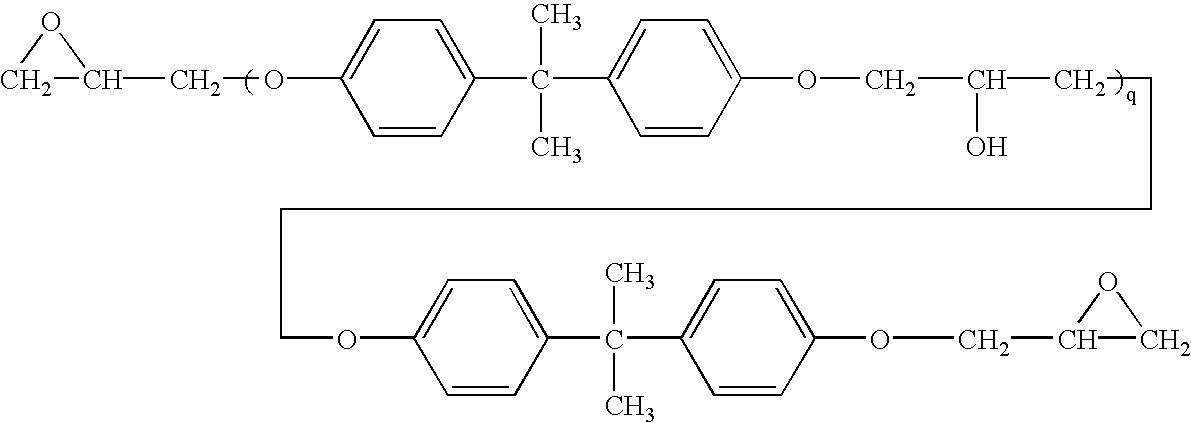
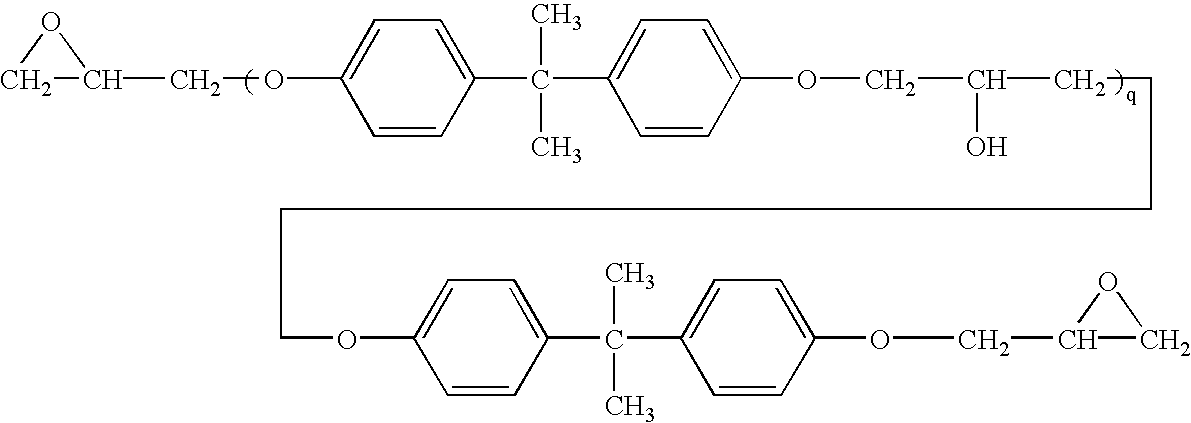
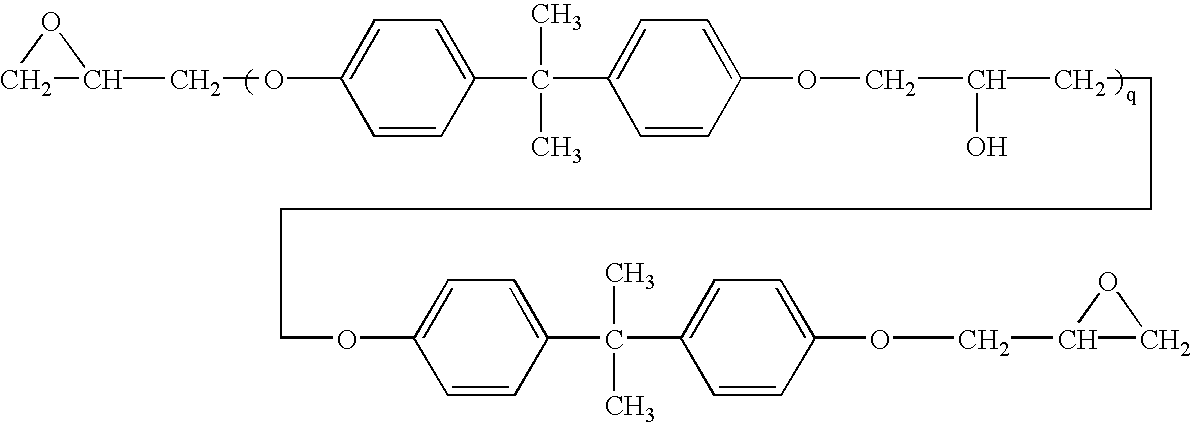
Patents
Literature
8965results about "Hot-dipping/immersion processes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20110027127A1Hot-dipping/immersion processesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteEngineering
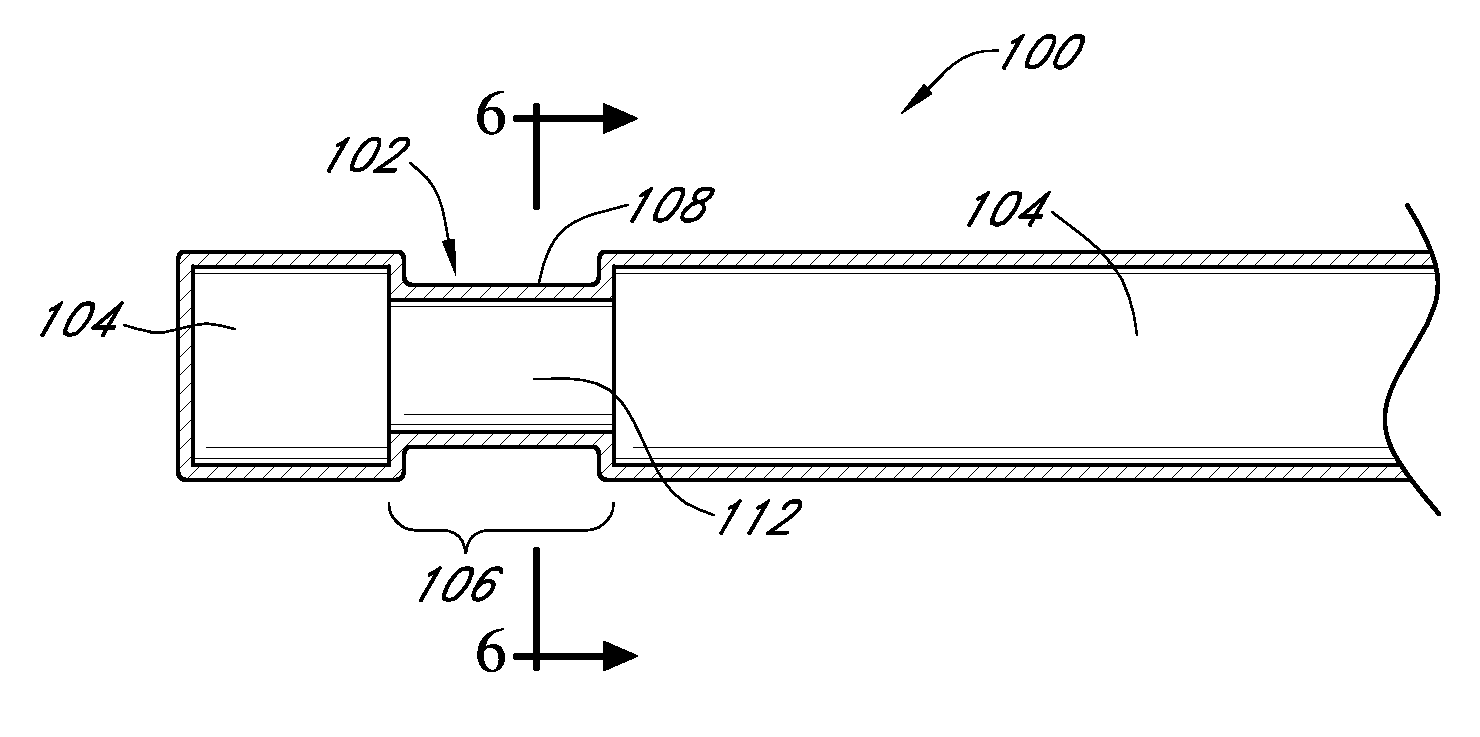
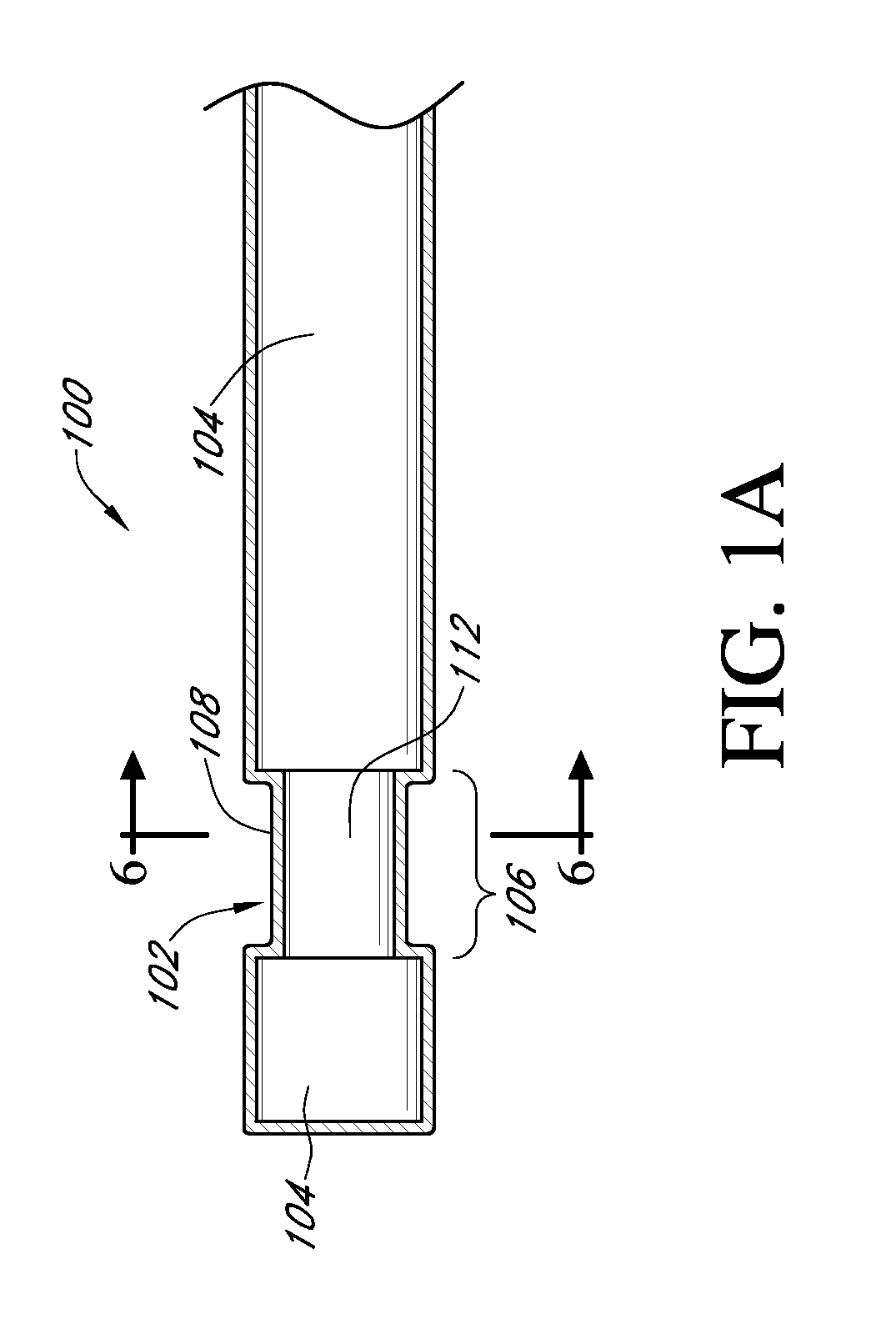
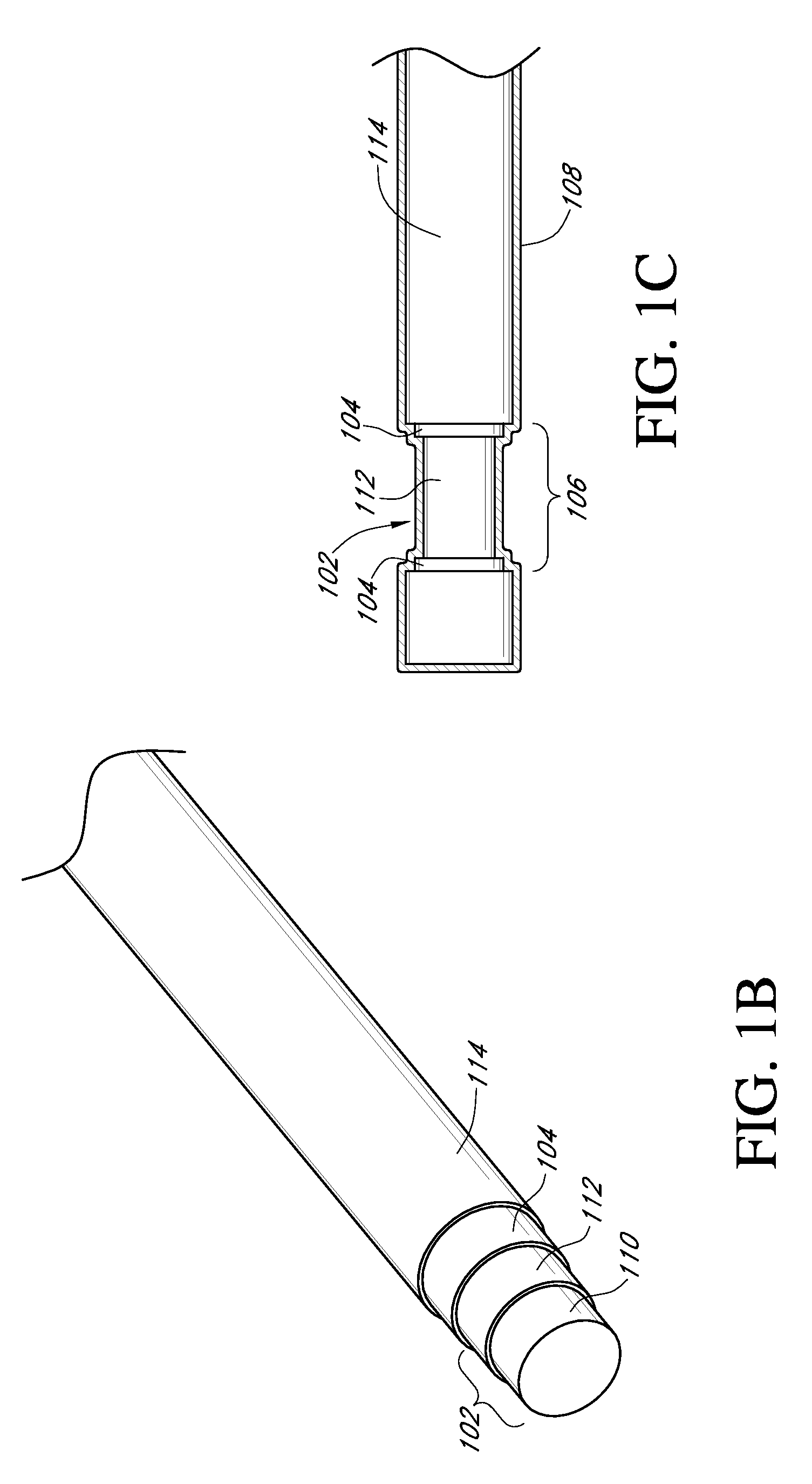
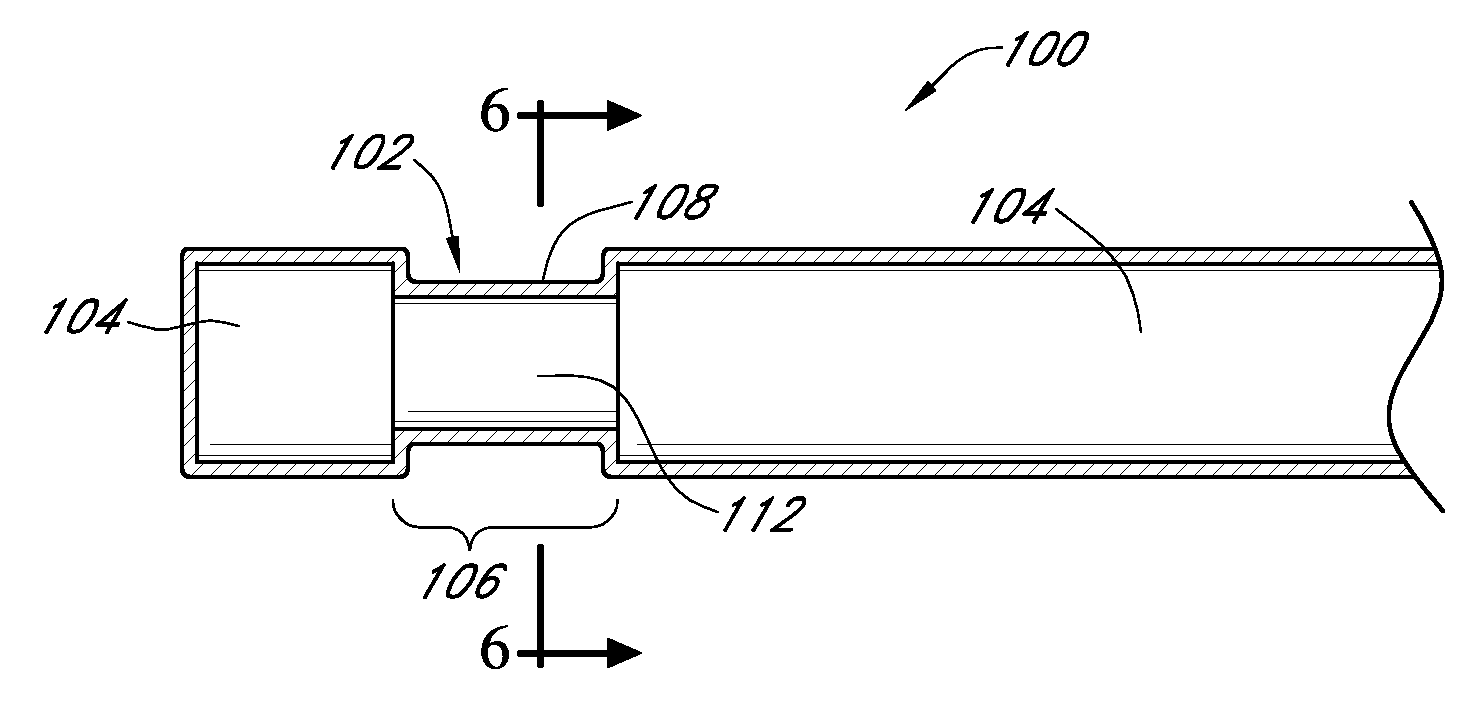
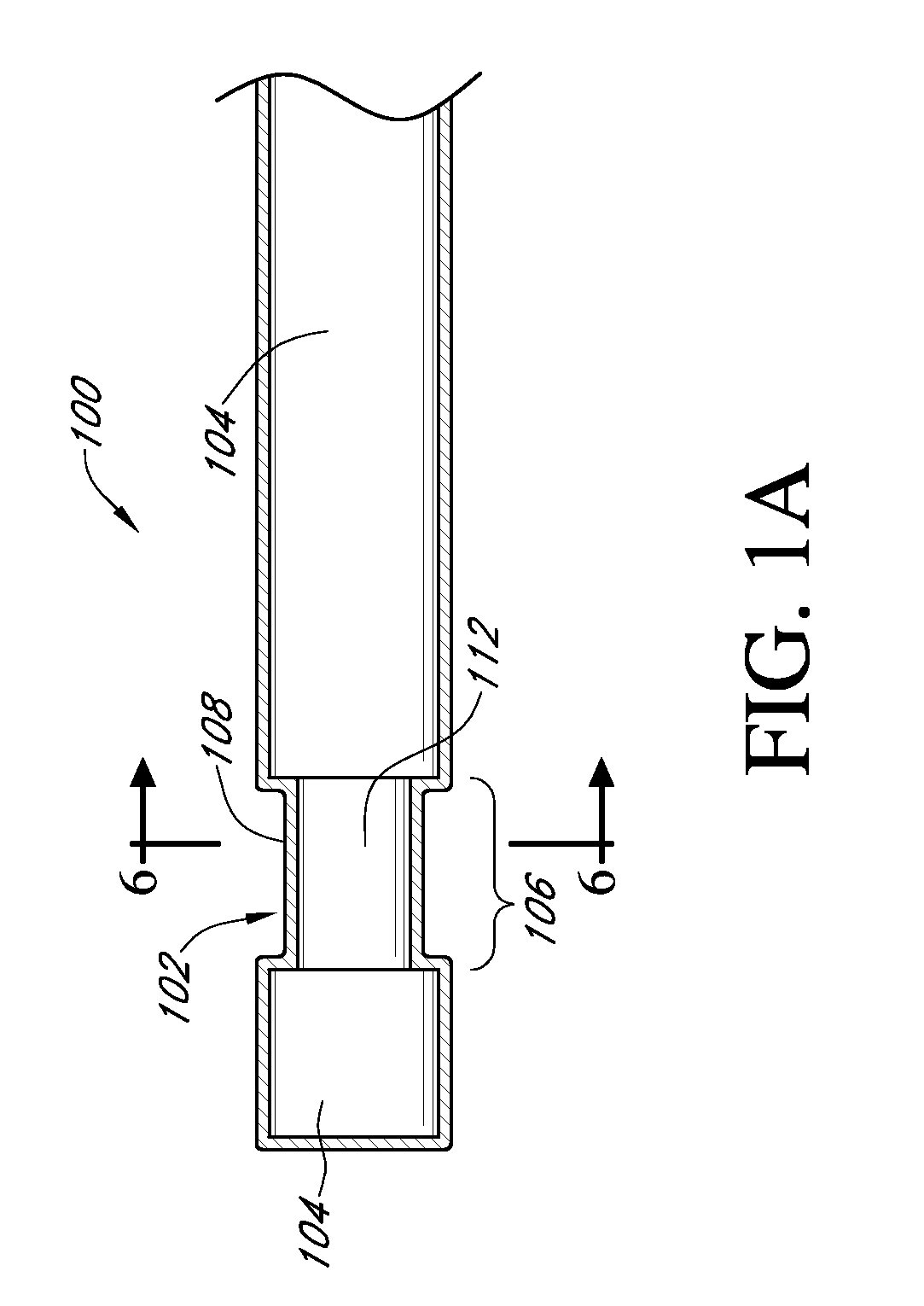
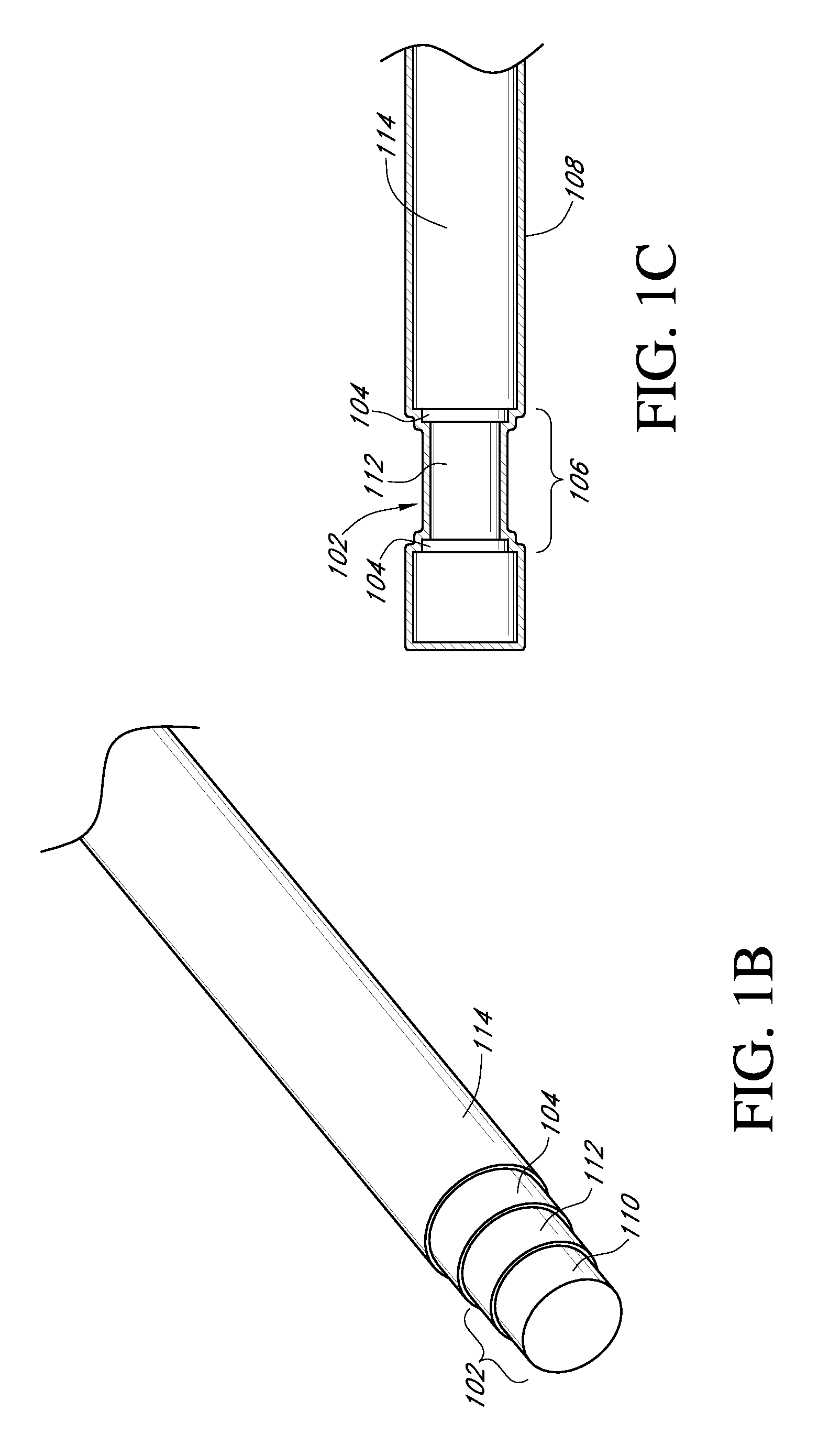
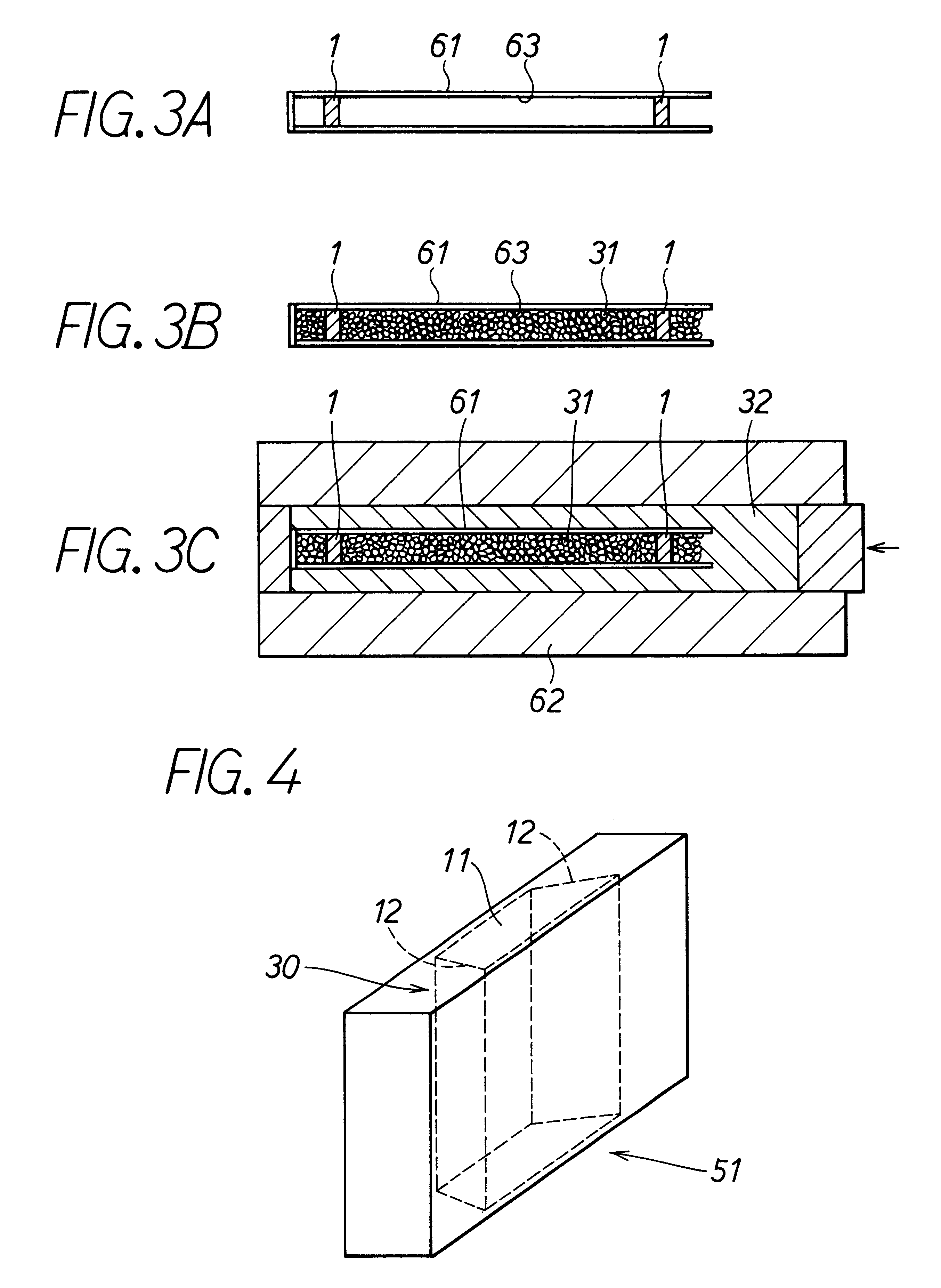
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same are provided, including analyte sensors comprising multi-axis flexibility. For example, a multi-electrode sensor system 800 comprising two working electrodes and at least one reference / counter electrode is provided. The sensor system 800 comprises first and second elongated bodies E1, E2, each formed of a conductive core or of a core with a conductive layer deposited thereon, insulating layer 810 that separates the conductive layer 820 from the elongated body, a membrane layer deposited on top of the elongated bodies E1, E2, and working electrodes 802′, 802″ formed by removing portions of the conductive layer 820 and the insulating layer 810, thereby exposing electroactive surface of the elongated bodies E1, E2.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same
Analyte sensors and methods of manufacturing same are provided, including analyte sensors comprising multi-axis flexibility. For example, a multi-electrode sensor system 800 comprising two working electrodes and at least one reference / counter electrode is provided. The sensor system 800 comprises first and second elongated bodies E1, E2, each formed of a conductive core or of a core with a conductive layer deposited thereon, insulating layer 810 that separates the conductive layer 820 from the elongated body, a membrane layer deposited on top of the elongated bodies E1, E2, and working electrodes 802′, 802″ formed by removing portions of the conductive layer 820 and the insulating layer 810, thereby exposing electroactive surface of the elongated bodies E1, E2.
