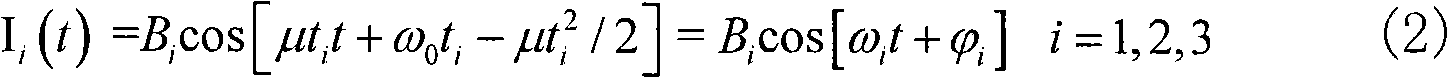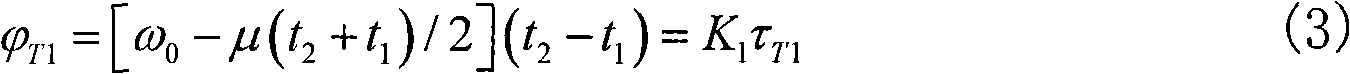Patents
Literature
105 results about "Surface micromachining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
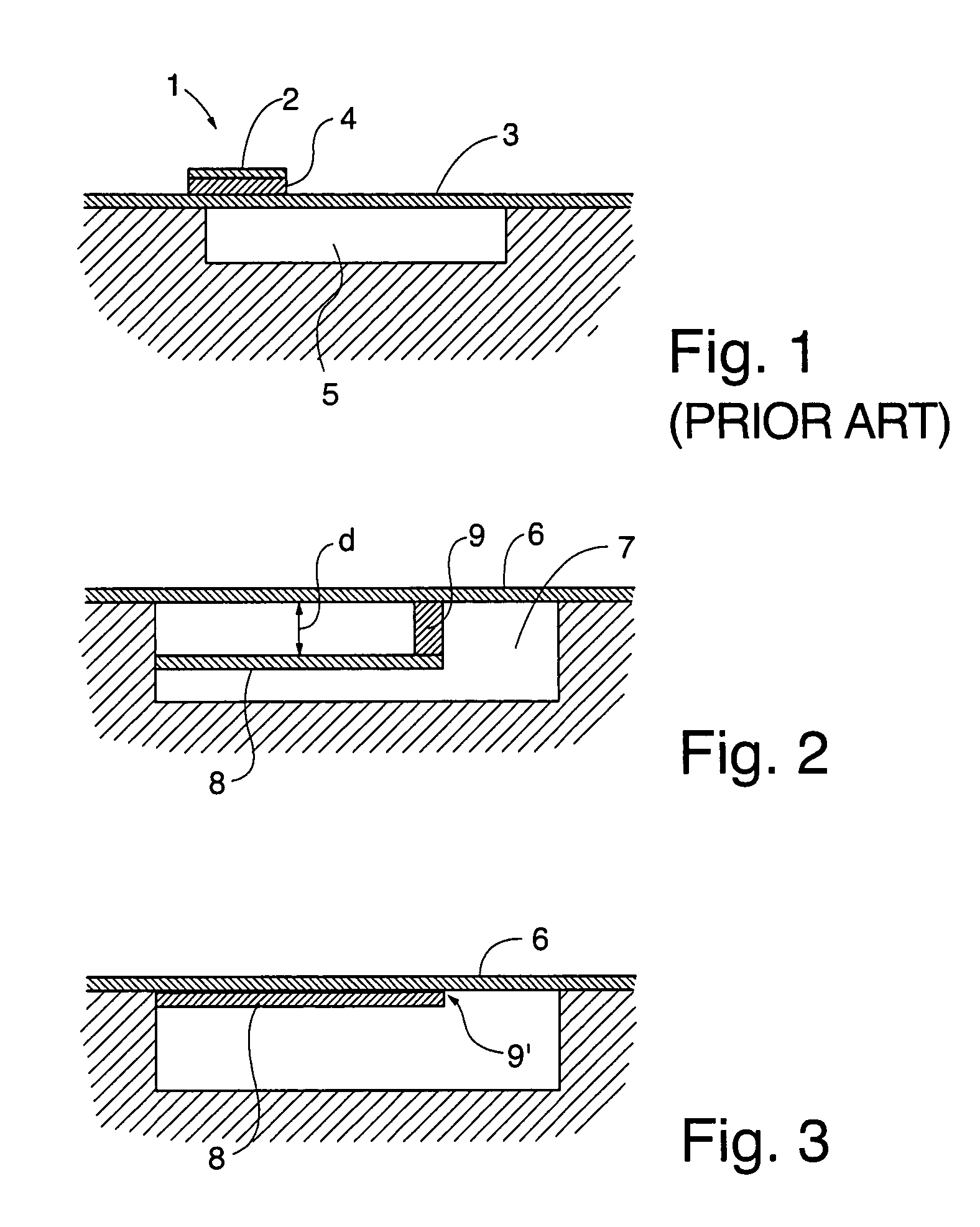
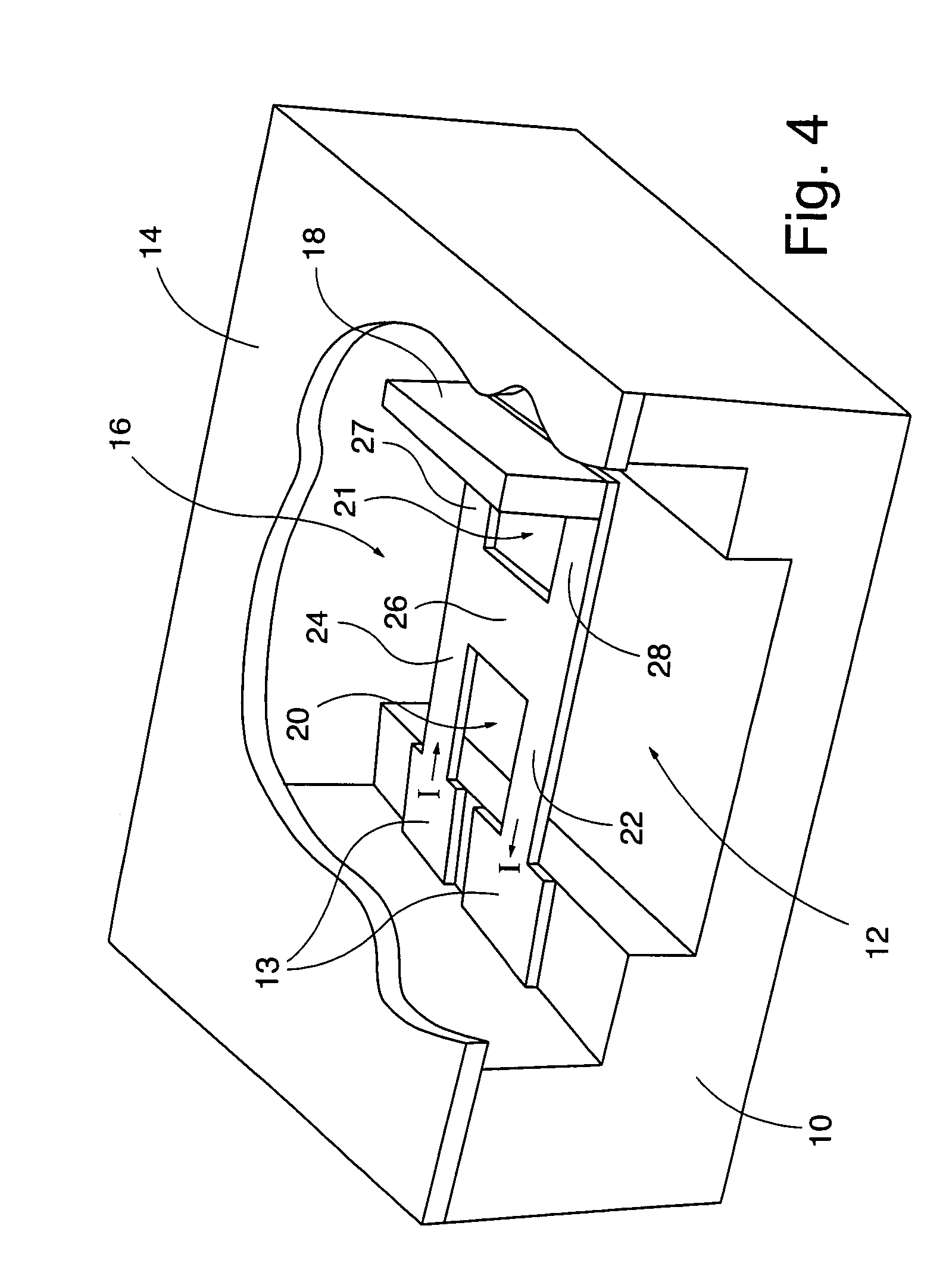
Surface micromachining builds microstructures by deposition and etching structural layers over a substrate. This is different from Bulk micromachining, in which a silicon substrate wafer is selectively etched to produce structures.
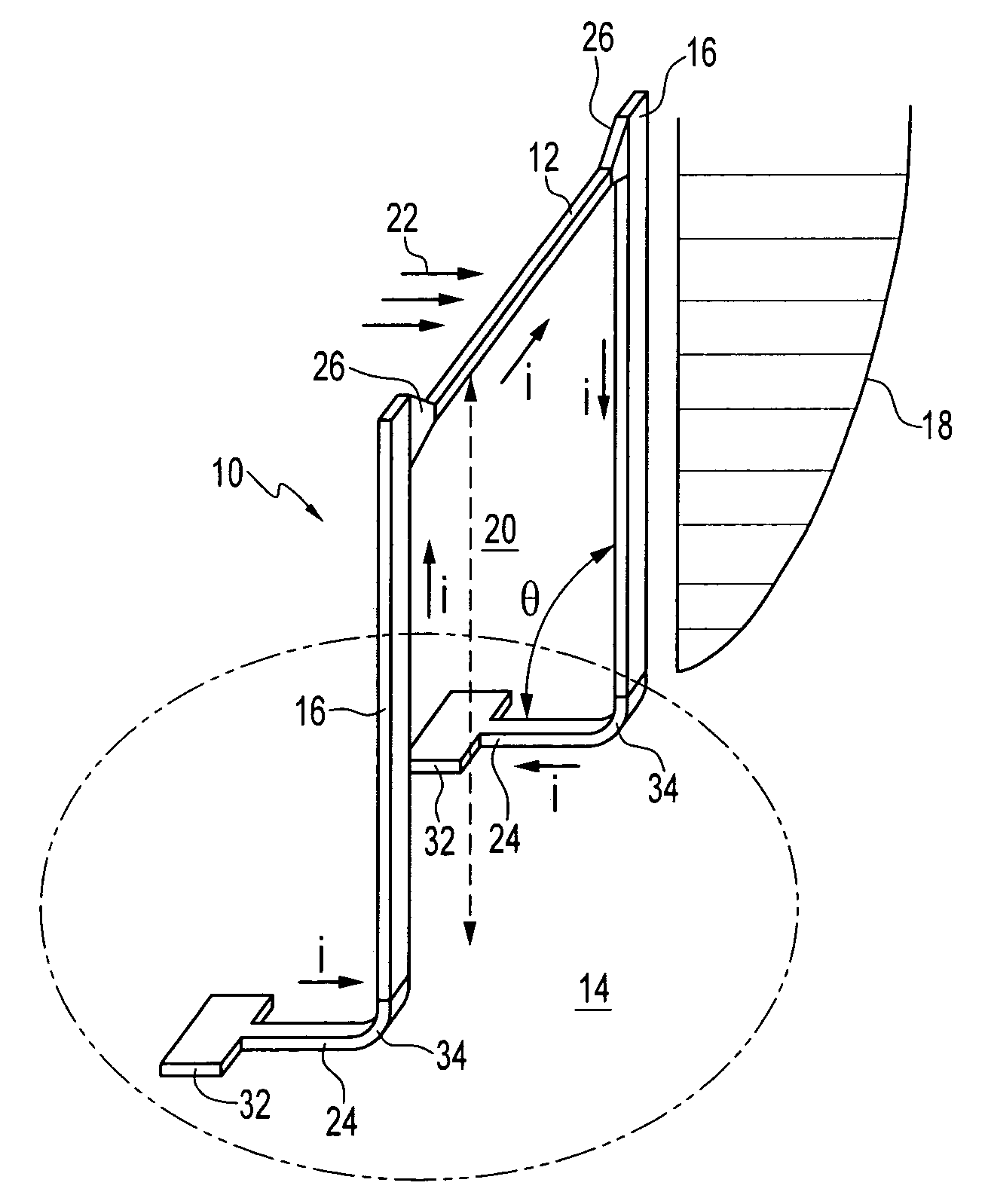
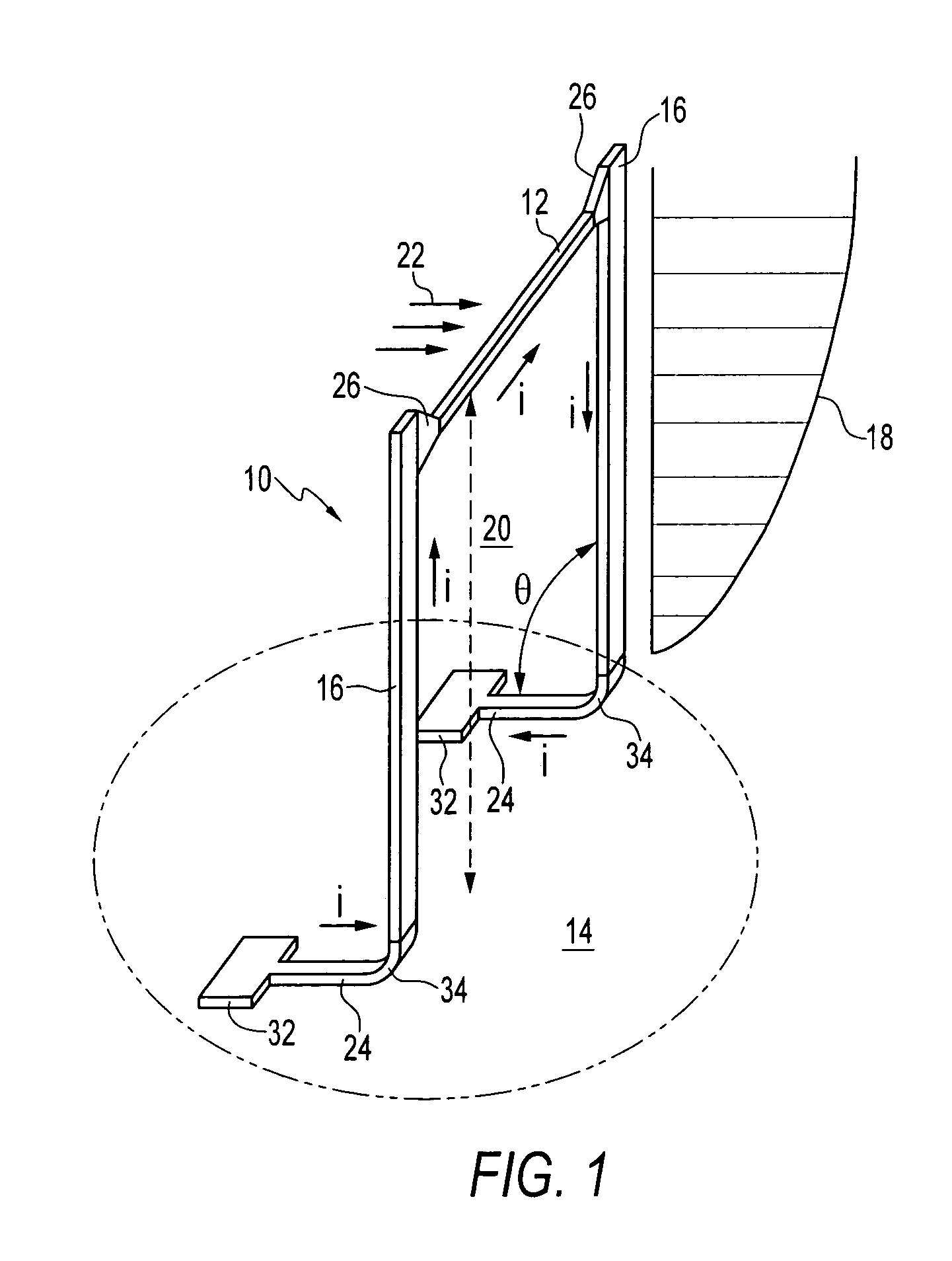
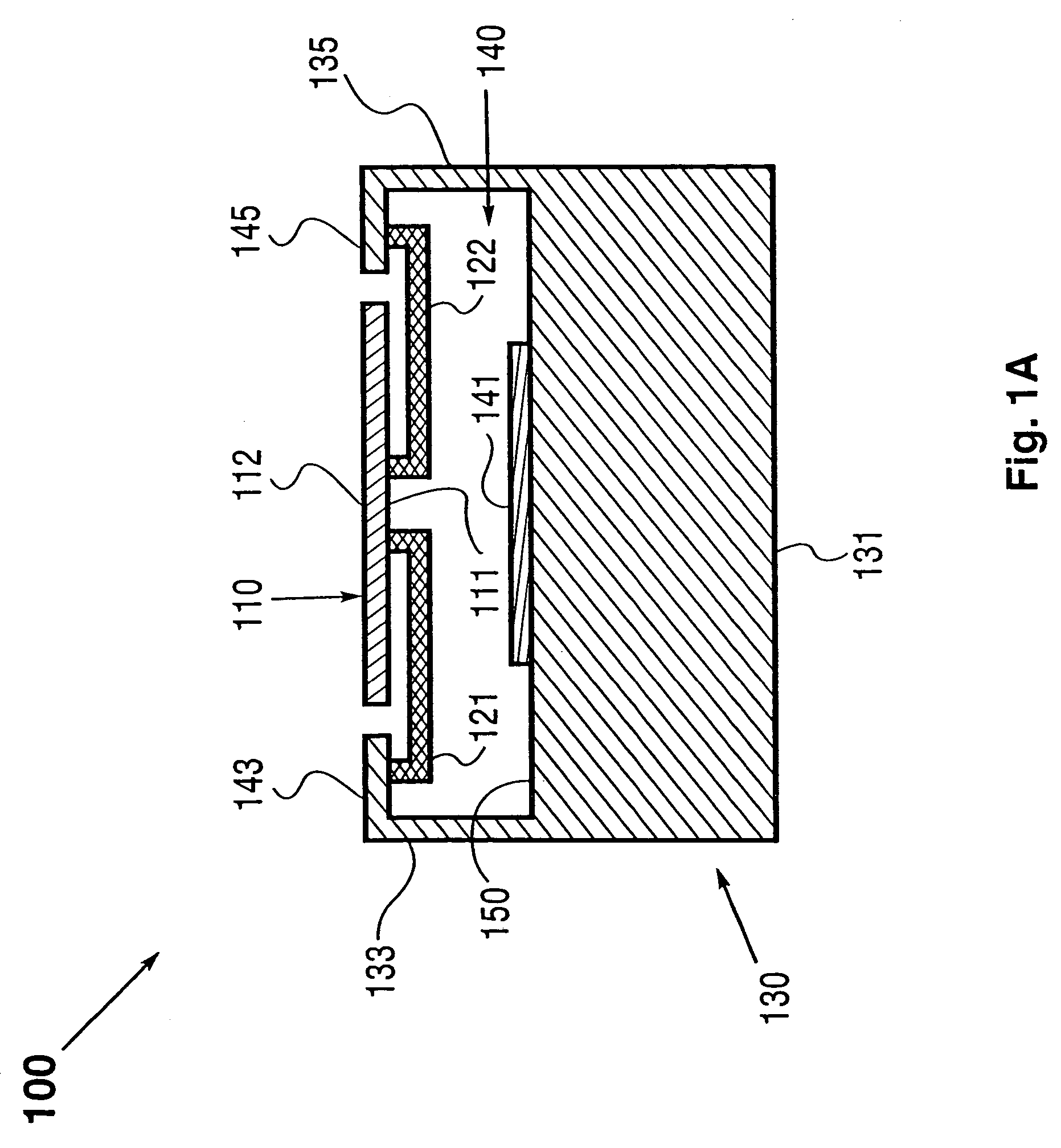
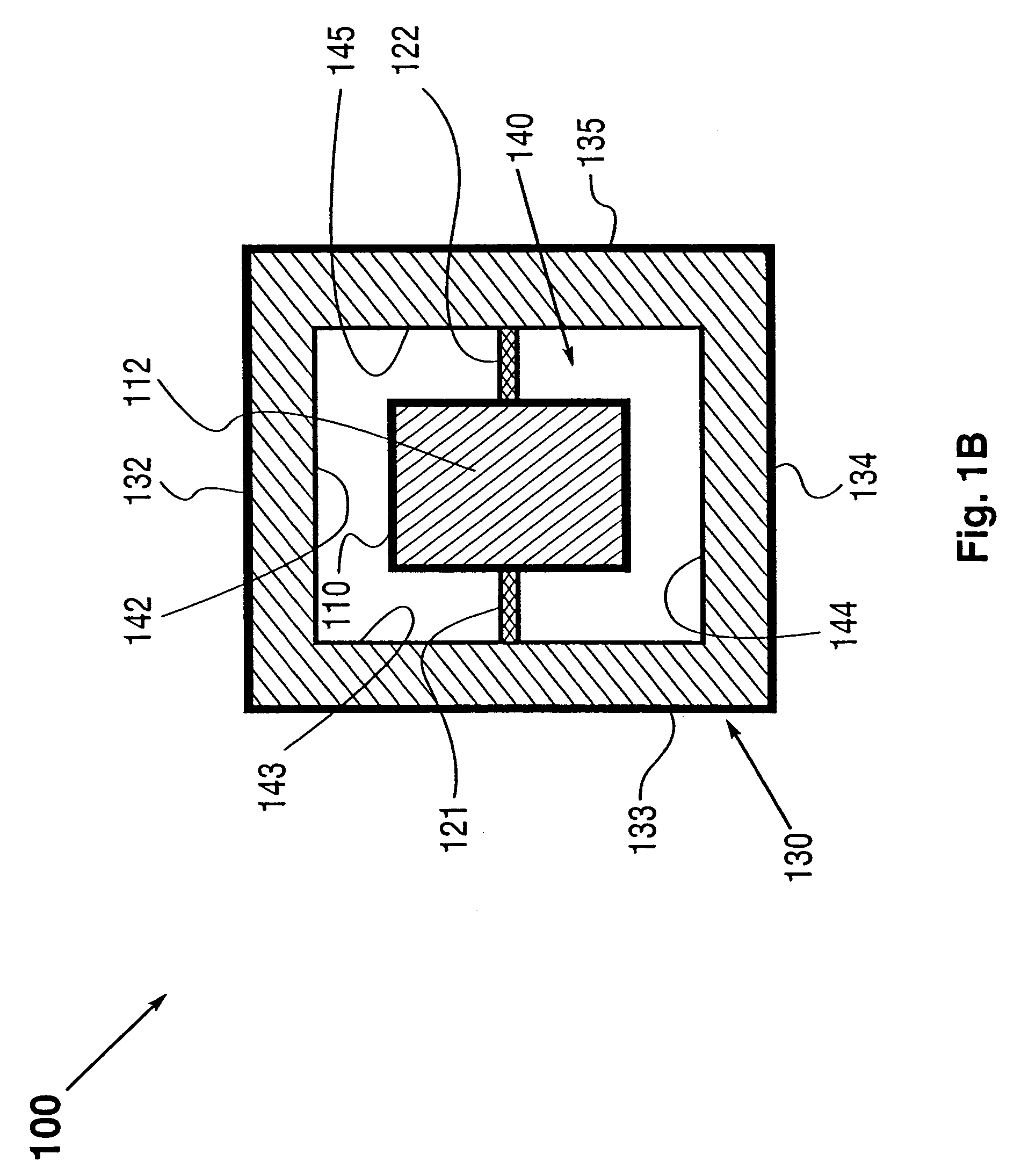
Gap tuning for surface micromachined structures in an epitaxial reactor
InactiveUS20050014374A1Increase chanceIncrease deposition rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSilicon dioxide
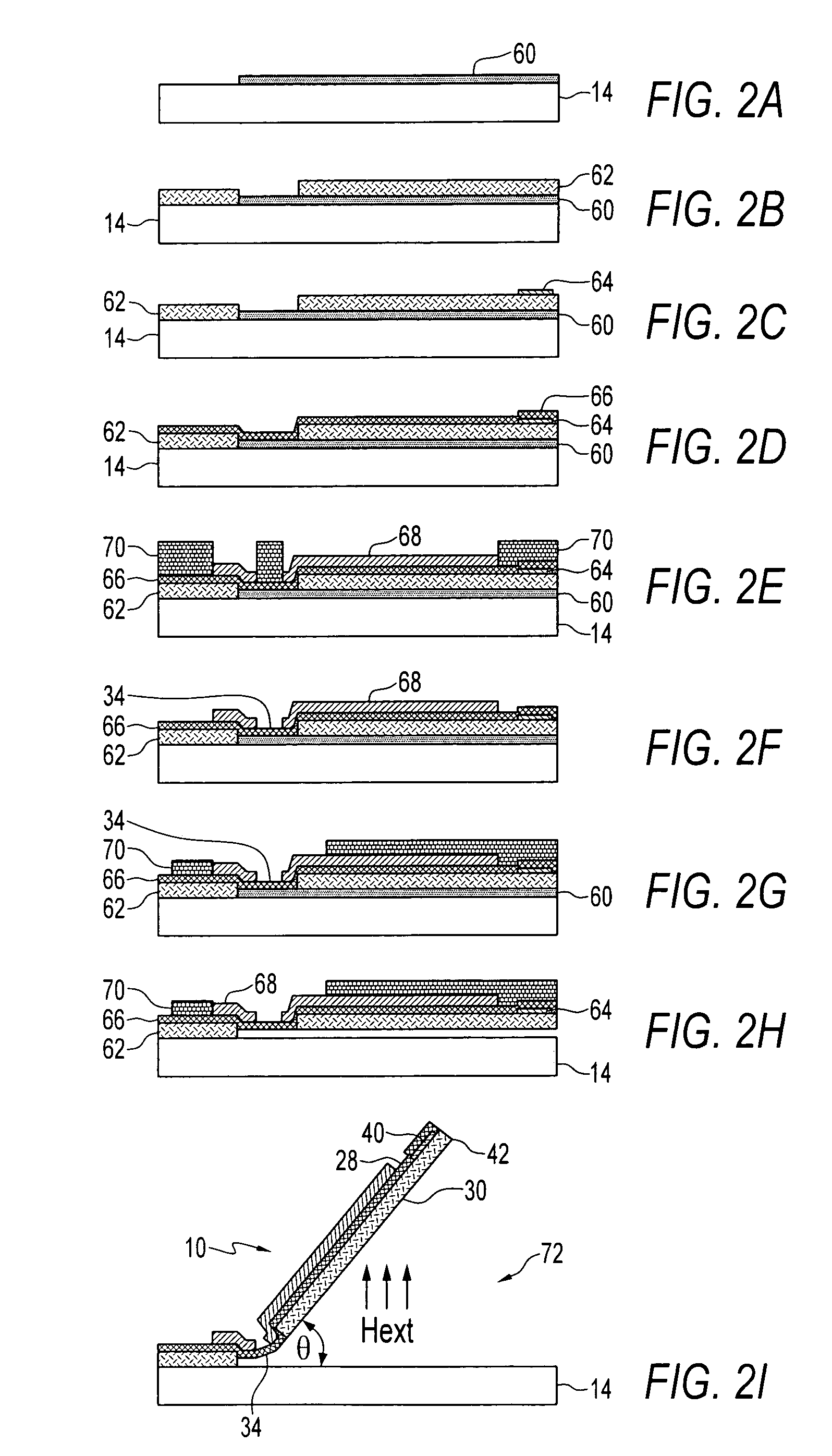
A method for adjusting with high precision the width of gaps between micromachined structures or devices in an epitaxial reactor environment. Providing a partially formed micromechanical device, comprising a substrate layer, a sacrificial layer including silicon dioxide deposited or grown on the substrate and etched to create desired holes and / or trenches through to the substrate layer, and a function layer deposited on the sacrificial layer and the exposed portions of the substrate layer and then etched to define micromechanical structures or devices therein. The etching process exposes the sacrificial layer underlying the removed function layer material. Cleaning residues from the surface of the device, then epitaxially depositing a layer of gap narrowing material selectively on the surfaces of the device. The selection of deposition surfaces determined by choice of materials and the temperature and pressure of the epitaxy carrier gas. The gap narrowing epitaxial deposition continues until a desired gap width is achieved, as determined by, for example, an optical detection arrangement. Following the gap narrowing step, the micromachined structures or devices may be released from their respective underlying sacrificial layer.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
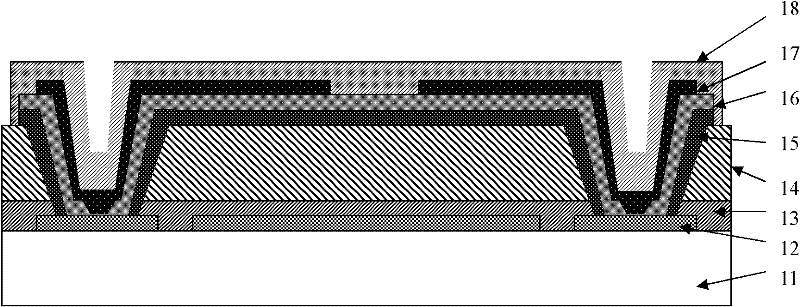
Stiffened surface micromachined structures and process for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050139542A1Increased bending stiffnessReduce stress deformationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesFlexible microstructural devicesBending stiffnessMachining
Stiffened surface micromachined structures and a method to fabricate the same. A silicon substrate (10) is first etched to produce a mold containing a plurality of trenches or grooves (14) in a lattice configuration. Sacrificial oxide (15) is then grown on the silicon substrate (10) and then a stiffening member (16) (silicon nitride) is deposited over the surface of the substrate, thereby backfilling the grooves with silicon nitride. The silicon nitride is patterned to form mechanical members and metal (40) is then deposited and patterned to form the leads and capacitors for electrostatic actuation of mechanical members. The underlying silicon and sacrificial oxides are removed by etching the mold from underneath the fabricated micromachined devices, leaving free-standing silicon nitride devices with vertical ribs. The devices exhibit increased out-of-plan bending stiffness because of the presence of stiffening ribs. Silicon nitride biaxial pointing mirrors with stiffening ribs are also described.
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY
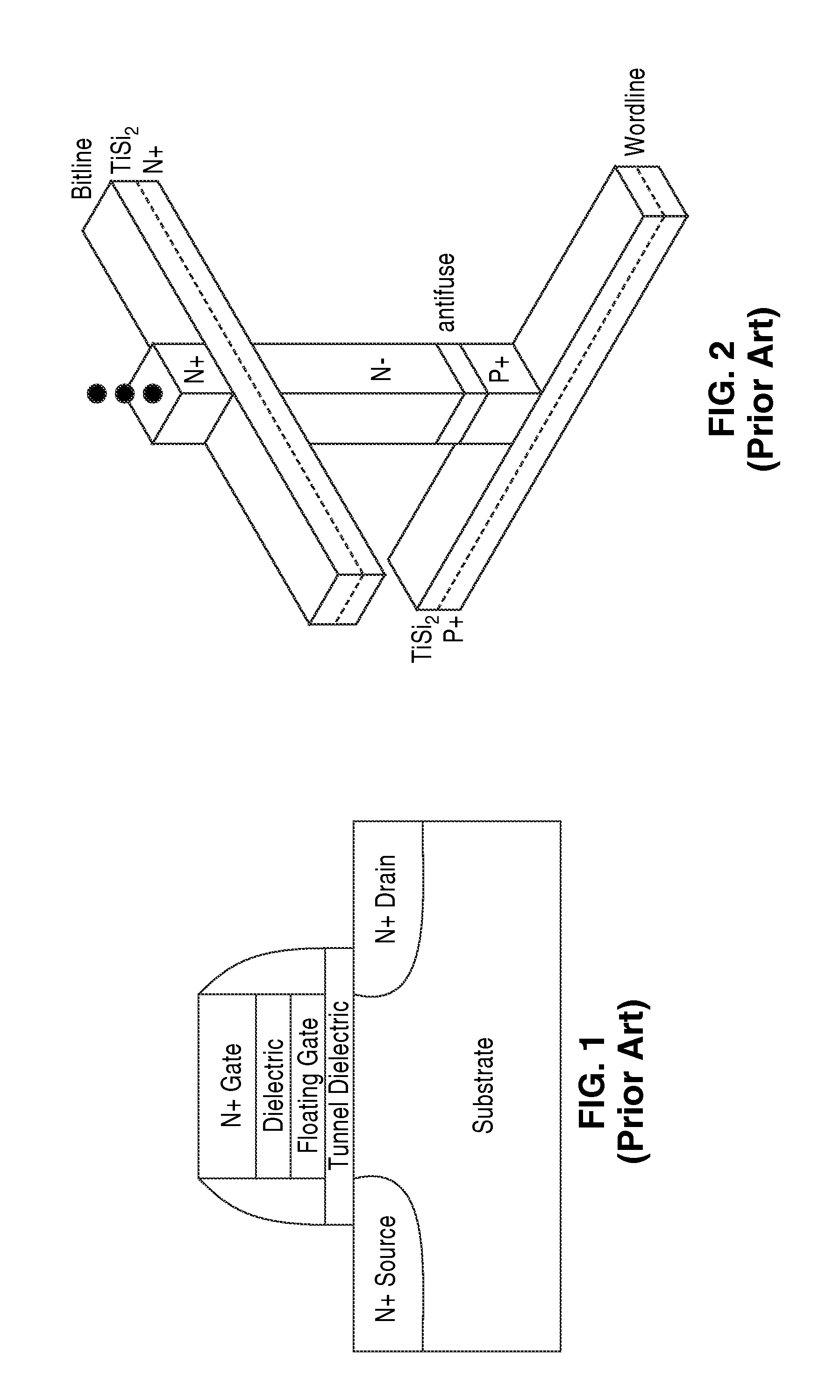
Method and apparatus for micro electro-mechanical systems and their manufacture
InactiveUS20020127760A1Less driving voltageSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOut of plane motionActuator
