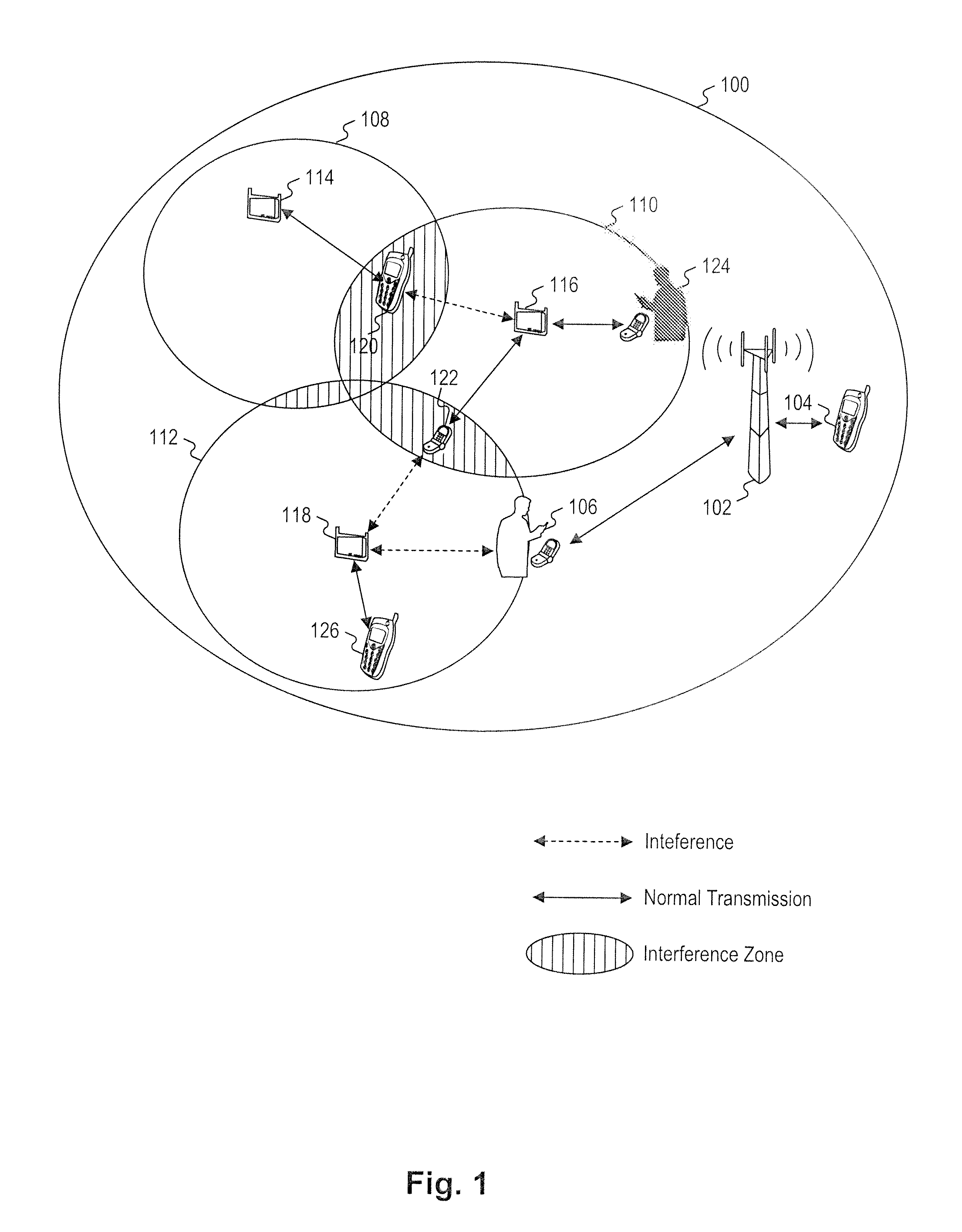
Integrated or autonomous system and method of satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse using signal attenuation and/or blockage, dynamic assignment of frequencies and/or hysteresis
InactiveUS6859652B2Efficient reuseInterference minimizationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentHysteresisUltrasound attenuation
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
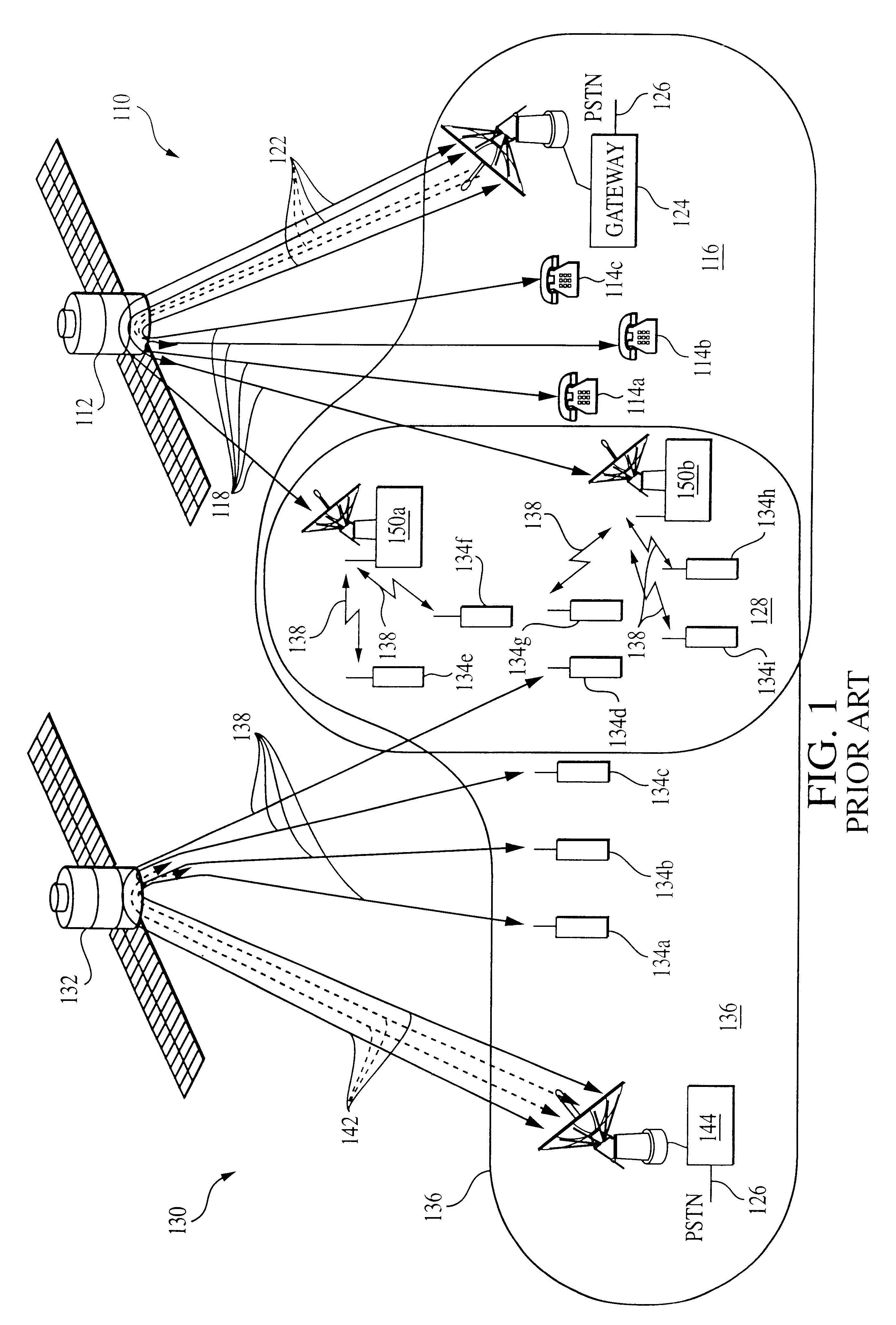
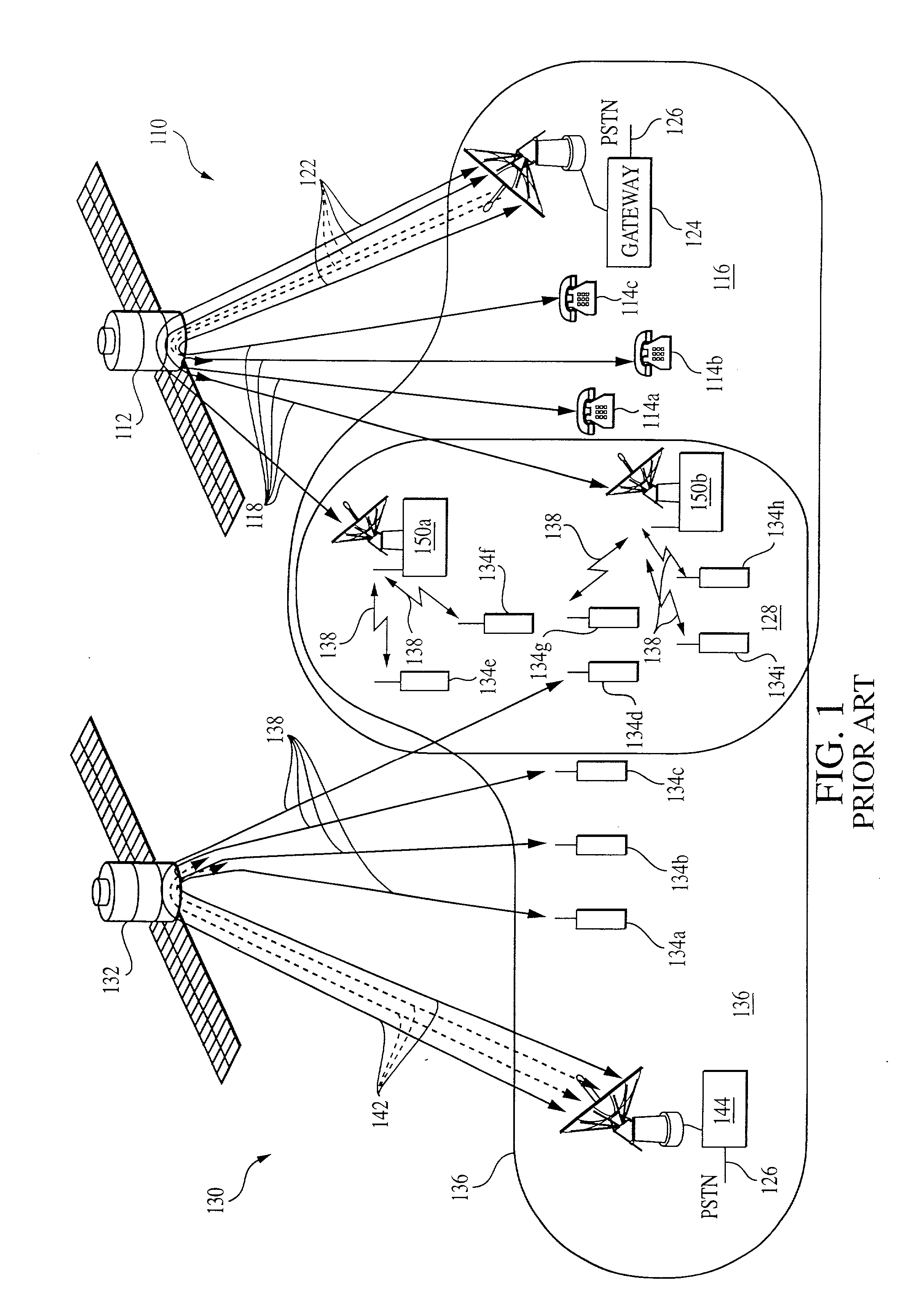
Coordinated satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse
InactiveUS6892068B2Facilitates assignmentEasy to shareRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumFrequency reuse
A system and method of operation for efficiently reusing and / or sharing at least a portion of the frequency spectrum between a first satellite spot beam and a second satellite spot beam, and / or an underlay terrestrial network associated with a second satellite spot beam. The spectrum is efficiently reused and / or shared between respective spot beams and / or associated underlay terrestrial systems in a manner minimizes interference between the respective satellite and terrestrial systems.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
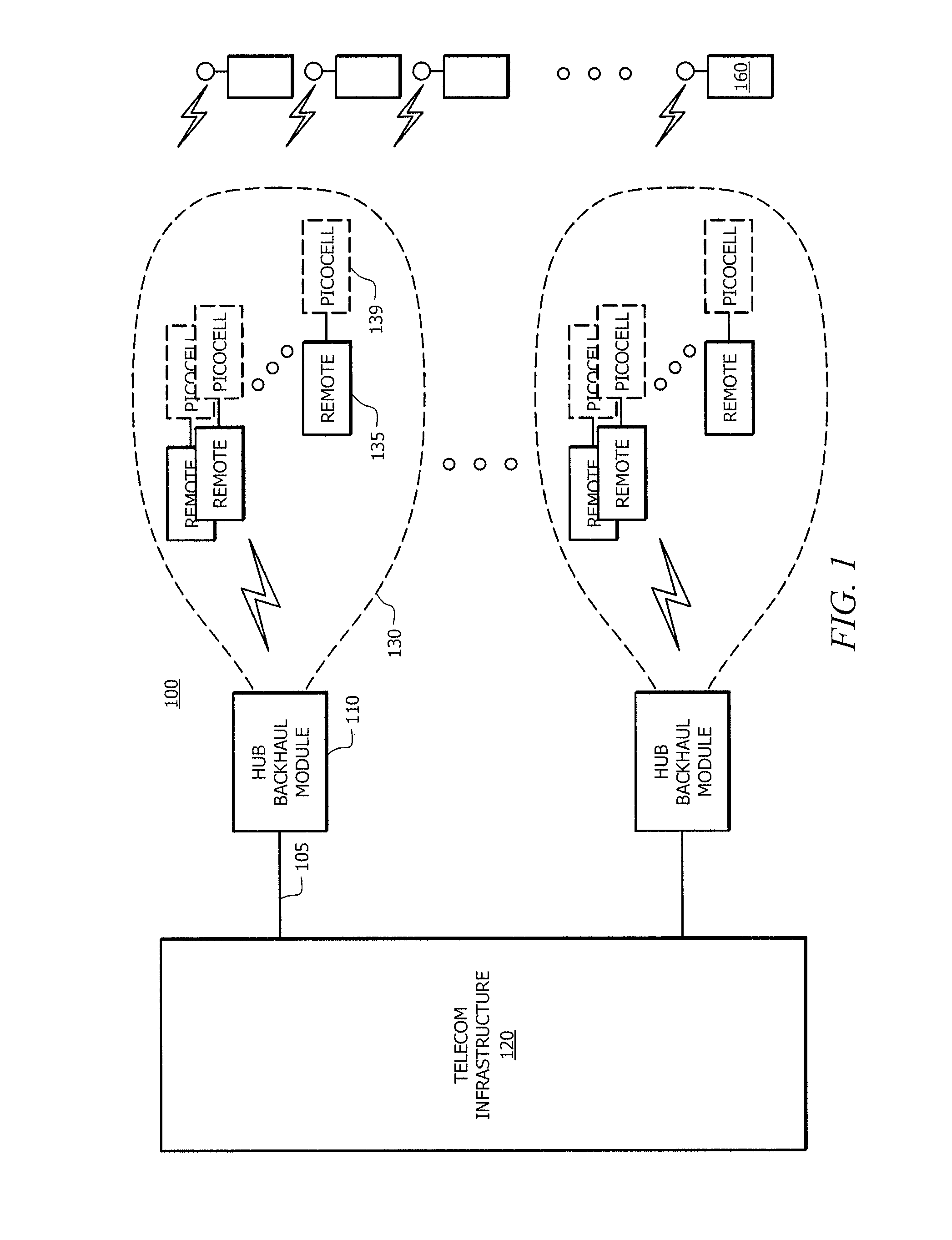
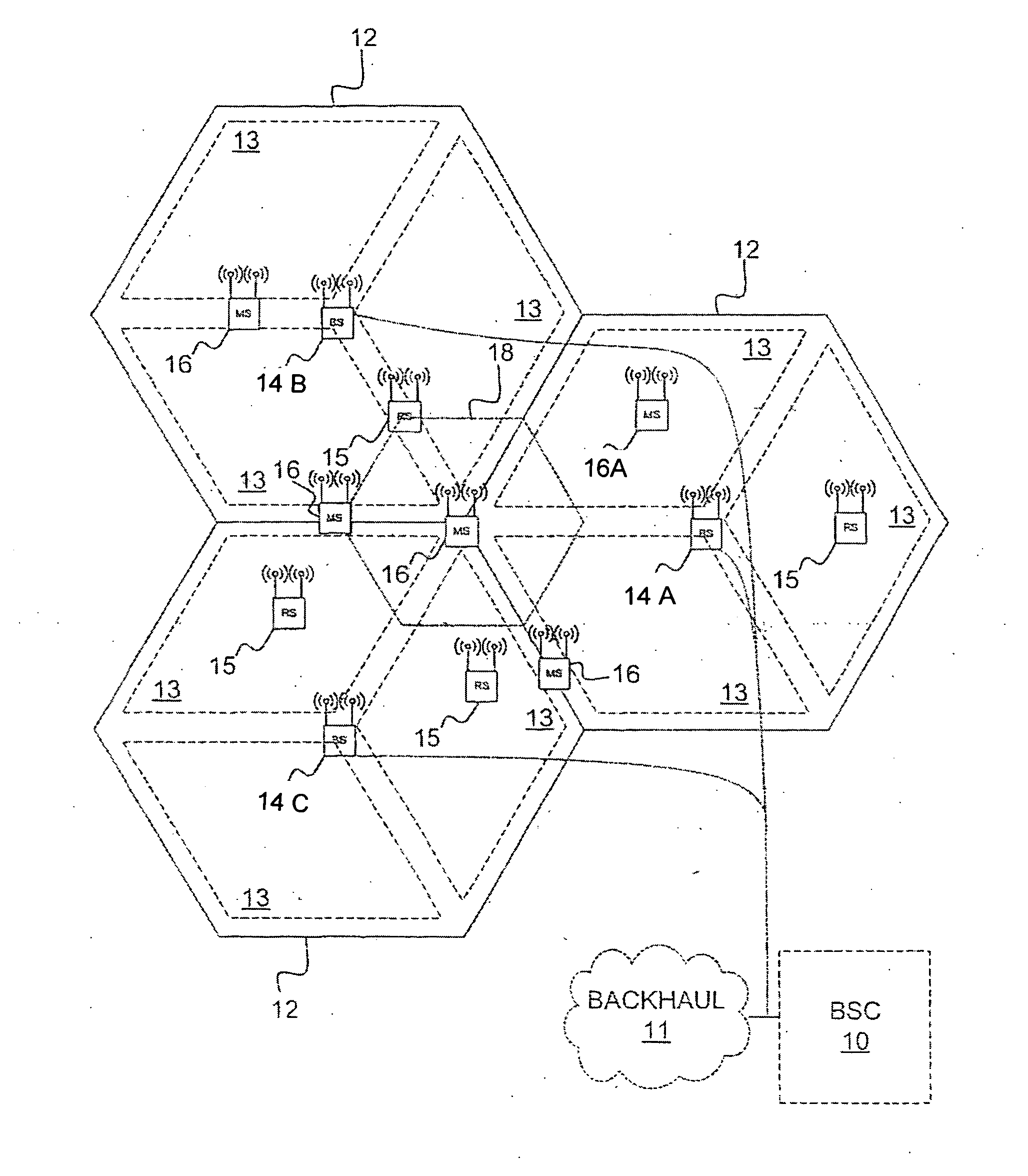
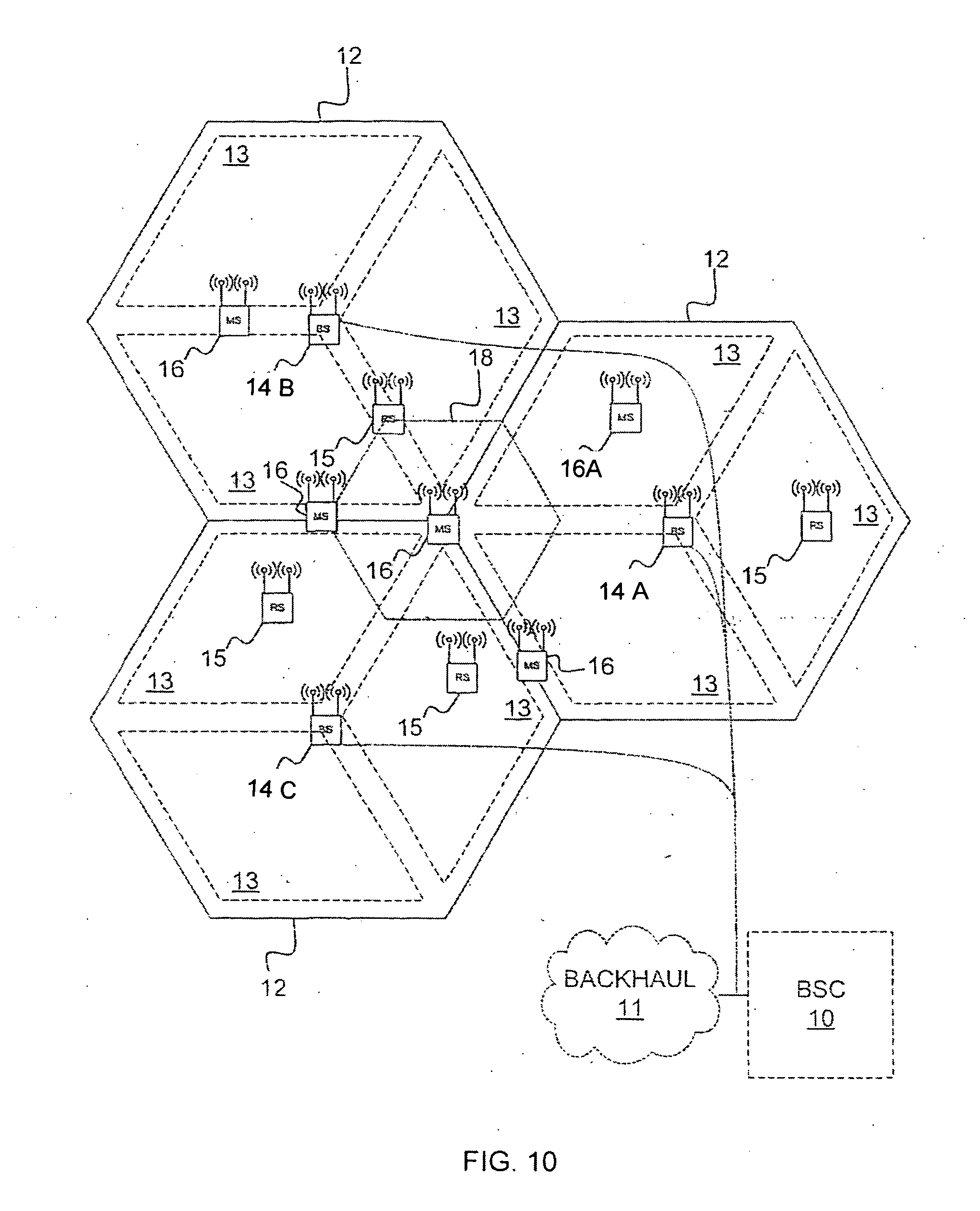
Methods and systems for frequency reuse in multi-cell deployment model of a wireless backhaul network
Systems and methods for frequency reuse in a multi-cell deployment model of a wireless backhaul network are shown. According to embodiments, a wireless backhaul network includes a plurality of cells, each of which includes one or more hubs supporting wireless backhaul communication utilizing a cell deployment geometry and wireless communication frequency assignments adapted to facilitate heterogeneous cell configurations within the wireless backhaul network. In particular, embodiments provide frequency planning for initial deployment, build out, and expansion of a plurality of cells providing wireless backhaul communication so as to implement a predetermined wireless frequency reuse pattern providing alternating utilization of a plurality of wireless communication frequencies by the cells of the backhaul network.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
Rate prediction in fractional reuse systems
ActiveUS20060014542A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemFrequency reuse
Apparatus and methods for rate prediction in a wireless communication system having fractional frequency reuse are disclosed. A wireless communication system implementing Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) can implement a fractional frequency reuse plan where a portion of carriers is allocated for terminals not anticipating handoff and another portion of the carriers is reserved for terminals having a higher probability of handoff. Each of the portions can define a reuse set. The terminals can be constrained to frequency hop within a reuse set. The terminal can also be configured to determine a reuse set based on a present assignment of a subset of carriers. The terminal can determine a channel estimate and a channel quality indicator based in part on at least the present reuse set. The terminal can report the channel quality indicator to a source, which can determine a rate based on the index value.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
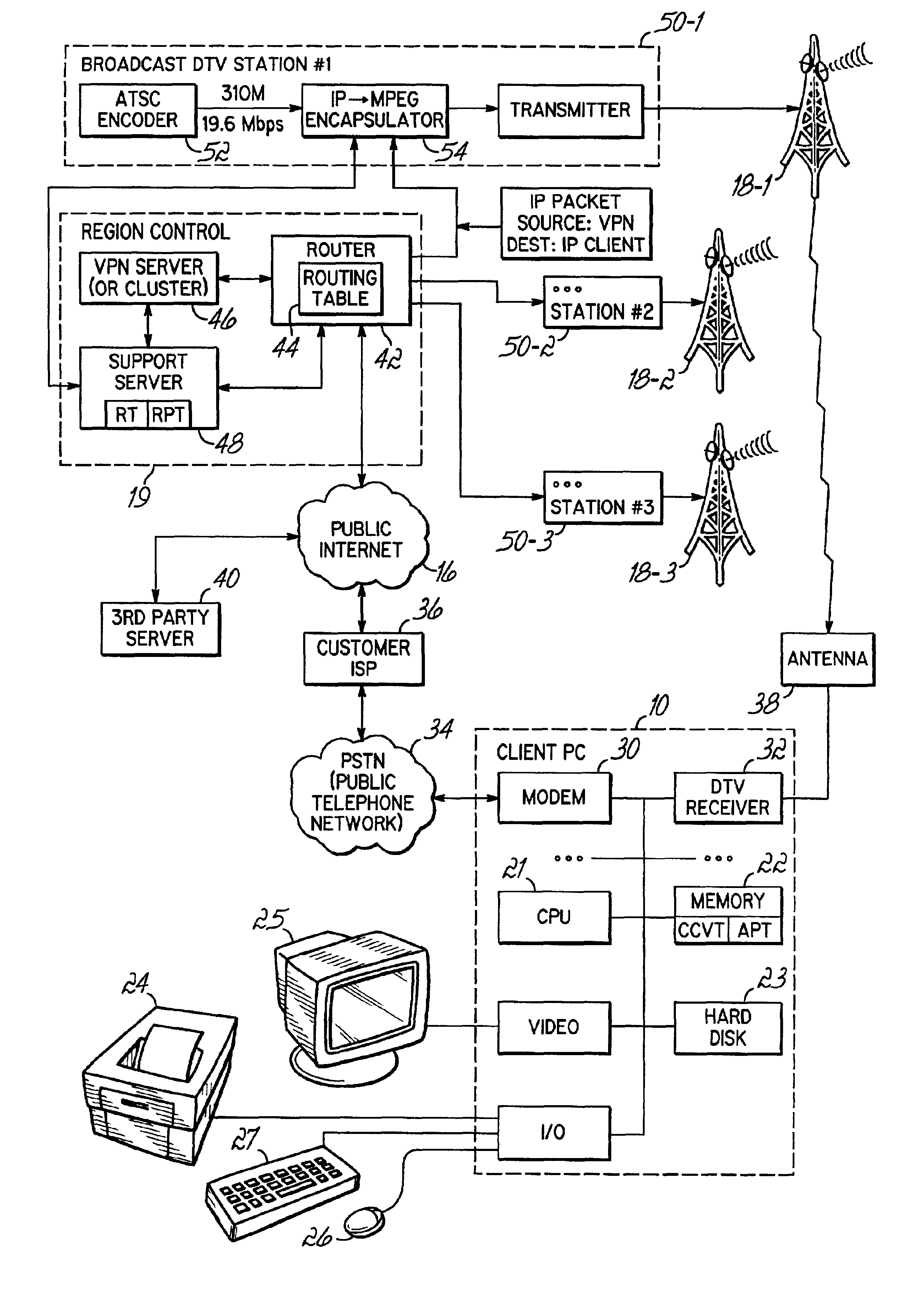
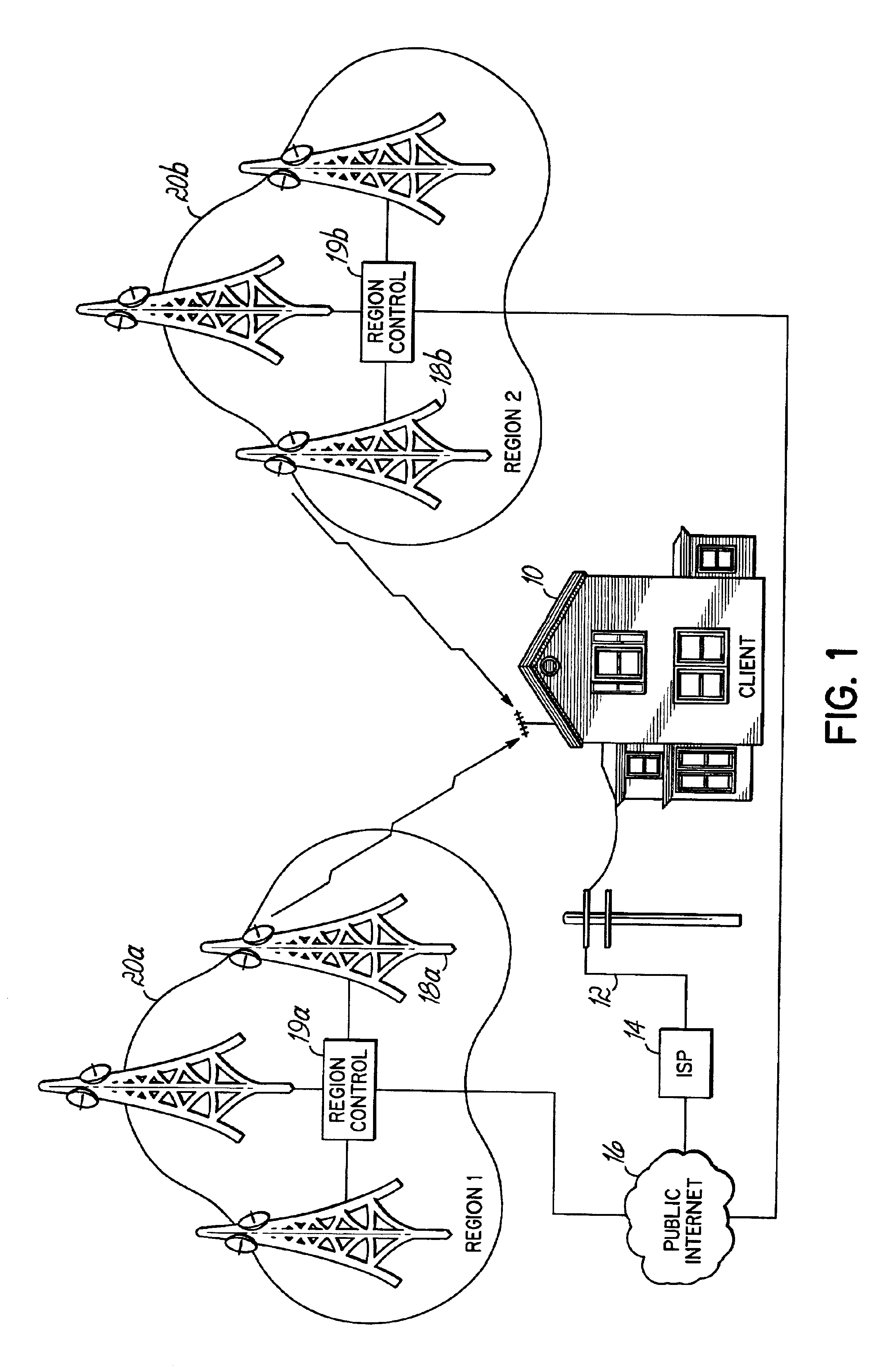
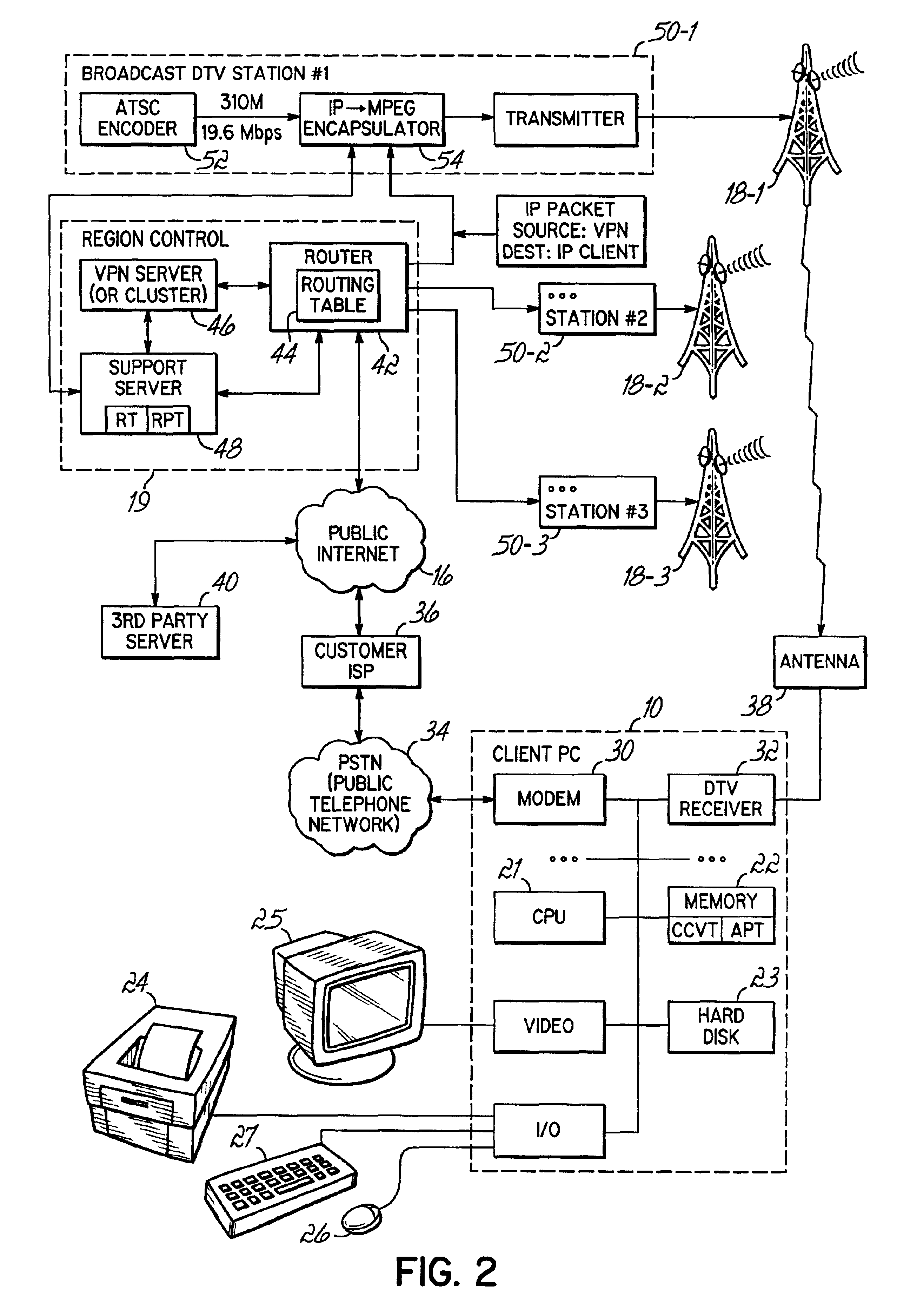
Provision of digital data via multiple broadcasts
InactiveUS6987734B2Facilitate provisionFacilitate automatic provisioningError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDistributed managementCable television
Internet access is provided through bandwidth available in broadcasted digital television signals, such as the digital television signals produced by terrestrial broadcast towers. Bandwidth is dynamically allocated or provisioned among clients, and is managed in part by the clients, thus providing dynamic, distributed management of spectrum allocation. Automatic provisioning may be applied among different terrestrial transmission towers, or different satellites, among transponders or channels on a given tower, or a given satellite, or among other forms of multiple broadcast origination points. The provisioning dynamically and automatically equalizes load among those multiple broadcast points. Principles of the present invention may also be applied to automatic provisioning of digital content among non-television broadcast sources, such as cellular telephone towers having available bandwidth, analog or digital radio broadcasts having available bandwidth, or satellite broadcast facilities, and / or dedicated broadcast towers or satellites operating in an allocated spectrum and limited to broadcasting requested digital content. In a satellite embodiment, provisioning may occur among multiple satellites as well as between transponders or time- or frequency-multiplexed channels provided by a single satellite.
