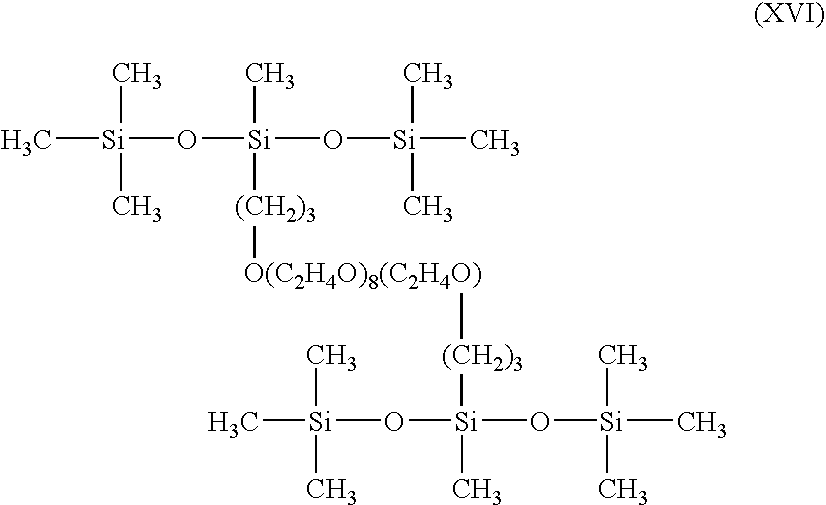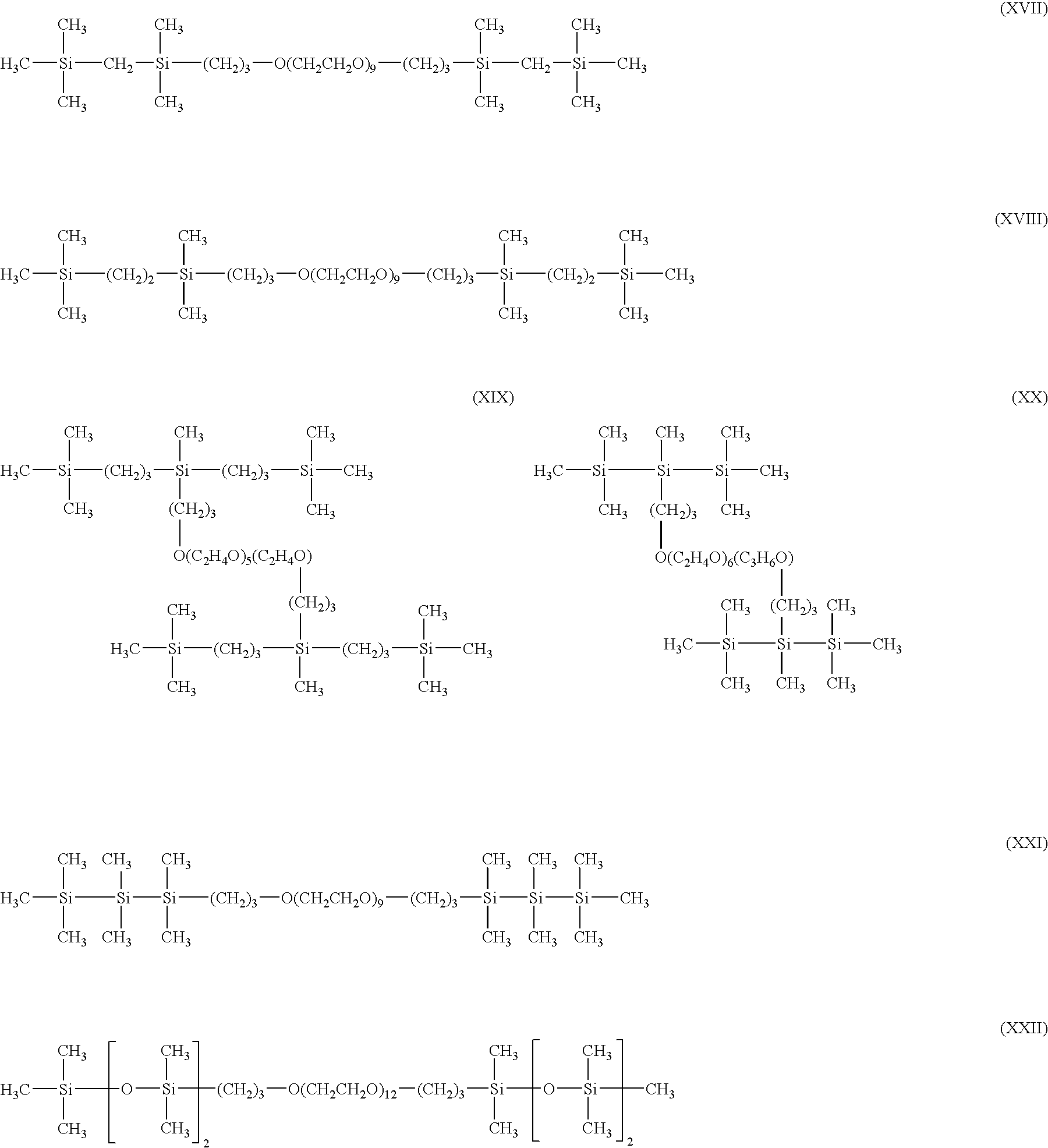Patents
Literature
362 results about "Hydrophobic moiety" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
So if we identify the meaning of hydrophilic moiety then this means that moiety which is soluble in water or which has a very strong affinity for water. Hydrophilic moiety or substance or part of a molecule are water loving. They get dissolved in water where as hydrophobic molecules are water fearing, they do not dissolve in water.
Water soluble metal and semiconductor nanoparticle complexes
The invention provides a water soluble complex comprising an inner core of a metal or semi-conductor nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is coated with a hydrophobic ligand, which is encapsulated in a micelle. In an aqueous medium, the micelle comprises a hydrophilic shell and a hydrophobic core, the hydrophilic shell comprising a plurality of hydrophilic moieties, the hydrophobic core comprising a plurality of hydrophobic moieties, each hydrophobic moiety comprising at least one chain, each chain comprising a minimum of 8 atoms; wherein the total number of atoms in all chains for each moiety comprises at least 24 atoms. The micelle has a minimum average diameter of approximately 5 nm and a maximum average diameter of approximately 45 nm.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
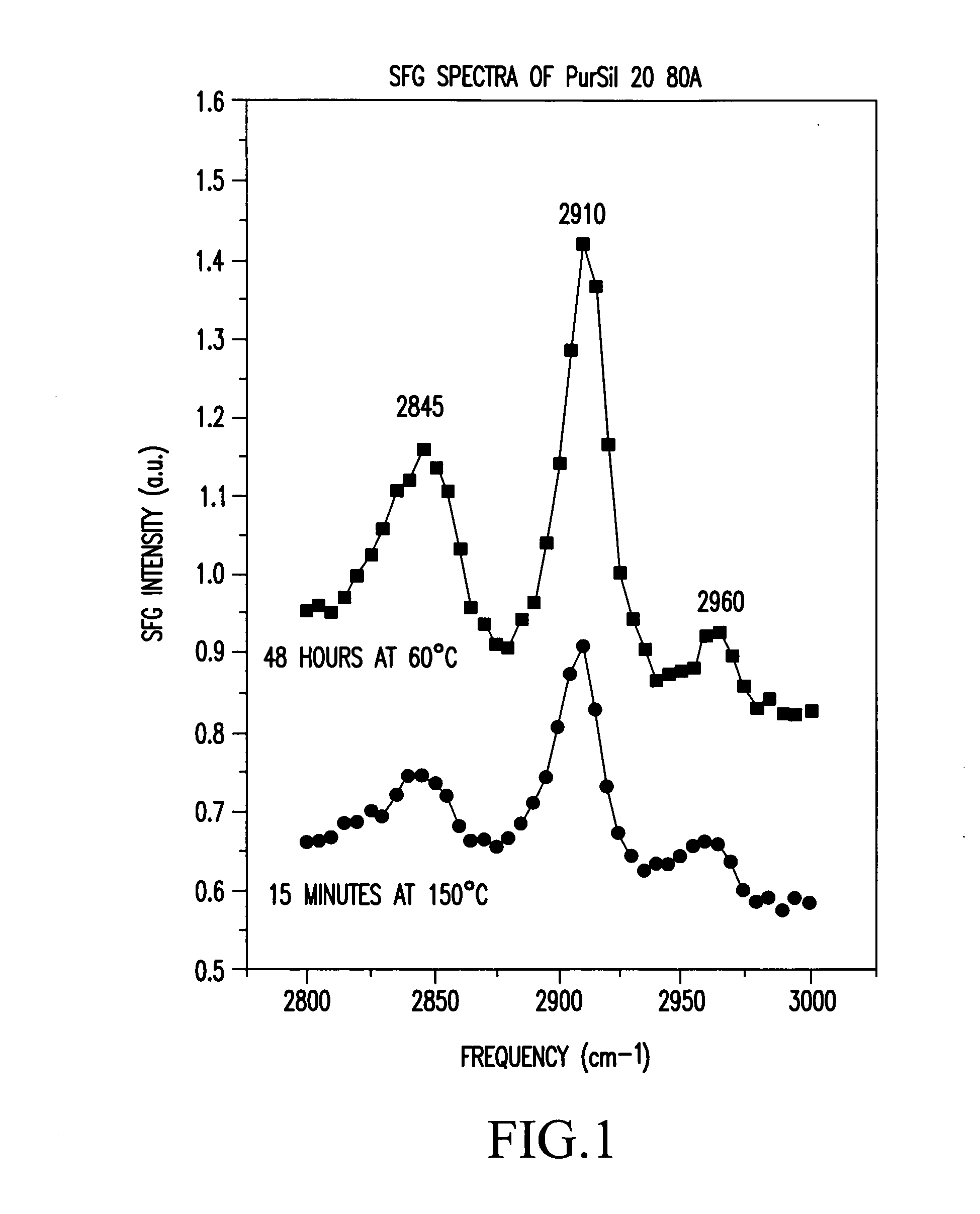
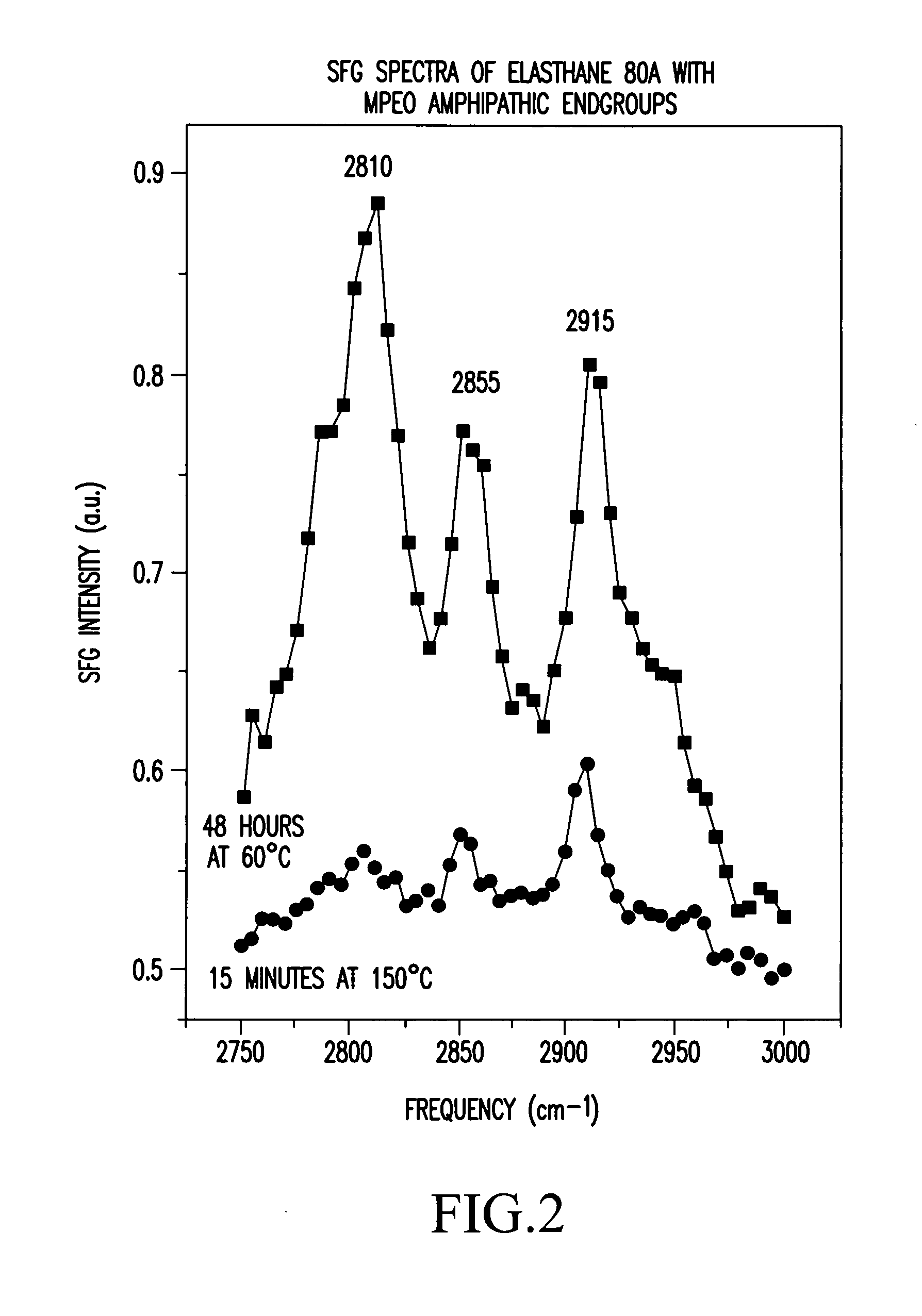
Control of polymer surface molecular architecture via amphipathic endgroups
ActiveUS20050282997A1Promote resultsReduce signal to noise ratioSurgeryCatheterPolymeric surfacePolyethylene oxide
Polymers whose surfaces are modified by endgroups that include amphipathic surface-modifying moieties. An amphipathic endgroup of a polymer molecule is an endgroup that contains at least two moieties of significantly differing composition, such that the amphipathic endgroup spontaneously rearranges its positioning in a polymer body to position the moiety on the surface of the body, depending upon the composition of the medium with which the body is in contact, when that re-positioning causes a reduction in interfacial energy. An example of an amphipathic surface-modifying endgroup is one that has both a hydrophobic moiety and a hydrophilic moiety in a single endgroup. For instance, a hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) terminated with a hydrophilic hydroxyl group is not surface active in air when the surface-modifying endgroup is bonded to a more hydrophobic base polymer. If the hydroxyl group on the oligomeric poly(ethylene oxide) is replaced by a hydrophobic methoxy ether terminus, the poly(ethylene oxide) becomes surface active in air, and allows the poly(ethylene oxide) groups to crystallize in the air-facing surface. In this example, immersion in water destroys the crystallinity as the poly(ethylene oxide) sorbs water and the hydrophobic methoxy group retreats below the surface of the polymer. Also disclosed are methods and articles of manufacture that make use of these polymers.
