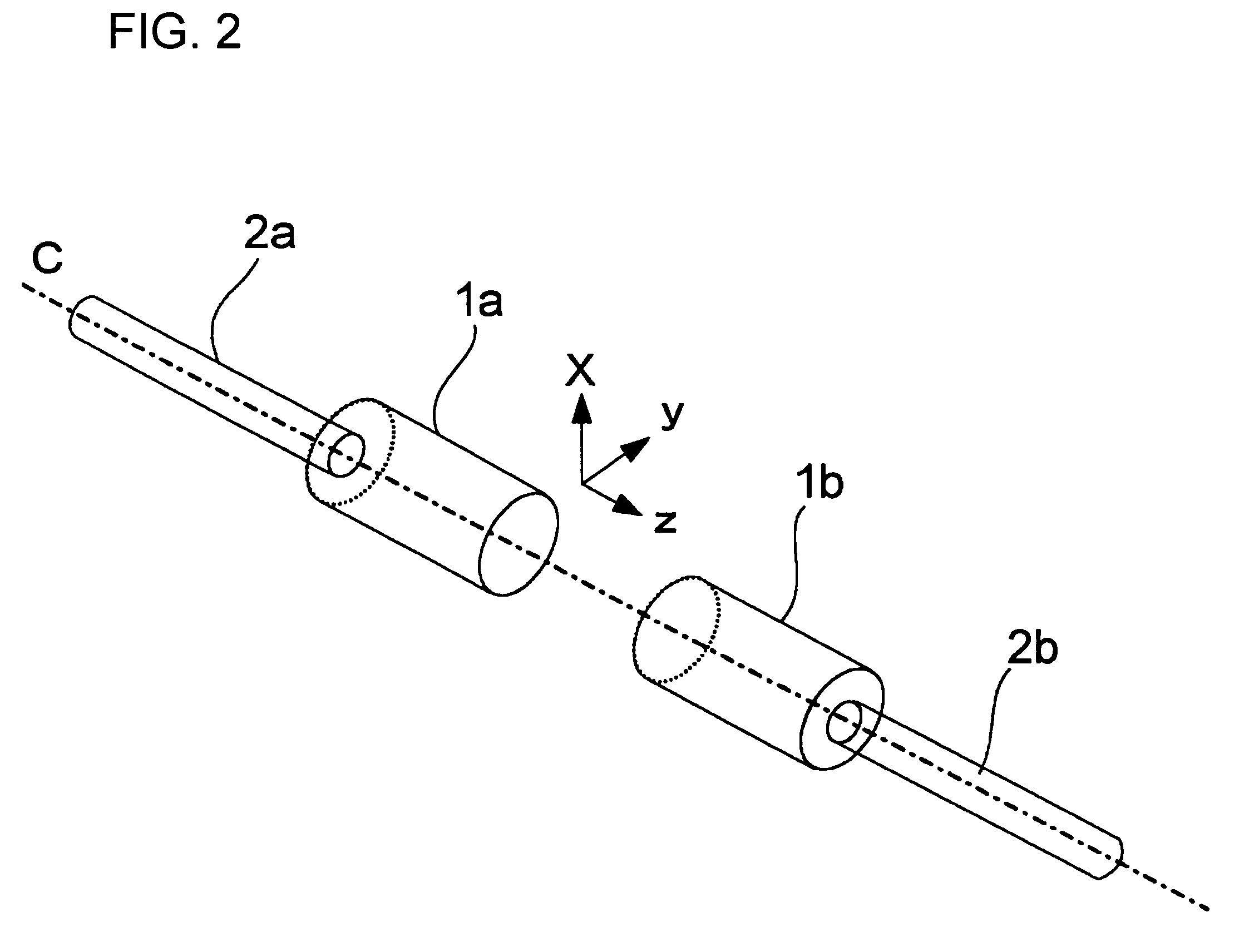
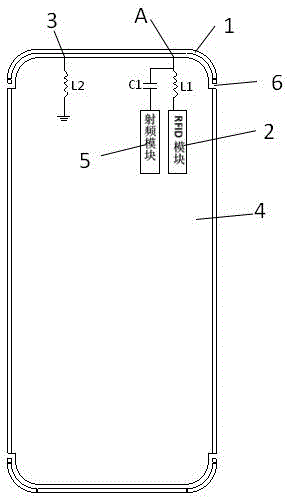
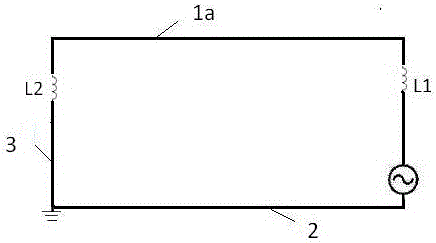
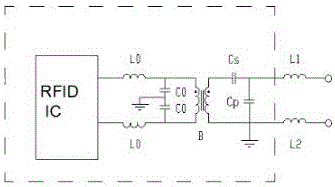
Patents
Literature
392 results about "Coupling loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
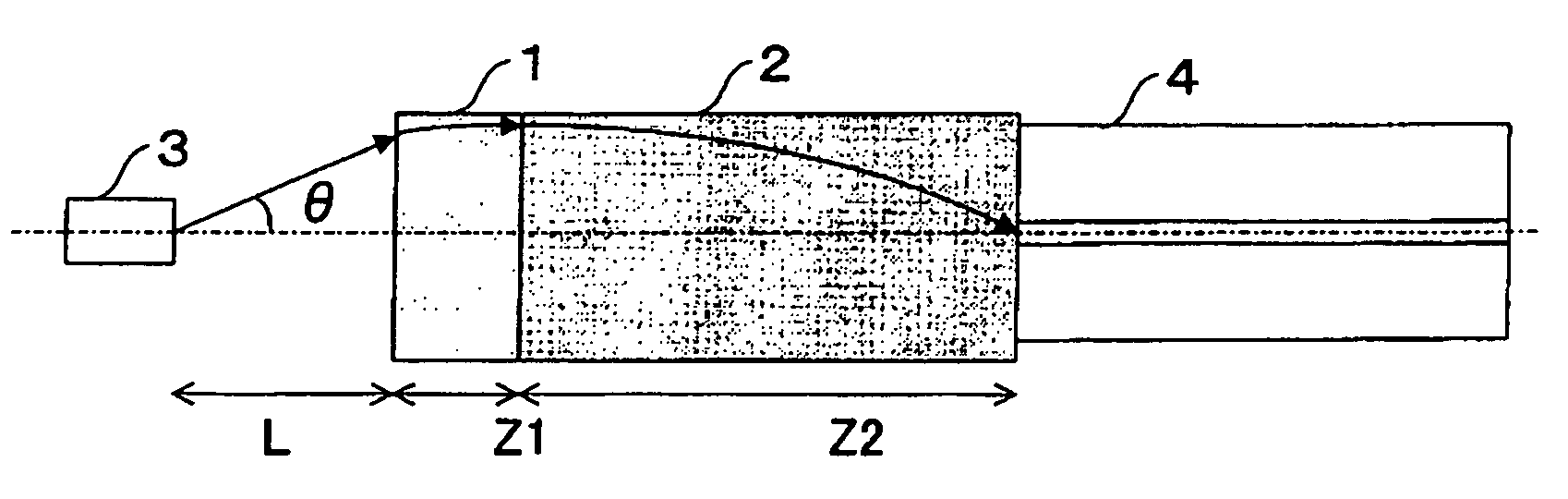
Coupling loss, also known as connection loss, is the loss that occurs when energy is transferred from one circuit, circuit element, or medium to another. Coupling loss is usually expressed in the same units—such as watts or decibels—as in the originating circuit element or medium.
Gas detecting method and gas sensors
InactiveUS20050186117A1Easy to detectImprove gas selectivityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCapacitanceCoupling loss
A gas detection method capable of solving the problem with respect to the operation at normal temperature that was impossible so far in the existent catalyst type sensor and detection with high sensitivity that was impossible by the light absorption type sensor. A multi-layered film formed of a first layer adsorbing a specified gas and a second layer having less adsorption are utilized as a detection film, and the detection film is disposed in the direction perpendicular to the optical channel and optically detects the change of stress caused in the detection film by gas adsorption as coupling loss. Alternatively, the stress generated in the detection film caused by gas adsorption is electrically detected by a piezoelectric element or capacitance element.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Connection apparatus for parallel optical interconnect module and parallel optical interconnect module using the same
InactiveUS7220065B2Minimize couplingIncrease optical powerSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesCoupling lossPrism
Provided is an optical connection apparatus for a parallel optical interconnect module and a parallel optical interconnect module using the same for reducing a coupling loss generated due to an alignment error when coupled with an optical fiber, comprising: a 2D reflector in a prism shape and having at least two rows of cylinder type lens attached thereto; a 2D optical waveguide having at least two layers of core arrays; at least two rows of 2D optical benches; and a 2D ferrule capable of loading at least two layers of optical fibers so as to facilitate the fixing of the 2D optical waveguide for optical interconnection.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Connection apparatus for parallel optical interconnect module and parallel optical interconnect module using the same
InactiveUS20050141823A1Minimize couplingSimple structureSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesCoupling lossPrism
Provided is an optical connection apparatus for a parallel optical interconnect module and a parallel optical interconnect module using the same for reducing a coupling loss generated due to an alignment error when coupled with an optical fiber, comprising: a 2D reflector in a prism shape and having at least two rows of cylinder type lens attached thereto; a 2D optical waveguide having at least two layers of core arrays; at least two rows of 2D optical benches; and a 2D ferrule capable of loading at least two layers of optical fibers so as to facilitate the fixing of the 2D optical waveguide for optical interconnection.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical module capable of improving coupling efficiency and suppressing fluctuation of coupling loss and its manufacturing method
ActiveUS6901185B2Coupling efficiency is improvedSuppress fluctuationsLaser detailsCoupling light guidesCoupling lossOptical Module
In an optical module, a package includes an array of first optical elements and at least one first positioning member. A microlens array plate including microlenses is fixed to the package, so that each of the microlenses corresponds to one of the first optical elements. An optical array connector mounts second optical elements thereon. The optical array connector has a light path bending portion for bending light paths of the second optical elements and at least one second positioning member. The optical array connector abuts against the package by aligning the second positioning member to the first positioning member so that each of the first optical elements corresponds to one of the second optical elements, A clamping member clamps the optical, array connector to the package.
Owner:NEC CORP
Integrated optics spot size converter and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060204175A1Enhanced couplingReduce lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCoupling lossOptical communication
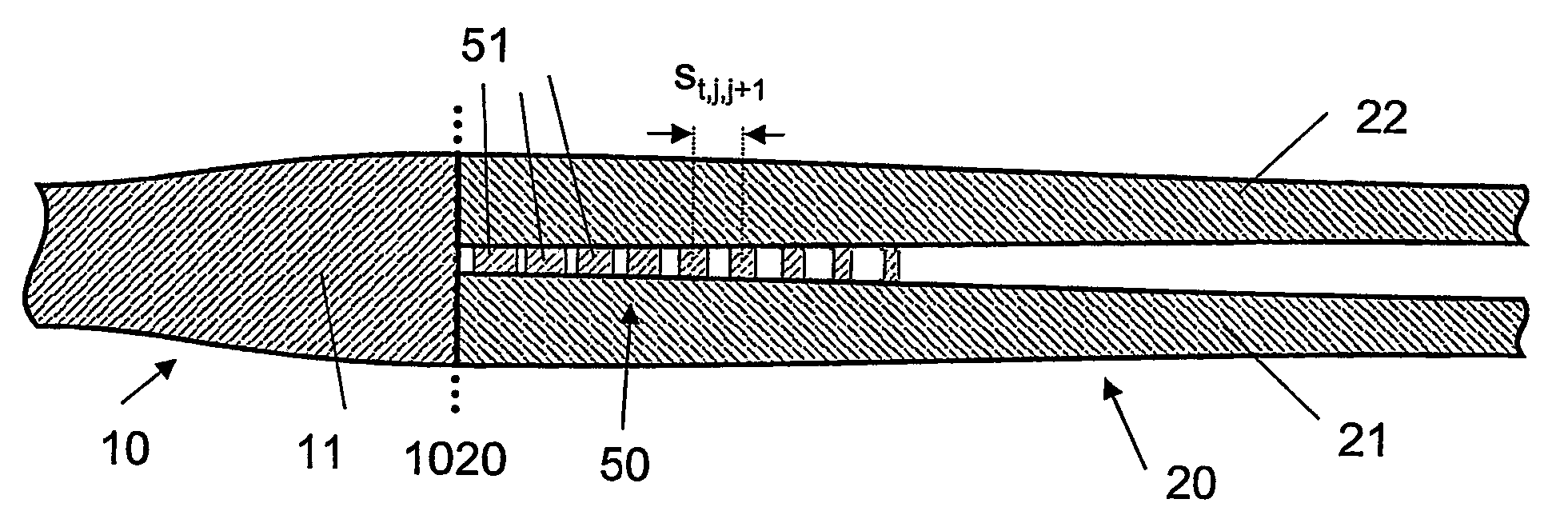
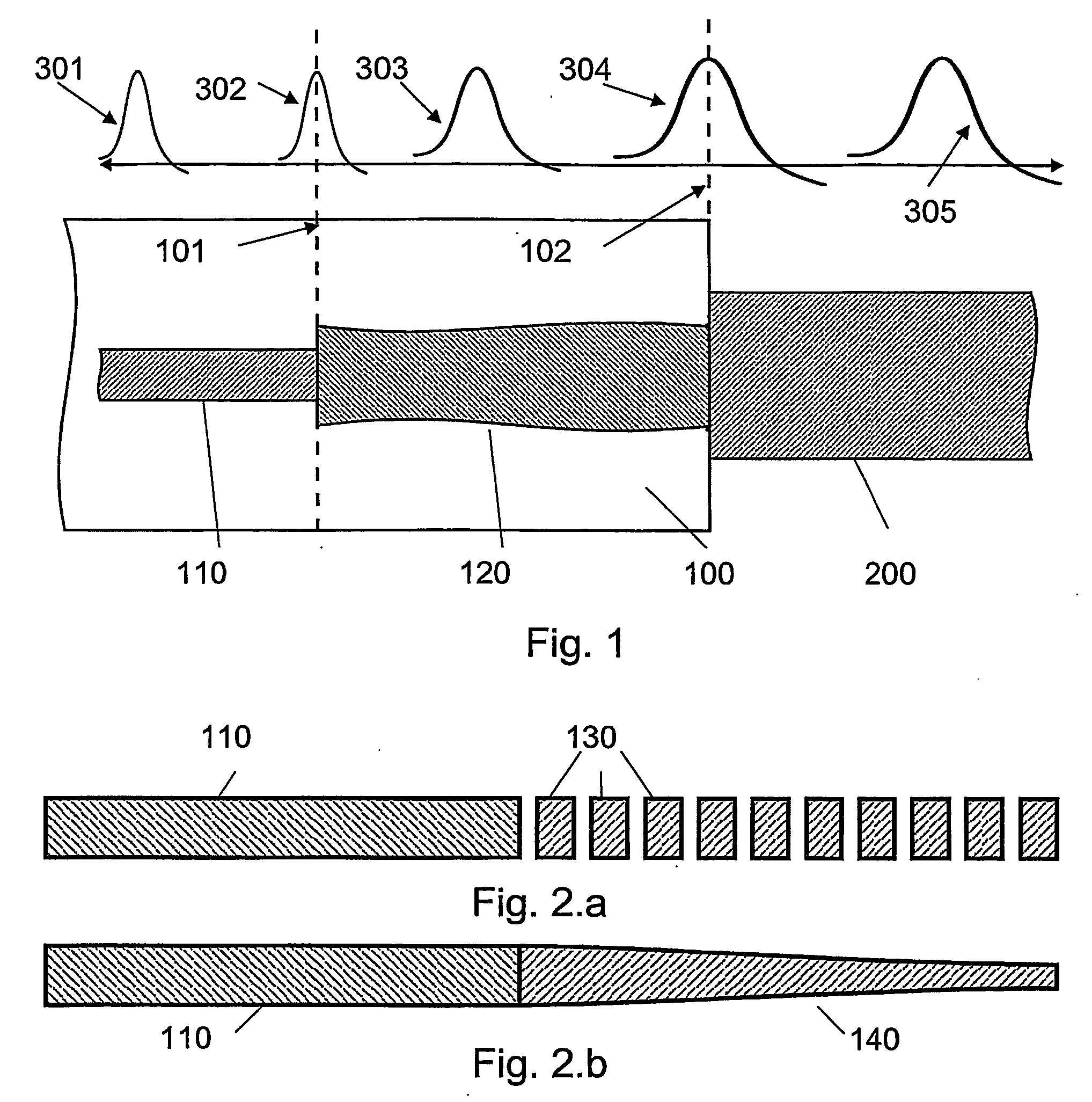
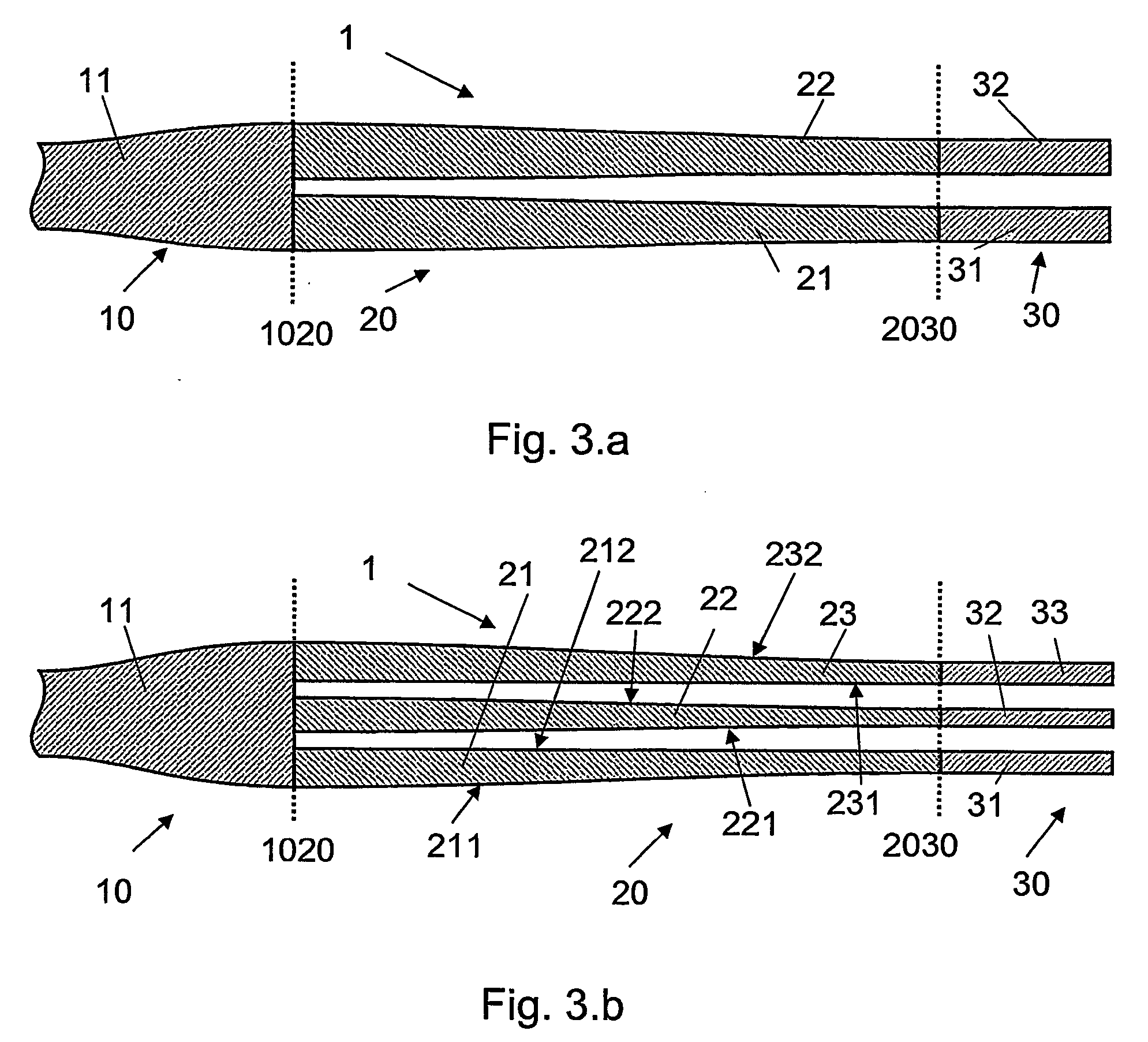
The invention relates to an optical component (1) comprising a combination of optical waveguide elements for modifying the spot size of a mode of an electromagnetic field propagated by an optical waveguide element, the optical waveguide elements being formed on a substrate. The object of the present invention is to provide a mode coupler with low coupling loss that is easy to manufacture and process tolerant. The problem is solved in that the optical component further comprises a) a first section (10), comprising a first optical waveguide element (11) adapted to sustain at least one mode of the electromagnetic field, b) a second section (20) comprising at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements (21, 22), each of said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements comprising at least one waveguide segment, said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements being optically connected to said first optical waveguide element of said first section; wherein said cooperating optical waveguide elements (21, 22) of said second section (20) are adapted to maintain optical coupling between said optical waveguide elements to ensure that said at least one mode of the electromagnetic field is sustained by said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements in cooperation. Preferably, the waveguides of the first and / or second sections are tapered according to a cosine function or to a 5th or 7th order polynomial. An advantage of an optical component according to the invention is that it provides a mode size converter that is relatively simple to manufacture in that it requires no extra process steps. A further advantage is that it is readily suitable for integration with other optical circuitry on a common substrate. The invention may be used in optical communication systems (e.g. systems employing WDM) where coupling of light between integrated optical circuits and optical fibres are needed.
