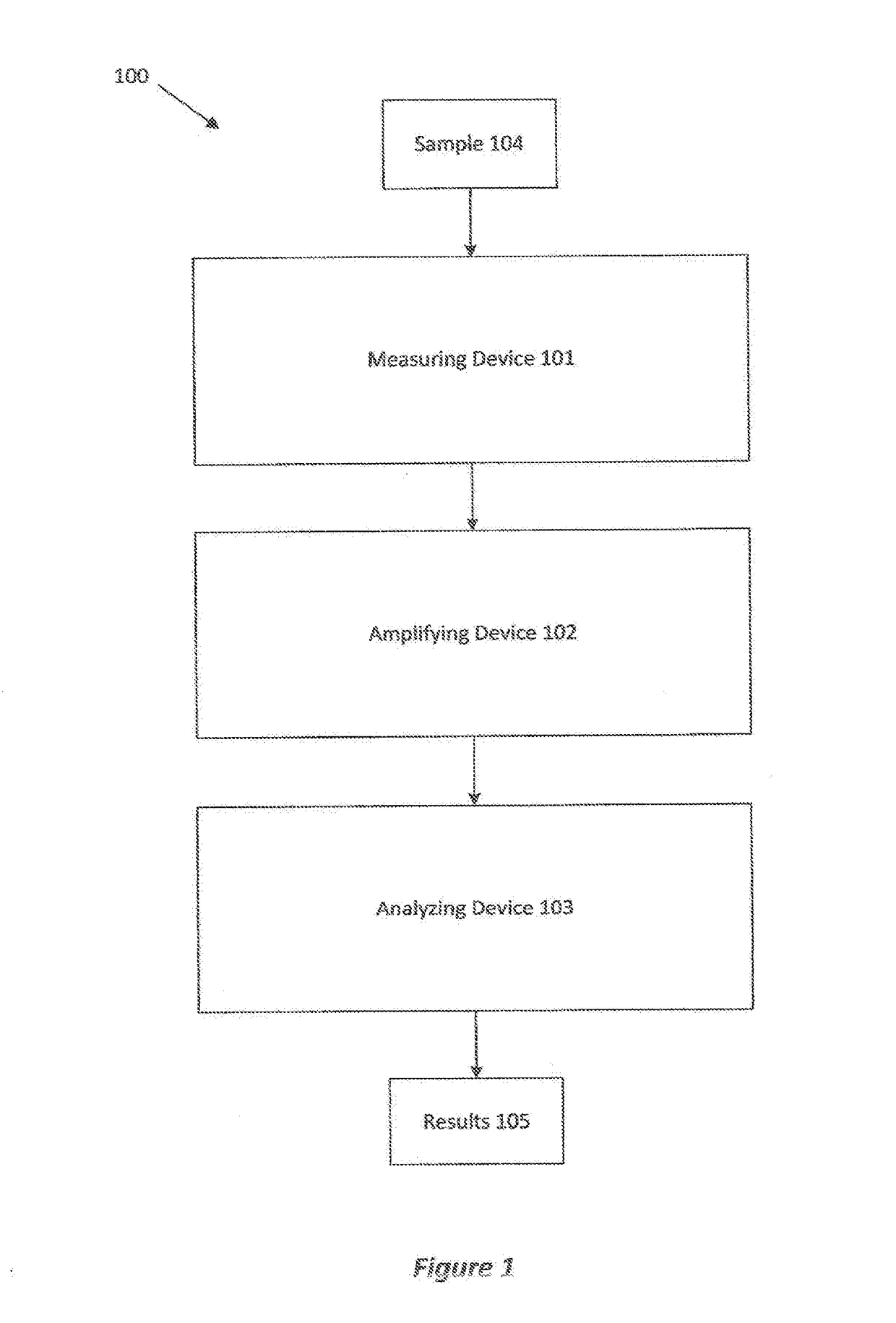
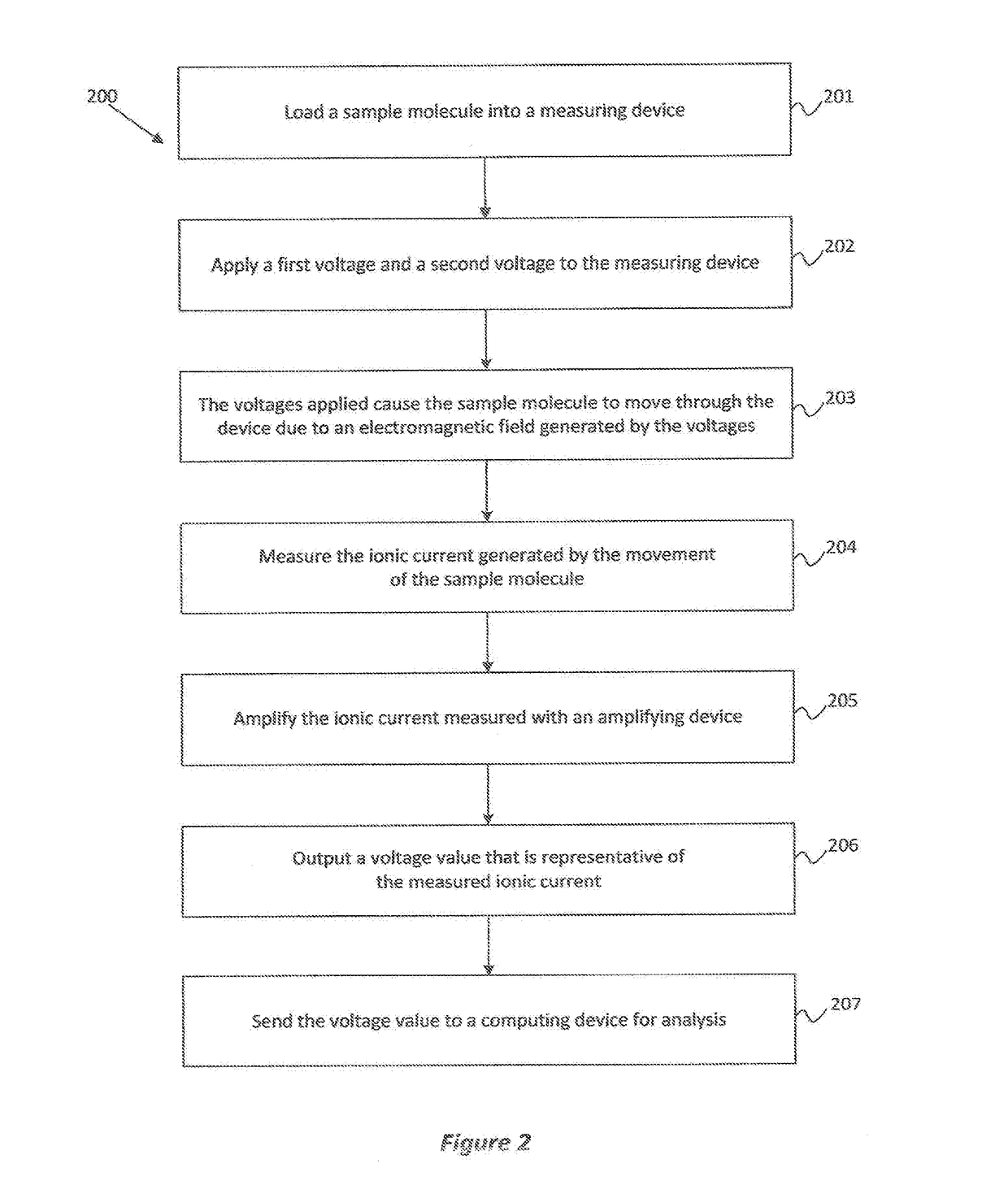
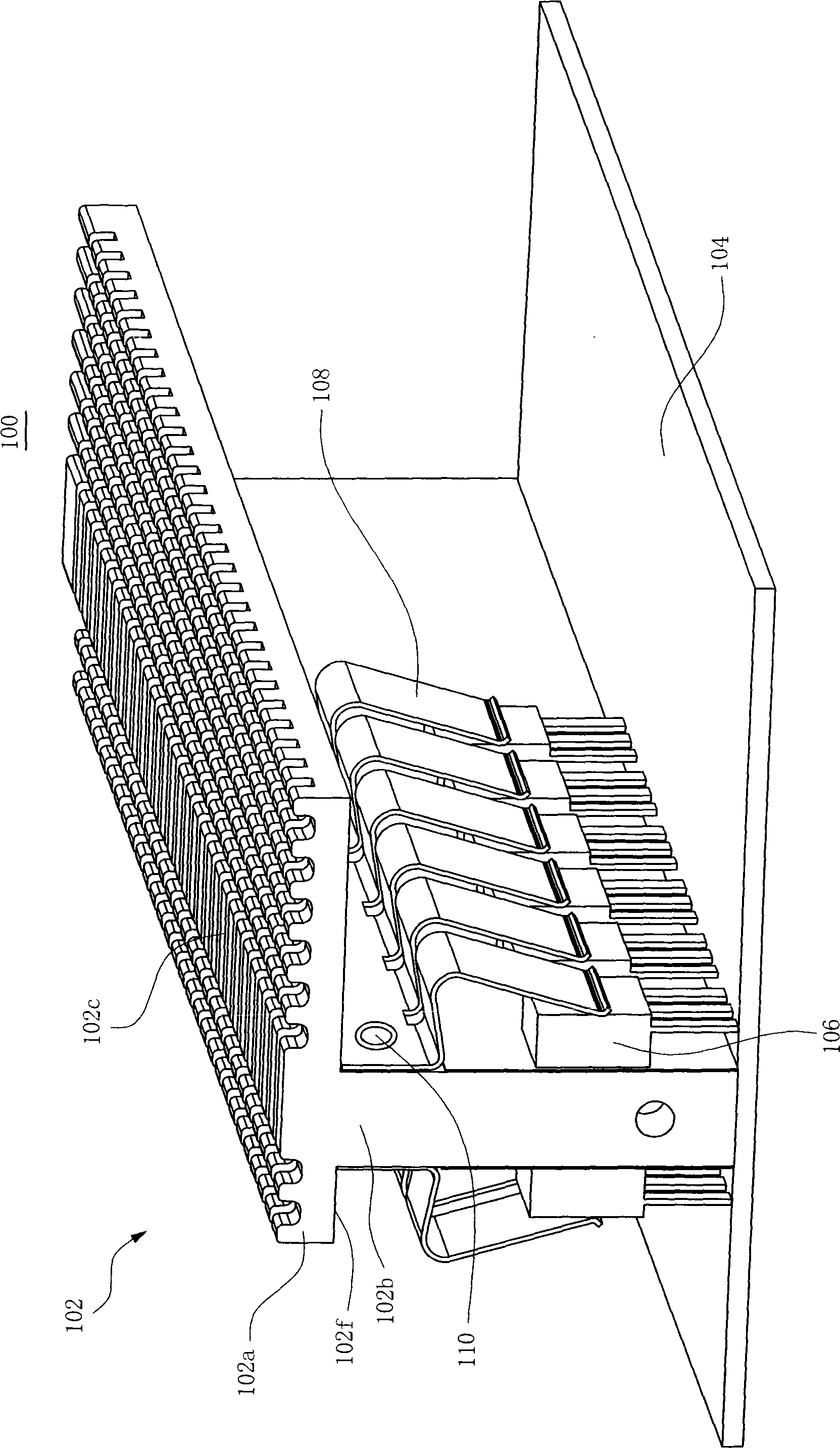
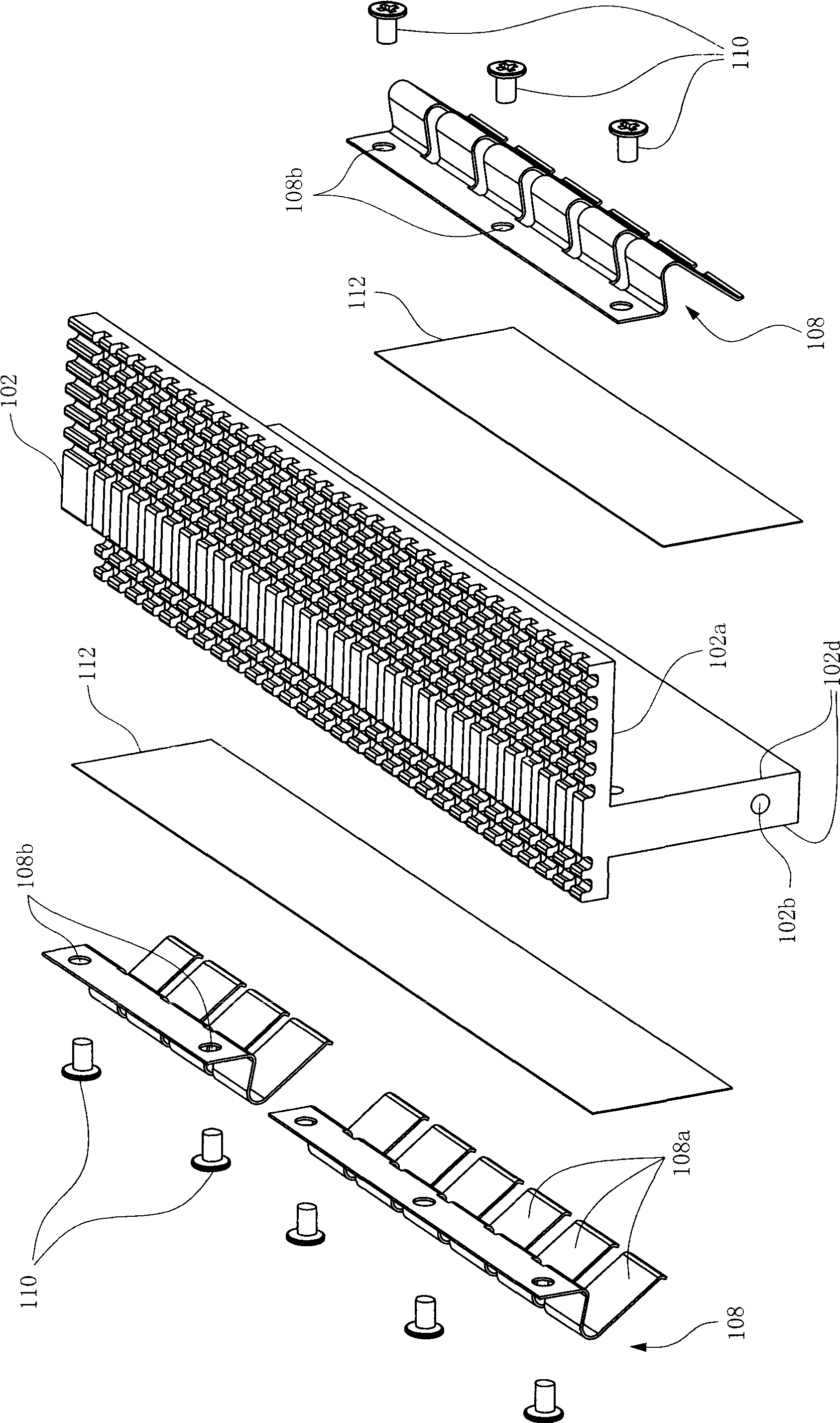
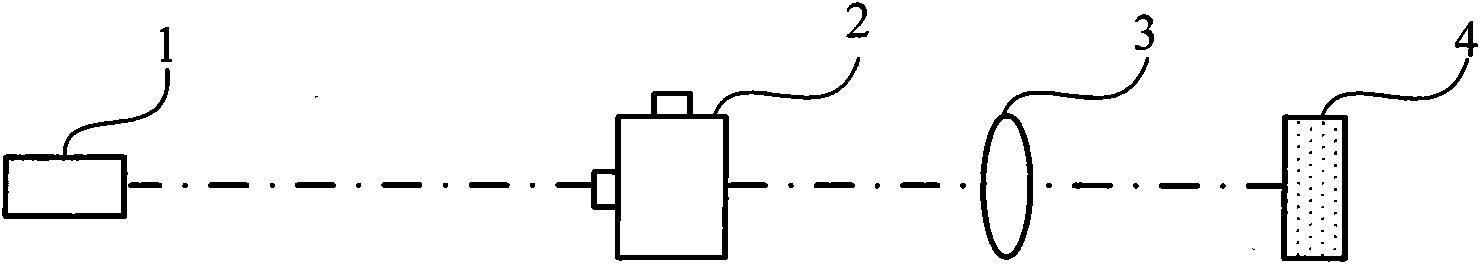Patents
Literature
211 results about "Patch clamp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
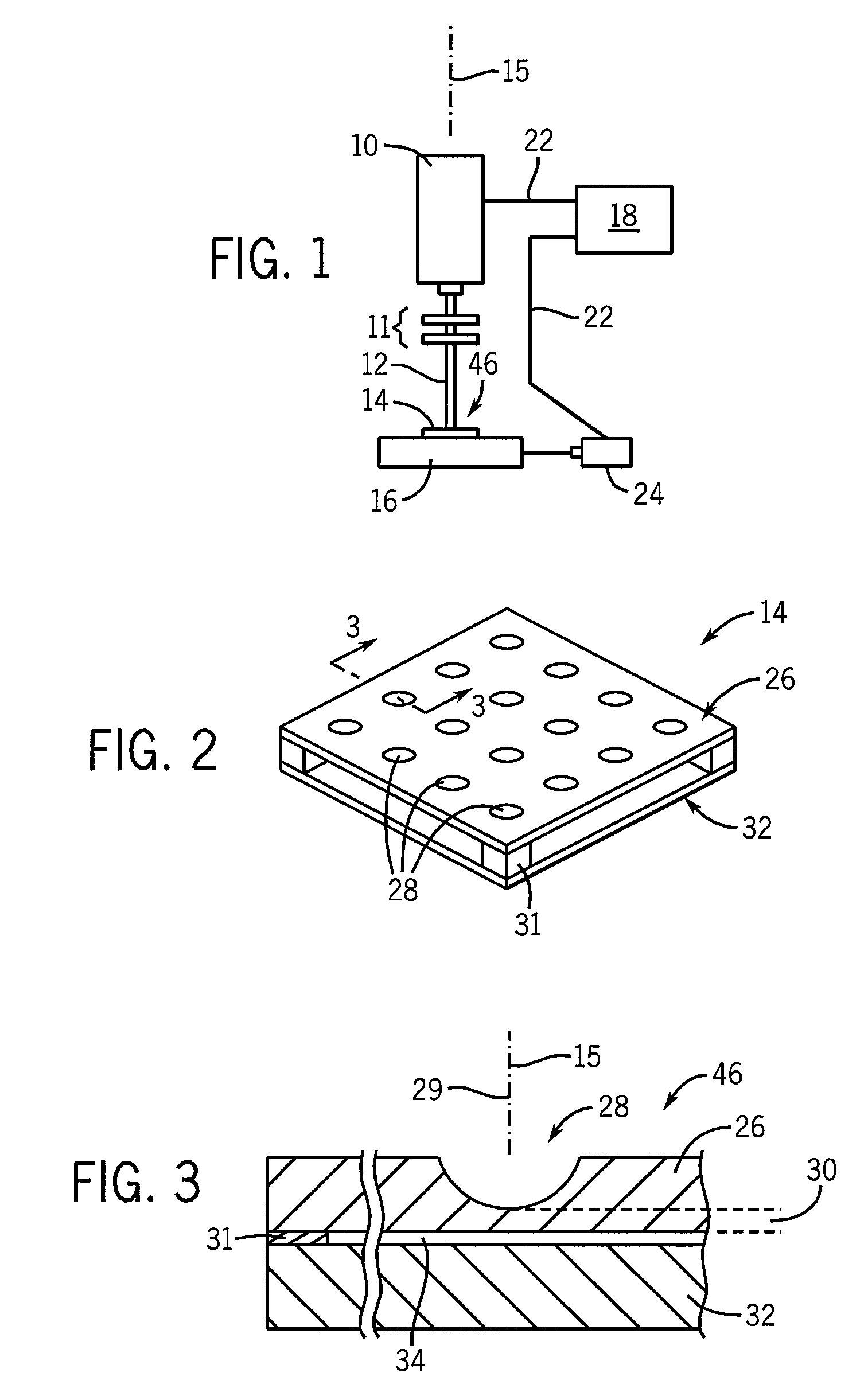
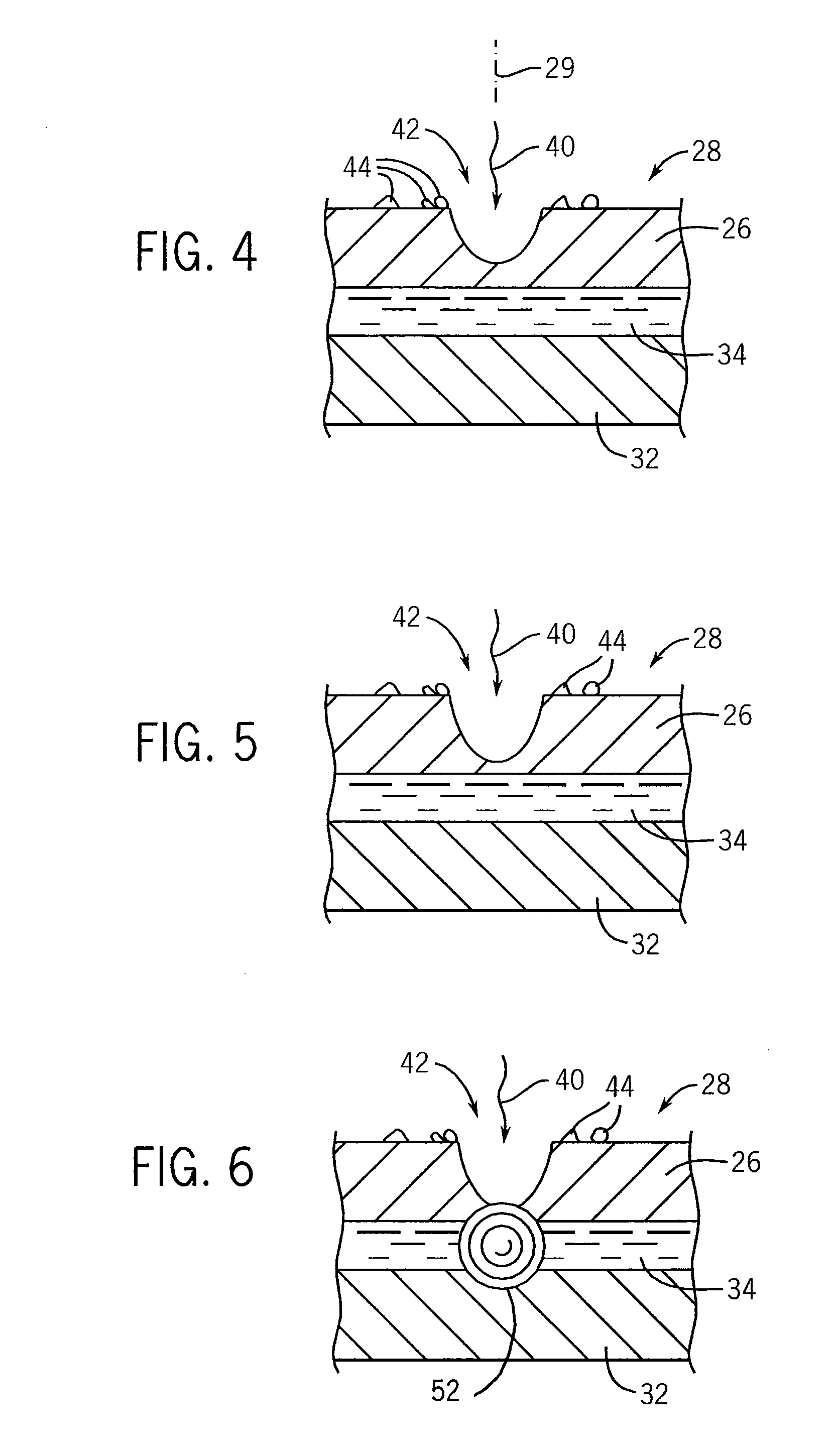
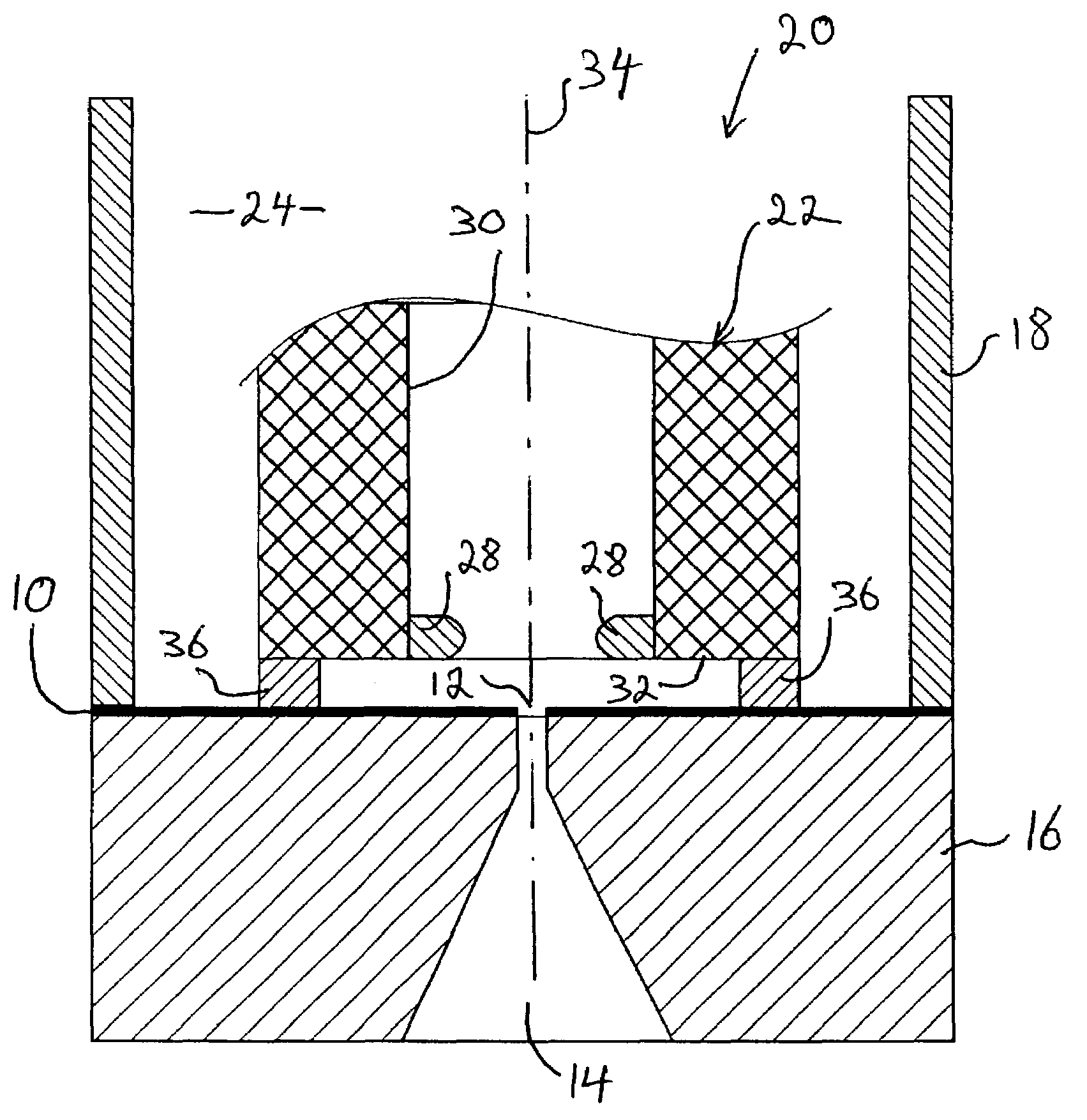
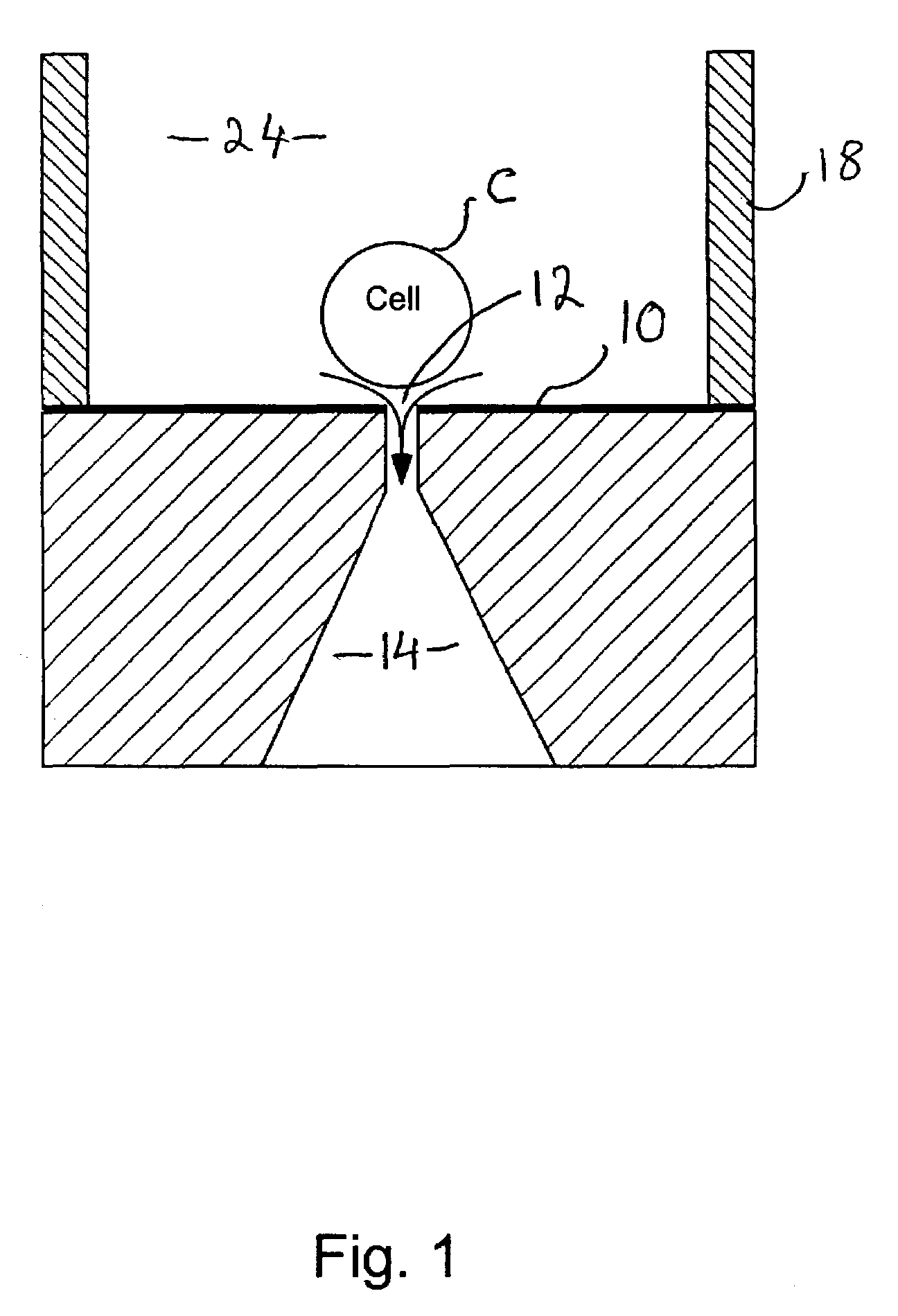
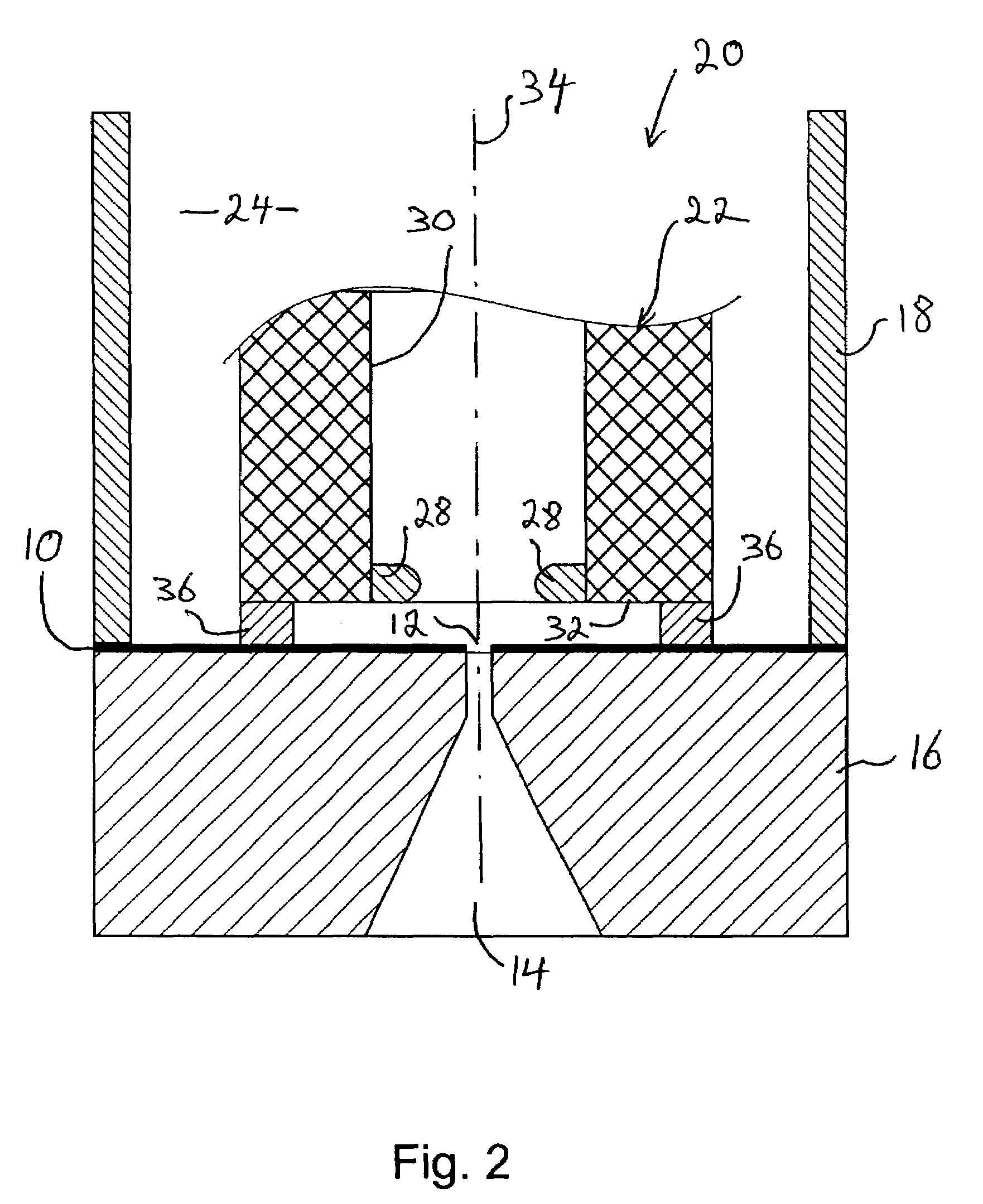
The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology used to study ionic currents in individual isolated living cells, tissue sections, or patches of cell membrane. The technique is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells, and can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.
