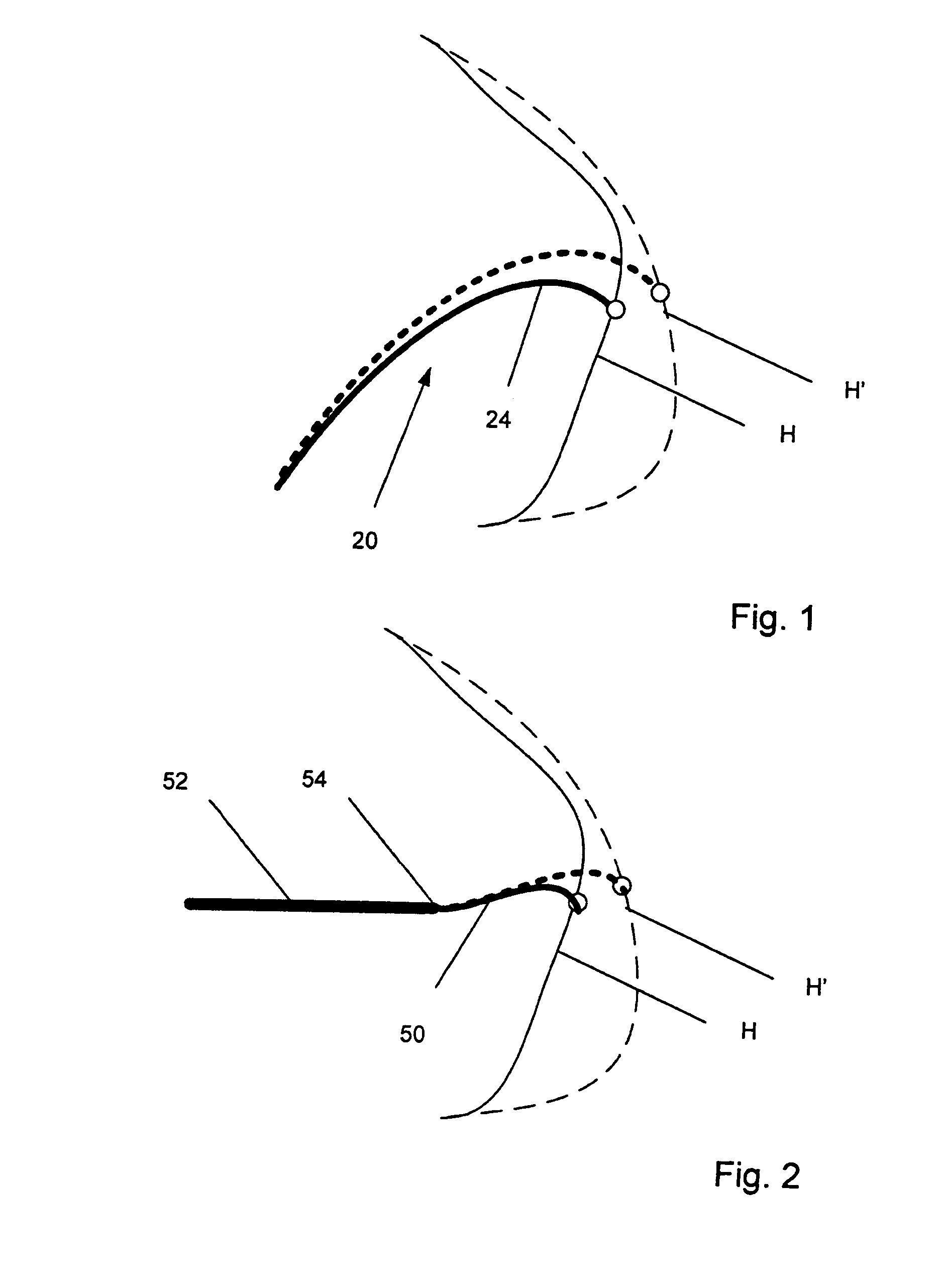
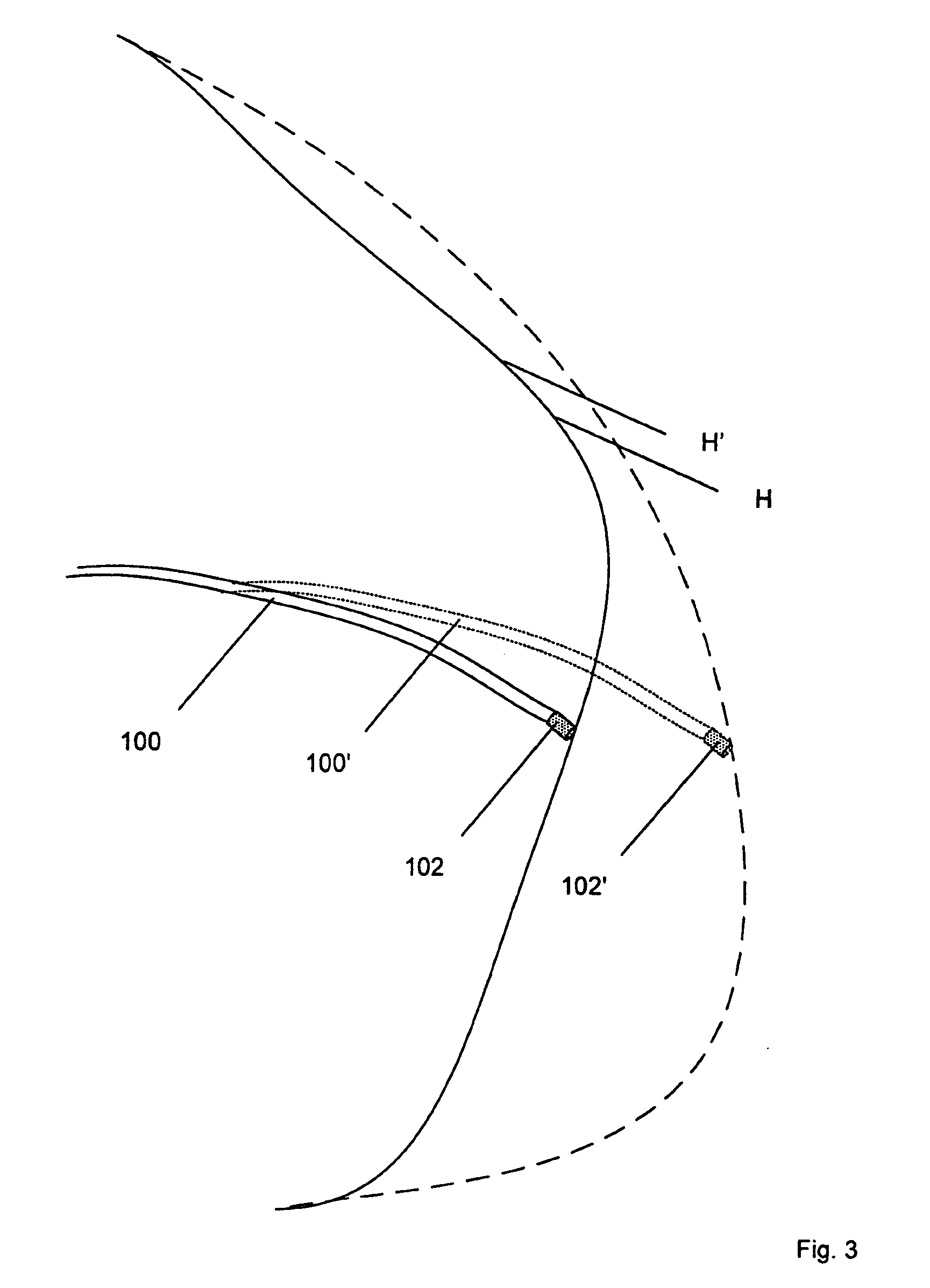
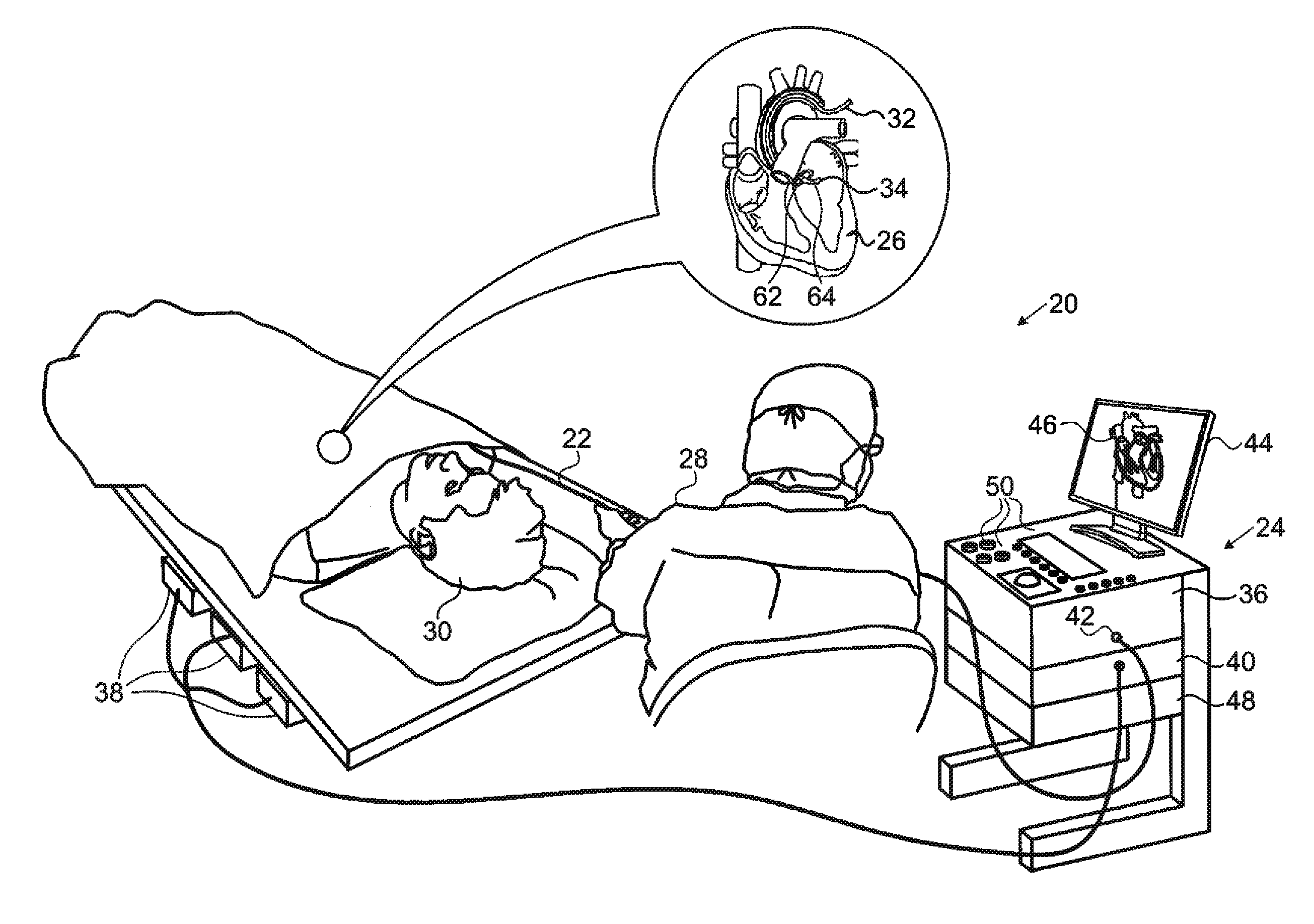
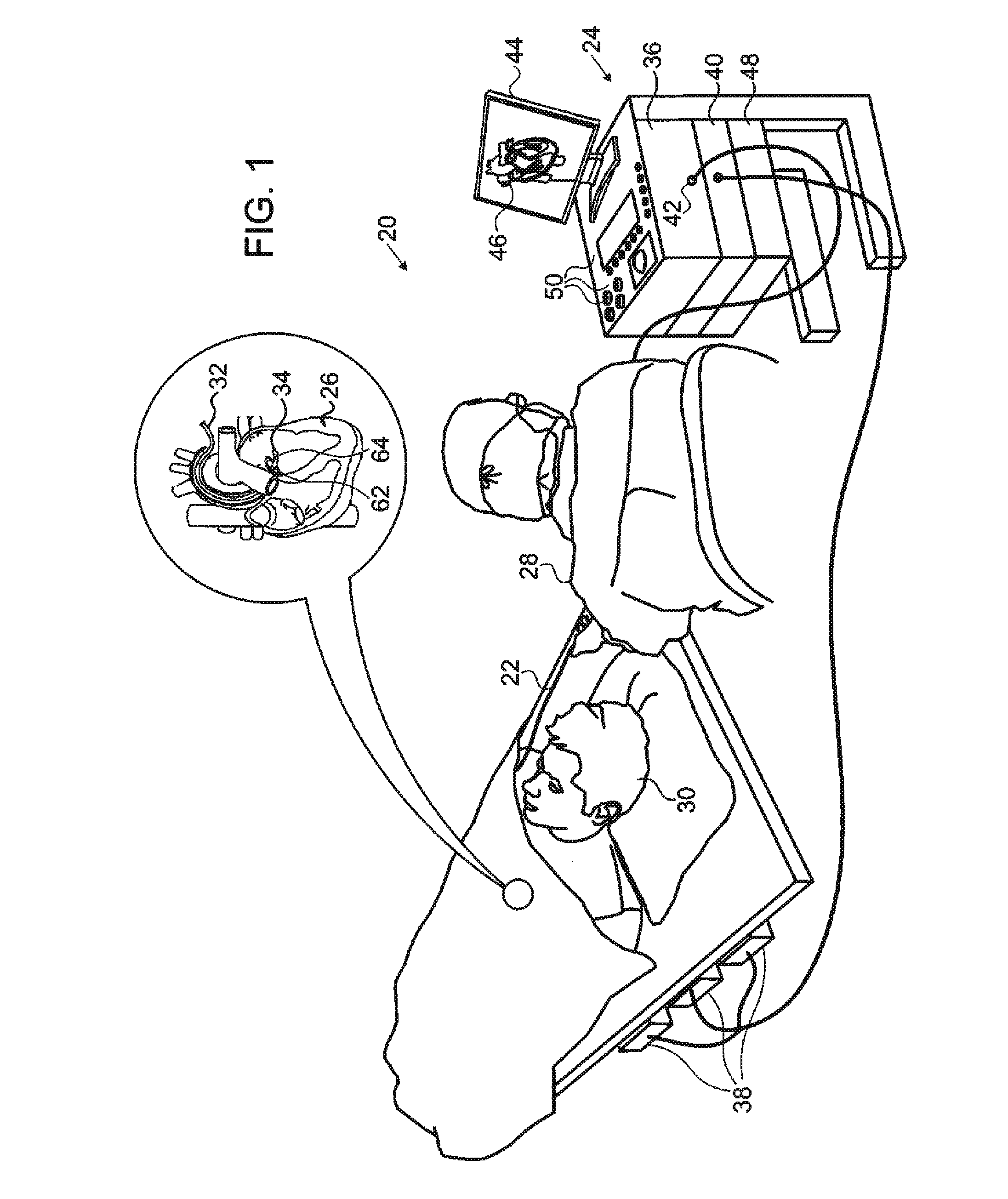
Patents
Literature
71 results about "Cell electrophysiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, "amber" [see the etymology of "electron"]; φύσις, physis, "nature, origin"; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues.
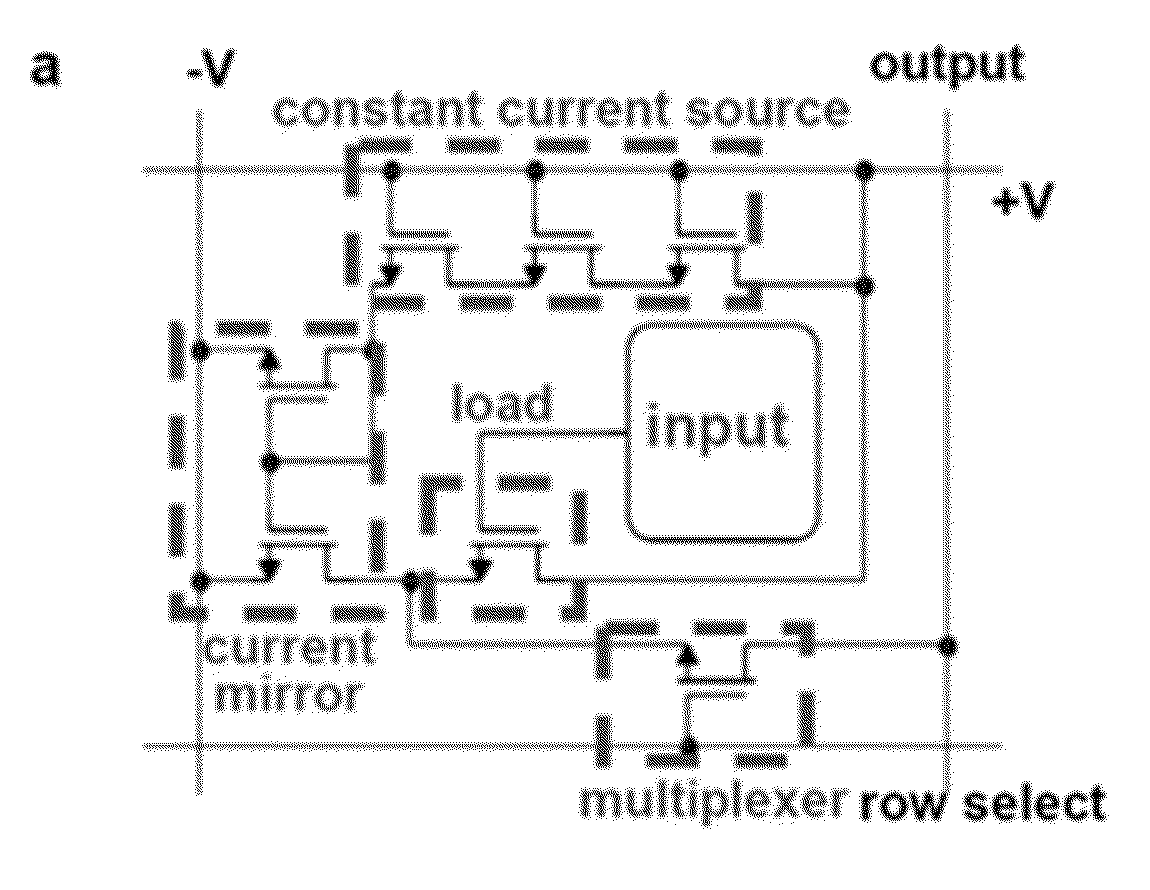
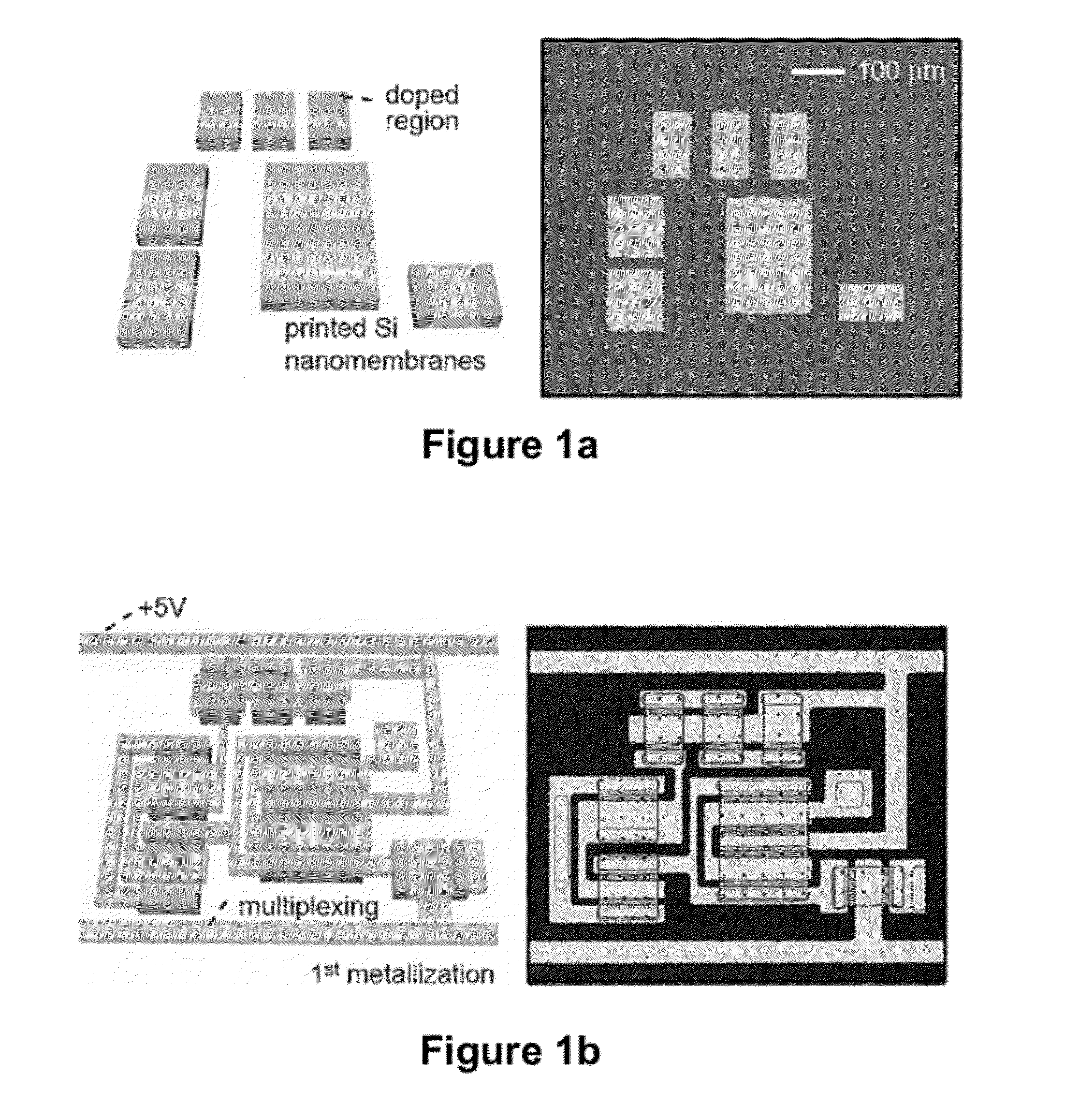
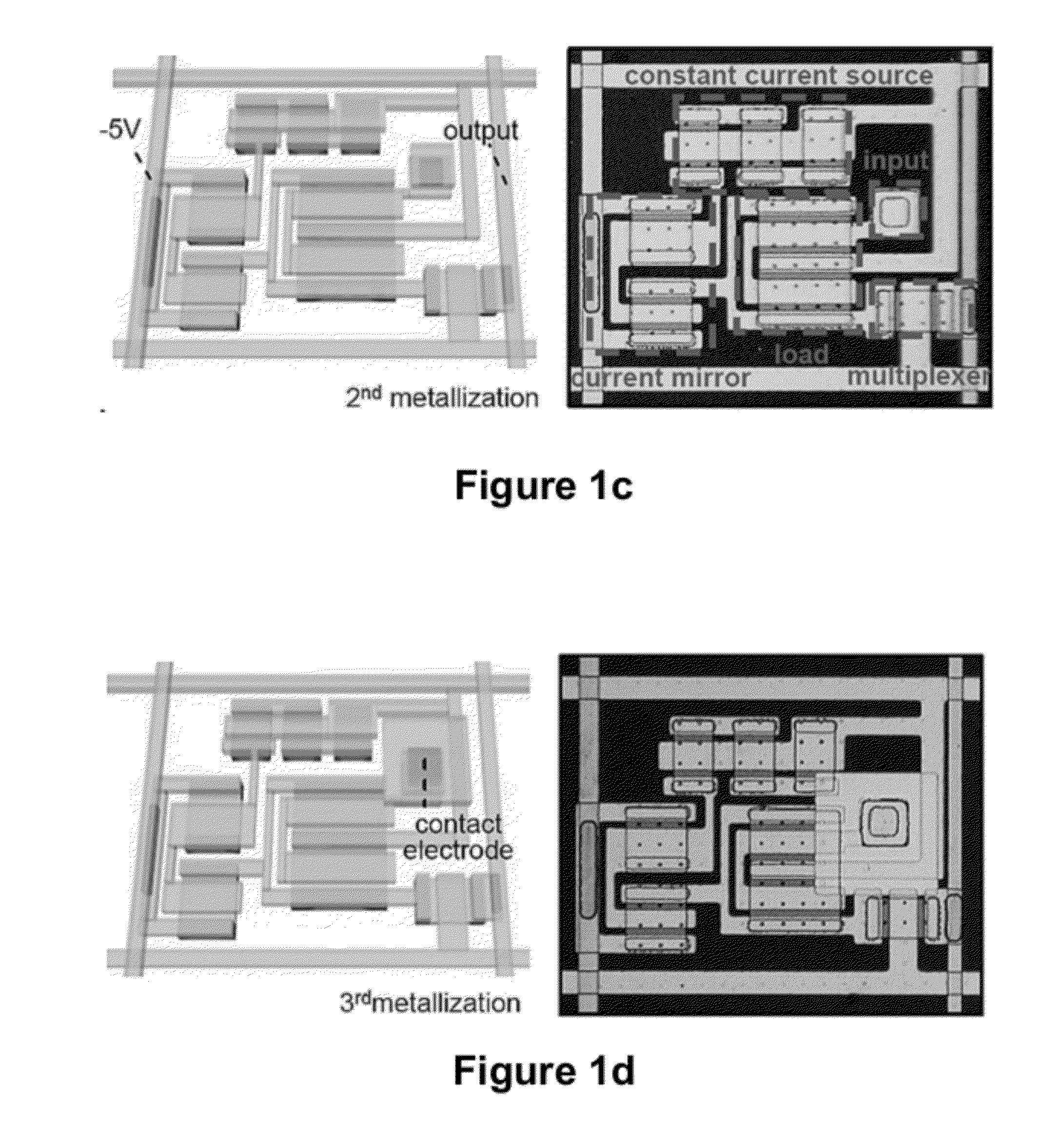
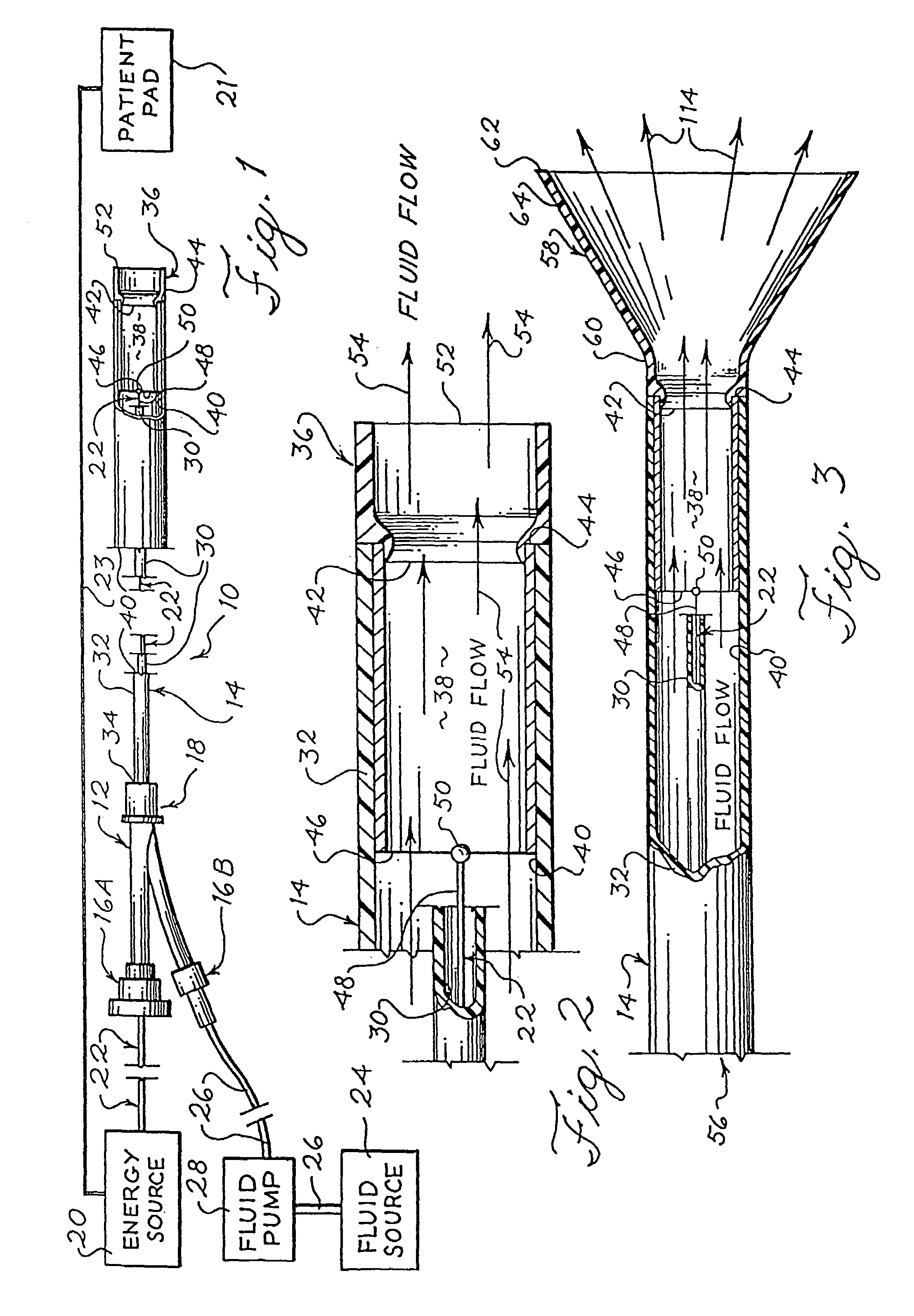
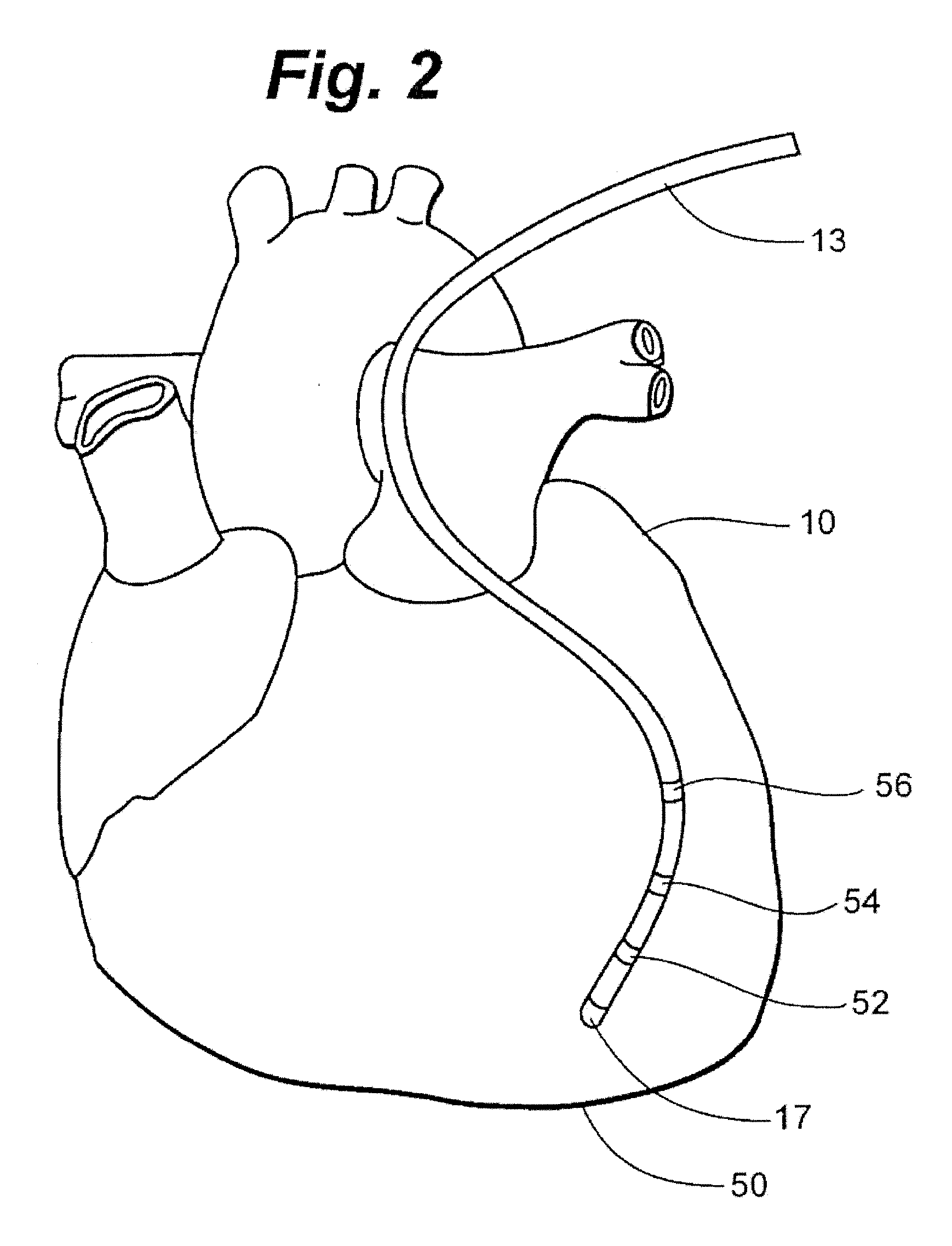
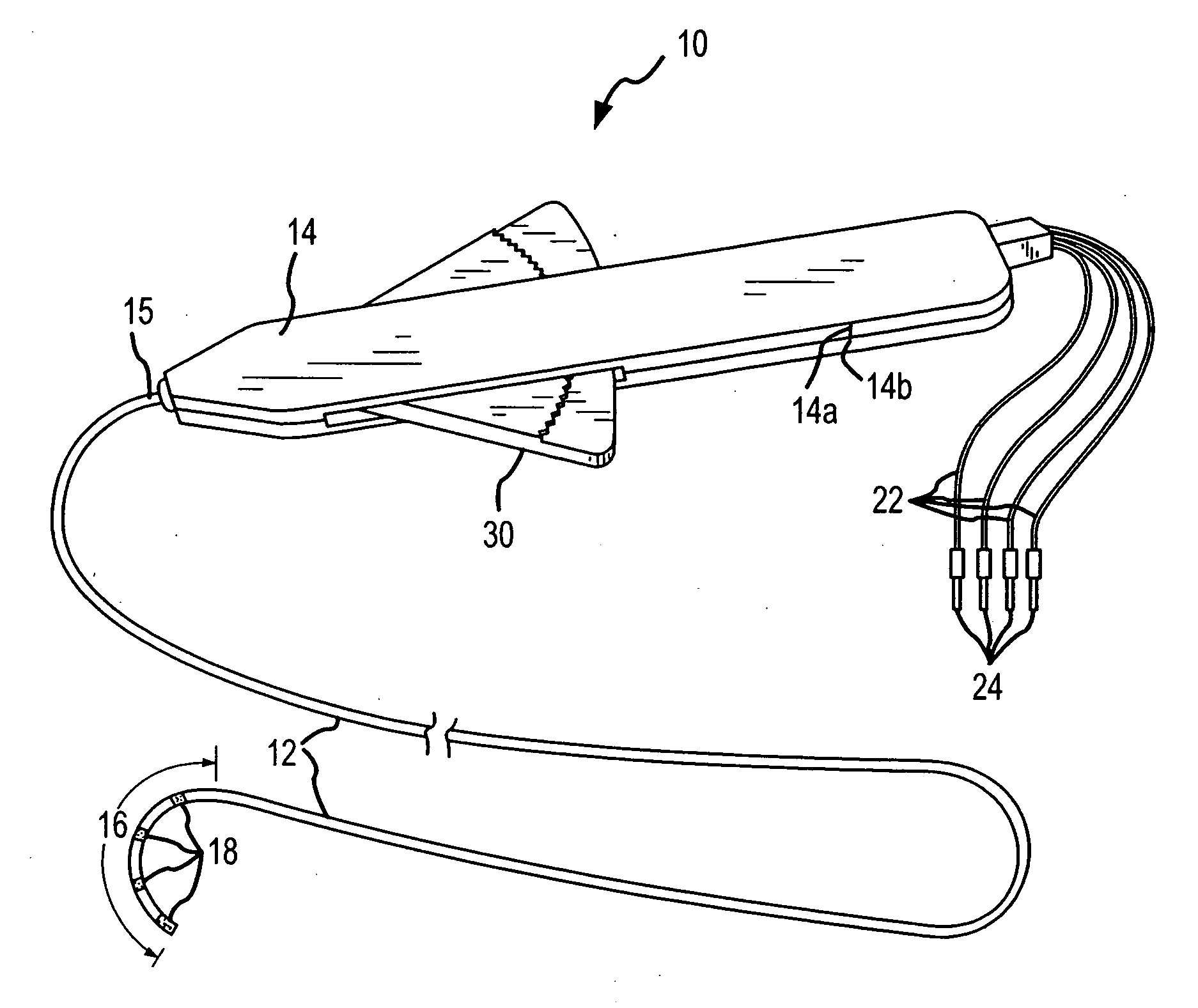
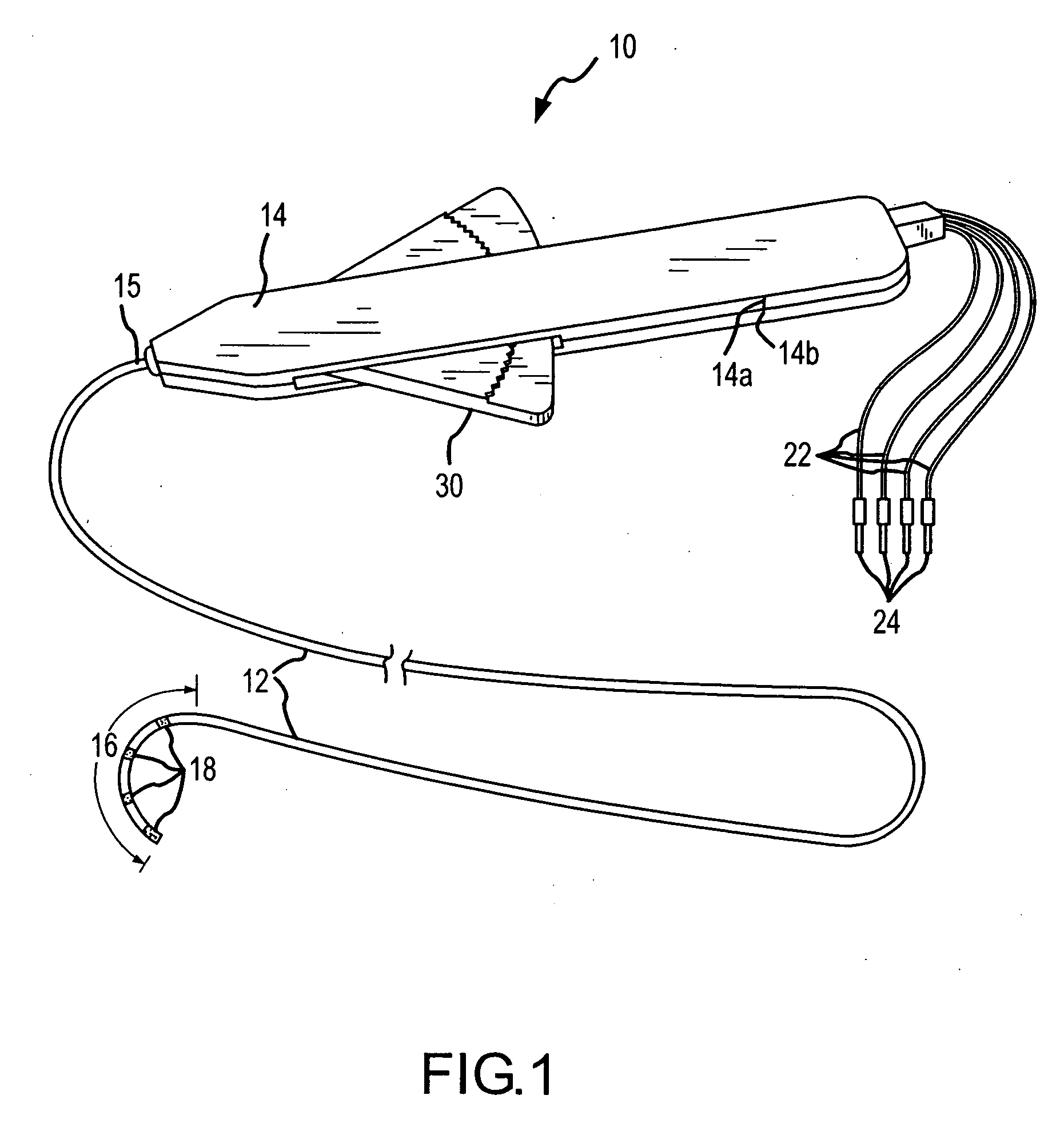
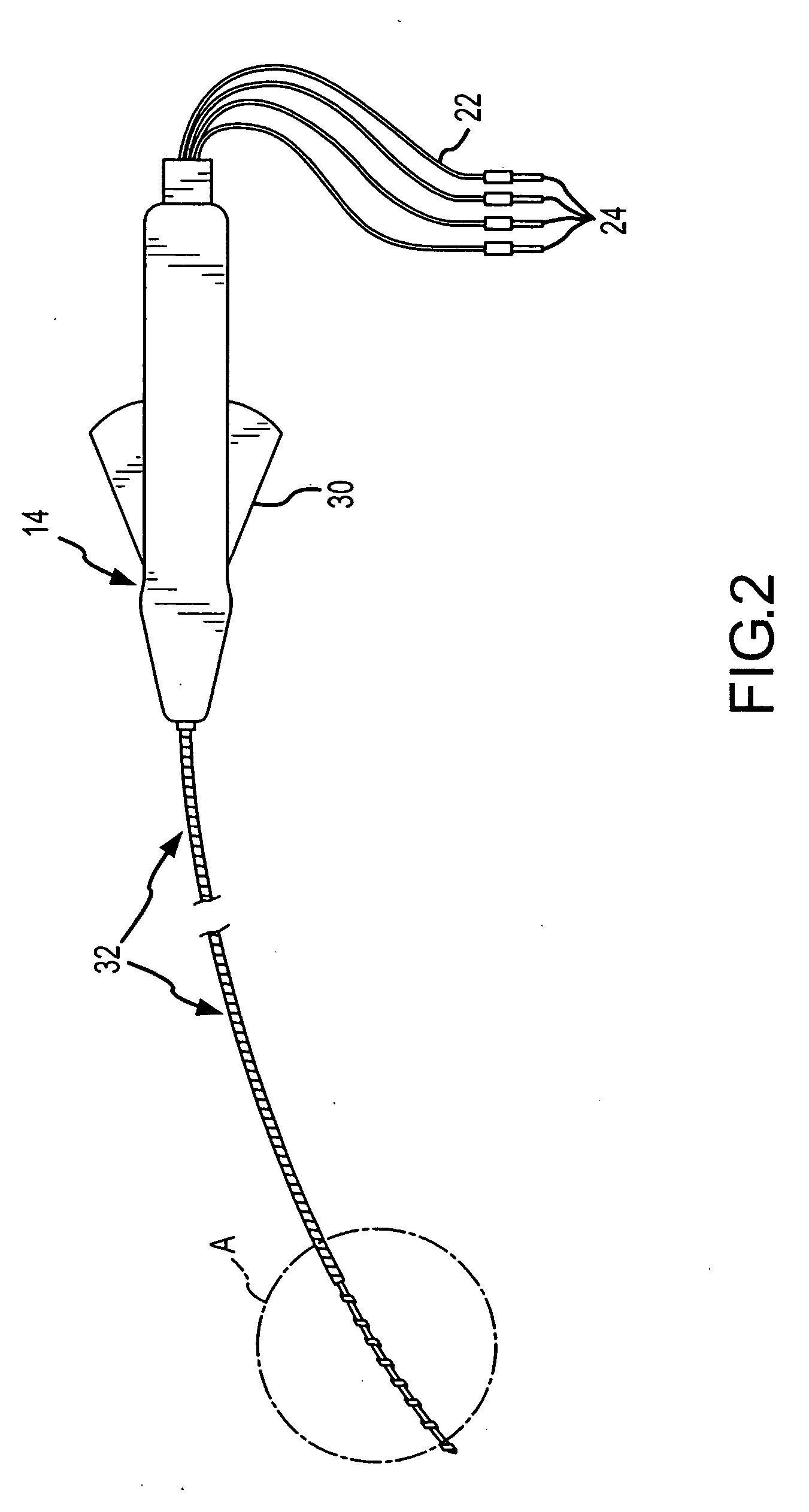
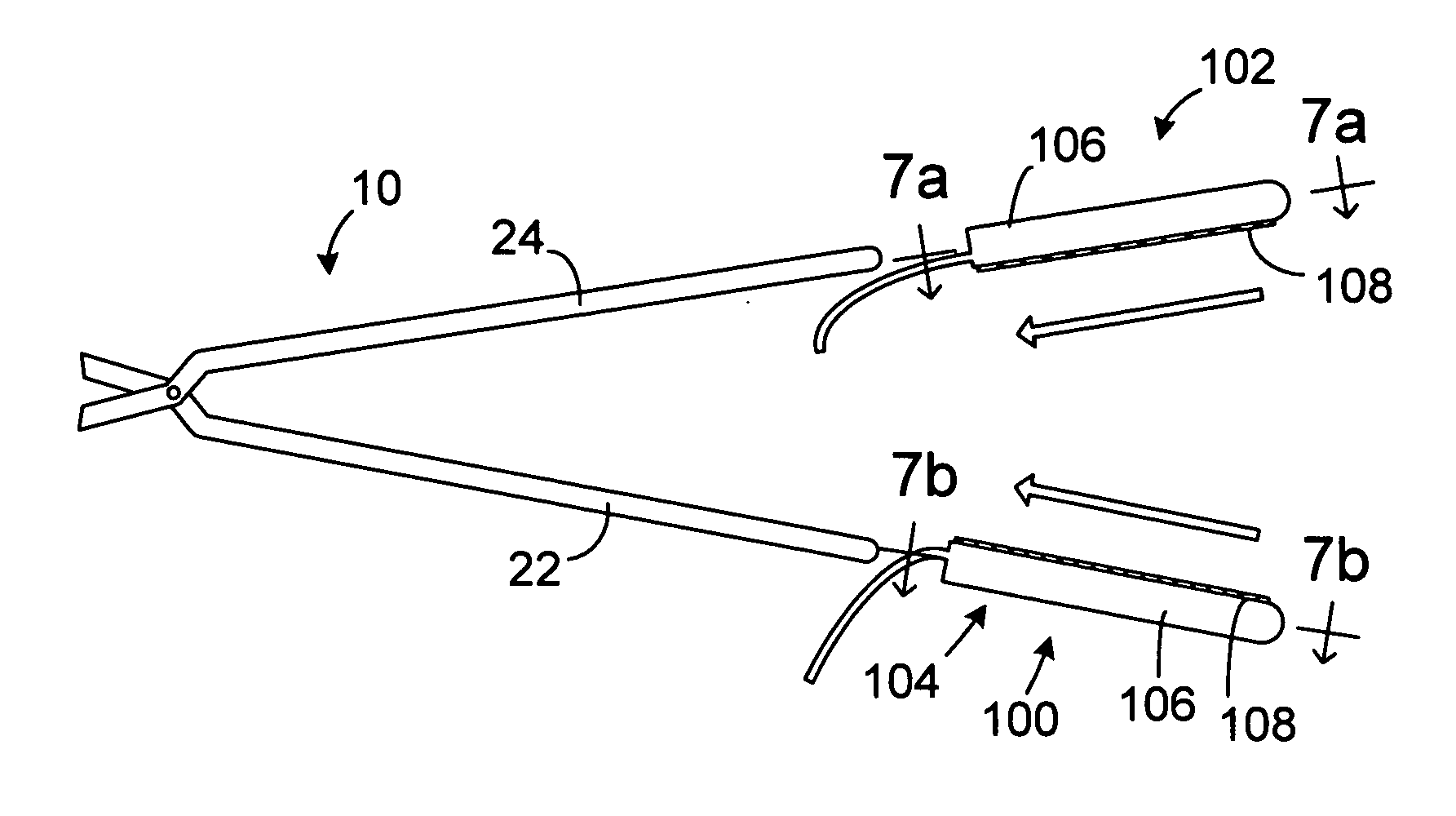
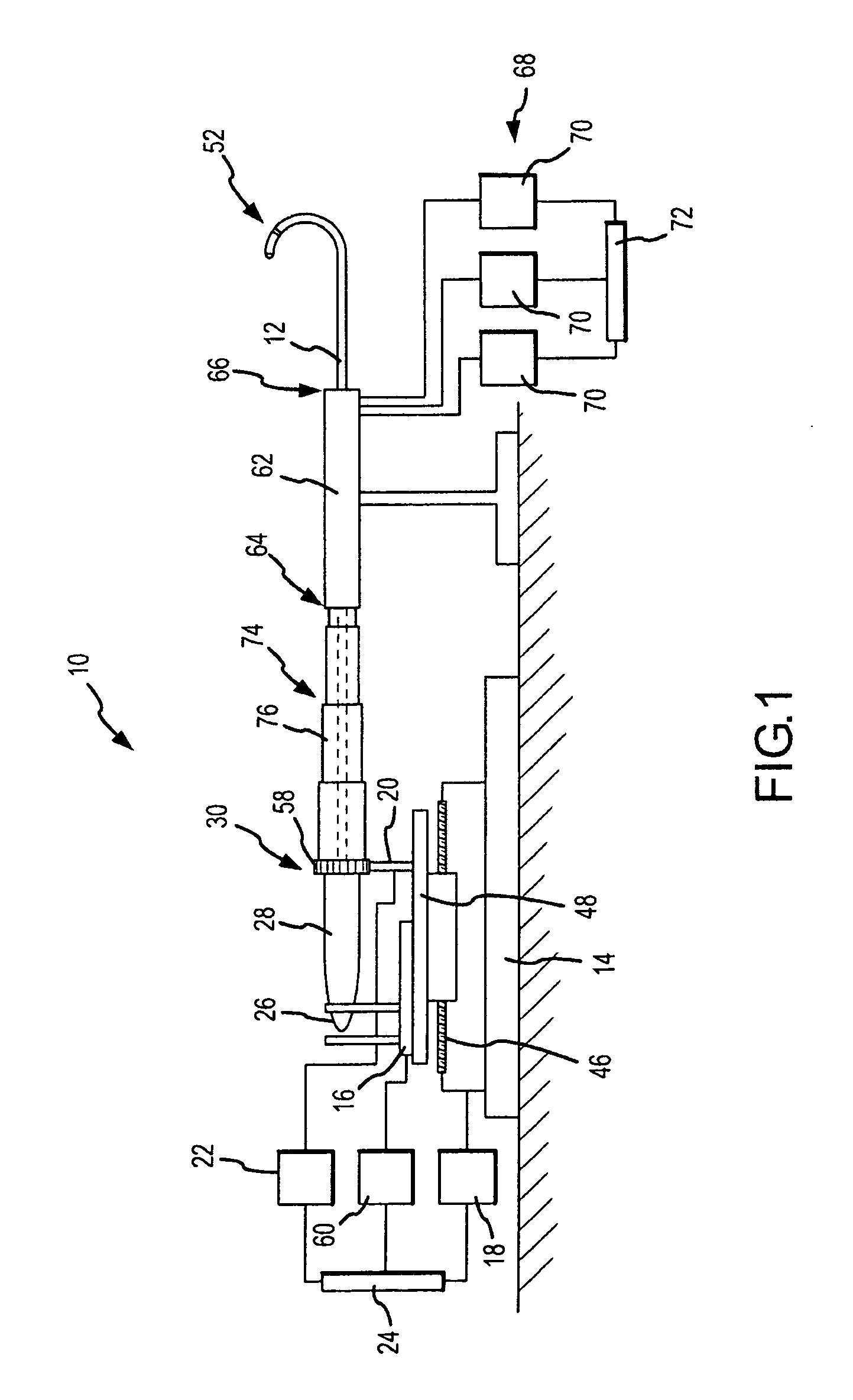
High-Speed, High-Resolution Electrophysiology In-Vivo Using Conformal Electronics
ActiveUS20120157804A1Limit leakage currentLow bending stiffnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIn vivoCell electrophysiology
Provided herein are biomedical devices and methods of making and using biomedical devices for sensing and actuation applications. For example, flexible and / or stretchable biomedical devices are provided including electronic devices useful for establishing in situ conformal contact with a tissue in a biological environment. The invention includes implantable electronic devices and devices administered to the surfaces(s) of a target tissue, for example, for obtaining electrophysiology data from a tissue such as cardiac, brain tissue or skin.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
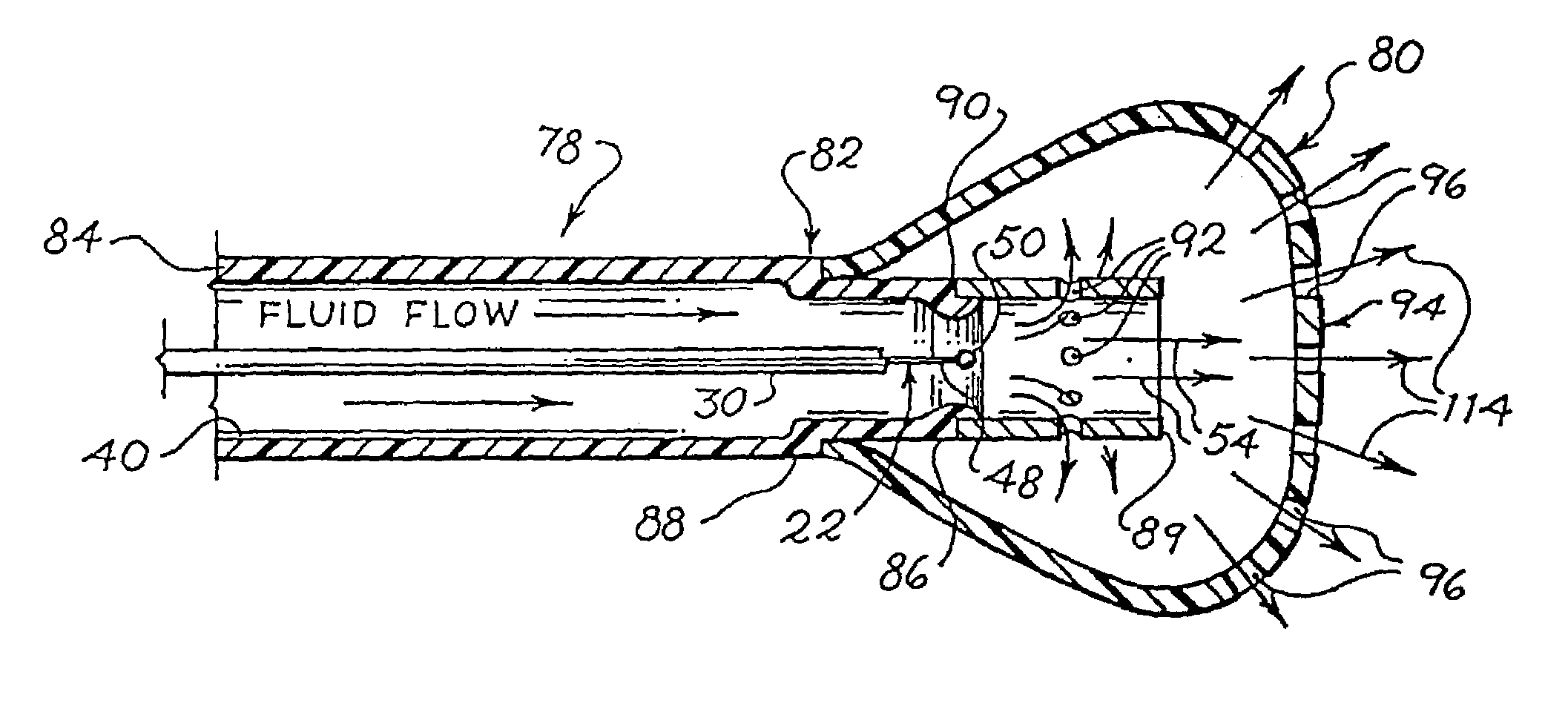
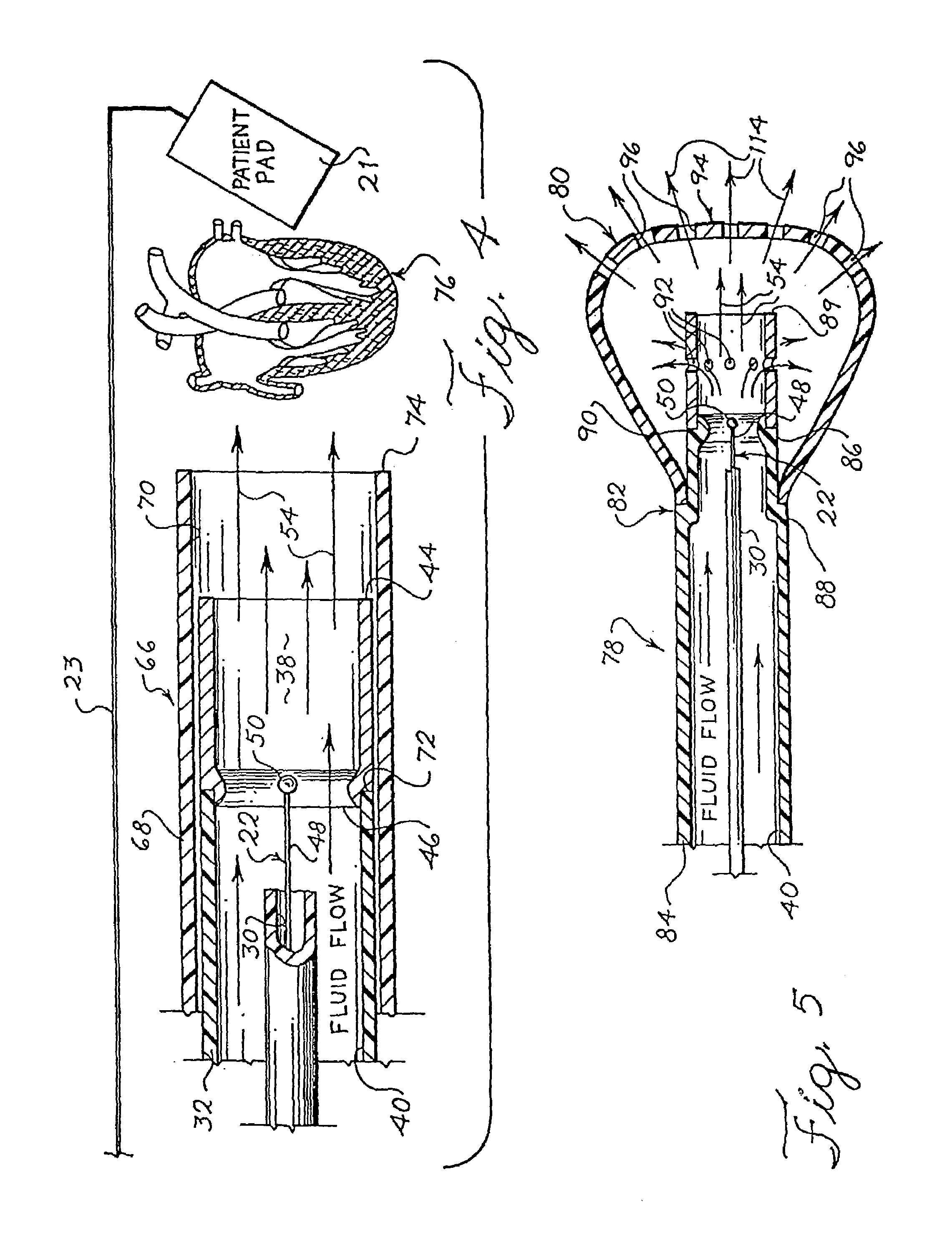
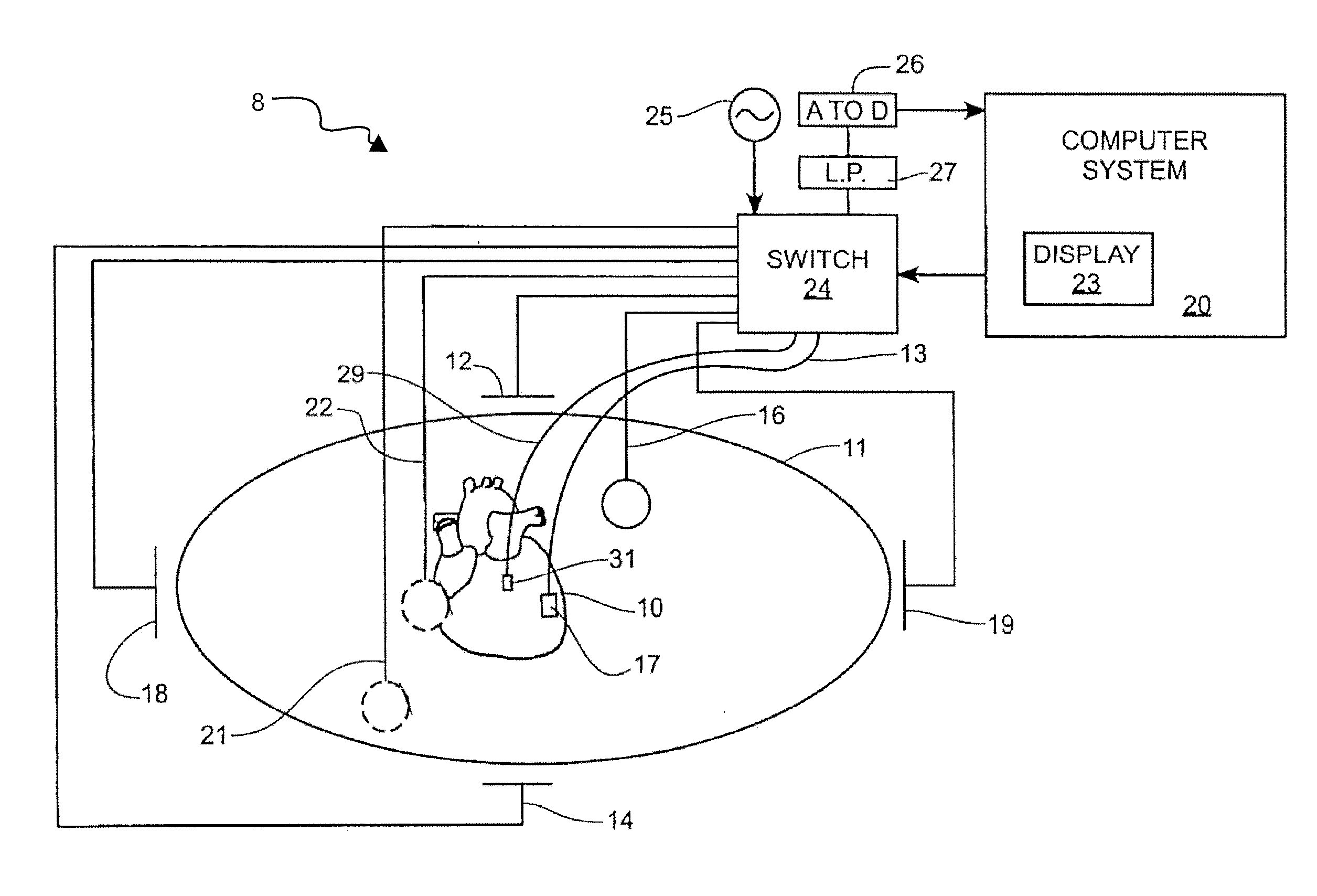
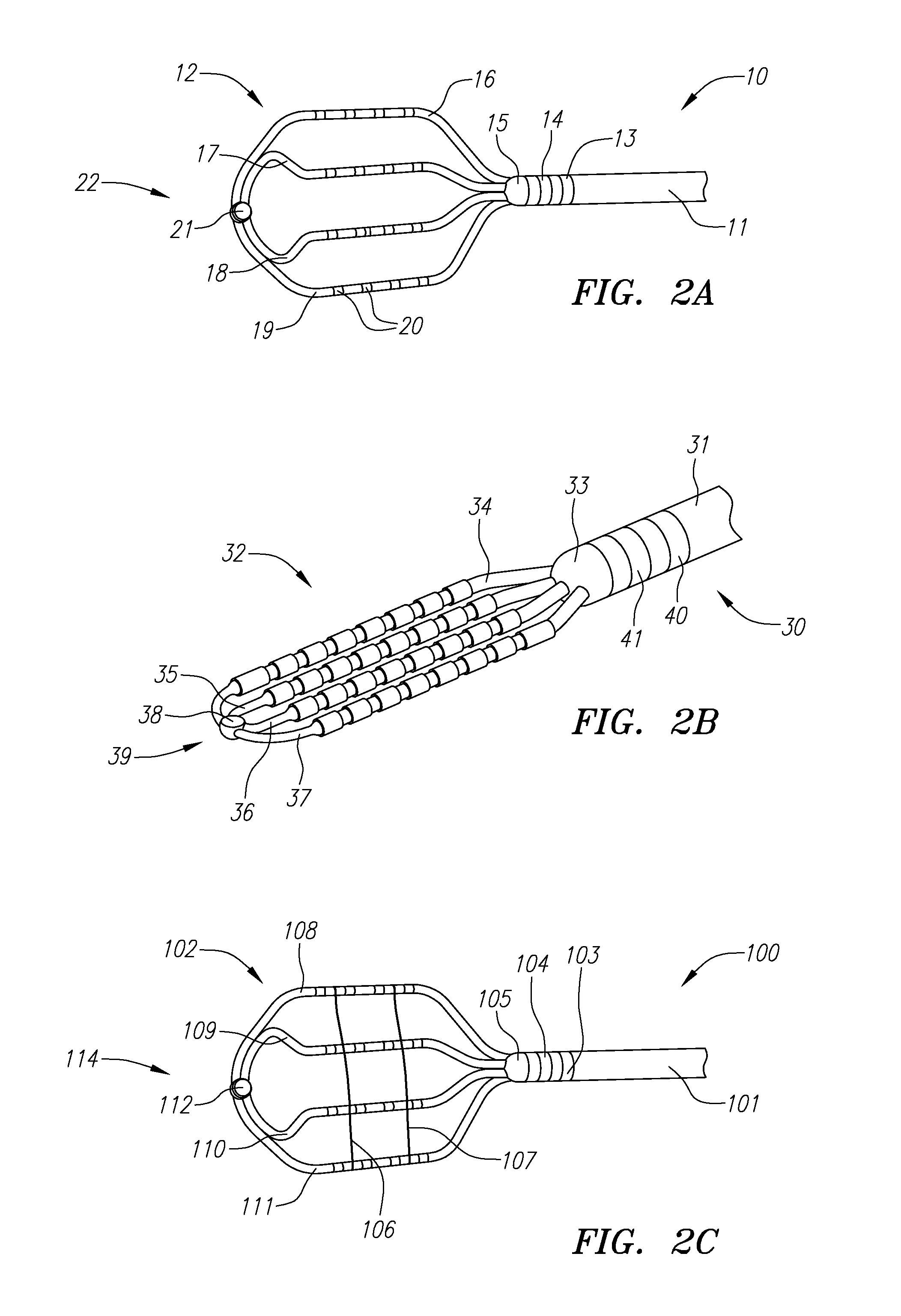
