Patents
Literature
1875 results about "Radio equipment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radio equipment, as defined in Federal Information Management Regulations, is any equipment or interconnected system or subsystem of equipment that is used to communicate over a distance by modulating and radiating electromagnetic waves in space without artificial guide. This does not include such items as microwave, satellite, or cellular telephone equipment.
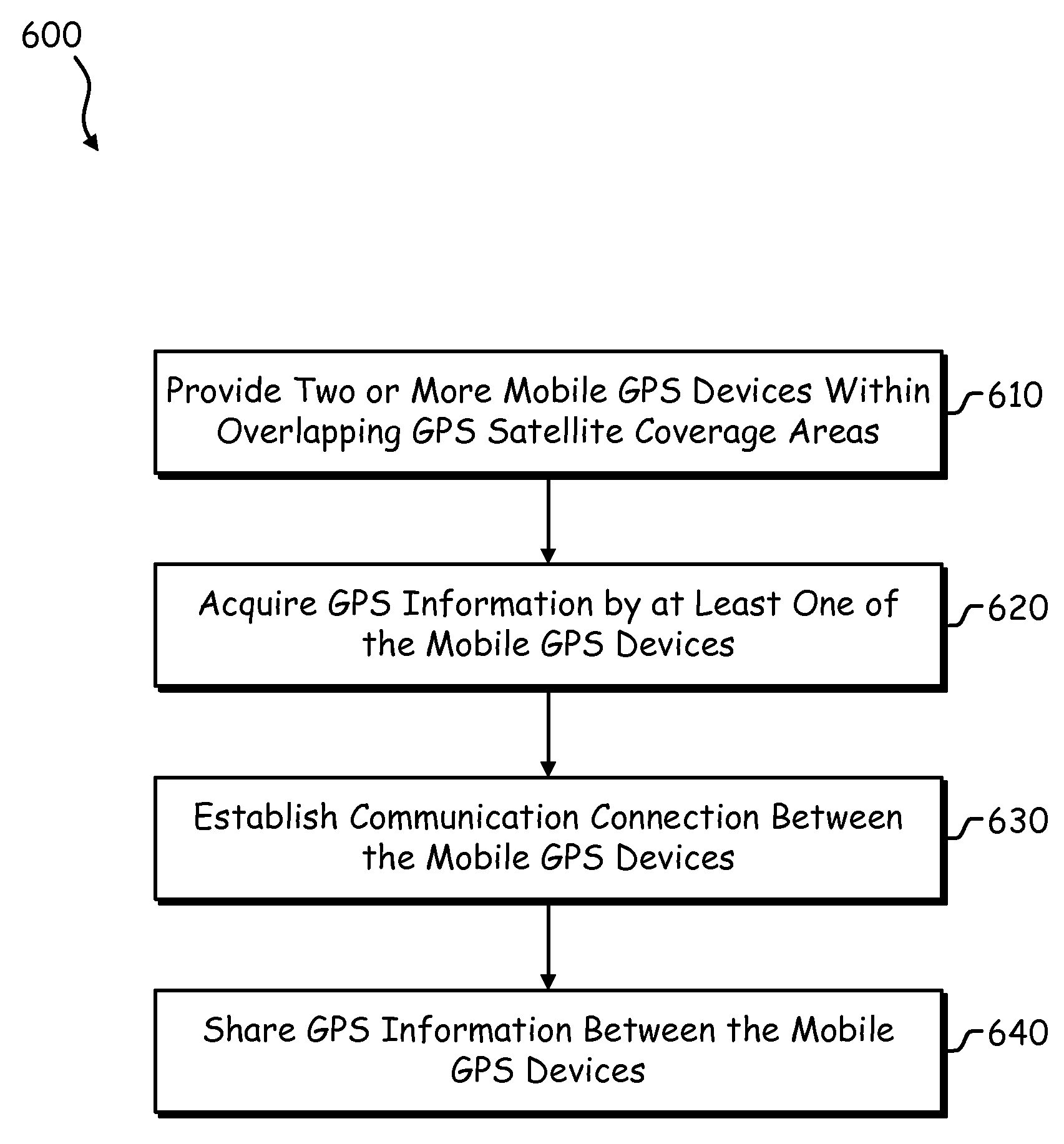
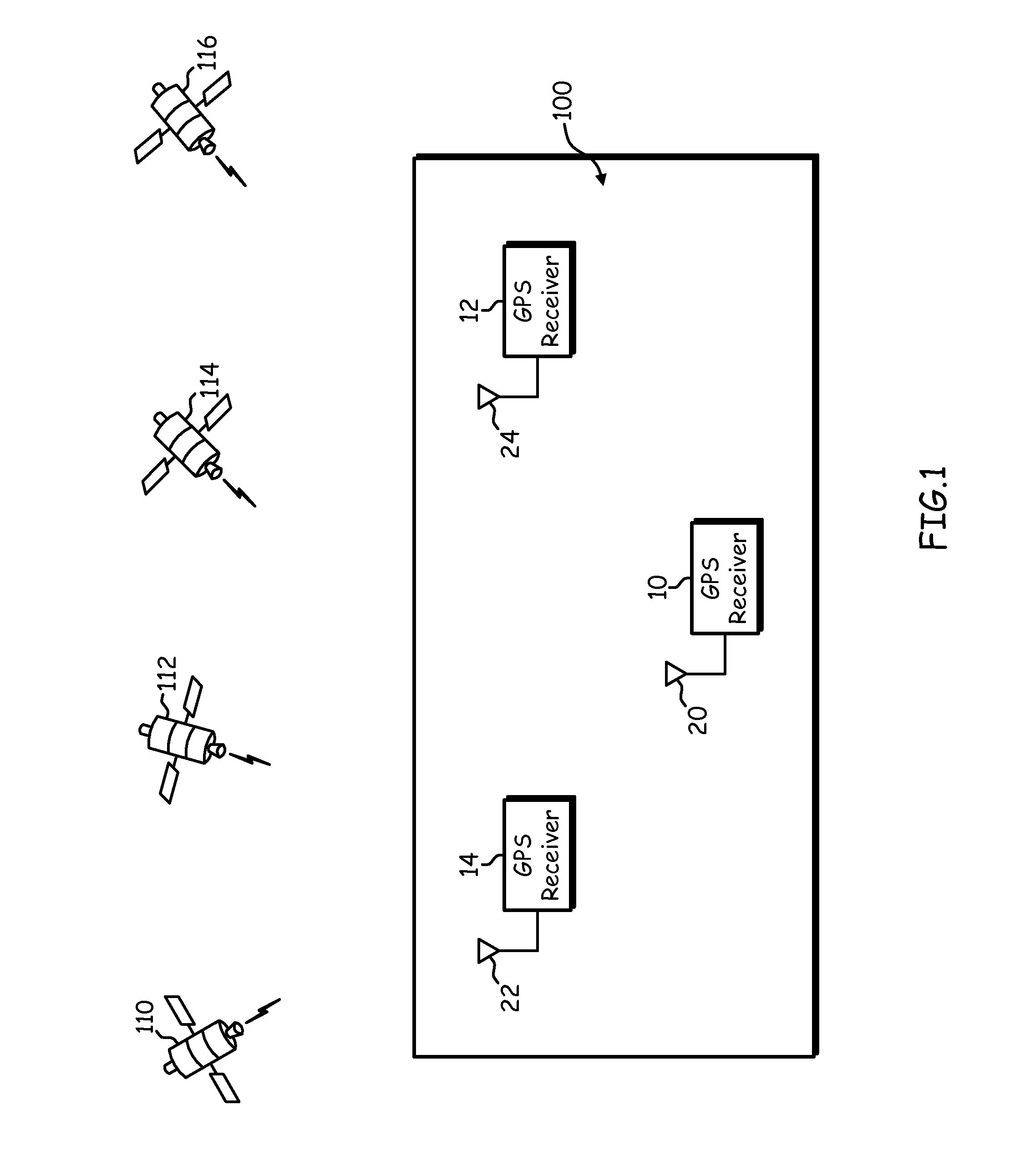
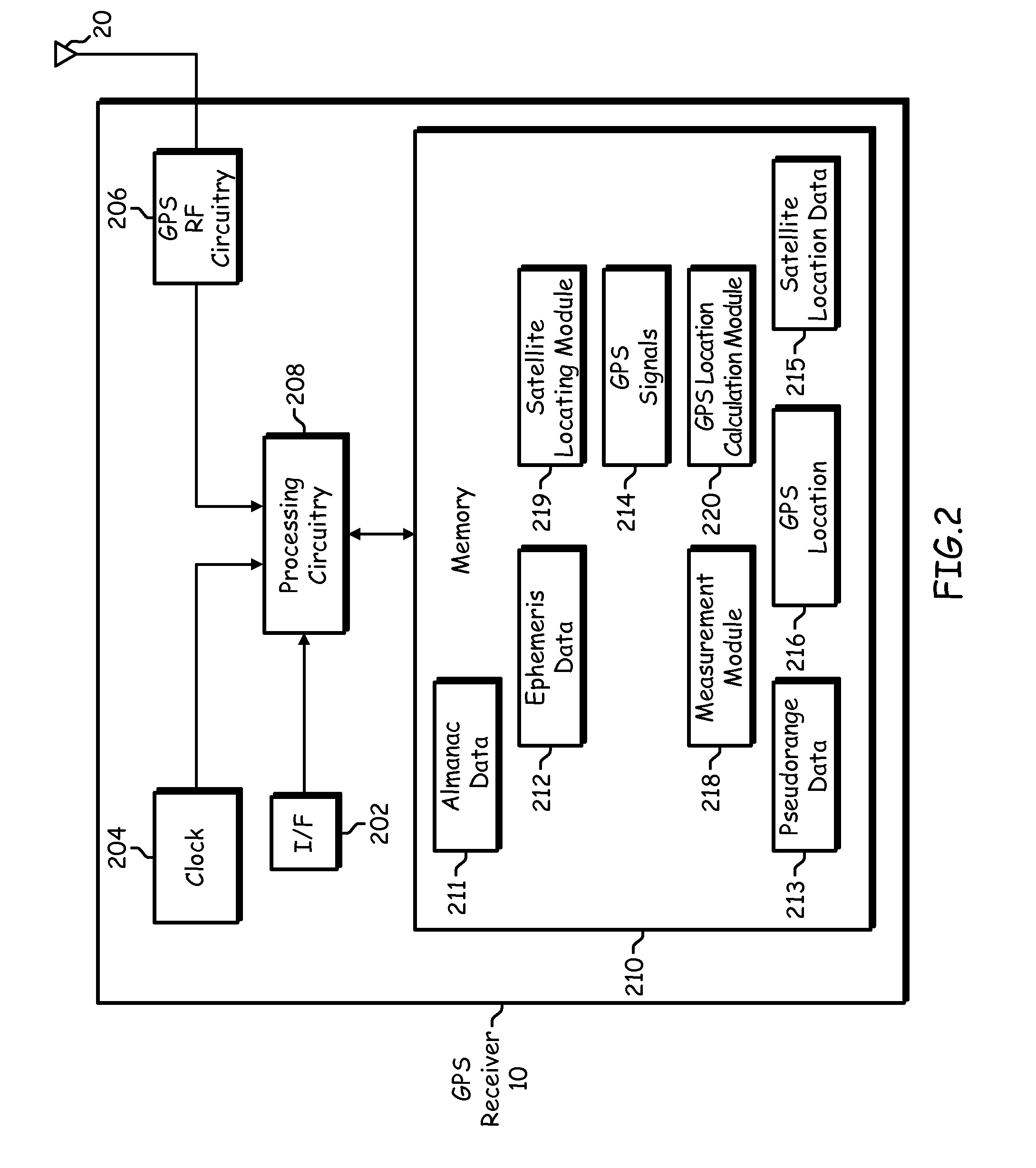
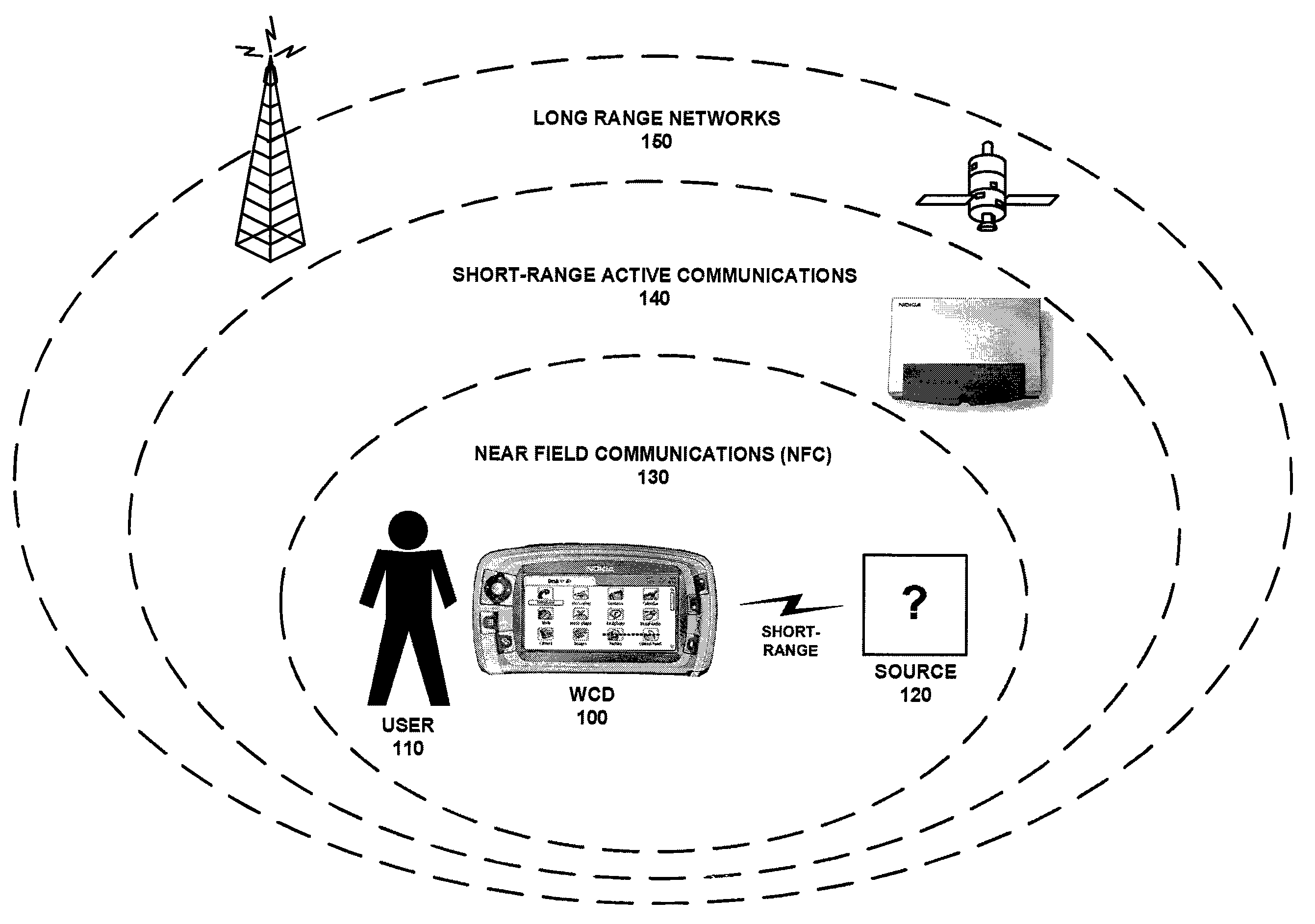
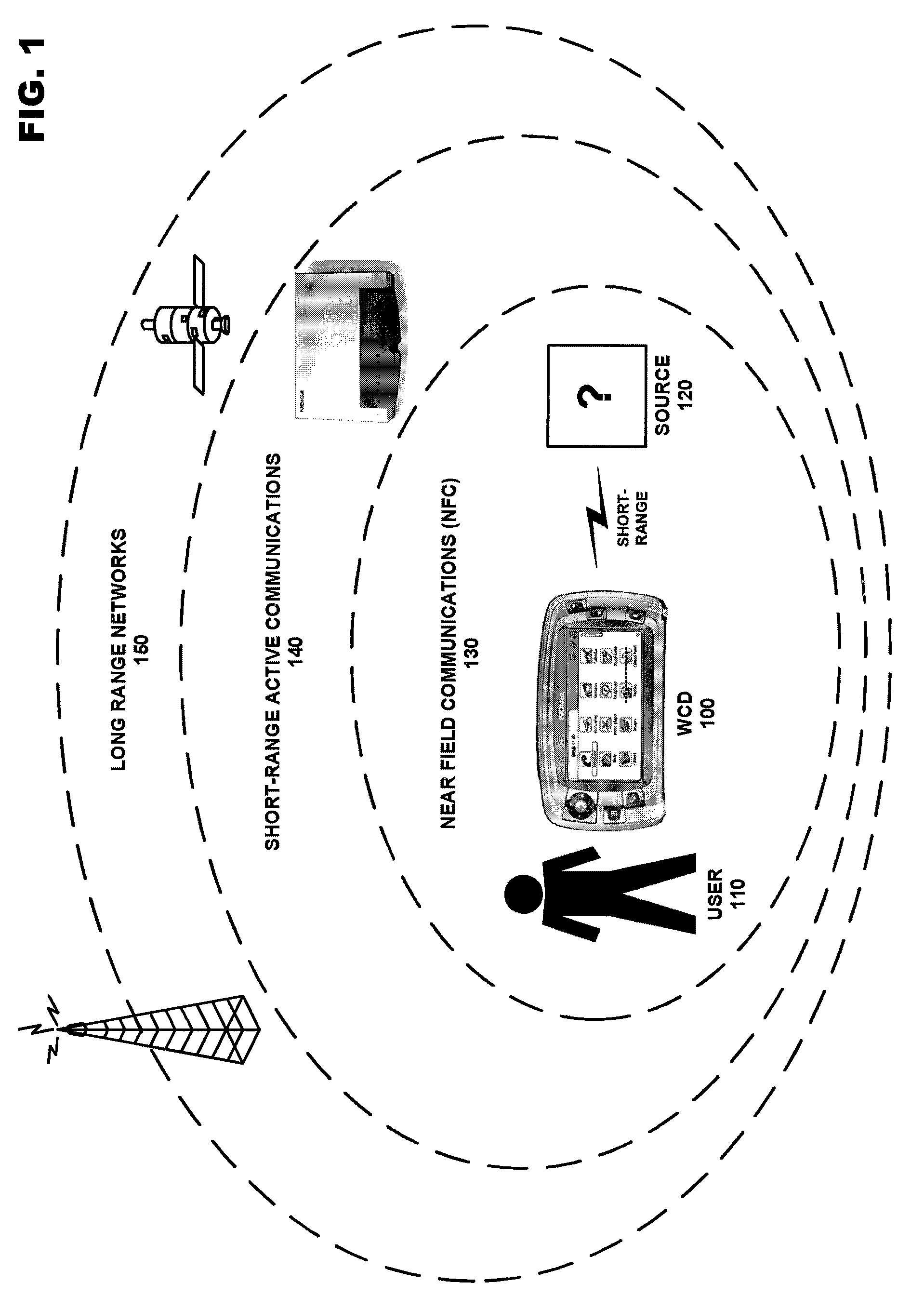
Sharing of GPS information between mobile devices
Mobile radio devices with Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers are able to share GPS information through a wireless communication connection. When one mobile radio device acquires GPS information associated with positioning of that mobile radio device, the mobile radio device can establish a communication connection with another mobile radio device via a wireless link to share that acquired GPS information with the other mobile radio device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Methods and apparatus for operating a radio device
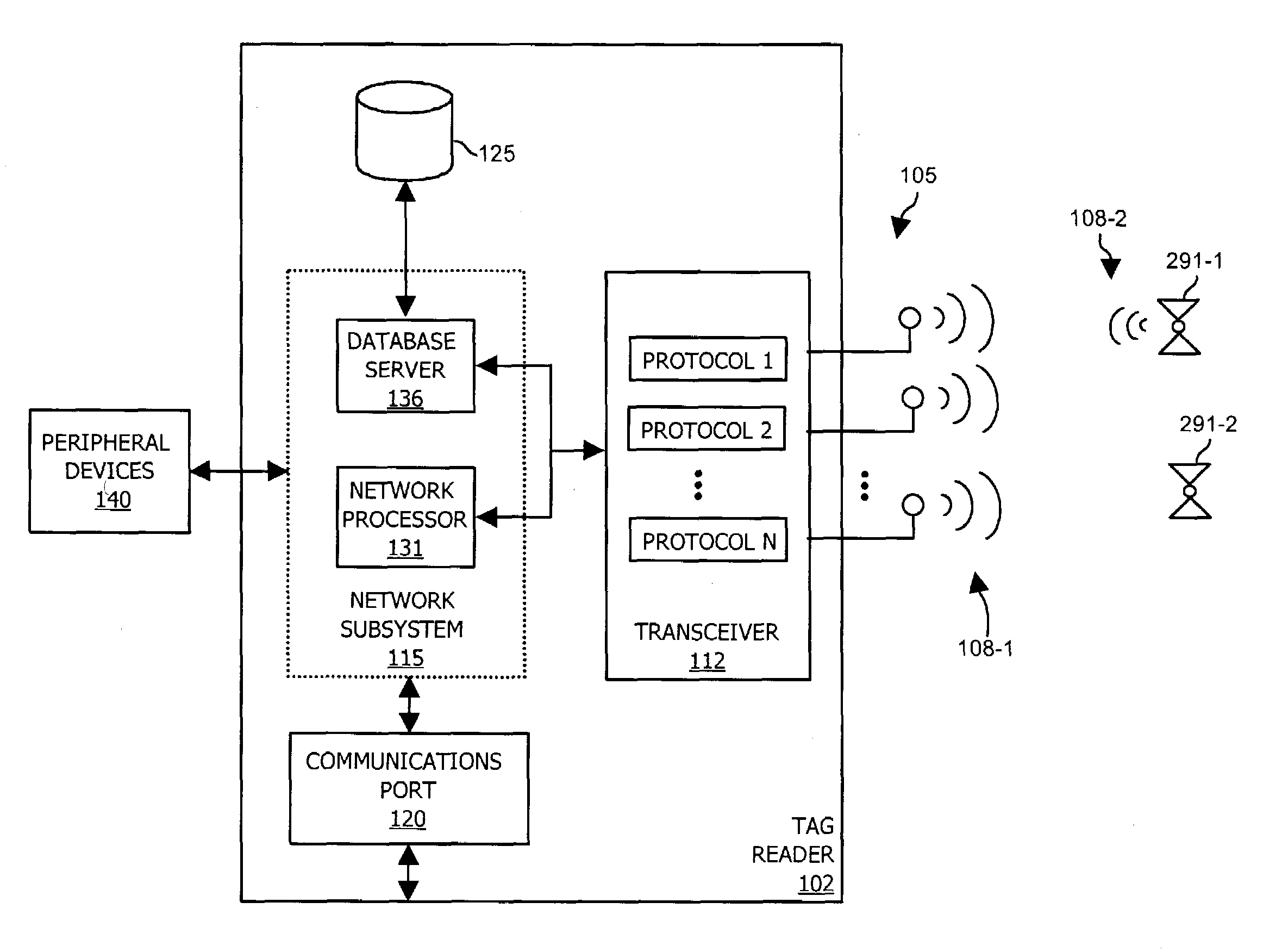
ActiveUS7075412B1Improve efficiencyMemory record carrier reading problemsSubscribers indirect connectionRadio equipmentNetwork interface
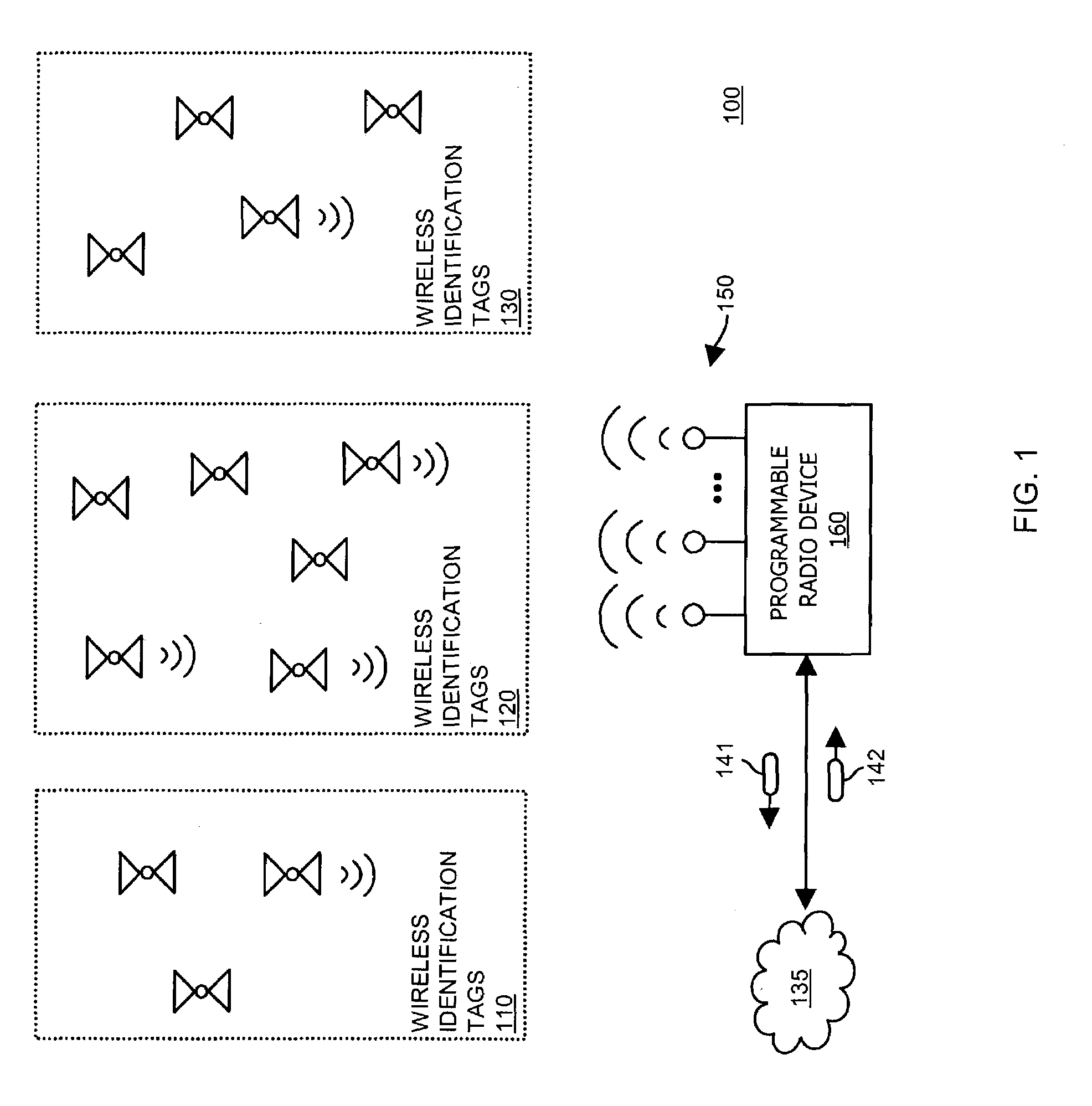
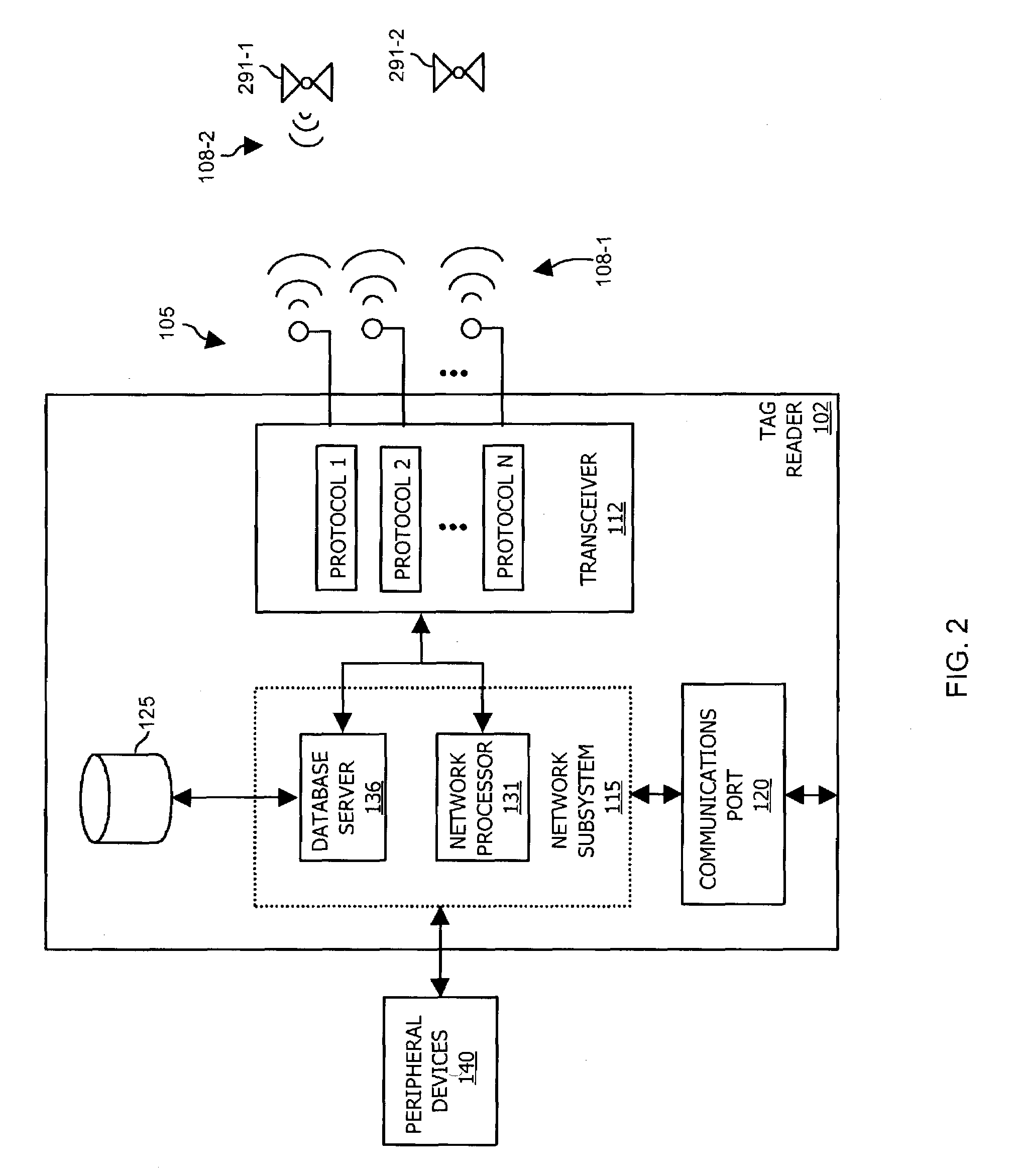
A radio device such as a wireless tag reader communicates with multiple types of wireless identification tags in a monitored region. The radio device includes a network interface to receive messages transmitted over a network. In response to receiving a message indicating to reconfigure the radio device to support an additional wireless tag protocol, the radio is reconfigured to support communications with a corresponding new type of wireless identification tag in a monitored region. Based on this technique of reconfiguring the radio device via network messages, the radio device optionally supports additional, new or latest versions of wireless tag protocols without having to physically reprogram or replace the radio device.