Owner:NEWPORT TELEVISION
Method and apparatus for using multicarrier interferometry to enhance optical fiber communications
InactiveUS7076168B1Increase diversityImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTModulated-carrier systemsSignal qualityFrequency reuse
A redundently modulated multicarrier protocol known as Carrier Interference Multiple Access (CIMA) is used in an optical-fiber network having wireless links at network nodes. CIMA is a protocol that can be used to create wireless protocols (such as TDMA and CDMA) having enhanced capacity and reduced system complexity. A CIMA optical-fiber network uses dispersion to enhance signal quality and facilitate switching. CIMA achieves both diversity benefits and capacity enhancements by providing redundancy in at least one diversity parameter while providing orthogonality in another diversity parameter. This basic operating principle of CIMA may be combined with multi-user detection to achieve frequency reuse and improved power efficiency. In the wireless link, diversity may be used to reduce the effects of small-scale fading on interferometry multiplexing.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Coordinated satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse
InactiveUS20020041575A1Improve efficiencyMinimize interferenceRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesFrequency spectrumFrequency reuse
A system and method of operation for efficiently reusing and / or sharing at least a portion of the frequency spectrum between a first satellite spot beam and a second satellite spot beam, and / or an underlay terrestrial network associated with a second satellite spot beam. The spectrum is efficiently reused and / or shared between respective spot beams and / or associated underlay terrestrial systems in a manner minimizes interference between the respective satellite and terrestrial systems.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
Integrated or autonomous system and method of satellite-terrestrial frequency reuse using signal attenuation and/or blockage, dynamic assignment of frequencies and/or hysteresis
InactiveUS20020090942A1Efficient reuseInterference minimizationSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionHysteresisUltrasound attenuation
A cellular communications system comprising a space based system comprising a first set of cells, and a ground based system comprising a second set of cells. The space and ground systems can optionally function substantially autonomously, with each using spectrum from at least one predetermined frequency band.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
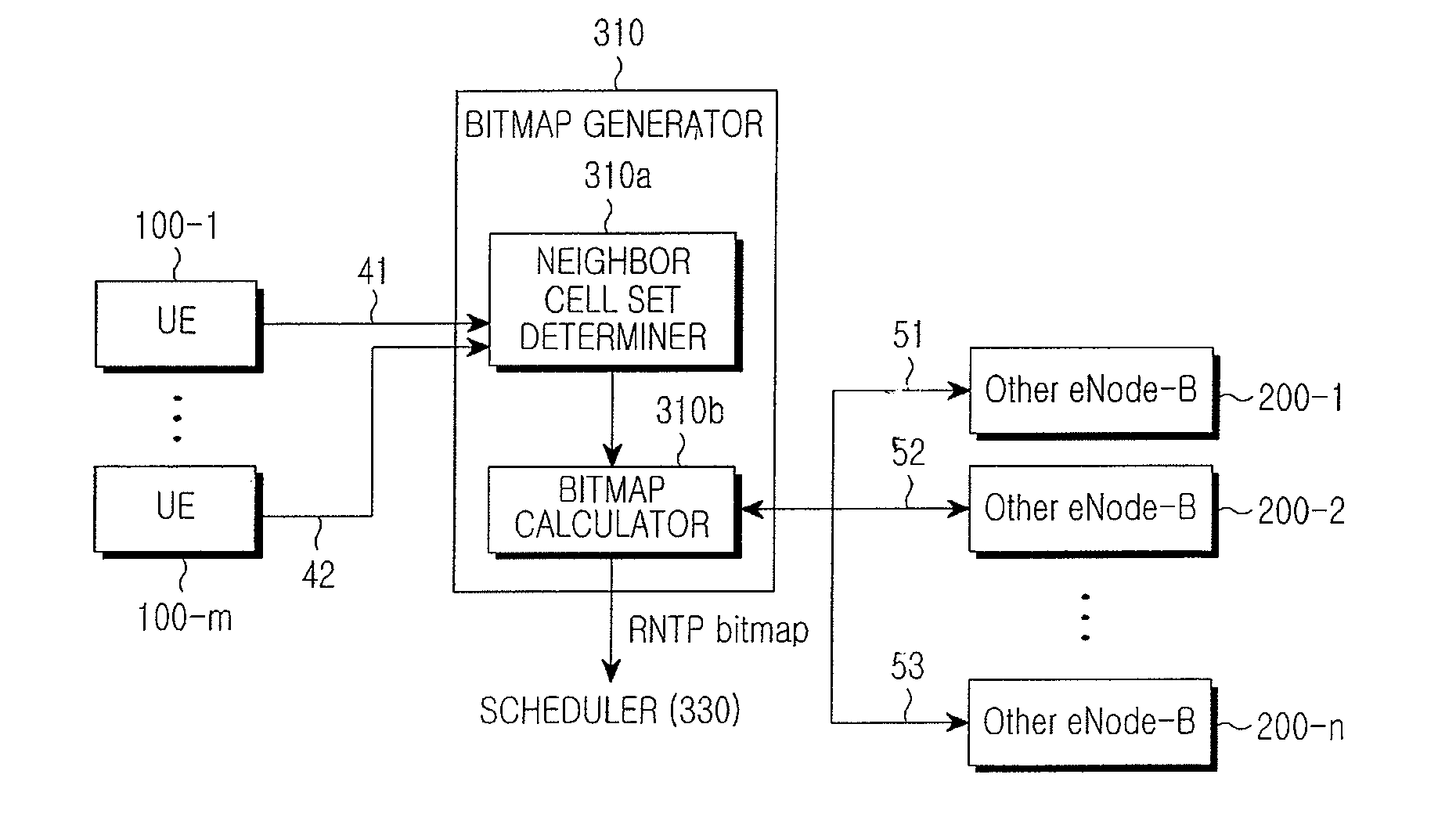
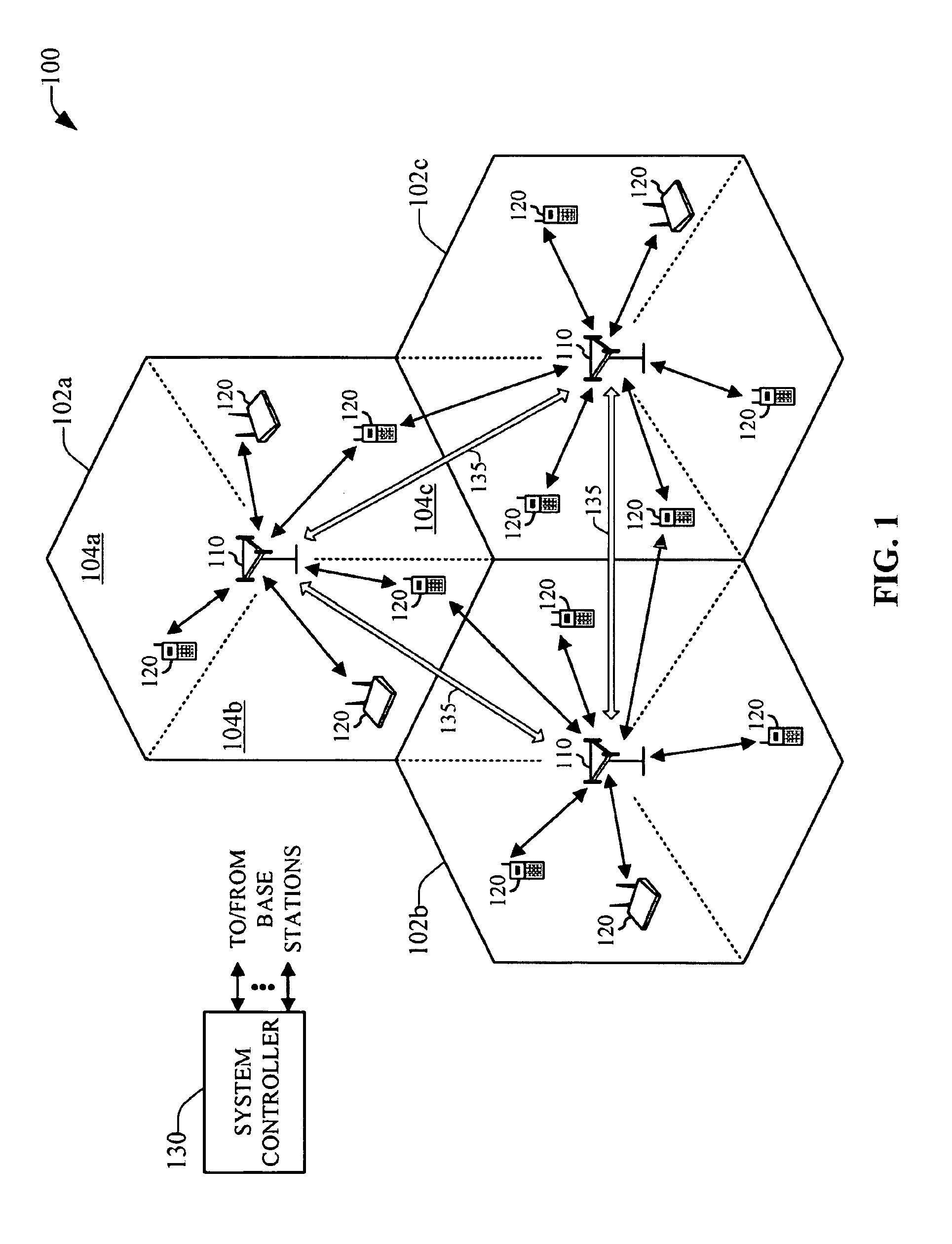
Method and apparatus for scheduling resource allocation to control inter-cell interference in a cellular communication system, and base station thereof
ActiveUS20110183679A1Efficient schedulingNetwork planningFrequency reuseCellular communication systems
A method and apparatus for controlling inter-cell interference in an evolved Node-B for a cellular communication system with a frequency reuse factor of 1 are provided. The apparatus includes a bitmap generator for receiving scheduling information from evolved Node-Bs of a plurality of neighbor cells, and for generating scheduling information including its cell's bitmap information for the resource allocation using the received neighbor cells' scheduling information, and a scheduler for scheduling the resource allocation for UEs in its cell based on the scheduling information provided from the bitmap generator and power allocation information of the UEs in its cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
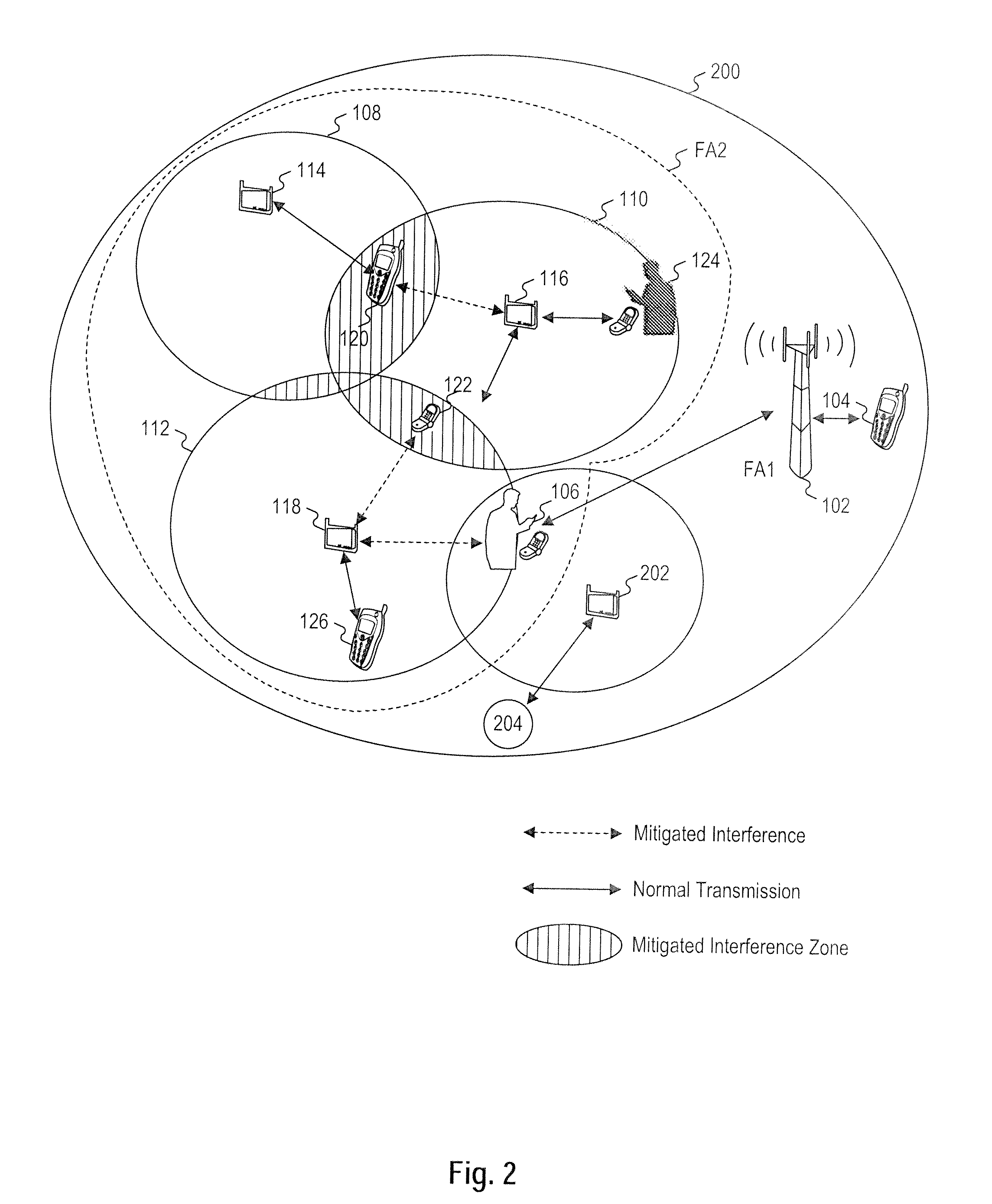
Intercell interference mitigation
ActiveUS20090264142A1Reduce Inter-Cell InterferenceImprove coordinationTransmission path divisionSignal allocationFrequency reuseInterference (communication)
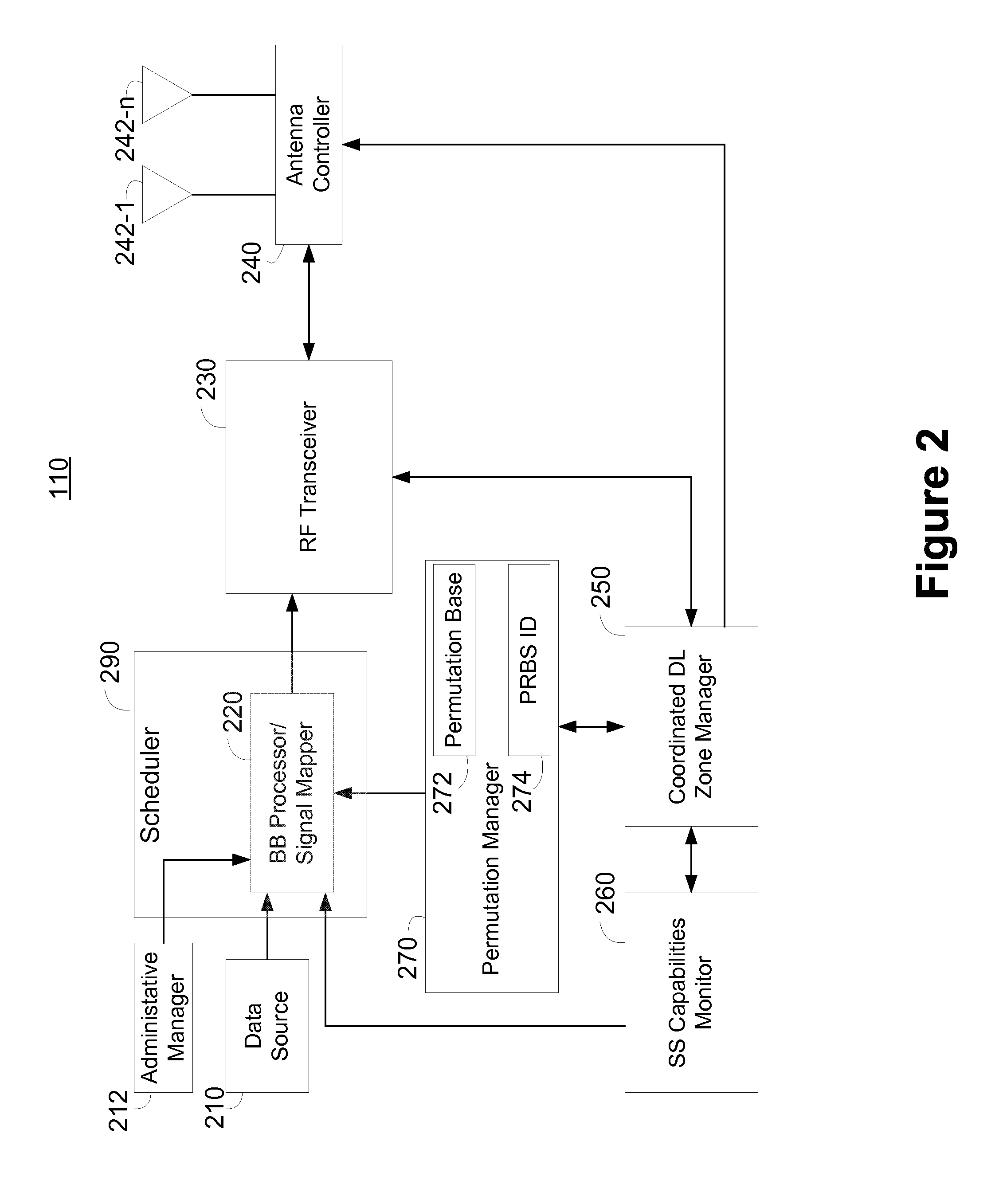
