Patents
Literature
4869 results about "GSM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is a standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets. It was first deployed in Finland in December 1991.By the mid-2010s, it became a global standard for mobile communications achieving over 90% market share, and operating in over 193 countries and territories.
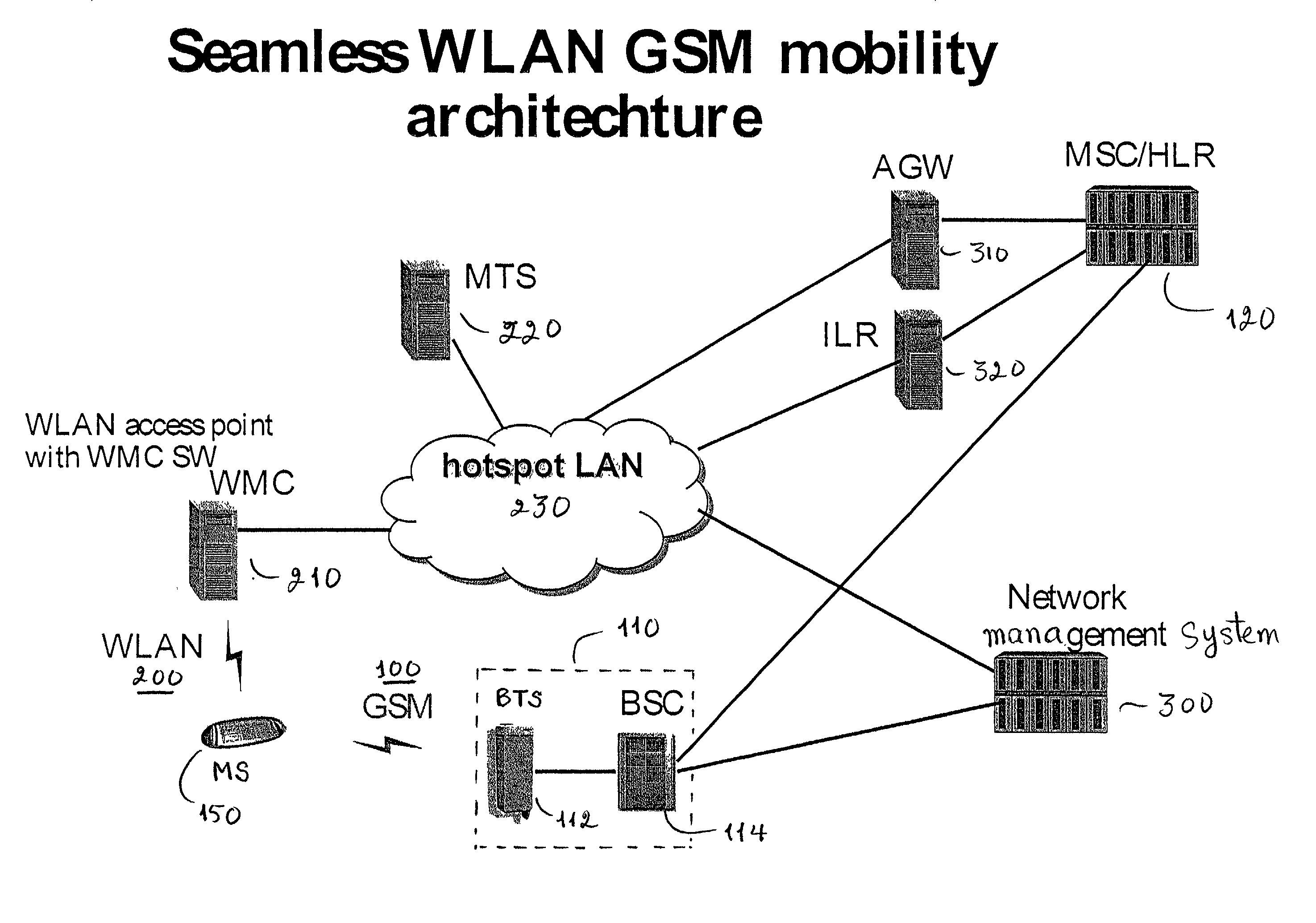
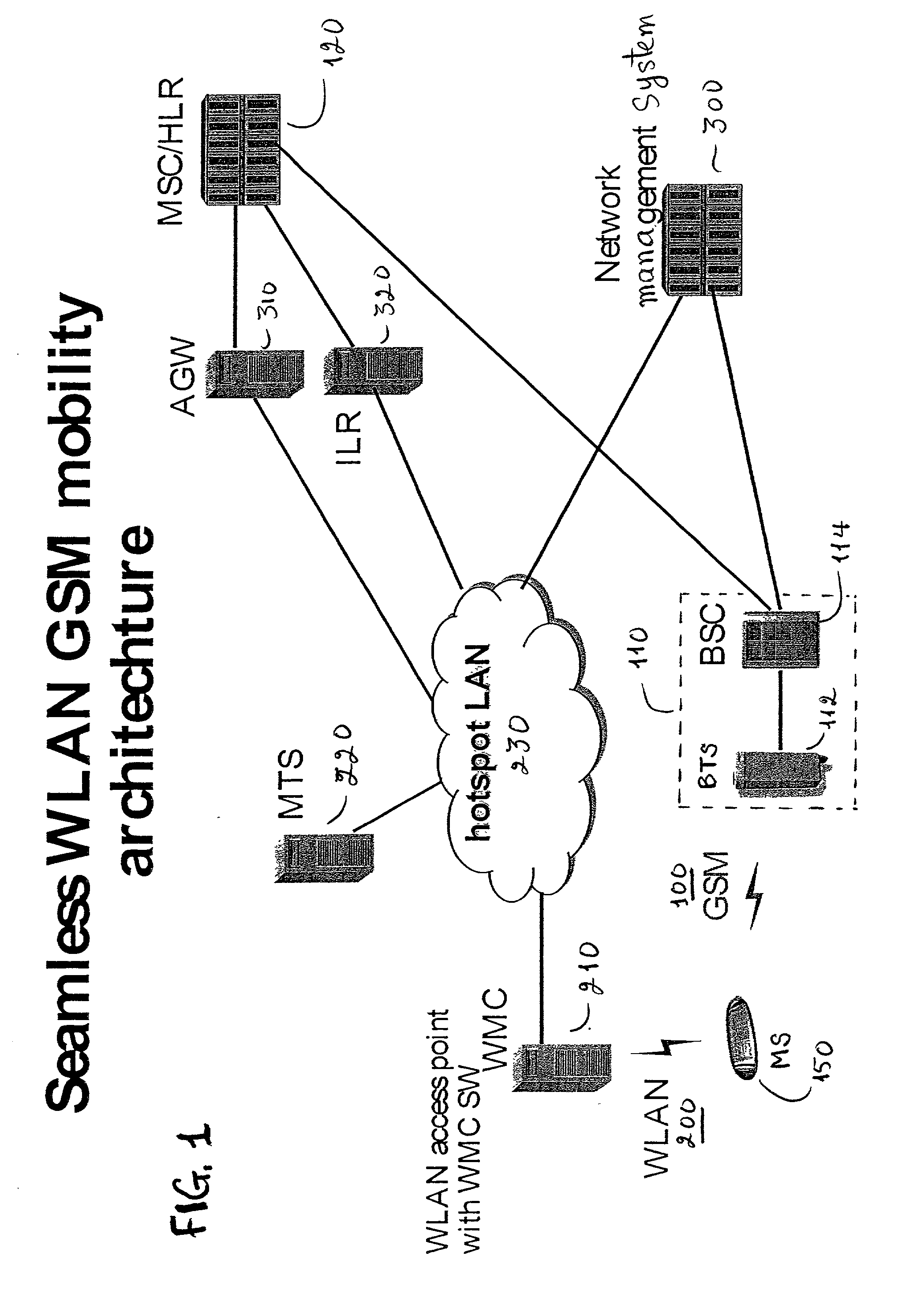
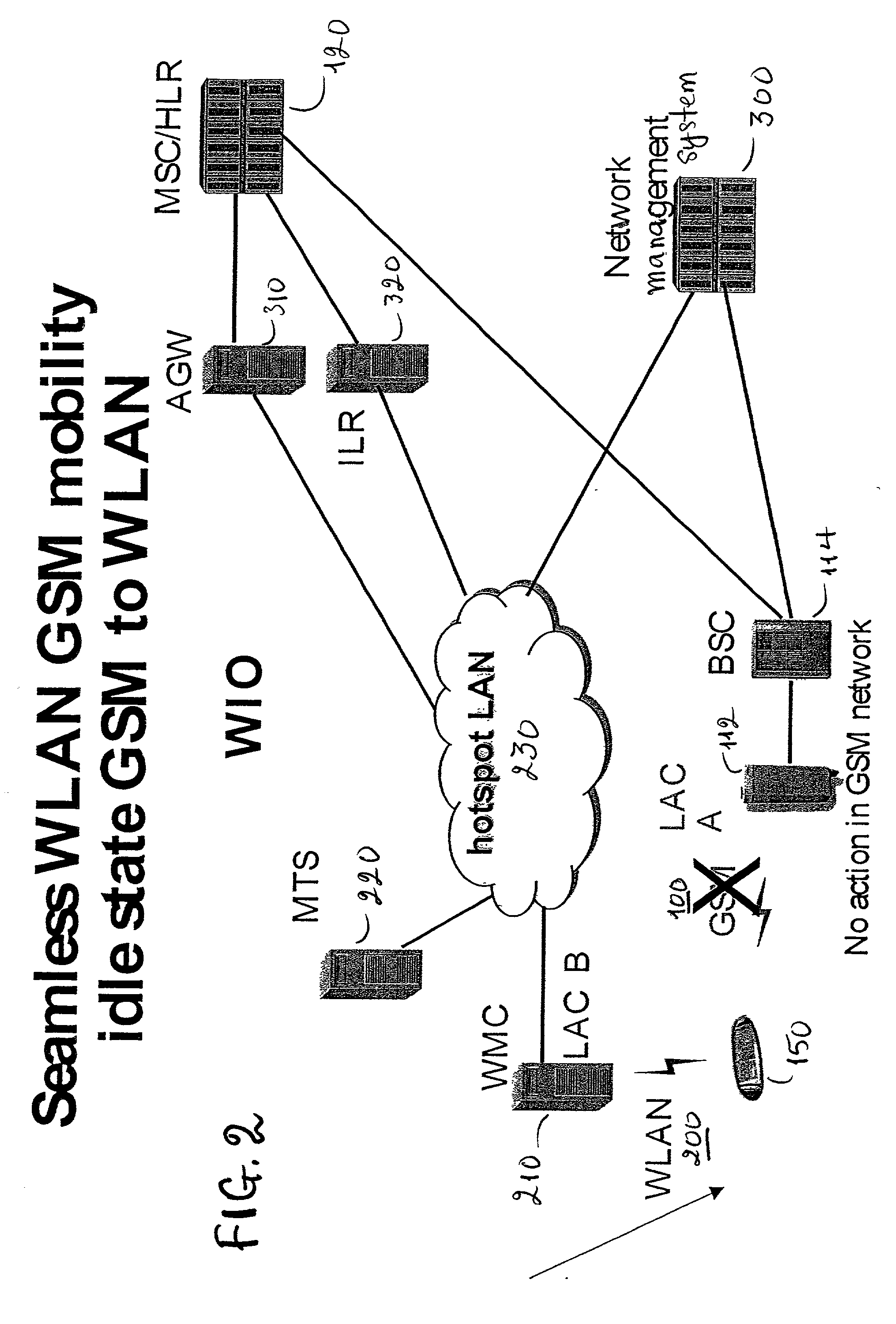
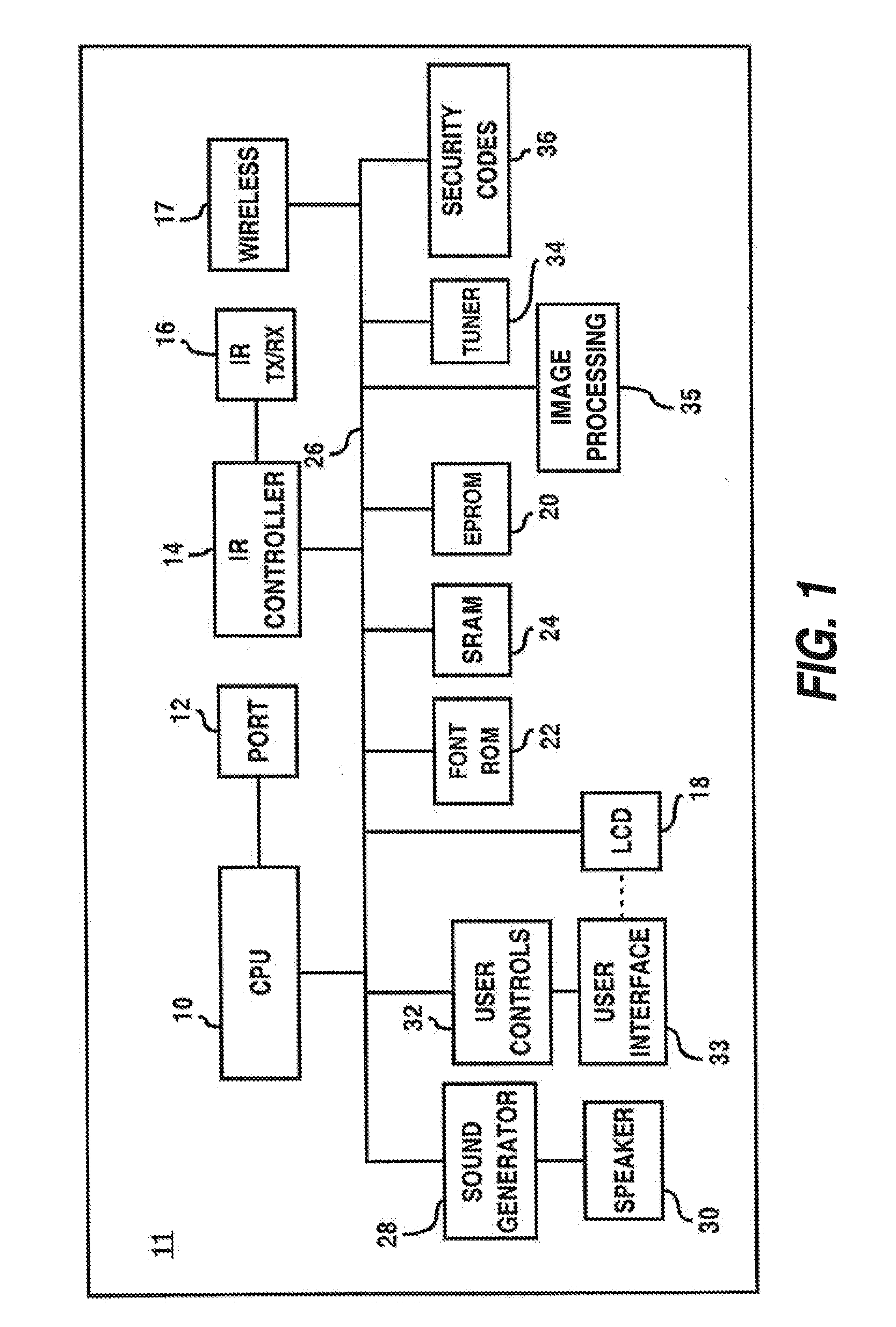
GSM Networks and solutions for providing seamless mobility between GSM Networks and different radio networks
InactiveUS20020147008A1Data switching by path configurationSubstation equipmentRadio networksDual mode
A network architecture for Wireless Intranet Office (WIO) applications including a local radio network such as a wireless local area network (WLAN) which comprises a Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) arranged to serve as a WLAN access point; a GSM network which comprises a Mobile Station (MS) in a form of a dual-mode cellular phone to access both WLAN and GSM radio technologies, a Base Station (BS) arranged to convert a radio signal from the Mobile Station (MS) for communication, a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) arranged to establish call connection; and a Handover Module implemented in either the Mobile Station (MS) or the Wireless Mobile Center (WMC) for providing seamless mobility between the GSM network and the wireless LAN, when the Mobile Station (MS) roams between the GSM network and the wireless LAN.
Owner:RPX CORP
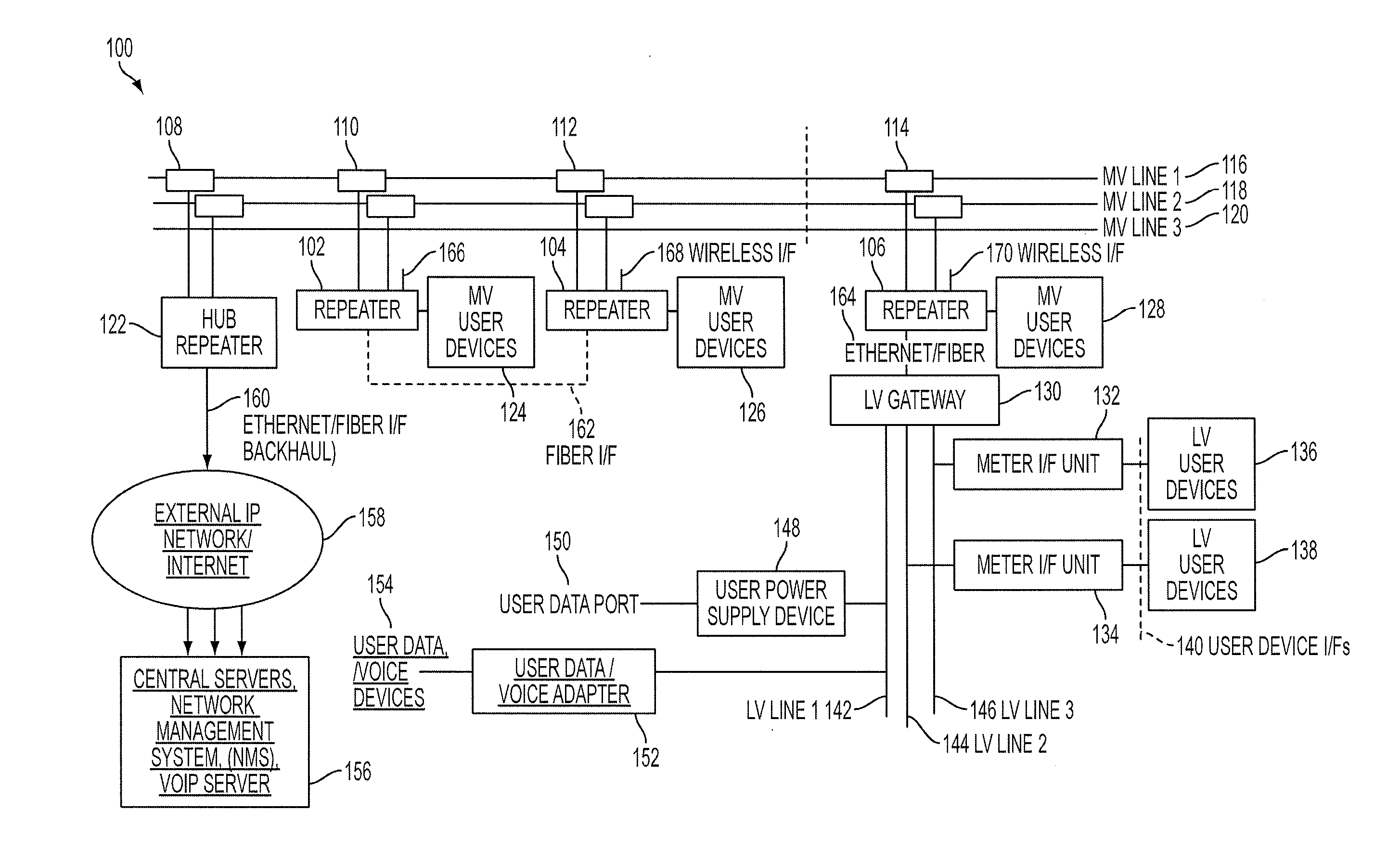
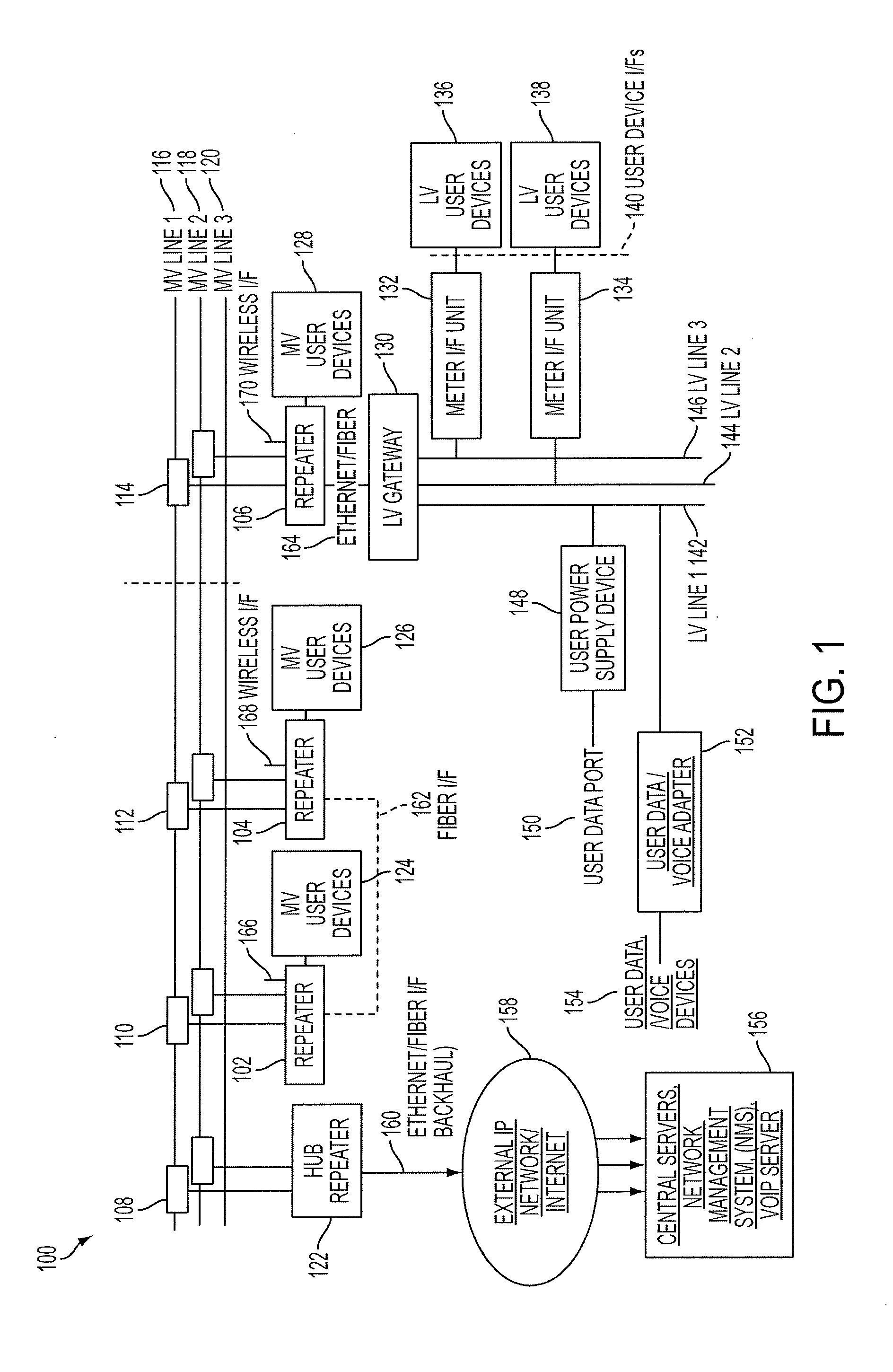
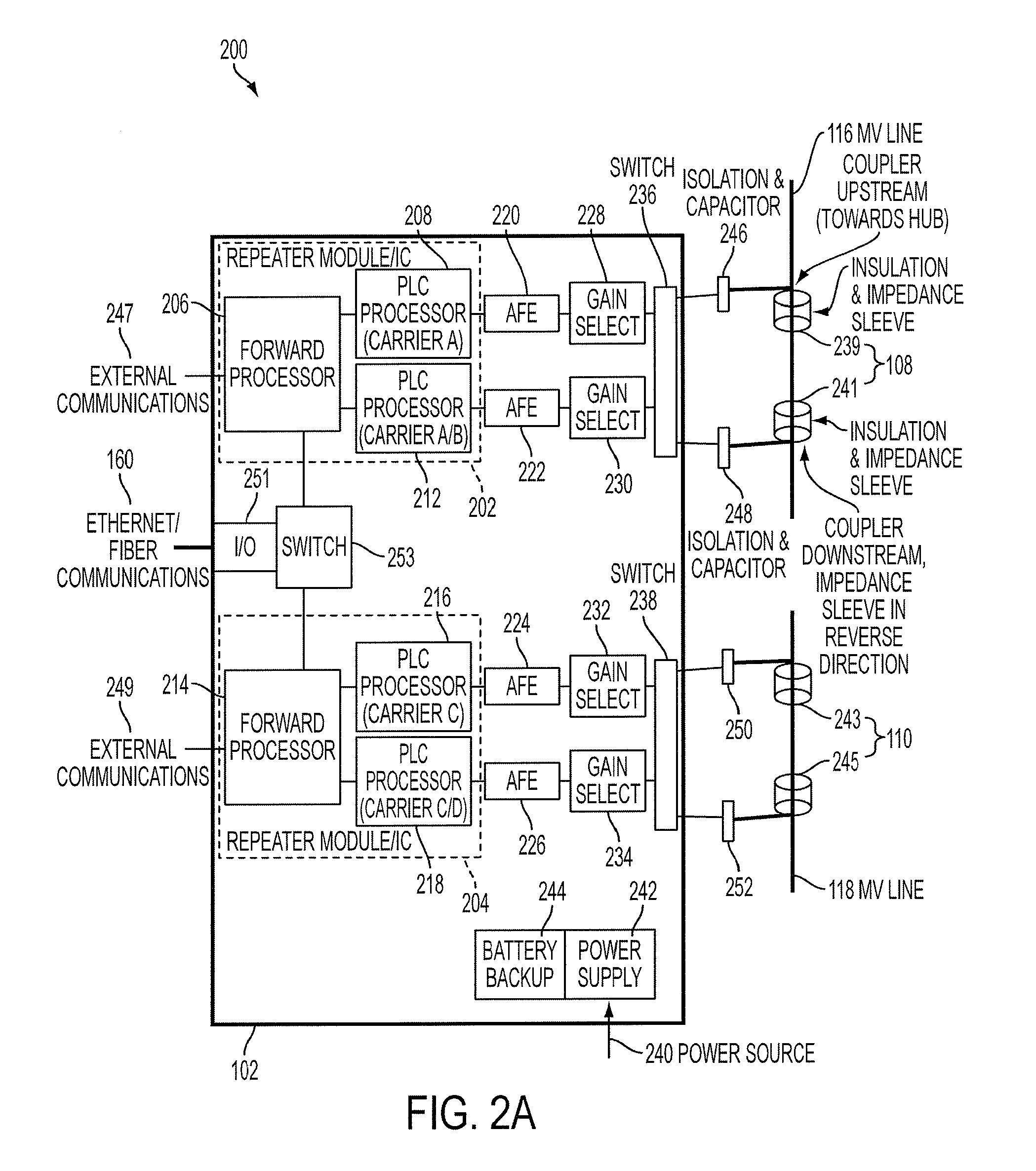
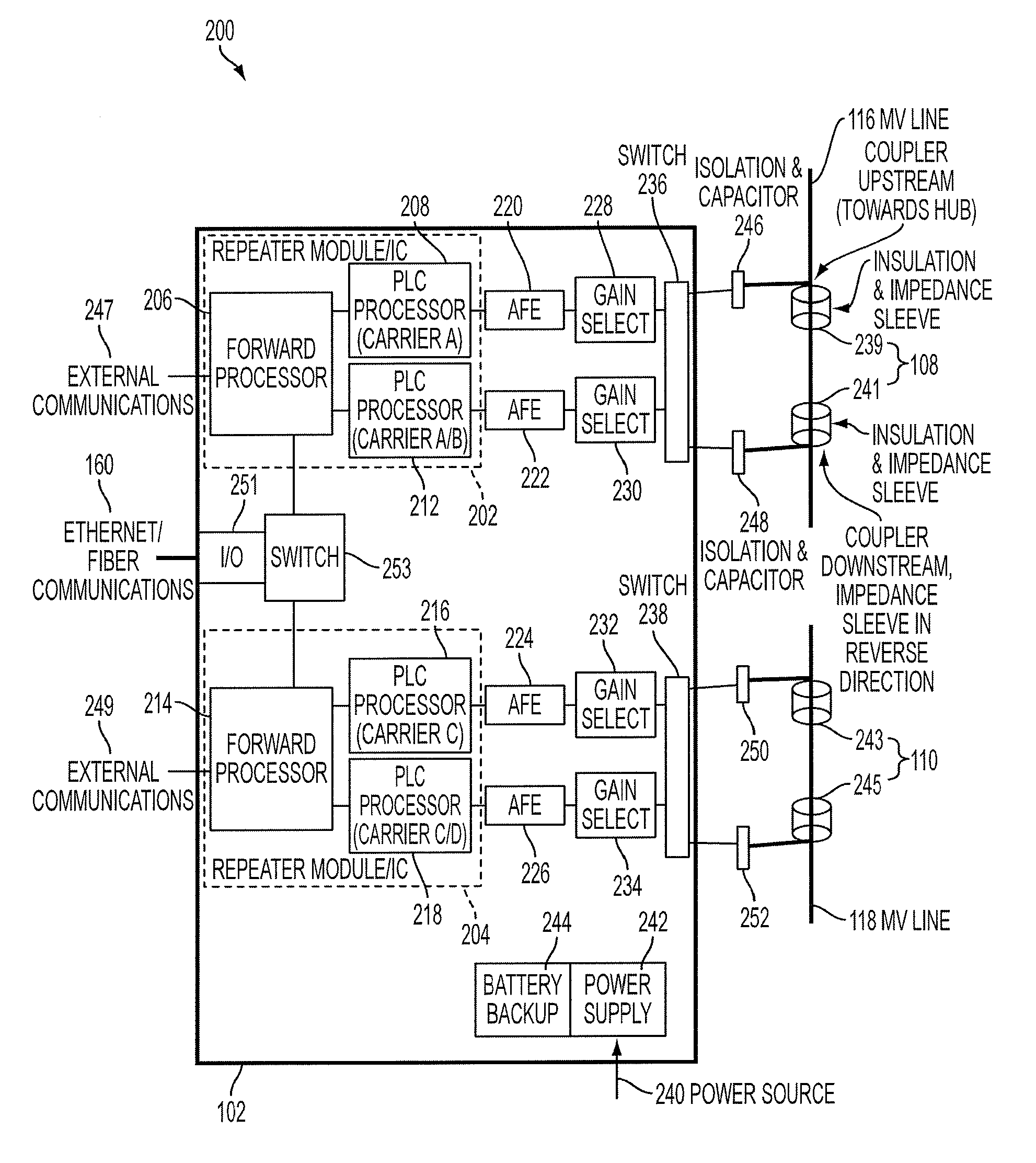
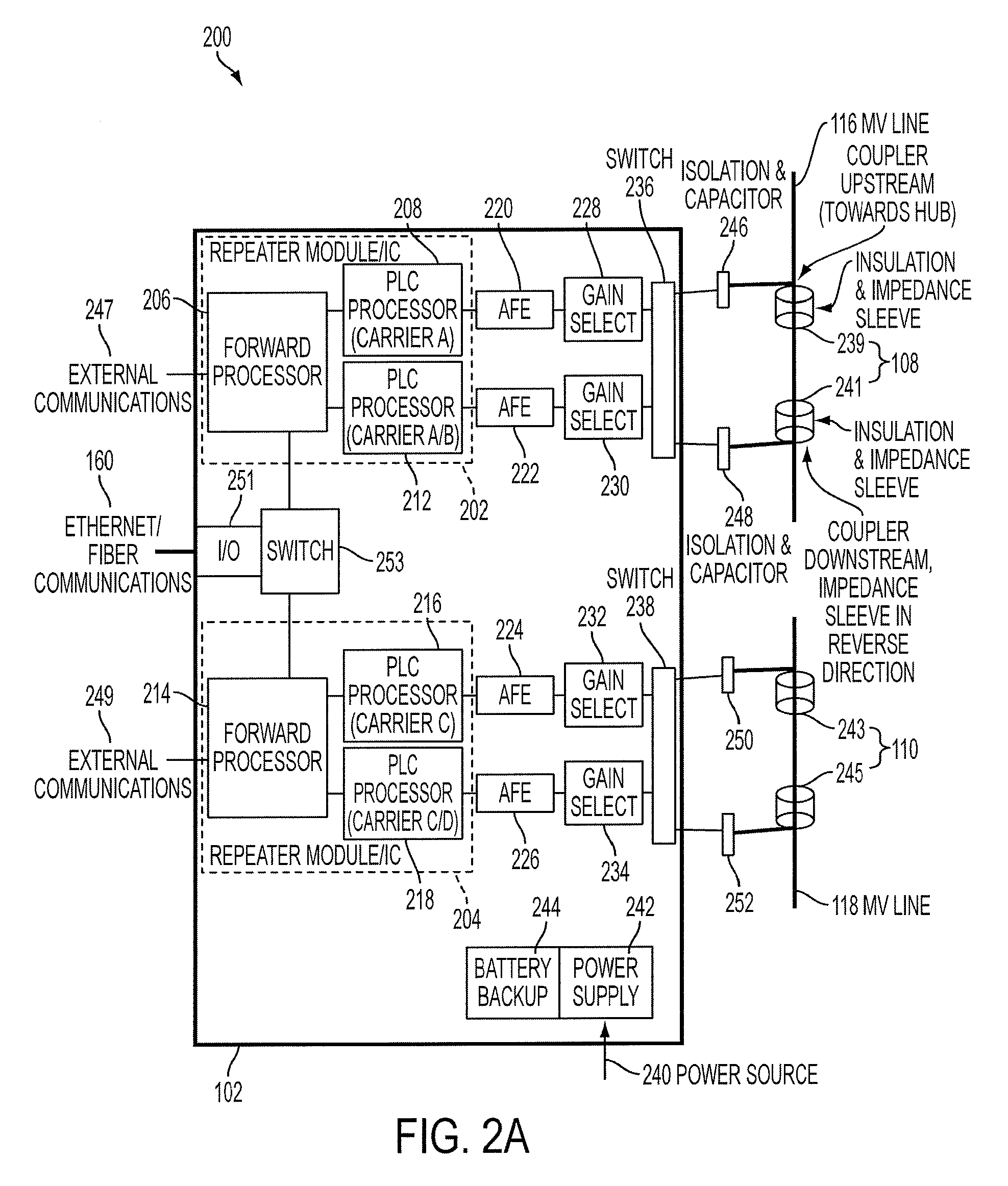
Reliable, long-haul data communications over power lines for meter reading and other communications services
InactiveUS20110140911A1Highly long-haulImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsPower distribution line transmissionPower qualitySignal quality
A system, method and computer program product provides for power line communications (PLC) over electric power lines includes a device mountable near an electrical distribution transformer (DT) to provide a high speed interface and communicates with one or multiple access devices, which provide low speed interfaces for analog signals or digital signals over RS 232, RS 485, optical, wireless and Ethernet. The device transmits data to / from these access devices over the electric lines to other repeaters over one or more wires of an electrical line or over multiple lines, and serves to strengthen and improve signal quality. Upon detecting a wire or line is having problems carrying data, the data is sent over other wires, and upon power line failures, wireless backup to mobile / GSM and WiMax networks is utilized. The device permits utilities and others to read electric meters, monitor the power quality of the distribution grid and detect power losses / failures / outages, and permits telecom service providers and others to provide a communications link to cell phone towers, WiFi Access Points and enable broadband Internet and telephony in rural, remote or sparely populated areas.