Owner:NOVANTA CORP
Multi-band planar antenna
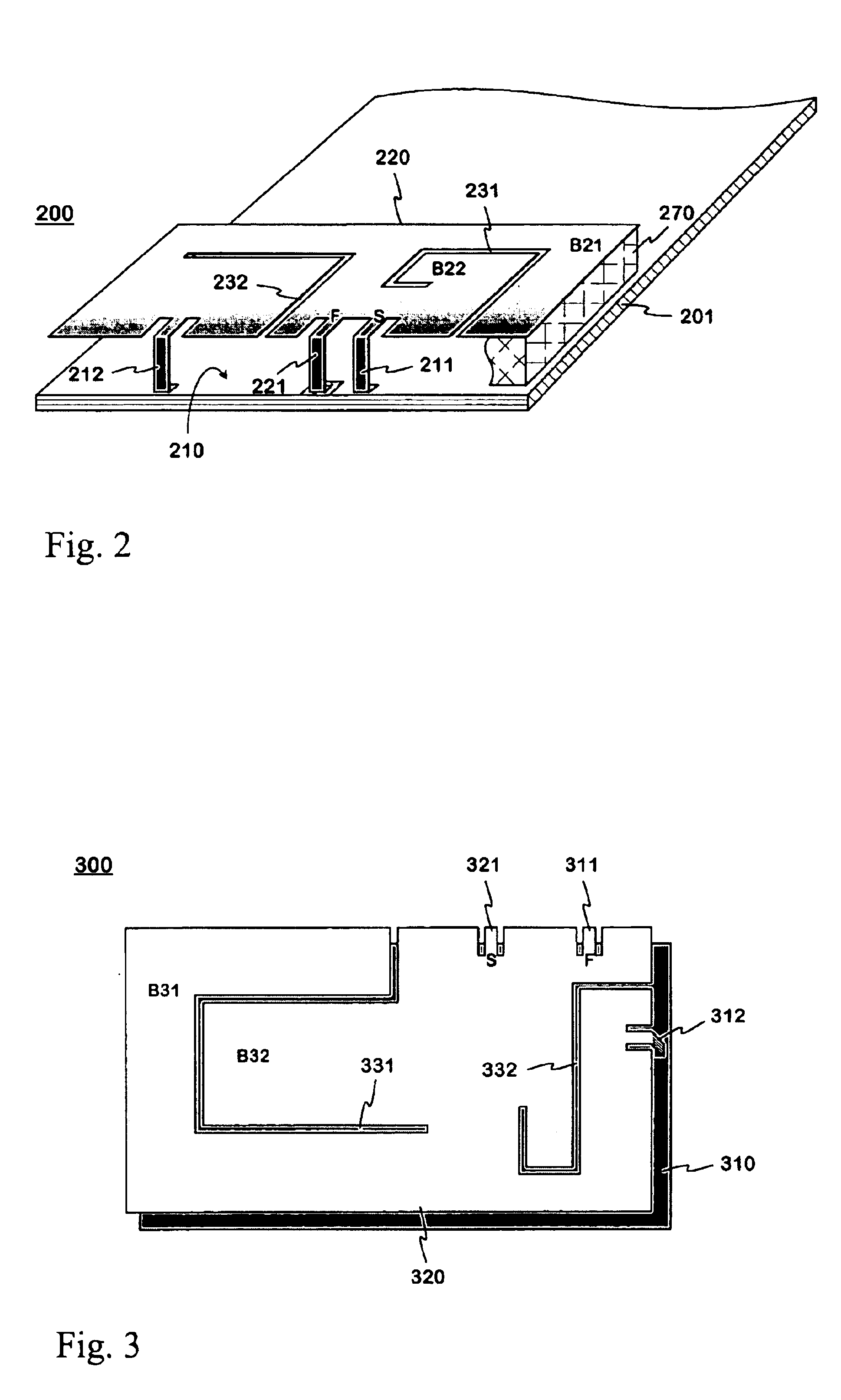
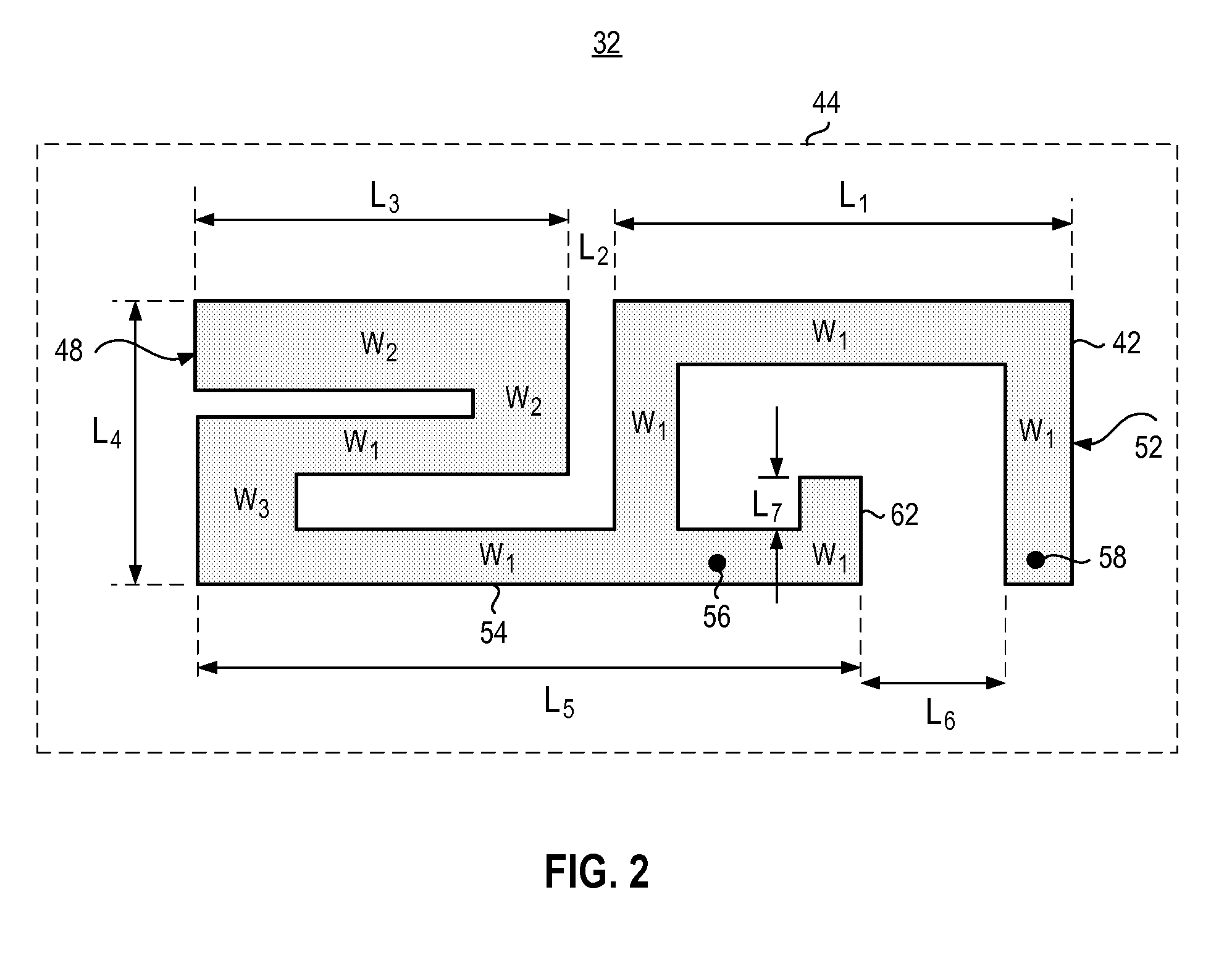
InactiveUS6911945B2Easy to manufactureImprove matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandRadio equipment
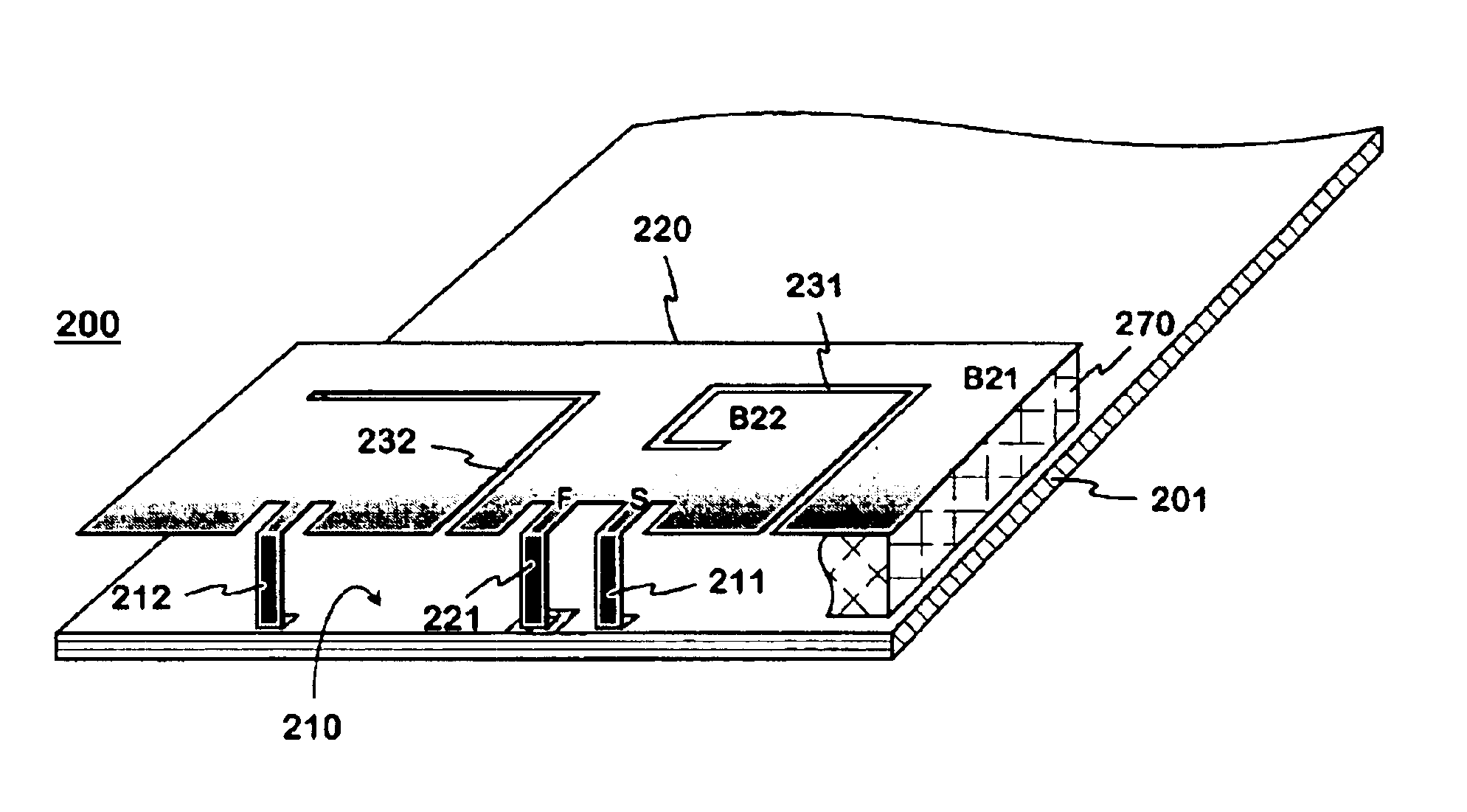
A multi-band planar antenna applicable as an internal antenna in small-sized mobile stations, and to a radio device including an antenna according to the invention. The basis is a conventional dual band PIFA with its feeding and shorting conductors and a non-conducting slot. The planar element (220) has a second slot (232) known as such, which starts at the edge of the planar element on the other side of the feeding conductor (221) and shorting conductor (211) than the above-mentioned slot (231). In addition the structure comprises a second shorting conductor (212) on the other side of the second slot, than the feeding conductor. The second slot acts as a radiator, which for instance broadens the upper band of a dual band antenna. The second shorting conductor facilitates a better matching of a multi-band antenna than in corresponding prior art antennas. The antenna is simple, and its manufacturing costs are relatively low.
Owner:CANTOR FITZGERALD SECURITIES
Mobile robotic with web server and digital radio links
InactiveUS6658325B2Programme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsWeb serviceNetwork Communication Protocols
The invention is a computerized mobile robot with an onboard internet web server, and a capability of establishing a first connection to a remote web browser on the internet for robotic control purposes, and a capability of establishing a second short range bi-directional digital radio connection to one or more nearby computerized digital radio equipped devices external to the robot. The short-range bi-directional digital radio connection will typically have a maximum range of about 300 feet. In a preferred embodiment, this short-range wireless digital connection will use the 2.4 gHz band and digital protocols following the IEEE 802.11, 802.15, or other digital communications protocol. By employing the proper set of external short-range digital radio devices capable of interfacing with the robot (such as sensors, mechanical actuators, appliances, and the like), a remote user on the internet may direct the robot to move within range of the external devices, discover their functionality, and send and receive commands and data to the external devices through the CGI interface on the robot's onboard web server.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Chip antenna and radio equipment including the same
InactiveUS6271803B1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio equipmentElectrical conductor
A chip antenna comprising a basic body made of a ceramic material; a first conductor and a second conductor respectively disposed at least either inside or on the surface of the basic body so as to be close to each other; a feeding terminal for applying a voltage to the first conductor disposed on the surface of the basic body and connected to the first conductor; and a grounding terminal disposed on the surface of the basic body and connected to the second conductor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method and device for authenticated access of a station to local data networks in particular radio data networks
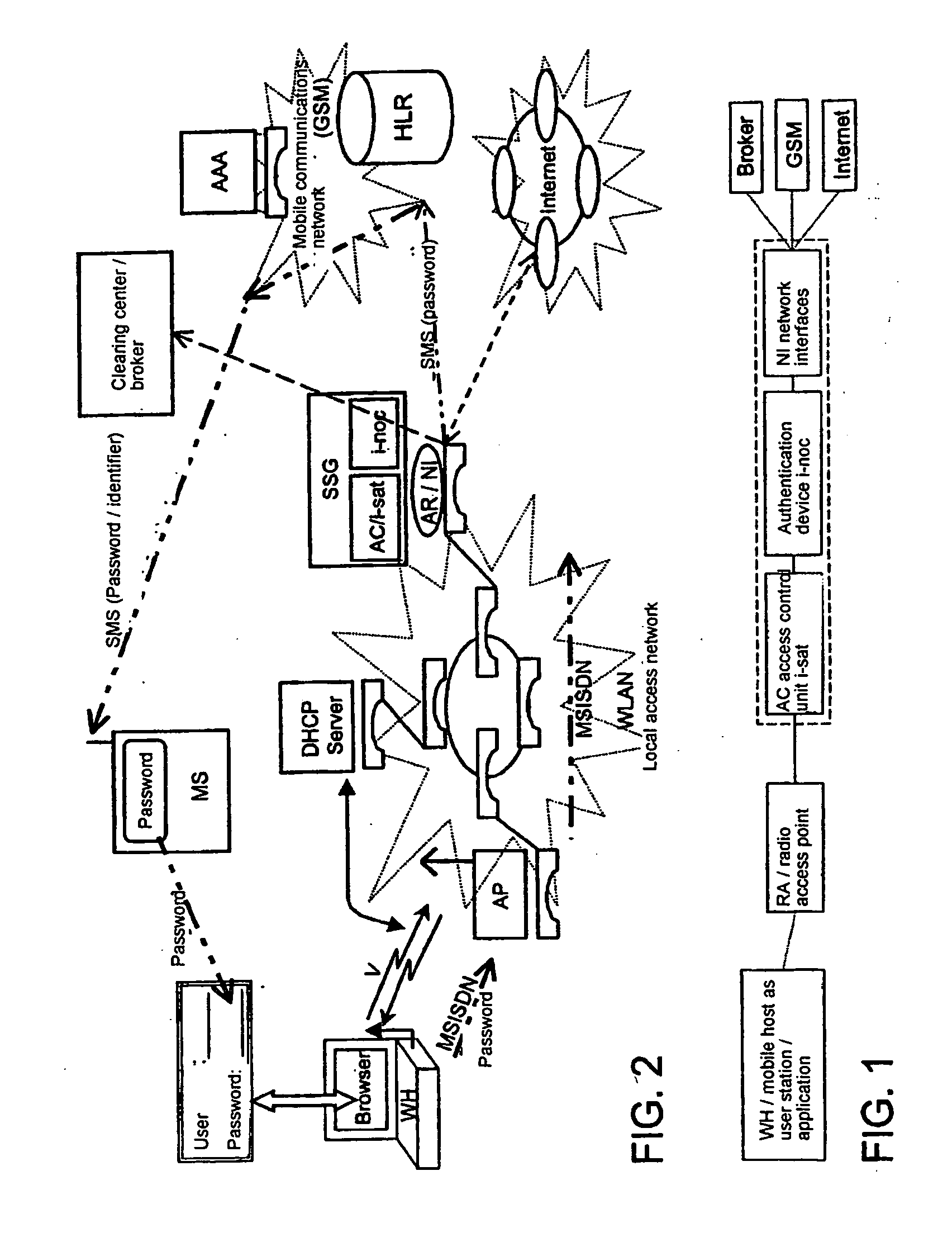
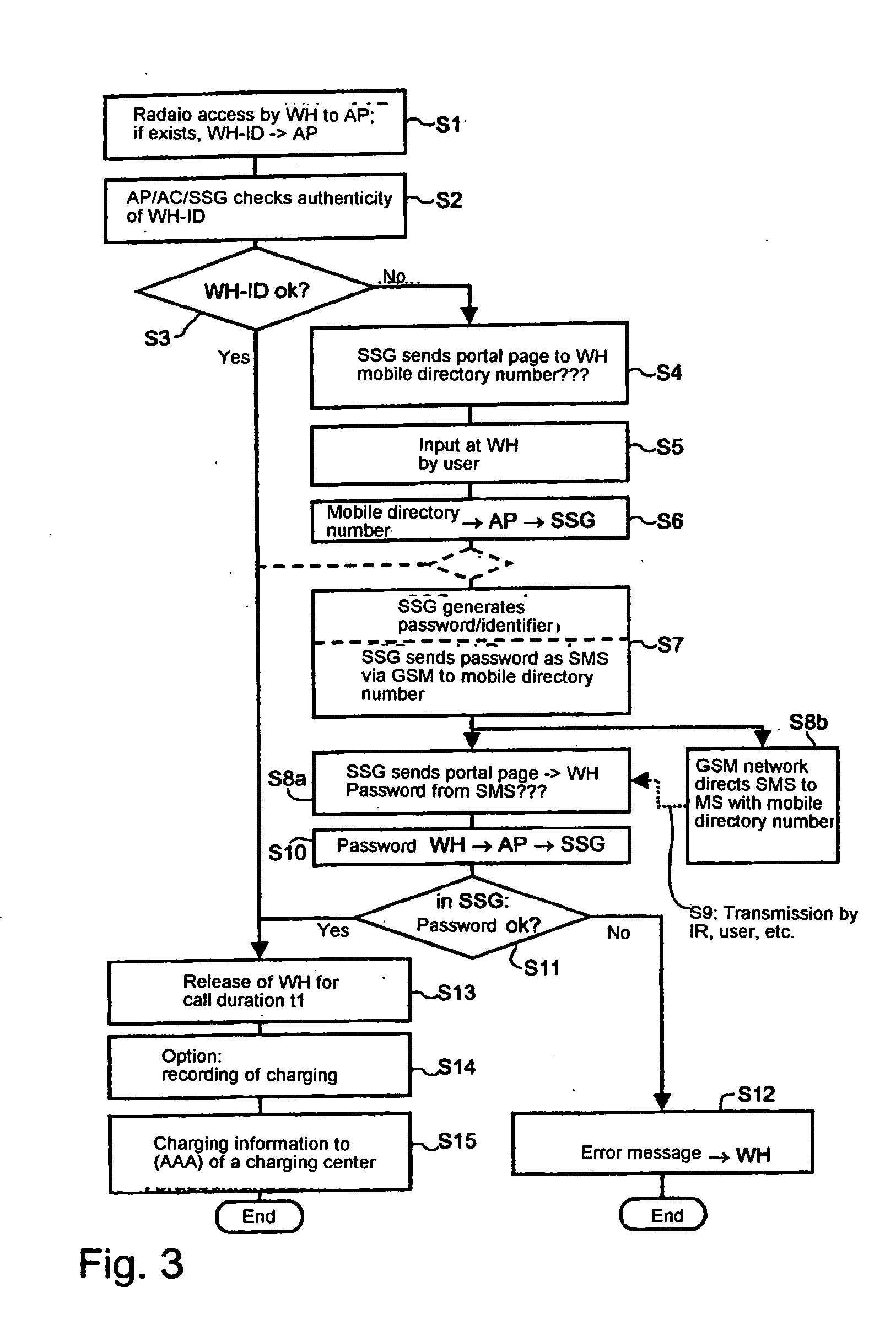
ActiveUS20050048950A1Authentication is simpleEasy to chargeMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionRadio equipmentCommunications system
The invention relates to methods, devices and systems for the authenticated access to a data network by means of a station (WH) compatible with a data network (WLAN), which permit an authentication of the station and user. A device, for example a mobile radio device, is used for the above, which is authenticated in another system. In addition to the authentication, in particular a charging of services in a data network or another communication system (GSM) which is accessible by means of the data network is thus possible.
Owner:MONARCH NETWORKING SOLUTIONS LLC
Mobile robotic with web server and digital radio links
InactiveUS20020173877A1Programme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorWeb serviceNetwork Communication Protocols
