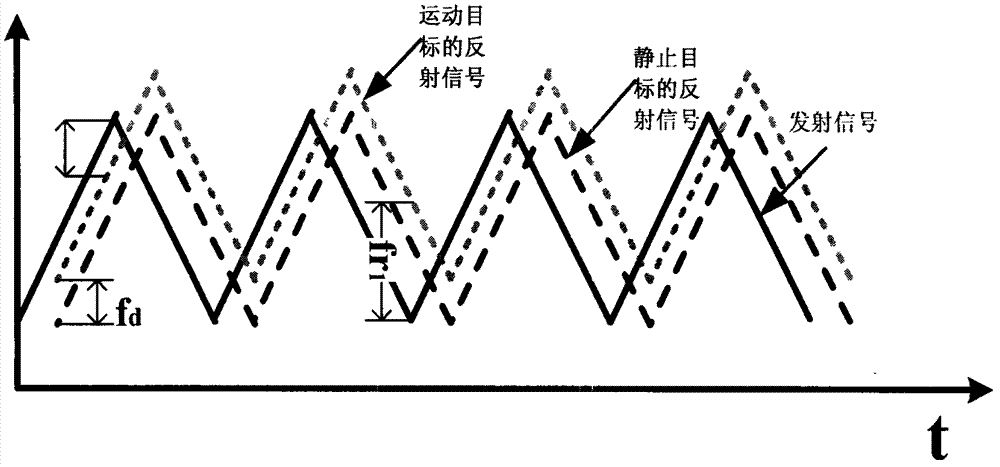
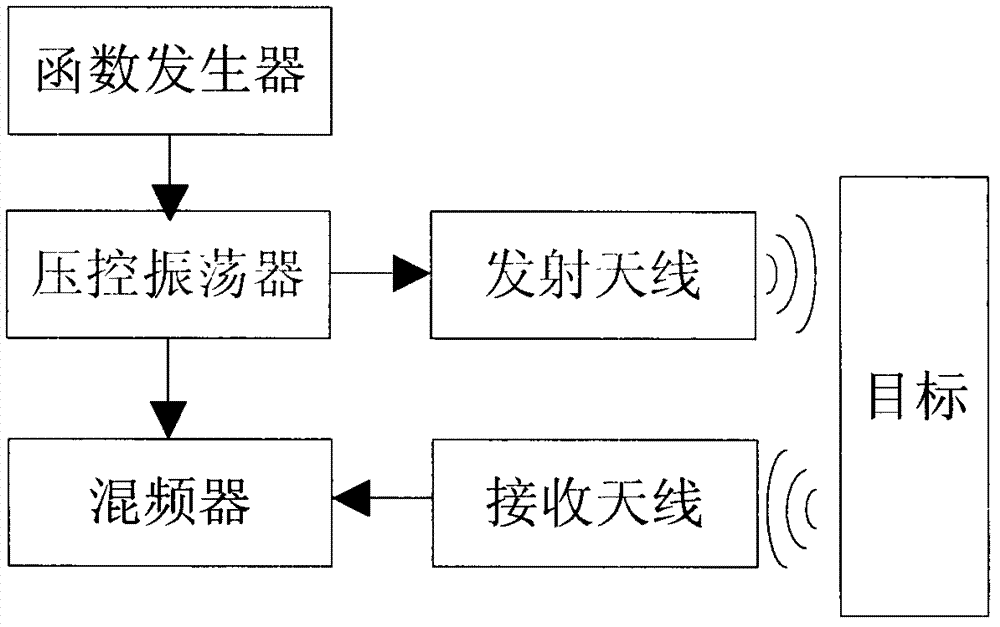
Patents
Literature
1707 results about "Frequency measurements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hertz (abbreviated: Hz) is the standard unit of measurement used for measuring frequency. Since frequency is measured in cycles per second, one hertz equals one cycle per second. Hertz is used commonly used to measure wave frequencies, such as sound waves, light waves, and radio waves.
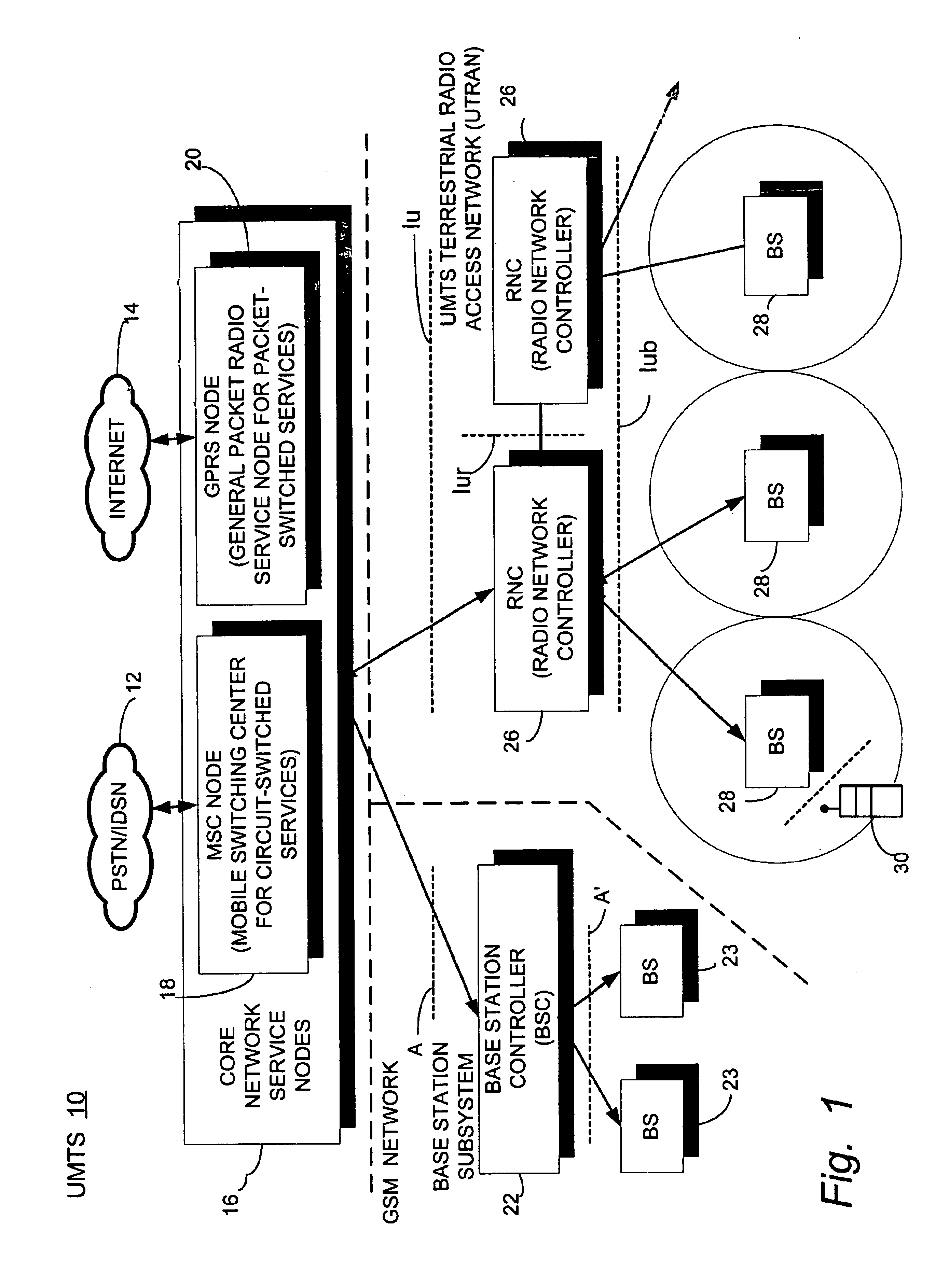
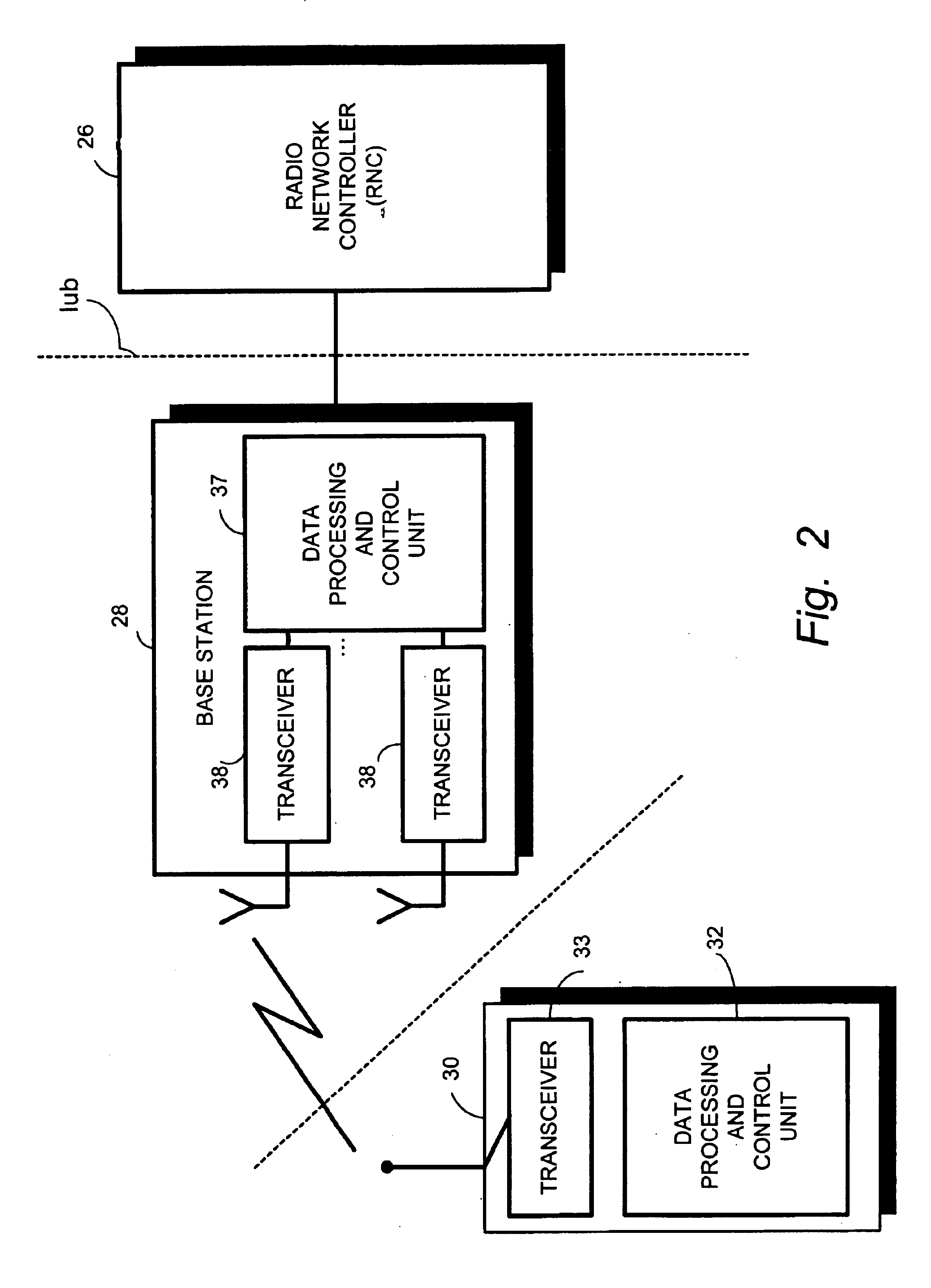
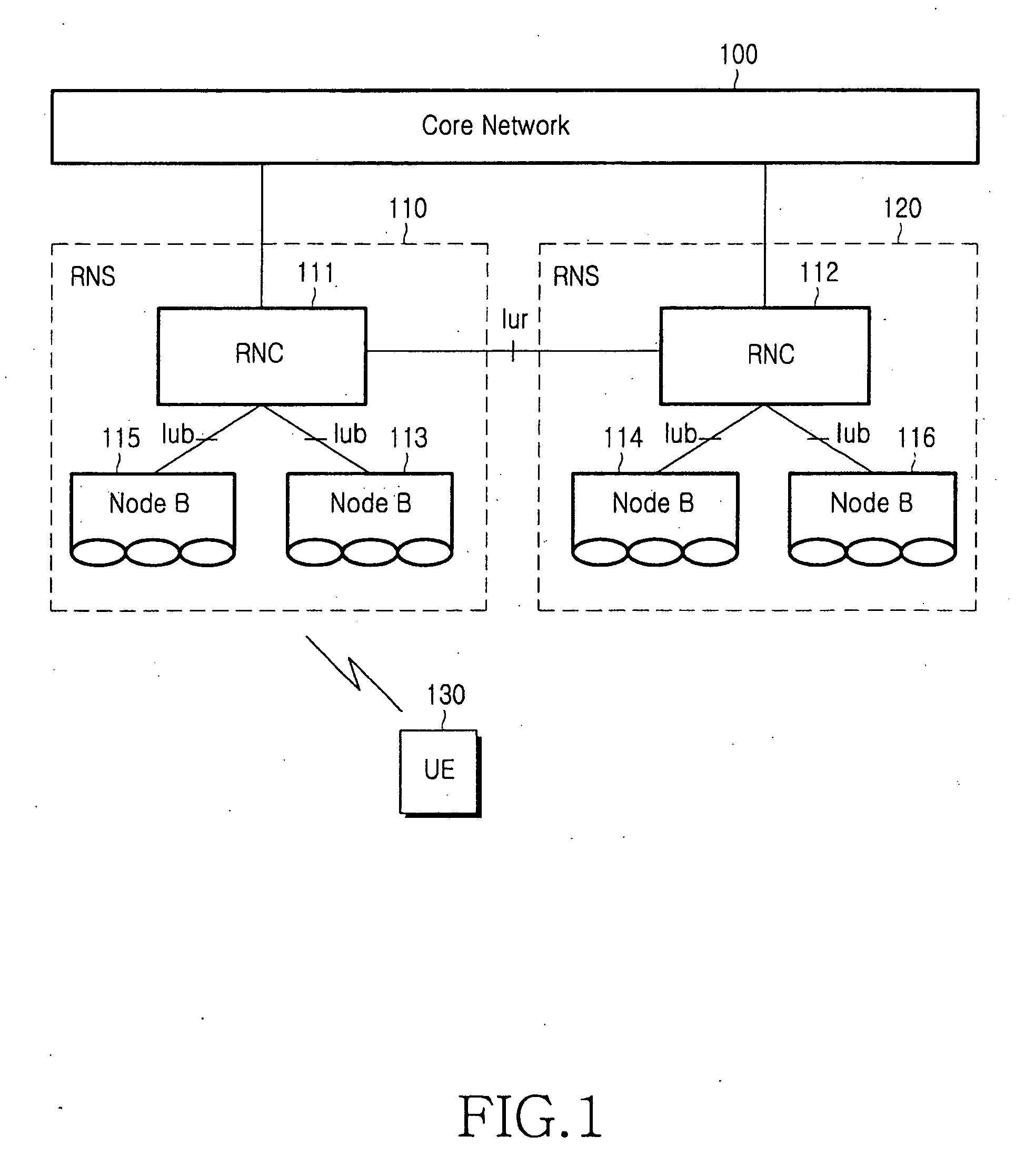
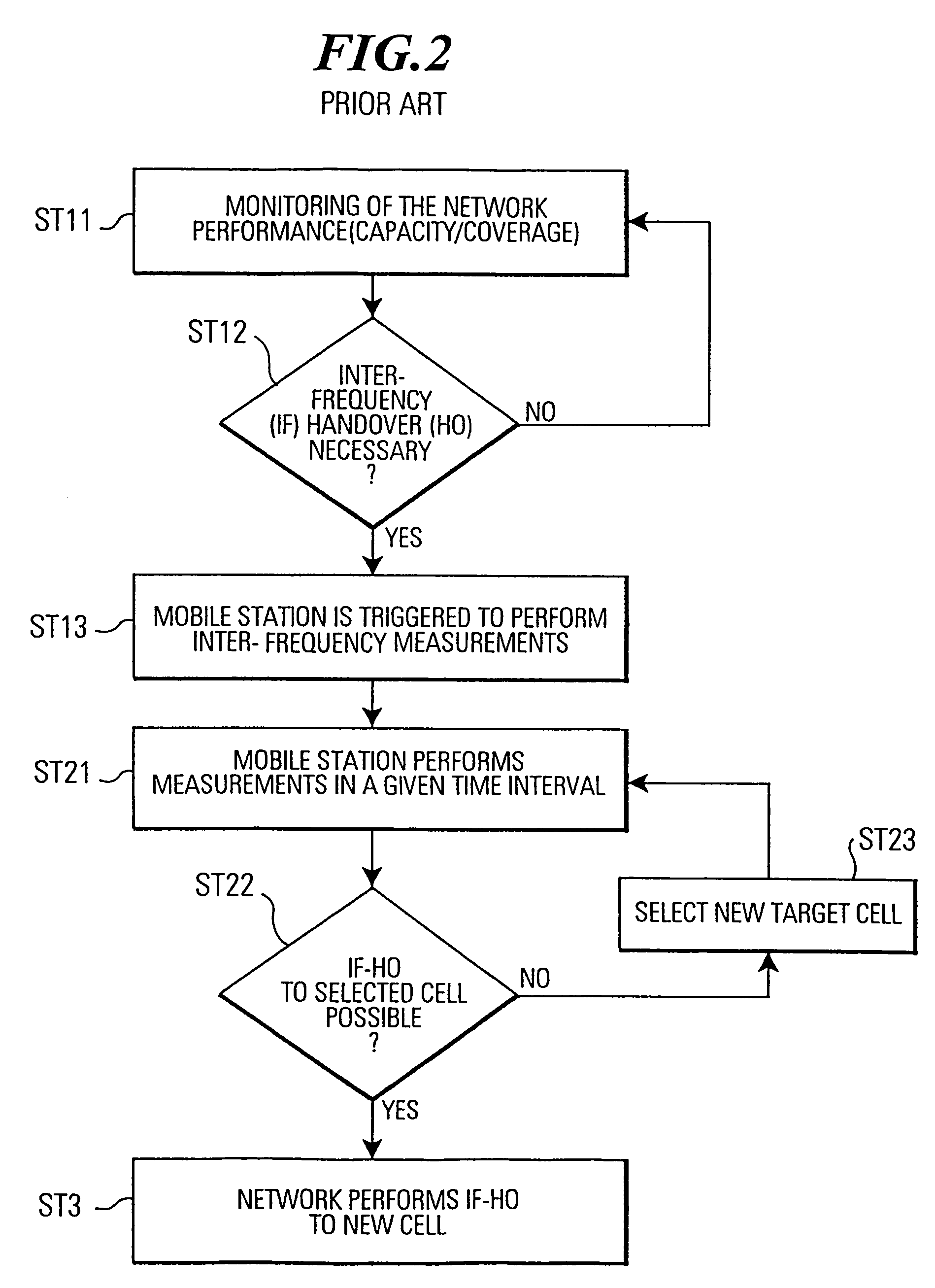
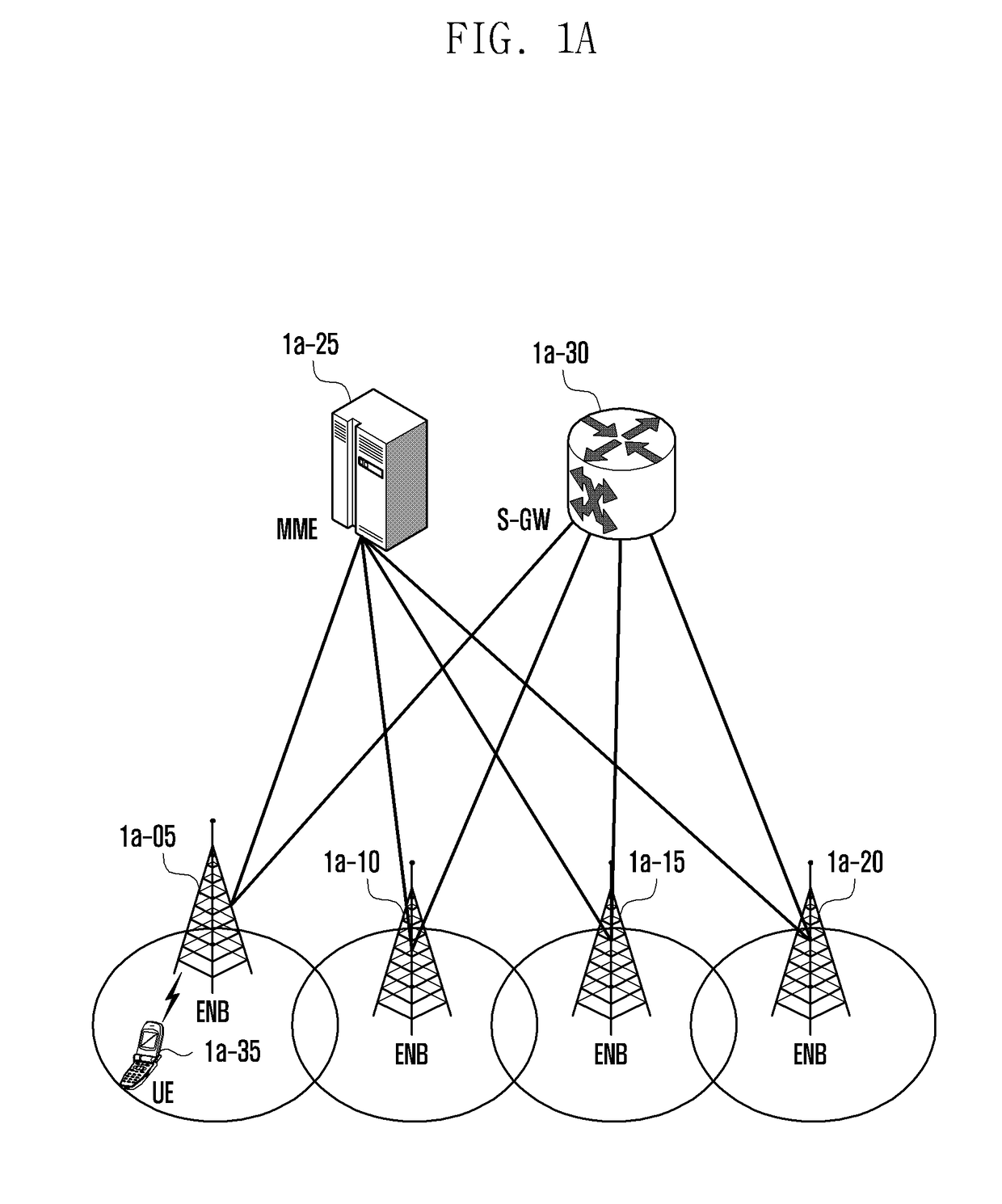
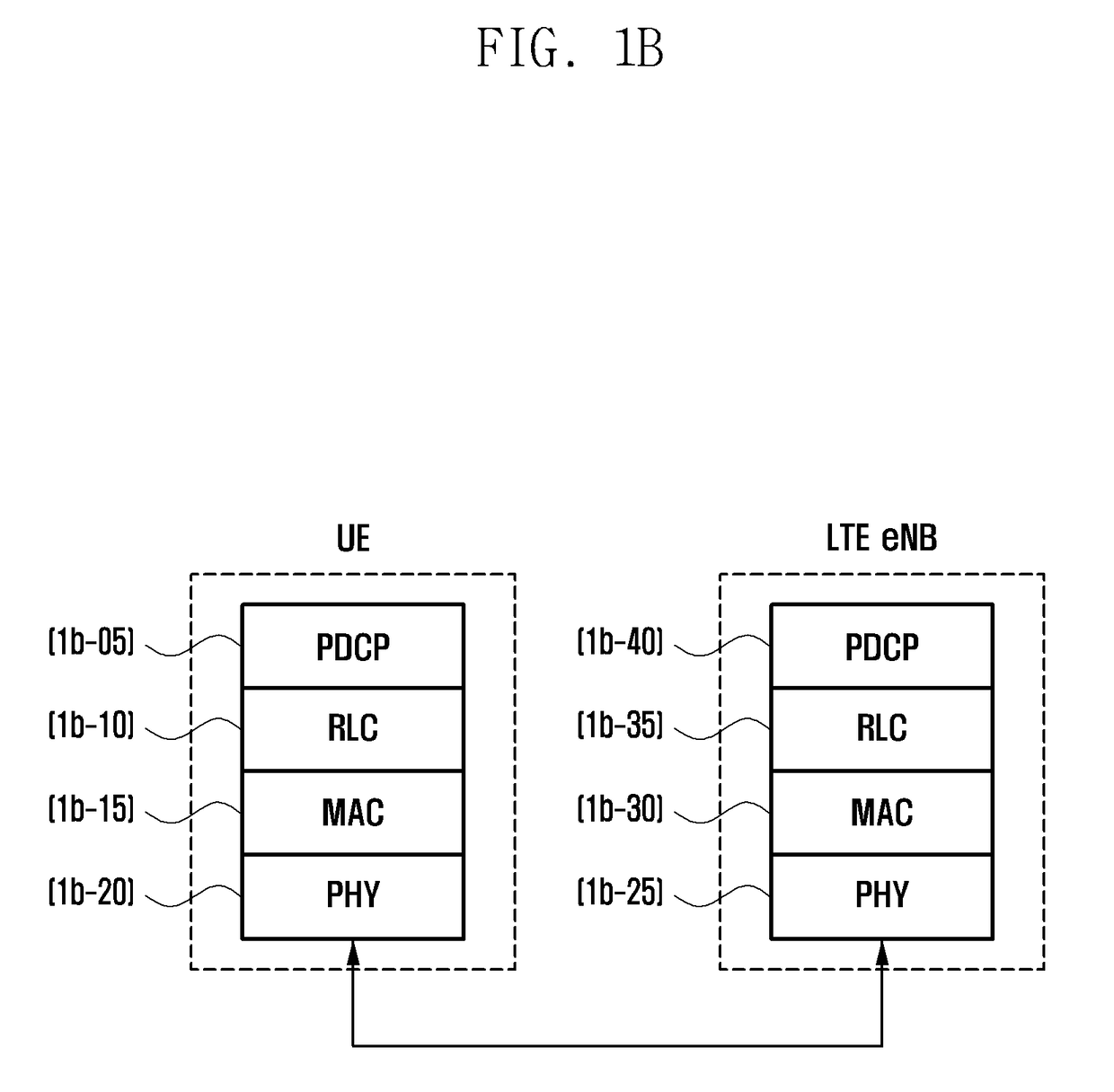
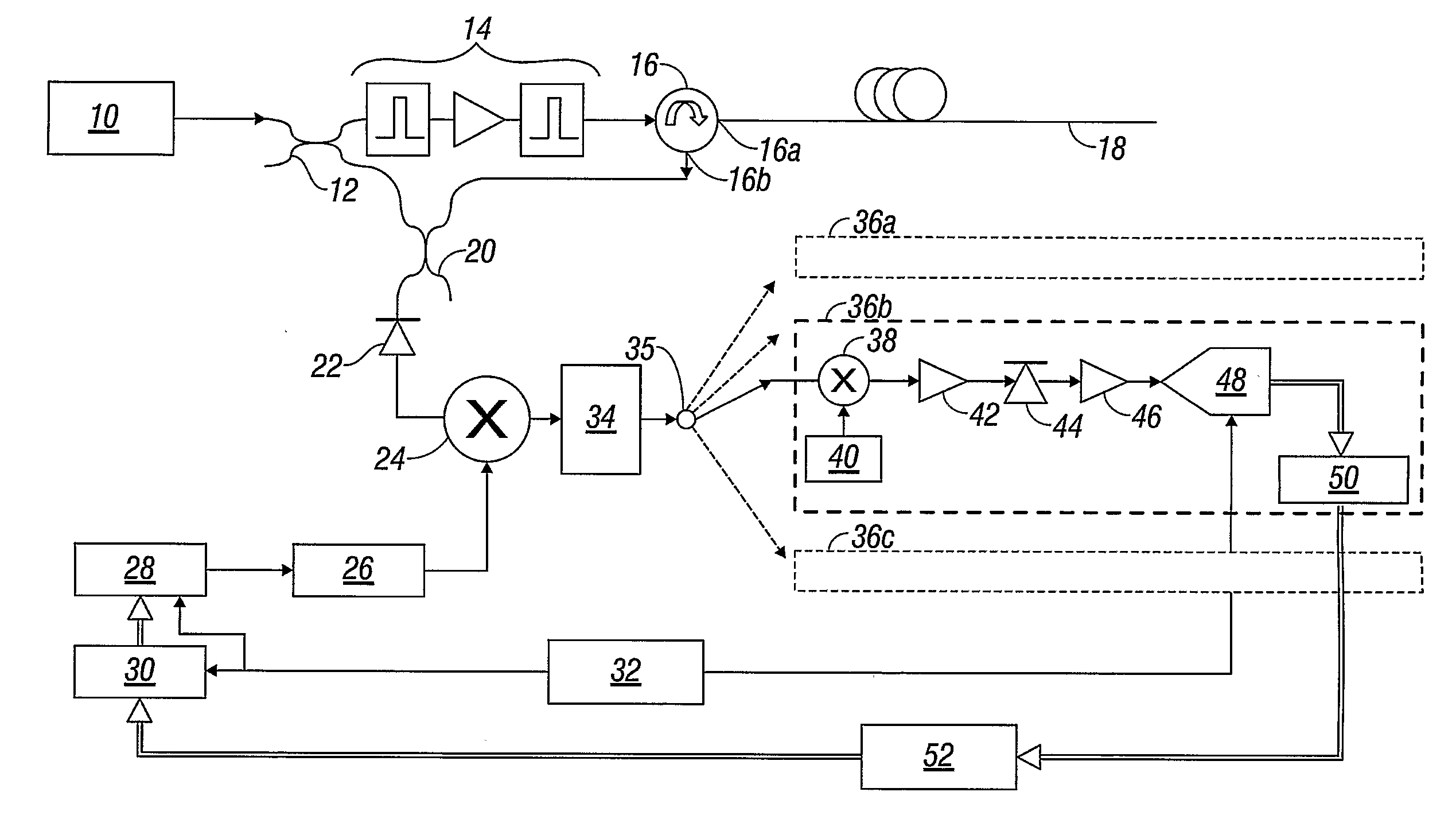
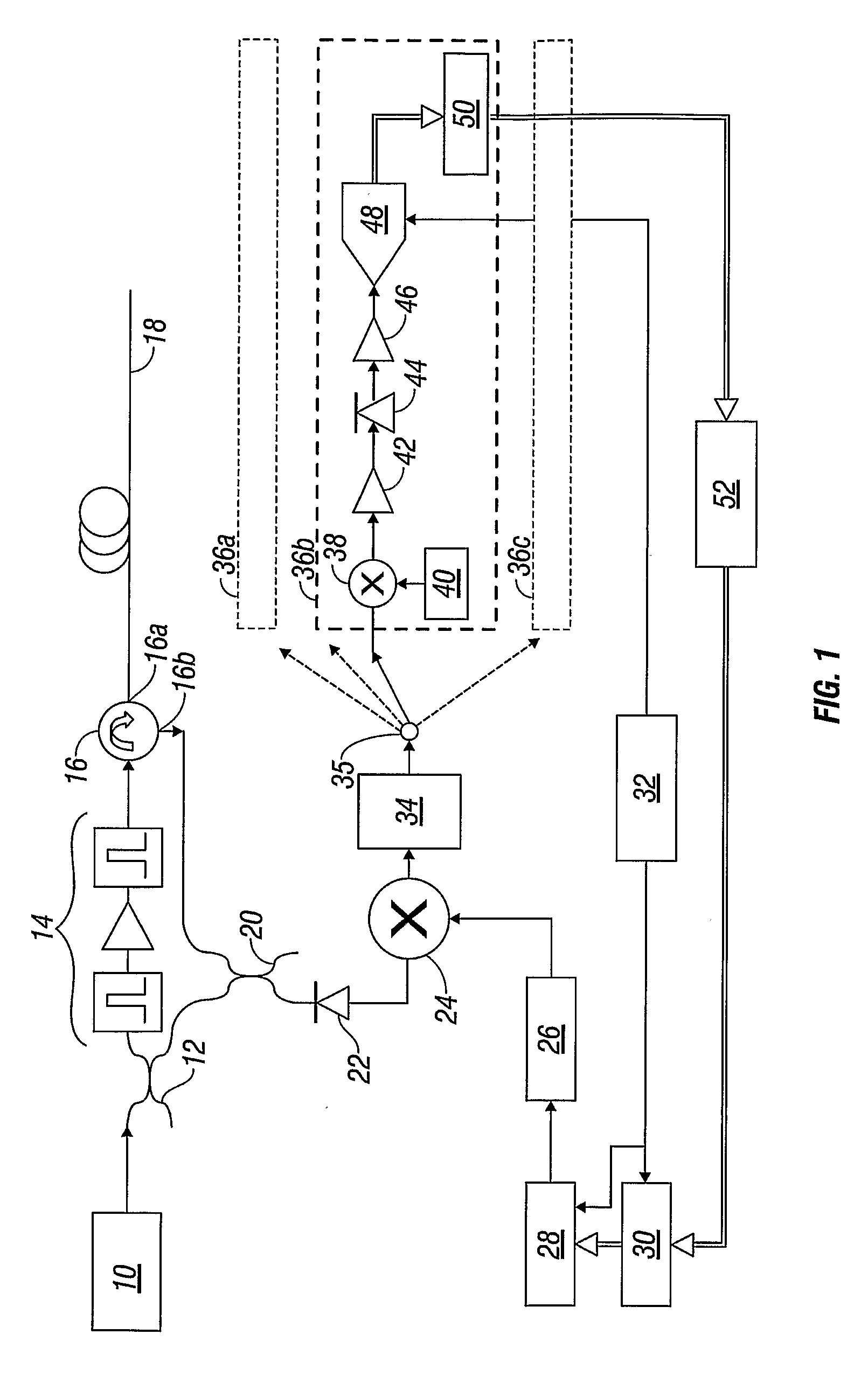
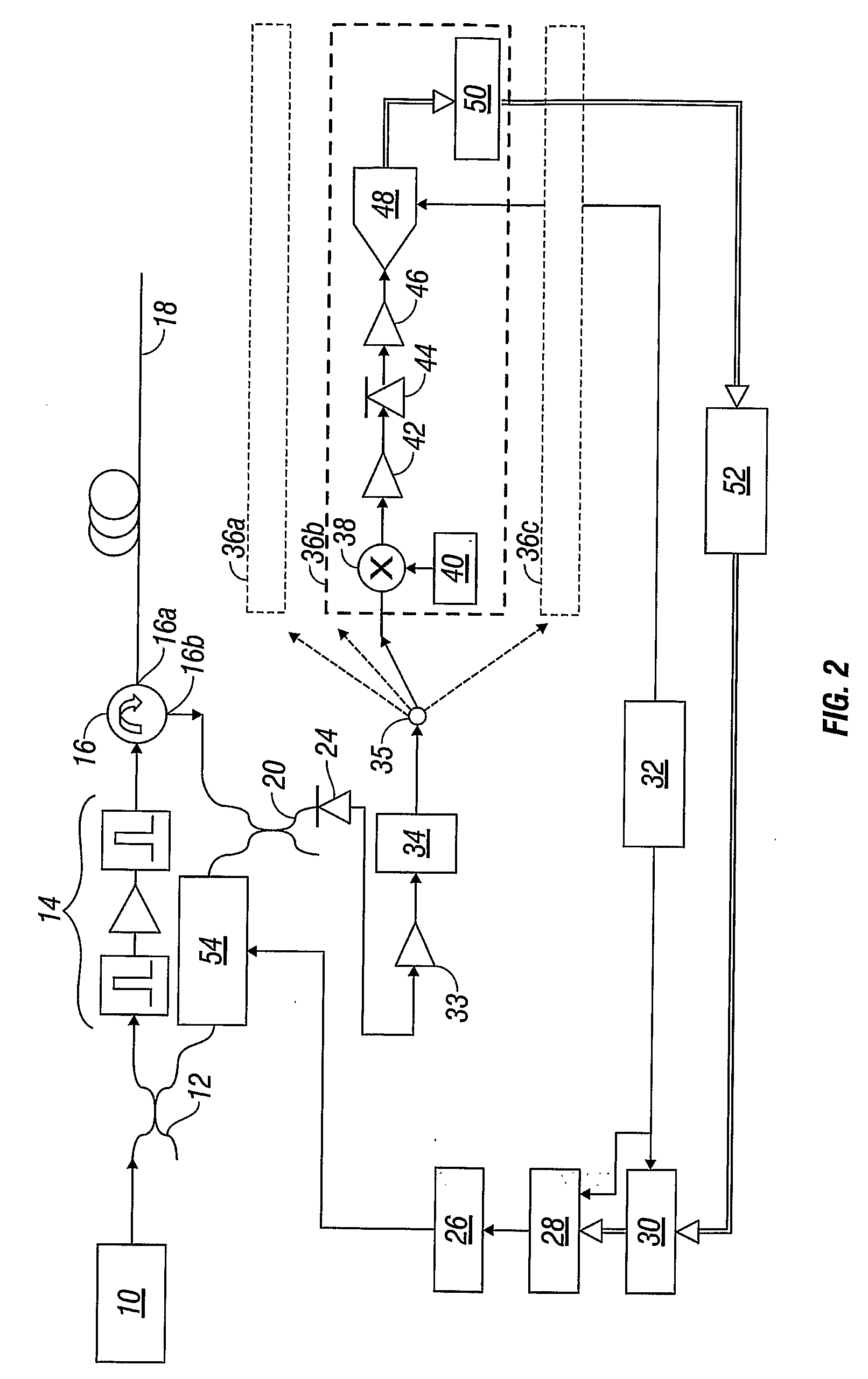
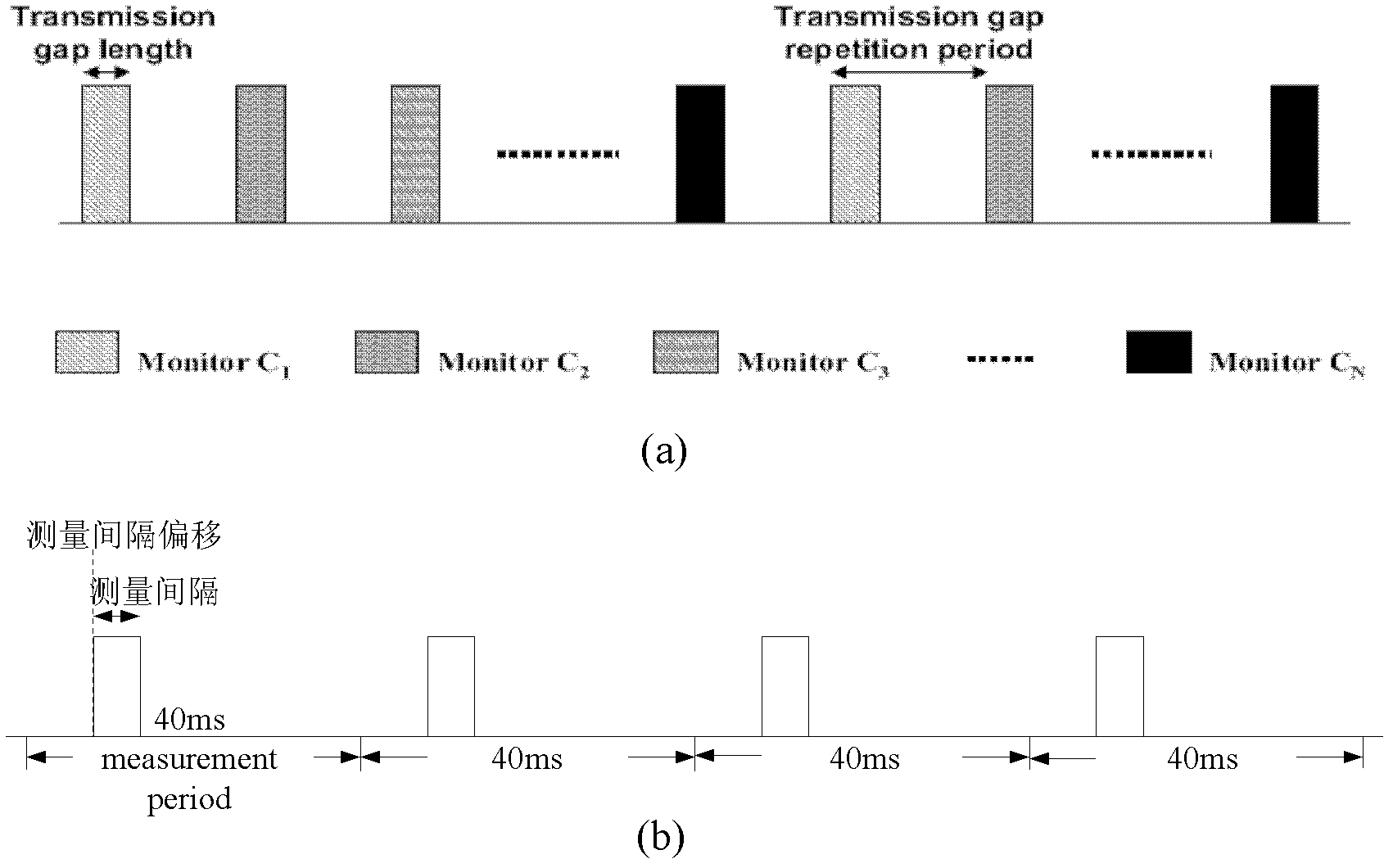
Inter-frequency measurement and handover for wireless communications
InactiveUS6845238B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesHysteresisTelecommunications network
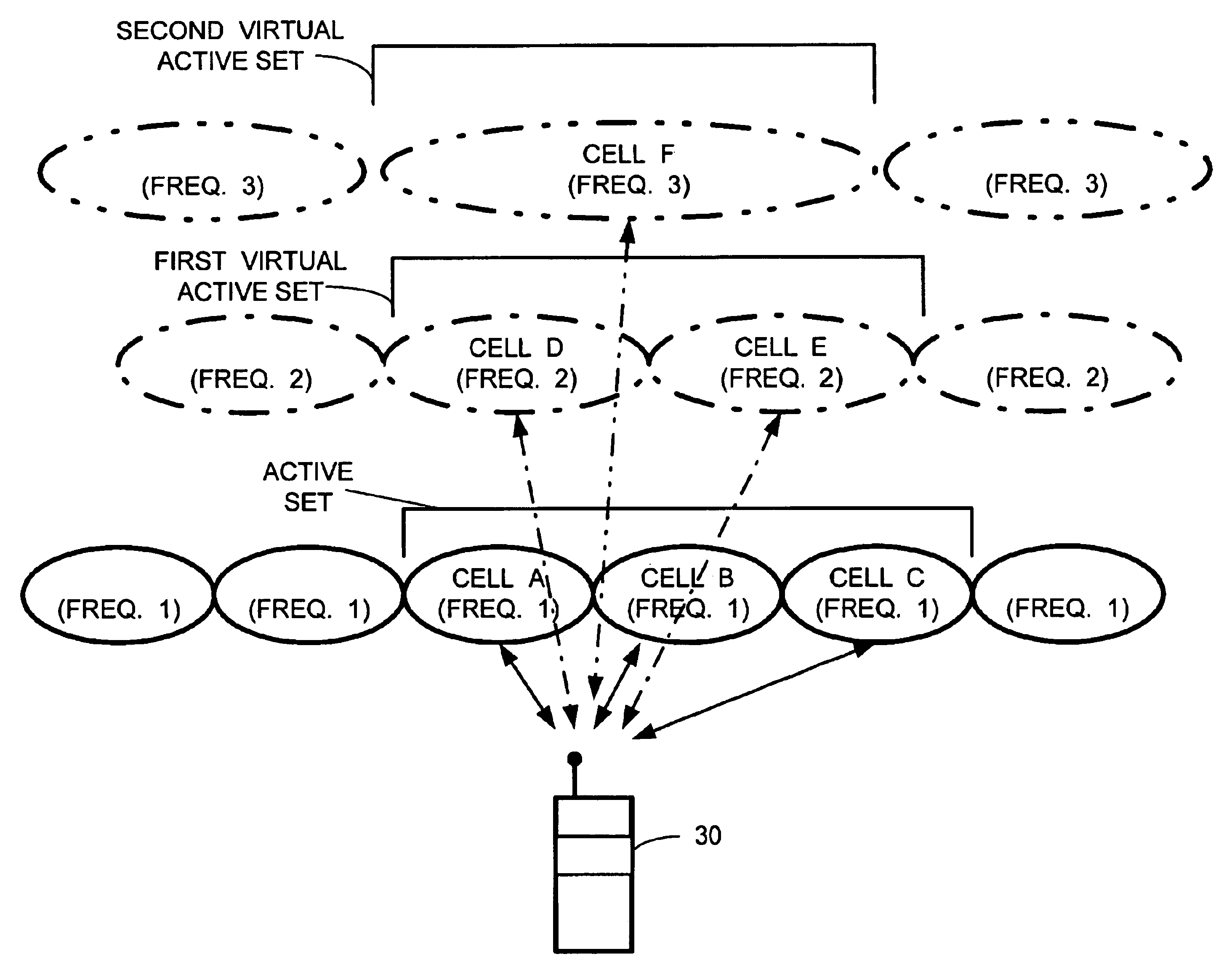
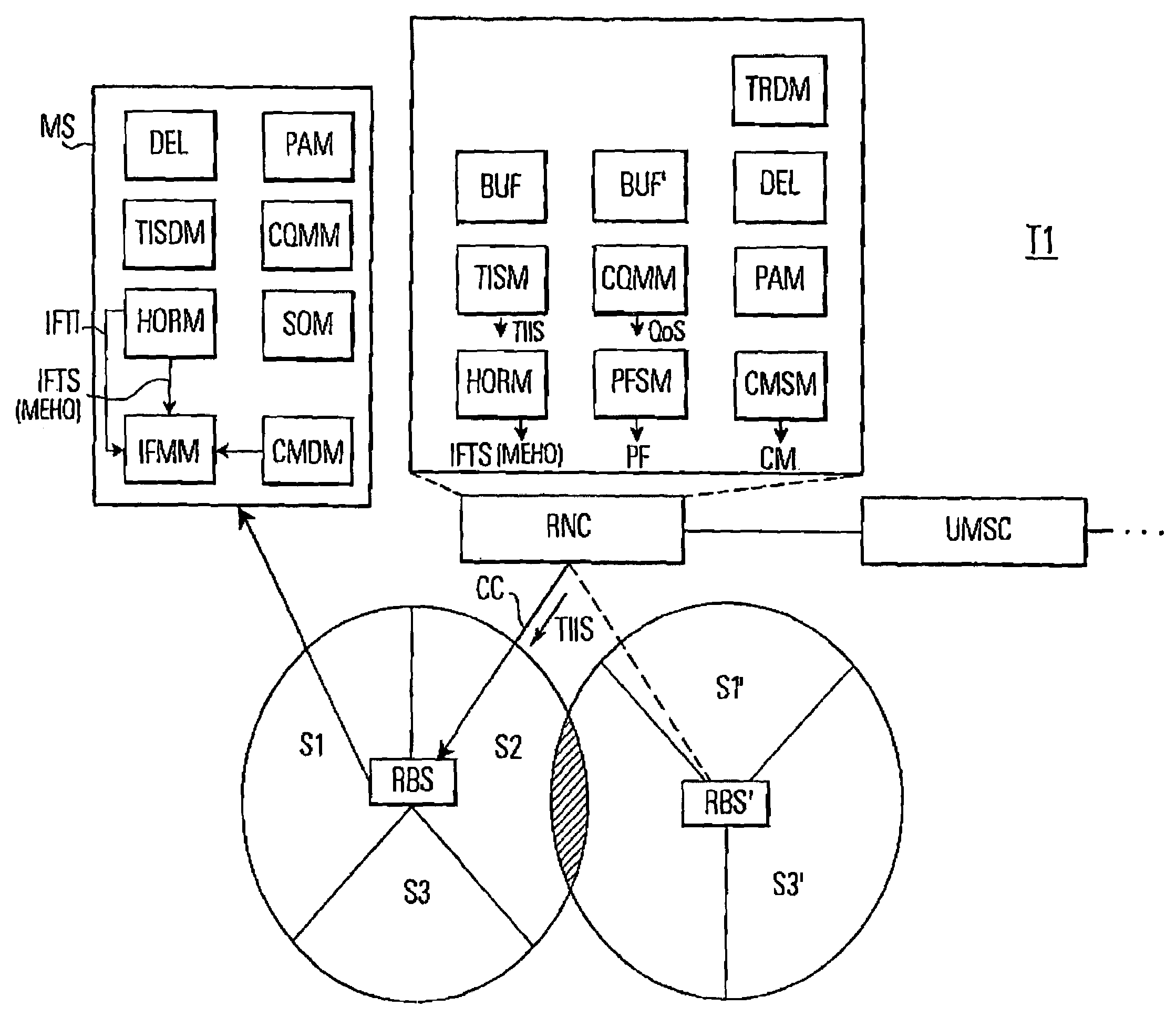
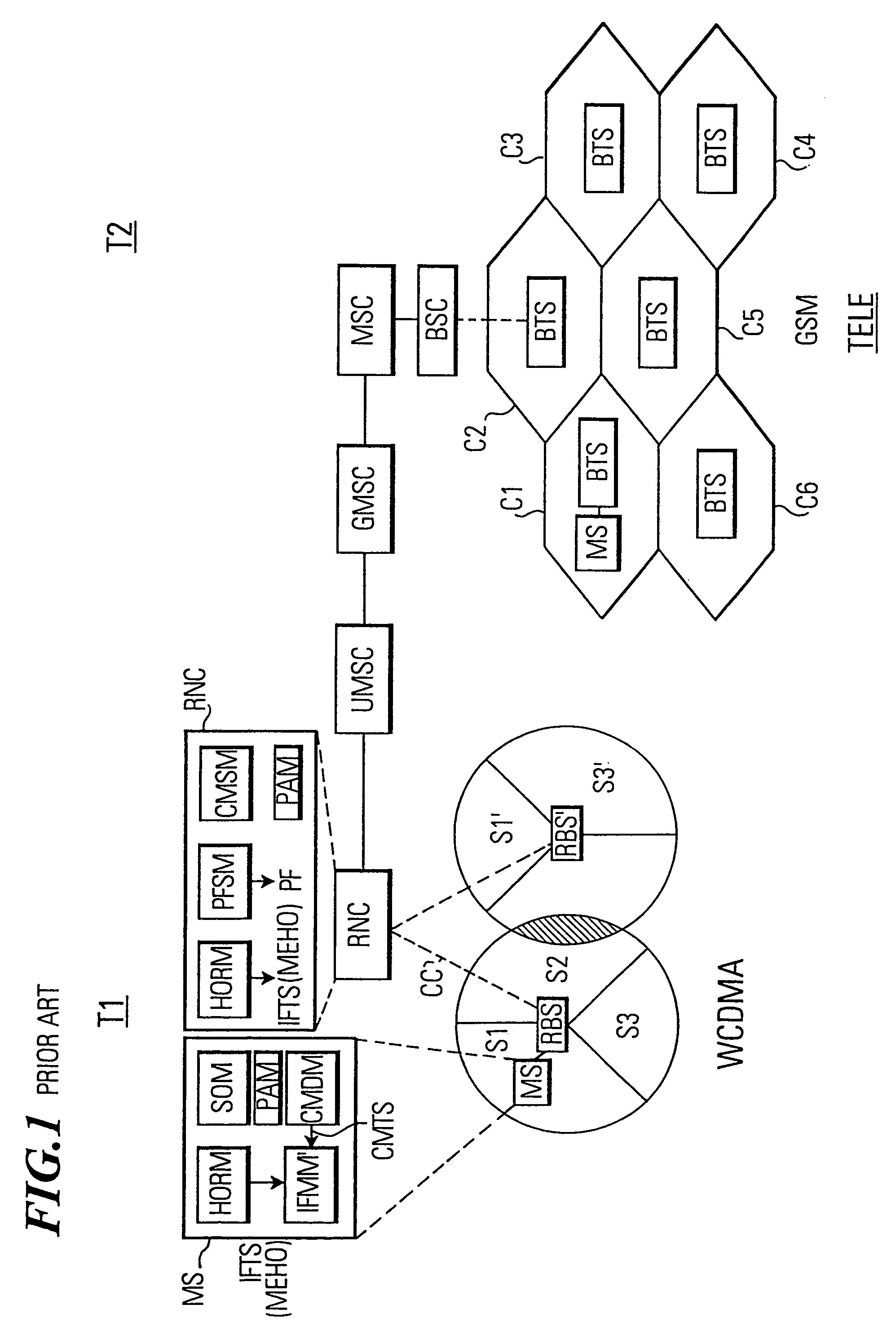
A telecommunications network performs an inter-frequency hard handover for a connection with a user equipment unit (UE) by switching either from a cell or a current active set of base stations on a first frequency to a virtual active set of base stations on another (new) frequency. The inter-frequency hard handover can be an inter-frequency handover within a same system, or an inter-system handover. The virtual active set of base stations is maintained at the user equipment unit (UE), and is updated in accordance with one of several updating implementations of the invention. In a first mode of the invention for implementing virtual active set updates, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to report to the network the occurrence of certain network-specified events which are acted upon by the network for communicating virtual active set update information to the user equipment unit (UE). In a second mode of the invention, the network authorizes the user equipment unit (UE) to perform an autonomous virtual active set update upon occurrence of certain network-specified events, with inter-frequency events being reported from the equipment unit (UE) to the network and the network issuing an inter-frequency handover command. Advantageously, events which trigger intra-frequency measurements can be reused for reporting inter-frequency measurements. In another of its aspects, the present invention provides the network with a quality estimate for a current active set as well as a quality estimate for the virtual active set. The quality estimate can be utilized in a context of a handover from one UTRAN frequency to another UTRAN frequency, or even in the context of an inter-system handover (e.g., a handover between a UTRAN system and a GSM system, for example). The quality estimate can be utilized to trigger a change or switch of frequencies / systems. Certain thresholds employed in the quality estimate-utilizing handovers provide hysteresis protection.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
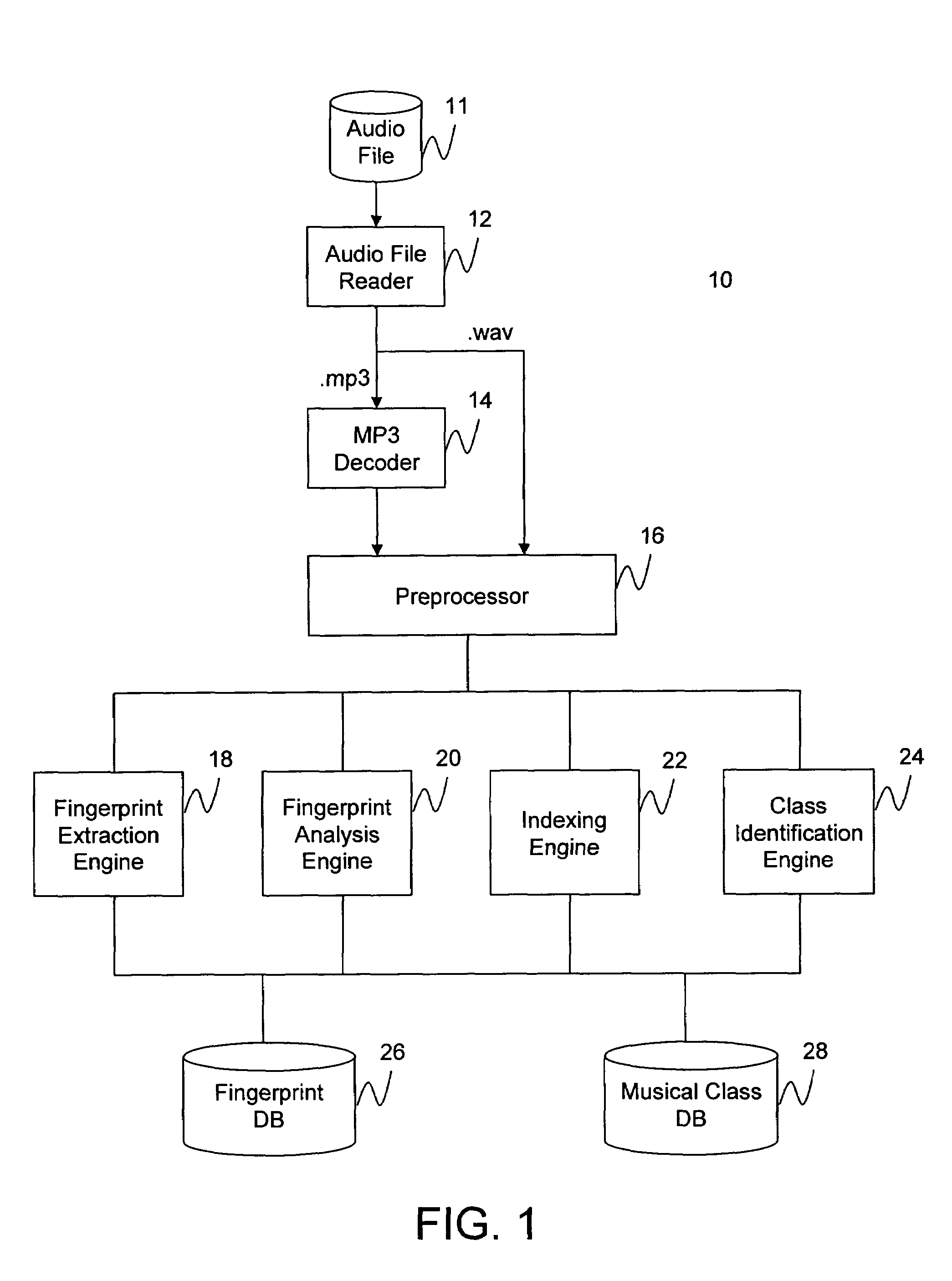
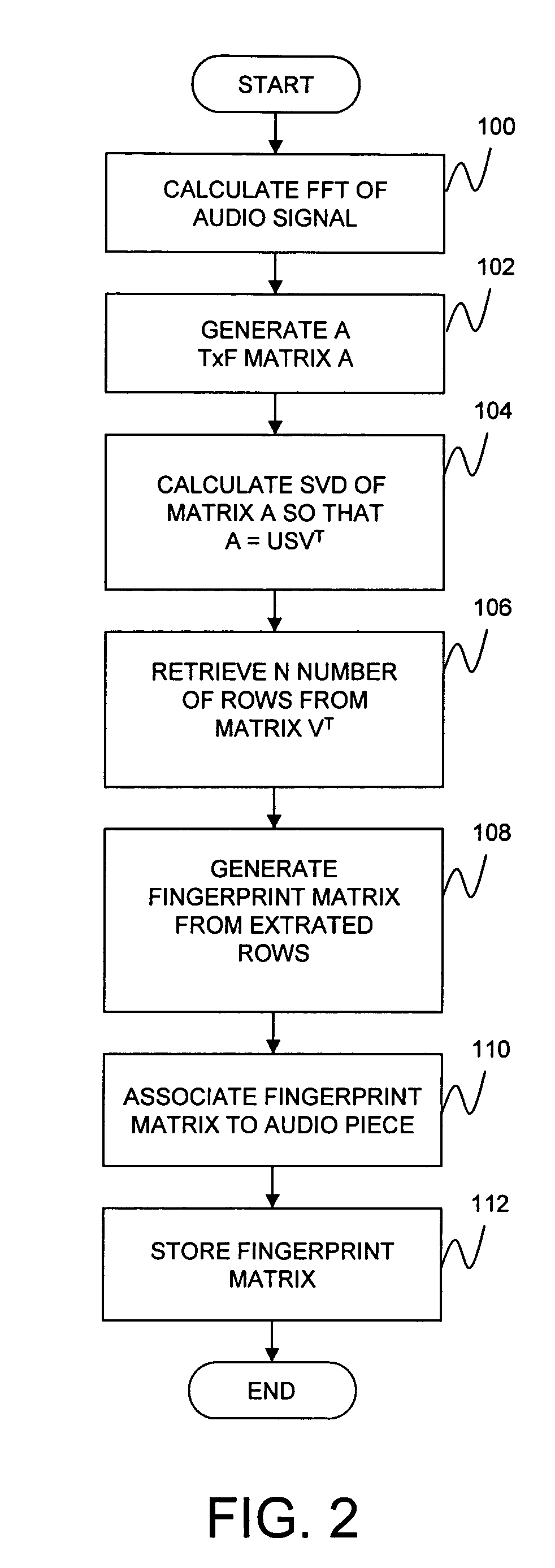
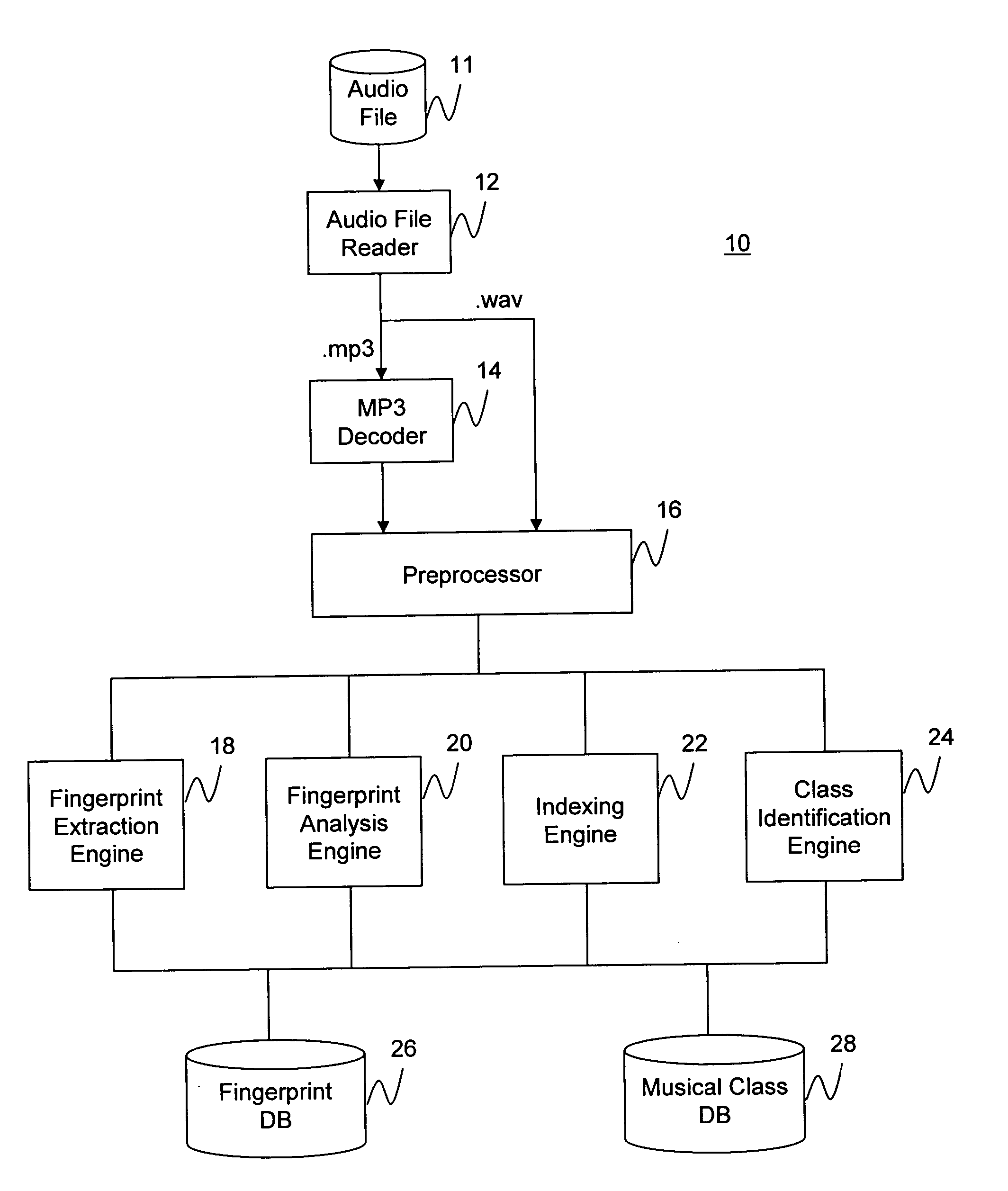
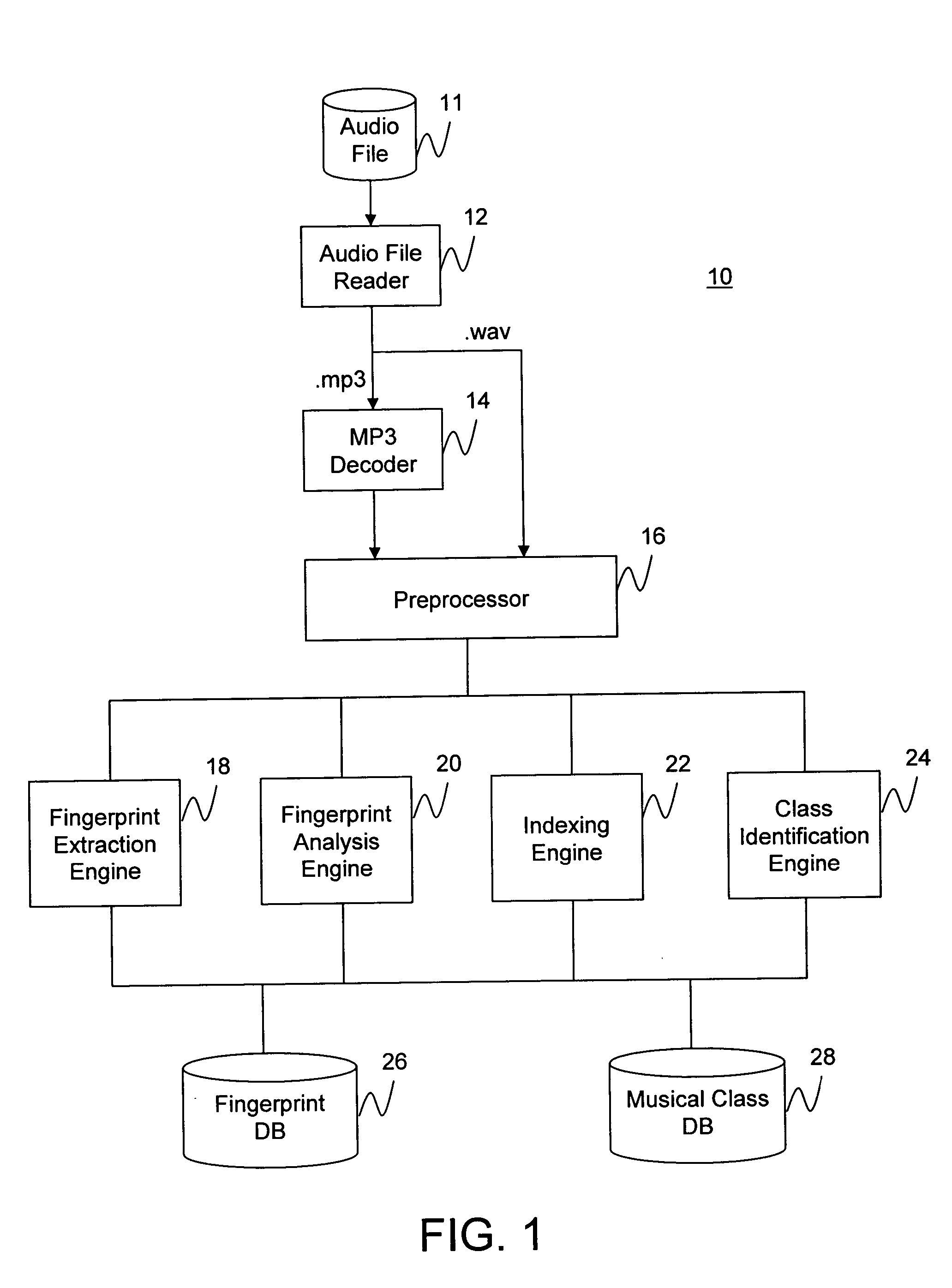
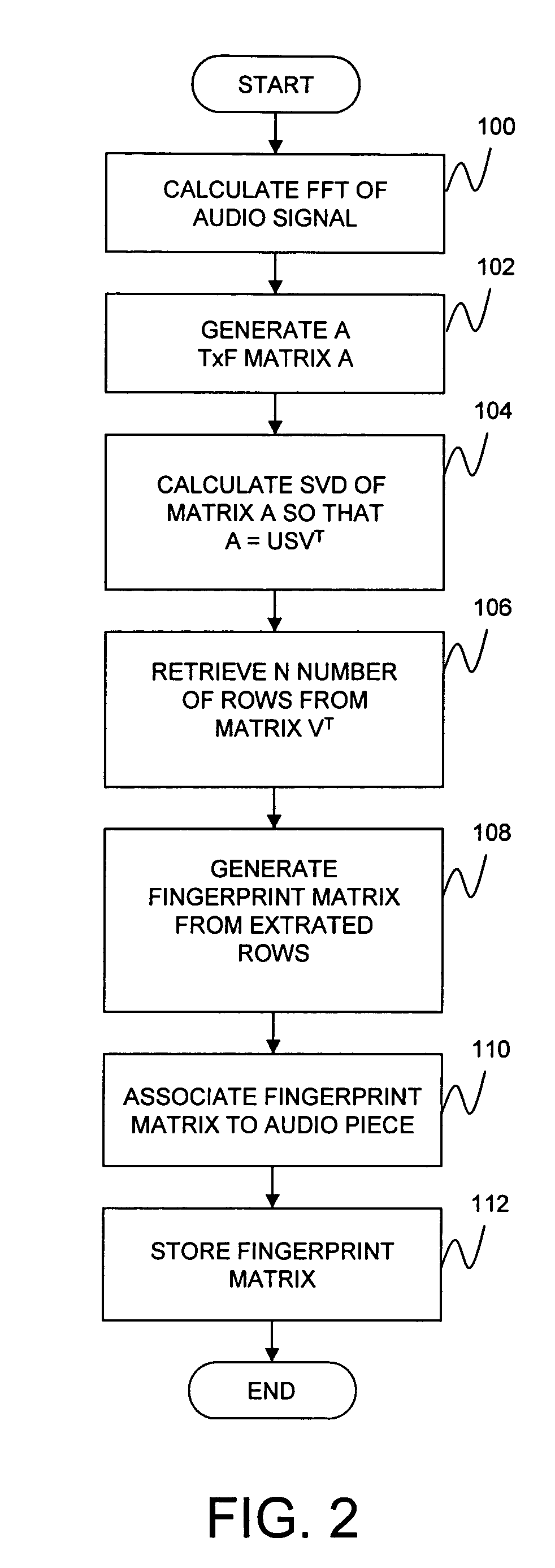
Audio fingerprinting system and method
ActiveUS7013301B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSingular value decompositionFrequency measurements
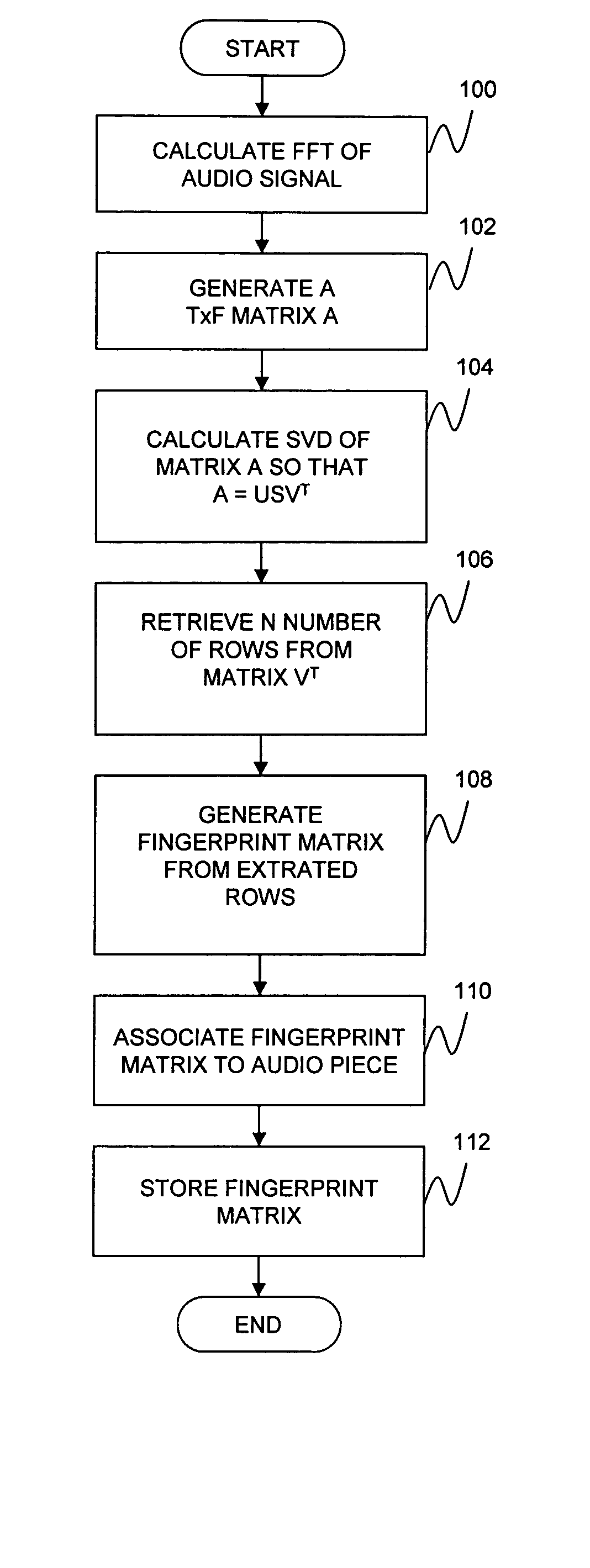
An audio fingerprinting system and method. A server receives an audio fingerprint of a first audio piece, searches a database for the audio fingerprint, retrieves an audio profile vector associated with the audio fingerprint, updates user preference information based on the audio profile vector, and selects a second audio piece based on the user preference information. The audio fingerprint is generated by creating a matrix based on the frequency measurements of the audio piece, and performing a singular value decomposition of the matrix. To expedite the search of the database and to increase matching accuracy, a subset of candidates in the database is identified based on the most prominent musical notes of the audio piece, and the search is limited to the identified subset. One of the attributes of the audio profile vector is a particular audio class. An identifier for the audio class is generated based on an average of audio fingerprints of the audio pieces belonging to the audio class.
