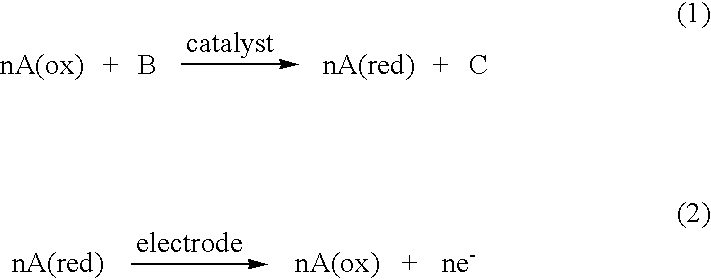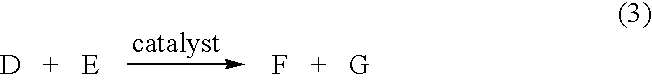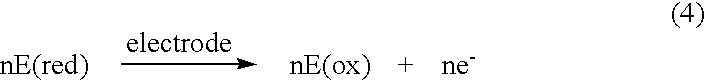Patents
Literature
6443 results about "Working electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
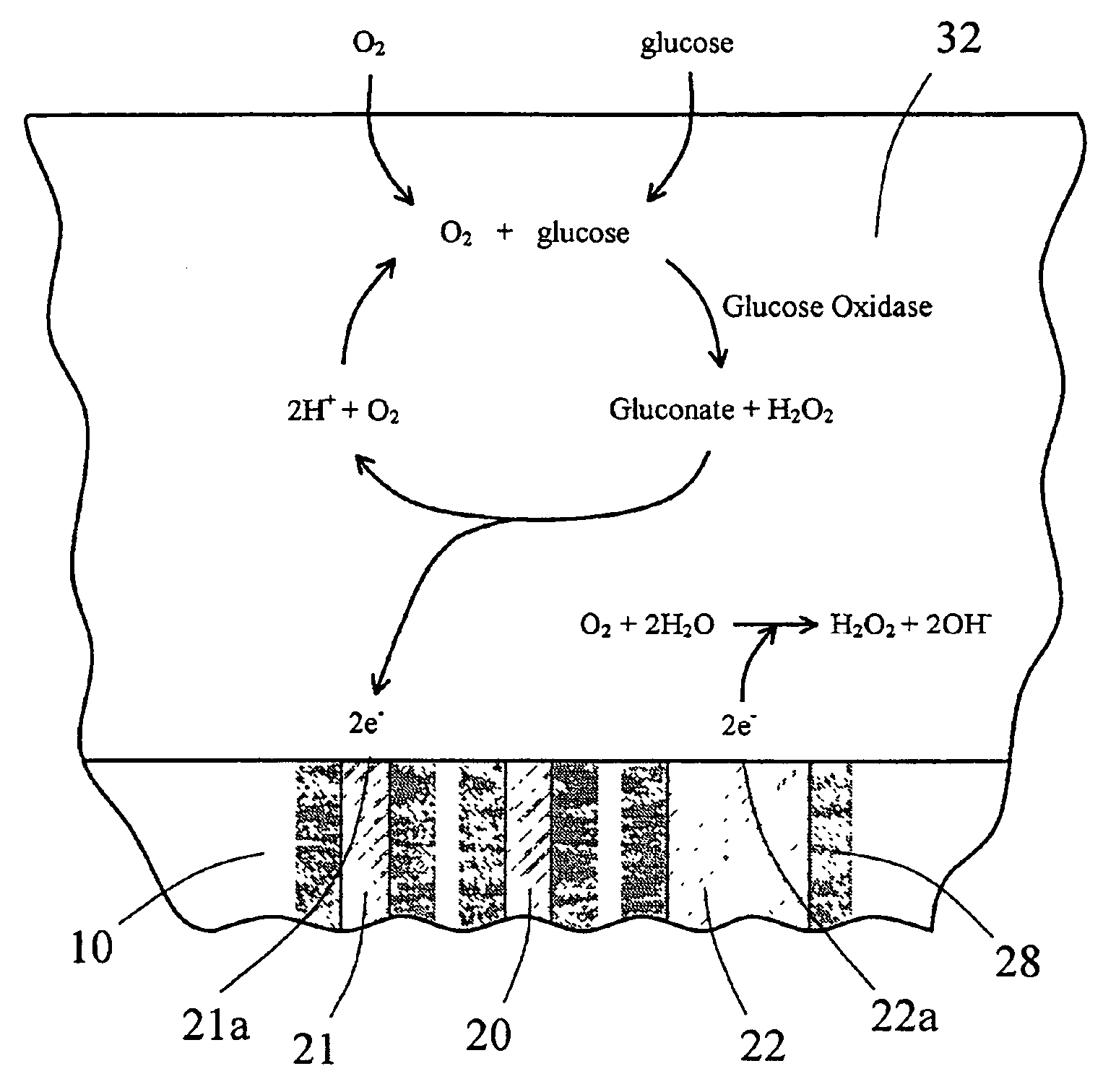
The working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three electrode system. Depending on whether the reaction on the electrode is a reduction or an oxidation, the working electrode is called cathodic or anodic, respectively. Common working electrodes can consist of materials ranging from inert metals such as gold, silver or platinum, to inert carbon such as glassy carbon, boron doped diamond or pyrolytic carbon, and mercury drop and film electrodes. Chemically modified electrodes are employed for the analysis of both organic and inorganic samples.
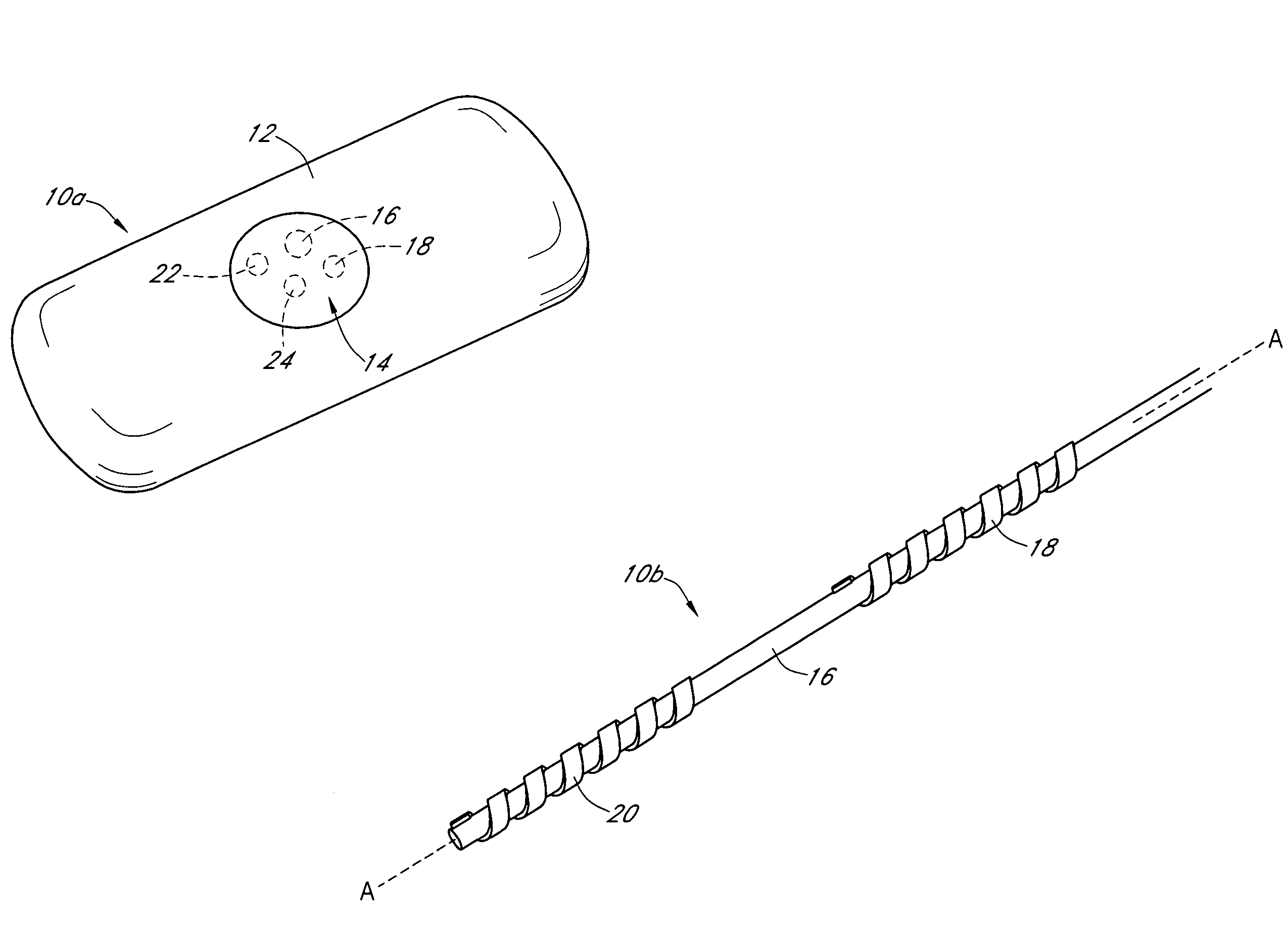
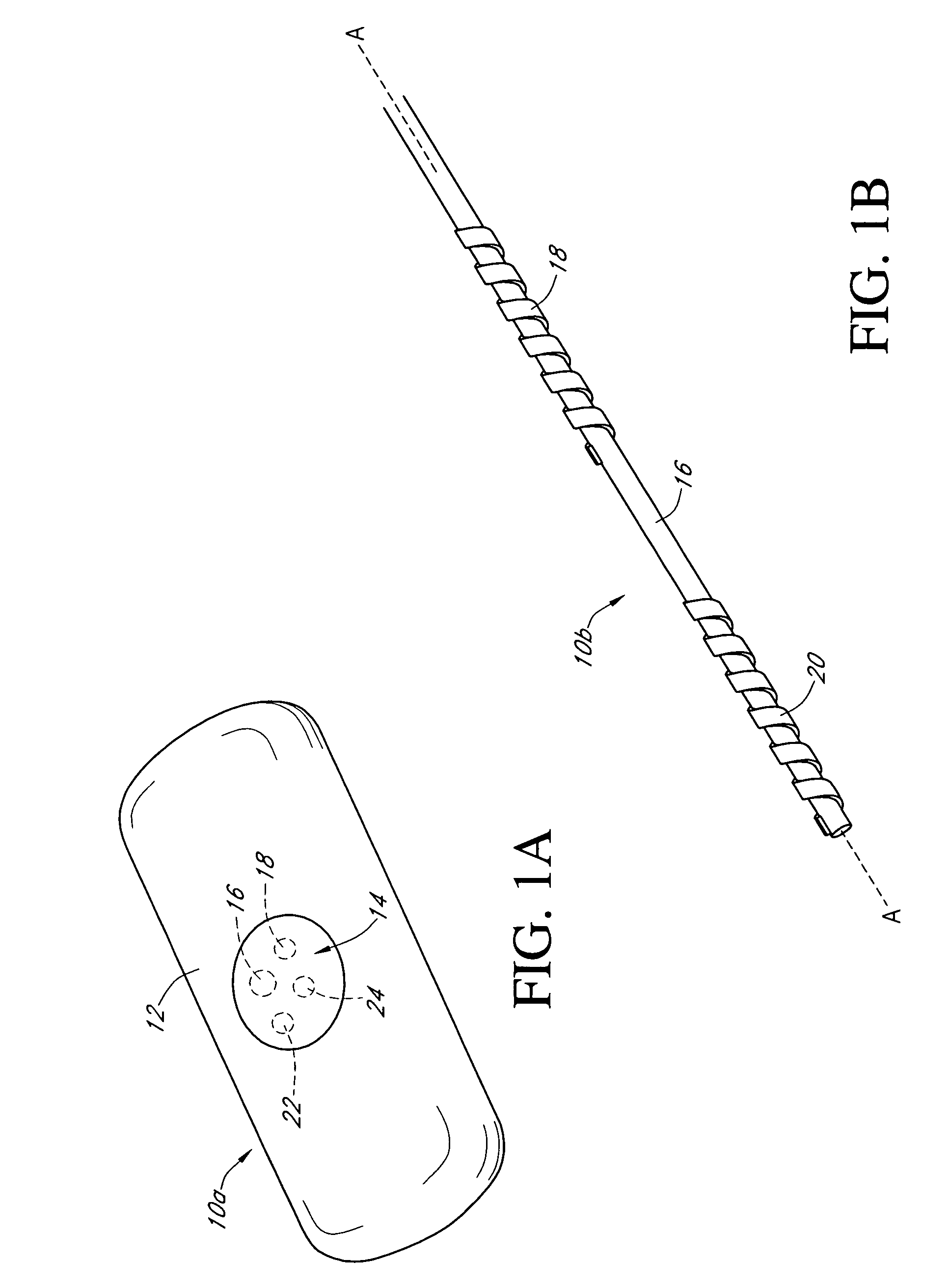
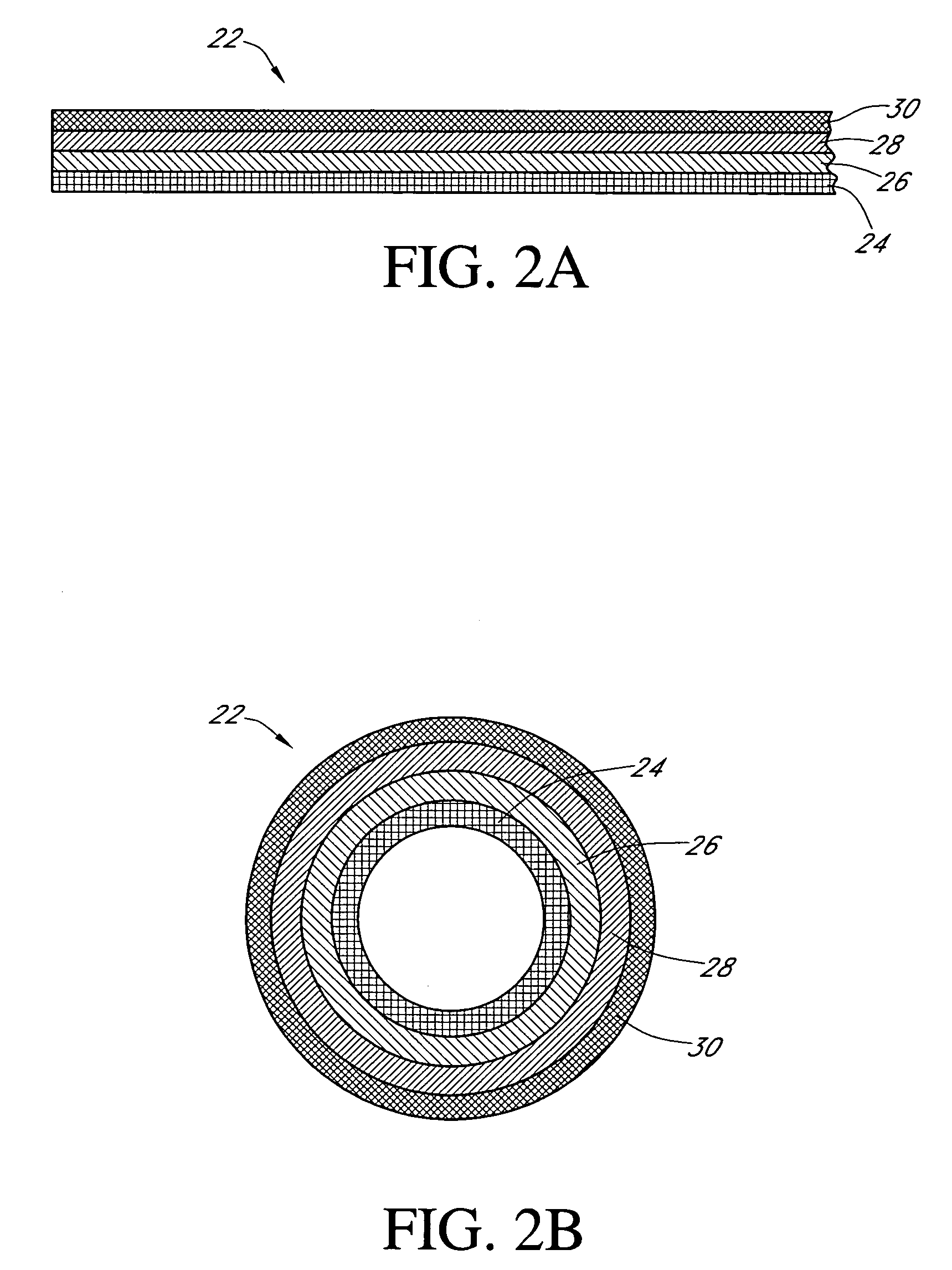
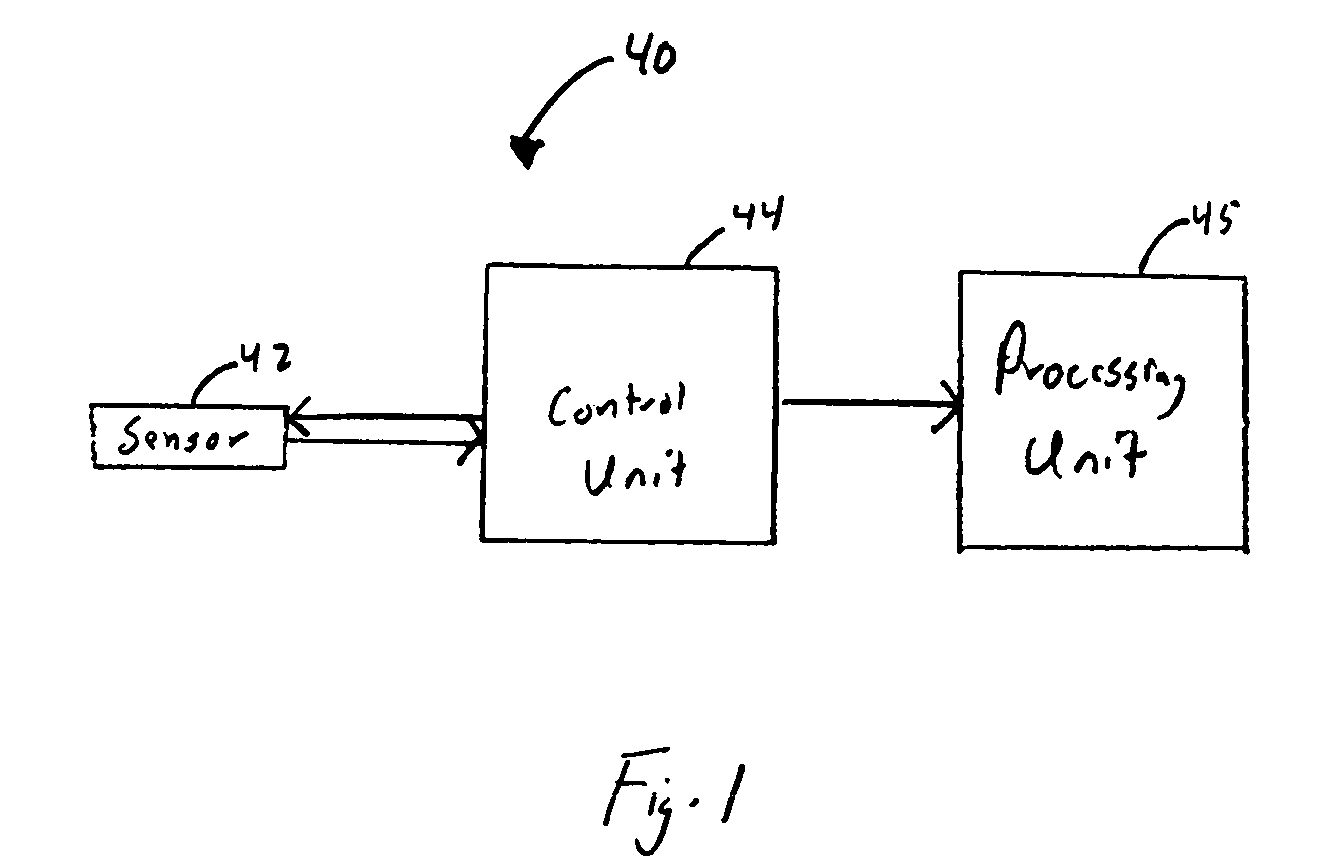
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS6484046B1Avoid and reduce corrosionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrolysis
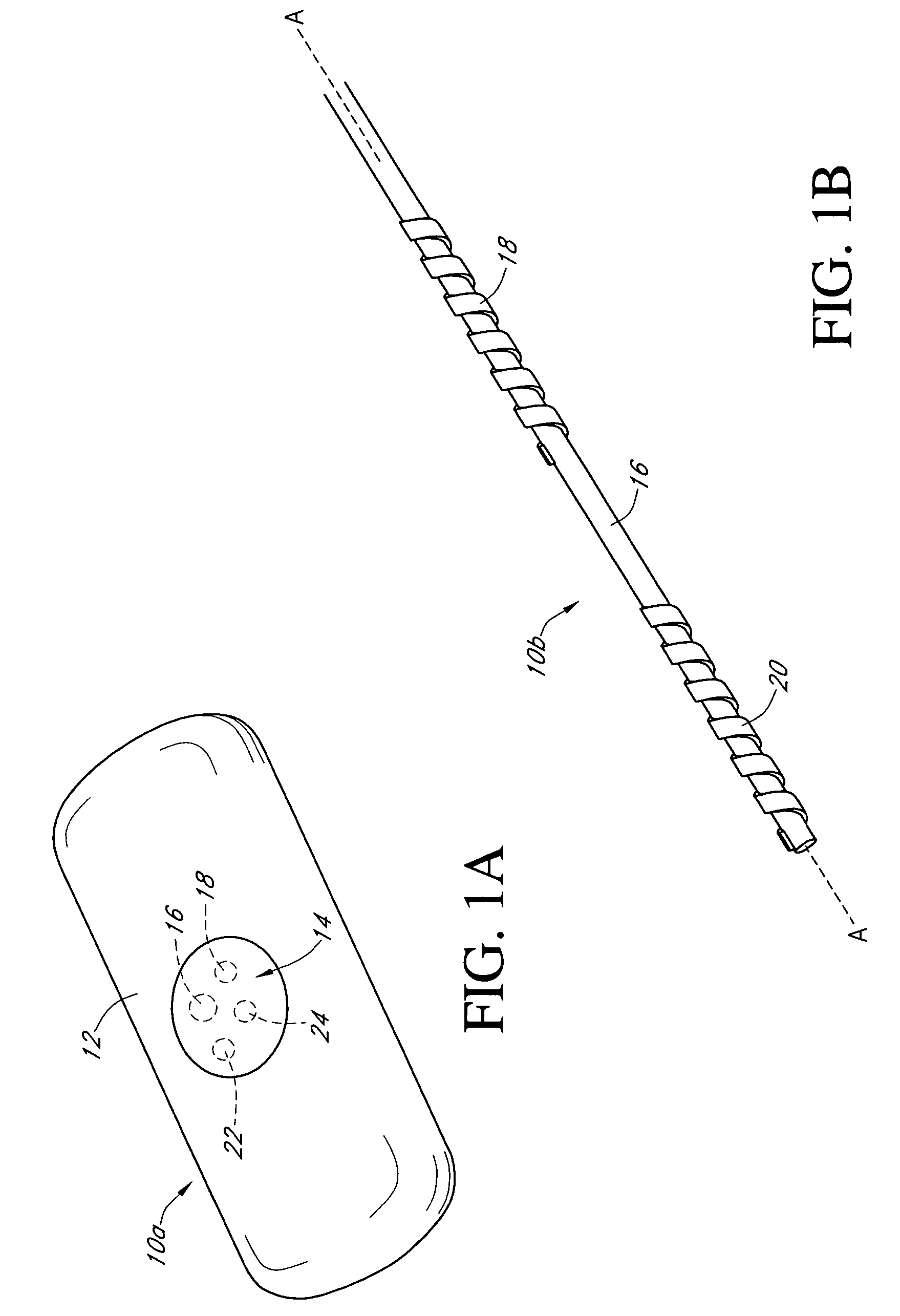
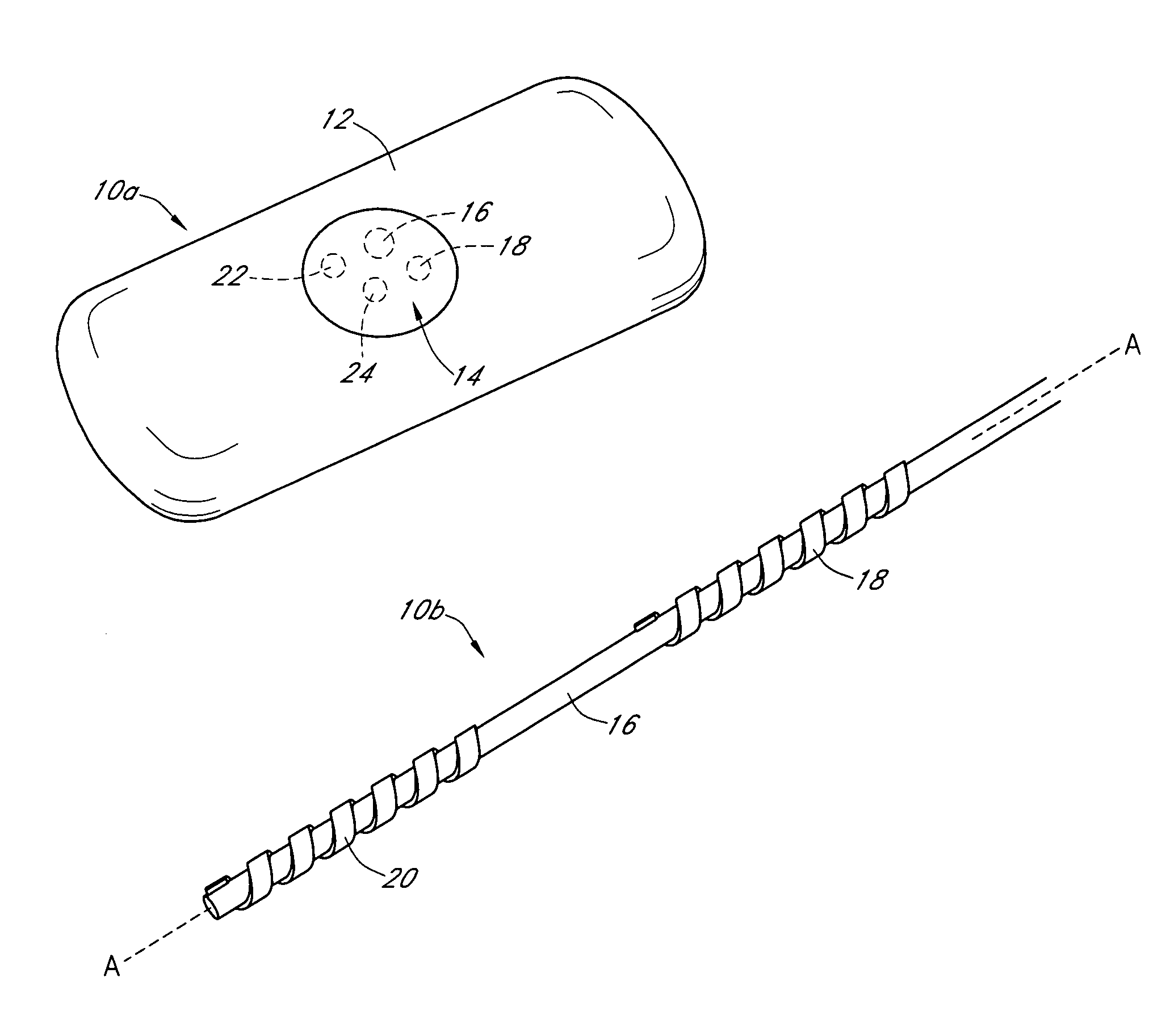
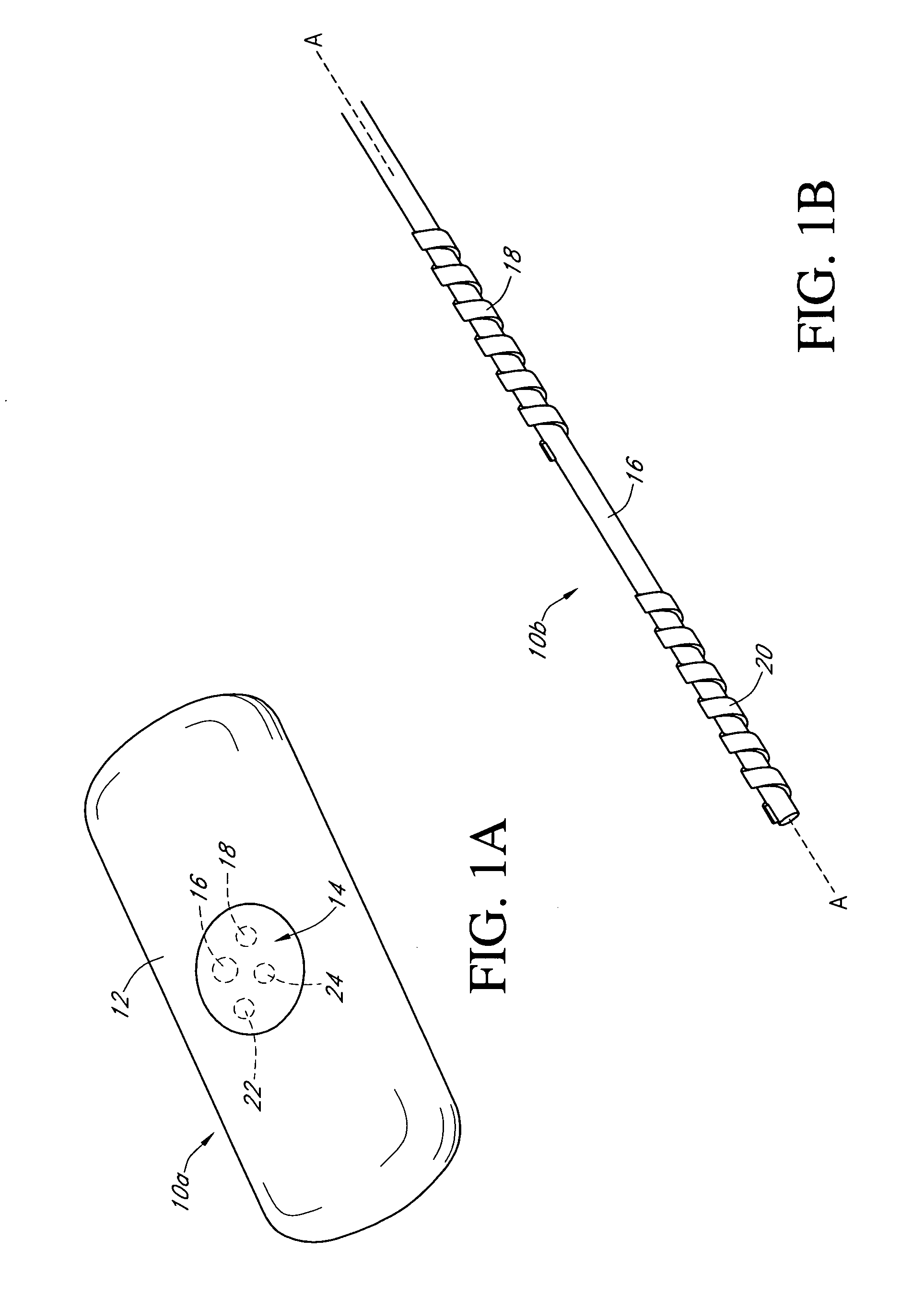
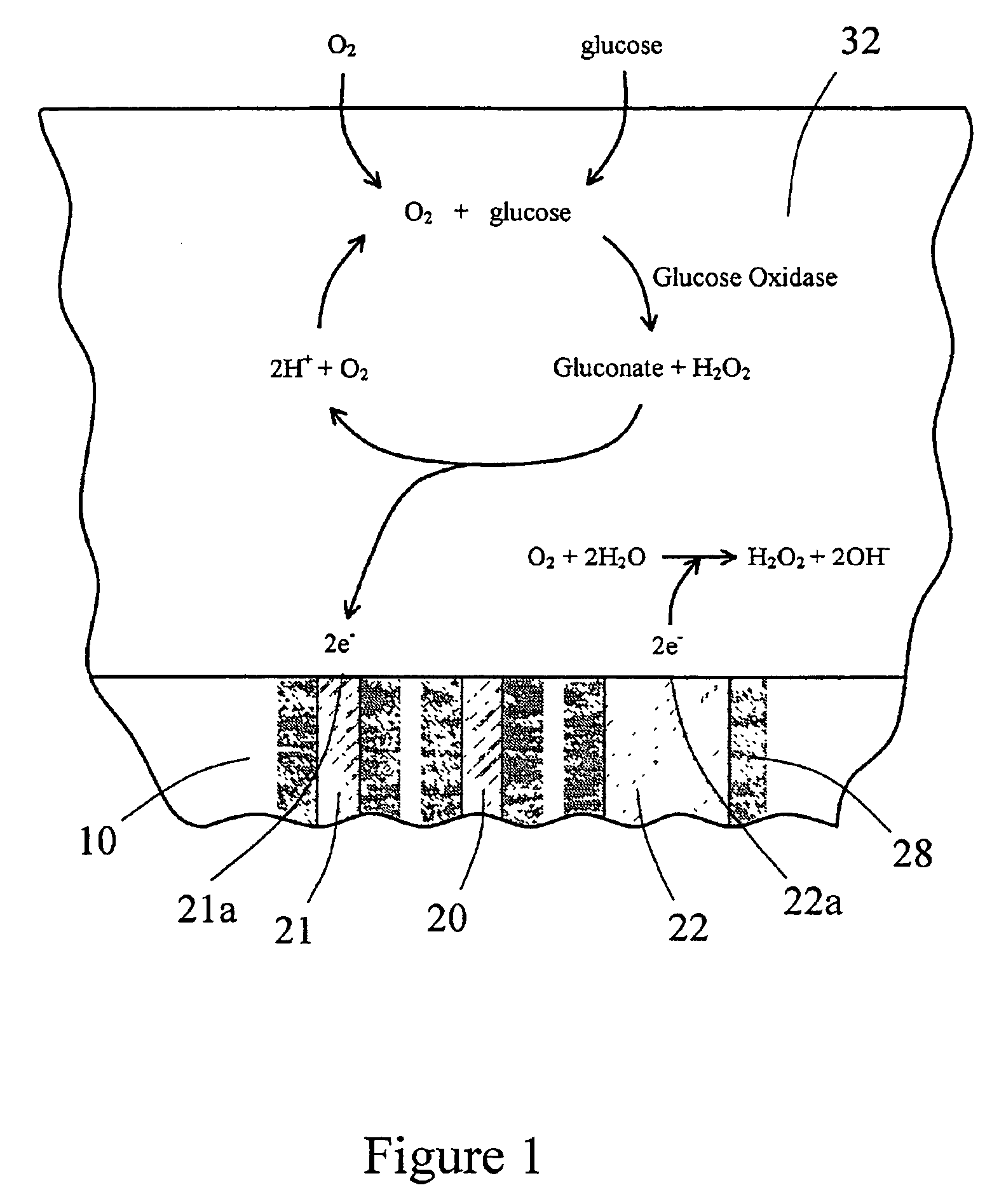
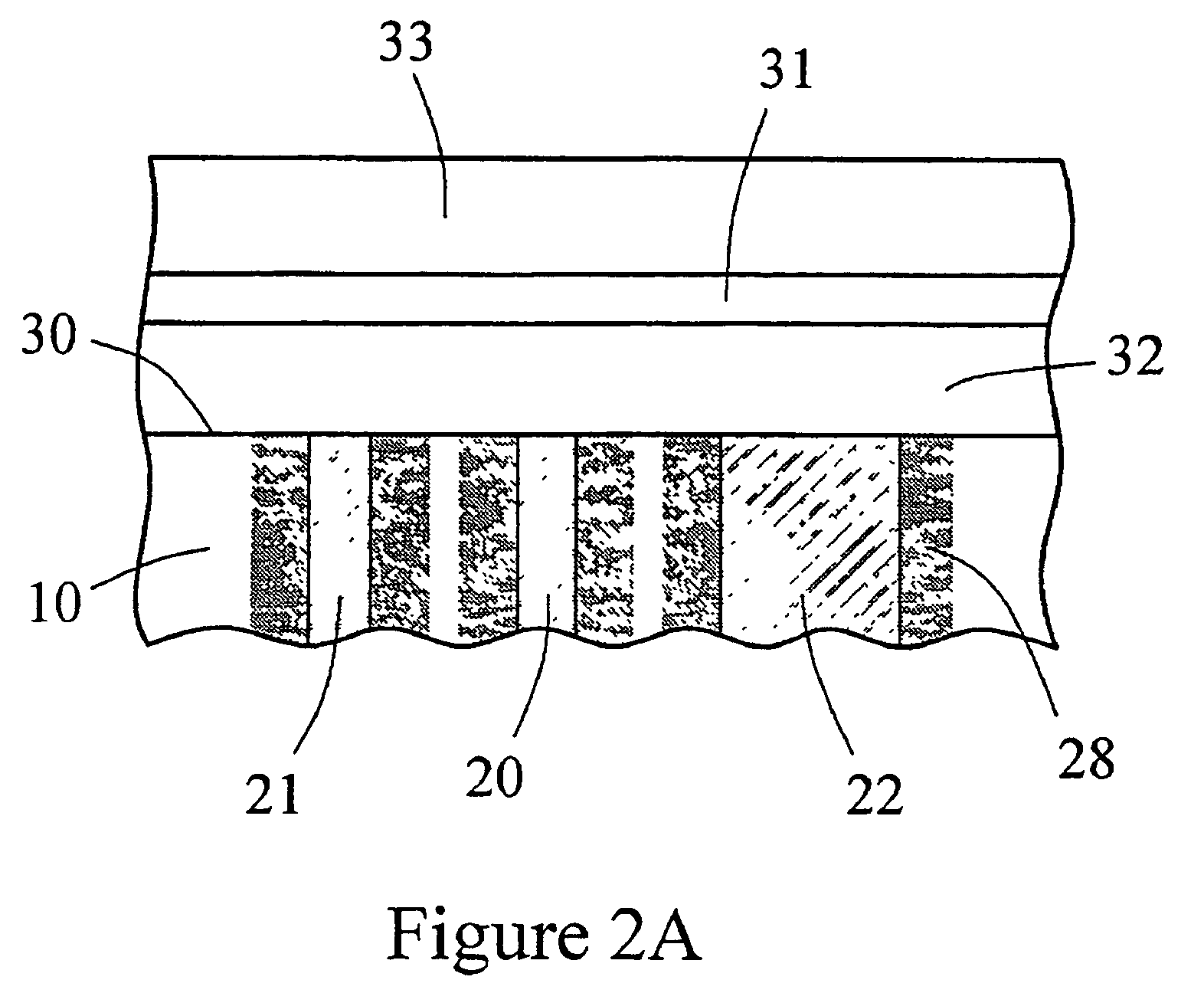
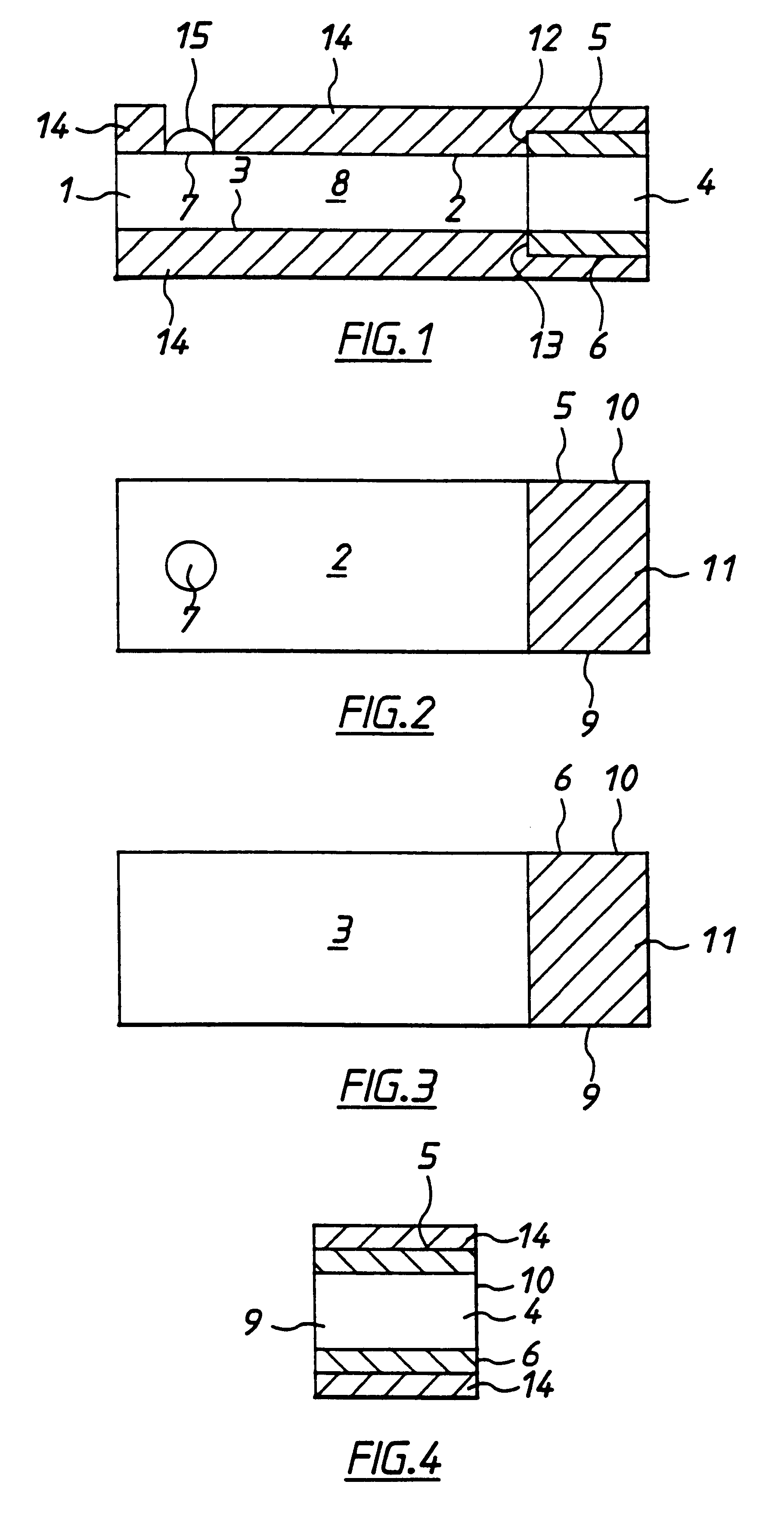
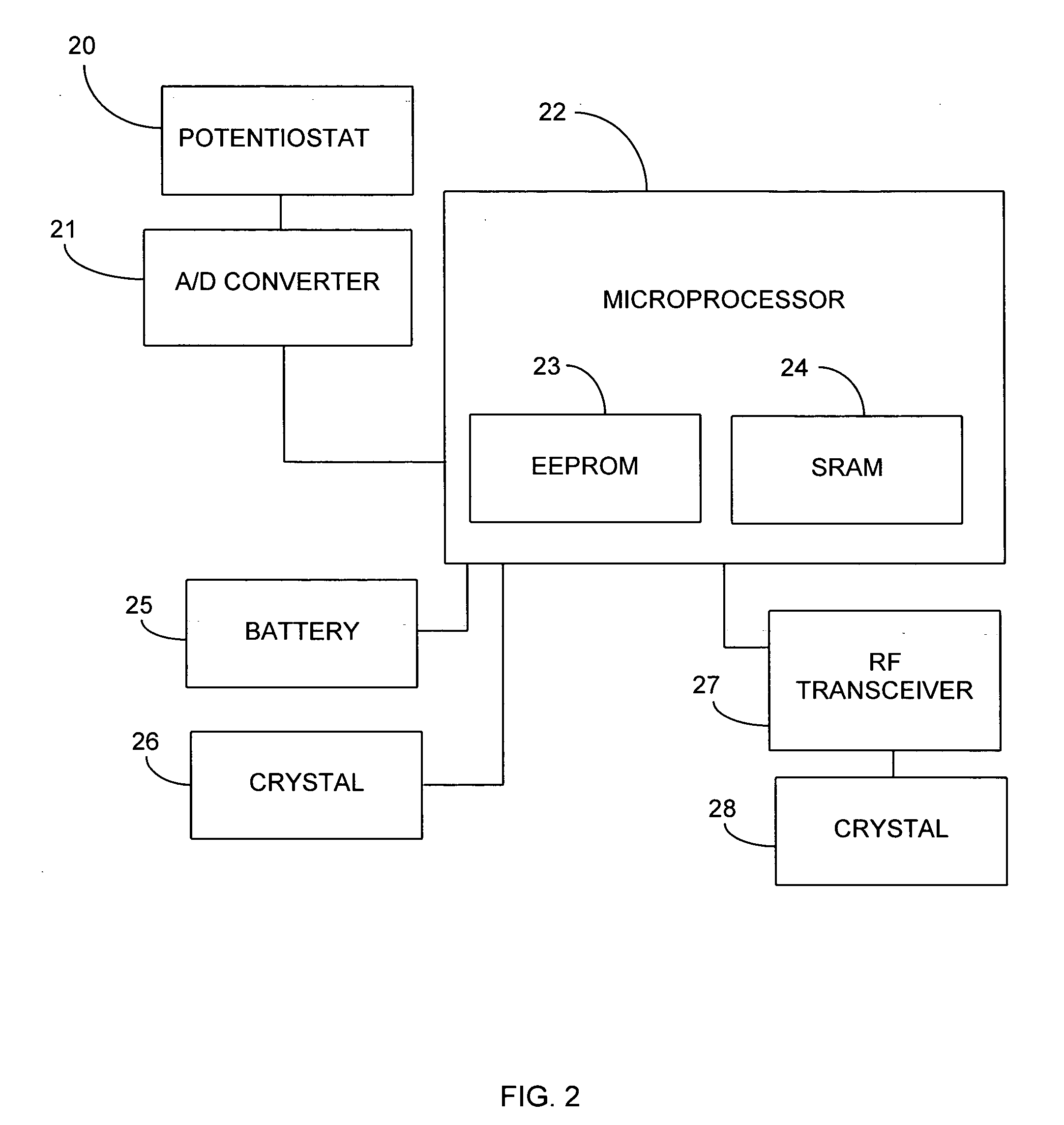
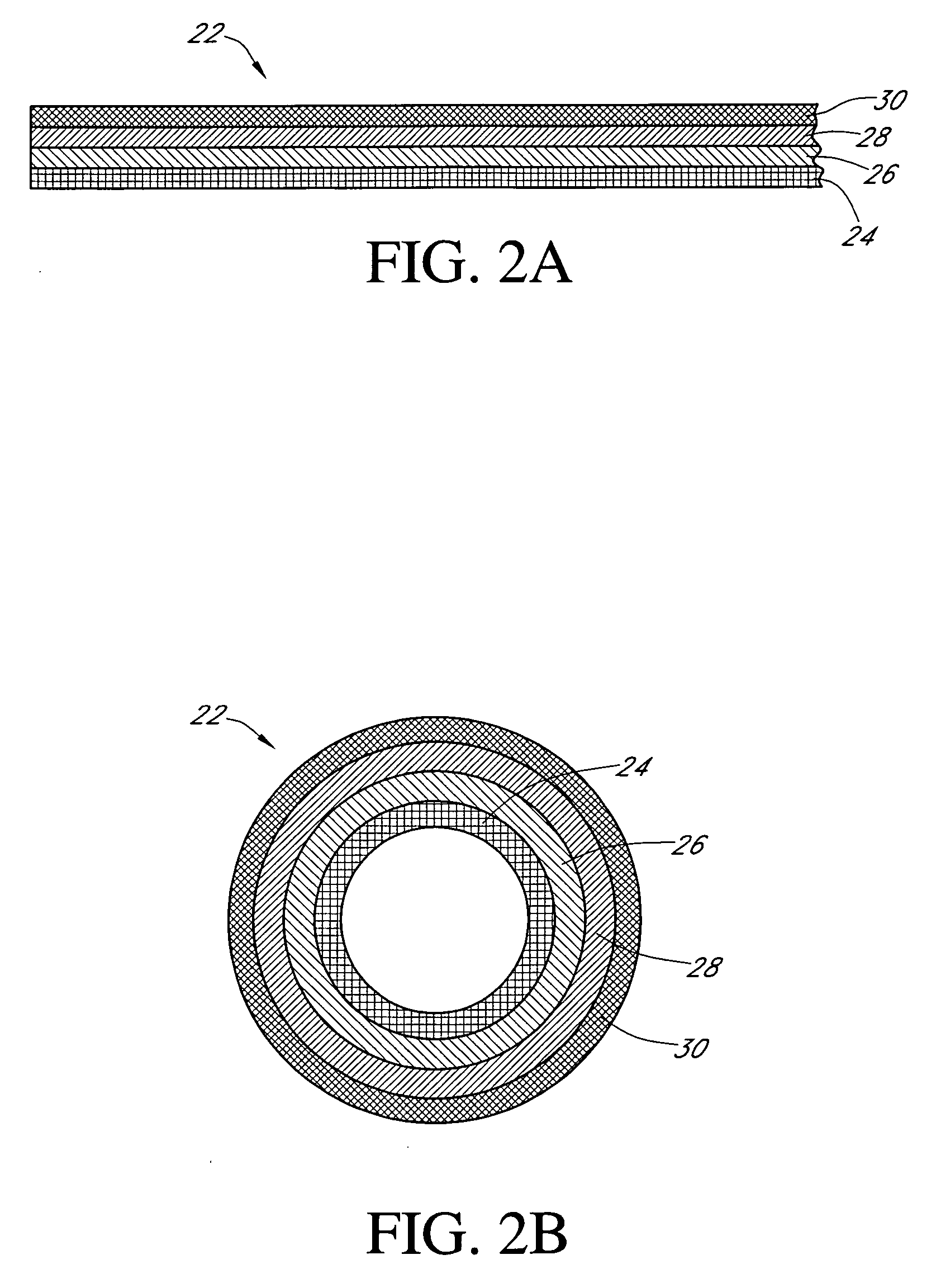
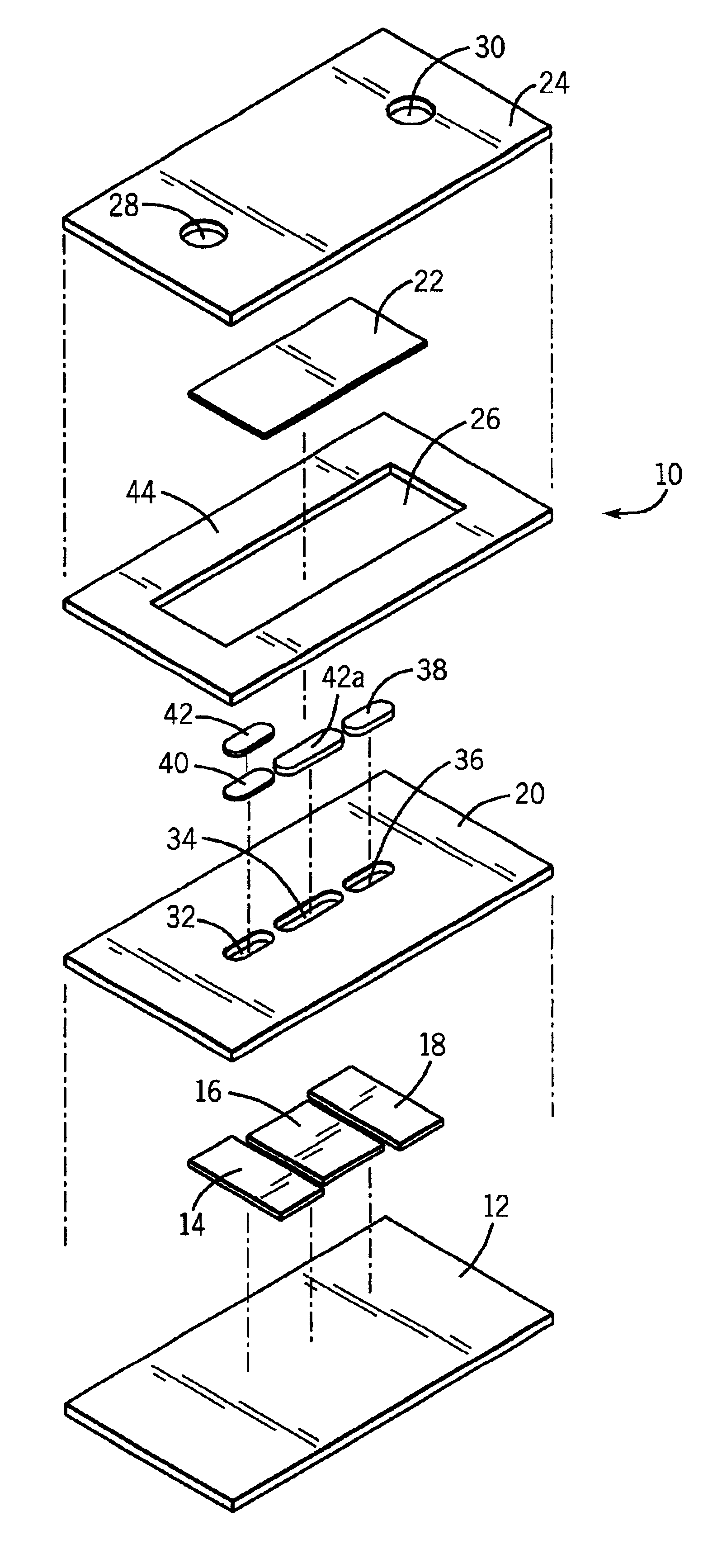
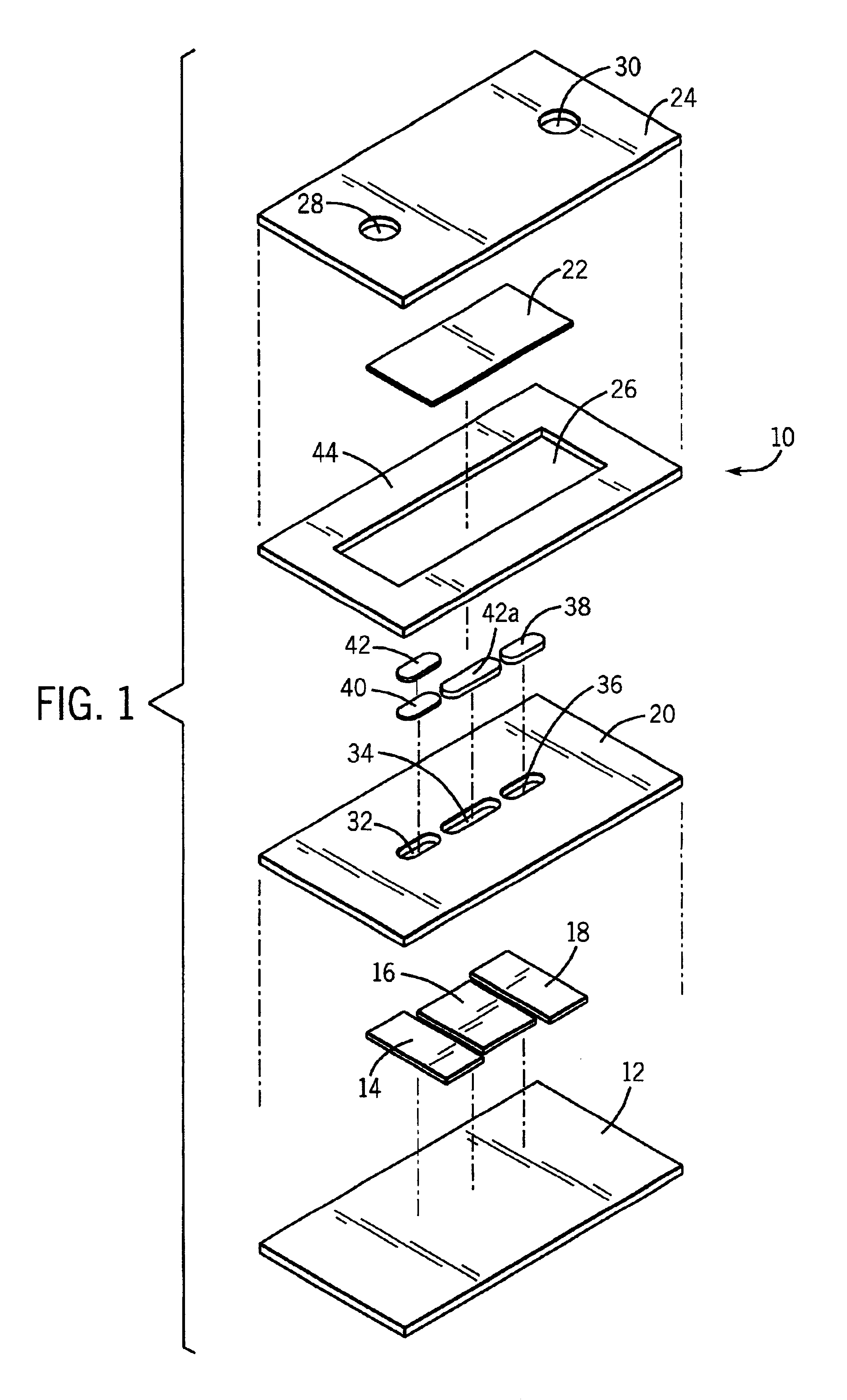
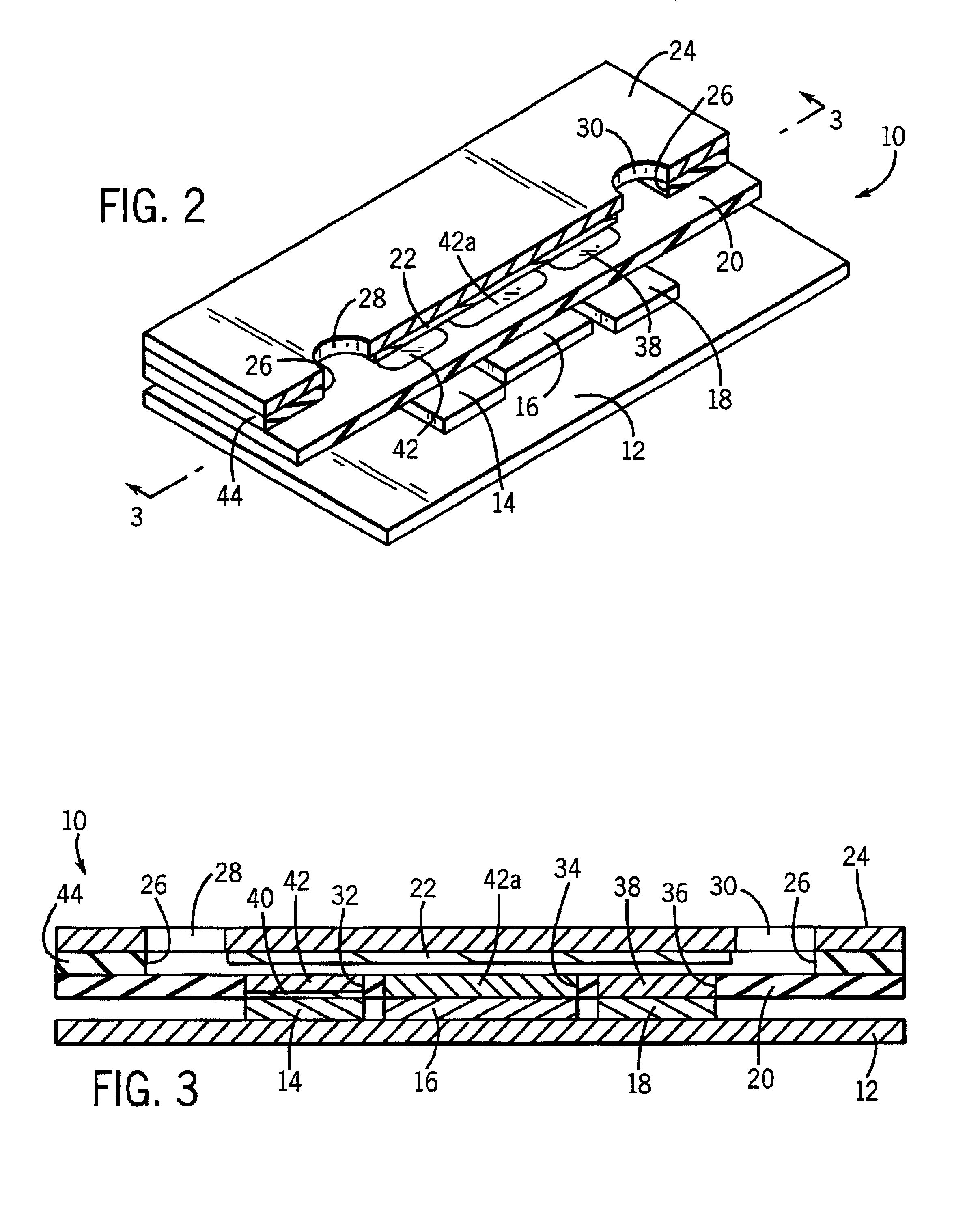
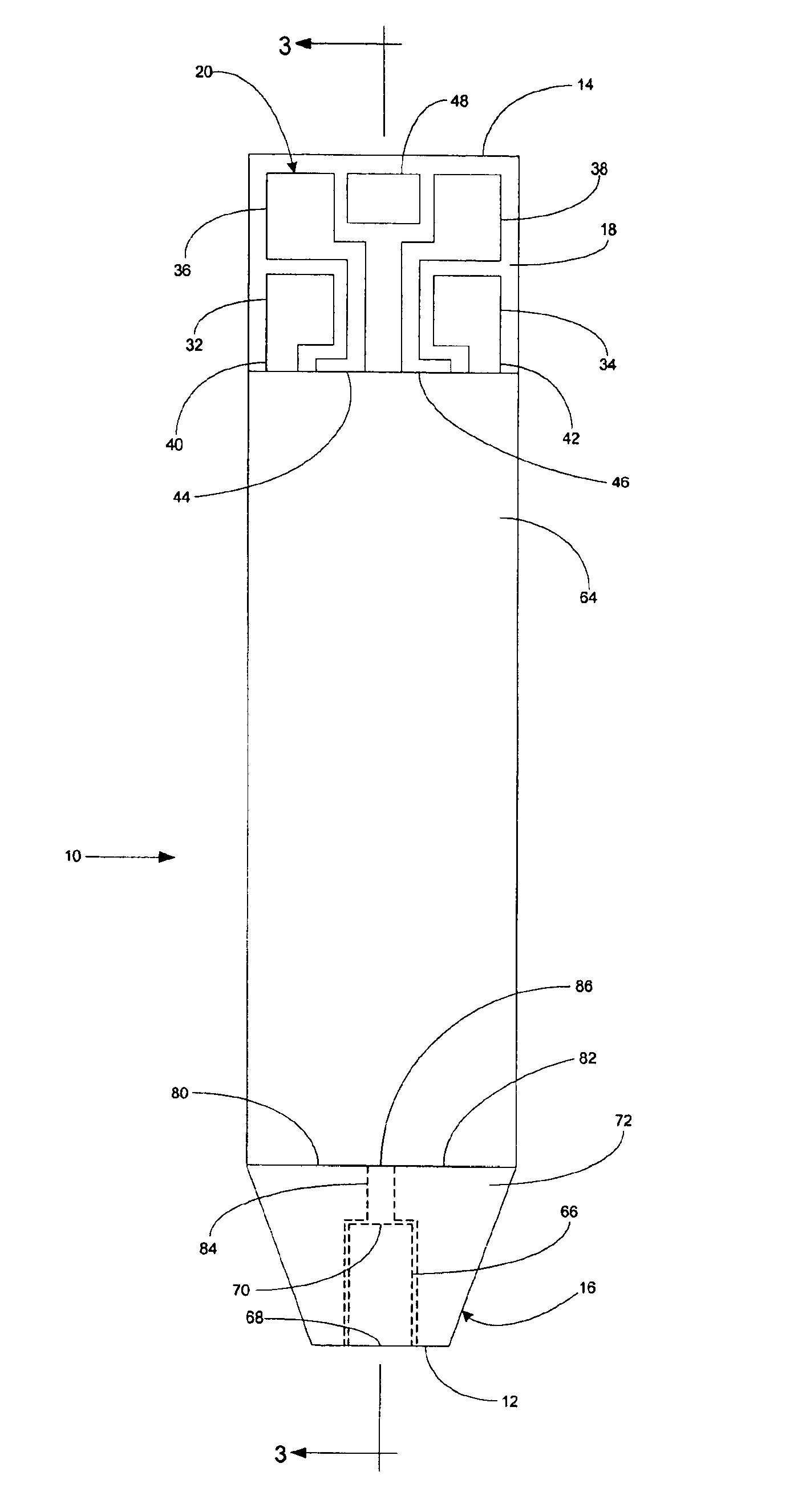
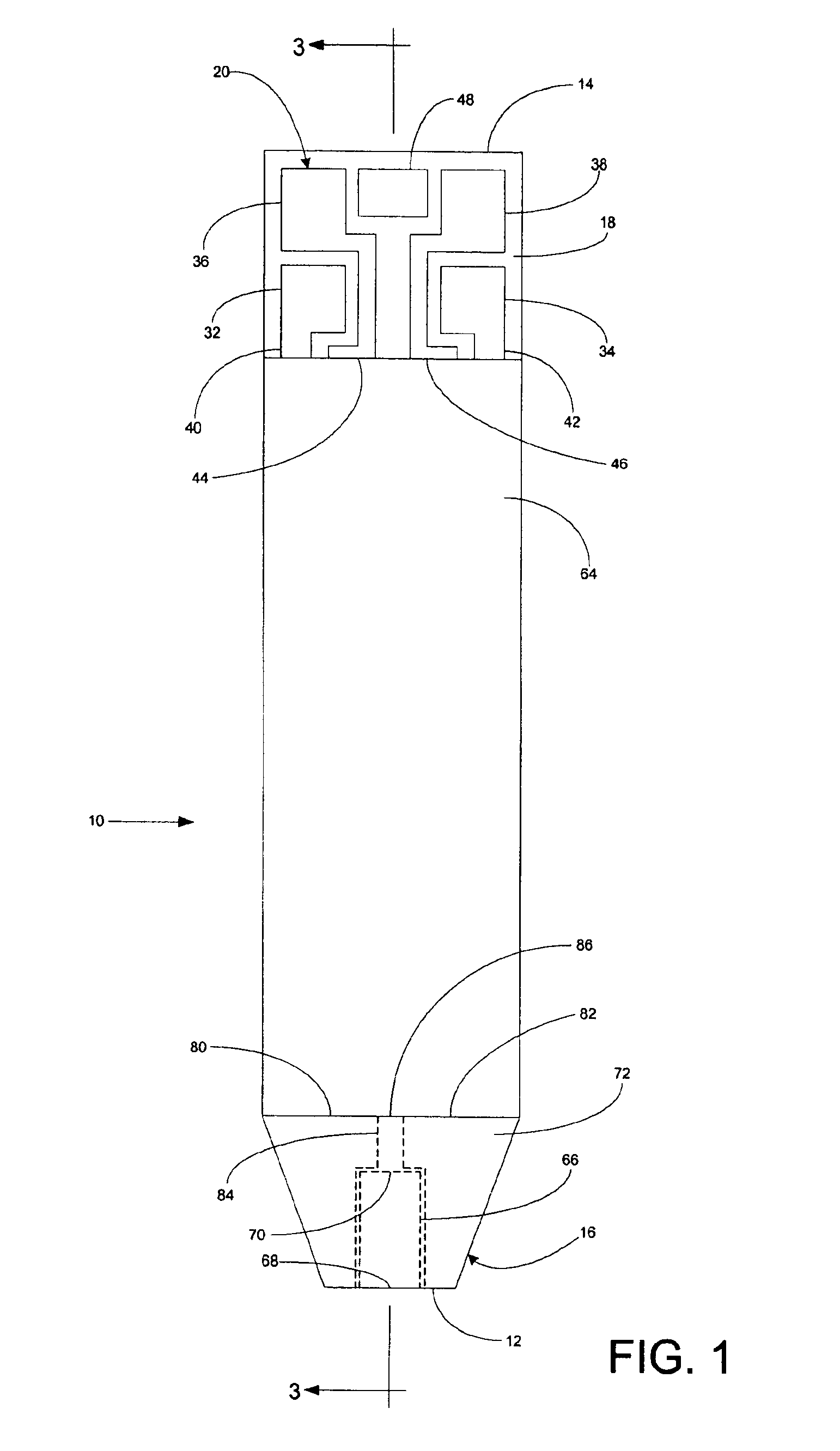
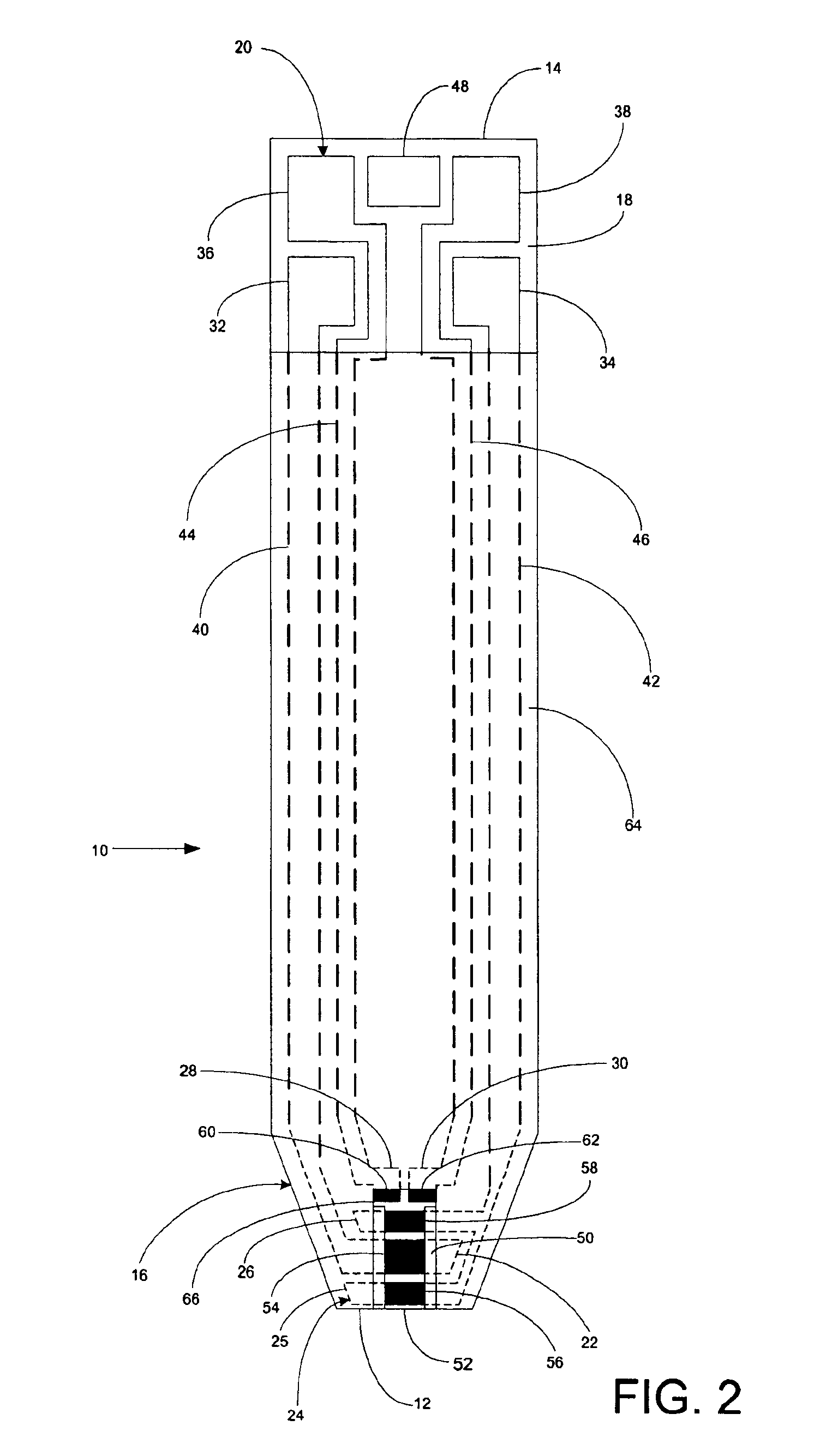
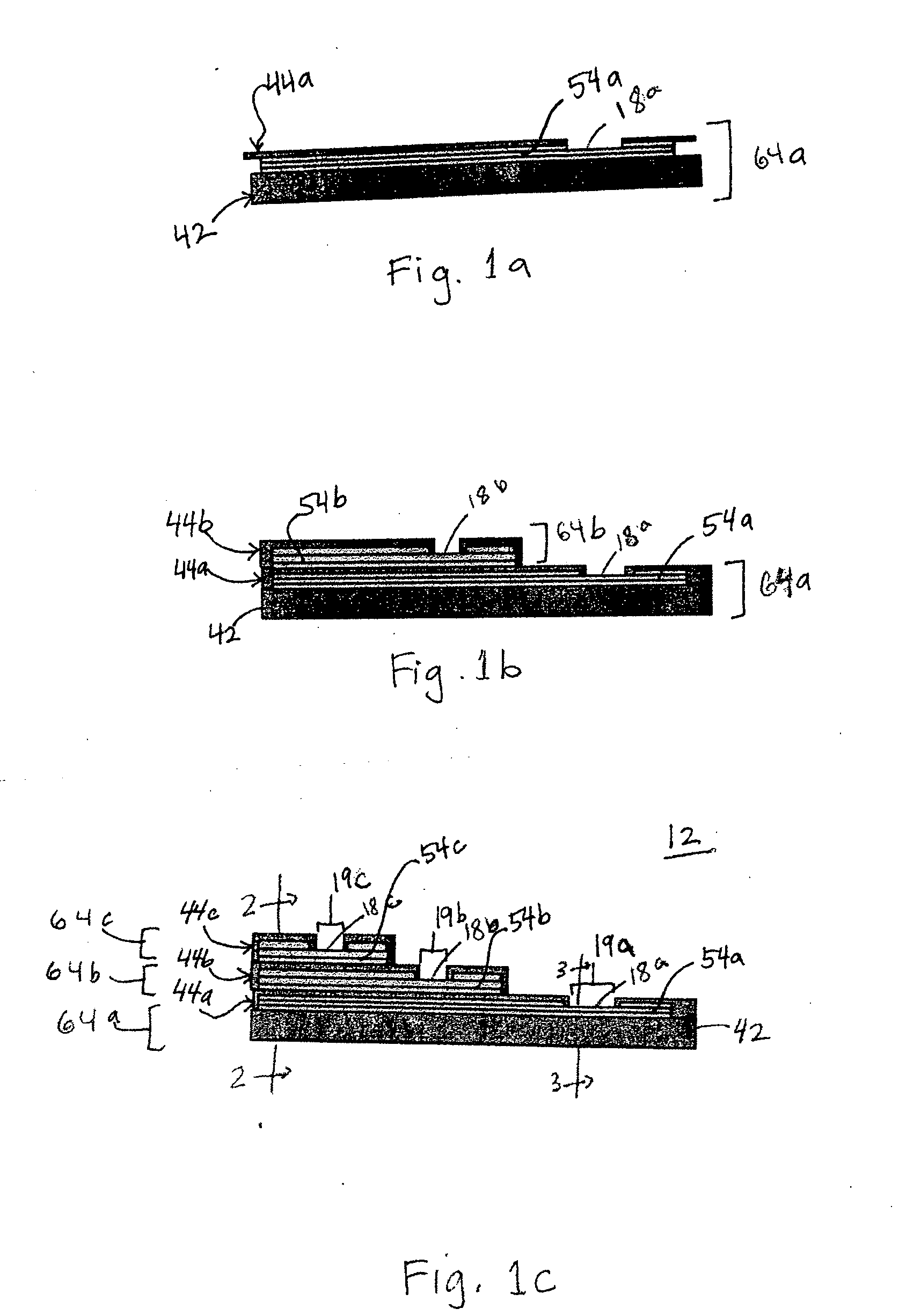
An electrochemical analyte sensor having conductive traces on a substrate is used to determine a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Enzyme electrode structure
InactiveUS6071391AEasy to manufactureEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzyme electrodeWorking electrode
