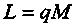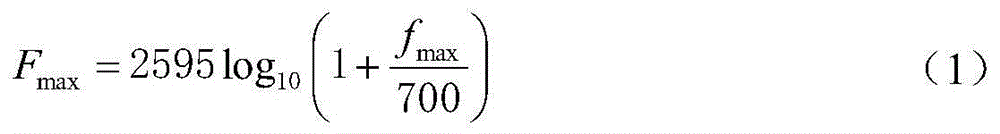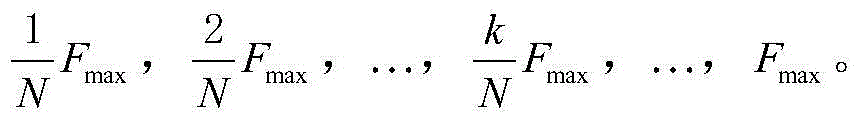Patents
Literature
321 results about "Frequency matching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Abstract. Frequency matching is a sampling design used in case–control studies to assure that cases and controls have the same distributions over strata defined by matching factors. Frequency matching is also used in cohort studies to insure that exposed and unexposed individuals have the same distributions over strata defined by known risk factors.
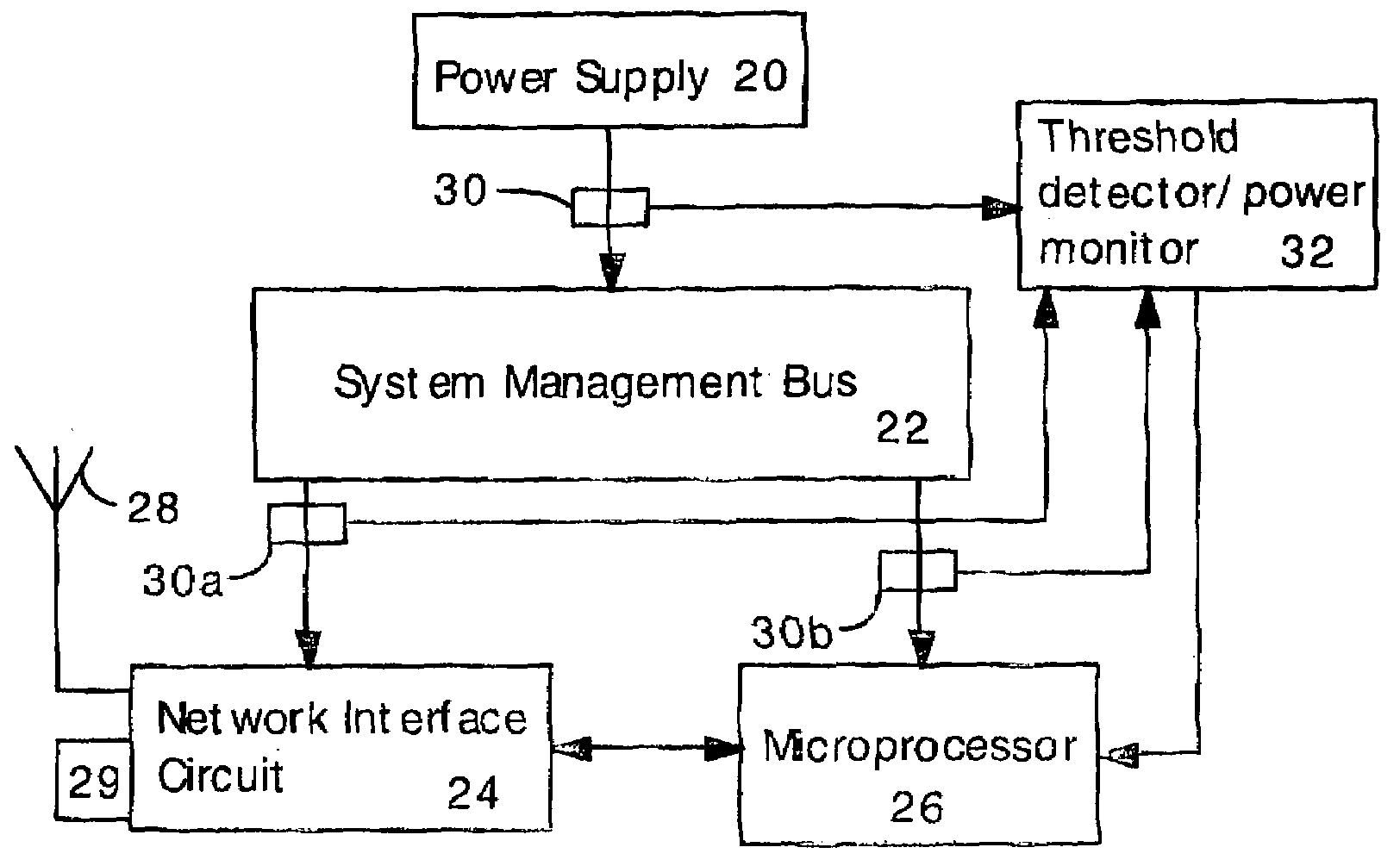
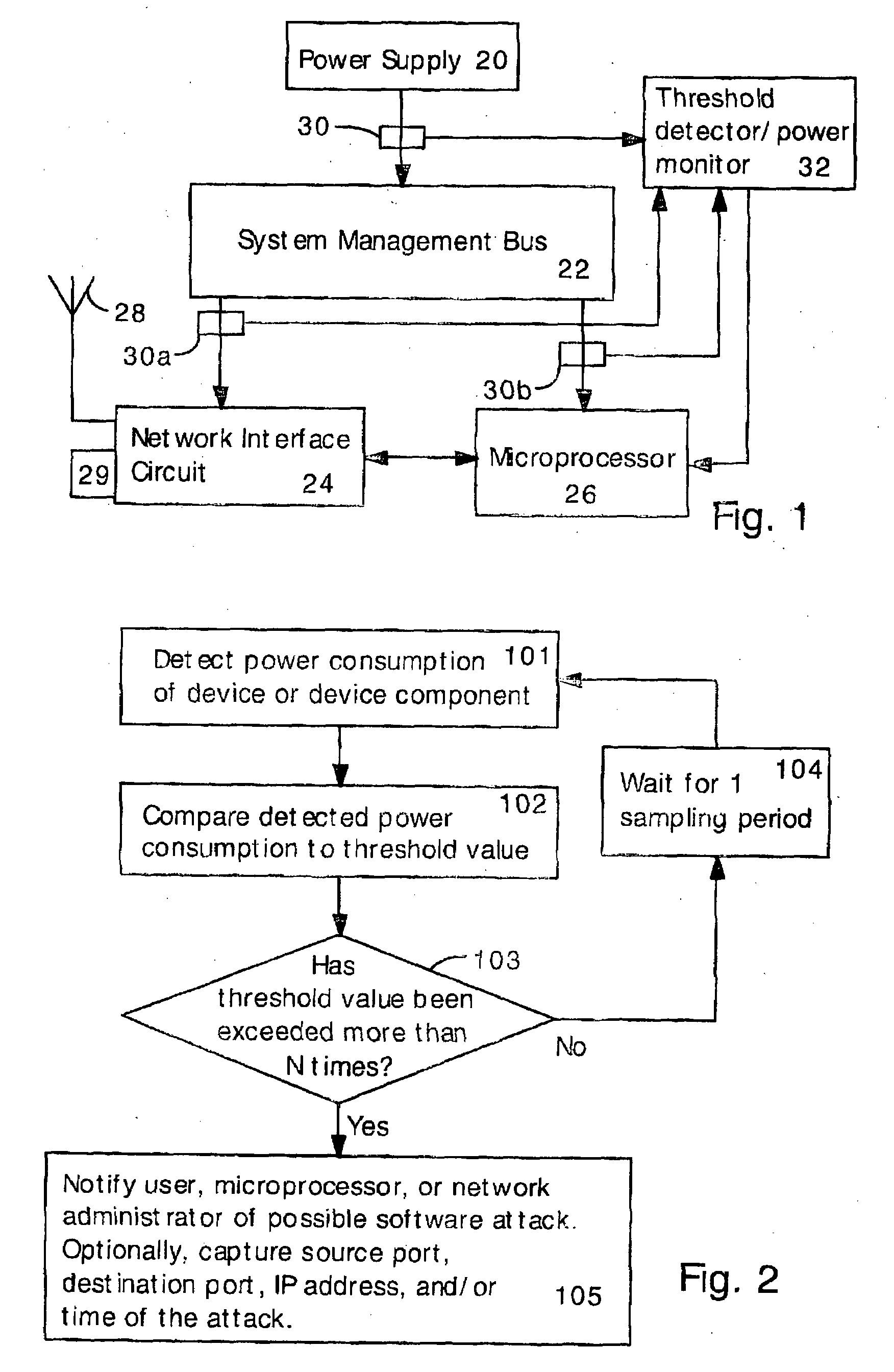
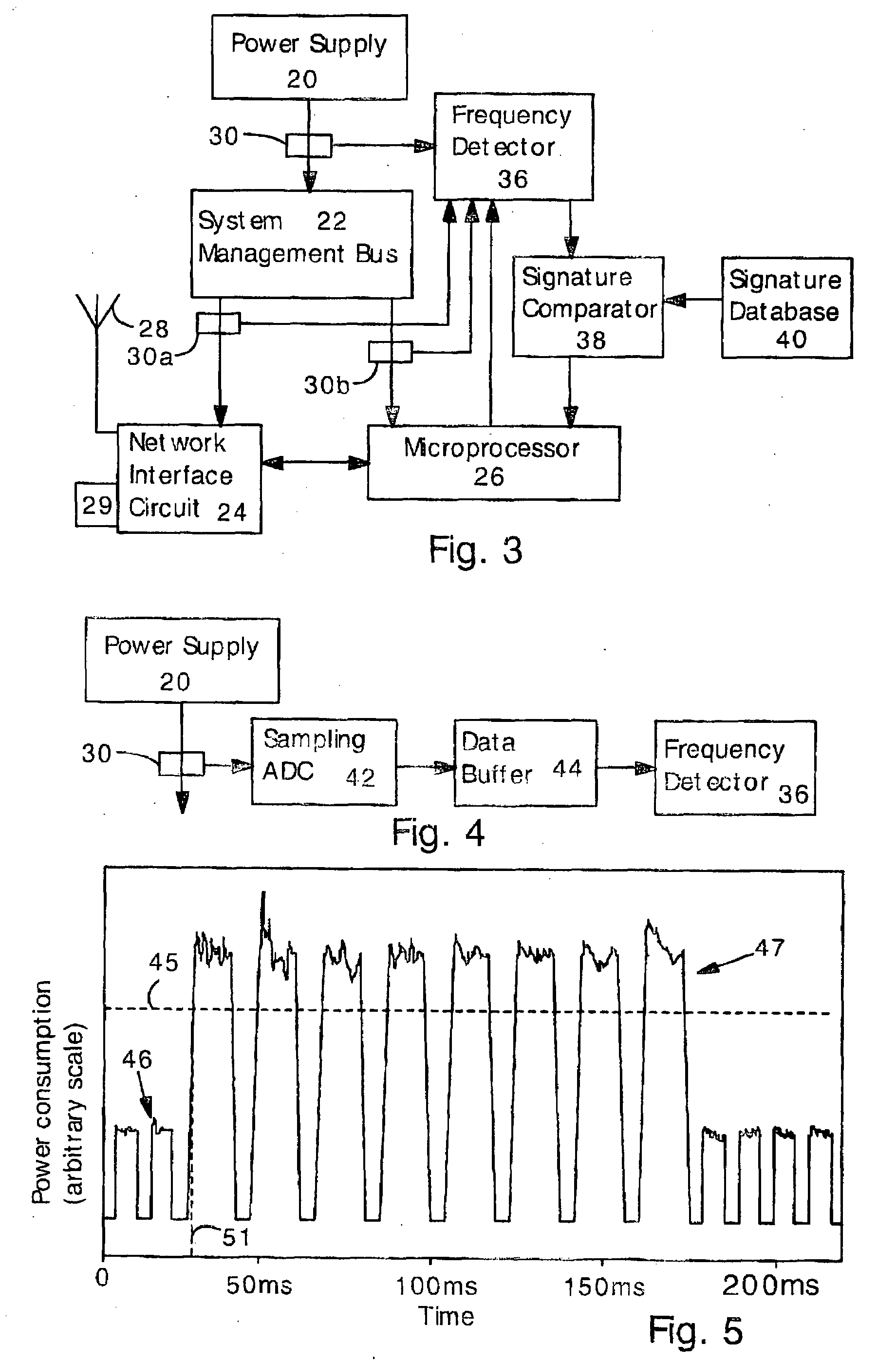
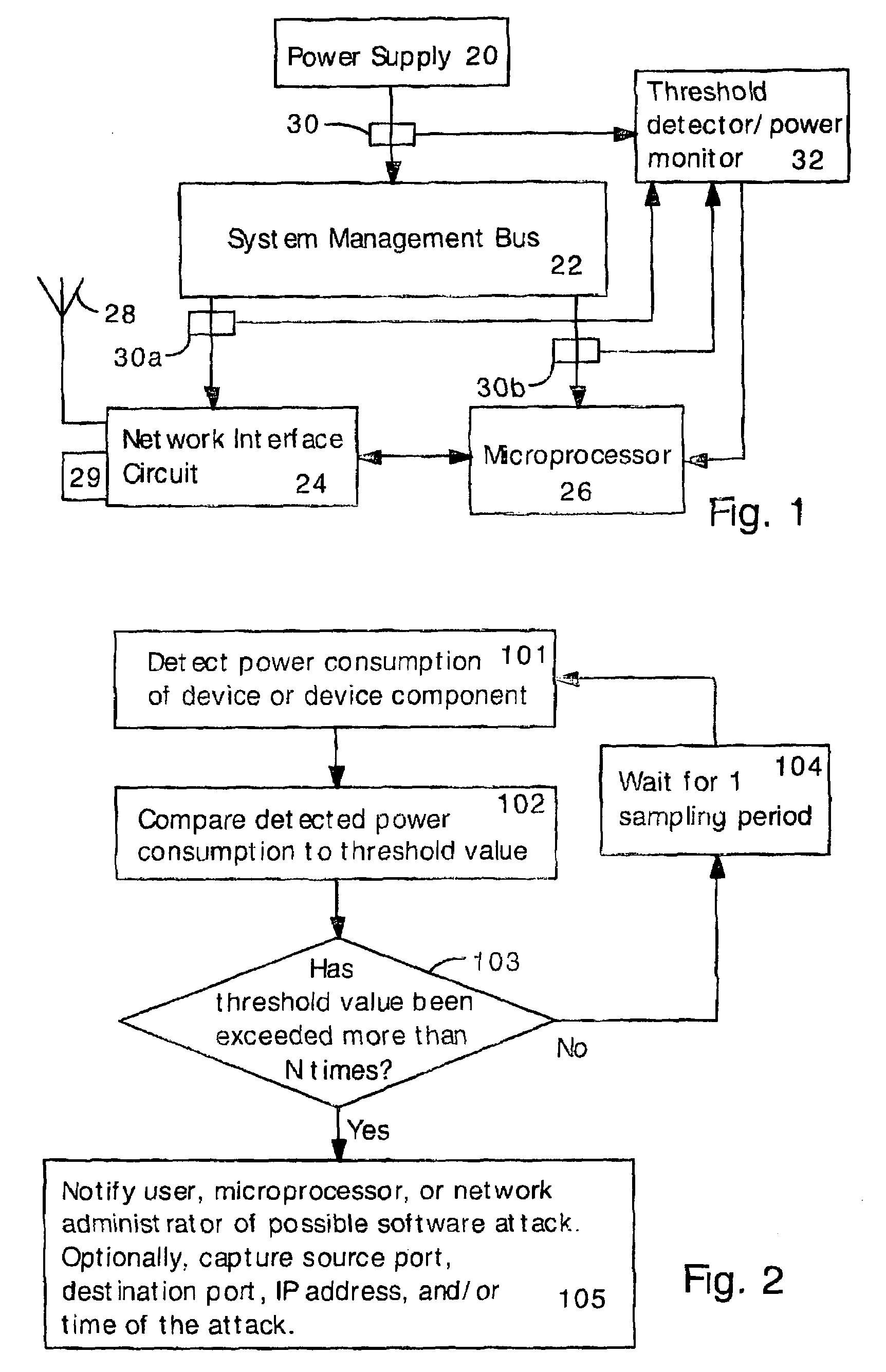
Detecting Software Attacks By Monitoring Electric Power Consumption Patterns
ActiveUS20080276111A1Reduce the valueMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
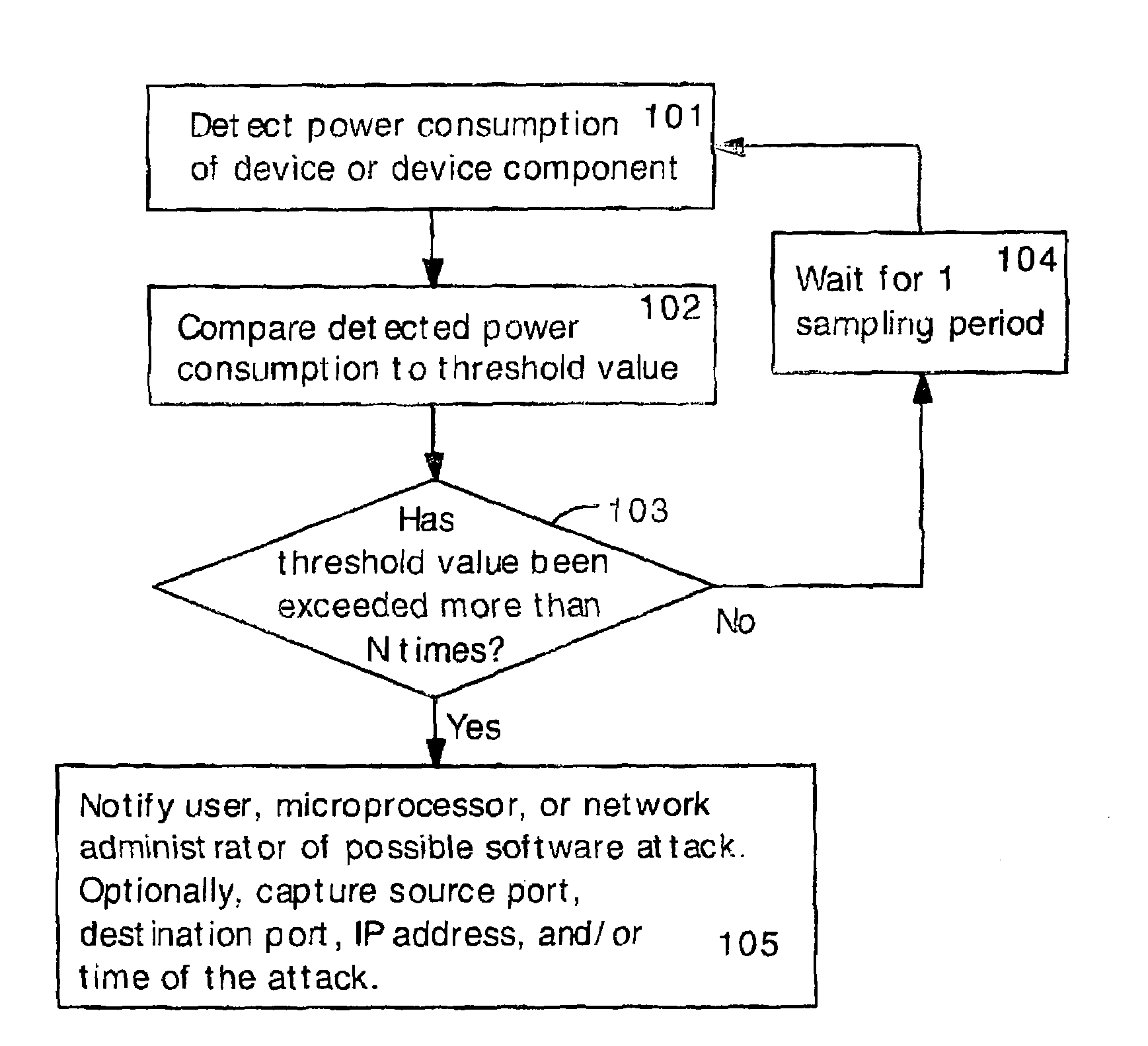
Software attacks such as worms and viruses are detected in an electronic device by monitoring power consumption patterns. In a first embodiment, software attacks are detected by an increase in power consumption. The increased power consumption can be caused by increased network traffic, or by increased activity in the microprocessor. Monitoring power consumption is particularly effective for detecting DOS / flooding attacks when the electronic device is in an idle state. In a second embodiment, a power consumption signal is converted to the frequency domain (e.g., by fast Fourier transform). The highest amplitude frequencies are identified. Specific software attacks produce characteristic frequencies in the power consumption signal. Software attacks are therefore detected by matching the highest amplitude frequencies with frequencies associated with specific worms and viruses. Identification of a particular software attack typically requires matching of 3 or more of the highest amplitude frequencies, and, optionally, amplitude information.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
Electromagnetic wave frequency filter
InactiveUS7321707B2Simple designEfficient extractionNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedFrequency matching
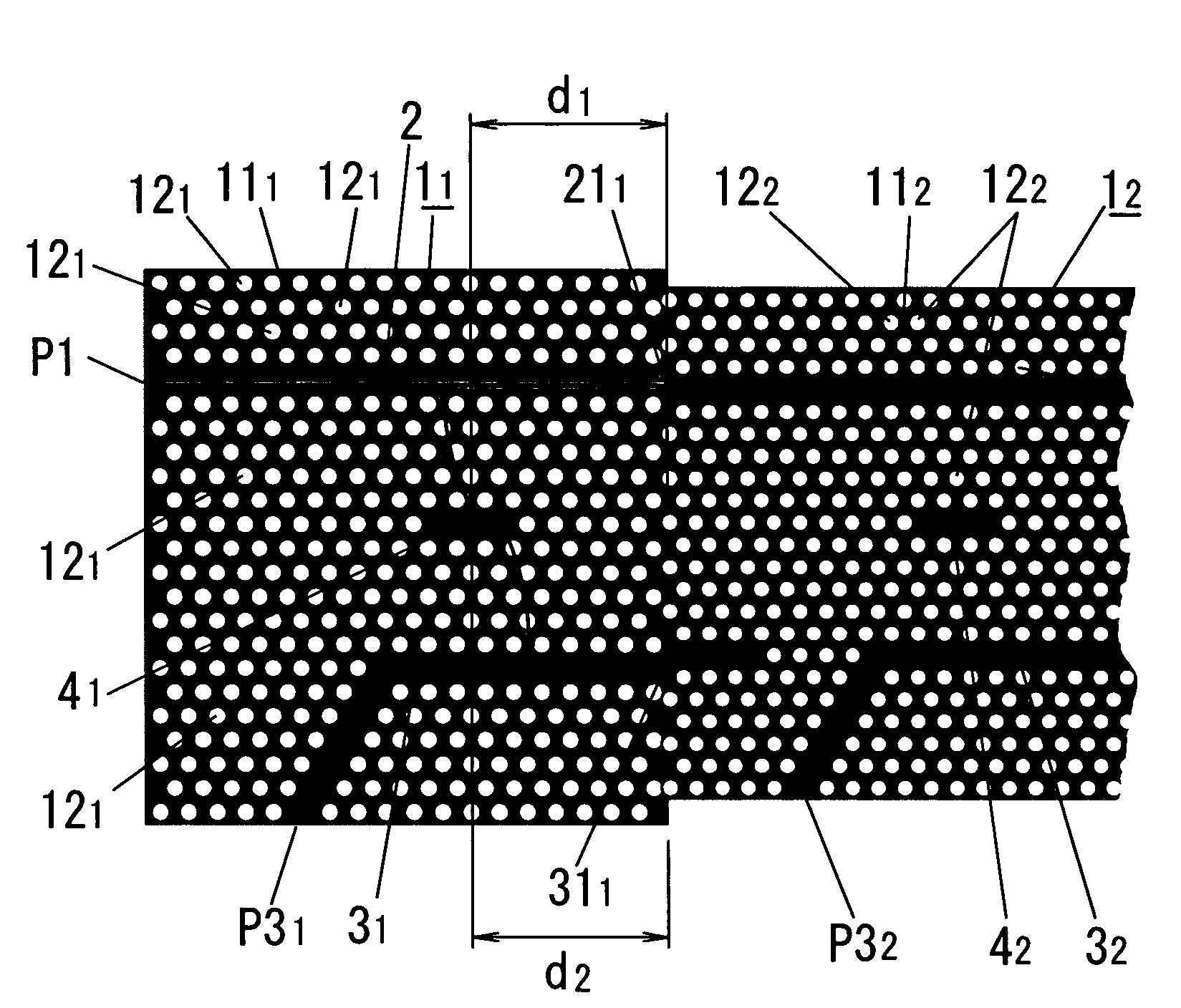
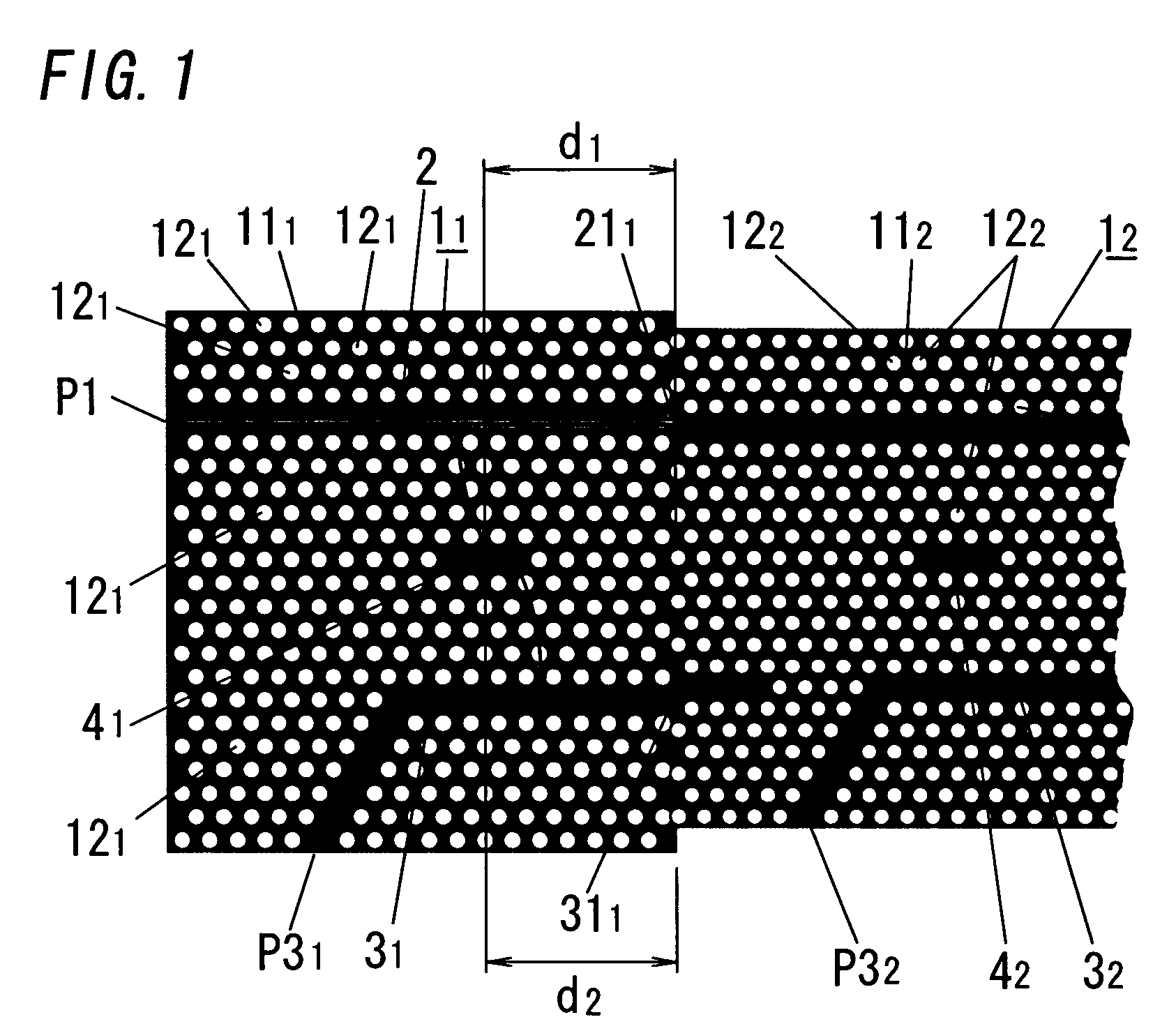
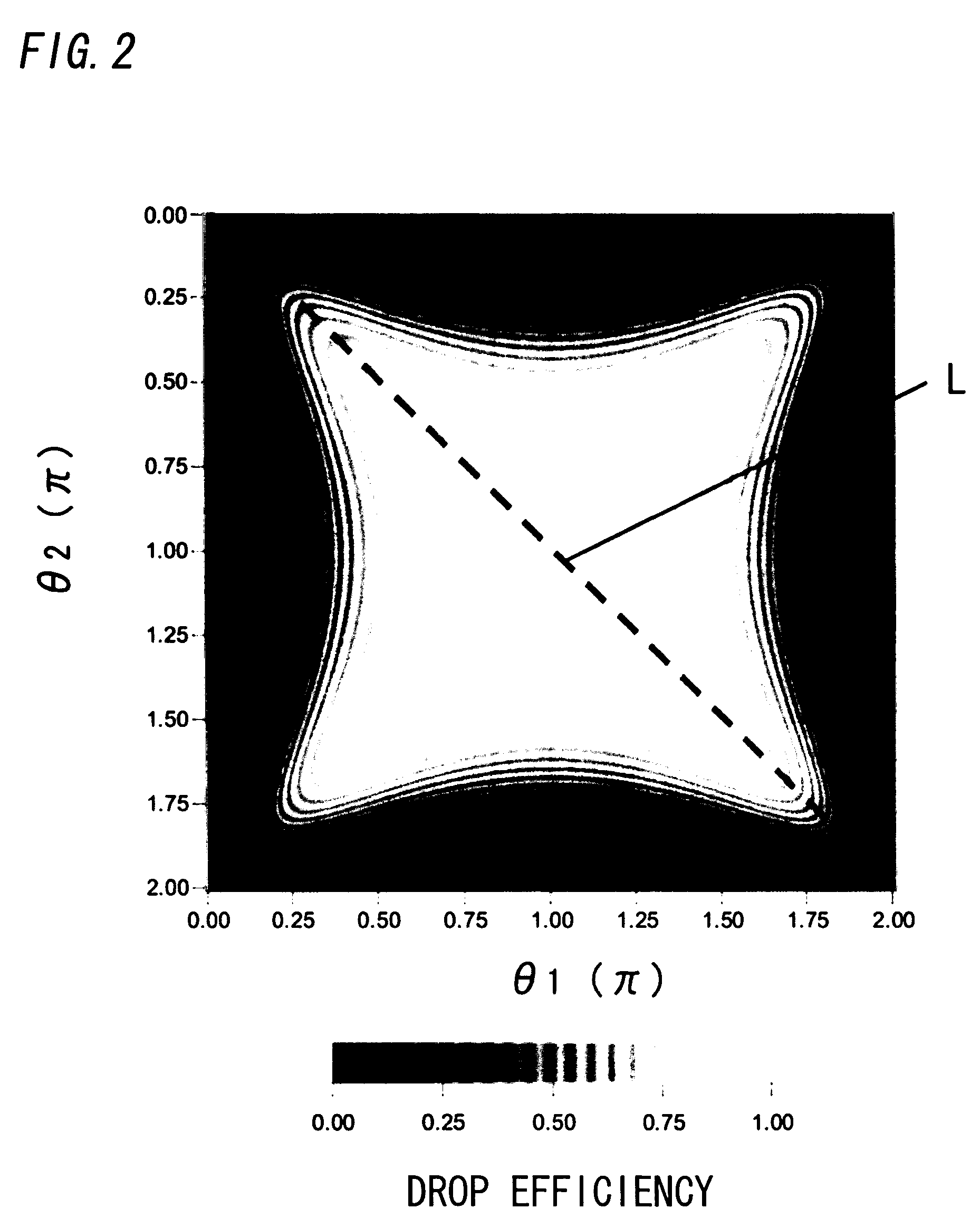
In this electromagnetic wave frequency filter, an electromagnetic wave of a predetermined frequency matching a resonant frequency of a resonator 41 is transmitted from an input waveguide 2 to an output waveguide 3 through the resonator 41, and is outputted from a drop port P31. This filter has an input-waveguide-side reflector 211 and an output-waveguide-side reflector 311, which reflect the electromagnetic wave of the predetermined frequency. The electromagnetic wave frequency filter satisfies the following relation:Qinb / (1−cos θ1)<<Qv,Qinb / (1−cos θ1)=Qinr / (1−cos θ2),θ1, θ2≠2Nπ(N=0, 1, . . . ),where θ1 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the input-waveguide-side reflector 211, θ2 is a phase shift amount of the electromagnetic wave reflected by the output-waveguide-side reflector 311, Qinb is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the input waveguide 2, Qinr is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and the output waveguide 31, and Qv is a Q-factor between the resonator 41 and free space.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