Owner:GRACENOTE
Audio fingerprinting system and method
ActiveUS20050065976A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalSingular value decompositionFrequency measurements
An audio fingerprinting system and method. A server receives an audio fingerprint of a first audio piece, searches a database for the audio fingerprint, retrieves an audio profile vector associated with the audio fingerprint, updates user preference information based on the audio profile vector, and selects a second audio piece based on the user preference information. The audio fingerprint is generated by creating a matrix based on the frequency measurements of the audio piece, and performing a singular value decomposition of the matrix. To expedite the search of the database and to increase matching accuracy, a subset of candidates in the database is identified based on the most prominent musical notes of the audio piece, and the search is limited to the identified subset. One of the attributes of the audio profile vector is a particular audio class. An identifier for the audio class is generated based on an average of audio fingerprints of the audio pieces belonging to the audio class.
Owner:GRACENOTE
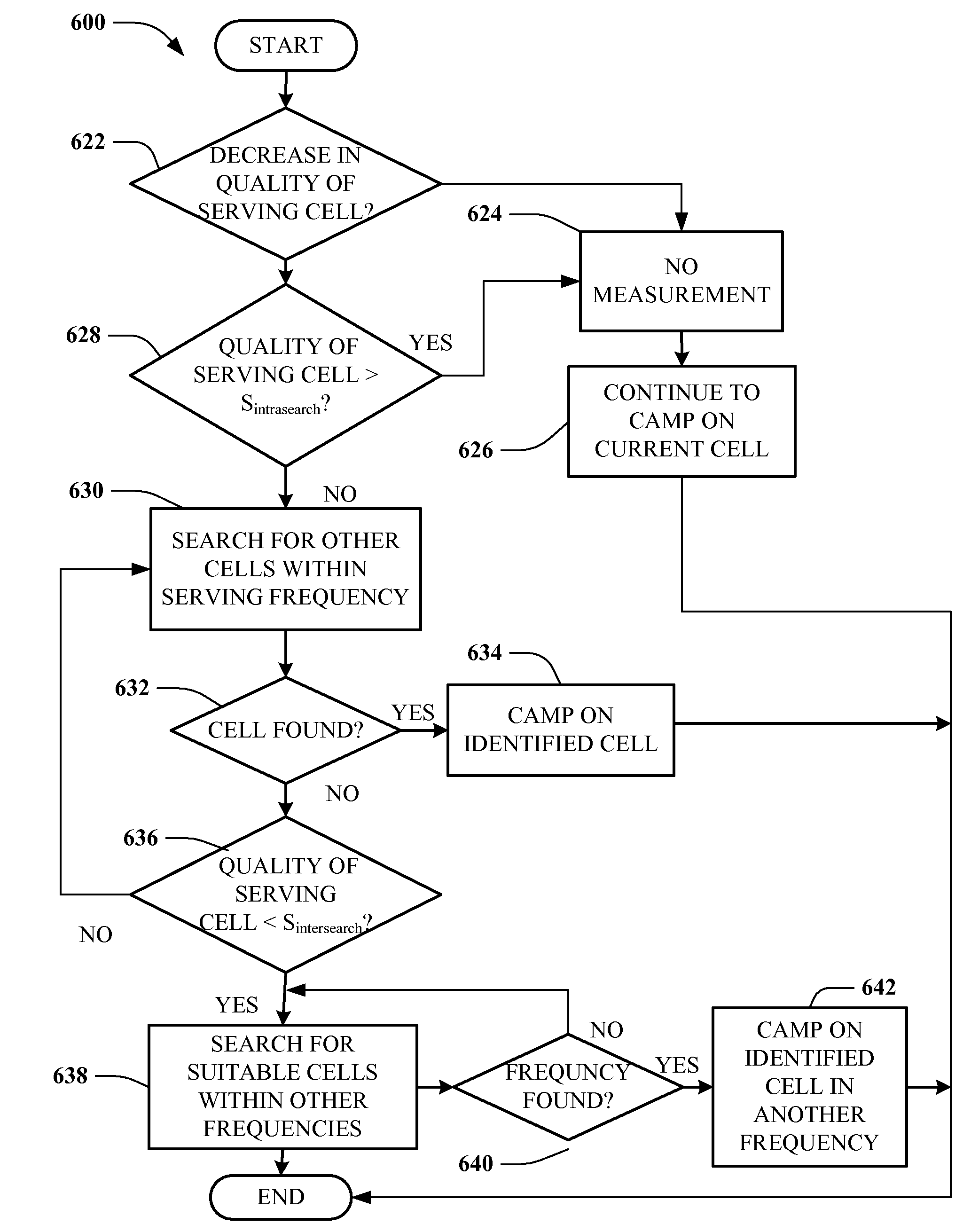
Method of performing cell reselection procedure in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100222055A1Reduce power consumptionReduce system loadConnection managementOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemFrequency measurements
A method of performing a cell reselection procedure in a wireless communication system includes evaluating priorities of a serving cell and neighbor cells, each of which use different frequency bands, performing inter-frequency measurement on a neighbor cell which has a higher priority than the serving cell, performing the inter-frequency measurement on a neighbor cell which has an equal or lower priority than the serving cell, when a signal characteristic of the serving cell is less than a threshold, and performing cell reselection according to the priorities.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method and apparatus for cell reselection enhancement for e-utran
InactiveUS20090067386A1Easy to determineFacilitate selection of cellAssess restrictionOrthogonal multiplexRelevant informationTelecommunications
A framework for the cell reselection and associated measurement behavior is proposed based on a state in which a UE is camped on the cell. If the UE is ‘camped in any cell state’, inter-frequency and / or inter-RAT measurements are prioritized over intra-frequency measurements. The proposed scheme helps the UE to find a suitable cell while in the camped on any cell state. If the UE subscribes to specific frequencies, separate measurement rules are implemented to aid the UE to find and camp on the preferred frequencies. The proposed scheme also considers access related information in addition to radio quality to help the UE in making cell selections thereby mitigating the UE from camping on restricted cells. Such aspects minimize situations wherein users are limited due to the service provided by an operator.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
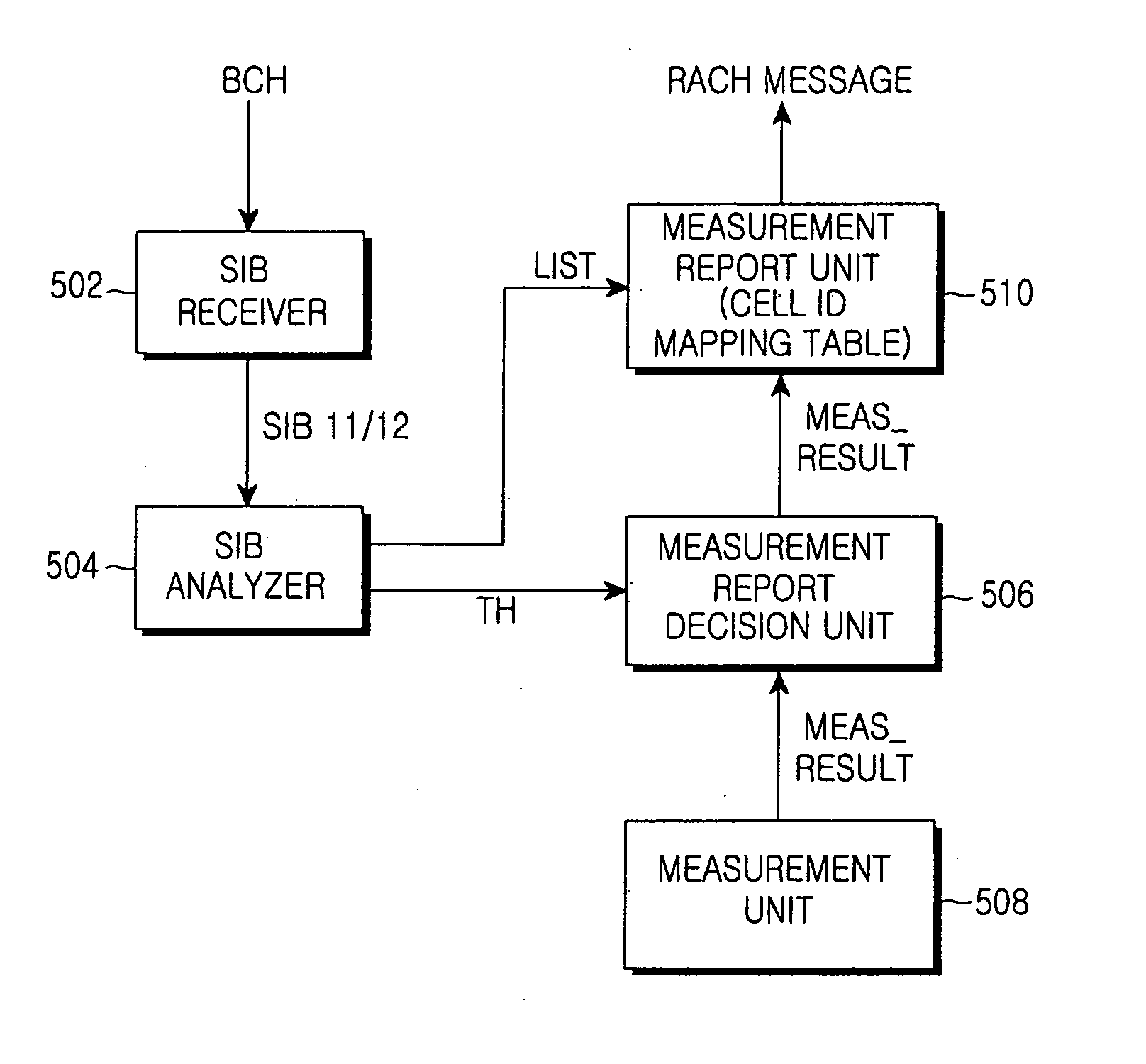
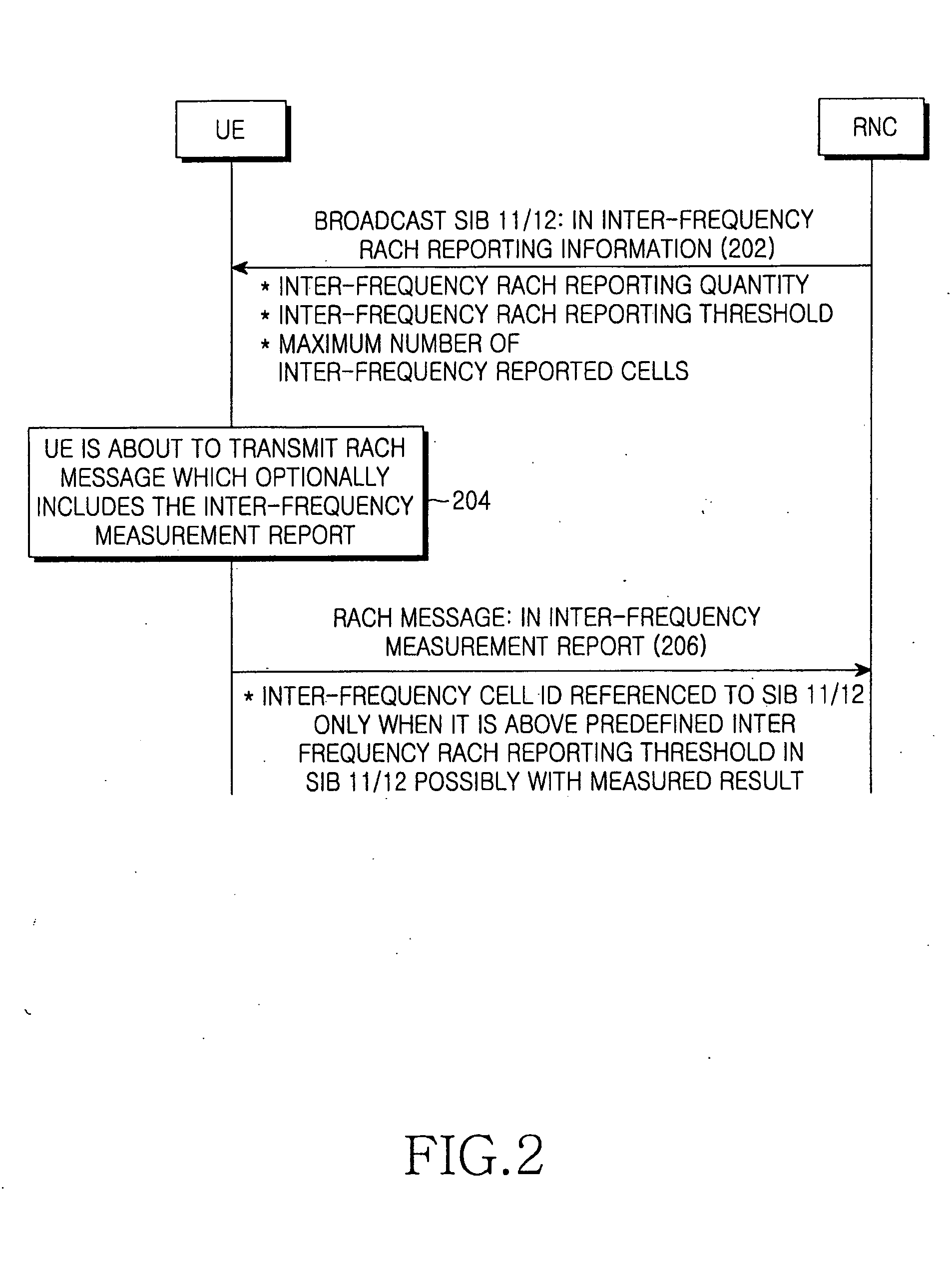
Method and apparatus for reporting inter-frequency measurement using RACH message in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20060252377A1Reduce signaling overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsFrequency measurements
A user equipment (UE) is provide which reduces uplink signaling overhead in the process of reporting inter-frequency measurement results over a RACH. For measurement reporting, the UE receives an SIB including a cell information list for non-used frequency cells and a threshold from an RNC, compares signal strengths of signals received from the non-used frequency cells with the threshold, and acquires at least one inter-frequency cell ID indicating at least one non-used frequency cell having signal strength exceeding the threshold from the cell information list. The at least one inter-frequency cell ID is included in a RACH message as measurement result information for the at least one non-used frequency cell, and transmitted to the RNC. The RNC determines that the cell corresponding to the inter-frequency cell ID has signal strength exceeding the threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
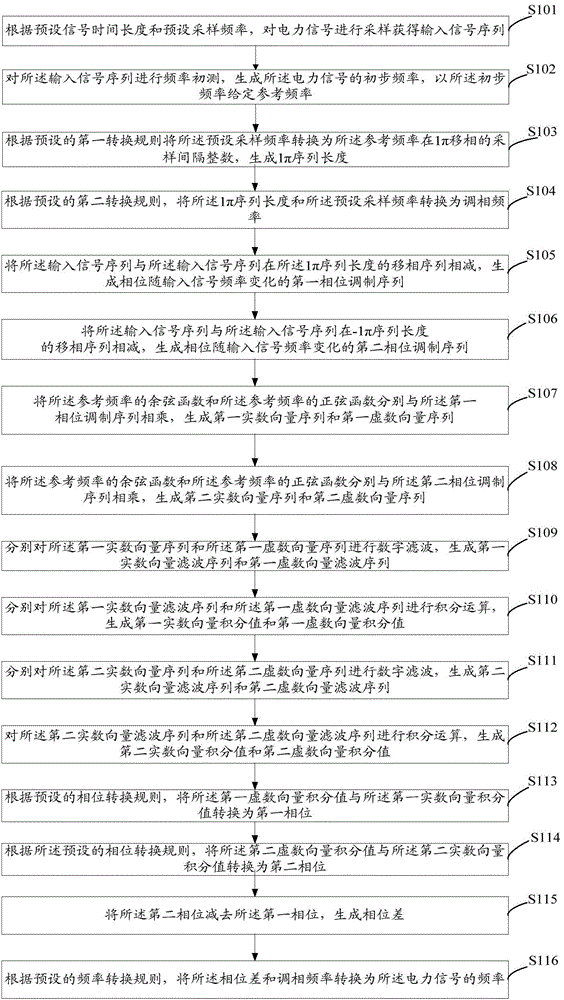
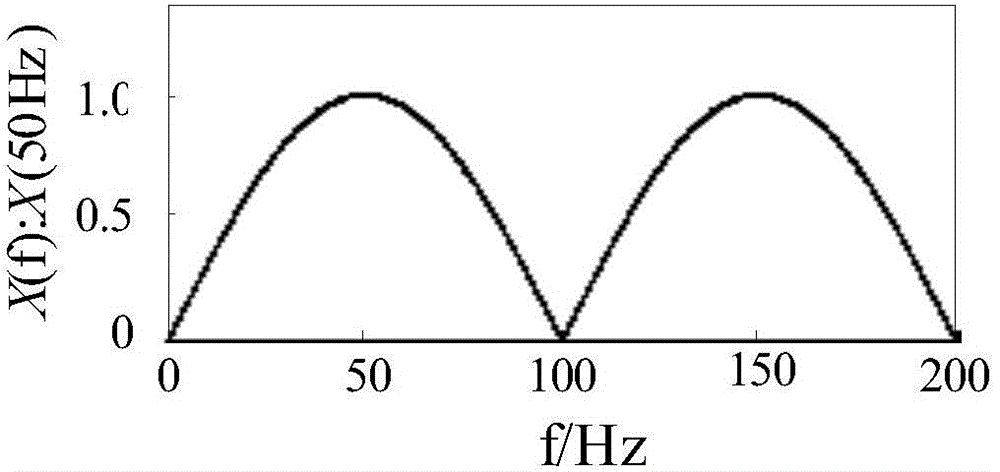