Methods and apparatus are described for mitigating intercell interference in wireless communication systems utilizing substantially the same operating frequency band across multiple neighboring coverage areas. The operating frequency band may be shared across multiple neighboring or otherwise adjacent cells, such as in a frequency reuse one configuration. The wireless communication system can synchronize one or more resource allocation regions or zones across the multiple base stations, and can coordinate a permutation type within each resource allocation zone. The base stations can coordinate a pilot configuration in each of a plurality of coordinated resource allocation regions. Subscriber stations can be assigned resources in a coordinated resource allocation region based on interference levels. A subscriber station can determine a channel estimate for each of multiple base stations in the coordinated resource allocation region to mitigate interference.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Cellular wireless network for passengers cabins
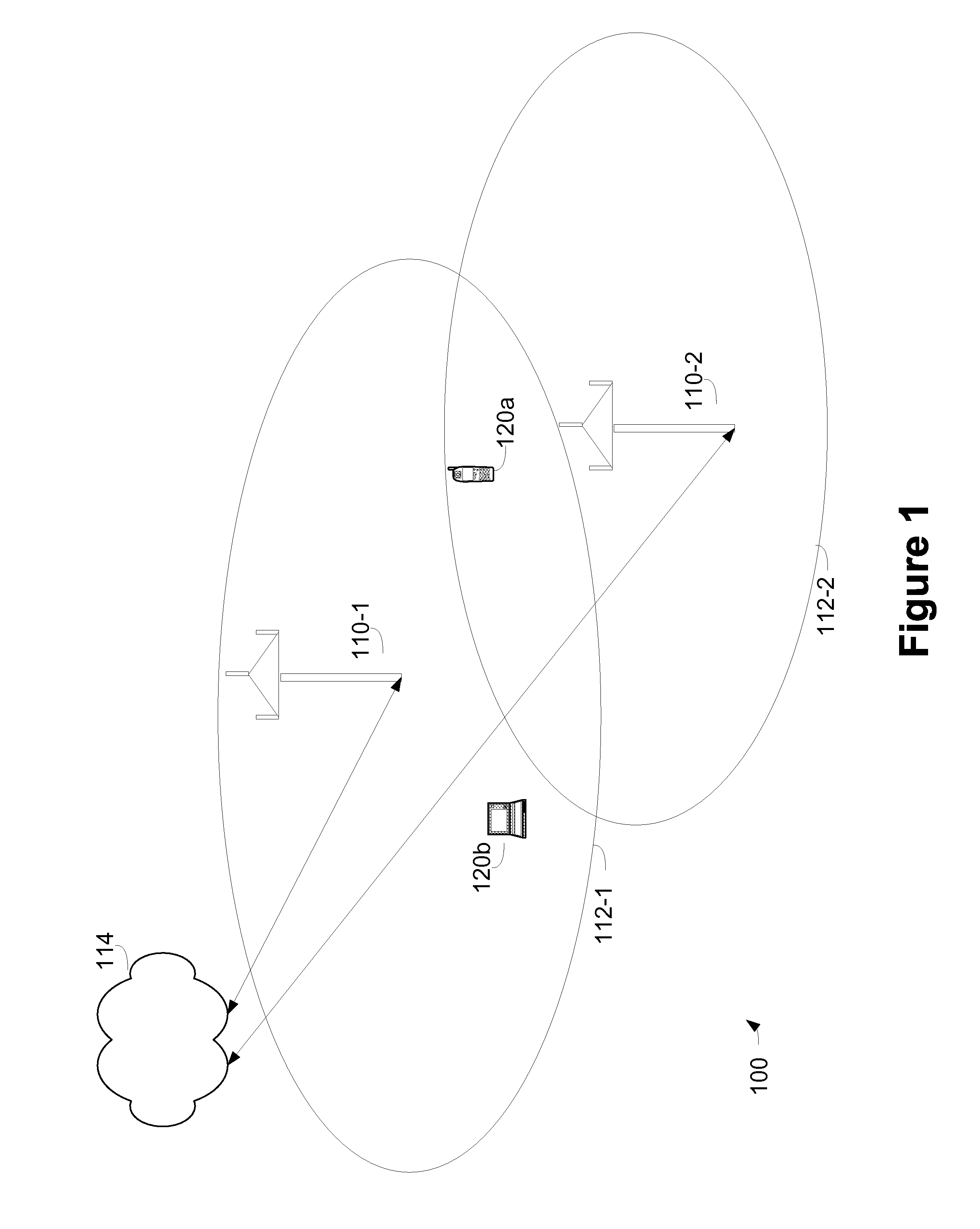
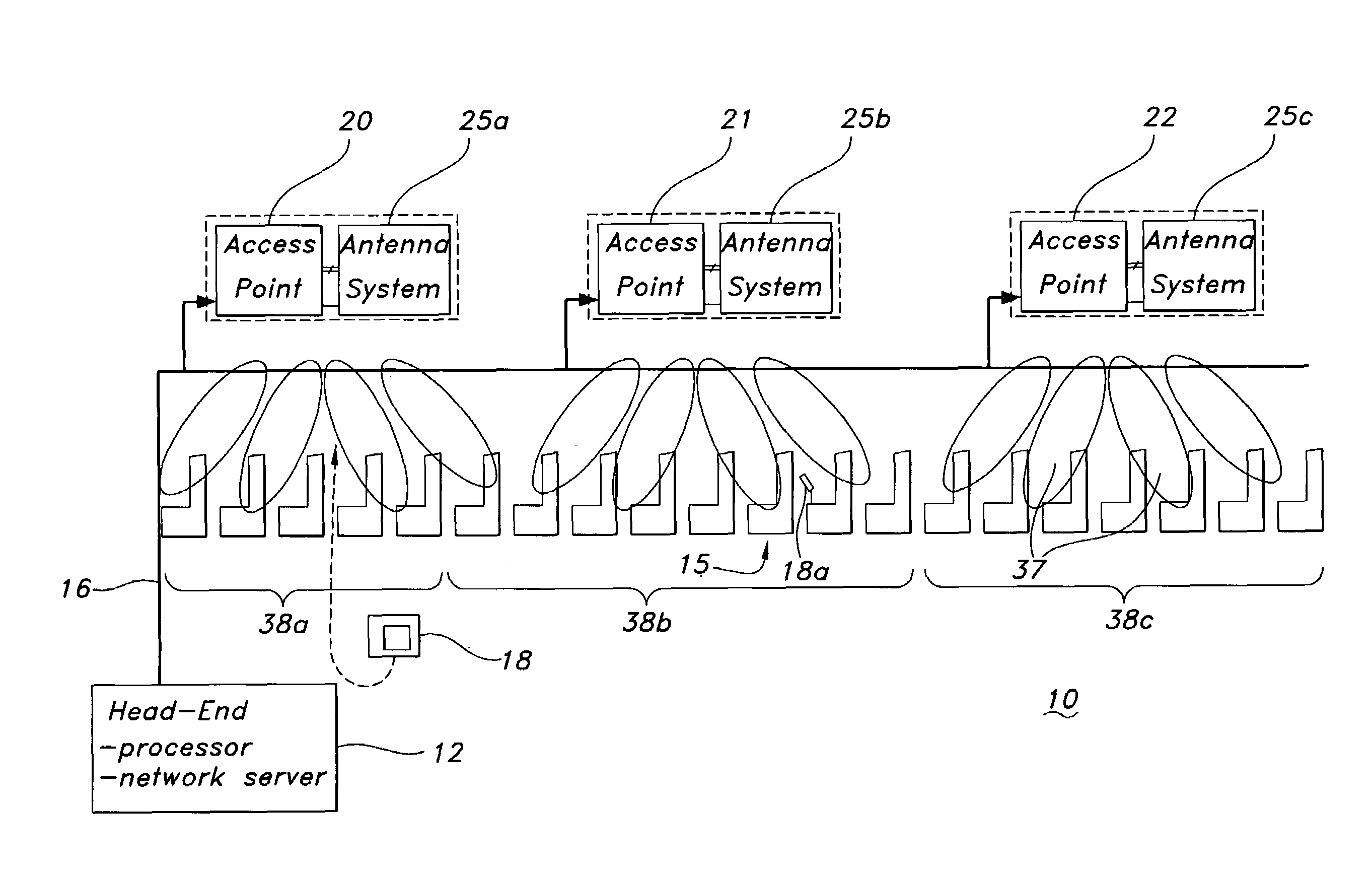
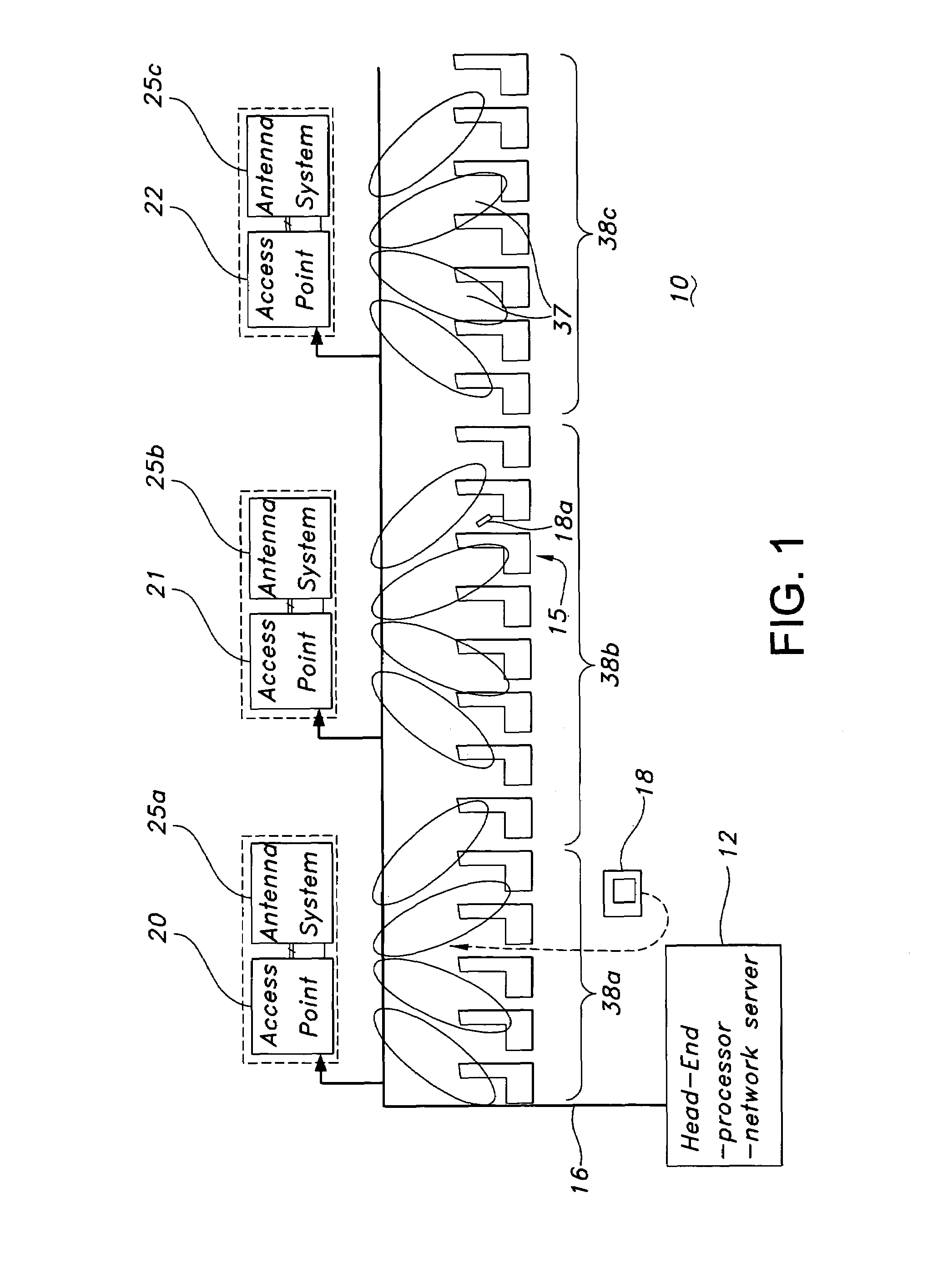
ActiveUS7483696B1Maximize connectivityAvoid OverloadingRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesReconfigurable antennaFrequency reuse
A cellular wireless in-flight entertainment (IFE) system is used in an aircraft for delivering programming to passengers. A head end server provides data and programming to cells. Each cell comprises a wireless access point / configurable antenna to receive the data and the programming. The wireless access point / configurable antenna is disposed at an optimum location in a passenger cabin and operates with a predetermined frequency, radiation pattern, and polarization to provide the programming at optimum coverage. Wireless seat displays receive the programming from the wireless access point / configurable antenna and have a seat display antenna with selectable polarization. The cellular wireless IFE system provides for frequency reuse within the cells, registration of passengers upon log in to identify placement of the wireless seat displays, load balancing to prevent exceeding a capacity of a wireless access point / configurable antenna, and a scalable architecture where data and video each utilize a different band and wireless access point / configurable antenna.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
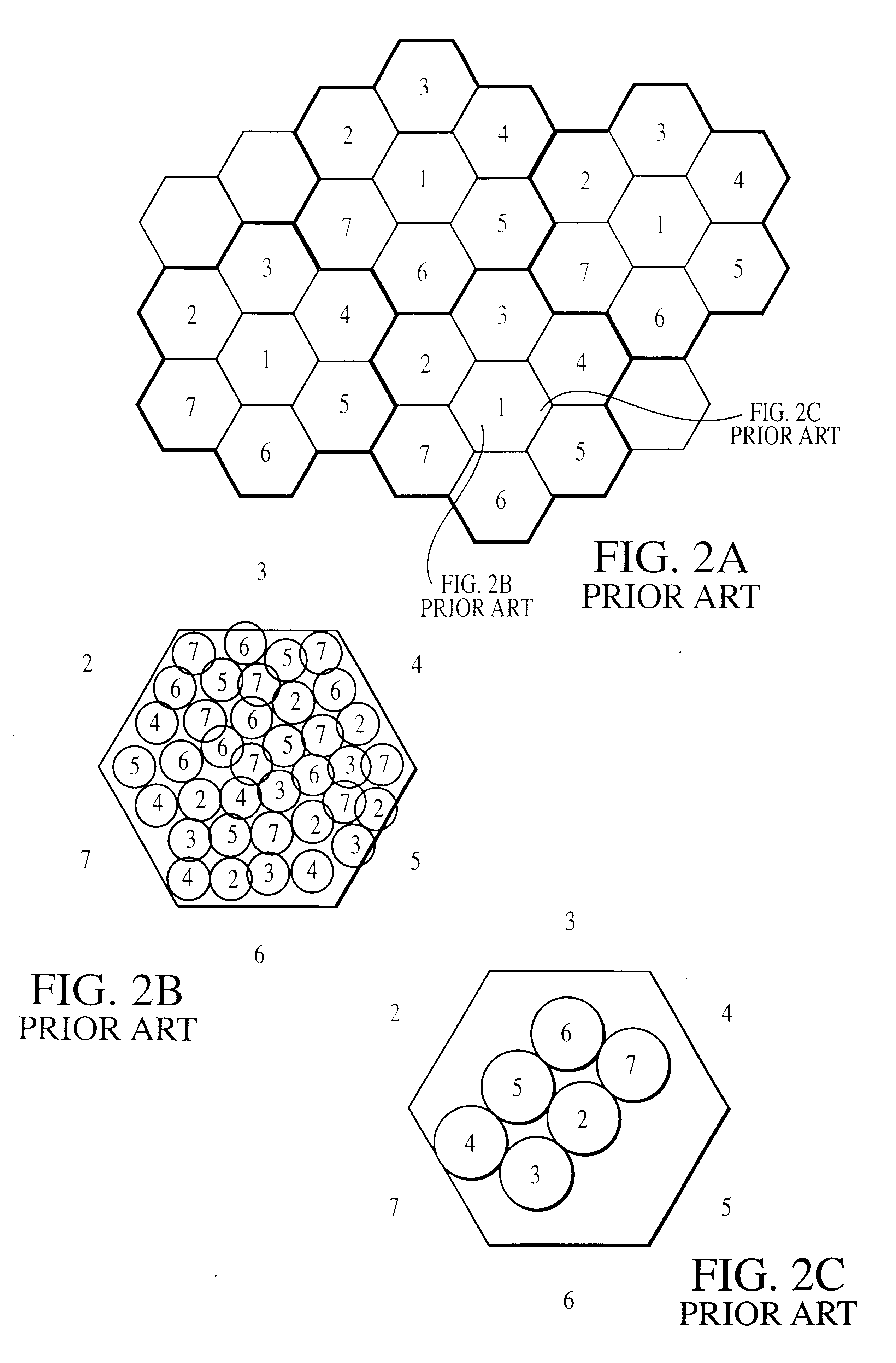
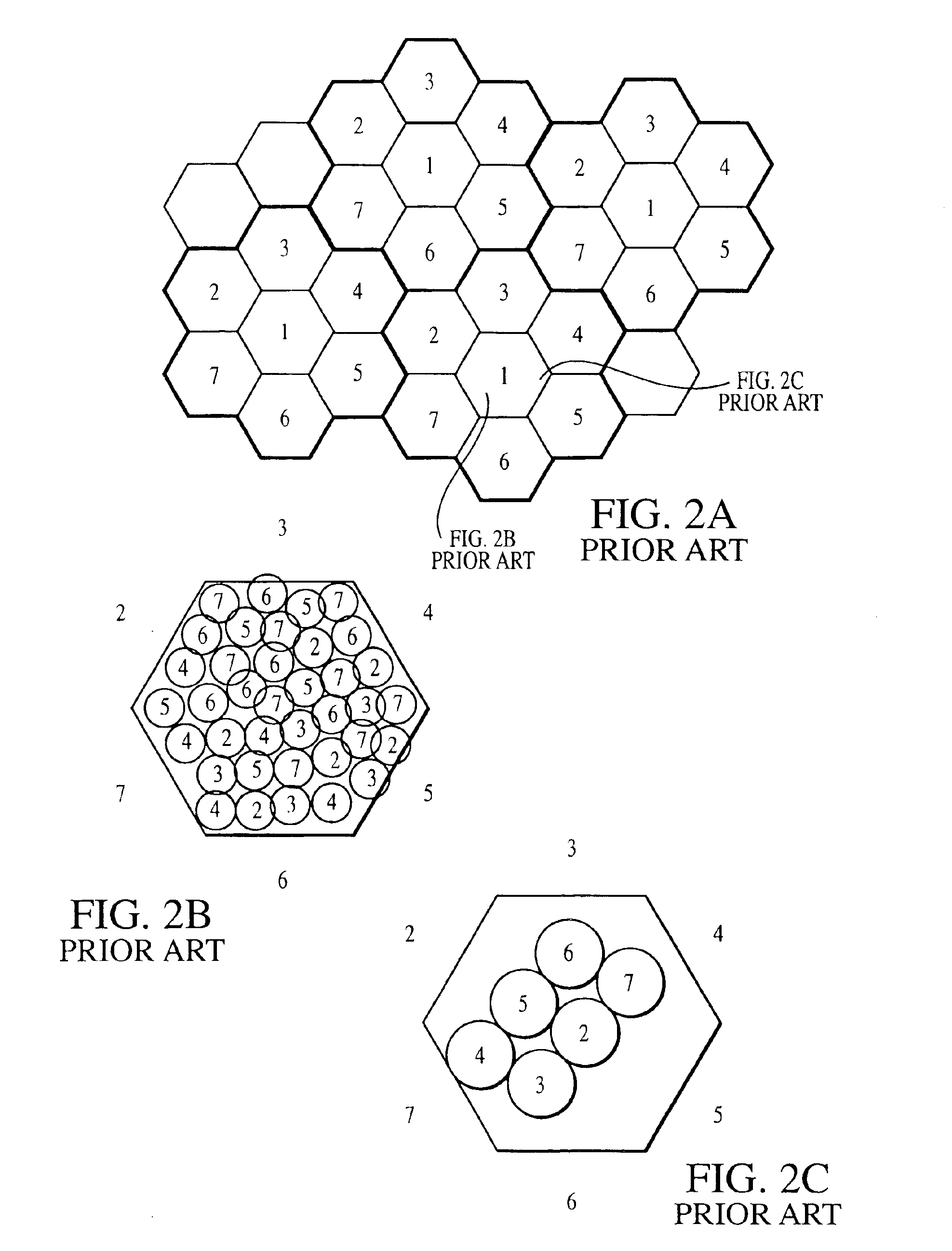
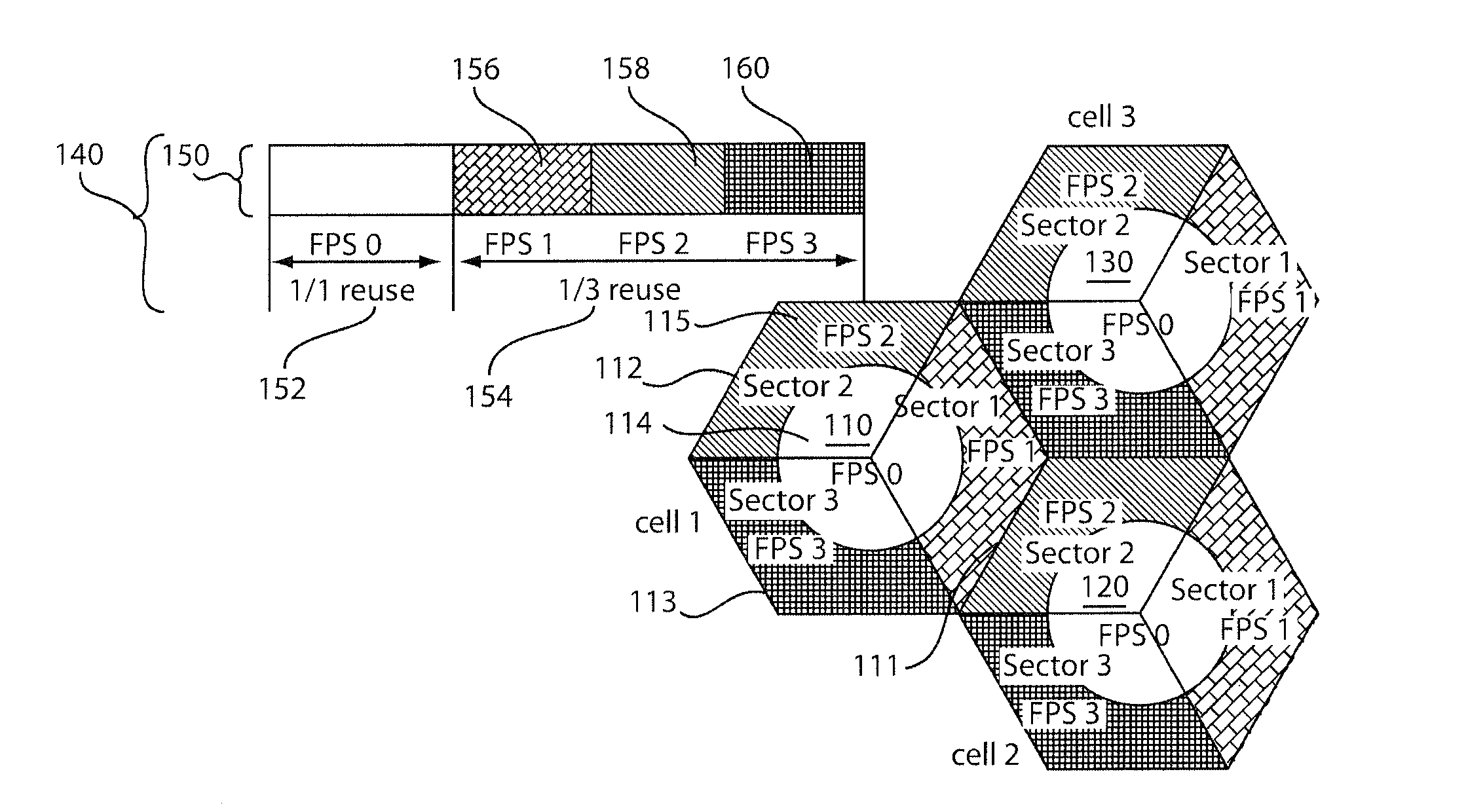
Method and system for solving cellular communications frequency planning problem
InactiveUS6522885B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningHigh bandwidthFrequency reuse
A method and system for use with wireless communications systems having a plurality of groups of channels, and wherein the method and system assign specific groups of channels such that channel interference is minimized. The method and system accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: define a geographic area; map the defined geographic area with at least one high bandwidth cell cluster wherein each cell has at least one sector; and eliminate channel adjacencies by selectively assigning channels, drawn from the plurality of groups of channels, to the at least one high bandwidth cell cluster. The method and system further accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: select a frequency reuse table having a predefined frequency reuse factor; and define a high bandwidth cell cluster over which the frequency reuse table is utilized such that the defined frequency reuse factor is effectively maintained while the communications efficiency of a wireless communications system is enhanced.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and System for User Equipment Location Determination on a Wireless Transmission System
ActiveUS20110286349A1Improve audibilityReduce signal to noise ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseResource block
Neighbor cell hearability can be improved by including an additional reference signal that can be detected at a low sensitivity and a low signal-to-noise ratio, by introducing non-unity frequency reuse for the signals used for a time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurement, e.g., orthogonality of signals transmitted from the serving cell sites and the various neighbor cell sites. The new reference signal, called the TDOA-RS, is proposed to improve the hearability of neighbor cells in a cellular network that deploys 3GPP EU-TRAN (LTE) system, and the TDOA-RS can be transmitted in any resource blocks (RB) for POSCH and / or MBSFN subframe, regardless of whether the latter is on a carrier supporting both PMCH and POSCH or not. Besides the additional TDOA-RS reference signal, an additional synchronization signal (TDOA-sync) may also be included to improve the hearability of neighbor cells.
