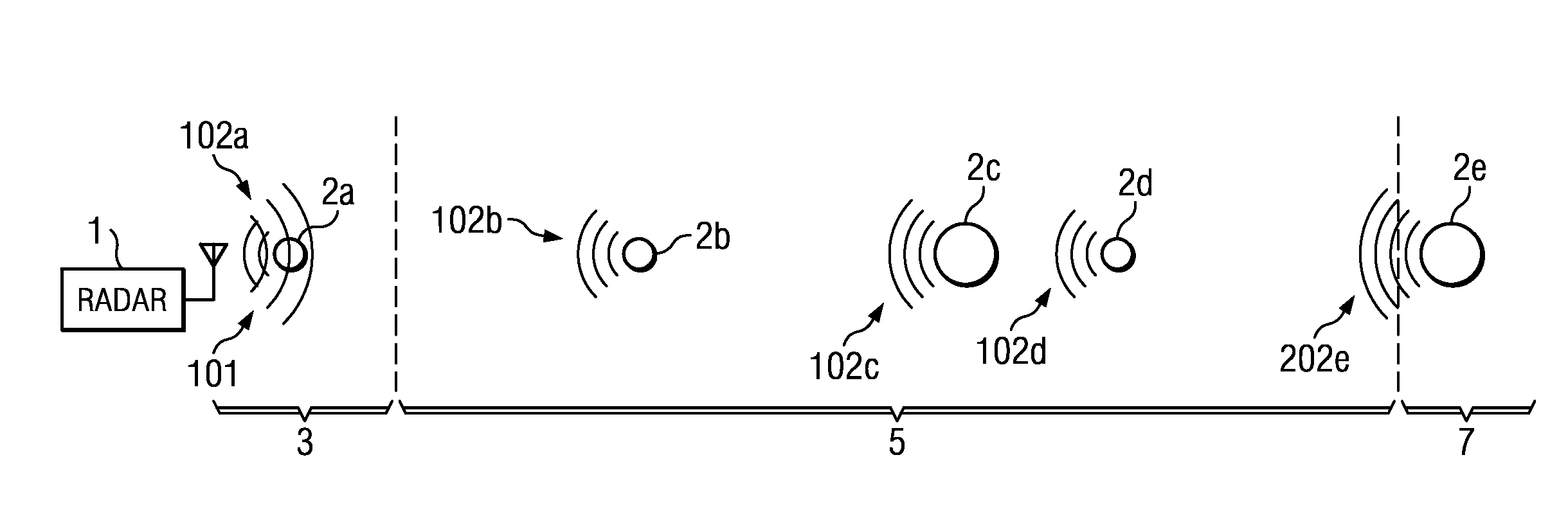Patents
Literature
991results about How to "Reduce signal to noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
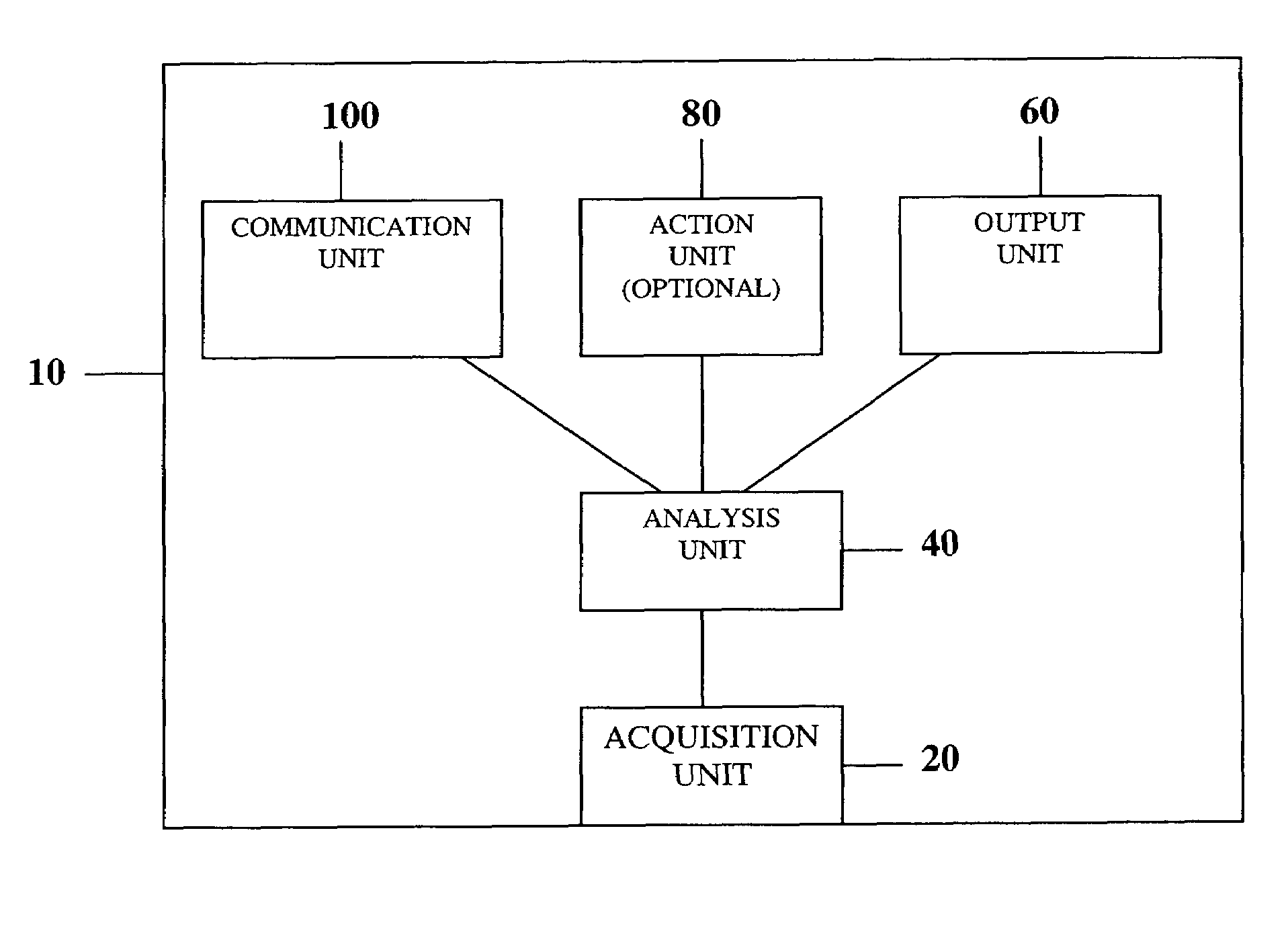
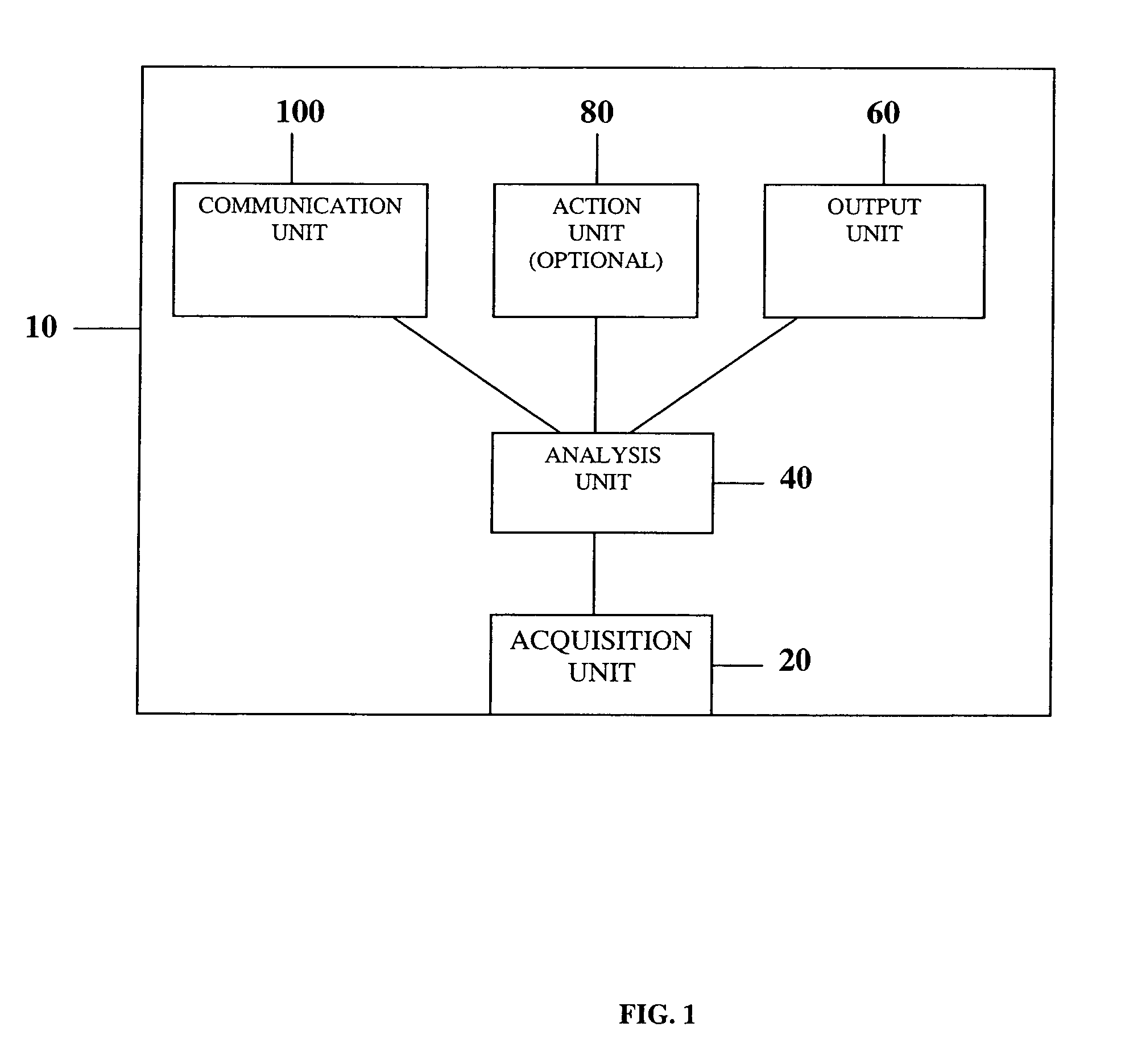
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
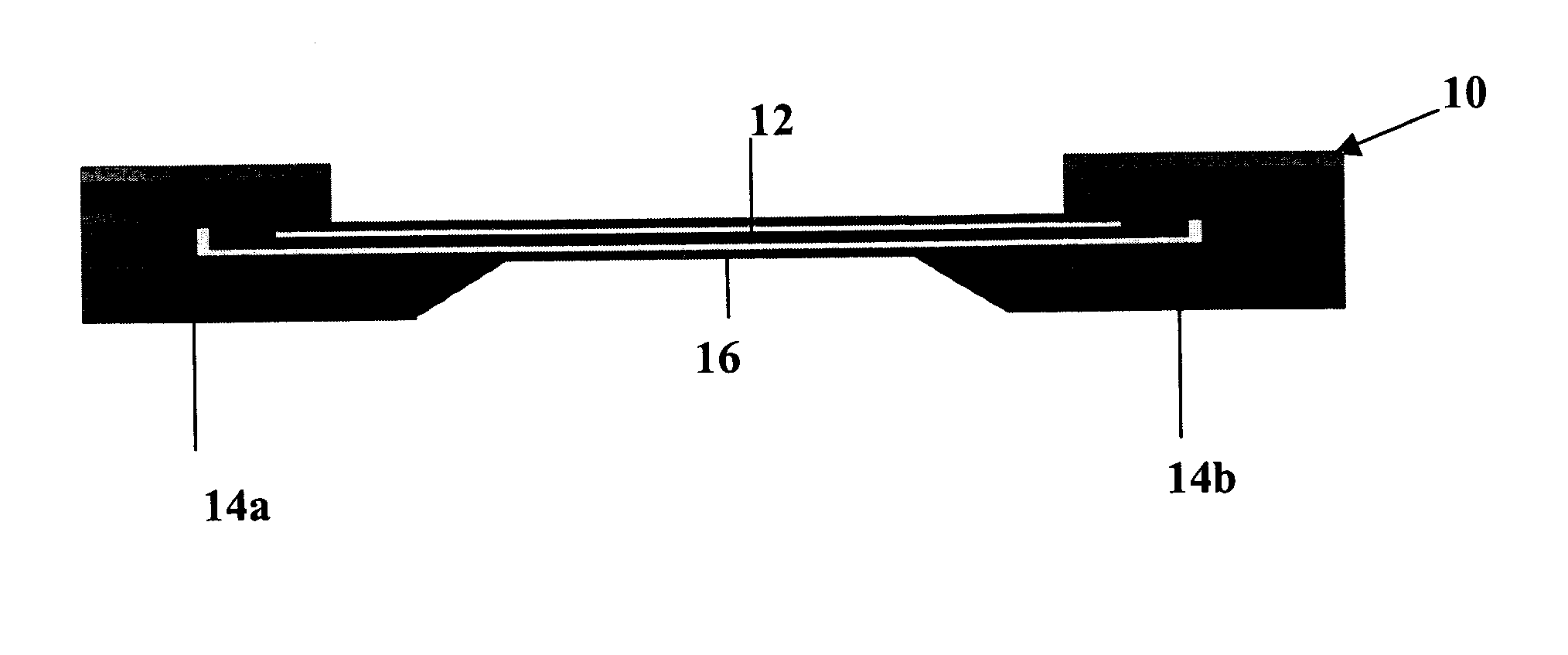
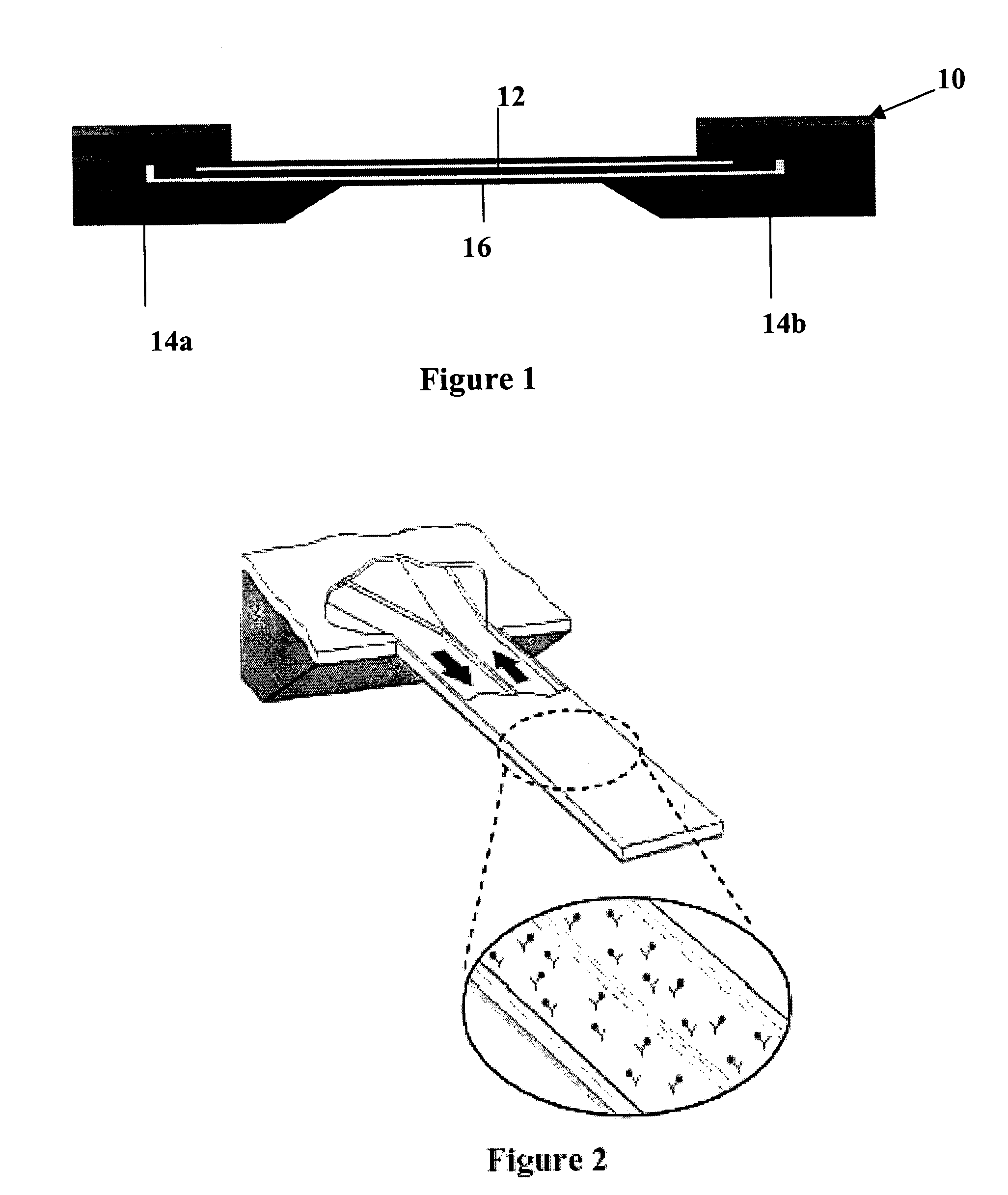
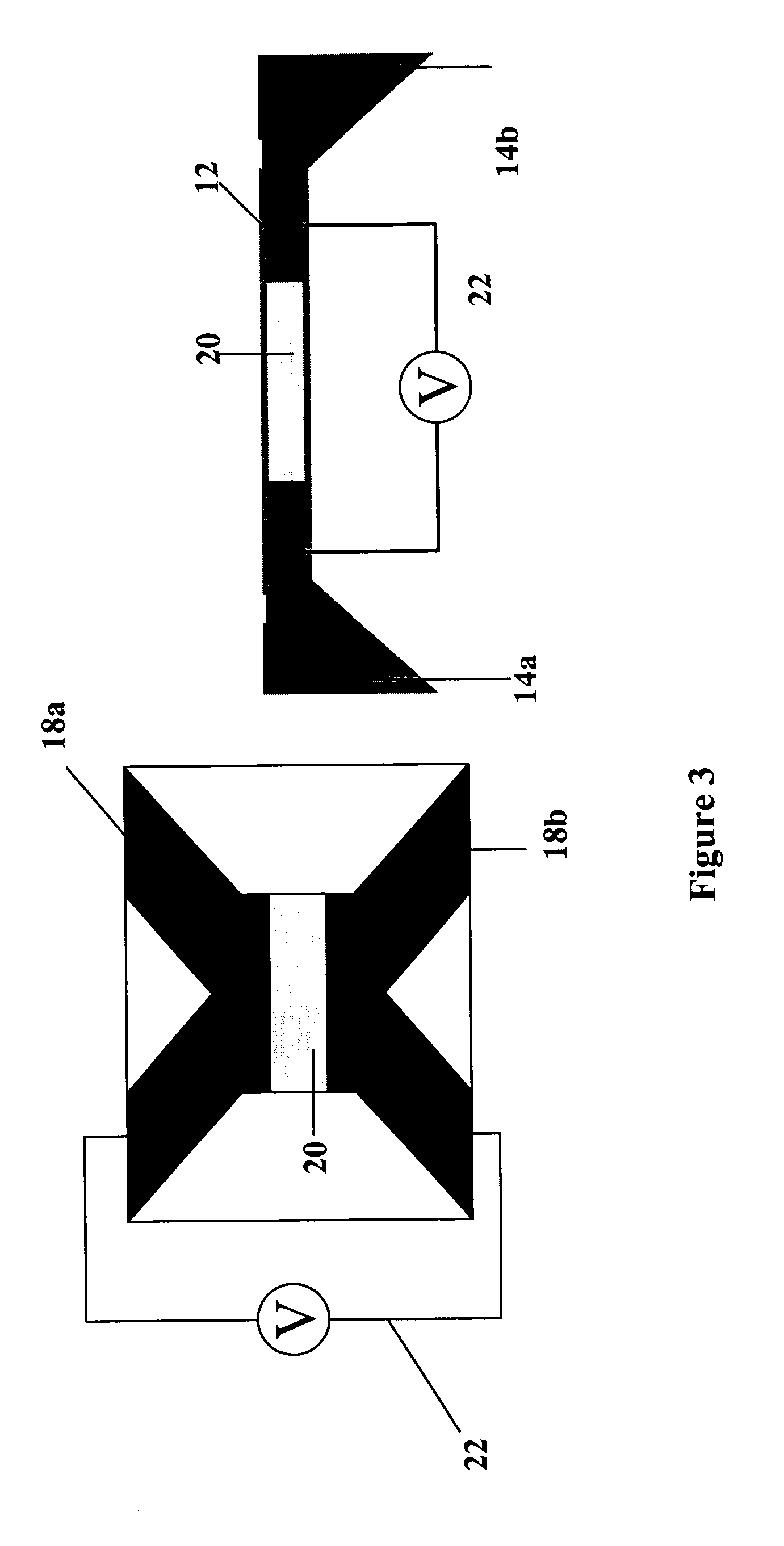
InactiveUS7485095B2Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
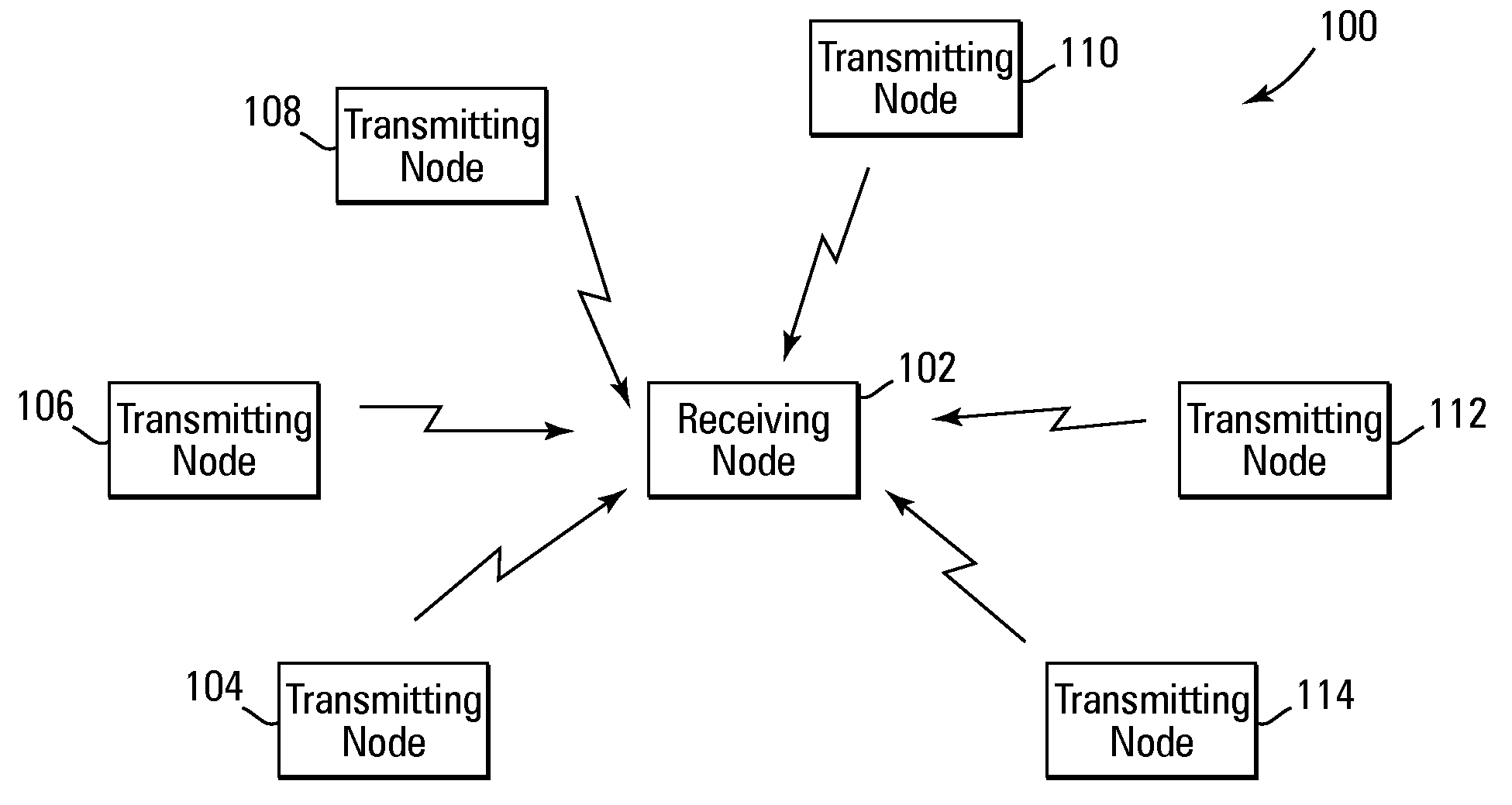
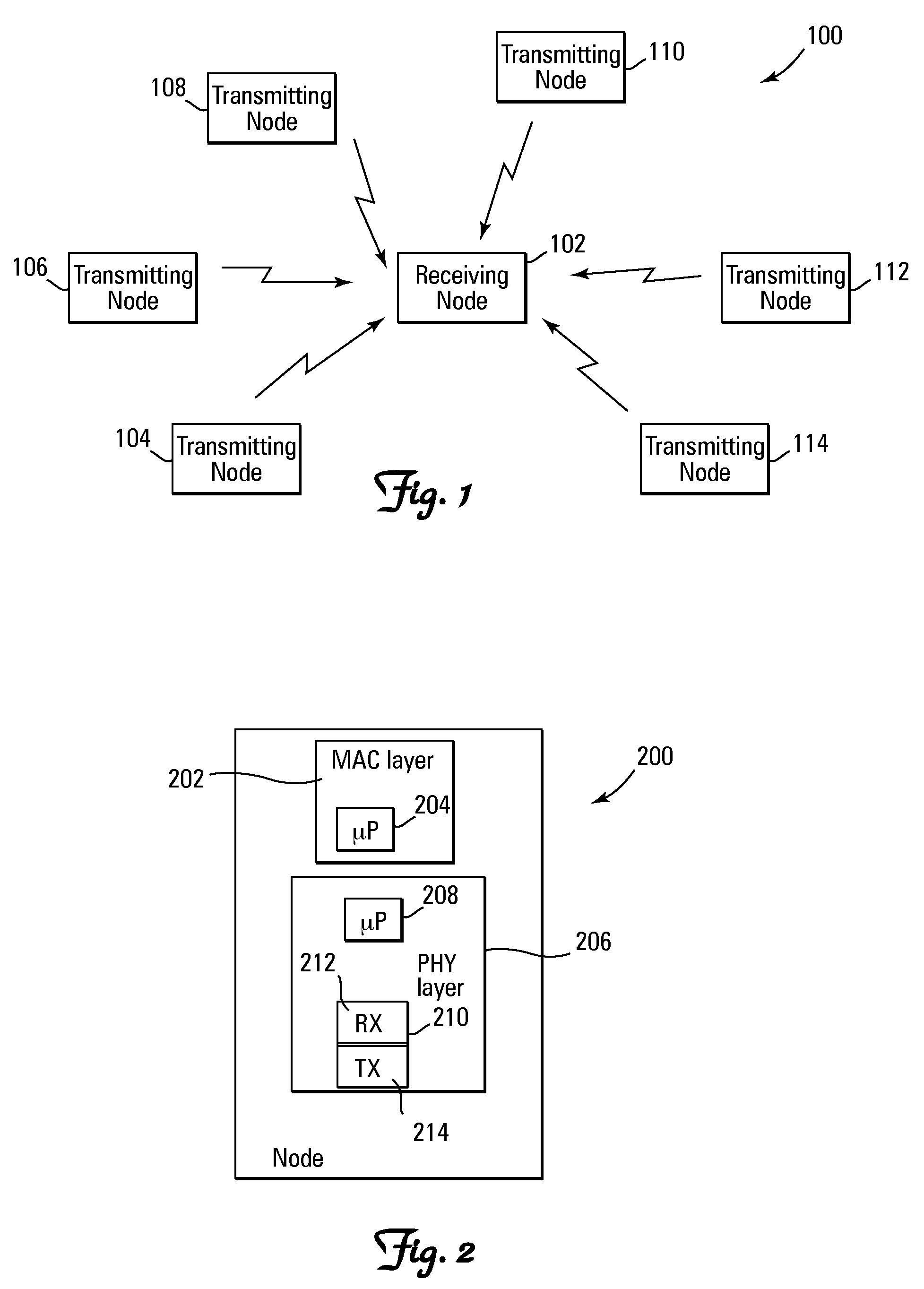
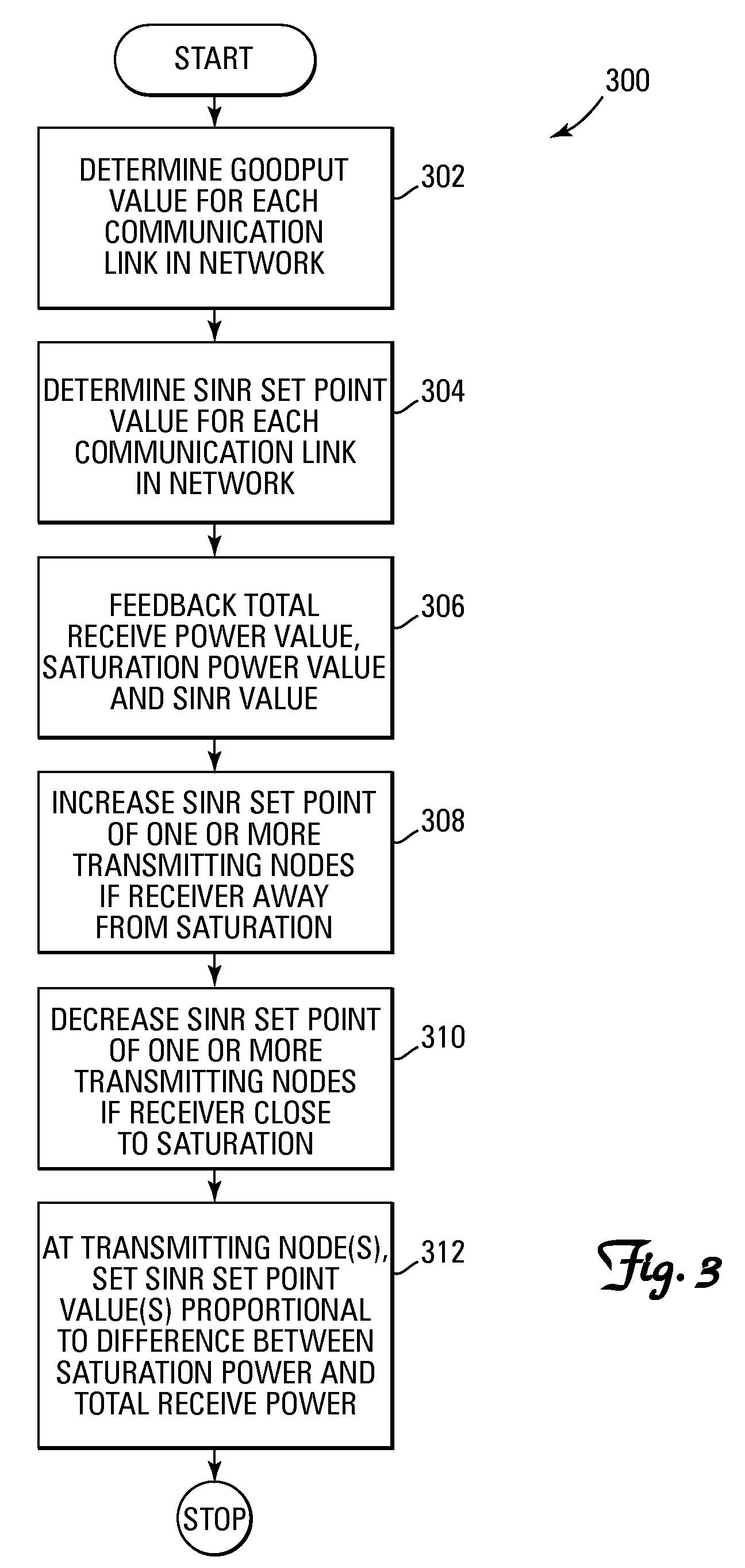
Method and system for performing distributed outer loop power control in wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20090093267A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce signal to noise ratioPower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioReceiver front end
A method and system for performing distributed outer loop power control in a wireless communication network are disclosed. The method includes the steps of determining a transmit power for a plurality of transmitting nodes such that signals sent from each of the transmitting nodes are received at a receiver associated with a receiving node at a predetermined signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) set point, increasing the SINR at the receiving node of one or more transmitting nodes of the plurality of transmitting nodes if a saturation value for a front end of the receiver associated with the receiving node is not near a predetermined saturation value, and decreasing the SINR at the receiving node of the one or more transmitting nodes of the plurality of transmitting nodes if the saturation value for the front end of the receiver associated with the receiving node is near the predetermined saturation value.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Measurement and analysis of trends in physiological and/or health data
InactiveUS20060122525A1Reduce signal to noise ratioCompensates the low SNRElectrocardiographyCatheterData systemPostural orientation
System comprised of a portable medical device and method for non-contact registering at least one of electrocardiographic (ECG), magnetocardiographic (MCG), physical activity, body position, respiration, temperature, blood pressure, vasomotor activity, blood flow, neural activity, and other physiological, and health data, extracting and representing the most significant parameters from time series (trends) of said data. The system achieves the necessary sensitivity (signal-to-noise ratio) in order to miniaturize the device by collecting data of at least one fiducial point in a cardiac complex over a period of at least one, and preferably, several seconds, and extracting the underlying typical patterns from these data. Due to the miniaturization (pocket-size), the system can be implemented in a shape of a pen (or another miniature shape) that can be worn in a pocket.