Owner:POWERMAX GLOBAL
Apparatus for and method of coordinating transmission and reception opportunities in a communications device incorporating multiple radios
InactiveUS20090180451A1Avoid interferenceDelay transitionNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentOperation modeMobile station
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of coordinating the allocation of transmission and reception availability and / or unavailability periods for use in a communications device incorporating collocated multiple radios. The mechanism provide both centralized and distributed coordination to enable the coordination (e.g., to achieve coexistence) of multiple radio access communication devices (RACDs) collocated in a single device such as a mobile station. A distributed activity coordinator modifies the activity pattern of multiple RACDs. The activity pattern comprises a set of radio access specific modes of operation, (e.g., IEEE 802.16 Normal, Sleep, Scan or Idle modes, 3GPP GSM / EDGE operation mode (PTM, IDLE, Connected, DTM modes), etc.) and a compatible set of wake-up events, such as reception and transmission availability periods. To prevent interference and possible loss of data, a radio access is prevented from transmitting or receiving data packets while another radio access is transmitting or receiving. In the event two or more RATs desire to be active at the same time, the mechanism negotiates an availability pattern between the MS and a corresponding BS to achieve coordination between the RATs.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
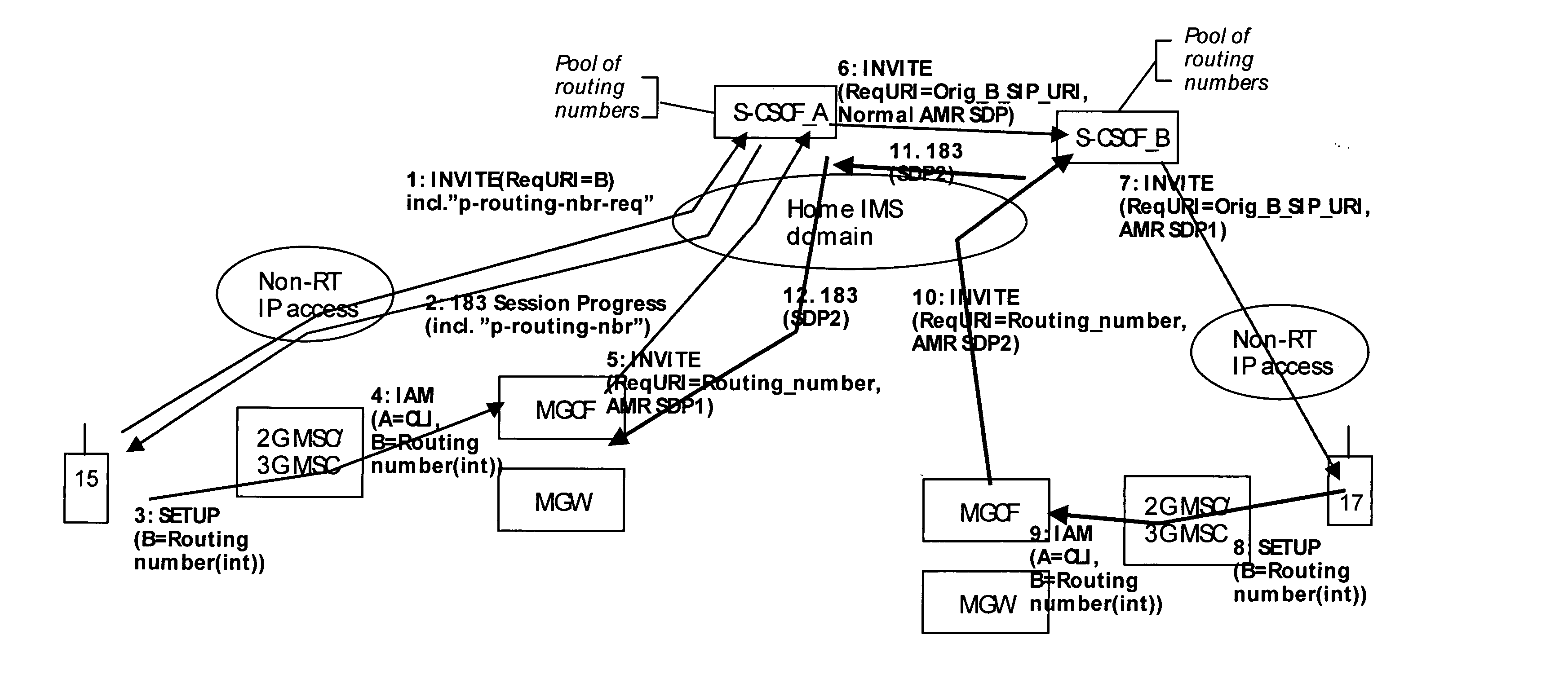
IP-based services for circuit-switched networks
ActiveUS20050058125A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsRadio access networkVoice over IP
A mechanism for providing a connection from an IP-based network to a circuit-switched network, such as a GSM network is disclosed. A temporary routing number for the circuit-switched network, such as an E.164 number, is delivered to a user terminal, and a circuit-switched call leg is established from the user terminal to the IP-based network using the routing number. Thereby, IMS-services are provided for end users which are located in the radio access network not having sufficient QoS required for voice over IP. In the example of a conference call service, a request for a conference call may forwarded via a data channel or data path to an application server which provides that conference call service. The application server then selects a conference routing number and returns the routing number to the conference host terminal via the data channel. Using the received conference routing number, the conference host terminal can then set up a circuit-switched connection as a call leg of the conference call.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Inter-frequency measurement and handover for wireless communications
InactiveUS6845238B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesHysteresisTelecommunications network
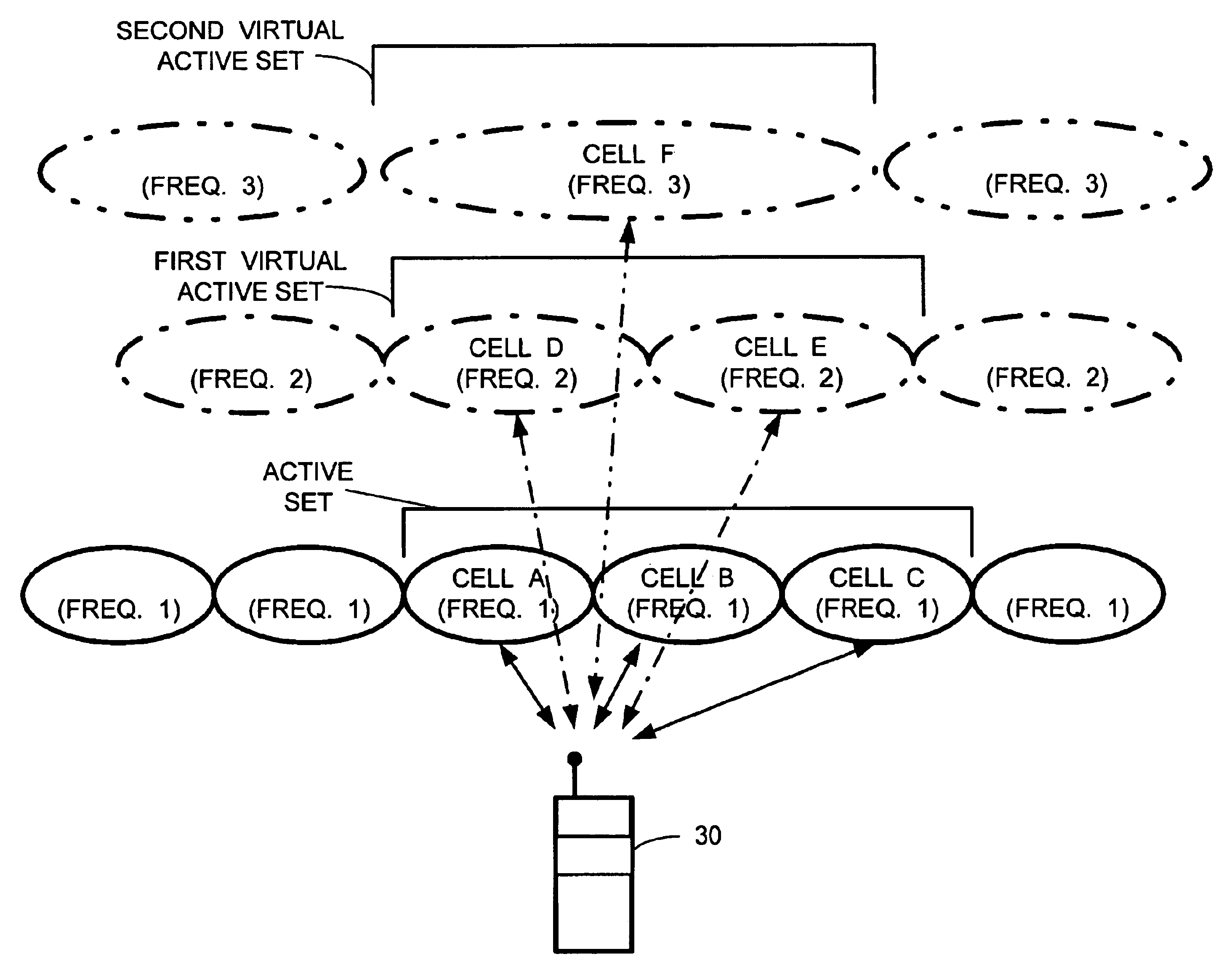
A telecommunications network performs an inter-frequency hard handover for a connection with a user equipment unit (UE) by switching either from a cell or a current active set of base stations on a first frequency to a virtual active set of base stations on another (new) frequency. The inter-frequency hard handover can be an inter-frequency handover within a same system, or an inter-system handover. The virtual active set of base stations is maintained at the user equipment unit (UE), and is updated in accordance with one of several updating implementations of the invention. In a first mode of the invention for implementing virtual active set updates, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to report to the network the occurrence of certain network-specified events which are acted upon by the network for communicating virtual active set update information to the user equipment unit (UE). In a second mode of the invention, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to perform an autonomous virtual active set update upon occurrence of certain network-specified events, with inter-frequency events being reported from the equipment unit (UE) to the network and the network issuing an inter-frequency handover command. Advantageously, events which trigger intra-frequency measurements can be reused for reporting inter-frequency measurements. In another of its aspects, the present invention provides the network with a quality estimate for a current active set as well as a quality estimate for the virtual active set. The quality estimate can be utilized in a context of a handover from one UTRAN frequency to another UTRAN frequency, or even in the context of an inter-system handover (e.g., a handover between a UTRAN system and a GSM system, for example). The quality estimate can be utilized to trigger a change or switch of frequencies / systems. Certain thresholds employed in the quality estimate-utilizing handovers provide hysteresis protection.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
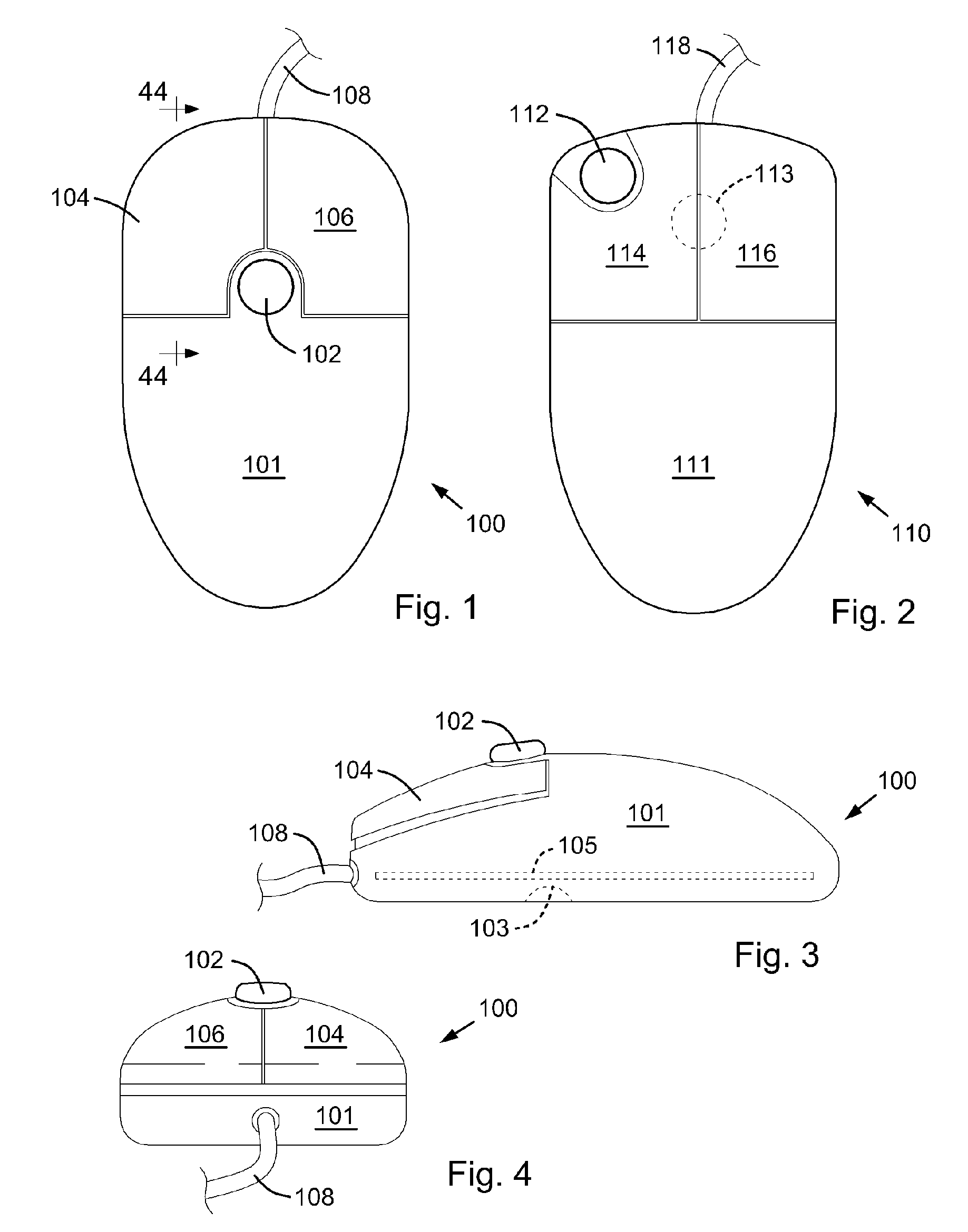
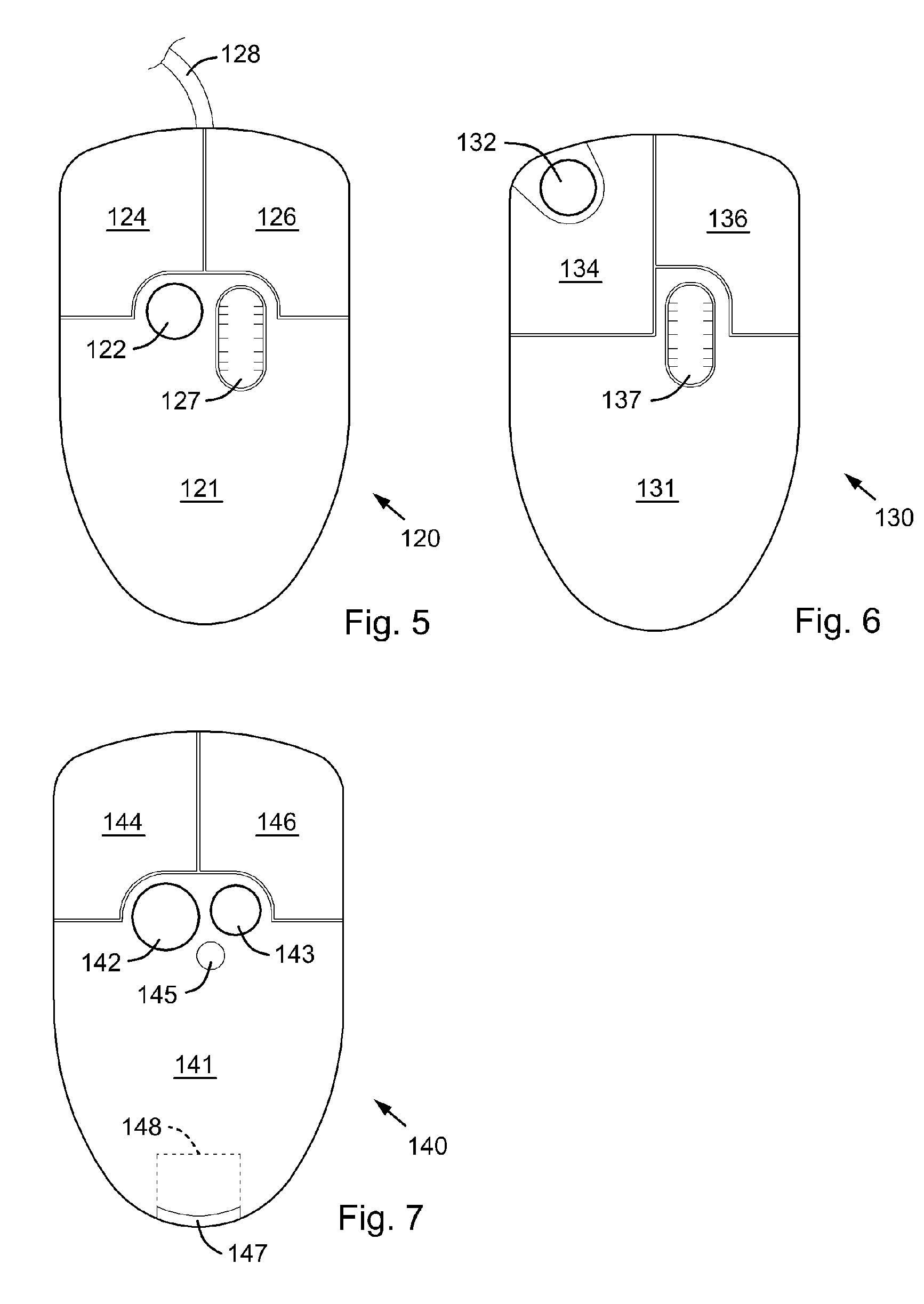
Computer Apparatus with added functionality
InactiveUS20060007151A1Add to and enhance functionLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHard disc driveWi-Fi
A computer apparatus such as a mouse, keyboard, or PC headset with additional devices disposed within the apparatus enclosure, which can enhance the functionality of such computer apparatus. In the preferred embodiment, the additional devices are disposed within or along the length of a mouse apparatus. The additional devices typically function independently of the mouse apparatus. However, the additional components may share one or more wired or wireless paths to a host PC and to other devices, or to a network. The additional devices either integrated within the mouse enclosure or removable from the mouse enclosure, include a wireless adapter (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 3G, GSM, etc. . . . ), RAM, ROM, a mini hard drive, a GPS receiver module, a flash memory, flash memory drive reader, a USB Hub, a Trackpoint™ device, a keyboard or keypad, a fingerprint reader, or a SIM card reader. Also disclosed, are software controls for mapping the mouse velocity to a cursor velocity and for controlling the function and settings of the Trackpoint device. Further disclosed is a method for assigning the mouse's data output to a variety of devices connected to a wired or wireless network.
Owner:RAM PRANIL
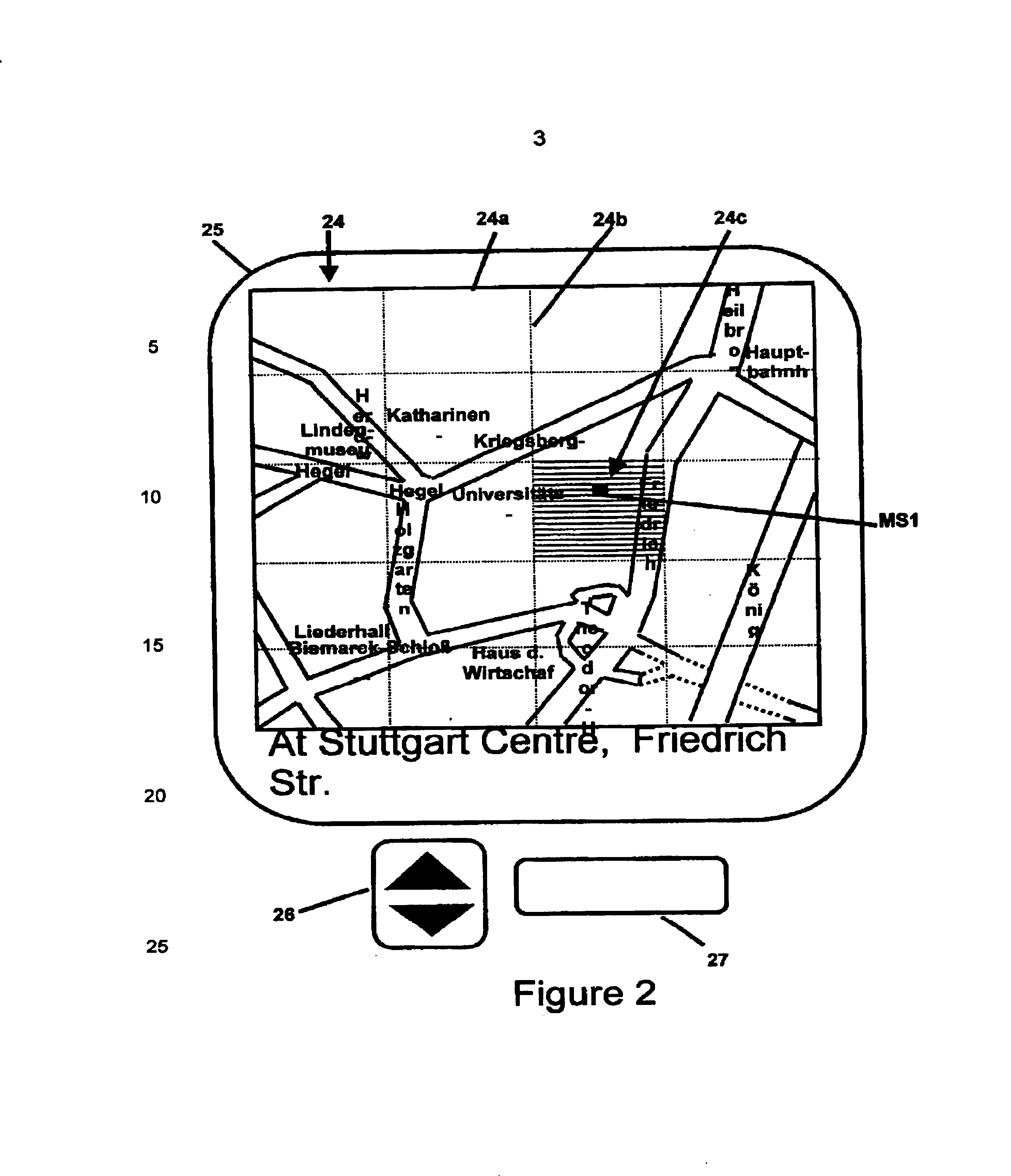
Downloading geographical data to a mobile station and displaying a map
InactiveUS6853911B1Low costSmall sizeInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationData displayWireless transmission
A mobile station (1) of a mobile communication network system (2), comprising a GPS / GSM or UMTS based geographical position localising module (3) for localising the geographical position (24c) of the mobile station, which has storage means for storing geographical related base data, and display means (4) for displaying geographical related base data as a map (24) or as a text string, is characterised in that the geographical related base data displayed has been at least partly provided by wireless transmission from the network system and is limited to a predetermined extent depending on the geographical position, travel modus and speed of the mobile station, and the mobile station itself calculates the geographical position which can be presented to others during call set-up or with SMS services and the mobile station can do routing using a navigational algorithm implemented in location finder module (31) of the mobile station.