Power signal frequency detection method and system based on phase modulation
ActiveCN104635045AHigh precisionSuppression of aliasing interference componentsFrequency measurement arrangementPhase shiftedFrequency measurements
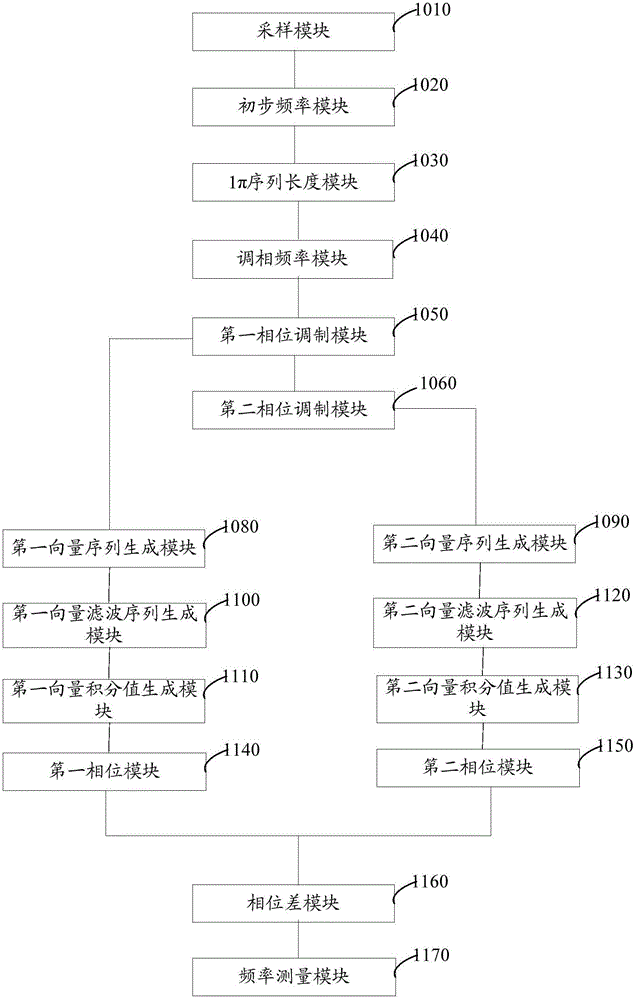
The invention discloses a power signal frequency detection method and a power signal frequency detection system based on phase modulation. The method comprises the steps: sampling a power signal according to preset signal time span and preset sampling frequency, so as to obtain an input signal sequence; measuring the frequency of the input signal sequence, so as to obtain the initial frequency of the power signal, and subtracting the input signal sequence and the plus or minus 1 Pi phase-shift sequence of the input signal sequence by using the initial frequency as reference frequency, so as to obtain two phase modulation sequences of which phases change along with the input signal frequency; respectively mixing, filtering and integrating the two phase modulation sequences, so as to obtain the phases of the two phase modulation phases for frequency measurement. By implementing the power signal frequency detection method and the power signal frequency detection system, frequency measurement results with higher accuracy can be obtained.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Subscriber station, network control means and method for carrying out inter-frequency measurements in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7016320B1Maintain qualityEasy to measurePower managementTransmission control/equalisingIdle timeFrequency measurements
In a mobile communication system (T1) a time interval selection means (TISM) in a network control means (RNC) determines a time interval and sends an indication about this time interval to a subscriber station (MS) in a time interval indication signal. A time interval signal determining means (TISDM) in the subscriber station (MS) detects the time interval and an IF measurement means (IFMM) carries out inter-frequency / inter-system measurements in the detected time interval specified by the network control means (RNC). In this time interval the temporary reduction of the quality of service QoS on the communication connection (CC) is planed by the network control means (RNC). However, independent as to whether a delay-sensitive or loss-sensitive data transmission is carried out, the network control means (RNC) can make provisions in order to compensate the temporary reduction of the quality of service. Such procedure is superior to performing IF measurements in an idle time interval of a compressed time slot in which a temporary degradation of the quality of service must always be accepted due to a compressed mode of operation.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Sampling packets for network monitoring
InactiveUS6920112B1Small amount of calculationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork packet
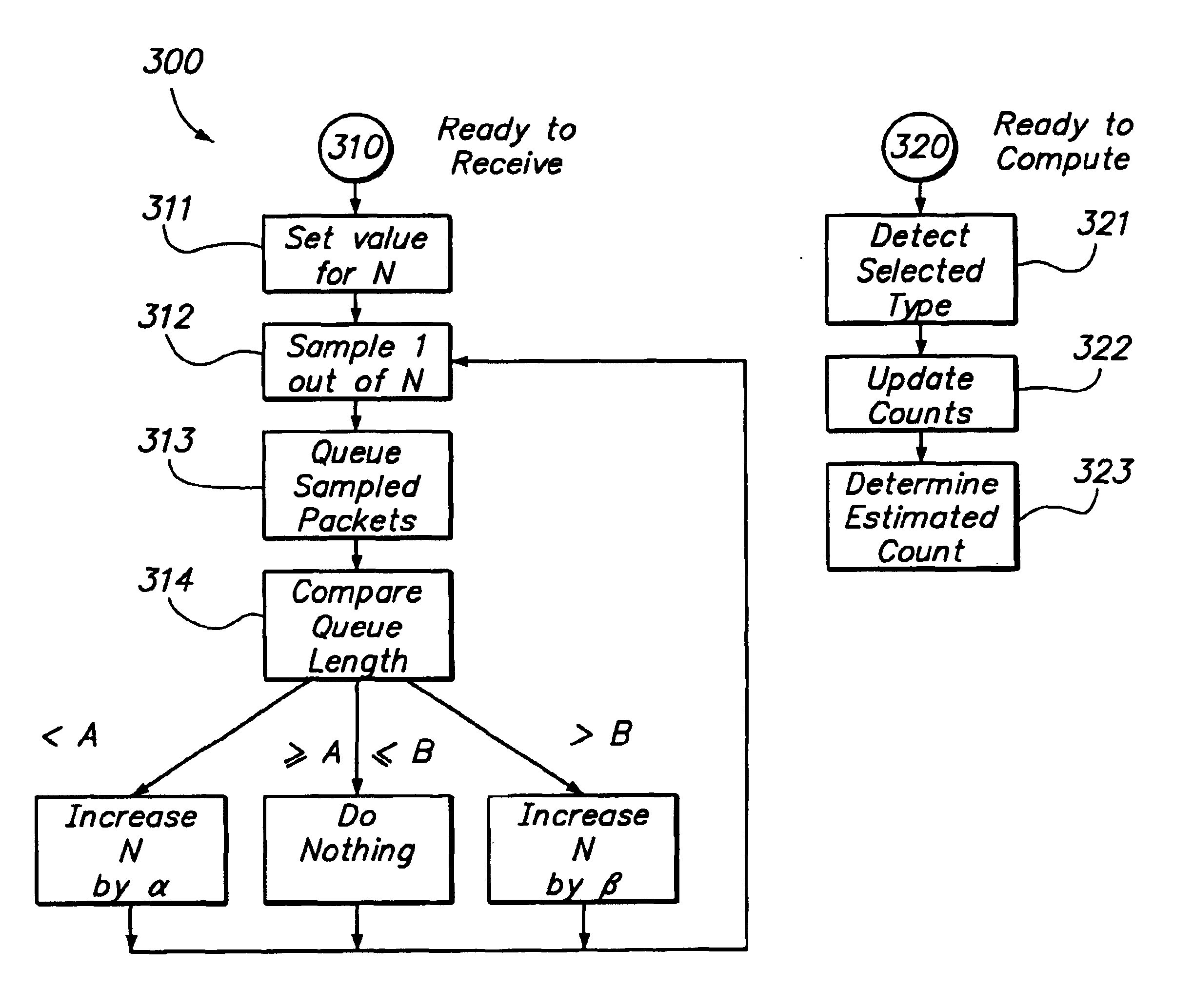
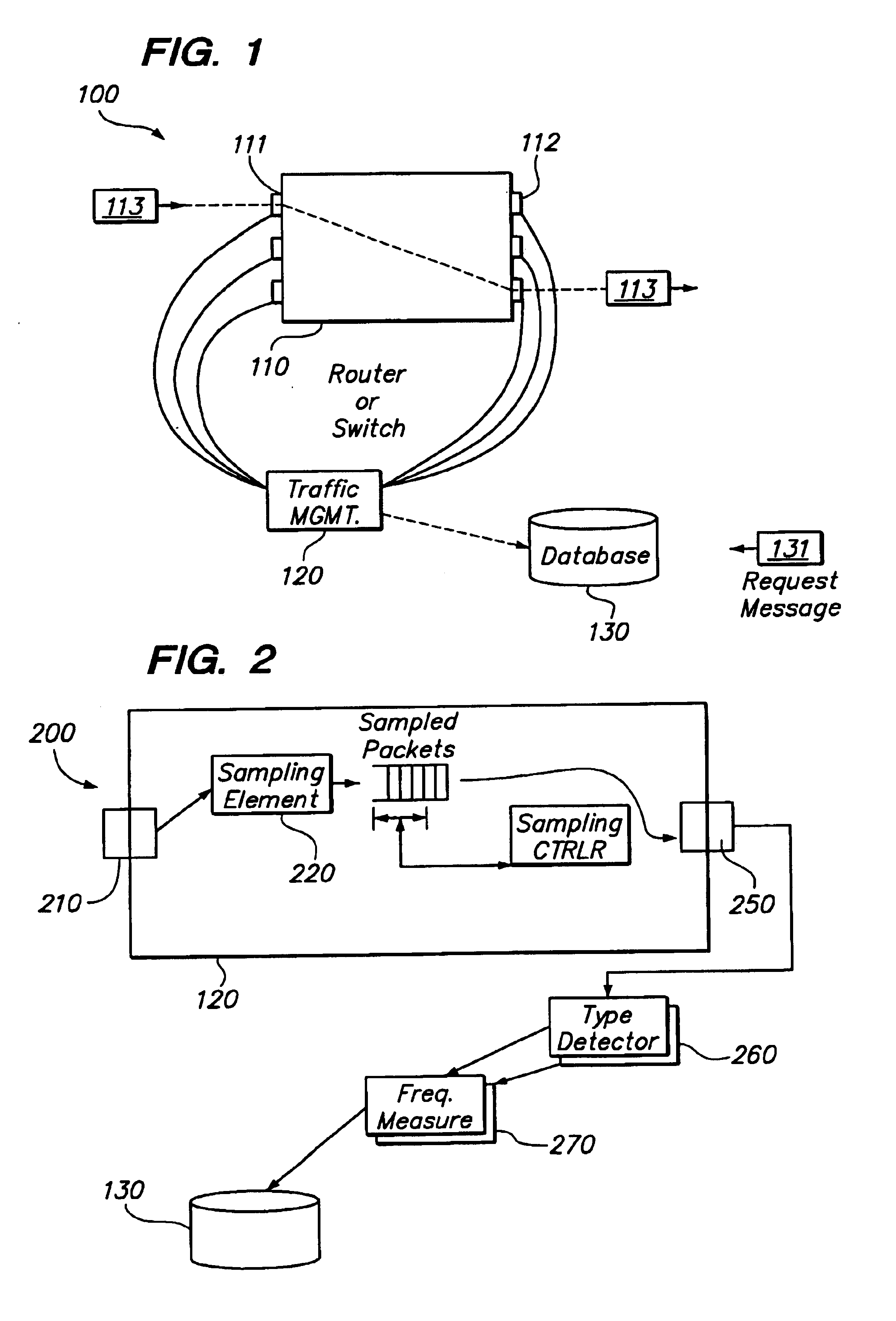
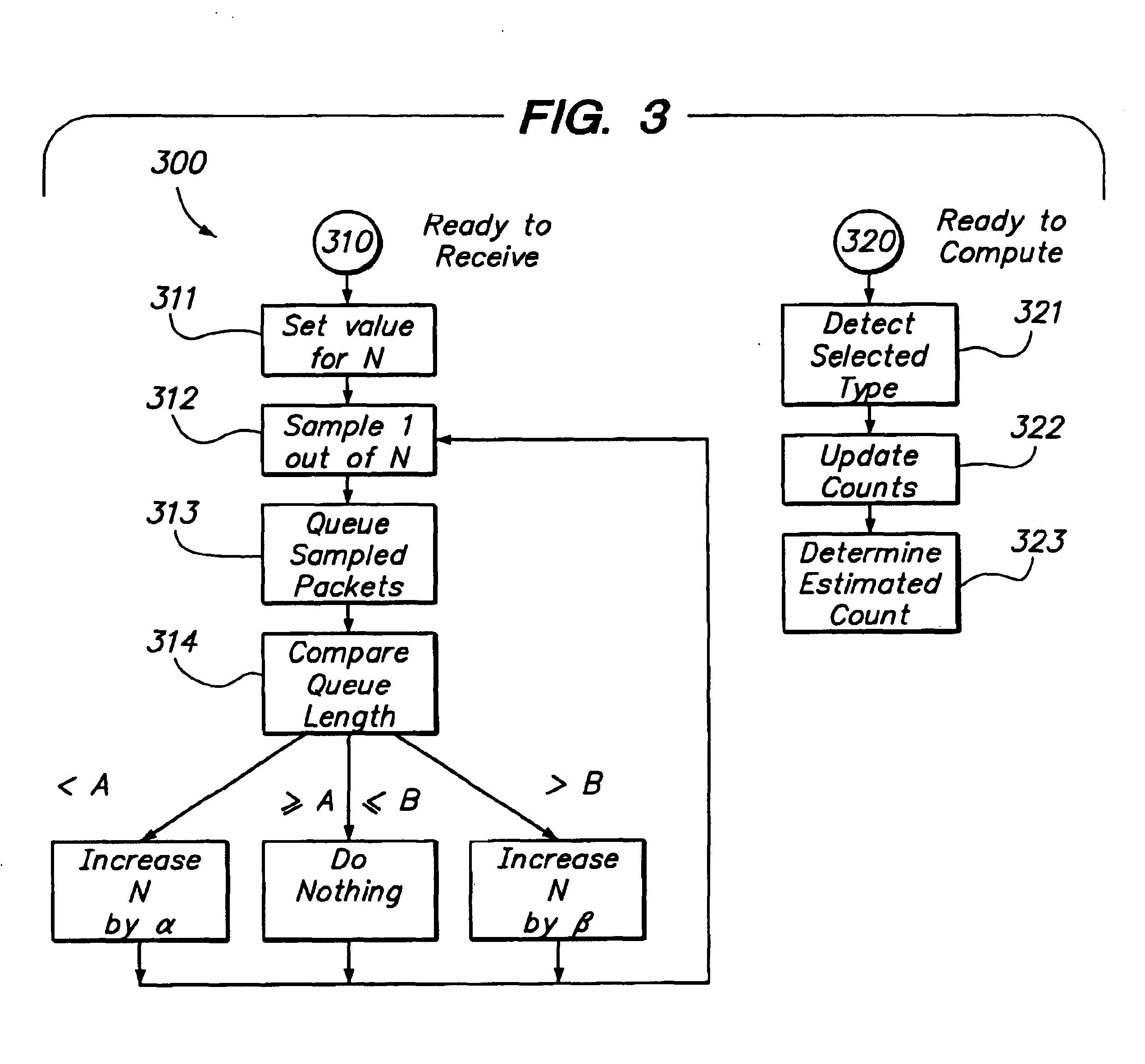
The invention provides a method and system for collecting aggregate information about network traffic, while maintaining processor load relatively constant despite substantial variation in network traffic, and capable of substantially accurate frequency measurement even for relatively infrequent events. A packet monitoring system includes an input port for receiving network packets, a sampling element for selecting a fraction of those packets for review, and a queue of selected packets. The packets in the queue are coupled to a packet-type detector for detecting packets of a selected type; the system applies a measurement technique for determining a frequency measure for those detected packets. The system includes a feedback technique for adaptively altering the sampling rate fraction, responsive to the queue length and possibly other factors, such as processor load or the detected frequency measure. The measurement technique also determines an error range and a measure of confidence that the actual frequency is within the error range of the measured frequency. The system can detect packets of multiple selected types essentially simultaneously, and provide measured frequencies and error ranges for all of the multiple selected types at once. Also, the measurement technique is selected so as to impose relatively light processor load per packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
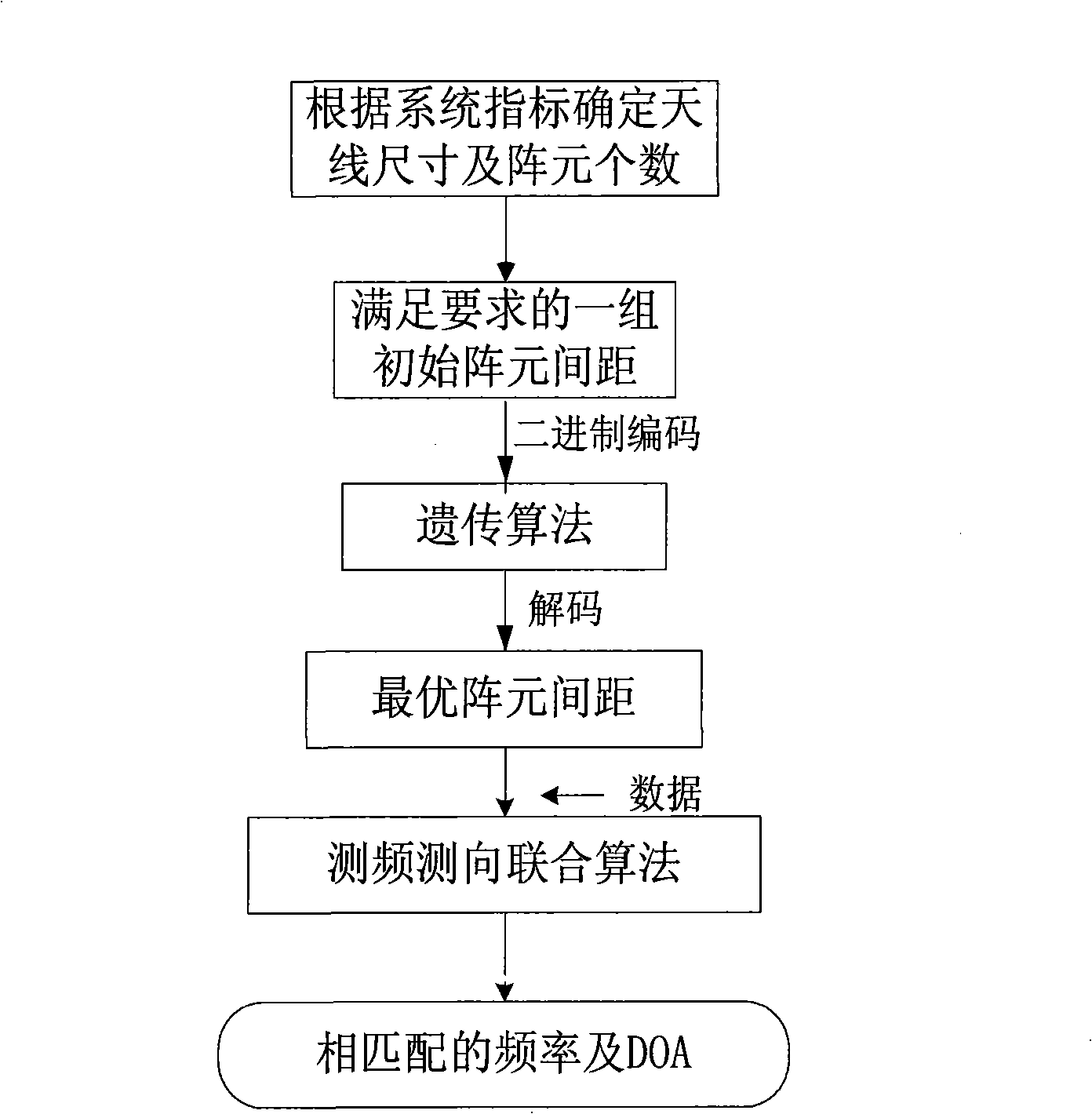
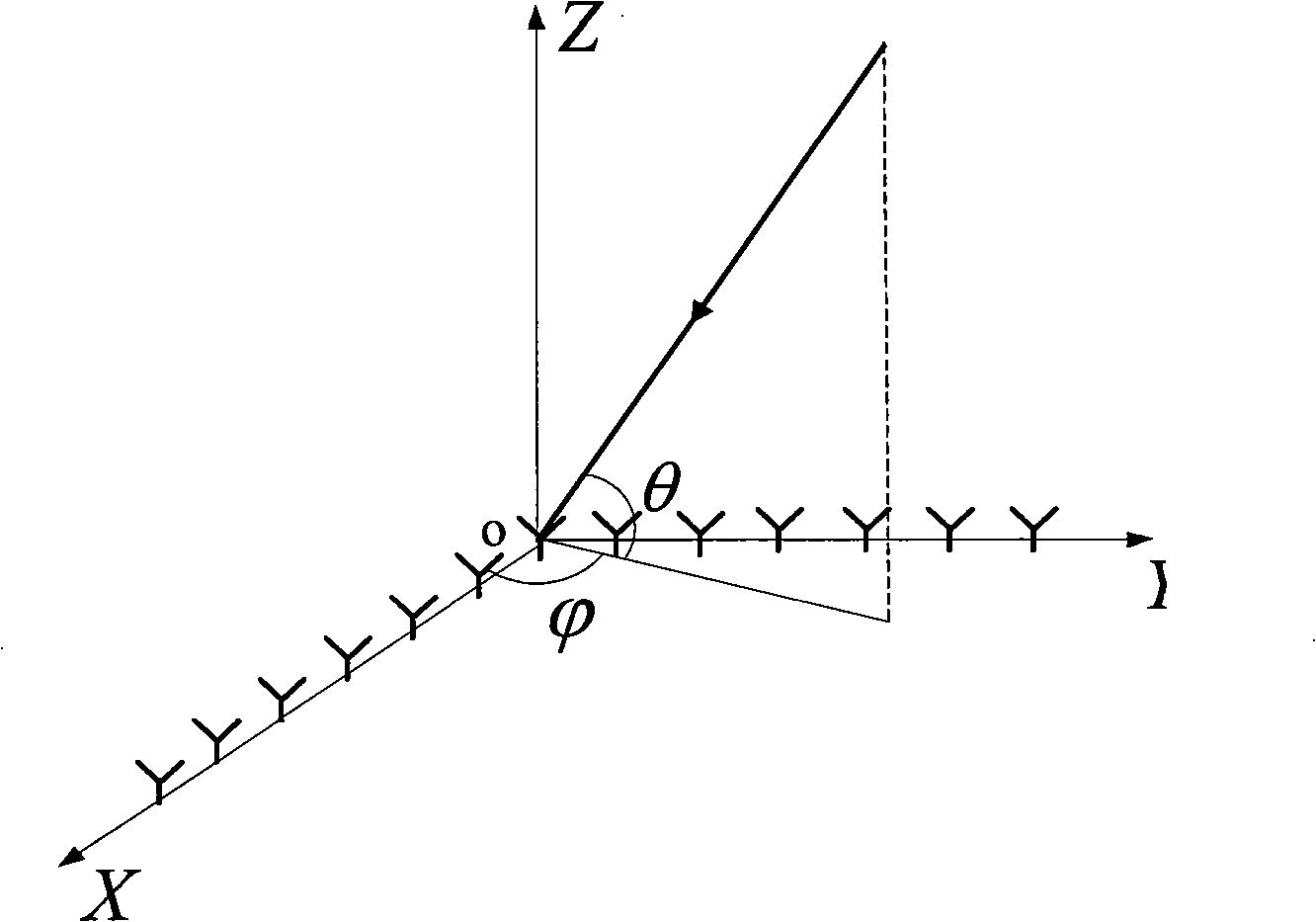