Owner:SHUSTERMAN VLADIMIR
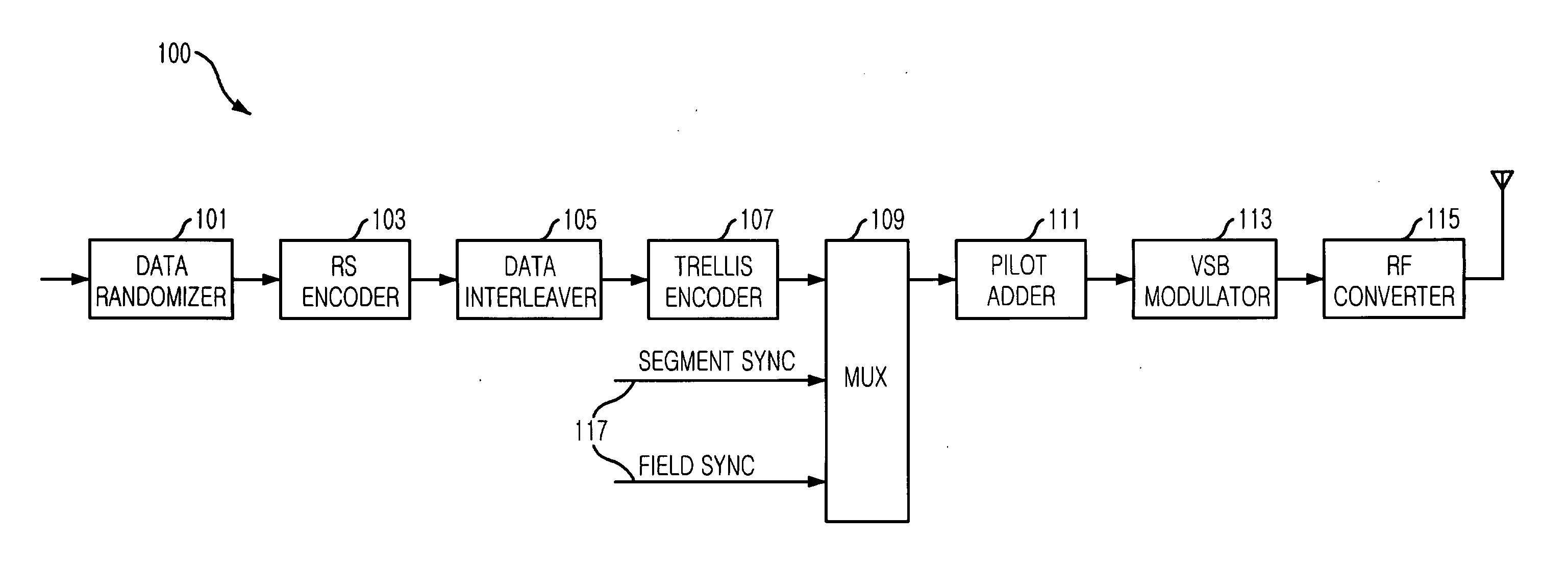
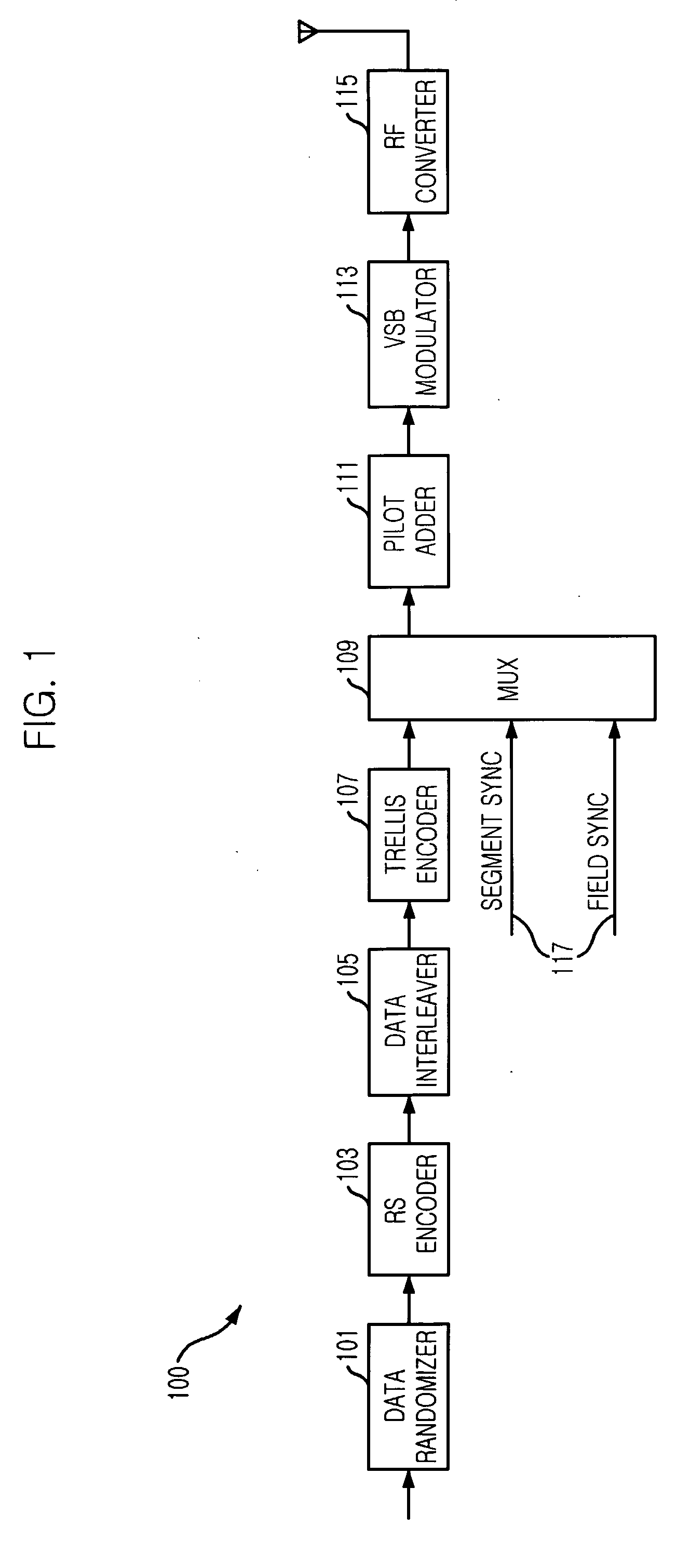
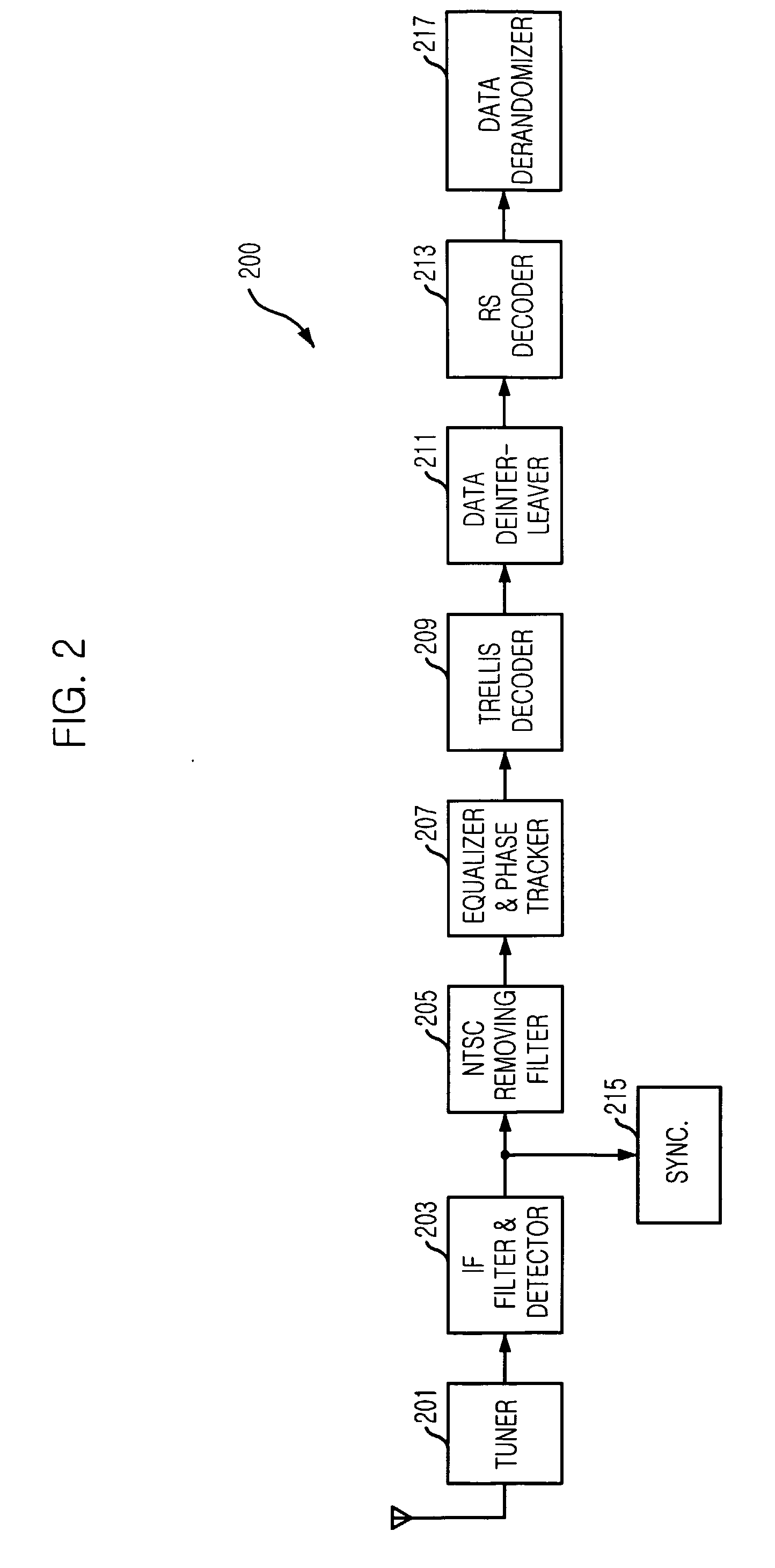
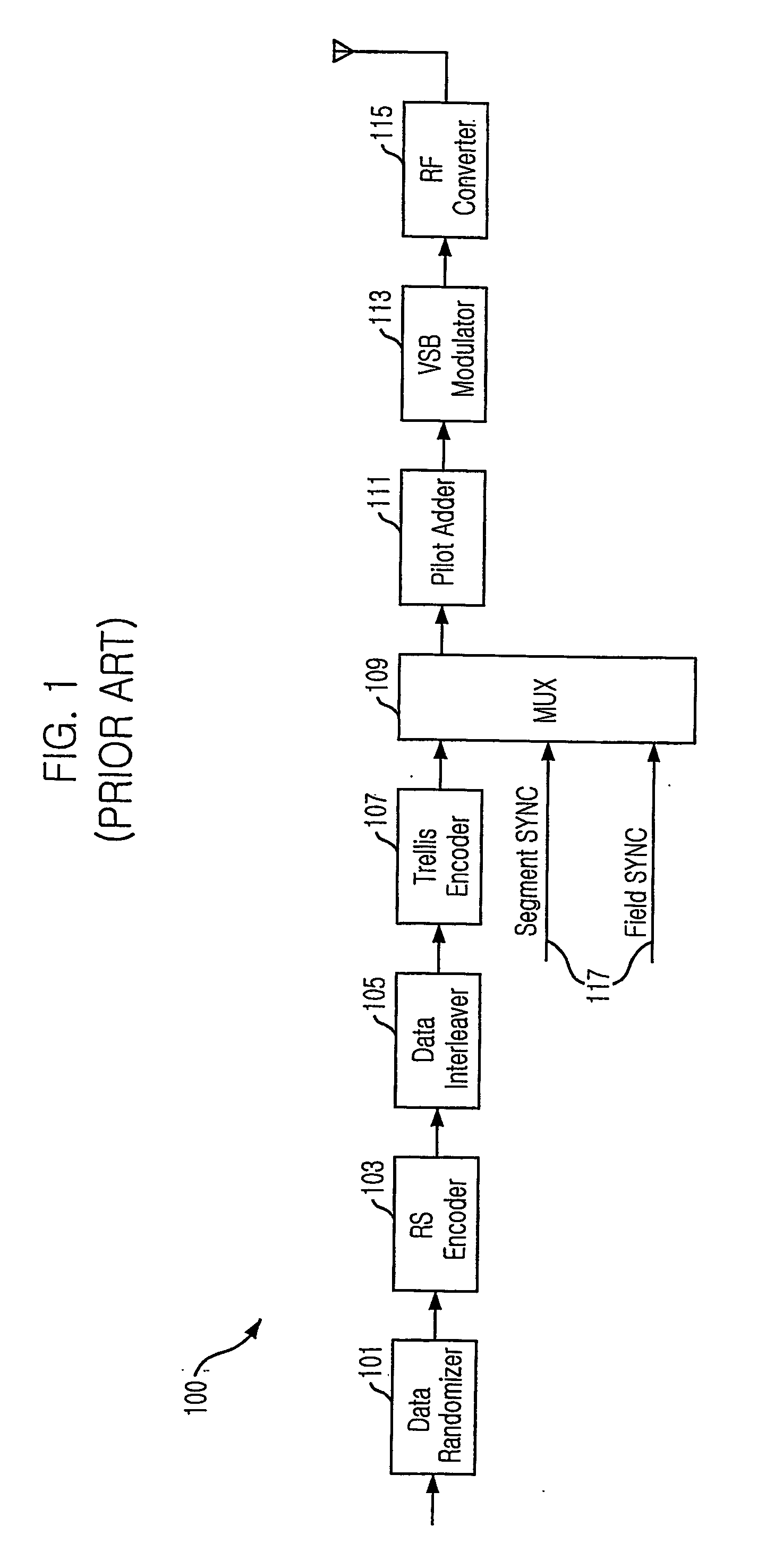
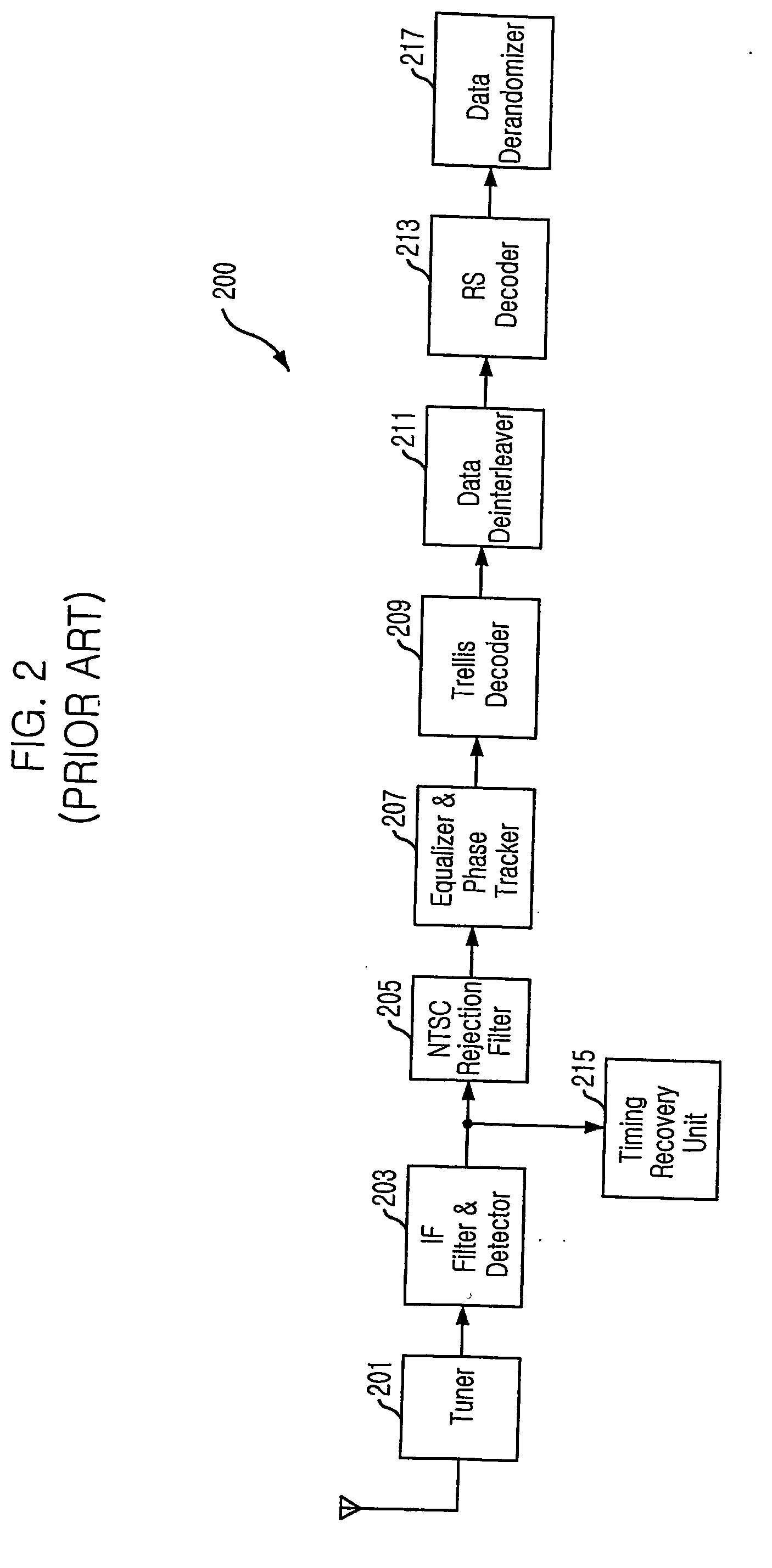
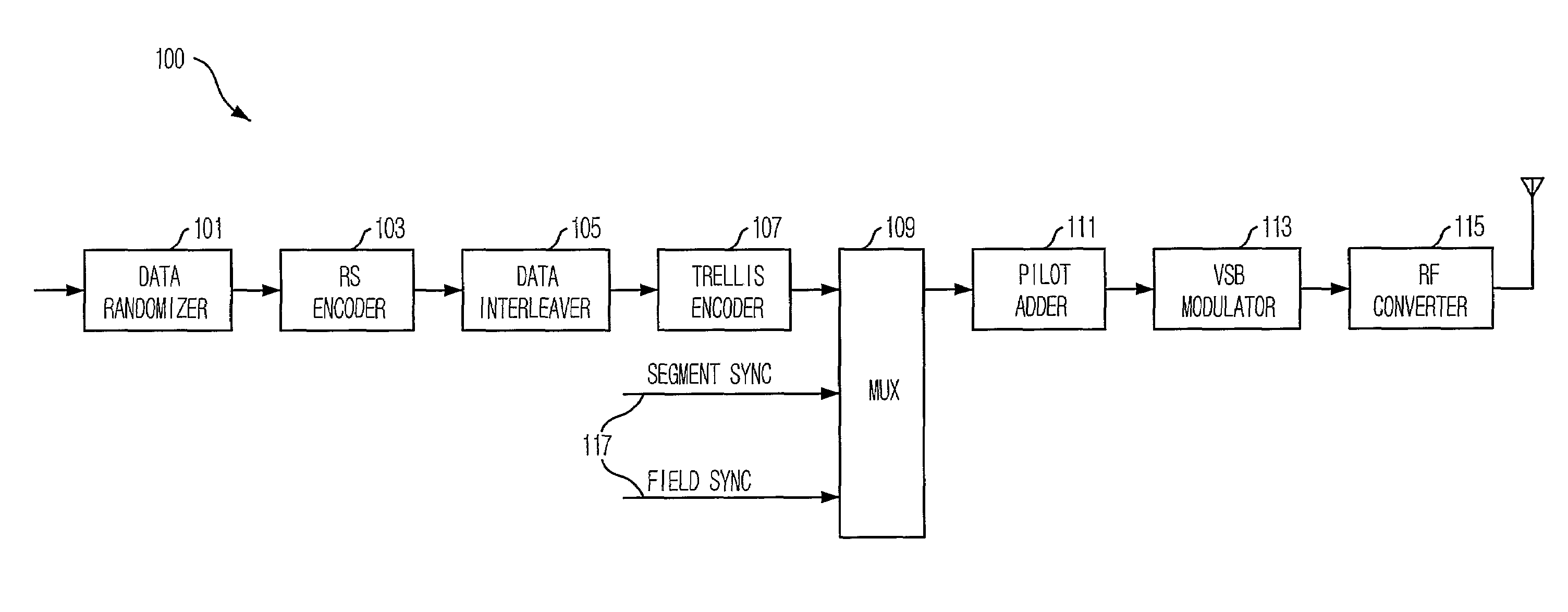
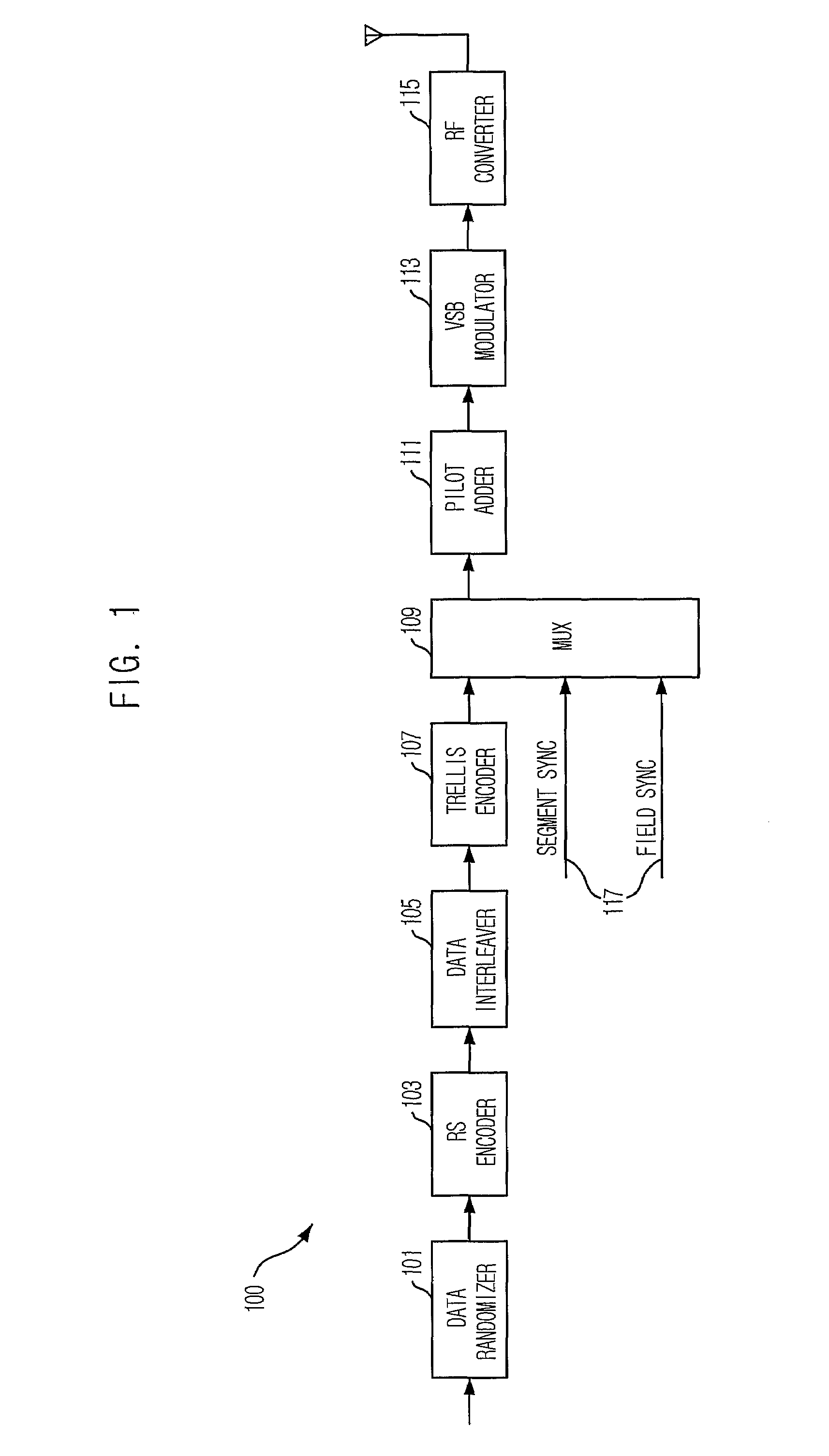
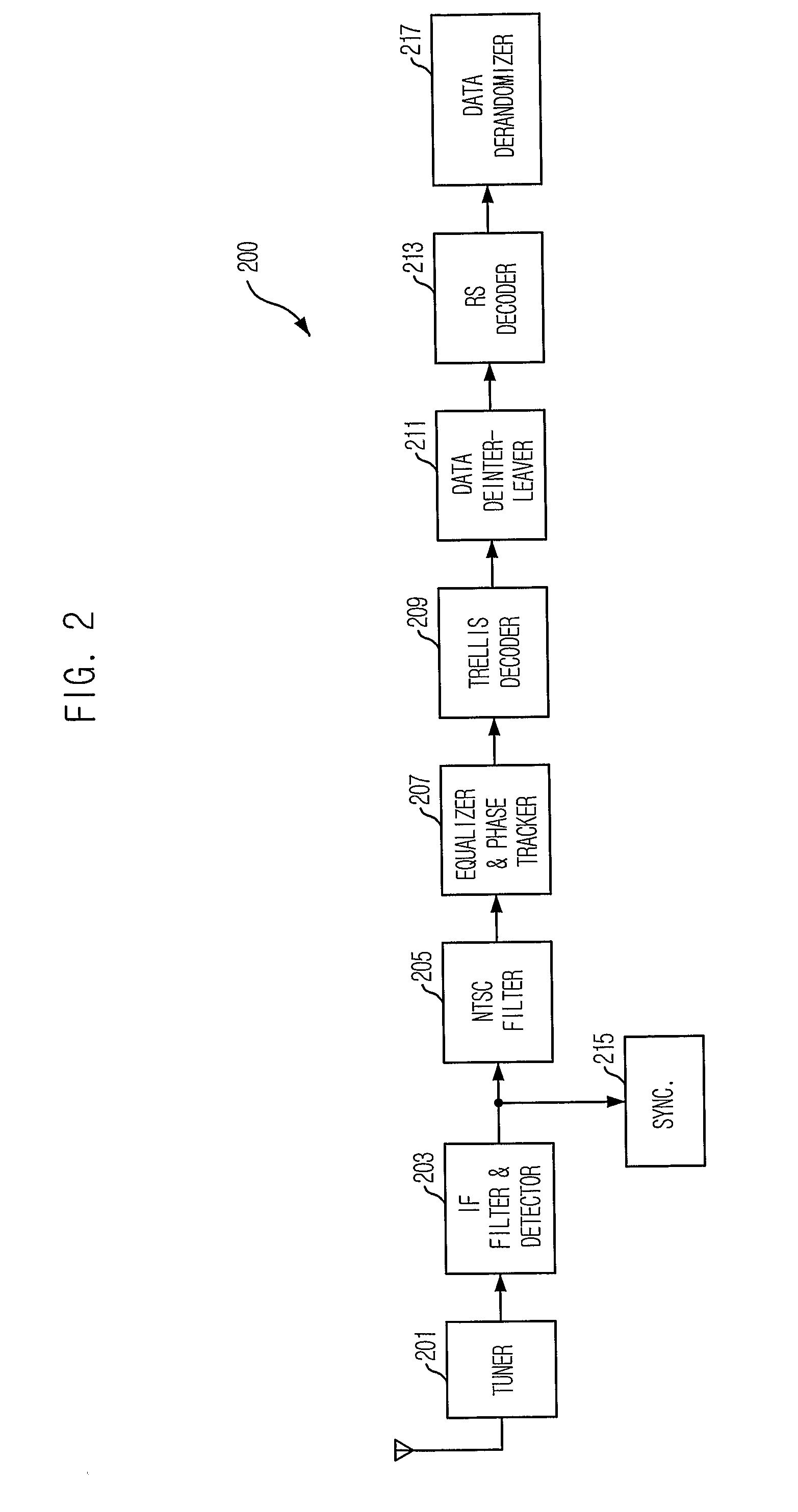
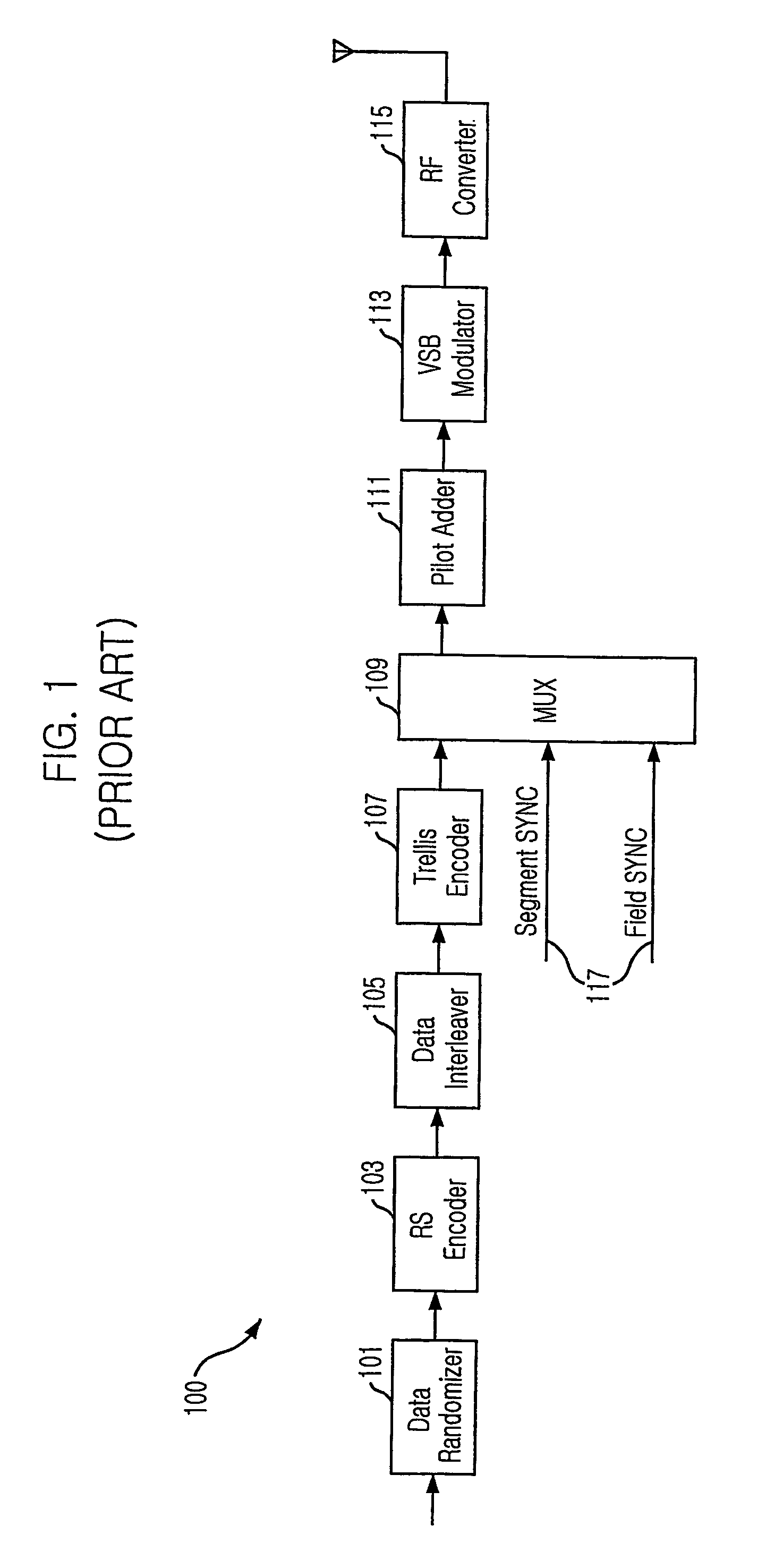
Robust signal transmission in digital television broadcasting
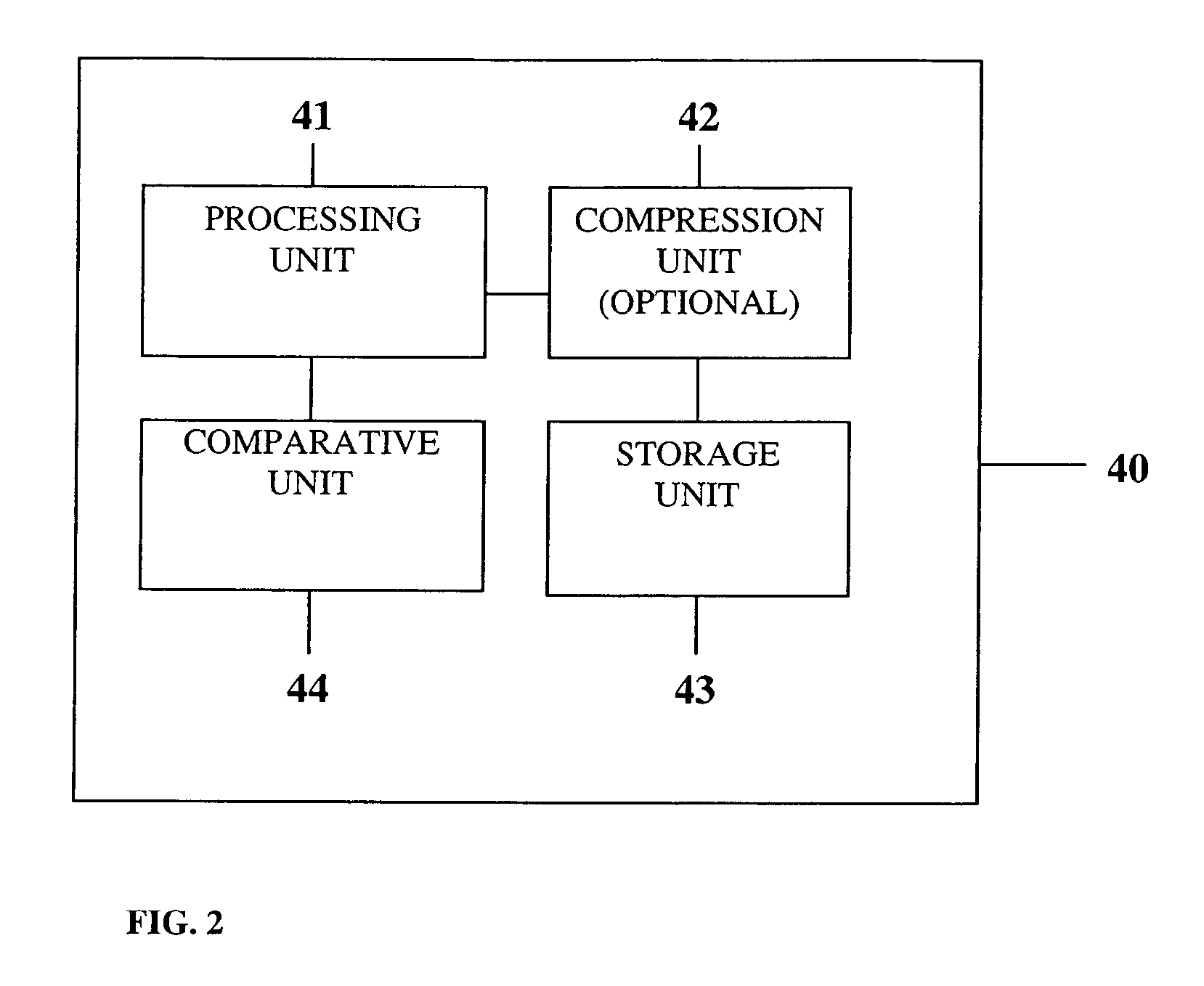
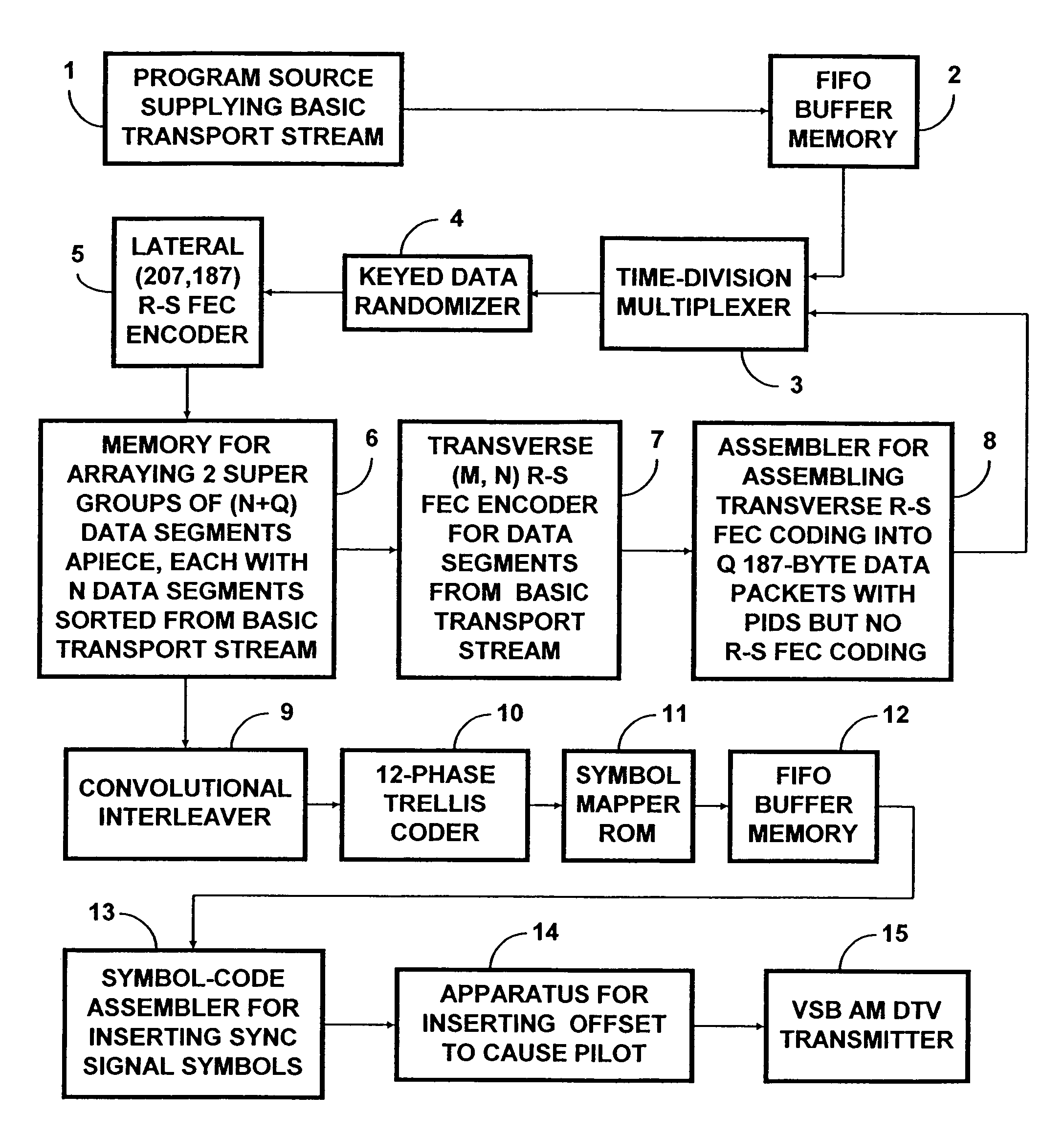
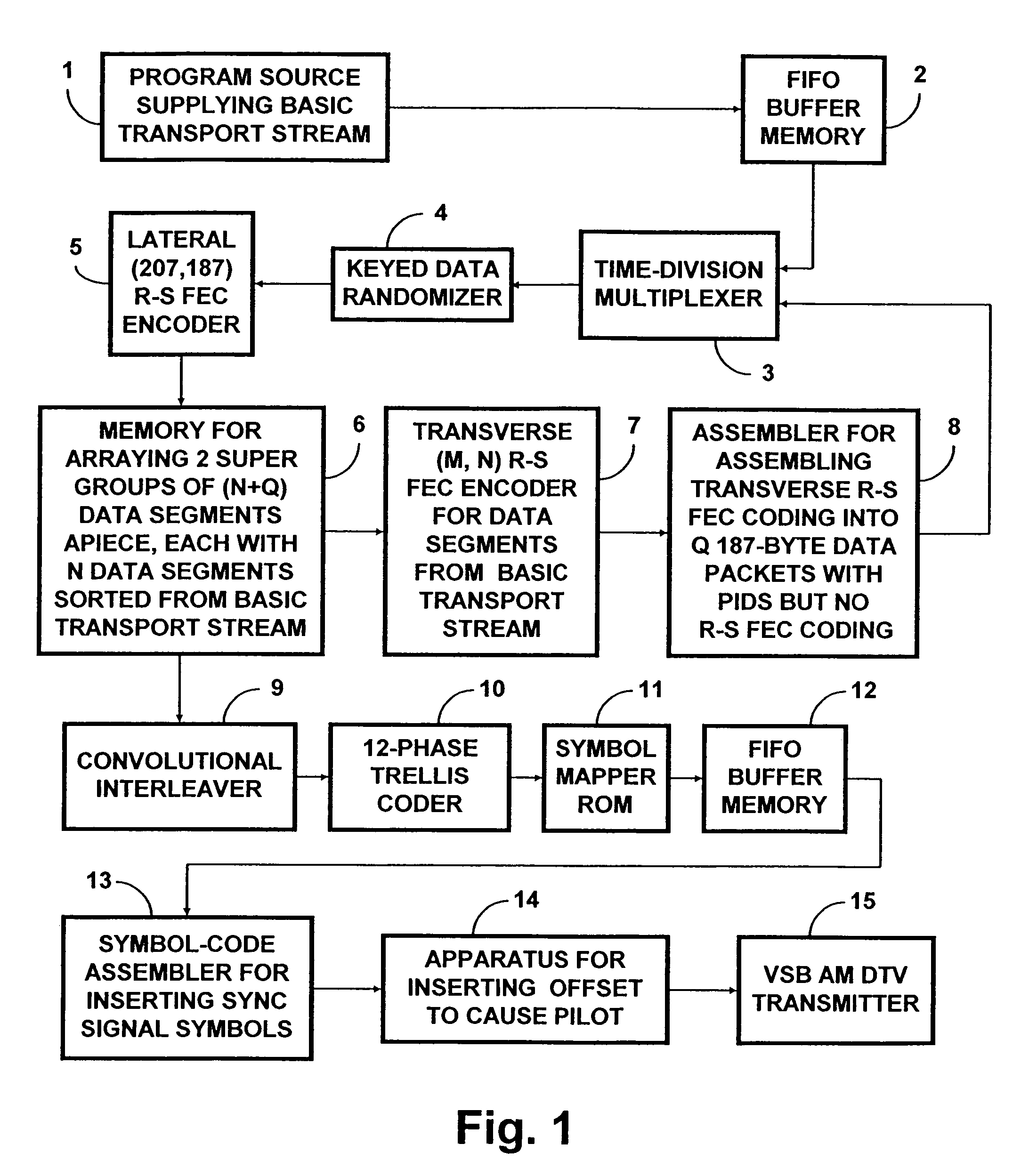
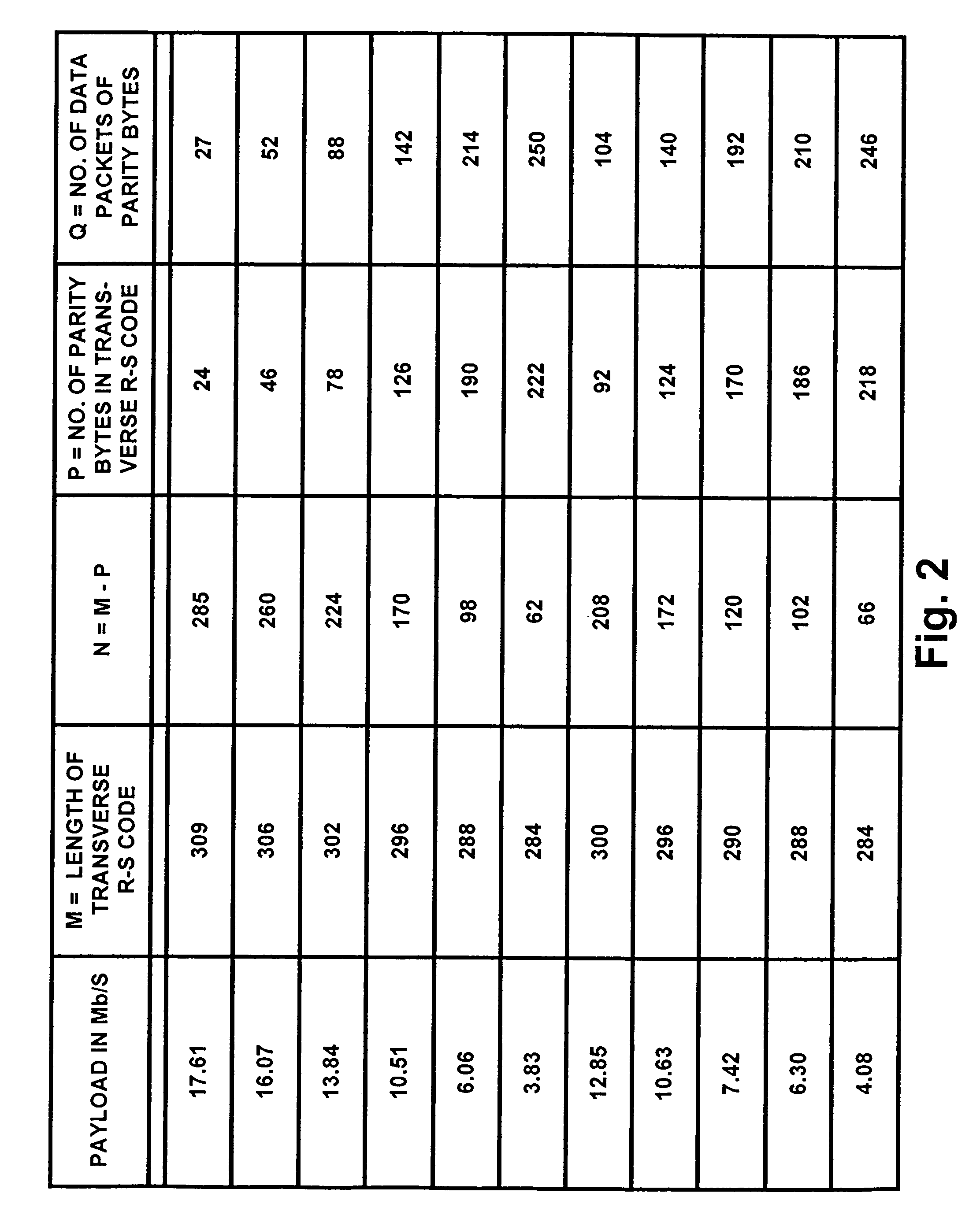
ActiveUS7197685B2Improve the level ofReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsData representation error detection/correctionData segmentData field
A data field of transmitted digital television signals includes a first set of A / 53-compliant data segments that convey payload information and further includes a second set of A / 53-compliant data segments that contain parity bytes for transverse Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction coding of the data contained within the first set of A / 53-compliant data segments. A digital television receiver uses the parity bytes in the second set of A / 53-compliant data segments to implement transverse Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction decoding that corrects byte errors in the data contained in the first set of A / 53-compliant data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
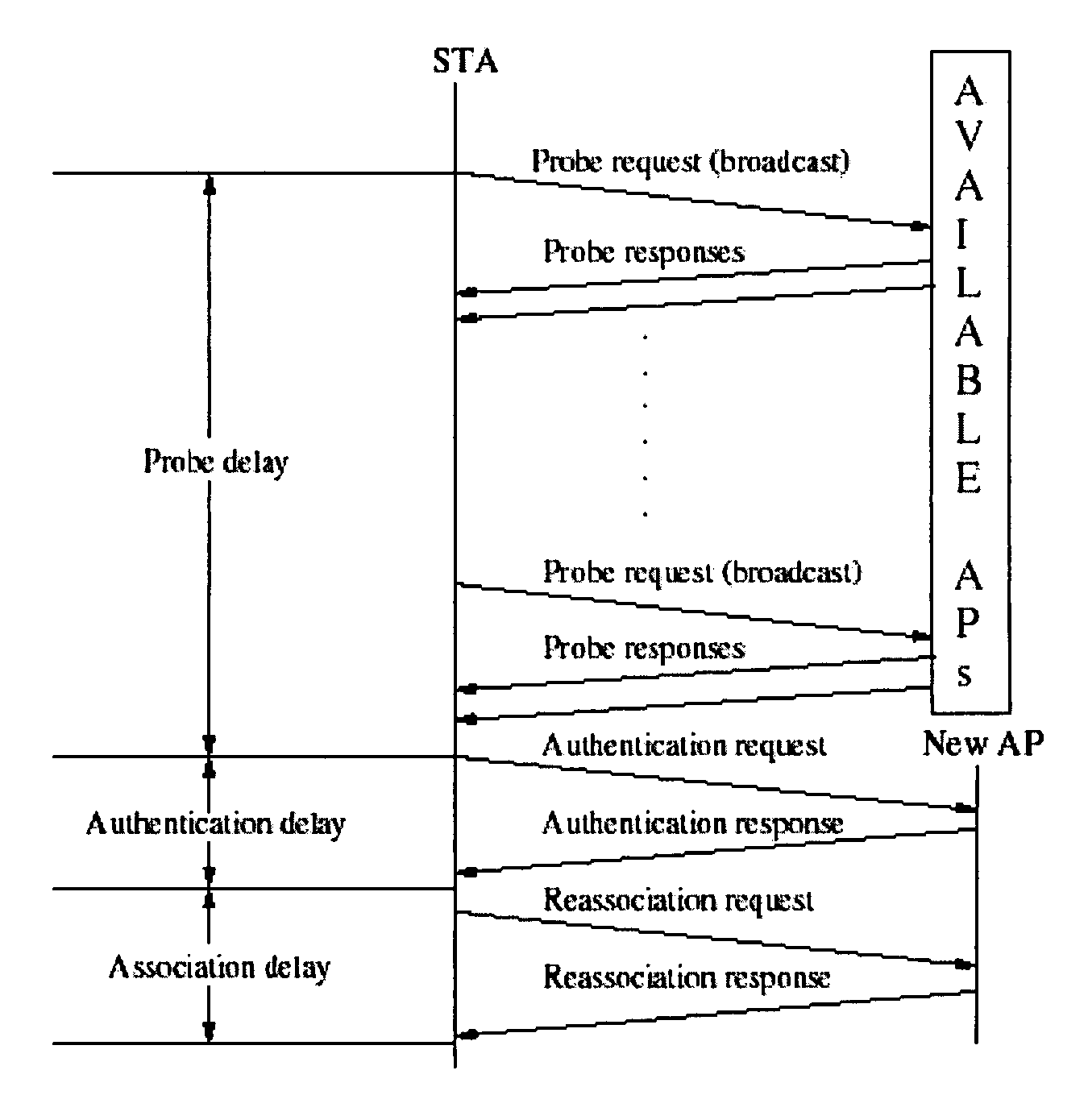
Methods and systems for reducing MAC layer handoff latency in wireless networks
ActiveUS20060062183A1Reduce switching delayReduce delaysRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCache algorithmsHandover latency
In accordance with the present invention, computer implemented methods and systems are provided for reducing handoff latency in a wireless network. In response to detecting that a handoff is necessary, the present invention uses a selective scanning algorithm that includes the use of a channel mask and / or a caching algorithm for detecting one or more new access points.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
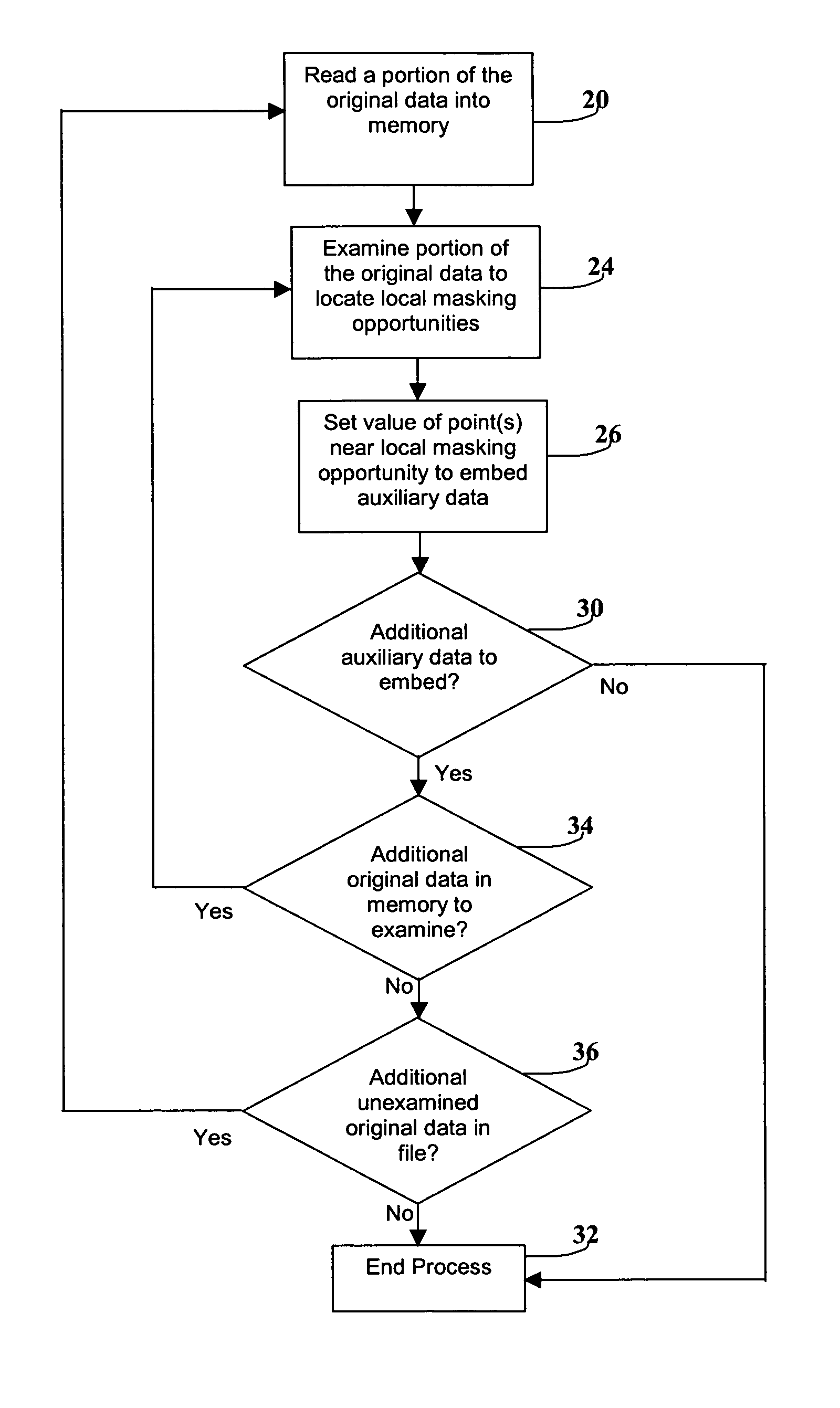
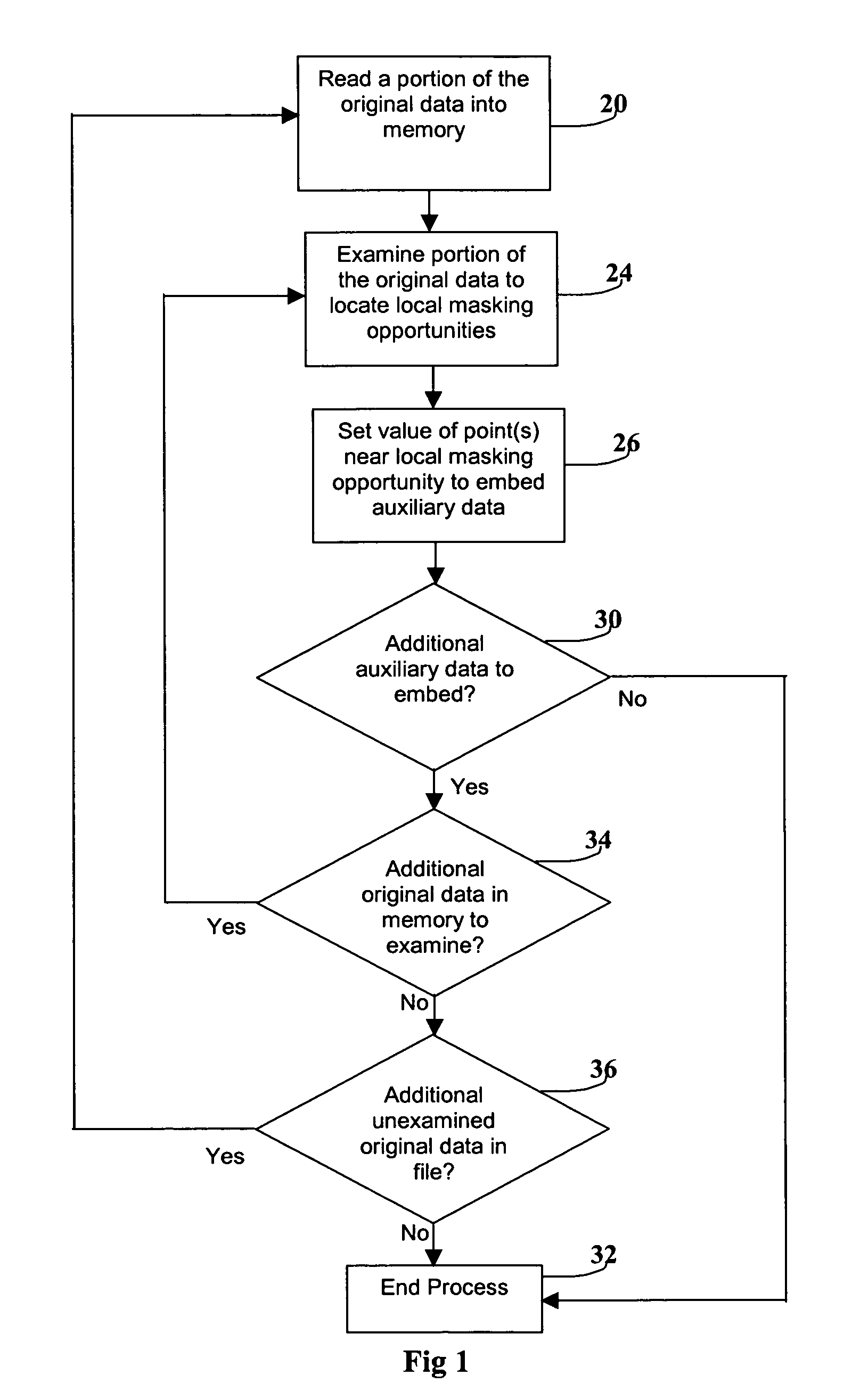
Method and apparatus for embedding auxiliary information within original data
InactiveUS7197156B1Extreme efficiencyDifficult to detect and removeTelevision system detailsUser identity/authority verificationEmbedded systemOriginal data