Owner:SAKARYA TASKIN
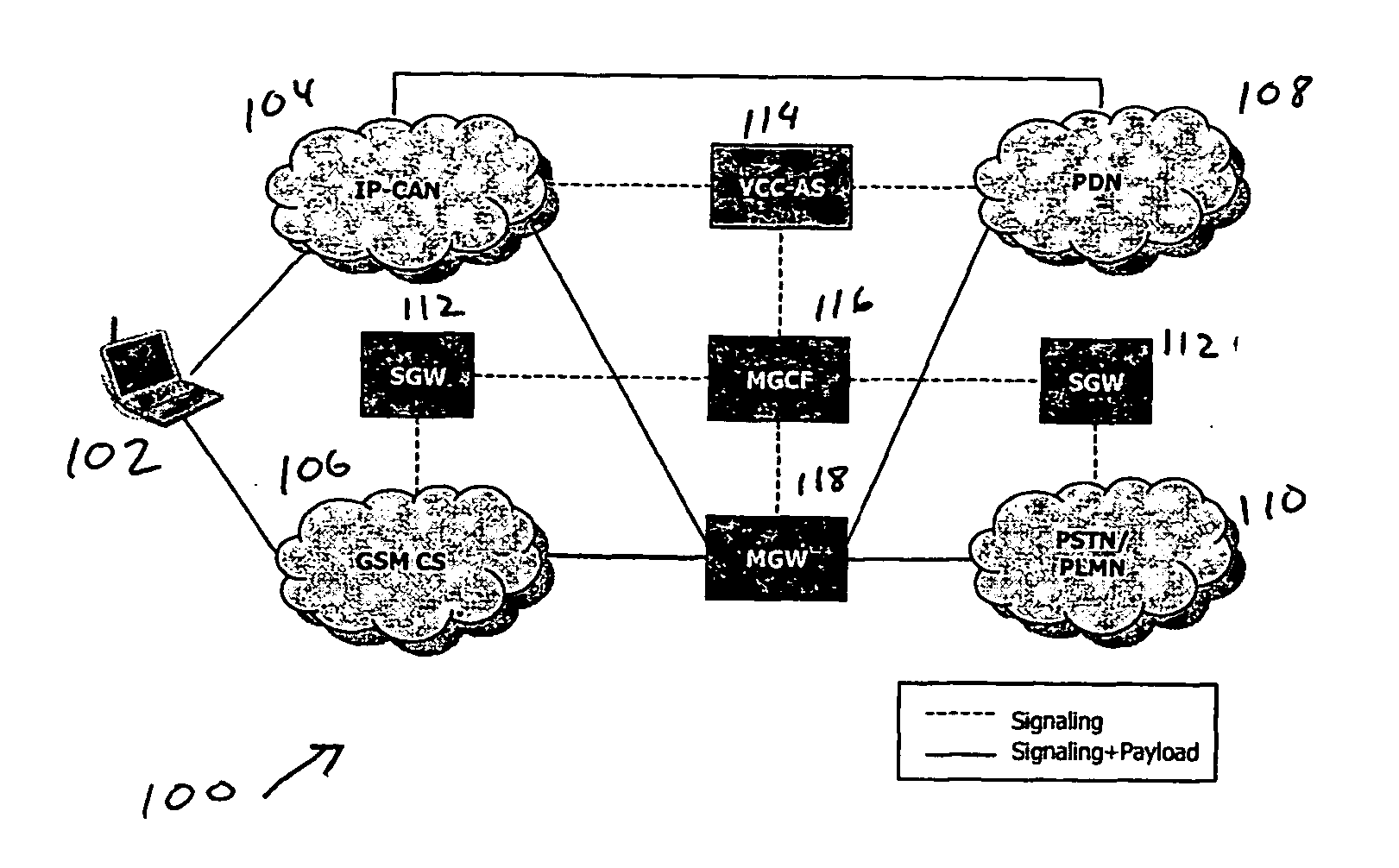
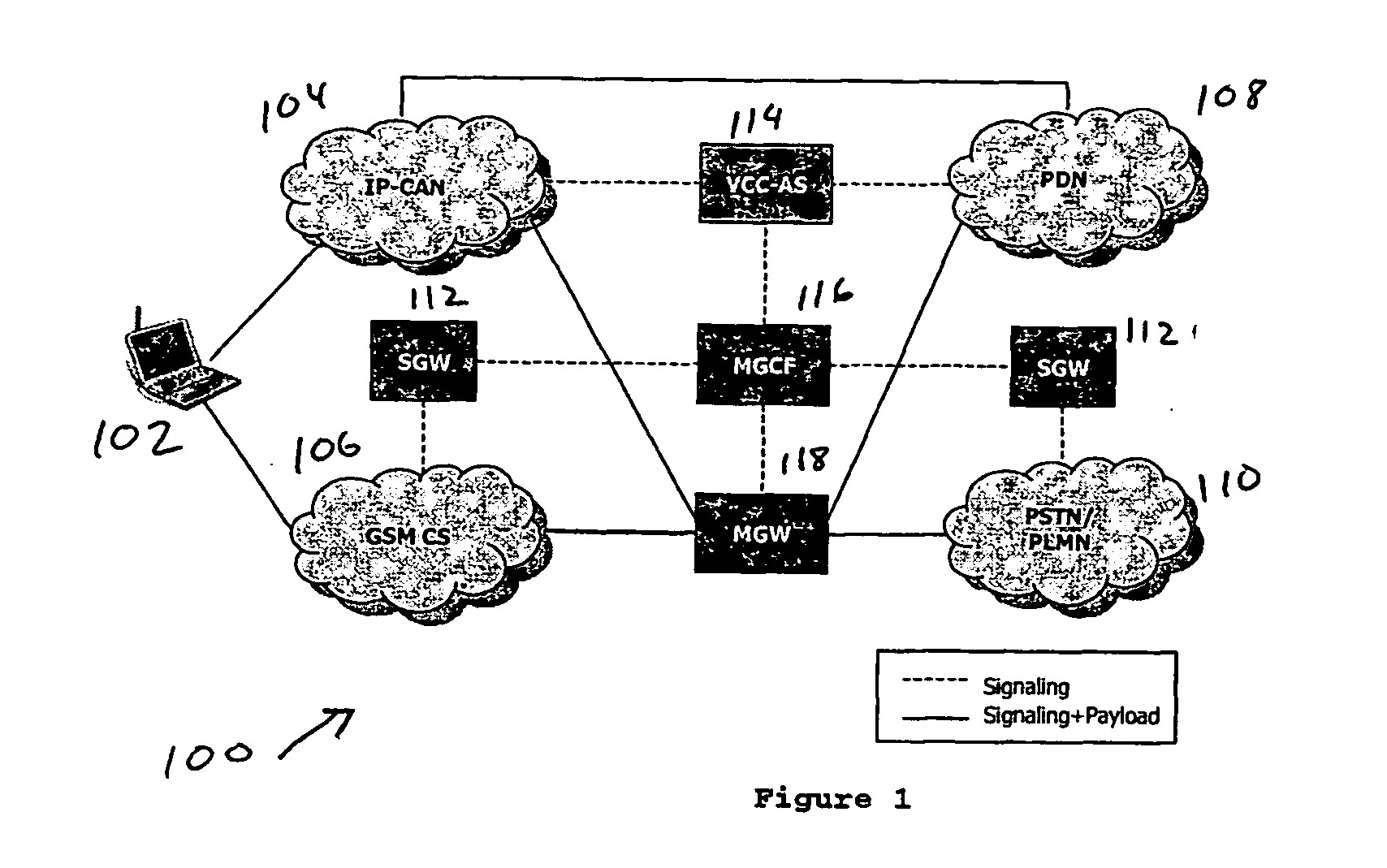
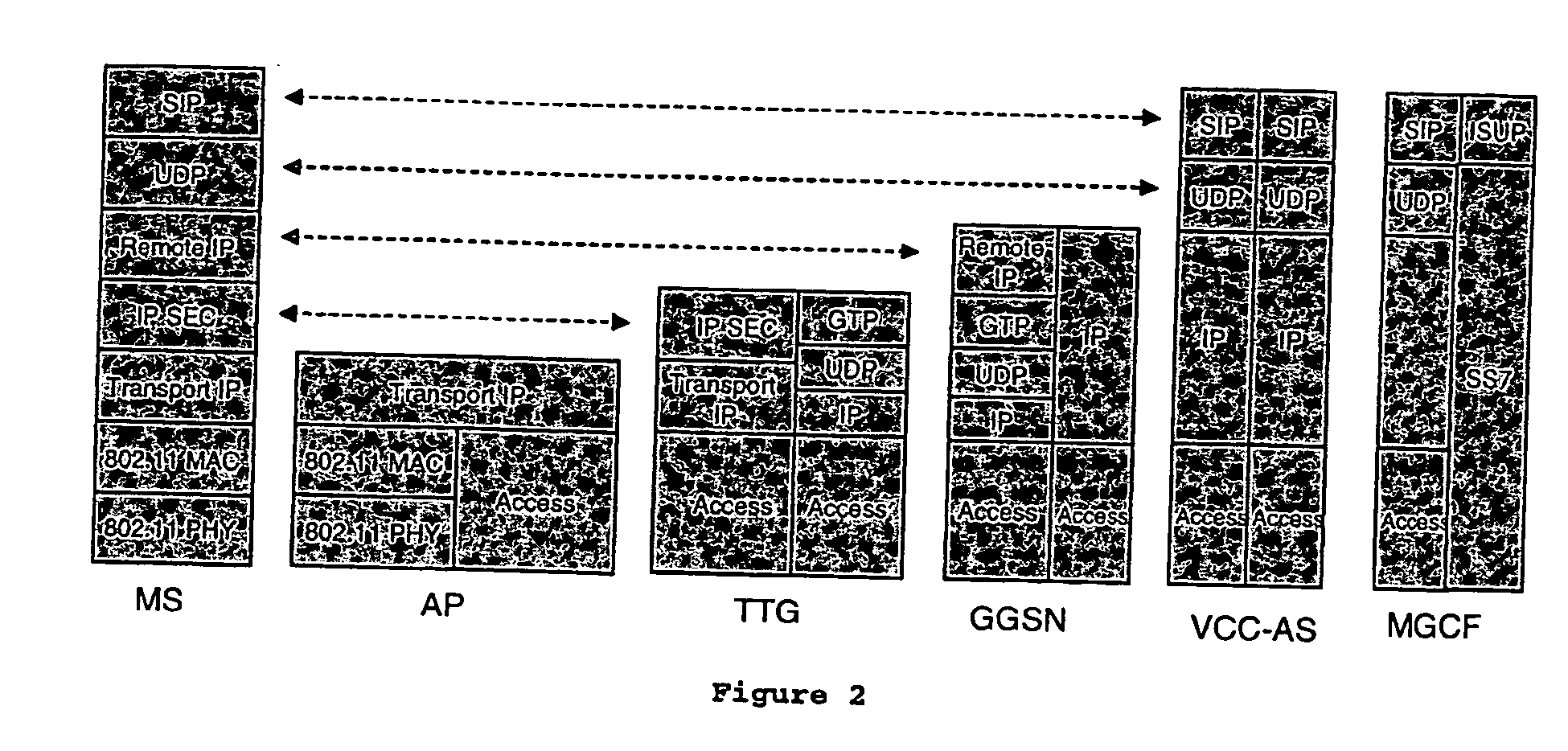
Voice call continuity application server between IP-CAN and CS networks
InactiveUS20070014281A1Accurate processingMultiplex system selection arrangementsConnection managementAccess networkApplication server
A system and method for continuous voice calls when a user switches between packet data and circuit switched access networks. In one example embodiment, the present innovations include an interworking system that supports voice call continuity for a user that moves between IP-CAN and CS networks (e.g., PSTN or GSM). In one example embodiment, the present innovations comprise a voice call continuity application server (VCC-AS) that serves as an anchor point for a voice call (i.e., it is the node from which a handover is initiated) and controls and handles voice calls to and from the user equipment (UE) regardless of the access network.
Owner:INTELLINET TECH
Method and device for authenticated access of a station to local data networks in particular radio data networks
ActiveUS20050048950A1Authentication is simpleEasy to chargeMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionRadio equipmentCommunications system
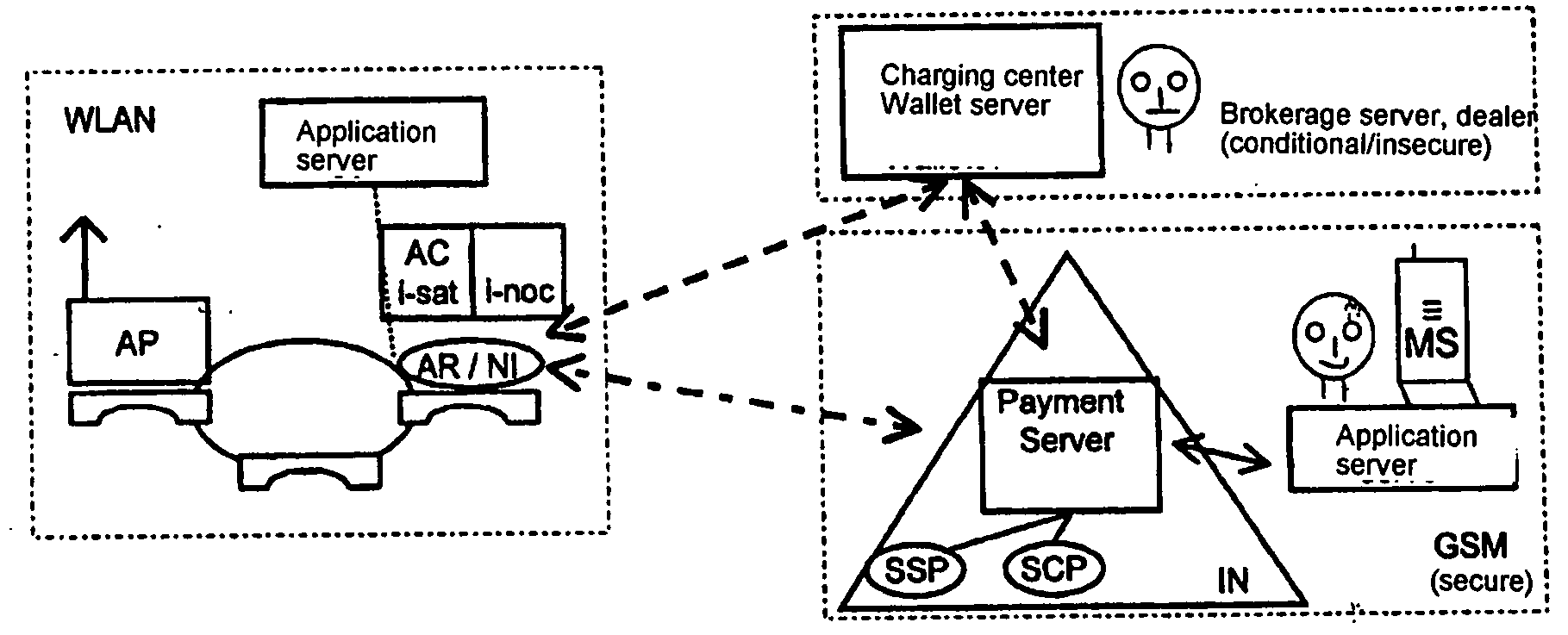
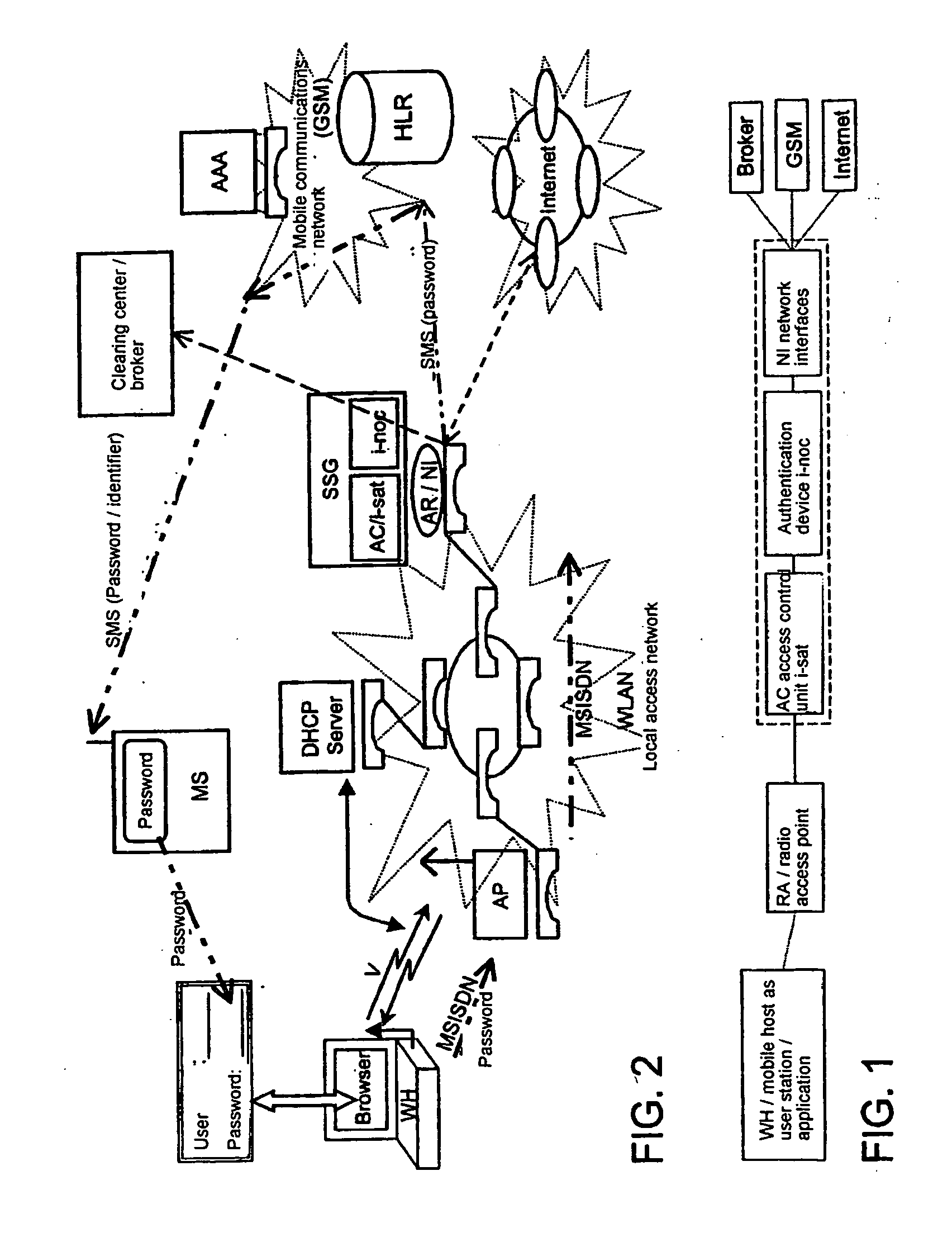
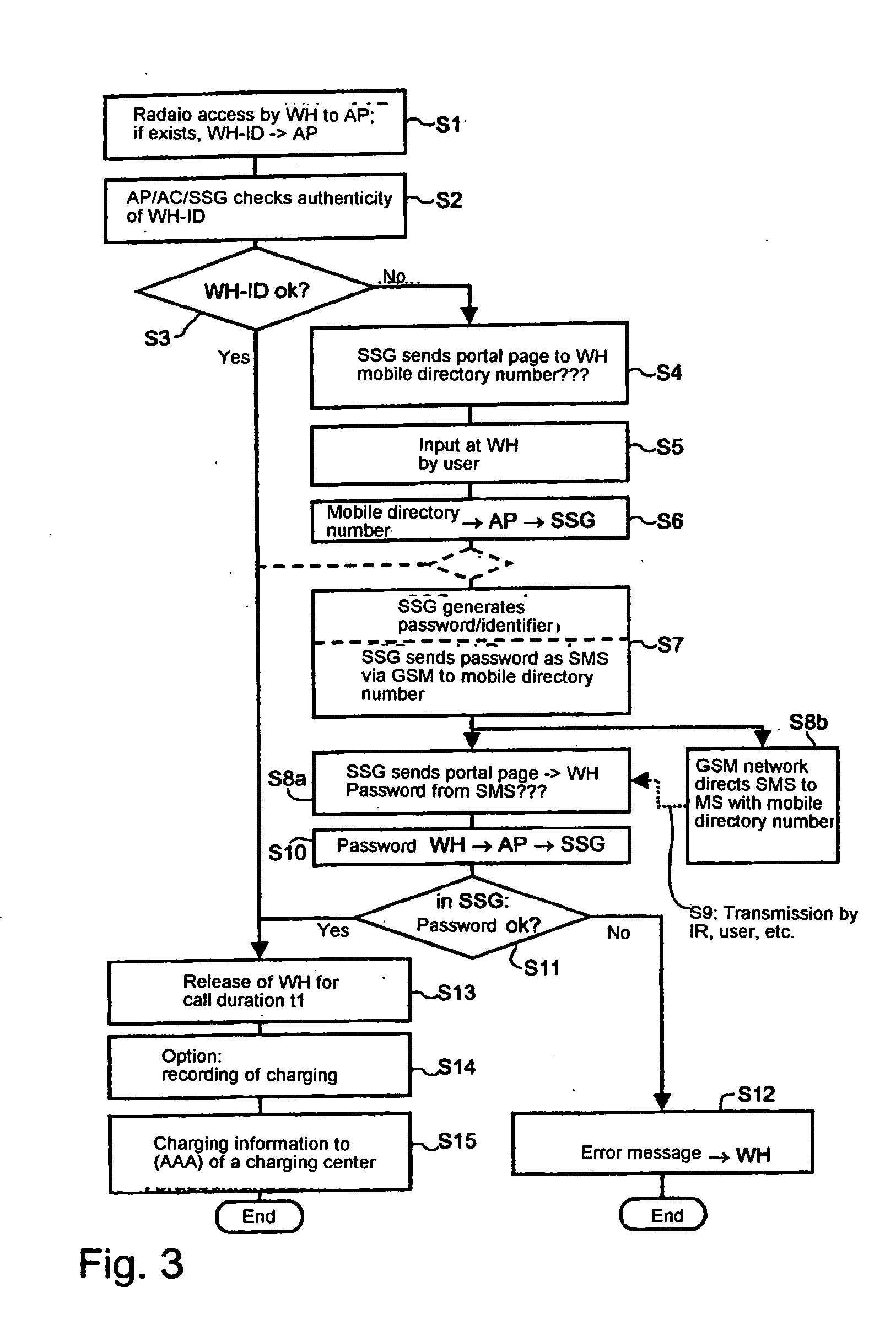
The invention relates to methods, devices and systems for the authenticated access to a data network by means of a station (WH) compatible with a data network (WLAN), which permit an authentication of the station and user. A device, for example a mobile radio device, is used for the above, which is authenticated in another system. In addition to the authentication, in particular a charging of services in a data network or another communication system (GSM) which is accessible by means of the data network is thus possible.
Owner:MONARCH NETWORKING SOLUTIONS LLC
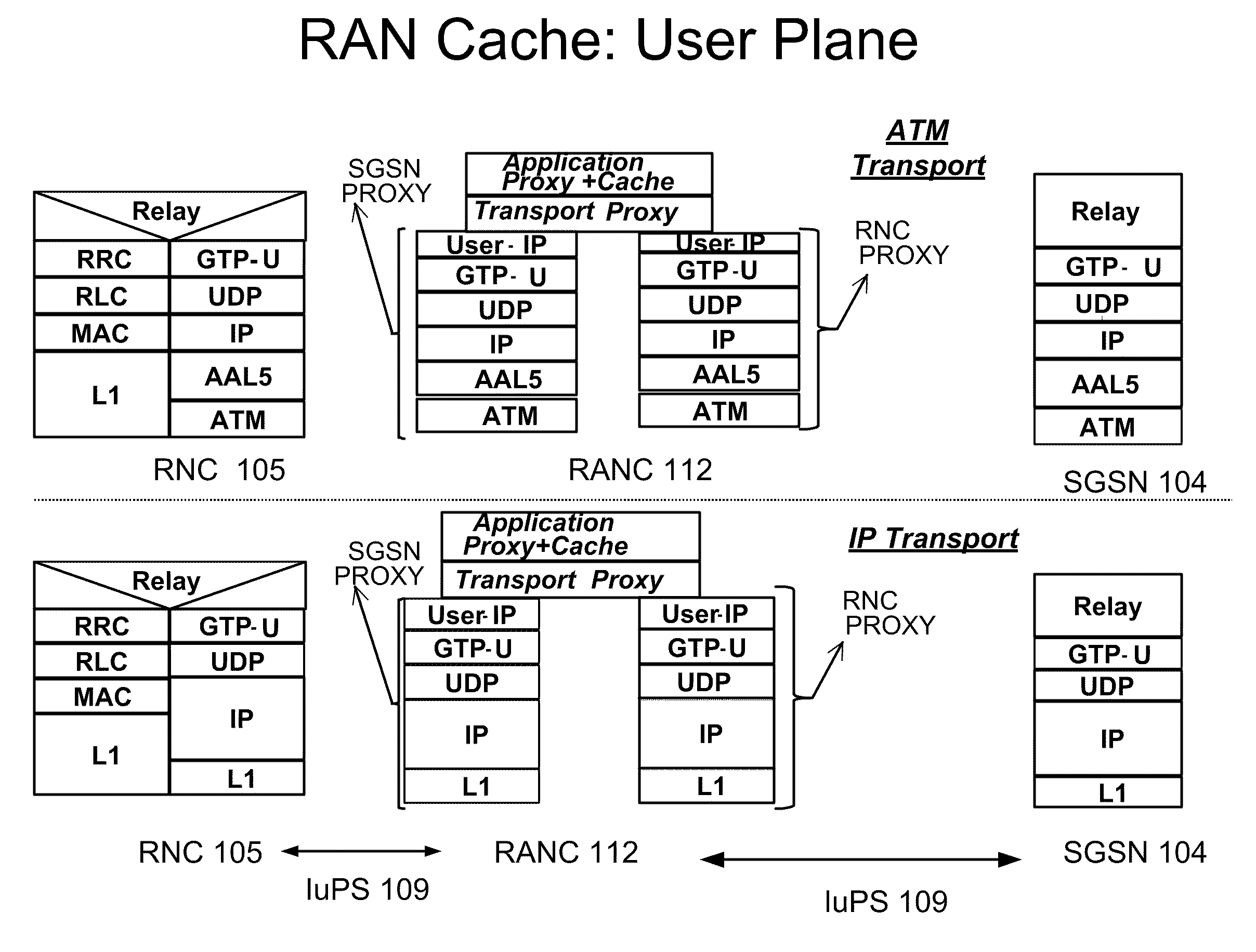
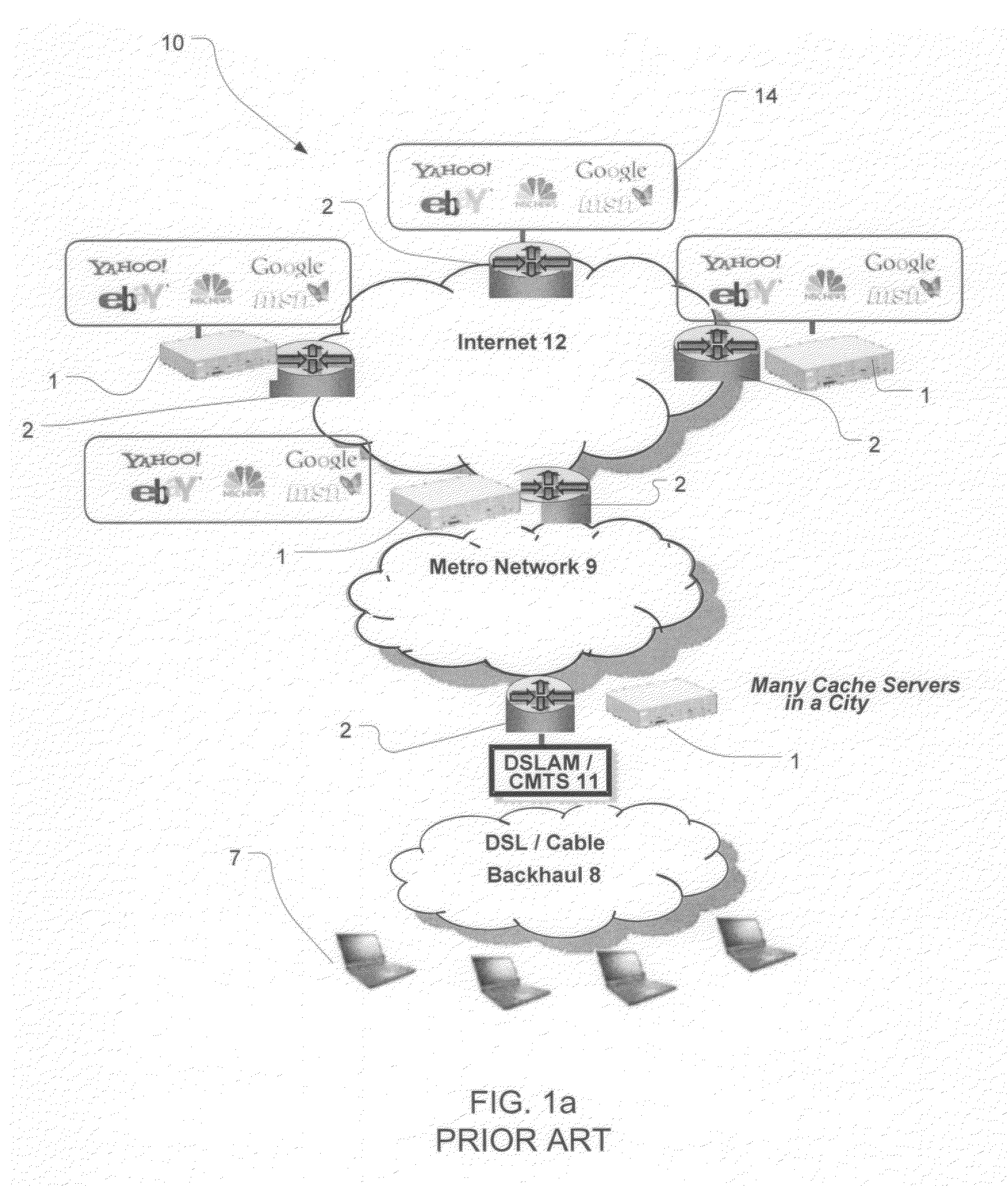
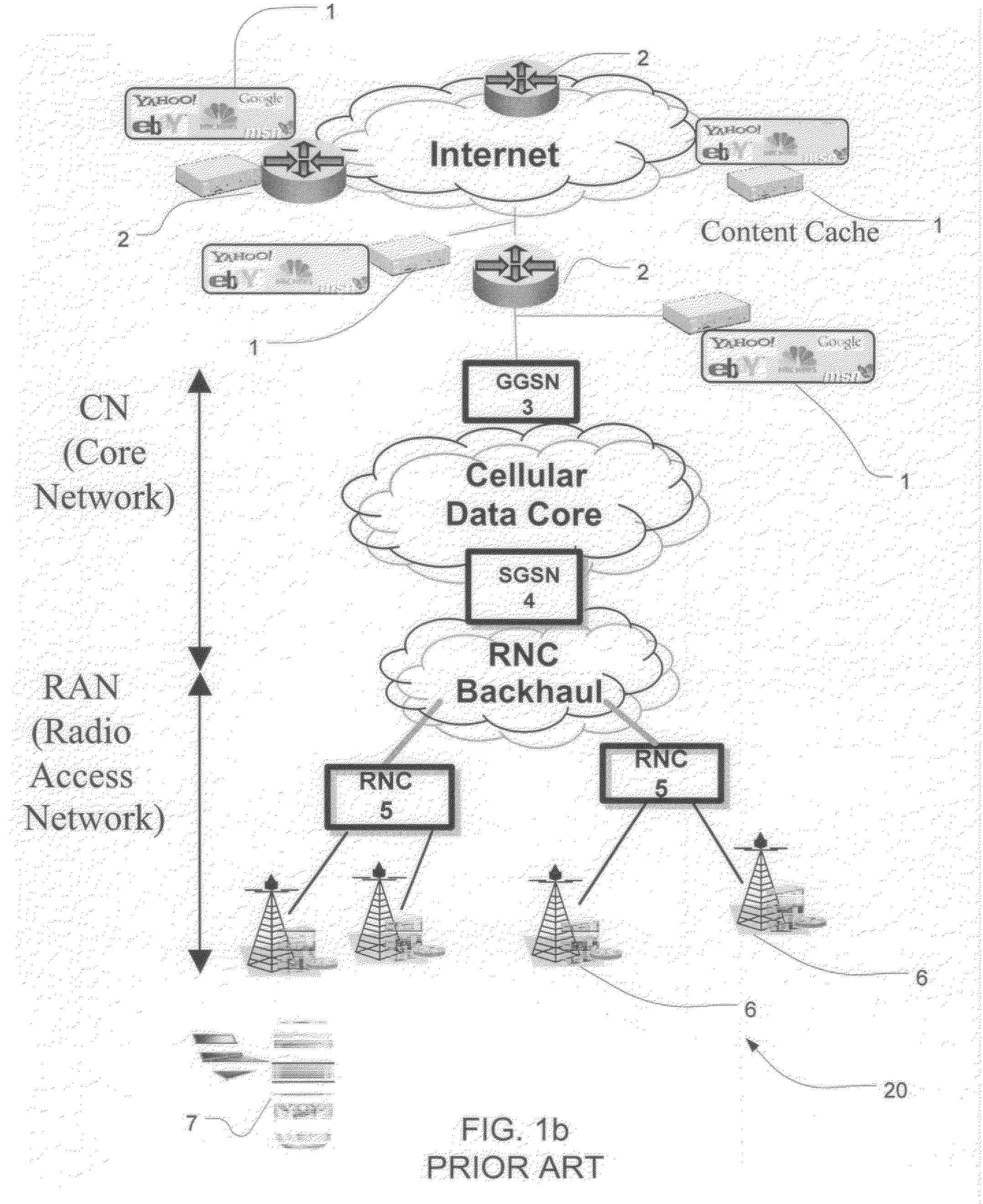
Content Caching in the Radio Access Network (RAN)
ActiveUS20100034089A1Reducing back-haul bandwidthImprove user experienceError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork packetRadio access network
A system and method to intercept traffic at standard interface points as defined by Cellular / Wireless networks (GSM / GPRS, 3G / UMTS / HSDPA / HSUPA, CDMA, WIMAX, LTE), emulate the respective protocols on either side of the interception point, extract user / application payloads within the intercepted packets, perform optimizations, and re-encapsulate with the same protocol, and deliver the content transparently is disclosed. The optimizations include but are not limited to Content Caching, prediction & pre-fetching of frequently used content, performance of content-aware transport optimizations (TCP, UDP, RTP etc.) for reducing back-haul bandwidth, and improvement of user experience. An additional embodiment of the current invention includes injecting opportunistic content (location based, profile based or advertisement content) based on the information derived while monitoring control plane protocols.
Owner:RIBBON COMM SECURITIES CORP
Secure, networked and wireless access, storage and retrival system and method utilizing tags and modular nodes
InactiveUS20050062603A1Quick and seamless handlingHigh levelIndividual entry/exit registersElectric signalling detailsComputer hardwareMedical equipment
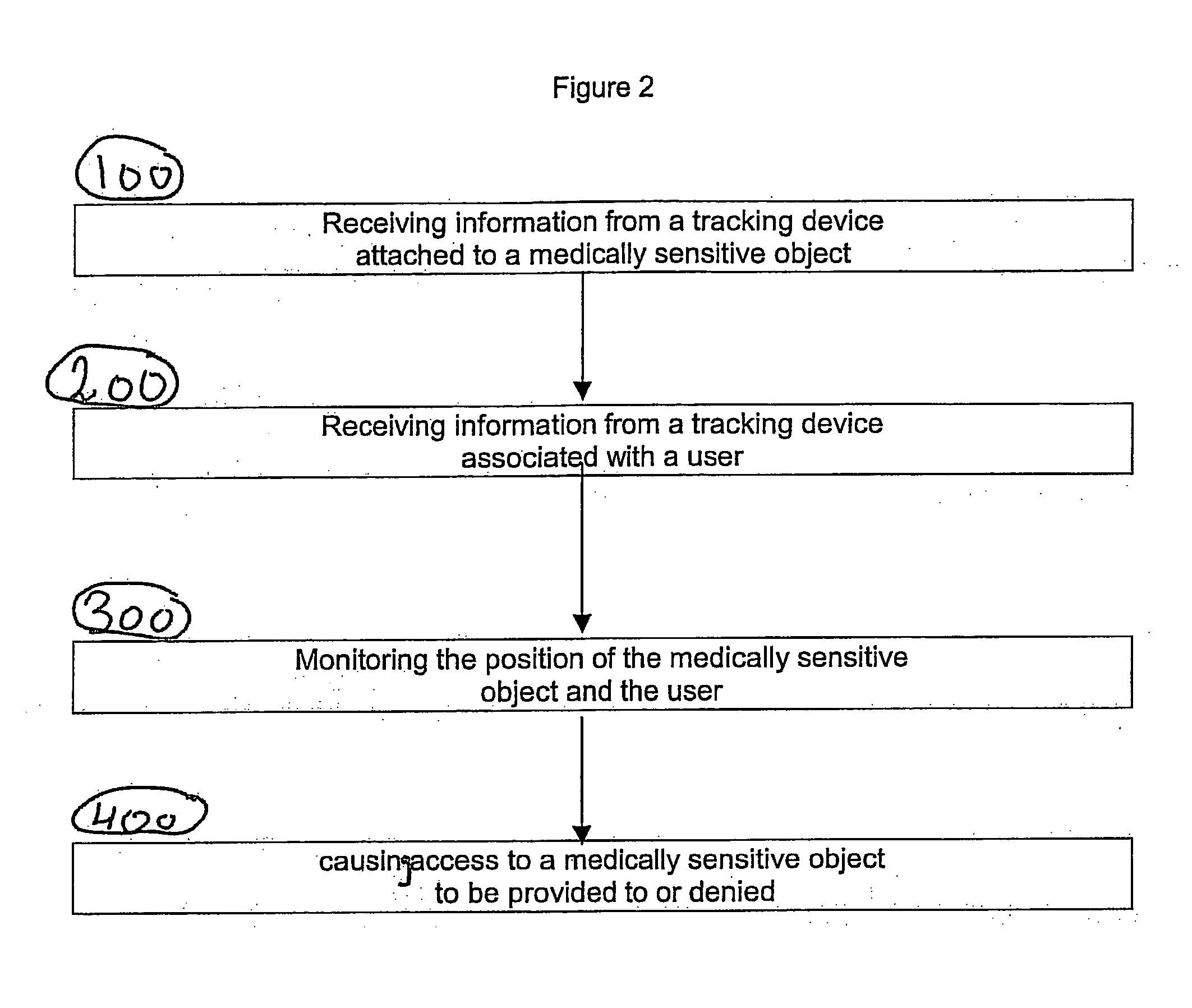
A system apparatus and method of monitoring in a secured fashion the access, storage and retrieval of information, using a networked modular wireless device. The system may include a network of wireless, Wi-Fi devices (or any other wireless communication mechanism such as GPRS, GSM, iDen), or Nodes, each one of them possibly controlling the access to a medically sensitive object, such as a drawer (or cabinet) or to a medical device, or to another information source, item of equipment, drug, etc as well as tracking via RFid readers the access to the records or information contained in it. In the case of a physical file, each file has an RFid tag on it that is being read when removed or returned to the cabinet. Access to the cabinet and physical records, or to the medical device is monitored by reading the RFiD identity card of personnel accessing the cabinet or medical devices. In addition to controlling the access to the cabinet or medical device by controlling the cabinet lock (or in the case of a small medical device, the lock of an IV, injection device, specimen collection unit, or of a large medical device such as a defibrillator), the node can alert electronically by sending a message to the controlling unit, or by sending a physical alert (such as an alarm signal), when unauthorized personnel is attempting to access the cabinet, the files or devices. The system is useful in the context of monitoring the information contained in physical files, such as medical information, and can be used for access to medical devices, in order to better monitor the authorization rights of personnel participating in processes such as drug delivery or specimen collection. A control unit monitors activity at a plurality of nodes, and assists in storing the list of authorized personnel and files, and can store electronically captured information regarding the physical files (for example, the reason for accessing the file and reasons for changes in it) or medical device. The system can communicate with other information management systems.