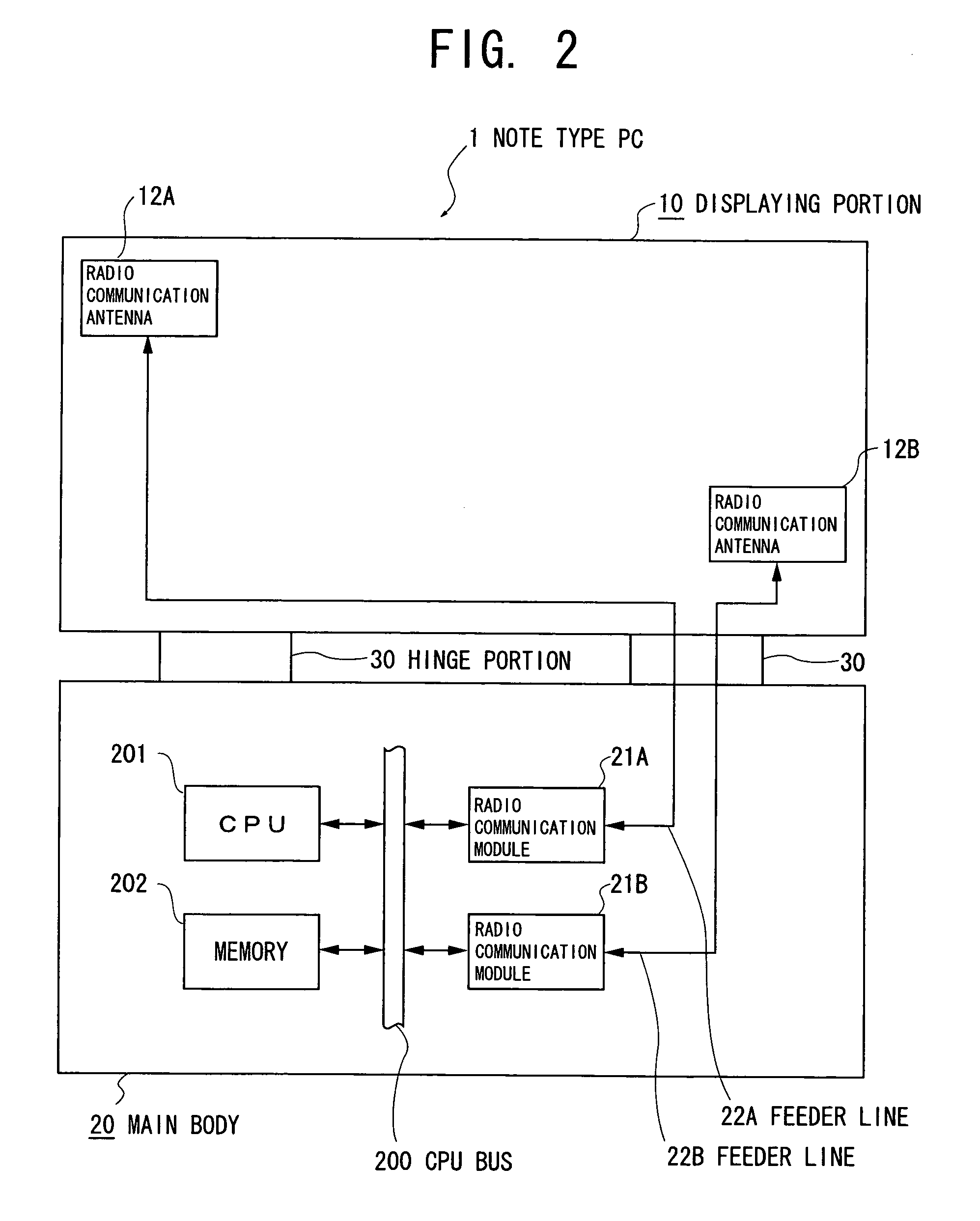
System and method for impedance matching an antenna to sub-bands in a communication band
InactiveUS7176845B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMultiple-port networksAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna impedanceMethod selection
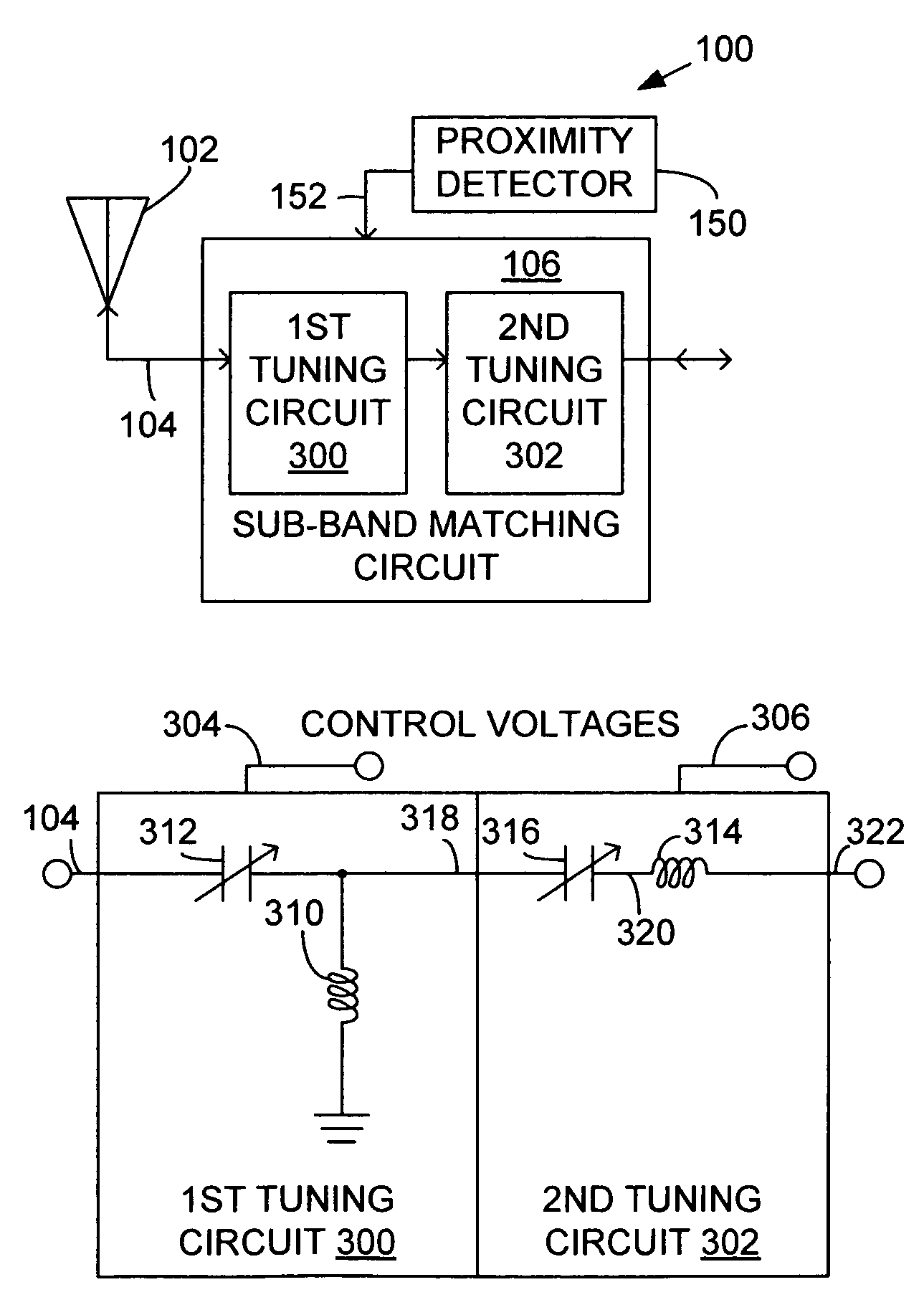
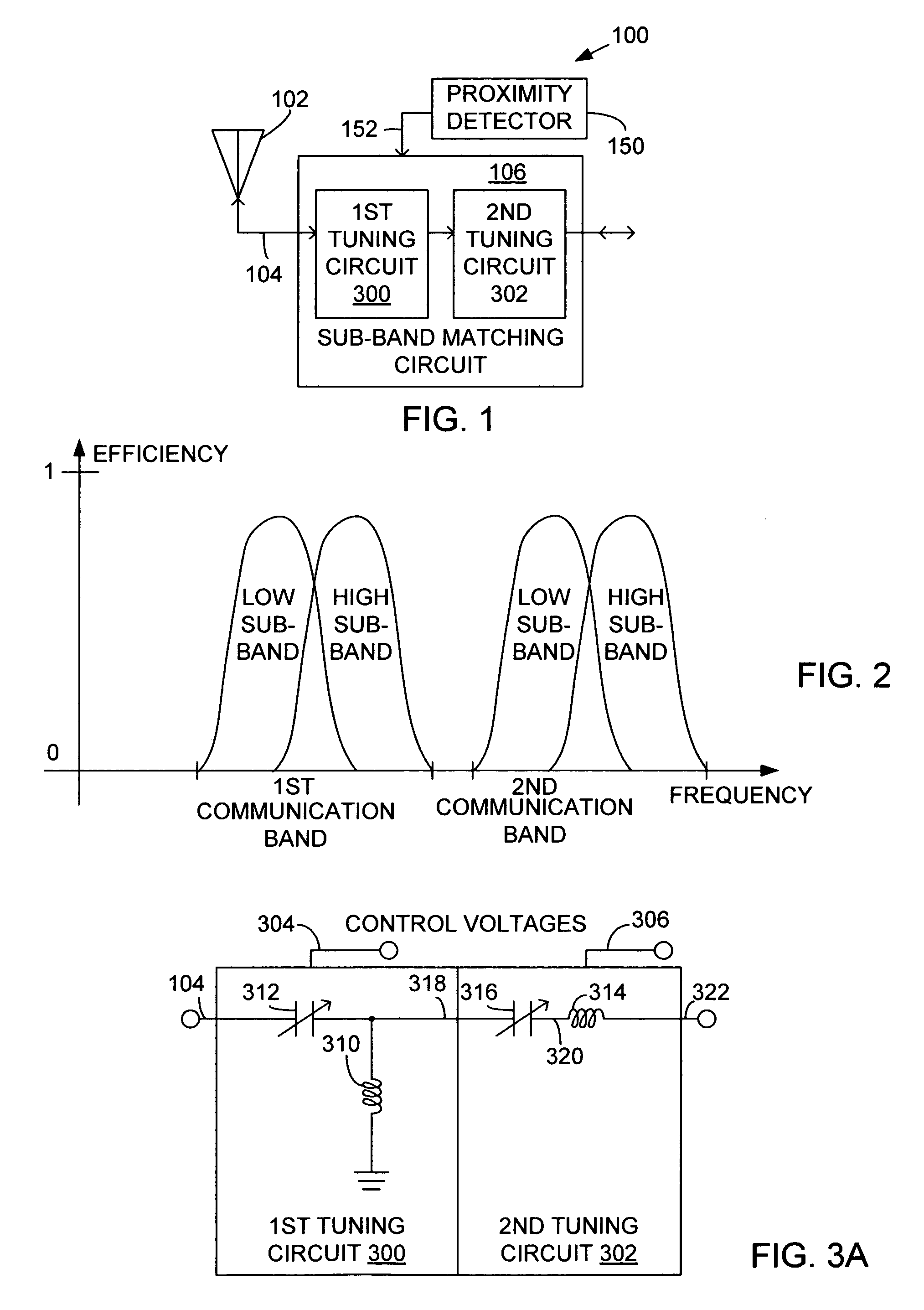
A sub-band antenna matching method and an antenna matching system for selectively matching a communication bandwidth segment impedance have been provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a first communication band. In some aspects, the method selectively supplies a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a second communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency to match the antenna at a low end of the first communication band. Likewise, the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency to match the antenna at a high end of the first communication band in response to the third and fourth frequencies.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Resonant controlled qubit system
Methods for coupling a superconducting qubit to a resonant control circuit. An interaction term between the qubit and the circuit initially has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to the qubit. The circuit is tuned so that a frequency of the qubit and circuit match. A second recoupling operation transforms the term to have only off-diagonal components. A method for entangling a state of two qubits coupled to a bus with a control circuit. An interaction term between at least one of the qubits and the circuit has a diagonal component. A recoupling operation is applied to at least one of the qubits such that the term has only off-diagonal components. The frequency of the circuit is tuned to the frequency of the first qubit, and then tuned to the frequency of the second qubit. The recoupling operation is reapplied to at least one of the qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
Coupling loop
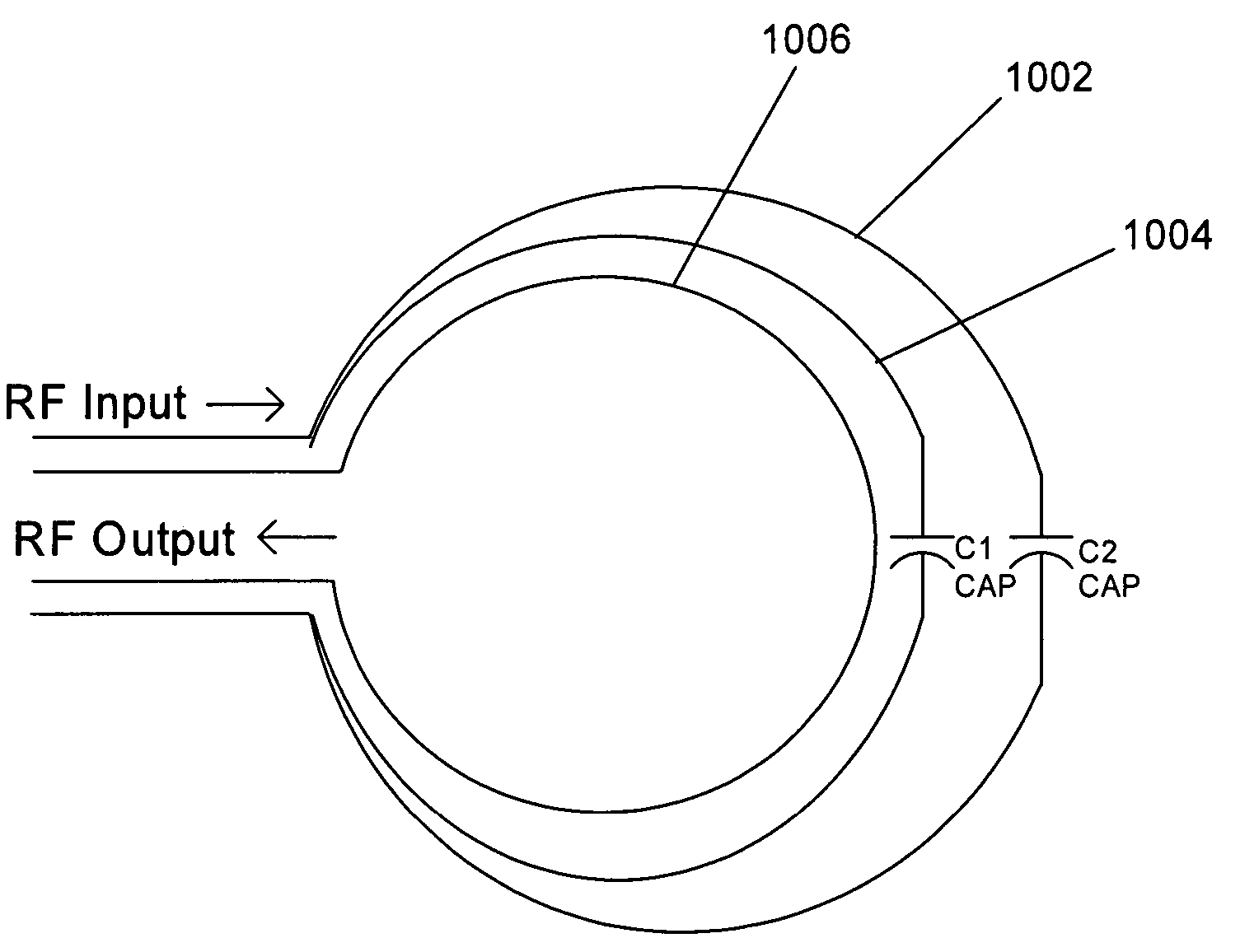
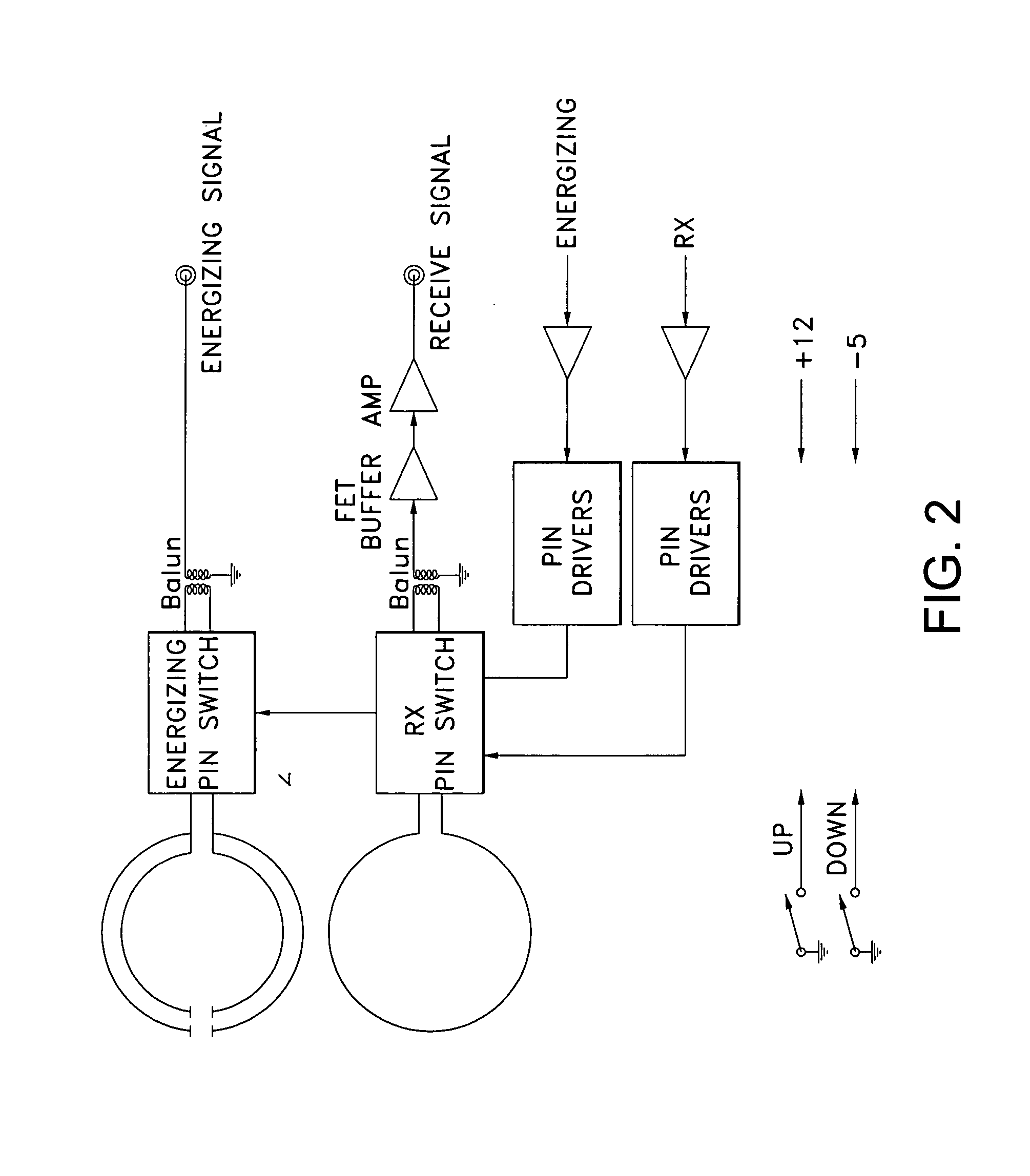
ActiveUS7432723B2Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingCoaxial cables/analogue cablesNear-field transmissionCouplingFrequency matching
A coupling loop or antenna is provided that can be used with a system that determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The coupling loop includes multiple loops. Preferably two tuned loops are used for transmitting the energizing signal to the sensor and an un-tuned loop is used for receiving the sensor signal from the sensor. Orientation features on the housing for the coupling loop and the sensor are provided to assist in positioning the coupling loop relative to the sensor to maximize the coupling between the sensor signal and the coupling loop.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
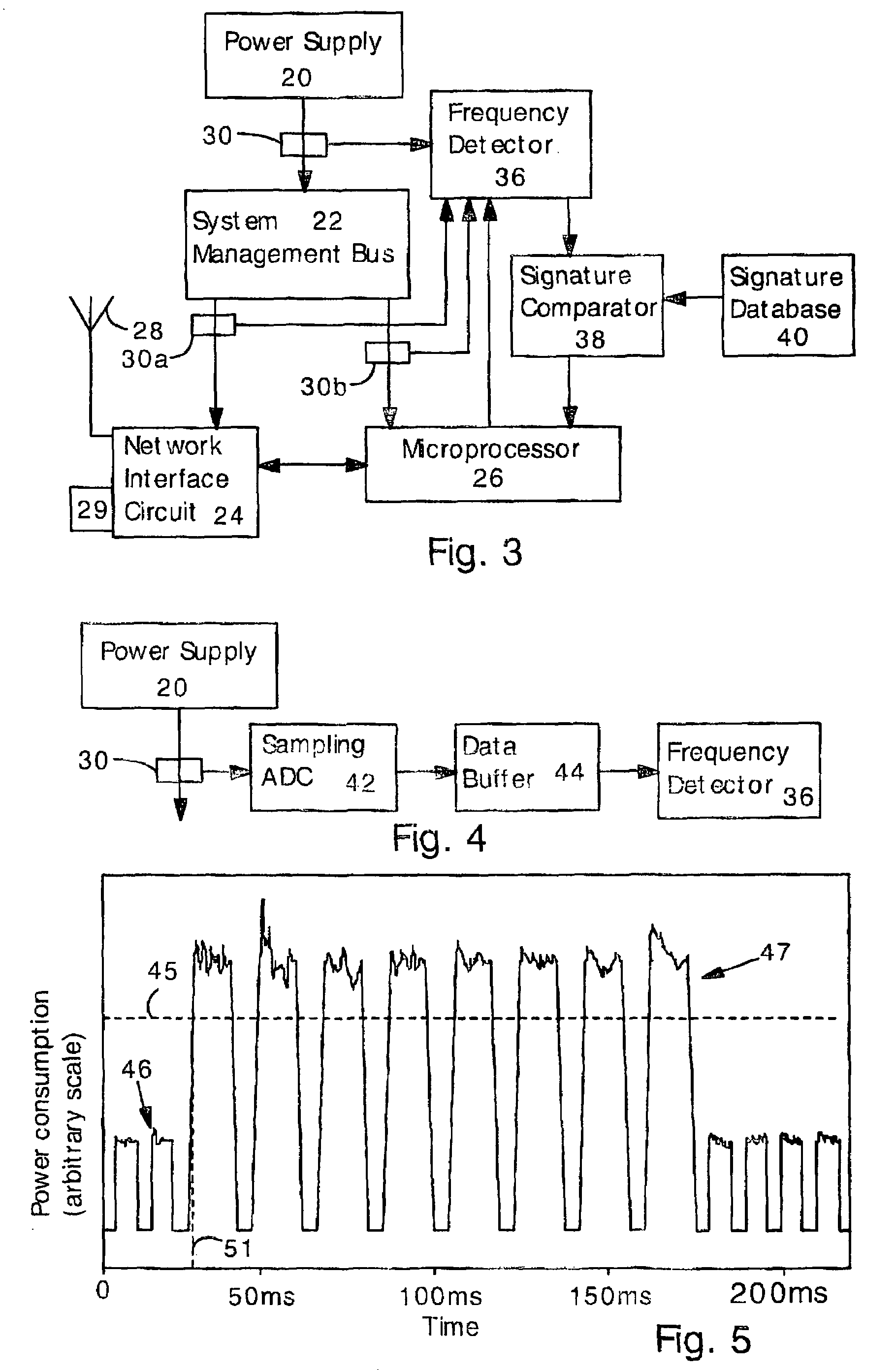
Detecting software attacks by monitoring electric power consumption patterns
ActiveUS7877621B2Reduce the valueMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionFourier transform on finite groupsFrequency matching