A biosensor comprises a space part for sucking and housing a sample formed of two upper and lower plates, the two plates being stuck together by an adhesive layer, the space part for sucking and housing the sample being constituted so as to be partially opened in the peripheral part and partially closed by the adhesive layer, and has a working electrode having at least glucose oxidase immobilized thereon and a counter electrode on the same plane of the plate.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
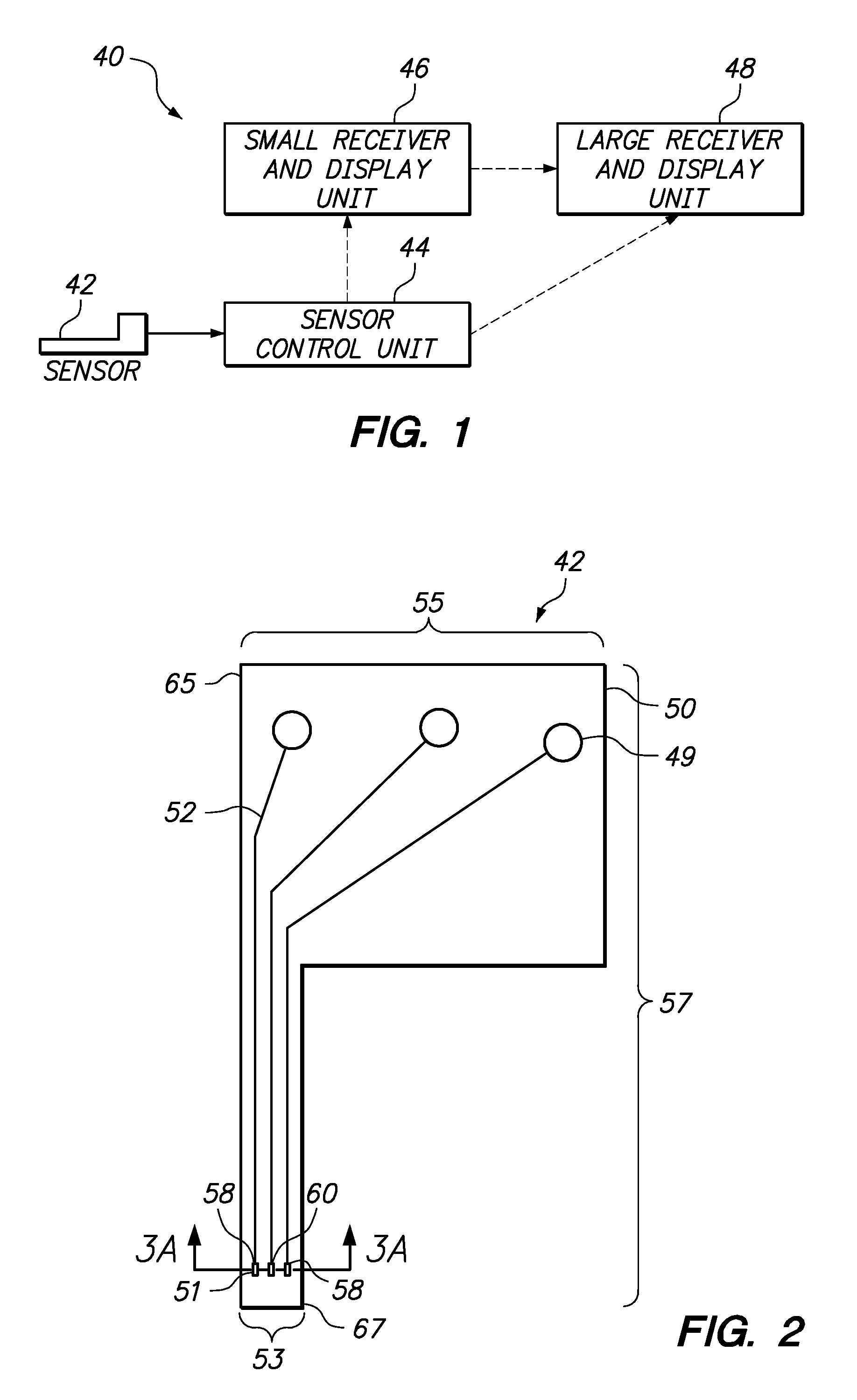
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
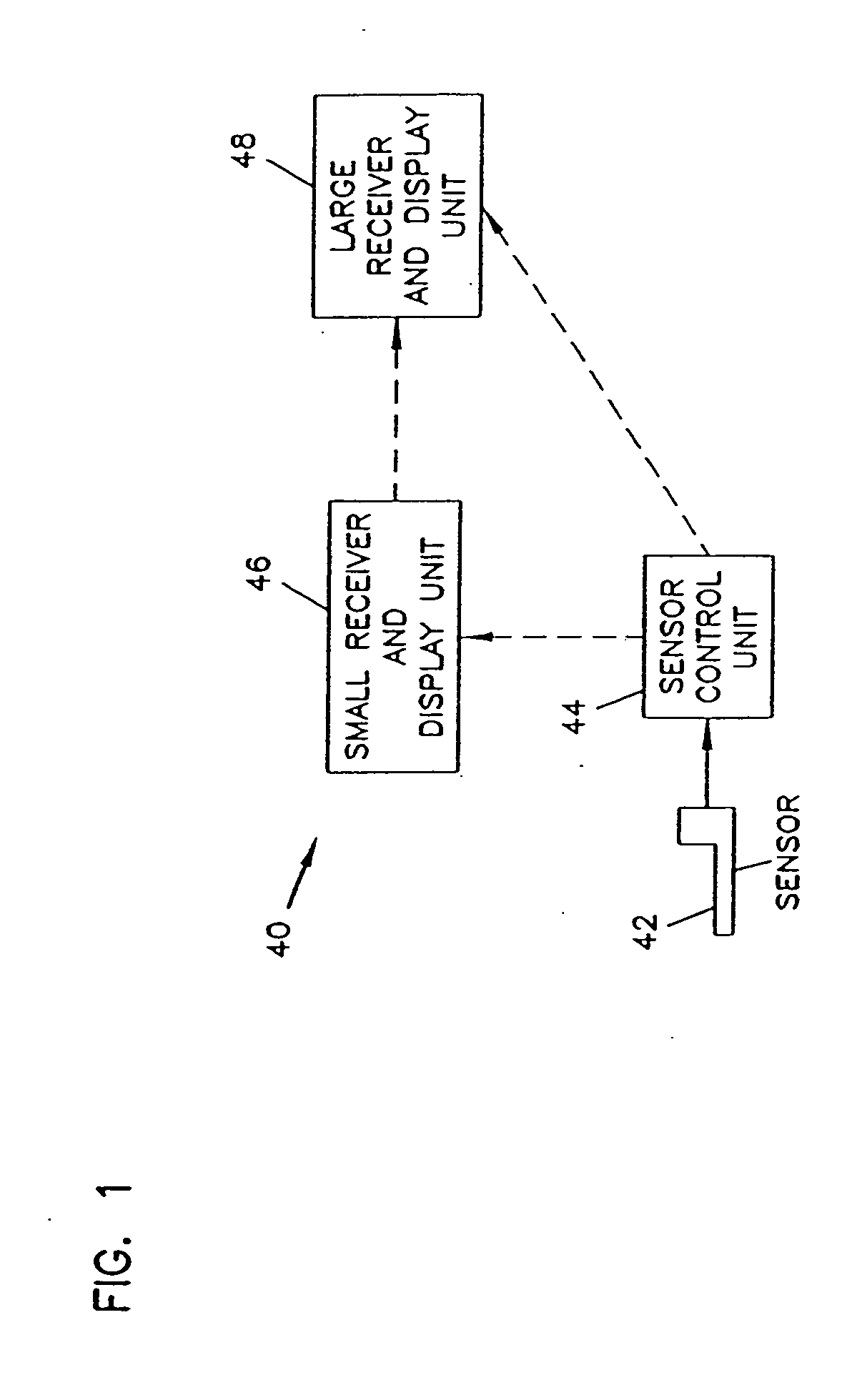
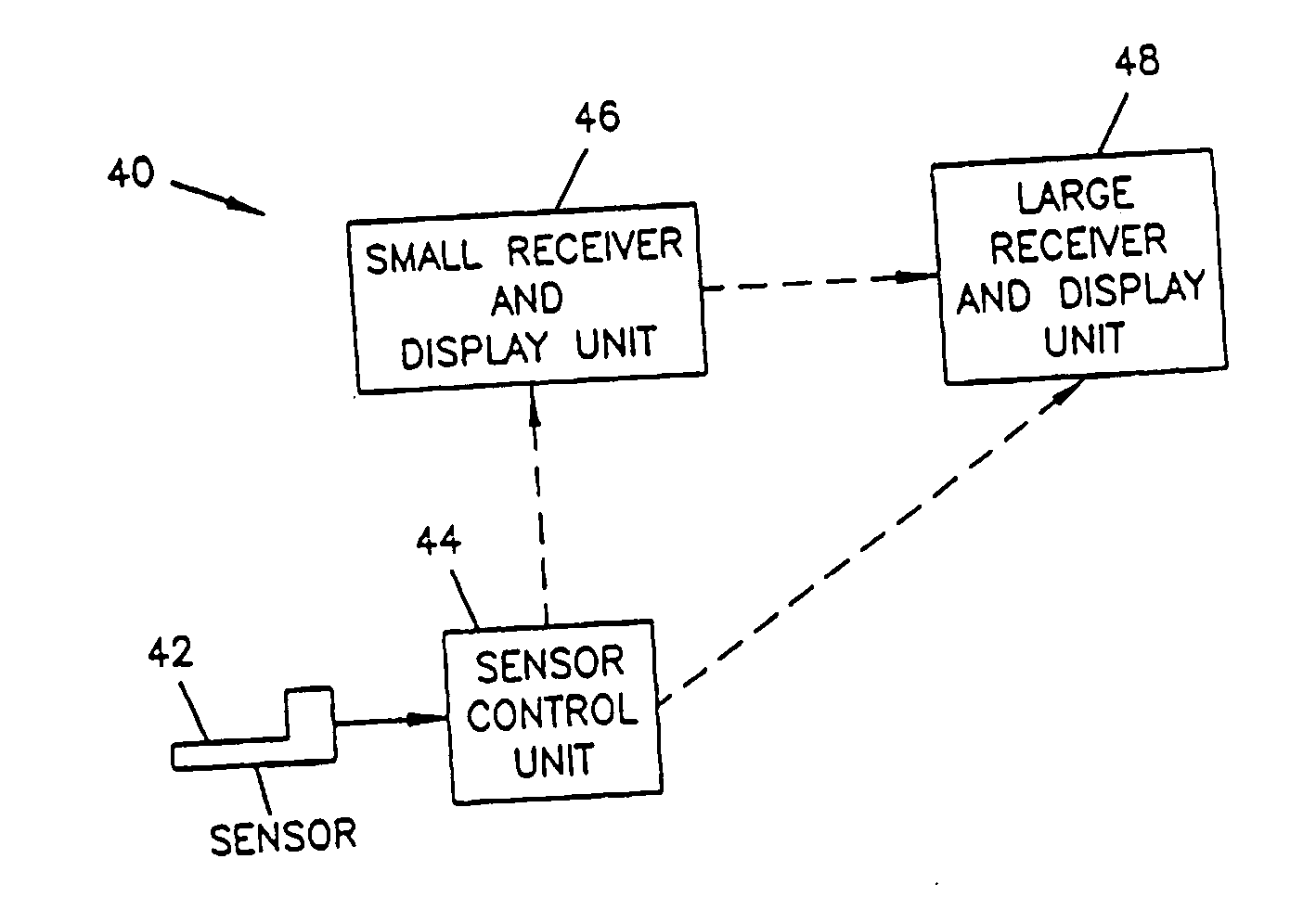
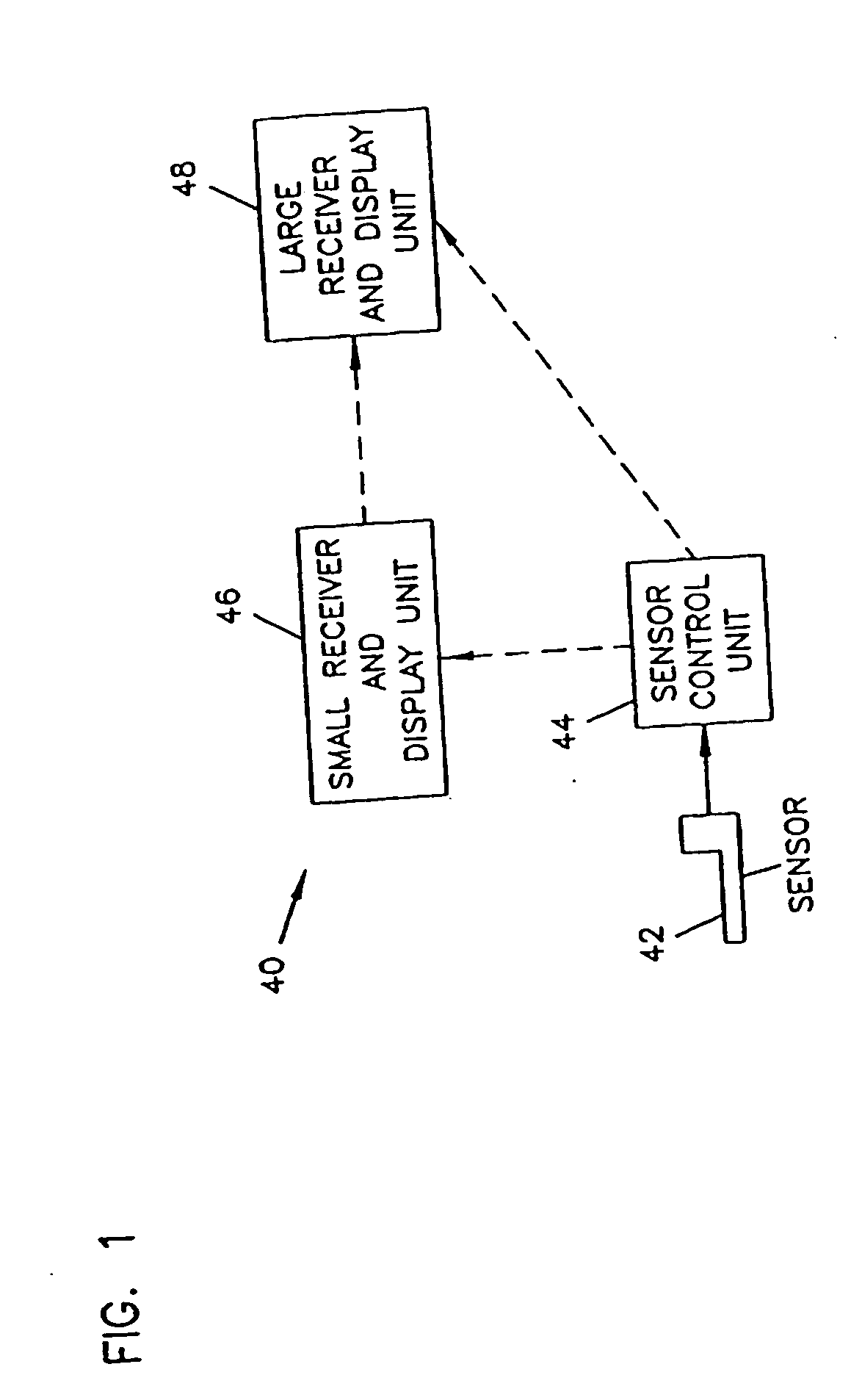
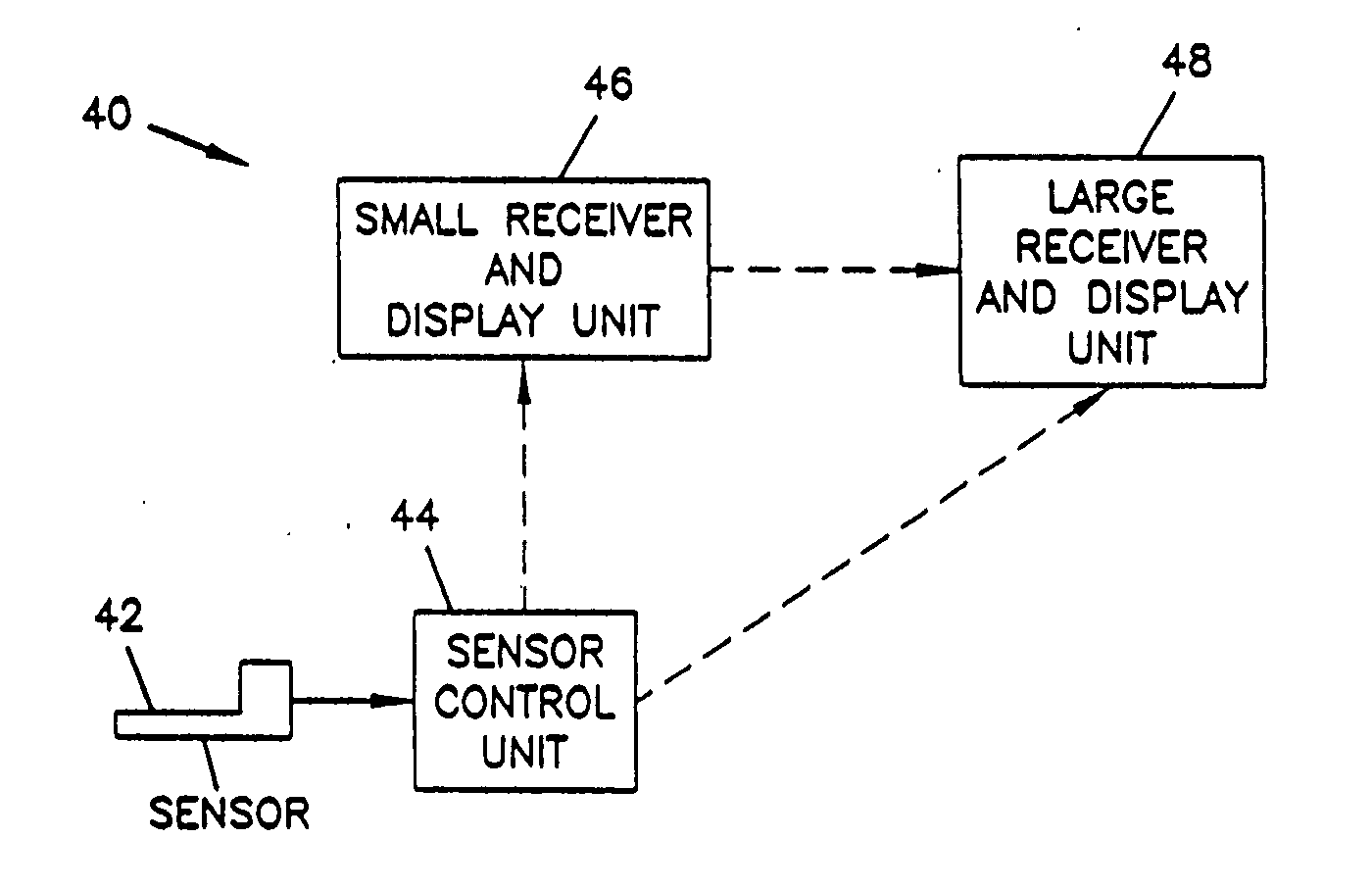
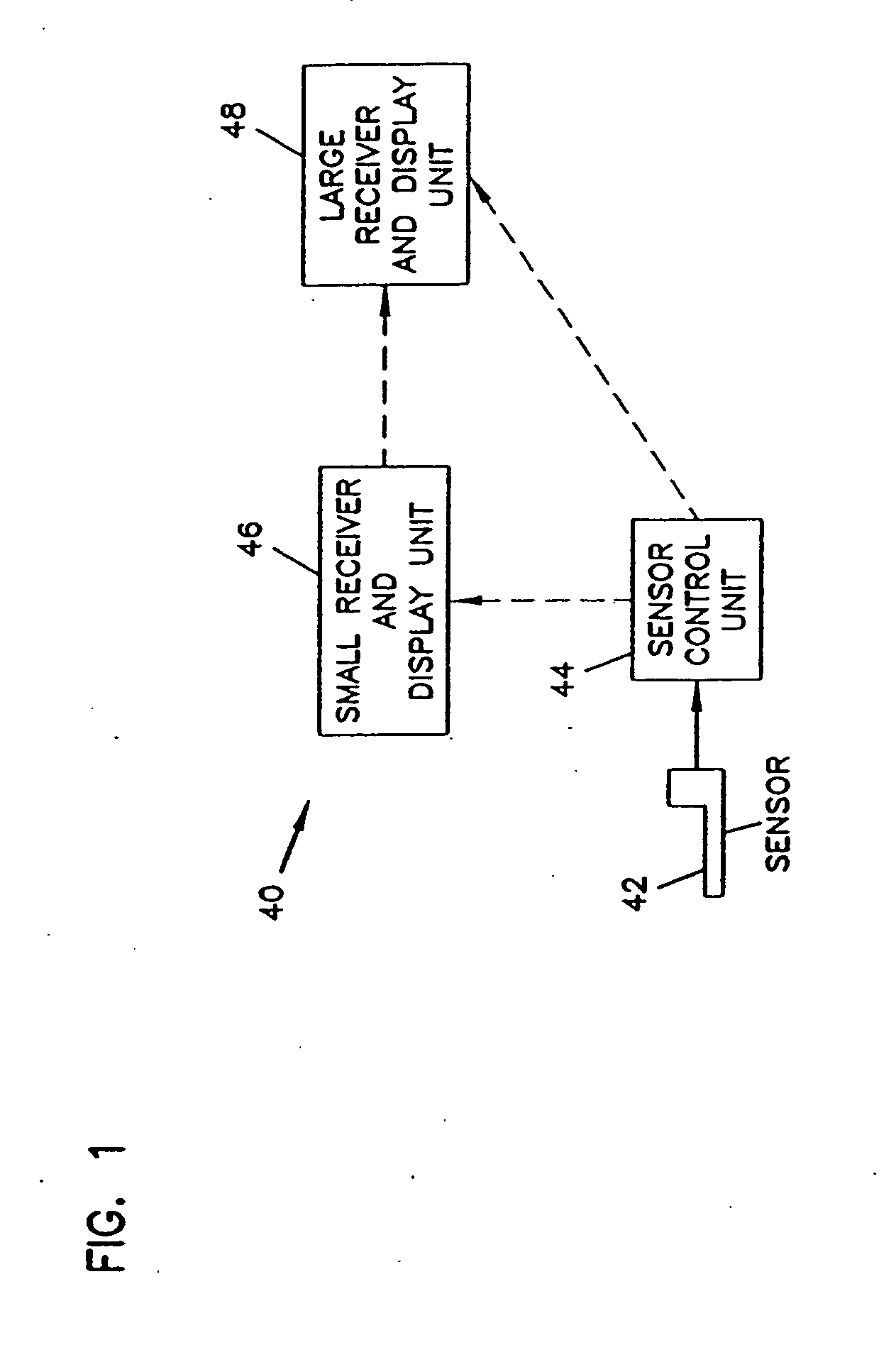
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:THERASENSE
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7366556B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
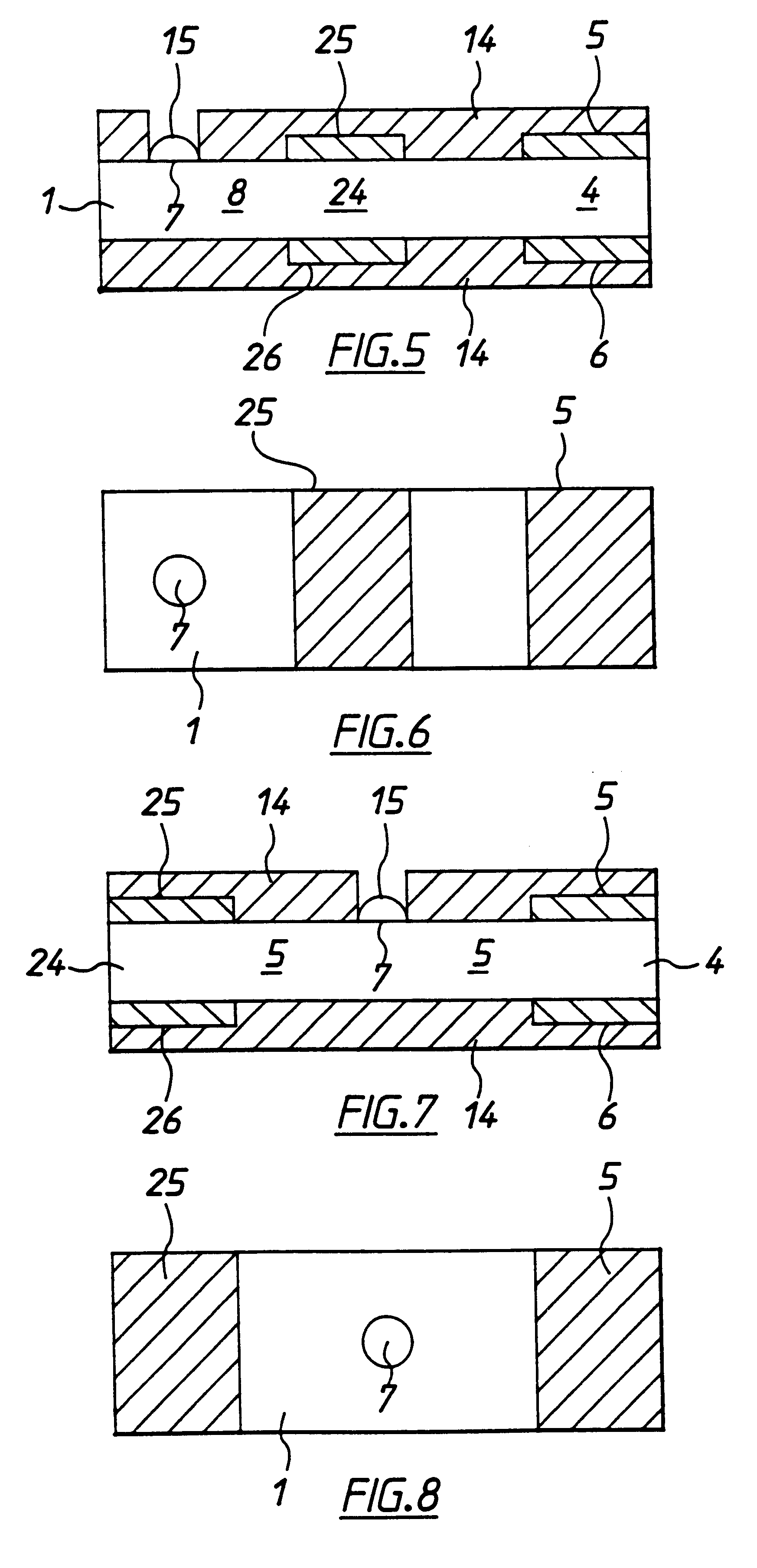
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20090099436A1Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCatheterAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7467003B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7460898B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS7424318B2Improve convenienceEasy CalibrationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
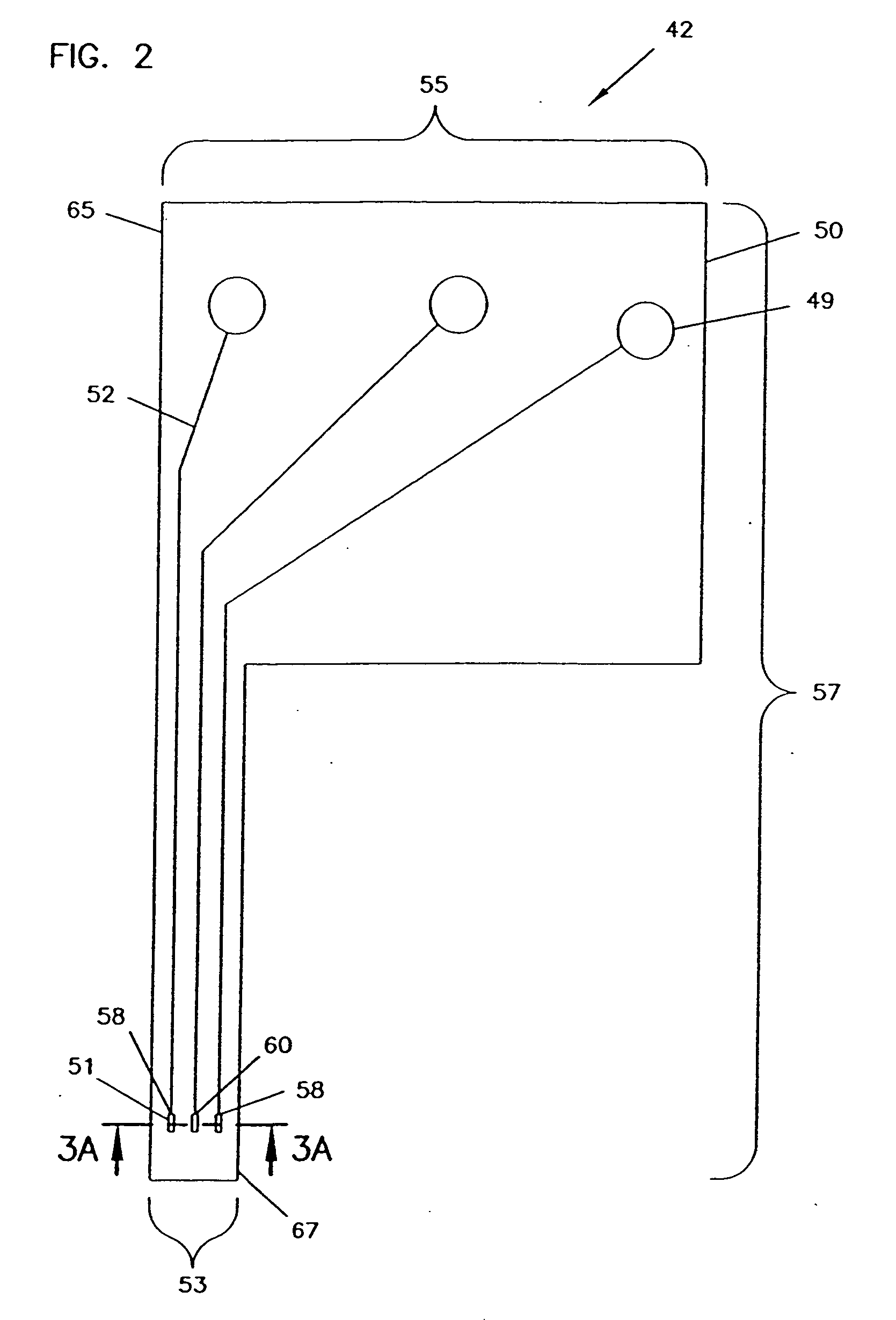
Sensor head for use with implantable devices
InactiveUS7471972B2Minimizing negative potential extremesImprove solubilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseAnalyte
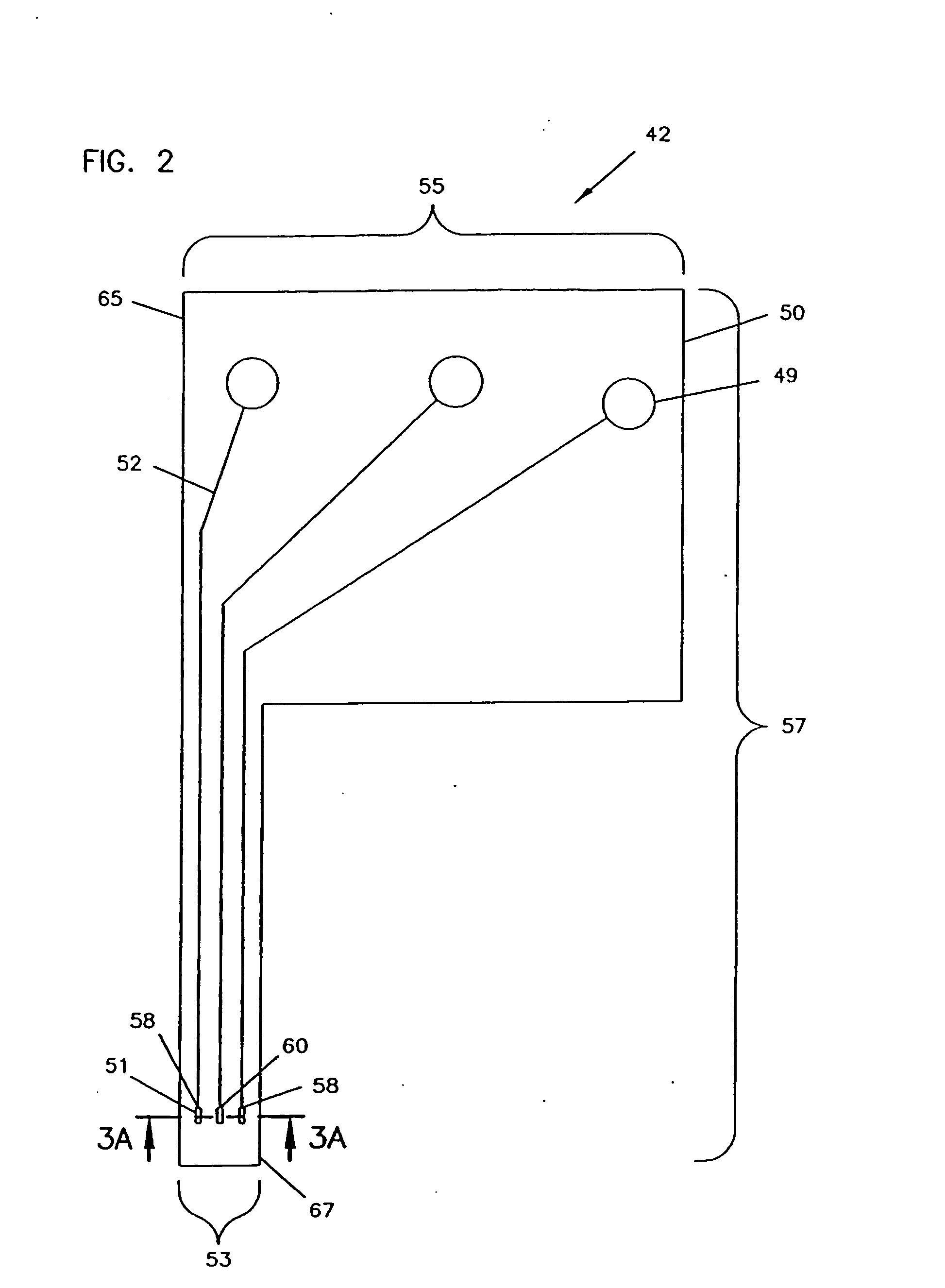
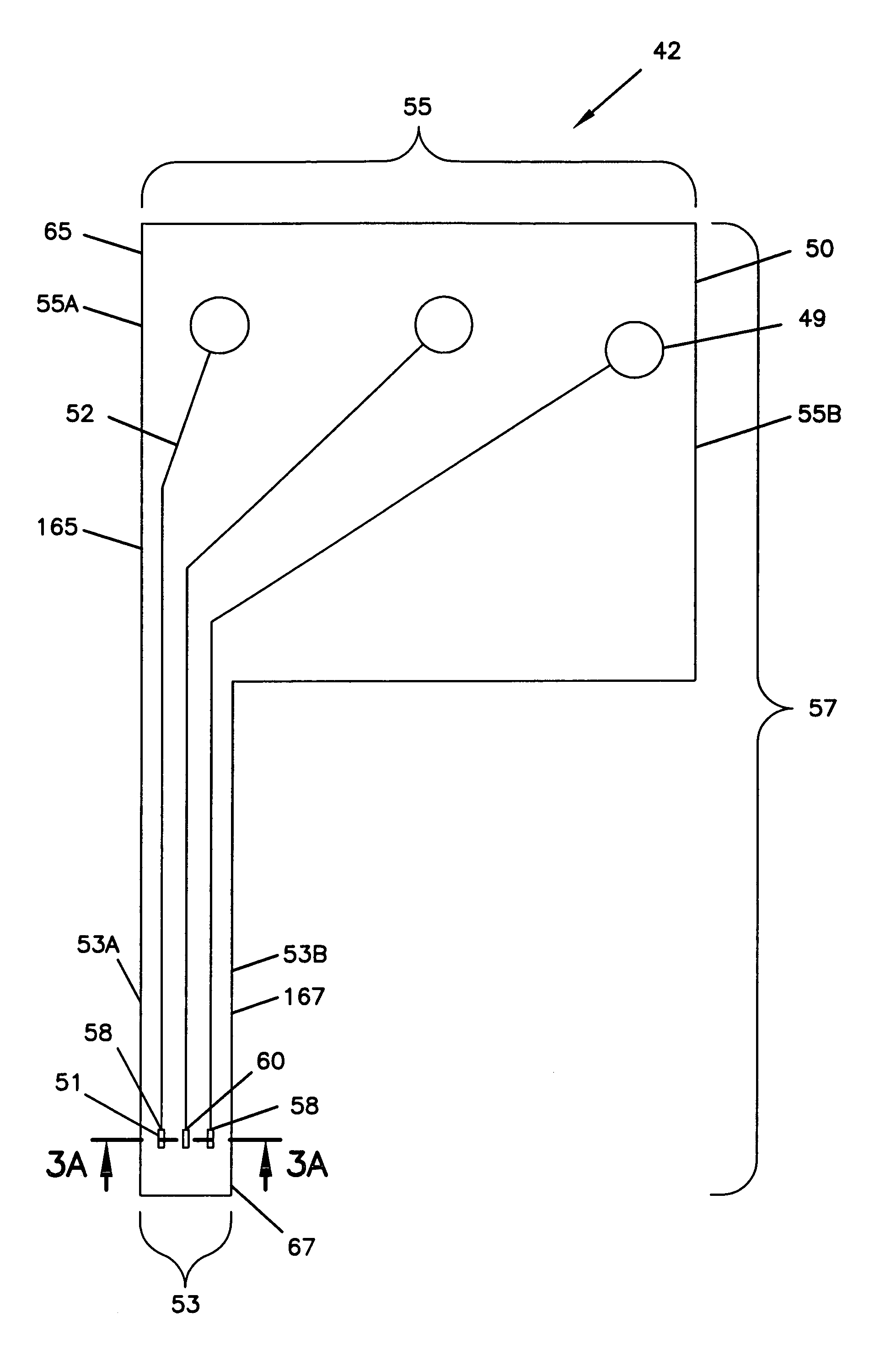
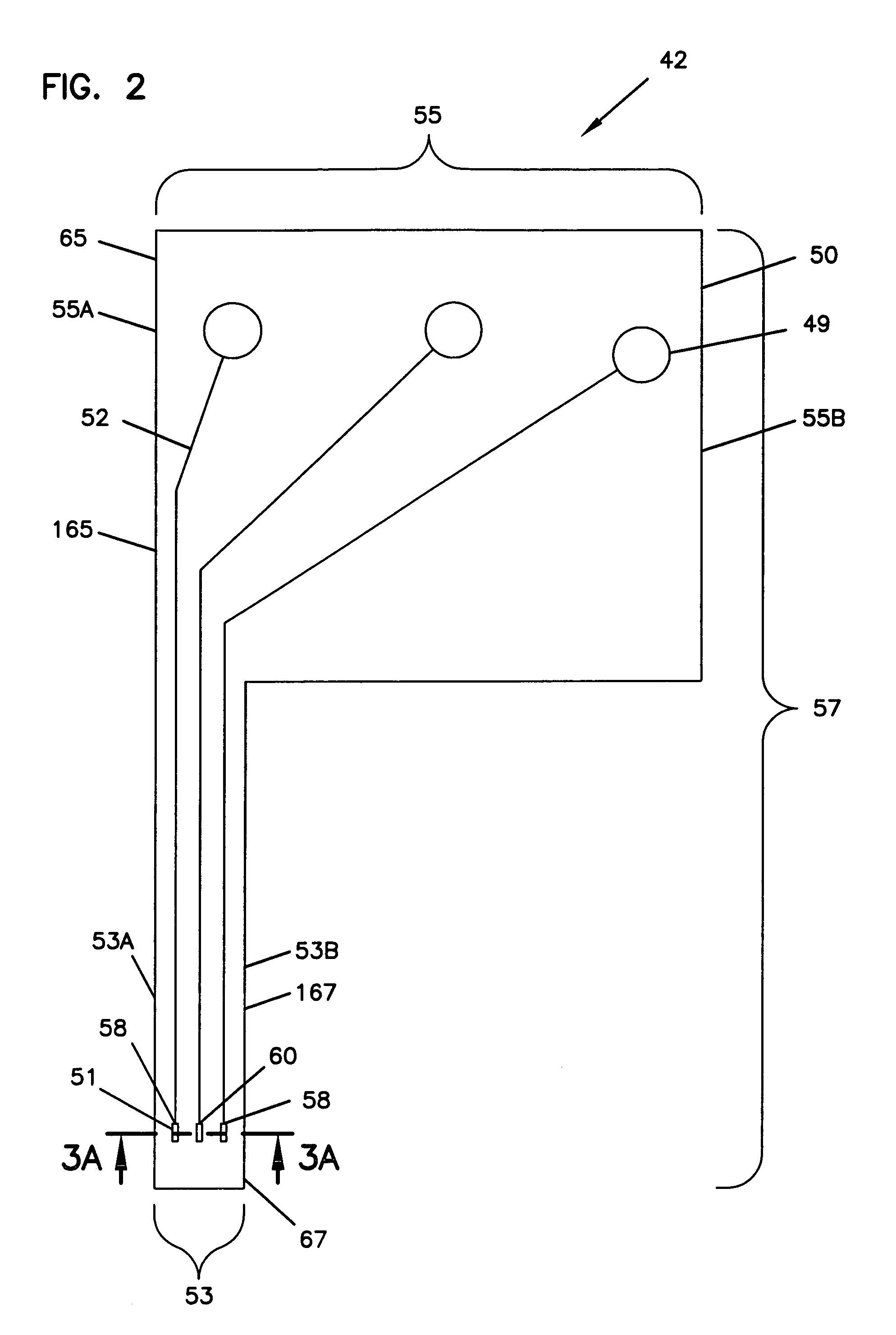