Owner:DEXCOM
Analyte sensor
InactiveUS20110024307A1Substantial linearityImmobilised enzymesHot-dipping/immersion processesContinuous measurementAnalyte
Devices and methods are provided for continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. The device can include a sensor having a plurality of sensor elements, each having at least one characteristic that is different from other sensor(s) of the device. In some embodiments, the plurality of sensor elements are each tuned to measure a different range of analyte concentration, thereby providing the device with the capability of achieving a substantially consistent level of measurement accuracy across a physiologically relevant range. In other embodiments, the device includes a plurality of sensor elements each tuned to measure during different time periods after insertion or implantation, thereby providing the sensor with the capability to continuously and accurately measure analyte concentrations across a wide range of time periods. For example, a sensor system 180 is provided having a first working electrode 150 comprising a first sensor element 102 and a second working electrode 160 comprising a second sensor element 104, and a reference electrode 108 for providing a reference value for measuring the working electrode potential of the sensor elements 102, 104.
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110027458A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingAnalyteSolvent
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110024043A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesAnalyteSolvent
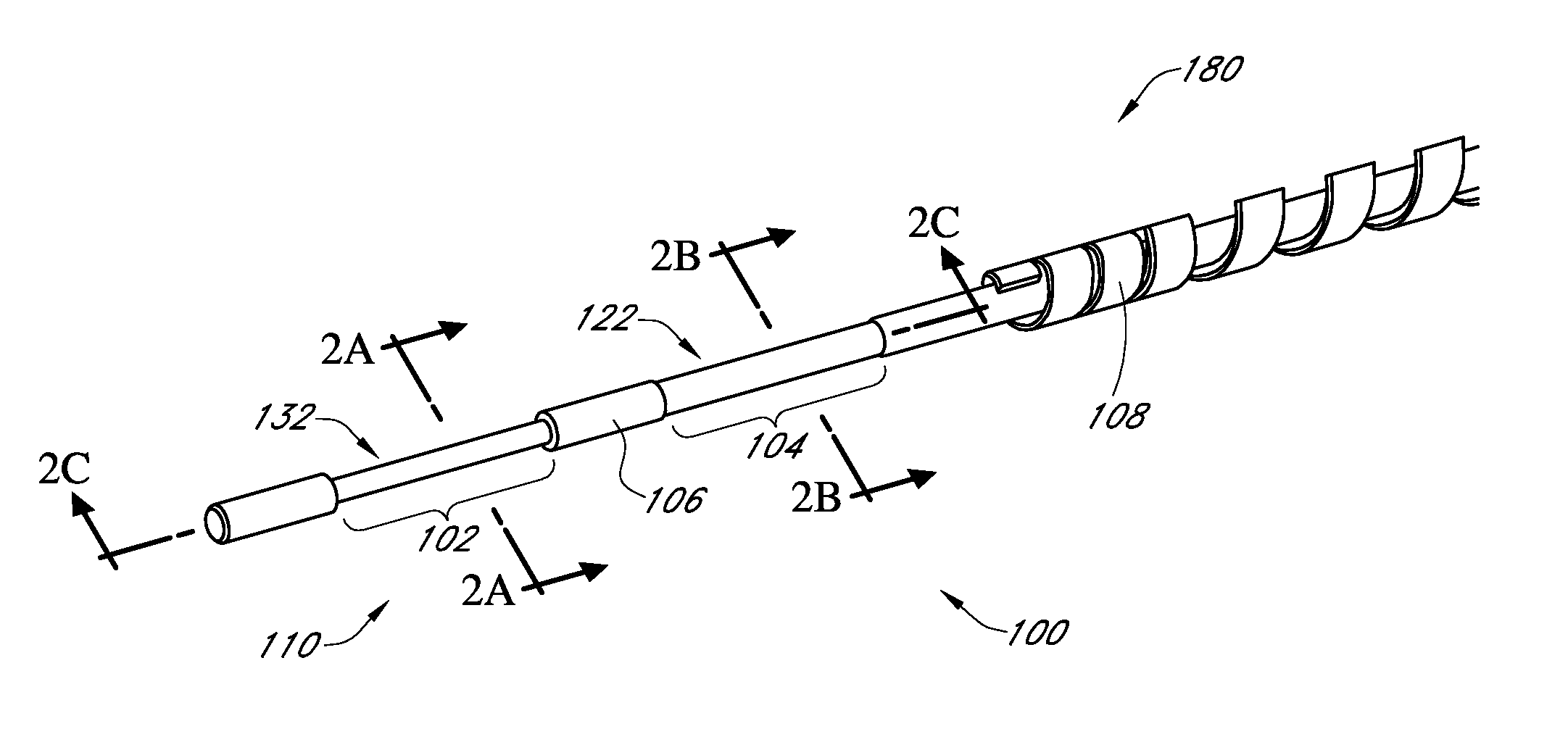