Method for optimizing space between broad band phased array elements and measuring frequency and direction of frequency domain multiple targets
InactiveCN101349742AImproved DF resolutionSolve the direction finding ambiguity problemRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency measurementsArray element
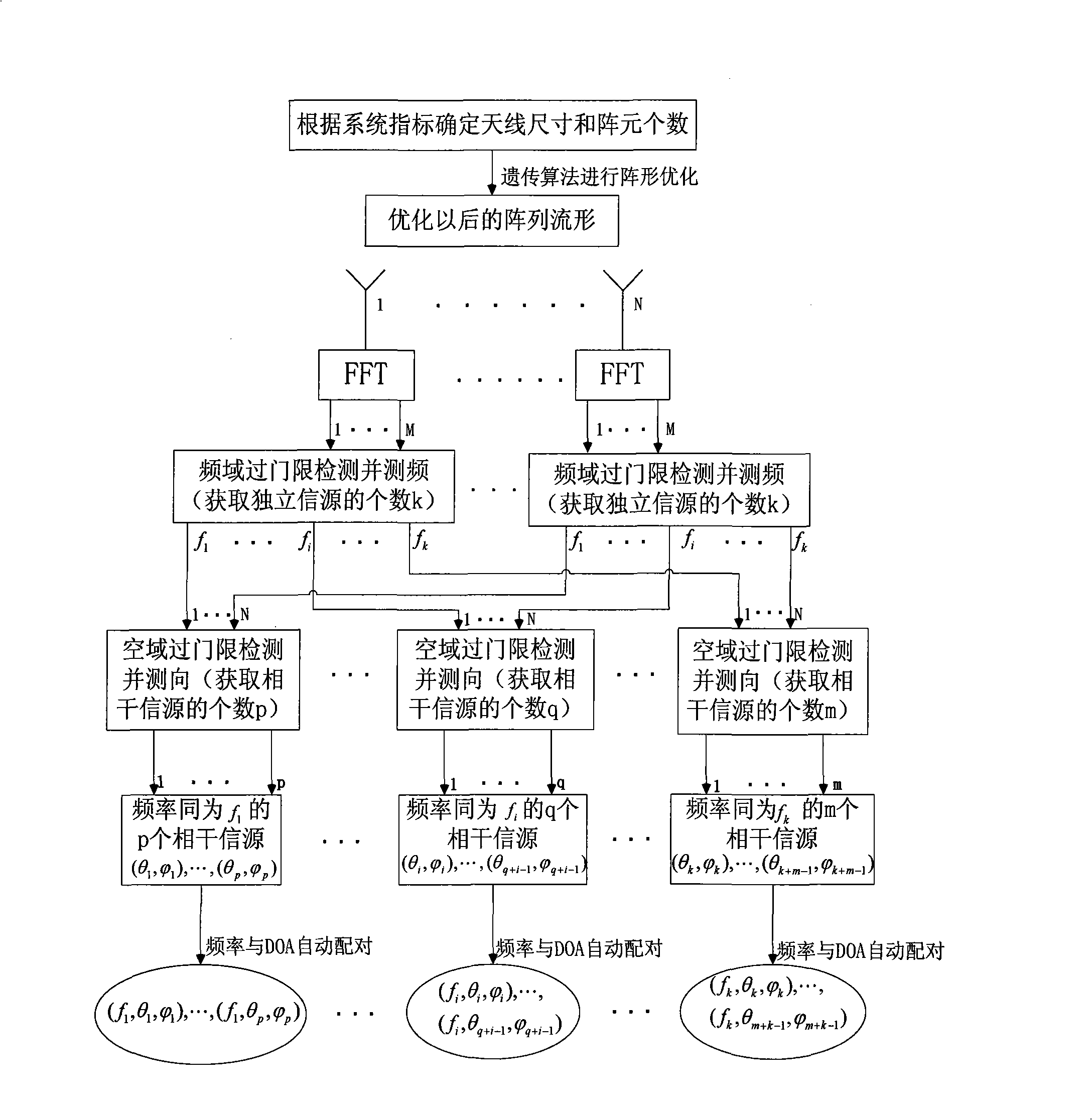
The invention discloses a method for matrix element distance optimization and frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement of wideband phased arrays, for realizing the direction measurement of multiple targets having narrow band coherence and irrelevance of a wideband receiver, resolving the contradiction between the direction measurement resolution and unambiguous direction measurement of sparse array, and realizing more accurate target detection under a certain channel error. The method comprises the steps of: first using uneven array, using genetic algorism to optimize the distance of array elements to satisfy the higher direction measurement resolution and high direction measurement accuracy of spatial unambiguous condition; based on the optimized array, realizing the frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement algorism as a DOA evaluation algorism which processes frequency domain accumulation, frequency domain check and frequency measurement for the data of each array element channel and realizes frequency automatic match. The algorism adopts array optimization, frequency domain peak snapshot frequency and direction measurement joint algorism. The invention can be applied for the multi narrow band target accurate frequency and direction measurement of wideband receivers in the airborne and satellite-borne electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-efficiency measurement method for sinusoidal signal frequency in undersampling and implementation device
ActiveCN101825660ASpectral/fourier analysisFrequency measurement arrangementDigital signal processingFrequency measurements
The invention belongs to the technical field of digital signal processing, and provides a high-efficiency measurement method of a sinusoidal signal frequency in undersampling and an implementation device which can estimate parameters such as frequency and the like under the condition of undersampling and can finish precise frequency measurement. The invention adopts the technical scheme that traditional FFT spectrum analysis and all phase FFT spectrum analysis are adopted to obtain a peak value spectrum G (q) and a peak value spectrum Ga (q); a phase value is directly read from the peak valuespectrum to take the square of a G (q) modulus to obtain a power spectrum value Pg (q); after performing modulus division on Pg (q) and Ga (q), amplitude estimation is obtained to take the differenceof the phase value of G (q) and the phase value of g(q), and the difference divided by tau=(N-1) / 2 to obtain frequency offset estimation delta k; and finally delta k delta omega and q delta omega aresuperposed to obtain digital angular frequency estimation which directly serves as the phase estimation and the amplitude estimation of the measured signal. The invention is mainly used for undersampling measurement in digital signal processing.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG RES INST NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Co-existing interference avoiding method and device
InactiveCN102378192AAvoid coexistence interferenceConnection managementNetwork planningFrequency measurementsUser equipment
The invention relates to a co-existing interference avoiding method and a device, which are used for solving the technical problem that the co-existing interference happens in user equipment (UE) on which multiple wireless technologies coexist. When co-existing interference is detected on the UE, a base station is allowed to know the co-existing interference at the UE side by transmitting a co-existing interference indication or switching a request message, so the UE is switched to a pilot-frequency neighboring region; or the base station ensures that the UE is selectively switched to the pilot-frequency neighboring region according to a reported measurement report by modifying a measuring configuration parameter; or the UE is directly re-connected to the pilot-frequency neighboring region satisfying the access condition through the pilot-frequency measurement. Due to the adoption of the method and the device, the UE is reselected to the pilot-frequency neighboring region so as to avoid the co-existing interference.