The present invention provides a sensor head for use in an implantable device that measures the concentration of an analyte in a biological fluid which includes: a non-conductive body; a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode, wherein the electrodes pass through the non-conductive body forming an electrochemically reactive surface at one location on the body and forming an electronic connection at another location on the body, further wherein the electrochemically reactive surface of the counter electrode is greater than the surface area of the working electrode; and a multi-region membrane affixed to the nonconductive body and covering the working electrode, reference electrode and counter electrode. In addition, the present invention provides an implantable device including at least one of the sensor heads of the invention and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the implantable device of the invention.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS7003340B2Avoid and reduce corrosionRotary clutchesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrolysisAnalyte
An electrochemical analyte sensor formed using conductive traces on a substrate can be used for determining and / or monitoring a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. For example, an implantable sensor may be used for the continuous or automatic monitoring of a level of an analyte, such as glucose, lactate, or oxygen, in a patient. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the body fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20080214918A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringAnalyteGlucose sensors
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Electrochemical cell
InactiveUS6284125B1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityDiffusion
A method for determining the concentration of a reduced (or oxidised) form of a redox species in an electrochemical cell of the kind comprising a working electrode and a counter electrode spaced from the working electrode by a predetermined distance, said method comprising the steps of: (1) applying an electric potential difference between the electrodes; (2) selecting the potential