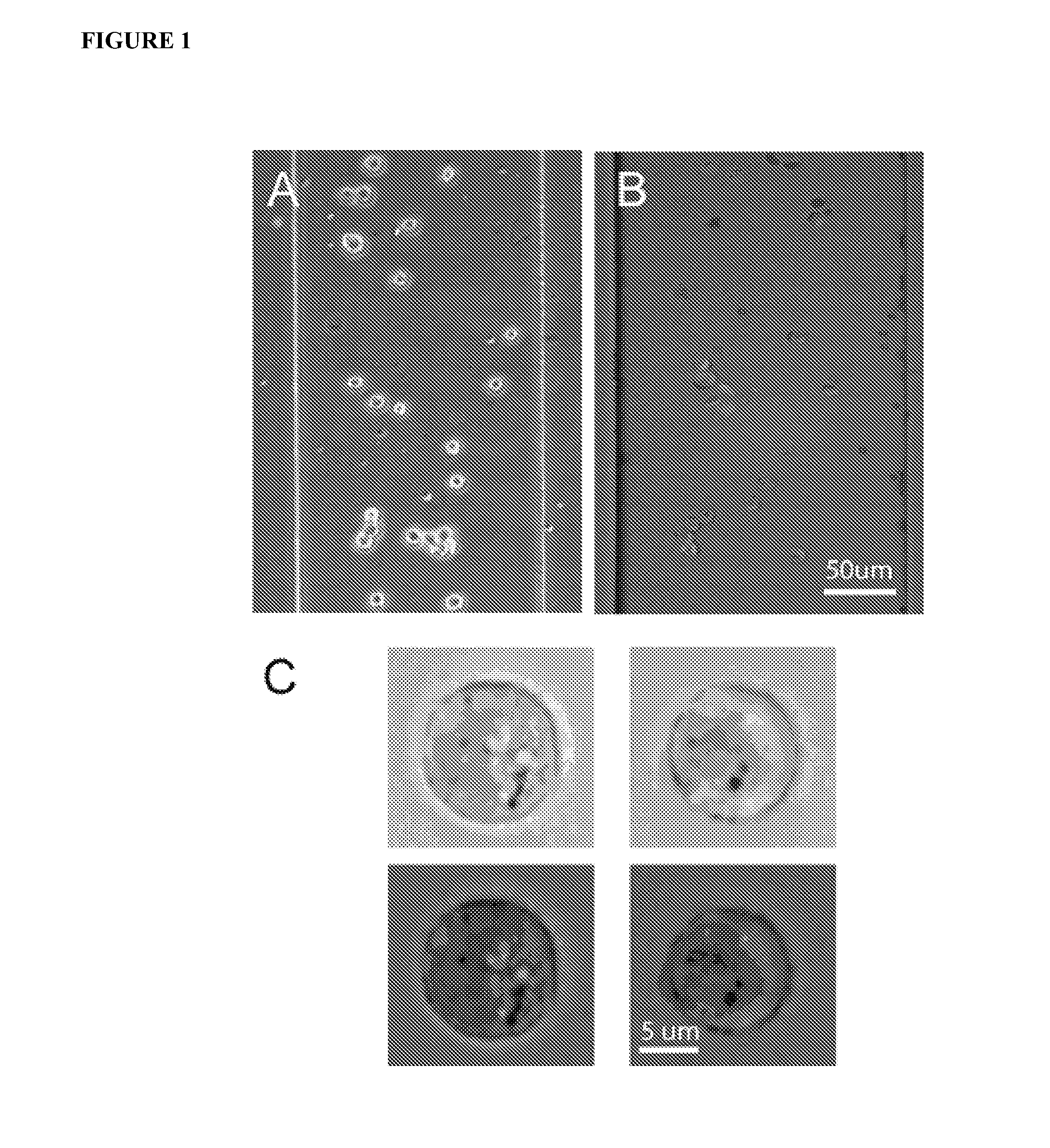
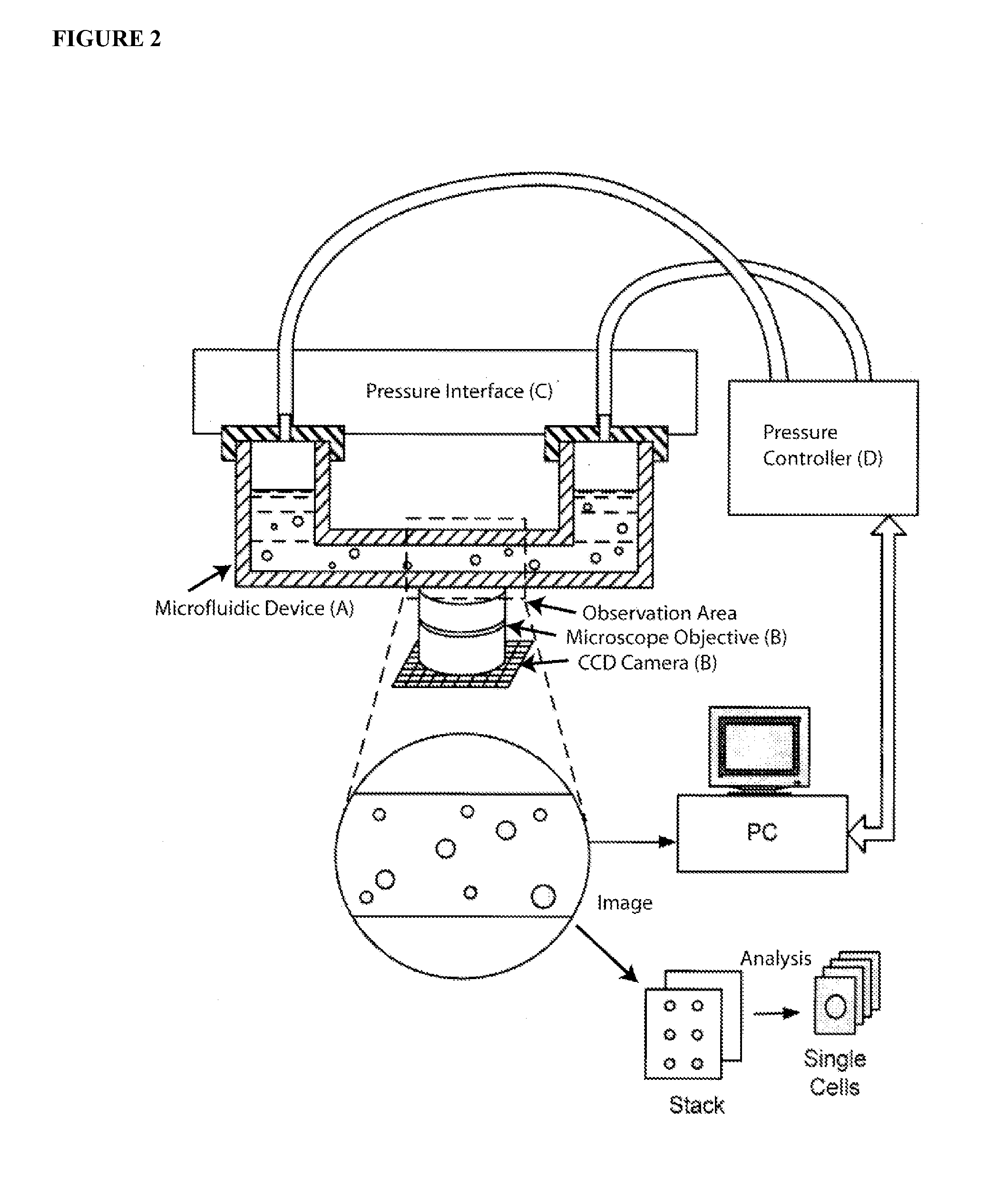
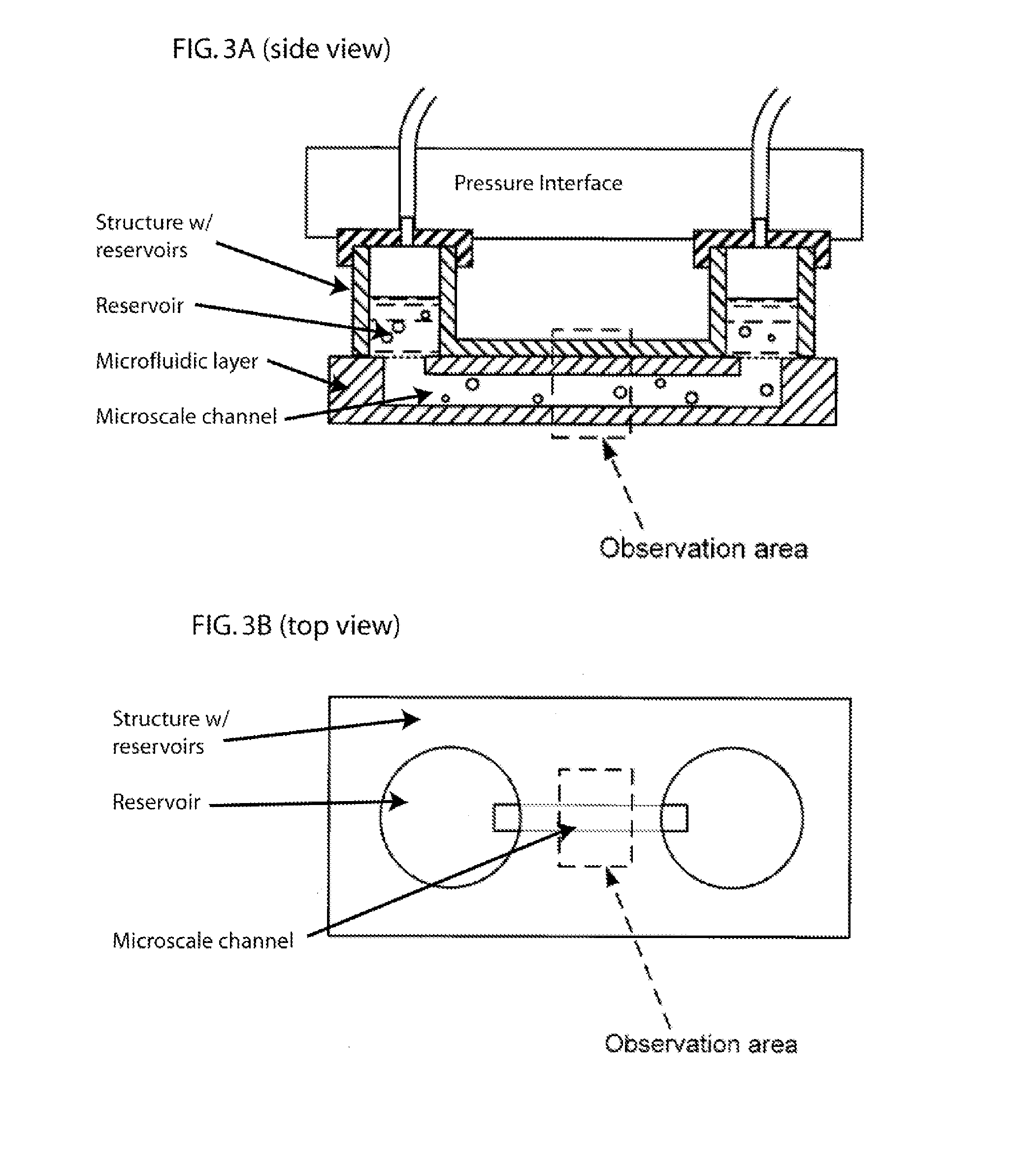
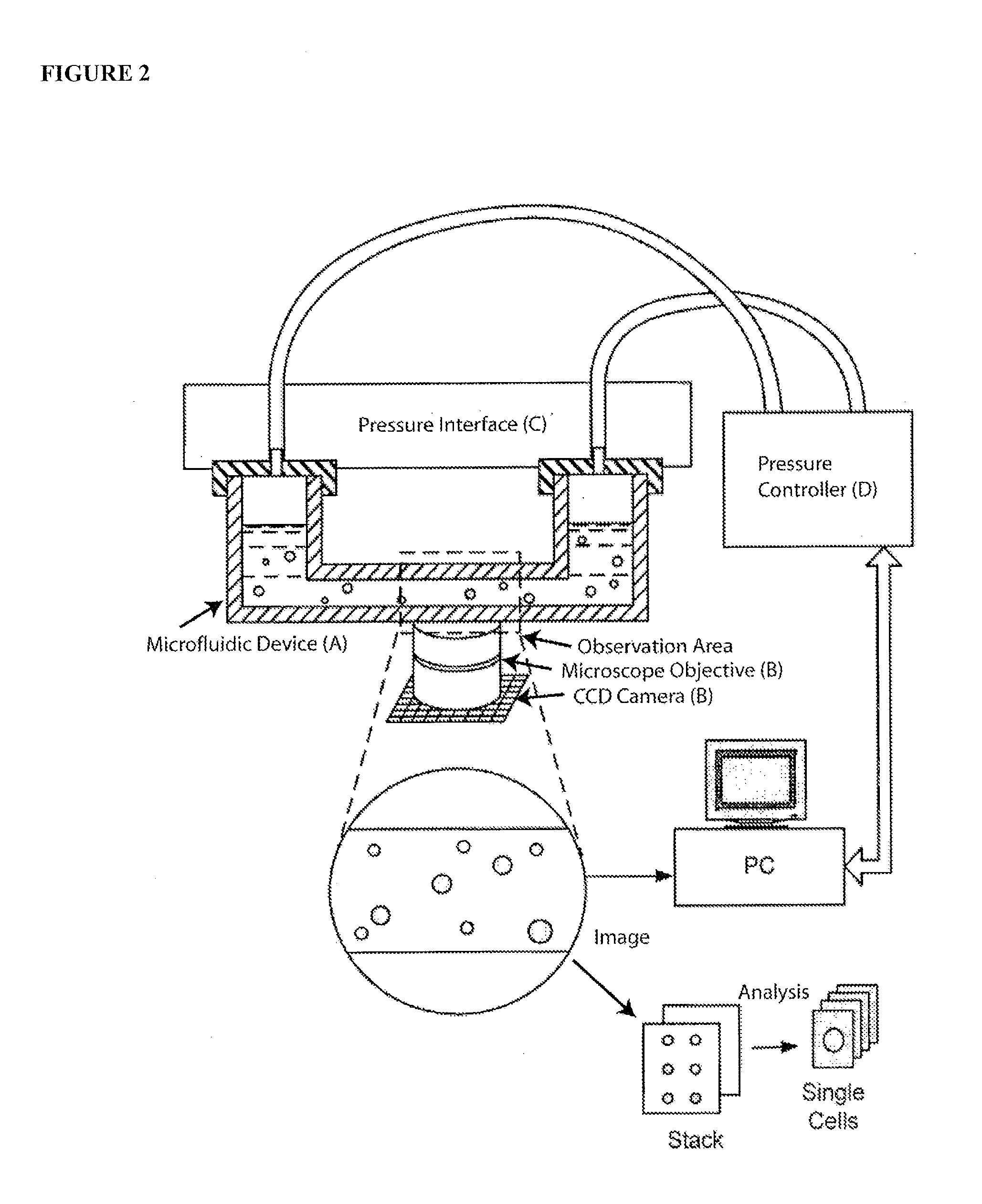
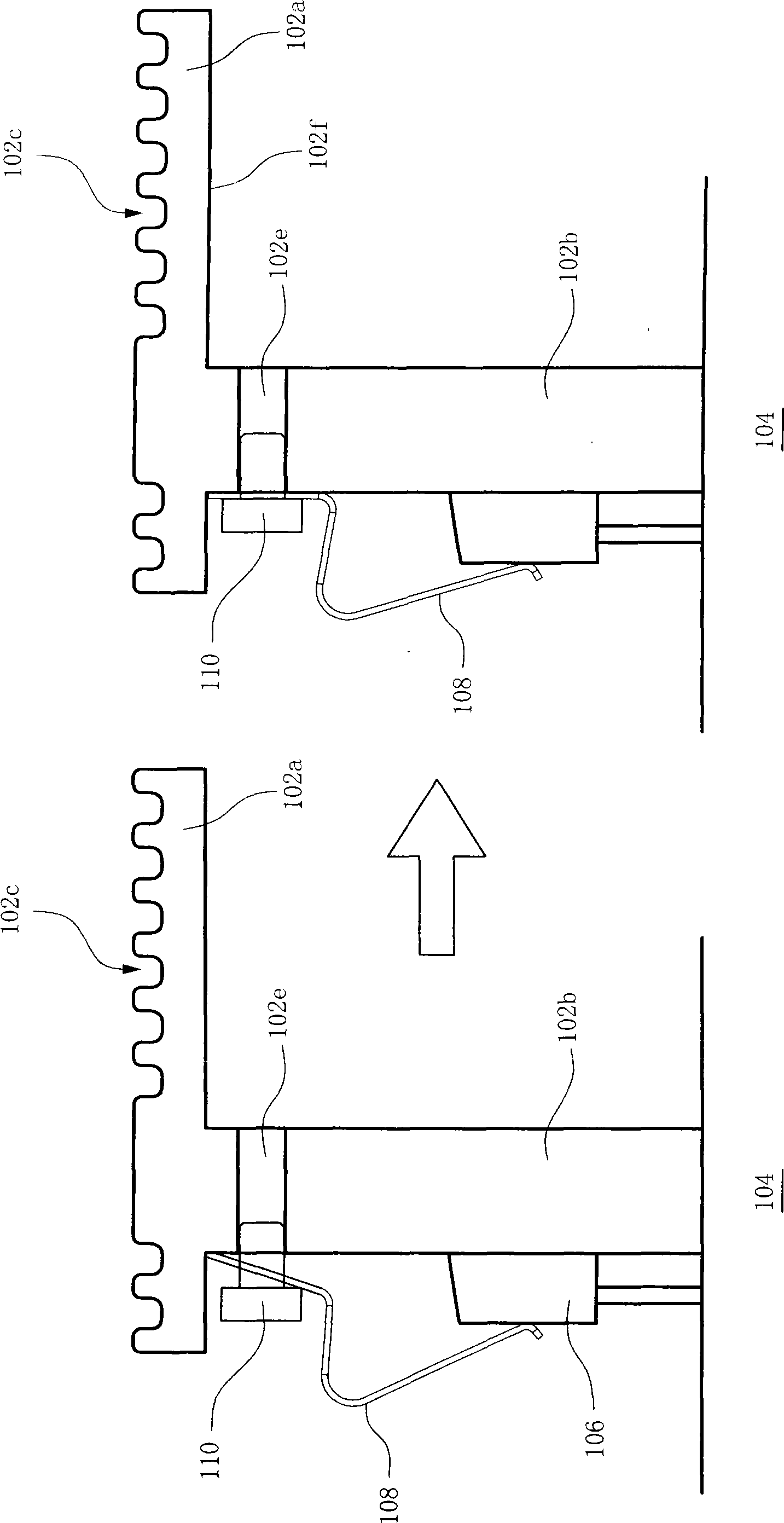
Methods and Apparatus for the Manipulation of Particle Suspensions and Testing Thereof
InactiveUS20070243523A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophysiology studyElectroporation
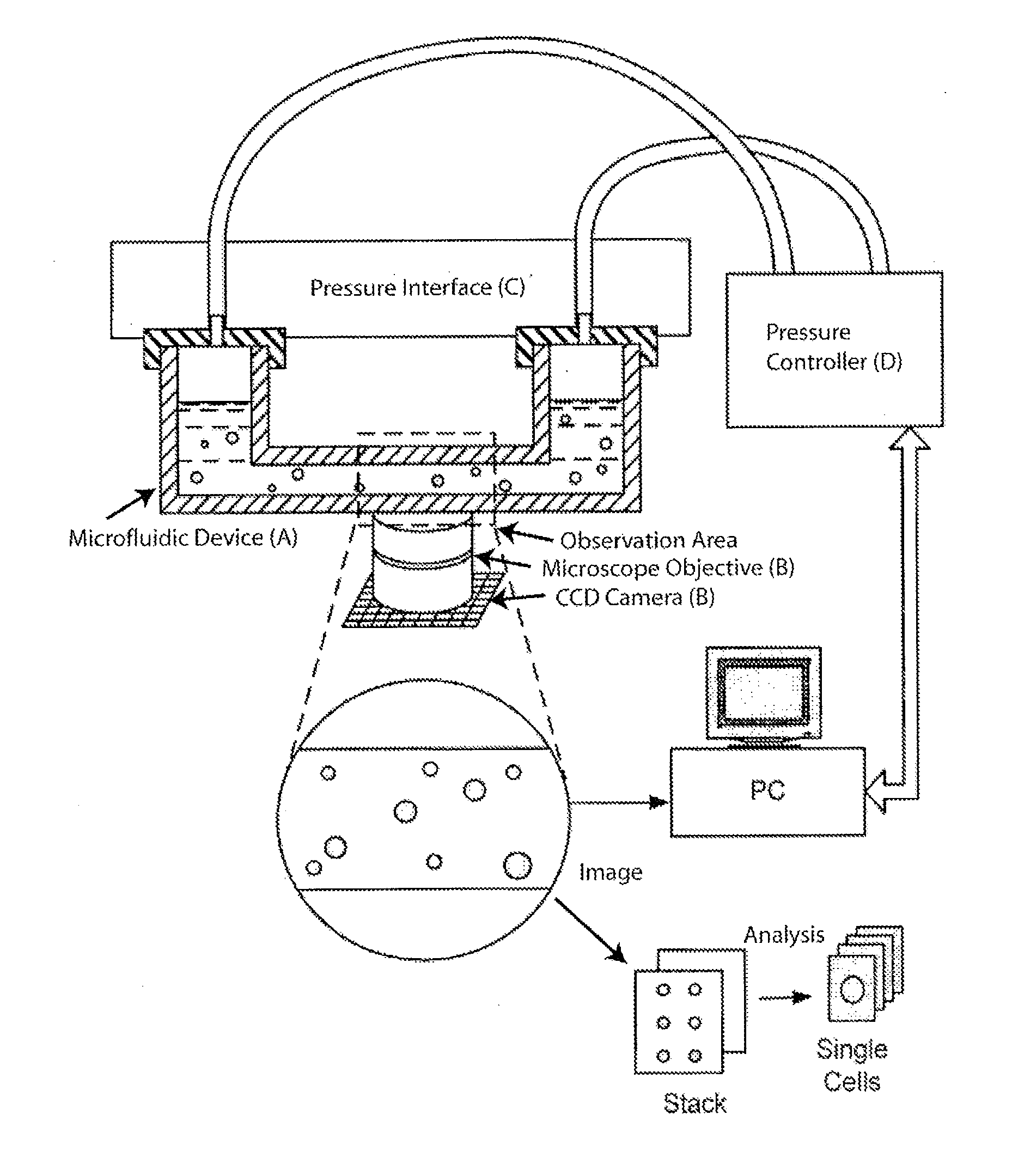
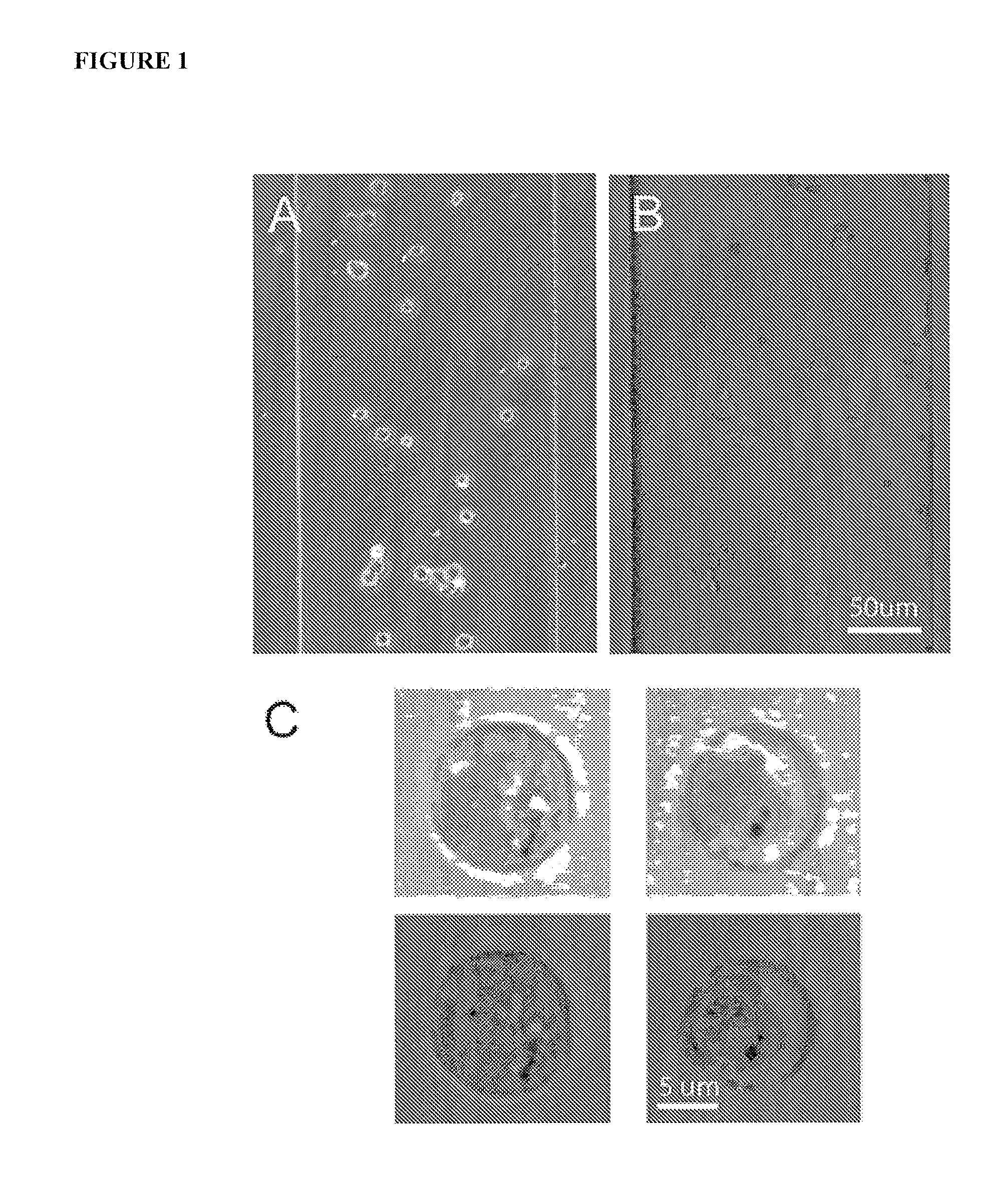
Apparatus and methods are provided for analysis of individual particles in a microfluidic device. The methods involve the immobilization of an array of particles in suspension and the application of experimental compounds. Such methods can also include electrophysiology studies including patch clamp recording, electroporation, or both in the same microfluidic device. The apparatus provided includes a microfluidic device coupled to a multi-well structure and an interface for controlling the flow of media within the microchannel device.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
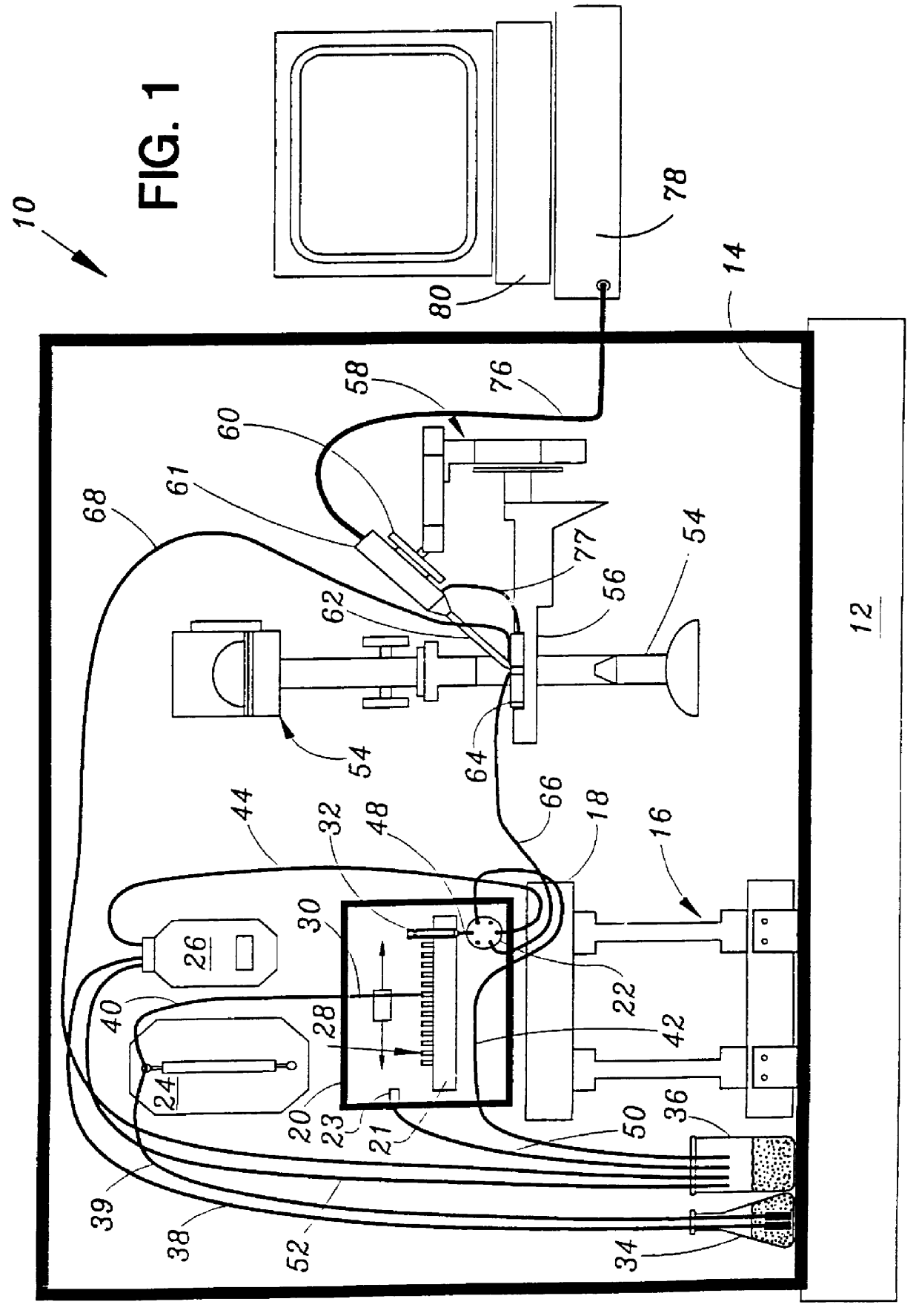
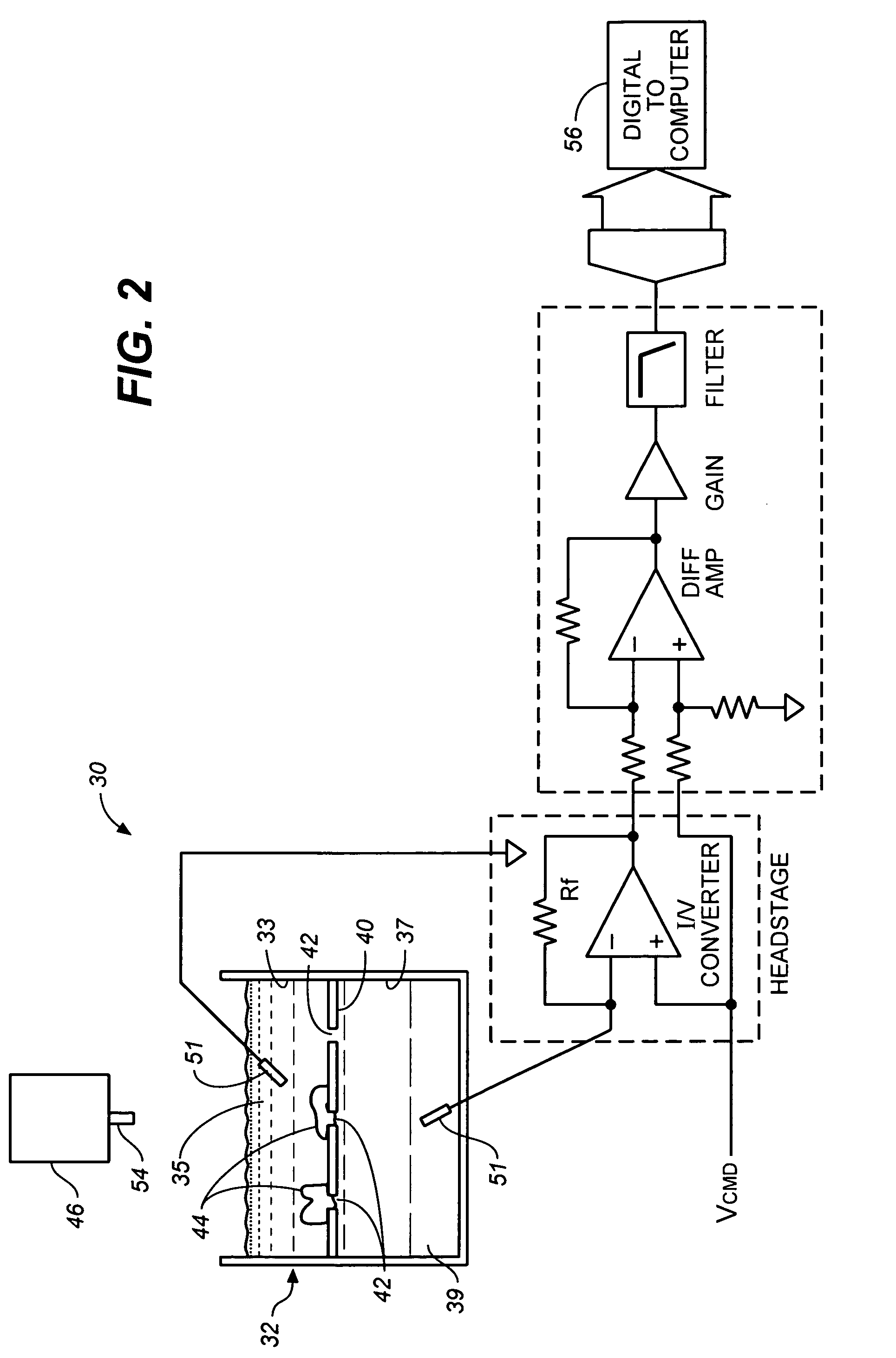
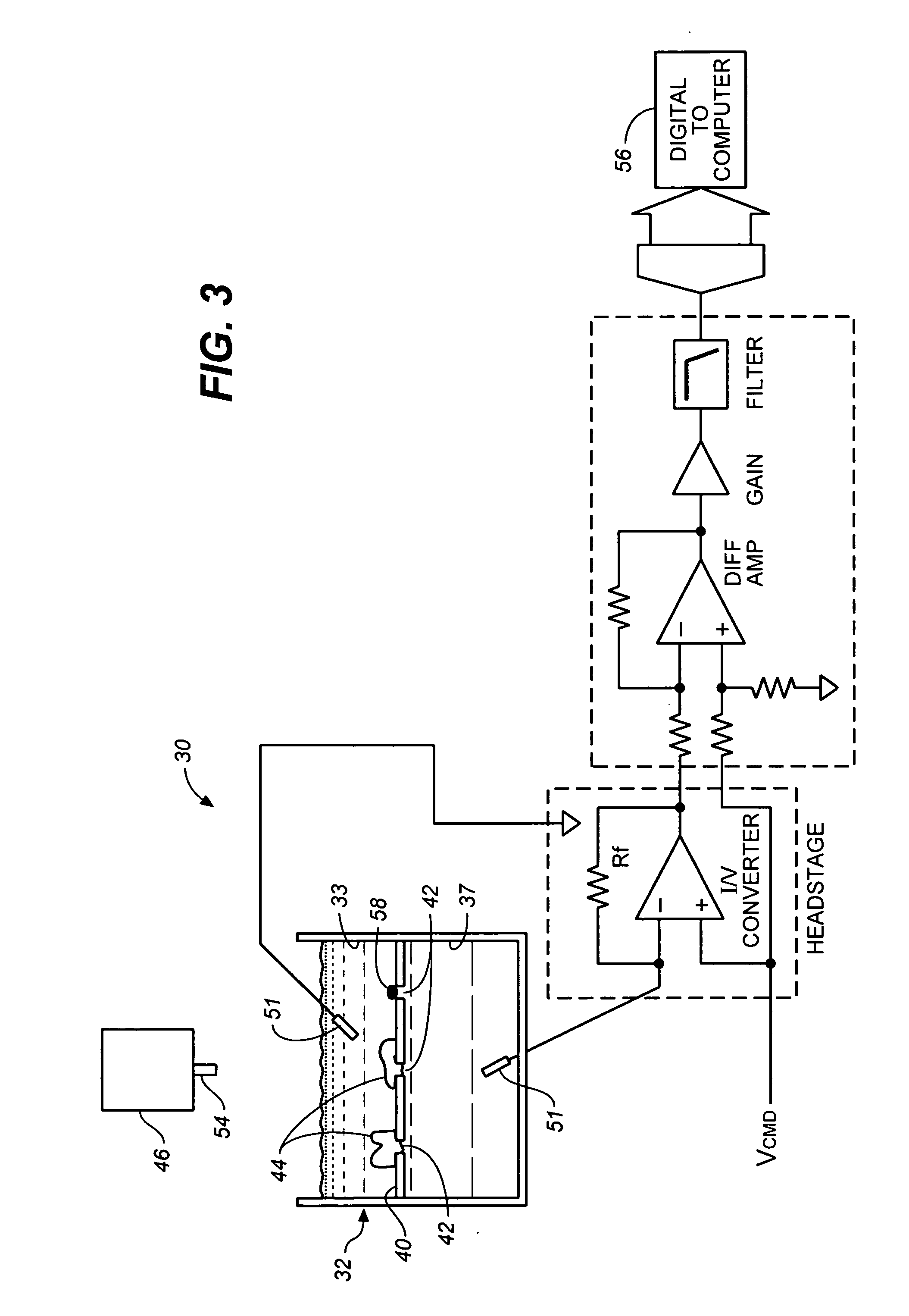
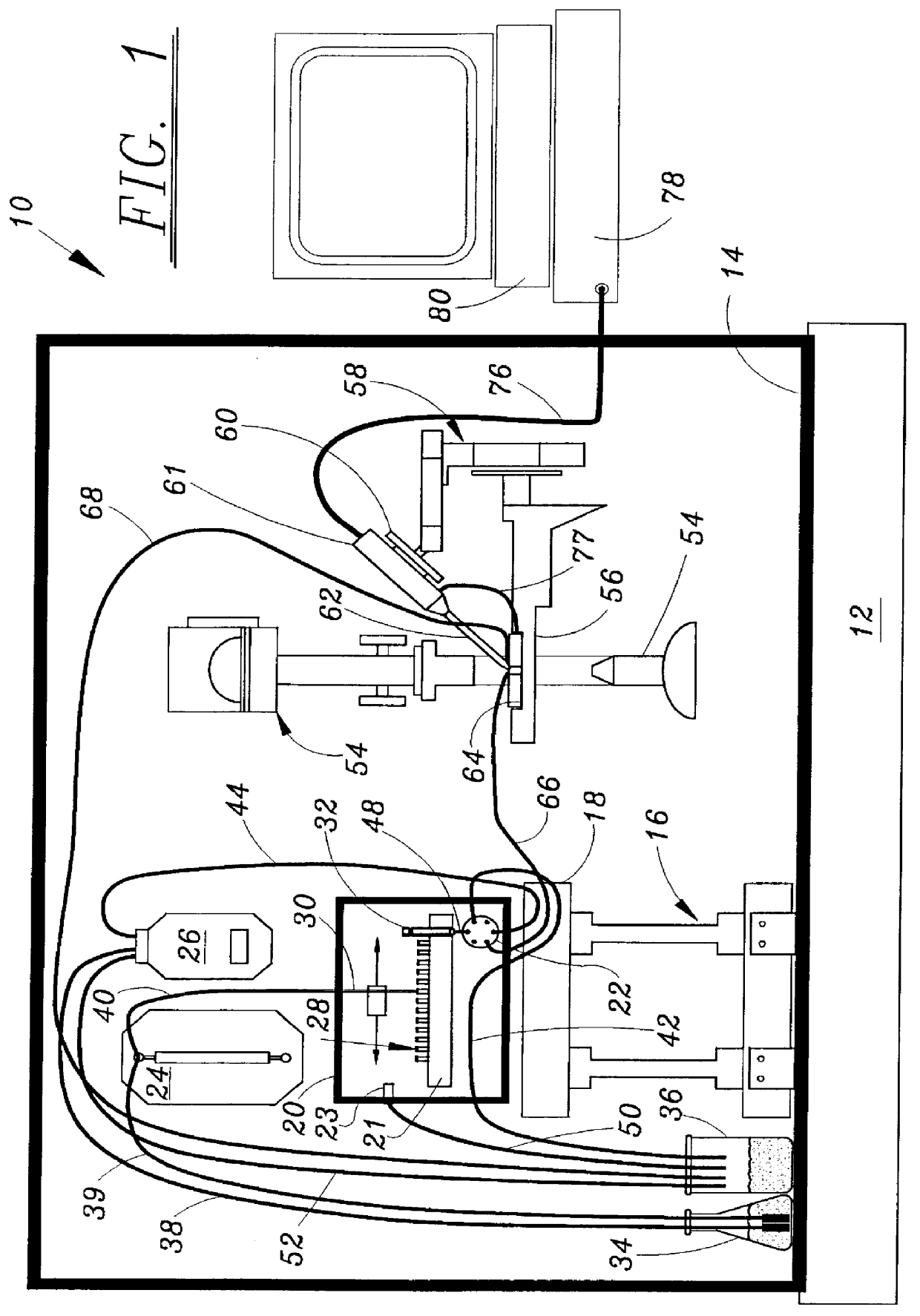
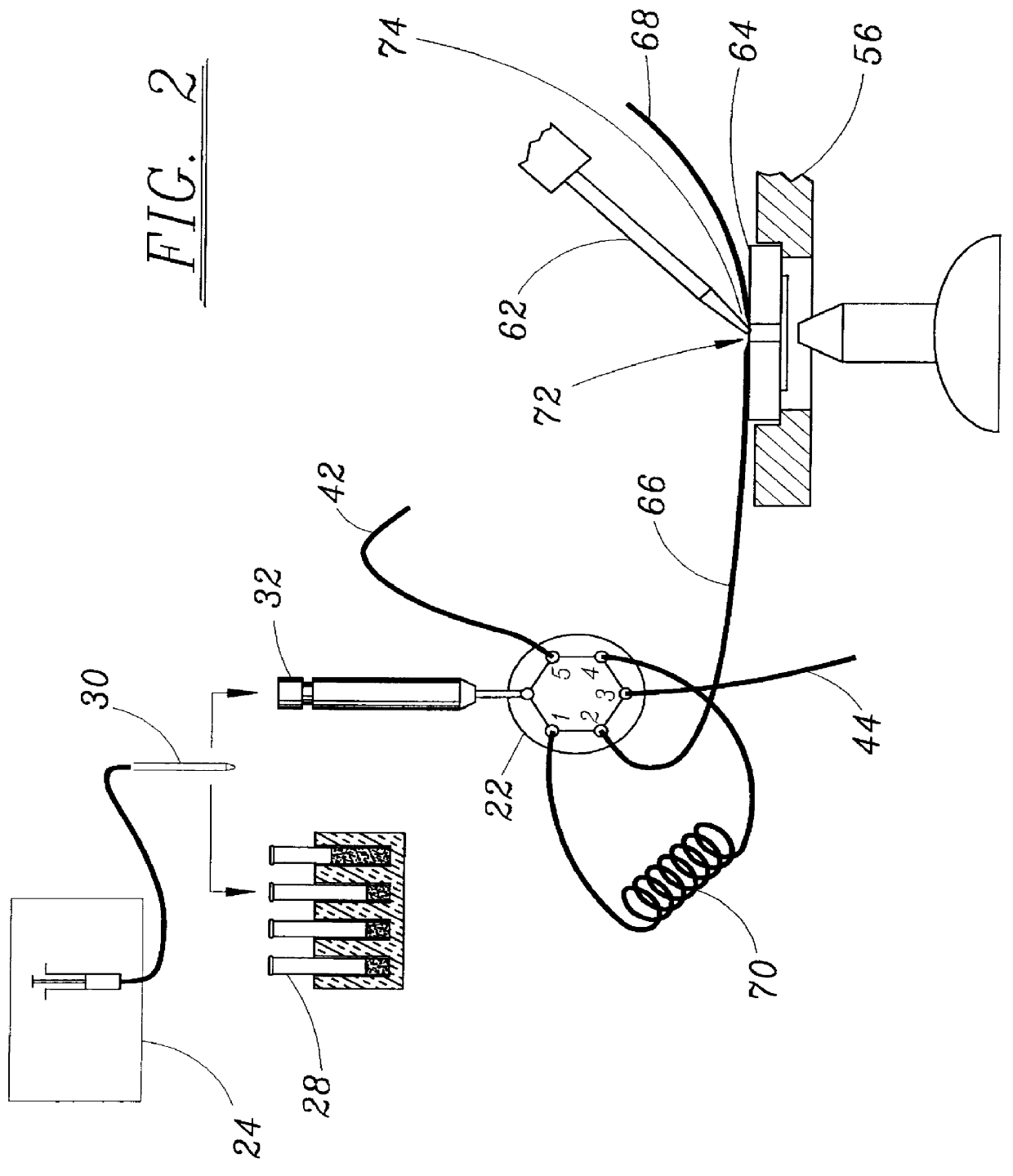
Patch clamp apparatus and technique having high throughput and low fluid volume requirements