Owner:IGNIS PHOTONYX AS
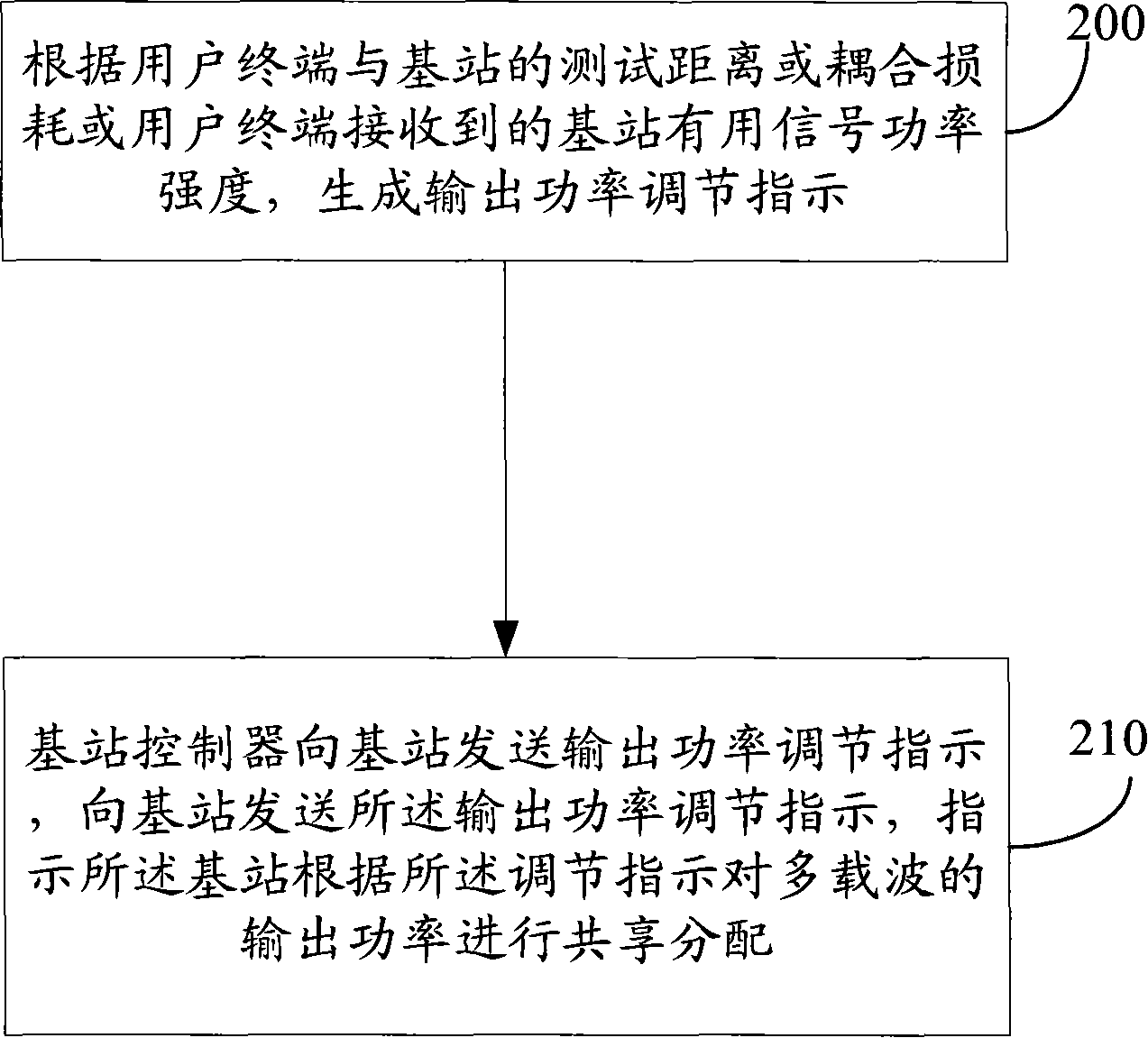
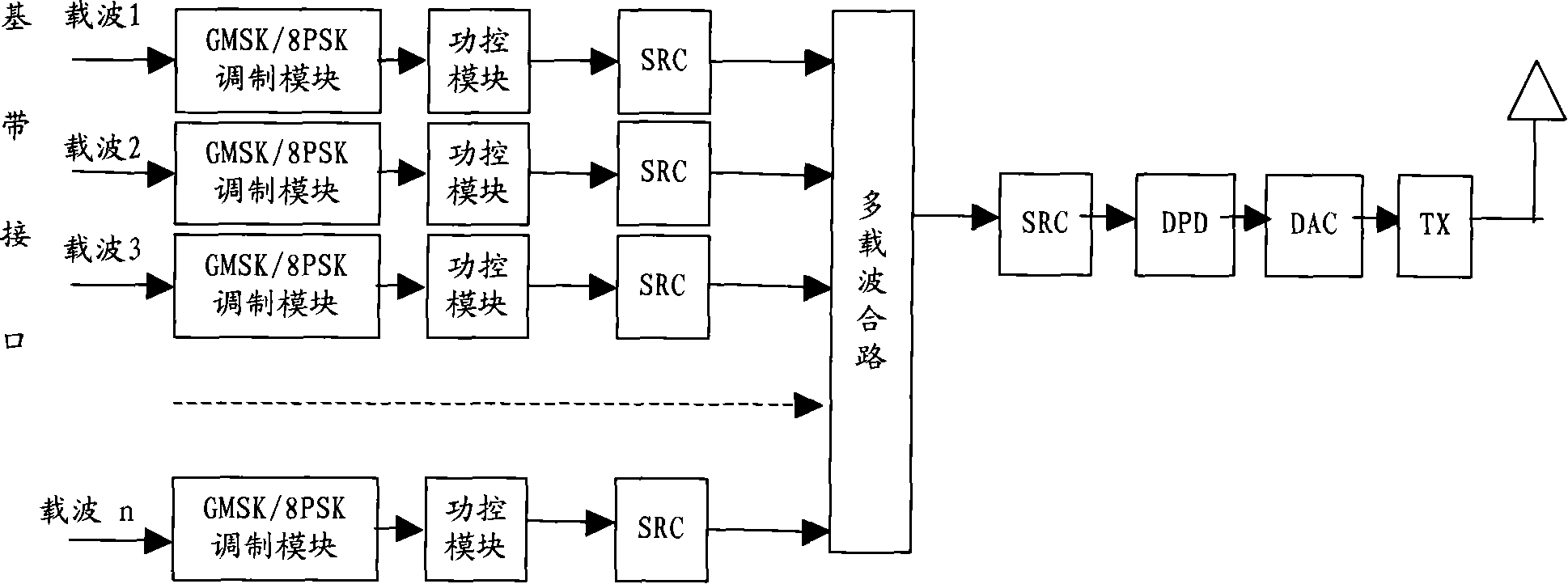
A realization method and device for multi-carrier wave power share
ActiveCN101242664AIncrease power sharingIncrease coveragePower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCoupling lossCarrier signal
The invention discloses a implementing method and device for multi-carrier power sharing. The inventive method includes steps of: generating output power modulating instruction according to test distance between user terminal and base station, or coupling loss, or available signal power intensity of base station; sending the mentioned output power modulating instruction to base station, so as to instruct base station to distribute output power of multi-carrier for sharing according to the instruction. The invention dynamically modulates output power of carrier, improves power sharing, equivalently enhances coverage, reduces cost through scheduling of base station according to distance between user terminal and base station, coupling loss and intensity of available signal power received by user terminal, without changes on main hardware such as power amplifier.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical coupling arrangement having low coupling loss and high production yield
InactiveUS6892004B1Effective width of gapCoupling loss of couplingCoupling light guidesCoupling lossMultiplexer
An optical coupling arrangement has a first transition region having a plurality of first segmented waveguides and a plurality of transverse segments of alternating indices of refraction with at least some of the transverse segments traversing the first segmented waveguides. The first segmented waveguides are formed by core segments in some of the transverse segments. The arrangement may also have a second transition region having a plurality of second segmented waveguides each aligned with a respective one of the first segmented waveguides. The arrangement is manufactured with a high production yield and is used in an optical coupling device for combining / splitting optical signals to reduce the insertion loss. The optical coupling device is also used in other devices such as Mach-Zehnder devices and arrayed waveguide grating demultiplexers / multiplexers.
Owner:YU GUOMIN
Optical device, optical device manufacturing method, and optical integrated device
ActiveUS20050259935A1Small coupling between dimensionsIncrease speedCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCoupling lossSignal light
In a multi-mode interference waveguide (MMI) of a sheet shape spreading in the length direction and the width direction, the length of the multi-mode interference waveguide is set to such a length that the unique mode interferes in the length direction, thereby reducing the coupling loss when inputting / outputting the signal light. The multi-mode interference waveguide has a maximum refraction factor portion in the thickness direction and has such a refraction factor distribution that the refraction factor is reduced as departing from the maximum refraction factor portion. Thus, it is possible to suppress mode dispersion in the thickness direction of the multi-mode interference waveguide and obtain a high transmission rate in the order of 10 Gb / s.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Hollow core photon crystal fiber-optic fiber gas sensor
InactiveCN1900696AReduce lossIncrease the lengthColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberCoupling loss
The disclosed sensor is gas sensor of optical crystal fiber with hollow core. The air sensor includes light source, light guiding gas-cell light path, reference light path of general optical fiber, and signal conversion part. Through general optical fiber, and light splitter, the light guiding gas-cell light path is connected to light source. Being setup at another end of the light guiding gas-cell light path and the reference light path, the said signal conversion part including photodiode, and phase-locked amplifier is in use for providing signal for circuit of monitoring external gas concentration. Optical crystal fiber with hollow core of containing gas permeable micropores in micro level is adopted in the light guiding gas-cell. Comparing current optical fiber gas sensor, the invention possesses advantages: simple system, easy of controlling absorbed light path, and coupling loss. The invention raises effective absorbed light path, and response seeped of parts so as to suit monitoring gas in site.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Optical fiber coupling part
ActiveUS7346237B2Send efficientlyLarge numerical apertureCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesCoupling lossSemiconductor
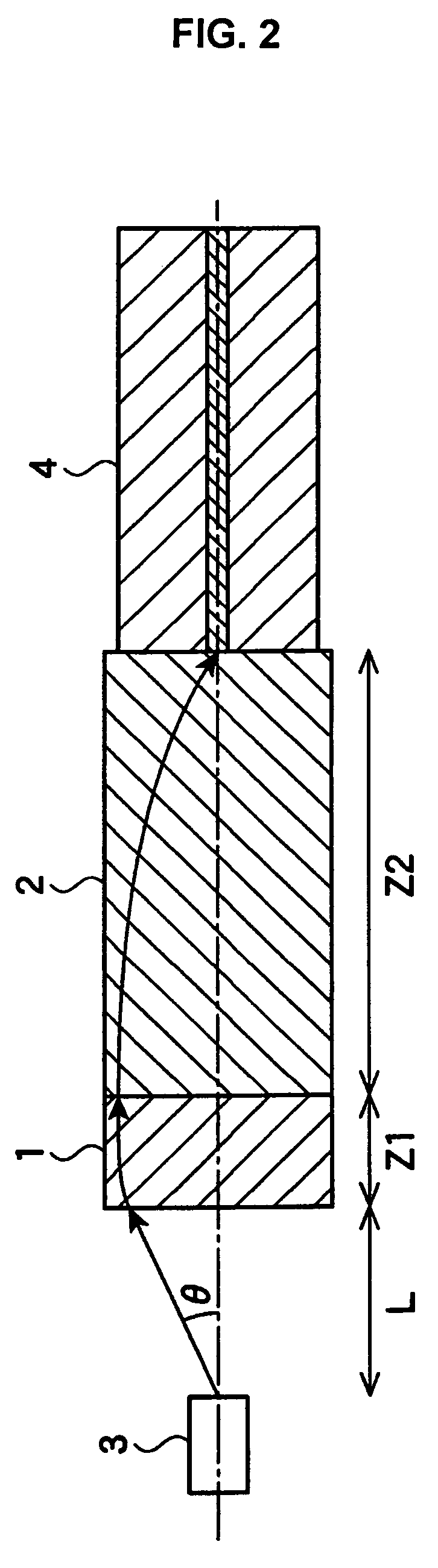
An optical fiber coupling part capable of reducing coupling loss while maintaining a large operating distance, and having a good module assembling property. AT least one GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA that is larger than numerical aperture NAs of a light-emitting source (such as a semiconductor laser) is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber. All lights emitted from the light-emitting source can enter the GRIN lens, and the loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In addition, a second GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA2 is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber having numerical aperture NAf, and further a first GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA1, which is larger than numerical aperture NA2, is fusion-spliced with the other end of the second GRIN lens. Thereby, the light emitted from the light-emitting source can efficiently enter the optical fiber, and loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In this case, the formula expressed by NAf≦NA2<NAs≦NA1 is desirable.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
Method for analyzing and predicting noise outside car
InactiveCN101661522AShorten the development cycleReduce development costsSpecial data processing applicationsCoupling lossPredictive methods
The invention discloses a method for analyzing and predicting noise outside a car, which aims at overcoming the problem that the noise outside the car is difficult to be predicted in the developing and designing stage of the car product. The method comprises the steps of: 1) establishing an SEA model of the car body structure: dividing the car body into a plurality of structural sub-systems, and connecting all structural sub-systems according to the correlations; 2) establishing an SEA model for an external acoustic cavity of the car: establishing SEA models for the external acoustic cavitiesof the car at two sides and on the external surface of the car body in the SEA model of the car body; 3) determining the SEA parameter of the car body and the external acoustic cavity sub-system of the car: determining the mode density of each sub-system, determining the internal loss factor of each sub-system, and determining the coupling loss factor of all sub-systems; 4) determining the external excitation energy of the car body: determining the acoustic excitation energy of an engine cabin, determining the excitation energy of suspended engine, determining the excitation energy of unevenness of the road surface on the car body, and determining the excitation energy of the wind pressure on the external surface of the car body; and 5) analyzing and predicting the noise outside the car.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Laser cleaning system for rubber module
InactiveCN102886363AEasy to cleanIncrease laser output powerCleaning processes and apparatusCoupling lossEngineering
The invention provides a laser cleaning system for a rubber module, and the laser cleaning system comprises a laser cleaning head and a laser control system, wherein the laser cleaning head comprises a laser device and a beam expander, a scanning galvanometer is arranged in the output light direction of the beam expander, a focusing lens is arranged on the reflecting light path of the scanning galvanometer, and the light path output end of the focusing lens is used for cleaning articles; the laser device comprises a total reflector, an acousto-optic Q-switch, a semiconductor pumping module and an output mirror which are sequentially arranged on the light path; and the light-emitting switch of the laser device, the Q-switching drive module of the acousto-optic Q-switch, the power supply of the semiconductor pumping module, and the drive unit of the scanning galvanometer are controlled by a laser control system respectively. According to the invention, the semiconductor pumping solid pulse laser device is adopted and integrated on a cleaning machining head, the output power of laser is increased by means of acousto-optic Q-switching, and the coupling loss caused by optical fibre transmission is avoided, so that portable-type machining in a handheld mode or a manipulator clamping mode can be realized, and efficient cleaning for the rubber module can be finished.