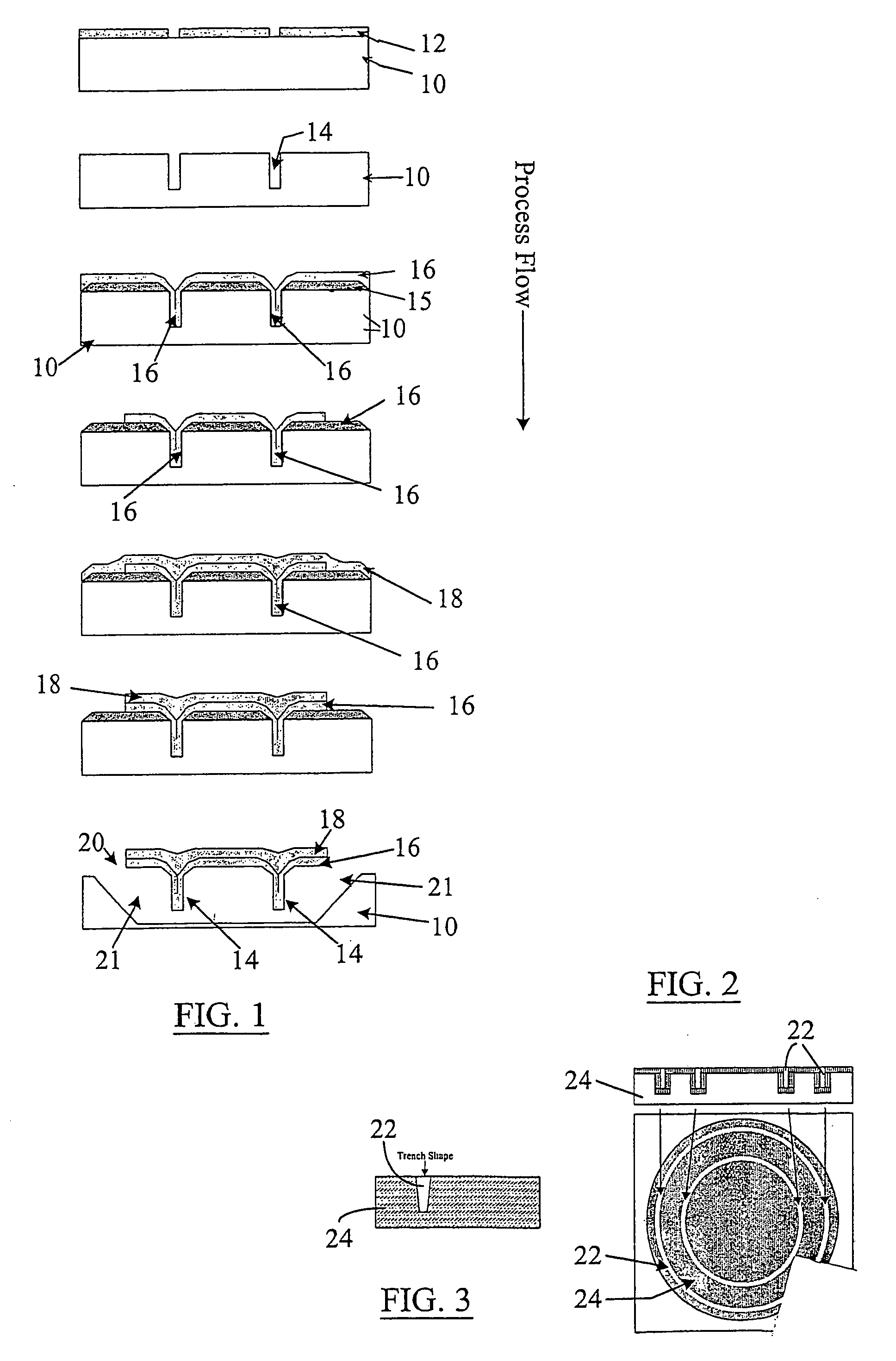
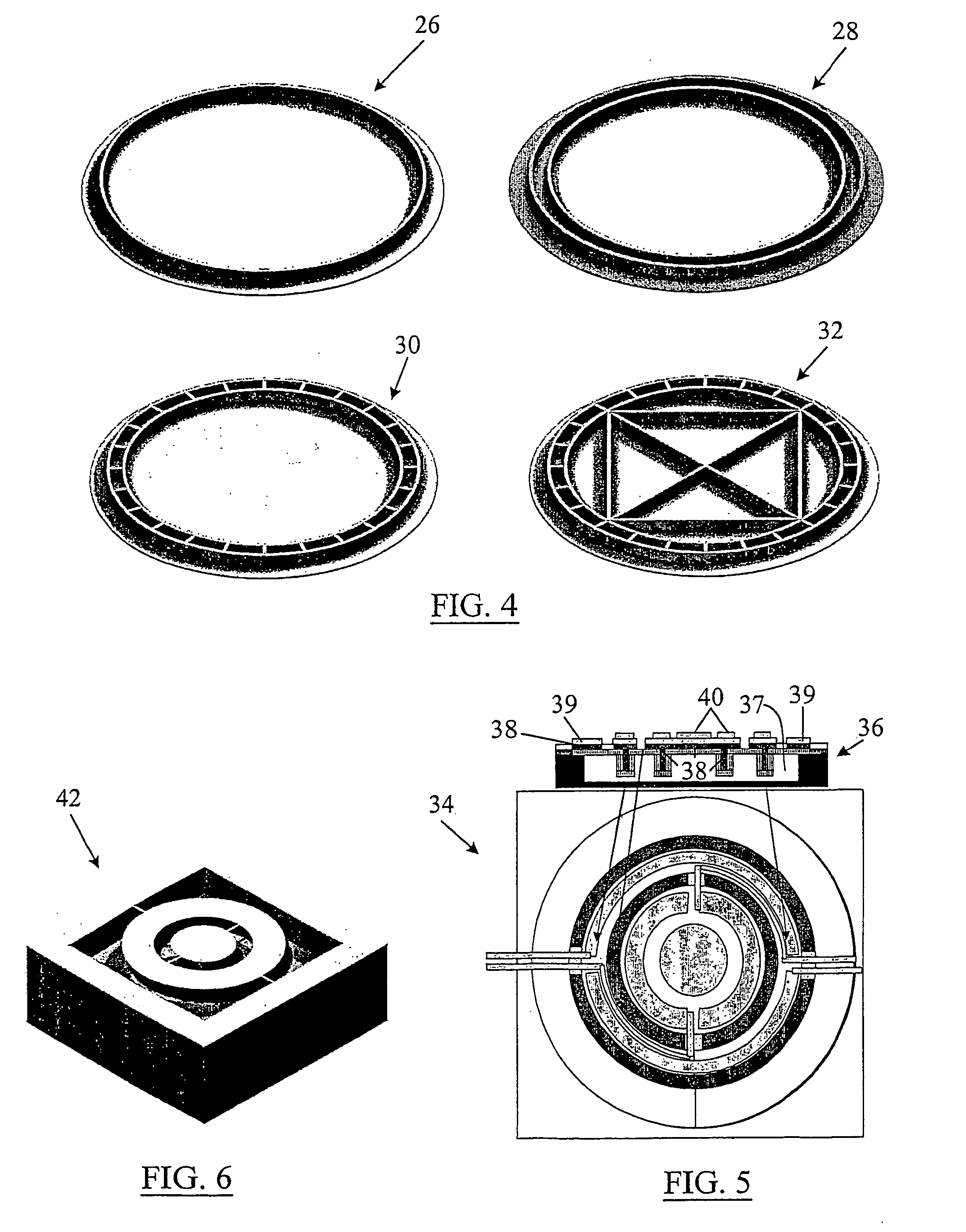
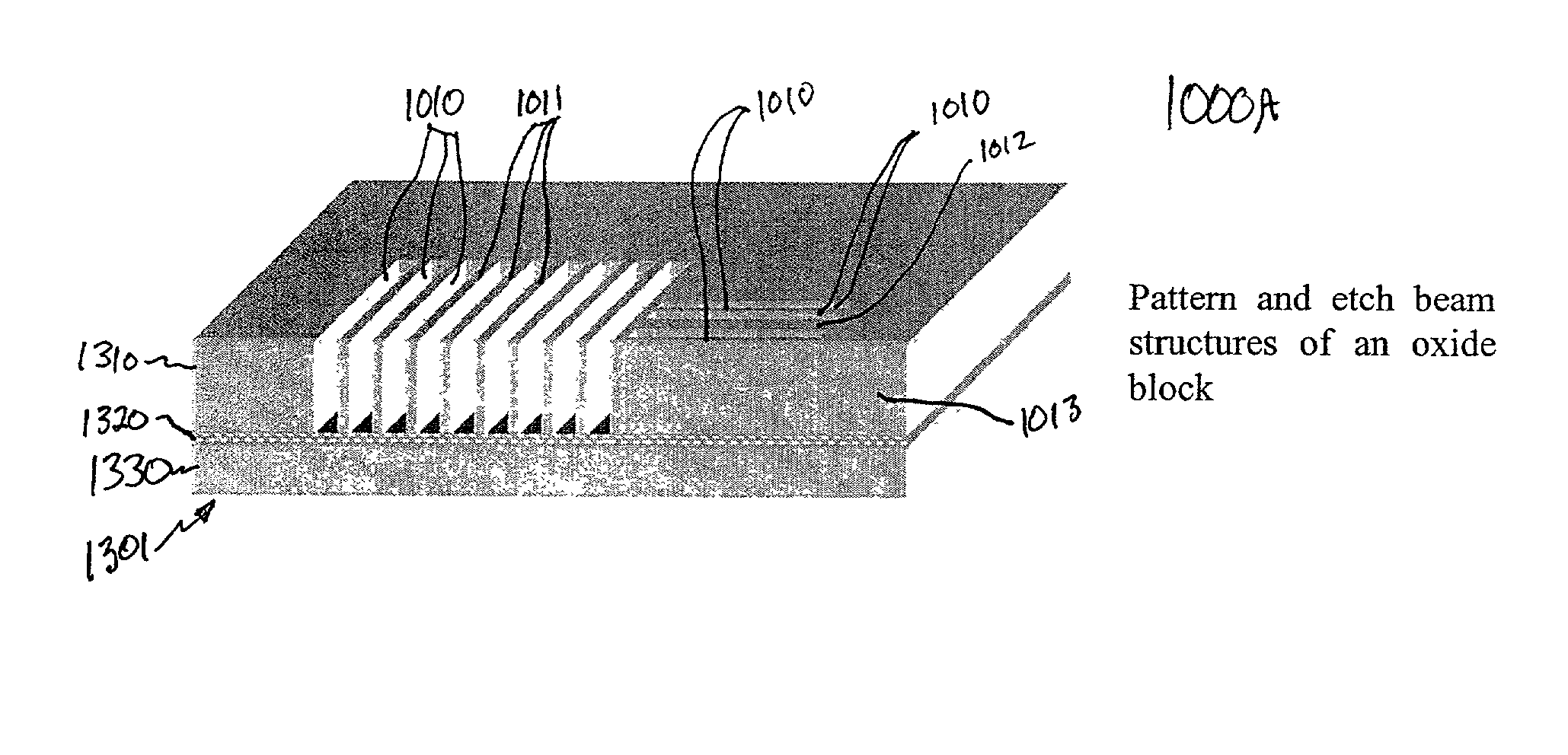
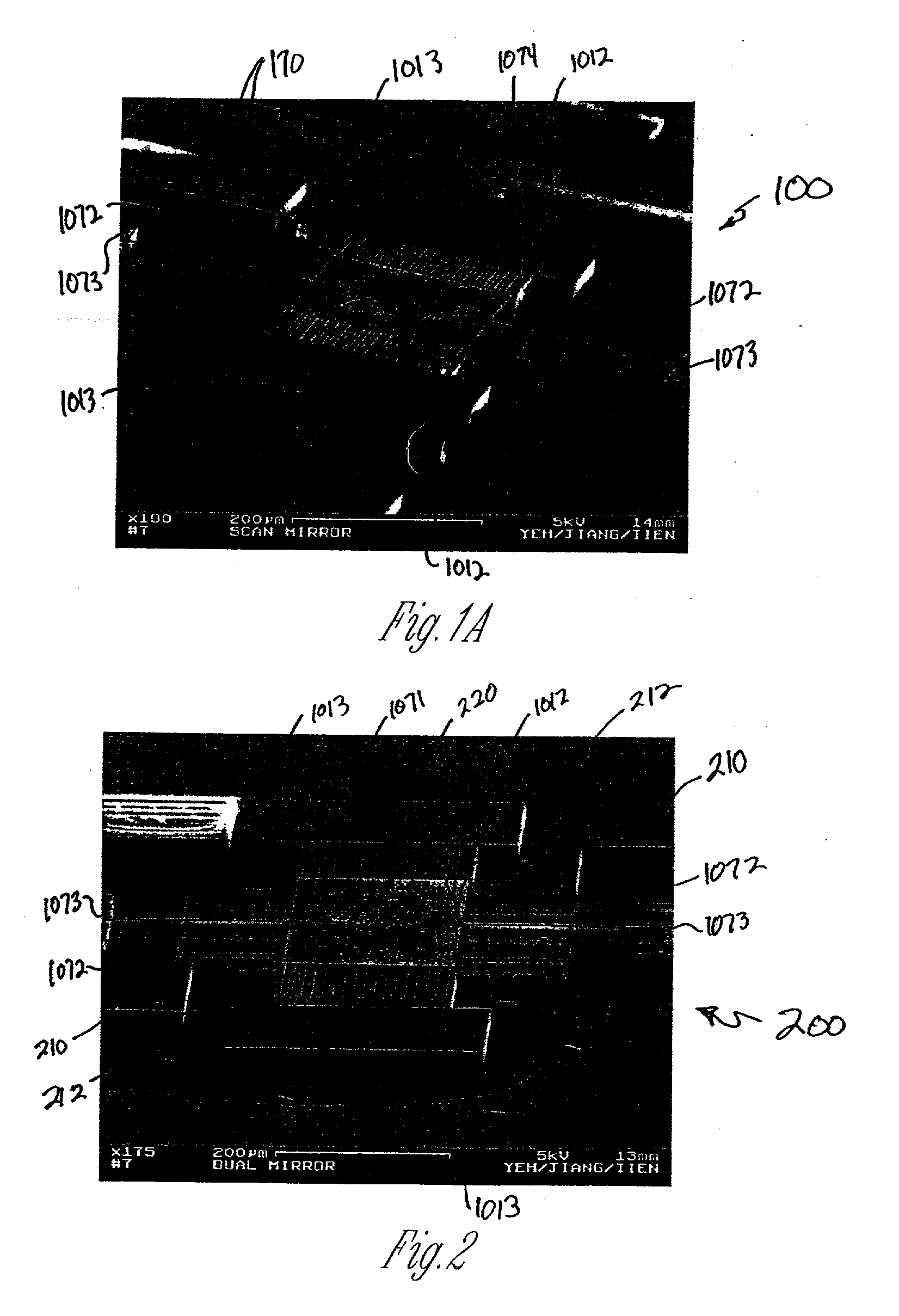
The present invention provides a fabrication process that integrates high-aspect-ratio silicon structures with polysilicon surface micromachined structures. In some embodiments the process includes forming an oxide block by etching a plurality of trenches to leave a plurality of vertical-walled silicon structures standing on the substrate, thermally and substantially completely oxidizing the vertical-walled silicon structures, and substantially filling spaces between the oxidized vertical-walled silicon structures with an oxide of silicon to form the oxide block. The process retains not only the high-aspect-ratio silicon structures possible with deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) but also the design flexibility of polysilicon surface micromachining. Using this process, polysilicon platforms have been fabricated, which are actuated by high-aspect-ratio combdrives for many applications such as x-y-z stages and scanning devices. The actuators include an asymmetric combdrive that actuates in torsional / out-of-plane motions, and a high-aspect-ratio combdrive that drives in translational motion.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Multi-stream microfluidic aperture mixers
Robust microfluidic mixing devices mix multiple fluid streams passively, without the use of moving parts. In one embodiment, these devices contain microfluidic channels that are formed in various layers of a three-dimensional structure. Mixing may be accomplished with various manipulations of fluid flow paths and / or contacts between fluid streams. In various embodiments, structures such as channel overlaps, slits, converging / diverging regions, turns, and / or apertures may be designed into a mixing device. Mixing devices may be rapidly constructed and prototyped using a stencil construction method in which channels are cut through the entire thickness of a material layer, although other construction methods including surface micromachining techniques may be used.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
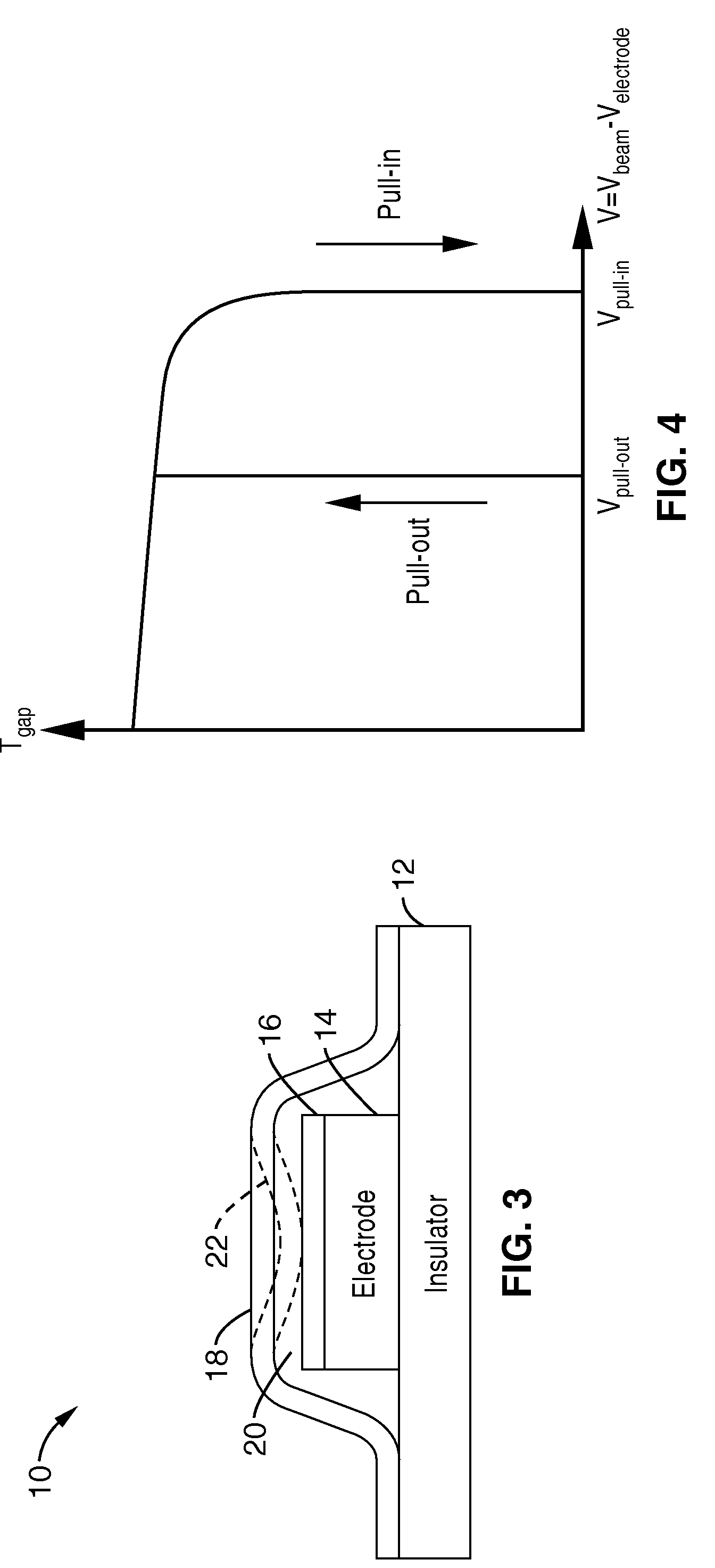
Resonant sensor and method of making a pressure sensor comprising a resonant beam structure
InactiveUS6182513B1Fluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLight beamResonant sensor
A resonant microbeam pressure sensor is disclosed, comprising a microbeam suspended in a diaphragm in at least one point by suspension elements. Pressure applied to the diaphragm will cause the resonance frequency of the beam to shift. This shift is detectable and proportional to the pressure. The device is manufactured by surface micromachining.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
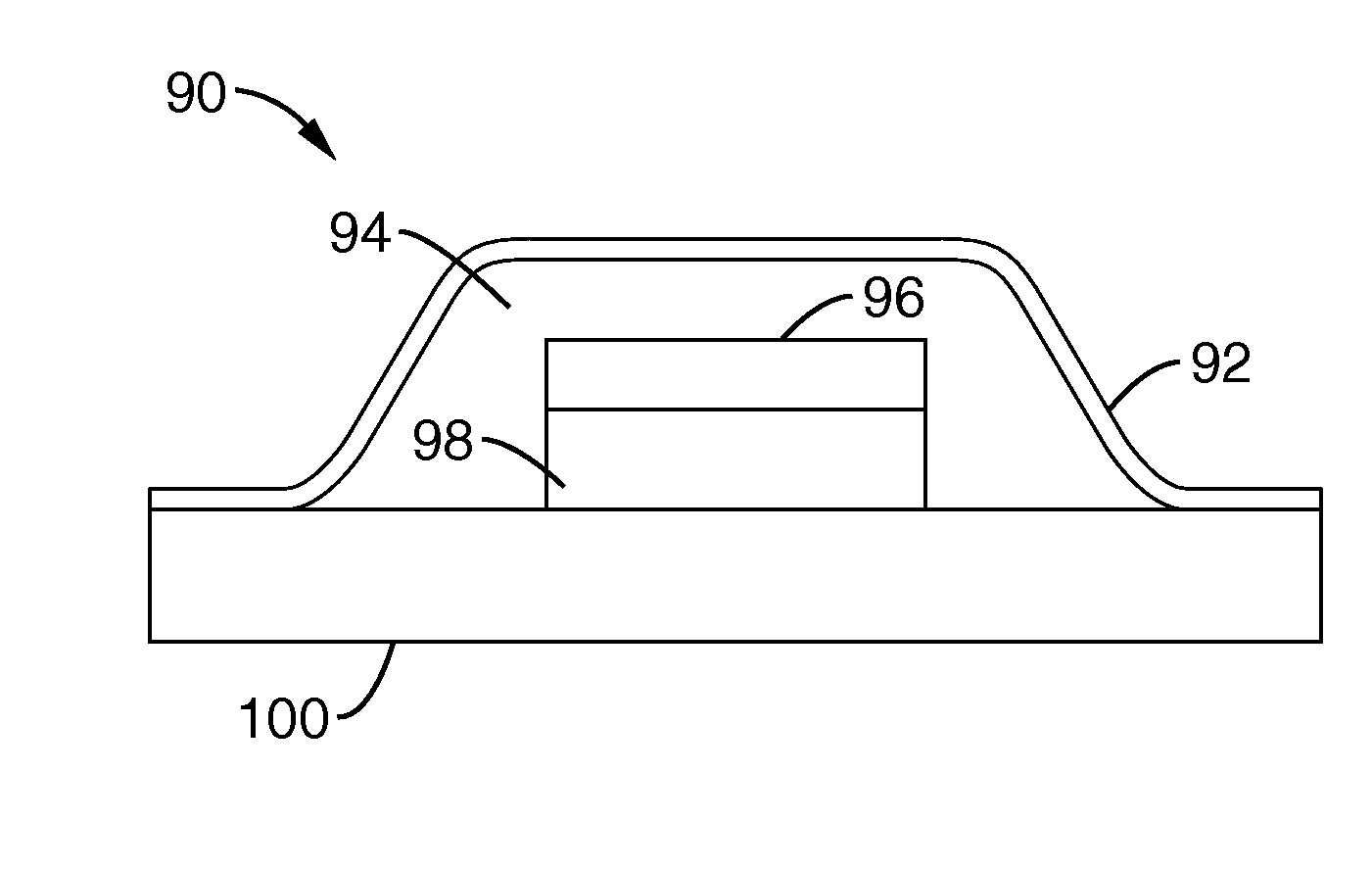
Surface micro-machined acoustic transducers
InactiveUS6249075B1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic cavity
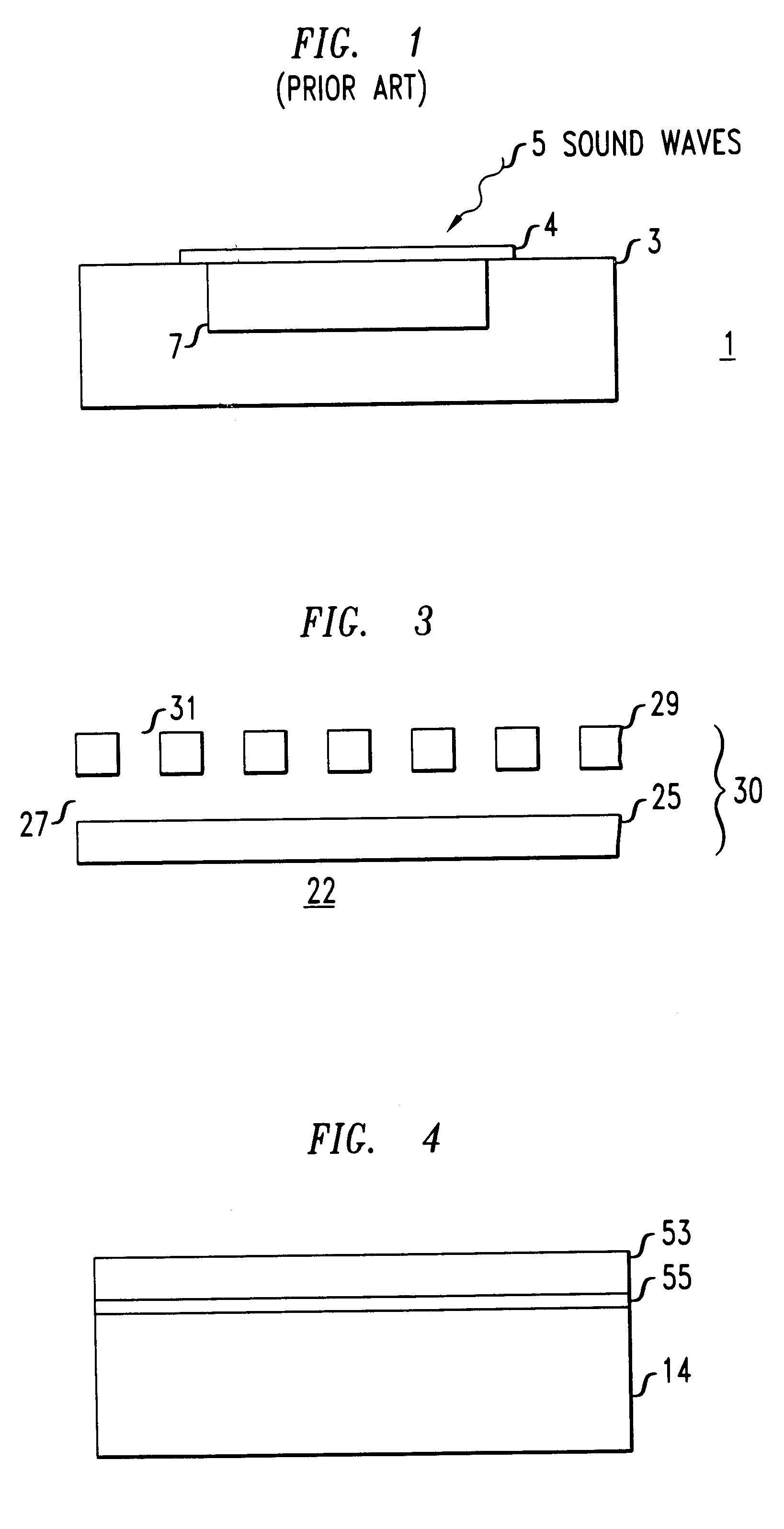
A micro-machined transducer having a structure in which an acoustic enclosure is formed on a substrate above the plane of the substrate surface is disclosed. Forming the acoustic enclosure on the substrate above the plane of the substrate surface, rather than an acoustic cavity in a surface of the substrate, provides an acoustic cavity whose size is not limited by the thickness of the substrate.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Microfabricated cylindrical ion trap
InactiveUS6870158B1Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationManufacturing cost reductionHigh pressure