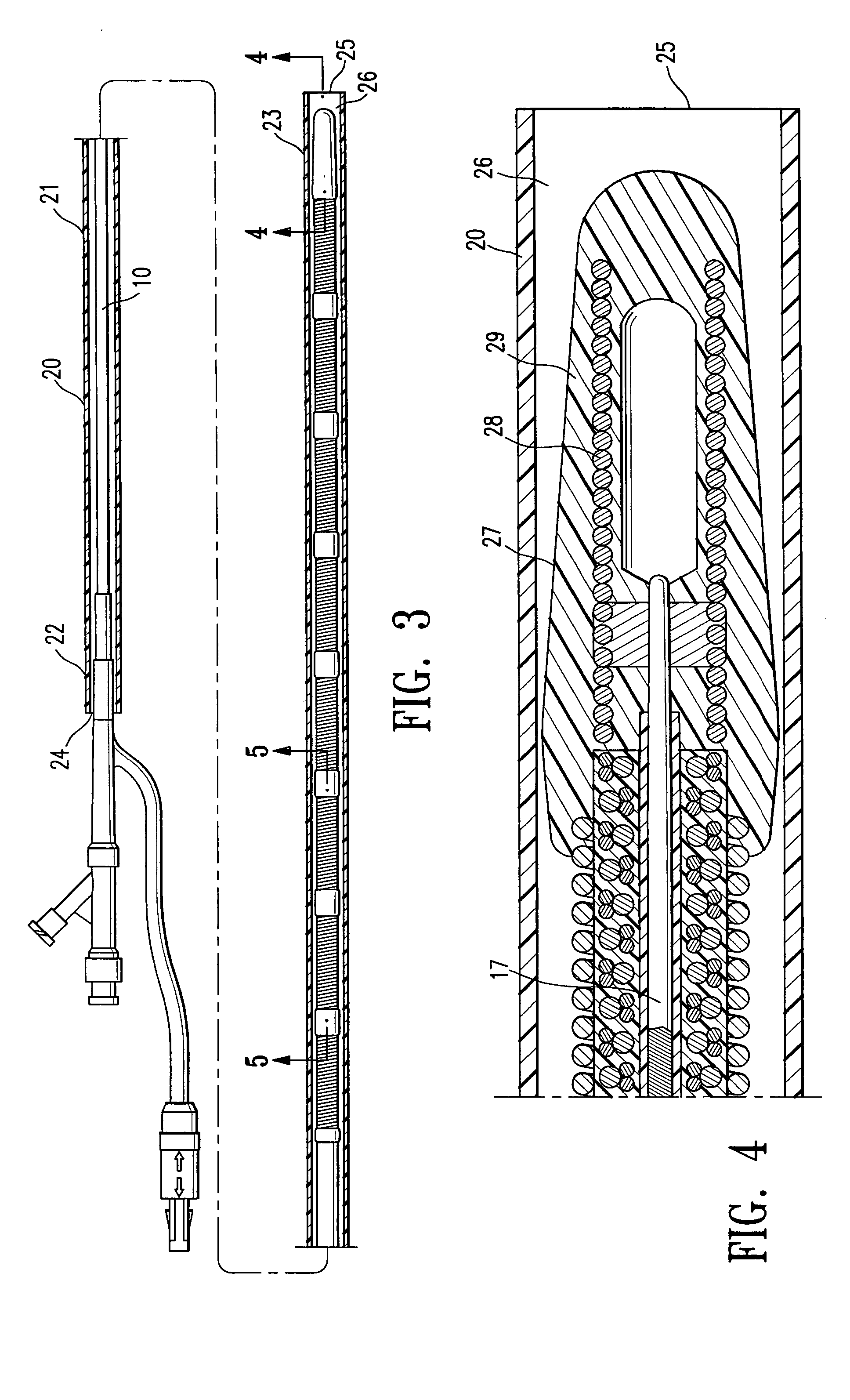
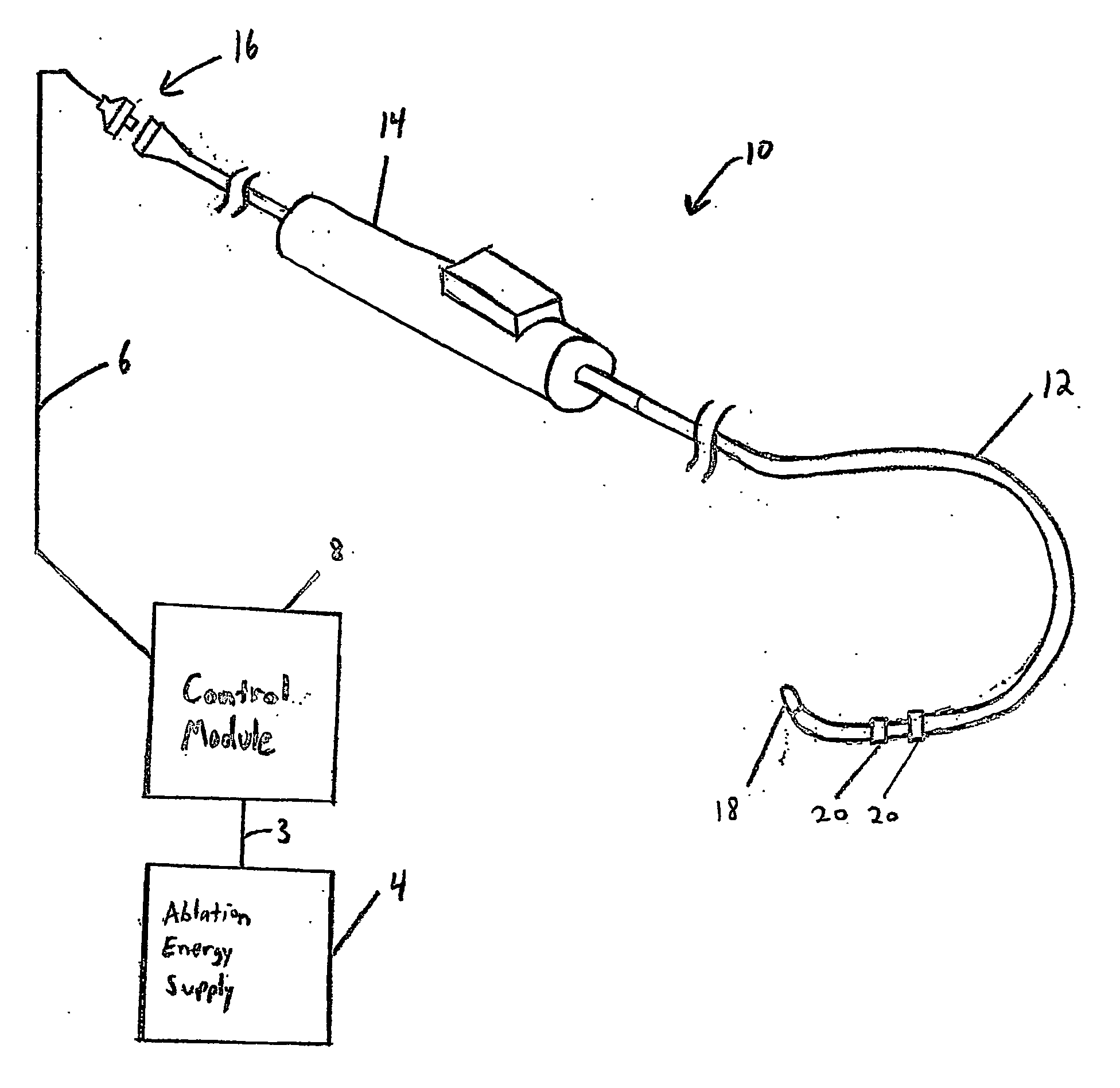
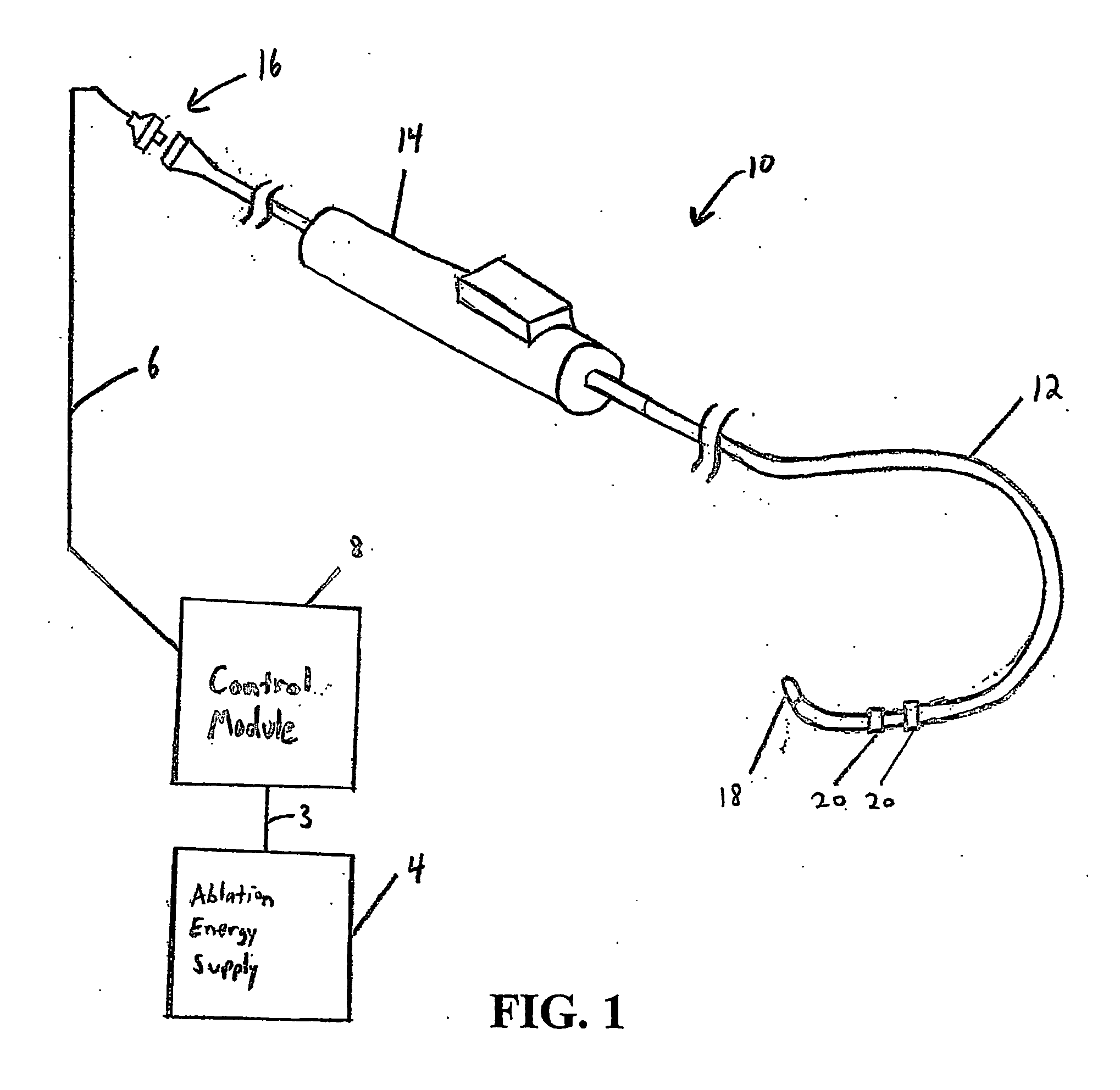
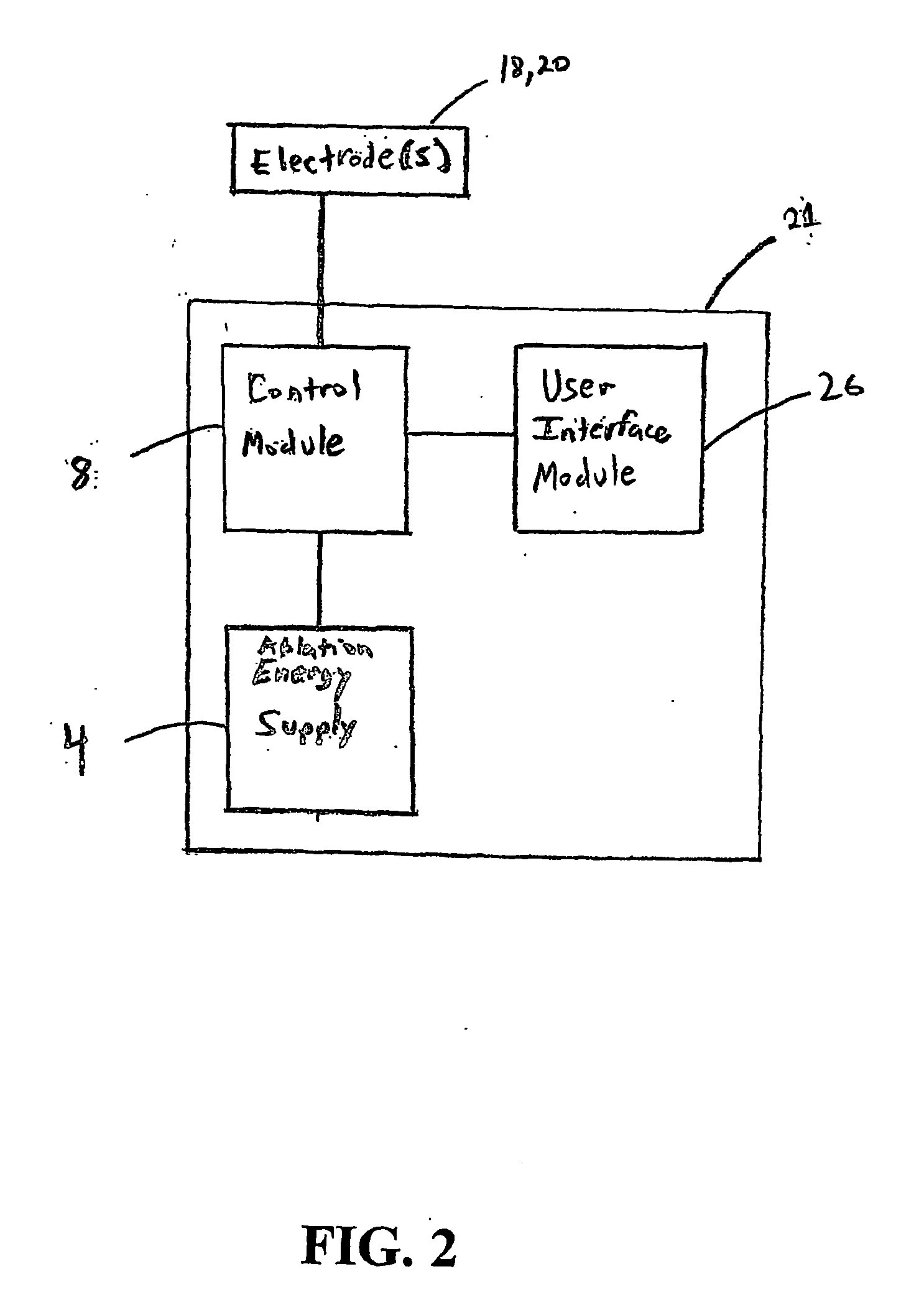
Electrophysiology energy treatment devices and methods of use
InactiveUS6923805B1Easy maintenanceElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingDistal portionCell electrophysiology
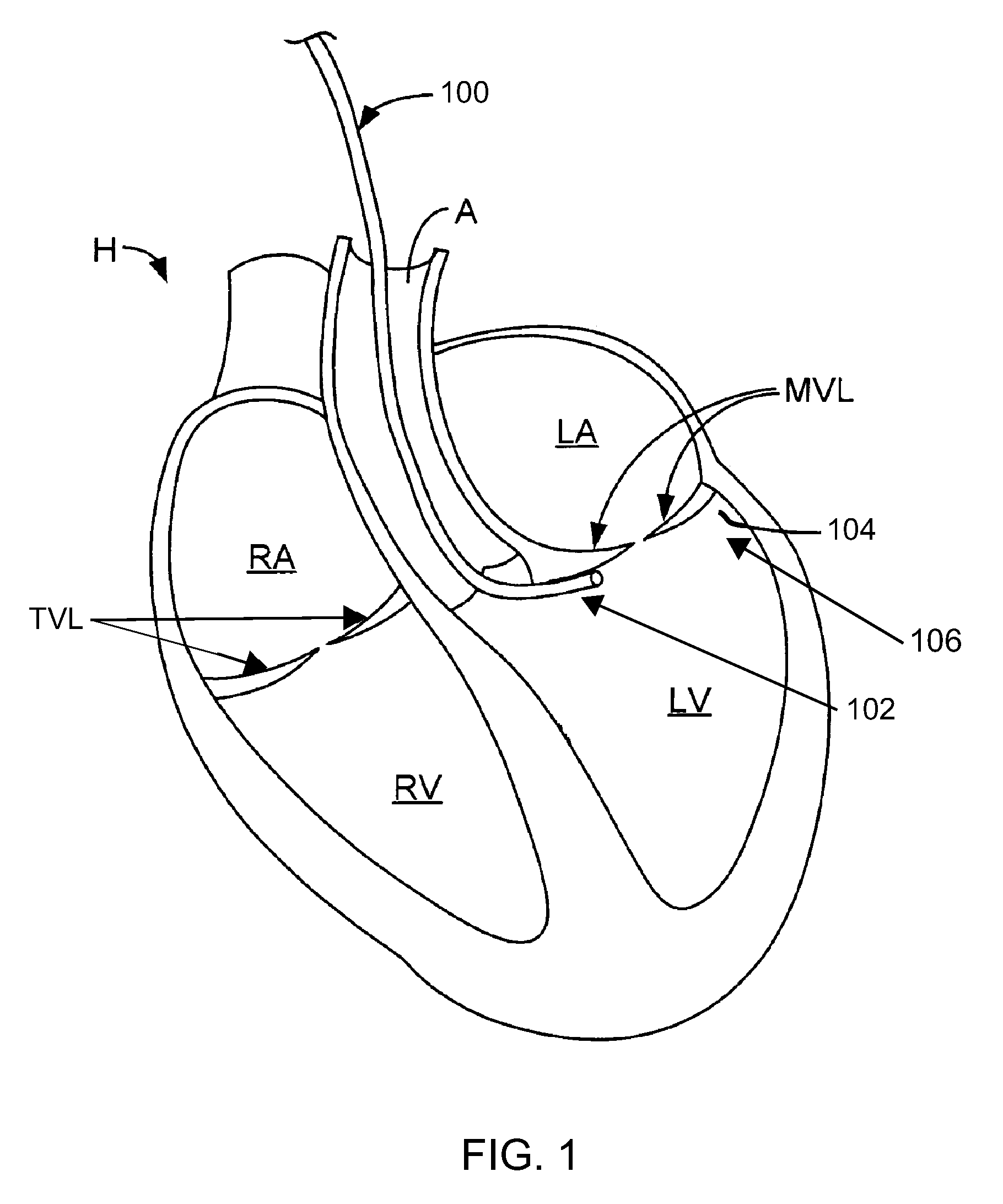
Apparatus and methods are provided for ablating body tissue using radio frequency (RF) energy. A catheter having a lumen for delivering fluid can be inserted into a patient's body. A porous member, which may be expandable, is attached to the distal portion of the catheter. The porous member defines an interior region in communication with the lumen, such that the interior region is capable of receiving electrolyte fluid delivered from the proximal portion of the catheter. An RF electrode is disposed in the interior region and is configured for coupling to a source of RF energy, whereby RF energy may be transferred from the electrode to selected tissue areas in a patient's body via electrolyte fluid delivered through the lumen and into the interior region of the porous member.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
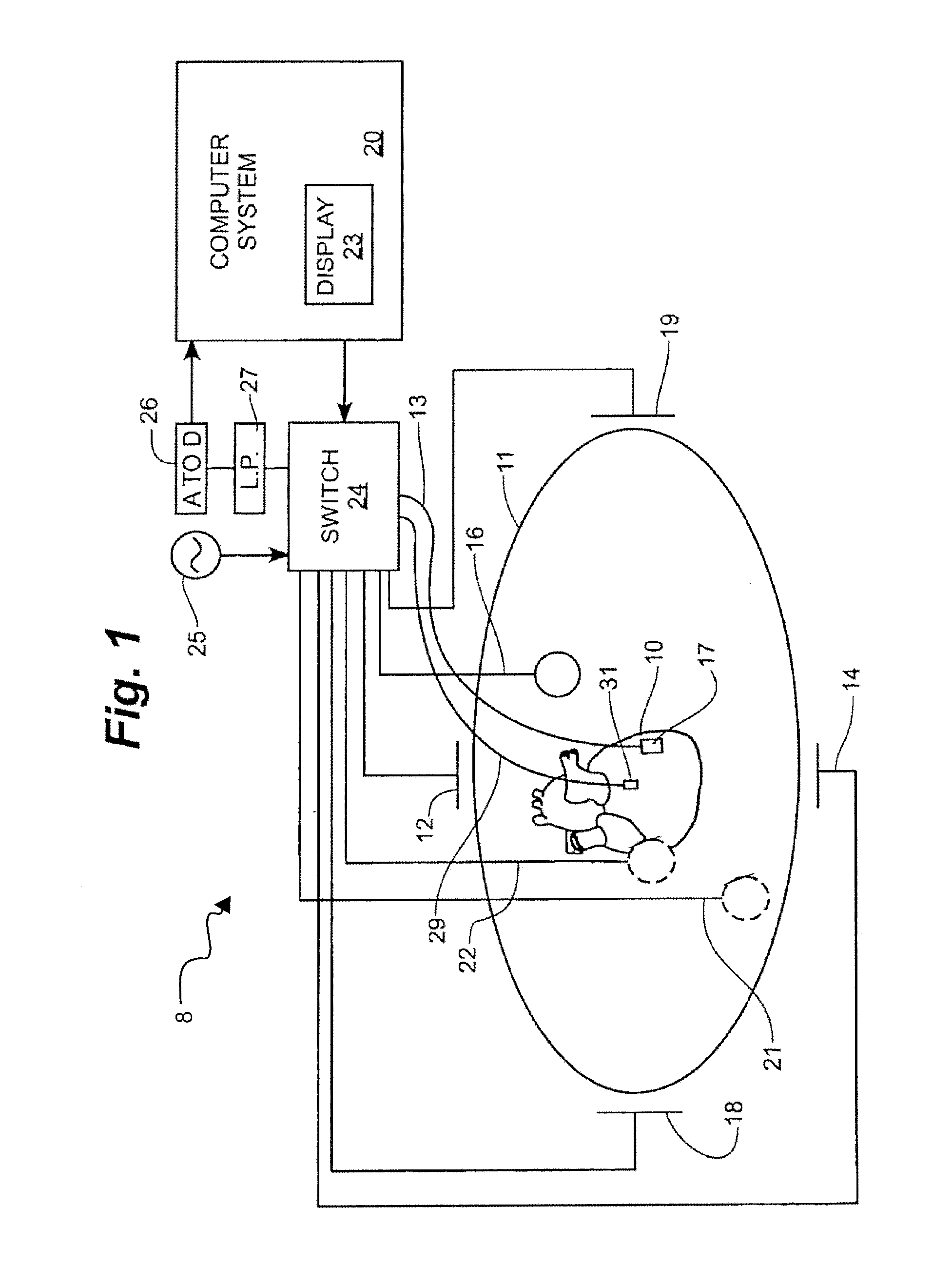
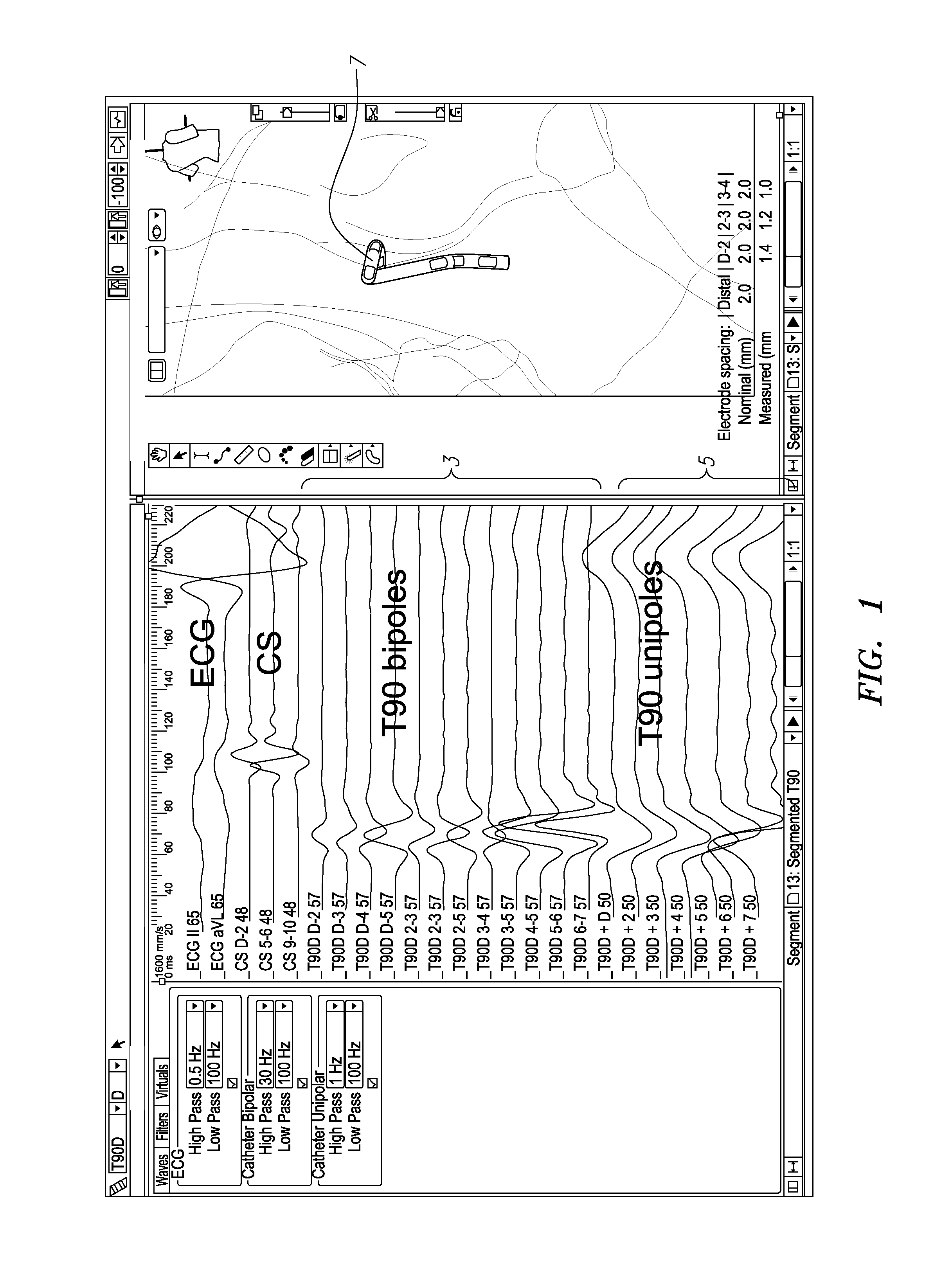
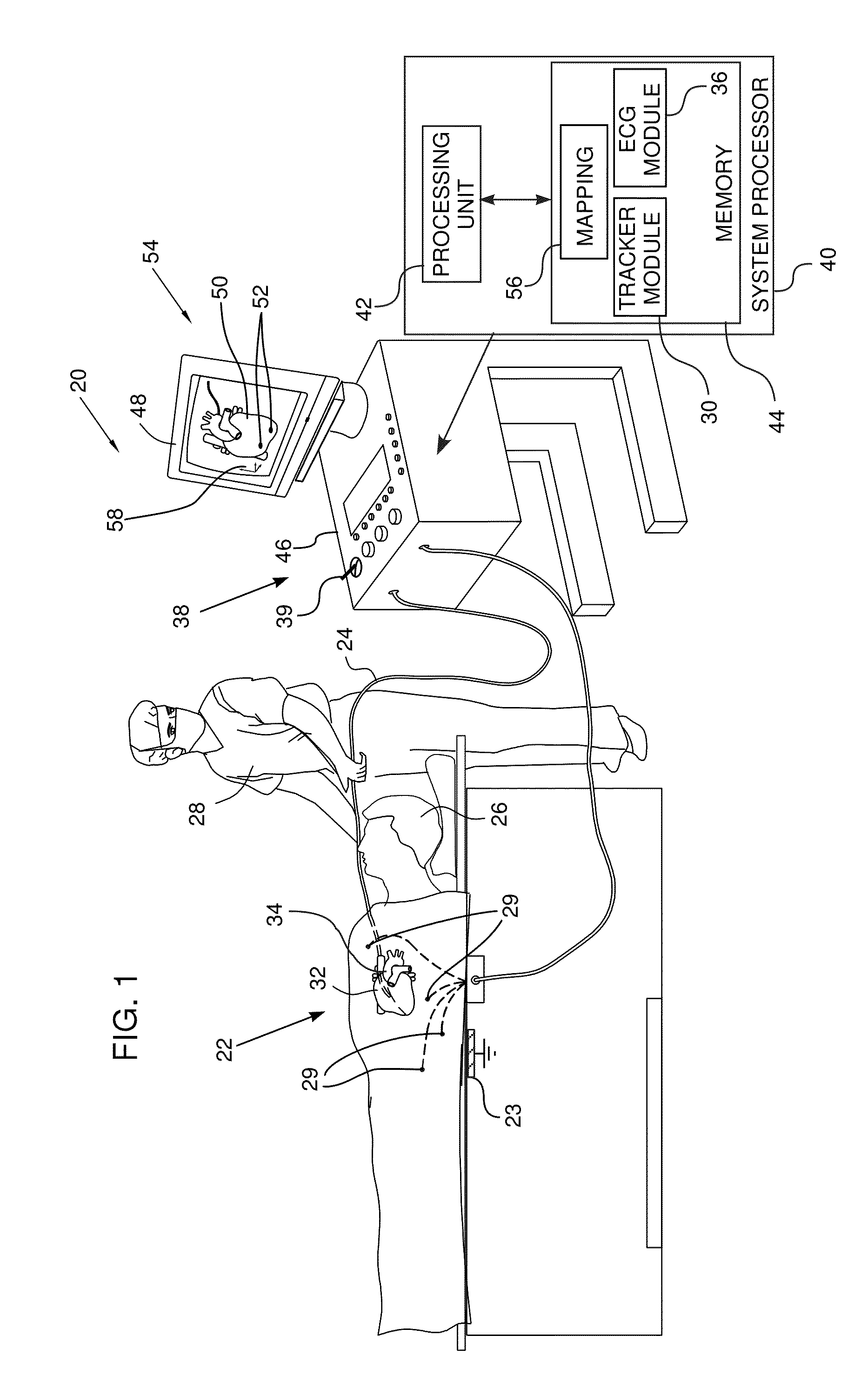
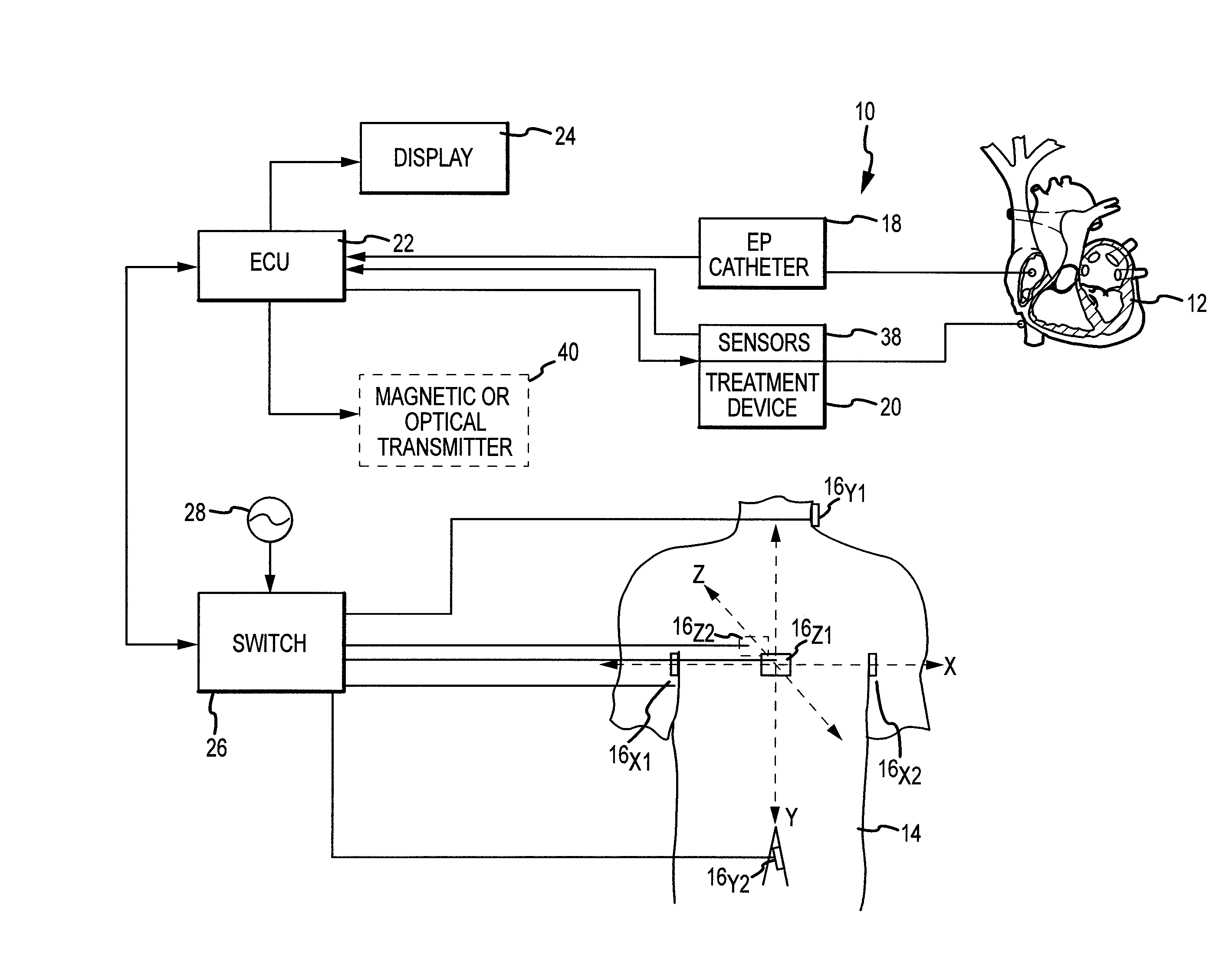
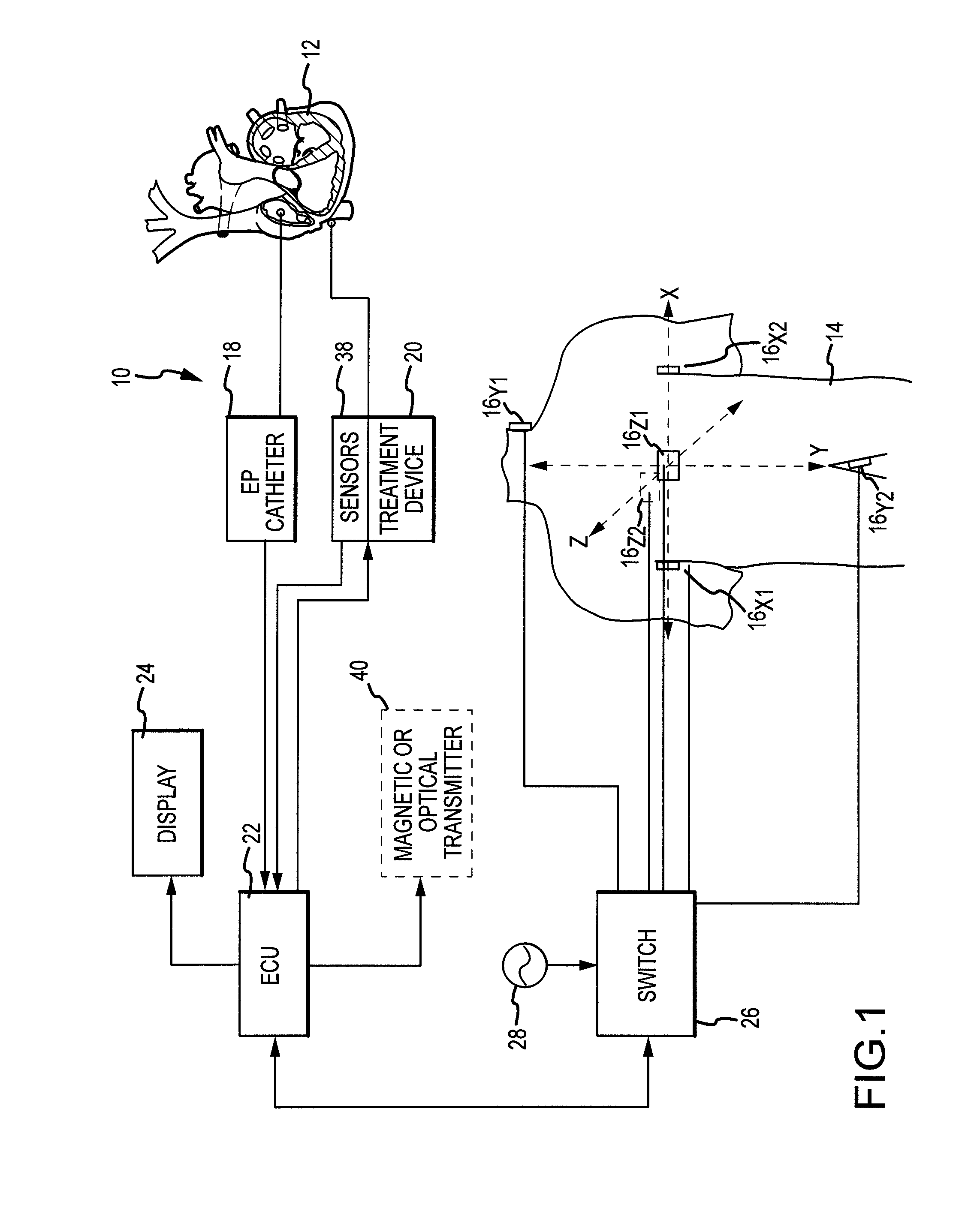
System and Method for Three Dimensional Mapping of Electrophysiology Information
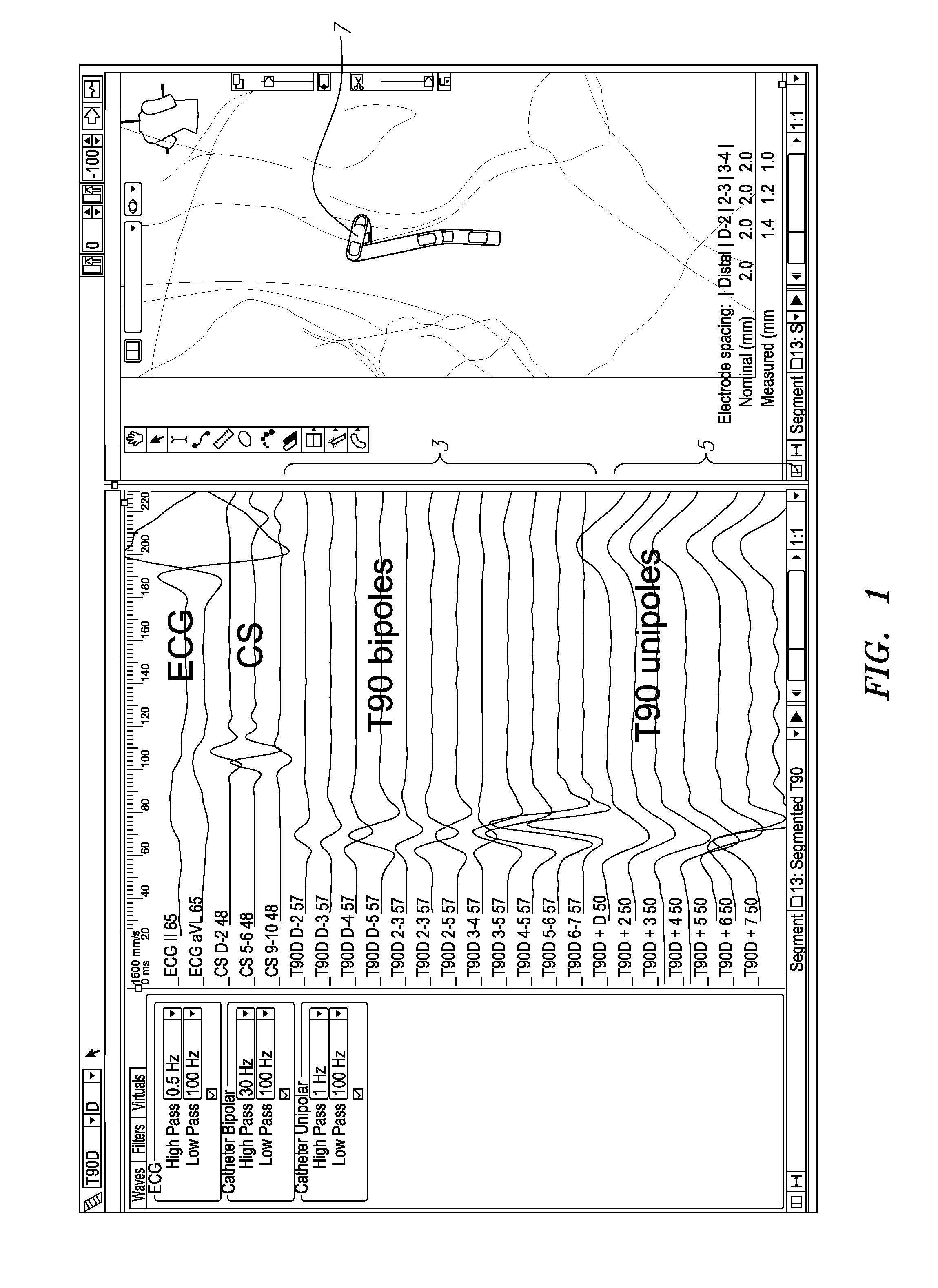