Owner:NO 717 INST CHINA MARINE HEAVY IND GRP
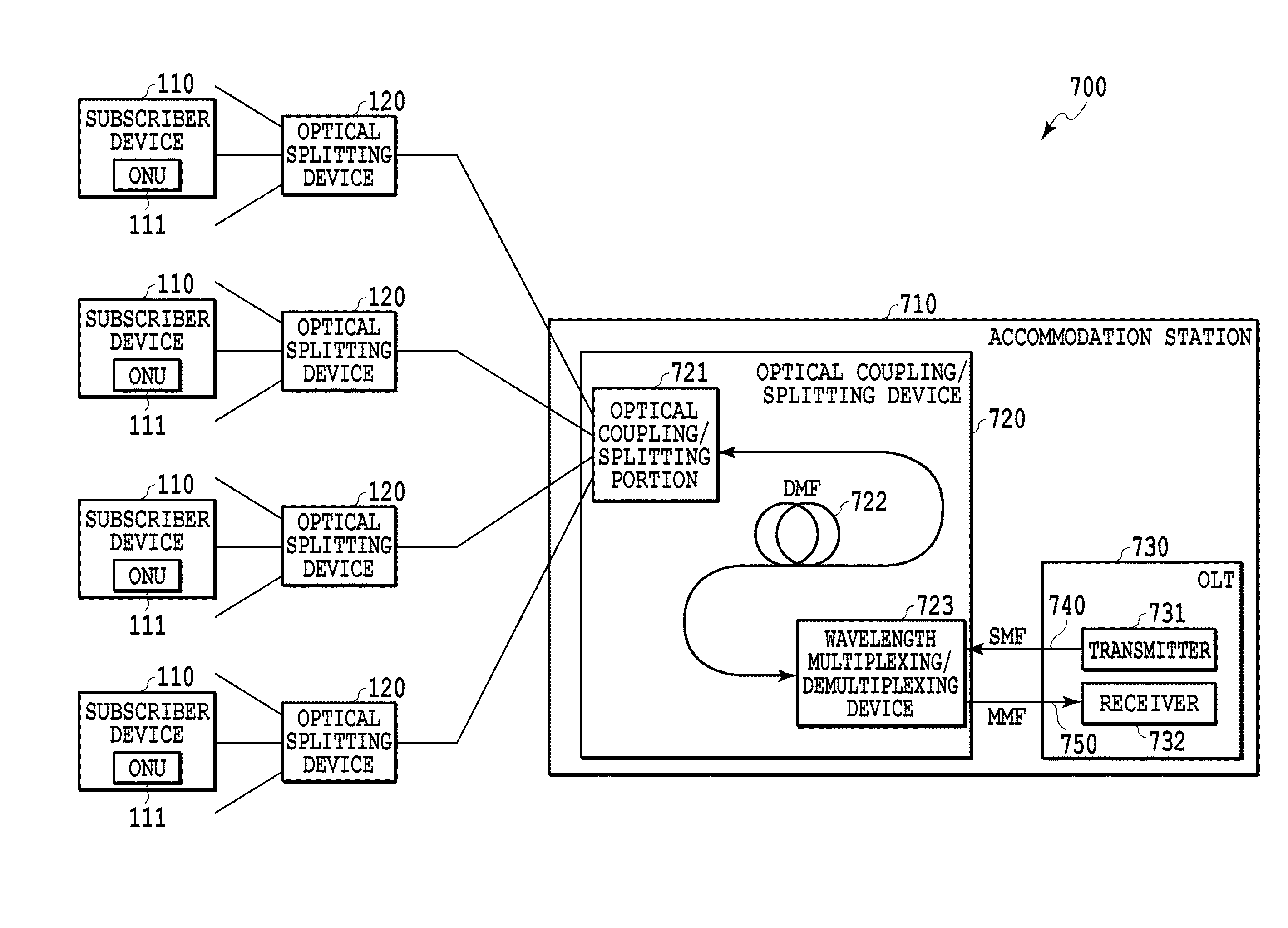
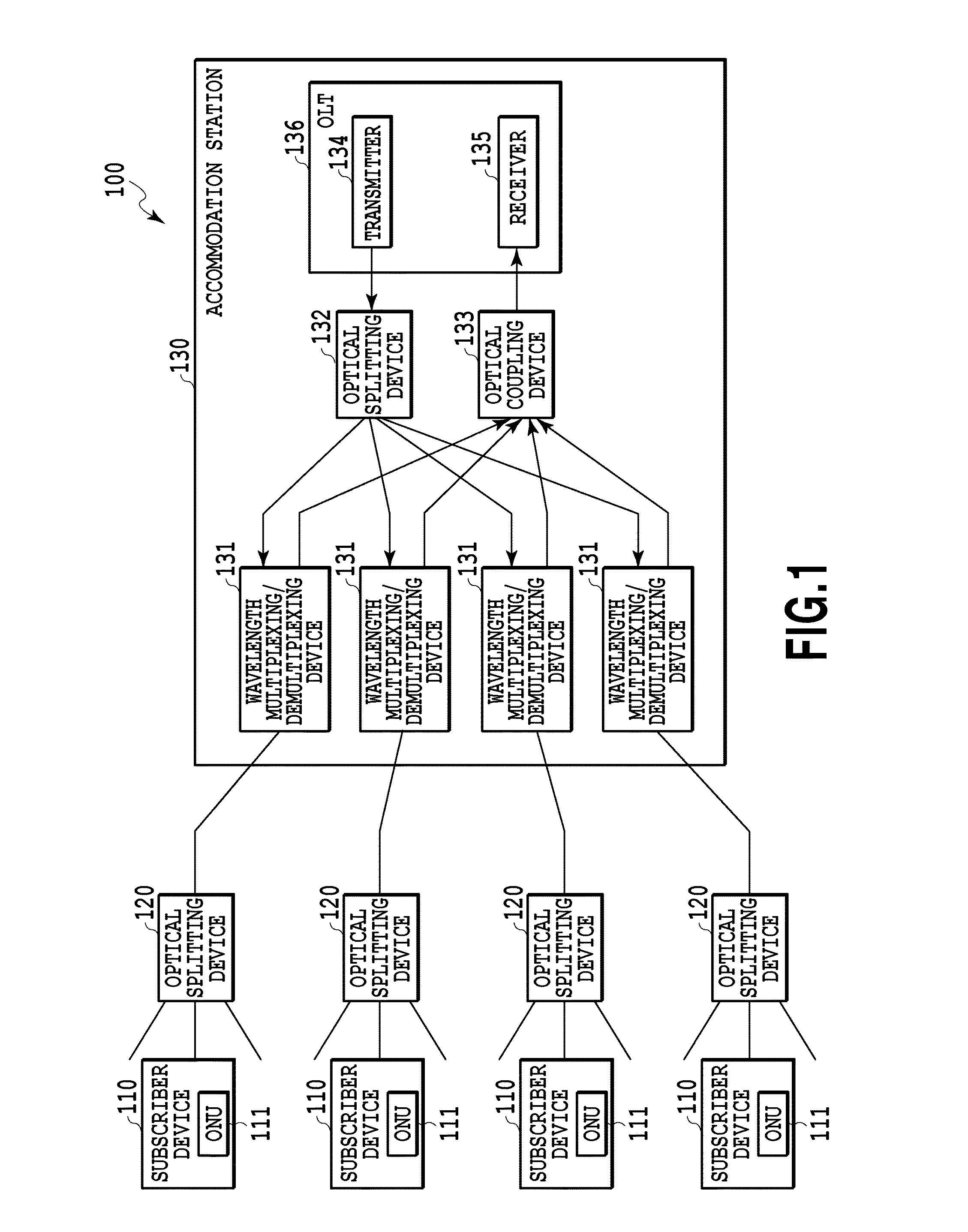
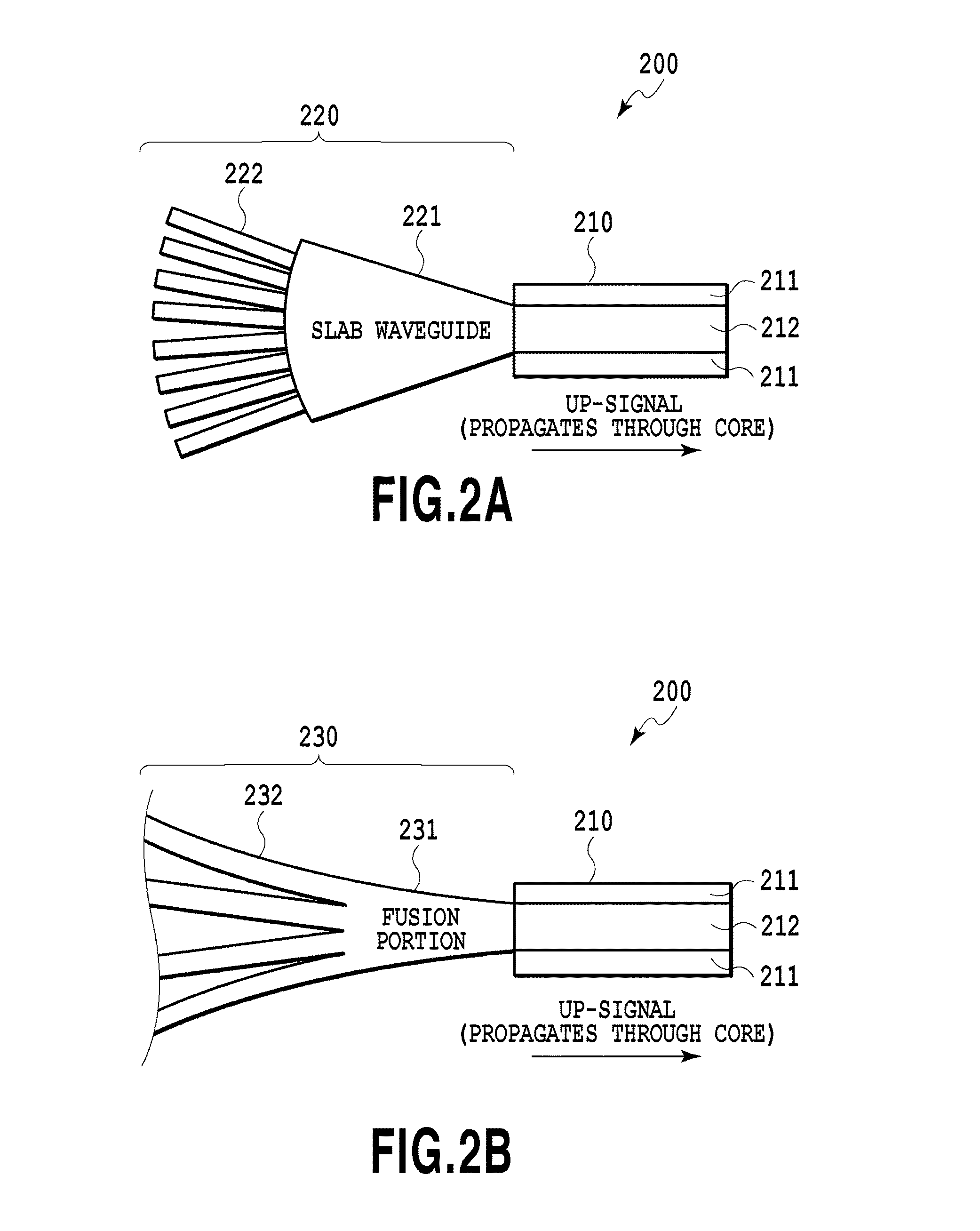
Light merging/branching device, bidirectional light propagation device, and light transmission/reception system
ActiveUS20140186040A1Reduce couplingIncreasing budgetCoupling light guidesOptical multiplexOptical propagationCoupling loss
The present invention relates to an optical coupling / splitting device that realizes the splitting of a down-signal and the coupling of up-signals by the same optical device, and reduces coupling losses of the up-signal. An optical coupling / splitting device in the present invention comprises an optical coupling / splitting means for coupling a plurality of up-signals in a multi-mode for output and splitting a down-signal in a single mode for output, and a two-way optical propagation means for propagating the up-signal that is output from the optical coupling / splitting means in a multi-mode for output and propagate the down-signal in a single mode to be output to the optical coupling / splitting means.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
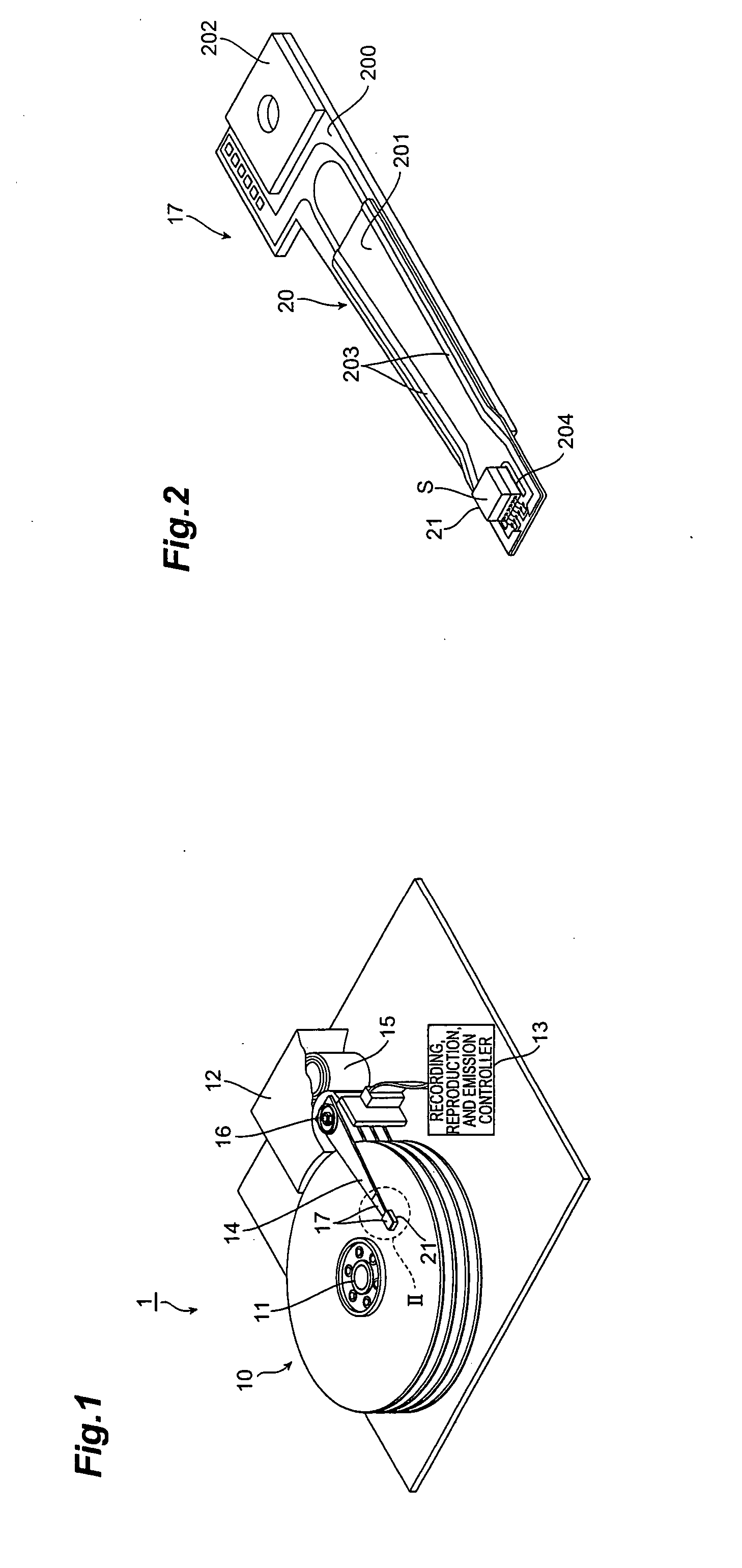
Thermally assisted magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive
ActiveUS20080055762A1Reducing characteristic variationReduce variationCombination recordingRecord information storageCoupling lossHard disc drive
A laser diode is fixed to a light source support substrate and a first surface of a slider substrate is fixed to a second surface of the light source support substrate; therefore, the slider substrate and the laser diode are kept in a fixed positional relation Since the laser diode faces a light entrance face of a core, long-distance propagation of light as in the conventional technology does not occur, and light emitted from, a light emitting element is guided well to a medium-facing surface, while permitting some mounting error and coupling loss of light A spot size w of a light intensity distribution along the X-axis in the XY plane including an incident-light centroid position on the light entrance face is set larger than a thickness of the core, whereby variation in incidence efficiency is well suppressed against positional deviation.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
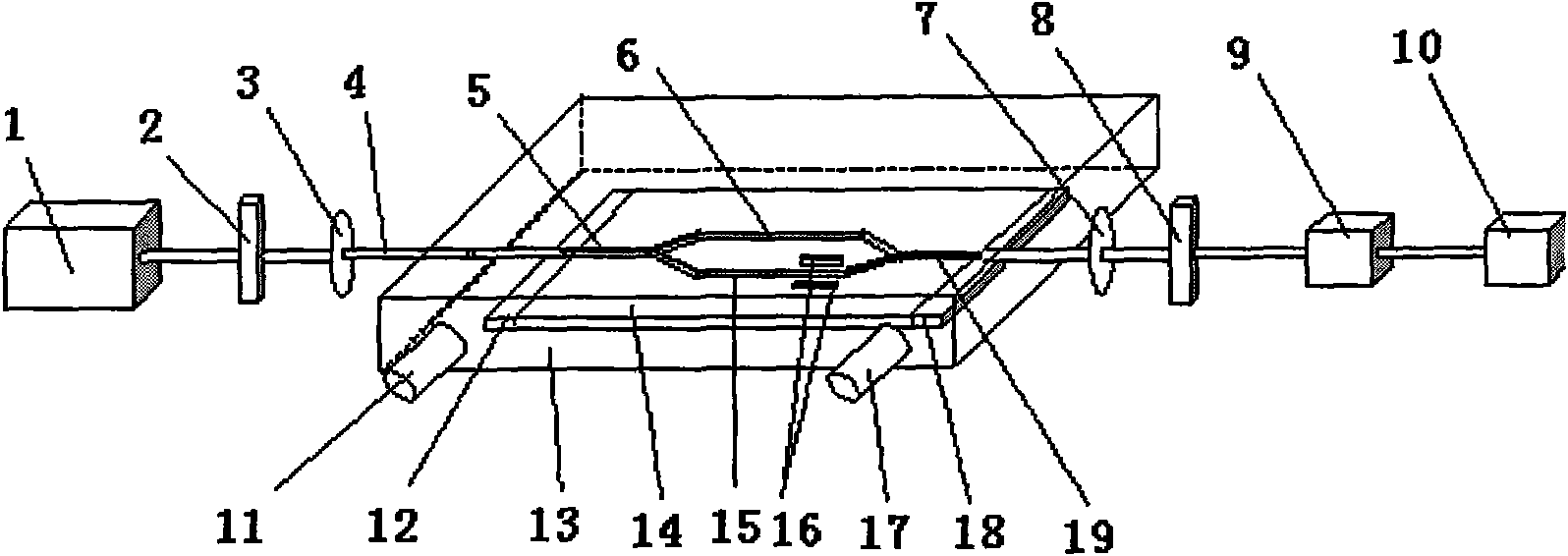
Optoelectronic hybrid integration sensor device of sulfureted hydrogen gas concentration and test method thereof
ActiveCN101576488AHigh detection sensitivityHigh selectivityPhase-affecting property measurementsCoupling lossLaser light
The invention discloses an optoelectronic hybrid integration sensor device of sulfureted hydrogen gas concentration, which has the characteristics: laser light led out from a laser (1) penetrates through a lens (3) via a polarizer (2), an optical fiber (4) transmits focused polarized light into a gas box (13), the coupling of the optical fiber with a wave guide is realized on an input coupling element (12), the coupled light enters a Mach-Zehnder wave guide interferometer (14), branch wave guides (5 and 19) are respectively connected with a reference arm wave guide (15) and a signal arm wave guide (6) in parallel, the end surface sizes of the two wave guides are determined by mode field matching so as to reduce coupling loss and improve coupling efficiency, a wave guide phase modulator (16) adopts a lumped type wave guide phase modulator structure and is arranged between the reference arm wave guide and the signal arm wave guide, the light interfered by the Mach-Zehnder wave guide interferometer is coupled out of the gas box by an output coupling element (18) to enter a photoelectric signal transforming and processing system and then is led into a photoelectric diode (9) by a lens (7) and an analyzer (8) via the optical fiber, after that, the light intensity is transformed into electric signals to be inputted to a micro signal processor (10), and finally the concentration value of the sulfureted hydrogen gas is obtained by calculation.
Owner:克拉玛依市金牛工程建设有限责任公司
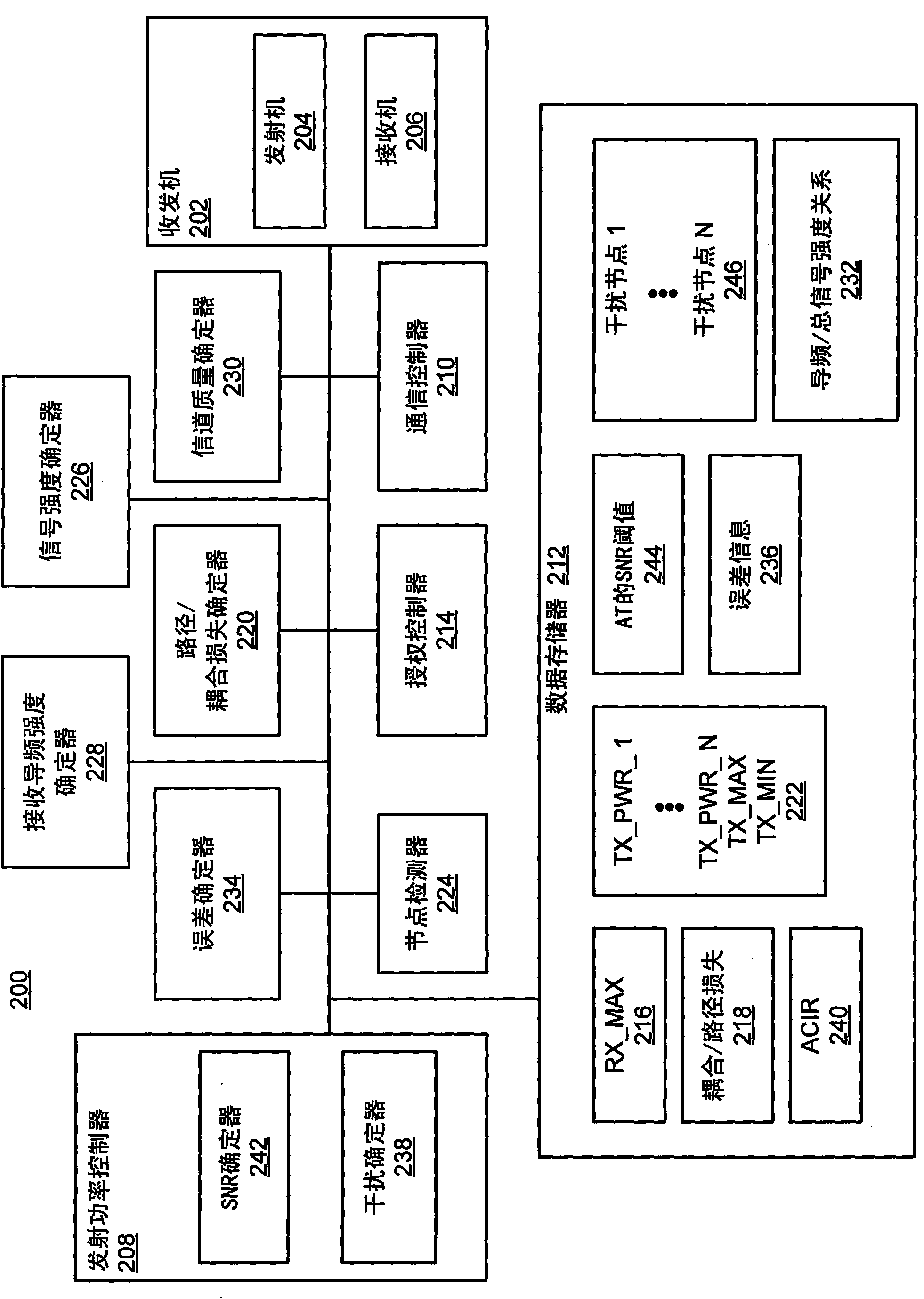
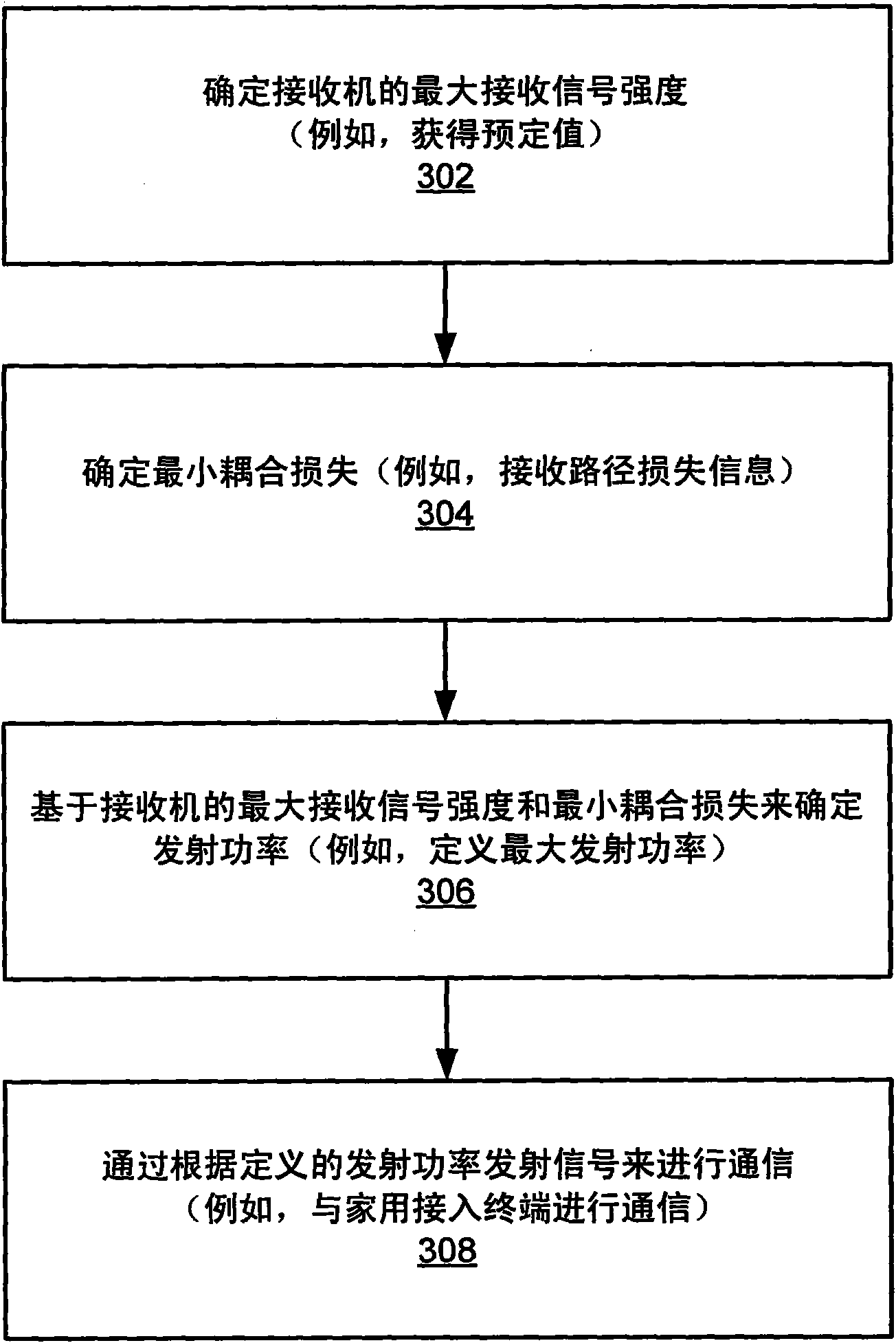
Adaptation of transmit power for neighboring nodes
