Patents
Literature
345 results about "Free spectral range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
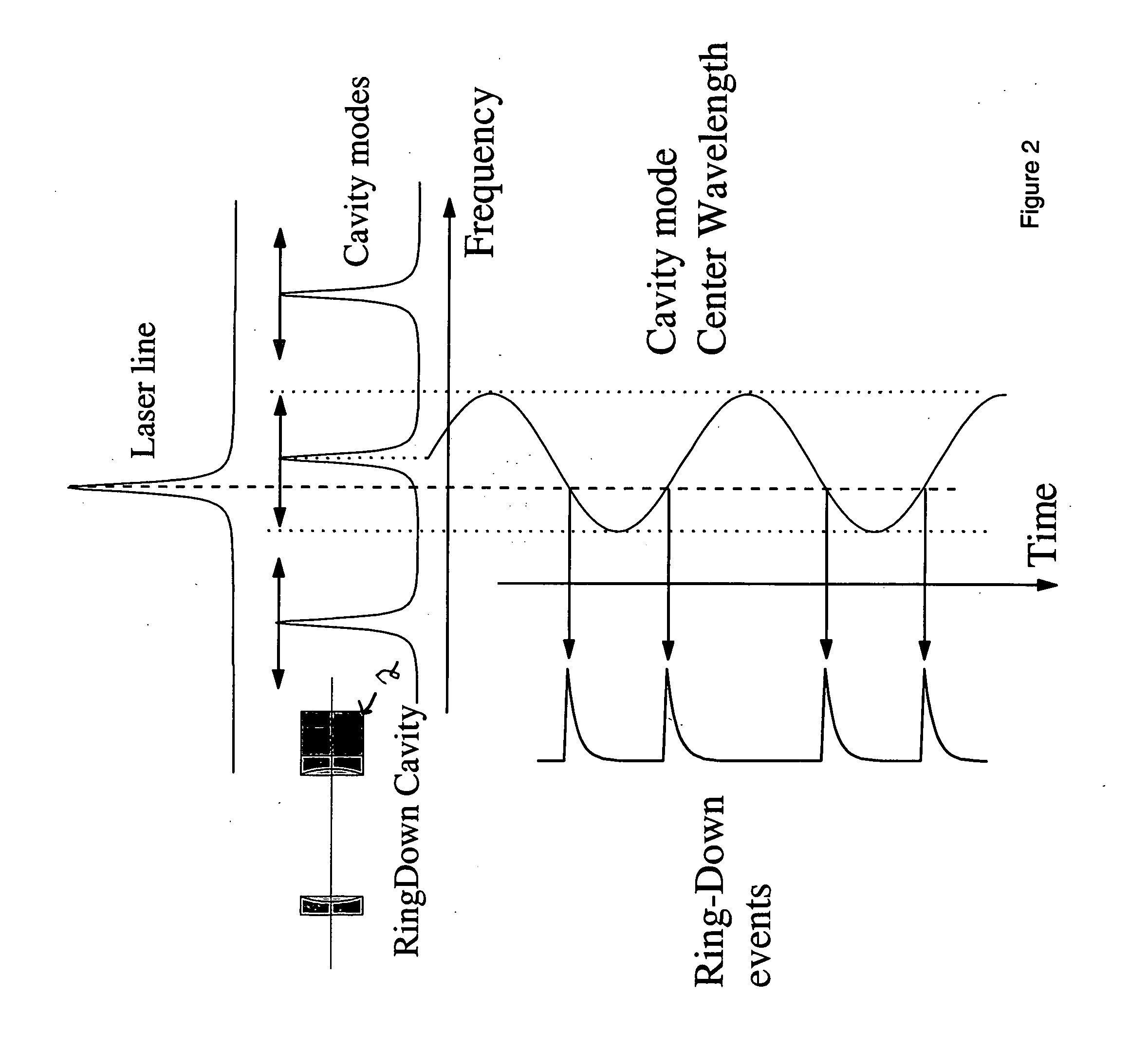
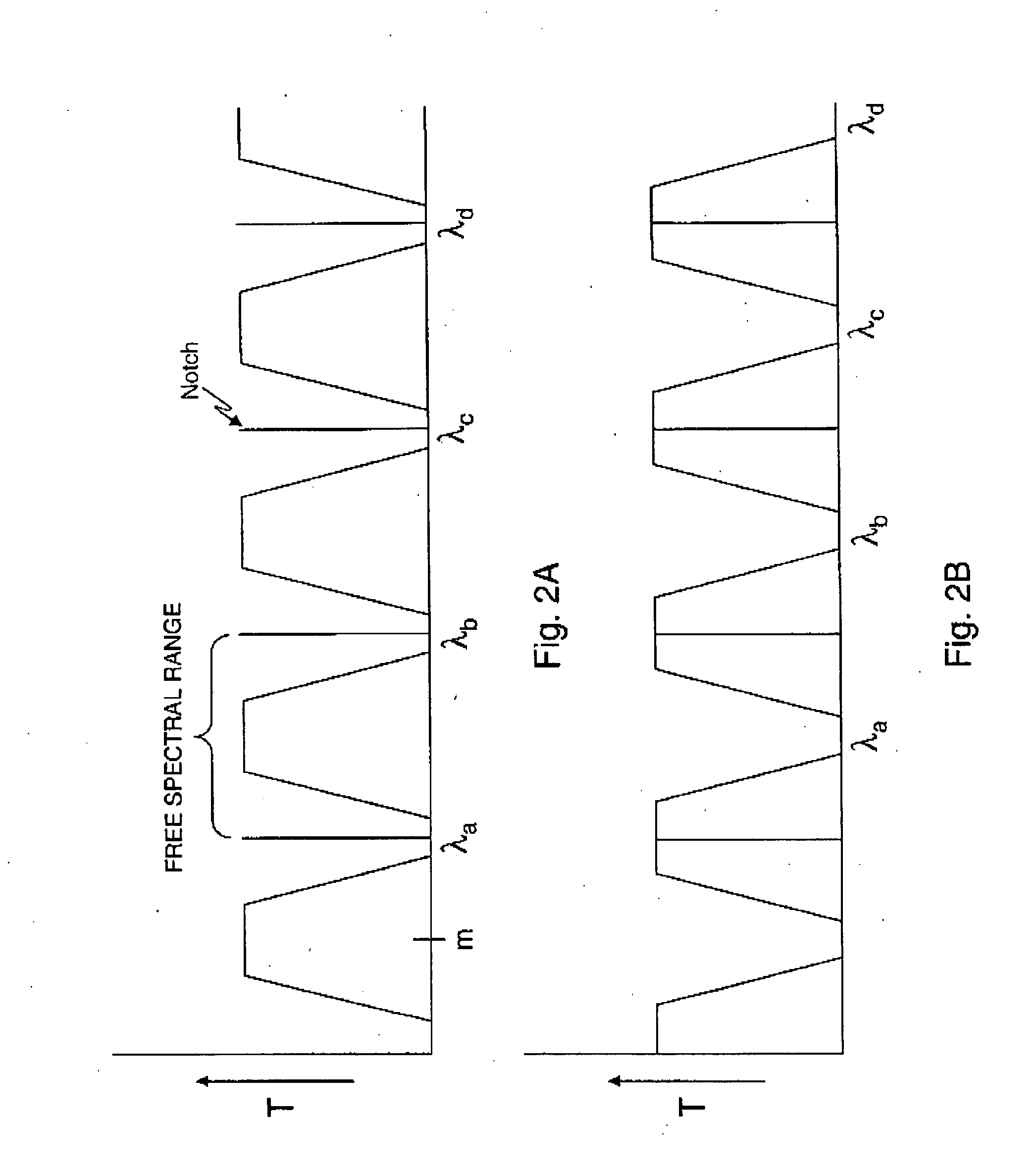
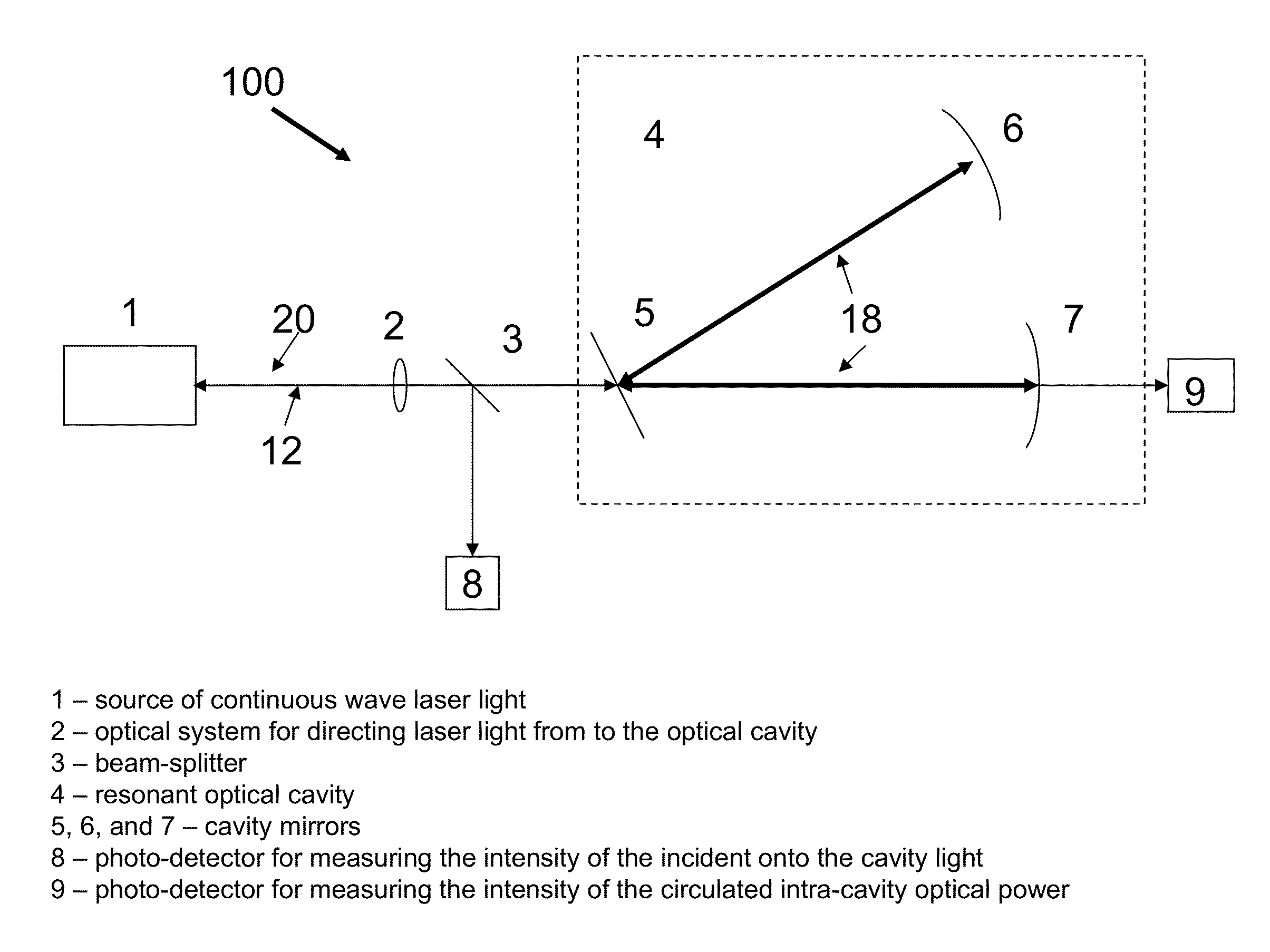
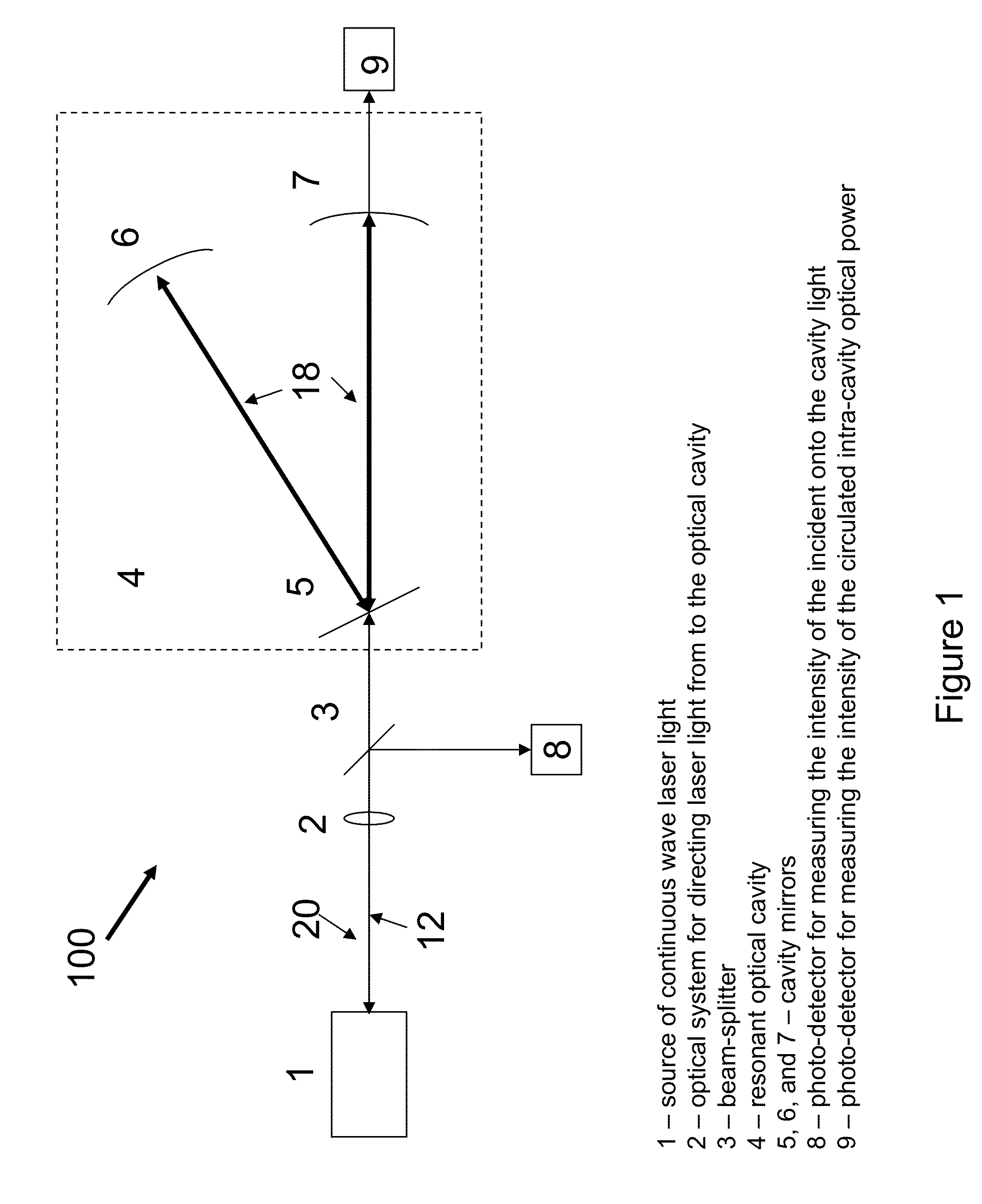
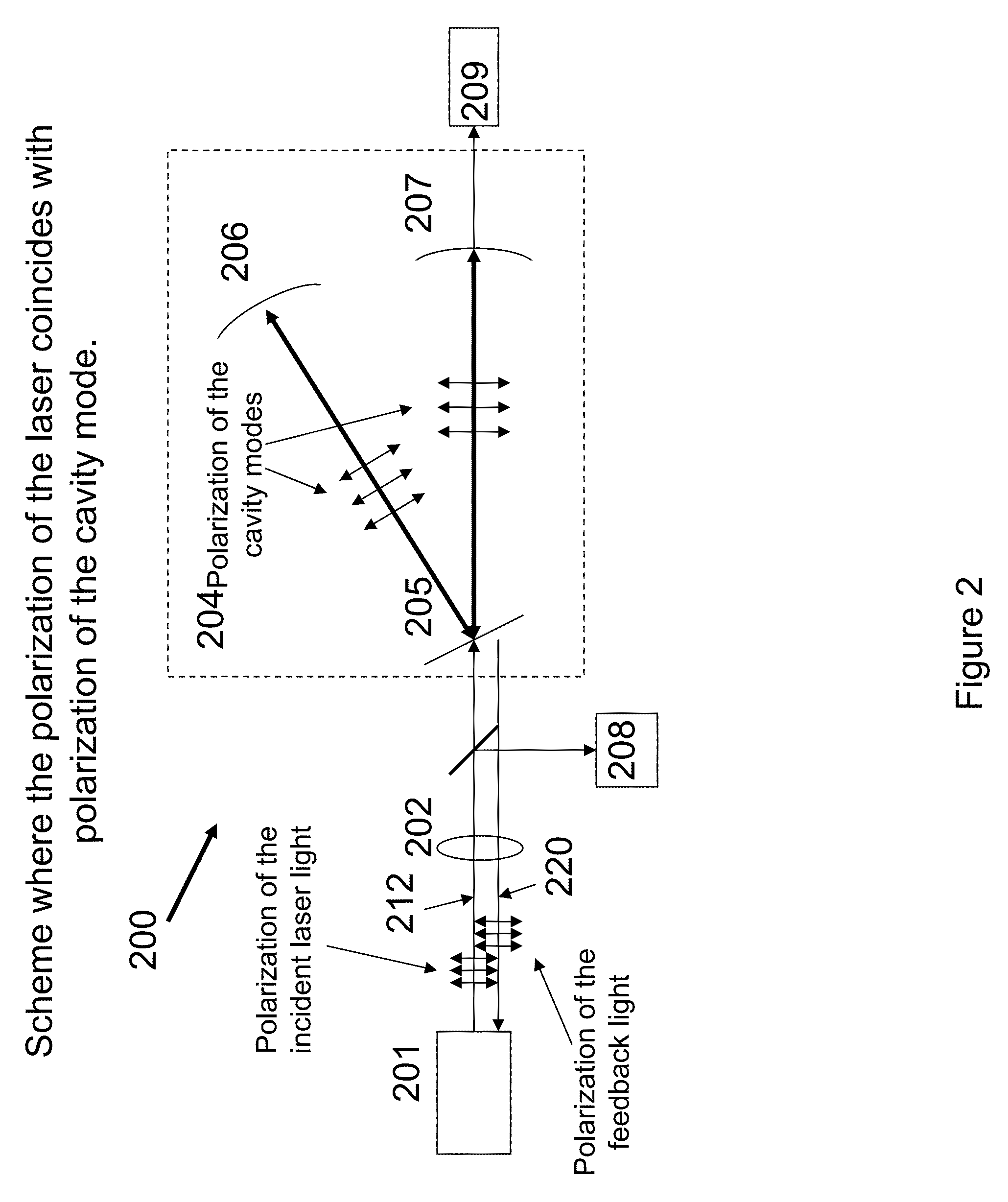
Free spectral range (FSR) is the spacing in optical frequency or wavelength between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element. The FSR is not always represented by Δν or Δλ, but instead is sometimes represented by just the letters FSR. The reason is that these different terms often refer to the bandwidth or linewidth of an emitted source respectively.
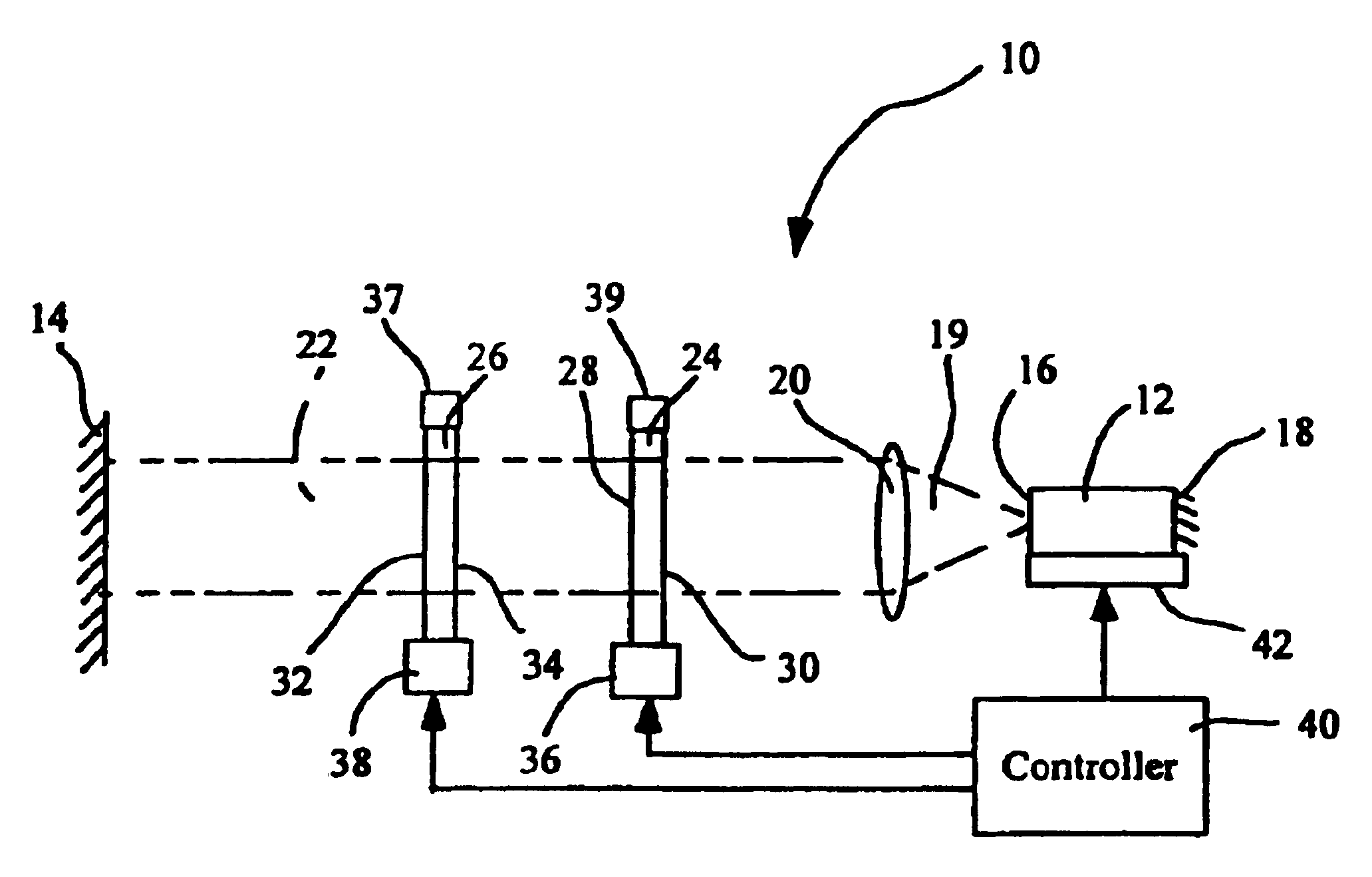
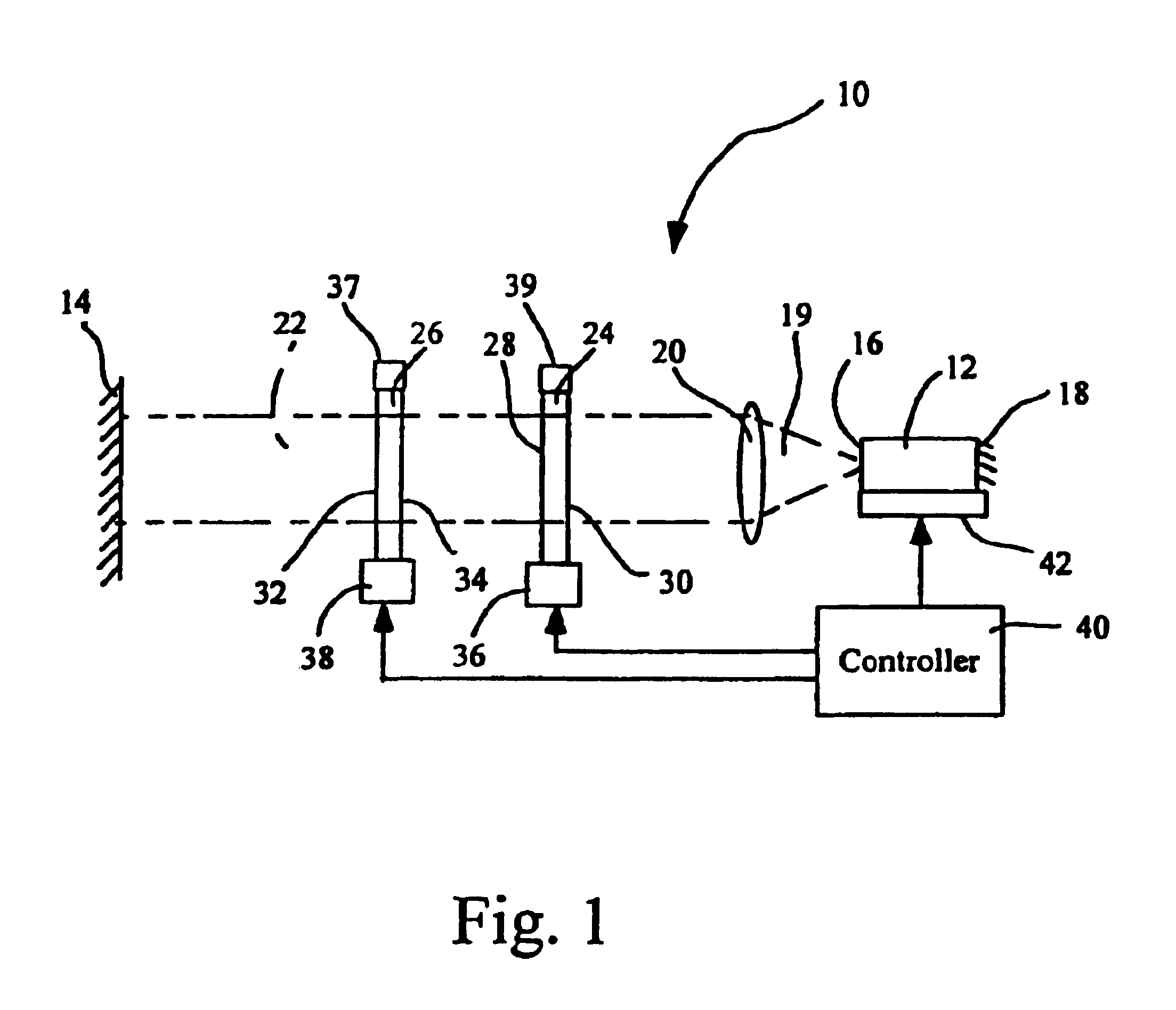
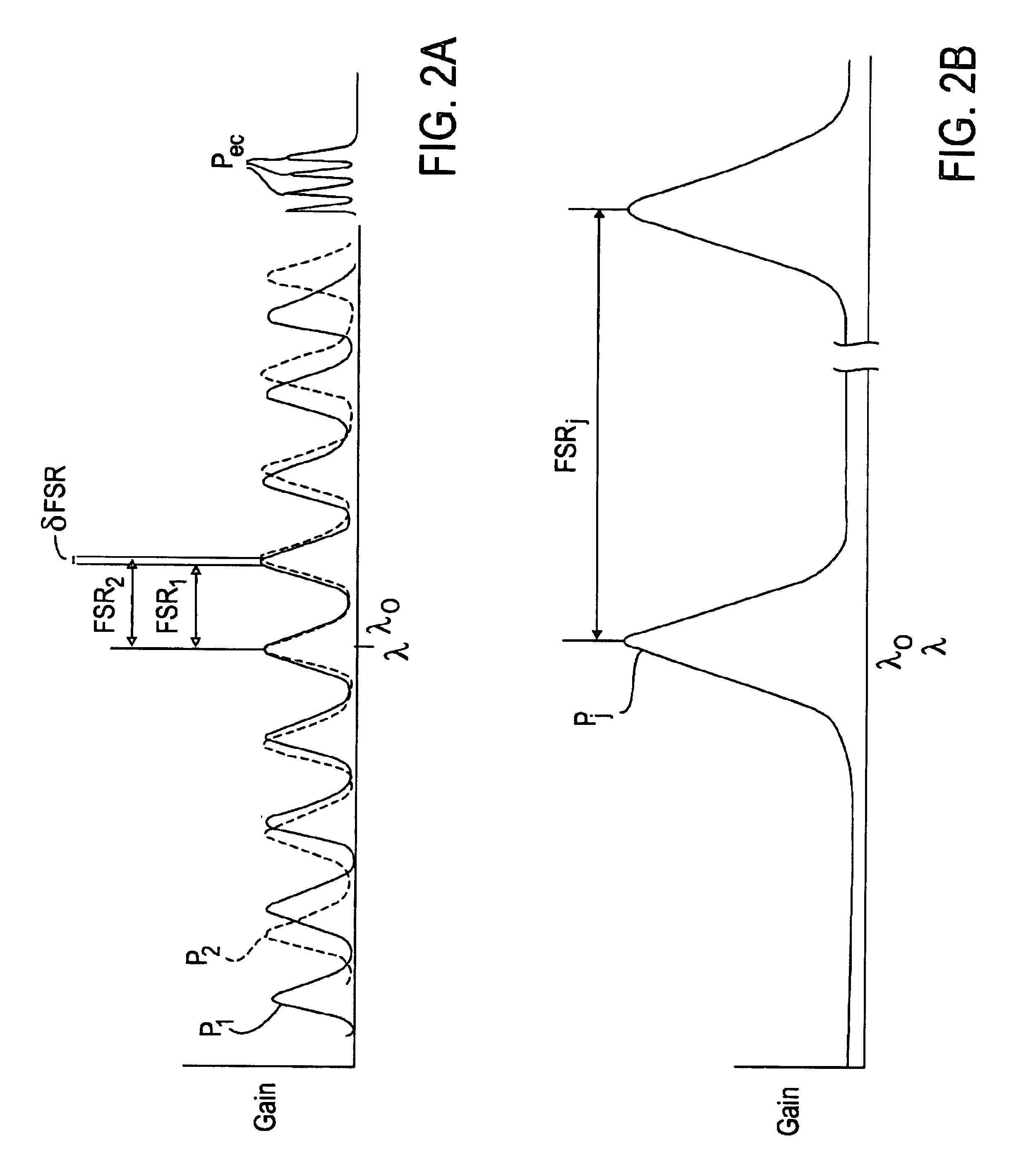
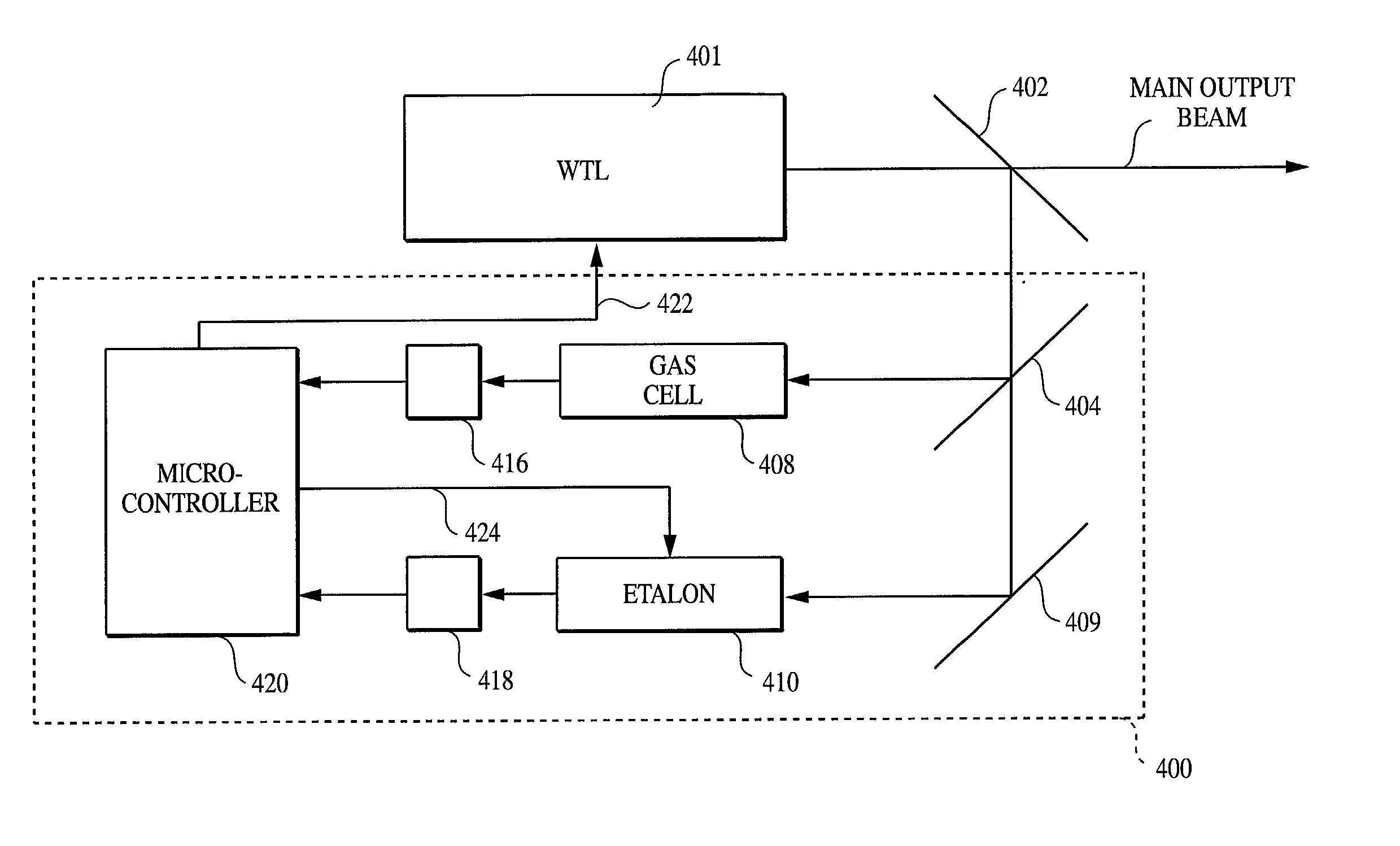
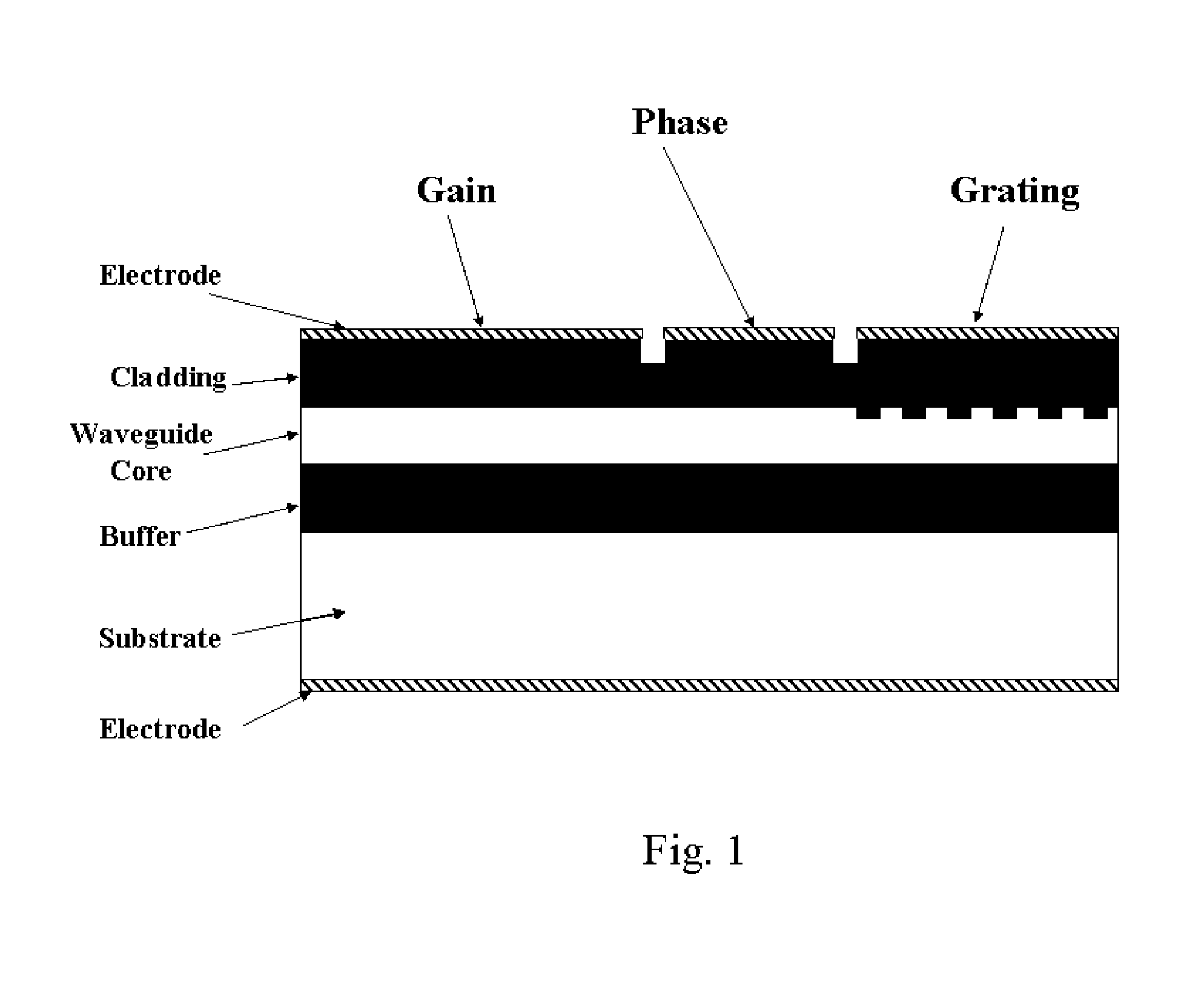
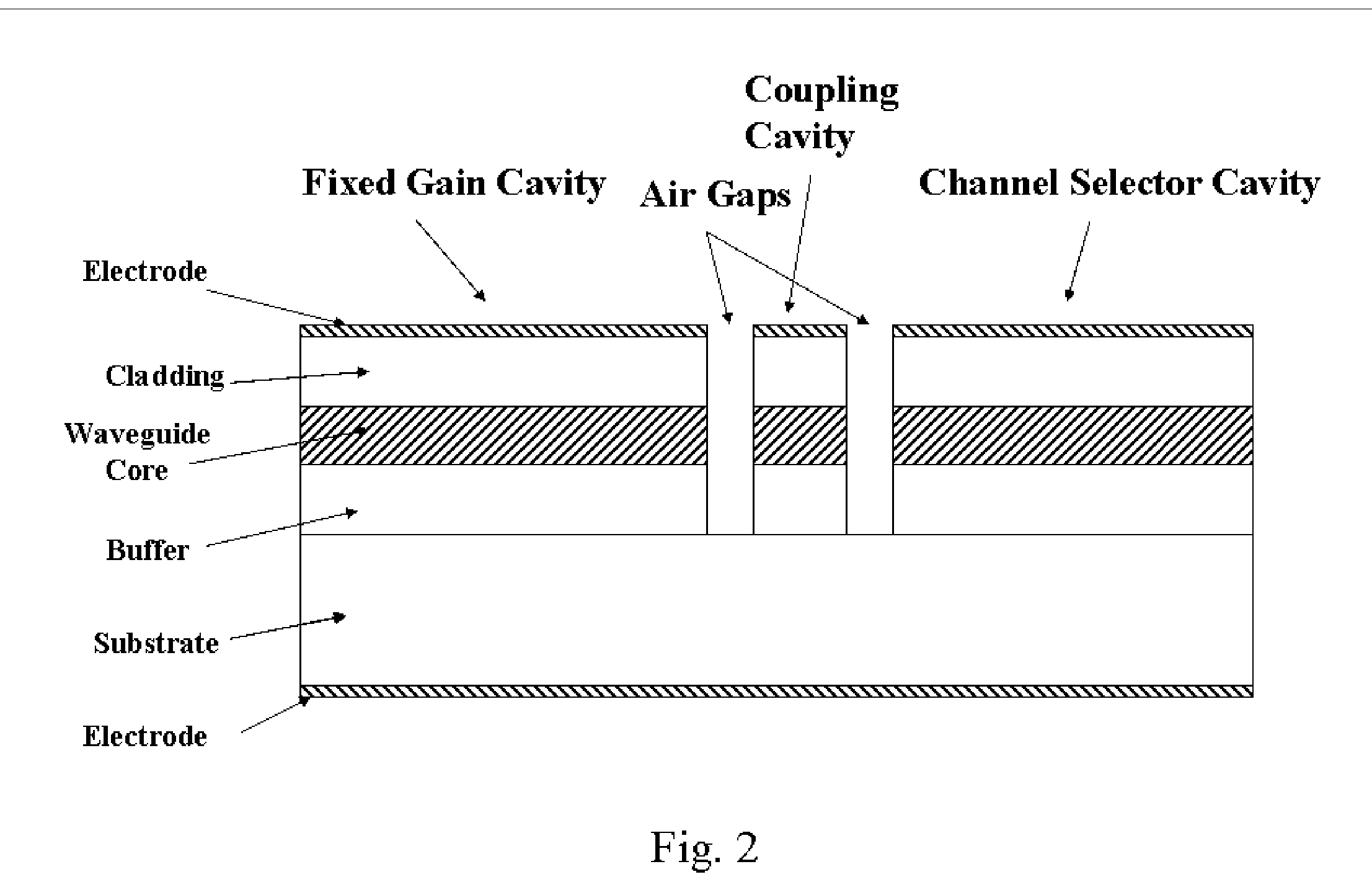
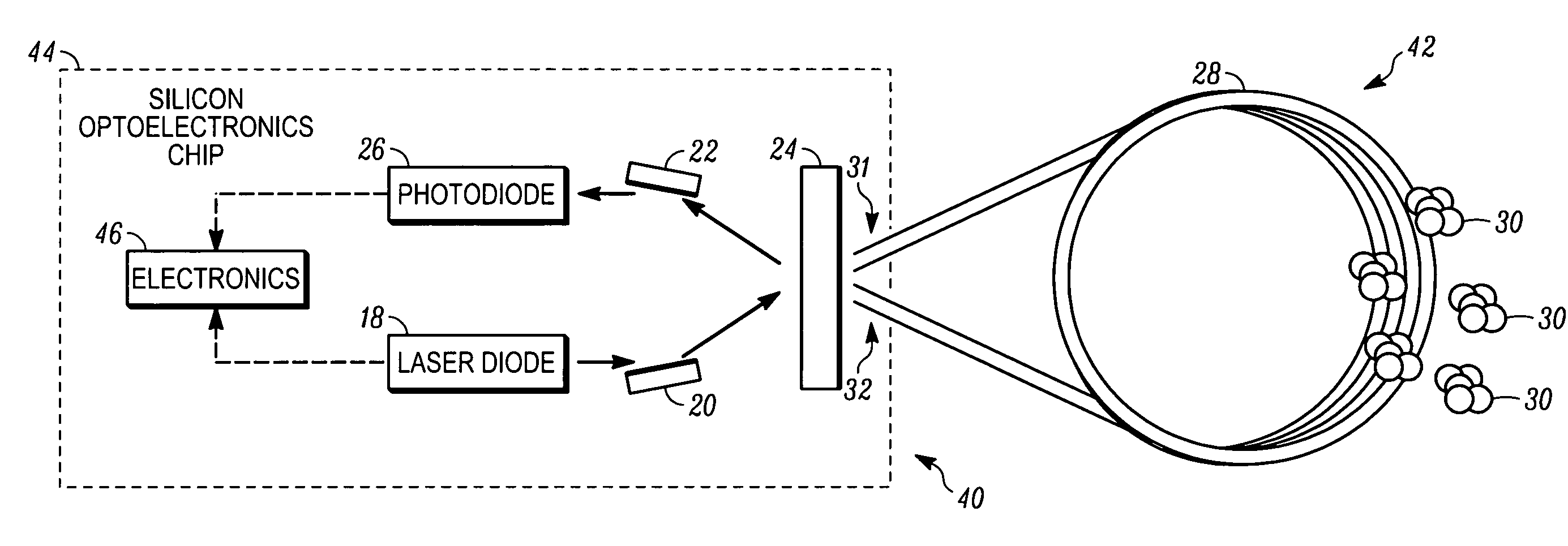
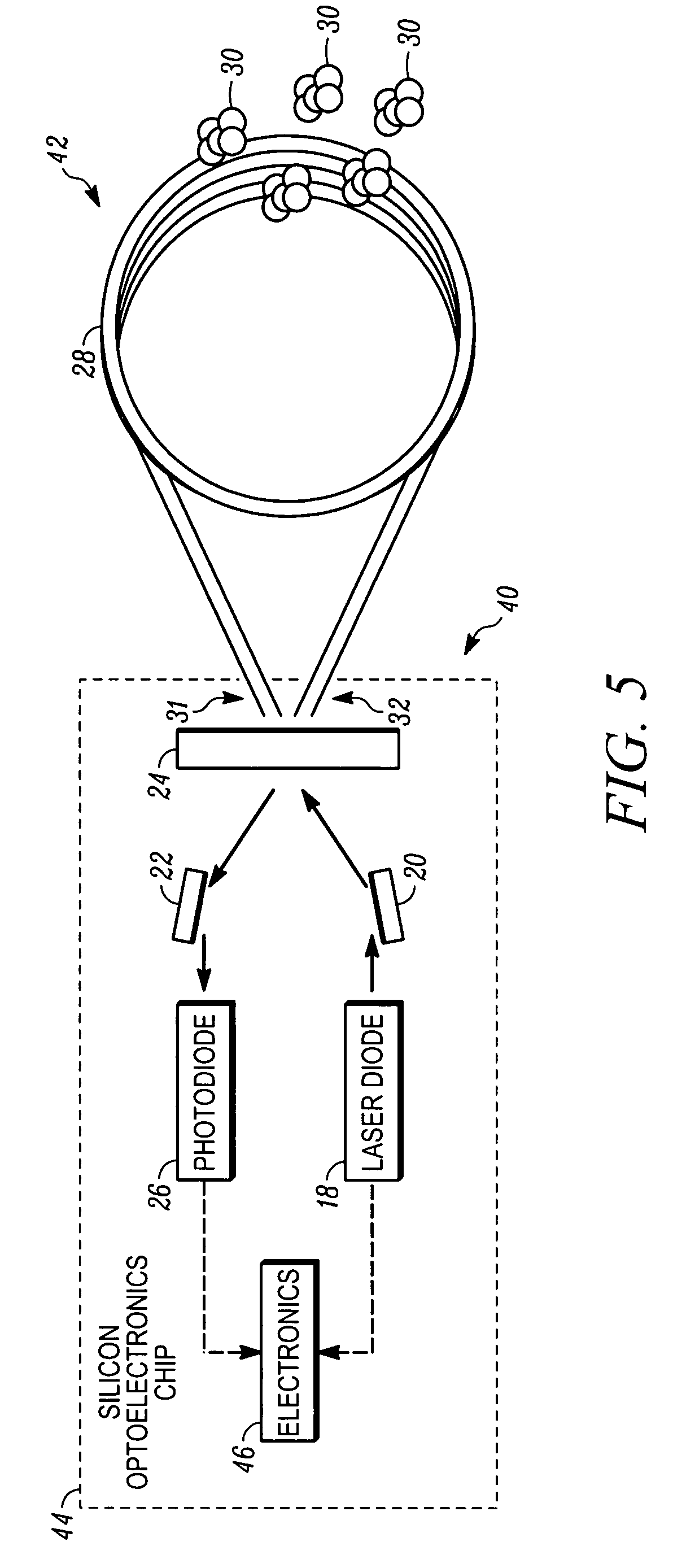
Tunable external cavity laser
InactiveUS6853654B2Avoids multimode lasingPrevent their lasingLaser optical resonator constructionWavelength-division multiplex systemsExternal cavity laserLight beam
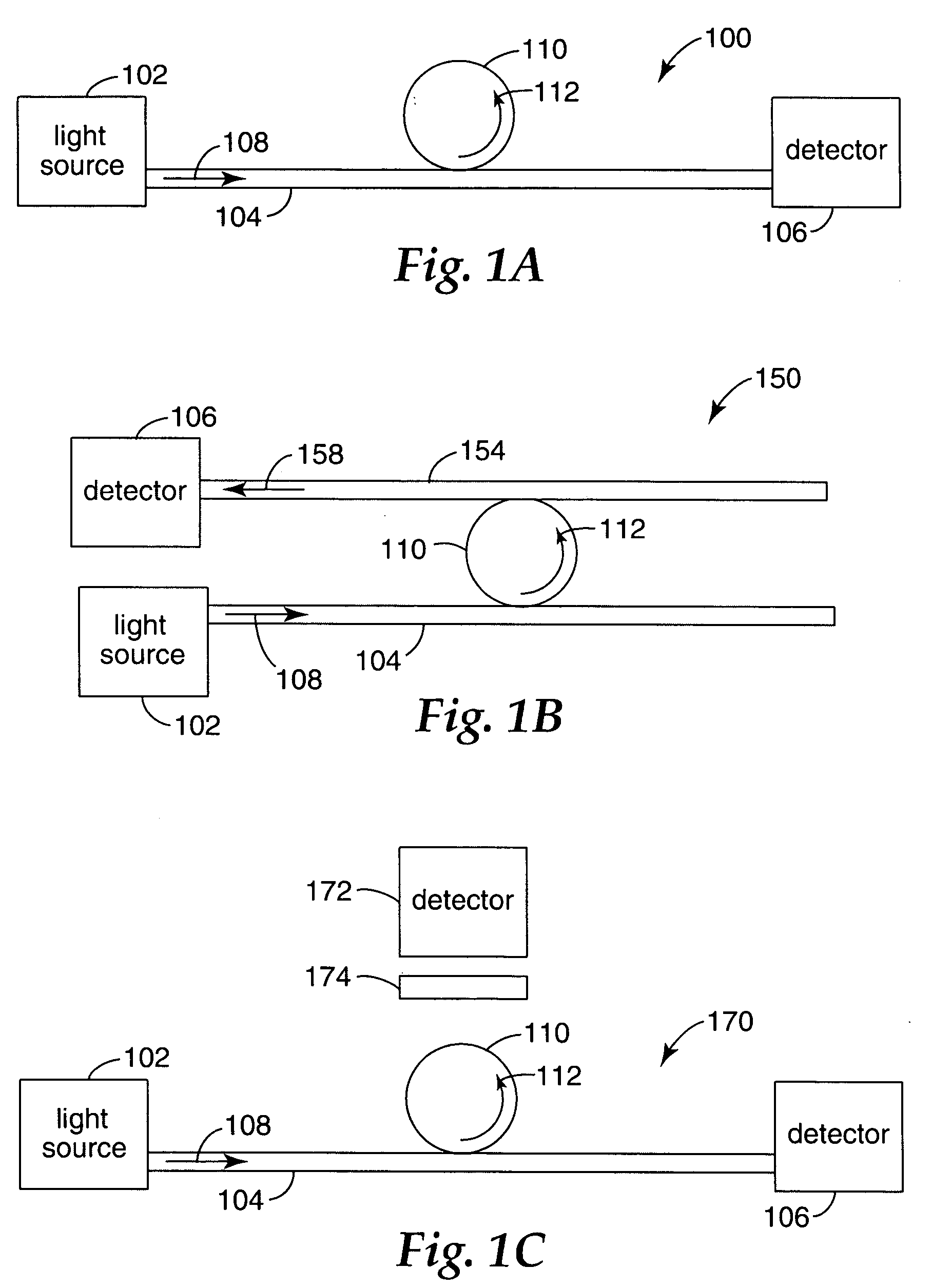
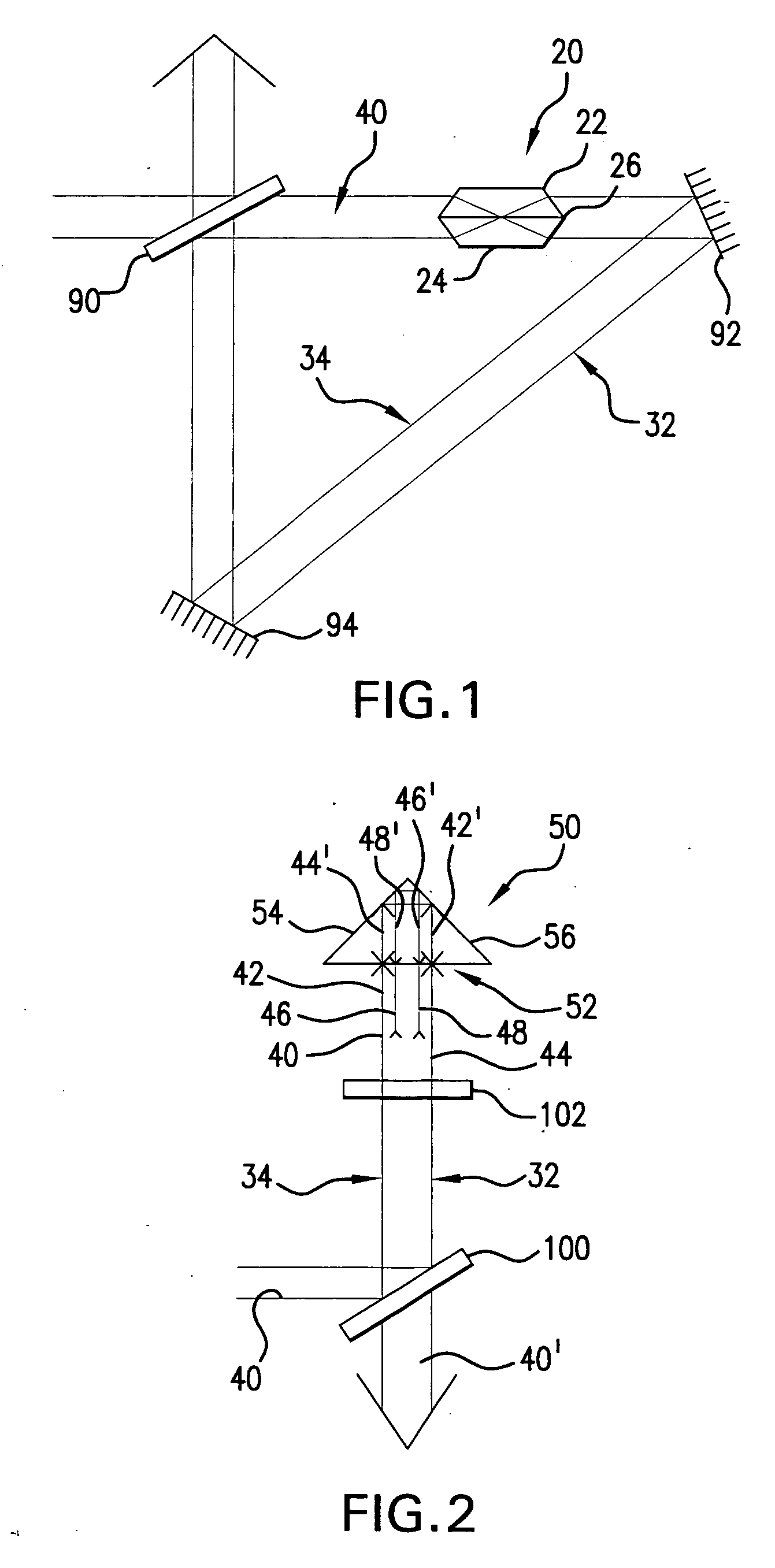
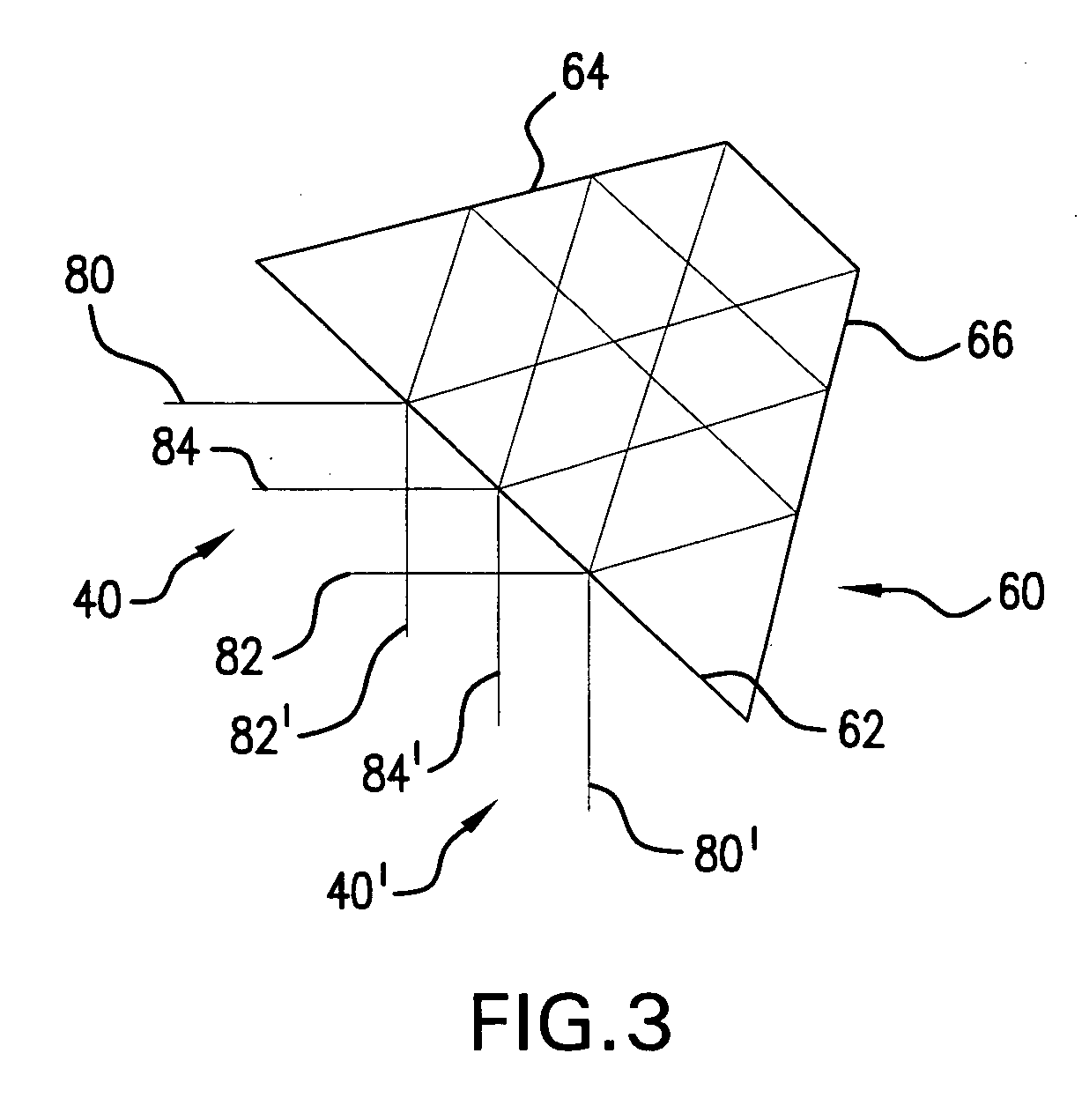
Apparatus and methods that utilize tunable elements to provide for selective wavelength tuning of a light beam. The apparatus comprises a first tunable wavelength selection element having a first adjustable free spectral range, a second tunable wavelength selection element having a second adjustable free spectral range, with the first and second tunable wavelength selection elements configured to define a tunable joint transmission peak. The first and second tunable wavelength selection elements respectively define first and second pluralities of tunable transmission peaks, wherein respective ones of each of the first and second plurality of transmission peaks are aligned to obtain a joint transmission peak that may be adjusted by tuning the wavelength selection elements. The free spectral ranges of the wavelength selection elements are configured to enable a Vernier tuning effect.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Device for measurement of optical wavelengths
InactiveUS6097487AGood repeatabilityAccurate scaleOptical measurementsSpectrum investigationGratingSource spectrum
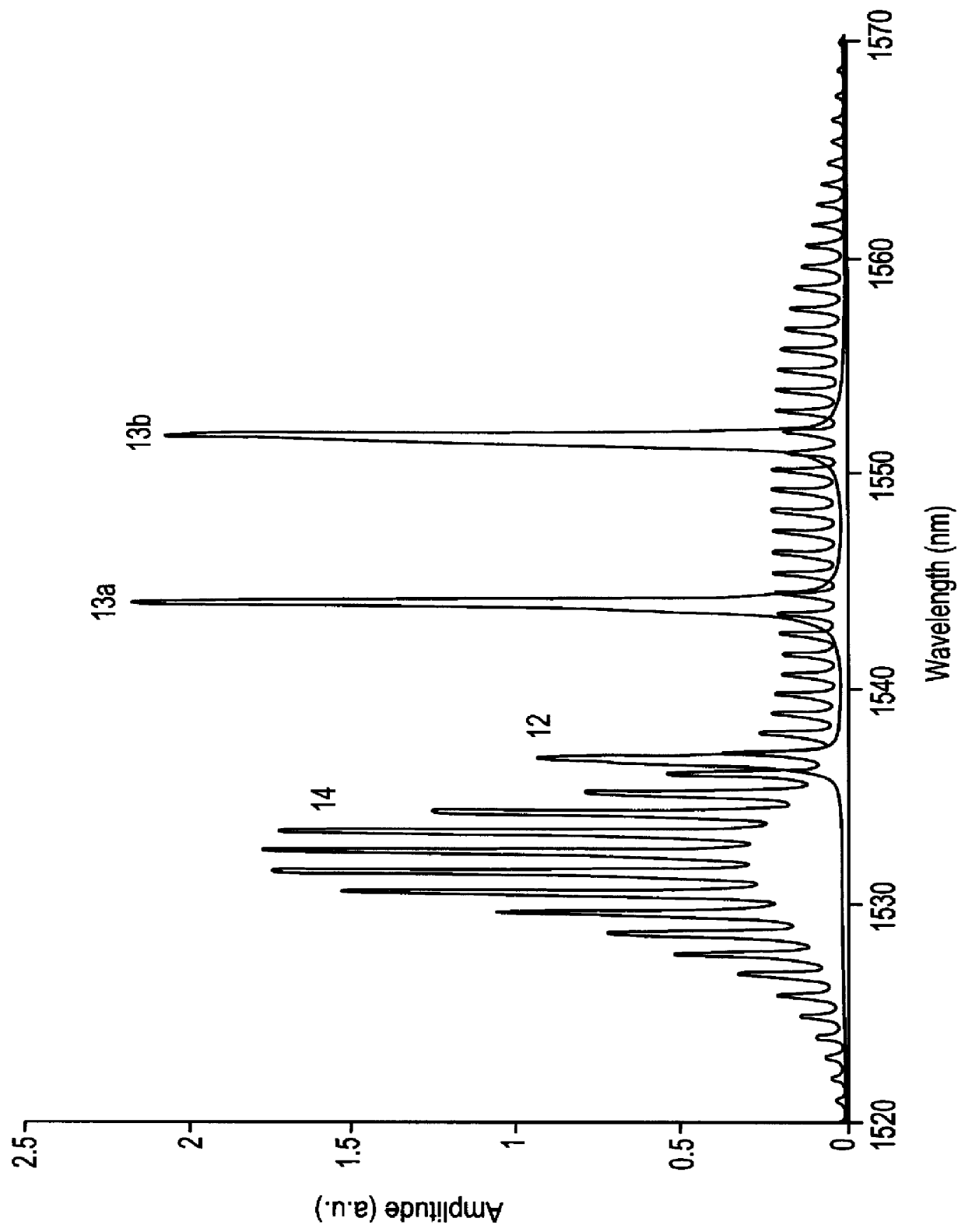
PCT No. PCT / NO98 / 00031 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 29, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 29, 1999 PCT Filed Jan. 29, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 36252 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 20, 1998A device for accurate and repeatable measurements of optical wavelengths, including an interrogation broadband light source (1) and a tuneable optical filter (2). A first part of the light is, in either order, transmitted through the filter (2) and reflected from, or transmitted through, at least one fibre Bragg grating (5) with known Bragg wavelength, providing an absolute wavelength reference, and directed to a first detector (7). A second part of the light is, in either order, transmitted through the filter and transmitted through, or reflected from a Fabry-Perot filter (8) with fixed and known free spectral range, creating a comb spectrum sampling the interrogation source spectrum to provide an accurate frequency / wavelength scale.