Owner:THE POLYMER TECH GROUP
Composition for long-acting peptide analogs
ActiveUS20090088387A1Increase perfusionImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeArginine
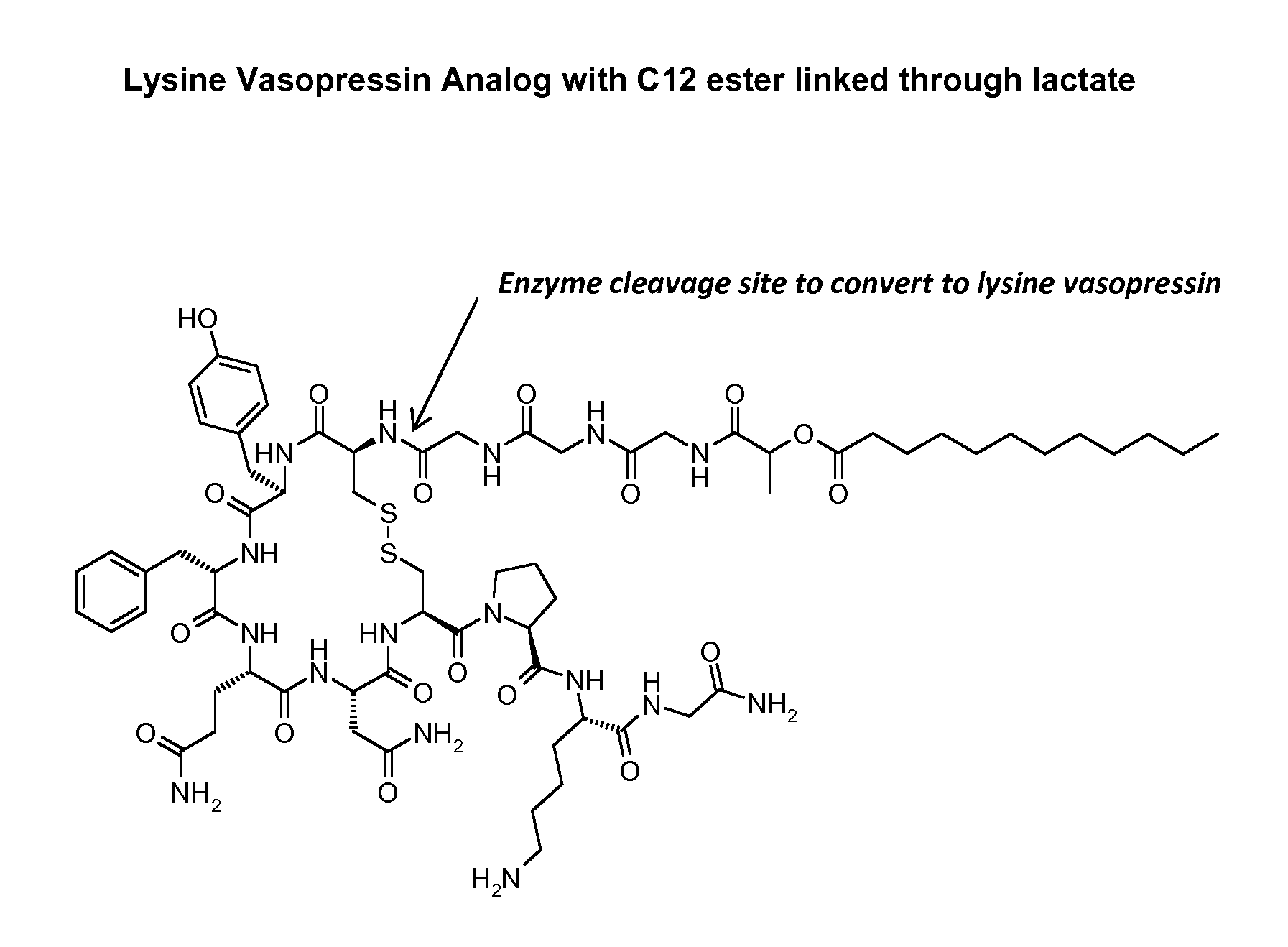
The invention describes compositions of peptide analogs that are active in blood or cleavable in blood to release an active peptide. The peptide analogs have a general formula: A-(Cm)x-Peptide, wherein A is hydrophobic moiety or a metal binding moiety, e.g., a chemical group or moiety containing 1) an alkyl group having 6 to 36 carbon units, 2) a nitrilotriacetic acid group, 3) an imidodiacetic acid group, or 4) a moiety of formula (ZyHisw)p, wherein Z is any amino acid residue other than histidine, His is histidine, y is an integer from 0-6; w is an integer from 1-6; and p is an integer from 1-6; wherein if A has alkyl group with 6 to 36 carbon units x is greater than 0; and Cm is a cleavable moiety consisting of glycine or alanine or lysine or arginine or N-Arginine or N-lysine, wherein x is an integer between 0-6 and N may be any amino acid or none. The peptide analogs are complexed with polymeric carrier to provide enhanced half-life.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
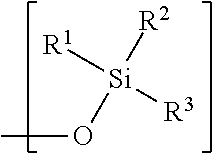
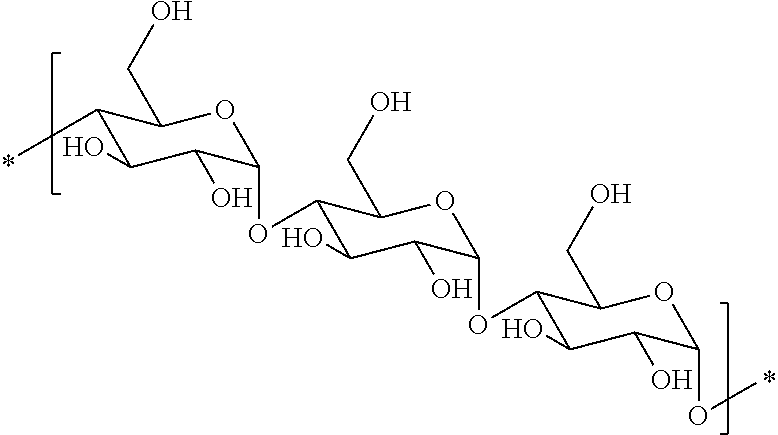
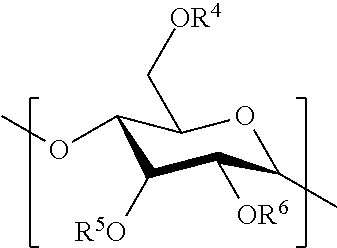
Hydrophobic polysaccharides with silyl ether linkages having enhanced degradation and medical articles made therefrom
ActiveUS8932616B2Improve degradation rateOvercome difficultiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceActive agent
Hydrophobic α(1→4)glucopyranose polymers with enhanced degradation properties are described. Between the α(1→4)glucopyranose polymeric portion and the hydrophobic portion exists a linker portion having a silyl ether chemistry that facilitates degradation of the polymer. Biodegradable matrices can be formed from these polymers, and the matrices can be used for the preparation of implantable and injectable medical devices wherein the matrix is capable of degrading in vivo at an increased rate. Matrices including and capable of releasing a bioactive agent in vivo are also described.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Polymeric micelles for polynucleotide encapsulation
InactiveUS8287910B2Enhance endolysosomal escapePrevent degradationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePolynucleotide
The present invention provides micelles having a polynucleotide encapsulated therein, the micelle comprising copolymers comprising hydrophobic moieties in a cationic complexing block. The invention further provides methods of preparing and using said micelles, and compositions thereof.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC
Water soluble metal and semiconductor nanoparticle complexes
The invention provides a water soluble complex comprising an inner core of a metal or semi-conductor nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is coated with a hydrophobic ligand, which is encapsulated in a micelle. In an aqueous medium, the micelle comprises a hydrophilic shell and a hydrophobic core, the hydrophilic shell comprising a plurality of hydrophilic moieties, the hydrophobic core comprising a plurality of hydrophobic moieties, each hydrophobic moiety comprising at least one chain, each chain comprising a minimum of 8 atoms; wherein the total number of atoms in all chains for each moiety comprises at least 24 atoms. The micelle has a minimum average diameter of approximately 5 nm and a maximum average diameter of approximately 45 nm.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Biosensor
InactiveUS20050175509A1Eliminate measurement errorsHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCompound (substance)Organic compound
The present invention relates to a biosensor which comprises an electrode system including at least one pair of electrodes, at least one insulating base plate for supporting the electrode system, a first reaction layer provided at least on a working electrode of the electrode system, including an organic compound having a functional group capable of bonding or being adsorbed to an electrode and a hydrophobic hydrocarbon group, a second reaction layer provided on the first reaction layer, including an amphiphilic lipid capable of bonding or being adsorbed to a hydrophobic portion of the first reaction layer, and a reagent system carried in a two-component membrane composed of the first and second reaction layers, including at least membrane-binding type pyrroquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase and an electron mediator.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Reversibly switchable surfactants and methods of use thereof
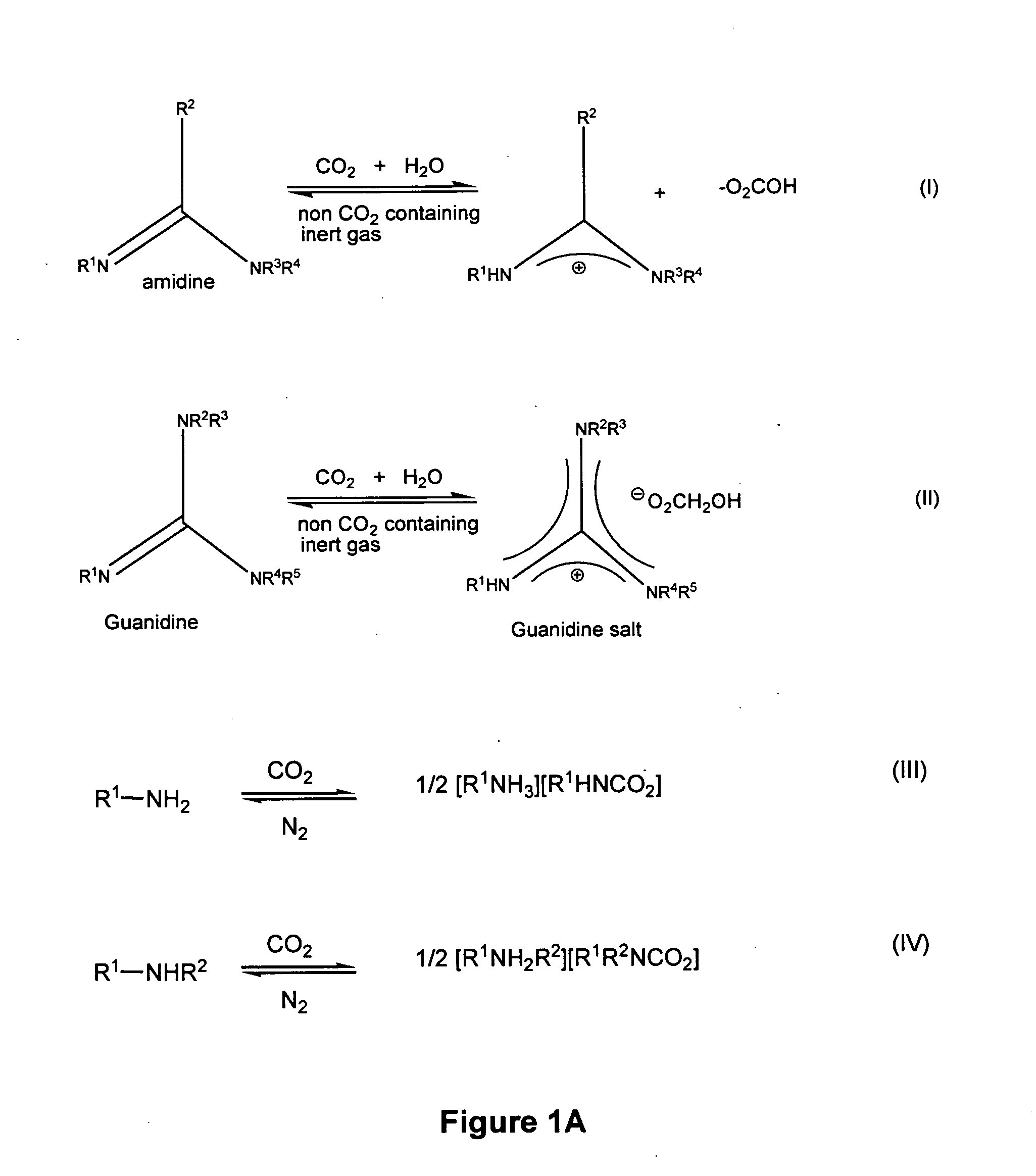
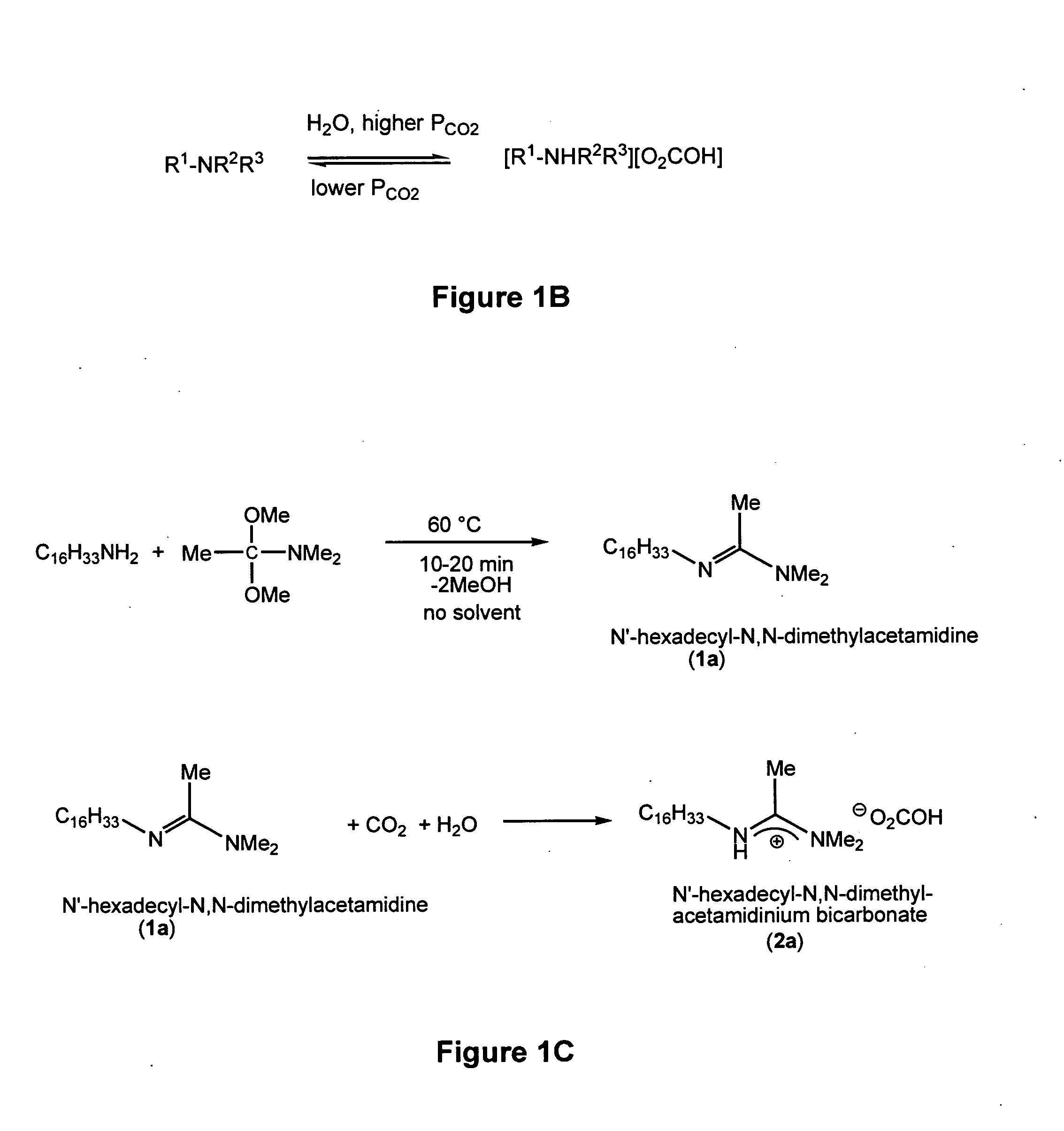
Reversible switchable surfactants are provided. A surfactant is the salt of an amidine or guanidine having at least one R group that is a hydrophobic moiety selected from the group consisting of higher aliphatic moiety, higher siloxyl moiety, higher aliphatic / siloxyl moiety, aliphatic / aryl moiety, siloxyl / aryl moiety, and aliphatic / siloxyl / aryl moiety. The other R groups are smaller moieties such as H, C1 to C4 aliphatic or the like. The surfactant is turned on by a gas that liberates hydrogen ions, such as, for example, carbon dioxide, which liberates hydrogen ions in the presence of water. The surfactant is turned off by exposure to a flushing gas and / or heating. When “on” the surfactants are useful to stabilize emulsions, and when “off” they are useful to separate immiscible liquids or a liquid and a solid. The surfactants find uses in polymerization and in the oil industry.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Sustained-Release Lipid Pre-Concentrate of Pharmacologically Active Substance And Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising The Same
ActiveUS20140206616A1Patient compliance is goodGood sustained releaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationSaturated fatty acid ester
Disclosed is a sustained release lipid pre-concentrate, comprising: a) a sorbitan unsaturated fatty acid ester having a polar head with at least two or more —OH (hydroxyl) groups; b) a phospholipid; and c) a liquid crystal hardener, free of an ionizable group, having a hydrophobic moiety of 15 to 40 carbon atoms with a triacyl group or a carbon ring structure. The lipid pre-concentrate exists as a liquid phase in the absence of aqueous fluid and forms into a liquid crystal in the presence of aqueous fluid. Also, a pharmaceutical composition further comprising a pharmacologically active ingredient plus the pre-concentrate is provided.
