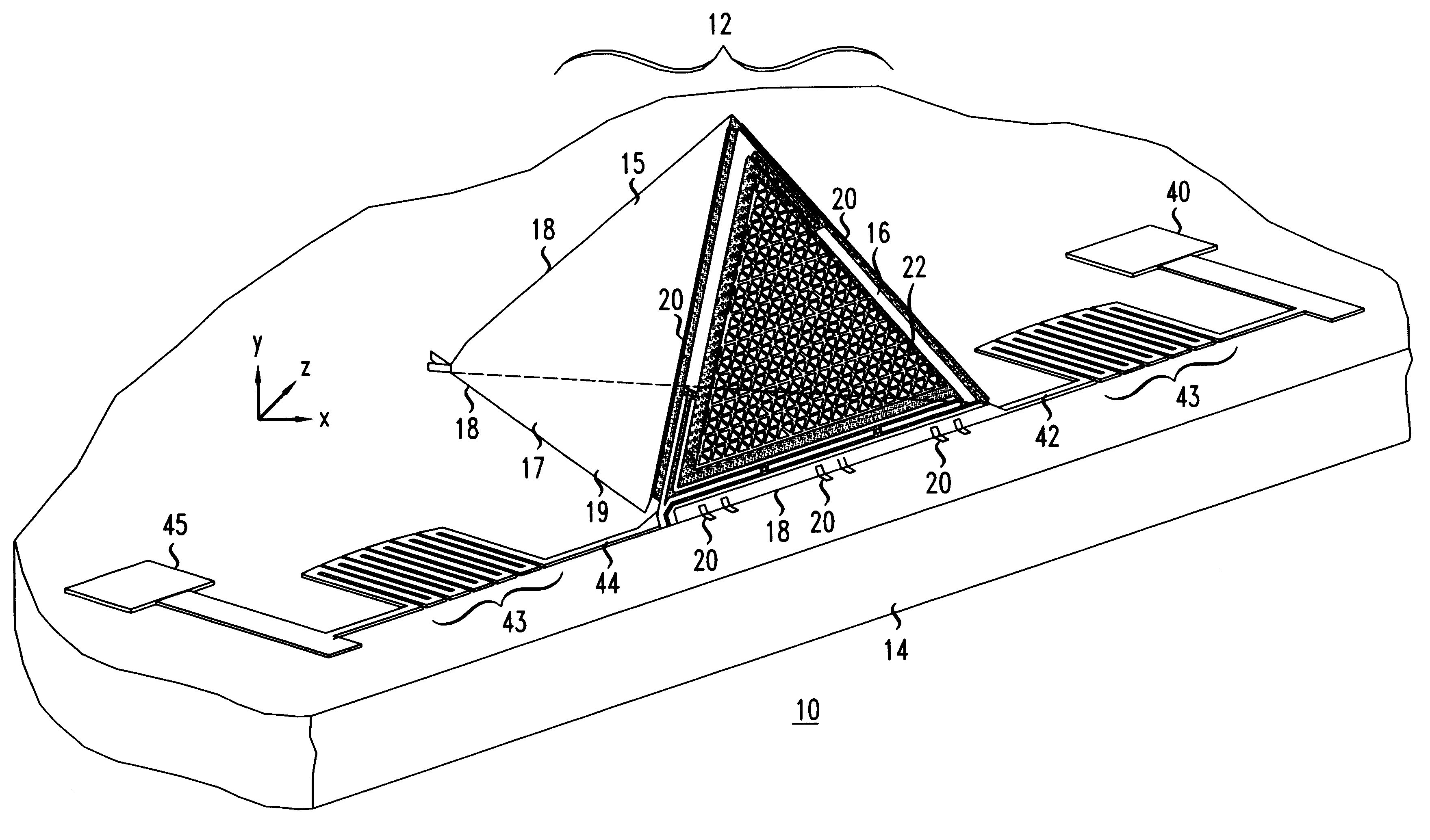
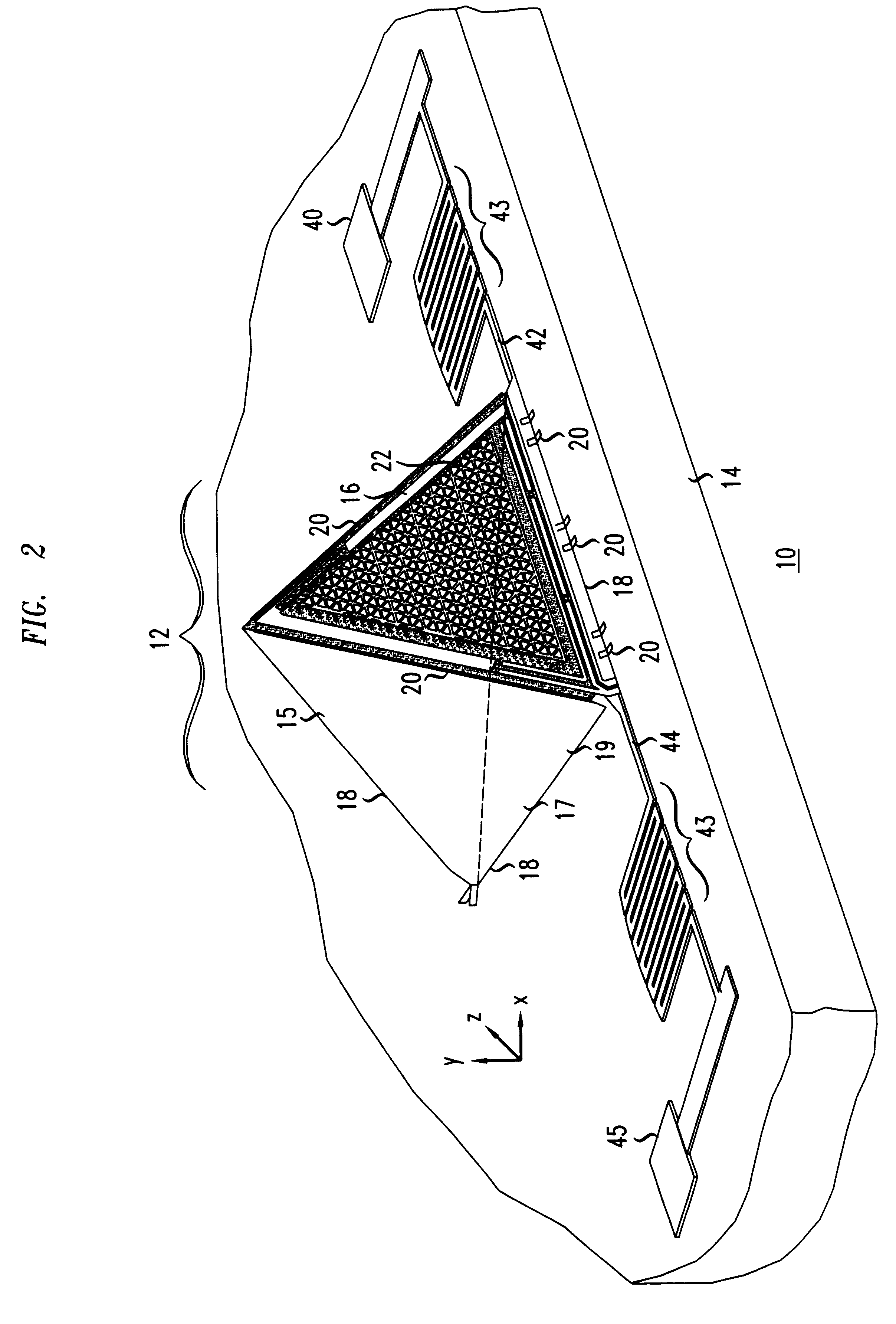
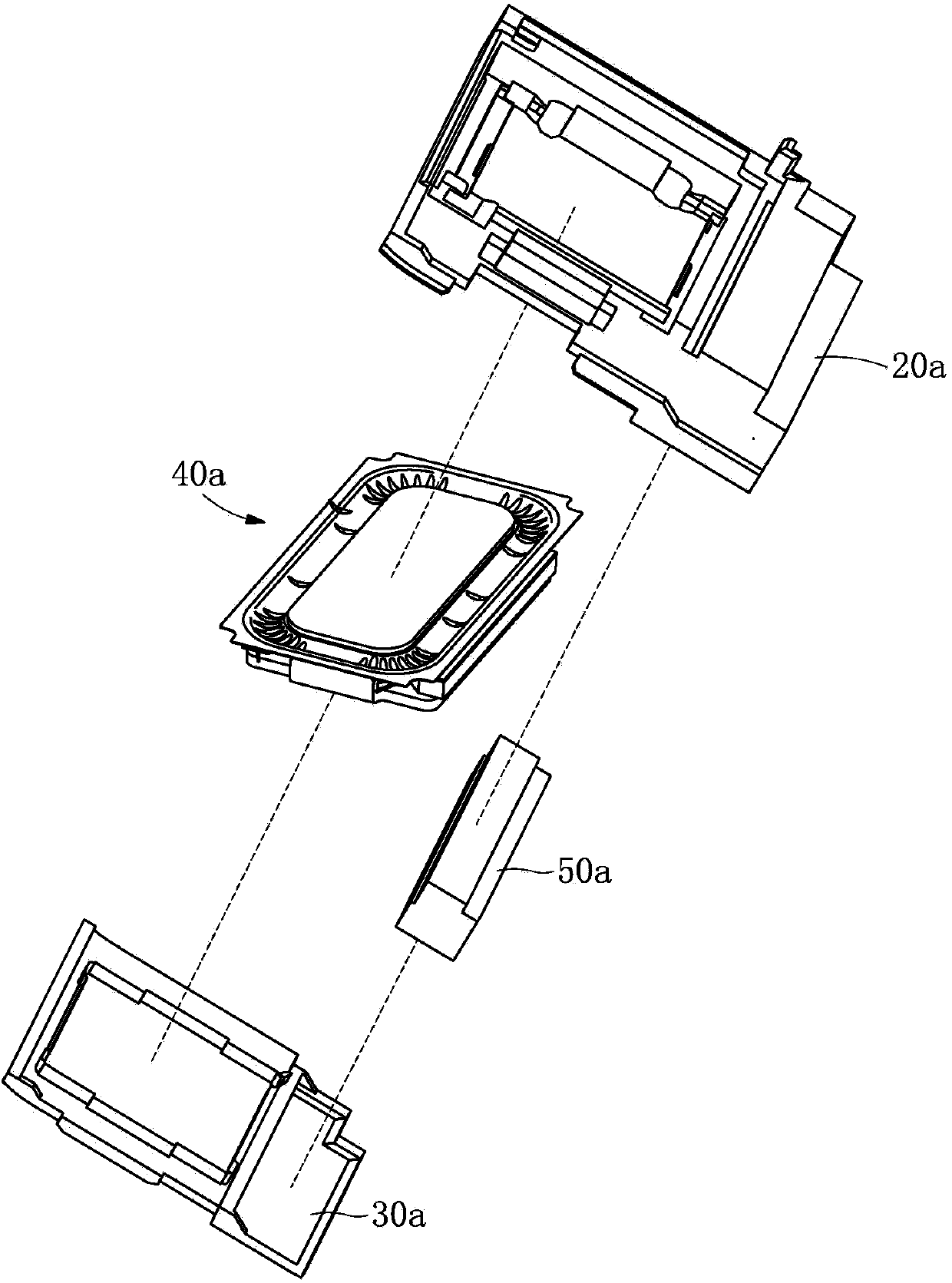
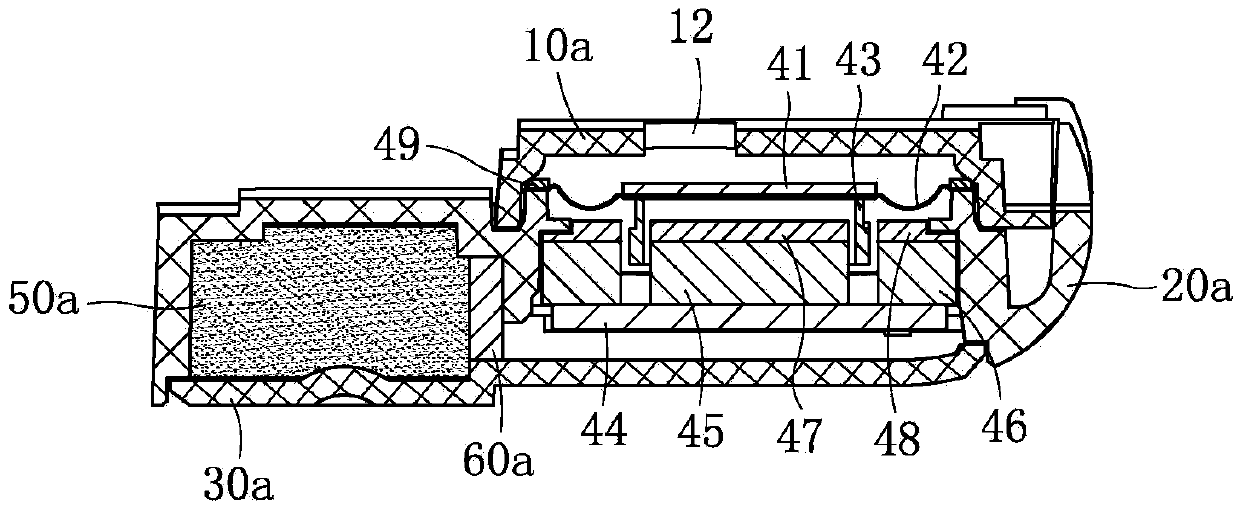
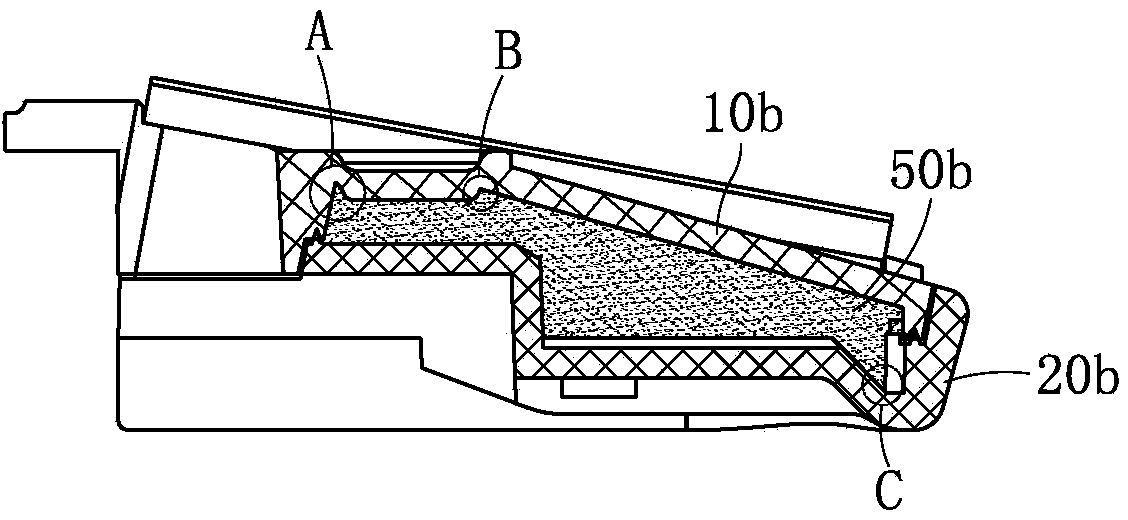
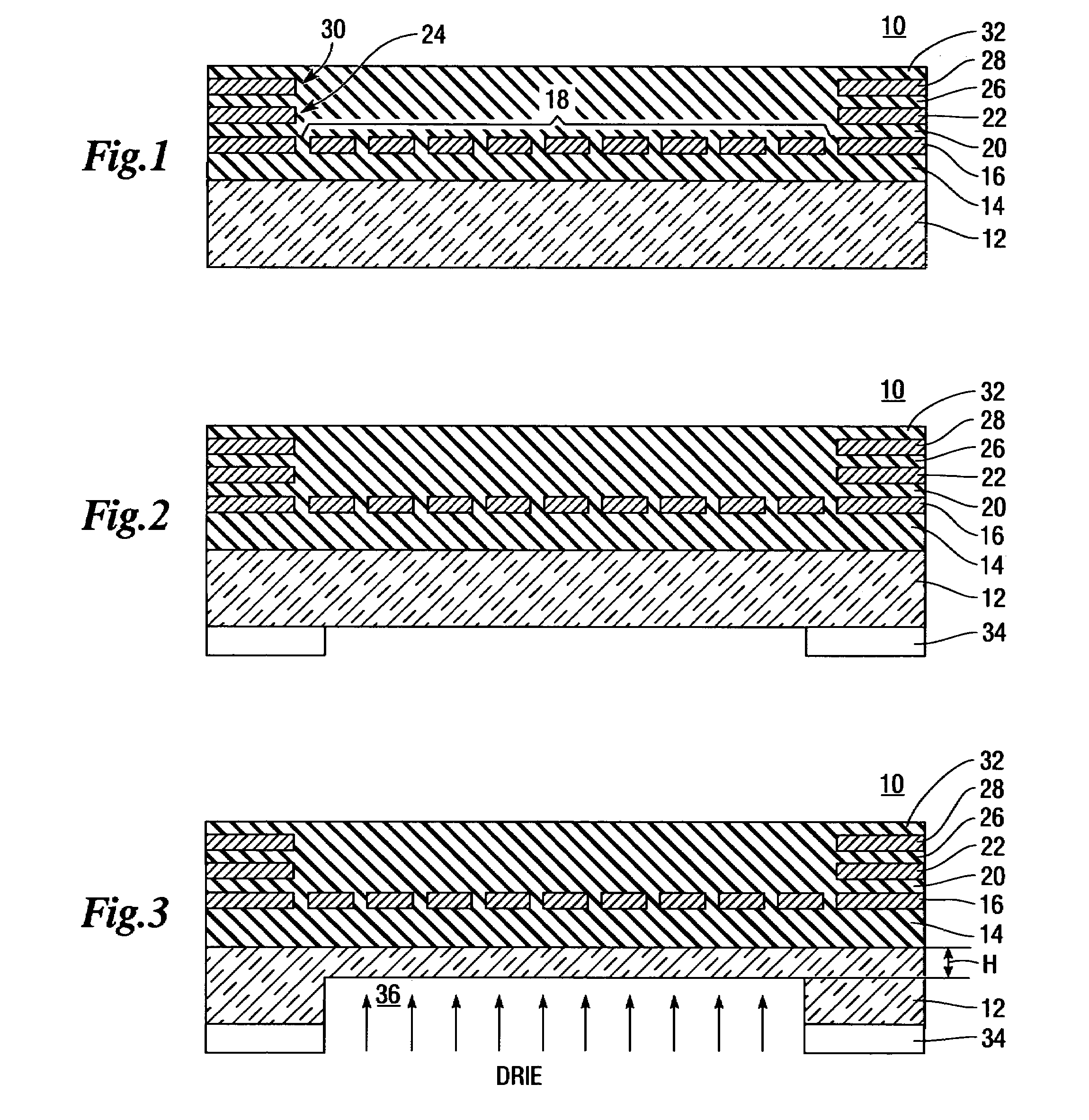
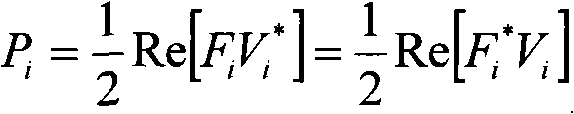Patents
Literature
839 results about "Acoustic cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
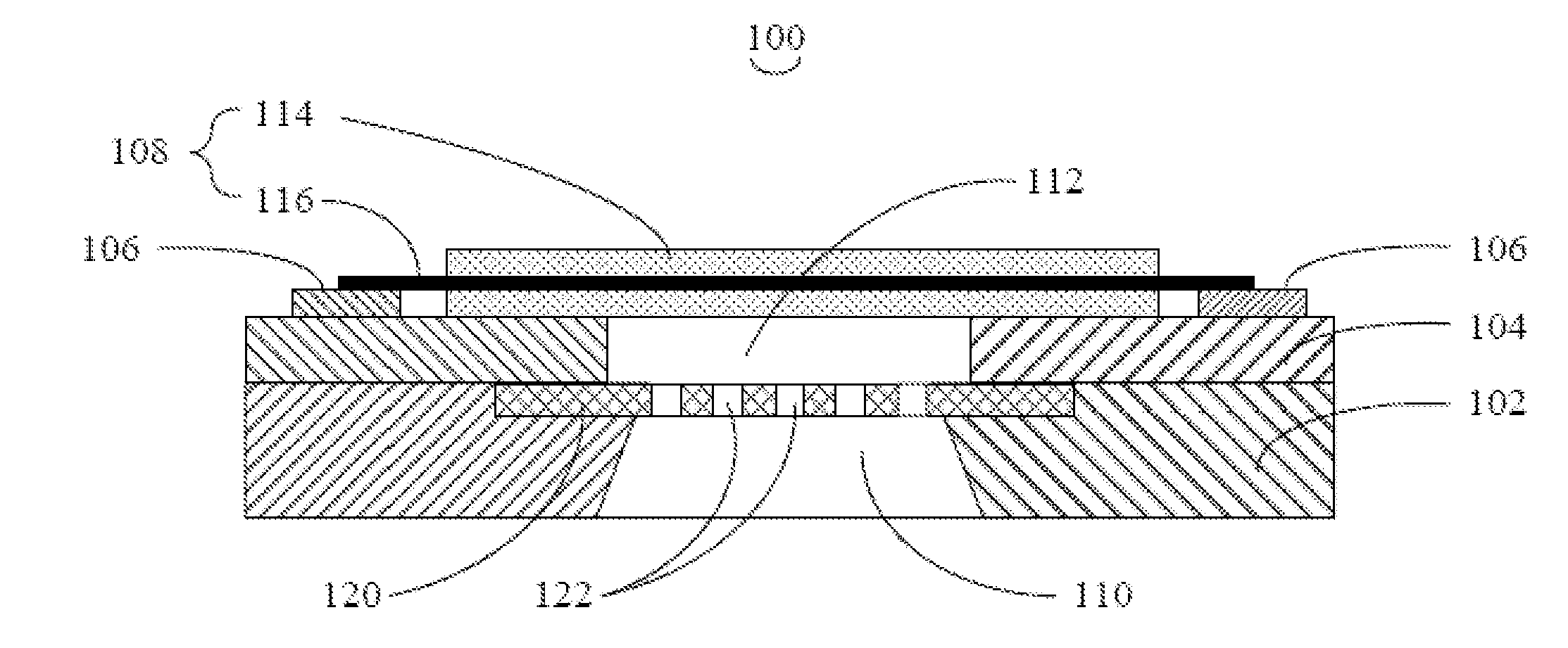
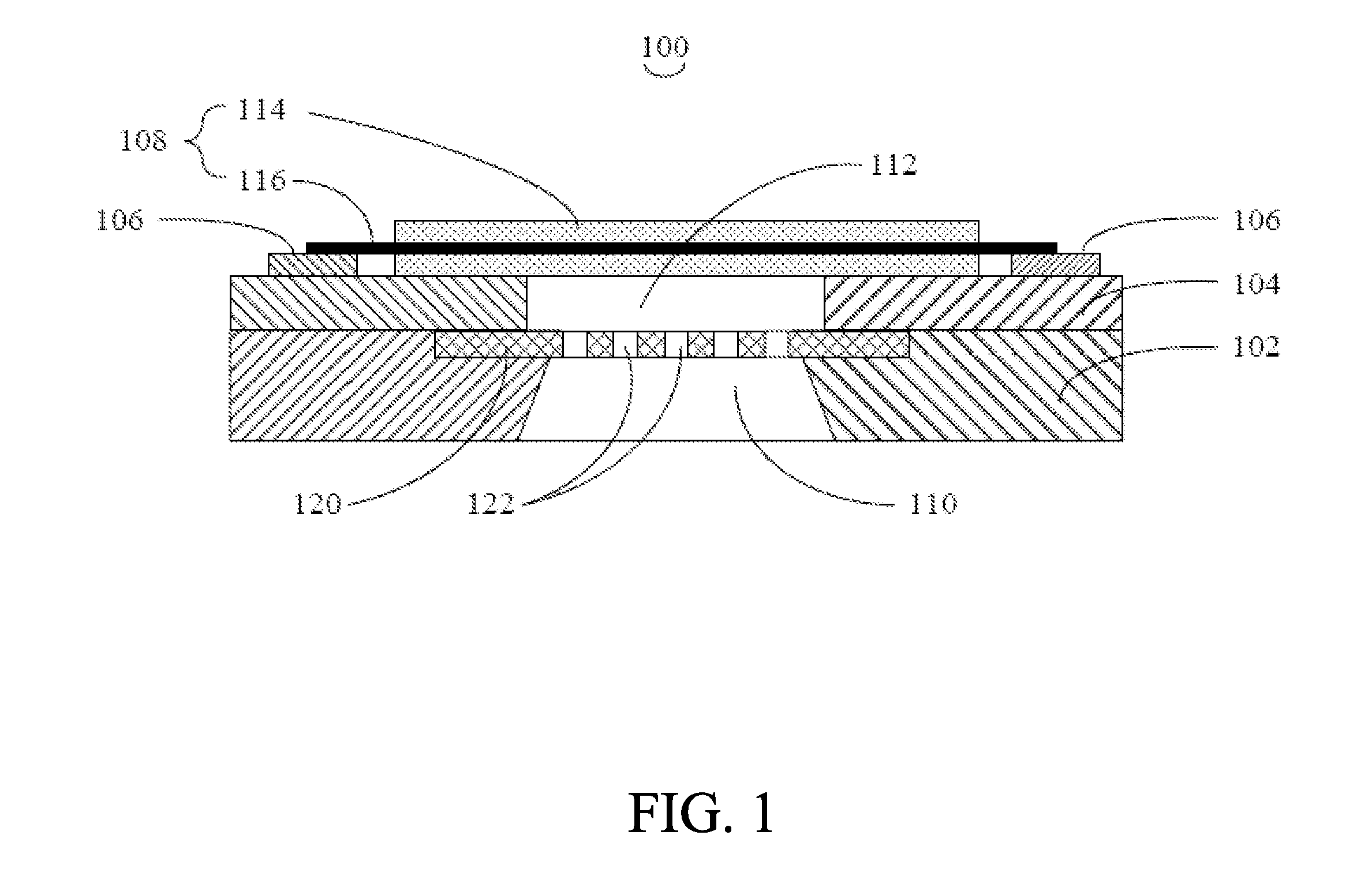
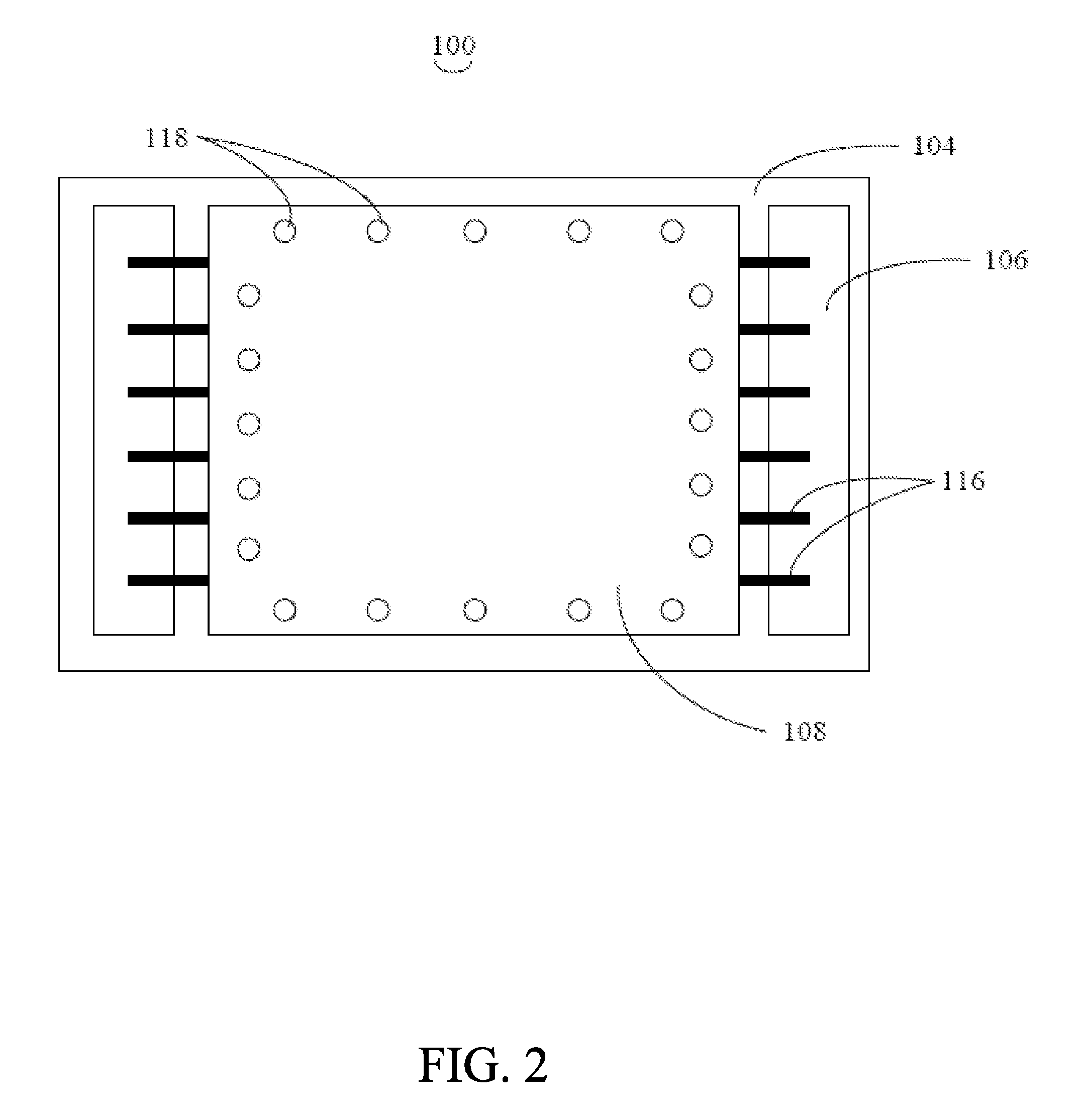
Capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducer and methods of making the same
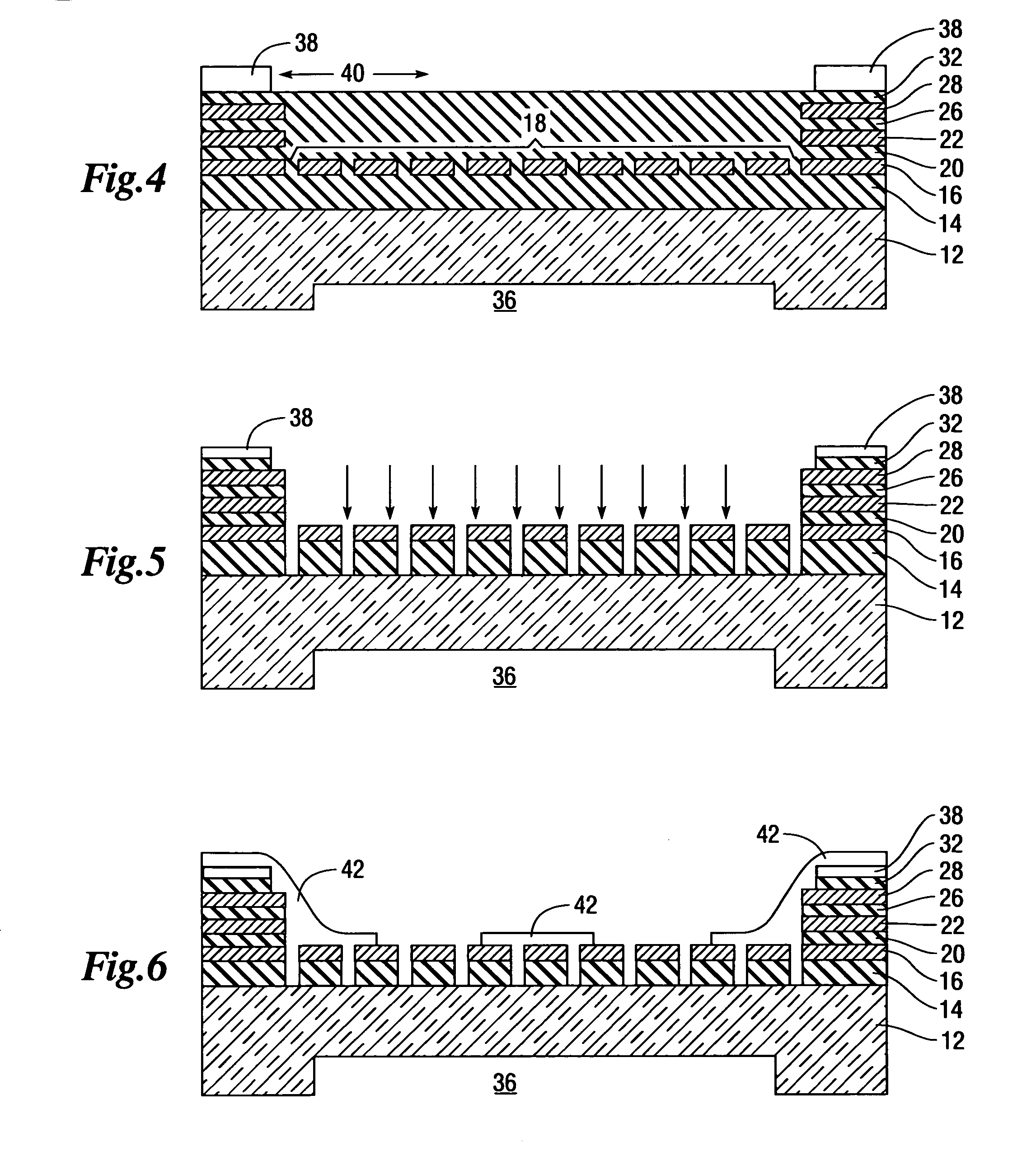
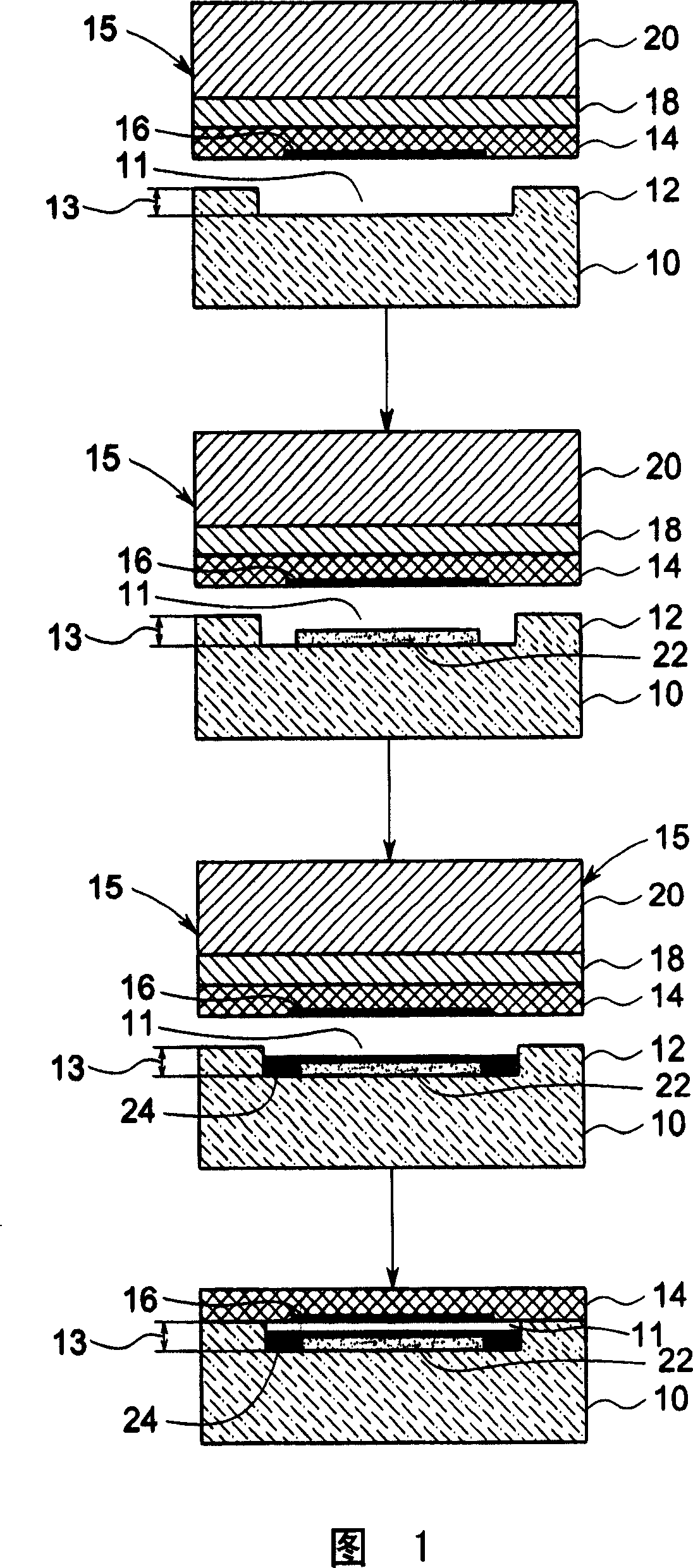
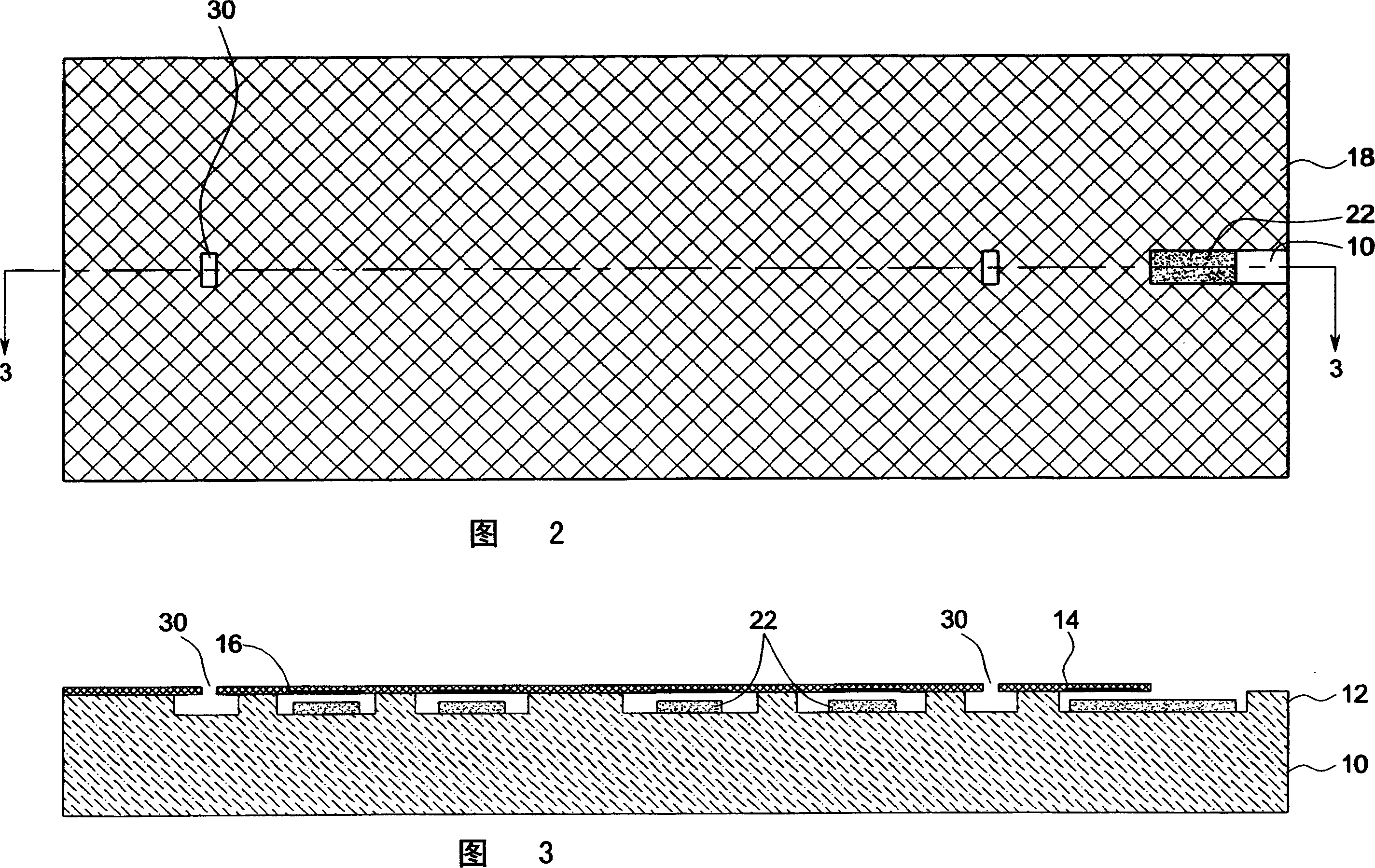
InactiveUS20070180916A1Electrical transducersMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCapacitanceUltrasonic sensor
A method of making a capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducer cell is provided. The method includes providing a carrier substrate, where