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Dielectric microcavity fluorosensors excited with a broadband light source
InactiveUS20050263679A1Solve narrow bandwidthRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsWhispering galleryBroadband light source
A microresonator sensor apparatus has a microcavity resonator that defines equatorial whispering gallery modes (EWGMs), whose frequencies are separated by the free spectral range (FSR). The EWGMs lie in a plane perpendicular to a microcavity resonator axis. A light source is optically coupled to inject light into the microcavity resonator. The light source produces output light having an output spectrum whose bandwidth is approximately equal to or broader than the FSR of the EGWMs. One or more fluorescent materials are excited using the excitation light coupled into the microcavity resonator. A fluorescent signal arising from fluorescence of the one or more fluorescent materials is then detected.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for the precise measurement of the wavelength of light
ActiveUS20060181710A1Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectrometerSpectral signature
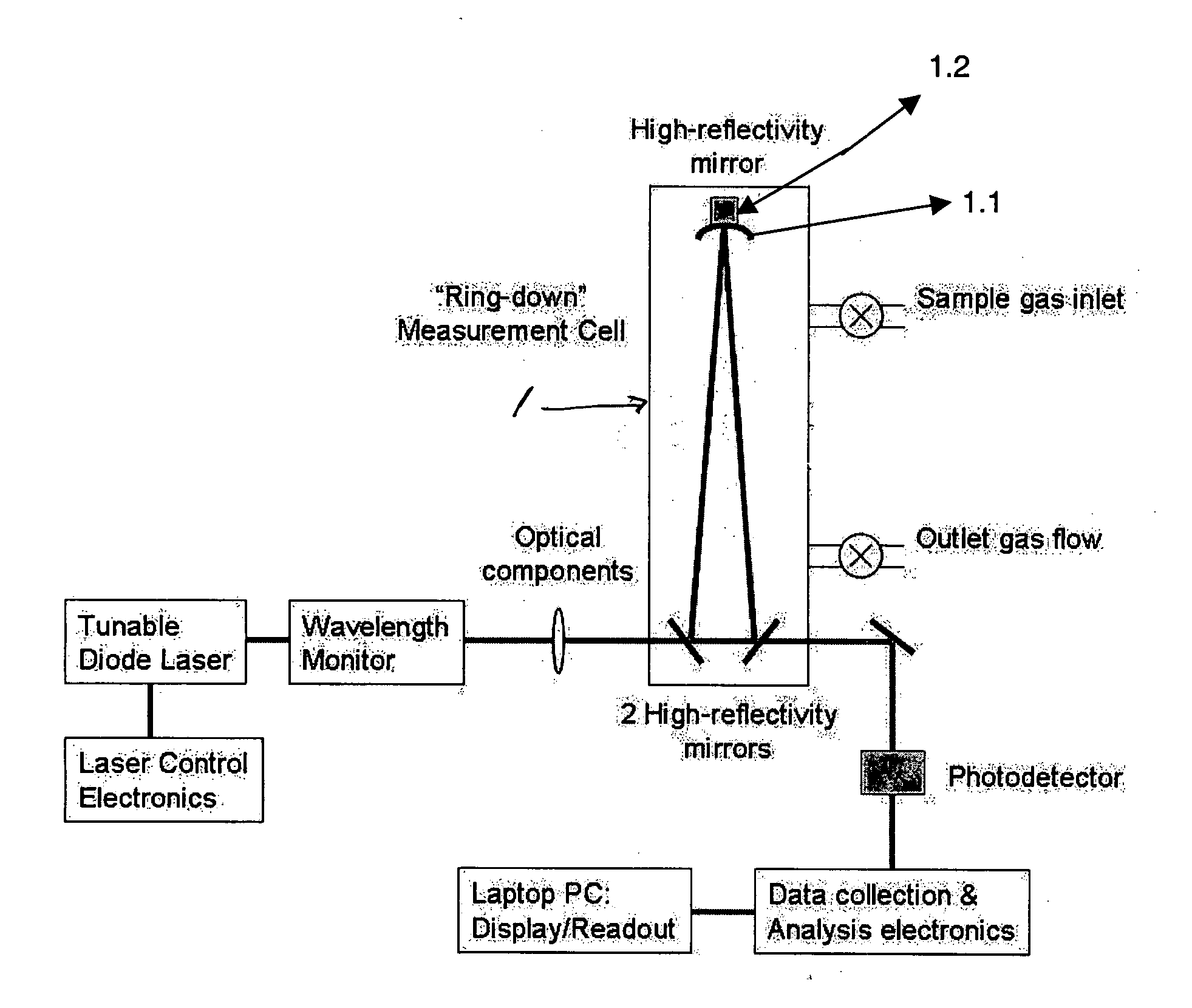
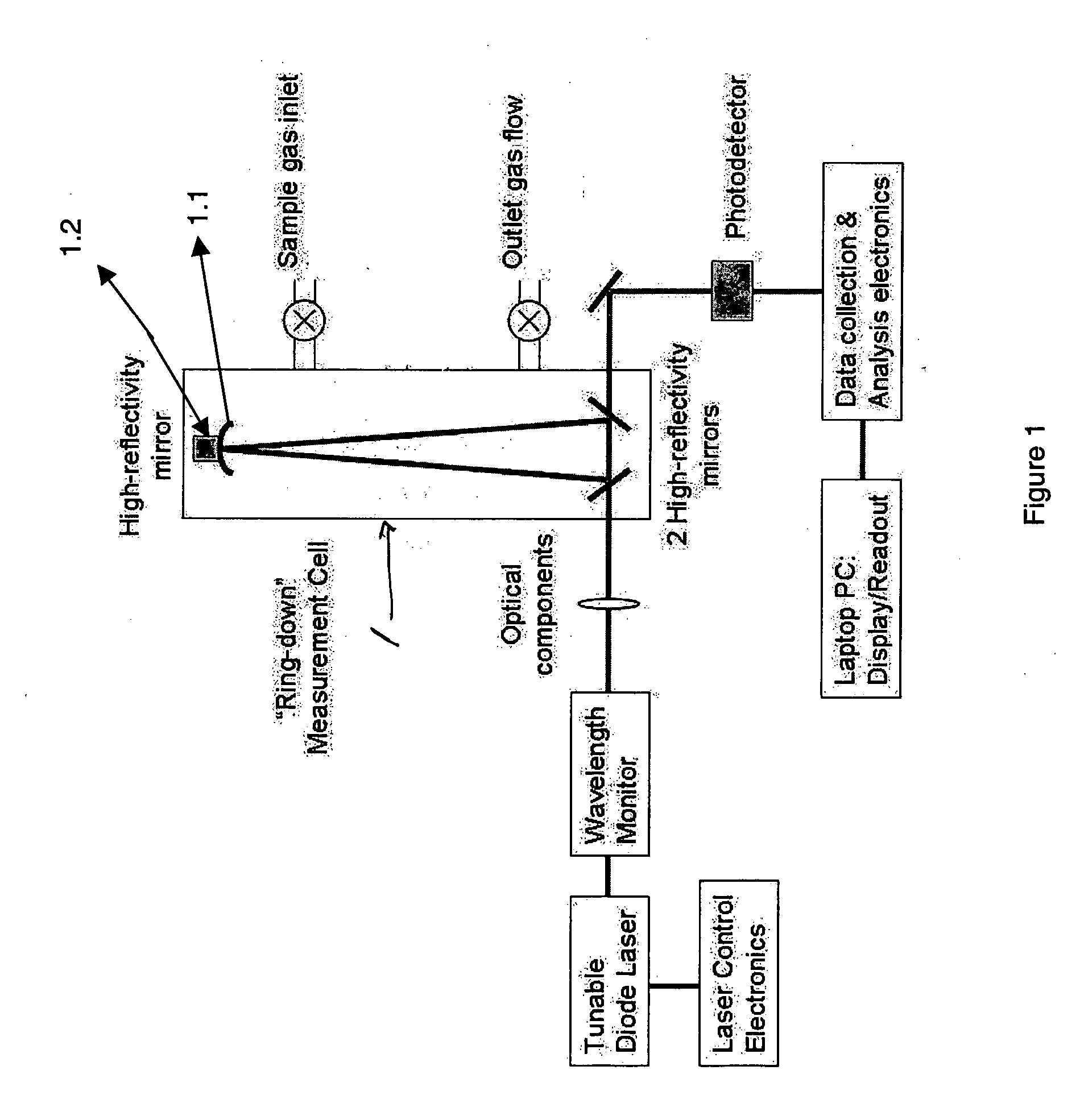
A process for measuring the absorption spectrum of a target analyte using a cavity ring down spectrometer, comprising the steps of: i) tuning the spectrometer laser so that the light transmitted from the laser into the spectrometer optical cavity is varied over a wavelength interval which encompasses both the absorption wavelength of a spectral feature of the target analyte and a plurality of the free spectral ranges of the optical cavity; ii) triggering a plurality of ringdown events; iii) for each ringdown event, recording the decay time constant and the trigger time at which the light into the cavity is shut off; iv) organizing the decay time constants, light wavelengths and trigger times as a function of trigger time; v) ordering said light wavelengths by increasing value and placing groups of wavelengths into individual bins; vi) computing the average wavelength of each bin group; vii) grouping the decay time constants and trigger times into bins that parallel said wavelength bins, with the decay time constants in each of said parallel bin being arranged by increasing trigger time; viii) computing the average decay time for each decay time bin and using this decay time average, together with the average wavelength from the parallel wavelength bin, to compute the optical loss for the target analyte at said average wavelength.