Software attacks such as worms and viruses are detected in an electronic device by monitoring power consumption patterns. In a first embodiment, software attacks are detected by an increase in power consumption. The increased power consumption can be caused by increased network traffic, or by increased activity in the microprocessor. Monitoring power consumption is particularly effective for detecting DOS / flooding attacks when the electronic device is in an idle state. In a second embodiment, a power consumption signal is converted to the frequency domain (e.g., by fast Fourier transform). The highest amplitude frequencies are identified. Specific software attacks produce characteristic frequencies in the power consumption signal. Software attacks are therefore detected by matching the highest amplitude frequencies with frequencies associated with specific worms and viruses. Identification of a particular software attack typically requires matching of 3 or more of the highest amplitude frequencies, and, optionally, amplitude information.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
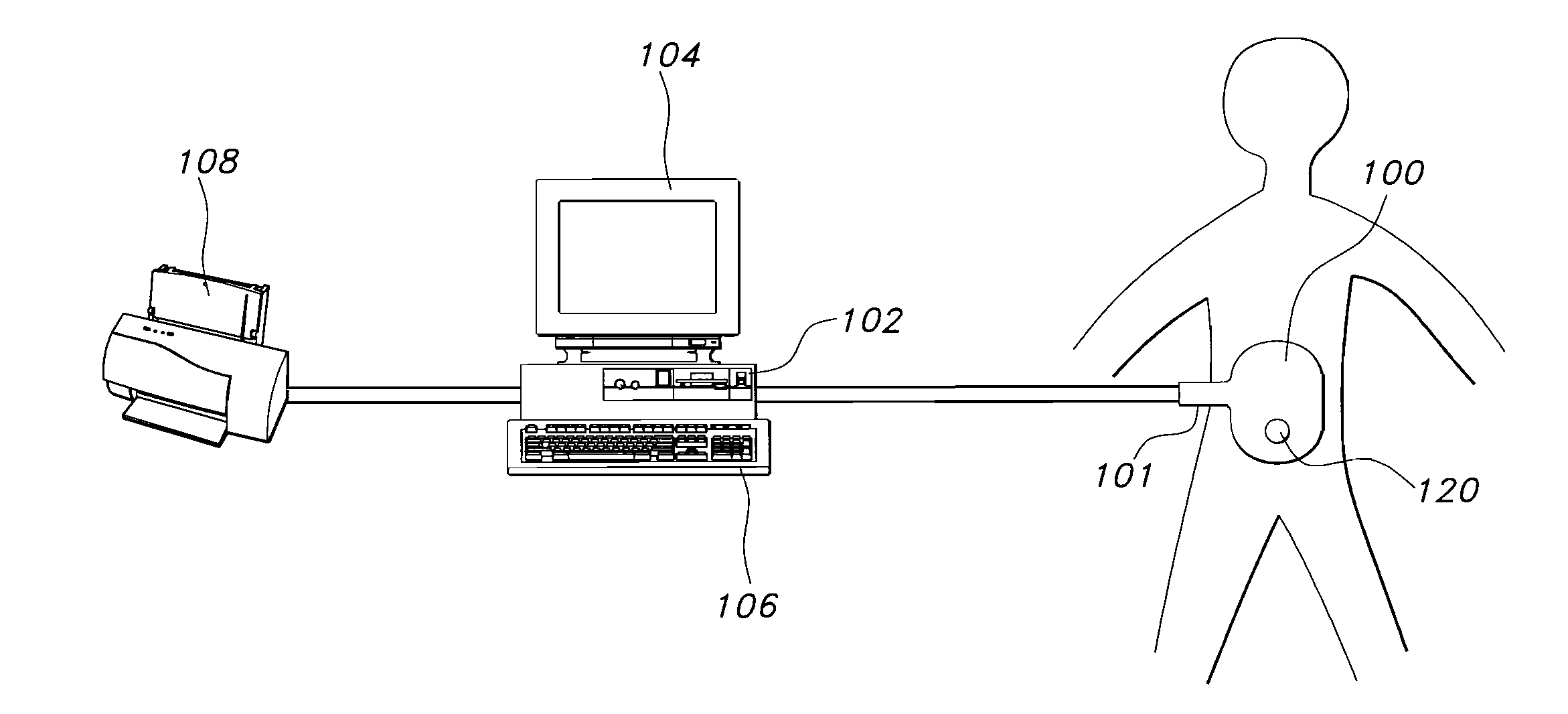
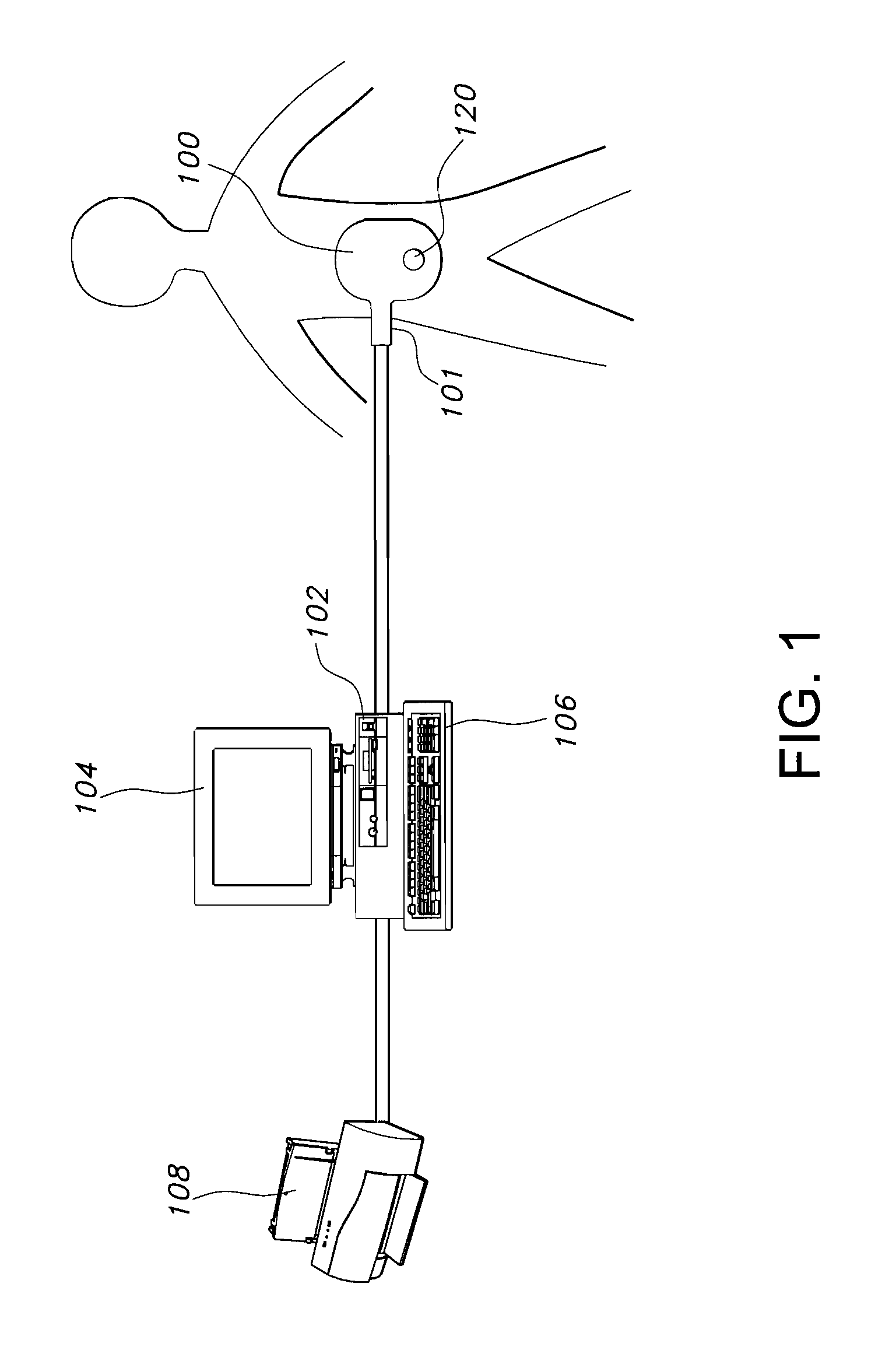
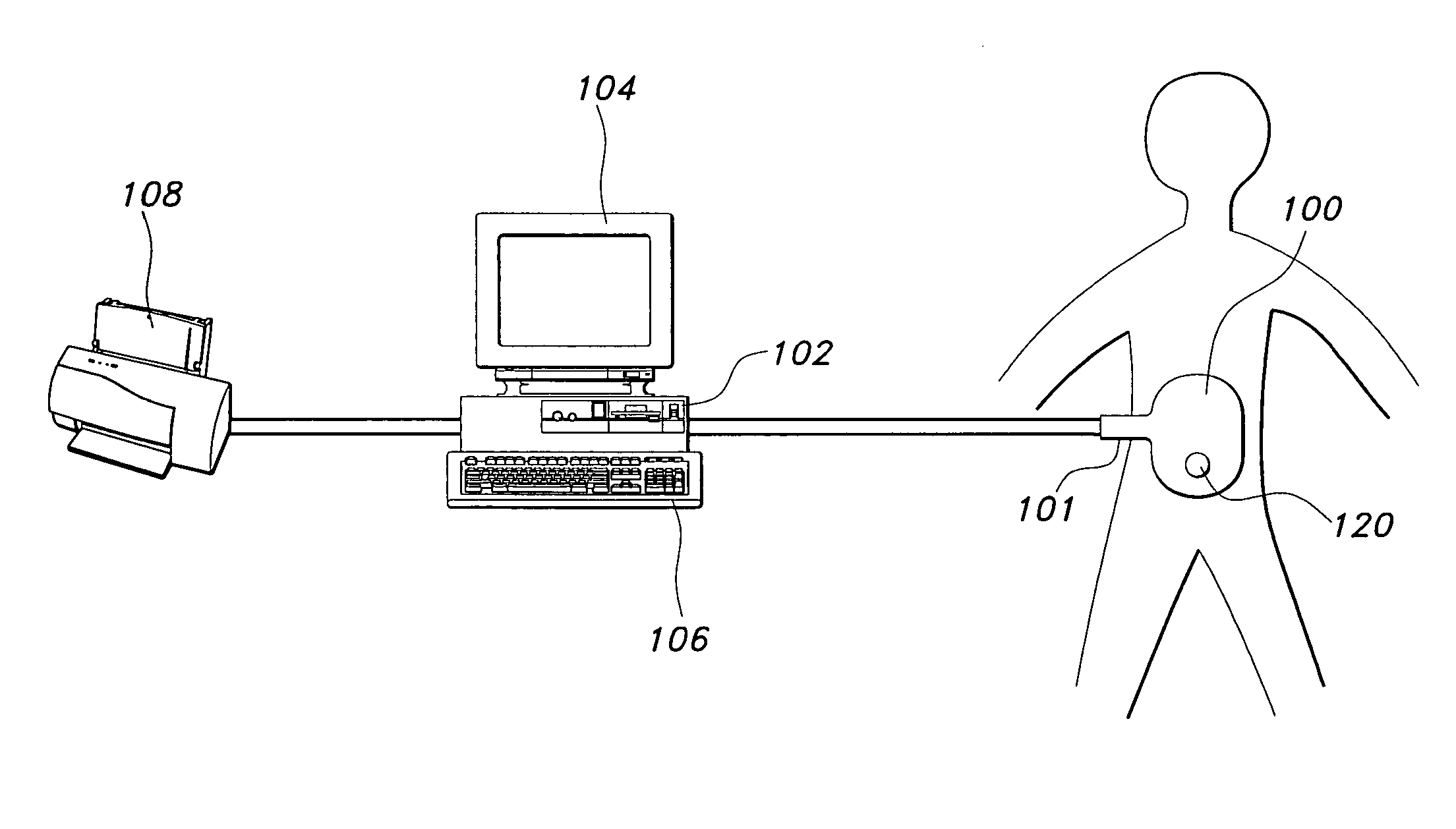
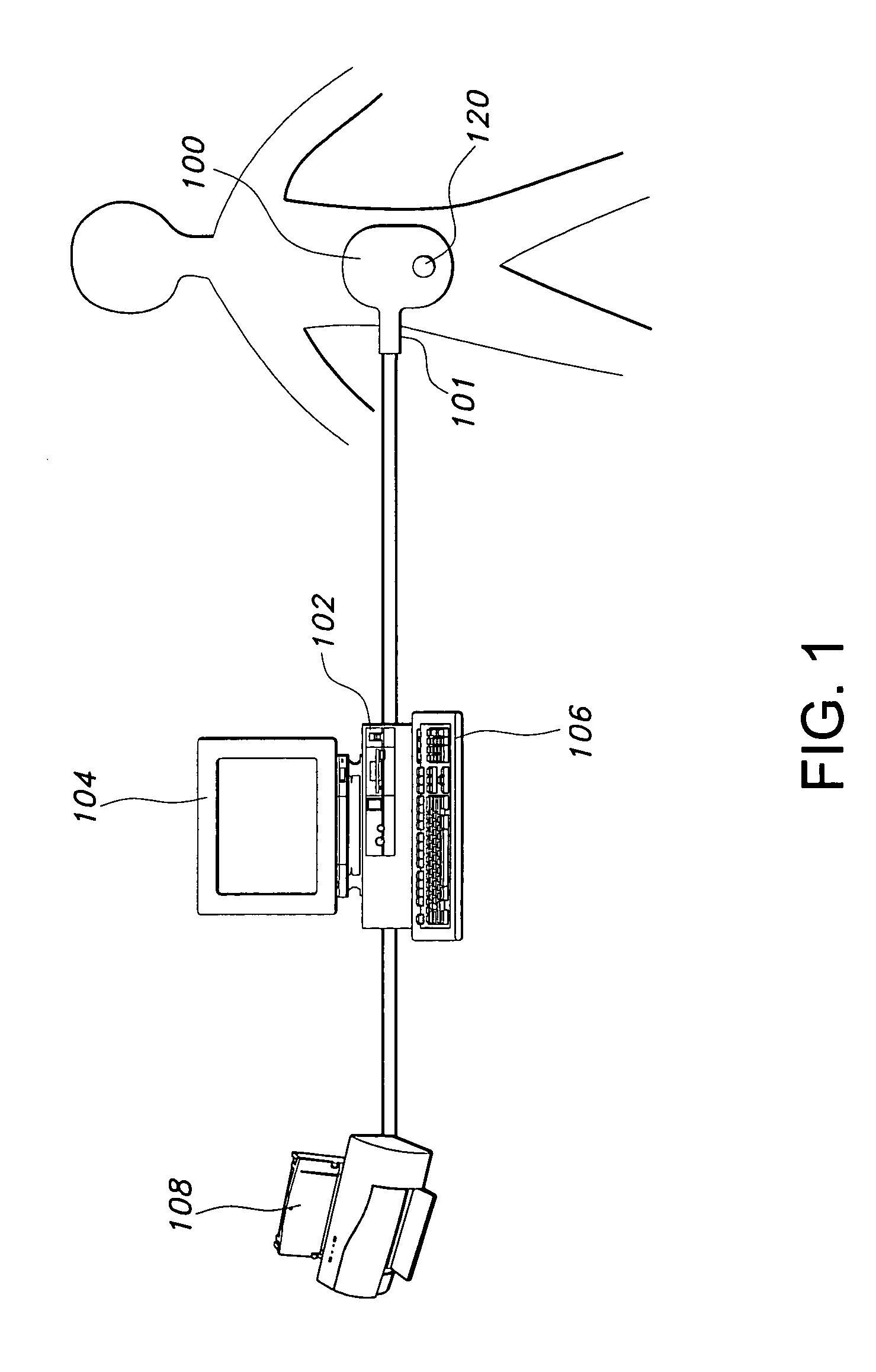
Communicating with an implanted wireless sensor
ActiveUS7439723B2Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingModulated-carrier systemsEndoradiosondesLine sensorRing down
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
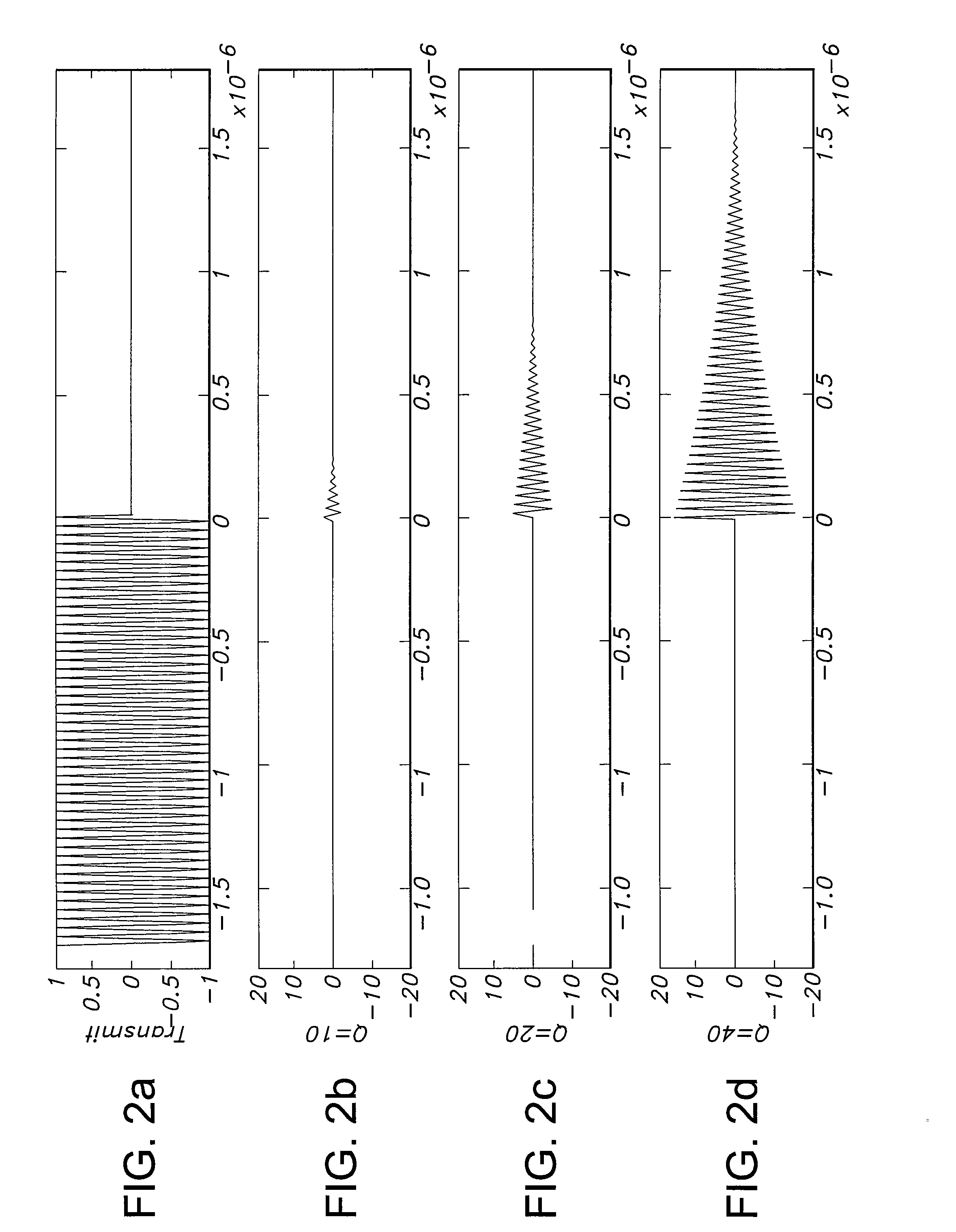
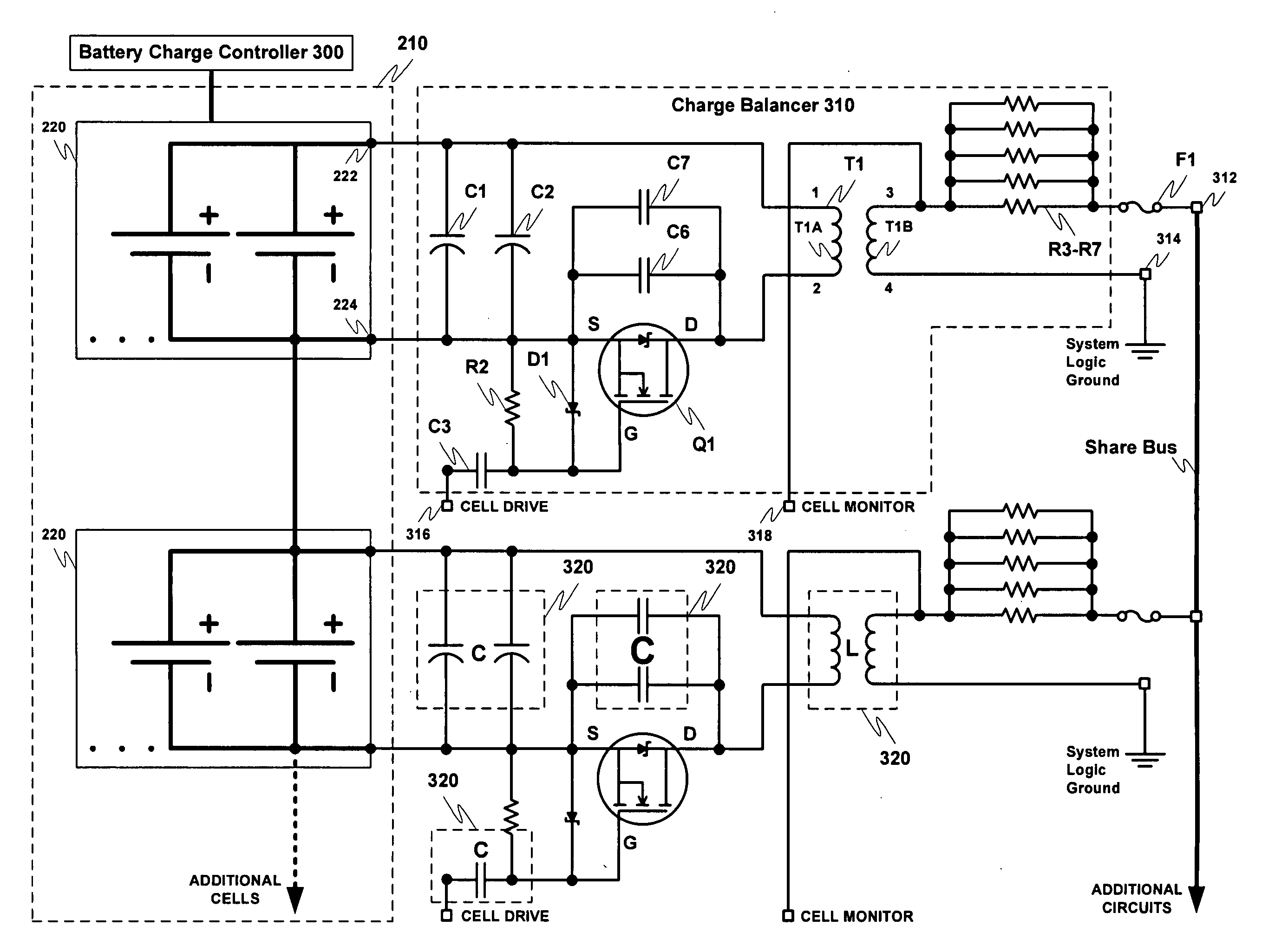
Battery balancing including resonant frequency compensation
ActiveUS20070279003A1Balance levelImprove performanceCharge equalisation circuitEfficient power electronics conversionFrequency compensationFrequency matching
A system for balancing charge between a plurality of storage battery cells within a storage battery. The battery balancing system sense changes, possibly caused by environmental influences, in the overall resonant frequency of charge balancing circuits contained within the battery balancing system. Using a phase locked loop based controller, the battery balancing system compensates for the change in resonant frequency by driving the battery balancing circuits at a frequency that matches the actual sensed resonant frequency of the battery balancing circuits.
Owner:COBHAM ADVANCED ELECTRONICS SOLUTIONS
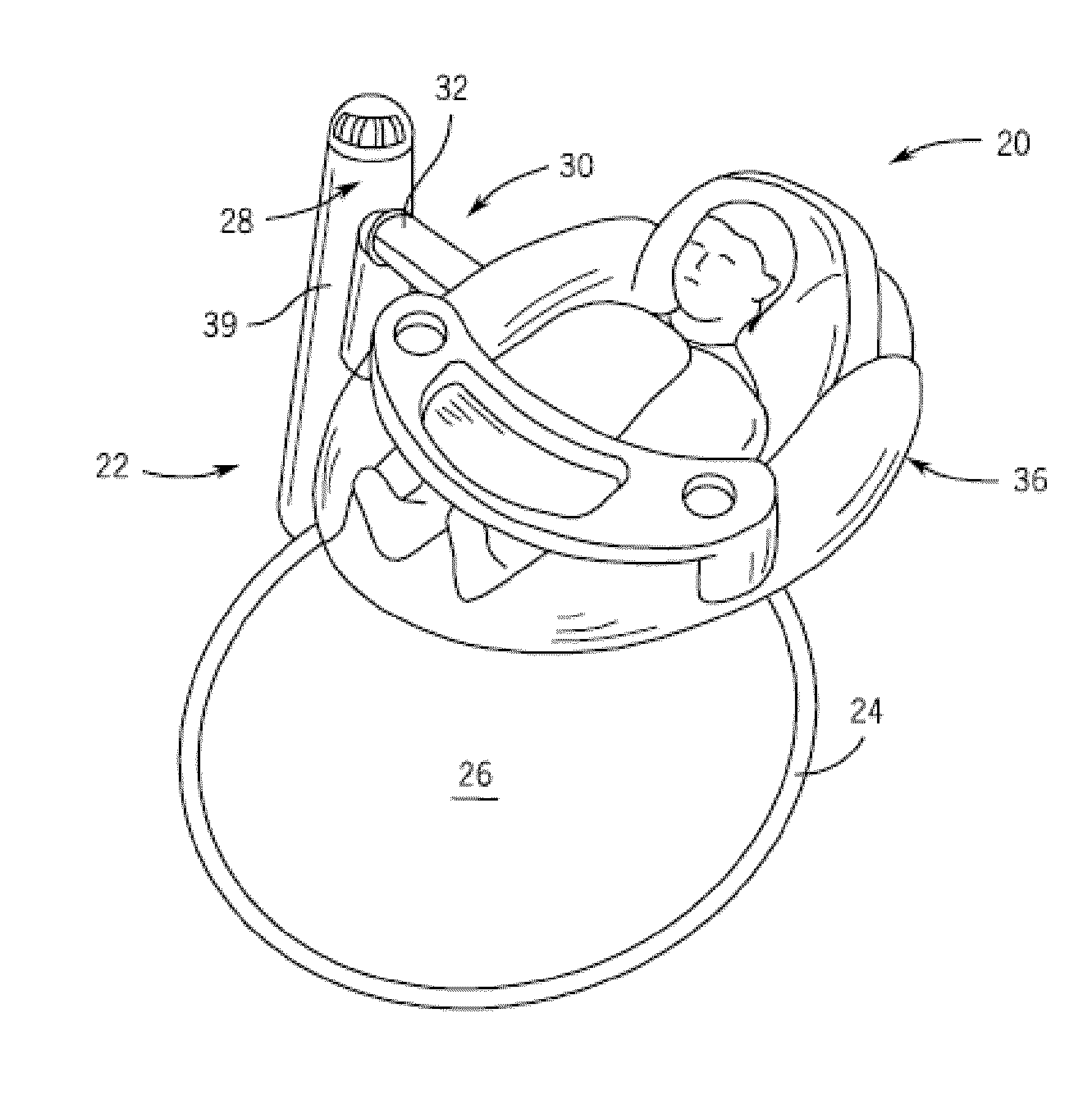
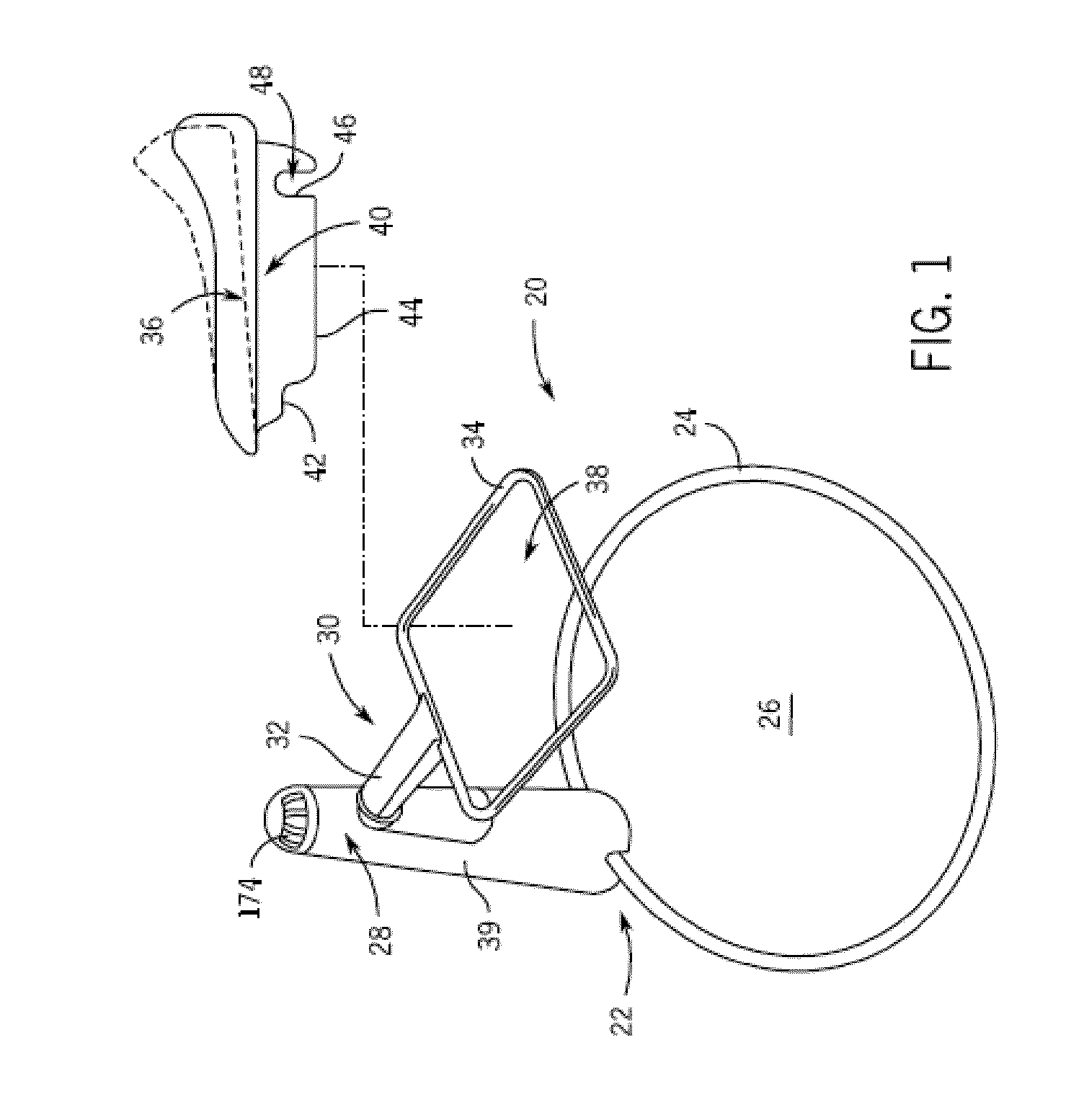
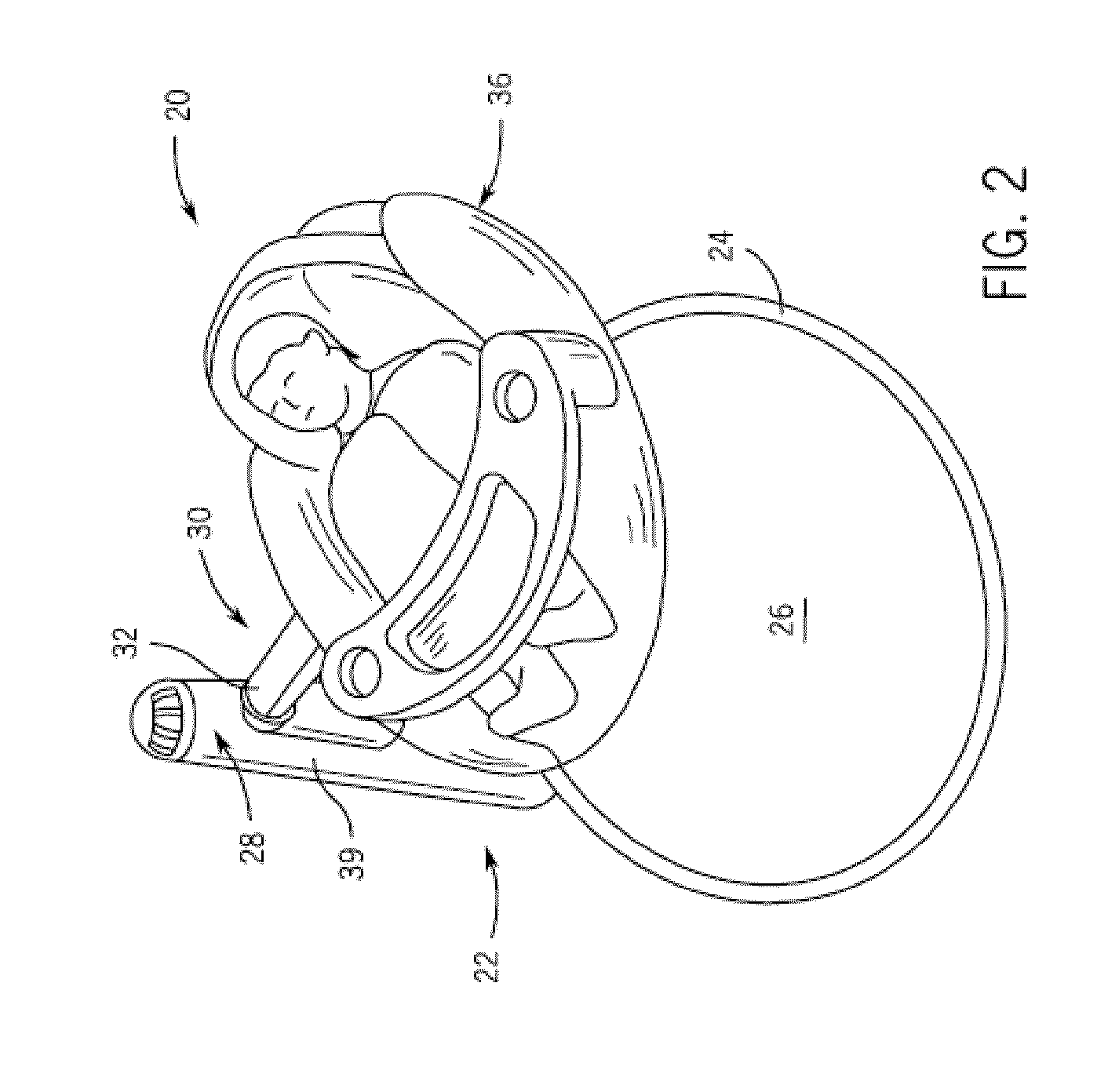
Child Motion Device
ActiveUS20100201171A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlReciprocating motionFrequency matching
A child motion device includes a frame providing a structural support relative to a reference surface and including an arm pivotably coupled to the structural support for reciprocating movement with a resonant frequency, a child supporting device coupled to the arm and spaced from the reference surface by the frame, and a drive system including a motor configured to drive the arm such that the child supporting device reciprocates along a motion path at a frequency matched to the resonant frequency. The drive system is configured to adjust a duty cycle of the motor to control a speed at which the child support device moves along the motion path.