ActiveCN101779500AReduce transmit powerImprove performancePower managementNetwork planningCoupling lossSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Transmit power (e.g., maximum transmit power) may be defined based on the maximum received signal strength allowed by a receiver and a minimum coupling loss from a transmitting node to a receiver. Transmit power may be defined for an access node (e.g., a femto node) such that a corresponding outage created in a cell (e.g., a macro cell) is limited while still providing an acceptable level of coverage for access terminals associated with the access node. An access node may autonomously adjust its transmit power based on channel measurement and a defined coverage hole to mitigate interference. Transmit power may be defined based on channel quality. Transmit power may be defined based on a signal-to-noise ratio at an access terminal. The transmit power of neighboring access nodes also may be controlled by inter-access node signaling.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Fiber optic collimator system, fiber optic collimator array, and manufacturing method of the fiber optic collimator system and fiber optic collimator array system
ActiveUS7357005B2Efficient manufacturingEasy to produceGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesCoupling lossFiber
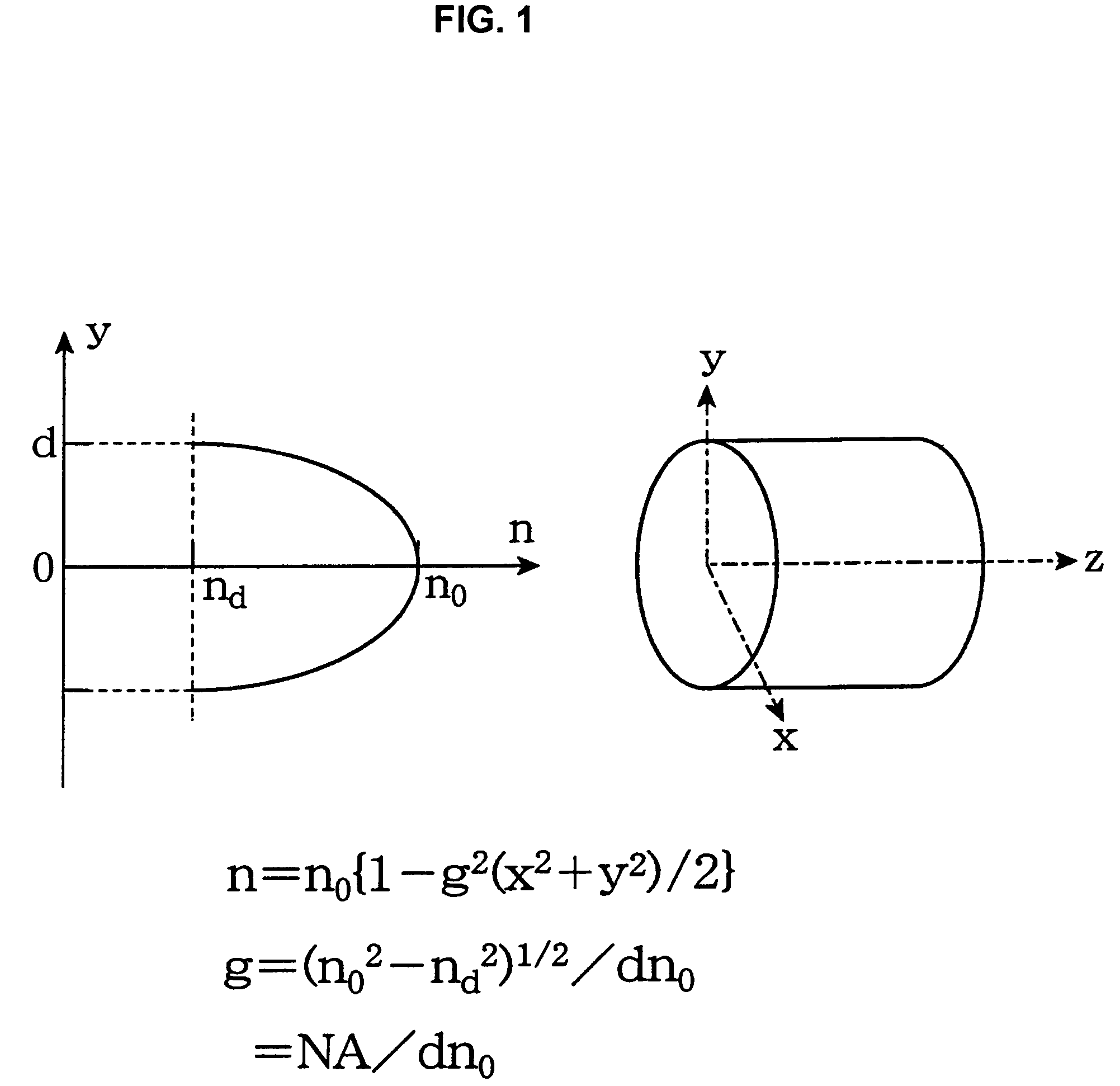
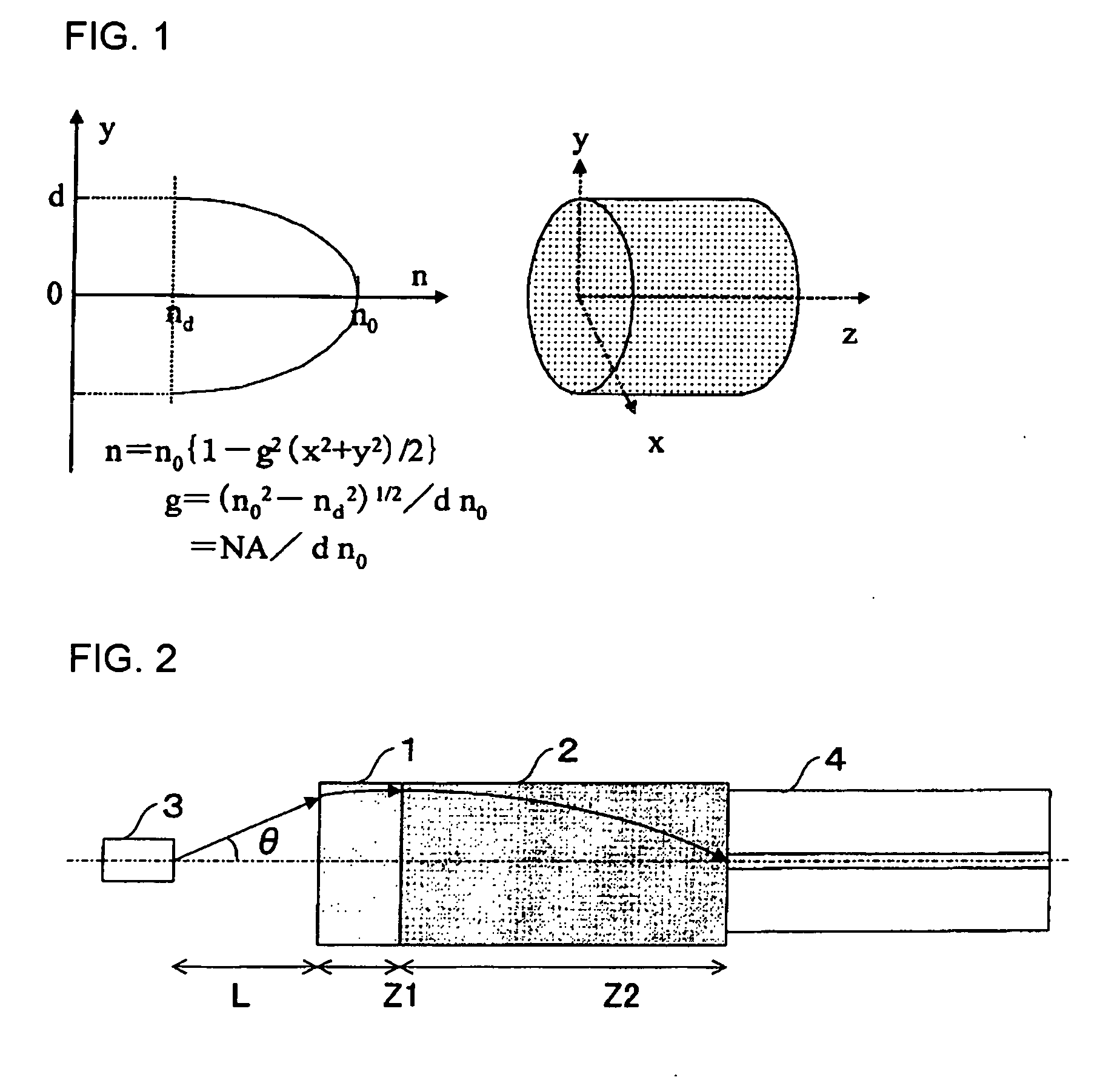
A fiber optic collimator system, a fiber optic collimator array, and a fiber optic collimator array system, which can reduce difficulty in an alignment process, minimize a coupling loss, and prevent the optical characteristics from deteriorating. An optical fiber is fused to one end of a GRIN lens made of quartz glass containing one or more selected from Sb2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2 and ZrO2 as a refractive index regulating substance, to form an optical fiber with a GRIN lens. Since an adhesive is not used, the core alignment of the GRIN lens and the optical fiber can be facilitated by a self alignment effect without deteriorating the optical characteristics. Moreover, the coupling loss is remarkably reduced by appropriately setting a refractive index distribution constant g of the GRIN lens. By fabricating the fiber optic collimator system, the fiber optic collimator array, the fiber optic collimator array system using the optical fiber with a GRIN lens can reduce the difficulty in the core alignment process, minimize the coupling loss, and prevent the optical characteristics from deteriorating.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
Near-field antenna apparatus for three-segment type metal rear cover
InactiveCN105826679AResolve interactionPlay the role of electric field radiationAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna equipments with additional functionsCoupling lossStructural engineering
The invention provides a near-field antenna apparatus for a three-segment type metal rear cover. The metal rear cover includes a metal frame and a metal backshell, wherein gaps are formed in the joint between the upper and lower ends of the metal frame and the metal backshell, so that a first segment, a second segment and a third segment are formed; the first segment is formed by the upper end of the metal frame and is used as a radiator; the second segment is formed by the middle part of the metal frame and the metal backshell; the third segment is formed by the lower end of the metal frame; the metal rear cover also includes a near-field antenna and a radio frequency antenna which are in feeding connection with the first segment; and the near-field antenna and the radio frequency antenna are set in a non-common ground mode. The near-field antenna apparatus for a three-segment type metal rear cover abandons a traditional mode for adding ferrite in a power supply coil, thus saving the cost; and the profile of a terminal has no demand for an extra gap opening design, so that the product is more beautiful and the coupling loss caused by coupled feeding is avoided; and at the same time, the antenna structure designed for a special three-segment type metal rear cover structure enables the antenna to have an efficient structural form in different forms of communication terminals.
Owner:HUIZHOU SPEED WIRELESS TECH CO LTD
Optical fiber coupling part and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7603008B2Easy alignmentEasy to manufactureGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesCoupling lossOptical property