Owner:ZTE CORP
On-line monitoring system for capacitive equipment dielectric loss angle
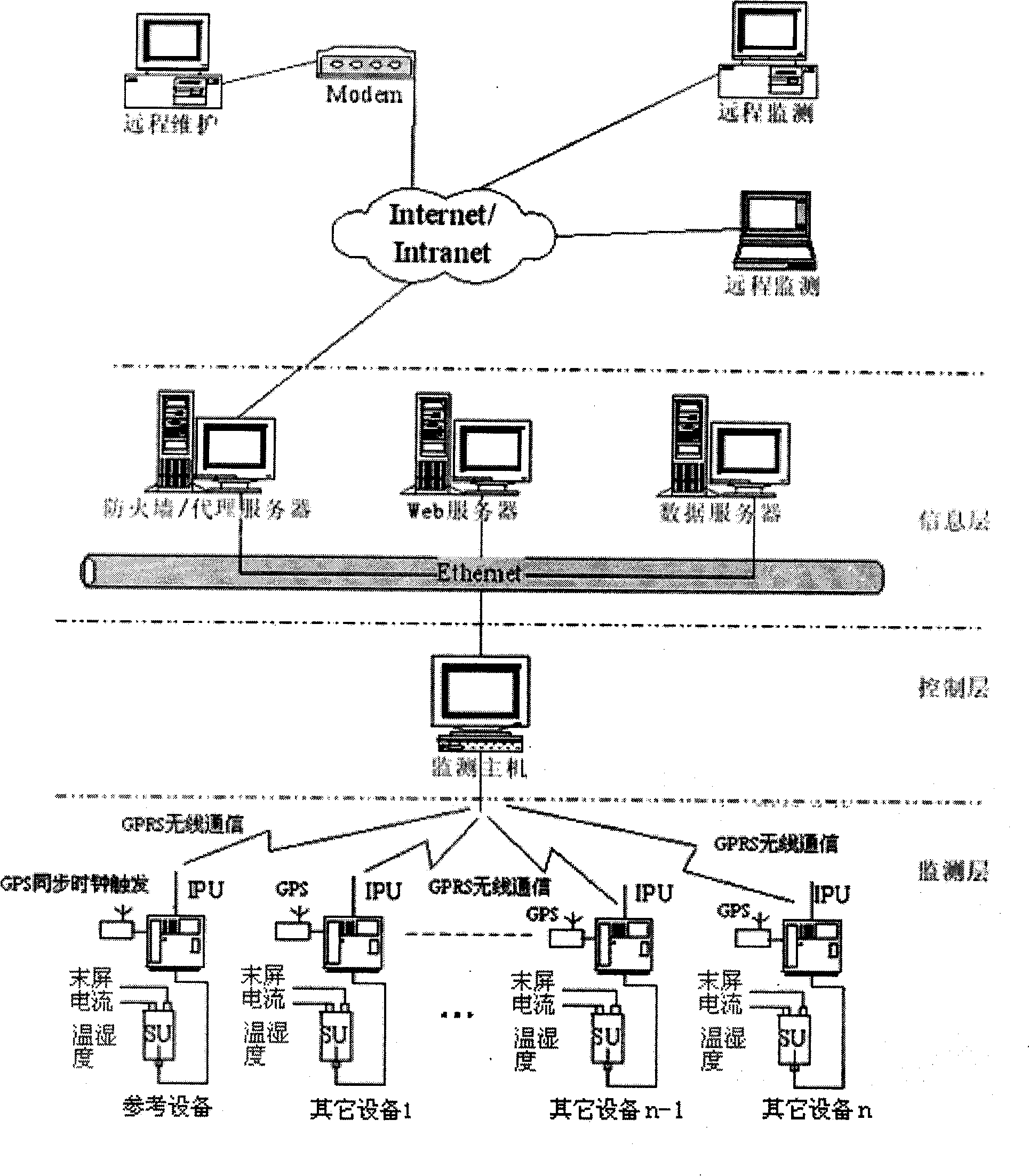
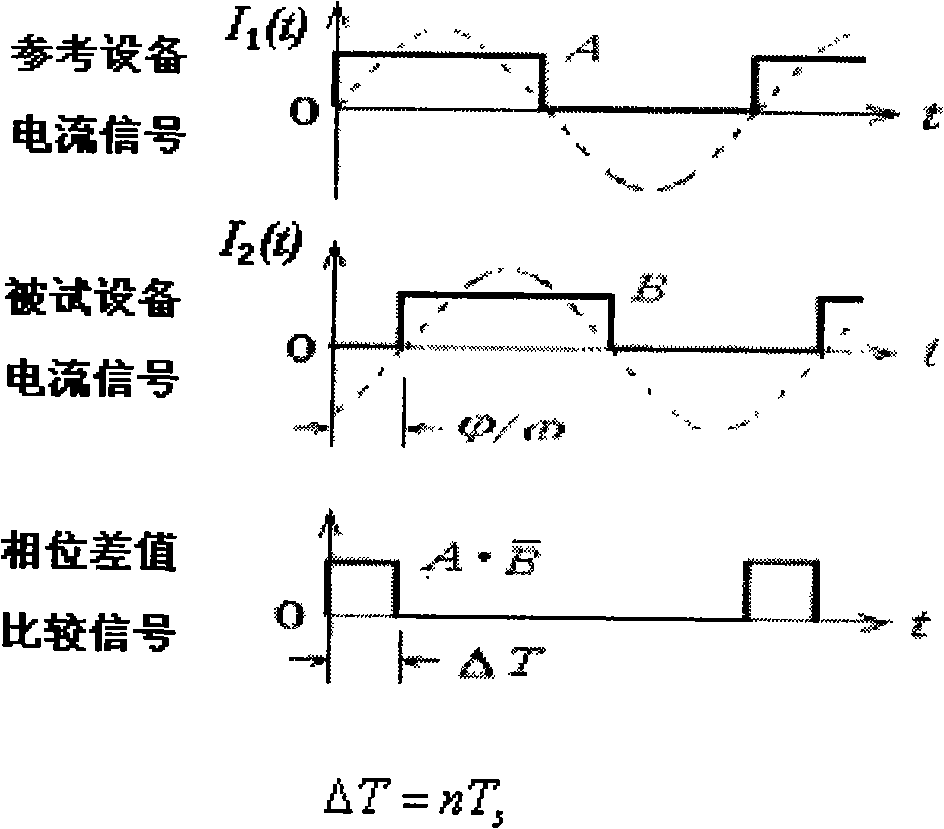
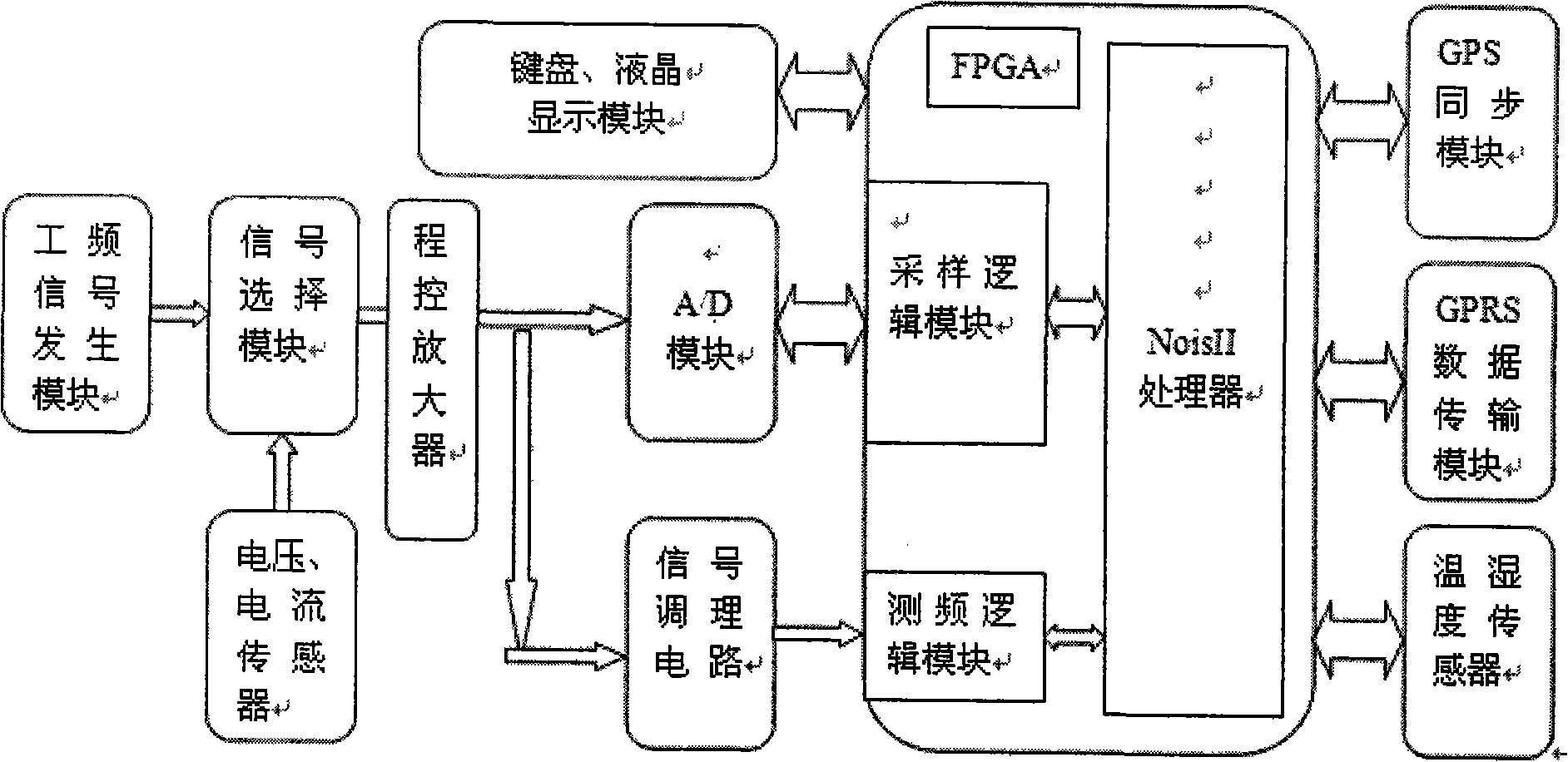
InactiveCN101493485AAvoid Transmission AttenuationImprove reliabilityResistance/reactance/impedenceInformation layerControl layer
The invention relates to a monitoring system for power transmission and transforming equipment, in particular to a capacitive equipment dielectric loss angle online monitoring system. The system is characterized by at least comprising a microprocessor, a leakage current signal acquisition module, a GPS synchronization module, a wireless communication module, an A / D sampling unit, and a frequency measurement sampling unit; in structure, a centralized management mode is used, a wireless data transmission technology and an Internet network technology are applied, and a layered distributed structure is achieved; according to the functional requirements, the invention divides the system into a monitoring layer, a control layer and an information layer. The manufacturer and operating management department (client) can visit the system in different places by only installing browser software and thus easily achieve remote maintenance and monitoring.
Owner:巨元智能电气(浙江)有限公司
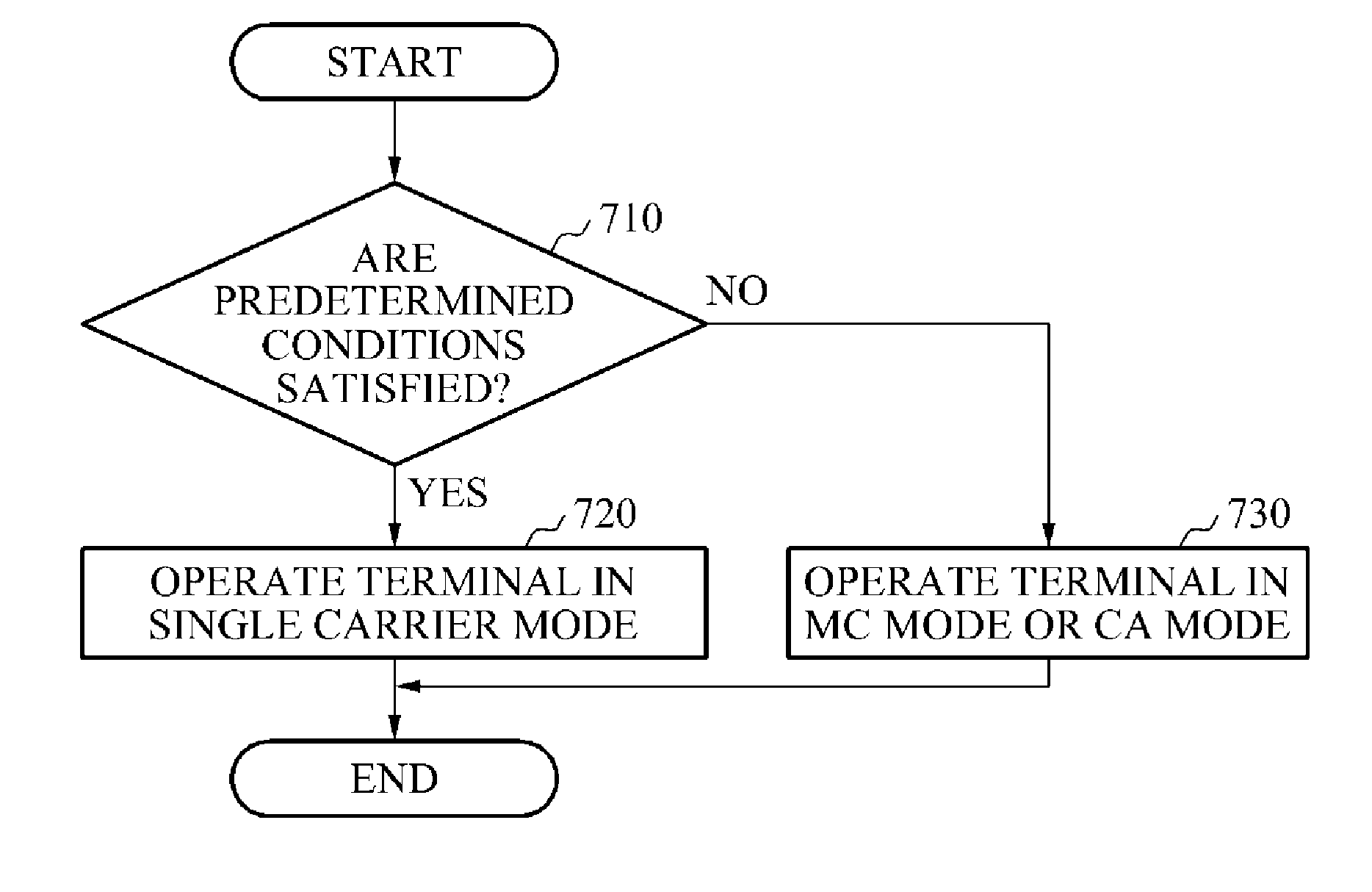
Apparatus and method for controlling multi-carrier supporting operation
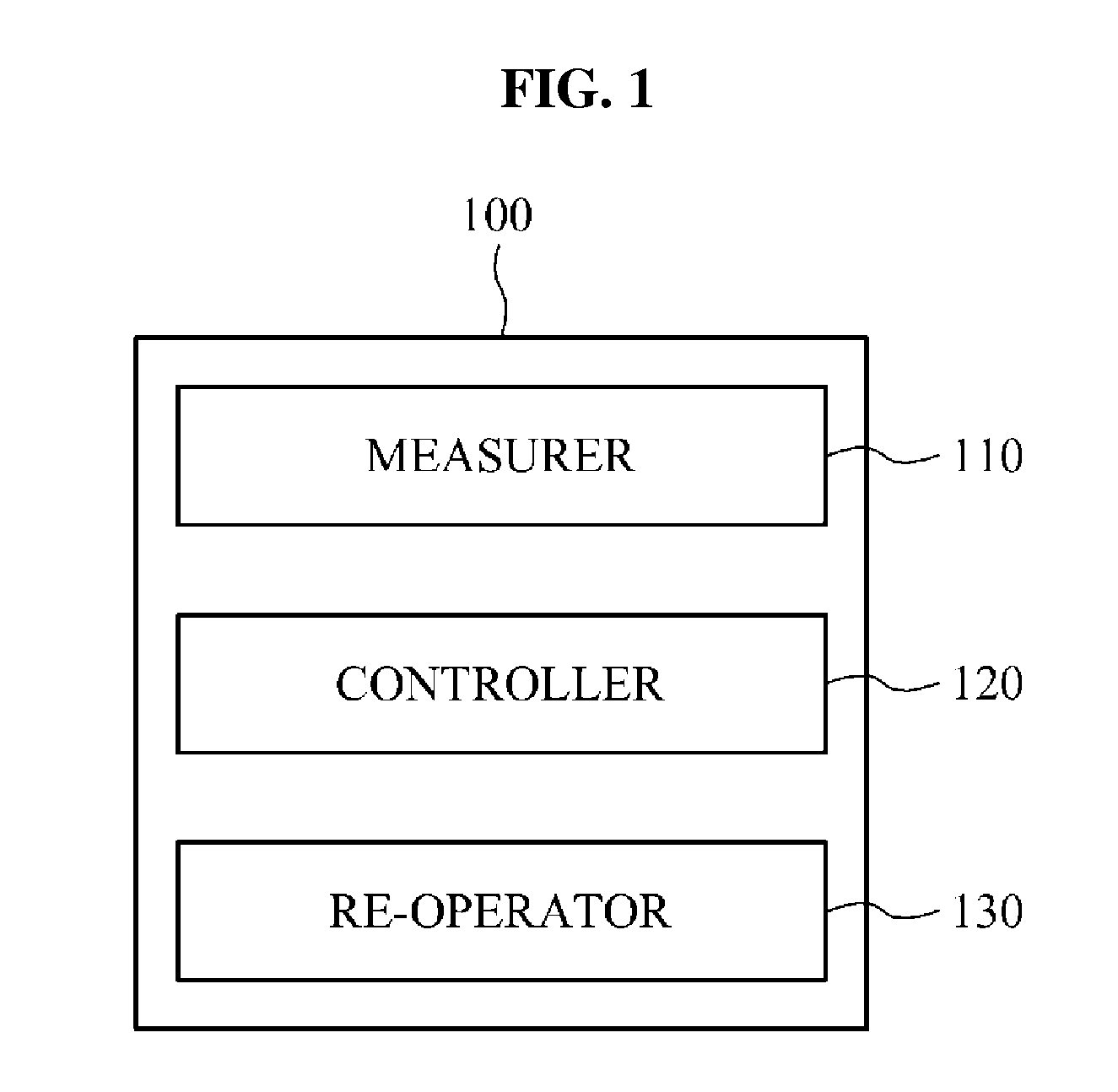
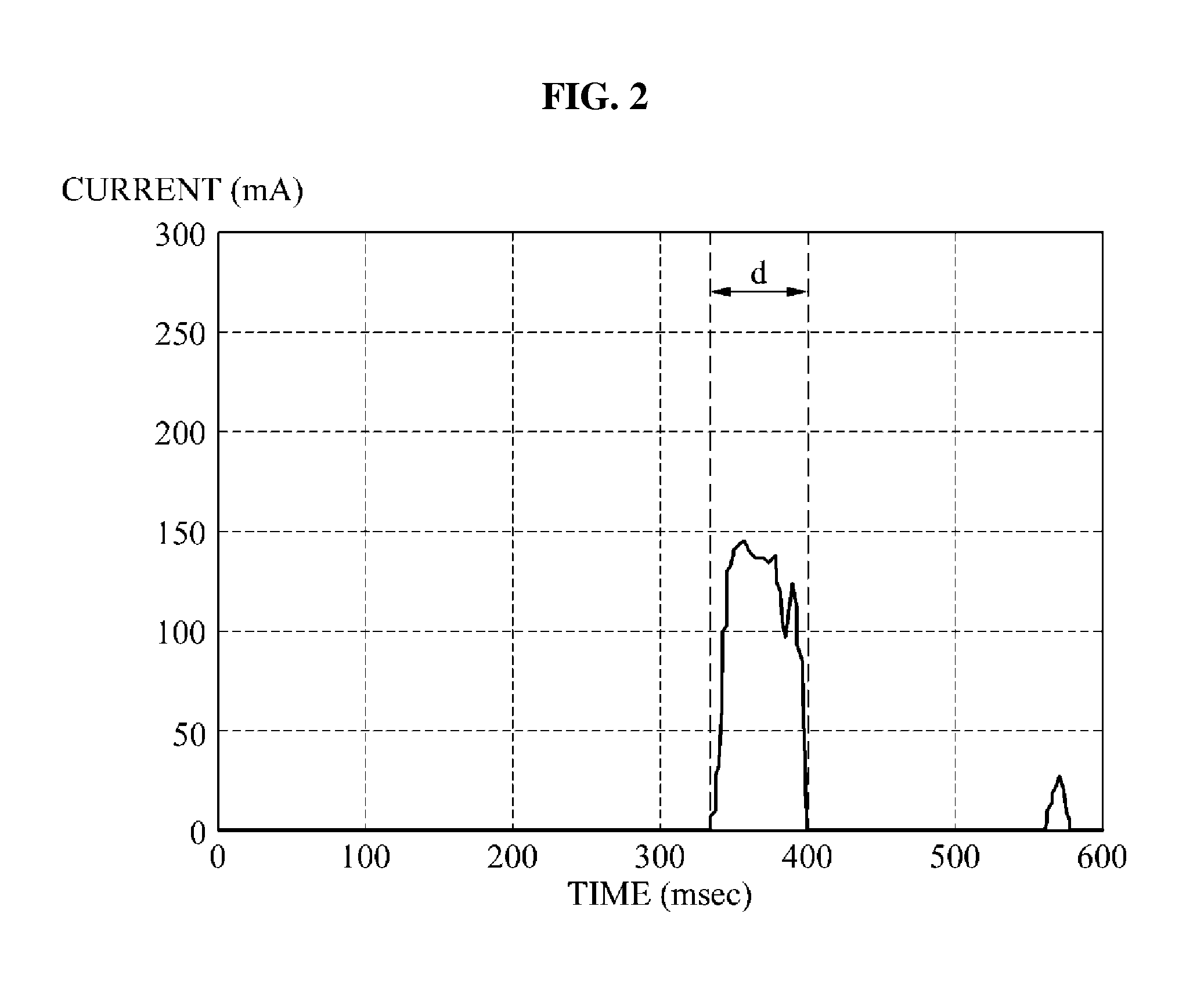
Provided is an apparatus and method for not performing an inter-frequency measurement to reduce a current to be used by a terminal providing a multi carrier (MC) function or a carrier aggregation (CA) function. When the terminal satisfies predetermined conditions, the terminal may be operated in a single carrier mode in which the inter-frequency measurement is not performed and thus, a current to be used for the inter-frequency measurement may be reduced.
Owner:PANTECH CO LTD
Measurement interval configuration method of pilot frequency measurement non-authorized frequency spectrum and service base station
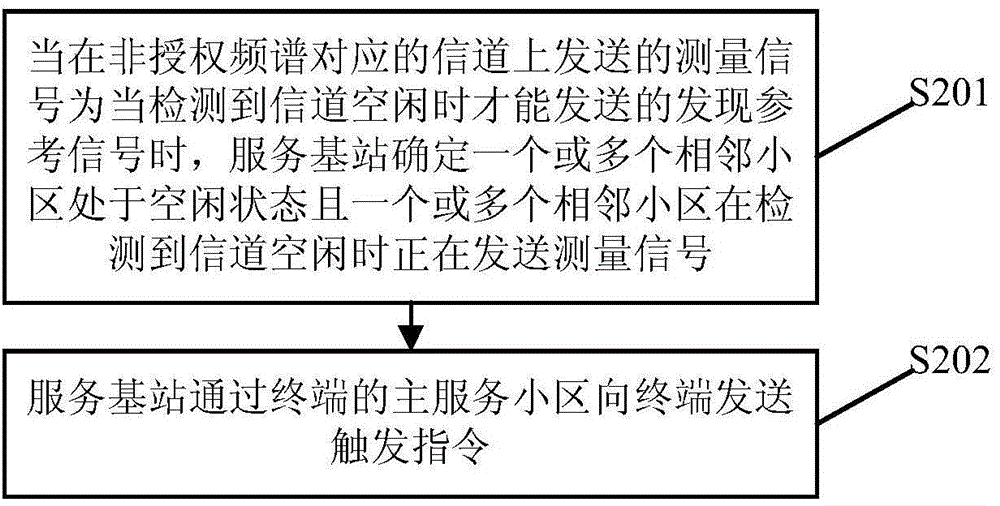
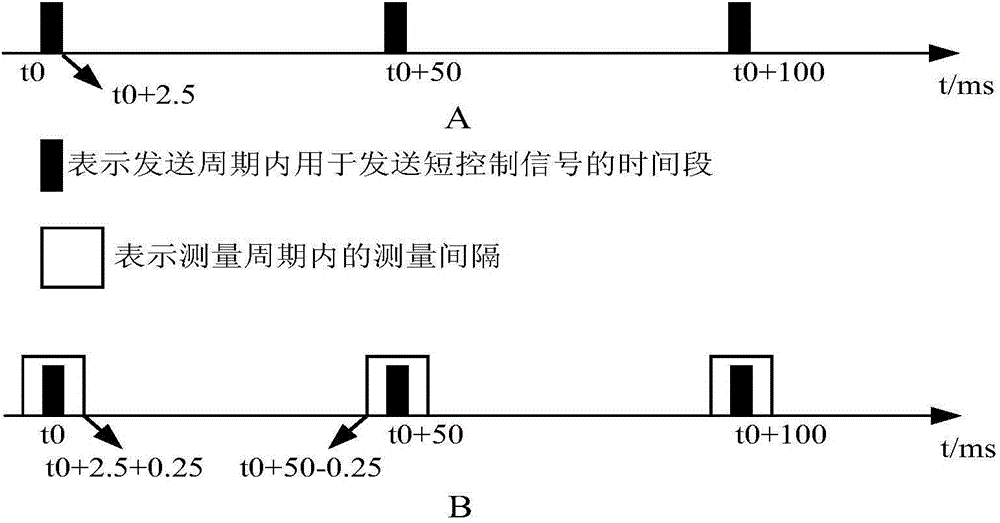
ActiveCN104602267AImprove throughputImprove accuracyWireless communicationFrequency spectrumControl signal
The embodiment of the invention discloses a measurement interval configuration method of a pilot frequency measurement non-authorized frequency spectrum and a service base station. The method comprises the following steps: when a measurement signal transmitted on a corresponding channel of the non-authorized frequency spectrum is a short control signal transmission manner, the service base station configures a measurement period of a measurement interval into transmission periods of transmitting the measurement signal by M adjacent cells and one measurement interval is configured in each measurement period according to a pre-set configuration rule, wherein the measurement interval in each measurement period covers a time period for transmitting the measurement signal in one transmission period of the measurement period. By the aid of the measurement interval configuration method, the accuracy of a measurement result of carrying out the pilot frequency measurement on the non-authorized frequency spectrum when the measurement signal is the short control signal transmission manner, and the throughput capacity of terminals in the service cells are can be improved, and the utilization rate of frequency spectrum resources is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN COOLPAD SOFTWARE TECH
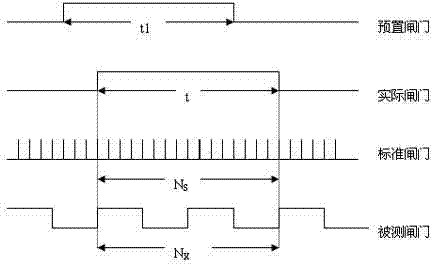
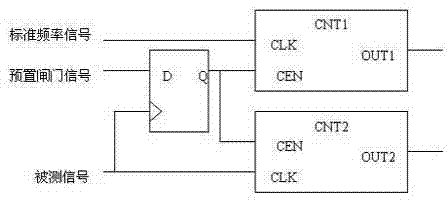
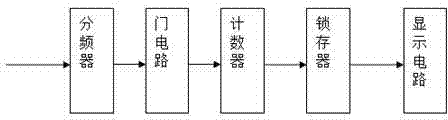
Frequency measurement method based on FPGA