Owner:PICARRO
Partial DPSK (PDPSK) Transmission Systems
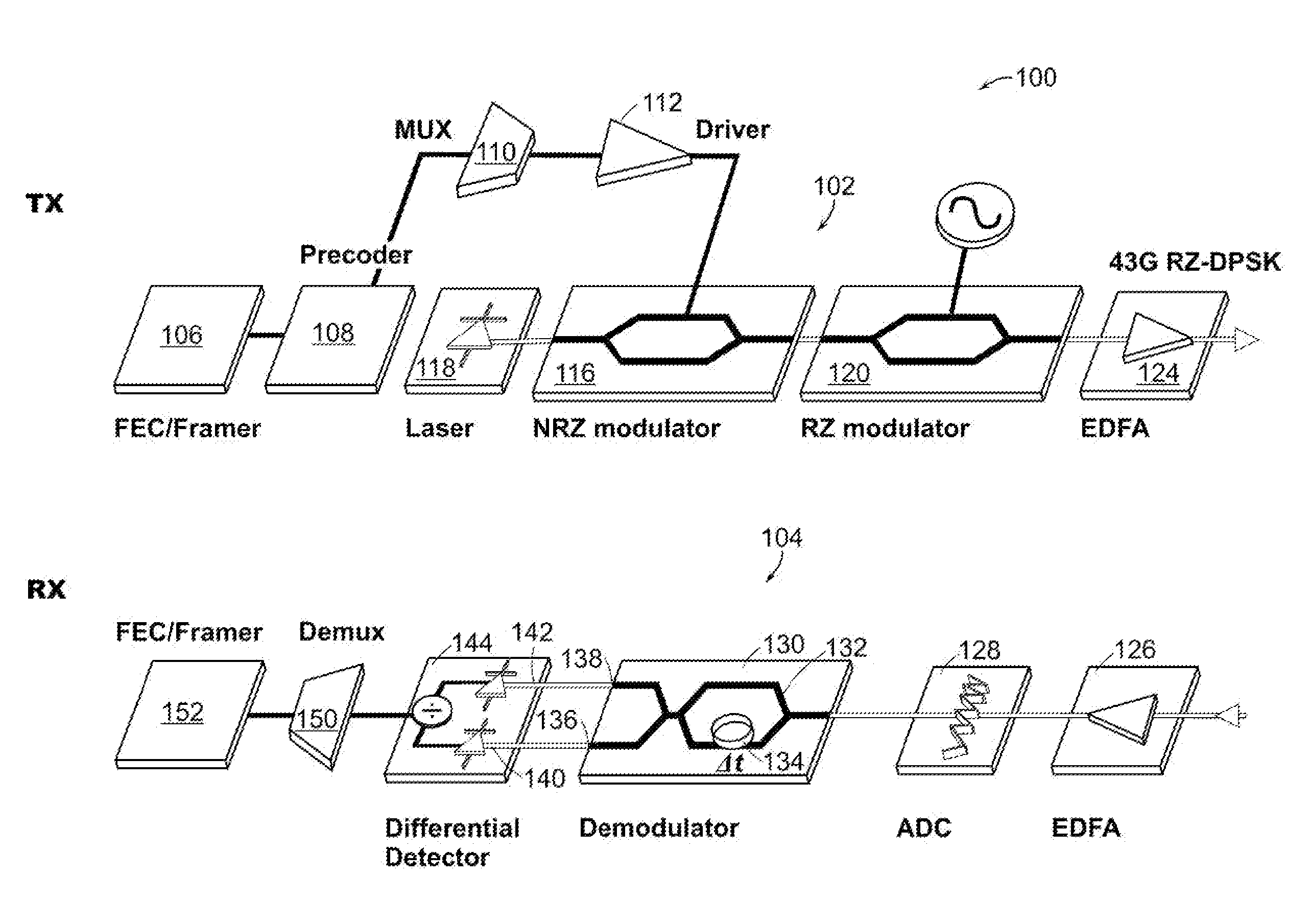
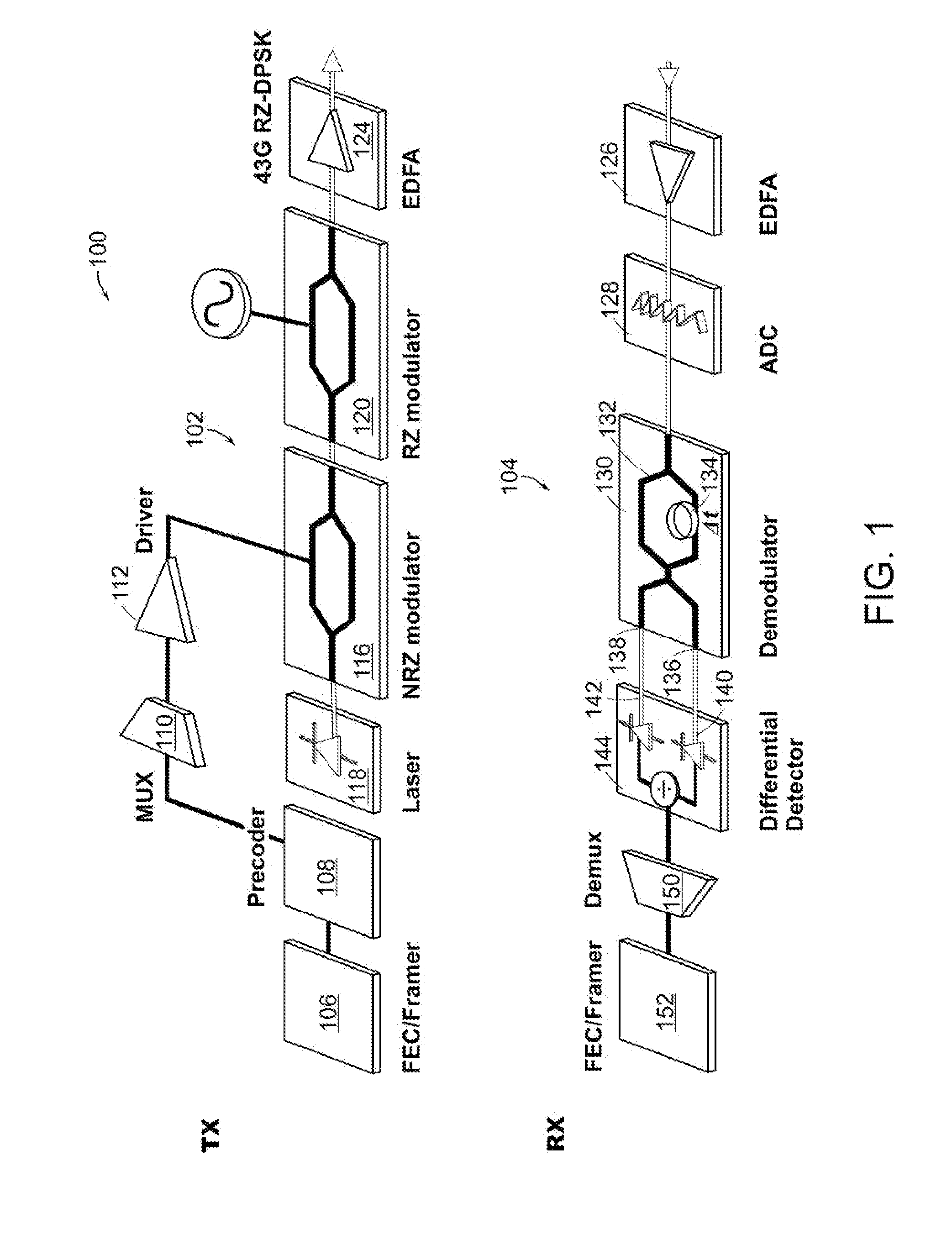
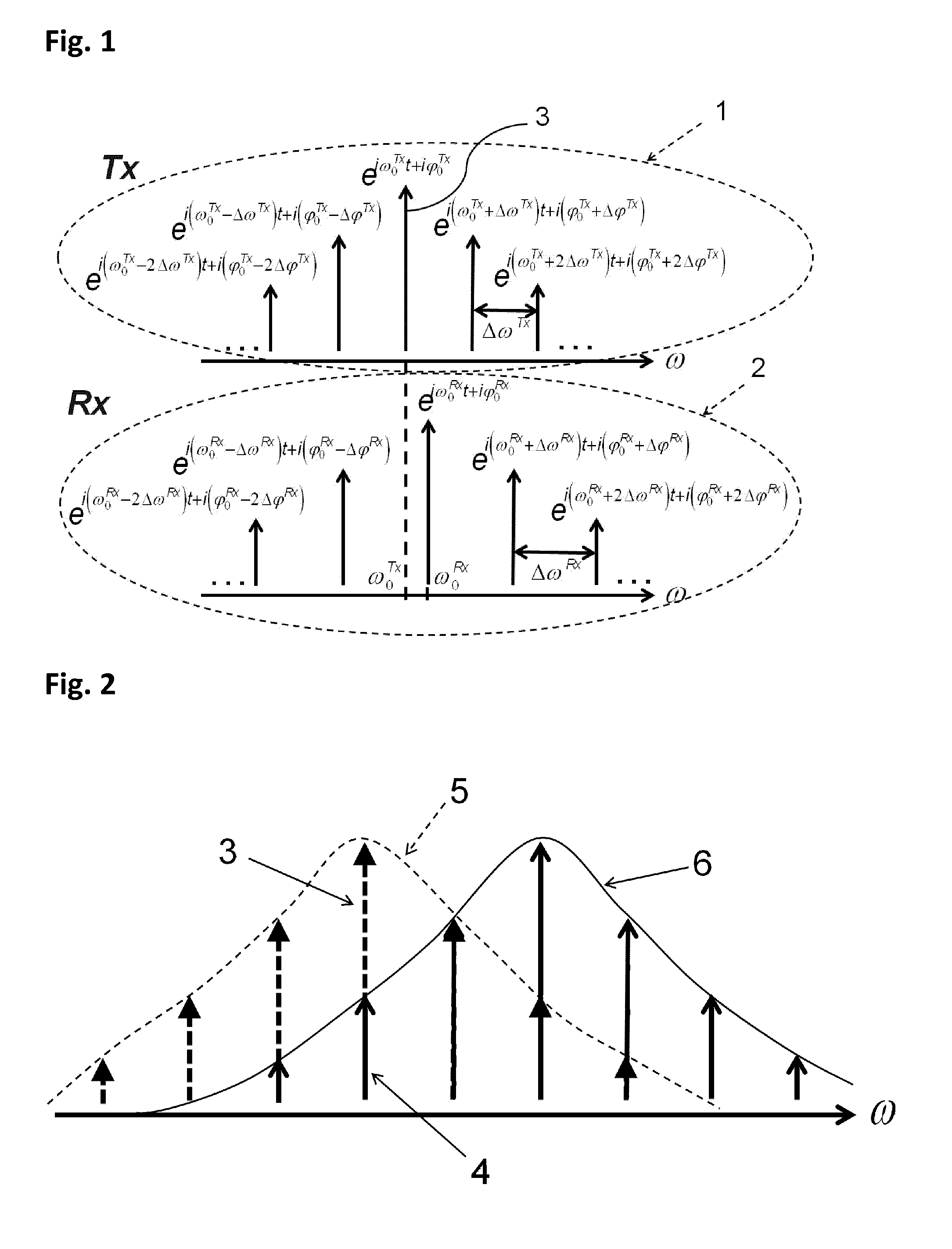
An optical receiver includes a demodulator having a delay interferometer comprising an optical input that receives a phase modulated optical signal from a bandwidth limited transmission system. The delay interferometer has a free spectral range that is larger than a symbol rate of the phase modulated optical signal by an amount that improves receiver performance. The receiver also includes a differential detector having a first and a second photodetector. The first photodetector is optically coupled to the constructive optical output of the delay interferometer. The second photodetector is optically coupled to the destructive optical output of the delay interferometer. The differential detector combines a first electrical detection signal generated by the first photodetector and a second electrical detection signal generated by the second photodetector to generate an electrical reception signal.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPTICS INC
Method and apparatus for gas discharge laser output light coherency reduction
A method and apparatus for producing with a gas discharge laser an output laser beam comprising output laser light pulses, for delivery as a light source to a utilizing tool is disclosed which may comprise a beam path and a beam homogenizer in the beam path. The beam homogenizer may comprise at least one beam image inverter or spatial rotator, which may comprise a spatial coherency cell position shifter. The homogenizer may comprise a delay path which is longer than, but approximately the same delay as the temporal coherence length of the source beam. The homogenizer may comprise a pair of conjoined dove prisms having a partially reflective coating at the conjoined surfaces of each, a right triangle prism comprising a hypotenuse face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or an isosceles triangle prism having a face facing the source beam and fully reflective adjoining side faces or combinations of these, which may serve as a source beam multiple alternating inverted image creating mechanism. The beam path may be part of a bandwidth measuring the bandwidths of an output laser beam comprising output laser light in the range of below 500 femtometers at accuracies within tens of femtometers. The homogenizer may comprise a rotating diffuser which may be a ground glass diffuser which may also be etched. The wavemeter may also comprise a collimator in the beam path collimating the diffused light; a confocal etalon creating an output based upon the collimated light entering the confocal etalon; and a detector detecting the output of the confocal etalon and may also comprise a scanning mechanism scanning the angle of incidence of the collimated light entering the confocal etalon which may scan the collimated light across the confocal etalon or scan the etalon across the collimated light, and may comprise an acousto-optical scanner. The confocal etalon may have a free spectral range approximately equal to the E95 width of the beam being measured. The detector may comprise a photomultiplier detecting an intensity pattern of the output of the confocal etalon.
Owner:CYMER INC
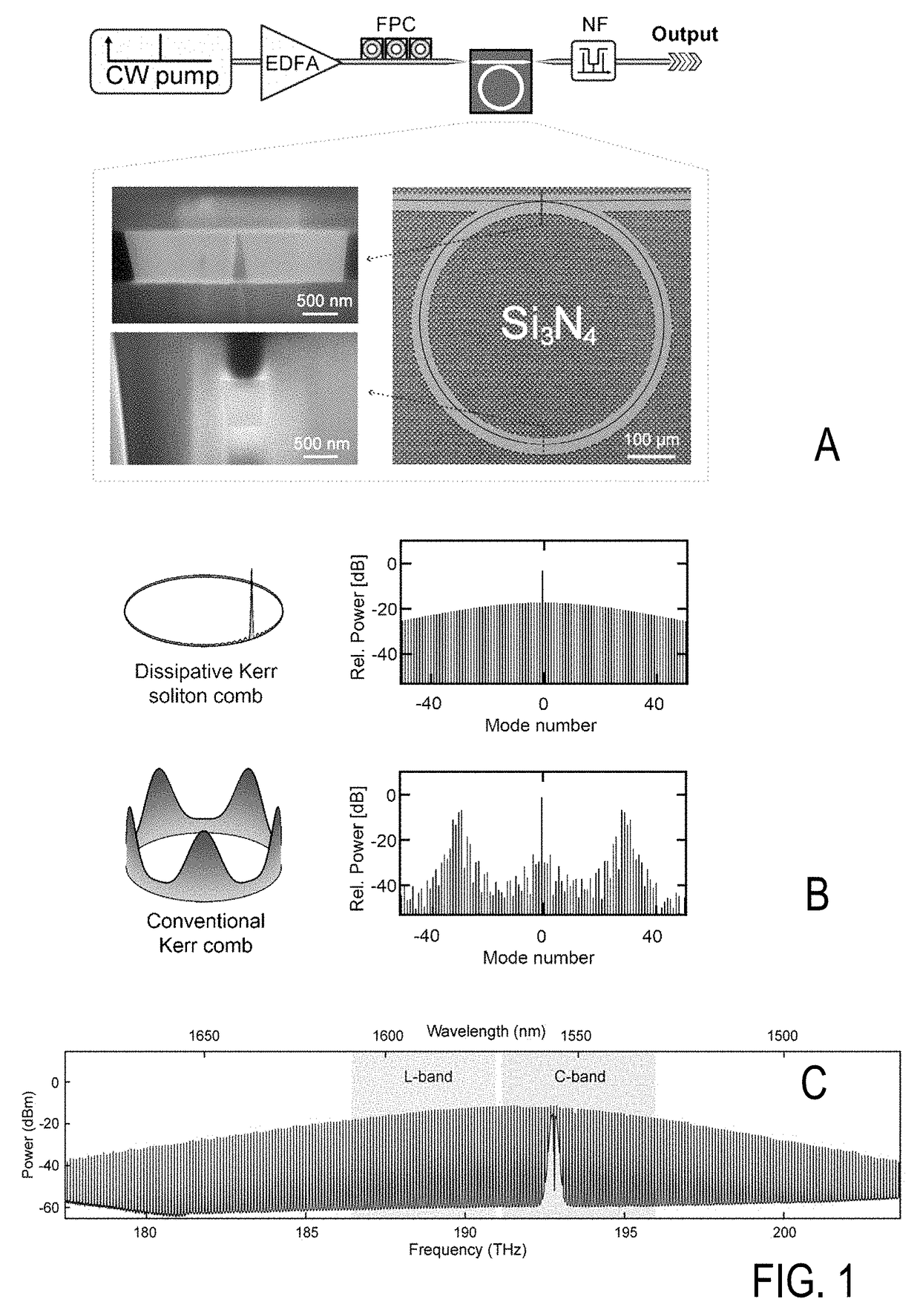
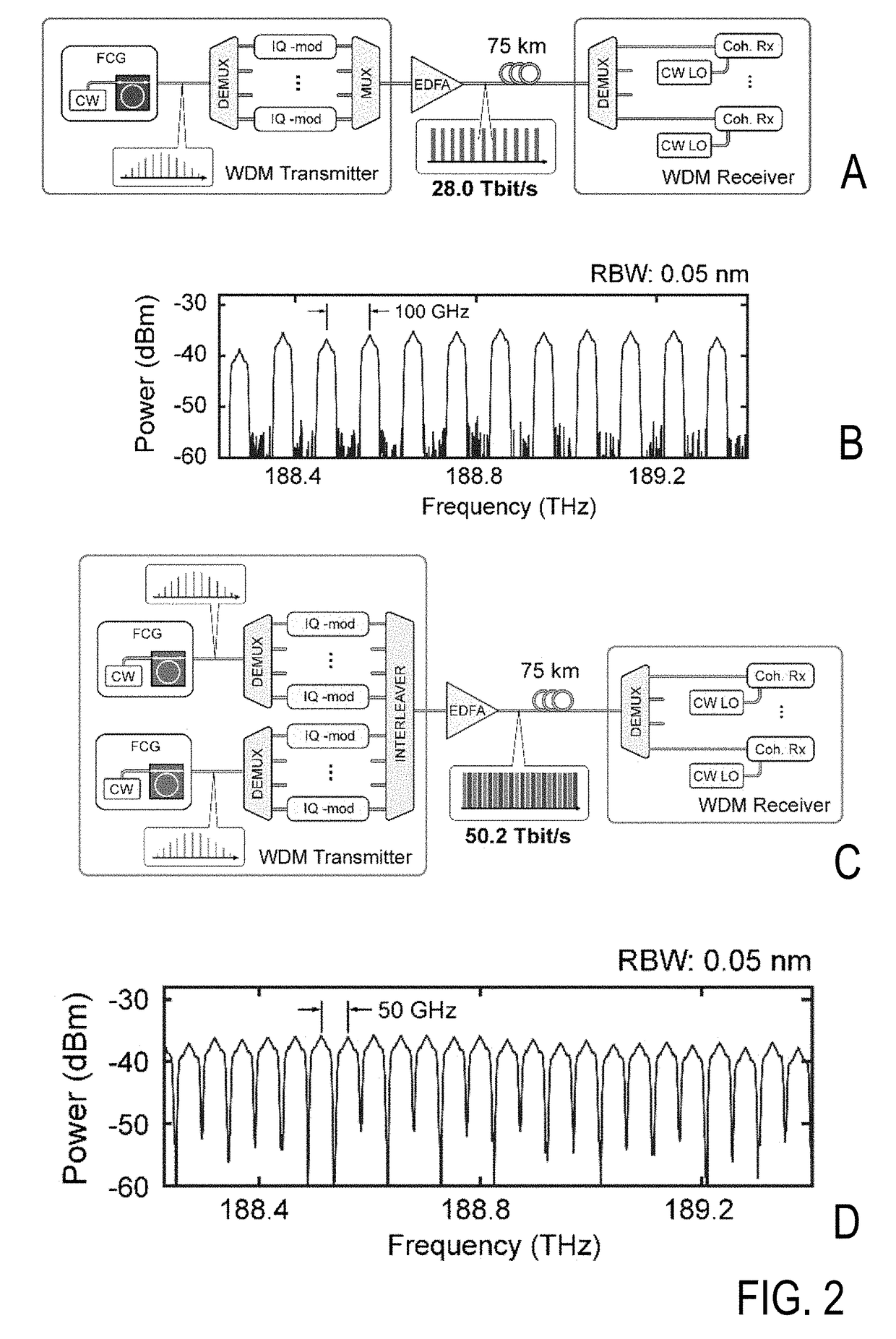
WDM telecommunications link with coherent detection and optical frequency comb sources
ActiveUS20140064734A1Increase the number ofReduce complexityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoherence multiplexingTelecommunications linkIntermediate frequency
An optical data link has a transmitter and a receiver with coherent detection at the receiver and more than one optical carrier frequency. The optical carrier frequencies are generated by a frequency comb source in both the transmitter and the receiver. The frequency comb sources generate frequency combs that have frequency components and a free spectral range. The optical carrier frequencies transport more than one optical channel. Either at least one frequency component or the free spectral range of the optical comb generated at the receiver is locked to the comb generated at the transmitter by an optical phase locked loop, or an electrical phase locked loop or a feed-forward carrier recovery generates an intermediate frequency carrier reference that is routed to more than one channel to demodulate the data.
Owner:RWTH AACHEN UNIV
Surface-emitting semiconductor laser
InactiveUS20020071463A1Easy to adaptEasy to useLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionAnti-reflective coatingSemiconductor package
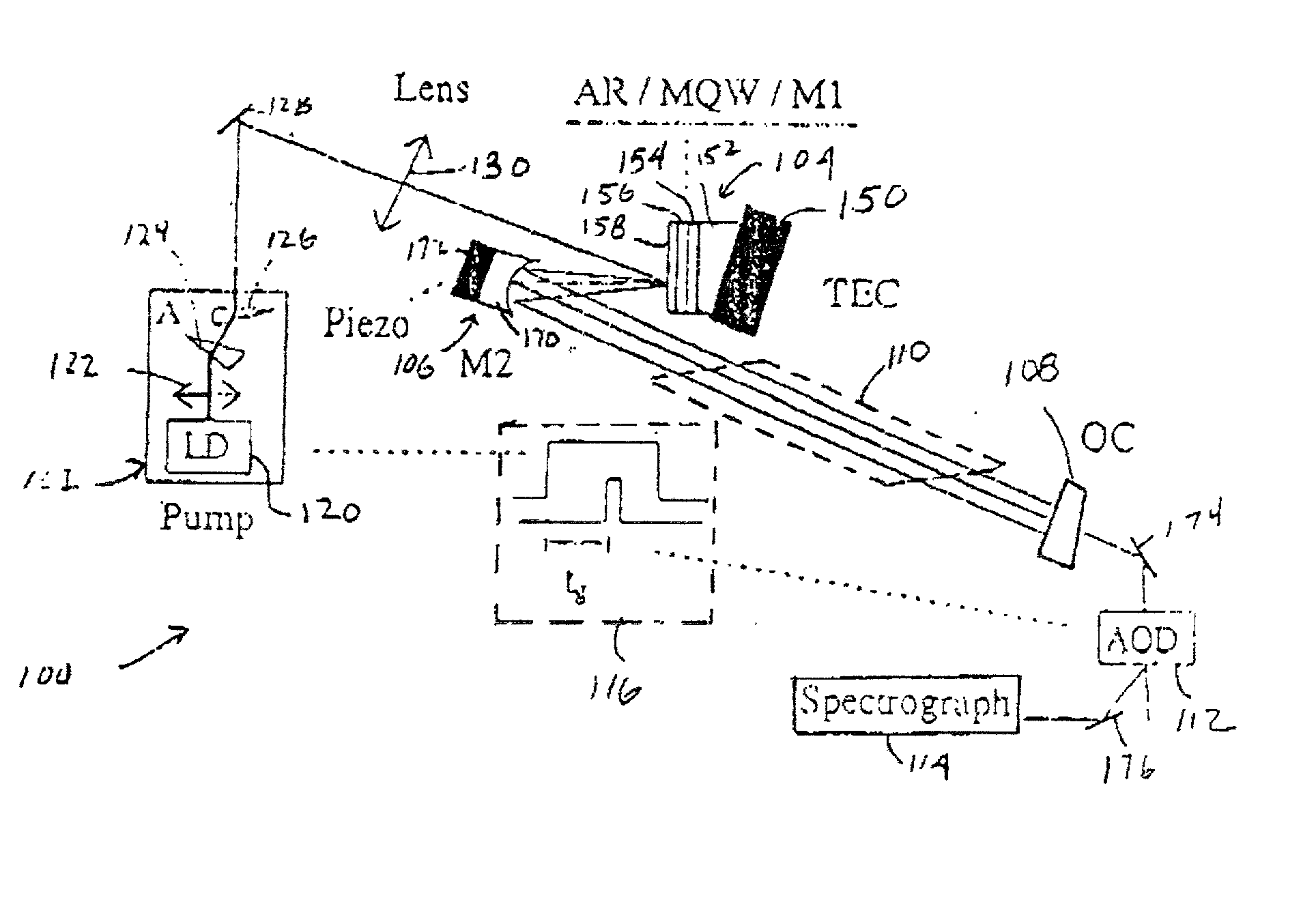
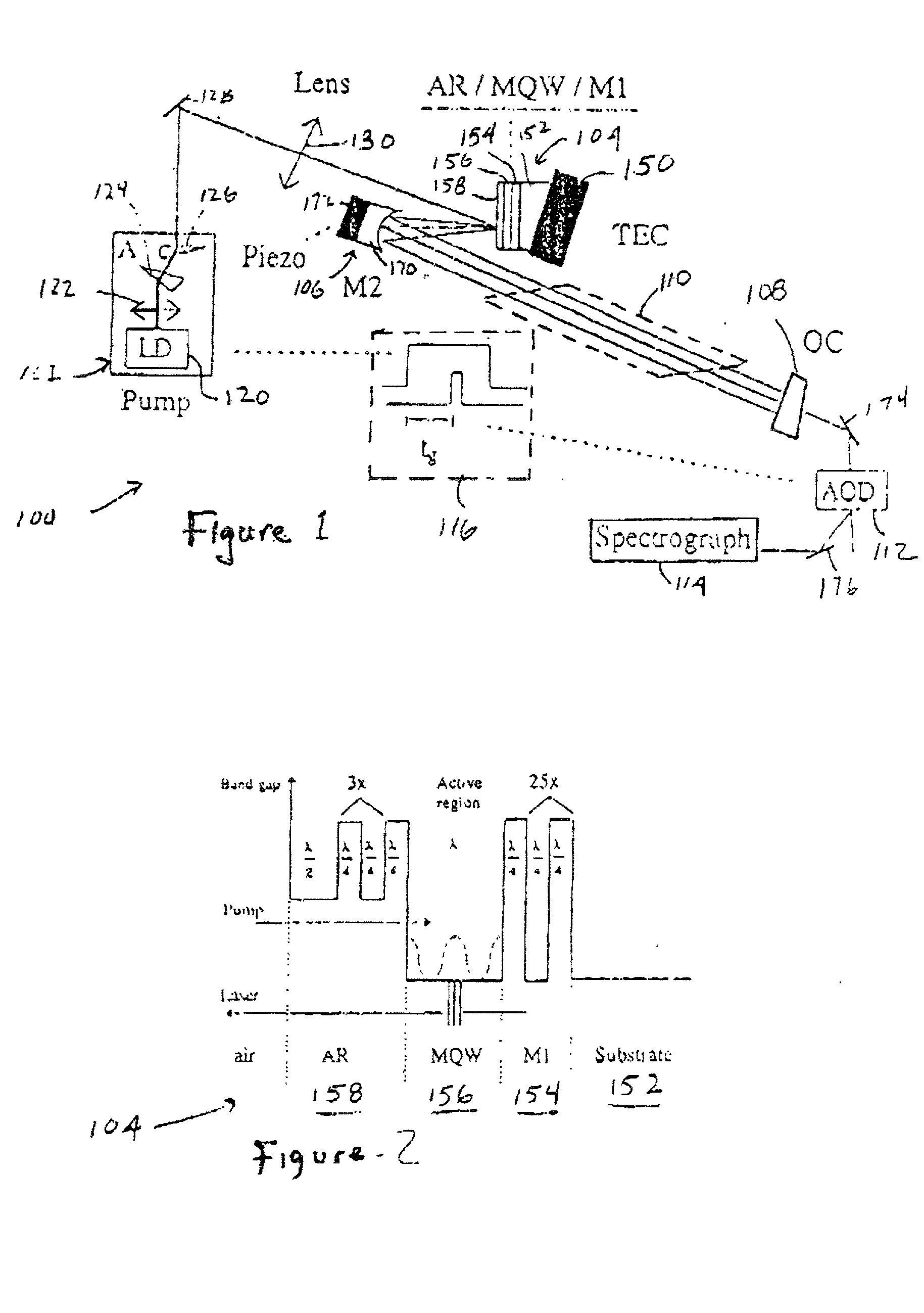
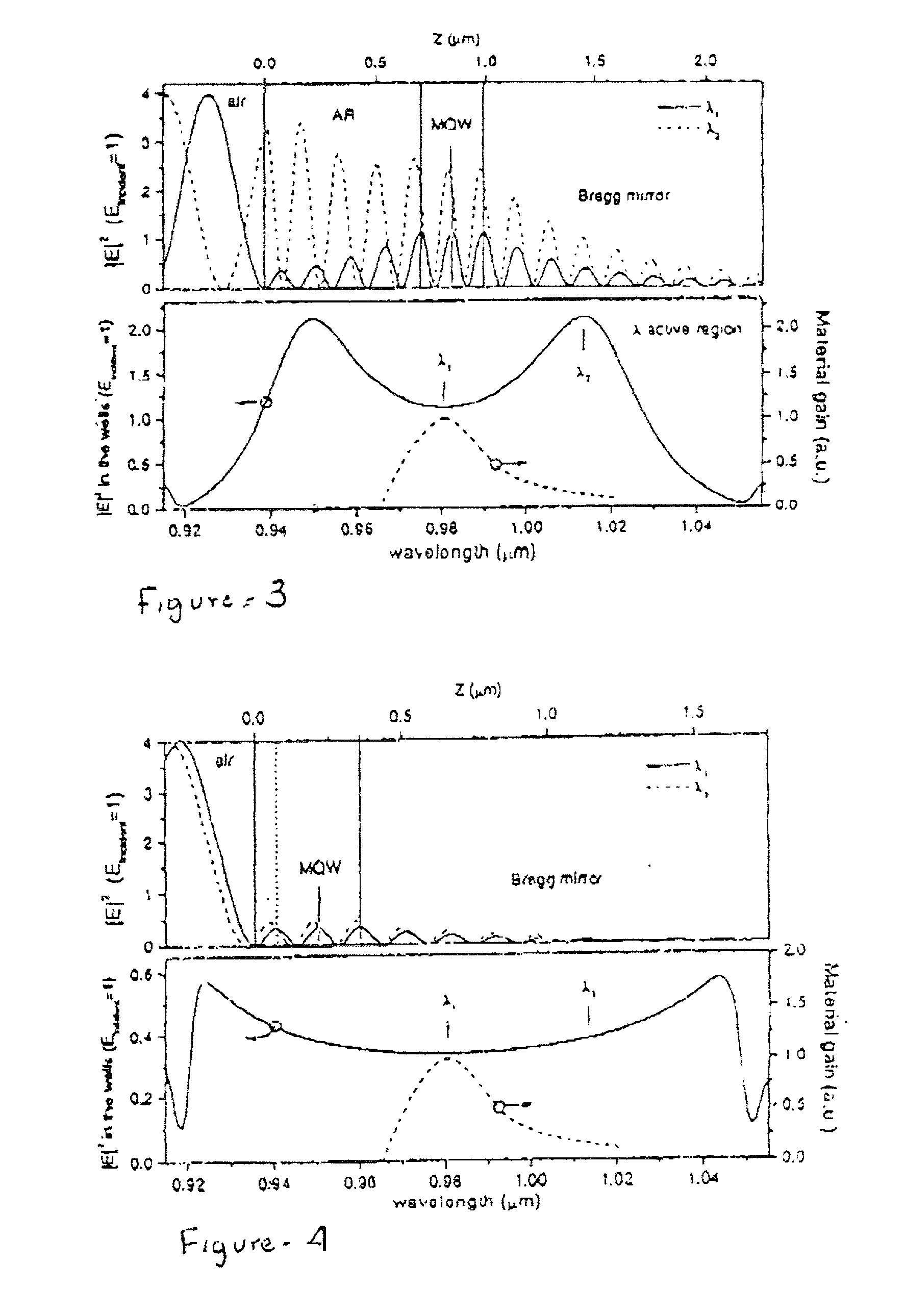
A laser suitable for intra-cavity laser absorption spectroscopy and for telecommunication system comprises a Bragg mirror, a multiple quantum well active region and an anti-reflective coating together with a second mirror spaced from the coating to define an external cavity, the free spectral range of the sub-cavity defined by the coating and the active region being less than two times the bandwidth of the coating and the bandwidth of the Bragg mirror being at least as great as the free spectral range of the sub-cavity.
