Patents
Literature
5904 results about "Reference electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A reference electrode is an electrode which has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The high stability of the electrode potential is usually reached by employing a redox system with constant (buffered or saturated) concentrations of each participant of the redox reaction.
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS6484046B1Avoid and reduce corrosionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteElectrolysis
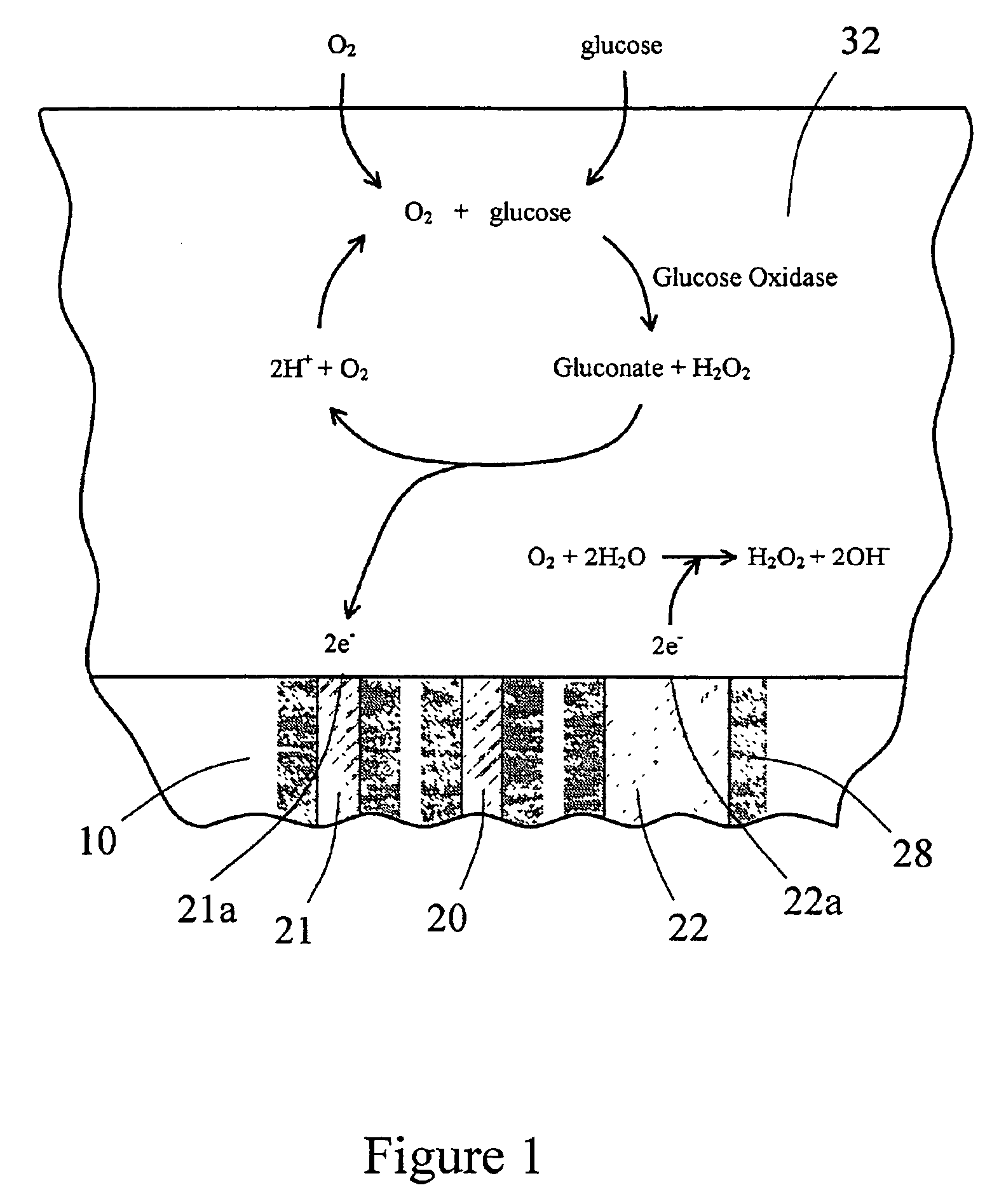
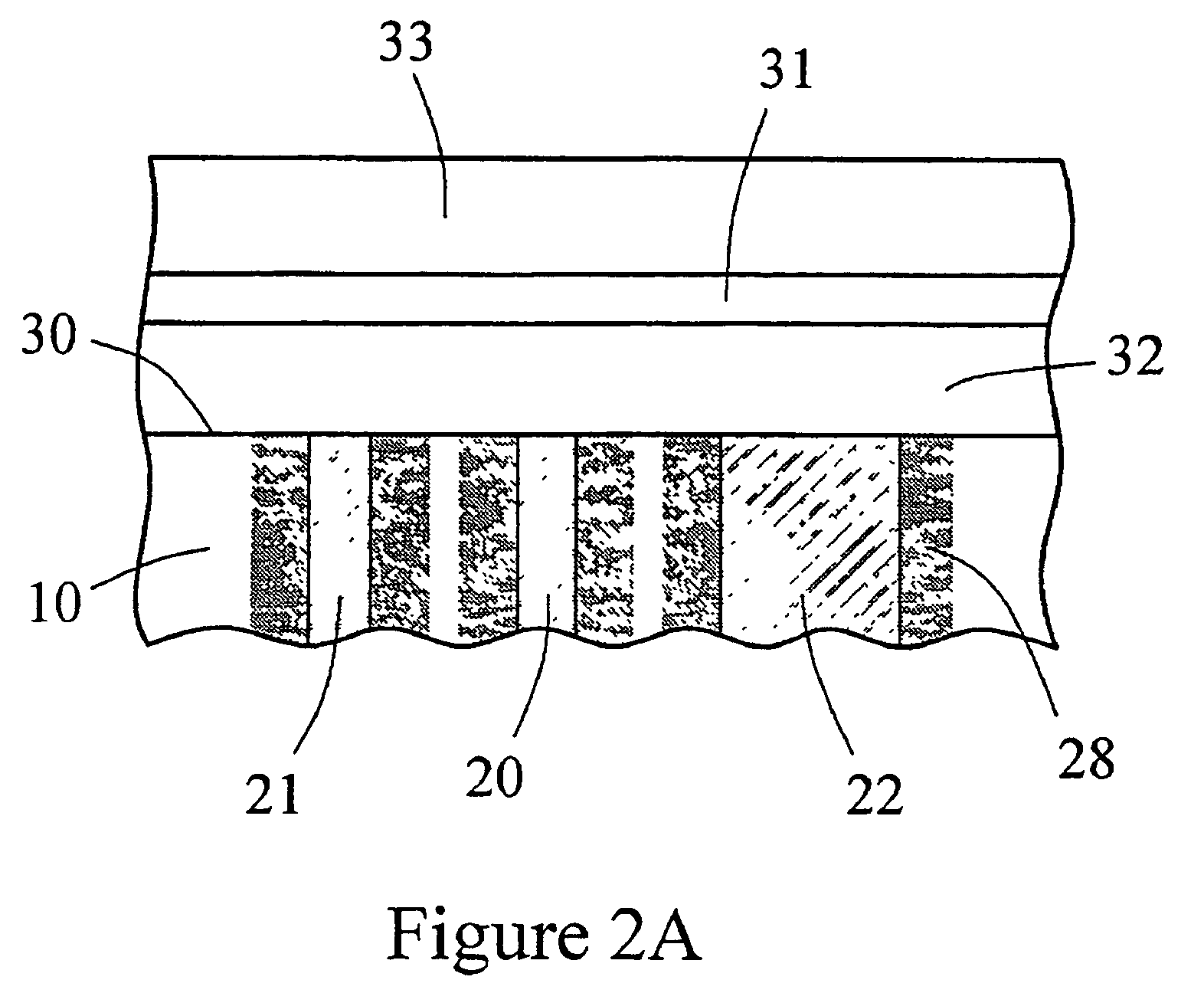
An electrochemical analyte sensor having conductive traces on a substrate is used to determine a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Sensor head for use with implantable devices
InactiveUS7471972B2Minimizing negative potential extremesImprove solubilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical responseAnalyte
The present invention provides a sensor head for use in an implantable device that measures the concentration of an analyte in a biological fluid which includes: a non-conductive body; a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode, wherein the electrodes pass through the non-conductive body forming an electrochemically reactive surface at one location on the body and forming an electronic connection at another location on the body, further wherein the electrochemically reactive surface of the counter electrode is greater than the surface area of the working electrode; and a multi-region membrane affixed to the nonconductive body and covering the working electrode, reference electrode and counter electrode. In addition, the present invention provides an implantable device including at least one of the sensor heads of the invention and methods of monitoring glucose levels in a host utilizing the implantable device of the invention.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Electrochemical analyte sensor
InactiveUS7003340B2Avoid and reduce corrosionRotary clutchesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrolysisAnalyte
An electrochemical analyte sensor formed using conductive traces on a substrate can be used for determining and / or monitoring a level of analyte in in vitro or in vivo analyte-containing fluids. For example, an implantable sensor may be used for the continuous or automatic monitoring of a level of an analyte, such as glucose, lactate, or oxygen, in a patient. The electrochemical analyte sensor includes a substrate and conductive material disposed on the substrate, the conductive material forming a working electrode. In some sensors, the conductive material is disposed in recessed channels formed in a surface of the sensor. An electron transfer agent and / or catalyst may be provided to facilitate the electrolysis of the analyte or of a second compound whose level depends on the level of the analyte. A potential is formed between the working electrode and a reference electrode or counter / reference electrode and the resulting current is a function of the concentration of the analyte in the body fluid.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte sensor
InactiveUS20110024307A1Substantial linearityImmobilised enzymesHot-dipping/immersion processesContinuous measurementAnalyte
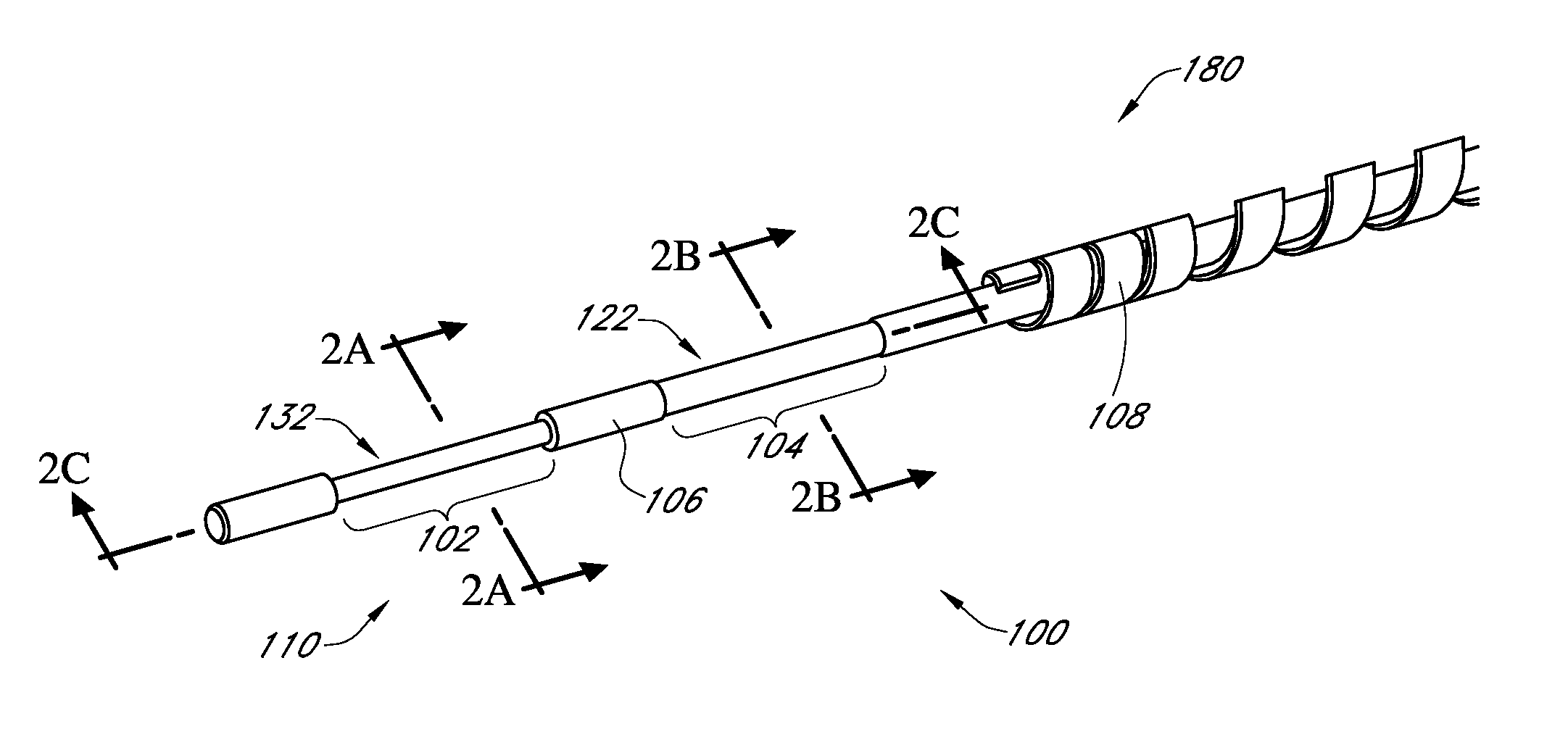
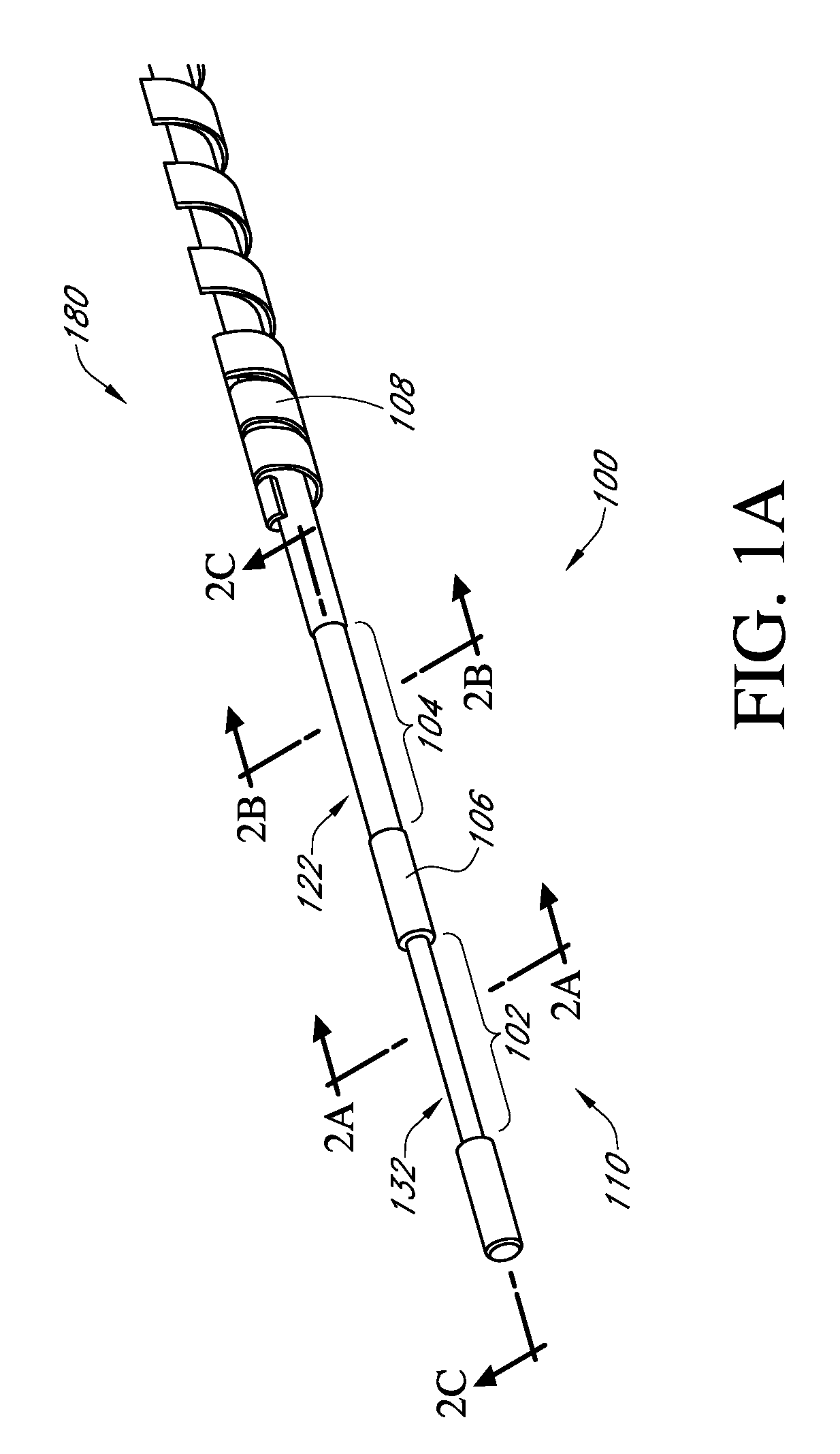
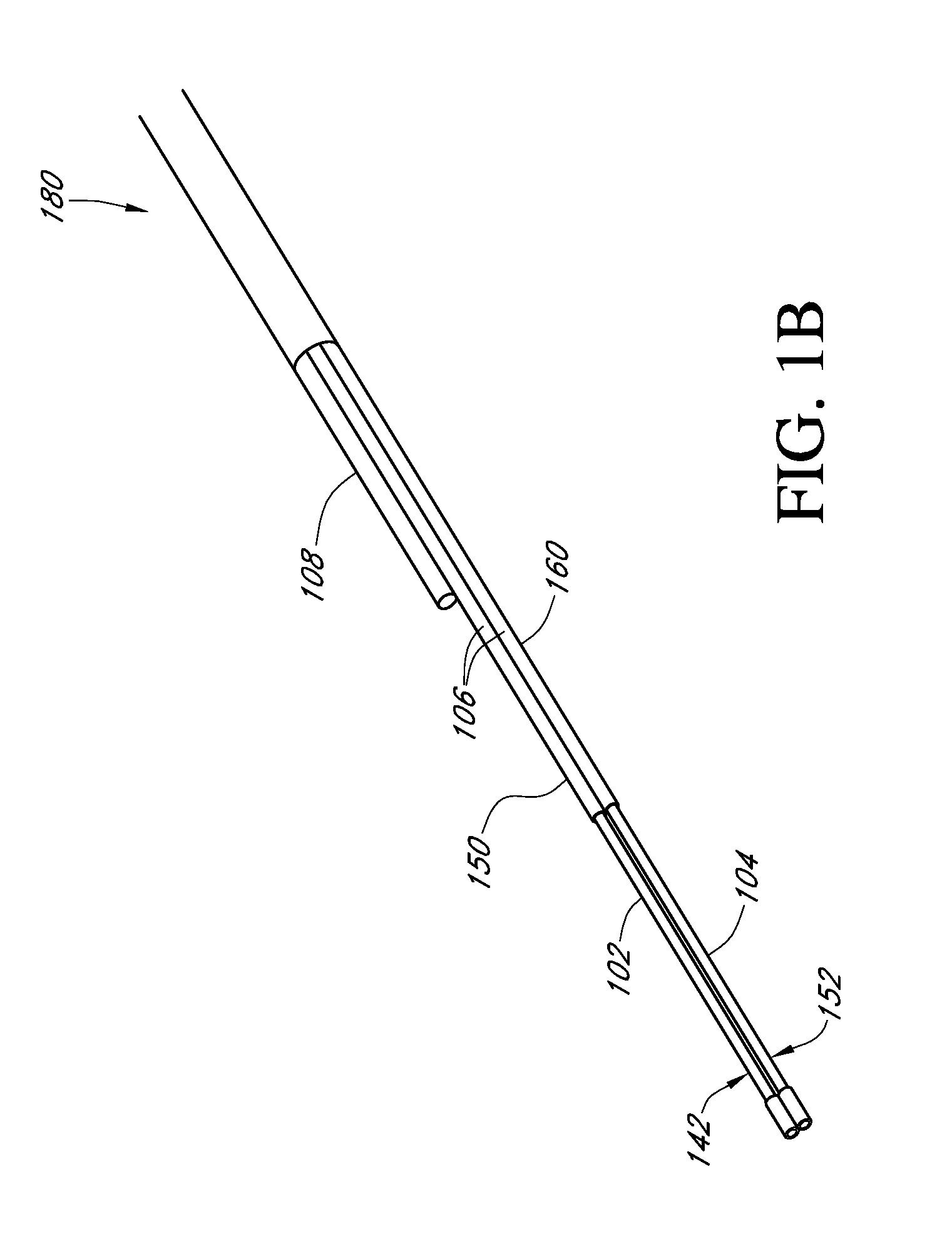
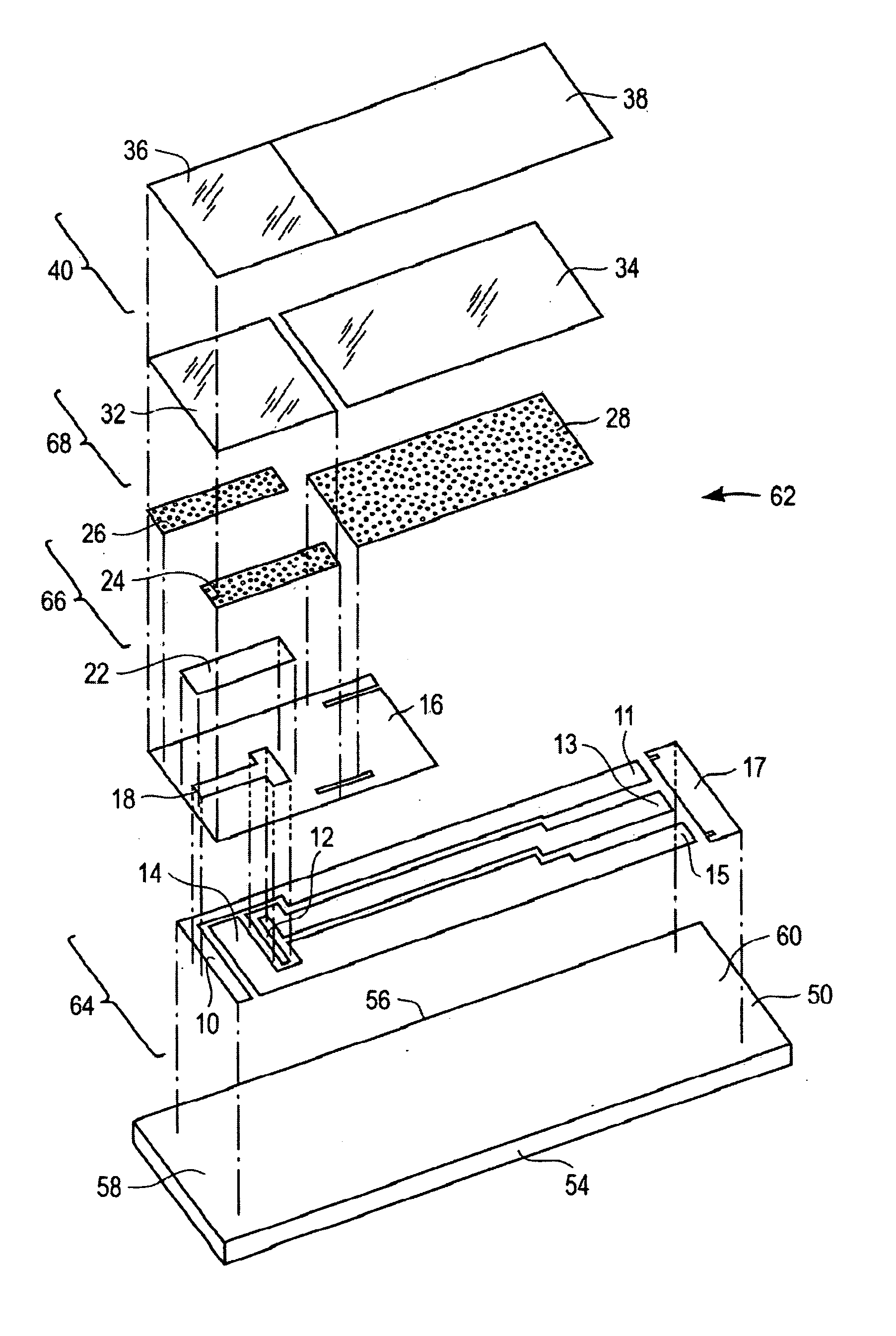
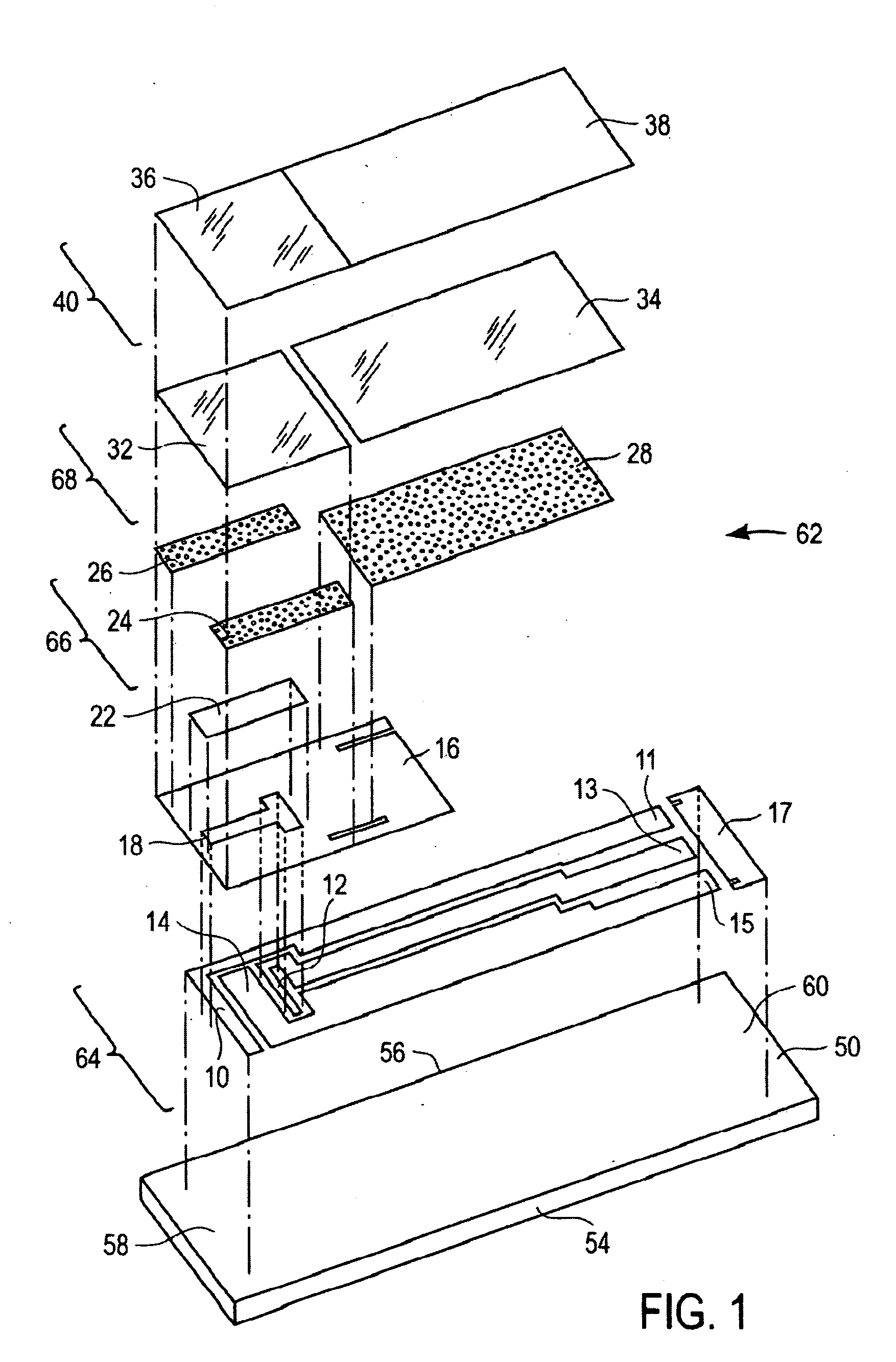
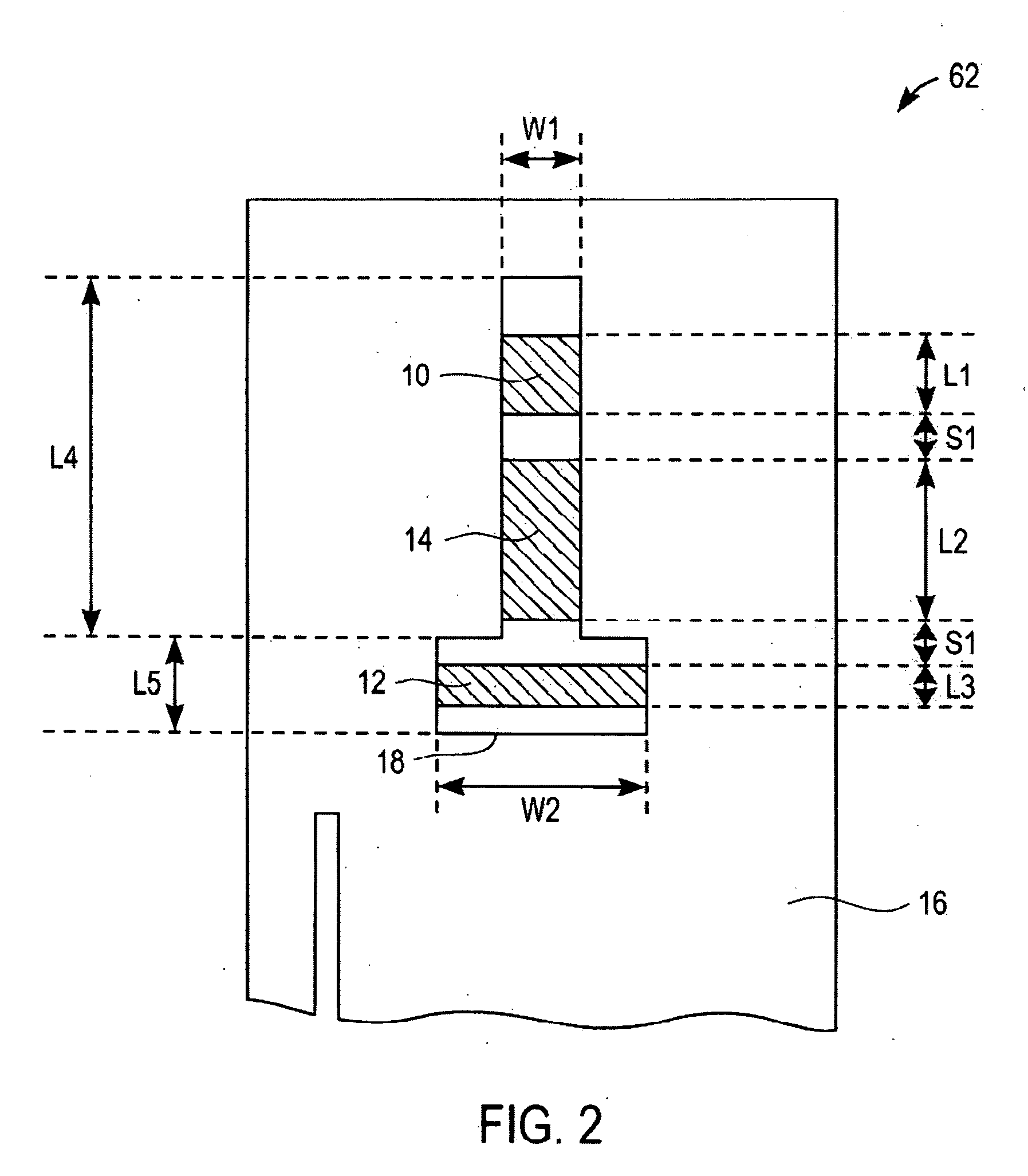
Devices and methods are provided for continuous measurement of an analyte concentration. The device can include a sensor having a plurality of sensor elements, each having at least one characteristic that is different from other sensor(s) of the device. In some embodiments, the plurality of sensor elements are each tuned to measure a different range of analyte concentration, thereby providing the device with the capability of achieving a substantially consistent level of measurement accuracy across a physiologically relevant range. In other embodiments, the device includes a plurality of sensor elements each tuned to measure during different time periods after insertion or implantation, thereby providing the sensor with the capability to continuously and accurately measure analyte concentrations across a wide range of time periods. For example, a sensor system 180 is provided having a first working electrode 150 comprising a first sensor element 102 and a second working electrode 160 comprising a second sensor element 104, and a reference electrode 108 for providing a reference value for measuring the working electrode potential of the sensor elements 102, 104.
Owner:DEXCOM
Sensor having electrode for determining the rate of flow of a fluid
InactiveUS6801041B2Accurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow by electric/magnetic effectsTarget analysisAnalyte
Sensors that are capable measuring the rate of flow of a fluid that passes over the electrodes of the sensor. In these sensors, an electrode, designated the flow rate-determining electrode, is used in conjunction with the conventional electrodes, e.g., the working electrode, the reference electrode, and the counter electrode, to determine the rate of flow of the fluid. In one aspect, this invention provides a sensor for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid when the sample flows continuously over the electrodes of the sensor, especially when the rate of flow of the sample is relatively low. In another aspect, this invention provides a method for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a sample of fluid, wherein the rate of flow of the sample varies during the period of time that the sensor is in place. In a preferred embodiment, the sensor employs four electrodes, namely, a working electrode, a reference electrode, a counter electrode, and a flow rate-determining electrode. Alternatively, a single electrode that performs both the function of the reference electrode and the function of the counter electrode can replace the reference electrode and the counter electrode. In addition, a dummy electrode or a blank electrode can be used to compensate for interference from electrochemically active species. The reagent(s) specific to the analyte of interest is required to be deposited on the working electrode.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS20060160164A1Reduce distractionsIncrease ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune profilingImmobilized Antibodies