InactiveCN103499739ASolve inaccurateImprove accuracyFrequency to pulse train conversionFrequency measurementsLow frequency band
The invention provides a frequency measurement method based on an FPGA. A standard reference clock is adopted to count the number of pulses of a measured signal in a unit time (1s) and the number of the pulses of the measured signal in the unit time (1s) is the frequency of the signal. Due to the fact that the starting moment of a gate and the finishing moment of the gate are random for the signal, a pulse period quantization error can be produced, and measurement accuracy needs to be analyzed further: the pulse period of a signal to be measured is set to be Tx, the frequency is set to be Fx, and when the measuring time T equals to 1s, the measurement accuracy & meets the equation that &=Tx / T=1 / Fx. The fact that measurement accuracy in a direct frequency measurement method is relevant to the frequency of the signal is known, the higher the frequency of the signal to be measured is, the higher the measurement accuracy is, and otherwise, the lower the frequency of the signal to be measured is, the lower the measurement accuracy is. The direct frequency measurement method is only suitable for measurement of the signal at the higher frequency and can not meet the demand that the measurement accuracy remains unchanged in the whole measurement frequency band. In order to overcome the defect of inaccuracy in low-frequency-band measurement, gating signals and the measured signal are used for carrying out dual control on enable signals of the counter, and therefore accuracy is improved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
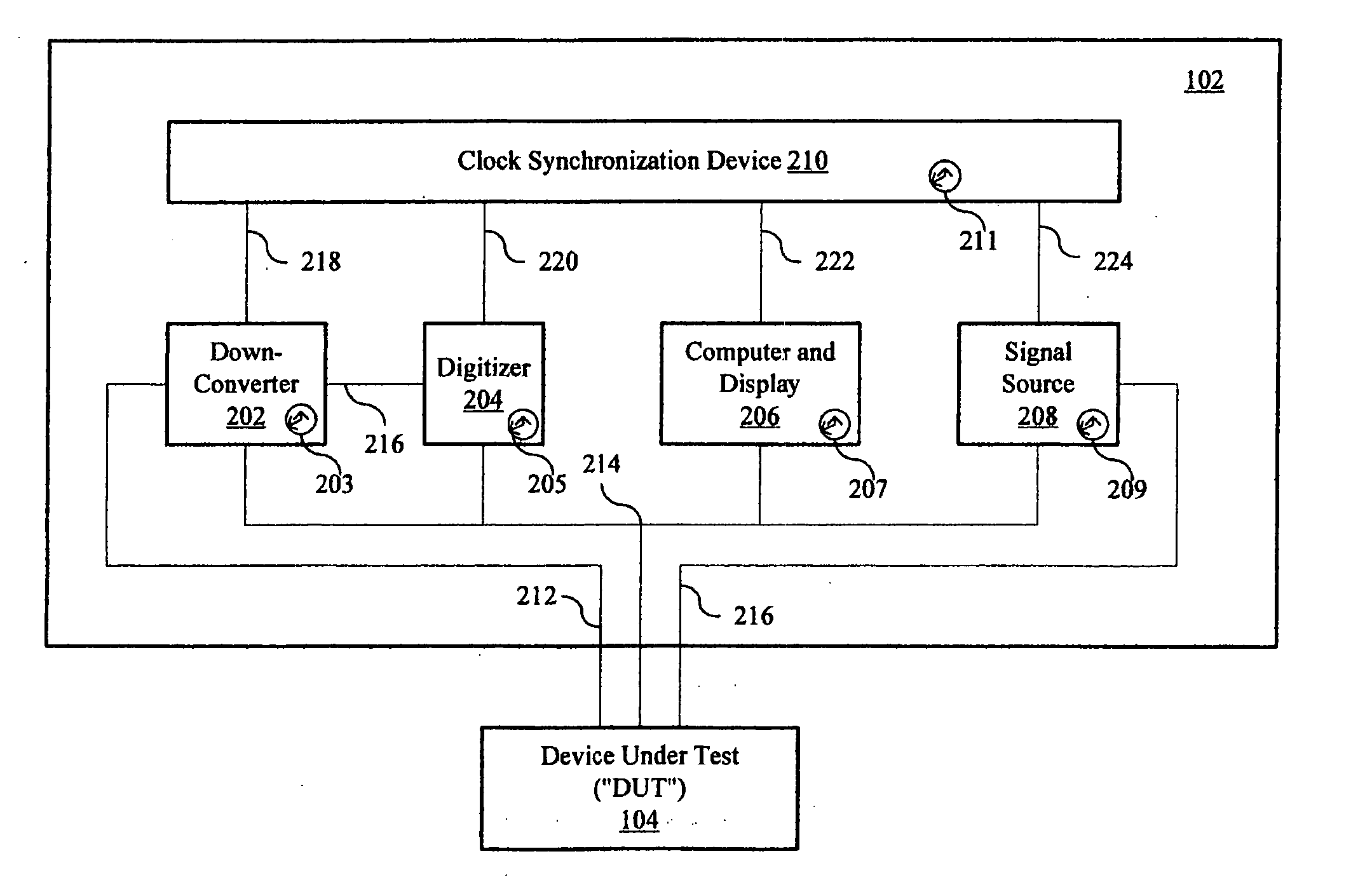
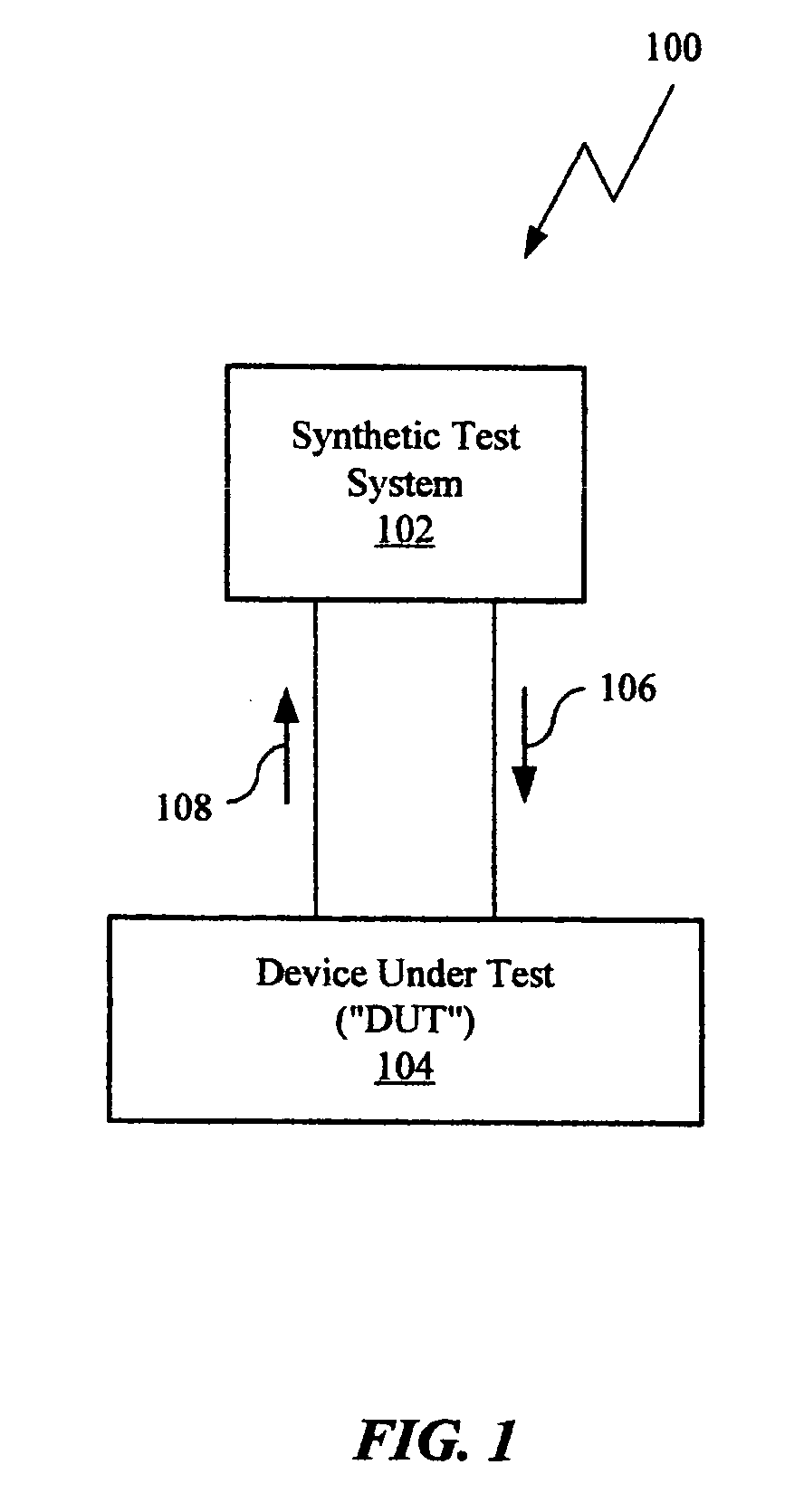
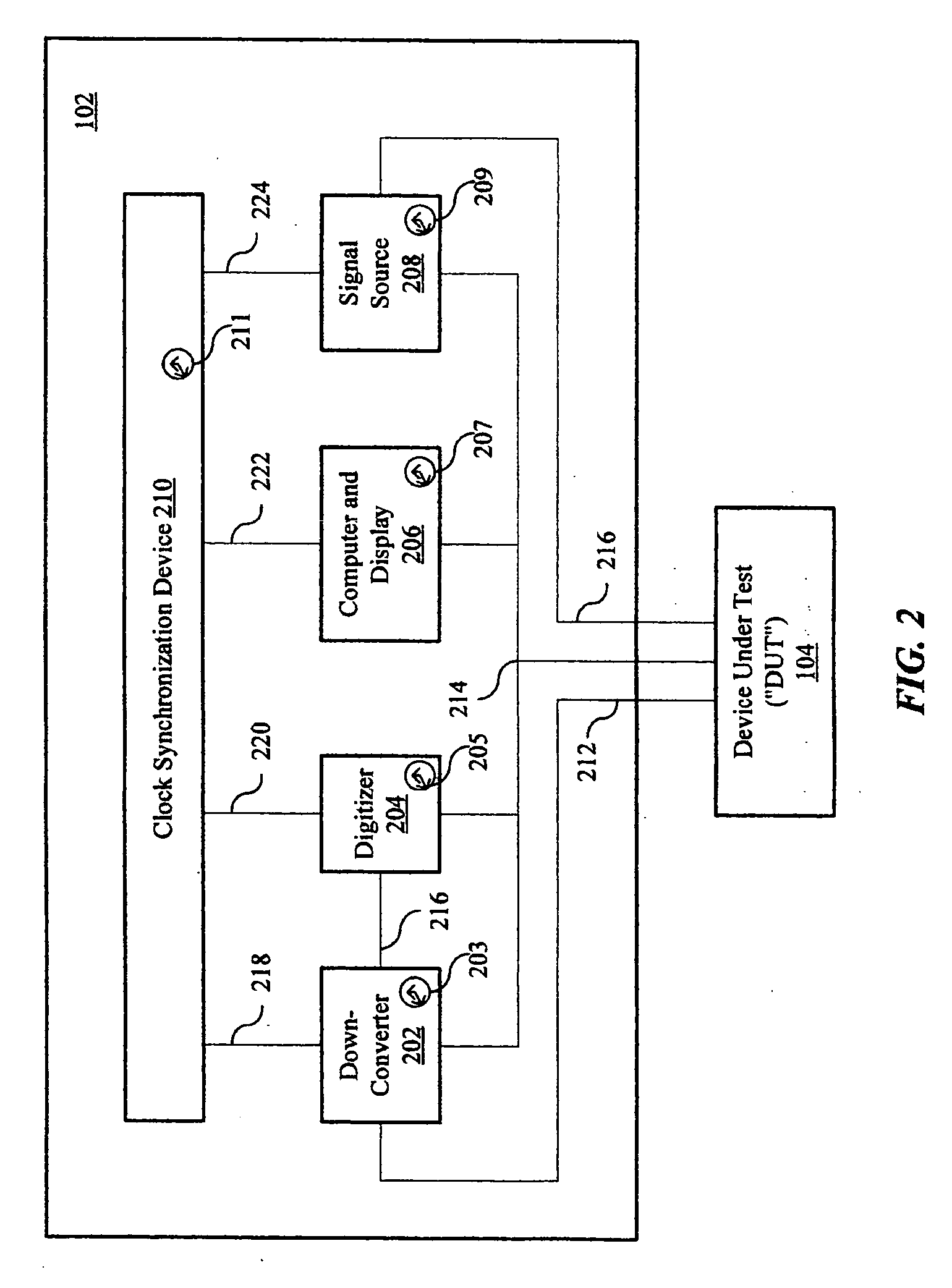
Swept-frequency measurements with improved speed using synthetic instruments
ActiveUS20070257660A1Spectral/fourier analysisPulse automatic controlCombined testSynthetic instrument
A synthetic test system for swept-frequency measurements that has a clock synchronization device to enable test boxes and devices that form the synthetic test system to have a common sense of time when conducting swept-frequency tests.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Method and device for measuring and stabilization using signals from a Fabry-Perot
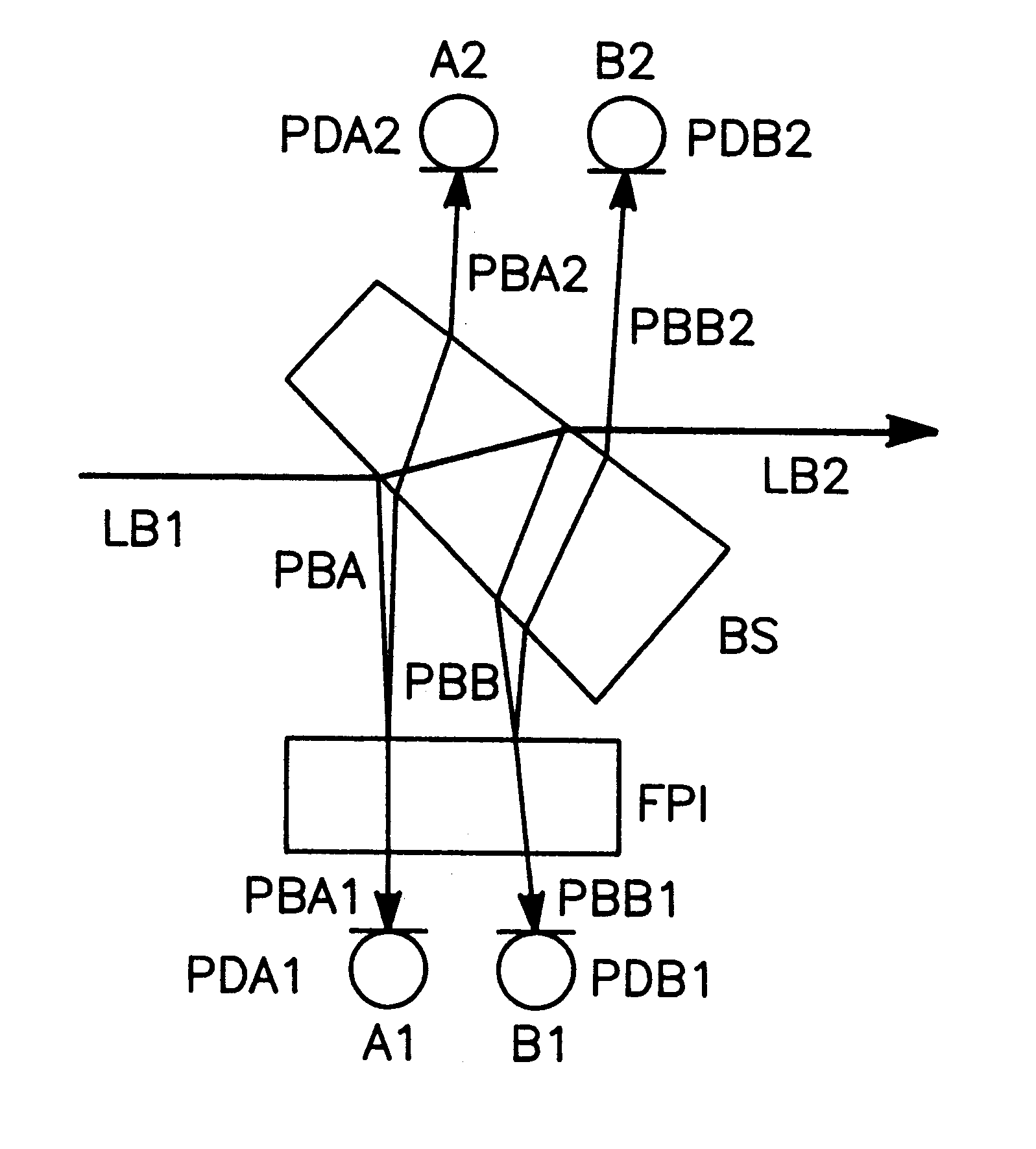
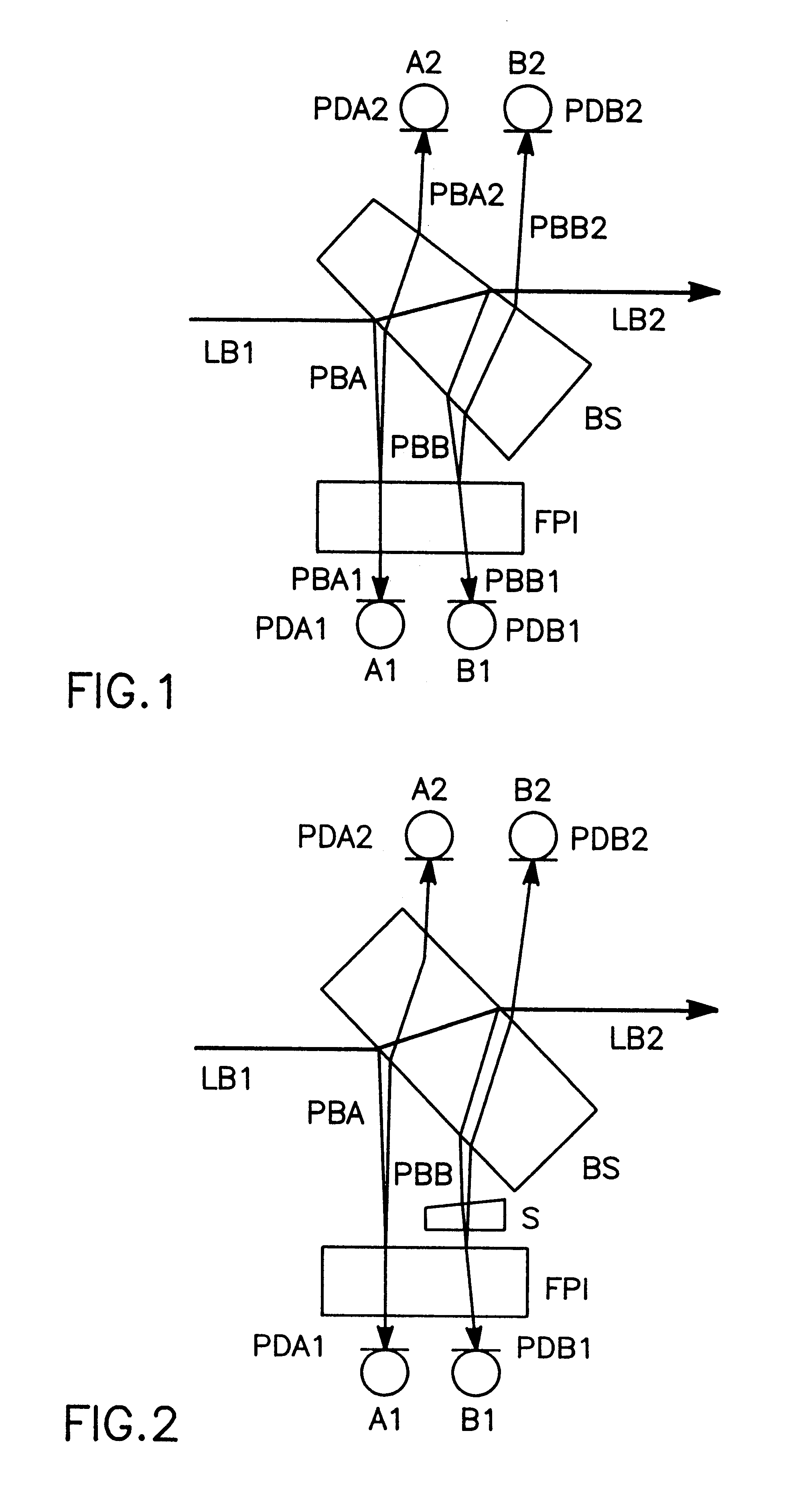
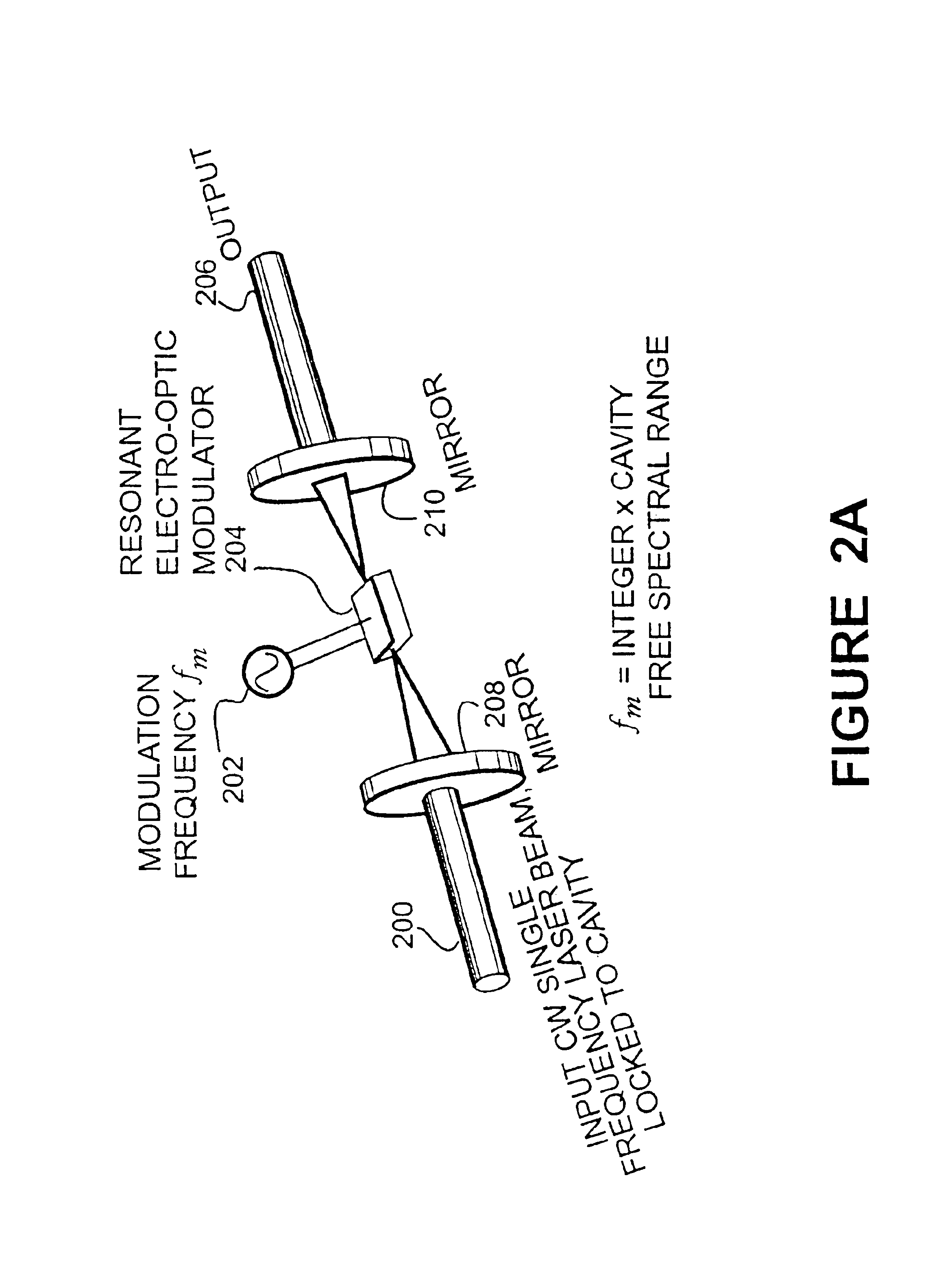
InactiveUS6178002B1Simple and low-cost and compact structureEasy to implementOptical measurementsLaser detailsPhase shiftedPath length
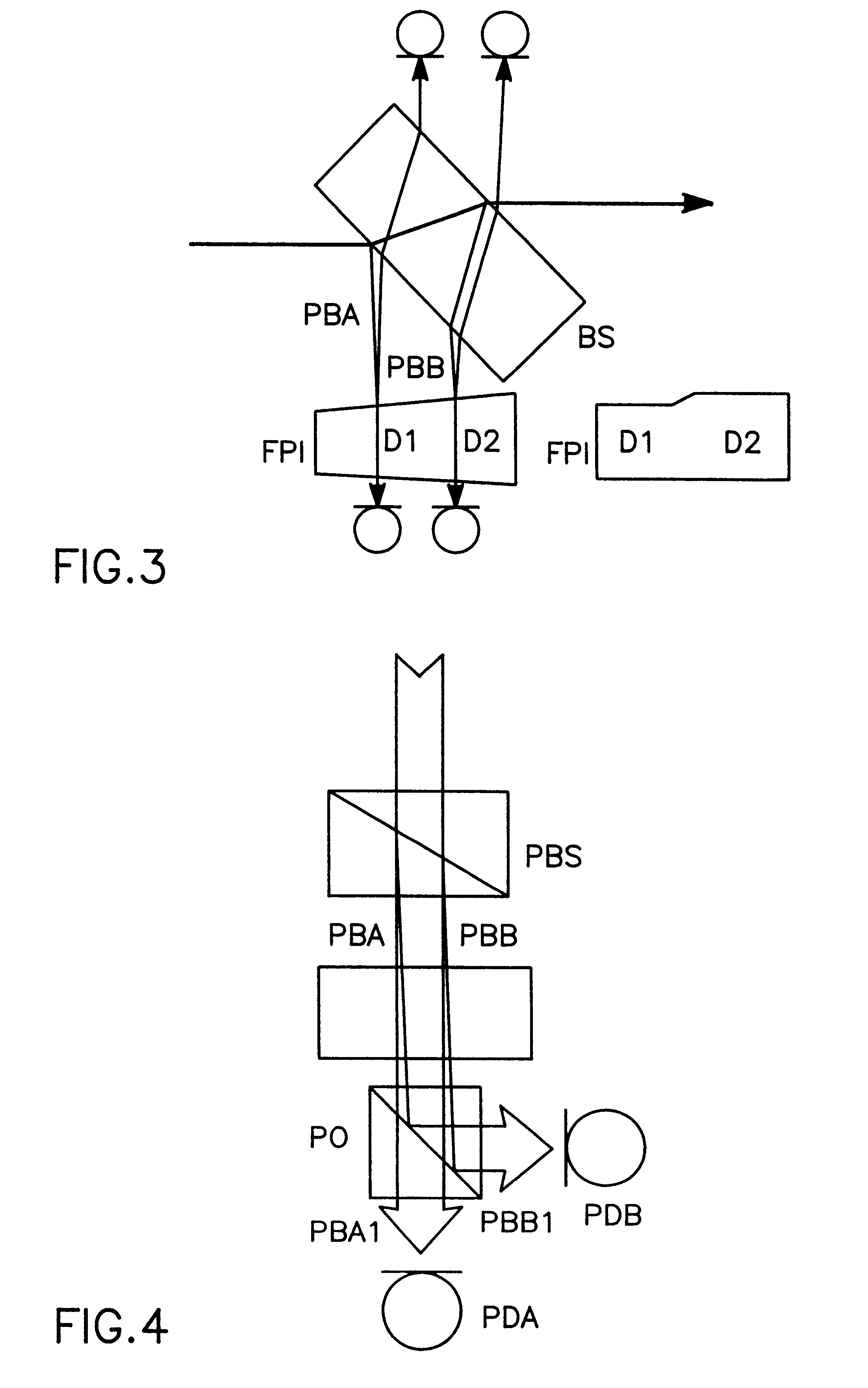
For measuring a laser frequency electronic signals can be generated by means of optical interferometers, especially Michelson, Mach-Zehnder and Fabry-Perot interferometers. These signals present profiles with a variation of the laser frequency which are practically identical but shifted in phase by 90°. It is common to generate such phase-shifted signals for frequency measurement in various systems, e.g. by means of a sigmameter, which present, however, disadvantages on account of the great number of the necessary high-quality optical components. The inventive method is based on the analysis of transmission and reflection signals of a Fabry-Perot interferometer (FPI) wherein the signals are obtained from two component beams (PBA and PBB) which are passed through slightly different path lengths within the interferometer. These differences in the length of the optical paths are so selected by different angles of incidence of the component beams into the Fabry-Perot interferometer or by an appropriate shape of the interferometer that the required 90° phase shift is adjusted between the detected intensity signals. From these signals electronic signals can be obtained for detection and also for a rapid correction of the laser frequency.