Owner:PICARRO +1
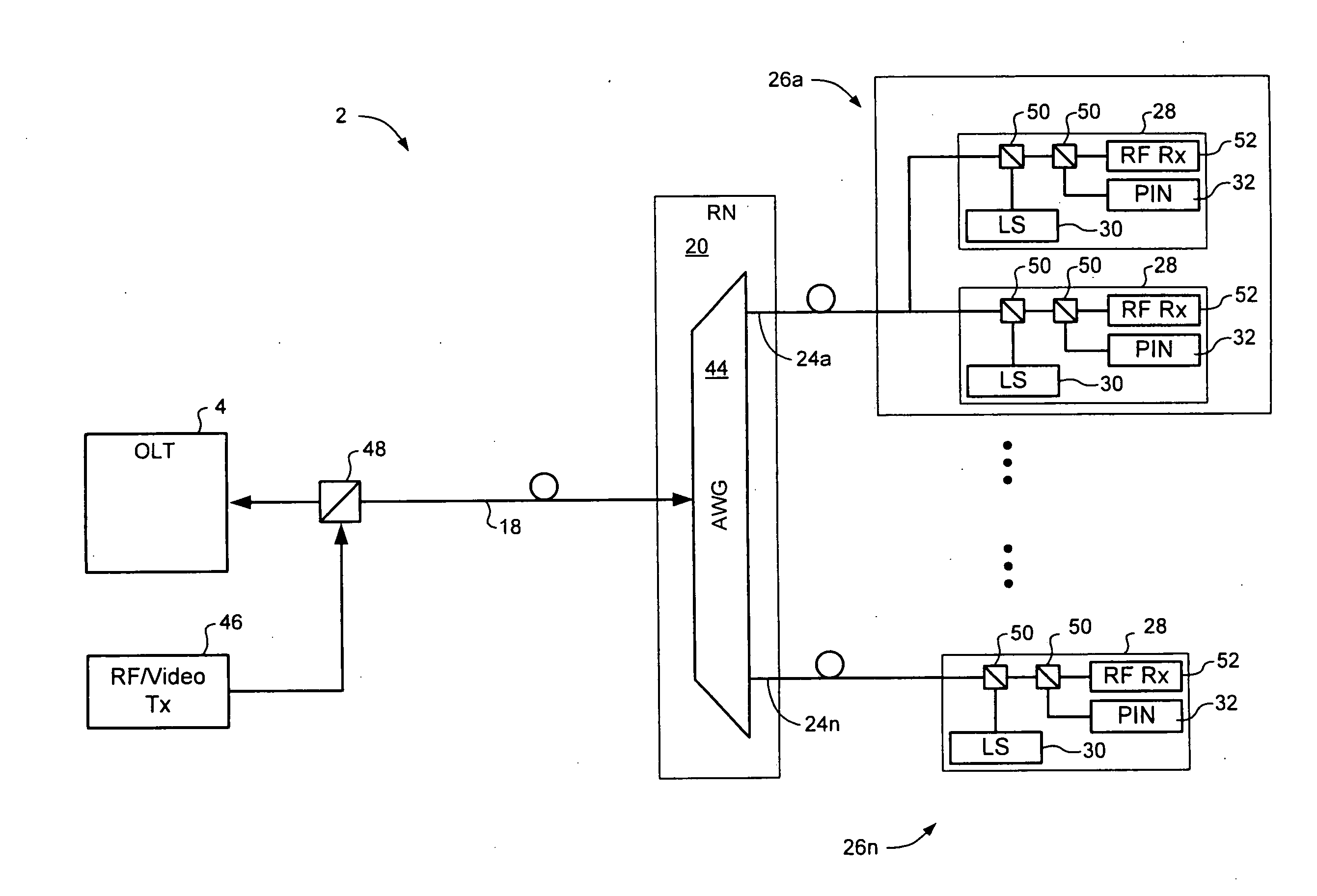
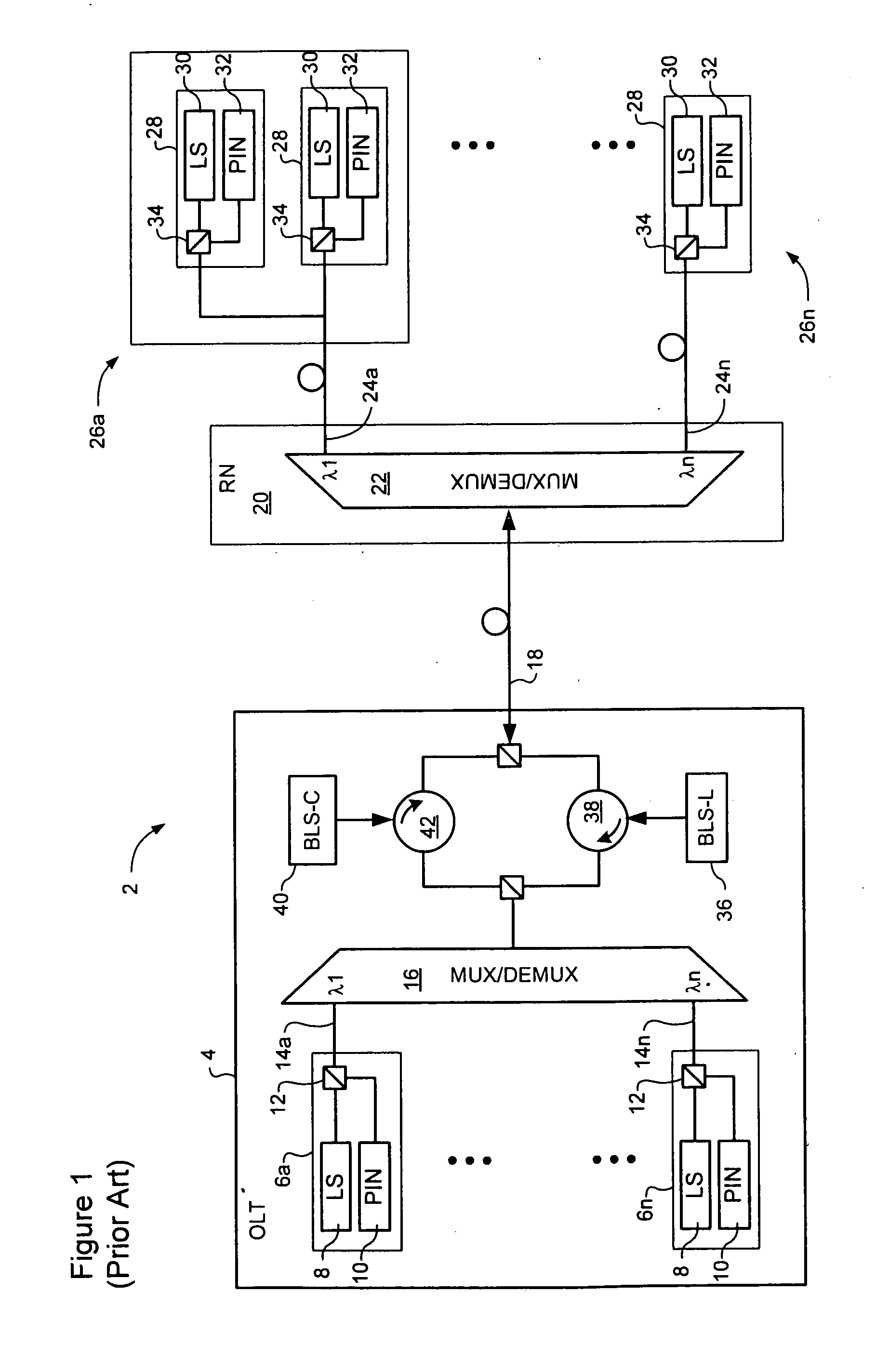
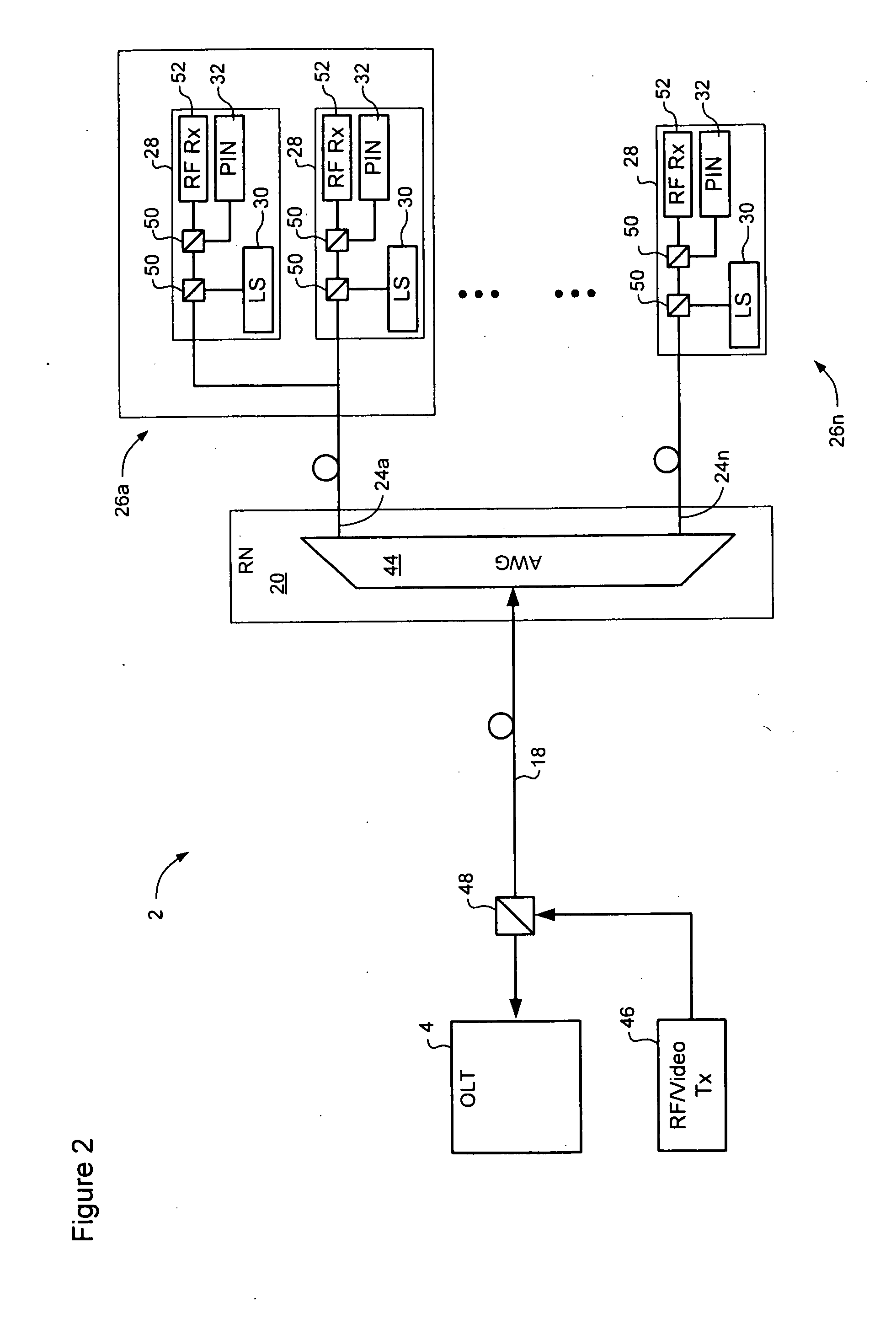
WDM PON with distribution via cyclic array waveguide grating
InactiveUS20100266283A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberLength wave
In a Wavelength Division Multiplexed Passive Optical Network (WDM-PON) including, a system for distributing uplink, downlink and RF / Video broadcast signalling. An Array Waveguide Grating (AWG) couples respective wavelength channels between a trunk fibre of the WDM-PON and a plurality of branch fibers of the WDM-PON. The AWG has a predetermined free spectral range and implements a channel plan comprising at least three spectral segments, each segment having a width equal to the free spectral range of the AWG. An Optical Line Terminal of the WDM-PON receives wavelength division multiplexed uplink signals within a first one of the spectral segments, and transmits wavelength division multiplexed downlink signals within a second one of the spectral segments. Respective channel plans within the first and second spectral segments are identical. An RF / Video broadcast transmitter generates an RF / Video broadcast signal within a third one of the spectral segments.
Owner:LG ERICSSON
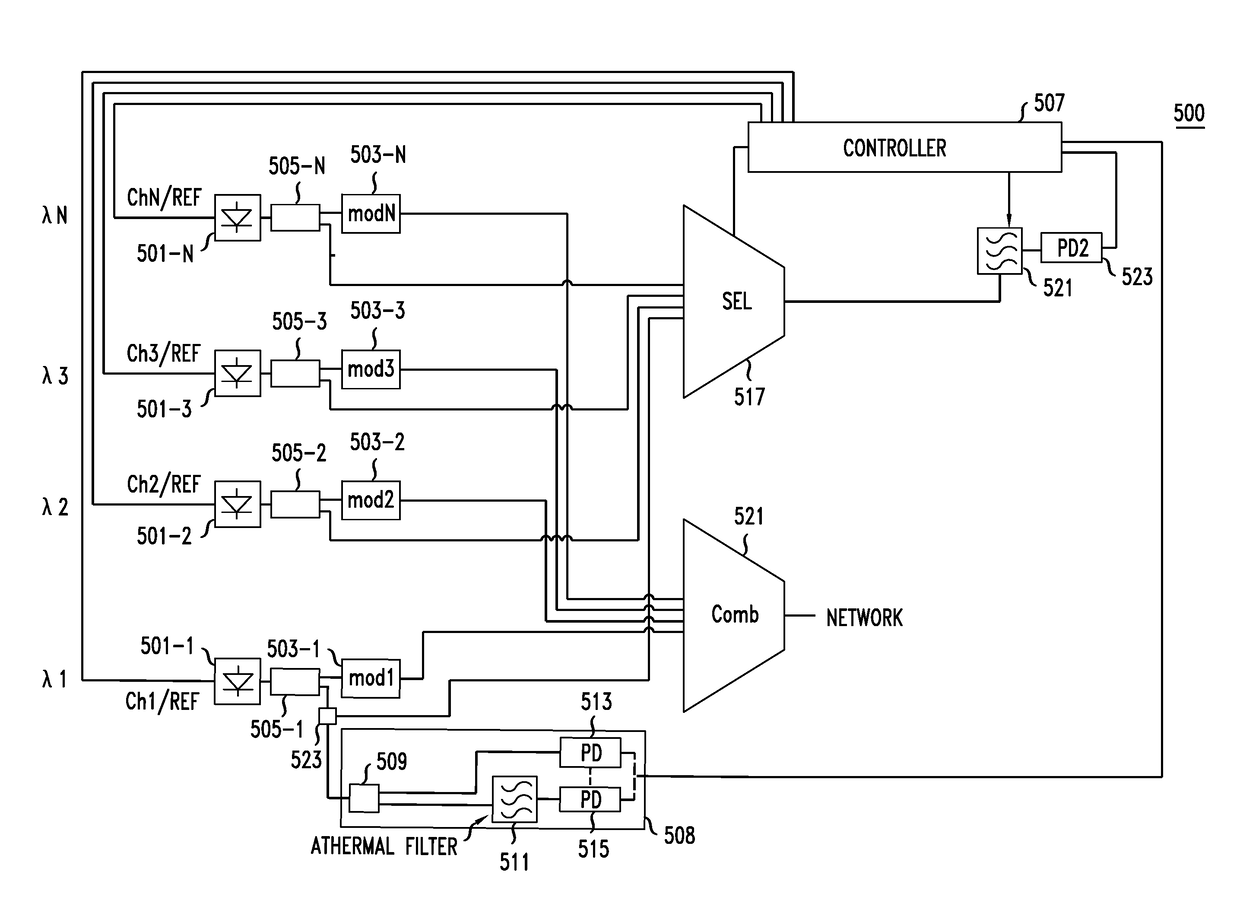
Method And Apparatus For Locking WDM Transmitter Carriers To A Defined Grid
ActiveUS20180115407A1Fabrication errorEliminate needWavelength-division multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansBandpass filteringCarrier signal
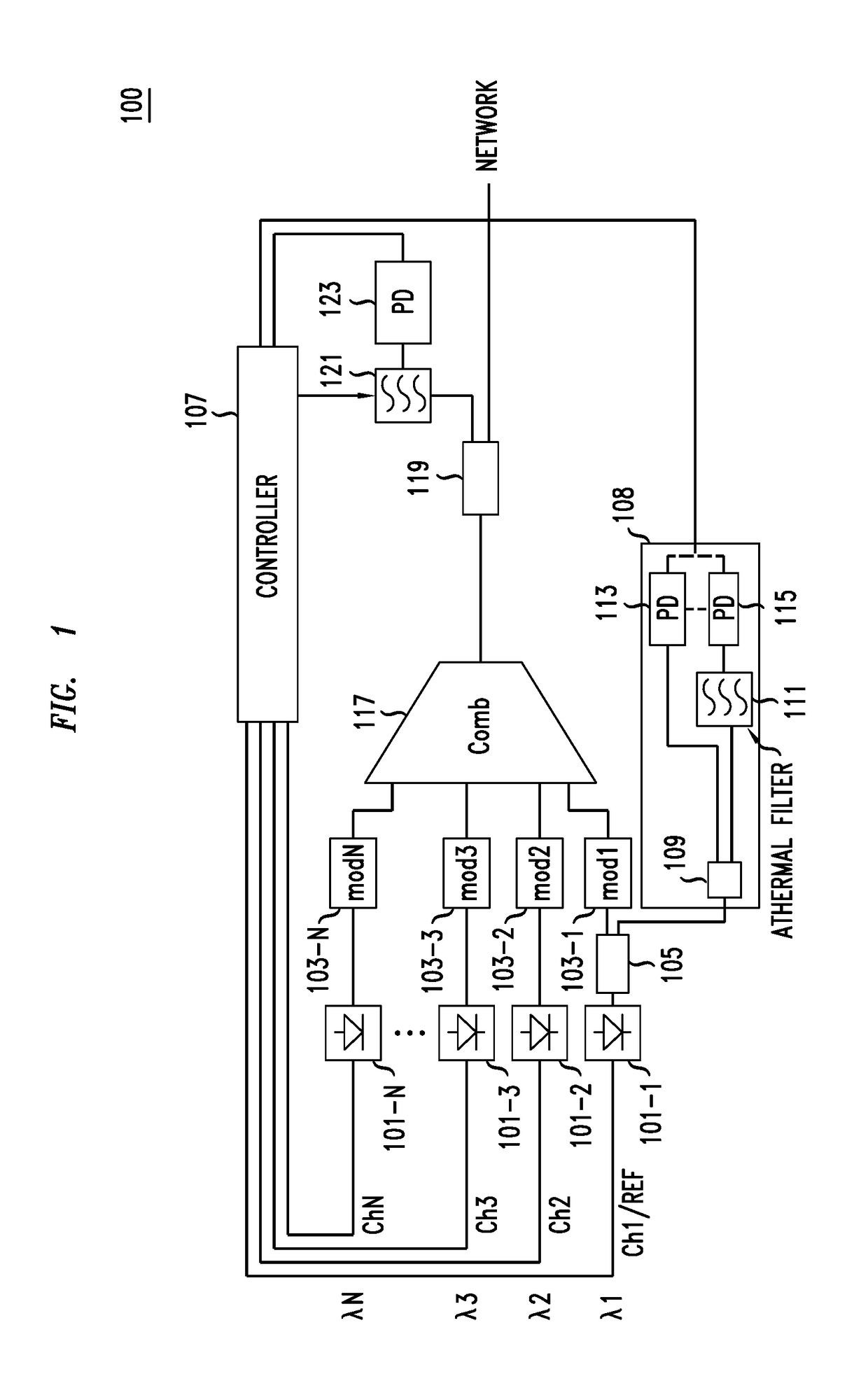
The locking of optical carriers to a grid can be achieved by employing an optical filter that exhibits athermal behavior in a frequency range to lock at least the frequency of a first channel to a target frequency. The locked frequency may be used to tune and lock the location of the free spectral range of a bandpass filter having transmission peaks at intervals, e.g., an FSR, corresponding to the target grid. The bandpass filter is used generate feedback signals that are used to lock the remaining frequencies to the grid. The athermal filter may be integrated on a silicon photonic integrated circuit.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
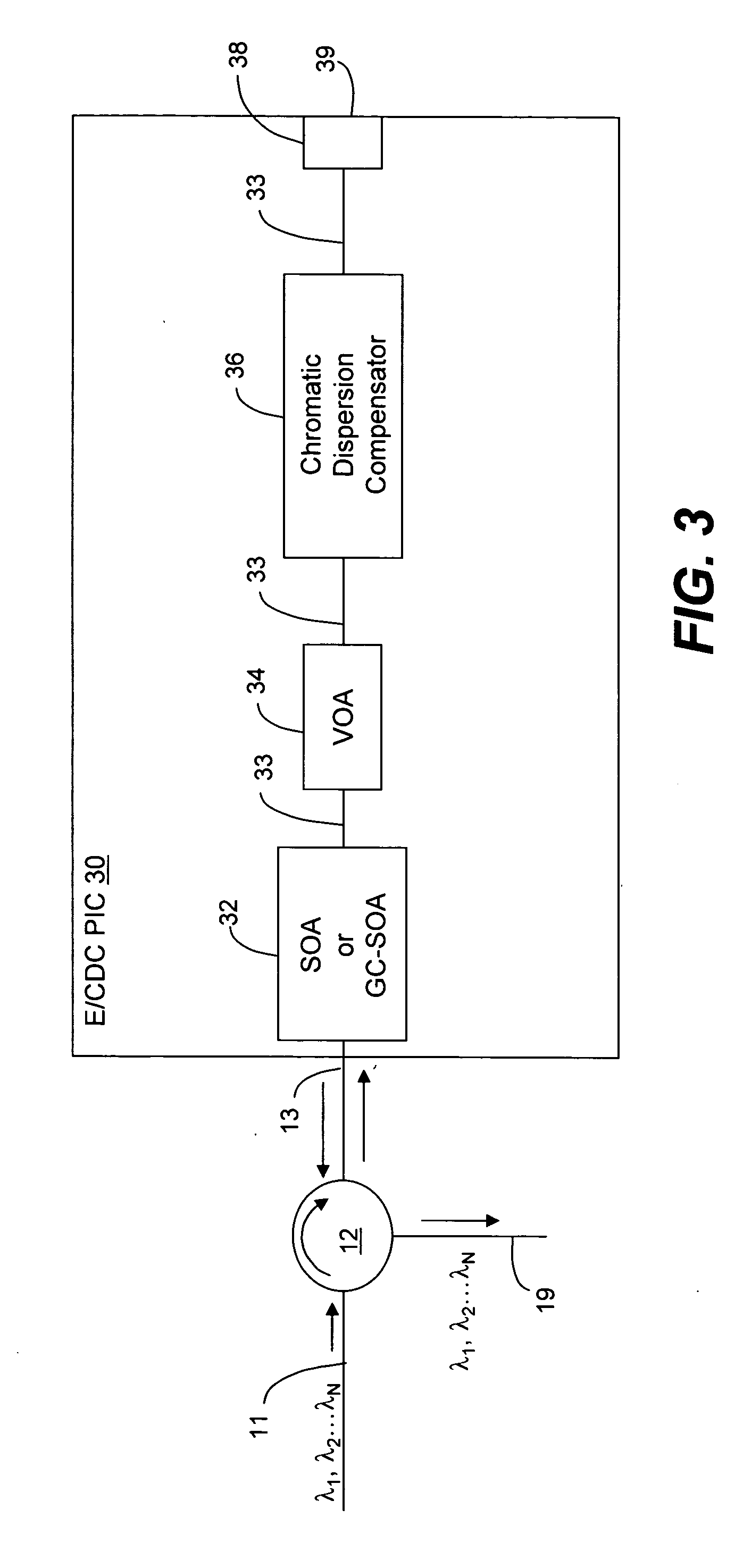
Chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip and method of operation
InactiveUS20050111848A1Effective functionOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingWavelength-division multiplex systemsGratingMach–Zehnder interferometer
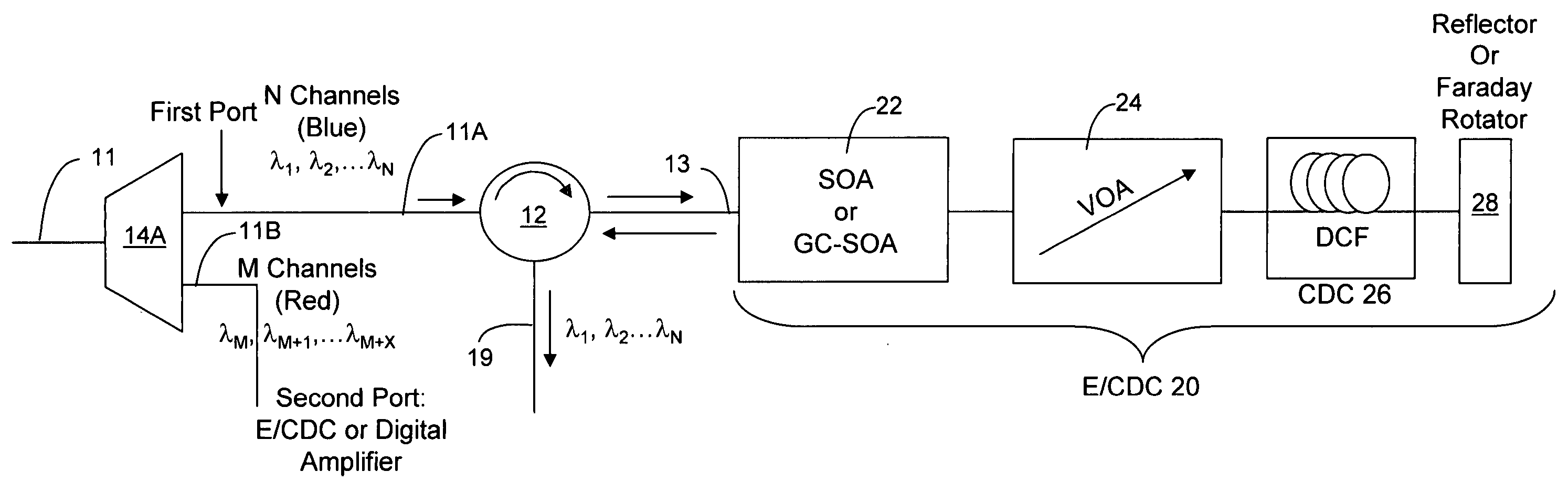
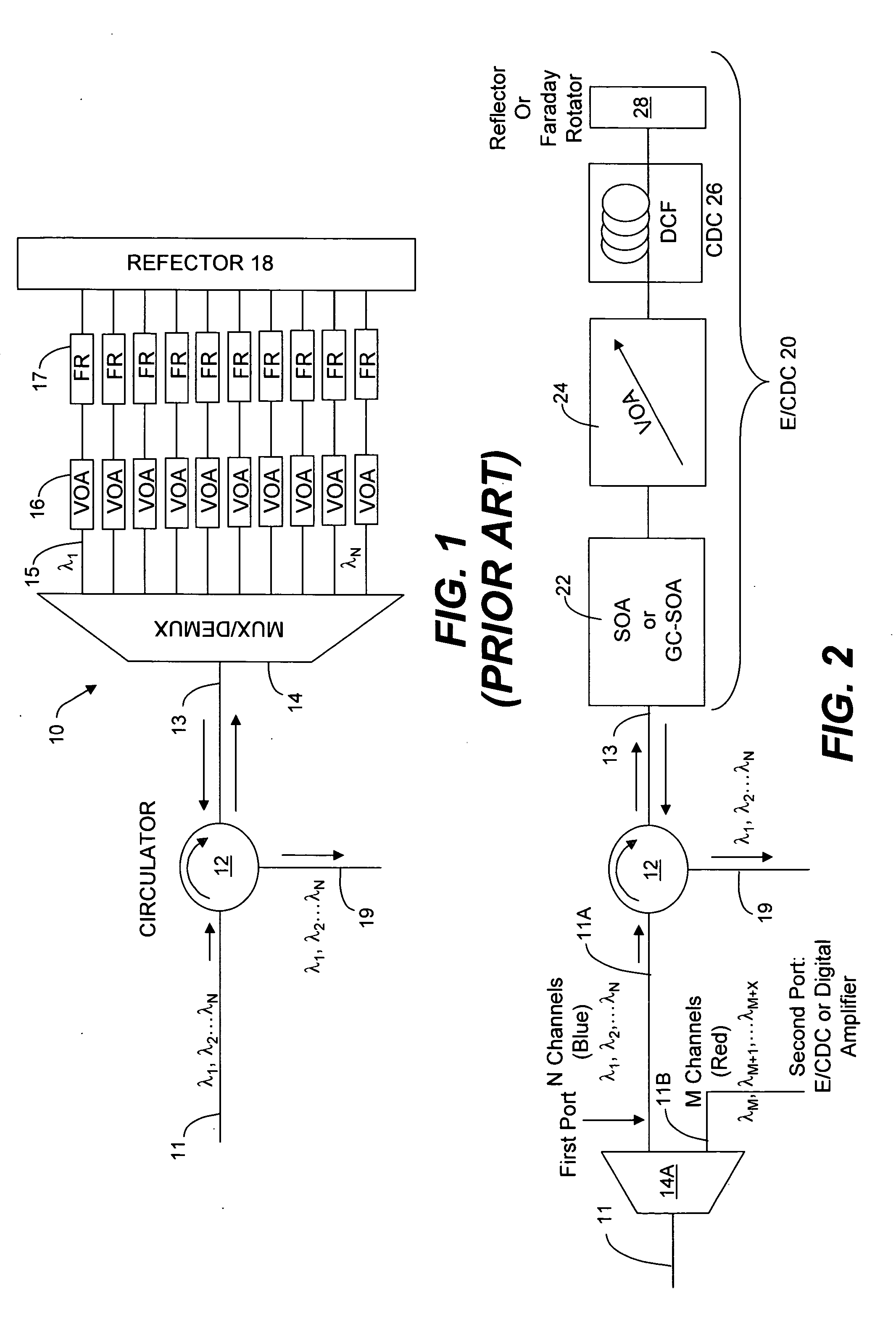
An optical equalizer / dispersion compensator (E / CDC) comprises an input / output for receiving a multiplexed channel signal comprising a plurality of channel signals of different wavelengths. An optical amplifier may be coupled to receive, as an input / output, the multiplexed channel signals which amplifier may be a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) or a gain clamped-semiconductor optical amplifier (GC-SOA). A variable optical attenuator (VOA) is coupled to the optical amplifier and a chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) is coupled to the variable optical attenuator. A mirror or Faraday rotator mirror (FRM) is coupled to the chromatic dispersion compensator to reflect the multiplexed channel signal back through optical components comprising the chromatic dispersion compensator, the variable optical attenuator and the optical amplifier so that the multiplexed channel signal is corrected partially for equalization and chromatic dispersion compensation with respect to each pass through these optical components. The E / CDC components may be integrated in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip. In several embodiments, a photonic integrated circuit (PIC) chip comprises an input into the chip that receives at least one channel signal having experienced chromatic dispersion, a chromatic dispersion compensator (CDC) that separates the at least one channel signal into separate wavelength components over a free spectral range (FSR) spanning only a signal channel width and subjects the wavelength components to a phase shift to change the wavelength group delay in the wavelength components and that recombines the wavelength components to reconstitute the at least one channel signal, and an output from the chip for the recombined at least one channel signal having reduced chromatic dispersion compared to the same channel signal received at the chip input. The CDC device may include a tuning section to vary the phase shift of wavelength components as they propagate through the device. Such a CDC device may include a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) or a cascaded group of Mach-Zehnder interferometers, or at least one arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) or at least one Echelle grating.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
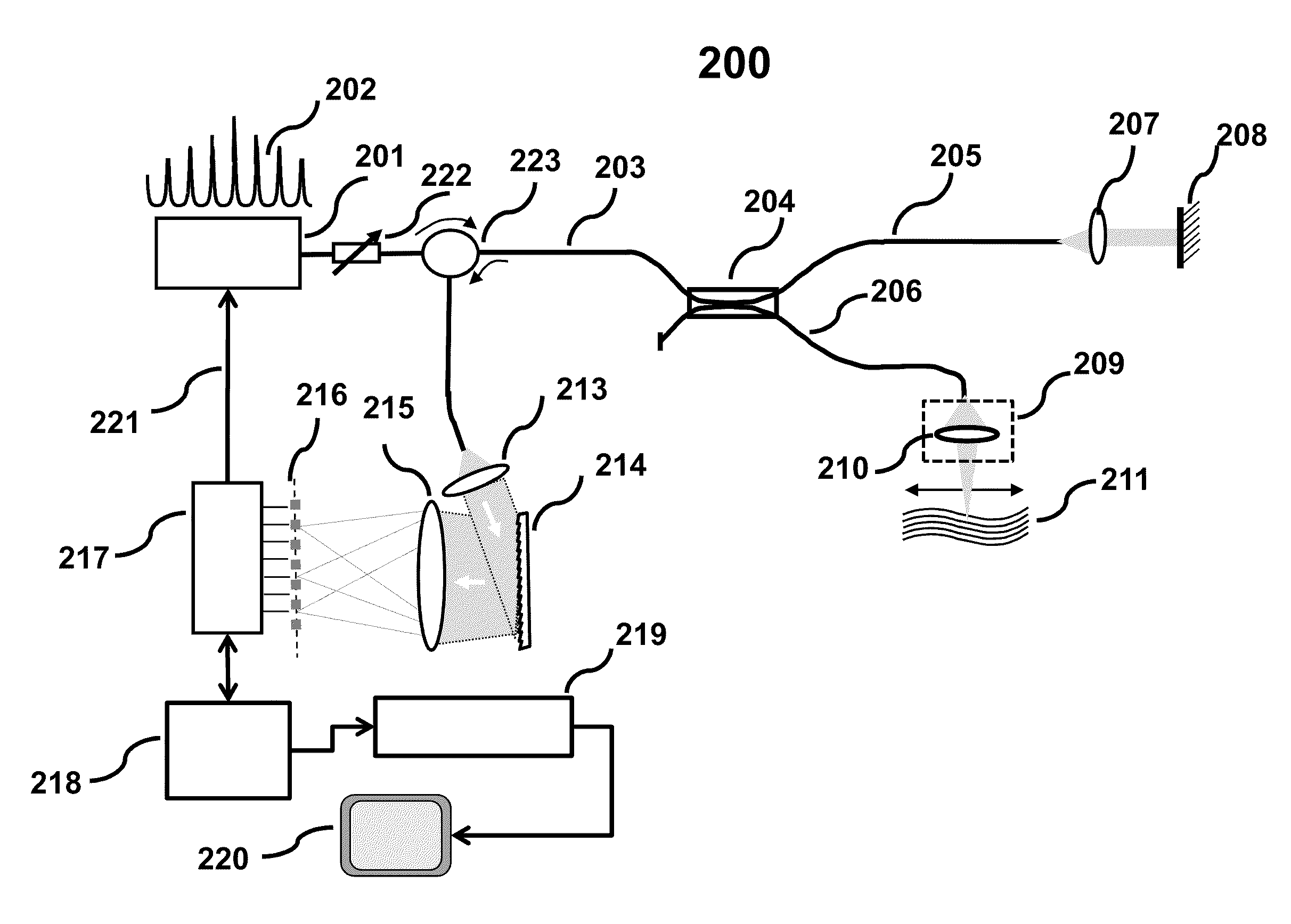
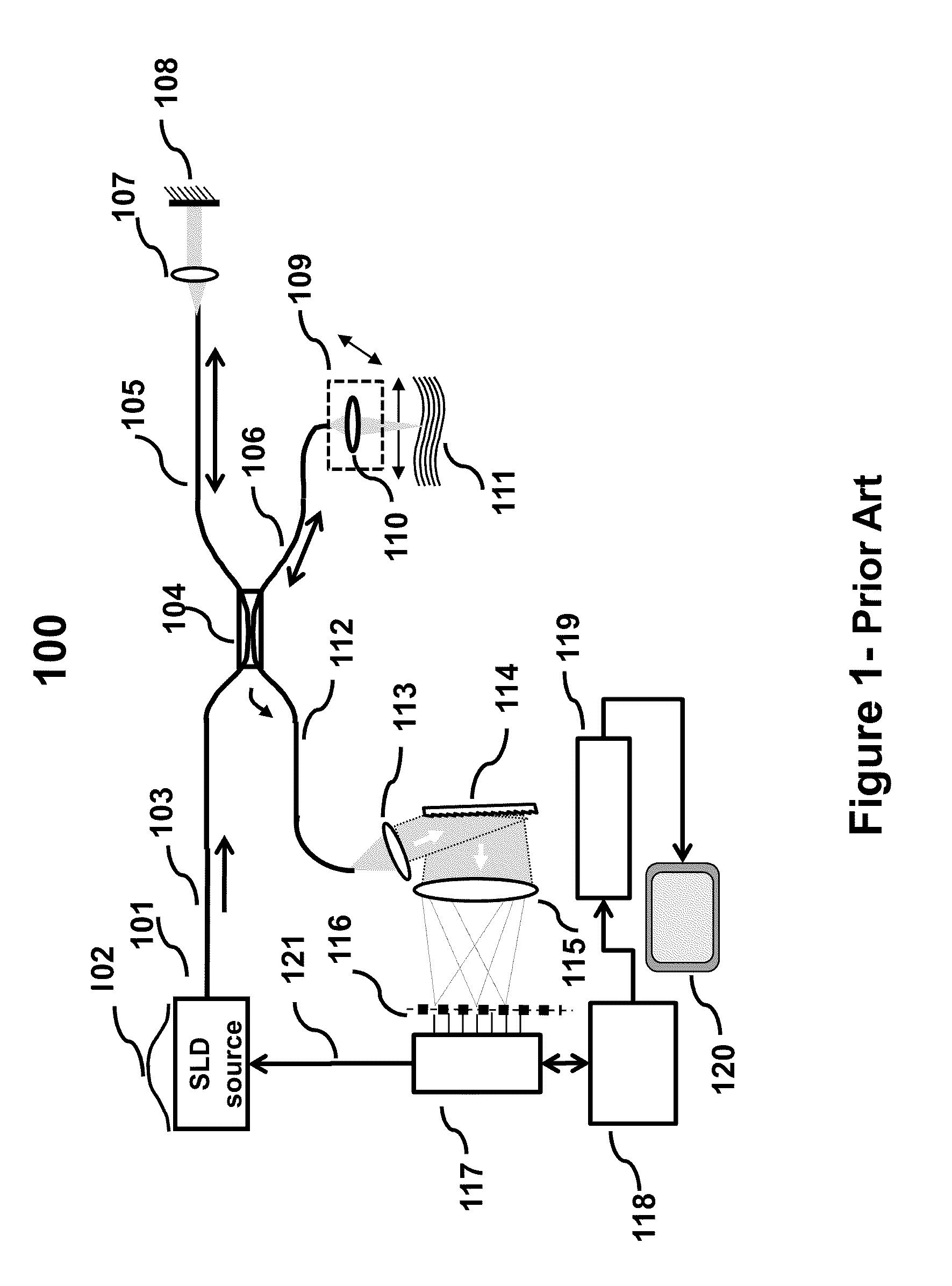
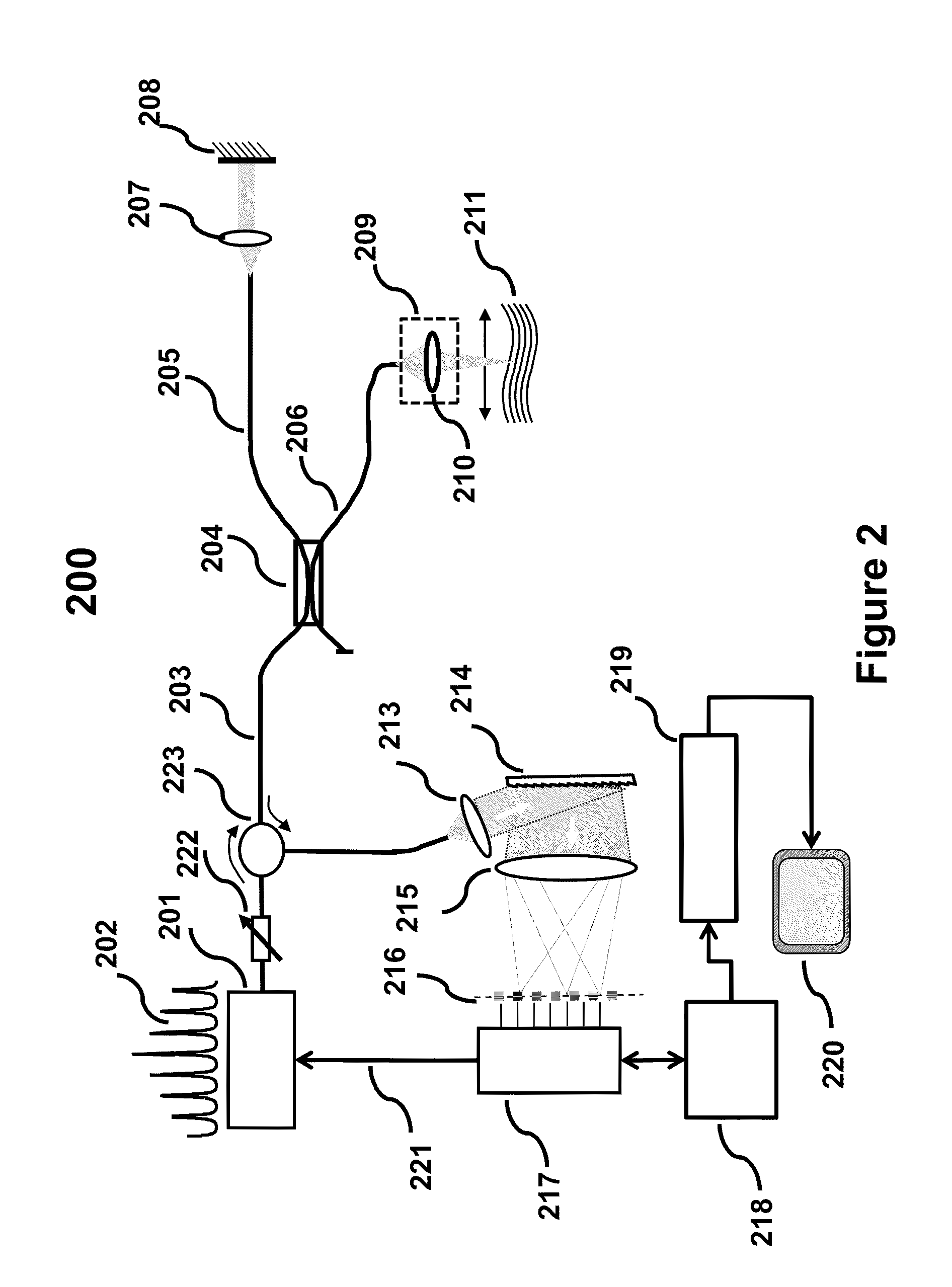
Discrete Spectrum Broadband Optical Source
ActiveUS20110292399A1Increase output peak powerHigh detection sensitivityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionSpectral emissionFrequency spectrum
A new broadband source having a discrete set of spectral emission lines having high peak power in each line is provided by placing a gain medium in a reflective cavity comprising reflective front and back surfaces. A cavity feedback factor less than unity is achieved by providing reflectivity of one surface substantially lower than the reflectivity of the other surface such that spontaneous emission in the gain medium is linearly amplified just below the lasing threshold. In an alternative arrangement, a movable external back surface placed at a prescribed distance from the gain medium provides a means to achieve a free spectral range and finesse of the emission lines to match a pitch of a detector array in a SD-OCT system. By simultaneously providing high power to each detector element of the array, sensitivity and imaging speed of SD-OCT system are significantly improved.