Owner:CHONG KUN DANG PHARMA CORP
Ink composition
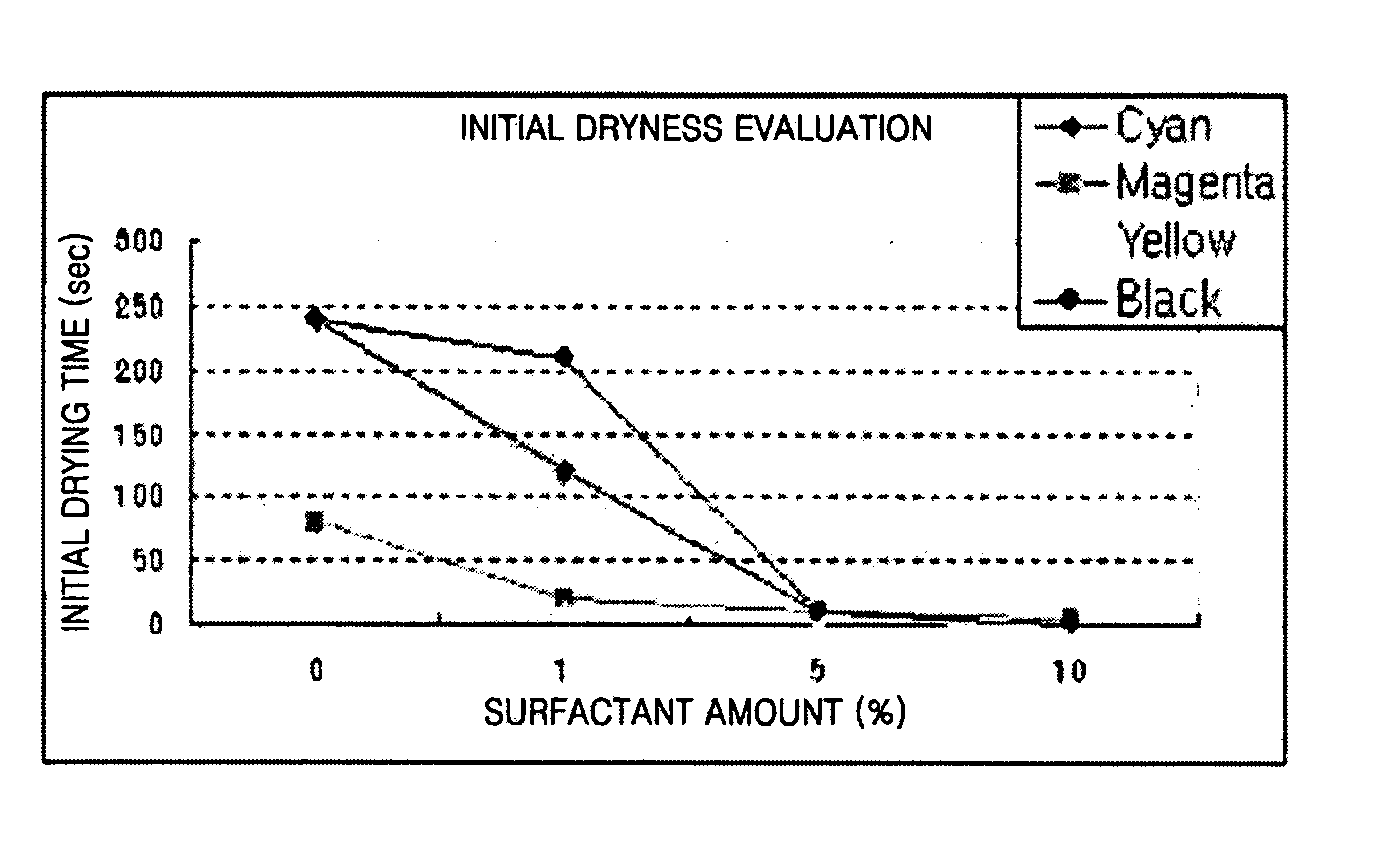
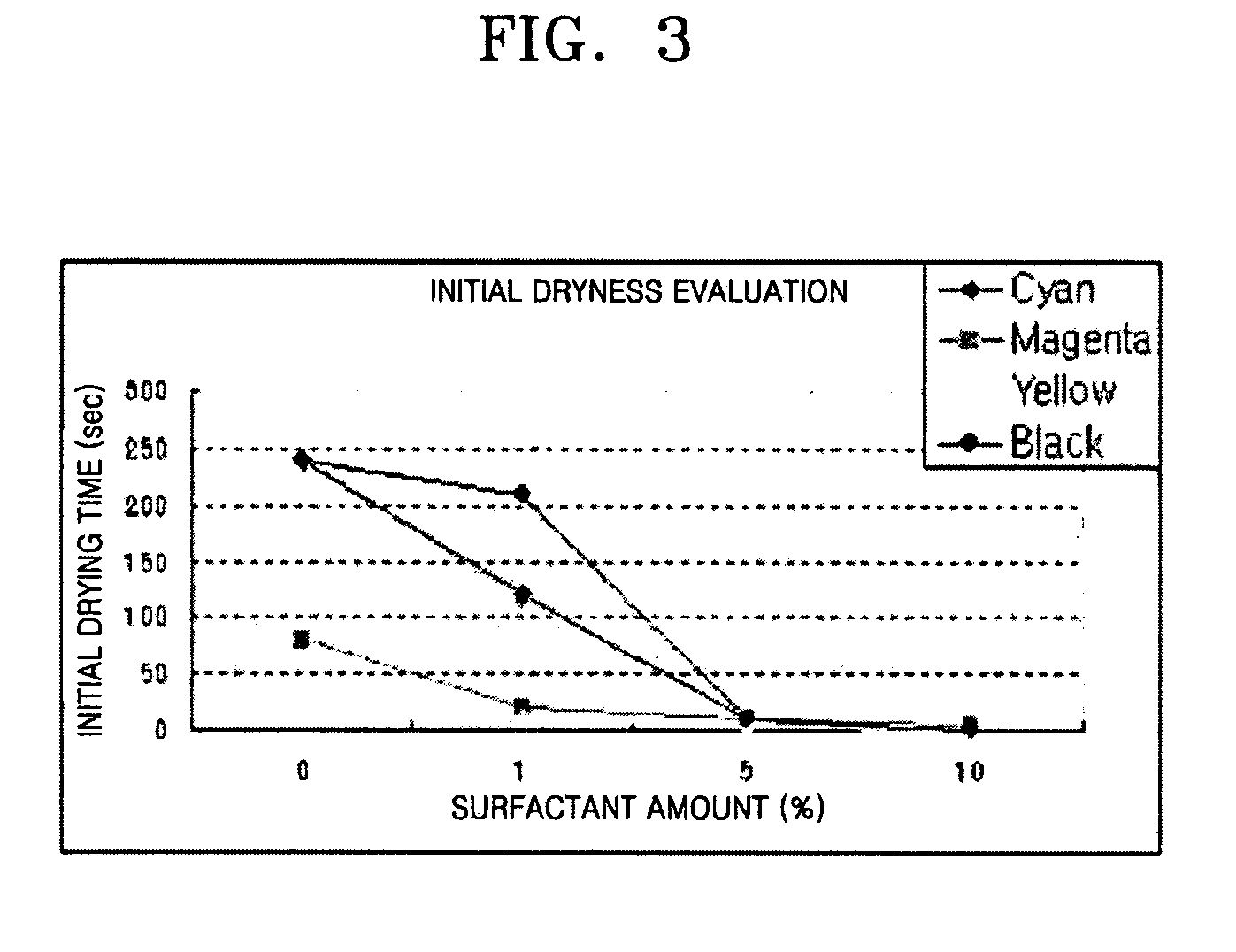
An ink composition including a colorant, a solvent, and a surface property treatment agent represented by the following formula (1): where each of Y1, Y2, and Y3 is independently —N(R3)- or —O—. R3 is H, a C1-C20 alkyl group, or a C6-C20 aryl group, each of R1 and R2 is independently a chemical bond, a C1-C10 alkylene group, a C2-C10 alkenylene group, a C2-C10 alkynylene group, or a C1-C20 alkyl group including a C2-C10 alkenylene group or a C2-C10 alkynylene group, 1≦a≦7, and b, c≧0 are integers, each of A and B is a hydrophobic moiety or are connected to each other to form a ring, A and B cannot simultaneously be H, and B can be a hetero atom. The ink composition can reduce smearing by increasing the rate of penetration into paper and may increase a duration of storage stability, while using little or no surfactant.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
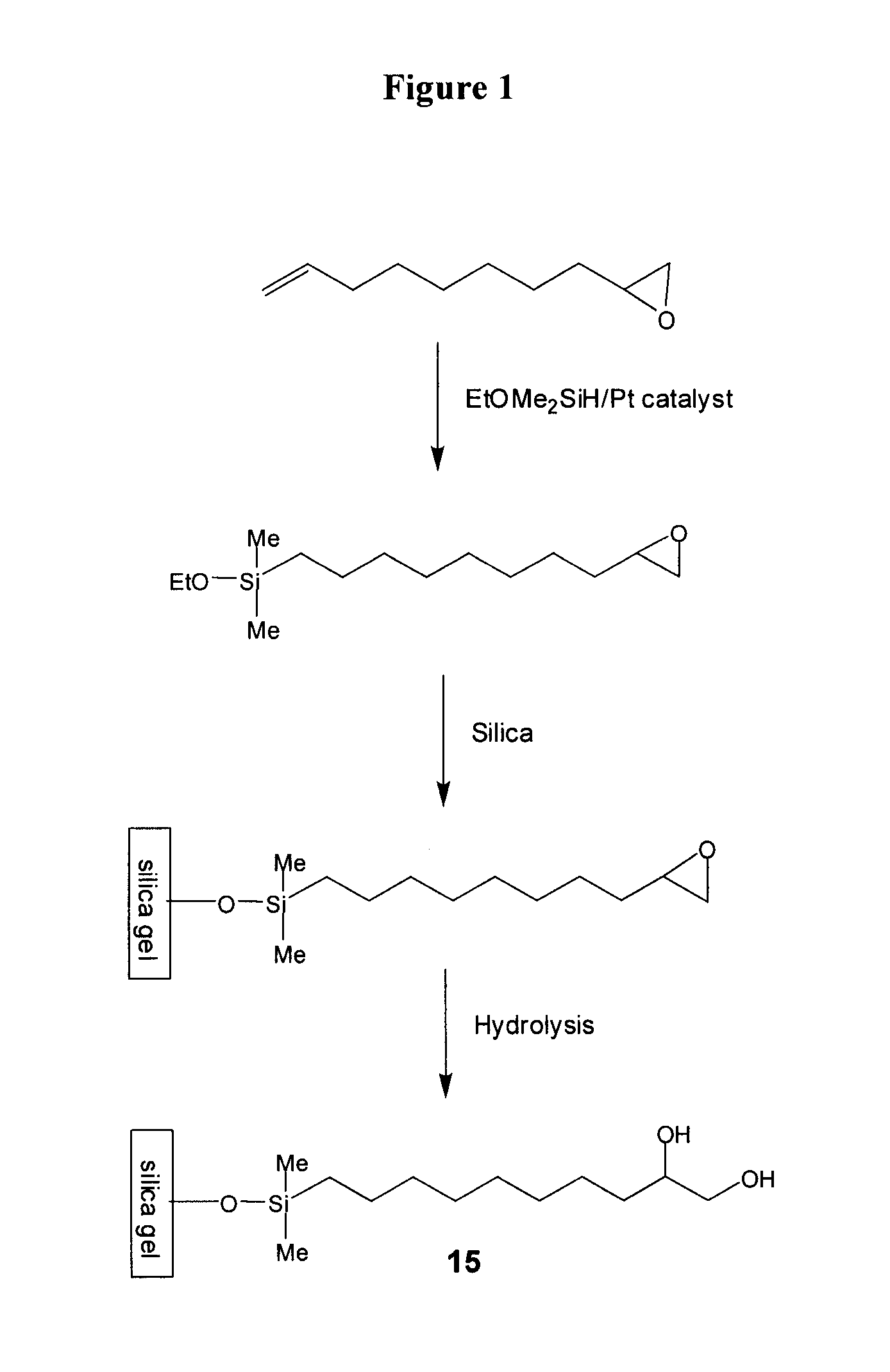
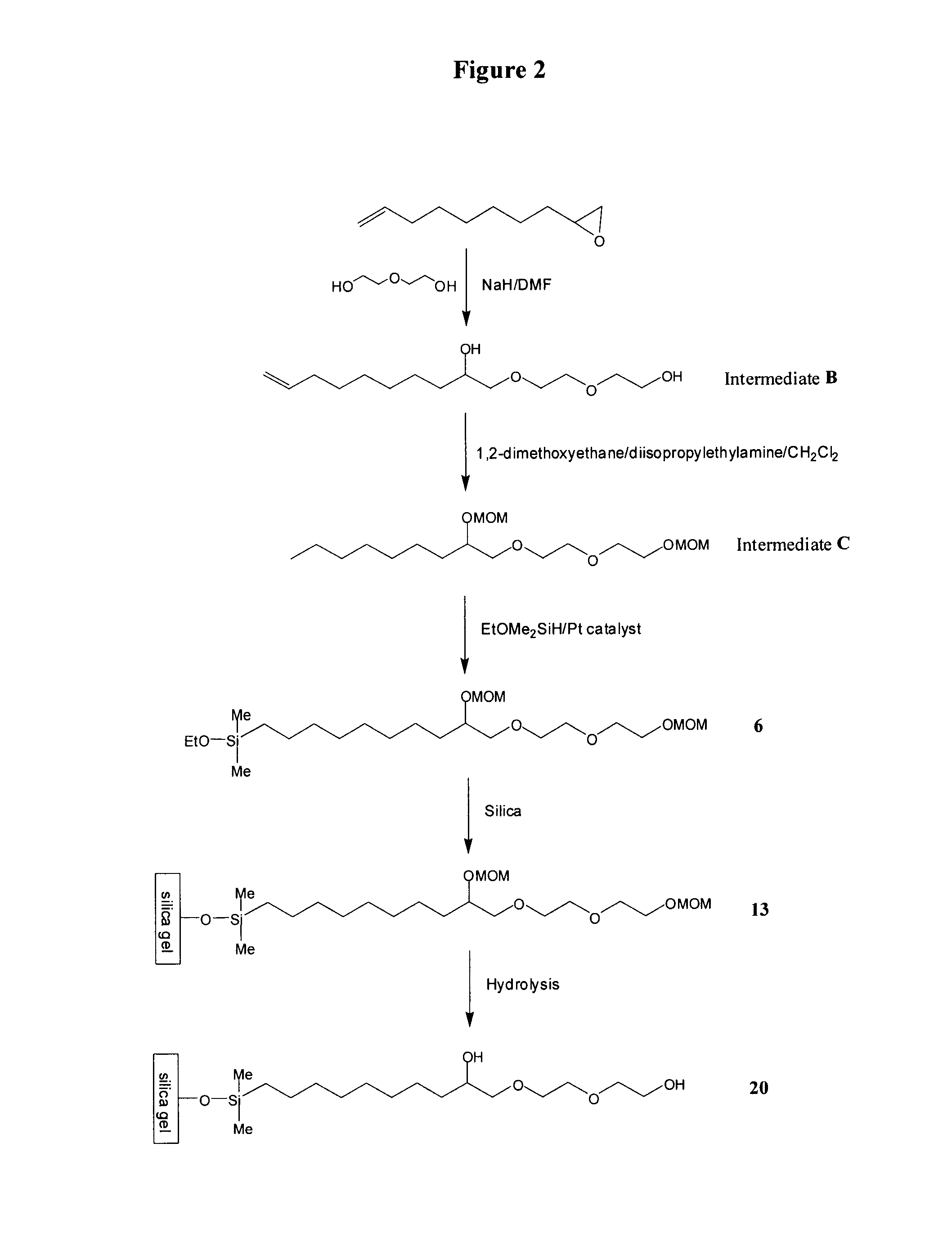
Compositions useful as chromatography stationary phases
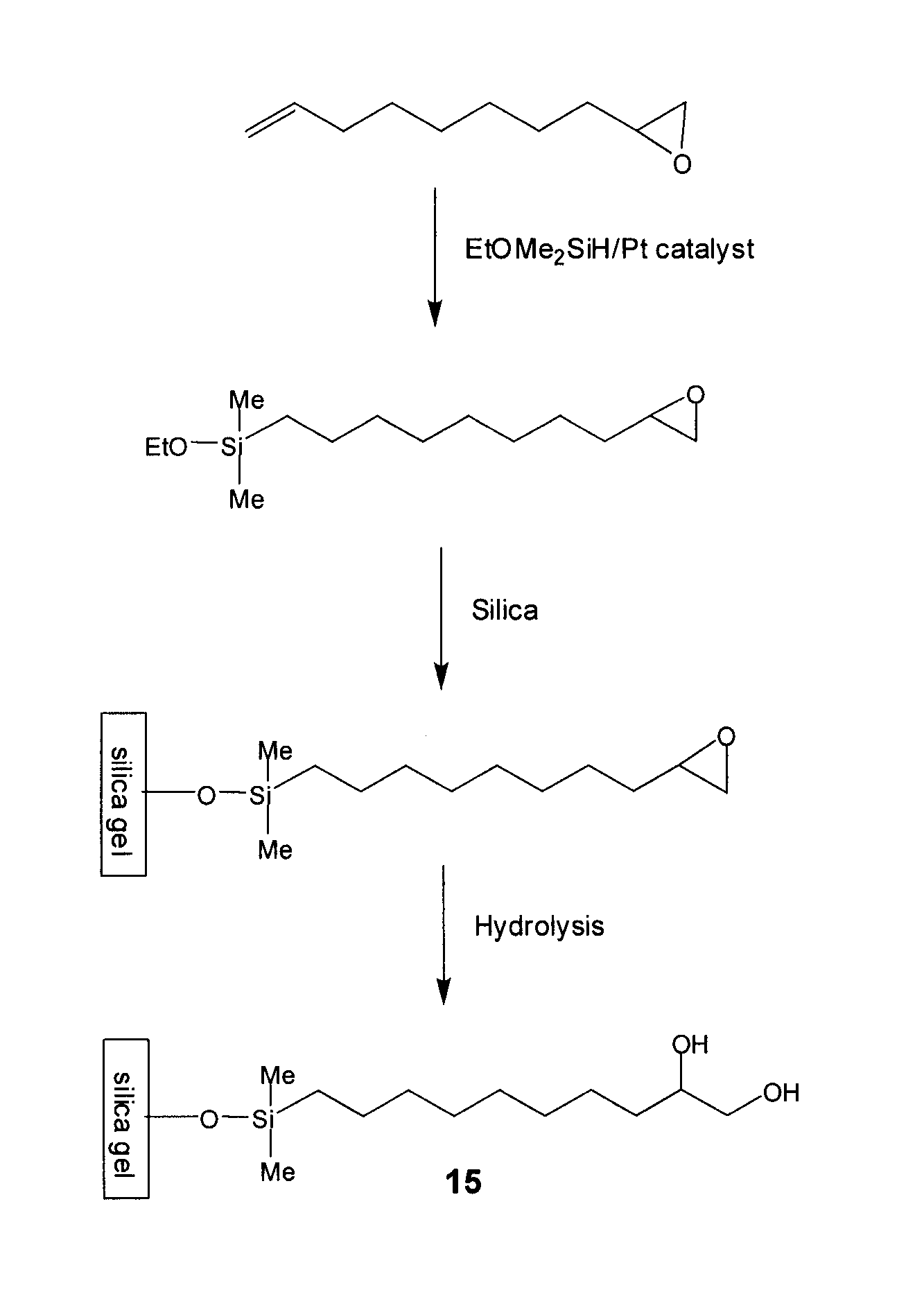
The current invention provides compositions, which are useful as stationary phases for a variety of chromatographic applications, such as high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The compositions include a substrate (e.g., silica gel), covalently bound to a compound, which includes both a hydrophobic moiety and a hydrophilic moiety, which is preferably a 1,2-diol moiety. The hydrophobic moiety is sufficiently hydrophobic for the compositions to exhibit reversed phase characteristics and typically incorporates at least 5 carbon atoms in sequence. Based on having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic functionalities, the new stationary phases exhibit unique chromatographic properties. For example, these media can be used in either hydrophilic (HILIC) mode, in which the mobile phase includes a high percentage of an organic solvent, or in reversed phase mode, in which the mobile phase contains a higher percentage of an aqueous solvent. The current invention also provides methods of making and using the compounds and compositions of the invention.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Surfactant compositions and associated method