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, and a second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
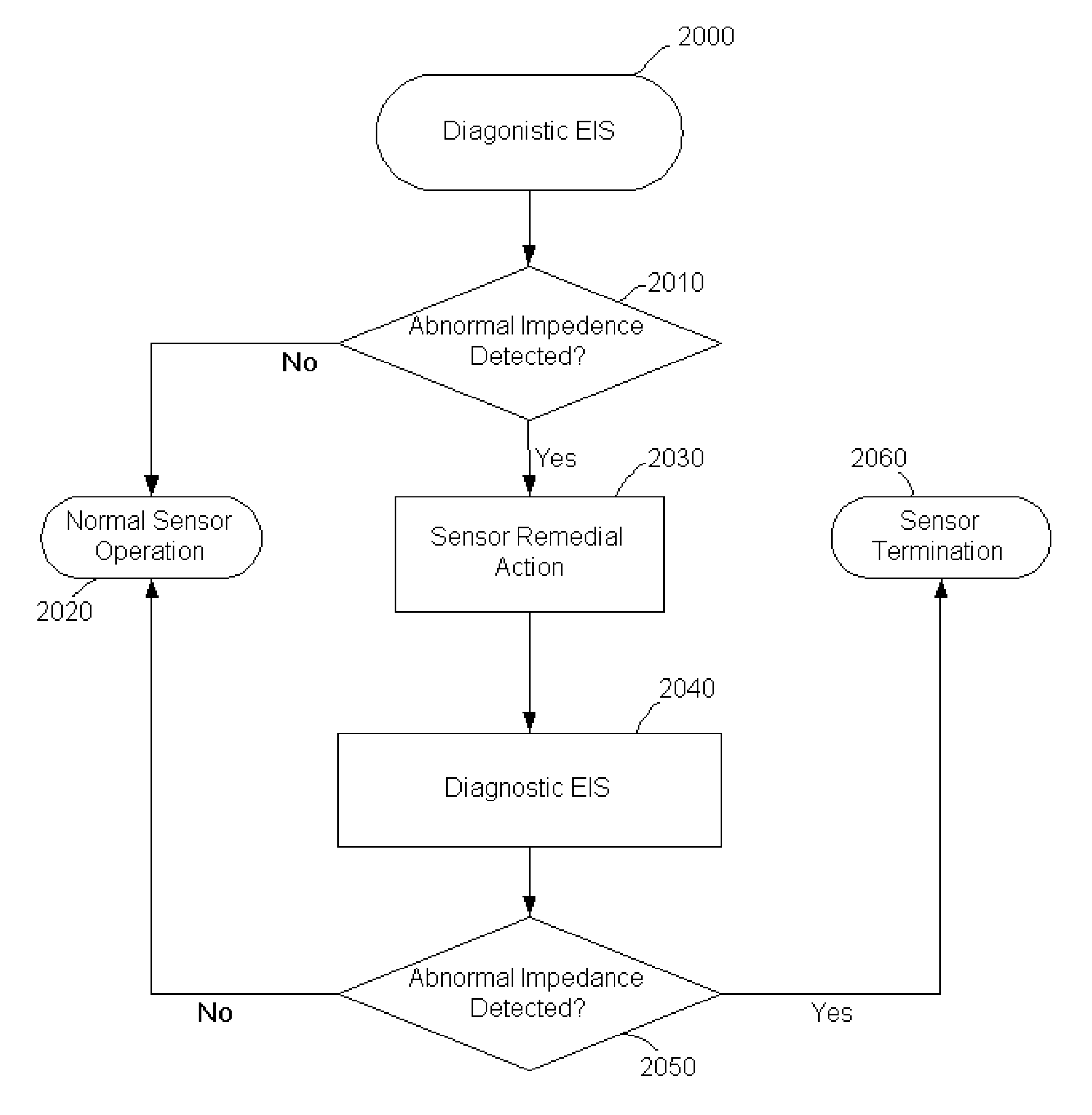
Method and system for remedying sensor malfunctions detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
A method and system that enables a user to maintain a sensor in real time. The present invention involves performing a diagnostic Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) procedure to measure sensor impedance value in order to determine if the sensor is operating at an optimal level. If the sensor is not operating at an optimal level, the present invention may further involve performing a sensor remedial action. The sensor remedial action involves reversing the DC voltage being applied between the working electrode and the reference electrode. The reversed DC voltage may be coupled with an AC voltage to extend its reach.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Sensor with layered electrodes
ActiveUS20070173711A1Easy and quick to placeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsThin film sensorGlucose sensors
A thin film sensor, such as a glucose sensor, is provided for transcutaneous placement at a selected site within the body of a patient. The sensor includes several sensor layers that include conductive layers and includes a proximal segment defining conductive contacts adapted for electrical connection to a suitable monitor, and a distal segment with sensor electrodes for transcutaneous placement. The sensor electrode layers are disposed generally above each other, for example with the reference electrode above the working electrode and the working electrode above the counter electrode. The electrode layers are separated by dielectric layer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Analyte sensor
InactiveUS7228162B2Easy to useSupplied with electric powerImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteDisplay device
A method of measuring an analyte concentration in body fluid in an animal body having skin and subcutaneous soft tissue that includes body fluid. The method comprises, introducing a portion of an analyte-measuring device into the subcutaneous soft tissue. The analyte-measuring device includes an analyte sensing element, having a sharpened distal end to facilitate introduction into the animal body. Additionally the sensing element has an indicating electrode that is adapted to be activated by electric power and to form a raw analyte measurement, when it is activated and in contact with the body fluid, in less than two minutes. The sensing device further has a reference electrode and an electric power and display device that is adapted to mate to the analyte-sensing element. The power and display device activates the analyte-sensing element by applying electric power to it. The analyte-sensing element is introduced into the animal body and is activated by the electric power and display device, thereby causing the analyte-sensing element to form a raw analyte measurement. The power and display device forms and displays a second analyte measurement that is related to the raw analyte measurement, within two minutes of the analyte sensing element being introduced into the body.
Owner:ISENSE ACQUISITION +1
System and method for determining the point of hydration and proper time to apply potential to a glucose sensor
ActiveUS8114269B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPotential measurementGlucose sensors
According to an embodiment of the invention, a method of determining hydration of a sensor having a plurality of electrodes is disclosed. In particular embodiments, the method couples a sensor electronics device to the sensor and measures the open circuit potential between at least two of the plurality of electrodes. Then, the open circuit potential measurement is compared to a predetermined value. In some embodiments, the plurality of electrodes includes a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode. In still further embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the reference electrode is measured. In other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the working electrode and the counter electrode is measured. In still other embodiments, the open circuit potential between the counter electrode and the reference electrode is measured.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Preparation for transmission and reception of electrical signals
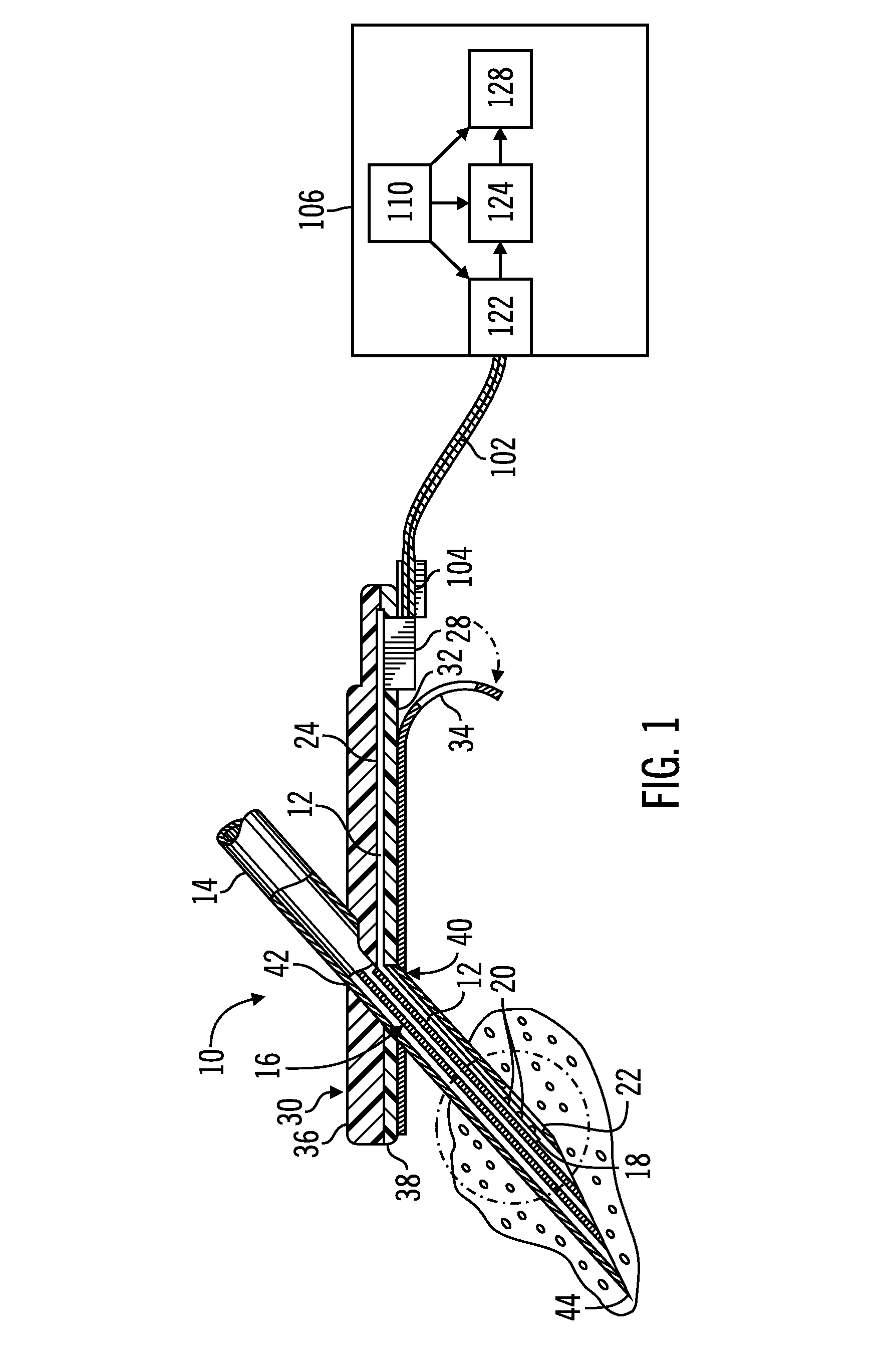
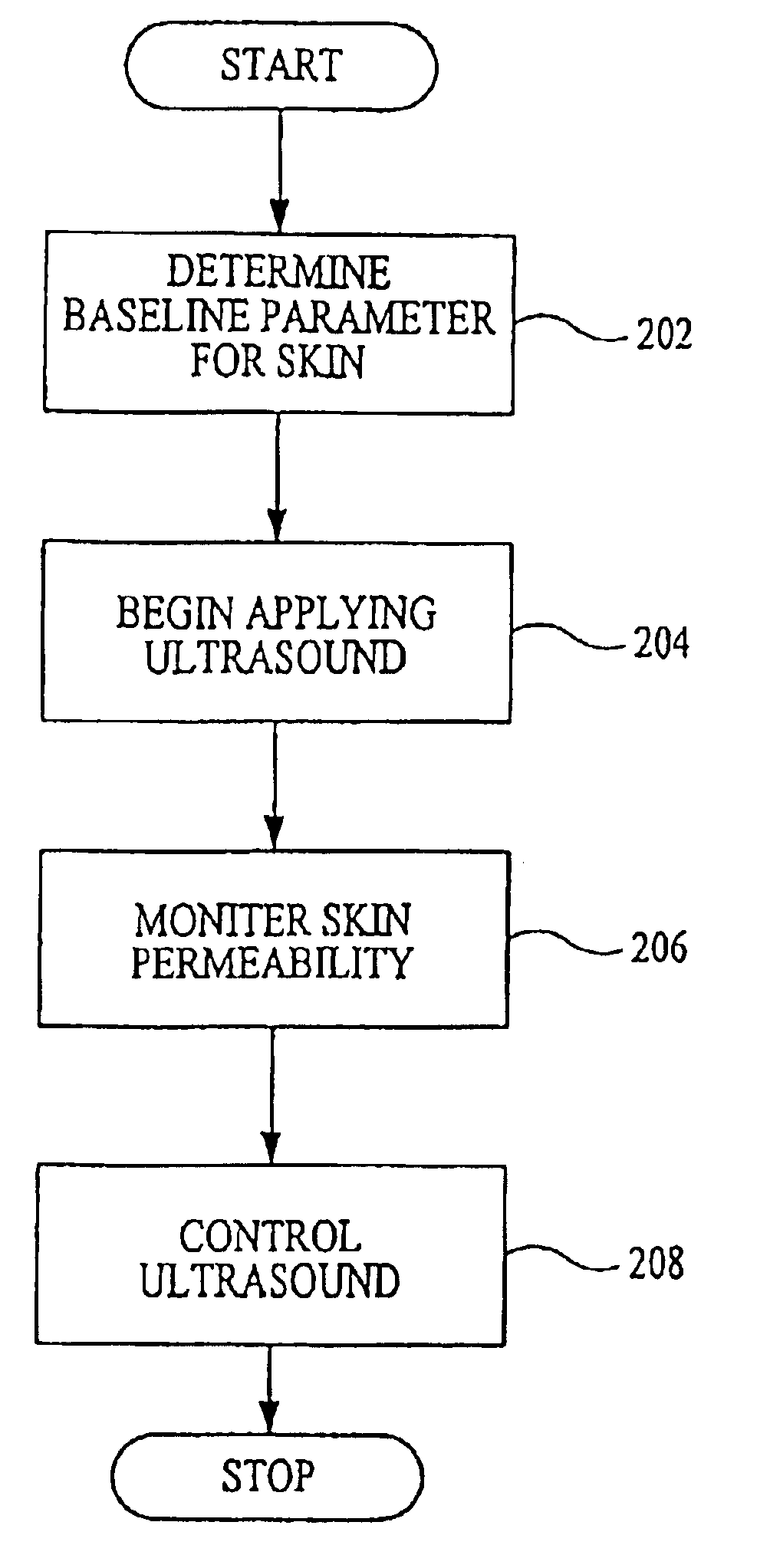
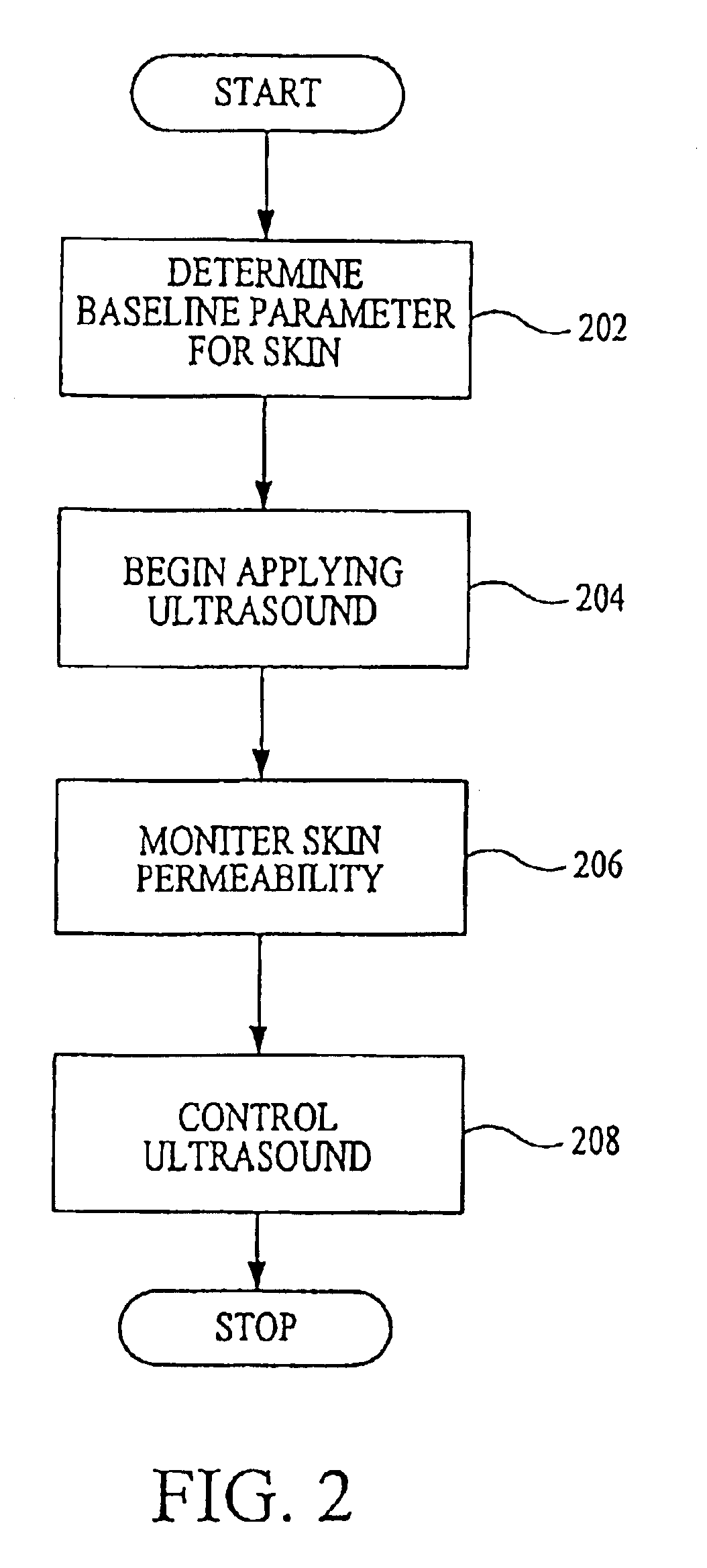
InactiveUS6887239B2Overcome or reduce one orThe process is convenient and fastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyElectricitySkin integrity
The invention provides a convenient and non-invasive means to prepare cells, tissues, and organs for electrical transmission and reception. In an embodiment of the invention, a control method comprises the use of at least one skin electrode, as a reference electrode, and an electrical sensor to measure periodically or continuously the skin's electrical conductance at the site of preparation. The dynamic change in the conductance through the skin is measured while the ultrasound is applied. Signal processing is performed on the measurement and the level of skin impedance change is controlled by performing a mathematical analysis and using the results of such analysis to control the application of ultrasonic energy. A desired level of skin impedance can be set at a predetermined value or based on a chosen level of skin integrity, subject's sensation of discomfort, or duration of the ultrasound application.