An optical fiber coupling part that reduces the difficulty in adjusting cores, minimizes coupling loss, and prevents optical characteristics from deteriorating. An optical fiber is fused to one end of a GRIN lens which includes a quartz glass containing one or more refractive index regulating substances selected from Sb2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2 or ZrO2. Optical characteristics are not deteriorated because an adhesive is not used, and self-alignment effects facilitate adjustment of the cores of the GRIN lens and the optical fiber. Furthemore, coupling loss can be minimized by setting a refractive index distribution constant g of the GRIN lens within an appropriate range.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
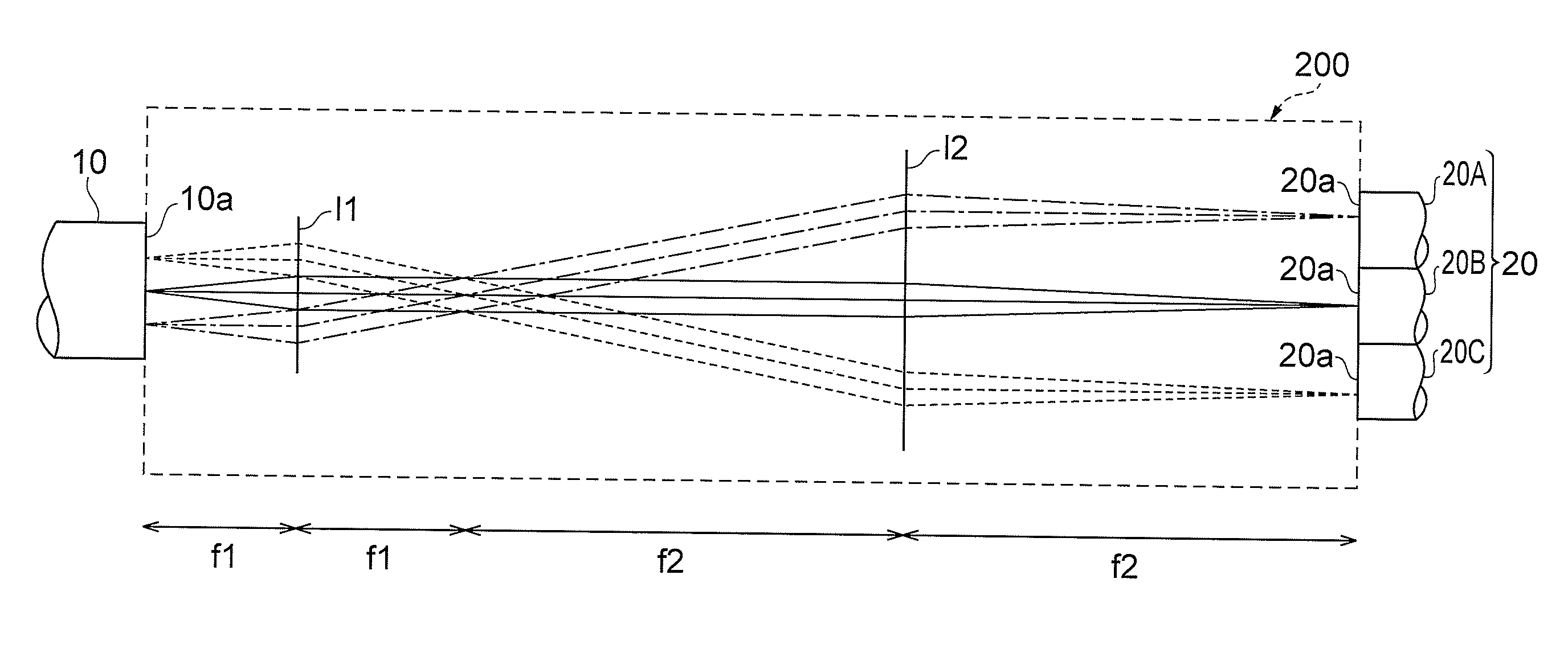
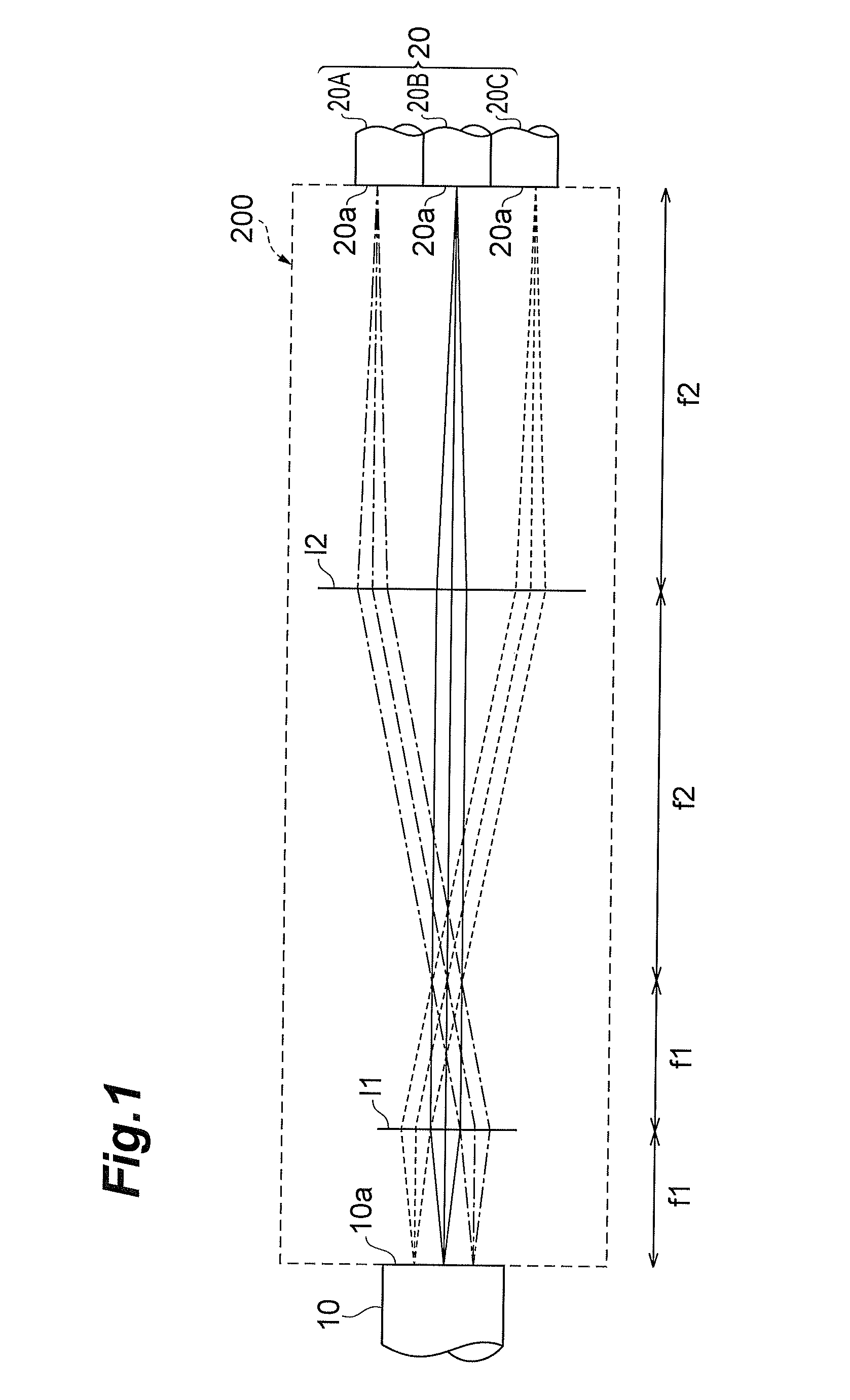
Optical device
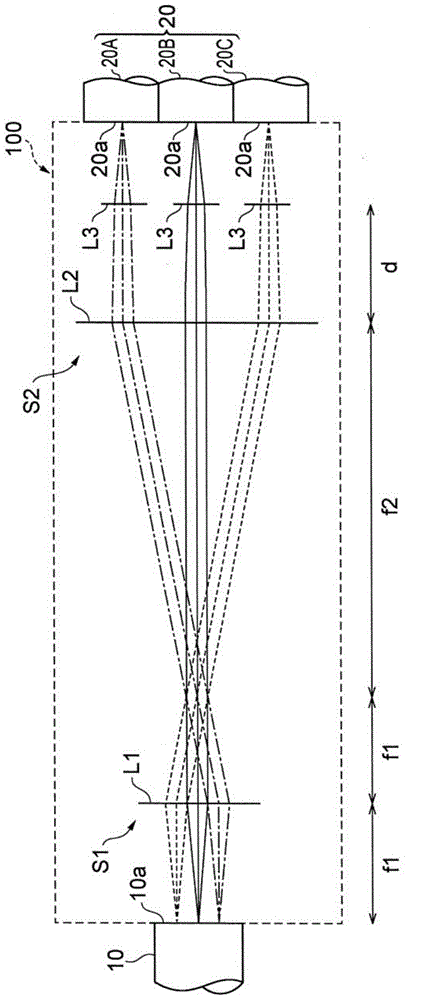
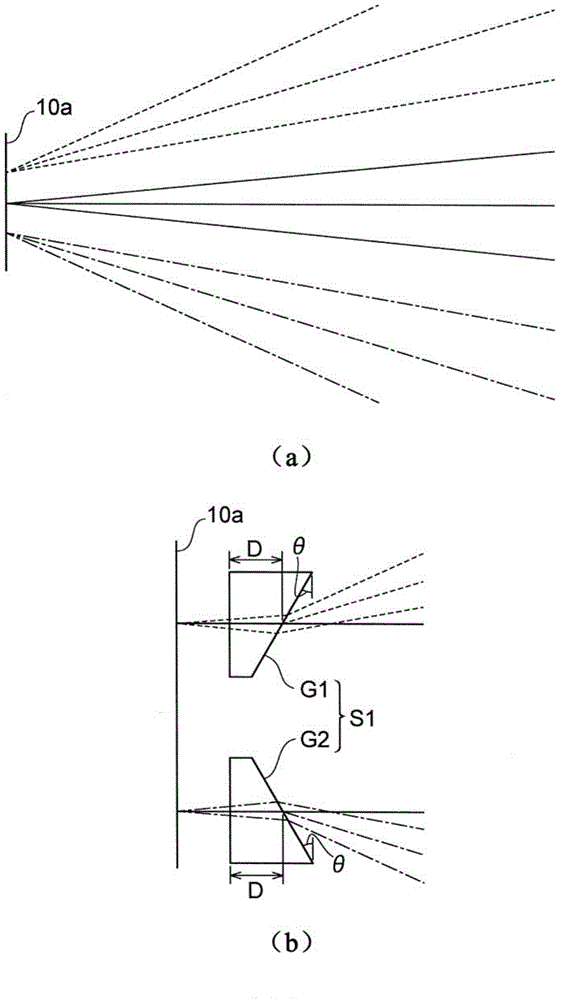
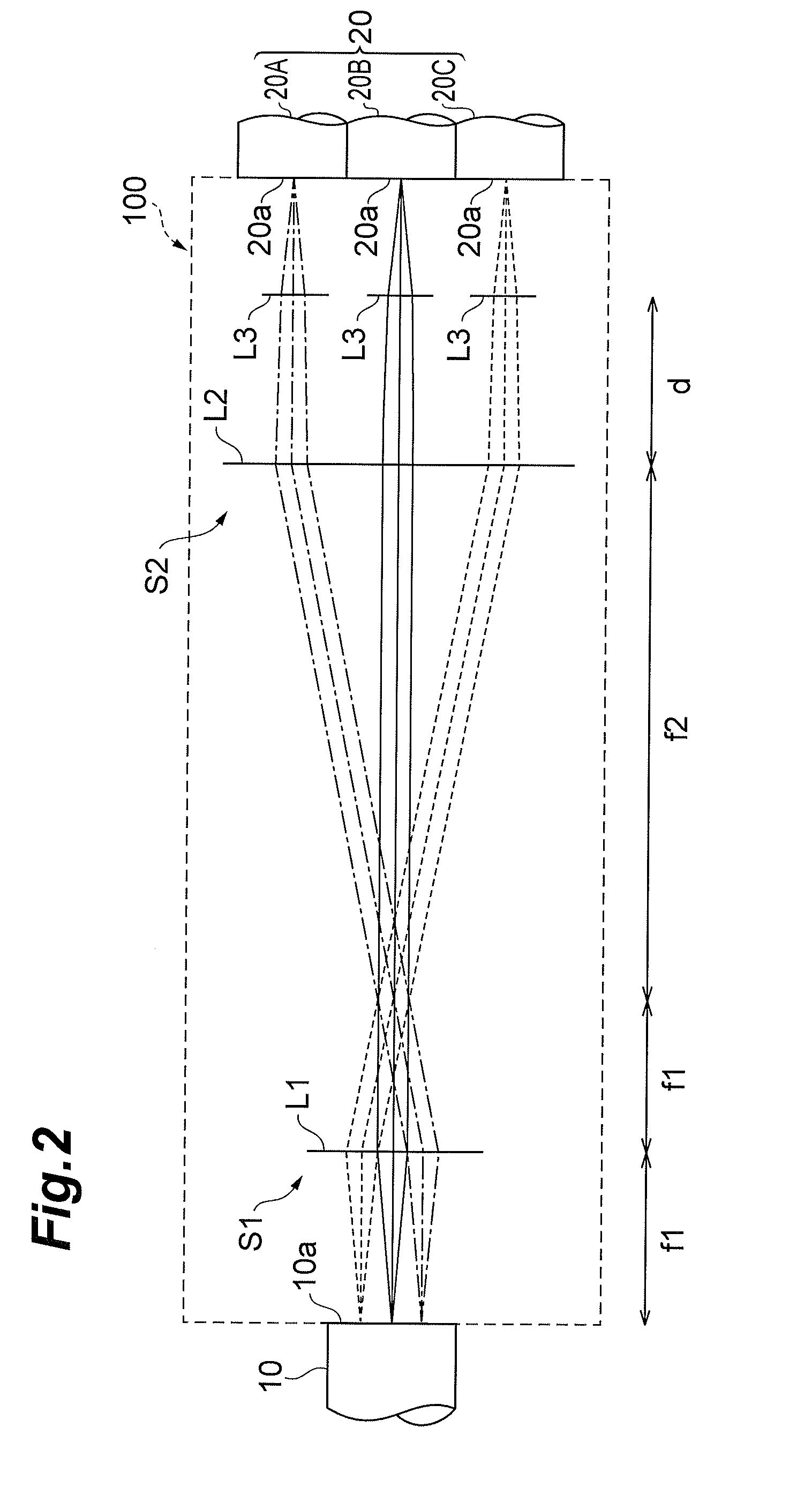
ActiveCN103608708AImprove practicalityReduce coupling lossCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreCoupling lossOptical axis
Provided is an optical device in which connection loss is reduced while practicality is enhanced. A multi-core fiber connection device (100) is an optical device for connecting a multi-core fiber (10) to a single-core fiber (20), and comprises a first optical system (S1) positioned on the optical axes of a plurality of beams emitted from a multi-core fiber (10), the first optical system for separating the optical axes of the beams from each other by making the optical axes non-parallel to each other, and a second optical system (S2) for making the optical axes of the plurality of beams substantially parallel to each other, the optical axes having been non-parallel to each other at the first optical system (S1).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Optical fiber devices and methods for interconnecting dissimilar fibers
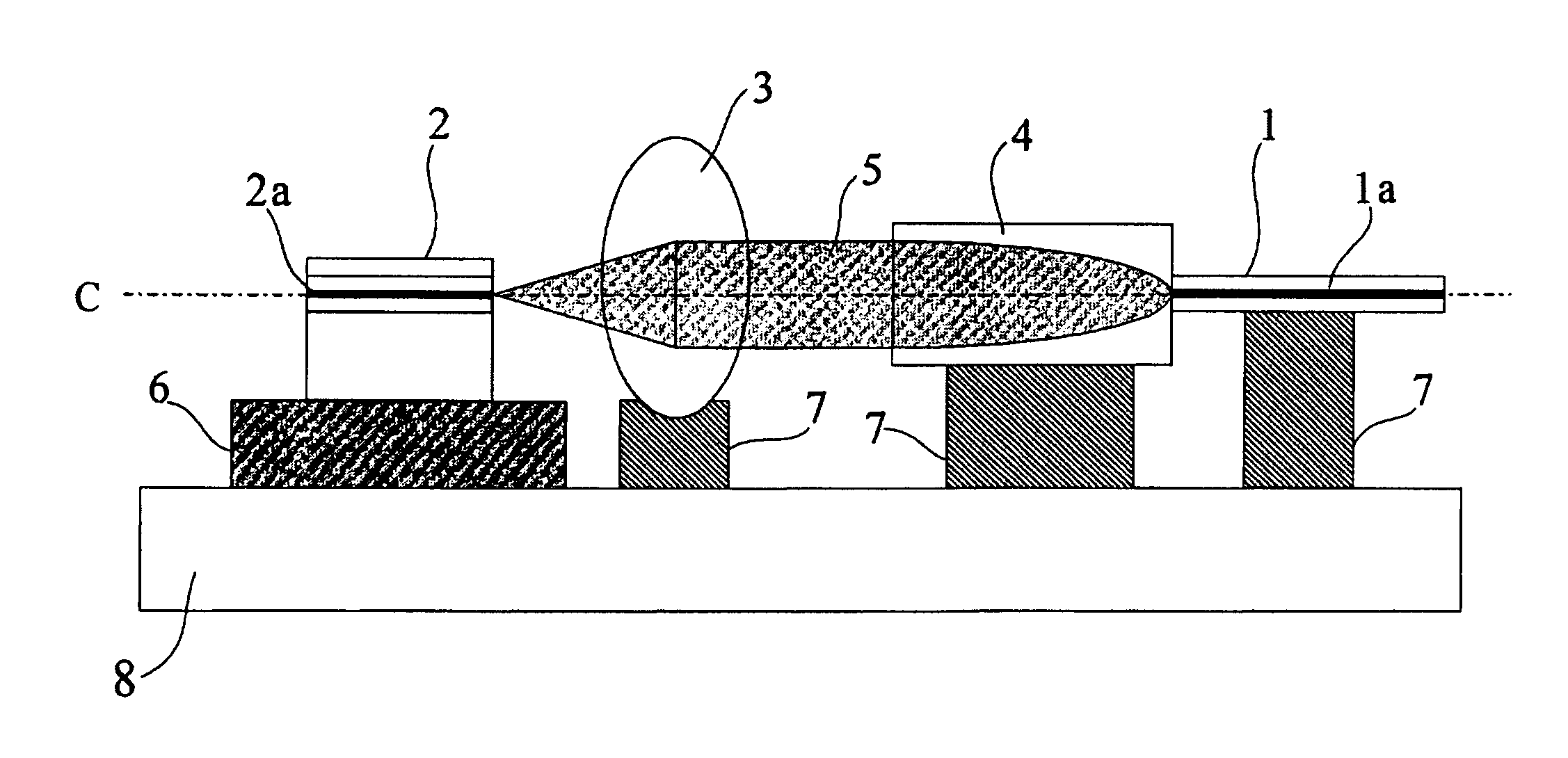
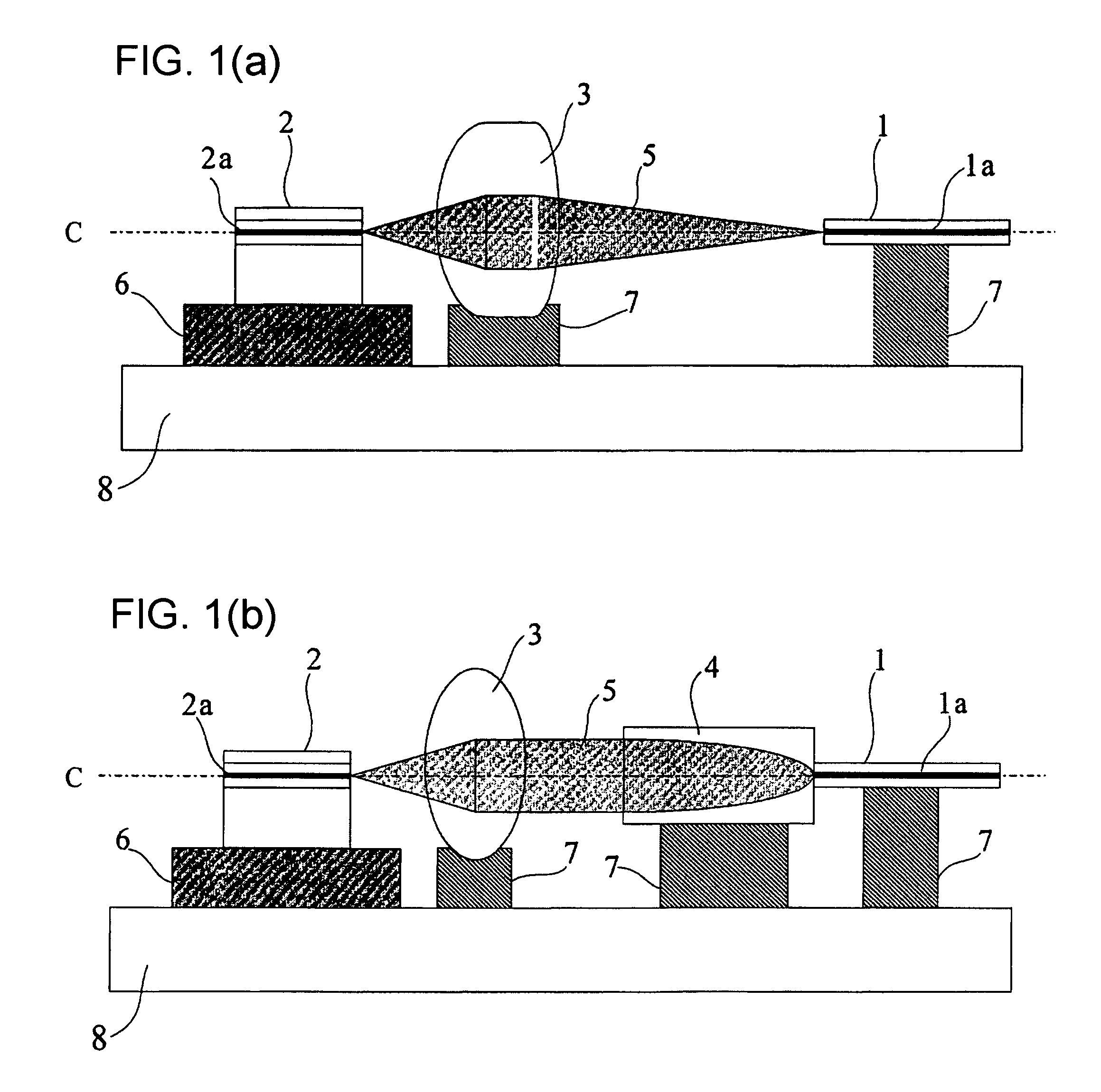
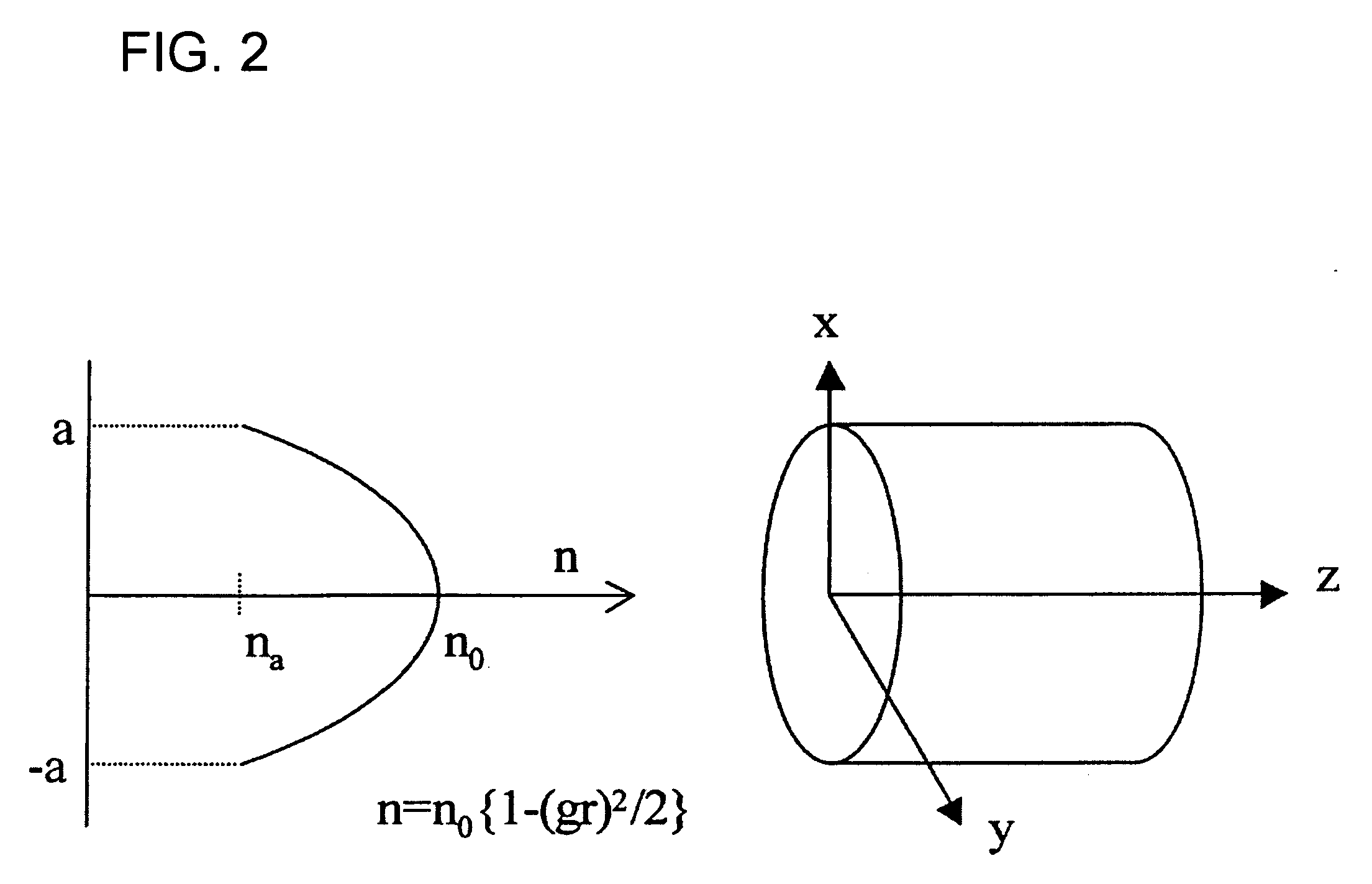
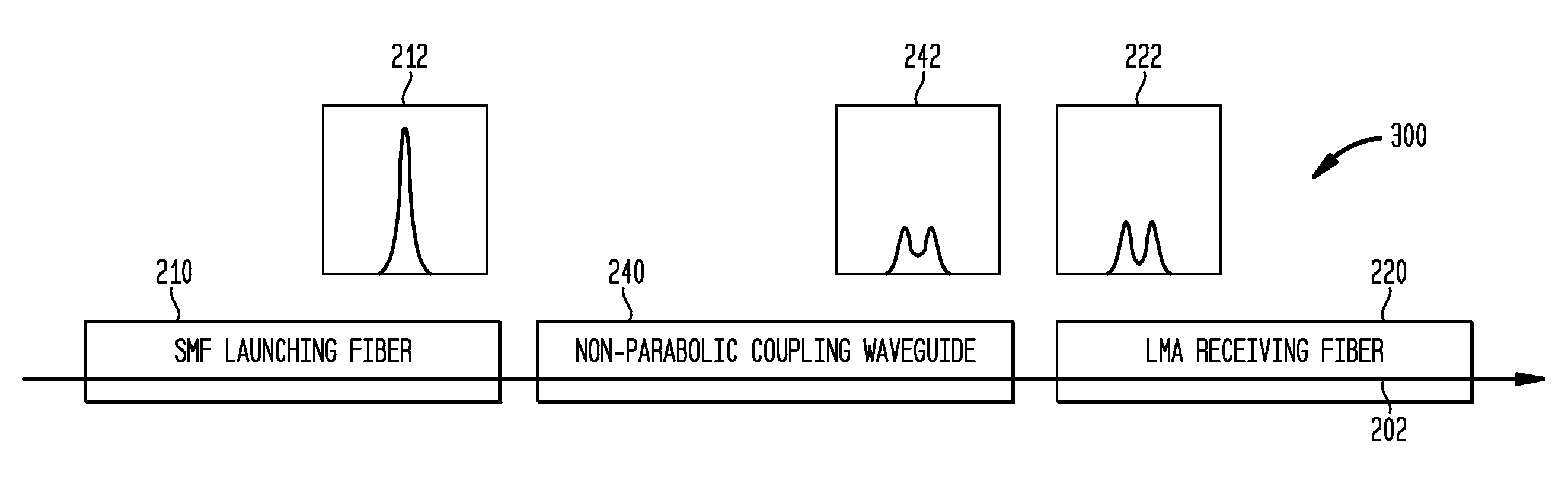
InactiveUS7340138B1Low loss couplingLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling lossFiber
A coupling waveguide is interconnected between a launching fiber and a receiving fiber to reduce coupling loss. The coupling waveguide includes an integrally formed graded index lens having a non-parabolic refractive index profile. The graded index lens receives as an input a coupling mode field of an optical signal launched by the launching fiber and transforms the coupling mode field into a transverse spatial distribution matching a corresponding coupling mode field of the receiving fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Optical waveguide element, manufacturing method for optical waveguide element, optical deflecting element, and optical switching element
InactiveUS6862393B2Reduce coupling lossIncrease the diameterCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical propagationCoupling loss
An optical waveguide element capable of being coupled with optical fibers at high coupling efficiency is to be provided. Also an optical waveguide element manufacturing method permitting accurate production of such optical waveguide elements is to be provided. The optical waveguide element is provided with a buffer layer formed over a monocrystalline substrate and an optical waveguide layer formed over the buffer layer, and a recess is formed in the buffer layer along the lengthwise direction of the monocrystalline substrate. The optical waveguide layer is provided to fit into this recess to form a channel optical waveguide. Over the upper face of the optical waveguide layer on the light incidence side and the light emission side, a cladding layer whose refractive index is smaller than that of the optical waveguide layer and whose thickness increases towards the end face(s) in a flared shape is provided in the same width as that of the monocrystalline substrate. By providing the cladding layer whose refractive index is smaller than that of the optical waveguide layer, it is made possible to expand the mode field diameter and substantially reduce the coupling loss between the optical fiber and the optical waveguide element. Further by increasing the thickness of the cladding layer in a flared shape toward the end face(s), it is made possible to gradually compress the mode field diameter and to reduce the optical propagation loss within the optical waveguide.