A microscale cylindrical ion trap, having an inner radius of order one micron, can be fabricated using surface micromachining techniques and materials known to the integrated circuits manufacturing and microelectromechanical systems industries. Micromachining methods enable batch fabrication, reduced manufacturing costs, dimensional and positional precision, and monolithic integration of massive arrays of ion traps with microscale ion generation and detection devices. Massive arraying enables the microscale cylindrical ion trap to retain the resolution, sensitivity, and mass range advantages necessary for high chemical selectivity. The microscale CIT has a reduced ion mean free path, allowing operation at higher pressures with less expensive and less bulky vacuum pumping system, and with lower battery power than conventional- and miniature-sized ion traps. The reduced electrode voltage enables integration of the microscale cylindrical ion trap with on-chip integrated circuit-based rf operation and detection electronics (i.e., cell phone electronics). Therefore, the full performance advantages of microscale cylindrical ion traps can be realized in truly field portable, handheld microanalysis systems.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method for making a microstructure by surface micromachining
InactiveUS20050059184A1Shorten the timeOptimize allocationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureComputer scienceMachining
Various methods for forming surface micromachined microstructures are disclosed. One aspect relates to executing surface micromachining operation to structurally reinforce at least one structural layer in a microstructure. Another aspect relates to executing the surface micromachining operation to form a plurality of at least generally laterally extending etch release channels within a sacrificial material to facilitate the release of the corresponding microstructure.
Owner:MEMX
Multi-stream microfludic mixers
Robust microfluidic mixing devices mix multiple fluid streams passively, without the use of moving parts. In one embodiment, these devices contain microfluidic channels that are formed in various layers of a three-dimensional structure. Mixing may be accomplished with various manipulations of fluid flow paths and / or contacts between fluid streams. In various embodiments, structures such as channel overlaps, slits, converging / diverging regions, turns, and / or apertures may be designed into a mixing device. Mixing devices may be rapidly constructed and prototyped using a stencil construction method in which channels are cut through the entire thickness of a material layer, although other construction methods including surface micromachining techniques may be used.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Nano superhydrophobic surface used for airplane antifreezing and deicing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101704410AImproved contact characteristicsReduce icingDe-icing equipmentsPhotomechanical apparatusSiliconFuselage
The invention belongs to the technical field of surface treatment, and relates to a nano superhydrophobic surface used for airplane antifreezing and deicing and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: making a hydrophobic microstructure on a substrate by non-silicon surface micromachining technology or microreplication method; coating a nano decorative film on the surface of the hydrophobic microstructure; and baking the prepared hydrophobic microstructure and the substrate coated with the nano decorative film to obtain the dry and clean superhydrophobic surface. The nano superhydrophobic surface improves the contact properties between the surface of an airplane and waterdrops and greatly reduces the degree that a fuselage is infiltrated by the waterdrops; and the nano decorative film can also further reduce the viscous force of the waterdrops when the waterdrops slip the surface of the fuselage, the number of the waterdrops condensed on the surface of the fuselage is reduced, the icing degree on the surface of the airplane is effectively reduced, and the aim of high-efficiency, clean and low-cost airplane ice prevention / removal is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Micromachine and Method for Manufacturing the Same