Owner:ECHO THERAPEUTICS INC
Electrochemical biosensor strip for analysis of liquid samples
InactiveUS6863800B2Easy to transportImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorConcentrations glucose
A biosensor in the form of a strip. In one embodiment, the biosensor strip comprises an electrode support, a first electrode, i.e., a working electrode, a second electrode, i.e., a counter electrode, and a third electrode, i.e., a reference electrode. Each of the electrodes is disposed on and supported by the electrode support. Each of the electrodes is spaced apart from the other two electrodes. The biosensor strip can include a covering layer, which defines an enclosed space over the electrodes. This enclosed space includes a zone where an analyte in the sample reacts with reagent(s) deposited at the working electrode. This zone is referred to as the reaction zone. The covering layer has an aperture for receiving a sample for introduction into the reaction zone. The biosensor strip can also include at least one layer of mesh interposed in the enclosed space between the covering layer and the electrodes in the reaction zone. This layer of mesh facilitates transporting of the sample to the electrodes in the reaction zone. In another embodiment, a biosensor strip can be constructed to provide a configuration that will allow the sample to be introduced to the reaction zone by action of capillary force. In this embodiment, the layer of mesh can be omitted. The invention also provides a method for determining the concentration of glucose in a sample of whole blood by using the biosensor of this invention.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Electrochemical test strip for reducing the effect of direct interference current
InactiveUS20050133368A1The result is accurateFully filledImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEngineering
This invention describes an electrochemical sensor which is adapted to reduce the effects of interfering compounds in bodily fluids when measuring an analyte in such fluids using an electrochemical strip. The sensor includes a substrate, a first and second working electrodes, and a reference electrode. A reagent layer is disposed on the electrodes such that, in one embodiment it completely covers all of the first working electrode, but only partially covers the second working electrode and, in a second embodiment, it only covers a portion of the first and the second working electrode. The portion of the working electrodes not covered by the reagent layer and is used to correct for the interference effect on the analyte measurement.
Owner:LIFESCAN SCOTLAND
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS7723099B2Increase ionic strengthReduce distractionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein insertionNon specific
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, anda second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Method and apparatus for determining local tissue impedance for positioning of a needle
