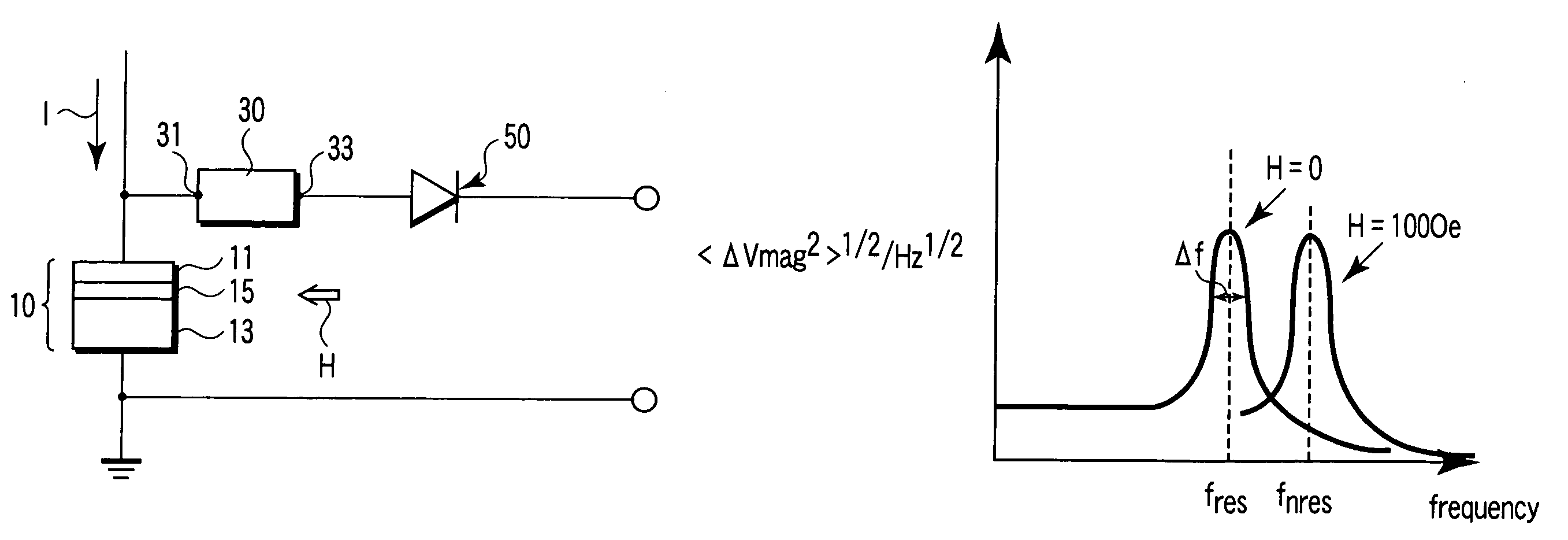Patents
Literature
772 results about "Frequency filtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
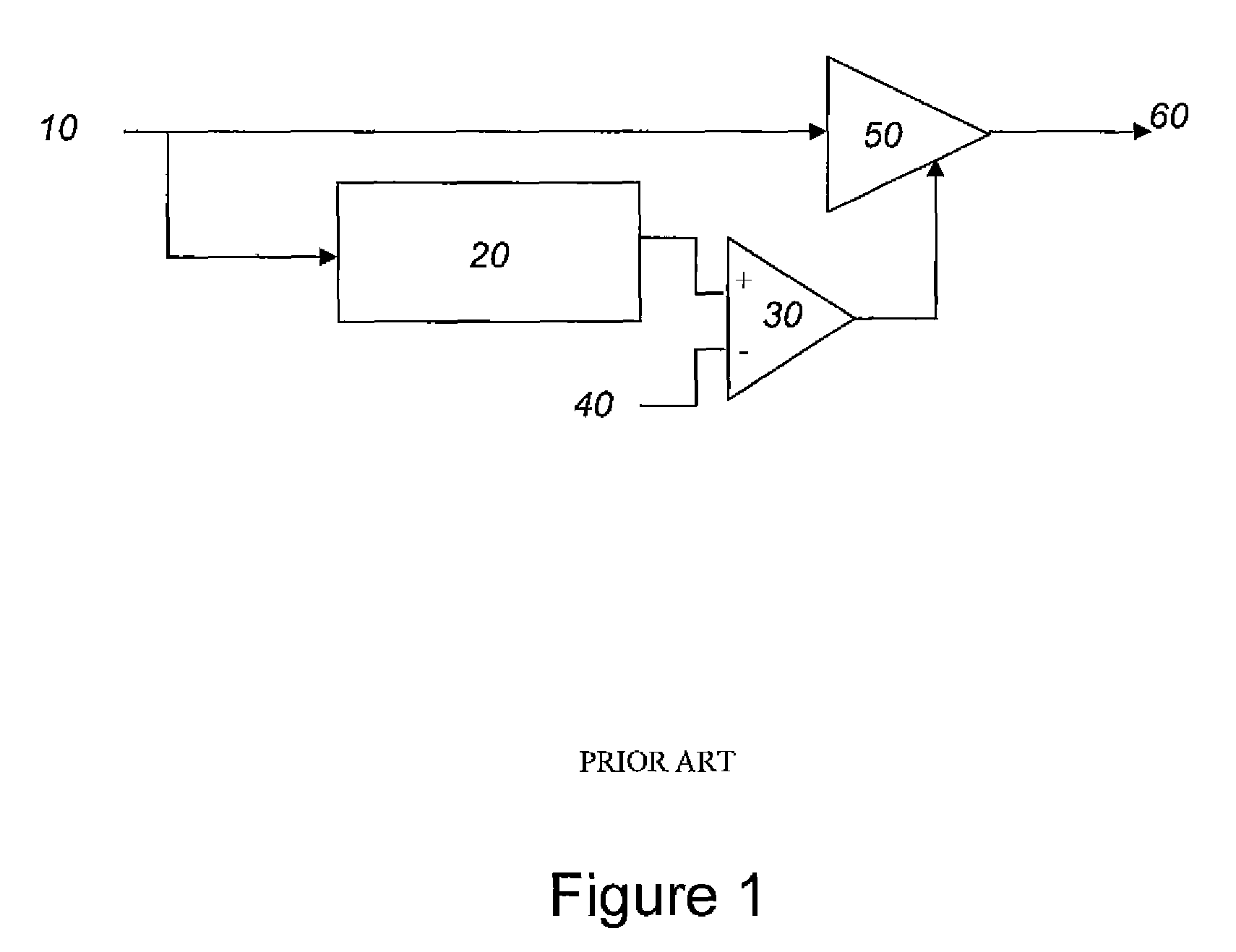
A frequency filter is an electrical circuit that alters the amplitude and sometimes phase of an electrical signal with respect to frequency. Filters are used in several electronic and telecommunications applications to emphasize signals in a particular frequency range while rejecting or suppressing those in the undesired frequency range.