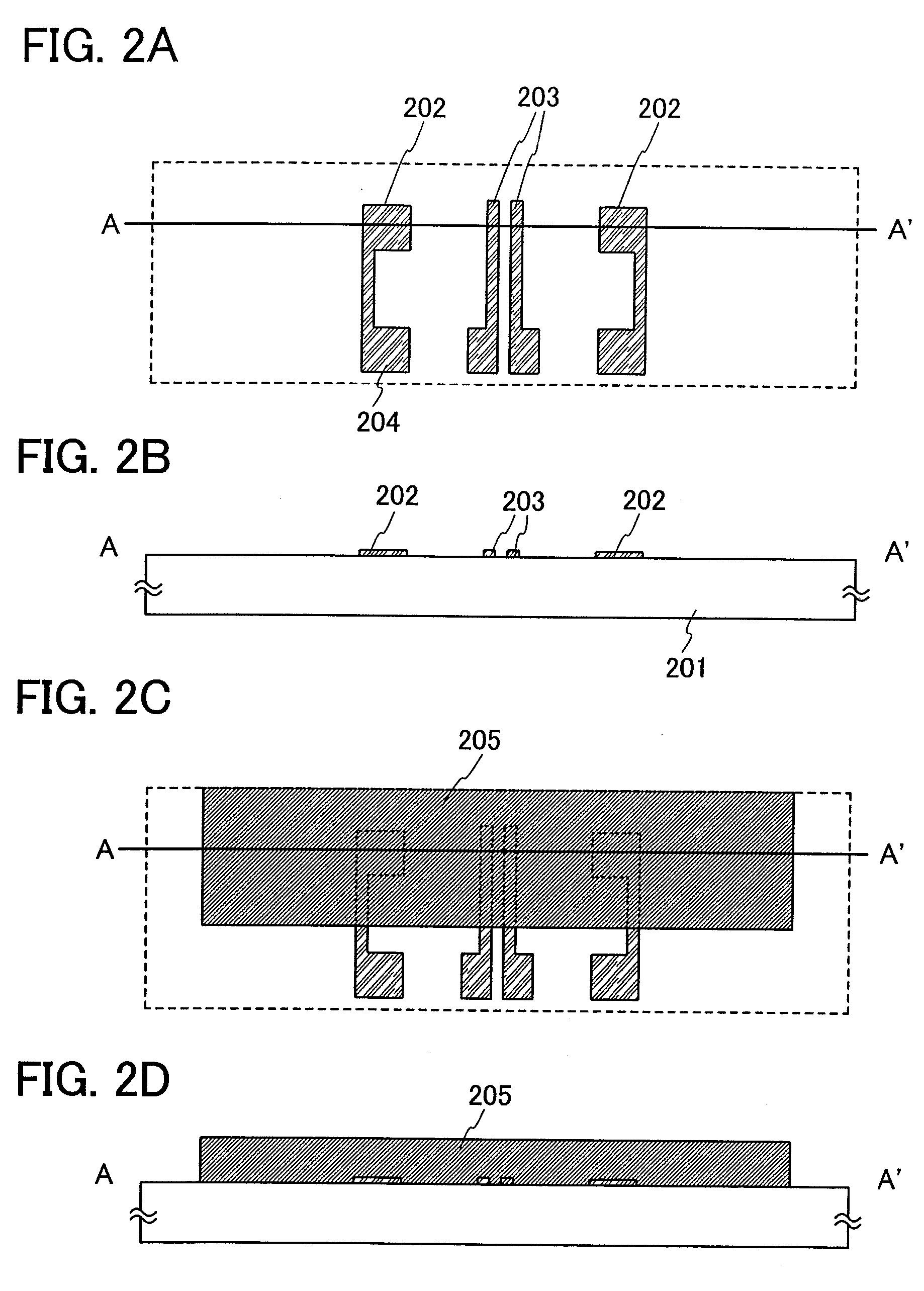
InactiveUS20090145629A1Improve reliabilityThinning and disconnection can be preventedElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysConductive pattern formationMachiningSurface micromachining
A structure which prevents thinning and disconnection of a wiring is provided, in a micromachine (MEMS structure body) formed with a surface micromachining technology. A wiring (upper auxiliary wiring) over a sacrificial layer is electrically connected to a different wiring (upper connection wiring) over the sacrificial layer, so that thinning, disconnection, and the like of the wiring formed over the sacrificial layer at a step portion generated due to the thickness of the sacrificial layer can be prevented. The wiring over the sacrificial layer is formed of the same conductive film as an upper driving electrode which is a movable electrode and is thus thin. However, the different wiring is formed over a structural layer, which is formed by a CVD method and has a rounded step, and has a thickness of 200 nm to 1 μm, whereby thinning, disconnection, and the like of the wiring can be further prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Erected mirror optical switch
A microelectromechanical (MEM) optical switching apparatus is disclosed that is based on an erectable mirror which is formed on a rotatable stage using surface micromachining. An electrostatic actuator is also formed on the substrate to rotate the stage and mirror with a high angular precision. The mirror can be erected manually after fabrication of the device and used to redirect an incident light beam at an arbitrary angel and to maintain this state in the absence of any applied electrical power. A 1×N optical switch can be formed using a single rotatable mirror. In some embodiments of the present invention, a plurality of rotatable mirrors can be configured so that the stages and mirrors rotate in unison when driven by a single micromotor thereby forming a 2×2 optical switch which can be used to switch a pair of incident light beams, or as a building block to form a higher-order optical switch.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method of making a pressure sensor comprising a resonant beam structure
A resonant microbeam pressure sensor is disclosed, comprising a microbeam suspended by a diaphragm at one or more points by suspension elements. Pressure applied to the diaphragm will cause the resonance frequency of the beam to shift. This shift is detectable and proportional to the pressure. The device is manufactured by surface micromachining.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
Miniaturized pressure sensor
InactiveUS7017420B2Reduce impactIncreased pressure sensitivityFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationChip sizeLight beam
An entirely surface micromachined free hanging strain-gauge pressure sensor is disclosed. The sensing element consists of a 80 μm long H-shaped double ended supported force transducing beam (16). The beam is located beneath and at one end attached to a square polysilicon diaphragm (14) and at the other end to the cavity edge. The sensor according to the invention enables a combination of high pressure sensitivity and miniature chip size as well as good environmental isolation. The pressure sensitivity for the sensor with a H-shaped force transducing beam, 0.4 μm thick was found to be 5 μV / V / mmHg.