the carrier substrate comprises glass. The step of providing the glass substrate may include forming vias in the glass substrate. Further, the method includes providing a membrane such that at least one of the carrier substrate, or the membrane comprises support posts, where the support posts are configured to define a cavity depth. The method further includes bonding the membrane to the carrier substrate by using the support posts, where the carrier substrate, the membrane and the support posts define an acoustic cavity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
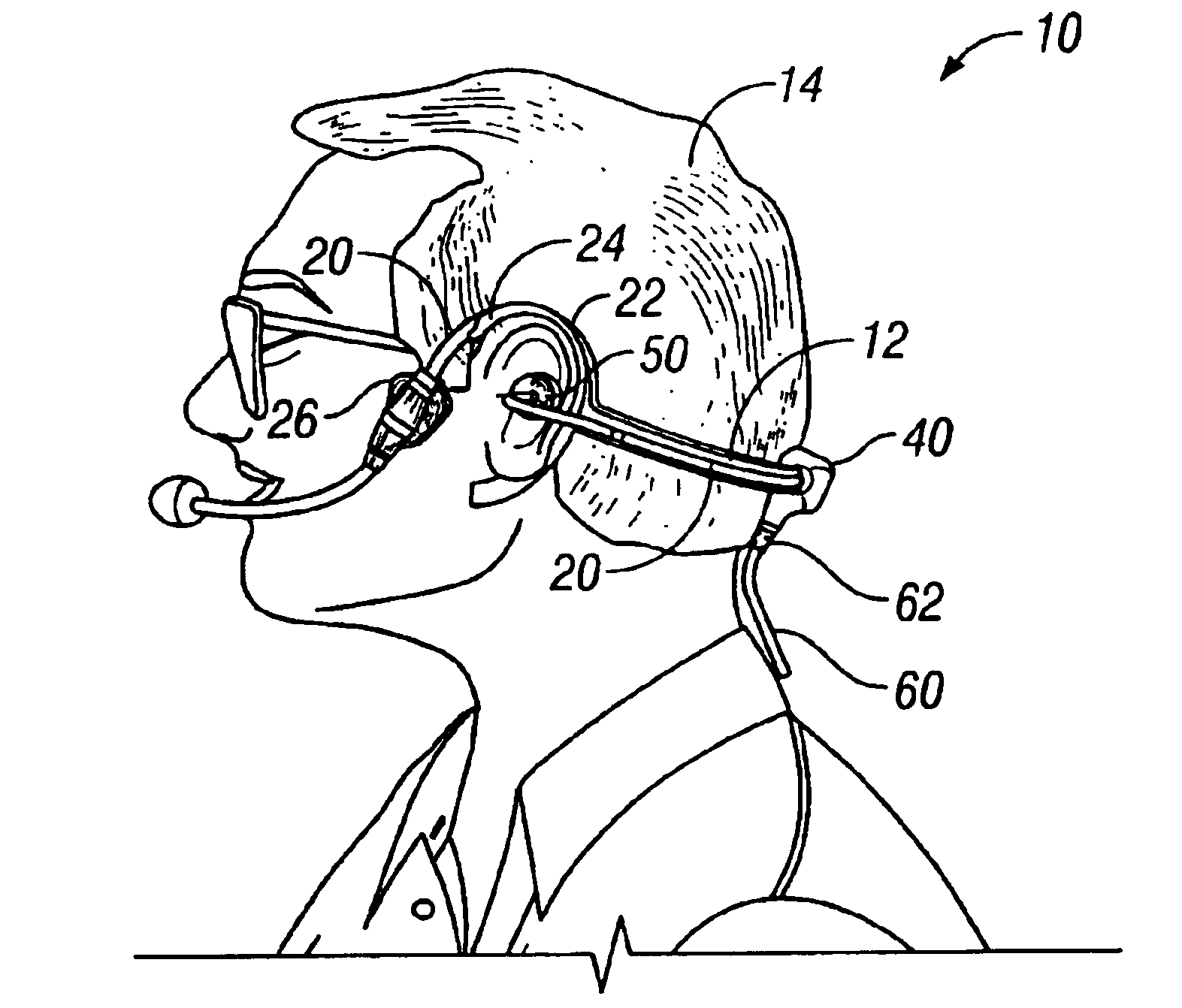
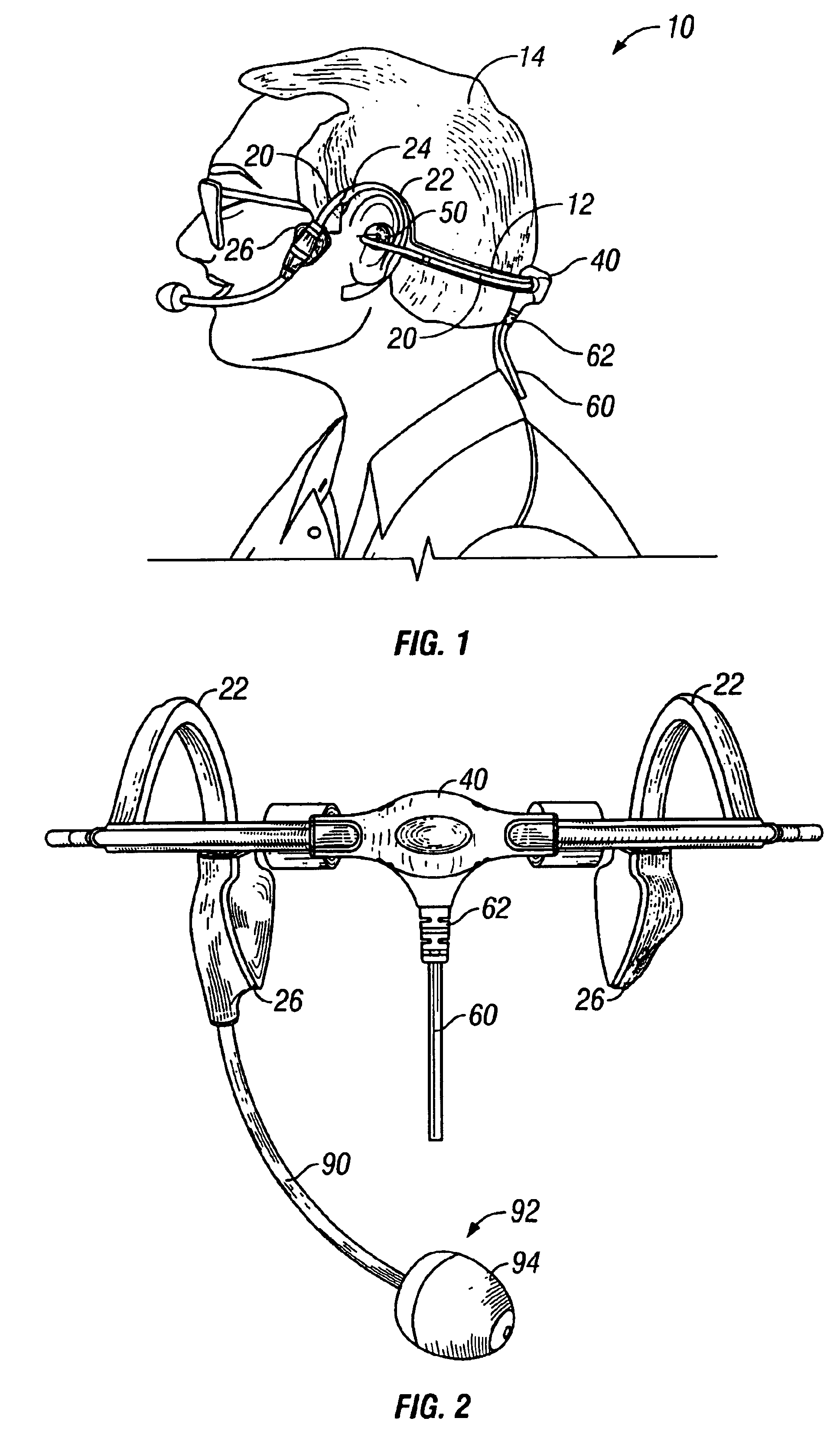
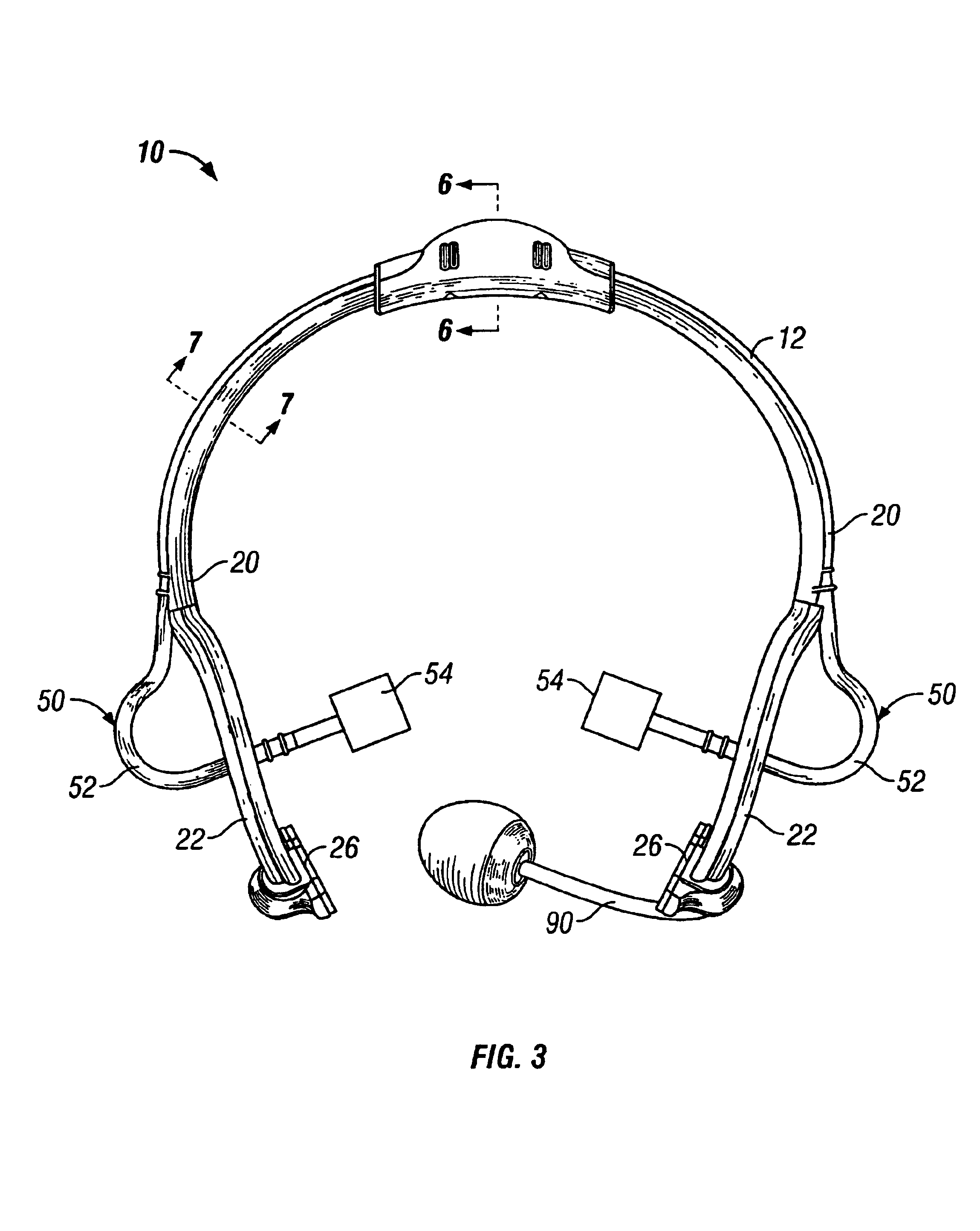
Head-worn, trimodal device to increase transcription accuracy in a voice recognition system and to process unvocalized speech
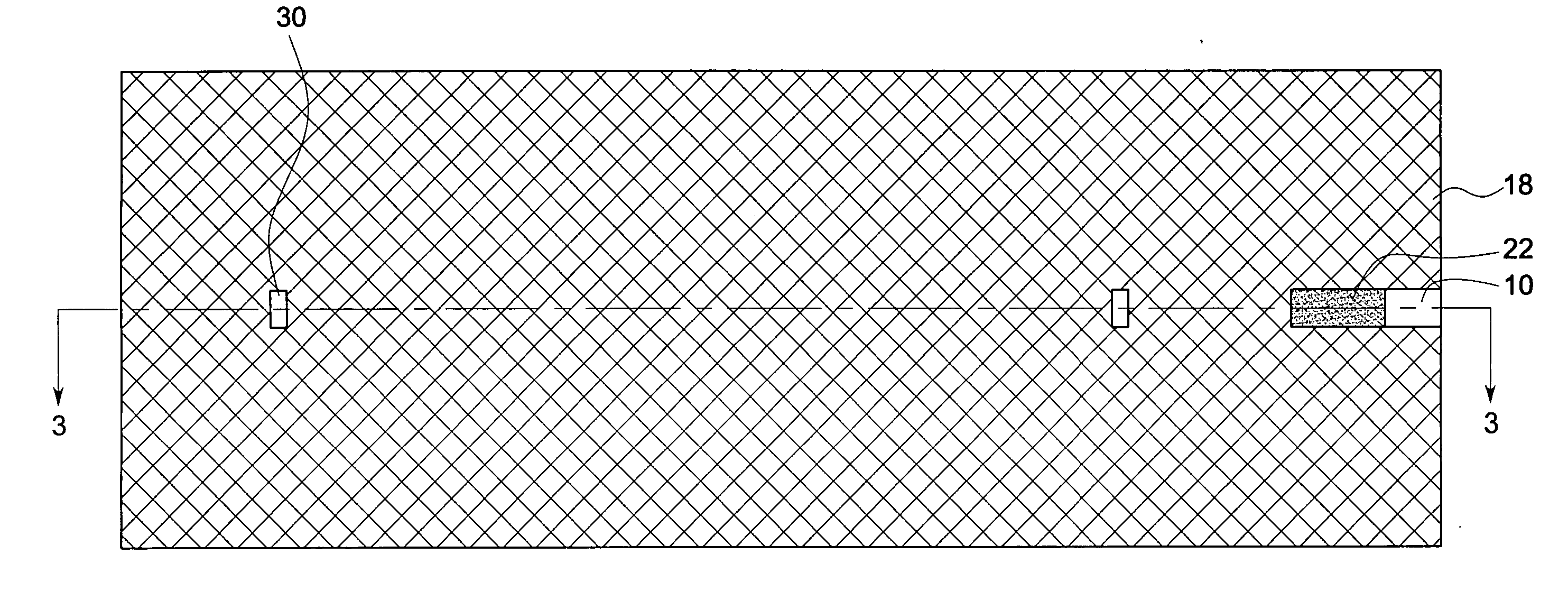
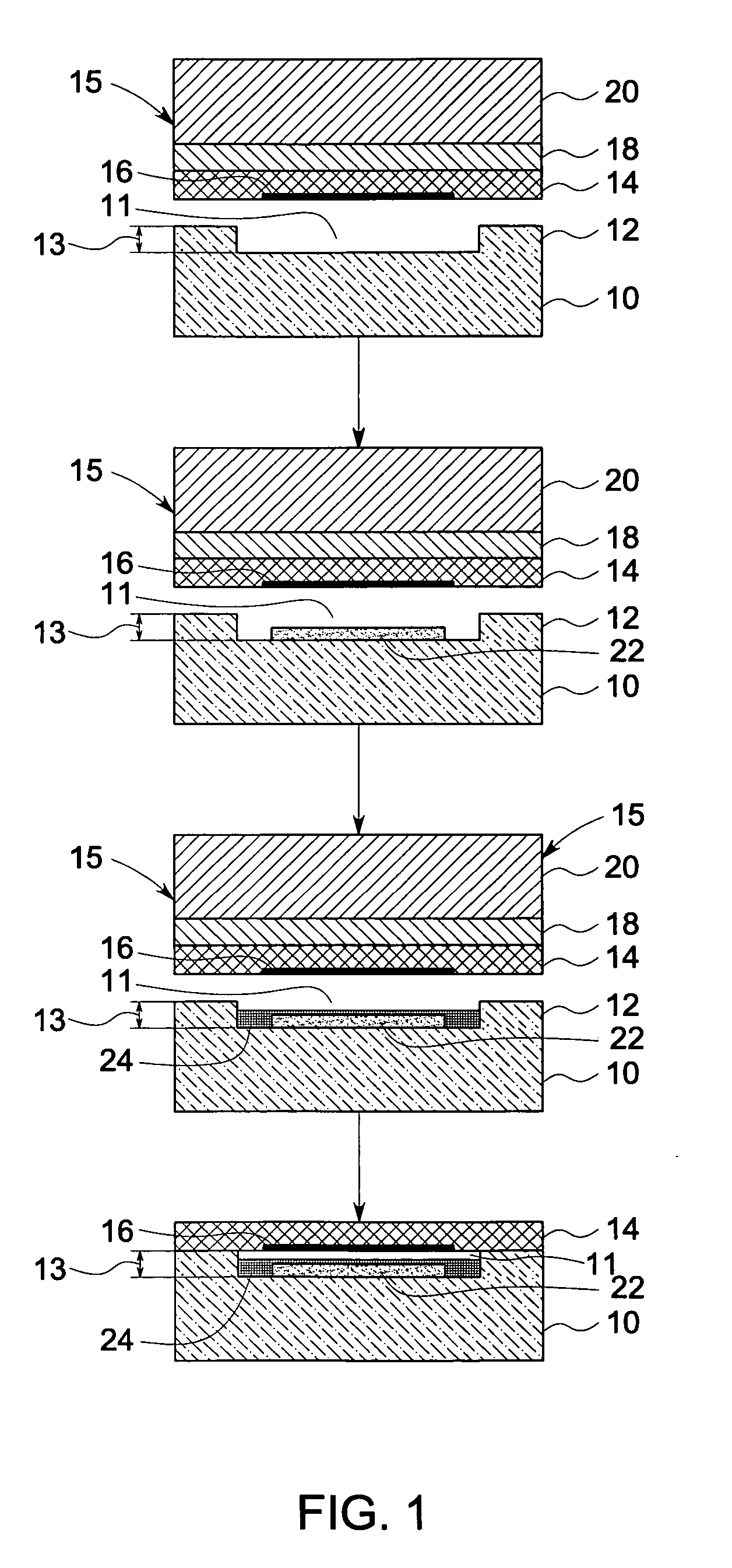
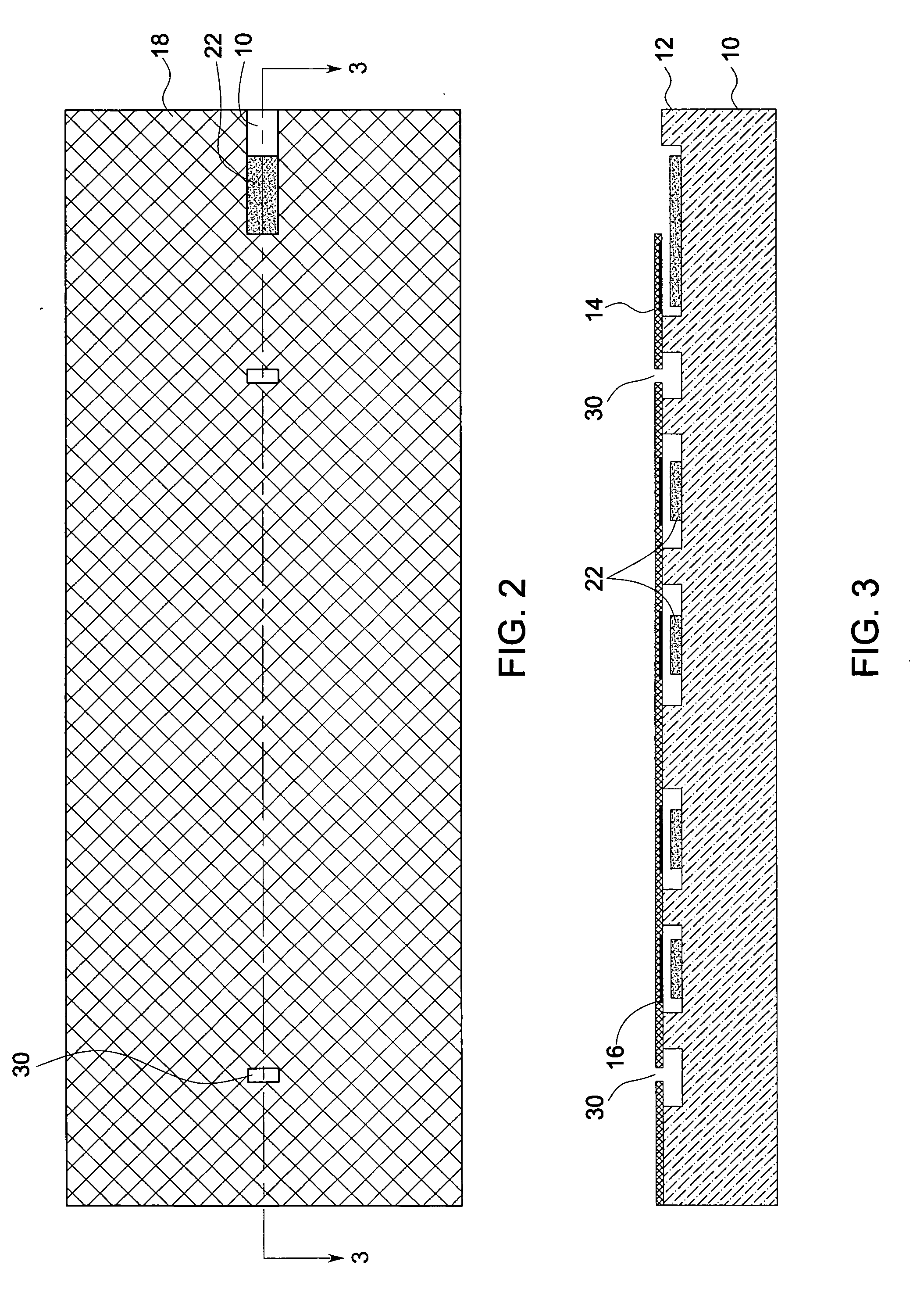
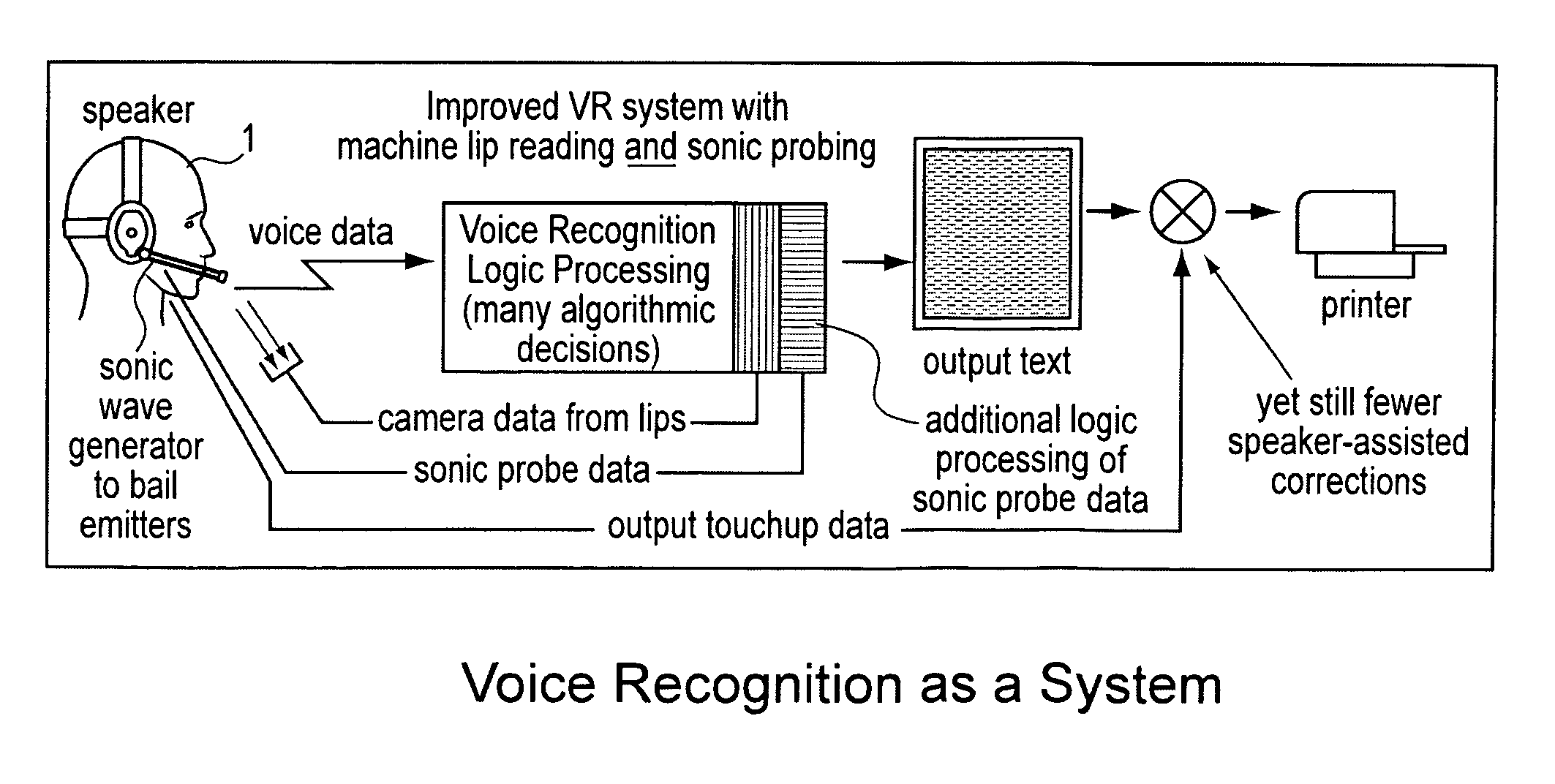