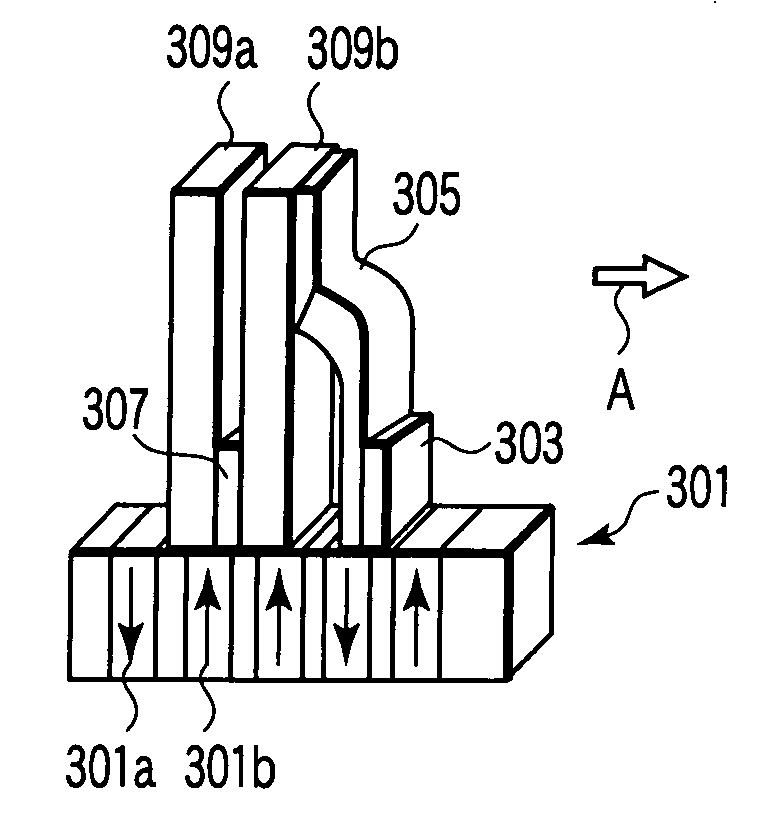
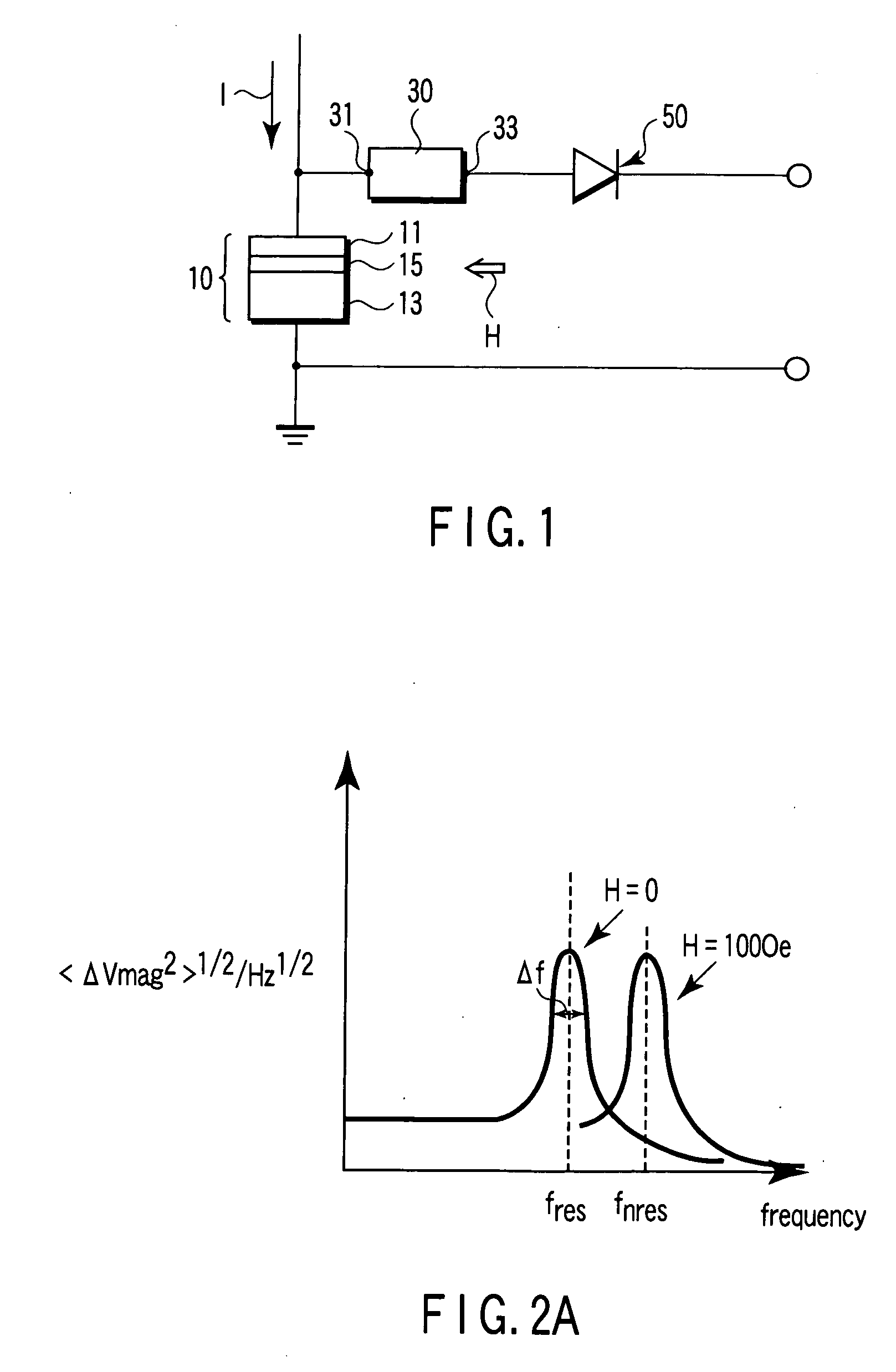
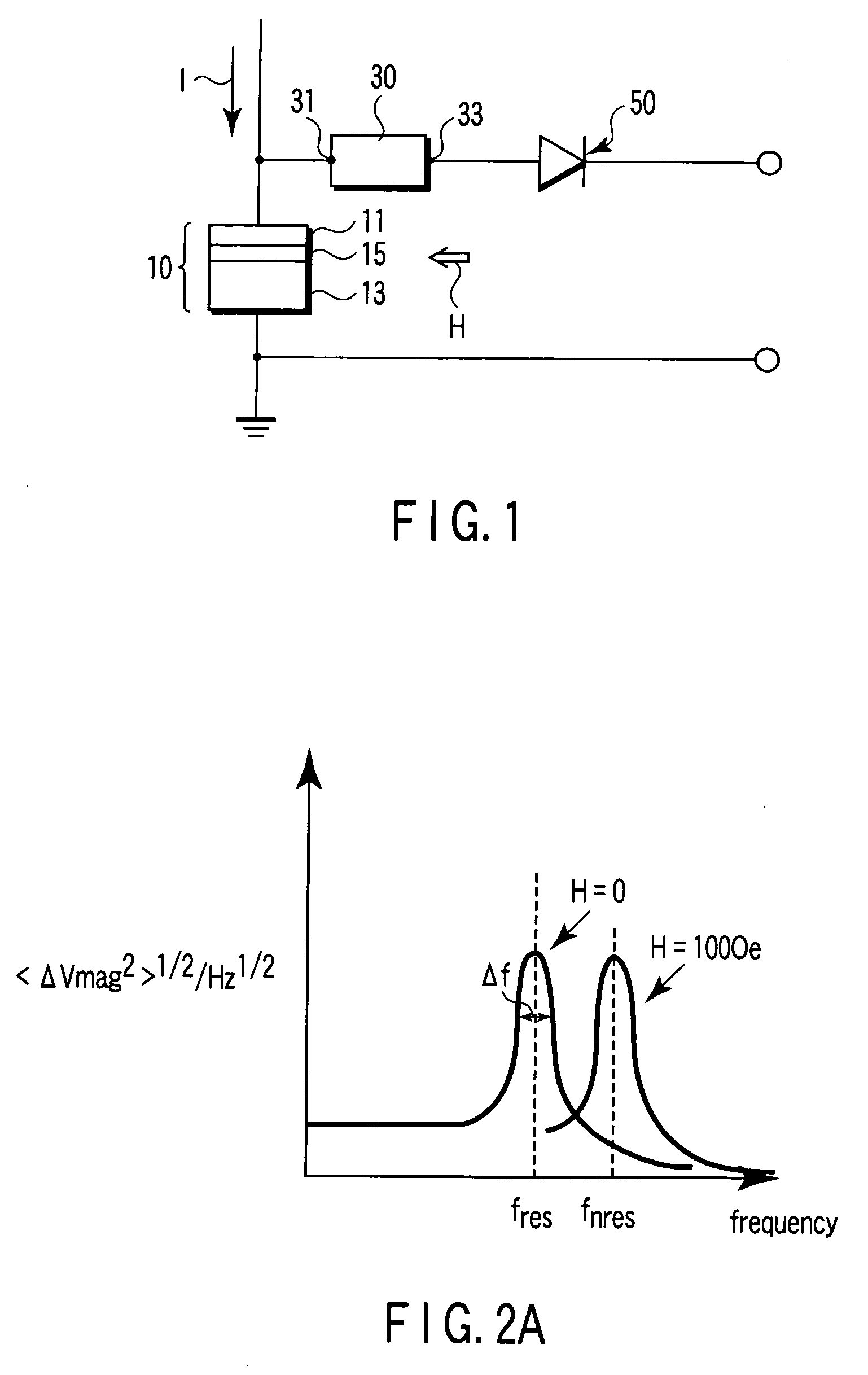
Magnetic sensor, magnetic field sensing method, semagnetic recording head, and magnetic memory device
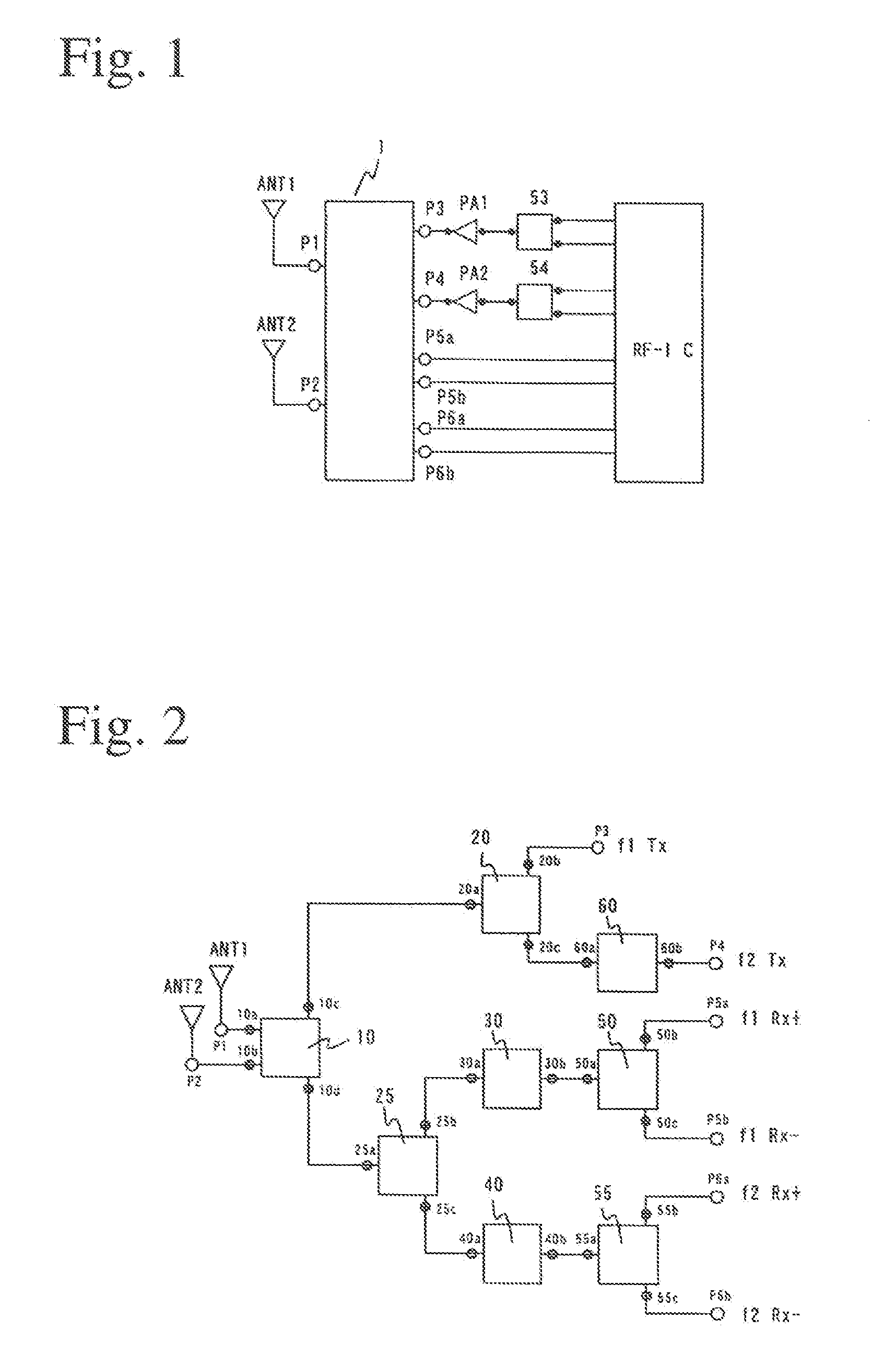
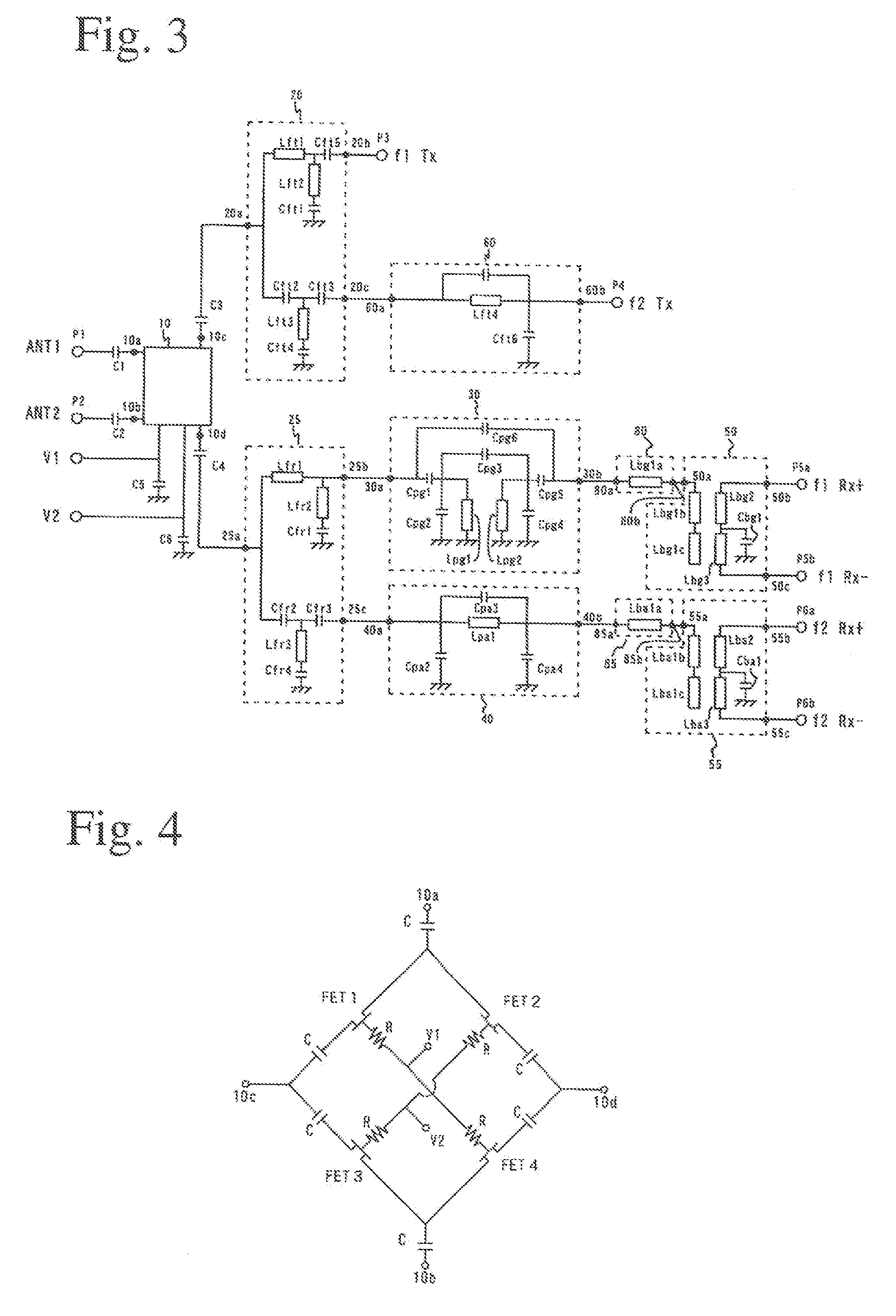
ActiveUS20050219771A1Modification of read/write signalsNanomagnetismFrequency filteringMagnetization
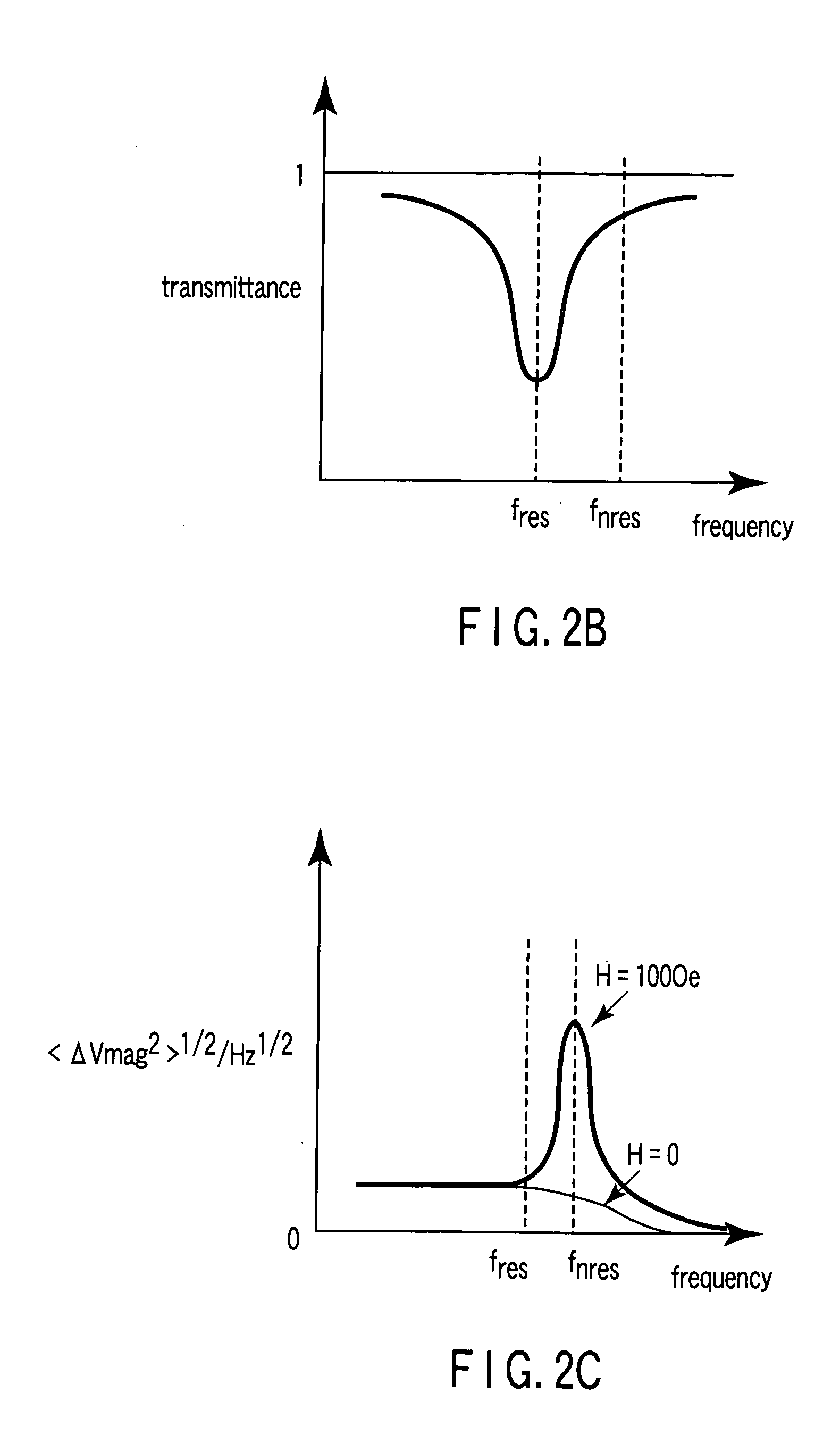
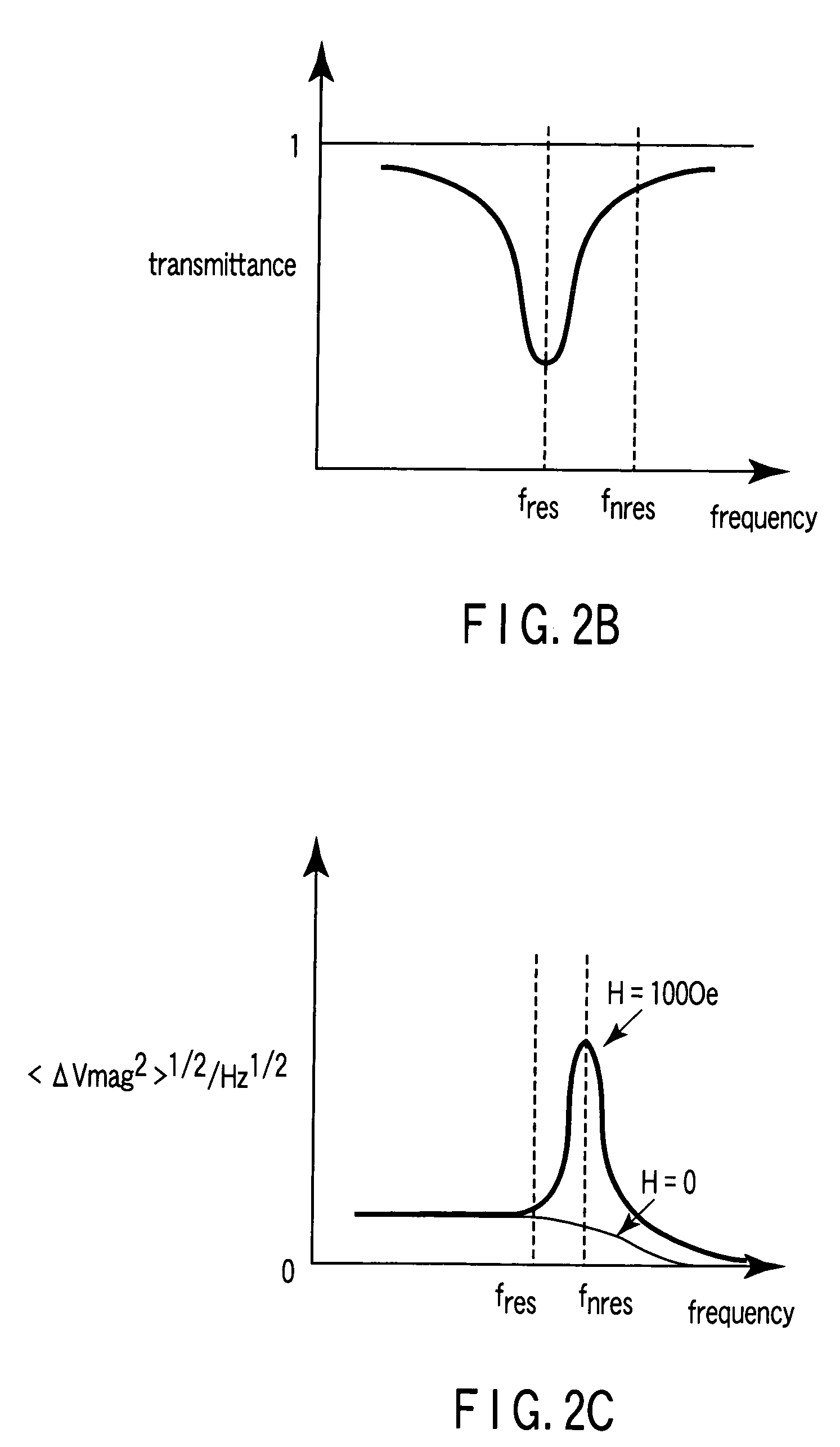
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