Owner:GRACO CHILDRENS PROD INC
Communicating with an Implanted Wireless Sensor
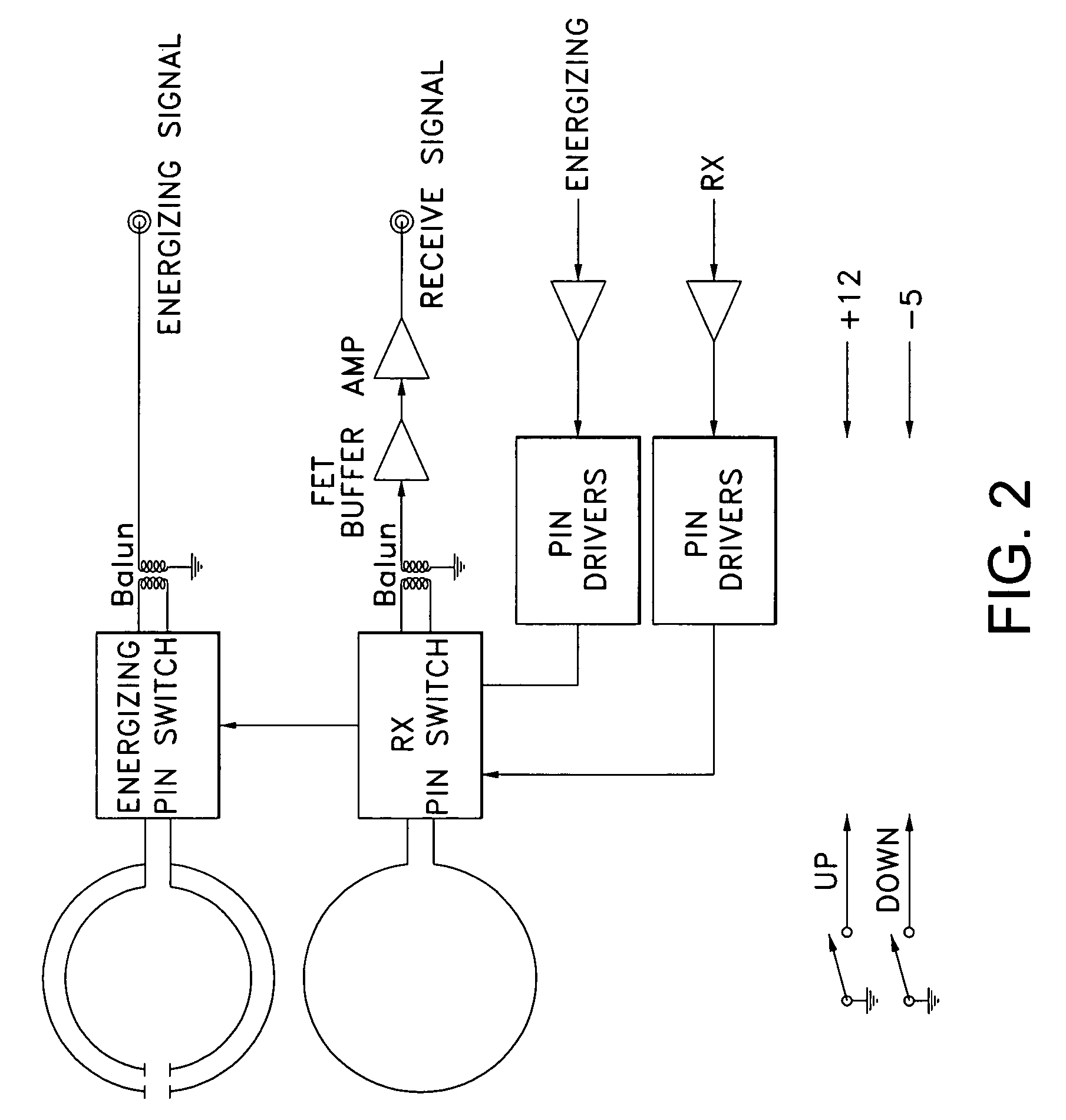
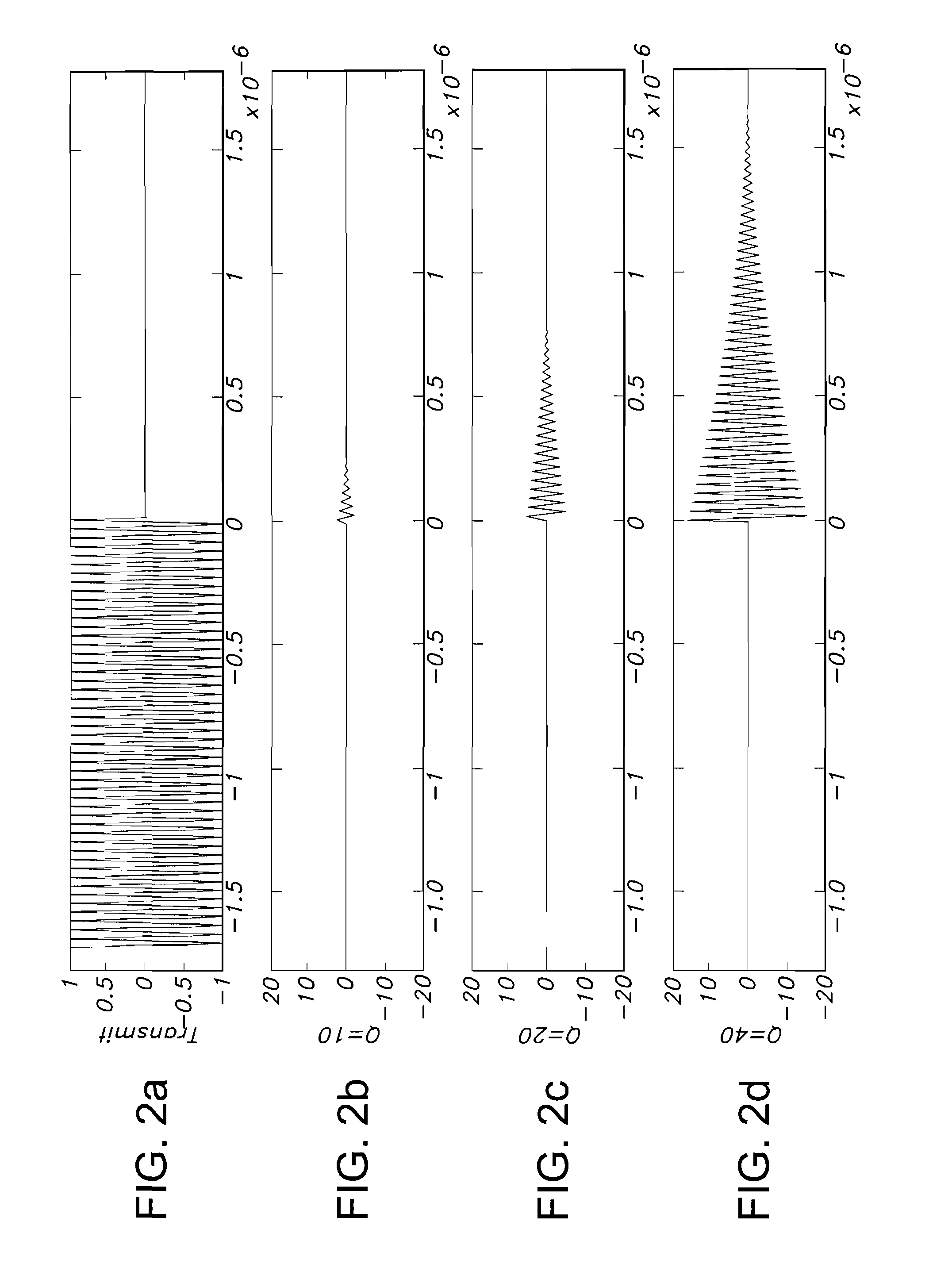
The present invention determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system energizes the sensor with a low duty cycle, gated burst of RF energy having a predetermined frequency or set of frequencies and a predetermined amplitude. The energizing signal is coupled to the sensor via magnetic coupling and induces a current in the sensor which oscillates at the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system receives the ring down response of the sensor via magnetic coupling and determines the resonant frequency of the sensor, which is used to calculate the measured physical parameter. The system uses a pair of phase locked loops to adjust the phase and the frequency of the energizing signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Coupling loop and method for positioning coupling loop
ActiveUS20060244465A1Avoid breakingIncrease opportunitiesCoaxial cables/analogue cablesNear-field transmissionCouplingFrequency matching
A coupling loop or antenna is provided that can be used with a system that determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The coupling loop includes multiple loops. Preferably two tuned loops are used for transmitting the energizing signal to the sensor and an un-tuned loop is used for receiving the sensor signal from the sensor. Orientation features on the housing for the coupling loop and the sensor are provided to assist in positioning the coupling loop relative to the sensor to maximize the coupling between the sensor signal and the coupling loop.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
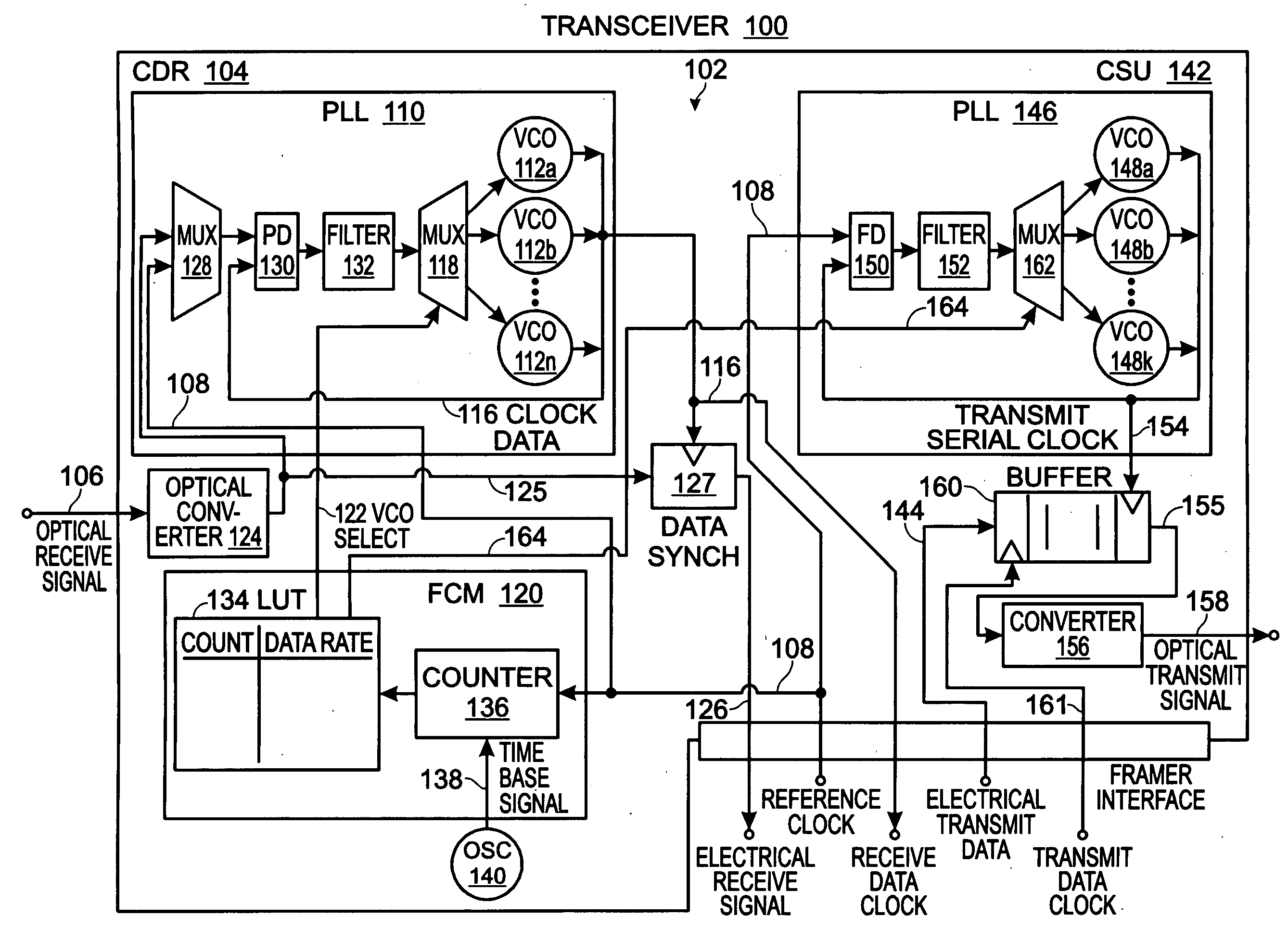
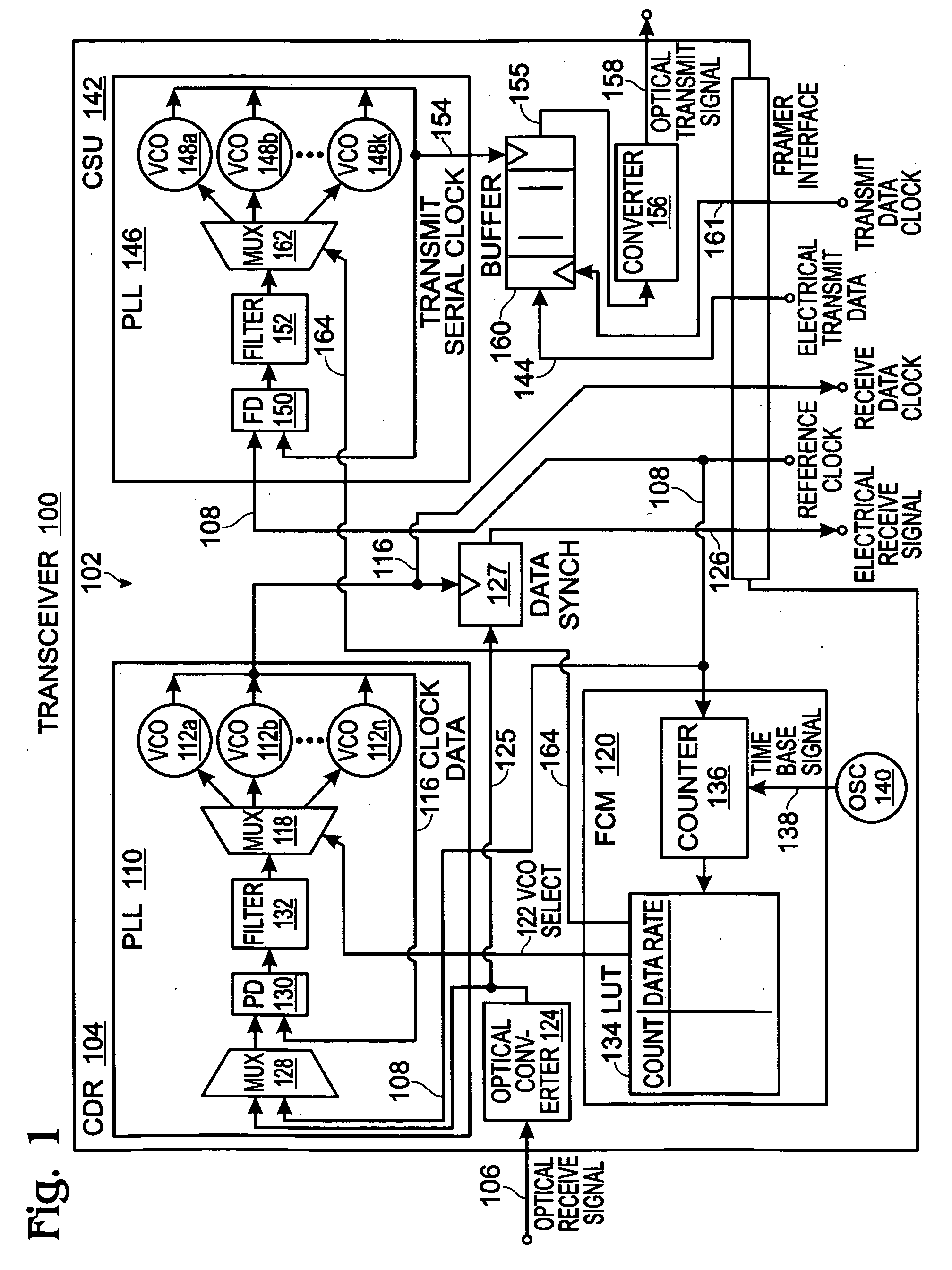
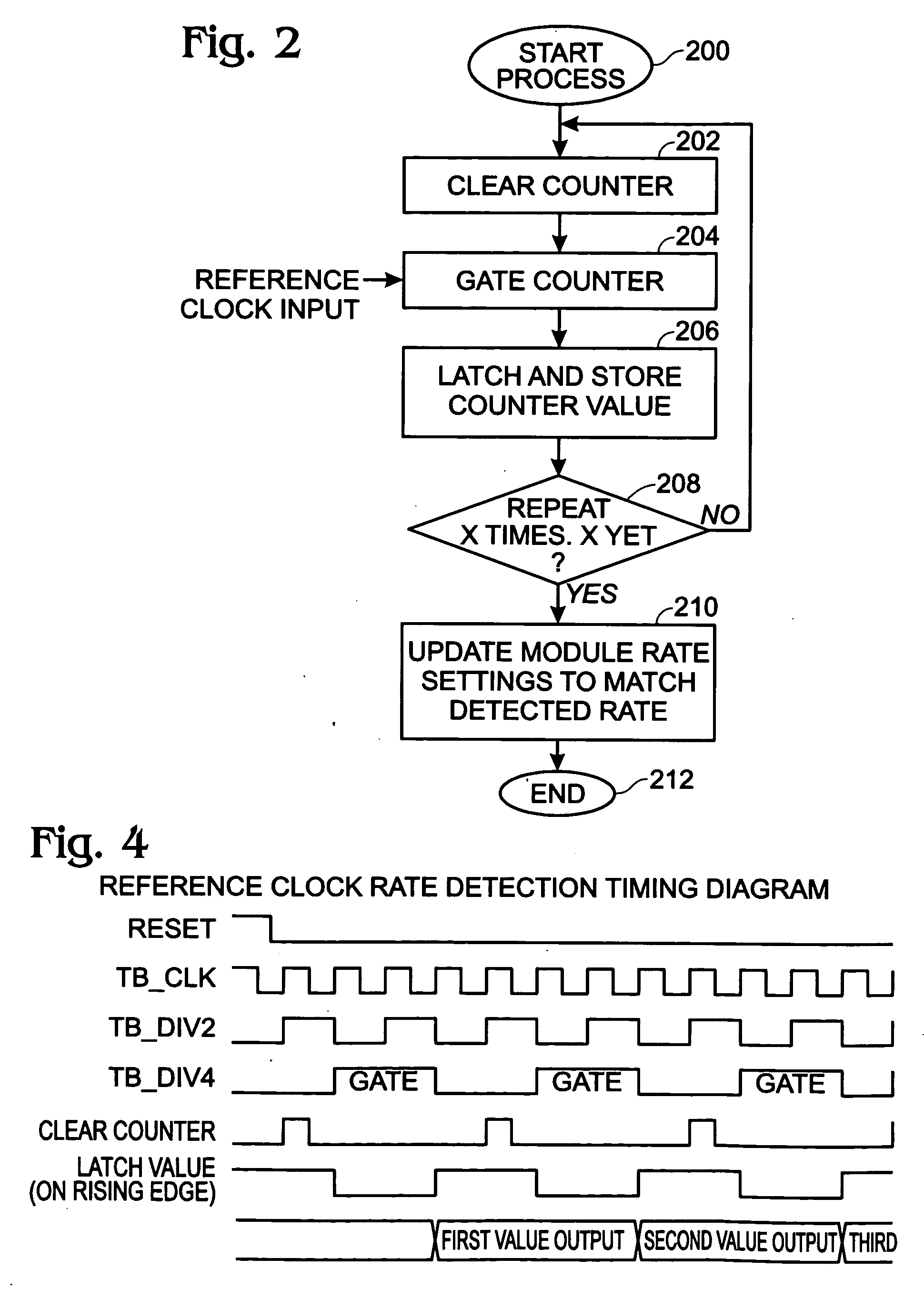
Reference Clock Rate Detection for Variable Rate Transceiver Modules
InactiveUS20100142967A1Eliminate human interventionModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransceiverClock rate
A system and method are provided for determining an optical signal frequency range in an optical / electrical transceiver. The method receives an optical receive signal having a non-predetermined data rate via a network interface, and also receives an electrical reference clock signal having a non-predetermined frequency via a framer interface. The reference clock signal frequency is cross-referenced to an optical receive signal frequency. In one aspect a clock and data recovery (CDR) voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) is selected having an output frequency matching the cross-referenced optical receive signal frequency. The optical receive signal is converted to an electrical receive signal. Initially, the VCO is frequency-locked to the reference clock. Subsequent to frequency-locking the VCO output frequency, the converted optical signal is phase-locked, generating a receive data clock. The CDR supplies a converted optical receive signal and receive data clock to the framer interface.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Communicating with an Implanted Wireless Sensor
ActiveUS20070096715A1Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingResistance/reactance/impedenceEndoradiosondesLine sensorRing down
The present invention determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system energizes the sensor with a low duty cycle, gated burst of RF energy having a predetermined frequency or set of frequencies and a predetermined amplitude. The energizing signal is coupled to the sensor via magnetic coupling and induces a current in the sensor which oscillates at the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system receives the ring down response of the sensor via magnetic coupling and determines the resonant frequency of the sensor, which is used to calculate the measured physical parameter. The system uses a pair of phase locked loops to adjust the phase and the frequency of the energizing signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