Owner:GDAC PHOTONICS INC
Method of making channel-aligned resonator devices
InactiveUS6934313B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsCross-linkResonant cavity
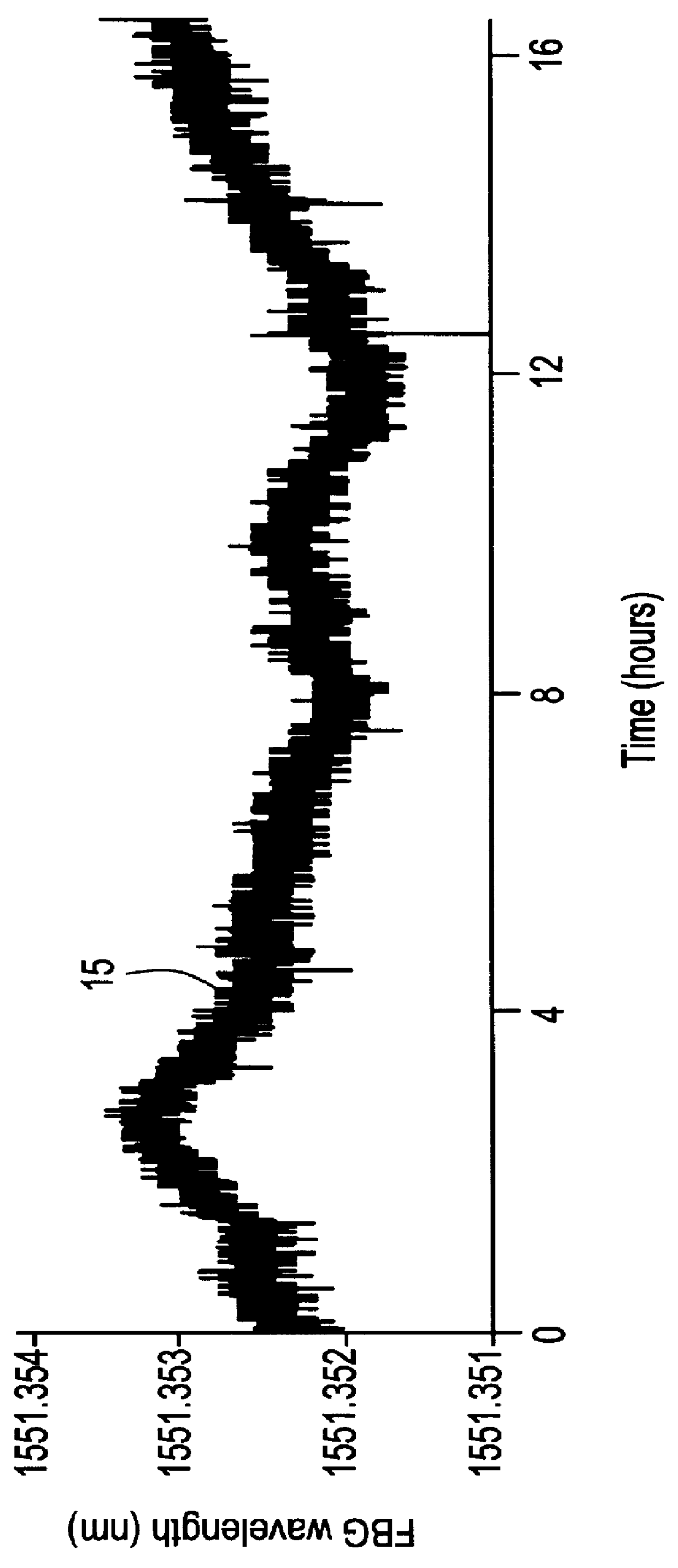
A method of making permanent adjustments to the resonant cavity of a laser device in order to match its free spectral range to a specified frequency interval involves monitoring the optical output produced during laser operation or cavity illumination with diagnostic light, determining the free spectral range from the monitored output, and then permanently modifying the effective refractive index of an intracavity waveguide segment of the laser device according to the determined free spectral range obtained from the monitoring step until the desired match is achieved. The permanent index changes can be done in several ways, including illumination of the intracavity segment with an energetic beam (e.g. UV light) to induce a chemical alteration in the waveguide material, such as polymer cross-linking in the waveguide cladding. Evaporative deposition or ablative removal of intracavity waveguide material would also produce the desired permanent modifications.
Owner:SPARKOLOR CORP +1
Extreme Temperature Robust Optical Sensor Designs And Fault-Tolerant Signal Processing
InactiveUS20090296776A1Eliminates multiple unwanted optical reflectionReduce ambiguityThermometer detailsSensing radiation from gases/flamesFrequency spectrumBlack body
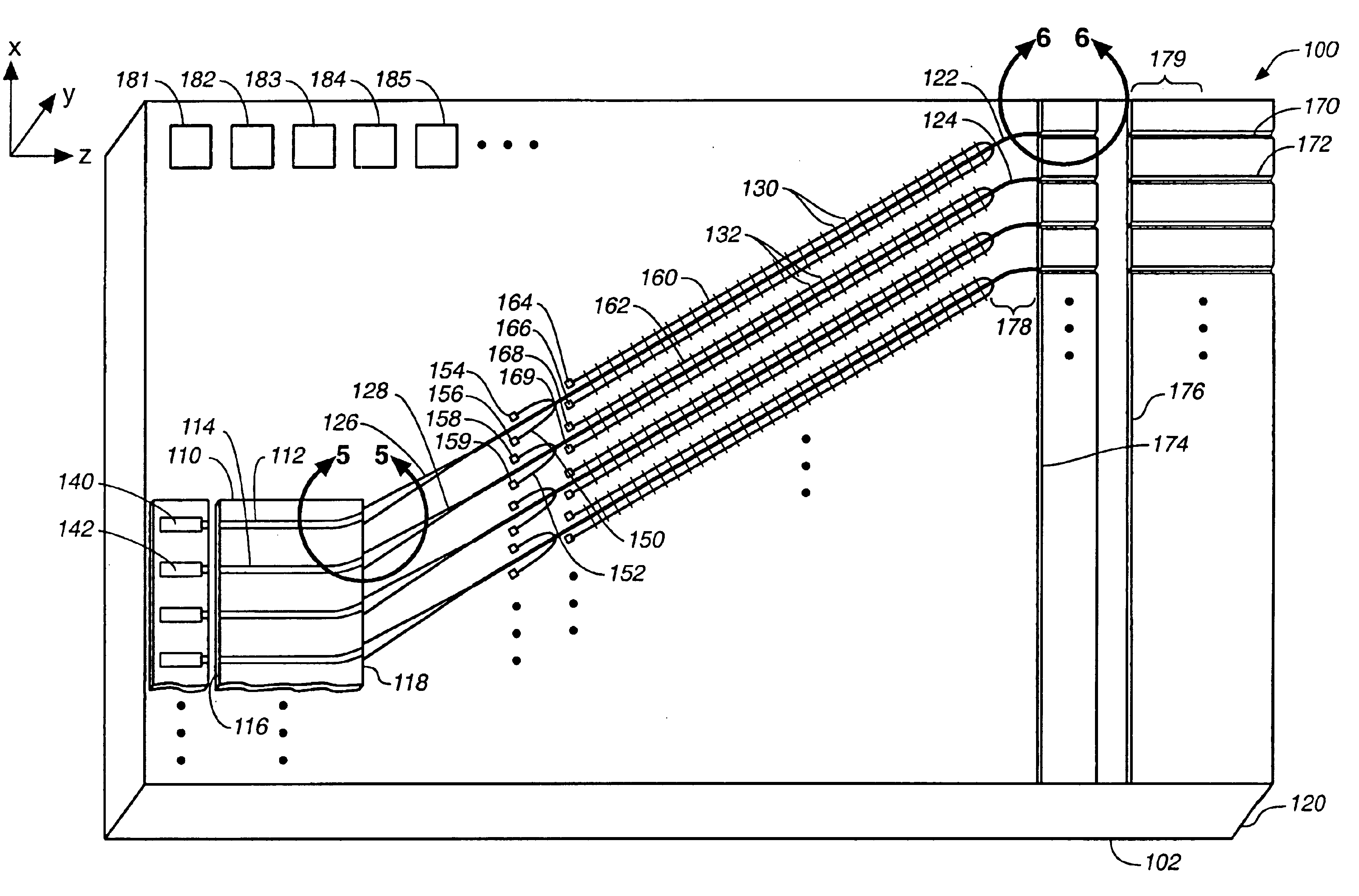
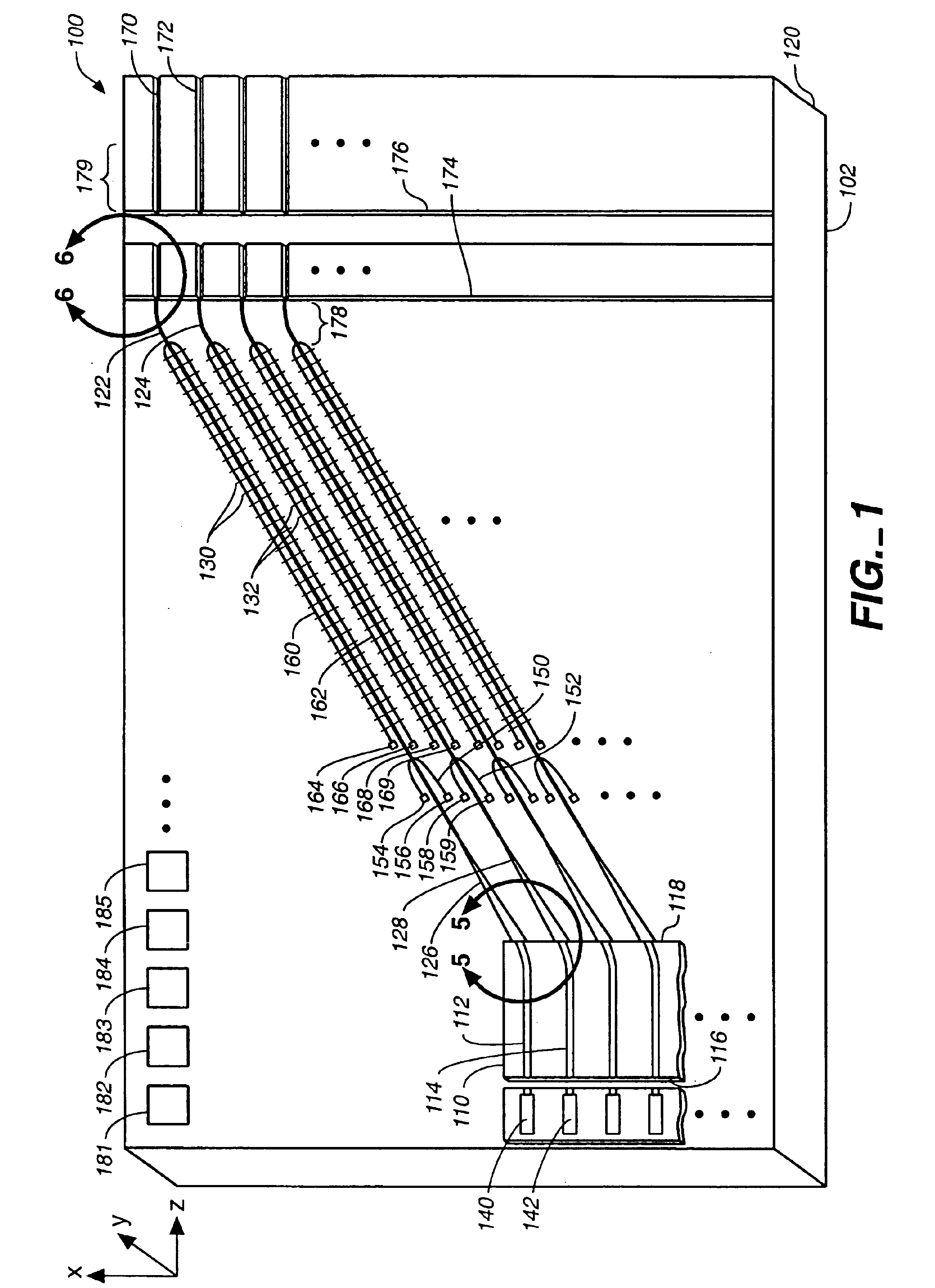
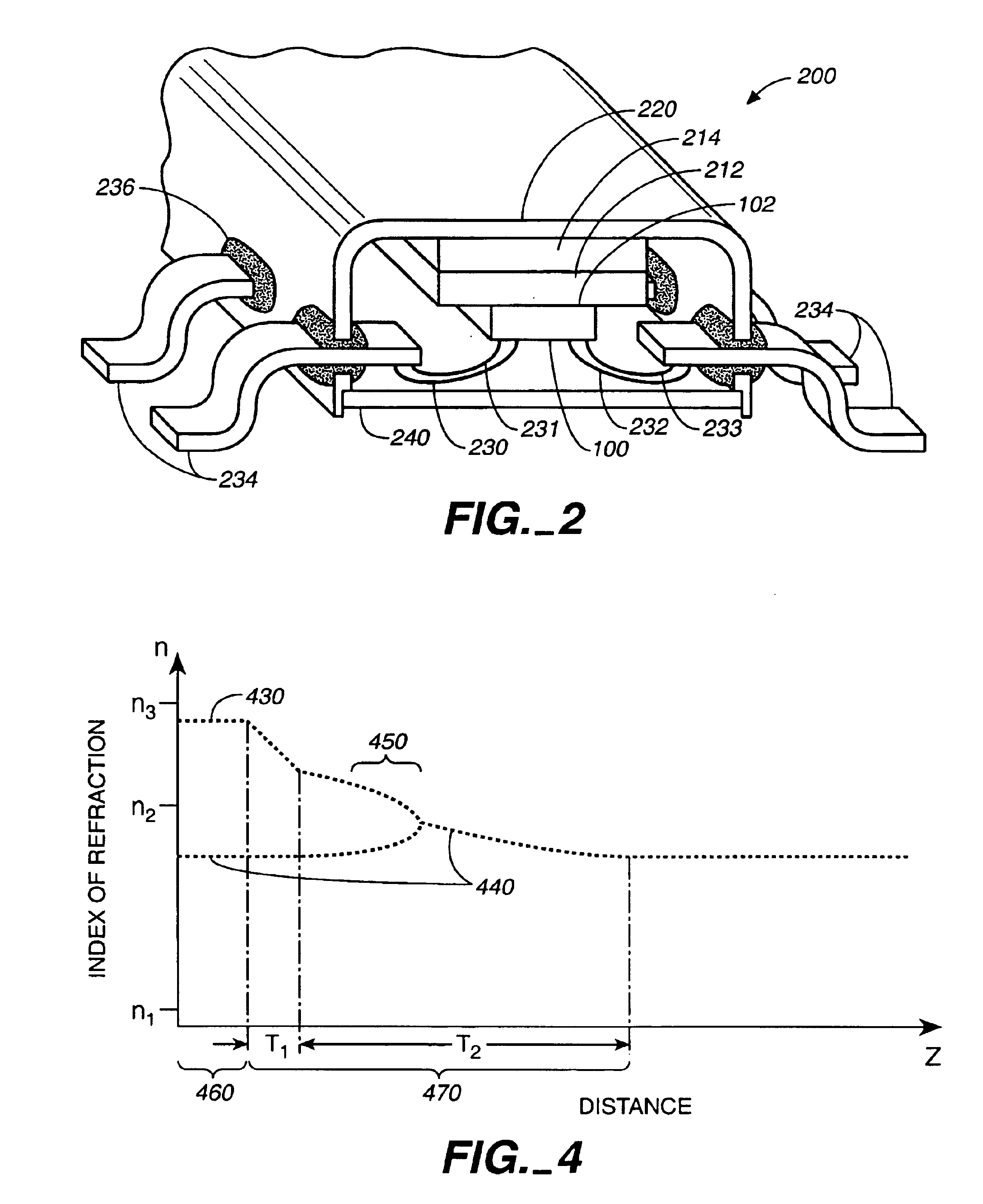
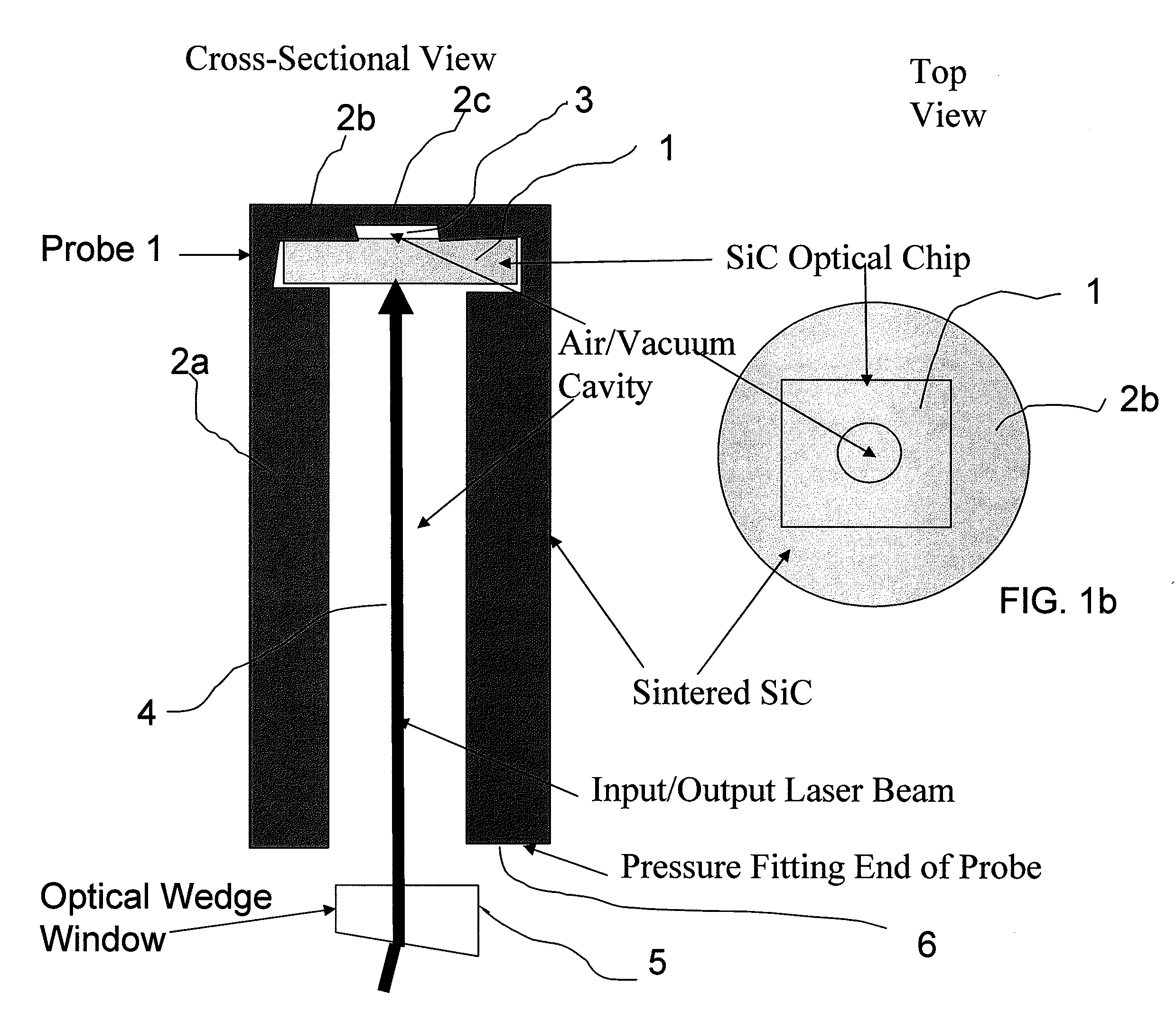
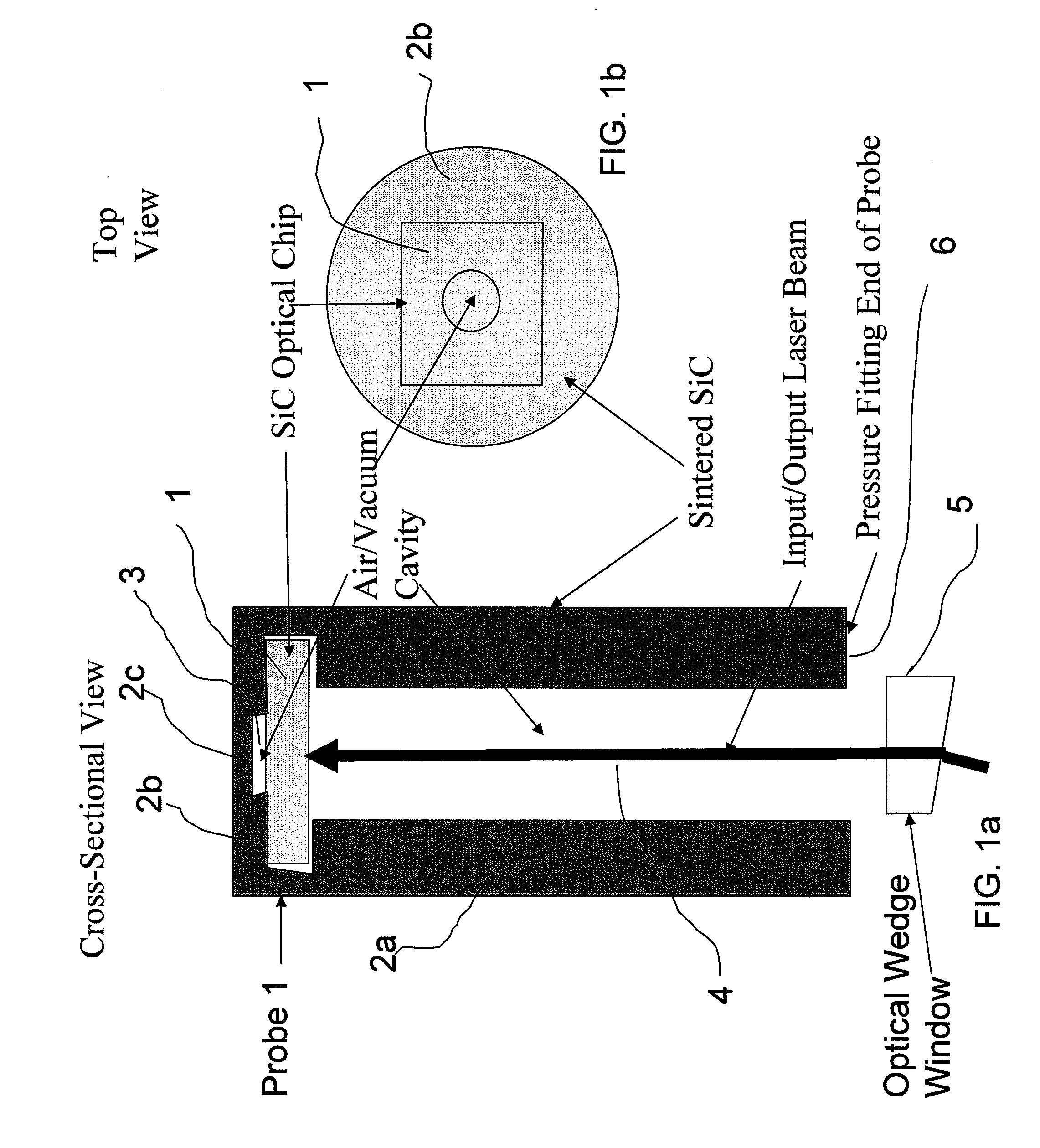
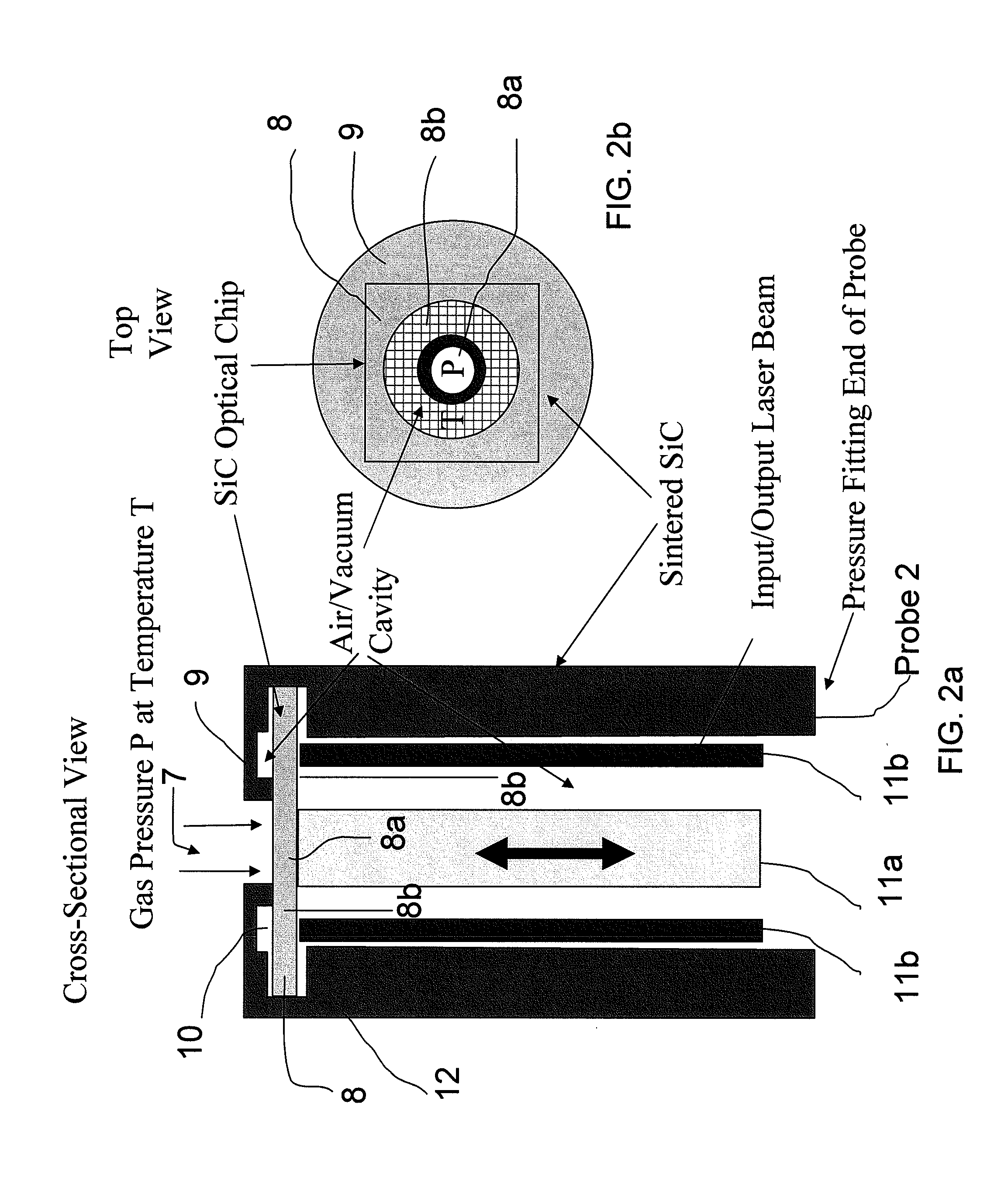
Silicon Carbide (SiC) probe designs for extreme temperature and pressure sensing uses a single crystal SiC optical chip encased in a sintered SiC material probe. The SiC chip may be protected for high temperature only use or exposed for both temperature and pressure sensing. Hybrid signal processing techniques allow fault-tolerant extreme temperature sensing. Wavelength peak-to-peak (or null-to-null) collective spectrum spread measurement to detect wavelength peak / null shift measurement forms a coarse-fine temperature measurement using broadband spectrum monitoring. The SiC probe frontend acts as a stable emissivity Black-body radiator and monitoring the shift in radiation spectrum enables a pyrometer. This application combines all-SiC pyrometry with thick SiC etalon laser interferometry within a free-spectral range to form a coarse-fine temperature measurement sensor. RF notch filtering techniques improve the sensitivity of the temperature measurement where fine spectral shift or spectrum measurements are needed to deduce temperature.