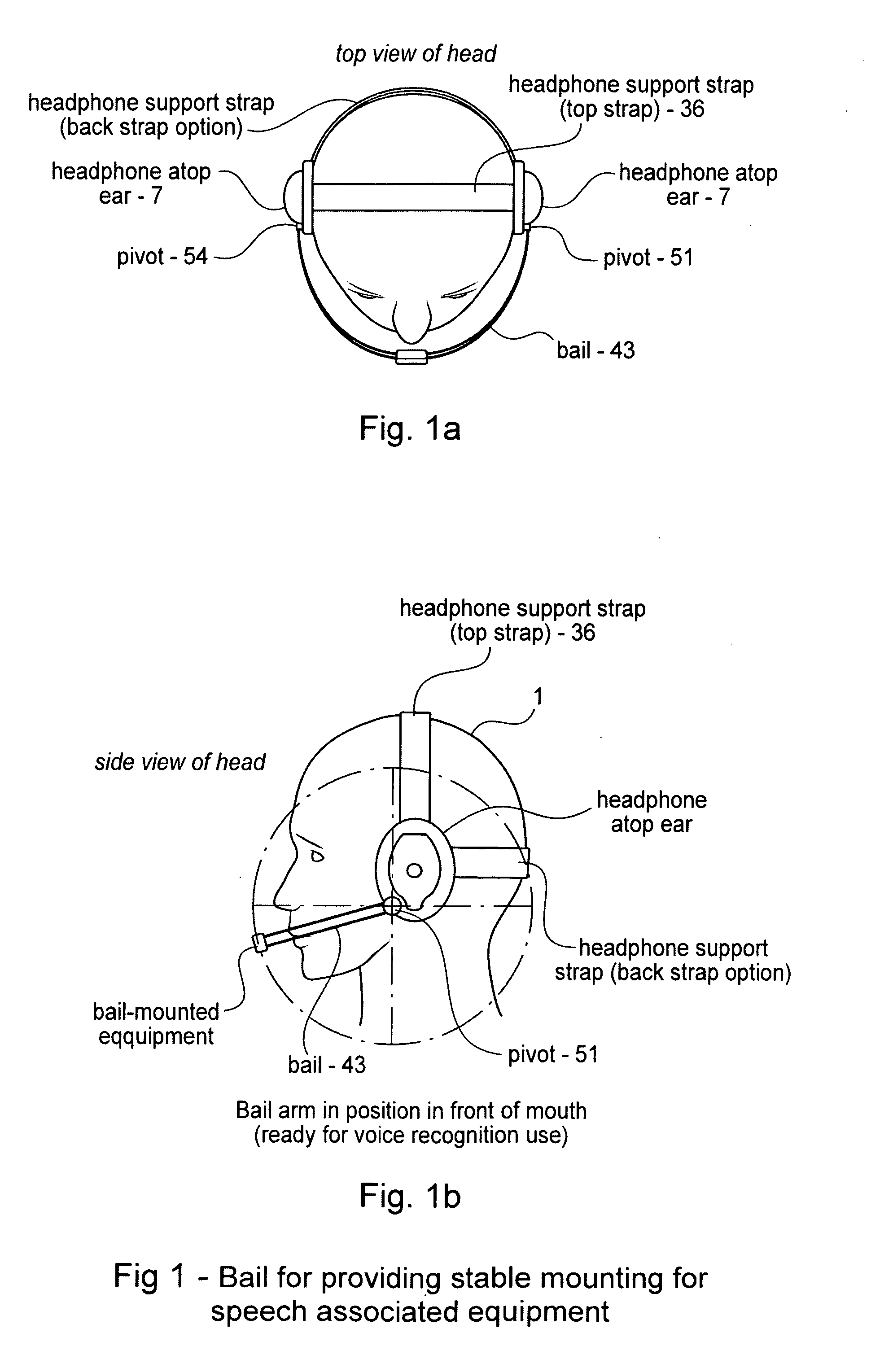
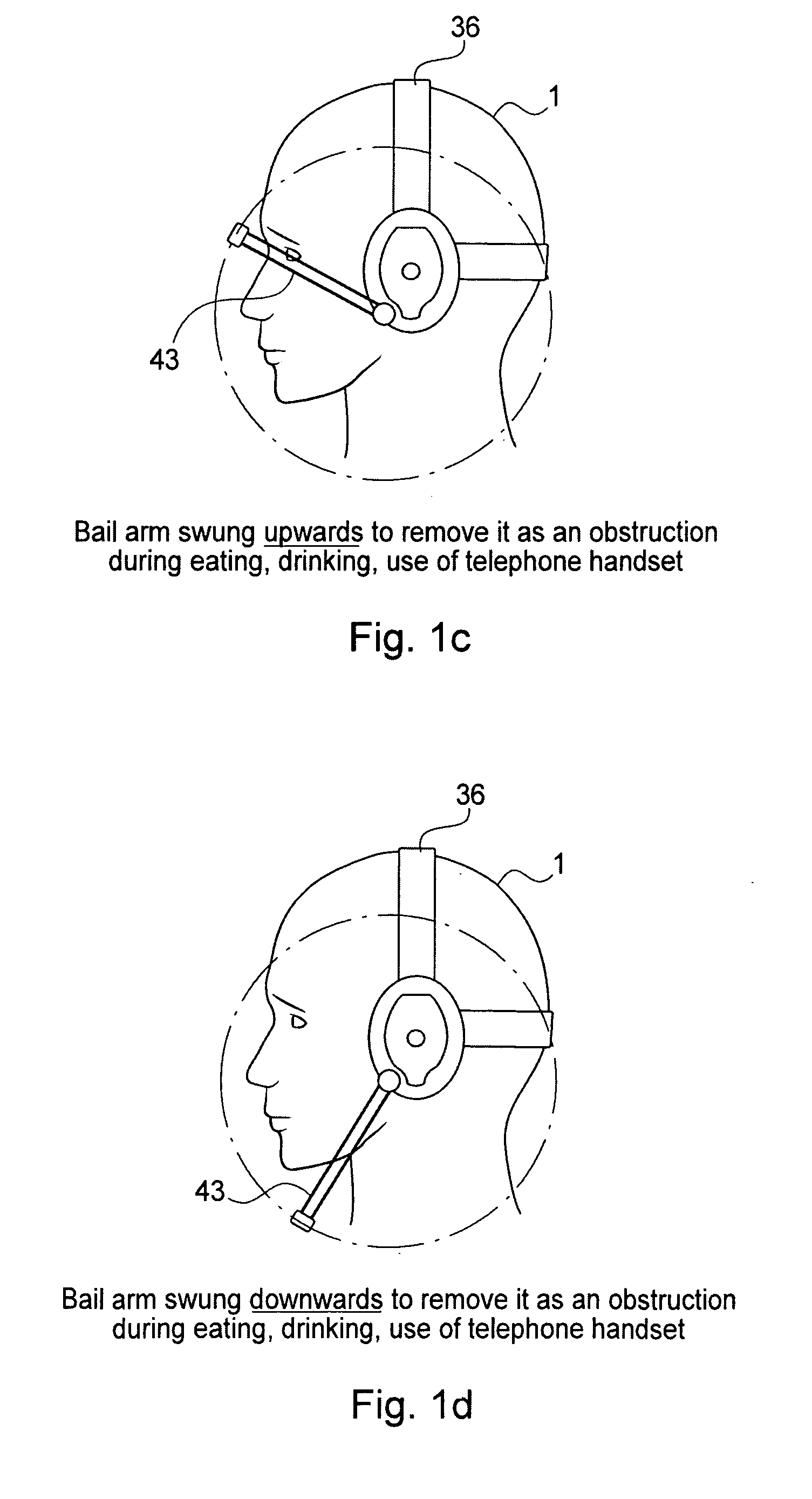
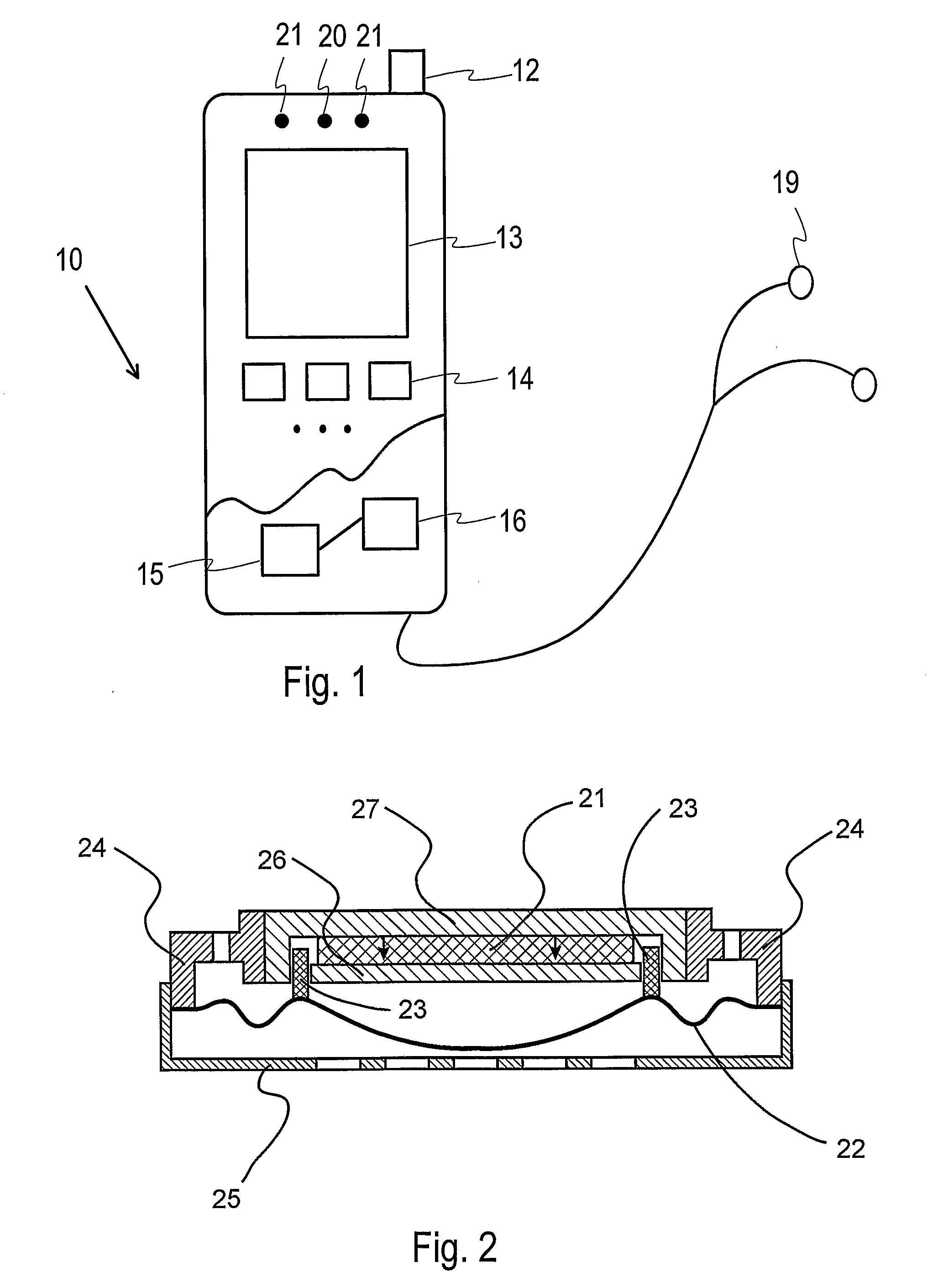
A voice recognition device and method allows position-stabilized capture of spoken sounds with great repeatability and accuracy. The voice recognition device may additionally provide two channels of lip movement information to supplement the usual audible speech component recognition system in selecting the proper pairing of data input to text output. The voice recognition device may provide a further channel of information about the speech generating motions via an ultrasonic injection of sound into the vocal cavity and subsequent decoding of the emitted sound after injection. The ultrasonic injection and decoding may also used to provide audible clues as to the unvoiced sound formed by speaking when the vocal cords are not energized. The ensemble of electronic equipment upon the bail band may be in microcircuit form, including placing the components on a copper layer polyimide flexible strip.