InactiveUS6063260ALow sample volume requirementLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutosamplerIon transfer
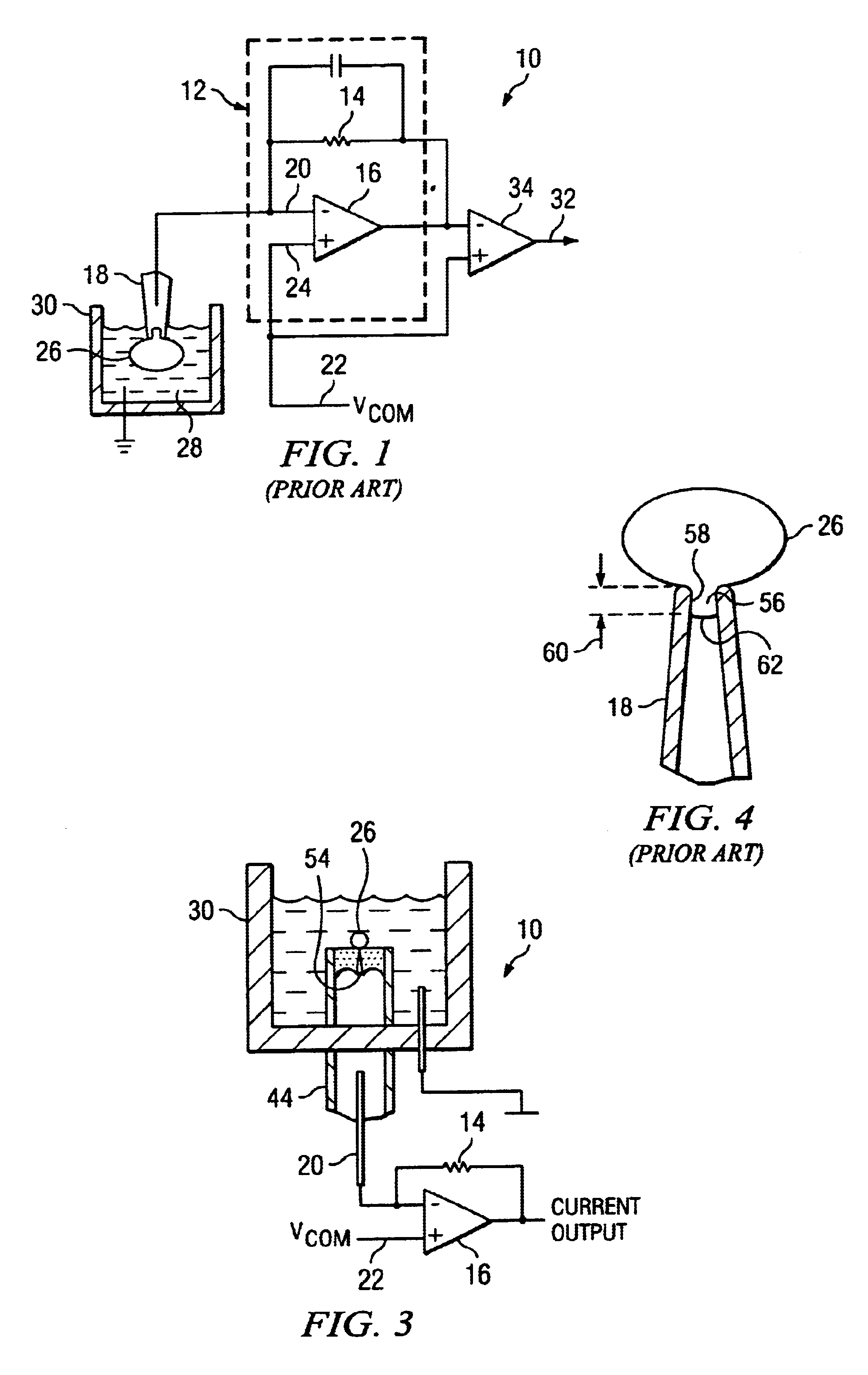
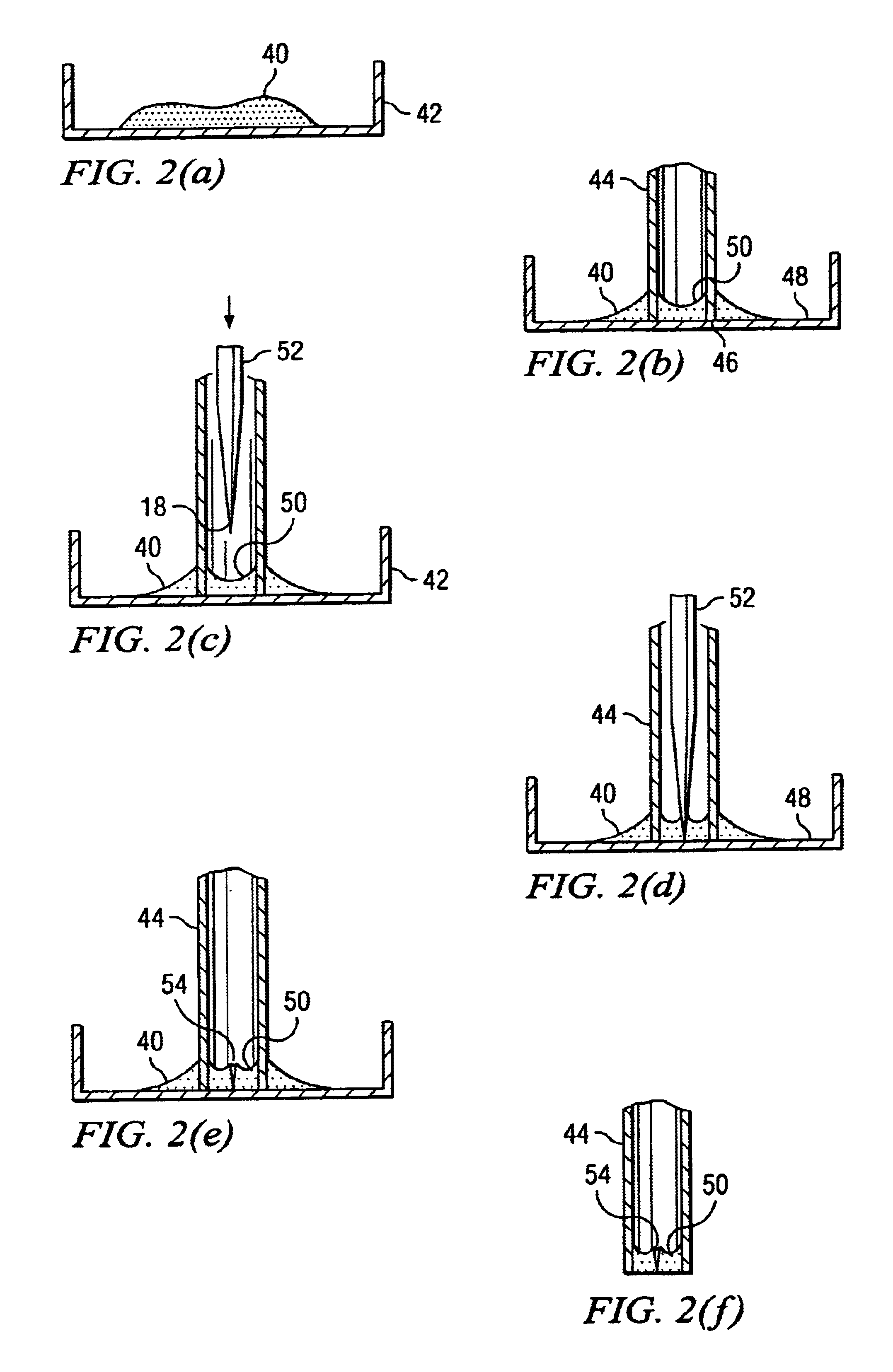
PCT No. PCT / EP95 / 02204 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 25, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 25, 1997 PCT Filed Jun. 7, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 13721 PCT Pub. Date May 9, 1996Apparatus for carrying out patch clamp technique utilized in studying the effect of certain materials on ion transfer channels in biological tissue, and more particularly patch clamp apparatus utilizing an autosampler, such as those utilized with HPLC apparatus, to provide high throughput, is disclosed. The invention additionally includes novel microperfusion chamber assemblies capable of utilizing only small amounts of material to be tested and only small amounts of liquid carrier, thereby enabling many tests to be completed in a short period of time. The invention more broadly relates to a novel electrophysiology drug handling and application set up for screening of chemical substances while providing high throughput and requiring only low volume of solutions and samples to be tested. The invention also comprises several novel procedures for utilizing the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