Owner:SILEX MICROSYST
Contact type micro piezoresistive shear-stress sensor
InactiveUS6877385B2Using electrical meansForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsEtchingEngineering
There is disclosed a semiconductor sensor for measuring the contact shear stress distribution between the socket of an above-knee (AK) prostheses and the soft tissue of an amputee's stump. The sensor is fabricated by the micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) technology, and its main sensing part is 2-X shaped with a flange structure. The sensor is prepared by anisotropic wet etching of bulk silicon in KOH solution and a square flange above the sensing diaphragm is formed through surface micromachining of deposited SiO2 thin film. This invention has the following characteristics: piezo-resistivity of the monolithic silicon will be utilized to convert shear deformation of the sensor into an electrical signal and a micro sensor which can measure the shear force vector acting on the sensing flange.
Owner:NAT SCI COUNCIL
Multi-dimensional micro-electromechanical assemblies and method of making same
InactiveUS20020170290A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesClosed-cycle gas positive displacement engine plantMicroelectromechanical systemsEngineering
A multi-dimensional, micro-electromechanical assembly and the method of fabricating same. The invention enables an assembly of three-dimensional (3D) microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) using surface tension or shrinkage self assembly. That is, the invention provides a surface tension self assembly technique for rotating a MEMS element with a controlled amount of deformation to a selected angle out of the plane of a substrate. In accordance with the inventive method, multi-dimensional, micro-electromechanical assemblies are fabricated by providing a phase change material on at least one substantially planar structure mounted in a first orientation. A phase change is induced in the phase change material whereby the phase change material changes from a first state, in which the structure is disposed in the first orientation, to a second state, in which the structure is disposed in a second orientation. The MEMS elements may be fabricated using conventional surface micromachining techniques. In the illustrative embodiment, each MEMS element is attached to a substrate by at least one hinge which allows rotation of the MEMS element out of the plane of the substrate to a selected angle. To enable mass assembly of the MEMS elements, the MEMS elements are rotated to the selected angle using either surface tension forces of a liquid phase change material or shrinkage of a solid phase change material. In the illustrative embodiment, the phase change material is solder and the step of inducing a phase change in the phase change material includes the step up applying heat.
Owner:BRIGHT VICTOR +6
Microscale out-of-plane anemometer
InactiveUS6923054B2Volume/mass flow by thermal effectsFluid speed measurement using thermal variablesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A microscale out-of-plane thermal sensor. A resistive heater is suspended over a substrate by supports raised with respect to the substrate to provide a clearance underneath the resistive heater for fluid flow. A preferred fabrication process for the thermal sensor uses surface micromachining and a three-dimensional assembly to raise the supports and lift the resistive heater over the substrate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
High fill-factor bulk silicon mirrors
InactiveUS7209274B2Improve performanceLarge optical surfaceMirrorsMountingsEngineeringAngular rotation
A method and apparatus for fabricating a MEMS apparatus having a device layer with an optical surface that is supported by a pedestal on a planar support layer that is suspended for movement with respect to a base support by hinge elements disposed in a different plane from the planar support layer. The surface area of the optical surface is maximized with respect to the base support to optimized the fill factor of the optical surface and afford a high passband. The height of the pedestal is selected to position the device layer sufficiently above the base support to afford an unobstructed predetermined angular rotation about each axis. The hinges may be made of thin-film material, fabricated by way of surface micromachining techniques. The hinges are disposed underneath the device layer enabling the optical surface to be maximized so that the entire surface becomes usable (e.g., for optical beam manipulation). MEMS devices afford an array of MEMS mirrors with a high optical fill factor and high passband. Further, use of both bulk and surface micromachining techniques gives a MEMS device with a large and flat mirror and flexible hinges capable of a substantial rotational range at modest electrostatic drive voltages.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
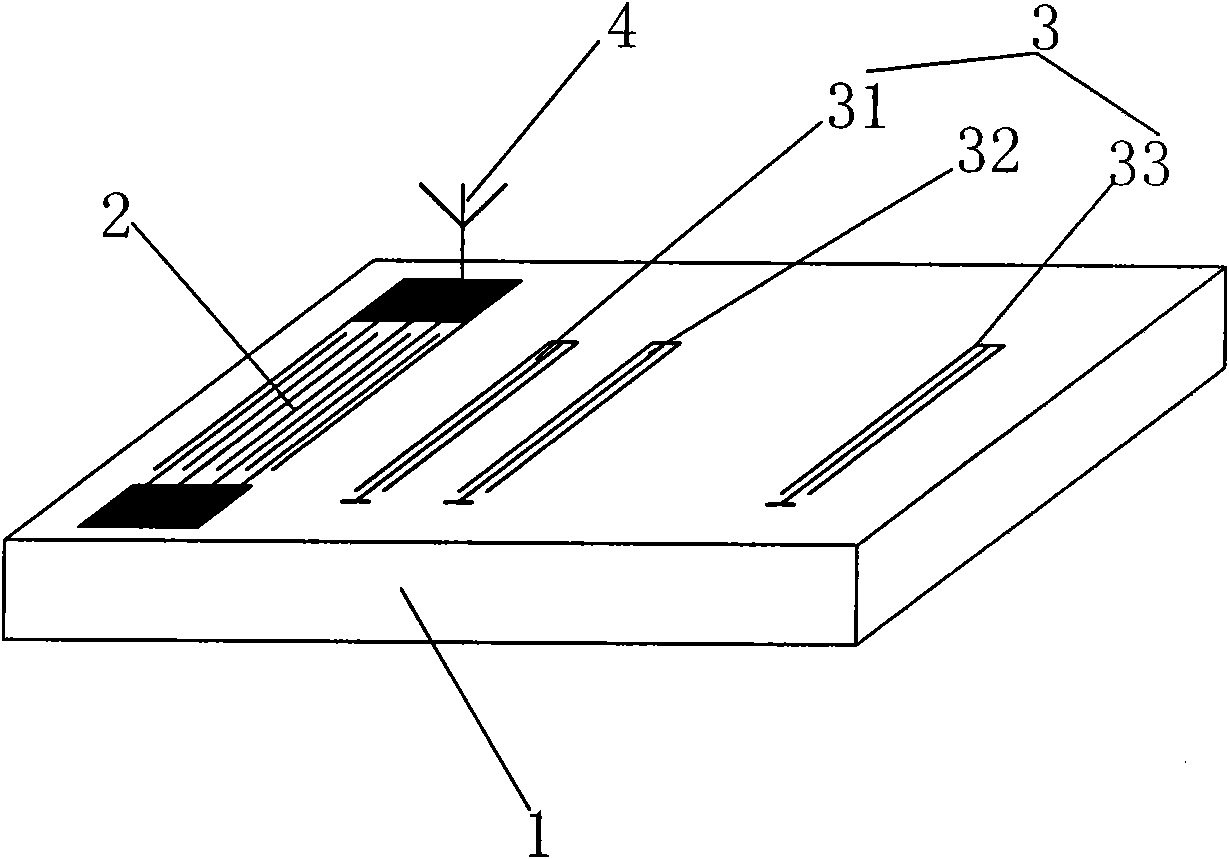
Sound surface wave measuring sensor and parameter analytical method