InactiveUS20090036794A1Eliminate impedanceGood distinctionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTissues typesSubcutaneous tissue
The invention relates to apparatus and methods for measuring local tissue impedance for subcutaneous tissue surrounding a needle tip inserted into a subject, impedance spectra and / or complex impedance values are determined. The invention applies a monopolar impedance measuring setup with a needle, a current-carrying electrode, an optional reference electrode. The setup is configured to eliminate contributions from the current-carrying electrode in order to measure local impedance of tissue in the close neighbourhood of the needle tip instead of an averaged value over the volume or current path between the needle and the electrode(s). The determined impedance can be correlated with either a tissue type or state, or with a position of the needle tip in the subject, and can thereby provide an insertion history to the operator in the form of impedance or corresponding tissue type as a function of insertion depth or time.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
Sensor systems having multiple probes and electrode arrays
ActiveUS20110319734A1Improve reliabilityImprove sensor accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensor arrayDiabetes mellitus
Embodiments of the invention provide amperometric analyte sensors having multiple related structural elements (e.g. sensor arrays comprising a working, counter and reference electrode) and algorithms designed for use with such sensors. While embodiments of the innovation can be used in a variety of contexts, typical embodiments of the invention include glucose sensors used in the management of diabetes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
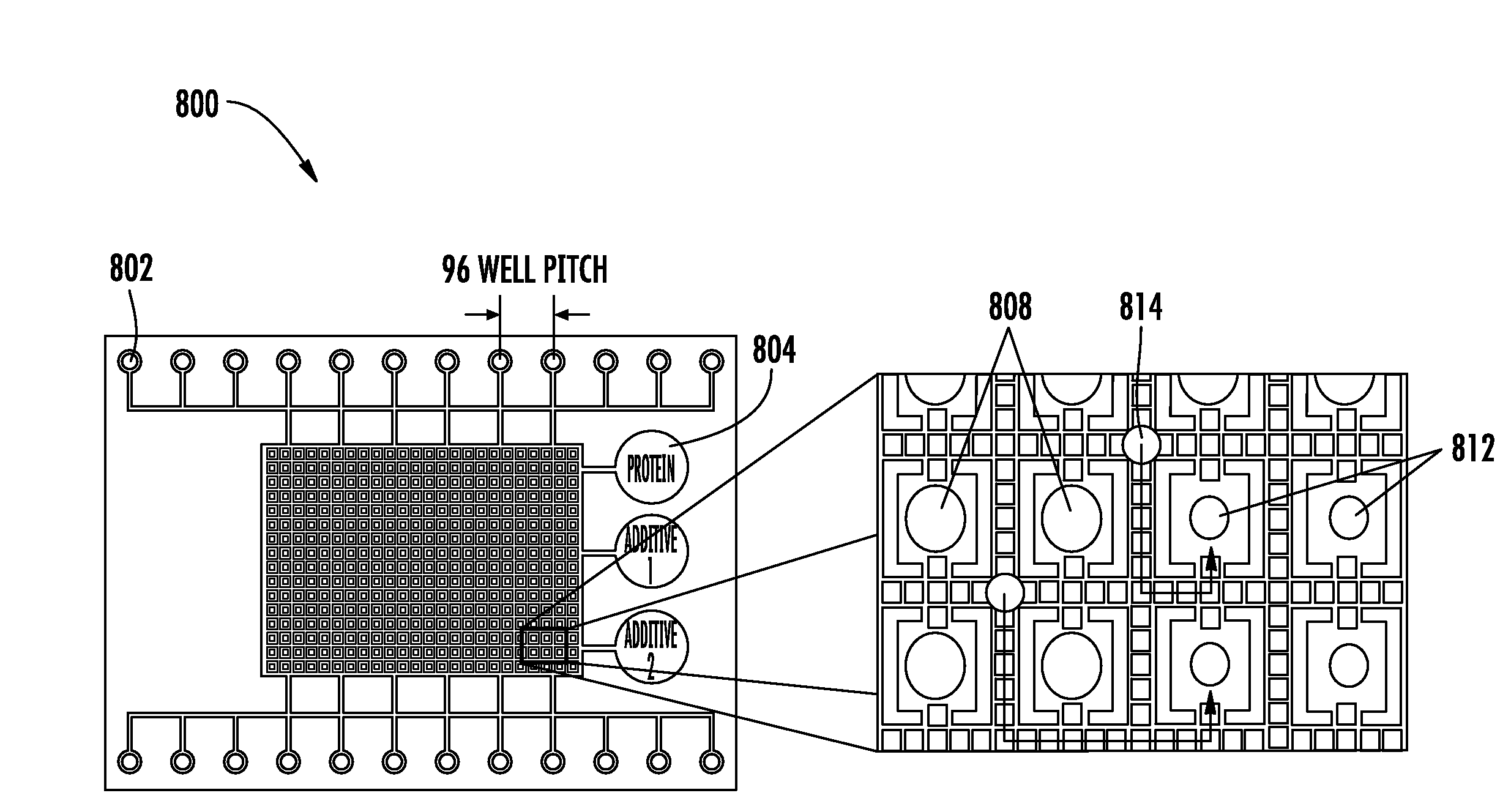
Sample Processing Droplet Actuator, System and Method
InactiveUS20080230386A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertySequential/parallel process reactionsSludge treatmentInterior spaceEngineering
Sample processing droplet actuators, systems and methods are provided. According to one embodiment, a stamping device including a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a first plate including a path or network of control electrodes for transporting droplets on a surface thereof; (b) a second plate mounted in a substantially parallel orientation with respect to the first plate providing an interior volume between the plates, the second plate including one or more stamping ports for transporting some portion or all of a droplet from the interior volume to an exterior location; (c) a port for introducing fluid into the interior volume between the plates; and (d) a path or network of reference electrodes corresponding to the path or network of control electrodes. Associated systems and methods including the stamping device are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Disposable sensor with enhanced sample port inlet
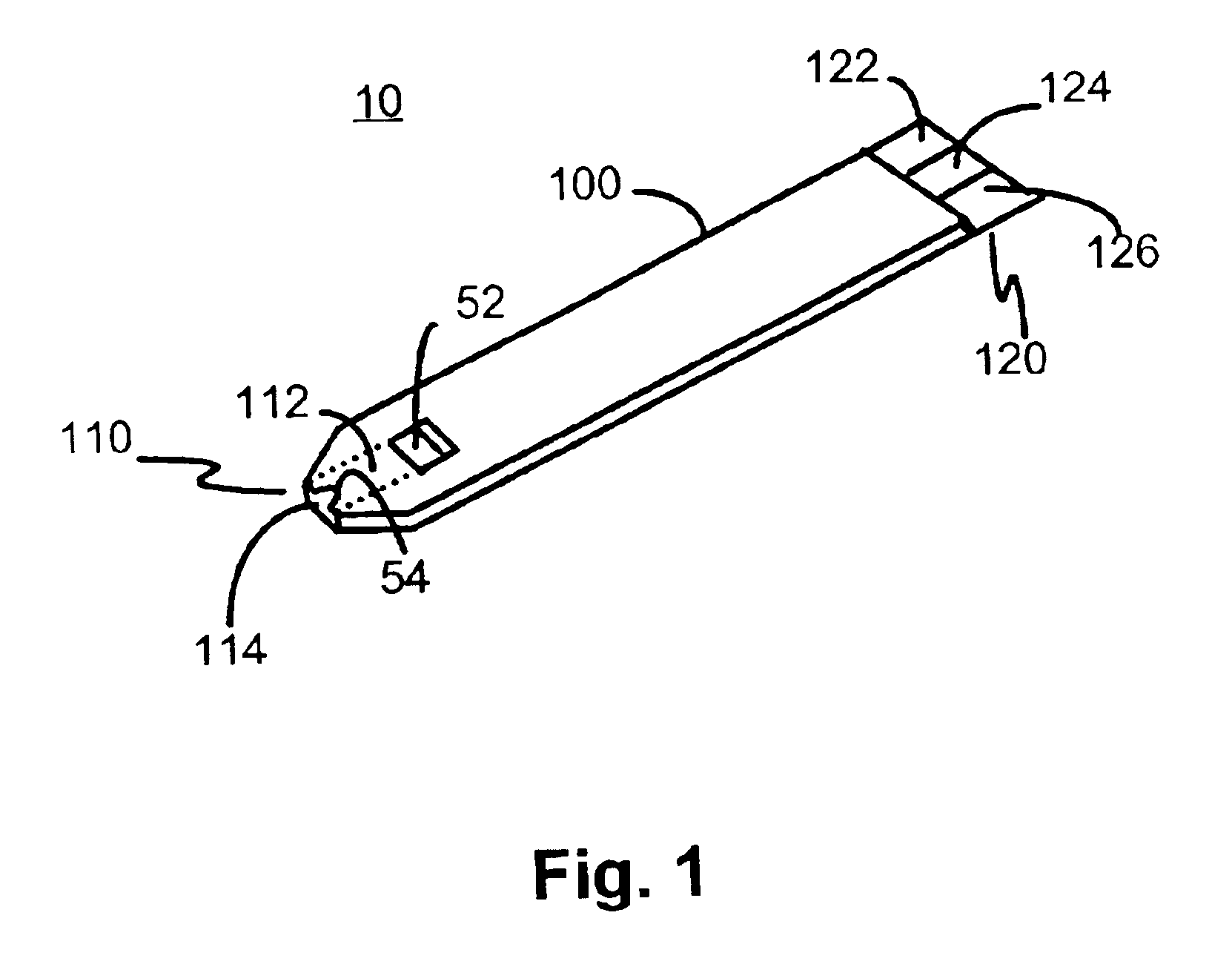