Owner:APPLE INC
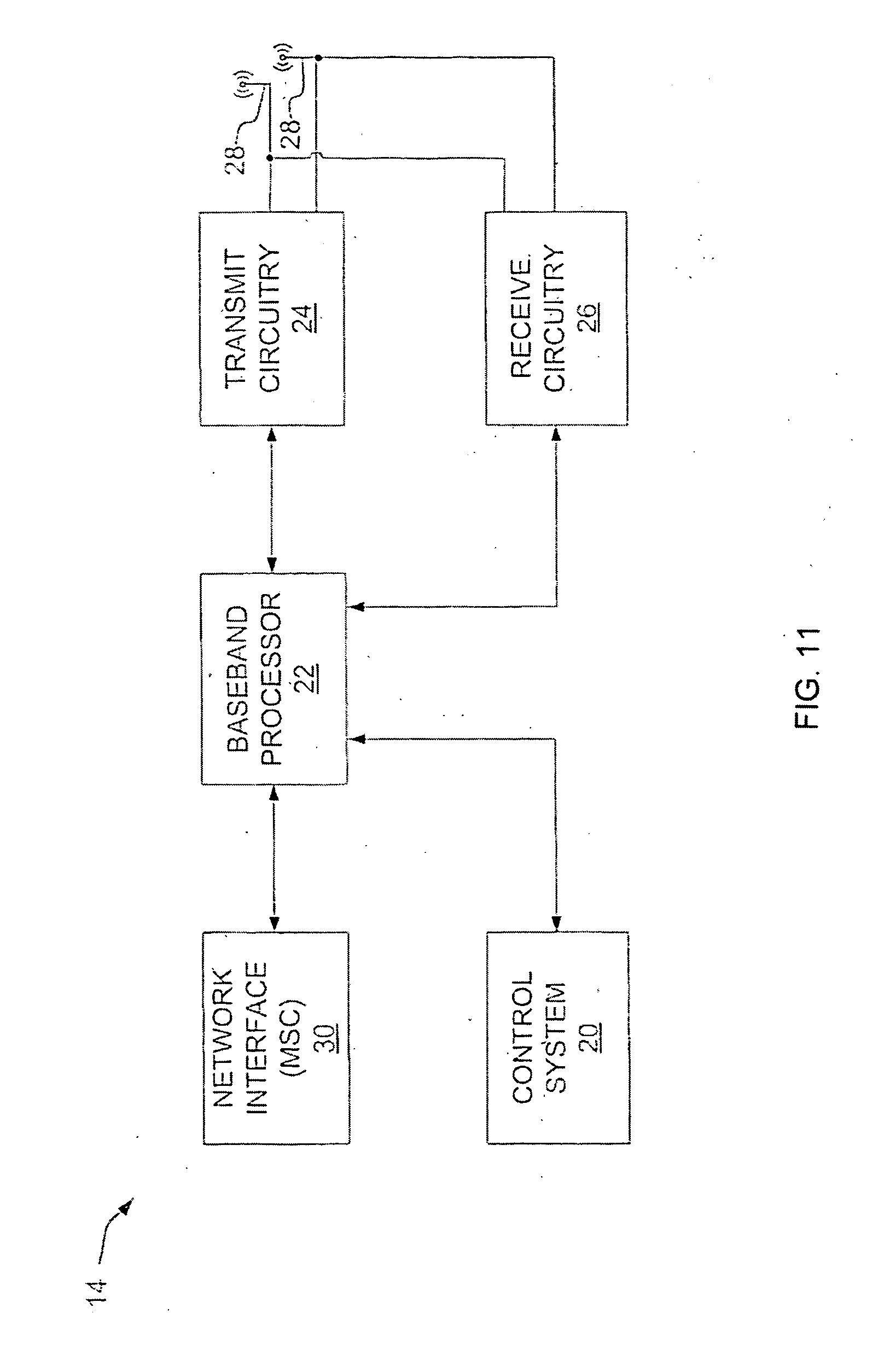
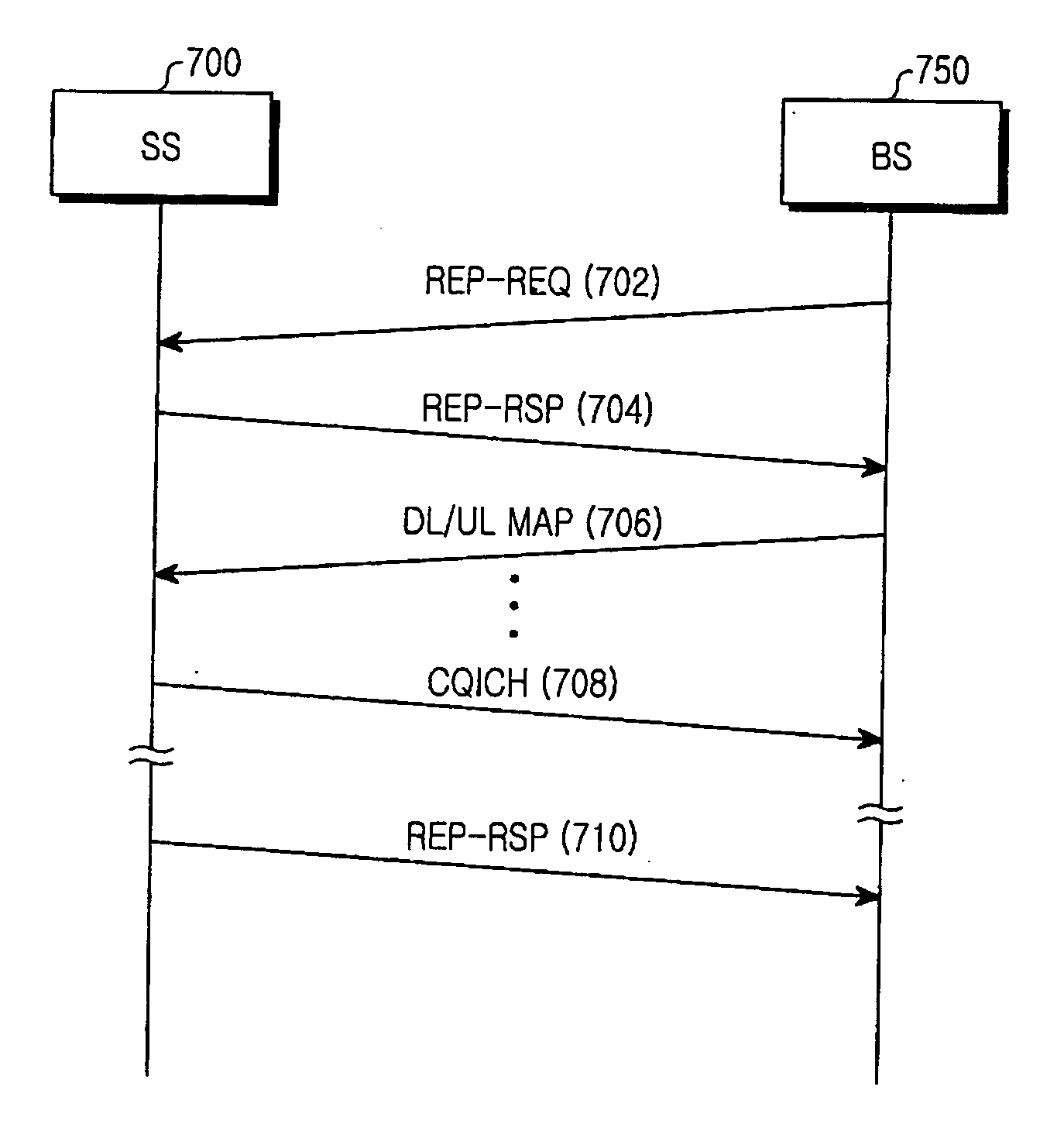
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving channel quality information in a communication system
ActiveUS20060148411A1Effective distributionReceivers monitoringModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemFrequency reuse
An apparatus and method for transmitting / receiving channel quality information (CQI) in a communication system having a frame including subchannels corresponding to the same frequency reuse factor or different frequency reuse factors. A base station (BS) allocates at least one of the subchannels in the frame to a subscriber station (SS), and sends a transmission request for a CQI for a subchannel desired to be received, to the SS. The SS measures channel quality for individual subchannels requested by the BS in response to the CQI request, and transmits the measured channel quality to the BS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cooperative beam-forming in wireless networks
ActiveUS8670390B2Site diversityFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseWireless mesh network
A beam-forming system comprises a cooperative array of wireless terminals coupled to at least one wireless wide area network (WWAN) and communicatively coupled to a wireless local area network (WLAN) configured to provide information exchanges between the wireless terminals. A cooperative beam-forming system employing the WLAN provides antenna-array processing benefits (such as frequency reuse, interference rejection, array-processing gain, antenna-switching diversity) to the individual wireless terminals. A network access operator facilitates network control functionality between the WWAN and the cooperative array of wireless terminals.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Method for dynamically allocating carriers in a wireless packet network, with reuse of carriers
InactiveUS6496490B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexMultiplexingDynamic channel
We disclose a method of dynamic channel assignment for wireless transmission systems that employ time or frequency multiplexing, or both time and frequency multiplexing. The invention is specifically addressed to the problem of avoiding interference in the channels of such systems. In a broad aspect, the invention involves partitioning base stations of a network into non-interfering sets. Channels are allocated to the non-interfering sets according to need. Stages of channel reallocation take place periodically. The reallocation takes place through coordinated activity by the base stations. That is, the channel reallocation is carried out in response to information that is exchanged between base stations, or it is centrally directed by the network in response to information passed to the network by the base stations.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and system for solving cellular communications frequency planning problem
InactiveUS6178328B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmissionHigh bandwidthFrequency reuse
A method and system for use with wireless communications systems having a plurality of groups of channels, and wherein the method and system assign specific groups of channels such that channel interference is minimized. The method and system accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: define a geographic area; map the defined geographic area with at least one high bandwidth cell cluster wherein each cell has at least one sector; and eliminate channel adjacencies by selectively assigning channels, drawn from the plurality of groups of channels, to the at least one high bandwidth cell cluster. The method and system further accomplish their objects via the use of communications equipment adapted to do the following: select a frequency reuse table having a predefined frequency reuse factor; and define a high bandwidth cell cluster over which the frequency reuse table is utilized such that the defined frequency reuse factor is effectively maintained while the communications efficiency of a wireless communications system is enhanced.