Owner:G D H
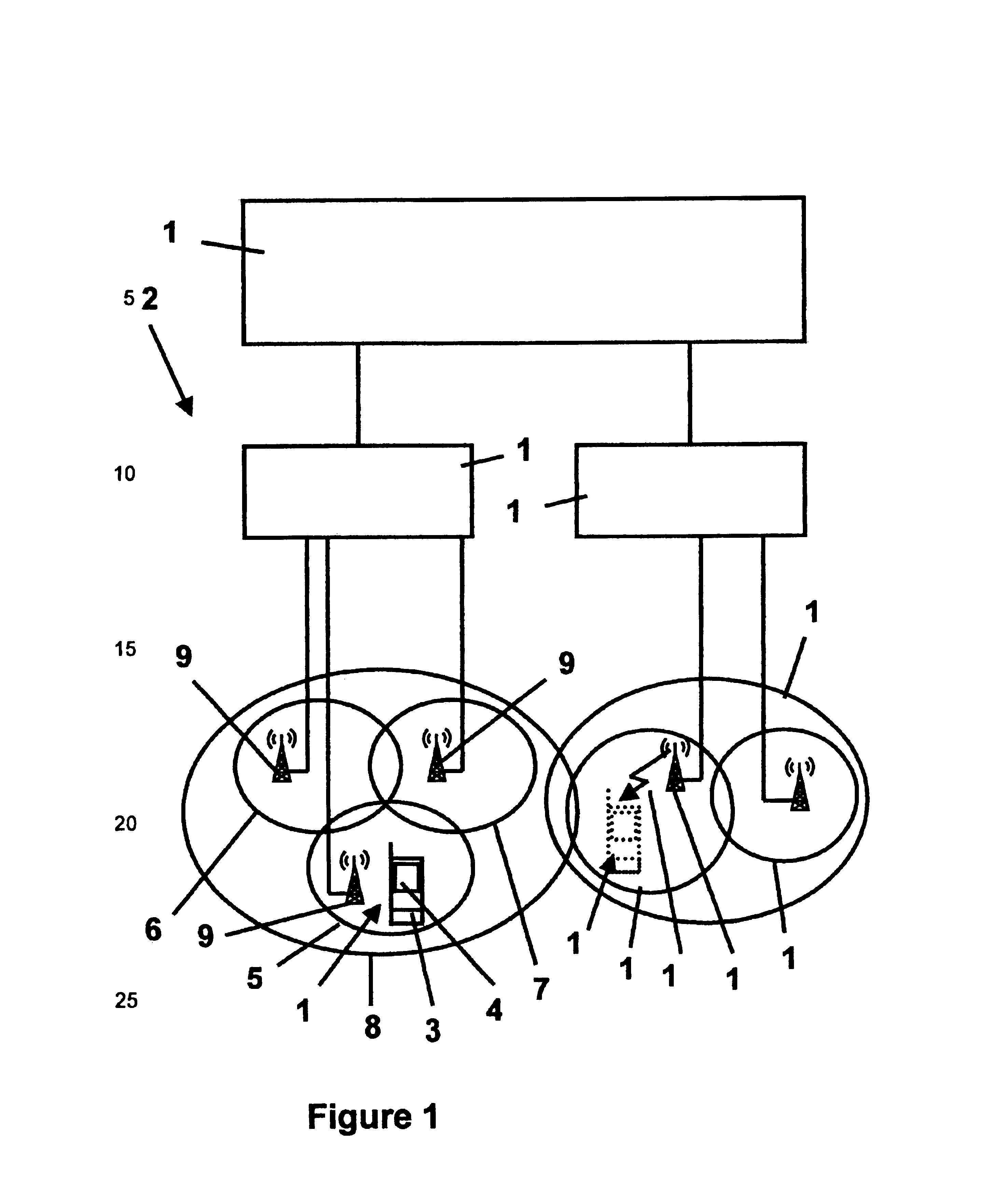
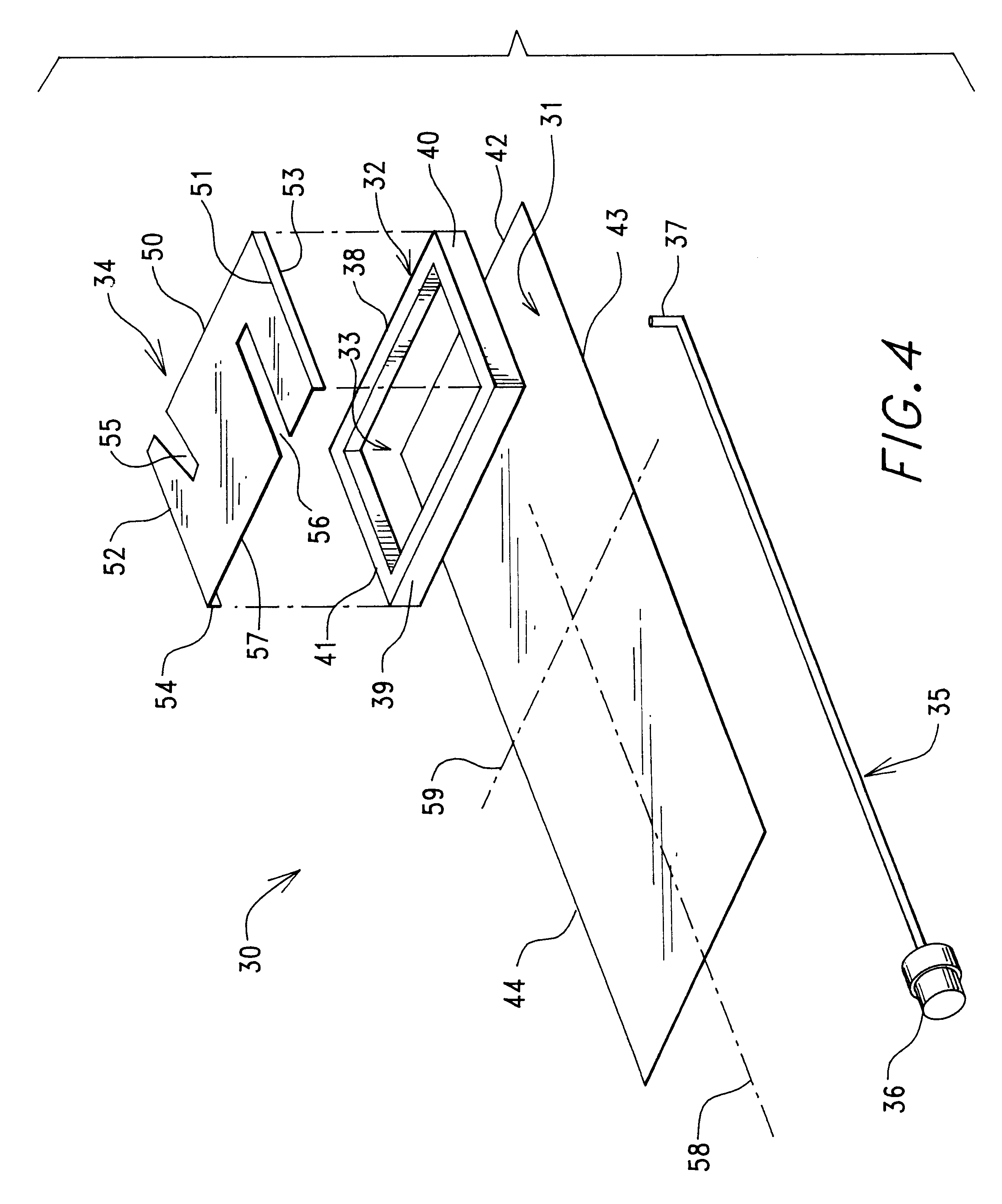
Monitoring of call information in a wireless location system
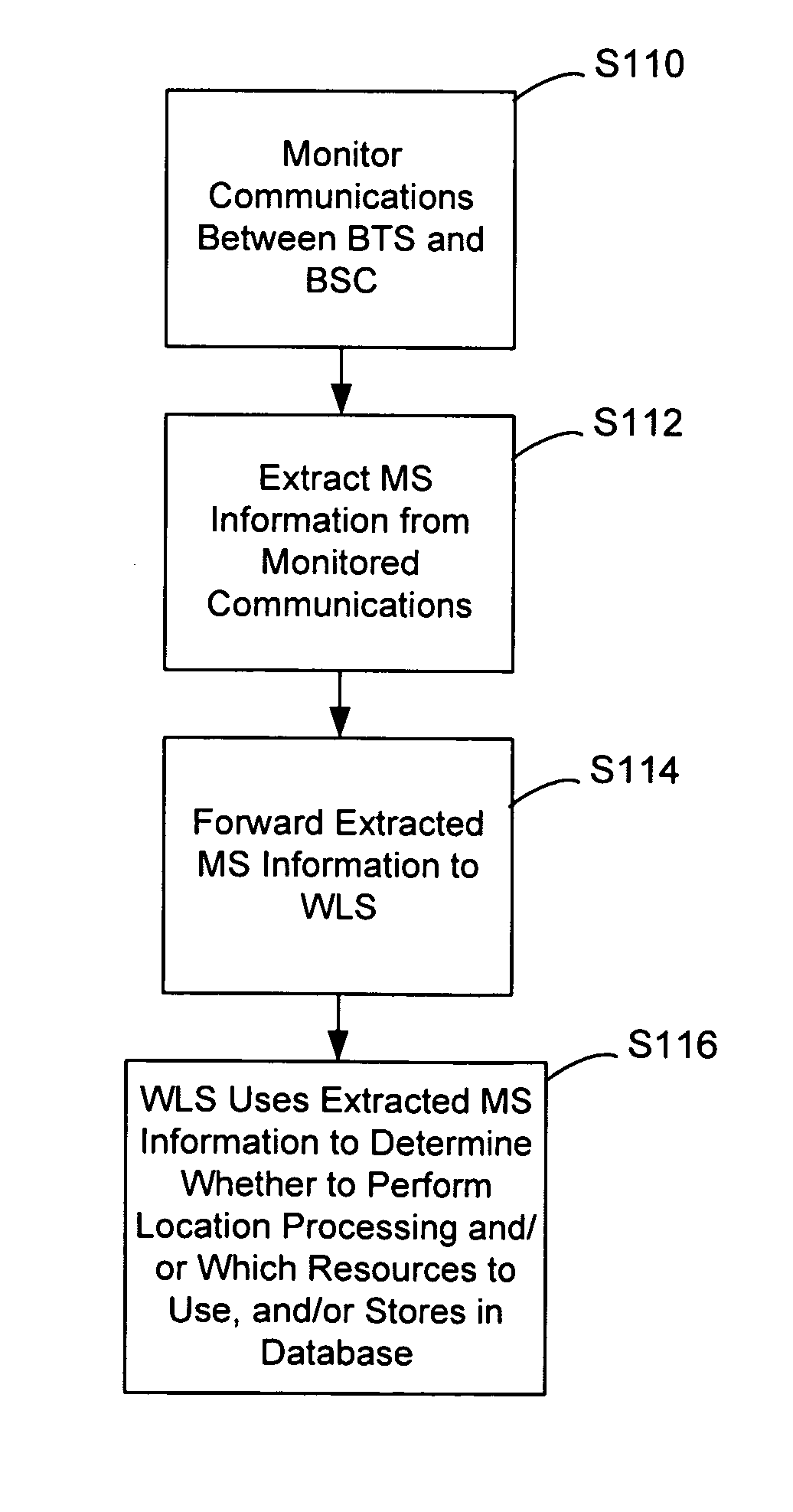
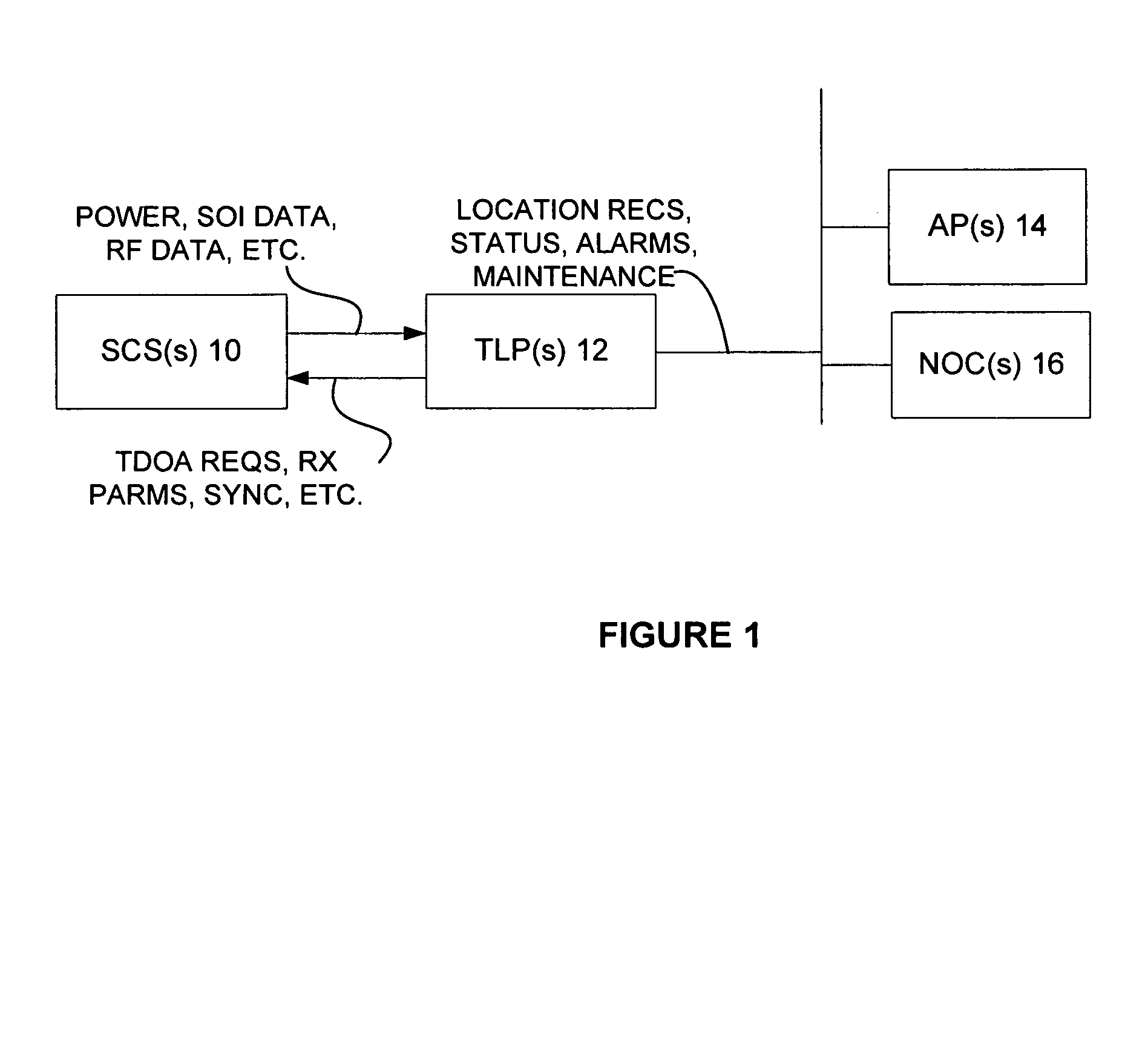
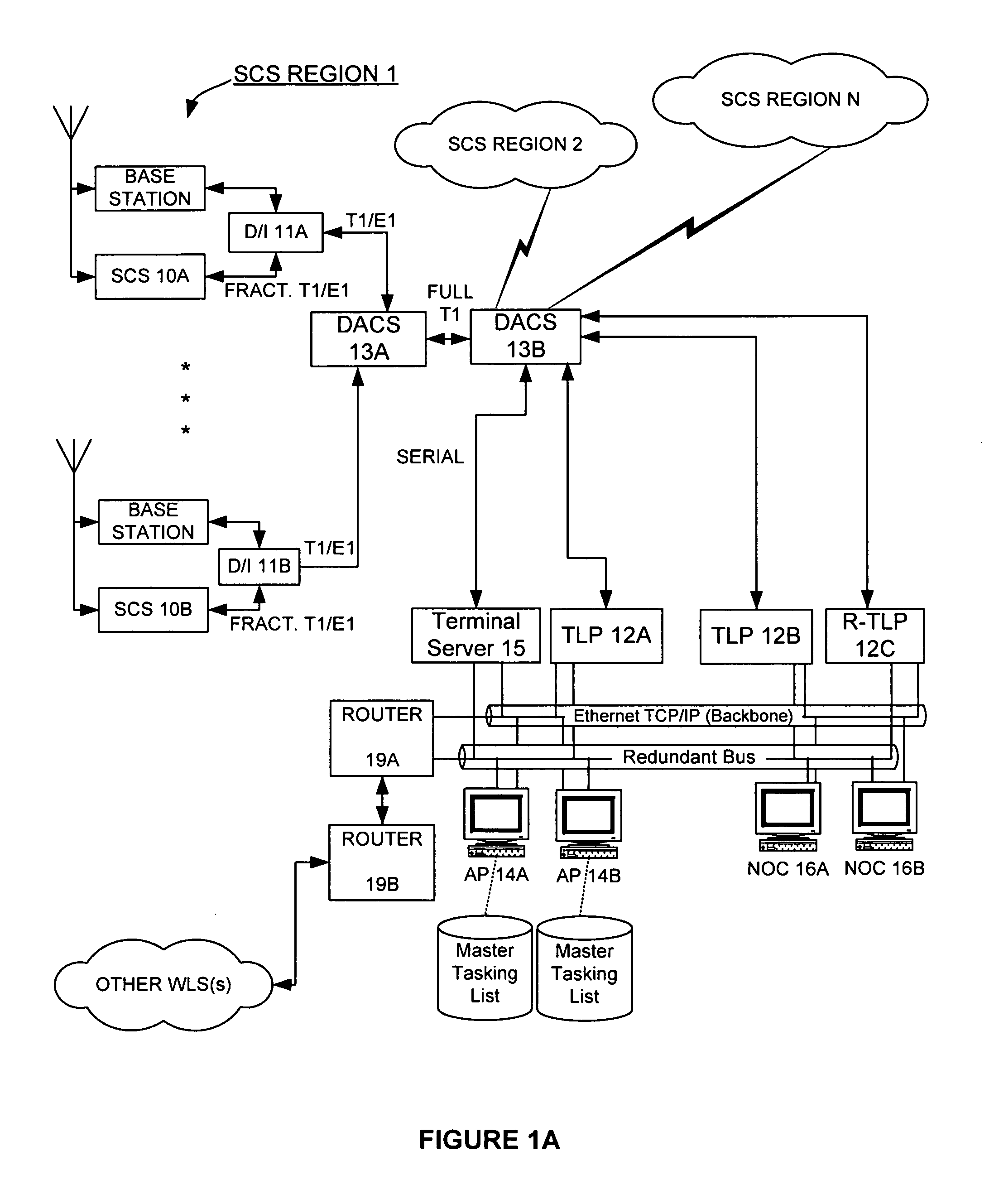
InactiveUS7167713B2Low costReduce functionEmergency connection handlingBeacon systems using radio wavesAir interfaceComputer science
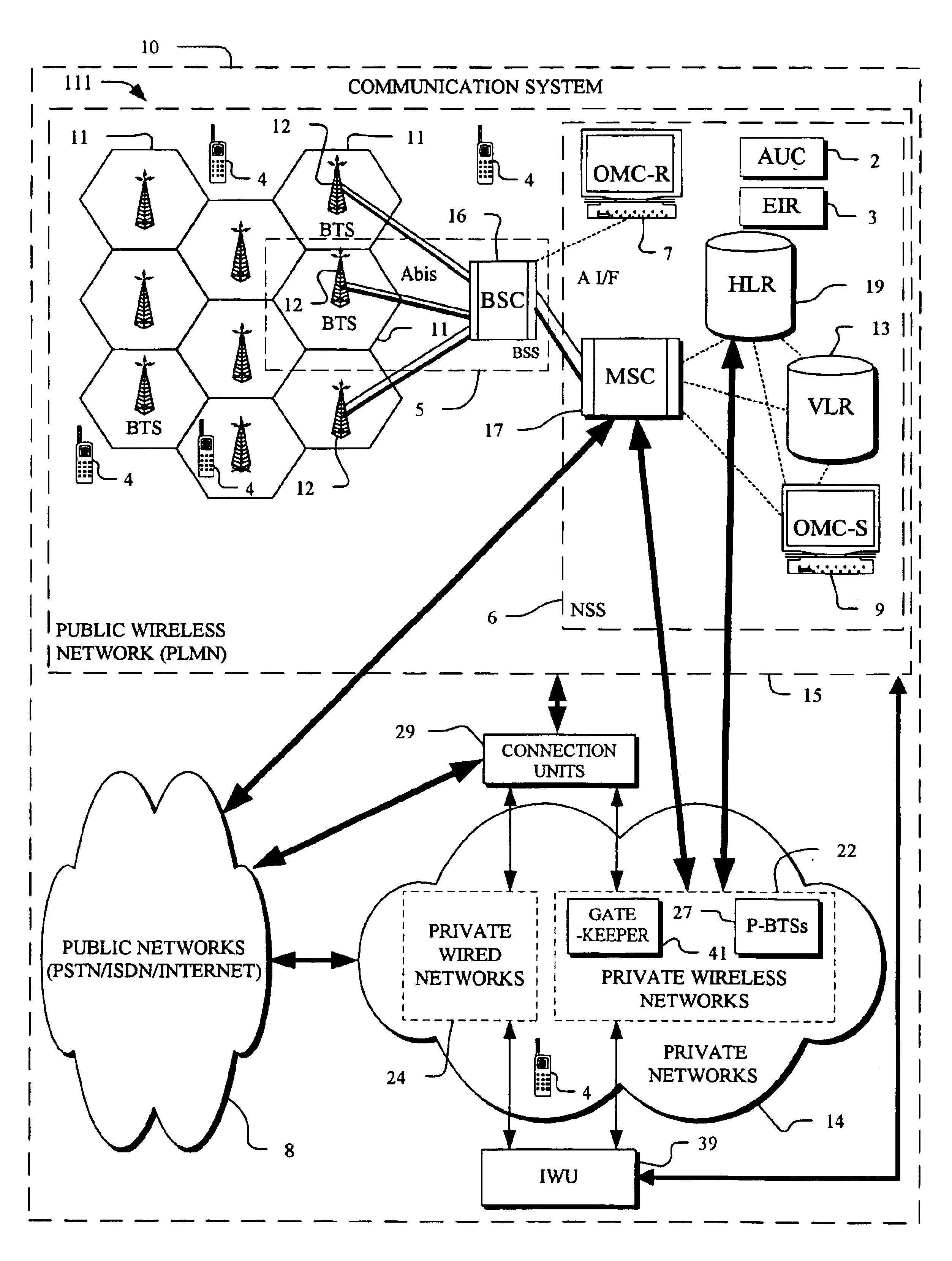
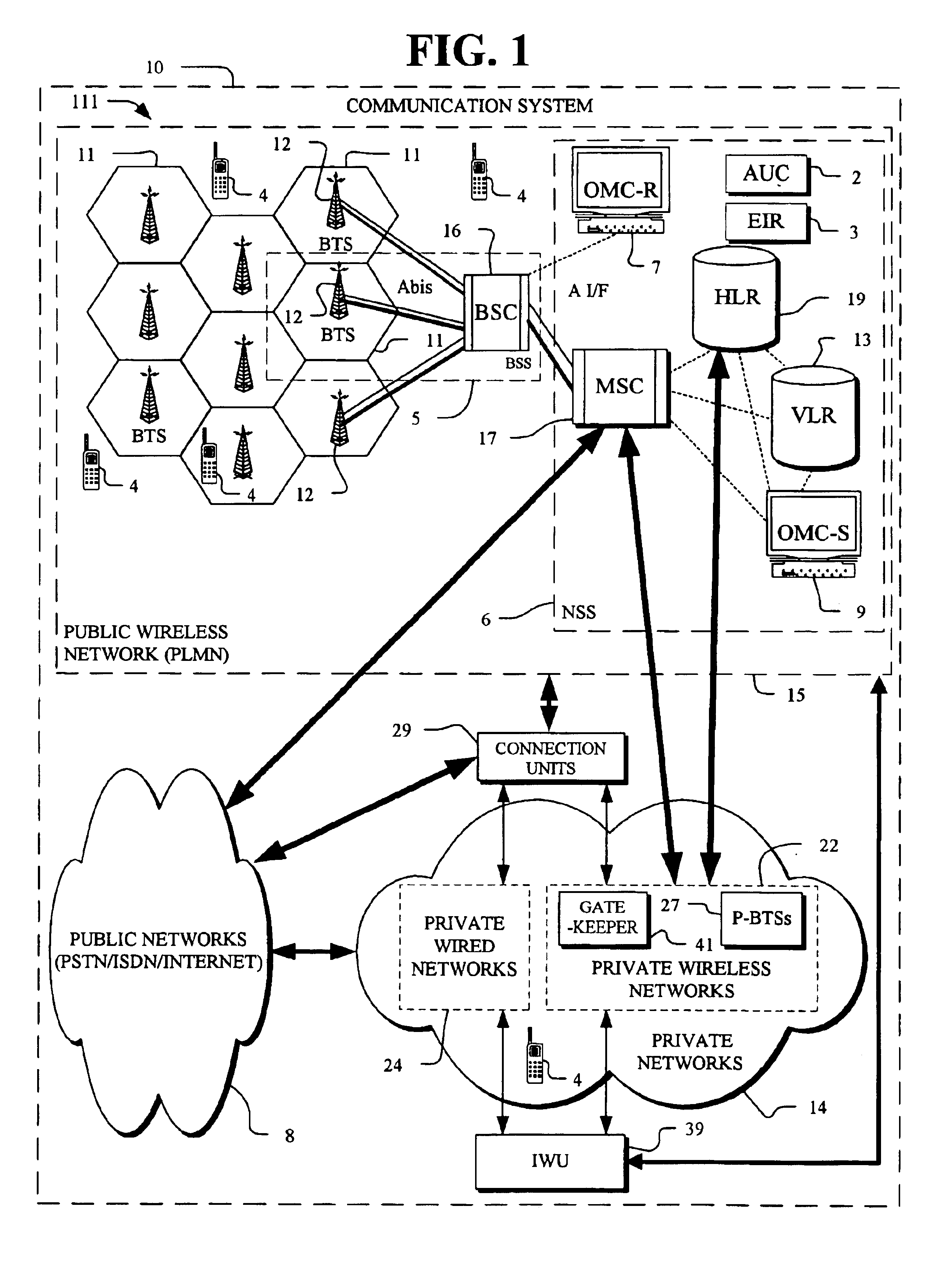
In an overlay Wireless Location System, an Abis interface is monitored to obtain information used to locate GSM phones. Signaling links of the Abis interface are passively monitored to obtain certain information, such as control and traffic channel assignment, called number, and mobile identification, which is not available from the GSM air interface of the reverse channel. This approach also applies to IDEN and can include CDMA systems where the GSM architecture has been used and the system includes a separated BTS to BSC interface.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Network for information transfer for mobile stations
InactiveUS20020123359A1Special service for subscribersRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsThe InternetMobile station
Search templates for a web portal search engine of the internet are provided and a method of use of such templates in customer transactions is provided. The method incorporates processing coded information in respect of a transaction by a customer and a merchant, the customer being a user of a mobile phone with a search template, which phone is connectable to an SMS server, which in turn is connectable to the Internet; the merchant having a GSM device connectable to a GSM terminal and to the Internet; each customer having a unique identification number ("UIN") for use in transactions; each merchant having a unique identification number for use in transactions; wherein the customer and merchant can complete a secure transaction.