Owner:RAST ASSOCS
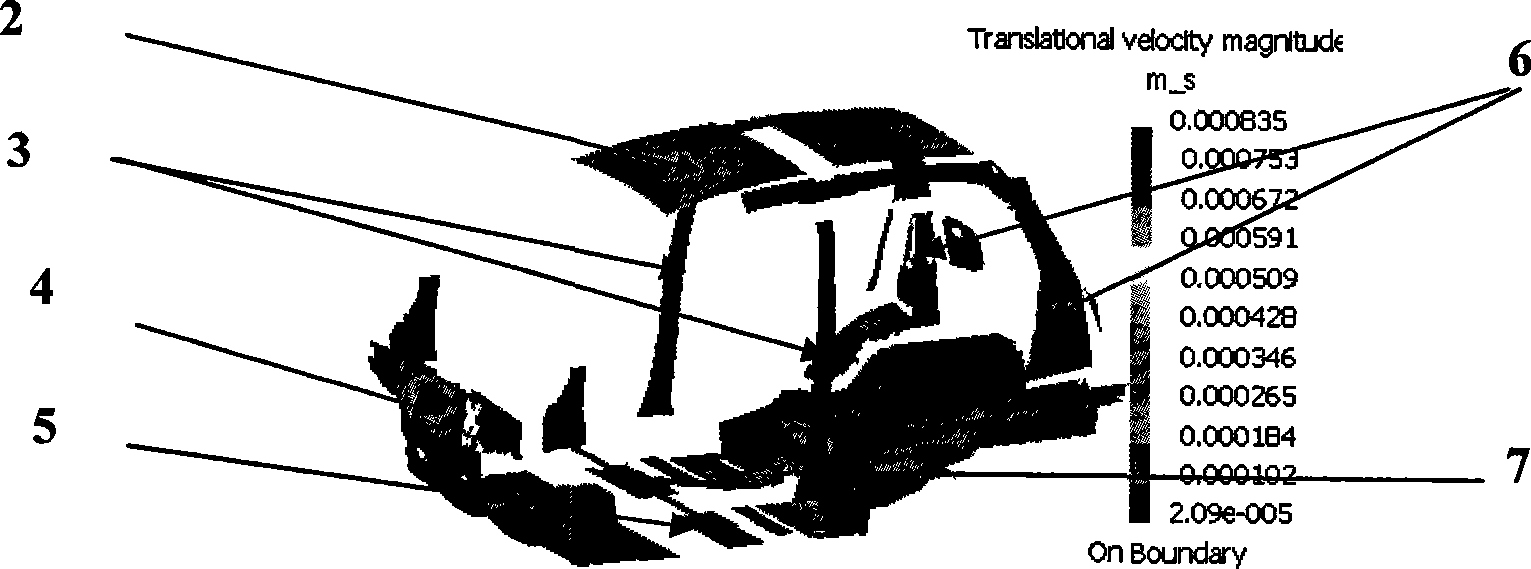
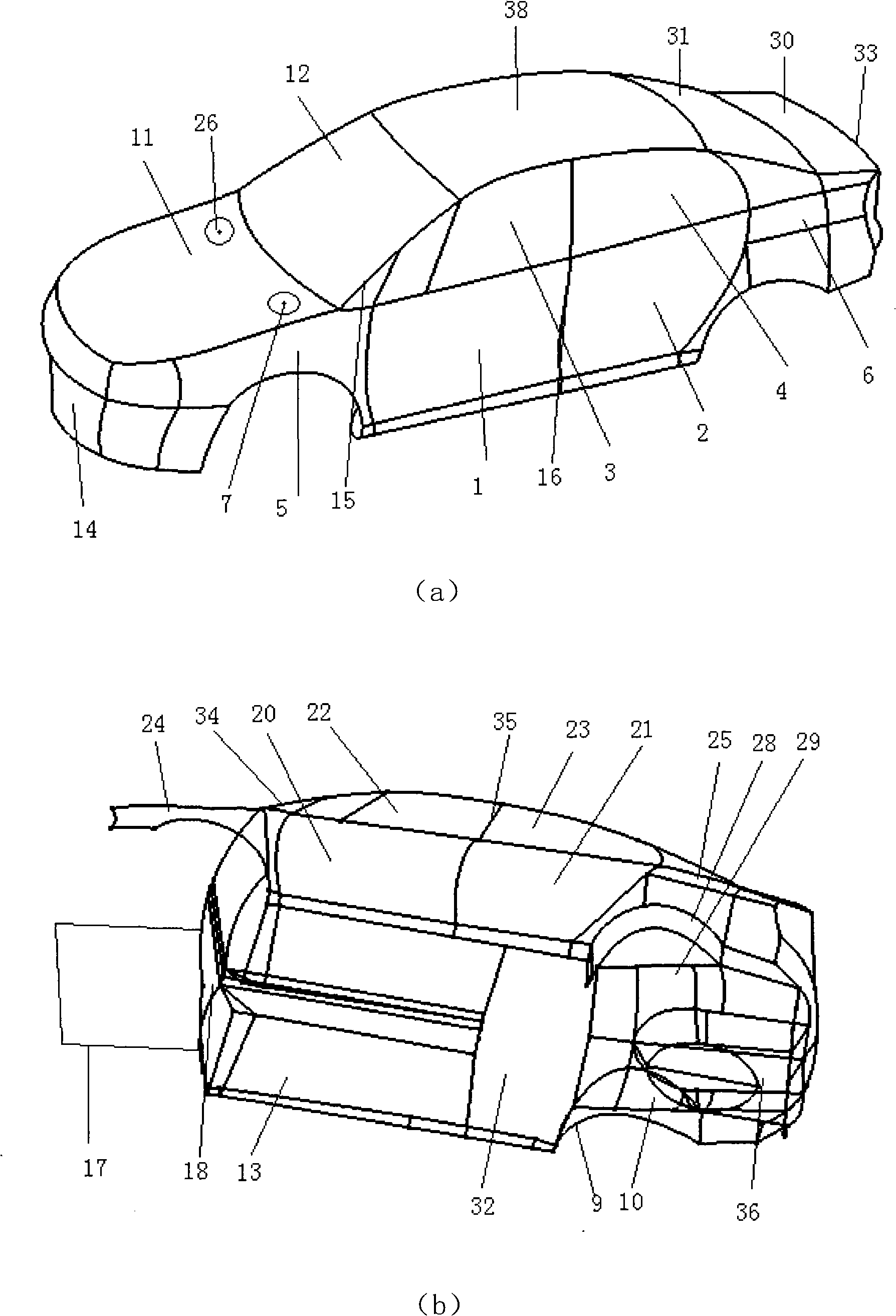
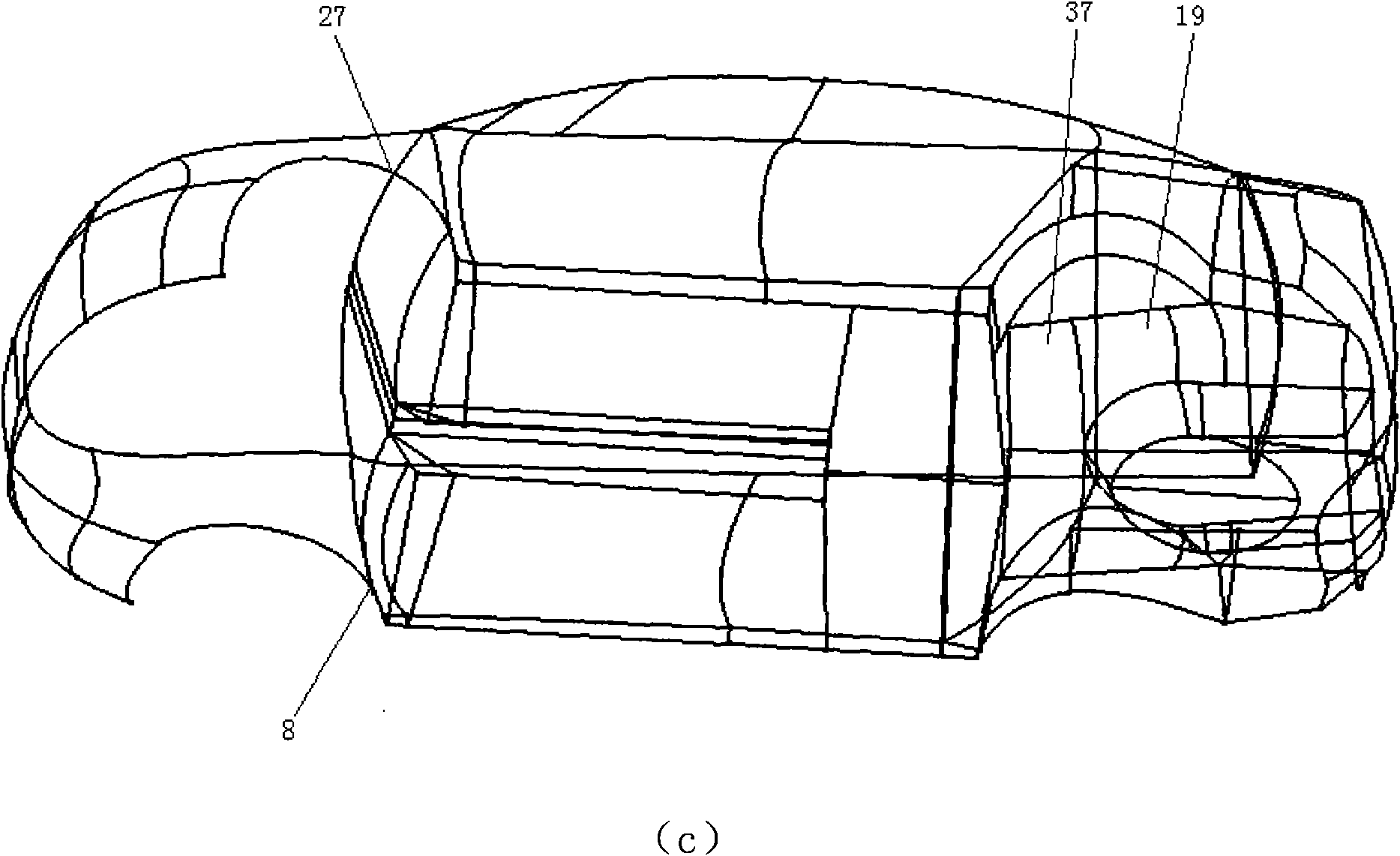
Transmission path detecting system for vehicle system structure vibration and noise
InactiveCN101271022AEasy to operateVehicle testingSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementPower flowAutomobile design
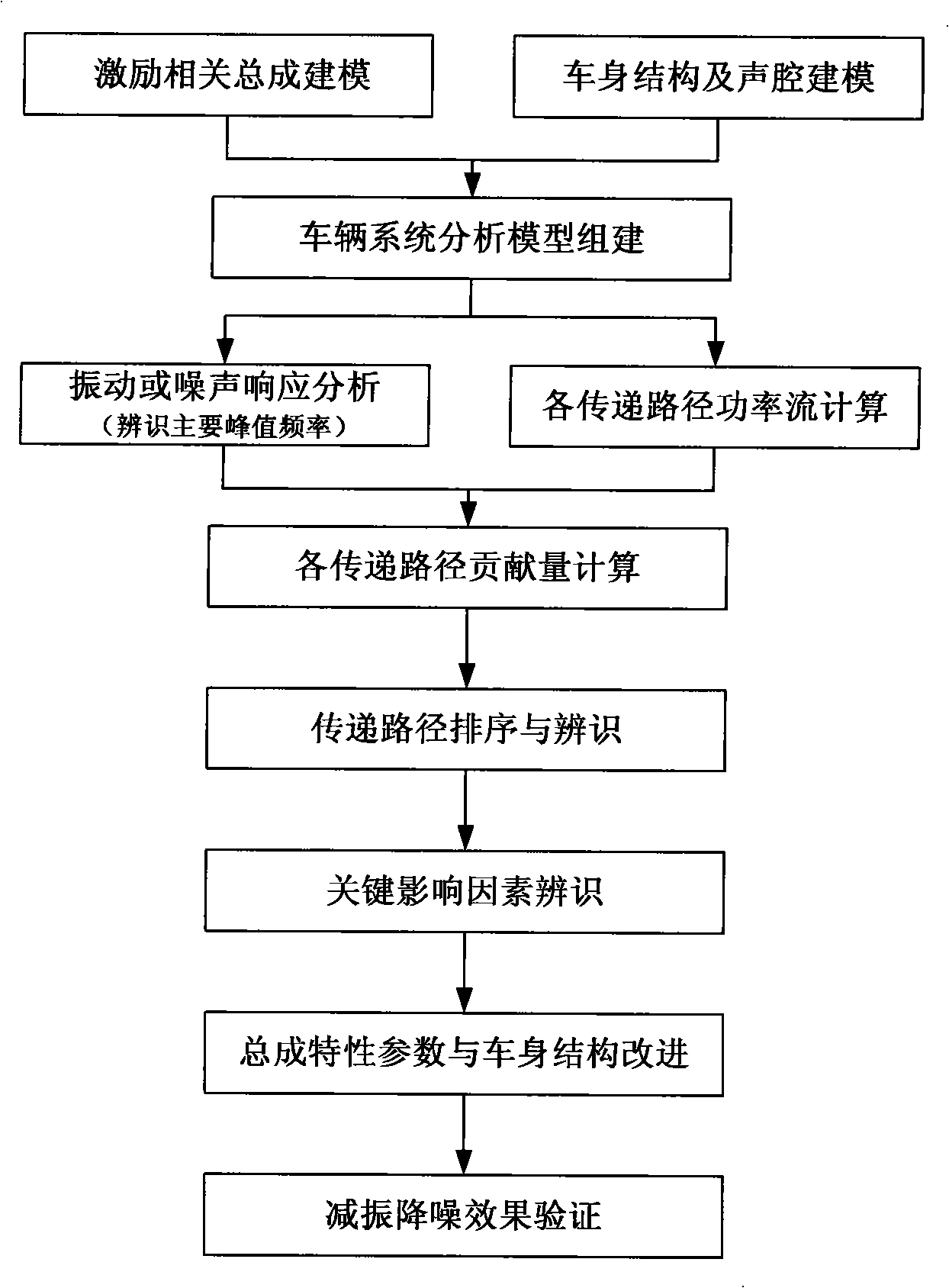
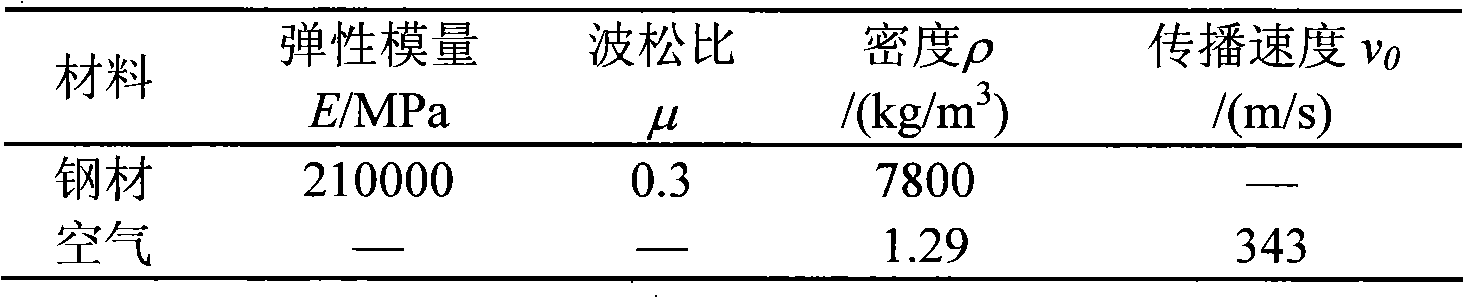
A vehicle system structure vibration and noise transmission path detecting system belongs to the technical field of automobile design. In the invention, a vehicle system analysis model building module builds incentive related bus, vehicle structure and acoustic cavity models and sets up a vehicle system analysis model; a vibration or noise response spectrum acquiring module acquires the vehicle structure vibration or passenger indoor structure noise response analysis; a transfer path power calculating module calculates the transfer power of all transfer paths and the total power transferred to the vehicle; a main transfer path detecting module calculates and orders the contribution of all the transfer paths, and identifies the main transfer paths; an optimized design module identifies the main influential factors for transfer of the power flow of the main transfer paths, applies an optimized design method to improve relevant bus characteristic parameters and structure types, and verifies the parameters in the vehicle system or the vibration absorbing and noise reducing effect after structure improvement. The vehicle system structure vibration and noise transmission path detecting system can improve the accuracy of transfer path identification and possibility of effective control to the transfer paths.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
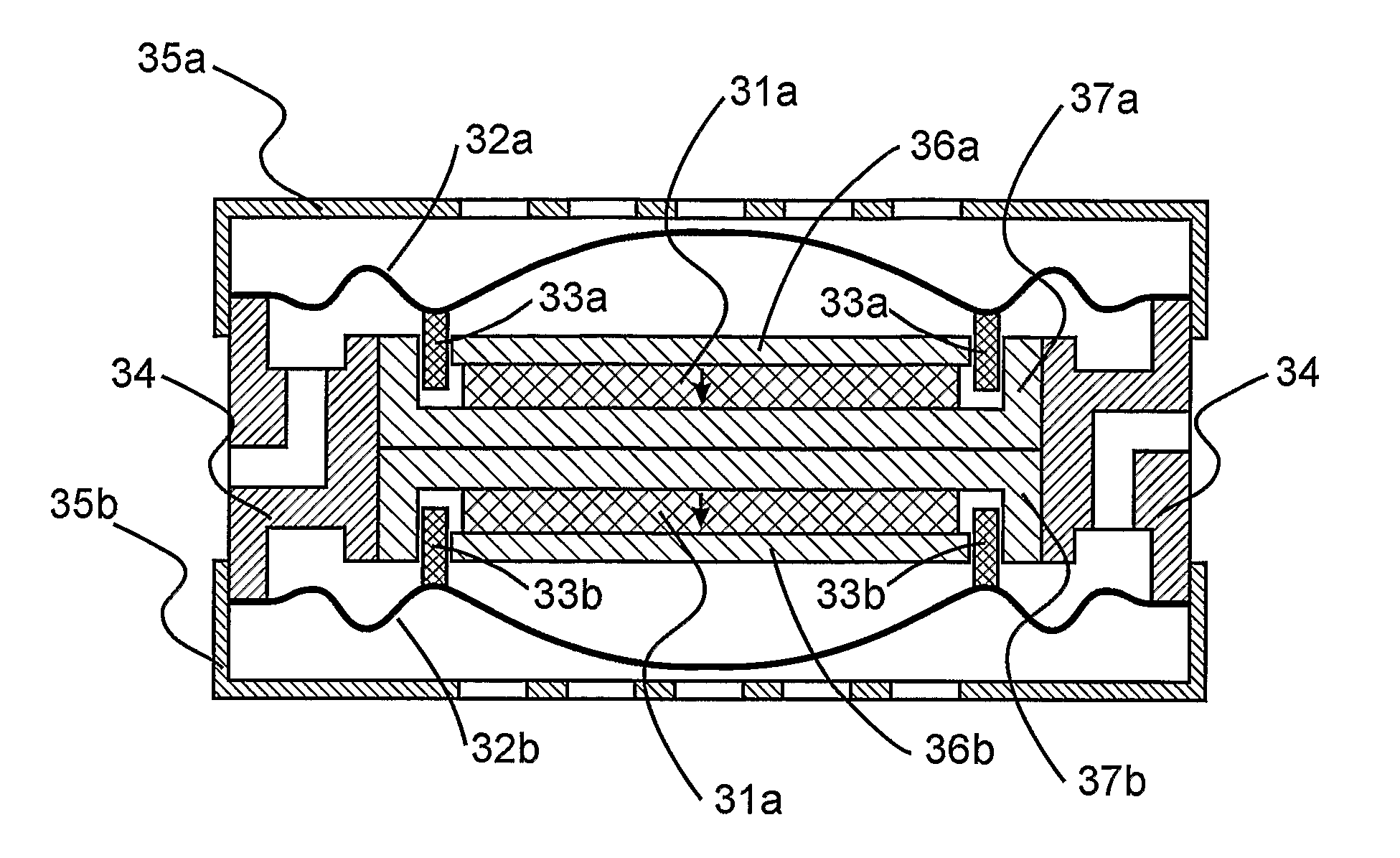
Surface micro-machined acoustic transducers
InactiveUS6249075B1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic cavity
A micro-machined transducer having a structure in which an acoustic enclosure is formed on a substrate above the plane of the substrate surface is disclosed. Forming the acoustic enclosure on the substrate above the plane of the substrate surface, rather than an acoustic cavity in a surface of the substrate, provides an acoustic cavity whose size is not limited by the thickness of the substrate.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
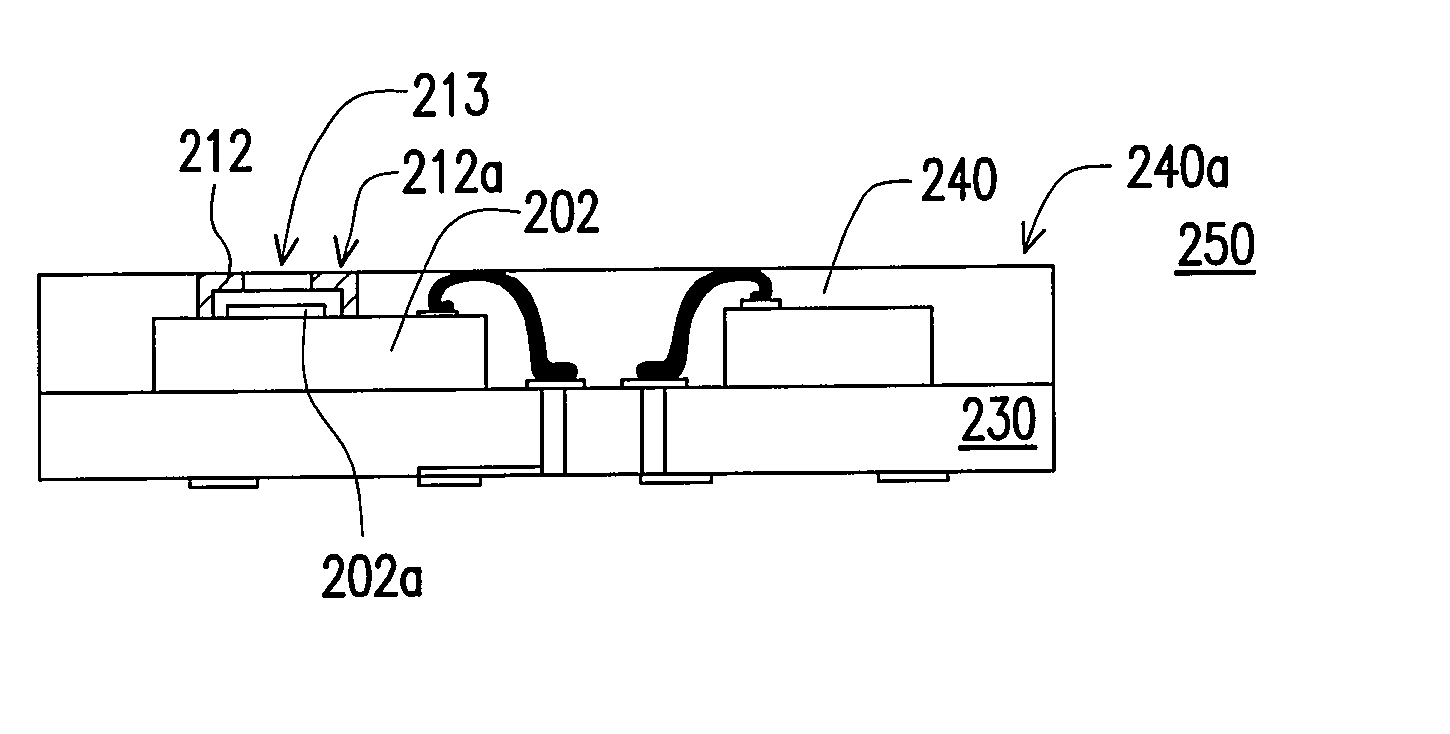
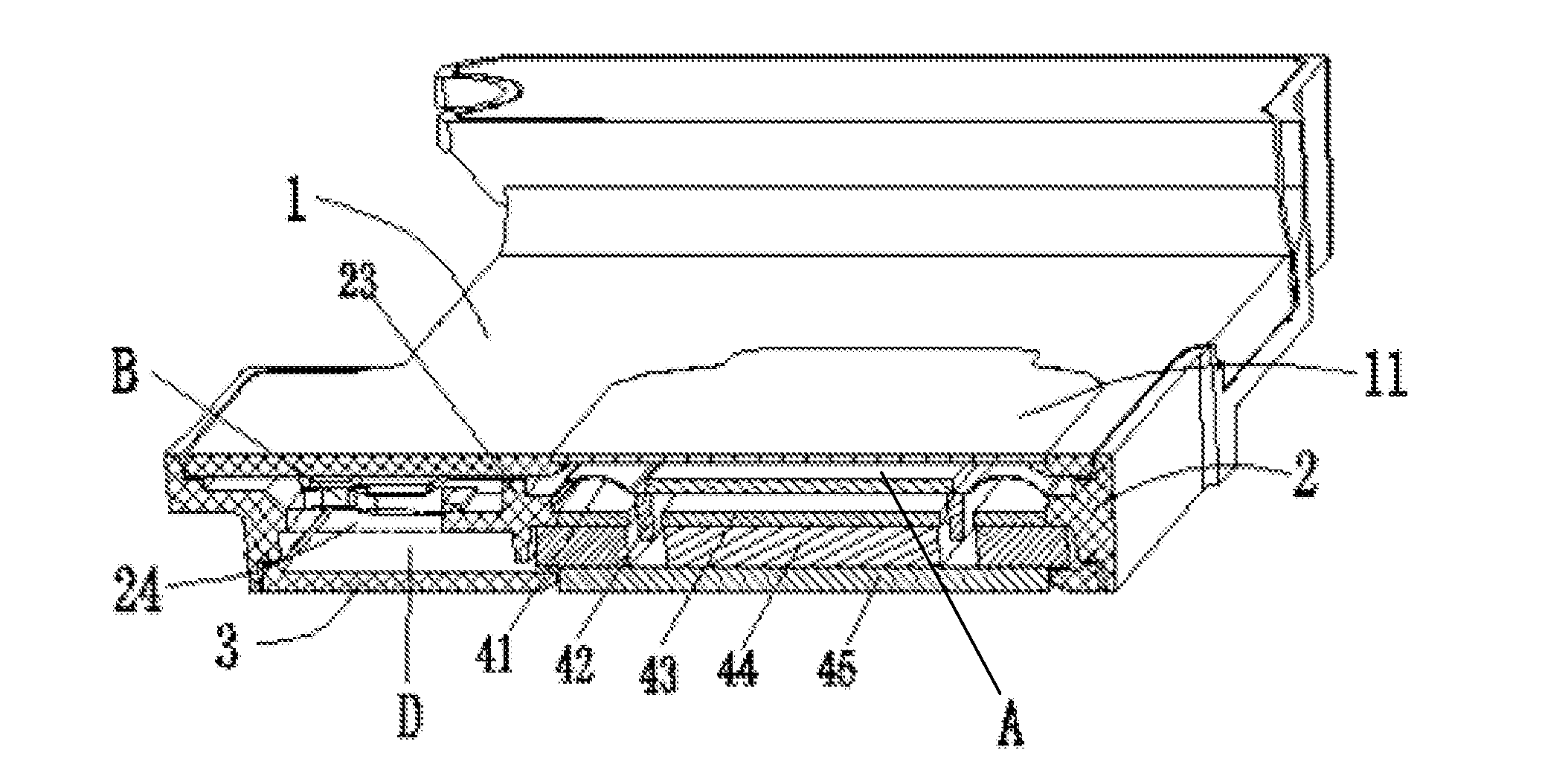
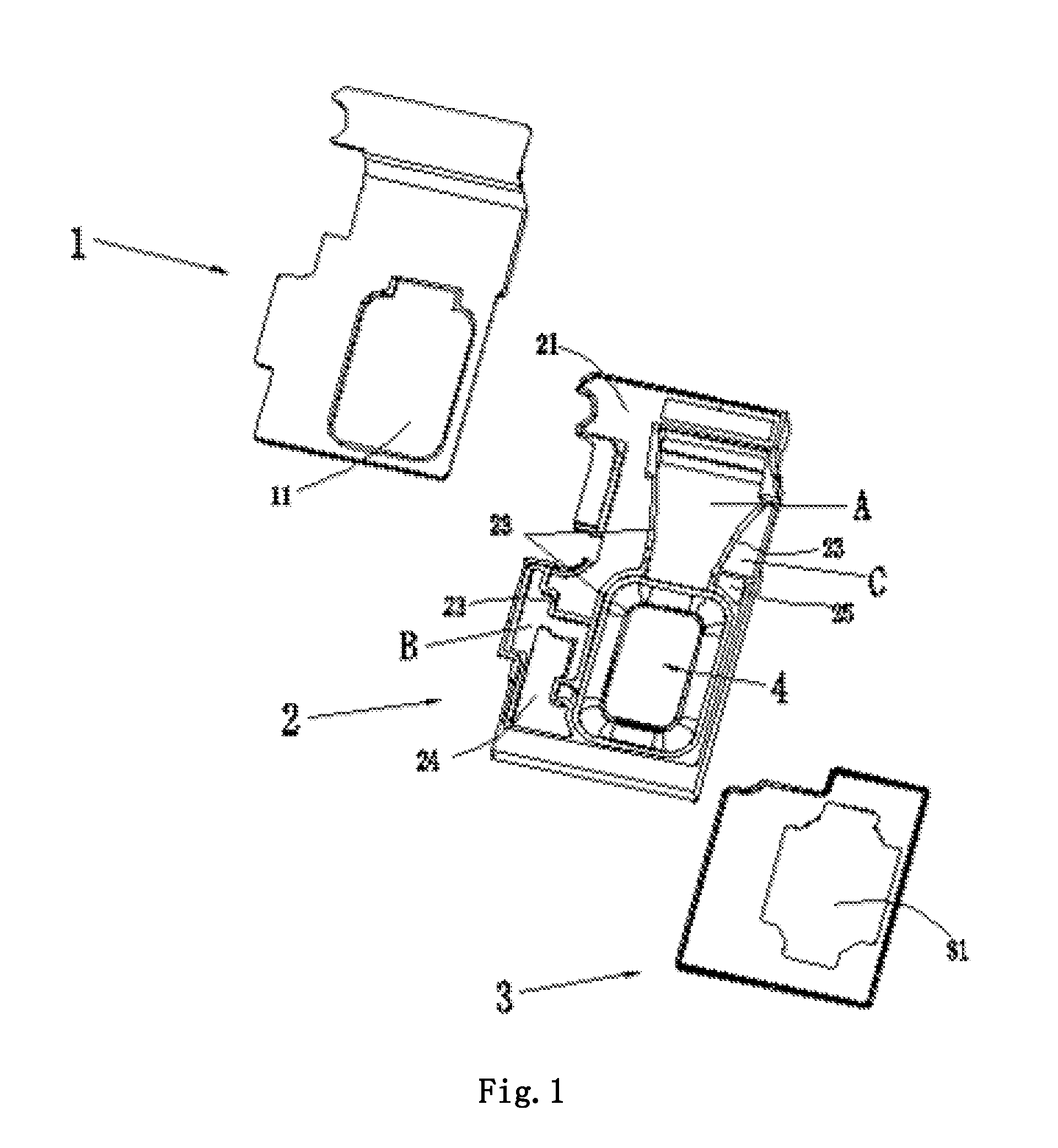
Package structure and packaging method of MEMS microphone
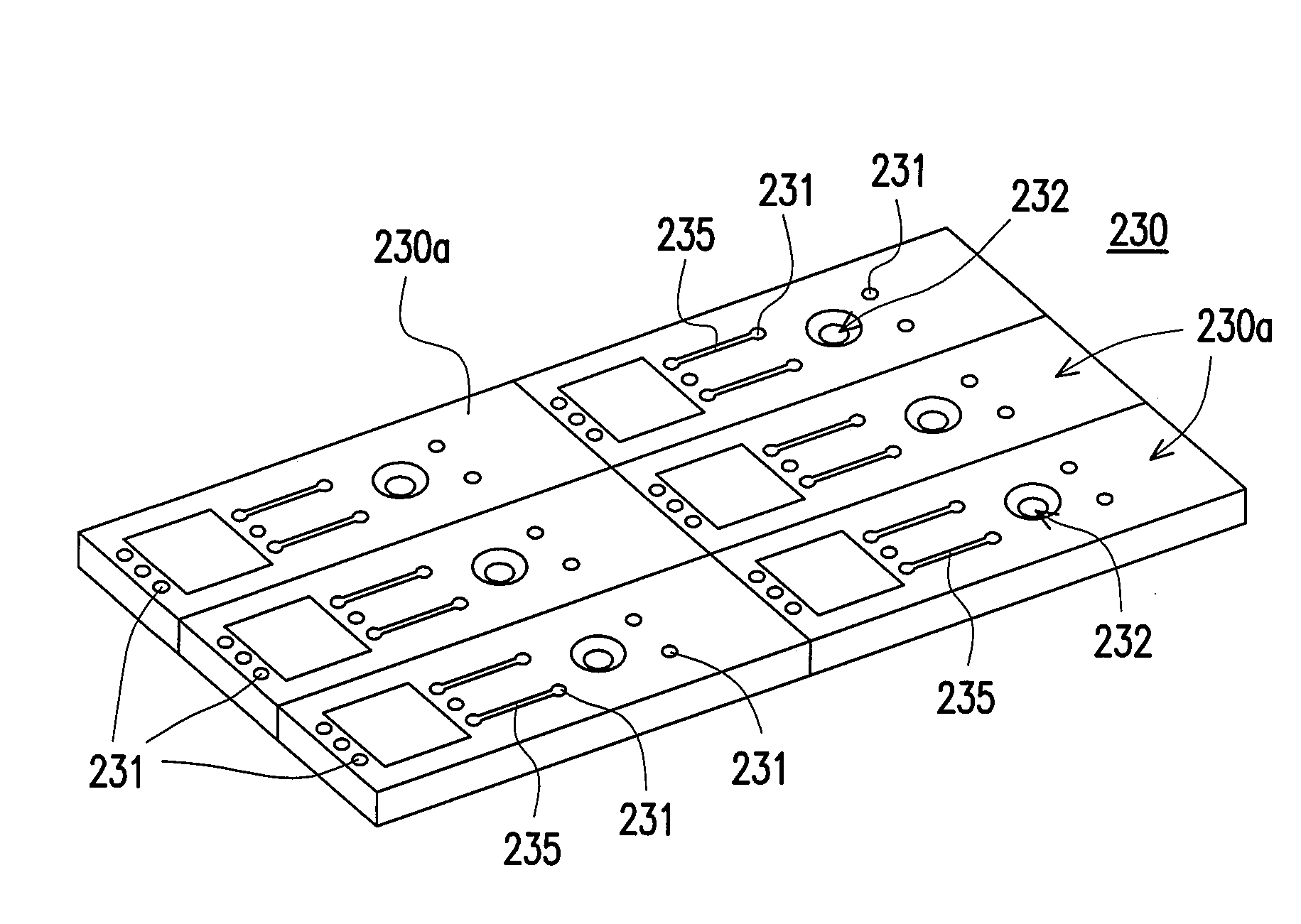
ActiveUS20080083960A1Improve throughputPrevent steppingPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor electrostatic transducersEngineeringMems microphone
A package structure of a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) type microphone is disclosed. The MEMS microphone comprises a substrate, a MEMS chip, an acoustic wave cover, and an encapsulant. The substrate has connection pads. The MEMS chip is electrically coupled to the connection pads. The MEMS chip includes an acoustic wave sensing portion. The acoustic wave cover is fixed on the MEMS chip for covering without contacting the acoustic wave sensing portion and defining an acoustic wave cavity space. The acoustic wave cover has an opening for allowing an acoustic wave to enter or exit out of the acoustic cavity space. The encapsulant encapsulates the substrate, the MEMS chip, and the acoustic wave cover, wherein a surface of the acoustic wave cover is exposed. The exposed surface of the acoustic wave cover is along the same level as the surface of the encapsulant.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Lightweight headset for high noise environments
A lightweight communications headset includes a headband adapted to be worn on user's head. A speaker housing is carried by the headband and defines an acoustic chamber. A speaker mounted within projects sound waves into the acoustic chamber. The headband carries a pair of earpieces which are positionable adjacent to the user's ears for delivering sound thereto. The acoustic chamber is coupled to earpieces through acoustic passages which transmit sound waves produced in the acoustic chamber to the earpieces. The earpieces preferably include removable in-ear inserts, which may be constructed for insertion into the auditory canals of the user's ears. Since the in-ear inserts are removable, the headset can readily be configured for a variety of applications.