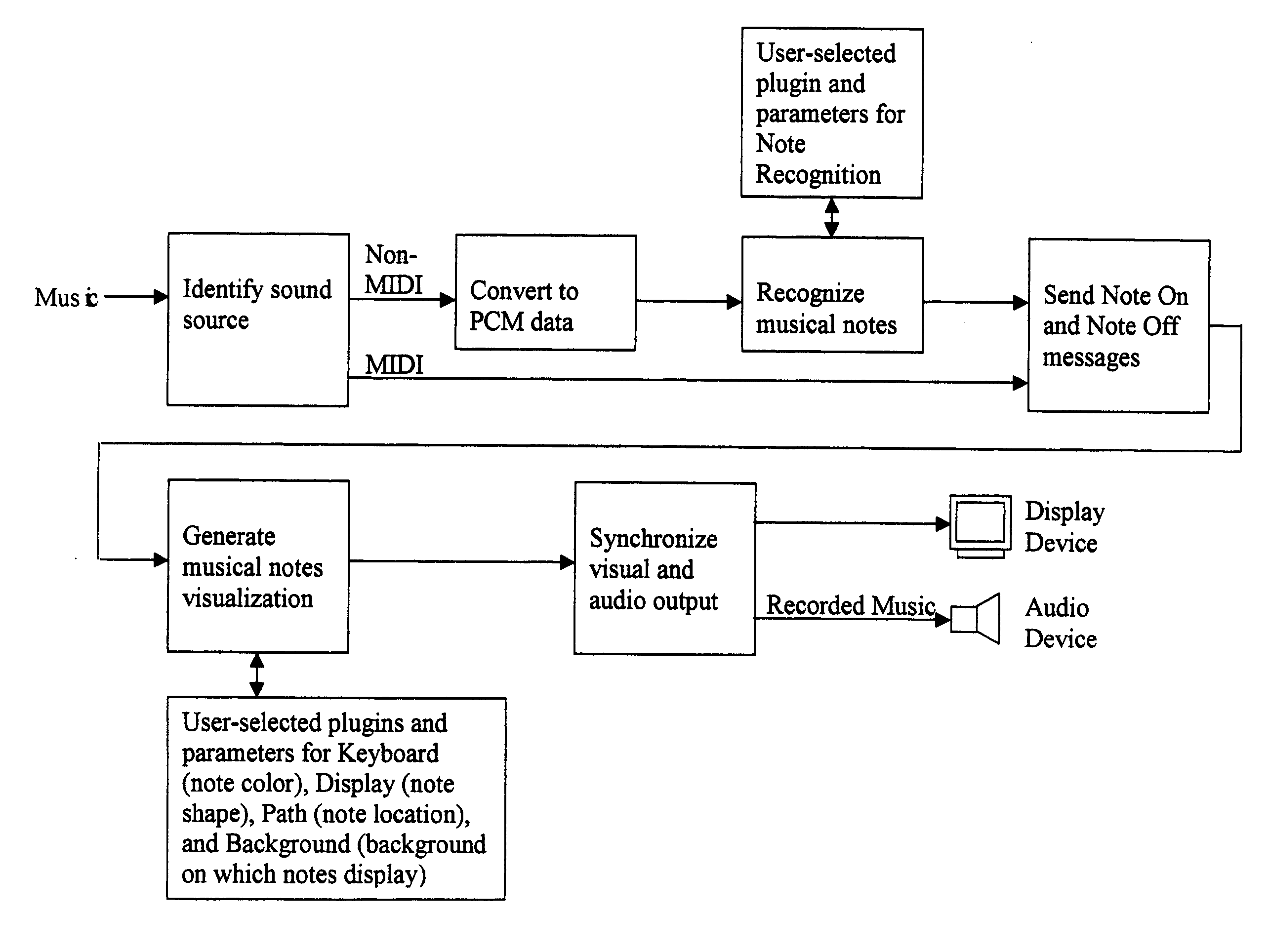
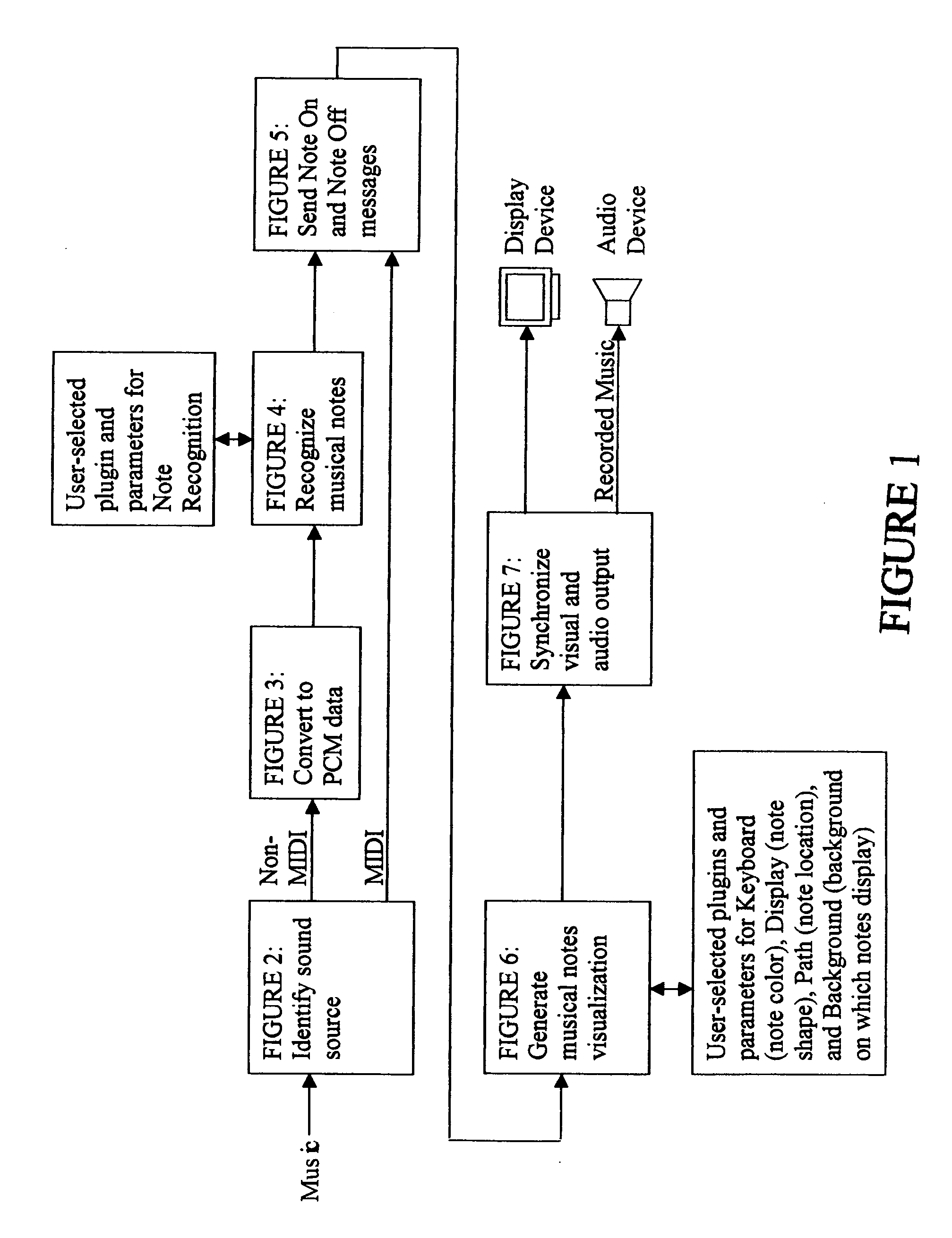
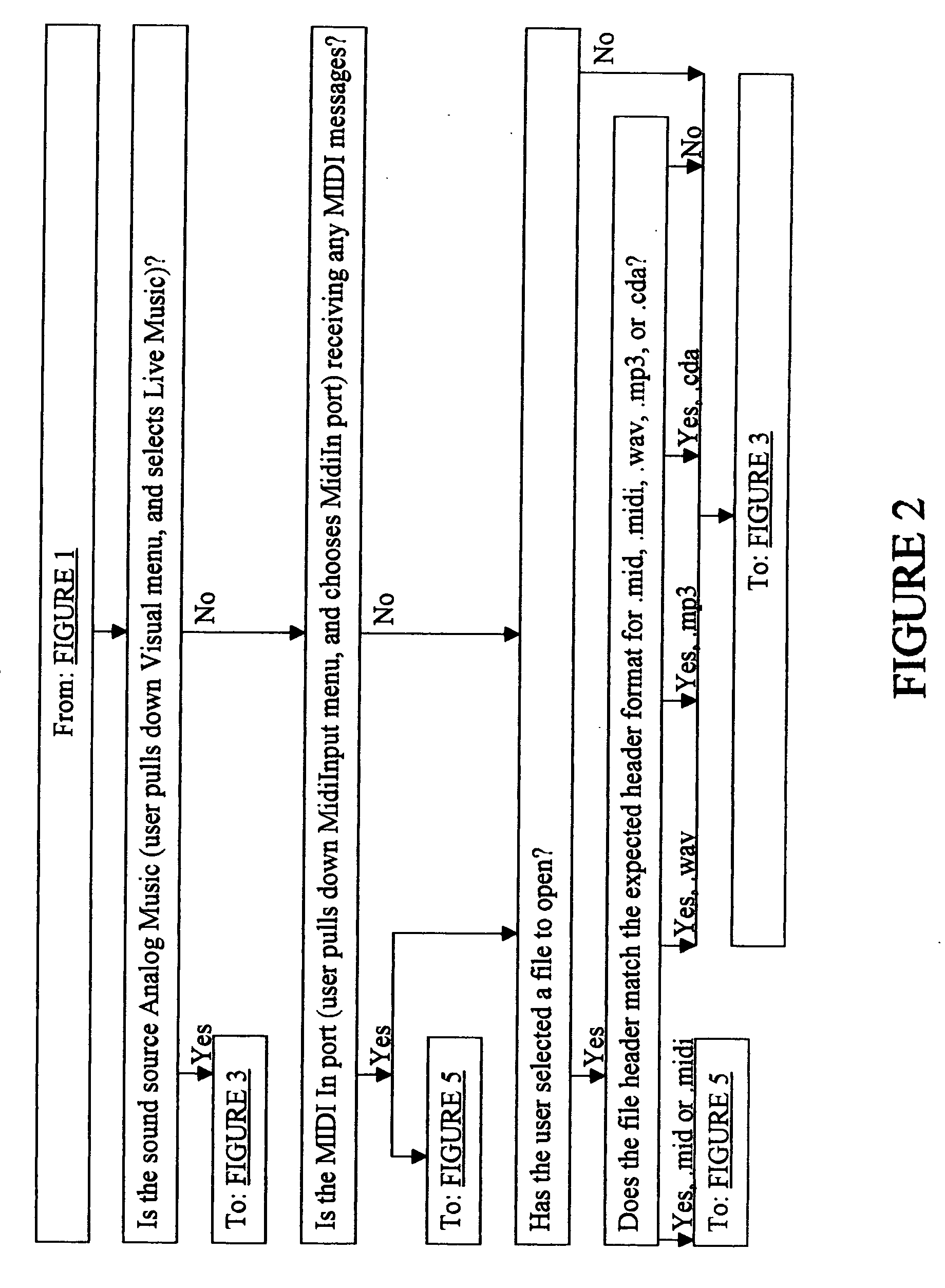
Apparatus and method for identifying and simultaneously displaying images of musical notes in music and producing the music
InactiveUS20050190199A1Reduce processor loadGearworksMusical toysDisplay deviceAnalog-to-digital converter
Our invention is an apparatus and method to identify and simultaneously visualize and hear musical notes contained in an analog or digital sound wave. Musical notes are expanded into a language for the eye as well as the ear. An analog-to-digital converter processes an analog sound wave to provide a digital sound wave. Component frequencies of the digital sound waves are identified, filtered and translated to their corresponding musical note and volume. As the original digital sound wave is sent through a digital-to-analog converter and output to an audio device, the identified musical notes are synchronously output to a display device. User-specified parameters, adjustable at any time before, during or after the music-playing process, control frequency filtering, the graphic display of the identified musical notes and the graphical background on which the musical notes are displayed. Users may also utilize existing, or create their own, computer programming code software modules, known as plug-ins, or hardware components, to interface with the invention to extend and control the invention's functionality. Because the synchronous musical note identification and visualization process occurs extremely quickly, the method applies and works in real-time for live music.