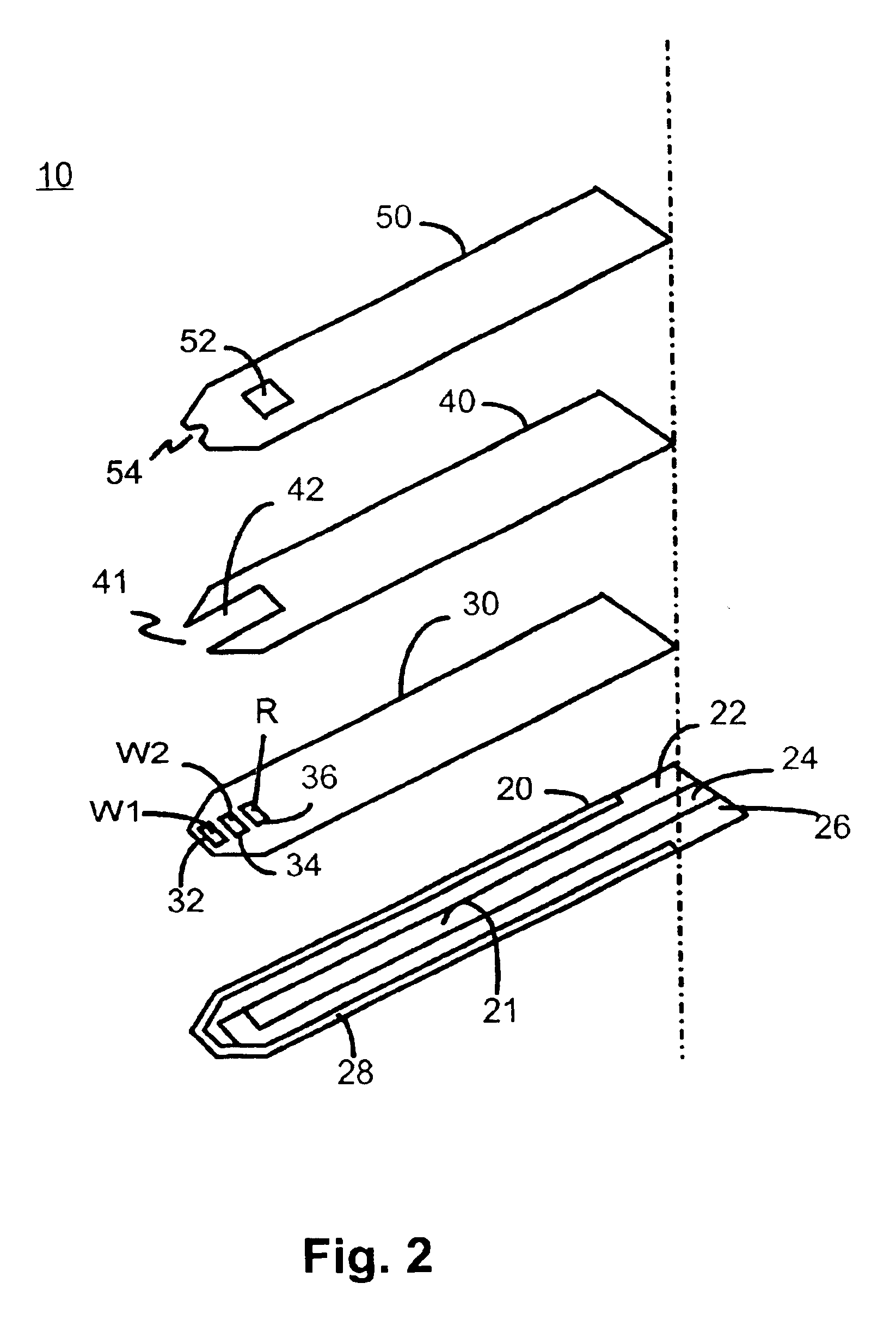
InactiveUS6837976B2Interference minimizationWide linear measurement rangeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProximateConductive coating
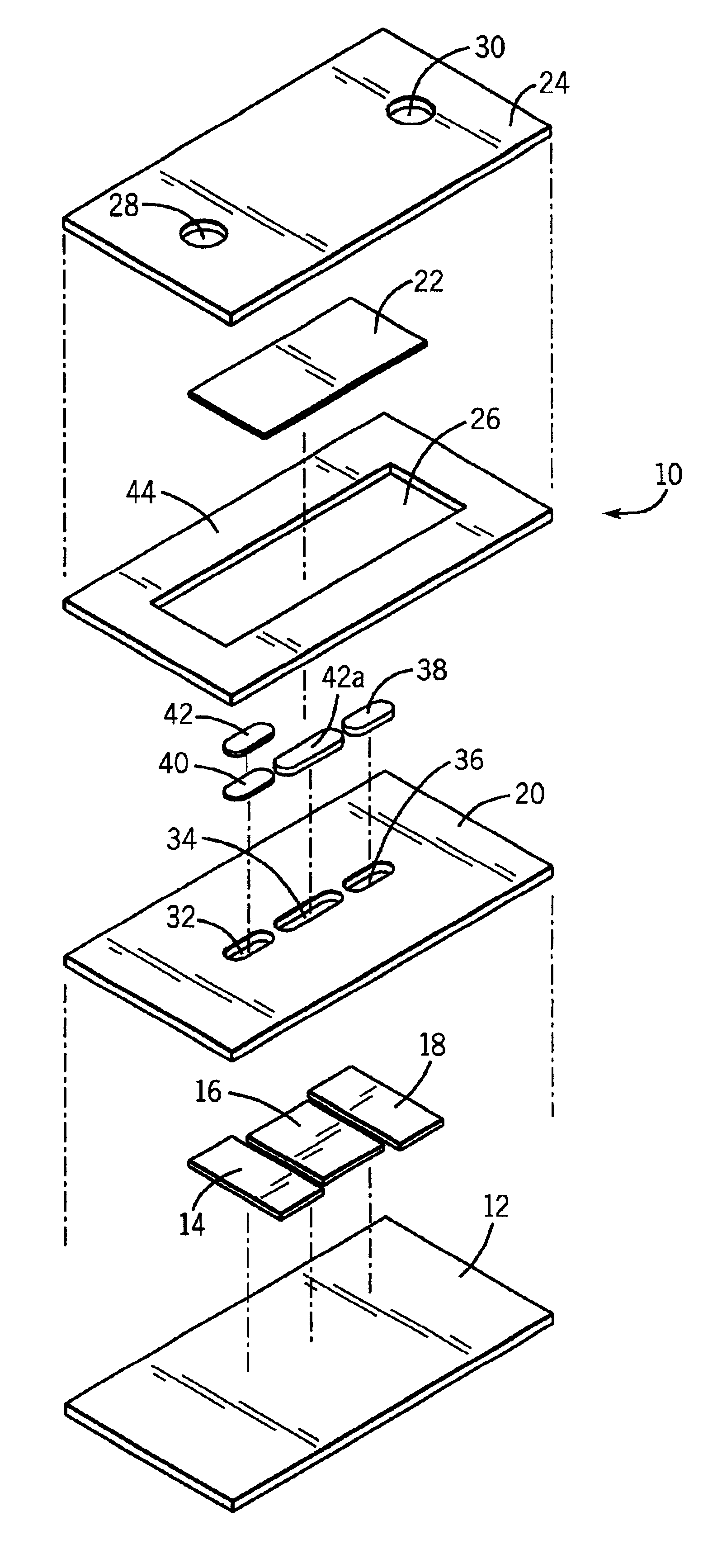
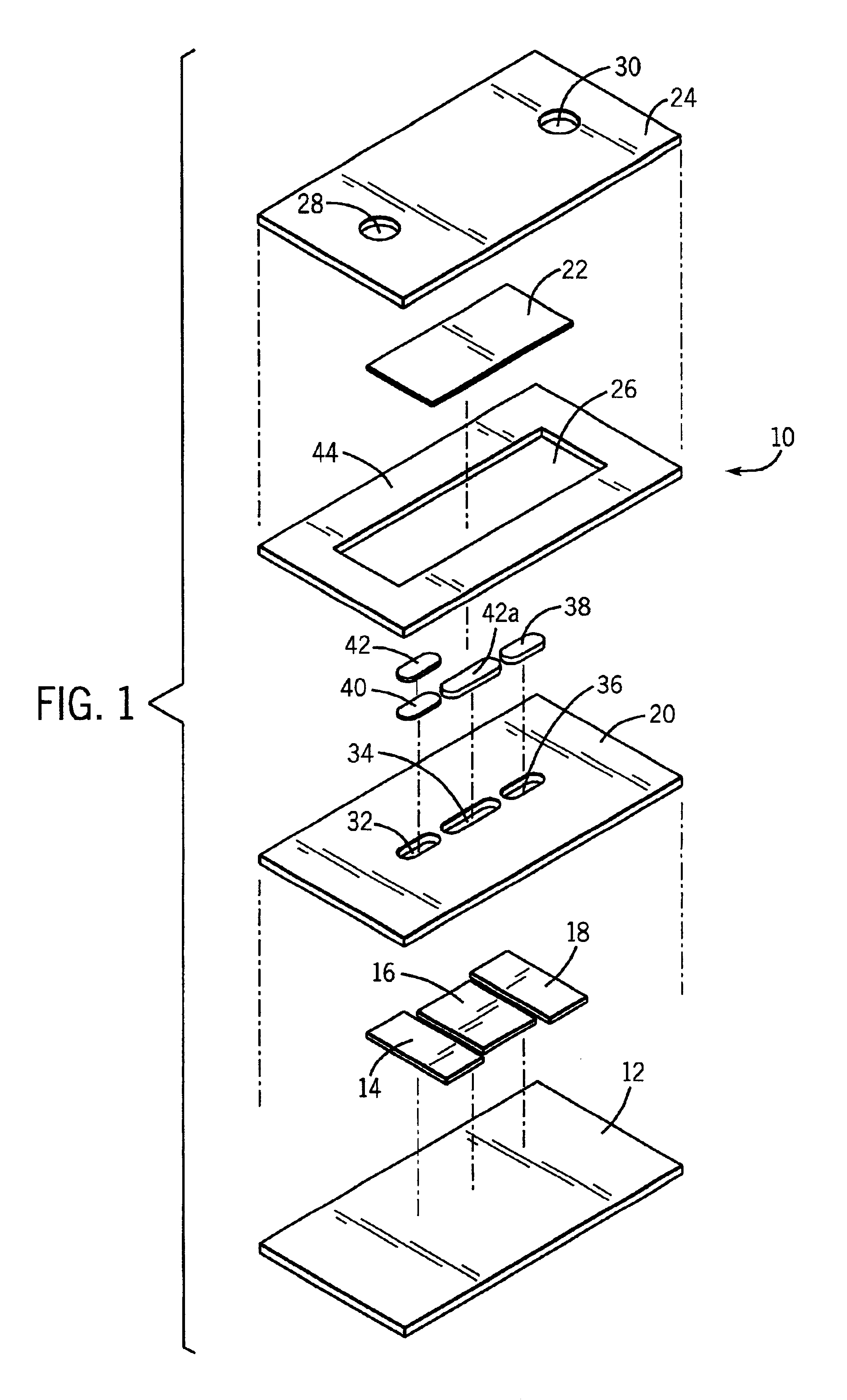
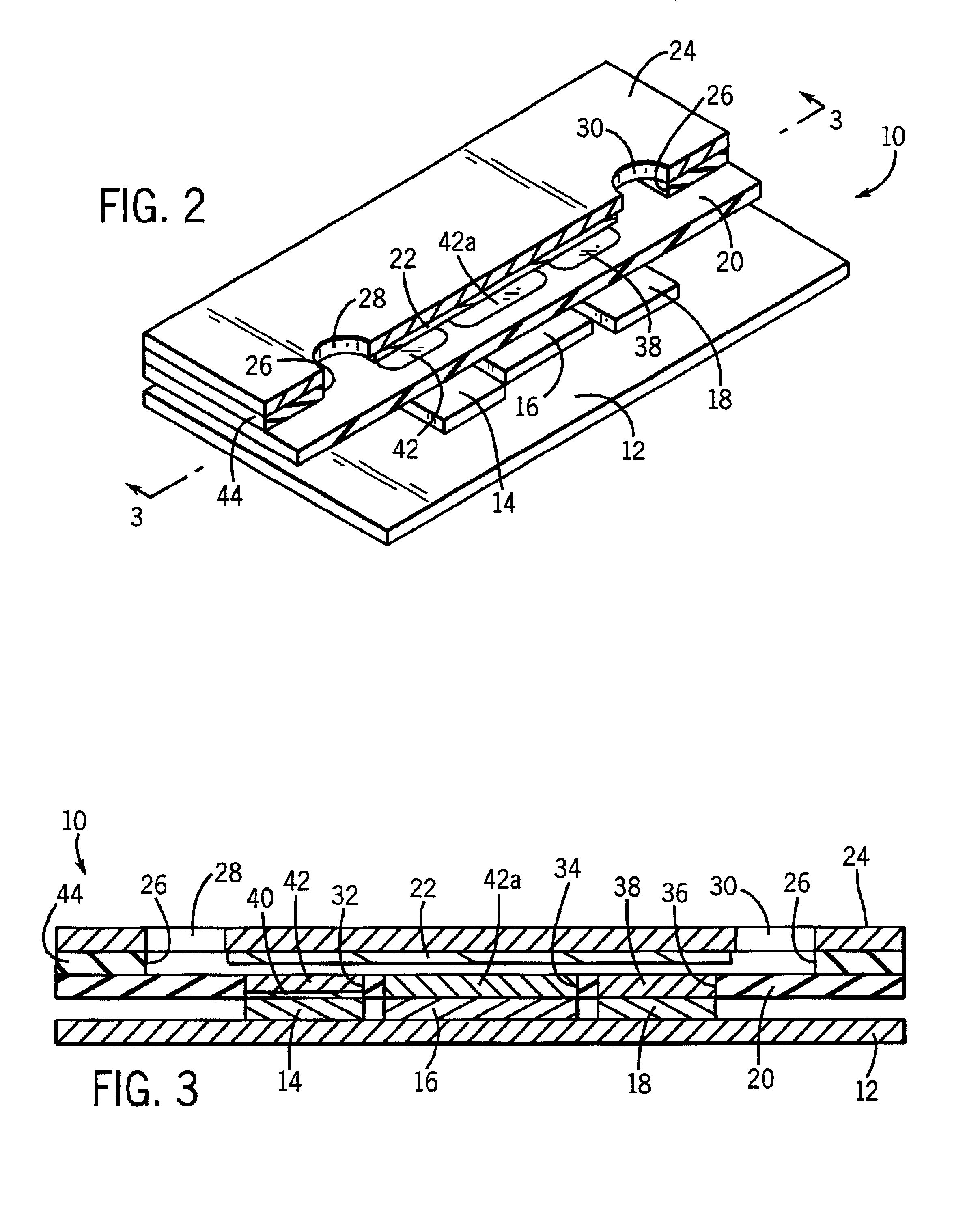
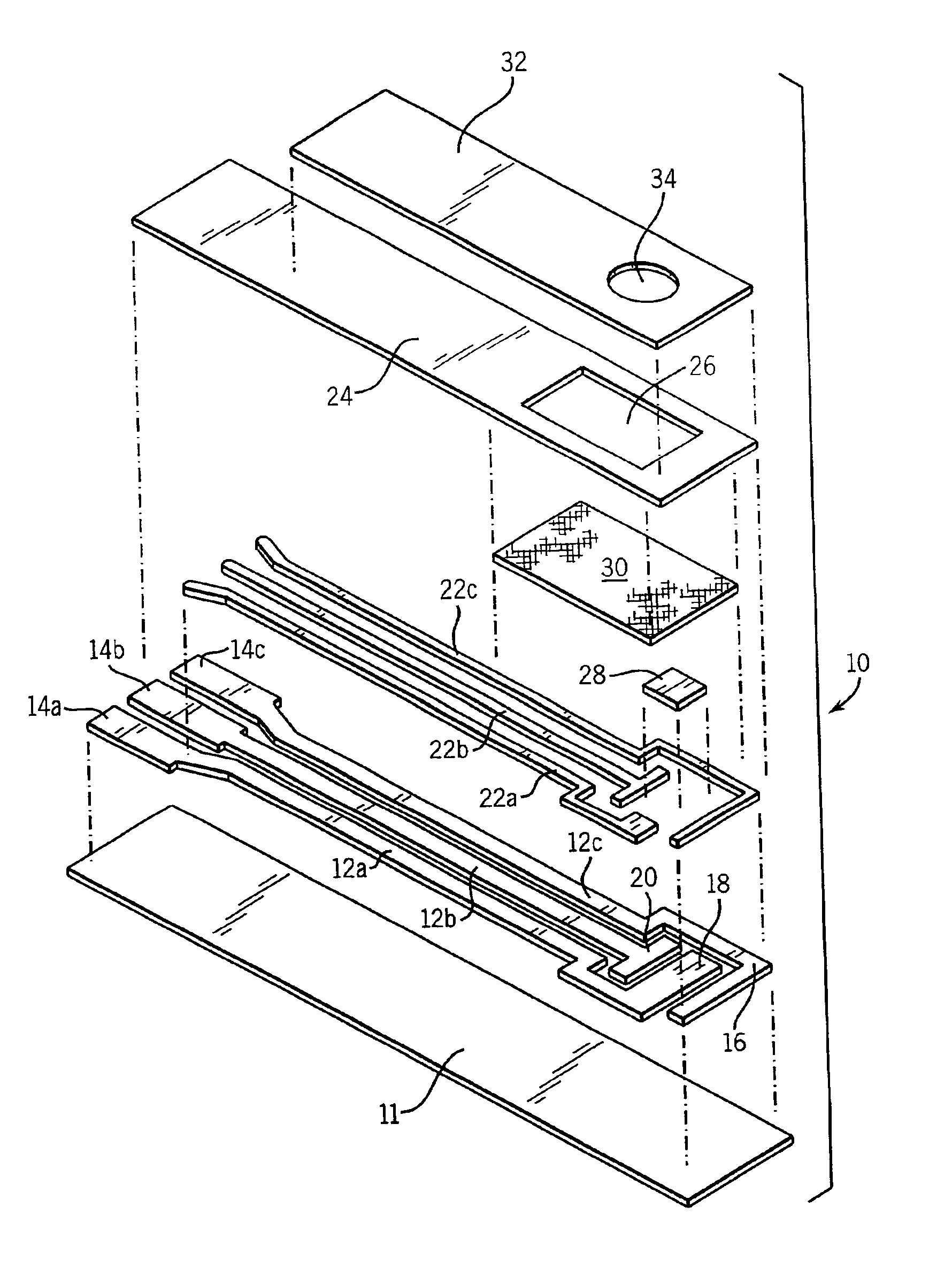
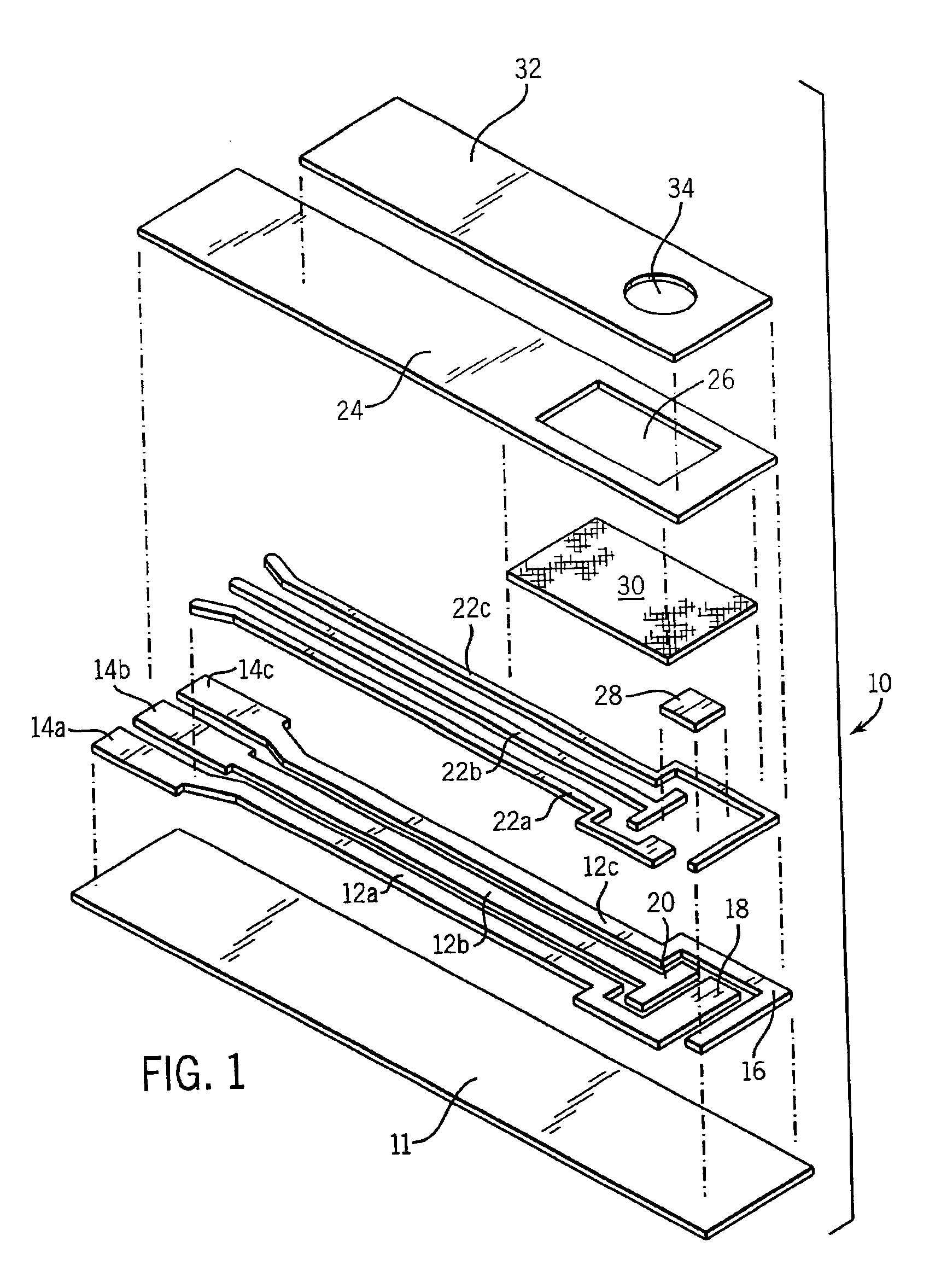
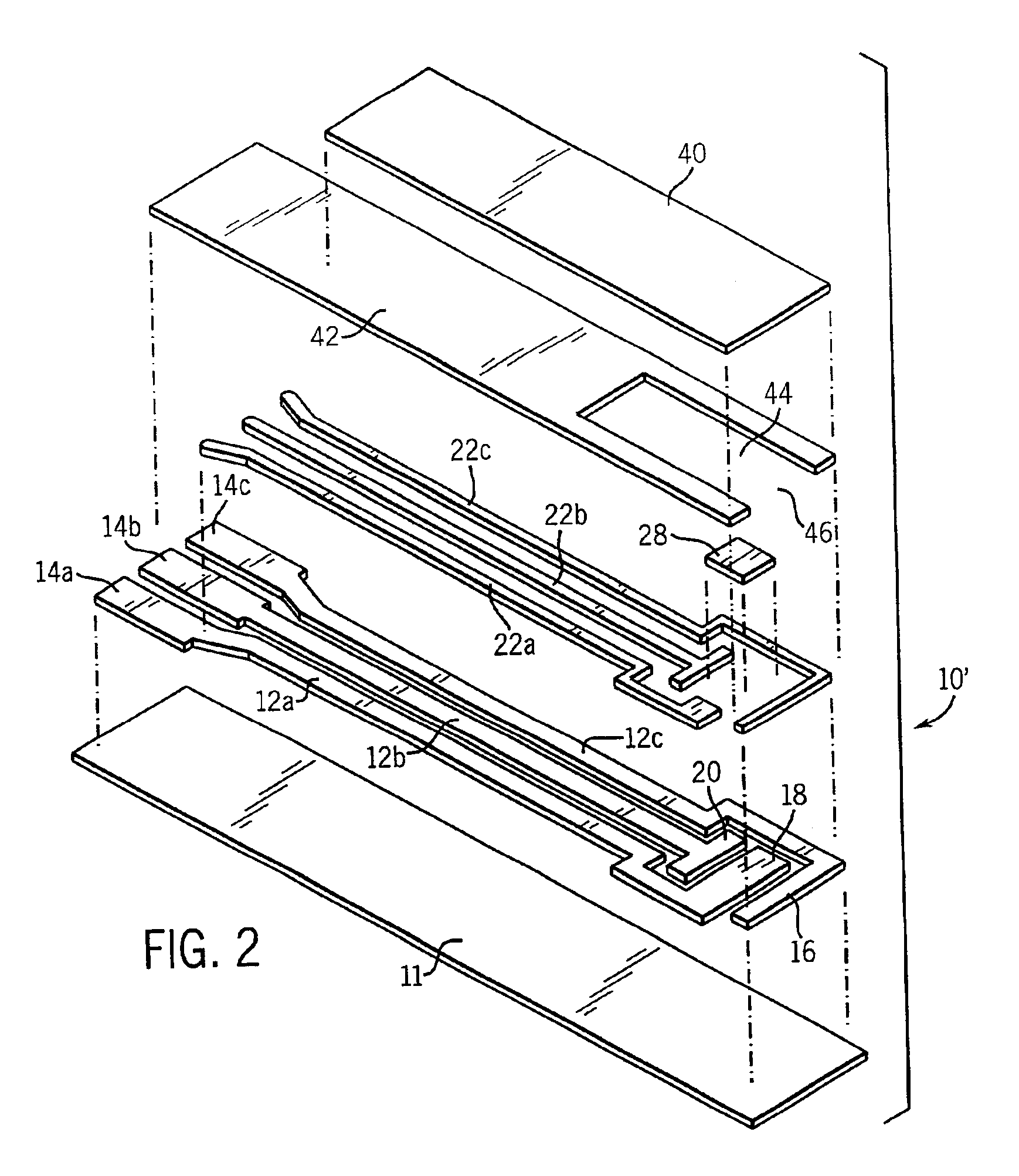
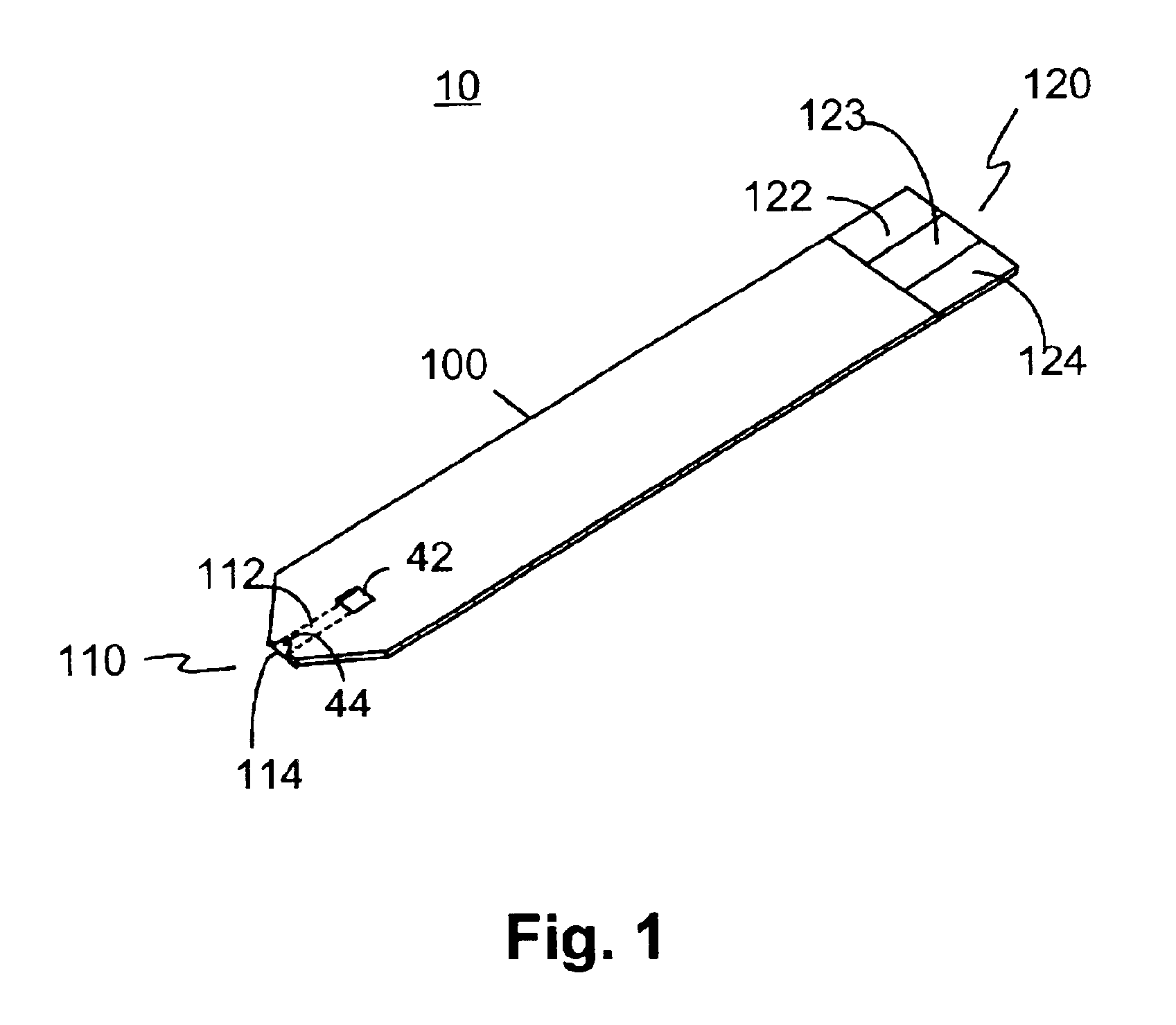
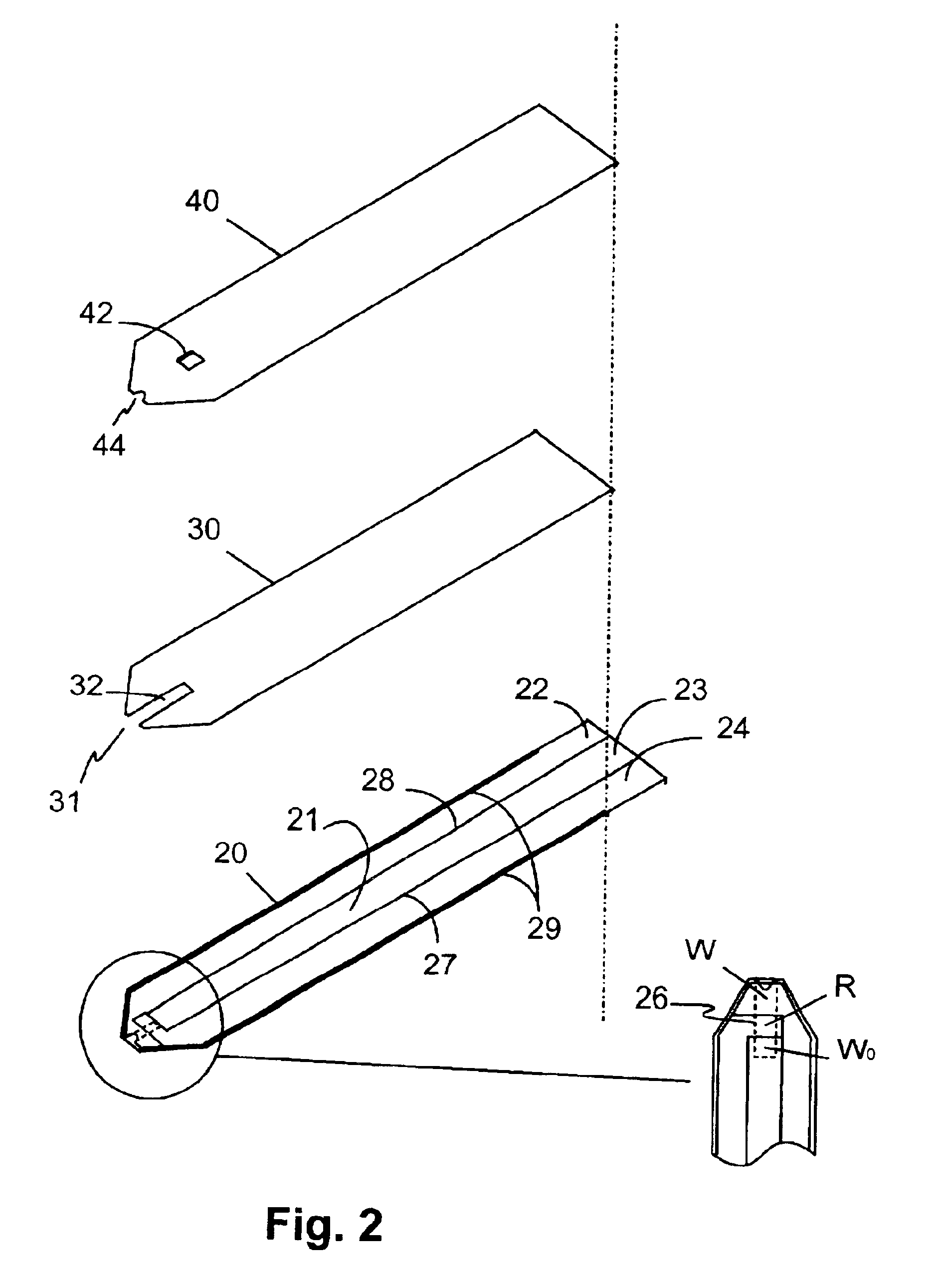
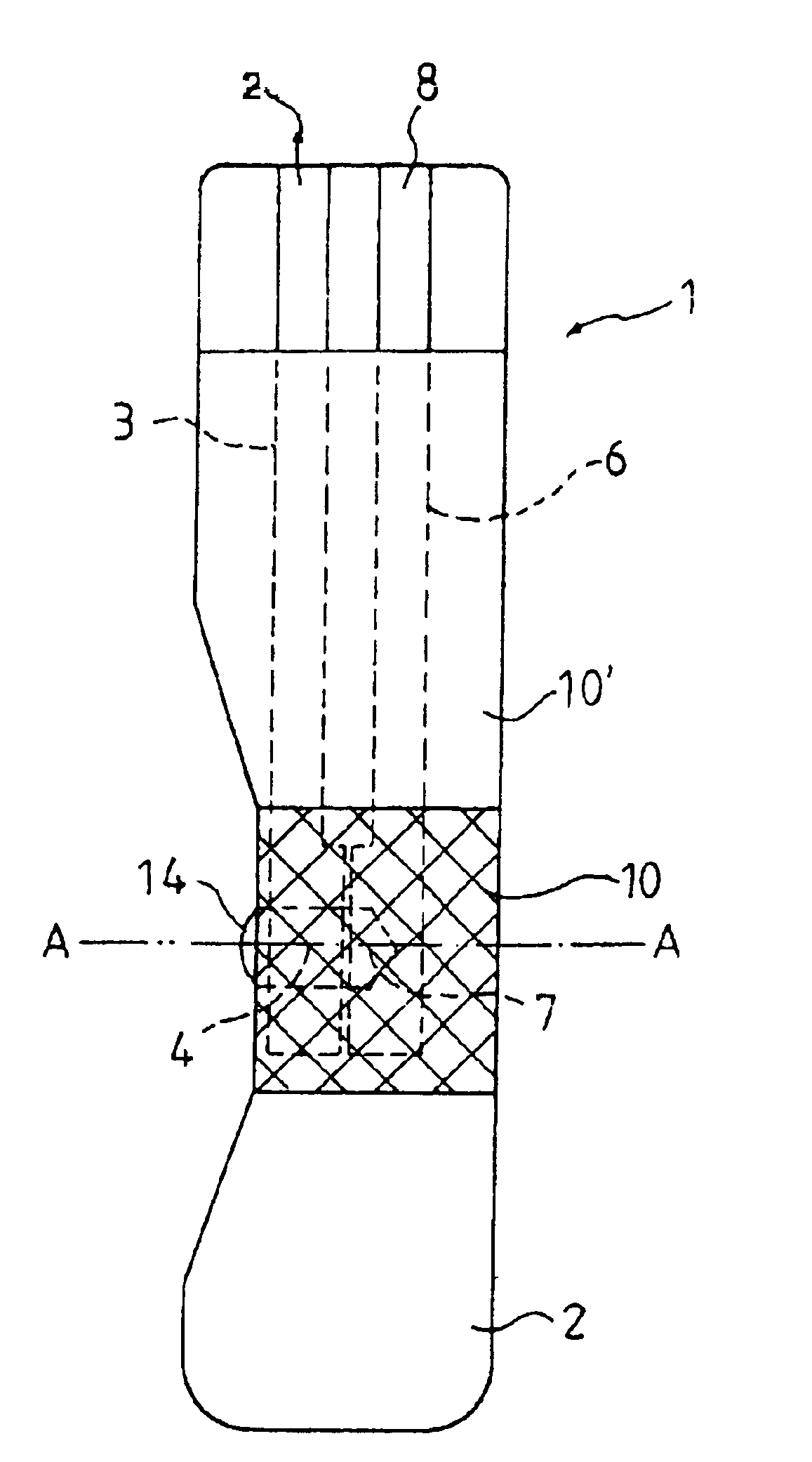
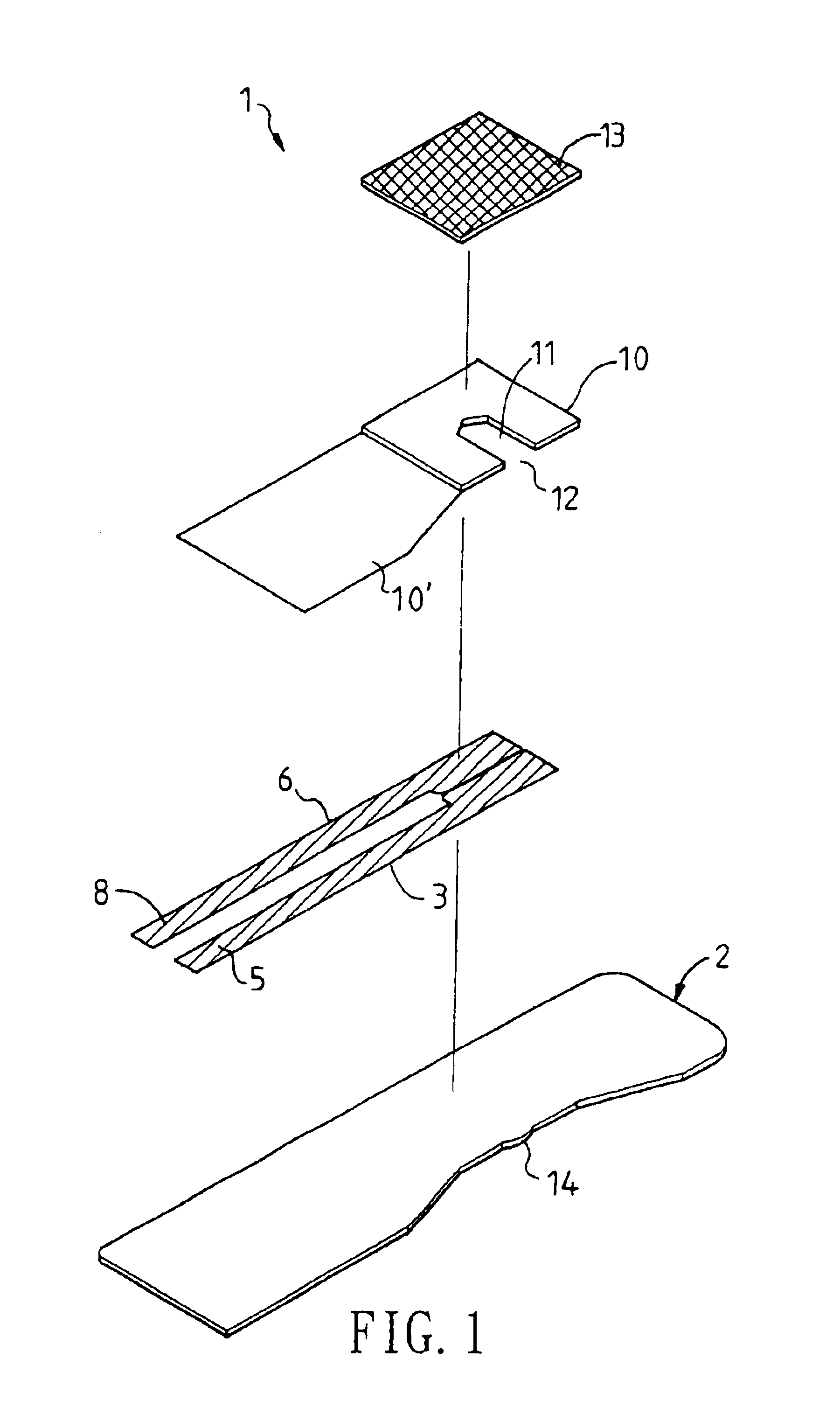
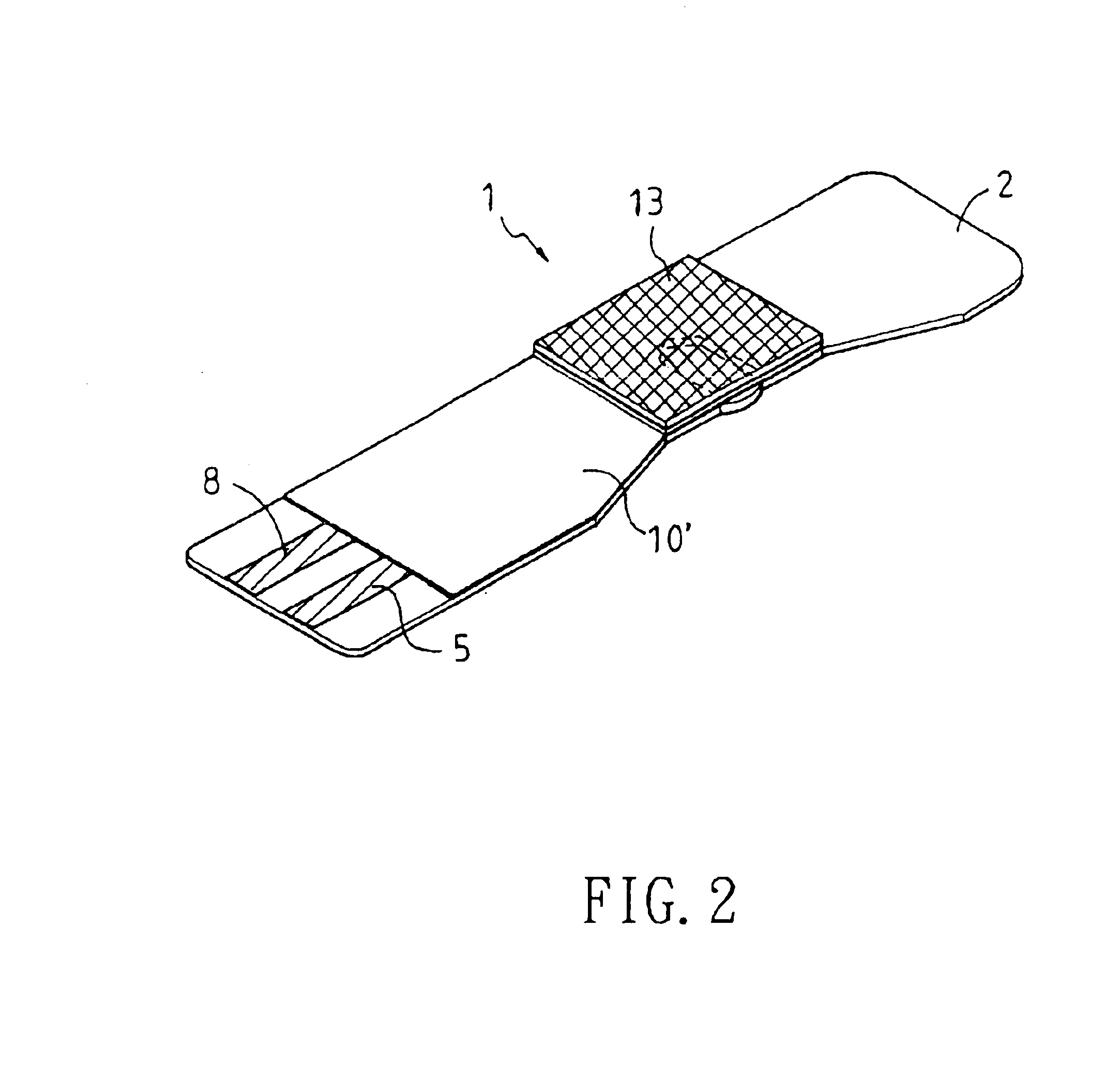
A disposable biosensor for testing a fluid sample including a laminated strip with a first and second end, a reference electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end, at least one working electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end and the reference electrode, an open path for receiving a fluid sample beginning from the first end and connecting to a vent spaced from the first end, the open path being sufficiently long to expose the reference electrode and the working electrode to the fluid sample, and conductive contacts located at the second end of the laminated strip. The laminated strip has a base layer with a conductive coating, a reagent holding layer, a channel forming layer and a cover having an inlet notch at the first end. The working electrode contains a reagent having an enzyme.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Analyte test sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060144704A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical resistance and conductanceAnalyte
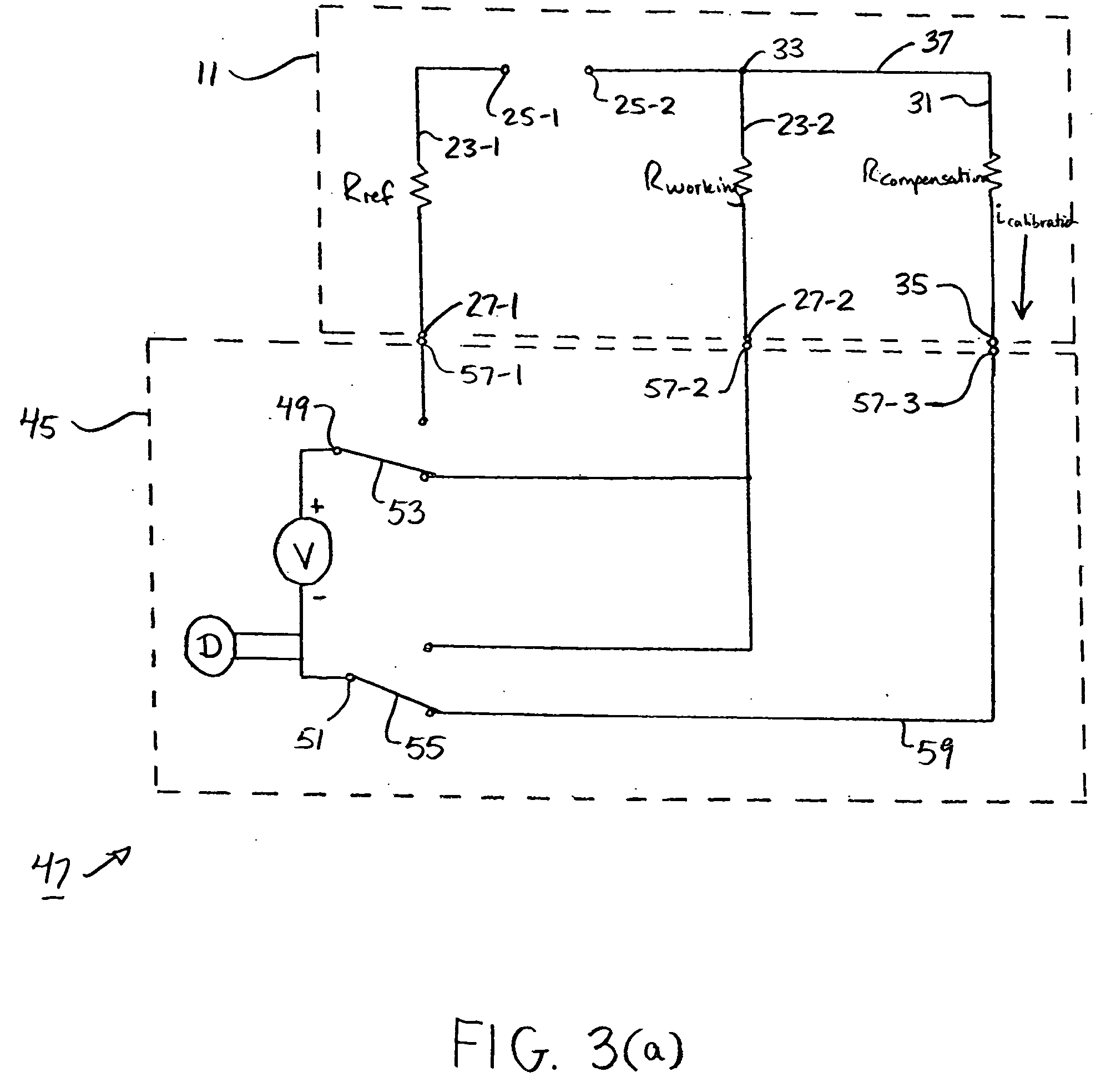
An analyte test sensor for use in measuring the concentration of a particular analyte in a test sample includes a non-conductive substrate, a reference electrode deposited on the substrate, a working electrode deposited on the substrate and a compensation electrode deposited on the substrate. The compensation electrode is provided with a resistive ladder and is designed to correct for test result inaccuracies which are the result of variances in the manufacturing of the test sensor. Specifically, in one embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in an analog manner by shunting a portion of the working current away from working electrode. In another embodiment, the compensation electrode corrects for test result inaccuracies in a digital manner by providing a calibration code which is proportional its resistance value. A batch of analyte test sensors are preferably manufactured in the following manner. An initial batch of the test sensors is constructed. Then, a limited sampling of the sensors is tested for accuracy using a control sample. Based on the test results, the resistance value of the compensation electrode for each remaining sensor in the batch is adjusted accordingly.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
System and Method for Three Dimensional Mapping of Electrophysiology Information