Owner:OTTO ENG
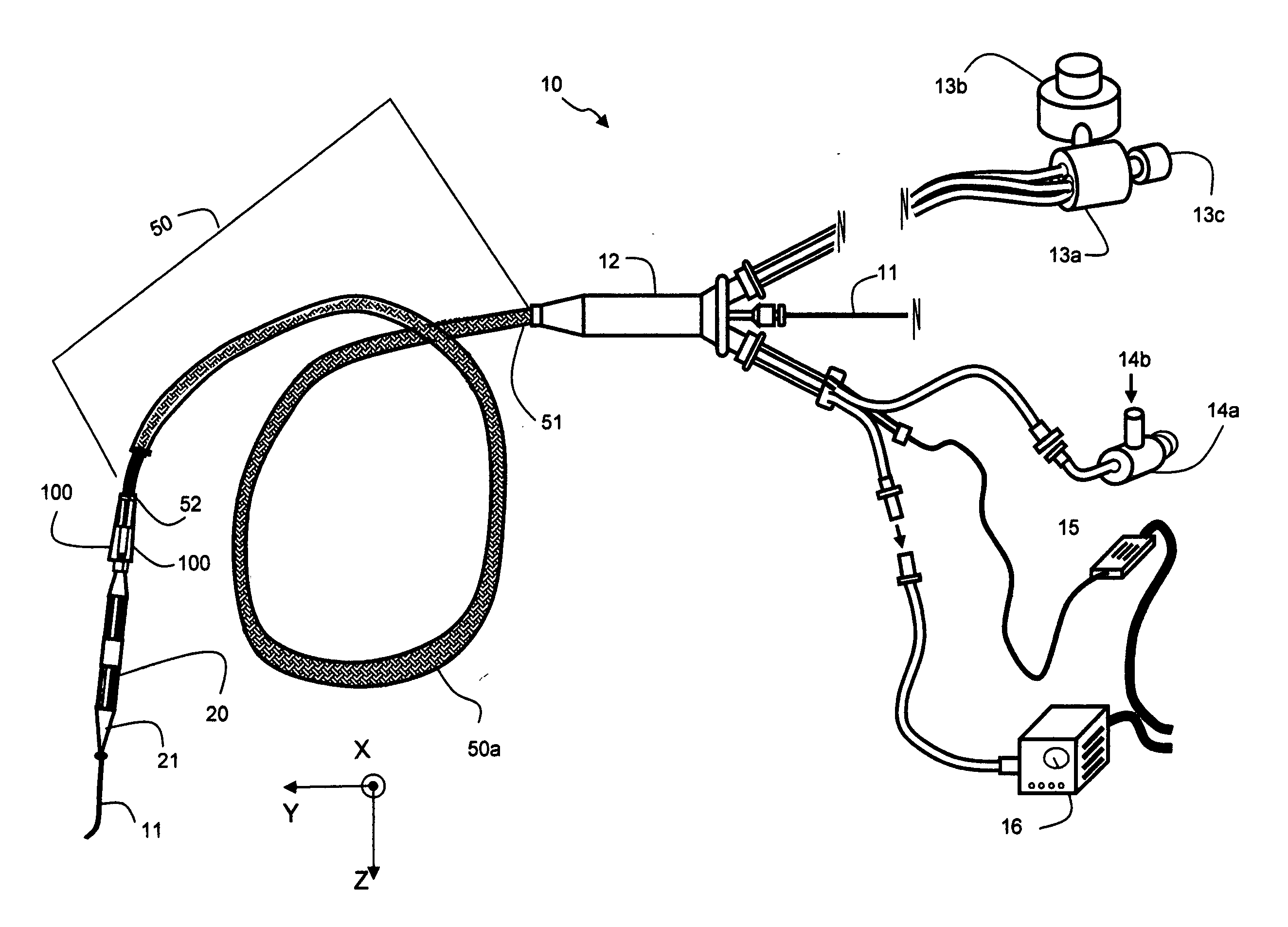
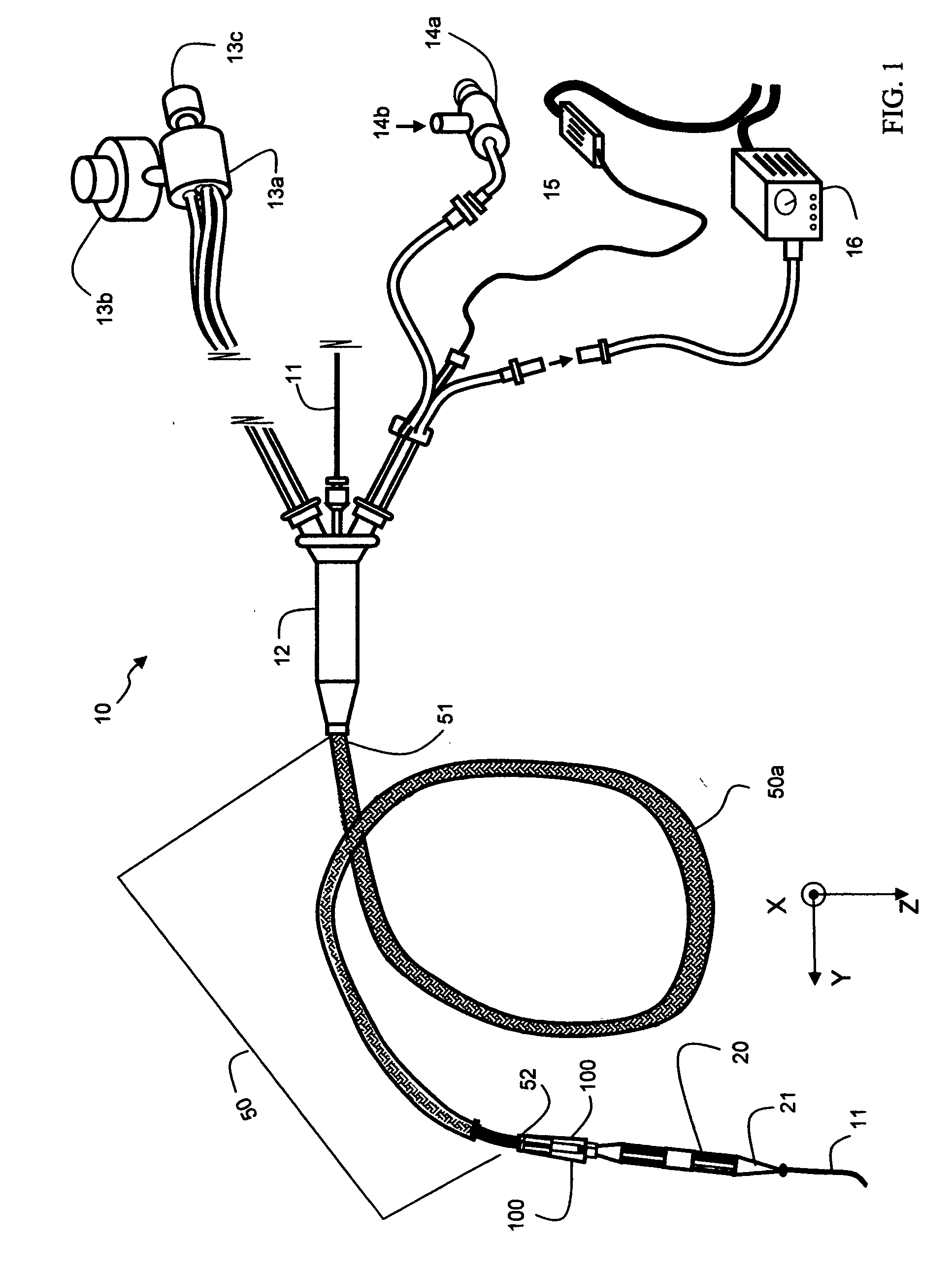
Intravascular ultrasound catheter device and method for ablating atheroma
InactiveUS20060241524A1Prolong time-integrated emulsificationEnhance reabsorptionChiropractic devicesMedical devicesCavitationUltrasound angiography
An intravascular catheter device having a catheter and an ultrasound ablation manifold is proposed for generating cavitations and acoustic jet streams in the blood to ablate atheroma. The ablation manifold has a power transducer and a coupled leaky acoustic cavity. The leaky acoustic cavity contains a first portion of ultrasonic power emission for intra-cavity ablation while allowing a second portion of ultrasonic power emission to leak outside for an extra-cavity ablation. The power transducer and the leaky acoustic cavity are configured to form a confocal resonant cavity. An intervening bird cage is coupled to the resonant cavity for stronger resonance while maintaining ultrasound leakage. A protective shield is mounted around the waist of bird cage to strengthen resonance and to prevent damaging the intima from an otherwise normal incidence of high intensity ultrasound. A microbubble releasing device and micro pump are also included to further increase the ablation efficacy.
Owner:YU QI
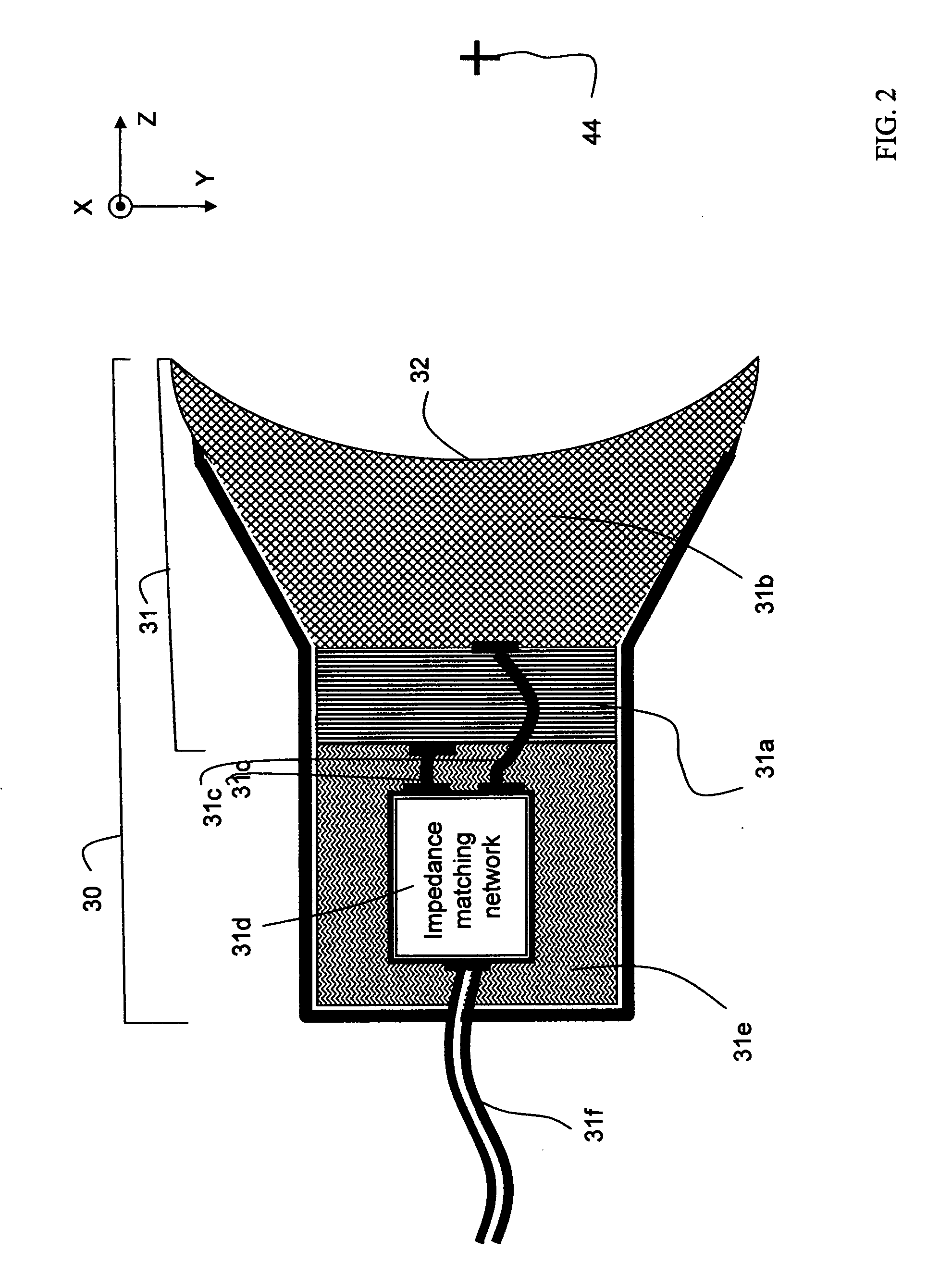
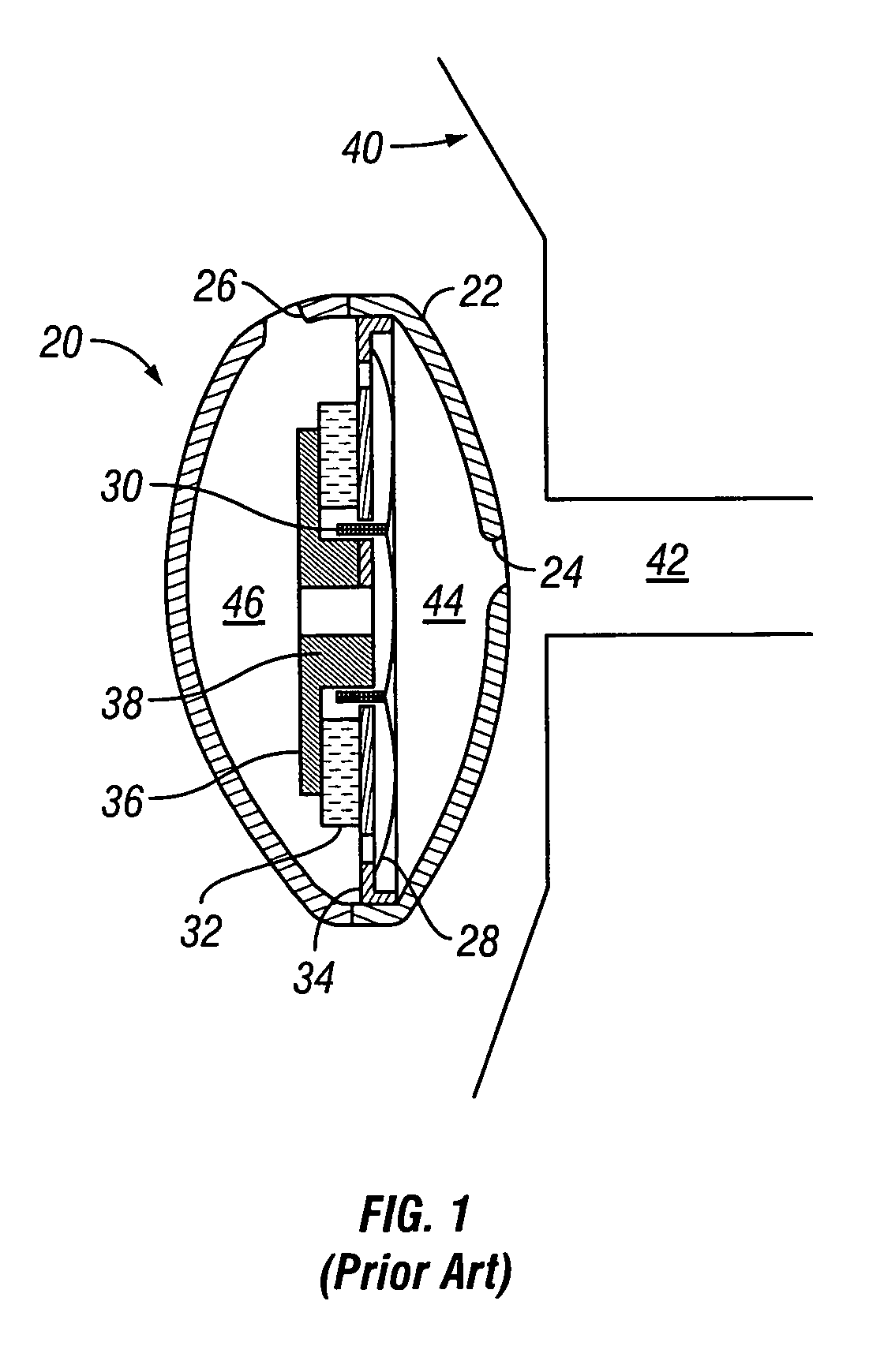
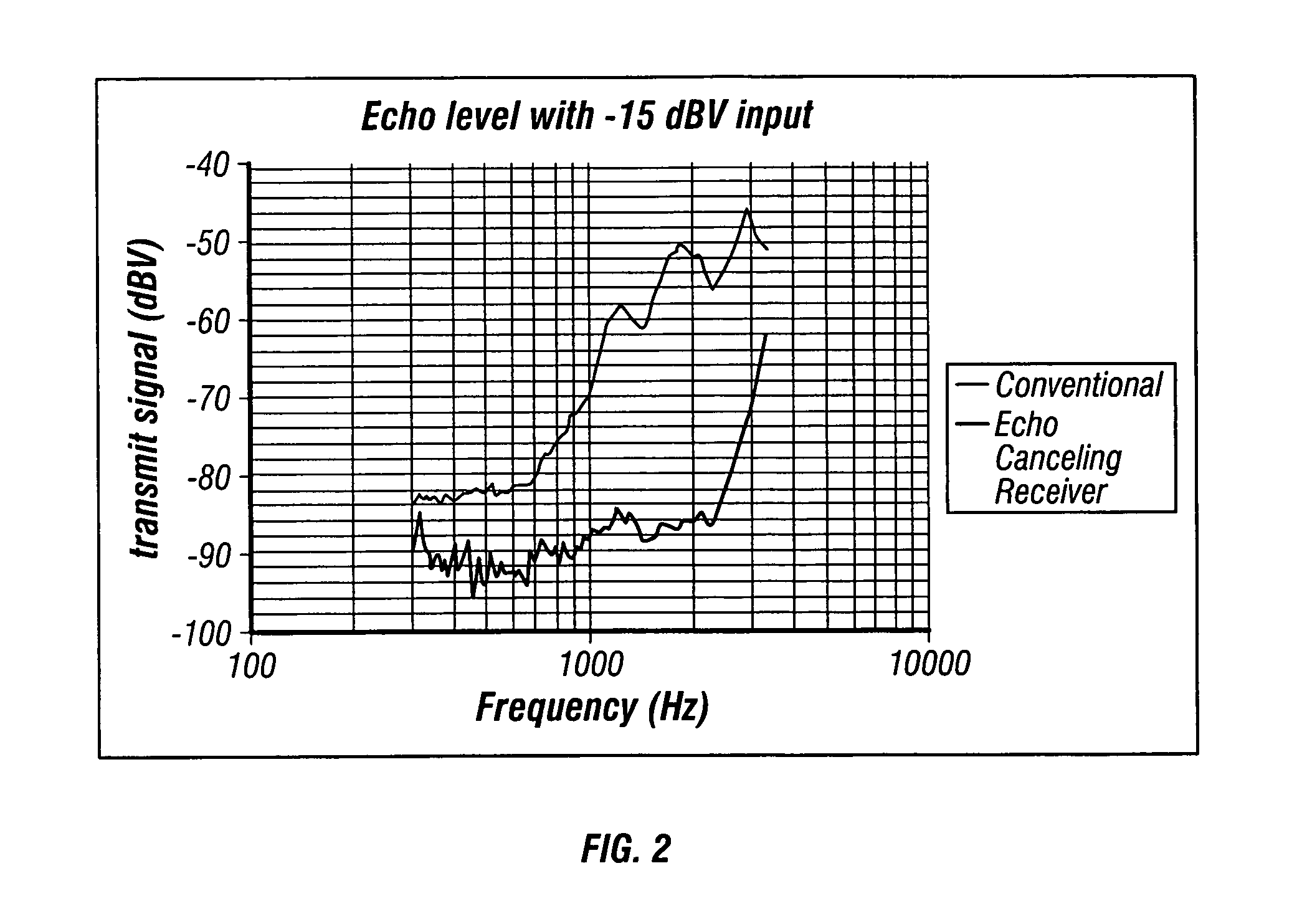
Personal communication method and apparatus with acoustic stray field cancellation
InactiveUS7499555B1Increase echo path lossReduce complexityEar treatmentHeadphones for stereophonic communicationComputer moduleHeadphones
Personal communication method and apparatus, such as telephone handsets and headsets, with acoustic stray field cancellation are disclosed. The personal communications device employs an echo canceling receiver generally including two displacement sources that are not in phase formed by at least one driver, an acoustic cavity corresponding to each displacement source, and an acoustic output port corresponding to and in acoustic connection with each displacement source via the corresponding acoustic cavity such that the acoustic length between the acoustic centers of the two ports is less than the distance between the acoustic center of each port and the acoustic center of the corresponding displacement source to which the port is acoustically connected. In another embodiment, the ports may be such that both ports are located on a same side of a surface of at least one of the displacement sources. As an example, the personal listening device may have at least two ports and a dedicated driver acoustically coupled to each port. The personal communication device may further include a transmit module. The ports may be driven and tuned such that when the device is worn, the ratio of acoustic pressure at a first location, e.g., the ear, to acoustic pressure at a second location, e.g. the transmit module, is substantially greater than that with either port acting alone. In another embodiment, the receiver ports are driven and tuned such that when the device is worn, the ratio of acoustic pressure at the first location to sound pressure gradient in a given direction at the second location is substantially greater than that with either port acting alone. The receiver thus achieves echo canceling for high frequencies.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
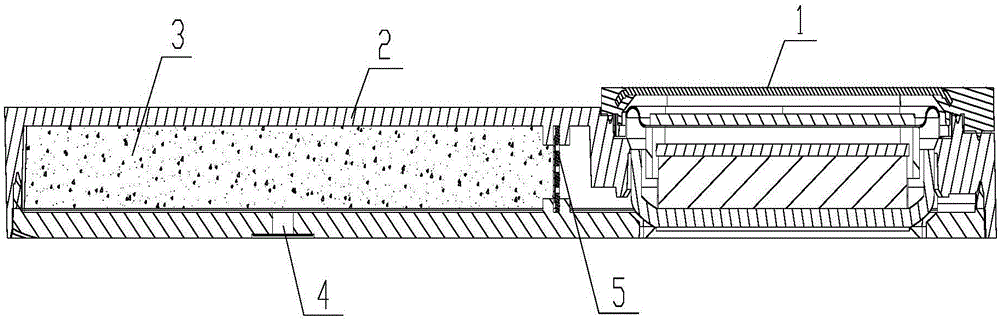
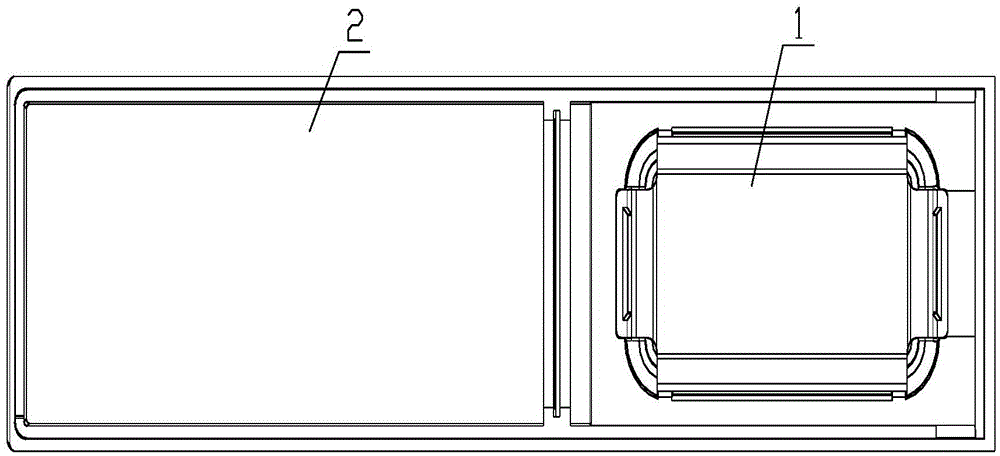
Loudspeaker die set
ActiveCN104202703ABandwidthSmooth IF CurveLoudspeaker transducer fixingFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsState of artEngineering
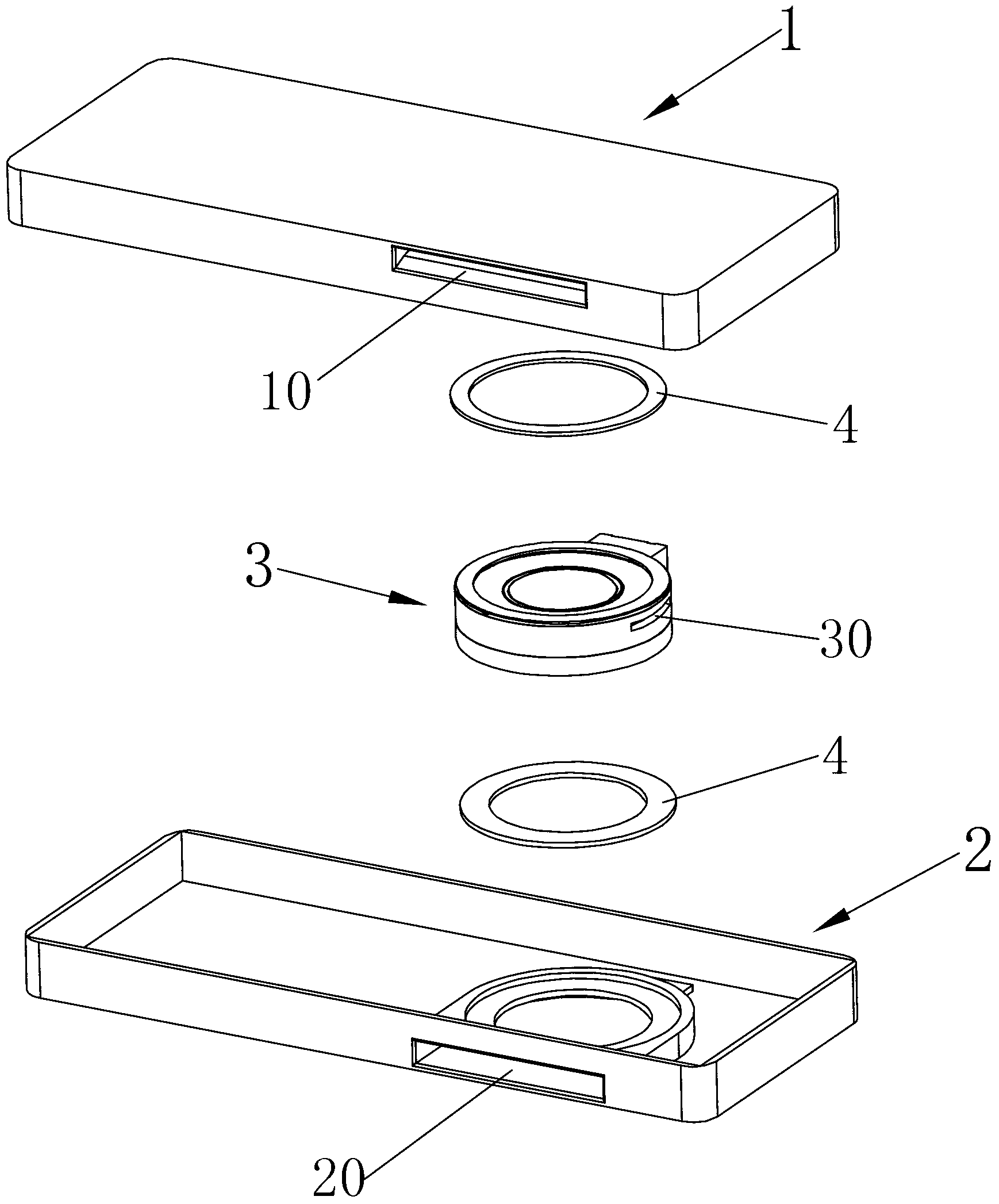
The invention discloses loudspeaker die set, and relates to the technical field of electroacoustic products. The loudspeaker die set comprises a housing in which a single loudspeaker body is contained; the single loudspeaker body comprises a vibrating system and a magnetic circuit system; an inner cavity of the whole die set is divided into two cavities, namely, a front vocal cavity and a rear vocal cavity, through the single loudspeaker body; a sound absorbing material is positioned in the rear vocal cavity; a separating structure for separating the sound absorbing material and the single loudspeaker body is also arranged in the rear vocal cavity; the whole rear vocal cavity is divided into a filling area and a non-filling area through the separating structure; the sound absorbing material which is foaming material is positioned in the filling area; the sound absorbing material is filled by foaming the foaming material and fully filled in the filling area. With the adoption of the loudspeaker die set, the technical problems of poor consistency and high production cost of the loudspeaker die set product in the prior art can be solved; the loudspeaker die set is high in acoustic performance, high in production efficiency, small in production cost, and high in product consistency.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Process for forming and acoustically connecting structures on a substrate
InactiveUS7049051B2Reduce thicknessPrecise alignmentCosmetic preparationsDecorative surface effectsParallel plateEngineering
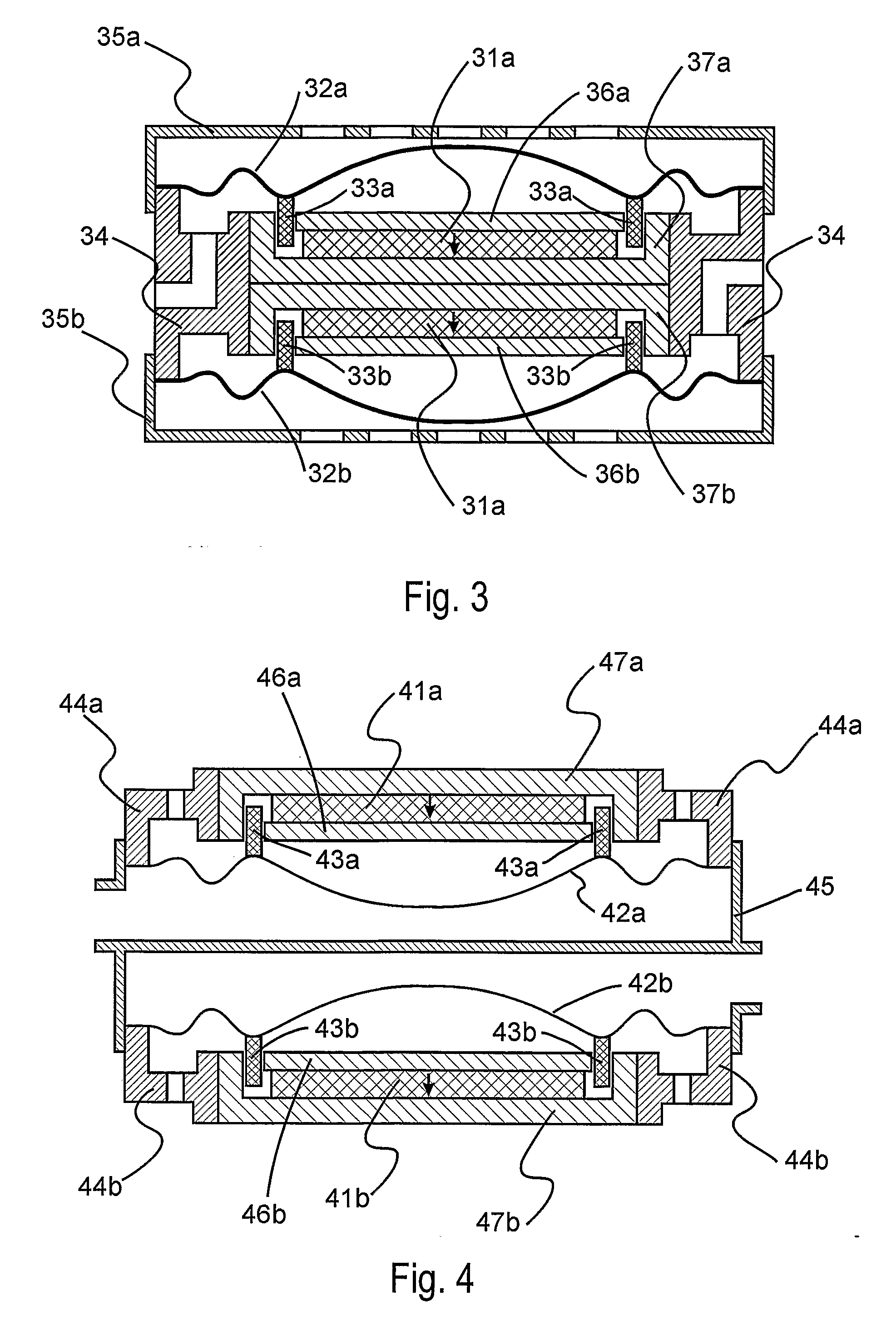
The present invention describes a processes that builds an acoustic cavity, a chamber, and vent openings for acoustically connecting the chamber with the acoustic cavity. The dry etch processes may include reactive ion etches, which include traditional parallel plate RIE dry etch processes, advanced deep and inductively coupled plasma RIE processes. Three embodiments for connecting the chamber to the cavity from the top side of the substrate, e.g. by using pilot openings formed using at least a portion of the mesh as an etch mask, by forming the vent openings using at least a portion of the mesh as an etch mask, or by having the chamber intersect the vent openings as the chamber is being formed, illustrate how the disclosed process may be modified. By forming the cavity on the back side of the substrate, the depth of the vent holes is decreased. Additionally, using at least a portion of the micro-machined mesh as an etch mask for the vent holes makes the process self-aligning.
Owner:AKUSTICA
Car body sound vibration roughness NVH design method based on low frequency acoustic sensitiveness inside vehicle
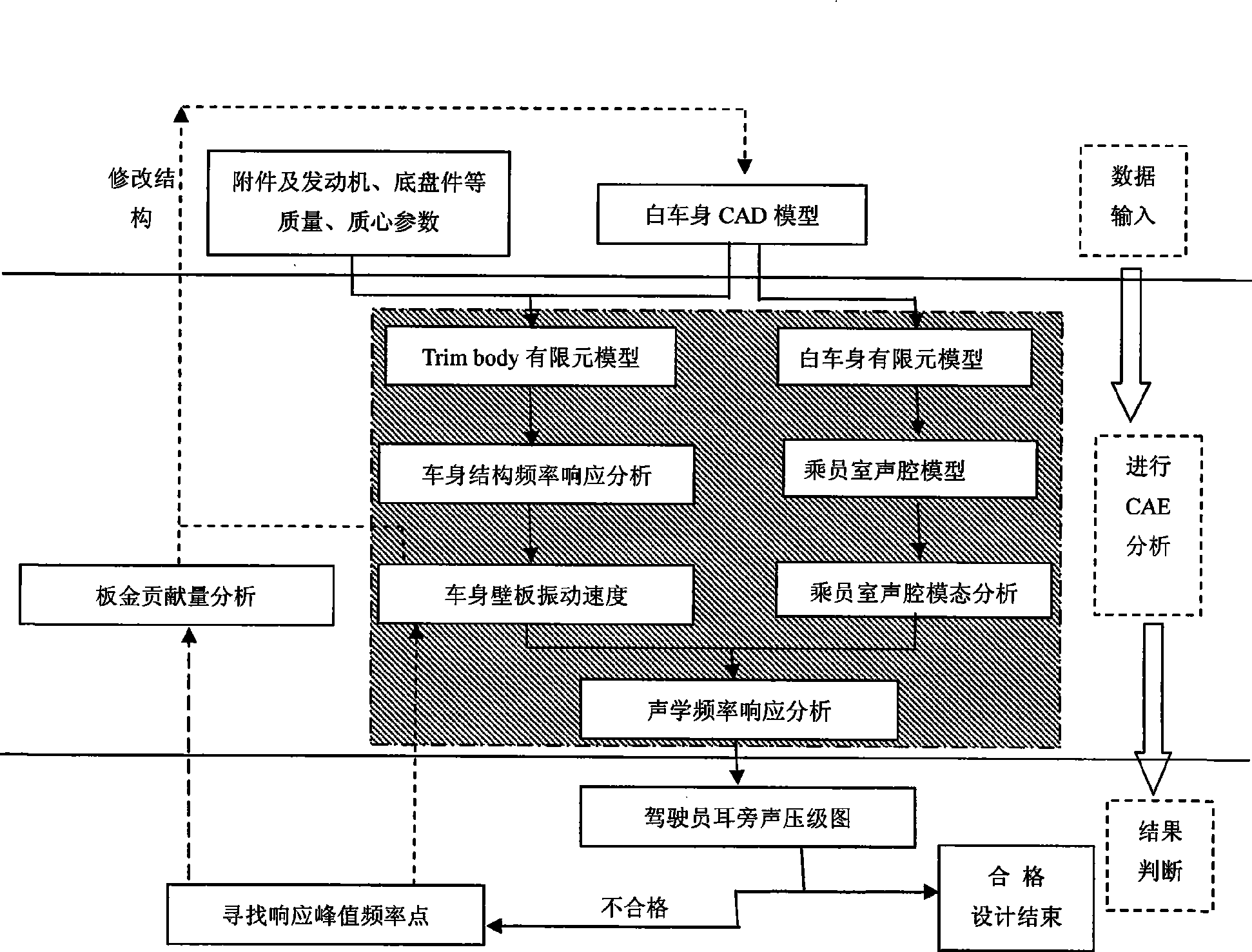