Owner:EPIPHOTONICS CORP
Optical fiber coupling componet
ActiveUS20060045419A1Send efficientlyLarge numerical apertureCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesCoupling lossNumerical aperture
An optical fiber coupling part capable of reducing coupling loss while maintaining a large operating distance, and having a good module assembling property. AT least one GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA that is larger than numerical aperture NAs of a light-emitting source (such as a semiconductor laser) is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber. All lights emitted from the light-emitting source can enter the GRIN lens, and the loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In addition, a second GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA2 is fusion-spliced with one end of the optical fiber having numerical aperture NAf, and further a first GRIN lens having numerical aperture NA1, which is larger than numerical aperture NA2, is fusion-spliced with the other end of the second GRIN lens. Thereby, the light emitted from the light-emitting source can efficiently enter the optical fiber, and loss of the light can thereby be reduced. In this case, the formula expressed by NAf≦NA2<NAs≦NA1 is desirable.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
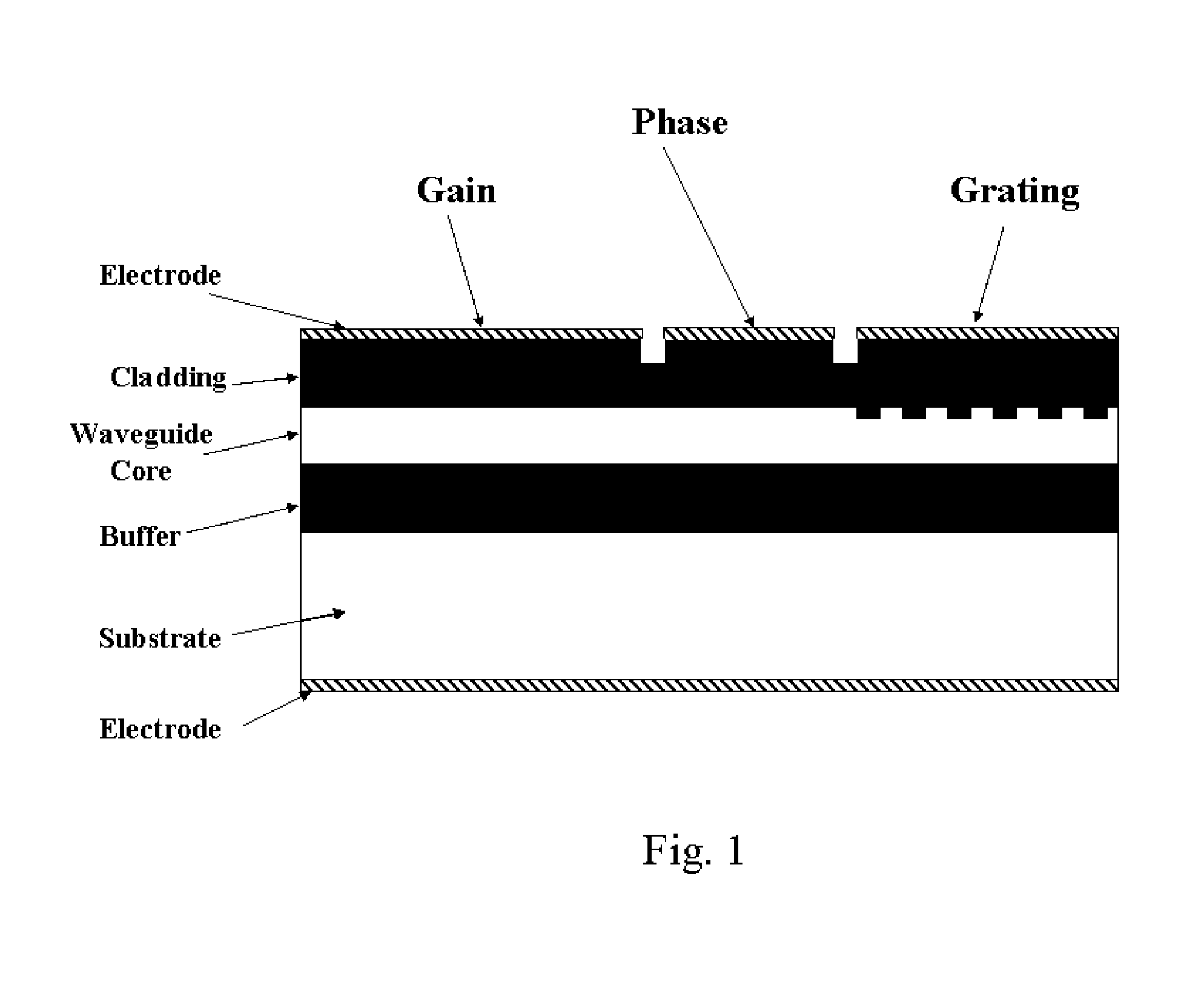
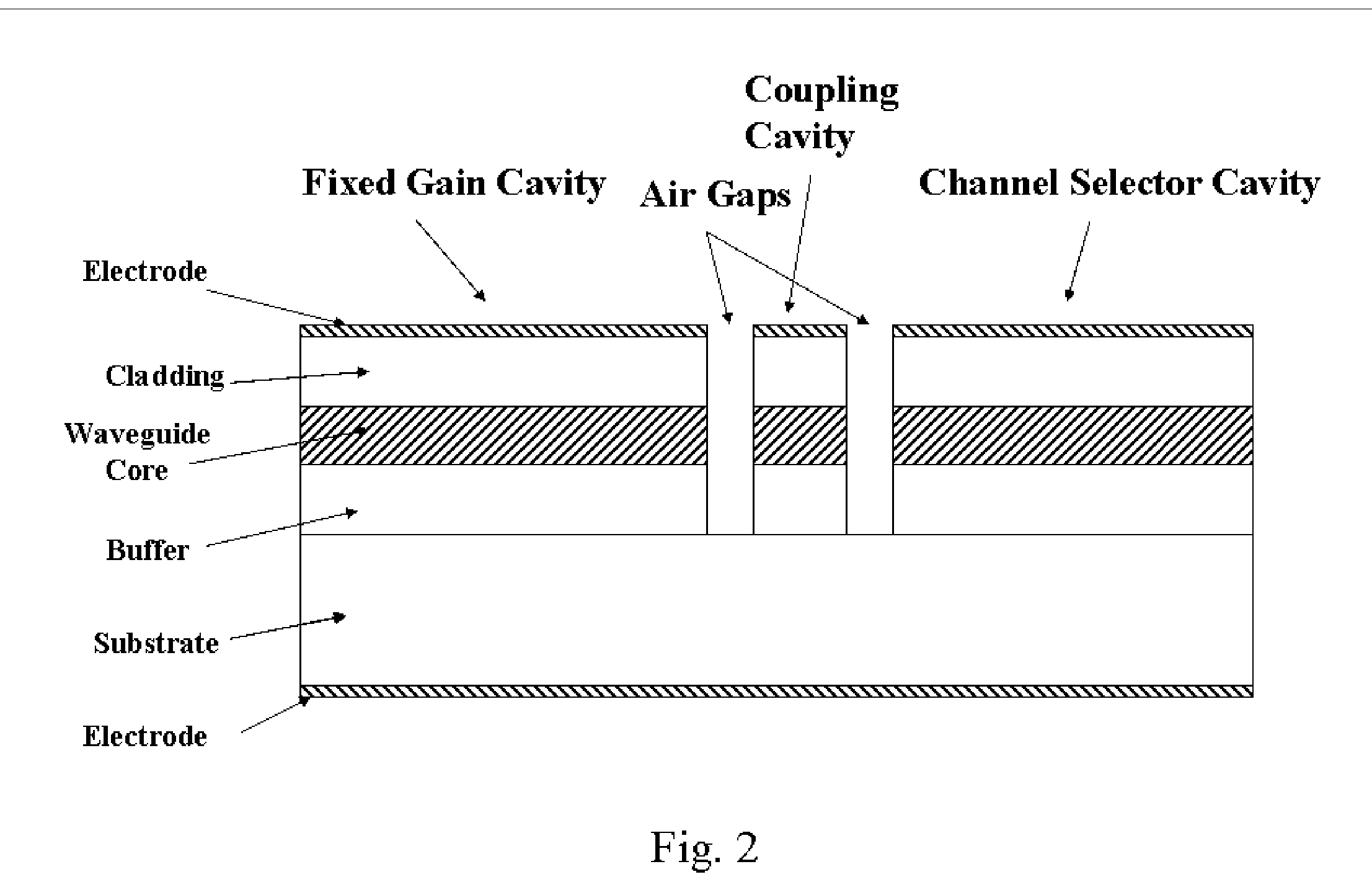
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser
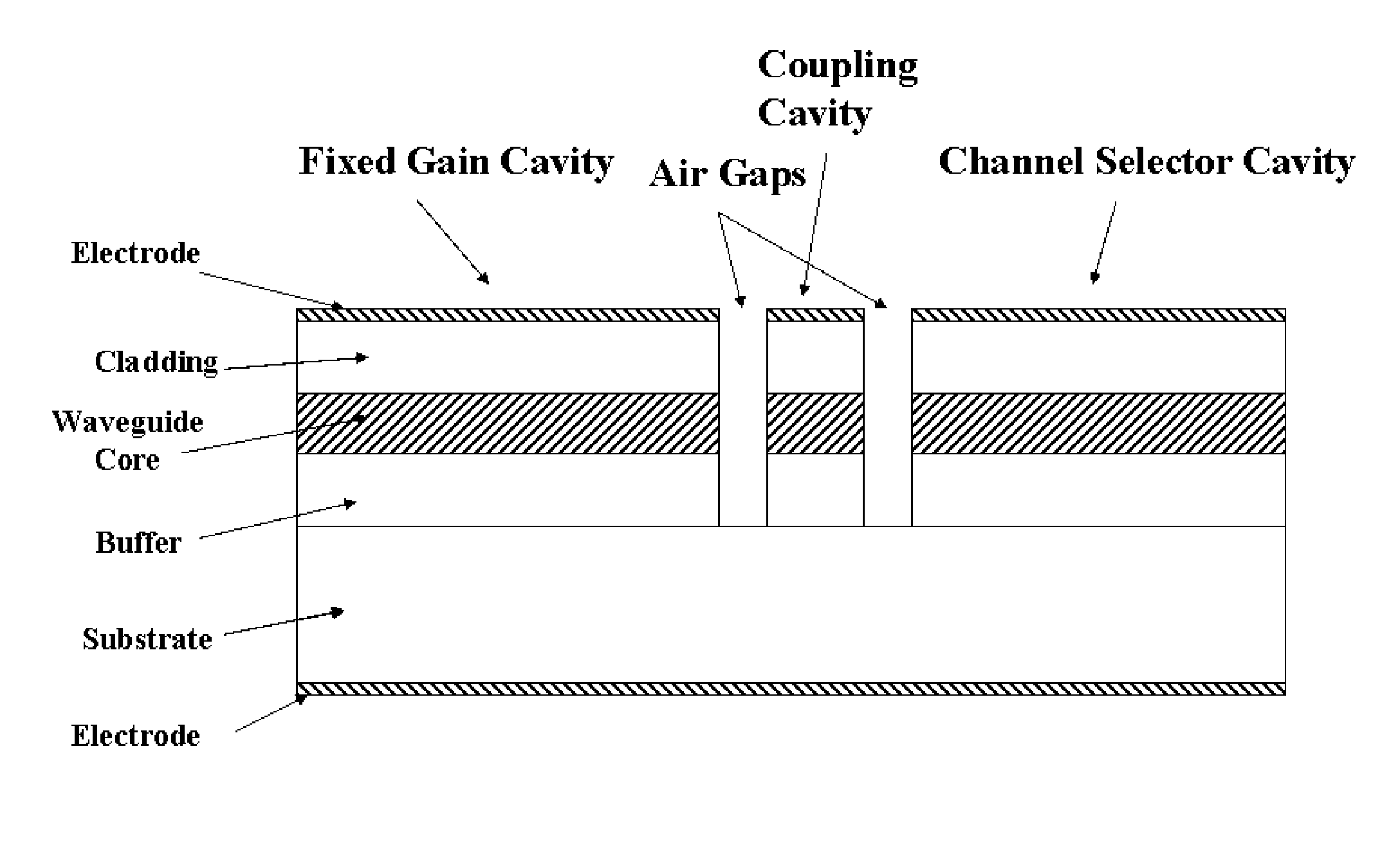
A monolithically integrated wavelength switchable laser comprises three coupled Fabry-Perot cavities. The length and consequently the free spectral range of the first cavity are designed such that the resonant peaks correspond substantially to a set of discrete operating wavelengths separated by a constant channel spacing. The second cavity has a slightly different length so that only one resonant peak coincides with one of the resonant peaks of the first cavity over the spectral window of the material gain. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. The two cavities are coupled through a third short cavity that produces a certain coupling loss and phase relationship between the first and the second cavities in order to achieve an optimal mode selectivity of the combined cavity laser. In operation, both the first and the second cavities are forward biased to provide optical gains for the laser action. The second cavity is tuned by varying the refractive index of at least a portion of the waveguide within the cavity through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching of the laser among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first cavity.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
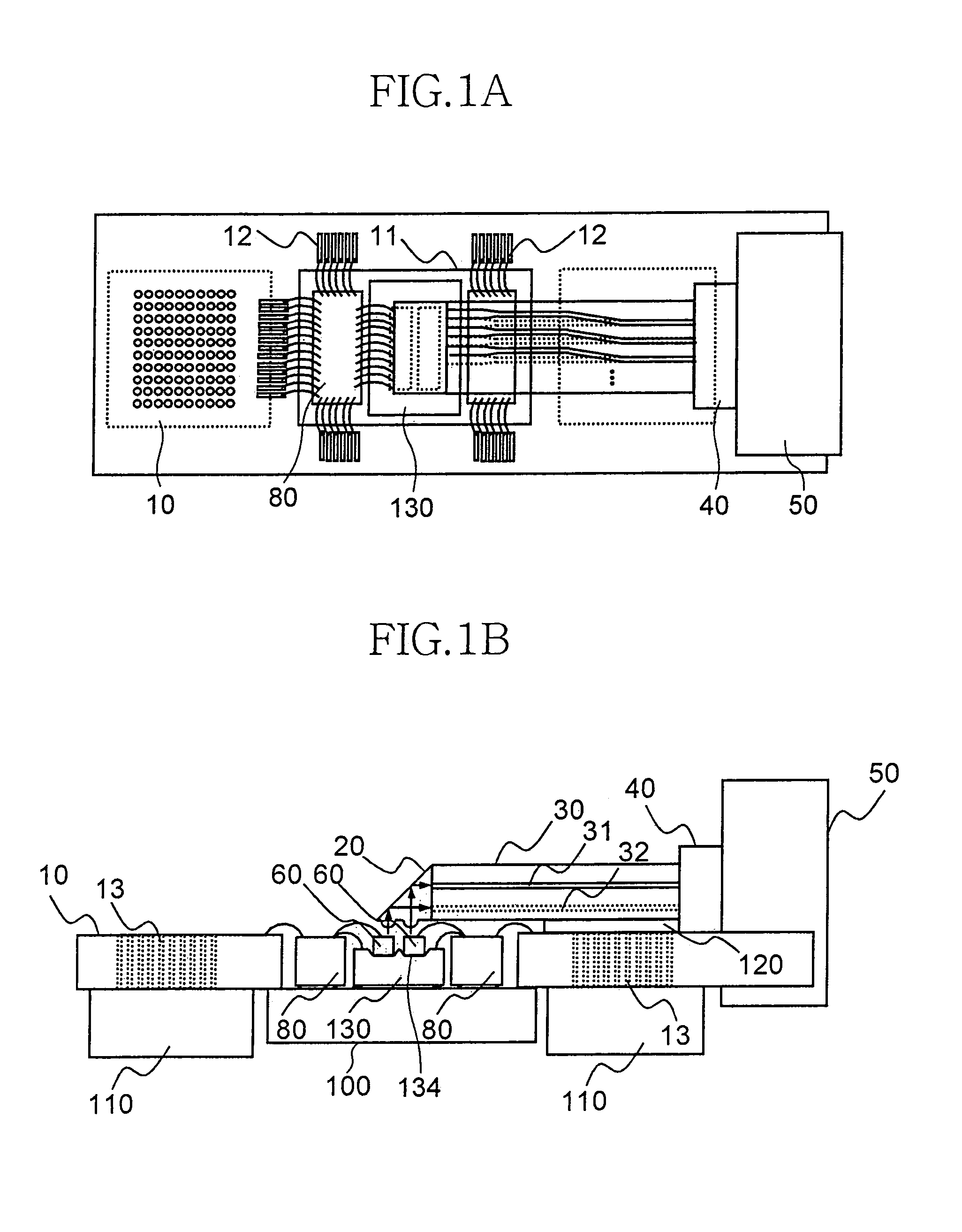
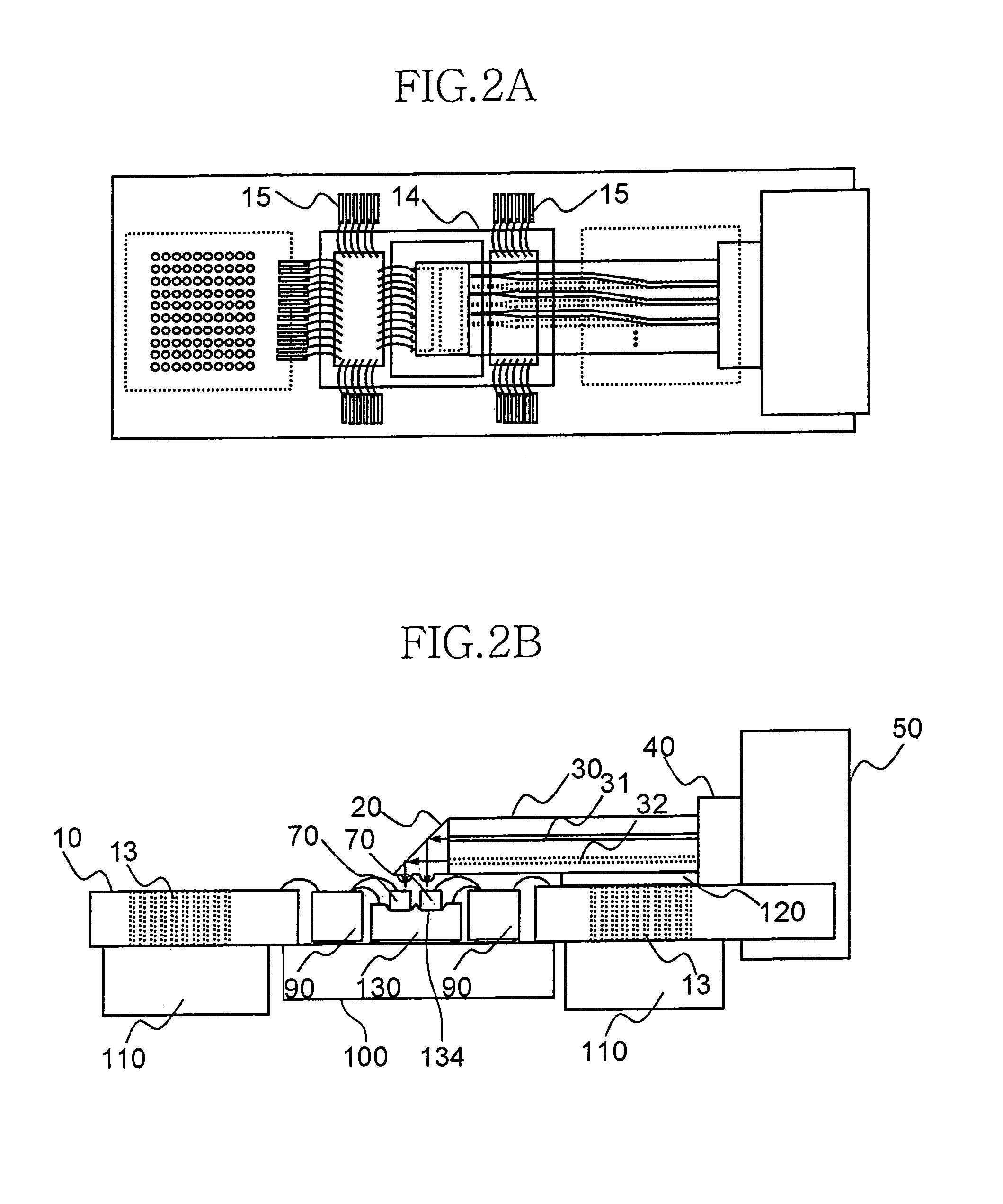
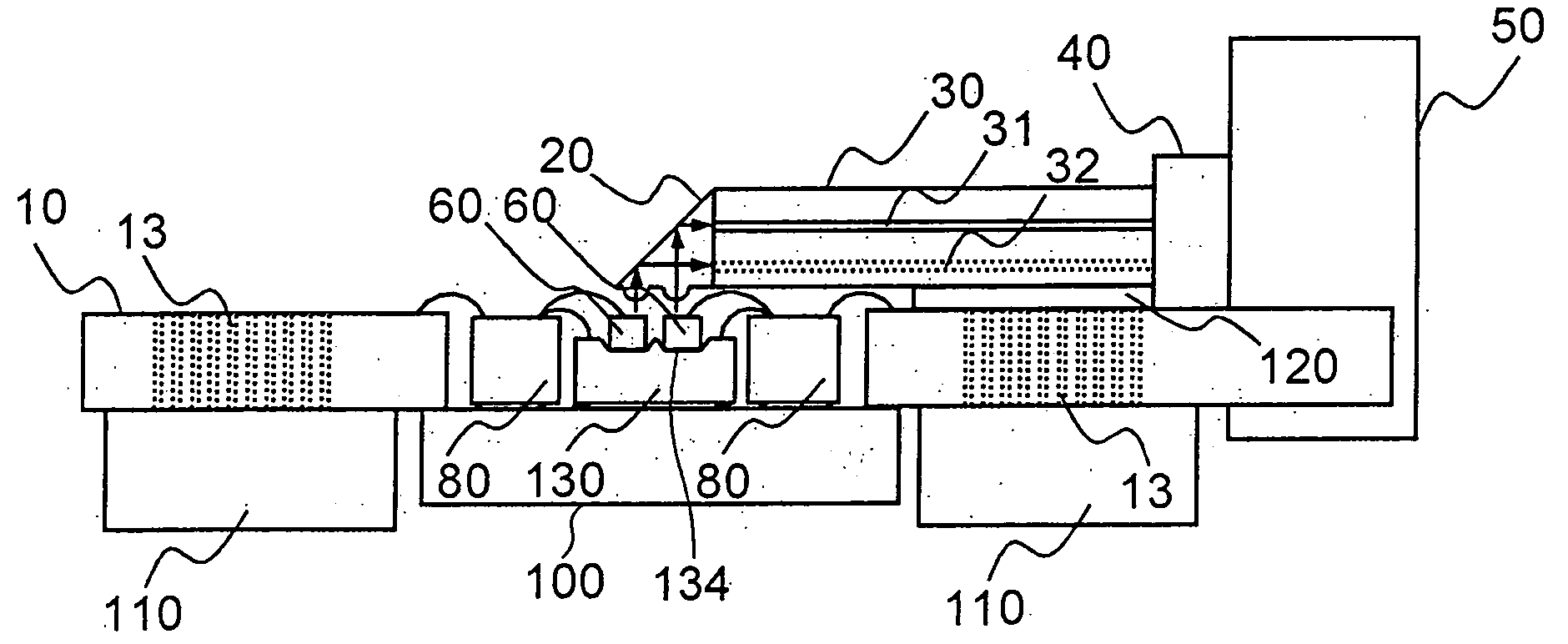
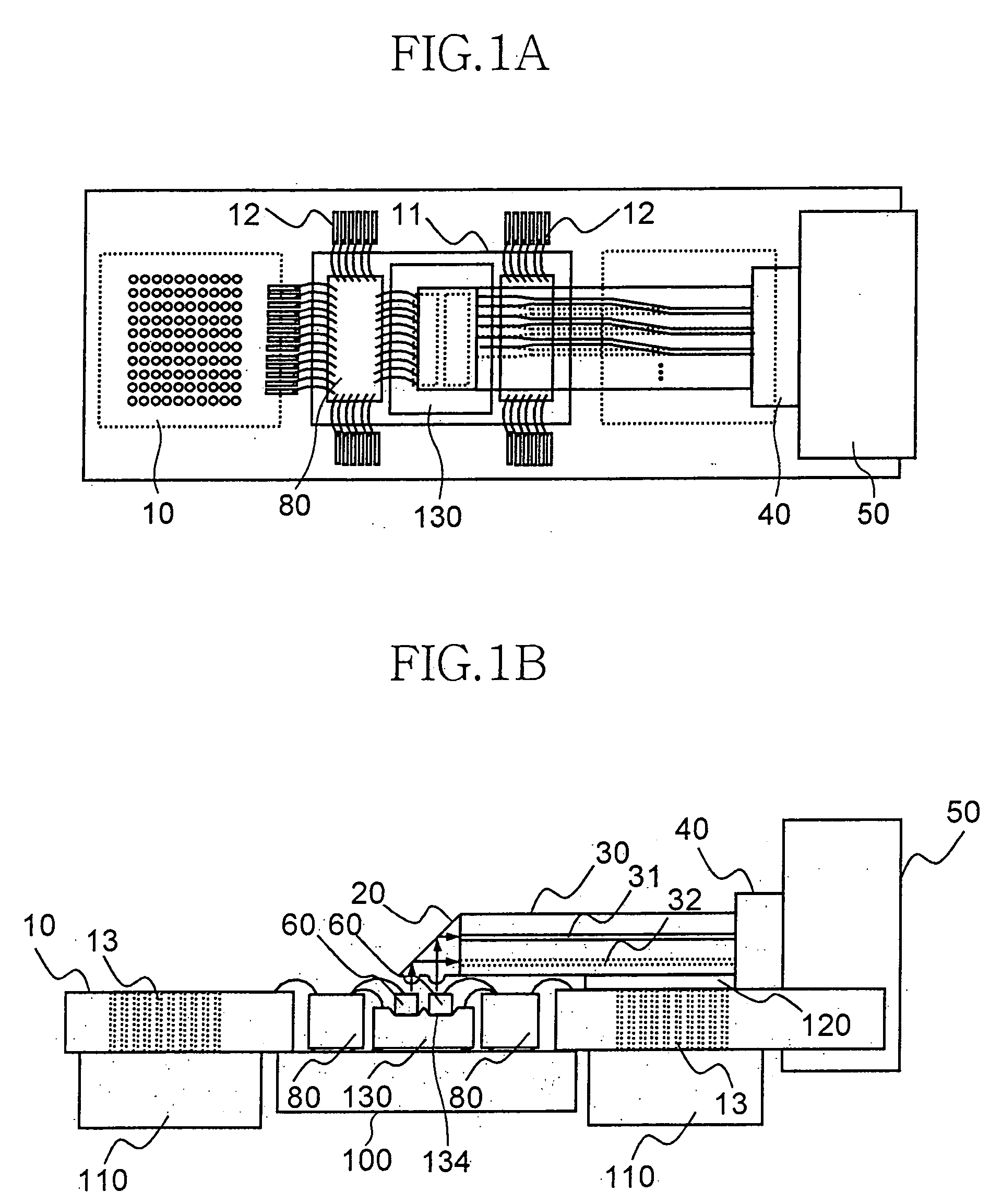
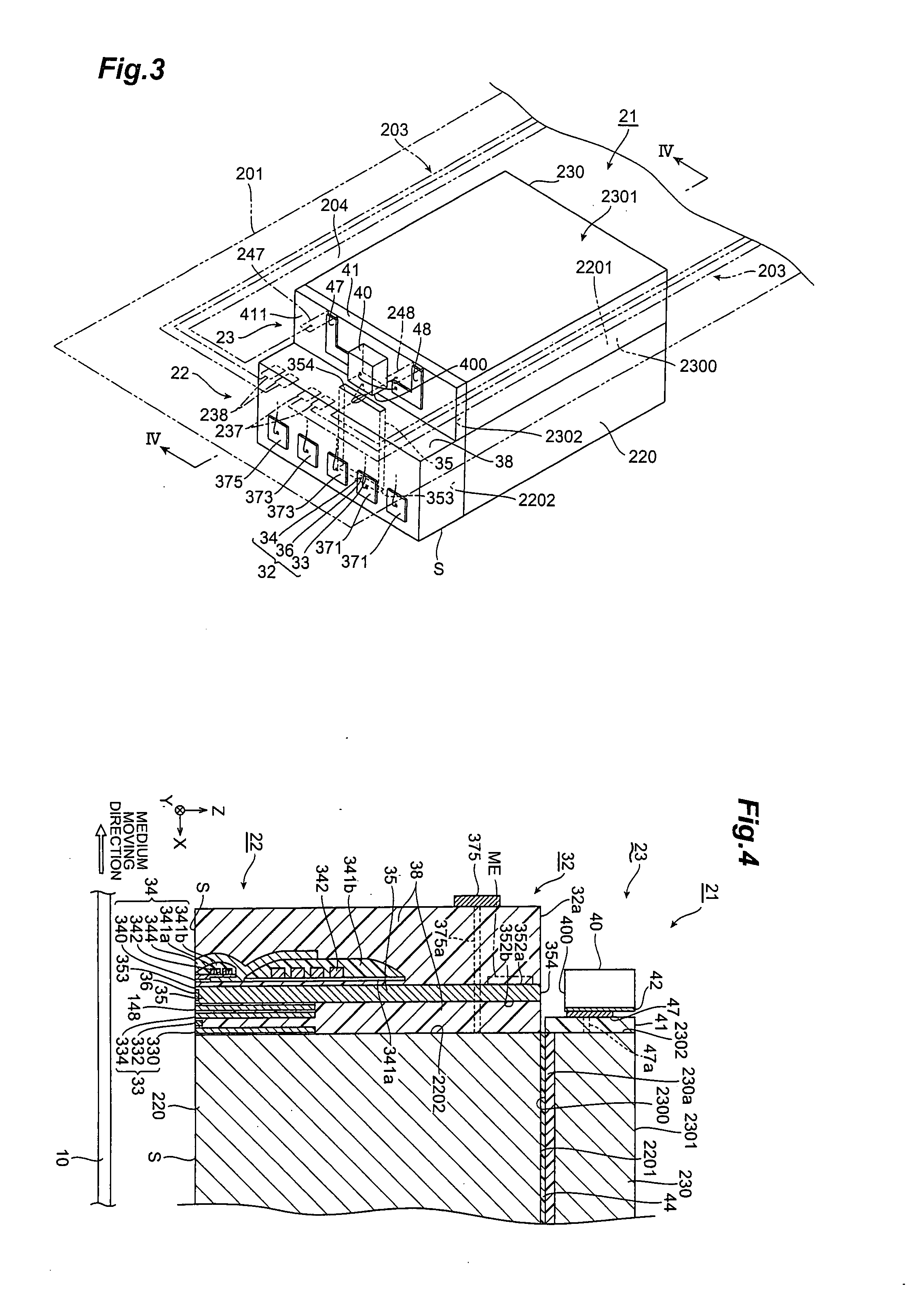
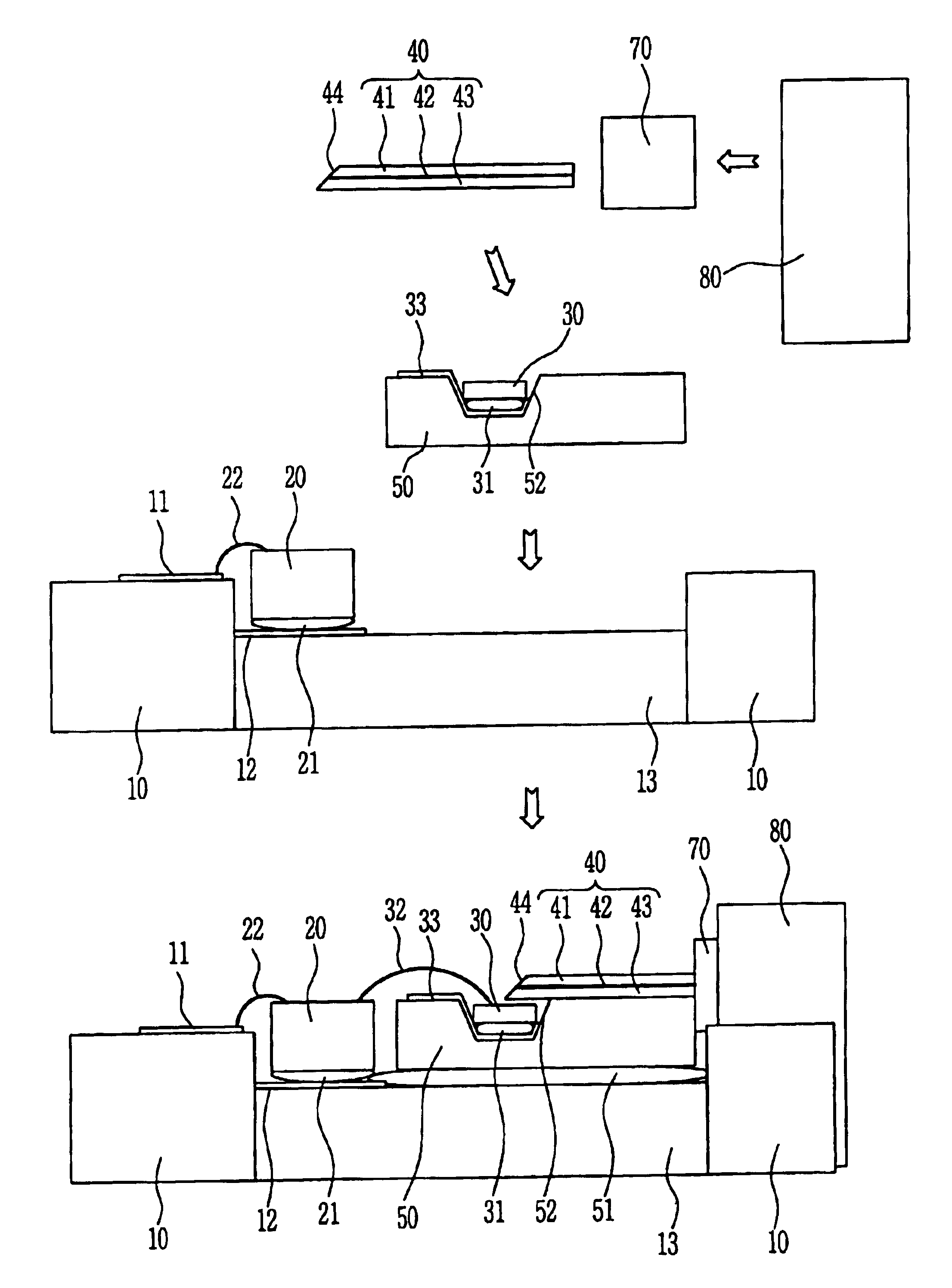
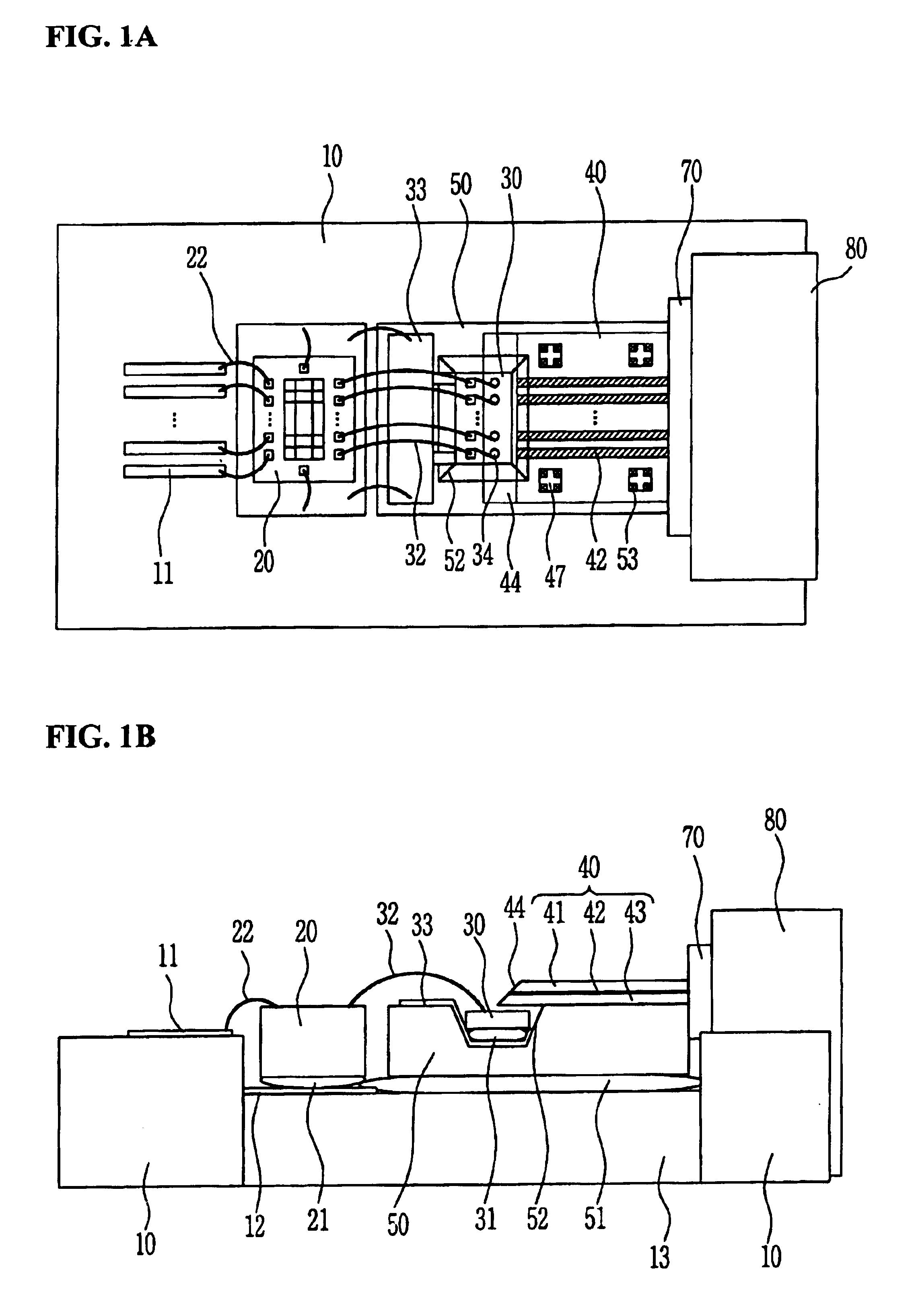
Parallel optical interconnection module and method for manufacturing the same
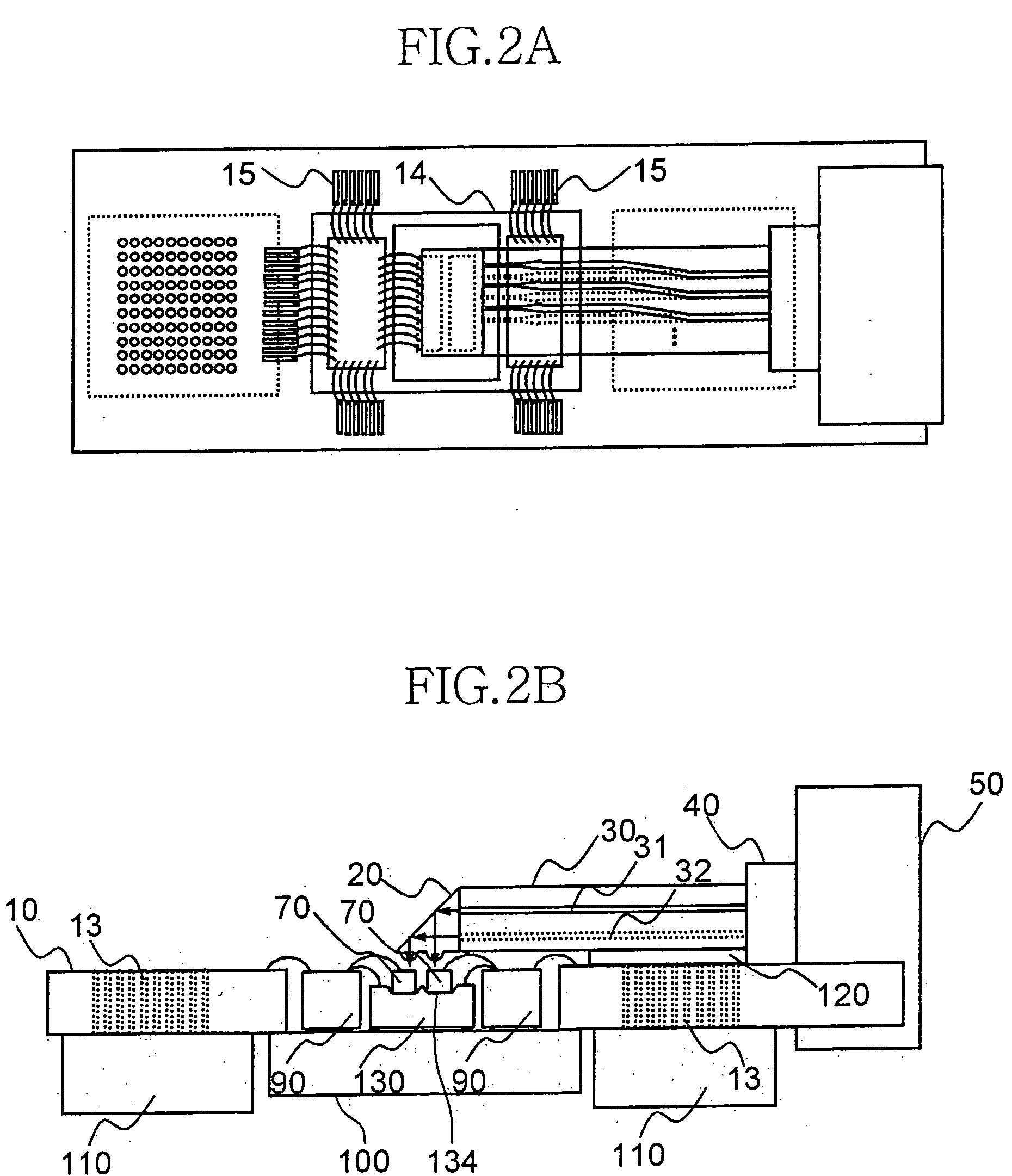
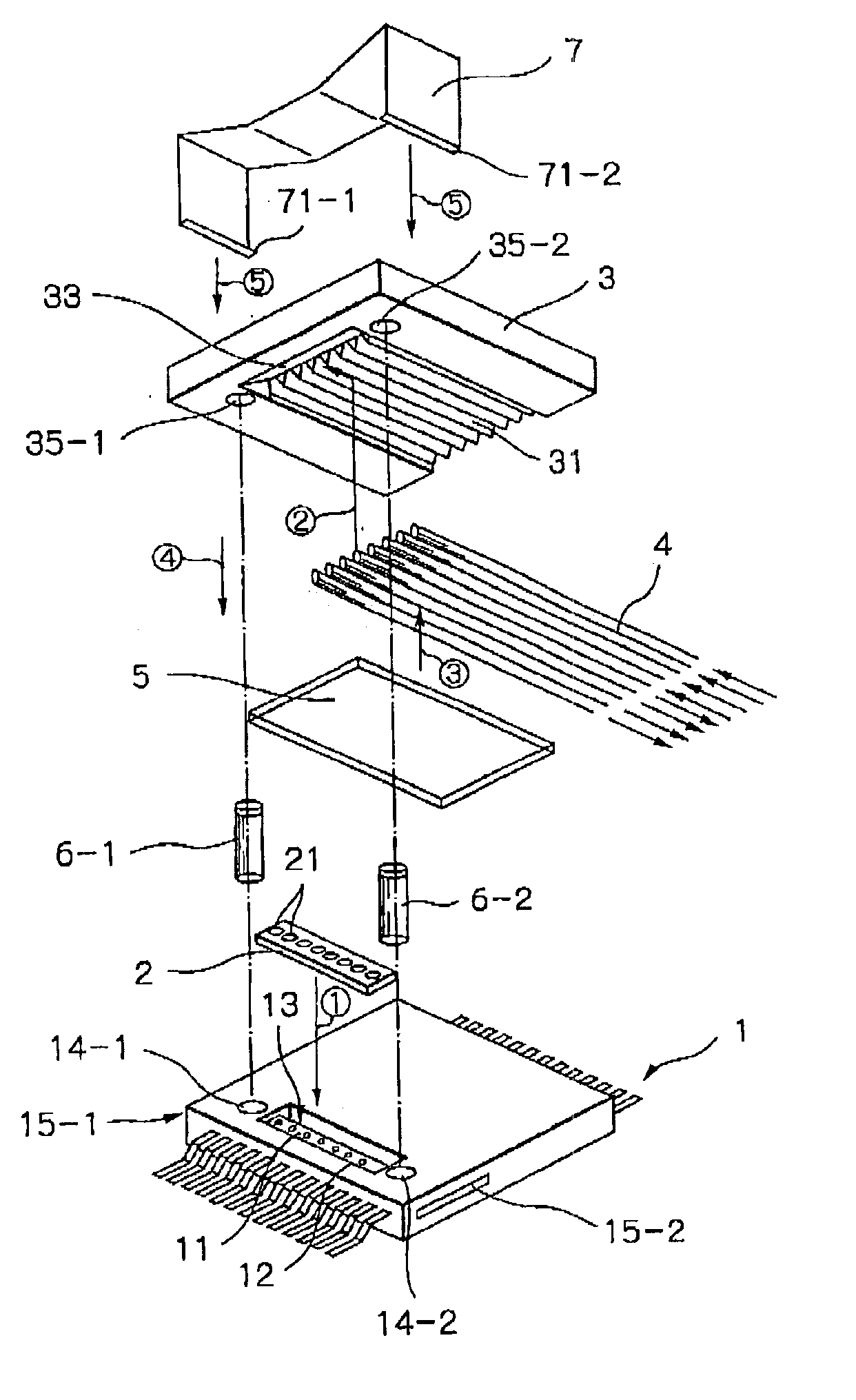
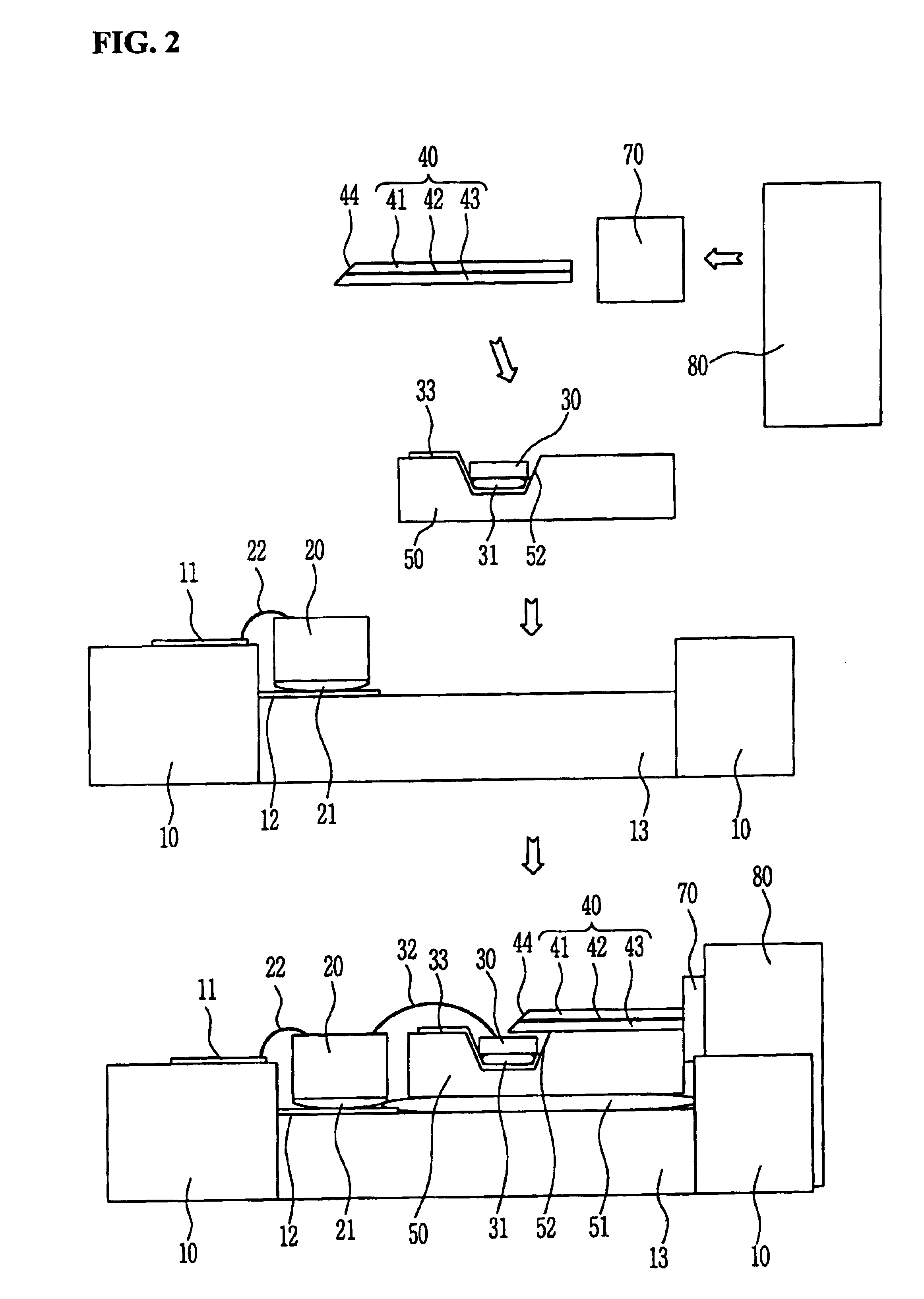
InactiveUS6912332B2Minimizing coupling lossImprove light outputSolid-state devicesCoupling light guidesCoupling lossPhotodetector