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
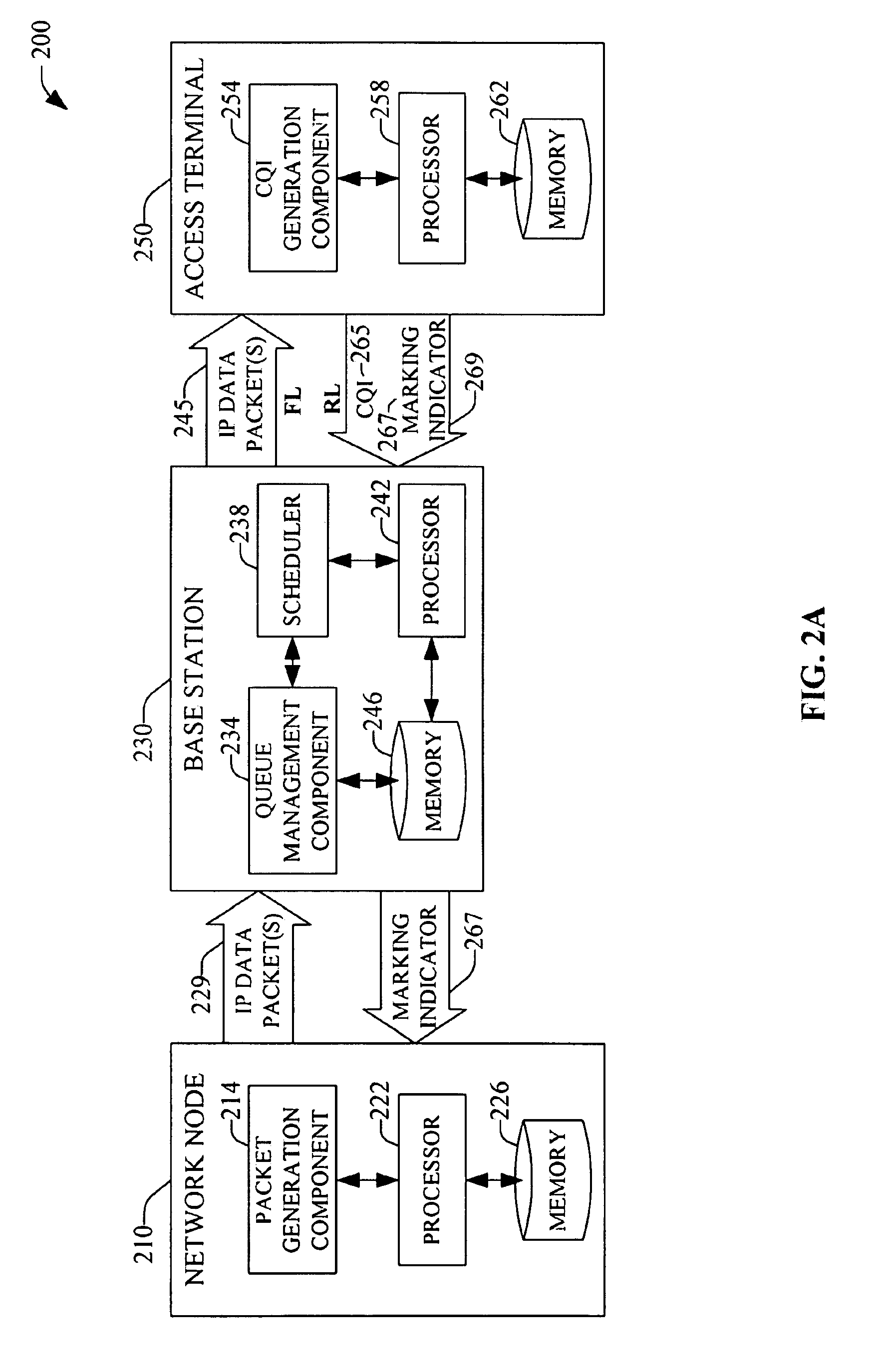
Method and system for reducing backhaul utilization during base station handoff in wireless networks
InactiveUS20080186918A1Well formedEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless mesh networkFrequency reuse
Systems and methods are provided that facilitate active queue management of internet-protocol data packets generated in a data packet switched wireless network. Queue management can be effected in a serving base station as well as in an access terminal, and the application that generates the data packets can be executed locally or remotely to either the base station or access terminal. Management of the generated data packets is effected via a marking / dropping of data packets according to an adaptive response function that can be deterministic or stochastic, and can depend of multiple communication generalized indicators, which include packet queue size, queue delay, channel conditions, frequency reuse, operation bandwidth, and bandwidth-delay product. Historical data related to the communication generalized indicators can be employed to determine response functions via thresholds and rates for marking / dropping data packets.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
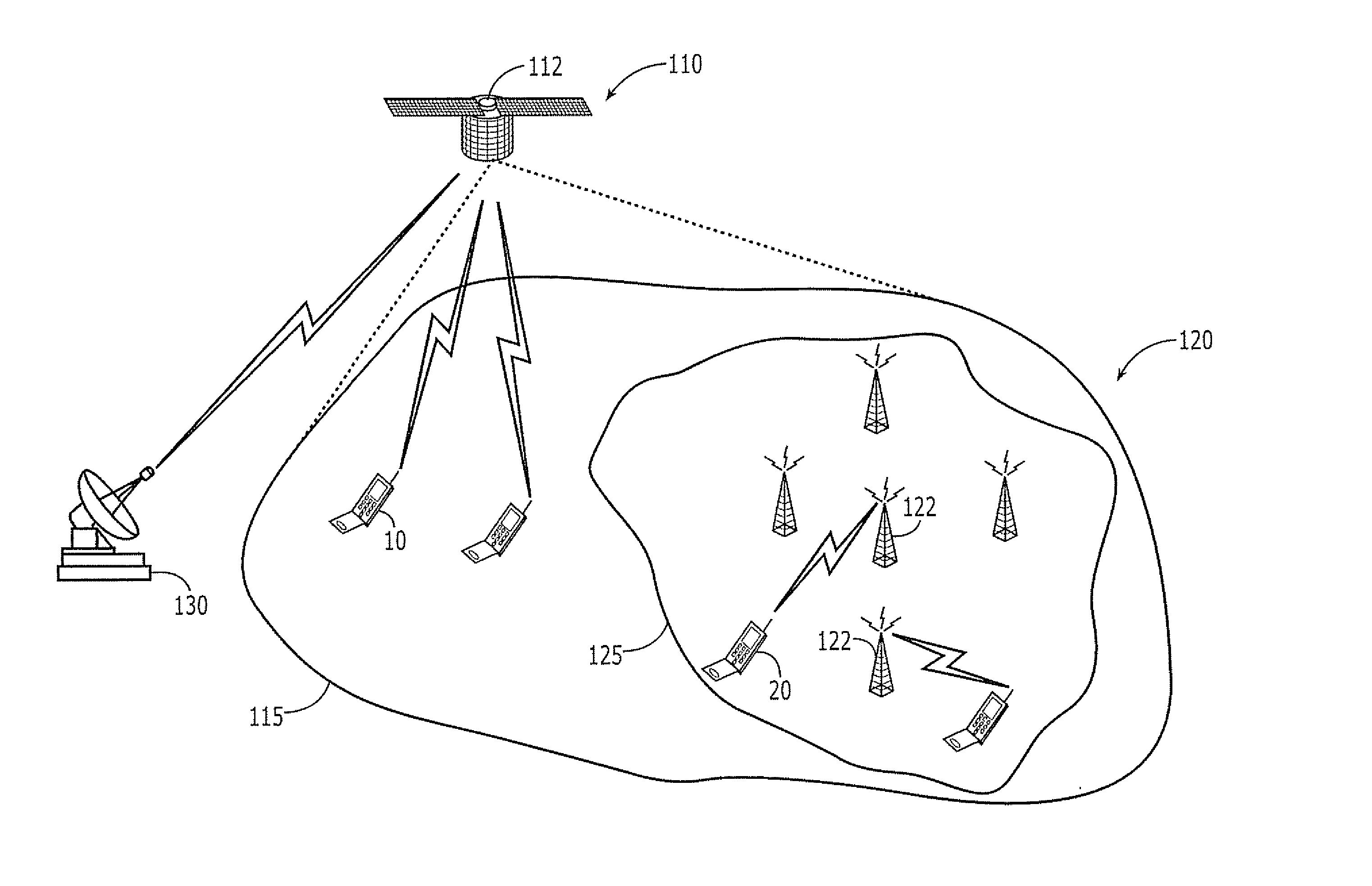
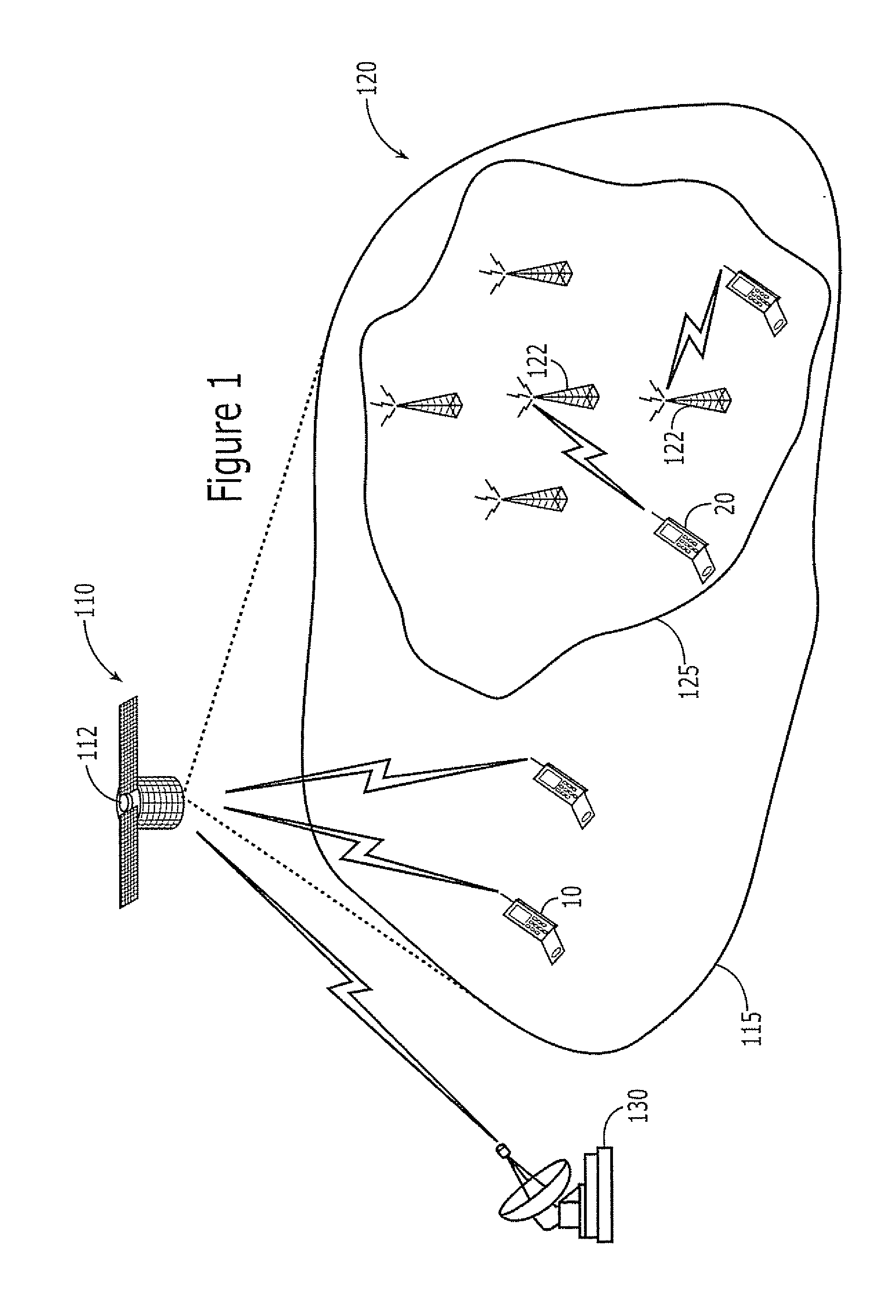
Satellite Communications Apparatus and Methods Using Asymmetrical Forward and Return Link Frequency Reuse
ActiveUS20070026867A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemFrequency reuse
Communications are conducted between a space-based component of the wireless communications system and radioterminals using a plurality of forward link cells and a plurality of return link cells, the return link cells having a greater number of cells per frequency reuse cluster than the forward link cells. At least some of the forward and return link cells may use at least some frequencies of a terrestrial wireless communications system having an adjacent and / or overlapping coverage area. Forward links of the at least some of the forward and return link cells may have a greater link bandwidth than return links of the at least some of the forward and return link cells.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
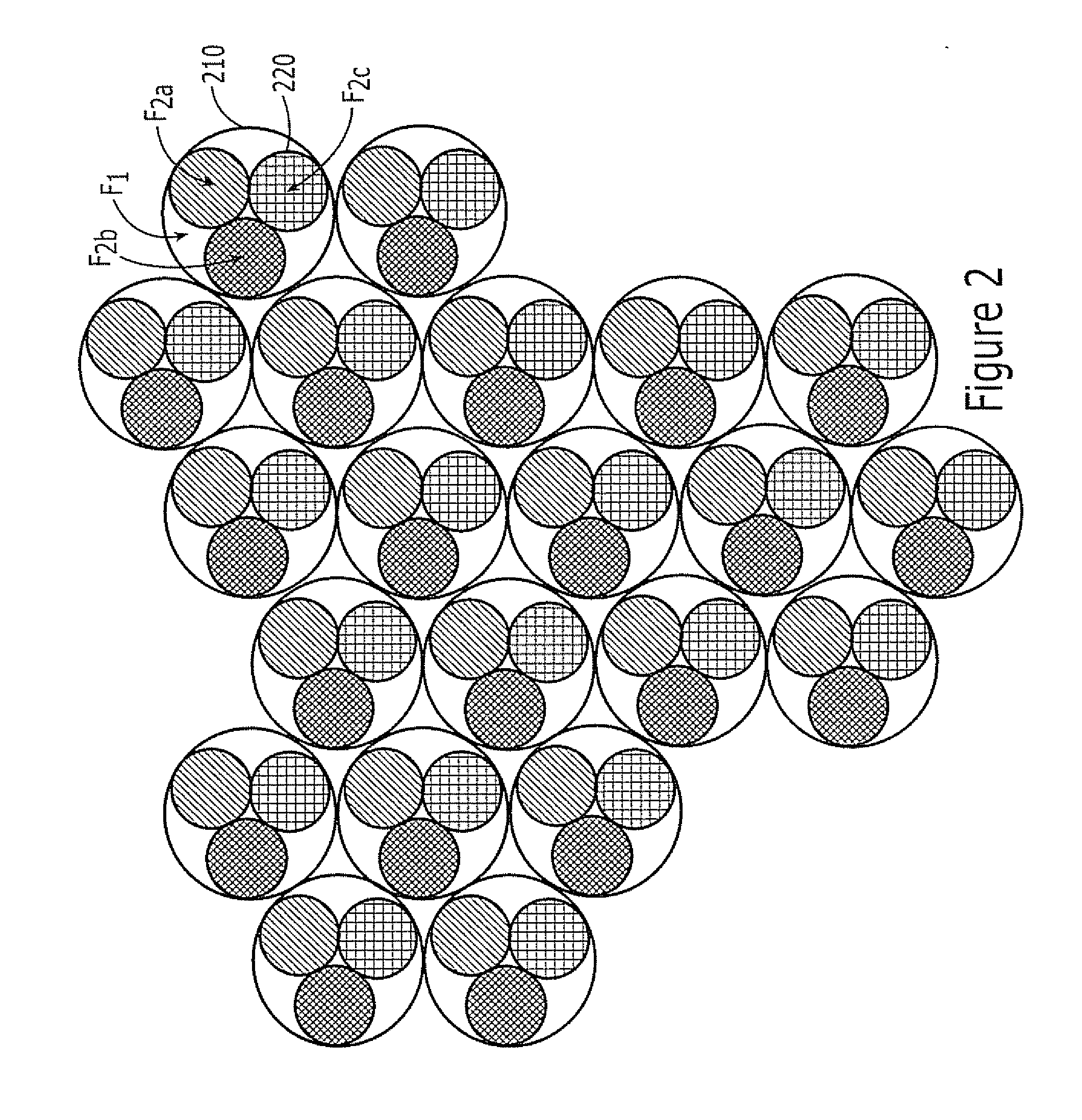
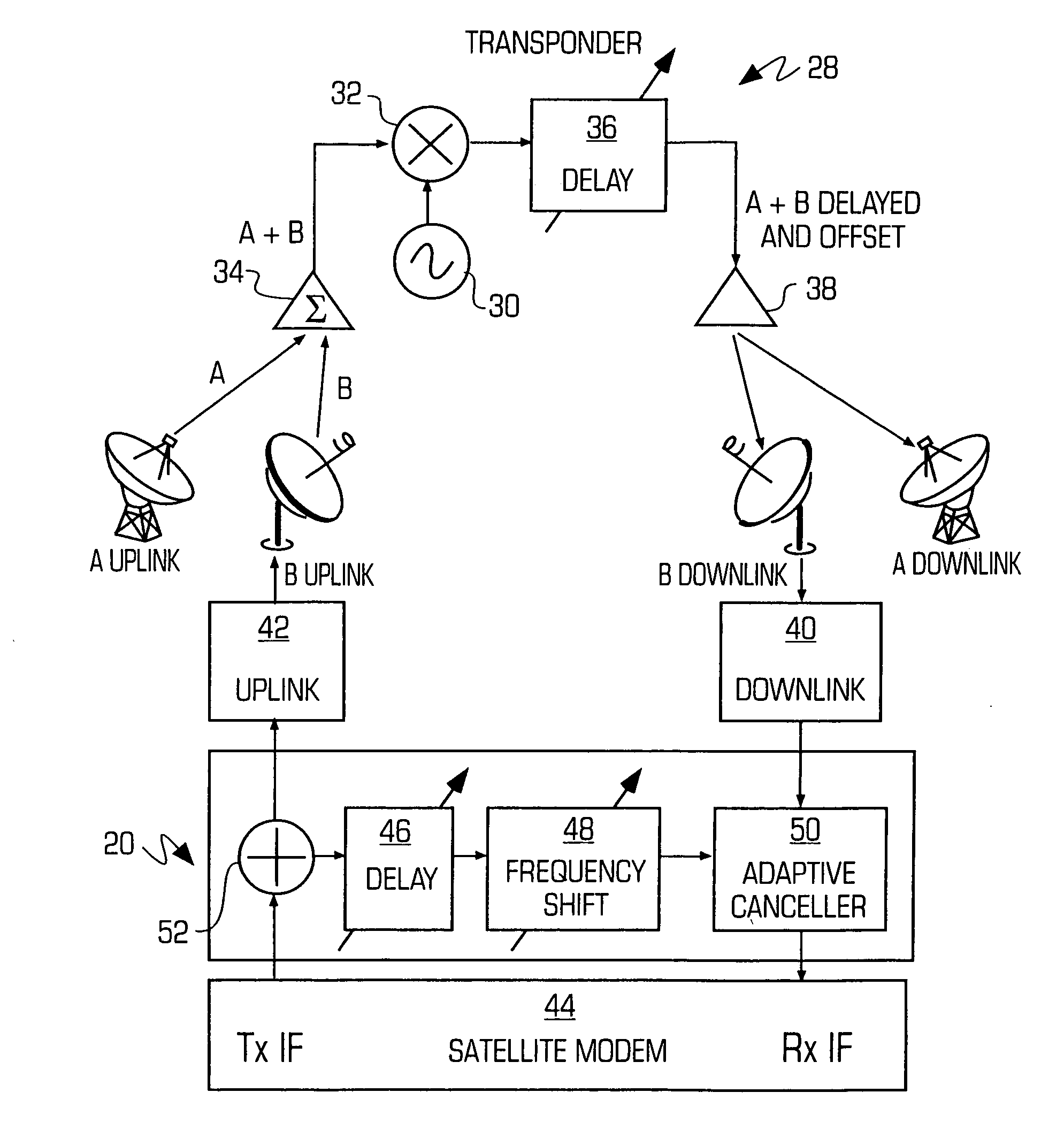
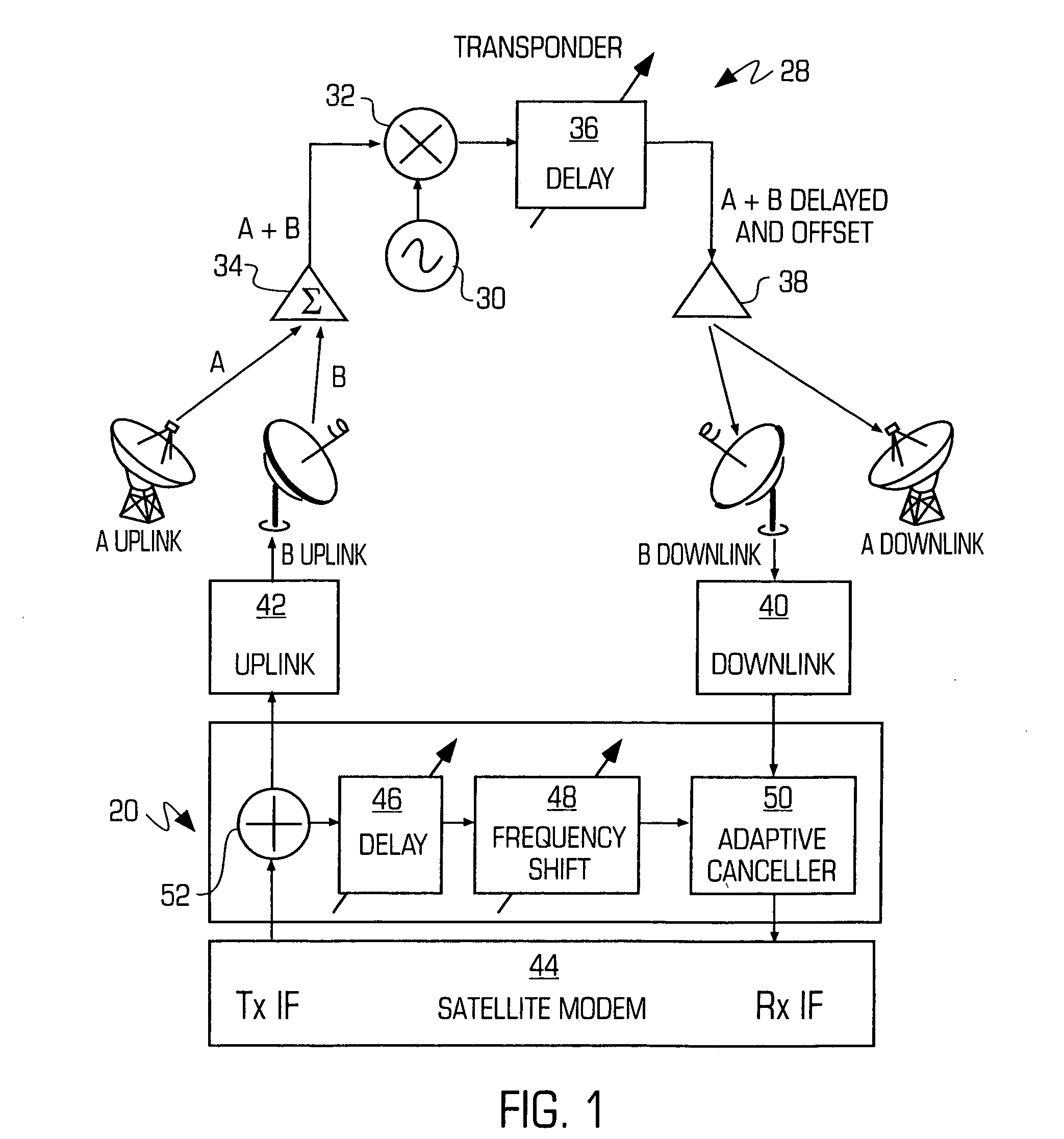
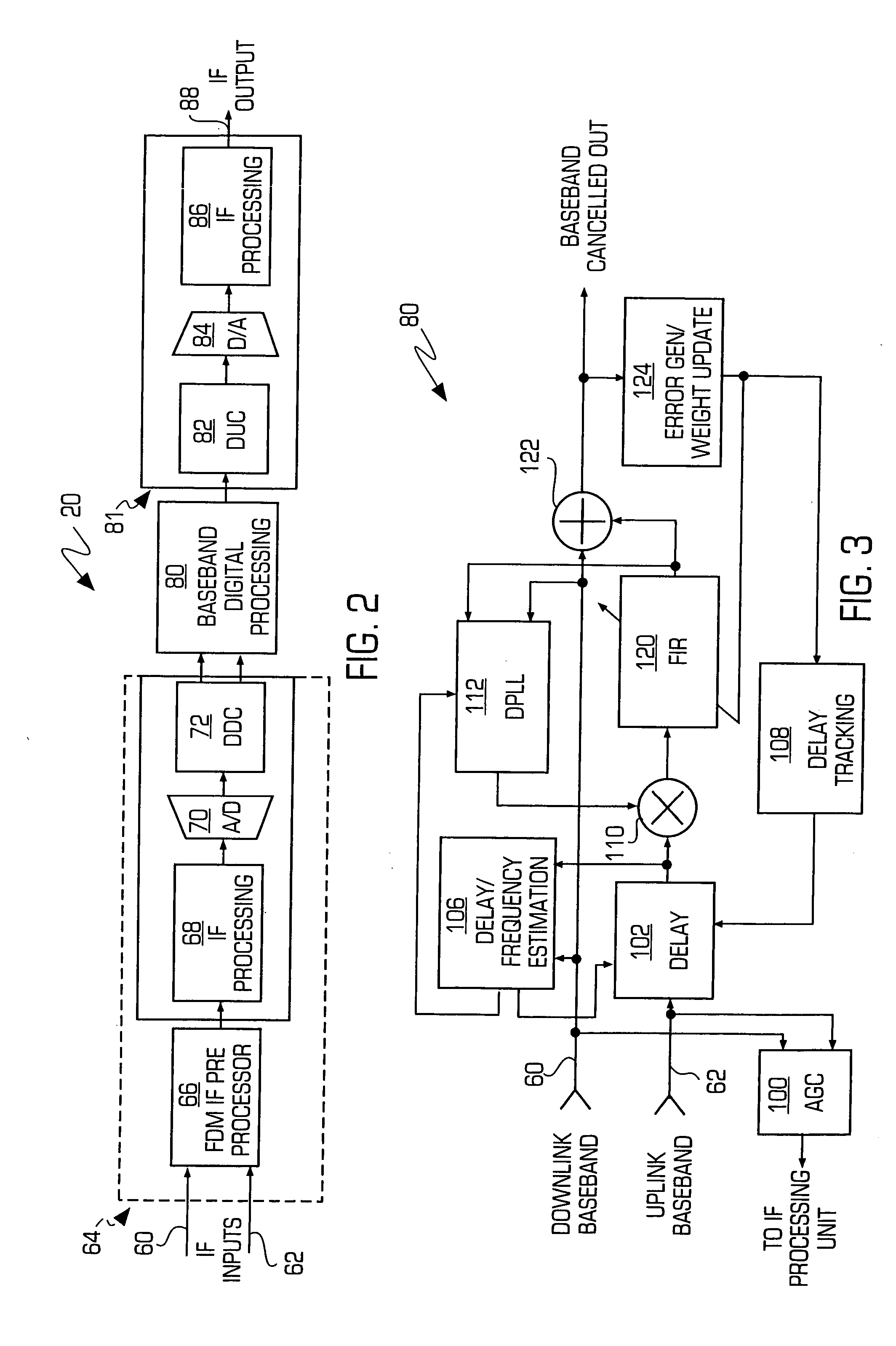
Adaptive canceller for frequency reuse systems
InactiveUS20050159128A1Easy to useHighly effectiveRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionFinite impulse responseAdaptive filter