The present invention relates generally to embedding and / or encoding auxiliary information within original data. For example, in one embodiment, a method of embedding auxiliary information in data is provided. The auxiliary information is not lost with compression of the embedded data. The embedded data initially includes a non-compressed form including the auxiliary information embedded therein. The method includes: (a) retrieving the auxiliary information from the non-compressed form of the embedded data; (b) compressing the non-compressed form of the embedded data; and (c) embedding the retrieved auxiliary information in the compressed embedded data, whereby the compressed embedded data comprises the auxiliary information embedded therein. Other embodiments are provided and claimed as well.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Control of polymer surface molecular architecture via amphipathic endgroups
ActiveUS20050282997A1Promote resultsReduce signal to noise ratioSurgeryCatheterPolymeric surfacePolyethylene oxide
Polymers whose surfaces are modified by endgroups that include amphipathic surface-modifying moieties. An amphipathic endgroup of a polymer molecule is an endgroup that contains at least two moieties of significantly differing composition, such that the amphipathic endgroup spontaneously rearranges its positioning in a polymer body to position the moiety on the surface of the body, depending upon the composition of the medium with which the body is in contact, when that re-positioning causes a reduction in interfacial energy. An example of an amphipathic surface-modifying endgroup is one that has both a hydrophobic moiety and a hydrophilic moiety in a single endgroup. For instance, a hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) terminated with a hydrophilic hydroxyl group is not surface active in air when the surface-modifying endgroup is bonded to a more hydrophobic base polymer. If the hydroxyl group on the oligomeric poly(ethylene oxide) is replaced by a hydrophobic methoxy ether terminus, the poly(ethylene oxide) becomes surface active in air, and allows the poly(ethylene oxide) groups to crystallize in the air-facing surface. In this example, immersion in water destroys the crystallinity as the poly(ethylene oxide) sorbs water and the hydrophobic methoxy group retreats below the surface of the polymer. Also disclosed are methods and articles of manufacture that make use of these polymers.