InactiveUS20070135329A1Cosmetic preparationsOrganic detergent compounding agentsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTActive ingredient
A composition having a first hydrophobic moiety linked to a spacer, which is linked to a second hydrophobic moiety to form a Gemini surfactant is provided. Each hydrophobic moiety of the foregoing composition may include silicon. A method for linking a first hydrophobic moiety to a second hydrophobic moiety using a spacer to form a Gemini surfactant is provided. A pesticide having an active ingredient and a composition having a first hydrophobic moiety linked to a spacer, which is linked to a second hydrophobic moiety to form a Gemini surfactant is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Self-assembly of organic-inorganic nanocomposite thin films for use in hybrid organic light emitting devices (HLED)
InactiveUS20050019602A1Improve light emission efficiencySuperior device lifetimeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid crystallineElectronic transmission
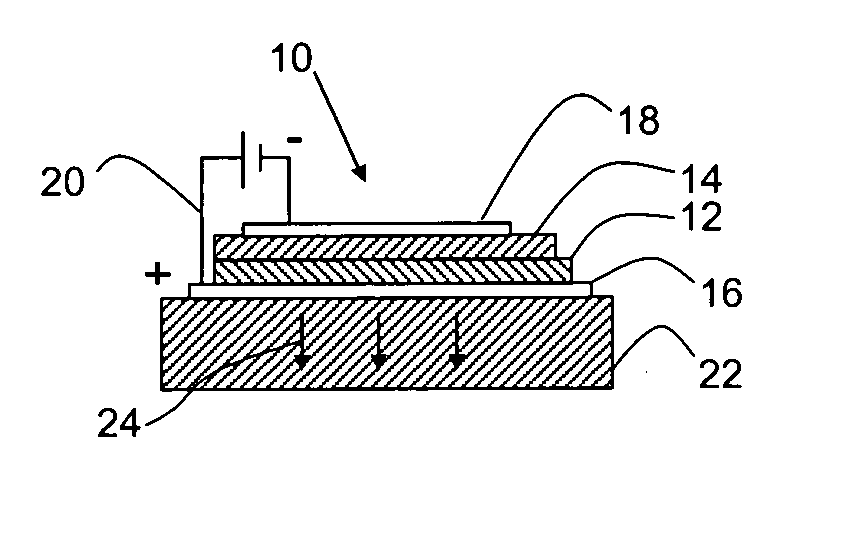
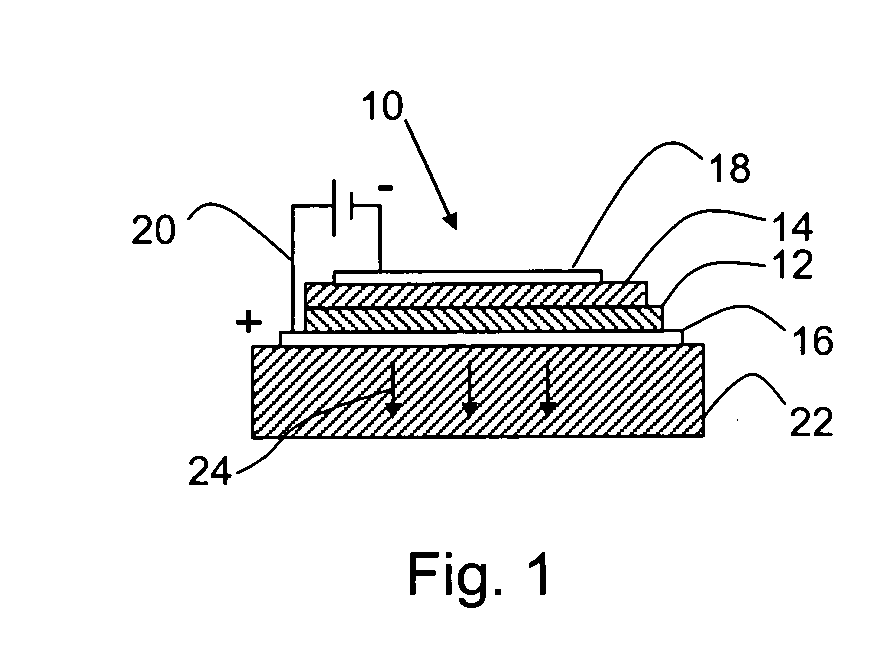
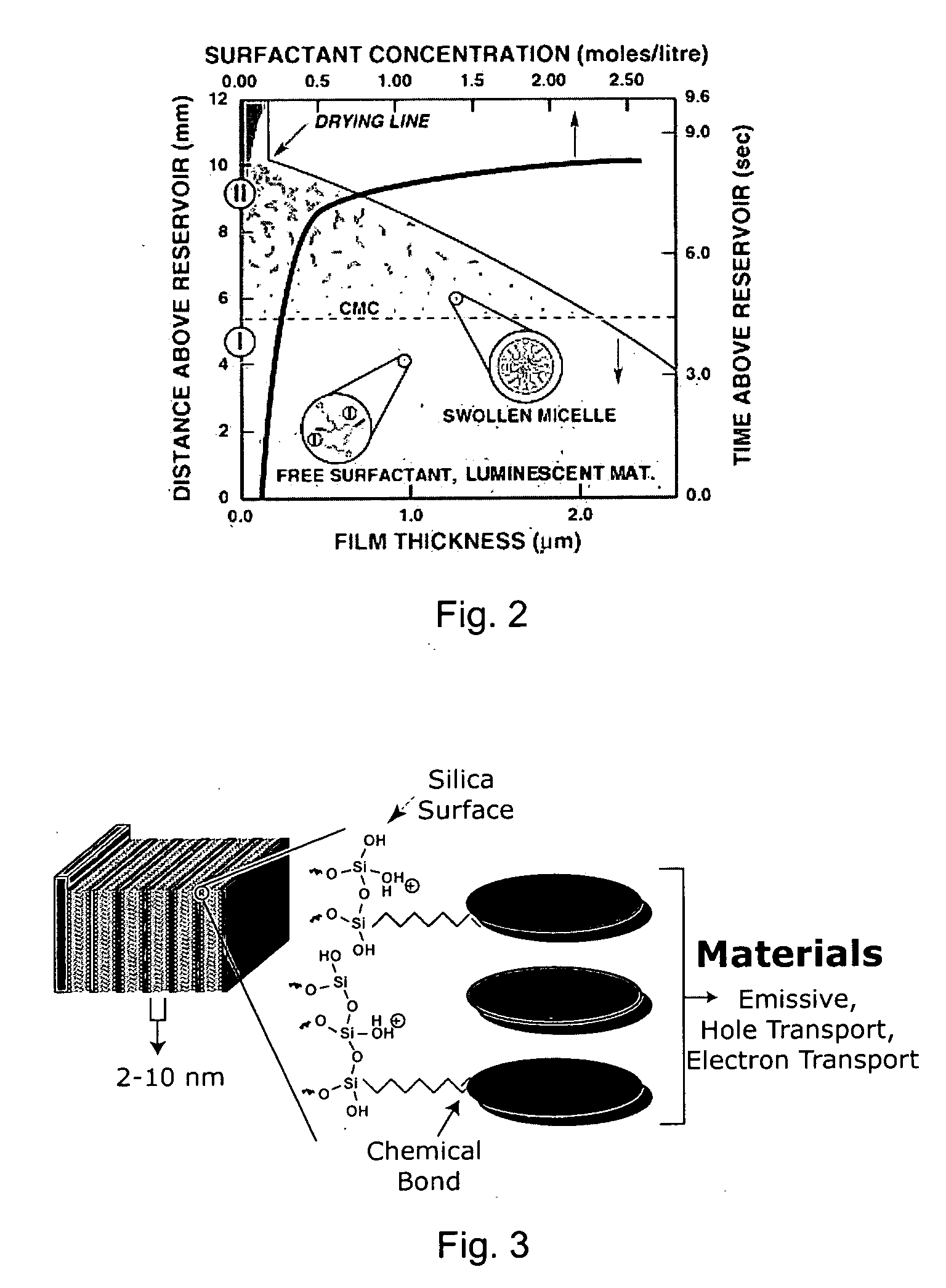
A self-assembly process for preparing luminescent organic-inorganic nanocomposite thin films is disclosed. A homogeneous solution in water and an organic solvent is obtained containing a soluble silicate, a silica coupling agent, a surfactant, and an organic material having a hole transport, electron transport, and / or emissive material moiety. The silica coupling agent is selected to chemically react with the organic material. A film of the homogeneous solution is deposited onto a substrate. Preferentially evaporating the organic solvent enriches the concentration of water and non-volatile solution components to promote micelle formation. Organic materials migrate into the hydrophobic portion of the forming micelles. Continued evaporation promotes self-assembly of the micelles into interfacially organized liquid crystalline mesophases. Reacting the organic material and silica coupling forms a nanostructure self-assembly. Luminescent ordered nanocomposite structures prepared by the process, and organic-inorganic HLED devices fabricated from the luminescent organic-inorganic nanocomposite structures are disclosed.