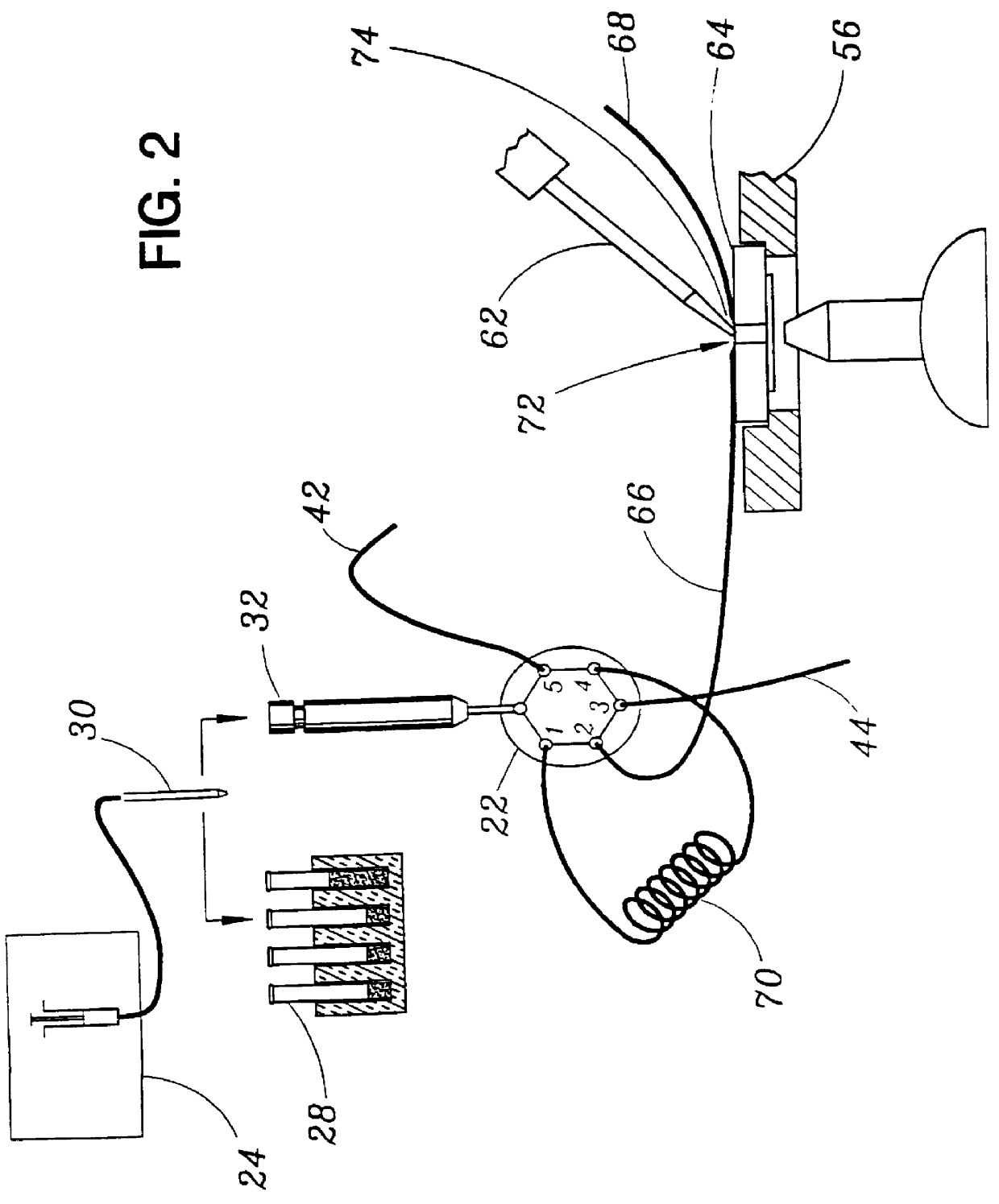
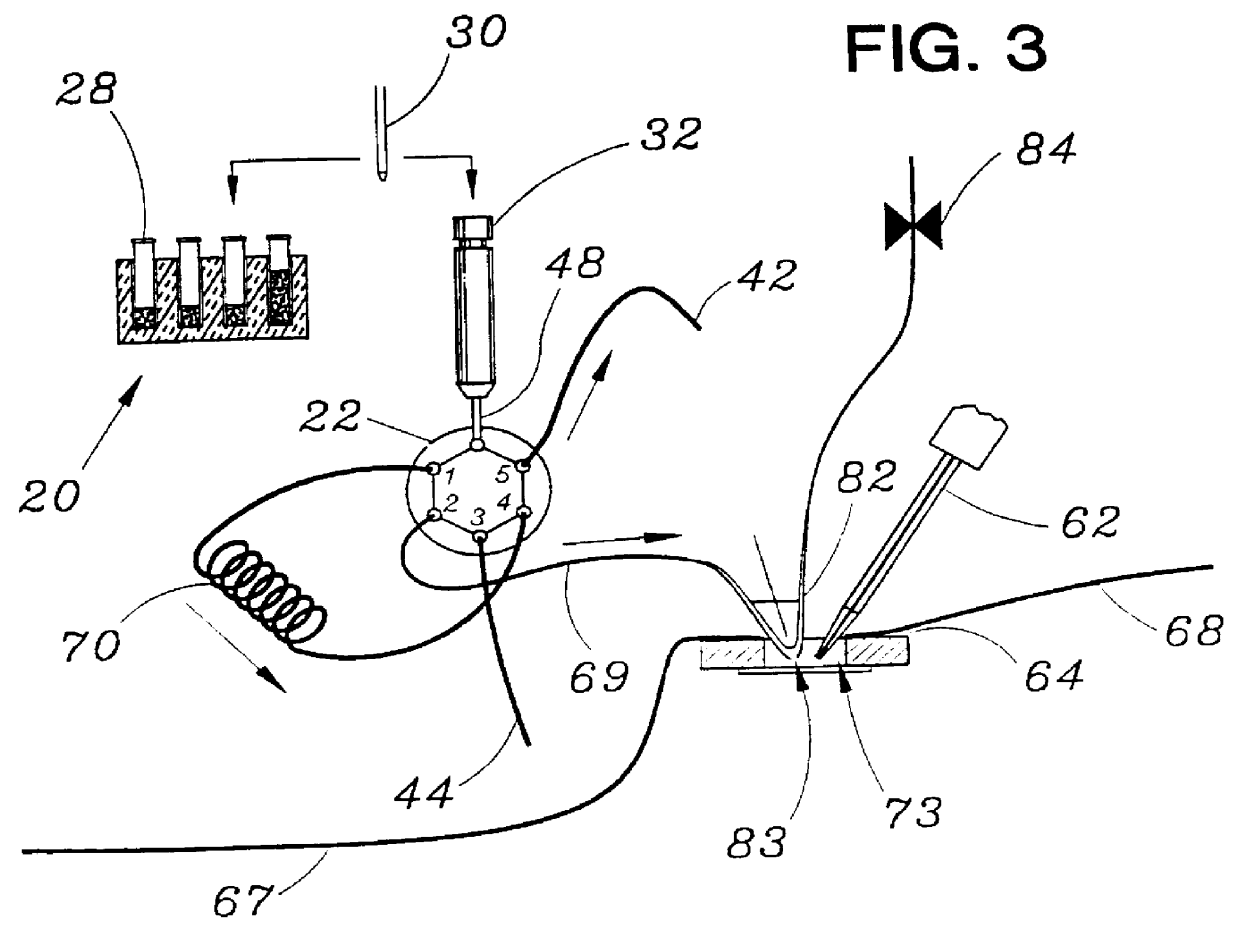
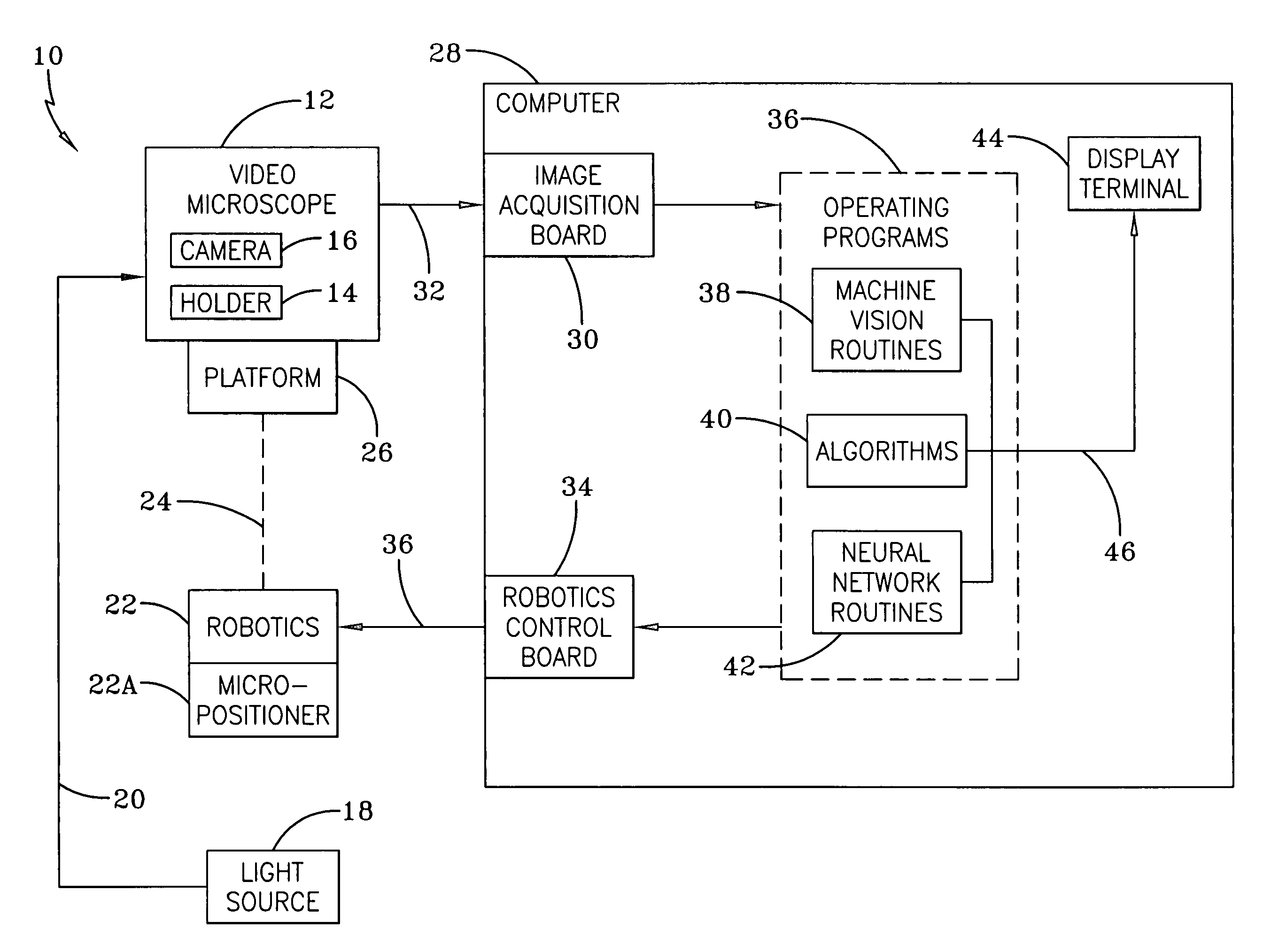
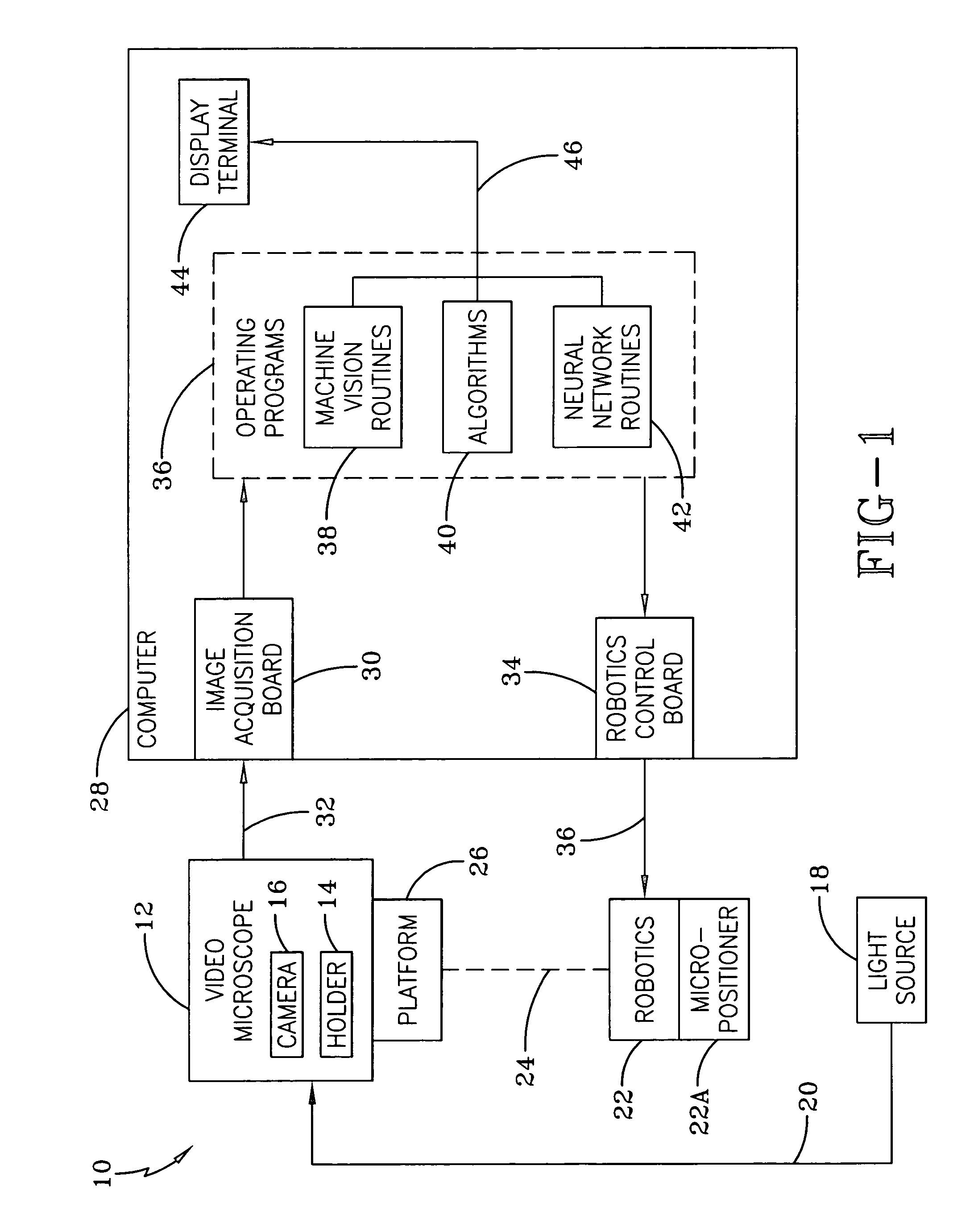
Identification of cells with a compact microscope imaging system with intelligent controls
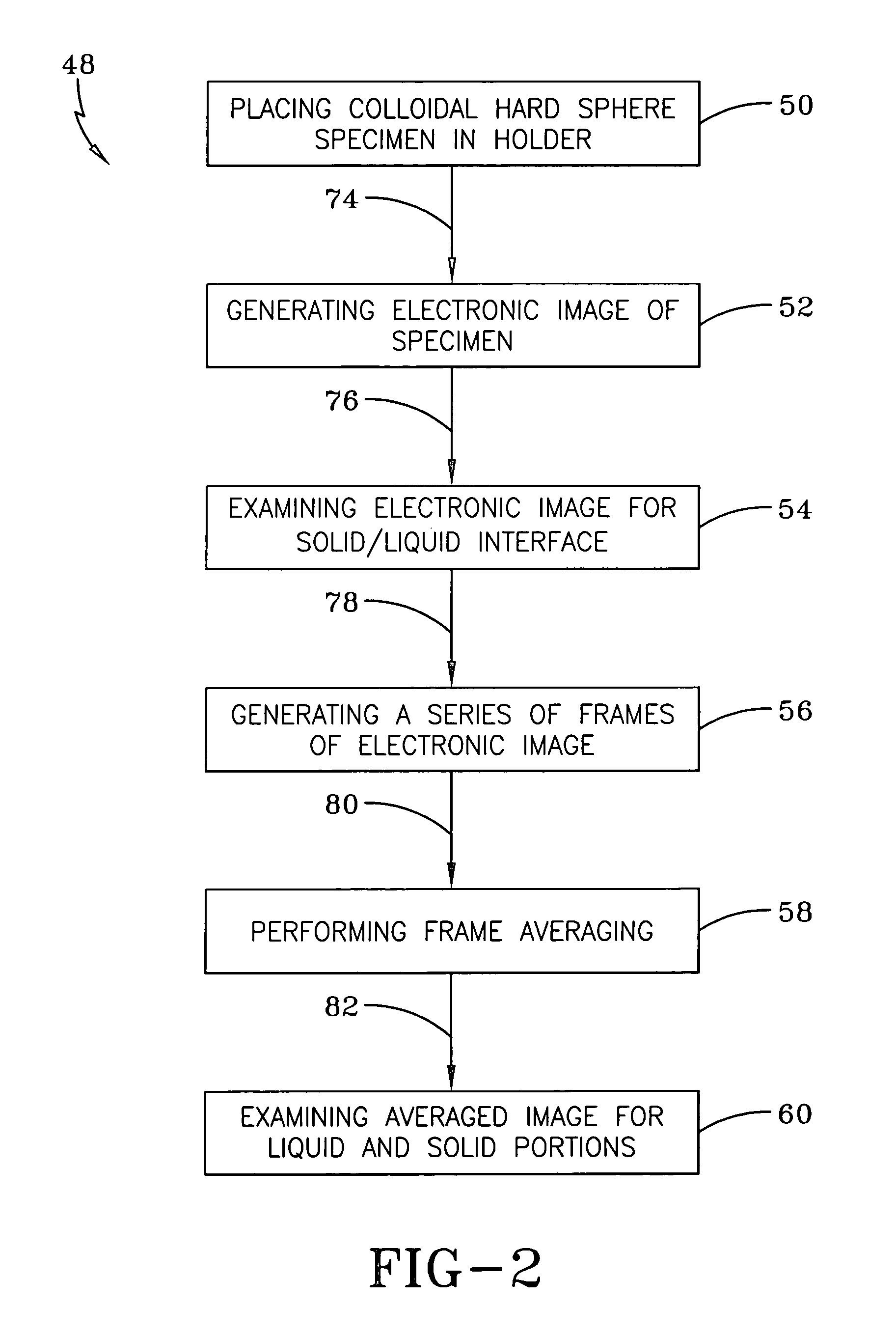
A Microscope Imaging System (CMIS) with intelligent controls is disclosed that provides techniques for scanning, identifying, detecting and tracking microscopic changes in selected characteristics or features of various surfaces including, but not limited to, cells, spheres, and manufactured products subject to difficult-to-see imperfections. The practice of the present invention provides applications that include colloidal hard spheres experiments, biological cell detection for patch clamping, cell movement and tracking, as well as defect identification in products, such as semiconductor devices, where surface damage can be significant, but difficult to detect. The CMIS system is a machine vision system, which combines intelligent image processing with remote control capabilities and provides the ability to auto-focus on a microscope sample, automatically scan an image, and perform machine vision analysis on multiple samples simultaneously.