The invention is a computerized mobile robot with an onboard internet web server, and a capability of establishing a first connection to a remote web browser on the internet for robotic control purposes, and a capability of establishing a second short range bi-directional digital radio connection to one or more nearby computerized digital radio equipped devices external to the robot. The short-range bi-directional digital radio connection will typically have a maximum range of about 300 feet. In a preferred embodiment, this short-range wireless digital connection will use the 2.4 gHz band and digital protocols following the IEEE 802.11, 802.15, or other digital communications protocol. By employing the proper set of external short-range digital radio devices capable of interfacing with the robot (such as sensors, mechanical actuators, appliances, and the like), a remote user on the internet may direct the robot to move within range of the external devices, discover their functionality, and send and receive commands and data to the external devices through the CGI interface on the robot's onboard web server.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
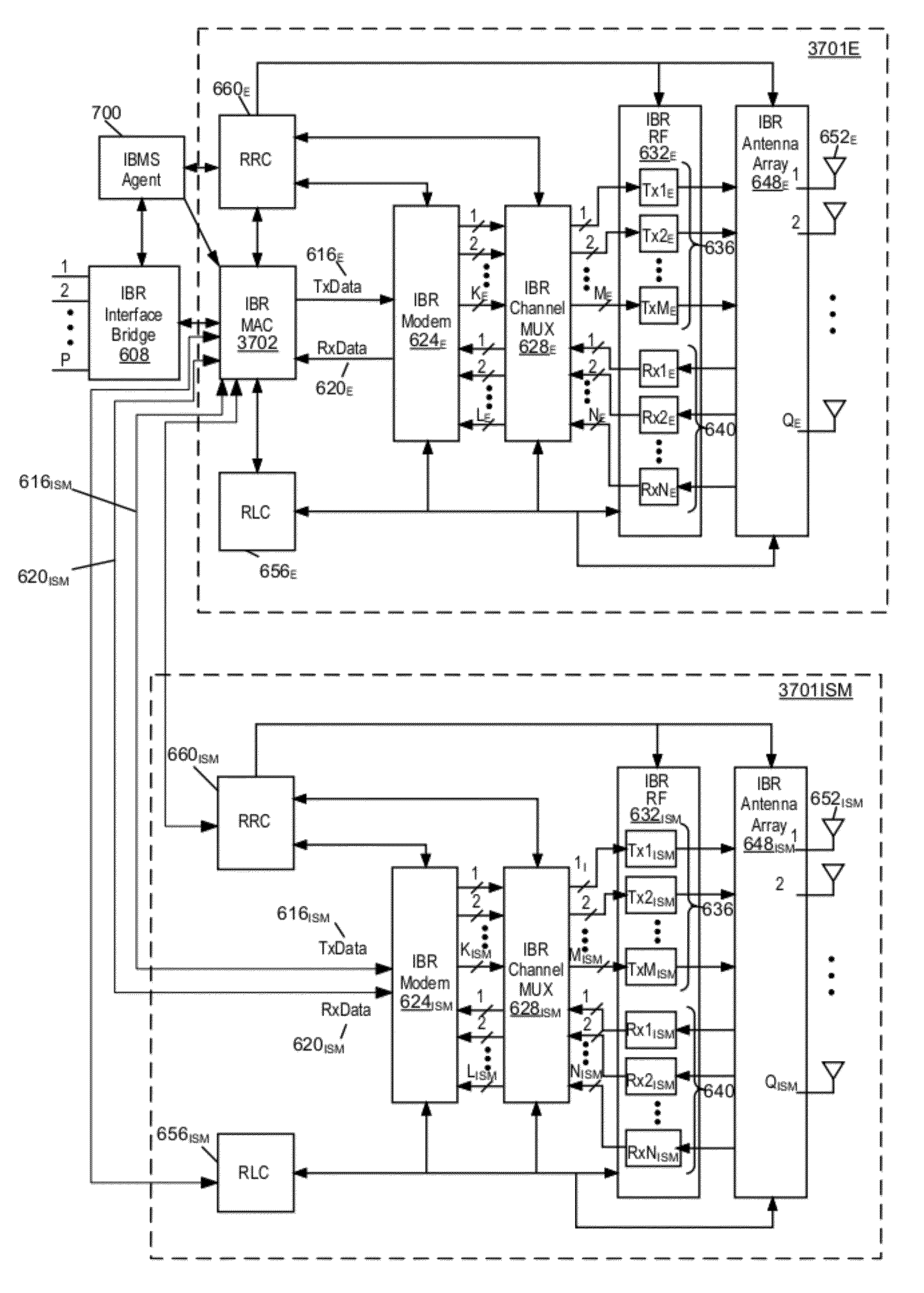
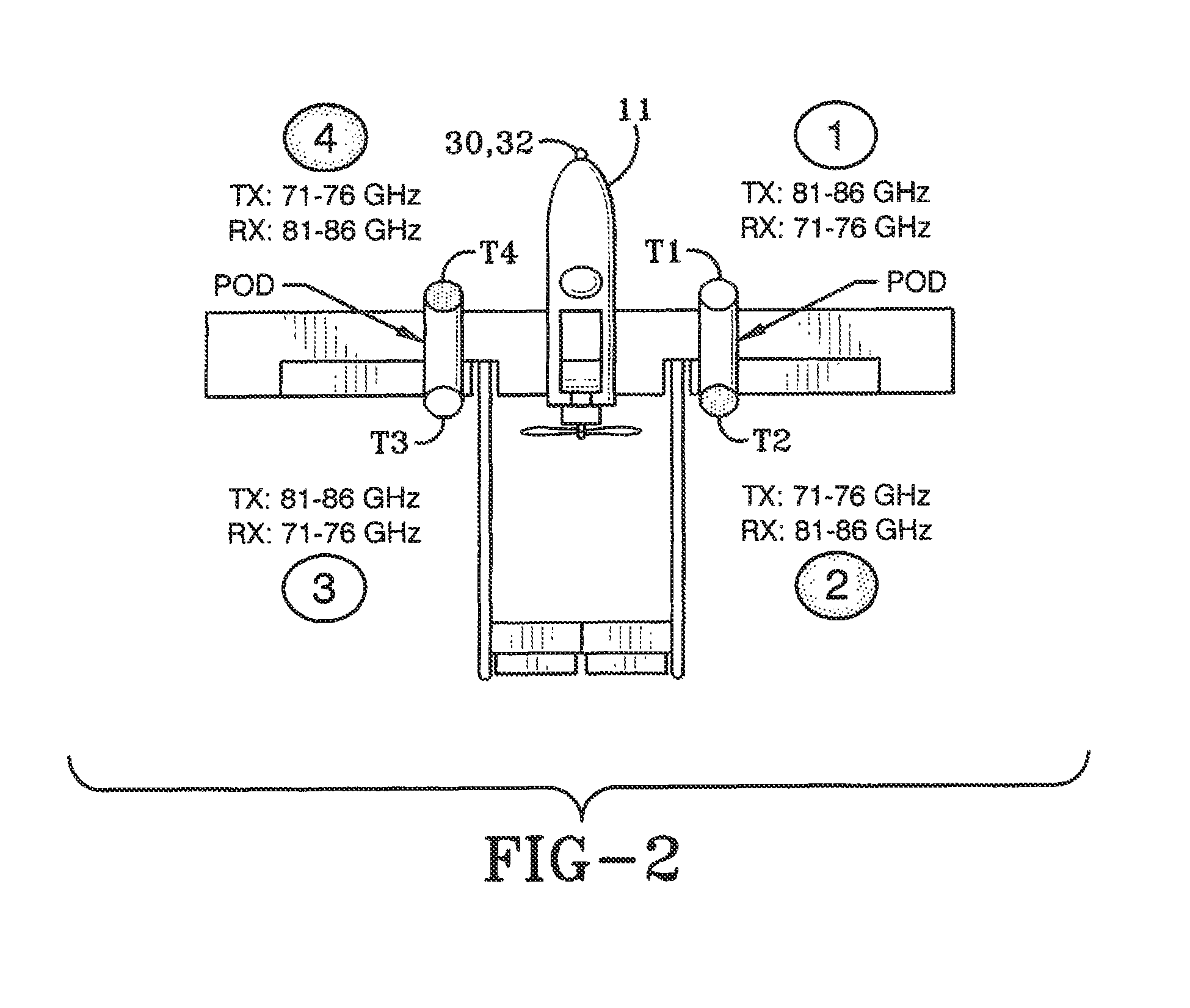
Hybrid band intelligent backhaul radio
ActiveUS8385305B1Reduce the time required for installationReduce installation costsNetwork topologiesFrequency-division multiplexRadio equipmentMedia access control
A hybrid band intelligent backhaul radio (HB-IBR) is disclosed that is a combination of two radios operating in different bands. Embodiments include a dual radio configuration wherein a first radio operates in a non-line of sight (NLOS) radio link configuration and a second ancillary radio operates in a near line of sight or line of sight configuration (n)LOS. For example, the HB-IBR may have an Intelligent Backhaul Radio (IBR) operating in the non-line of sight mode of operation within the 5.8 GHz unlicensed band, and have an ancillary radio link operating in the FCC part 101E band of operation at 60 GHz. A common medium access control (MAC) block may be utilized between the dual radios.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Techniques for ad-hoc mesh networking
ActiveUS20050282494A1Maximize efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesUltra-widebandRadio equipment
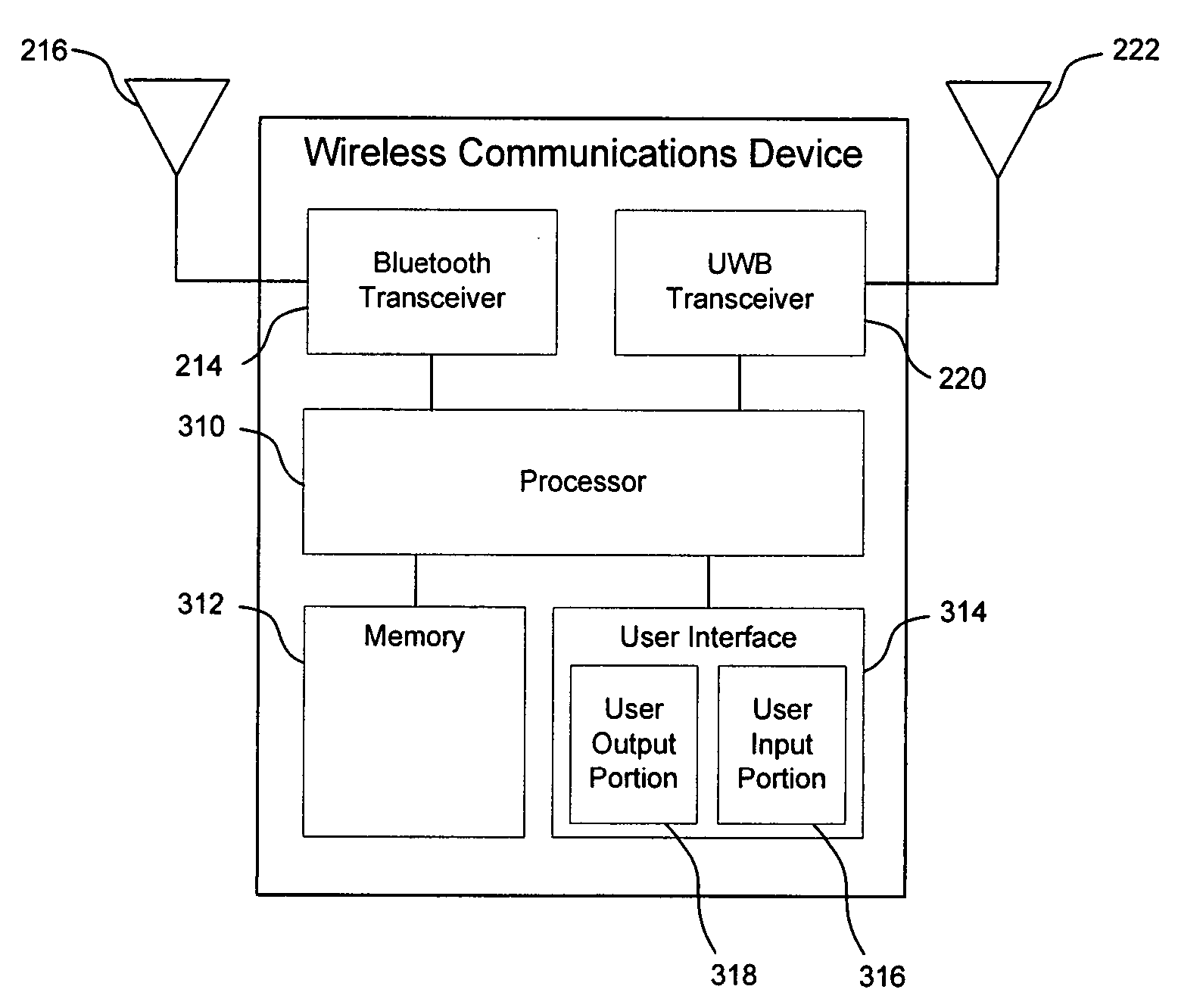
A wireless communications device includes a first radio and a second radio. The first radio is receives information regarding an ad-hoc mesh wireless network from at least one remote device. The second radio exchanges user data with the ad-hoc wireless mesh network. The wireless communications device also includes a buffer and a scheduler. The buffer stores user data for transmission to one or more remote devices in the ad-hoc wireless mesh network. The scheduler schedules transmissions by the second radio of the user data based on the received information. The first and second radios may employ various communications technologies. Examples of such technologies include Bluetooth, wireless local area network (WLAN), and ultra wideband (UWB). The information received from the remote device may include one or more of the following: configuration information (e.g., topology information) corresponding to the ad-hoc wireless mesh network; routing information; and information regarding communications capabilities of one or more nodes within the ad-hoc wireless mesh network.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS6462716B1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS20020044092A1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
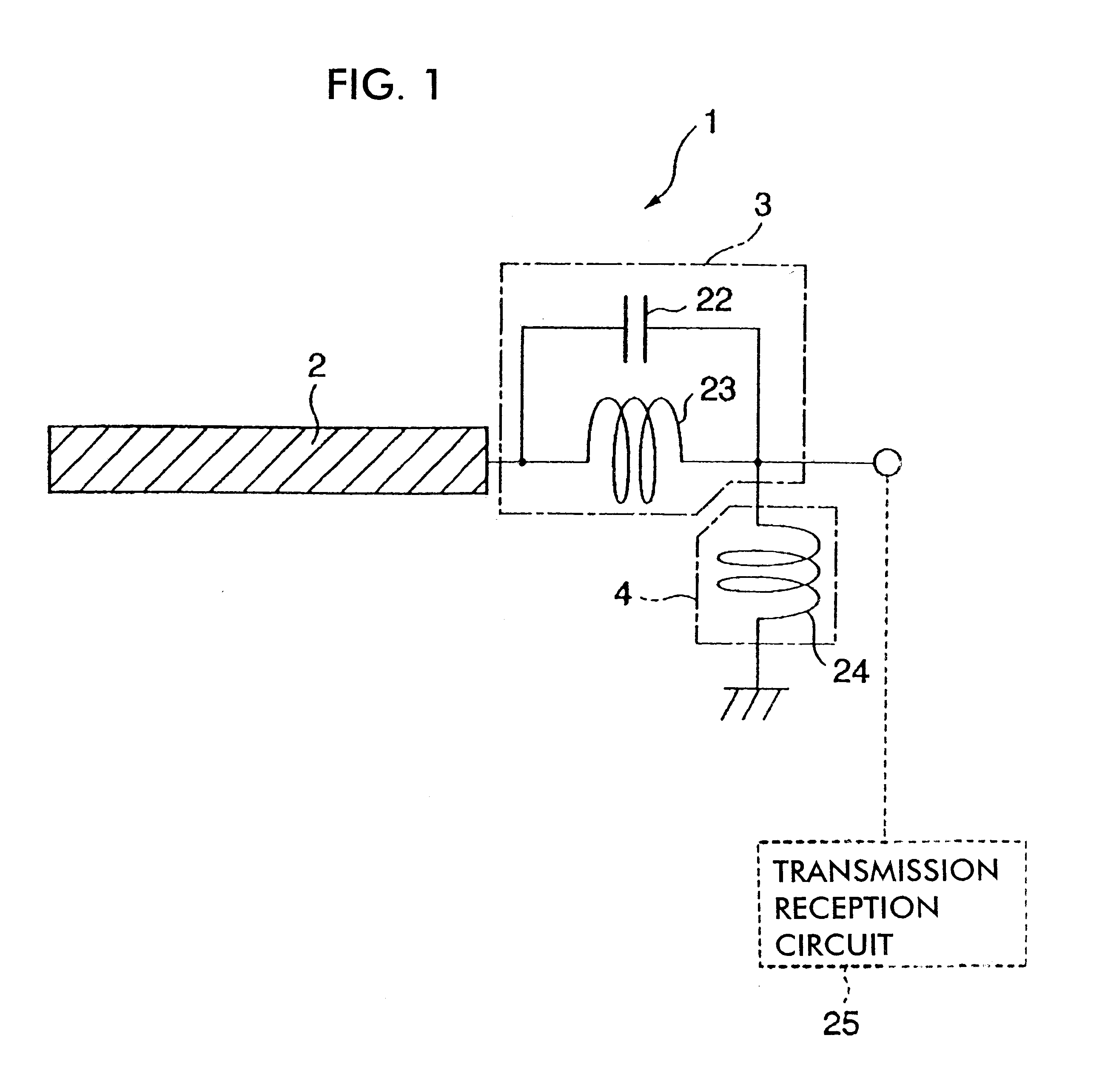
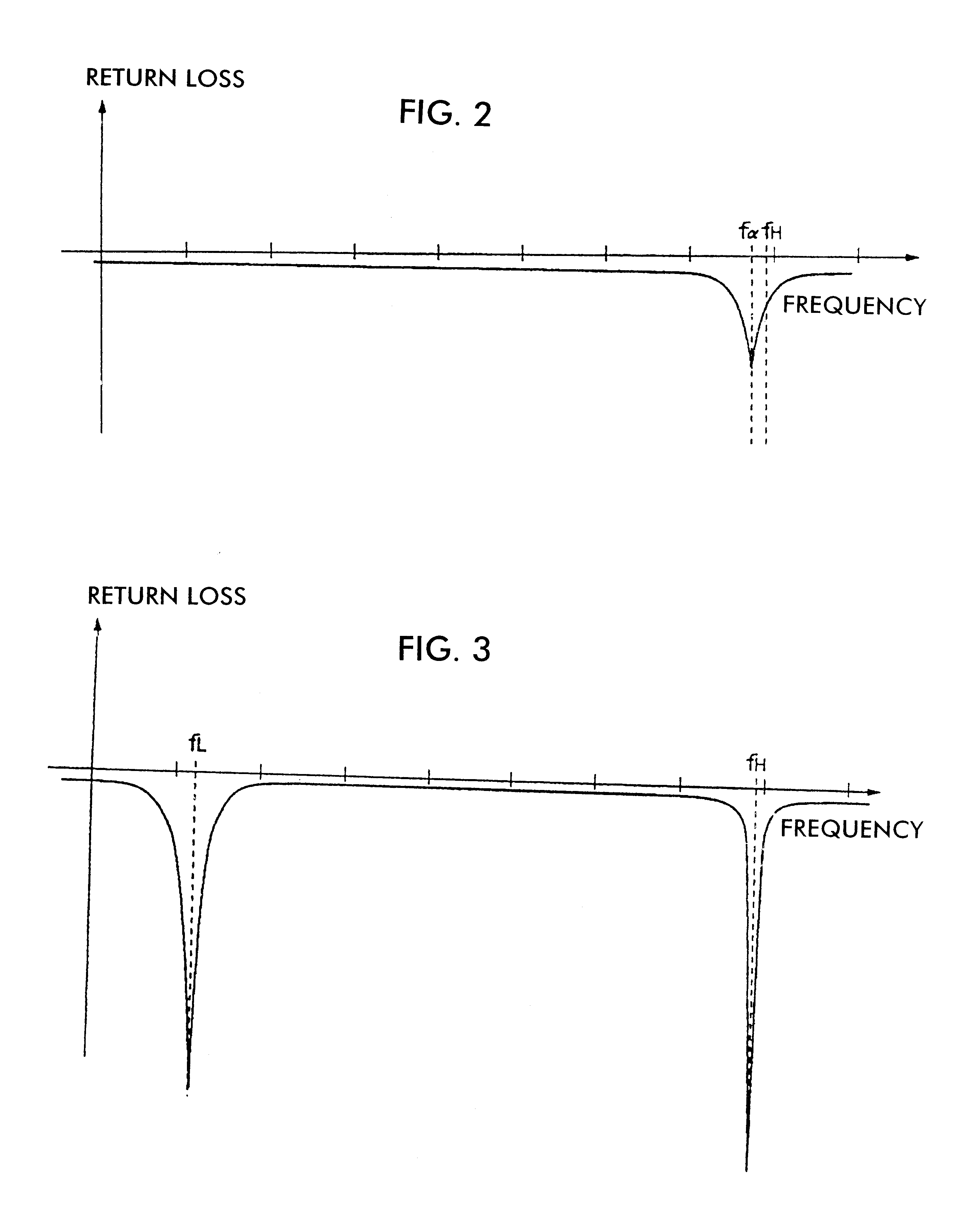
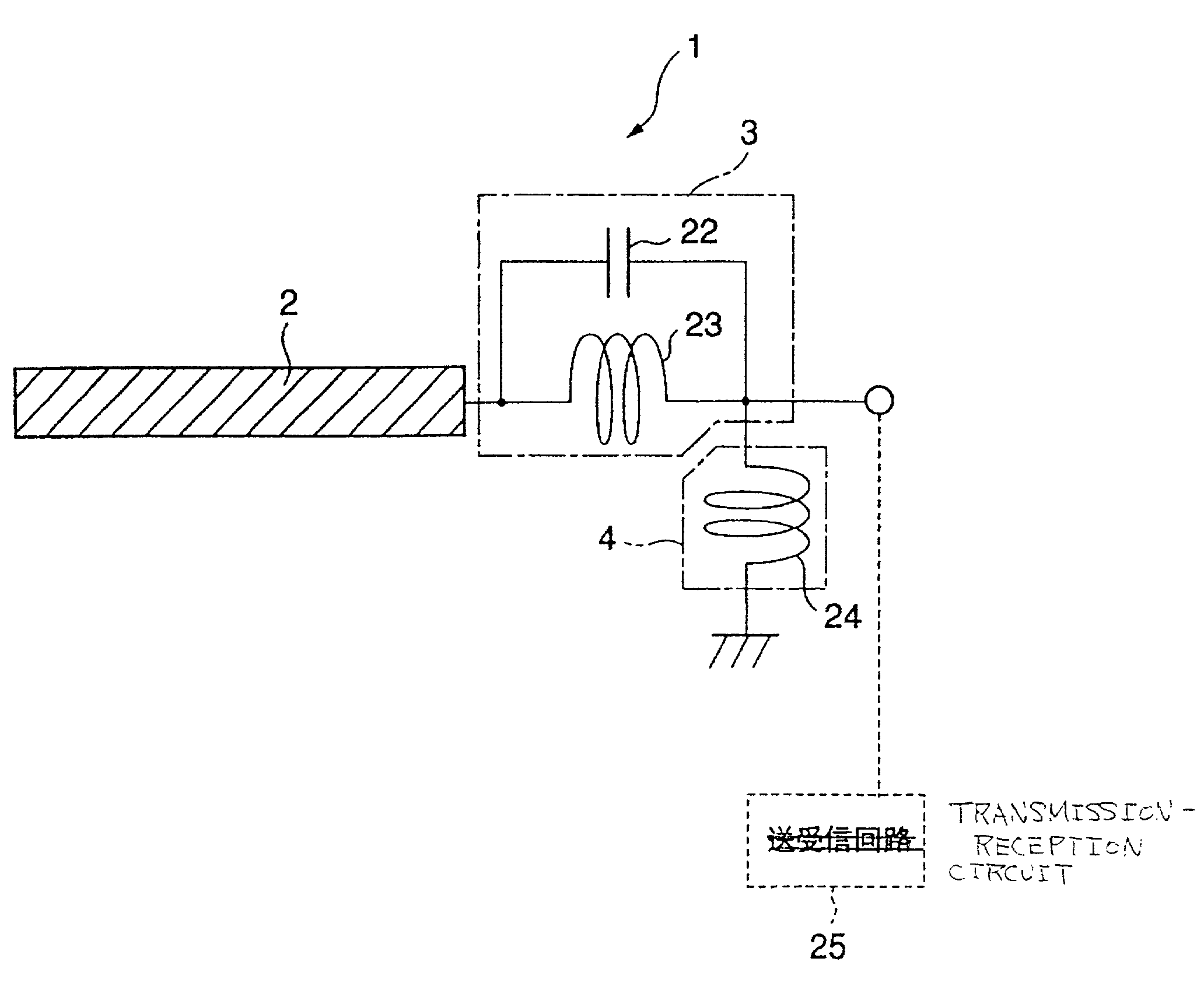
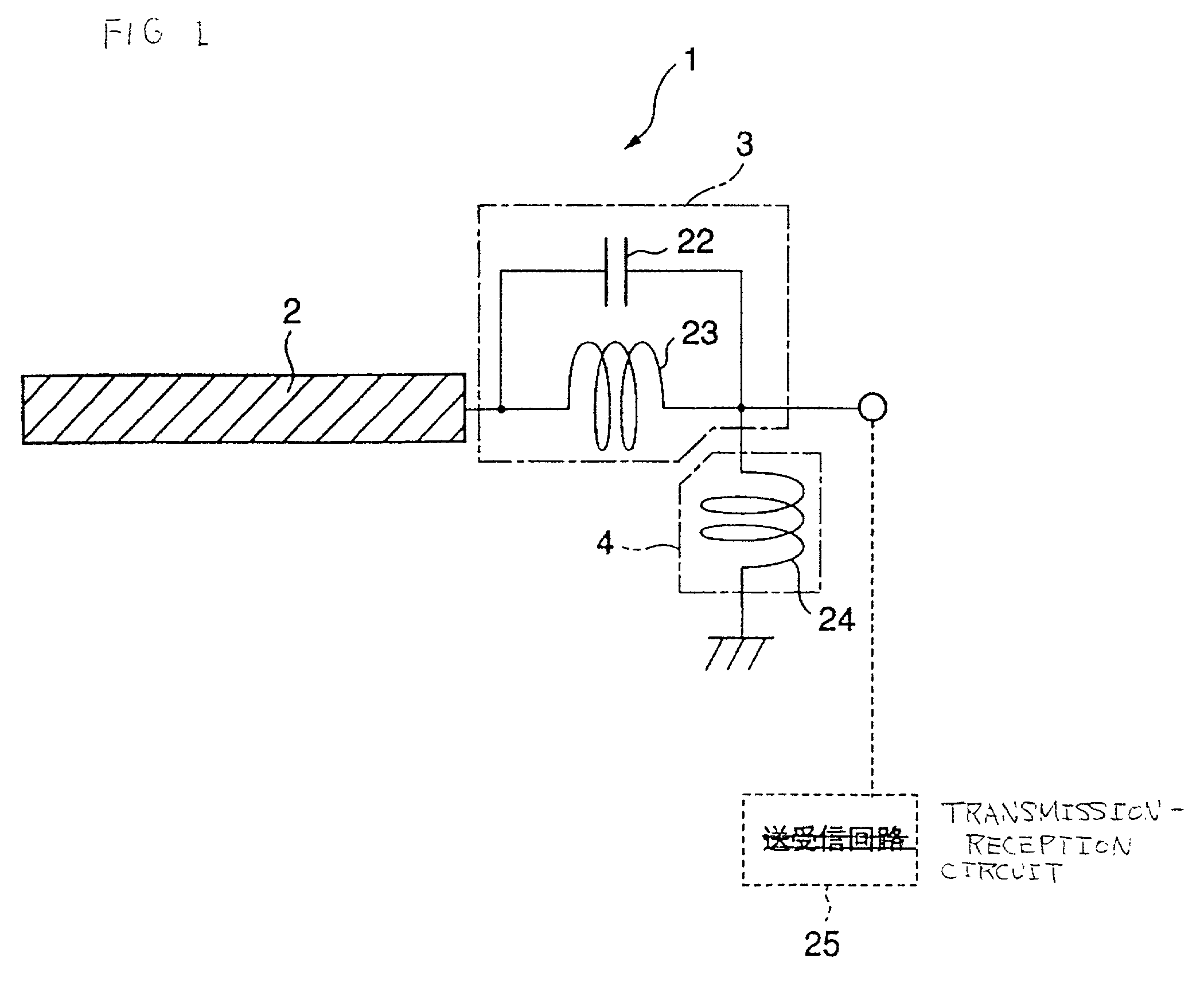
An LC parallel resonance circuit is connected in series with the power supply side of the antenna conductor portion. The antenna conductor portion is configured so as to resonate at a frequency slightly lower than the center frequency in the higher frequency band of two frequency bands for transmitting and receiving radio waves. The LC parallel resonance circuit is configured so as to resonate substantially at the center frequency in the lower frequency band for transmitting and receiving a radio wave and be capable of providing to the antenna conductor portion a capacitance for causing the antenna conductor portion to resonate at the center frequency in the higher frequency band. Thus, a circuit for changing the upper and lower frequency bands is not needed. Such a change-over circuit, which is complicated, causes problems in that the conduction loss increases, and the antenna sensitivity deteriorates. Without need of the change-over circuit, the conduction loss can be reduced, the antenna sensitivity can be enhanced and costs can be reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Content output device