Owner:THE POLYMER TECH GROUP
Method and System for User Equipment Location Determination on a Wireless Transmission System
ActiveUS20110286349A1Improve audibilityReduce signal to noise ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseResource block
Neighbor cell hearability can be improved by including an additional reference signal that can be detected at a low sensitivity and a low signal-to-noise ratio, by introducing non-unity frequency reuse for the signals used for a time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurement, e.g., orthogonality of signals transmitted from the serving cell sites and the various neighbor cell sites. The new reference signal, called the TDOA-RS, is proposed to improve the hearability of neighbor cells in a cellular network that deploys 3GPP EU-TRAN (LTE) system, and the TDOA-RS can be transmitted in any resource blocks (RB) for POSCH and / or MBSFN subframe, regardless of whether the latter is on a carrier supporting both PMCH and POSCH or not. Besides the additional TDOA-RS reference signal, an additional synchronization signal (TDOA-sync) may also be included to improve the hearability of neighbor cells.
Owner:APPLE INC
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20100081011A1Secure run stabilityIncrease in dropout and error rateRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMagnetic layerAgglomerate
A magnetic recording medium includes, in the following order: a backcoat layer; a nonmagnetic support; a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder; and a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder, wherein the backcoat layer contains particles having an average primary particle size D50 of from 0.05 to 1.0 μm and forming substantially no aggregates nor agglomerates in the backcoat layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic recording medium
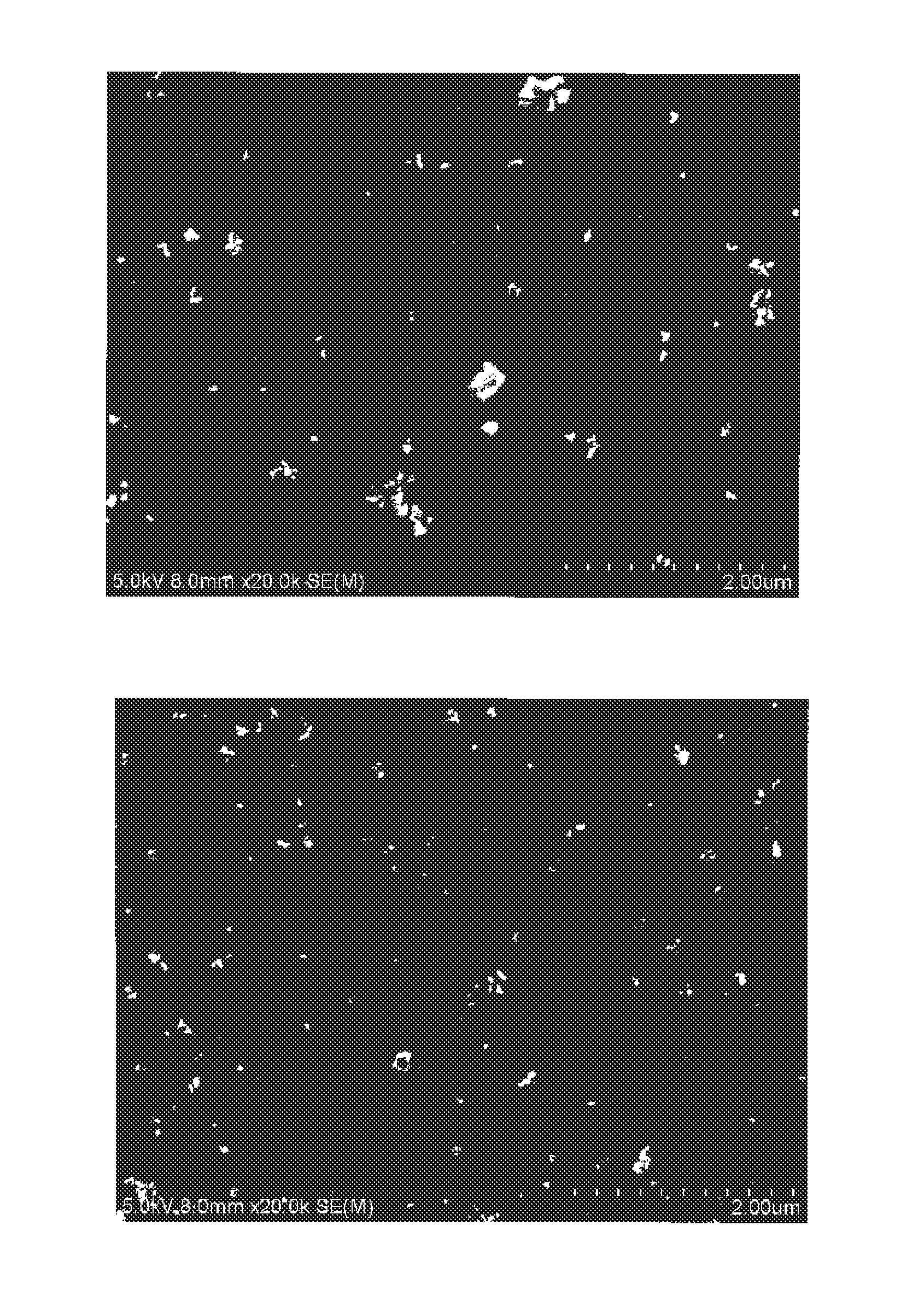
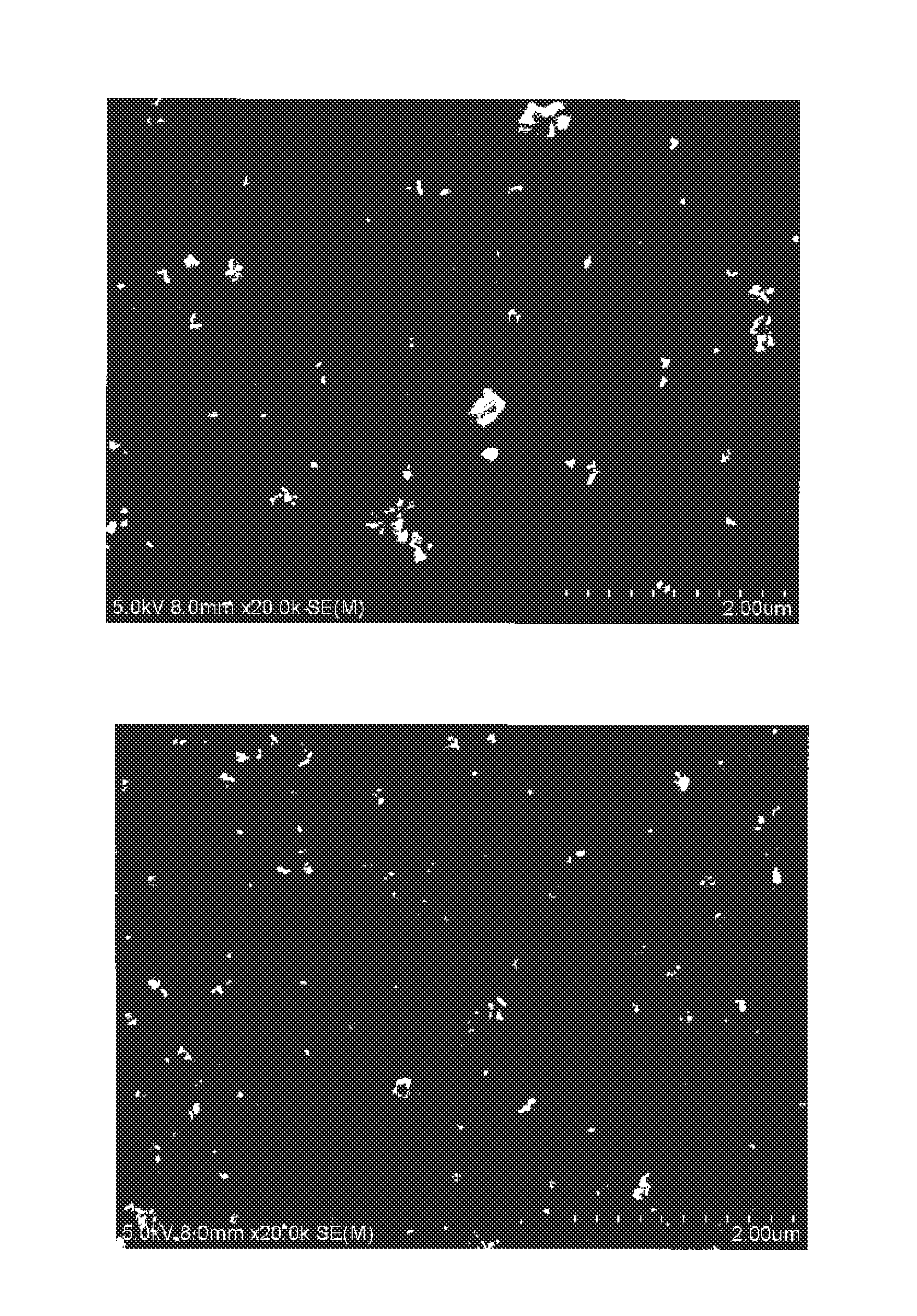
ActiveUS20140272474A1Increased durabilityReduce runningRecord information storageMaterials with non-metallic substancesScanning electron microscopeElectron microscope
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium, which comprises a magnetic layer comprising ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the ferromagnetic powder is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder comprising 3 to 12 weight percent of Al, based on Al2O3 conversion, relative to 100 weight percent of a total weight of the powder, the magnetic layer further comprises abrasive, and a maximum plan view surface area of the abrasive as determined for a 4.3 μm×6.3 μm rectangular region of the magnetic layer by a scanning electron microscope is less than 0.06 percent relative to 100 percent of a total surface area of the region.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
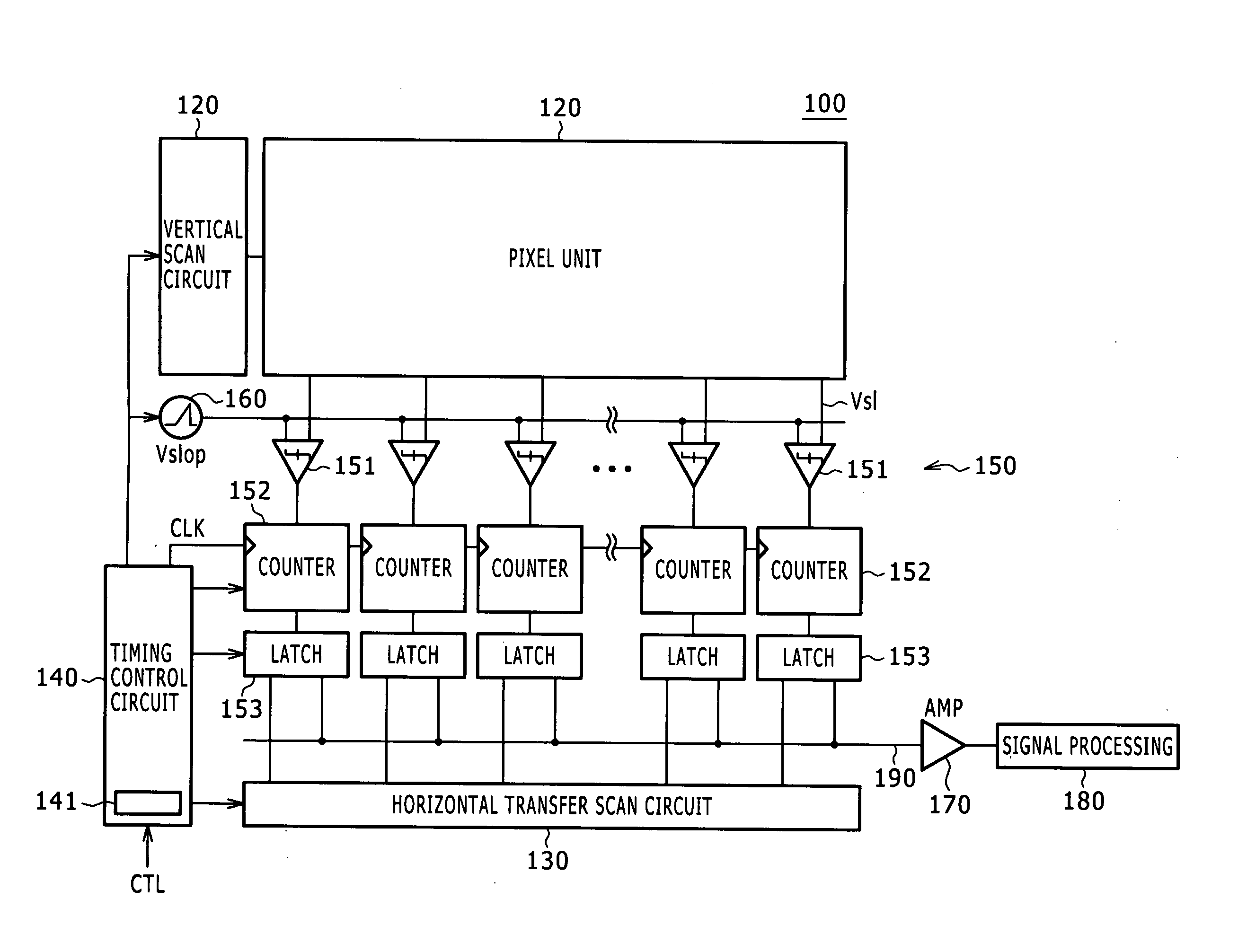
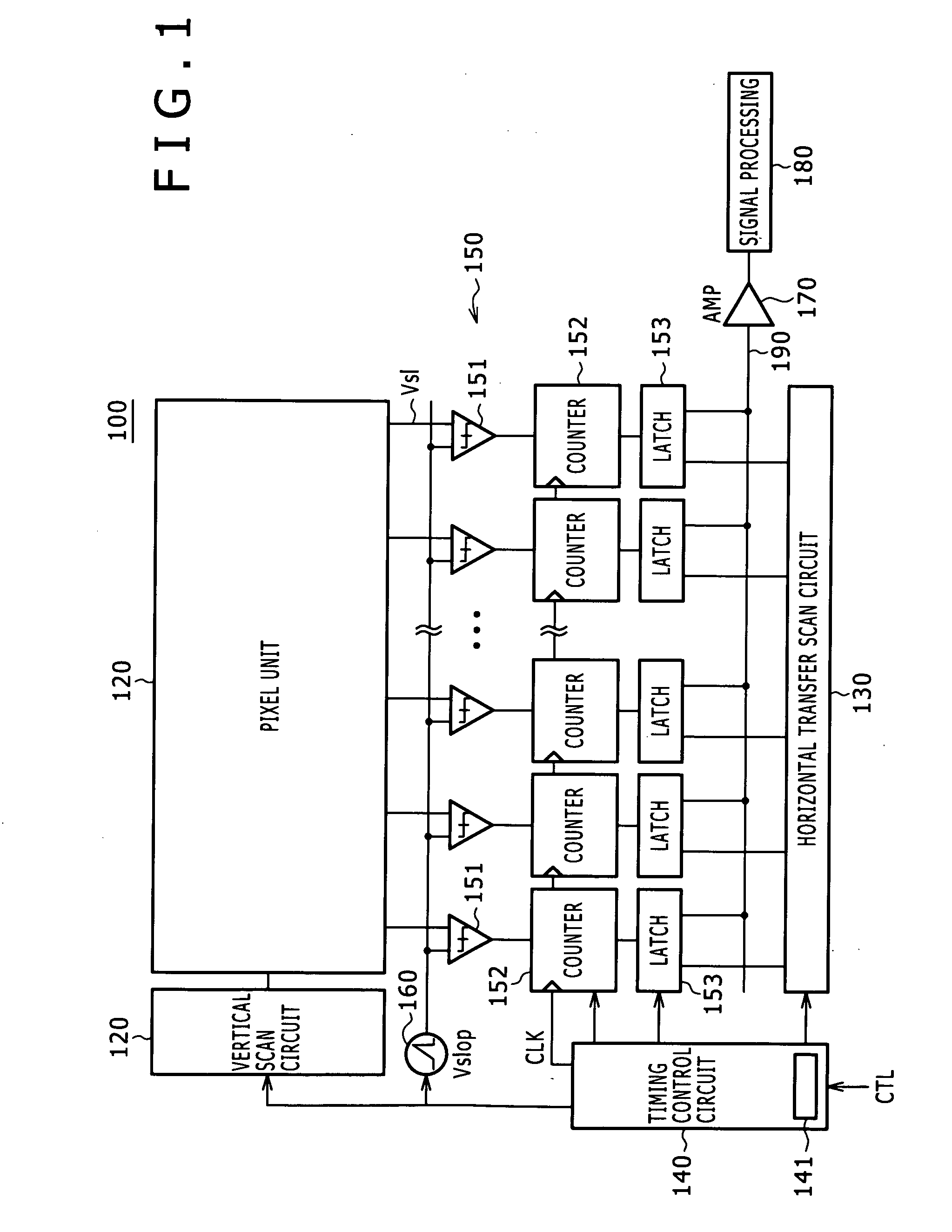
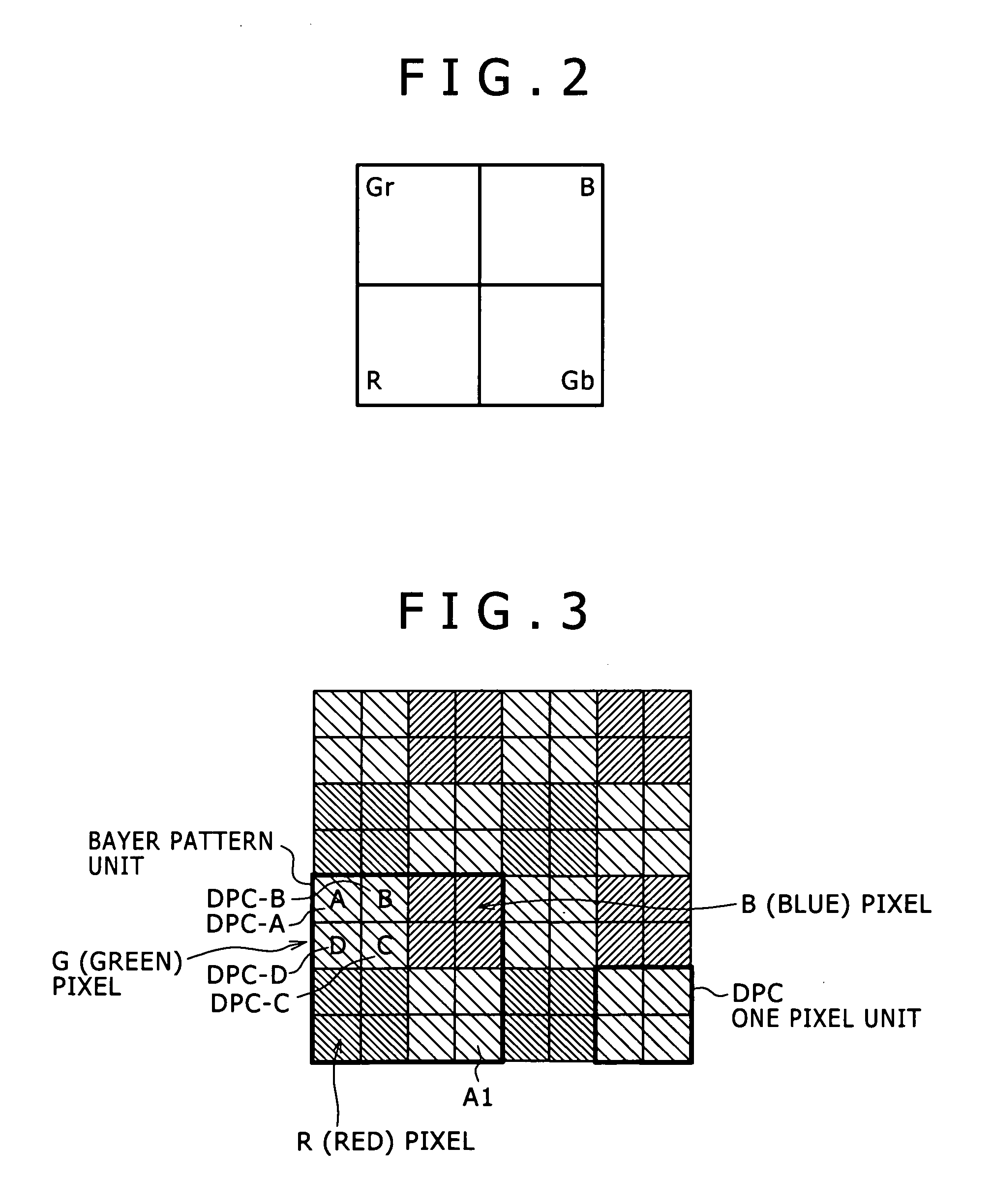
Solid-state imaging element and camera system
ActiveUS20100013969A1Wide dynamic rangeHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital conversionComputer vision
Disclosed herein is a solid-state imaging element including a pixel unit configured to include a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix and a pixel signal readout unit configured to include an analog-digital conversion unit that carries out analog-digital conversion of a pixel signal read out from the pixel unit. Each one of the pixels in the pixel unit includes a plurality of divided pixels arising from division into regions different from each other in optical sensitivity or a charge accumulation amount. The pixel signal readout unit reads out divided-pixel signals of the divided pixels in the pixel. The analog-digital conversion unit carries out analog-digital conversion of the divided-pixel signals that are read out and adds the divided-pixel signals to each other to obtain a pixel signal of one pixel.