Owner:CANON KK
Lipids and lipid assemblies comprising transfection enhancer elements
ActiveUS20080306153A1Promote absorptionImprove fusion effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideLipid formationLiposome
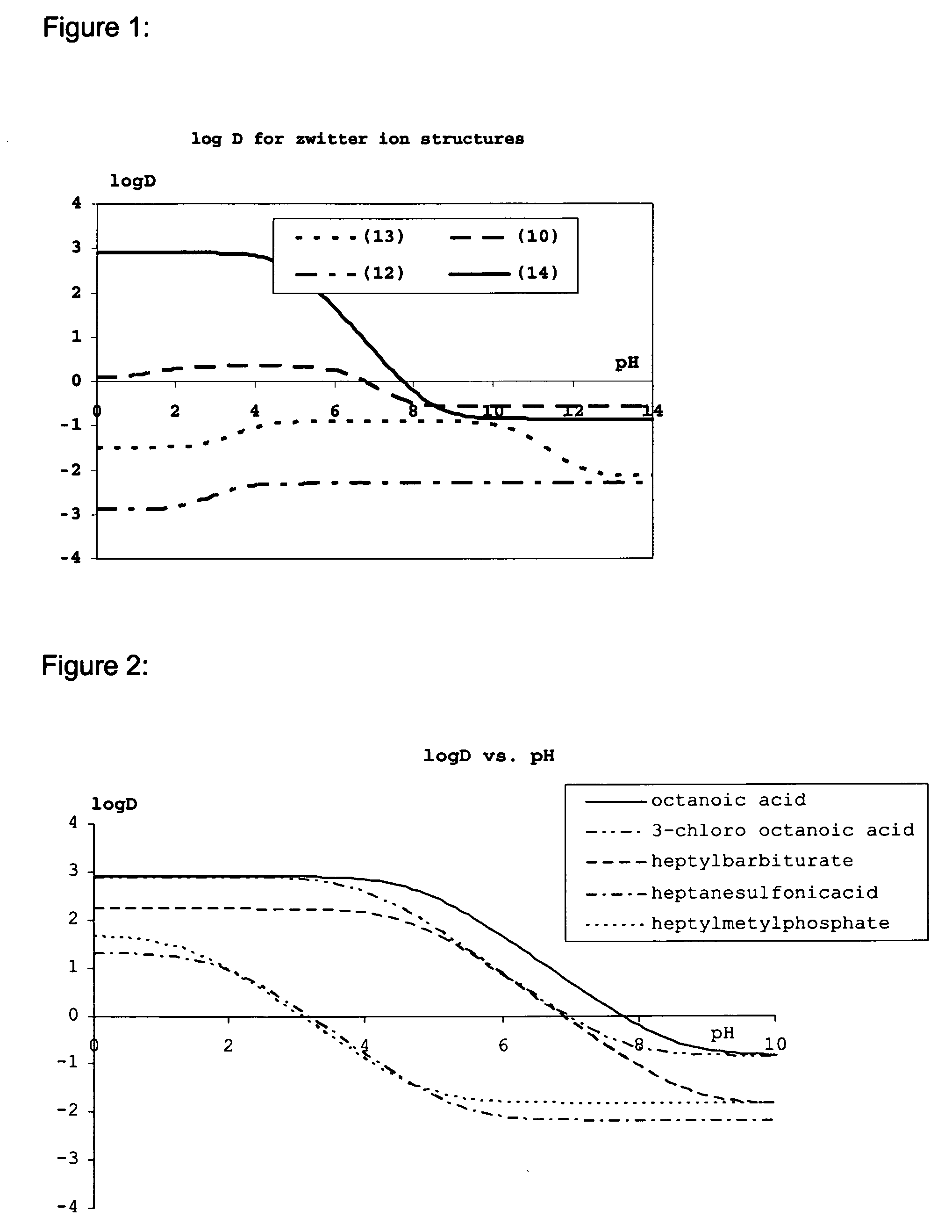
Lipid assemblies, such as liposomes, comprising transfection enhancer elements (TEE's), which are complexed with the lipid assemblies by means of ionic interactions, or lipids incorporating such TEE's are disclosed for enhancing the fusogenicity of the lipid assemblies. The TEE's have the formula:hydrophobic moiety-pH sensitive hydrophilic moiety (II)The pH sensitive hydrophilic moiety of each TEE is a weak acid having a pka of between 2 and 6 or a zwitterionic structure comprising a combination of acidic groups with weak bases having a pKa of between 3 and 8. Lipids incorporating one or more such TEEs have the formula (I):Lipid moiety-[Hydrophobic moiety-pH sensitive hydrophilic moiety] (I)
Owner:BIONTECH DELIVERY TECH GMBH
Surfactant-based composition and associated methods
Provided are a pesticide, a coating formulation, a cosmetic, a cleaner, and a foamable fire-fighting composition, which may include a Gemini surfactant. The Gemini surfactant may include a first hydrophobic moiety linked to a spacer, which is linked to a second hydrophobic moiety. Each hydrophobic moiety may include silicon. A method is provided that may include linking a first hydrophobic moiety to a second hydrophobic moiety using a spacer to form a Gemini surfactant, and each hydrophobic moiety may include silicon. Water may be added to the Gemini surfactant to form an aqueous mixture. The method may include one or more of applying the aqueous mixture to an agricultural field, cleaning a soiled article using the aqueous mixture, or extinguishing a fire using the aqueous mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Particulate Constructs For Release of Active Agents
InactiveUS20080299205A1Increase load capacityLow toxicityCosmetic preparationsBiocideParticulatesActive agent
Particulate constructs stabilized by amphiphilic copolymers and comprising at least one active coupled to a hydrophobic moiety provide sustained release of the active in both in vitro and in vivo environments.
Owner:CELATOR PHARMA INC +1
Mixed-Modal Anion-Exchanged Type Separation Material
ActiveUS20080164211A1Improve performanceImprove productivityIon-exchanger regenerationChromatographic anion exchangersHybrid typeBinding site
The present invention relates to mixed-modal anion-exchange materials composed of a support on which a ligand is immobilized. The ligand combines at least one basic domain based on cyclic monobasic derivatives with two or more rings as anion-exchange domain and at least one non-ionic binding domain. The basic domain is ionized under the conditions of use and may contain secondary, tertiary, or quaternary nitrogen forming a weakly (WAX) or strongly (SAX) basic anionic exchange domains. The non-ionic binding domain allows adjustment of the overall hydrophobicity / hydrophilicity of the material and represents a second binding site for the solute to be separated. Binding to this second binding site is based on reversed phase (RP), hydrophobic interaction (HIC) or hydrophilic interaction (HILIC). Linker sites, which can be represented by a chemical bond or by hydrophobic moieties like alkyl(ene) chains or hydrophilic moieties like amide structures connect the support to the binding domains and the binding domains to each other.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Hydrophobically midified saccharide surfactants
InactiveUS20040248761A1Cosmetic preparationsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsHigh concentrationFructan