InactiveUS20060190577A1Improve responsivenessImprove response characteristicsDigital computer detailsTransmissionInternet radio deviceRadio equipment
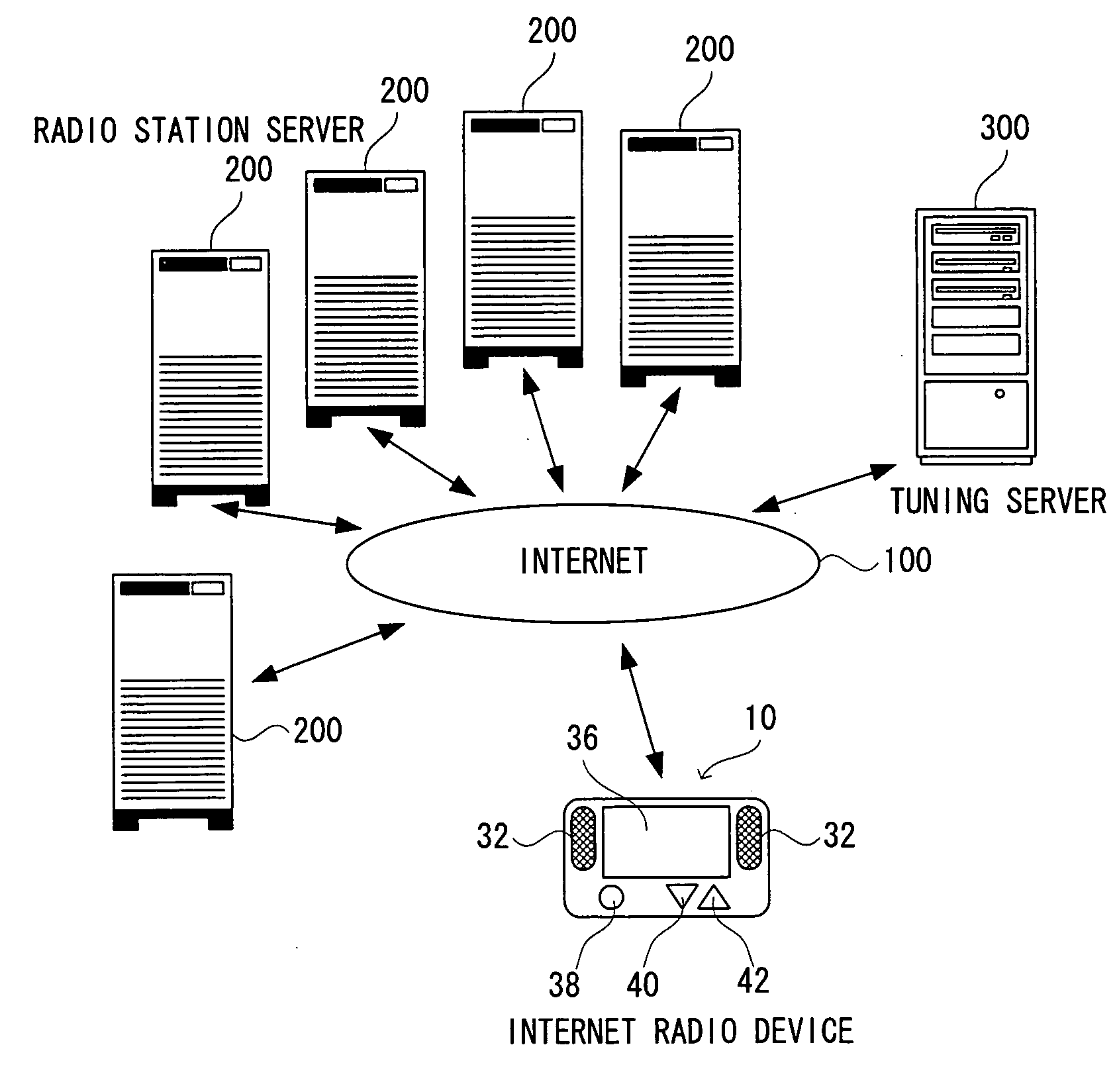
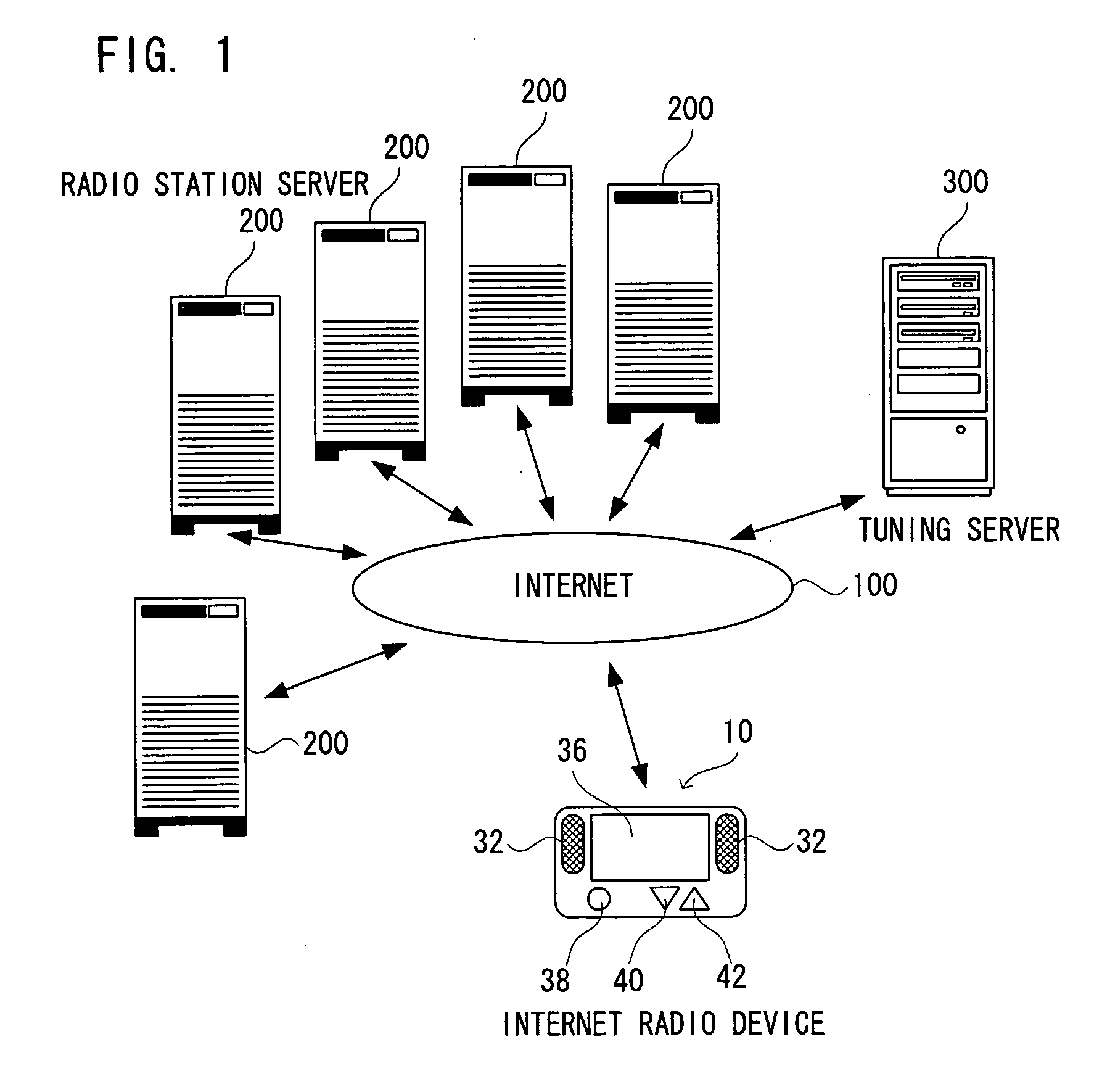
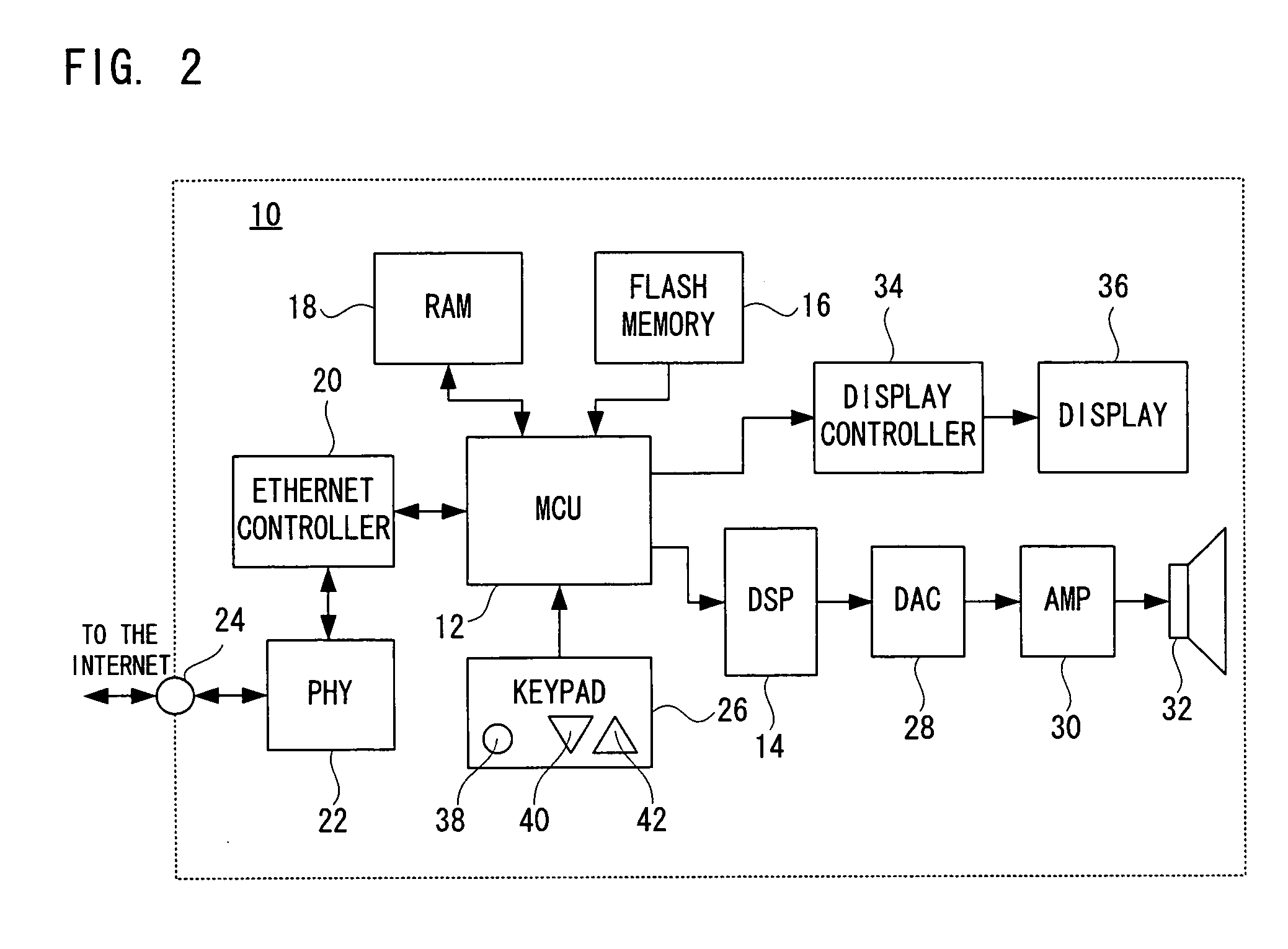
An Internet radio device (10), when an N-th radio station server (200) is selected, receives streaming contents from five N−2-th to N+2-th radio station servers (200, 200, . . . ), writes them respectively into five buffers, and reads only the streaming content from the N-th radio station server (200) via the buffer and reproduces it. After that, when a station change operation is performed for a change to a neighboring station, that is, the N−1-th or N+1-th radio station server (200), the Internet radio device (10) reads only the streaming content from the N−1-th or N+1-th radio station server (200) via the buffer and reproduces it.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
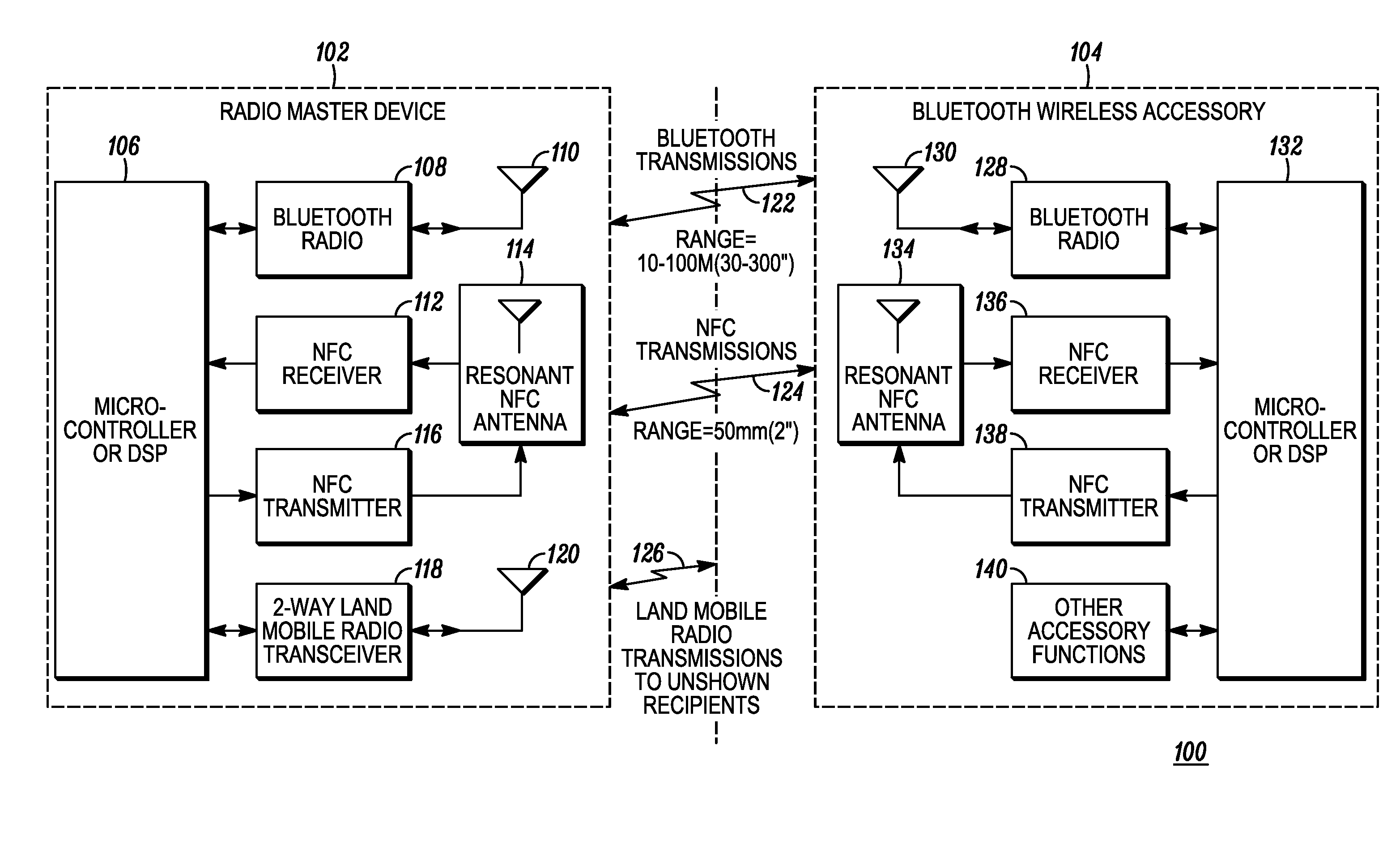
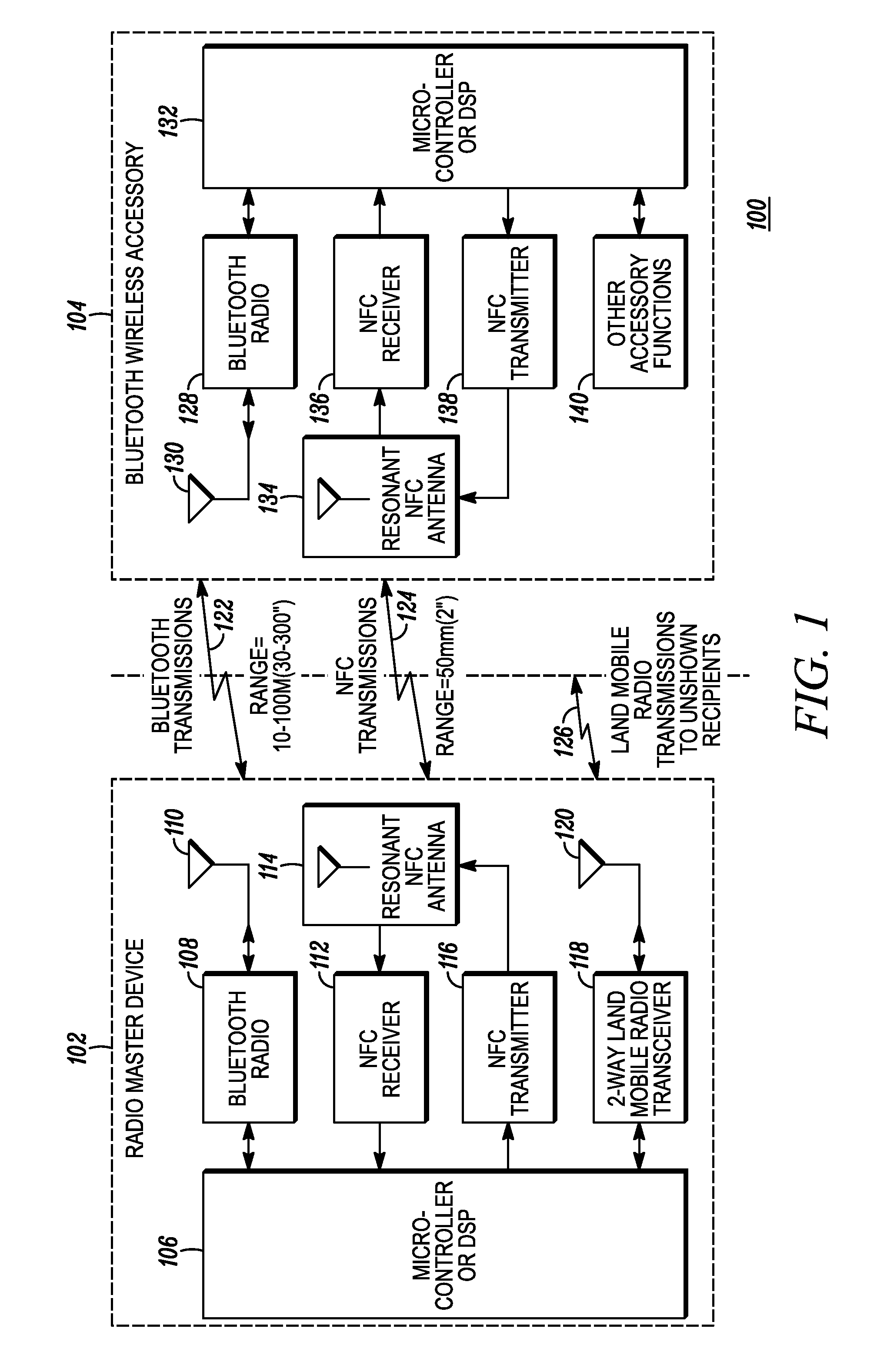
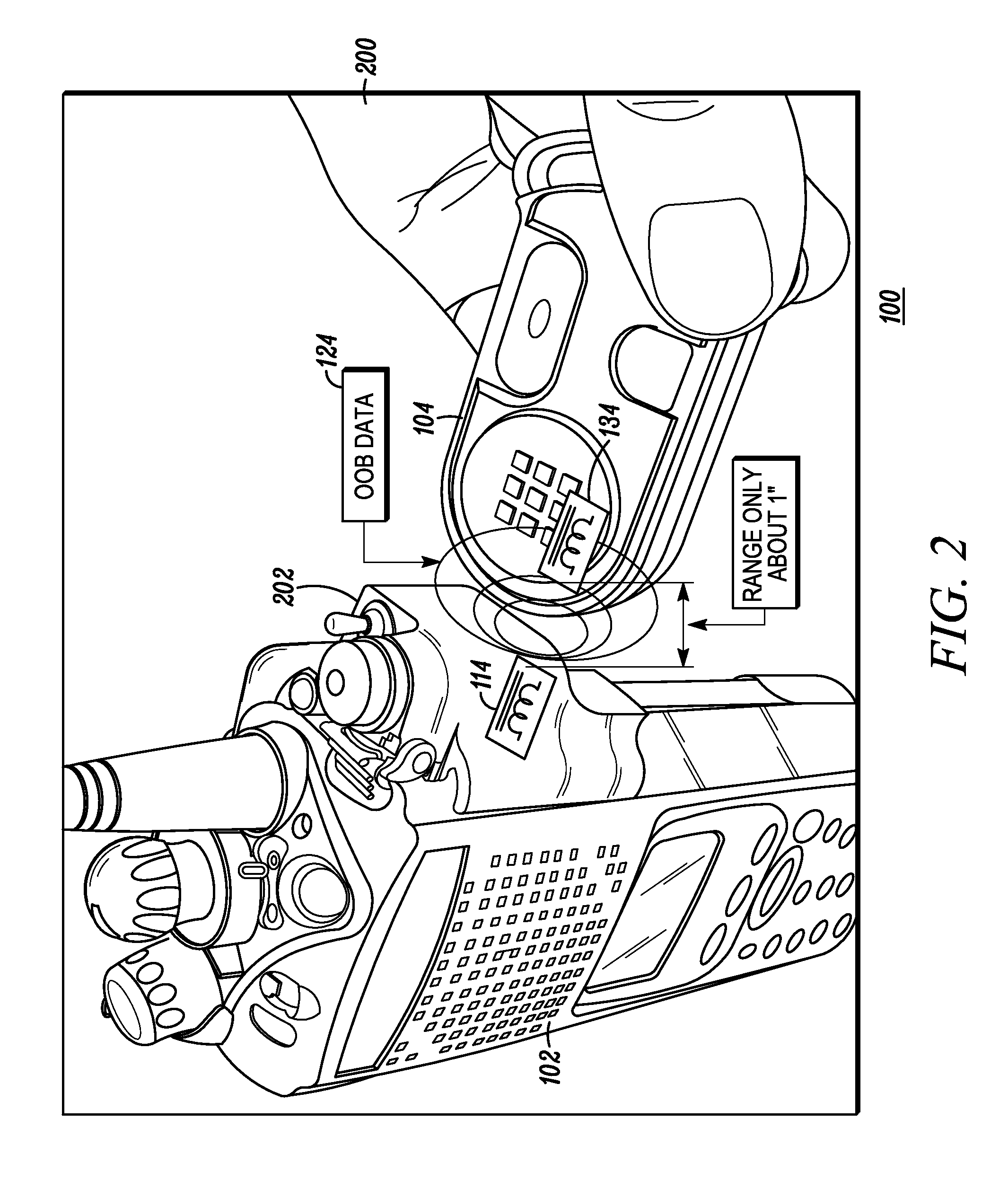
Method and system for near-field wireless device pairing
A first communication device (e.g., a radio) and a second communication device (e.g., an accessory) implement a wireless device pairing procedure to exchange numerical credentials so that the devices can subsequently form a link for communications using electromagnetic radio signals. The accessory transmits a beacon comprises a pairing request. Upon a user bringing the radio and accessory in close enough proximity, the radio receives the beacon using near-field apparatus included in the radio. In response to receiving the beacon, the radio initiates a pairing procedure, wherein the pairing procedure comprises a data exchange between the radio and accessory, and wherein the beacon and the data exchange comprise a non-propagating radio signal generated using the near-field apparatus. Upon completing the pairing procedure, the radio forms a link with the accessory to communicate using propagating electromagnetic radio signals.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
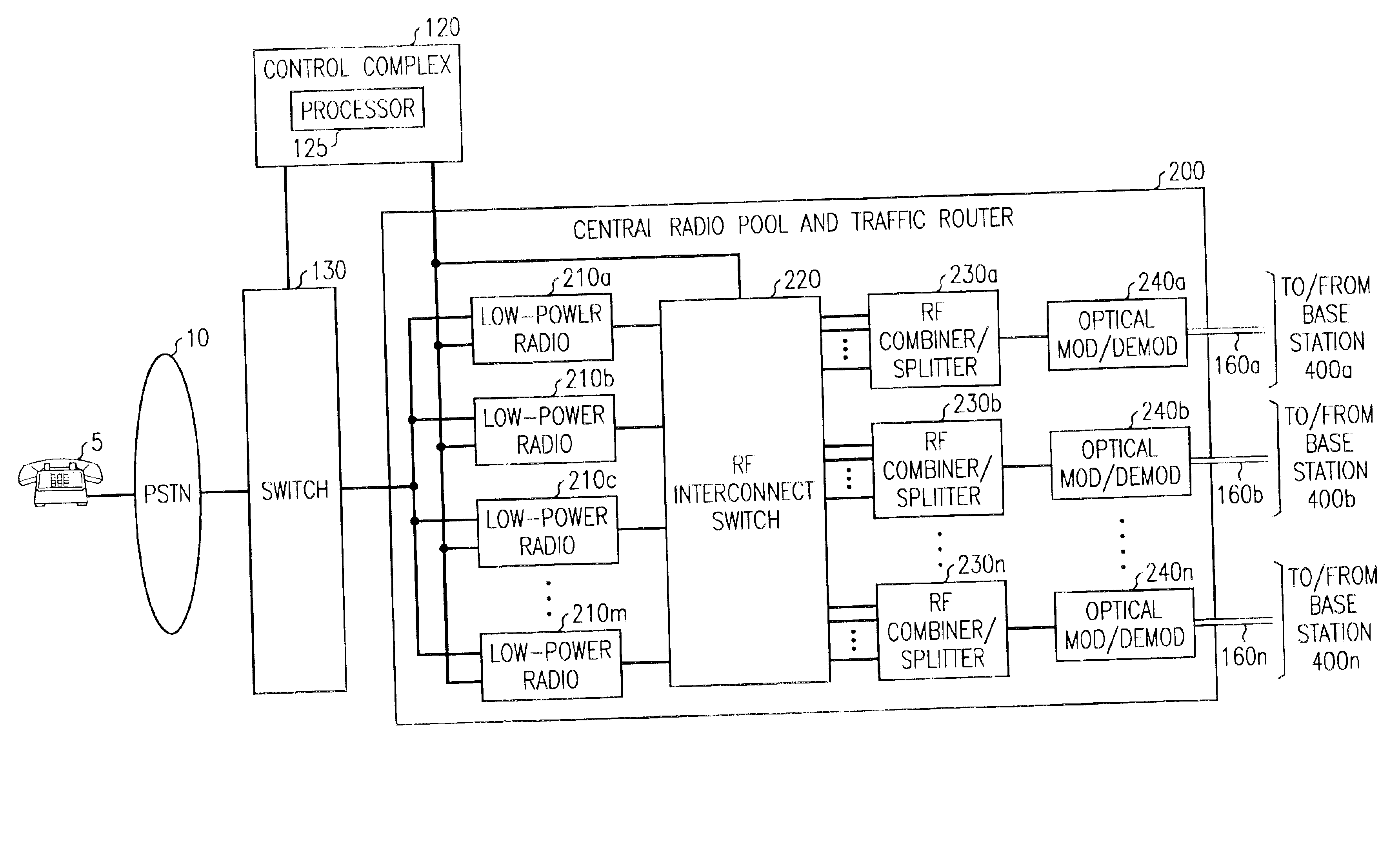
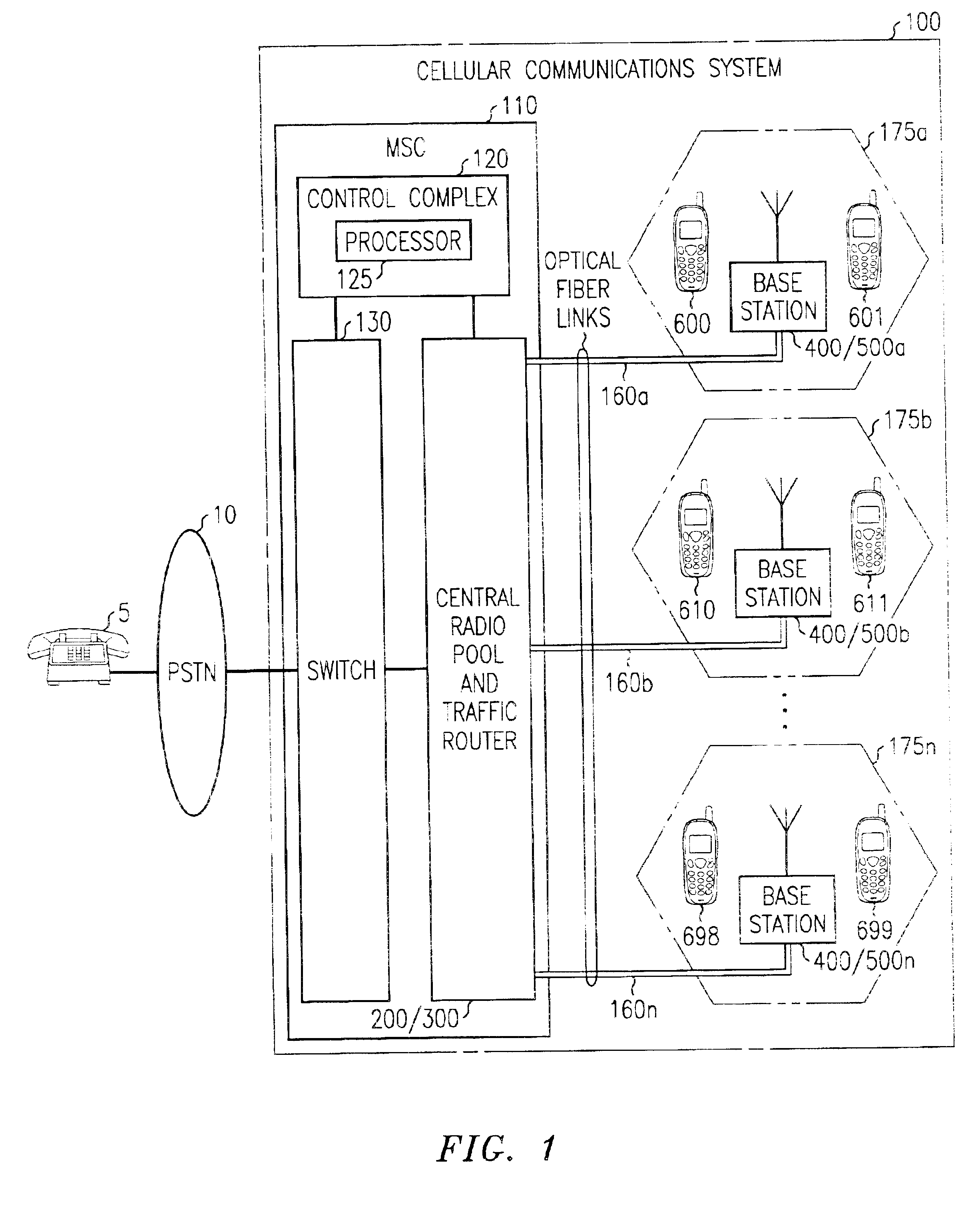
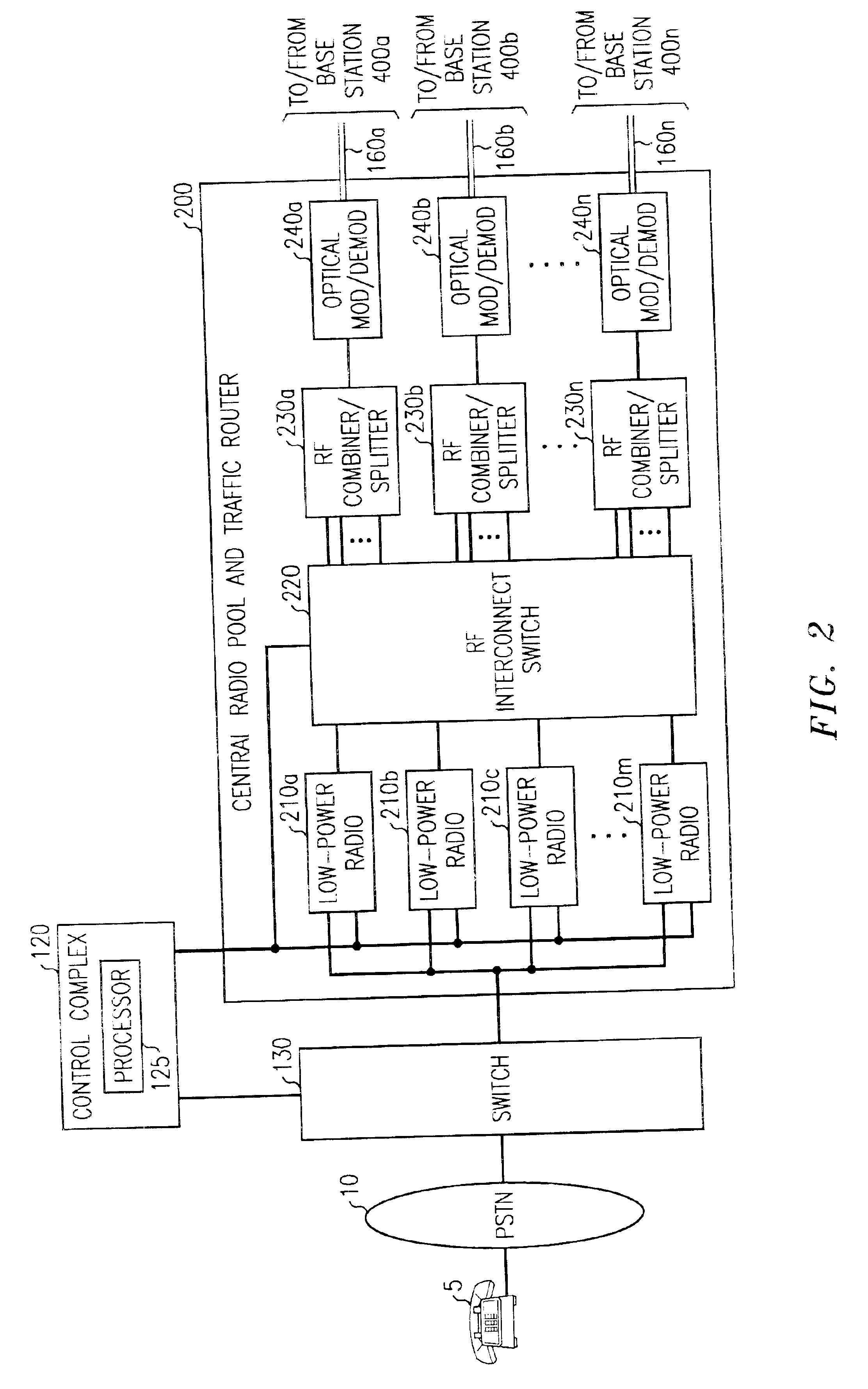
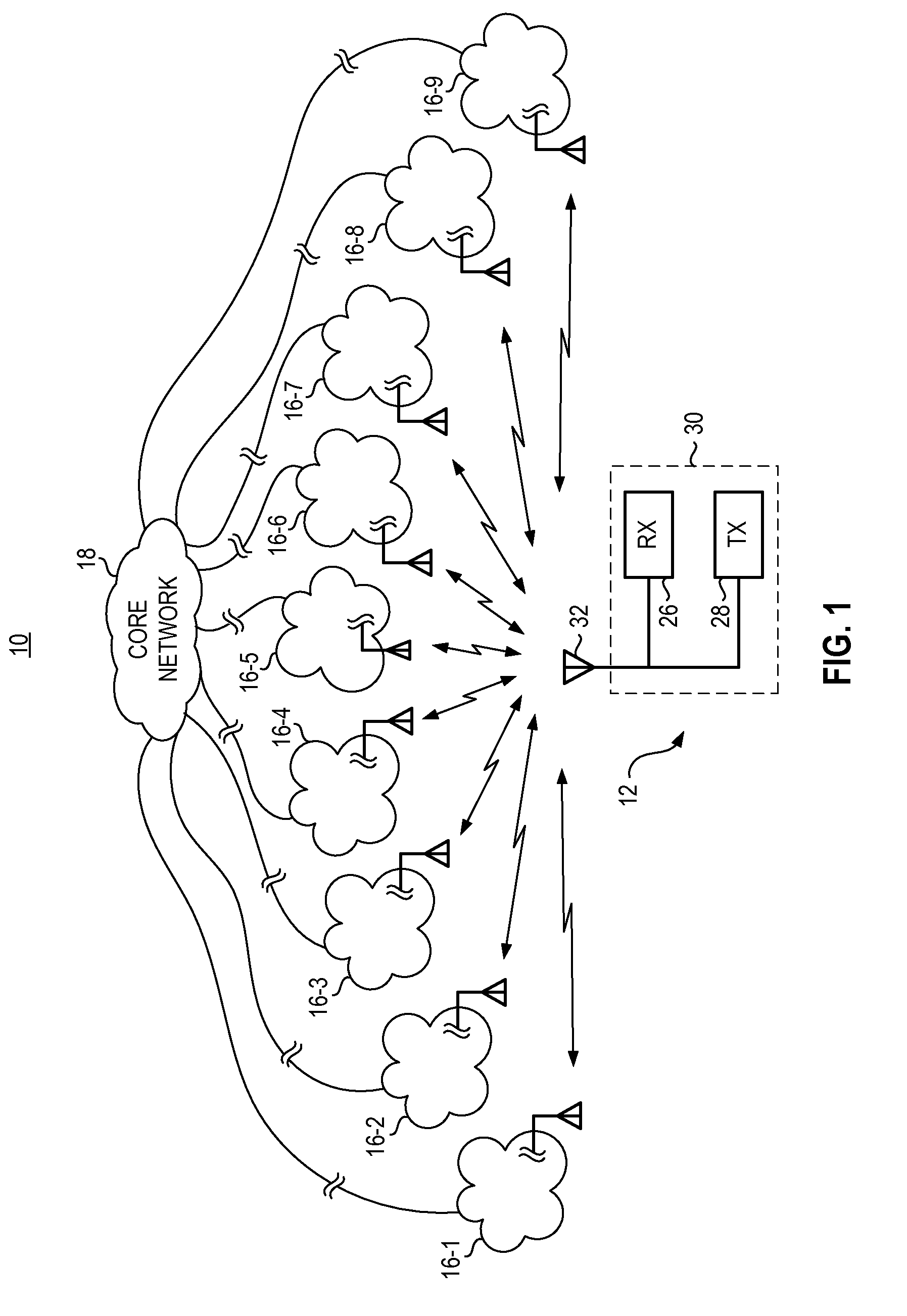
Cellular communications system featuring a central radio pool/traffic router
InactiveUS6865390B2Easy to useEasy maintenanceSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFiberRadio equipment
The present invention provides a cellular communication system that includes a central radio pool / traffic router (CRP / TR) that sends control and traffic signals over fiber optic transmission links that connect the CRP / TR with base stations of the cellular communication system. The high bandwidth capacity of each fiber link allows a large band of radio frequencies representing many radio channels to pass between the CRP / TR and individual base stations. Radio resources can be shared by all base stations in the cellular communication system, dynamically, when and where needed, to meet access demands throughout the system. The CRP / TR includes low-powered digital and / or analog radios and also switching and modulation means used to convey signals between the radios and various base stations within the system.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
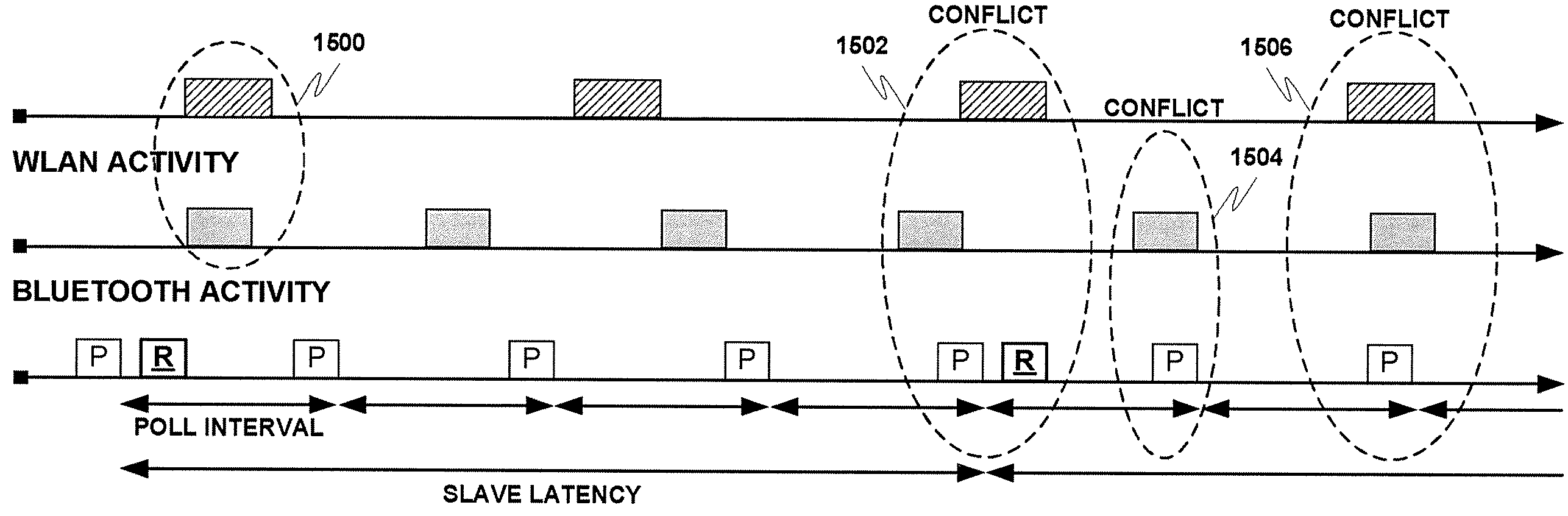
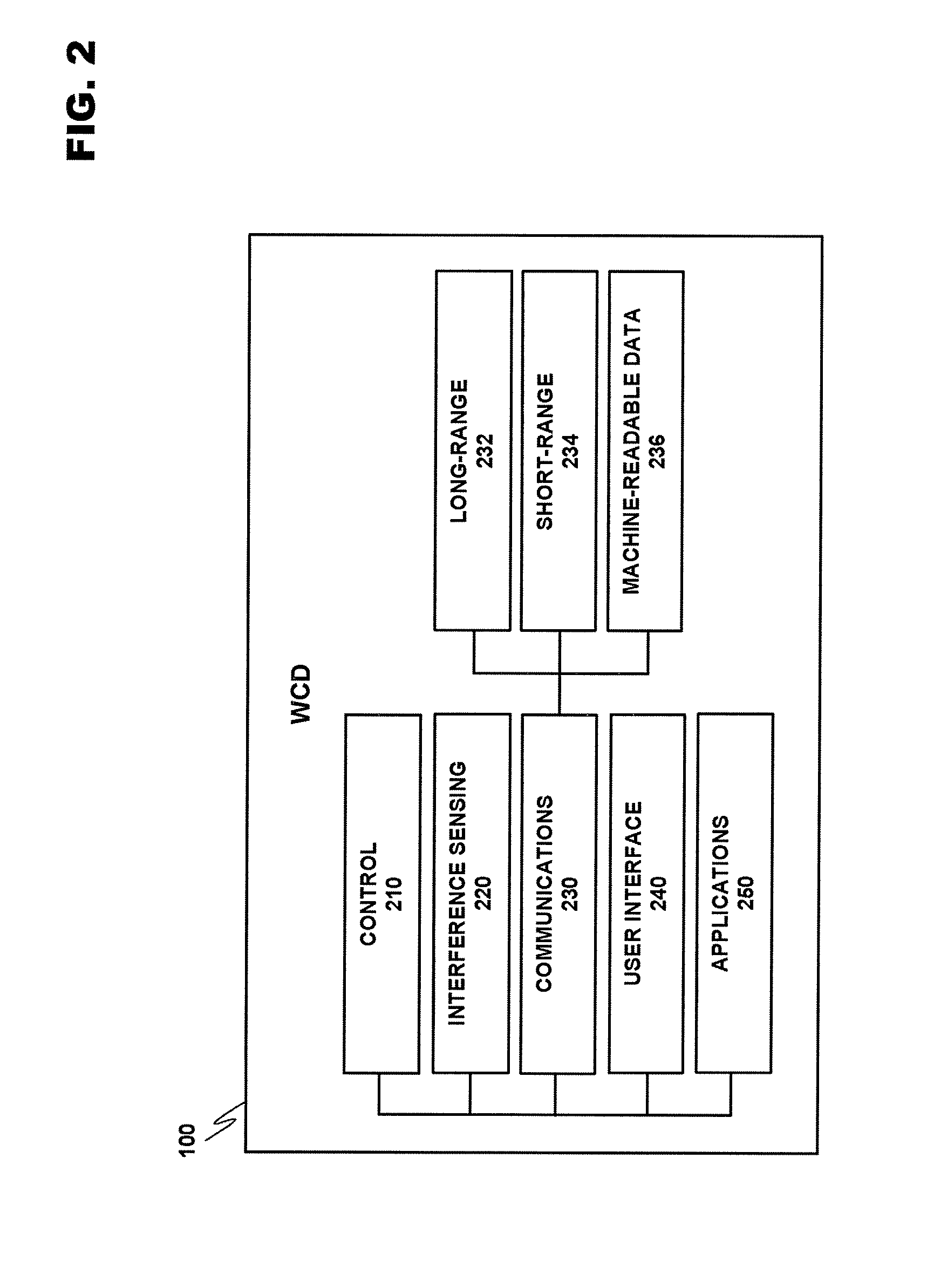
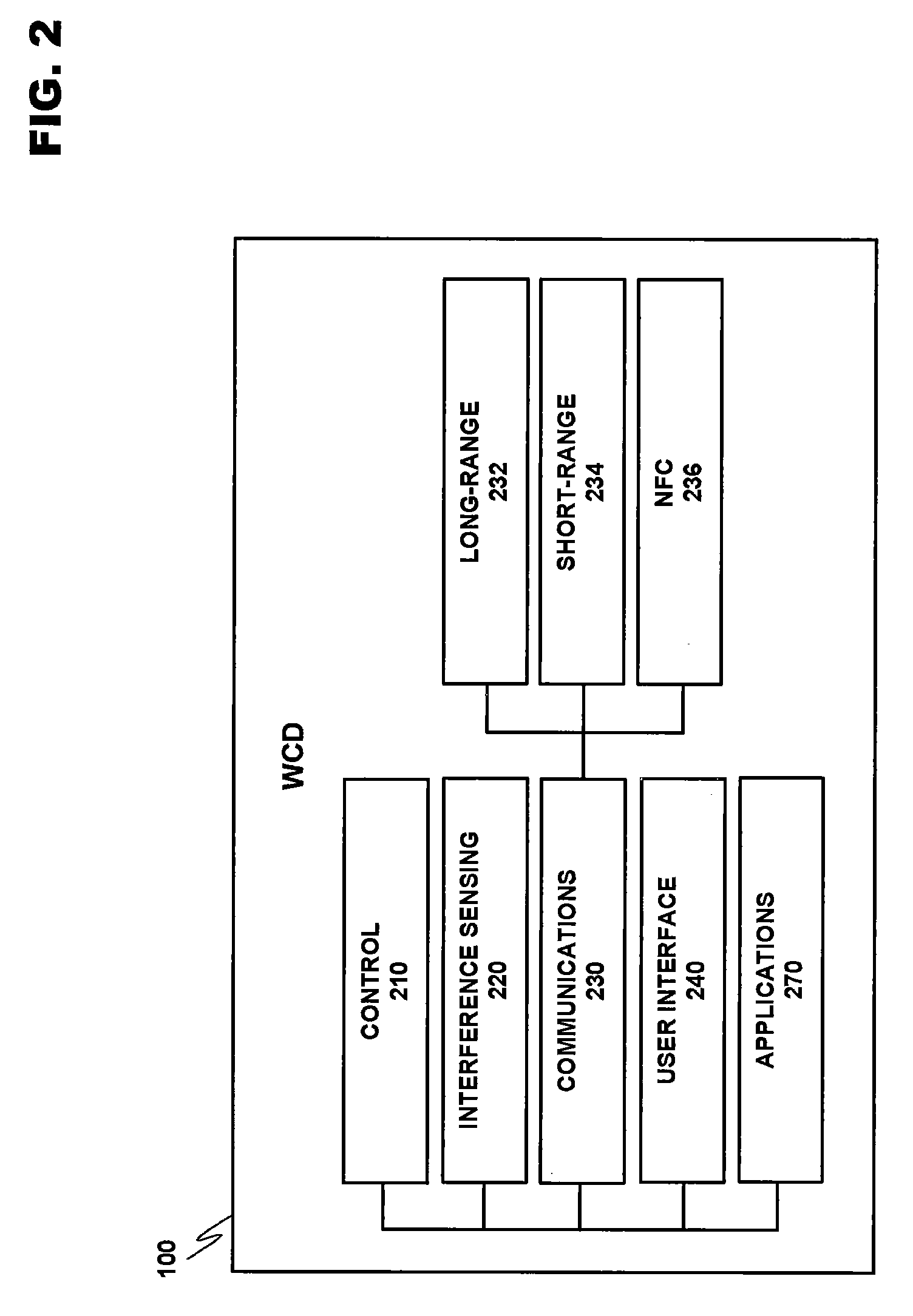
Managing low-power wireless mediums in multiradio devices
ActiveUS7809012B2Stay connectedAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesRadio equipmentCommunication device