Owner:SONY CORP
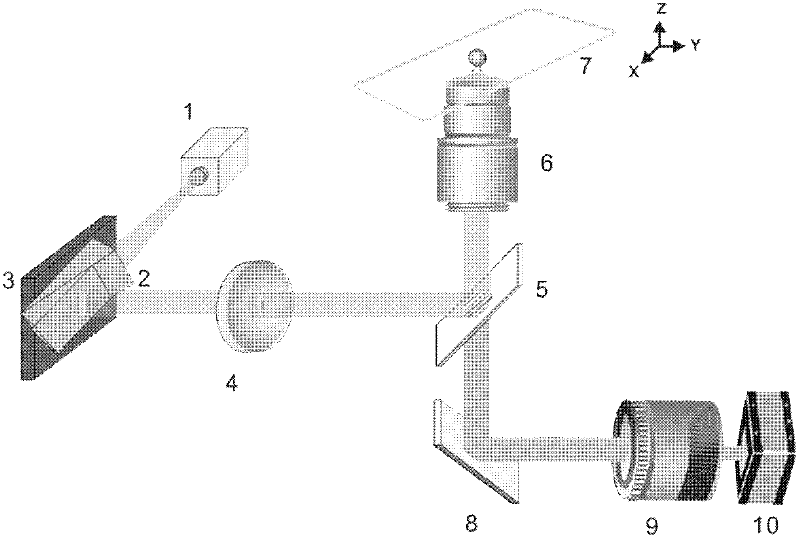
High-speed structure illumination optical microscope system and method based on digital micromirror device
InactiveCN102540446AImaging refresh rate is fastImprove light energy utilizationMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesCcd cameraOptical path
The invention relates to a high-speed structure illumination optical microscope system and a method based on a digital micromirror device. The high-speed structure illumination optical microscope system comprises an illumination light source, a light splitting prism, a structure light generator, a lens, a spectroscope, a microobjective, an objective table, a reflector, a tubular mirror and a charge coupled device (CCD) camera, wherein the light splitting prism is arranged on a light path of the illumination light source, the structure light generator is arranged on a reflection light path of the light splitting prism, the lens is arranged on a transmission light path of the light splitting prism, the spectroscope is arranged on a lens light path, the microobjective and the objective table are arranged on a light path above the tubular mirror, the reflector and the tubular mirror are arranged on a light path under the spectroscope, and the CCD camera is arranged behind the tubular mirror. The system and the method aim at the technical problems of low optical energy utilization rate and low speed of the existing structure illumination microscope and have the advantages that the image refreshing speed is high (32KHz), and the optical energy utilization rate is high (higher than 90 percent). The system and the method are more applicable to the real-time three-dimension image study and high-speed dynamic process observation of living biological cells.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
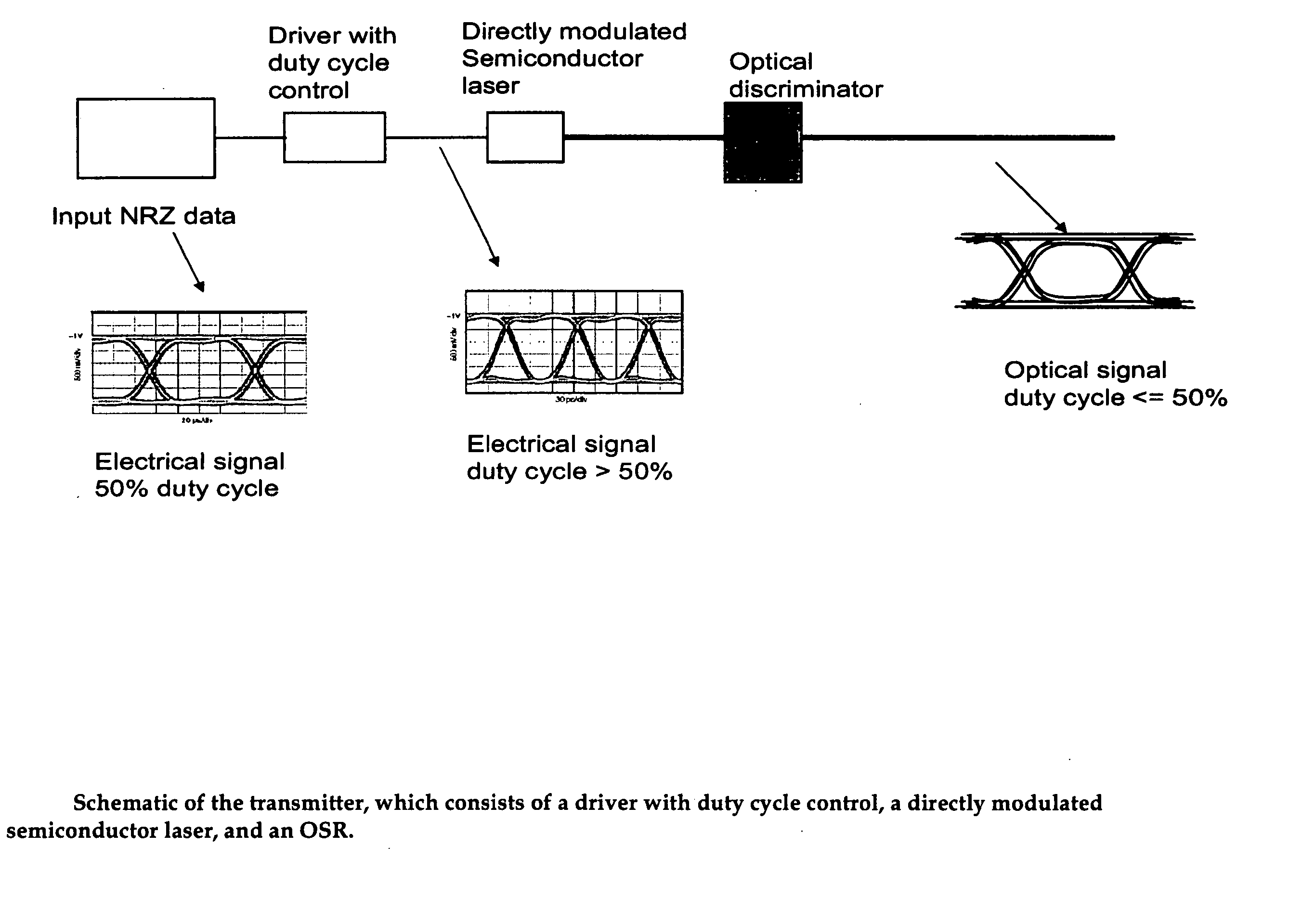
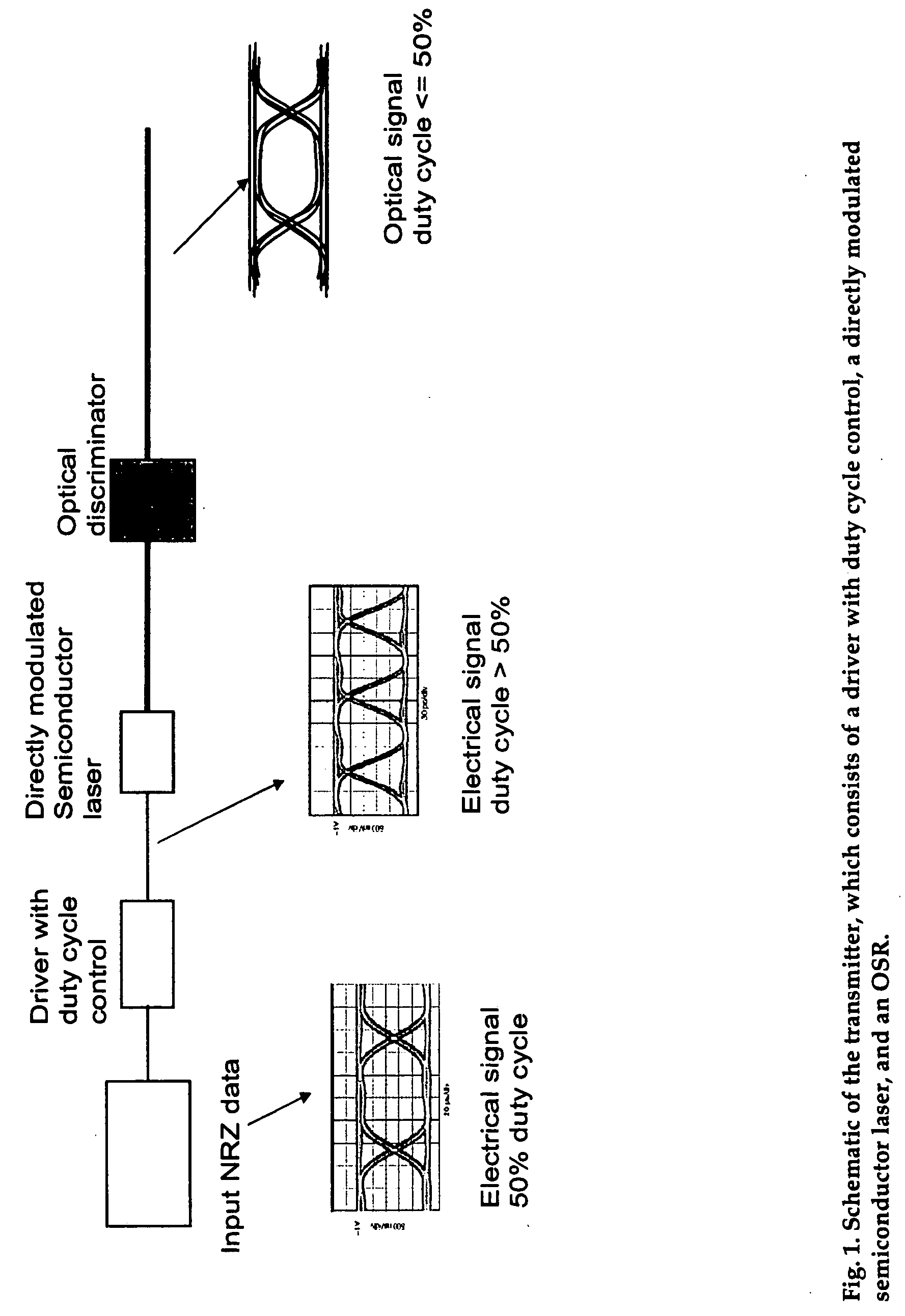
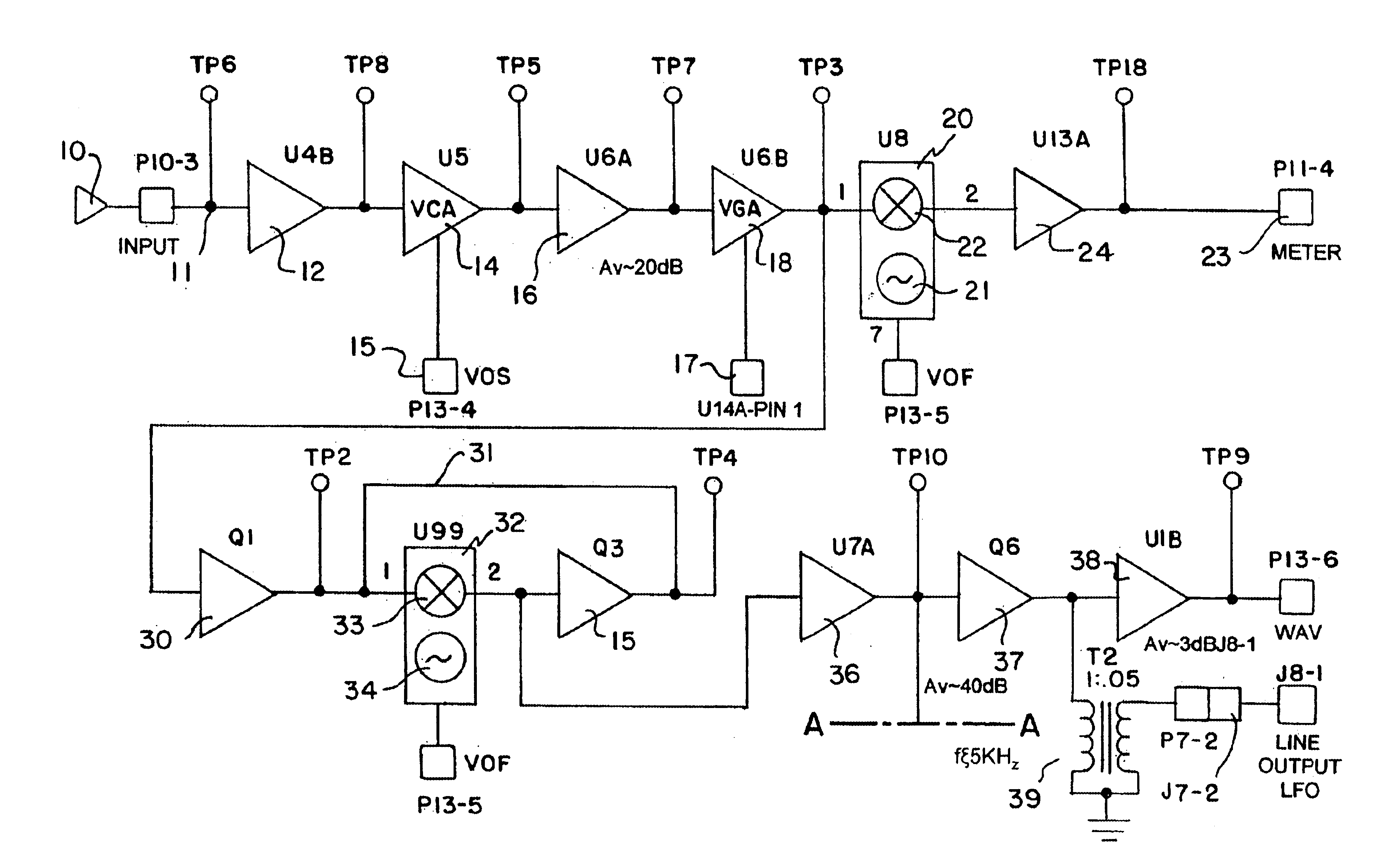
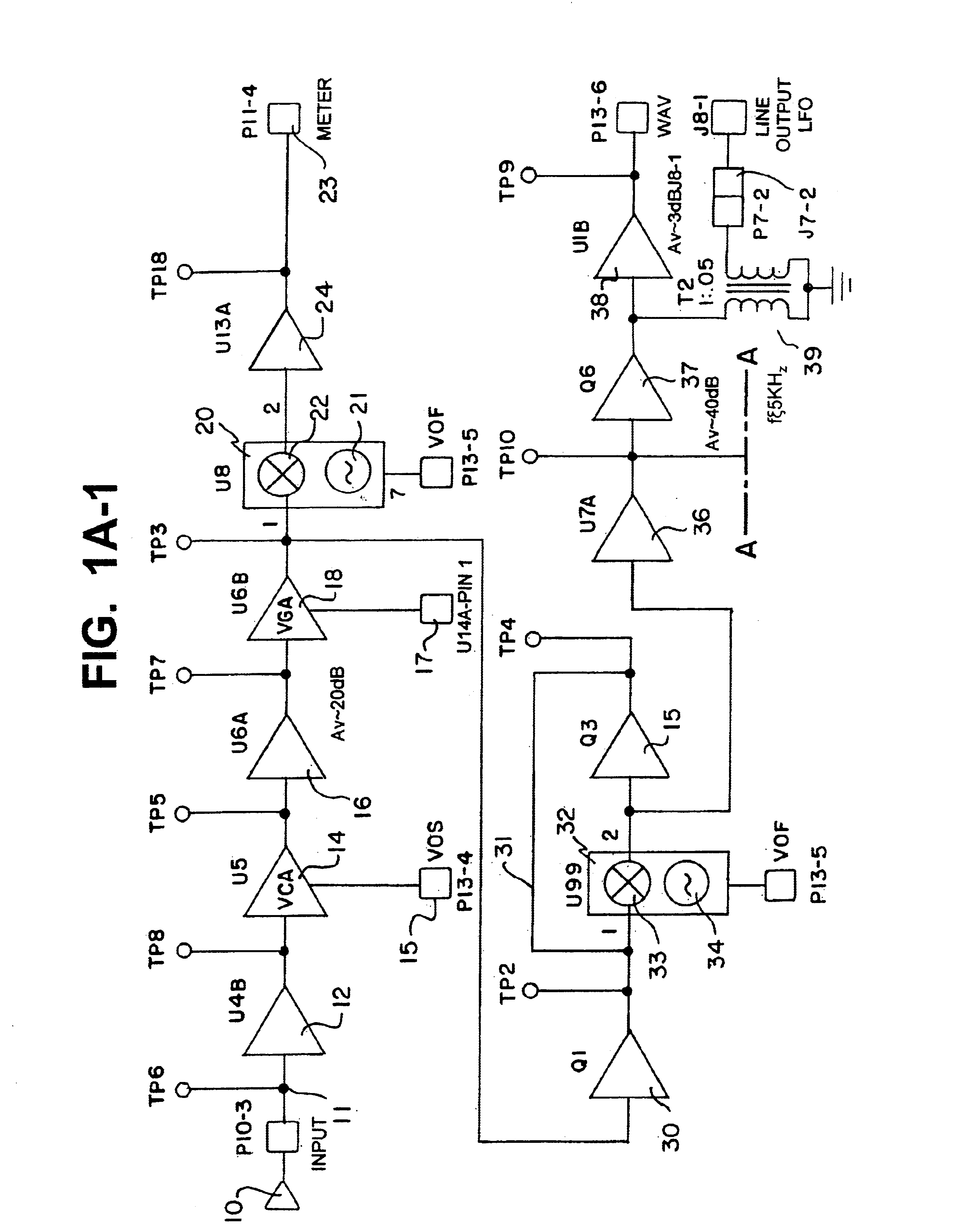
Method and apparatus for transmitting a signal using thermal chirp management of a directly modulated transmitter
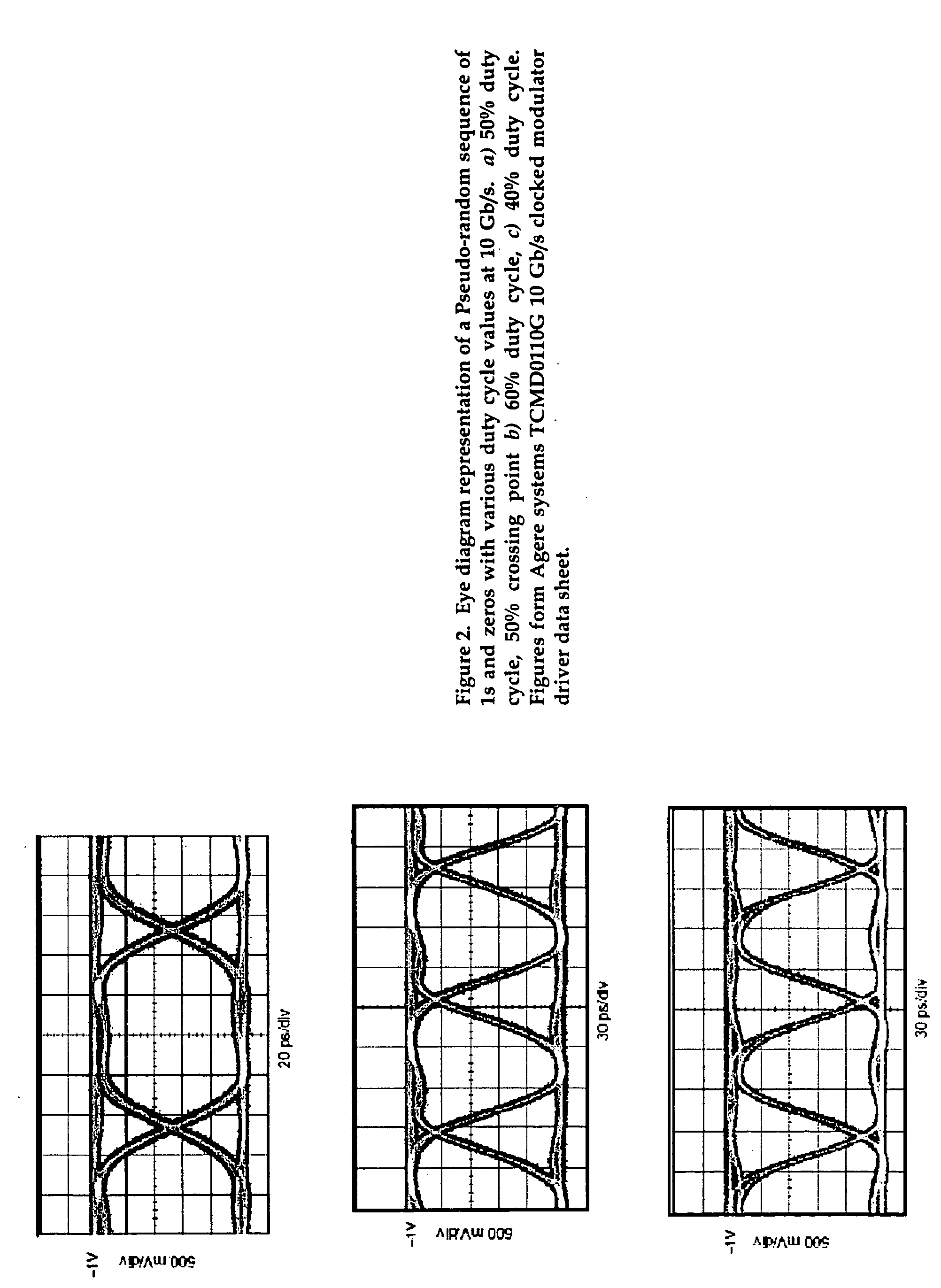
ActiveUS20050111852A1Reduce thermal chirp of optical signalReducing “ overshoot ”Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersChirpLight source
A fiber optic transmitter comprising a digital driver adapted to adjust the crossing point of a digital base signal, an optical source adapted to receive the digital base signal and produce a frequency modulated optical signal, and an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to convert the frequency modulated optical signal to an amplitude modulated optical signal. A method for transmitting a signal, comprising: adjusting the crossing point of a digital base signal; providing the adjusted signal to an optical source to produce a frequency modulated optical signal; and providing the frequency modulated optical signal to an optical spectrum reshaper to convert the frequency modulated optical signal to an amplitude modulated optical signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Readout technique for increasing or maintaining dynamic range in image sensors
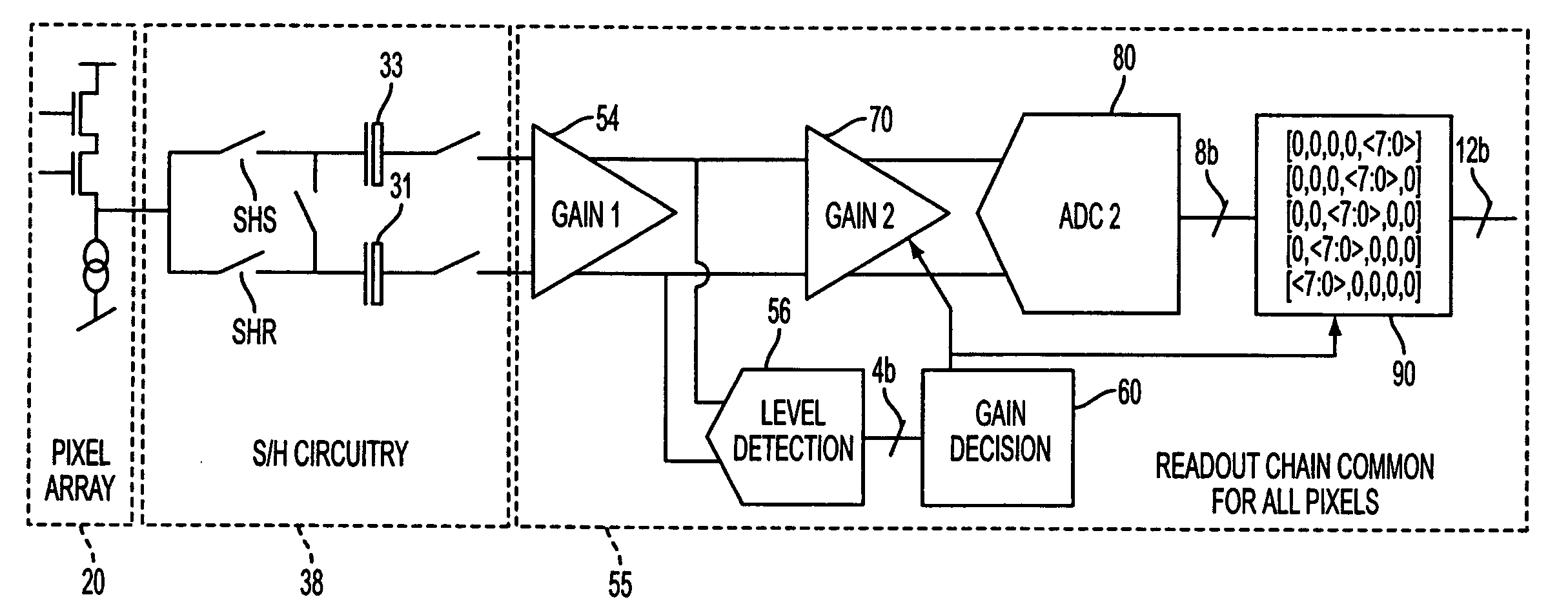
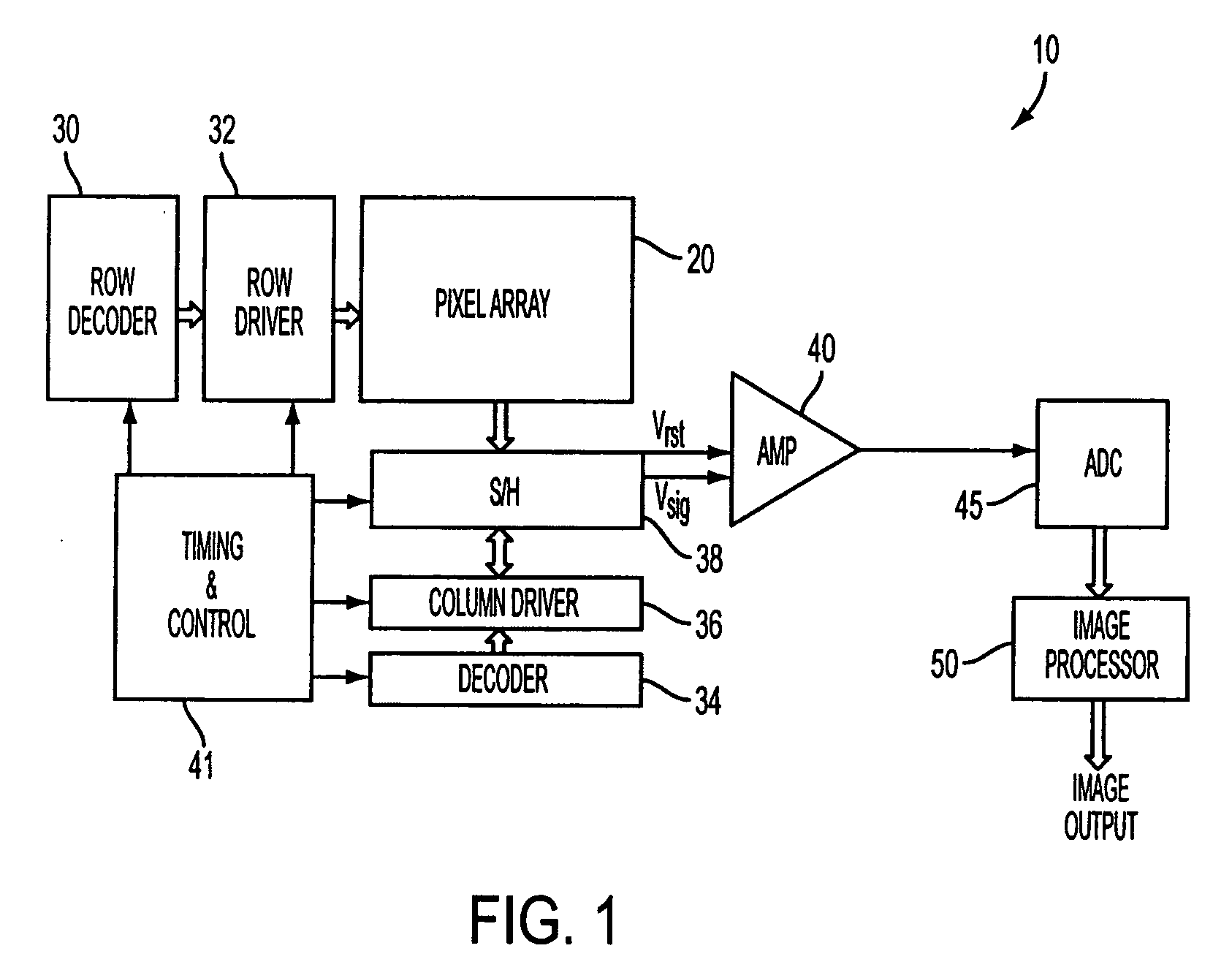
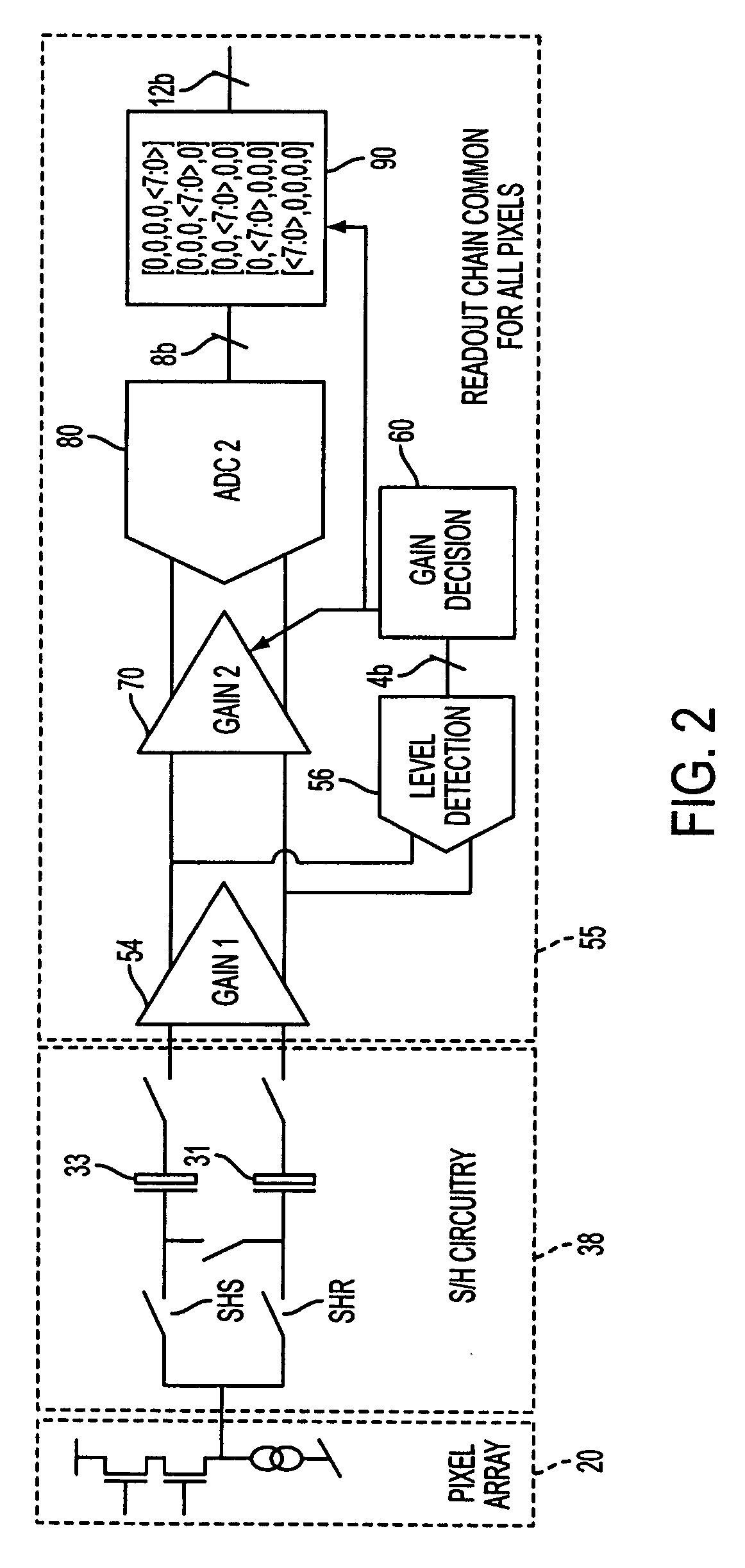
ActiveUS20060214085A1Extended imaging rangeReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system detailsNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The apparatus and method provide a readout technique and circuit for increasing or maintaining dynamic range of an image sensor. The readout technique and circuit process each pixel individually based on the magnitude of the readout signal. The circuit includes a gain amplifier amplifying the readout analog signal, a level detection circuit for determining the signal's magnitude, a second gain amplifier applying a gain based on the signal magnitude and an analog-to-digital converter digitizing the signal and a circuit for multiplying or dividing the signal. The method and circuit allow for a lower signal-to-noise ratio while increasing the dynamic range of the imager.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS9530444B2Increased durabilityReduce runningMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageScanning electron microscopeElectron microscope
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
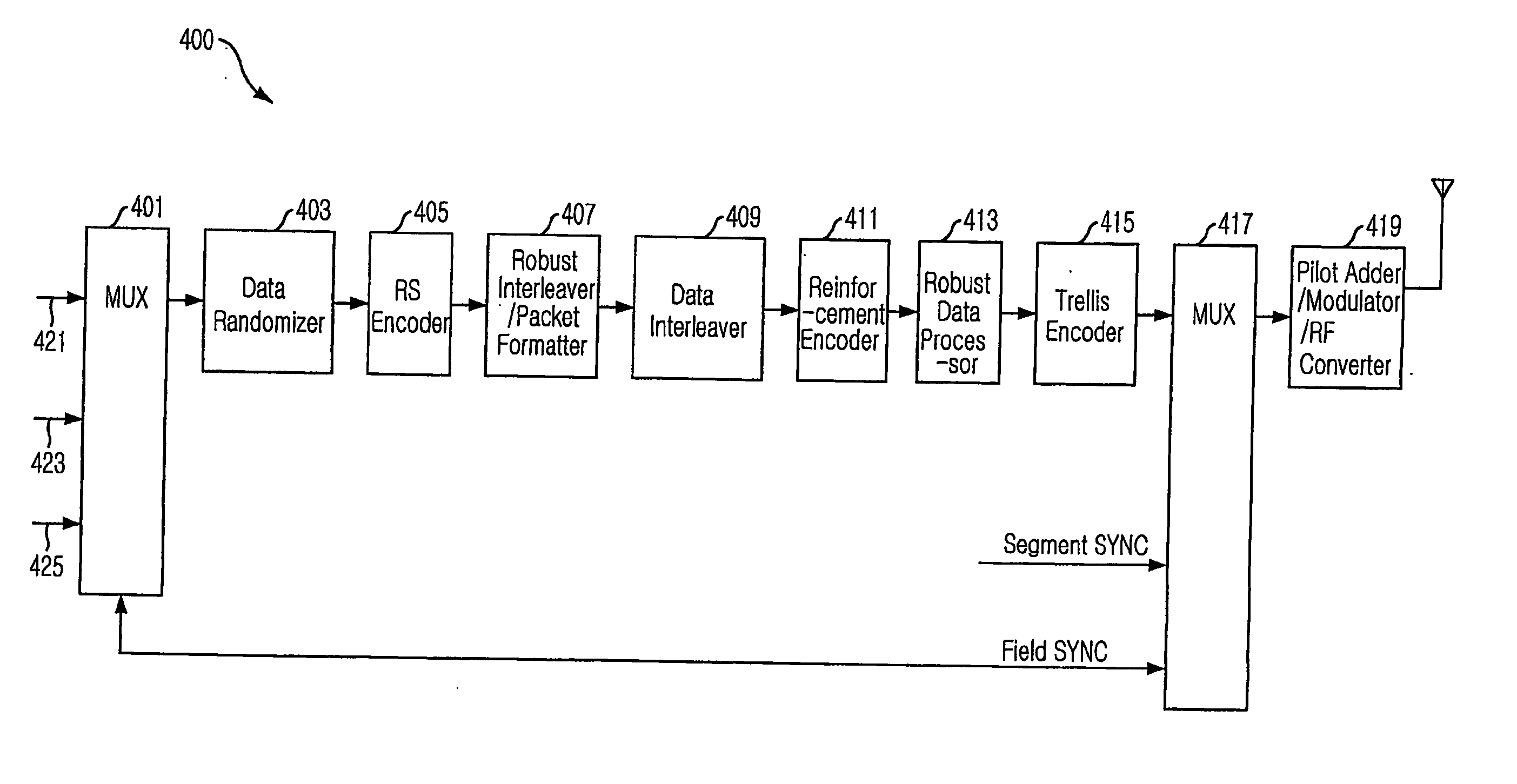
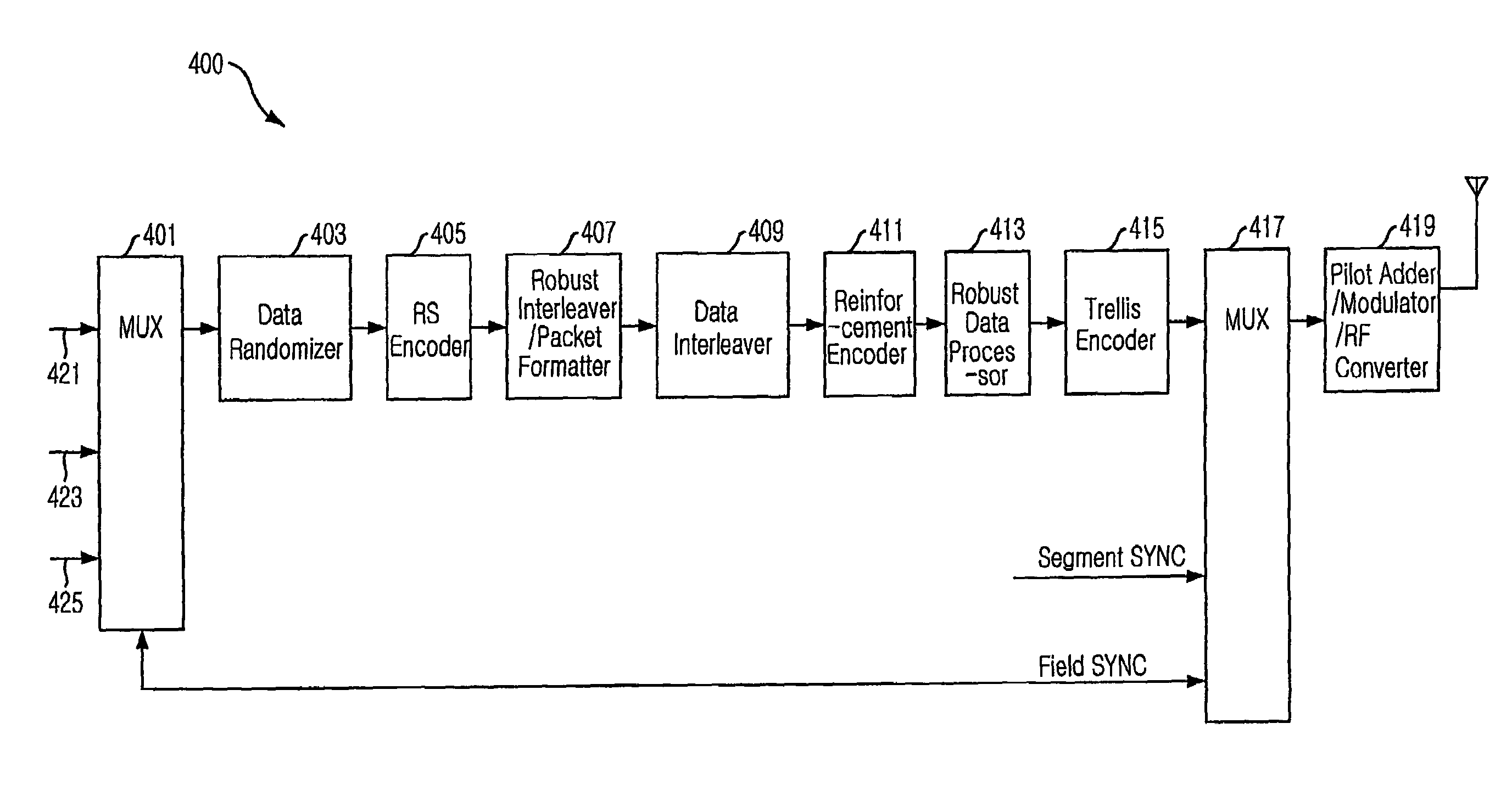
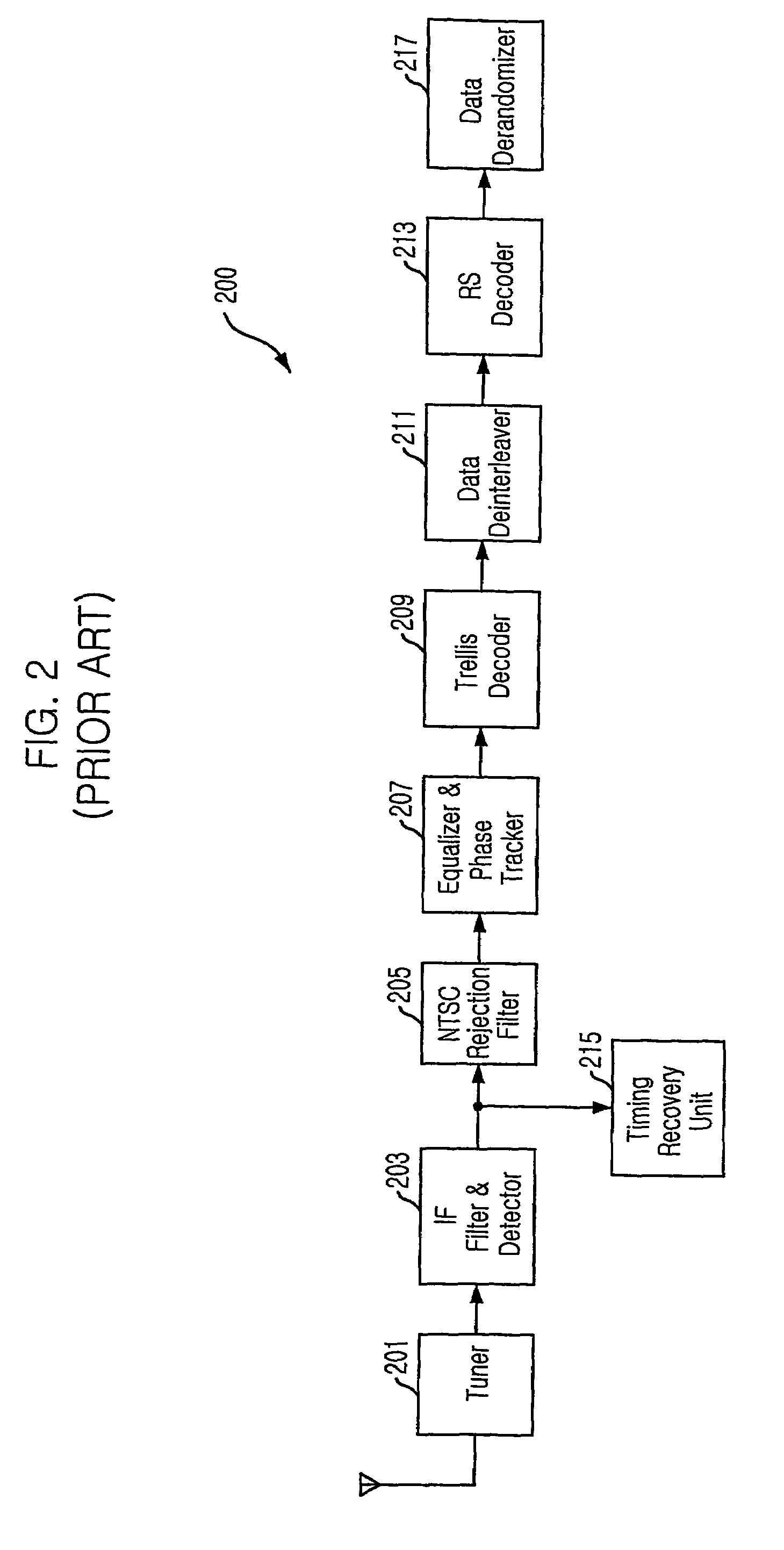
Digital television transmitter and receiver for using 16 state trellis coding
InactiveUS20070140368A1Improve reception performanceReduce signal to noise ratioData representation error detection/correctionError correction/detection using concatenated codesTelevision systemData stream