The invention relates to the use as surfactant, for the preparation of dispersions of multiphase systems that comprise a continuous aqueous phase containing a high concentration of electrolytes, of hydrophobically modified saccharides of general formula (I) and (II) [A]n(-M)s (I) [B]m(-M)s'(II) wherein [A]n represents a fructan-type saccharide [B]m represents a starch-type saccharide (-M) represents a hydrophobic moiety that substitutes a hydrogen atom of a hydroxyl group of the fructosyl and / or glucosyl units of the fructan-type and starch-type saccharides, which is selected from the group consisting of an alkylcarbamoyl radical of formula R-NH-CO- and an alkylcarbonyl radical of formula R-CO-, wherein R represents a linear or branched, saturated or unsaturated alkyl group with from 4 to 32 carbon atoms, and s and s', which can have the same value or not, represent the number of said hydrophobic moieties that substitute the fructosyl or glucosyl unit, expressed as average degree of substitution (av. DS) which ranges from 0.01 to 0.5. The invention also relates to a method for the preparation and / or stabilisation of dispersions of multiphase systems that comprise a continuous aqueous phase containing a high concentration of electrolytes, by using as surfactant one or more hydrophobically modified saccharides of general formula (I) and / or (II) defined above. Also dispersions of multiphase systems are disclosed that comprise a continuous aqueous phase containing a high concentration of electrolytes and that comprise as surfactant one or more hydrophobically modified saccharides of general formula (I) and / or (II) defined above.
Owner:TIENSE SUIKERRAFINADERIJ
Photosensitive compositions, quantum dot polymer composite pattern prepared therefrom, and electronic devices including the same
ActiveUS20170059988A1Process environmental protectionOptical filtersNanoopticsQuantum dotCarboxylic acid
A photosensitive composition including: a plurality of quantum dots, wherein the quantum dot includes an organic ligand with a hydrophobic moiety bound to a surface of the quantum dot; a binder; a photopolymerizable monomer having a carbon-carbon double bond; a photoinitiator; and a solvent, wherein the binder includes a multiple aromatic ring-containing polymer including a main chain including a carboxylic acid group and a backbone structure incorporated in the main chain, wherein the backbone structure includes a quaternary carbon atom, which is a part of a cyclic group, and two aromatic rings bound to the quaternary carbon atom, and wherein the plurality of quantum dots are dispersed in the binder.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Polyglyceryl compounds and compositions
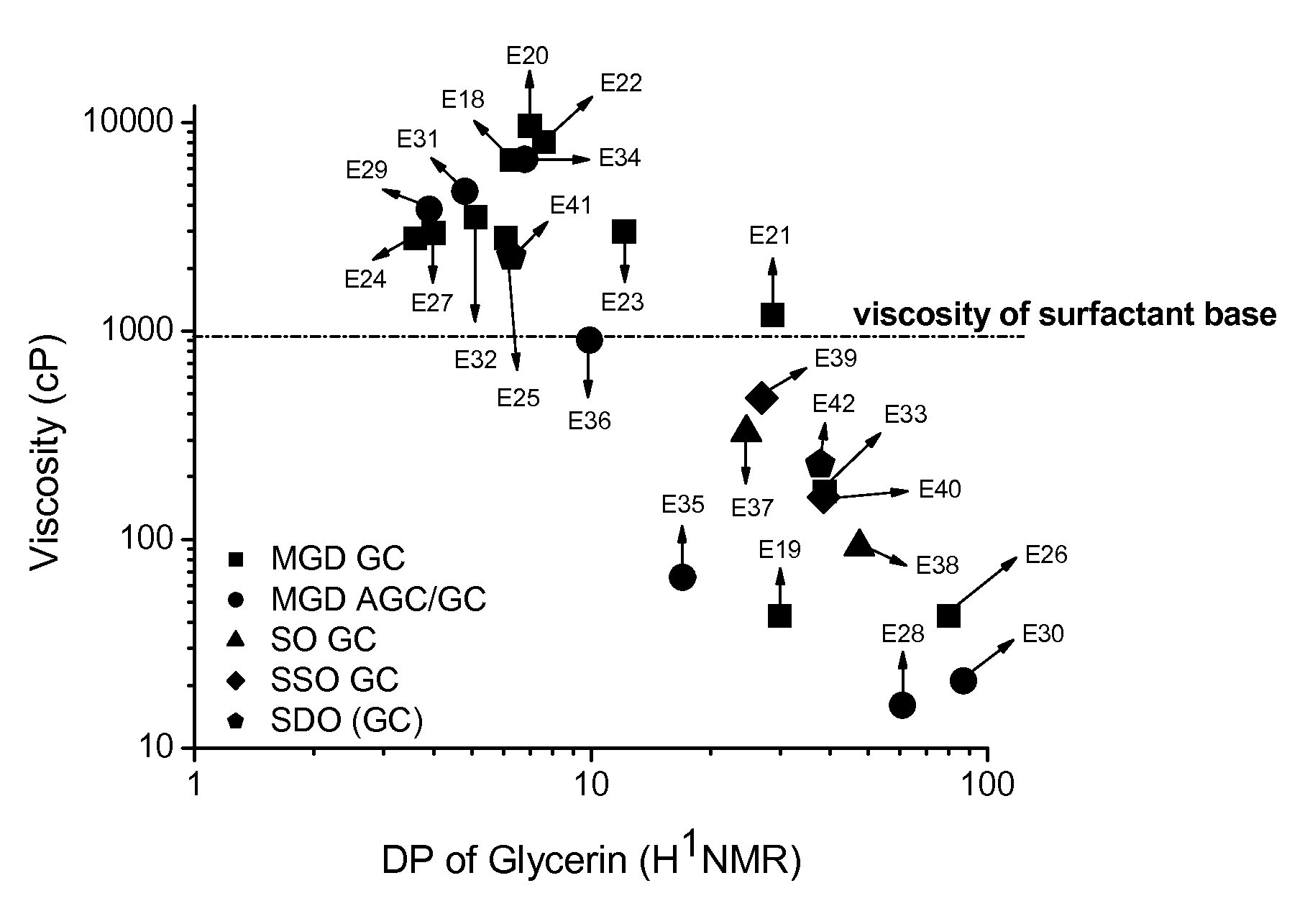
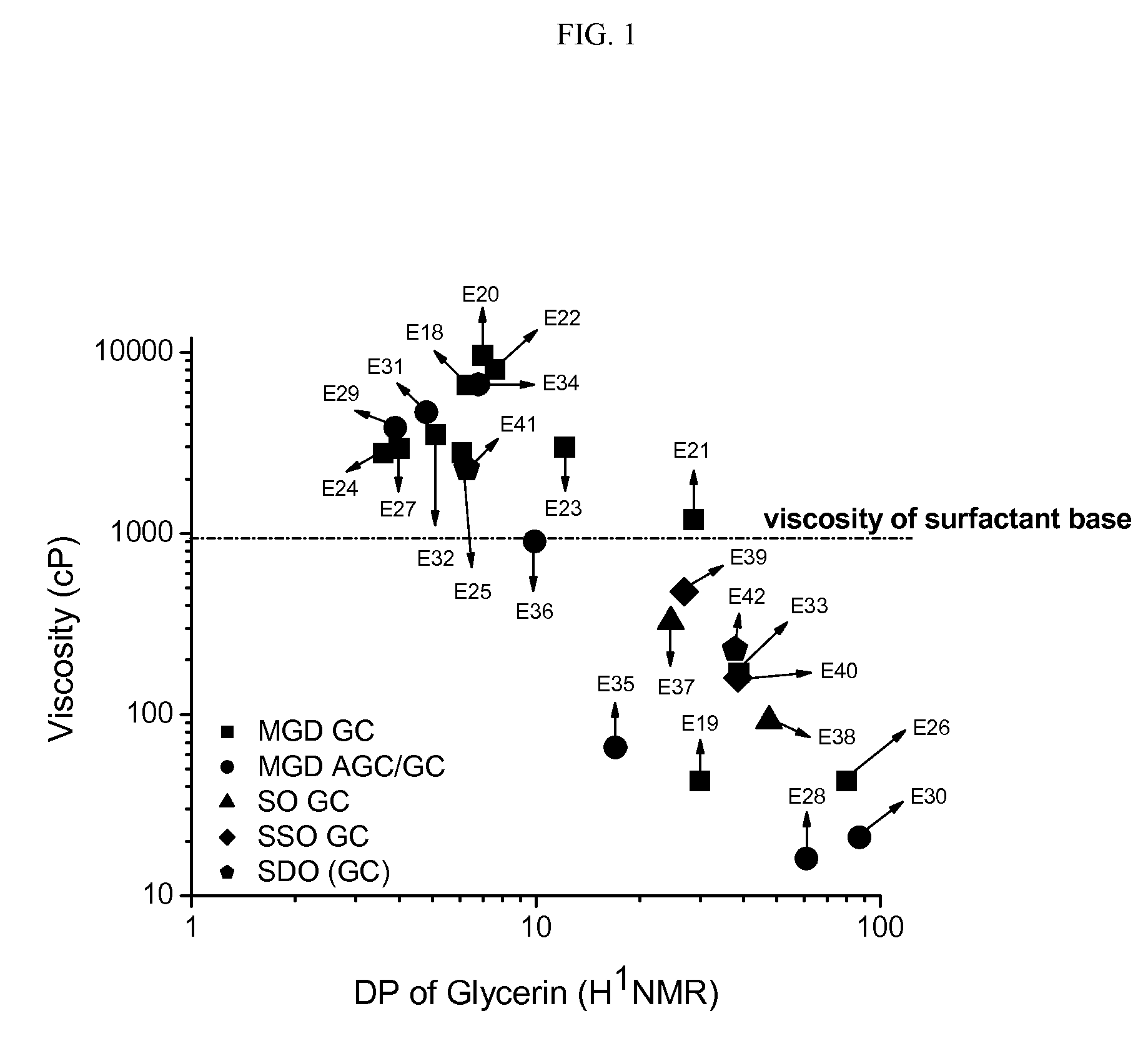
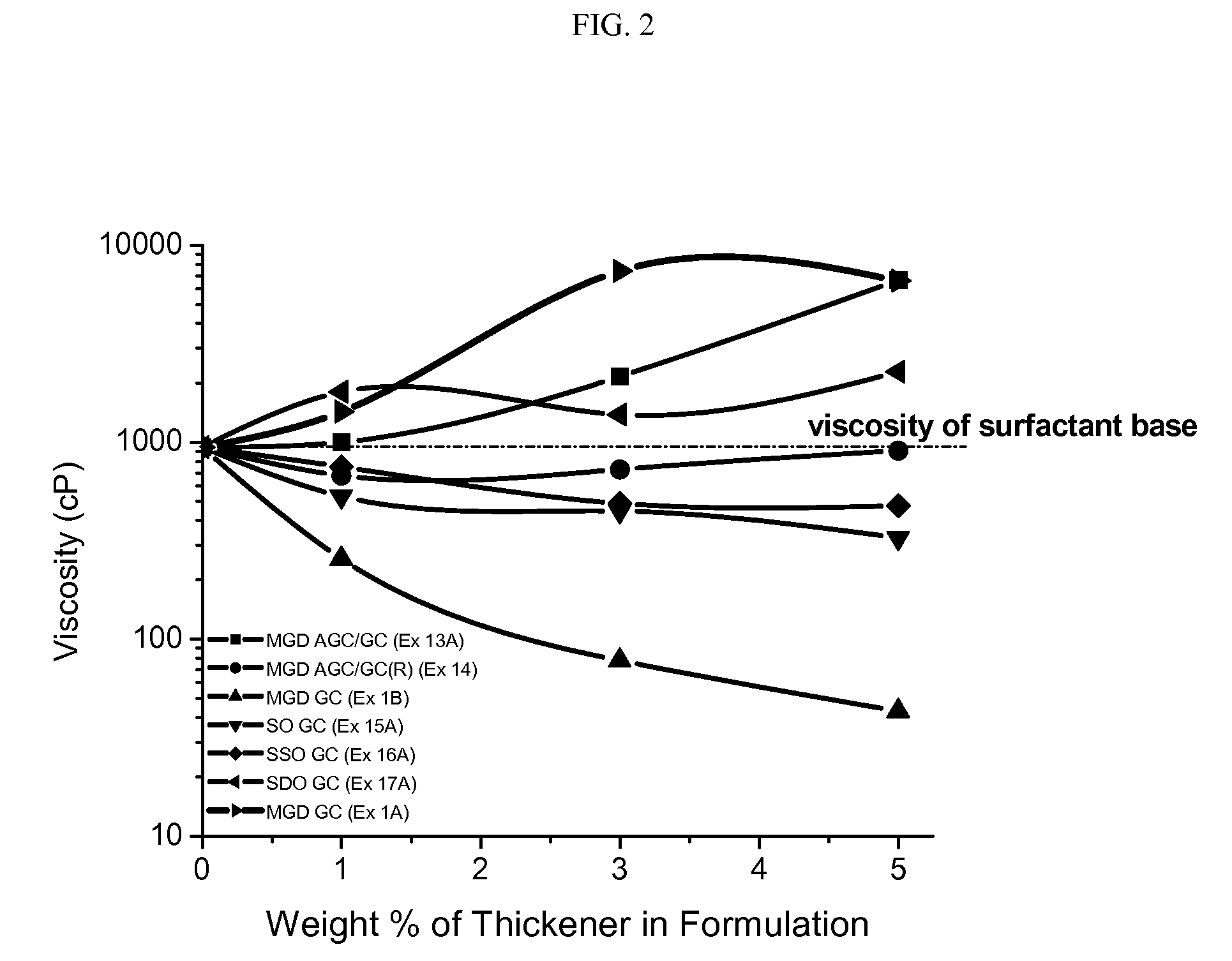
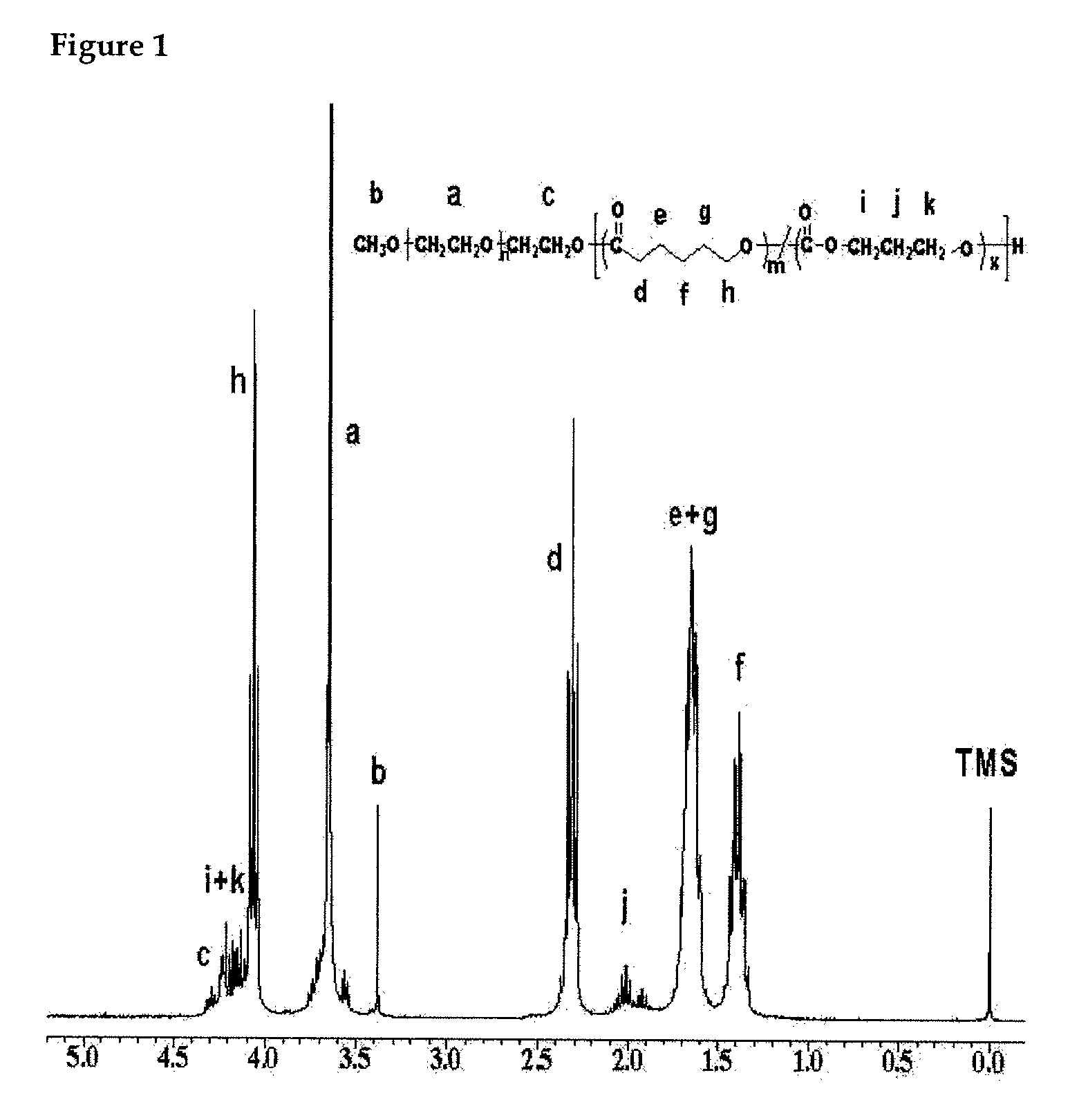
ActiveUS8211850B2High viscosityOvercome disadvantagesEsterified saccharide compoundsCosmetic preparationsOrganic chemistrySURFACTANT BLEND
Provided are compositions comprising one or more compounds having a structure comprising a node structure with from four to twelve carbon atoms, one or more (poly)glyceryl groups, and one or more hydrophobic moieties, wherein each of the one or more (poly)glyceryl groups is linked to the node structure by a first primary linking group, the one or more hydrophobic moieties are each independently linked either to the node structure by a primary linking group or to one of the (poly)glyceryl groups by a secondary linking group, and wherein the polyglyceryl thickener has an average degree of glyceryl polymerization of from greater than 3 to less than about 11 and an average number of hydrophobic groups per primary linking group of about 0.35 or greater. Also provided are polyglyceryl compounds, compositions comprising water, a surfactant, and a polyglyceryl thickener, as well as, methods of making polyglyceryl compounds and compositions of the present invention.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