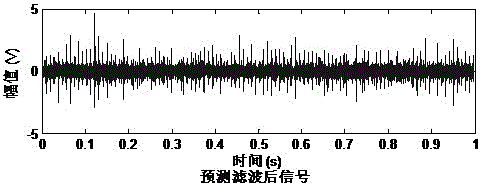
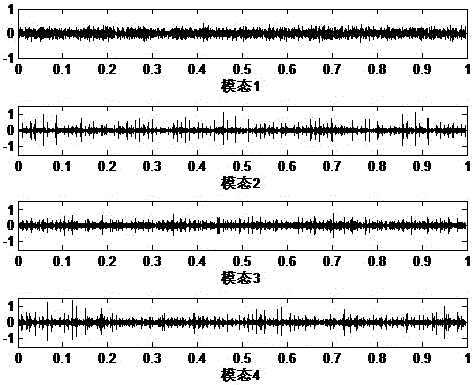
Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on variational mode decomposition
InactiveCN106017926ASuppress spectral noiseOptimal predictive filter orderMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency matchingVariational mode decomposition
The invention discloses a rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on variational mode decomposition, which is used to analyze a rolling bearing fault based on a vibration signal. First, fault information enhancement processing is performed on a signal collected by a sensor using a predictive filtering method; then, variational mode decomposition is performed on the filtered signal to get four modes; next, a mode most relevant to a rolling bearing fault is selected according to a fault information index; and finally, an envelope autocorrelation spectrum analysis of the filtered signal is made, and fault characteristic frequency matching is performed to get fault information.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
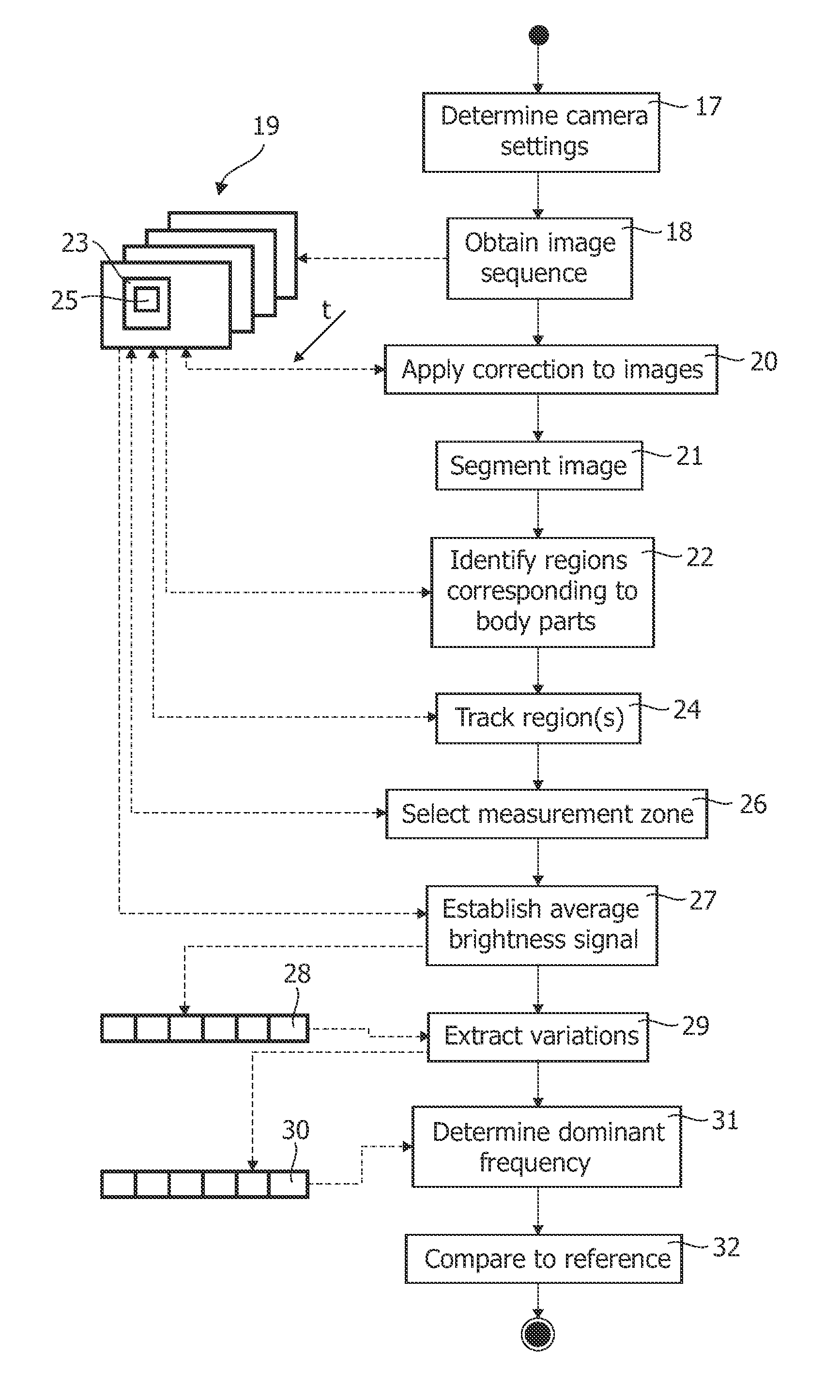
Method of controlling a function of a device and system for detecting the presence of a living being
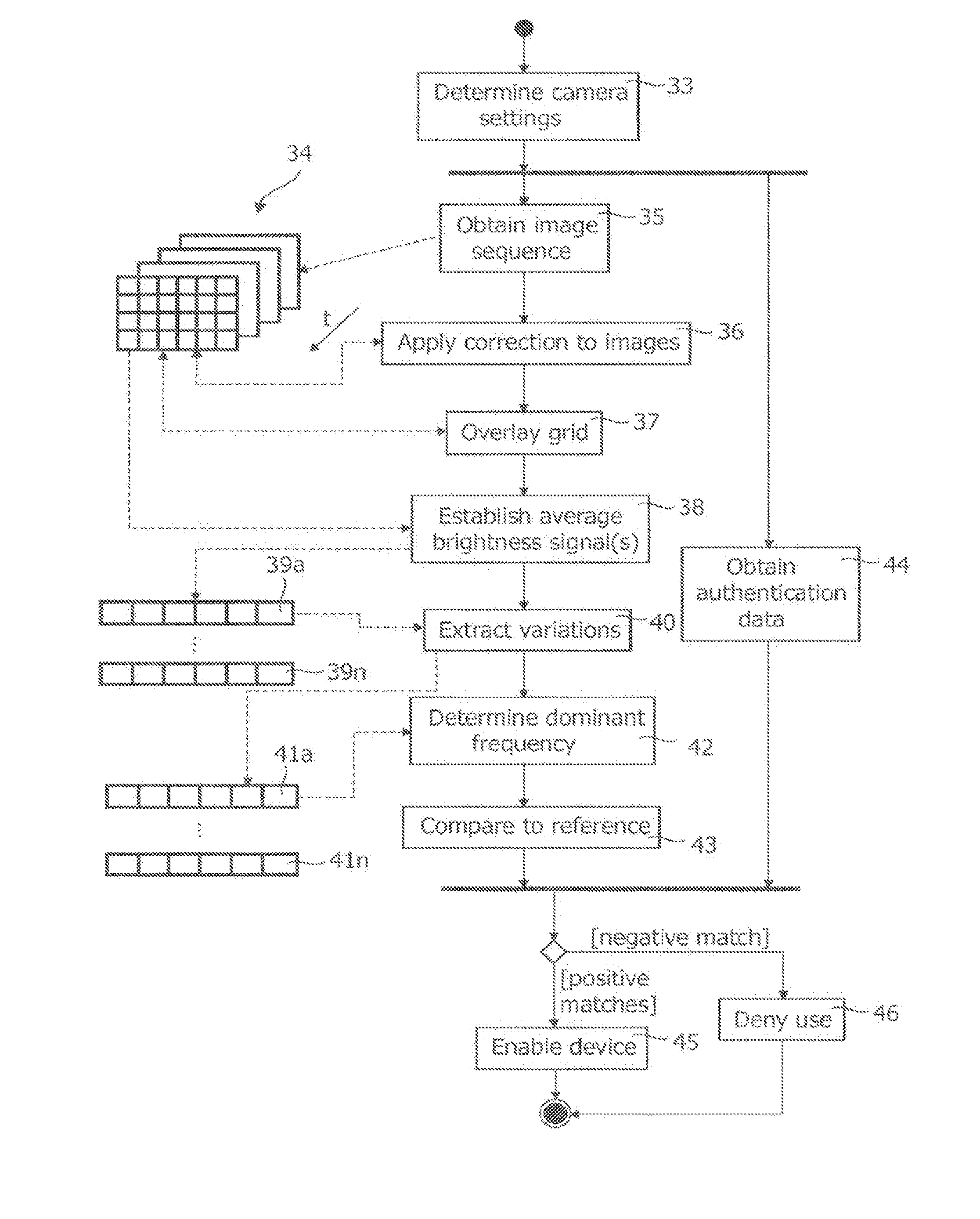
InactiveUS20110311143A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSufficient degree of accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumFrequency matching
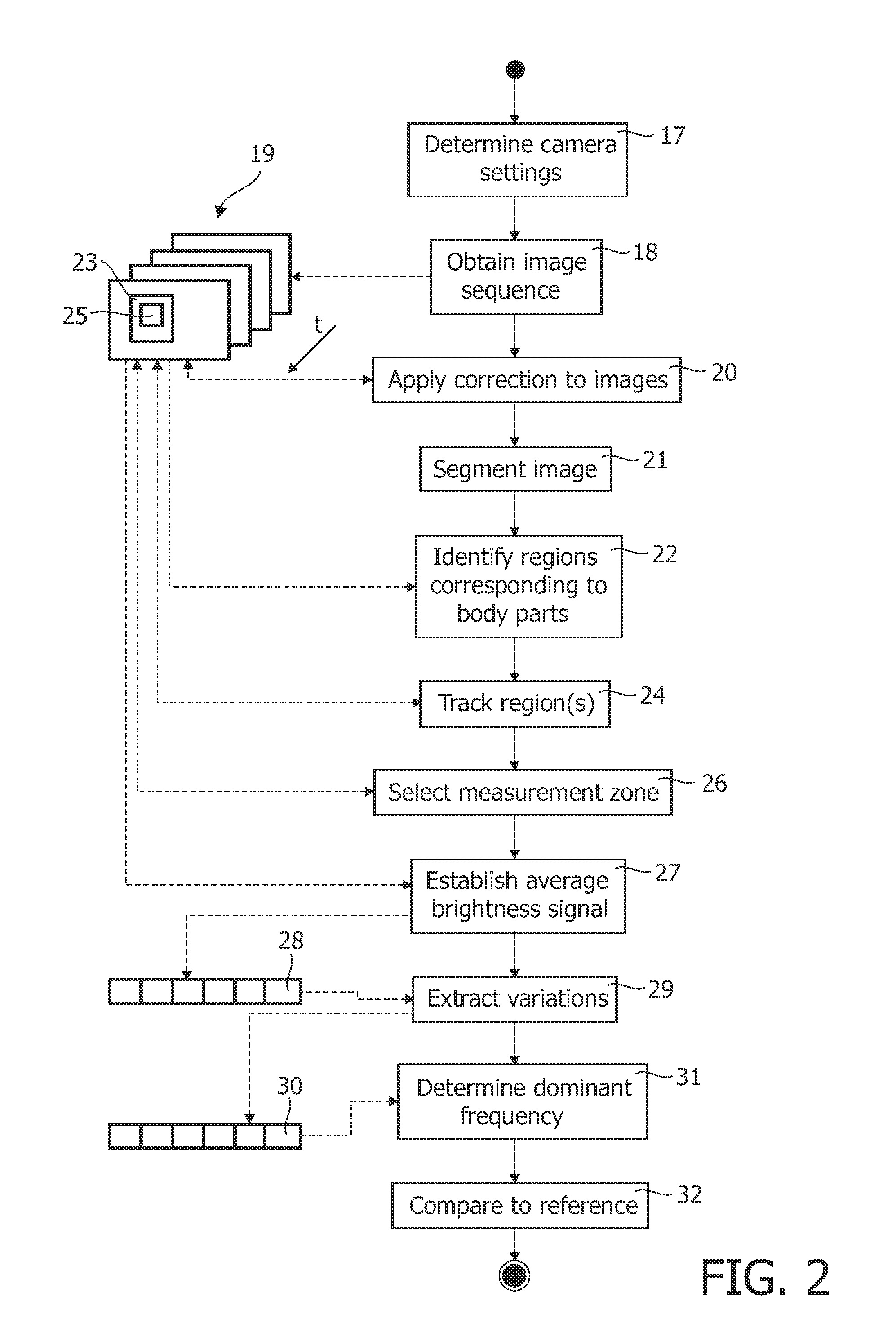
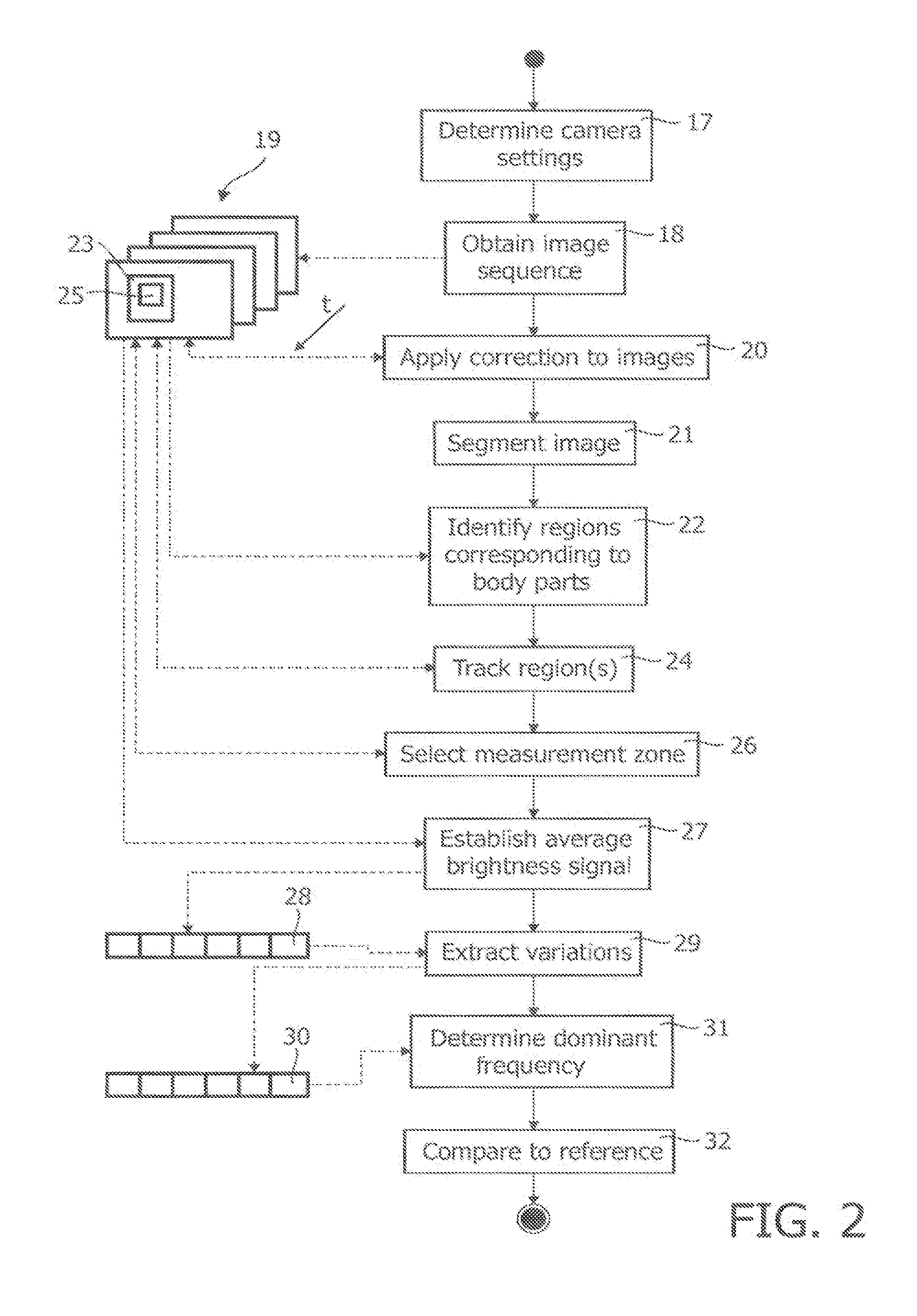
A method of controlling a function of a device, includes obtaining a sequence (19;34;48) of digital images taken at consecutive points in time. At least one measurement zone (25) including a plurality of image points is selected. For at least one measurement zone (25), a signal (30;41;55) representative of at least variations in a time-varying value of a combination of pixel values at least a number of the image points is obtained and at least one characteristic of the signal (30;41;55) within at least a range of interest of its spectrum relative to comparison data is determined. The determination comprises at least one of: (i) determining whether the signal (30;41;55) has a spectrum with a local maximum at a frequency matching a comparison frequency to a certain accuracy; and (ii) determining whether at least a certain frequency component of the signal (30;41;55) is in phase with a comparison signal to a certain accuracy. The function is controlled in dependence on whether the determination is positive.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Smartcards, RFID devices, wearables and methods
ActiveUS20180123221A1Improve performanceImprove the coupling effectAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsCapacitanceDiamond-like carbon
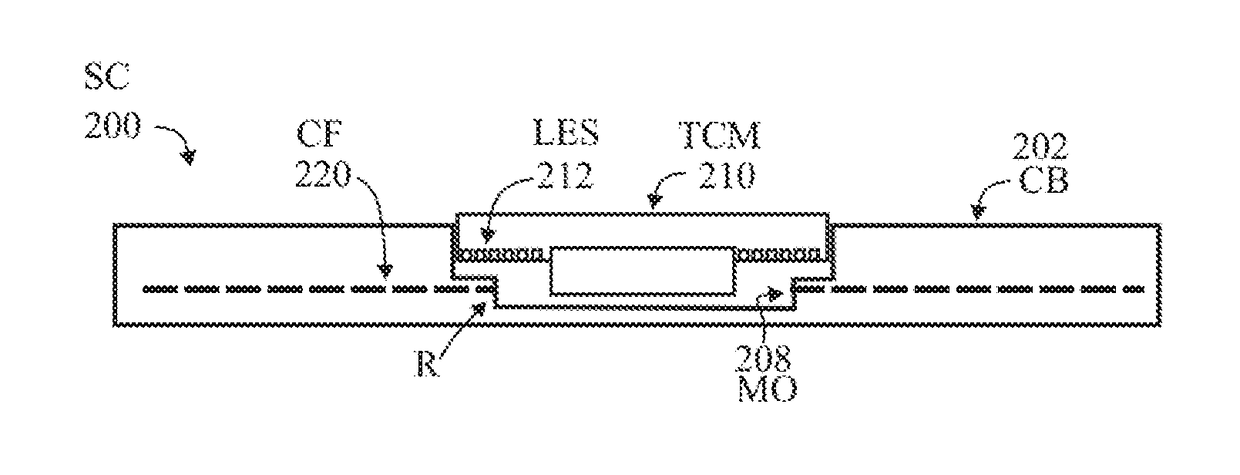
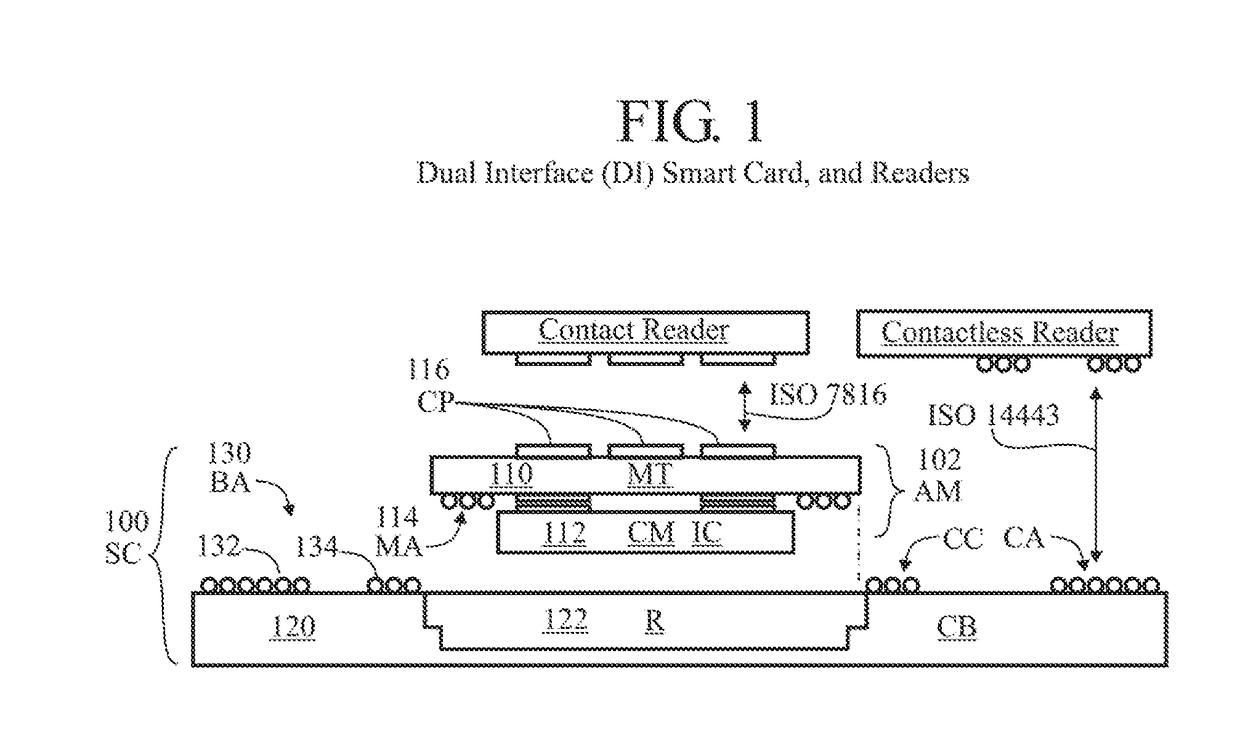
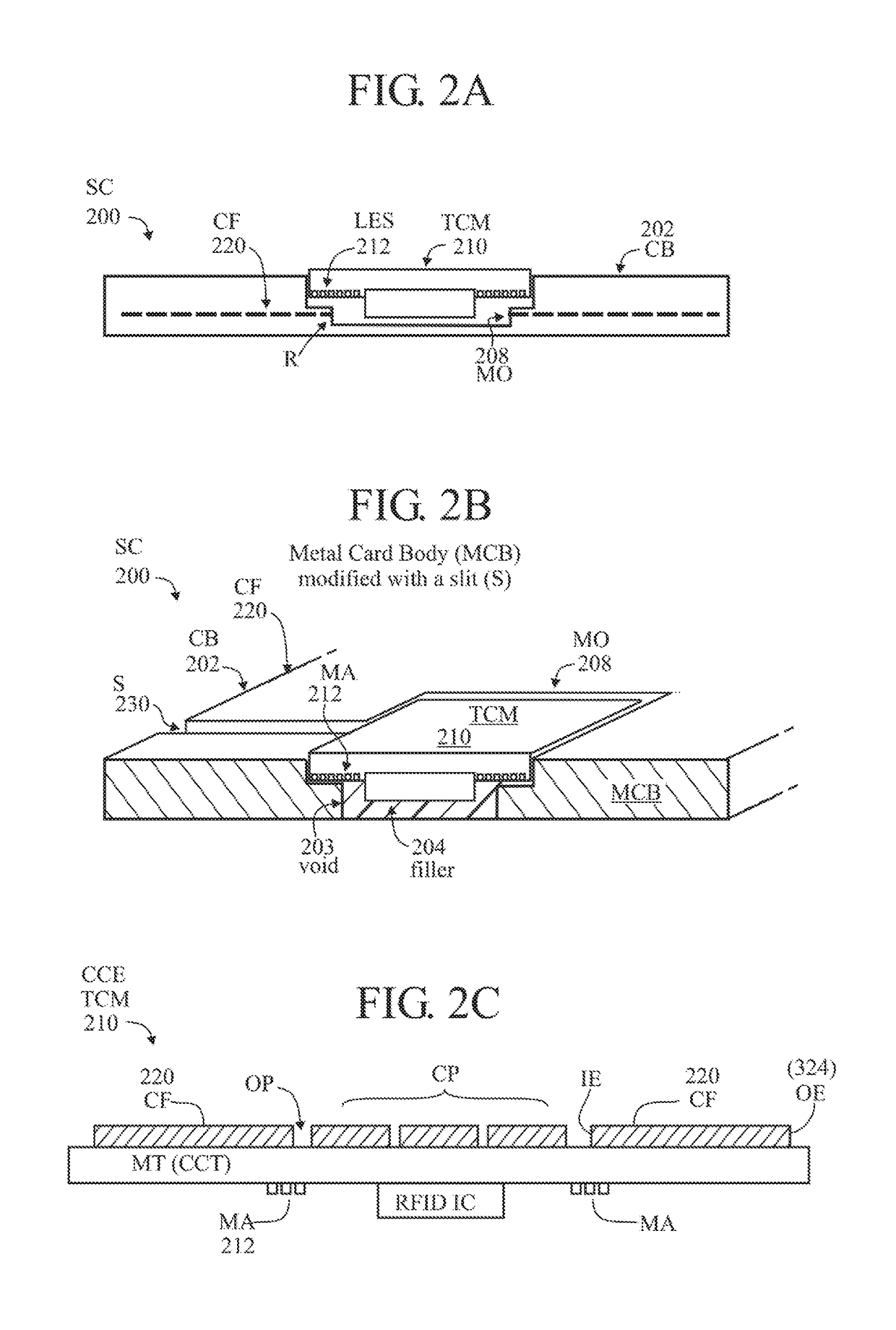
Coupling frames comprising a conductive (metal) surface with a slit (S) or non-conductive stripe (NCS) extending from an outer edge to an inner position thereof, and overlapping a transponder device. A coupling frame with slit for coupling with an inductive or capacitive device (inductor or capacitor) may be used at any ISM frequency band to concentrate surface current around the slit. The coupling frame can be tuned to operate at a frequency of interested by introducing a resistive, inductive or capacitive element. The resonance frequency of the coupling frame can be matched to that of the transponder chip module to achieve optimum performance. Coupling frames with or without a transponder device may be integrated, overlapping, stacked or placed adjacent to one another to enhance system performance. Multiple coupling frames may be electrically isolated from one another by the application of a dielectric coating such Diamond Like Carbon (DLC).