Provided are a Vestigial Side Band (VSB) Digital Television (DTV) transmitter and receiver based on the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC) A / 53, and a method thereof. The present invention provides 8-VSB DTV transmitter and receiver that can improve reception performance of the receiver by transmitting and double streams formed of normal data and robust data without increasing an average power level, regardless of the ratio of the normal data and robust data, by including an encoding unit for performing 16-state trellis coding on the robust data when a data stream includes robust data, and a method thereof.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital television transmitter and receiver for transmitting and receiving dual stream using 4 level vestigial side band robust data
ActiveUS20060269012A1Improve reception performanceReduce signal to noise ratioError preventionTelevision system scanning detailsSidebandDigital television transition
The present invention relates to a Vestigial Side Band (VSB) Digital Television (DTV) in agreement with the DTV standards (A / 53) of the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC), and to a method thereof. More particularly, it provides 4-VSB DTV transceiver that improves reception performance of a receiver by transmitting and receiving dual streams formed of normal data and robust data without increasing average power, regardless of a mixing rate of the normal and robust data. The 4-VSB DTV transceiver of the present research includes an encoding unit for encoding the robust data to be mapped to one of two groups having 4 levels {−5, −3, 1, 7} and {−7, −1, 3, 5}.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital television transmission and receiving apparatus and method using 1/4 rate coded robust data
ActiveUS20090201997A1Decreased signal to noise ratioImprove decoding performanceTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionStreamDigital video
Provided is a Vestigial Side Band Digital Television (DTV) transmitter / receiver based on Advanced Television System Committee A / 53. The invention provides DTV transmitter / receiver having a dual stream structure through generation of robust data which has a transmission rate a fourth as fast as that of normal data, and a method thereof. The DTV transmitter includes: input means for receiving digital video data stream including normal and robust data; encoding means for performing ¼ rate coding on the digital video data stream so that one bit can be transmitted through two symbols; and transmitting means for modulating / transmitting output signals of the encoding means. This invention can reduce SNR and satisfy TOV of robust data by performing additional FEC on robust data, transmitting / receiving ¼ rate coded robust data, which are capable of transmitting one-bit data for two symbols, and improving decoding ability of an equalizer and a trellis decoder of a DTV receiver.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Receiver
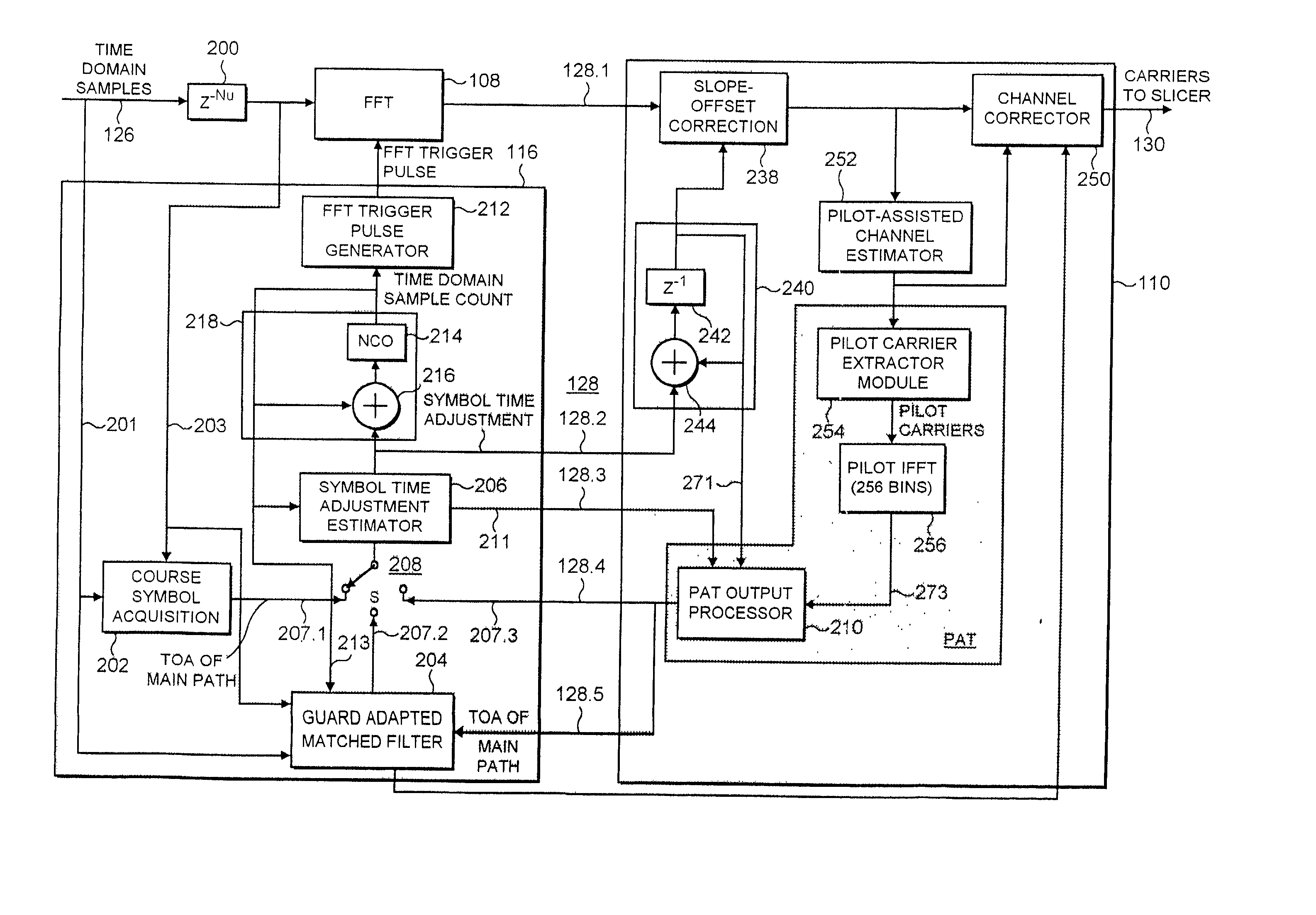
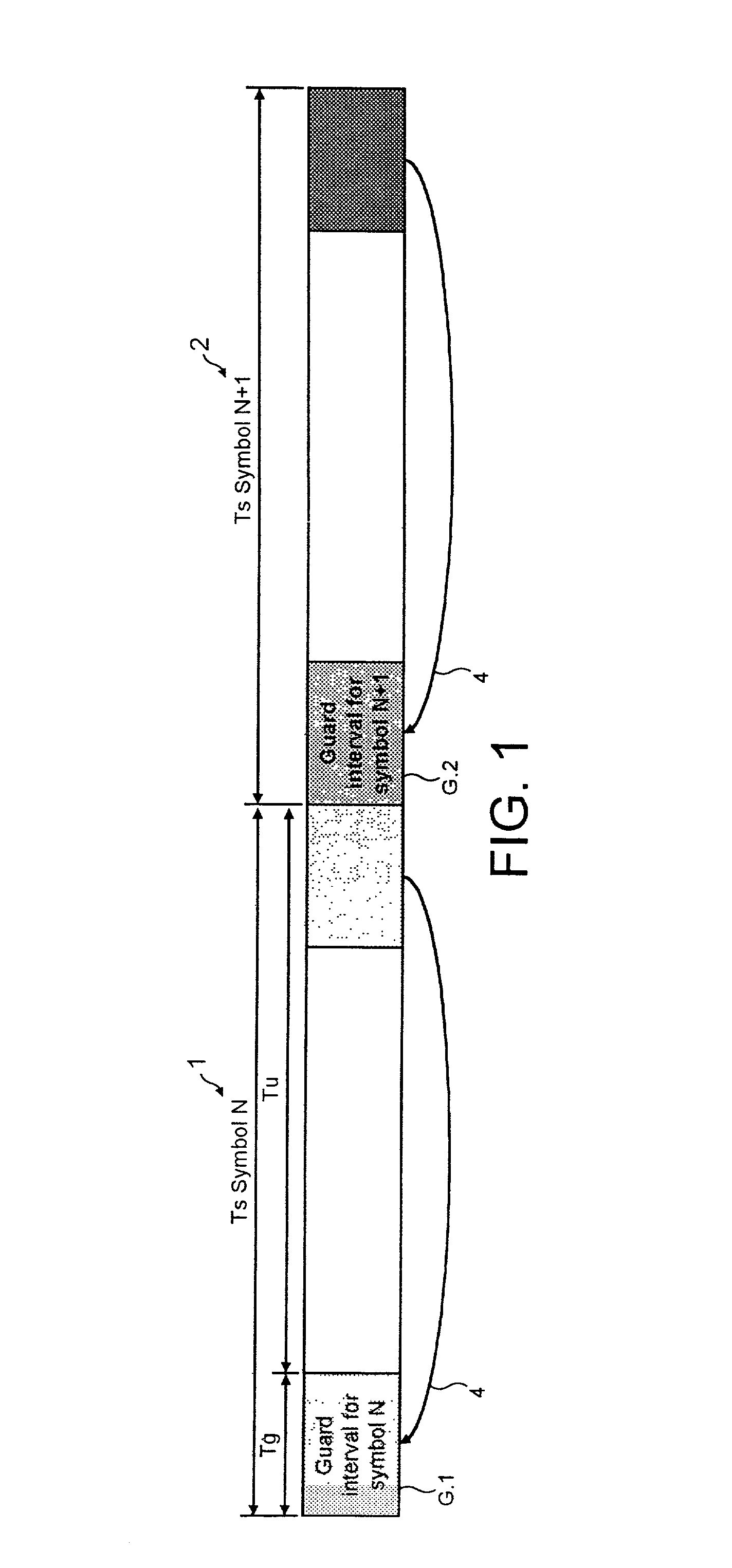
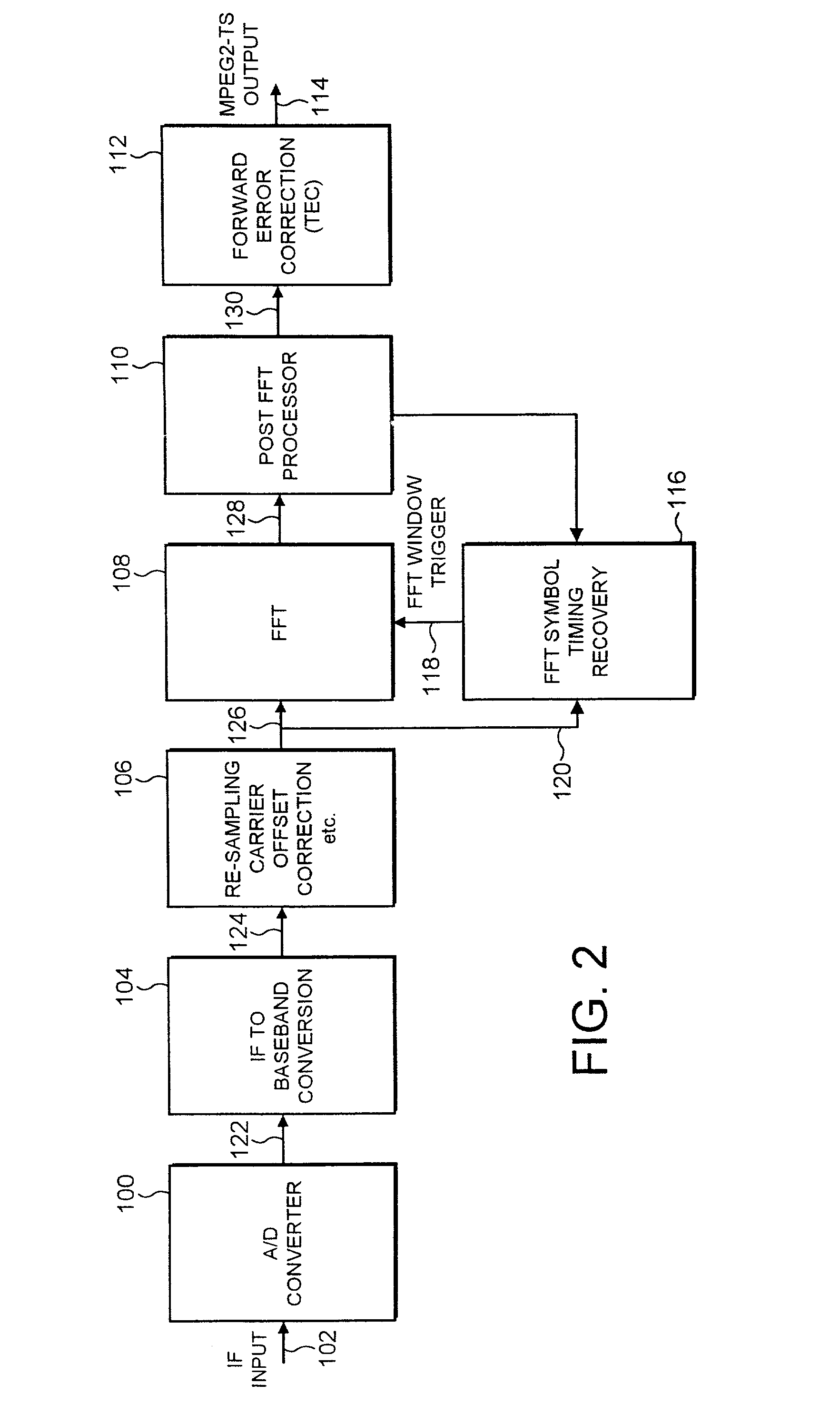
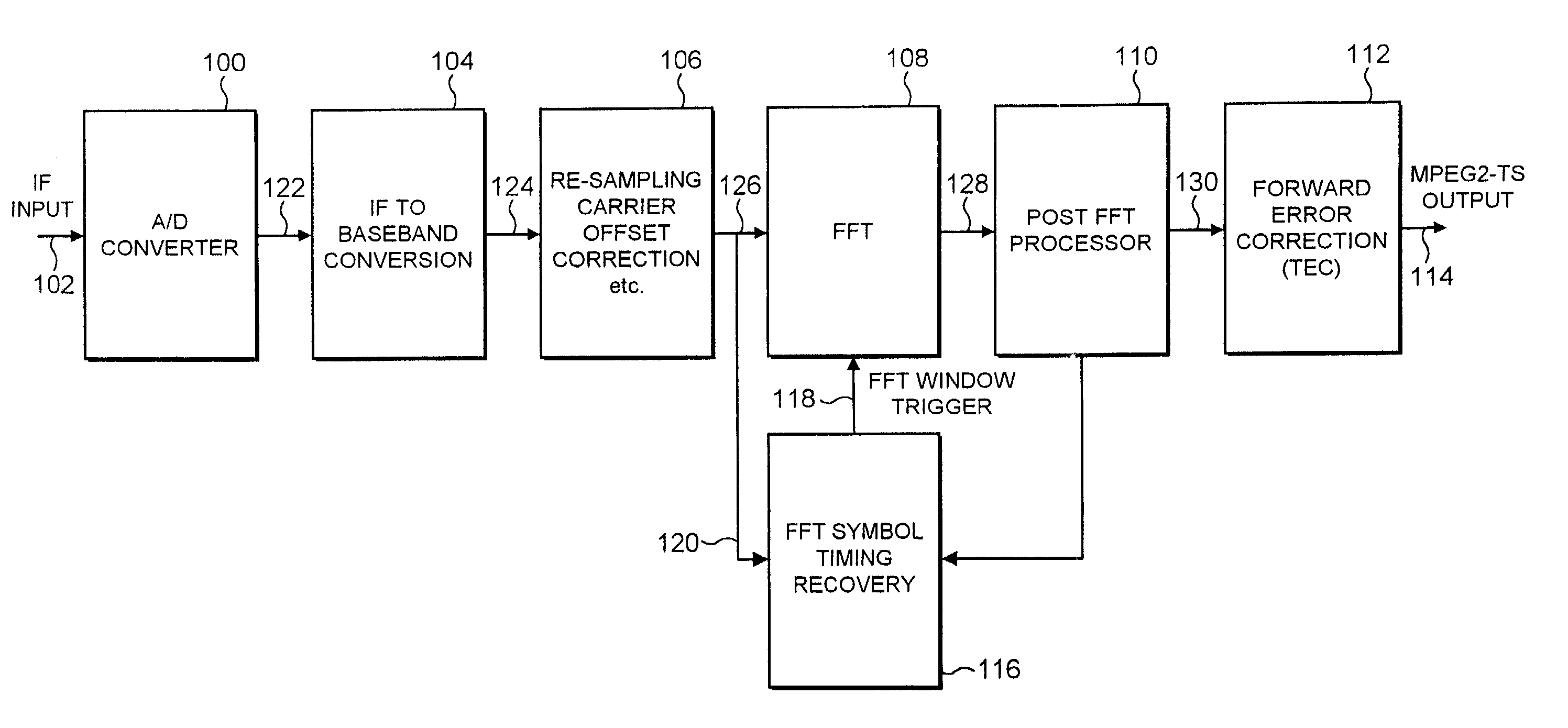
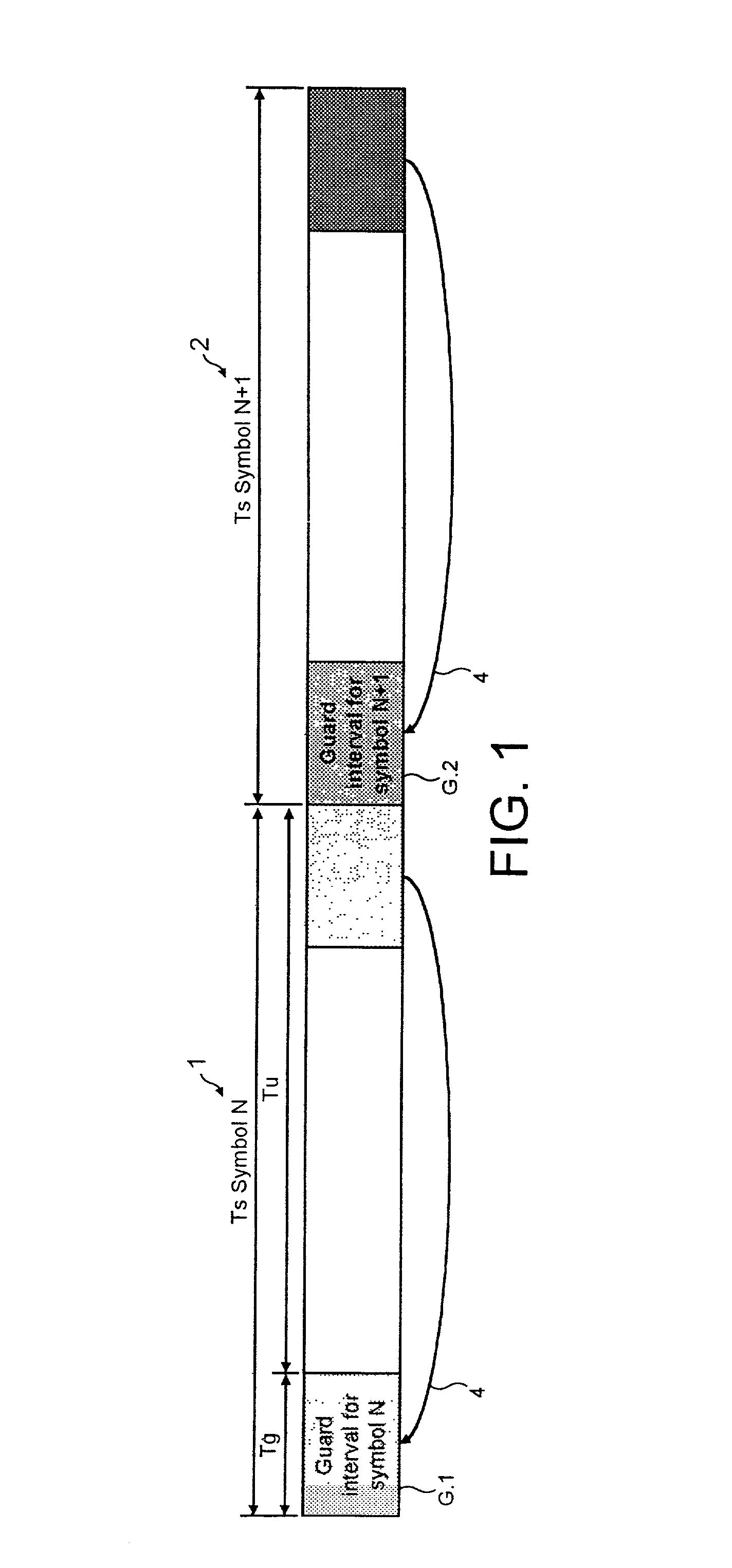
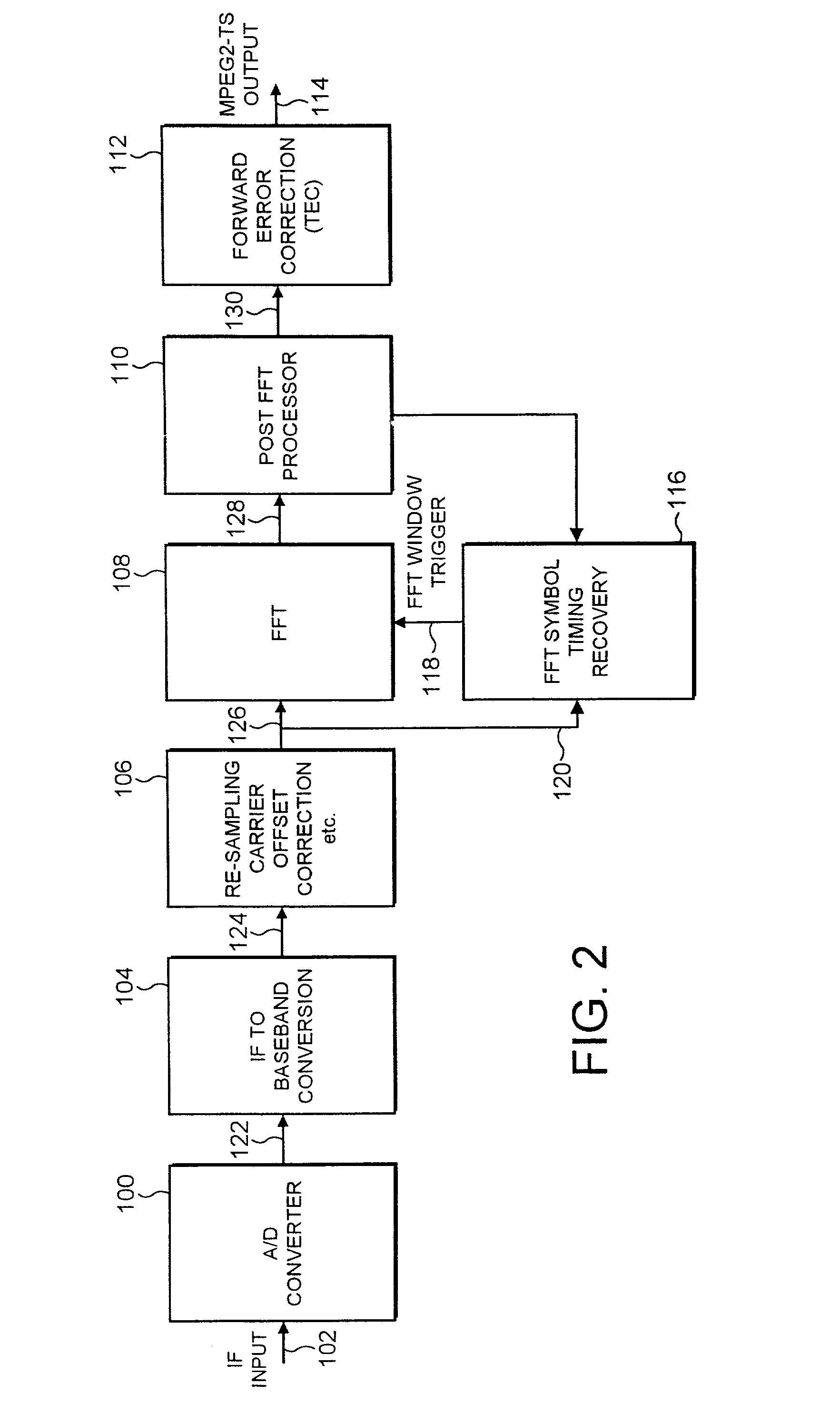
ActiveUS20030016773A1Reduce signal to noise ratioReduced likelihoodAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlAdaptive filterChannel impulse response
A receiver determines a symbol synch time for recovering data from a symbol of signal samples generated in accordance with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. Each symbol includes a guard period which carries data repeated from a data bearing part of the symbol and pilot signal samples. The receiver comprises a pilot assisted tracker which is operable to determine an adjustment to the symbol synch time from a pilot assisted channel impulse response estimate, a guard adapted filter processor comprising a filter and a filter controller operable to adapt the impulse response of the filter to the signal samples from the guard period. The controller is operable to excite the filter with the symbol signal samples to generate an output signal which provides a further representation of the channel impulse response. A symbol time adjustment estimator is operable to adjust the symbol synch time in accordance with the adjustment provided by at least one of the pilot assisted tracker and the guard adapted filter processor. The receiver provides an improved estimate of the symbol synch time by combining a pilot assisted tracker with a guard adapted filter processor. The pilot assisted tracker estimates the symbol synch time from a channel impulse response estimate generated from pilot signal samples. By combining the synch time adjustment estimated from the pilot assisted channel impulse response, with the adjustment estimated by the guard adapted filter processor, an ambiguity in a relative time of arrival of signal paths of the channel impulse response with respect to the main signal path is obviated.