An electrophysiology apparatus is used to measure electrical activity occurring in a heart of a patient and to visualize the electrical activity and / or information related to the electrical activity. A three-dimensional map of the electrical activity and / or the information related to the electrical activity is created. Exemplary maps include a time difference between action potentials at a roving electrode and a reference electrode, the peak-to-peak timing of action potentials at the roving electrode, the peak negative voltage of action potentials at the roving electrode, complex fractionated electrogram information, a dominant frequency of an electrogram signal, a maximum peak amplitude at the dominant frequency, a ratio of energy in one band of the frequency-domain to the energy in a second band of the frequency-domain, a low-frequency or high-frequency passband of interest, a frequency with the maximum energy in a passband, a number of peaks within a passband, an energy, power, and / or area in each peak, a ratio of energy and / or area in each peak to that in another passband, and a width of each peak in a spectrum. Colors, shades of colors, and / or grayscales are assigned to values of the parameters and colors corresponding to the parameters for the electrograms sampled by the electrodes are updated on the three-dimensional model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
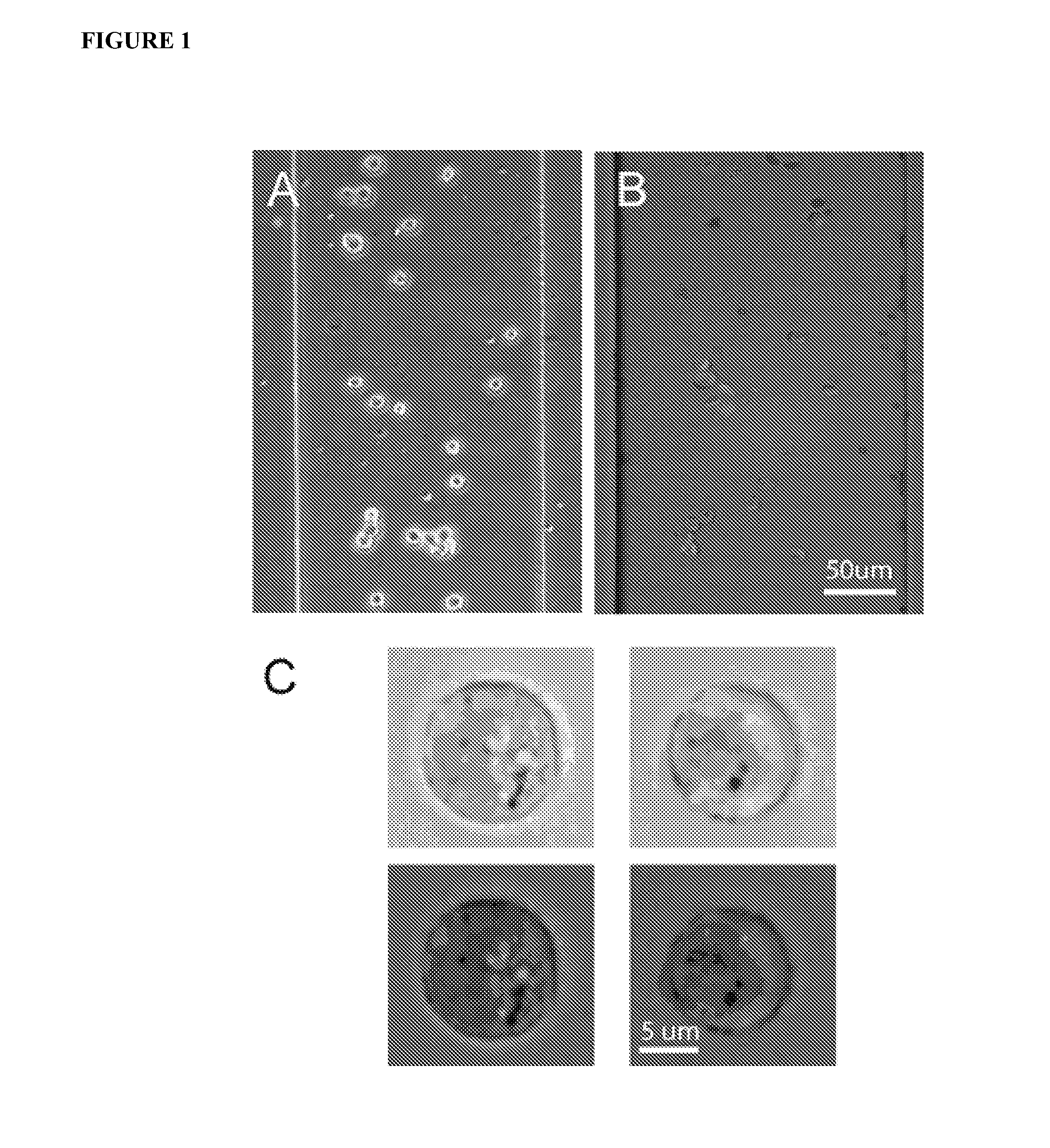
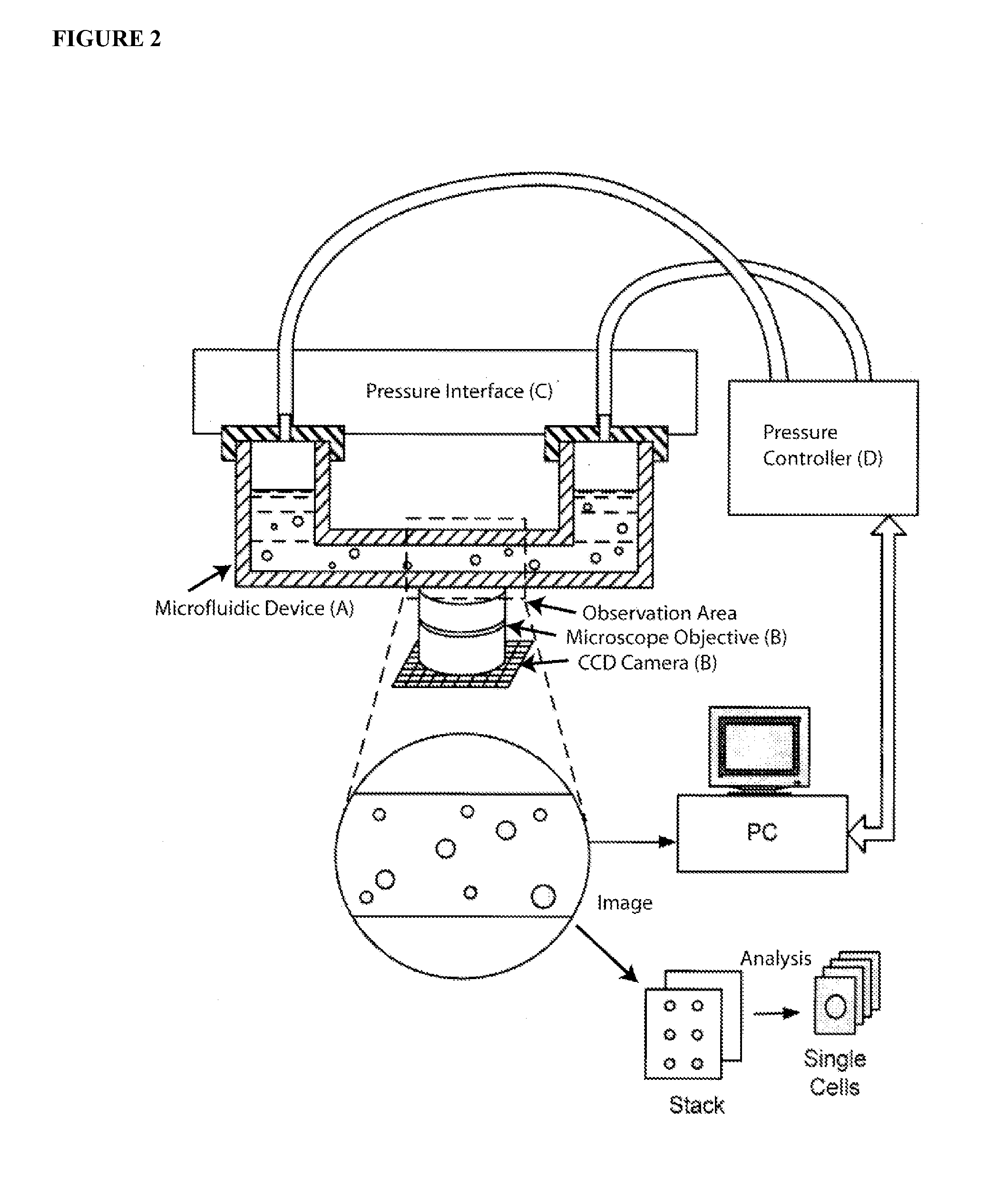
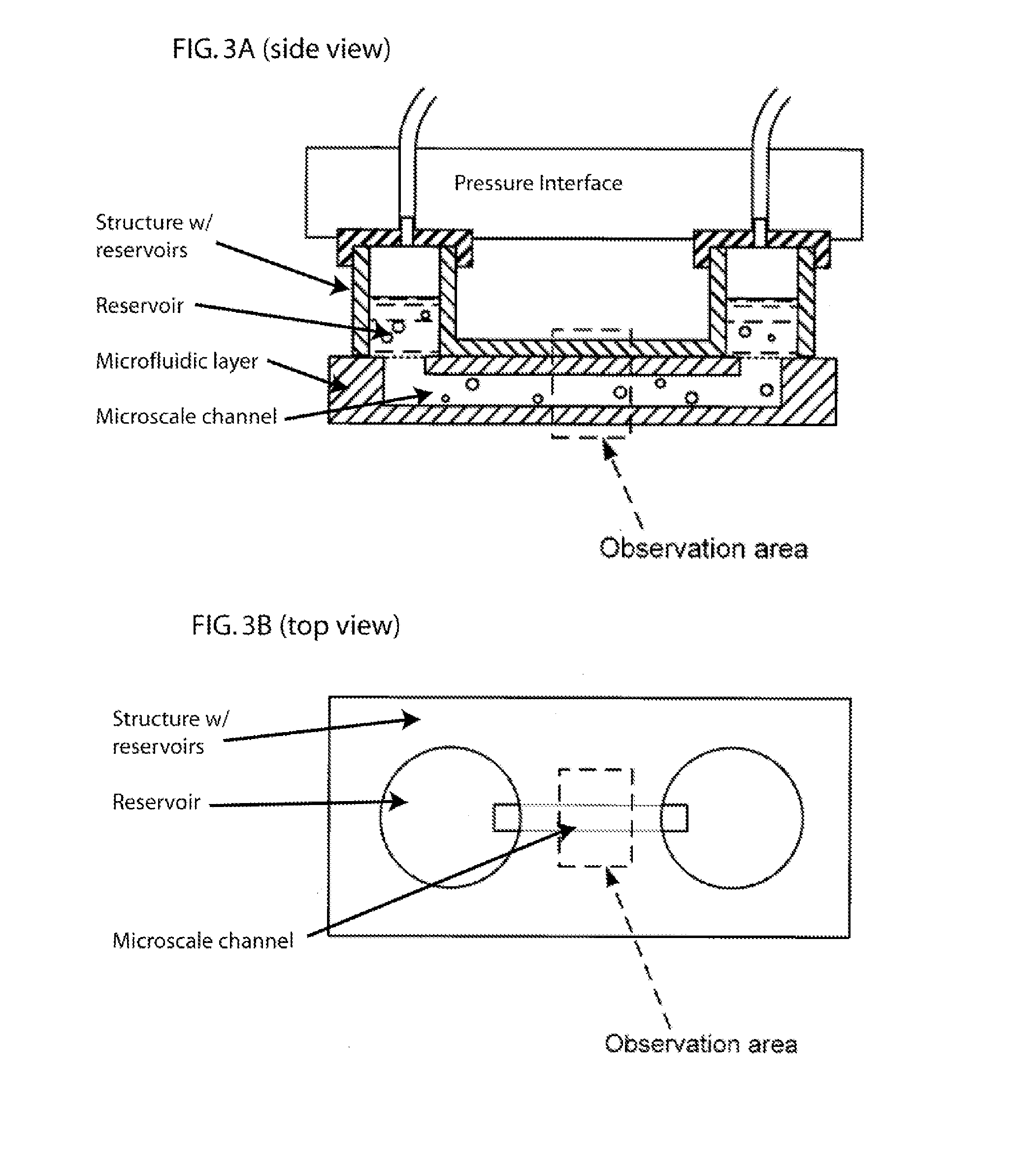
Methods and Apparatus for the Manipulation of Particle Suspensions and Testing Thereof
InactiveUS20070243523A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophysiology studyElectroporation
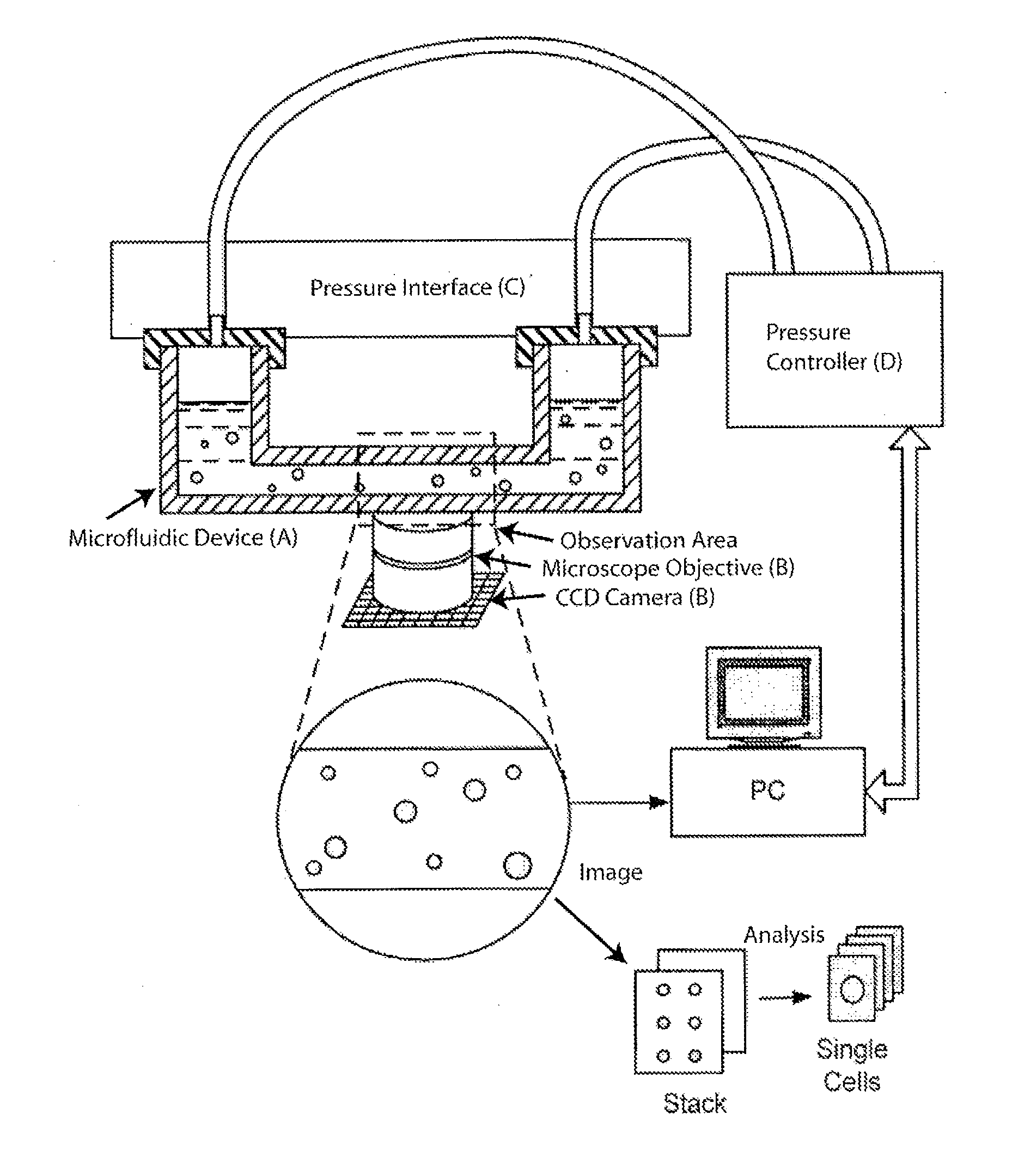
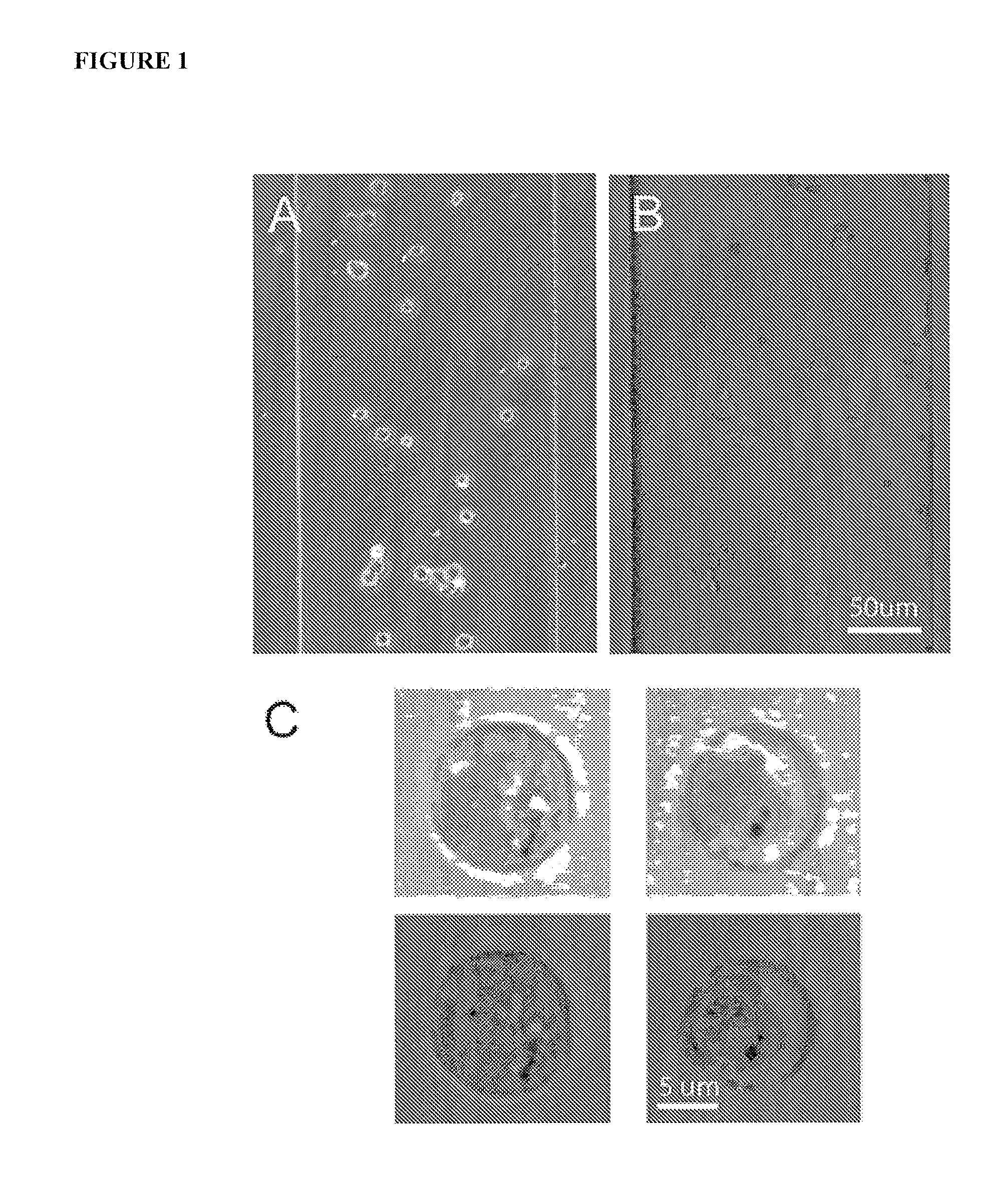