The present invention relates to a parallel optical interconnection module for transmitting an optical signal over an optical fiber and receiving an optical signal from the optical fiber. According to the present invention, a reflection surface is formed at the end of the optical waveguide forming a core so that the path of light can be exactly changed and is focused. A light source / photodetector is buried within a trench using the silicon optical bench and an optical waveguide is manually aligned on the surface of the silicon optical bench, so that alignment error between the light source / photodetector and the optical waveguide can be minimized. A ferrule into which the optical waveguide is inserted is fixed to an adaptor so that alignment error between the optical waveguide and the light source / photodetector is minimized. Therefore, the present invention can minimize the coupling loss in the process during which the optical signal is transmitted to increase the optical output. Further, the present invention allows easy optical interconnection by means of a manual alignment and can increase the productivity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device and method for stabilizing any bias point of external modulator
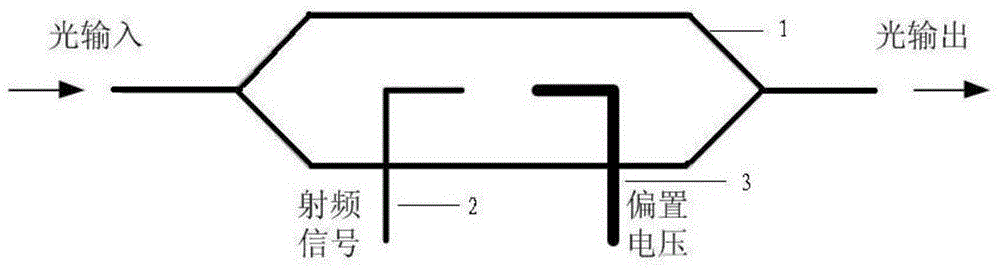
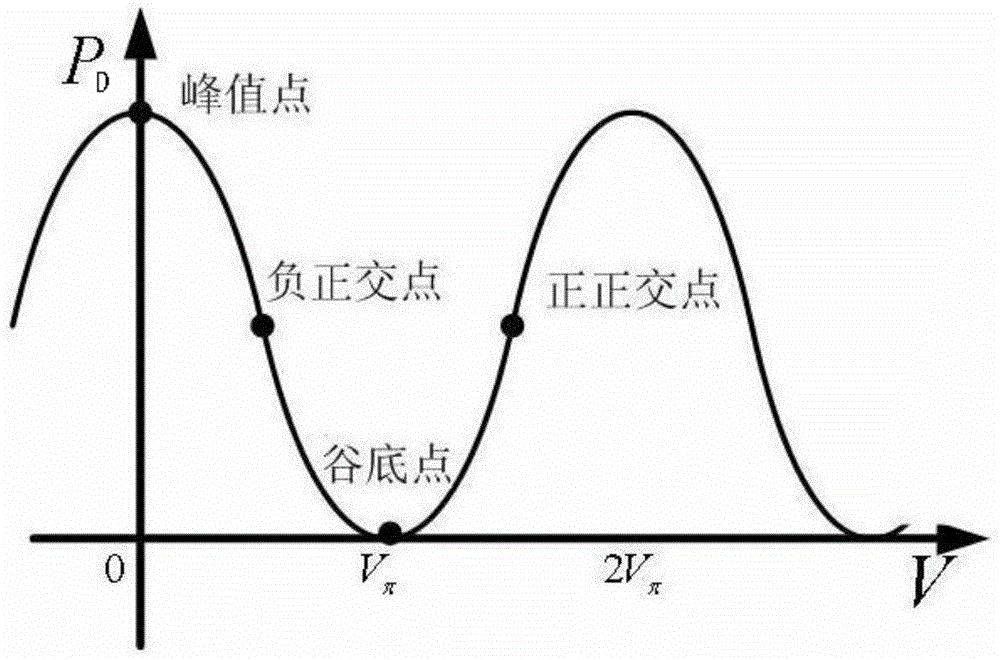
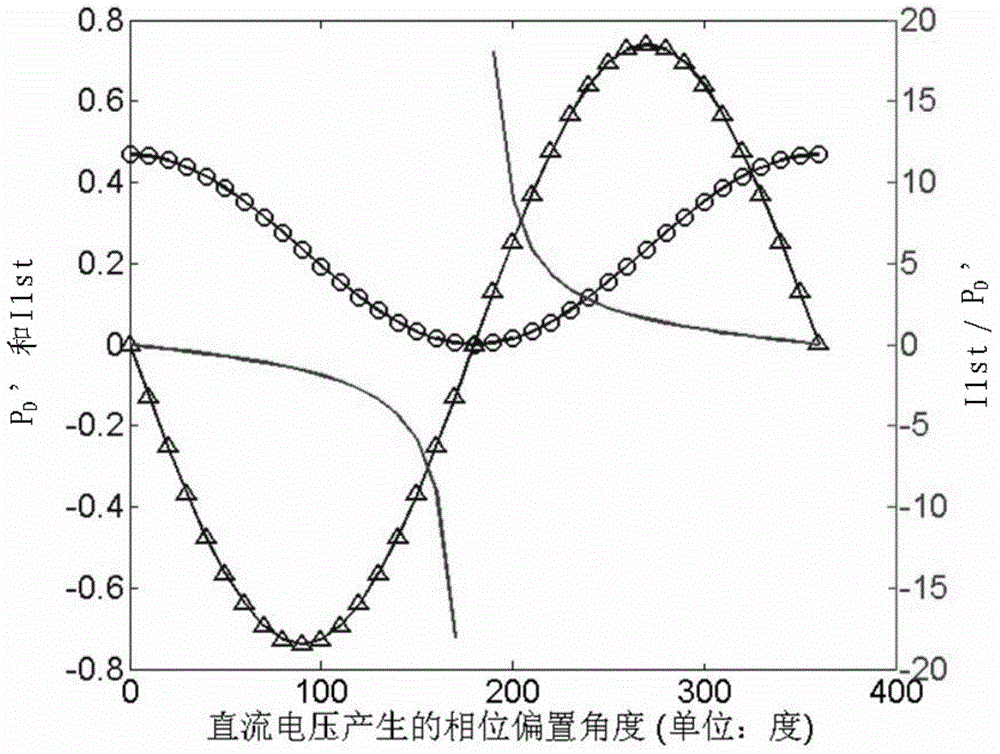
The invention relates to a device and method for stabilizing any bias point of an external modulator, wherein the device comprises a laser, a variable optical attenuator, a lithium niobate modulator, an optical coupler, a signal source, a driving amplifier and a feedback control part; the device can be used for collecting a feedback signal and setting a bias voltage via a data acquisition board in the feedback control part so as to stabilize any bias point. The device and the method of the invention solve the problem that an optimal bias point of the modulator is drifted and an output signal is degraded because of changes of factors such as time, environment temperature, laser luminous power, and optical fiber inserting and coupling loss. The device and the method can be applied in the optical communication field, especially high-speed long distance communication in the optical communication field.
Owner:一叁一九(北京)光电科技有限公司
Grating coupler with adjustable refractive index and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of photonic devices, in particular to a method for manufacturing a grating coupler with an adjustable refractive index. The method is characterized in that a grating groove is of a sub-wavelength structure with different transverse duty ratios, and a grating has different duty ratios fy in the transverse direction, namely, the direction y, at different positions x in the longitudinal direction, namely, the direction x; the value of the duty ratio fx of the grating in the longitudinal direction is a fixed value between zero and one; the transverse duty ratio fy of the sub-wavelength structure forming the grating grooves at different positions x in the longitudinal direction is determined by leakage factor distribution alpha (x) needed by output Guassian field distribution G (x). The grating coupler of the structure can effectively reduce coupling losses in the optical fiber and waveguide coupling process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
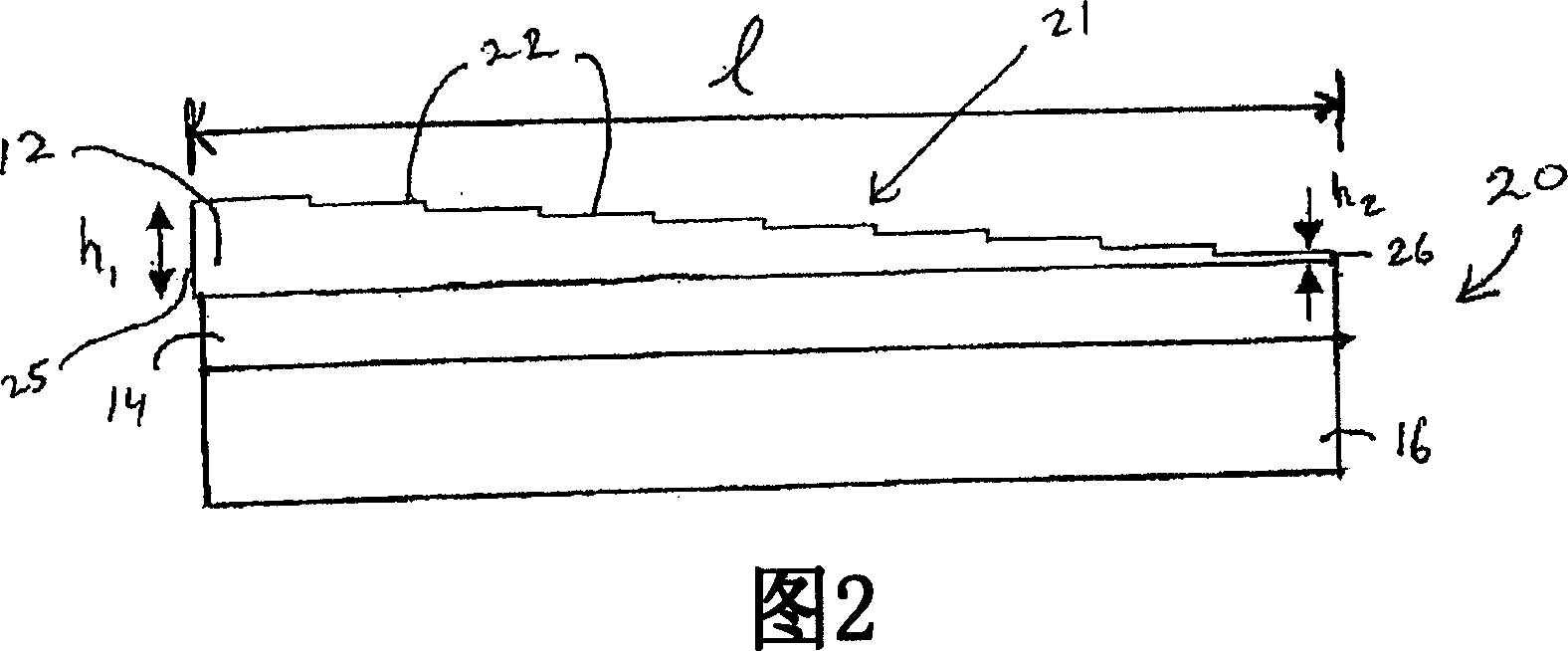
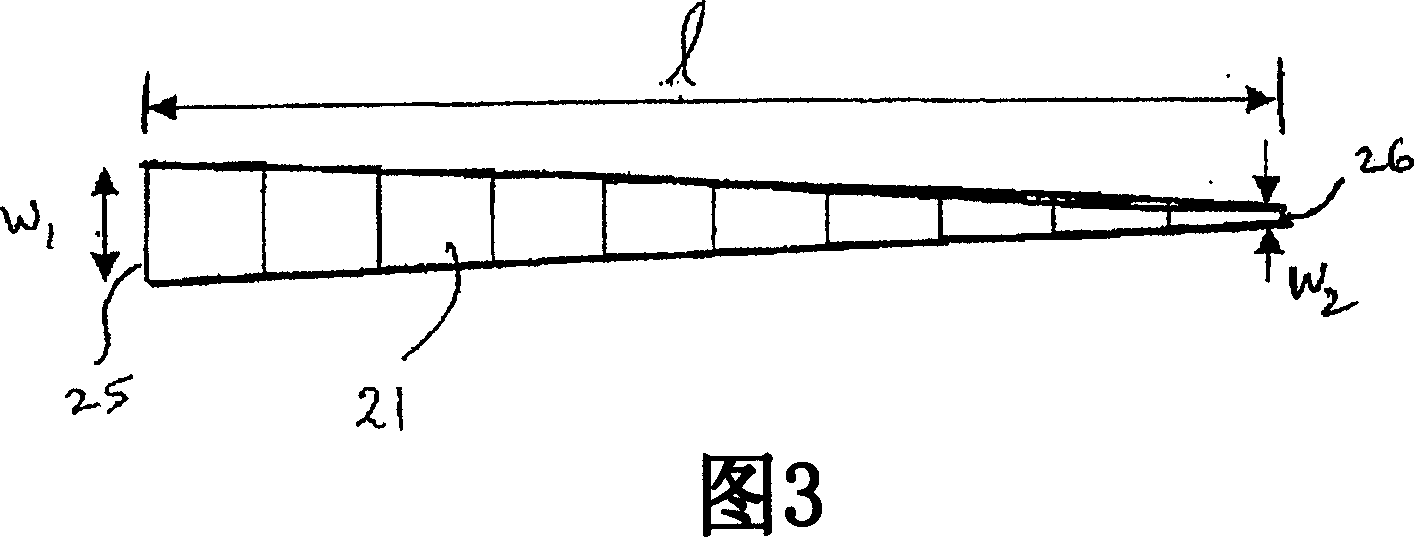