An adaptive interference canceller for canceling an interfering signal corresponding to a delayed, frequency translated, amplitude and phase offset version of a transmitted signal contained in a composite received signal relayed through a relay system such as a satellite transponder. The canceller digitally downconverts the received signal and a local replica of the transmitted signal from IF to baseband, applies a variable delay and frequency compensation to the replica as a coarse delay and frequency correction, and tracks fine delay, amplitude and phase differences using an adaptive finite impulse response filter to generate a cancellation signal corresponding to the delayed and frequency shifted version. A minimum output power process produces an error signal that drives the variable delay and adaptive filter to minimize the power in the signal of interest to maximize cancellation of the interfering signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON APPLIED SIGNAL TECH
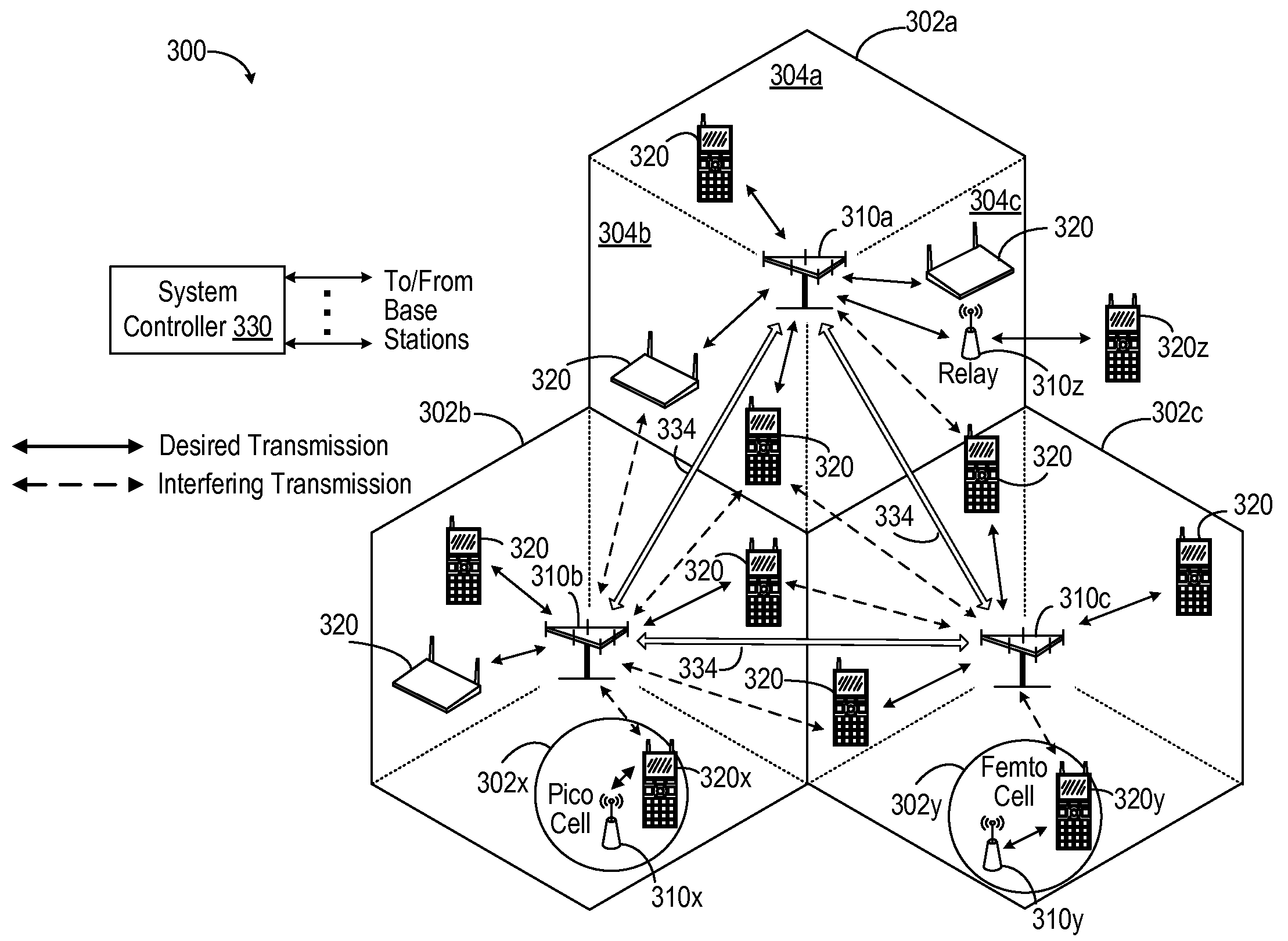
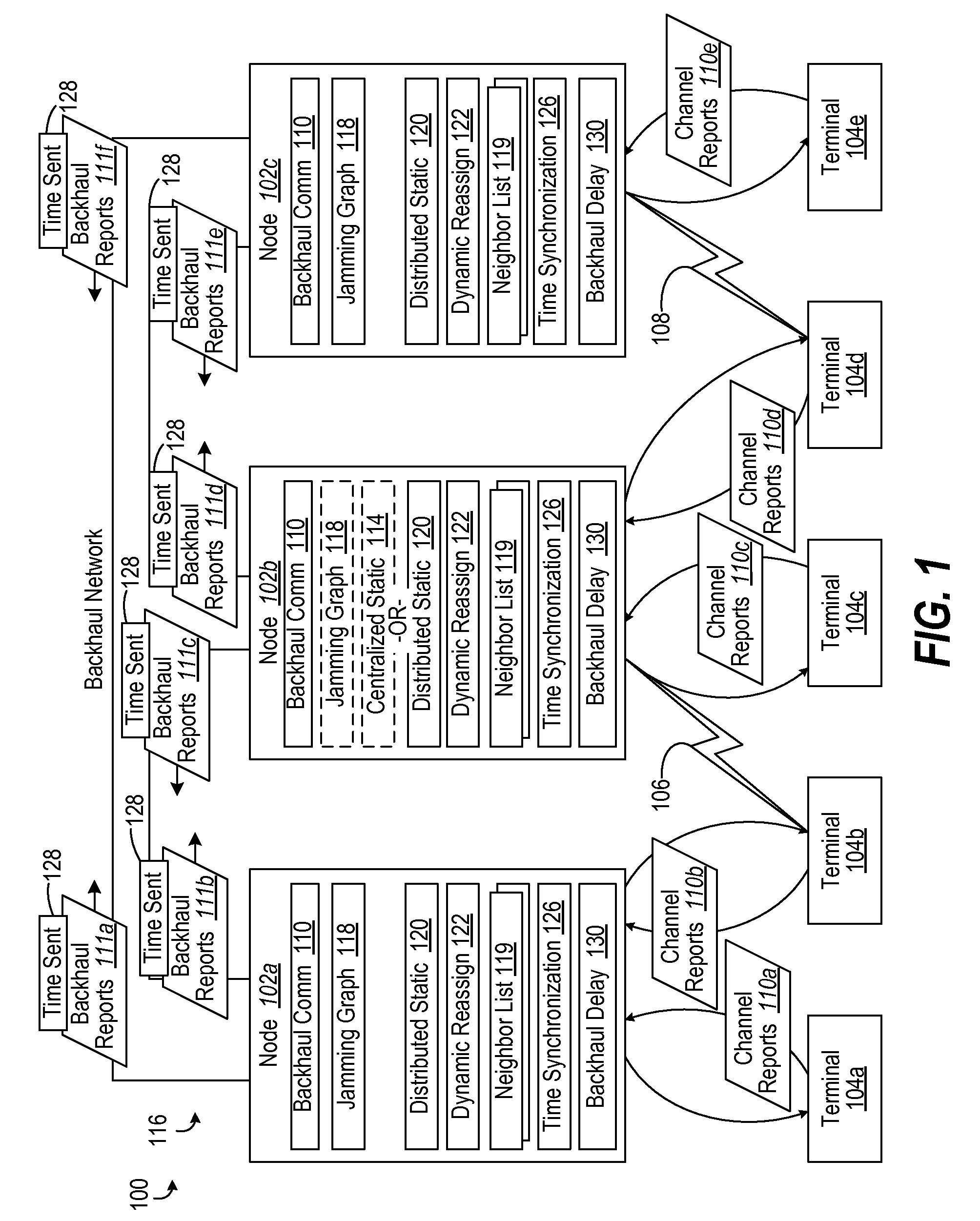
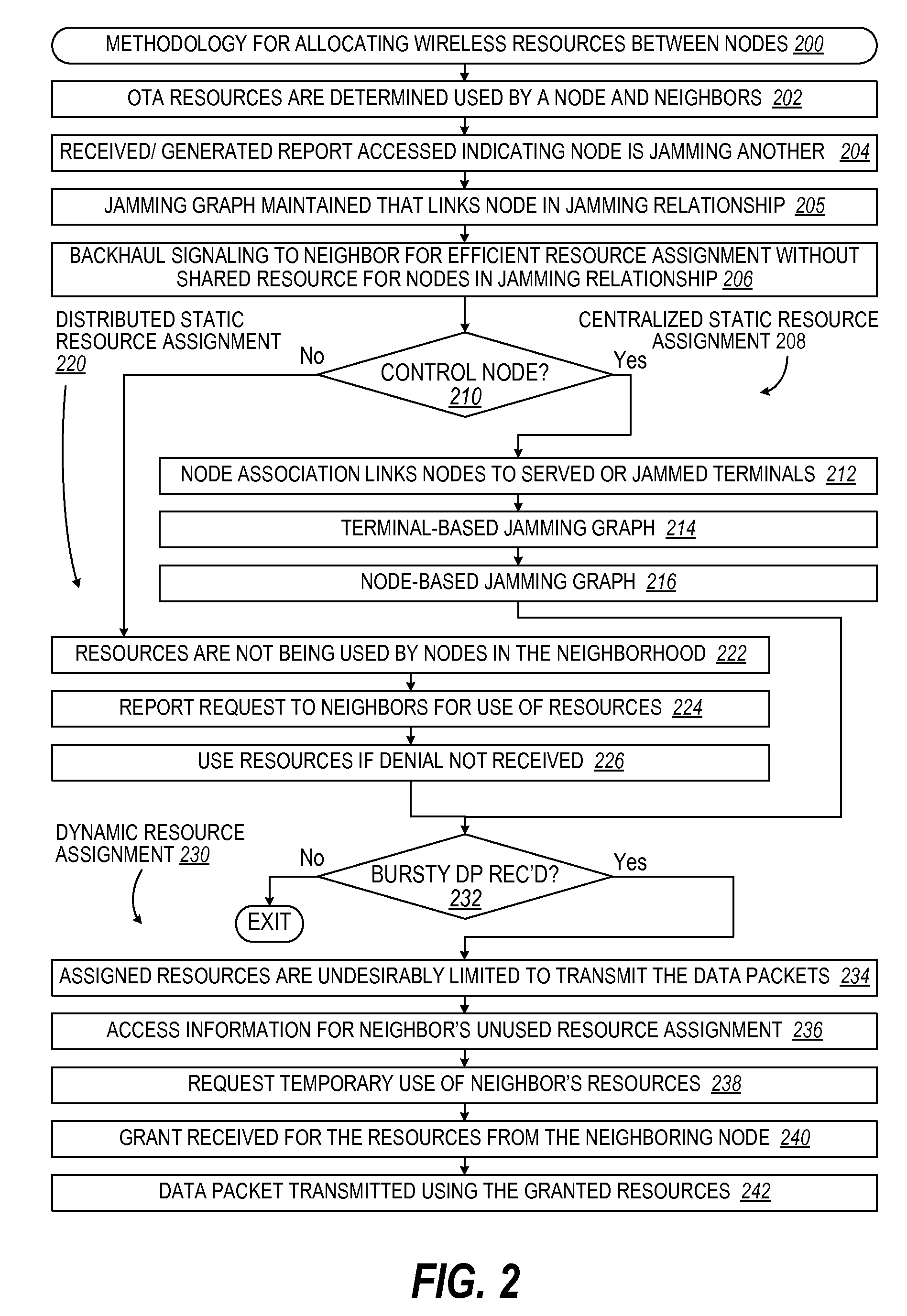
Jamming graph and its application in network resource assignment
InactiveUS20090310554A1Well formedNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionResource assignmentFrequency reuse
A wireless communication network uses backhaul negotiation based upon static and dynamic resource assignment on jamming graphs. Static reuse factor design methods including fractional frequency reuse (FFR) are addressed. The jamming graph is used to summarize the interfering relationship between transmitters (nodes in the jamming graph). Negotiation-based algorithm is used to arrive at a static resource assignment so that a large reuse factor can be achieved while jamming scenario can be avoided. As a result of such algorithm, each transmitter is assigned some resources, over which traffic transmission can be done instantaneously to reduce the packet delay for short packets. Based on the result of static resource negotiation algorithm, a dynamic resource algorithm can be run, such that the resources assigned to different nodes can be share in a bursty traffic scenario to further reduce packet delay for larger packet size cases, while jamming be also avoided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
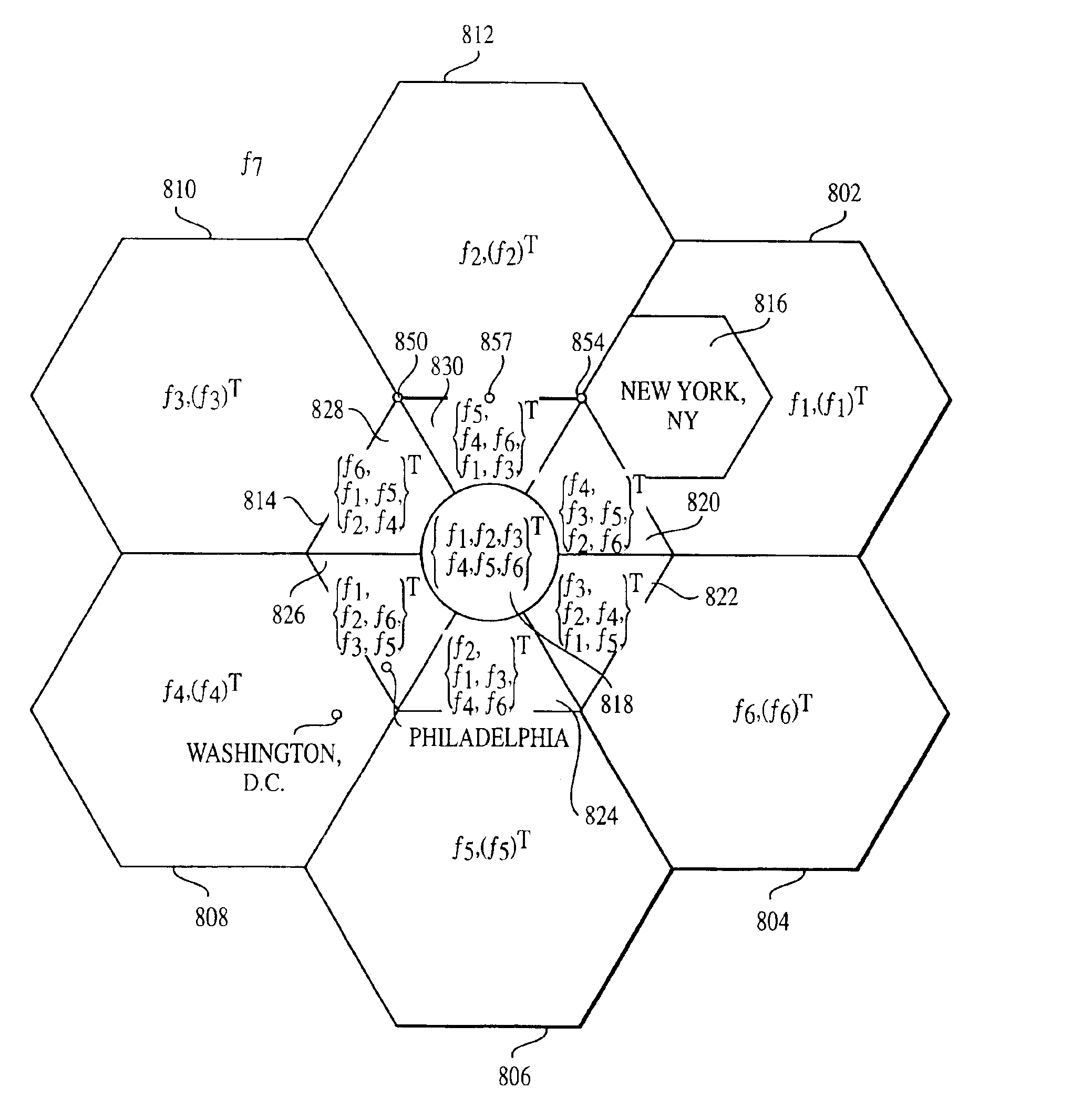
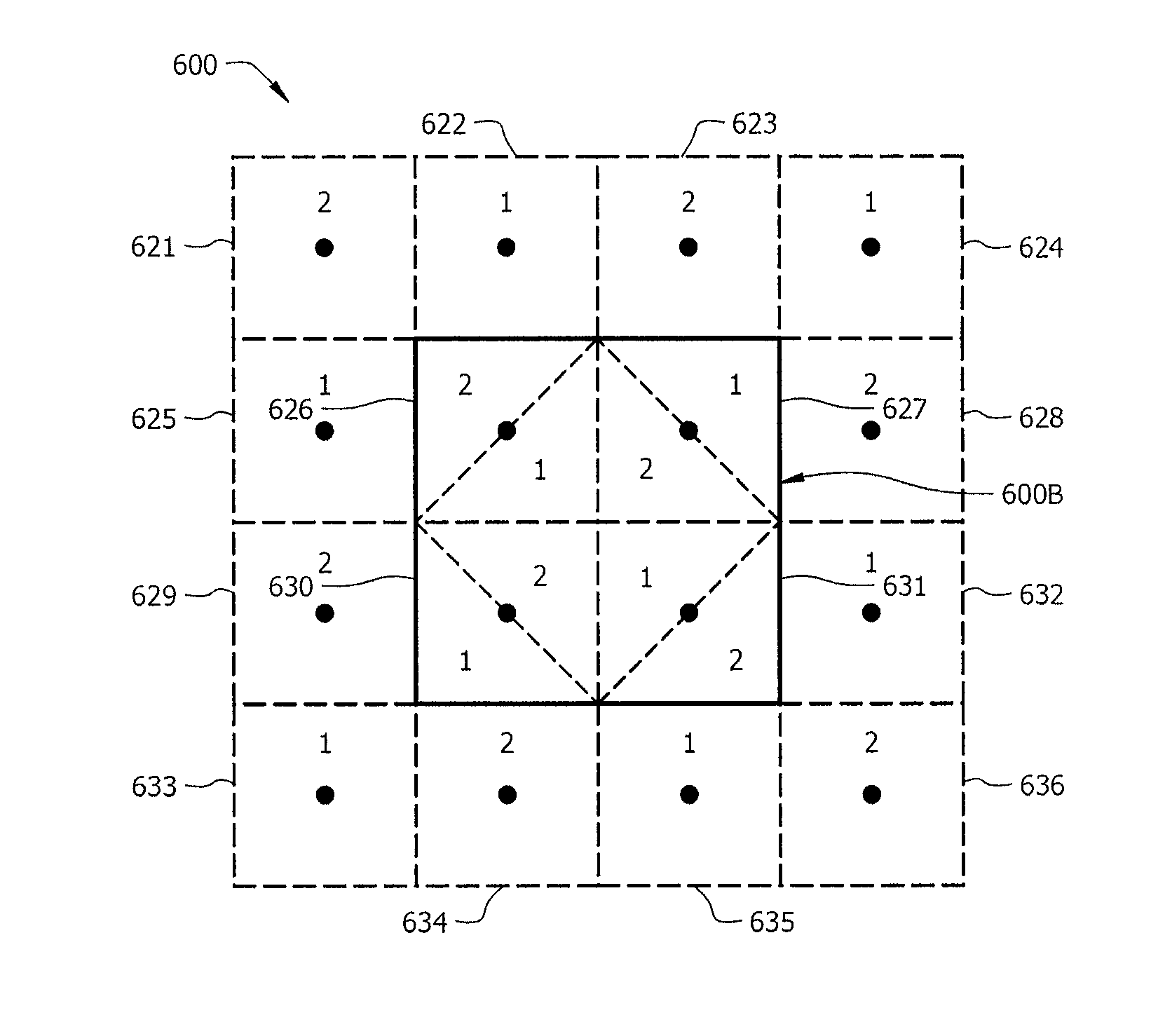
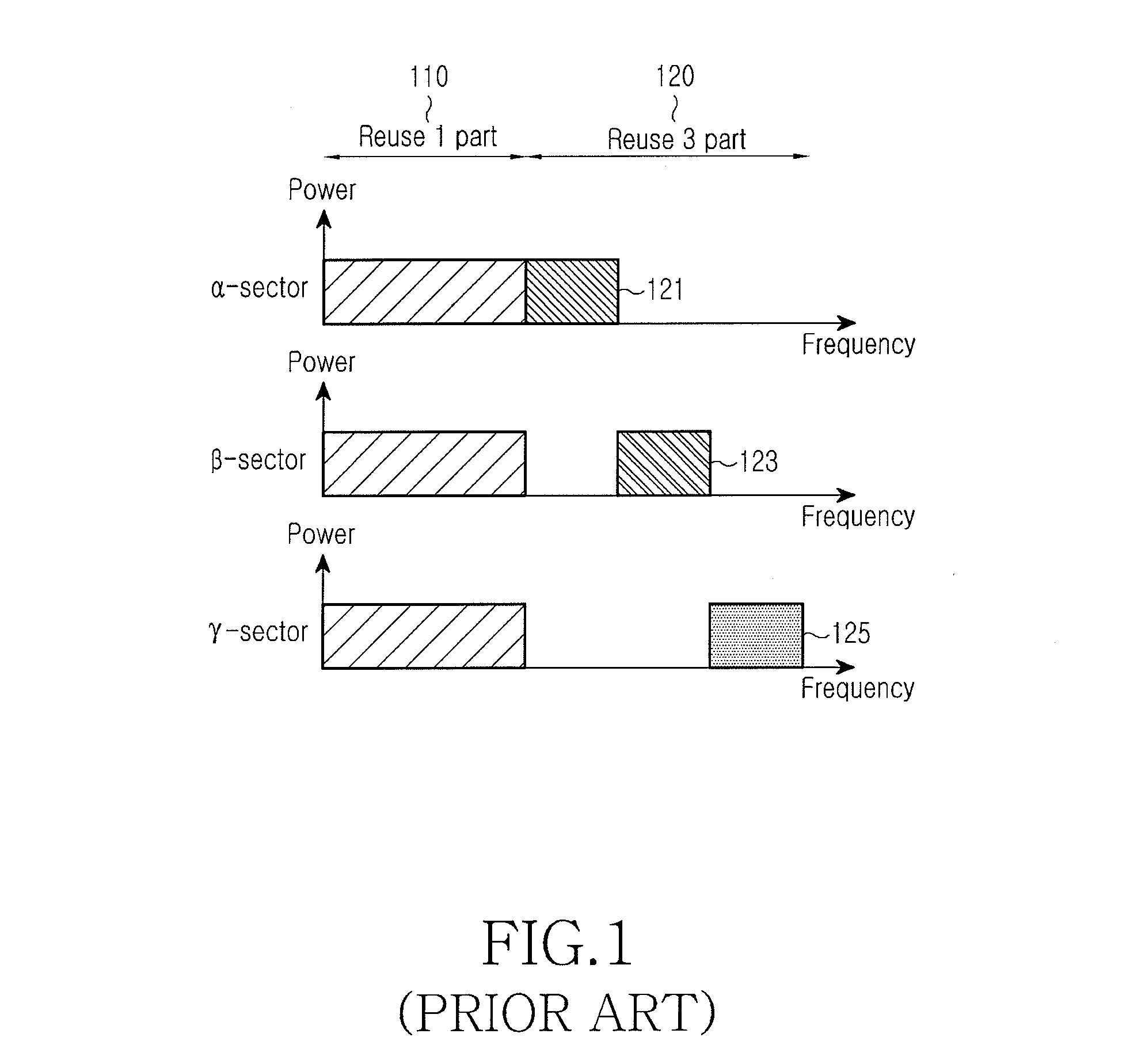
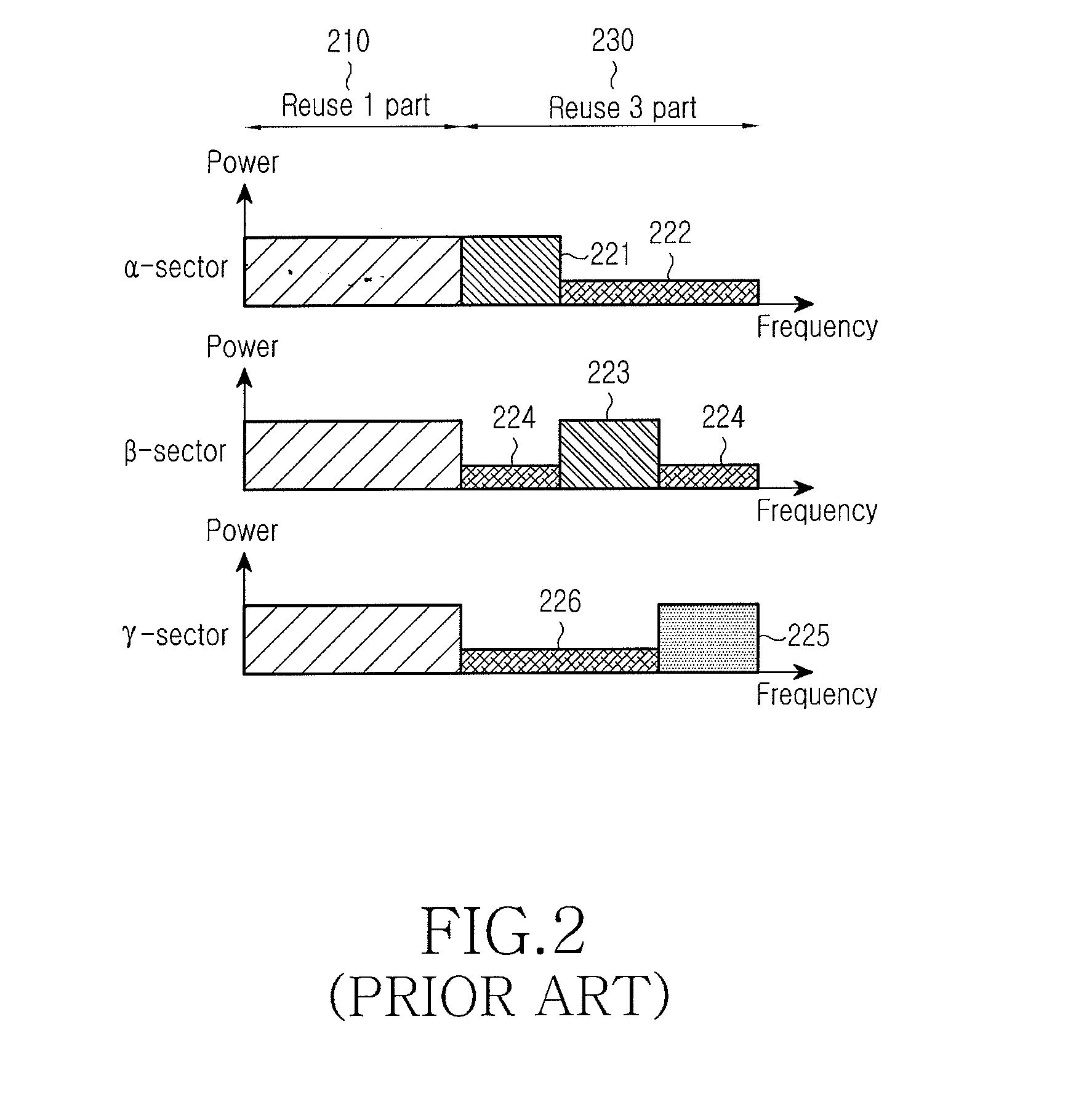
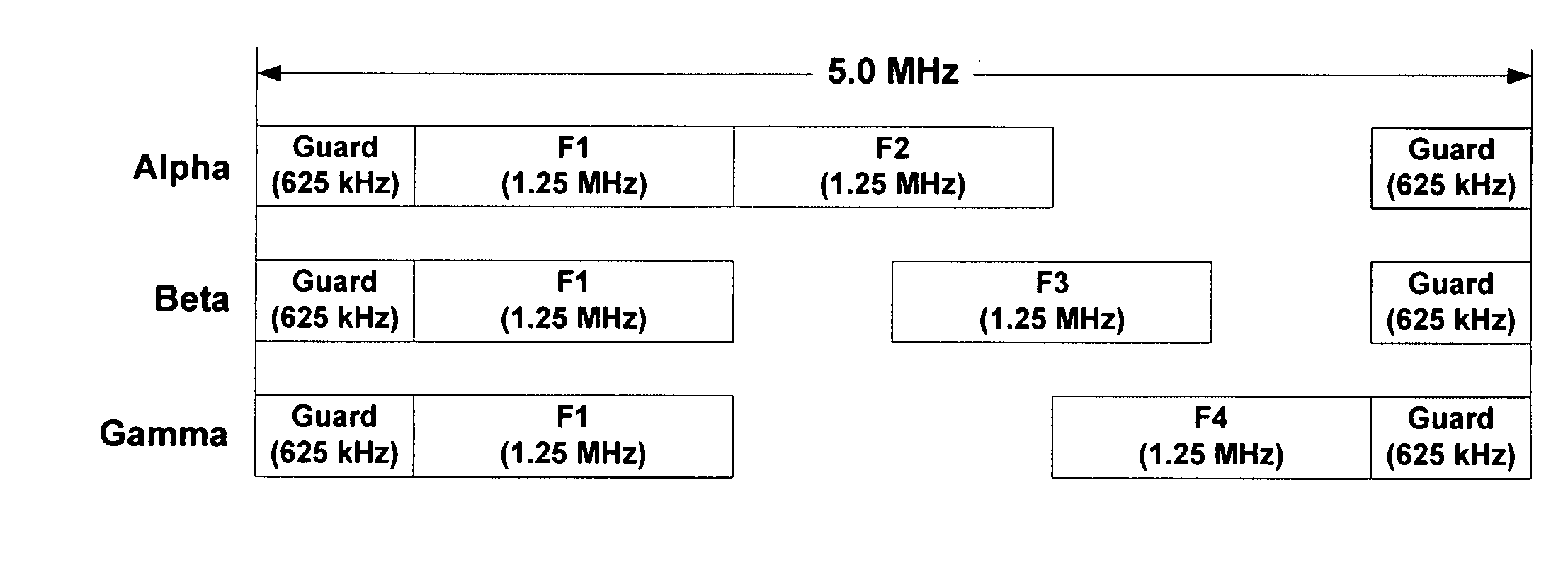
Method and system using overlapping frequency bands in a hybrid frequency reuse plan
ActiveUS20070298807A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency reuseTelecommunications network
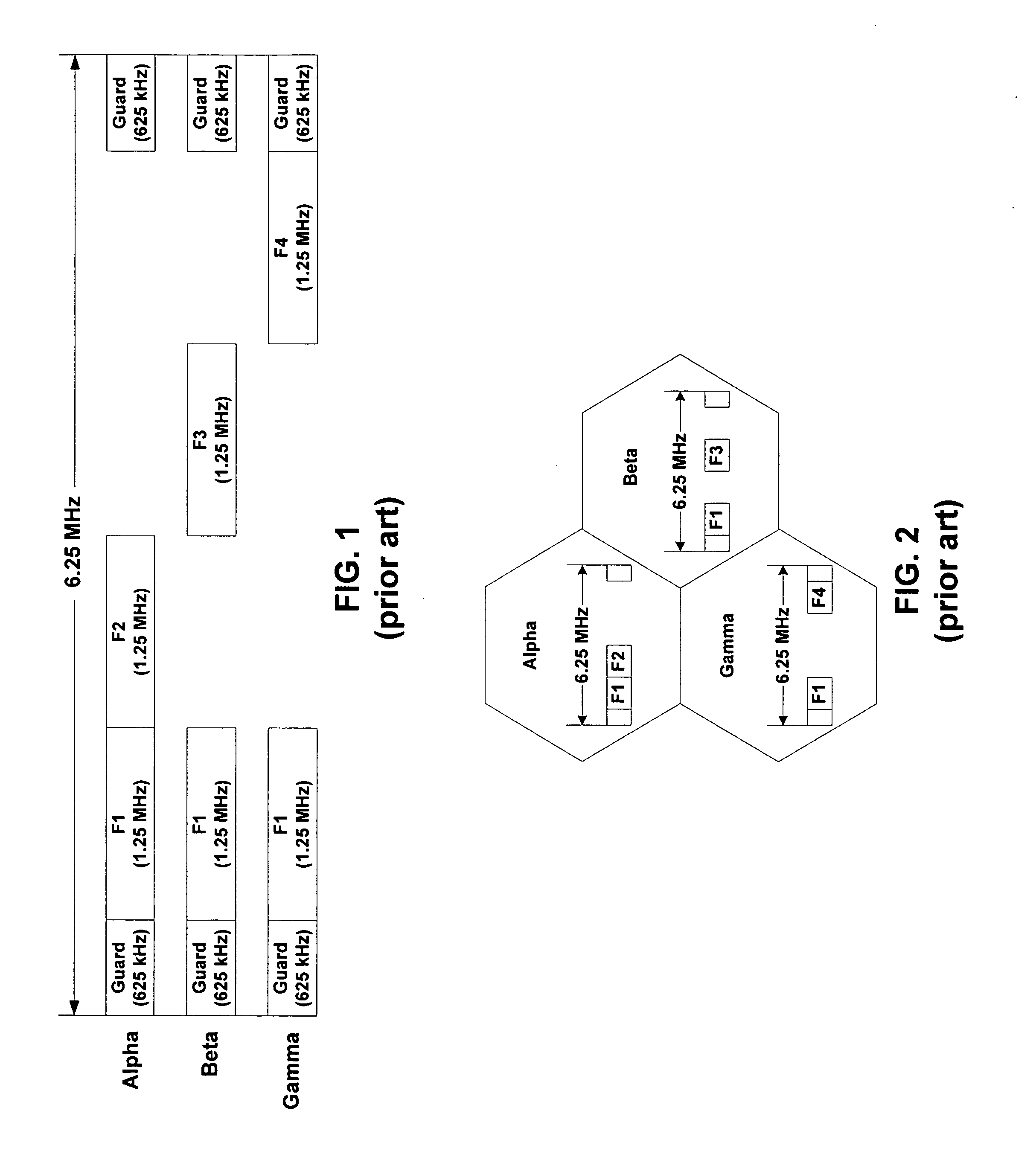
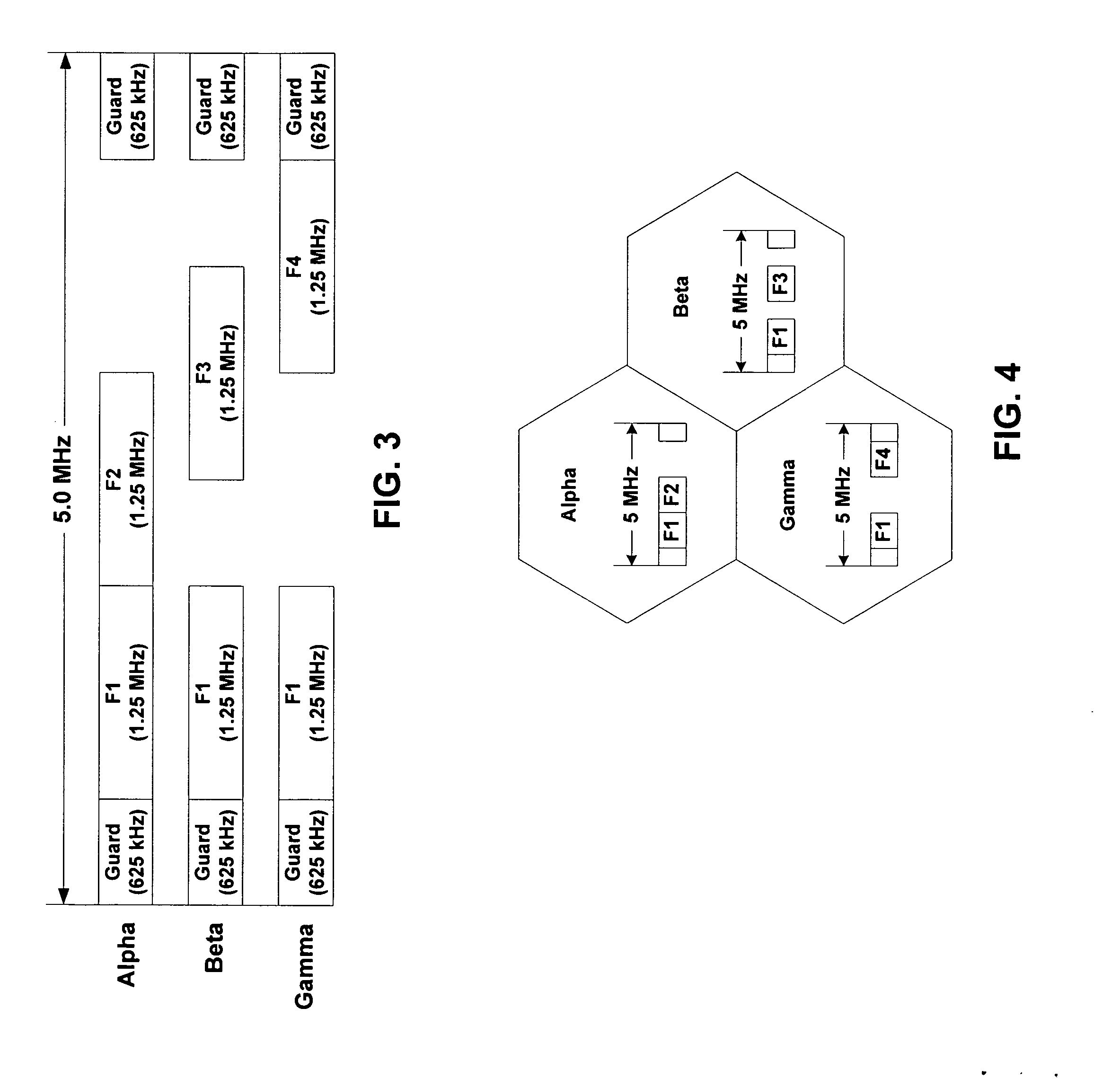
The wireless coverage of a wireless telecommunications network is divided into a plurality of cells, and each cell is further divided into an alpha sector, a beta sector, and a gamma sector. The alpha sectors are provided with a first frequency assignment that includes a first frequency band and a second frequency band. The beta sectors are provided with a second frequency assignment that includes the first frequency band and a third frequency band. The gamma sectors are provided with a third frequency assignment that includes the first frequency band and a fourth frequency band. The second and third frequency bands partially overlap in frequency. The third and fourth frequency bands also partially overlap in frequency. By using overlapping frequency bands, the benefits of hybrid frequency reuse may be achieved in a more spectrally efficient manner.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
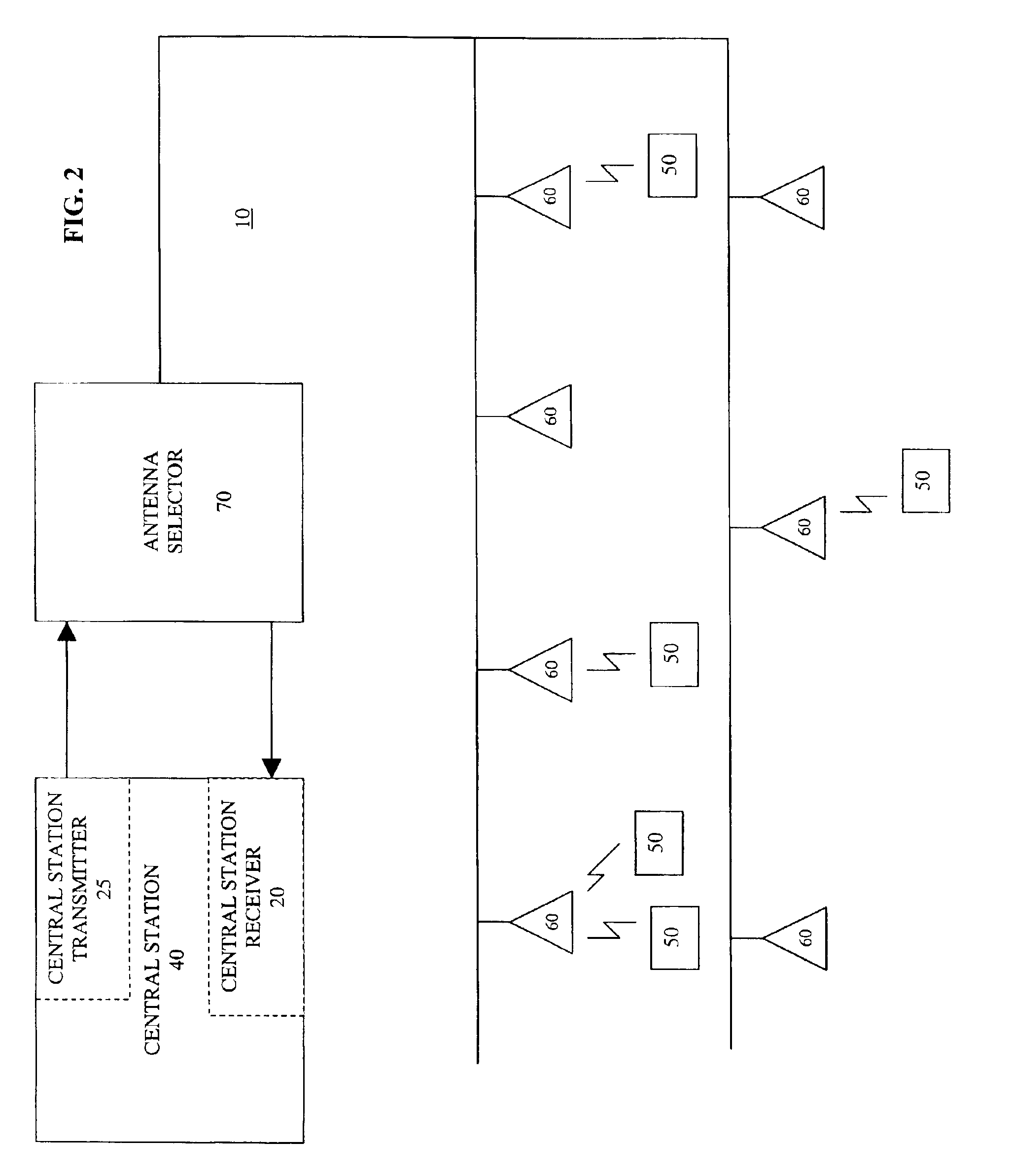
System and method for a low rate, in-band broadcast communication for medical telemetry
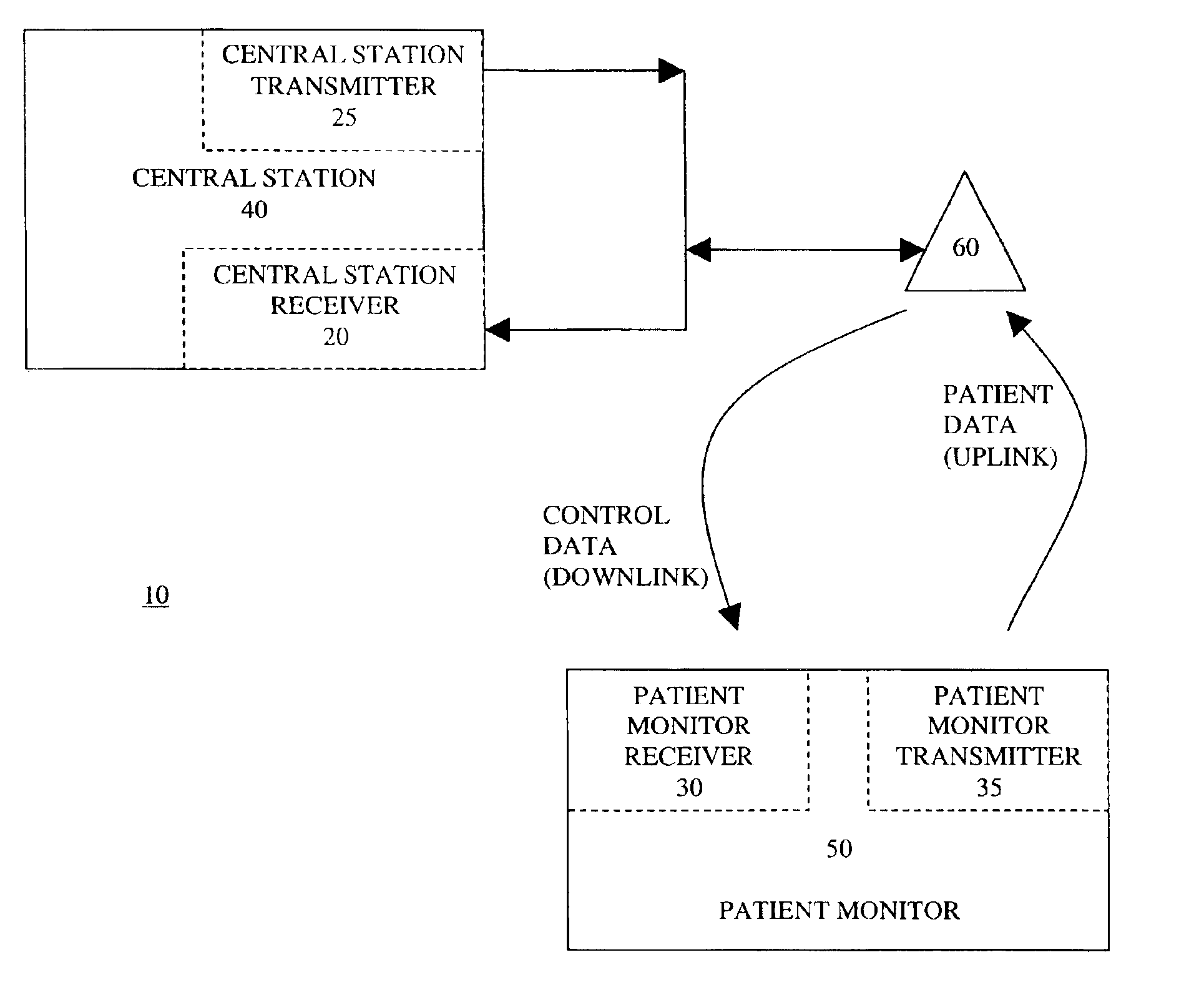
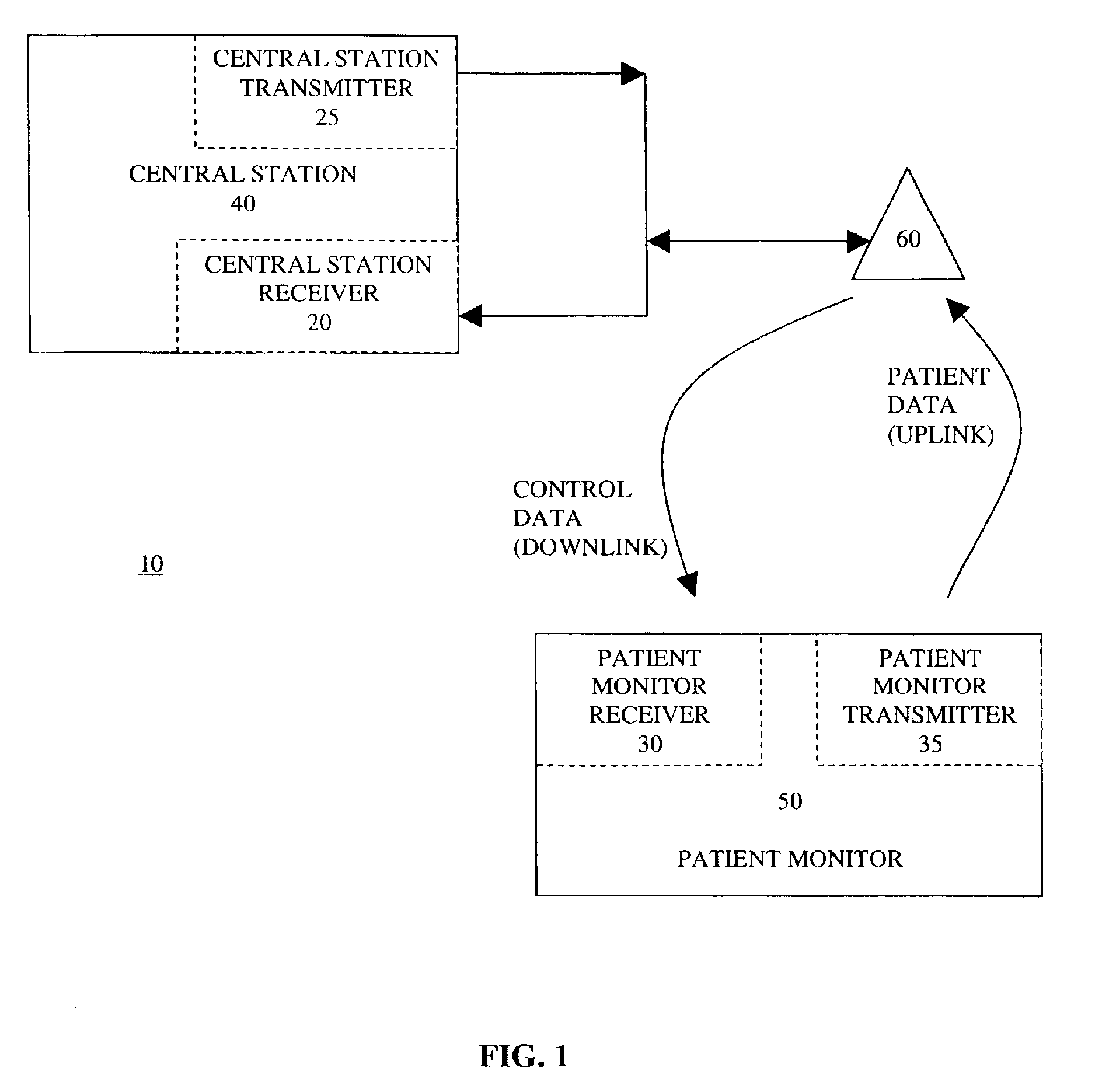
ActiveUS6914539B2Electric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsFrequency reuseData information