The invention relates to a method for designing the automobile body acoustic vibration unevenness NVH based on a low frequency automobile acoustic sensitivity. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a body-in-white finite element modeling, and establishing an acoustic finite element modeling for a cab on the basis of the body finite element modeling; secondly, carrying the frequency response analysis on the positions of a suspending point of an engine on the automobile body, a suspension mounting point, an exhaust hanging point, and the like; thirdly, taking the vibration speed of a body wall plate obtained by the frequency response analysis as a boundary condition, and the sound pressure level beside ears of a driver by solving the acoustic response of the cab; further, the influence level of larger sheet metal parts and mounting points which have great influence on the sound pressure level are acquired by checking the vibration situation of the body wall plate displayed by the frequency response analysis result at higher sound pressure response frequency points, and analyzing the sheet metal contribution; and finally, amending the design proposal of the sheet metal parts and the design proposal of the local rigidity of the mounting points.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Method for analyzing and predicting noise outside car
InactiveCN101661522AShorten the development cycleReduce development costsSpecial data processing applicationsCoupling lossPredictive methods
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and predicting noise outside a car, which aims at overcoming the problem that the noise outside the car is difficult to be predicted in the developing and designing stage of the car product. The method comprises the steps of: 1) establishing an SEA model of the car body structure: dividing the car body into a plurality of structural sub-systems, and connecting all structural sub-systems according to the correlations; 2) establishing an SEA model for an external acoustic cavity of the car: establishing SEA models for the external acoustic cavitiesof the car at two sides and on the external surface of the car body in the SEA model of the car body; 3) determining the SEA parameter of the car body and the external acoustic cavity sub-system of the car: determining the mode density of each sub-system, determining the internal loss factor of each sub-system, and determining the coupling loss factor of all sub-systems; 4) determining the external excitation energy of the car body: determining the acoustic excitation energy of an engine cabin, determining the excitation energy of suspended engine, determining the excitation energy of unevenness of the road surface on the car body, and determining the excitation energy of the wind pressure on the external surface of the car body; and 5) analyzing and predicting the noise outside the car.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Micro-electro-mechanical pressure sensor
ActiveUS20090013792A1Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectricityVibrating membrane
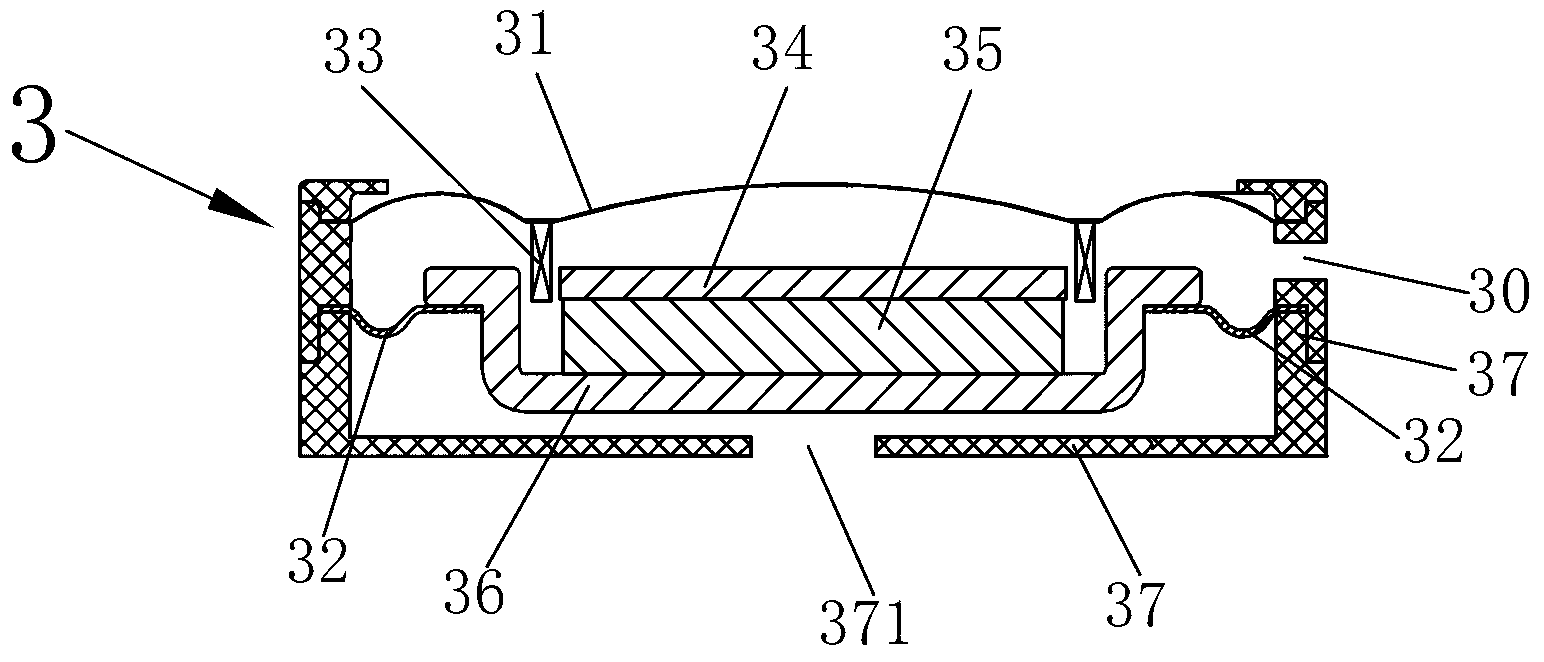
The present micro-electro-mechanical pressure sensor includes a substrate, a dielectric isolation layer, at least two electrodes, and a vibrating membrane. The substrate includes an acoustic cavity. The dielectric isolation layer is formed on the substrate, and the dielectric isolation layer includes a through hole corresponding to the acoustic cavity. The at least two electrodes are separately formed on the dielectric isolation layer. The vibrating membrane covers the through hole, and the vibrating membrane includes at least one carbon nanotube structure with two opposite ends. The two opposite ends of the carbon nanotube are respectively connected to at least a given one of the at least two electrodes.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Audio Transducer Component
An audio transducer component comprises at least two independent voice coils, each voice coil associated with a diaphragm and an acoustic cavity. The audio transducer component further comprises magnetic means for driving the at least two independent voice coils with independent signals.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Structure and manufacturing method of inversed microphone chip component
ActiveUS20080075309A1Reduce the impactLower the volumePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesEngineeringAcoustic cavity
An inversed microphone module is provided. The module includes a substrate, a microphone chip, a back acoustic cavity cover, and a sealing material. The substrate has a plurality of connection pads and an acoustic hole. The microphone chip has a first surface and an opposite second surface. A plurality of electrically bonding portions and an acoustic sensing are disposed on the first surface. The microphone chip is electrically coupled to the connection pads of the substrate through the electrically bonding portions, and the acoustic hole corresponds to the acoustic sensing portion. The back acoustic cavity cover is fixed to the second surface and defines a back acoustic cavity with the acoustic sensing portion and the microphone chip. The sealing material encapsulates the microphone chip and covers the substrate, so that the sealing material, the substrate, the acoustic sensing portion, and the first surface define a front acoustic cavity.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Acoustic wave touch actuated switch
InactiveUS7106310B2Simple circuitOvercome disadvantagesInput/output for user-computer interactionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerAcoustic wave
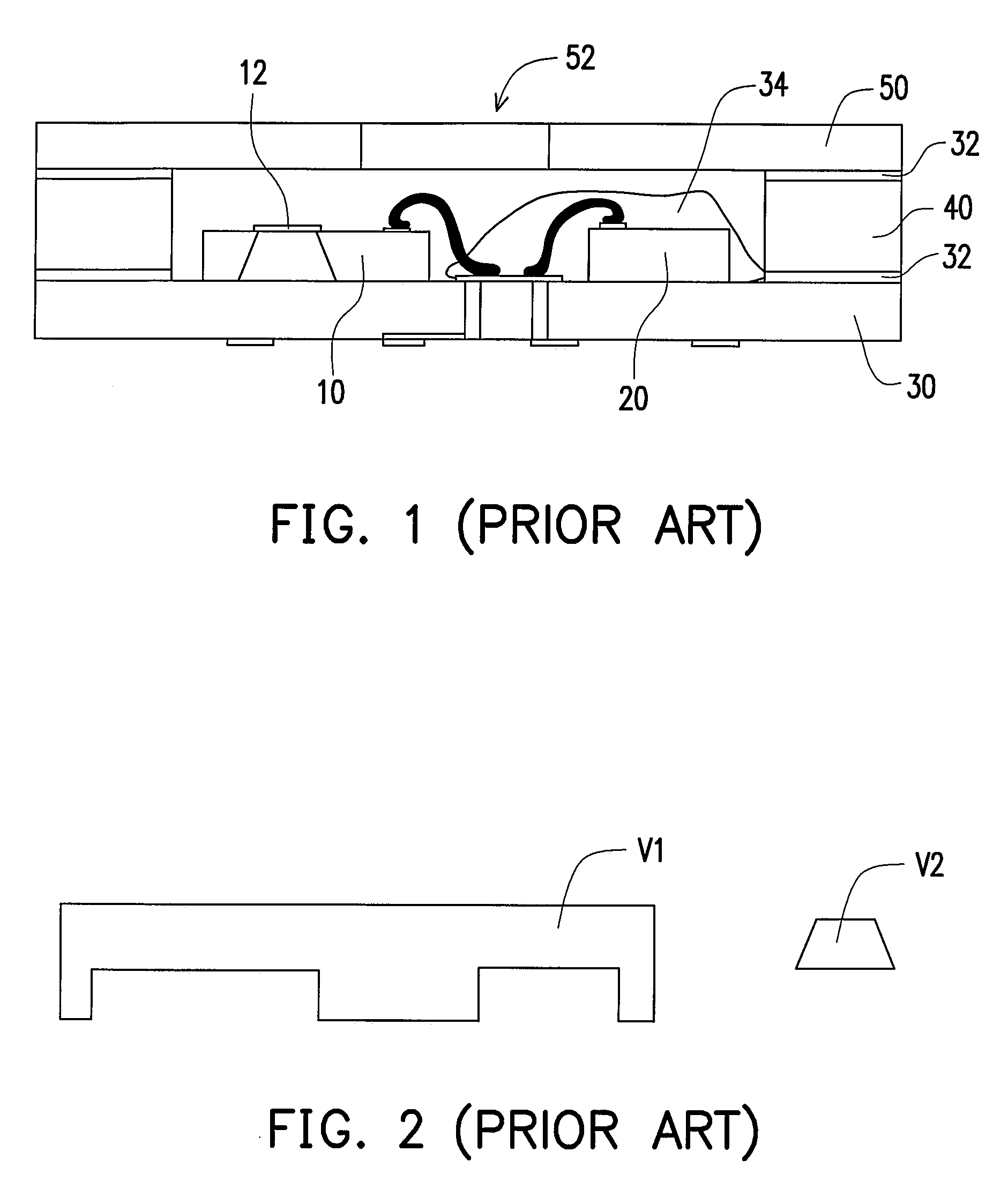
An acoustic wave switch includes a substrate with an acoustic wave cavity formed therein such that the mass per unit area of the acoustic cavity is greater than the mass per unit area of the substrate adjacent the cavity. A transducer is mounted on the acoustic cavity for generating an acoustic wave that is substantially trapped in the cavity. A touch on the touch surface of the acoustic wave cavity absorbs acoustic wave energy and produces a detectable change in the impedance of the transducer. The acoustic wave switch has a high Q so as to enable a touch to be detected by extremely simple, low-cost circuitry. The acoustic wave switch of the present invention is rugged, explosion proof, operates in the presence of liquids and other contaminants, has a low power consumption and can be incorporated and integrally formed in a wall of a housing for a device.