of the working electrode such that the rate of electro-oxidation of the reduced form (or electro-reduction of the oxidised form) of the species is diffusion controlled, (3) selecting the spacing between the working electrode and the counter electrode so that reaction products from the counter electrode arrive at the working electrode; (4) determining current as a function of time after application of the potential and prior to achievement of a steady state; (5) estimating the magnitude of the steady state current, and (6) obtaining from the change in current with time and the magnitude of the steady state current, a value indicative of the diffusion coefficient and / or of the concentration of the reduced form (or the oxidised form) of the species. Also disclosed is an apparatus for determining the concentration of a redox species in an electrochemical cell comprising: an electrochemical cell having a working electrode and a counter (or counter / reference) electrode, means for applying and electric potential difference between said electrodes, means for measuring the change in current with time, and characterised in that the working electrode is spaced from the counter electrode by less than 500 mum.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Integrated Lancing and Measurement Device
InactiveUS20080017522A1Accurate and efficient measurementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMeasurement device
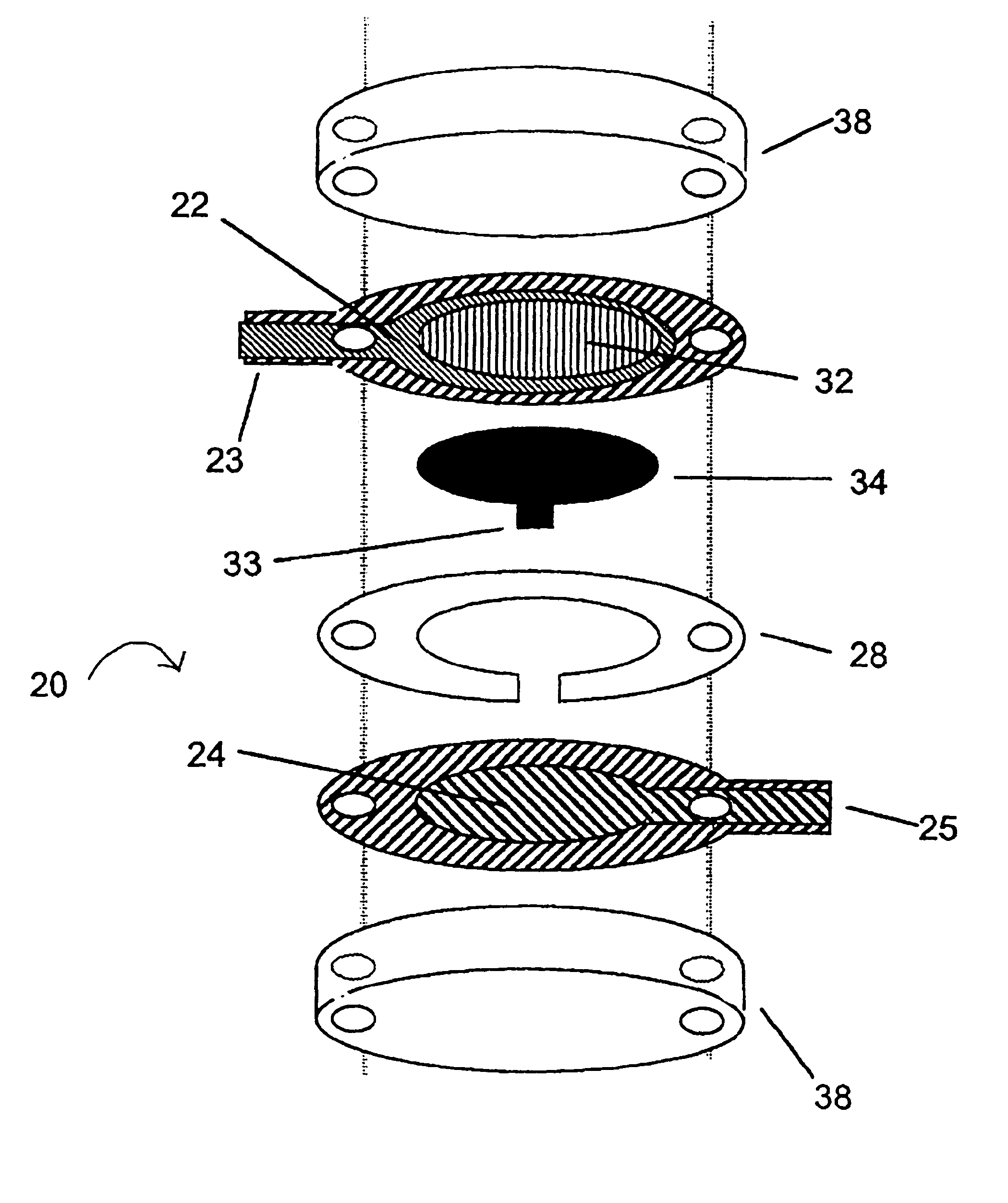
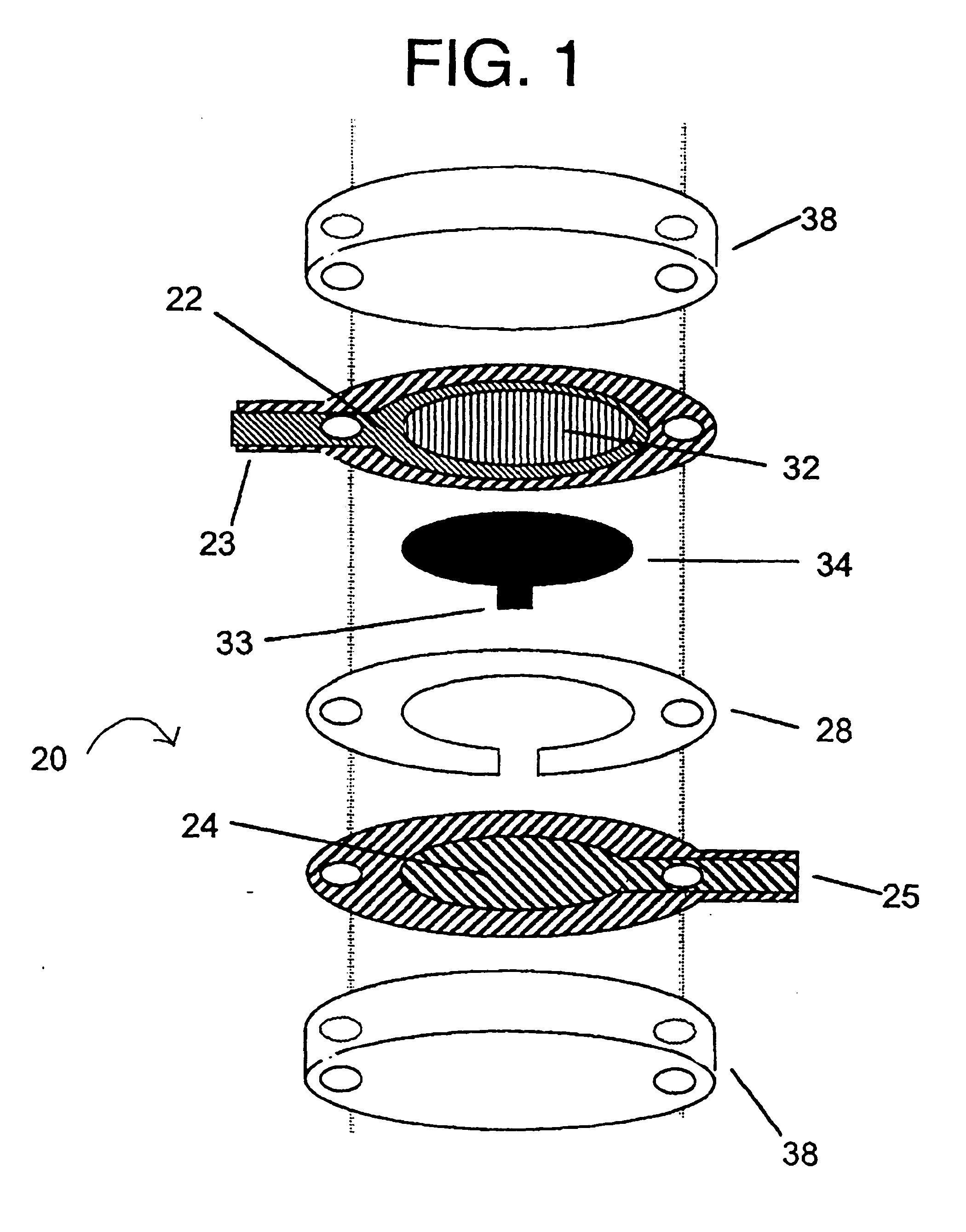
An integrated lancing and measurement device is provided comprising a sensor designed to determine the amount and / or concentration of analyte in a biological fluid having a volume of less than about 1 μL. A piercing member is adapted to pierce and retract from a site on the patient to cause the fluid to flow therefrom, and the sensor is positioned adjacent to the site on the patient so as to receive the fluid flowing from the site to generate an electrical signal indicative