A system for optimizing the operation of a plurality of radio modules incorporated within a wireless communication device (WCD) connected as a slave on a low-power wireless network, wherein a low-power device is acting as the master of the wireless network. The timing of communication between master and slave may be established by the master, and as a result, the WCD may utilize a control strategy to allow substantially concurrent active communication in one or more of the plurality of radio modules while still operating under the parameters set forth by the low-power master device.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
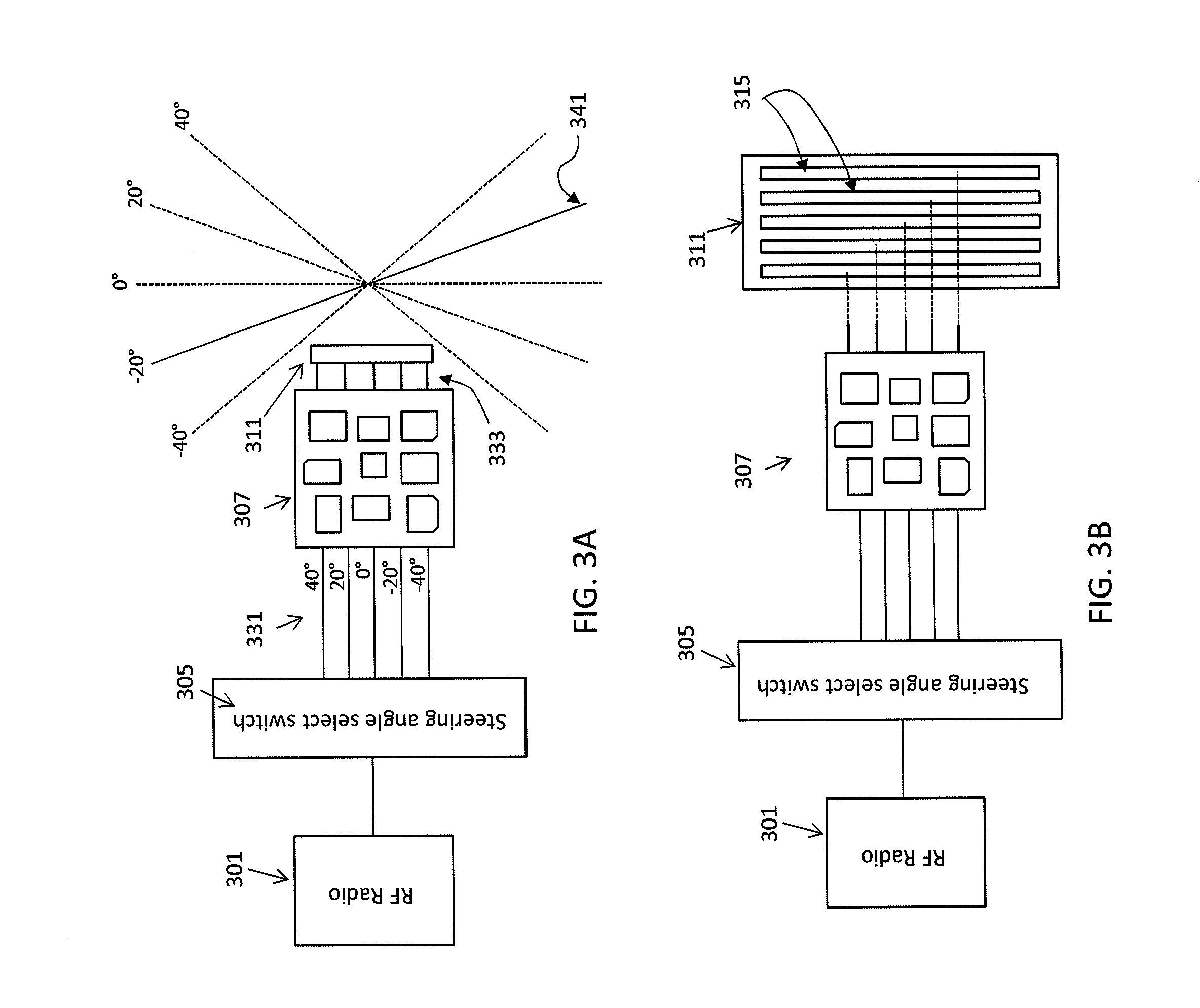
Array antennas having a plurality of directional beams
ActiveUS20150263424A1Comparable and superior performanceIncrease path lengthAntenna supports/mountingsNetwork topologiesRadio equipmentDirectional antenna
Multi-directional antenna apparatuses, which may include phased array antennas and / or arrays of multiple antennas, and methods for operating these directional antennas. In particular, described herein are apparatuses configured to operate as an access point (AP) for communicating with one or more station devices by assigning a particular directional beam to each access point, and communicating with each station device using the assigned directional beam at least part of the time. Methods and apparatuses configured to optimize the assignment of one or more directional beam and for communicating between different station devices using assigned directional beams are described. Also described are methods of connecting a radio device to an antenna by connecting a USB connector on the radio device to a USB connector on an antenna and identifying the antenna based on a voltage of the ground pin on the antenna's USB connector.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
Multiple access frequency hopping network with interference anticipation
InactiveUS6920171B2Spreading over bandwidthSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsMessage queueRadio equipment
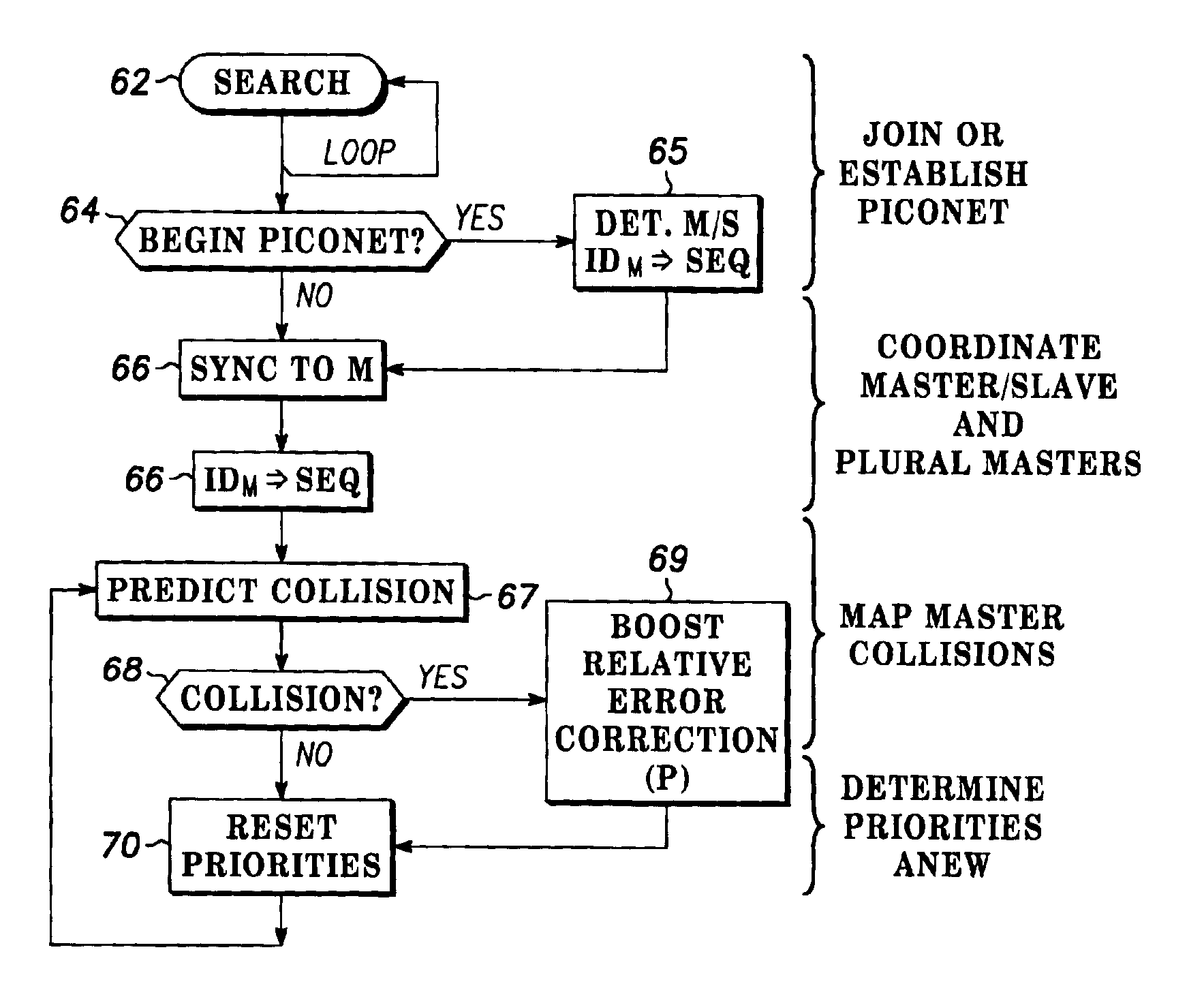
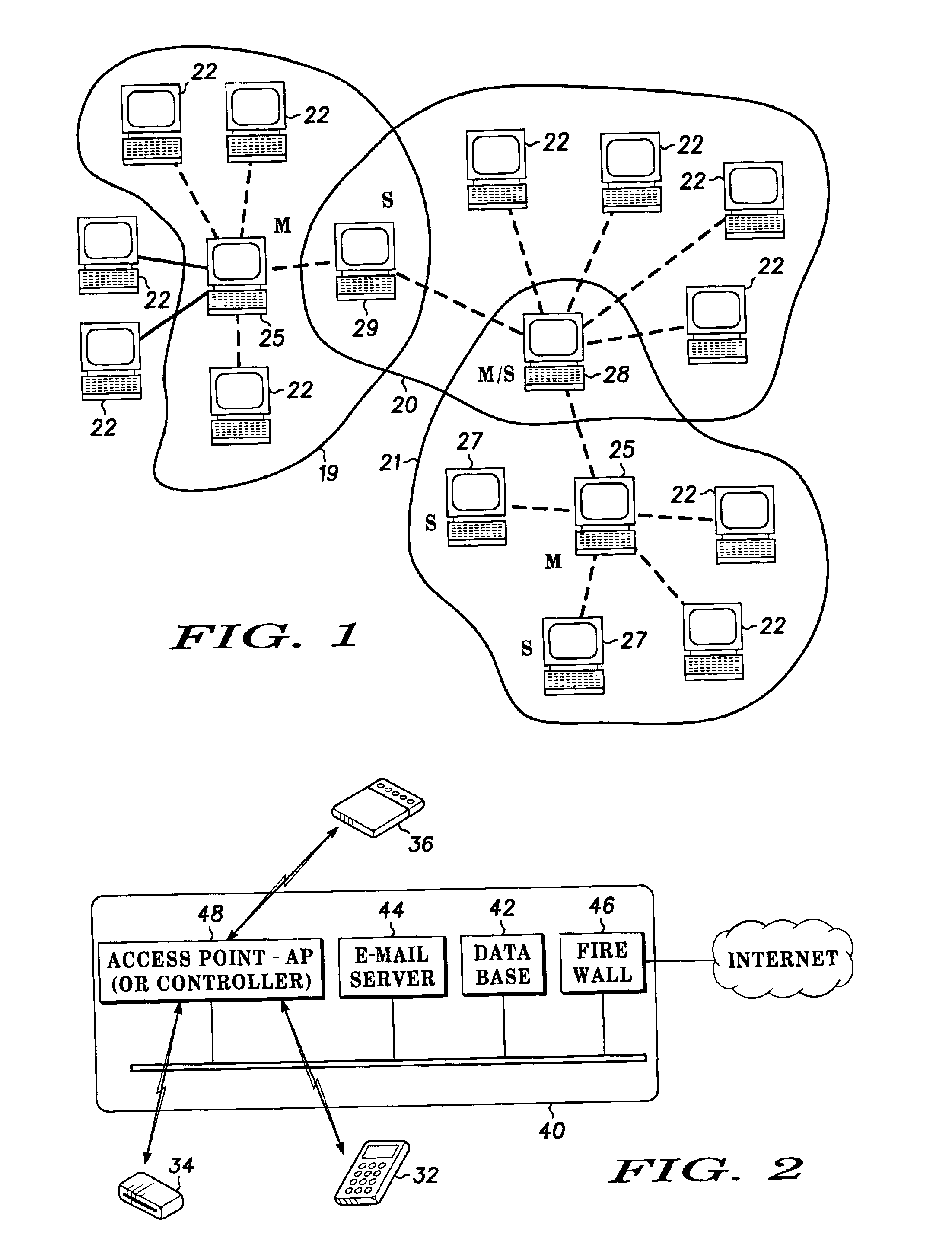
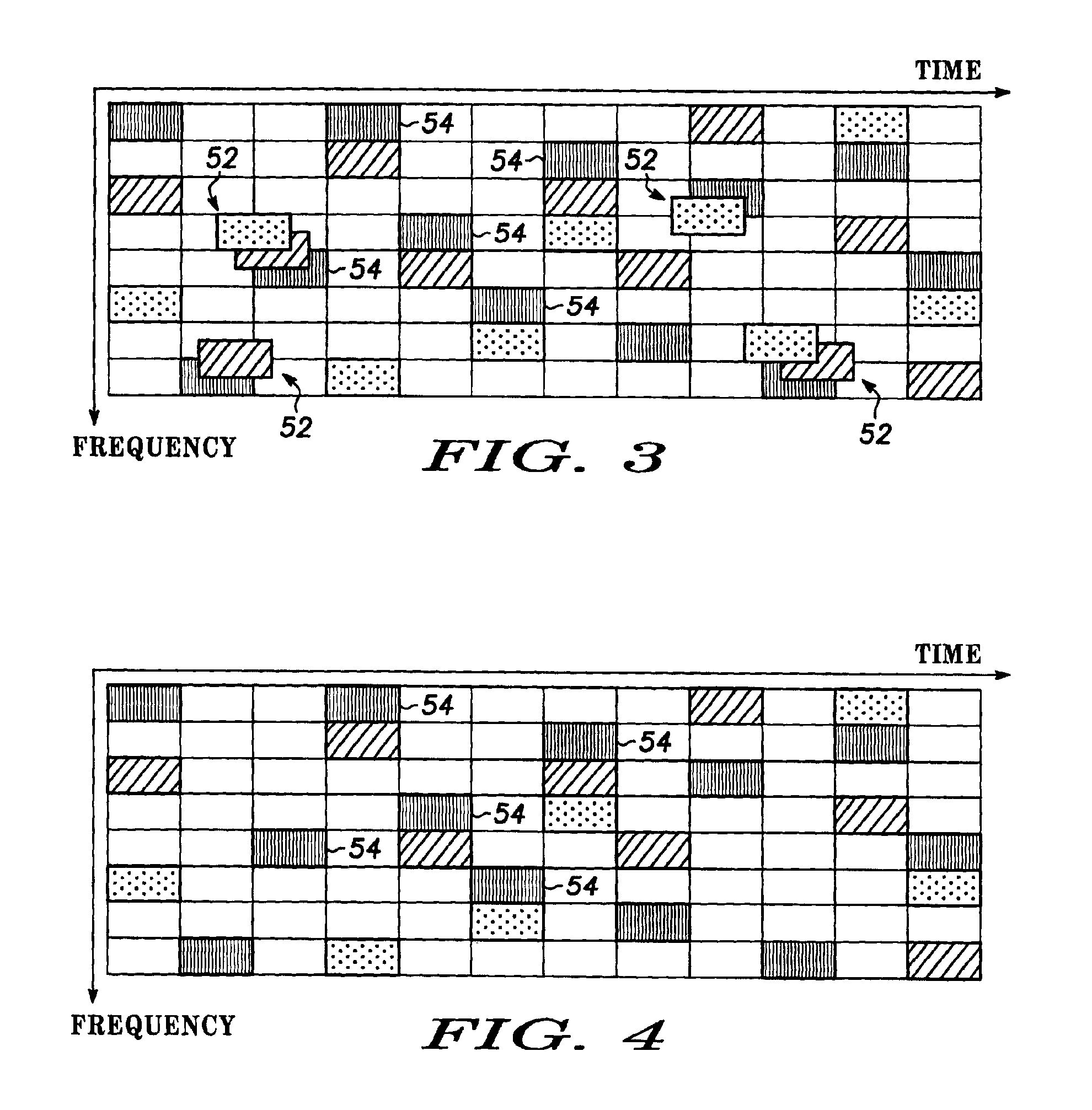
Spread spectrum packet-switching radio devices (22) are operated in two or more ad-hoc networks or pico-networks (19, 20, 21) that share frequency-hopping channel and time slots that may collide. The frequency hopping sequences (54) of two or more masters (25) are exchanged using identity codes, permitting the devices to anticipate collision time slots (52). Priorities are assigned to the simultaneously operating piconets (19, 20, 21) during collision slots (52), e.g., as a function of their message queue size or latency, or other factors. Lower priority devices may abstain from transmitting during predicted collision slots (52), and / or a higher priority device may employ enhanced transmission resources during those slots, such as higher error correction levels, or various combinations of abstinence and error correction may be applied. Collisions are avoided or the higher priority piconet (19, 20, 21) is made likely to prevail in a collision.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
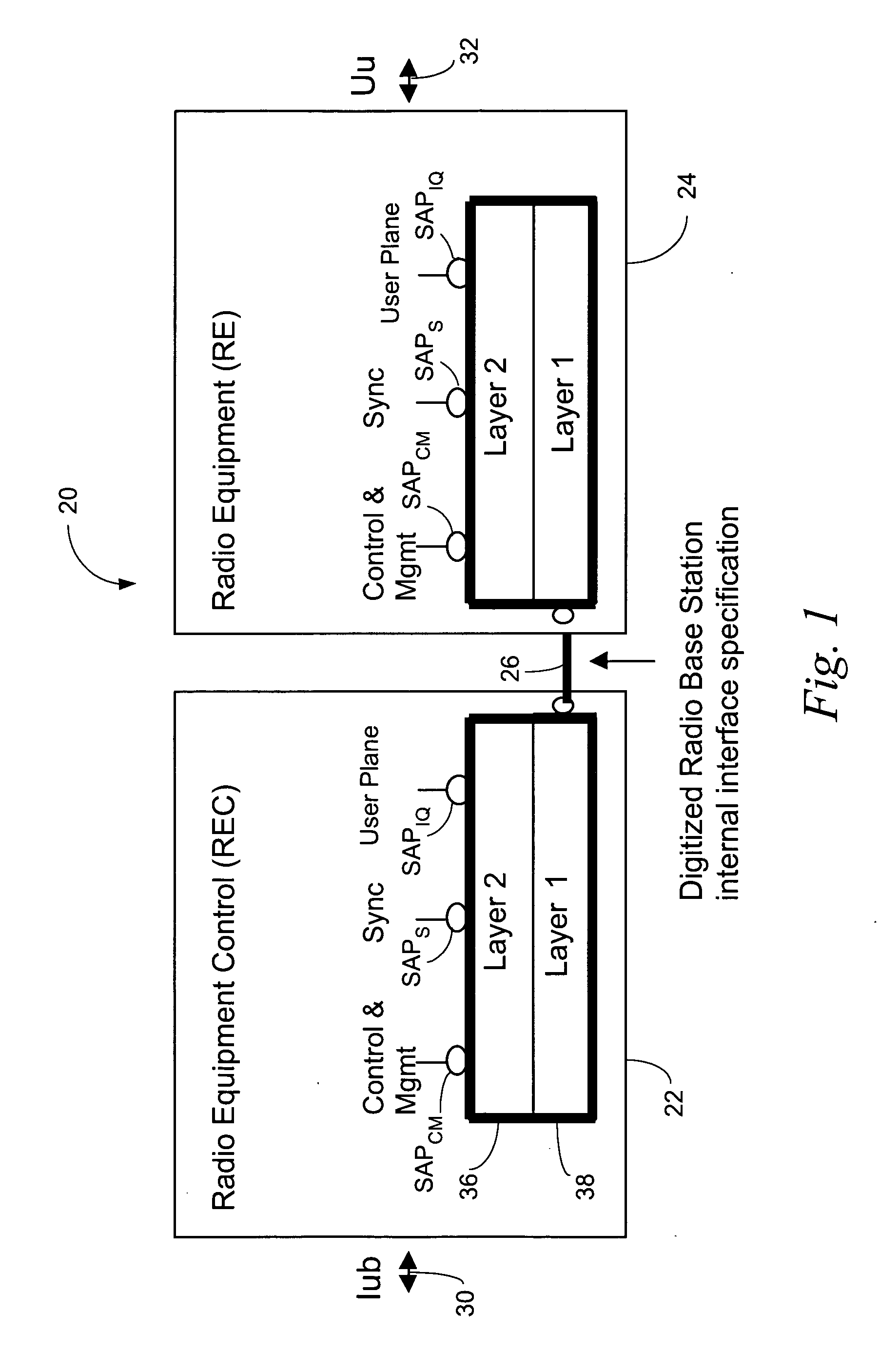
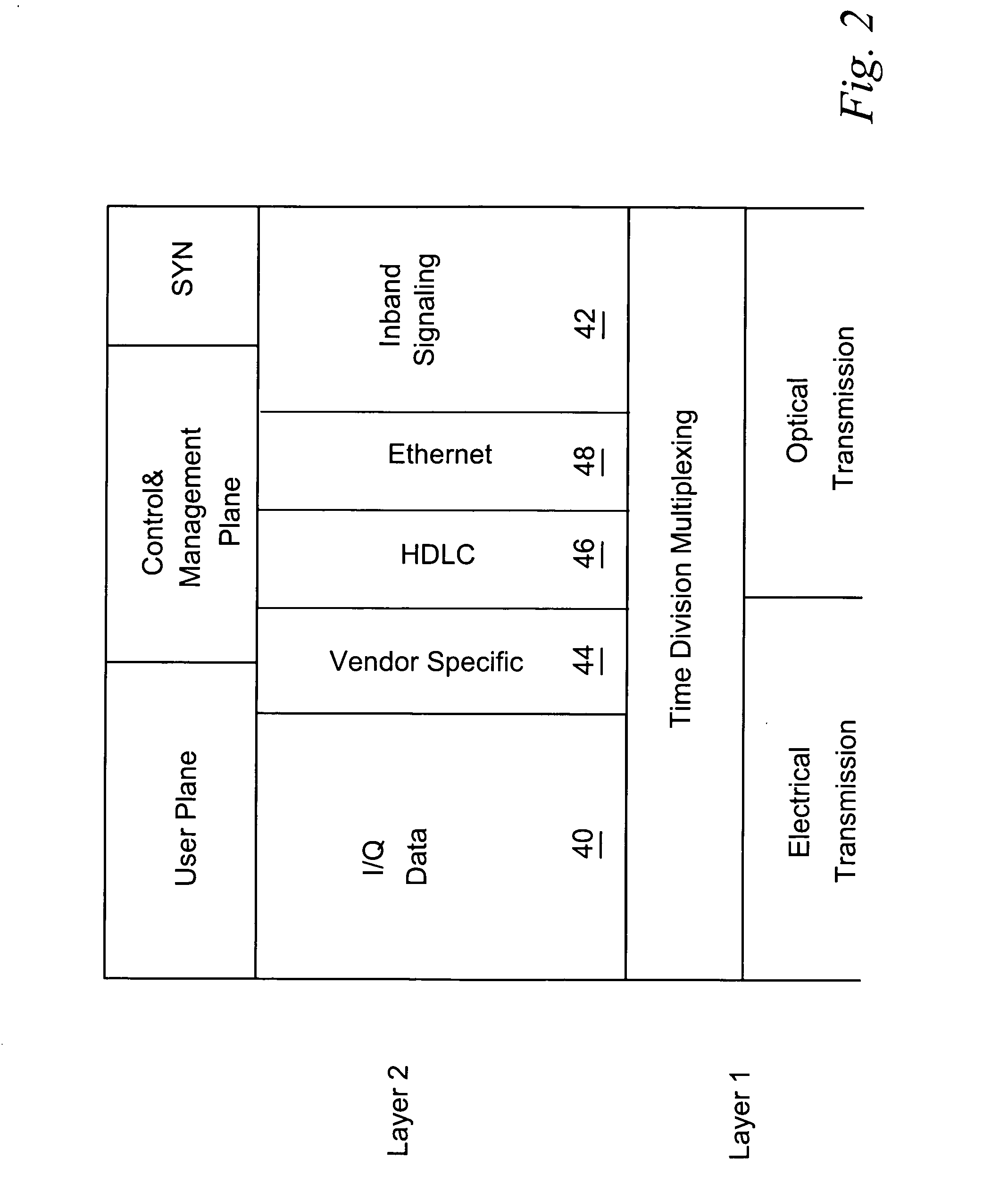
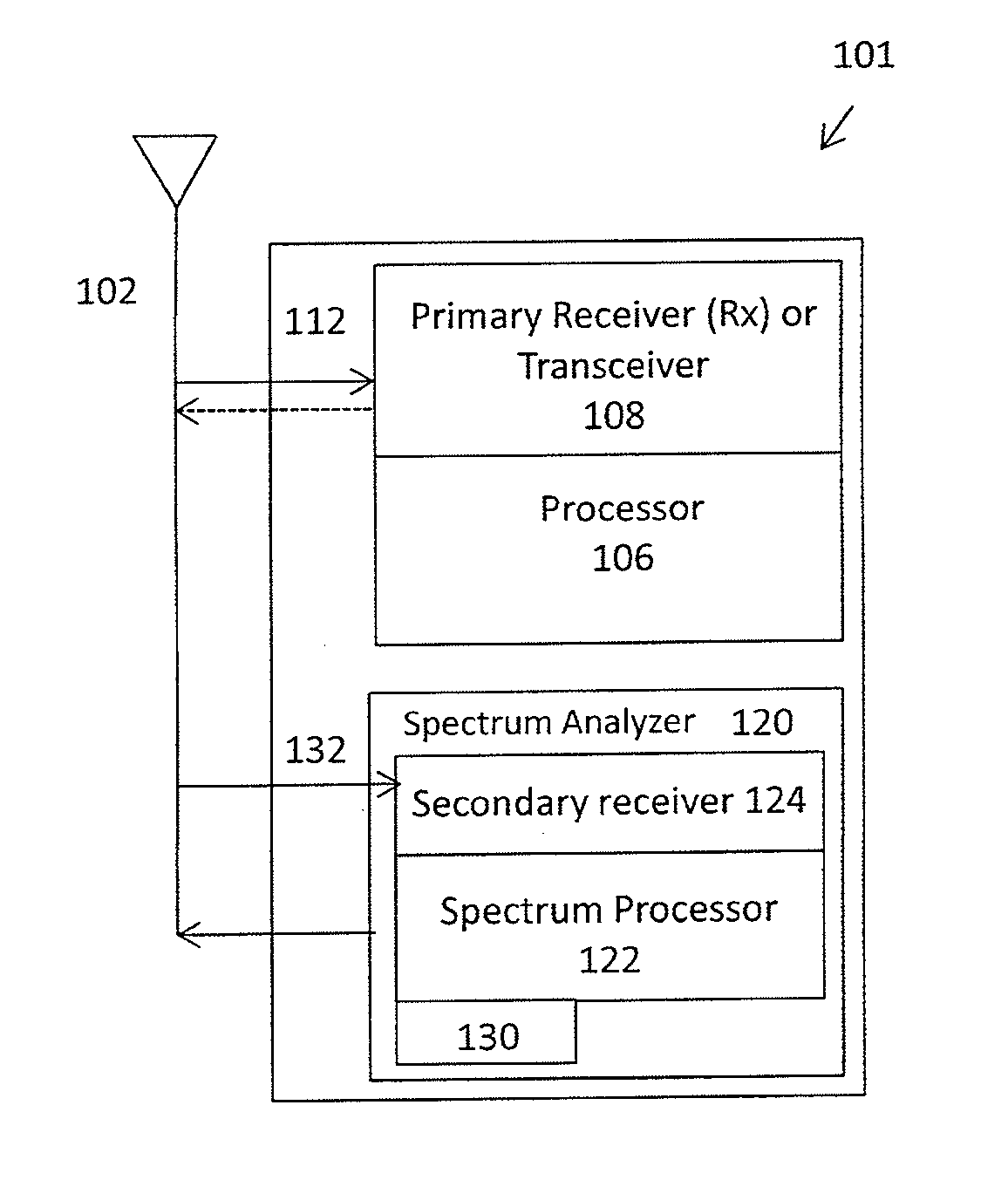
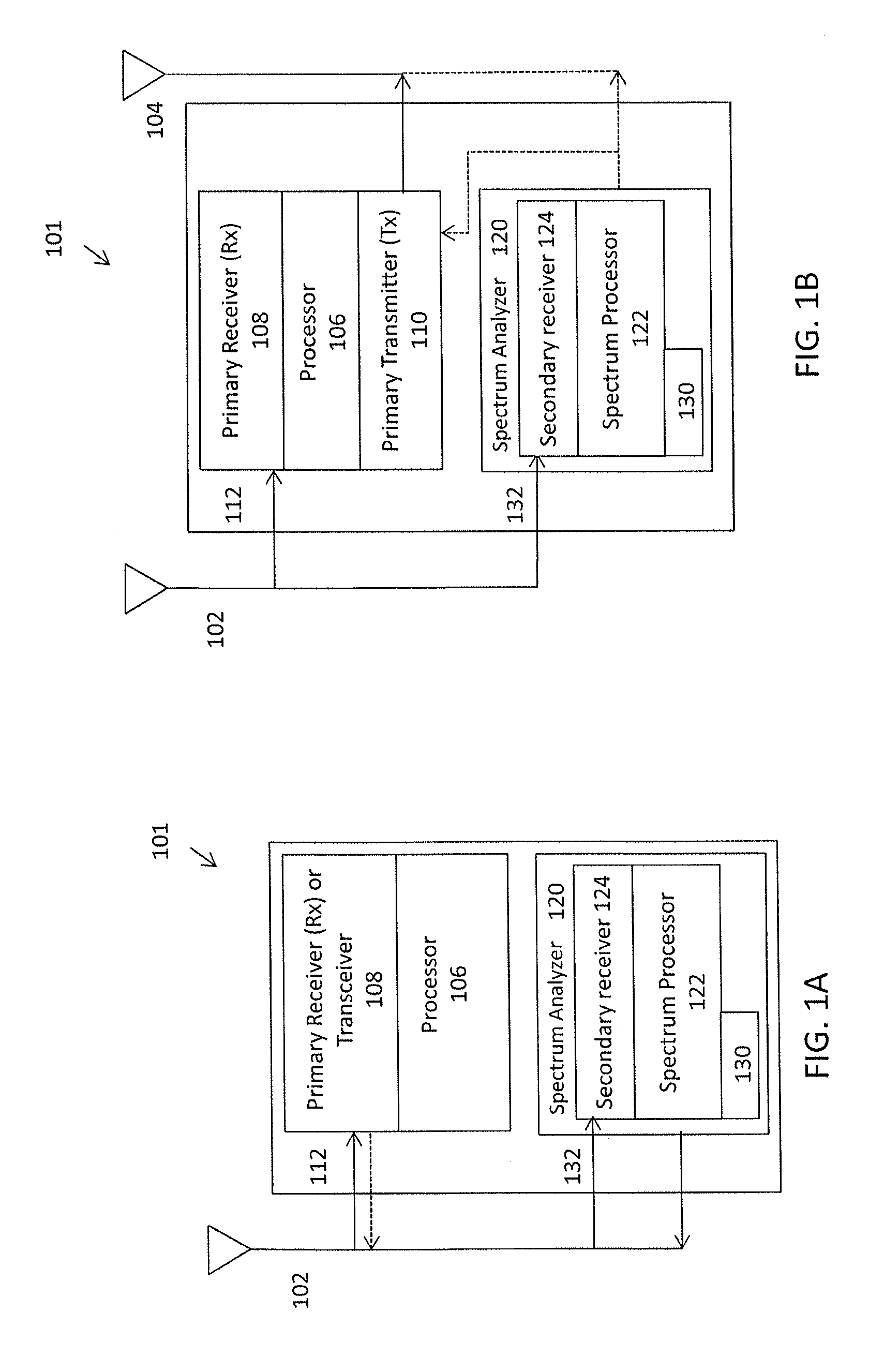
Encapsulation of independent transmissions over internal interface of distributed radio base station
ActiveUS20050105552A1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexRadio equipmentEngineering
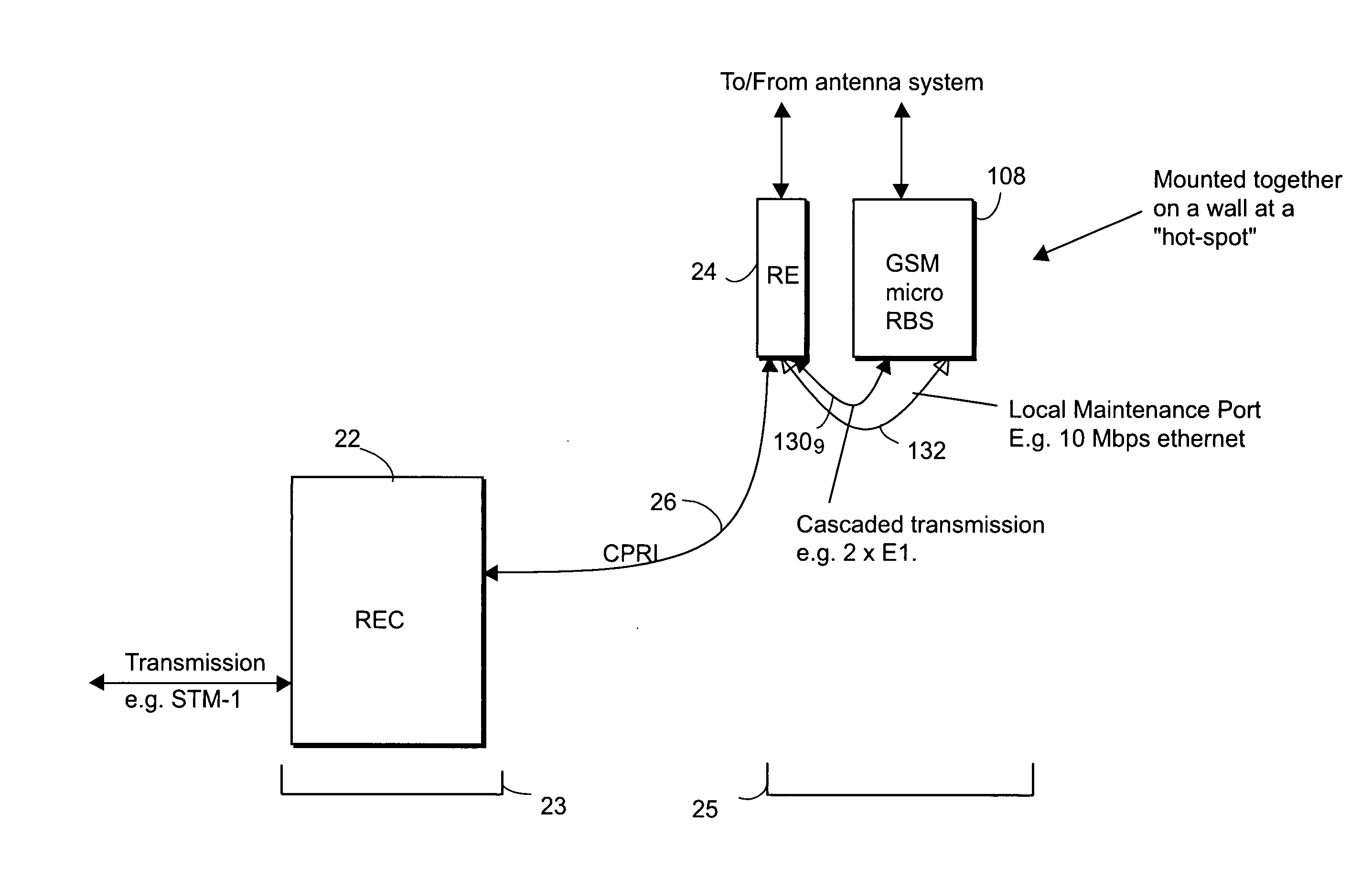
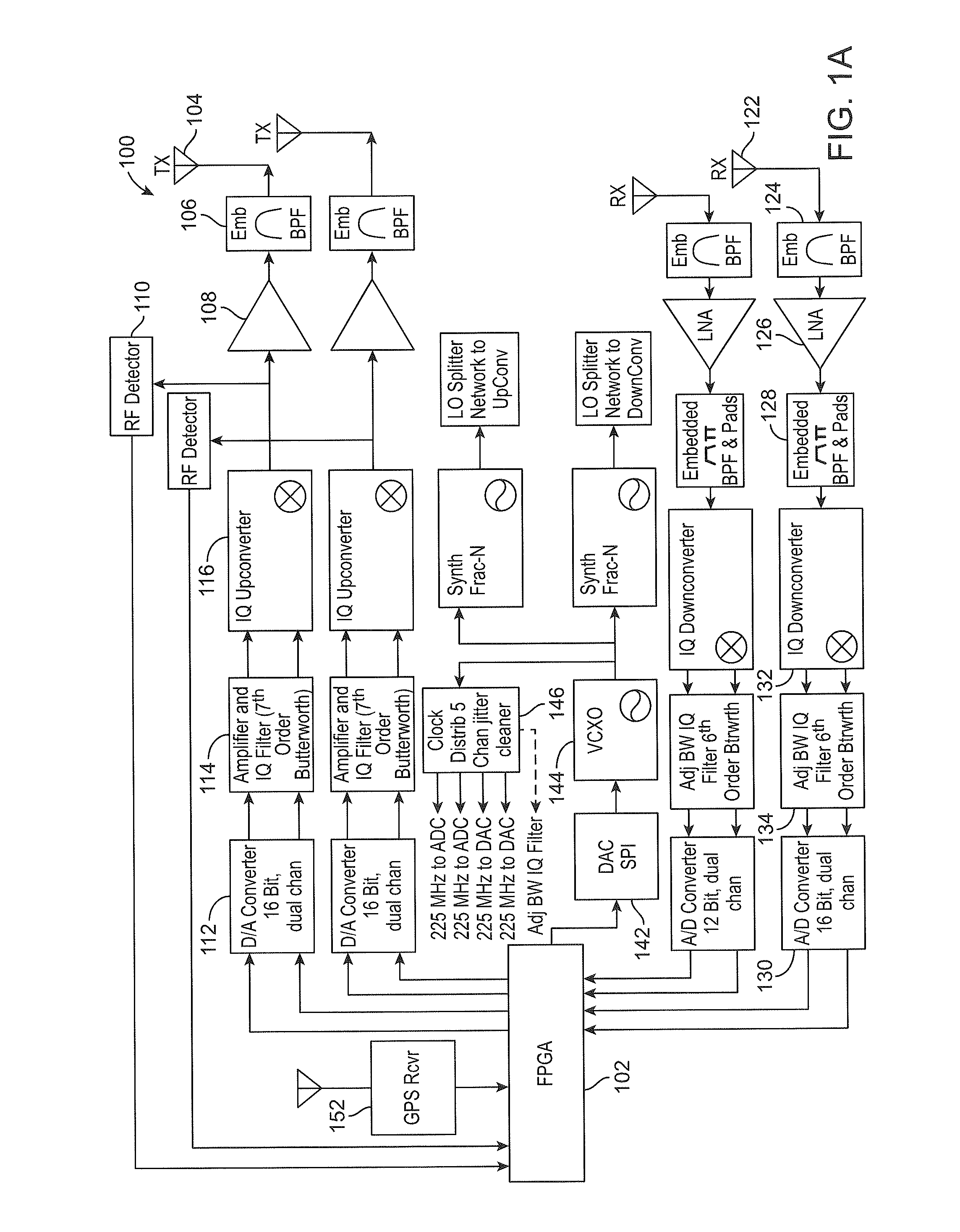
A distributed radio base station (20) comprises a radio equipment controller (REC) (22) situated at a main site (23) and a radio equipment (RE) (24) situated at a remote site (25). A remote unit (102, 104, 106, 108, 110, 124) configured to engage in direct communications with the radio equipment controller (REC) is also situated at the remote site (25). An internal interface (26) connects the radio equipment controller (REC) and the radio equipment (RE). Advantageously, the internal interface (26) also encapsulates the direct communications between the radio equipment controller (REC) (22) and the remote unit, thereby obviating a separate physical link between the radio equipment controller (REC) and the remote unit. A new physical link (130) transmits, between the radio equipment (RE) and the remote unit, the direct communications between the radio equipment controller (REC) and the remote unit which are encapsulated over the internal interface (26). The remote unit can take various differing forms, including that of an antenna (102) with remote electrical tilt control; a tower mounted amplifier (TMA) (104); a Transmission network unit (106); a separate radio base station (108) which is co-located at the remote site; a proprietary equipment unit (110); or even one or more cascaded radio equipments (RE) (124).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