Apparatus and methods are provided for analysis of individual particles in a microfluidic device. The methods involve the immobilization of an array of particles in suspension and the application of experimental compounds. Such methods can also include electrophysiology studies including patch clamp recording, electroporation, or both in the same microfluidic device. The apparatus provided includes a microfluidic device coupled to a multi-well structure and an interface for controlling the flow of media within the microchannel device.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
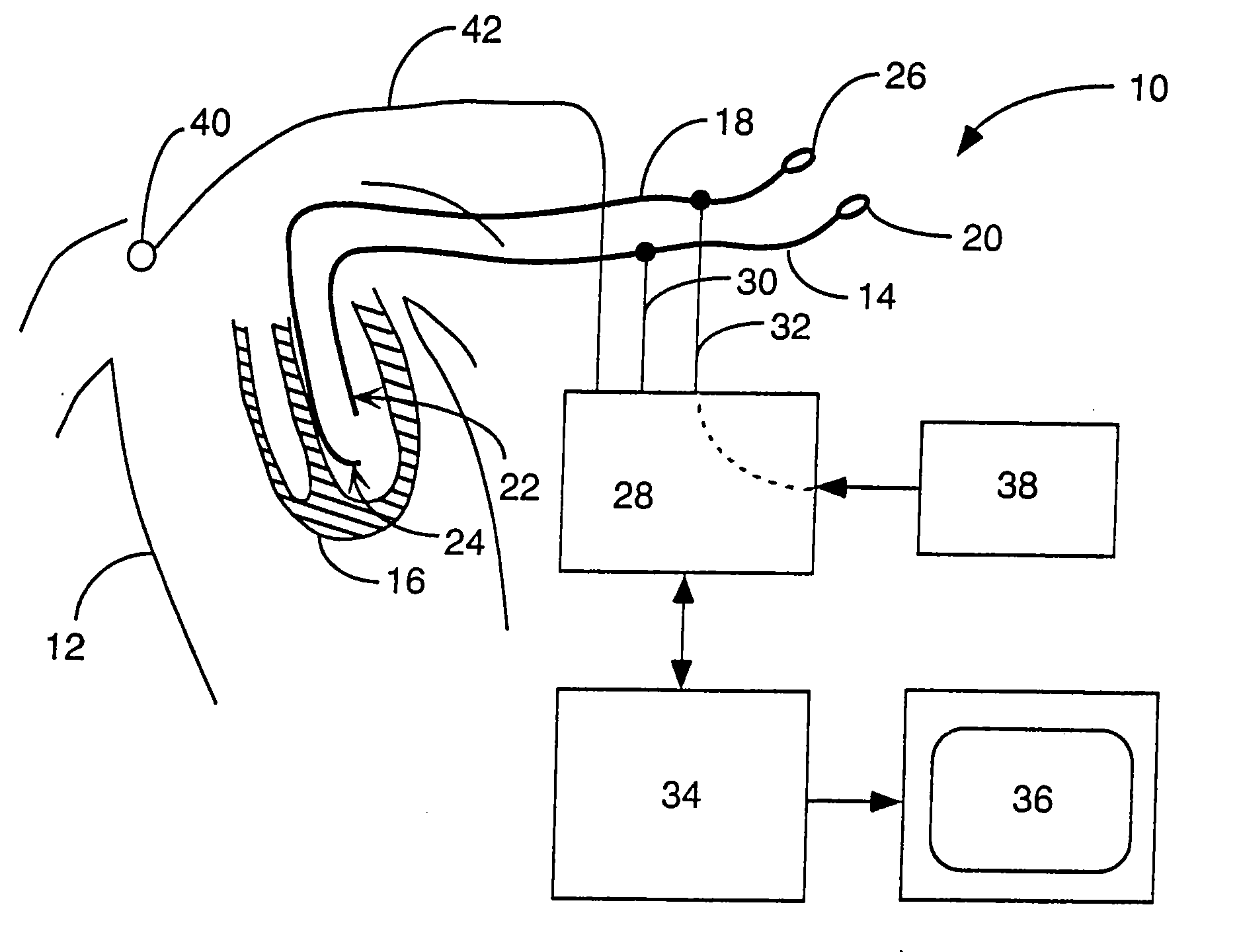
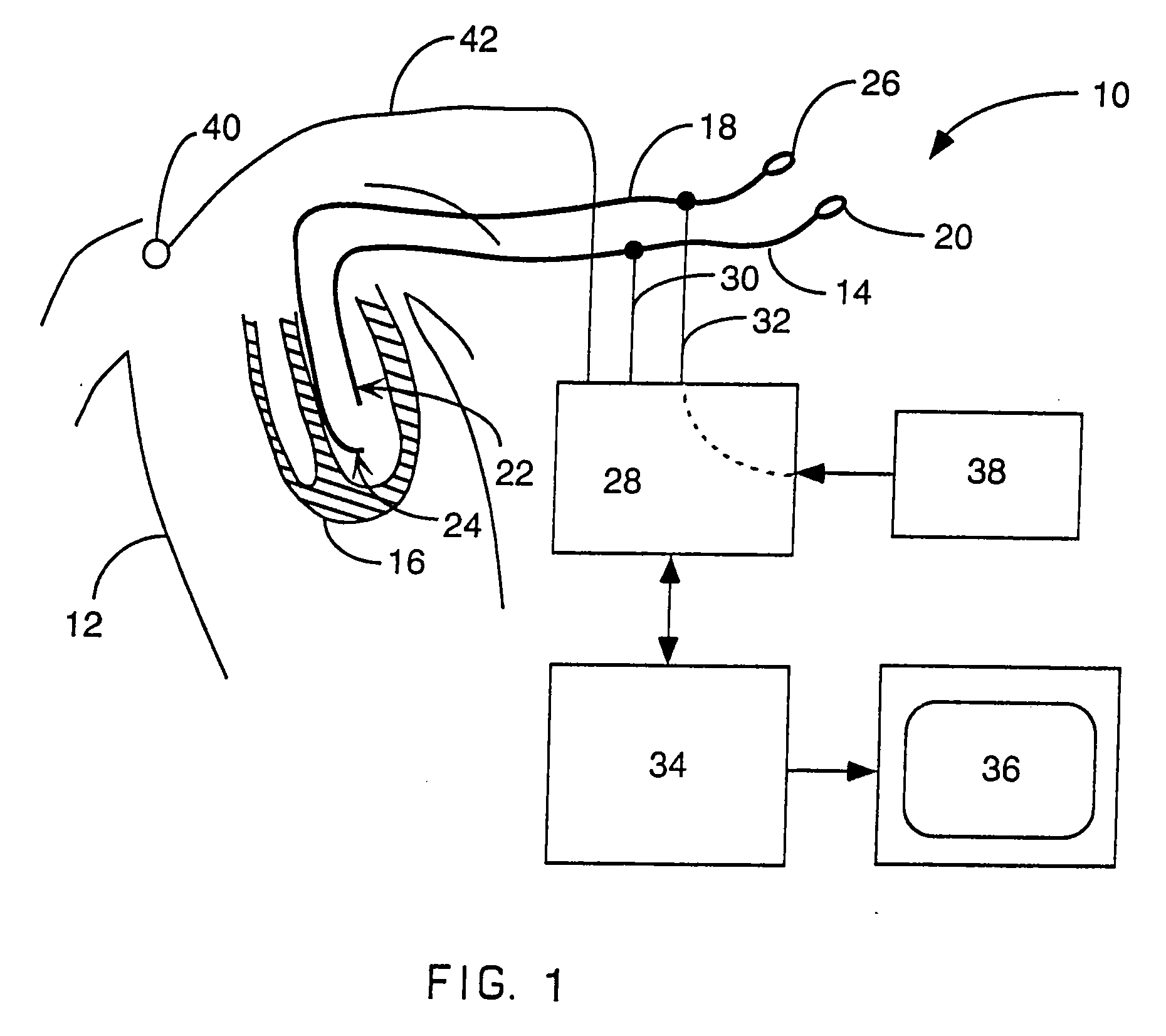
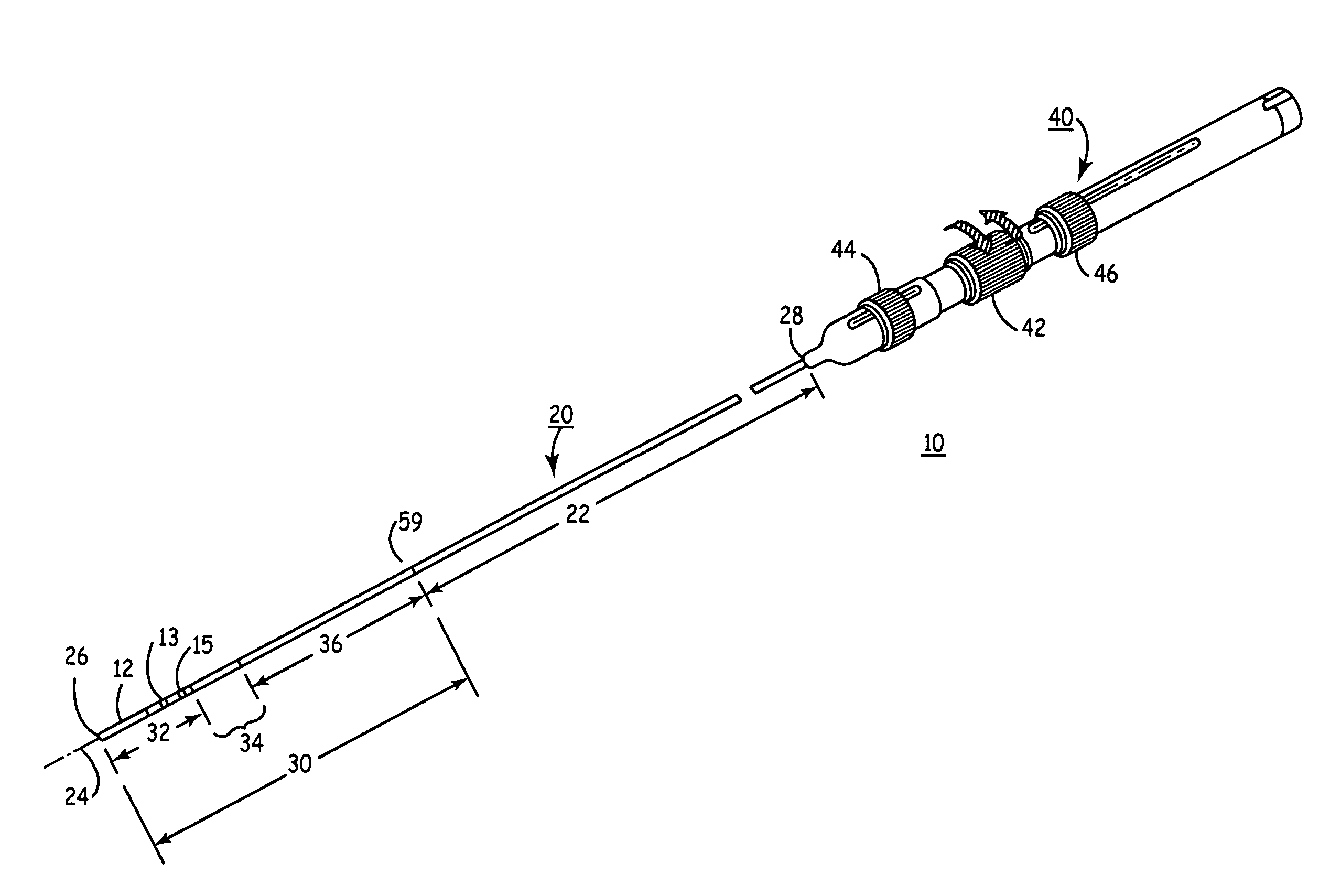
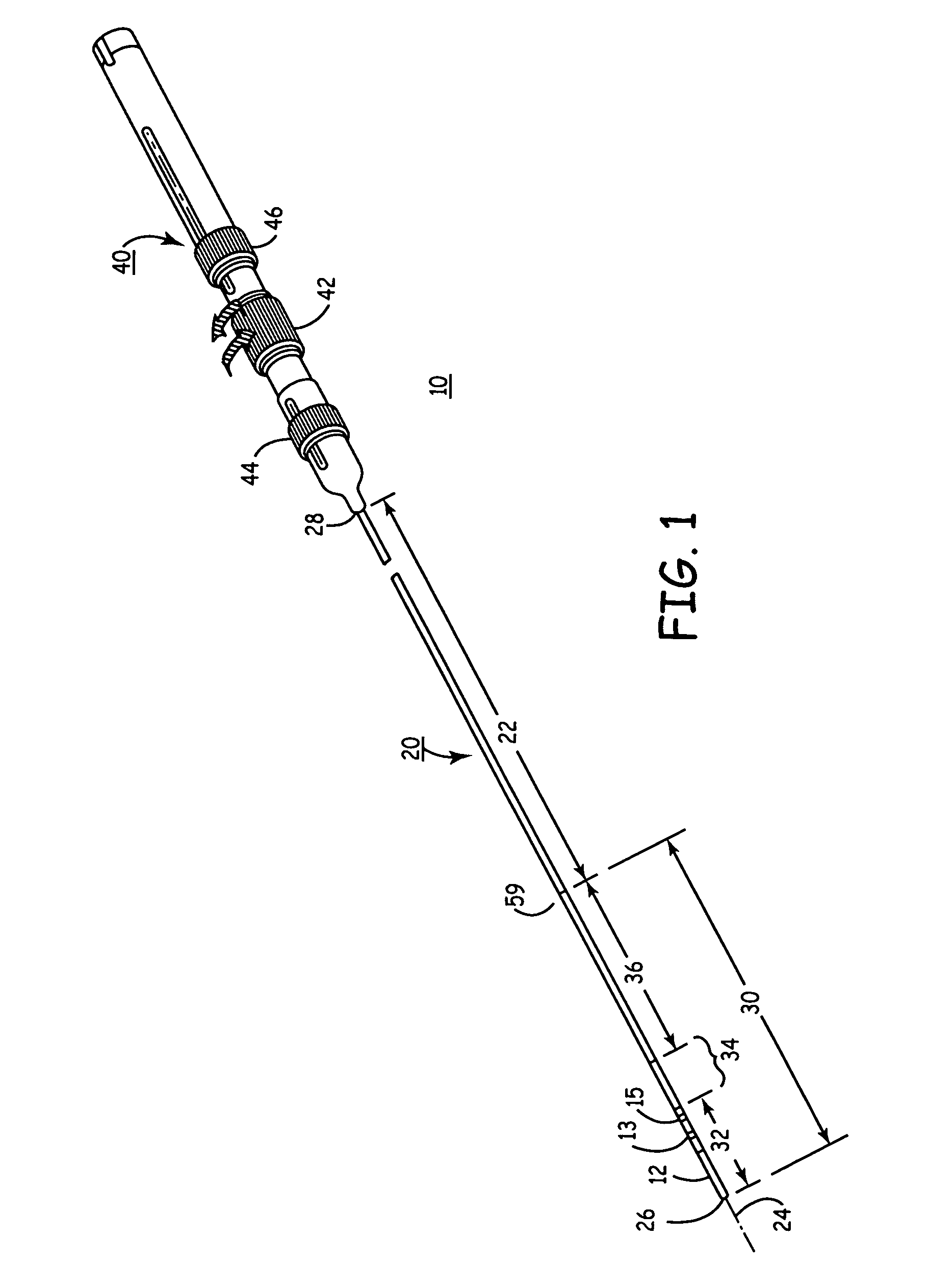
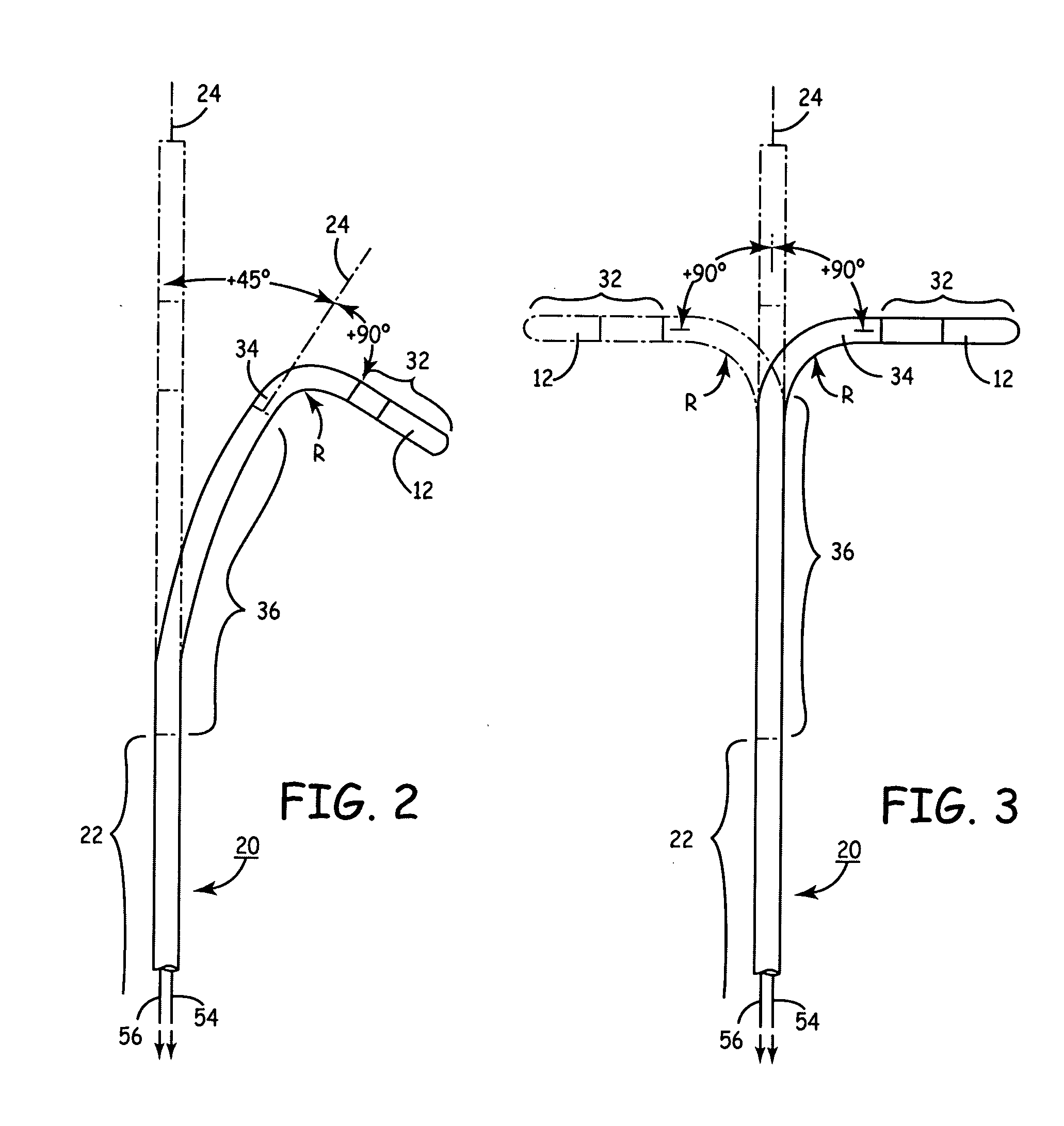
Electrophysiology catheter system
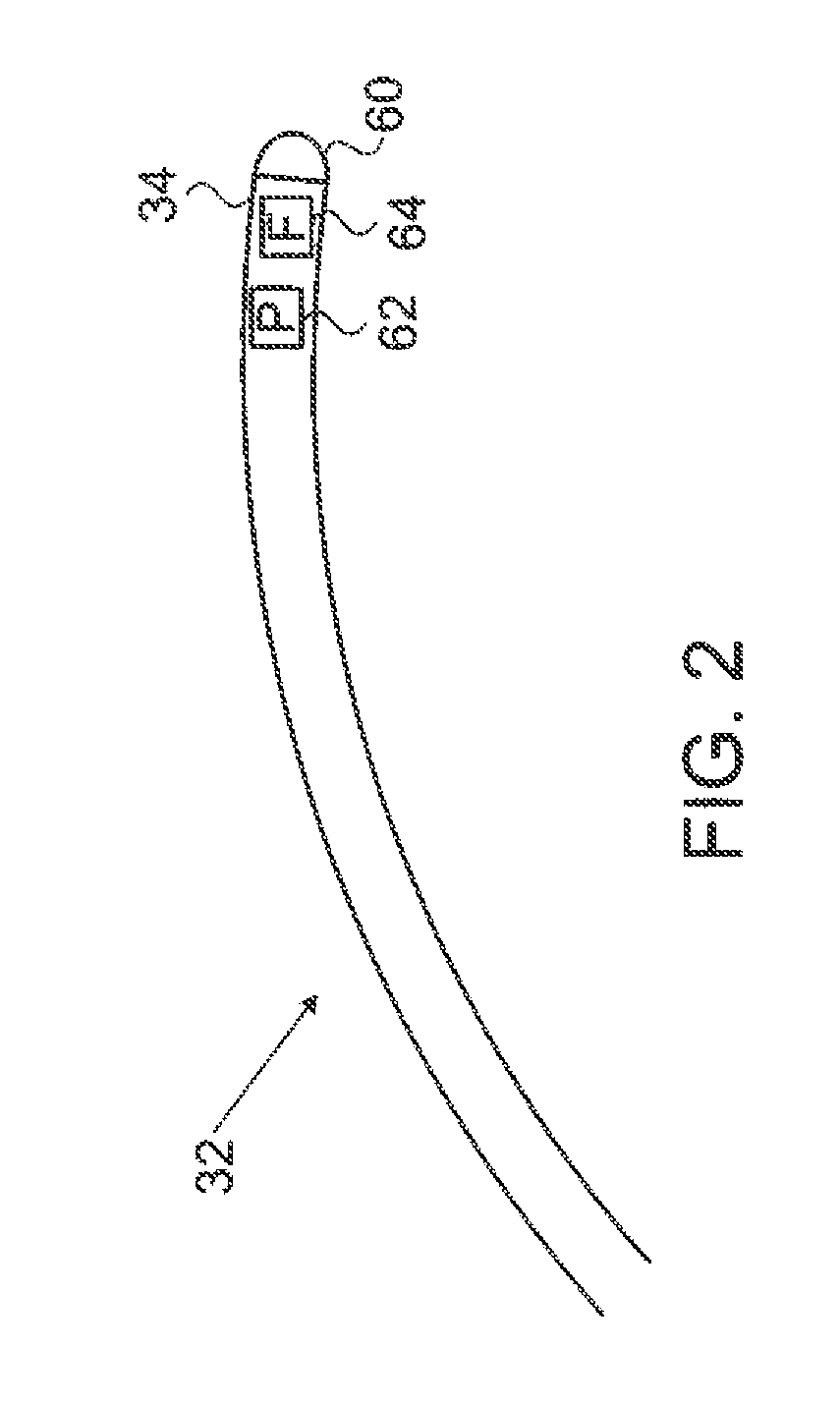
InactiveUS20090209950A1Reduce needConvenient guidanceSuture equipmentsUltrasound therapyRadiologyCell electrophysiology
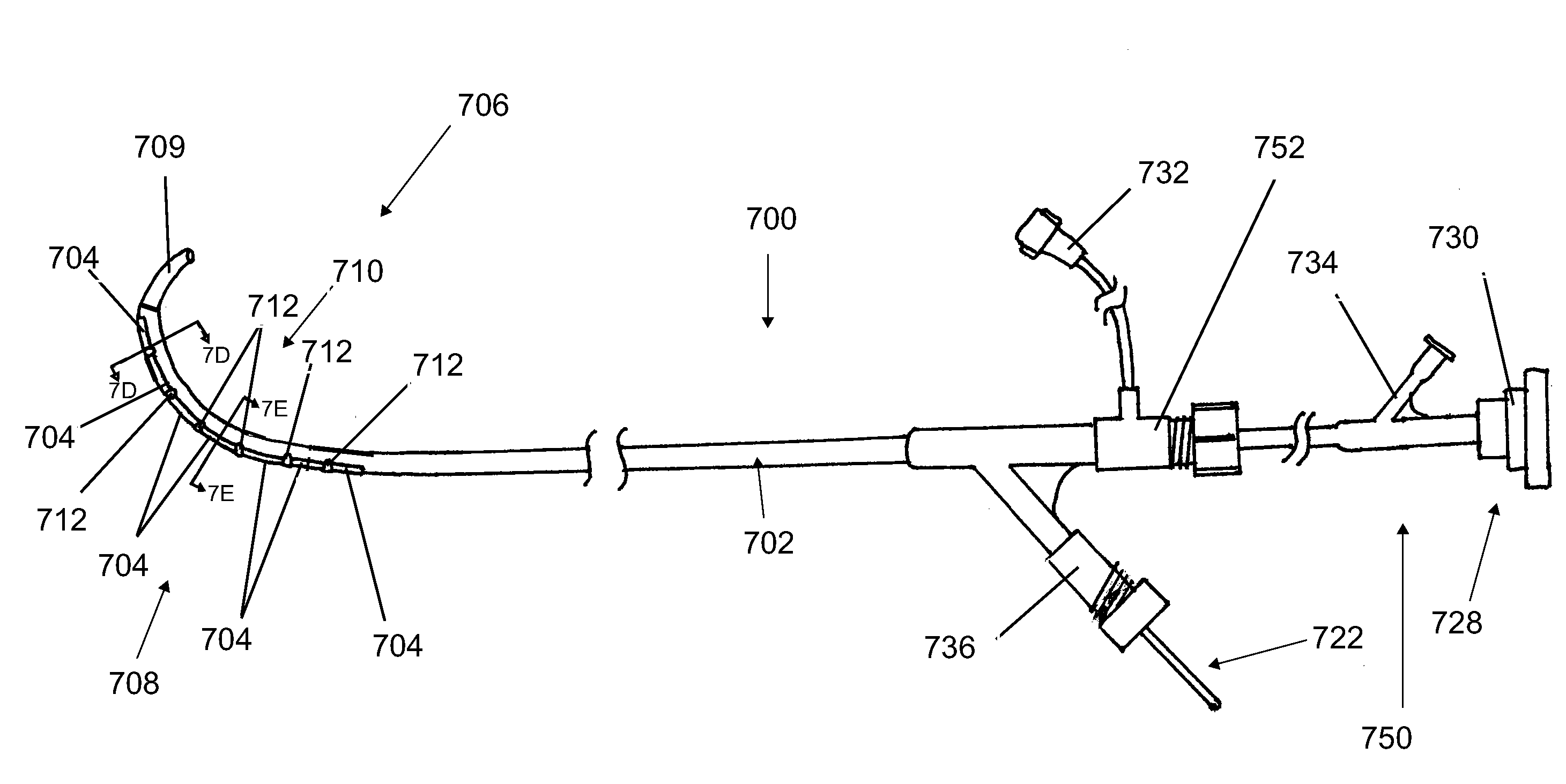
Described herein are devices and methods for treating tissue, comprising a catheter with a plurality of access sites and a plurality of sensors associated with the access sites. The catheter may be positioned along a tissue surface and the sensors may be used to identify a target site along the tissue surface using the plurality of sensors. Analysis of the tissue surface by the sensors is performed without requiring repositioning of the catheter. In some examples, the access sites of the catheter are side openings along a length of the catheter and the plurality of sensors are electrodes configured to measure electrophysiology parameters. In these examples, the catheter may comprise an internal lumen which permits a treatment device, such as an ablation catheter, to be slidably positioned at the desired target site without requiring displacement of the catheter. In other examples, the catheter may comprise a plurality of fixed ablation elements associated with the plurality of access sites.