Owner:AMATECH GRP LTD
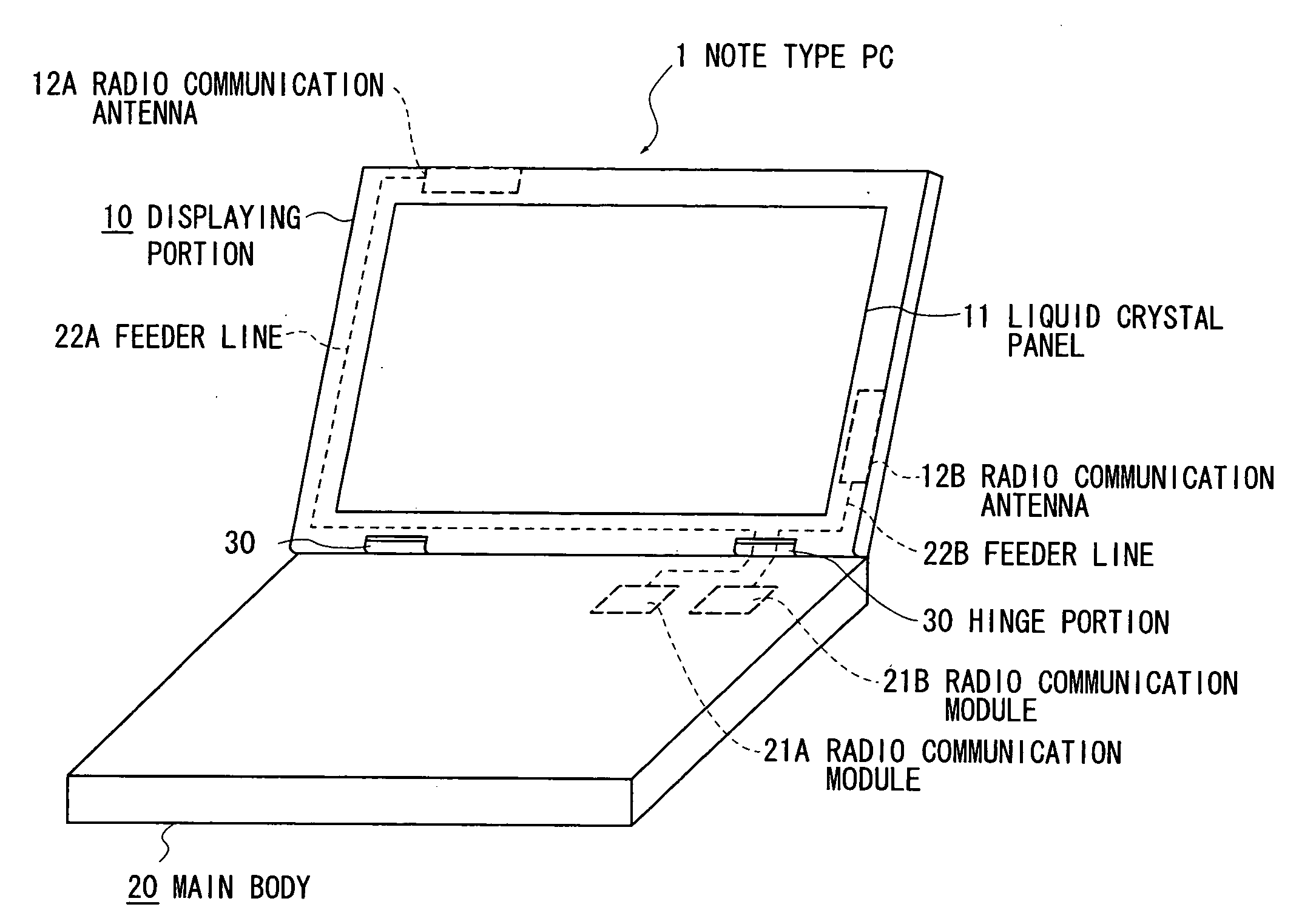
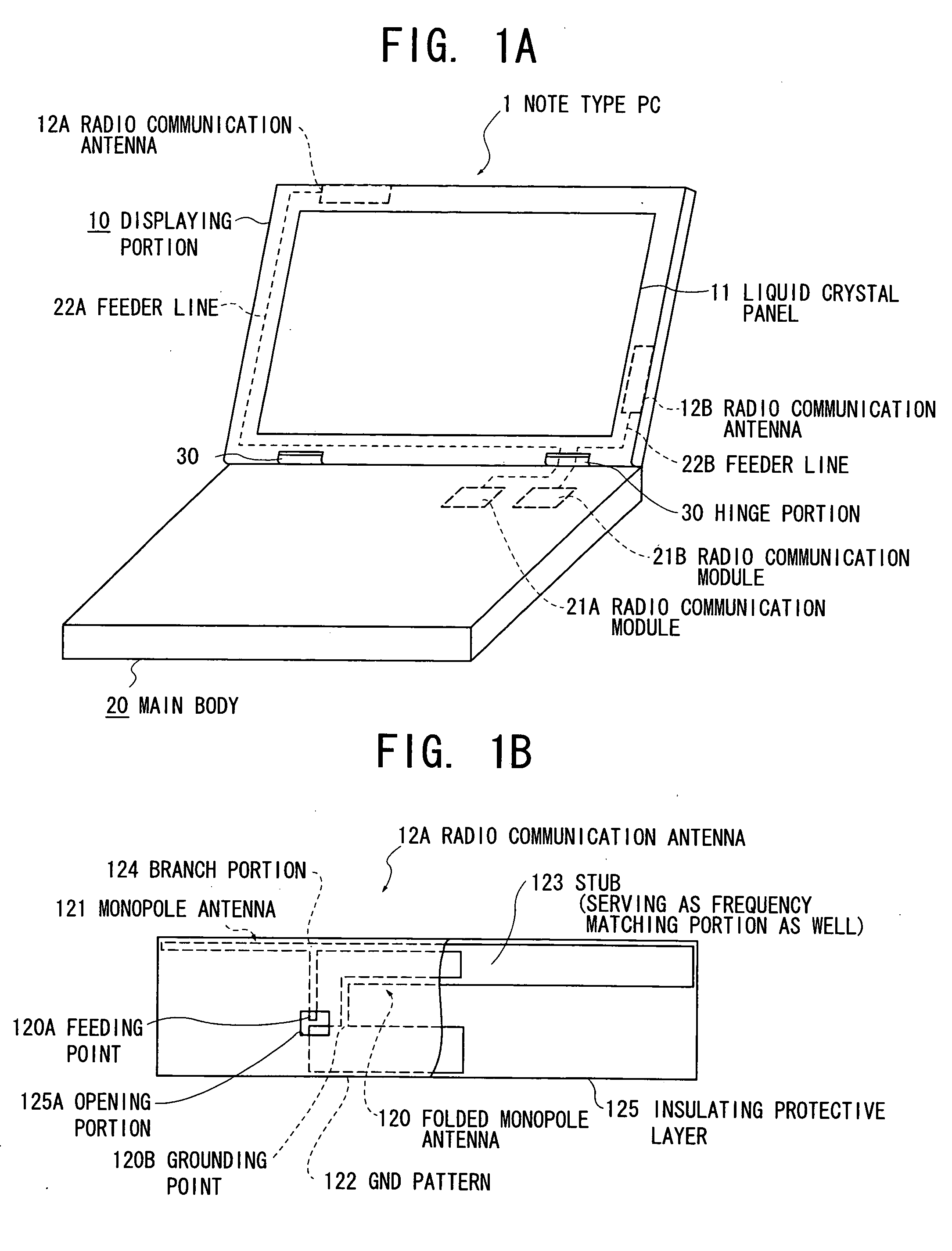
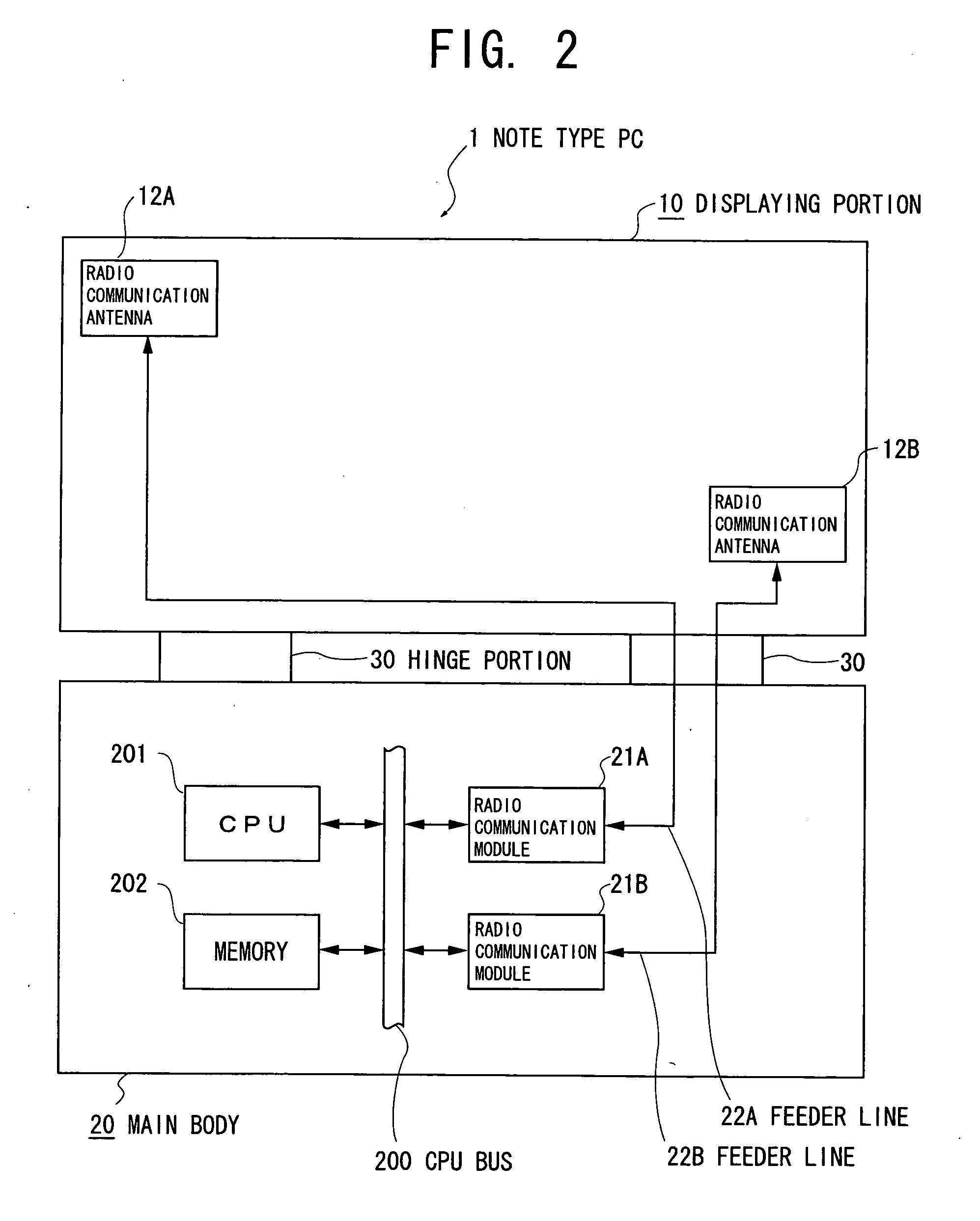
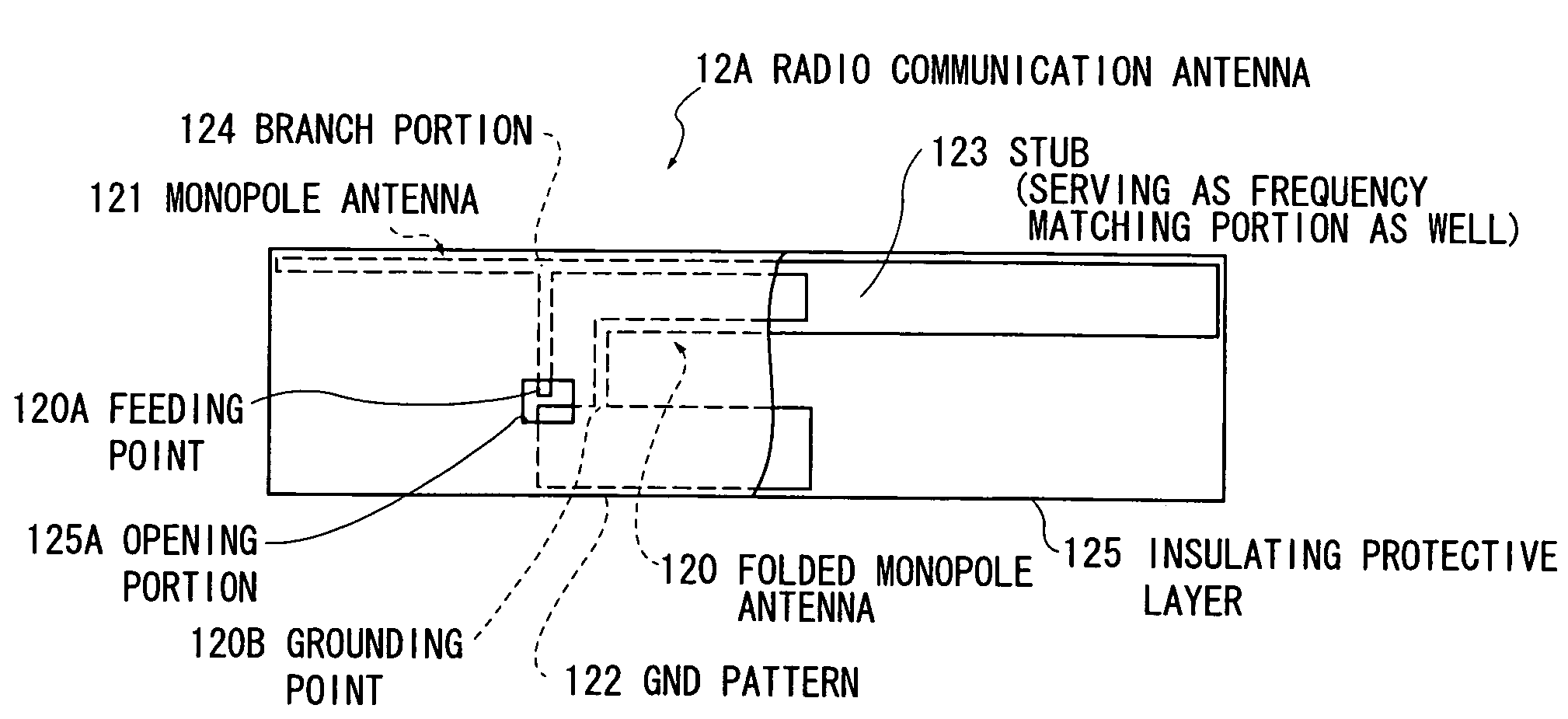
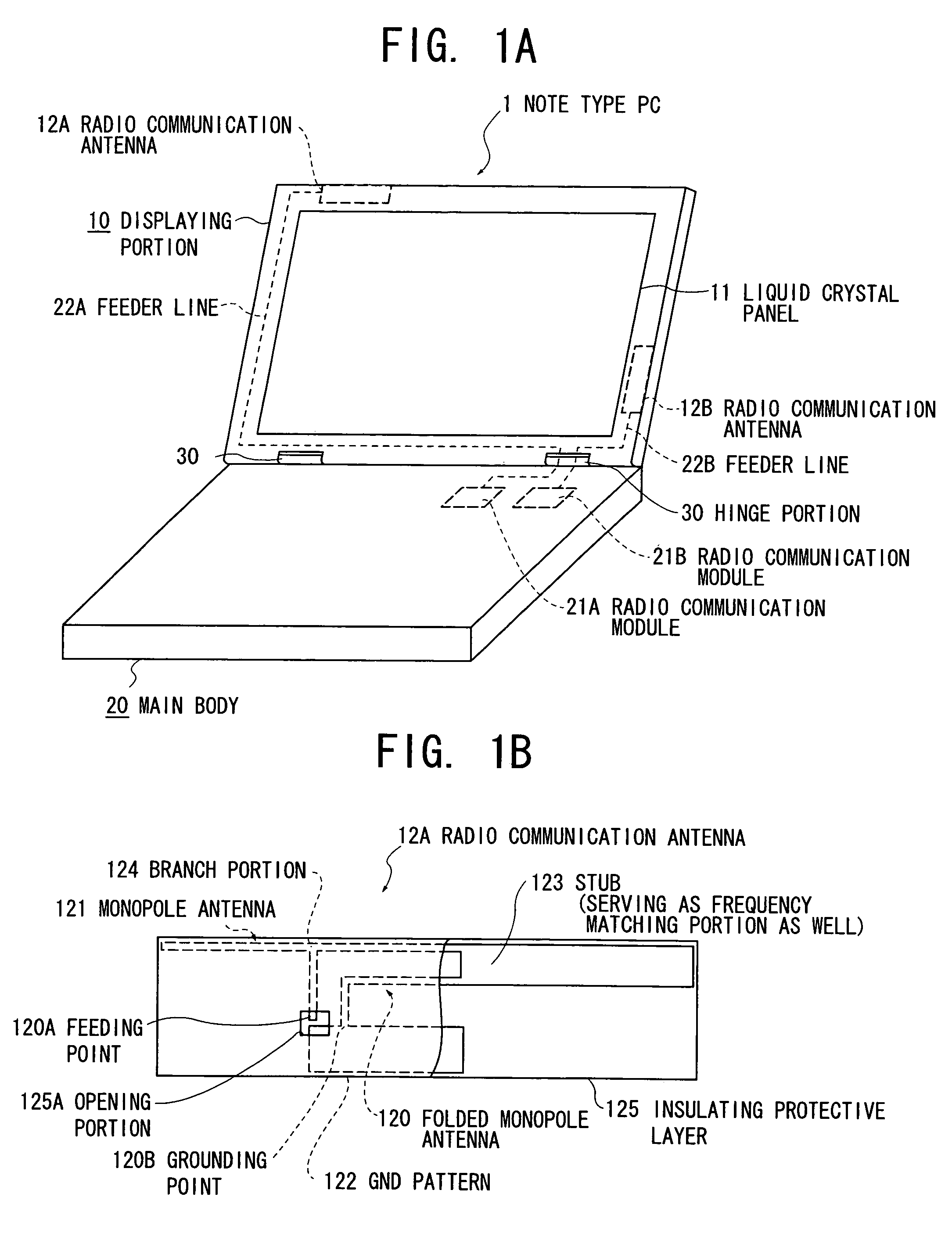
Radio device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20070115188A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMonopole antennaFrequency matching
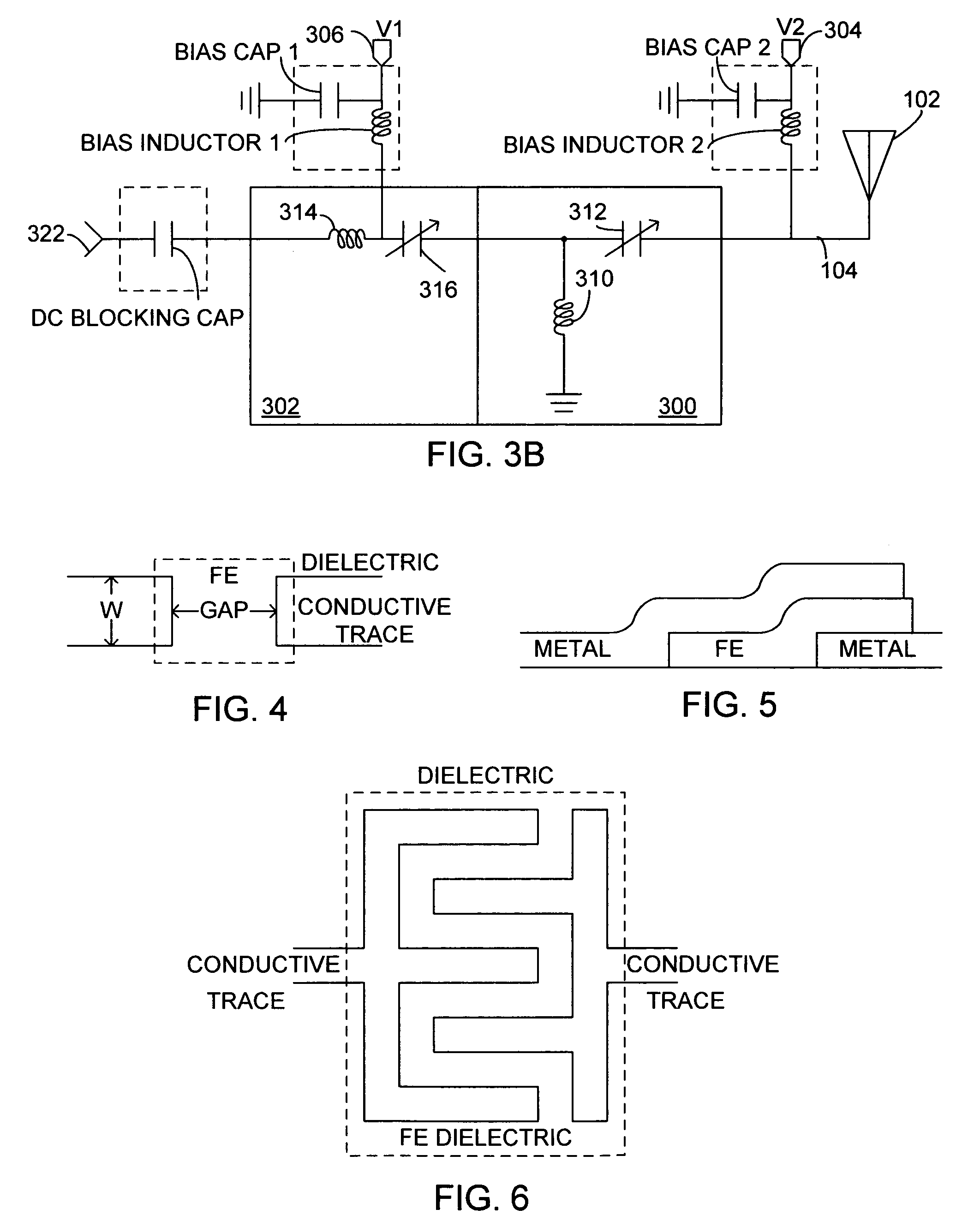
The invention provides a radio device in which multi-resonance promotion and impedance adjustment can be readily performed and a restriction in a mounting space can be dissolved, and an electronic apparatus having the same installed therein. Provision of a stub (123) having a large area and serving as a frequency matching portion as well in a folded monopole antenna (120) results in that a conductor area can be increased, and a resonance frequency can be shifted to lower frequencies. In addition, a frequency of a radio communication antenna can be readily adjusted because the resonance frequency is adjusted by cutting the stub (123).
Owner:TOSHIBA CLIENT SOLUTIONS CO LTD
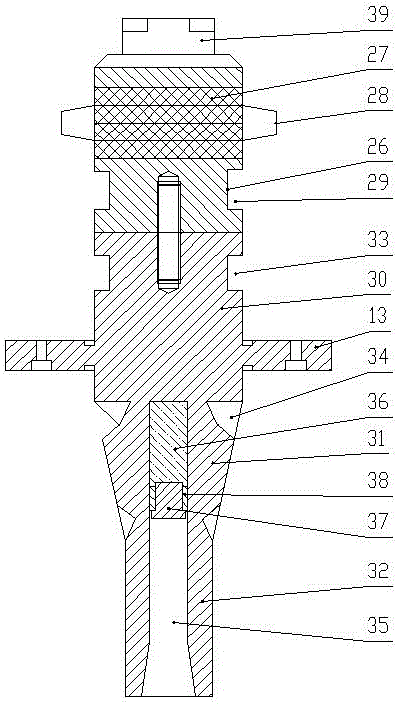
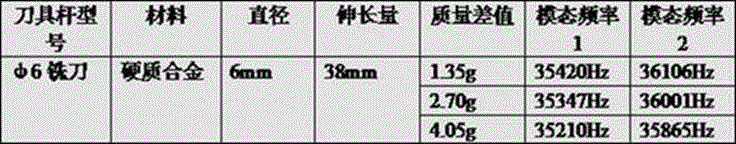
General frequency matching longitudinal-torsional compound ultrasonic vibration milling and drilling device
The invention discloses a general frequency matching longitudinal-torsional compound ultrasonic vibration milling and drilling device. The device comprises a machine tool main shaft, a main shaft shell, an ultrasonic power supply, an ultrasonic wireless electric energy transmission system, a mounting cylinder, a sleeve, a longitudinal ultrasonic vibration transducer, a hollow spiral groove amplitude change rod, an elastic chuck, a pressing nut and a cutter. The device adjusts the positions of a rubber plug and a sealing ring to change the volume of a fluid in a cylindrical groove or to replace the type of the fluid so as to change the mass of a longitudinal-torsional compound ultrasonic vibrator to compensate the frequency loss or increment in clamping of different cutter rods; and when the different cutter rods are clamped, the consistency of the resonant frequency, the vibration mode and the vibration shape of an ultrasonic device is realized, and the generality of the device is greatly improved. The longitudinal vibration and torsional vibration effects are both enhanced to a certain extent; the working efficiency is greatly improved; and the advantages of longitudinal-torsional compound vibration are preferably exerted.
Owner:CONPROFE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
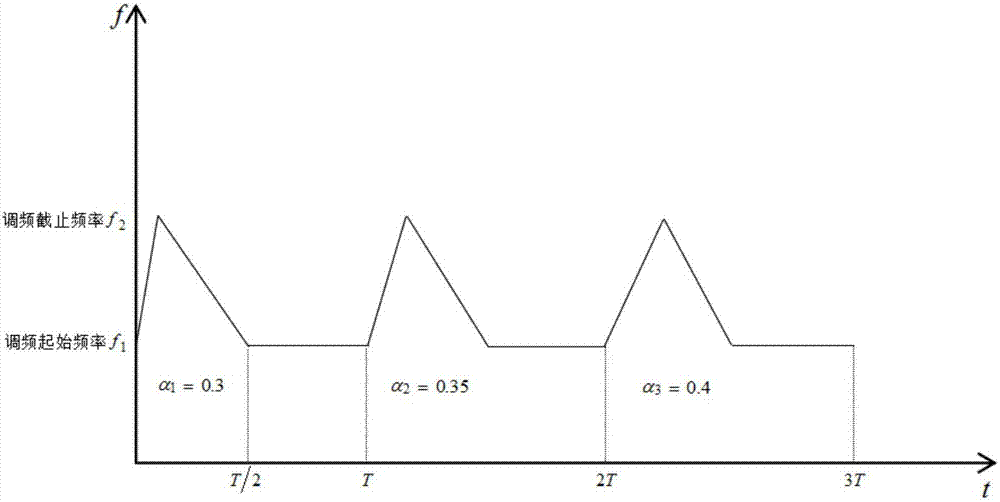
Vehicle collision avoidance radar multi-target frequency matching method based on combined waveform of LFM triangular wave and constant frequency wave
ActiveCN105182341ASolve the technical problems of multi-target frequency matchingGood matching accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionConstant frequencyWave shape
A vehicle collision avoidance radar multi-target frequency matching method based on a combined waveform of an LFM triangular wave and a constant frequency wave belongs to the field of vehicle collision avoidance radar multi-target frequency matching, solves the technical problem of multi-target frequency matching, and eliminates constant false alarms. According to the technical scheme, over-threshold detection is carried out on upper and lower frequency sweep segments of the triangular wave and the constant frequency wave separately; beat frequencies of the upper and lower frequency sweep segments of the triangular wave are combined pair-wise and two matrices (A1 and B1) are generated; a difference matrix C1 of the matrix A1 and a first Doppler frequency value detected from the constant frequency wave is calculated, and the minimal value of the matrix C1 is found; and corresponding Doppler frequency values and beat frequencies and values in the matrix A1 and the matrix B1 are output. The beneficial effects are that the technical problem of multi-target frequency matching is solved and false alarms are removed.
Owner:DALIAN ROILAND SCI & TECH CO LTD
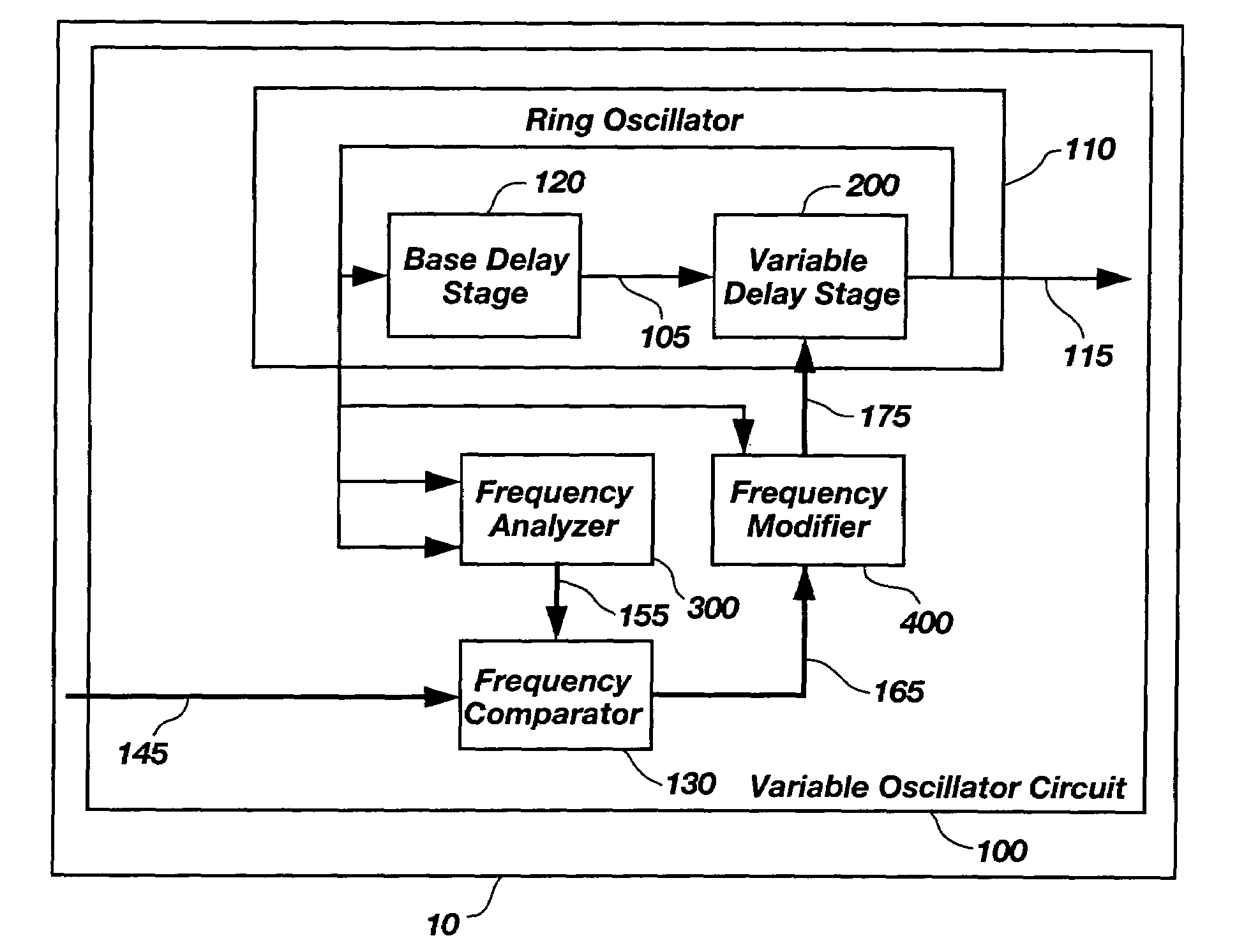
On-chip variable oscillator method and apparatus
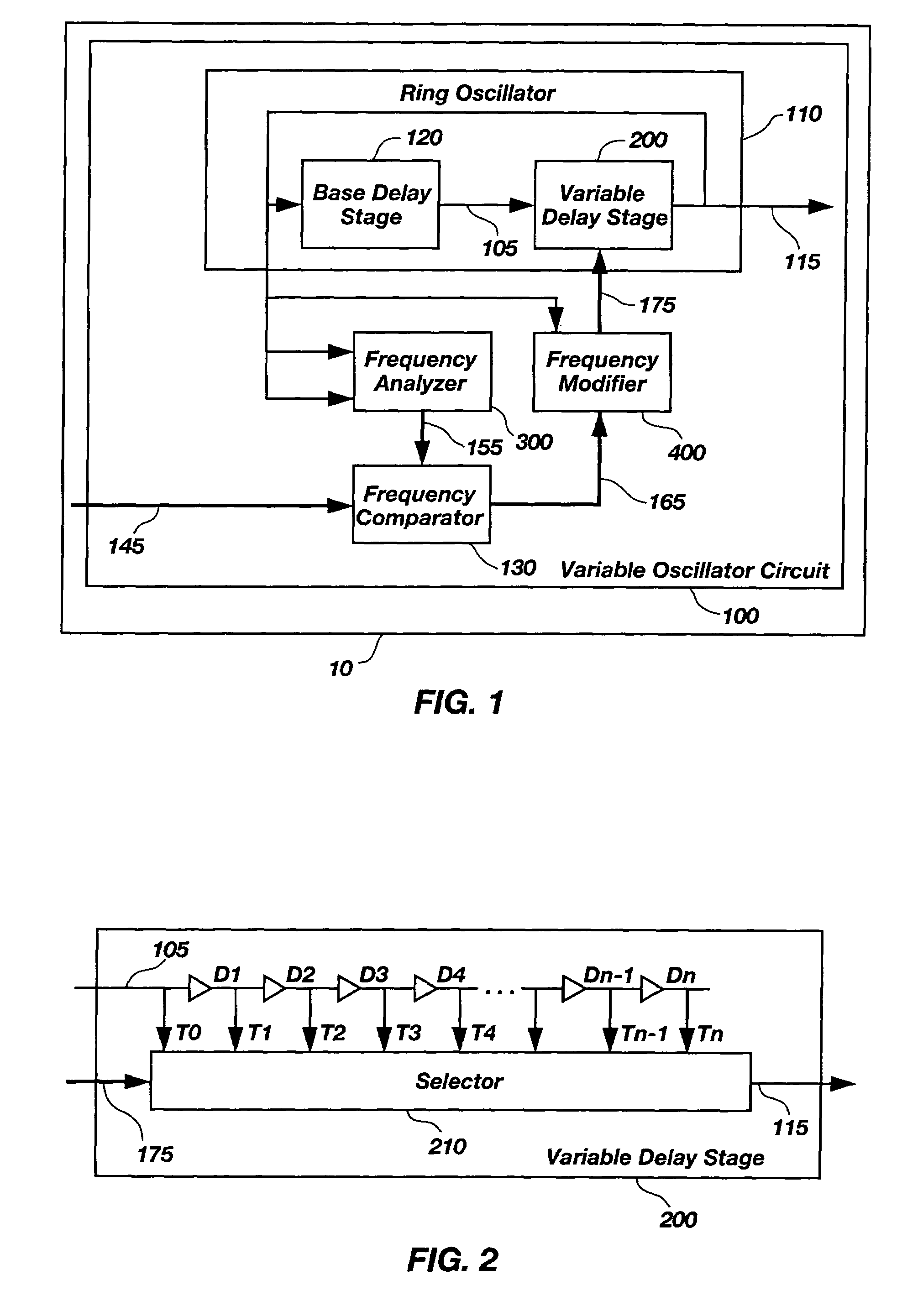
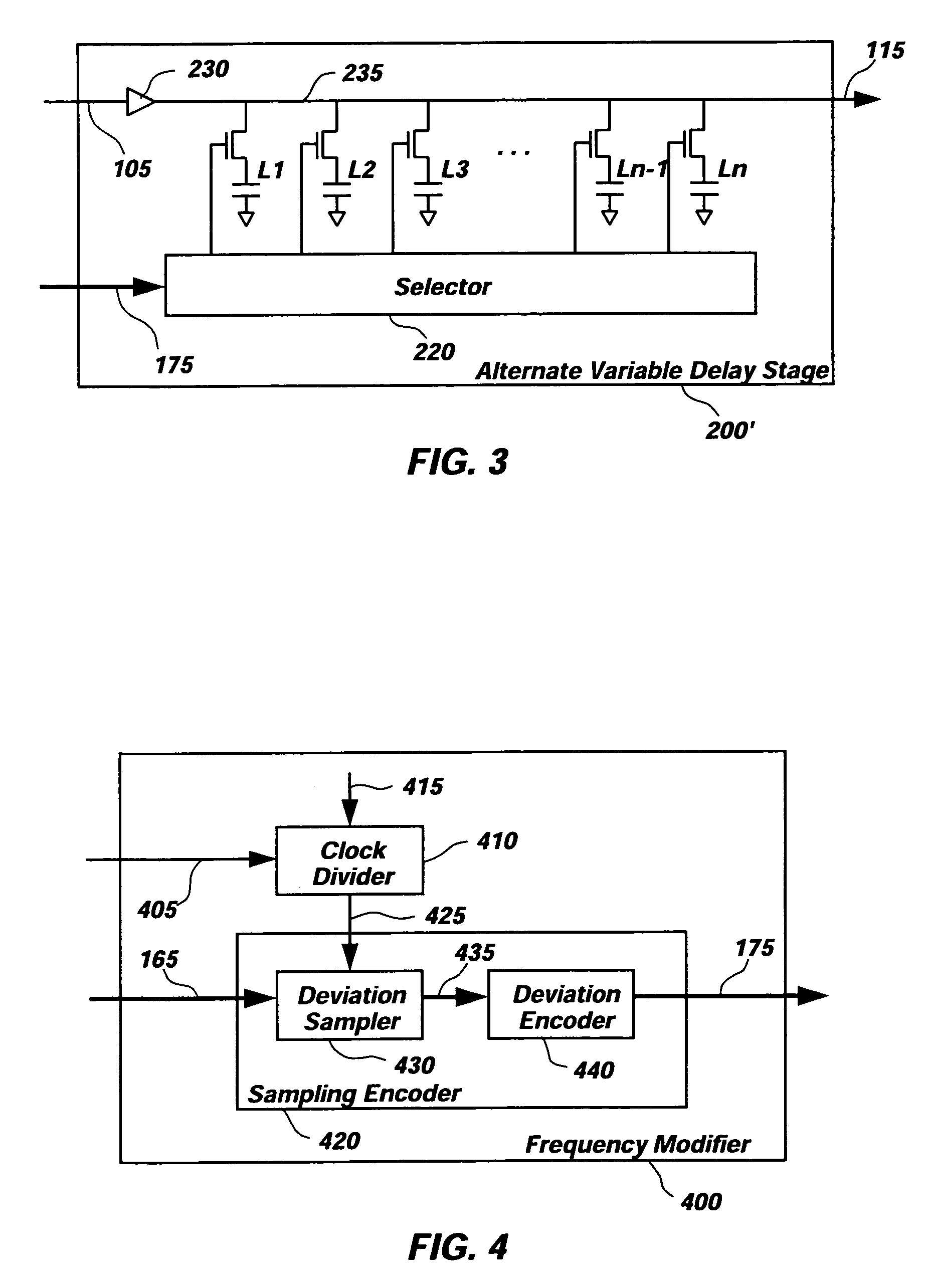
InactiveUS6995621B1Large dynamic rangePulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsSignal onEngineering
A method and apparatus for creating a variable frequency-oscillating signal on a semiconductor device. The frequency of a ring oscillator is varied by inserting or removing additional delay into the ring. The frequency of the oscillating signal is periodically compared to an encoded input signal indicating the desired frequency. The comparison result modifies the desired frequency by modifying the amount of delay in the ring oscillator. In an alternate reference clock is converted to an encoded representation of the input reference clock's current frequency. This resultant encoded representation is compared to the encoded representation of the variable frequency-oscillating signal to determine whether the delay in the ring oscillator should be modified so the frequency of the variable oscillating signal matches the frequency of the input reference clock.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of controlling a function of a device and system for detecting the presence of a living being
InactiveUS20140023235A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSufficient degree of accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFrequency spectrumFrequency matching