of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid. The sensor is comprised of a working electrode comprising an analyte-responsive enzyme and a redox mediator, and a counter electrode. An analyte monitor is operatively connected to the sensor and adapted to measure the signal generated by the sensor. Also provided are analyte measuring methods that optionally employ the integrated lancing and measurement device.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Increasing bias for oxygen production in an electrode system
InactiveUS20050056552A1Improve device performanceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementProcess engineeringOxygen
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for electrochemical sensing. Particularly, the invention relates to optimizing bias settings in an electrode system to increase oxygen production at the working electrode.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070027385A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte monitoring device and methods of use
An analyte monitor includes a sensor, a sensor control unit, and a display unit. The sensor has, for example, a substrate, a recessed channel formed in the substrate, and conductive material disposed in the recessed channel to form a working electrode. The sensor control unit typically has a housing adapted for placement on skin and is adapted to receive a portion of an electrochemical sensor. The sensor control unit also includes two or more conductive contacts disposed on the housing and configured for coupling to two or more contact pads on the sensor. A transmitter is disposed in the housing and coupled to the plurality of conductive contacts for transmitting data obtained using the sensor. The display unit has a receiver for receiving data transmitted by the transmitter of the sensor control unit and a display coupled to the receiver for displaying an indication of a level of an analyte. The analyte monitor may also be part of a drug delivery system to alter the level of the analyte based on the data obtained using the sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte sensor with insertion monitor, and methods