Owner:GUIDED DELIVERY SYST INC
System and method for local electrophysiological characterization of cardiac substrate using multi-electrode catheters
A system for determining electrophysiological data comprising an electronic control unit configured to acquire electrophysiology signals from a plurality of electrodes (130) of one or more catheters, select at least one clique of electrodes from the plurality of electrodes (136) to determine a plurality of local E field data points, determine the location and orientation of the plurality of electrodes, process the electrophysiology signals from the at least one clique from a full set of bipole subcliques to derive the local E field data points associated with the at least one clique of electrodes, derive at least one orientation independent signal from the at least one clique of electrodes (138) from the information content corresponding to weighted parts of electrogram signals, and display or output catheter orientation independent electrophysiologic information to a user or process.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Electrophysiology Therapy Catheter
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
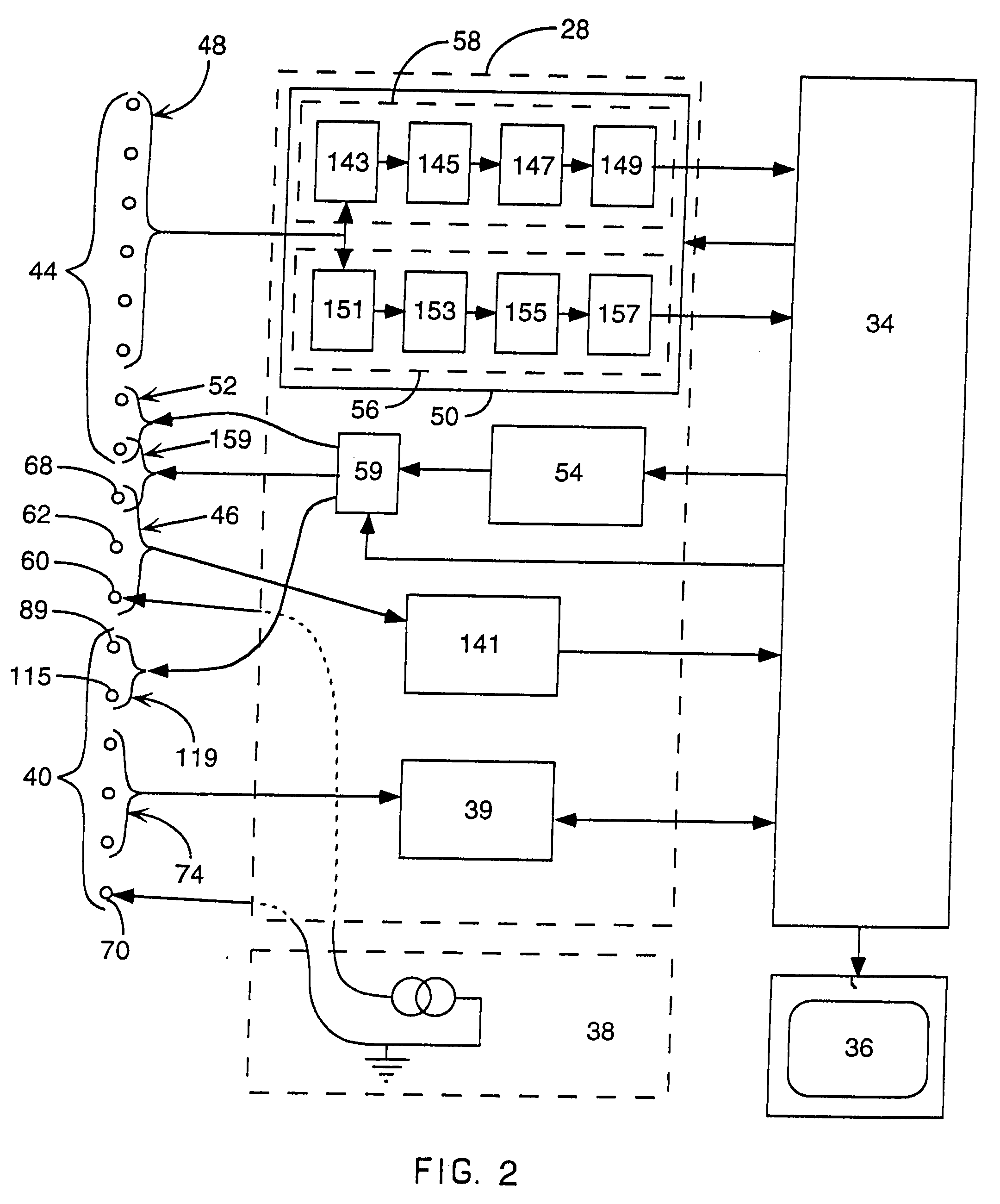
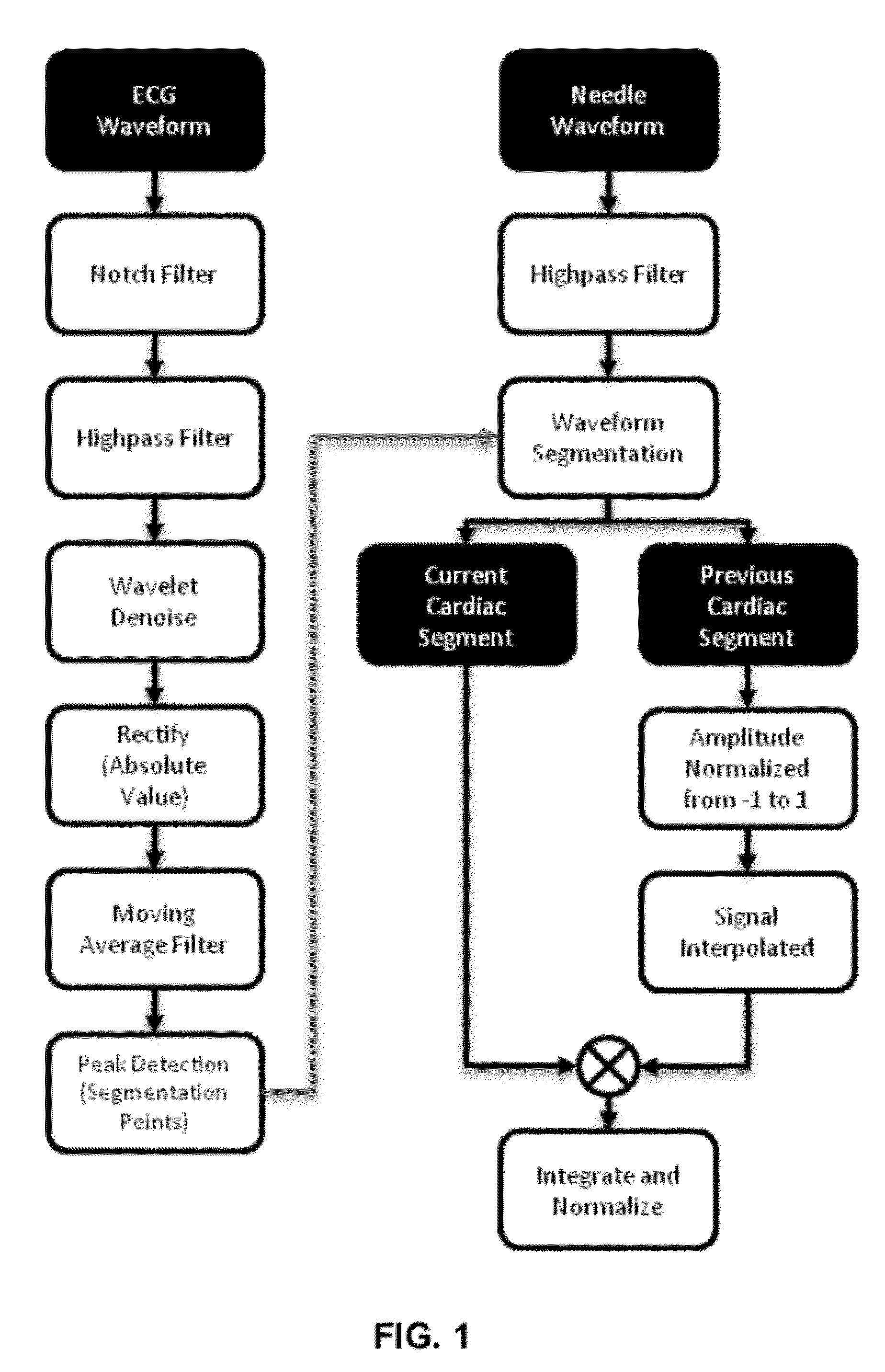
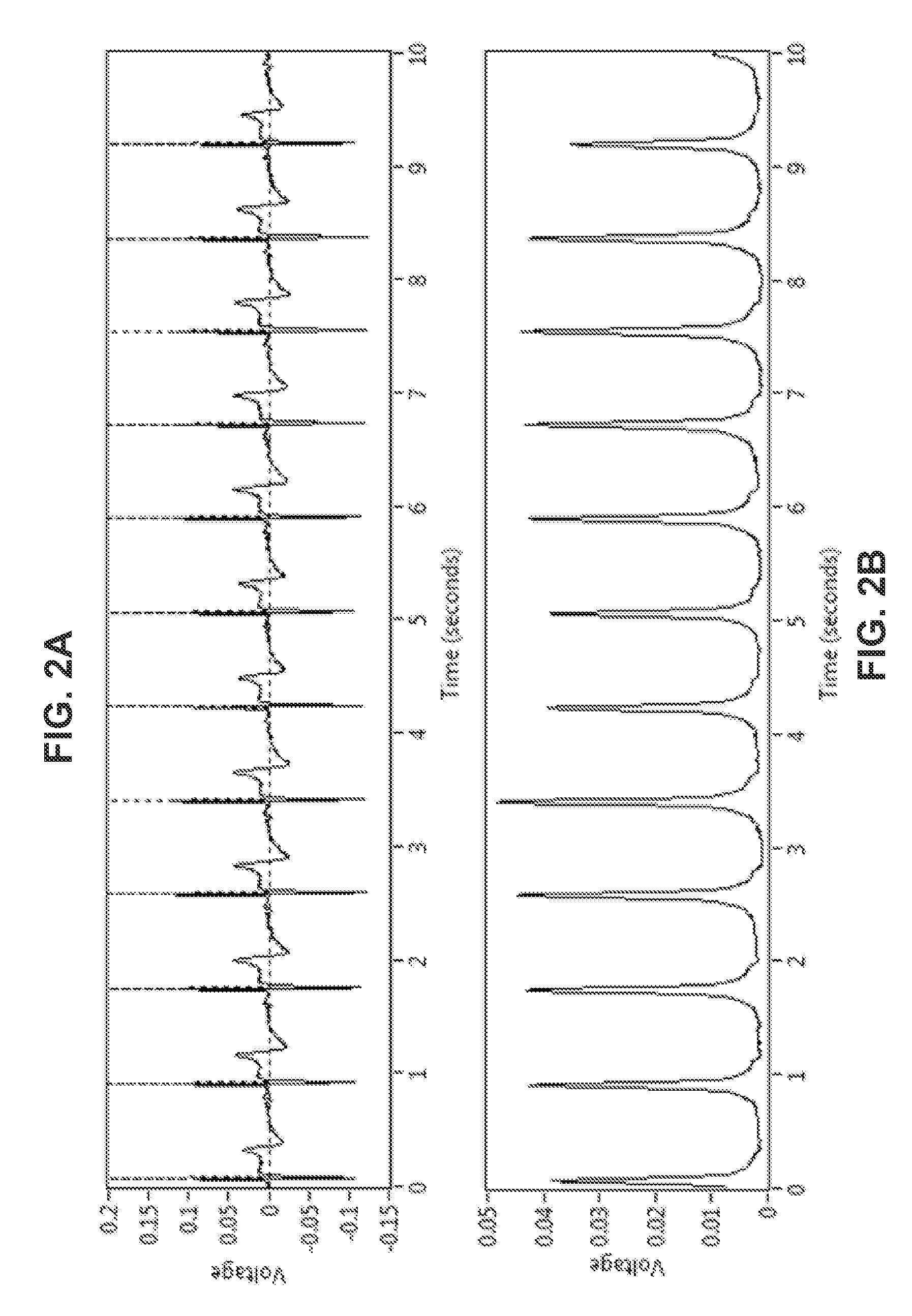
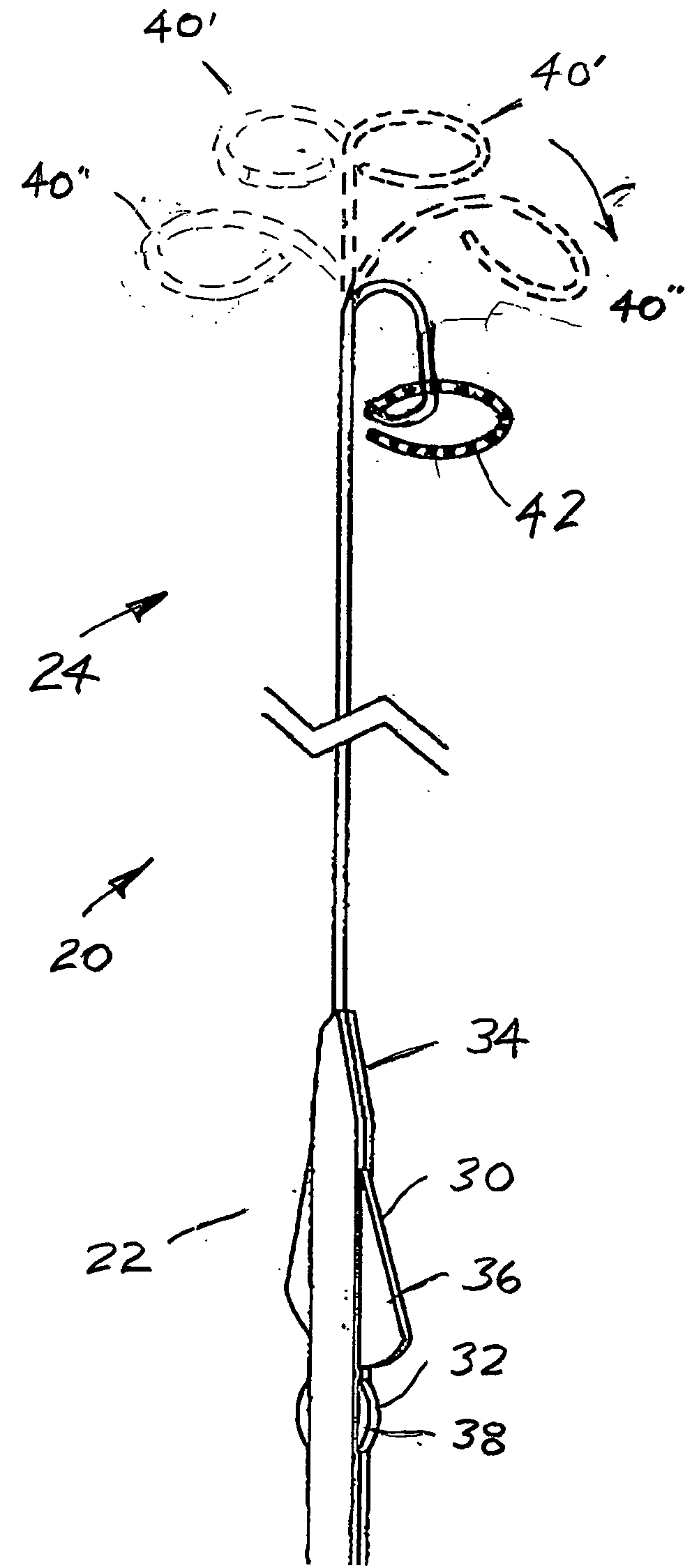
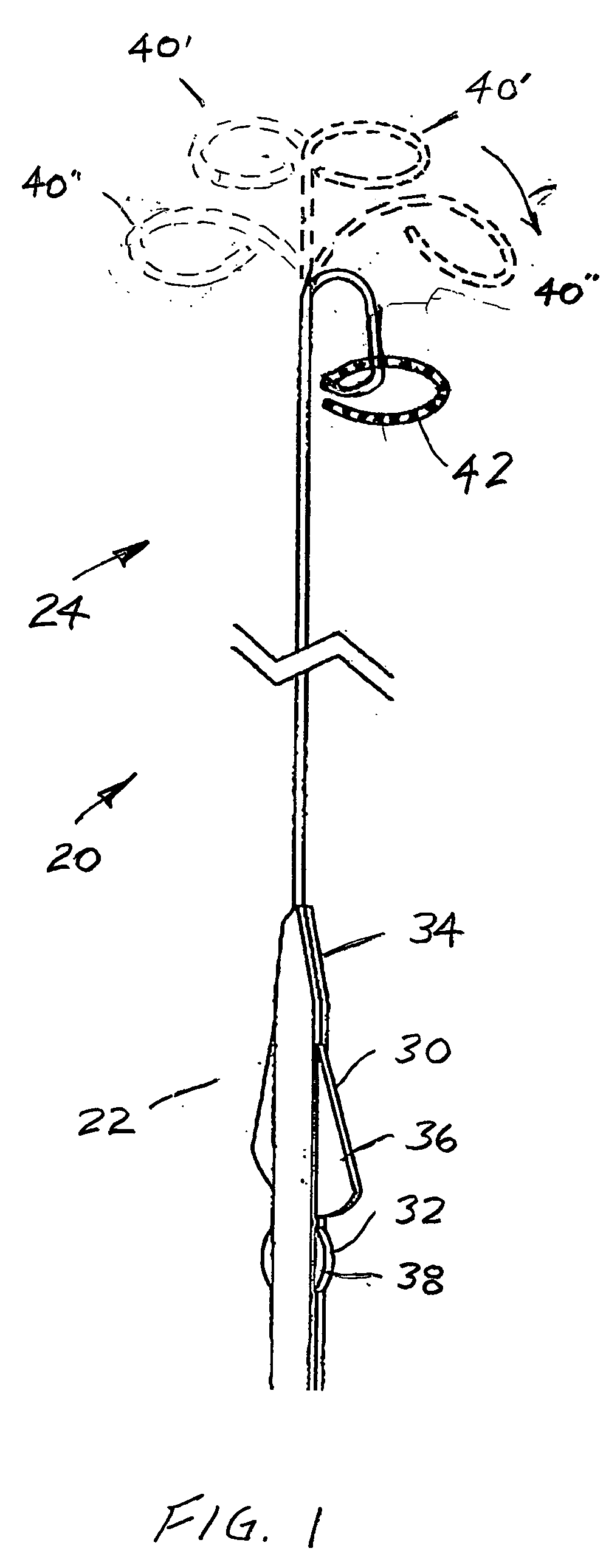
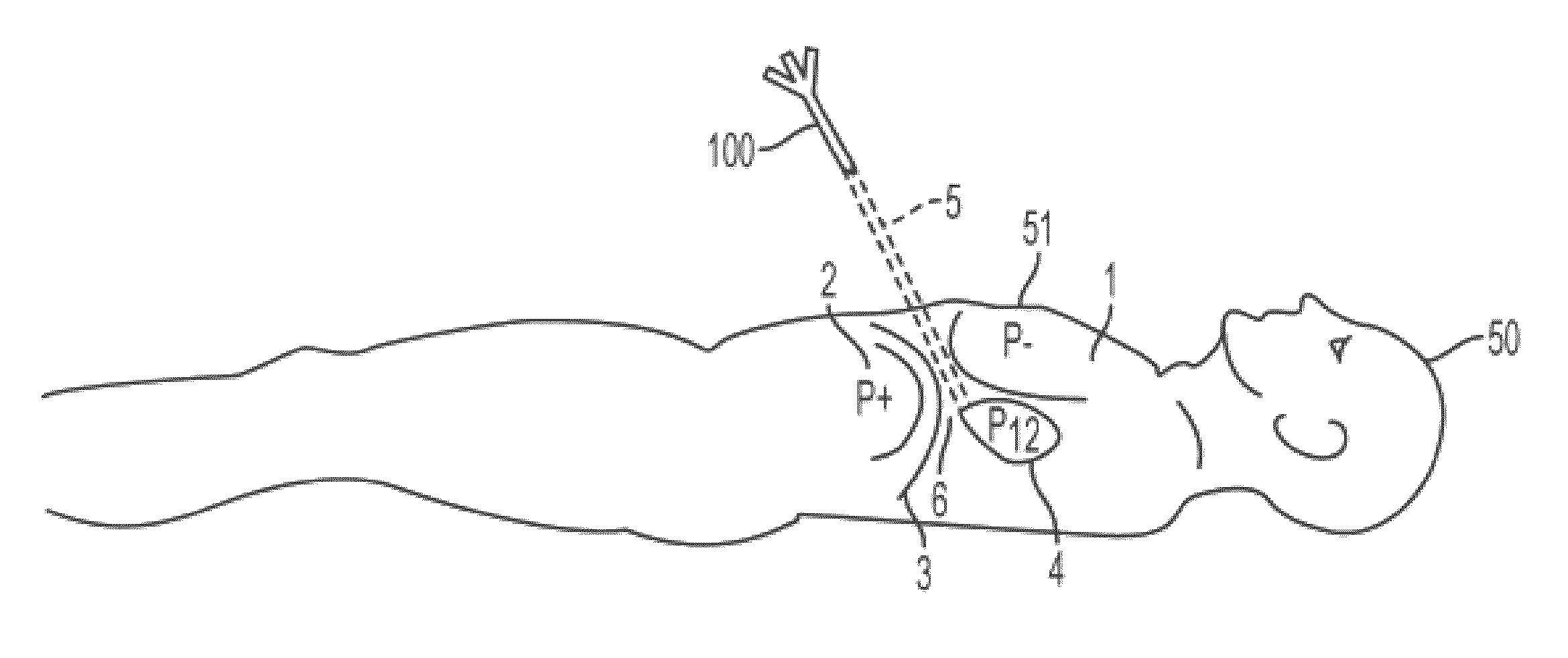
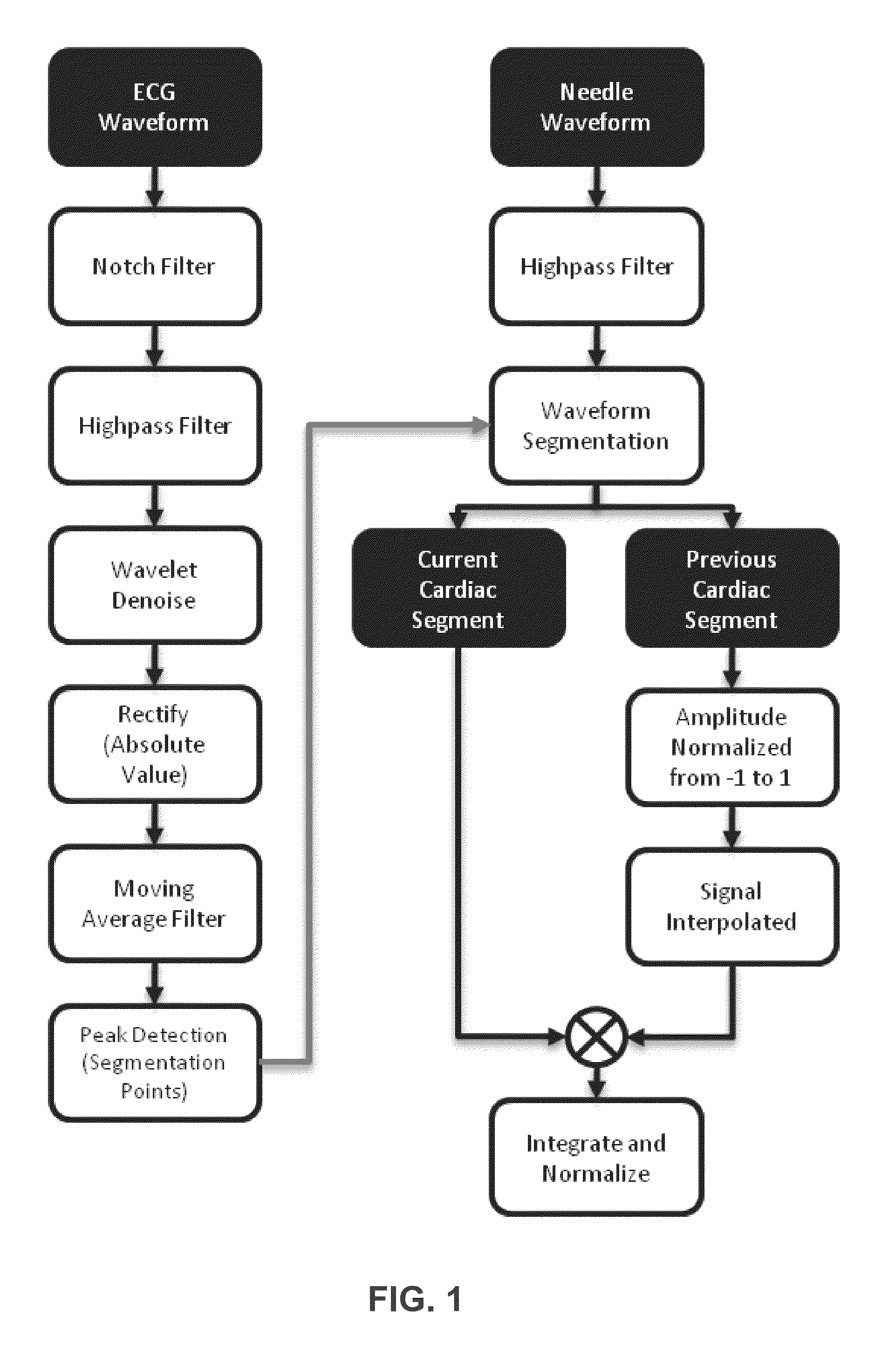
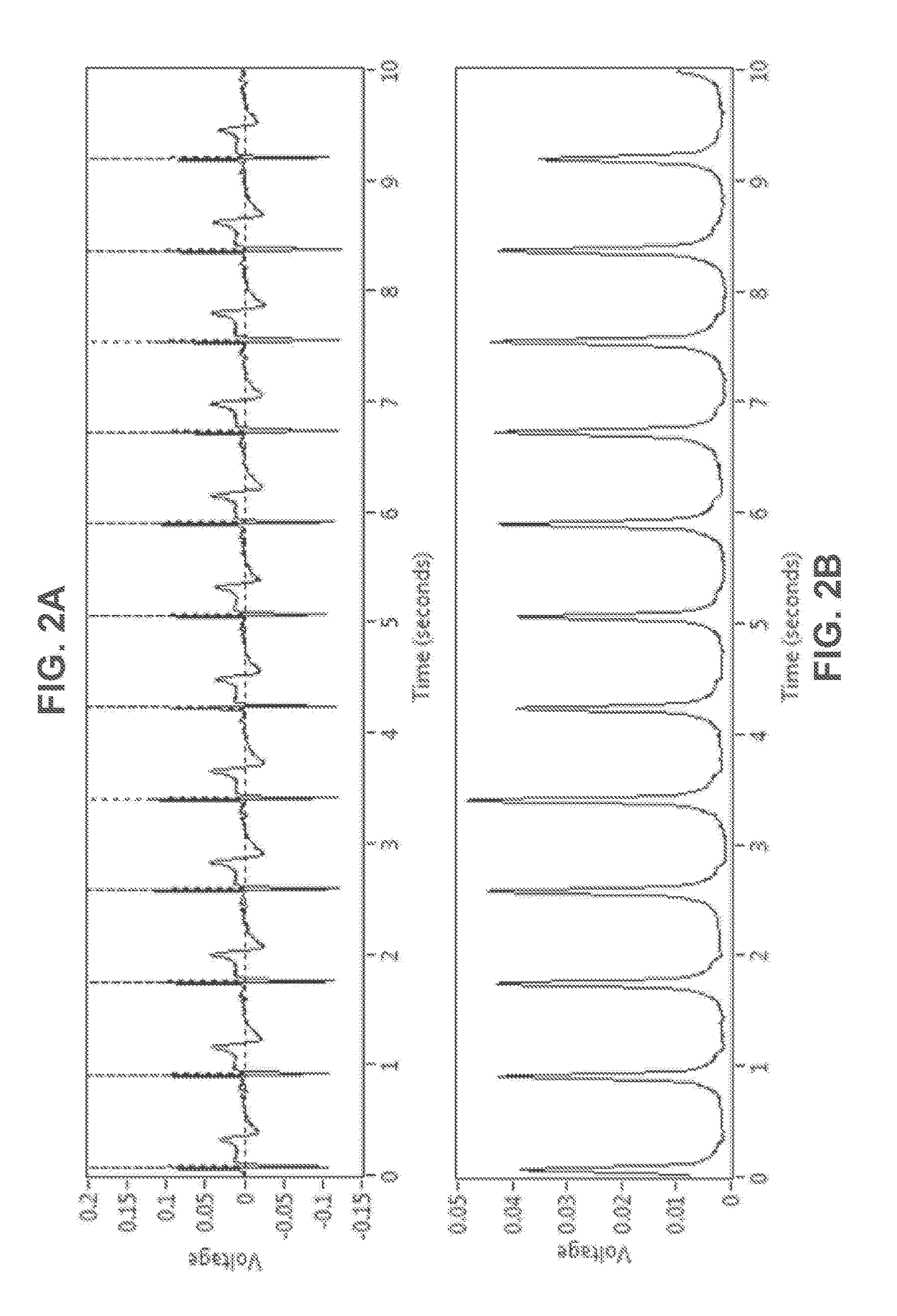
Systems and methods for determining location of an access needle in a subject
ActiveUS20120310052A1Reduce clinical riskImprove efficacySurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsCell electrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
Systems and methods for epicardial electrophysiology and other procedures are provided in which the location of an access needle may be inferred according to the detection of different pressure frequencies in separate organs, or different locations, in the body of a subject. Methods may include inserting a needle including a first sensor into a body of a subject, and receiving pressure frequency information from the first sensor. A second sensor may be used to provide cardiac waveform information of the subject. A current location of the needle may be distinguished from another location based on an algorithm including the pressure frequency information and the cardiac waveform information.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
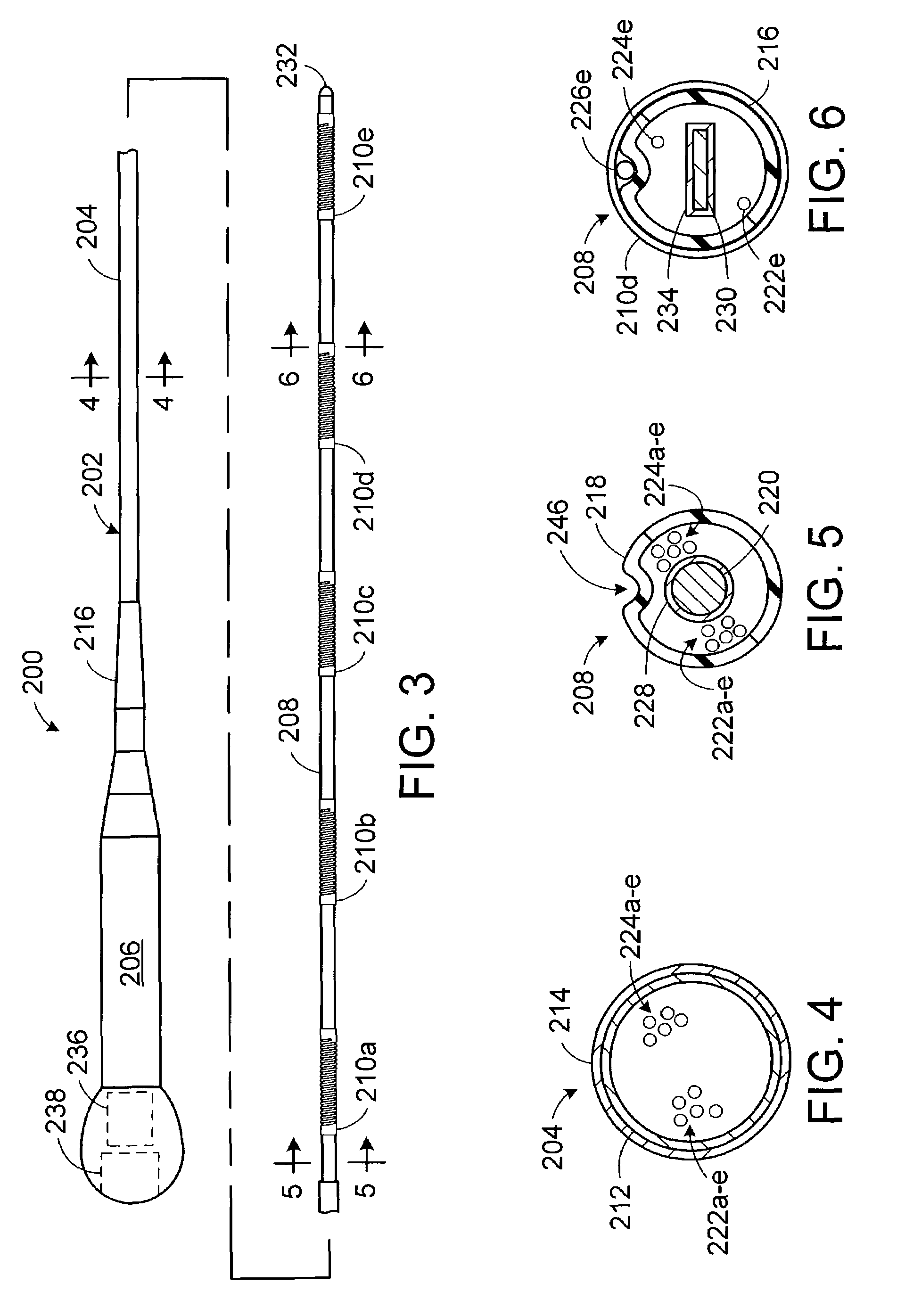
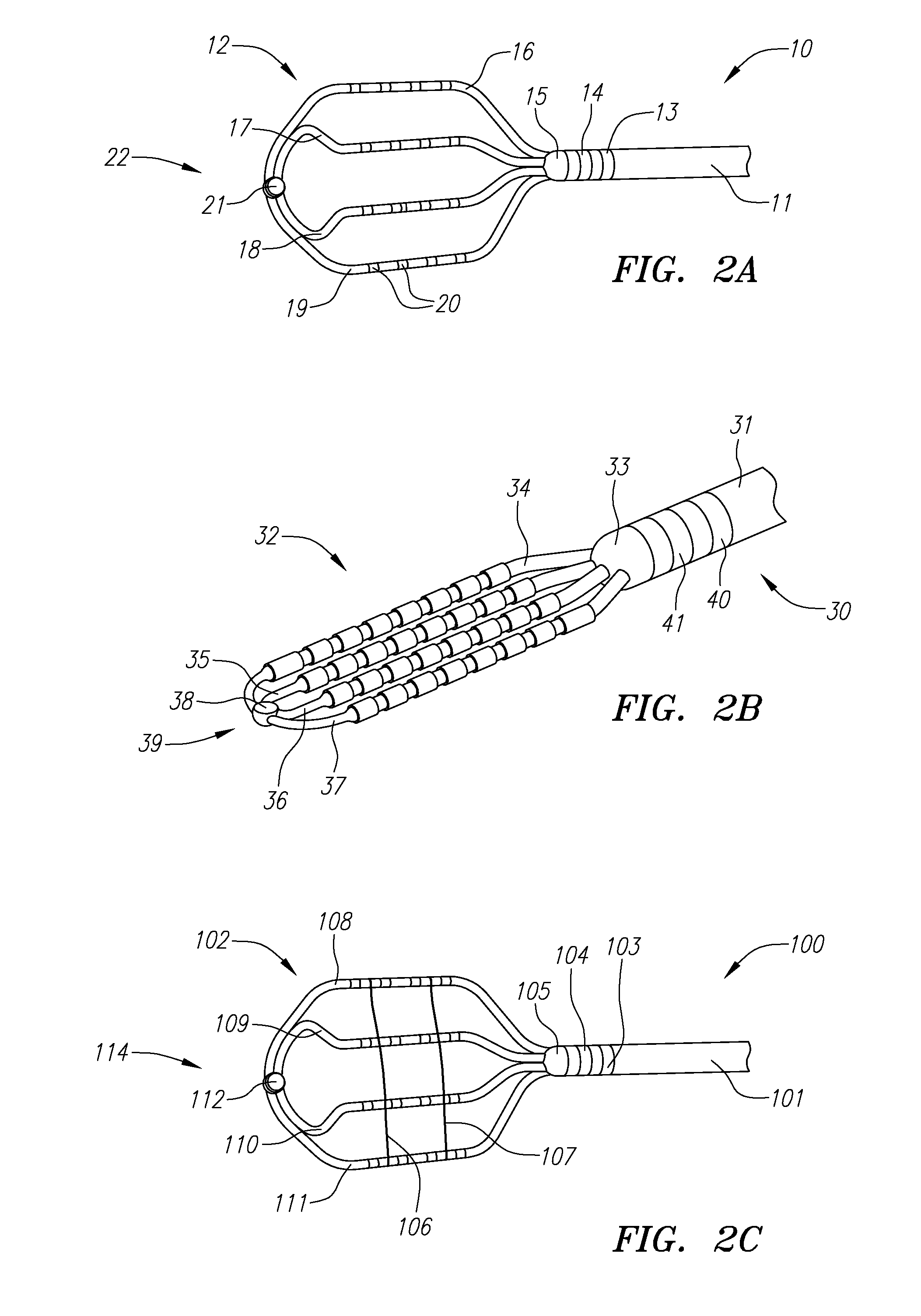
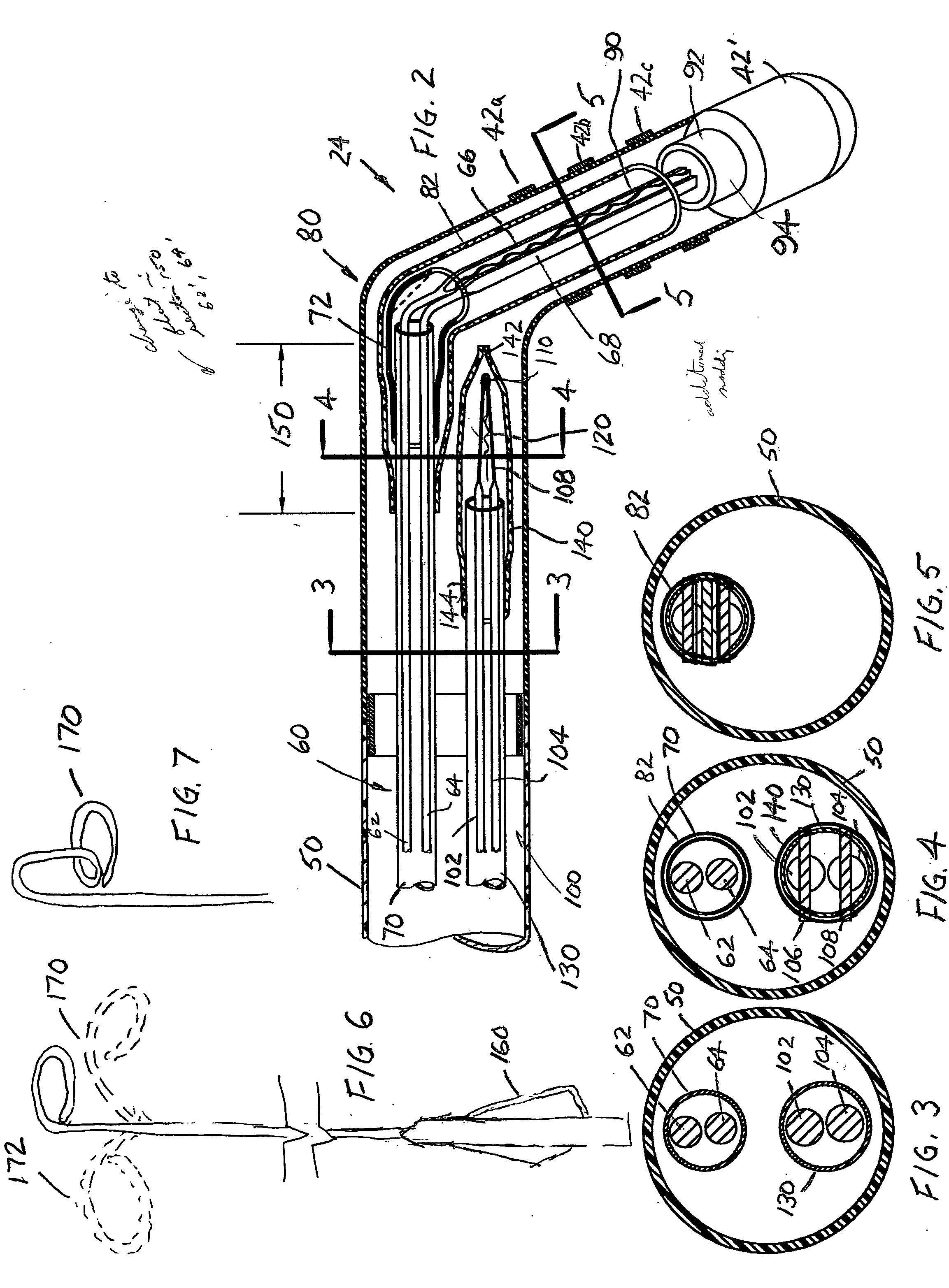
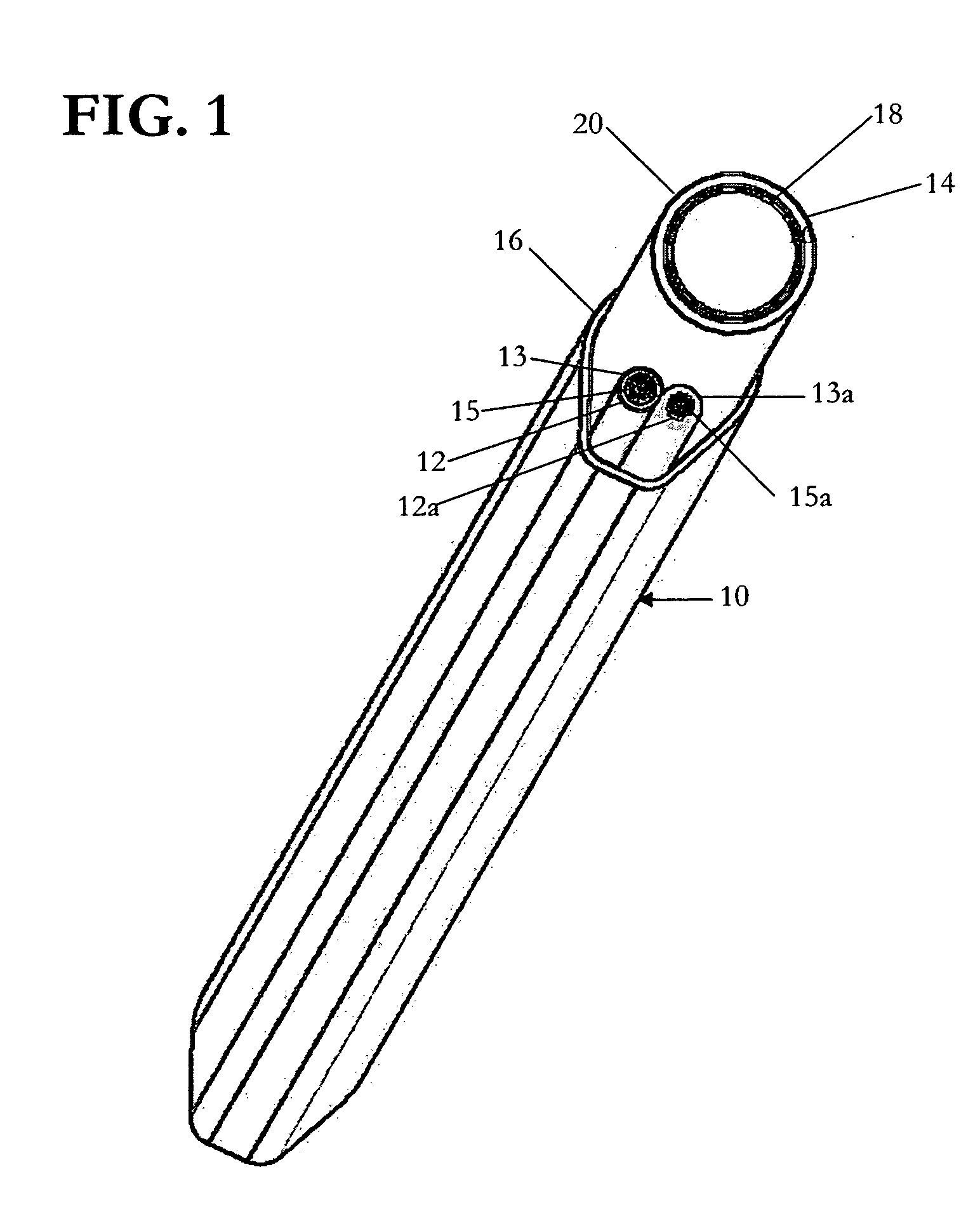
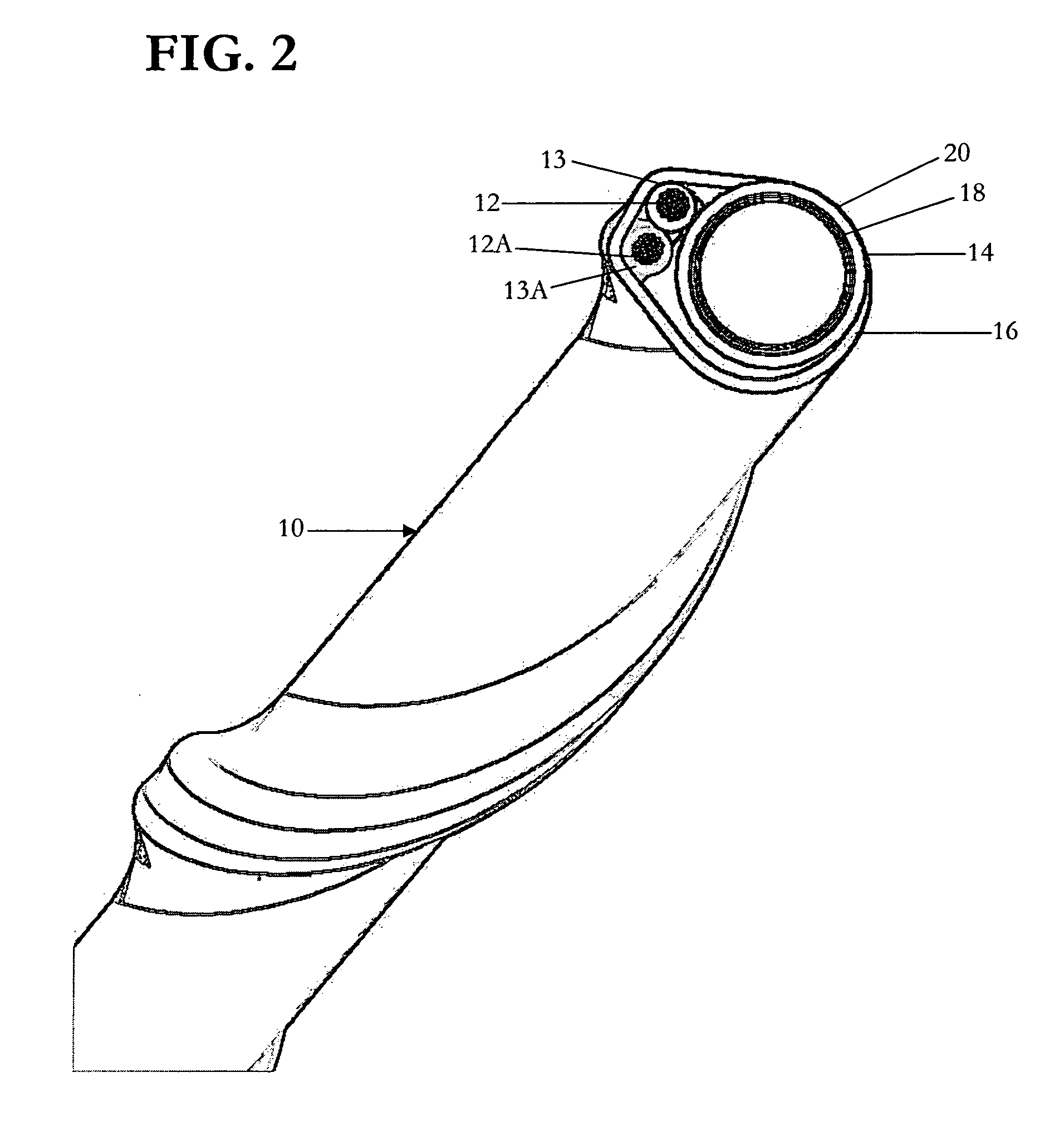
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter having deflection assembly
An electrophysiology / ablation catheter assembly includes an elongated flexible casing that received a first catheter deflection assembly. Electrical leads are connected to each electrode on a distal portion of the catheter assembly and extend through the casing for external connection at a proximal end of the catheter assembly. A first actuator is operatively connected to the first catheter deflection assembly and operable upon movement to selectively effect displacement of the distal end. A second catheter deflection assembly is also disposed in the casing. A second actuator is connected adjacent the proximal end of the catheter deflection assembly and operable upon movement to selectively effect lateral displacement of the catheter at a location spaced from the first curved configuration of the distal end.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
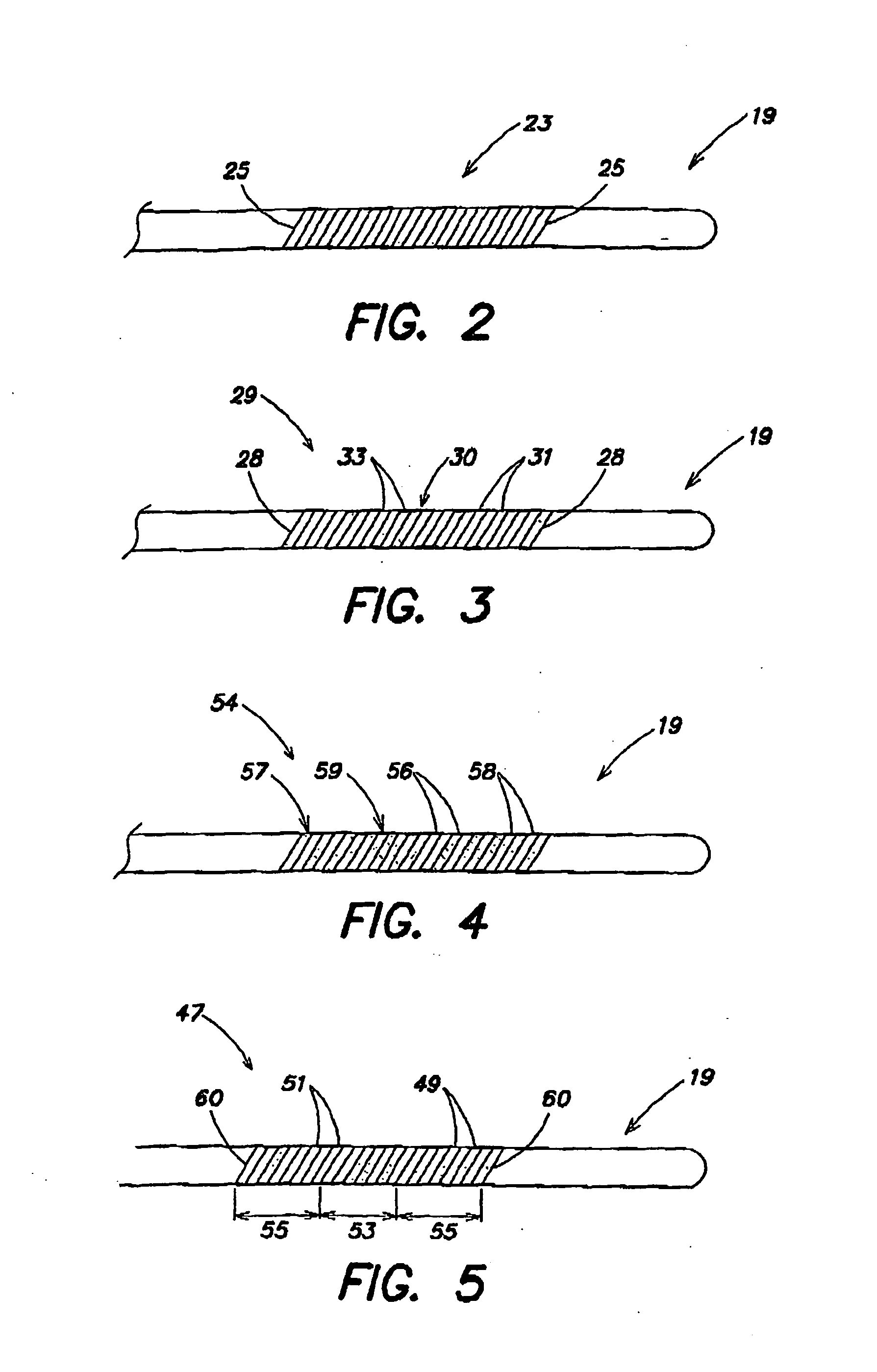
Electrophysiology catheter and system for gentle and firm wall contact
InactiveUS20060278248A1Easy to controlSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringContact pressureCell electrophysiology
A method of applying an electrode on the end of a flexible medical device to the surface of a body structure, the method including navigating the distal end of the device to the surface by orienting the distal end and advancing the device until the tip of the device contacts the surface and the portion of the device proximal to the end prolapses. Alternatively the pressure can be monitored with a pressure sensor, and used as an input in a feed back control to maintain contact pressure within a pre-determined range.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
In-vivo calibration of contact force-sensing catheters using auto zero zones
A method for the in vivo re-calibration of a force sensing probe such as an electrophysiology catheter provides for the generation of an auto zero zone. The distal tip of the catheter or other probe is placed in a body cavity within the patient. Verification that there is no tissue contact is made using electrocardiogram (ECG) or impedance data, fluoroscopy or other real-time imaging data and / or an electro-anatomical mapping system. Once verification that there is no tissue contact is made, the system recalibrates the signal emanating from the force sensor setting it to correspond to a force reading of zero grams and this recalibrated baseline reading is used to generate and display force readings based on force sensor data.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Electrophysiology catheter and system for gentle and firm wall contact