Owner:NASA
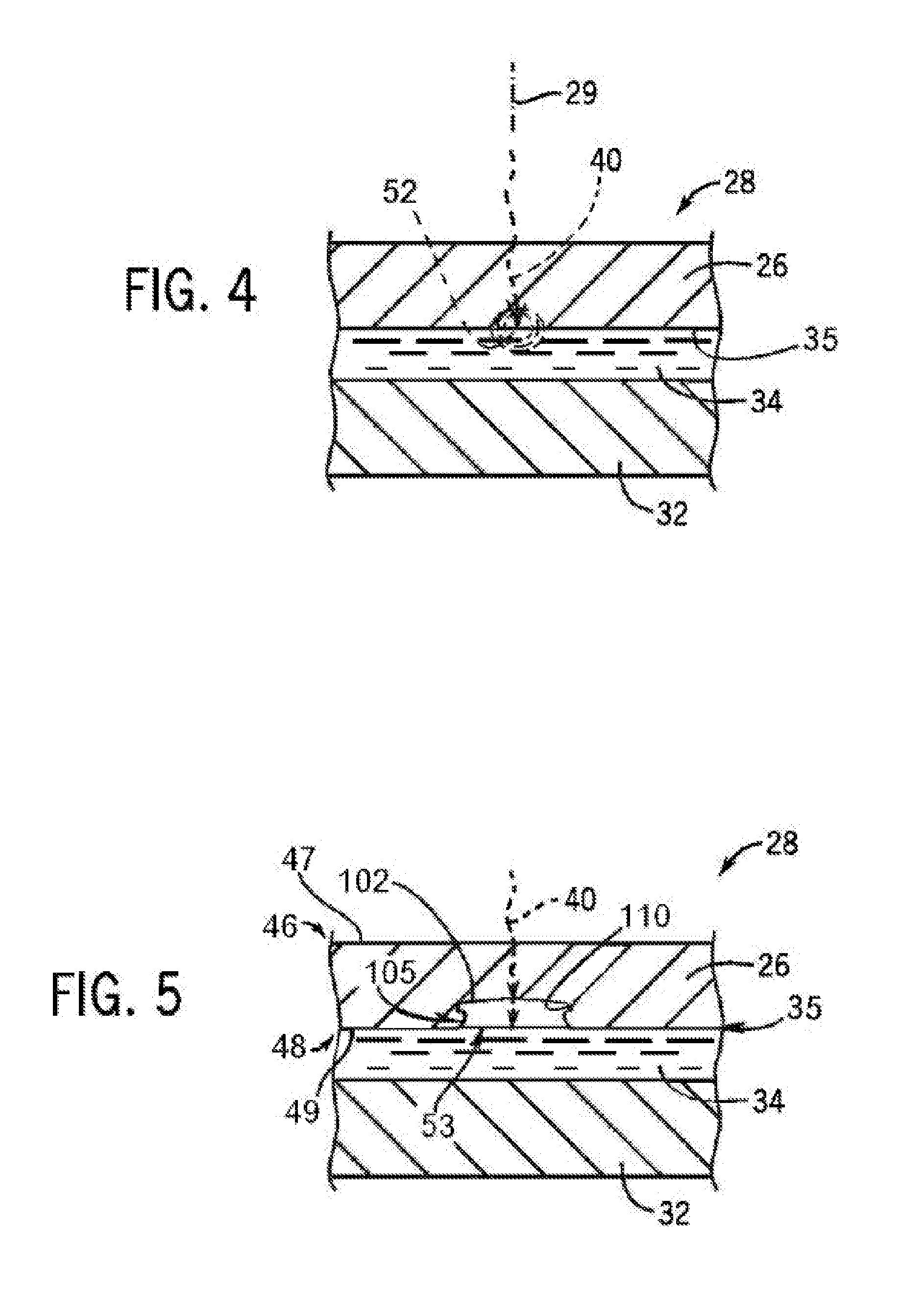
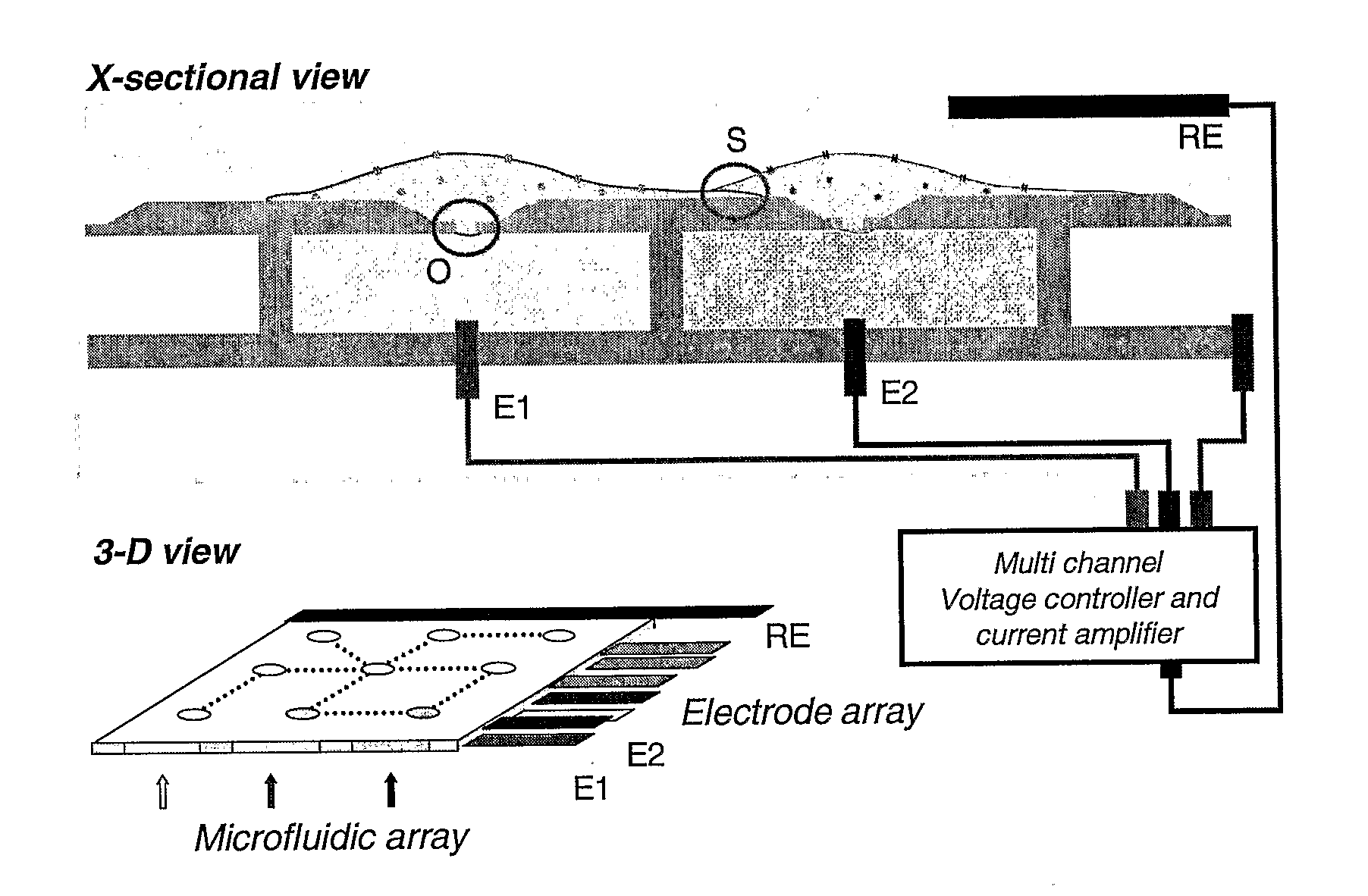
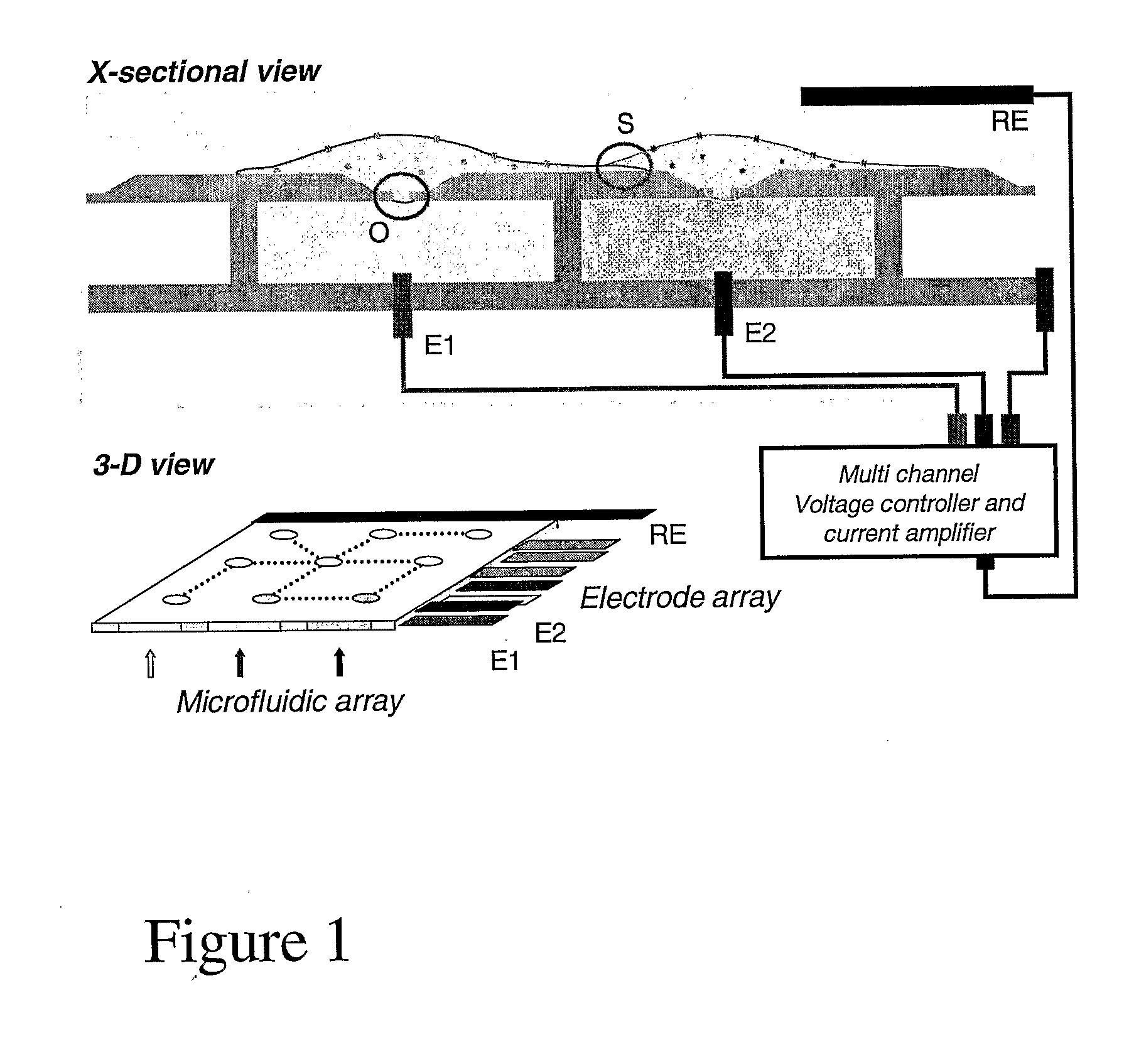
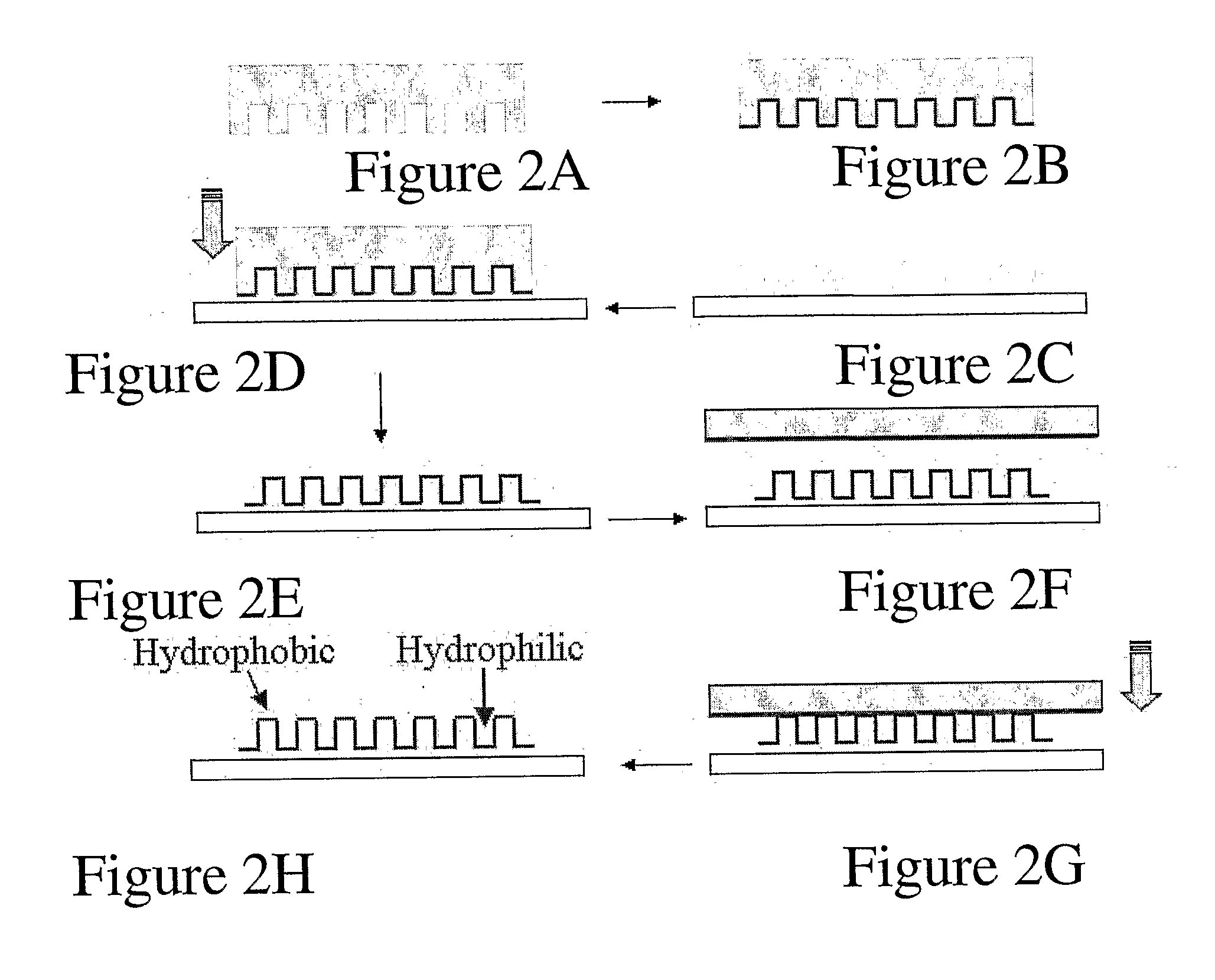
High-density ion transport measurement biochip devices and methods
InactiveUS20050196746A1Low costImprove production efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFluidicsHigh density
The present invention provides novel biochips, biochip-based devices, and device configurations that can be used for ion transport measurement. The chips, devices, and designs of the present invention are particularly suited to high-throughput assays such as compound screening assays using patch clamping techniques. The invention includes high-density biochips made by novel methods and methods of making high density biochips, and also provides novel upper chamber configurations and fluidics designs for upper chambers of ion transport measurement devices that can be used in high throughput patch clamp assays. The present invention also includes methods of using ion transport measuring chips and devices of the present invention.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Retro-percussive technique for creating nanoscale holes
ActiveUS20100129603A1Improve abilitiesResistance sealLayered productsThin material handlingShock waveCell membrane
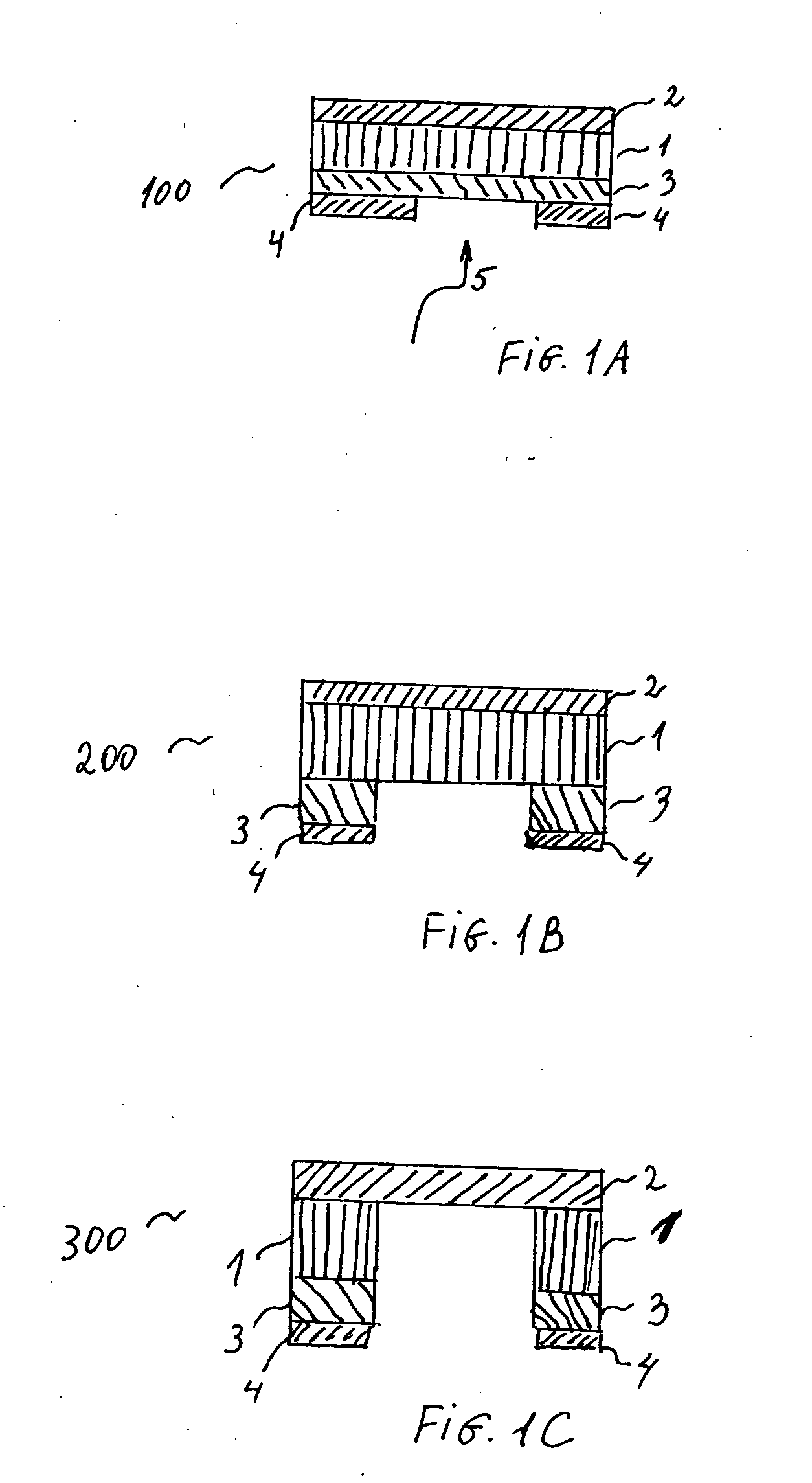
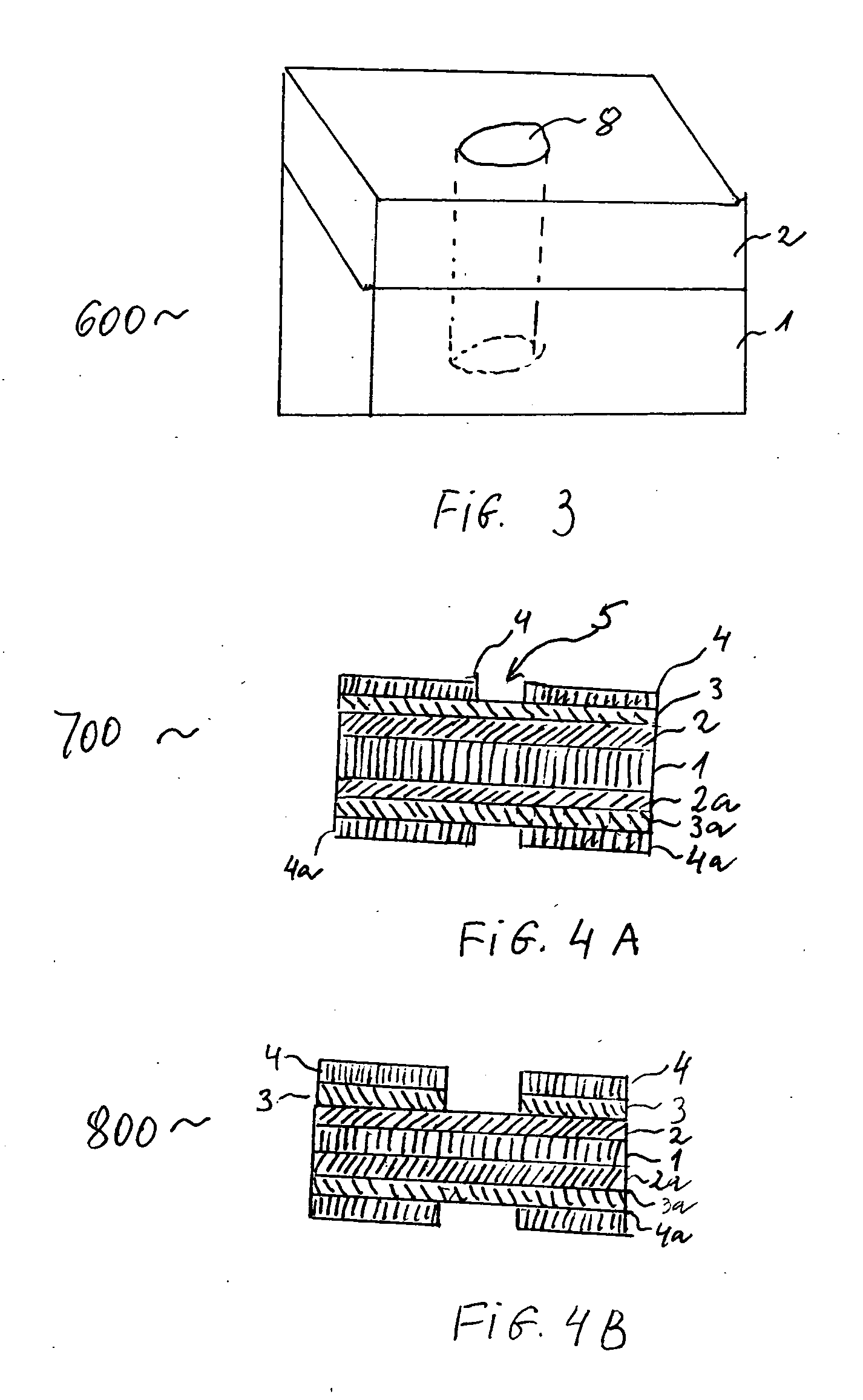
A method of forming extremely small pores in glass or a similar substrate, useful, for example, in patch clamp applications, that employs a backer plate to contain energy of a laser-induced ablation through the front surface of the substrate so as to create a rear surface shock wave providing a fire polishing of the exit aperture of the pore such as produces improved sealing with cell membranes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Parallel patch clamp system
ActiveUS20060194255A1Increase success rateLow costImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCurrent sensorEngineering
A system for high-throughput analysis of membranous samples having ion channels including at least one membranous sample, a multi-compartment structure including an extracellular chamber, an opposing intracellular chamber and a partition separating the extracellular and intracellular chambers, the partition having a plurality of apertures fluidly and electrically coupling the extracellular and intracellular chambers, wherein at least one of the apertures is sealed by the at least one membranous sample, and another of the apertures is unsealed, a electric source configured to apply a current between the extracellular and intracellular chambers, wherein a portion of the current travels through the unsealed aperture, and a current sensor configured to measure the current between the extracellular and intracellular chambers. A method of using the system is also disclosed.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
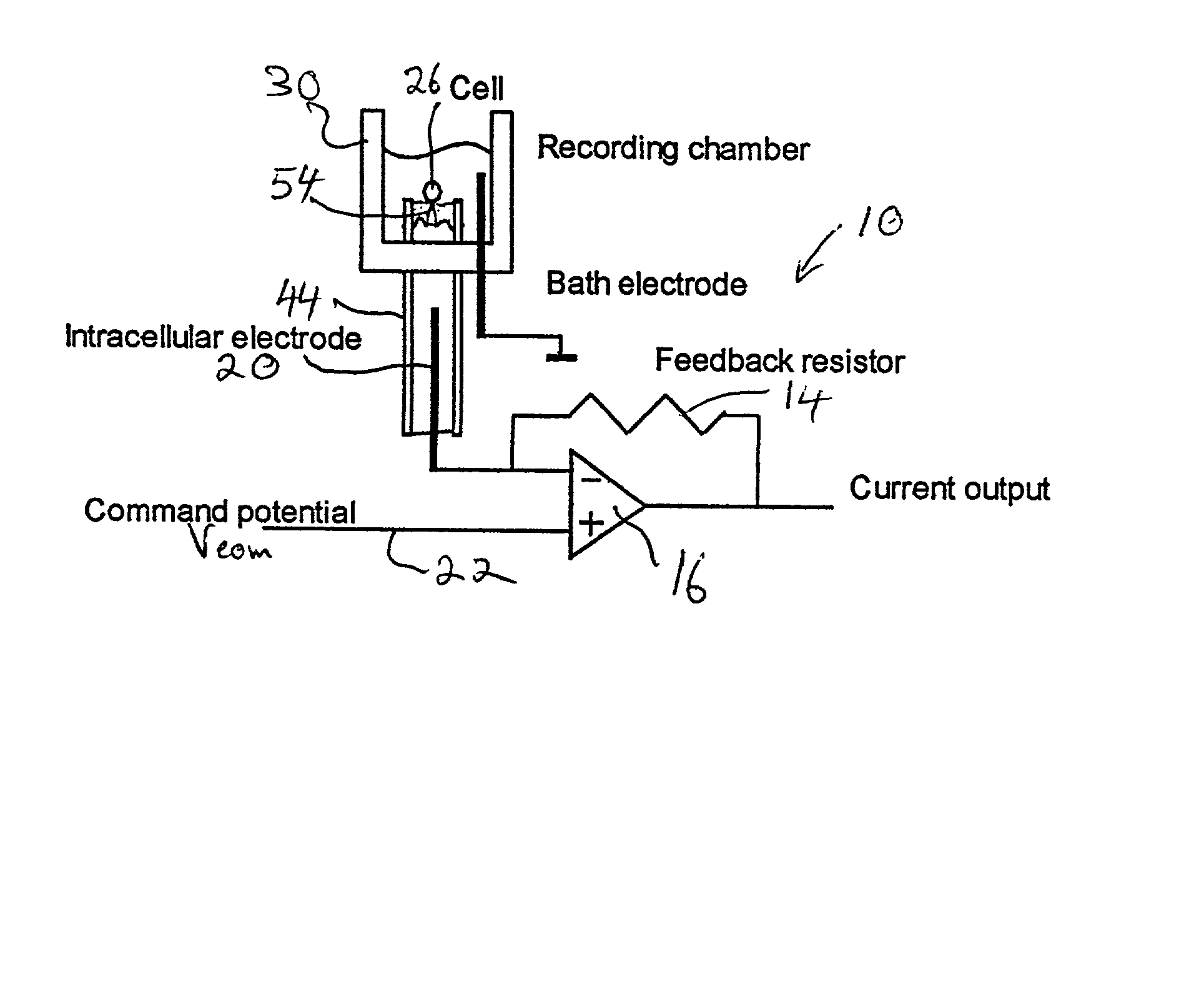
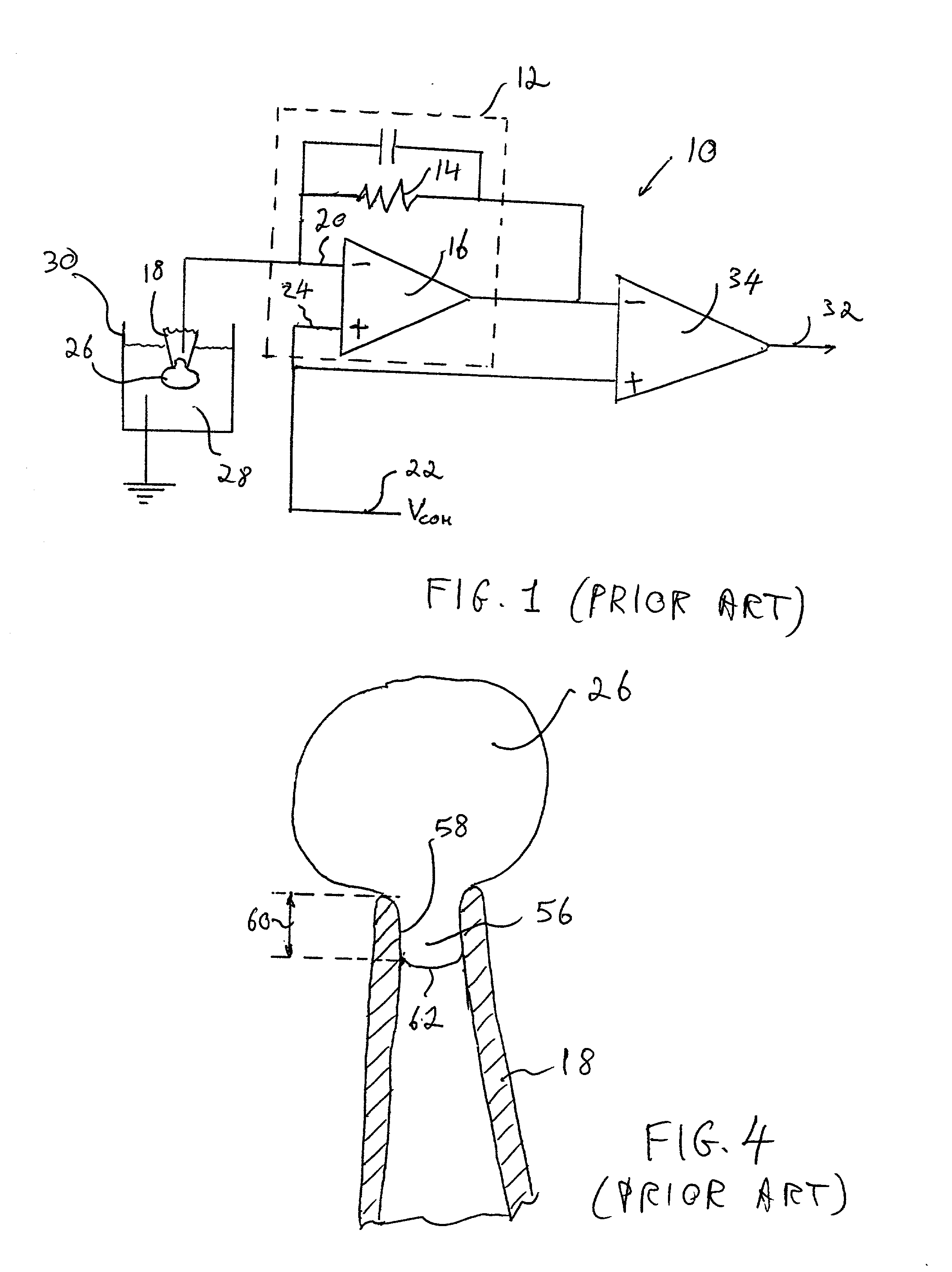
Microperfusion chamber assembly with base comprising silver chloride coated silver
InactiveUS6117291AImprove throughputLower requirementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutosamplerIon transfer
Apparatus for carrying out patch clamp technique utilized in studying the effect of certain materials on ion transfer channels in biological tissue, and more particularly patch clamp apparatus utilizing an autosampler, such as those utilized with HPLC apparatus, to provide high throughput, is disclosed. The invention additionally includes novel microperfusion chamber assemblies capable of utilizing only small amounts of material to be tested and only small amounts of liquid carrier, thereby enabling many tests to be completed in a short period of time. The invention more broadly relates to a novel electrophysiology drug handling and application set up for screening of chemical substances while providing high throughput and requiring only low volume of solutions and samples to be tested. The invention also comprises several novel procedures for utilizing the apparatus of the invention.