Owner:SONY UK LTD +1
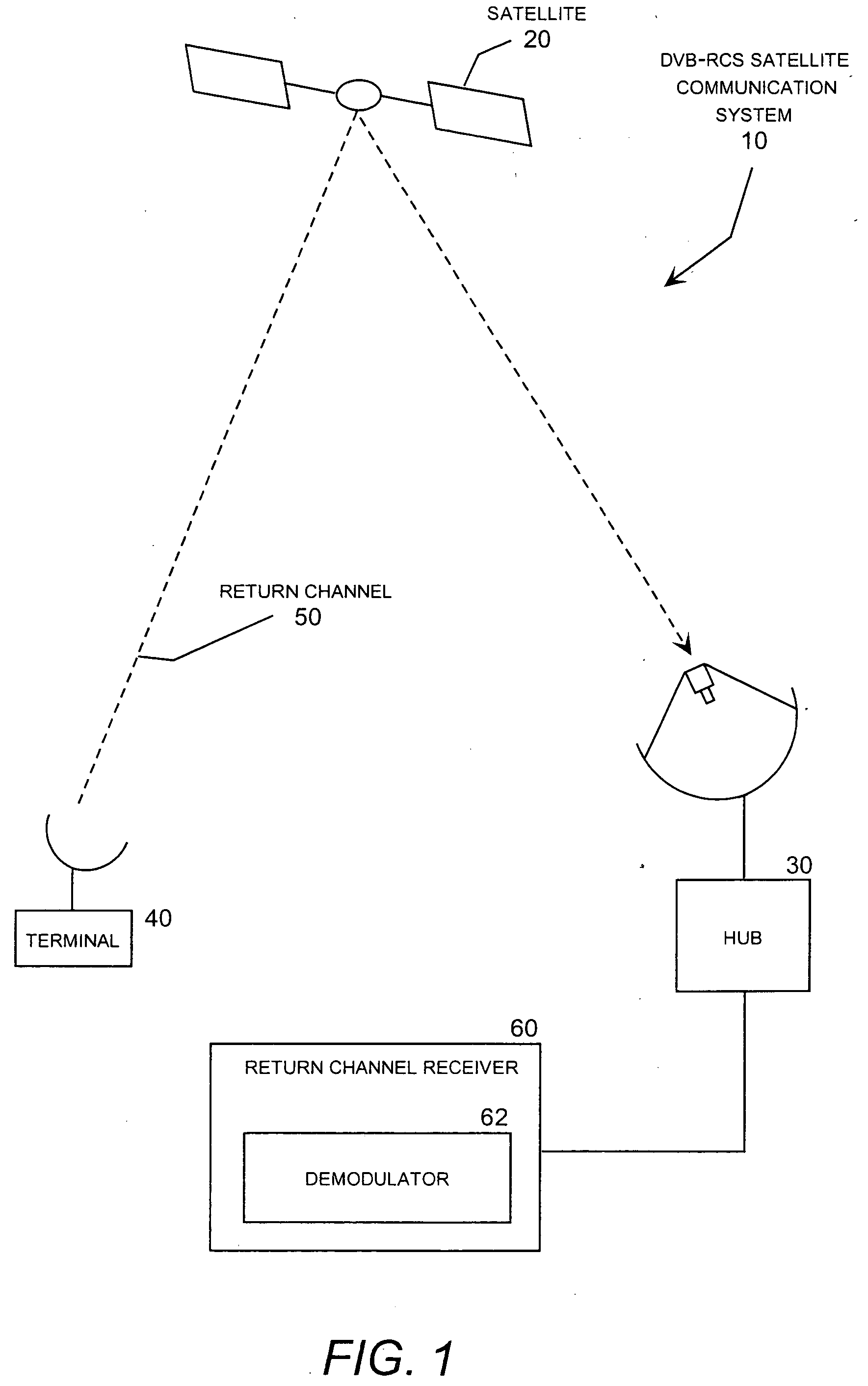
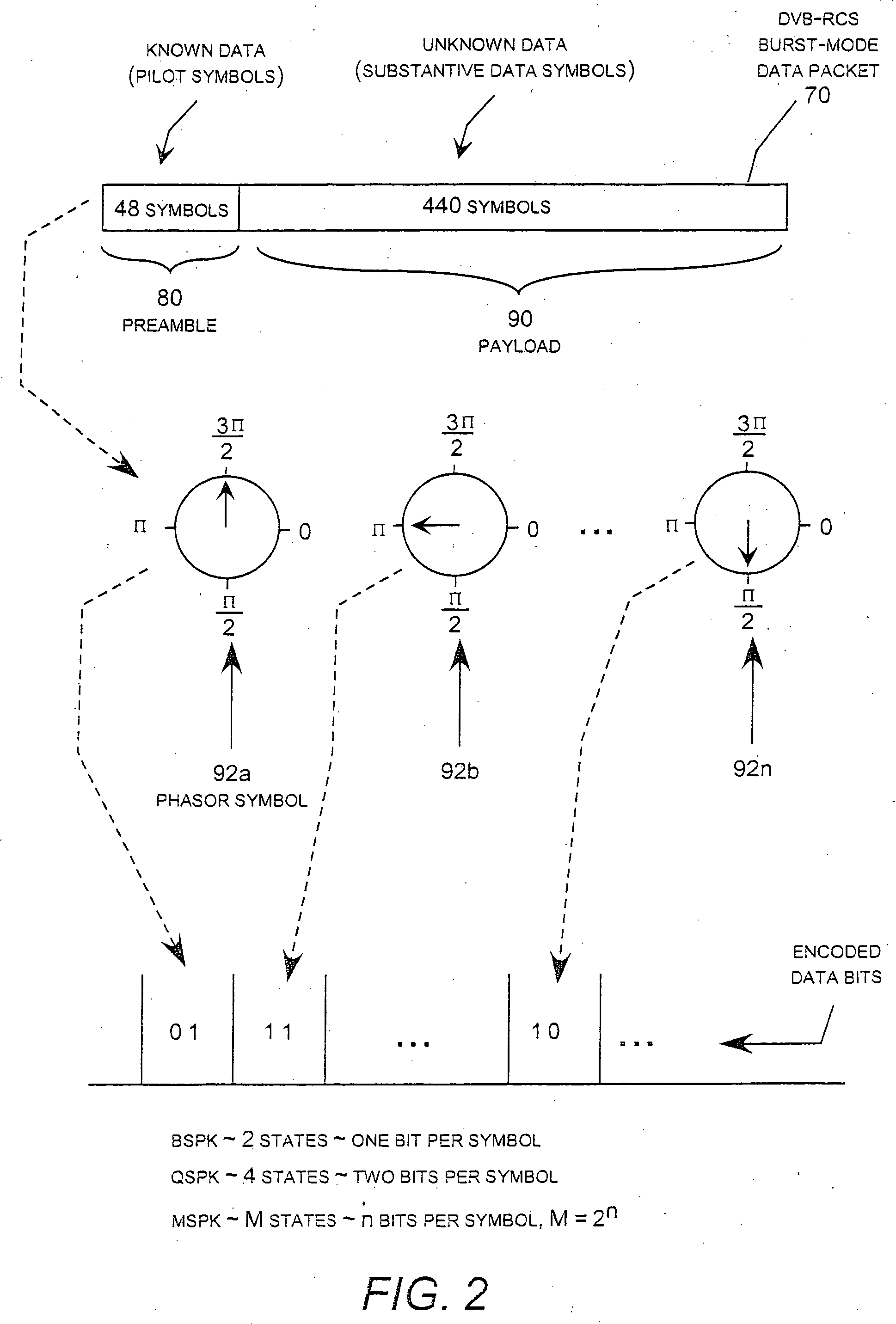
Hybrid frequency offset estimator
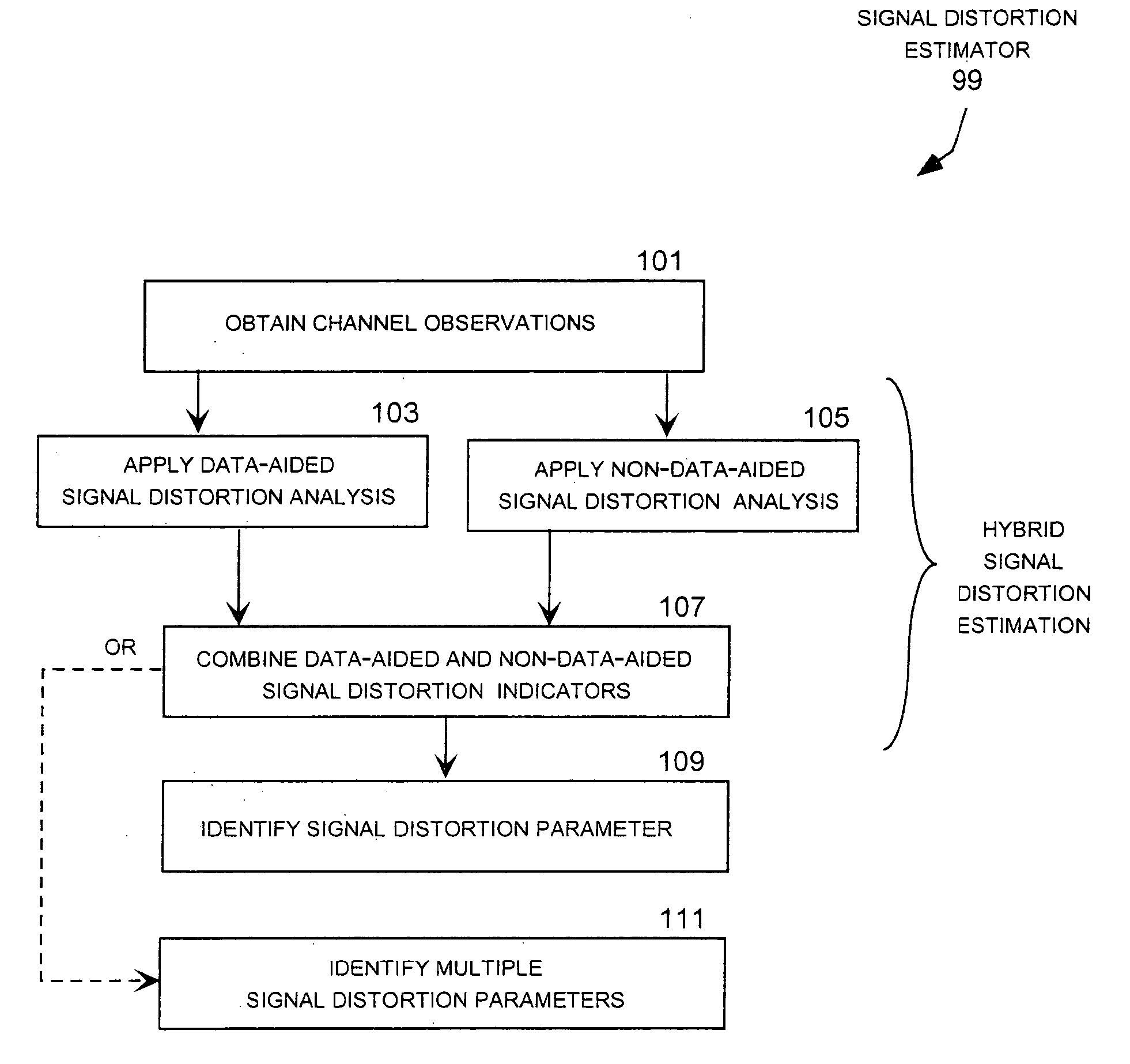
ActiveUS20050058229A1Improve frequency performanceImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionPacket lossSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A hybrid carrier frequency offset estimator that uses data-aided and non-data-aided signal processing techniques to produce multiple candidates for the carrier frequency offset within a return channel receiver in a DVB-RCS system using turbo coding and quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) data modulation. In this system, the invention is employed to estimate signal distortion caused by carrier frequency offset so that this particular source of signal distortion can be removed to improve the ability of the receiver to maintain synchronization in low signal-to-noise conditions. This, in turn, allows the receiver to meet the DVB-RCS performance target, measured in terms of packet loss ratio, in low signal-to-noise ratio conditions and in particular for burst-mode data transmission with a short data packet size.
Owner:ADVANTECH SATELLITE NETWORKS
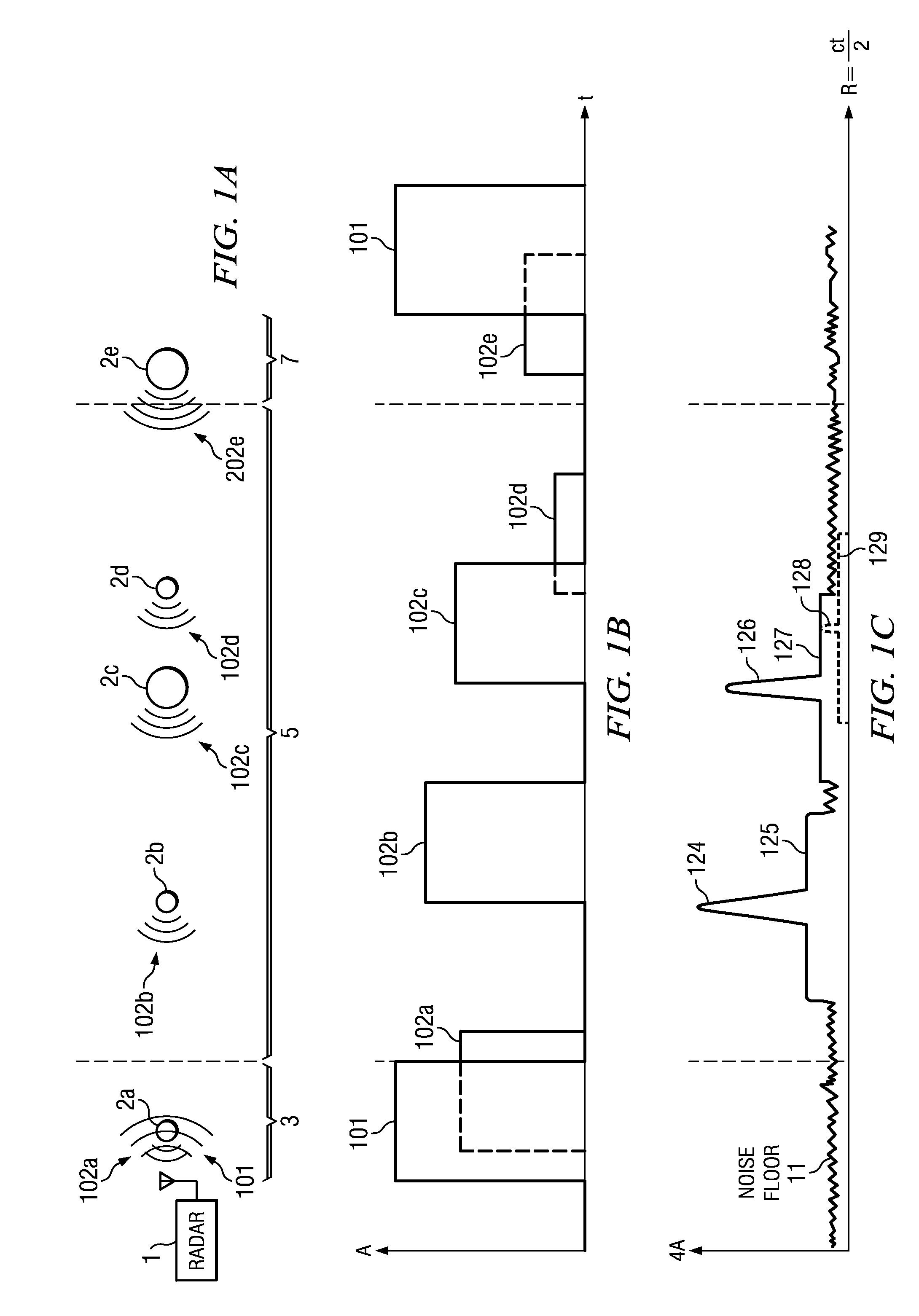
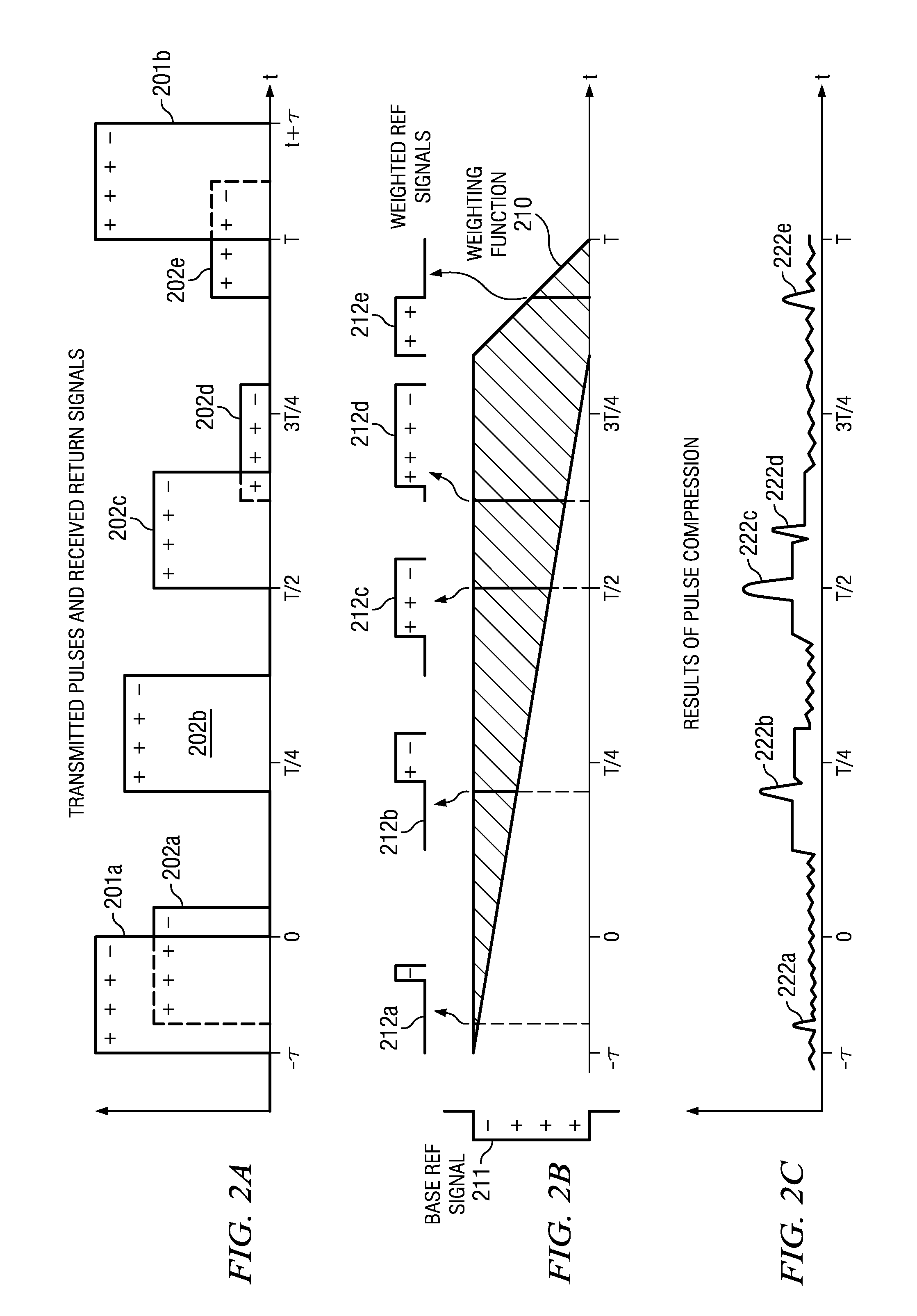
High Duty Cycle Radar with Near/Far Pulse Compression Interference Mitigation
ActiveUS20110279307A1High resolutionReduce signal to noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPulse transmissionVIT signals
In conventional pulse compression processing, sidelobes from strong return signals may hide correlation peaks associated with weaker return signals. Example embodiments include methods of mitigating this near / far interference by weighting a received return signal or corresponding reference signal based the return signal's time of arrival, then performing pulse compression using the weighted signal to produce a correlation peak that is not hidden by sidelobes from another return. Multi-frequency processing can also be used to reduce the pulse width of the transmitted pulses and received return signals, thereby mitigating near / far interference by decreasing the overlap between signals from nearby targets. Weighting can be combined with multi-frequency pulse transmission and reception to further enhance the fidelity of the processed correlation peak. Weighting and multi-frequency processing also enable higher duty cycles than are possible with conventional pulse compression radars.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Detection of analytes using electrochemistry
InactiveUS6100045ALow costReduce lossesImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseMatrix solution
The present invention relates to diagnostic assays whereby the detection means is based on electrochemical reactions. This means that the label to be detected provides an electric signal. Preferred labels are enzymes giving such a signal. Provided is a flow cell whereby a solid phase is provided in a flow stream of the sample, in close proximity to a working electrode to detect any electrical signal. In a typical embodiment, a sample is mixed with molecule having specific binding affinity for an analyte of which the presence in the sample is to be detected, whereby said specific binding molecule is provided with a label. The conjugate of labelled specific binding molecule and analyte is then immobilized on the solid phase in the vicinity of the working electrode, the flow cell is rinsed with a solution and afterwards a substrate solution for the label (an enzyme) is provided upon which an electrical signal is generated and can be detected by the working electrode. The methods and devices of the present invention are particular useful for liquids which comprise many substances that may disturb measurement in conventional assays. The design of the flow cell allows for removal of said interfering substances before measurement. In a preferred embodiment at least part of the solid phase is provided in the form of magnetic beads. In this embodiment the solid phase can be mixed with the sample thereby creating a longer reaction time, a better sensitivity and a higher speed of the assay.