Owner:STEINBERG GRIMM
Surface acoustic wave device with KNb03 piezoelectric thin film, frequency filter, oscillator, electronic circuit, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS6720846B2Polycrystalline material growthPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTectorial membraneFrequency filtering
Surface acoustic wave device having a high k<2>, and a frequency filter, oscillator, electronic circuit and electronic device employing this surface acoustic wave device is provided, wherein a first oxide thin film layer comprising SrO or MgO and a second oxide thin film layer comprising SrTiO3 are sequentially formed on top of a (110) Si substrate, or a first oxide thin film layer comprising CeO2, ZrO2 or yttrium-stabilized zirconia and a second oxide thin film layer comprising SrTiO3 are sequentially formed on top of a (100) Si substrate, a KNbO3 piezoelectric thin film being then formed on top of either of these second oxide thin film layers, and then, a protective film comprising oxide or nitride is formed on top of the KNbO3 piezoelectric thin film, finally, at least one electrode is formed on top of this protective film, to form a surface acoustic wave device, which surface acoustic wave device is employed to form a frequency filter, oscillator, electronic circuit, or electronic device.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
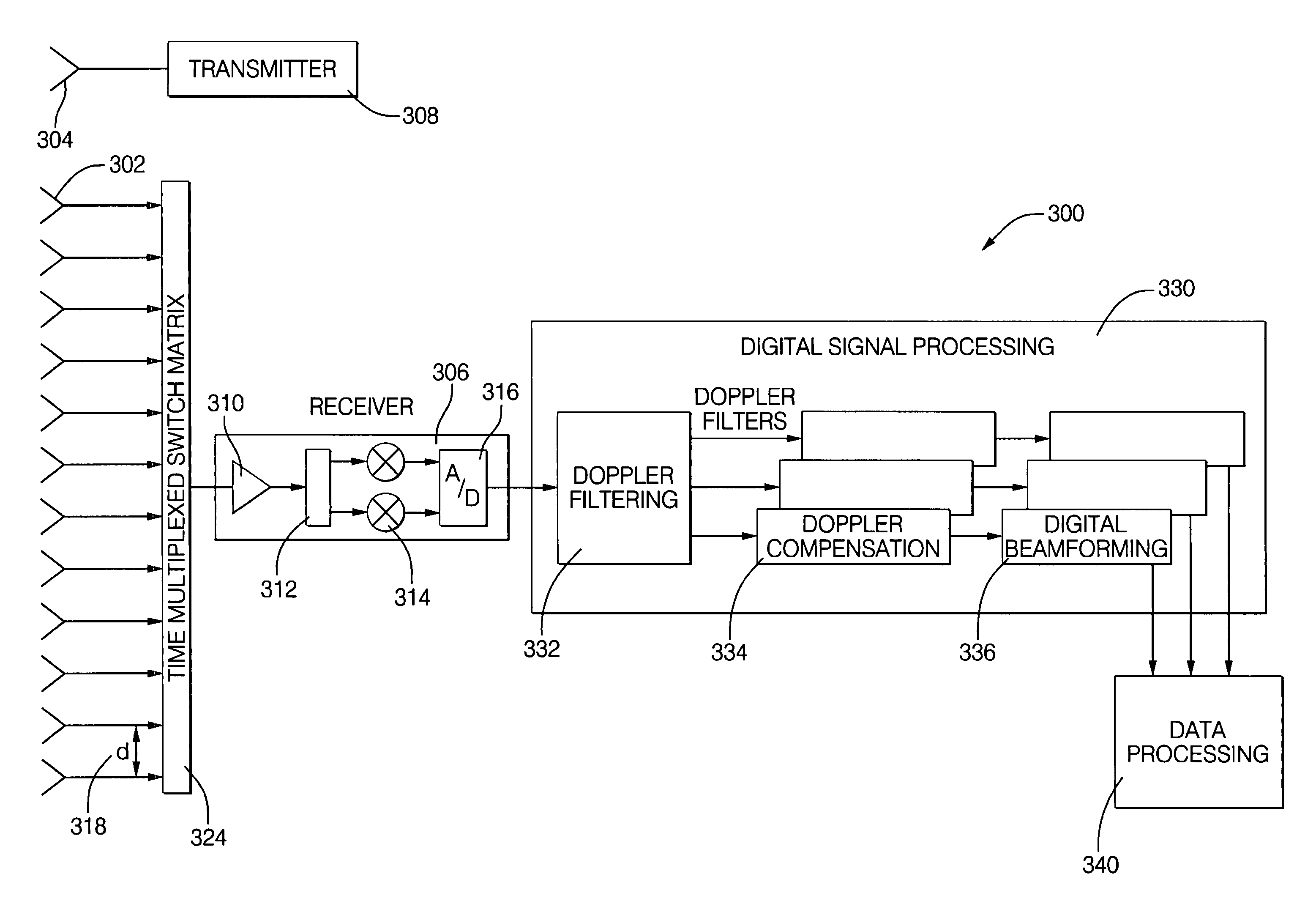
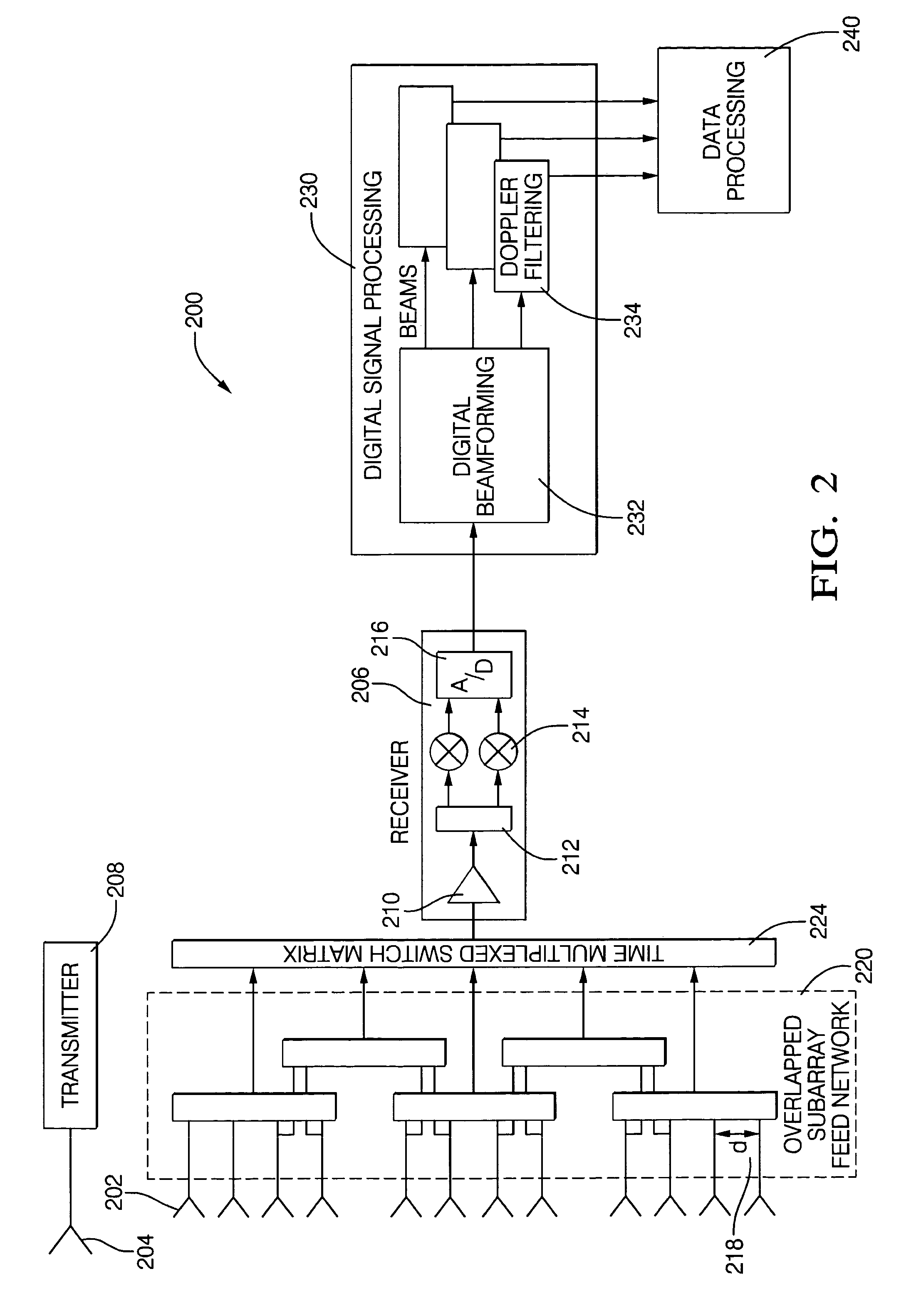
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS20070001897A1Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsGrating lobe
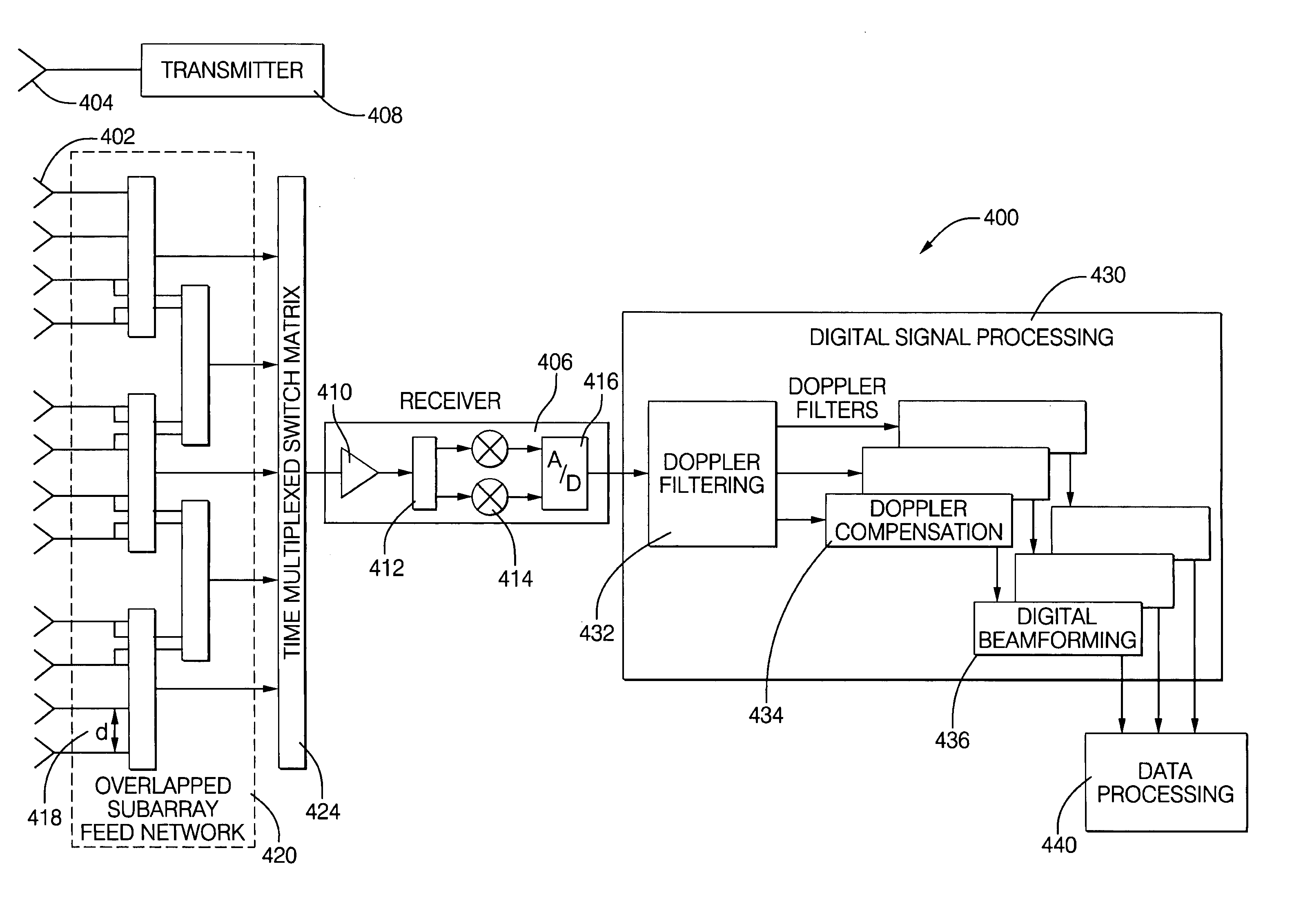
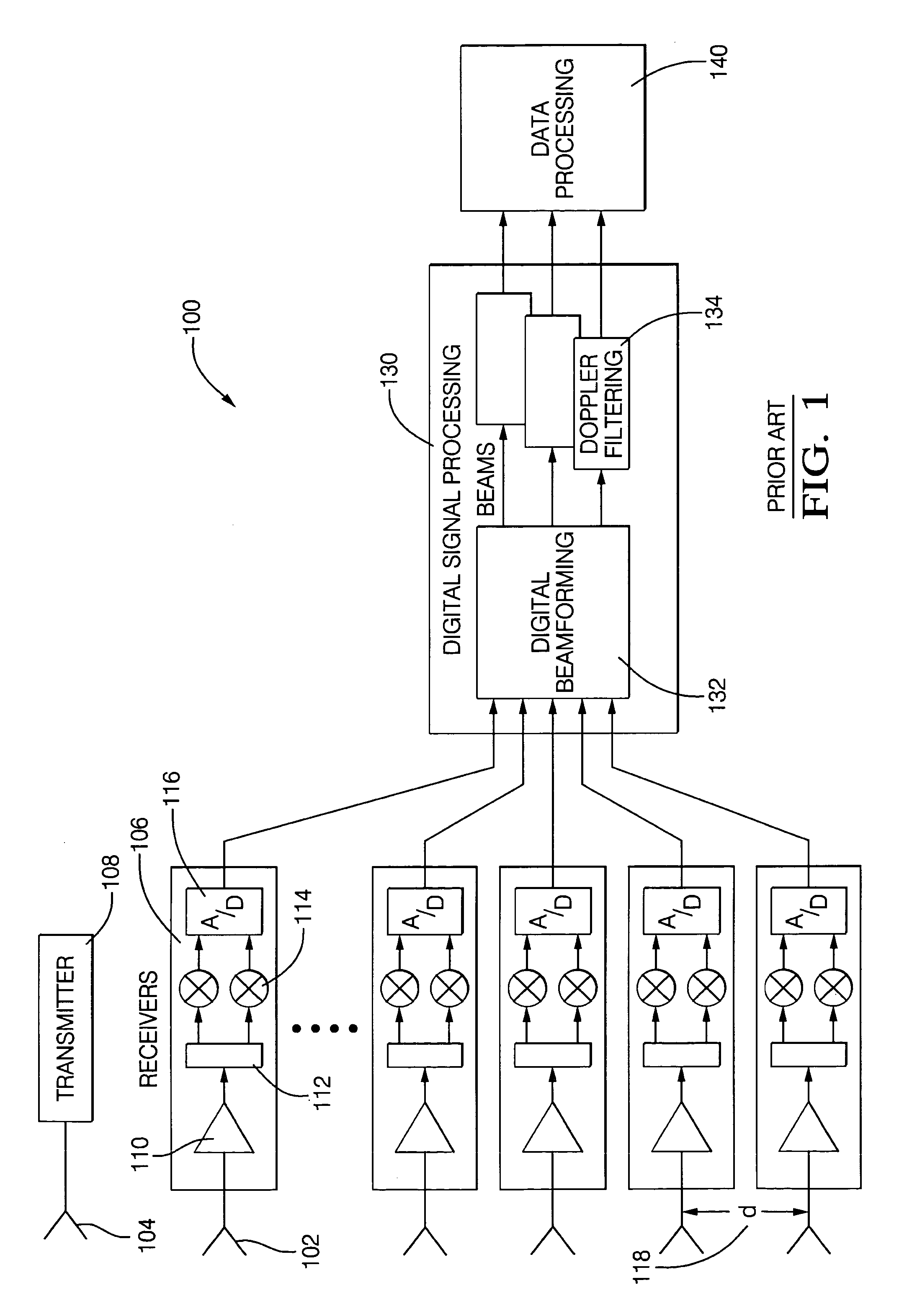
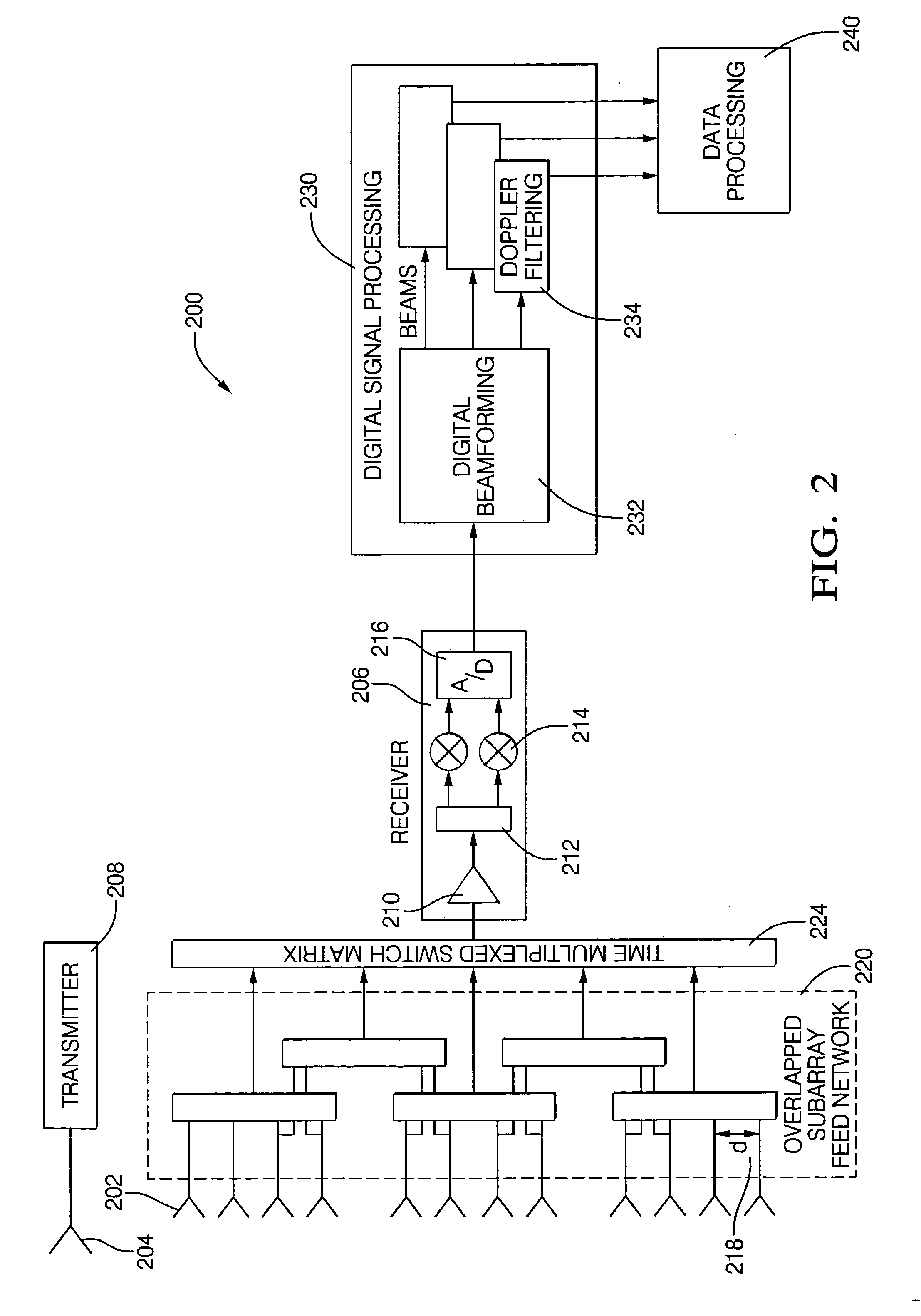