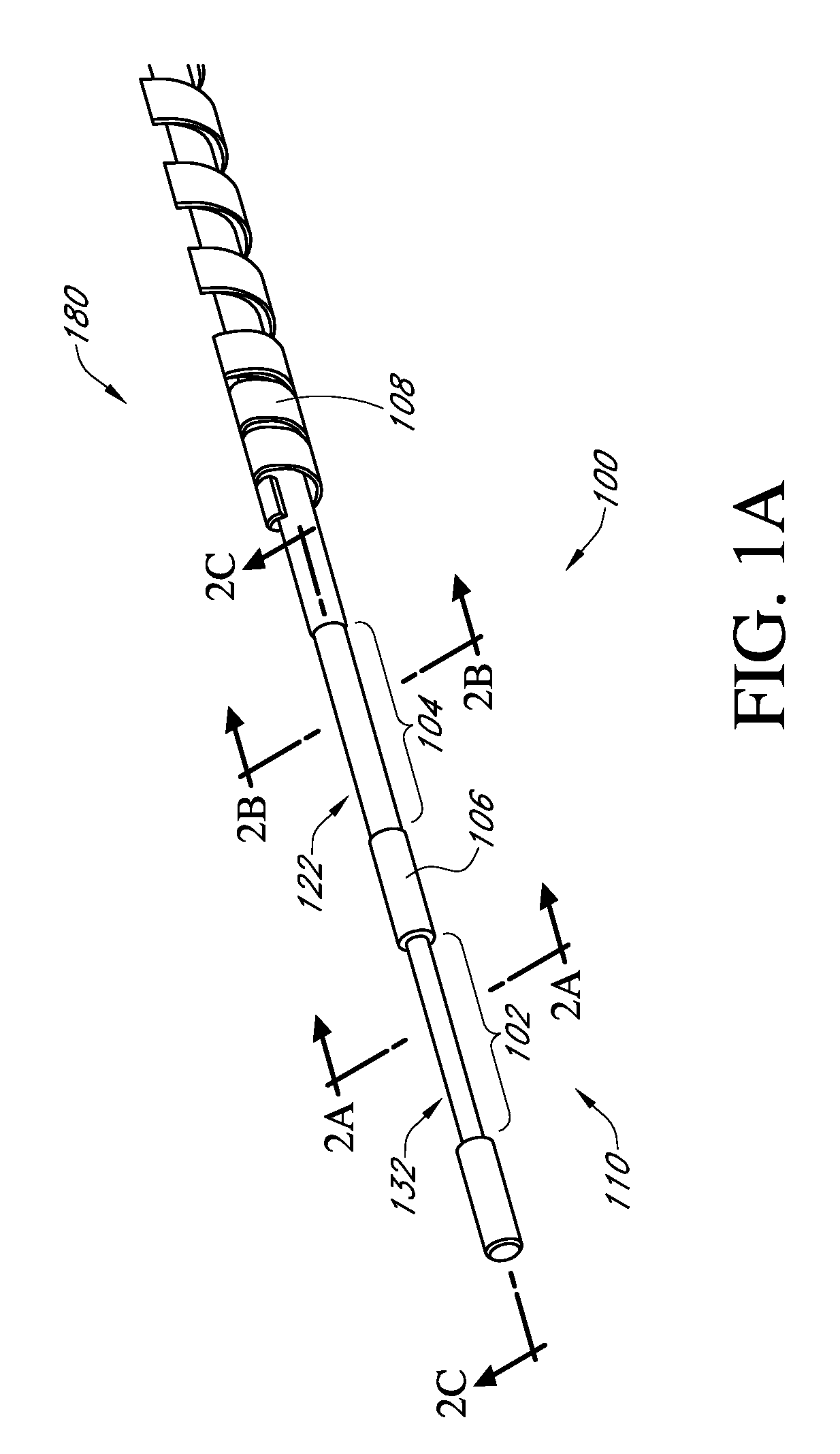
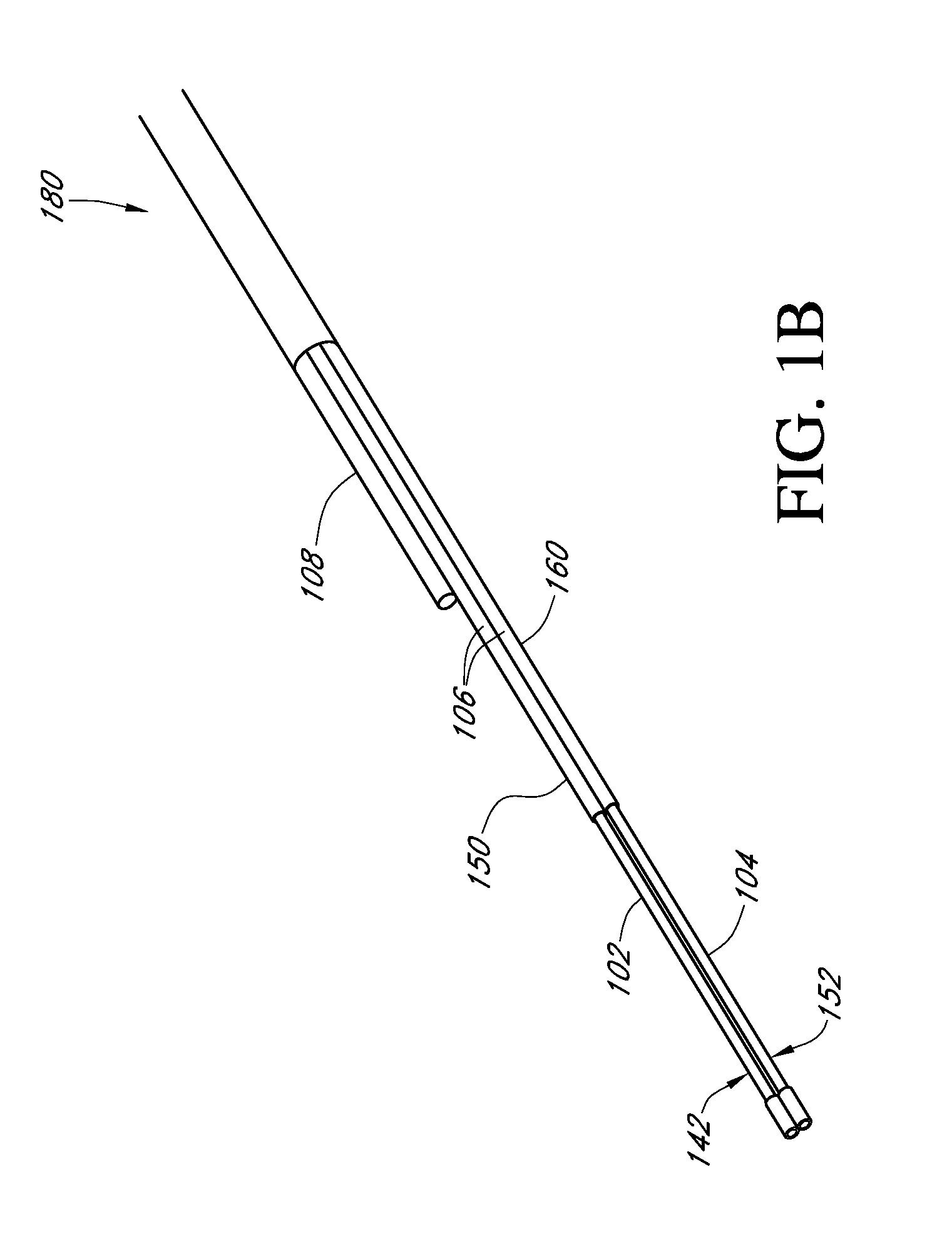
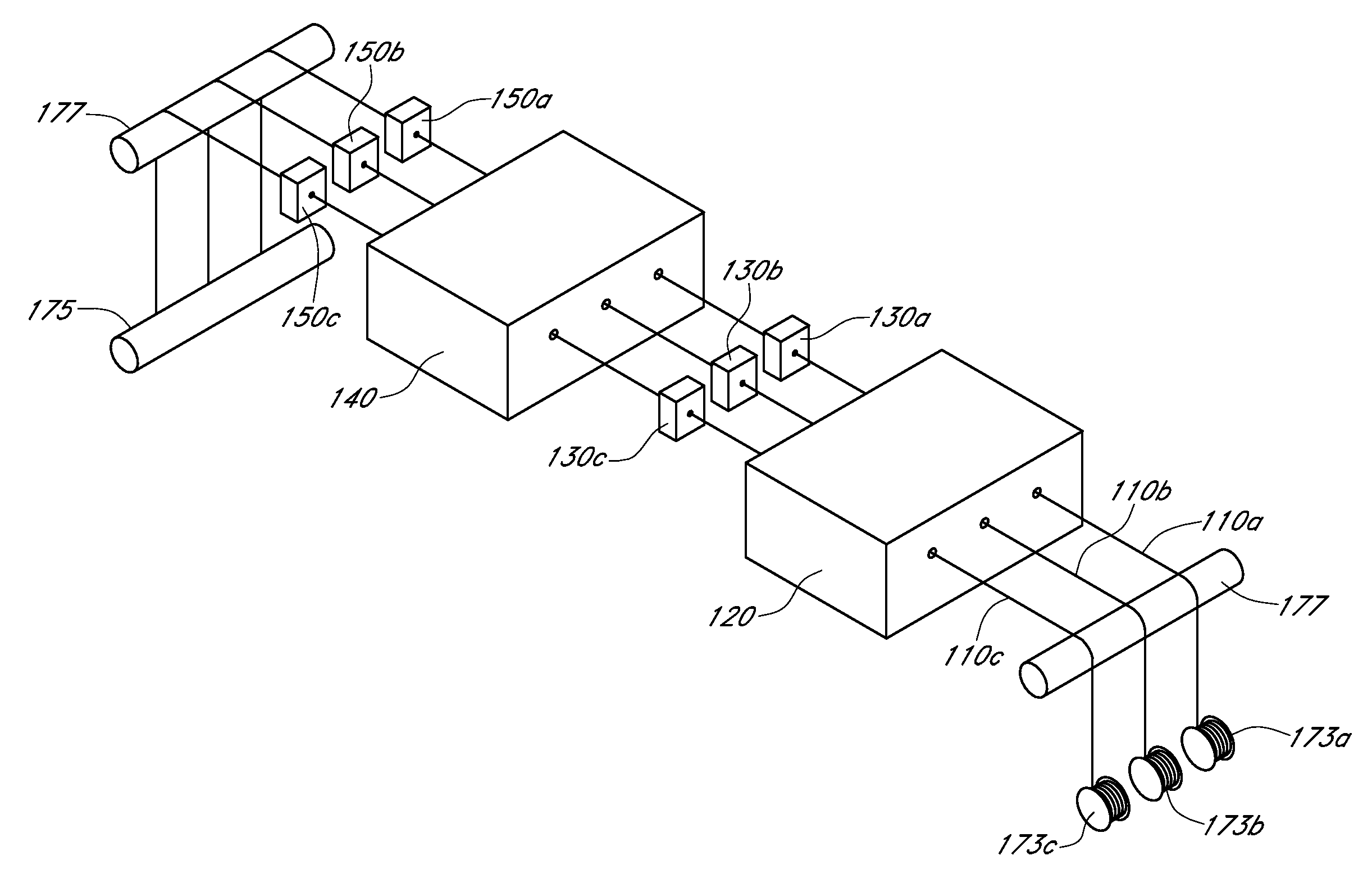
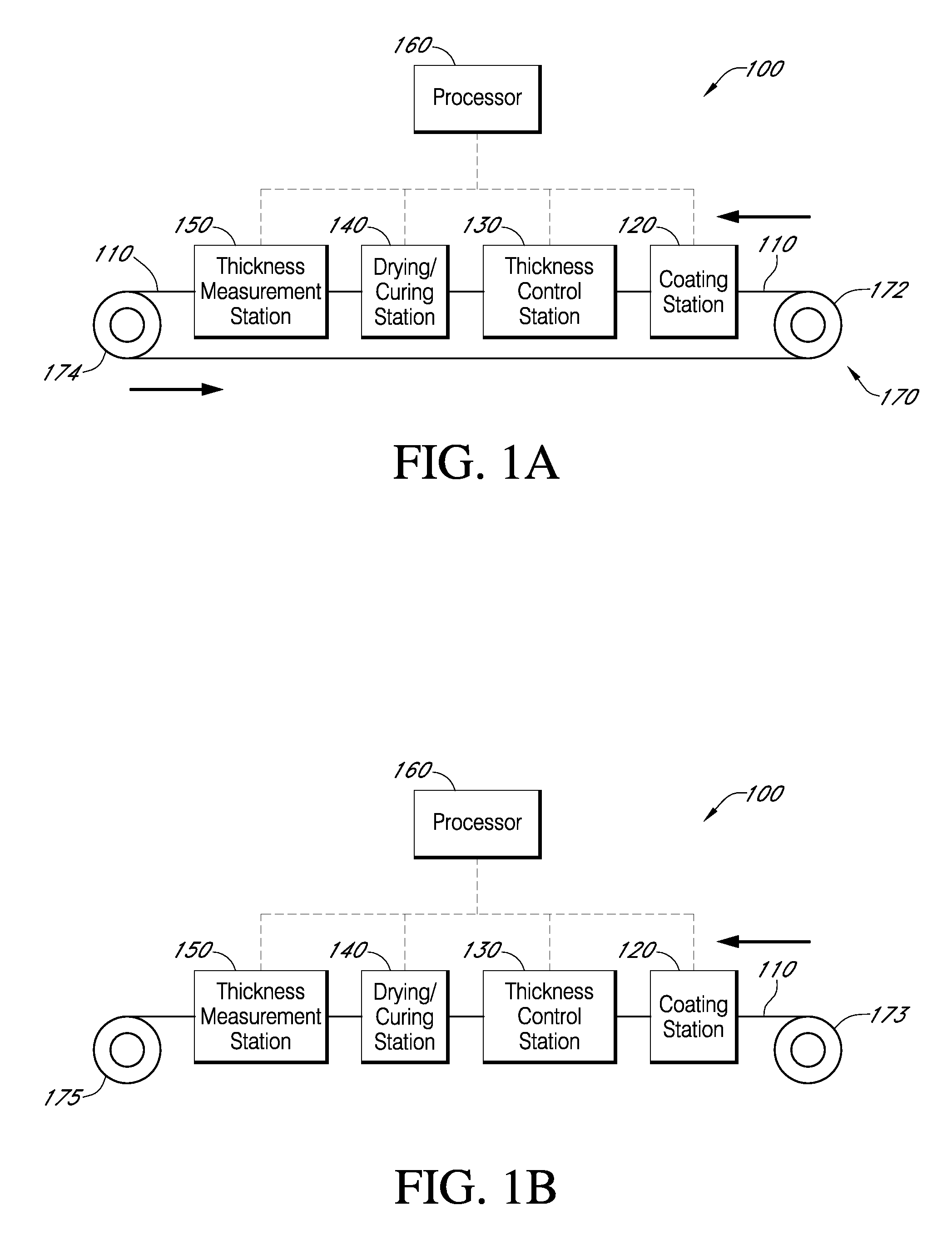
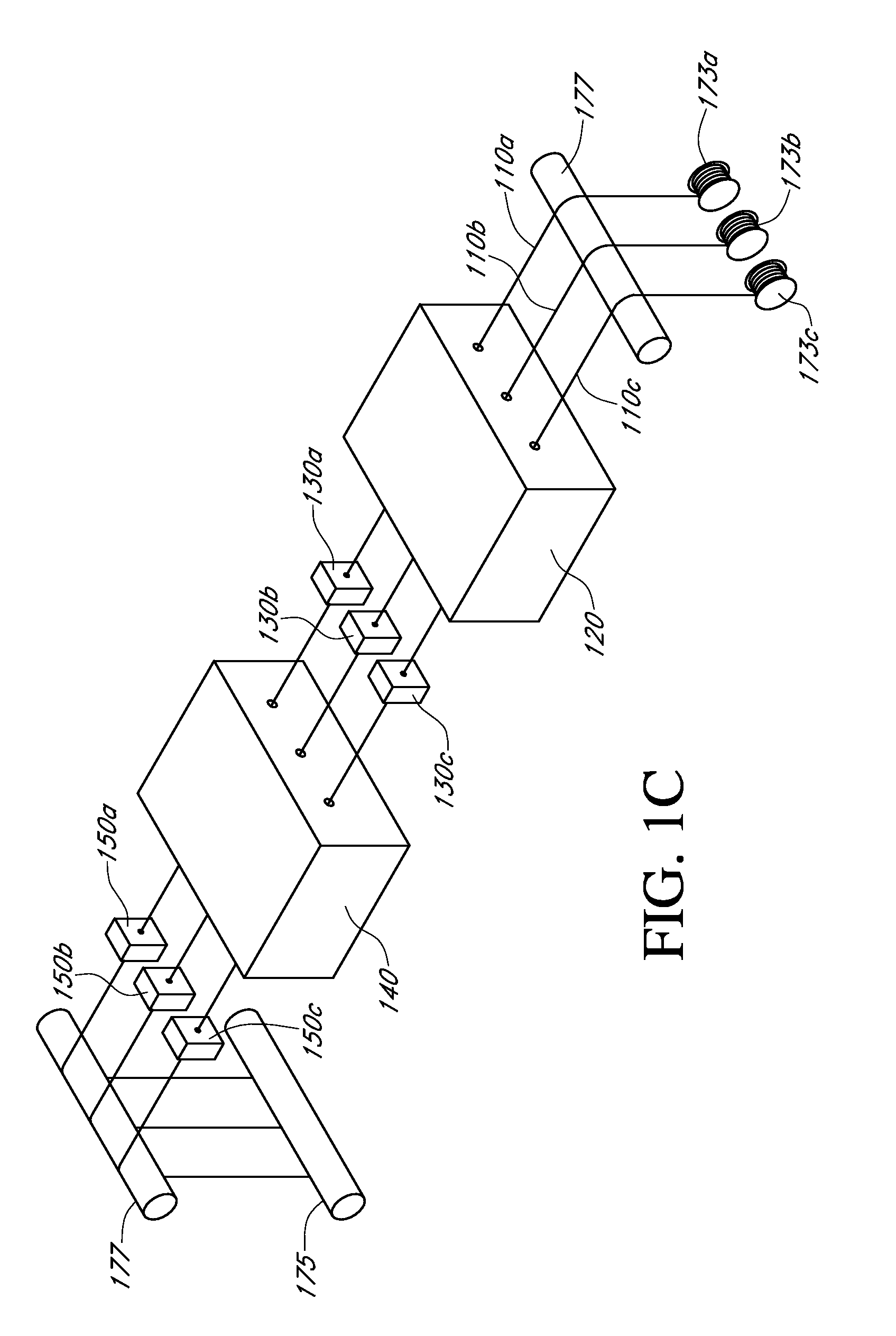
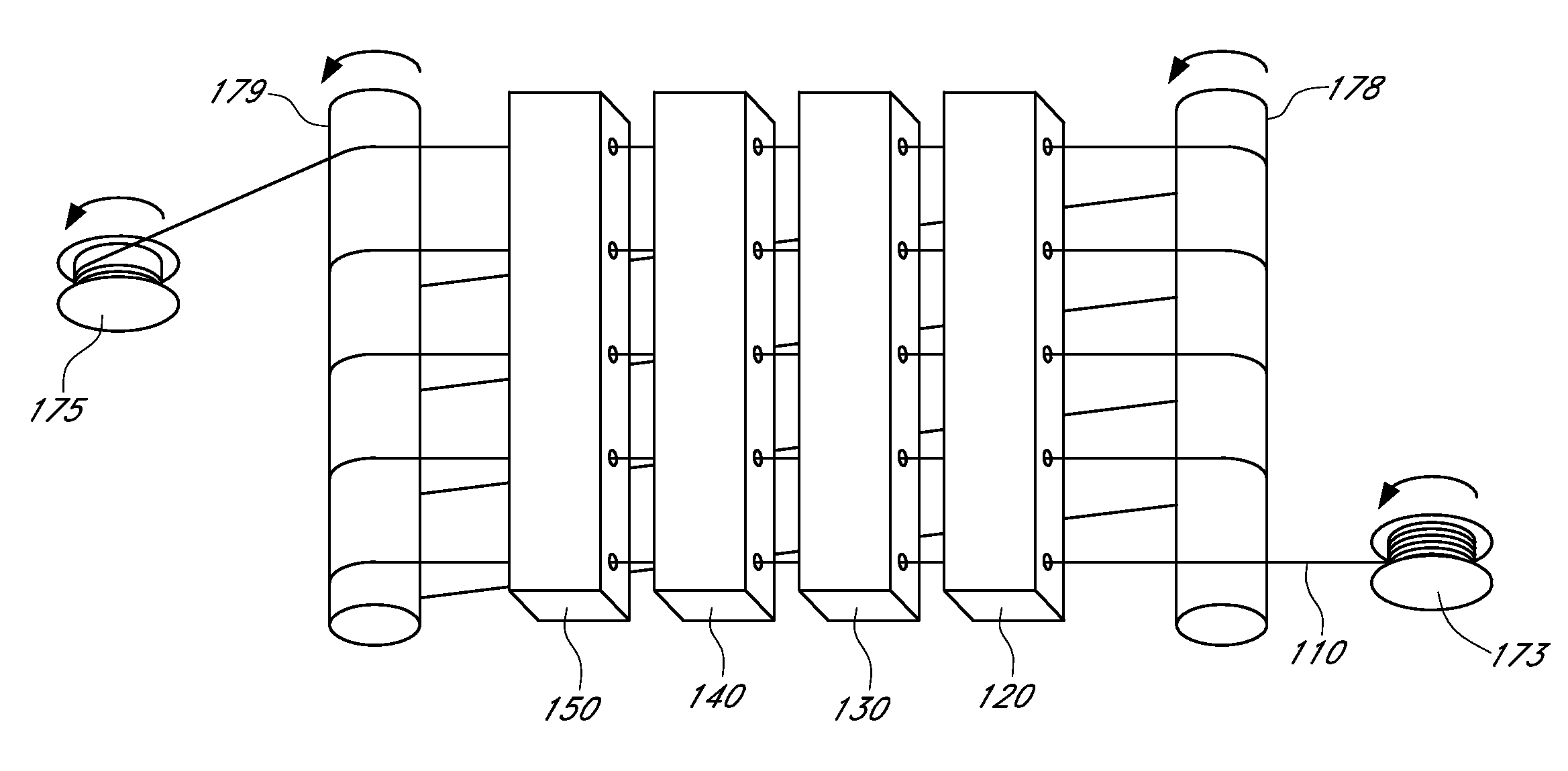
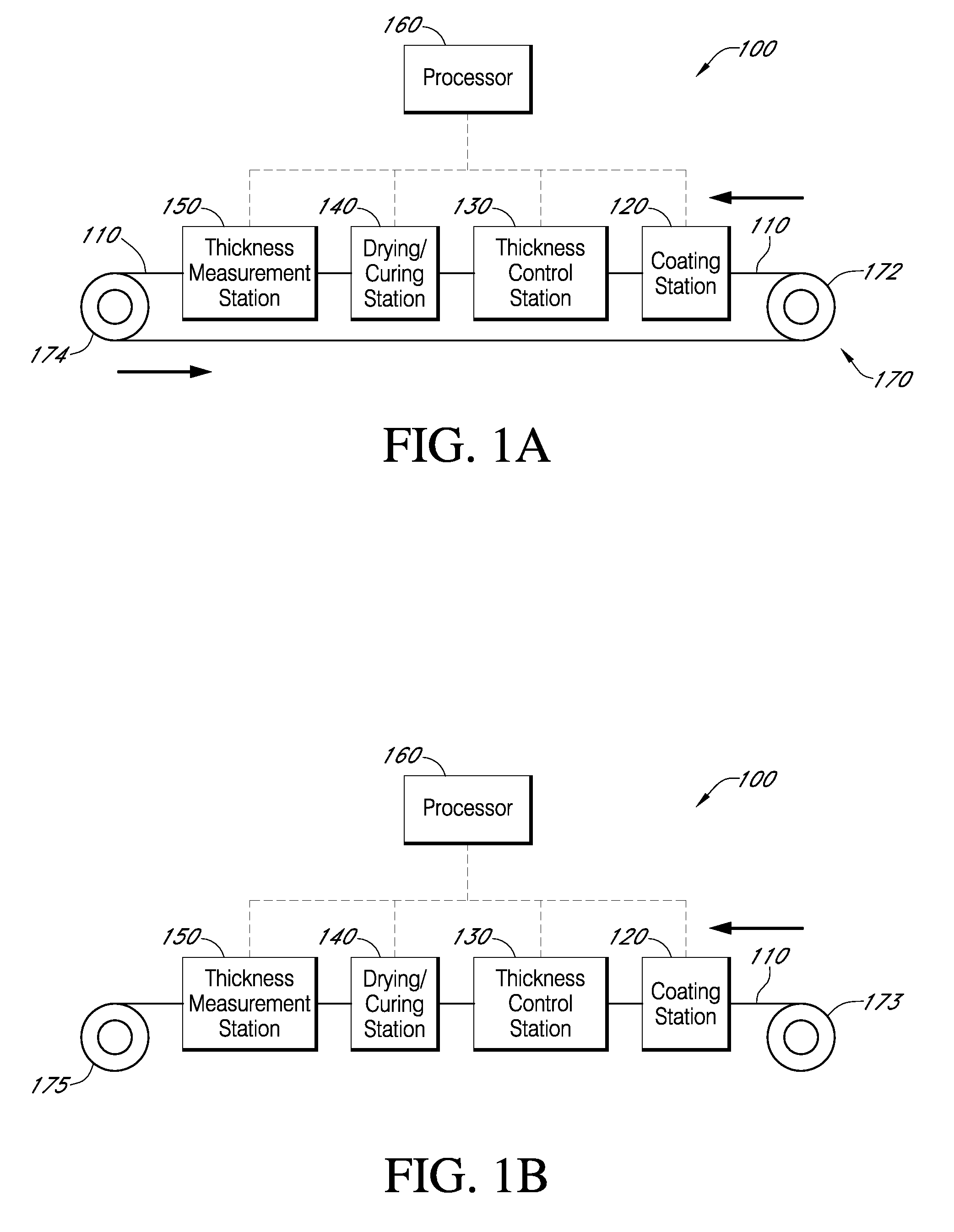
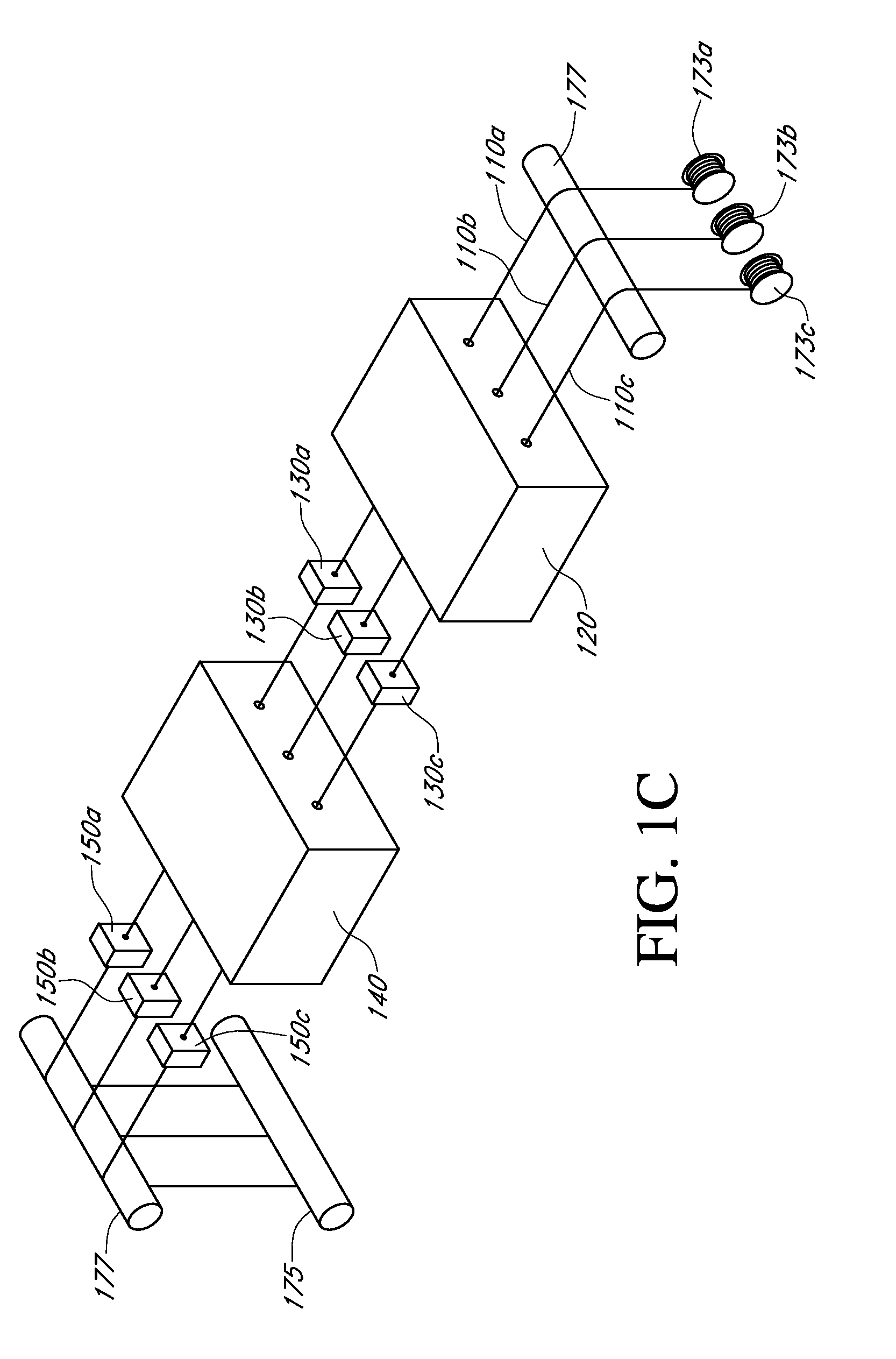
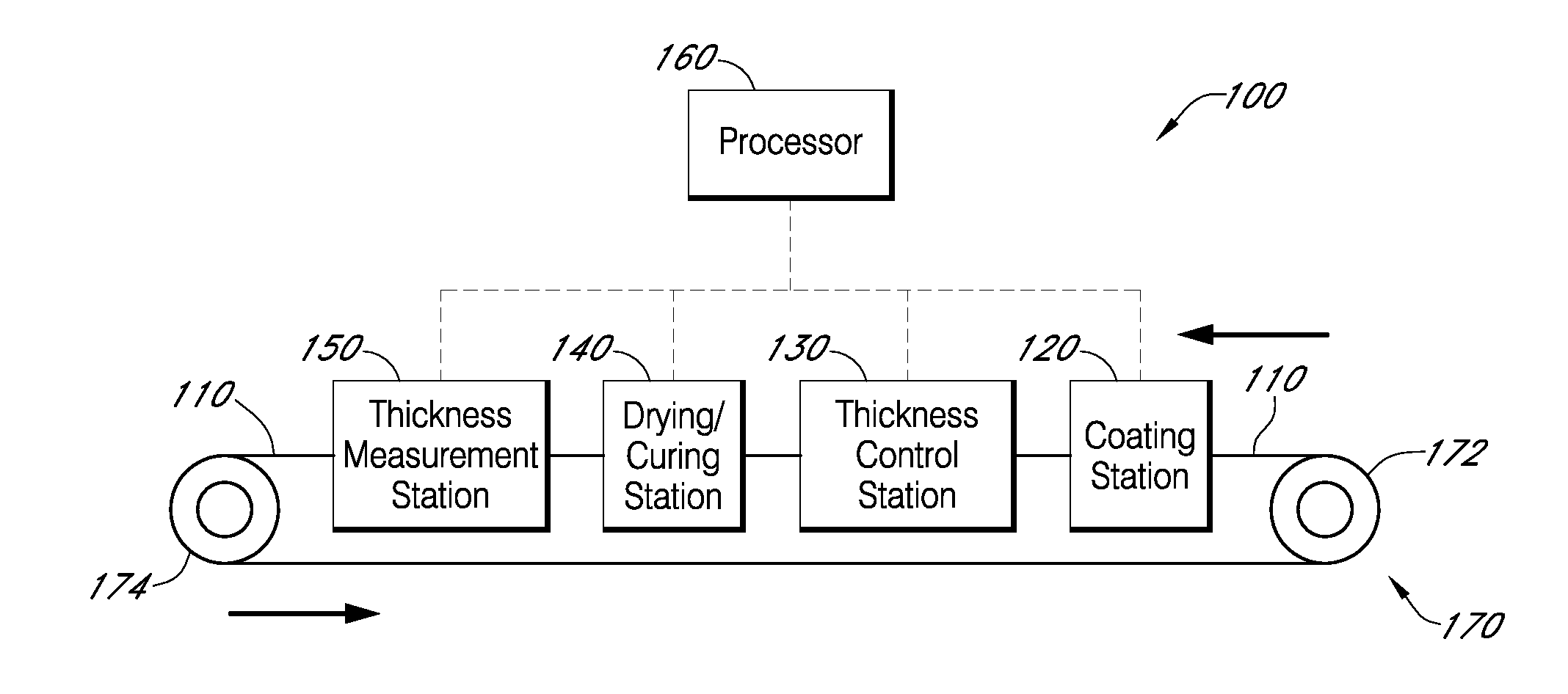
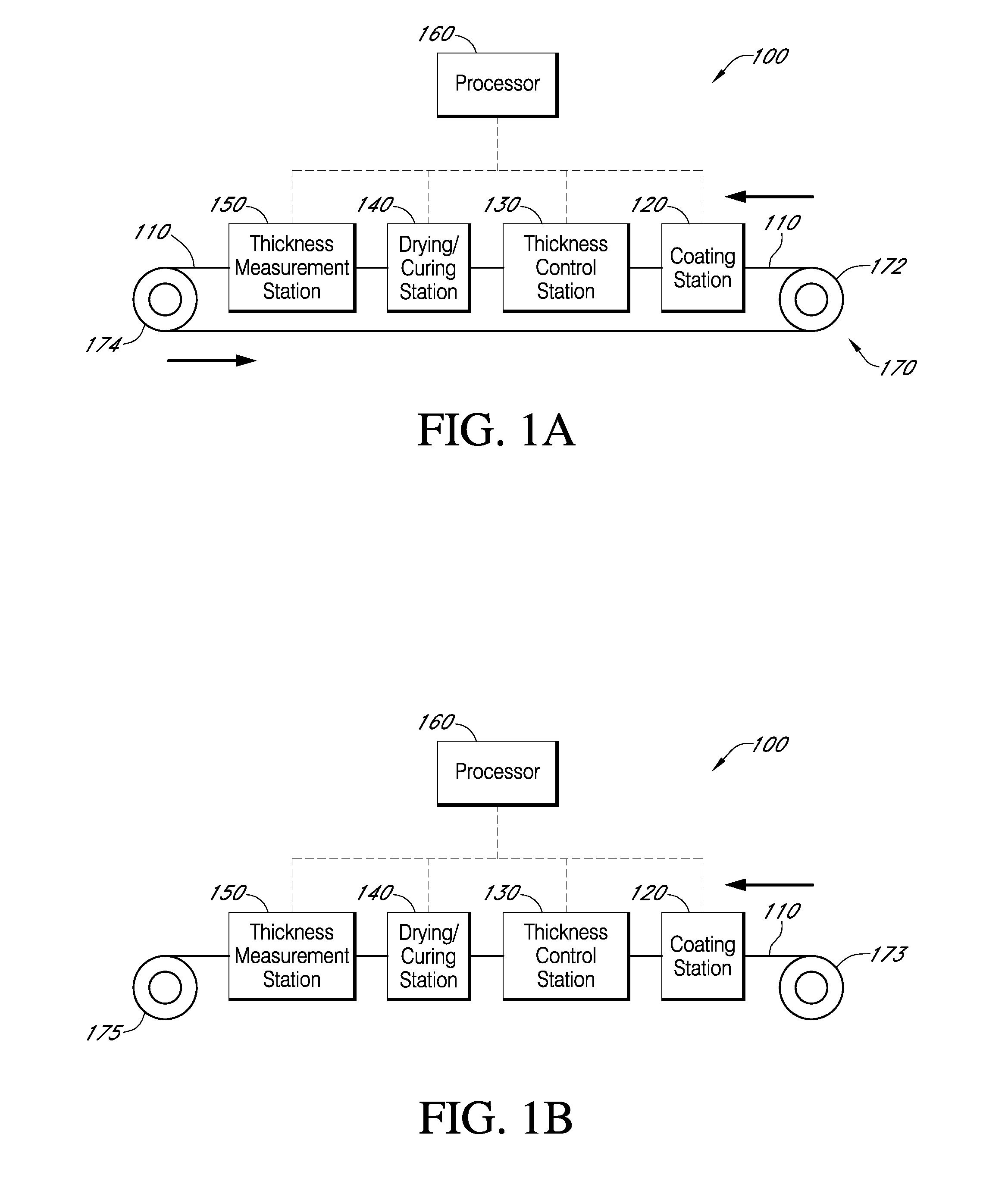
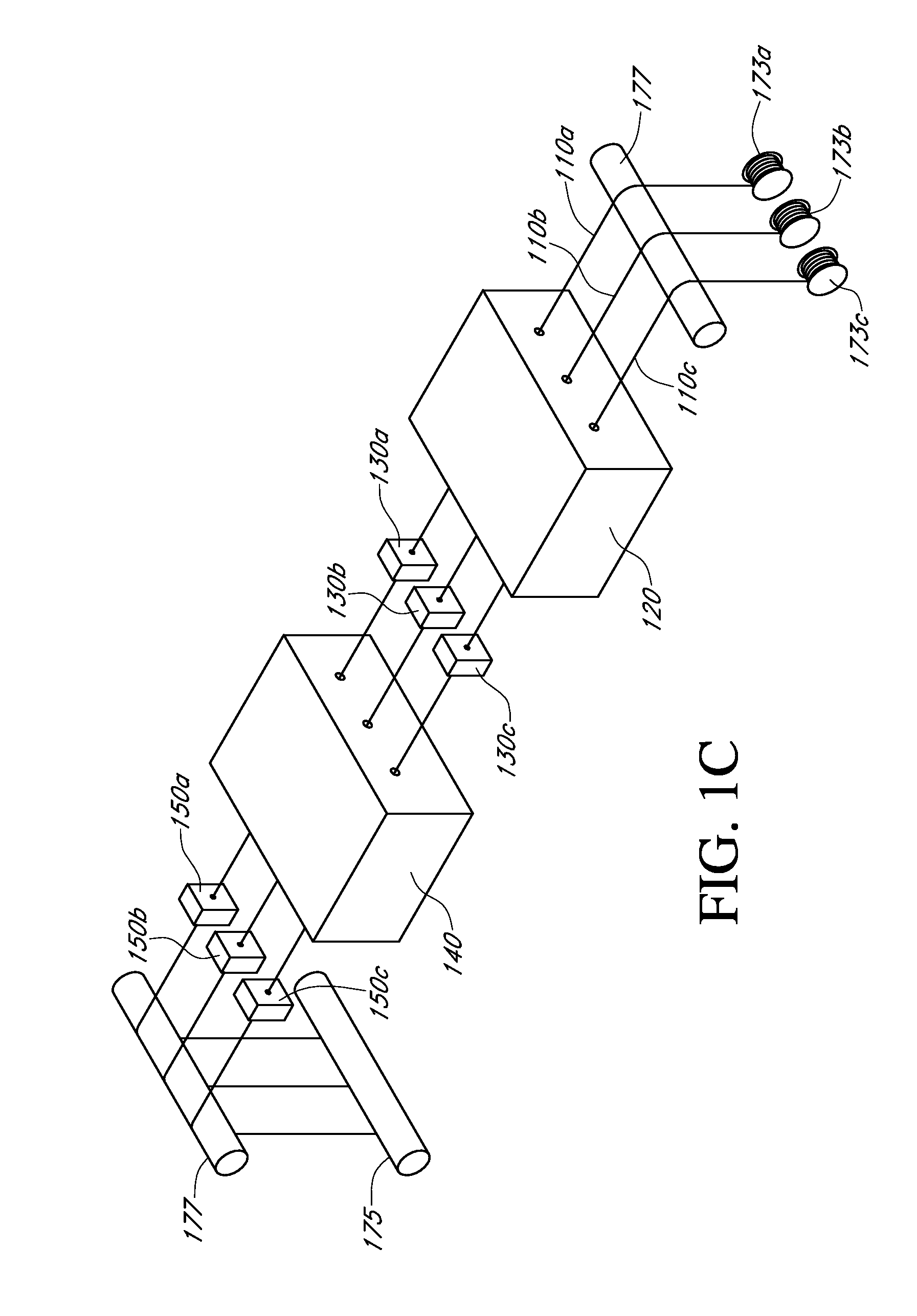
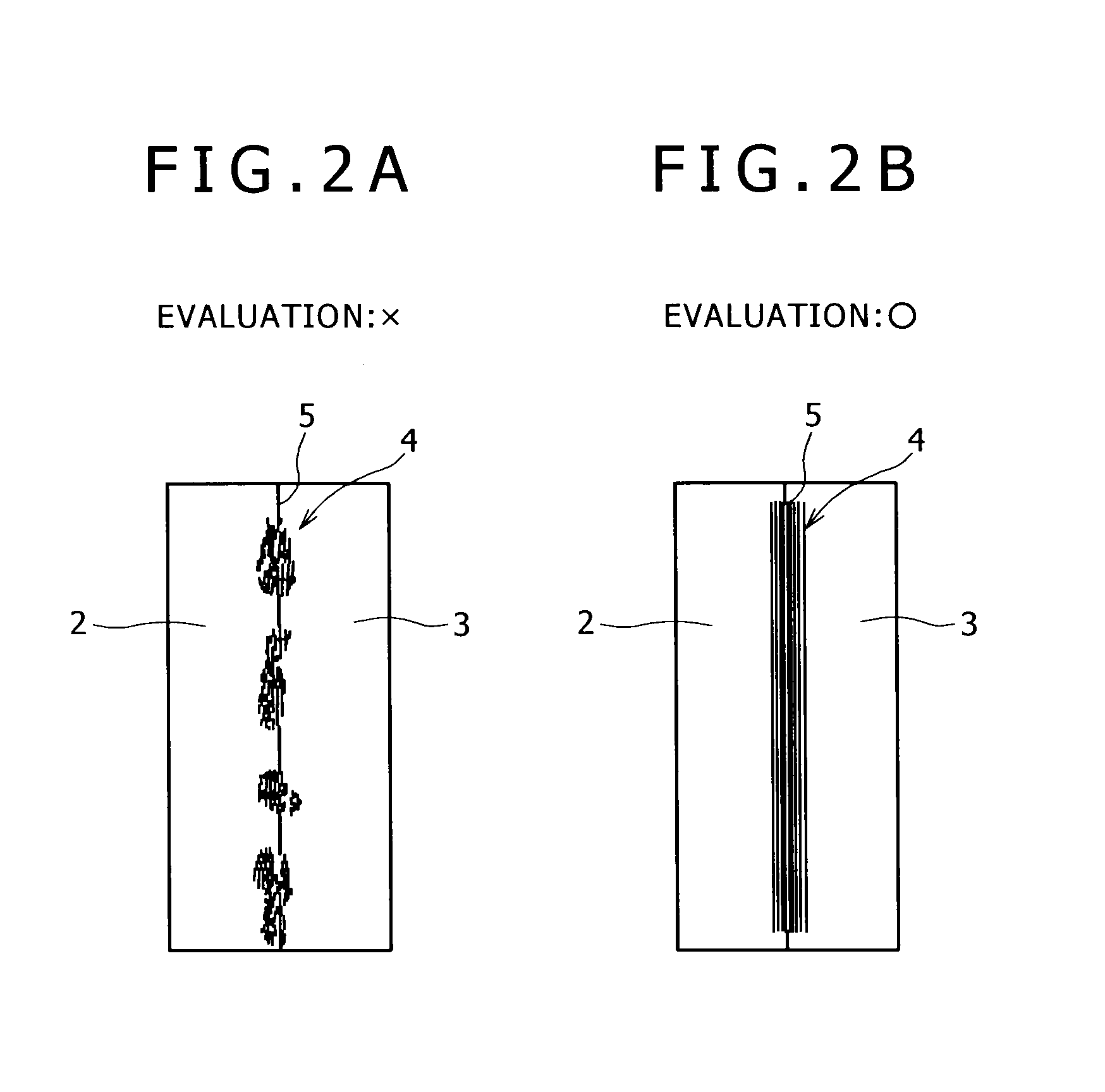
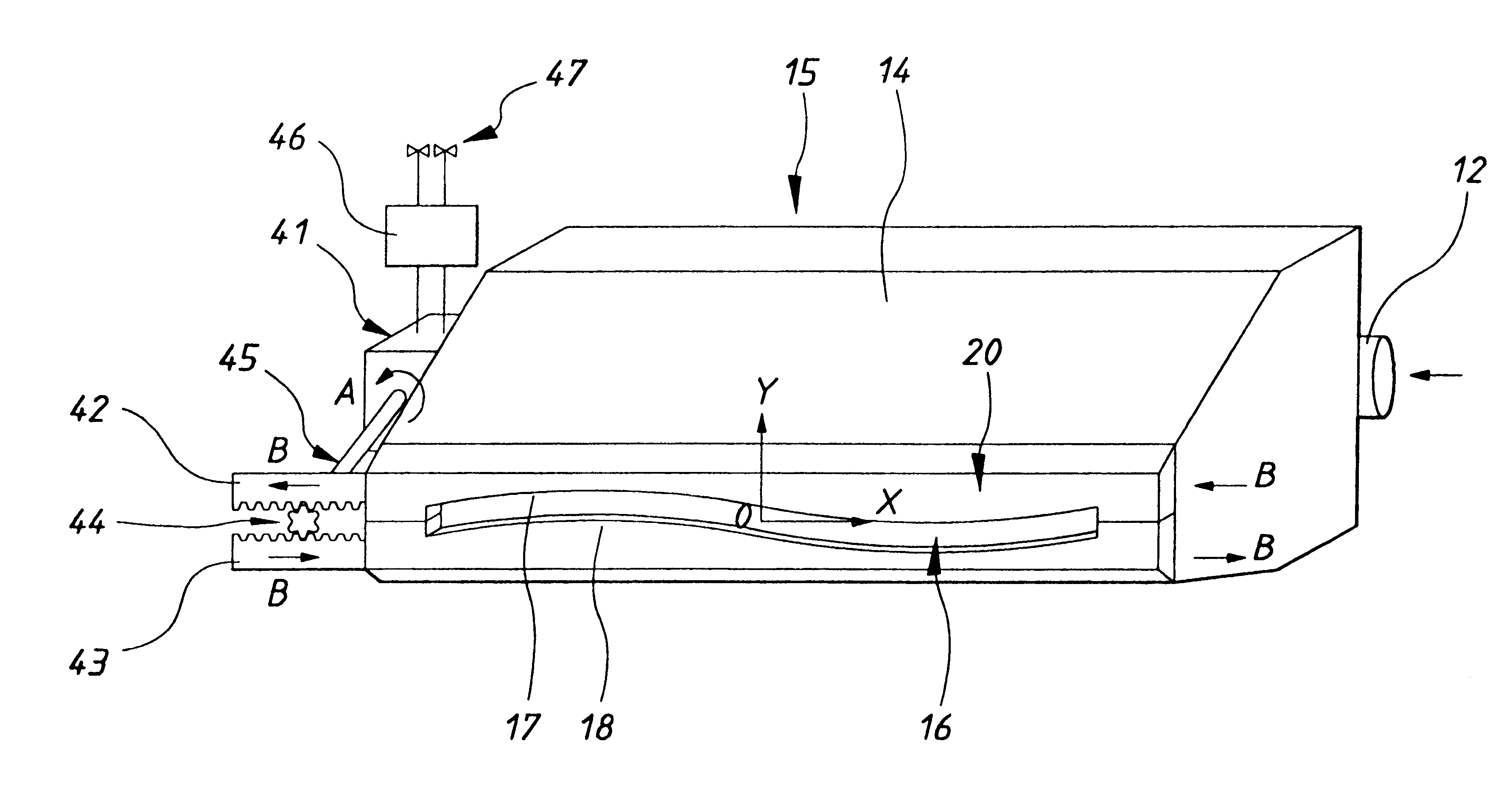
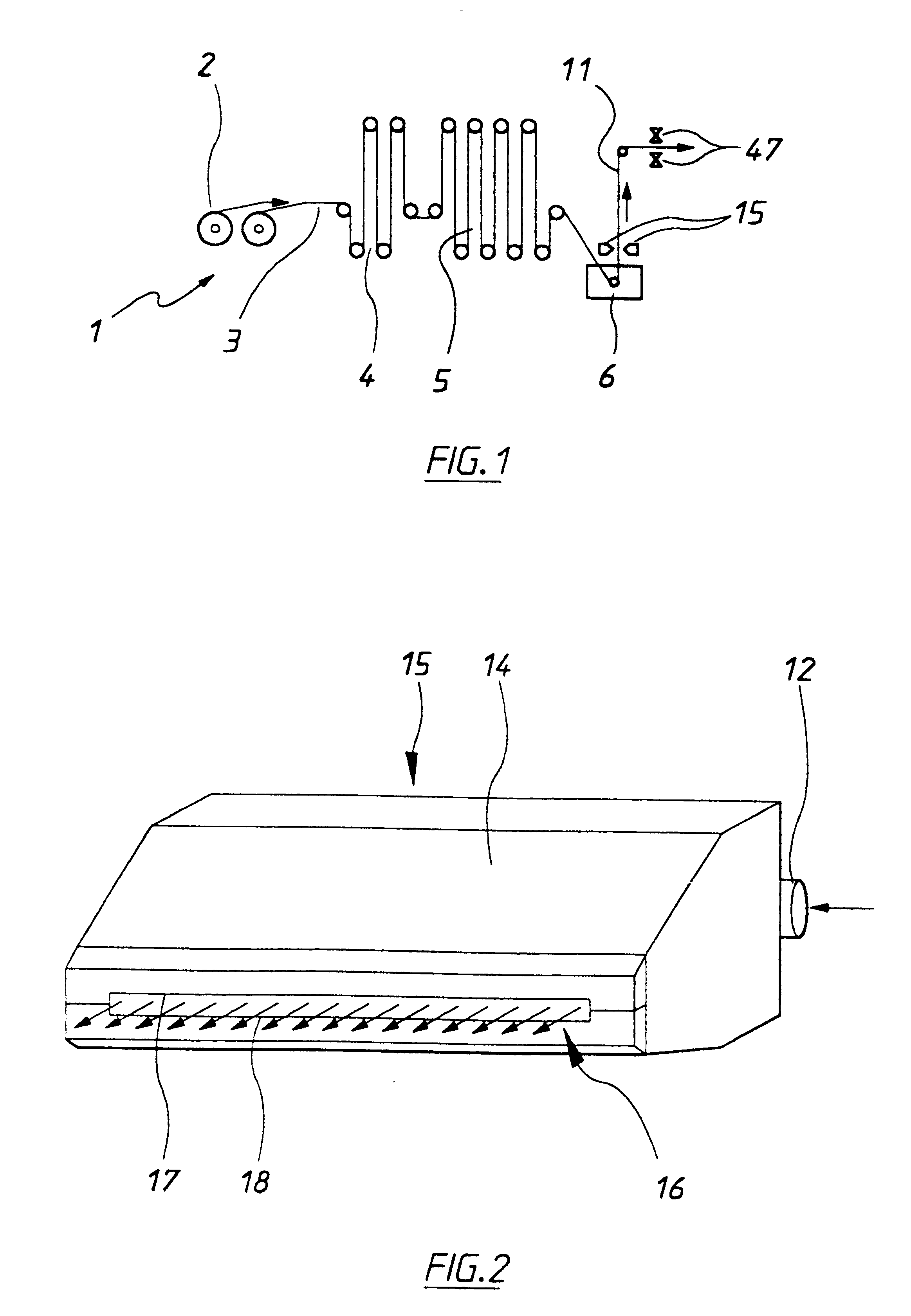
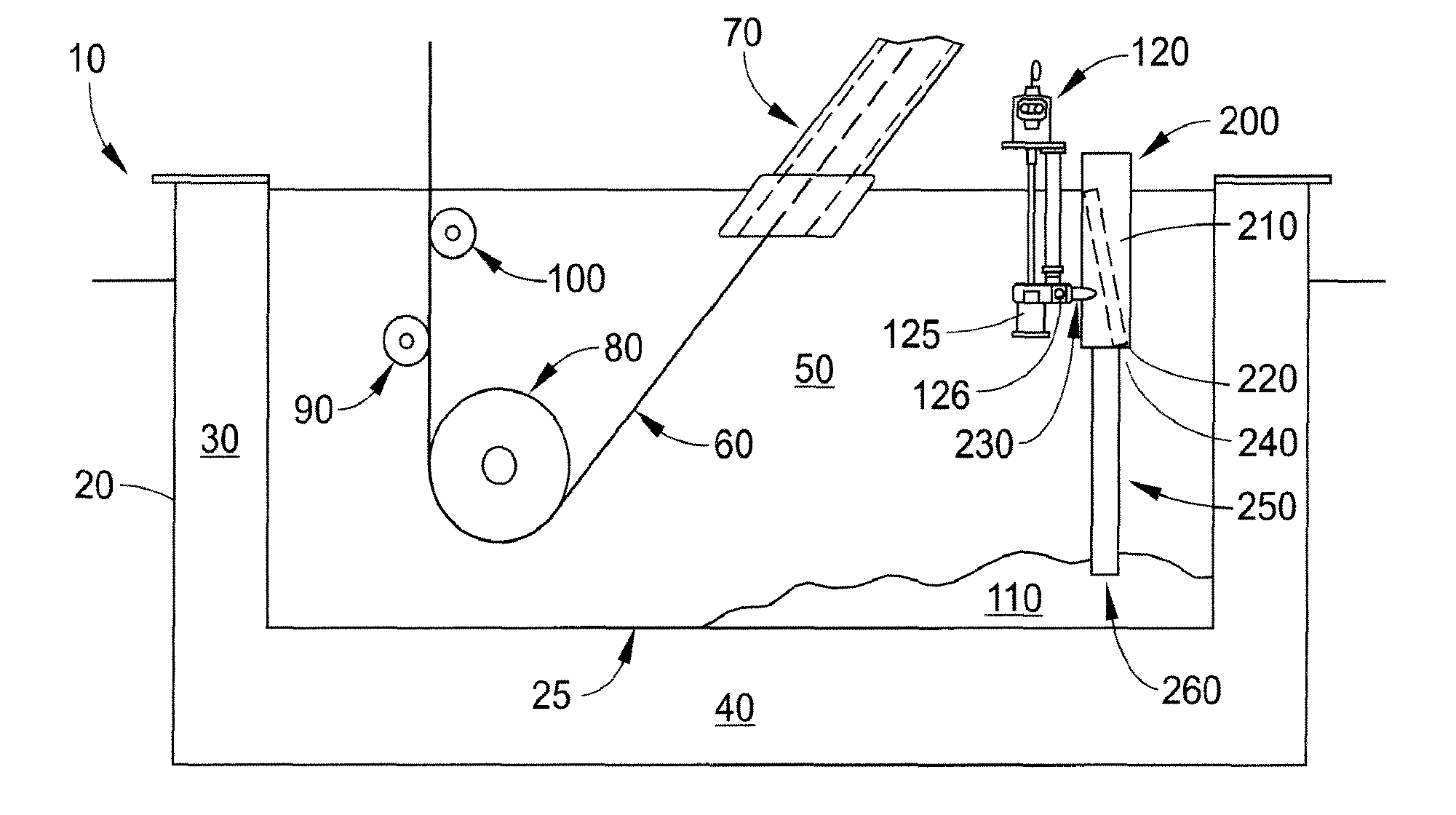
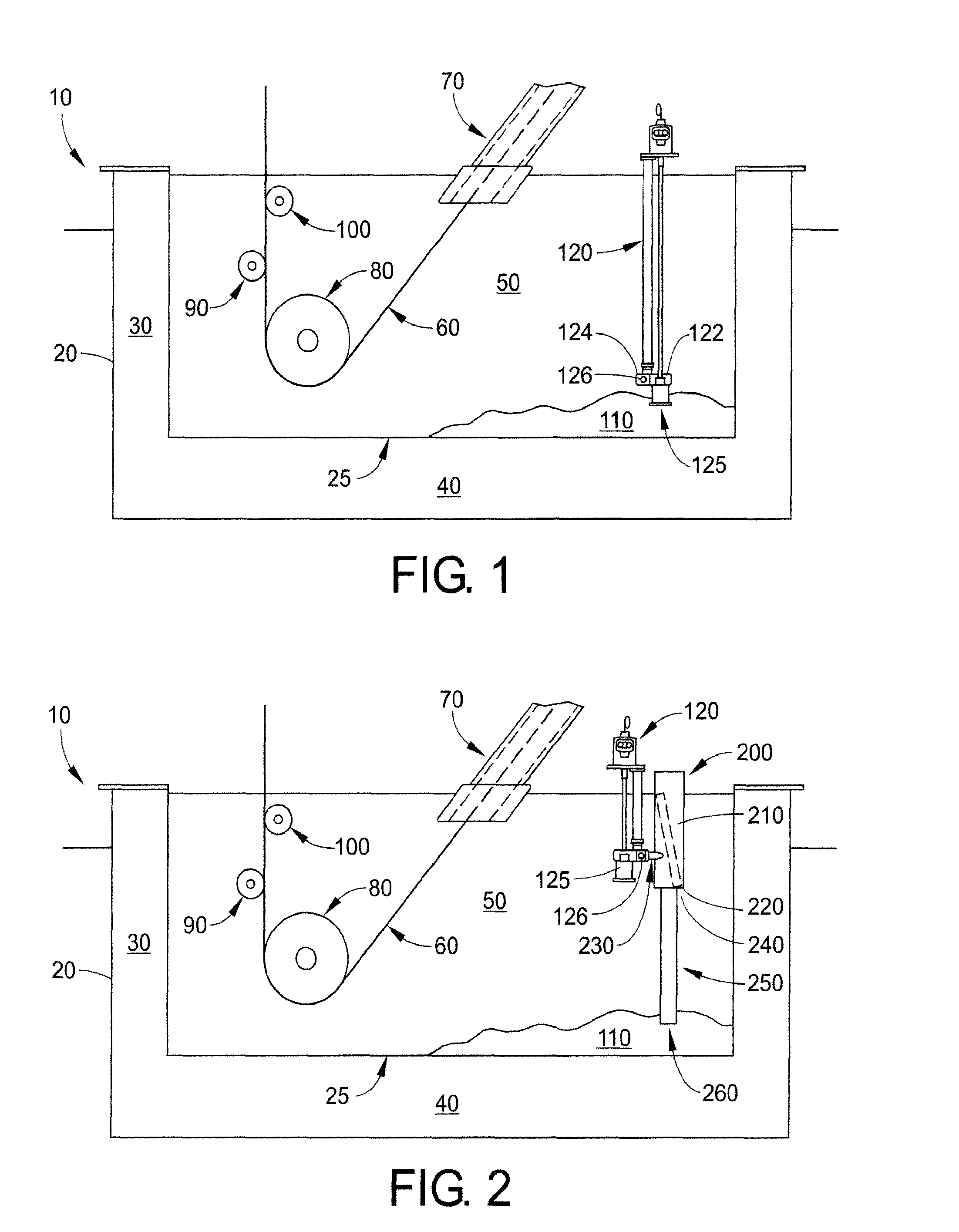
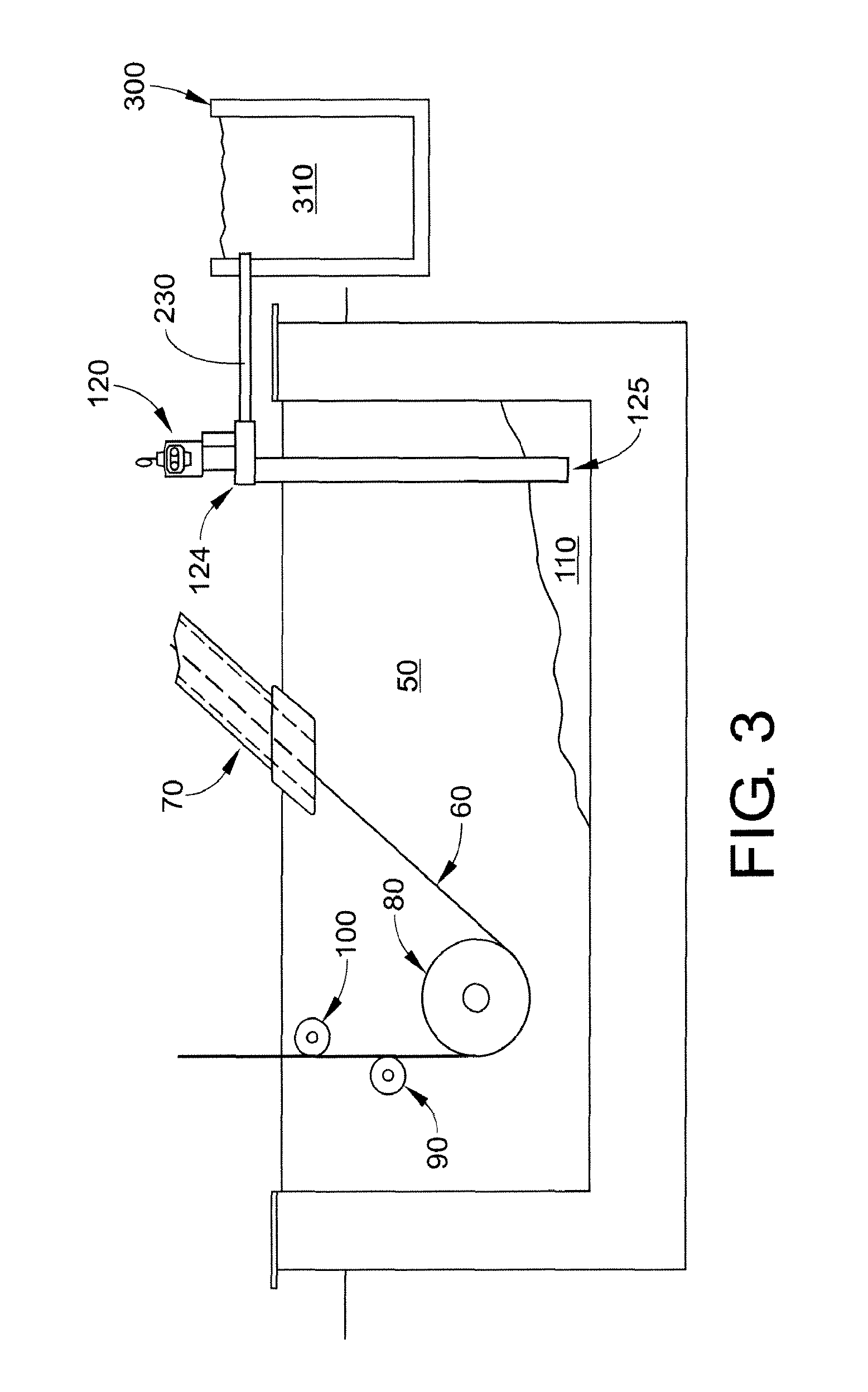
Described here are embodiments of processes and systems for the continuous manufacturing of implantable continuous analyte sensors. In some embodiments, a method is provided for sequentially advancing an elongated conductive body through a plurality of stations, each configured to treat the elongated conductive body. In some of these embodiments, one or more of the stations is configured to coat the elongated conductive body using a meniscus coating process, whereby a solution formed of a polymer and a solvent is prepared, the solution is continuously circulated to provide a meniscus on a top portion of a vessel holding the solution, and the elongated conductive body is advanced through the meniscus. The method may also comprise the step of removing excess coating material from the elongated conductive body by advancing the elongated conductive body through a die orifice. For example, a provided elongated conductive body 510 is advanced through a pre-coating treatment station 520, through a coating station 530, through a thickness control station 540, through a drying or curing station 550, through a thickness measurement station 560, and through a post-coating treatment station 570.
Owner:DEXCOM
Continuous analyte sensors and methods of making same
InactiveUS20110027453A1Low production costMinimize changesHot-dipping/immersion processesPharmaceutical containersAnalyteSolvent
Described here are embodiments of processes and systems for the continuous manufacturing of implantable continuous analyte sensors. In some embodiments, a method is provided for sequentially advancing an elongated conductive body through a plurality of stations, each configured to treat the elongated conductive body. In some of these embodiments, one or more of the stations is configured to coat the elongated conductive body using a meniscus coating process, whereby a solution formed of a polymer and a solvent is prepared, the solution is continuously circulated to provide a meniscus on a top portion of a vessel holding the solution, and the elongated conductive body is advanced through the meniscus. The method may also comprise the step of removing excess coating material from the elongated conductive body by advancing the elongated conductive body through a die orifice. For example, a provided elongated conductive body 510 is advanced through a pre-coating treatment station 520, through a coating station 530, through a thickness control station 540, through a drying or curing station 550, through a thickness measurement station 560, and through a post-coating treatment station 570.