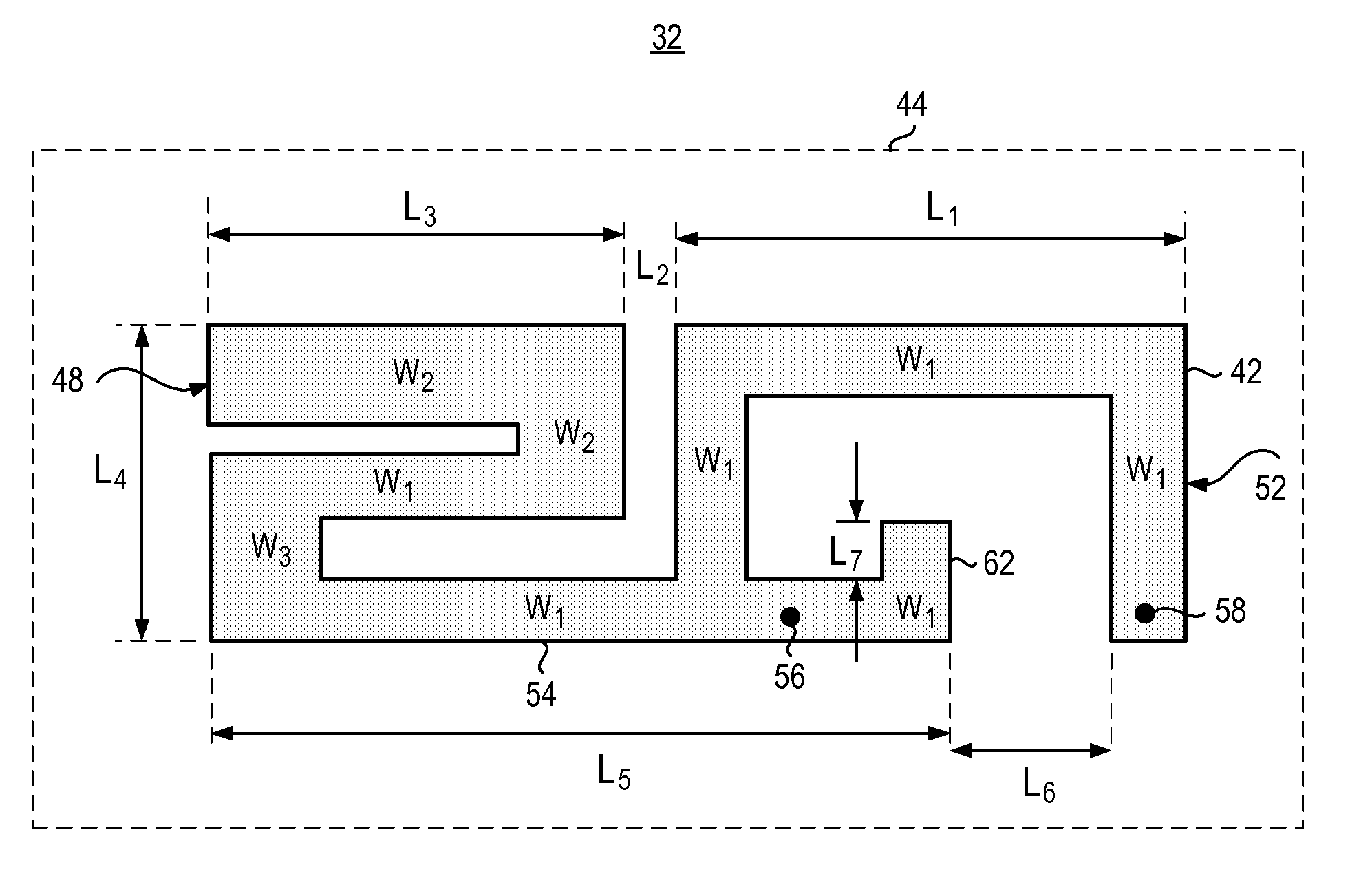
Slot-strip antenna apparatus for a radio device operable over multiple frequency bands
ActiveUS7705783B2Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsRadio equipmentEngineering
A hybrid slot-strip antenna apparatus, and an associated methodology, for a multi-mode mobile station or other radio device. The antenna is formed of a plurality of slot-strips disposed upon a printed circuit board, or other substrate. The antenna is defined by width and length design parameters, the selections of which are determinative of the antenna functionality. Through appropriate selection of the design parameters, the antenna is operable, that is, resonant, at each of the frequency bands of the multi-mode mobile station.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Managing unscheduled wireless communication in a multiradio device
A system for managing the operation of a plurality of radio modules integrated within the same wireless communication device. A control strategy may be employed to manage both more predictable and more spontaneous wireless communication mediums, wherein a local controller may be employed in a radio module utilizing an unscheduled wireless medium, like WLAN, for determining whether adequate time has been allocated to complete a transaction. If the transaction cannot be completed in the allowed time, it may be delayed until adequate time exists, and the delay may be reported so that the time may be reallocated to other radio modules. The radio module may then enter a power-saving mode until the transaction can be completed.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
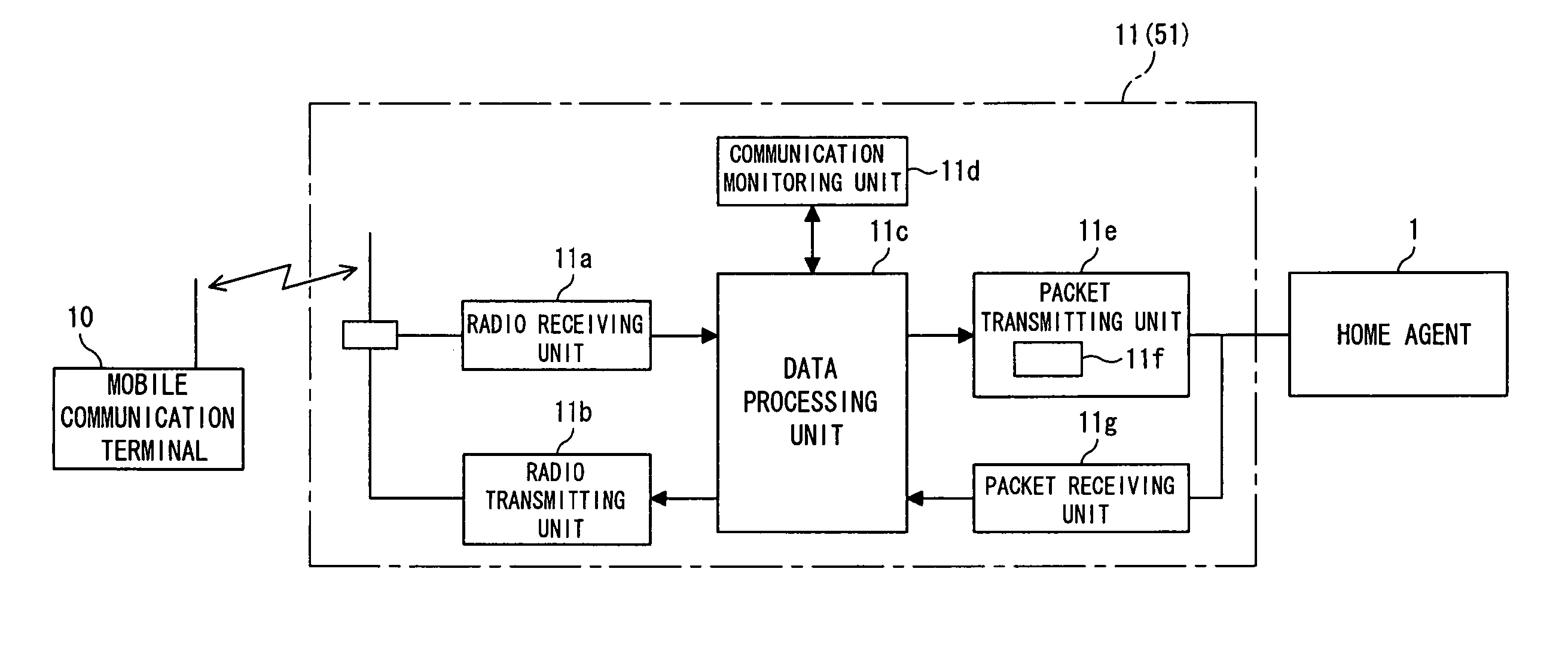
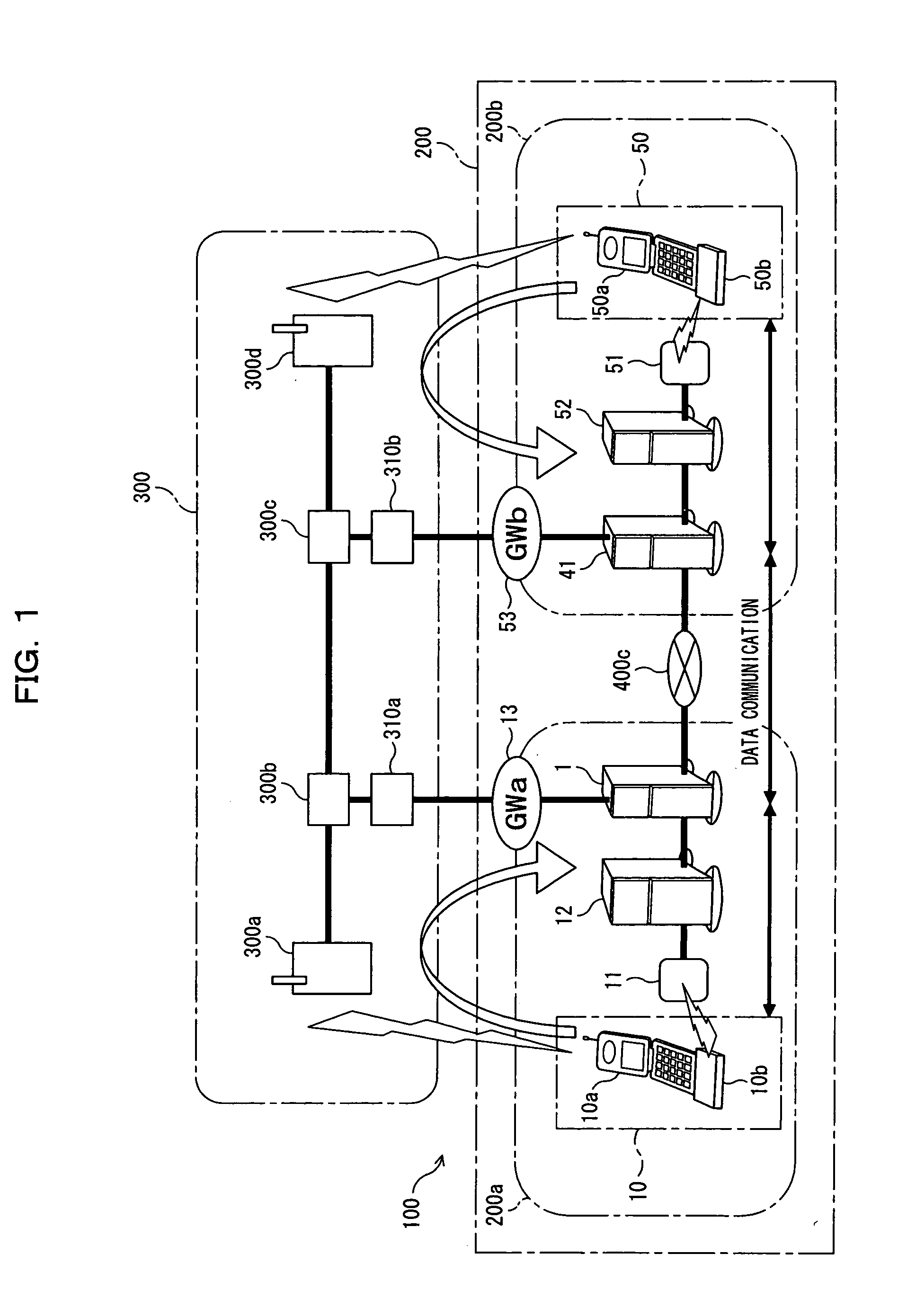
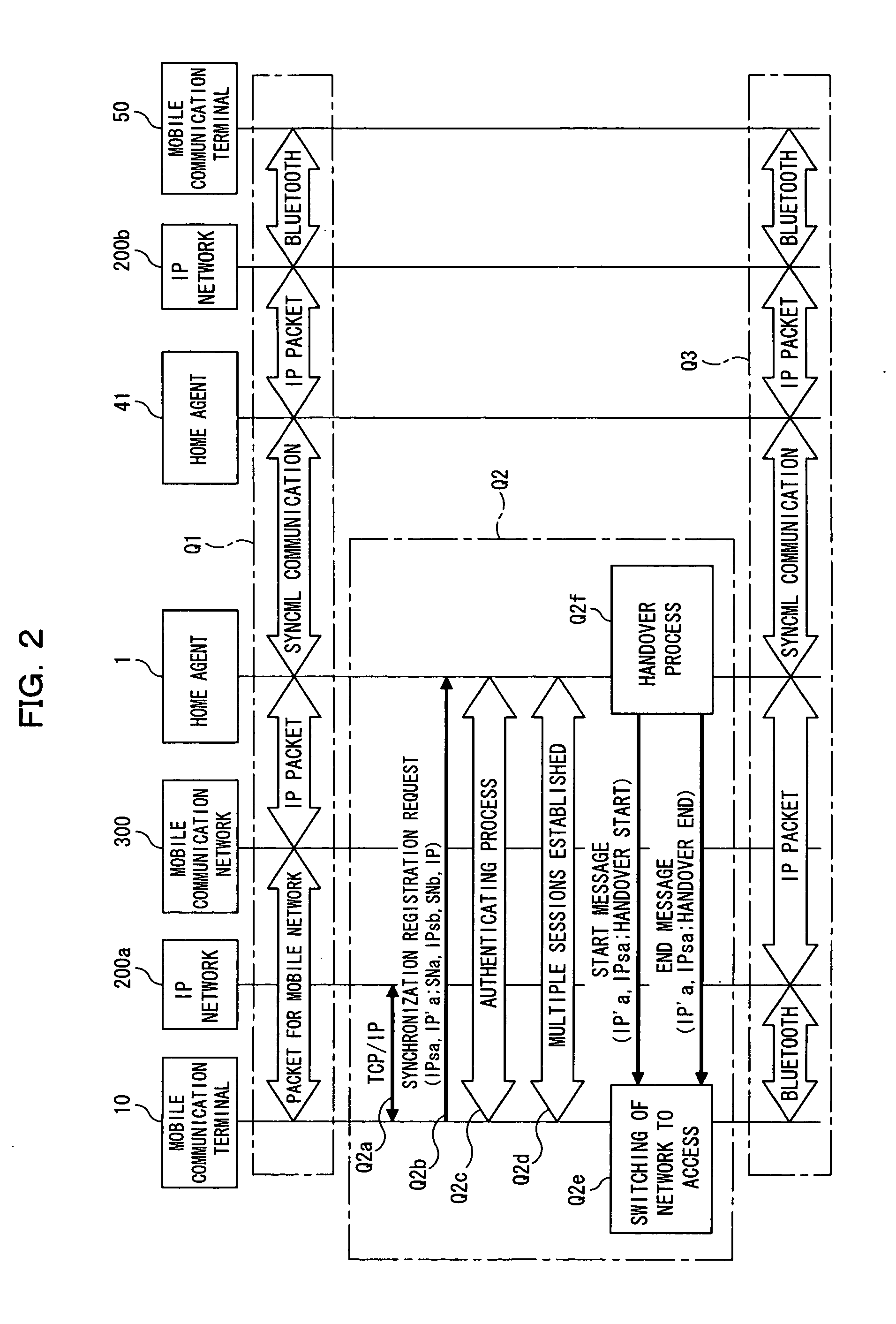
Server, mobile communication terminal, radio apparatus, communication method in communication system and communication system
InactiveUS20040151186A1Freedom of movementReduce loadConnection managementData switching by path configurationRadio equipmentCommunications system
A server for enabling a first terminal to switch between a mobile communication network and a packet network, with the first terminal continuing a communication with a second terminal. The server comprises a session managing unit storing a first address of the first terminal assigned to a first session and a second address of the second terminal assigned to a second session, a receiving unit receiving a packet containing user data from the second terminal, a switching unit switching from the first session of a packet having the first address as a destination and containing the user data to the second session of a packet having the second address as the destination and containing the user data on the basis of the addresses in the session managing unit, and a transmitting unit transmitting the packet using the second session switched by the switching unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Skypoint for mobile hotspots
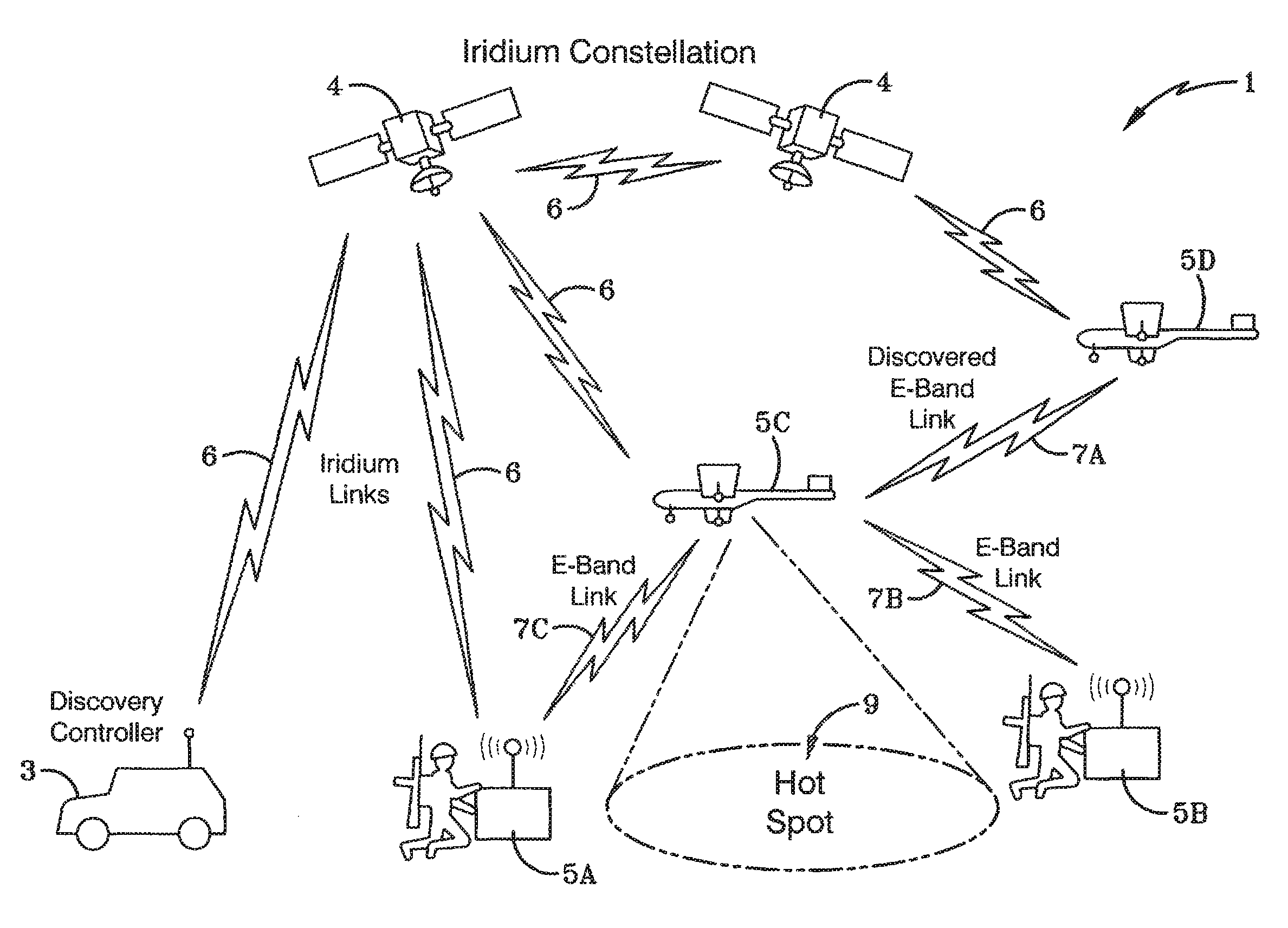
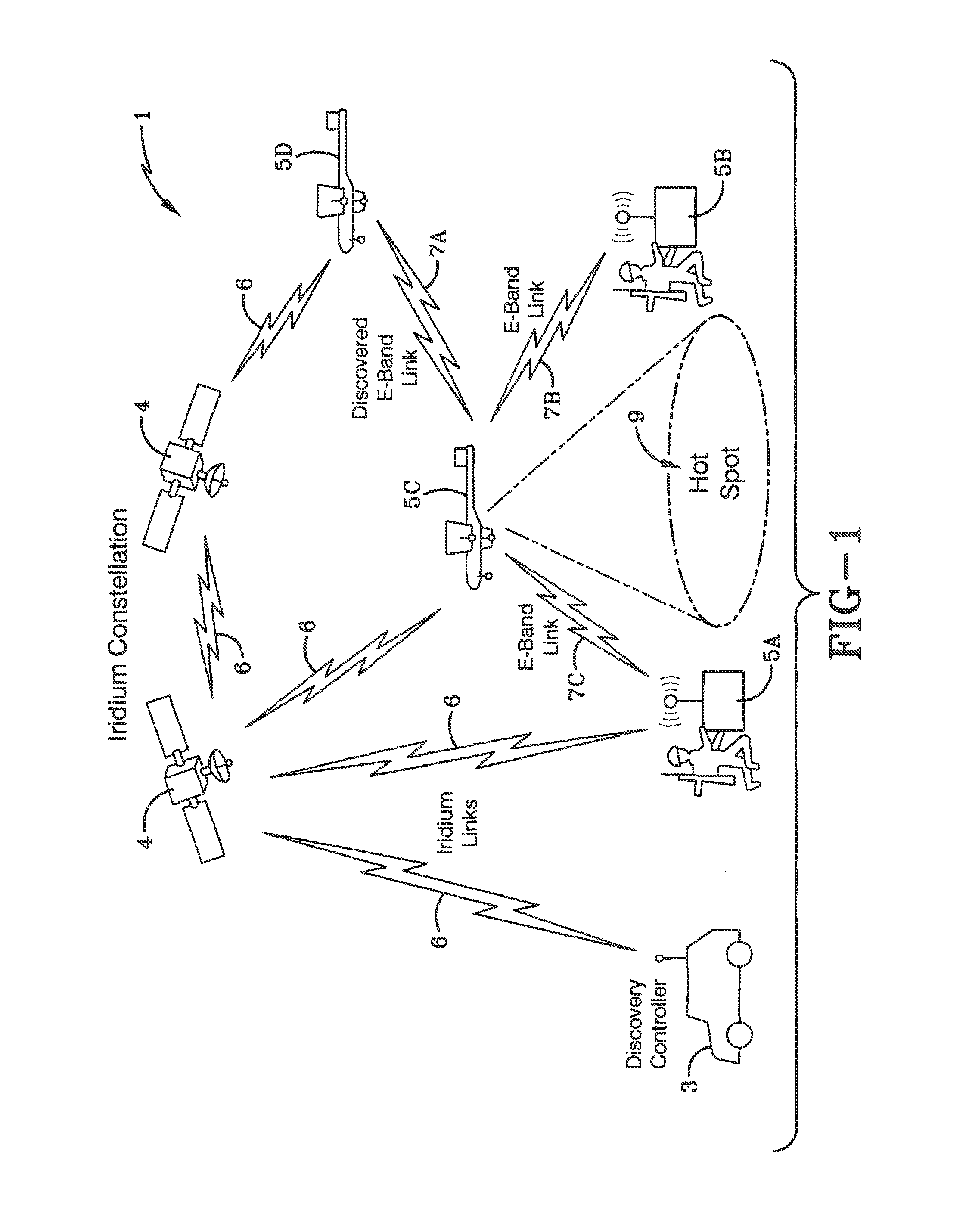
A system and method for dynamically planning a network is presented. One method may begin by determining network parameters for connecting nodes to a network and decision variables associated with radios and / or nodes in the network. Constraints may be established to narrow possible values of the network parameters and / or the decision variables. The constraints may be based on one or more of: values associated with connecting a radio to a node in the network, values associated with connecting two nodes in the network together over a communication link, whether a node can connect to a GIG node and a flow balance in the GIG node. To find possible links in the network that are optimal, the method may minimize an equation based on the network parameters, constraints and decision variables to determine optimal communication links between pairs of nodes in the network, pairs of nodes and radios and / or pairs of radios.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Methods and tools for assisting in the configuration of a wireless radio network