InactiveUS20060091006A1Efficient and reliable methodEfficient methodImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose polymers
A sensor, and methods of making, for determining the concentration of an analyte, such as glucose or lactate, in a biological fluid such as blood or serum, using techniques such as coulometry, amperometry, and potentiometry. The sensor includes a working electrode and a counter electrode, and can include an insertion monitoring trace to determine correct positioning of the sensor in a connector.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
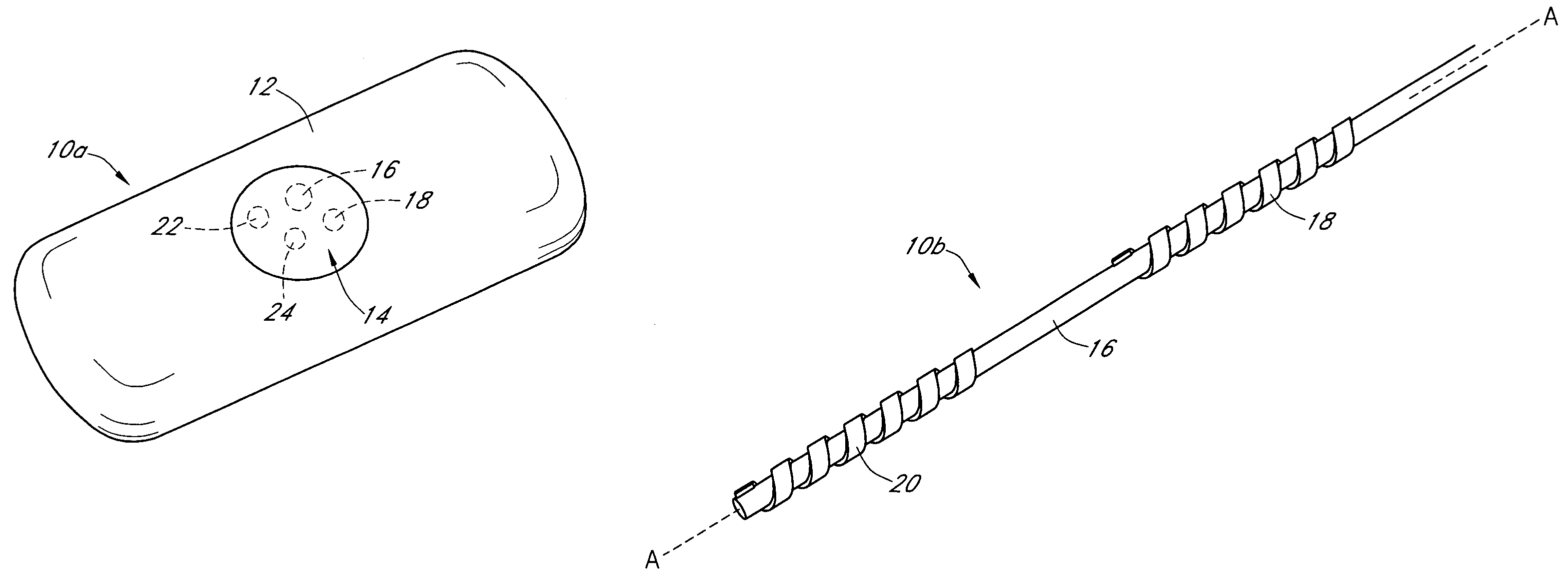
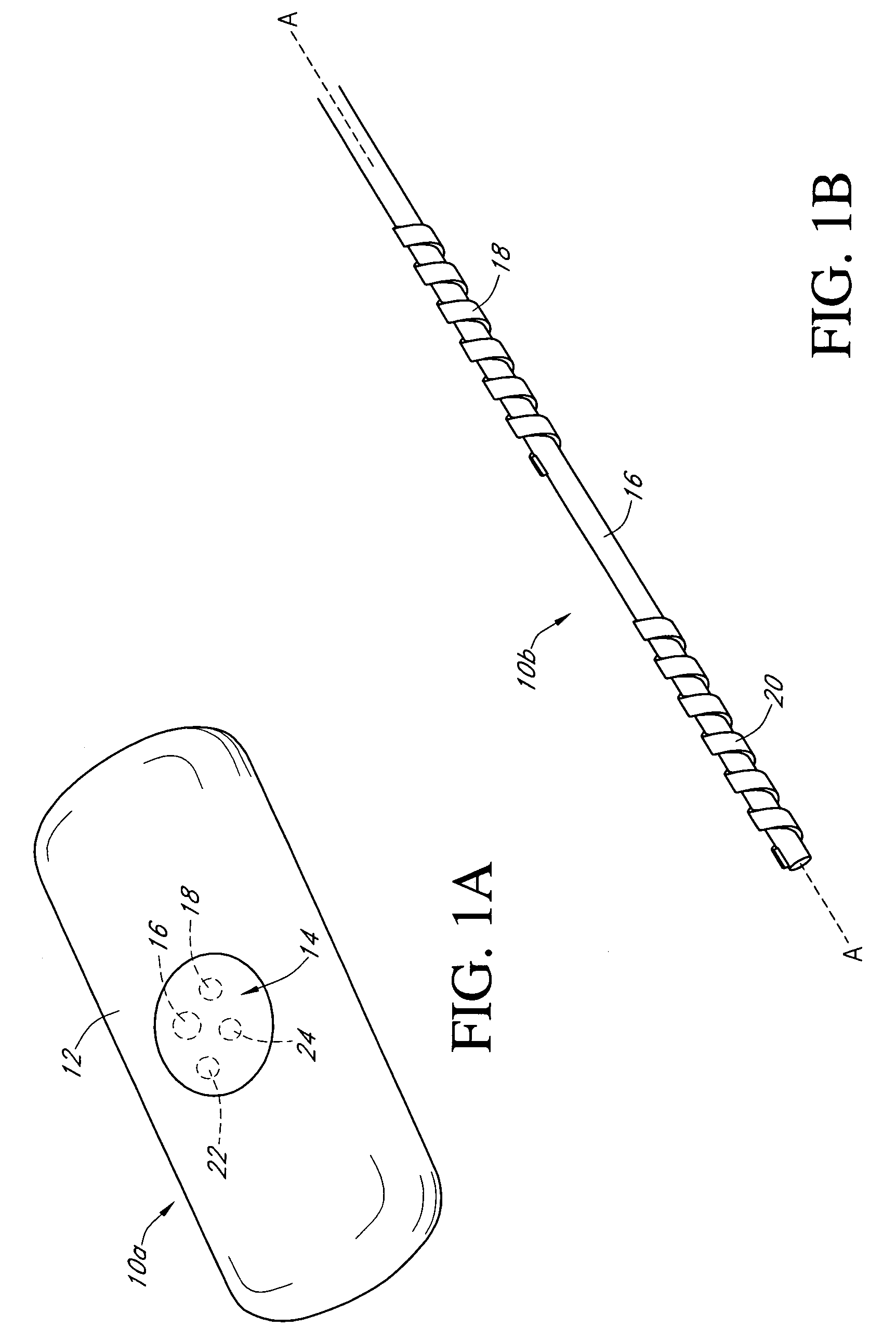
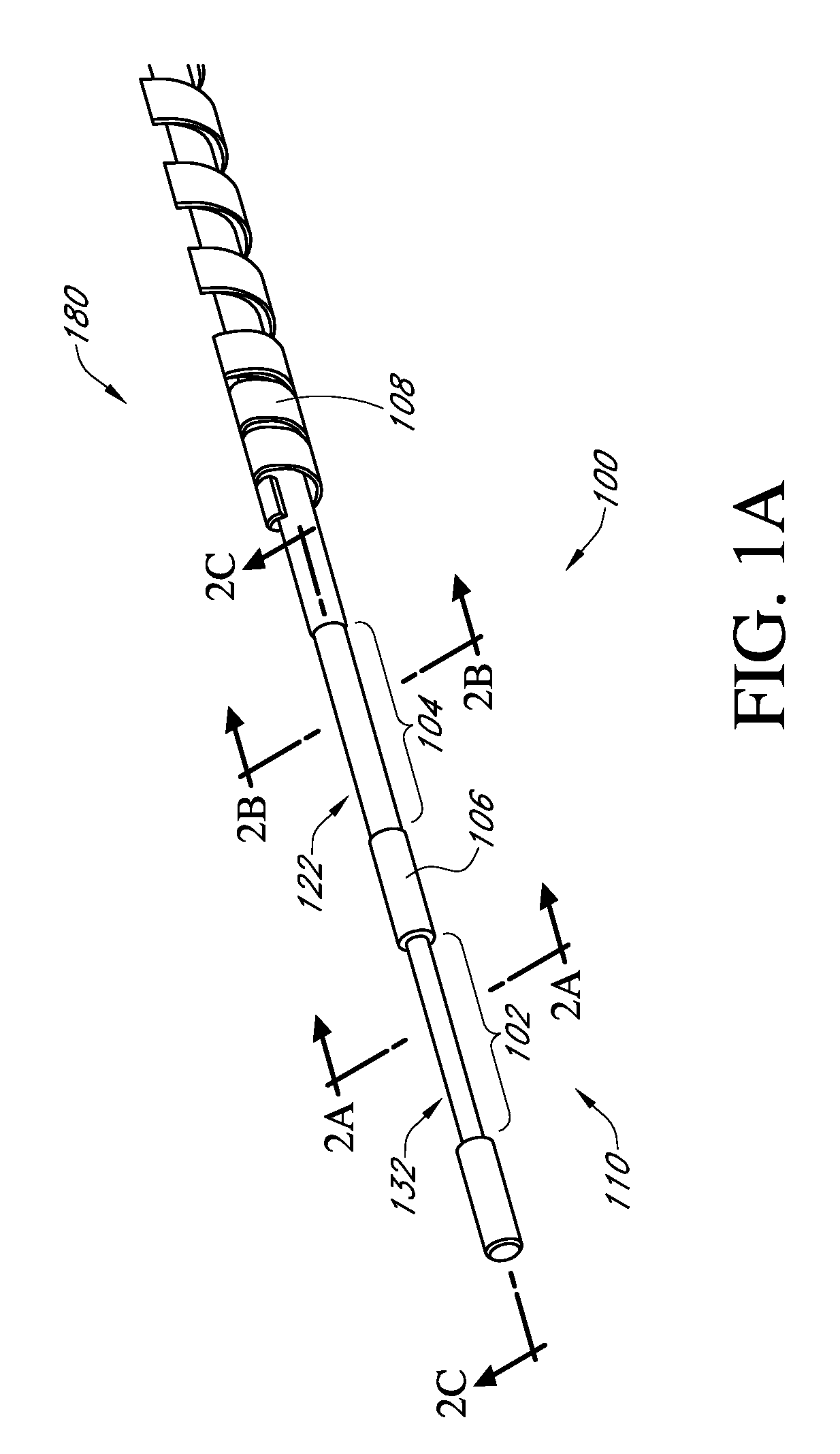
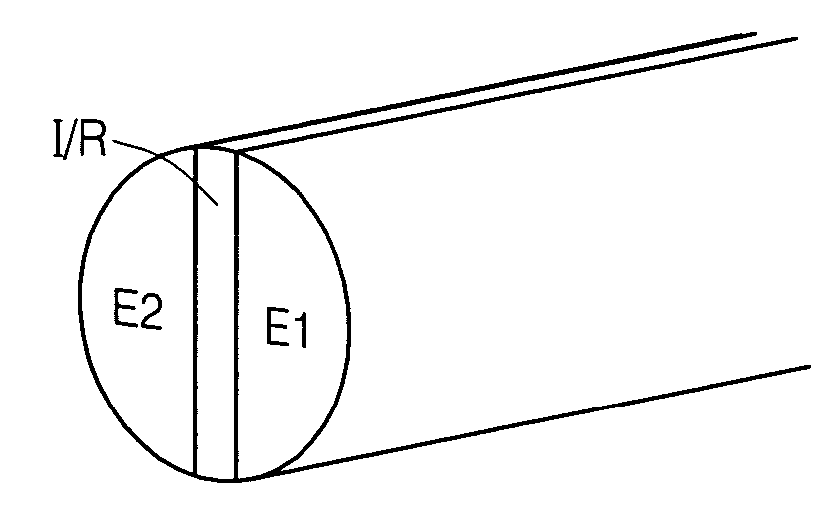
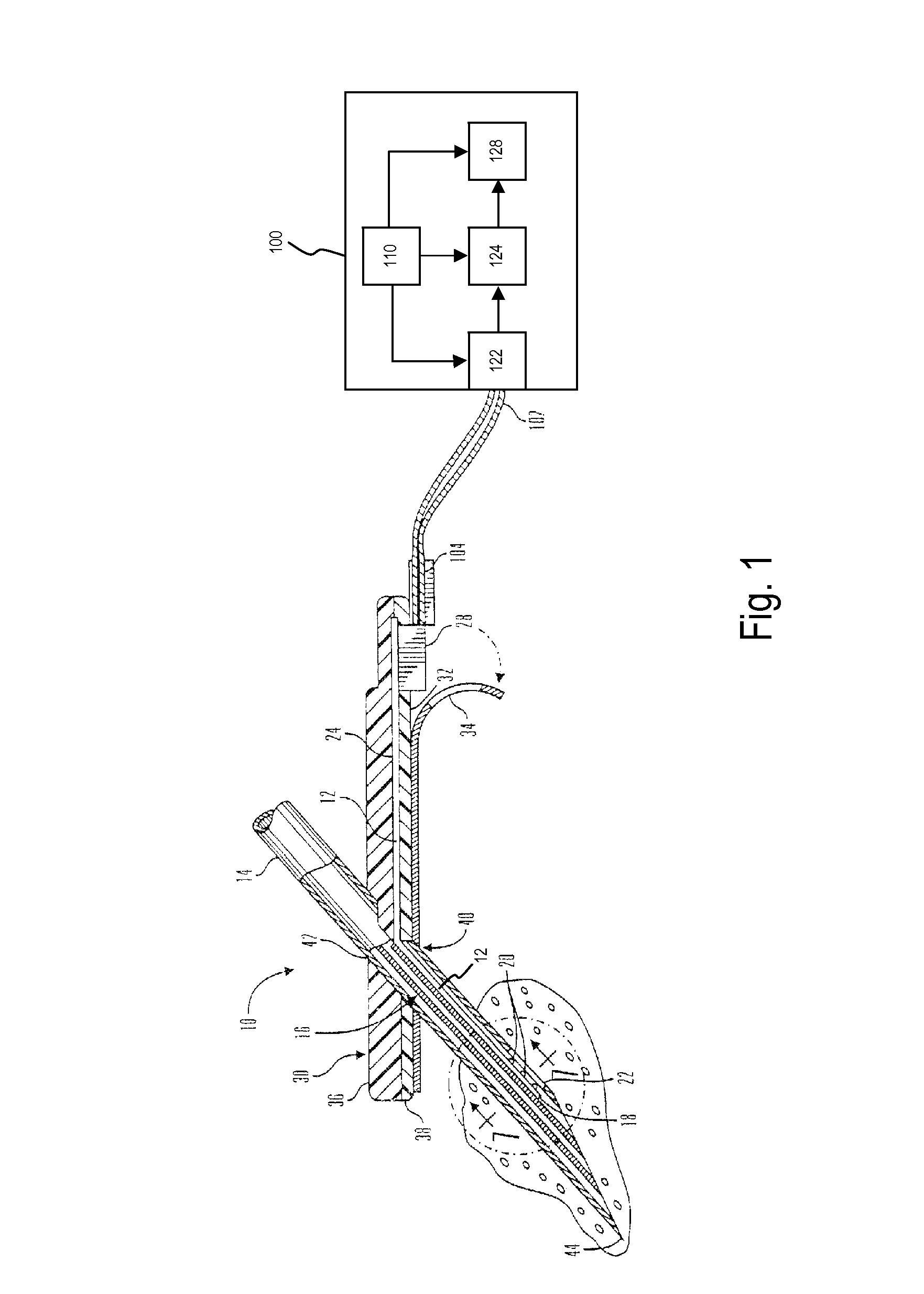
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same
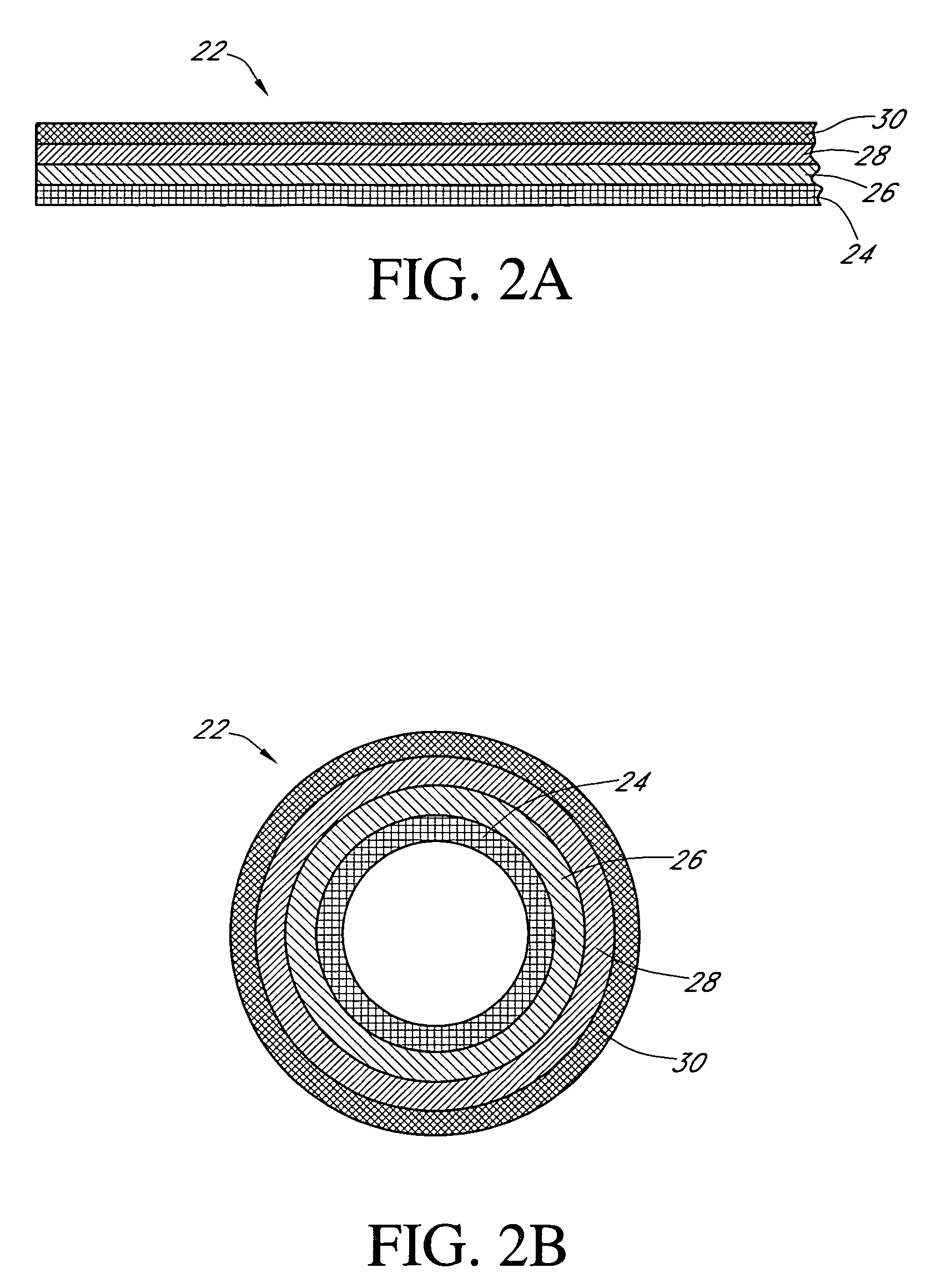
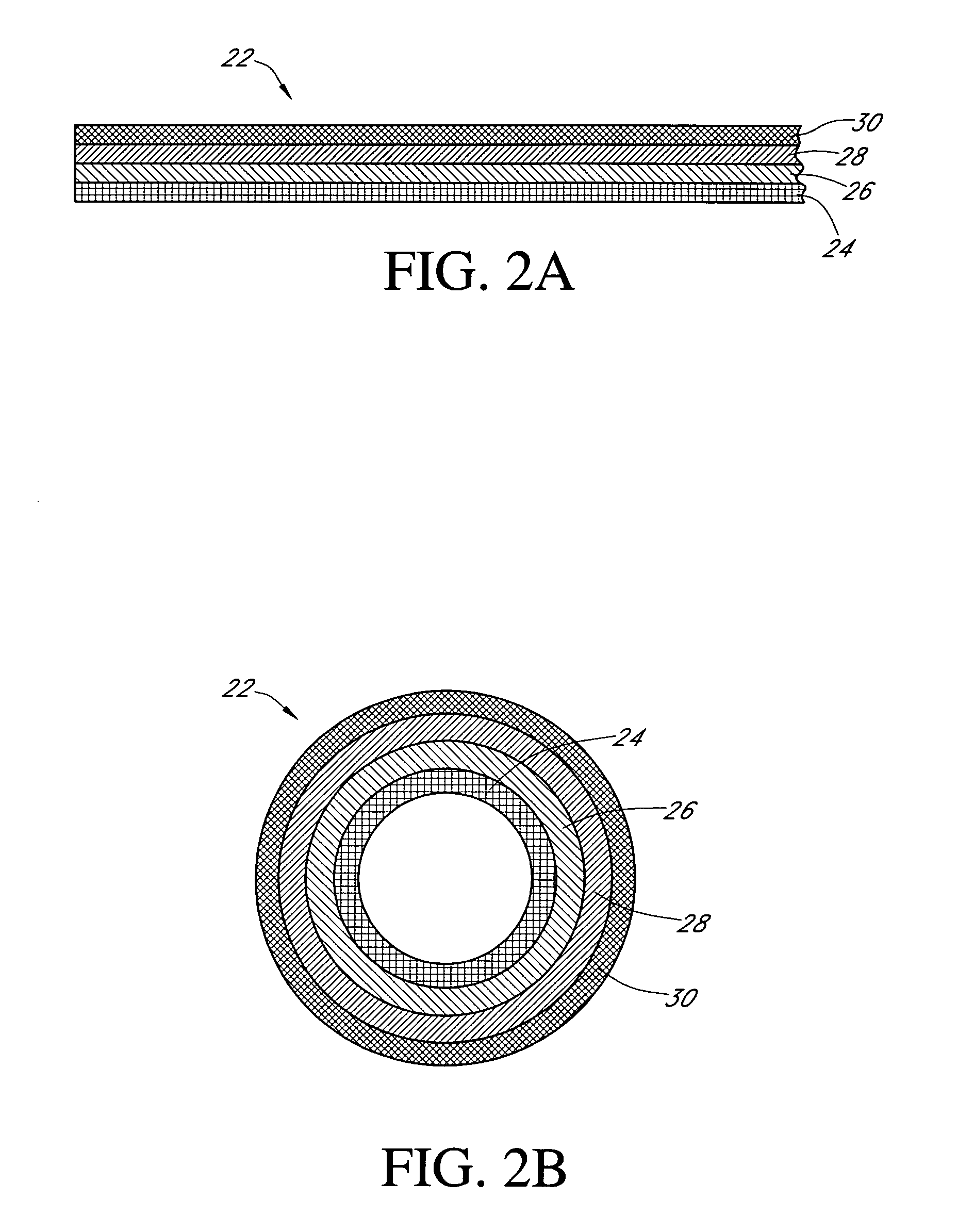
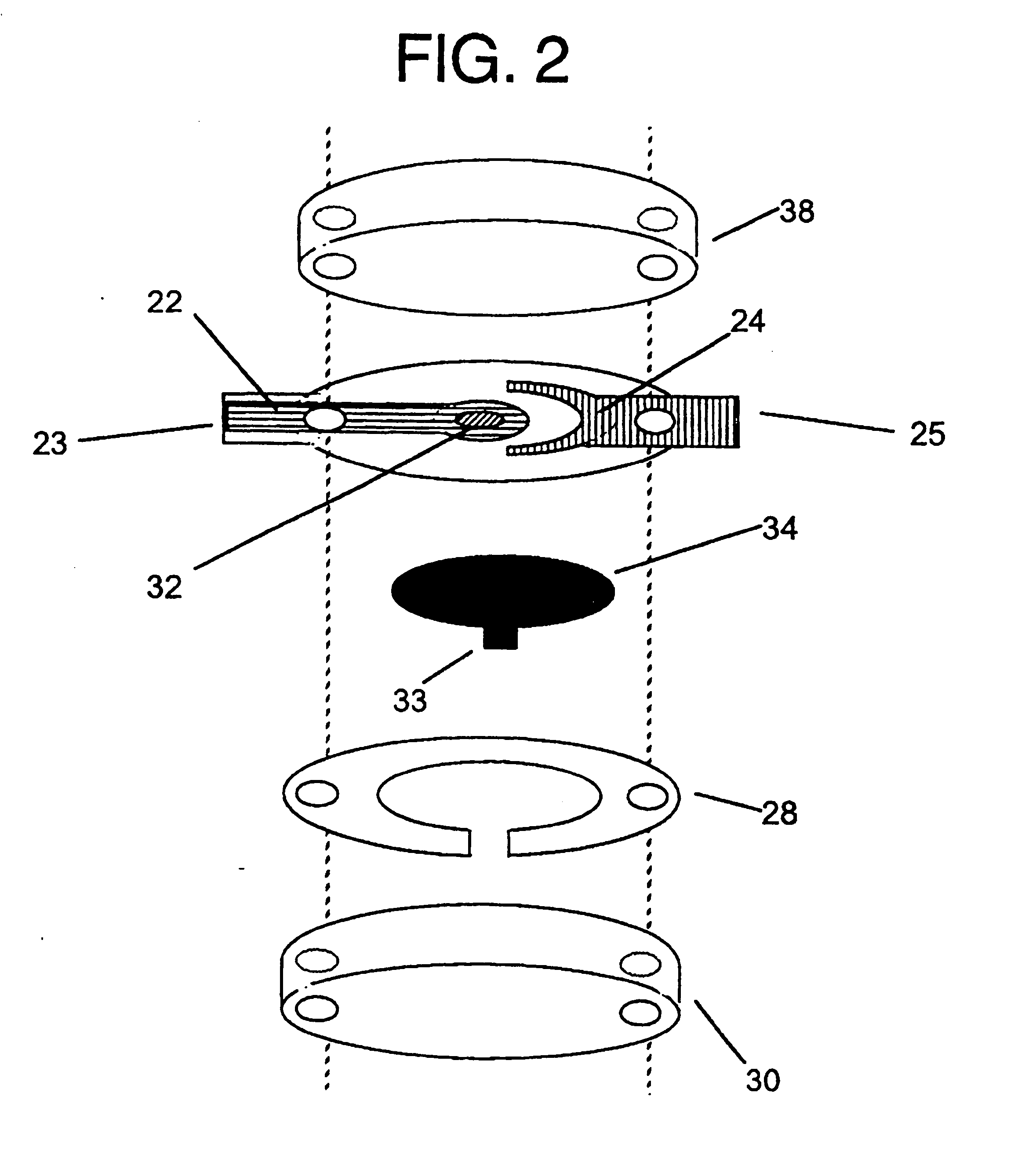
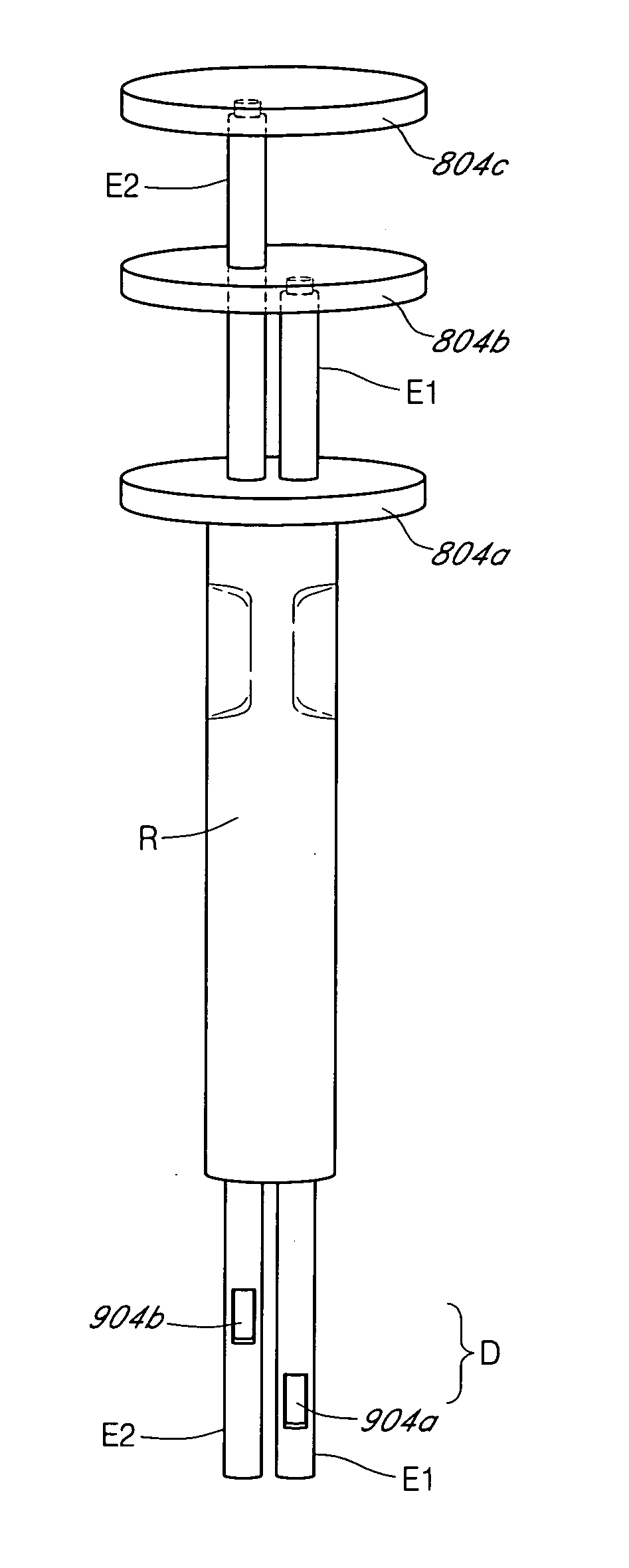
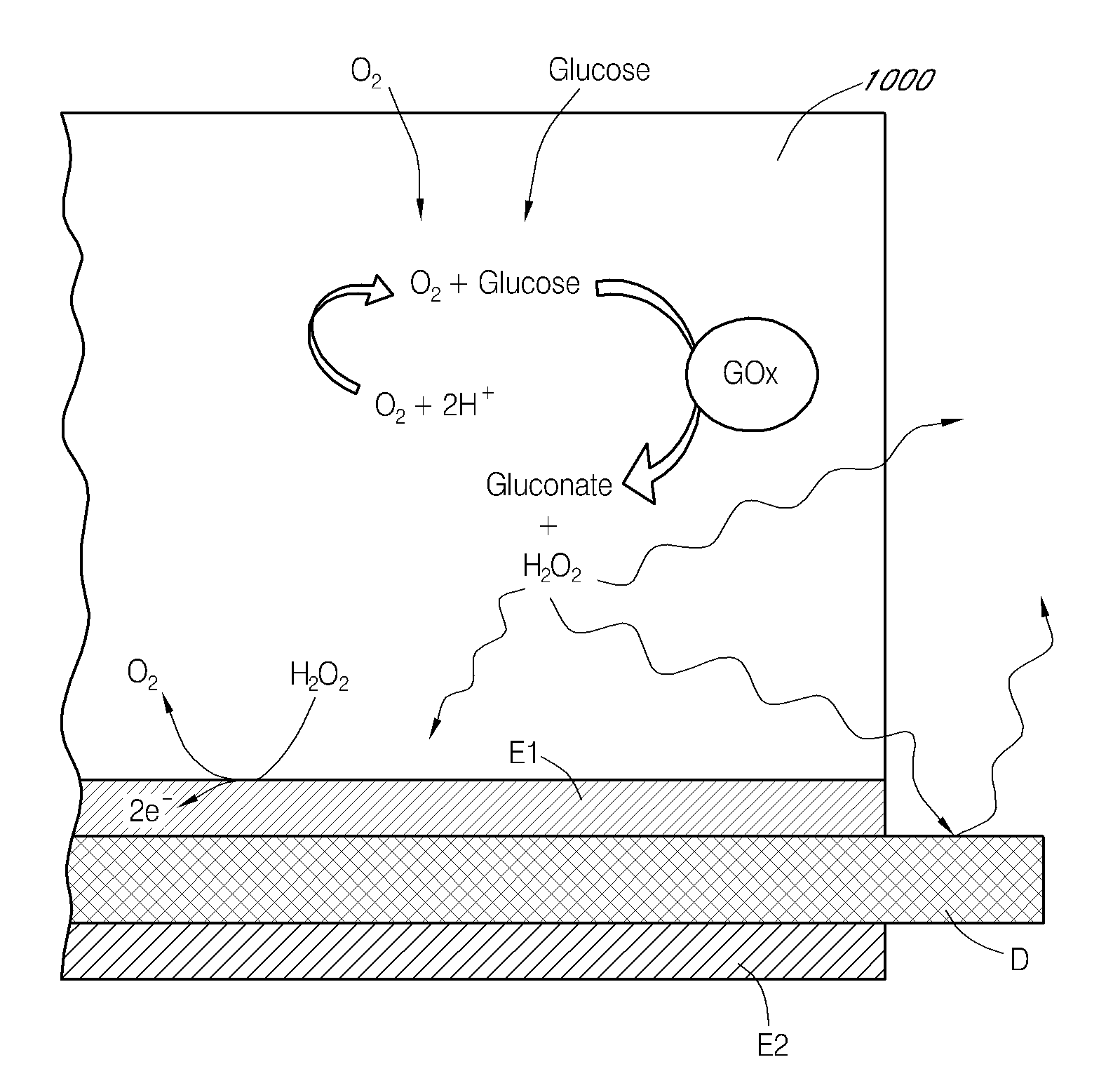
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same are provided, including analyte sensors comprising multi-axis flexibility. For example, a multi-electrode sensor system 800 comprising two working electrodes and at least one reference / counter electrode is provided. The sensor system 800 comprises first and second elongated bodies E1, E2, each formed of a conductive core or of a core with a conductive layer deposited thereon, insulating layer 810 that separates the conductive layer 820 from the elongated body, a membrane layer deposited on top of the elongated bodies E1, E2, and working electrodes 802′, 802″ formed by removing portions of the conductive layer 820 and the insulating layer 810, thereby exposing electroactive surface of the elongated bodies E1, E2.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