Owner:SOPHION BIOSCI
Polymeric electrode for electrophysiological testing
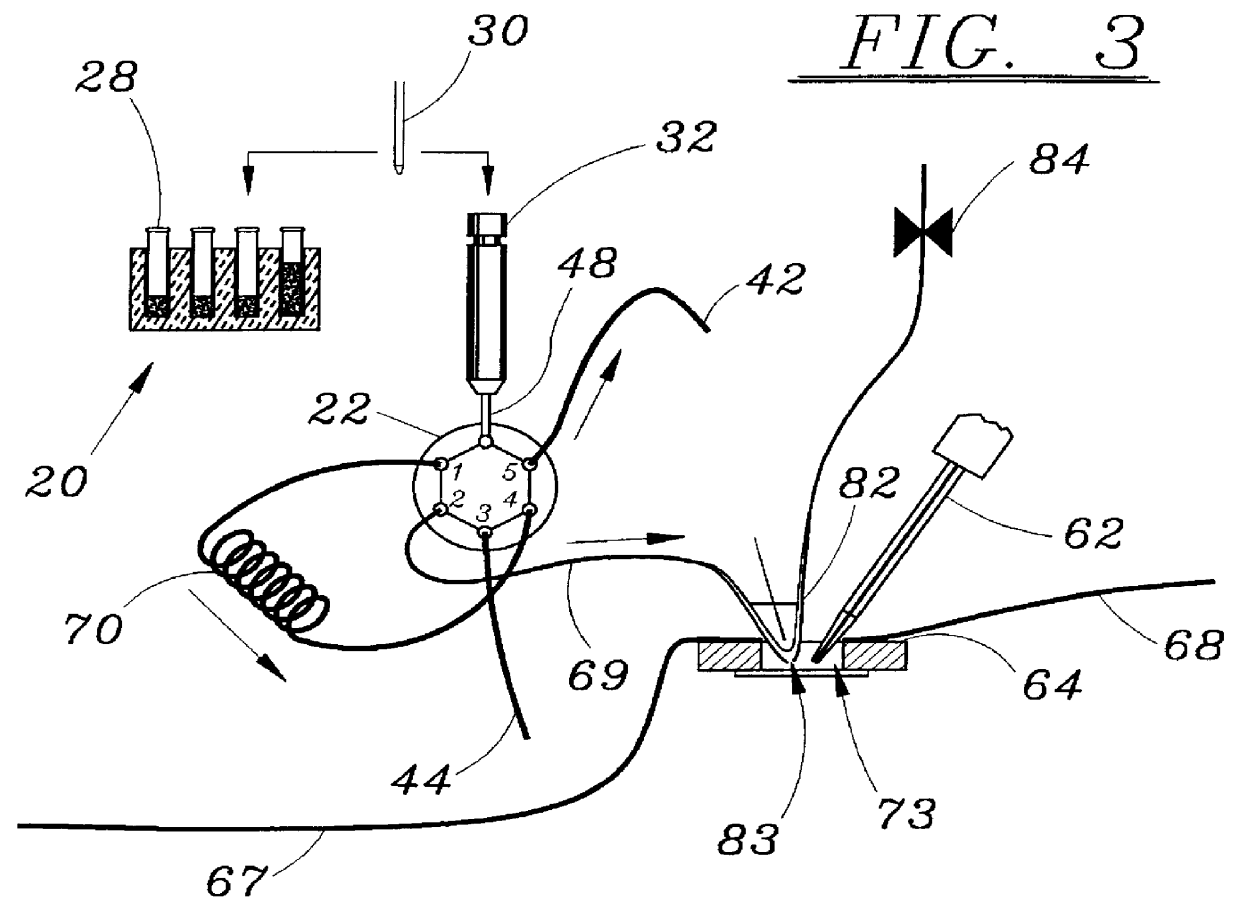
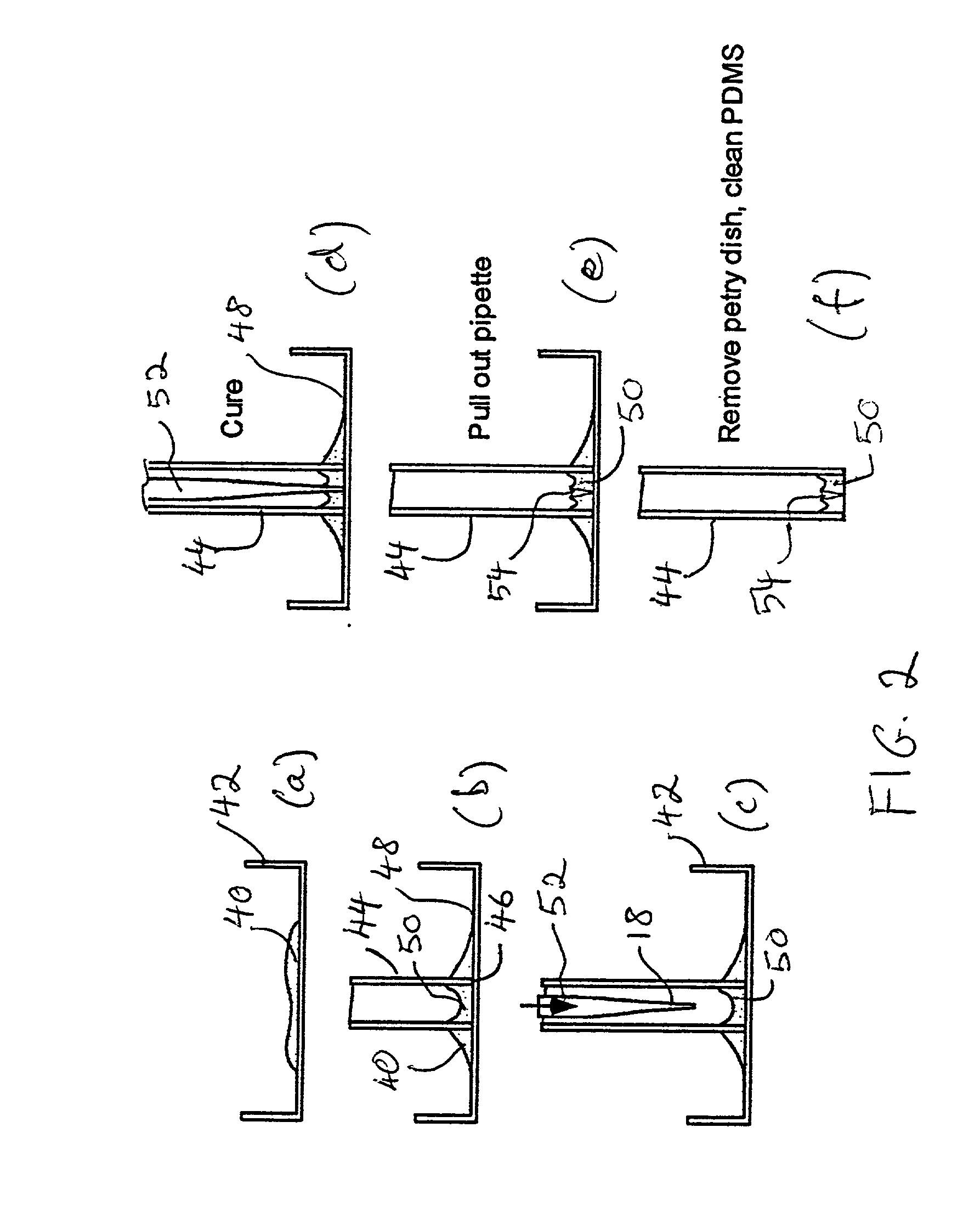
InactiveUS20020195337A1Reduce manual operationsSuitable for useImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological membraneBiomedical engineering
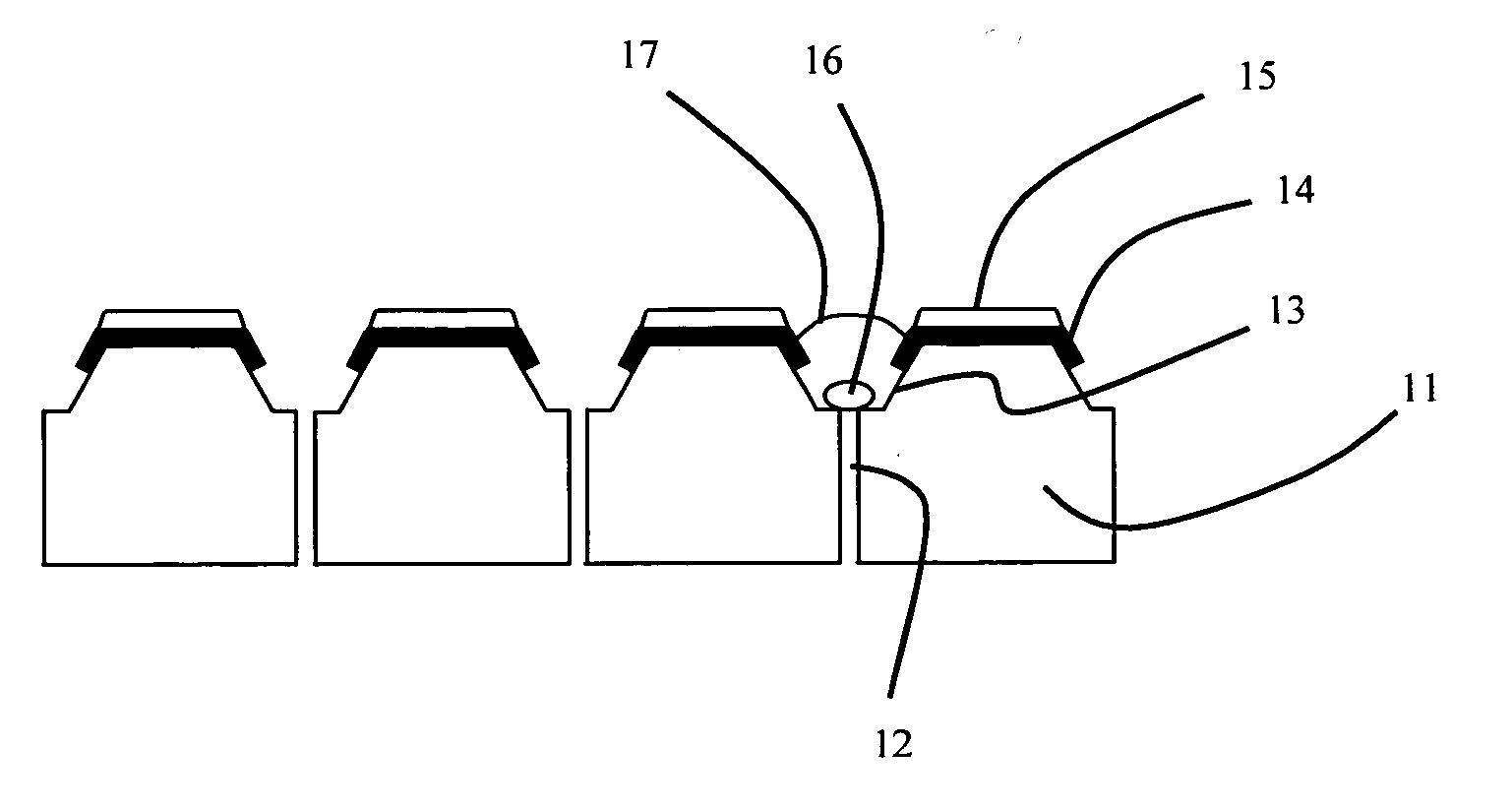
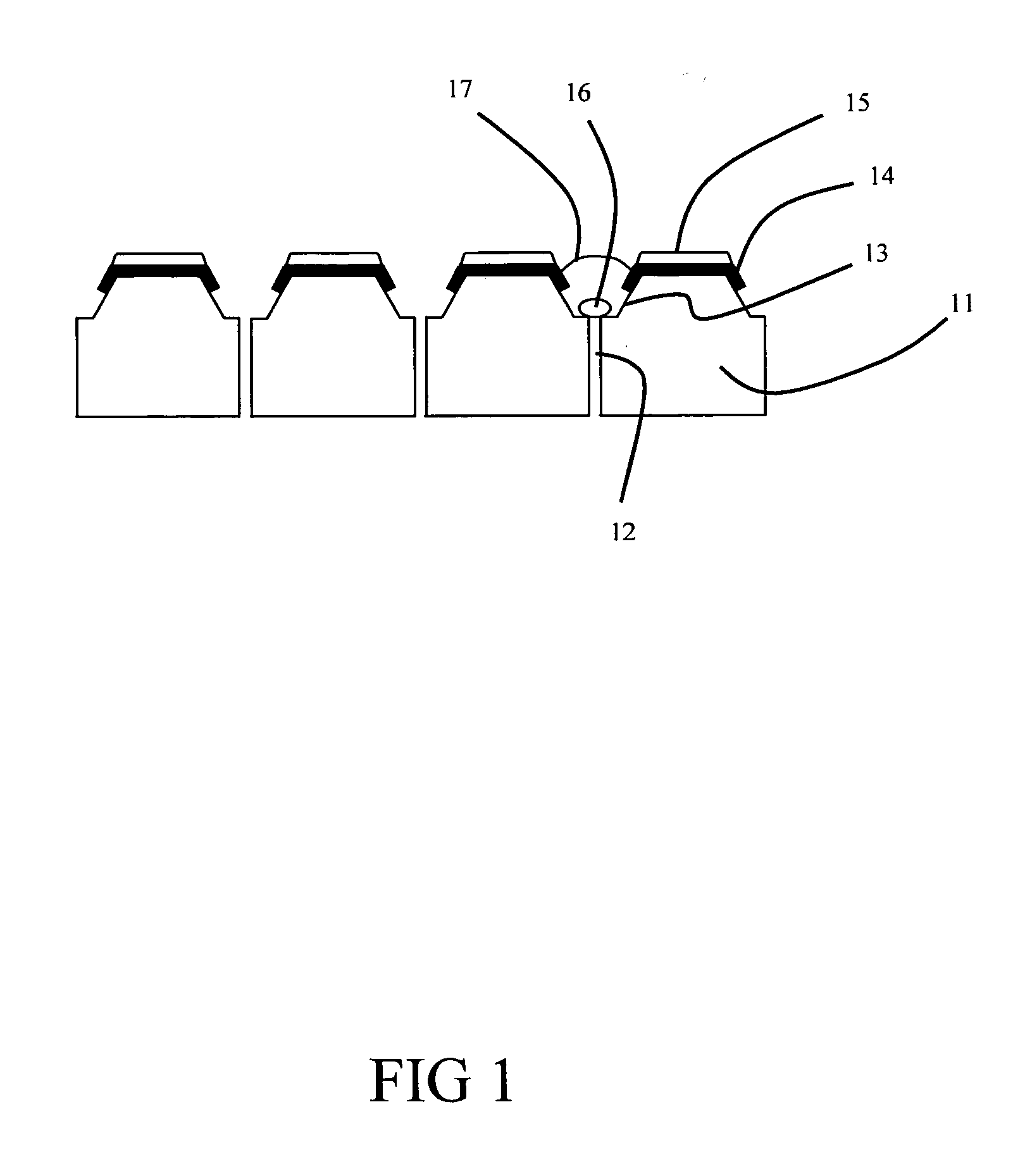
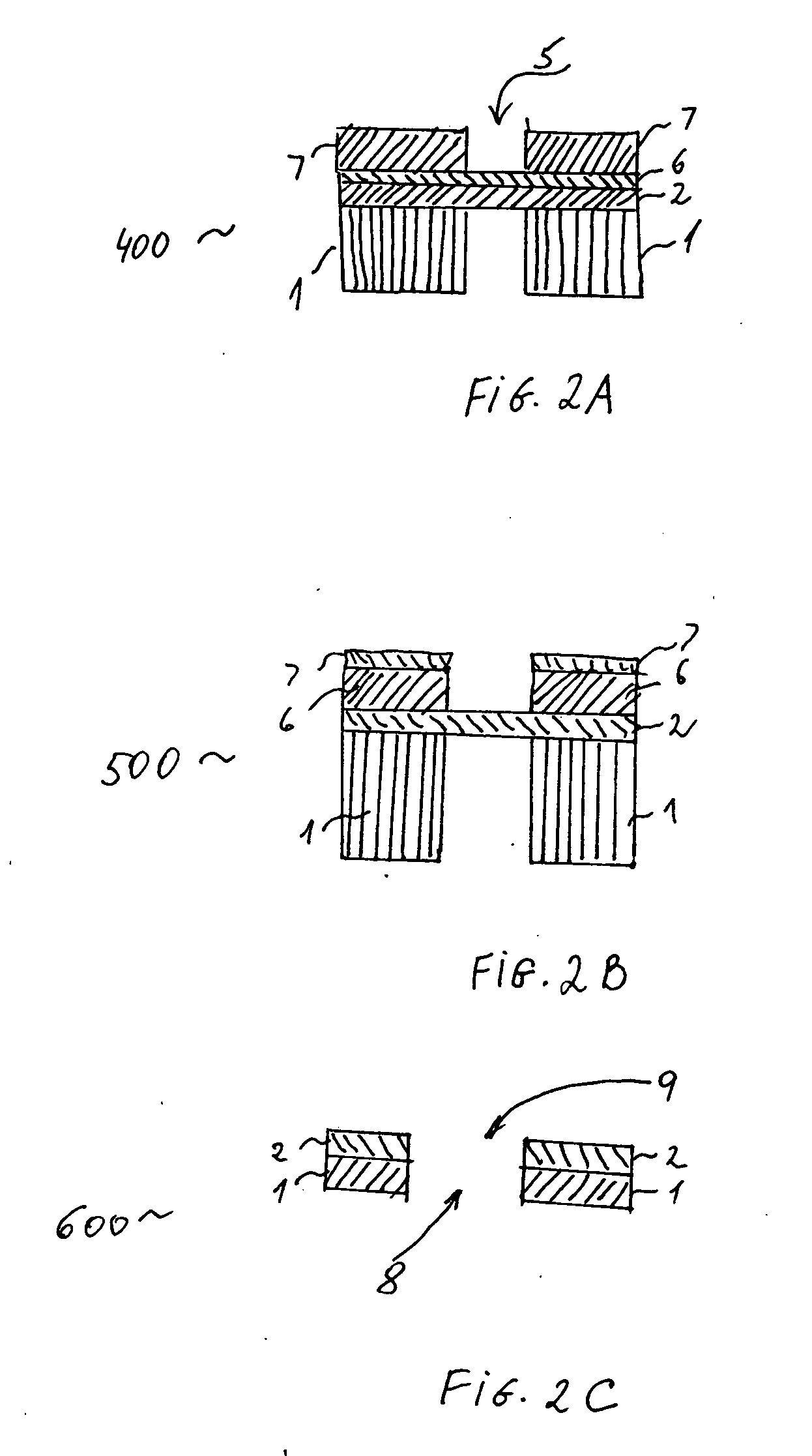
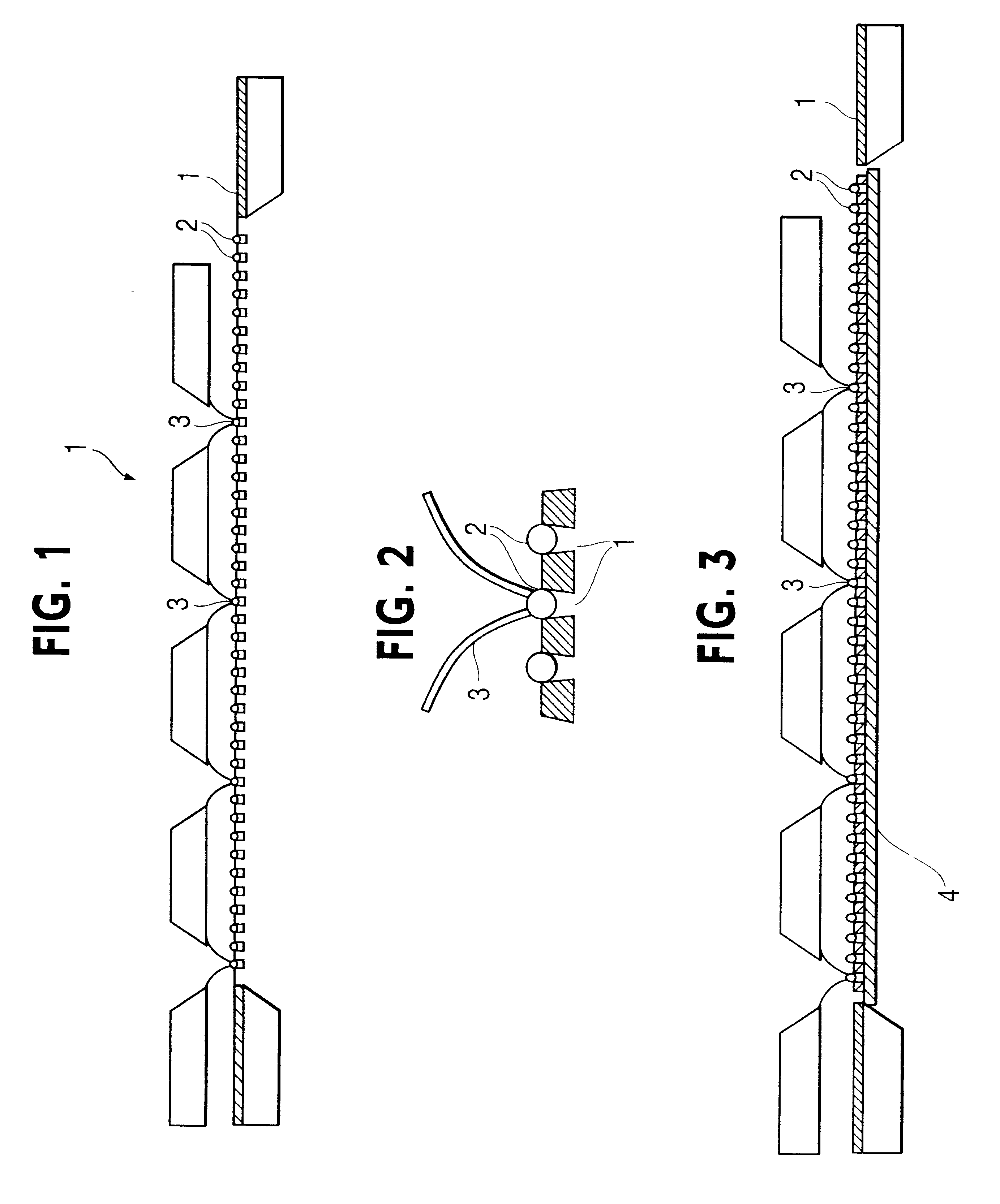
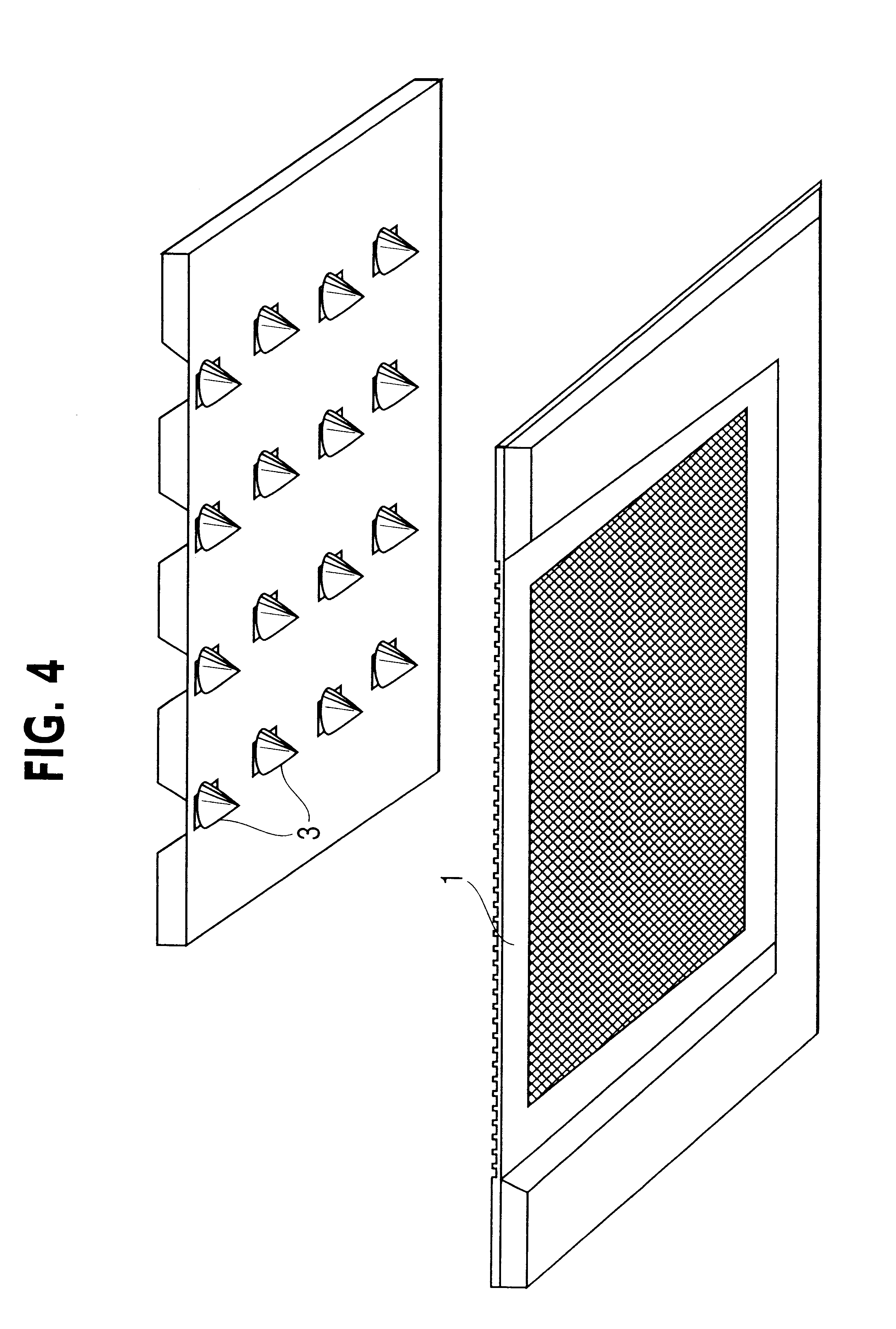
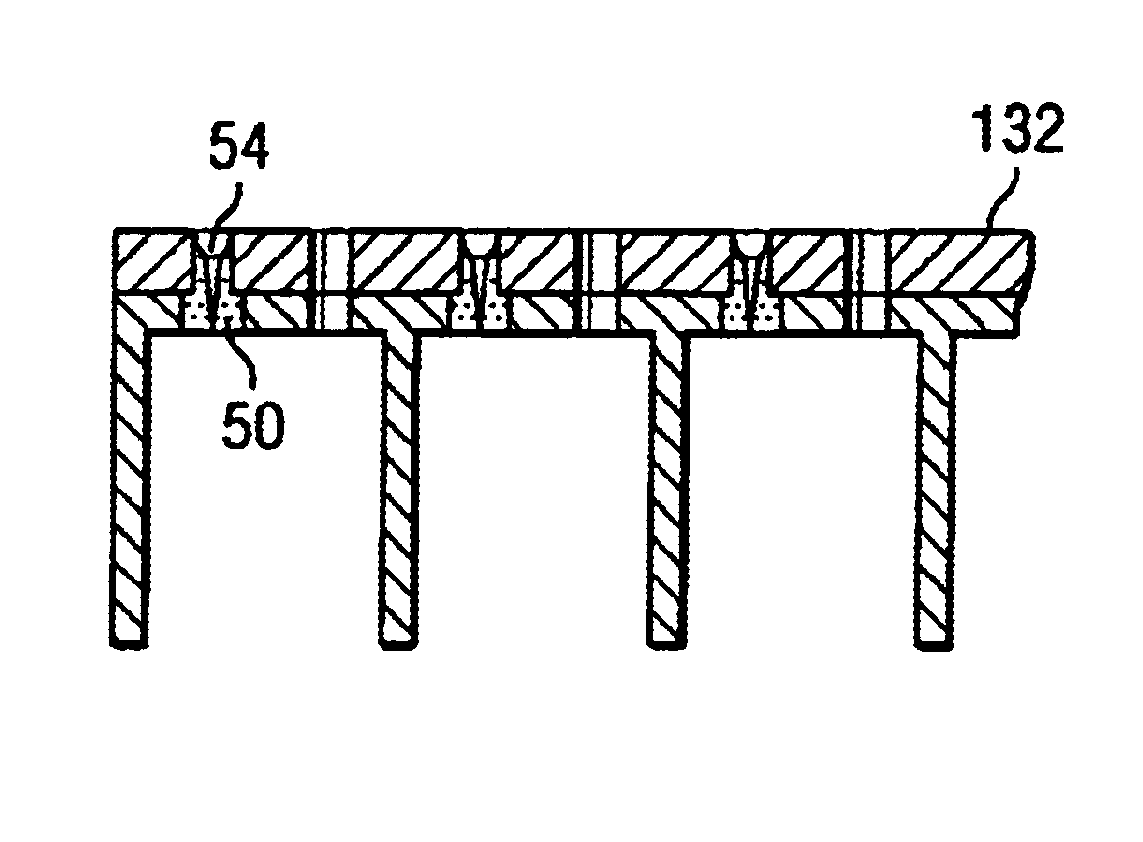
A polymeric material such as PDMS is molded into an electrode structure containing a micron-size aperture for receiving and forming a giga-ohm seal with a biological membrane One end of a tube is filled with uncured polymeric material and pressed against a support surface to prevent drainage. A conventional micropipette having a size suitable for sliding through the tube is introduced, tip first, into the tube and is allowed to fall through the polymeric material and rest against the support surface. The assembly is heated to cure the polymer and the micropipette is removed from the tube, thereby leaving a polymeric plug at the end of the tube with an aperture suitable in shape and size for patch-clamp giga-ohm seal electrode applications. A multi-well tray with a polymeric electrode plug in each well is constructed using the same approach.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Ultra-smooth microfabricated pores on a planar substrate for integrated patch-clamping
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Device and process for the examination of cells using the patch-clamp method
InactiveUS6379916B1Compact measuringEvenly distributedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteEngineering
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Methods and apparatus for the manipulation of particle suspensions and testing thereof
InactiveUS20120264134A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrophysiology studyCell electrophysiology
Apparatus and methods are provided for analysis of individual particles in a microfluidic device. The methods involve the immobilization of an array of particles in suspension and the application of experimental compounds. Such methods can also include electrophysiology studies including patch clamp recording, electroporation, or both in the same microfluidic device. The apparatus provided includes a microfluidic device coupled to a multi-well structure and an interface for controlling the flow of media within the microchannel device.