A method of controlling a function of a device, includes obtaining a sequence (19;34;48) of digital images taken at consecutive points in time. At least one measurement zone (25) including a plurality of image points is selected. For at least one measurement zone (25), a signal (30;41;55) representative of at least variations in a time-varying value of a combination of pixel values at at least a number of the image points is obtained and at least one characteristic of the signal (30;41;55) within at least a range of interest of its spectrum relative to comparison data is determined. The determination comprises at least one of:(i) determining whether the signal (30;41;55) has a spectrum with a local maximum at a frequency matching a comparison frequency to a certain accuracy; and(ii) determining whether at least a certain frequency component of the signal (30;41;55) is in phase with a comparison signal to a certain accuracy. The function is controlled in dependence on whether the determination is positive.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Radio frequency navigation using frequency response matching
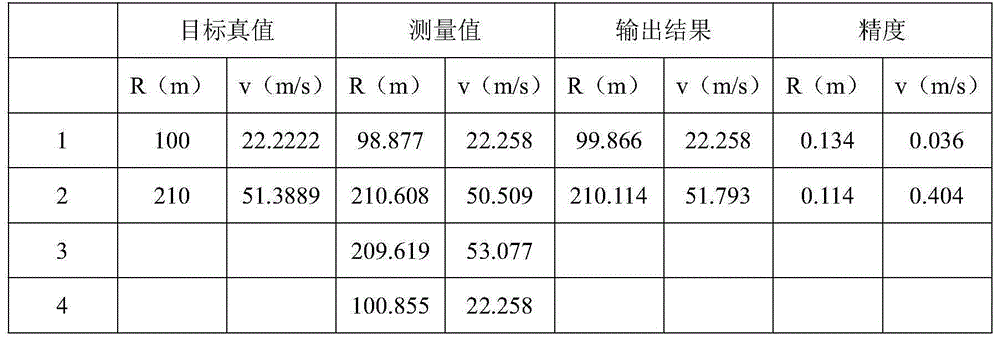
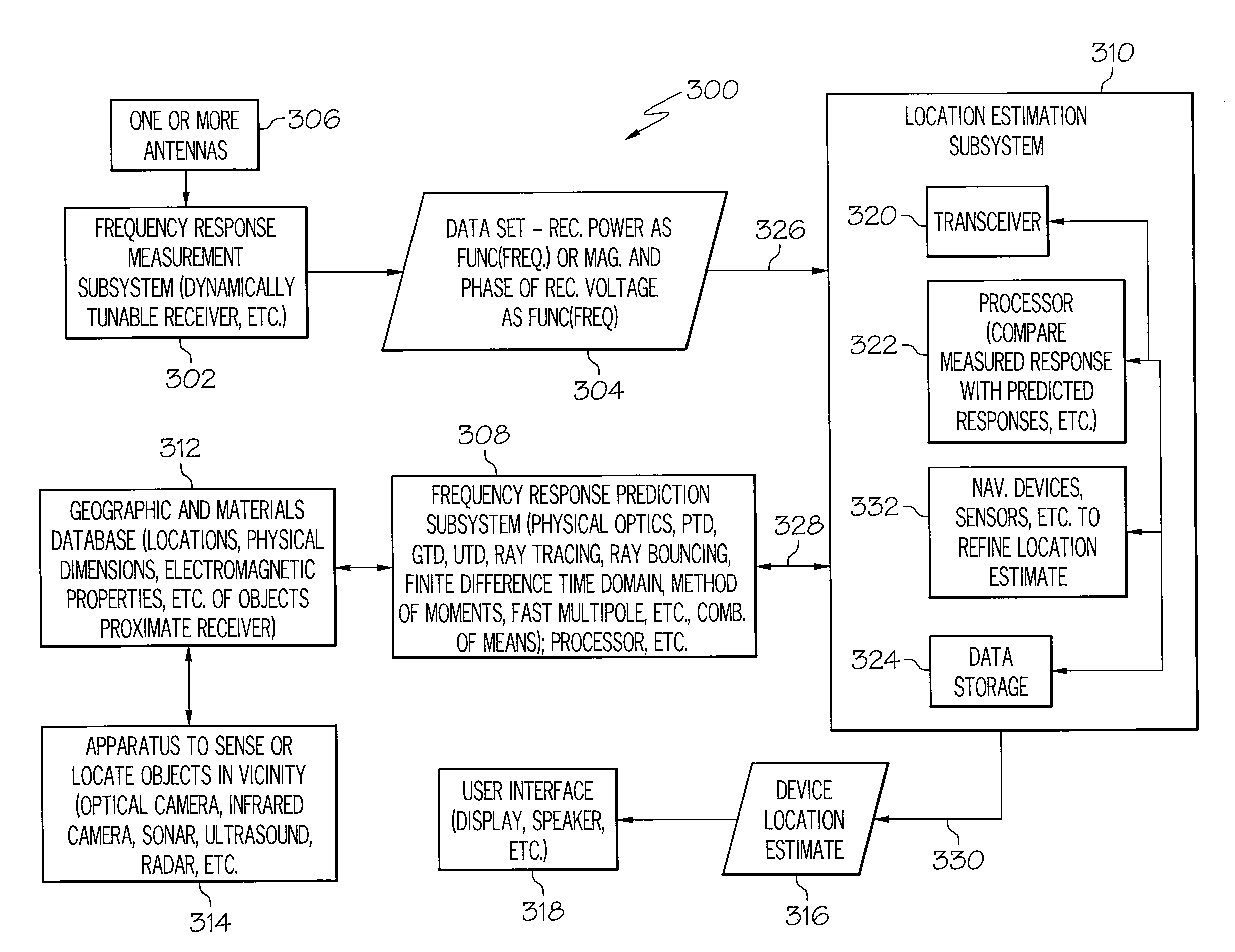
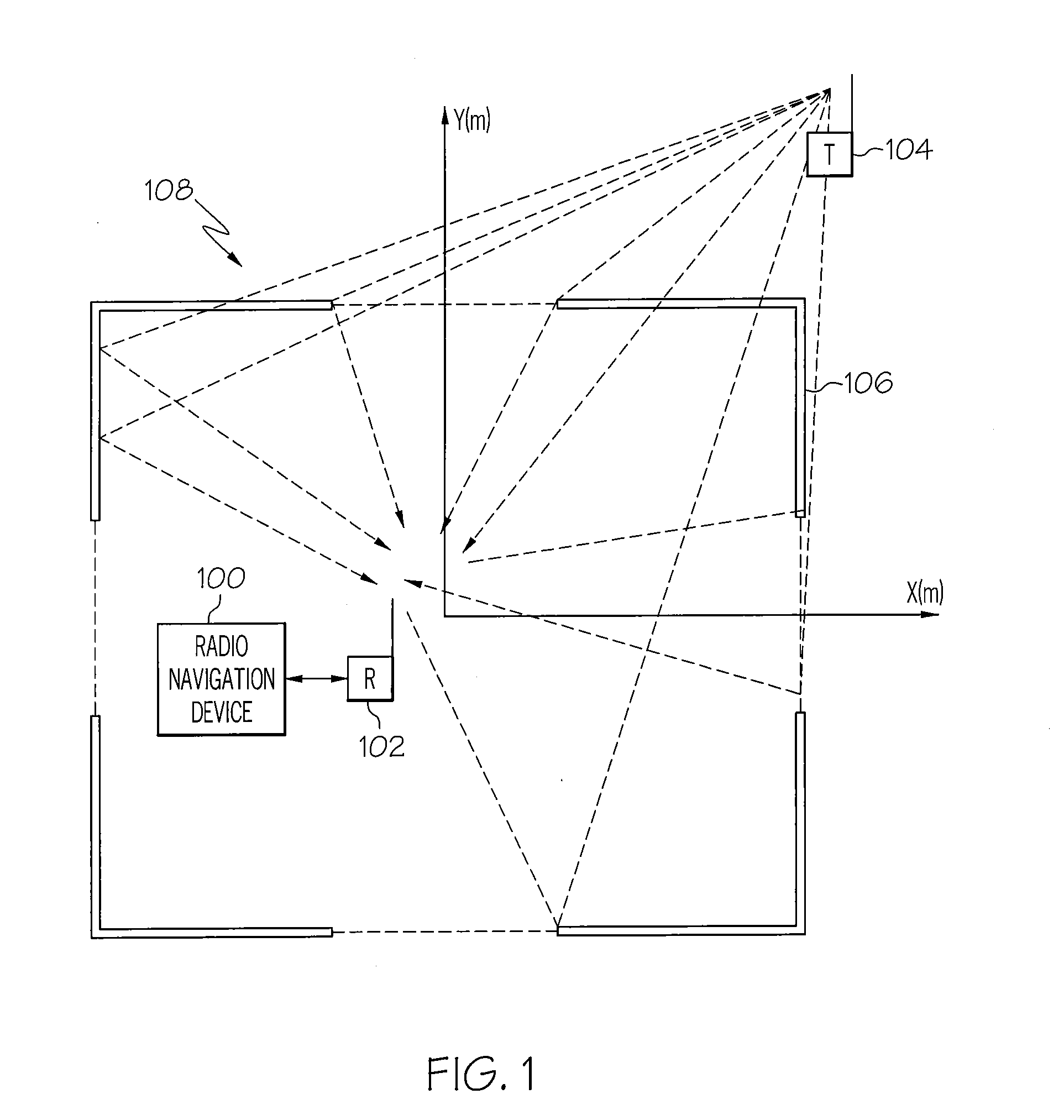
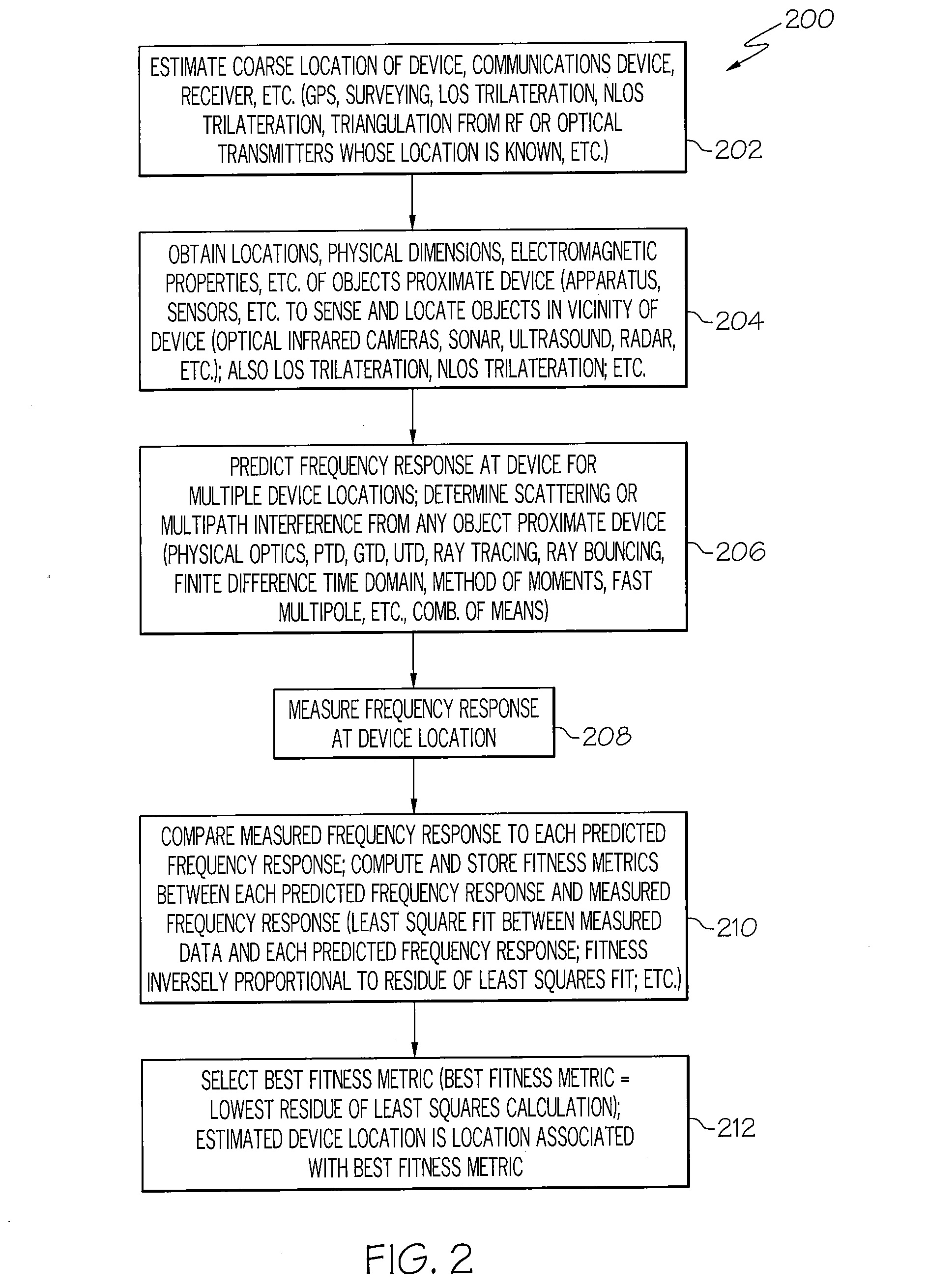
InactiveUS20080143605A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringFrequency matching
A method for radio navigation may include predicting a frequency response for each of a multiplicity of possible device locations. The method may also include measuring a frequency response at an actual device location. The method may further include matching the measured frequency response to one of the predicted frequency responses to determine an estimated device location, wherein the estimated device location corresponds to the possible device location associated with the one predicted frequency response that most closely matches the measured frequency response.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method for extracting fault features of rotating mechanical equipment
ActiveCN104655380AReduce the hidden danger of failureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingTime domainMoving average
The invention provides a method for extracting the fault features of rotating mechanical equipment, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out equal-time-interval sampling on a vibration signal and carrying out time domain processing, and extracting time domain features; (2) carrying out envelope detection processing on an equal-time-interval sampling vibration signal x(n) so as to obtain an equal-time-interval sampling envelope signal, and extracting the features of the envelope signal; (3) reconstituting an equal-angle-interval sampling envelope signal y(n) by using the equal-time-interval sampling envelope signal and rotating speed information; (4) carrying out equal-angle moving average filter processing on the equal-angle-interval sampling envelope signal y(n) so as to obtain a signal z (n); and (5) solving the Fourier transform of the signal z (n), seeking feature frequencies by using a feature frequency matching method, and extracting the fault features of a frequency domain. The method not only can suppress interferences under the condition that the resolution ratio of a frequency domain is not reduced, but also can extract actual feature frequencies under the condition that rotating speeds and mechanical parts have deviations, and therefore, smaller potential faults can be effectively found.
Owner:北京昊鹏智能技术有限公司
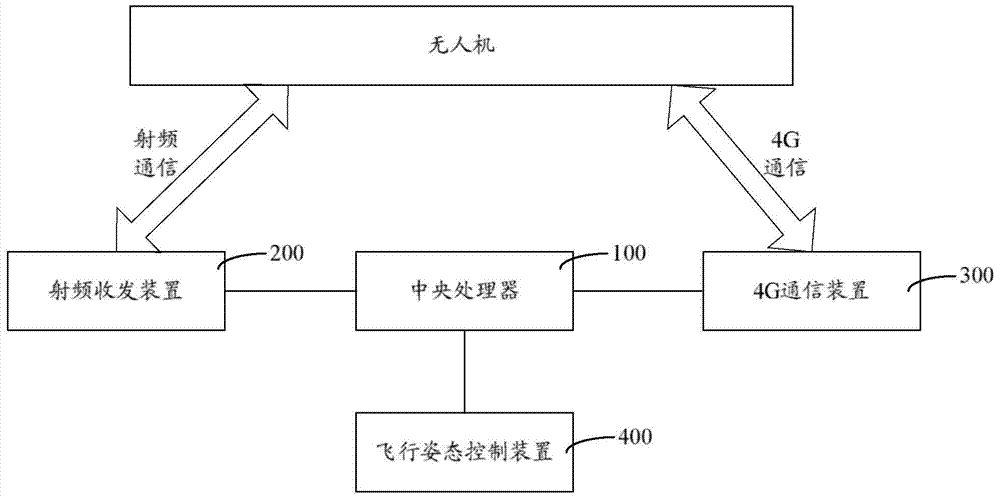
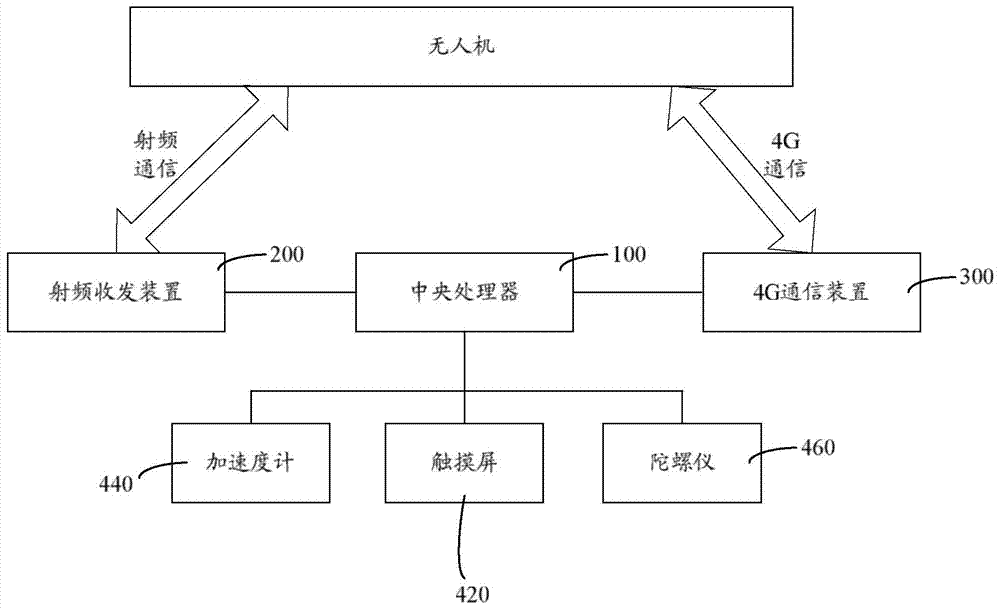
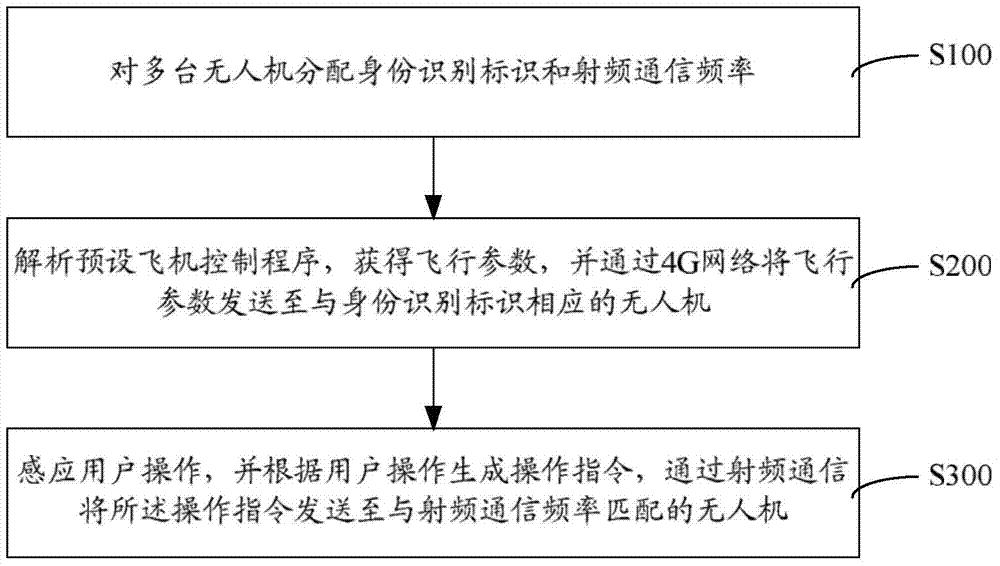
Unmanned plane control apparatus and method based on 4G communication
The invention provides an unmanned plane control apparatus and method based on 4G communication. A central processor distributes identity recognition identifiers (such as IP addresses) and radio frequency communication frequencies to each unmanned plane, and the central processor parses a preset airplane control program, obtains flight parameters, sends the flight parameters through a 4G network to the unmanned planes corresponding to the identity recognition identifiers, at the same time, senses manual operation of users, generates operation instructions, and sends the operation instructions through radio frequency communication to the unmanned planes matching the radio frequency communication frequencies. The 4G communication distance is long, the execution cost is low, the bandwidth capacity is large, and the message transmission rate is high. By using the 4G communication to undertake major communication tasks, the control cost of the unmanned planes can be remarkably reduced. Besides, the 4G communication is employed for long-distance transmission, the defect that conventional radio frequency communication cannot realize long-distance accurate communication can be overcome, and the unmanned planes can be stably controlled.
Owner:湖南基石信息技术有限公司
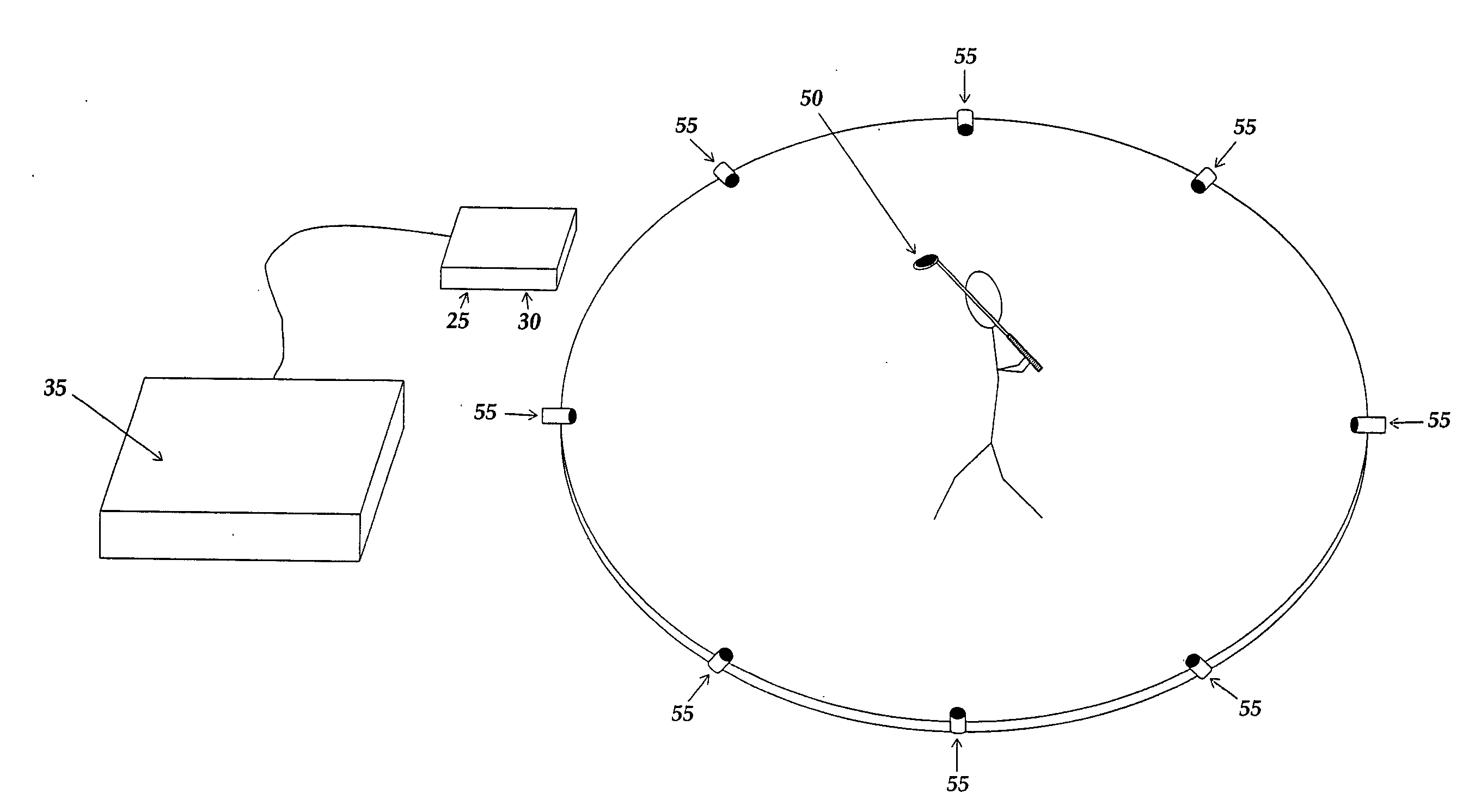
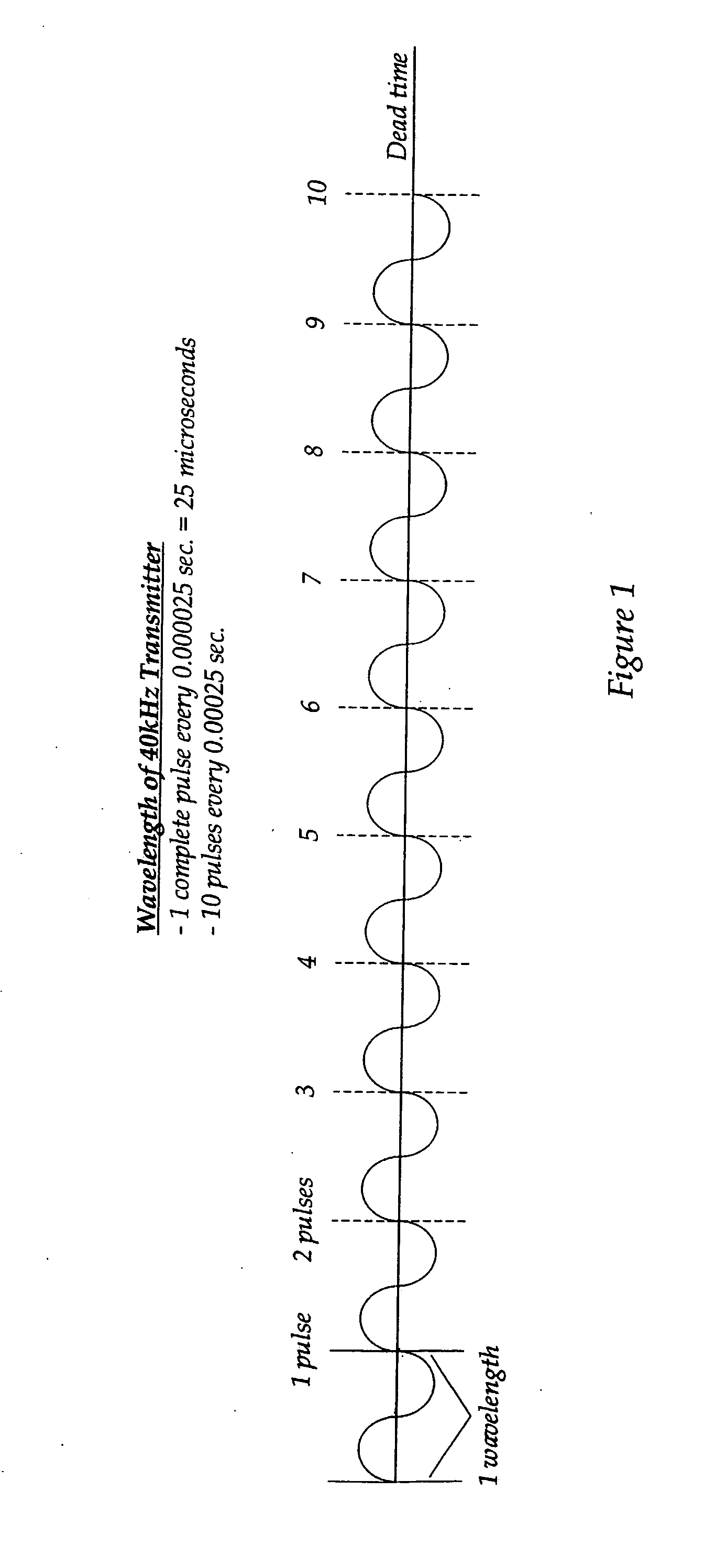
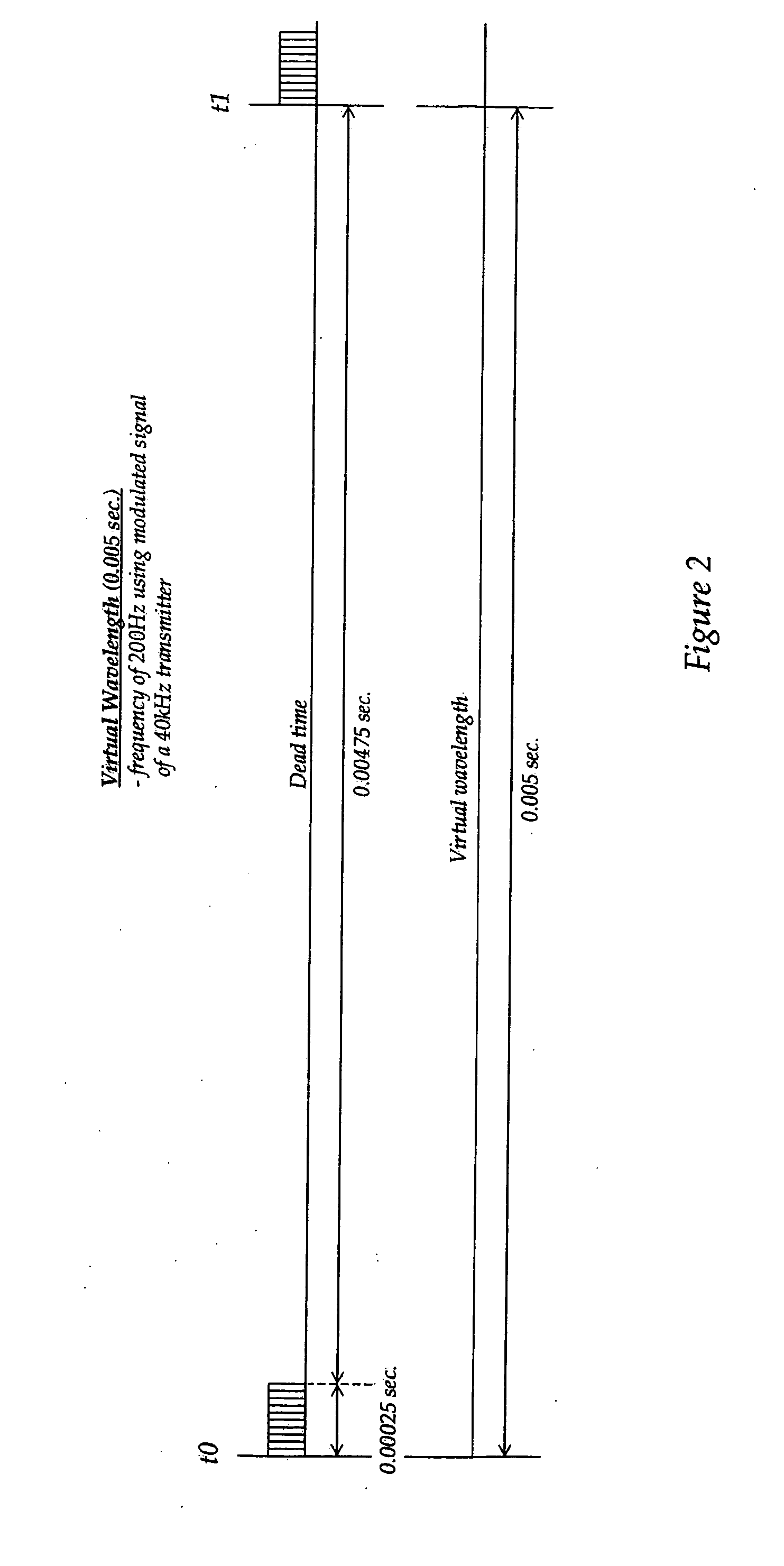
Frequency matched relative position tracking system
InactiveUS20070237029A1Save energyProlong transmitter lifeDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationTransceiverTriangulation
A method and system for relative positional tracking of a signal source is disclosed that requires no phase synchronization between the tracked source and tracking system. A signal source transmits a repeating signal. The virtual wavelength of the repeating signal establishes zones of coverage. The system's sampling rate (or sync clock) corresponds to the frequency of the repeated signal. One or more ultrasonic transceivers placed within the desired coverage area capture the transmitted signal. Before tracking begins, a coordinate system origin (X=0, Y=0, Z=0) is established so that all tracking calculations are relative to the origin. Relative time-of-flight measurements are made by comparing the received signals against a sync clock. Tracking is accomplished by triangulating distance measurements received from the ultrasonic transceivers.