Owner:RIZA NABEEL +2
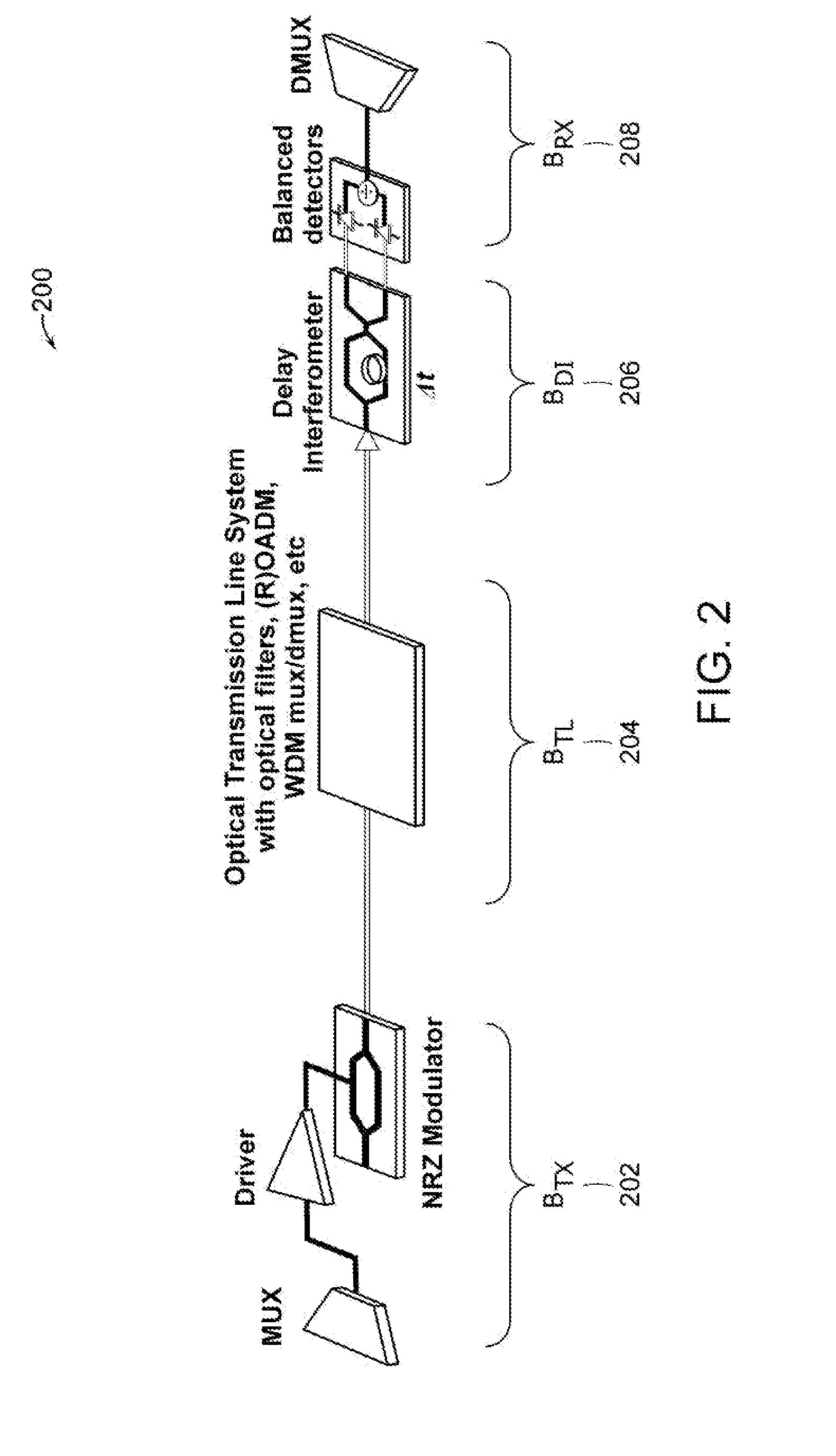
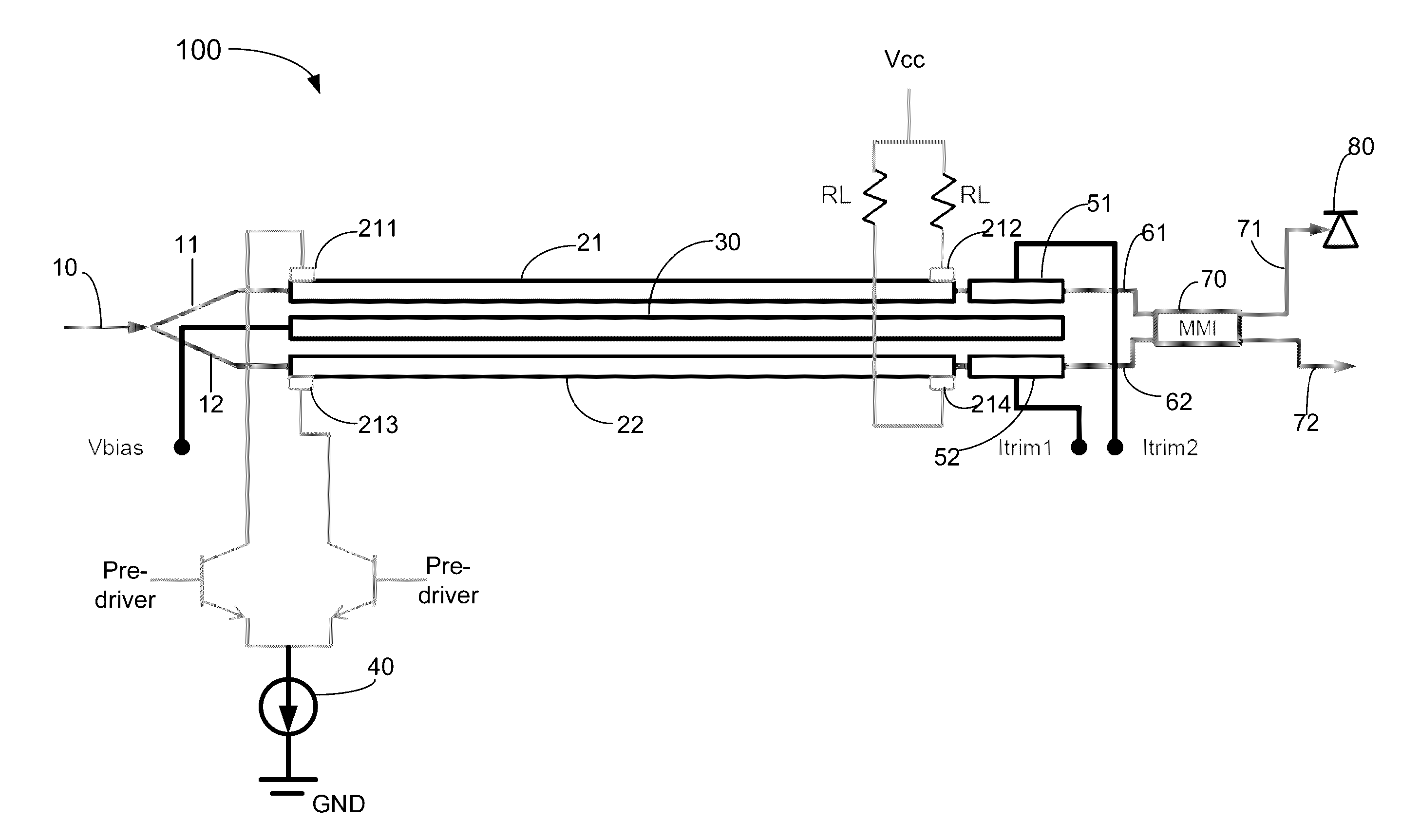
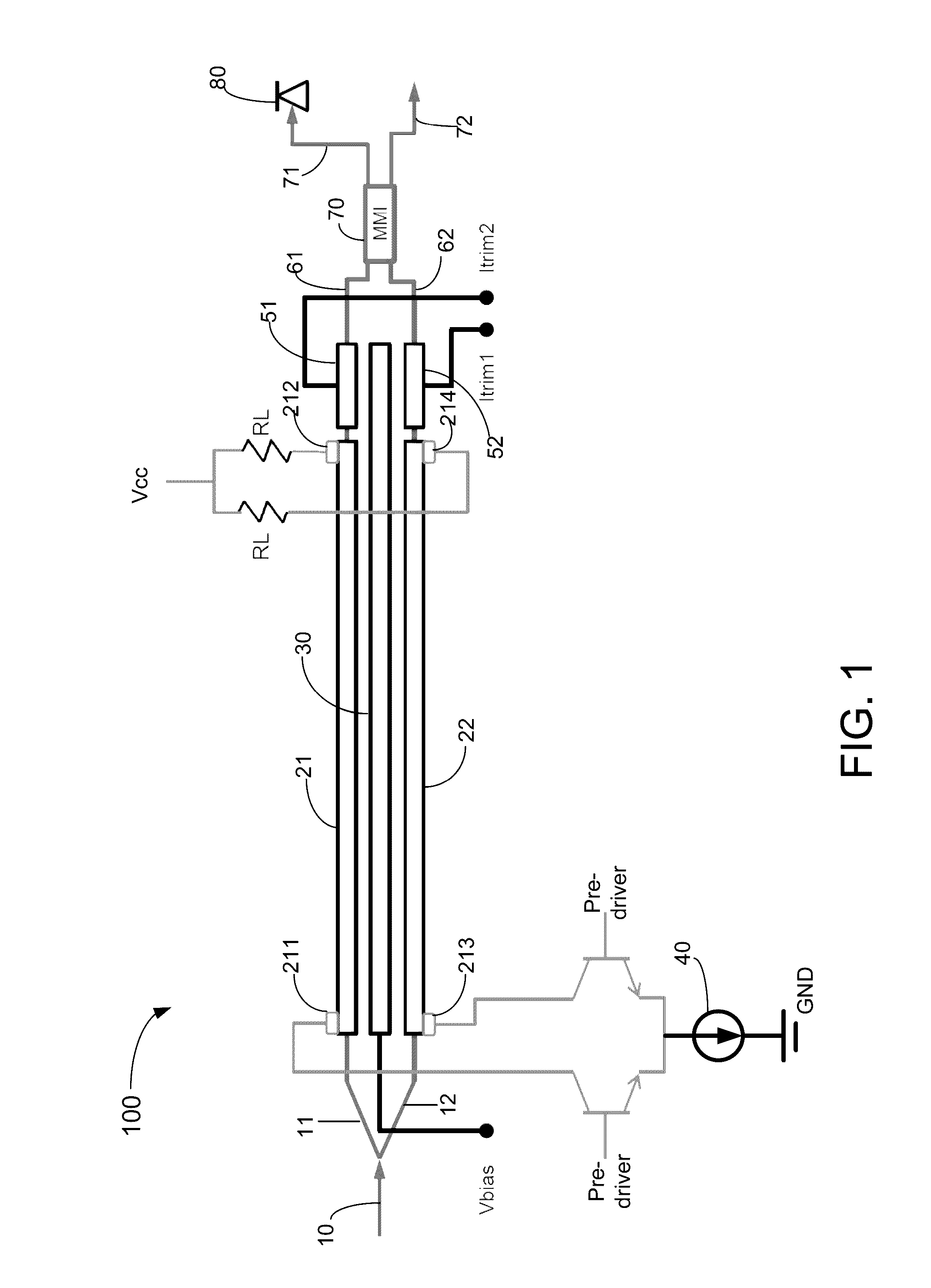
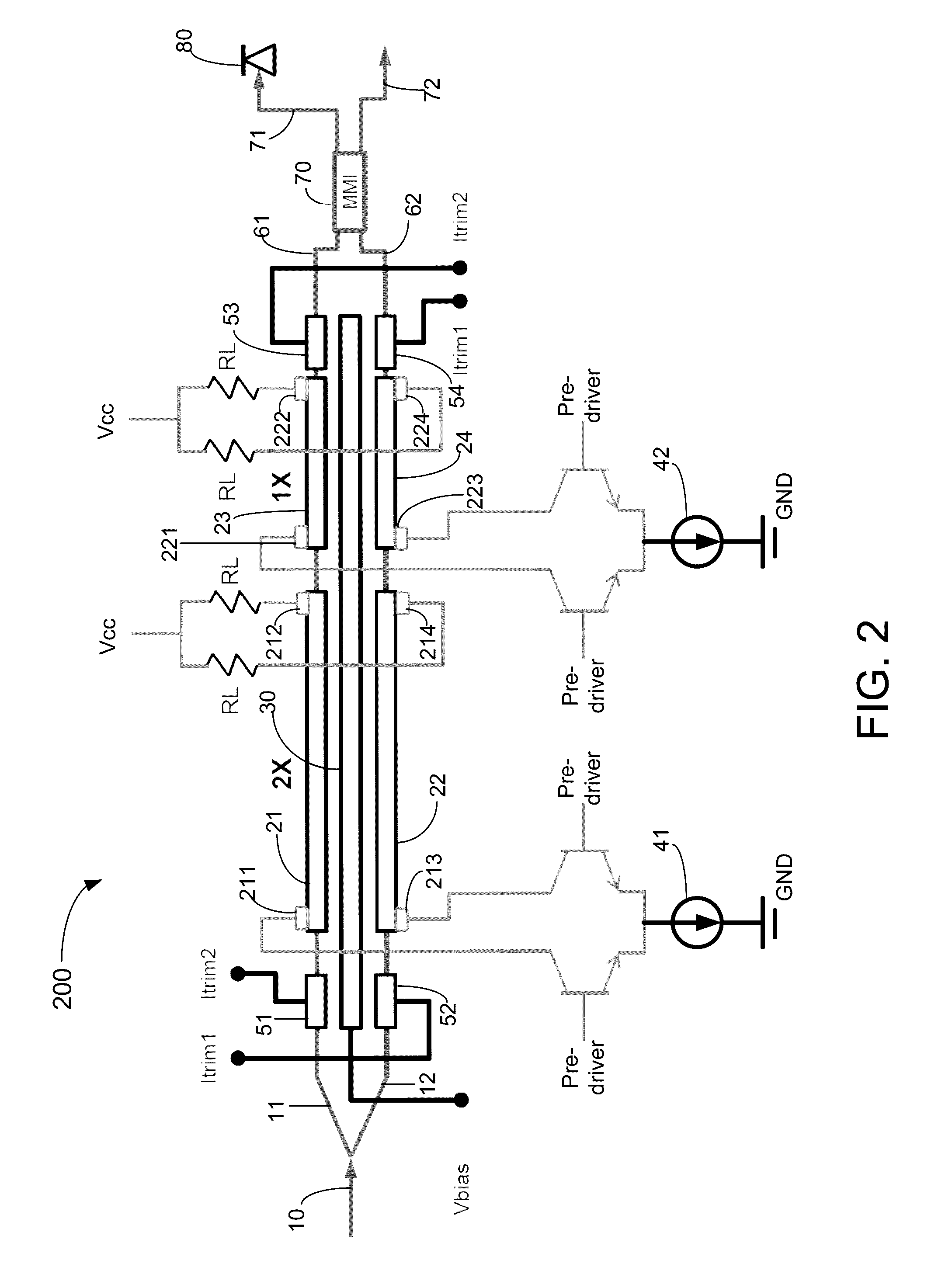
Mzm linear driver for silicon photonics device characterized as two-channel wavelength combiner and locker
The present invention includes a Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) linear driver configured in a differential form with two waveguides carrying two traveling waves which supports a two-channel spectral combiner integrated with a wavelength locker. By coupling a DC current source supplied with a modulation voltage with each segment thereof for providing electrical modulation signal overlapping with each of the two traveling waves. The modulated traveling waves in the two waveguides then are combined in one output signal by a multimode interference coupler. Two optical signals at ITU grid channels are separately modulated by two MZMs and combined into a silicon waveguide-based delayed-line interferometer built on a SOI substrate to produce an output signal having a free spectral range equal to twice of the spacing of the two ITU grid channels. Two dither signals can be added respectively to the two optical signals for identifying and locking corresponding two channel wavelengths.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
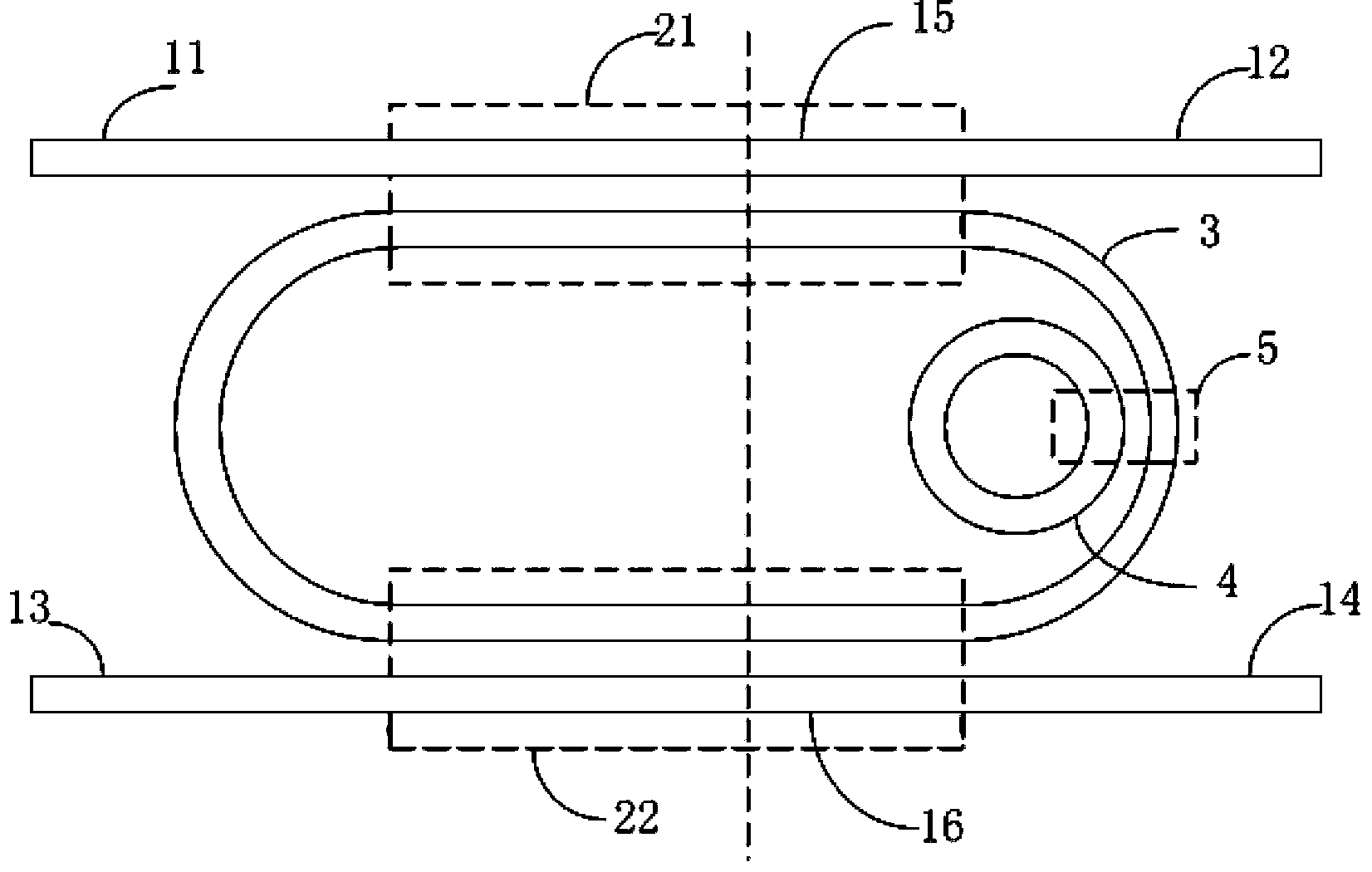
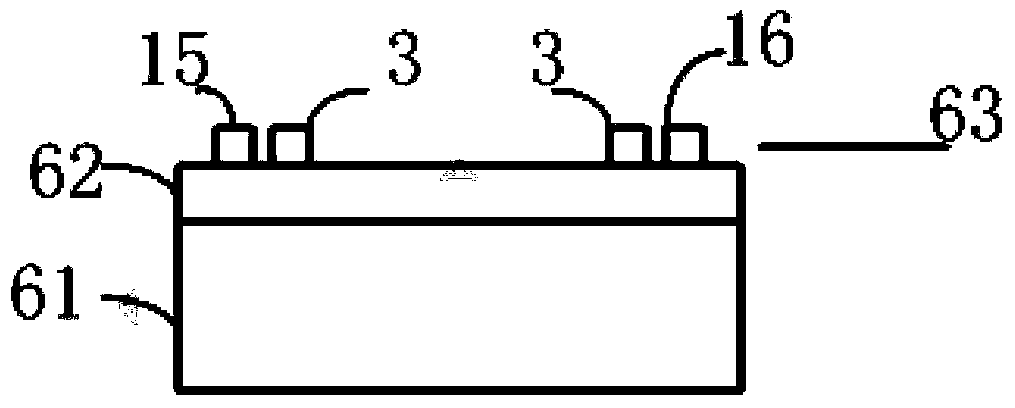
Double-microring resonator optical biochemical sensing chip based on vernier effect
InactiveCN103411924AReduce volumeEase of mass productionPhase-affecting property measurementsMiniaturizationWaveguide
The invention provides a double-microring resonator optical biochemical sensing chip based on the vernier effect and aims to solve the detection problem of some biochemistry matters. The double-microring resonator optical biochemical sensing chip mainly comprises an input straight waveguide, an output straight waveguide and two microring resonators, wherein the first microring resonator comprises an annular waveguide and is coupled with the input straight waveguide and the output straight waveguide; the second microring resonator is positioned on the inner side of the annular waveguide of the first microring resonator and has a free spectral range different from that of the first microring resonator, and the two microring resonators are connected in an optical coupling manner. Through the above scheme adopted by the optical biochemical sensing chip, the second optical resonator is positioned on the inner side of the first optical resonator and connected with the first optical resonator in a lateral coupling manner to form the vernier effect and detect the influence on an optical signal from external substances. Under the condition of meeting the same sensing performance, the size of the optical biochemical sensing chip is greatly reduced, and miniaturization of the optical biochemical sensor and the on-chip sensing system are favorably realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
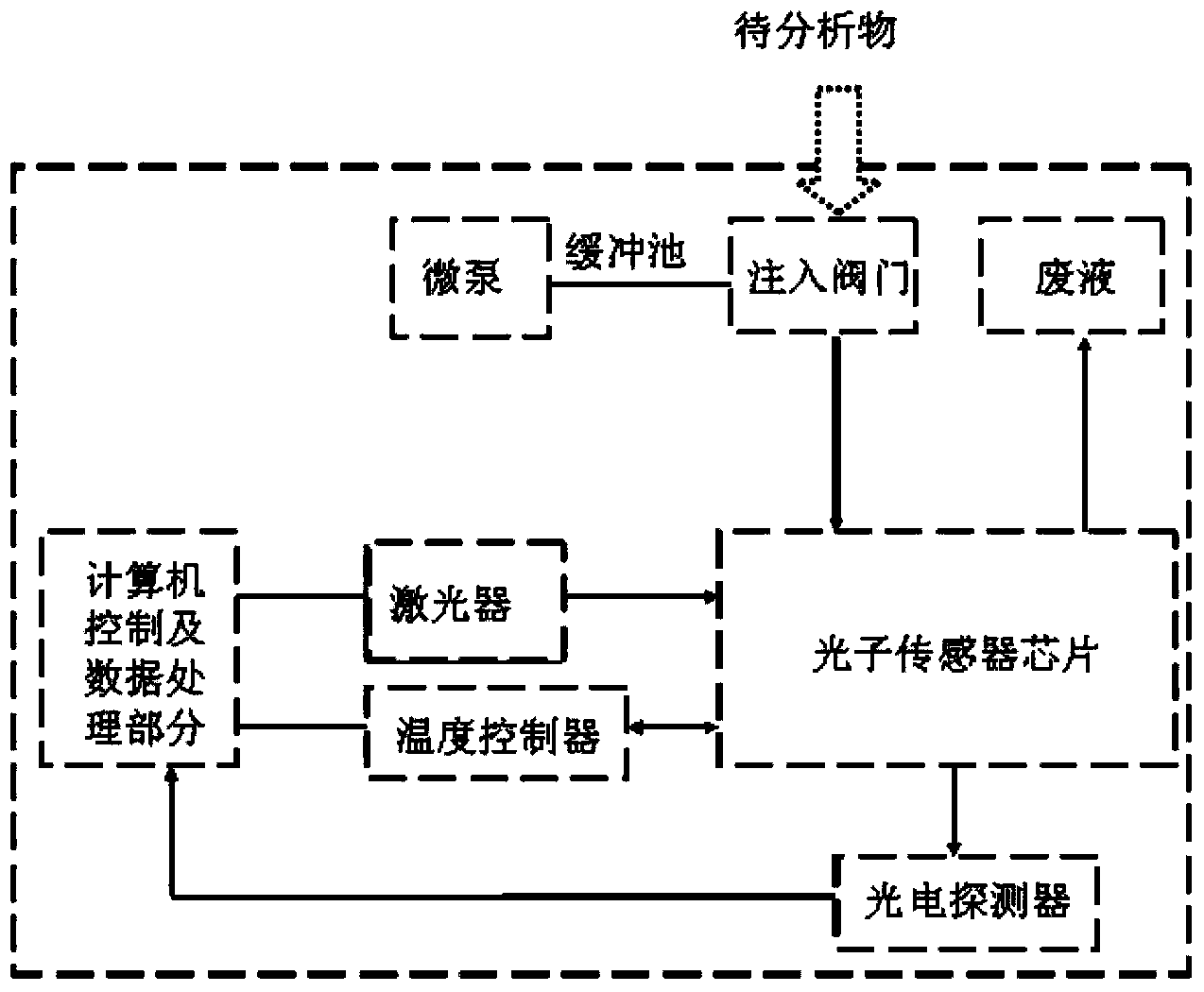
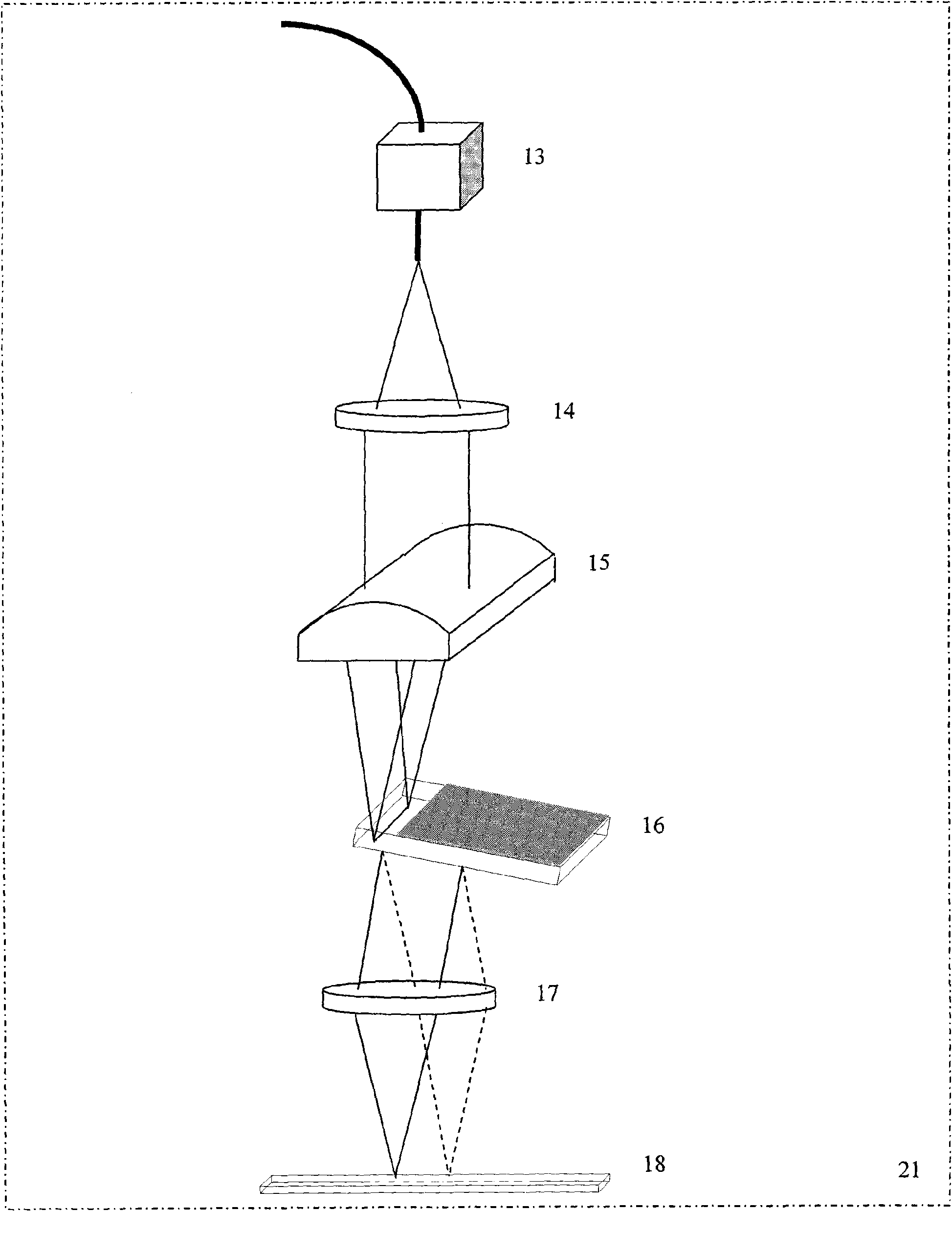
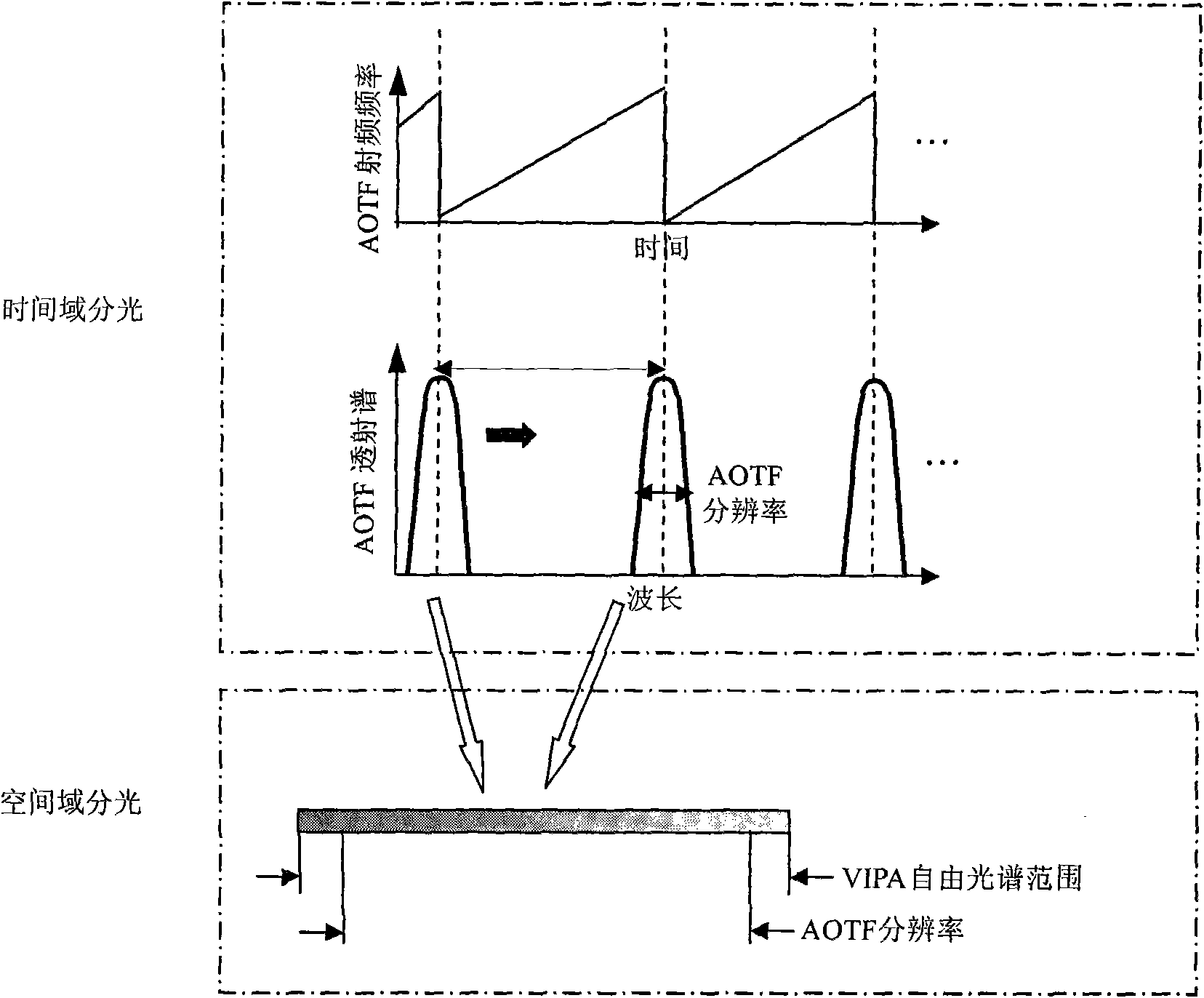
Method and system for wide-spectrum and high-resolution detection based on space-time light splitting in OCT
InactiveCN101617935AHigh resolutionSmall field of viewPhase-affecting property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSample imageOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a method and a system for wide-spectrum and high-resolution detection based on space-time light splitting in OCT. Low-coherence lights emitted from a broadband light source enter a broadband optical fiber coupler through an optical isolator, and respectively enter a scanning probe and a reference arm after light splitting by the coupler. The returned lights generate interference in the broadband optical fiber coupler, a detection arm detects interference signals after the interference signals are decomposed into different spectral components, and then the interference signals are sent to a computer so as to reconstruct a sample image. In the detection arm, interference spectral signals firstly pass through a time domain light splitting device with low resolution and wide free spectrum range, then pass through a space domain light splitting device with high resolution and narrow free spectrum range, and then are detected by a spectrum imaging system. On the premise of satisfying the requirement of high spectrum resolution, the invention can reduce a visual field of the spectrum imaging system, and solves the problems of field curvature, spectrum interference and the like existing during large visual field spectrum imaging, thereby spectral domain OCT imaging with high signal-to-noise ratio and high resolution is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Signal processing apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving coherent parallel optical signals
ActiveUS20180083599A1Simple signal processingAvoid restrictionsPolarisation multiplex systemsImpedence networksCarrier signalLocal oscillator
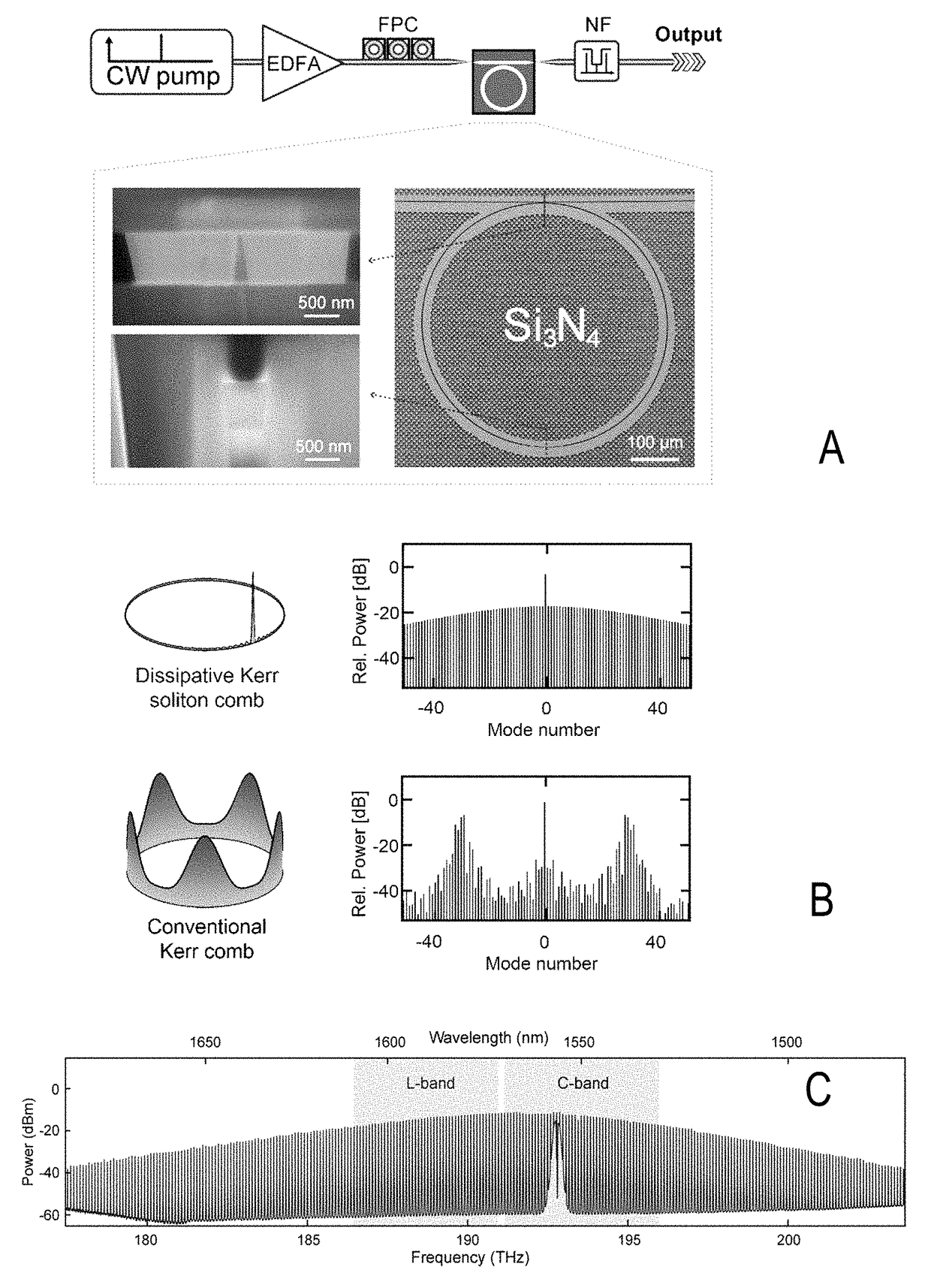
A signal processing apparatus, being configured for transmitting and receiving coherent parallel optical signals, comprises a transmitter apparatus including a first single soliton micro-resonator device and a modulator device, wherein the first single soliton micro-resonator device is adapted for creating a single soliton providing a first frequency comb, wherein the first frequency comb provides a plurality of equidistant optical carriers with a frequency spacing corresponding to a free spectral range of the first single soliton micro-resonator device, and the modulator device is adapted for modulating the optical carriers according to data to be transmitted, and a receiver apparatus including a coherent receiver device with a plurality of coherent receivers and a local oscillator device providing a plurality of reference optical signals, wherein the coherent receiver device and the local oscillator device are arranged for coherently detecting the transmitted modulated optical carriers, wherein the signal processing apparatus further includes at least one second single soliton micro-resonator device having a free spectral range being equal or approximated to the free spectral range of the first single soliton micro-resonator device and being adapted for creating at least one single soliton providing at least one second frequency comb, wherein the at least one second frequency comb provides at least one of additional optical carriers and the reference optical signals. Furthermore, a signal processing method, including transmitting and receiving coherent parallel optical signals via a communication channel is described.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