Owner:FLUXION BIOSCI
Single molecular nucleic acid sequencing process for exonuclease-nanometer hole
InactiveCN1932039AImprove recognition accuracyHigh hardnessMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
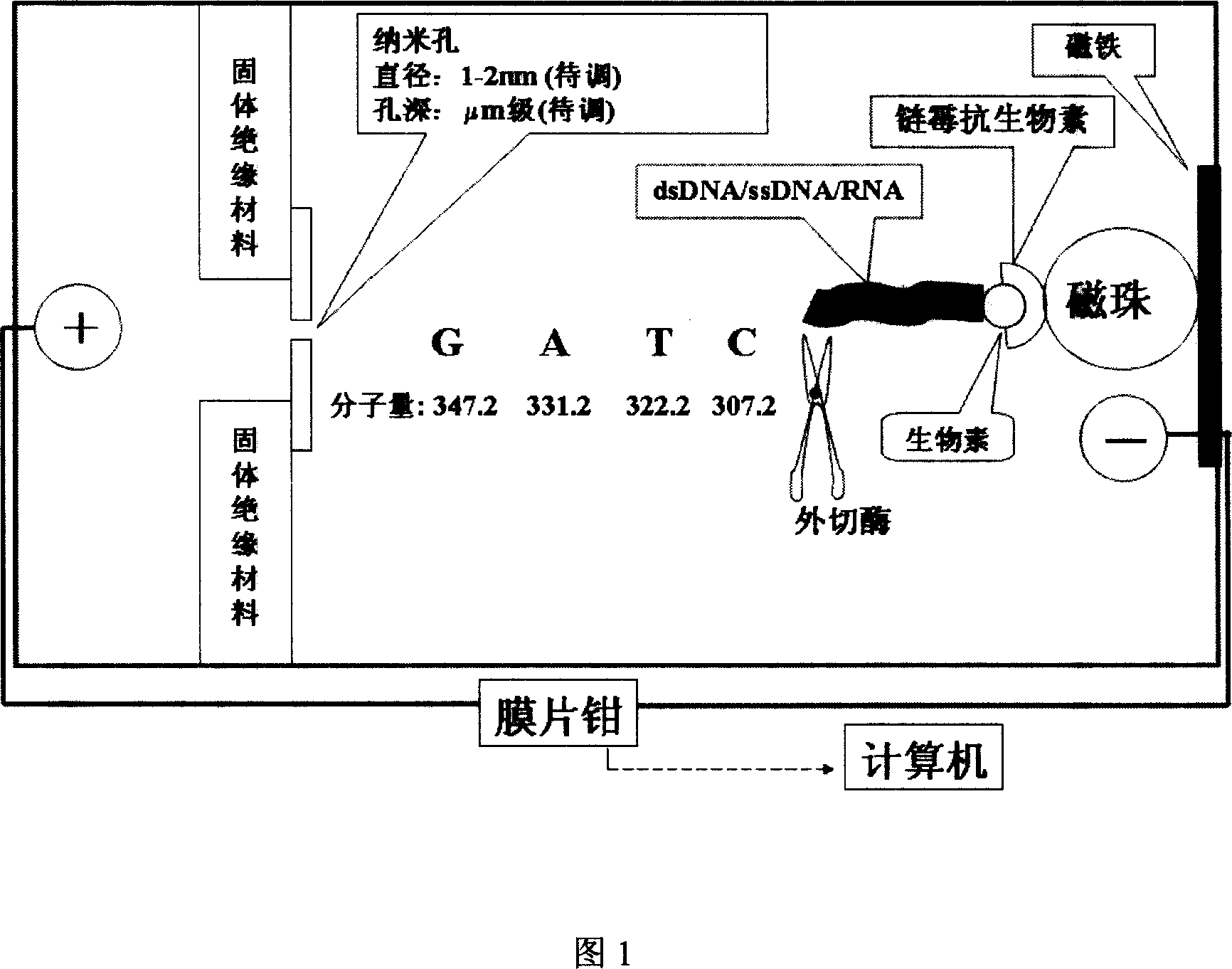
The present invention relates to biotechnology, and is single molecular nucleic acid sequencing process for exonuclease-nanometer hole. The process includes the following steps: 1. detecting electric signal of single molecular nucleotide to set up standard curve; 2. fixing nucleic acid in the negative pole of electrophoresis tank, degrading nucleotides with exonuclease and detecting the electric signal with the patch clamp while passing through the nanometer hole; and 3. converting the electric signal into specific nucleotide based on the standard curve and obtaining the base sequence of the nucleotide according to the cutting direction of the exonuclease. The present invention has high nucleoside and deoxynucleoside-phosphate recognizing accuracy, and may be used in detecting nucleoside and deoxynucleoside5'-phosphate, nucleoside and deoxynucleoside3'-phosphate and methylated cytidine in natural eukaryote DNA.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Laser drilling technique for creating nanoscale holes
ActiveUS20110111179A1Smooth poresLarge caliberLayered productsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnergy absorptionEngineering physics
A method of forming extremely small pores in a substrate that is used, for example, in patch clamp applications is provided that employs an energy absorbing material beyond a back side of the substrate to allow a laser to be focused adjacent the exit side of the substrate so as to generate a pore through the substrate and can also form a crater in the back side of the substrate and in which the pore may propagate from the crater in a drilling direction that can oppose a laser transmission direction.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Patterned Cell Network Substrate Interface and Methods and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070231850A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell membraneCell network
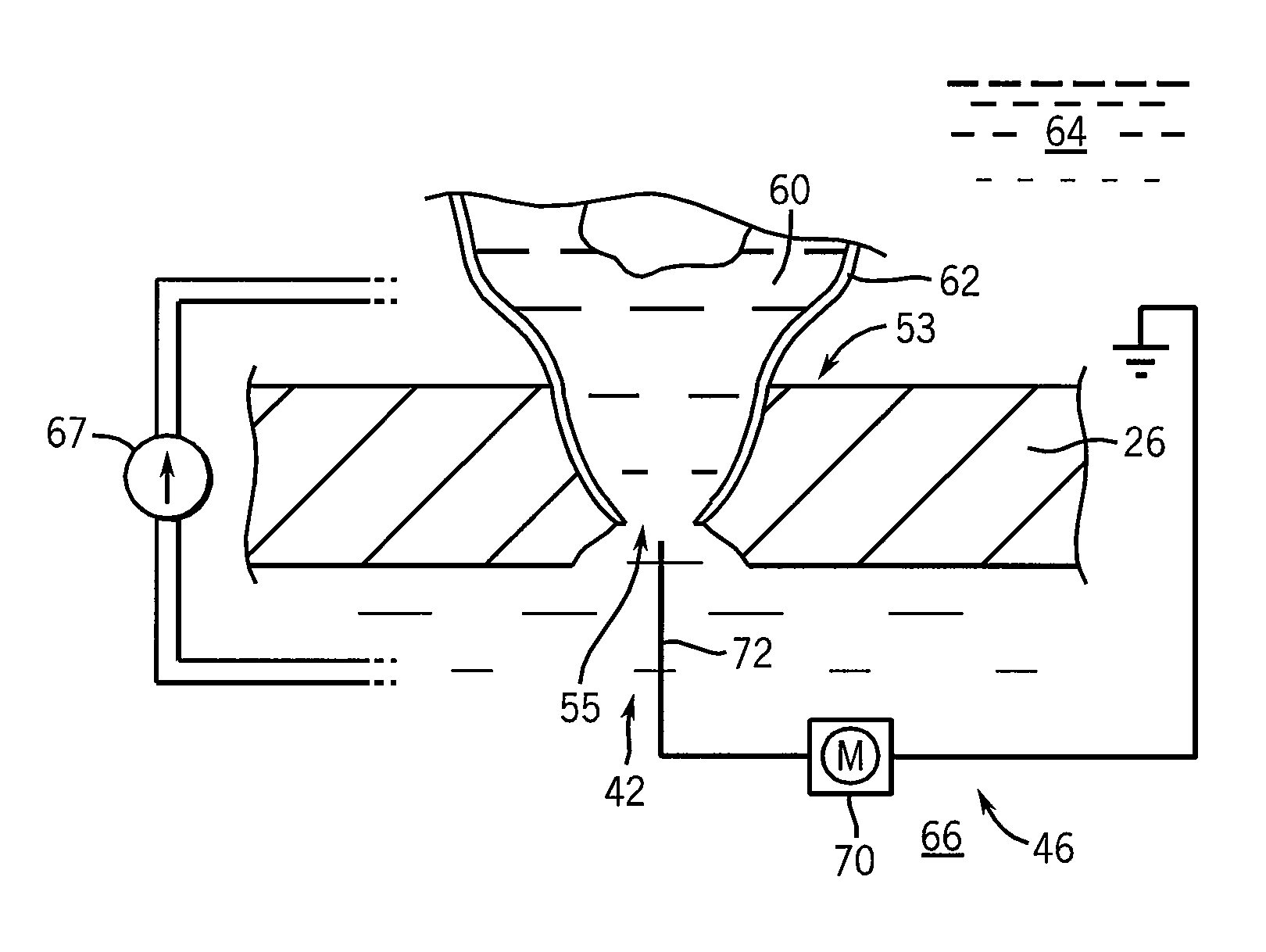
There is provided herein a method and apparatus suitable for use in studying cell membrane related activities. Activities of interest include patch-clamp related studies of networks of cells on a solid substrate. Cells are grown, preferably in a patterned manner, on a substrate having microholes therein. Seals between the cells and the microholes are formed. Each microhole is attached to a channel. In many cases only one hole will be attached to a single channel, allowing examination of effects of a stimulus at a number of different points in a network of one or more cell types. This may be interest, for example, to those wishing to study interactions between neurons or neuromuscular junctions.
Owner:GEOFFREY MEALING +6
Detachable cell-delivery system for patch-clamp unit
ActiveUS7056430B1Improve throughputLow costImmobilised enzymesElectrostatic separatorsCell sorterEngineering
The cell-delivery unit of a high-throughput electrophysiological testing system is implemented as a reusable movable unit suitable for repetitive delivery of cells to a disposable, multi-aperture patch-clamp tray. An electric field emanating from the patch aperture is used to align the dispenser with the aperture. A set of electrodes in the nozzle of the dispenser is used to detect the electric field and effect the alignment. According to another aspect of the invention, dielectrophoretic fields produced by sets of electrodes in the nozzle form a retaining cage that is used first to suspend a test cell directly above the patch aperture and then to urge the cell toward it. A movable cell sorter may also be coupled to the cell-delivery unit.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
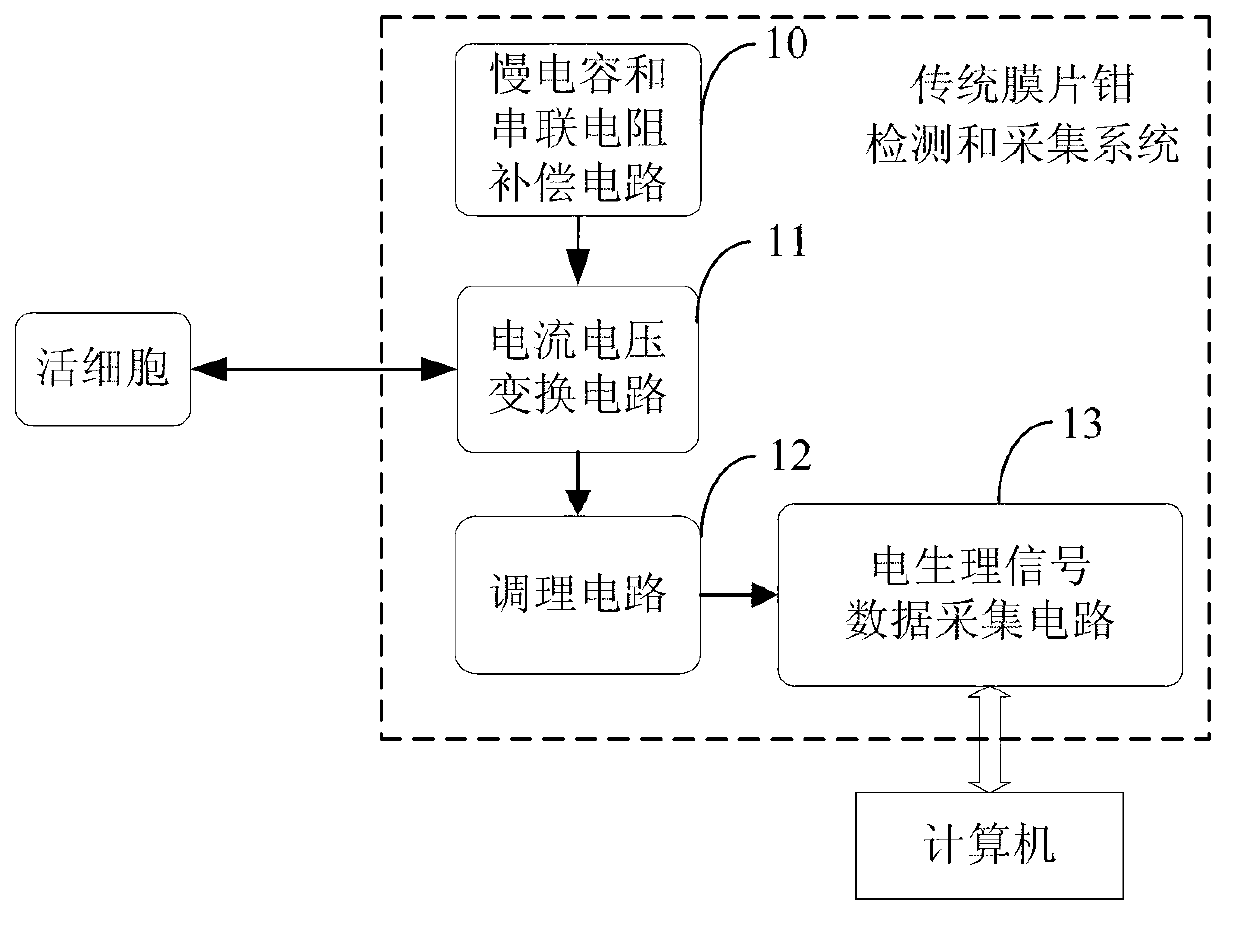
Detection and acquisition system for solid-state nano-pore nucleic acid sequencing electric signals
ActiveCN103275867ASimple structureReduce volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage resolutionData acquisition
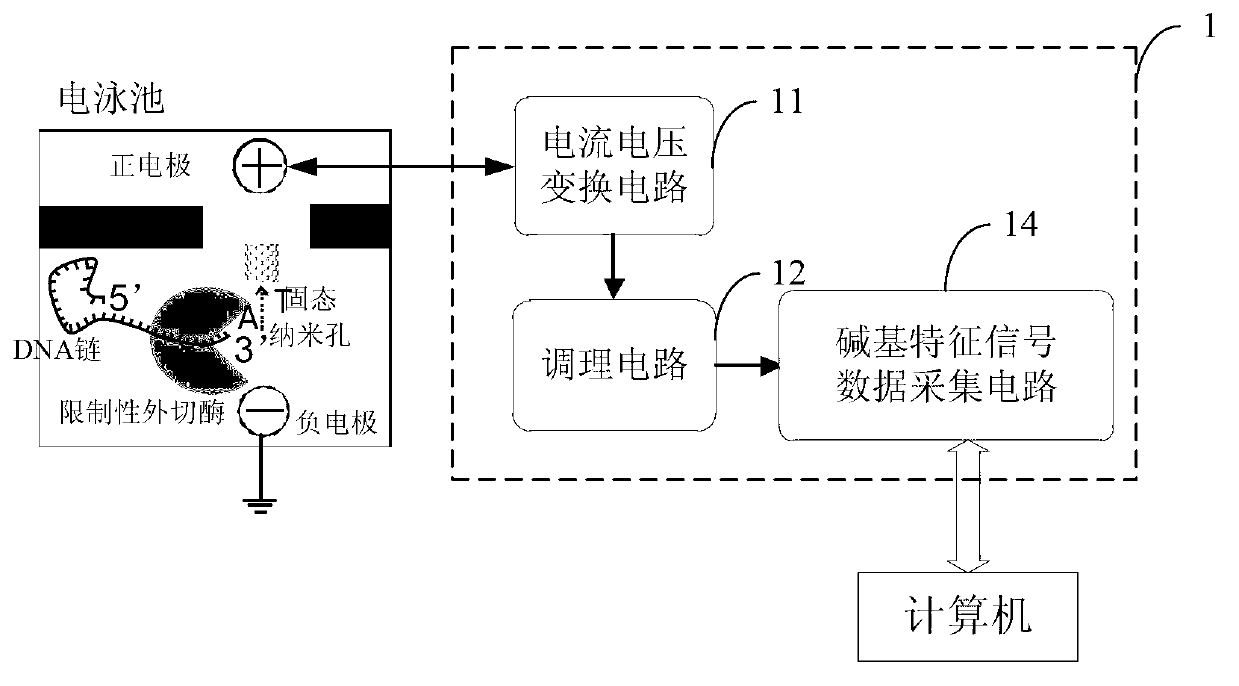
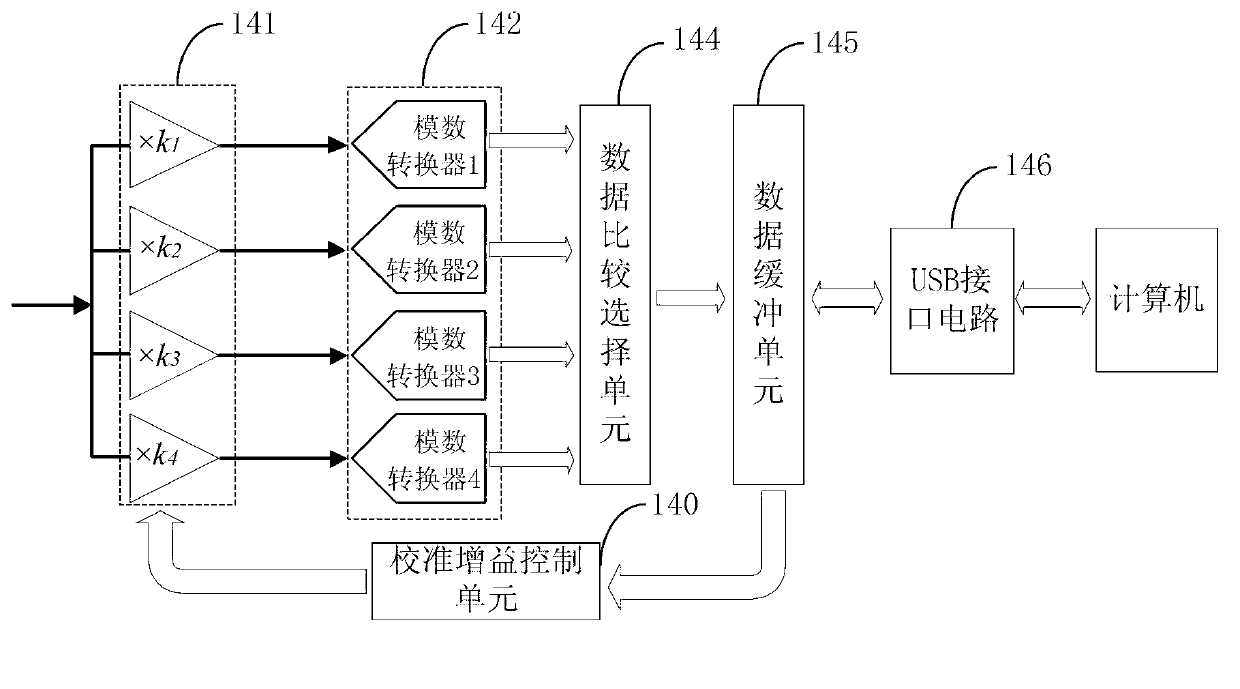
The invention relates to the fields of genetics and molecular biology, and provides a detection and acquisition system for solid-state nano-pore nucleic acid sequencing electric signals. The system comprises a current-voltage conversion circuit, a conditioning circuit and a base characteristic signal data acquisition circuit which are successively connected to one another; the current-voltage conversion circuit is used for converting characteristic current signals into voltage signals, the characteristic current signals are generated by passing bases through solid-state nano-pores under the driving of an electric field, the conditioning circuit is used for amplifying and filtering the voltage signals, and the base characteristic signal data acquisition circuit is used for longtime continuously acquiring output signals of the conditioning circuit and outputting acquisition data to a computer for processing. The system overcomes the disadvantages of detection of electric signals in a solid-state nano-pore nucleic acid sequencing in a patch clamp system, employs detection channels which are mutually independent with one another and different gains aiming at four kinds of bases, realizes detection and acquisition of greatly changeable pA-nA grade current signals, improves the speed and the resolution of base characteristic current signal acquisition, and thereby increasing the identification precision.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light stimulation device
InactiveCN101776791AGuaranteed beam scanning qualityReduce volumeMicroscopesNon-linear opticsAcousto-opticsNerve cells
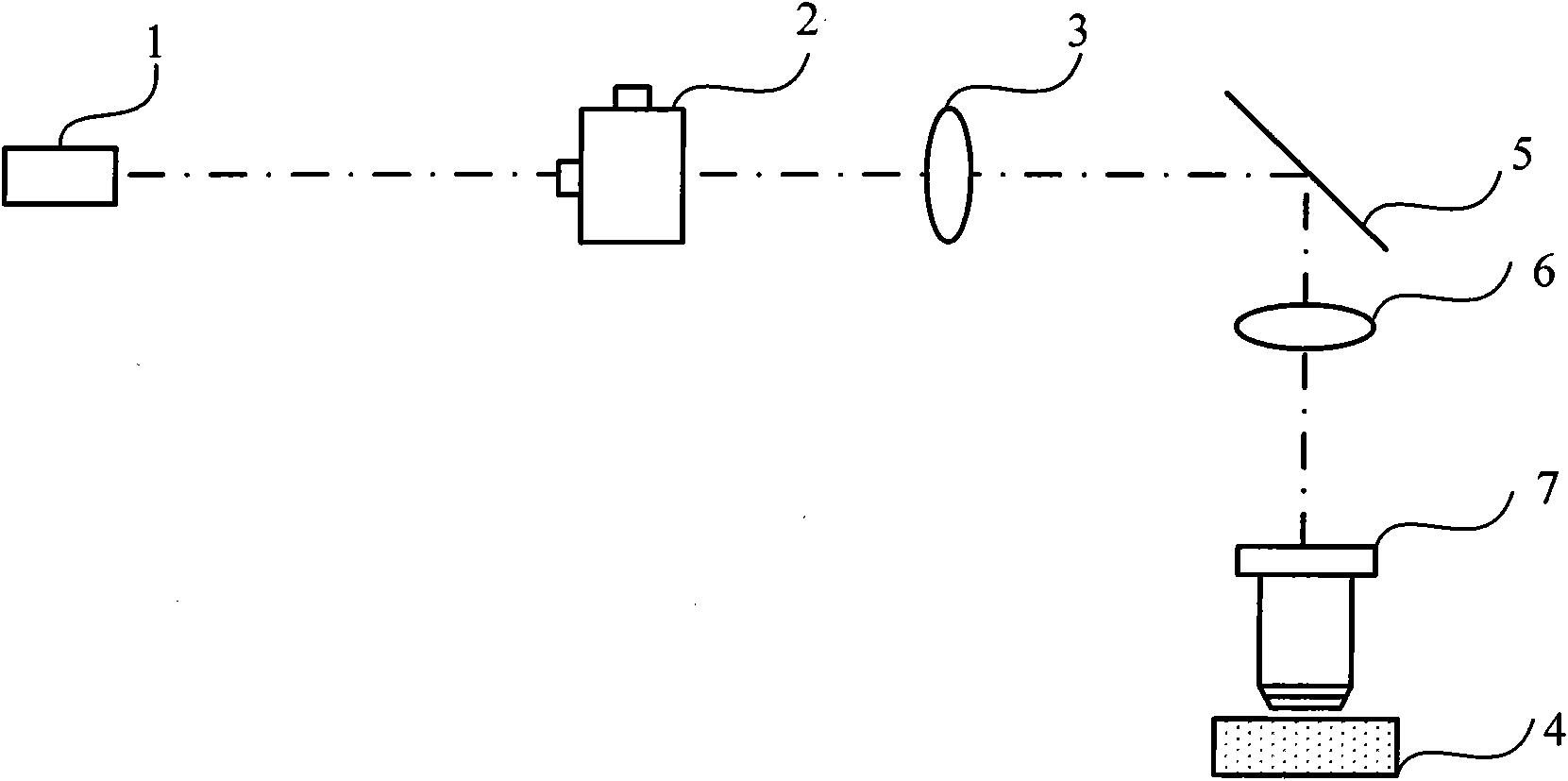
The invention discloses a light stimulation device, which can be applied to the fields of biology, chemistry, life sciences and the like. The structure of the device is that a laser, a scanning unit and a lens are arranged sequentially and are coincident with the center of an optical axis; the center of the scanning unit is positioned on an object focal plane of the lens; and the scanning unit comprises two acousto-optic deflection devices arranged orthogonally. The device adopts the acousto-optic deflection devices as the scanning elements and can carry out high-speed random light stimulation on cell biological samples comprising nerve cells, tissues and the like so as to carry out various psychological research. The device adopts the optical fiber and the optical fiber bundle to guide light to make the system miniaturized and convenient for integration, and is very convenient to carry out cooperative work with other systems such as the microscope and the patch clamp.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electromagnetic method and device for controlling single-chain nucleic acid perforating speed
InactiveCN1986832AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to identify base perforation electrical signalsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMagnetic beadBio engineering
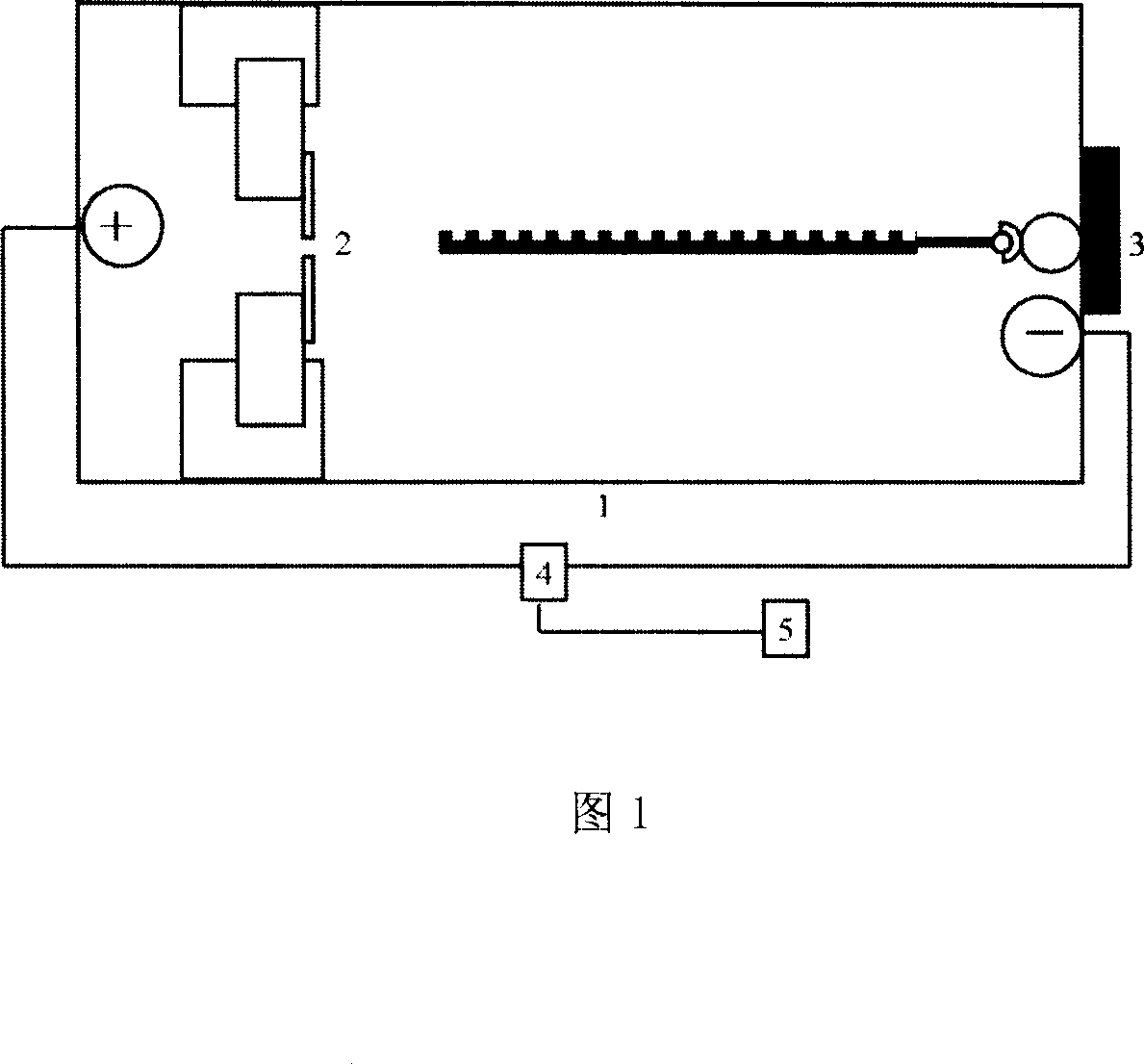
The present invention relates to bioengineering technology, and is electromagnetic method and equipment for controlling single-chain nucleic acid perforation. The method includes the following steps: 1. fixing the composition of one single-chain target DNA or RNA and one connected magnetic bead onto the negative pole of electrophoresis tank with two nanometer hole separated poles by using one electromagnet; and 2. turning on the power source to apply the free end of the negatively charged target molecule with one pull force towards the positive pole, trimming the electromagnetic force to release the magnetic bead while maintaining certain attraction of the electromagnet on the magnetic bead so as to make the target molecule to move slowly towards the positive pole and control the nanometer hole passing speed in 0.5-1 base / ms, recording the signal with the patch clamp and converting the signal into sequence information in the computer. The equipment includes electrophoresis tank, nanometer element, computer, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
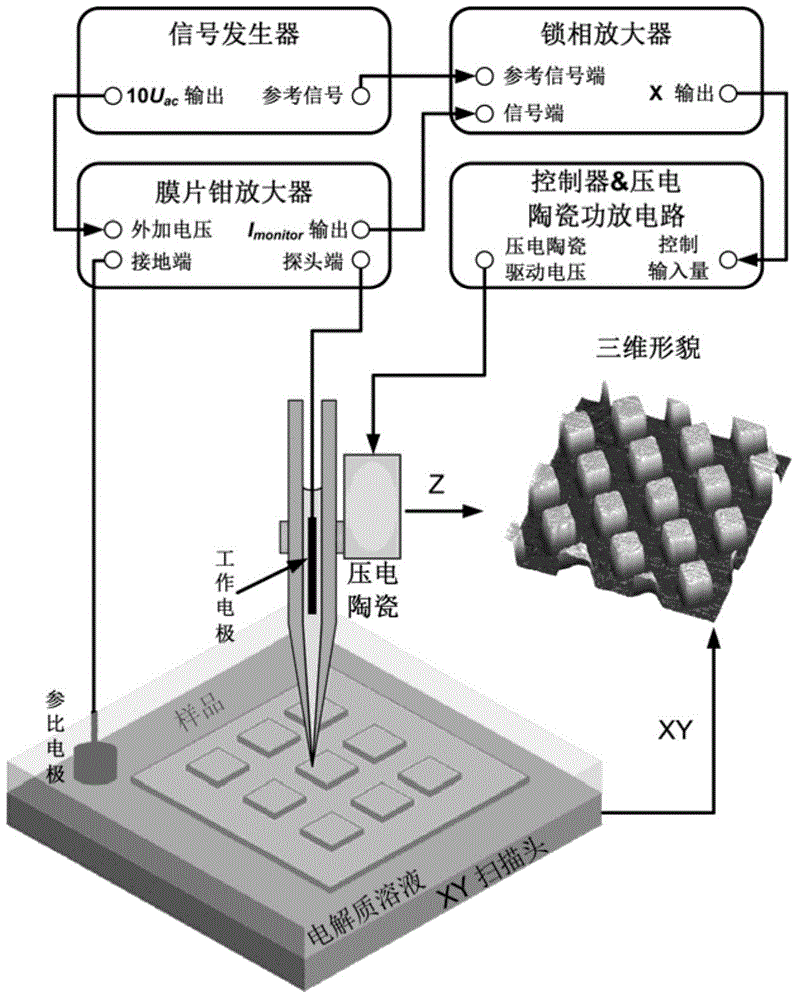
Apparatus and method for rapidly assessing nano-material on biological security of breathing system
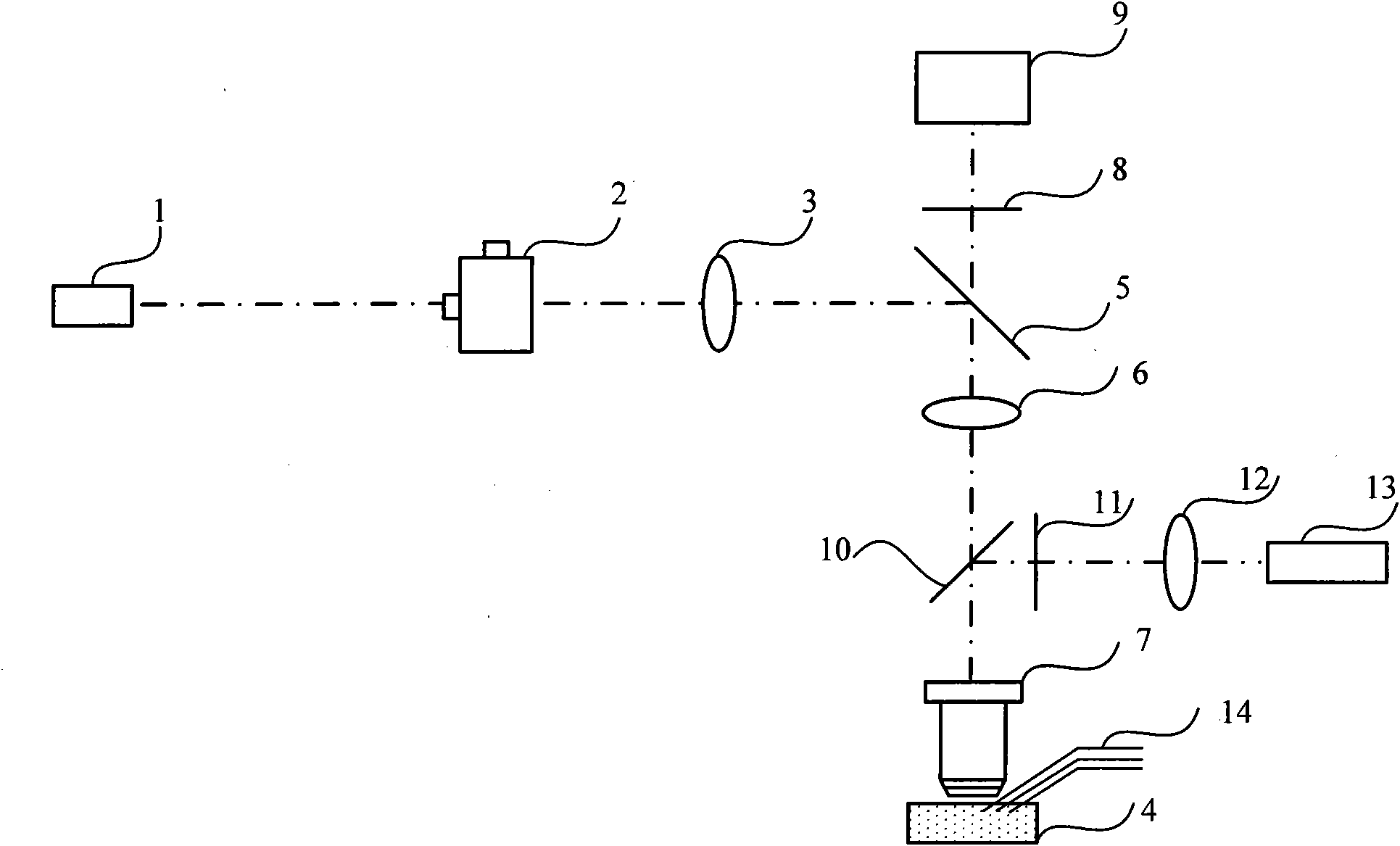
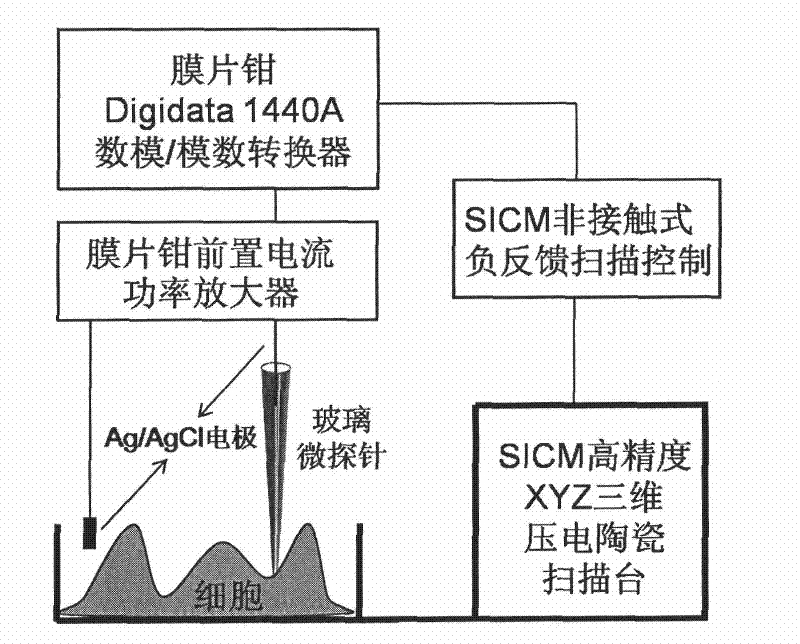
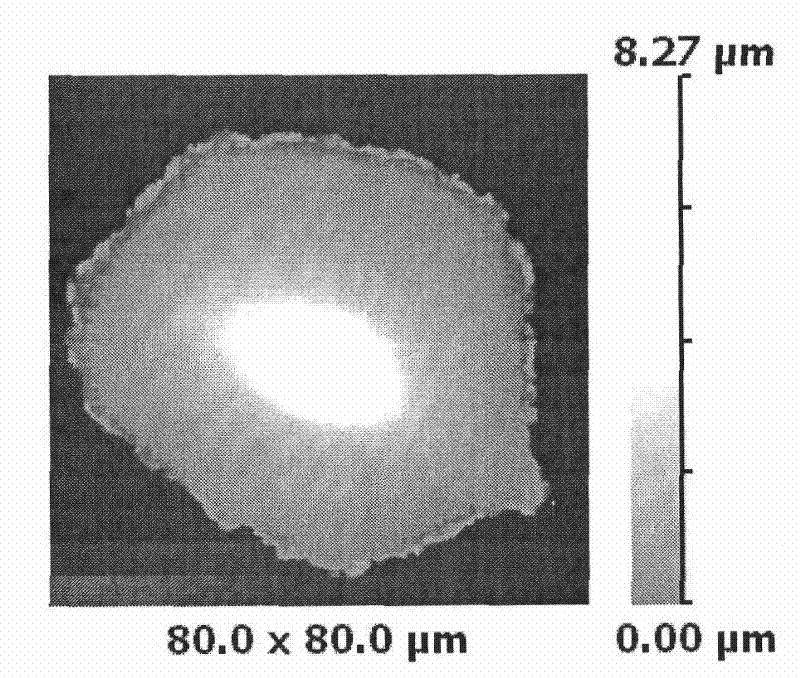
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for rapidly assessing a nano-material on biological security of a breathing system, the apparatus comprises a glass microprobe, an Ag / AgCl electrode placed in the glass microprobe, a reference Ag / AgCl electrode, a culture dish with cells and cell culture fluid, a patch clamp preposed current power amplifier, a patch clamp digital-analog / analog-to-digital converter, a SICM negative feedback scanning control circuit and a SICM high precision XYZ three dimensional piezoelectricity ceramic scanner. The method comprises the following steps: using a SICM technology for detecting the surface three dimensional structure of an in-vivo biological sample under the physiological liquid state culture condition, the change of microscopic appearance of cell surface before adding nano-material on the vivo-cell and after adding nano-material on the vivo-cell can be observed; influence of nano-material on vivo-cell function can be researched, a traditional patch clamp technology is employed, the biological security of the nano-material can be assessed by recording the voltaic change of the ion channels before adding the nano-material and after adding the nano-material. The apparatus and method of the invention have the advantages of easy realization and rapidity by using combination of SICM and the patch clamp technology, the security of the nano-material can be assessed from the structure and function.