Owner:HUP
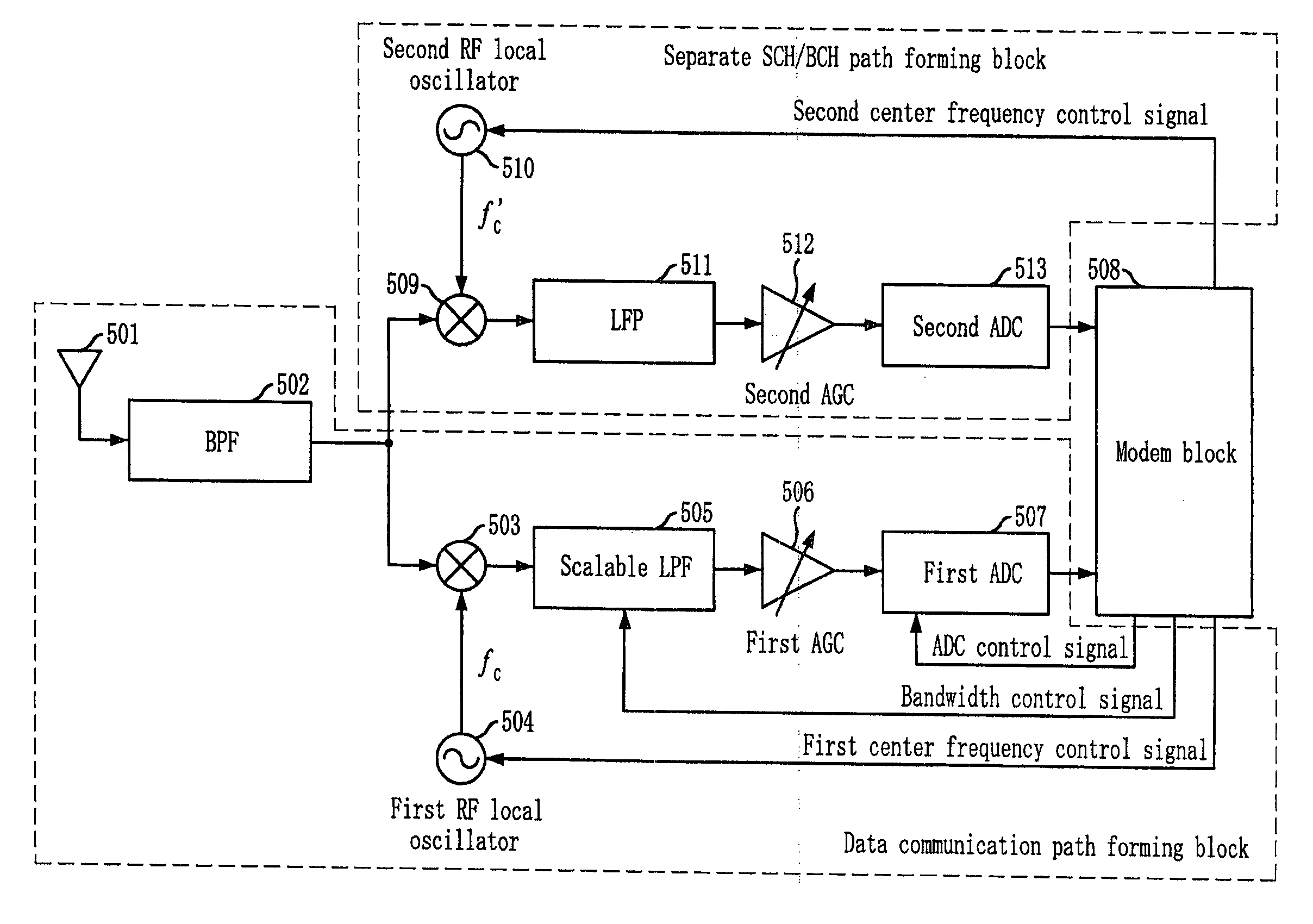
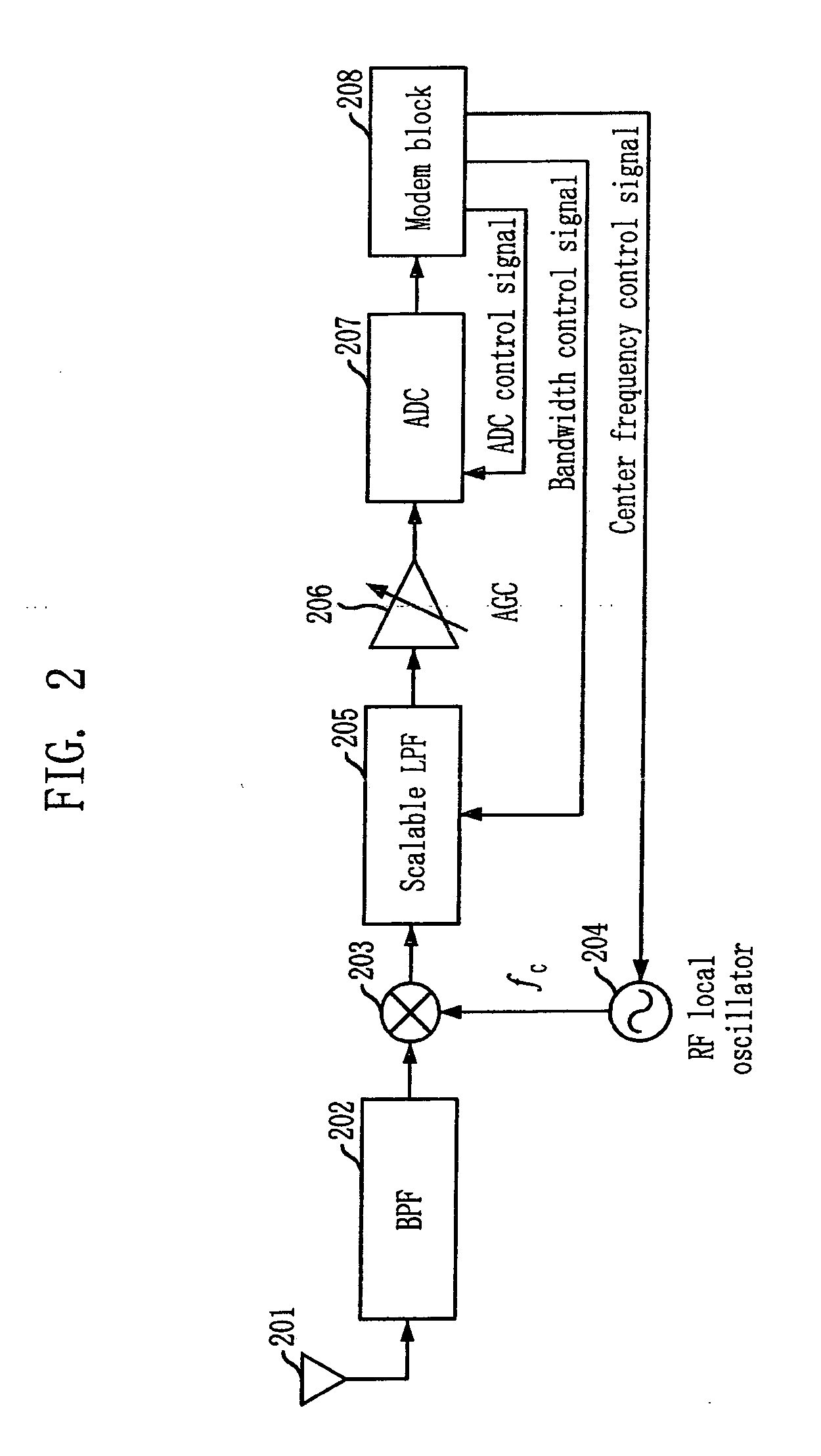
Receiver and receiving method for scalable bandwith
ActiveUS20100104001A1Scalable can be supportedFlexible bandwidthResonant long antennasFrequency-division multiplexControl signalAnalog signal
Provided are a receiver and a receiving method for a scalable bandwidth in a mobile station of an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. The receiving method includes the steps of: (a) filtering a received RF signal; (b) oscillating a frequency according to a center frequency control signal to output a local oscillation frequency; (c) down-converting the filtered RF signal by using the local oscillation frequency; (d) scalable-filtering the down-converted signal while adjusting a bandwidth according to a bandwidth control signal; (e) controlling gain of the scalable-filtered signal; (f) converting the gain-controlled analog signal into a digital signal by using a sampling frequency matching with a corresponding bandwidth according to an ADC control signal; and (g) demodulating the converted digital signal, outputting the center frequency control signal, the bandwidth control signal, and the ADC control signal according to control information received from an upper layer.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Tinnitus detecting method and tinnitus therapeutic apparatus
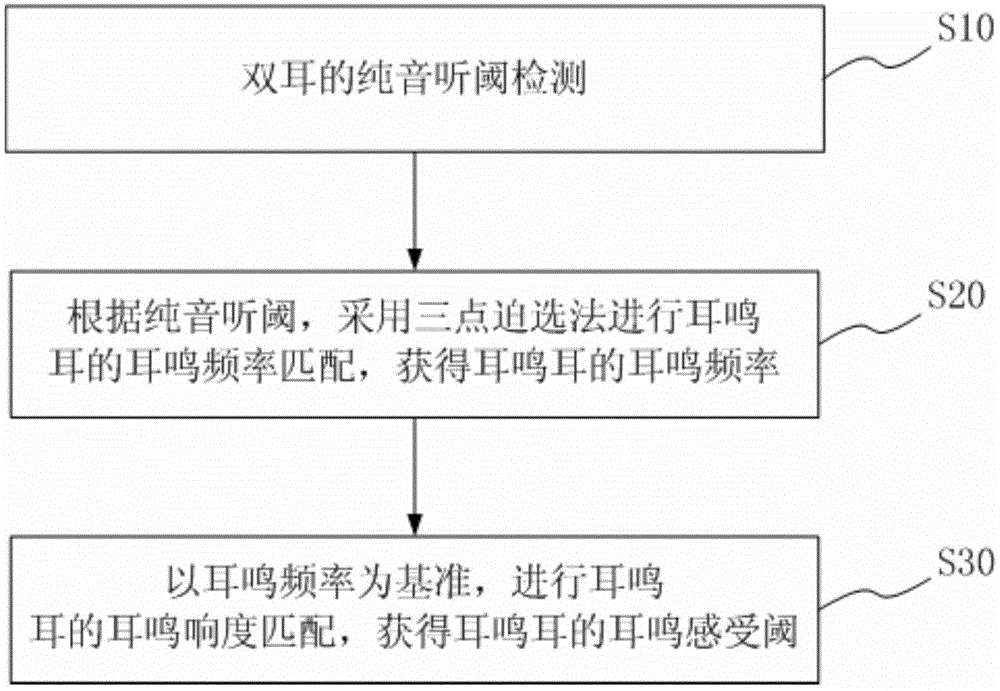
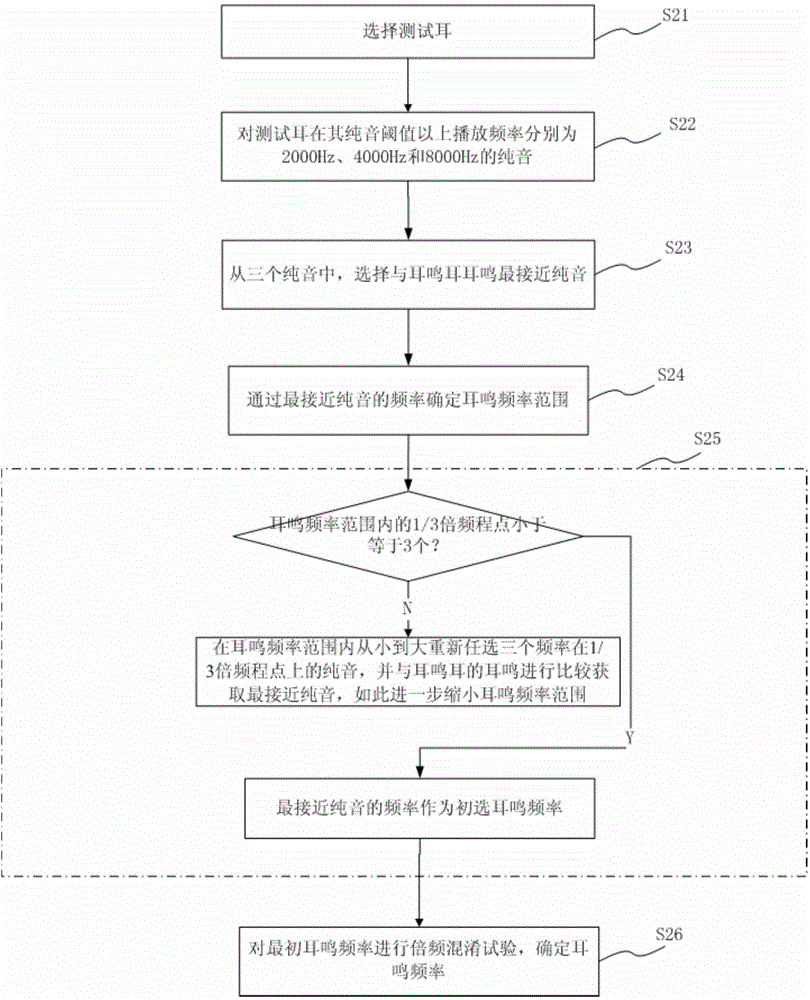
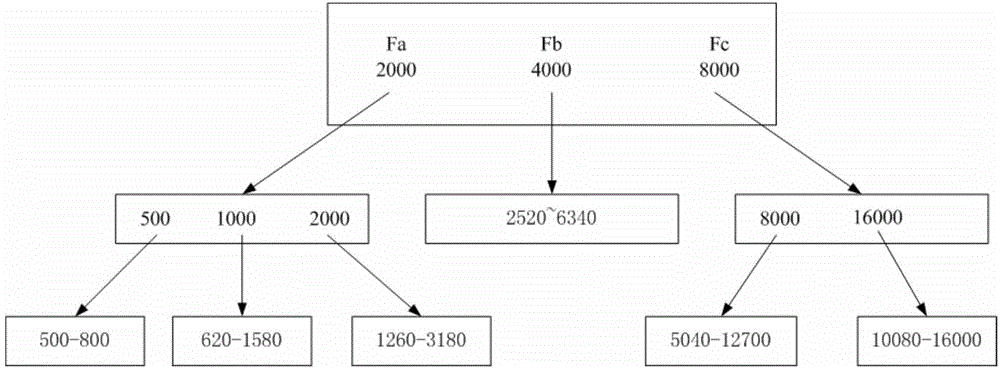
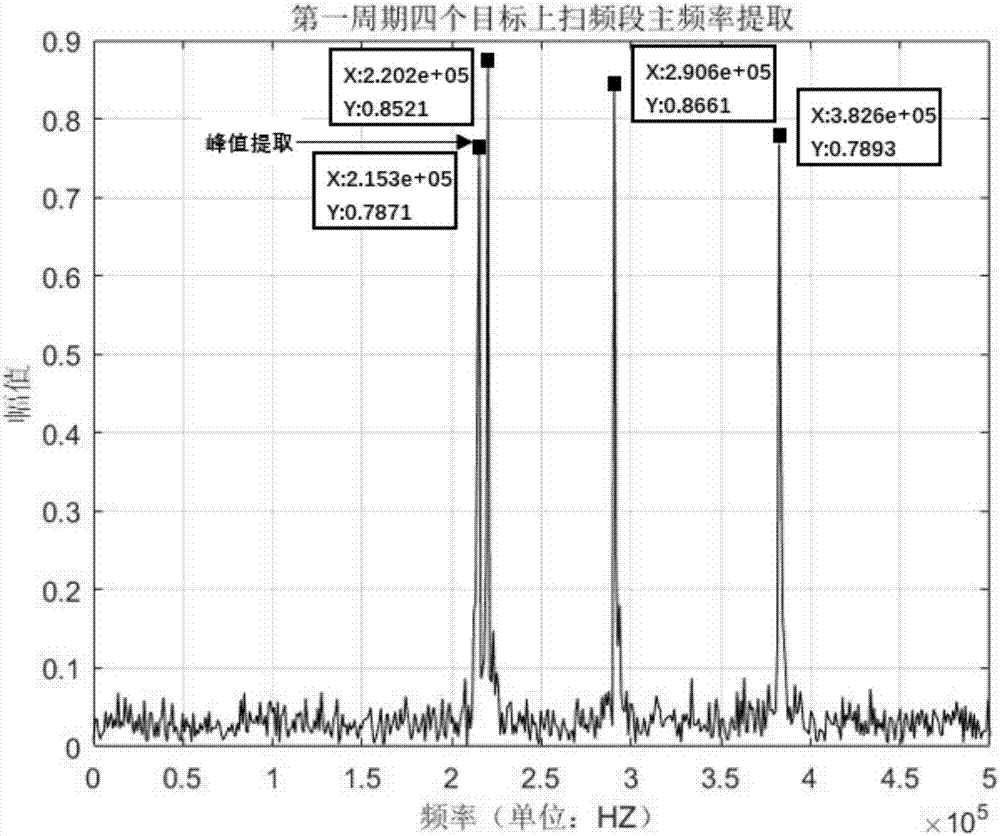
ActiveCN104783808AImprove the efficiency of medical treatmentReduce the cost of medical visitsEar treatmentAudiometeringFault toleranceSOUND STIMULATION
The invention provides a tinnitus detecting method and a tinnitus therapeutic apparatus. The method includes the steps of conducting pure tone threshold detection of two ears, selecting the tested ear according to the result of the pure tone threshold detection, conducting tinnitus frequency matching of the tinnitus ear through a three-point forced choice method to obtain the tinnitus frequency, and conducting tinnitus loudness matching of the tinnitus ear with the tinnitus frequency as the datum to obtain a tinnitus perception threshold. By means of a sound stimulation strategy, the tinnitus therapeutic apparatus comprises a computer readable medium, a detection control unit, a treatment control unit, a headset and a feedback unit. The detection control unit is used for conducting tinnitus detection and involves pure tone threshold detection, tinnitus frequency matching and tinnitus loudness matching. The treatment control unit processes audio files for treatment according to the result of the tinnitus detection, and therefore the individual treatment scheme is obtained. By means of the method and the apparatus, the tinnitus detection time is shortened, and the fault tolerance capacity is improved; by means of the tinnitus therapeutic apparatus, diagnosis and treatment are integrated, the treatment efficiency is improved, and the treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:FOSHAN BOZHI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Multi-target recognition method of vehicle radar based on FMCW
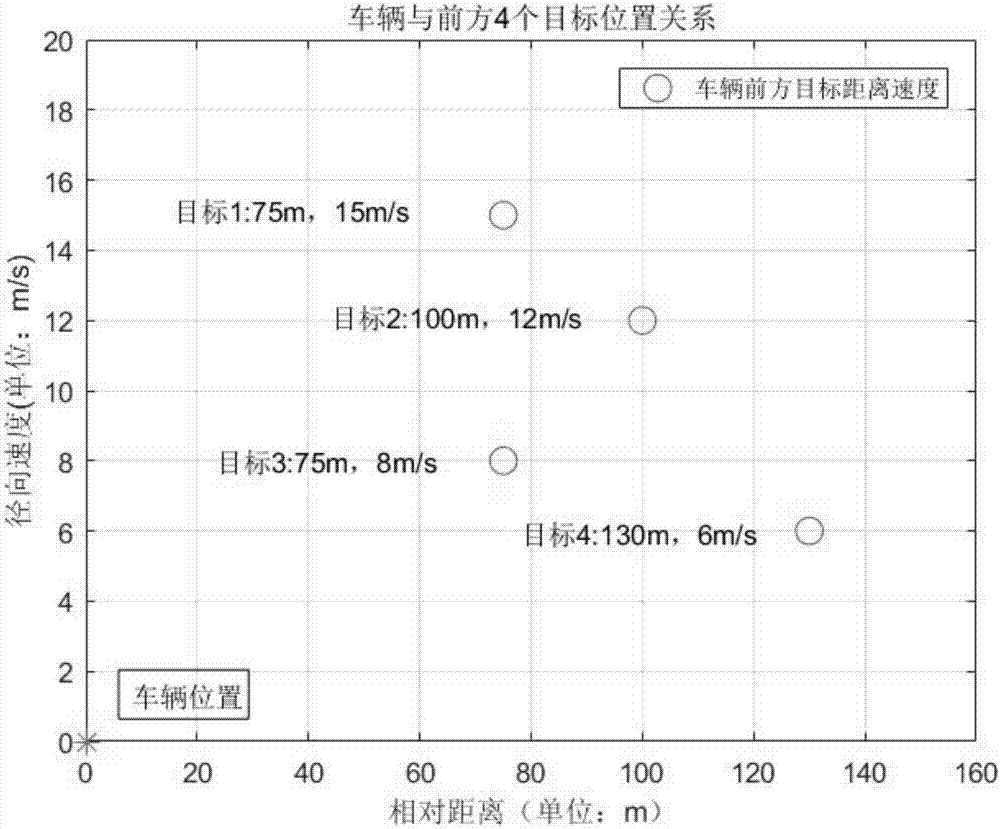
ActiveCN108008391AAvoid formingModerate calculation speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionConstant frequencyRadar
The invention discloses a multi-target recognition method of vehicle radar based on FMCW. The method includes the following steps: vehicle radar continuously emits frequency modulated continuous wavesto the front, wherein the frequency modulated continuous wave in each period is composed of three sub periodic modulated waves, the periods of the sub periodic modulated waves are T, and each sub periodic modulated wave is composed of a triangular wave band and a constant frequency band; mixing the emitted frequency modulated continuous waves and the received echo, and outputting beat signals; performing FFT operation on the beat signals of the upper sweep frequency band, the lower sweep frequency band and the constant frequency band in the same period, and extracting the main frequency; matching the upper sweep frequency band, the lower sweep frequency band and the constant frequency band corresponding to each target in the same period; calculating the speed and distance of each target according to a corresponding frequency group obtained; and finally, taking the distance and speed simultaneously detected in three periods as the distance and speed of a real target. The false judgmentrate of false targets is reduced, and the correctness of target recognition is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Radio device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7345637B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentElectrical conductor
The invention provides a radio device in which multi-resonance promotion and impedance adjustment can be readily performed and a restriction in a mounting space can be dissolved, and an electronic apparatus having the same installed therein. Provision of a stub (123) having a large area and serving as a frequency matching portion as well in a folded monopole antenna (120) results in that a conductor area can be increased, and a resonance frequency can be shifted to lower frequencies. In addition, a frequency of a radio communication antenna can be readily adjusted because the resonance frequency is adjusted by cutting the stub (123).
Owner:TOSHIBA CLIENT SOLUTIONS CO LTD
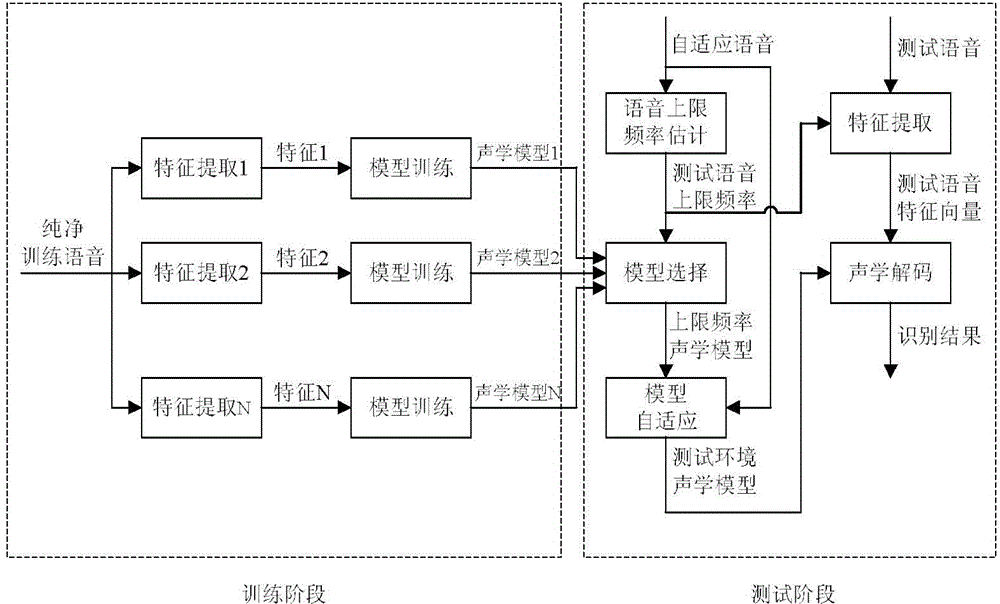
Robust voice recognition method based on acoustic model array
ActiveCN104392718AMinimize the impact of adaptationHigh precisionSpeech recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
The invention discloses a robust voice recognition method based on an acoustic model array. The robust voice recognition method comprises a training phase and a testing phase. At the training phase, a plurality of upper limiting frequencies are set for training voice according to the highest frequency of the voice, a plurality of groups of characteristic vectors are extracted and model training is performed to obtain the acoustic model array. At the testing phase, firstly, the upper limiting frequency of test voice is estimated according to a small quantity of self-adaptive voice in the testing environment; secondly, an acoustic model matched with the upper limiting frequency of the test voice is selected from the acoustic model array, and the parameters of the acoustic model are adjusted to obtain a testing environment acoustic model; finally, characteristic extraction is performed according to the upper limiting frequency of the test voice so as to obtain a characteristic vector of the noise-containing test voice, and acoustic decoding is performed on the characteristic vector by use of the testing environment acoustic model to obtain an identification result. The robust voice recognition method based on the acoustic model array is capable of improving the performance of a voice recognition system in a noise environment and improving the robustness of the system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com