InactiveCN102042844ASolve the problem of accurate detection of physical quantitiesGuaranteed StrengthConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationThermometers using physical/chemical changesElectricitySurface acoustic wave sensor
The invention relates to a sound surface wave measuring sensor and a parameter analytical method. The sensor comprises a piezoelectric base, an interdigital transducer and a reflector, wherein the piezoelectric base is used for inducting physical quantity to be measured; the interdigital transducer and the reflector are deposited on the upper surface of the piezoelectric base through a surface micromachining process; the interdigital transducer is used for receiving drive energy required by the operation of the sound surface wave measuring sensor through an antenna connected with the interdigital transducer and returning a radio frequency pulse echo signal through the antenna; and the reflector is used for generating the radio frequency pulse echo signal. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following technical characteristics: the physical quantity can be detected with high precision in a wide range on the premise of ensuring certain signal intensity; the problem that the sound surface wave sensor in the prior art can only meet one index in the range and the precision of signal measurement and the range and the precision of signal measurement cannot be met simultaneously is solved; the sound surface wave measuring sensor has simple structure; and by using a certain parameter analytical method, the measured physical quantity generates a corresponding feedback signal and the problem that the physical quantity can be accurately detected by the sensor in a wide range can be solved.
Owner:李天利 +1
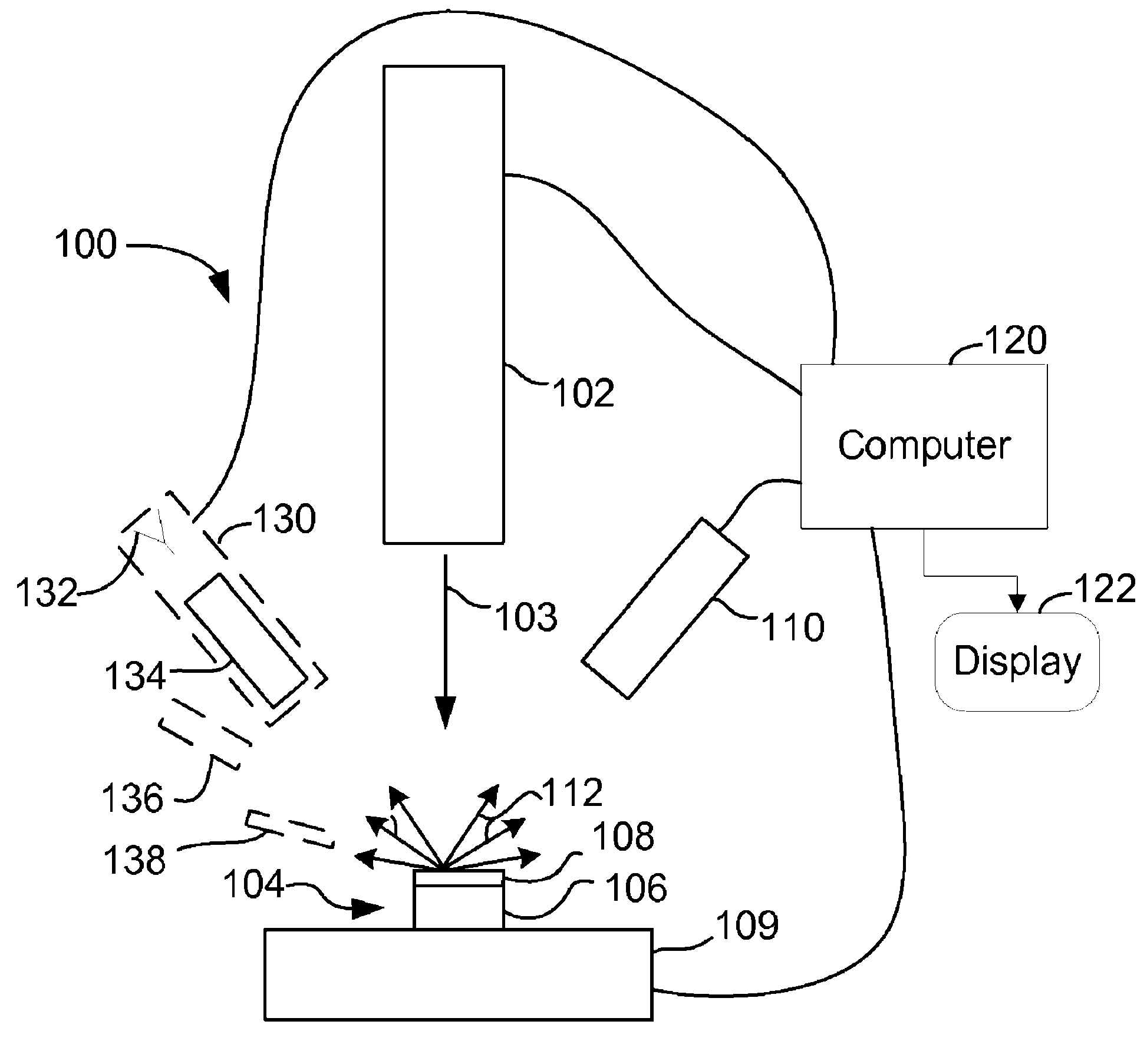
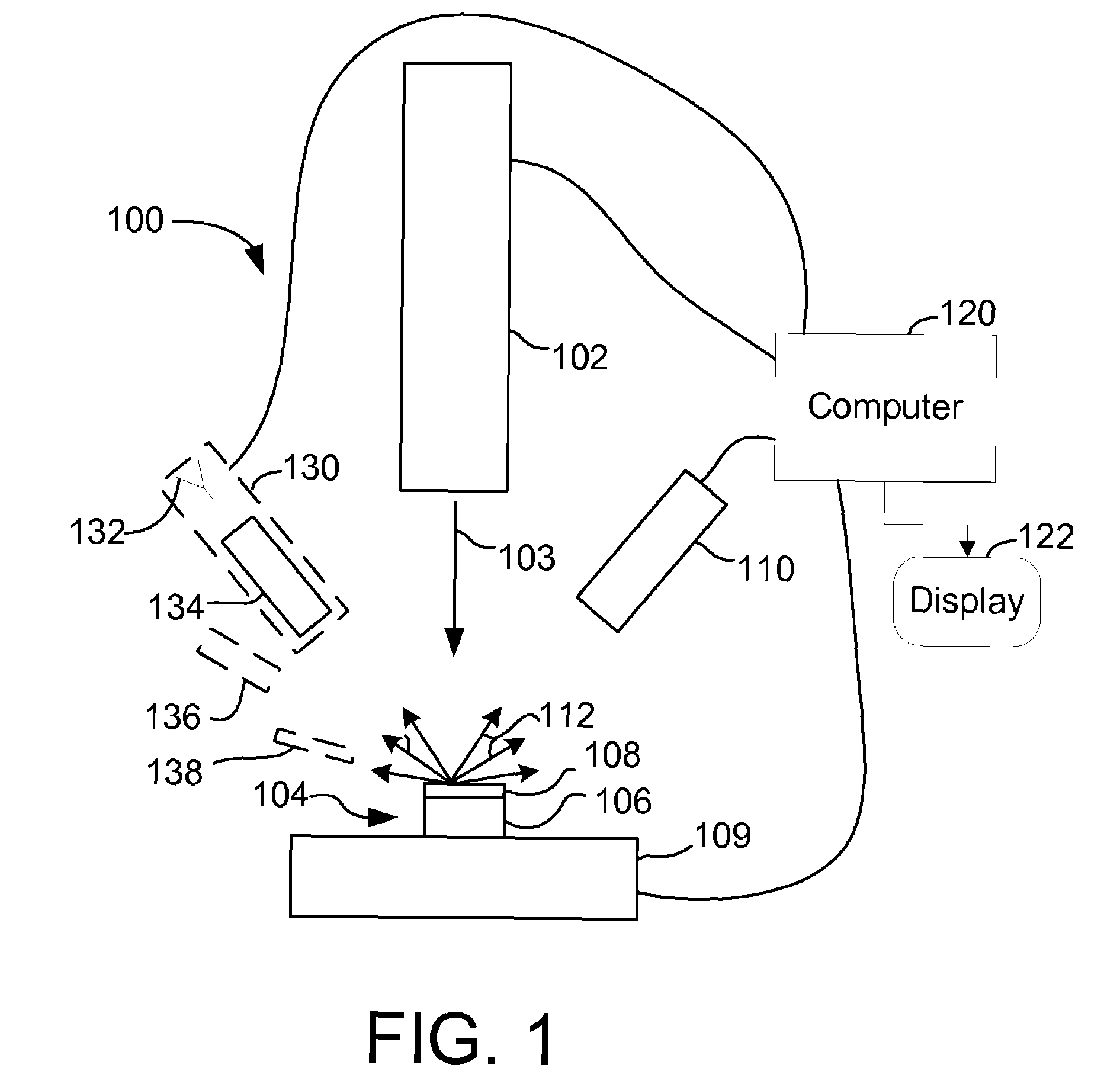
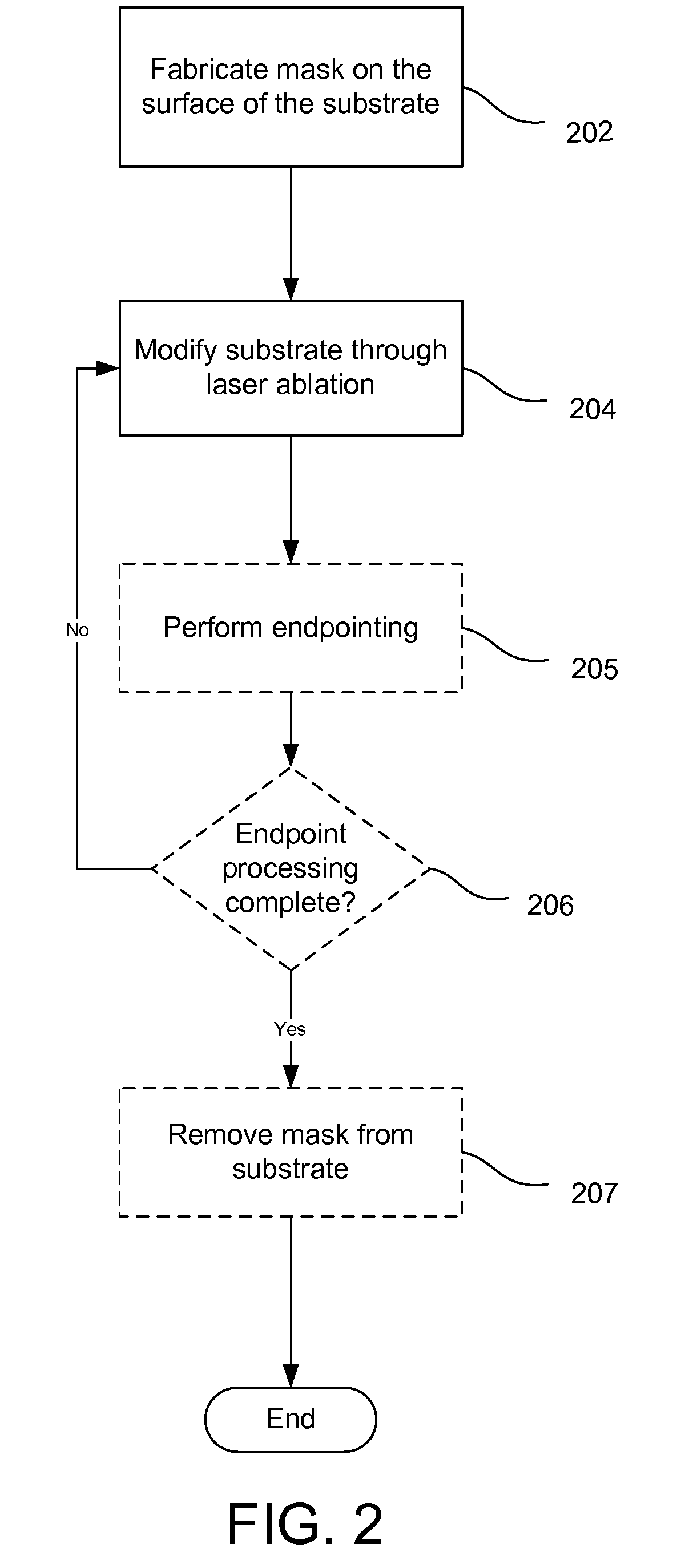
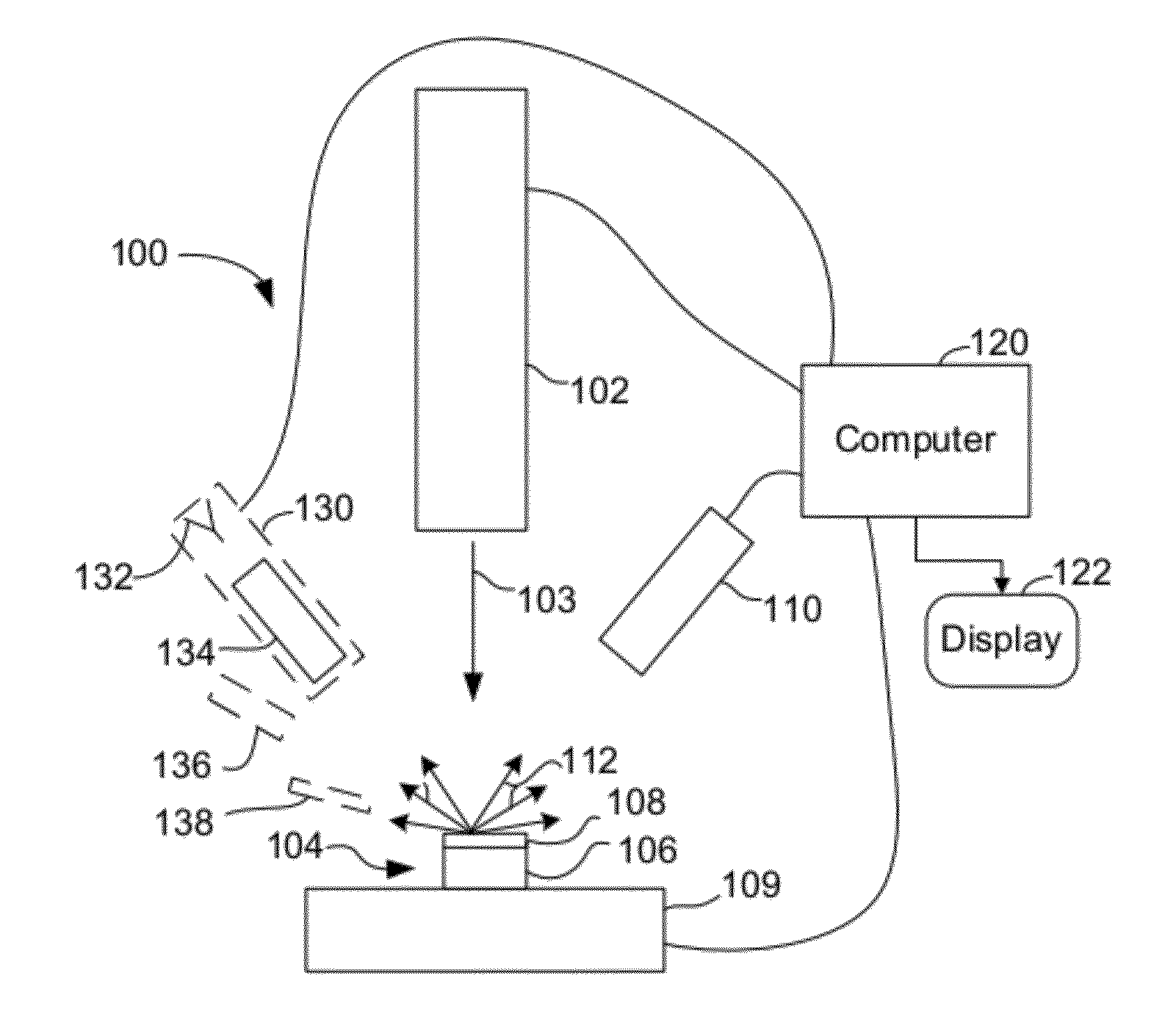
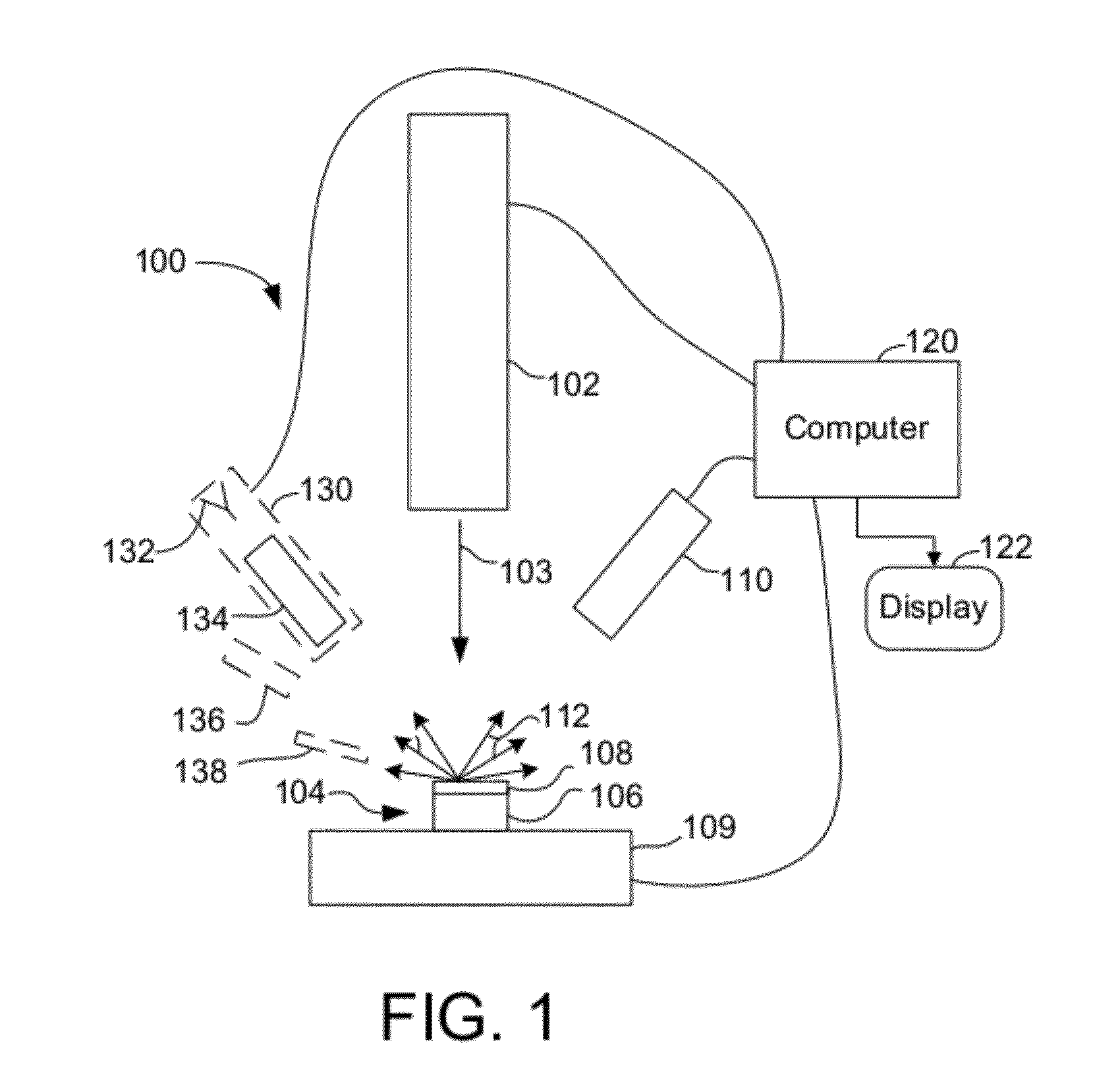
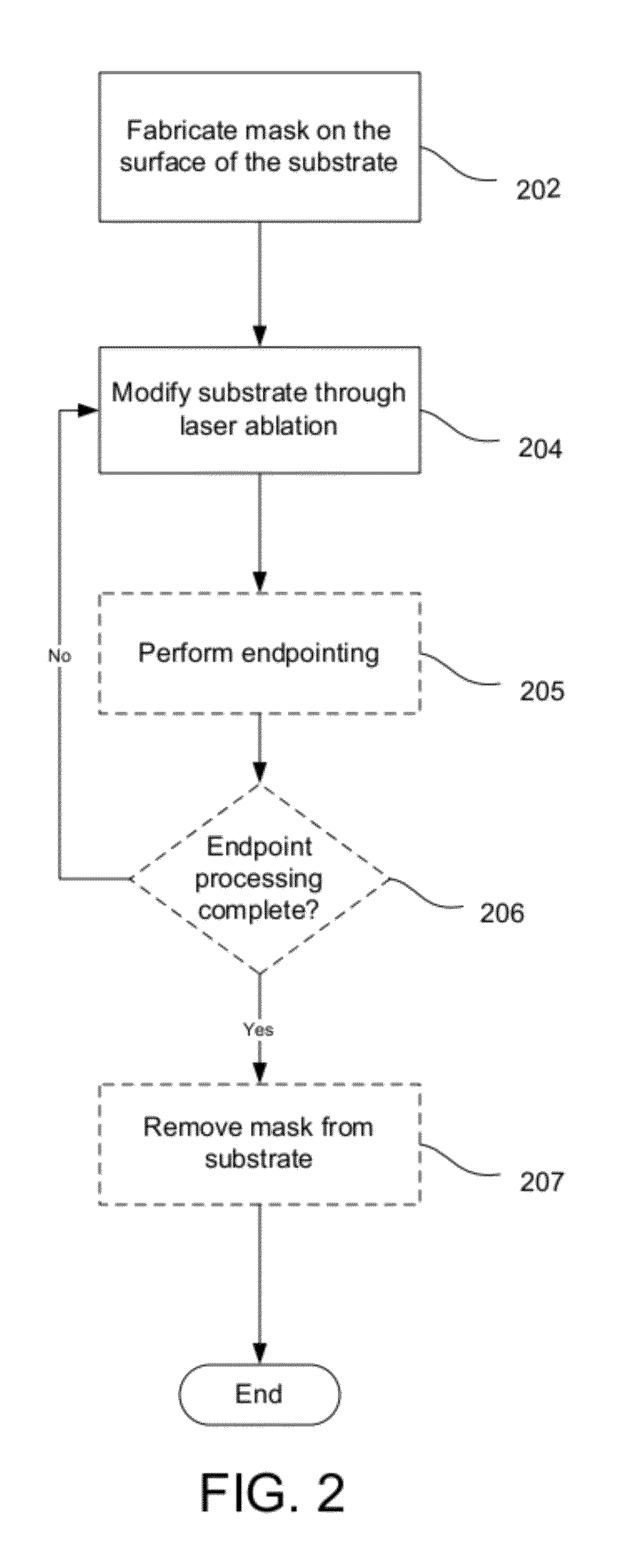
Charged particle beam masking for laser ablation micromachining
ActiveUS8168961B2High resolutionHigh processing of sampleElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusTemporal resolutionCharged particle beam
An improved method for substrate micromachining. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide improved methods for the utilization of charged particle beam masking and laser ablation. A combination of the advantages of charged particle beam mask fabrication and ultra short pulse laser ablation are used to significantly reduce substrate processing time and improve lateral resolution and aspect ratio of features machined by laser ablation to preferably smaller than the diffraction limit of the machining laser.
Owner:FEI CO
Manufacturing method of infrared detector based on temporary release protective layer
ActiveCN102683475APerformance impactDoes not directly affect the structureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCMOSO2 plasma
The invention discloses a surface micromachining method for a microelectromechanical system based on a temporary release protective layer and particularly relates to a manufacturing method of an uncooled infrared detector. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: sequentially depositing a metal layer, an amorphous silicon sacrificial layer, a first temporary release protective layer of polyimide on a CMOS (complentary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor) silicon substrate; manufacturing a sensitive layer and a metal electrode layer in a cascading way, and imaging the sensitive layer, the electrode layer and a microbridge structure; and finally manufacturing a second temporary release protective layer. When the sacrificial layer is released, firstly XeF2 is adopted for releasing the amorphous silicon sacrificial layer, and then O2 plasma is utilized for removing the temporary release protective layers after the release is completed. According to the manufacturing method of the infrared detector provided by the invention, compared with the prior art, the adopted temporary release protective layers are completely removed in the later period of manufacturing, thus not causing any influence on the microbridge performance, and being beneficial to the reduction of process difficulty and improvement of the performance of the detector.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DALI TECH
Charged Particle Beam Masking for Laser Ablation Micromachining
ActiveUS20120200007A1High resolutionHigh processing of sampleElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusTemporal resolutionImage resolution
An improved method for substrate micromachining. Preferred embodiments of the present invention provide improved methods for the utilization of charged particle beam masking and laser ablation. A combination of the advantages of charged particle beam mask fabrication and ultra short pulse laser ablation are used to significantly reduce substrate processing time and improve lateral resolution and aspect ratio of features machined by laser ablation to preferably smaller than the diffraction limit of the machining laser.