ActiveUS20160014613A1Improve network coverageMaximizing improvementData switching by path configurationCommunication jammingRadio equipmentGeographic regions
Tools and methods for optimizing the selection and placement of wireless radio devices in a wireless network within a geographic region using a remote database that includes a geographic mapping of existing wireless devices within the network and / or adjacent networks, device characteristics for the wireless devices within the network and / or adjacent networks, and radio frequency spectral information across times for a plurality of regions (e.g., corresponding to locations of existing wireless devices). A tool may include a local user interface, a remote database, and a processor that communicates with the user interface and remote database. The methods and tools described herein may receive user input indicating a desired location and / or operational characteristics of new wireless radio device and may determine and suggest an optimal type, location and / or operational parameters for the additional device, or may suggest other modifications to the current network to optimize the network including the new device.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
Cellular wireless internet access system using spread spectrum and internet protocol
InactiveUS6865169B1Reduce environmental impactOvercome lossMultiplex communicationNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexingUser equipment
A cellular wireless internet access system which operates in the 2.5 to 2.68 GHz band and which must comply with complex government regulations on power levels, subscriber equipment and interference levels yet which provides high data rates to users and cell sizes of 1½ miles radius or more from base stations with subscriber equipment and antennas mounted indoors. Such base stations are mounted low and use spread-spectrum transmission to comply with interference rules with respect to adjacent license areas. An unidirectional tear-drop coverage pattern is used at multiple cells to further reduce interference when required. Time division duplex is used to allow the system to operate on any single channel of varying bandwidth within the 2.5 to 2.68 GHz band. Backhaul transmission from base stations to the Internet is provided using base station radio equipment, operating either on a different frequency in the band or on the same frequency using a time-division peer-to-peer technique. Different effective data-rates are provided by a prioritization tiering technique.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
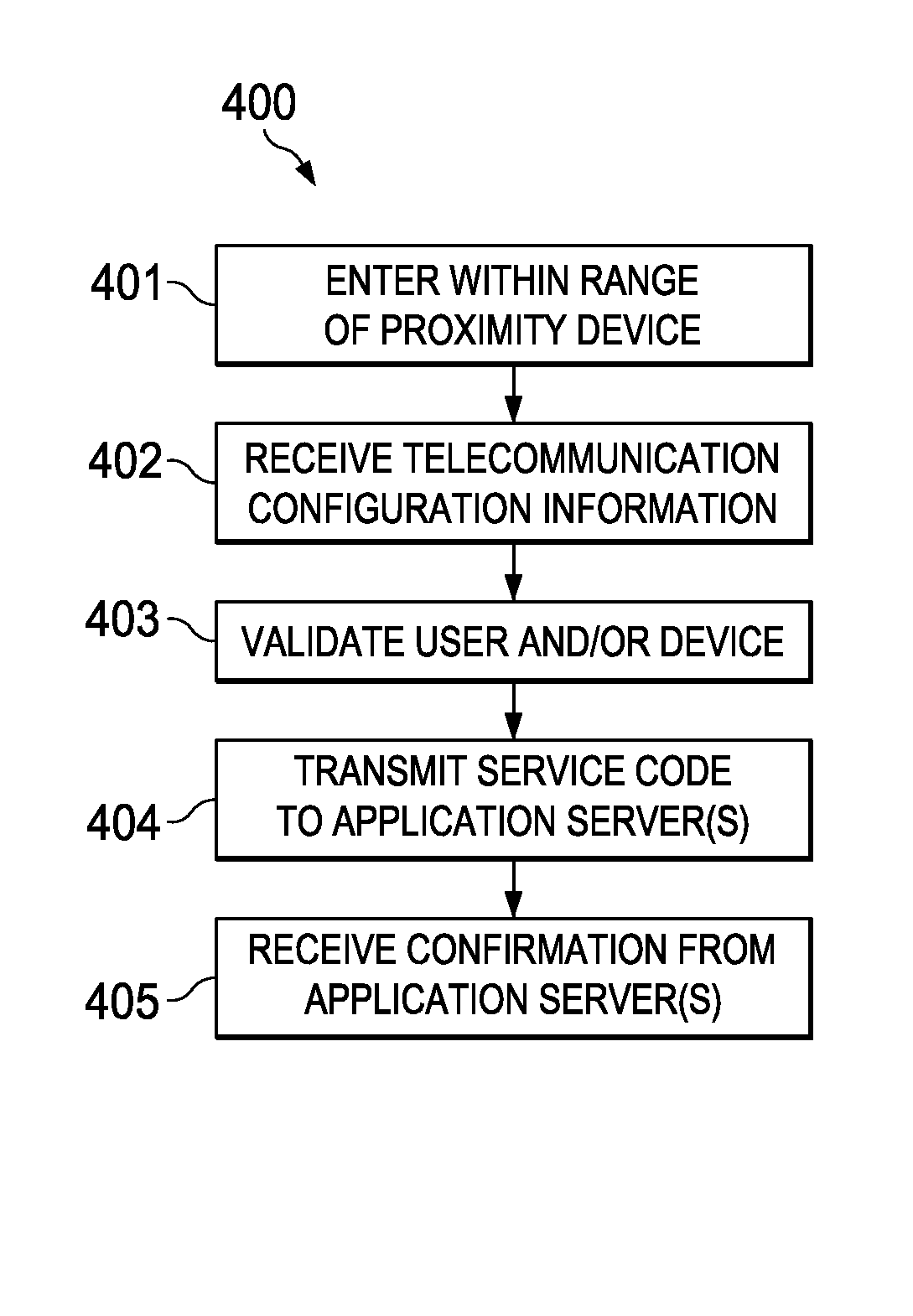
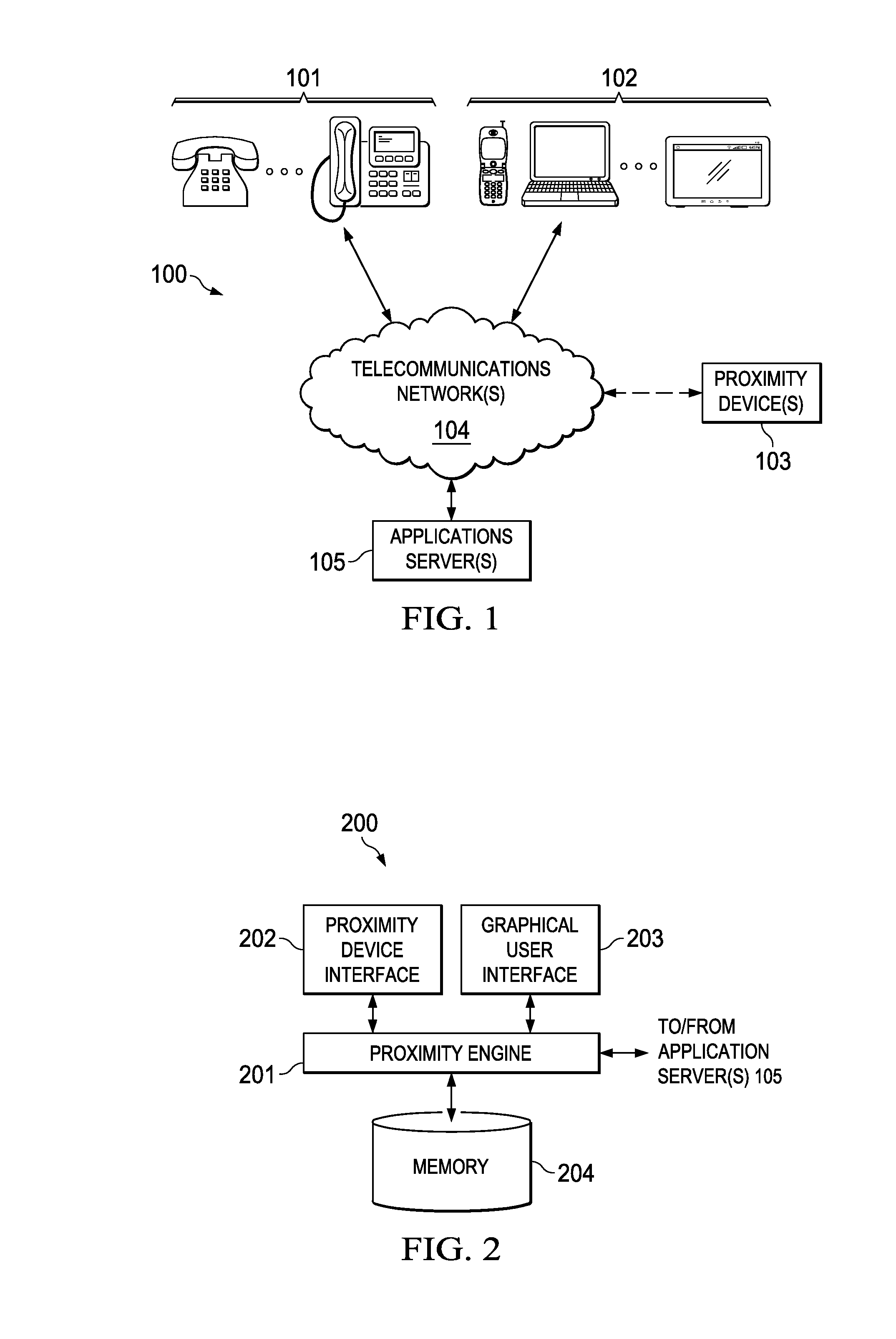
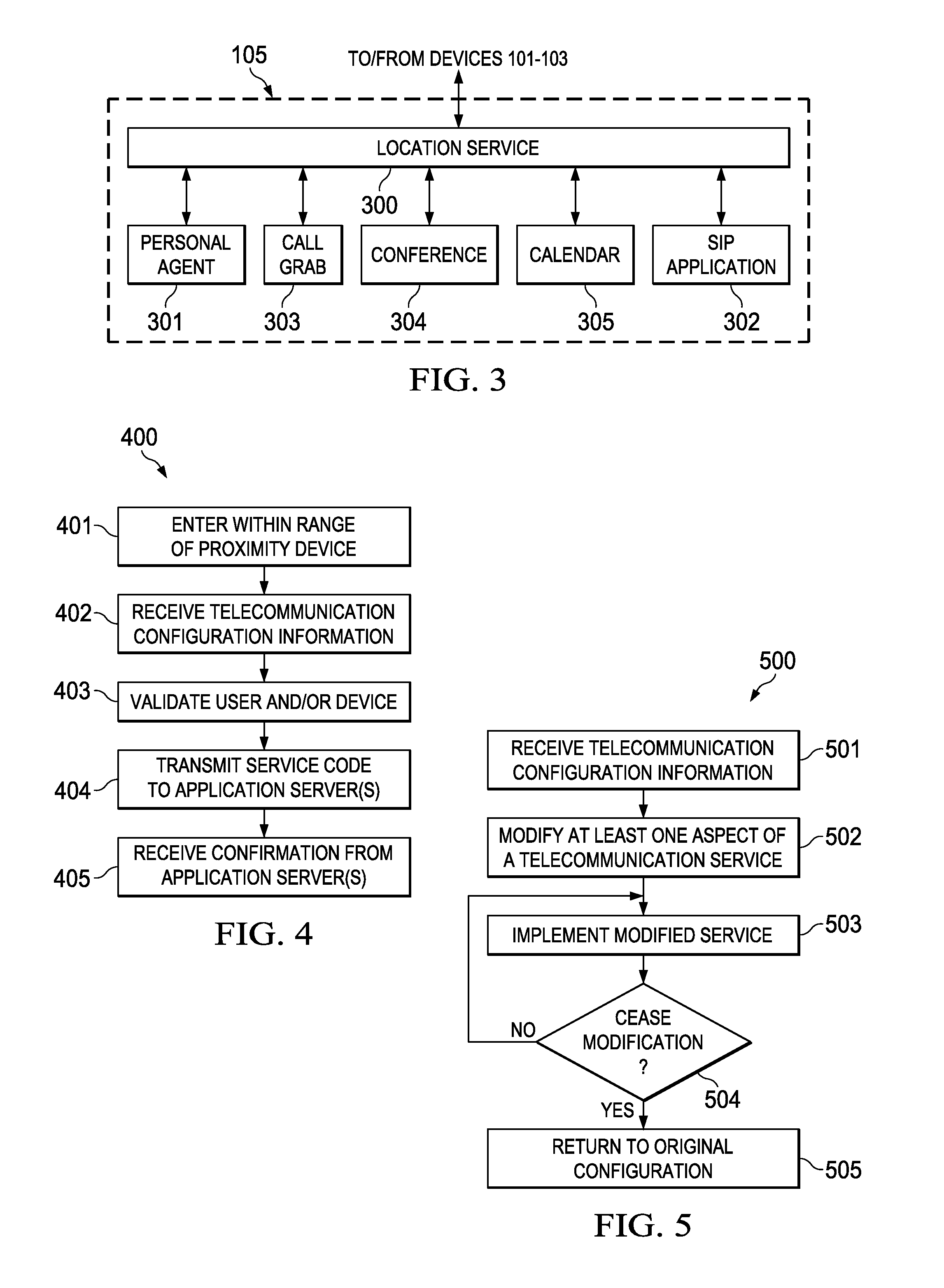
Managing Telecommunication Services using Proximity-based Technologies
InactiveUS20140073300A1Reduce in quantityReduce and minimize and eliminate numberService provisioningNetwork topologiesTablet computerRadio equipment
Systems and methods for managing telecommunication services using proximity-based technologies are described. In some embodiments, a method may include detecting, by a first communication device (e.g., a laptop computer, a netbook computer, a tablet computer, a cellular phone, a smartphone, etc.), a proximity device (e.g., a Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tag, a Near Field Communications (NFC) tag, etc.) coupled to or integrated within a second communication device. The method may also include triggering an operation configured to manage a telecommunication service based, at least in part, upon the detection of the proximity device. In some implementations, the operation may be configured to reduce a number of manual operations that would otherwise be involved in managing the telecommunication service. For instance, in a non-limiting example, the operation may cause a routing of a communication directed at the first communication device to the second communication device. Numerous other telecommunication services are described herein.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
Method and system for sharing a single antenna on platforms with collocated Bluetooth and IEEE 802.11 b/g devices