InactiveUS20070062546A1Easy to controlSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringContact pressureCell electrophysiology
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Magnetic navigation maneuvering sheath
The inventive apparatus may be slid onto a guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters, solid catheters, such as Electrophysiology catheters and multi-lumen tubing and advanced to the distal end of the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters, solid catheters, such as Electrophysiology catheters and multi-lumen tubing to assist in holding the distal end of the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters, solid catheters, such as Electrophysiology catheters and multi-lumen tubing at a target location within a patient, by utilizing an externally applied magnetic field to hold a plurality of magnetic elements on the apparatus in alignment with the target location. A medical device may then be advanced through the guiding catheter, for example, to the target location in the patient, without the guiding catheter backing out. The apparatus in combination with magnetic navigation thus provides support to hold the guiding catheter or other thru-lumen catheters, solid catheters, such as Electrophysiology catheters and multi-lumen tubing in place to prevent back out of the catheter.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
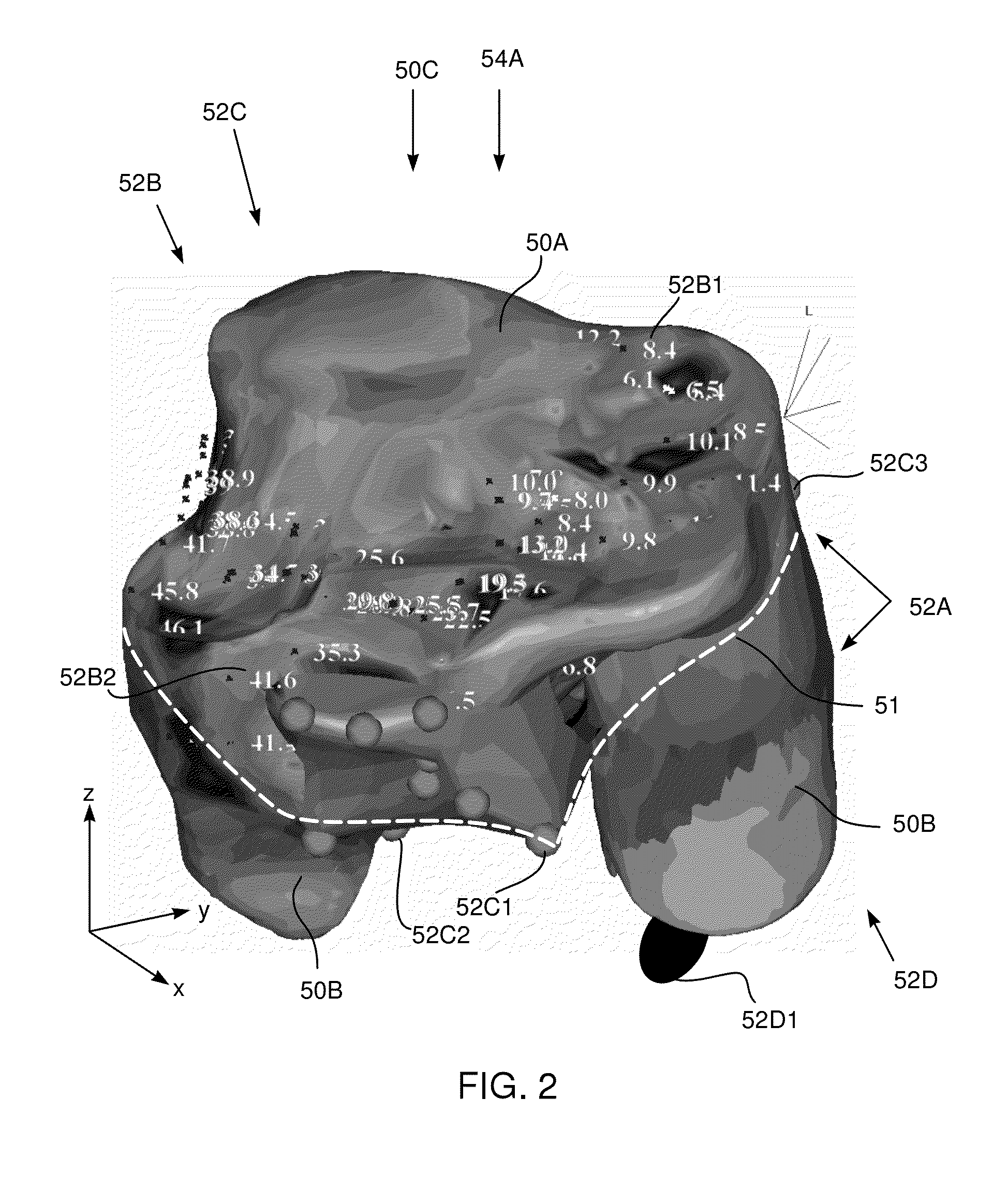
Selectably transparent electrophysiology map
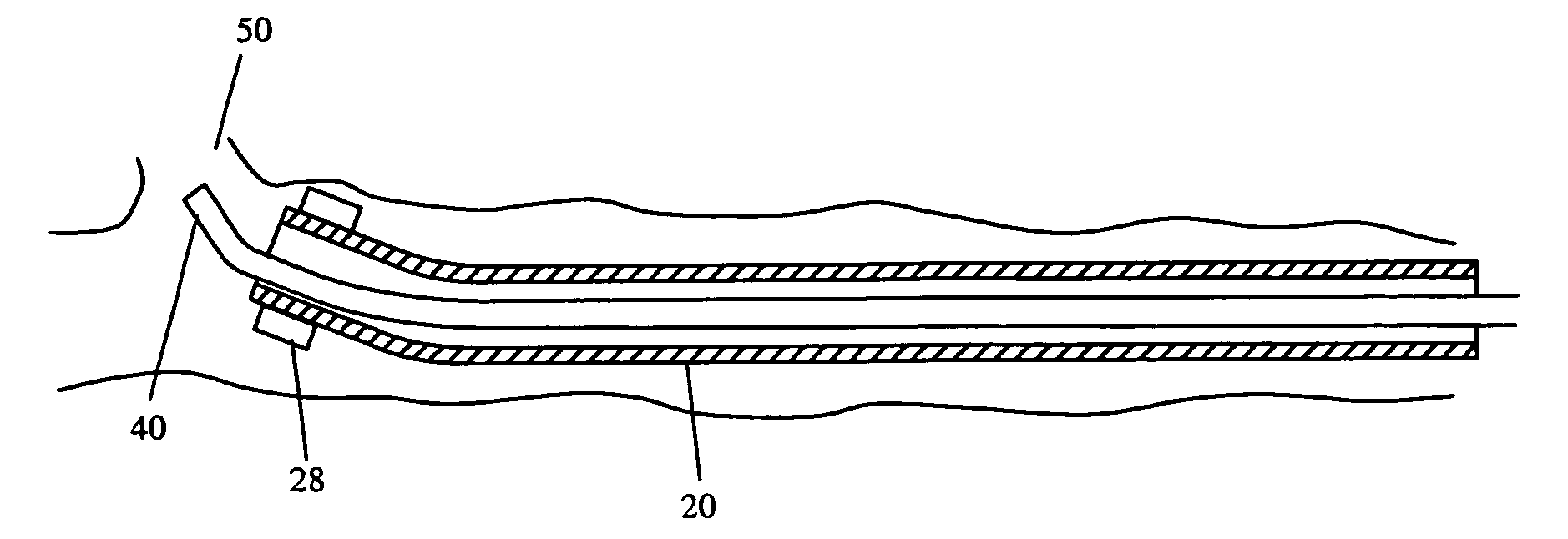
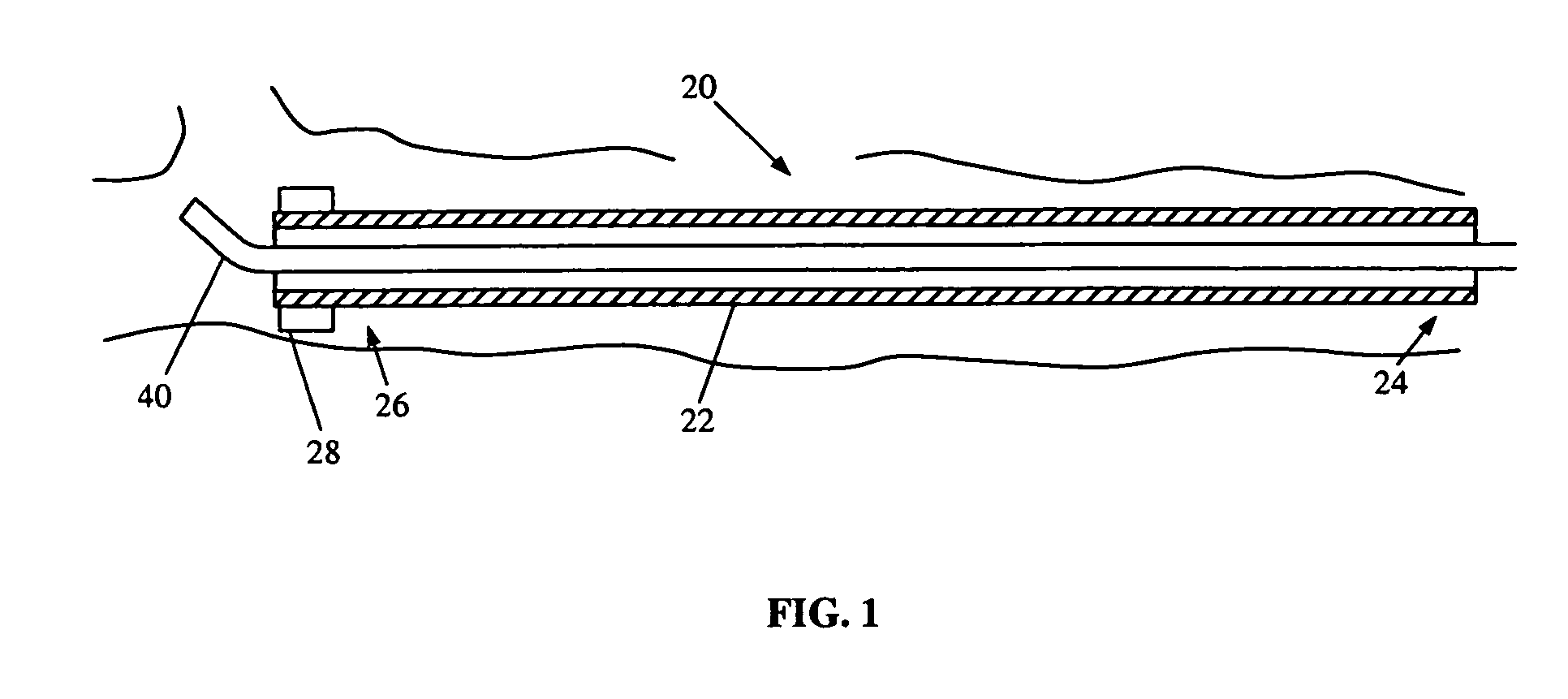
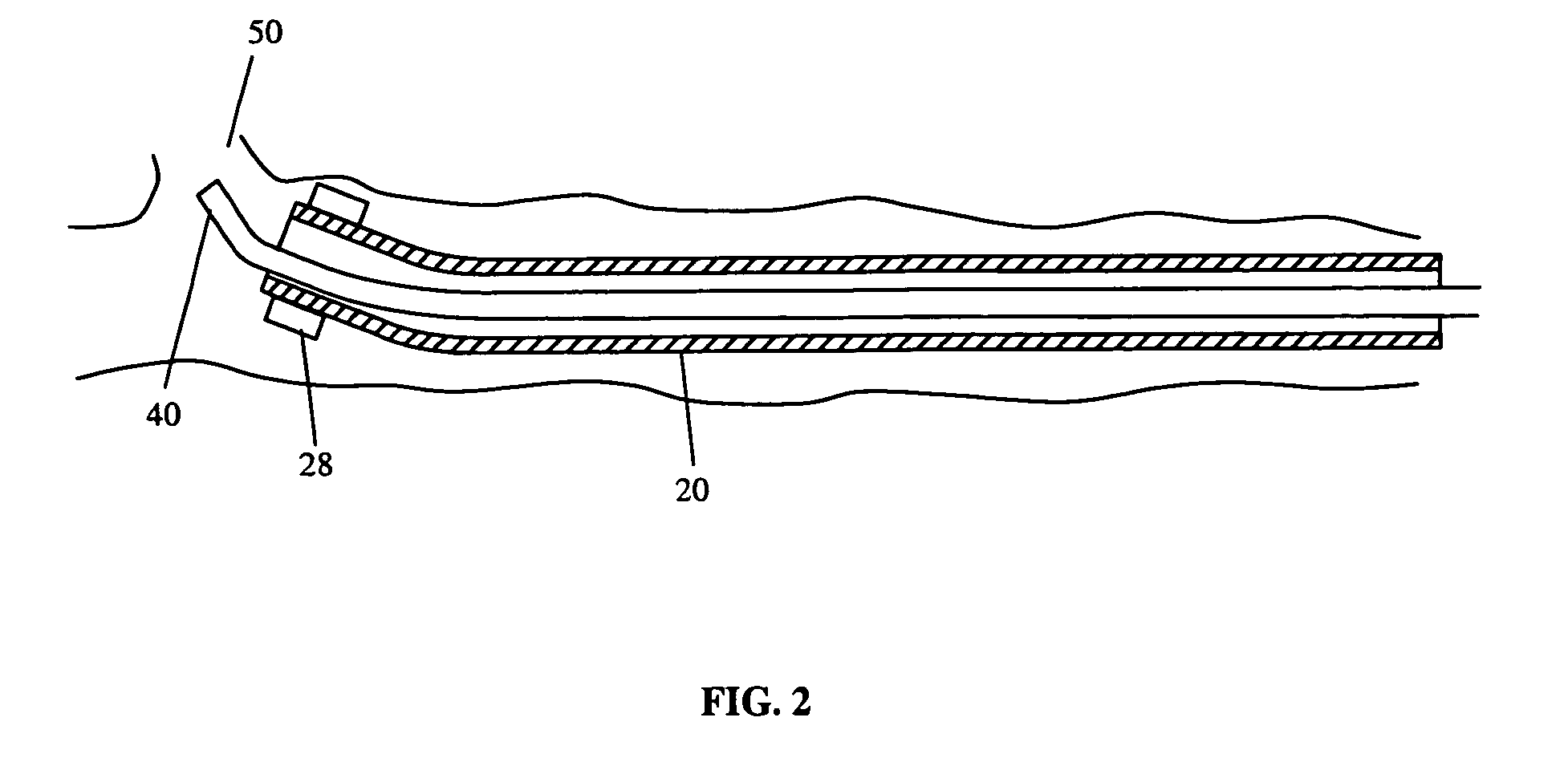
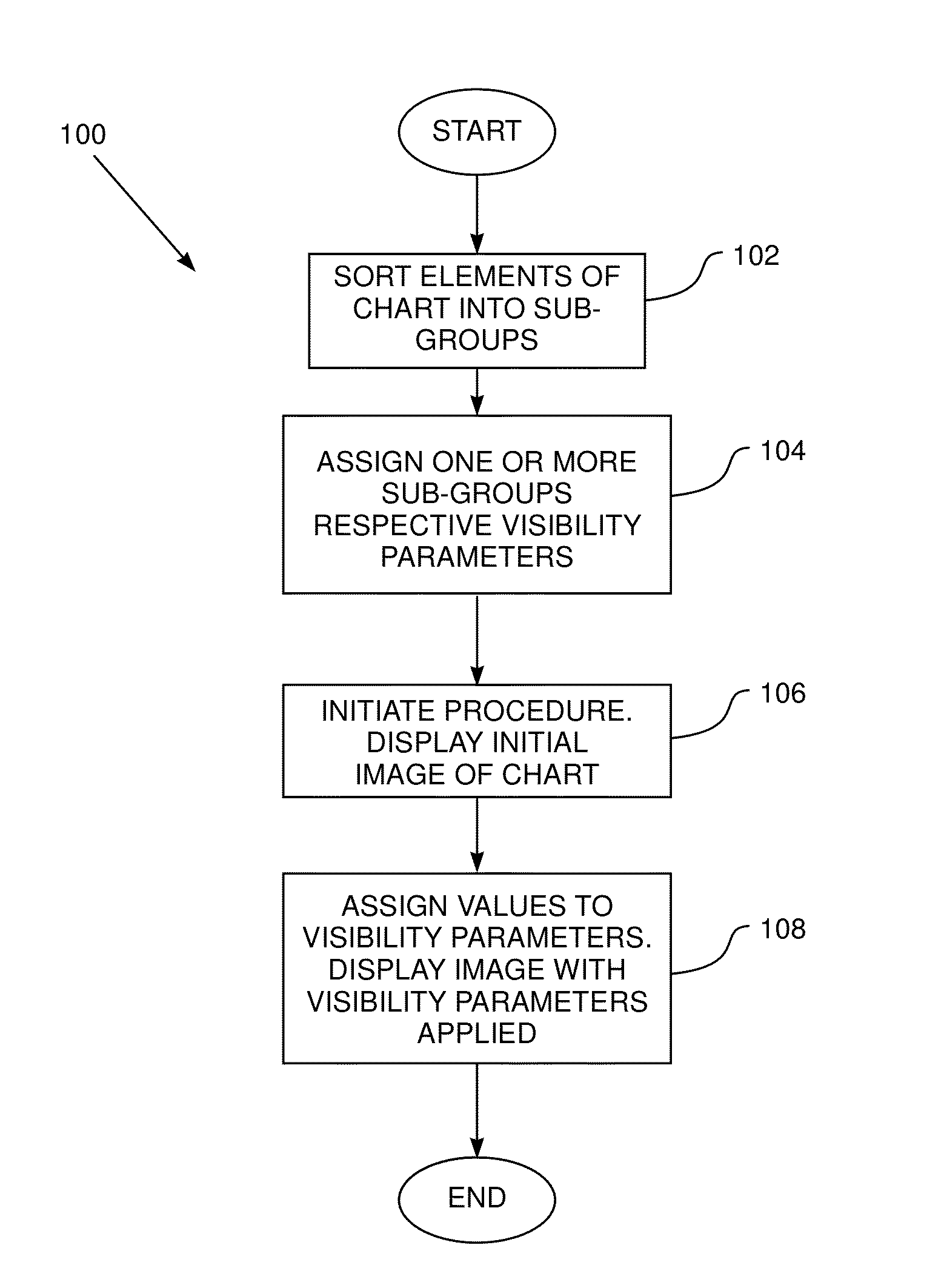
A method for mapping a body organ, including receiving a three-dimensional (3D) map of the body organ together with items of auxiliary information having respective location coordinates in a frame of reference of the 3D map and apportioning the items into a plurality of sub-groups. The method further includes assigning to a selected sub-group a visibility parameter indicative of a relative visibility of the selected sub-group in relation to the map and to other sub-groups. The method also includes displaying the 3D map of the body organ in a selected orientation while selectively superimposing on the 3D map one or more of the items in the selected sub-group responsively to the orientation, the respective location coordinates of the items, and the assigned visibility parameter.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
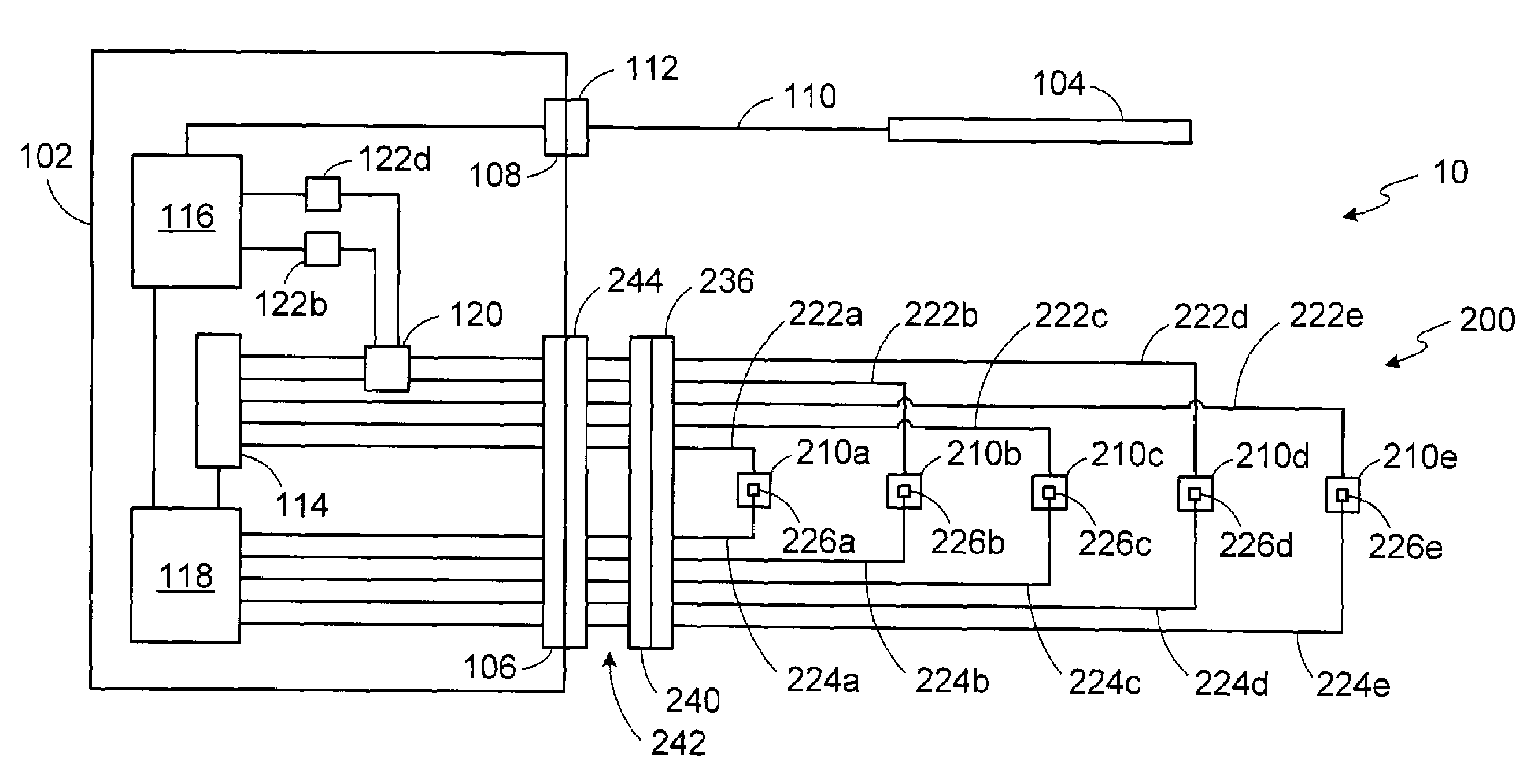
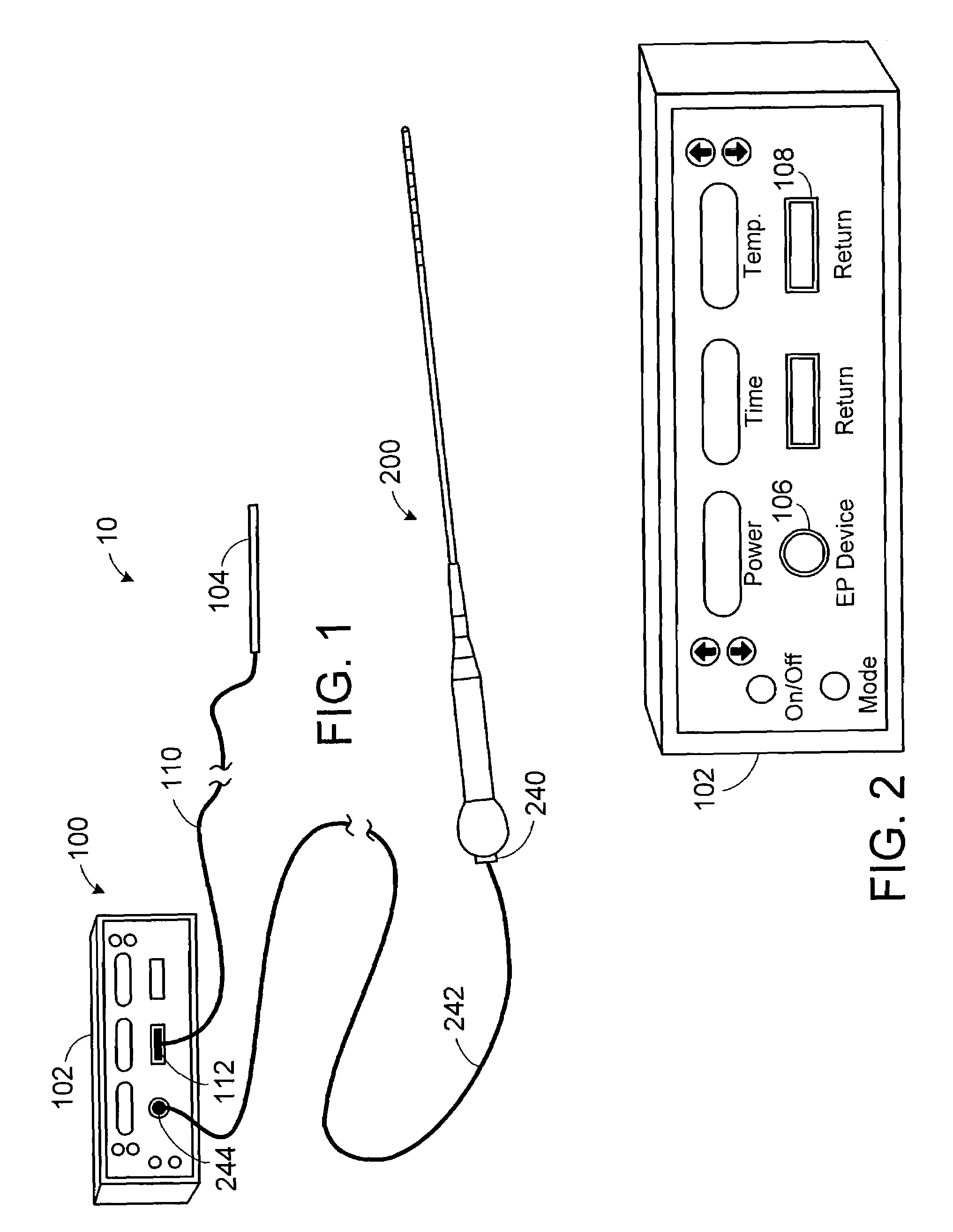
Power supply and control apparatus and electrophysiology systems including the same
ActiveUS7357800B2Easy to createHigh densityDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingElectricityEngineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS20050273006A1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a range of about −180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
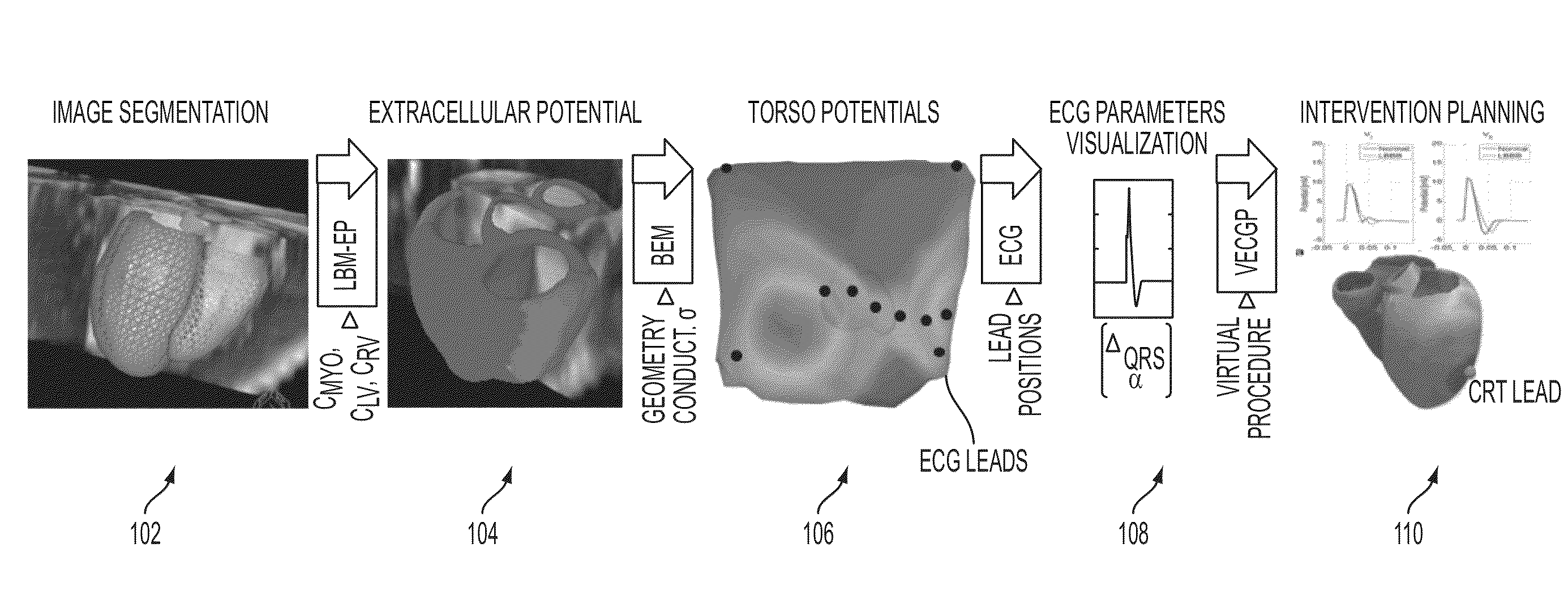
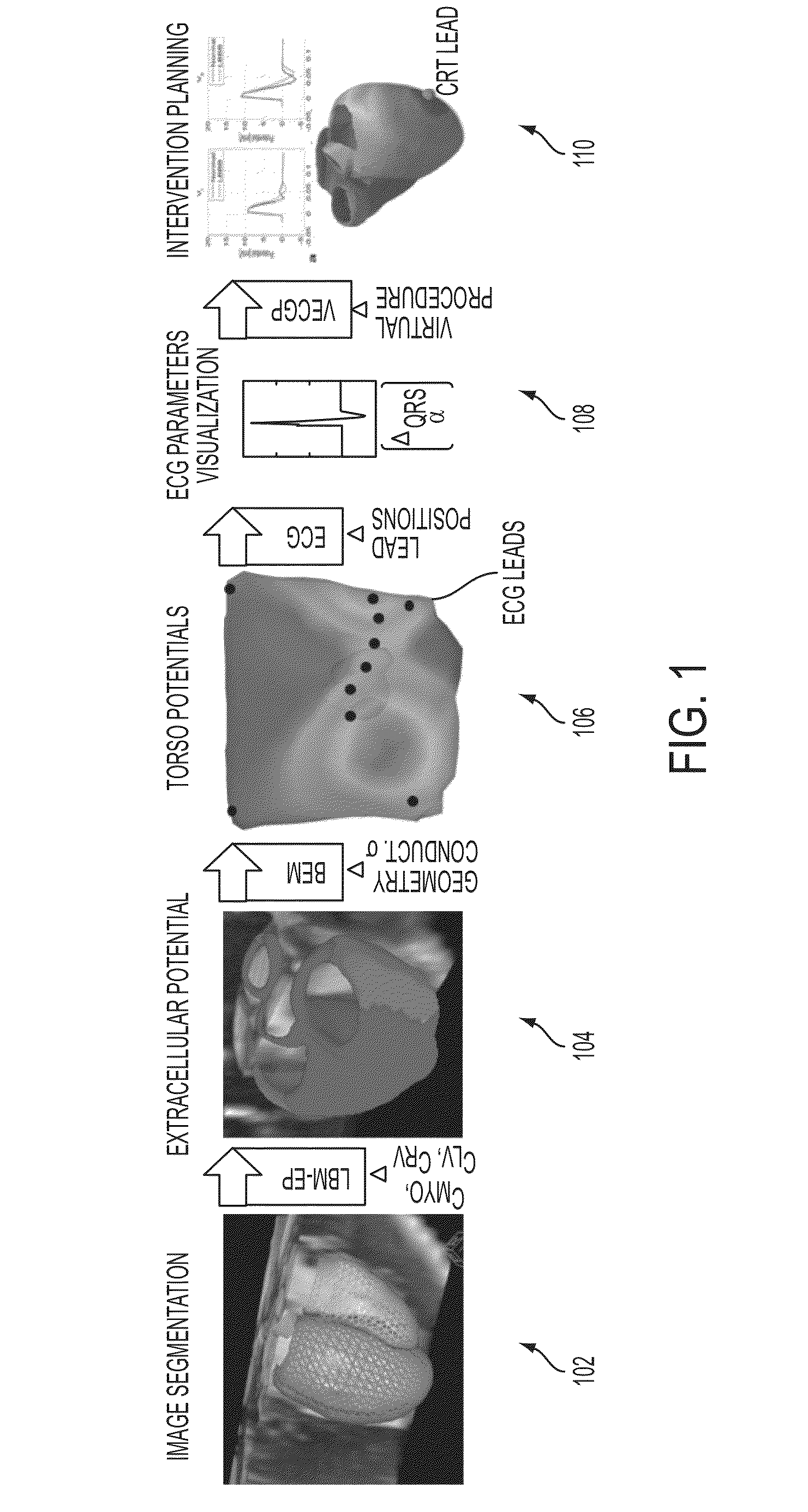
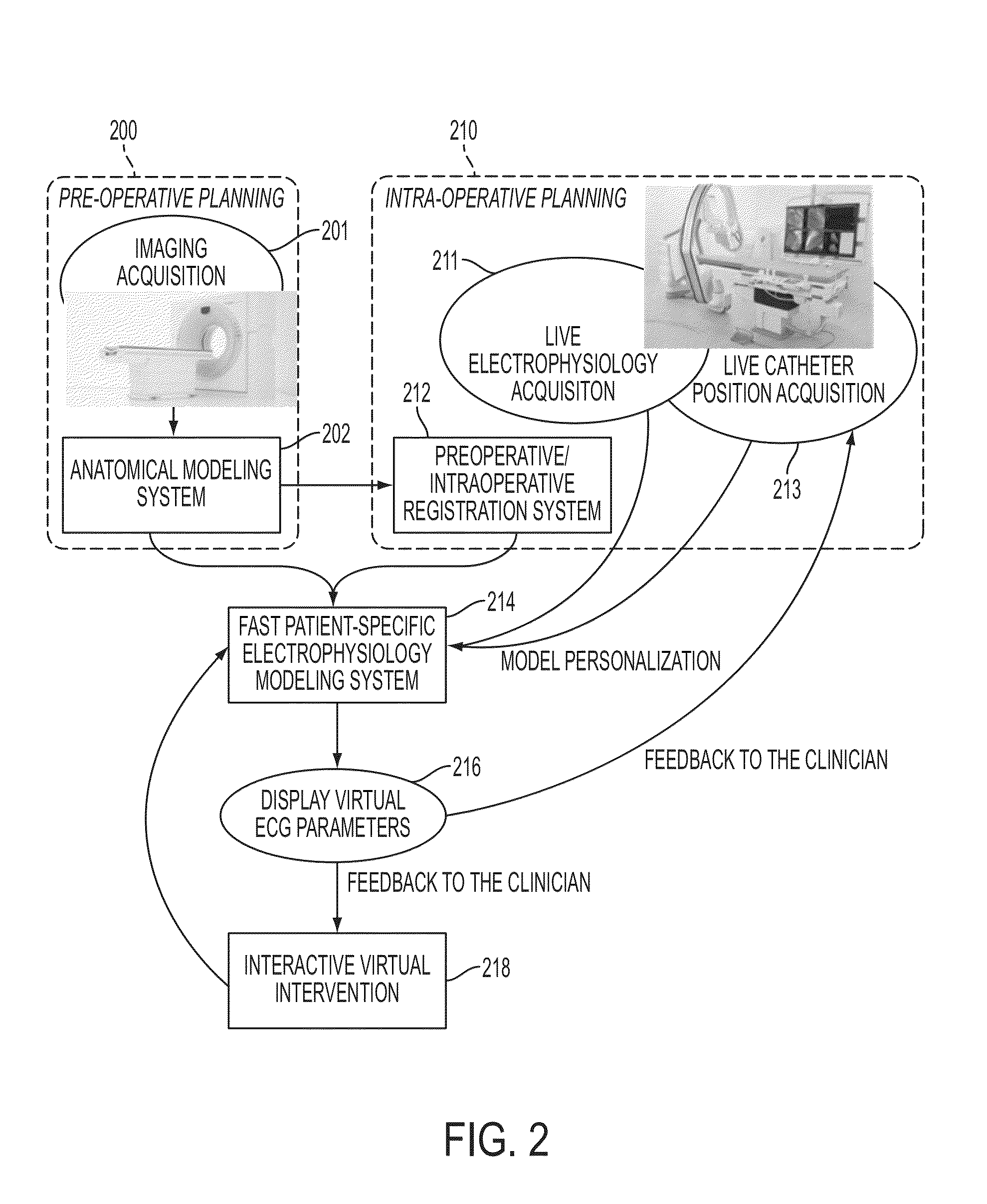
System and Method for Patient Specific Planning and Guidance of Electrophysiology Interventions
ActiveUS20150042646A1Physical therapies and activitiesDetails involving processing stepsRadiologyCell electrophysiology
A method and system for patient-specific planning and guidance of electrophysiological interventions is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from cardiac image data of a patient. A patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model and patient-specific electrophysiology measurements. Virtual electrophysiological interventions are performed using the patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. A simulated electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is calculated in response to each virtual electrophysiological intervention.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for using electrophysiology properties for classifying arrhythmia sources
ActiveUS20170049348A1Easy to identifyDiagnostic signal processingElectrocardiographyVelocity conductionCell electrophysiology
A method for determining electrophysiology properties of tissue comprising acquiring electrical signal data from a plurality of electrodes (130) of one or more catheters, determining at least one electrode clique from the plurality of adjacent electrodes (136), computing local conduction velocity vectors for the at least one electrode clique (138), determining at least one catheter orientation independent indicator from which to classify an arrhythmia source based on one or more of an angular dependence parameter associated with a flow field of the local velocity conduction vectors, an eccentricity parameter reflecting the uniformity of local conduction velocity, and divergence and curl-like sums or closed path integral parameters associated with the local velocity vectors, and displaying a rhythm classification responsive to catheter movement thereby facilitating identification of types and causes of arrhythmia disorders.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
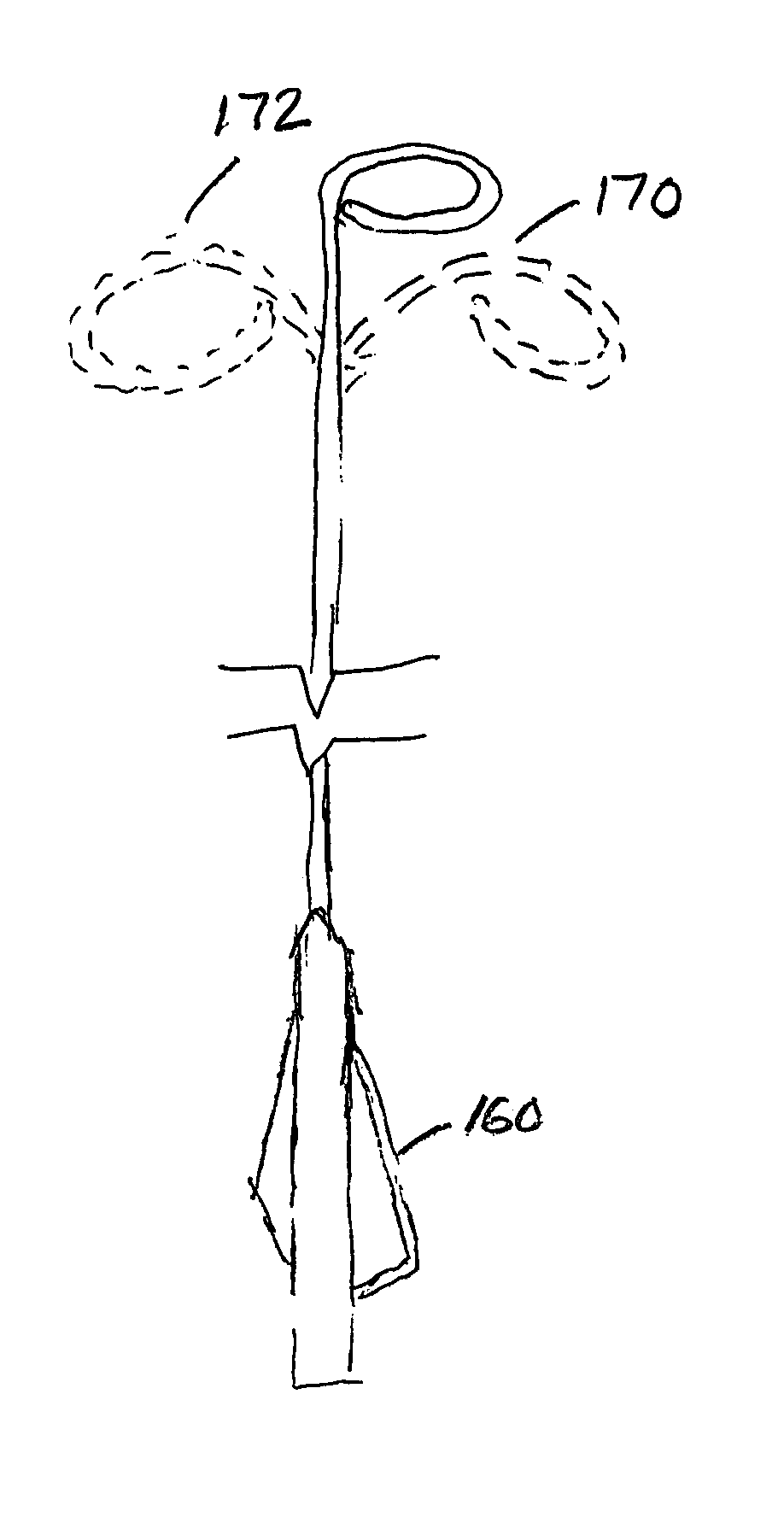
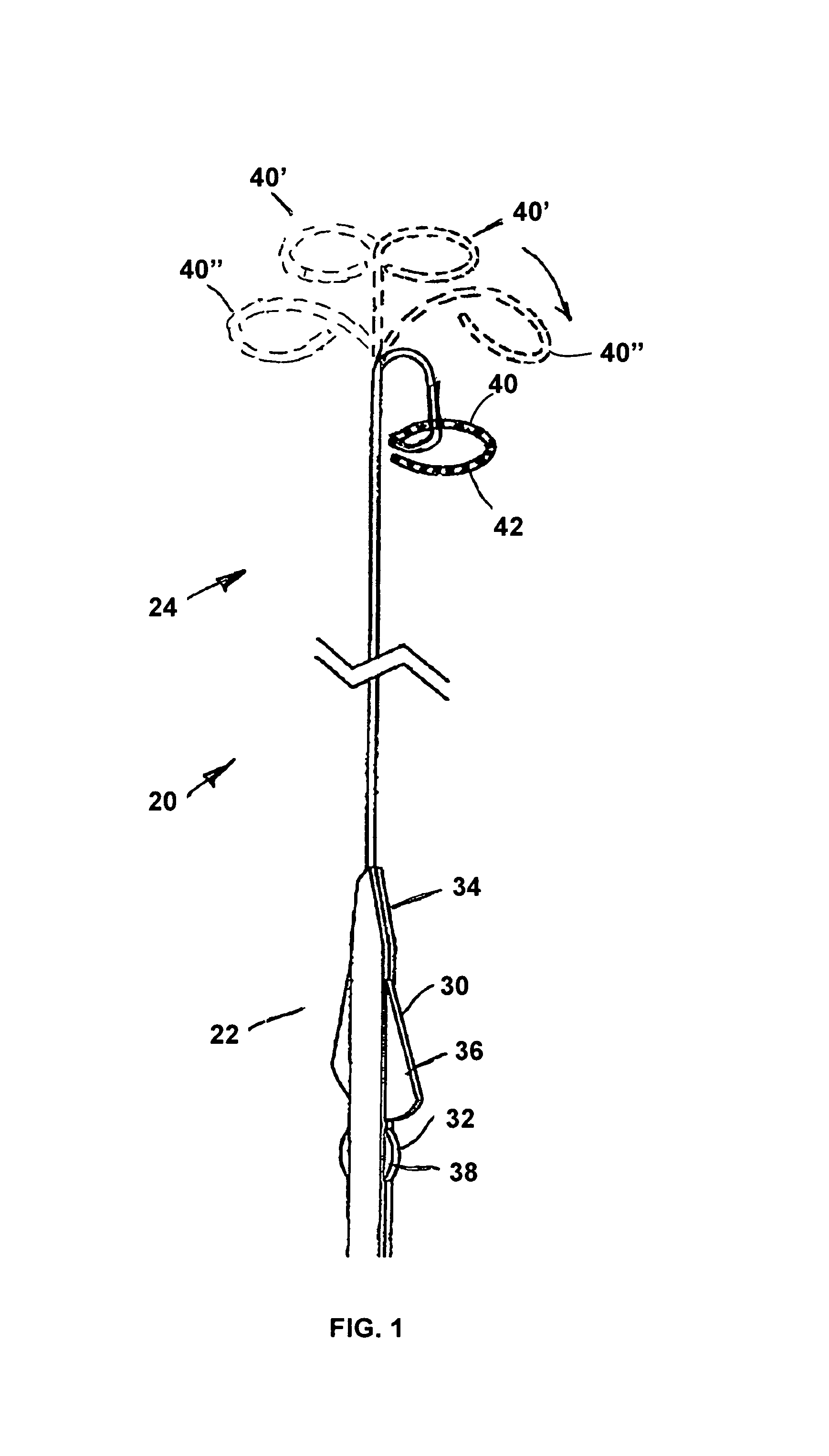
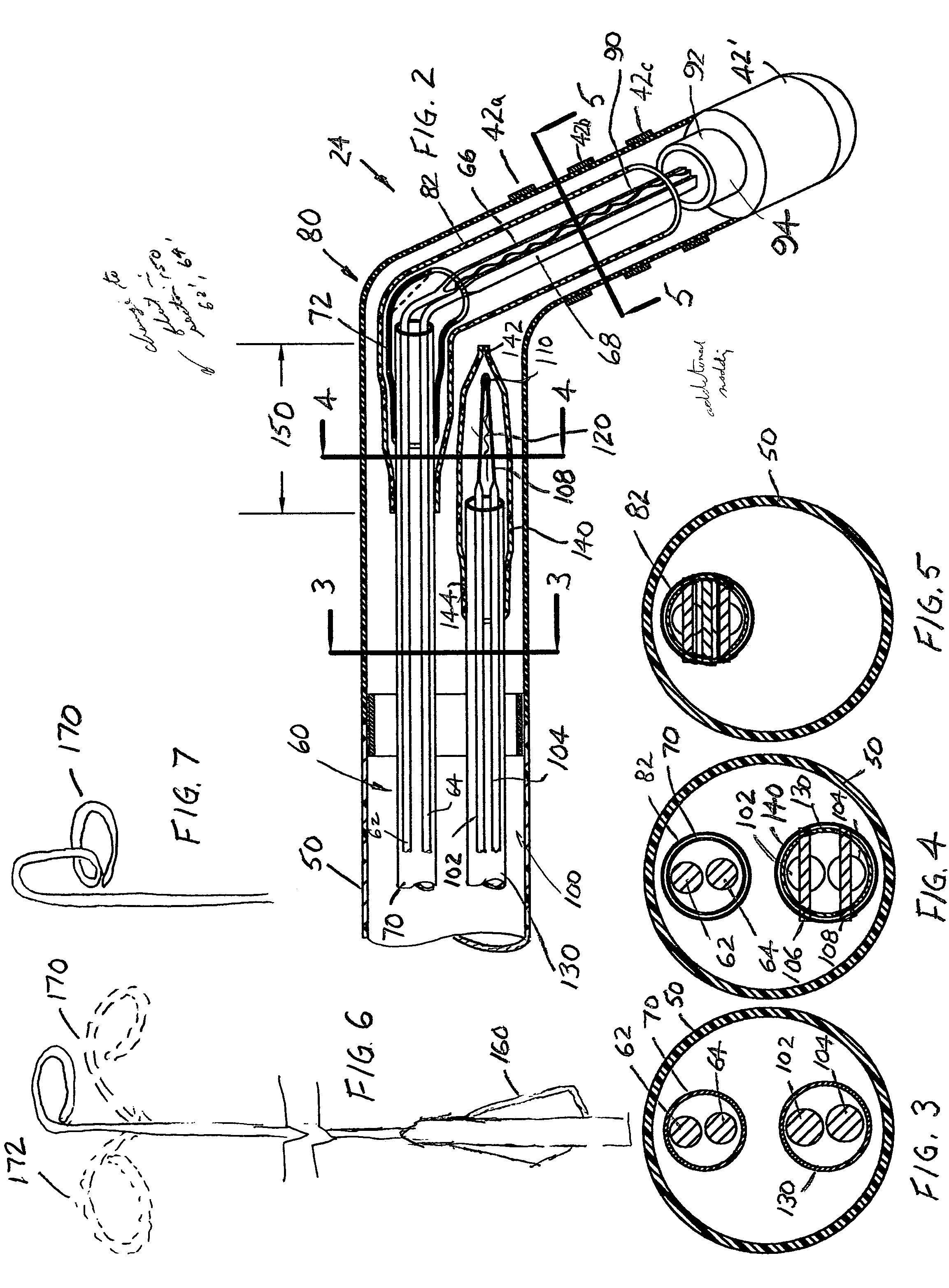