Owner:FEI CO
Electromagnetic-driven miniature two-dimensional scanning mirror device
ActiveCN103399402ARealize 2D area scanningRealize two-dimensional deflection scanningOptical elementsClassical mechanicsMagnetic poles
The invention discloses an electromagnetic-driven miniature two-dimensional scanning mirror device which belongs to the technical field of micro scanning and MEMS, is manufactured by adopting bulk silicon and surface micro machining technology and is actually a miniature two-dimensional scanning mirror device with two pairs of orthogonal magnetic poles. The scanning mirror device comprises a reflecting mirror surface, an inner baseplate, an outer baseplate, a base, inner torsion beams and outer torsion beams, wherein the reflecting mirror surface is integrally arranged on the inner baseplate; the inner baseplate is connected with the outer baseplate through a pair of opposite inner torsion beams; the outer baseplate is connected with the fixed base through the pair of opposite outer torsion beams; the inner torsion beams and the outer torsion beams are orthogonal. The scanning mirror device adopts a duralumin structure for encapsulation; two groups of magnet poles and magnetic yokes are arranged inside to form an orthogonal magnetic field; input signals are led in through the side wall of the encapsulating structure; a transparent glass seal cover is arranged at the top end of the encapsulating structure. The scanning mirror device has the advantages of high actuating efficiency, large torsion force and compact structure, and can realize two-dimensional scanning at larger angle.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF NANOENERGY & NANOSYST
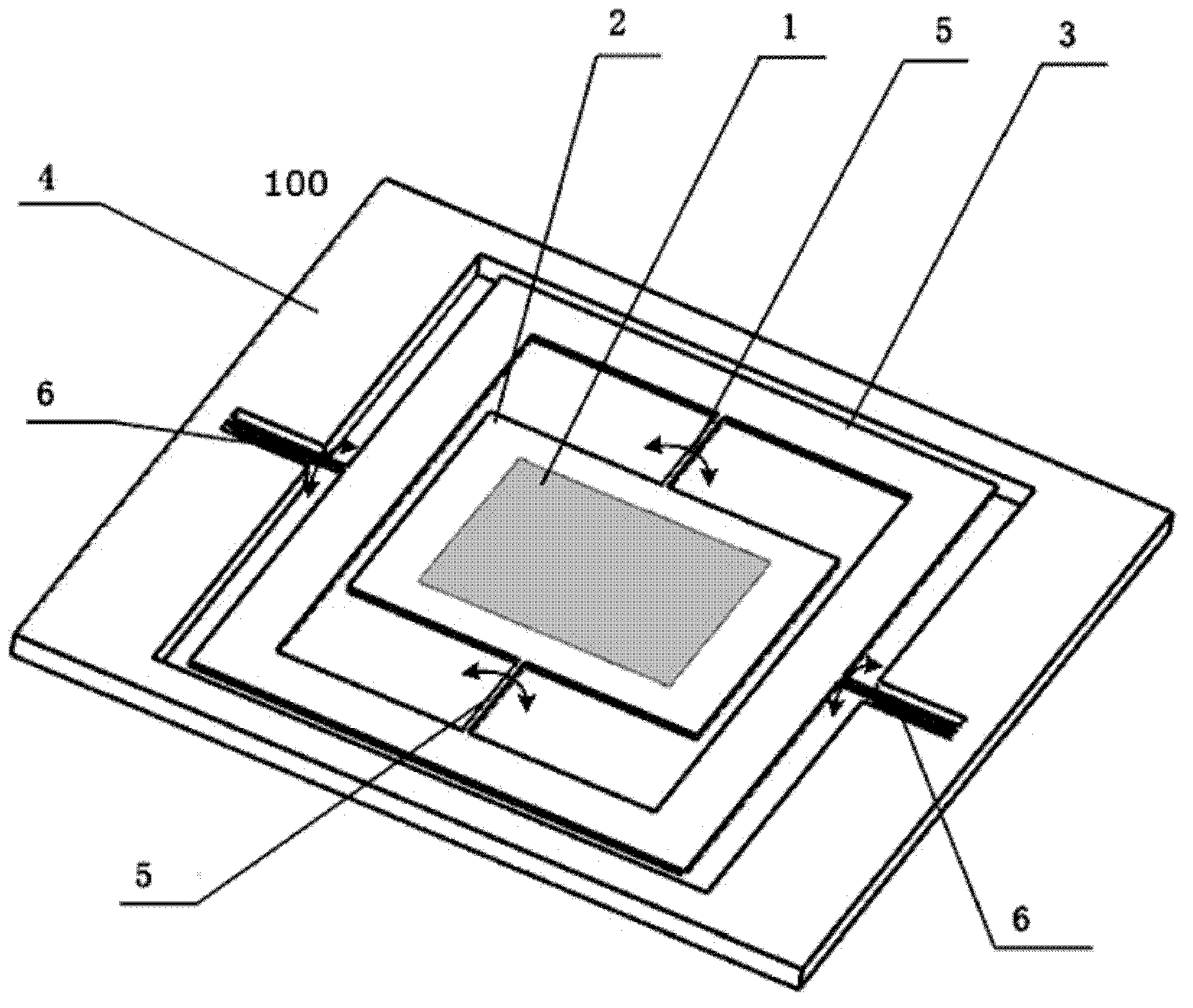
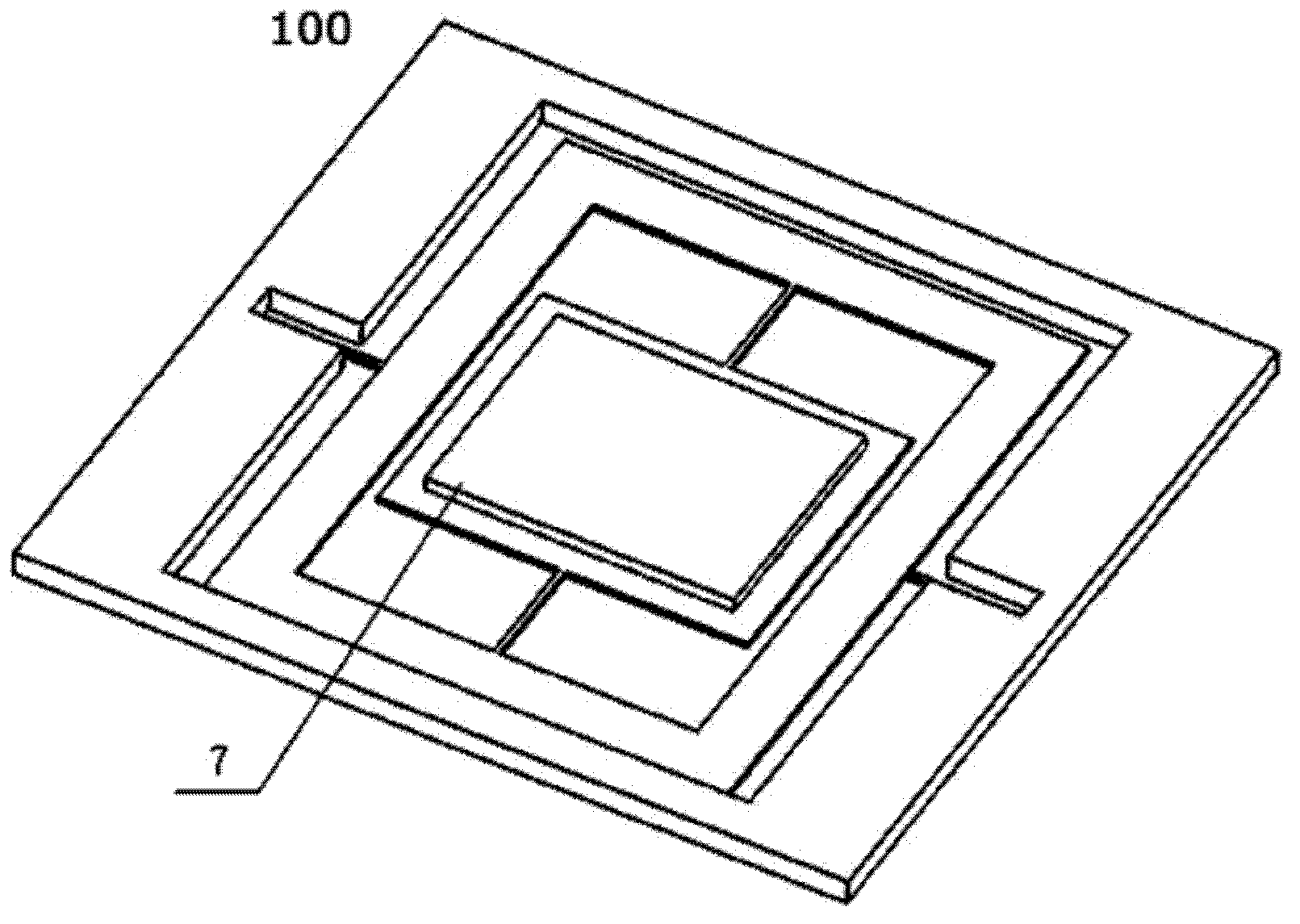
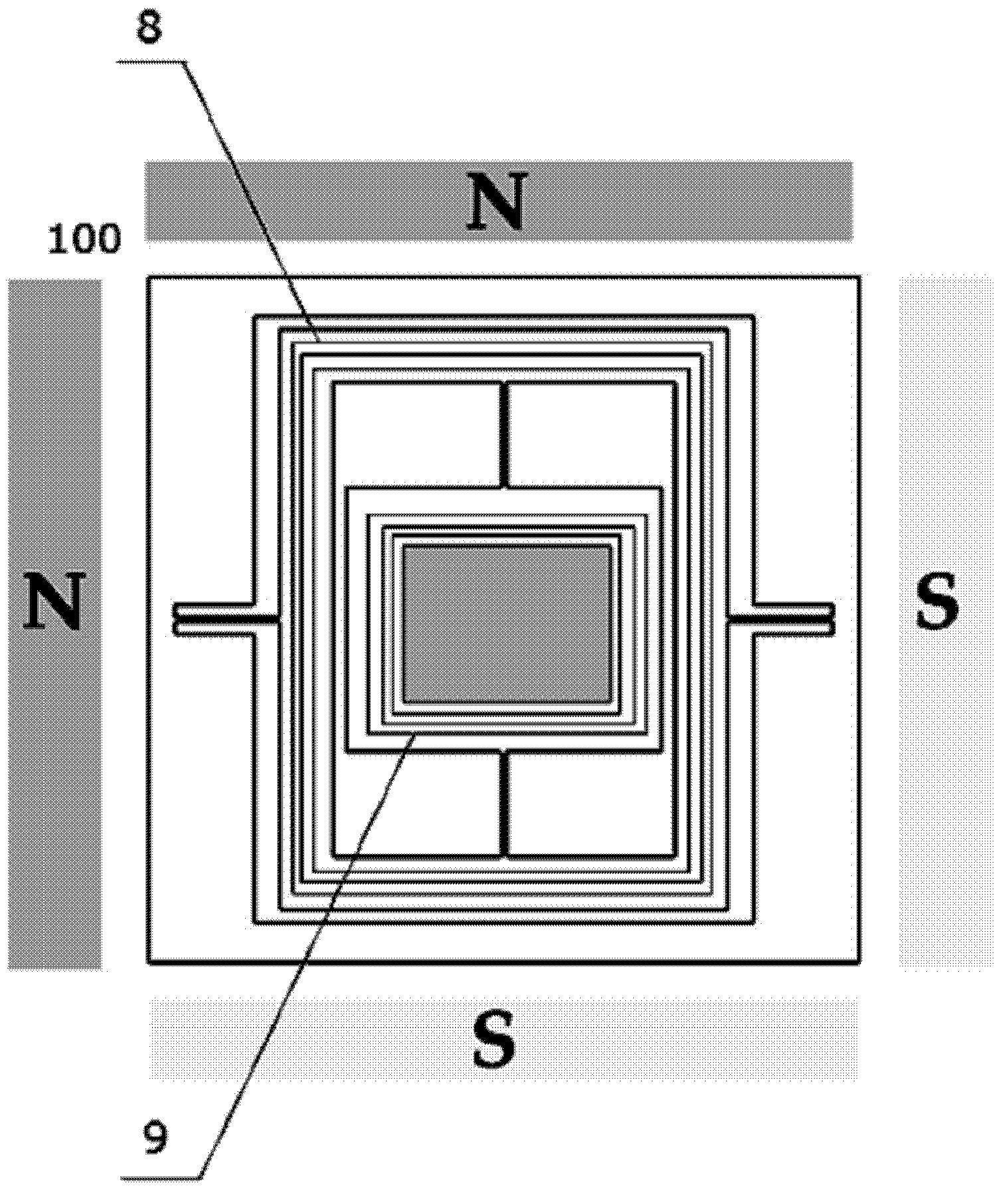
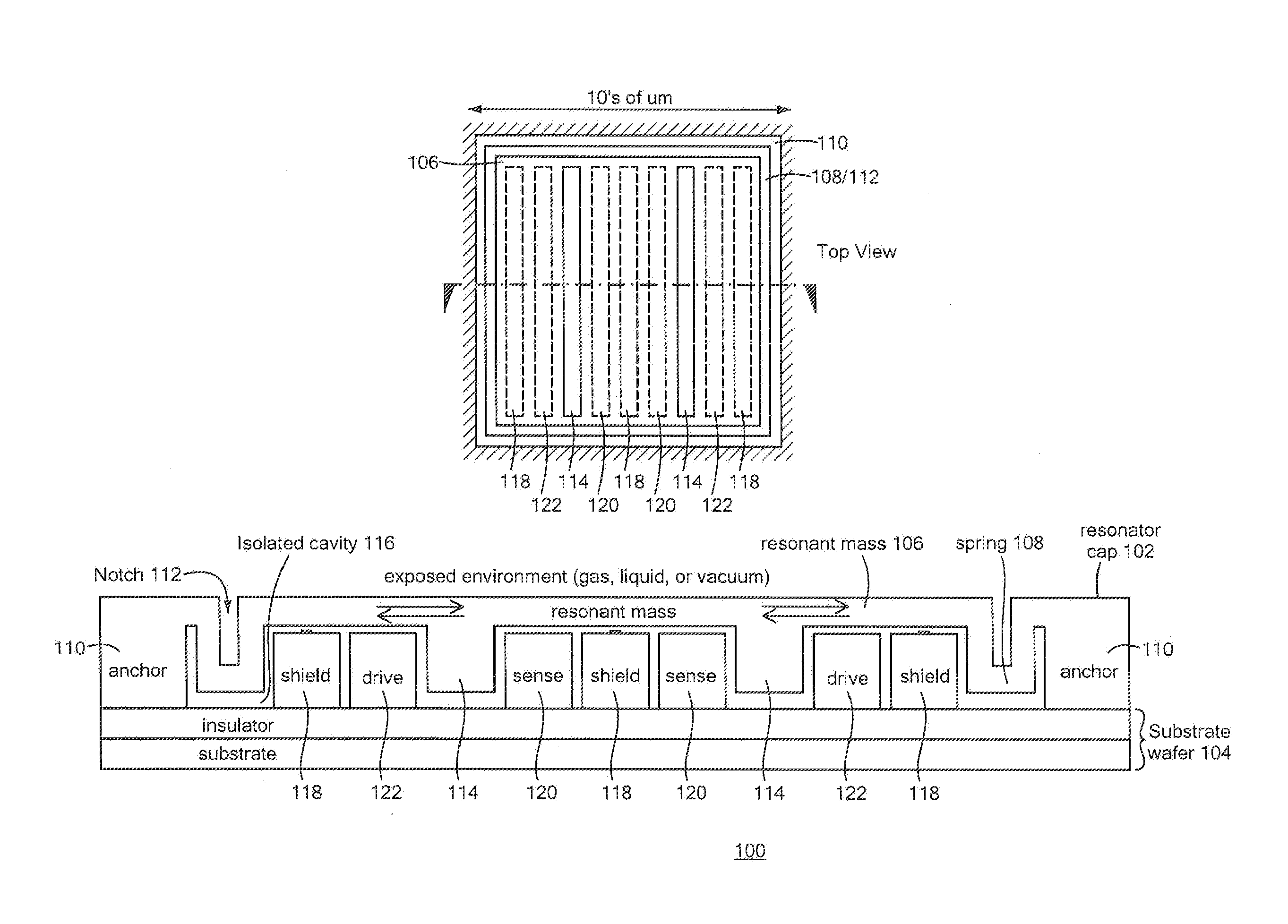
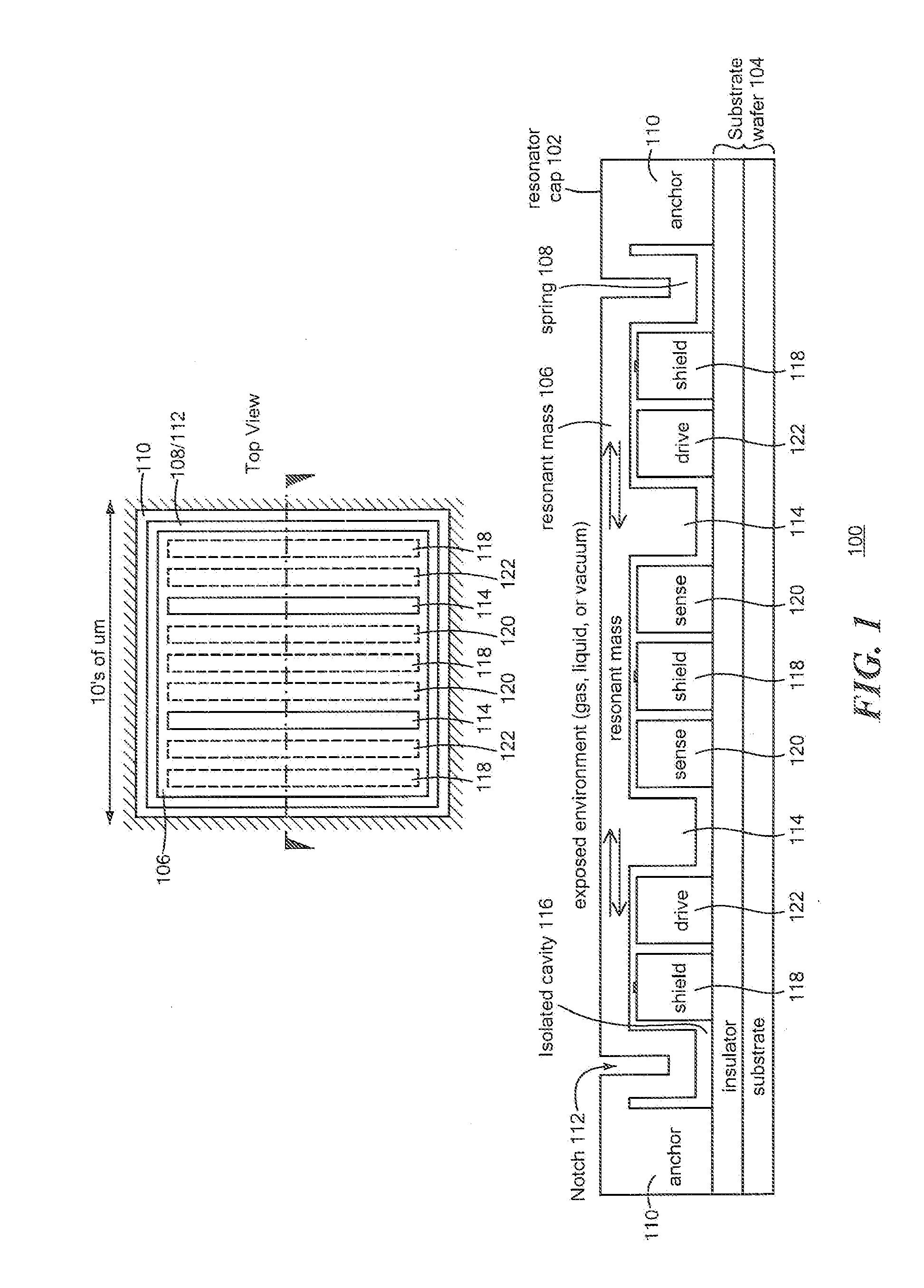
MEMS In-Plane Resonators
ActiveUS20120112765A1Decrease in damping performanceLower performance requirementsVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesIn planeWafer fabrication
MEMS in-plane resonators include a substrate wafer, at least one resonant mass supported by the substrate wafer and configured to resonate substantially in-plane, and at least one transducer coupled to the at least one resonant mass for at least one of driving and sensing in-plane movement of the at least one resonant mass, wherein at least part of one surface of the resonant mass is configured for exposure to an external environment and wherein the at least one transducer is isolated from the external environment. Such MEMS in-plane resonators may be fabricated using conventional surface micromachining techniques and high-volume wafer fabrication processes and may be configured for liquid applications (e.g., viscometry, densitometry, chemical / biological sensing), gas sensing (e.g., where a polymer film is added to the sensor surface, further degrading the damping performance), or other applications.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
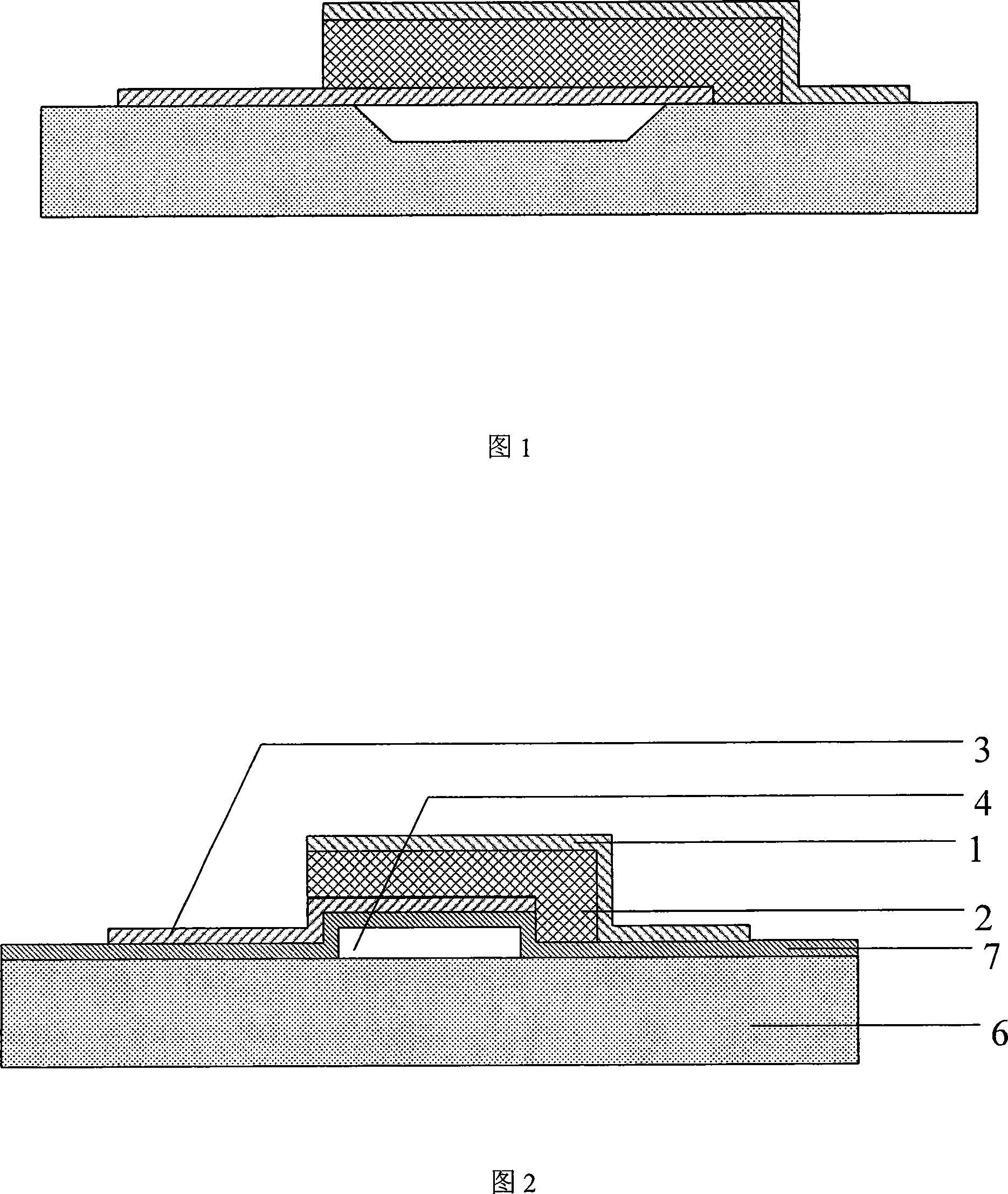
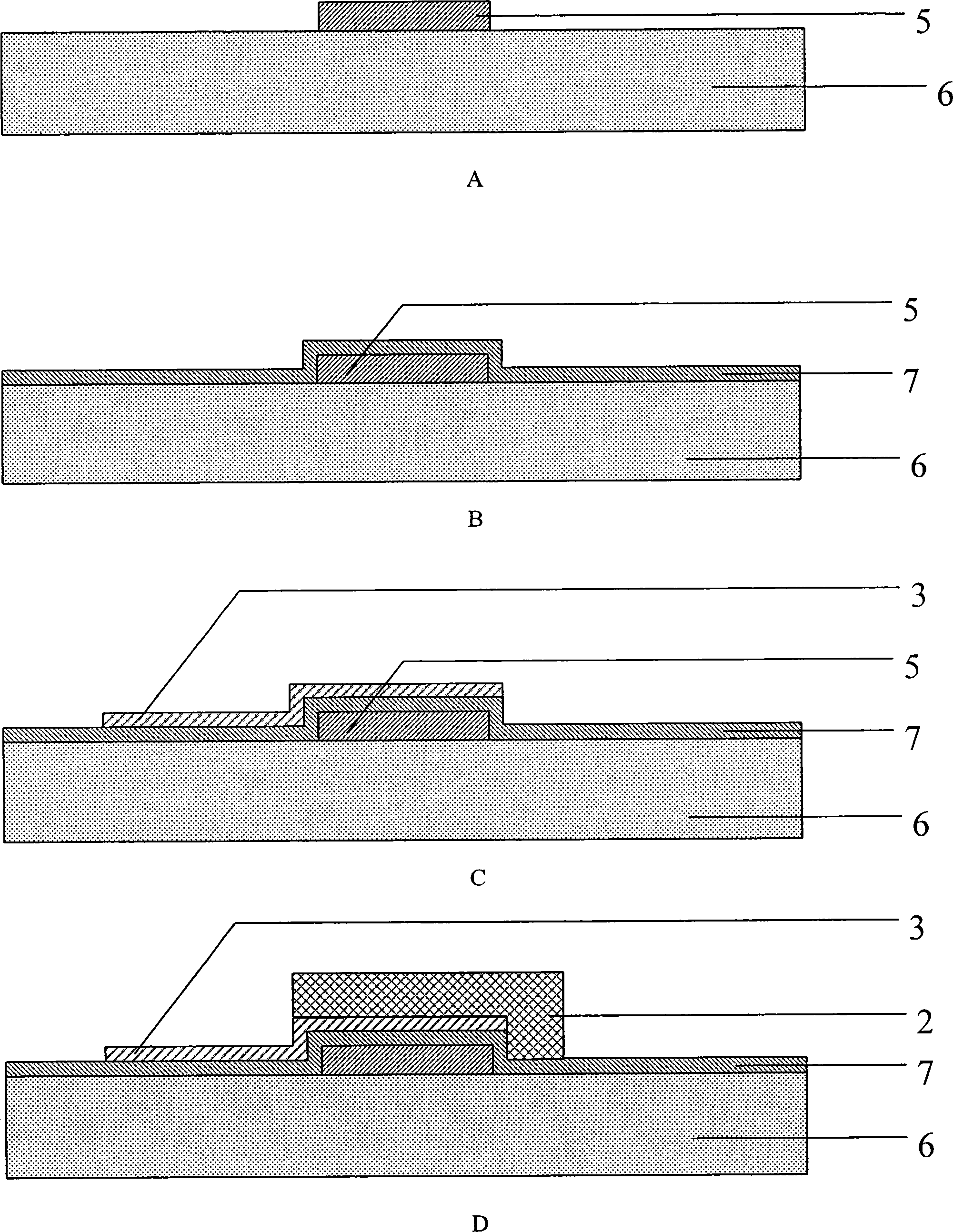
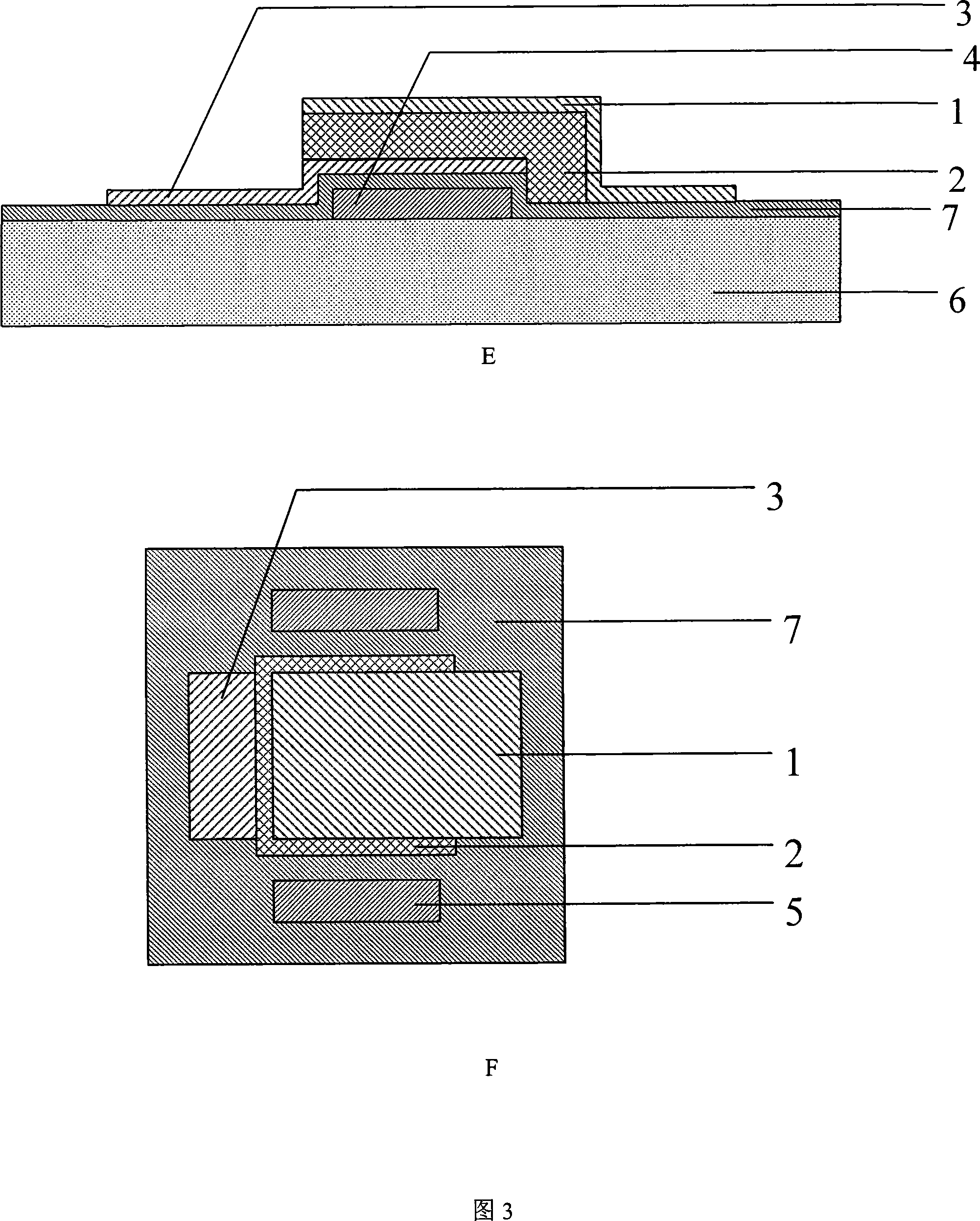
Absolute pressure transducer chip based on surface micro-machining and its production method
ActiveCN101487747AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityTelevision system detailsSemi-permeable membranesPolycrystalline siliconResistor
The invention relates to an absolute pressure sensor chip based on surface micromachining and a manufacturing method. The manufacturing method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adopting a low-stress silicon nitride film as a core structural layer of the pressure sensor chip and using a polycrystalline silicon film to form a force-sensitive resistor track; designing a film area of the low-stress silicon nitride film into a long rectangle, fully utilizing longitudinal piezoresistive effect of the polycrystalline silicon resistor track according to the stress distribution of the film area, and making the most of a tensile stress area on the film to put part of a pair of resistor tracks on the external surface of the film and arrange another two resistor tracks on the central position of the film; and separately contacting a folded bent angle part of each resistor track with a hole depositing metal to conduct the bent angle part. By adopting surface micromachining technology compatible with IC technology, the method can manufacture the absolute pressure sensor chip with a measuring range of 1KPa-1MPa and with high sensitivity, good stability and high precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resonant sensor and method of making a pressure sensor comprising a resonant beam structure