Owner:MULTISCI SYST PTE
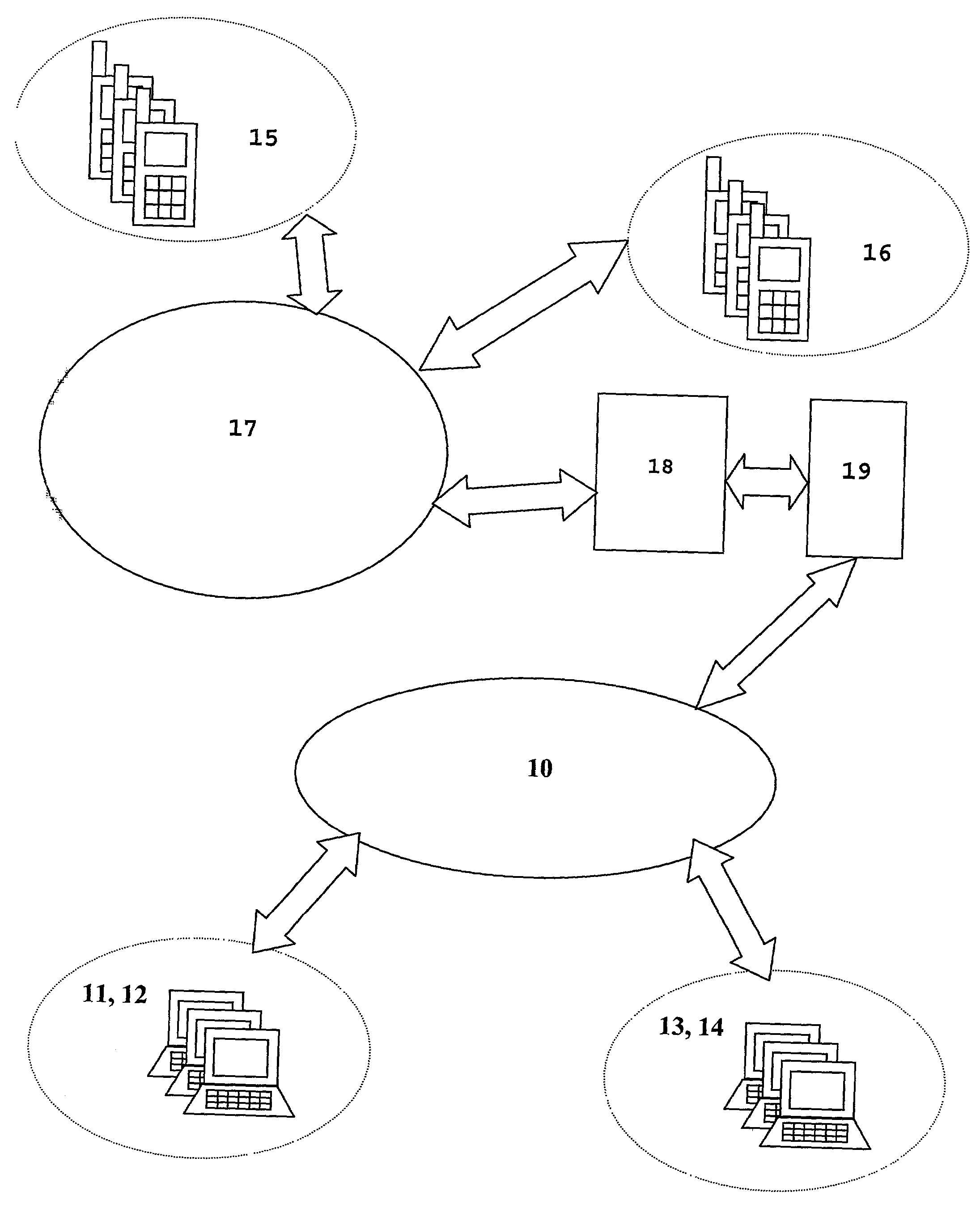
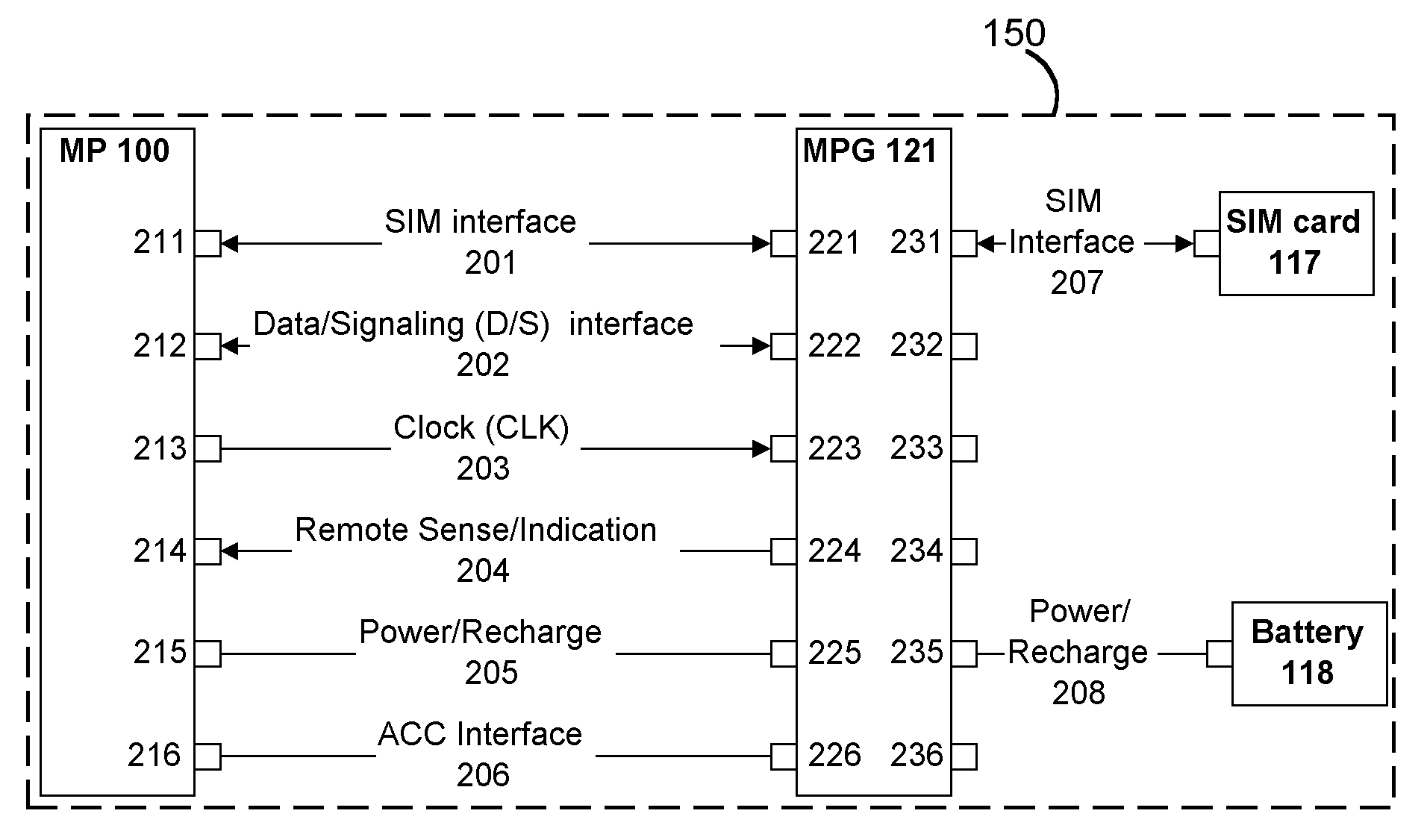
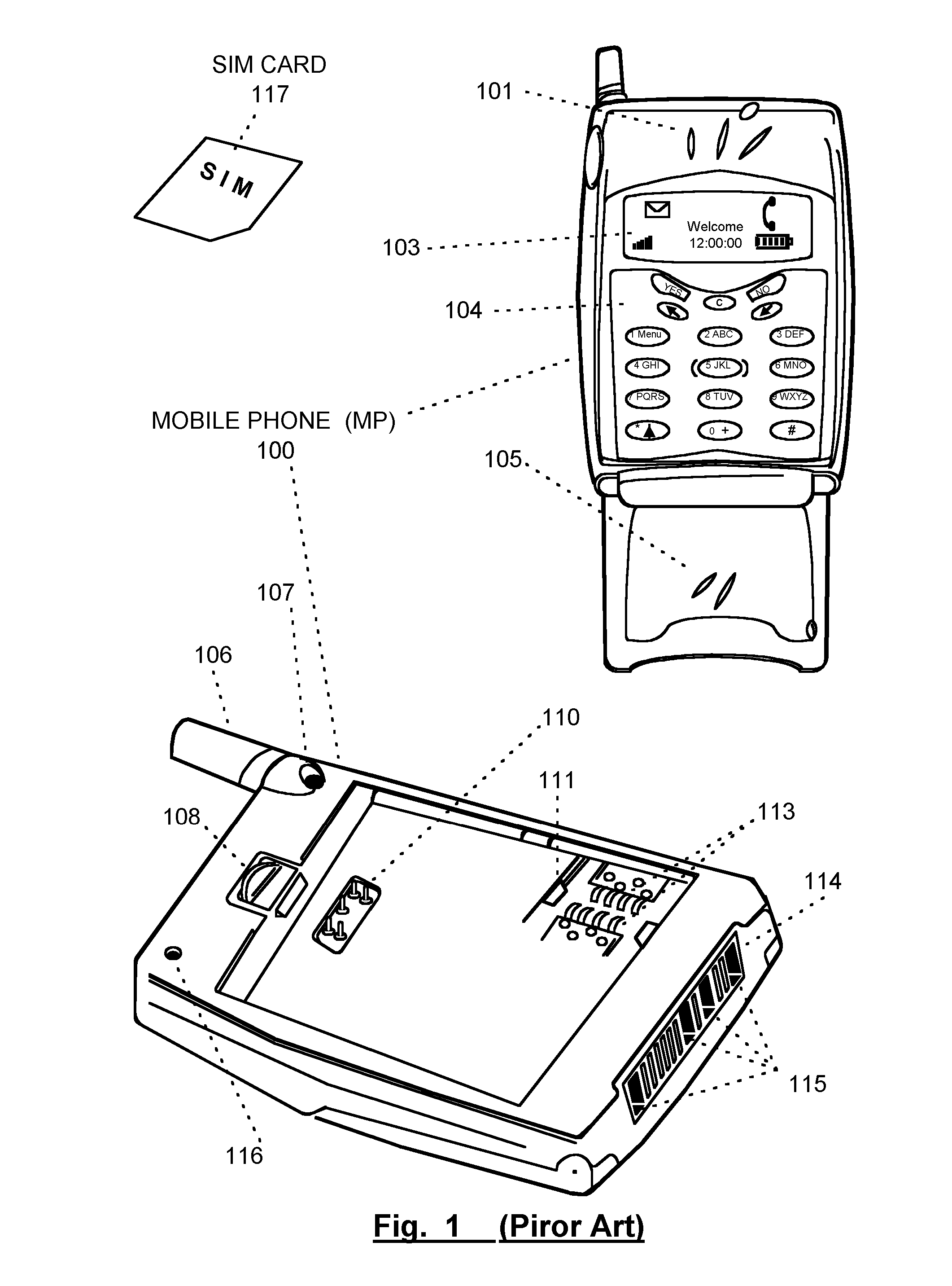
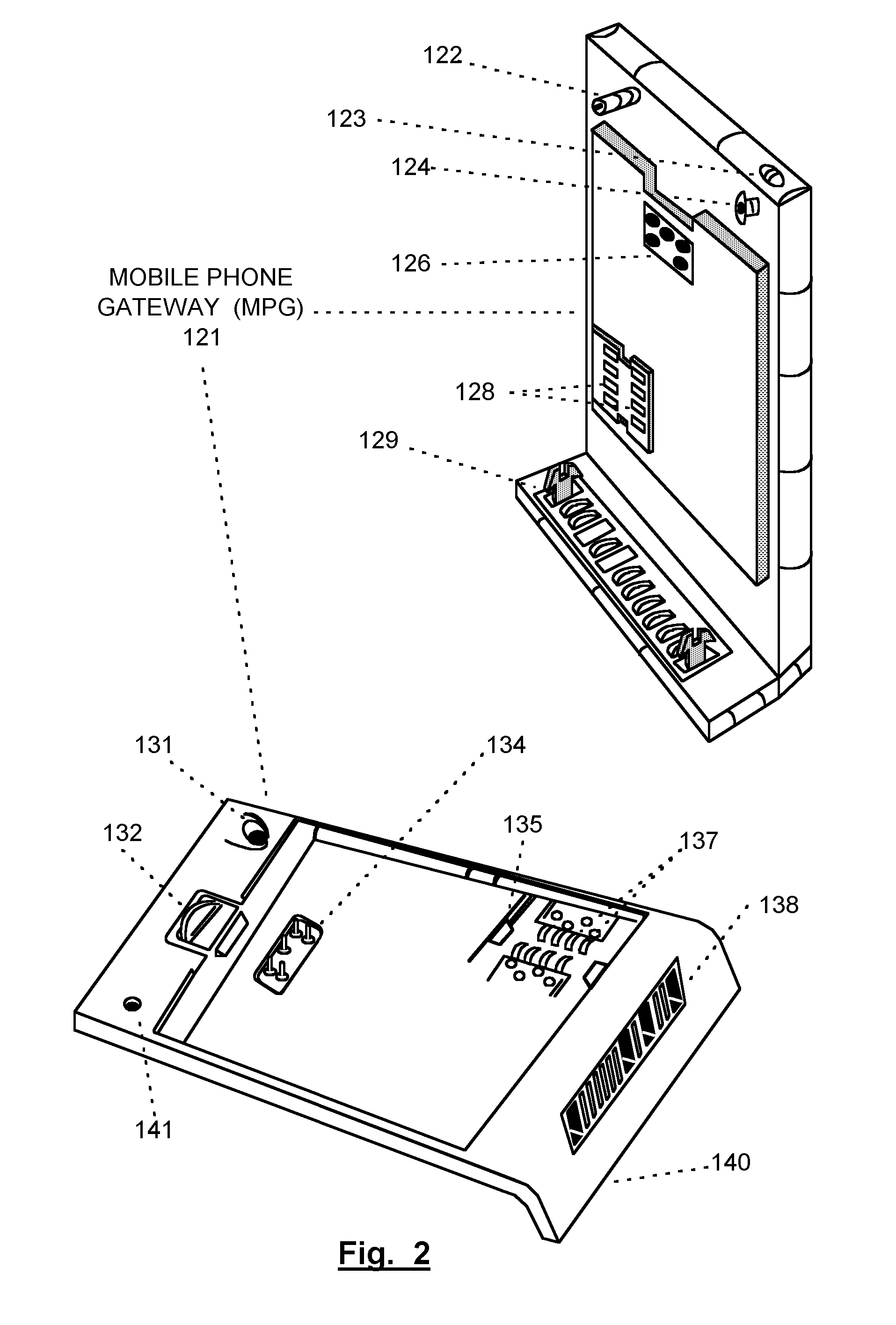
Mobile Telephone Gateway Apparatus, Communication System, and Gateway Operating System
InactiveUS20060291483A1Facilitates proper initializationImprove coordinationDevices with wireless LAN interfaceData switching by path configurationOperational systemWireless data
A mobile telephone gateway and communication routing device (MPG) (121) disclosed by the present invention is coupled through an electrical signaling transmission medium with a mobile telephone (100) operative on a first communication network in accordance with a first communication protocol, for adding communication capabilities through at least a second communication network in accordance with a second communication protocol. A mobile communication system (150) is disclosed, comprising MPG (121) placed in-between mobile phone (100) and battery (118) and Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) card (117). MPG connects to the SIM interface of mobile phone (100), using which it wraps SIM functionalities and controls call management. It connects to the data / signaling interface of mobile phone (100), using which it communicates with it, while communicating with the second network using another communication means. It may optionally connects to an accessory device interface of mobile phone (100) such as a Terminal Adapter / Terminal Equipment (TA / TE) or a USB OTG interface, thereby enabling communication between the mobile phone and wireless data terminals of the second network. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a MPG is provided for use with a mobile phone operative on a mobile communication network such as GSM, adding communication capabilities through a wireless communication network such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. Furthermore, gateway applications are provided to facilitate or support communication through at least the second network in accordance with mobile web protocols and technologies such as Mobile IP, mobile SIP, and mobile VoIP.
Owner:SELA YOSSY
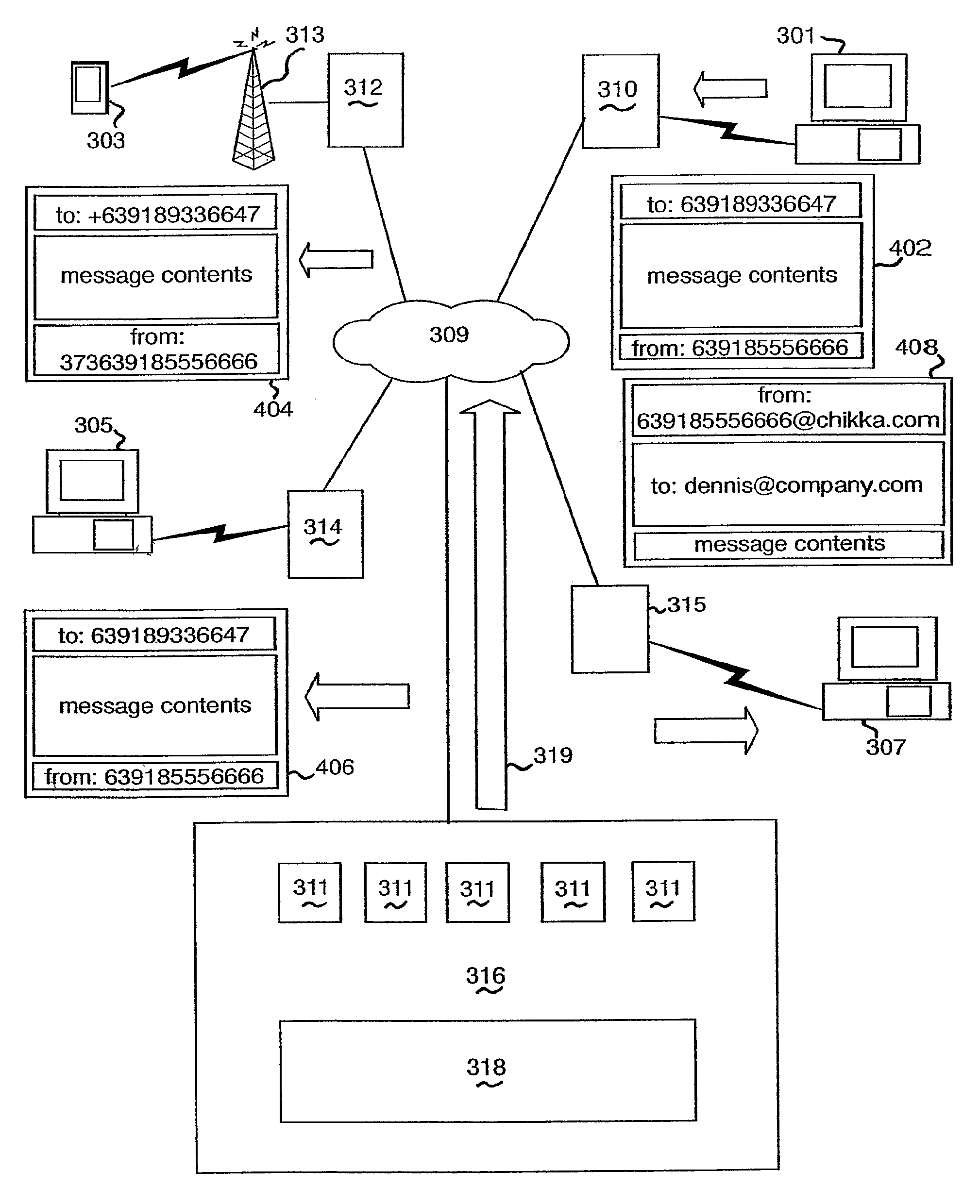
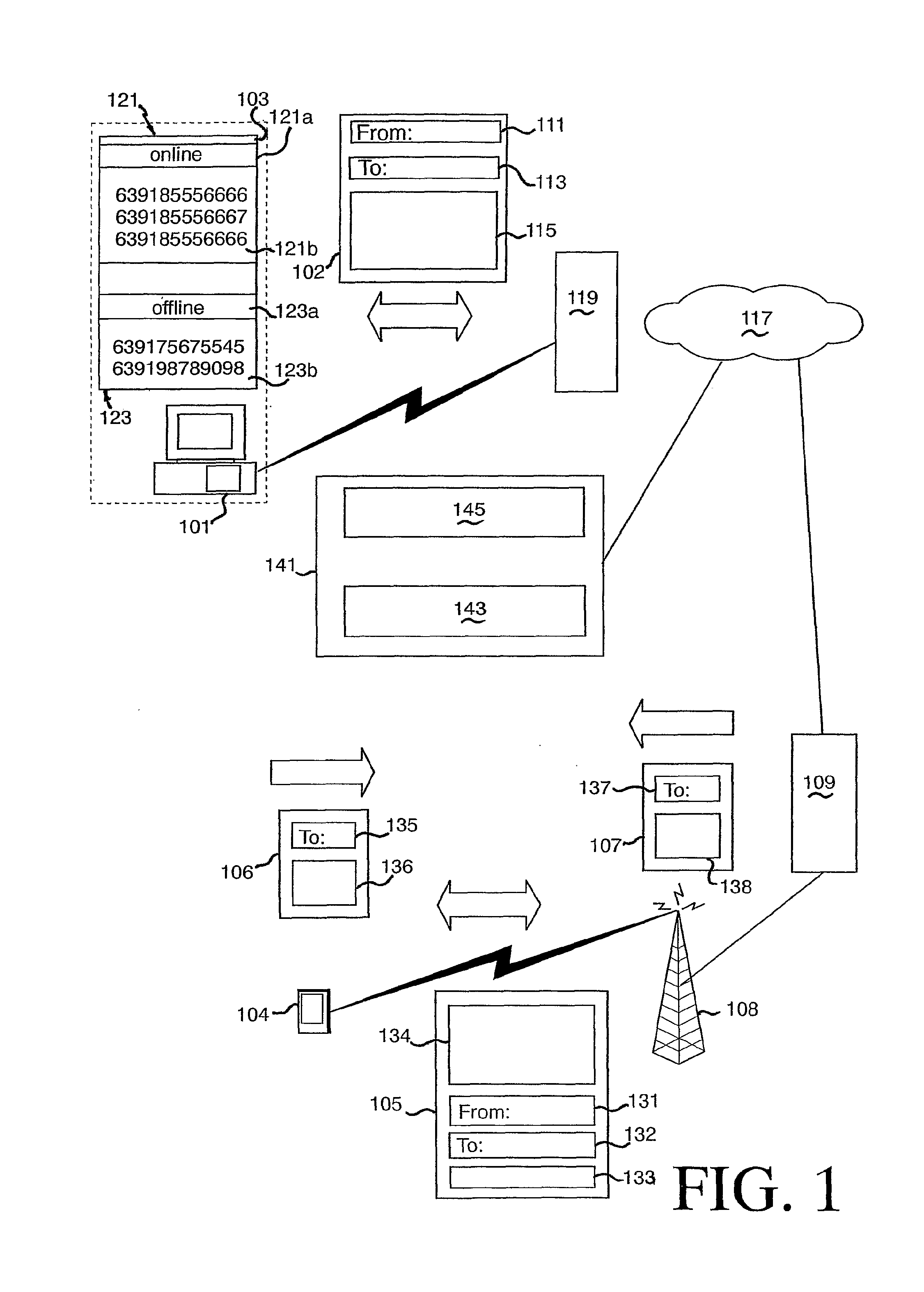
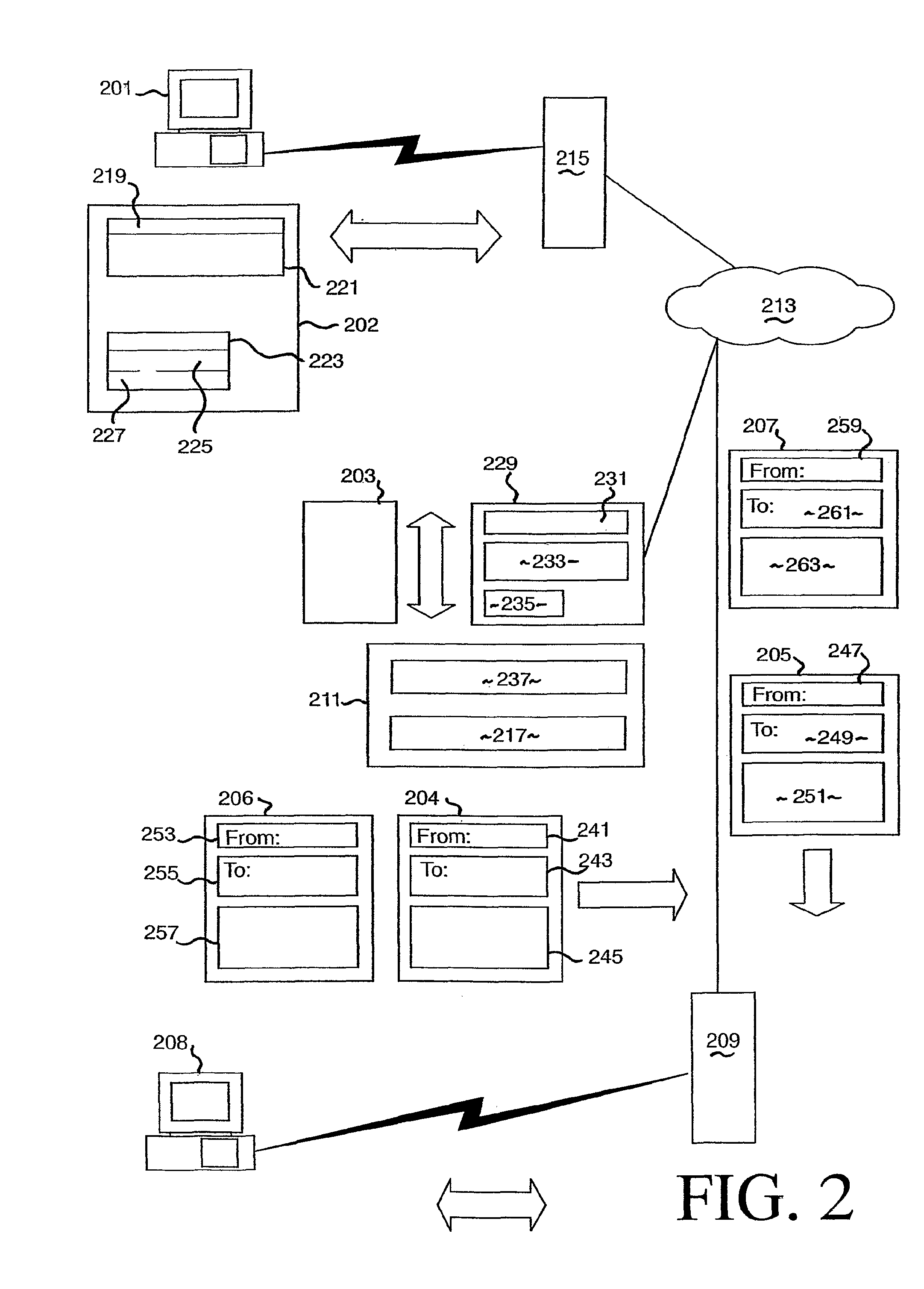
Instant messaging account system
InactiveUS7200634B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksThe InternetUnique identifier
An instant messaging system and a method of instant messaging between a plurality of clients having IM applications of the same or different types. The IM system includes a plurality of clients having IM client applications of the following types: a PC-based instant messaging client application program (101, 301); a GSM device (104, 303) forming part of a GSM network; an internet browser-based client application 201, 305; and an email-based client application (208, 307). An IM system host (141, 211, 316) including an IM server (143, 217, 311) is selectively connected to each of the clients via the direct electronic links or the internet (117, 213, 309) and provides a prescribed range of functionality to the clients. This functionality includes sending an IM, receiving an IM and identifying which members of a group of clients that a client is a member, or prospective member, of are online. Each client type has a unique identifier to enable access thereto via the internet (117, 213, 309) and each client has a single account on the IM host / server for all of its client types that can access the IM server (143, 217, 311). The account is identified by a unique identification number (“UIN”) common to all of the client types of that client and each unique identifier of each client type of a client is matched to the UIN of the particular client.