Owner:DEXCOM
High strength steel sheet having excellent formability and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7090731B2Good molding effectHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityHardness
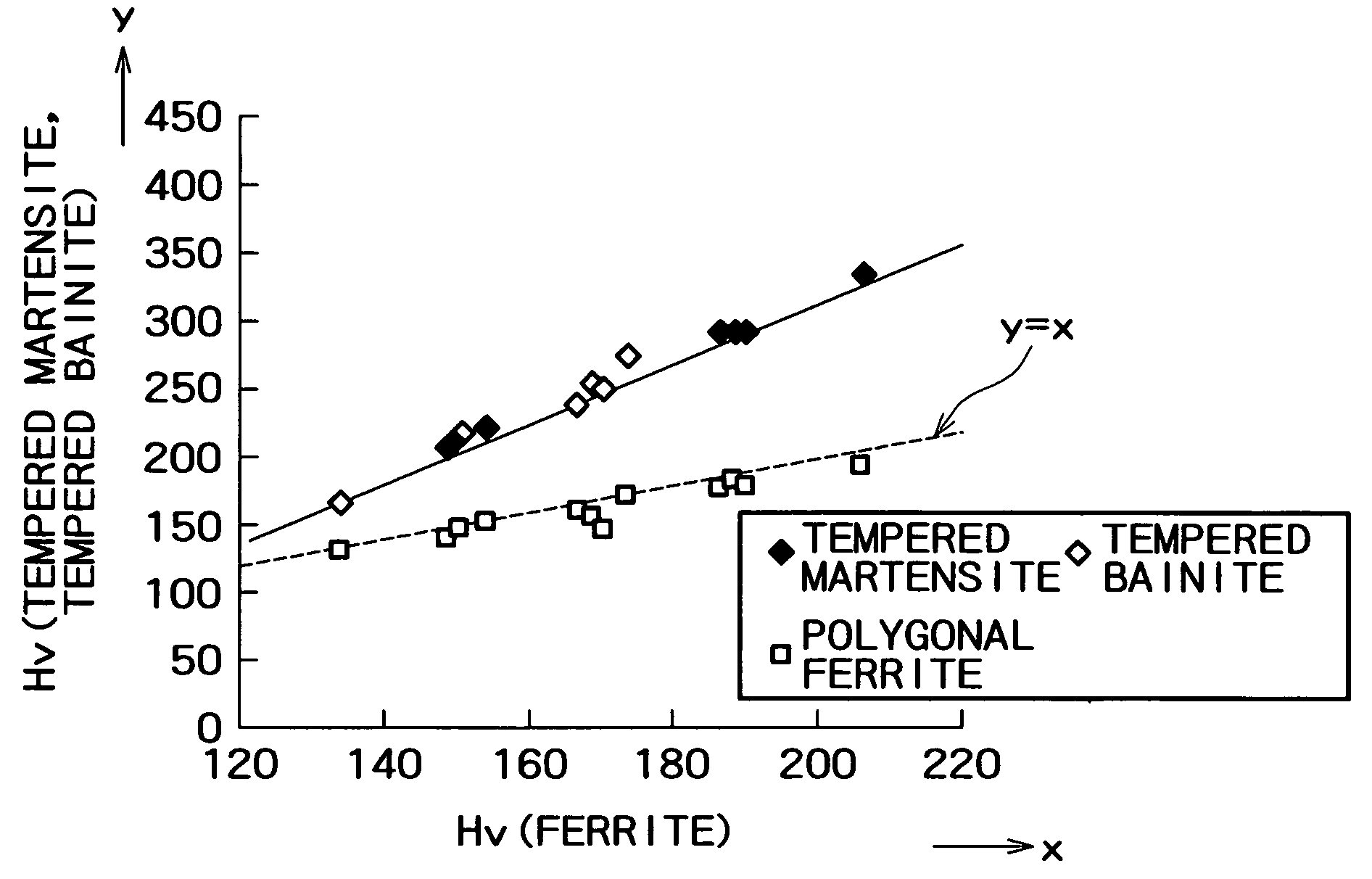
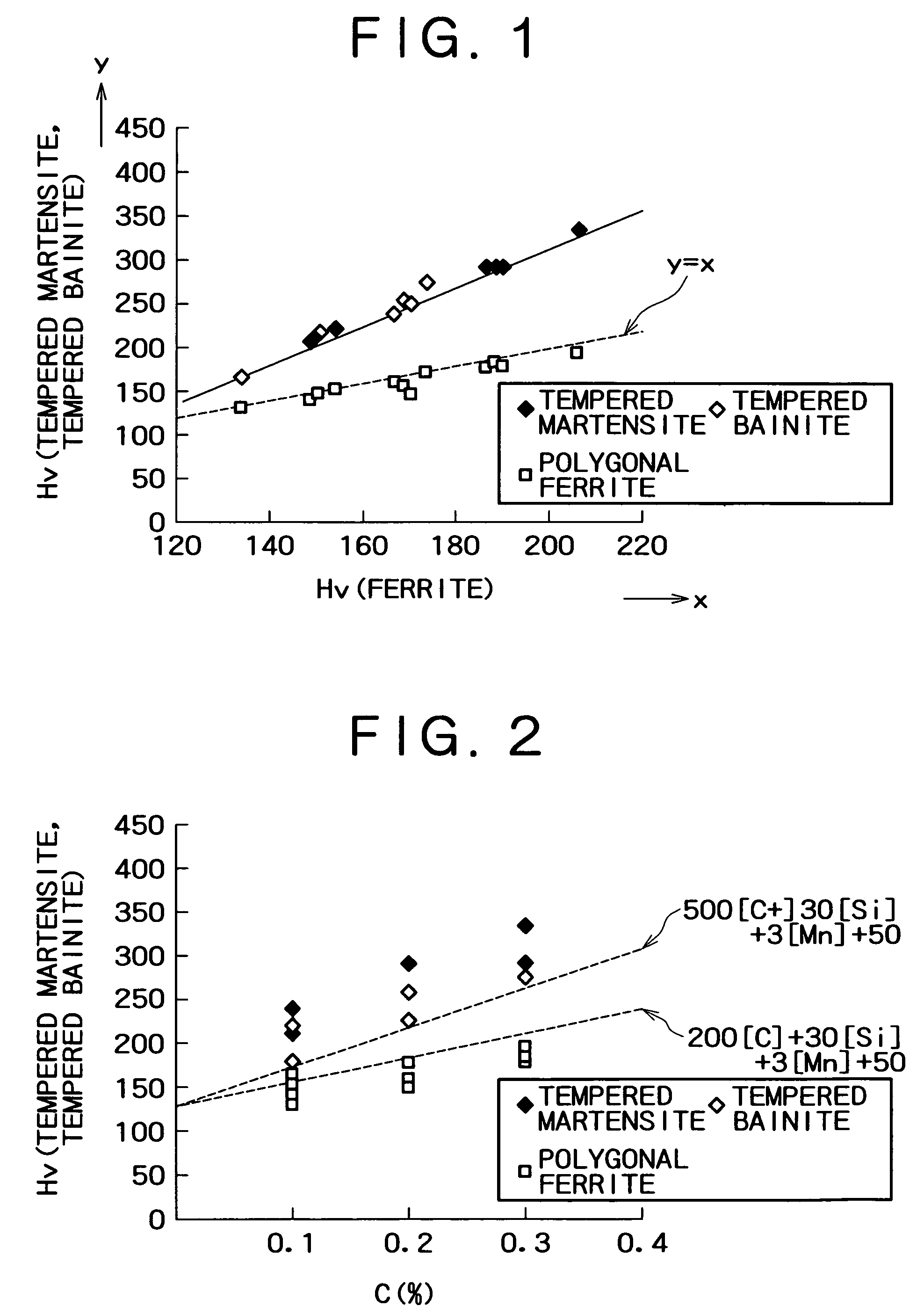
A high strength steel sheet having (2-1) a base phase structure, the base phase structure being tempered martensite or tempered bainite and accounting for 50% or more in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure, or the base phase structure comprising tempered martensite or tempered bainite which accounts for 15% or more in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure and further comprising ferrite, the tempered martensite or the tempered bainite having a hardness which satisfies the relation of Vickers hardness (Hv)≧500[C]+30[Si]+3[Mn]+50 where [ ] represents the content (mass %) of each element, and (2-2) a second phase structure comprising retained austenite which accounts for 3 to 30% in terms of a space factor relative to the whole structure and optionally further comprising bainite and / or martensite, the retained austenite having a C concentration (CγR) of 0.8% or more.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
-Zn coated steel material, ZN coated steel sheet and painted steel sheet excellent in corrosion resistance, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS6465114B1Improve corrosion resistanceResistance to red rustHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelAlloy coating
A coated steel material excellent in corrosion resistance and a method of producing the same, wherein a coated steel material has on the surface of the steel sheet a Zn-alloy coating layer containing 1-10 wt % of Mg, 2-19 wt % of Al and 0.01-2 wt % of Si, where Mg and Al satisfy Mg (%)+Al (%)<=20%, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities, and has a coating layer structure of a Mg intermetallic compound or the like. As a base metal treatment, it is preferably provided with a Ni coating layer. The coated Zn-alloy coated steel sheet may have provided on the coating layer, as an intermediate layer, a chromate film layer, and, as an upper layer, an organic coating layer. The Zn-alloy coating layer may further contain one or more of 0.01-1 wt % of In, 0.01-1 wt % of Bi and 1-10 wt % of Sn. The coated steel material may be painted.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and production thereof
InactiveUS6312536B1High strengthGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
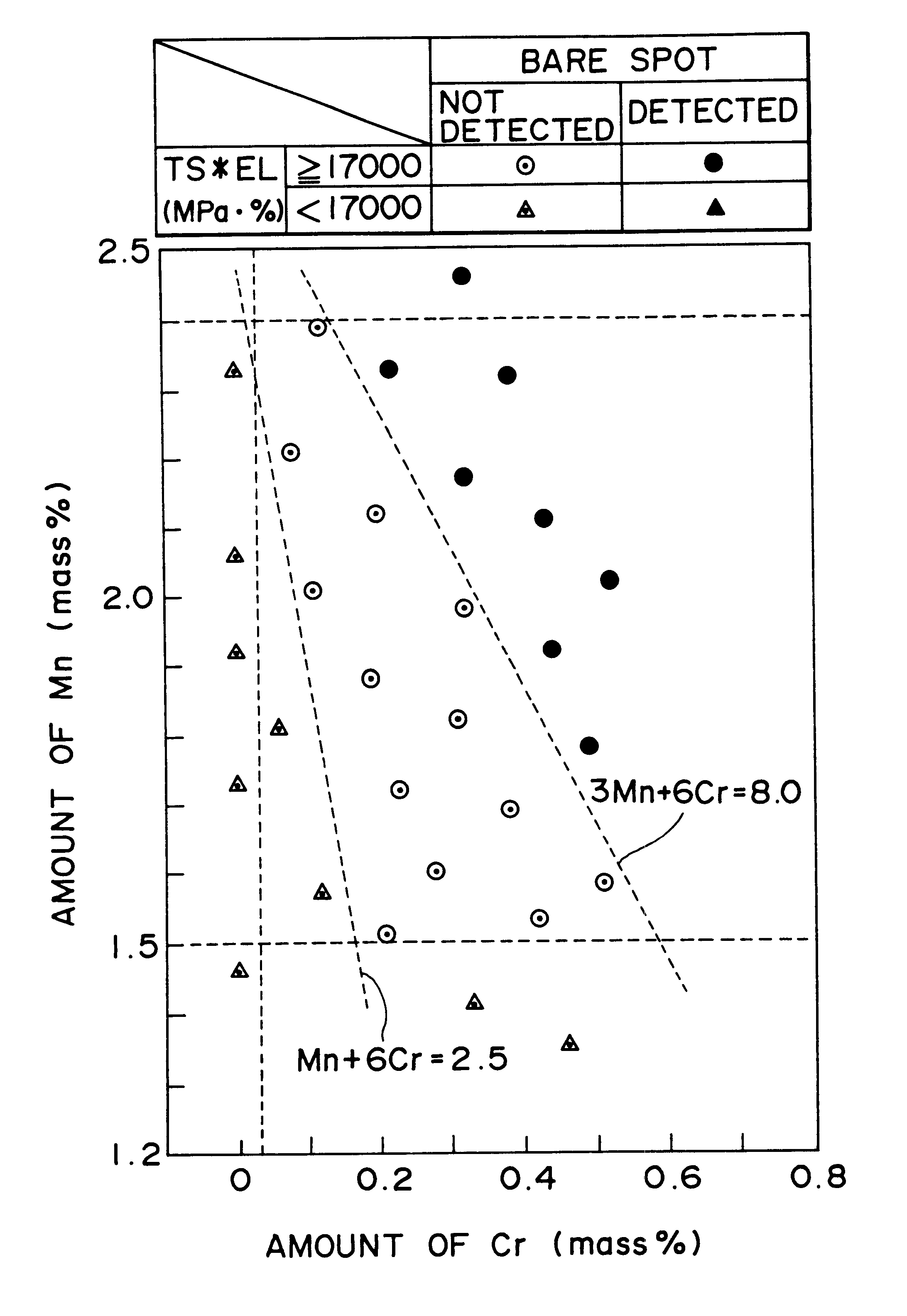
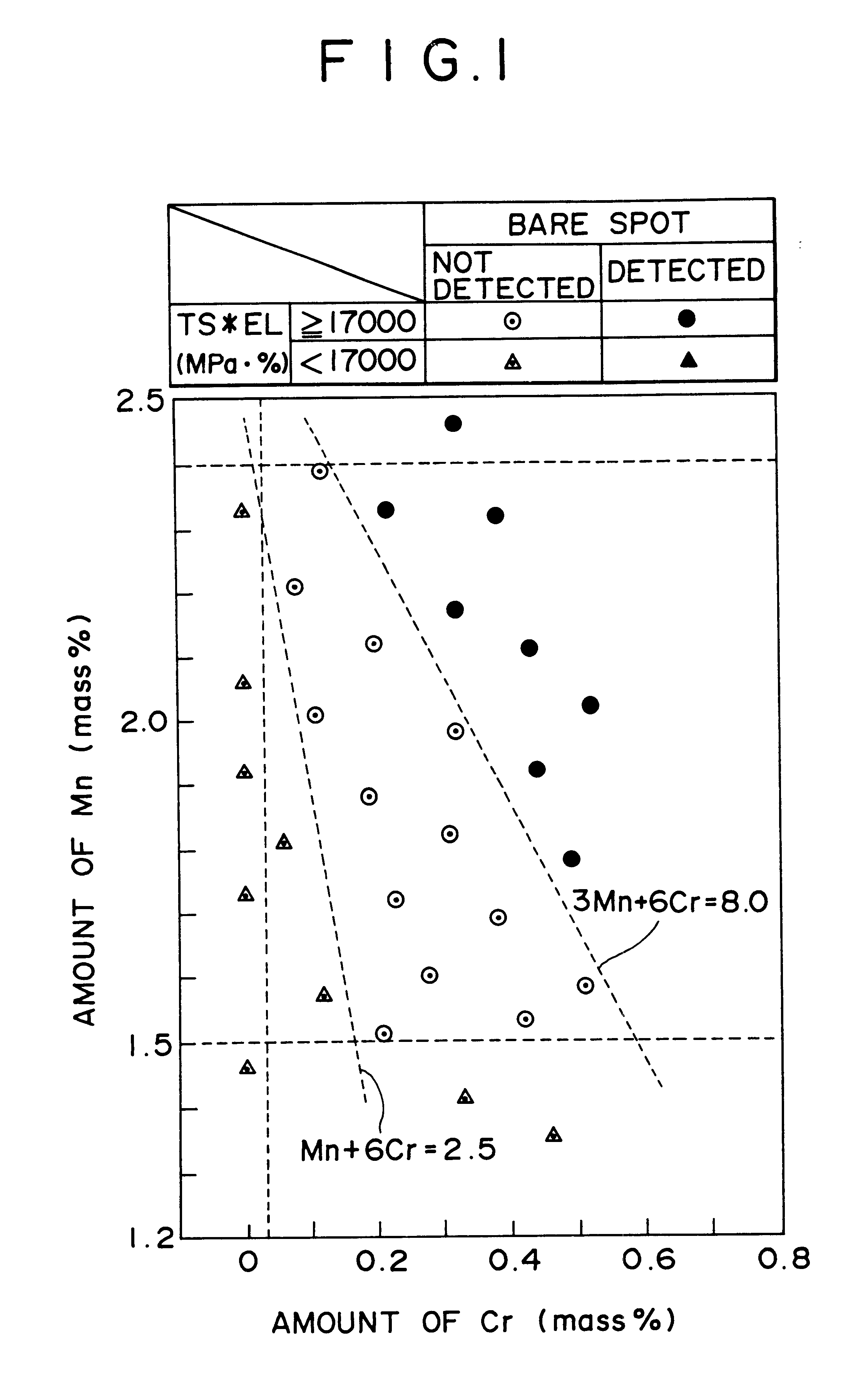
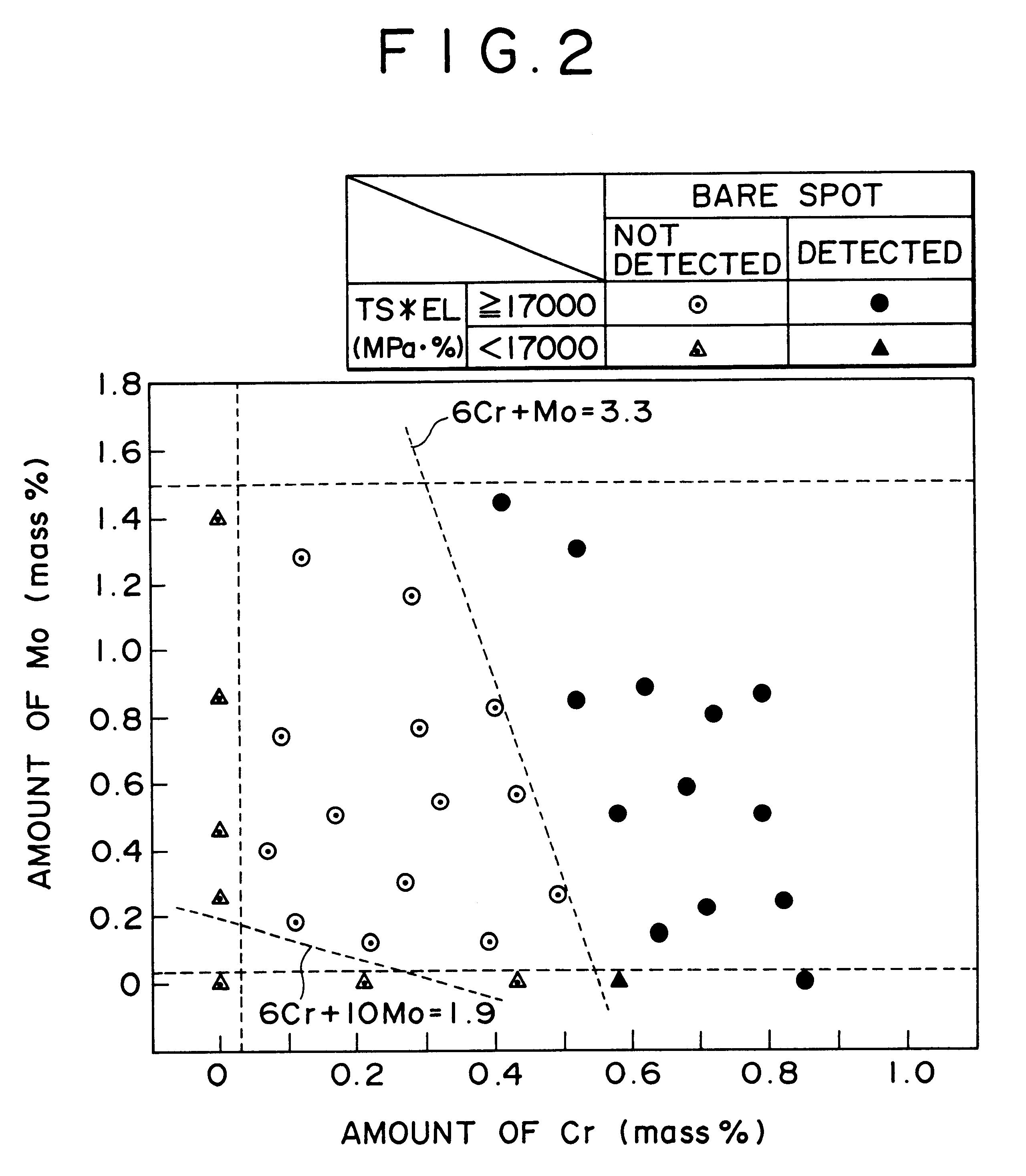
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having both high strength and good formability. A process for producing said hot-dip galvanized steel sheet without requiring additional steps of surface grinding and pre-plating.The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is produced by forming a hot-dip galvanizing layer on a base cold-rolled steel sheet composed of C (0.02-0.20 mass %), Mn (1.50-2.40 mass %), Cr (0.03-1.50 mass %), Mo (0.03-1.50 mass %), 3Mn+6Cr+Mo (no more than 8.1 mass %), Mn+6Cr+10 Mo (no less than 3.5 mass %), Al (0.010-0.150 mass %), and Fe as the principal component, with Ti limited to 0.01 mass % or less, Si limited to 0.04 mass % or less, P limited to 0.060 mass % or less, and S limited to 0.030 mass % or less, and said base steel sheet having the composite microstructure composed mainly of ferrite and martensite.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Flux-cored wire for different-material bonding and method of bonding different materials
InactiveUS20090017328A1High bonding strengthRaise checkHot-dipping/immersion processesArc welding apparatusHigh intensityChloride
There are provided a flux cored wire for joining dissimilar materials with each other, capable of enhancing a bonding strength upon joining an aluminum-base material with a steel-base material, and excellent in bonding efficiency, a method for joining the dissimilar materials with each other, and a bonded joint obtained by the method. In particular, there is provided a method for joining dissimilar materials with each other, in the case of melt weld-bonding of high-strength dissimilar materials with each other, that is, the high-strength steel member with the high-strength 6000 series aluminum alloy member and in the case of the steel member being a galvanized steel member. In one mode, use is made of a flux cored wire wherein the interior of an aluminum alloy envelope is filled up with a flux, the flux has fluoride composition containing a given amount of AlF3 without containing chloride, and the aluminum alloy of the envelope contains Si in a range of 1 to 13 mass %. If such a flux cored wire is use, it is possible to obtain a high bonding strength in the case of melt weld-bonding of high-strength dissimilar materials with each other, that is, the high-strength steel member with the high-strength 6000 series aluminum alloy member.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Coating thickness control
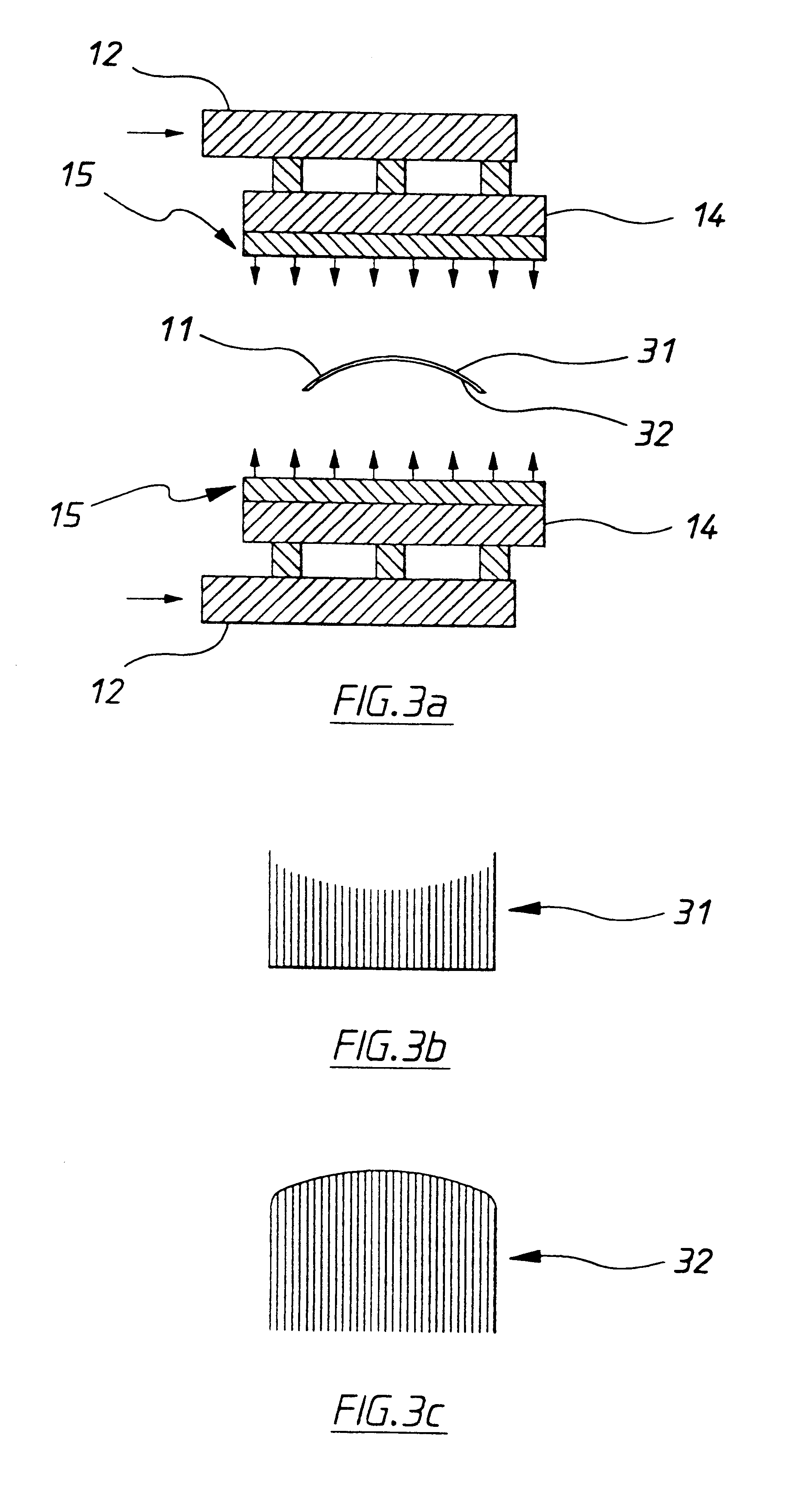
An air knife mouth arrangement for use in an air knife assembly having a laterally extending mouth through which pressurized fluid passes to operate on a coating applied to a surface of a sheet material passing the mouth in a longitudinal direction to control the thickness of the coating. In the preferred form of the invention shown the air knife mouth arrangement comprises a mouth defined by a pair of facing lips, each lip having in front elevation a curved shape along its length. The curved shapes of the two lips face each other. The lips of the air knife mouth arrangement are selectively laterally displaceable relative to each other by a moving means so as to thereby vary the separation of the lips and hence the width of the mouth along the length of the mouth. It is to be noted that the term "length" refers to the dimension of the mouth in the lateral direction (indicated by the X axis), while the term "width" refers to the dimension of the mouth in the longitudinal direction (indicated by the Y axis).
Owner:HATCH LTD
Quick change conveyor roll sleeve assembly and method
InactiveUS8915830B2Hot-dipping/immersion processesElectrolysis componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A quick change conveyor roll assembly for metal or glass processing comprising an inner roll shaft having a rigid and elongated cylindrical surface supported and rotationally driven by an associate rotor mean. At least one removable spool having a cylindrical body with a first diameter, a hollow interior therethrough and a collar rigidly adapted at a first end, the collar having a second diameter whereby the second diameter is greater than the first diameter. At least one removable and replaceable insulated roll sleeve being slidably mounted over at least a portion of said removable spool and abutting said collar, the insulated roll sleeve including at least one layer of an insulation material and a securing means operably adjustable to hold said roll sleeve about said removable spool at a second end in a predetermined location on said inner roll shaft.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
Film formation source, vacuum film formation apparatus, and method of manufacturing organic EL panel
InactiveUS20060045958A1Easy to adjustAvoid position deviationHot-dipping/immersion processesVacuum evaporation coatingElectrical and Electronics engineeringSurface plate
It is an object of the present invention to easily adjust the percentage of each component when mixing together several film formation materials, so as to prevent deviation among film formation areas. A film formation source of a vacuum film formation apparatus comprises: a plurality of material accommodating units containing a plurality of film formation materials; a plurality of heating means for heating the film formation materials contained within the material accommodating units; a plurality of discharge outlets for discharging atom flows or molecule flows of film formation materials; a plurality of discharge passages for air-tightly communicating the material accommodating units with discharge outlets. Two groups of discharge outlets each for discharging an identical film formation material are arranged in one direction, in a manner such that two elongated discharge areas formed by linearly connecting the outer edges of the discharge outlets are at least partially overlapped with each other when viewed from overhead.