A medical telemetry system includes a central station having a central station receiver and a central station transmitter that both operate on a frequency bandwidth having frequency multiplexed transmission channels and guard bands. A guard band separates each of the frequency-multiplexed transmission channels. The central station receiver wirelessly receives patient data from one of the frequency-multiplexed transmission channels. The central station transmitter wirelessly transmits control data information via each of the guard bands. At least one patient monitor is provided that includes a patient monitor receiver and a patient monitor transmitter that both operate on the frequency bandwidth. The patient monitor is wirelessly connected to the central station. The patient monitor receiver is configured for wirelessly receiving the control data information from the central station transmitter via the guard bands. The patient monitor transmitter is configured for wirelessly transmitting the patient data to the central station receiver via one of the frequency multiplexed transmission channels.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
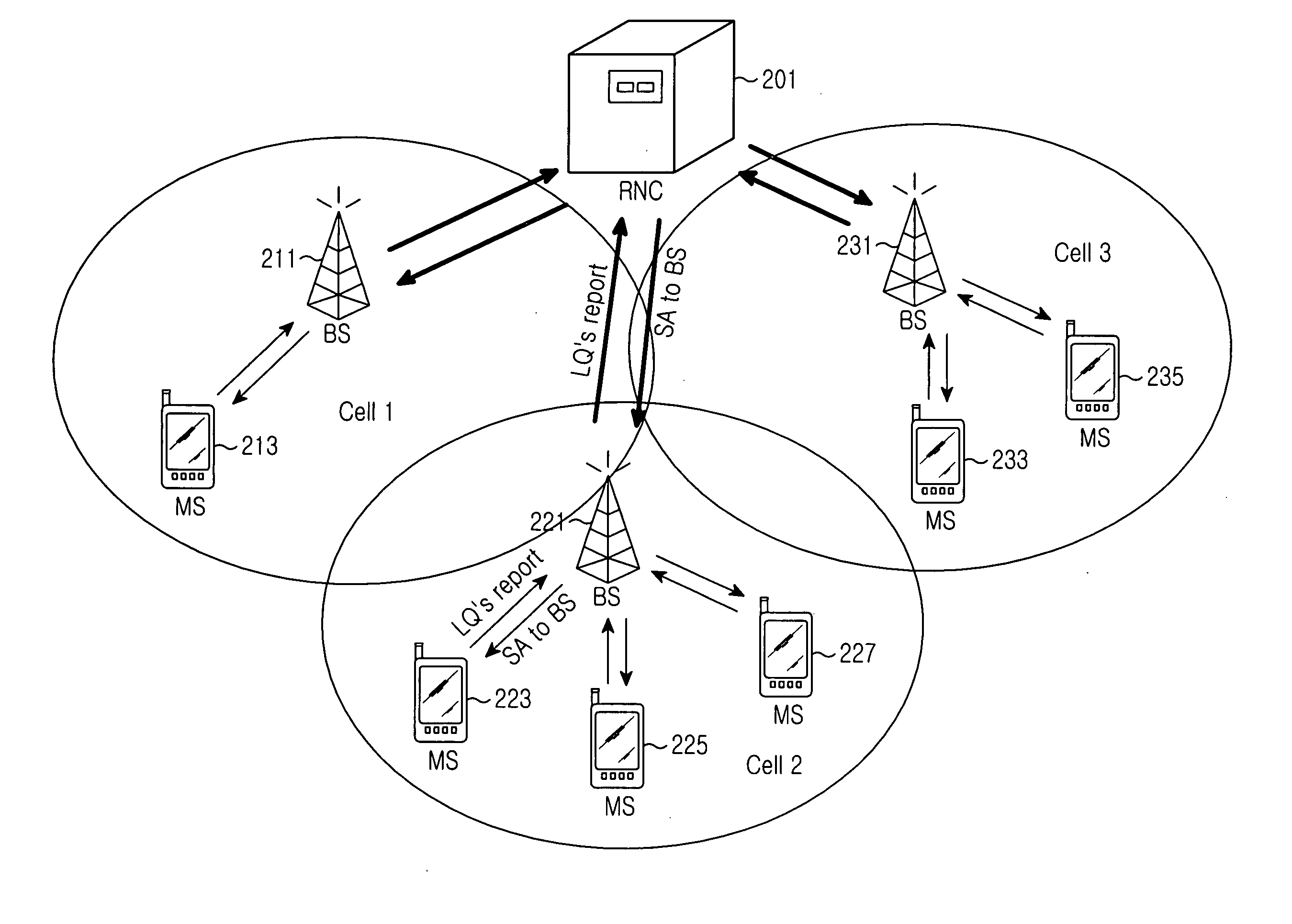
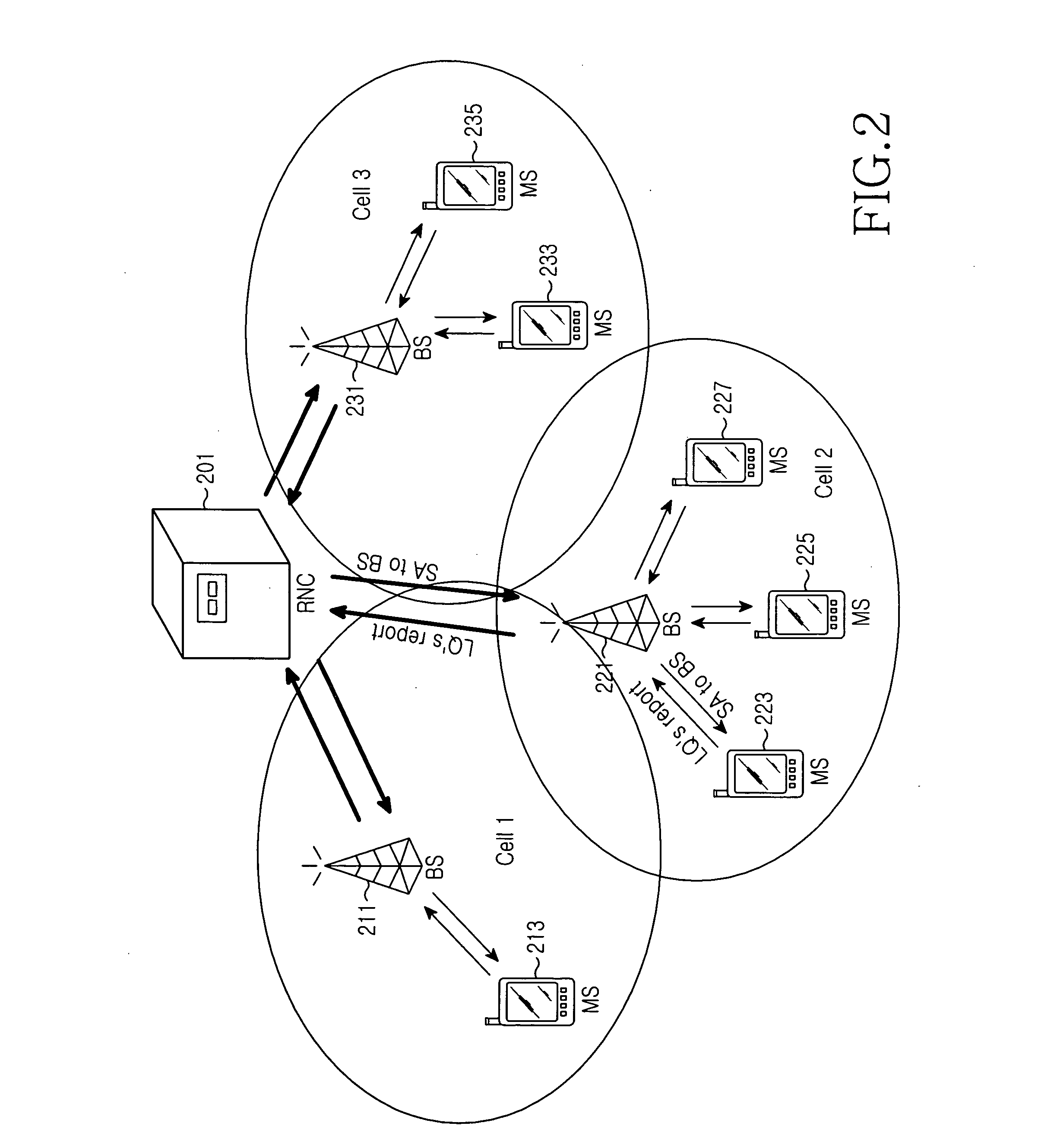
Method and apparatus for uplink power control in a frequency division multiple access communication system
A communication system optimizes cell edge performance and spectral efficiency by determining an adaptive power control parameter based on system performance metrics measured by a serving Node B and further measured by, and reported to the serving Node B by, neighboring Node B's. The adaptive power control parameter is then used to determine an uplink transmit power of a user equipment (UE) served by the serving Node B. The uplink transmit power may be determined by the Node B and then conveyed to the UE, or the Node B may broadcast the adaptive power control parameter to the UE and the UE may self-determine the uplink transmit power. In addition, as a frequency reuse factor of one has been proposed for such communication systems, interference levels may be even further improved by employment of an intra-site interference cancellation scheme in the sectors serviced by the Node B.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
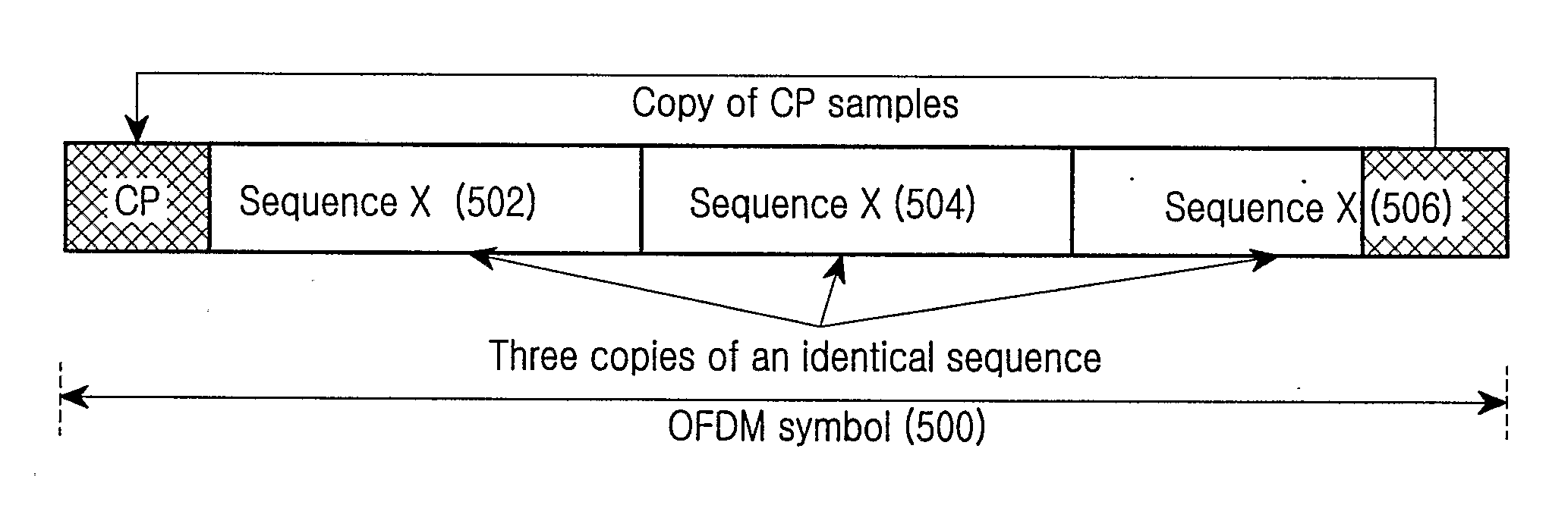
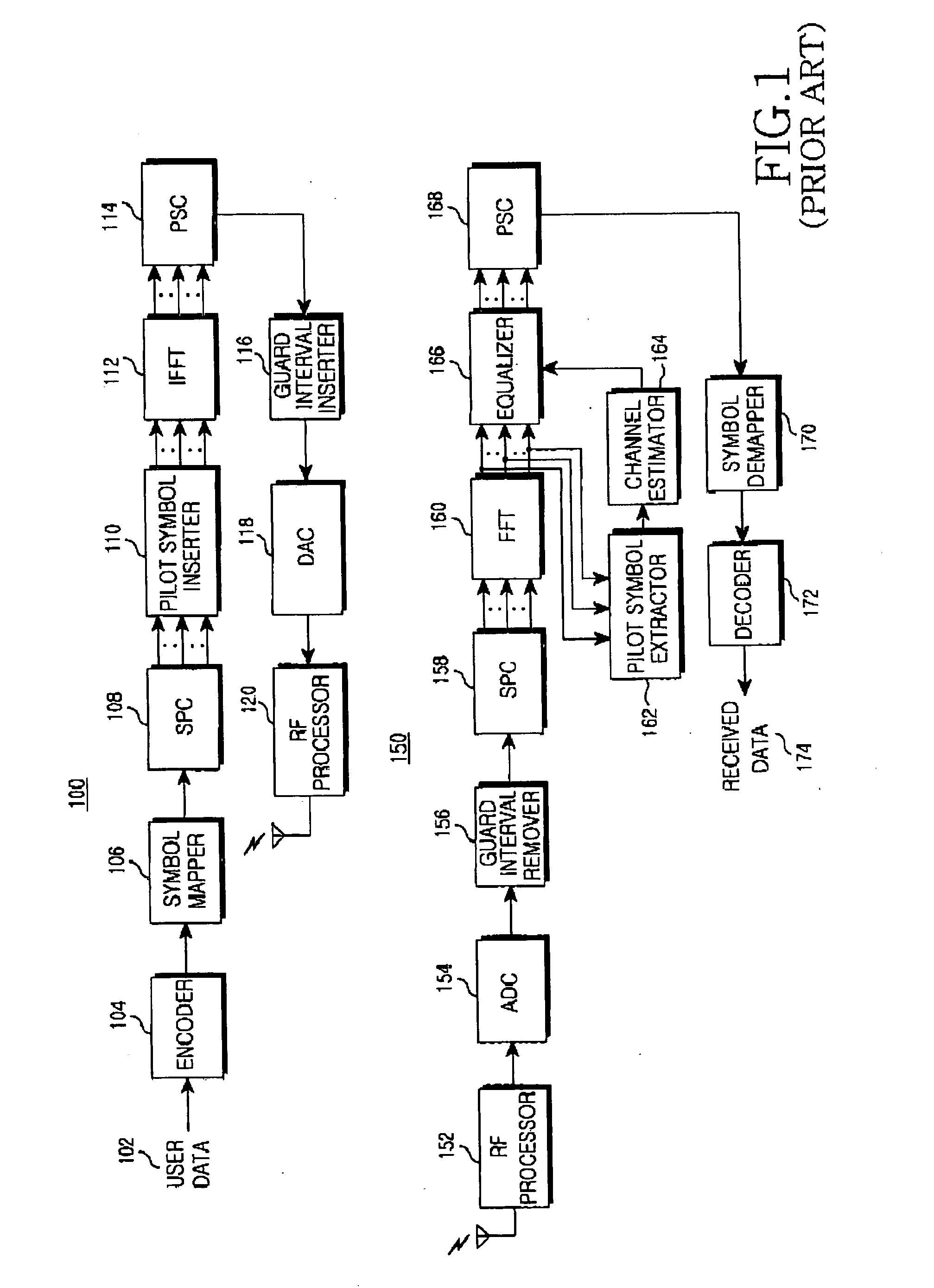
Method and apparatus for transmitting synchronization signals in an OFDM based cellular communication system
ActiveUS20090219883A1Process stabilityInterference minimizationSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionCell specificFrequency reuse
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for transmitting the synchronization signal in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based cellular system. The cell search process widely used in the OFDM based cellular system is divided into two steps for obtaining the frame timing synchronization and obtaining the cell-specific scrambling code. When designing the channel for obtaining the frame timing synchronization and the channel for obtaining the cell-specific scrambling code, different frequency reuse factors are applied to the synchronization channels of different steps according to the characteristics of each synchronization obtainment step in order to improve the performance of each step.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
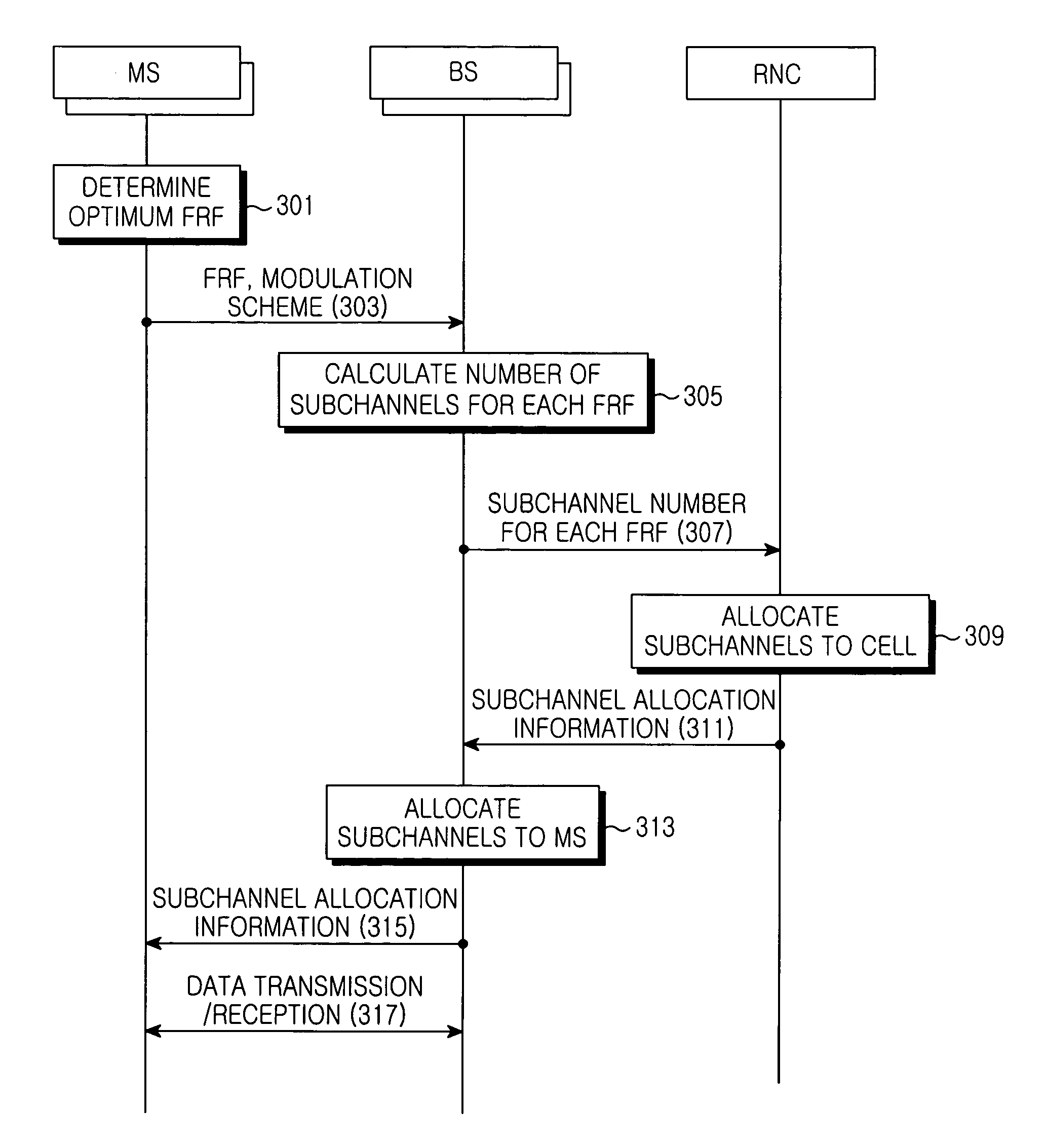
Apparatus and method for allocating subchannels adaptively according to frequency reuse rates in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access system
ActiveUS7423991B2Effective distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionFrequency reuseSelf adaptive