Owner:CHINA NAT ACAD NANOTECH & ENG
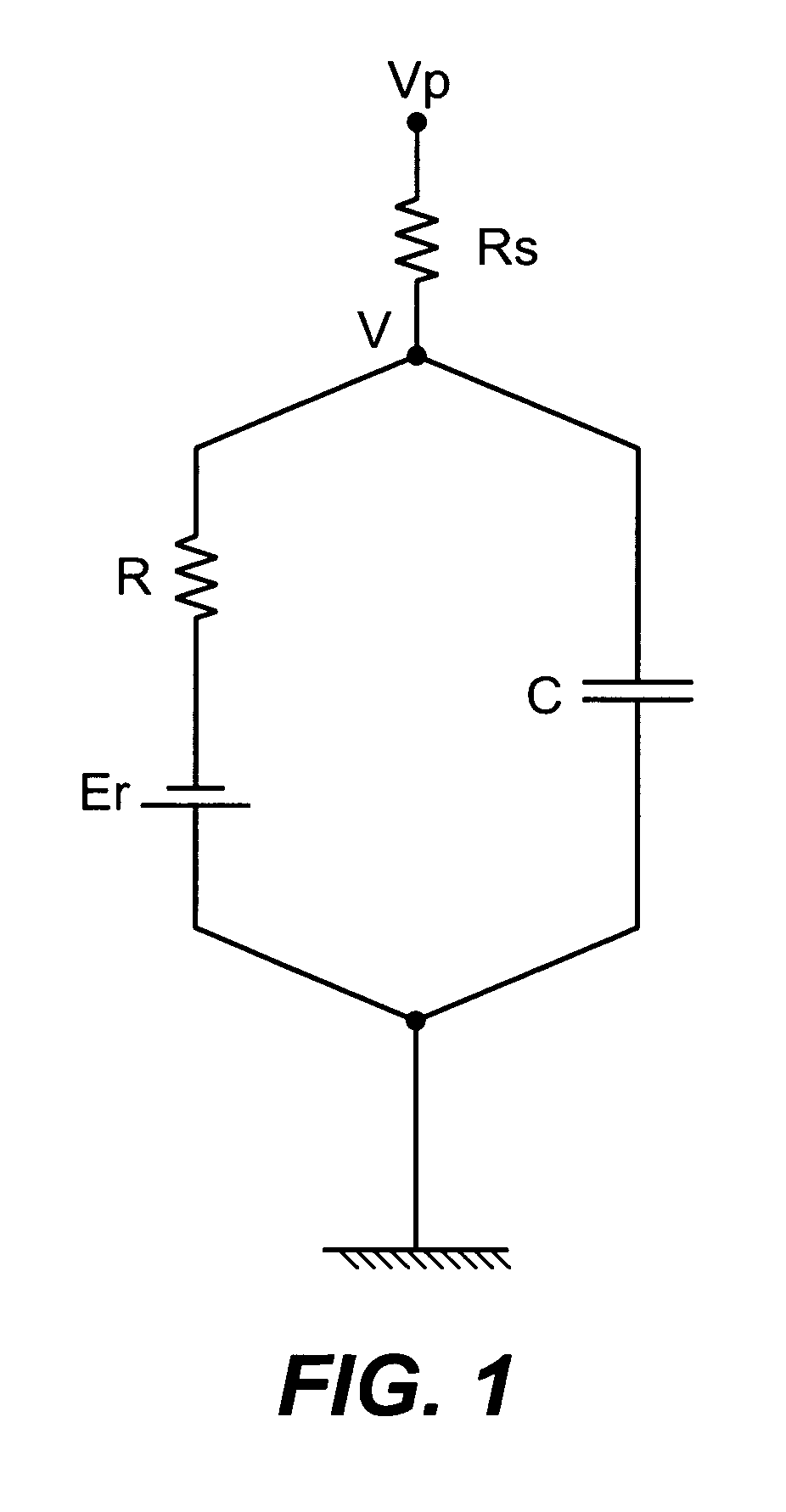
Compensated patch-clamp amplifier for nanopore polynucleotide sequencing and other applications
InactiveUS20130341192A1Avoid saturationCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesPolynucleotideAmplifier
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polymeric electrode for electrophysiological testing
InactiveUS6899800B2Simple and reliable processReduce manual operationsImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological membraneBiomedical engineering
A polymeric material such as PDMS is molded into an electrode structure containing a micron-size aperture for receiving and forming a giga-ohm seal with a biological membrane. One end of a tube is filled with uncured polymeric material and pressed against a support surface to prevent drainage. A conventional micropipette having a size suitable for sliding through the tube is introduced, tip first, into the tube and is allowed to fall through the polymeric material and rest against the support surface. The assembly is heated to cure the polymer and the micropipette is removed from the tube, thereby leaving a polymeric plug at the end of the tube with an aperture suitable in shape and size for patch-clamp giga-ohm seal electrode applications. A multi-well tray with a polymeric electrode plug in each well is constructed using the same approach.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Capacitive feedback (transimpedance) amplifier for use with nanopore detection and sequencing device
InactiveUS20170145481A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsMicrobiological testing/measurementCapacitanceMultiplexing
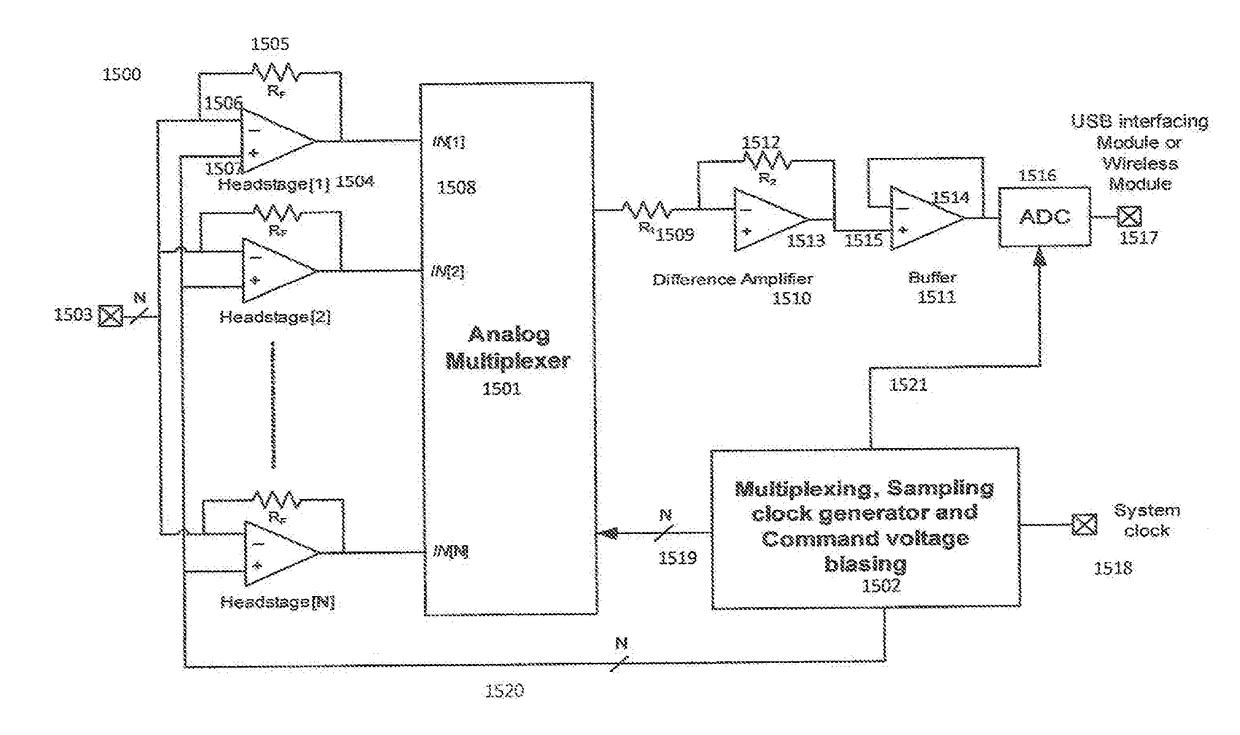
A multiplexed nanopore sensing network comprising an integrated and multiplexed network of patch clamp capacitive integrator-differentiator amplifiers with small feedback capacitors using pseudo-resistors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Radiating structure and use method thereof
ActiveCN101511159AEasy to fixSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPatch clampPetroleum engineering
The invention provides a radiator structure which is used in a plurality of right-angle type heating element. The radiator structure includes a radiator piece and a clamping part. The radiator structure has a supporting plate. One end of the clamping part has a plurality of spring patches, anther end of the clamping part is fixed on the supporting plate, the spring patch clamp the right-angle type heating element for adhibiting the supporting plate.
Owner:ASUSTEK COMPUTER INC
Method for screening crude delta sleep-inducing peptide extract from milk source in virtue of patch clamp technique
ActiveCN105548531AUniversally adaptableEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationHydrolysateSteel columns
The invention provides a method for screening crude delta sleep-inducing peptide extract from a milk source in virtue of a patch clamp technique. The method comprises the following steps: adding water, trypsin and pepsin in cow's milk for enzymatic hydrolysis and carrying out spray drying after enzyme killing so as to obtain powdery casein hydrolysate; separating the casein hydrolysate through isoelectric precipitation; subjecting a purified product obtained after isoelectric precipitation to preparative liquid chromatography via a reversed-phase steel column so as to separate and purify samples again, dividing the samples into a plurality of sections according to different polarities of the samples and carrying out modeling to evaluate the activity of the crude delta sleep-inducing peptide extract; employing the whole cell patch clamp technique, giving an evoked action potential with a size of 30-60 Pa / 3000-4000 ms, delivering a drug with a dosage of 100 to 150 [mu]mol / L, recording an electrophysiological spectrum and screening out good active sleep-inducing fragments via discharging number and frequency. The method is simple to operate and has good separation effect; and the crude extract can shorten time for going to sleep and adjust sleep rhythm and provides better guarantee for health of patients with insomnia.
Owner:GREENCREAM BIOTECH
Process of controlling monochain nucleic acid punching speed by optical nickle
InactiveCN100999764AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMagnetic beadPass rate
The present invention relates to biotechnology, and is especially optical forceps method of controlling the hole passing rate of single chain nucleic acid. The method includes the following steps: 1. capturing single chain DNA or RNA connected magnetic bead with optical forceps in the negative pole of electrophoresis tank; 2. separating the two poles of the electrophoresis tank with film possessing single nanometer hole so as to perform ion exchange only through the nanometer hole; and 3. turning on the power source for the current to draw the free end of the DNA towards the positive pole, controlling the moving speed of the optical forceps in 0.5-1 base / ms to control the motion of DNA, recording the electric signal during penetrating the nanometer hole with the patch clamp and converting the electric signal into sequence information in the computer. The present invention is superior to available technology, which has too fast nucleic acid speed for patch clamp to recognize.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Compensated patch-clamp amplifier for nanopore polynucleotide sequencing and other applications
InactiveUS20150377856A1Avoid saturationElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementPolynucleotideAmplifier
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Probe arrangement
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
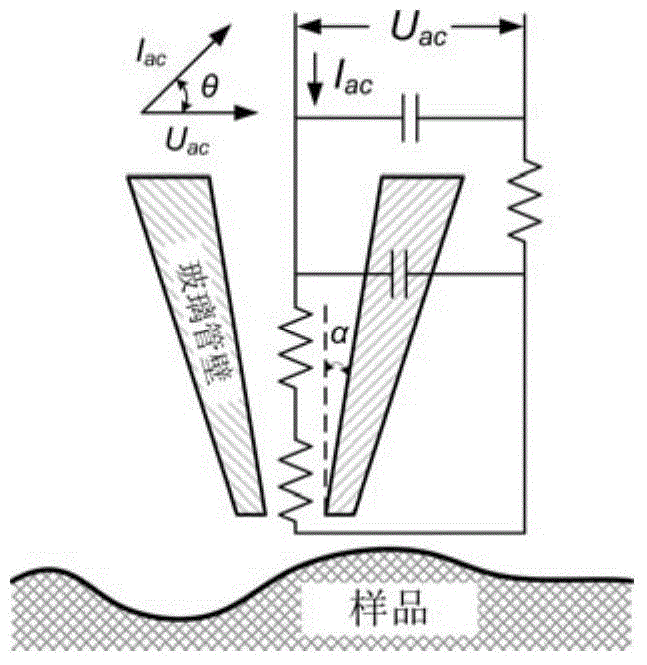
Phase modulation imaging mode scanning device and method of SICM
ActiveCN105301290AHigh frequencyReduced amplitude detection timeScanning probe microscopyCapacitanceElectricity
The invention relates to a phase modulation imaging mode scanning device of an SICM. The scanning device comprises a signal generator, a phase-locked amplifier, a patch clamp amplifier, a controller, a probe, an XY nanometer platform and a Z-direction nanometer piezoelectric ceramic. The signal generator, the patch clamp amplifier, the phase-locked amplifier and the controller are connected in sequence; the signal generator is connected with the phase-locked amplifier; and the patch clamp amplifier is connected with the probe. The method comprises the following steps: the signal generator outputs two paths of AC signals to the phase-locked amplifier and the patch clamp amplifier respectively; the compensation capacitance of the patch clamp amplifier is adjusted; the phase-locked amplifier extracts current component and feeds back the amplitude to the controller; and the controller controls the height of the probe in real time according to the amplitude, and scanning of a sample is realized. According to the phase modulation imaging mode scanning device and method, only the alternating current component under some frequency is extracted to serve as the feedback value, so that the defects of DC drifting and easy electrical noise influence under a DC mode and the like can be overcome; and compared with a conventional AC mode, the method realizes higher modulation frequency, and the purpose of accelerating scanning can be realized.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
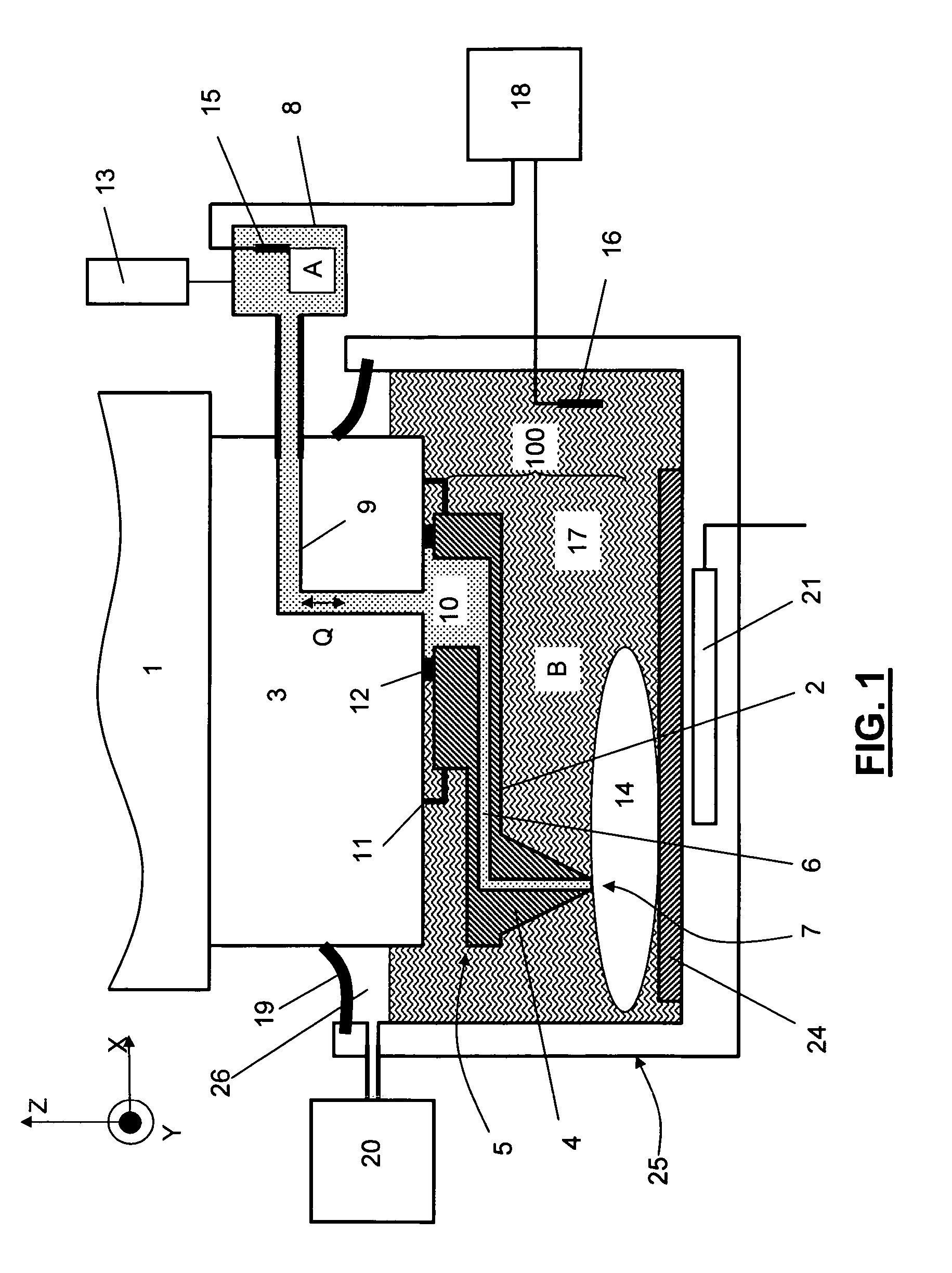
Micromachined patch-clamp apparatus
ActiveUS8323955B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell membraneEngineering
A micromachined patch-clamp apparatus is disclosed for holding one or more cells and providing electrical, chemical, or mechanical stimulation to the cells during analysis with the patch-clamp technique for studying ion channels in cell membranes. The apparatus formed on a silicon substrate utilizes a lower chamber formed from silicon nitride using surface micromachining and an upper chamber formed from a molded polymer material. An opening in a common wall between the chambers is used to trap and hold a cell for analysis using the patch-clamp technique with sensing electrodes on each side of the cell. Some embodiments of the present invention utilize one or more electrostatic actuators formed on the substrate to provide mechanical stimulation to the cell being analyzed, or to provide information about mechanical movement of the cell in response to electrical or chemical stimulation.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
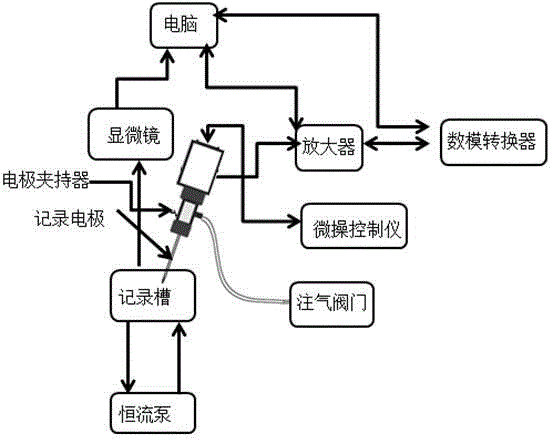
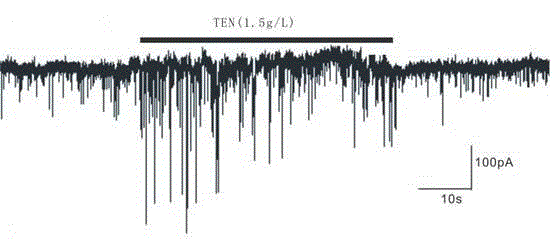
Experiment method for studying effect of tenuigenin on synaptic transmission of rat hippocampal neuron
InactiveCN104132965AGuaranteed accuracyPrecisionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHippocampal regionNeural cell
The invention discloses an experiment method for studying the effect of tenuigenin on synaptic transmission of rat hippocampal neuron. The method adopts a micro control instrument, a microscopic, and a recording electrode to monitor the spontaneous current state of neuron in tenuigenin with different concentrations, and then the monitor current data is analyzed so as to obtain the influence mechanism and effect of tenuigenin on rat hippocampal neuron. The method adopts a whole-cell patch-clamp technology to research the effect of tenuigenin on spontaneous postsynaptic current in the rat brain hippocampal CA1 area so as to disclose the regulating effect and mechanism of tenuigenin on neuron synaptic transmission, thus the requirements of scientific research and drug development are fulfilled, and at the same time a basis is provided for the further research on the signal transmission mechanism of neuron. The method can be widely used in the pharmaceutical theory researches on neuron, the experiment method and equipment design are scientific and reasonable, and requirements of scientific research can be met.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com