Owner:TOHOKU PIONEER CORP
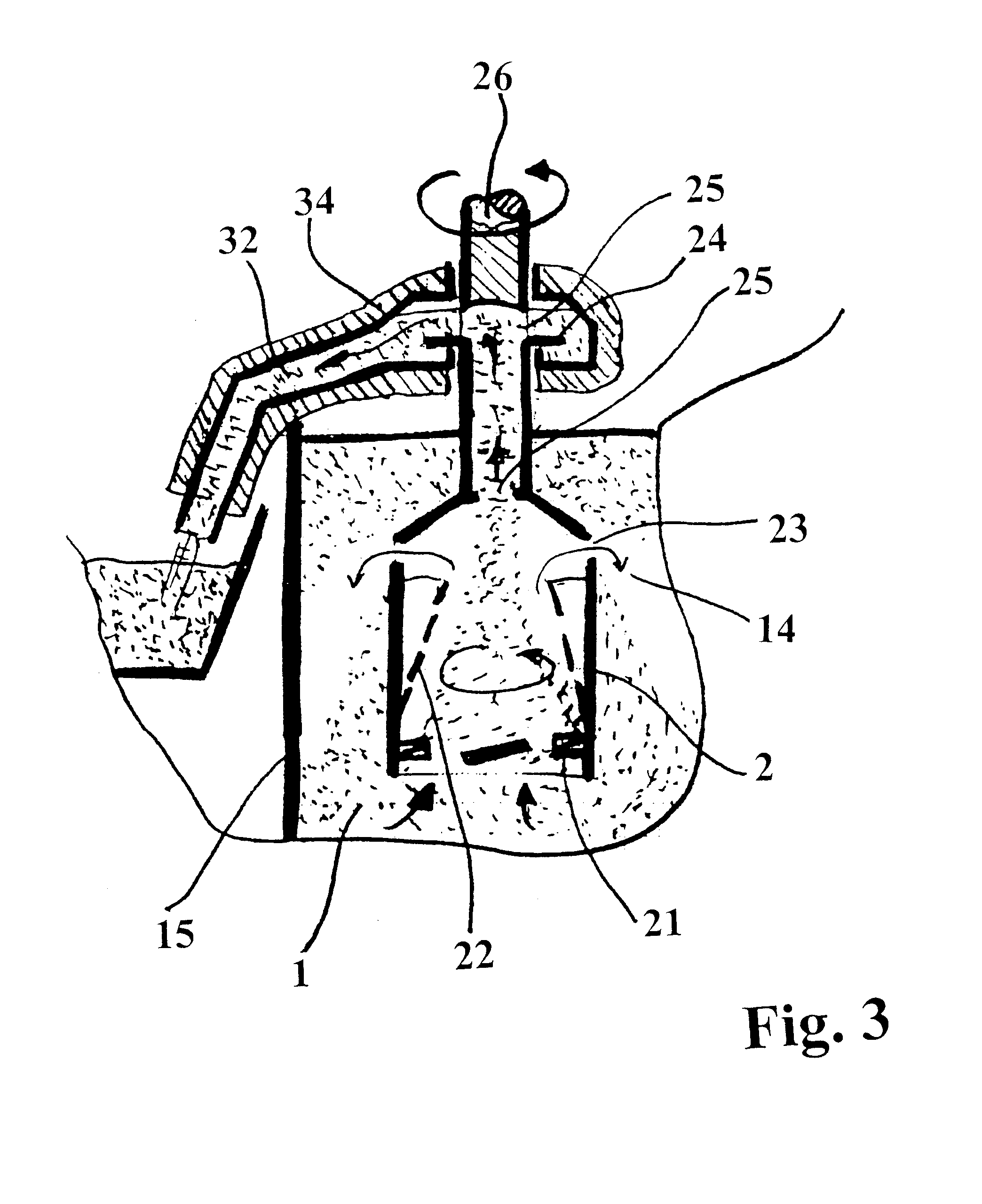
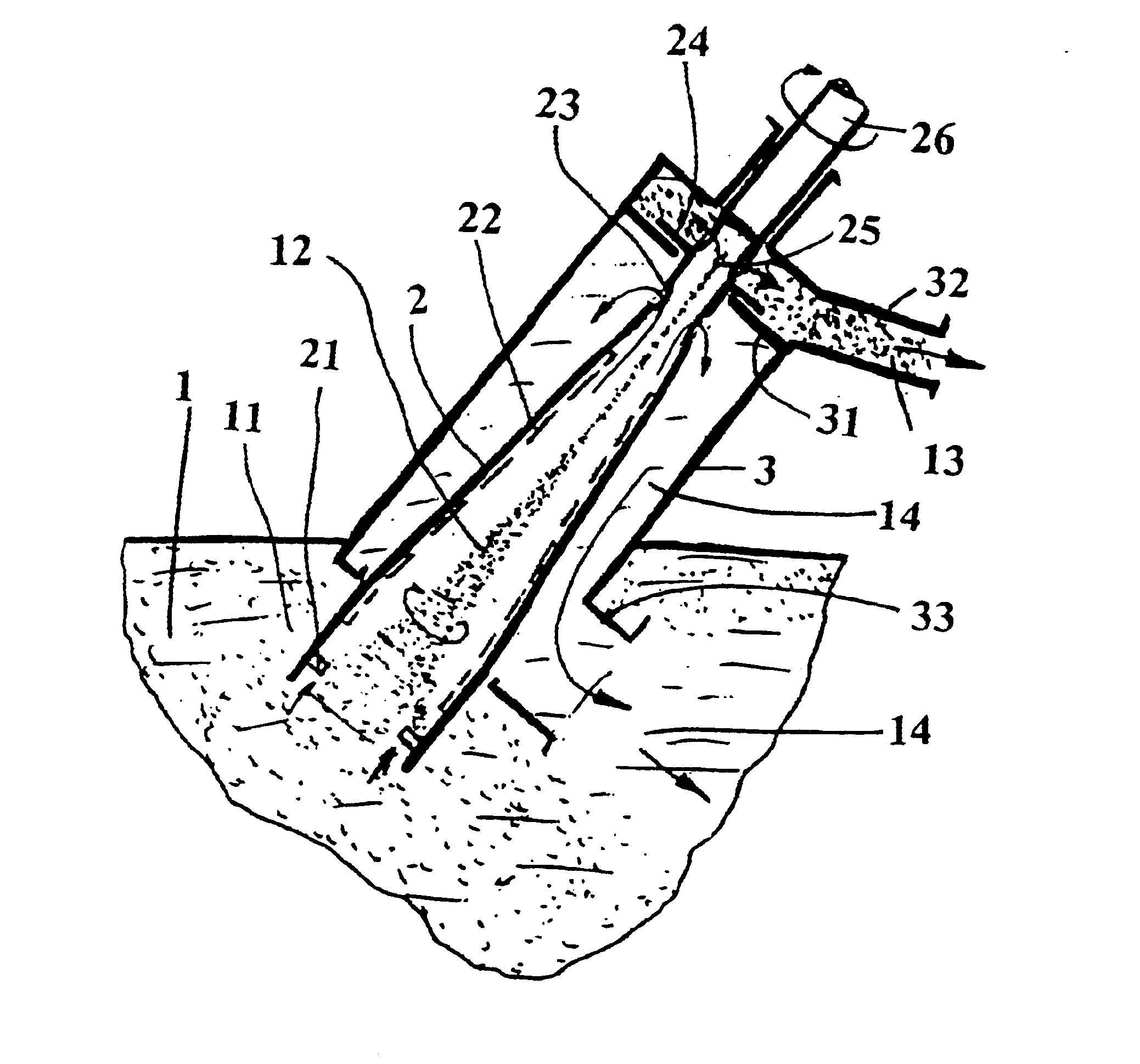
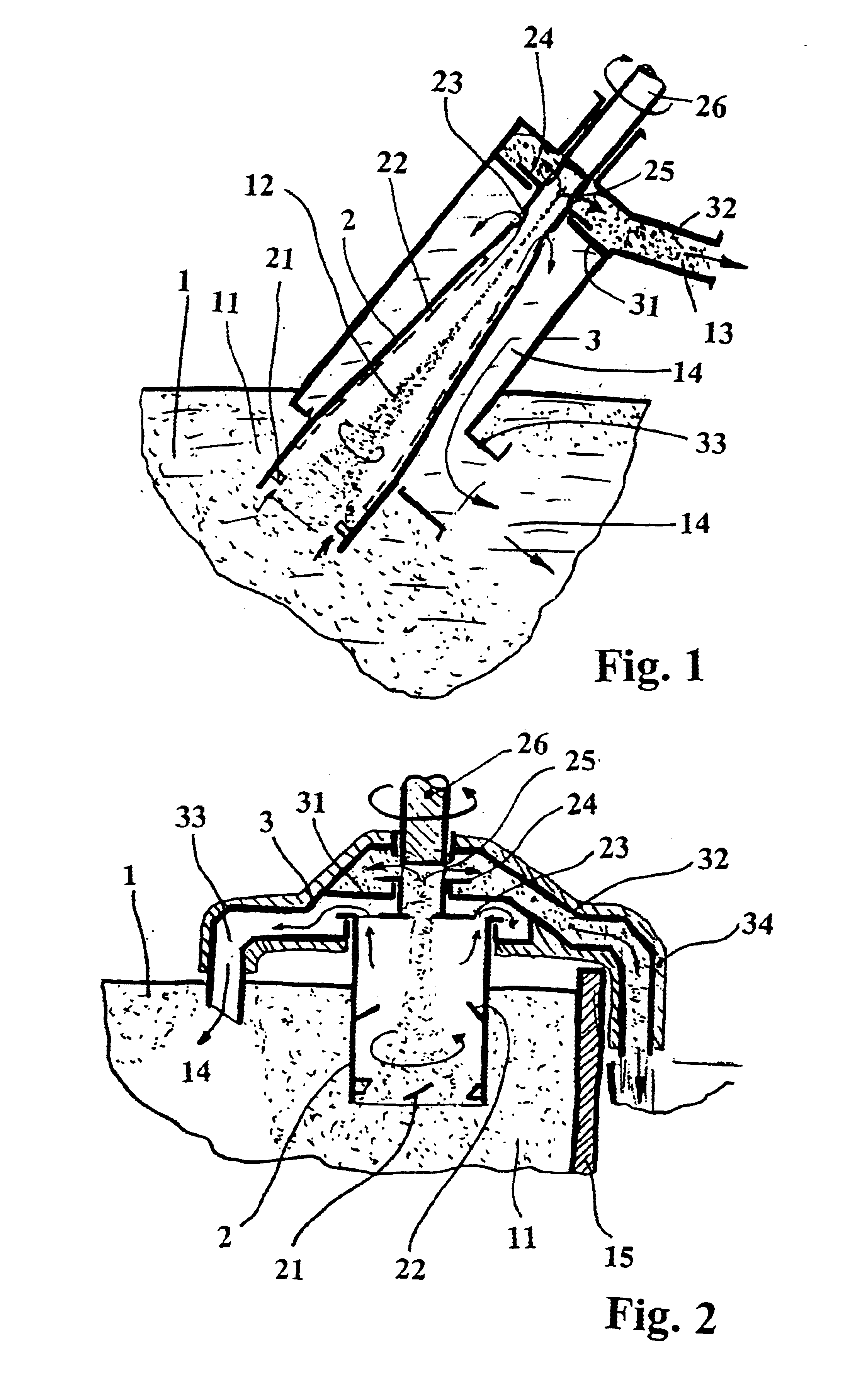
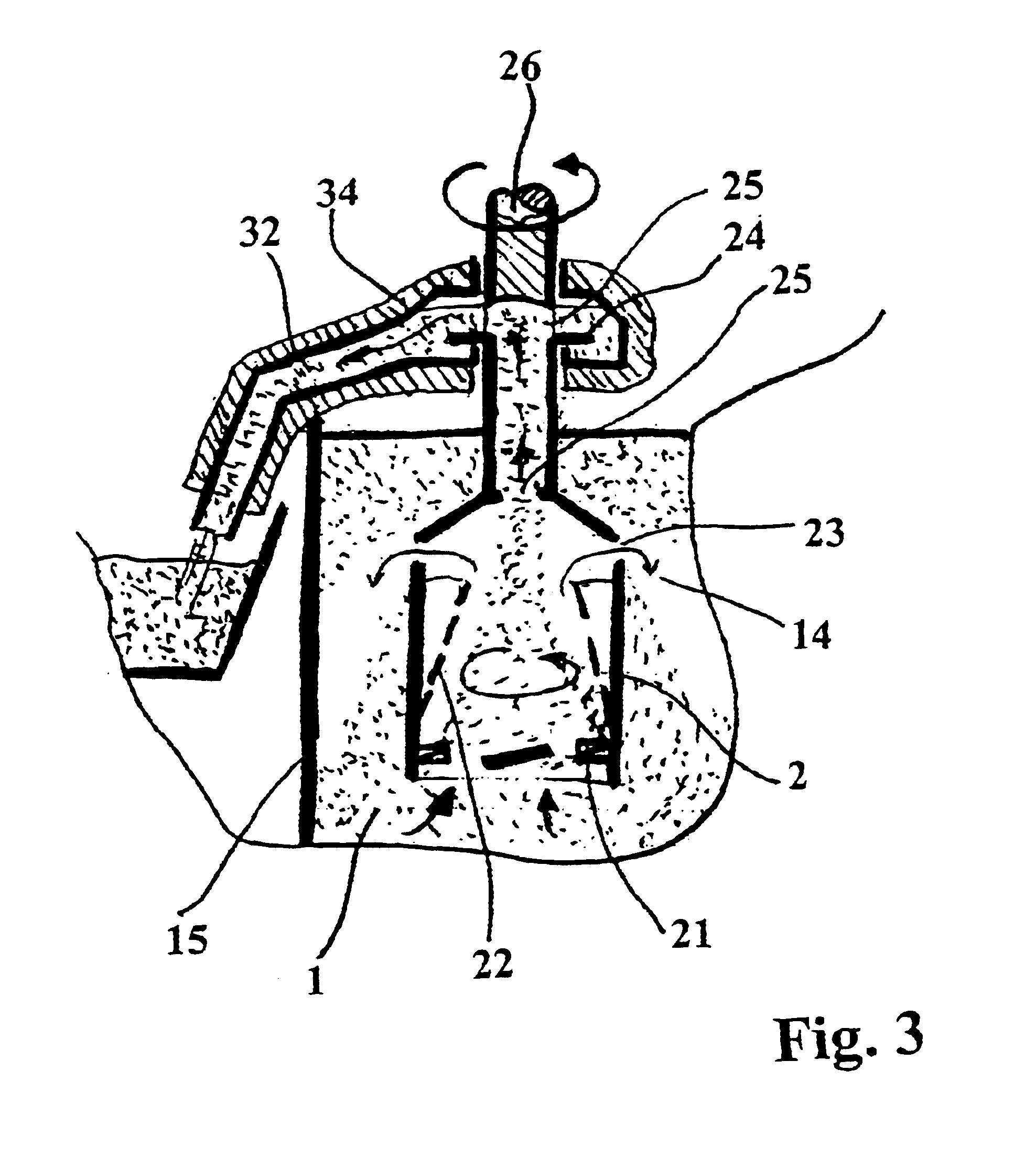
Process for precipitating compounds from zinc metal baths by means of a hollow rotary body that can be driven about an axis and is dipped into the molten zinc
InactiveUS6364930B1High acceleration of the metalRapid and highly effective separationHot-dipping/immersion processesSpecific fluid pumpsZinc metalLiquid metal
A process and device are disclosed for precipitating solid compounds from the liquid zinc or liquid zinc-based alloys of a metal bath. According to the disclosed process, partial amounts of the metal phase containing the compound(s) are exposed to an acceleration higher than the acceleration due to gravity and at least partially dissociated thereby into fractions containing heavier and / or lighter components. The molten mass depleted of solid compounds is returned to the metal bath and the part of the molten mass enriched with the desired compounds is discharged. The disclosed device is substantially characterized in that a hollow rotary body (2) is introduced into the molten mass (1). The hollow rotary body (2) can be driven about an axis and is fitted in the submerged or lower area with conveyor means (21) which project into the cavity. In its discharge or upper area, the hollow rotary body (2) is provided with at least one discharge opening (23) for the depleted molten mass (14) eccentrically arranged in its wall and with at least one further discharge opening (25) for the liquid metal enriched with the desired compounds centrally arranged and / or eccentrically arranged on the discharge side. At least one of the upper molten mass discharge openings (23, 24) in the rotary body (2) opens into a discharge area of a housing (3) which at least partially surrounds the rotary body (2).
Owner:ANDRITZ PATENTVERW GES
Process and device for precipitating compounds from zinc metal baths by means of a hollow rotary body that can be driven about an axis and is dipped into the molten zinc
InactiveUS6656415B2High acceleration of the metalRapid and highly effective separationHot-dipping/immersion processesSpecific fluid pumpsLiquid stateZinc metal
Process and device for precipitating solid compounds from zinc metal baths. Partial amounts of the metal phase containing these compounds are exposed to an acceleration higher than gravity and dissociated into fractions containing heavier or lighter components. The molten mass depleted of solid compounds is returned to the metal bath. The device has a hollow rotary body for introduction into the molten mass and provided with a discharge opening for the depleted molten mass and a discharge opening for the liquid metal enriched with the solid compounds.
Owner:ANDRITZ PATENTVERW GES
Composite structure type high tensile strength steel plate, plated plate of composite structure type high tensile strength steel and method for their production
InactiveUS20030129444A1Lower yield stressImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingSheet steelHigh intensity
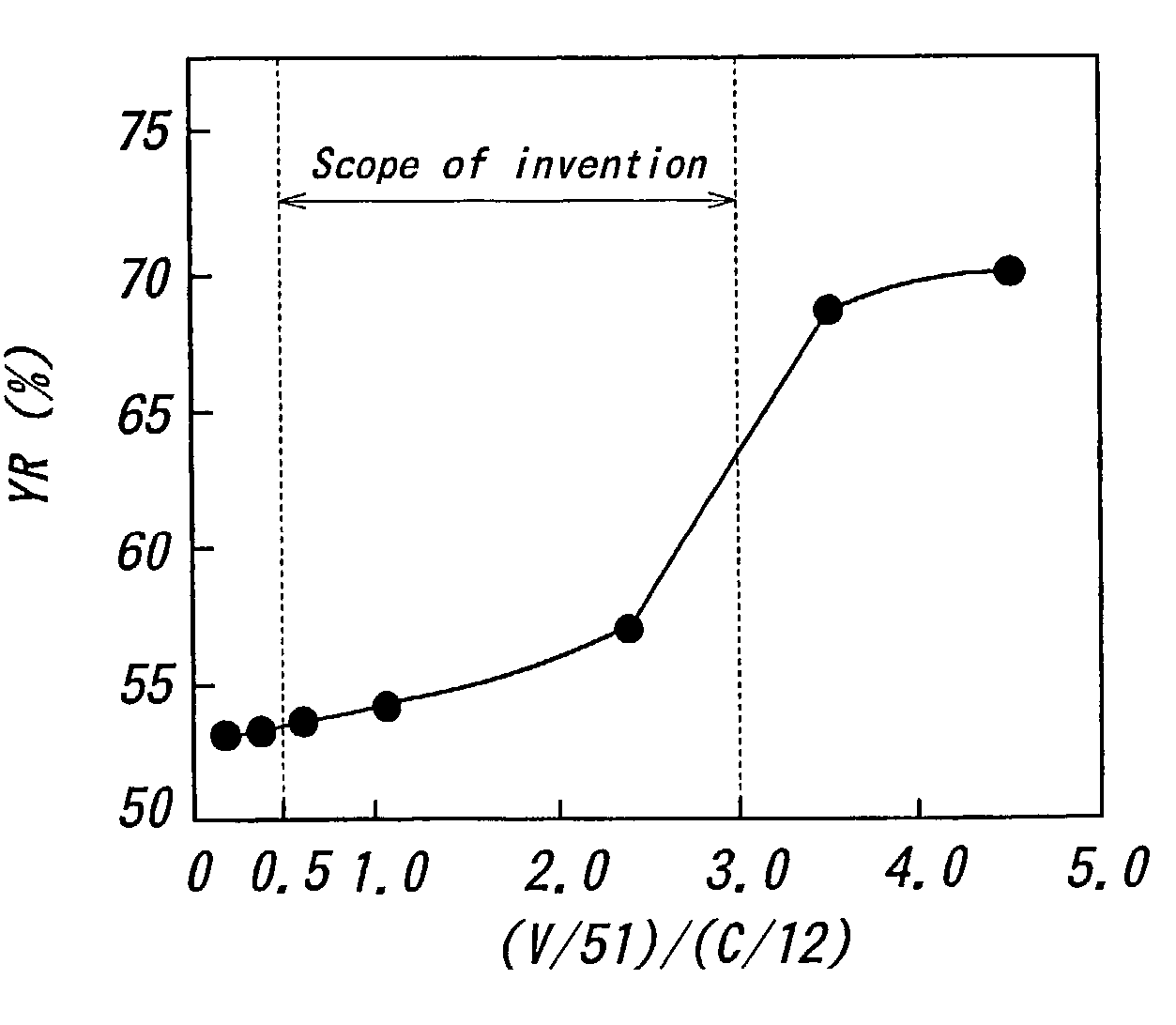
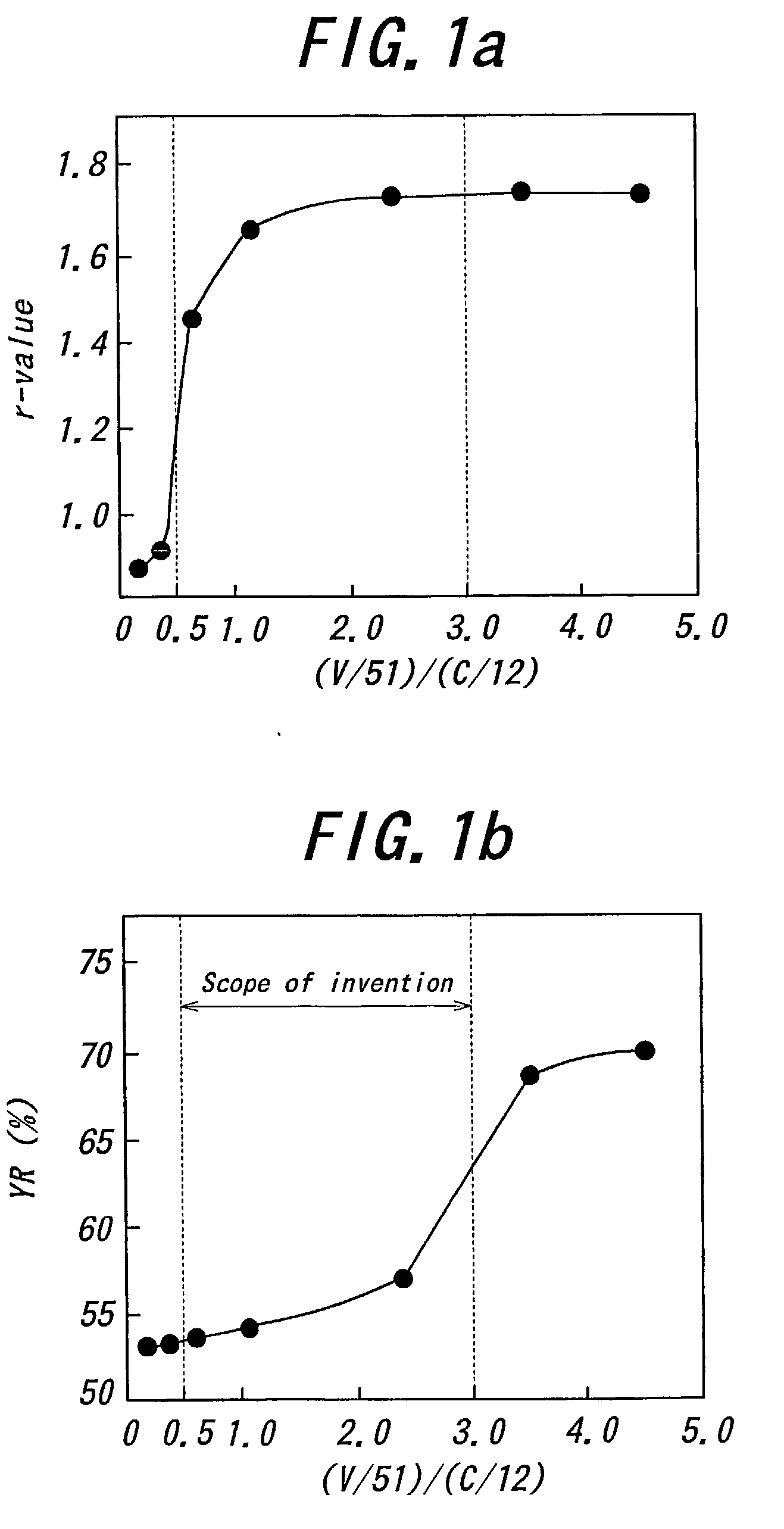
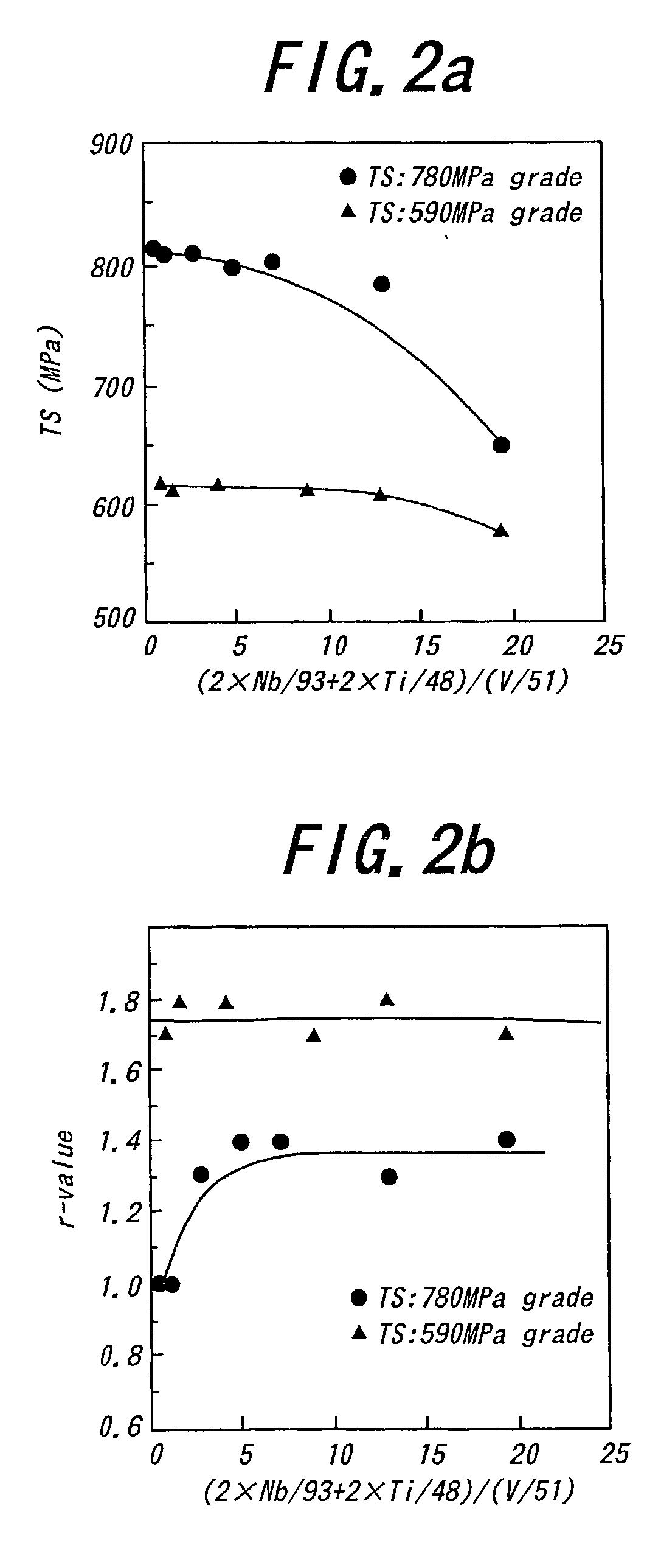
The invention proposes a high-strength dual-phase cold rolled steel sheet having an excellent deep drawability, wherein the steel sheet has a composition comprising C: 0.01-0.08 mass %, Si: not more than 2.0 mass %, Mn: not more than 3.0 mass %, P: not more than 0.10 mass %, S: not more than 0.02 mass %, A1: 0.005-0.20 mass %, N: not more than 0.02 mass % and V: 0.01-0.5 mass %, provided that V and C satisfy a relationship of 0.5xC / 12<=V / 51<=3xC / 12, and the remainder being Fe and inevitable impurities, and has a microstructure consisting of a ferrite phase as a primary phase and a secondary phase including martensite phase at an area ratio of not less than 1% to a whole of the microstructure and a high-strength dual-phase galvanized steel sheet comprising a galvanized coating on the above steel sheet as well as a method of producing the same.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Flux and process for hot dip galvanization
InactiveUS20030219543A1Improve the immunityConvenient coatingHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsAlkaline earth metalChloride
A flux for hot dip galvanization comprises from:&Circlesolid;60 to 80 wt. % of zinc chloride (ZnCl2); 7 to 20 wt. % of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl); 2 to 20 wt. % of a fluidity modifying agent comprising at least one alkali or alkaline earth metal; 0.1 to 5 wt. % of a least one of the following compounds: NiCl2, CoCl2, MnCl2; and 0.1 to 1.5 wt. % of at least one of the following compounds: PbCl2, SnCl2, BiCl3, SbCl3.