Owner:DSM NV
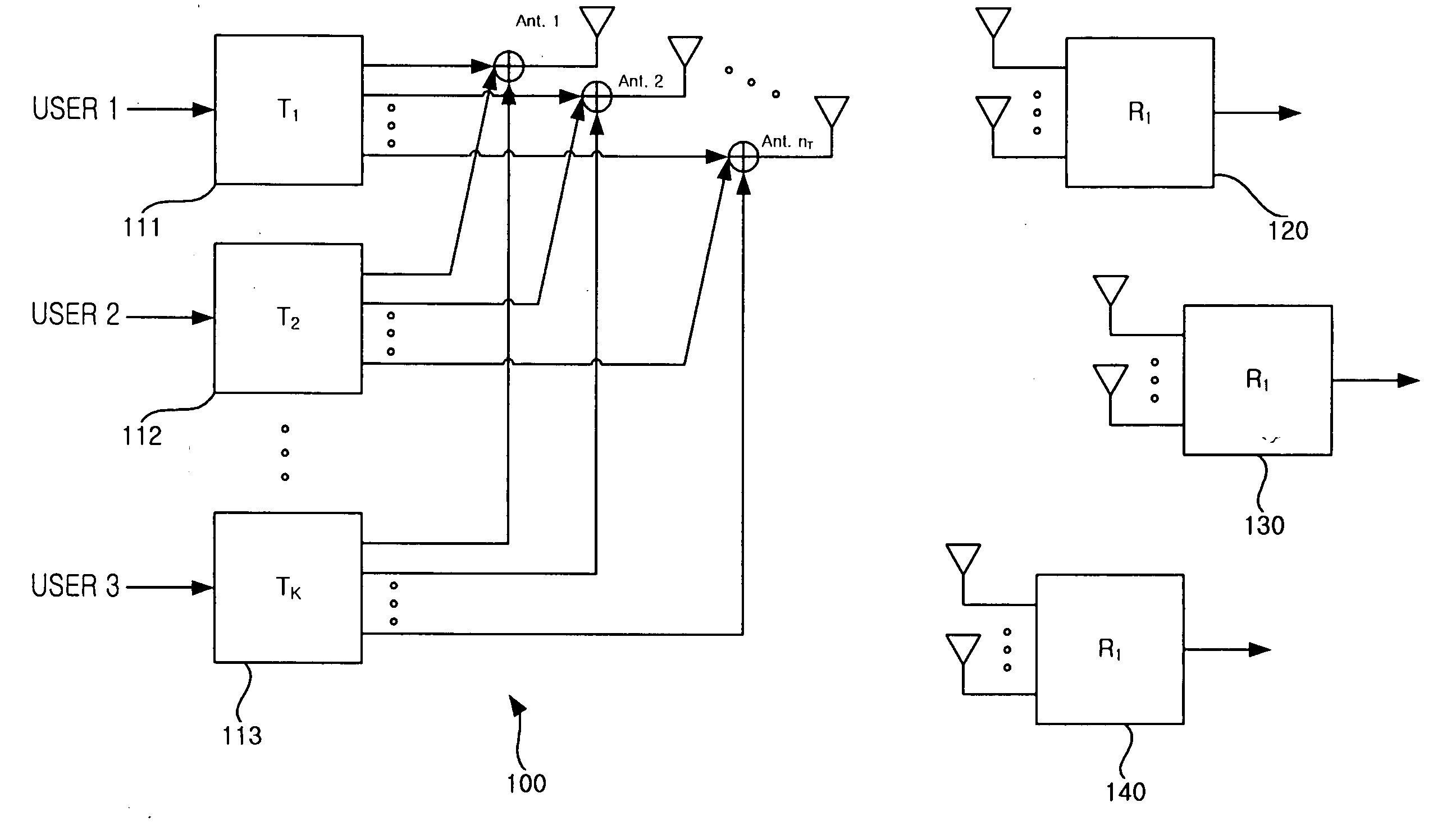
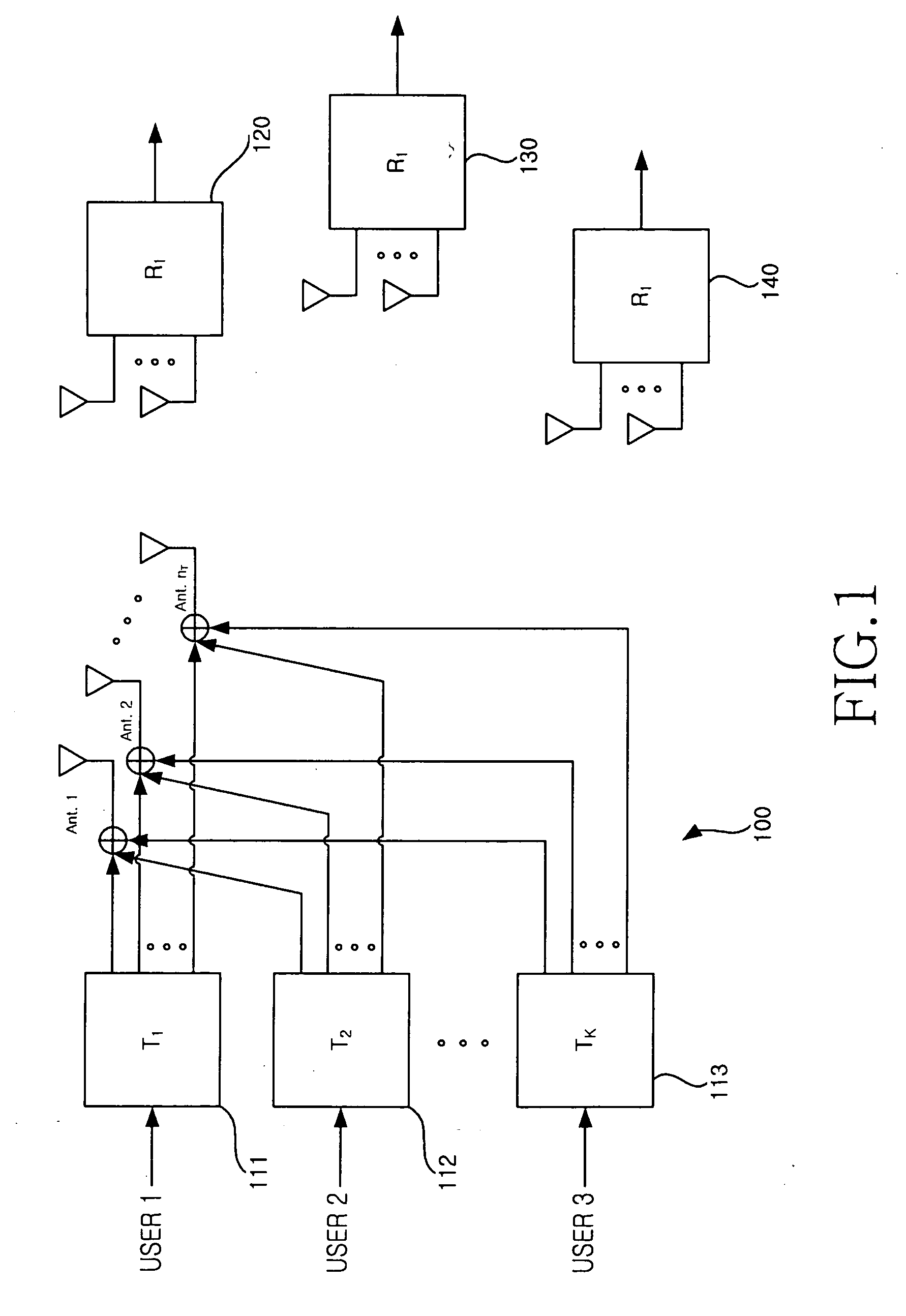
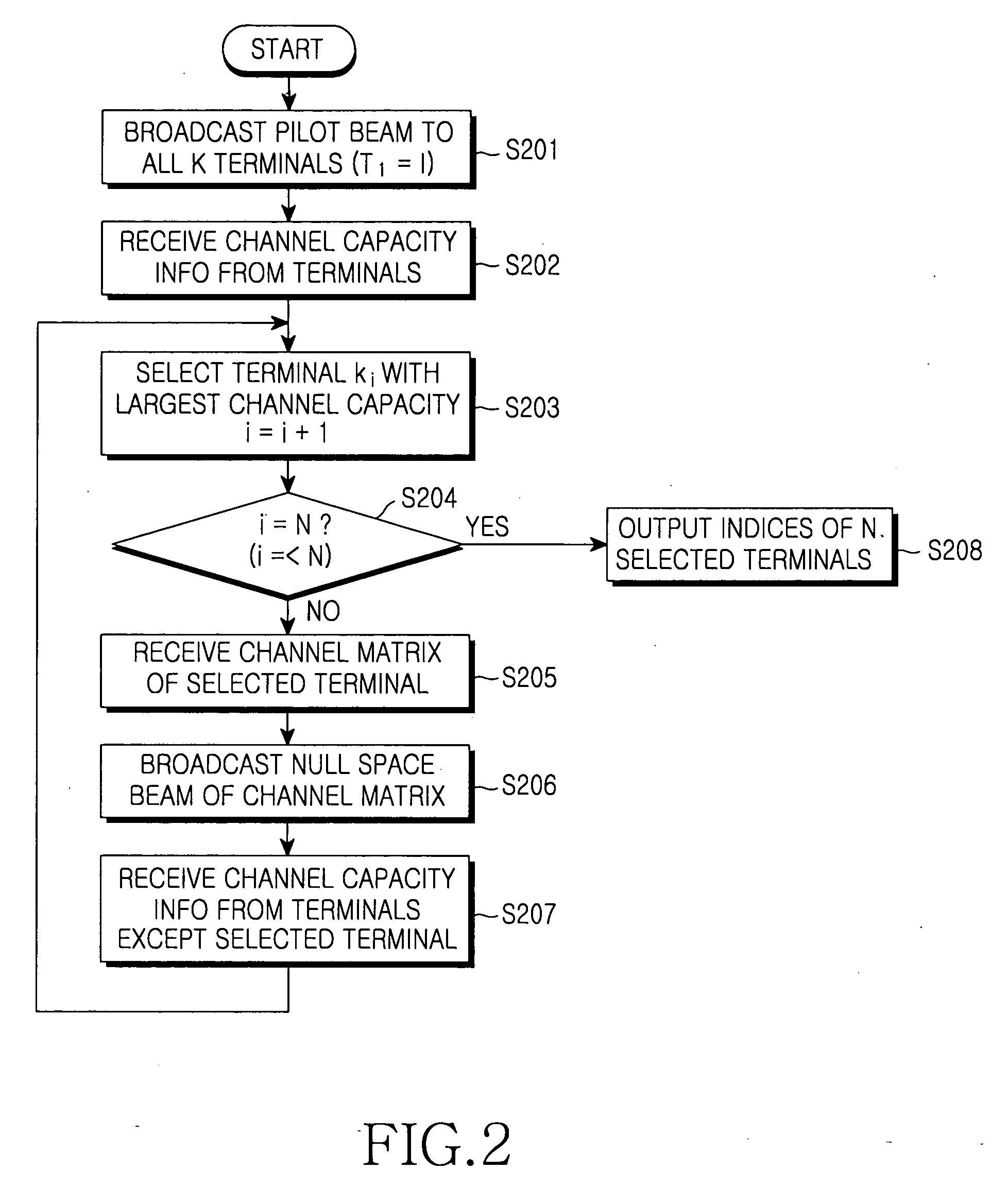
User selection method in a zero-forcing beamforming algorithm
InactiveUS20070058590A1Improve performanceIncrease throughputDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSubstation equipmentChannel capacityEngineering
In a method for selecting a transmission target terminal in a zero-forcing beamforming algorithm, information about a channel capacity of each terminal is received from all K terminals. A terminal with a largest channel capacity is selected as an initial transmission target terminal. A determination is made as to whether the number of currently selected terminals, i, is equal to the predefined number N. If the number of currently selected terminals, i, is different from the predefined number N, information about channel capacities of remaining terminals except previously selected transmission target terminals is received until i is equal to N and a terminal with a largest channel capacity is selected as a transmission target terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Digital television transmitter and receiver for transmitting and receiving dual stream using 4 level vestigial side band robust data
ActiveUS7653143B2Improve decoding performanceReduce signal to noise ratioTelevision system scanning detailsModulated-carrier systemsDigital television transitionTelevision system
The present invention relates to a Vestigial Side Band (VSB) Digital Television (DTV) in agreement with the DTV standards (A / 53) of the Advanced Television System Committee (ATSC), and to a method thereof. More particularly, it provides 4-VSB DTV transceiver that improves reception performance of a receiver by transmitting and receiving dual streams formed of normal data and robust data without increasing average power, regardless of a mixing ratio of the normal and robust data. The 4-VSB DTV transceiver of the present research includes an encoding unit for encoding the robust data to be mapped to one of two groups having 4 levels {−5, −3, 1, 7} and {−7, −1, 3, 5}.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
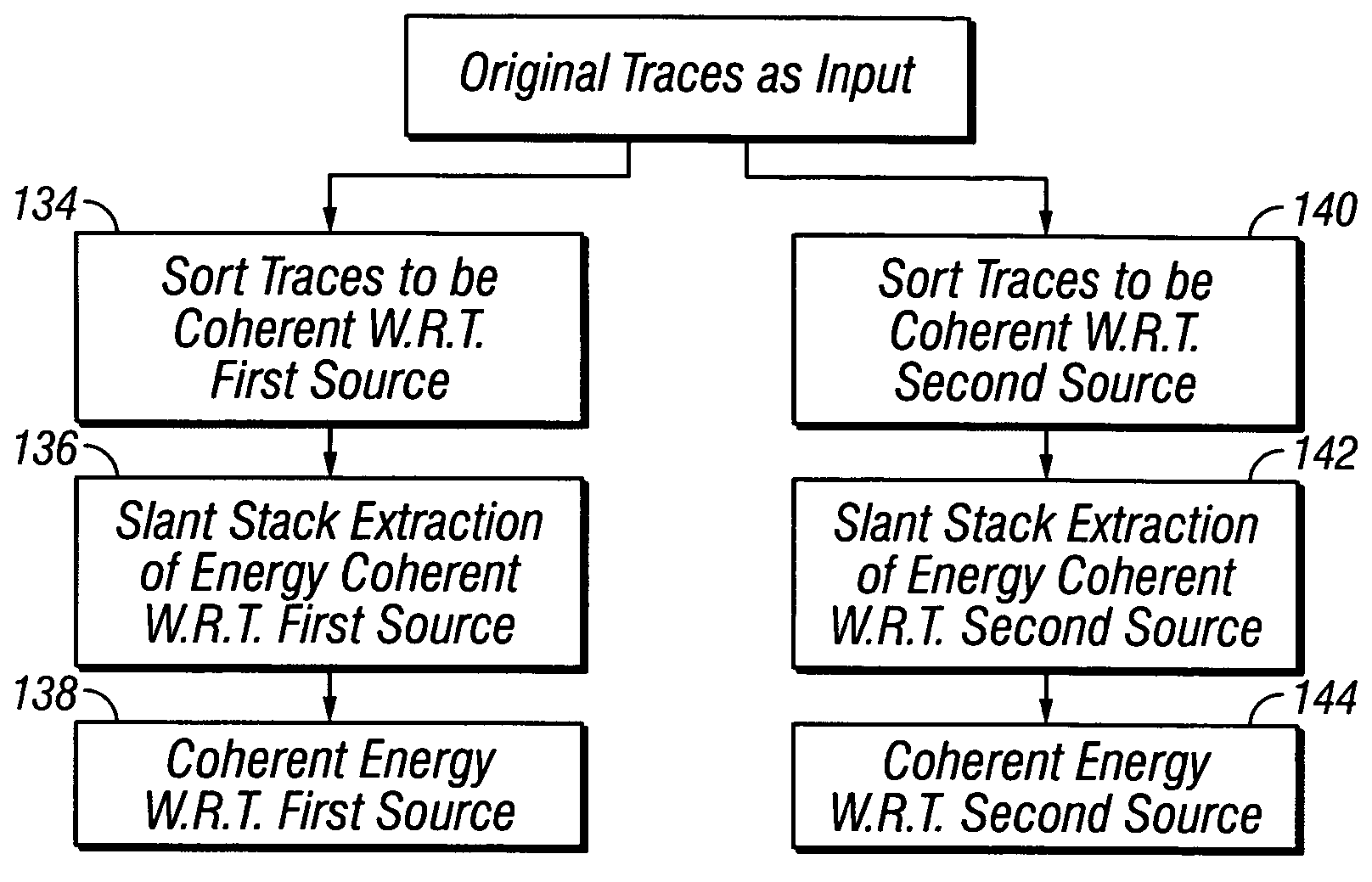
Method for separating seismic signals from two or more distinct sources
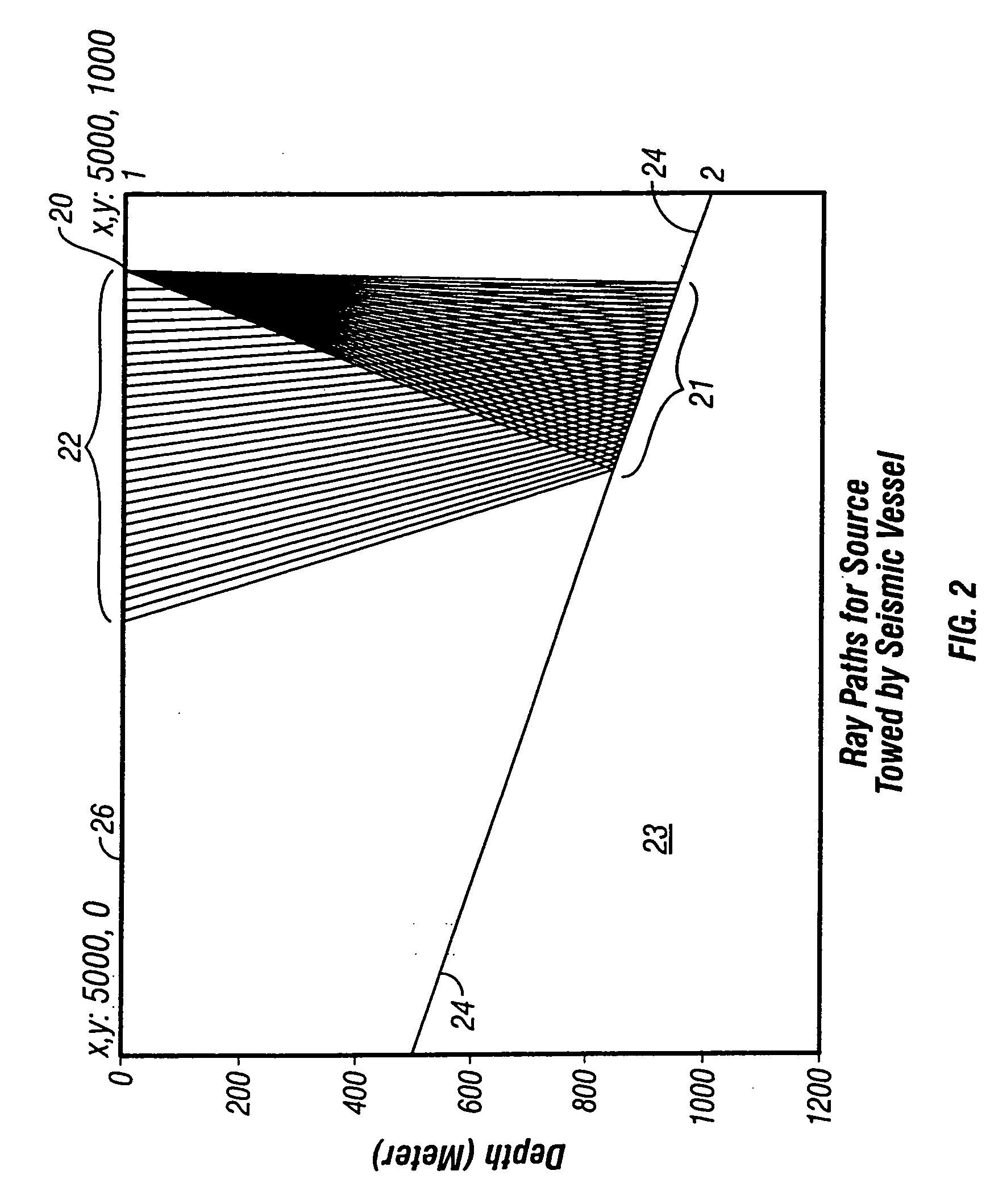
InactiveUS20050027454A1Increase effective subsurface length of coverageEasy to foldSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial directionSeismic energy
A method is disclosed for separating energy resulting from actuating at least two different seismic energy sources from seismic signals. The sources are actuated to provide a variable time delay between successive actuations of a first one and a second one of the sources. The method includes sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the first source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, coherency filtering the first source coherency sorted signals, sorting the seismic signals such that events therein resulting from actuations of the second source are substantially coherent in all spatial directions, and coherency filtering the second source coherency sorted signals.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Apparatus and associated method of symbol timing recovery using coarse and fine symbol time acquisition
ActiveUS7177376B2Reduce signal to noise ratioReduced likelihoodAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlChannel impulse responseEngineering
A receiver determines a symbol synch time for recovering data from a symbol of signal samples generated in accordance with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing. Each symbol includes a guard period which carries data repeated from a data bearing part of the symbol and pilot signal samples. The receiver compromises a pilot assisted tracker, a guard adapted filter processor and a filter controller. The controller is operable to excite the filter with the symbol signal samples to generate an output signal which provides a further representation of the channel impulse response. A symbol time adjustment estimator is operable to adjust the symbol synch time in accordance with the adjustment provided by at least one the pilot assisted tracker and the guard adapted filter processor. The pilot assisted tracker estimates the symbol synch time from a channel impulse response estimate generated from pilot signal samples.
Owner:SONY UK LTD +1
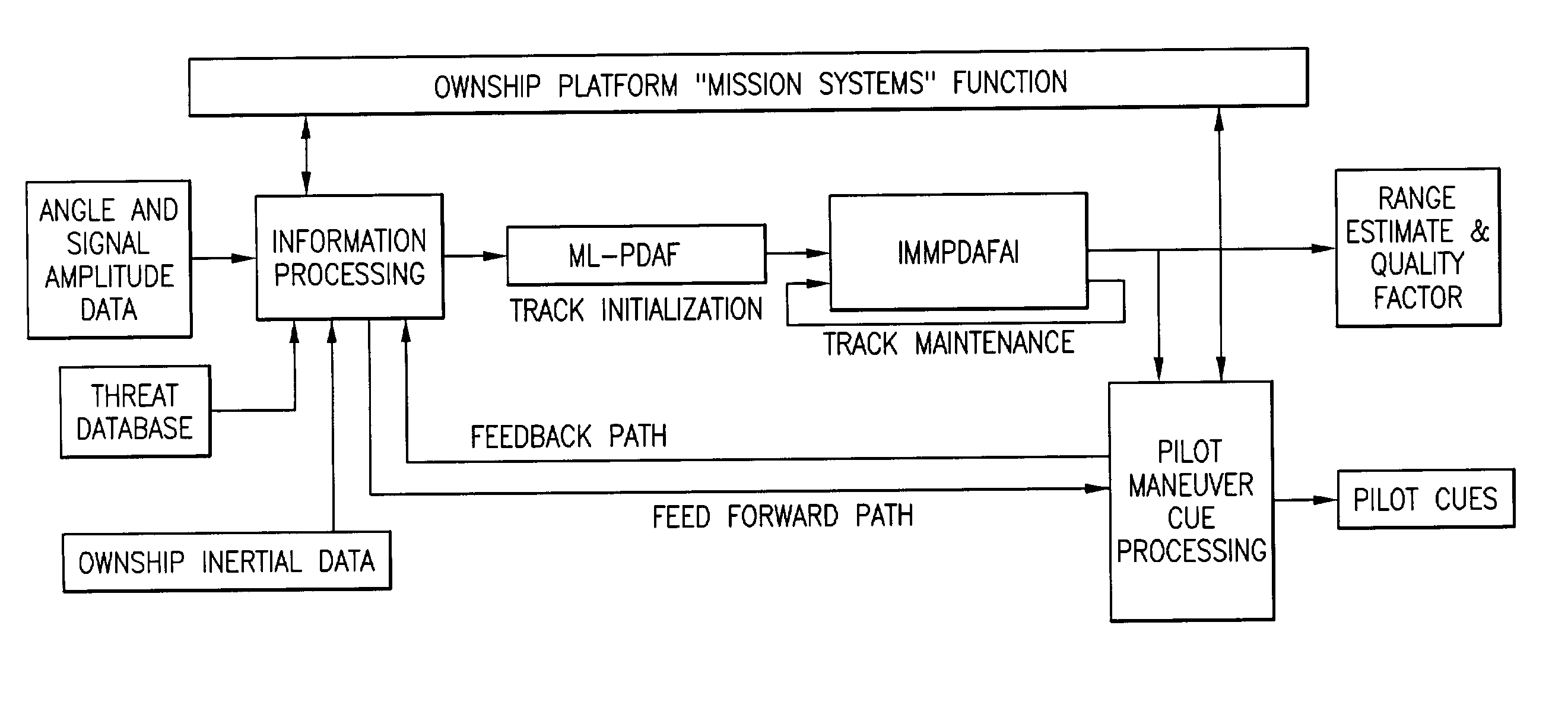
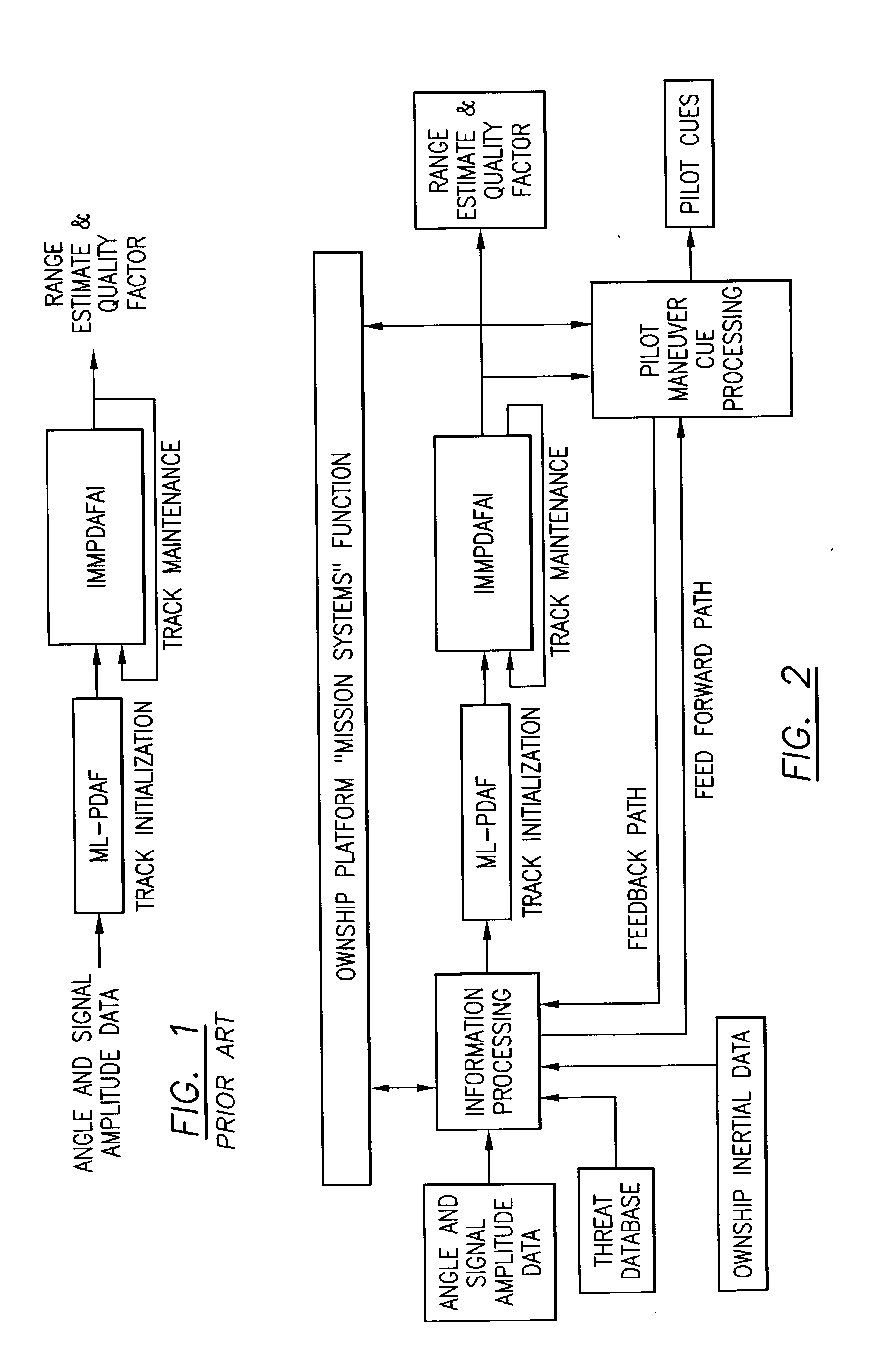
Method for passive "360-degree coverage" tactical fighter target tracking incorporating adaptive pilot maneuver cue processing
InactiveUS20040027257A1Reduce signal to noise ratioEasy to trackNavigation instrumentsAlarmsInformation processingPresent method
A method and system to rapidly, passively, estimate target range, speed and heading for non-maneuvering and maneuvering radio frequency airborne emitters (enemy targets and threats) for tactical fighters using batch based recursive estimators for track initialization and track maintenance that includes providing information processing that operates on interferometer cosine (cone angle) measurements, and estimated SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) data, threat database, and feedback information from pilot maneuver cue algorithm. The present method will initialize airborne tracks using varying degrees of real time and a priori information to quickly estimate coarse airborne emitter heading using real time interferometer cosine (cone angle) measurements and provide pilot aircraft maneuver cues that will accelerate passive range (target speed and heading estimates) convergence. The system includes pilot maneuver cue processing which computes airborne emitter (target and threat) initial heading and corresponding accuracy to determine if sufficient accuracy is available to present the pilot with the proper pilot cue.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
System and method for heterodyning an ultrasonic signal
InactiveUS6707762B1Large dynamic rangeControls are responsiveNon-metal conductorsDetection of fluid at leakage pointSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A method and apparatus for detecting leaks and mechanical faults by way of an ultrasonic device. An output from a variable gain amplifier is supplied to a pair of heterodyning circuits, i.e., a dual heterodyning circuit. At each respective heterodyning circuit, the output signal from the variable gain amplifier is multiplied by a local oscillator that is internal to each circuit. The dual heterodyning circuit is used to provide an enhanced input transducer signal for spectral analysis. This permits the capture of low level frequency components for extraction during spectral analysis. The dual heterodyning circuit of the present invention to provide the enhanced spectrum to thereby permit an easy determination of whether the resonance is mechanical or electrical becomes clear. In addition, fault frequencies are also more easily discernable. In other words, the enhanced signal output provides a lower signal to noise ratio such that the ease with which frequency components are analyzed is increased.
Owner:U E SYST
Multi-frequency synchronous modified large range high precision fast laser ranging method and apparatus
InactiveCN1825138AGood effectGuaranteed speedElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingFast measurement
The invention relates to a wide range high accuracy fast laser distance measuring method and device based on multiple frequency synchronous condenser. The multiple frequency modulating signals are taken characteristic pre-compensation weight summarizing at laser emitting unit. After compounding, the laser power is modulated to take distance measuring. Synchronous band pass filter frequency selection and phase determination method is used to taken signal process. The method could gain the distance measuring result of distance measuring frequency in multiple frequency modulating distance measuring, and gain the final distance result. The distance measuring speed and real time is ensured. It also avoids measuring error coursed by the location movement of the target.'
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fabrication and packaging of suspended microchannel detectors
InactiveUS20050064581A1Reduce signal to noise ratioHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteLight beam
An apparatus for detecting an analyte in solution that has a suspended beam containing at least one microfluidic channel containing a capture ligand that bonds to or reacts with an analyte. The apparatus also includes at least one detector for measuring a change in the beam upon binding or reaction of the analyte. A method of making the suspended microfluidic channels is disclosed, as well as, a method of integrating the microfluidic device with conventional microfluidics having larger sample fluid channels.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com