Owner:MUELLER WIRTS THOMAS
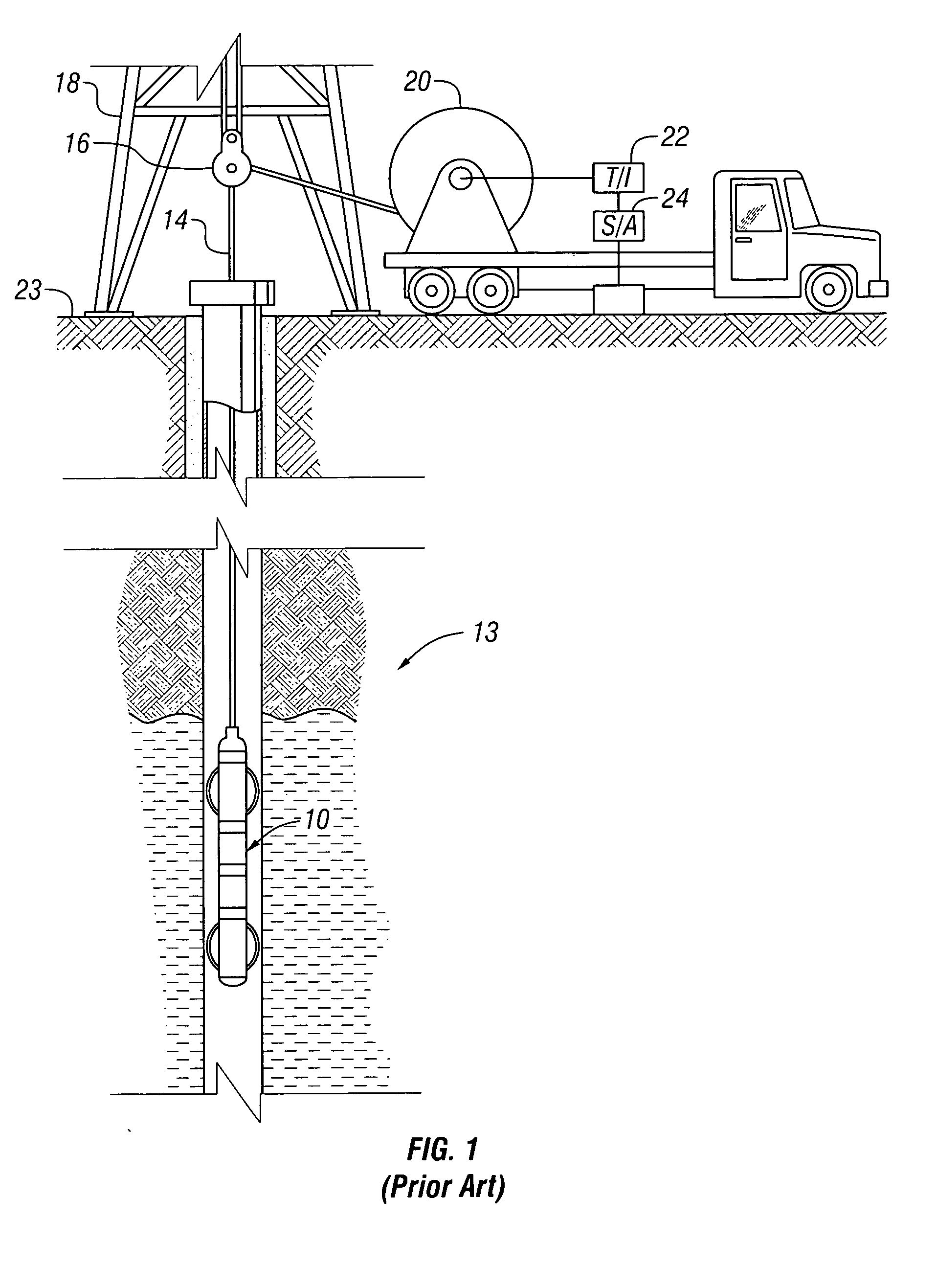
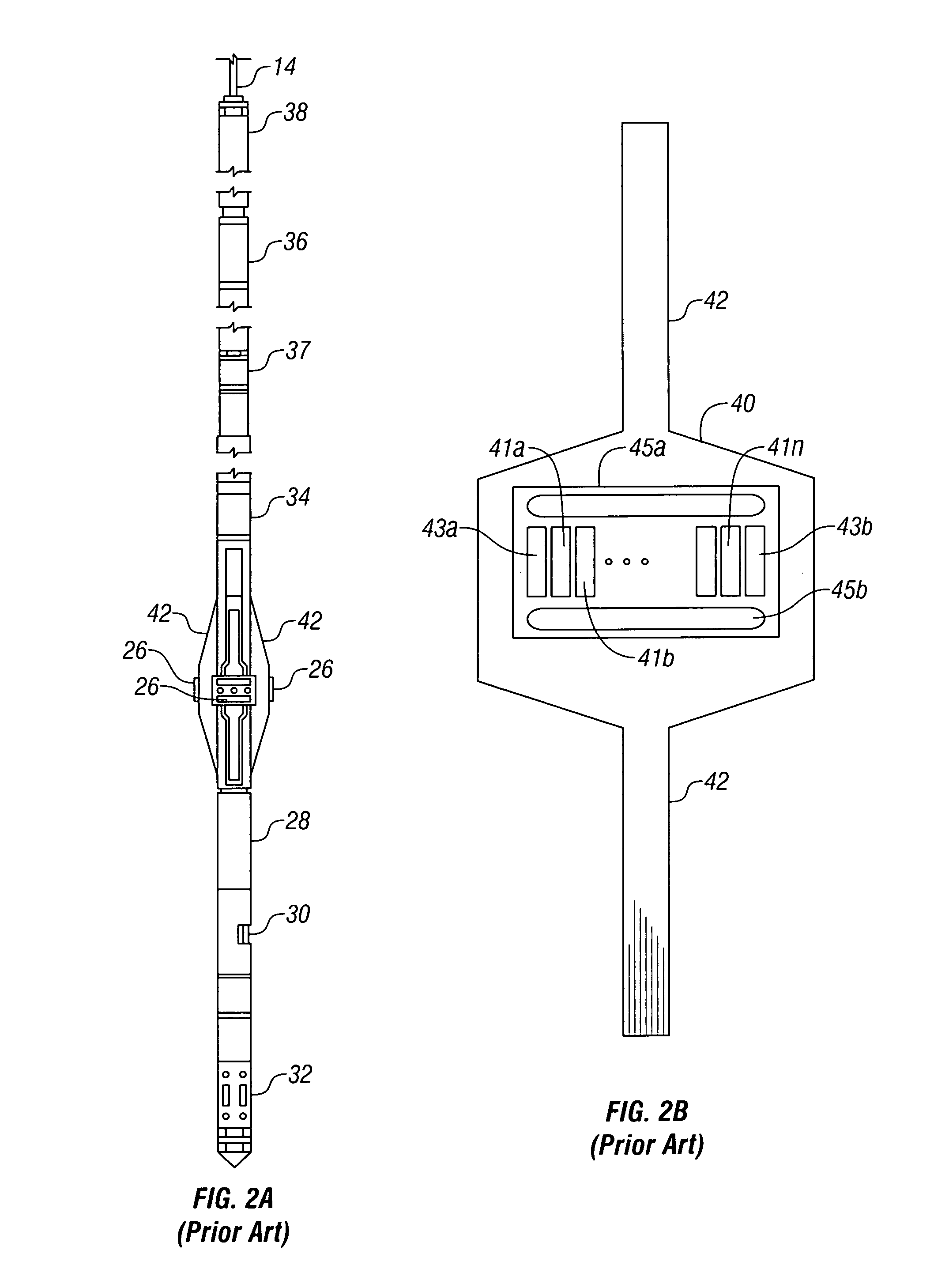
High resolution resistivity earth imager
ActiveUS7397250B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationDielectricCapacitance
Phase-sensitive measurements are made by a resistivity imaging tool in a borehole having non-conductive mud in a conductive earth formation at a plurality of frequencies. From the phase sensitive measurements, the formation resistivity can be determined with higher sensitivity than is possible with the single frequency measurements. Tool standoff can also be determined from a knowledge of the mud resistivity and / or dielectric constant. Formation resistivity may also be determined when the effect of formation capacitance cannot be ignored.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
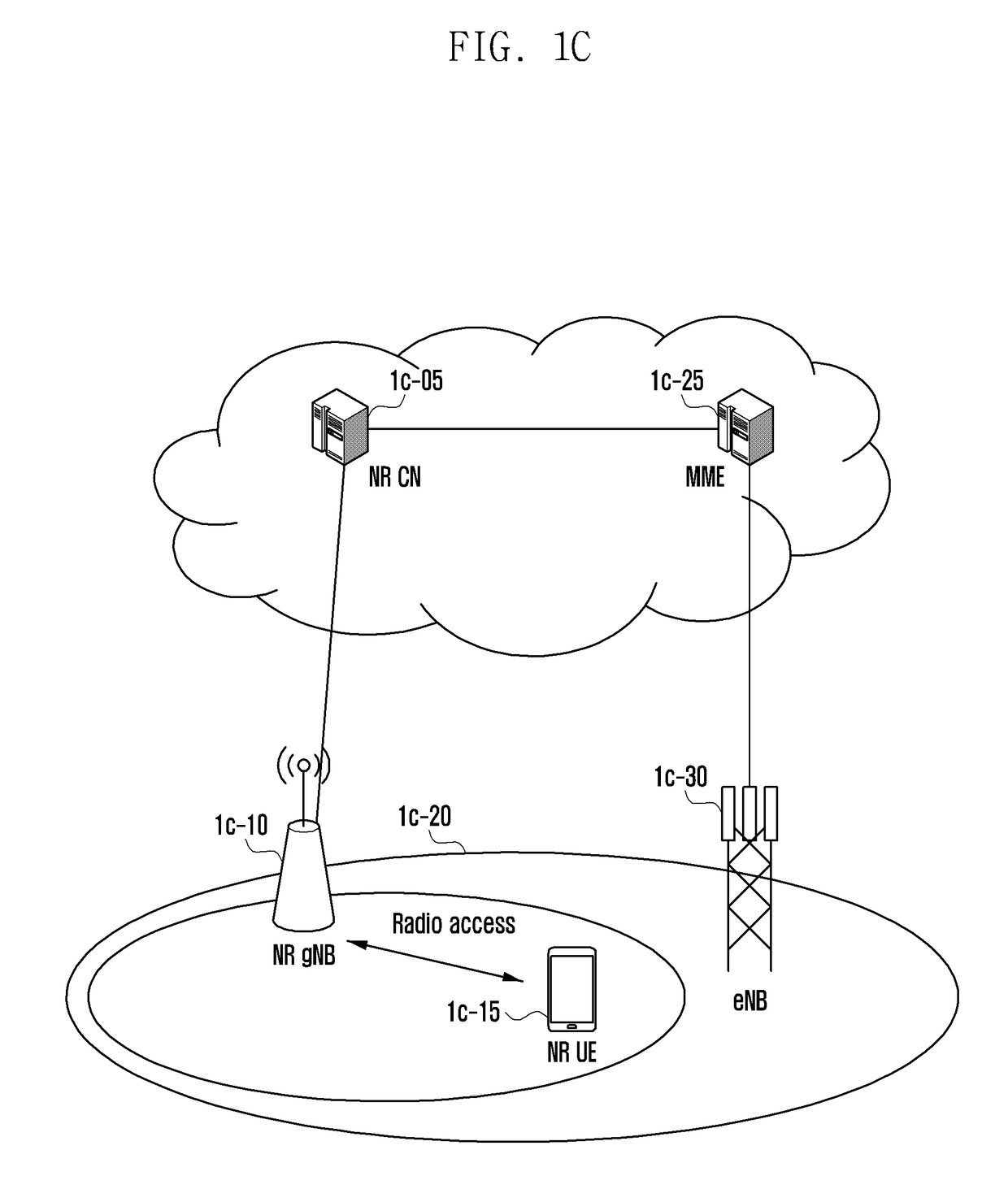
Method and apparatus for rapidly reporting frequency measurement results in next generation mobile communication system
ActiveUS20180368018A1Receive quicklyNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemFrequency measurements
The present disclosure relates to a communication method and system for converging a 5th-Generation (5G) communication system for supporting higher data rates beyond a 4th-Generation (4G) system with a technology for Internet of Things (IoT). The present disclosure may be applied to intelligent services based on the 5G communication technology and the IoT-related technology, such as smart home, smart building, smart city, smart car, connected car, health care, digital education, smart retail, security and safety services. A control method of a user equipment (UE) in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes receiving packet data conversion protocol (PDCP) configuration information including information indicative of whether a PDCP layer supports out-of-sequence delivery; identifying whether the PDCP layer supports out-of-sequence delivery based on the PDCP configuration information; and processing a PDCP packet data unit (PDU) based on a result of identifying whether the PDCP layer supports out-of-sequence delivery.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High resolution resistivity earth imager
ActiveUS20070046290A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationCapacitanceDielectric
Phase-sensitive measurements are made by a resistivity imaging tool in a borehole having non-conductive mud in a conductive earth formation at a plurality of frequencies. From the phase sensitive measurements, the formation resistivity can be determined with higher sensitivity than is possible with the single frequency measurements. Tool standoff can also be determined from a knowledge of the mud resistivity and / or dielectric constant. Formation resistivity may also be determined when the effect of formation capacitance cannot be ignored.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
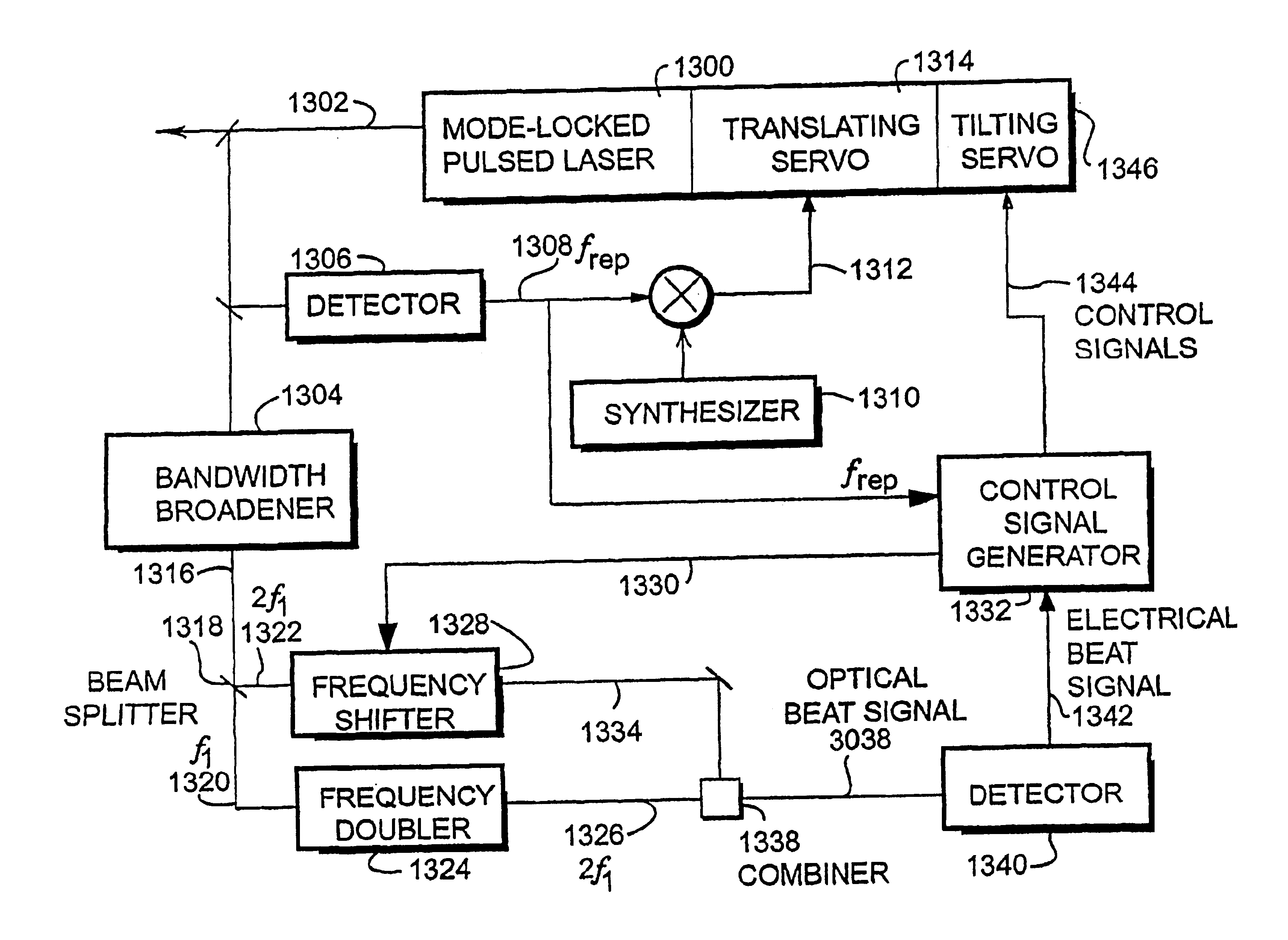
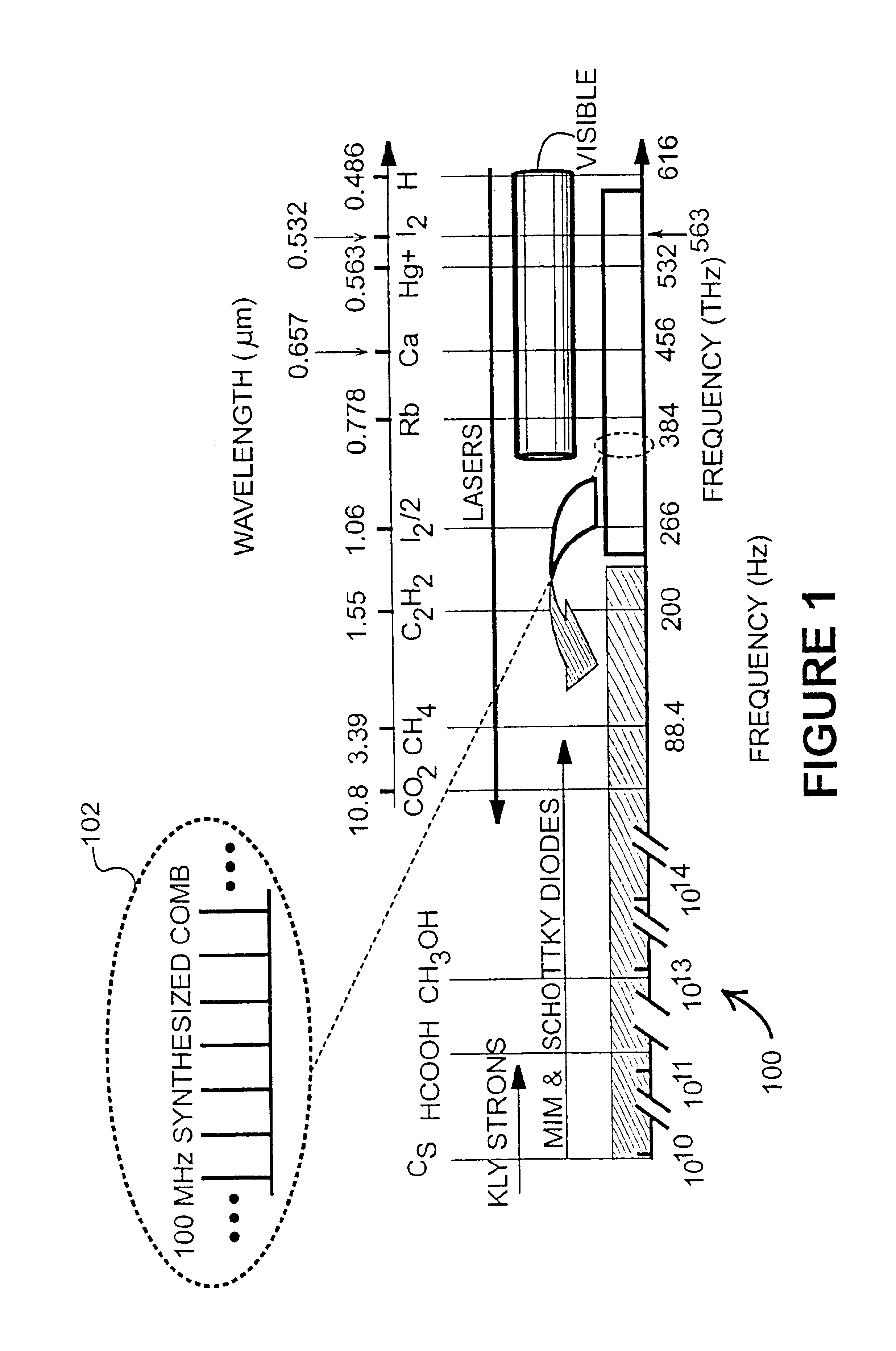
Mode-locked pulsed laser system and method
InactiveUS6850543B2Compact and relatively inexpensiveInexpensive and highly accurateActive medium materialMicrowaveFrequency measurements
Disclosed is a system and method for stabilizing the carrier-envelope phase of the pulses emitted by a femtosecond mode-locked laser by using the powerful tools of frequency-domain laser stabilization. Control of the pulse-to-pulse carrier-envelope phases was confirmed using temporal cross correlation. This phase stabilization locks the absolute frequencies emitted by the laser, which is used to perform absolute optical frequency measurements that were directly referenced to a stable microwave clock.
Owner:GOVERMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE +2
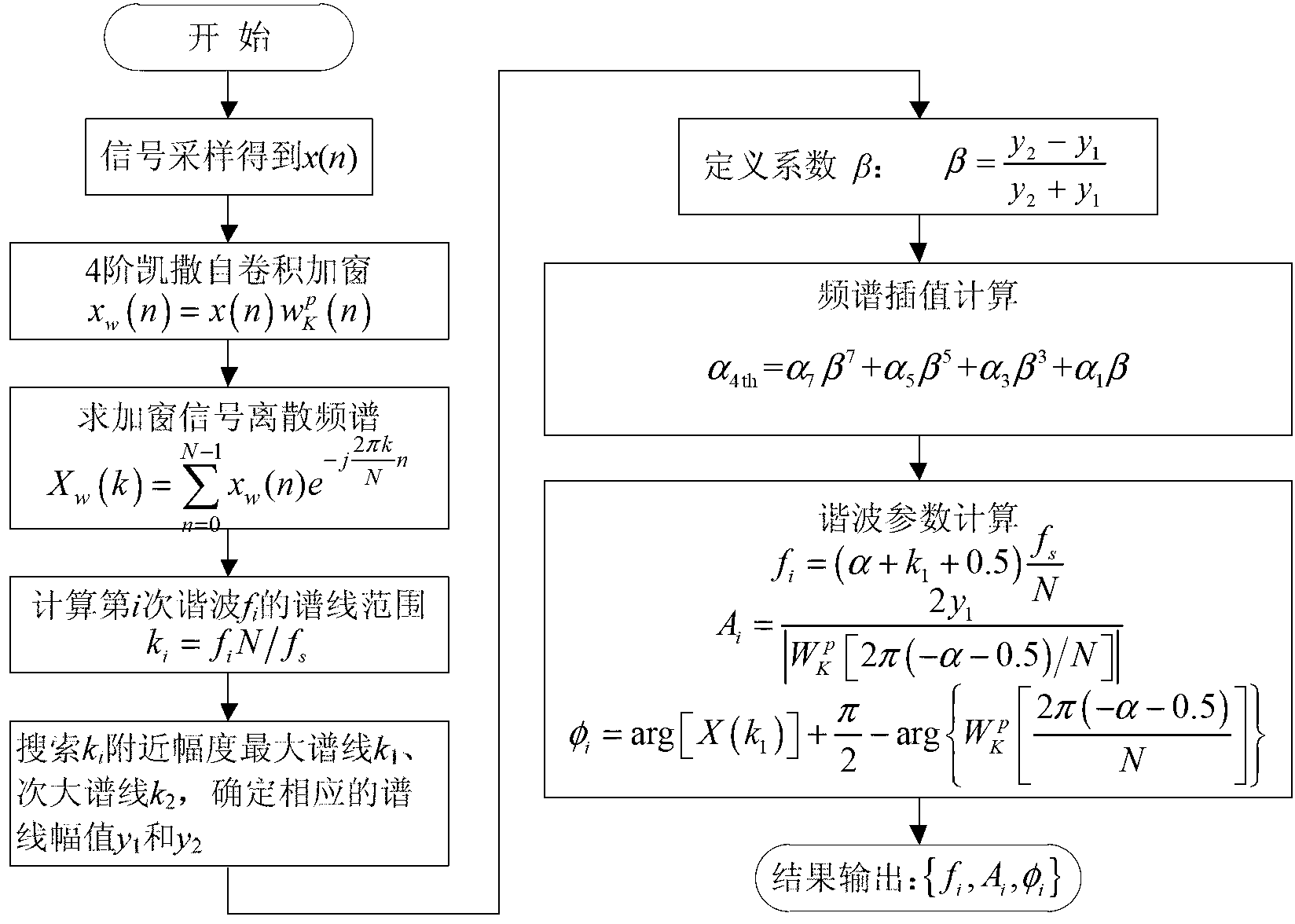
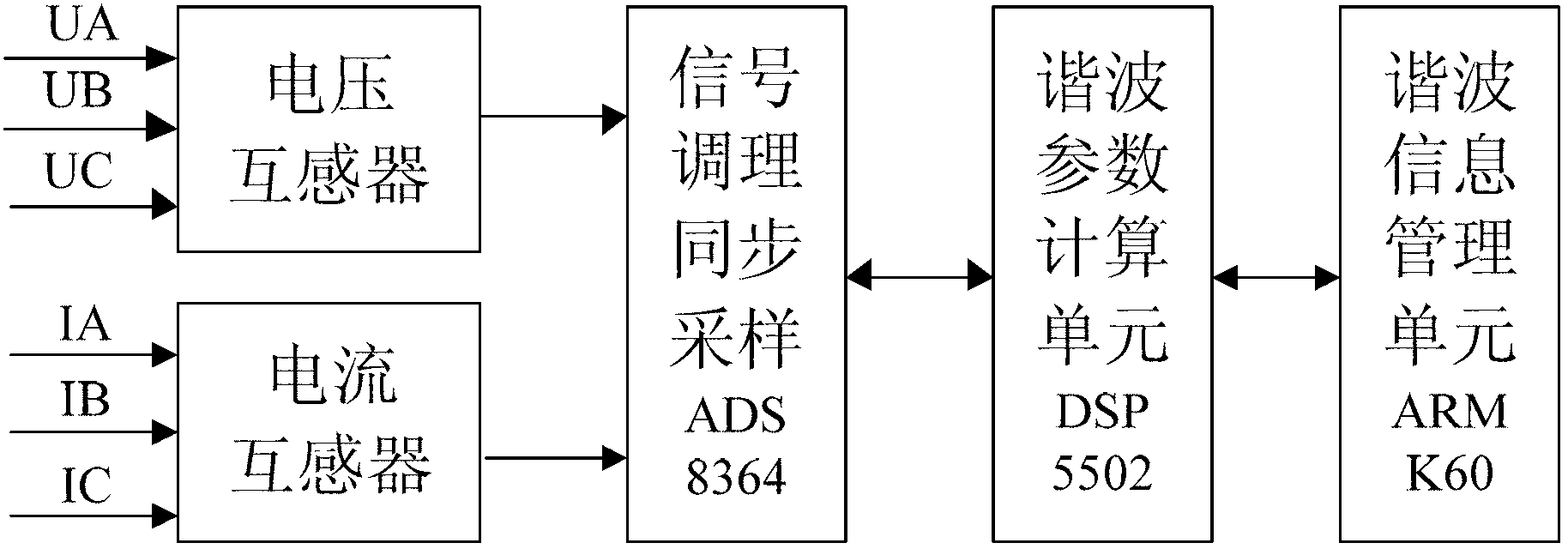
Harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and device thereof
InactiveCN103308766AQuick checkAccurate detectionFrequency analysisFrequency spectrumFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a harmonic analysis method based on Kaiser self-convolution window dual-spectrum line interpolation FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps of sampling a signal: sampling a time-domain continuous signal, and discretizing to obtain an infinitely long discrete sequence; windowing a four-order Kaiser self-convolution window function: performing four-order Kaiser self-convolution window operation on the infinitely long discrete sequence; performing N-point FFT on a windowed and truncated signal to obtain the discrete spectrum of the signal; determining the peak parameter of the discrete spectrum: searching the local spectrum peak of each integer harmonic frequency around the integer harmonic frequency; and calculating a harmonic parameter: solving a coefficient alpha by adopting a discrete spectrum interpolation correction formula based on an LSM (Least Square Method), and calculating parameters such as a harmonic frequency, an amplitude, an initial phase angle and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, the fundamental and harmonic components of a tested signal can be detected rapidly and accurately, and accurate frequency measurement is realized; and the method is convenient for implementing an embedded system, and the tested signal can be detected continuously for a long time.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator
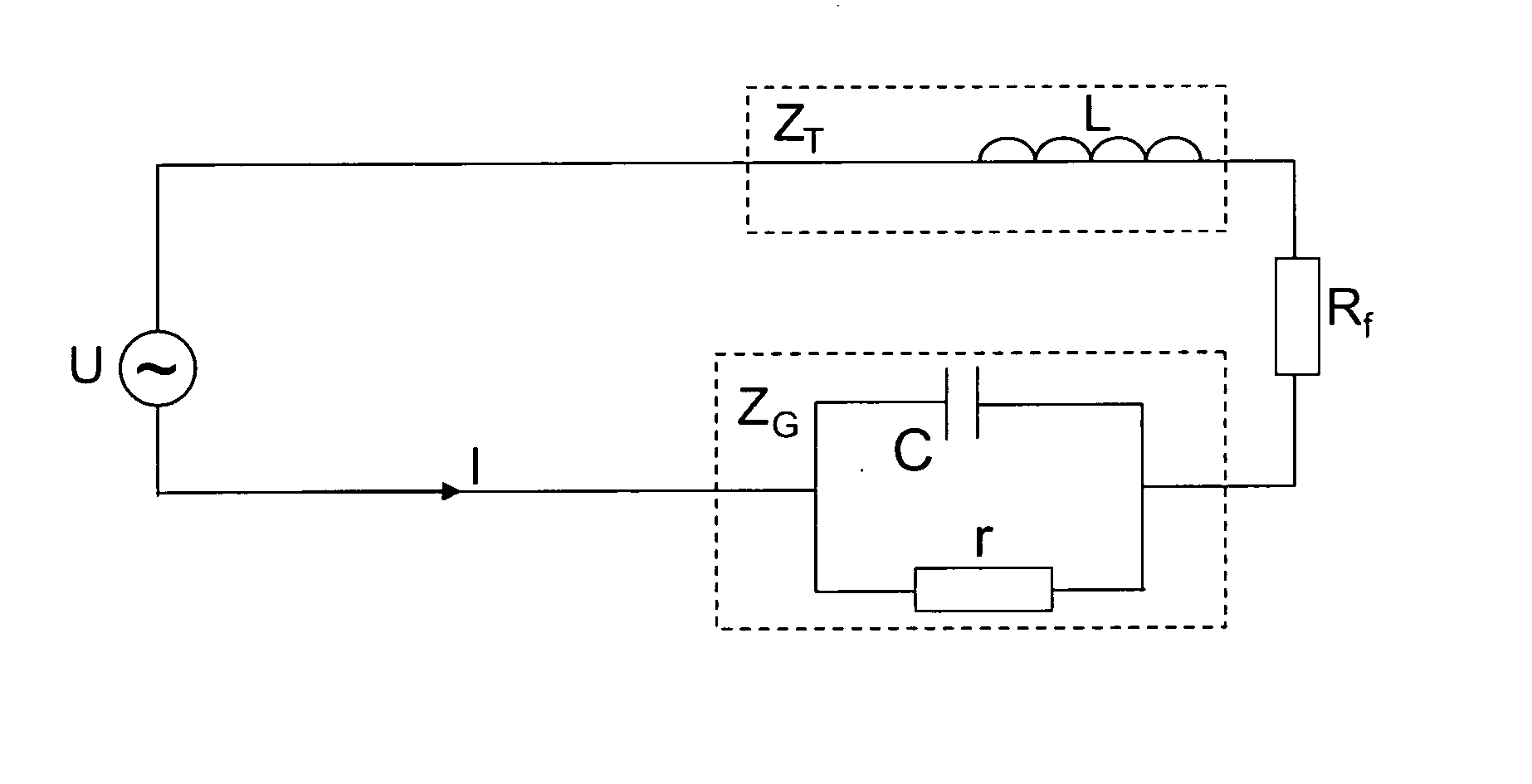
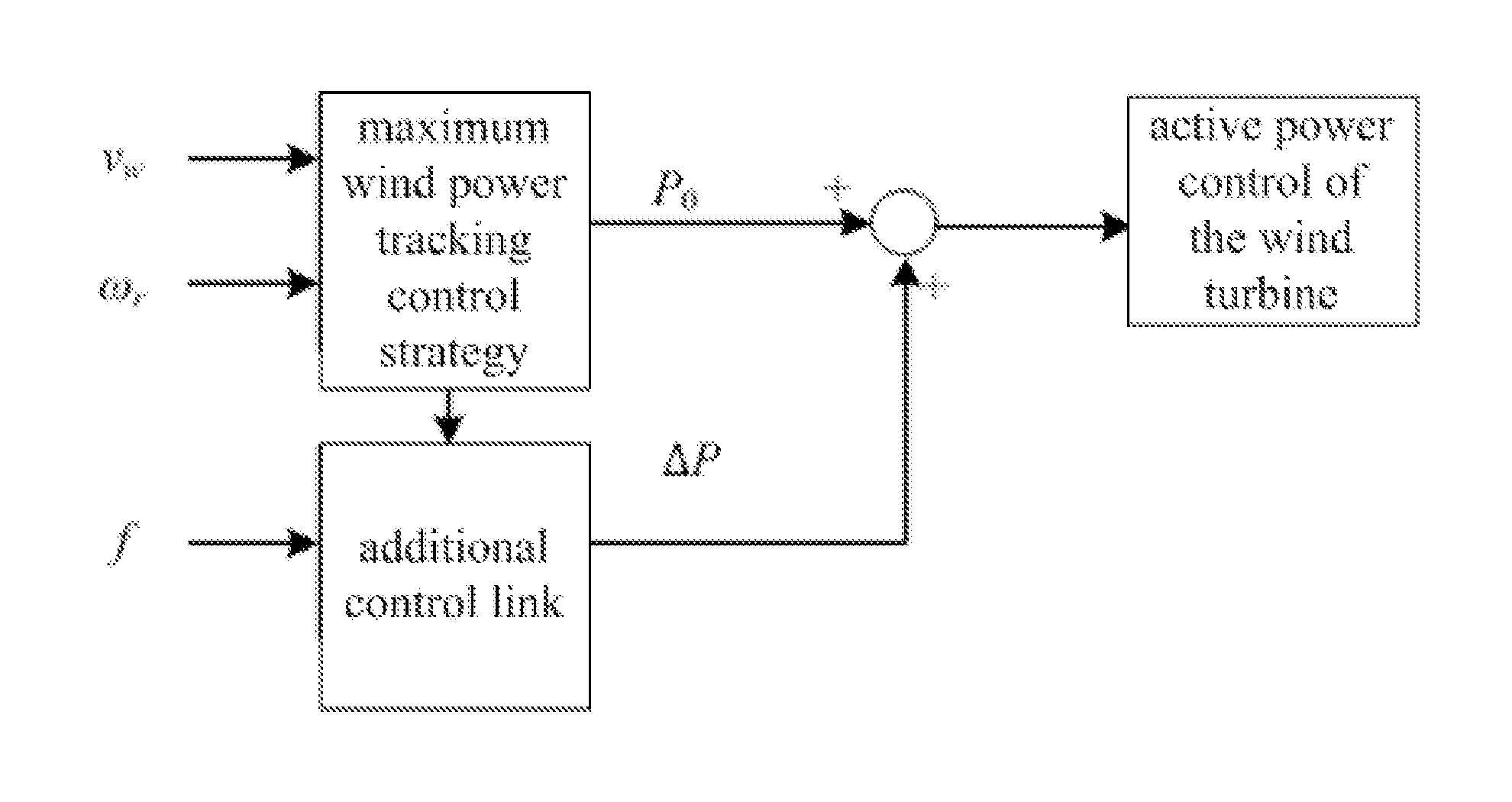
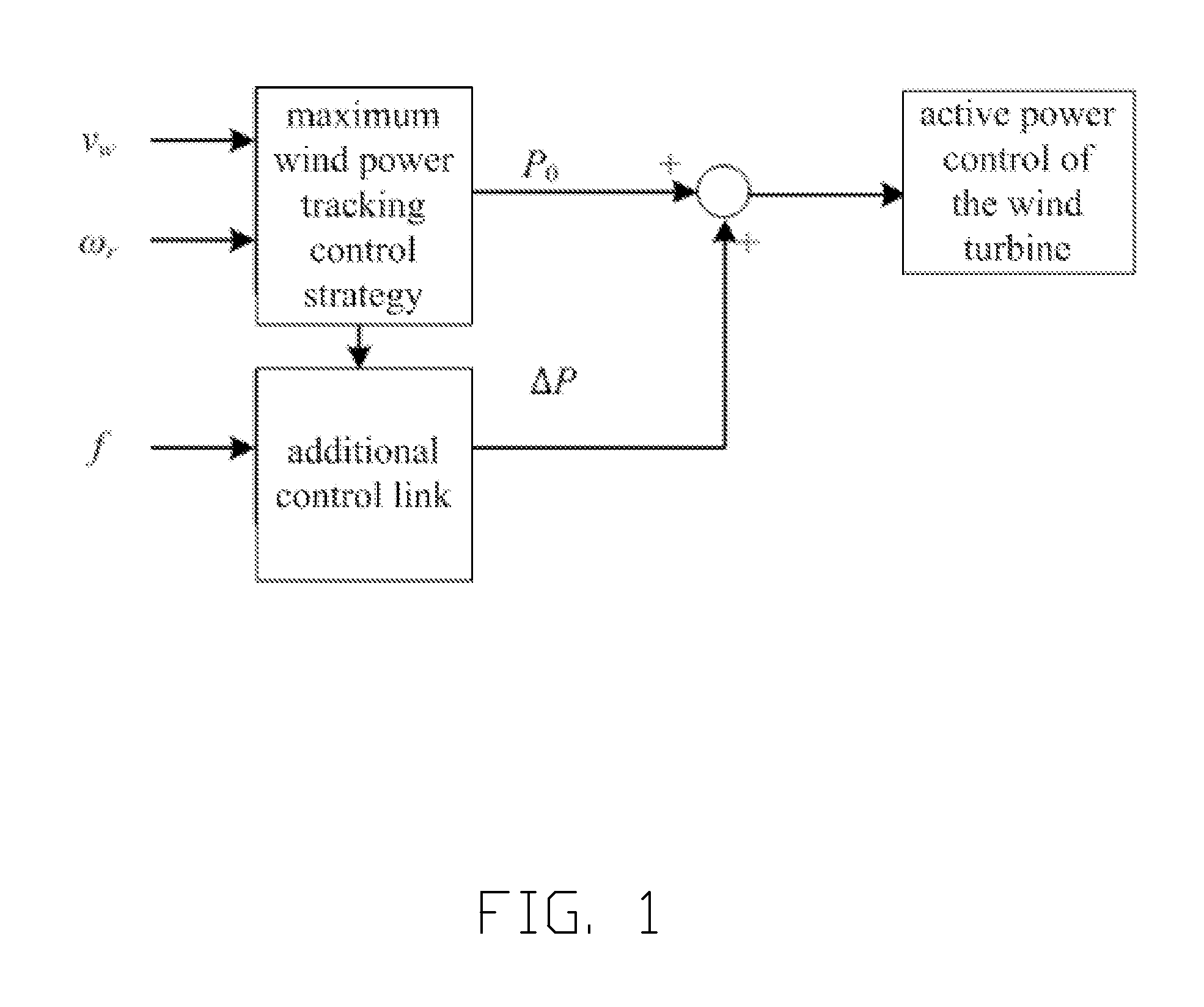
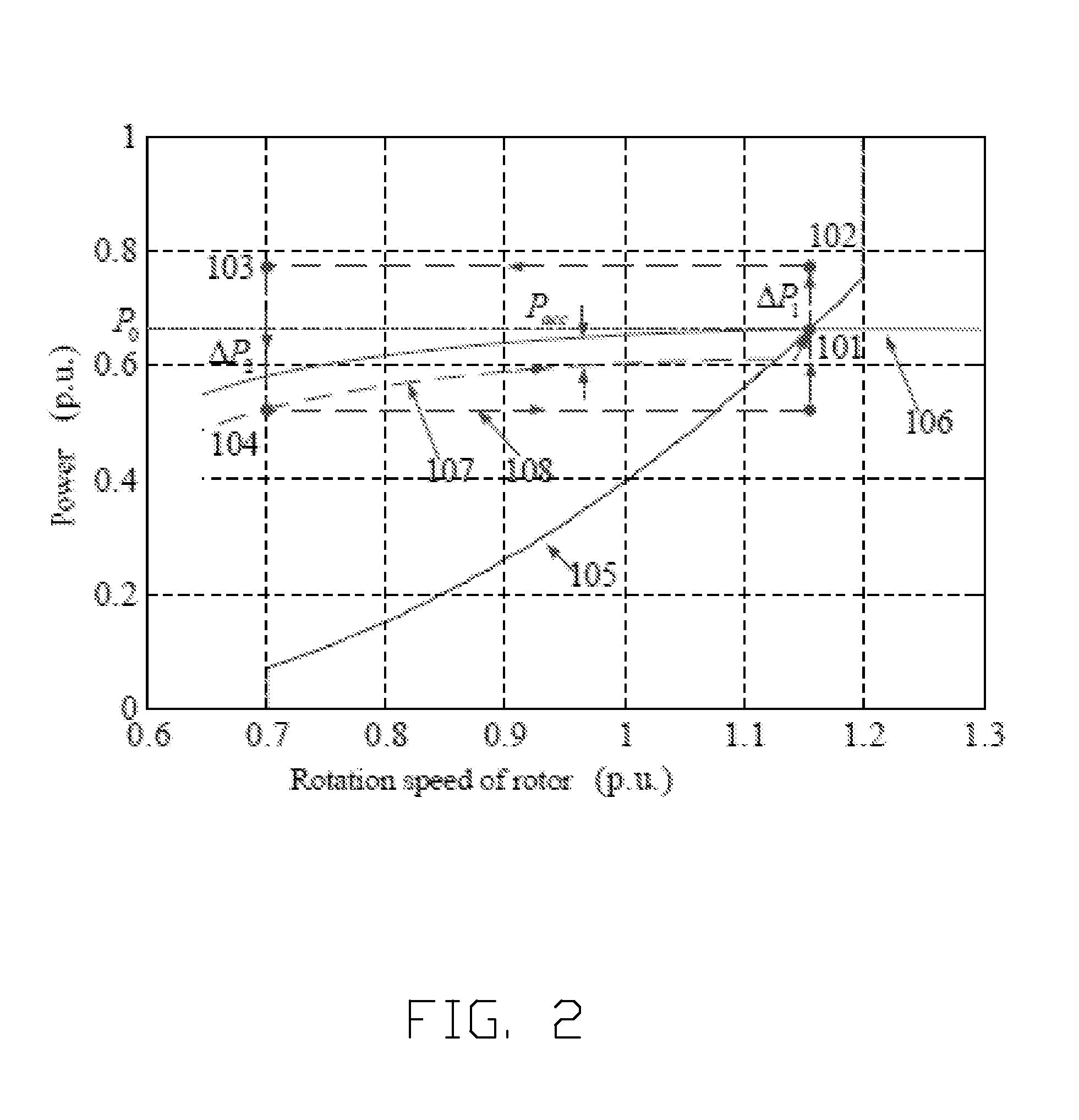
A method of controlling inertia response of variable-speed wind turbine generator includes following steps. A maximum wind power of the wind turbine is gotten through a wind speed νw and a rotation speed ωr at the hub of the wind turbine based on a maximum wind power tracking control strategy. The maximum wind power is set as an active power control reference value P0 of the wind turbine. A grid frequency f is obtained via a frequency measurement equipment. An additional active power control reference value ΔP of the wind turbine is generated based on the grid frequency f via an additional control block, and the additional active power control reference value ΔP is added on the active power control reference value P0, wherein a total of active power control reference value of the wind turbine is P0+ΔP.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
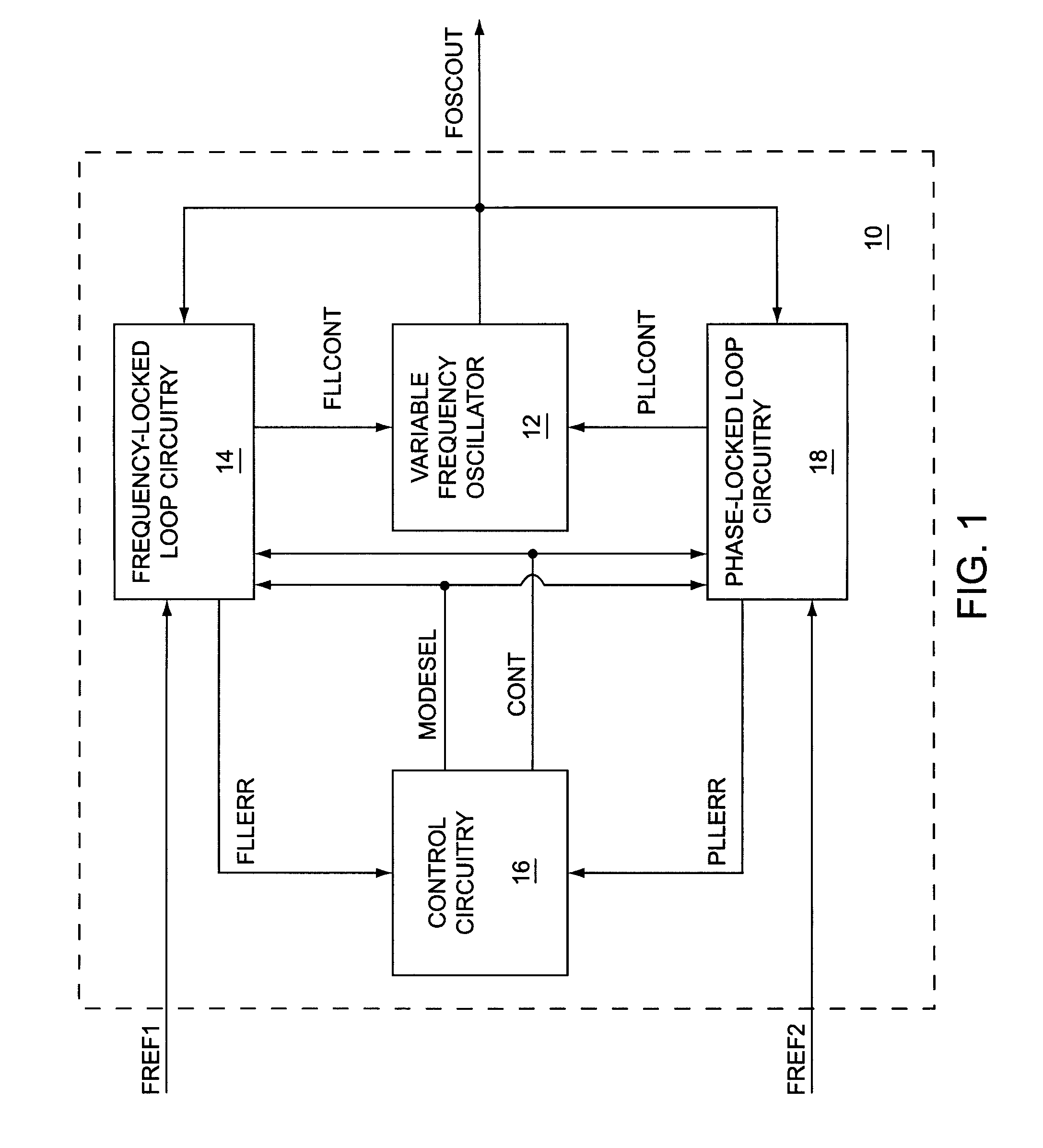
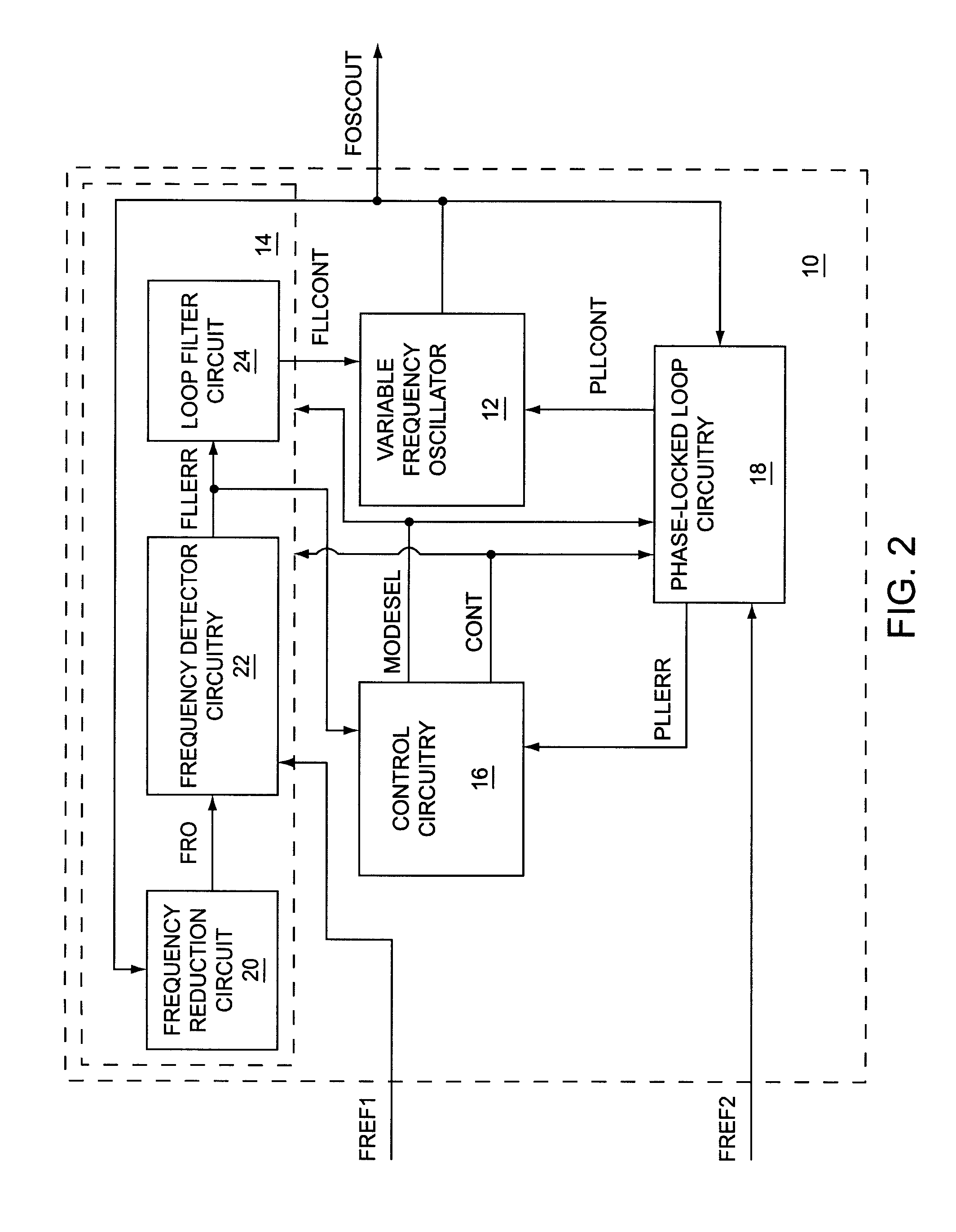
Frequency measurement based frequency locked loop synthesizer
ActiveUS7750685B1Fast settling timeReduce frequencyMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlFrequency measurementsEngineering
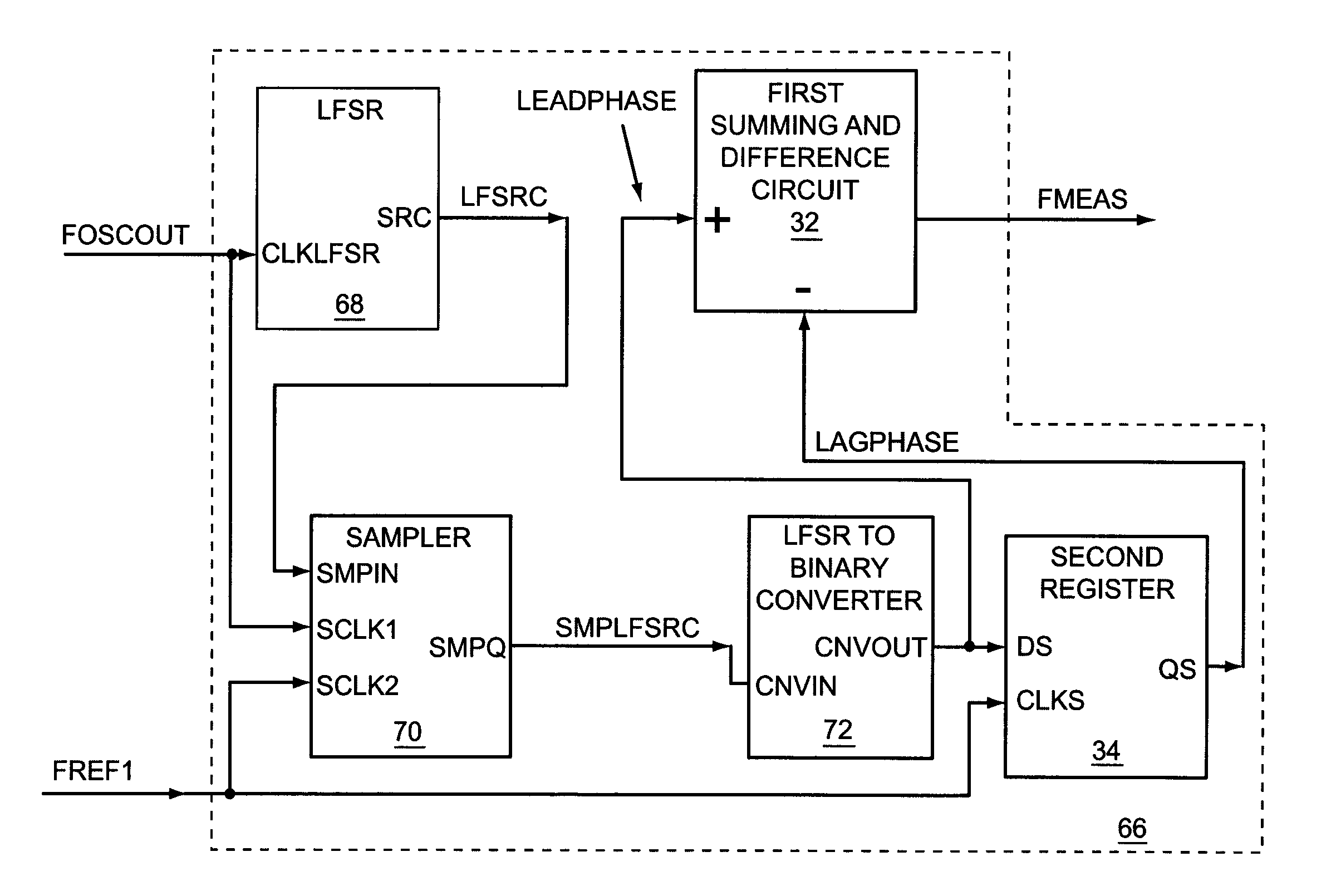