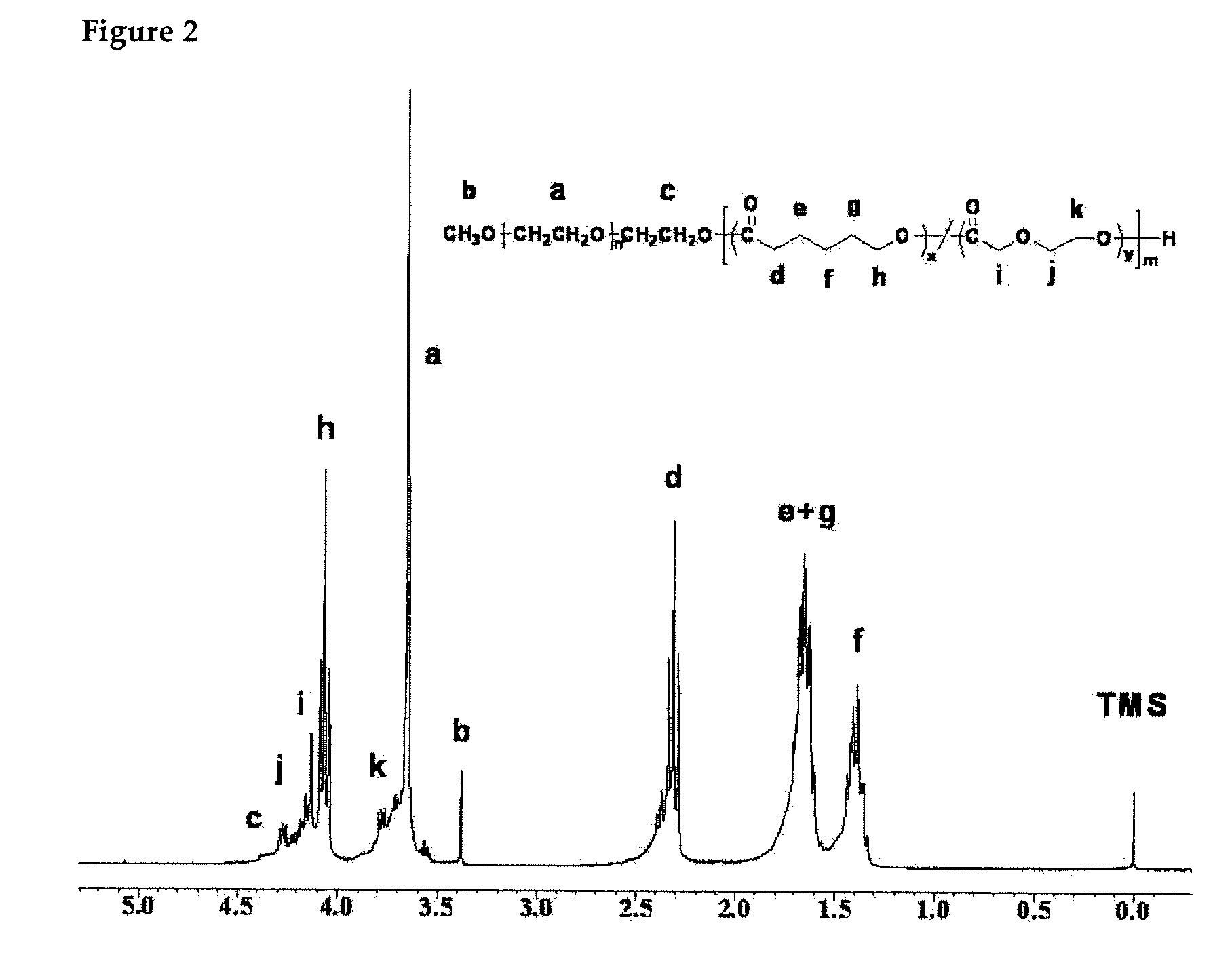
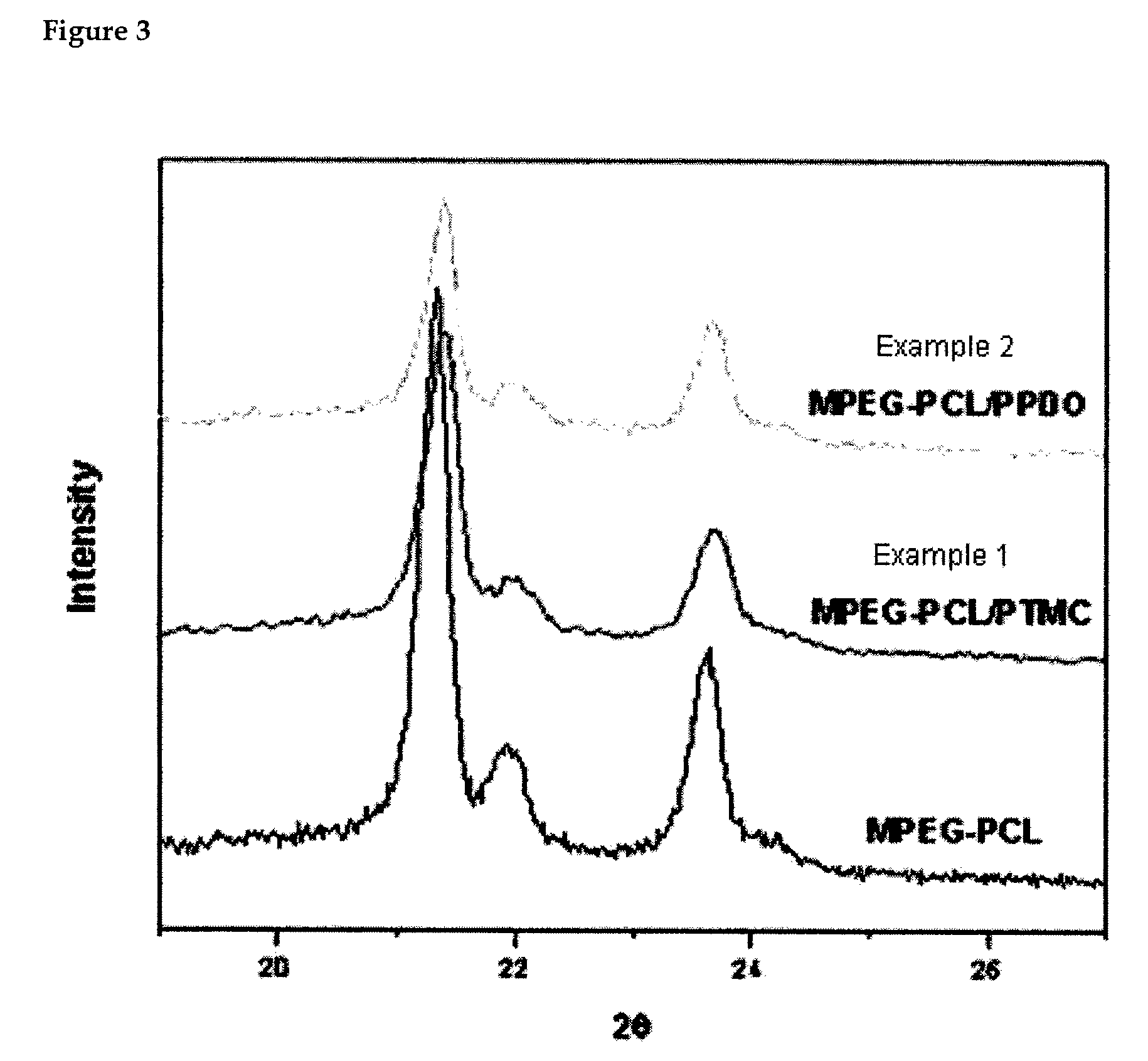
Preparation and characterization of polyethyleneglycol/polyesters as biocompatible thermo-sensitive materials
InactiveUS20070218099A1Reduce molecular weightWell formedPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisPolyesterPolymer science
The present invention relates to a biocompatible and thermosensitive poly(ethylene glycol) / polyester block copolymer and a method of its preparation thereof, and particularly to a multi-functional intelligent hydrogel polymer comprising a hydrophilic part of a poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) having a low molecular weight and a hydrophobic part comprising an ester-based caprolactone (CL) segment as an essential ingredient and further comprising a para-dioxanone (PDO) segment, a trimethylene carbonate (TMC) segment or a PDO / TMC copolymer containing the PDO and the TMC segments in a predetermined ratio, which easily forms a desired-shaped gel and decomposes or disperses without necessitating the operation process for removing the gel due to the temperature-dependent phase transition caused by the coagulation and the expansion of polymer micelles comprising a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part, thus being applicable to a drug delivery system or a porous support for tissue engineering purpose.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Dihydroxyalkyl substituted polygalactomannan, and methods for producing and using the same
ActiveUS20150098921A1Cosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHydrophobic moiety
Owner:HERCULES LLC
Hydrophobically modified polysaccharide in personal care products
A personal care composition is composed of:(a) from about 0.1% to about 99% by weight of a vehicle system which comprises a hydrophobically modified nonionic water soluble polysaccharide polymer which comprises a water soluble polysaccharide polymer backbone and a hydrophobic moiety selected from the group consisting of 3-alkoxy-2-hydroxypropyl group wherein the allyl moiety is a straight or branch chain having 2-6 carbon atoms, C3-C7 alky aryl alkyl, alkyl aryl groups and mixtures thereof, wherein the ratio of the hydrophilic portion to the hydrophobic portion of the polymer is from about 2:1 to 1000:1, and(b) at least one other personal care ingredient.This compostion can be used in a wide range of personal care products such as shampoos, conditioners, hair coloring and styling agents, soaps, body washing agents, underarm products, lubricating agents, oral care products, denture adhesives, sunscreen agents, make-up products, and the like.
Owner:HERCULES INC
Delivery Agents for enhancing mucosal absorption of therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20050260237A1Reduce decreaseEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsSterolDipeptide
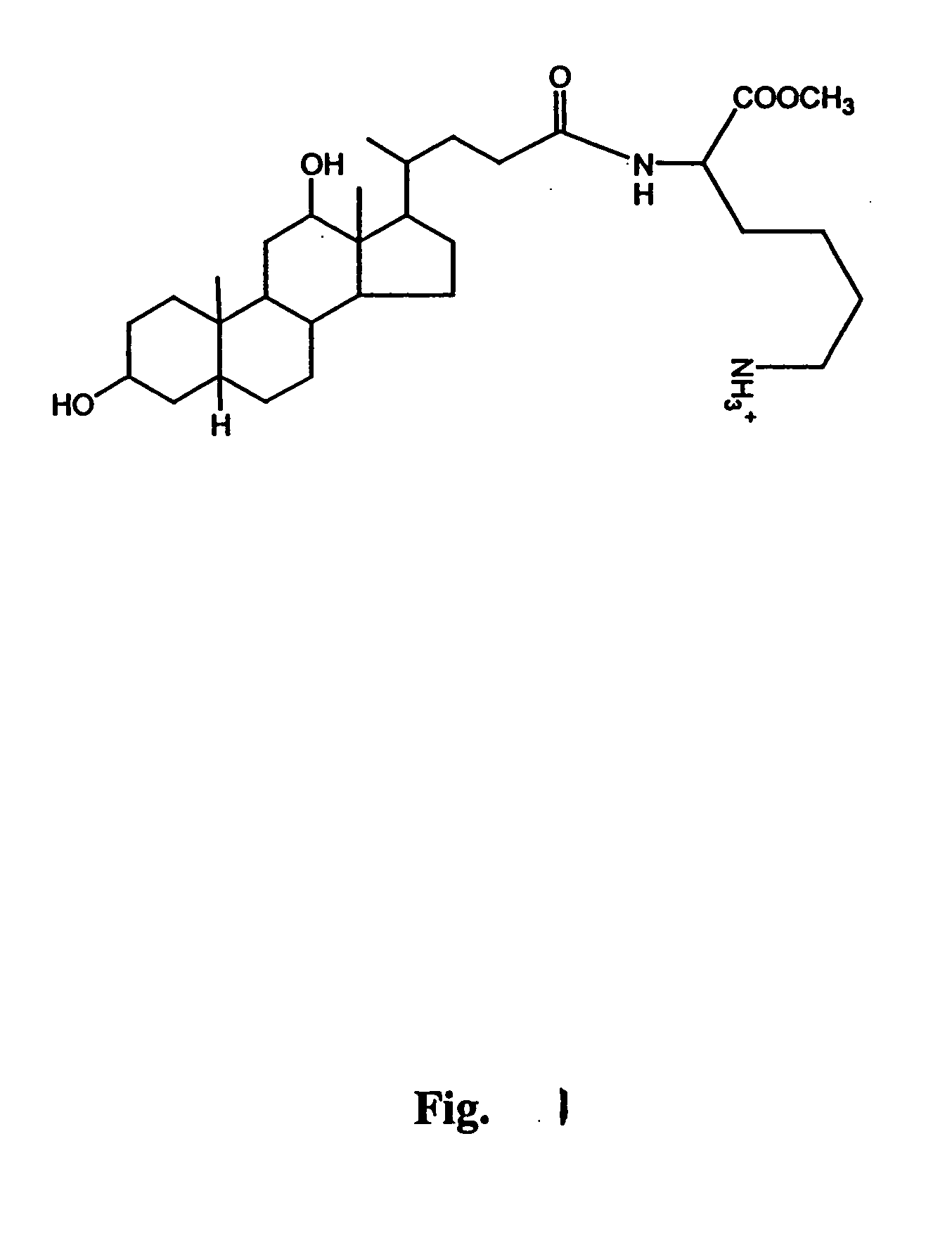
A delivery agent for delivering a biologically active agent to a warm-blooded animal includes a hydrophobic moiety covalently bonded to a hydrophilic moiety. The hydrophobic moiety can include bile acids, sterols, or hydrophobic small molecules. The hydrophilic moiety can include α-amino acids, dipeptides or tripeptides, or hydrophilic small molecules. An illustrative delivery agent is Nα-deoxycholyl-L-lysine-methylester. The delivery agent and the biologically active agent are mixed together to form a complex, which is then administered to the animal. These complexes are particularly useful for oral administration of biologically active agents, but other routes of administration may be used.