Owner:FONTAINE HLDG NV
Bonded body of galvanized steel sheet and adherend, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110008644A1Firmly connectedGood adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsPolyolefinSheet steel
The invention is a technique for strongly integrating a galvanized steel sheet and a resin molded article. A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet “Z18” is immersed in an aqueous solution for aluminum degreasing at 75° C. for 7 minutes, to form roughness having an RSm of 0.8 to 2.3 μm and an Rz of 0.3 to 1.0 μm on the surface. The surface is covered with convex protrusions having a diameter of about 100 nm, and a chromate treatment layer appears in the surface. In other words, three conditions suitable for bonding are satisfied thereby. A resin composition comprising 70 to 97 wt % of polyphenylene sulfide and 3 to 30 wt % of a polyolefin resin is injected onto the surface. The resin composition penetrates into ultra-fine irregularities and is cured in that state, whereby a composite in which the galvanized steel sheet and the resin molded article are strongly integrated is obtained. The shear rupture strength of the composite is extremely high, in excess of 20 MPa.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
Metal matrix composite casting and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6245442B1Well formedEasy to processHot-dipping/immersion processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal matrix compositeCompound s
A metal matrix composite casting comprises a metal matrix composite and a processed member inserted in the metal matrix composite by enveloped casting. By the processed member which is easier to process than the metal matrix composite, a processed portion of a predetermined shape can be formed in the metal matrix composite. That is, by a simple processing such that the processed member is removed from the metal matrix composite or the processed portion is formed in the processed member itself, the processed portion having a desired shape can be easily formed in the metal matrix composite.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
HIGH STRENGTH STEEL PLATE WITH ULTIMATE TENSILE STRENGTH OF 900 MPa OR MORE EXCELLENT IN HYDROGEN EMBRITTLEMENT RESISTANCE AND METHOD OF PRODUCTION OF SAME
ActiveUS20120222781A1Reduce resistanceImprove plasticityHot-dipping/immersion processesSurface reaction electrolytic coatingCarbideUltimate tensile strength
High strength steel plate with an ultimate tensile strength of 900 MPa or more which is excellent in hydrogen embrittlement resistance characterized in that, in the structure of the steel plate, (a) by volume fraction, ferrite is present in 10 to 50%, bainitic ferrite and / or bainite in 10 to 60%, and tempered martensite in 10 to 50%, and (b) iron-based carbides which contain Si or Si and Al in 0.1% or more are present in 4×108 (particles / mm3) or more.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
1000MPa grade cold rolling hot dip galvanizing two-phase steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention provides 1,000 MPa cold-rolled hot-dip galvanized dual-phase steel and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cold-rolled hot-dip galvanized high-strength steel plates. The chemical components in mass percentage of the cold-rolled hot-dip galvanized dual-phase steel are: 0.06 to 0.18 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of Si, 1.2 to 2.5 percent of Mn,0.05 to 0.5 percent of Mo, 0.05 to 0.6 percent of Cr, 0.005 to 0.05 percent of Al, 0.01 to 0.06 percent of Nb, 0.01 to 0.05 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.02 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of N, the balance being Fe and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing method adopts Cr or Mo to replace Si, so as to enlarge an austenitic and ferritic two-phase region and improve the hardenability of the dual-phase steel, and meanwhile, the manufacturing method improves the strength of toughness of the steel by adding Nb or Ti refined grains, so as to ensure that the steel has good weldability and usability, and the strength grade of the steel can reach over 1,000 Mpa.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Galvanizing bath apparatus
InactiveUS8475594B2Reduce buildSpeed up the conversion processHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesHigh concentrationDross
A continuous galvanizing line uses a coating pot containing a molten zinc bath having bottom dross and further comprises a pump. The pump agitates the bottom dross so the bottom dross interacts with aluminum and converts to top dross, which can be removed without needing to stop the galvanizing line. A reaction vessel may also be used to provide a higher concentration of aluminum to react with the bottom dross.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy for hot dipping steel
InactiveCN101457320AAvoid gatheringDeterioration of surface propertiesHot-dipping/immersion processesRare earthZinc alloys
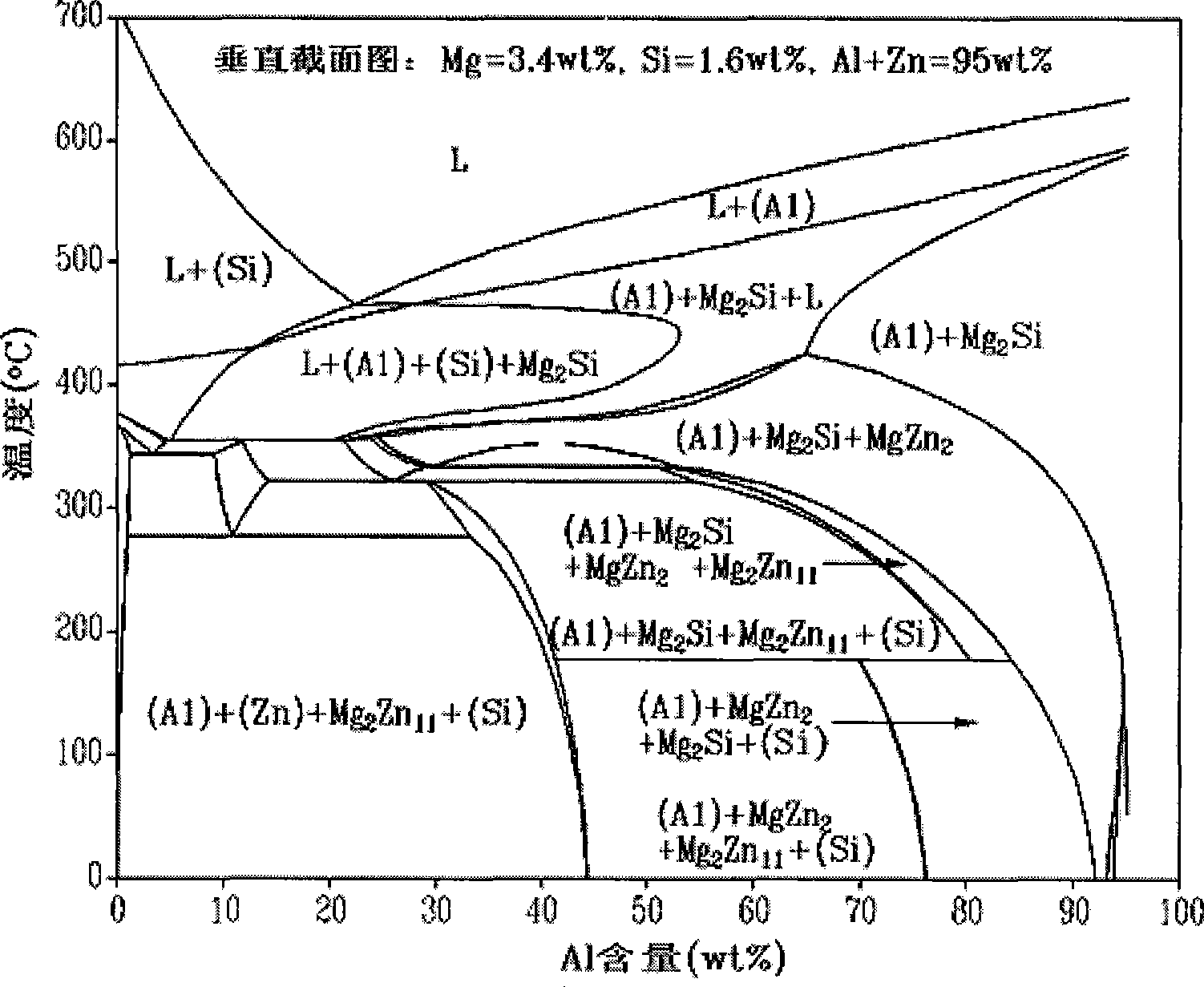
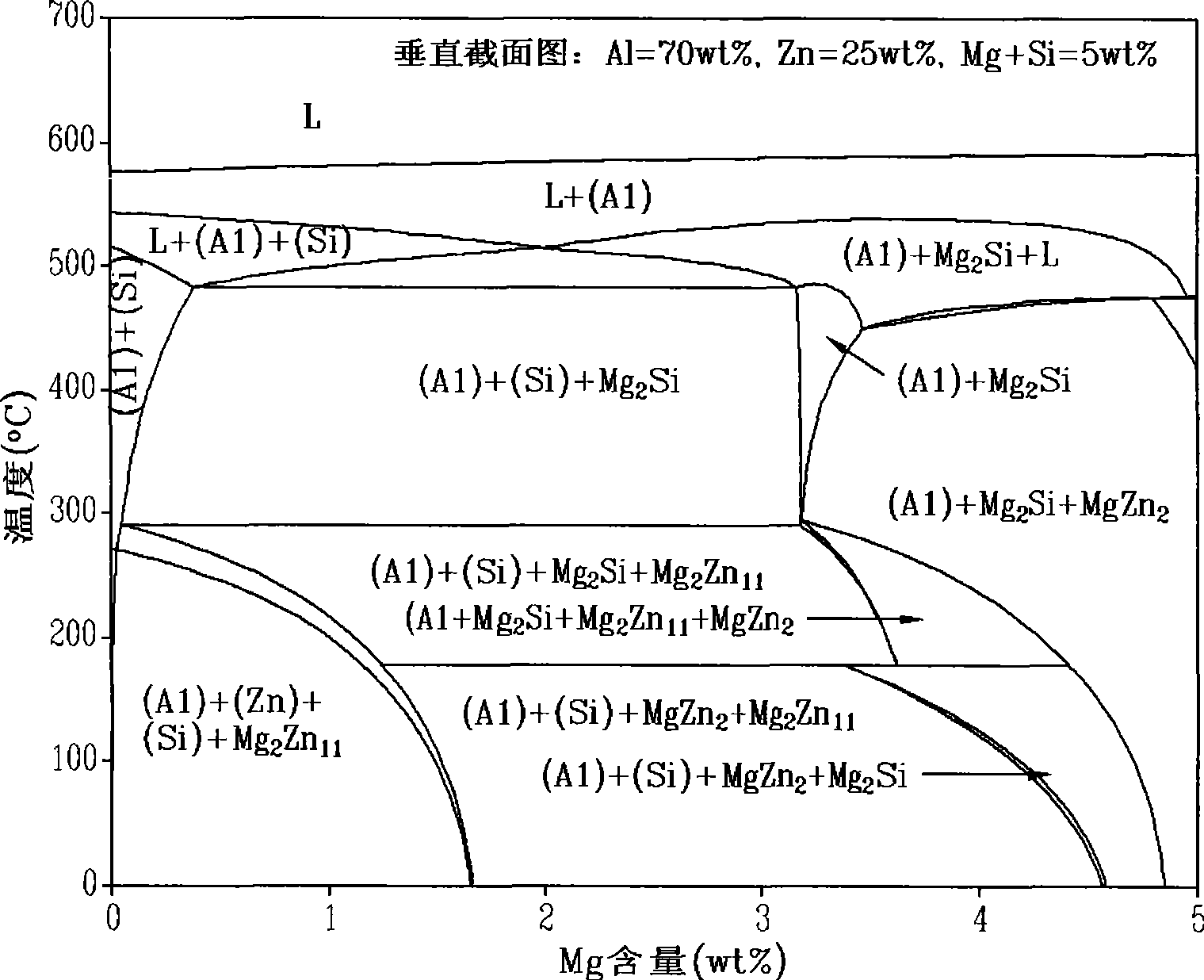
The invention provides a rare earth-containing Al-Zn-Mg-Si alloy with high aluminum content for hot-dipping steel products, comprising the following compositions by weight percent as follows; Al: 50-75%, Mg: 1-5%, Si: 0.5-2.5%, the addition of 0.002-0.1% of Ti, 0.001-0.045% of B and 0.05-1% of rare earth (La or Ce), and the balance of Zn and unavoidable impurities. The invention utilizes corrosion resistance of Mg2Si and grain-refining effect of the rare earth, the Ti and the Bi elements to improve quality of plating solution and obtain a high aluminum content aluminum-zinc alloy cladding with ,a bright and smooth surface and great corrosion resistance property. In addition, the content of aluminum in the alloy is up to 50-75%, thereby lowering production cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
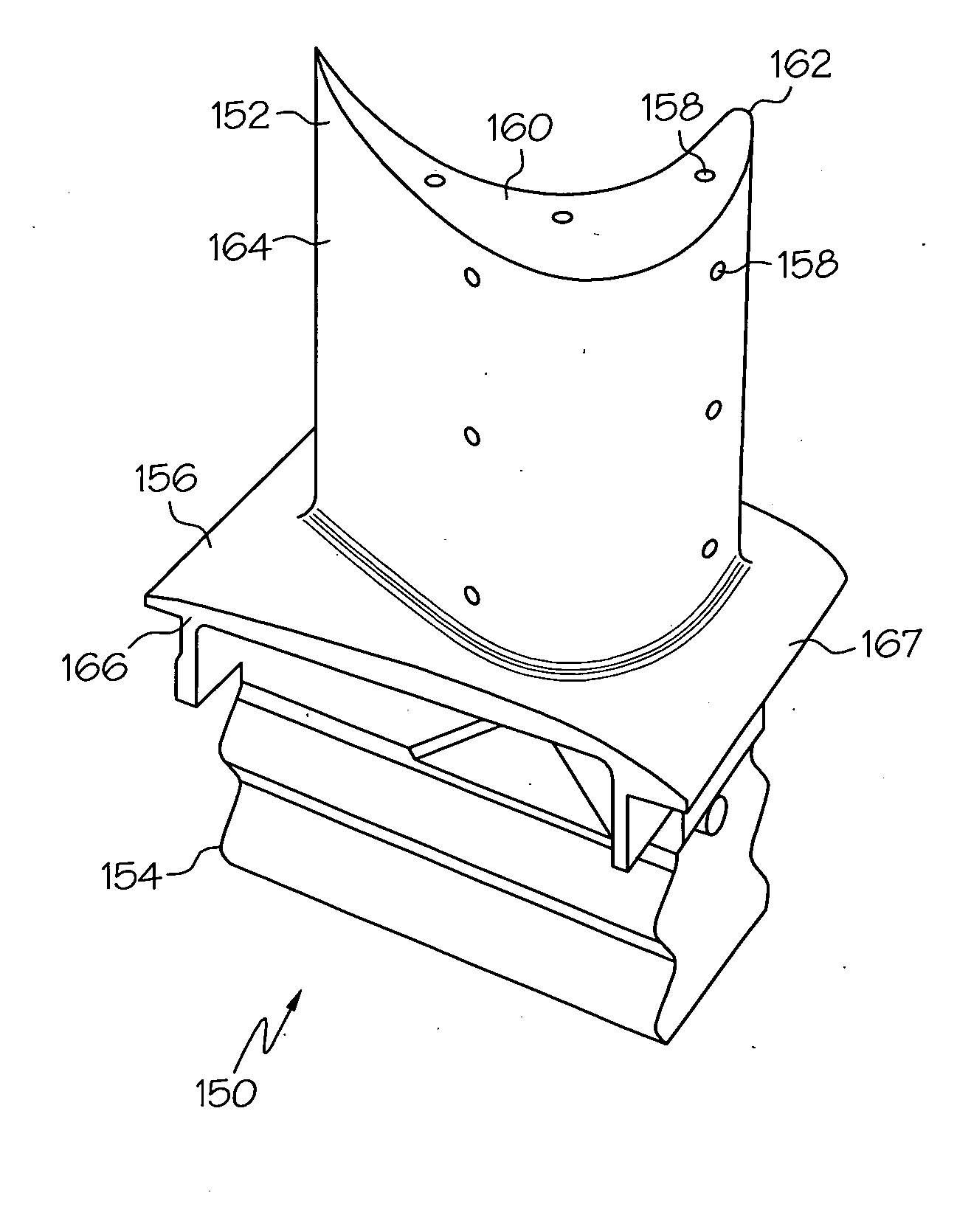
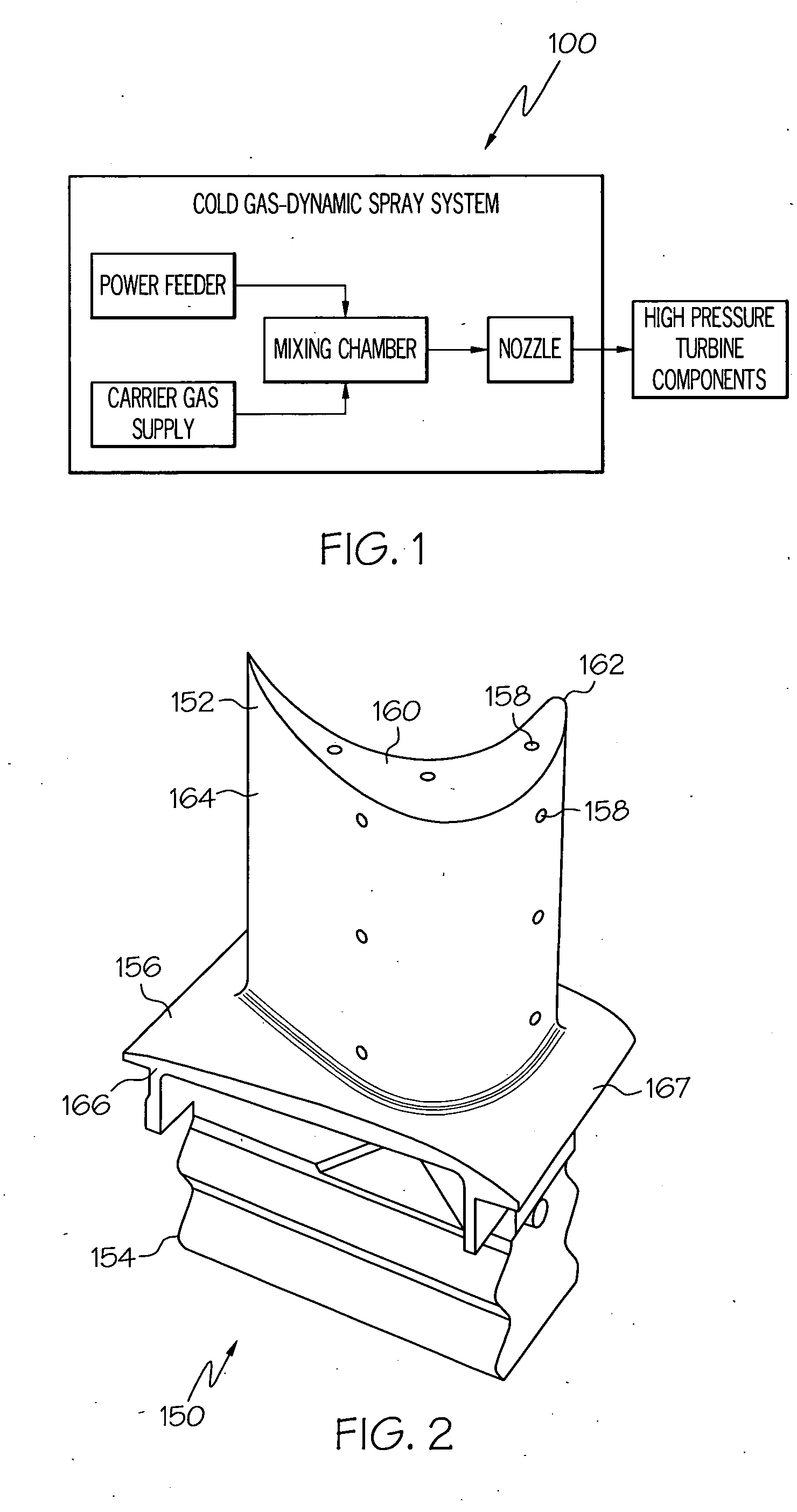
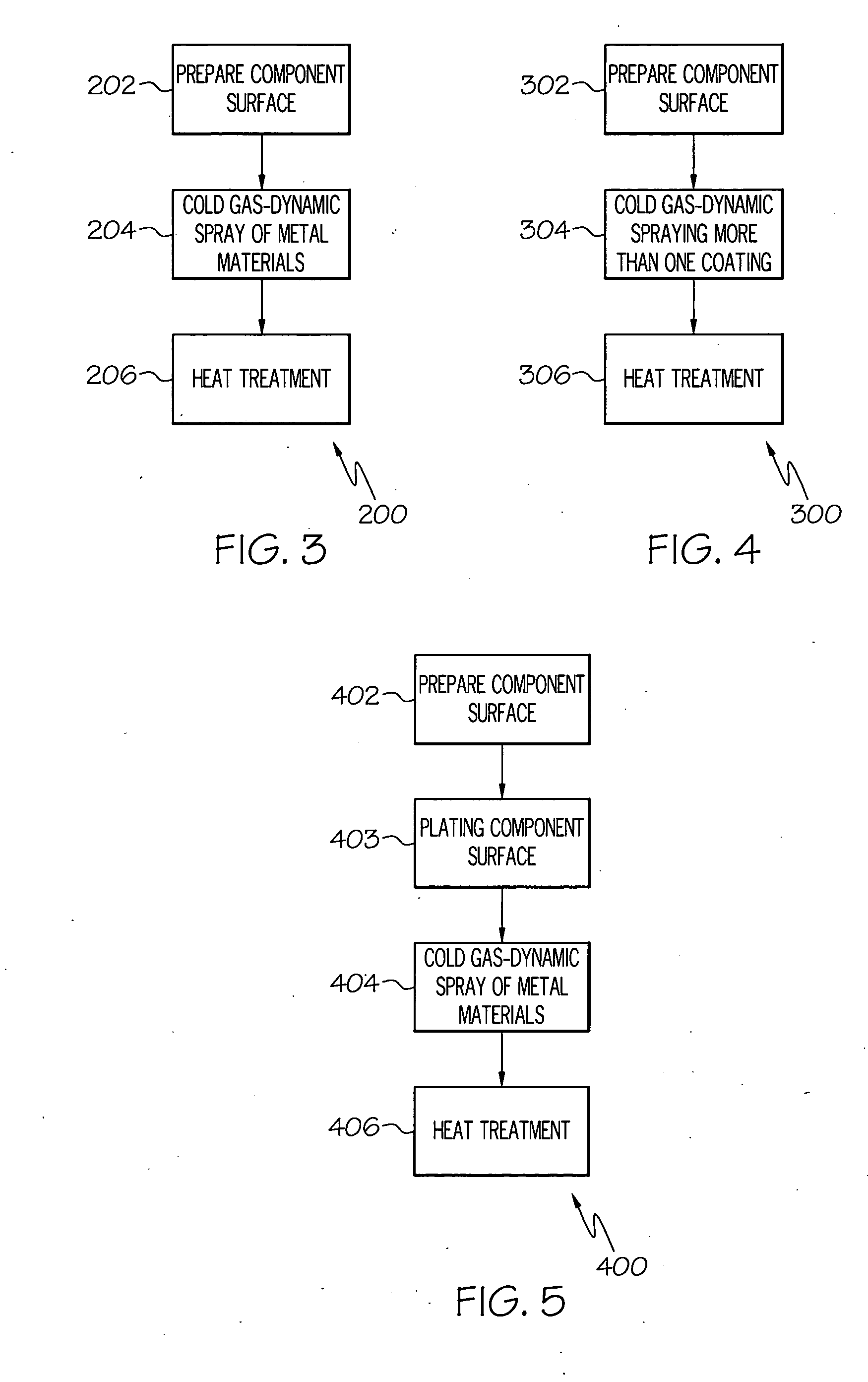
Environment-resistant platinum aluminide coatings, and methods of applying the same onto turbine components
In a method for coating a surface of a turbine component with an environment-resistant aluminide, a coating is formed by cold gas-dynamic spraying a powder material on the turbine component surface, the powder material comprising aluminum, platinum, and at least one additional metal selected from the group consisting of nickel, chromium, hafnium, silicon, yttrium, rhenium, zirconium, cobalt, and tantalum. After forming the coating, at least one thermal diffusion treatment is performed on the turbine component to metallurgically homogenize the coating and thereby form an aluminide coating that includes by weight about 12 to about 30% aluminum, up to about 50% platinum, about 2 to about 25% chromium, about 1 to about 5% hafnium, about 1 to about 5% silicon, about 0.1 to about 1% yttrium, and about 1 to about 3% Zr, and nickel.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High-strength steel sheet and process for production thereof