A first embodiment of the present invention relates to a frequency and phase locked loop (FPLL) synthesizer having a frequency-locked loop (FLL) operating mode and a phase-locked loop (PLL) operating mode. The FLL operating mode is used for rapid coarse tuning of the FPLL synthesizer and is followed by the PLL operating mode for fine tuning and stabilization of the frequency of an output signal from the FPLL synthesizer. A second embodiment of the present invention relates to a high resolution frequency measurement circuit that is capable of directly measuring the frequency of a high frequency signal to provide a high resolution frequency measurement using a lower frequency reference signal, and may include linear feedback shift register (LFSR) circuitry and LFSR-to-binary conversion circuitry. A third embodiment of the present invention relates to an FPLL having an FLL that includes the high resolution frequency measurement circuit.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Method of Handling Handover Measurement in a Discontinuous Reception Mode and Related Communication Device
A method of handling measurement in a DRX mode is for a mobile device in a wireless communication system. The method comprises being requested to perform inter-frequency measurement or inter-radio access technology (RAT) measurement after the mobile device performs a handover procedure or a re-establishment procedure and performing the inter-frequency measurement or inter-RAT measurement when the mobile device stays in a DRX period of the DRX mode.
Owner:HTC CORP
Automobile anticollision radar system based on frequency-modulated continuous wave
InactiveCN102788980ALimit ranging distanceEffective filteringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingDistance discrimination
The invention relates to an automobile anticollision radar system based on frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) and belongs to the technical field of automobile protection. The system can measure the distance and velocity of a target and effectively avoid car crashes. The system comprises the following components: a radar sensor, a filter, an automatic gain control amplifier, an analog-to-digital converter, a digital signal processor and a corresponding early-warning device. The radar sensor collects signals including leaked modulation, intermediate-frequency and high-frequency signals; the filter filters off the leaked modulation waves and high-frequency component; in the digital signal processor, the spectral analysis is performed by means of FFT and the frequency measurement results are converted into distance information and velocity information; and different warning modes are adopted according to the measurement results. The maximum acceptance range of the system can reach 150 m, the distance discrimination is 1 m, the velocity discrimination is 1 m / s, and the working environment is -40 DEG C to -80 DEG C.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Measuring brillouin backscatter from an optical fibre using a tracking signal
ActiveUS20100002226A1Narrow down the frequency rangeReduce the amount requiredReflectometers using simulated back-scatterConstructionsFrequency measurementsFrequency shift
A method for measuring Brillouin backscattering from an optical fibre (18), comprises frequency mixing a first signal with a frequency f B (t) representative of the Brillouin frequency shift in backscattered light received from a deployed optical fibre with a second signal at a frequency f i (t) that varies in time in the same manner as a Brillouin shift previously measured from the fibre to produce a difference signal with a difference frequency iF(t) that has a nominally constant value corresponding to the situation where the received light has a Brillouin shift that matches the previously measured shift. The difference signal is acquired and processed to determine properties of the Brillouin shift and corresponding physical parameters producing the shift. The frequency mixing can be carried out. optically or electrically. Techniques for acquisition of the difference signal include the use of parallel frequency measurement channels and fast rate digital sampling.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Different frequency measurement configuration method and device
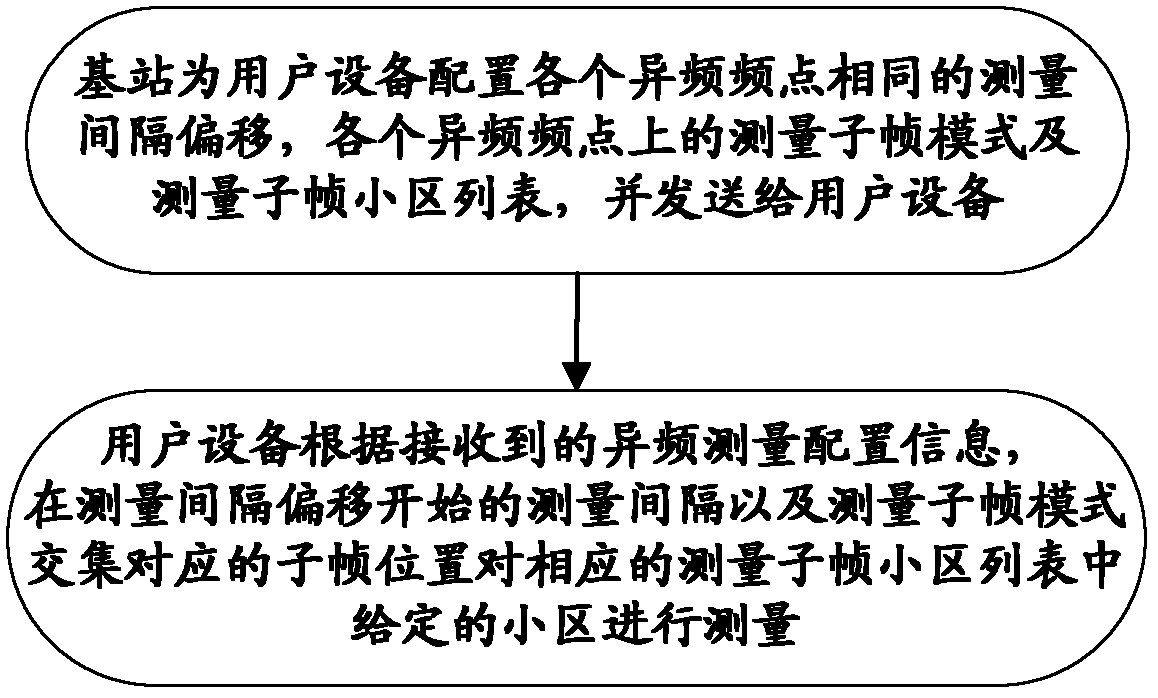
InactiveCN103037399AGuaranteed accuracyAccurate judgmentWireless communicationFrequency measurementsComputer science
The invention discloses a different frequency measurement configuration method and a device. A base station configures different frequency measurement for user equipment according to nearly blank subframe model information of adjacent cells on each frequency point for the user equipment to perform different frequency measurement and sends different frequency measurement configuration information to the user equipment, wherein the different frequency measurement information at least comprises measurement interval deviation or a measurement subframe model; and the user equipment measures the adjacent cells on the corresponding frequency points according to the received different frequency measurement configuration information. By means of the different frequency measurement configuration method and the device, the fact that the user equipment accurately measures different frequency cells in the scene of interference coordination can be guaranteed so that the user equipment can correctly judge and switch to an appropriate different frequency cell.
Owner:ZTE CORP
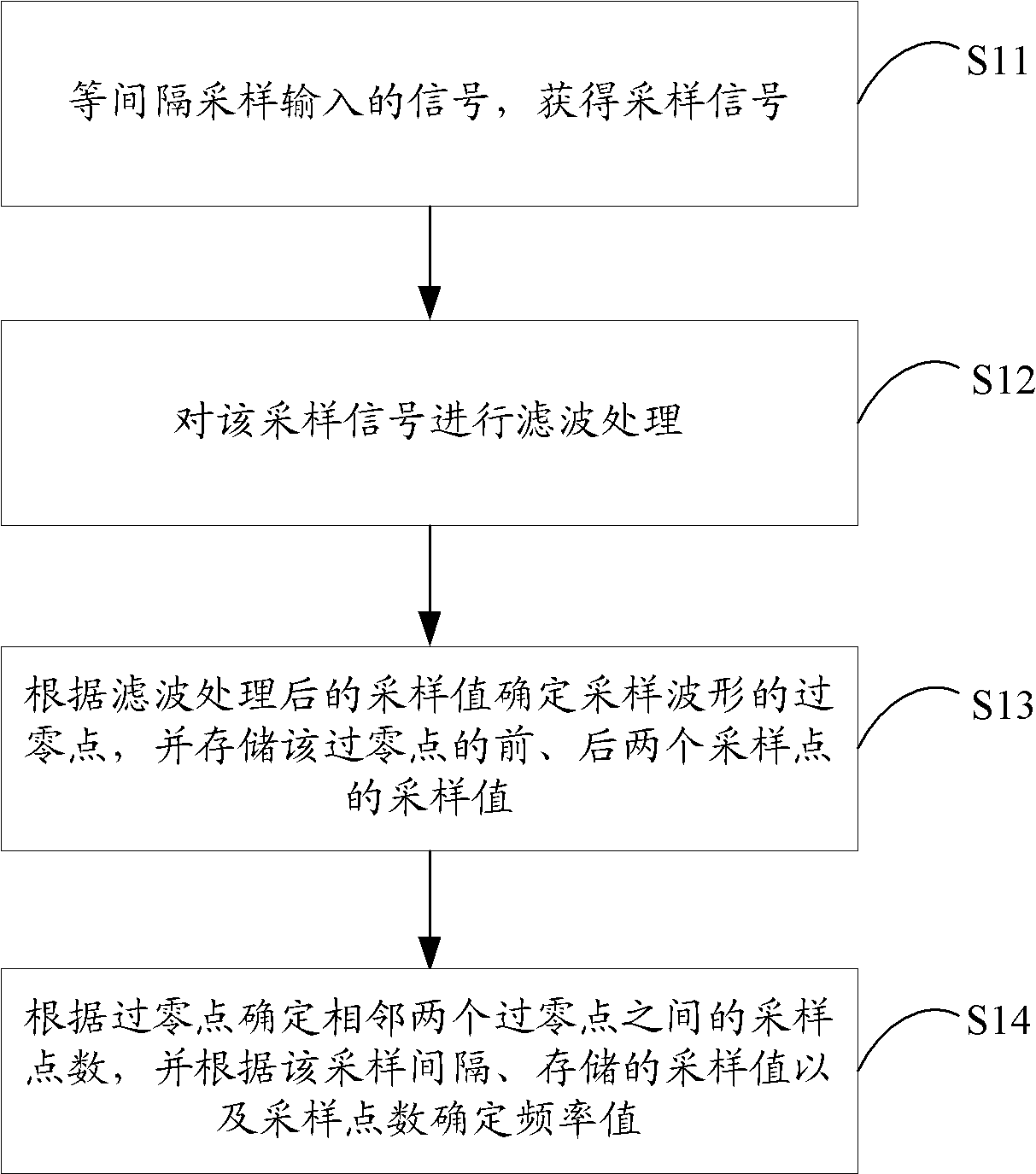
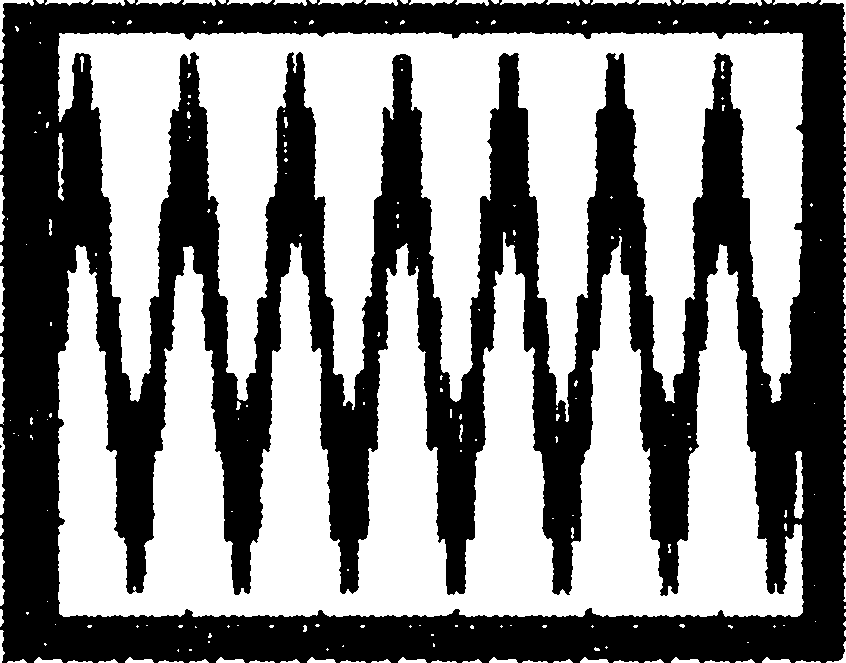
Power grid frequency measurement method and device
InactiveCN102116798AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionFrequency measurement arrangementFrequency measurementsHarmonic
The invention is applicable to the power field and provides a power grid frequency measurement method and a device. The method comprises the following steps: sampling inputted signals at equal intervals and obtaining sampled signals with equal sampling intervals; carrying out filtering treatment on the sampled signals; determining a zero crossing point of a sampled waveform according to the sampling value after the filtering treatment and storing the sampling values of front and rear sampling points of the zero crossing point; determining the number of sampling points between the adjacent zero crossing points and measuring the frequency value according to the sampling intervals, the sampling values and the sampling points. As the high-frequency filtering treatment is carried out before the base wave frequency measurement, the embodiment of the invention can effectively eliminate the interference of harmonic waves in the practical power network operation, thereby improving the detection accuracy of the zero crossing point and further improving the reliability and the accuracy of the base wave frequency measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN RENERGY TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com