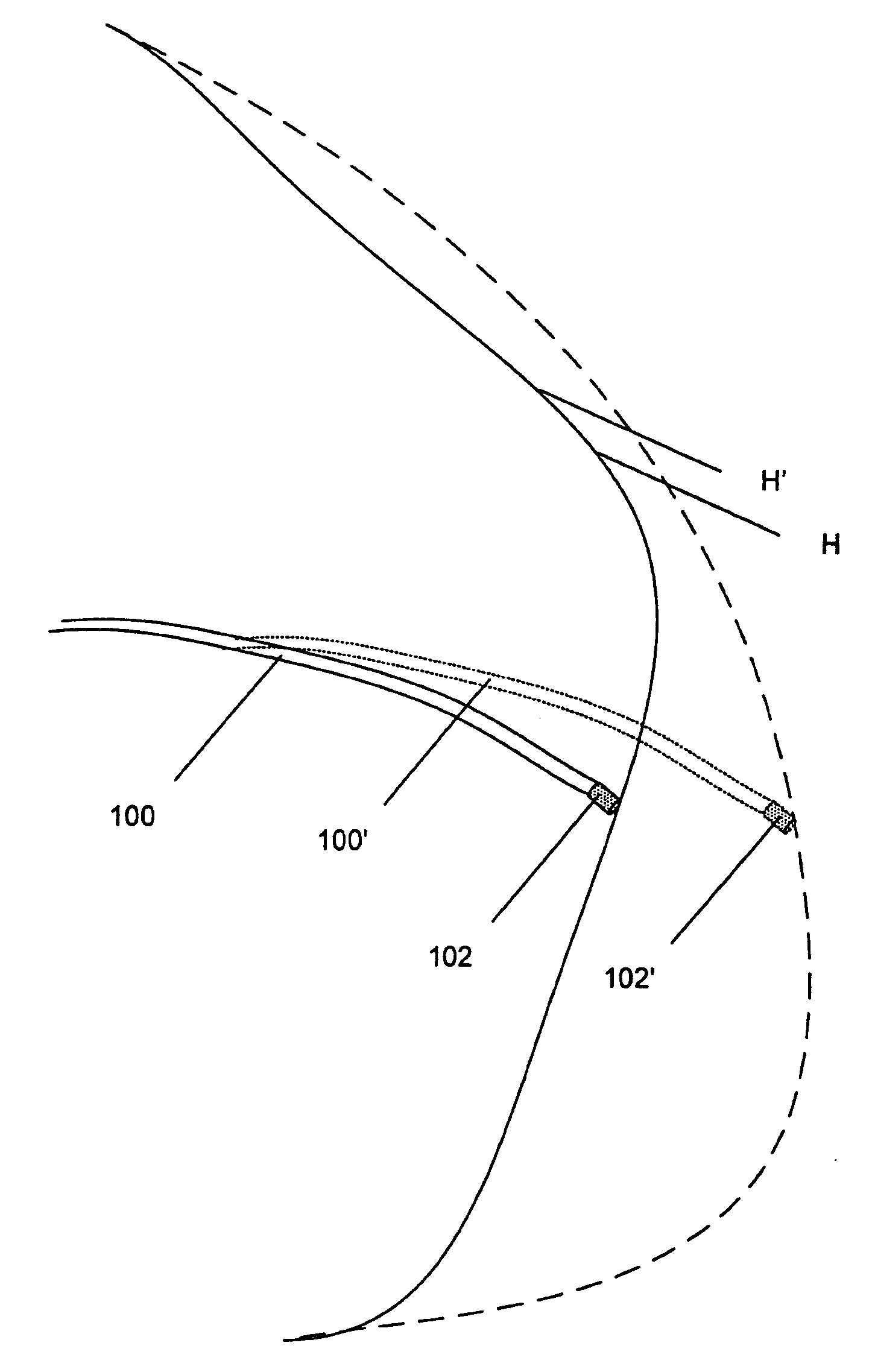
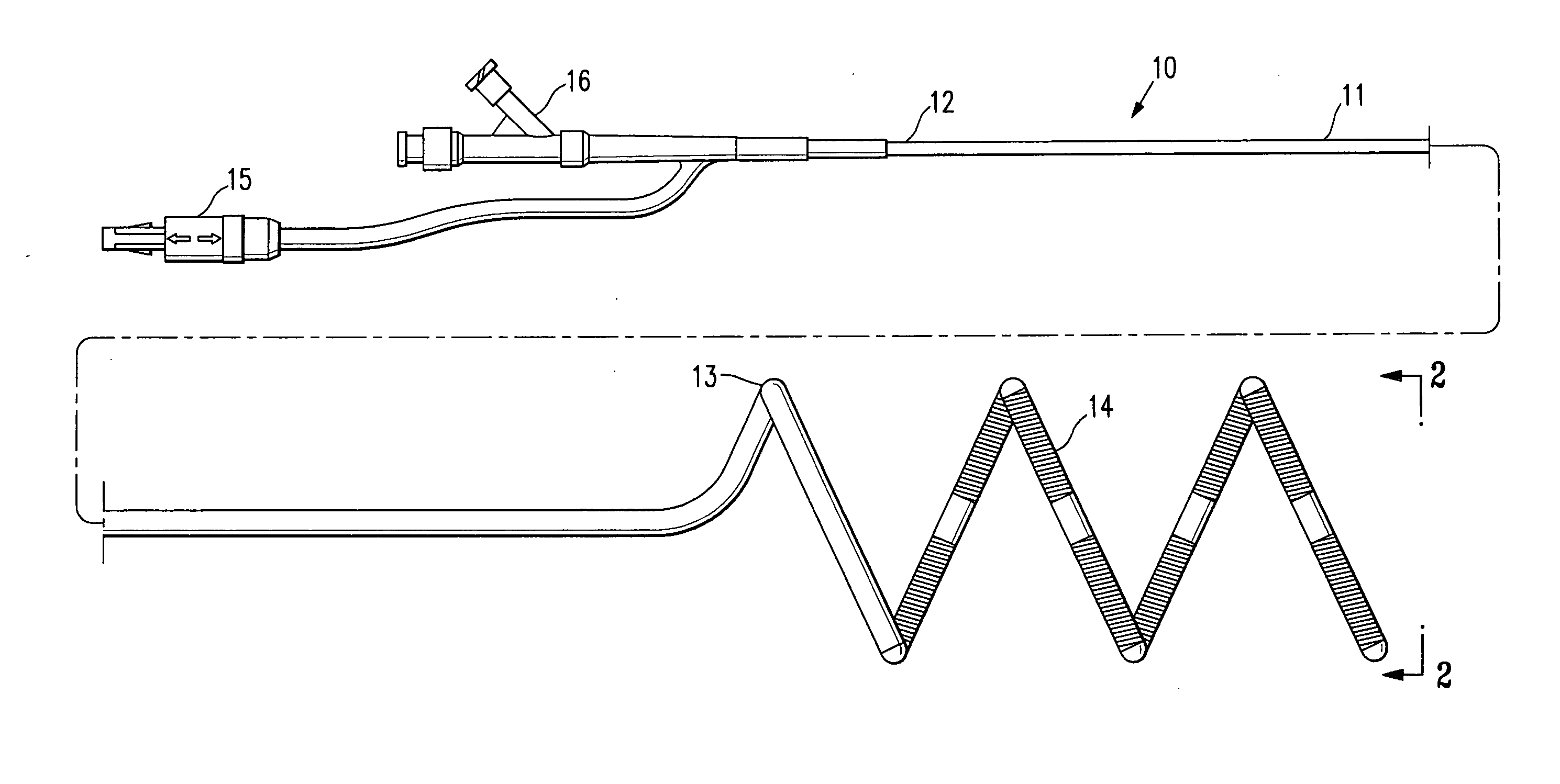
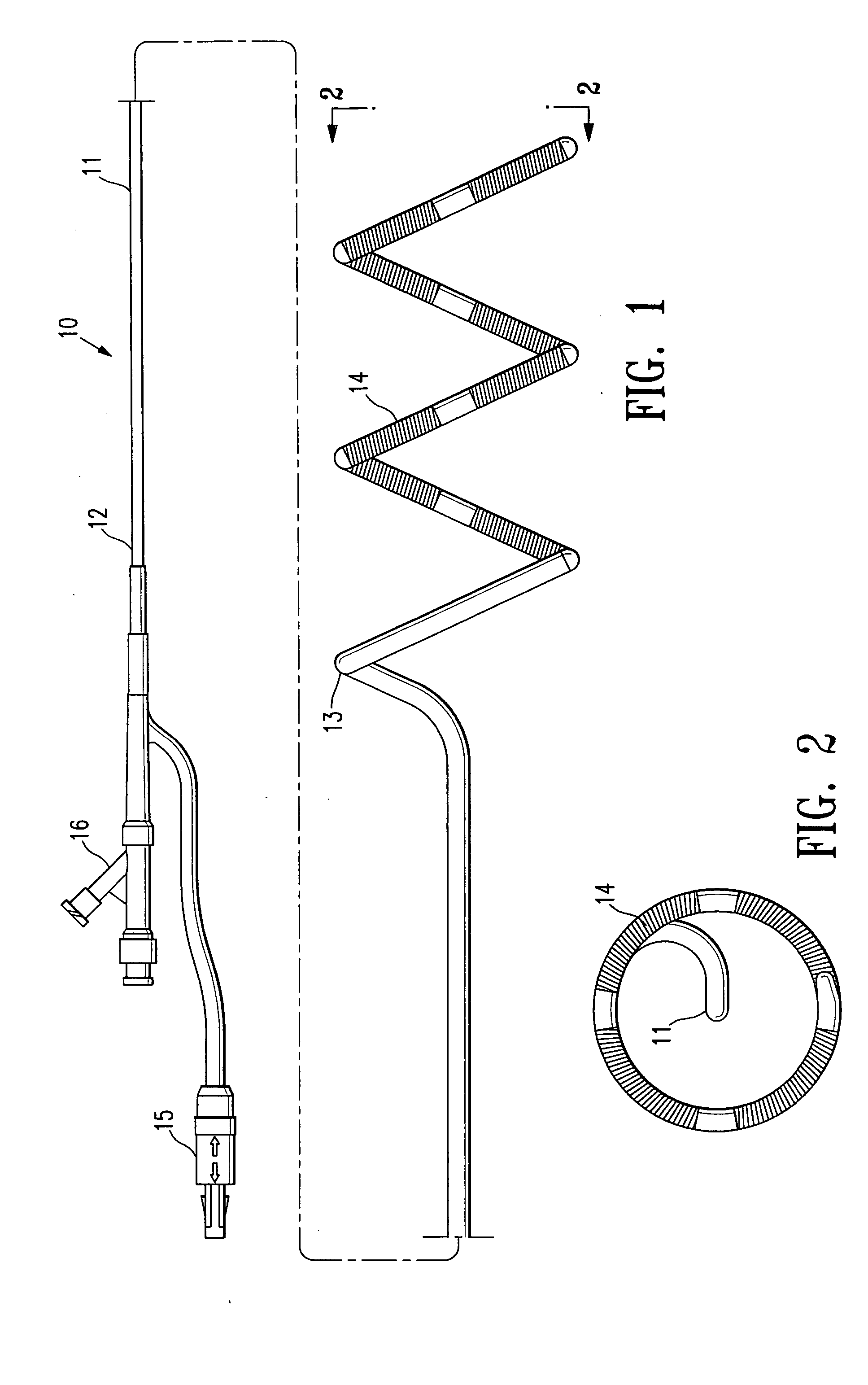
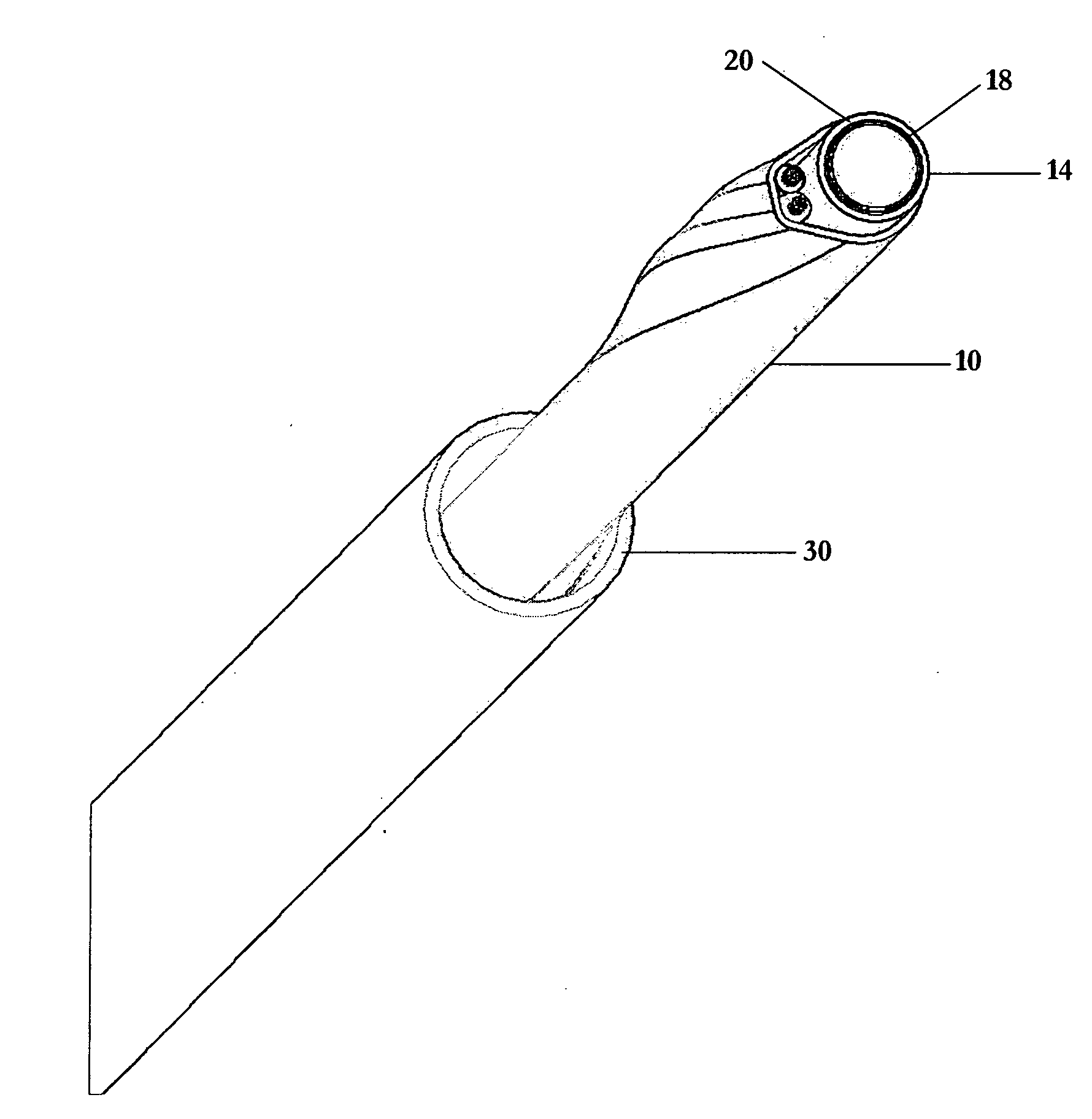
Helically shaped electrophysiology catheter
InactiveUS20050015084A1Reduce configurationEasy to deploySurgical instruments for heatingCell electrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
An electrophysiology (EP) device suitable for ablating tissue within a patient's body lumen. The EP device of the invention generally comprises an elongated shaft having a distal shaft section with a helical shape and at least one electrode on an exterior portion thereof. One aspect of the invention comprises a method of performing a medical procedure, such as treating a patient for atrial arrhythmia, by forming a lesion using an EP device embodying features of the invention.
Owner:CARDIMA
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter having deflection assembly
ActiveUS20050187455A1Increase usageIncrease capacityElectrocardiographyCatheterDistal portionActuator
An electrophysiology / ablation catheter assembly includes an elongated flexible casing that received a first catheter deflection assembly. Electrical leads are connected to each electrode on a distal portion of the catheter assembly and extend through the casing for external connection at a proximal end of the catheter assembly. A first actuator is operatively connected to the first catheter deflection assembly and operable upon movement to selectively effect displacement of the distal end. A second catheter deflection assembly is also disposed in the casing. A second actuator is connected adjacent the proximal end of the catheter deflection assembly and operable upon movement to selectively effect lateral displacement of the catheter at a location spaced from the first curved configuration of the distal end.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
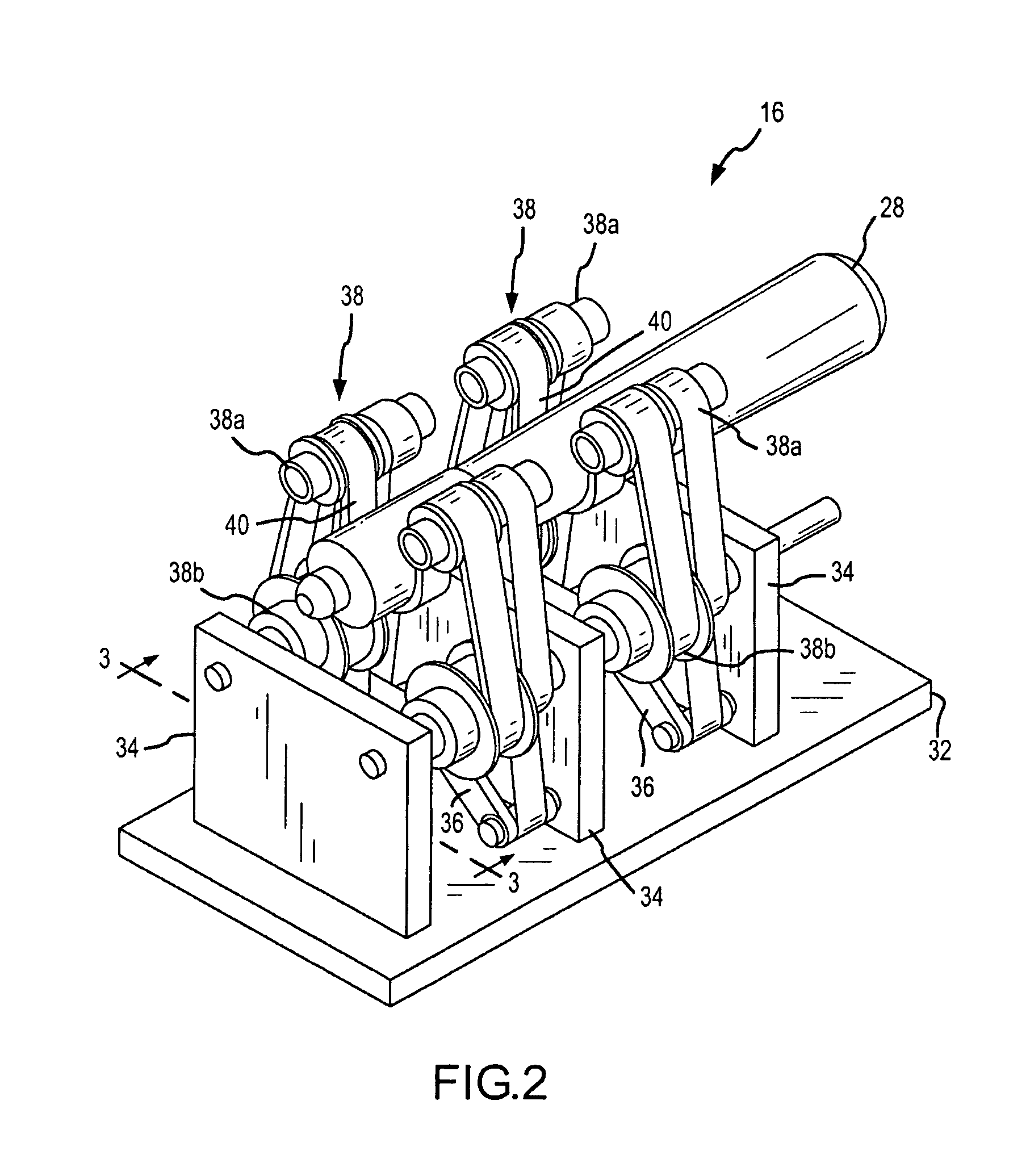
Long travel steerable catheter actuator
The present invention is an electrophysiology, RF ablation, or similar catheter (i.e., catheter or sheath) that includes an actuator that significantly increases the length of travel (i.e., steering travel) of the actuation wires, as compared to the length of travel provided by prior art actuators. The catheter includes a hollow flexible tubular body, a pair of actuation wires disposed in a side-by-side relationship in the body, a handle attached to a proximal end of the body, an actuator pivotally mounted to the handle, an arcuate internal gear rack disposed on the actuator, one or more pulleys pivotally mounted on the handle and coaxially coupled to a pinion gear engaged with the gear rack, and a guide block mounted within the handle. The one or more pulleys include a first channel in which the first actuation wire resides and a second channel in which the second actuation wire resides. The actuation wires pass through holes in the guide block, which aligns the wires into their respective channels. The actuation wires enter into their respective channels on opposite sides of the axis of the one or more pulleys. As the actuator is pivoted relative to the handle, the gear rack rotates the pinion gear and the one or more pulleys. This causes one of the actuation wires to be in-hauled (i.e., wound about the one or more pulleys) and the other actuation wire to be paid-out (i.e., unwound from the one or more pulleys).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
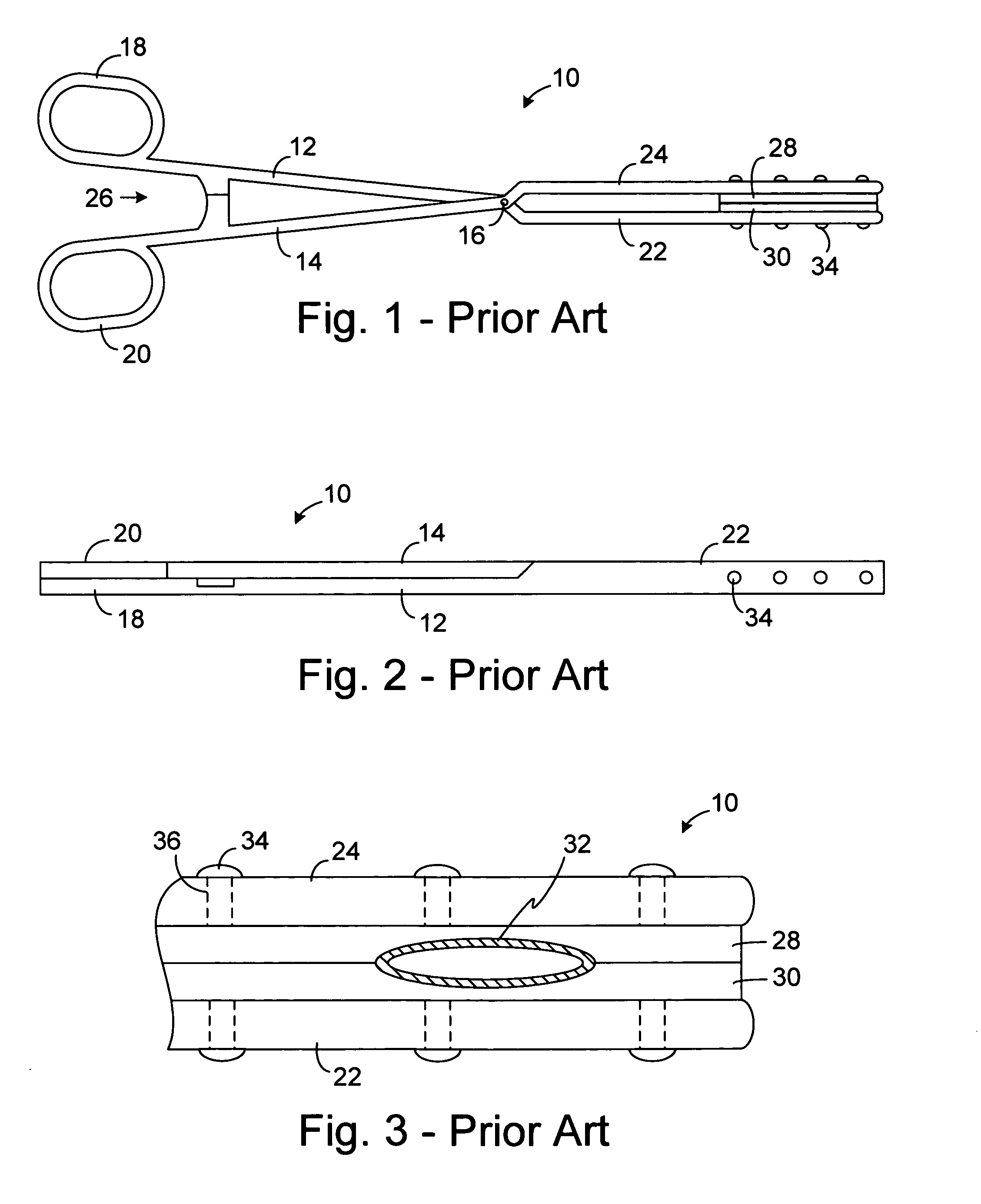
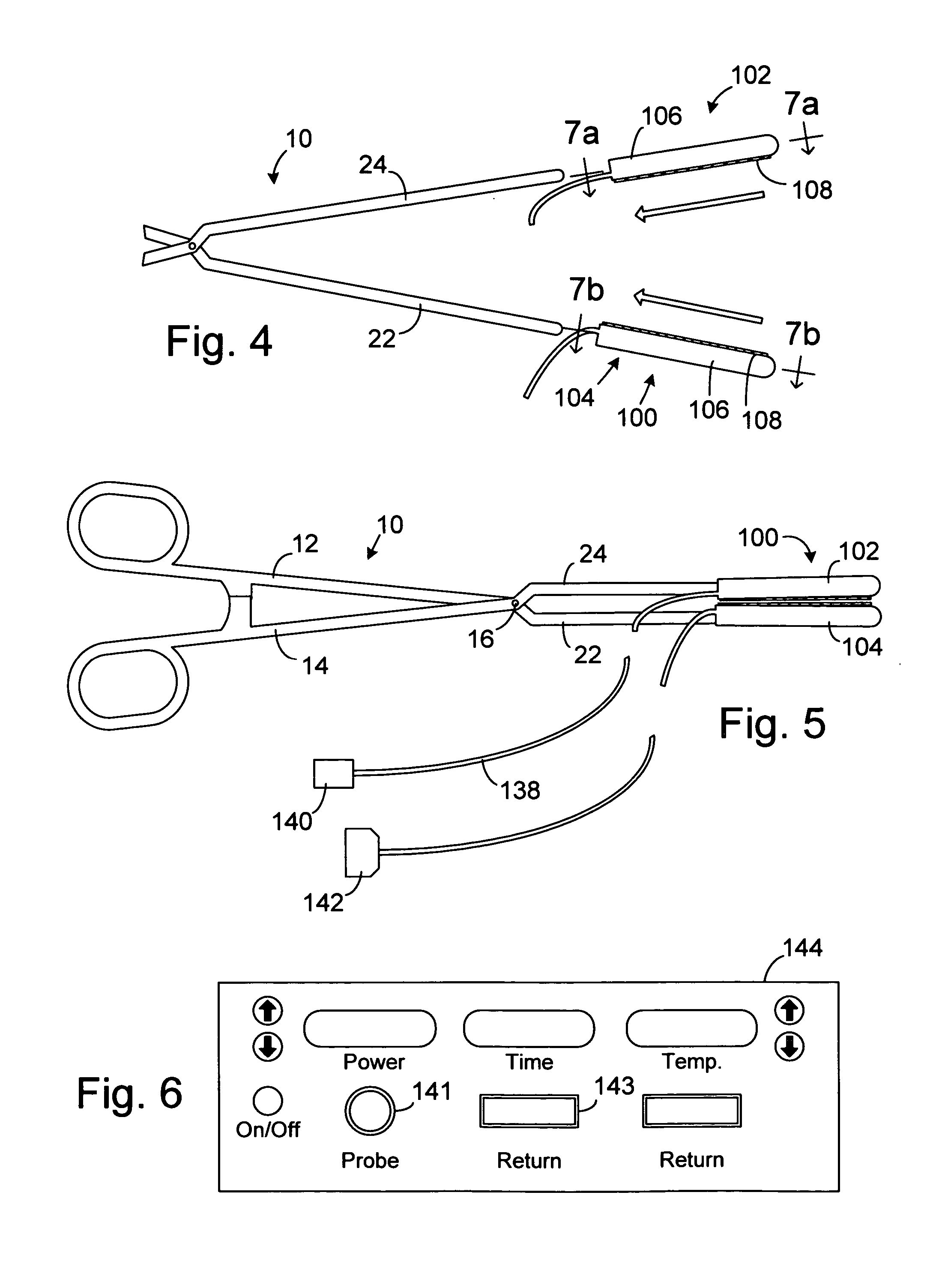
Apparatus for converting a clamp into an electrophysiology device
InactiveUS20050215993A1Quick conversionLow costSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsEngineeringCell electrophysiology
An apparatus for use with a clamp including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and at least one energy transmission device carried by the base member. An apparatus for use with a clamp and a probe that carries at least one energy transmission device including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and an engagement device associated with the base member and configured to engage the probe. A clamp including first and second clamp members, at least one of which is malleable, and a movement apparatus that moves at least one of the first and second clamp members relative to the other. A surgical system including a clamp with first and second clamp members and a device that removably mounts at least one electrode on at least one of the first and second clamp members.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Electrophysiology catheter with ablation electrode
In one embodiment, a shaft-mounted electrode for ablating tissue comprises an end portion and a middle portion. The end portion is configured differently than the middle portion such that, when the electrode is energized, the ratio of a first density of ablation energy that is emitted in a vicinity of the end portion to a second density of ablation energy that is emitted in a vicinity of the middle portion is lower than the ratio would be if the end portion were configured the same as the middle portion. In another embodiment, a shaft-mounted electrode for ablating tissue comprises at least two separate coiled conductors having interleaved spirals.