System and tapered waveguide for improving light coupling efficiency between optical fibers and integrated planar waveguides and method of manufacturing same
InactiveCN1922519AImprove optical coupling efficiencyCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCoupling lossTransformer
A tapered waveguide optical mode transformer (20) includes a tapered core formed on a planar substrate structure (16). To vertically taper the core (21), steps (22) are etched into the top surface of the core. The steps have depths and lengths along the optical axis of tapered waveguide that are selected to transform the optical mode characteristics of a desired optical fiber to the optical mode characteristics of a desired planar waveguide. The core can also be tapered horizontally to form a 2-D tapered waveguide. The tapered waveguide can be integrally included in planar lightwave circuits (PLCs) to reduce light coupling losses between optical fibers and the PLC waveguides.
Owner:克咯拉姆达技术有限公司
Optical device
ActiveUS20120328238A1Reduce couplingImprove practicalityCoupling light guidesCoupling lossOptical axis
An optical device which reduces coupling loss while improving practicality is provided. A multi-core fiber coupling device is an optical device which couples a multi-core fiber to single core fibers, and includes a first optical system which is located on optical axes of a plurality of beams emitted from the multi-core fiber, and which makes the optical axes of the respective beams non-parallel to each other, thereby making the beams in a state of being separated from each other, and a second optical system S2 which makes the optical axes of the plurality of beams in a state of being non-parallel to each other on the side of the first optical system, in a state of being approximately parallel to each other.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Manufacturing method for optical fiber array for optical coupling and coupling method and device
The invention provides a manufacturing method for an optical fiber array for optical coupling and a coupling method and device.The manufacturing method for the optical fiber array comprises the following steps that naked fibers of the optical fiber array are pressed into a V-shaped groove, the tail end of a bare wire is aligned to the tail end of the V-shaped groove, the bare wire pressed into the V-shaped groove is covered with cover glass to be fixed, the cover glass does not cover the tail end of the V-shaped groove, the distance between the tail end of the cover glass and the tail end of the V-shaped groove is larger than the depth distance between steps of a silicon optical chip coupled to the optical fiber array, and the tail end of the optical fiber array is supported under the V-shaped groove to form one step; an adhesive is dispensed on the portion, not covered with the cover glass, of the bare wire so as to fix the bare wire; a filler aligned to the tail end of the V-shaped groove is applied to the step at the tail end of the optical fiber array; the end face of the optical fiber array is polished, the filler is removed after polishing is performed, and the step is exposed.By adopting the step-type optical fiber array, the problem that coupling losses are large due to the fact that a common optical fiber array is far away from the coupling end face of the chip is solved.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com