InactiveUS20110024307A1Substantial linearityImmobilised enzymesHot-dipping/immersion processesContinuous measurementAnalyte
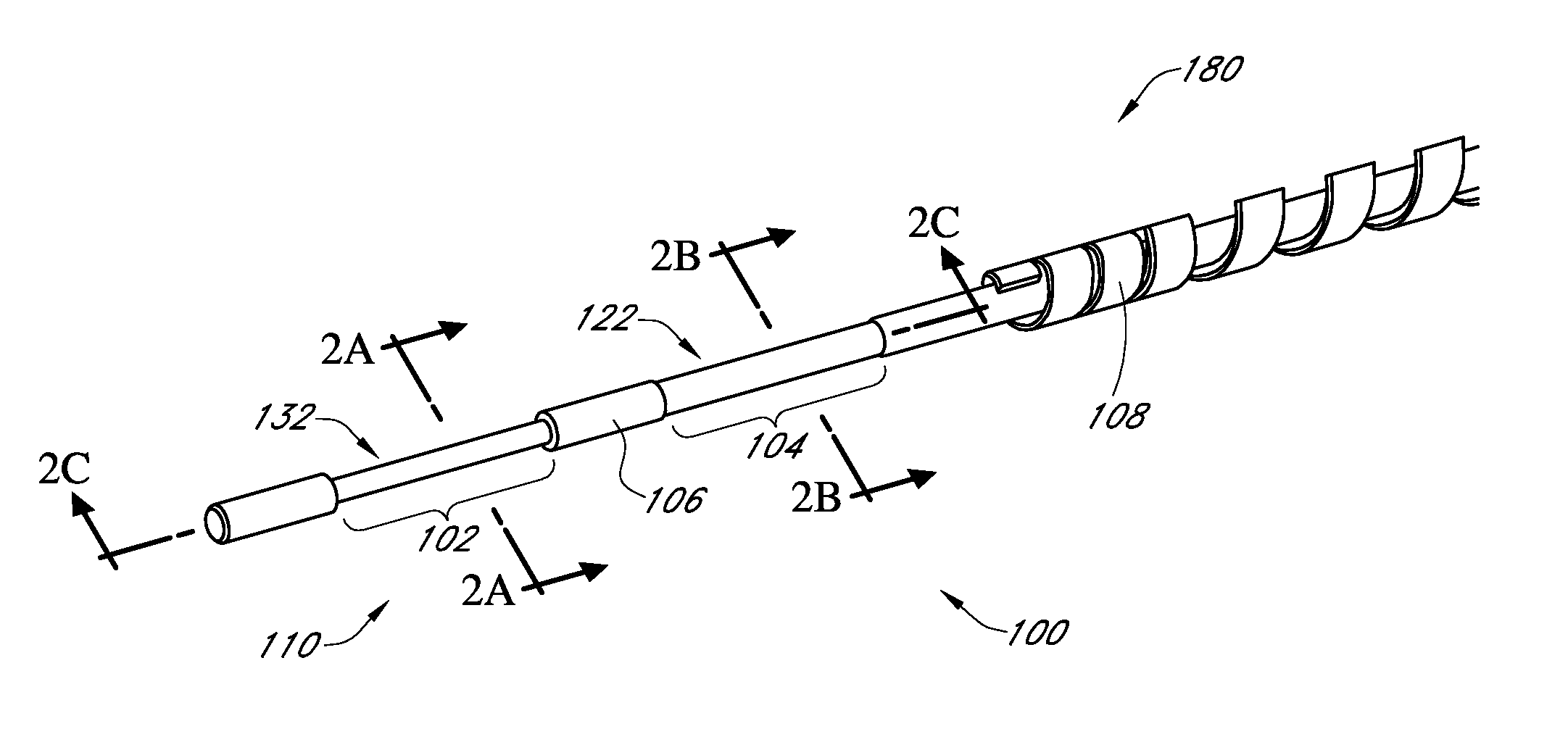
Devices and methods are provided for continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. The device can include a sensor having a plurality of sensor elements, each having at least one characteristic that is different from other sensor(s) of the device. In some embodiments, the plurality of sensor elements are each tuned to measure a different range of analyte concentration, thereby providing the device with the capability of achieving a substantially consistent level of measurement accuracy across a physiologically relevant range. In other embodiments, the device includes a plurality of sensor elements each tuned to measure during different time periods after insertion or implantation, thereby providing the sensor with the capability to continuously and accurately measure analyte concentrations across a wide range of time periods. For example, a sensor system 180 is provided having a first working electrode 150 comprising a first sensor element 102 and a second working electrode 160 comprising a second sensor element 104, and a reference electrode 108 for providing a reference value for measuring the working electrode potential of the sensor elements 102, 104.
Owner:DEXCOM
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
ActiveUS20070032717A1Cancel noiseImprove convenienceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGlucose sensorsAnalyte
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for a continuous analyte sensor, such as a continuous glucose sensor. One such system utilizes first and second working electrodes to measure additional analyte or non-analyte related signal. Such measurements may provide a background and / or sensitivity measurement(s) for use in processing sensor data and may be used to trigger events such as digital filtering of data or suspending display of data.