Owner:CHIKKA COM
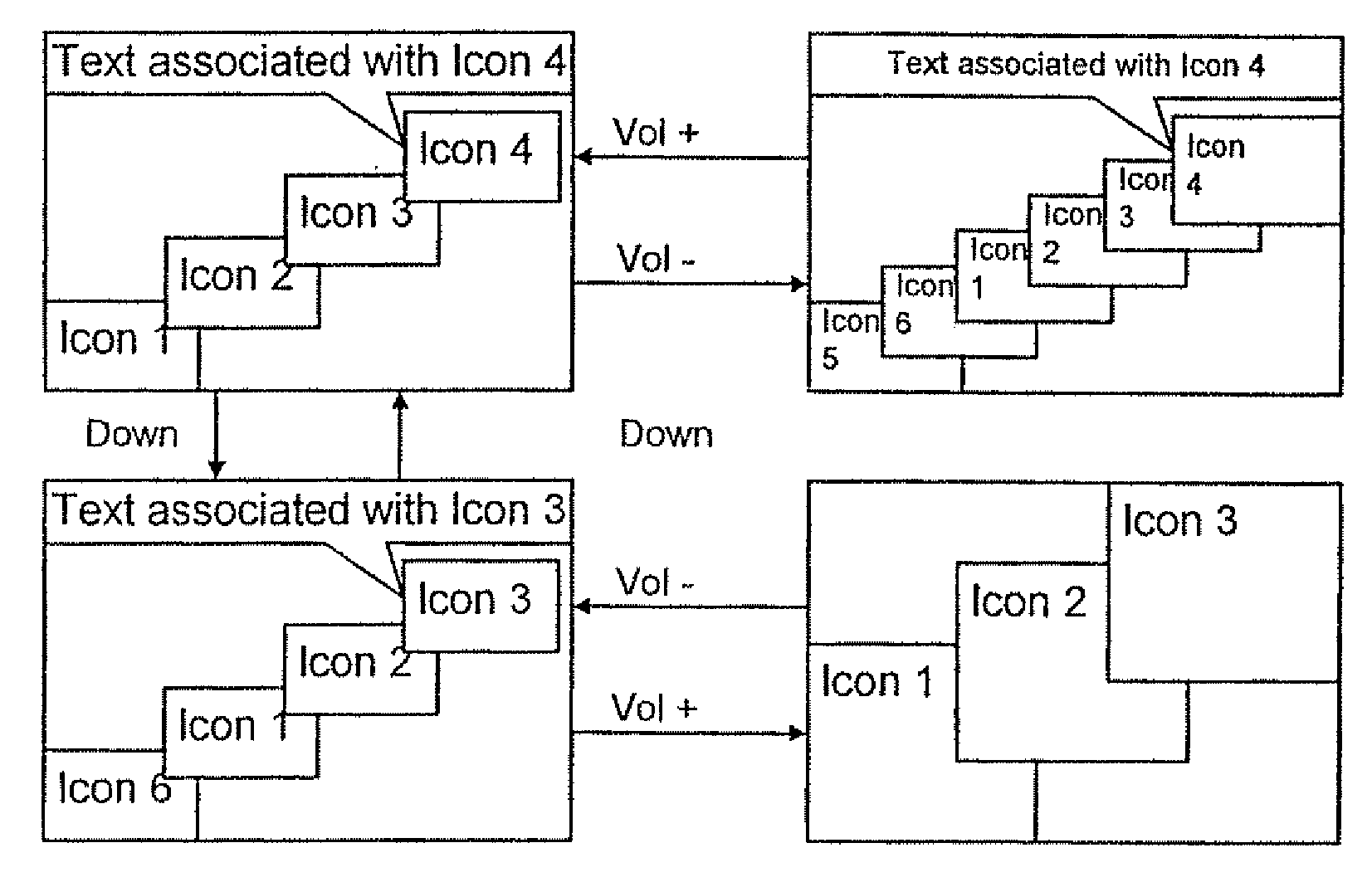
Mobile telephone with improved man machine interface
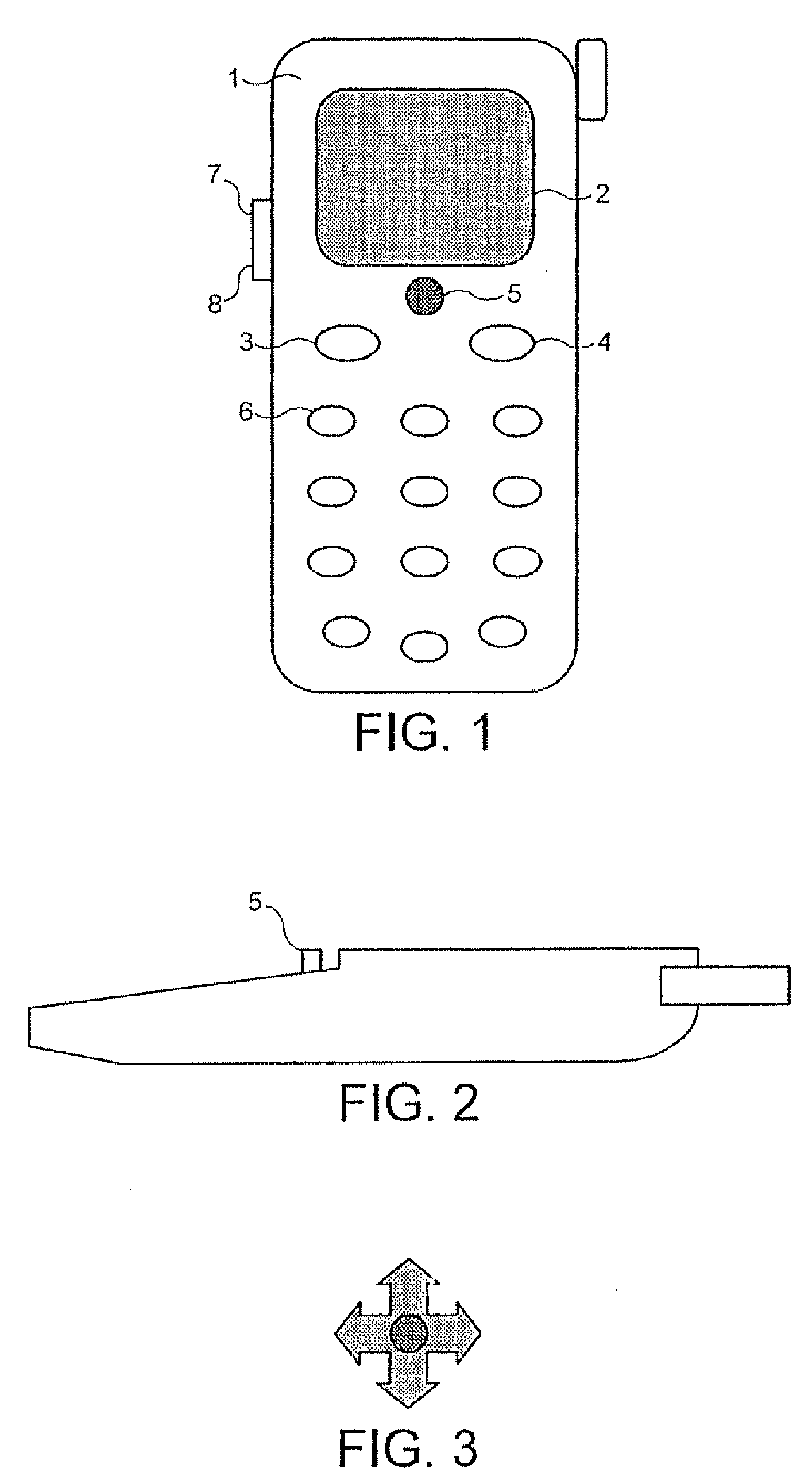
InactiveUS20070213099A1Save memoryEliminate needSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionHuman–machine interfaceCall forwarding
The present invention envisages a GSM mobile telephone in which a line of icons is displayed on a display. As a user navigates through the displayed line of icons, the positions of the icons alter so that the selectable icon moves to the head of the line. This approach makes it very clear (i) which icon is selectable at any time and (ii) where that icon sits in relation to other icons at the same functional level (e.g. only first level icons will be present in one line). First level icons typically relate to the following functions: phonebook; messages; call register; counters; call diversion; telephone settings; network details; voice mail and IrDA activation.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Method and apparatus for inter-cell handover in wireless networks using multiple protocols
InactiveUS6993359B1Increase data rateNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsWireless mesh networkCommunications system
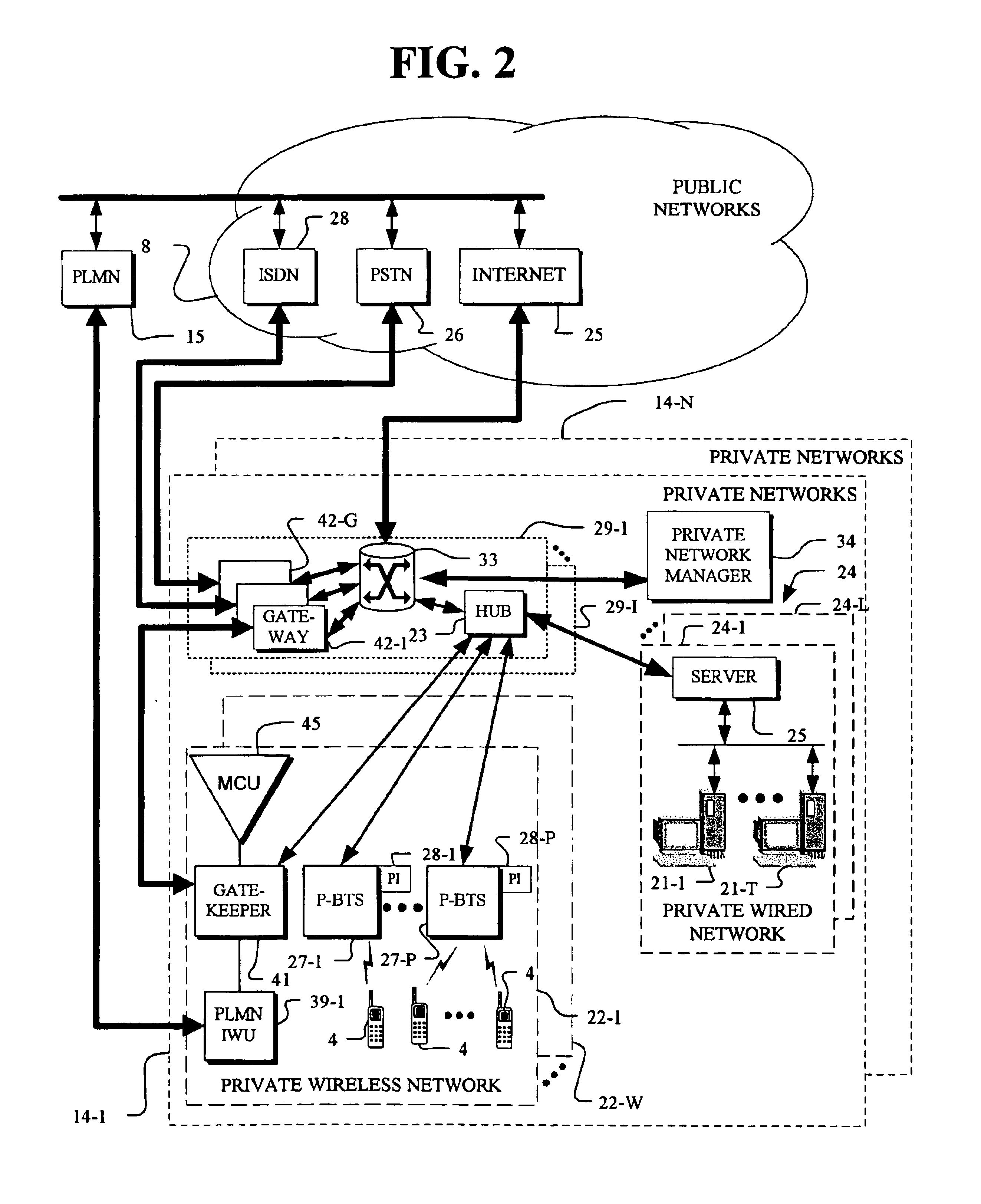
A communication system formed by a private wireless network that can be used with public wireless networks using a public wireless protocol, such as GSM, and typically includes public networks, such as PSTN, ISDN and the Internet, using a wired-packet protocol, such as IP. The private network also typically includes a local area network (LAN) and the private network typically connects to the public networks using the wired-packet protocol, such as IP. The public and private wireless networks operate with the same public wireless protocol, such as GSM, and the private wireless network additionally operates with the wired-packet protocol, such as IP. In this environment, multiple wireless cells are present and inter-cell handovers employ multiple protocols including the wired-packet protocol.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Voice call redirection for enterprise hosted dual mode service
ActiveUS7664495B1Network topologiesCommmunication supplementary servicesDevice registerSpecific function
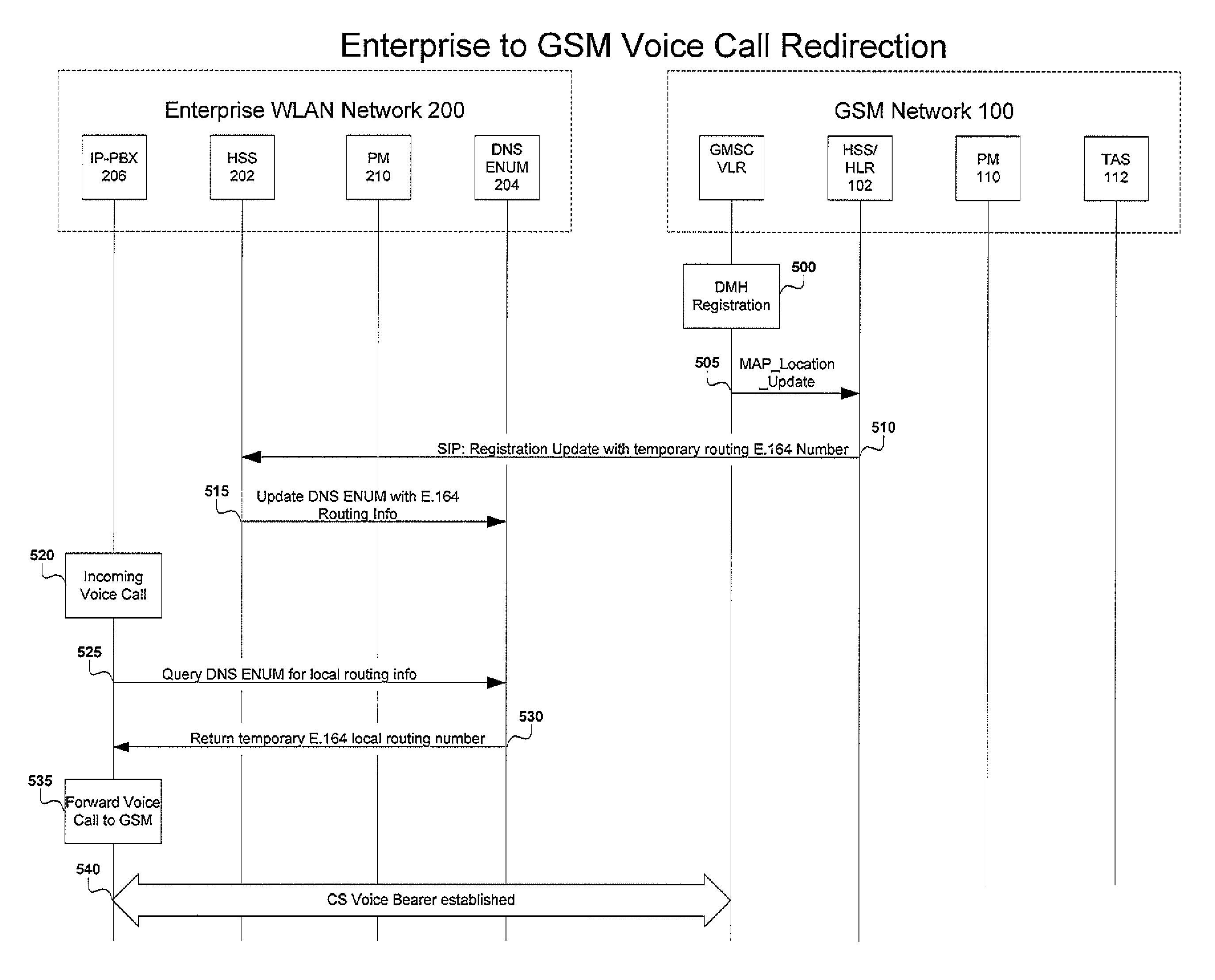
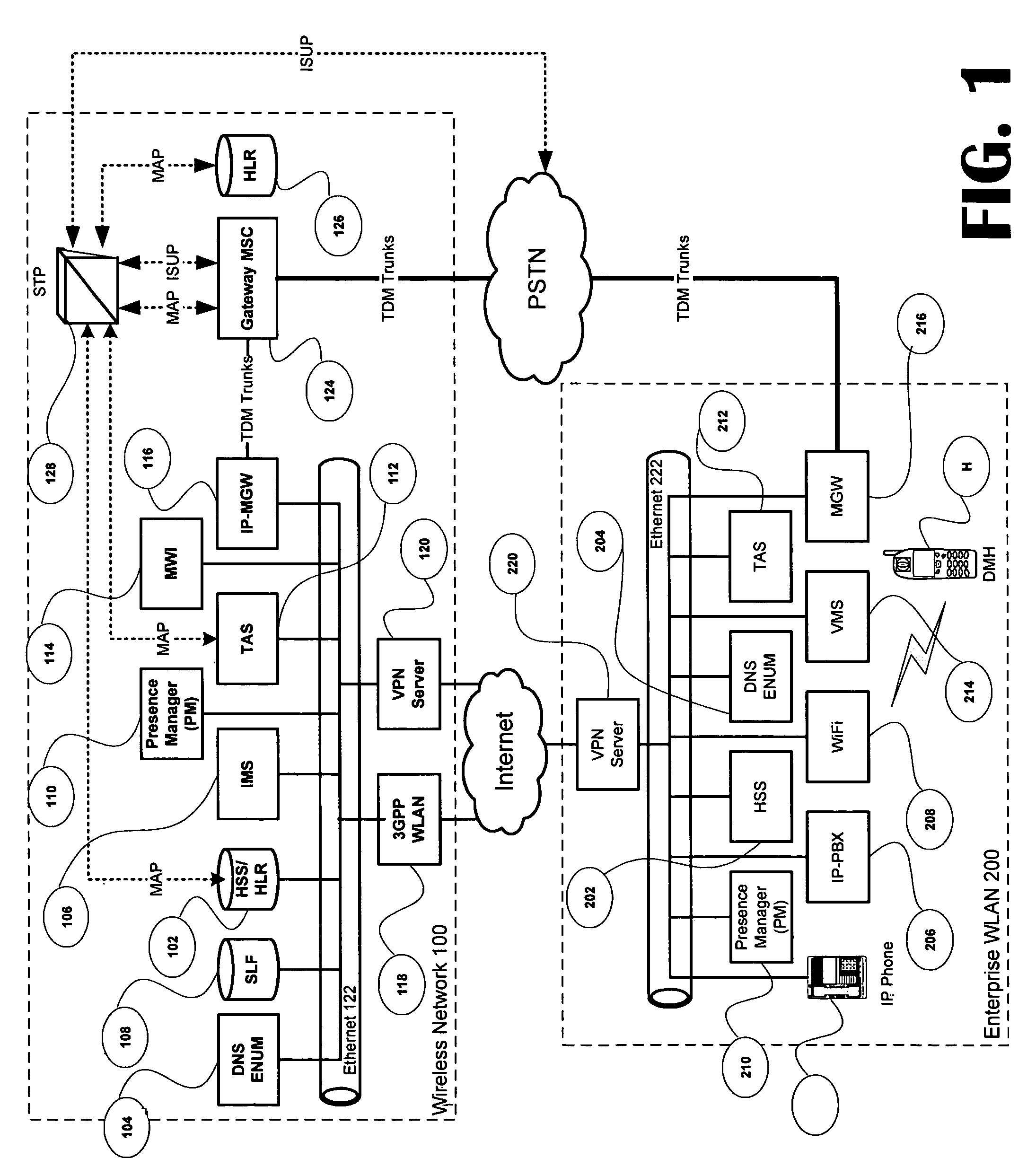
Systems and methods provide a single E.164 number for voice and data call redirection and telephony services such as caller identification, regardless of in which type of network a dual mode mobile device operates. When the dual mode device registers and is active in a GSM network, temporary routing and status updates are triggered and resultant information is maintained in both networks. A mobile terminated call is routed through an enterprise WLAN with call control within the enterprise being handled by SIP or H.323 signaling, and the call is redirected to the mobile device in the GSM network, where call control is assumed by the SS7 network. Services are provided using the protocols native to the active network, and the single E.164 is used consistently along with or lieu of the temporary routing information for subscriber identity specific functions, such as caller identification and voice mail.
Owner:MITEL NETWORKS INC +1
Reliable, long-haul data communications over power lines for meter reading and other communications services
InactiveUS8947258B2Highly long-haulImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsPower distribution line transmissionPower qualityLow speed
Owner:POWERMAX GLOBAL
Mobile Telephone Firewall and Compliance Enforcement System and Method
ActiveUS20090325615A1Improve protectionSubstation equipmentMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsComputer softwareSubscriber identity module
Methods, systems, and software for mediating SMS messages, and especially type 0 SMS messages, in a wireless mobile communications device configured to send and receive data using a GSM protocol and including a subscriber identity module (“SIM”) including electronic hardware and computer software executed by the hardware such that the SIM is configured to send, receive, and process messages using a Short Message System (“SMS”) between the wireless mobile communications device and a communications network. One aspect includes a method for mediating SMS messages comprising: configuring electronic hardware on the wireless mobile communications device to implement a firewall on the wireless mobile communications device, the firewall configured to identify and optionally mediate infrastructure SMS messages.
Owner:MANTECH ADVANCED SYST INT
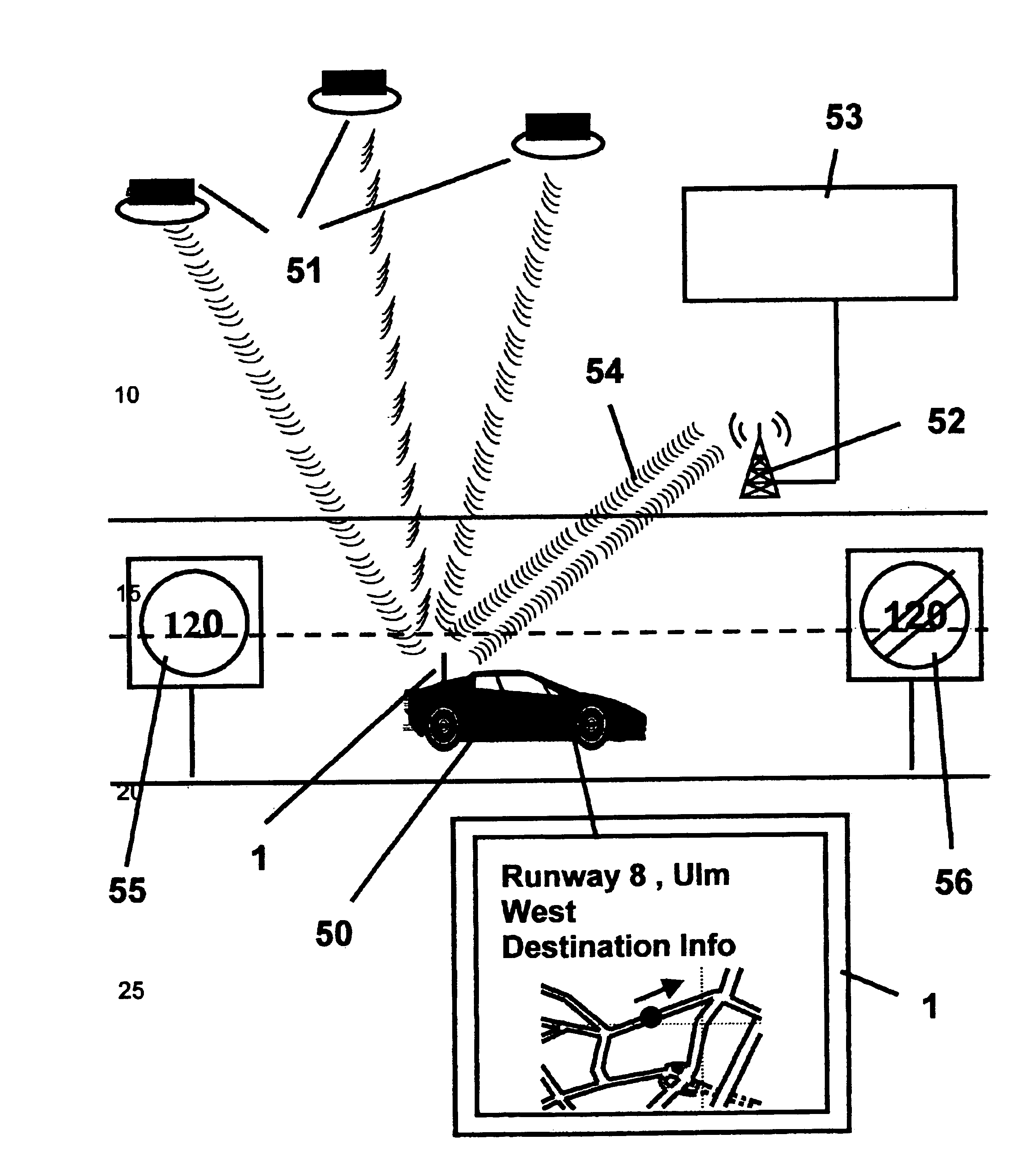
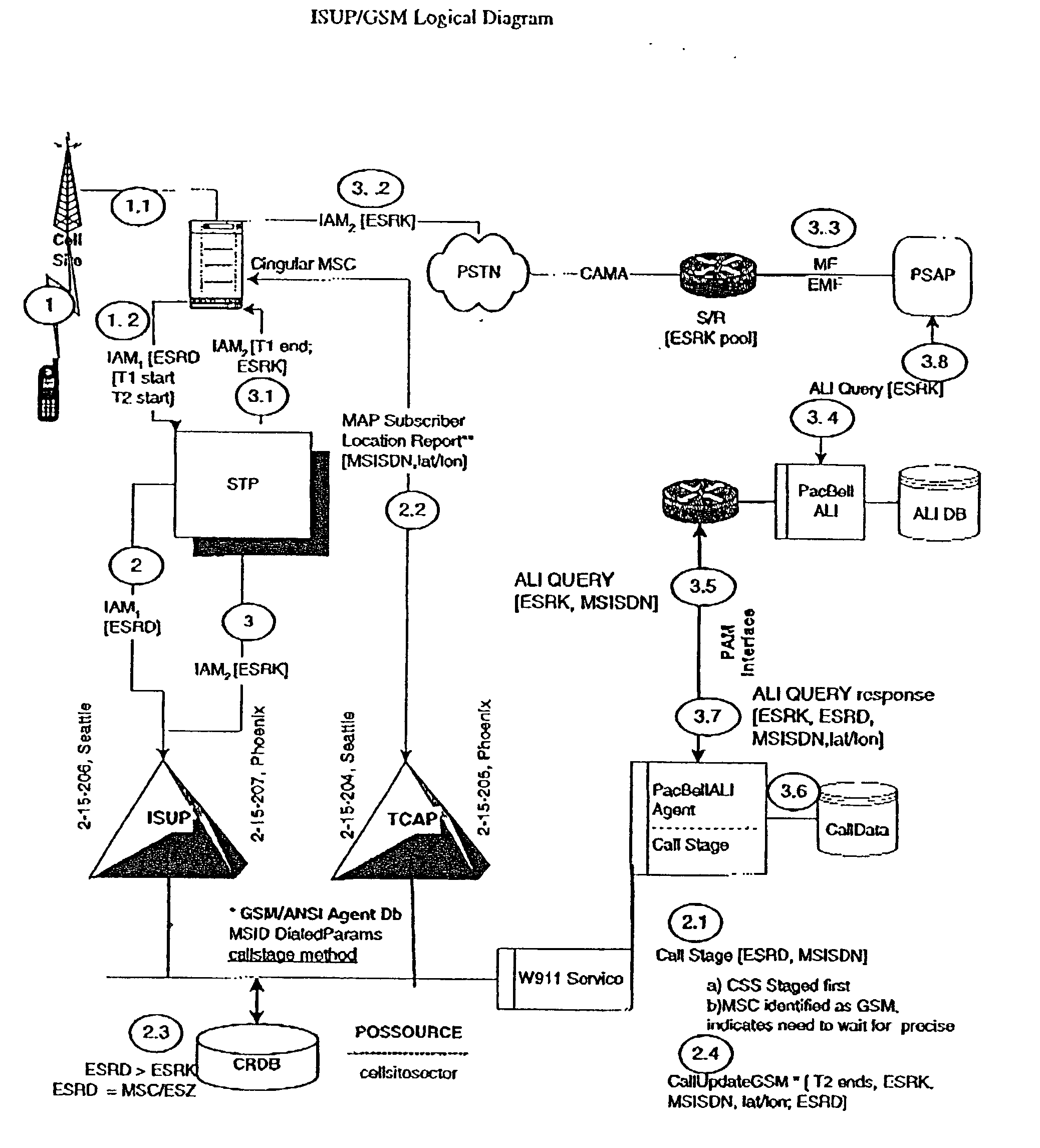
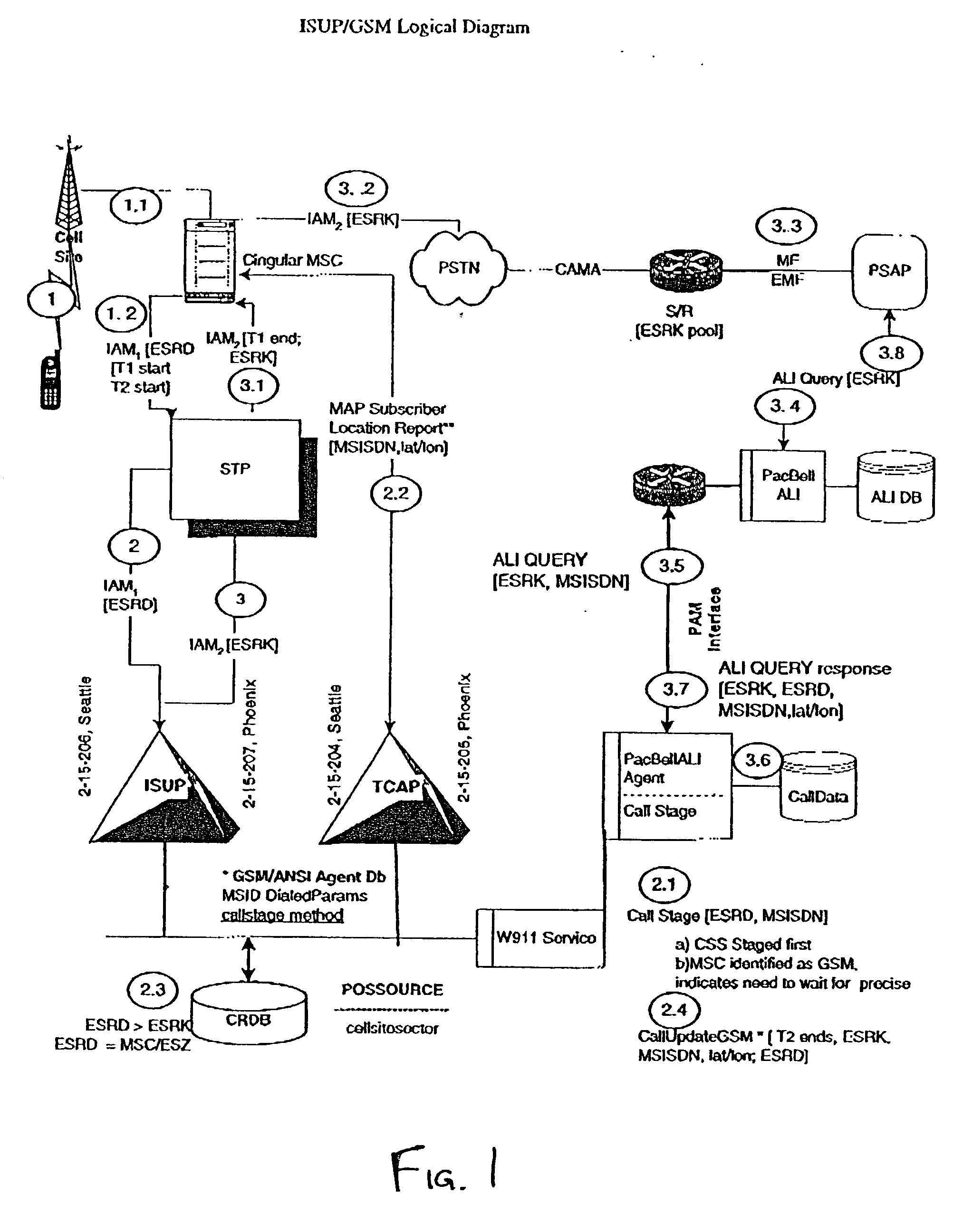
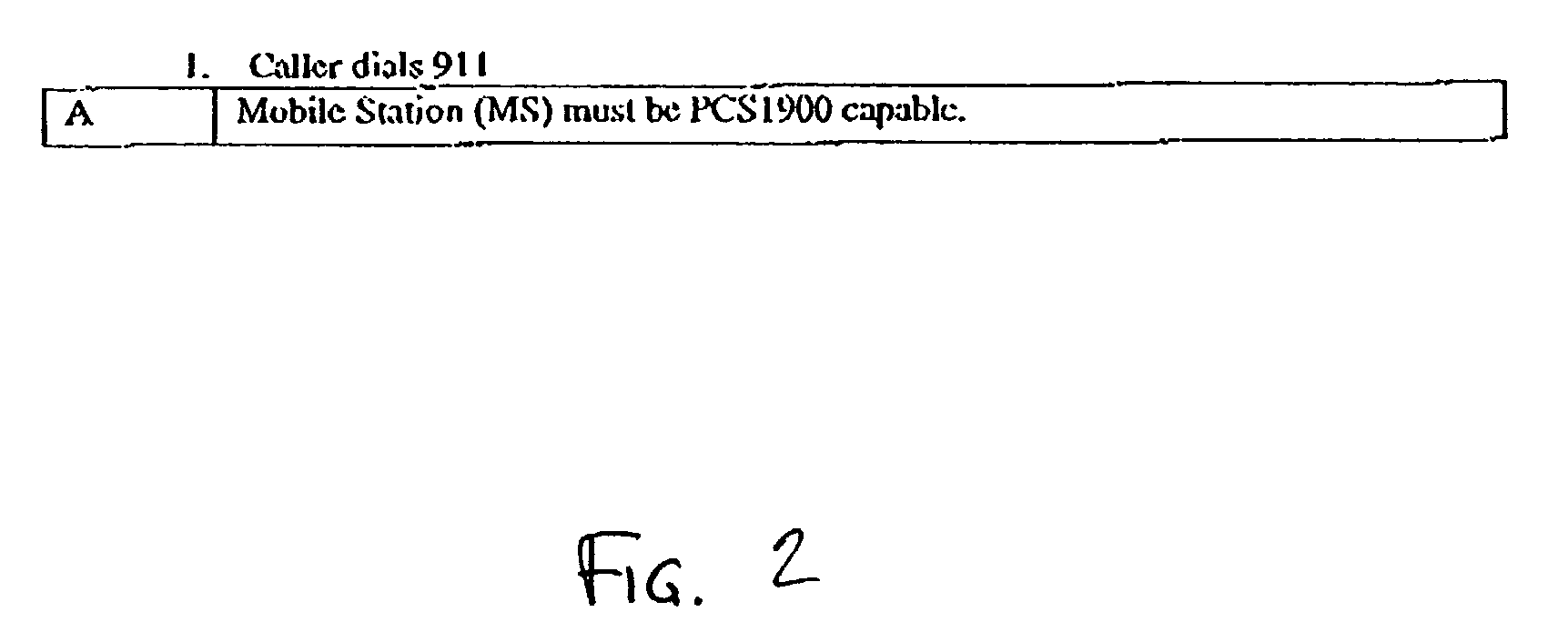
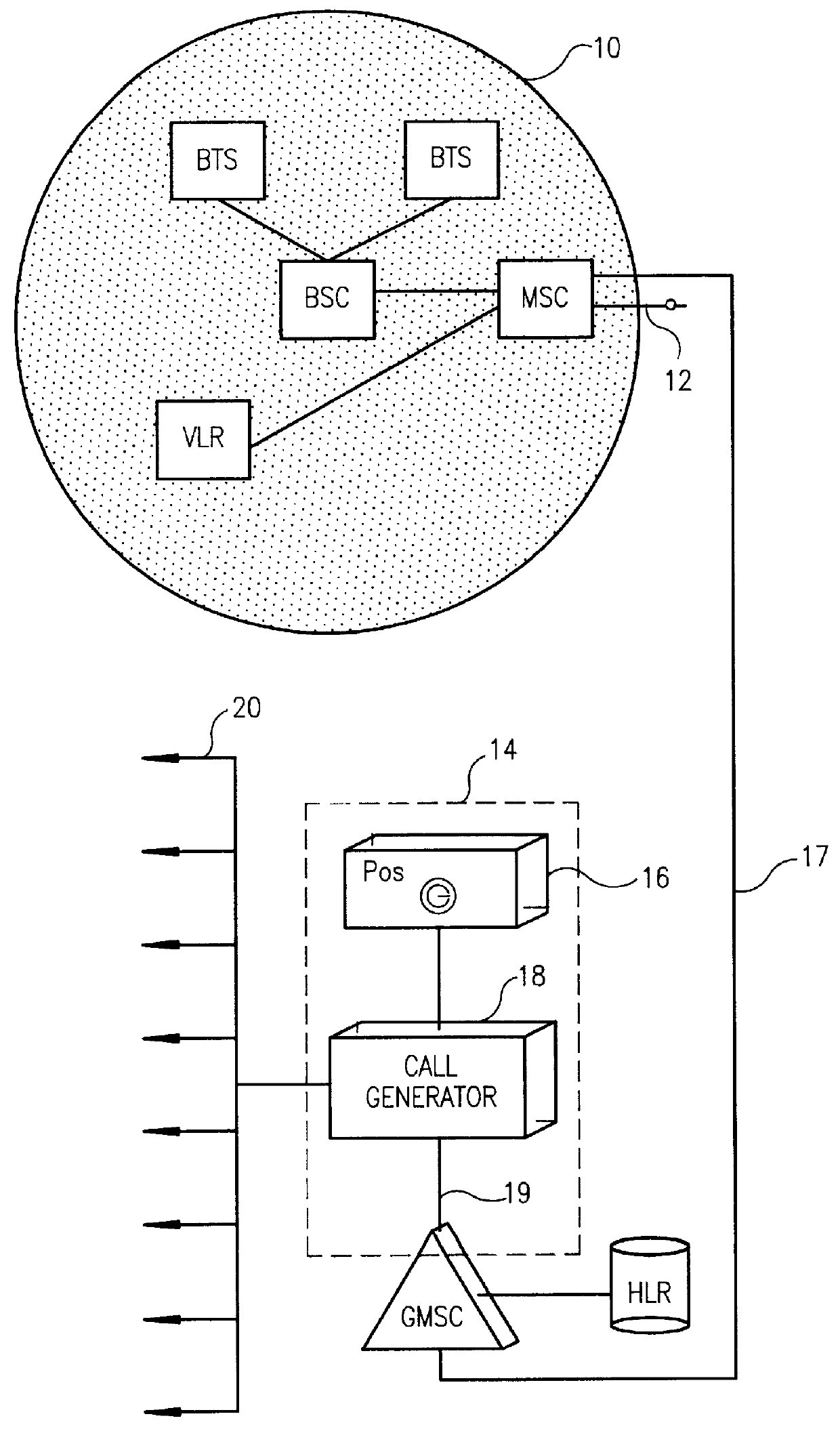
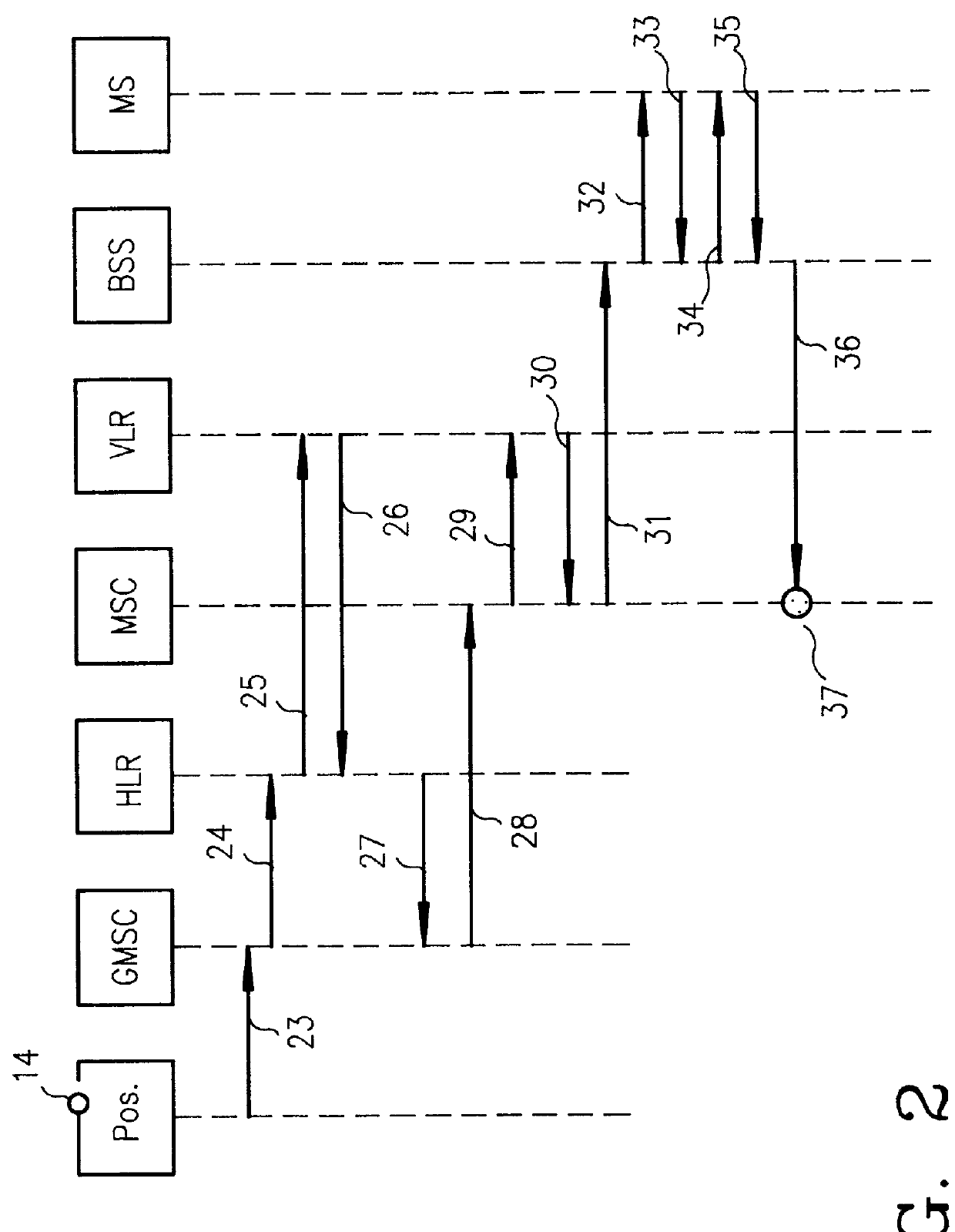
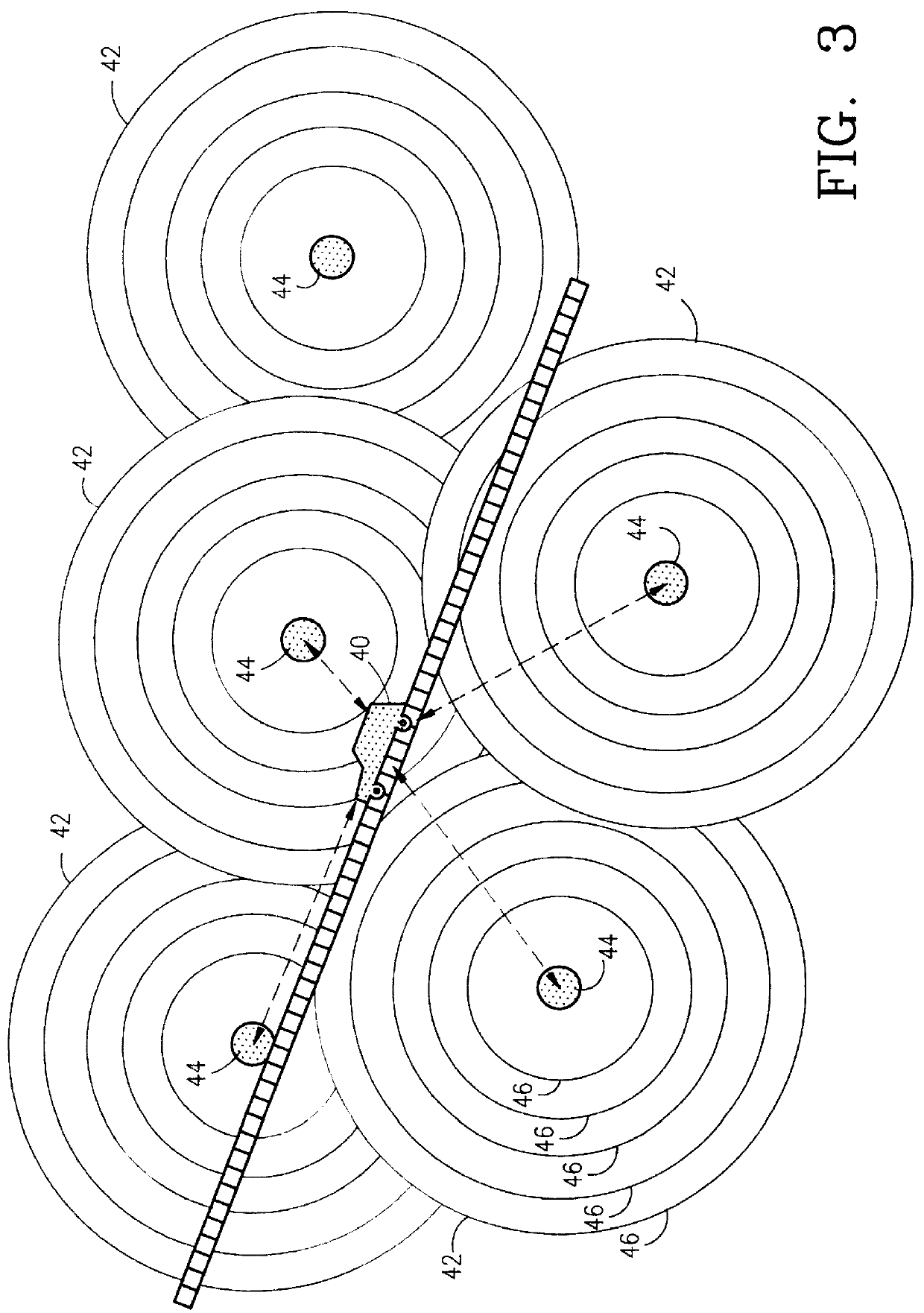
Public safety access point (PSAP) selection for E911 wireless callers in a GSM type system
Public safety access points are selected in a wireless network for E911 calls based on ESRD substitution when ESRKs are not being used. The present invention was conceived as an ESRK workaround solution to implement Phase II of the E911 rules from the starting point of a Phase I implementation. ESRKs, ESRDs or ESRVs are initially obtained and managed for each PSAP in a particular carrier's area. Then, Phase I processes are modified to wait to see if Phase II GSM location information will be reported in a timely manner (e.g., within a second or two or so) before committing to a default selection of a particular PSAP based on information available (e.g., based on the location of a serving cell site).