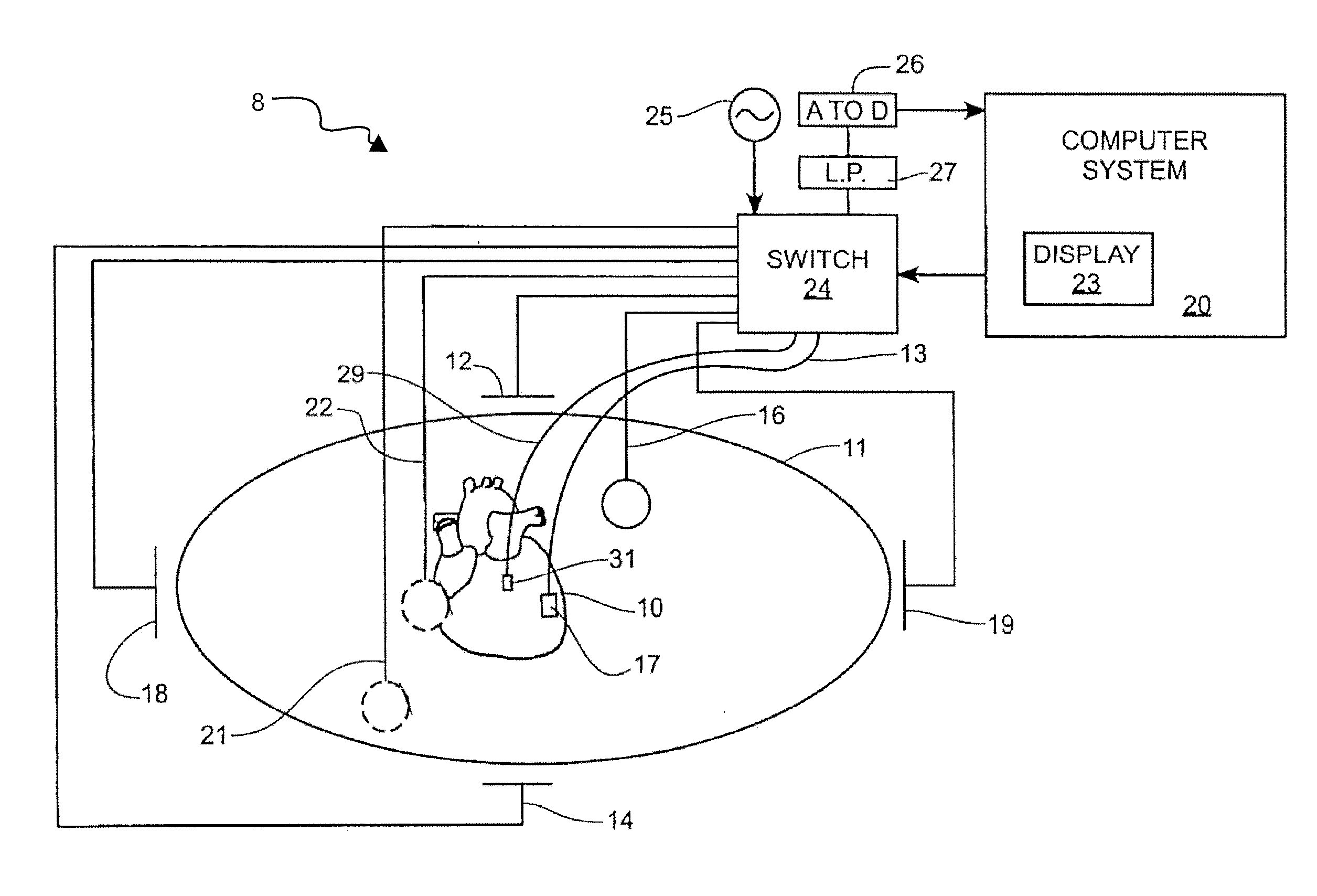
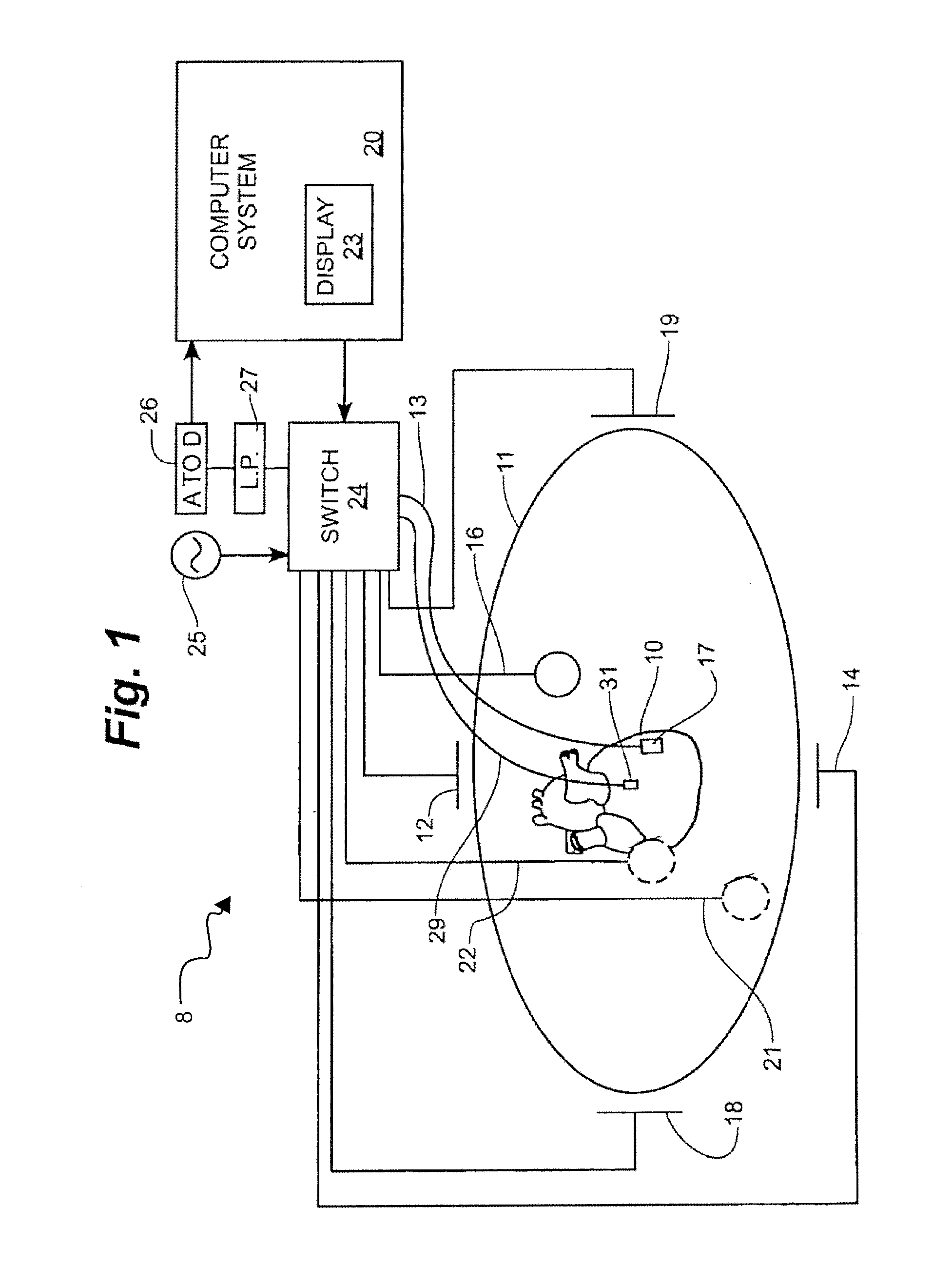
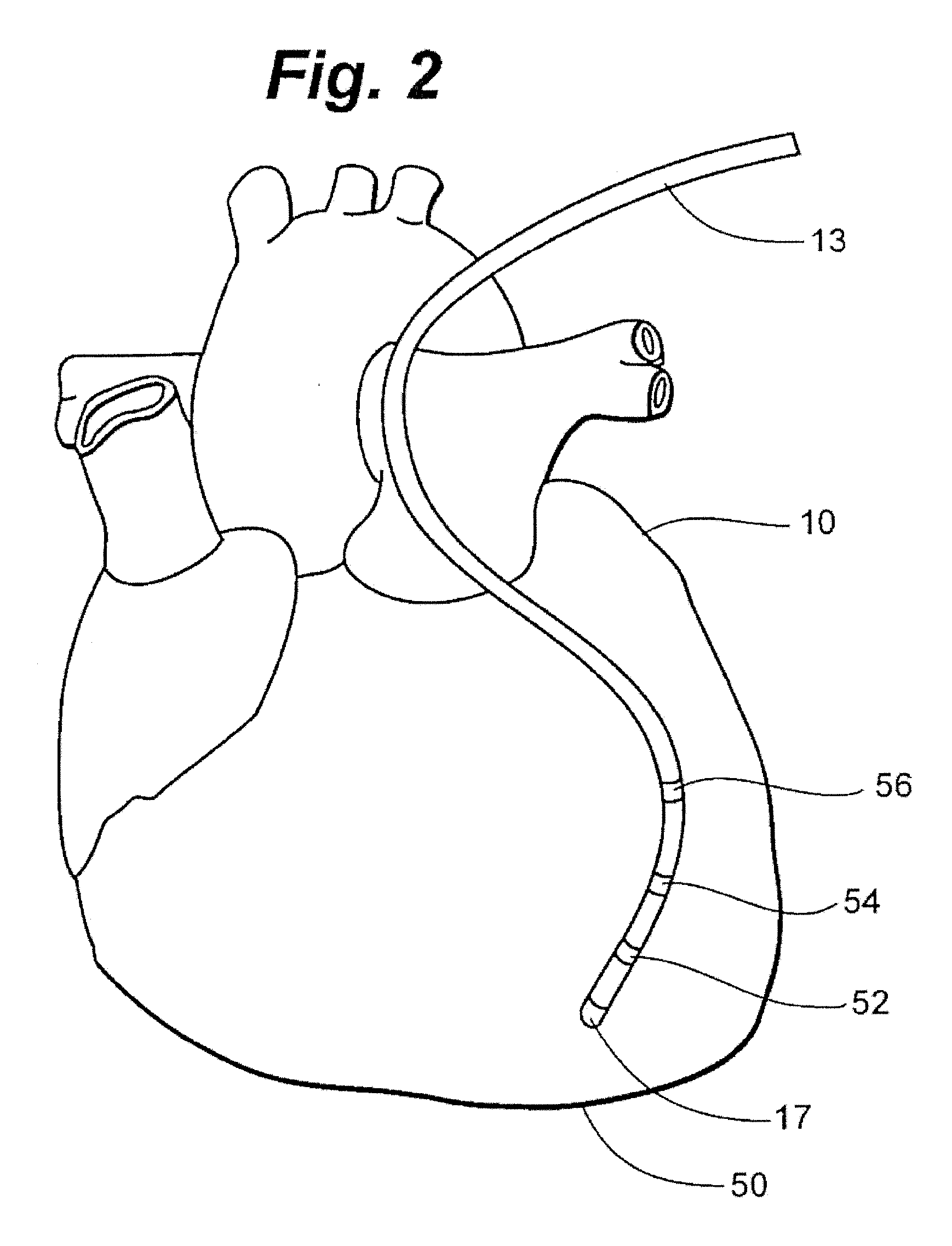
An electrophysiology apparatus is used to measure electrical activity occurring in a heart of a patient and to visualize the electrical activity and / or information related to the electrical activity. A three-dimensional map of the electrical activity and / or the information related to the electrical activity is created. Exemplary maps include a time difference between action potentials at a roving electrode and a reference electrode, the peak-to-peak timing of action potentials at the roving electrode, the peak negative voltage of action potentials at the roving electrode, complex fractionated electrogram information, a dominant frequency of an electrogram signal, a maximum peak amplitude at the dominant frequency, a ratio of energy in one band of the frequency-domain to the energy in a second band of the frequency-domain, a low-frequency or high-frequency passband of interest, a frequency with the maximum energy in a passband, a number of peaks within a passband, an energy, power, and / or area in each peak, a ratio of energy and / or area in each peak to that in another passband, and a width of each peak in a spectrum. Colors, shades of colors, and / or grayscales are assigned to values of the parameters and colors corresponding to the parameters for the electrograms sampled by the electrodes are updated on the three-dimensional model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Electrochemical screening and early diagnosing instrument for malignant tumor
InactiveCN1866018AEasy to useOvercoming the deficiency of tumor-associated antigen specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
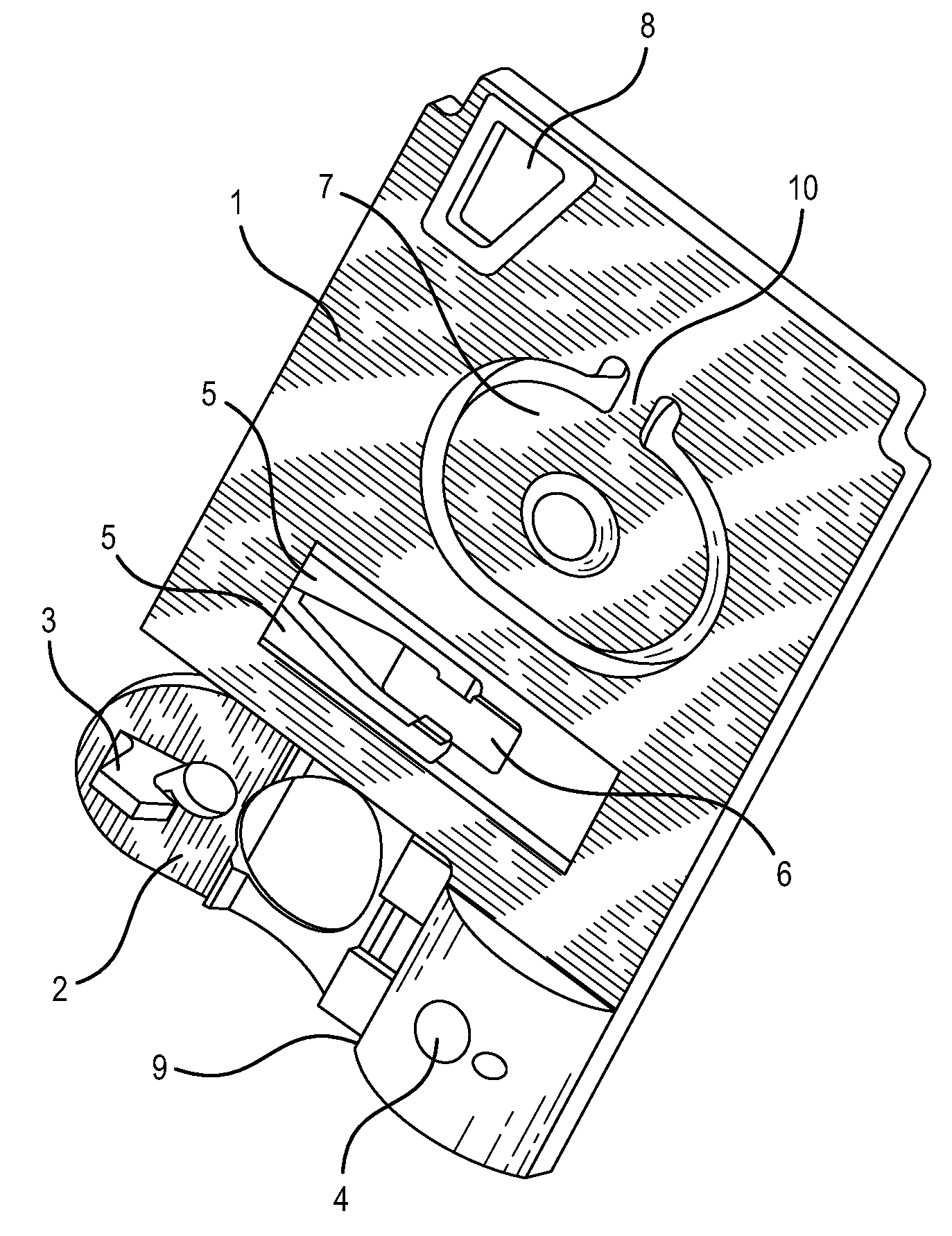
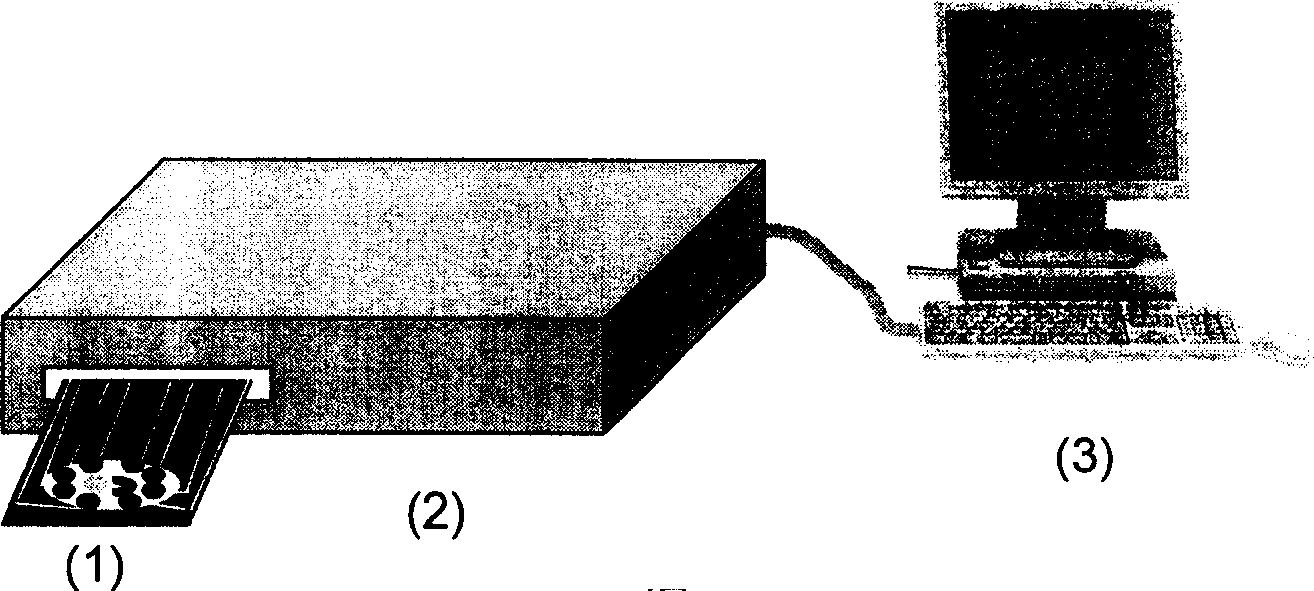
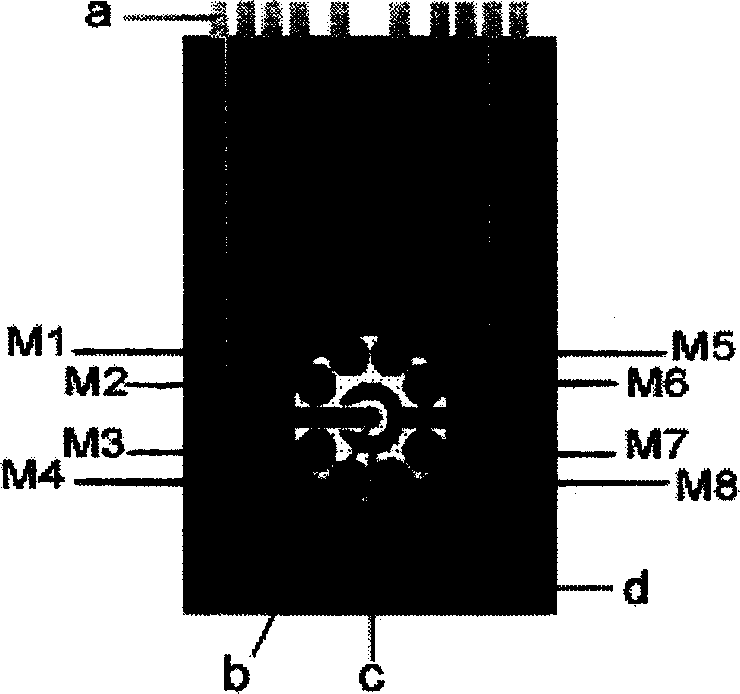
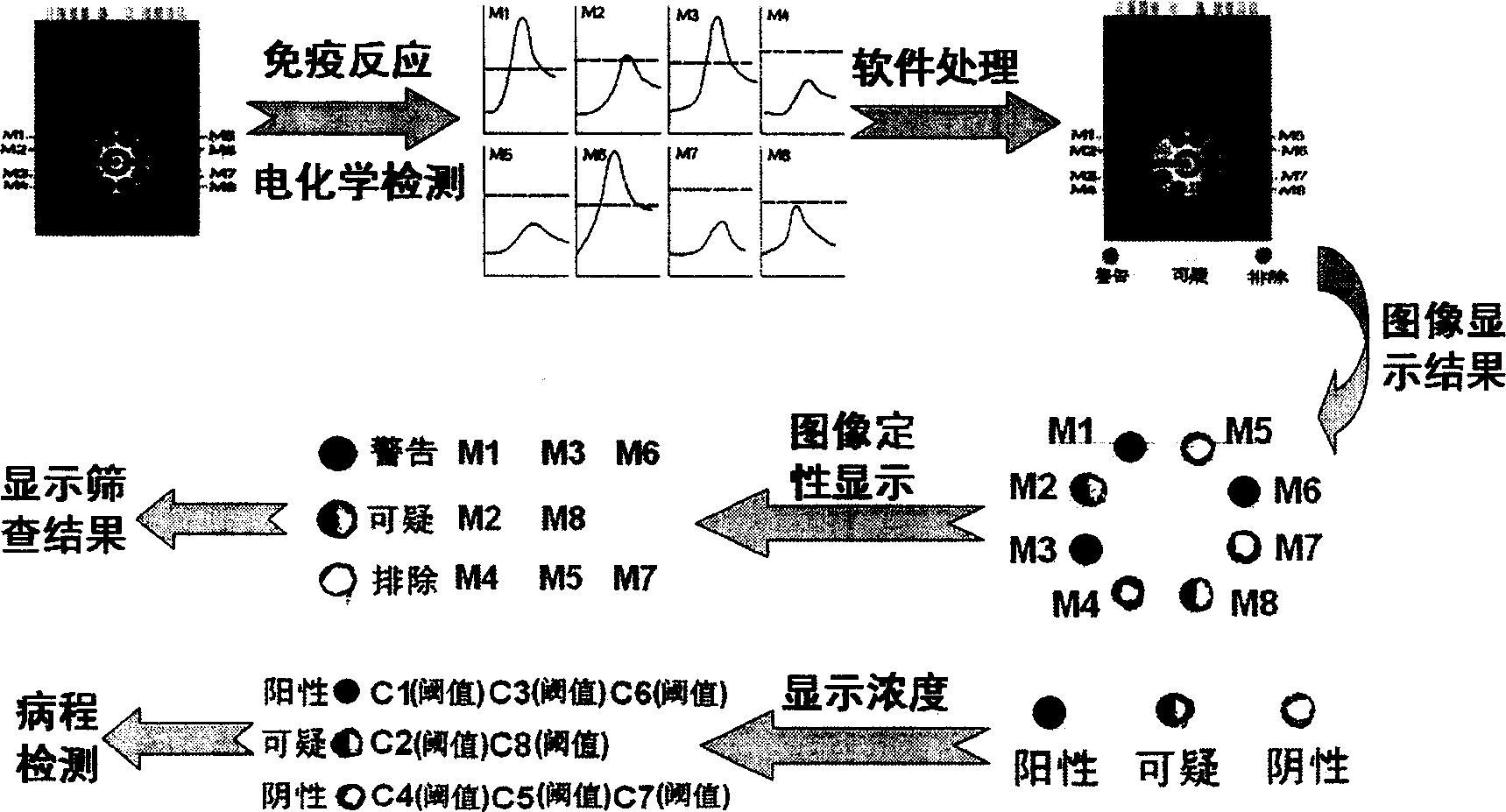
The disclosed electrochemical screening and early diagnostic device for malignant tumor comprises: an immune detection chip (1) connected to a time-resolution multichannel potentiostat (2) that connects to a data process and display system (3) by an interface. Wherein, the chip (1) comprises eight working electrodes fixed different antigen films and Ag wire (a), Ag / AgCl reference electrode (b), a carbon-pair electrode (c), and an insulation film (d). This invention needs low cost, has intelligence and fit to fast detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Disposable sub-microliter volume biosensor with enhanced sample inlet
InactiveUS6942770B2Wide linear measurement rangeReduce waiting timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringOpen path