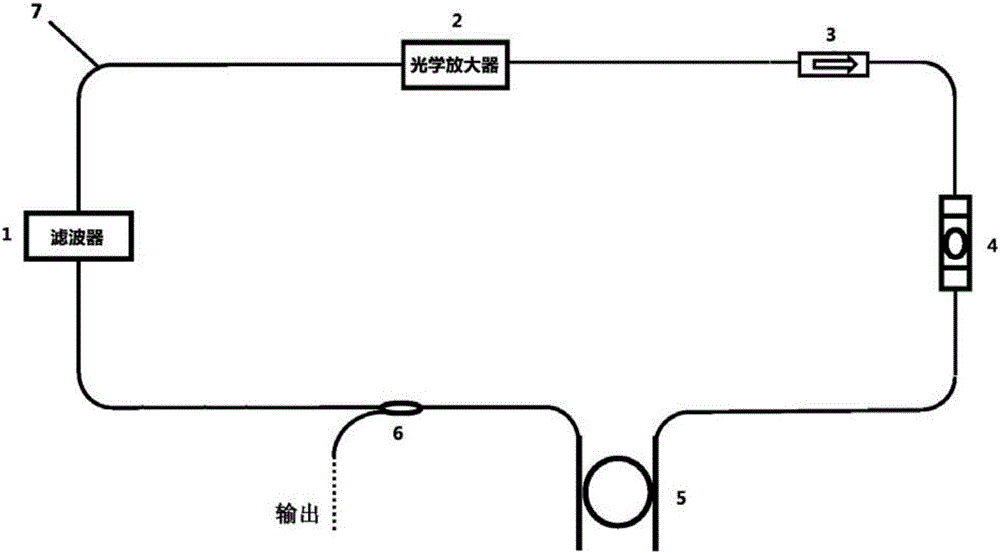
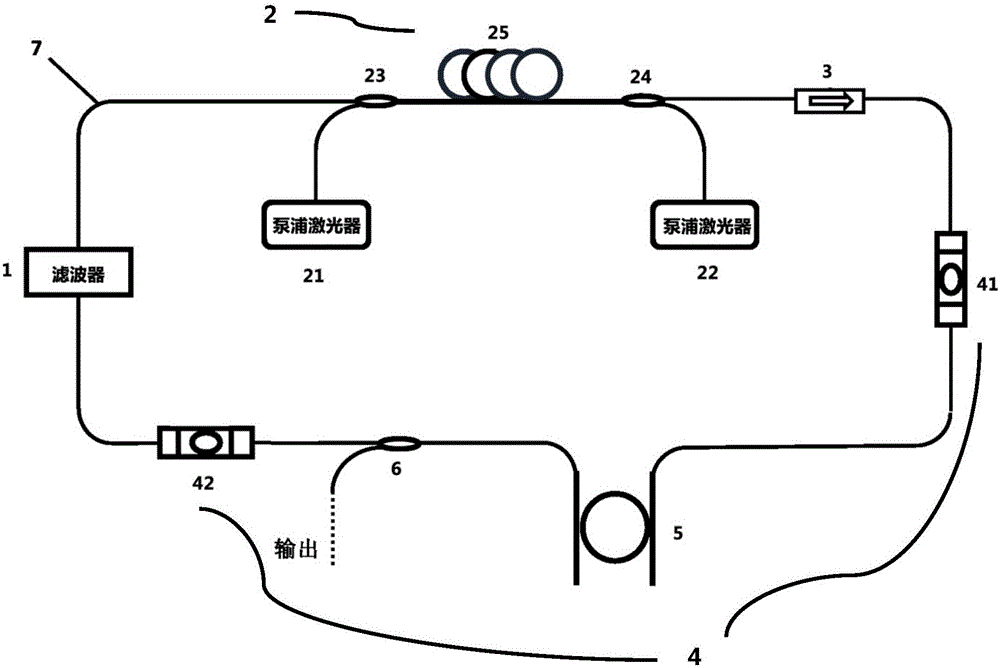
Micro-ring resonator-based system and method for generating optical frequency comb with adjustable frequency interval
ActiveCN105680301AThe frequency interval is freely adjustableNo obvious threshold phenomenonLaser detailsBeam splitterDual wavelength
The invention relates to a micro-ring resonator-based system and method for generating an optical frequency comb with an adjustable frequency interval, and aims at solving the problems that an existing system for generating the optical frequency comb is poor in stability and the frequency interval of the optical frequency comb is fixed or is adjustable only within a few of free spectrum ranges. The system comprises a closed optical fiber ring cavity which is formed by connecting an optical amplifier, an optical isolator, a polarization controller, an upload / download micro-ring resonator, a beam splitter and an adjustable dual-wavelength filter through a single mode fiber in series; and the beam splitter is located behind the upload / download micro-ring resonator along the propagation path of a laser signal in the optical fiber ring cavity. By the system and the method provided by the invention, the optical frequency comb with the freely adjustable frequency interval can be generated; meanwhile, the self-terminating phenomenon of a traditional micro-ring resonator-based system is eliminated; the micro-ring resonator-based system and method have the advantages of being simple to operate and convenient to adjust; and the system is easy to integrate.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tunable optical filter
ActiveUS20090263142A1Small sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionFrequency spectrumRetroreflector
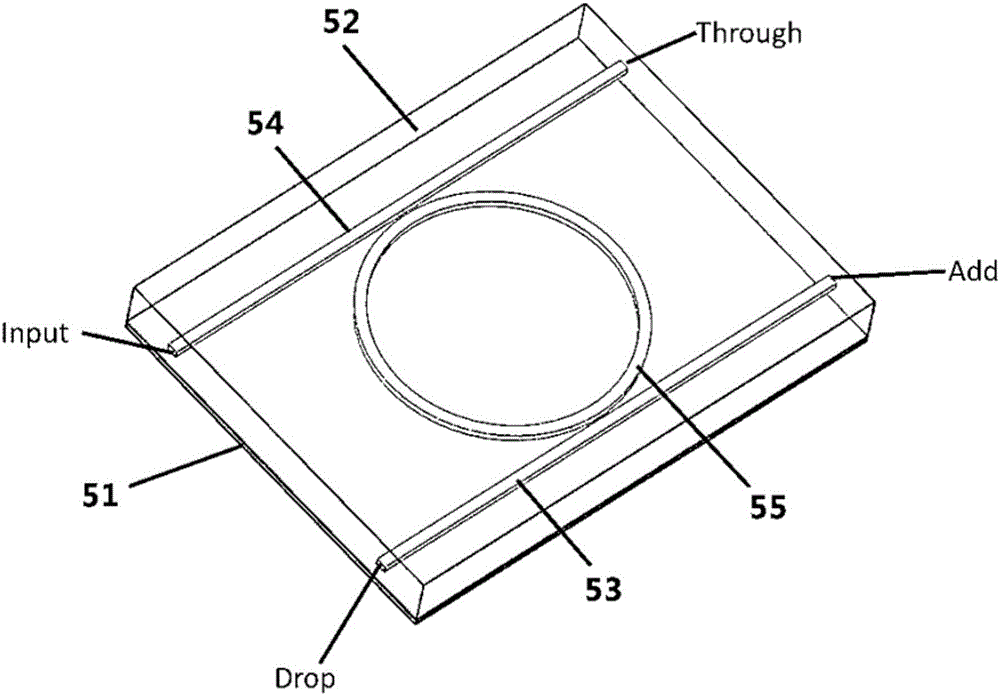
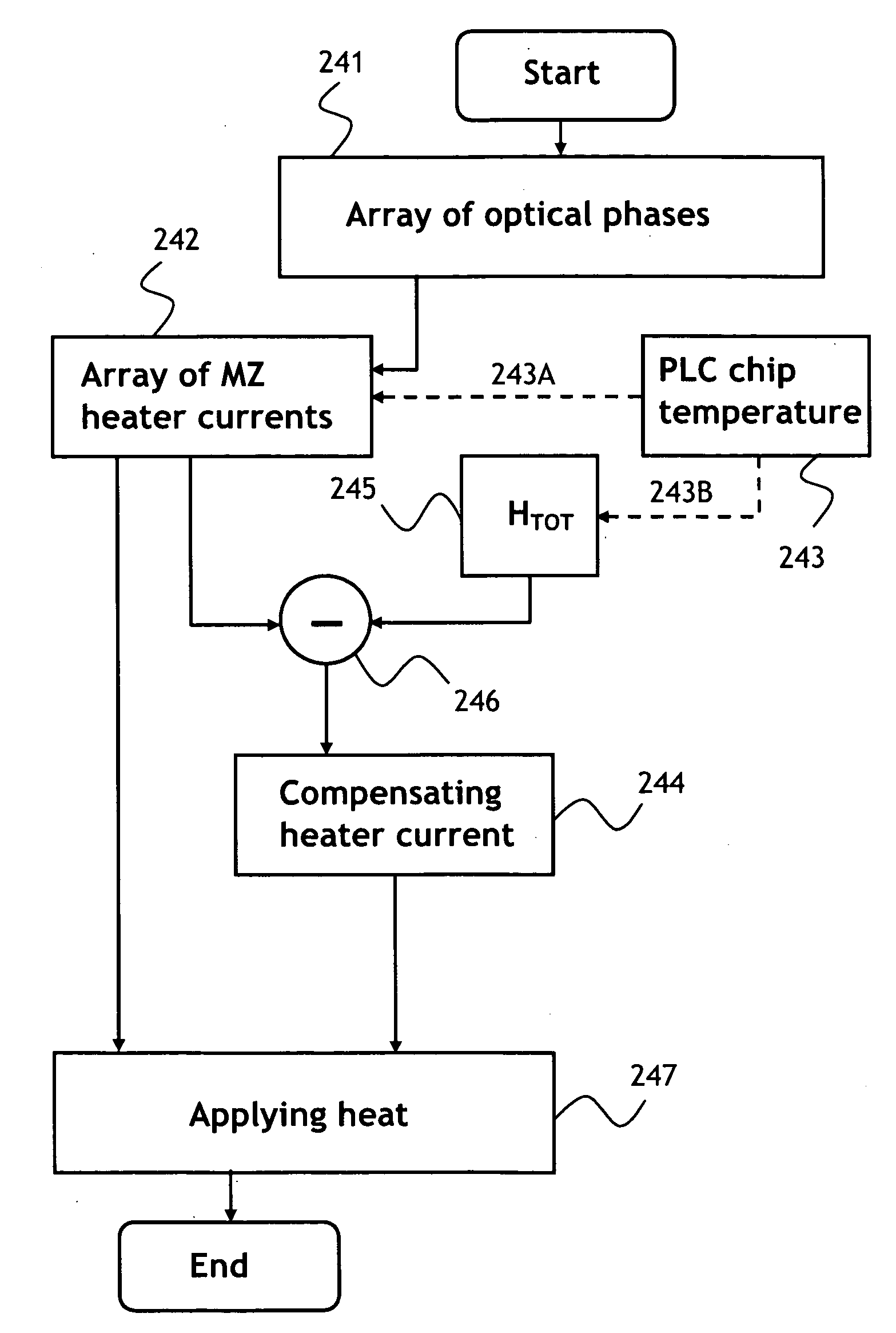
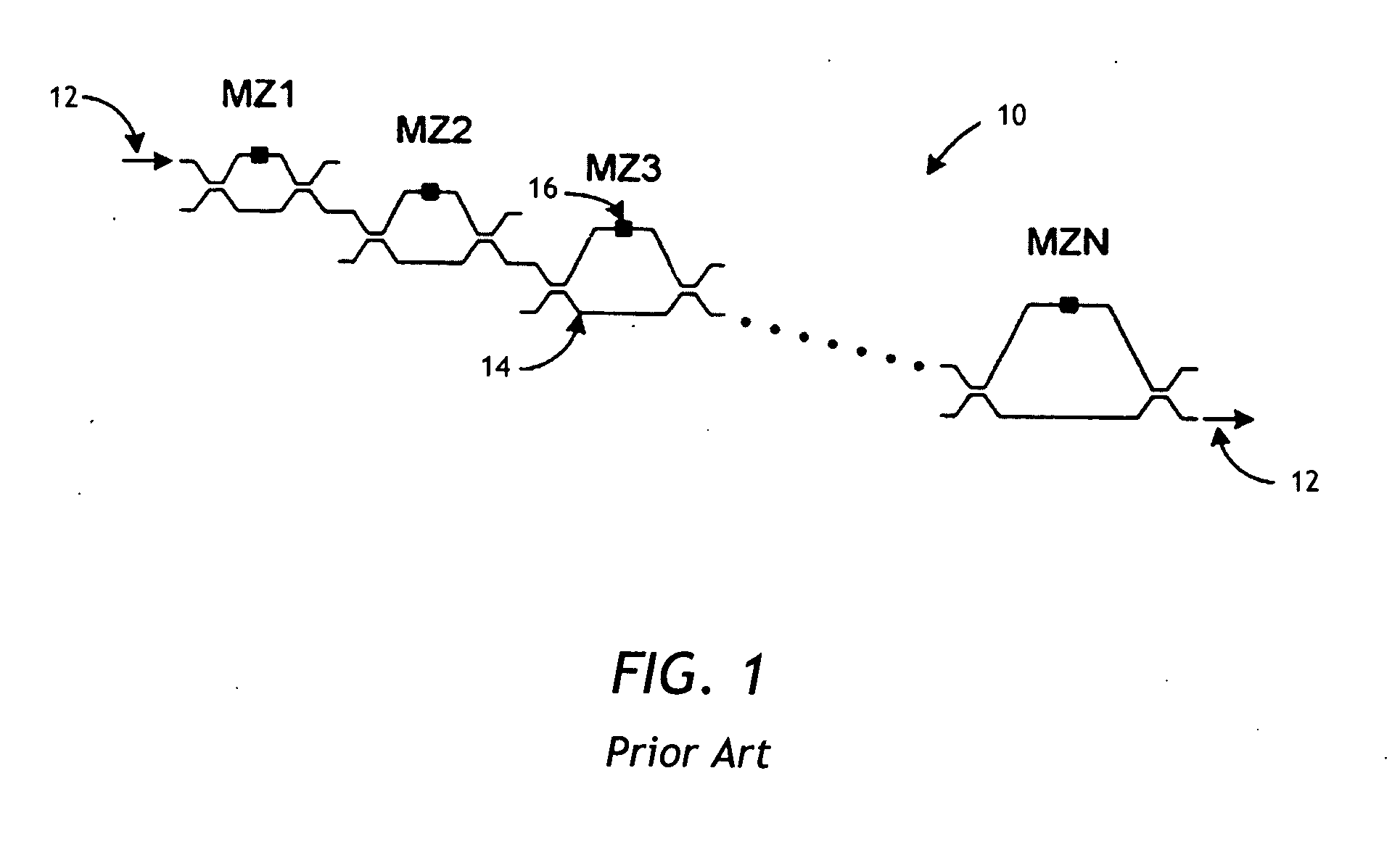
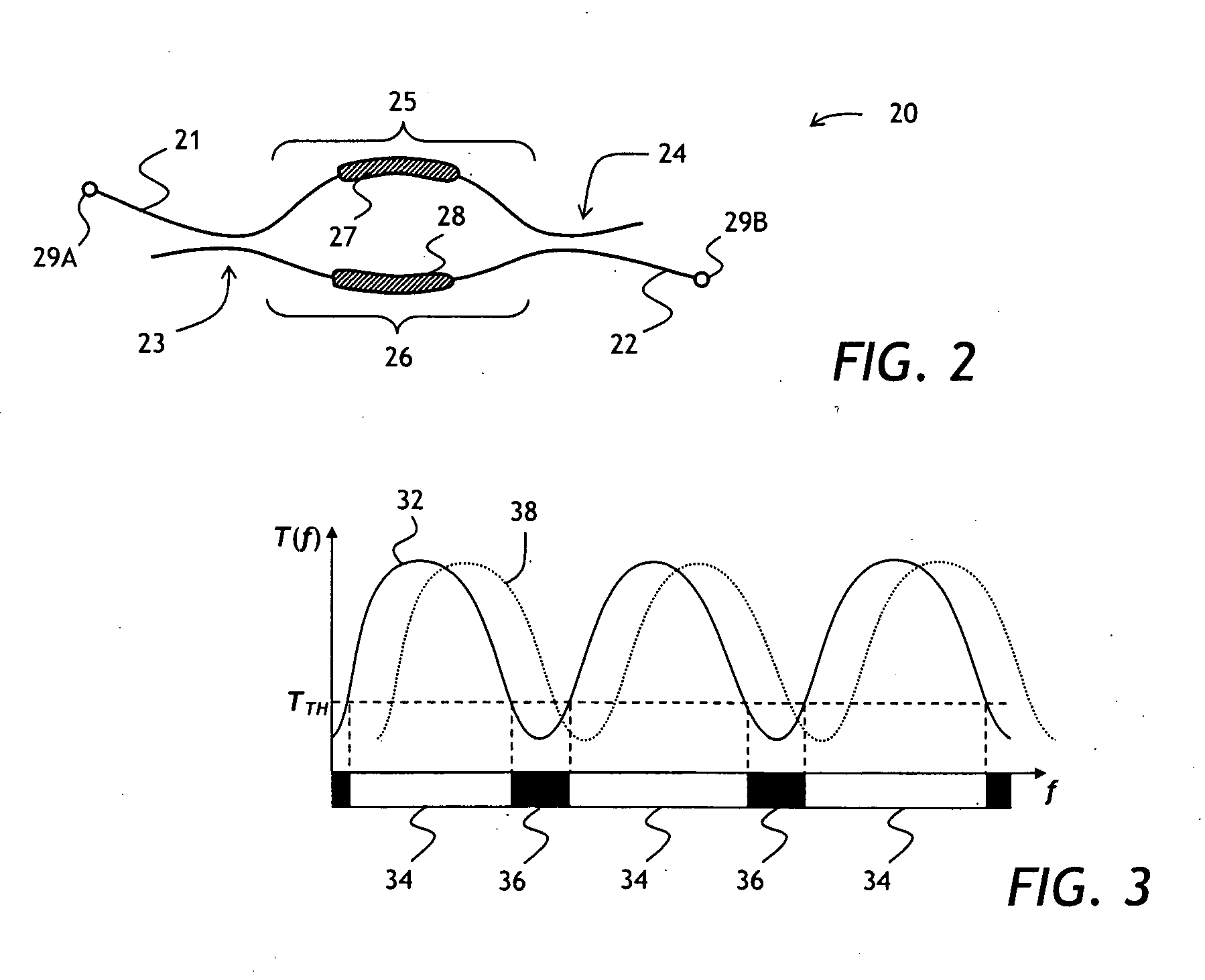
A tunable PLC optical filter having sequentially connected thermally tunable Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometers is described. The MZ interferometers, having free spectral ranges matching ITU frequency grid spacing, are tuned so as to have a common passband centered on the frequency of the signal being selected, while having at least one of the stopbands centered on any other ITU frequency. Any other optical channel that may be present at any other ITU frequency is suppressed as a result. The PLC chip, including a zero-dispersion lattice-filter interleaver stage, a switchable fine-resolution stage and, or a retroreflector for double passing the filter, is packaged into a hot-pluggable XFP transceiver package. A compensation heater is used to keep constant the amount of heat applied to the PLC chip inside the XFP package, so as to lessen temperature variations upon tuning of the PLC optical filter.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
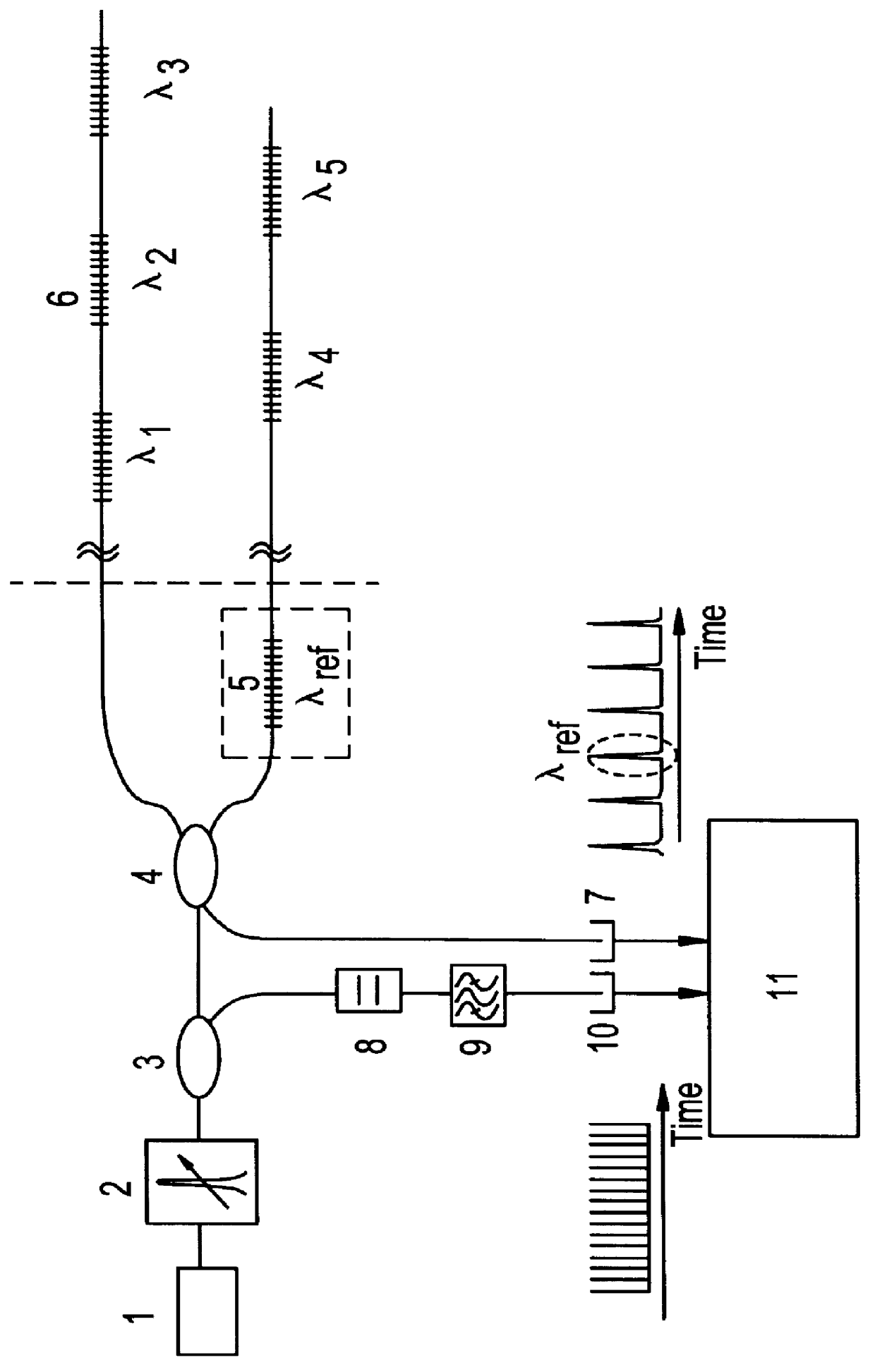
Method and system for locking transmission wavelengths for lasers in a dense wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS20020163650A1Heat is lostChange in refractive indexSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser output parameters controlFiberFinesse
Owner:SPECTRASENSORS INC
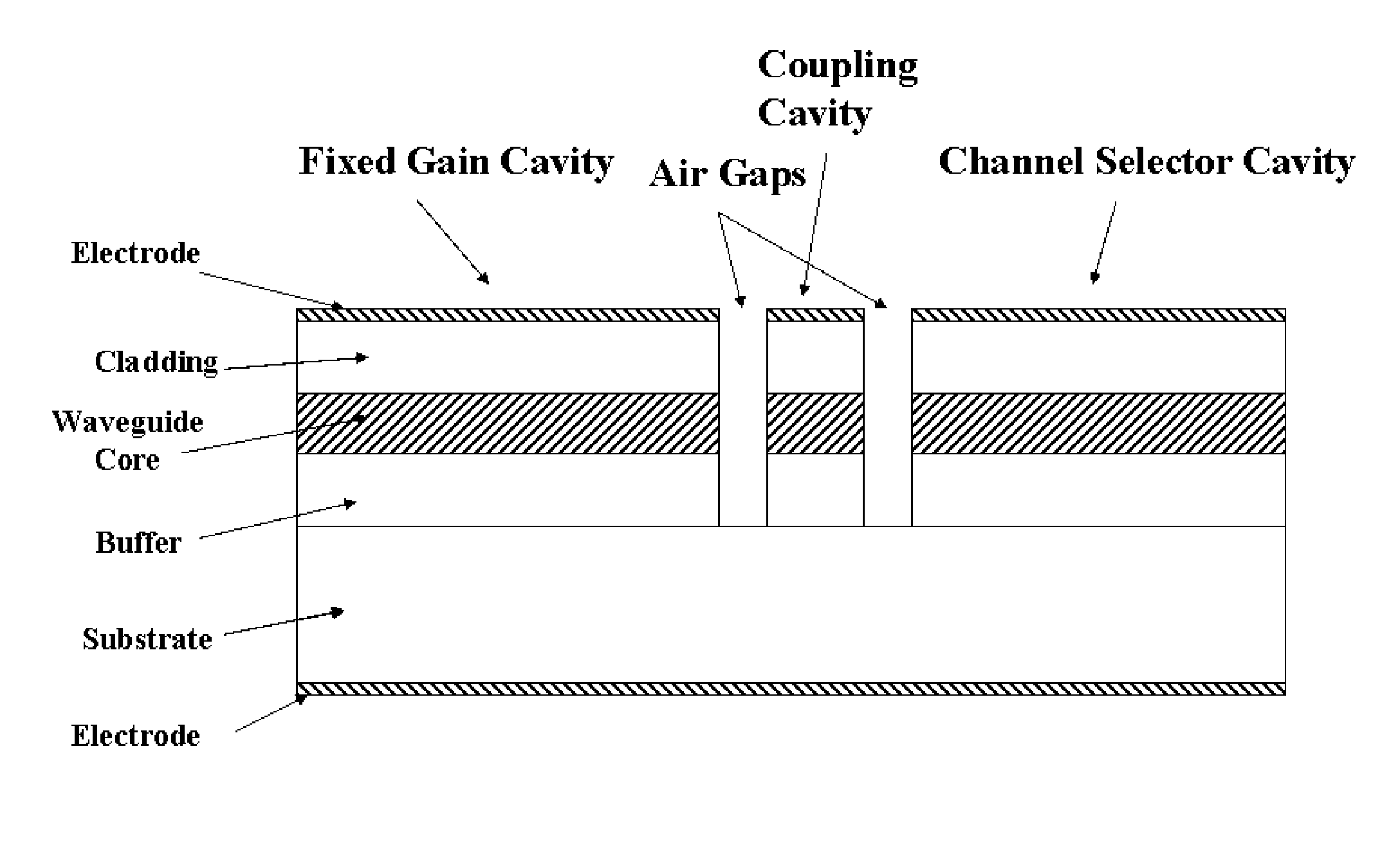
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser
A monolithically integrated wavelength switchable laser comprises three coupled Fabry-Perot cavities. The length and consequently the free spectral range of the first cavity are designed such that the resonant peaks correspond substantially to a set of discrete operating wavelengths separated by a constant channel spacing. The second cavity has a slightly different length so that only one resonant peak coincides with one of the resonant peaks of the first cavity over the spectral window of the material gain. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. The two cavities are coupled through a third short cavity that produces a certain coupling loss and phase relationship between the first and the second cavities in order to achieve an optimal mode selectivity of the combined cavity laser. In operation, both the first and the second cavities are forward biased to provide optical gains for the laser action. The second cavity is tuned by varying the refractive index of at least a portion of the waveguide within the cavity through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching of the laser among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first cavity.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
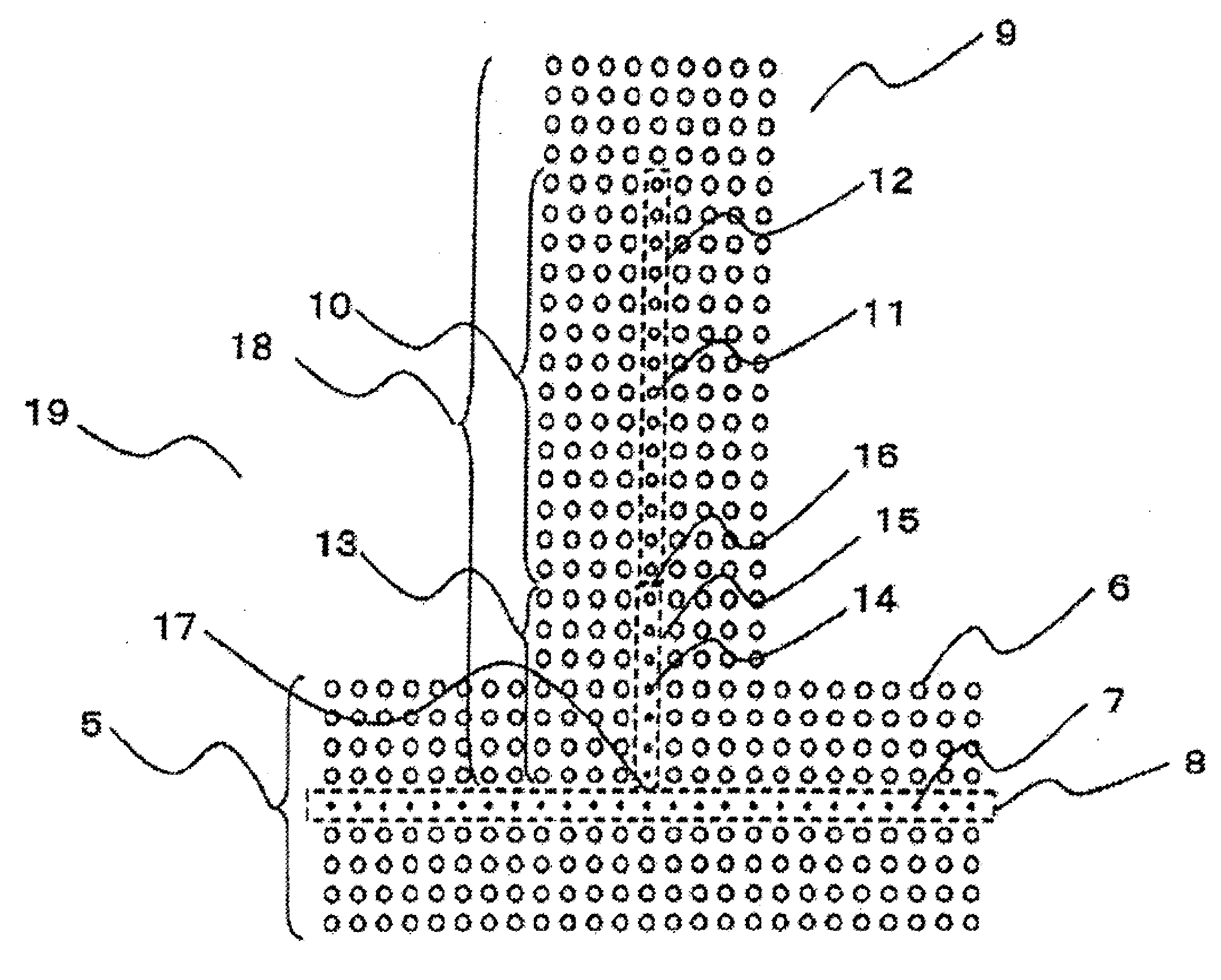
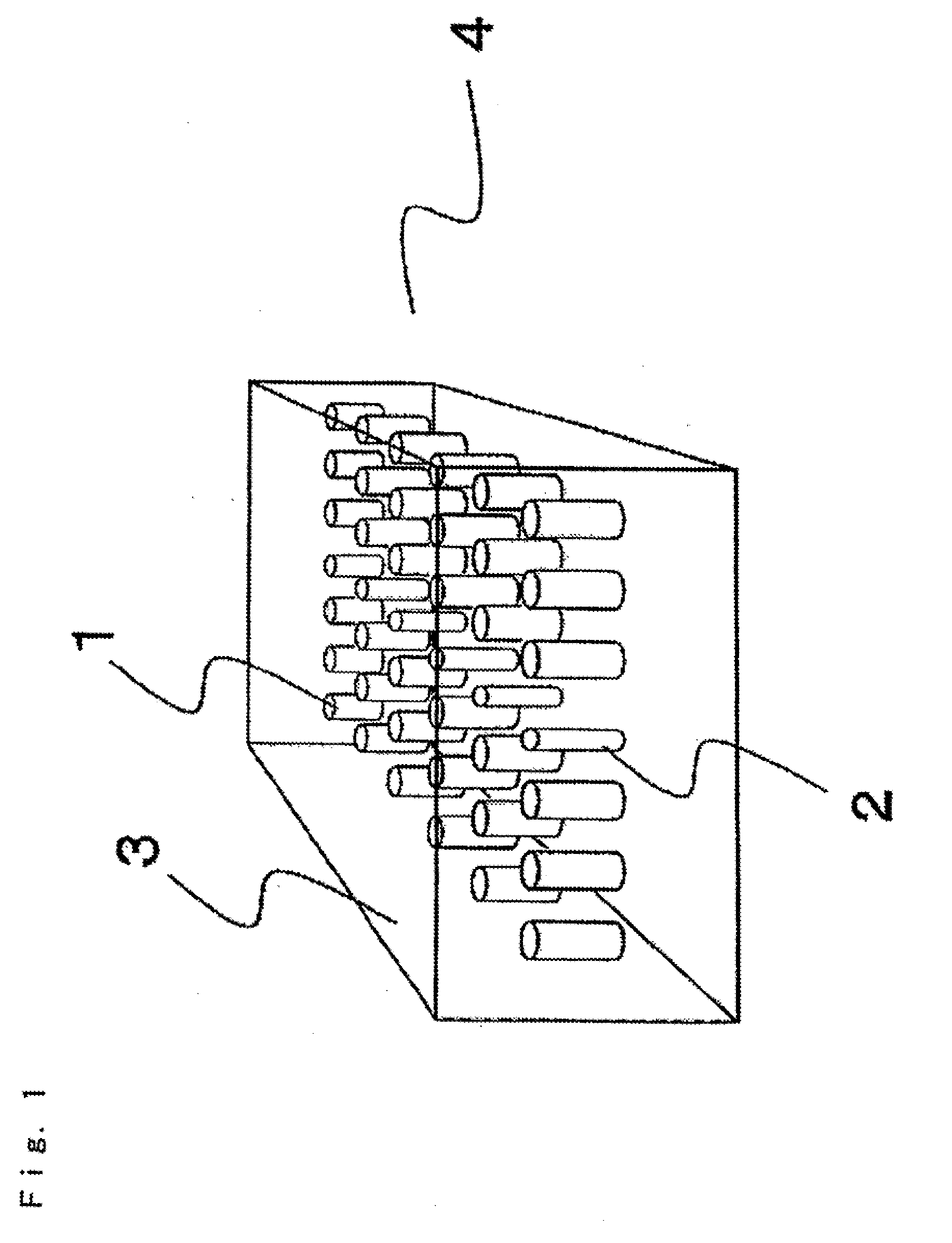
Photonic crystal element
A waveguide stub is connected to a pillar-type square-lattice photonic crystal waveguide. Within the waveguide stub, the diameter of a defect is made larger than that of the original photonic crystal waveguide thereby reducing the group velocity of a guided light. The original waveguide and the waveguide stub are smoothly connected via a taper waveguide. Because of low group velocity of light in the waveguide stub, free spectral range (FSR) decreases thereby allowing the size of the waveguide stub to be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
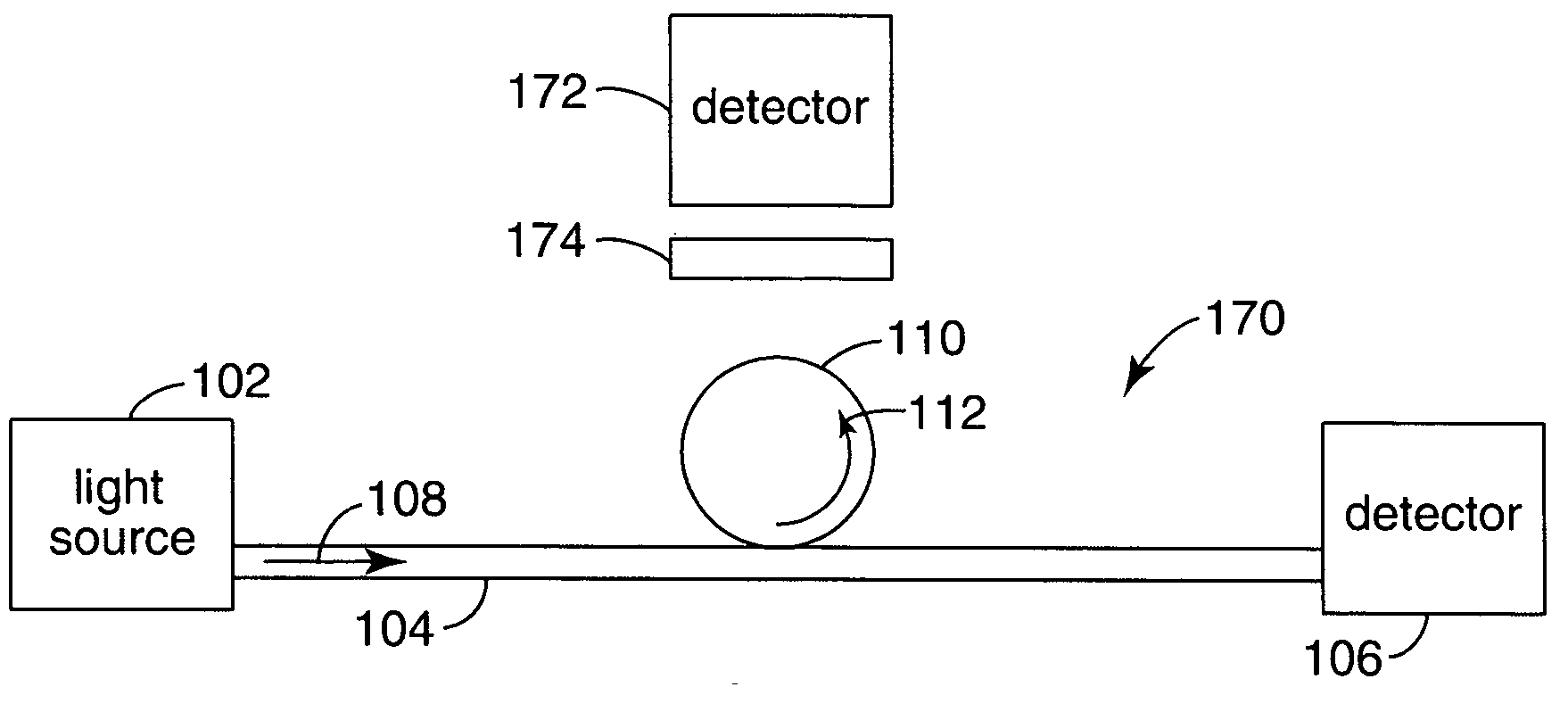
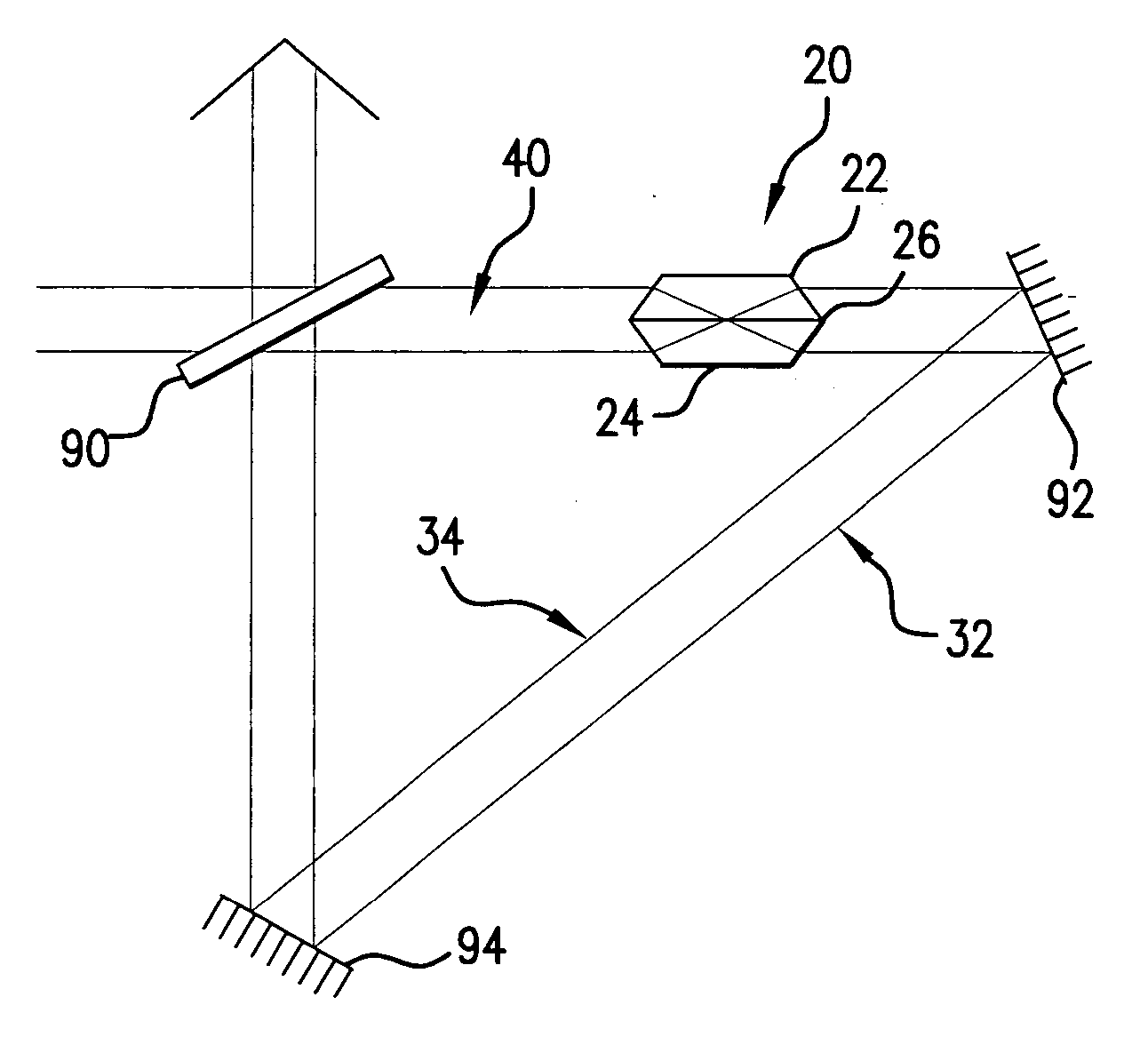
Wavelength reference apparatus and method
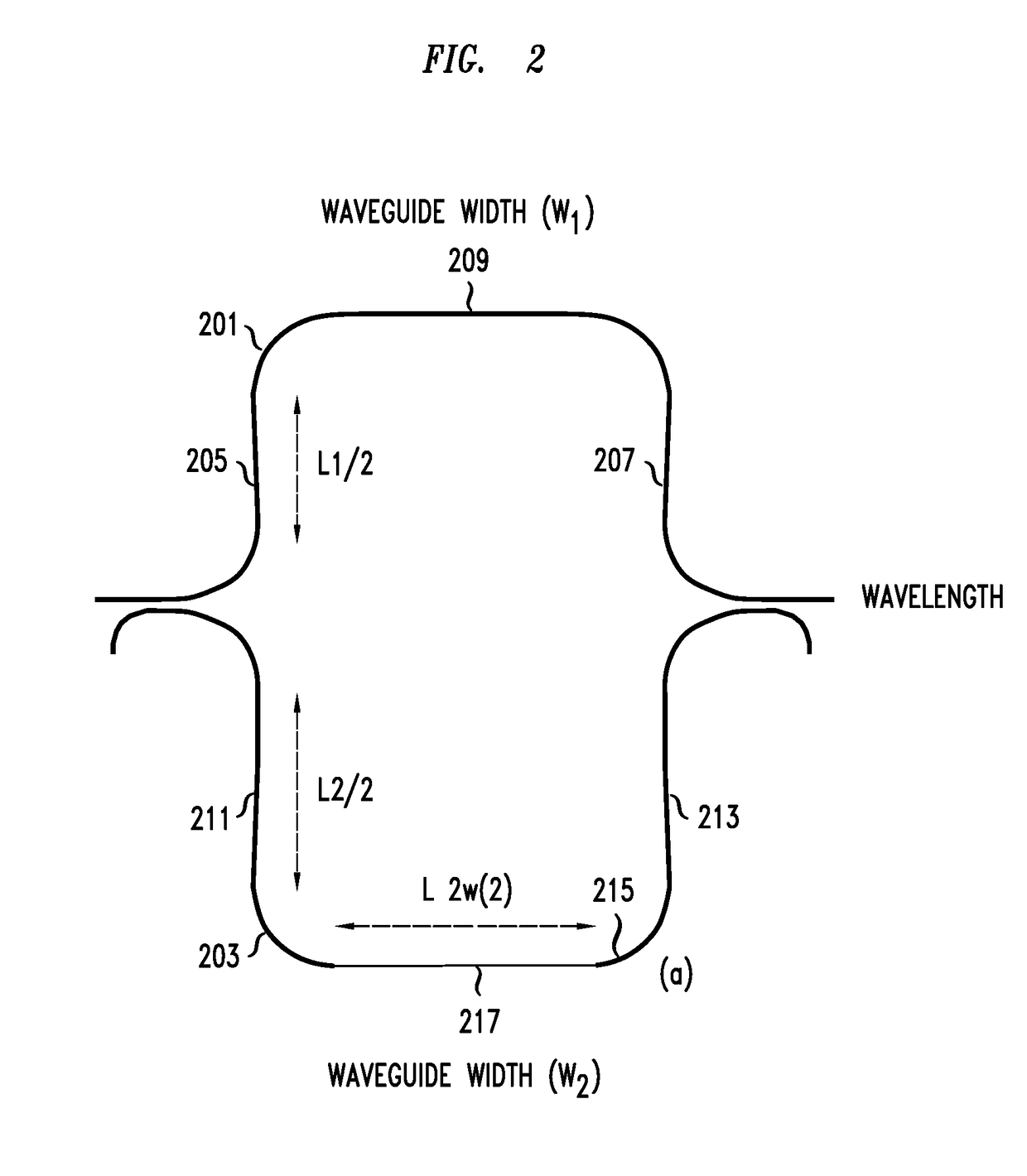
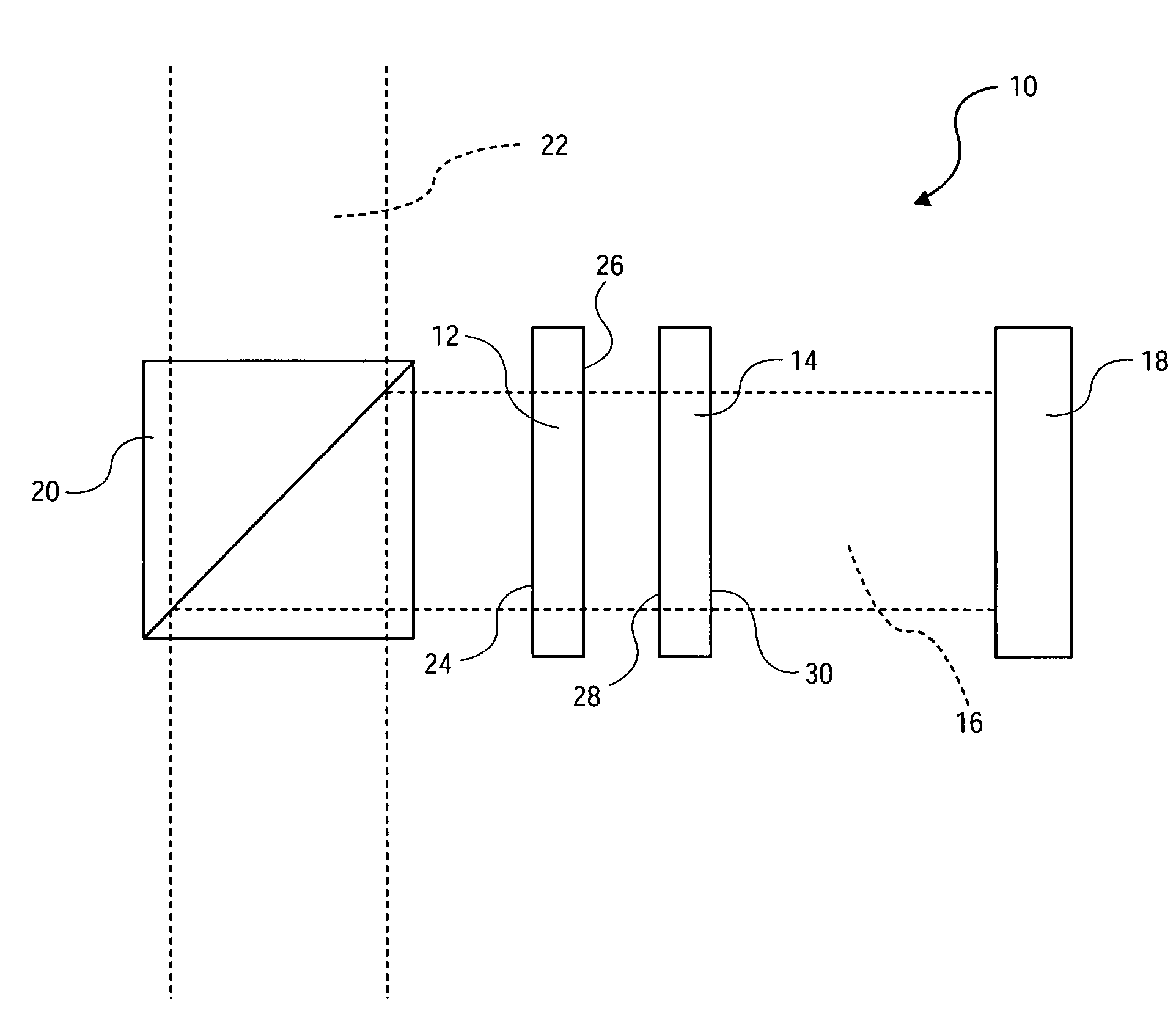
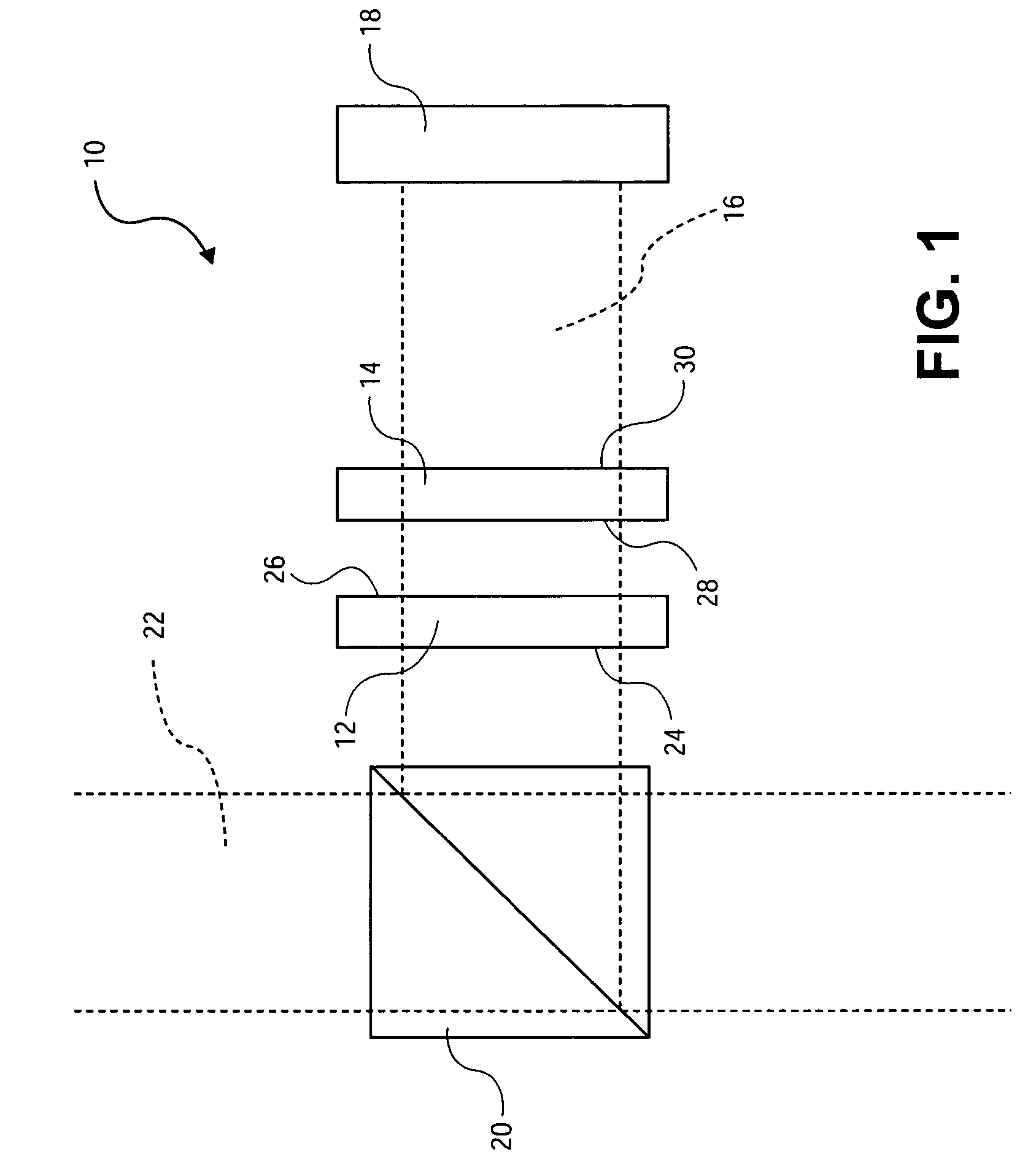
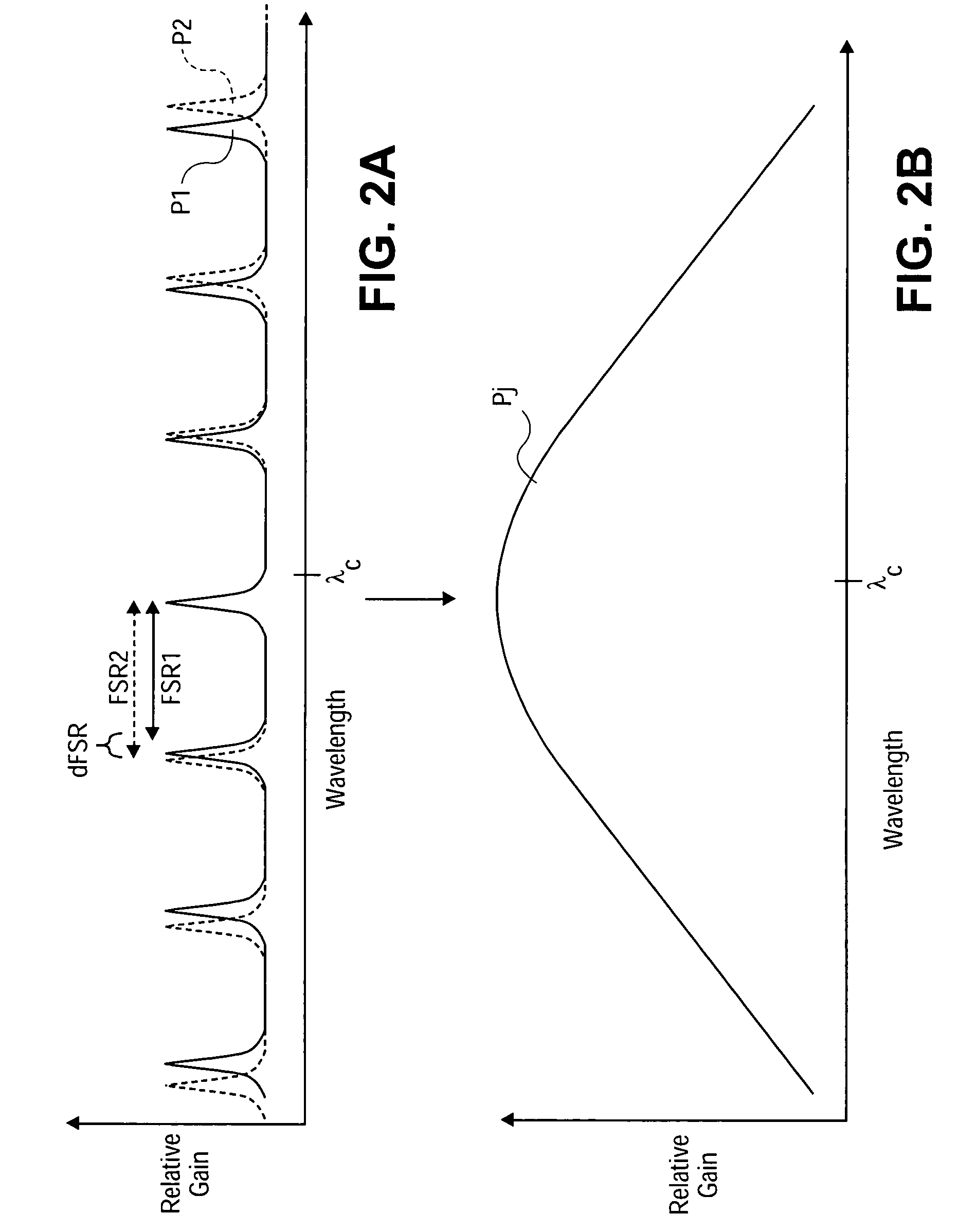
Apparatus and methods usable for wavelength references and measurement of wavelength of a light beam. The apparatus comprise at least two wavelength reference or filter elements positioned in a light beam, each wavelength reference element having a different free spectral range and operable to define a joint free spectral range, and a detector positioned in the beam after the wavelength reference elements. The joint free spectral range provided by the multiple wavelength reference elements results in a joint transmission peak that is centered at a unique wavelength, and maximum optical power detectable from the beam by the detector occurs at the center wavelength of the joint transmission peak.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and method for resonant chemical and biological sensing