Owner:TEXZEC
Induction system with air flow rotation and noise absorber for turbocharger applications
InactiveUS8651800B2Minimized pressure lossAssists functionalityPropellersInternal combustion piston enginesImpellerTurbine wheel
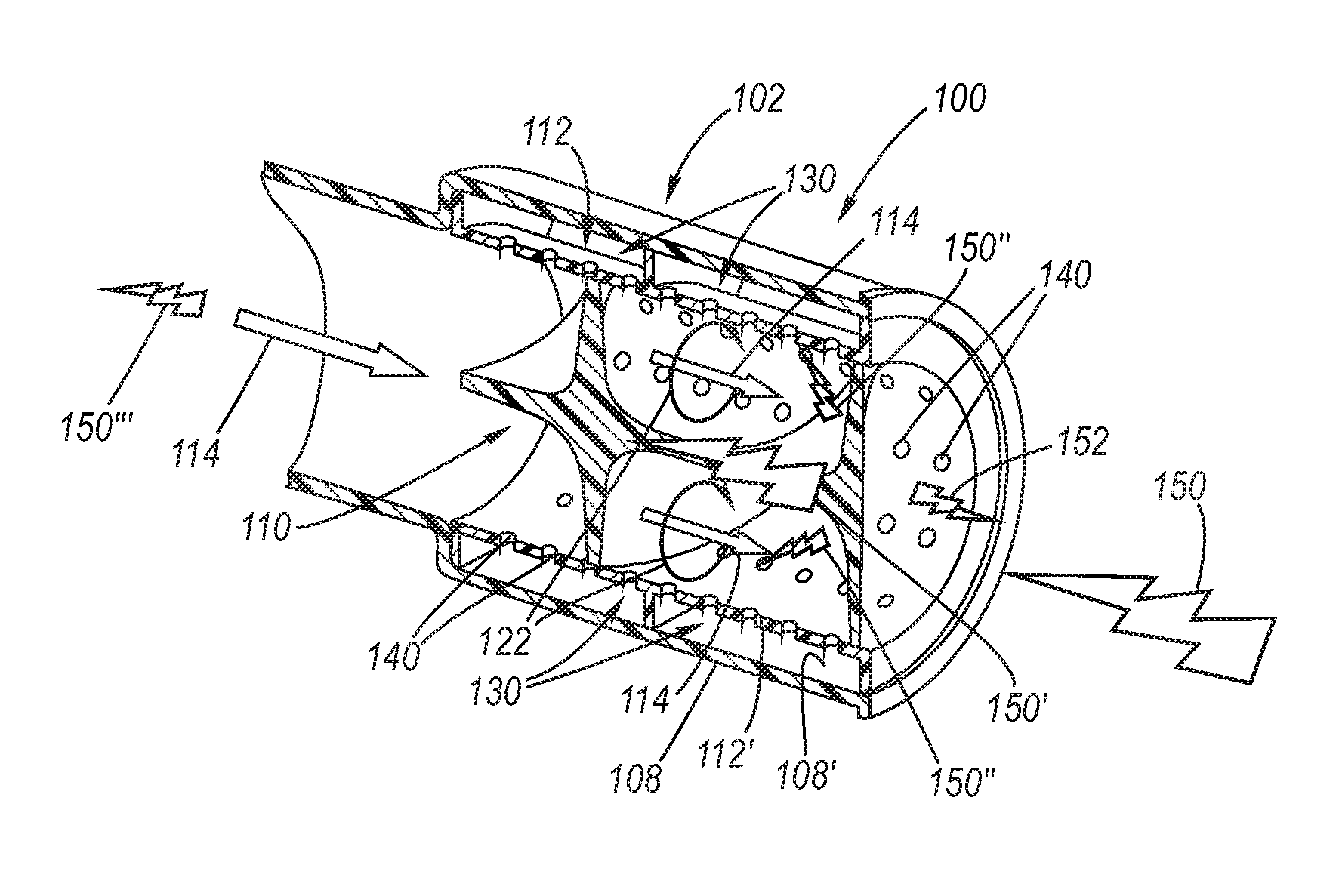
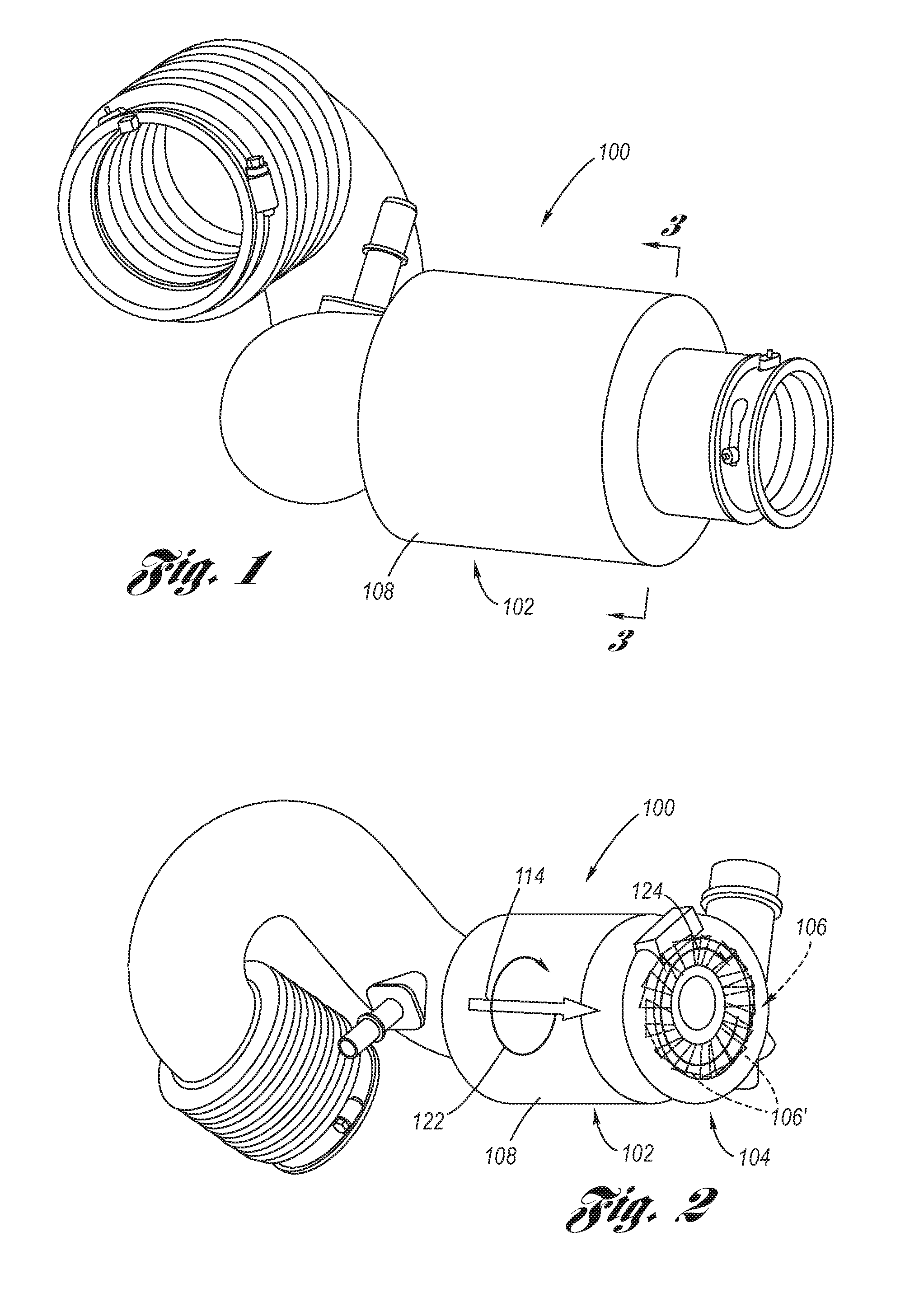
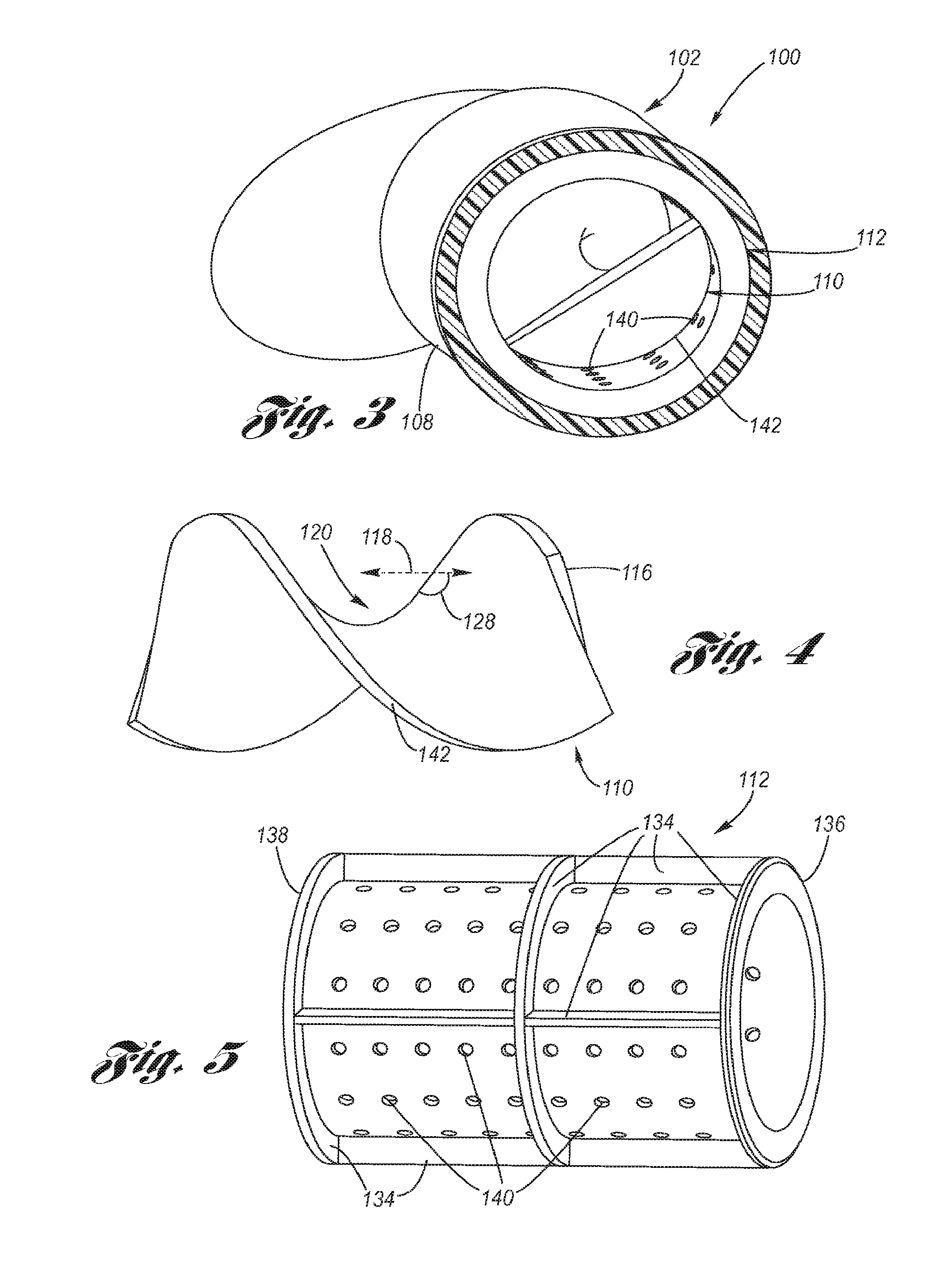
An air induction system consisting of a cylindrical main flow tube, a helical vane disposed within the main flow tube, and, preferably, a noise absorbing perforated tube disposed within the main flow tube in concentric relation to the helical vane. The twist direction of the helical vane provides air flow rotation in the same direction of rotation as the turbine wheel. The helical vane causes noise reflection and enhancement of noise attenuation by the perorated tube and its adjoining one or more acoustic cavities.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Loudspeaker module
ActiveCN105142074AImprove acoustic performanceAvoid adsorptionSingle transducer incorporationLoudspeaker transducer fixingCrystal structureHeteroatom
The invention provides a loudspeaker module. The loudspeaker module comprises a shell and a loudspeaker monomer contained in the shell, wherein the loudspeaker monomer divides a cavity formed by the shell into a front vocal cavity and a rear vocal cavity; the rear vocal cavity is filled with acoustic materials; heteroatoms are doped in the crystal structures of the acoustic materials. The loudspeaker module provided by the invention can reduce the adsorption of acoustic materials inside the loudspeaker module to heterogeneous molecules, and even reject the heterogeneous molecules, so as to guarantee that the acoustic materials are long-term effective and improve the stability of the acoustical property of the loudspeaker module.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Evacuation of liquid from acoustic space
An acoustic module, such as a microphone or speaker module, includes an acoustic membrane that vibrates to produce acoustic waves and an acoustic cavity through which acoustic waves produced by the membrane travel. A liquid removal mechanism removes liquid from the acoustic cavity. Such a liquid removal mechanism may include the acoustic membrane, heating elements, hydrophobic and / or hydrophilic surfaces, and so on. In some cases, the liquid removal mechanism may remove liquid from the acoustic cavity upon connection of the acoustic module and / or an associated electronic device to an external power source.
Owner:APPLE INC
Audio headset with active noise control of the non-adaptive type for listening to an audio music source and/or for "hands-free" telephony functions
InactiveUS20130129105A1High gainIncreased phase marginOcclusion effect electronic compensationMicrophonesBandpass filteringNoise control
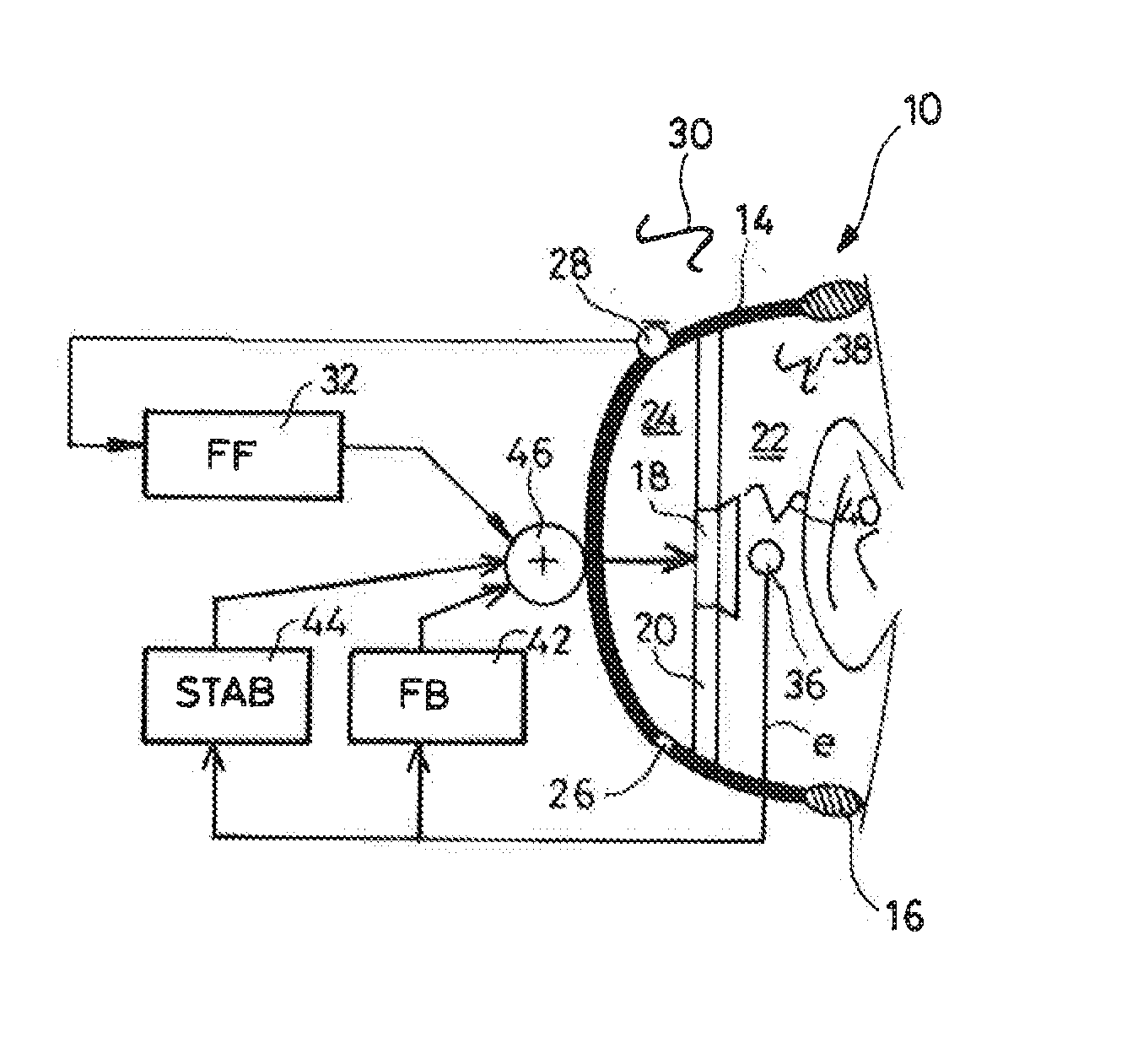
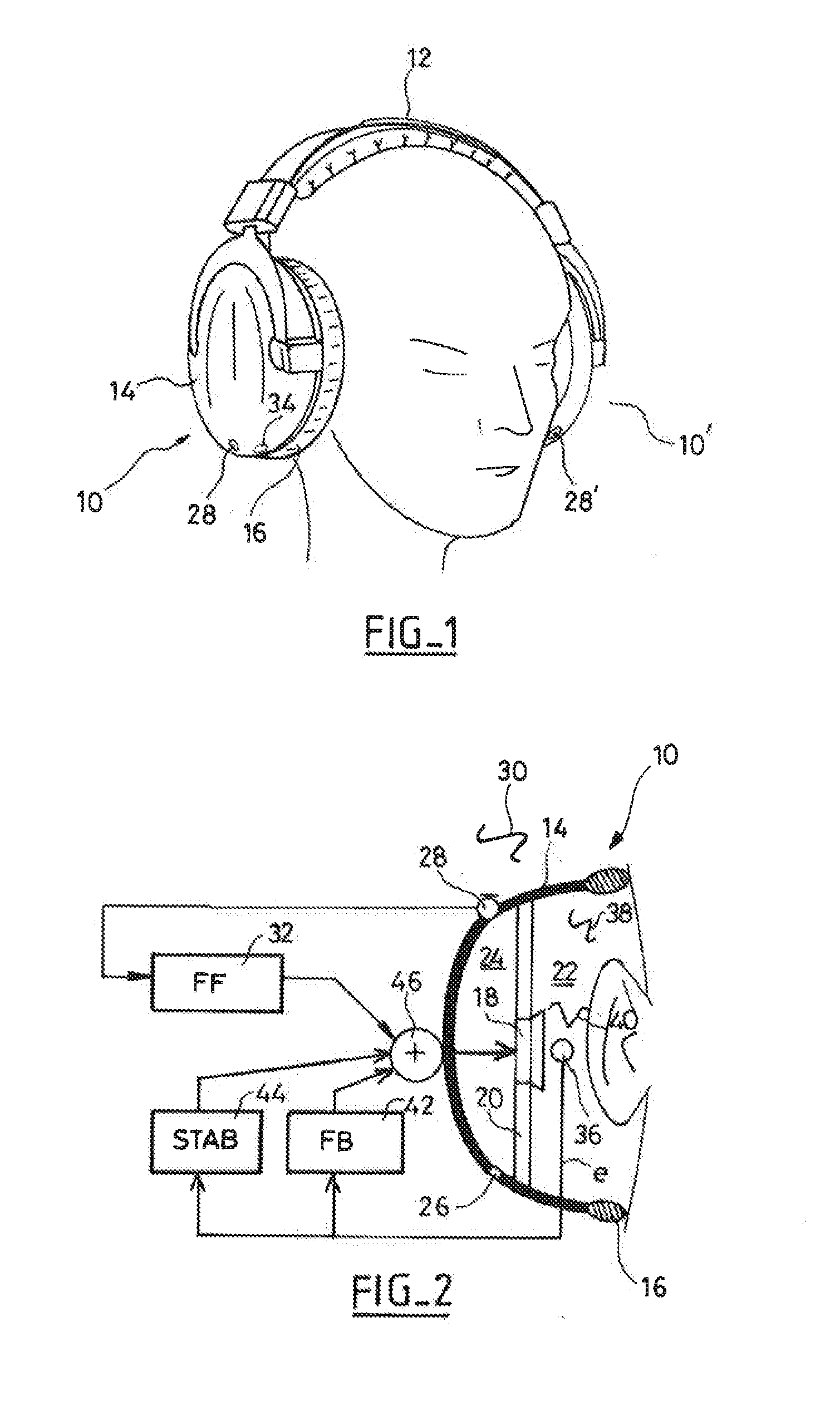
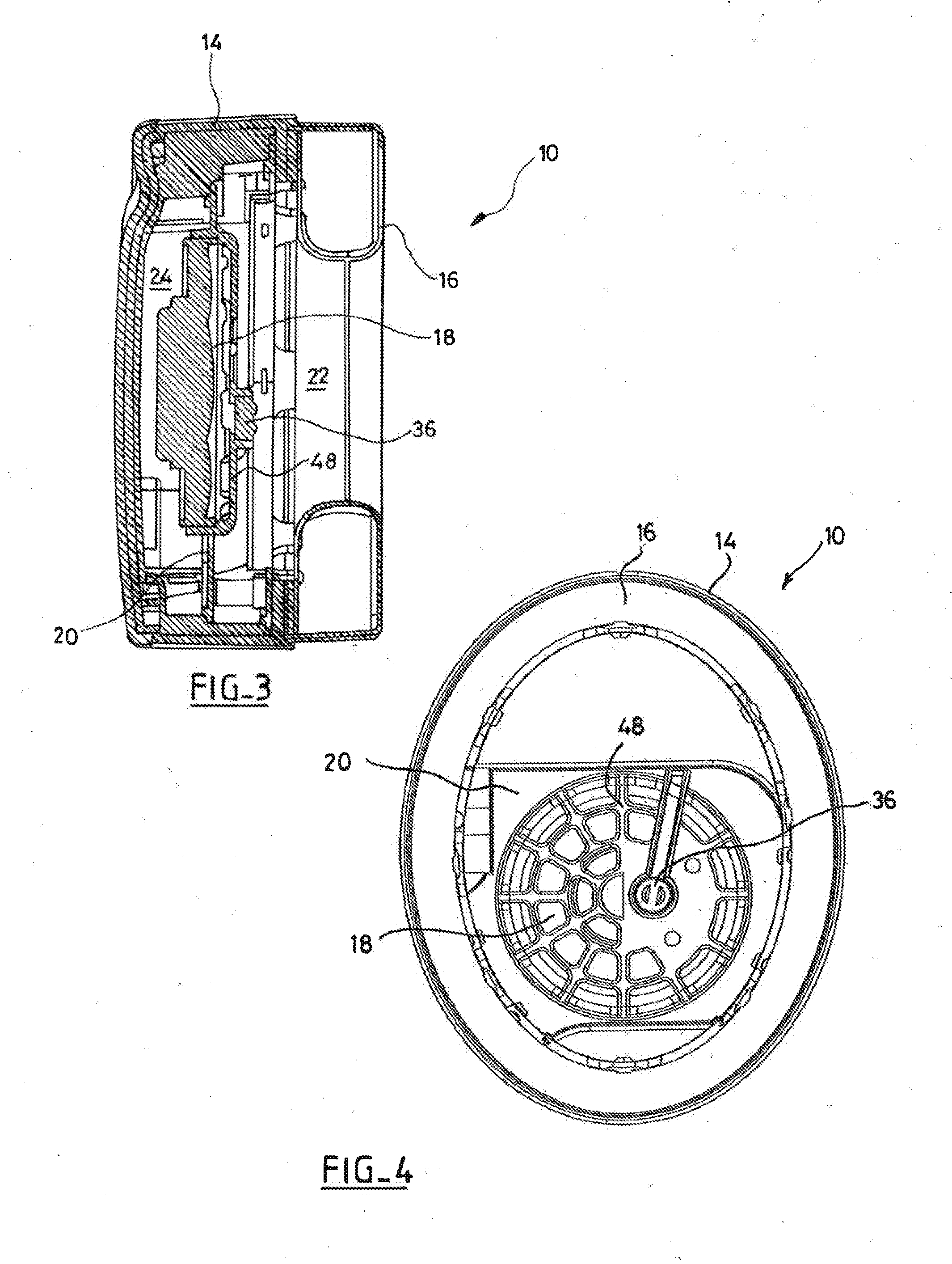
The headset comprises two earpieces each having a transducer for playing back the sound of an audio signal and received in an acoustic cavity defined by a shell having an ear-surrounding cushion. The active noise control comprises, in parallel, a feedforward bandpass filter receiving the signal from an external microphone, a feedback bandpass filter receiving as input an error signal delivered by an internal microphone, and a stabilizer bandpass filter locally increasing the phase of the transfer function of the feedback filter in an instability zone, in particular a waterbed effect zone around 1 kHz. A summing circuit delivers a weighting linear combination of the signal delivered by these filters together with the audio signal to be played back. Control is non-adaptive, with the parameters of the filters being static.