A disposable electrode strip for testing a fluid sample including a laminated strip with a first and second end, a vent, an open path for receiving a fluid sample of less than one microliter beginning from the first end and connecting to the vent, a working electrode, a reference electrode and a pseudo-working electrode embedded in the laminated strip within the open path and proximate to the first end, a reagent matrix coextensive within the open path and covering the three electrodes, and conductive contacts located at the second end of the laminated strip.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Biological fluid analysis device
InactiveUS7144496B2Reduce passageEarly detectionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringBiological fluids
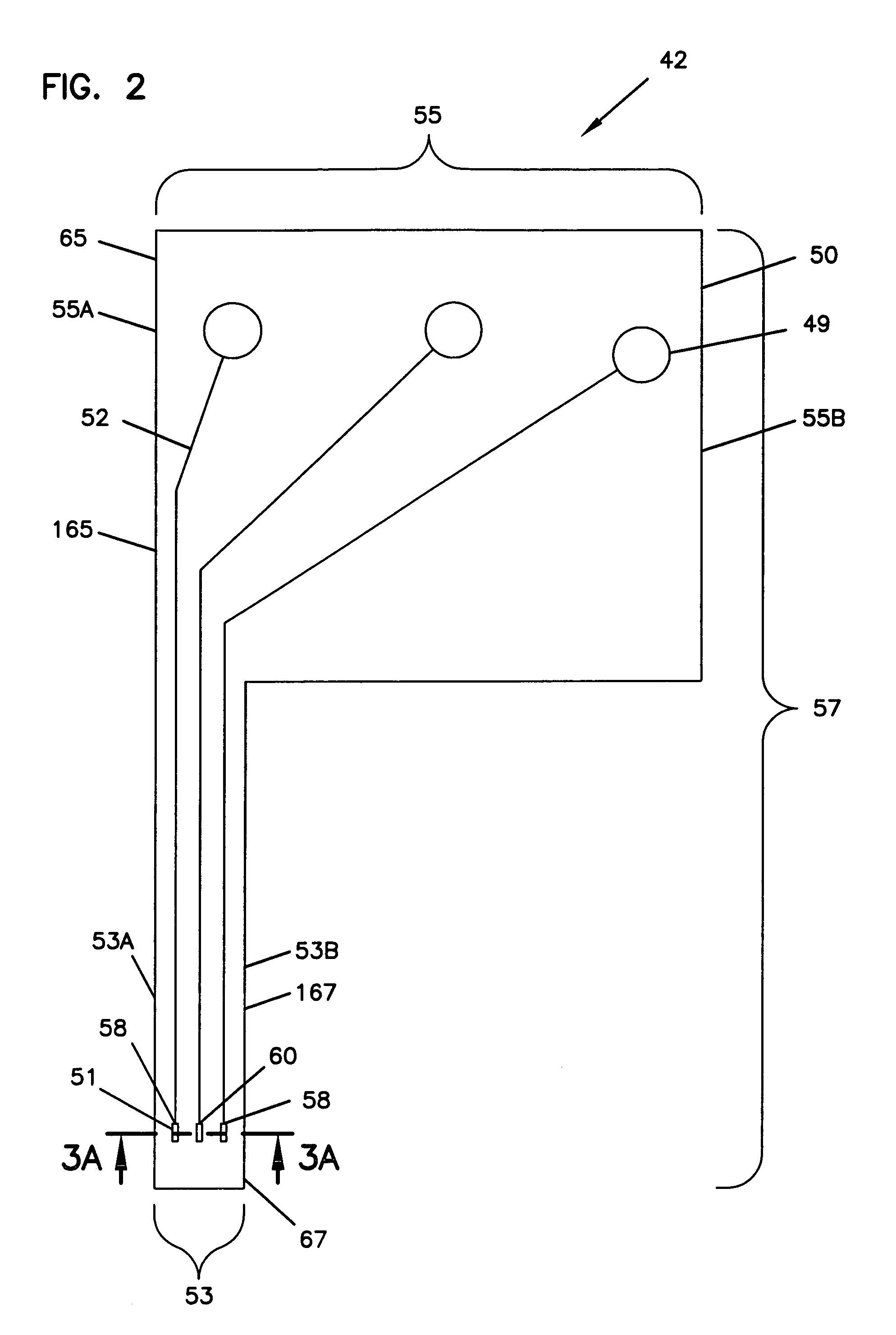
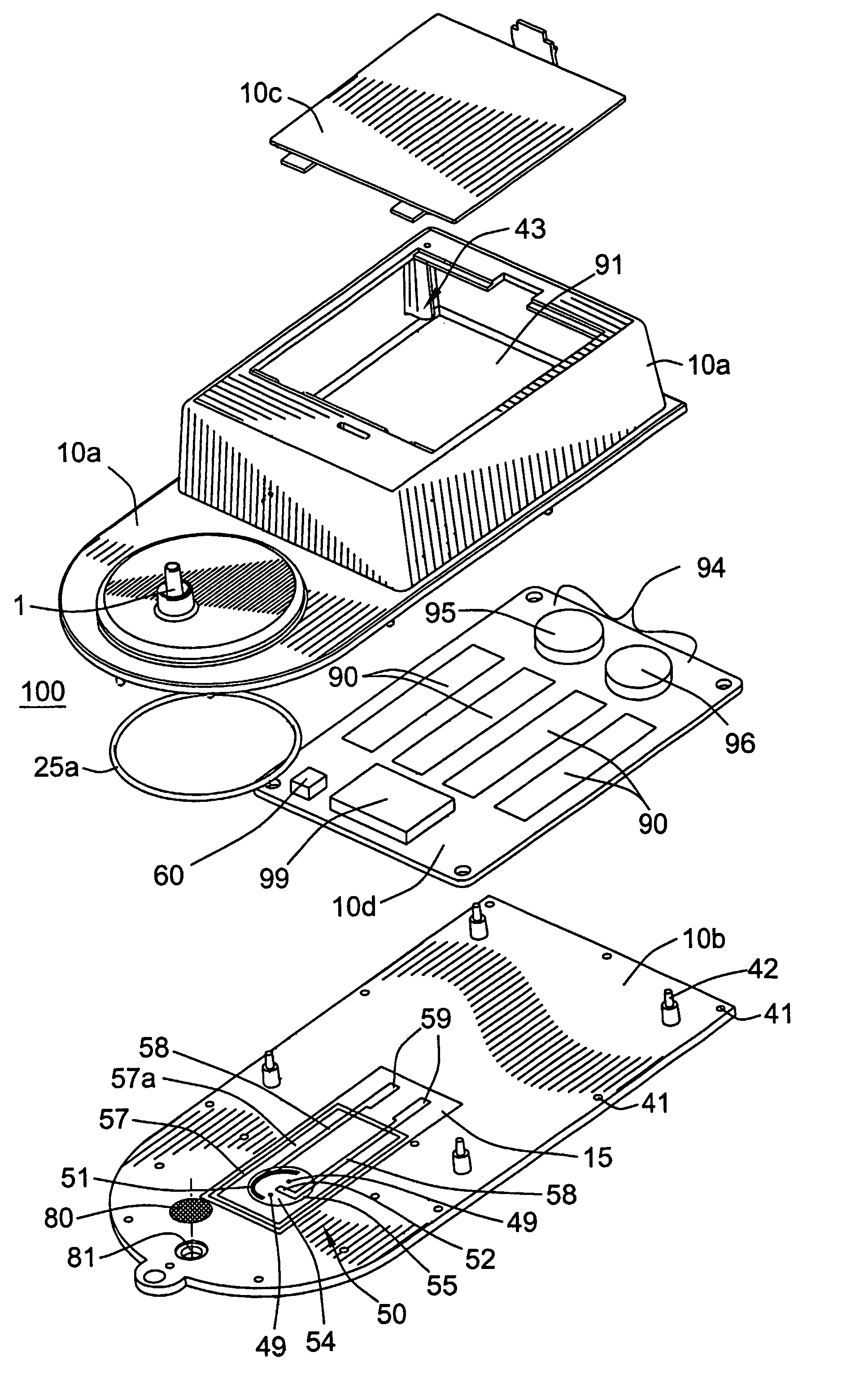
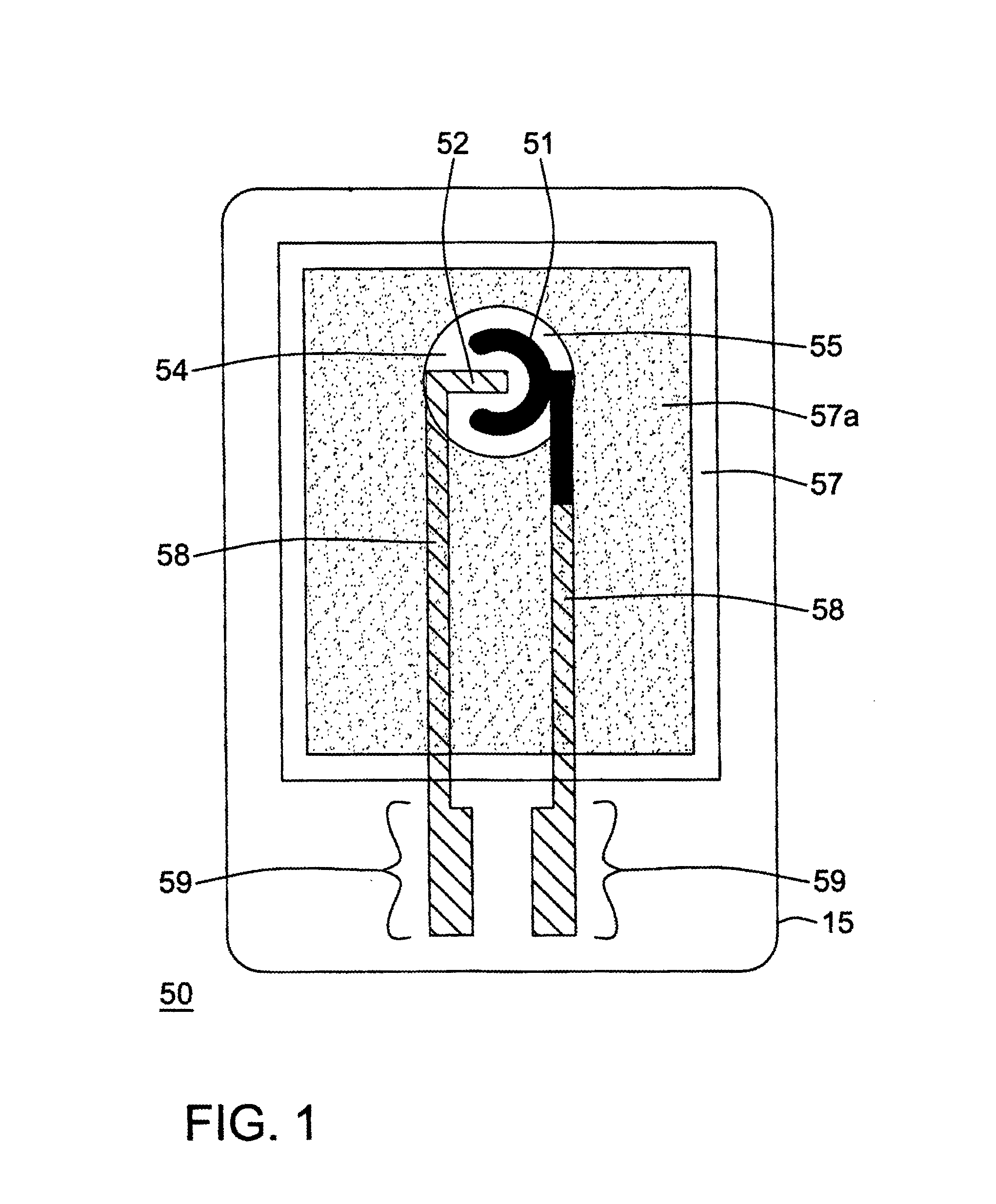
A biological fluid analysis device (100) including a biosensor (50) comprising an electrochemical-enzymatic sensor including a working electrode (51) and a reference electrode (52), is disclosed.
Owner:PALL CORP
Electronic circuit
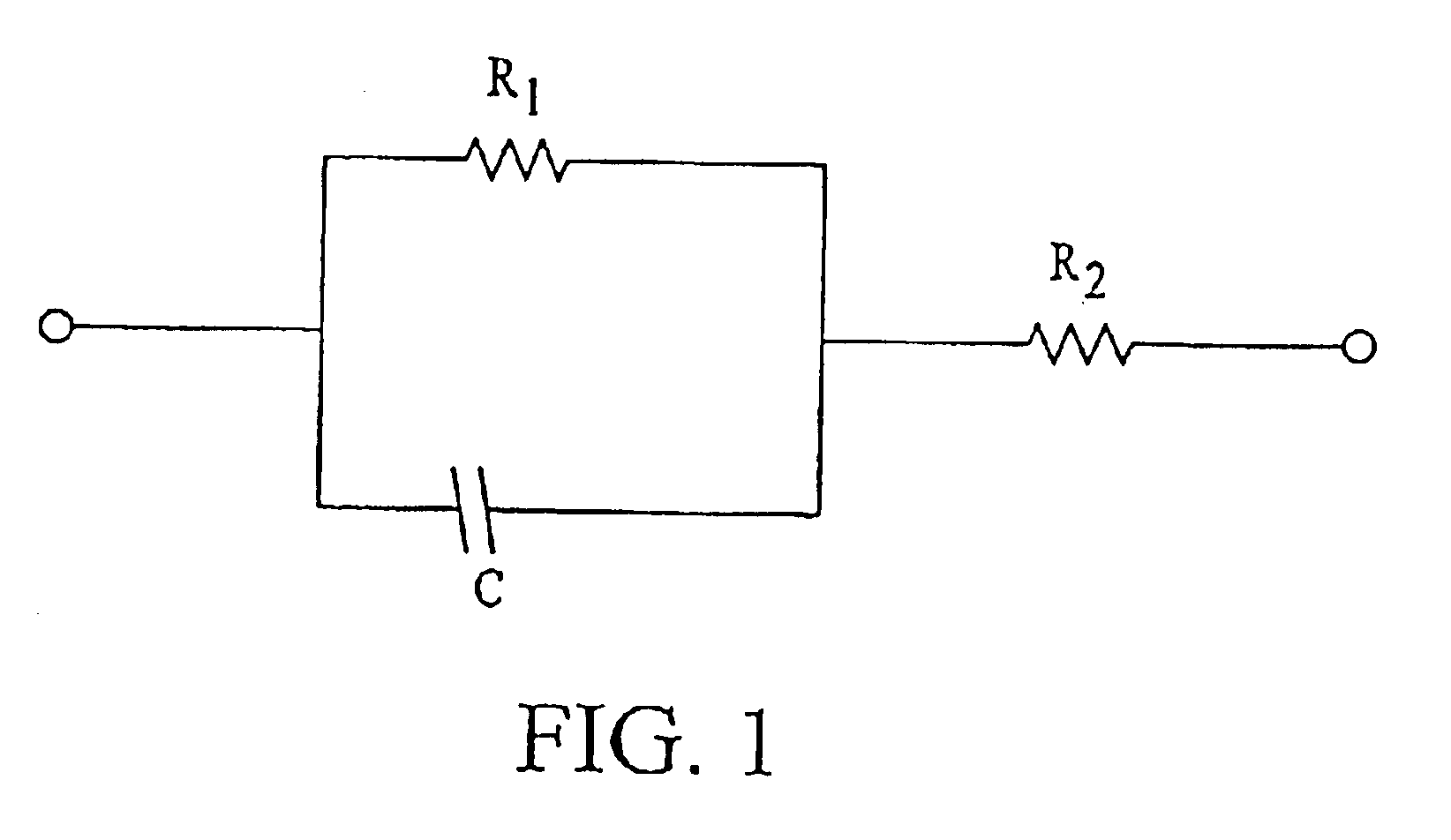
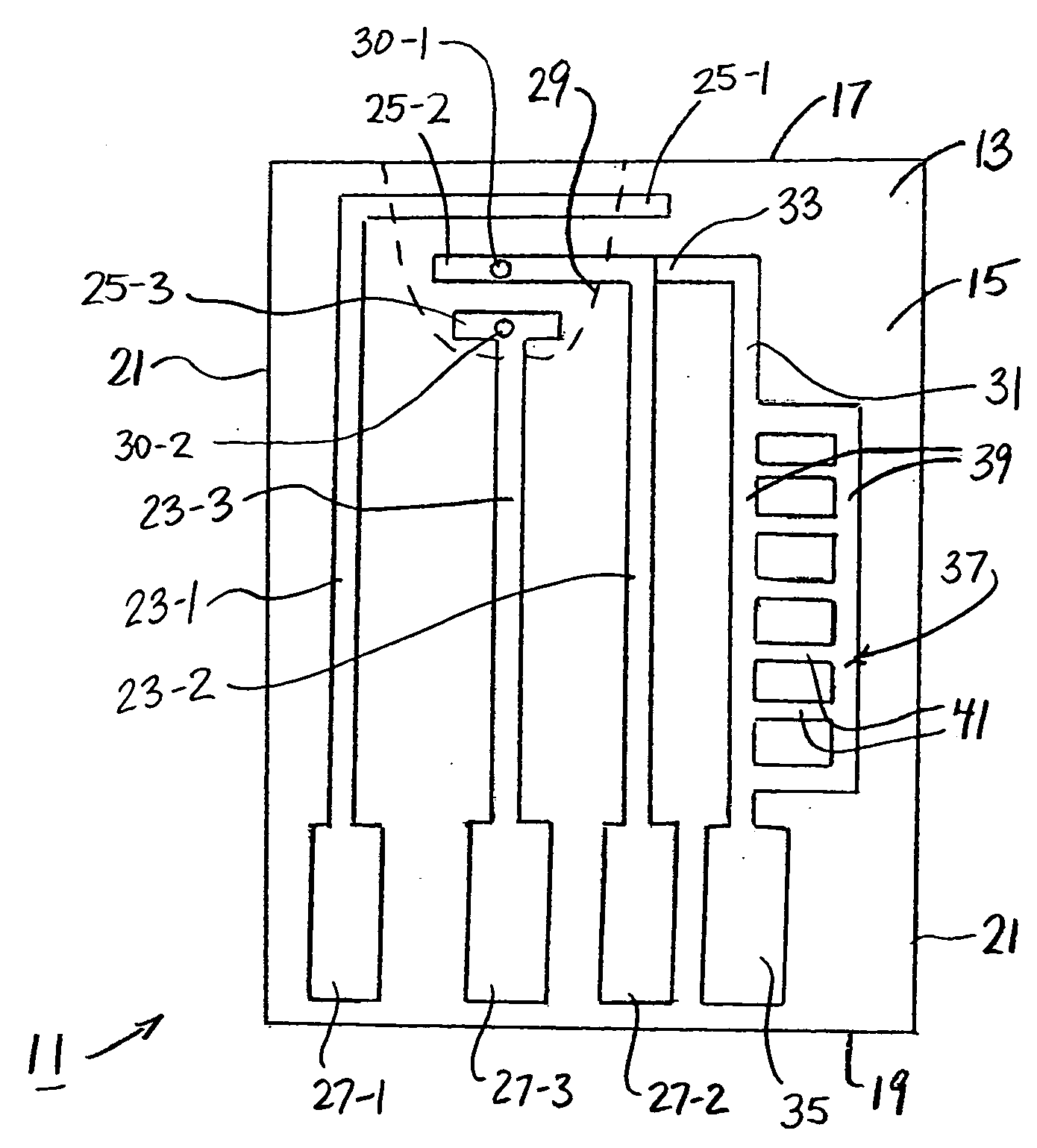
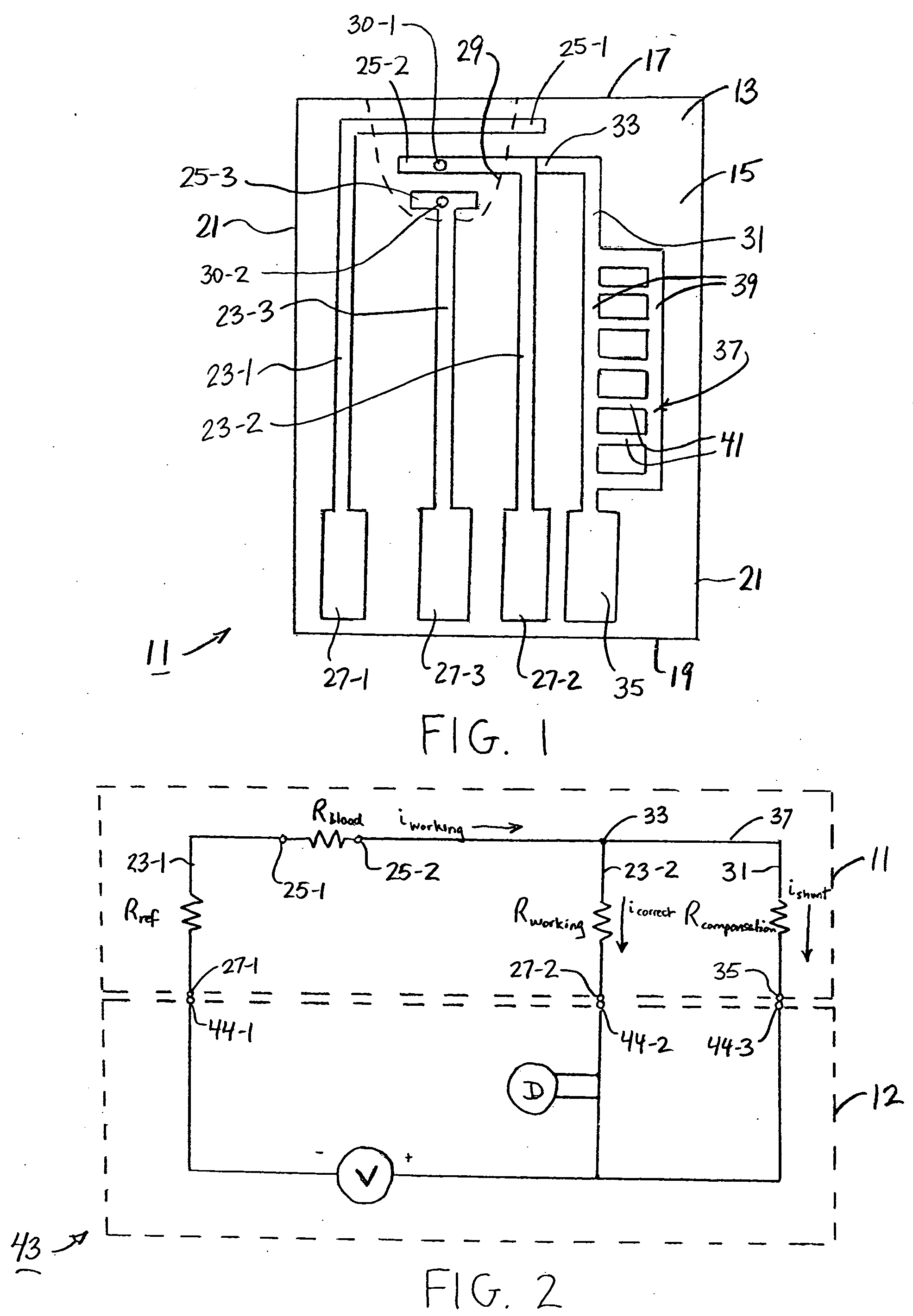
InactiveUS6353324B1Improve performanceLimits of linearityPhotometry electrical circuitsMeasurement using digital techniquesCapacitanceEngineering
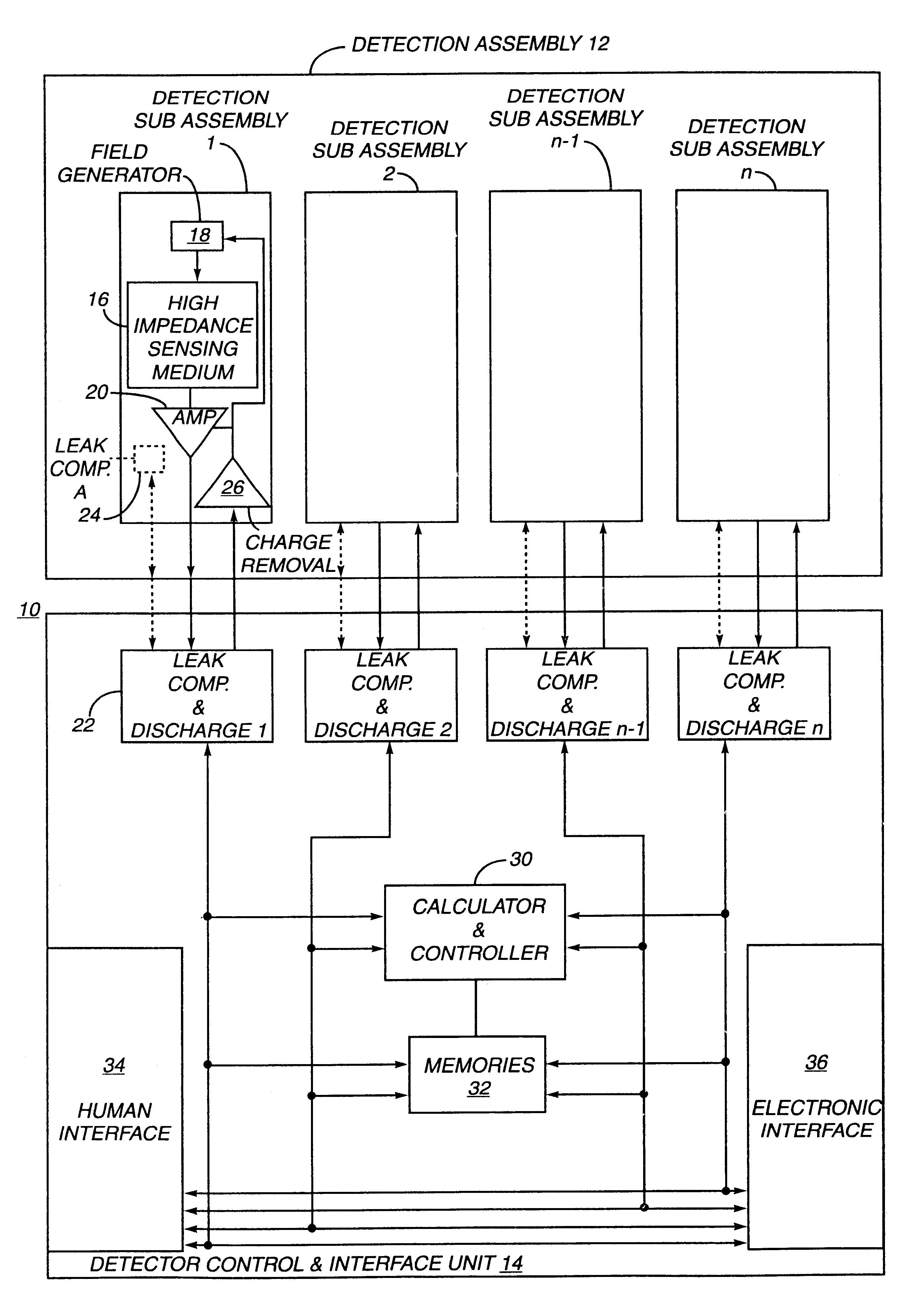
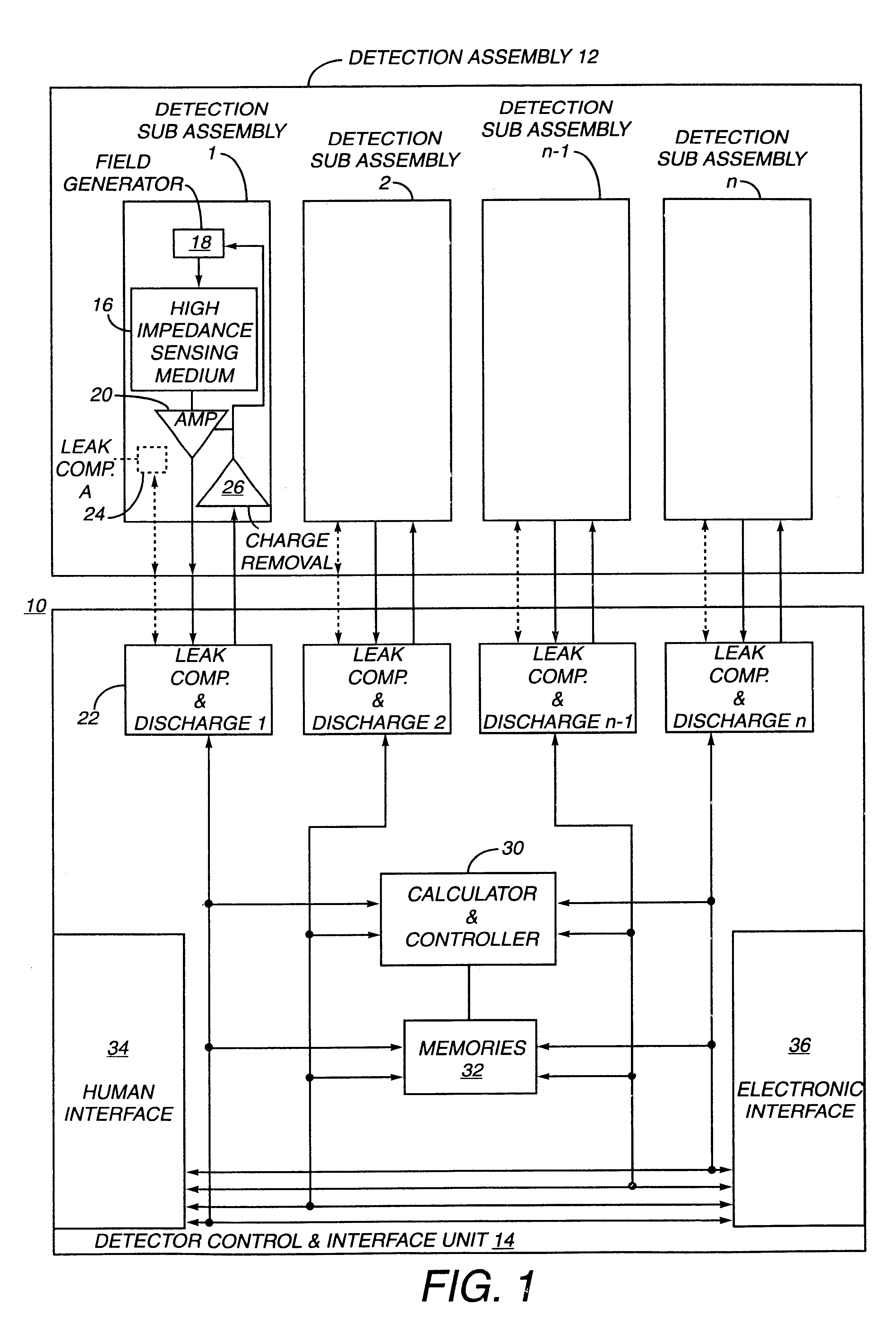
The present invention relates to an electronic circuit and an array of such circuits for precisely measuring small amounts or small changes in the amount of charge, voltage, or electrical currents. One embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic circuit for measuring current or charge that can be used with a variety of sensing media (including high impedance sensing media) that produce a signal by either charge or current production or induction in response to physical phenomena occurring within the sensing media. In another embodiment, the voltage level (bias) of either the sensing or reference electrode can be switched relative to the other upon receipt of a triggering pulse. This changes the polarity of the electric field to cause charge of the opposite polarity to be driven to the sensing electrode, thereby eliminating the need to electrically connect a discharge path to the sensing electrode to clear the charge accumulated at the sensing electrode. This can be supplemented by capacitively coupling a compensation signal to the sensing electrode to cause the amplifier output signal to lessen in magnitude below a threshold level that permits additional charge or current measurements of the same polarity before performing bias reversal. Alternately or in combination with bias reversal and capacitive compensation, sensor performance can be improved by minimizing inaccuracies caused by leakage currents or current drawn from the sensor. Other described methods of reducing leakage currents that can be used alone or in combination with the aforementioned features include the use of guard rings, physical switches or relays, the controlled creation of charges or currents of a specific polarity in a specific region of the sensing medium, controlled leakage over the surface of an insulator, and controlling the environment in which the circuit operates.