An apparatus and method for adaptively allocating subchannels according to frequency reuse rates in an OFDMA system are provided. To allocate one or more subchannels to one or more MSs, information related to an optimum FRF and a modulation scheme is received from the plurality of MSs, the number of subchannels required for each FRF is calculated according to the received information, subchannels are allocated to the BS for each FRF, based on the calculated subchannel numbers from the BS and neighboring BSs, and the allocated subchannels are allocated to the MSs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
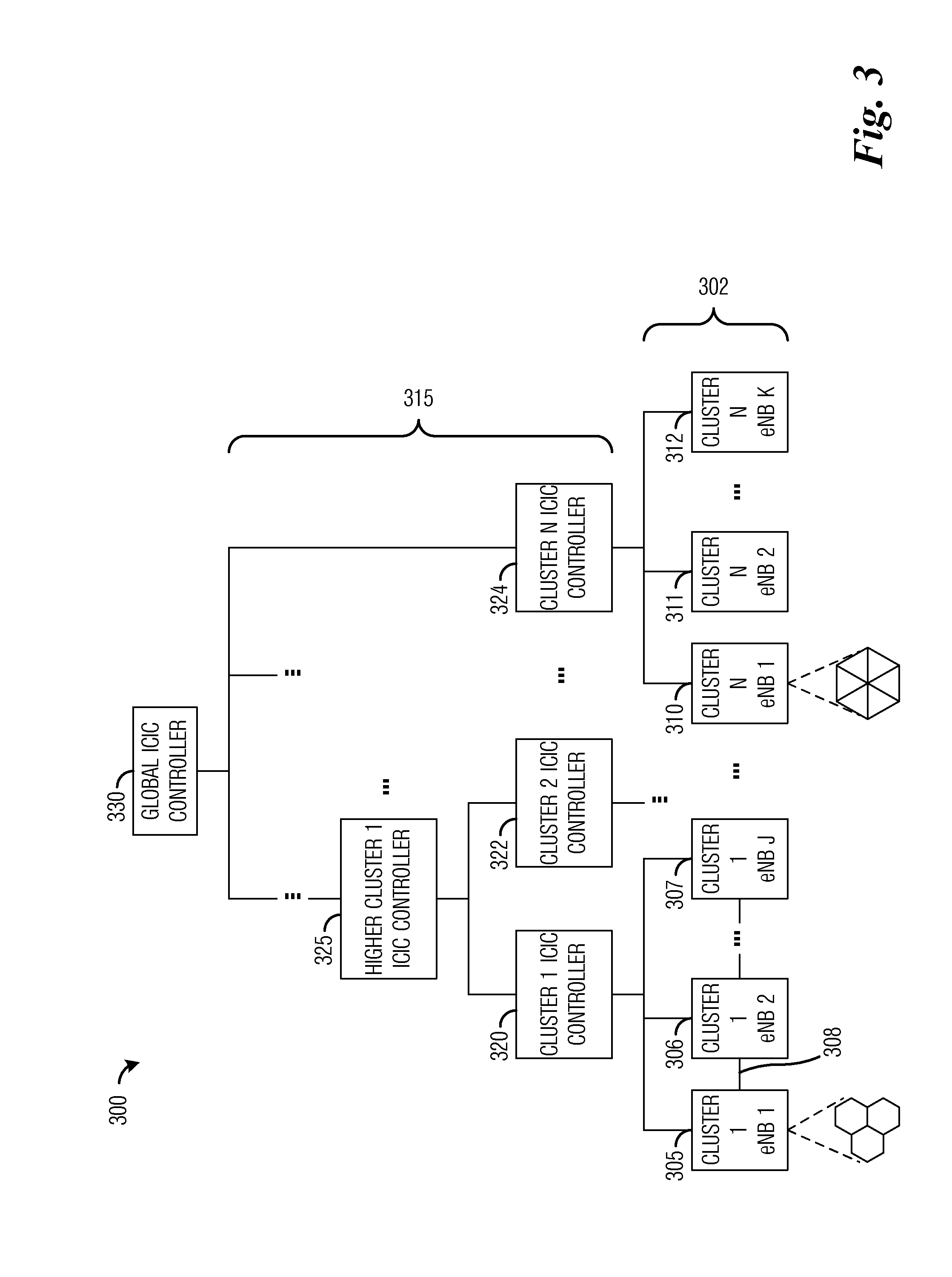
System and Method for Self-Organized Inter-Cell Interference Coordination
ActiveUS20120028584A1Operation efficiency can be improvedReduce operating costsTransmission noise suppressionNetwork planningFrequency reuseEngineering
A system and method for self-organized inter-cell interference coordination are provided. A method for controller operations includes receiving signal power measurements at a controller, determining an interference level based on the signal power measurements, generating relationship information based on the interference level, and determining frequency reuse modes for communications controllers controlled by the controller based on the relationship information.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Apparatus and method for allocating subchannels adaptively according to frequency reuse rates in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access system
ActiveUS20050169229A1Effective distributionNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionFrequency reuseFrequency-division multiple access
An apparatus and method for adaptively allocating subchannels according to frequency reuse rates in an OFDMA system are provided. To allocate one or more subchannels to one or more MSs, information related to an optimum FRF and a modulation scheme is received from the plurality of MSs, the number of subchannels required for each FRF is calculated according to the received information, subchannels are allocated to the BS for each FRF, based on the calculated subchannel numbers from the BS and neighboring BSs, and the allocated subchannels are allocated to the MSs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Communication network method and apparatus including macro base station and femto base station
A communications network comprises a macro base station for providing service to a macrocell and a femto base station in a femtocell, wherein the femtocell overlies the macrocell, the femto base station is configured to perform self-configuration using resource profiles, and resource profiles include pre-configured profiles and frequency reuse information.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
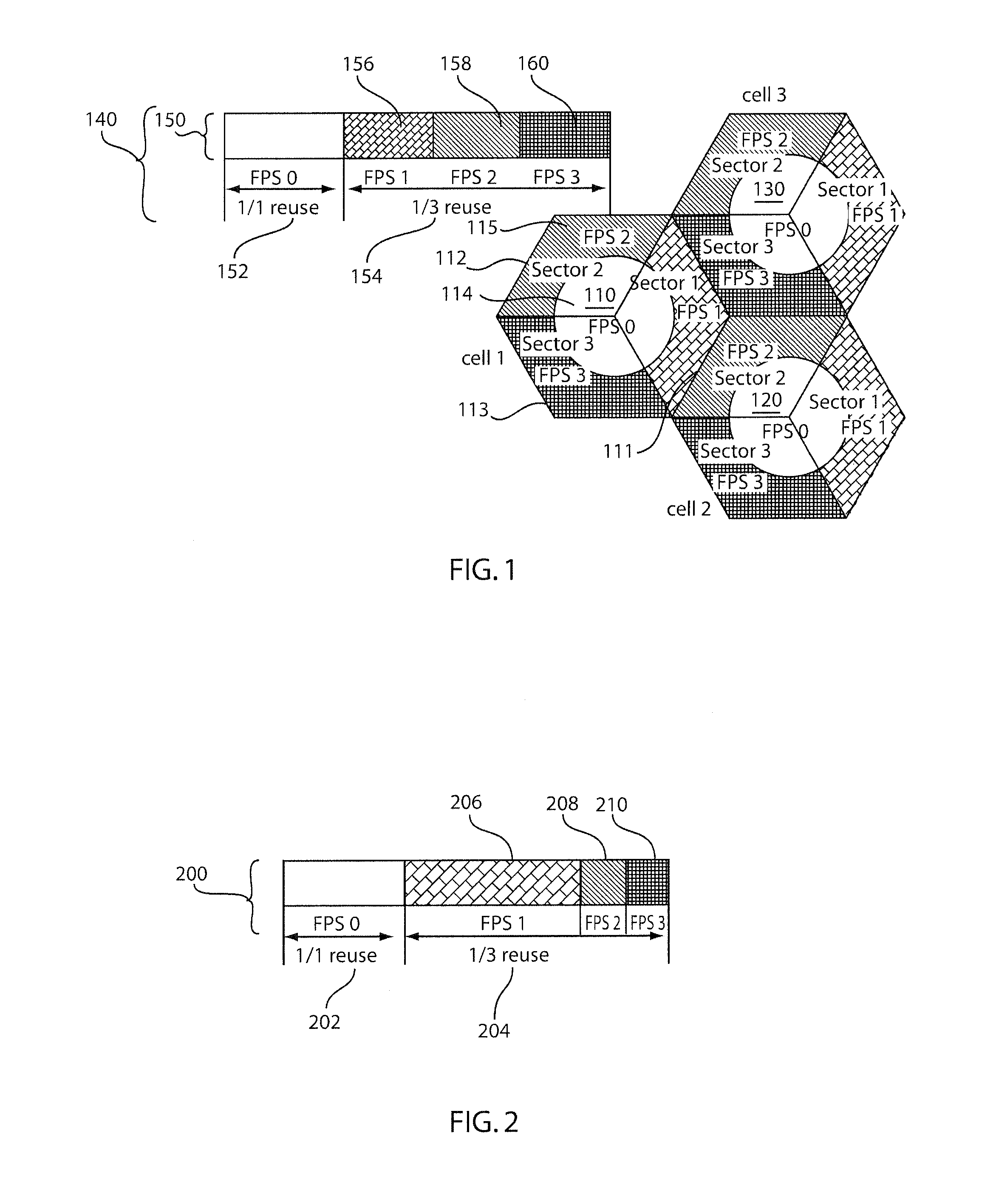
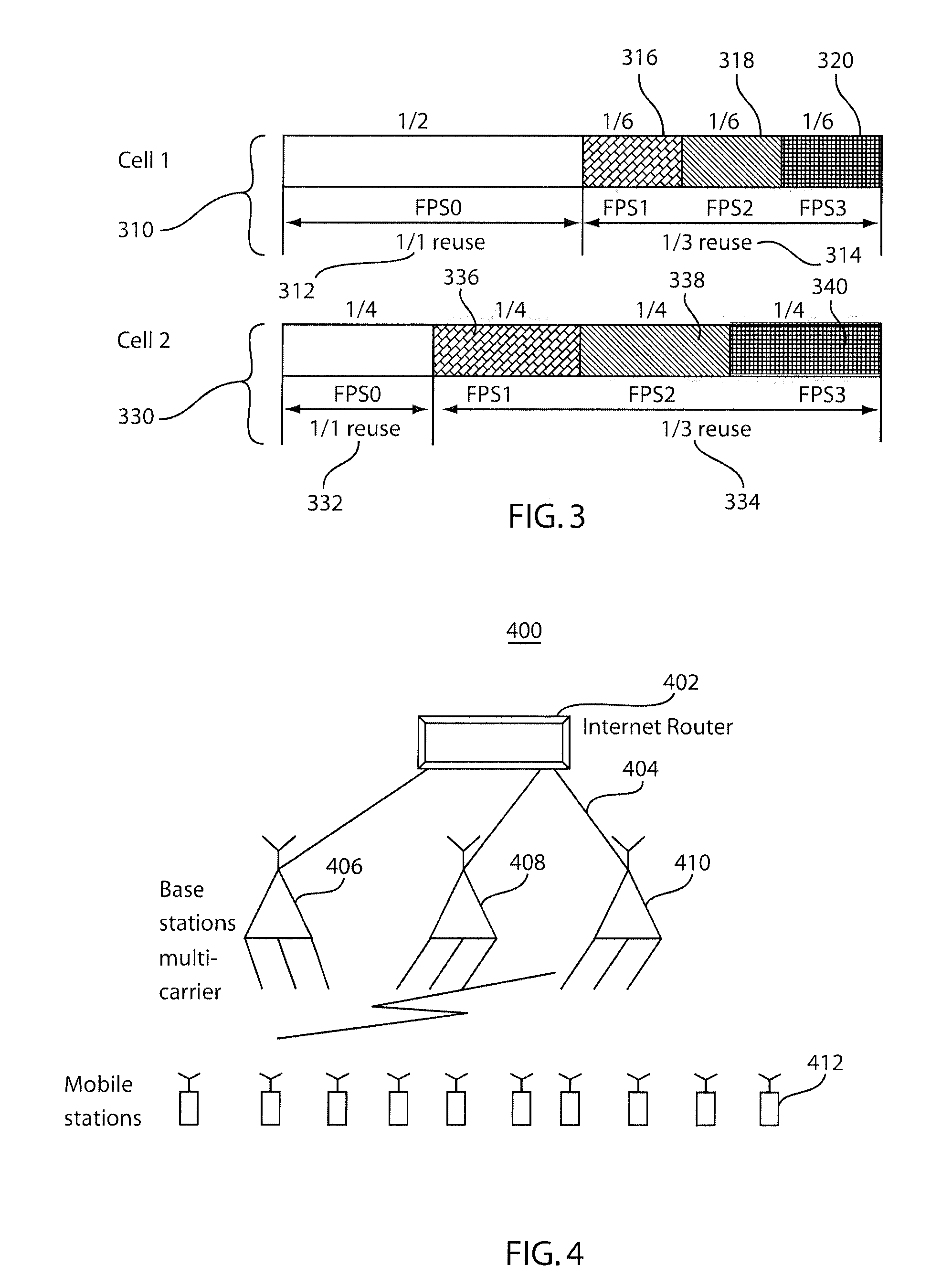
Methods and systems for dynamic and configuration based fractional frequency reuse for uneven load distributions
ActiveUS20110070911A1Reduce the impact of interferenceMaximize throughputTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionFrequency reuseEngineering
Fractional frequency reuse systems and methods for assigning physical resource units of an available frequency band to sectors of cells are disclosed. In particular, the systems and methods permit adaptation of frequency configuration partitions to mobile station or throughput distribution within cells while at the same time ensuring mitigation of interference between neighboring sectors of different cells.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com