Owner:CR BARD INC
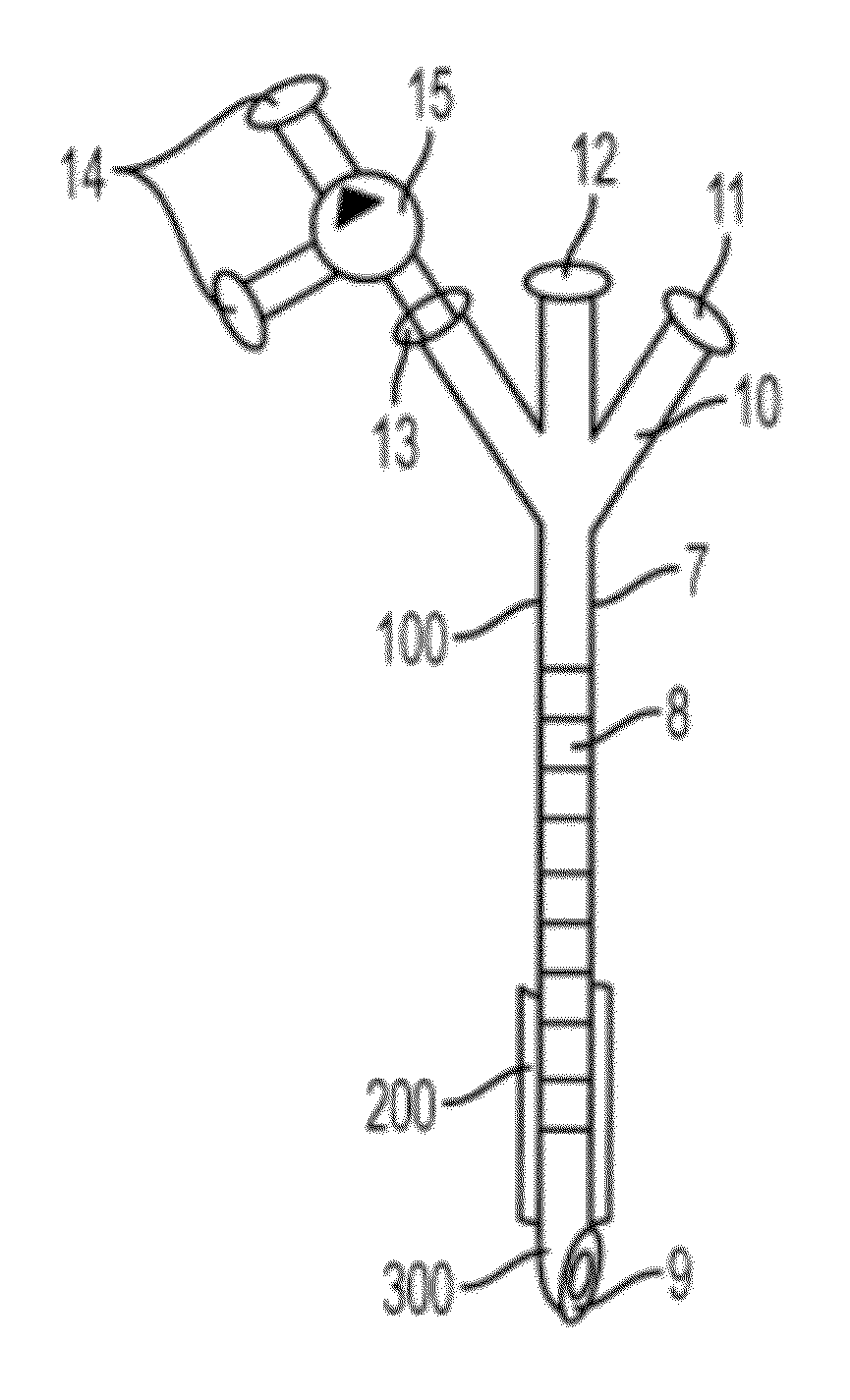
Access needle with direct visualization and related methods
ActiveUS20160100797A1Reduce clinical riskImprove efficacyElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCell electrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
Systems and methods for epicardial electrophysiology and other procedures are provided in which the location of an access needle may be inferred according to the detection of different pressure frequencies in separate organs, or different locations, in the body of a subject. Methods may include inserting a needle including a first sensor into a body of a subject, and receiving pressure frequency information from the first sensor. A second sensor may be included with the access needle to provide image data and / or cardiac waveform information of the subject.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and apparatus for selecting operating parameter values in electrophysiology procedures
InactiveUS20070167940A1Surgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesEnergy supplyCell electrophysiology
Methods of selecting operating parameter values for tissue ablation procedures are disclosed. Energy supply parameters may be selected based on inputs such as fluid flow rate, impedance, and the distance from an ablation electrode surface to a target tissue surface. The distance to place an ablation electrode surface from a target tissue surface may be selected based on various operating parameter values and / or operating condition values. Operating curves, lookup tables, or processors may be used to select operating parameter values.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Robotic surgical system and method for diagnostic data mapping
ActiveUS20070185404A1Reduce exposureShorten the timeSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsGraphicsDiagnostic data
A method of generating a diagnosis map of at least a portion of the heart includes inserting an electrode within the portion of a heart, robotically moving the electrode therein, measuring electrophysiology information at a point on the surface of the heart, associating the measured electrophysiology information with position information for the point on the surface of the heart, repeating the measuring and associating steps for a plurality of points on the surface of the heart, thereby generating a plurality of surface diagnostic data points, and generating the diagnosis map therefrom. The electrode may be moved within the heart randomly, pseudo-randomly, or according to one or more predetermined patterns. A three-dimensional model of the portion of the heart may be provided and presented as a graphical representation, either with or without information indicative of the measured electrophysiology information superimposed thereon.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
System for displaying data relating to energy emitting treatment devices together with electrophysiological mapping data
InactiveUS20090163801A1Minimizing potential riskLess riskUltrasound therapyElectrocardiographyGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system and method for treatment of tissue is provided. An electronic control unit is configured to generate displays signals used to create a graphical user interface. The display signals are generated in response to a first set of position signals indicative of the position of an electrophysiology mapping electrode relative to the tissue and a second set of position signals indicative of the position of a treatment device, such as a high intensity focused ultrasound transducer, that is configured to generate a beam of energy towards a selected region in the tissue. The graphical user interface displays an electrophysiology map of the tissue and an image of at least one of the treatment device and the beam of energy which may be superimposed on the electrophysiology map.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Implantable electrophysiology lead body
ActiveUS20070106144A1Spinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical conductorFluoropolymer
The invention is an electrophysiology lead body comprising two or more longitudinal elements, each having an outer surface, the longitudinal elements comprising electrical insulation material, the electrical insulation material consisting essentially of fluoropolymer; at least one conductor disposed within at least one of the longitudinal elements; and a cover consisting essentially of fluoropolymer, wherein the cover surrounds the longitudinal elements.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Methods and apparatus for the manipulation of particle suspensions and testing thereof
InactiveUS20120264134A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophysiology studyCell electrophysiology
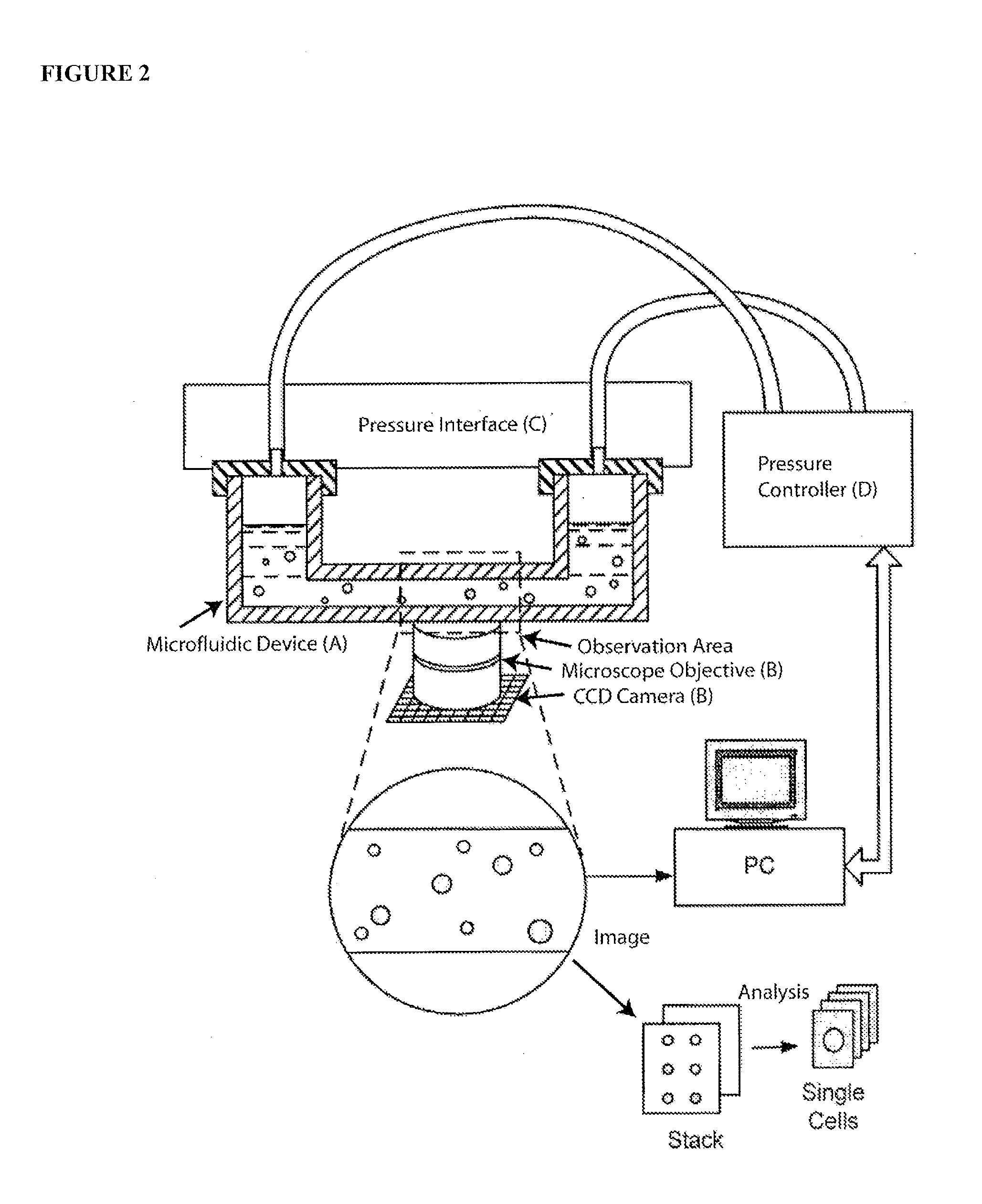
Apparatus and methods are provided for analysis of individual particles in a microfluidic device. The methods involve the immobilization of an array of particles in suspension and the application of experimental compounds. Such methods can also include electrophysiology studies including patch clamp recording, electroporation, or both in the same microfluidic device. The apparatus provided includes a microfluidic device coupled to a multi-well structure and an interface for controlling the flow of media within the microchannel device.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
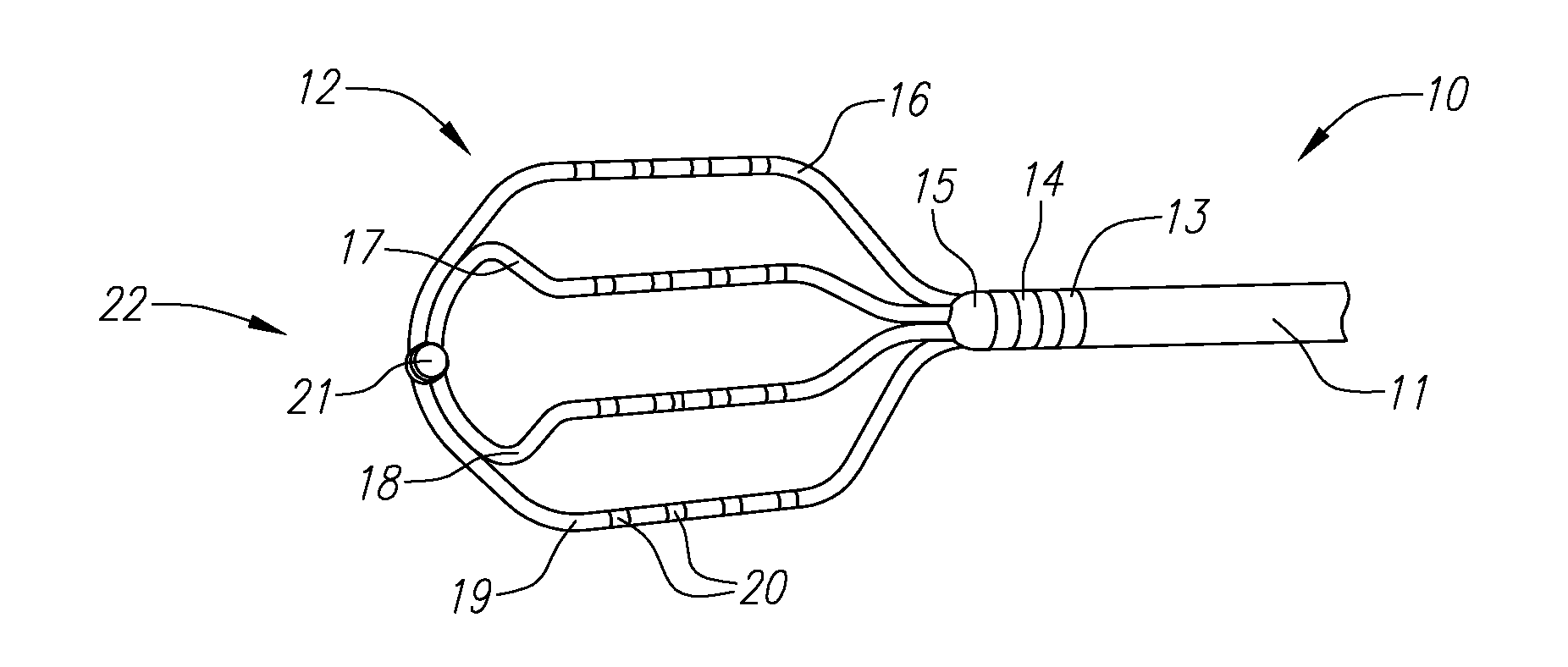
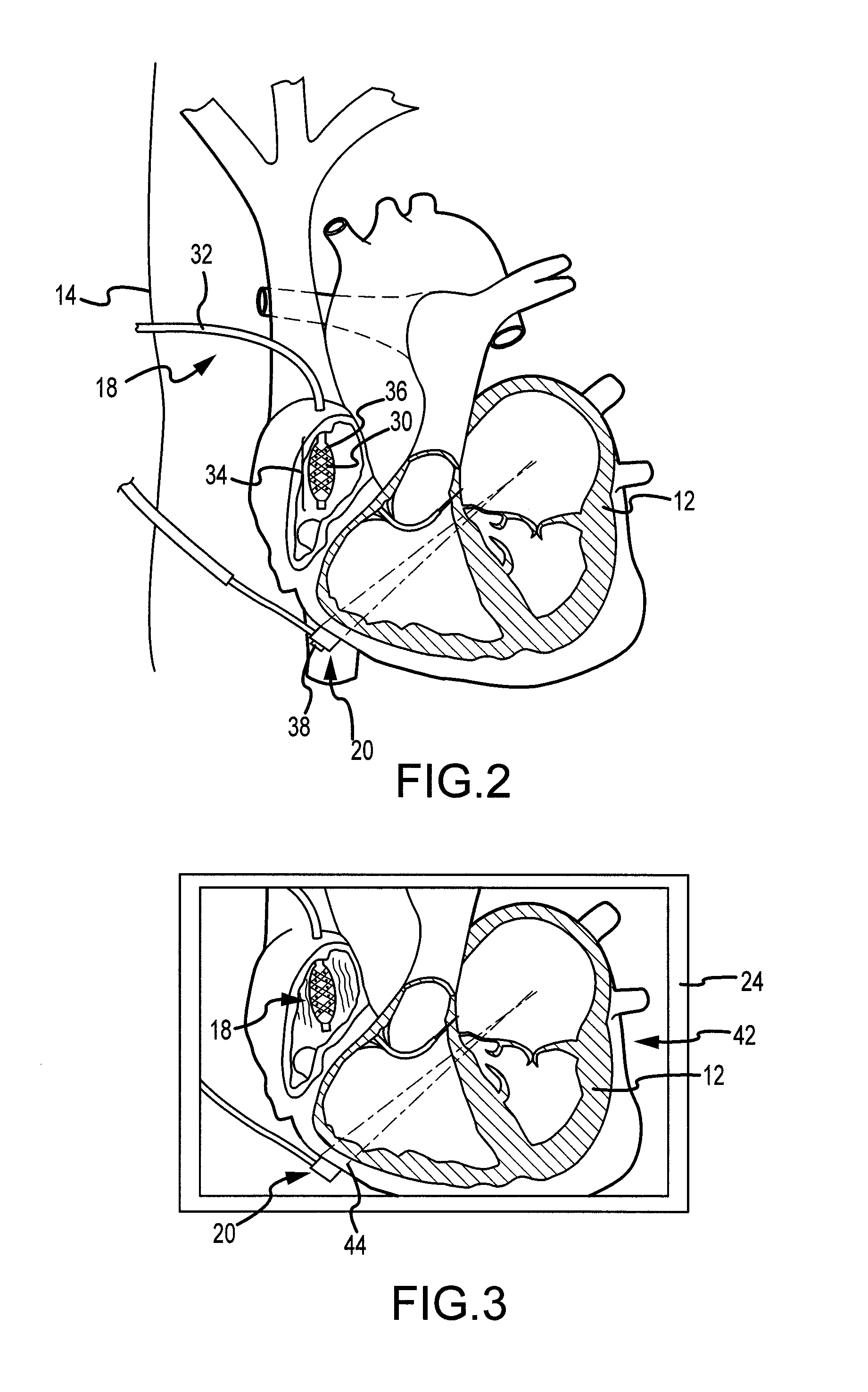
Electrophysiology ablation device
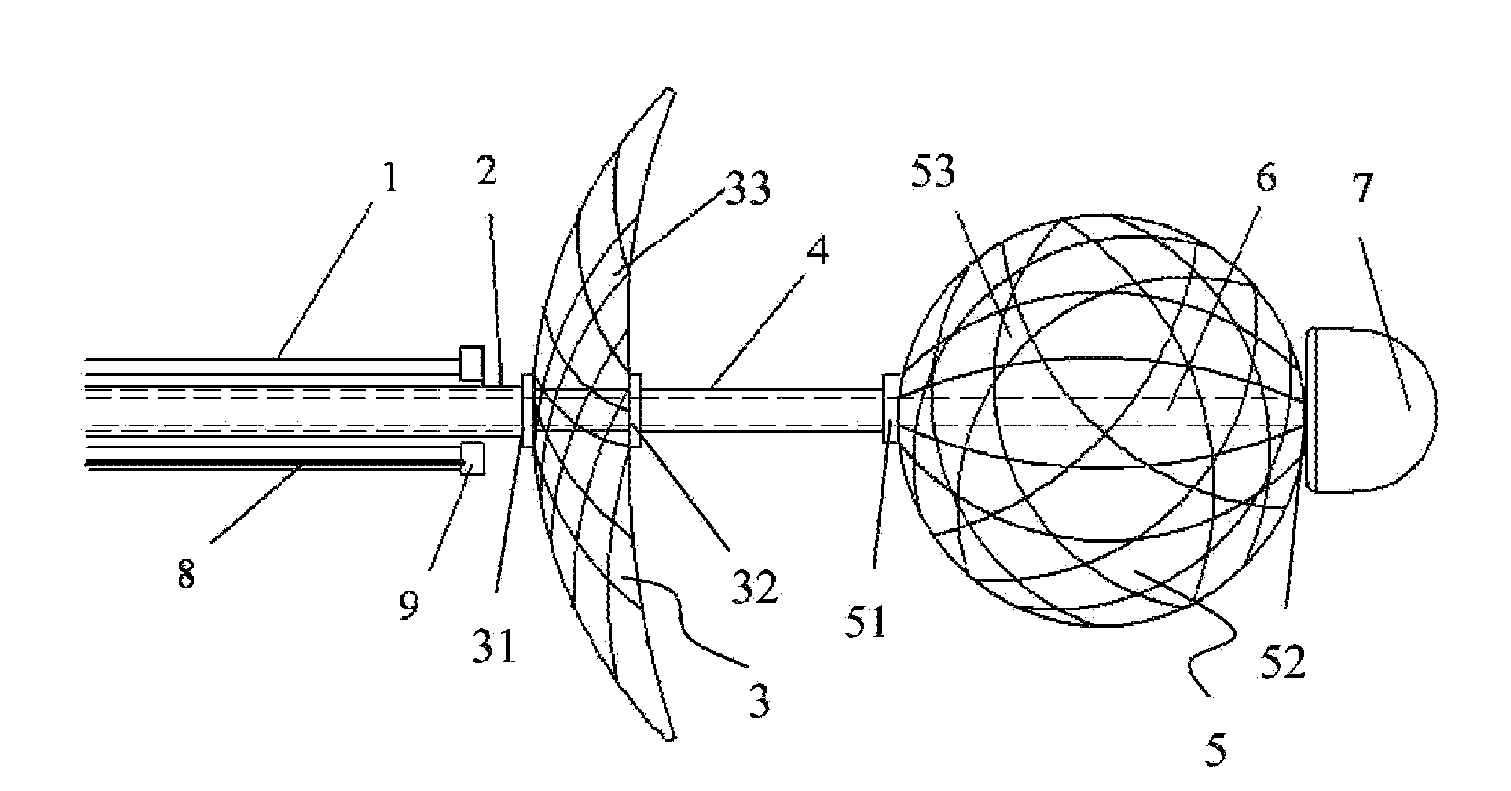
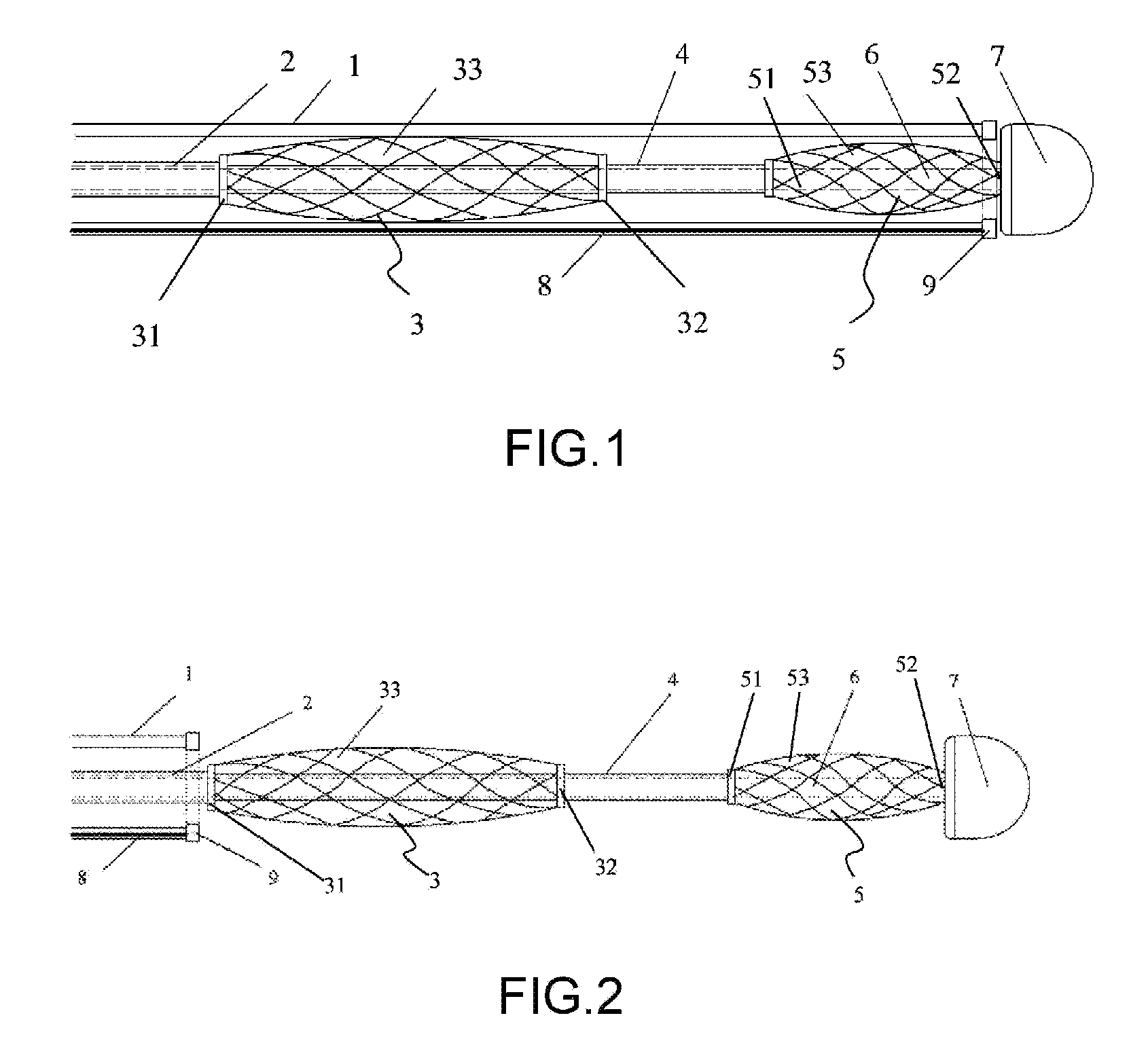
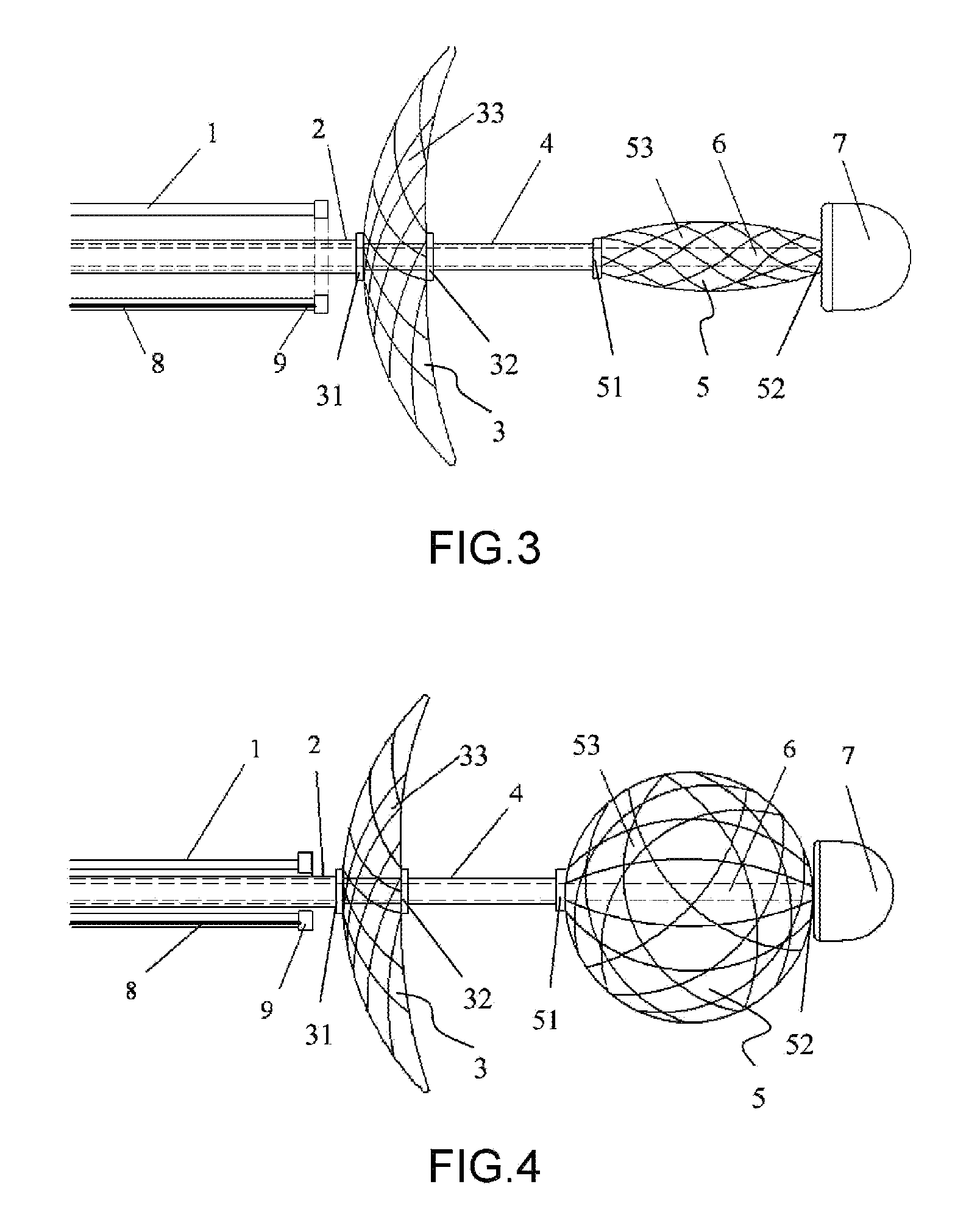
ActiveUS8454596B2Easy to observeInhibition formationInternal electrodesSurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringSpherical shaped
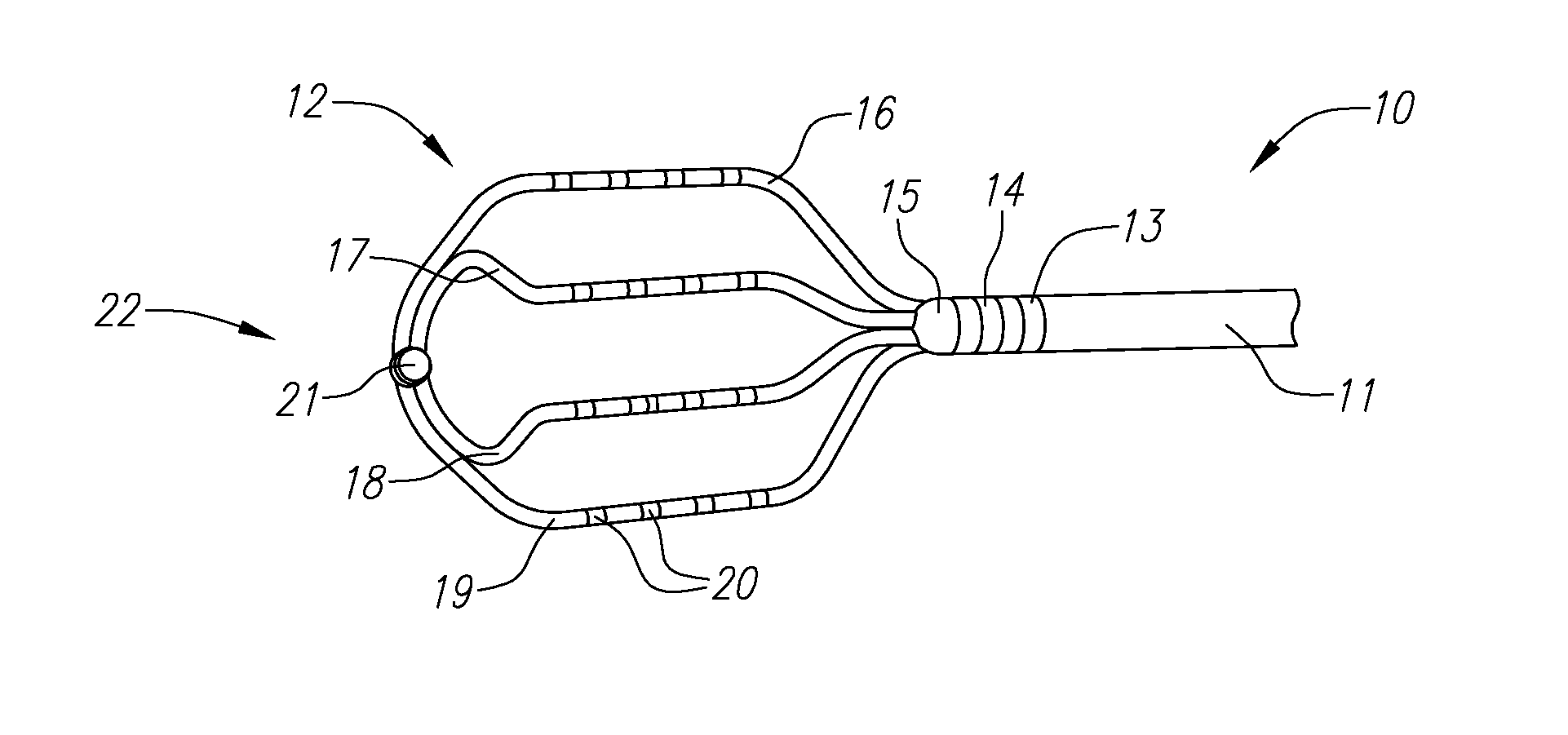
An electrophysiology ablation device includes a catheter sleeve (1), an electrode sleeve (2), a steering ball sleeve (4), a central rod (6), an ablation electrode (3) and a steering ball (5). The catheter sleeve (1), the electrode sleeve (2), the steering ball sleeve (4) and the central rod (6) are muff-coupled together, and the steering ball (5) can be deployed radially to define a meshed spherical shape, in order to steer the positioning of the ablation electrode (3) which can be deployed to define a meshed disk shape, so the ablation electrode (3) can be positioned at the ostium of the pulmonary vein accurately.
Owner:BEIJING AMSINO MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com