Apparatus and method are provided for chemical and biological agent sensing. The sensing apparatus includes a resonator having a resonance frequency. The resonator includes a coil of a photonic crystal fiber. The photonic crystal fiber has a solid region configured to guide a substantially single optical mode of light having an evanescent tail, a first cladding surrounding an exterior of the solid region, and a polymer coating the first cladding. The polymer has an embedded indicator. The first cladding and polymer are together configured to extend a portion of the evanescent tail into the polymer. The resonator is configured to produce a resonance shape centered at the resonance frequency. A predetermined change in the resonance shape or the free spectral range indicates a reaction of the indicator to the agent.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Fabry-perot etalon with independently selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range
InactiveUS6947218B2Substantial linearityGood dispersionUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumResonance
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components for optical signal generation and processing using optical interference filters and interferometers are presented. The invention provides optical interference filters and interferometers having a selected cumulative reflectance phase dispersion capable of providing substantially independent selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides a multi-peak transmission spectrum with substantially independent, selectable control over absolute transmission band frequencies and relative transmission band spacing. The methods and devices provided herein are particularly well suited for frequency matching optical signals to a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Fabry-perot etalon with independently selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range
InactiveUS20040042083A1Substantial linearityConstant lengthUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumResonance
The invention relates generally to optical interference filters and interferometers. Methods, devices and device components for optical signal generation and processing using optical interference filters and interferometers are presented. The invention provides optical interference filters and interferometers having a selected cumulative reflectance phase dispersion capable of providing substantially independent selectable resonance frequency and free spectral range. An exemplary interference filter of the present invention provides a multi-peak transmission spectrum with substantially independent, selectable control over absolute transmission band frequencies and relative transmission band spacing. The methods and devices provided herein are particularly well suited for frequency matching optical signals to a selected frequency standard, such as the International Telecommunication Union frequency standard.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Wavelength division multiplexed optical communication system with rapidly-tunable optical filters
ActiveUS20070258714A1Accurate monitoringWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical light guidesEngineeringOptical communication
The present invention provides a WDM optical system that includes a tunable filter for selecting one or more optical channels from a WDM optical signal. A portion of a WDM signal enters a first optical filter stage that exhibits a periodic transmission spectrum and possesses individually tunable filter elements. A second optical filter stage receives throughput from the first filter stage and has a periodic transmission spectrum and individually tunable filter elements. A controller electrically communicates with the optical filter to select individual optical channels from the portion of the wavelength division multiplexed optical signal received through the filter input port; each selected optical channel is output via a filter throughput port. In an exemplary embodiment, each tunable filter element is a micro-ring resonator and the micro-ring resonators in the first filter stage have a different free spectral range (FSR) than the micro-ring resonators of the second filter stage.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Laser based cavity enhanced optical absorption gas analyzer with laser feedback optimization
ActiveUS8659758B2Promote absorptionGood reproducibilityInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical frequenciesSpectroscopy
Owner:LI COR
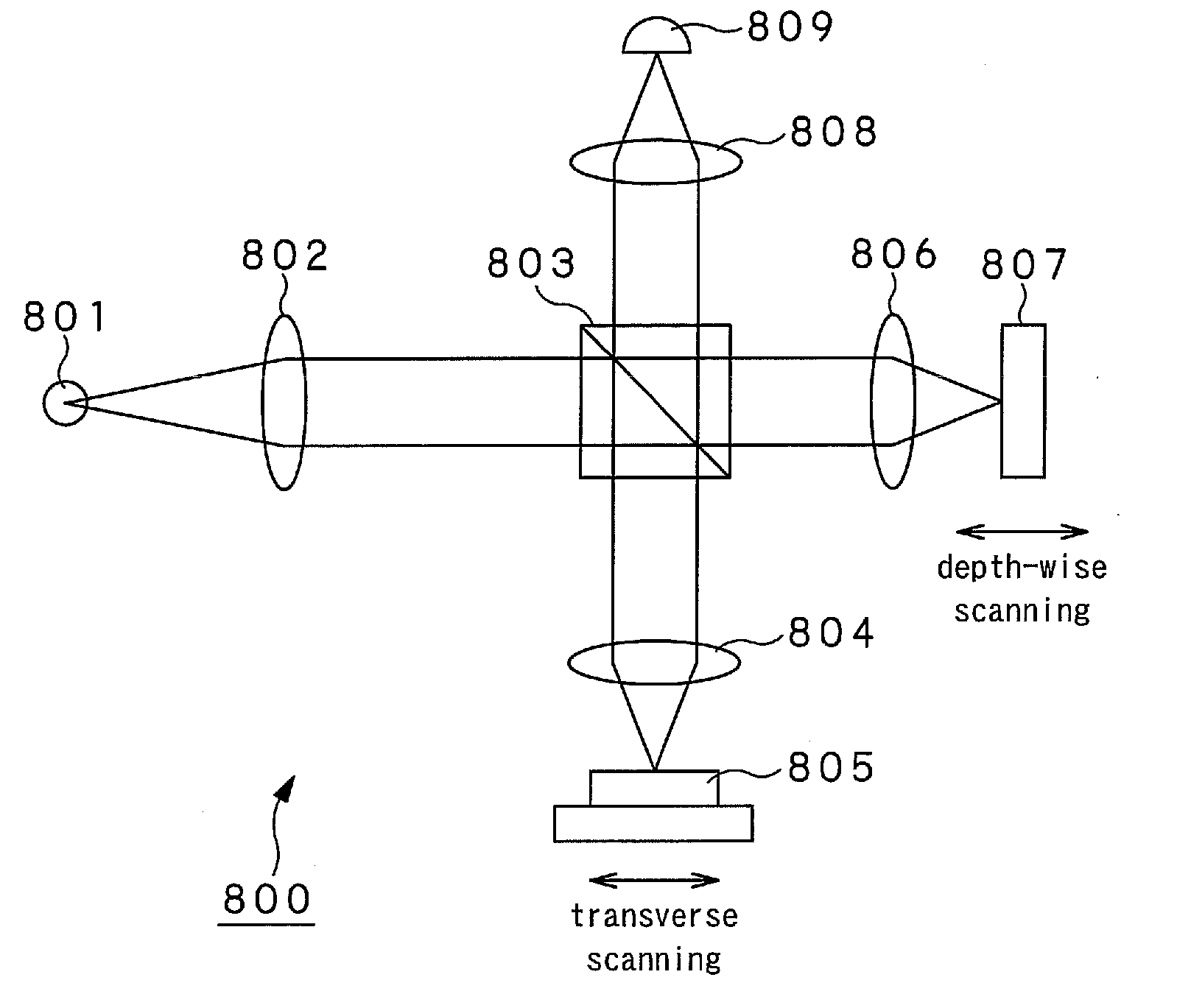
Wavelength scanning light source and optical coherence tomography device
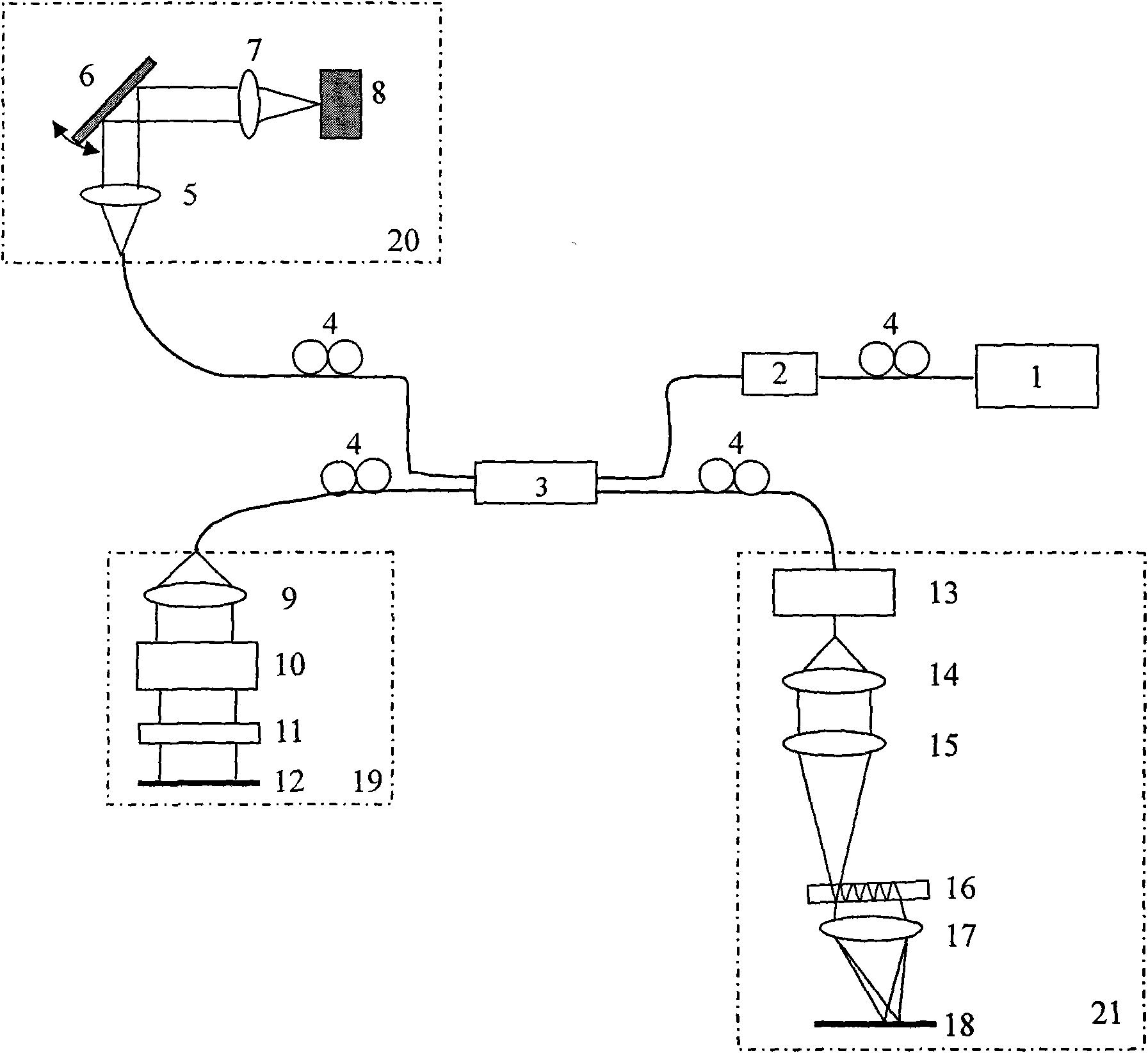
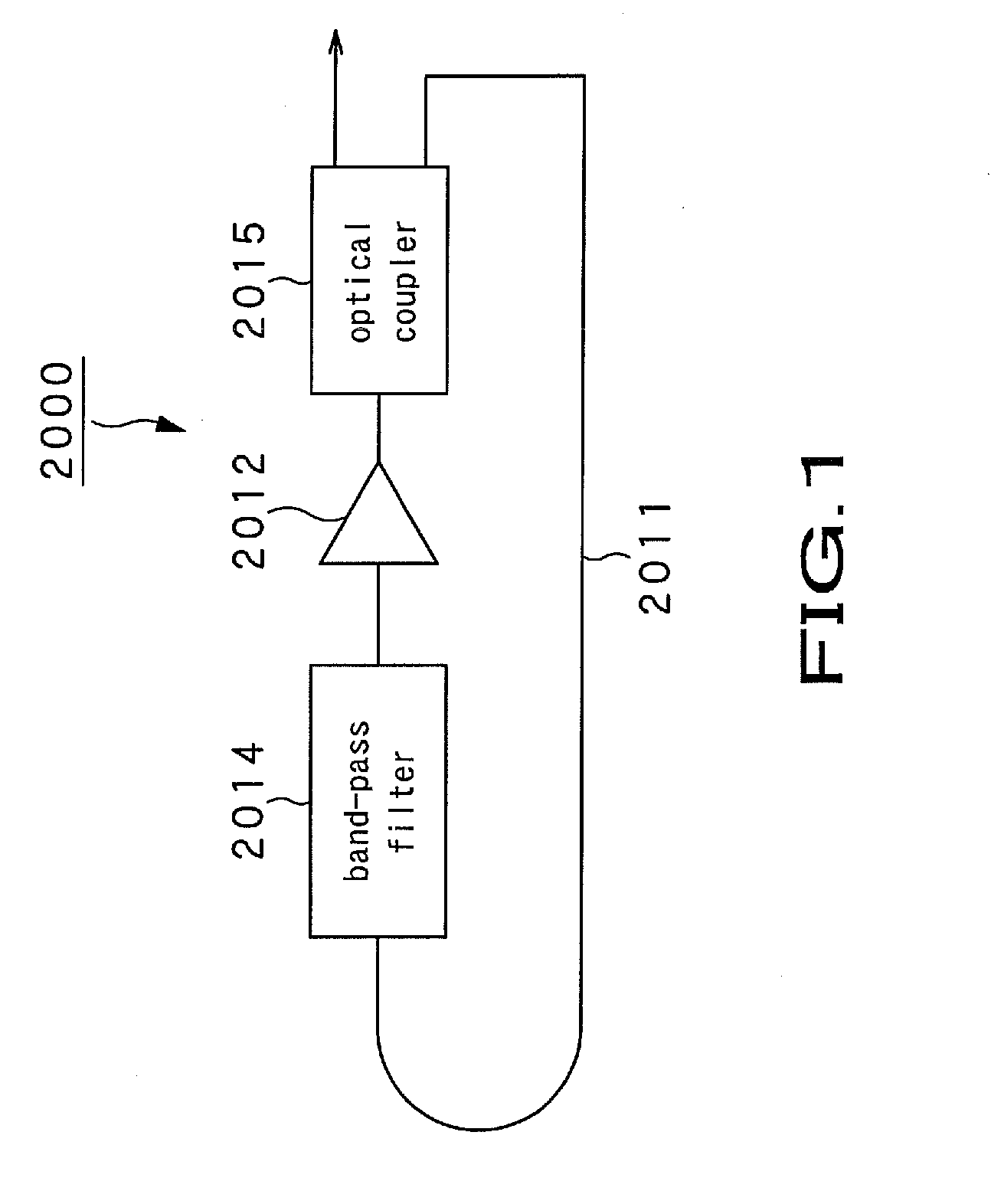
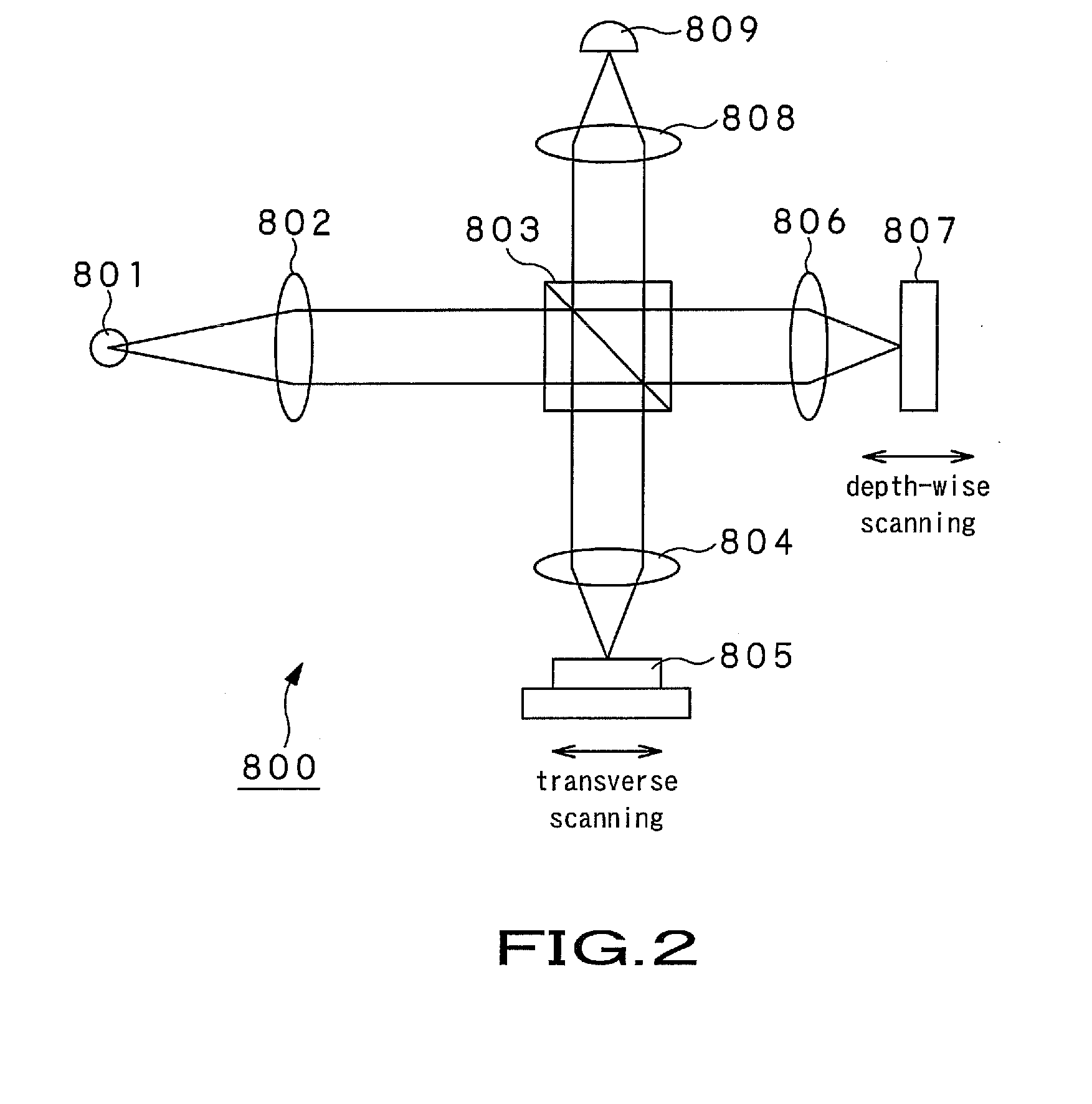
InactiveUS20100097614A1Increase speedContinuous scanMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographyLaser lightLength wave
An optical coherence tomography device includes a wavelength scanning laser light source (10) provided with two Fabry-Perot resonators (13A, 13B) provided in a light path for laser oscillation. The values of FSR (free spectral range) of the Fabry-Perot resonators are set so as to be proximate to each other. The resonator length of at least one of the two Fabry-Perot resonators is periodically varied within a preset range to cause the two Fabry-Perot resonators (13A, 13B) to operate as a wavelength length varying filter of a narrow pass band capable of varying the selection wavelength by the vernier effect to output laser light that has wavelength temporally scanned. The optical coherence tomography device also includes an interference optical system (20) that causes the laser light output from the wavelength scanning laser light source (10) to be branched into light for reference and light for observation to be illuminated on an object for observation (60) and that generates interference light of reflected light of the light for observation illuminated on the object for observation (60) and the light for reference. The optical coherence tomography device further includes a signal processing means (50) that receives the interference light obtained from the interference optical system (20) for transforming the received interference light into an electrical signal to calculate the optical tomographic image information of the object for observation (60).
Owner:OPTICAL COMB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com