Owner:DEXCOM
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
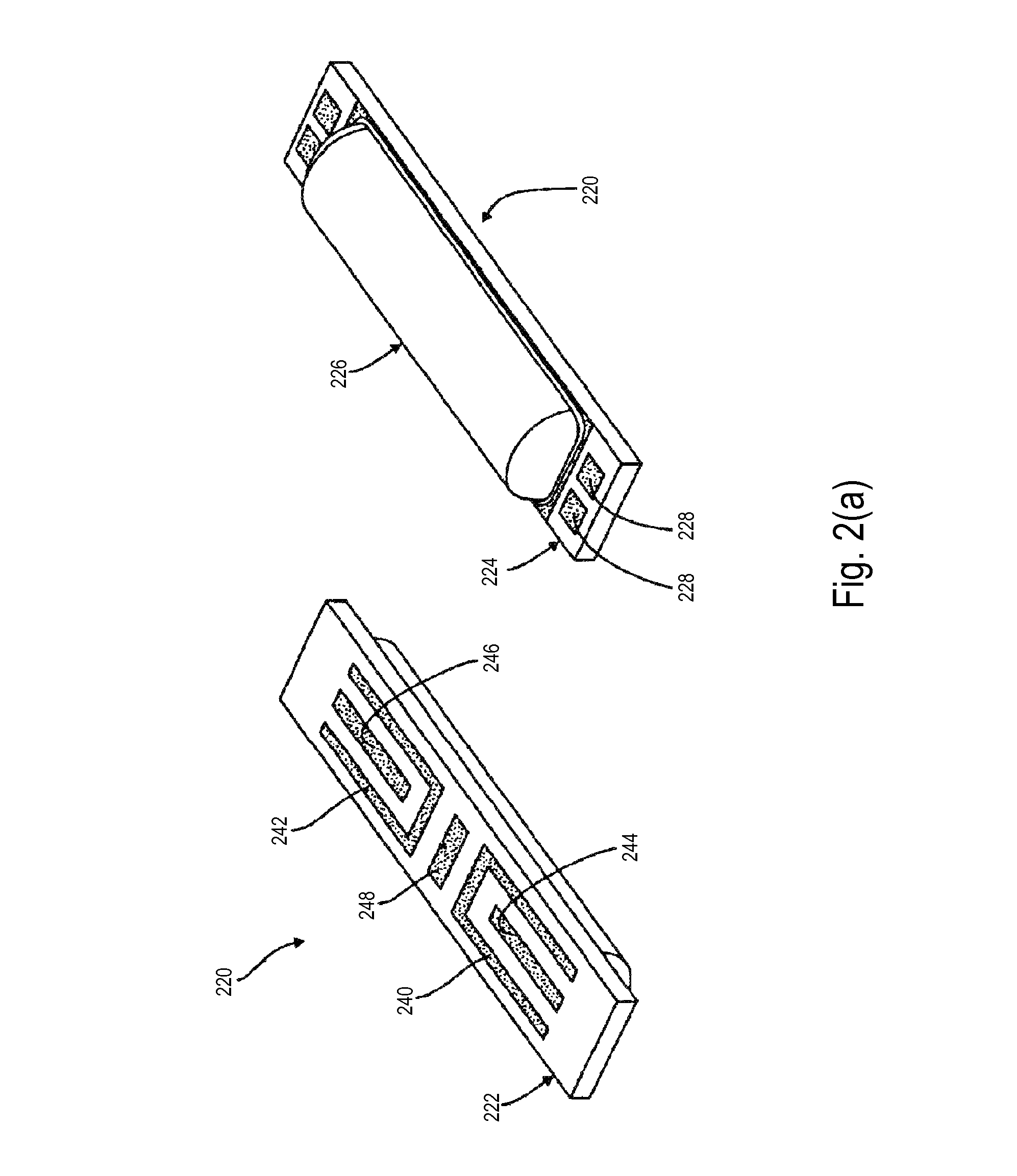
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Dual electrode system for a continuous analyte sensor
InactiveUS20100185071A1Noise-free signalImprove convenienceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteGlucose sensors
Owner:DEXCOM
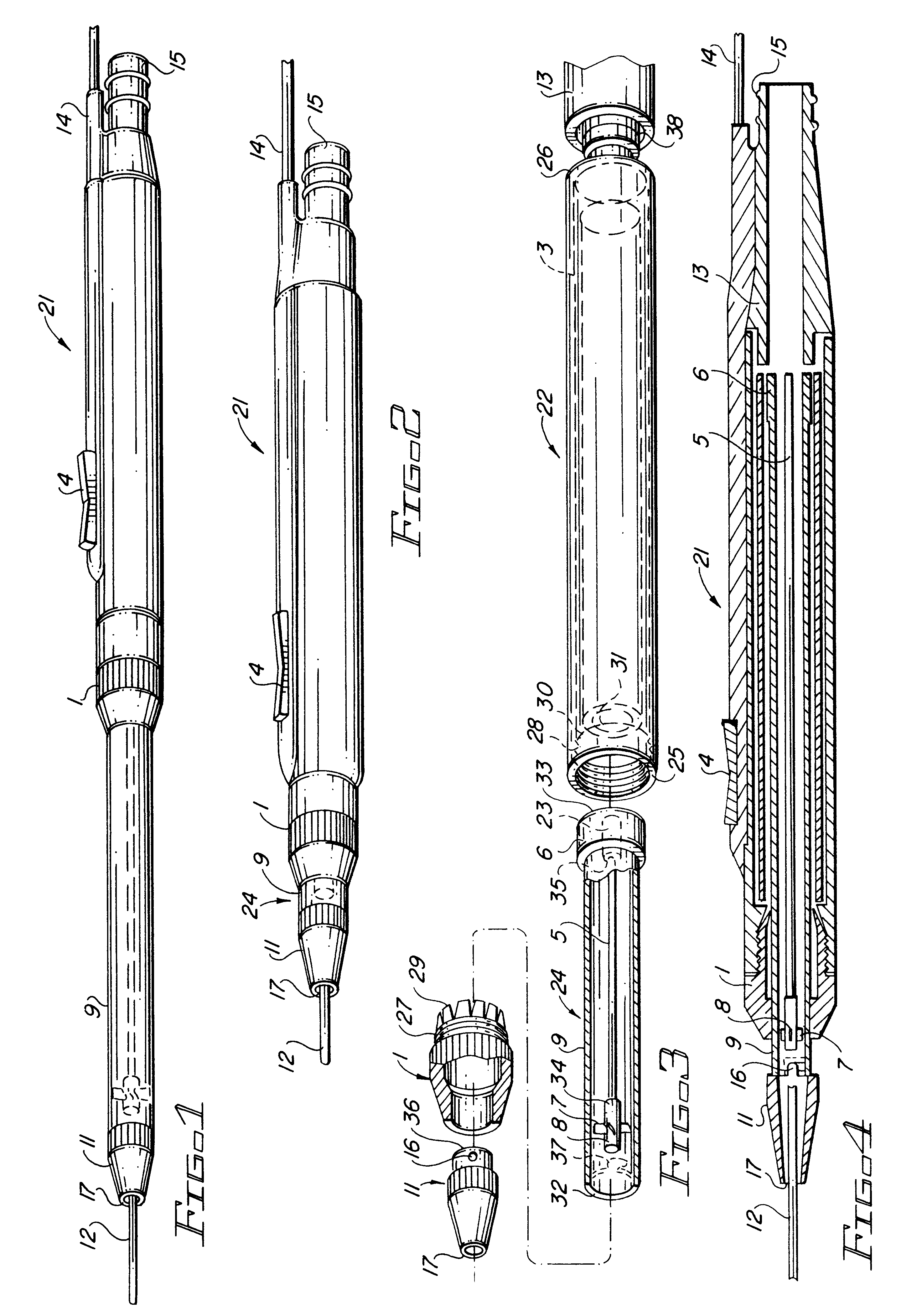
Electro-surgical unit pencil apparatus and method therefor
InactiveUS6458125B1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesArgon beamElectrosurgical unit
An electro-surgical unit (ESU) pencil apparatus is disclosed in which an improved handpiece enables the surgeon to vary the length of working electrode without having to use cutting electrodes of varying lengths. This is achieved by installing the electrode in an assembly that may, as desired by the surgeon, be extended from, or retracted into, the body of the ESU pencil apparatus. Means are provided for supplying uninterrupted RF supply to the electrode tip and uninterrupted smoke evacuation for the ESU pencil apparatus as the electrode assembly is expanded or retracted. Additionally, means are provided for locking the electrode assembly at the desired length, so that it does not move during the operation. The ESU pencil apparatus is also adapted for use with an ESU-argon beam coagulator pencil.
Owner:IC MEDICAL INC
Analyte monitoring: stabilizer for subcutaneous glucose sensor with incorporated antiglycolytic agent
ActiveUS20090018425A1Reduce in quantityReading can be lowImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProximateAnalyte
An analyte sensor including an antiglycolytic agent or a precursor thereof and a chelating agent that stabilizes the antiglycolytic agent positioned proximate to the working electrode of the sensor. Also provided are systems and methods of using the electrochemical analyte sensors in analyte monitoring.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
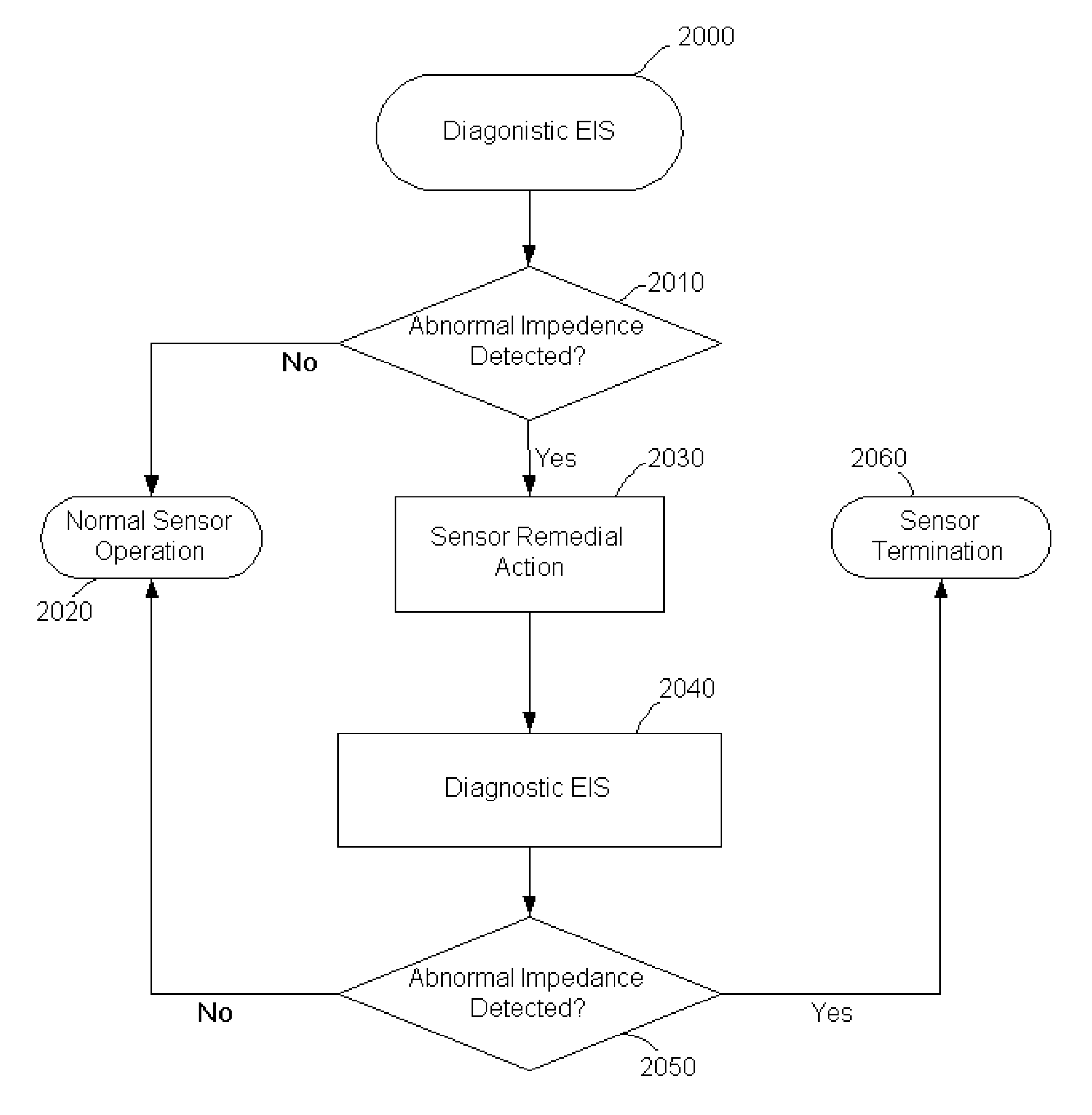
Method and system for remedying sensor malfunctions detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
A method and system that enables a user to maintain a sensor in real time. The present invention involves performing a diagnostic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) procedure to measure sensor impedance value in order to determine if the sensor is operating at an optimal level. If the sensor is not operating at an optimal level, the present invention may further involve performing a sensor remedial action. The sensor remedial action involves reversing the DC voltage being applied between the working electrode and the reference electrode. The reversed DC voltage may be coupled with an AC voltage to extend its reach.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS6946299B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorGlucose polymers
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the sample chamber. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
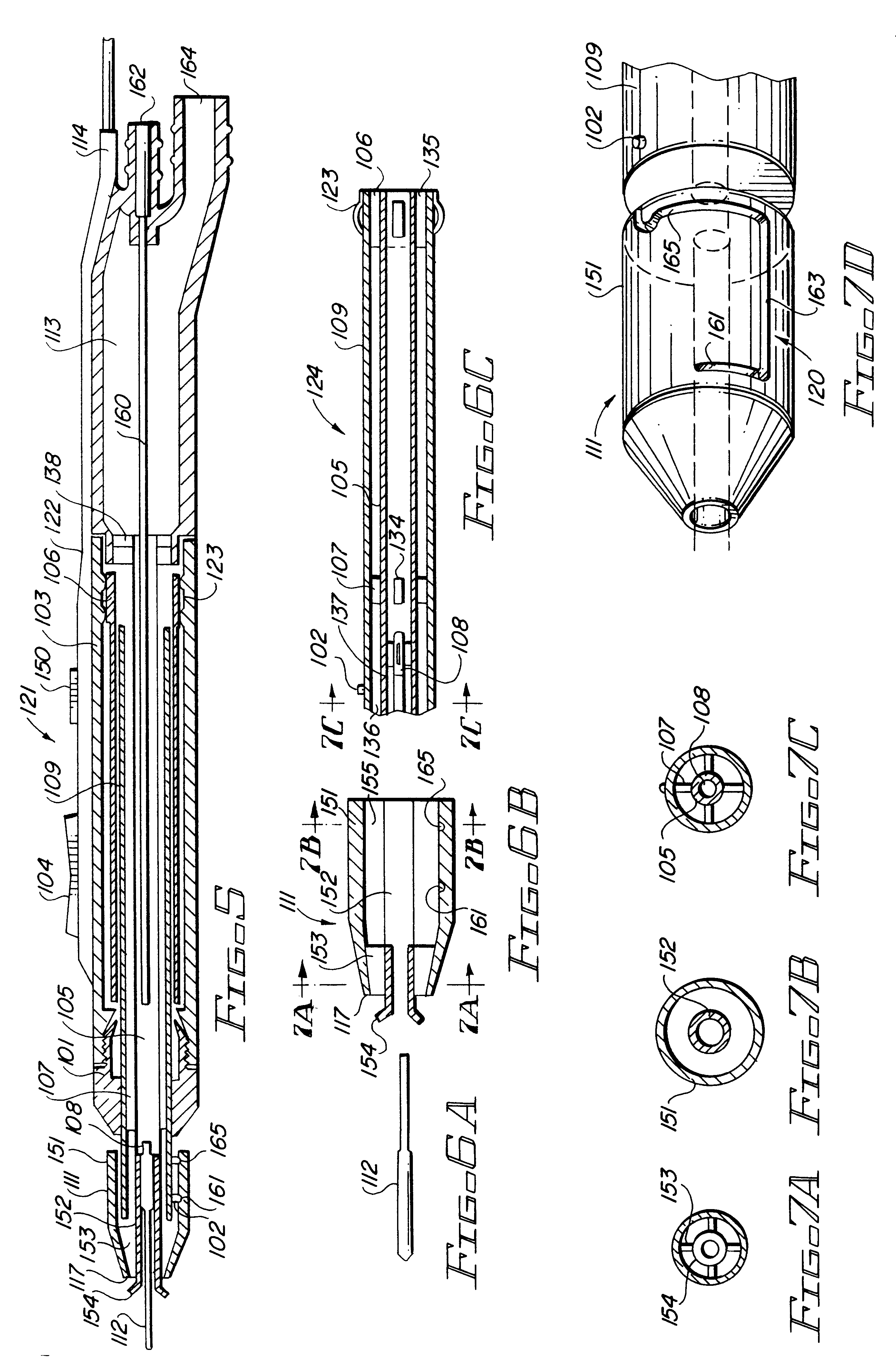
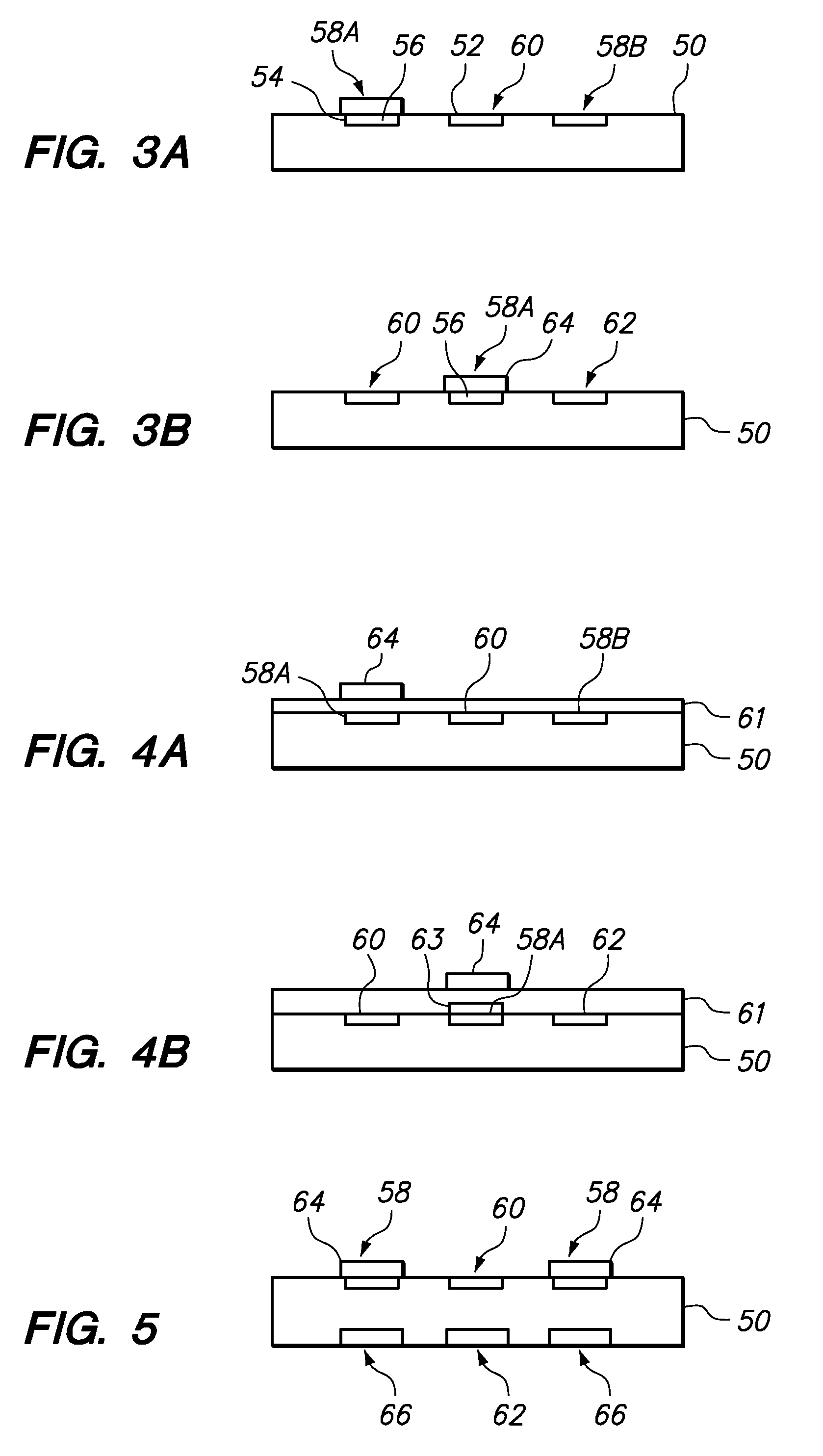
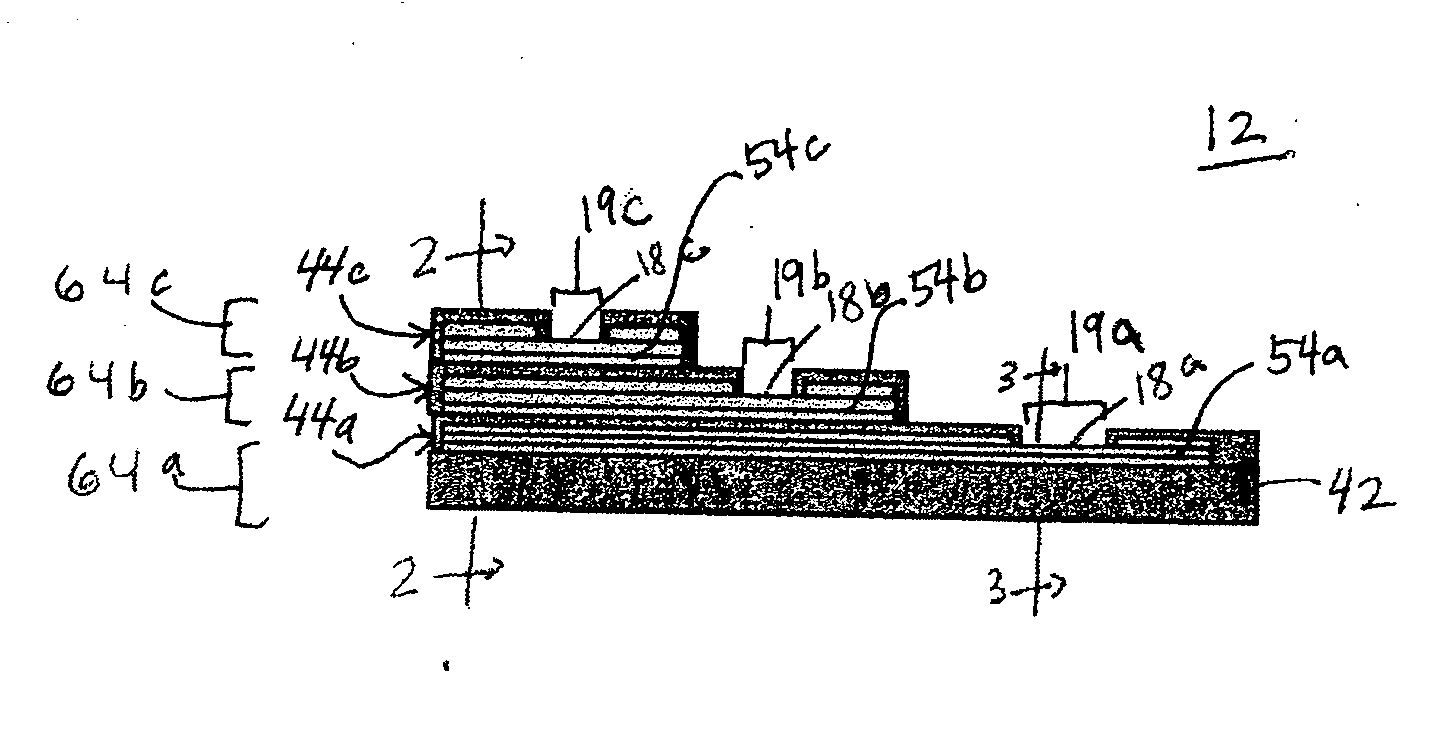
Sensor with layered electrodes
ActiveUS20070173711A1Easy and quick to placeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsThin film sensorGlucose sensors
A thin film sensor, such as a glucose sensor, is provided for transcutaneous placement at a selected site within the body of a patient. The sensor includes several sensor layers that include conductive layers and includes a proximal segment defining conductive contacts adapted for electrical connection to a suitable monitor, and a distal segment with sensor electrodes for transcutaneous placement. The sensor electrode layers are disposed generally above each other, for example with the reference electrode above the working electrode and the working electrode above the counter electrode. The electrode layers are separated by dielectric layer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com