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Short message service initiated cellular mobile positioning system
InactiveUS6052597ADirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMobile Telephone ServiceGeolocation
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00210 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 15, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 15, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 16, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 25830 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 22, 1996The position of a mobile station in a cellular mobile telephone system, particularly a GSM system, is determined by carrying out a simulated call setup, i.e., the call setup is interrupted subsequent to a telephone switching center (MSC) having received a paging response containing the identity of the cell and, optionally, a timing advance. The simulated call setup is initiated by generating a modified short message signal (SMS) which is not registered in the SMS catalogue of the mobile station and which is not shown to the user of the mobile station. The SMS commands the mobile station to carry out a position determining sequence in order to establish parameters for use in establishing the position of the mobile station, for example by commanding the mobile station to connect itself to a base station contained in its neighbor list, analyze the geographical position of the base station, and subsequently send the position determining parameters to a position handler. The geographical position of the base station is analyzed from the cell identity and, if available, the timing advance, the position of the mobile station being presented graphically on a picture screen and constantly updated after each call setup. The call setups are generated by the position handler.
Owner:EUROPOLIGRAFICO
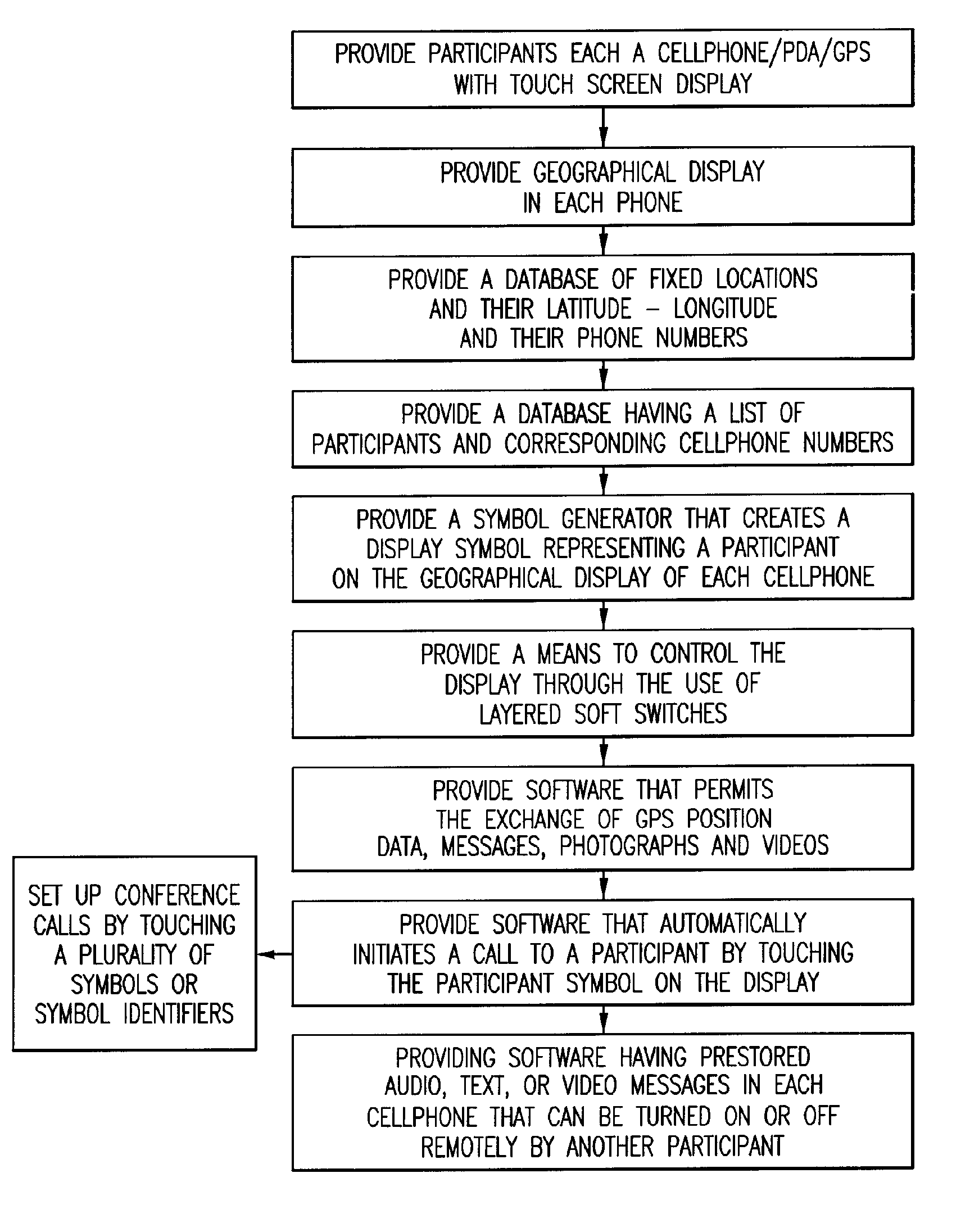
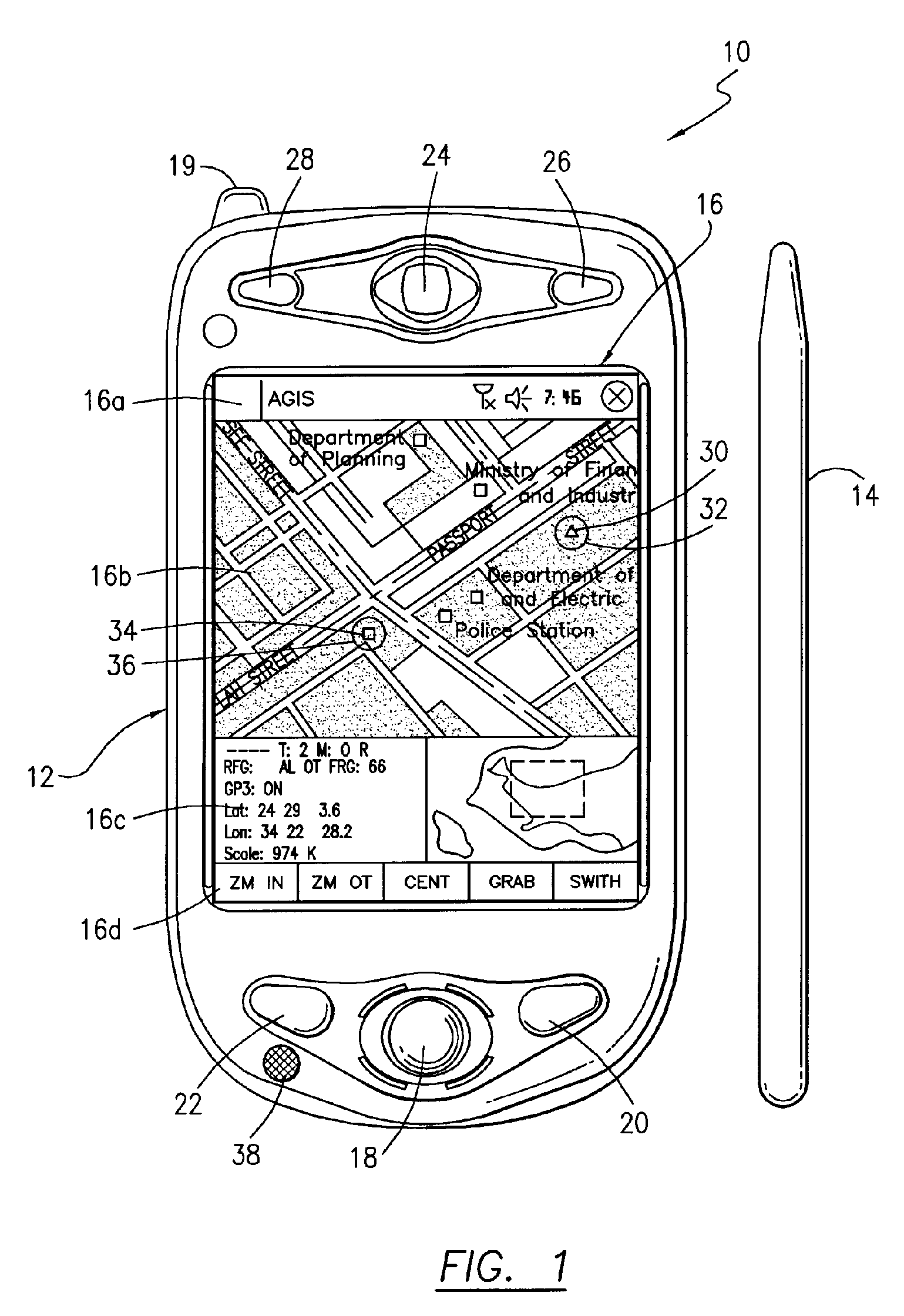
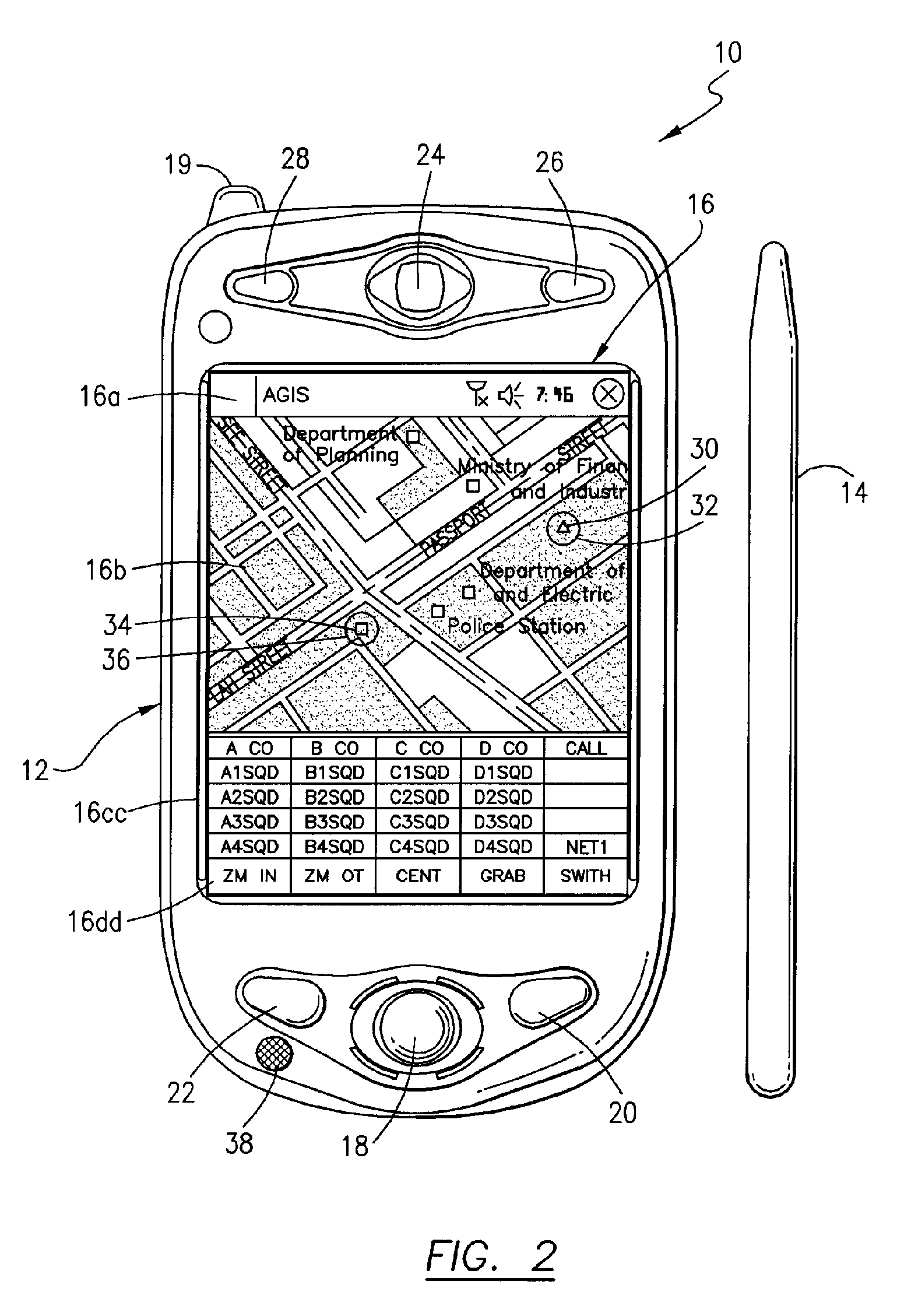
Method of providing a cellular phone/pda communication system
ActiveUS20060199612A1Transmission easilyDecreasing the operator actions necessaryDevices with GPS signal receiverDevices with wireless LAN interfaceVideo transmissionDisplay device
A cellular, PDA communication device and communication system for allowing a plurality of cellular phone users to monitor each others' locations and status, to initiate cellular phone calls by touching a symbol on the touch screen display with a stylus which can also include point to call conferencing calling. Each participant's cellular phone PDA device includes GPS navigation receiver with application software for point to call cellular phone initiation to participants and geographical entities including vehicles, persons or events, conference calls and video transfers. The method and system also includes automatic shifting from GPRS / EDGE / CDMA / 1XEVDO to SMS when any of the cellular phones in the communication network is in the voice mode and in use and for automatic shifting back to GPRS / EDGE / CDMA / 1XEVDO upon completion of the voice phone call. In addition, using the system, a full transfer of photographs, video clips and high speed data can be used between any cellular phones regardless of who the cellular phone vendors or cellular phone companies are and in either CDMA, GSM, WiFi or a combination of the two.
Owner:AGIS SOFTWARE DEVEMENT LLC +1
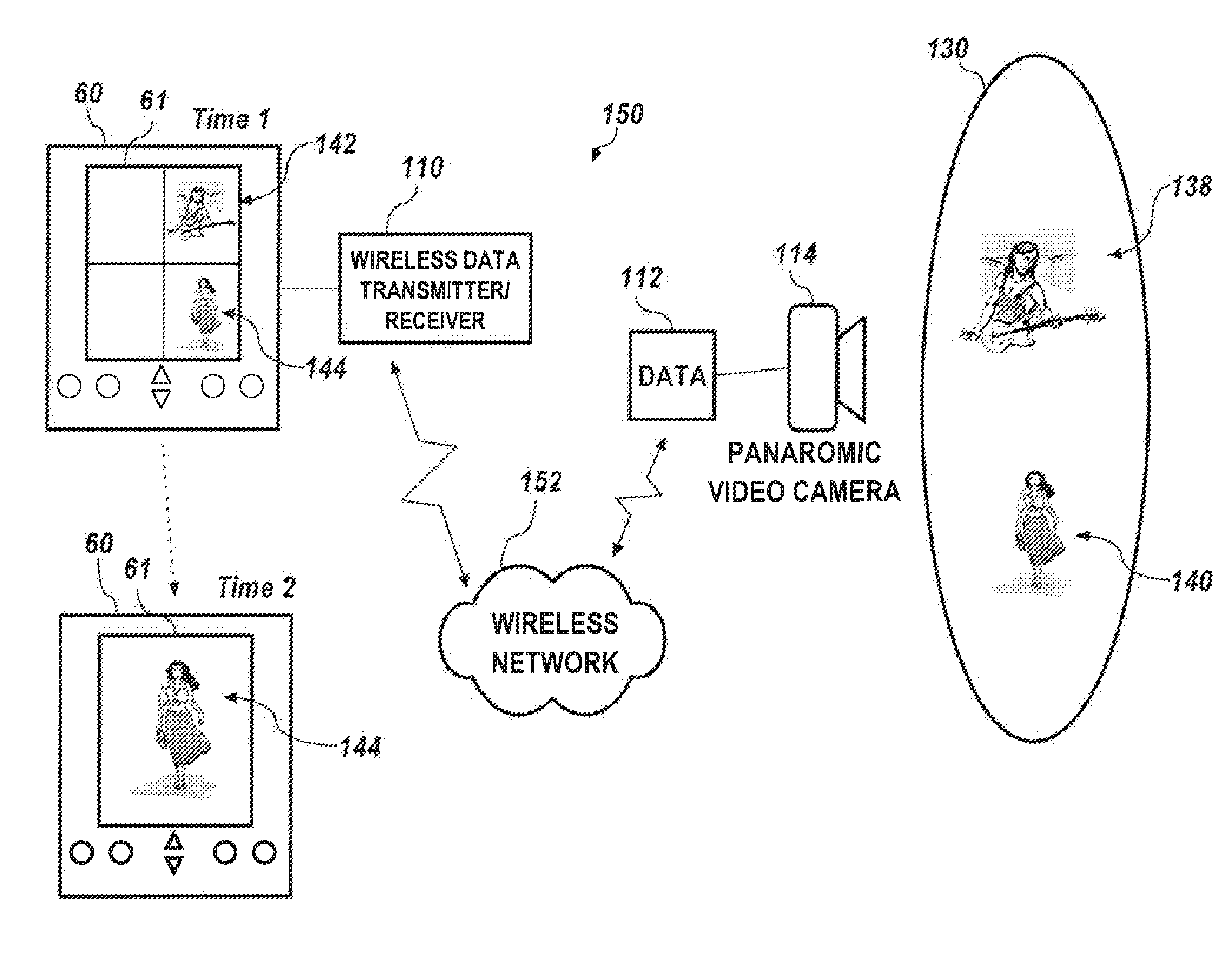
Providing video of a venue activity to a hand held device through a cellular communications network
InactiveUS20070216783A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDisplay deviceHand held
Systems and methods for providing video of a live venue event to a hand held device. A hand held device wirelessly receives data containing two or more video streams conveying live video venue event content, the venue event content including moving images of action occurring at the live venue event held at a venue. A cellular communications network (e.g., CDMA, GSM, GPRS, TDMA, 3G, etc.) is provided through which the data containing the two or more video streams is transmitted to the hand held device for display via a display associated with the hand held device.