Owner:PARROT
Vibration and noise complex experiment equipment
ActiveCN102004022ASubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingEngineeringSound production
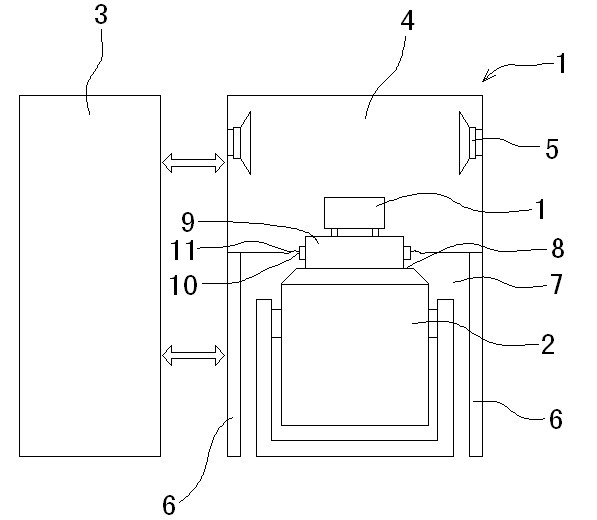
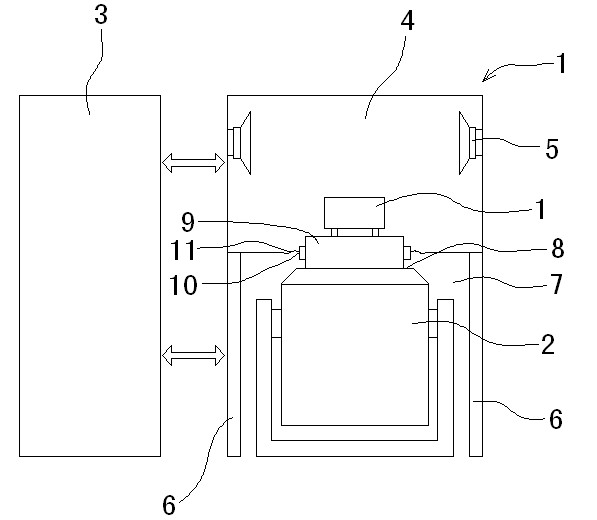
The invention discloses vibration and noise complex experiment equipment which is characterized by mainly comprising a noise experiment box, a vibration table and a control box, wherein the noise experiment box is an airtight box body and is internally provided with a sound cavity which is internally provided with at least one set of sound production device; the noise experiment box is provided with a bracket support over the ground, an accommodation space is formed below the noise experiment box, and the vibration table is arranged in the accommodation space; the table board of the vibration table is fixedly provided with an extending head, the bottom surface of the noise experiment box is provided with an interface corresponding to the extending head, the extending head extends into the sound cavity through the interface, and a sealing device is arranged between the circumferential direction of the extending head and the interface for connection; and the control box is internally provided with a control circuit used for controlling the noise experiment box and the vibration table. The invention not only can simultaneously provide complex experiments of the vibration experiment and the noise experiment, but also can provided single vibration experiment or single noise experiment, which fills in a blank in the field in China.
Owner:苏州苏试广博环境可靠性实验室有限公司
Double-vibrating-diaphragm speaker module
ActiveCN103297904ABoost low frequency soundImprove acoustic performanceLoudspeaker transducer fixingLoudspeakersLoudspeakerVoice coil
The invention discloses a double-vibrating-diaphragm speaker module which comprises a single speaker body and a peripheral shell for accommodating the single speaker body. The single speaker body comprises a first vibrating diaphragm, a voice coil, a magnetic circuit and a second vibrating diaphragm, a first sound outlet and a second sound outlet communicating with the outside are formed in the peripheral shell, a first sound cavity communicating with the first sound outlet is formed between the first vibrating diaphragm and the peripheral shell, a second front sound cavity communicating with the second sound outlet is formed between the second vibrating diaphragm and the peripheral shell, a space between the first vibrating diaphragm and the second diaphragm is communicated with a rear sound cavity. The double-vibrating-diaphragm speaker module of the structure can be used with a double-vibrating-diaphragm speaker, so that low-frequency sound effect of the speaker module is improved, and acoustic performance of the double-vibrating-diaphragm speaker module is improved.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducer and methods of making the same
InactiveCN101018428AEasy to understandUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrets selectrostatic transducerCapacitanceUltrasonic sensor
A method of making a capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducer cell is provided. The method includes providing a carrier substrate, where the carrier substrate comprises glass. The step of providing the glass substrate may include forming vias in the glass substrate. Further, the method includes providing a membrane such that at least one of the carrier substrate, or the membrane comprises support posts, where the support posts are configured to define a cavity depth. The method further includes bonding the membrane to the carrier substrate by using the support posts, where the carrier substrate, the membrane and the support posts define an acoustic cavity.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
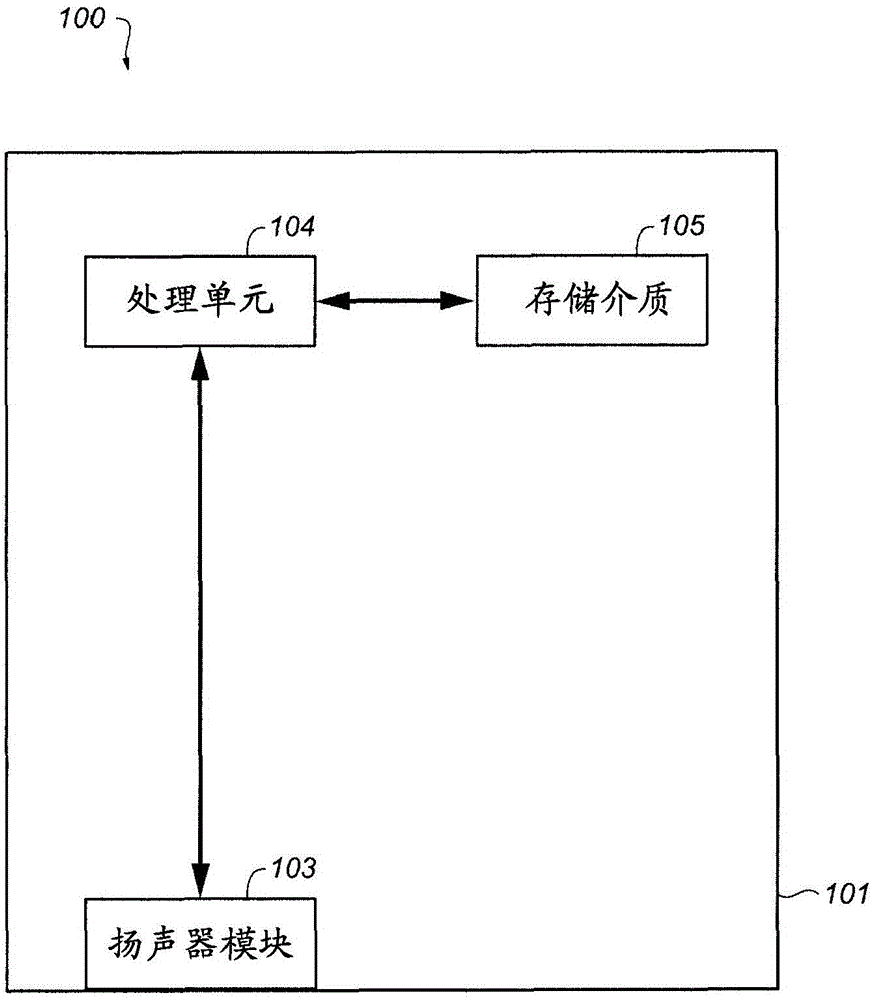
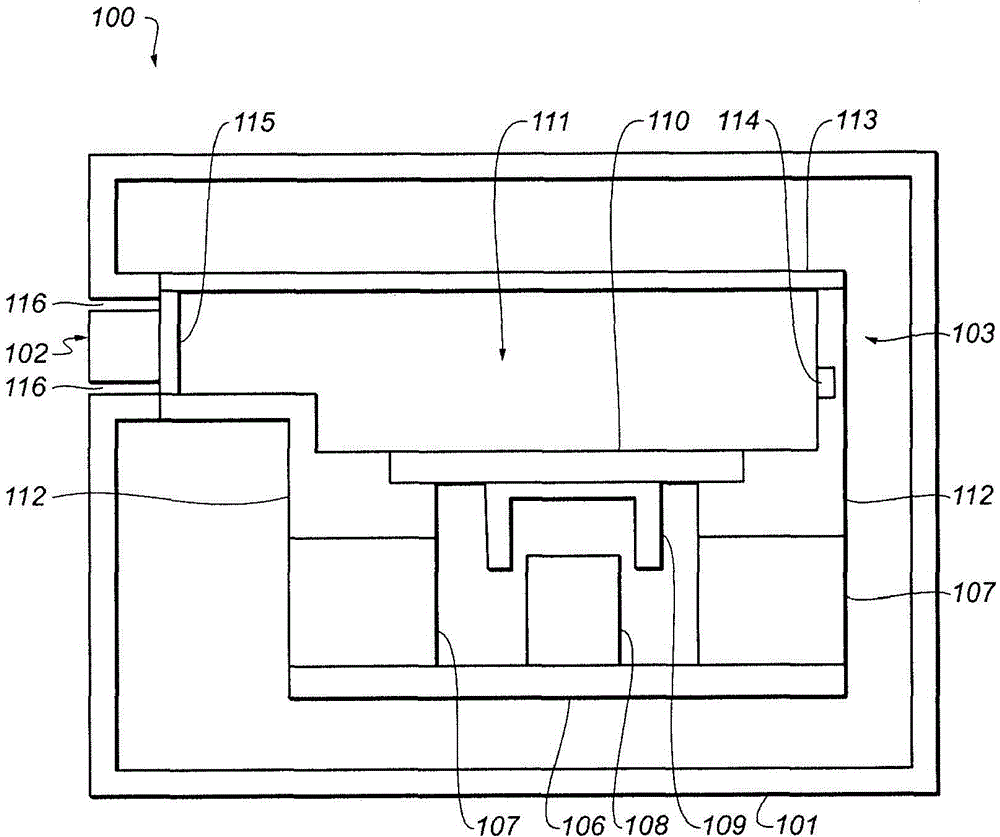
Portable handset with integrated speaker
InactiveUS7565178B1Enhanced acoustic functionImprove sound qualityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesInterconnection arrangementsAcoustic energyEngineering
A portable wireless handset with enhanced acoustic functions is disclosed having a chamber gasket that has an opening sized to receive a speaker. When inserted into the opening, the speaker seals to the chamber gasket. The chamber gasket also seals to a support surface, so that a sealed acoustic chamber is created. The keypad has an opening in the user interface area for receiving a speaker, and a navigation input key may be positioned over the speaker. In this way, the speaker shares an area with the navigation key, and projects sounds through vents in the navigation key. With the speaker sealed to the keypad, and the keypad sealed to a printed circuit board, a sealed acoustic chamber is formed. Acoustic energy emitted from the back of the speaker is received into the sealed chamber, thereby improving the sound quality for sound projected from the front of the speaker.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Acoustic wave touch actuated switch
InactiveUS20020126103A1Simple circuitOvercome disadvantagesElectronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsTransducerAcoustic wave
An acoustic wave switch includes a substrate with an acoustic wave cavity formed therein such that the mass per unit area of the acoustic cavity is greater than the mass per unit area of the substrate adjacent the cavity. A transducer is mounted on the acoustic cavity for generating an acoustic wave that is substantially trapped in the cavity. A touch on the touch surface of the acoustic wave cavity absorbs acoustic wave energy and produces a detectable change in the impedance of the transducer. The acoustic wave switch has a high Q so as to enable a touch to be detected by extremely simple, low-cost circuitry. The acoustic wave switch of the present invention is rugged, explosion proof, operates in the presence of liquids and other contaminants, has a low power consumption and can be incorporated and integrally formed in a wall of a housing for a device.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
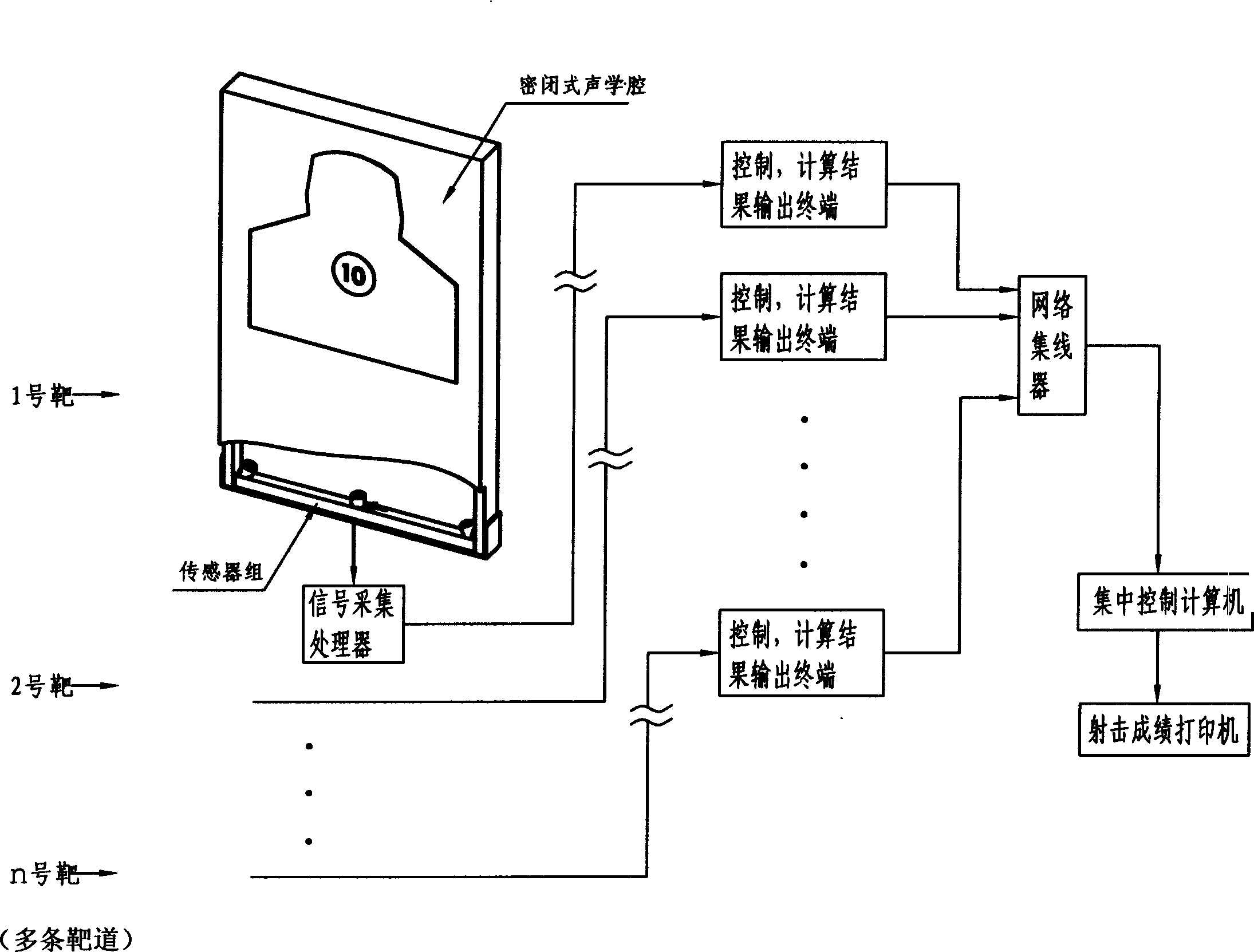
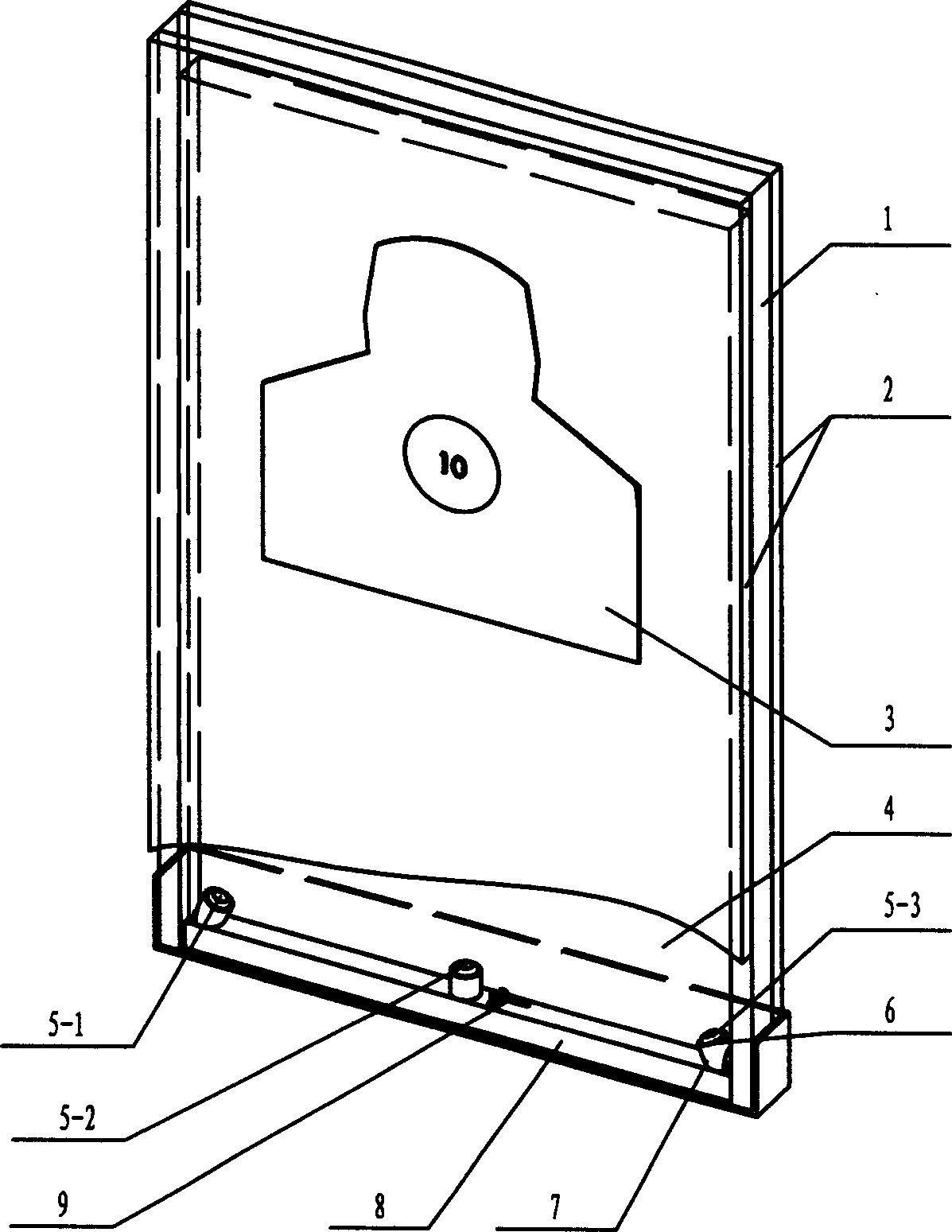
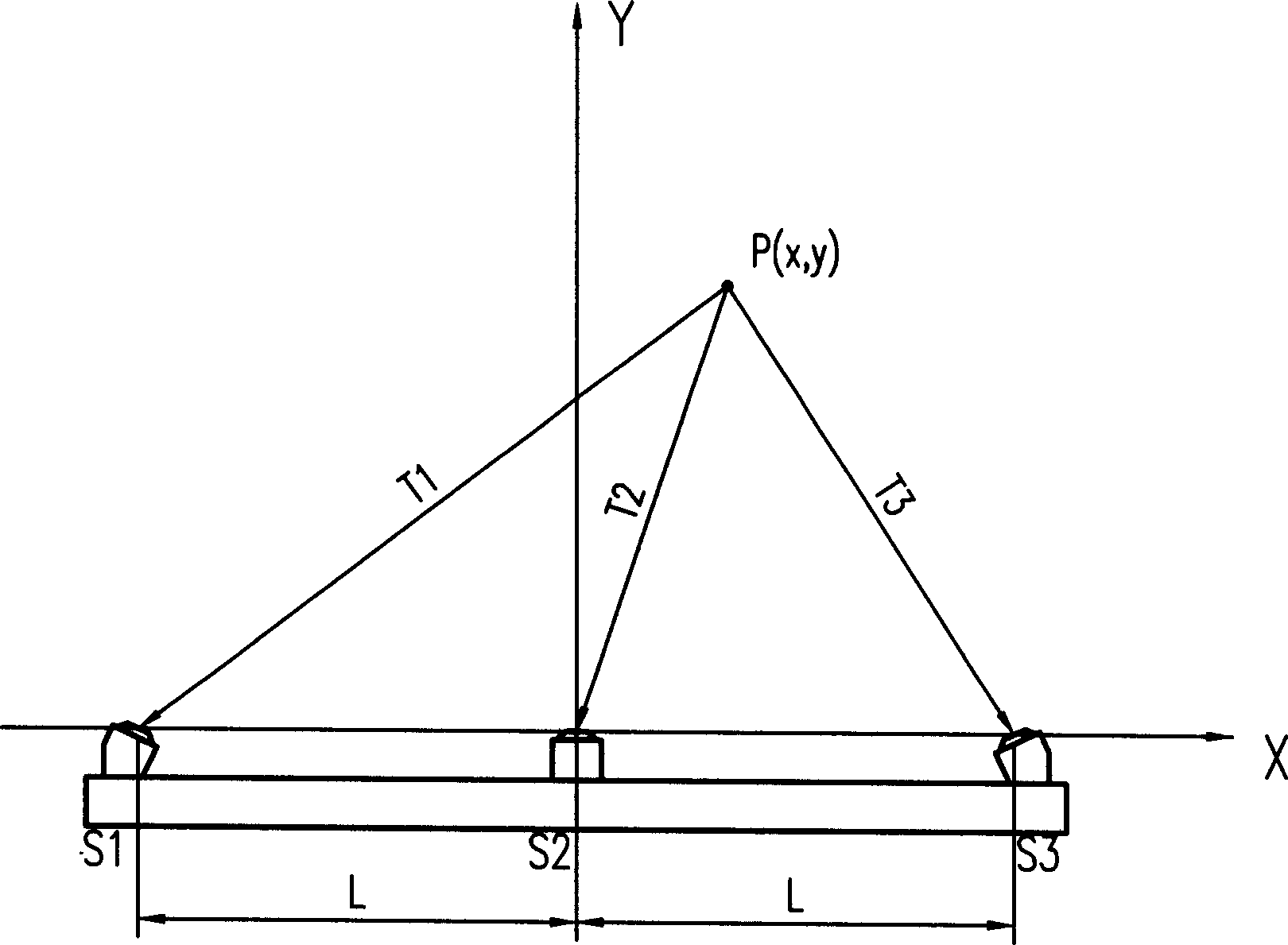
Horizontal battle setted ultrasonic automatic target reporting system
ActiveCN1560555AReduce weightImprove real-time performanceTarget detectorsSonificationDisplay device
The invention is a parallel embattling supersonic automatic target reporting system relating to an automatic target reporting device for indoor and outdoor direct pointing weapon fire. The system includes closed acoustics cavity, three parallel embattling acoustic sensors and environment temperature compensating sensors, fixing base, signal gathering and processor, monitor, network connector, total computer, printer; three parallel embattling acoustic sensors and environment temperature compensating sensor are arranged below the closed acoustic cavity, the output ends of the acoustic sensor and the temperature sensor are connected to the signal gathering processor with signal cable, the processor is connected to the back monitor through series bus, the monitor is connected to the total control computer with network wiring device, sends the calculated to the total control computer, then printing the first results.
Owner:NANJING RES INST ON SIMULATION TECHN +1
Ultrathin speaker module
ActiveUS20150358705A1Reduce the impactIncrease volumeTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsComputer moduleEngineering
The invention provides an ultrathin speaker module, comprising: a casing, which is provided with a sound hole thereon; a speaker unit, which comprises a diaphragm; a first separating wall, which is provided with a diaphragm accommodating hole, wherein the diaphragm of the speaker unit is fixed in the diaphragm accommodating hole, and the first separating wall and the diaphragm separate the internal space of the casing into an upper space and a lower space; and a second separating wall, which separates the upper space into one first upper cavity and at least one second upper cavity, wherein the first upper cavity comprises the diaphragm and forms a front acoustic cavity, and the front acoustic cavity is in communication with the outside through the sound hole on the casing; and the at least one second upper cavity is in communication with the lower space through a through hole on the first separating wall, and forms a rear acoustic cavity. The speaker module of the invention utilizes the internal space to increase the volume of the rear acoustic cavity thereby reducing the impact of the thinning on the low frequency acoustic characterstics of the speaker module.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Loudspeaker module
InactiveCN104811831ASimple structureImprove acoustic performanceTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEngineeringLoudspeaker
The invention discloses a loudspeaker module which comprises a shell and a single loudspeaker. A cavity for fixedly containing the single loudspeaker is formed in the shell, the cavity is divided into a front sound cavity and a rear sound cavity by the single loudspeaker, a sound outlet hole is formed in the shell, the front sound cavity is communicated with the sound outlet hole, a partition plate is arranged in the rear sound cavity and matched with the shell to separate an independent cavity from the rear sound cavity, the independent cavity is filled with sound absorption particles, and a through hole penetrating the partition plate is formed in the partition plate. The loudspeaker module is simple in structure and overcomes the shortcoming that the sound absorption particles enter the single loudspeaker along with airflow, the number of the sound absorption particles is increased, sound absorption effects are improved, and the acoustic performance of the loudspeaker module is improved.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Earphone
ActiveCN104244130AGood bassImprove mid-range sound qualityEarpiece/earphone attachmentsElectricityCurve shape
The invention discloses an earphone which comprises a loudspeaker single body, an audio signal line electrically connected with the loudspeaker single body, a shell used for containing the loudspeaker single body and a front cover laid on the shell. A front acoustic cavity is formed in the space between the front cover and the loudspeaker single body, and a rear acoustic cavity is formed in the space between the shell and the loudspeaker single body; the rear acoustic cavity is divided by a dividing wall into a main rear cavity and a low-pitch rear cavity, an acoustic tube is laid in the cavity body of the low-pitch rear cavity, is bent in a curve shape and arranged in the cavity body of the low-pitch rear cavity, one end of the acoustic tube is connected with the main rear cavity through a through hole of the dividing wall, and the other end of the acoustic tube is communicated with the outside through a sounding hole in a shell of the low-pitch rear cavity. By means of the structure, low-frequency performance and medium-frequency performance of the earphone are effectively improved, and the appearance of the earphone is more attractive on the basis that stability of the earphone is guaranteed.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Loudspeaker module
ActiveCN105872917ALower F0Improve acoustic performanceElectrical transducersEngineeringSound quality
The invention discloses a loudspeaker module, and relates to the technical field of an electroacoustic product. The loudspeaker module comprises a module housing; a loudspeaker monomer is accommodated in the module housing; the loudspeaker monomer divides an integral module inner cavity into two cavities, i.e. a front sound cavity and a rear sound cavity; the rear sound cavity comprises an accommodating cavity and a sound adsorption cavity which are communicated; the loudspeaker monomer is positioned in the accommodating cavity; the sound adsorption cavity is filled with sound adsorption particles; the accommodating cavity is formed by the surrounding of the module housing; the sound adsorption cavity is formed by the surrounding of a sound adsorption cavity housing; the sound adsorption cavity housing is combined with the module housing; and a netted isolation part is arranged between the sound adsorption cavity and the accommodating cavity. The sound adsorption particles of the loudspeaker module disclosed by the invention cannot be influenced by a module production assembling process, and have a good sound adsorption effect; acoustic performance of the module is obviously improved; sound quality is higher; and meanwhile, the loudspeaker module is low in assembling difficulty and high in production efficiency.
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com