ActiveCN101932745AHigh strengthHelps to reduce weightHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelCarbide
Disclosed are an ultra-high-strength steel sheet having both a tensile strength of as high as 1400MPa or above and excellent formability and an advantageous process for manufacturing the same. A high-strength steel sheet having both a composition which contains by mass C: 0.12 to 0.50%, Si: 2.0% or less, Mn: 1.0 to 5.0%, P: 0.1% or less, S: 0.07% or less, Al: 1.0% or less, and N: 0.008% or less with the balance being Fe and unavoidable impurities, and a structure which comprises, in terms of area fraction, autotempered martensite: 80% or more, ferrite: less than 5%, bainite: 10% or less, and retained austenite: 5% or less and in which the average number of precipitated iron carbide particles of 5nm to 0.5[mu]m in the autotempered martensite is 5OE04 or above per mm2.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Continuous Annealing and Hot Dip Plating Method and Continuous Annealing and Hot Dip Plating System of Steel sheet Containing Si
InactiveUS20090123651A1Suppress surface concentrationImprove adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesSheet steelHydrogen
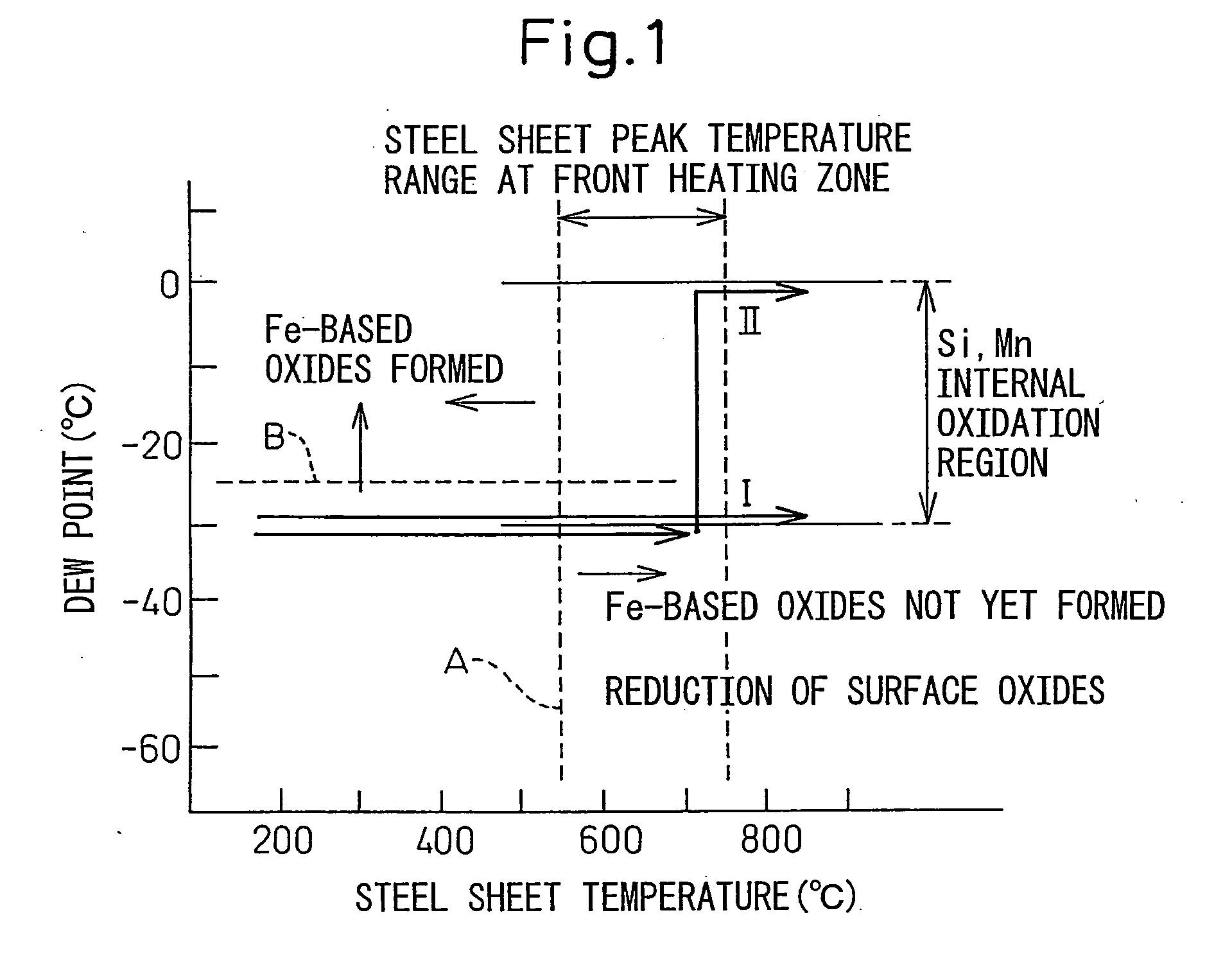
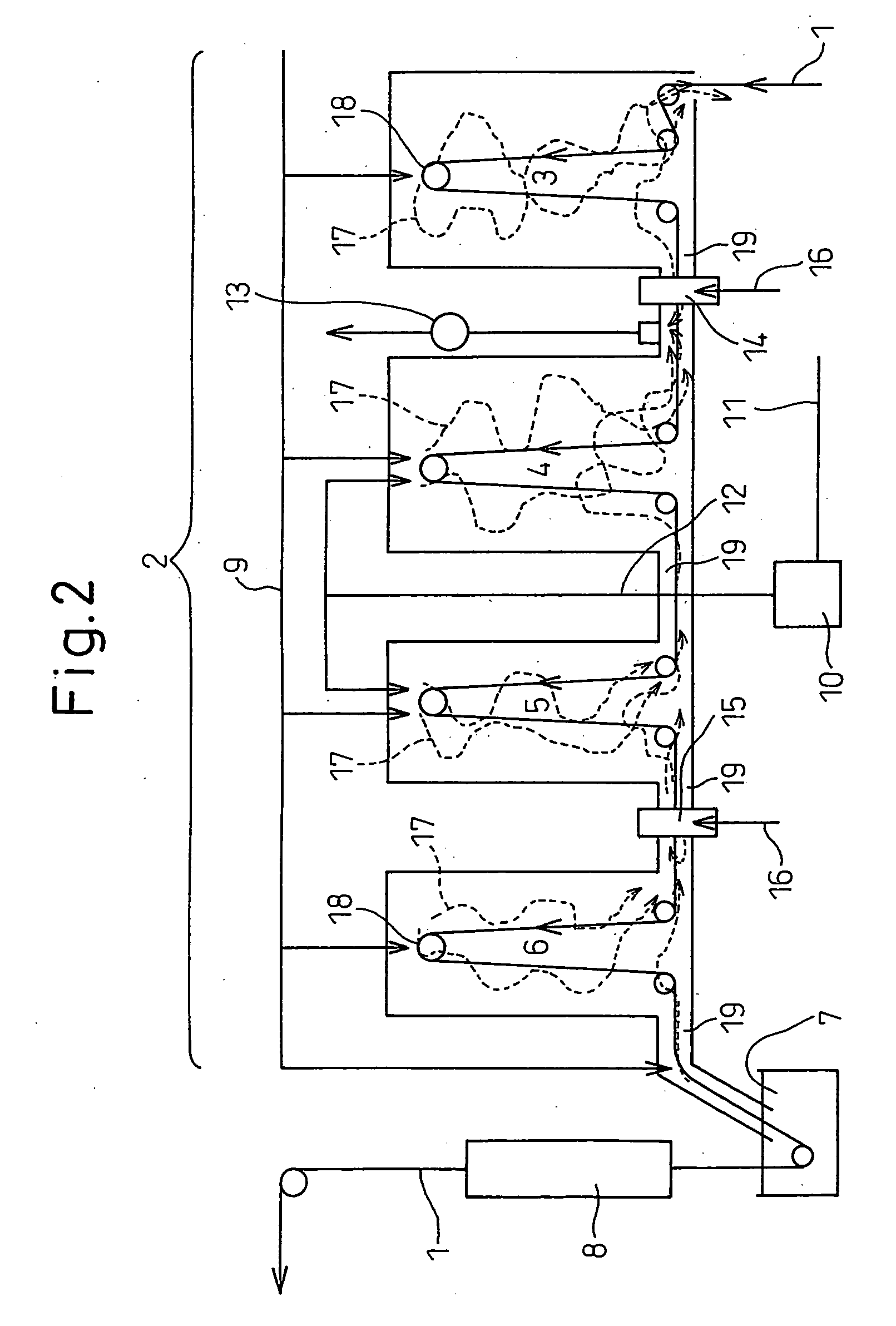
The present invention provides, in a hot dip plating system having an annealing furnace for hot dip plating steel sheet containing Si, a continuous annealing and hot dip plating method and system causing internal oxidation without causing surface oxidation of the Si in the steel and avoiding a drop in the plating ability of the steel sheet and retardation of alloying, that is, a continuous annealing and hot dip plating method using an annealing furnace having, in order, a front heating zone, rear heating zone, soaking zone, and cooling zone and a hot dip plating bath, comprising heating or soaking the steel sheet at a steel sheet temperature of a temperature range of at least 300° C. or more by indirect heating, making an atmosphere of the zones one comprised of hydrogen H: 1 to 10 vol % and a balance of nitrogen and unavoidable impurities, making a steel sheet peak temperature during heating at the front heating zone 550 to 750° C. and making the dew point less than −25° C., making dew points of the following rear heating zone and soaking zone −30° C. to 0° C., and making a dew point of the cooling zone less than −25° C.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL CORP
Steel sheet having enhanced ductility for a molding member, molding member, and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN103392022AHigh strengthImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesUltimate tensile strengthImpurity
Owner:浦项股份有限公司
Cold-rolled galvanized duplex steel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102021482APlatability EliminationHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesManufacturing convertersHigh rateOxygen
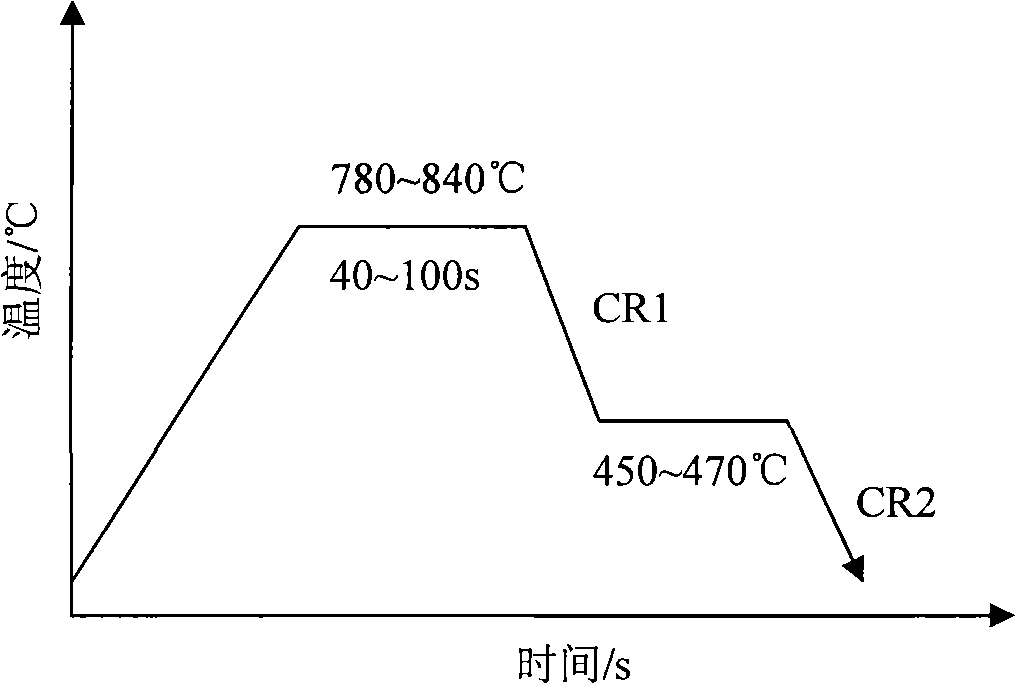
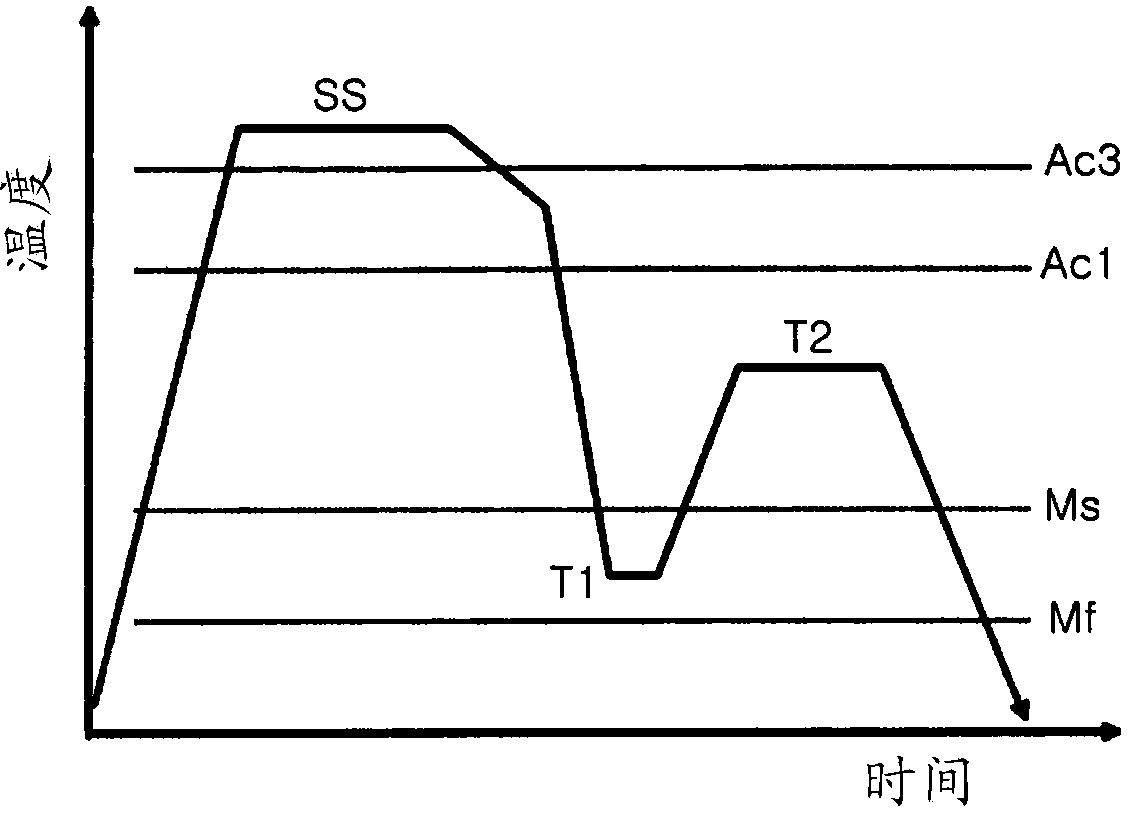
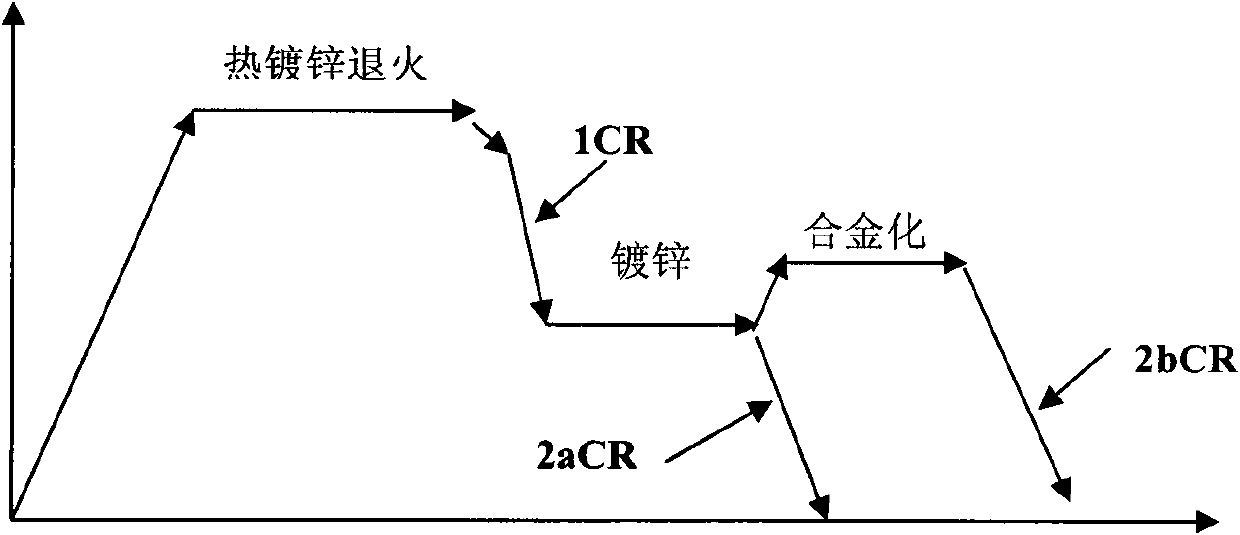
The invention relates to a cold-rolled galvanized duplex steel, wherein the substrate thereof comprises the following components by weight percentage: 0.08 to 0.18 wt.% of C, 0.50 to 1.50 wt.% of Si, 1.50 to 2.5 wt.% of Mn, 0.10 to 1.0 wt.% of Cr, 0.02 to 0.5 wt.% of Mo, 0.005 to 0.05 wt.% of Nb, 0.005 to 0.05 wt.% of Ti, 0.002 to 0.05 wt.% of T.Al, less than or equal to 0.02 wt.% of P, less thanor equal to 0.01 wt.% of S and less than or equal to 0.006 wt.% of N, and the balance of Fe. The manufacturing method thereof comprises the steps of: smelting in an oxygen top-blown convertor, refining in a heating steel ladle, continuously casting into a slab, and then conventionally hot rolling, pickling tandem rolling, galvanizing and annealing, wherein the critical annealing temperature is between 760 and 840 DEG C; the annealing is finished in the two-phase area of ferrite and austenite; 1CR section cooling has a cooling speed of 1 to 40 DEG C / S from the annealing temperature to the zincpool, putting the substrate into the zinc pool having a temperature of 450 to 465 DEG C so as to galvanize; and 2a CR section cooling has a cooling speed more than 3 DEG C / S. The steel of the invention has the advantages of high tensile strength, low yield ratio, capable of being press formed, excellent matching between strength and toughness, high rate of initially work-hardening and being free from yield extending.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Steel sheet having organic coating and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030072962A1Hot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelZinc alloys
Steel sheet having organic coating comprises: a zinc or a zinc alloy plated steel sheet or an aluminum or an aluminum alloy plated steel sheet; a composite oxide coating formed on the surface of the plated steel sheet and containing at least one metal selected from the group consisting of Mn and Al; and an organic coating formed on the composite oxide coating and containing a rust-preventive additive component.
Owner:NIPPON KOKAN KK
High-strength alloyed aluminum-system plated steel sheet and high-strength automotive part excellent in heat resistance and after-painting corrosion resistance
InactiveCN1531604AImprove heat resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesSuperimposed coating processSheet steelCorrosion
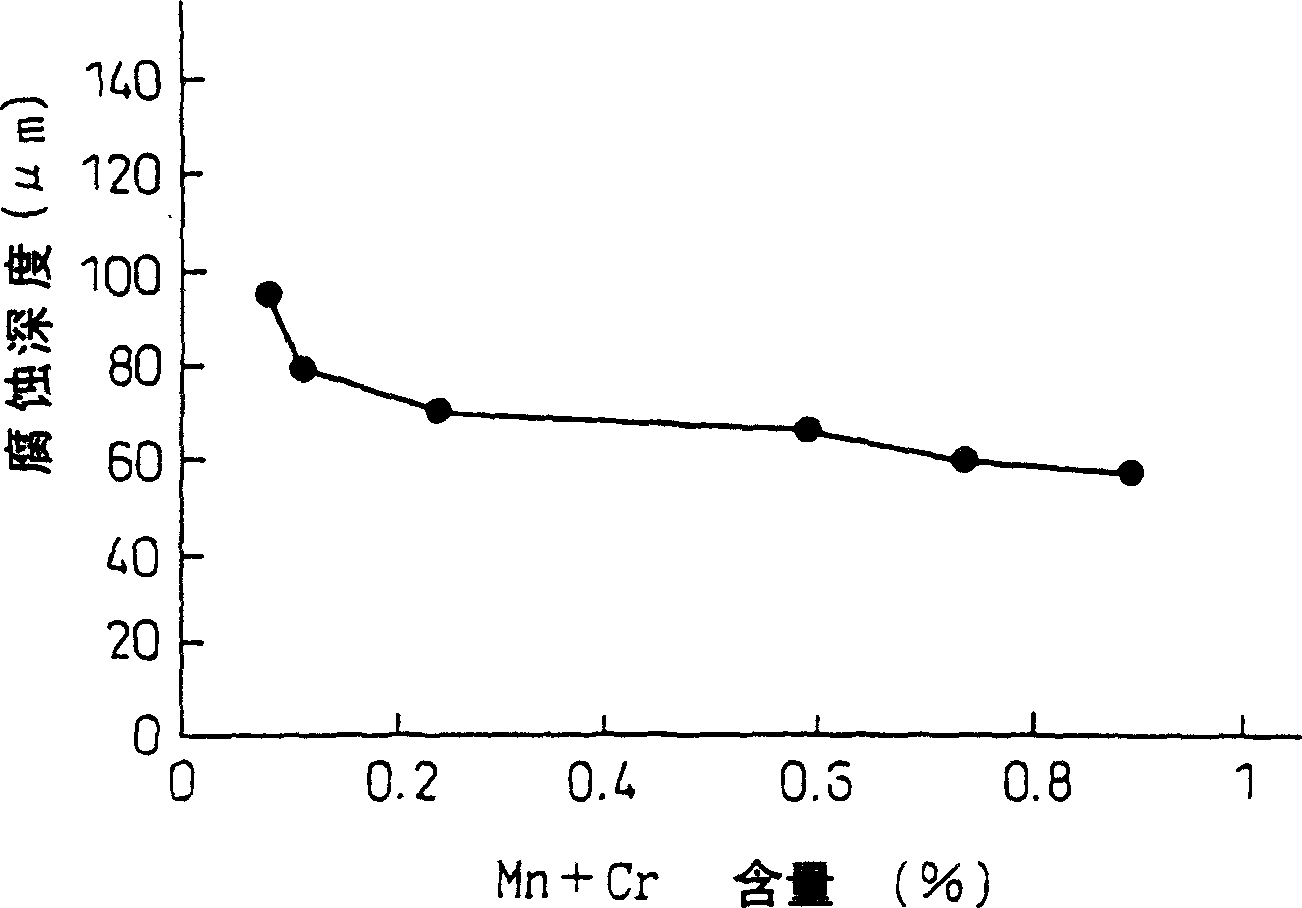
The present invention provides a hot press method used for producing a high-strength member for an automobile and, in particular, a part which requires high-strength, such as an undercarriage component of an automobile. More specifically, the present invention provides an aluminum plated steel sheet or an aluminum-zinc plated steel sheet suitable for high temperature forming (hot forming) wherein high strength is obtained after high temperature forming, and a method of producing the same. Also, the present invention provides a hot dip aluminum plated steel sheet which suppresses the alloying reaction of a plated layer during press forming and has beautiful appearance, and an aluminum-system plated steel sheet for hot press having excellent after-painting corrosion resistance. Concretely, the present invention is a high-strength aluminum-system plated steel sheet excellent in heat resistance and after-painting corrosion resistance, characterized by having an Fe-Al-system coating containing, in mass, Mn and Cr of more than 0.1% in total on the surface of the steel containing, in mass, C: 0.05 to 0.7%, Si: 0.05 to 1%, Mn: 0.5 to 3%, P: not more than 0.1%, S: not more than 0.1% and Al: not more than 0.2%, and, in addition, one or more element(s) selected from among Ti: 0.01 to 0.8%, Cr: not more than 3% and Mo: not more than 1%, so as to satisfy the following expression (1): Ti + 0.5xMn + Cr + 0.5xMo > 0.4 ... 1
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com