Owner:FRONT ROW TECH
Antenna with a conductive layer and a two-band transmitter including the antenna
InactiveUS20020003499A1Improve matchSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual modeTwo band
The antenna of said transmitter is a microstrip antenna. A rear edge of its patch is provided with a short circuit by means of which a quarter-wave primary resonance can be excited by a coplanar line formed by two coupling slots in an area. Separator slots separate said area from another area in which a secondary resonance can be established at twice the frequency of the primary resonance from a slotted line extending one slot of the coplanar line. The invention applies in particular to the production of a dual-mode mobile telephone to the GSM and DCS standards.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
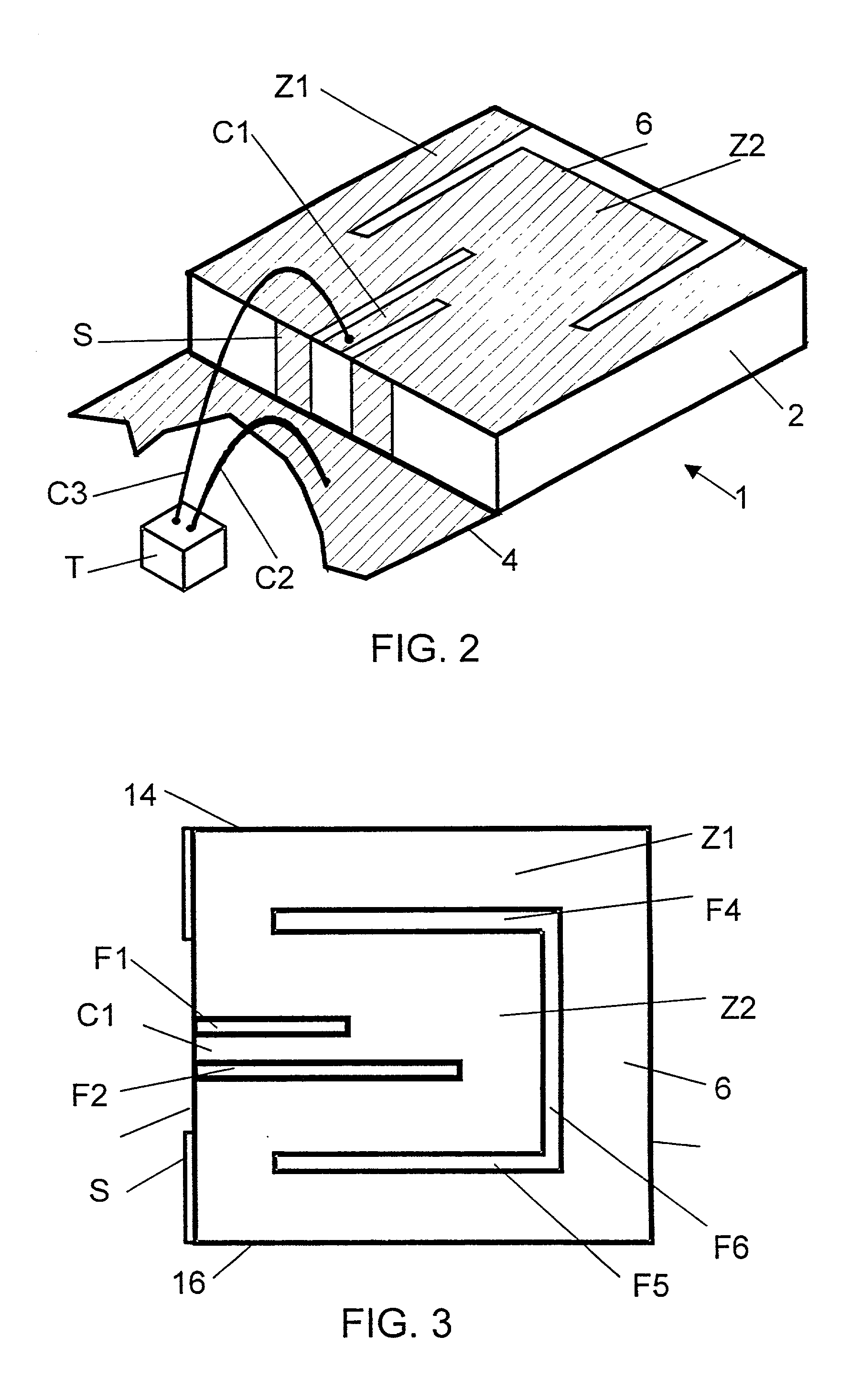
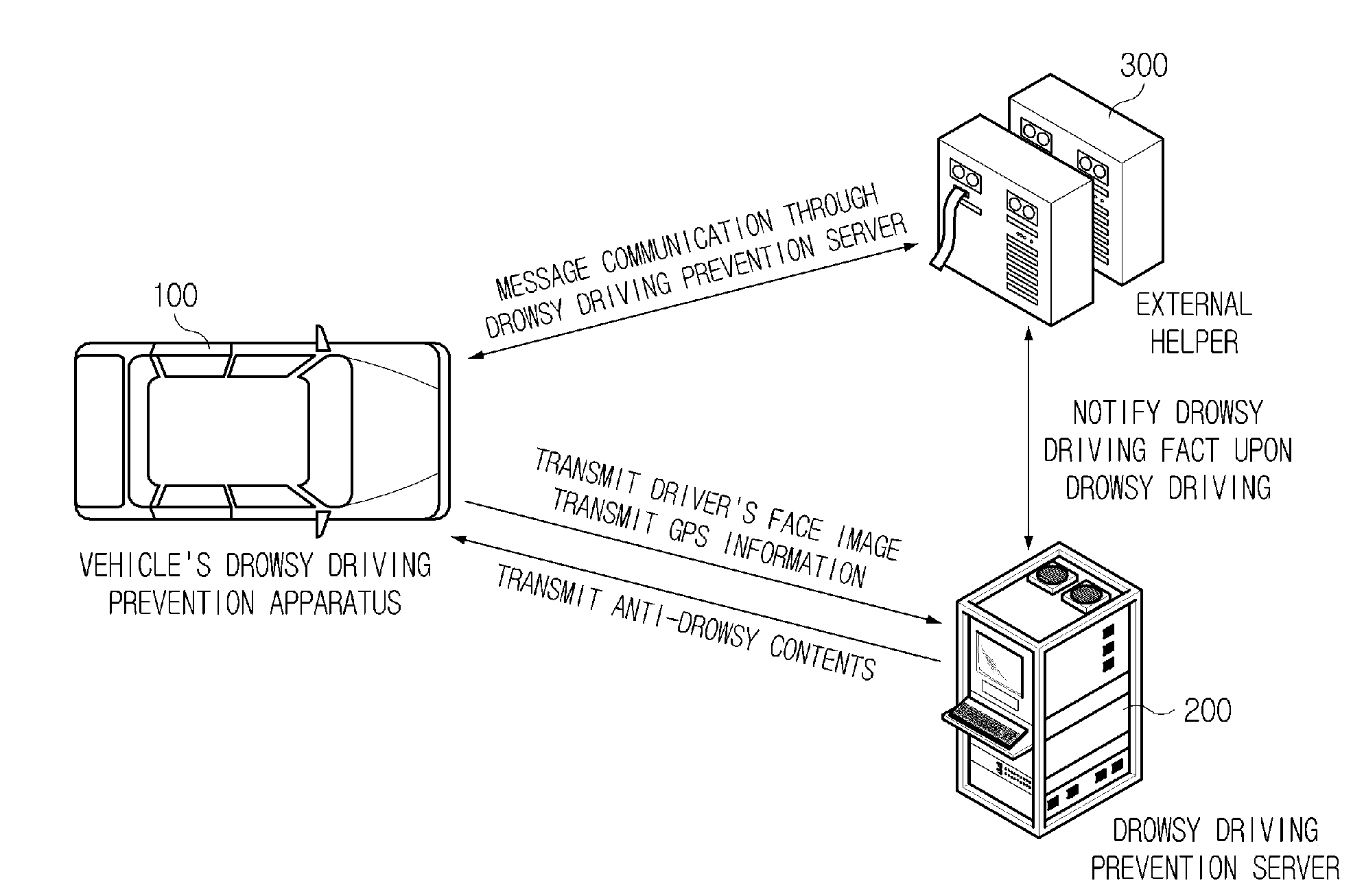
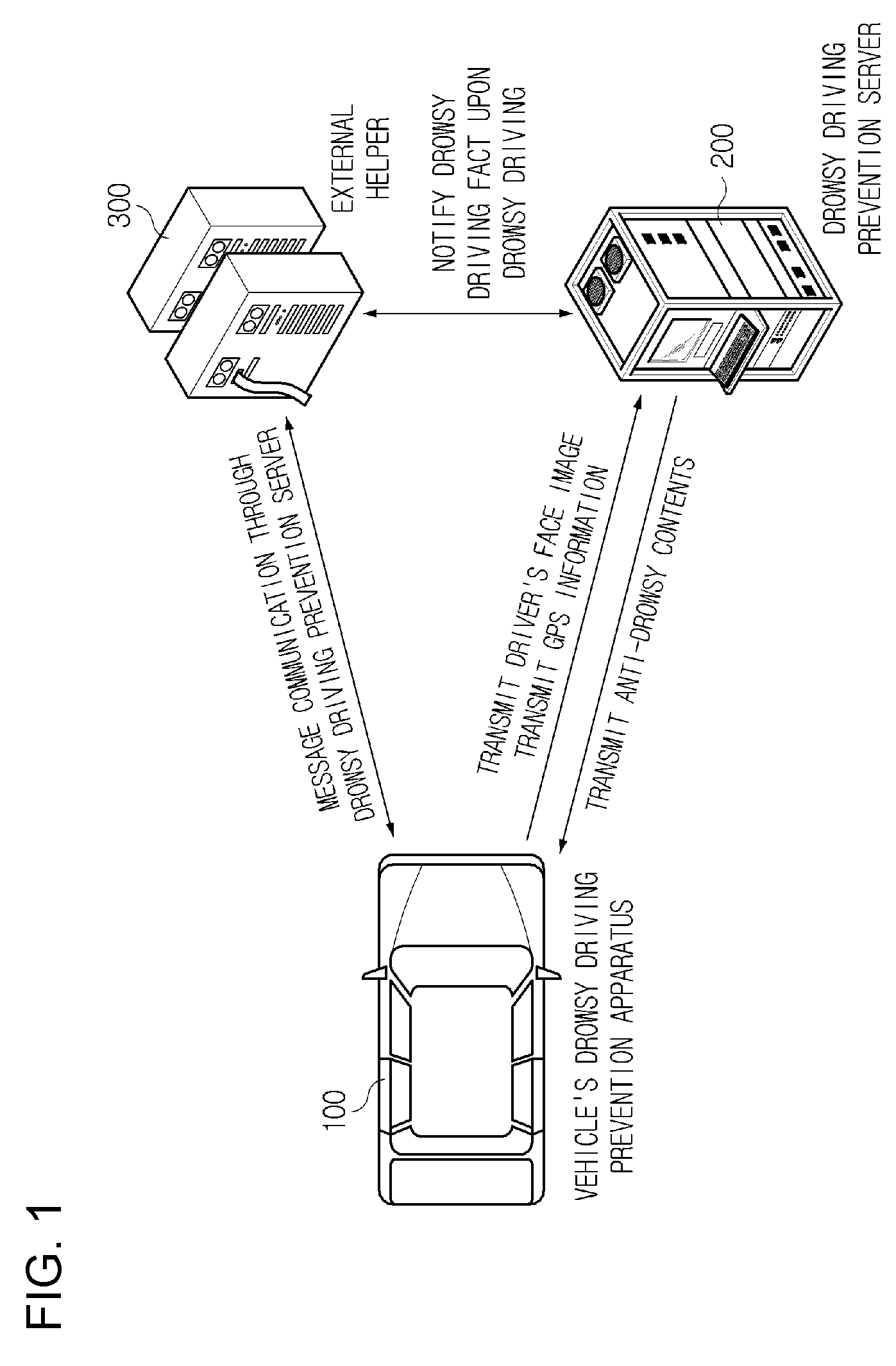
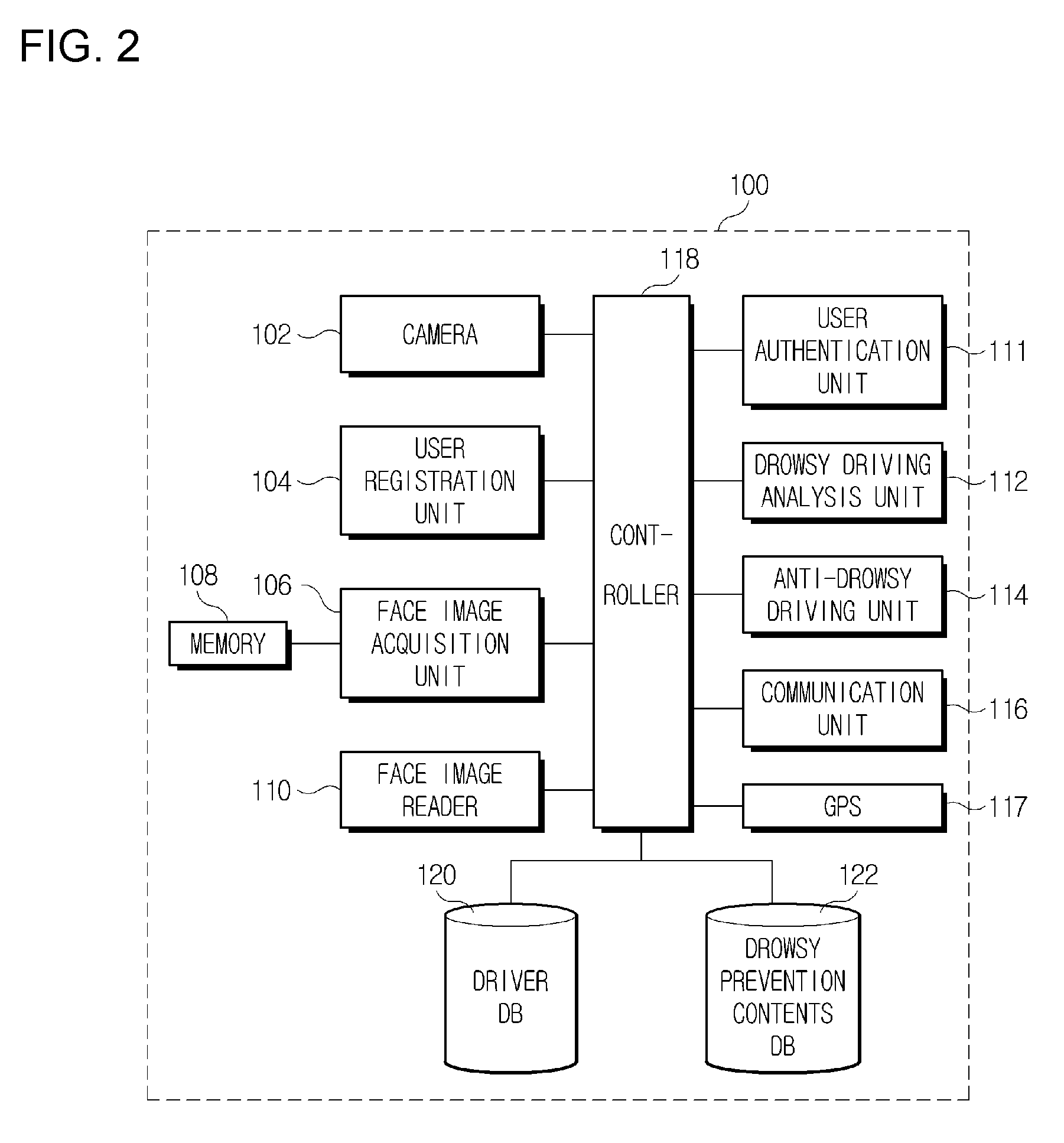
Preventive terminal device and internet system from drowsy and distracted driving on motorways using facial recognition technology
InactiveUS20080291008A1Avoid driving fatigueCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDriver/operatorTerminal equipment
A drowsy driving prevention apparatus employing a facial recognition technology and a drowsy driving prevention system employing the same is provided. A GPS and a communication unit for informing a central control center or a traffic accident prevention management institute of information about a drowsy driving state and the position of a vehicle are mounted in the drowsy driving prevention apparatus. Thus, traffic accidents can be prevented. A management server is informed of a driver's drowsiness and a driver can access a portable telephone of an external helper over a network using wireless Internet communication technologies, such as Wibro (also called Mobile WiMAX), HSDPA & HSUPA, Long Term Evolution (LTE), Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB), TD-SCDMA, TRS, GPRS GSM and CDMA. It is therefore possible to prevent traffic accidents caused by drowsy driving in synthetic and multidimensional ways.
Owner:TELICSTA
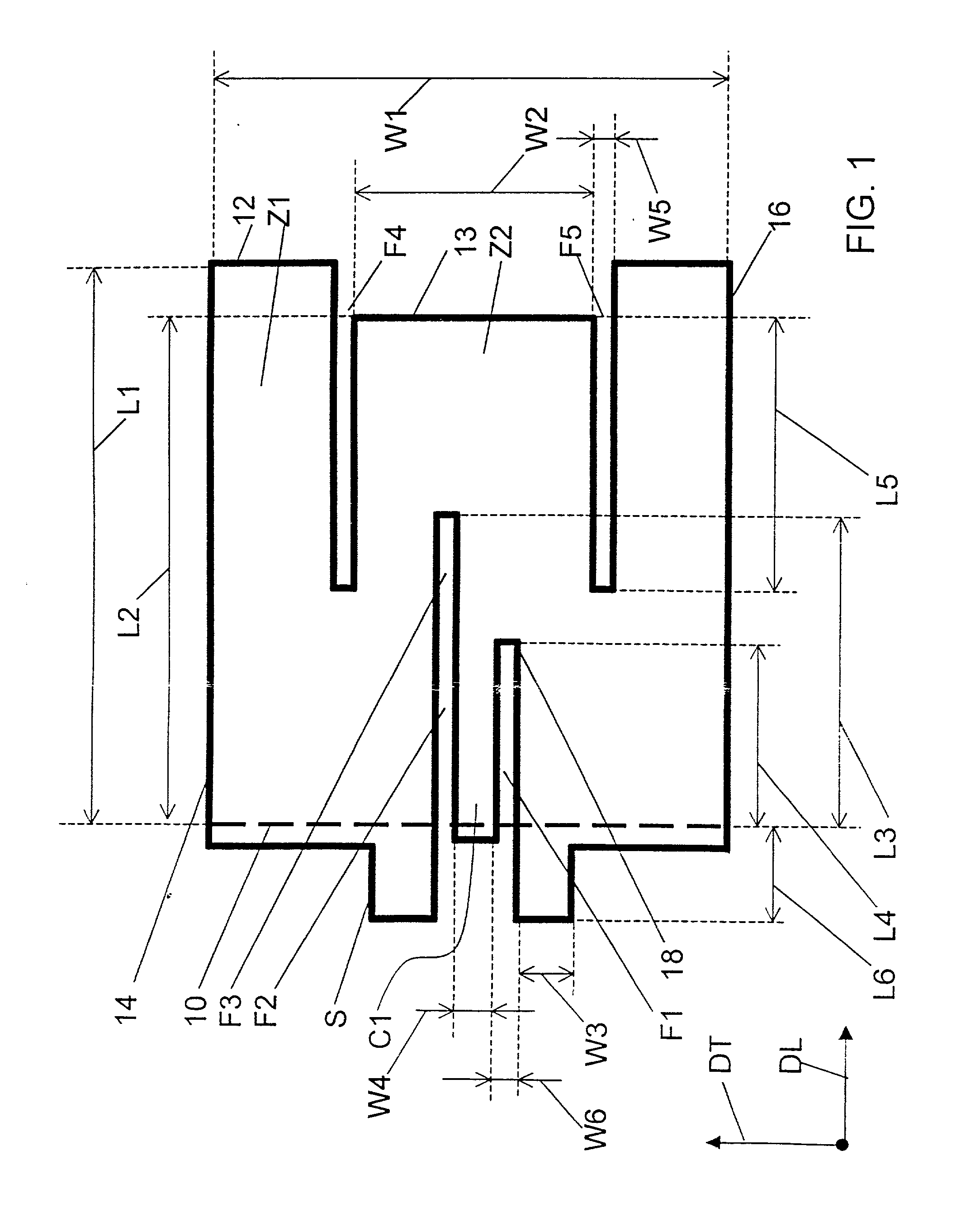
Absorbent article with high absorbent material content
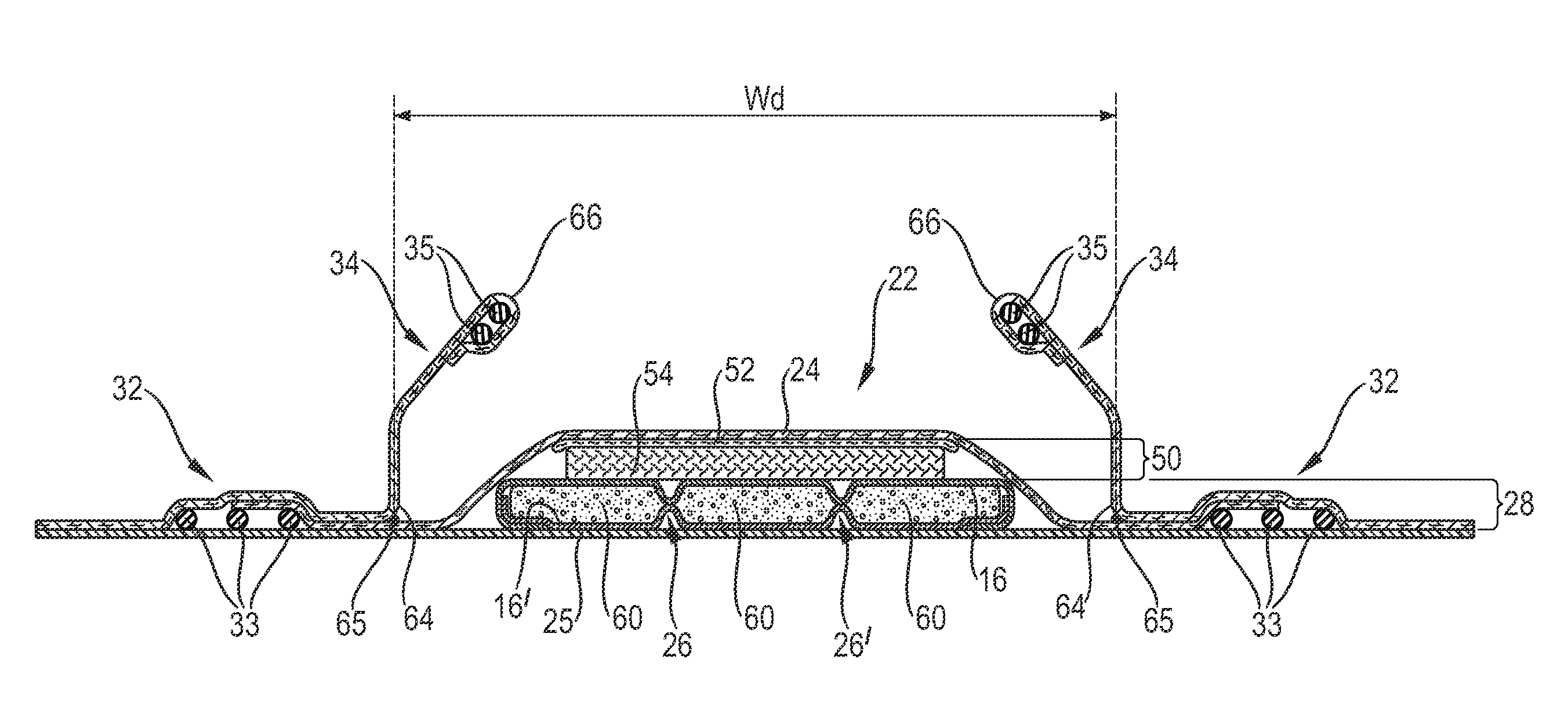
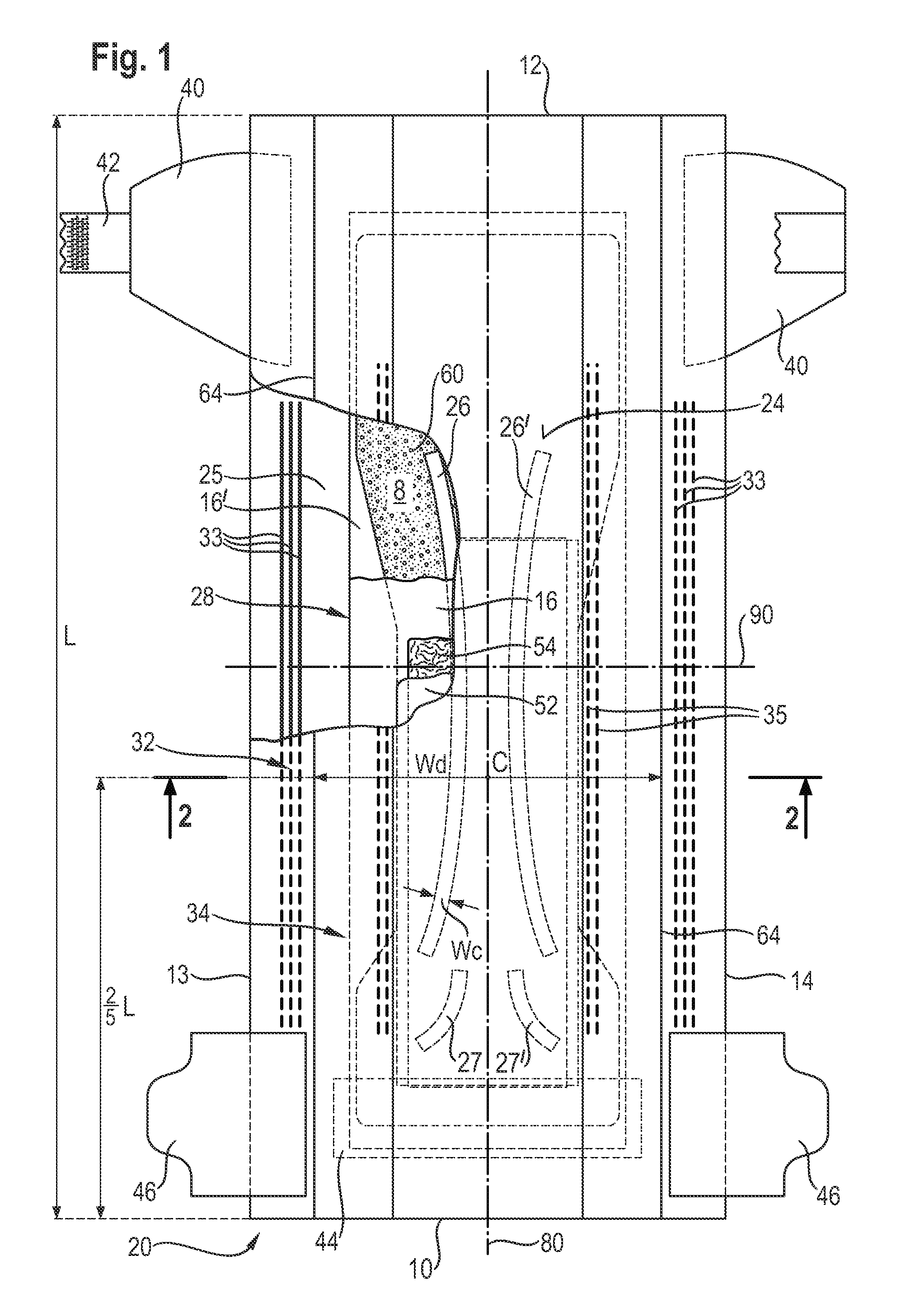
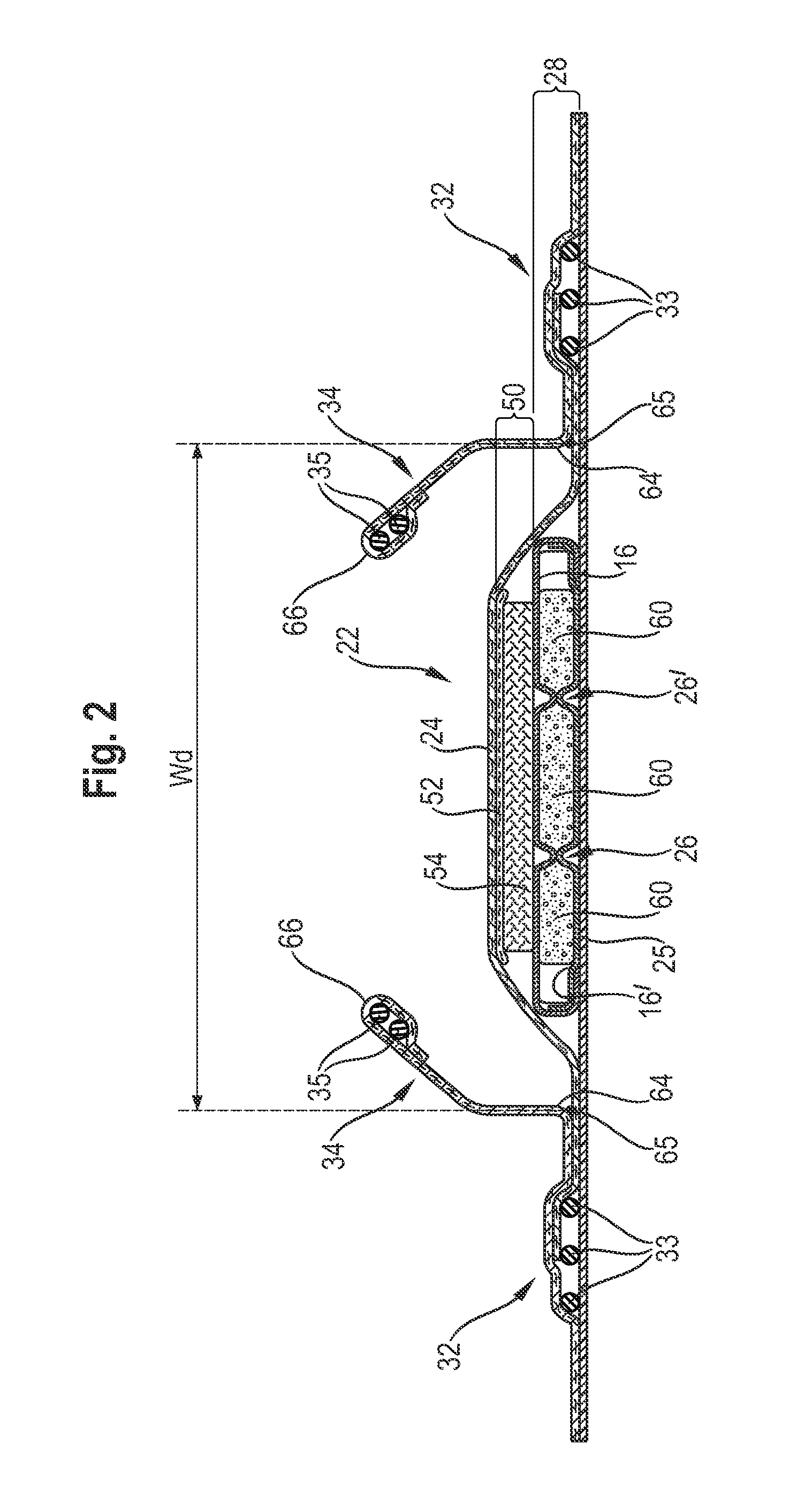
An absorbent article having an absorbent core comprising a core wrap (16, 16′) enclosing an absorbent material (60), which comprises at least 80% of superabsorbent polymers (“SAP”) by weight. The absorbent core further comprises at least one channel (26, 26′) and an acquisition-distribution system (ADS) between the topsheet and the absorbent core, the ADS comprising one, two or more layers wherein the ADS does not comprise a layer comprising at least 50% by weight of synthetic fibers and having a basis weight above 150 gsm.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Intelligent utilization of resources in mobile devices
InactiveUS7026984B1Save battery powerSave network bandwidthPower managementPosition fixationComputer moduleBiological activation
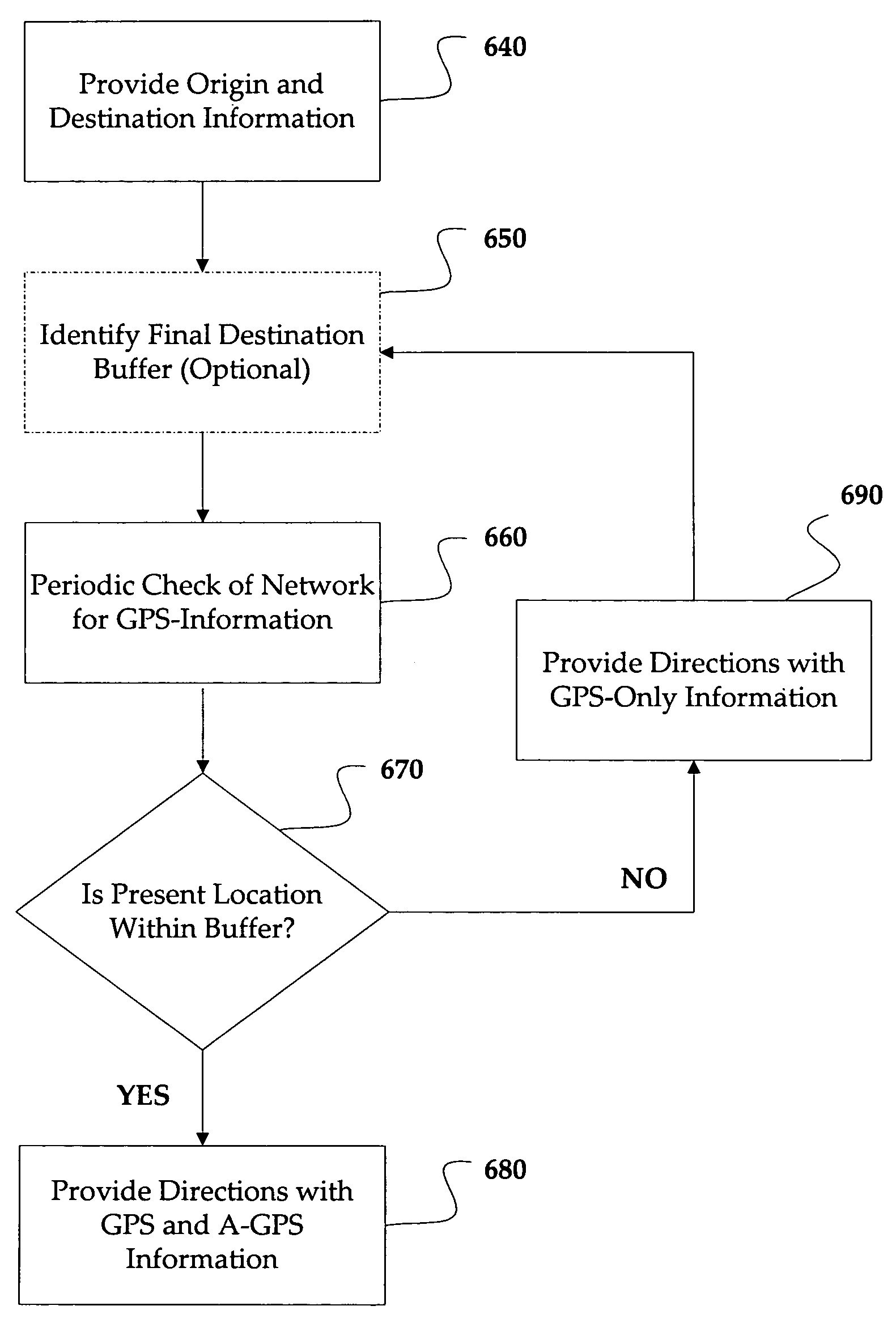
A programmable intelligent activation module to intelligently allow access to GPS resources is provided. In accordance with pre-programmed settings, an intelligent activation module will control the frequency by which a GPS module is allowed to access a GPS or GSM network in order to acquire location information of a mobile device equipped with GPS equipment. By controlling access to a GPS or GSM network, network resources such as bandwidth are conserved unless actually needed as is determined by the intelligent activation module. Similarly, battery resources for the mobile device are also conserved in that unnecessary activation of the GPS module is prevented until such activation is actually needed. The intelligent activation module can be programmed with a variety of settings including speed, map deltas, final destination information, or settings as pre-determined by a user of the mobile device.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Dual feel multi-band planar antenna
InactiveUS6670923B1Reduce Design ComplexityCompromise performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandPlanar inverted f antenna
A three-band, two-antenna, assembly includes a planar inverted-F antenna (PIFA) having a radiating / receiving element that is spaced from and extends generally parallel to a ground plane element. The planar radiating / receiving element of an inverted-F antenna (IFA) is located in an open space that exists between the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA and the ground plane element. The radiating / receiving element of the IFA extends either perpendicular to, or parallel to, the radiating / receiving element of the PIFA. The radiating / receiving element of the PIFA includes one or more open slot configurations that operate to provide dual resonant frequencies for the IPFA (AMPS / PCS or GSM / DCS). The radiating / receiving element of the IFA operates in a non-cellular frequency band (ISM or GPS).
Owner:LAIRD CONNECTIVITY LLC
Monitoring of call information in a wireless location system
InactiveUS20050003831A1Low costReduce functionEmergency connection handlingBeacon systems using radio wavesAir interfaceGSM
In an overlay Wireless Location System, an Abis interface is monitored to obtain information used to locate GSM phones. Signaling links of the Abis interface are passively monitored to obtain certain information, such as control and traffic channel assignment, called number, and mobile identification, which is not available from the GSM air interface of the reverse channel. This approach also applies to IDEN and can include CDMA systems where the GSM architecture has been used and the system includes a separated BTS to BSC interface.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com