A method and system for sharing a single antenna on platforms with collocated Bluetooth and IEEE 802.11 b / g devices are provided. A single antenna may be utilized for communication of Bluetooth HV3 frame traffic and wireless local area network (WLAN) communication based on a time multiplexing approach. At least one antenna switch may be utilized to configure an antenna system to enable Bluetooth and WLAN coexistence via the single antenna. Configuration signals may be generated by a Bluetooth radio device and / or by a WLAN radio device to configure the antenna system. A default configuration for the antenna system may provide WLAN communication between a station and a WLAN access point until Bluetooth communication becomes a priority.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
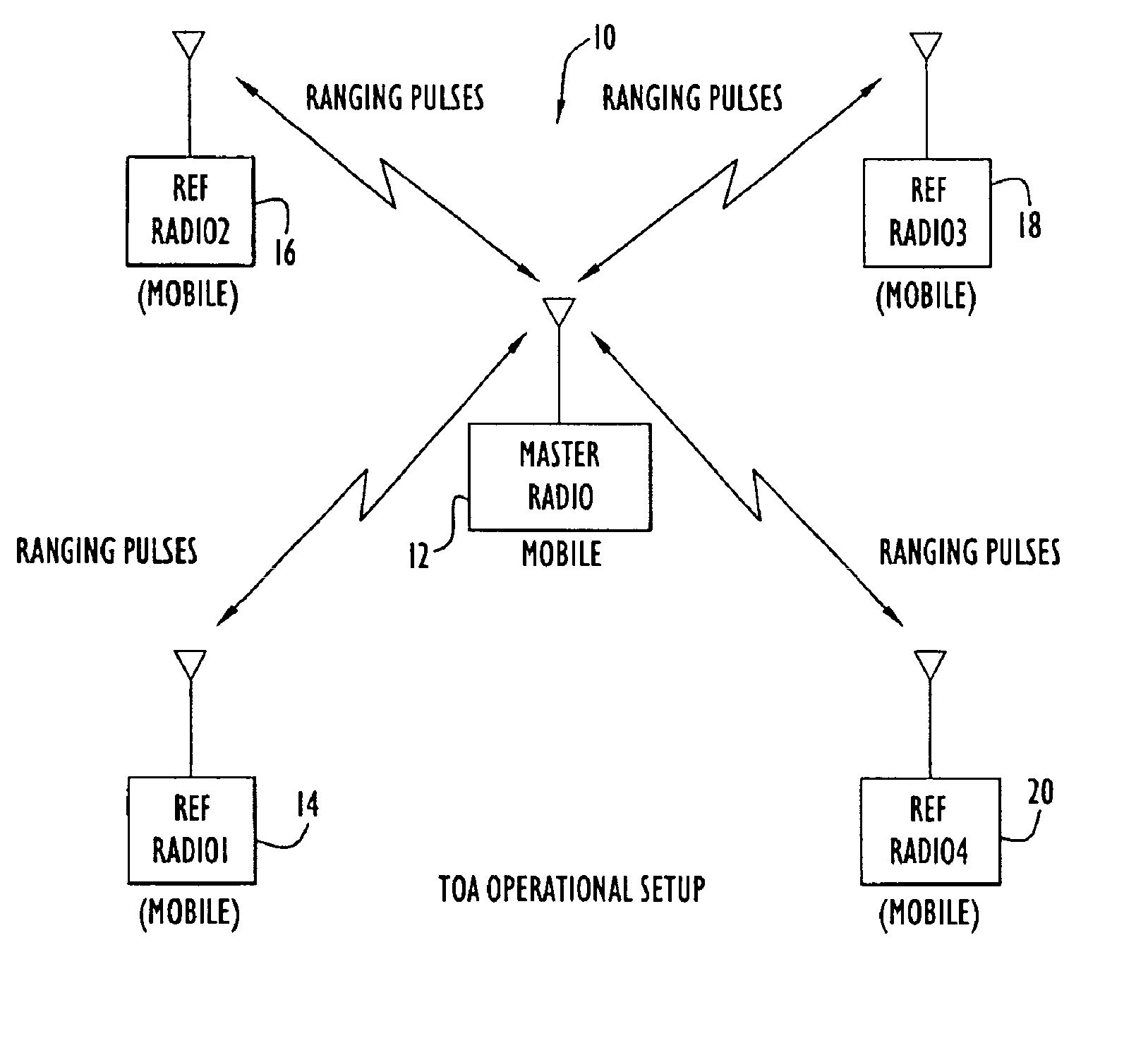
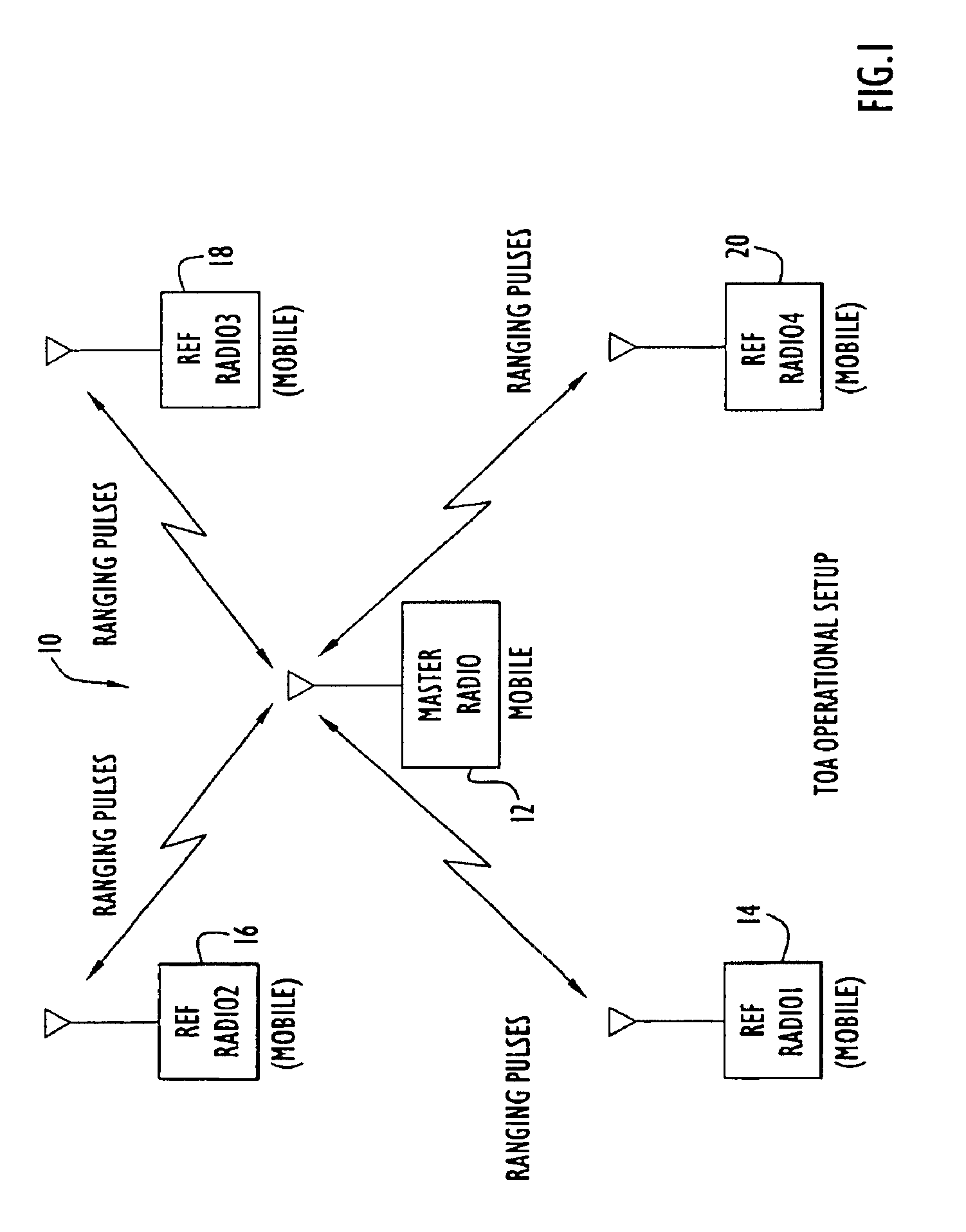
Method and apparatus for high-accuracy position location using search mode ranging techniques
InactiveUS6876326B2Improve abilitiesReduce impactDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesRadio equipmentCommunications system
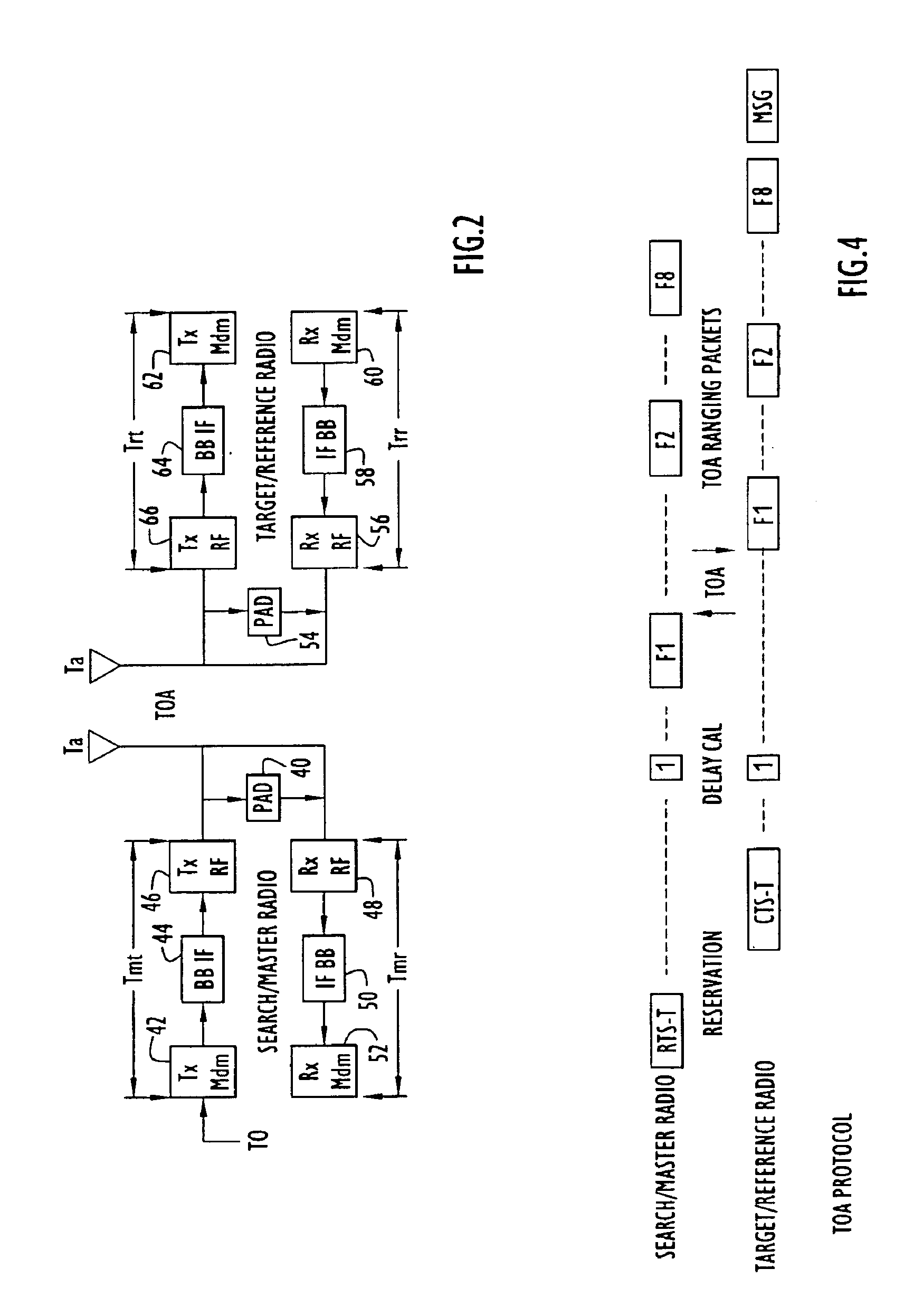
A high accuracy search and tracking system that uses a round-trip messaging scheme in which the time of arrive (TOA) of ranging signals is accurately determined to yield the range estimates between a target communications device and one or more search communications devices. Successive ranging estimates are used by a search device to home in upon the target device. The physical location pinpoint communications system can be used alone, or in combination with other location estimation systems that can be used initially, or throughout the search and tracking process to pinpoint the physical location of the target device. The search radio(s) transmits ranging signals to the target radio which responds by transmitting reply ranging signals. Upon reception of the reply ranging signal, the search radio determines the range to the reference radio from the signal propagation time. Errors in TOA estimates can be minimized using advanced processing techniques, if required.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
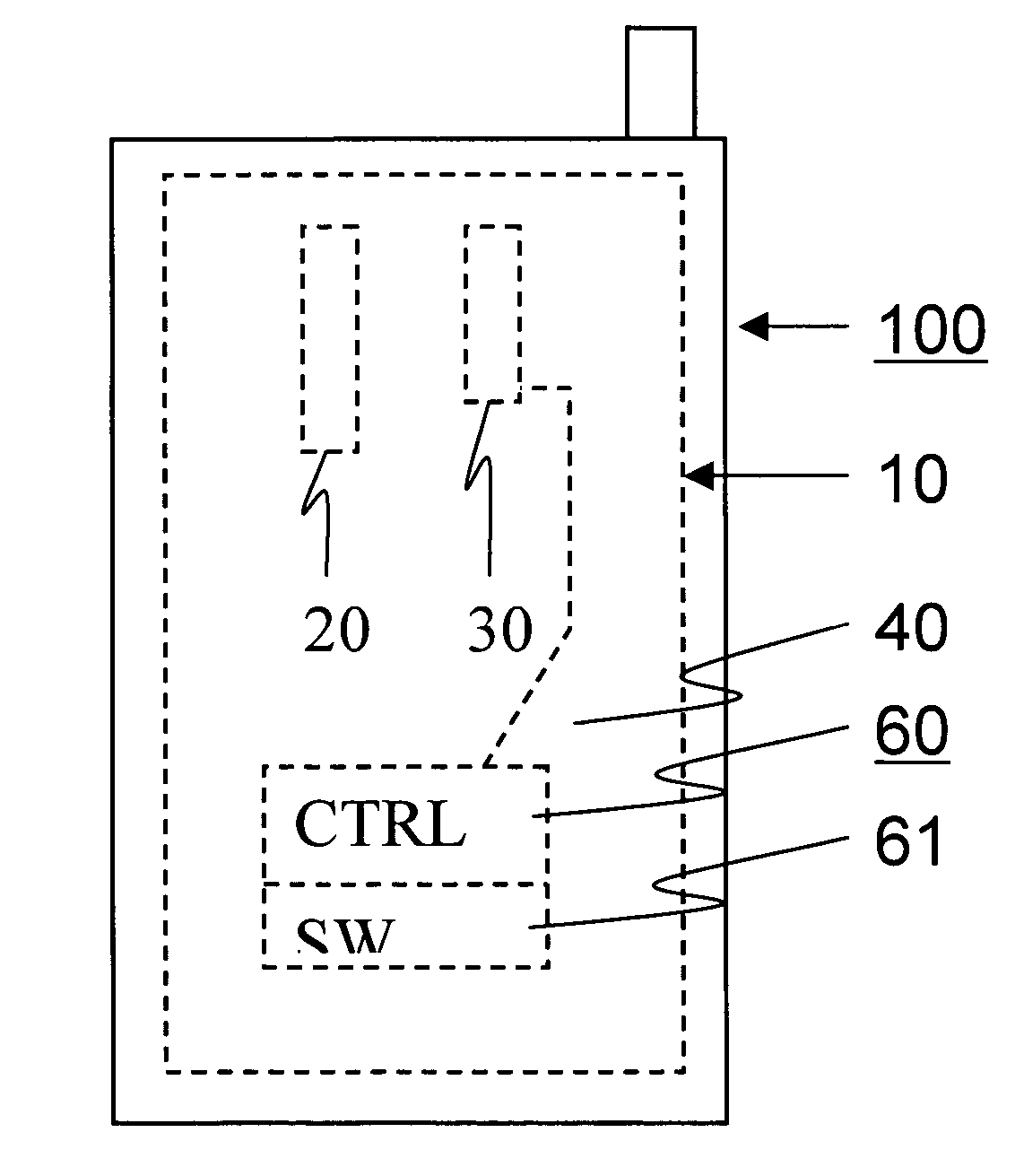
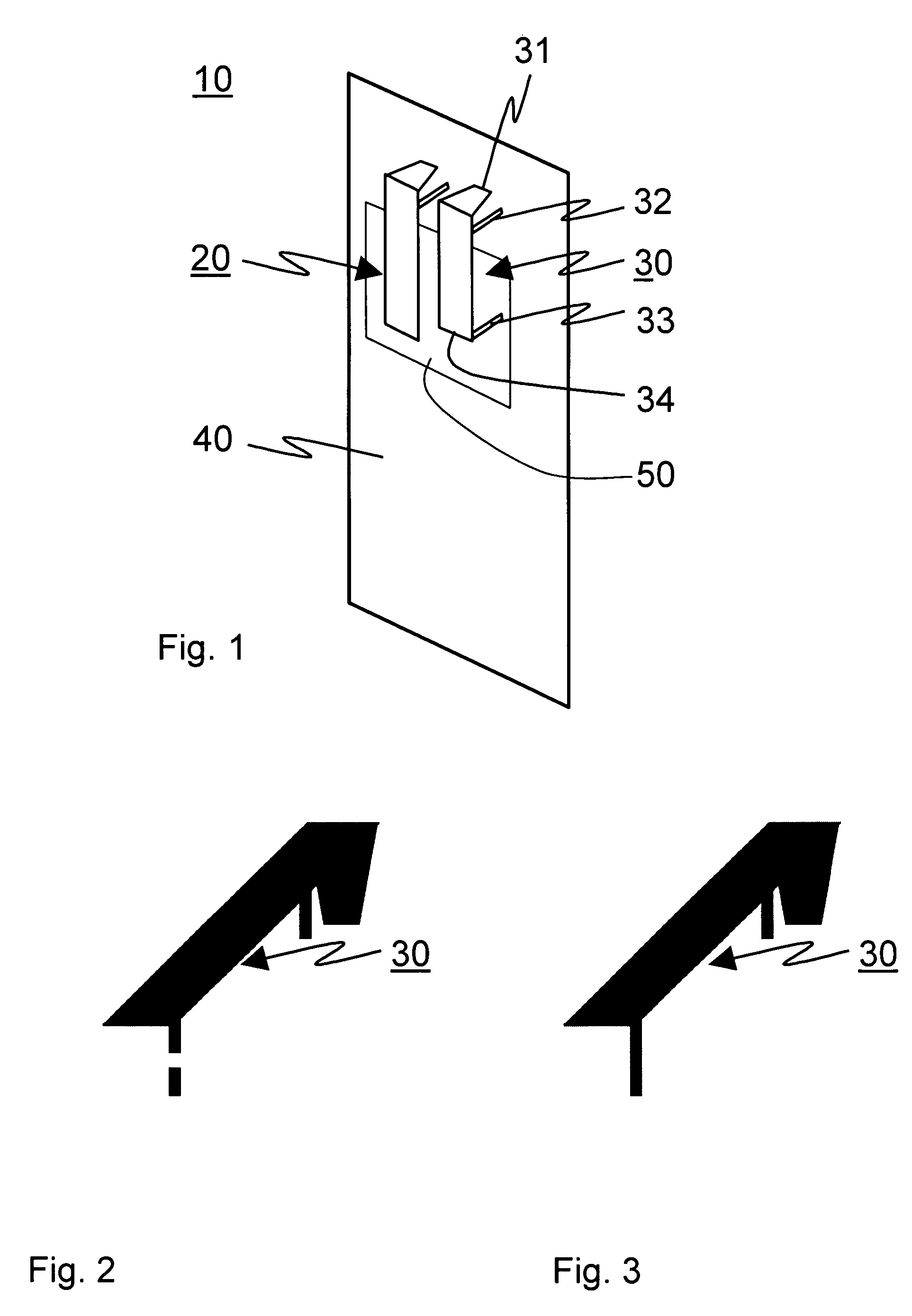
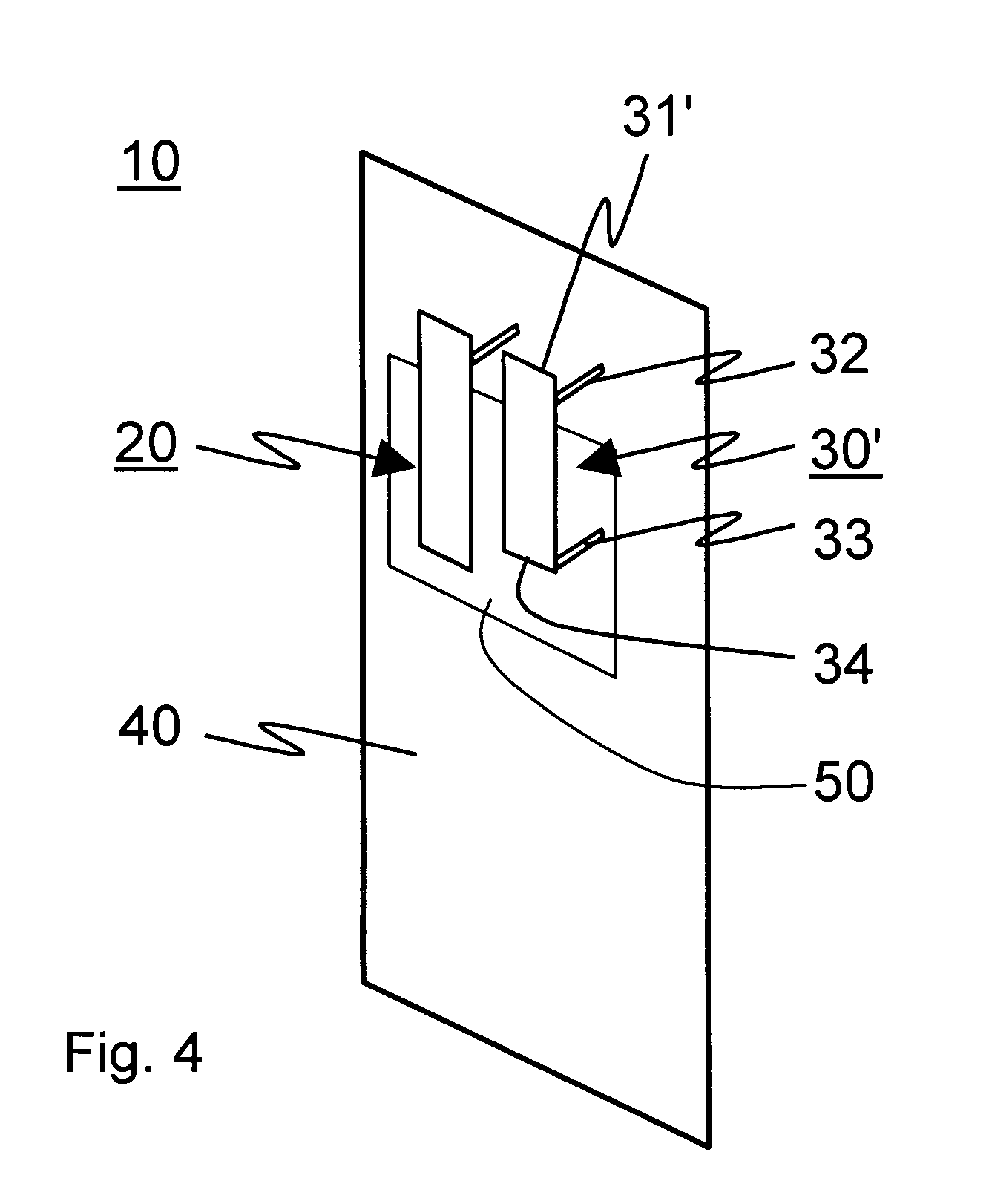
Method and arrangement for detecting load mismatch, and a radio device utilizing the same
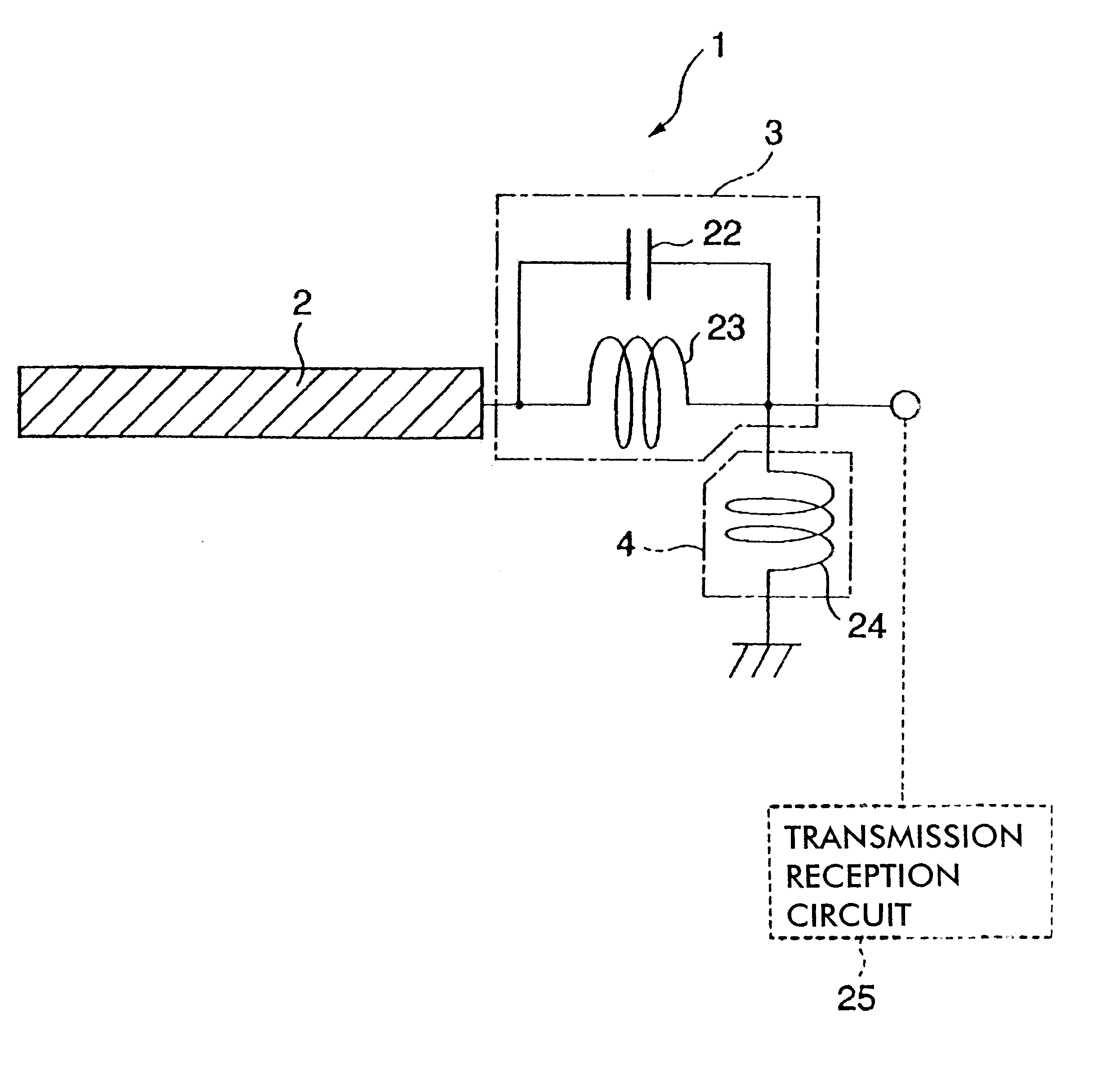
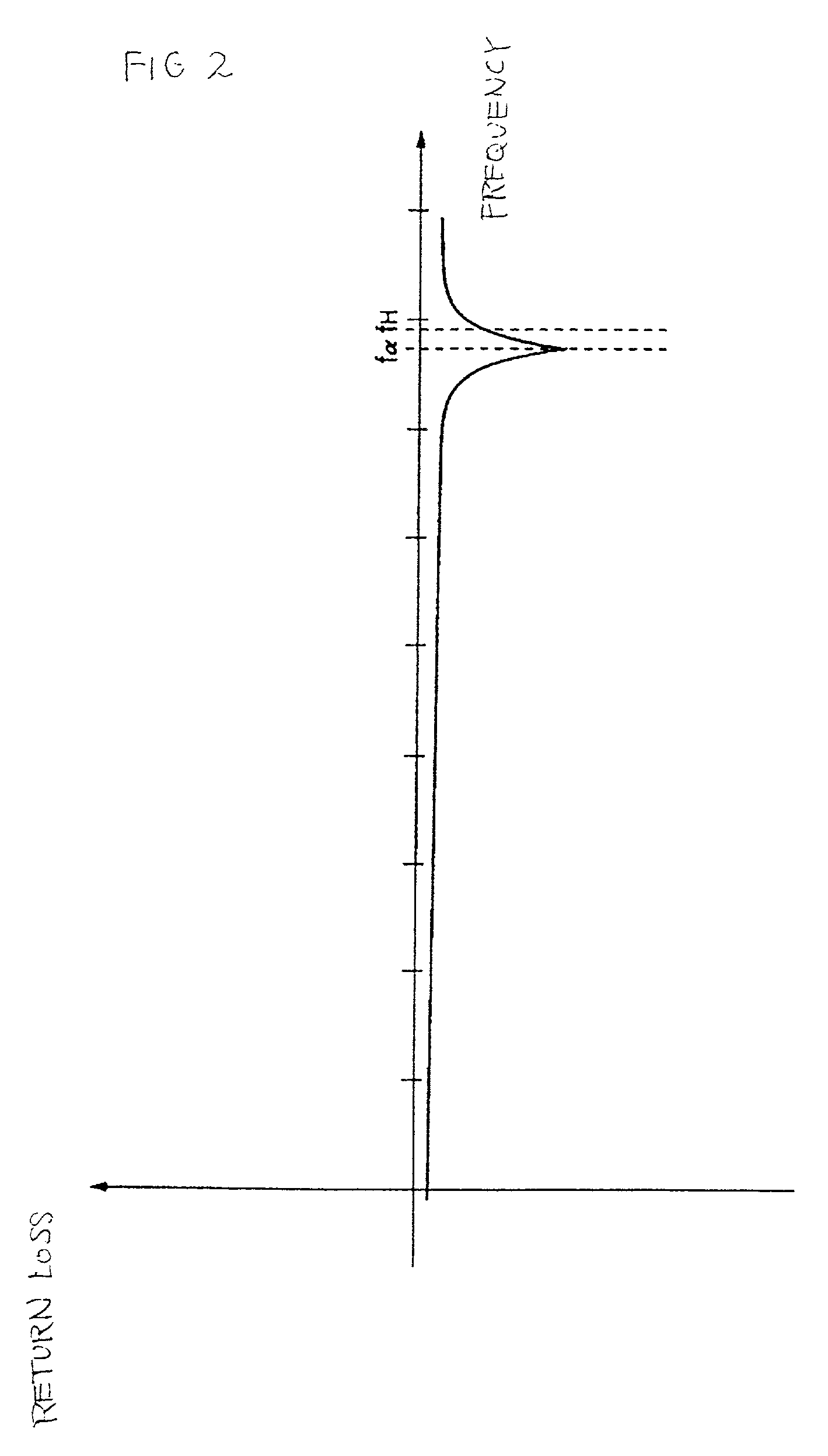
ActiveUS6965837B2Reduce lossesAccurate and reliable detectionResonant long antennasResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio equipmentEngineering
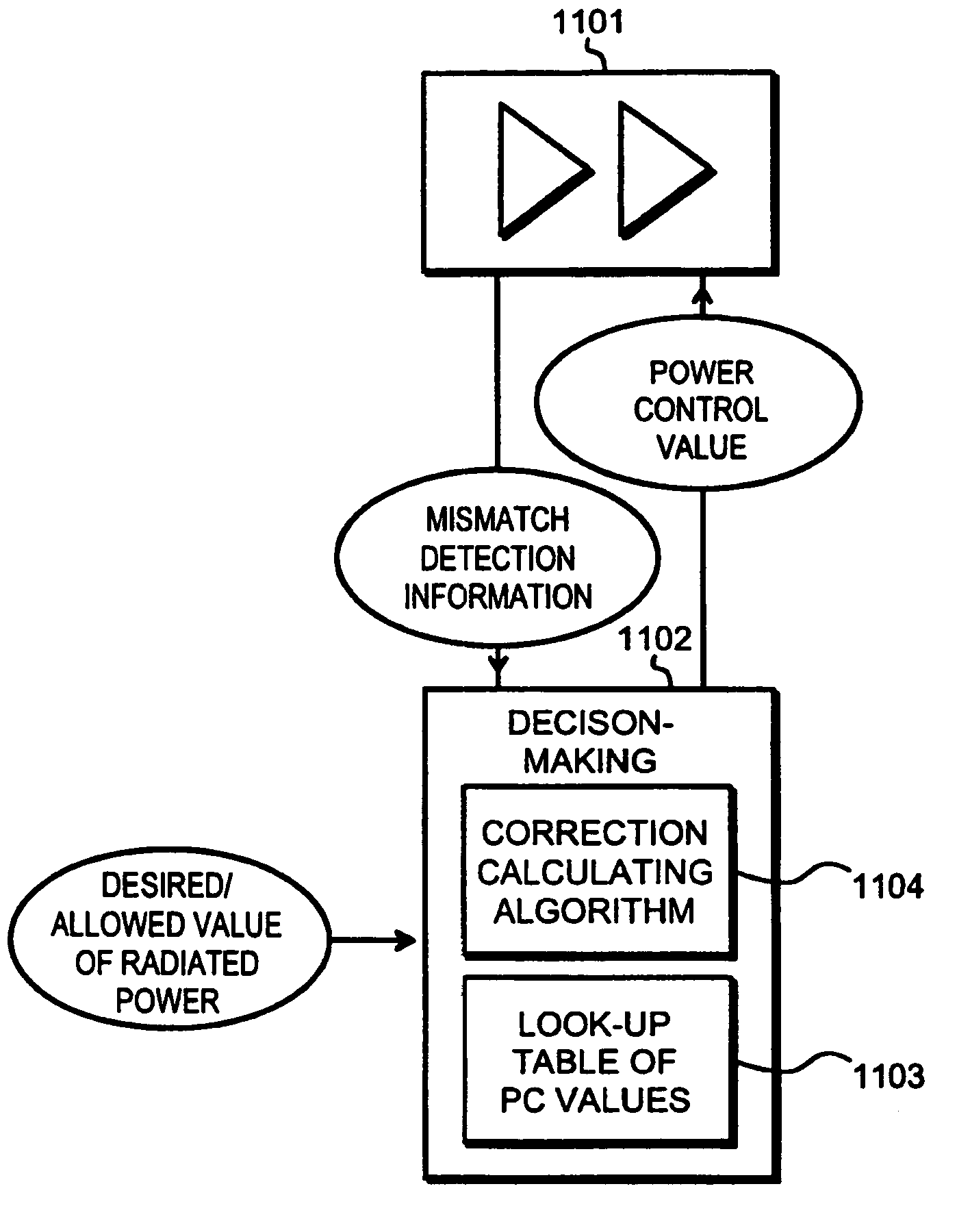
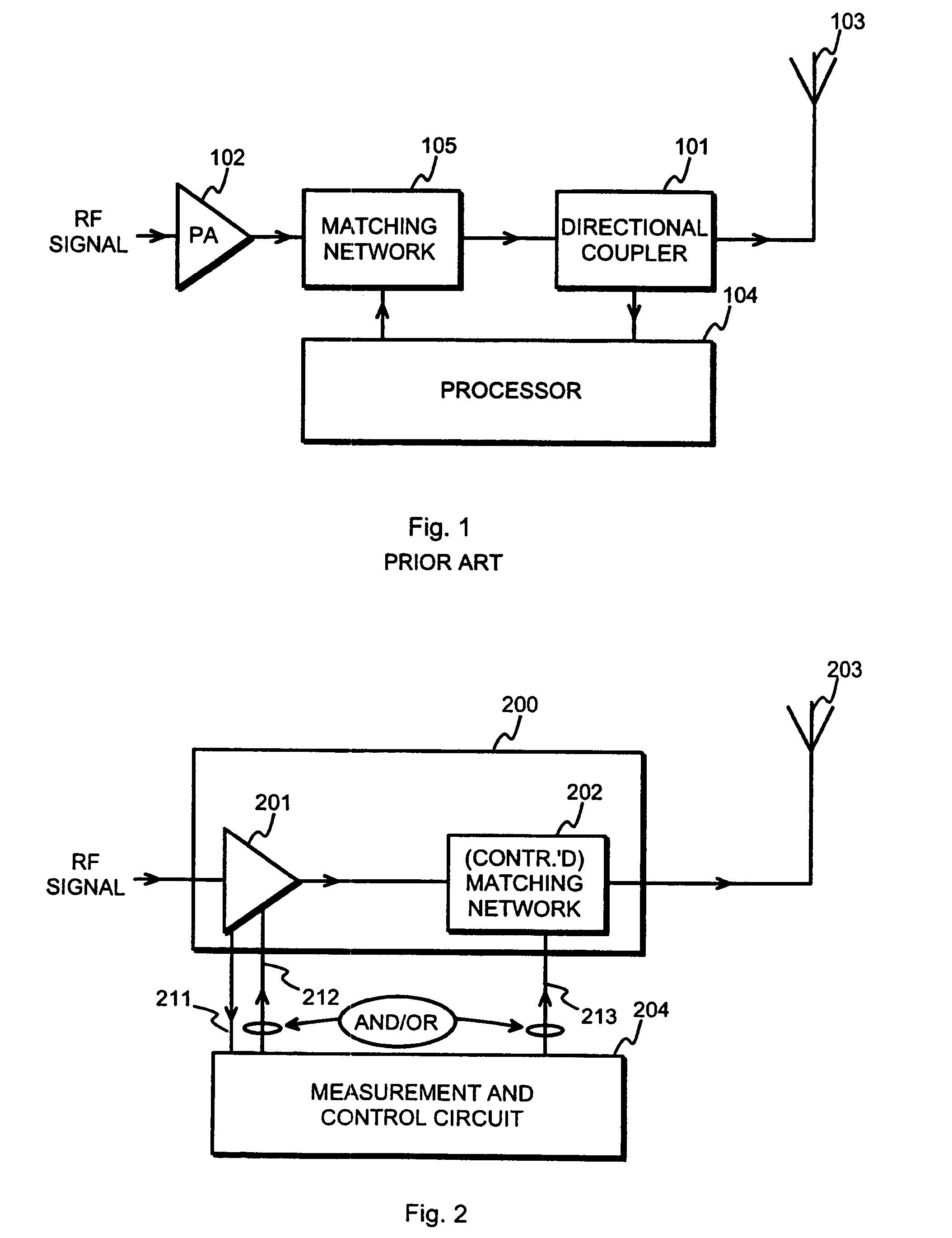
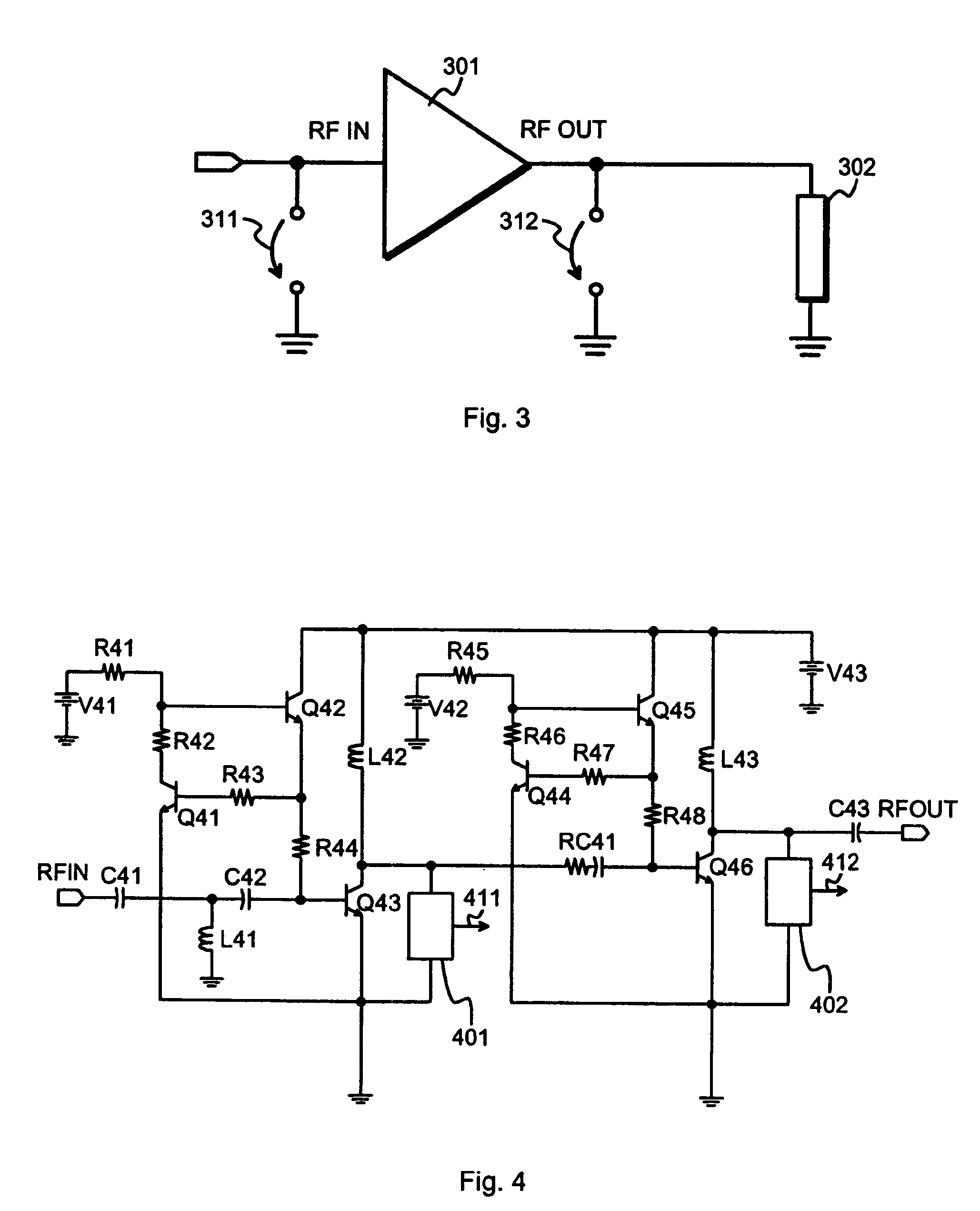
A method and an arrangement for detecting impedance mismatch between an output of a radio frequency amplifier (200, 901, 911, 921, 1101) which has an amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and an input of a load (203, 302) coupled to the output of the radio frequency amplifier having: first monitoring means (401) to monitor a measurable electric effect (311) at a side of the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) other than the load (203, 302) and to produce a first measurement signal (411). Second monitoring means (402) monitor a measurable electric effect (312) between the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and the load (203, 302) and produce a second measurement signal (412). Decision-making means (204, 902, 912, 923, 1102) receive said first (411) and second (412) measurement signals and decide, whether said first and second measurement signals together indicate impedance mismatch.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Mobile communication
InactiveUS7058434B2Reduce power consumptionAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentRadio equipmentDual mode
An antenna arrangement for dual mode radio devices such as WCDMA / GSM or Bluetooth radio devices. The arrangement contains two antennas close to each other, where a shorting switch is used at an open end of one antenna to increase isolation by effectively converting the one antenna from a quarter wave length antenna to a half wave length antenna when not needed in order to improve the efficiency of the other antenna. The shorting switch is typically a MEMS switch and the antennas are typically PIFA antennas. A radio device containing the arrangement has also been disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Dual receiver/transmitter radio devices with choke
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com