Owner:BRIDGE SEMICON
Biosensor with multiple sampling ways
InactiveUS6923894B2Solve the complicated productionEasy to detectImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerOptoelectronics
A biosensor for detecting contents of biochemical components in a sample, comprising an electrically insulating substrate, a working electrode disposed on said substrate, a reference electrode disposed on said substrate, which is spaced from said working electrode, a reaction layer disposed on said working electrode and said reference electrode, wherein said reaction layer and said electrodes form a reaction area for reacting with the sample, an electrically insulating layer disposed on said substrate and having an opening for receiving the sample, wherein said opening exposes a portion of said reaction area and the end of said opening is located at the edge of the biosensor; and a reticular covering layer which covers said opening and the end of said opening of said insulating layer wherein said reticular layer and said insulting layer form a sampling area from said reticular covering area to the edge of said biosensor.
Owner:APEX BIOTECH
Electrochemical methods and devices for use in the determination of hematocrit corrected analyte concentrations
InactiveUS20050176153A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical batteryBlood cell
Methods and devices for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. In the subject methods, the physiological sample is introduced into an electrochemical cell having a working and reference electrode. A first electric potential is applied to the cell and the resultant cell current over a period of time is measured to determine a first time-current transient. A second electric potential of opposite polarity is then applied and a second a time-current transient is determined. The preliminary concentration of the analyte is then calculated from the first and / or second time-current transient. This preliminary analyte concentration less a background value is then multiplied by a hematocrit correction factor to obtain the analyte concentration in the sample, where the hematocrit correction factor is a function of the preliminary analyte concentration and the variable γ of the electrochemical cell. The subject methods and devices are suited for use in the determination of a wide variety of analytes in a wide variety of samples, and are particularly suited for the determination of analytes in whole blood or derivatives thereof, where an analyte of particular interest is glucose.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Fluid-type multiple electrochemical system and preparation thereof
InactiveUS6969451B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityAuxiliary electrode
A fluid-type multiple electrochemical system. The system includes a substrate for an electric circuit having a plurality of electrode parts formed at regular intervals. The electrode parts each include a reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode. Also provided is a fluid-type substrate having a fluid injection part, a fluid ejection part and a plurality of fluid storages. The fluid storages are formed at the same regular intervals as the electrode parts of the substrate and are connected with each other through fluid passages. The system also includes a sensor substrate having a plurality of unit sensors formed at the same regular intervals as the electrode parts of the substrate. Each unit sensor has an electrode part, an electrode pad for supplying power voltage simultaneously, and an electrode wiring.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
FET-based sensor for detecting ionic material, ionic material detecting device using the FET-based sensor, and method of detecting ionic material using the FET-based sensor
ActiveUS7859029B2Reduce concentrationHigh sensitivityDrying solid materials without heatSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectric current
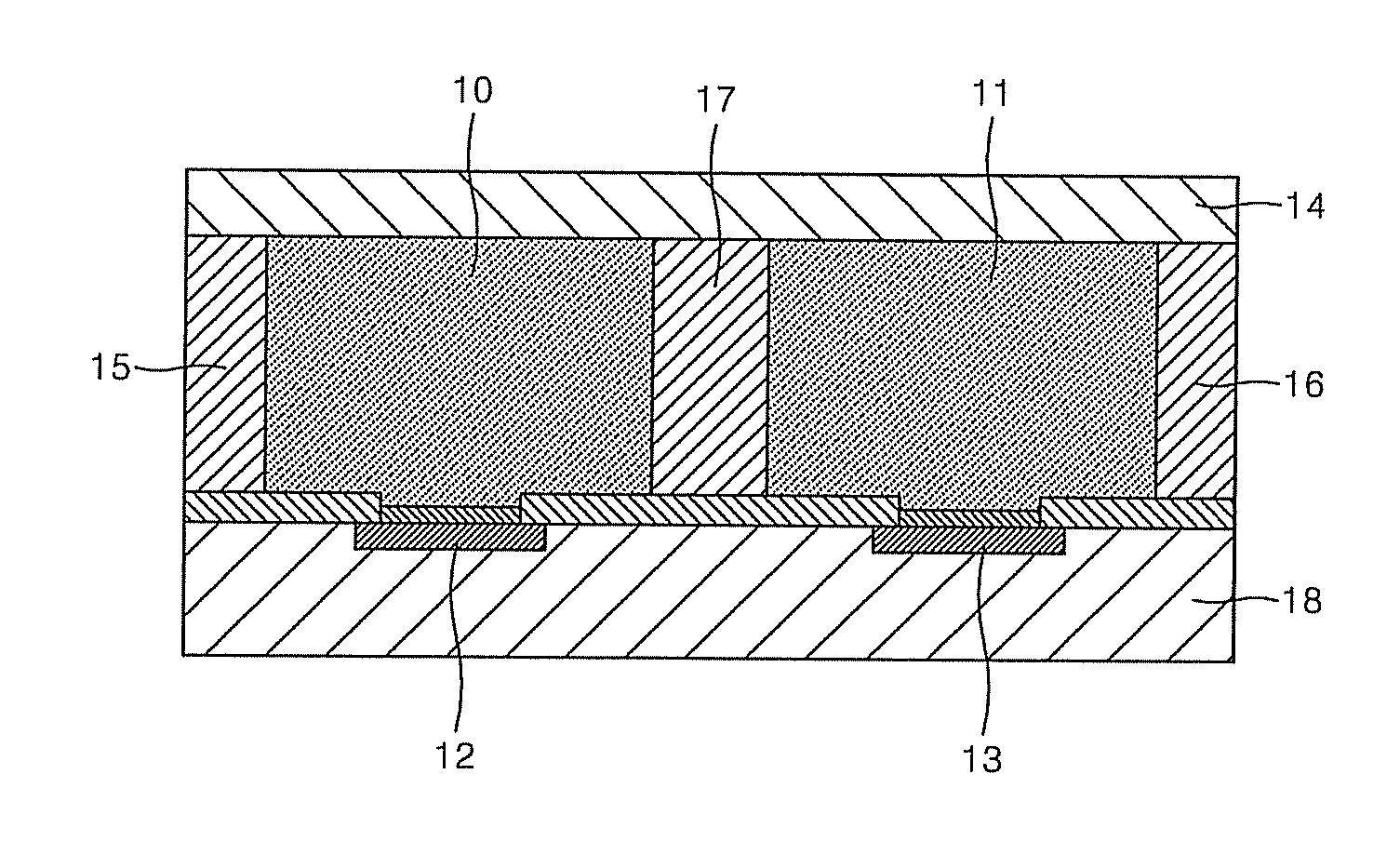
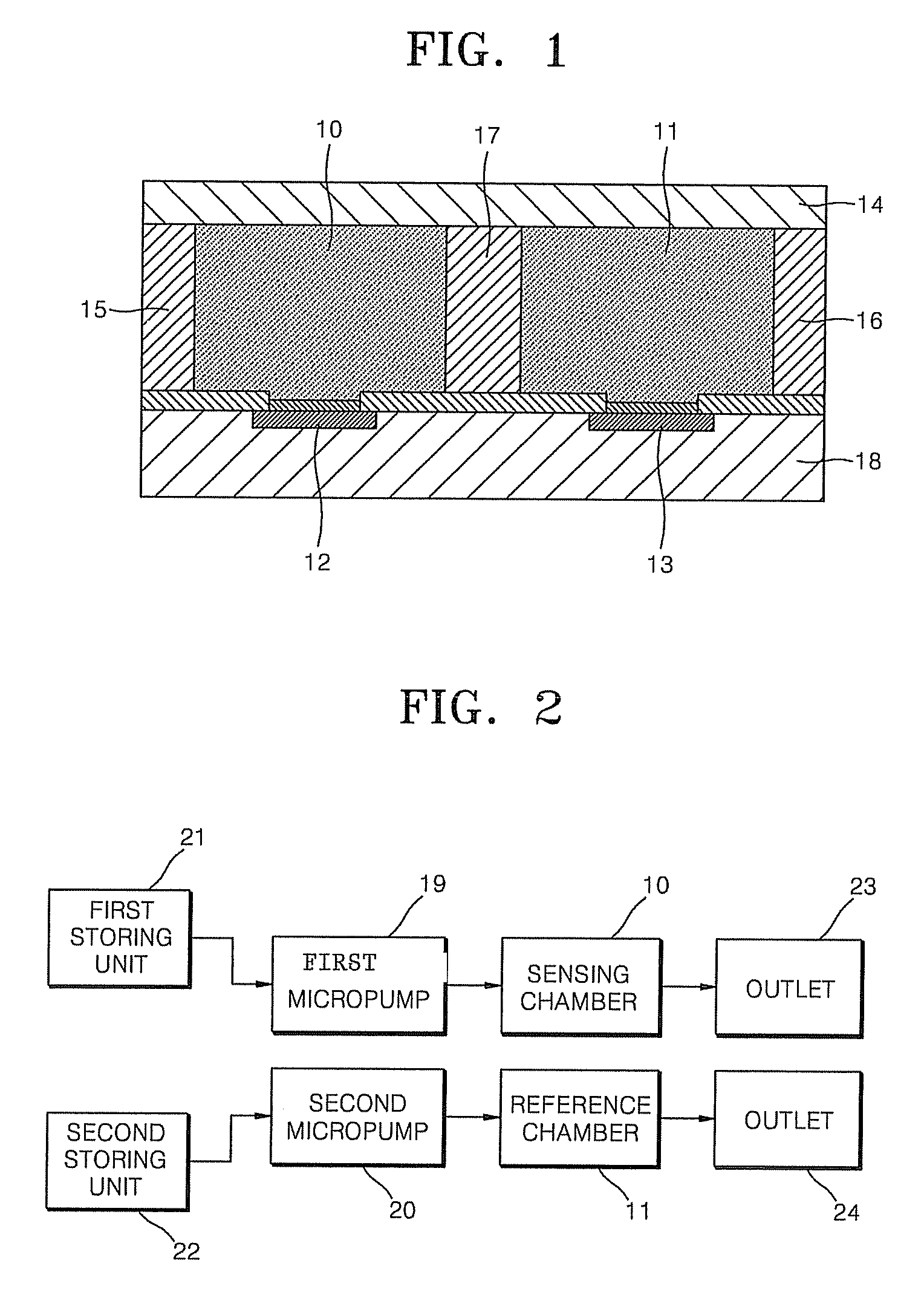
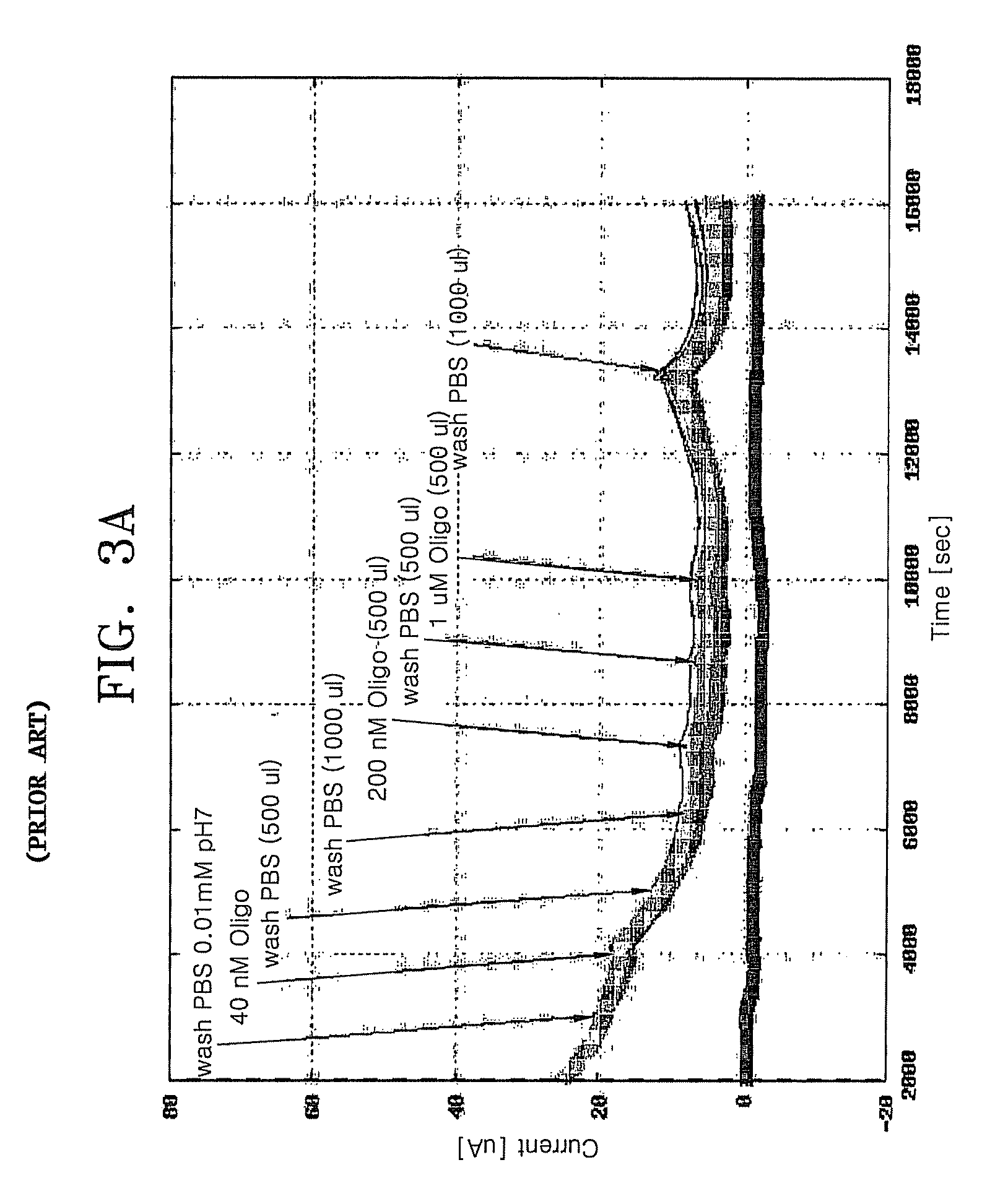
Provided are a FET-based sensor for detecting an ionic material, an ionic material detecting device including the FET-based sensor, and a method of detecting an ionic material using the FET-based sensor. The FET-based sensor includes: a sensing chamber including a reference electrode and a plurality of sensing FETs; and a reference chamber including a reference electrode and a plurality of reference FETs. The method includes: flowing a first solution into and out of the sensing chamber and the reference chamber of the FET-based sensor; flowing a second solution expected to contain an ionic material into and out of the sensing chamber while continuously flowing the first solution into and out of the reference chamber; measuring a current in a channel region between the source and drain of each of the sensing and reference FETs; and correcting the current of the sensing FETs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gene detection field-effect device and method of analyzing gene polymorphism therewith
ActiveUS7695907B2High degreeReduction of size and costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesBiology
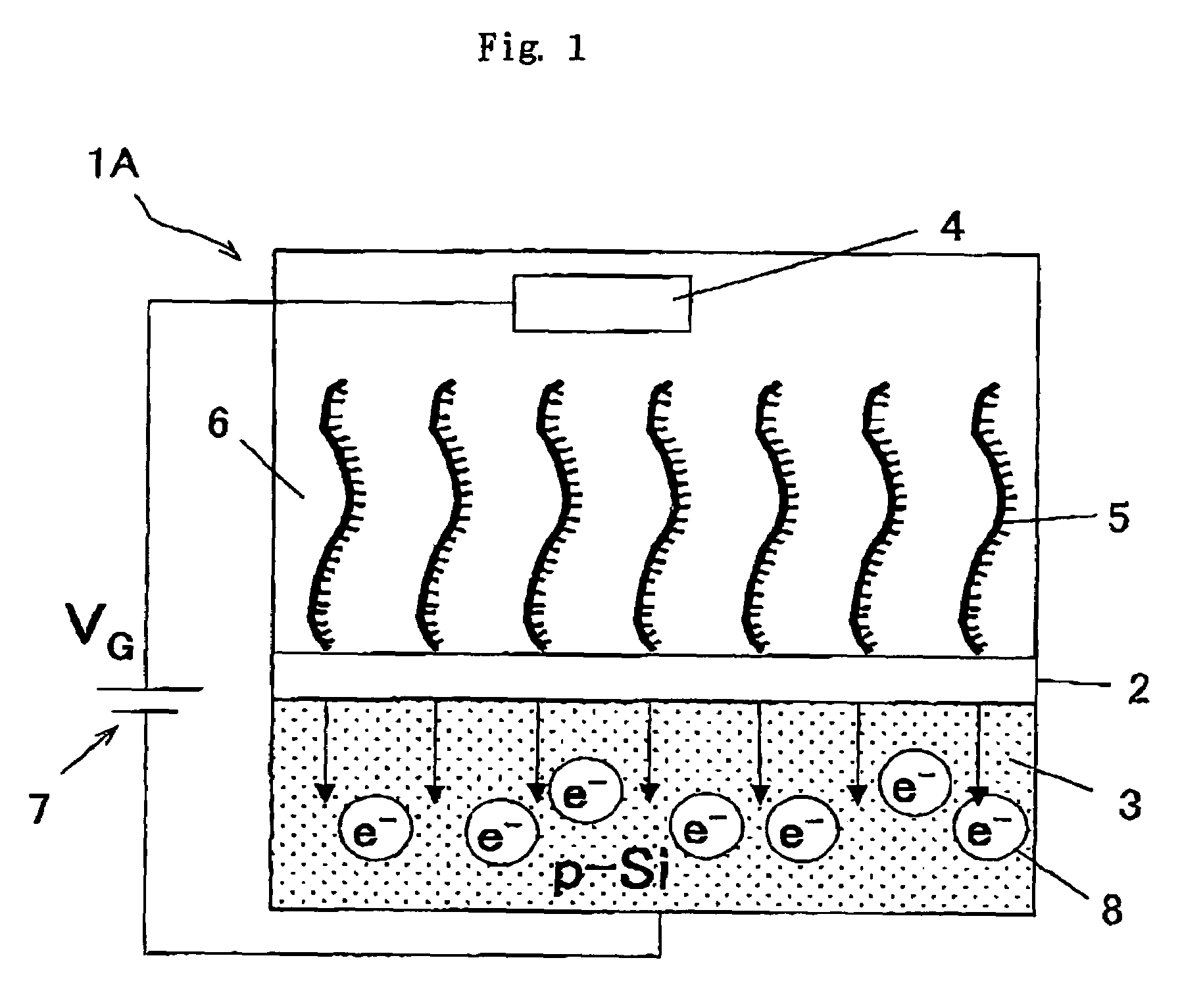
A gene detection field-effect device provided with an insulation film (2), a semiconductor substrate (3), and a reference electrode (4), includes: (a) the insulation film (2) including a nucleic acid probe (5) immobilized on one of the surfaces thereof and is in contact with a sample solution (6) containing at least one type of a target gene (601) for detection and analysis; (b) the semiconductor substrate (3) being installed so as to abut against the other surface of the insulation film (2); and (c) the reference electrode (4) being provided in the sample solution (6).
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Nanopost arrays and process for making same
InactiveUS6185961B1Efficient depositionEfficiently magnetic materialNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismNanopillarEngineering
A nanopost glass array contains up to 1012 / cm2 of magnetizable nanoposts having diameter of 10-1000 nm that are straight and parallel to each other and are typically of a uniform diameter relative to each other and along the post length. The array is made using a reference electrode and a nanochannel glass template structure connected to each other electrically through an electrical source and both disposed in a plating solution. A magnetizable material is electroplated from the plating solution into the channels of the template structure.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com