InactiveUS20020157473A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsLight beamResonant sensor
A resonant microbeam pressure sensor is disclosed, comprising a microbeam suspended in a diaphragm in at least one point by suspension elements. Pressure applied to the diaphragm will cause the resonance frequency of the beam to shift. This shift is detectable and proportional to the pressure, The device is manufactured by surface micromachining.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL COORDINATION CENT
A novel acoustic wave syntonizer and the corresponding preparation method
The invention discloses a novel film bulk acoustic wave resonator, comprising an underlay, a piezoelectric film, an upper metal electrode layer and a lower metal electrode layer. The invention is characterized in that the invention also comprises a film support layer which is arranged on the underlay and is provided with the air gap structure in the contacting surface with the underlay; the film support layer, the lower metal electrode layer, the piezoelectric film and the upper metal electrode layer are overlapped successively upwards so as to form a resonance area. The resonator overcomes the defects in the prior art, and makes use of surface-micromachining technique and sacrificial layer technique without needing groove etching technique to silicon substrate and without needing chemical mechanical polishing technique. The invention greatly improves the feasibility of technique preparation, reduces production cost to a large extent, still has higher Q value and ensures the characteristics of the resonator.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN103976703AProcessing size is smallImprove excitationSurgeryCatheterSonificationAnnular array
The invention discloses an optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system. The optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system is composed of an endoscope lens, a light source, a controlling and processing device, an impulse voltage generator, an interface module, a cable, a display screen, a crystal oscillator circuit and a power circuit. The optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system can achieve endoscopic type optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal imaging. According to the optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system, a high density CMUT ring array manufactured by using surface micro fabrication technology is used, an excitation unit and a sensing unit are designed into coaxial and homocentric integrative microstructure, and integration, microminiaturization and practical performance of optoacoustic and ultrasonic excitation and sensing are achieved. The optoacoustic and ultrasonic bimodal endoscope imaging system can be widely used in fields of medical endoscopic diagnosis, jewelry identification, industrial inspection and flaw detection and the like.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Micromachined relay with inorganic insulation
A micromechanical relay is made by surface micromachining techniques. It includes a metallic cantilever beam deflectable by an electrostatic field and a beam contact connected to the beam and electrically insulated from the beam by an insulating segment. During operation, the beam deflects, and the beam contact establishes an electrical contact between two drain electrodes.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
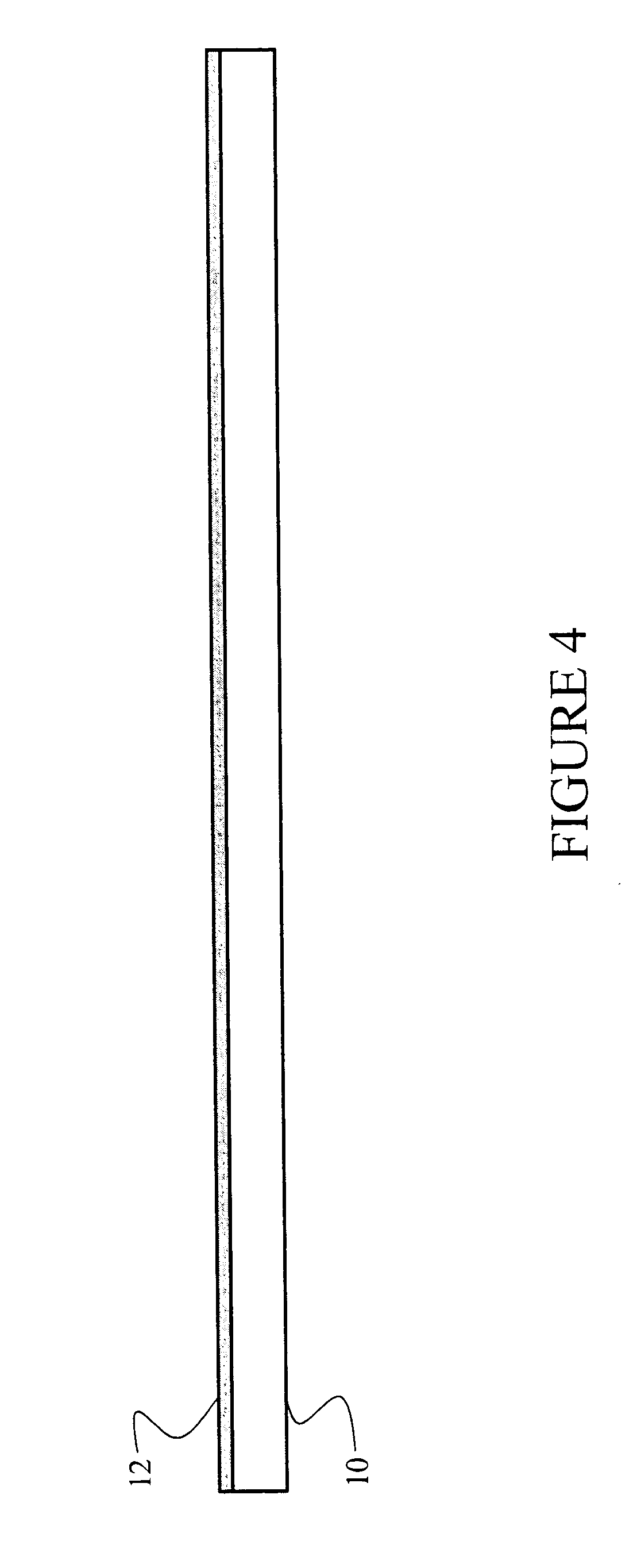
Nano-electro-mechanical memory cells and devices
A scalable nano-electro-mechanical memory cell design that requires only conventional semiconductor fabrication materials and surface micromachining technology, and is suited for use in cross-point memory arrays for very high density non-volatile storage. This design also leverages well established surface-micromachining technology and electro-mechanical device phenomena to achieve an elegantly simple and scalable memory cell structure that can potentially operate with low voltage. An elongate beam is held between a non-deflected state and a deflected state, or between two deflected states, therein defining two binary memory states. Stiction, buried charge layers, or a combination of stiction and buried charge layers can be incorporated to modify the stability of one or both deflected states for the cell. Current through the moveable portion of the elongate beam within the memory cell can be registered utilizing one or more access transistors for reading the data state.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com