Owner:MEDIPLEX CORP
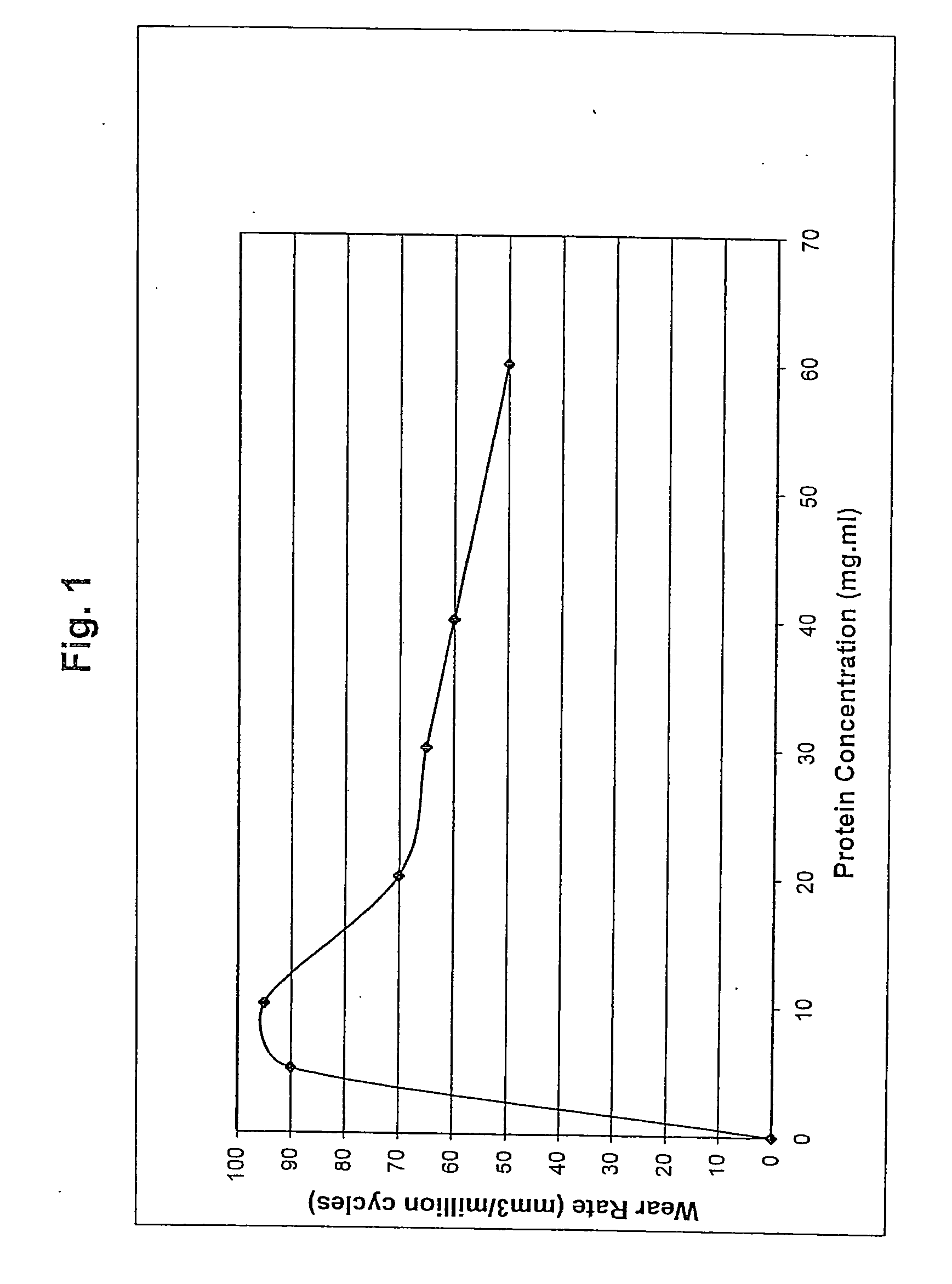
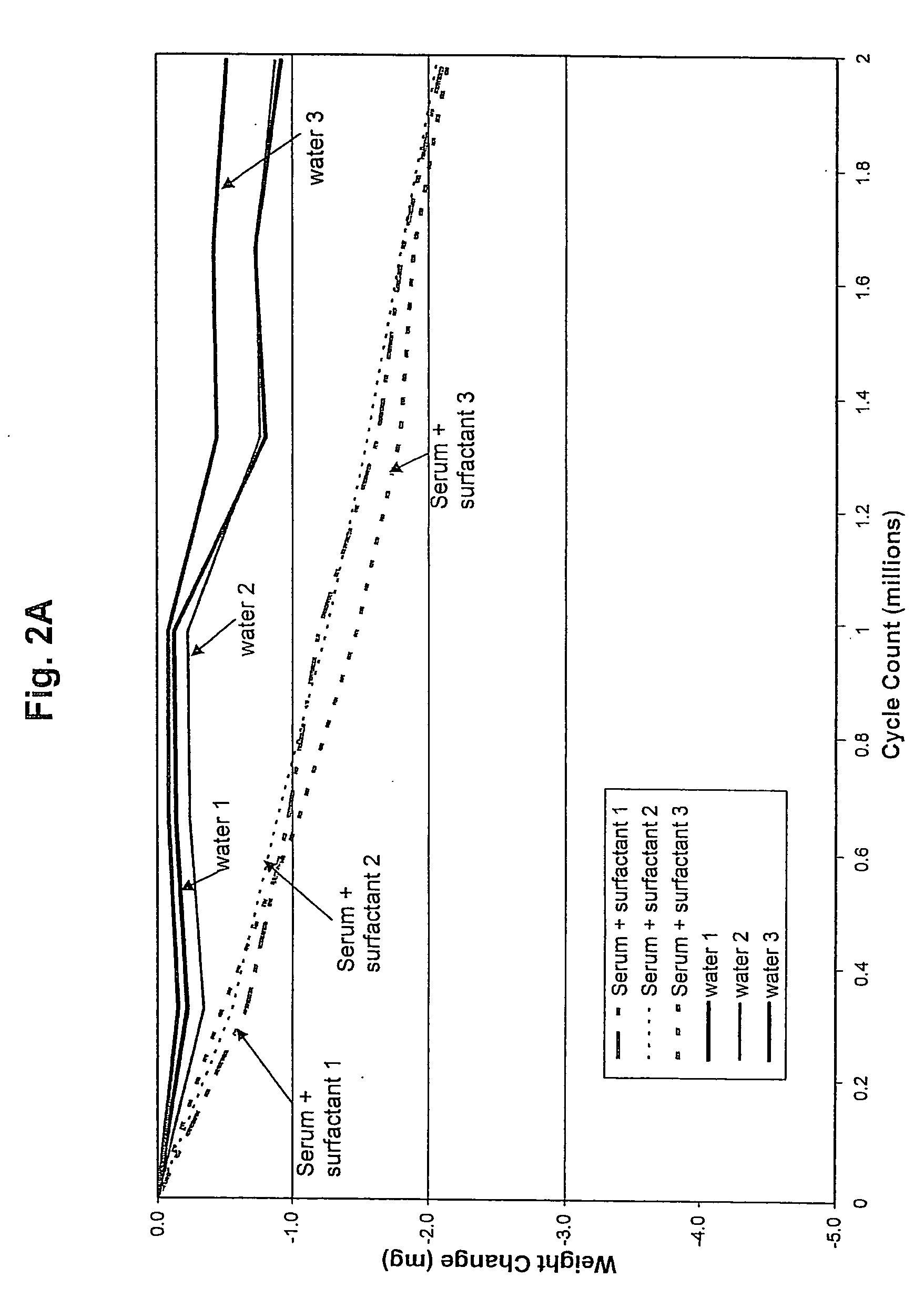
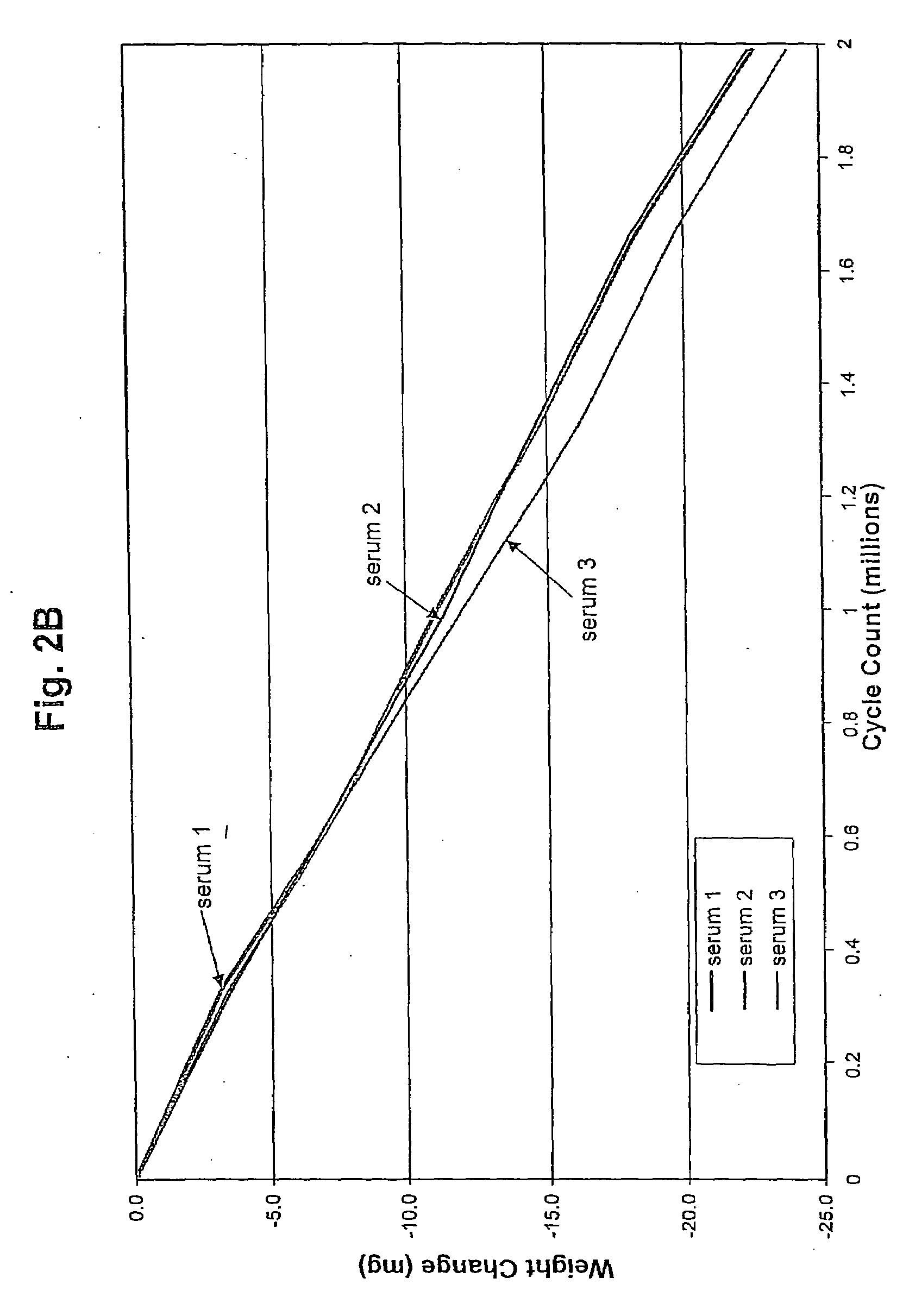
Bearing material of medical implant having reduced wear rate and method for reducing wear rate
Disclosed is a bearing material of a medical implant comprising a polymer such as UHMWPE and a surface active agent that is not covalently bonded to the polymer. The surface active agent includes a hydrophilic moiety or segment, such as an ethoxylated moiety, and a hydrophobic moiety or segment, such as an alkanol, alkenol, aromatic alcohol, alkylamine, alkenyl amine, alkyl aromatic alcohol, alkanoic acid, alkenoic acid, or any combination thereof. The bearing material has a reduced wear rate. Also disclosed is a method of reducing the wear rate of a polymeric bearing material of a medical implant when it articulates against a hard counterface in the presence of synovial fluid, the method comprising providing a surface active agent in the synovial fluid in close proximity to the bearing surface, the hard counterface, or both.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
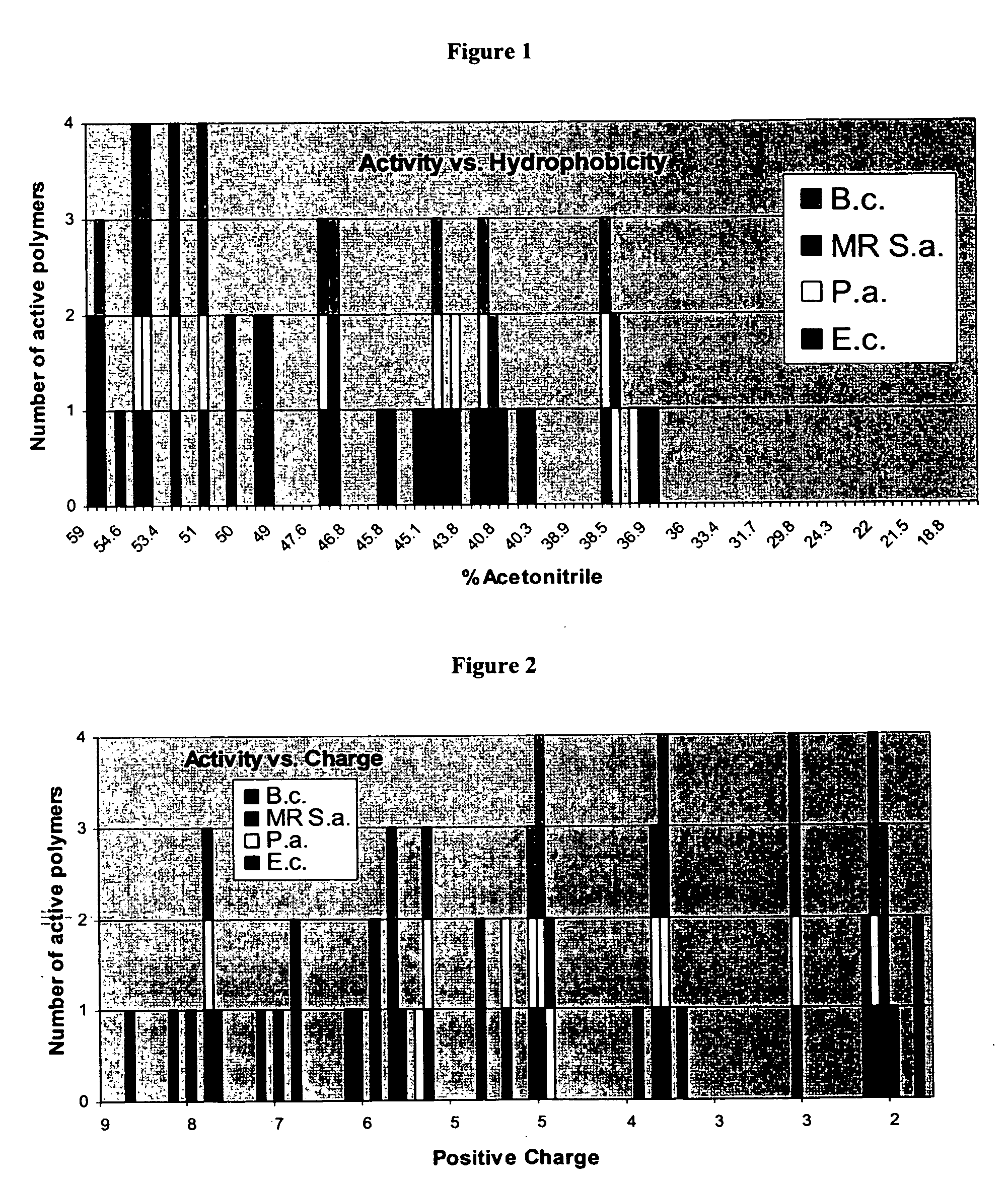
Novel antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS20060074021A1High efficacyStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismMedical device
A novel class of antimicrobial polymeric agents which are designed to exert antimicrobial activity while being stable, non-toxic and avoiding development of resistance thereto and a process of preparing same are disclosed. Further disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions containing same and a method of treating medical conditions associated with pathological microorganisms, a medical device, an imaging probe and a food preservative utilizing same. Further disclosed are conjugates of an amino acid residue and a hydrophobic moiety residue and a process of preparing same.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Hydrophobically-modified protein compositions and methods
InactiveUS6897297B1Improve biological activityImprove stabilityBiocideHydrocarbon active ingredientsLipid formationChemical reaction
Hydrophobically-modified proteins and methods of making them are described. A hydrophobic moiety is attached to a surface amino acid residue of the protein. The hydrophobic moiety can be a lipid or a peptide. Alternatively, the protein can be derivatized by a wide variety of chemical reactions that append a hydrophobic structure to the protein. The preferred protein is of mammalian origin and is selected from the group consisting of Sonic, Indian, and Desert hedgehog. The hydrophobic moiety is used as a convenient tether to which may be attached a vesicle such as a cell membrane, liposome, or micelle.
Owner:CURIS INC +1
Mesh-adjustable molecular sieve
InactiveUS20080184881A1Group 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOther chemical processesMetal clustersMolecular sieve
Metal-organic framework-based molecular sieves comprising pores with a temperature-adjustable pore opening. The temperature-adjustable pore size molecular sieves comprise a plurality of metal clusters bound with a plurality of amphiphilic ligands, each ligand comprising a functionalized hydrophobic moiety and a functionalized hydrophilic moiety, and wherein the metal clusters and amphiphilic ligand hydrophilic moieties form a metal cluster layer, the metal cluster layer forming at least one hydrophilic pore. On each side of the metal cluster layer, a plurality of associated amphiphilic ligand hydrophobic moieties cooperate with the metal cluster layer to form a tri-layer and a plurality of tri-layers are held in proximity with each other to form at least one hydrophobic chamber. The hydrophobic moieties form temperature-adjustable pore size hydrophobic pores. When adjusted to a pre-selected temperature the temperature-adjustable pore openings allow for the passage of molecules having a size less than the size of the pre-selected temperature-adjustable pore opening.
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERSITY
Cleansing composition and cleansing sheet
A cleansing composition according to the present invention comprises (A) an aqueous phase containing 1 to 25% by weight of a water-soluble compound (a), which has a polyoxypropylene structure having 3 or more addition number of propylene oxide but neither an alkyl group having 4 or more carbon atoms nor a polyoxyethylene structure, in the aqueous phase and (B) an oil phase which is liquid at 30° C., wherein the weight ratio (A):(B) of the aqueous phase (A) and the oil phase (B) is 97:3 to 40:60, and water is contained more than 10% by weight in the total composition. Moreover, a cleansing sheet according to the present invention comprises a nonwoven fabric which is made of a fiber having a cellulose content of at least 70% by weight and has a density of about 0.15 to 0.3 g / cm3 impregnated with an oil-in-water emulsion composition comprising (A) an aqueous phase containing 1 to 25% by weight, in the aqueous phase, of a water-soluble compound (a) which has a polyoxypropylene structure having 3 or more addition number of propylene oxide but neither an alkyl group having 4 or more carbon atoms nor a polyoxyethylene structure, (B) an oil phase containing 50% by weight or more of an oil (b) having a boiling point of 160 to 300° C. at 1,013.25 hPa and (C) 0.01 to 1% by weight of an aqueous thickening agent having a hydrophobic part, wherein the weight ratio (A):(B) of the aqueous phase (A) and the oil phase (B) is 97:3 to 40:60.
Owner:KAO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com