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Resonator, frequency filter, duplexer, electronic device, and method of manufacturing resonator
InactiveUS20130234805A1Low mechanical strengthImprove productivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFrequency filteringAcoustic wave
A resonator according to the present invention includes a supporting substrate, a piezoelectric layer, a pair of excitation electrodes, and a bonding layer. The piezoelectric layer is made of a piezoelectric material. The pair of excitation electrodes is formed on the upper surface of the piezoelectric layer so as to excite bulk acoustic waves. The bonding layer has a cavity formed therein so as to face the excitation electrode pair through the piezoelectric layer, and the bonding layer bonds the supporting substrate to the lower surface of the piezoelectric layer.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
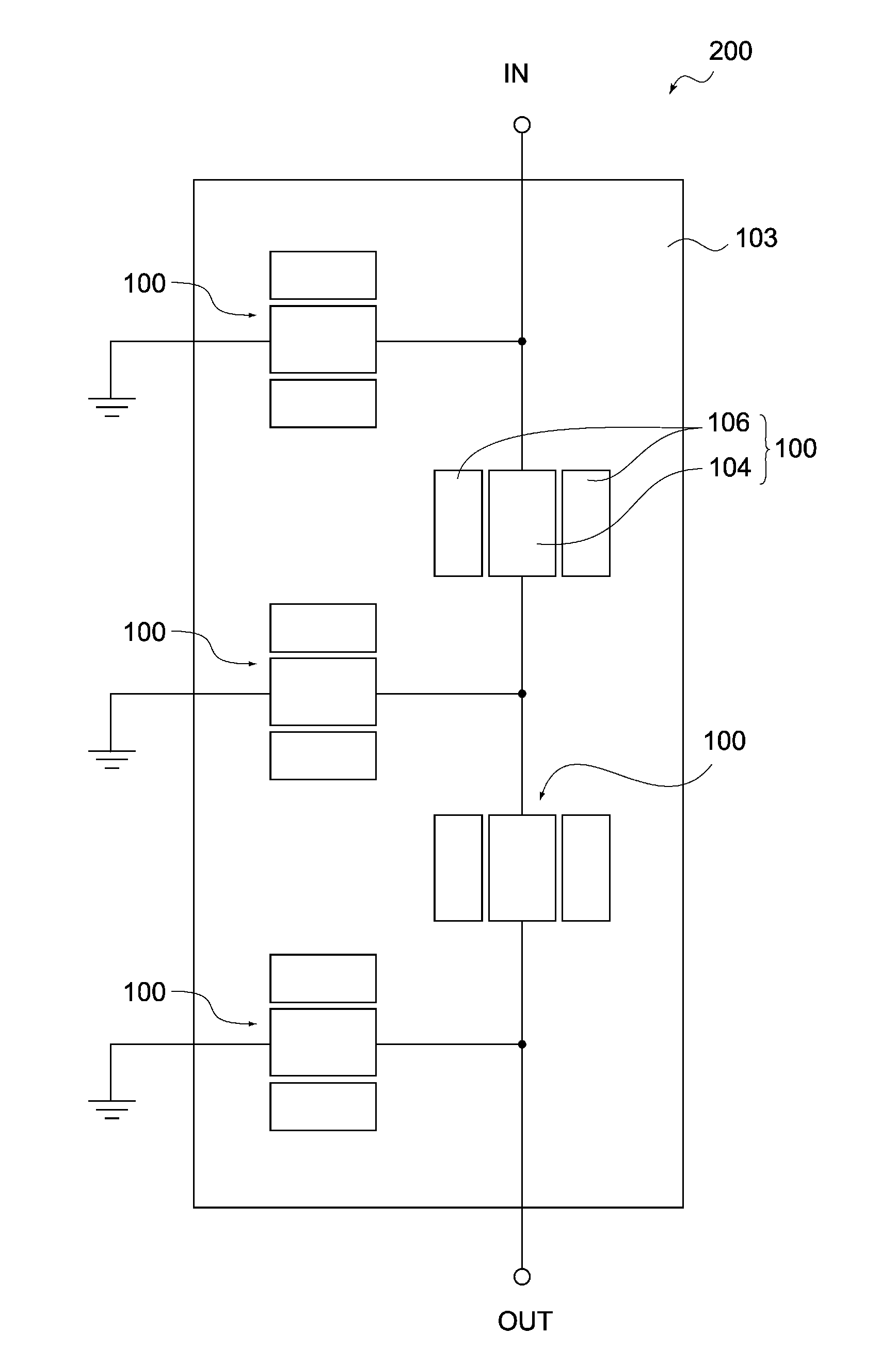
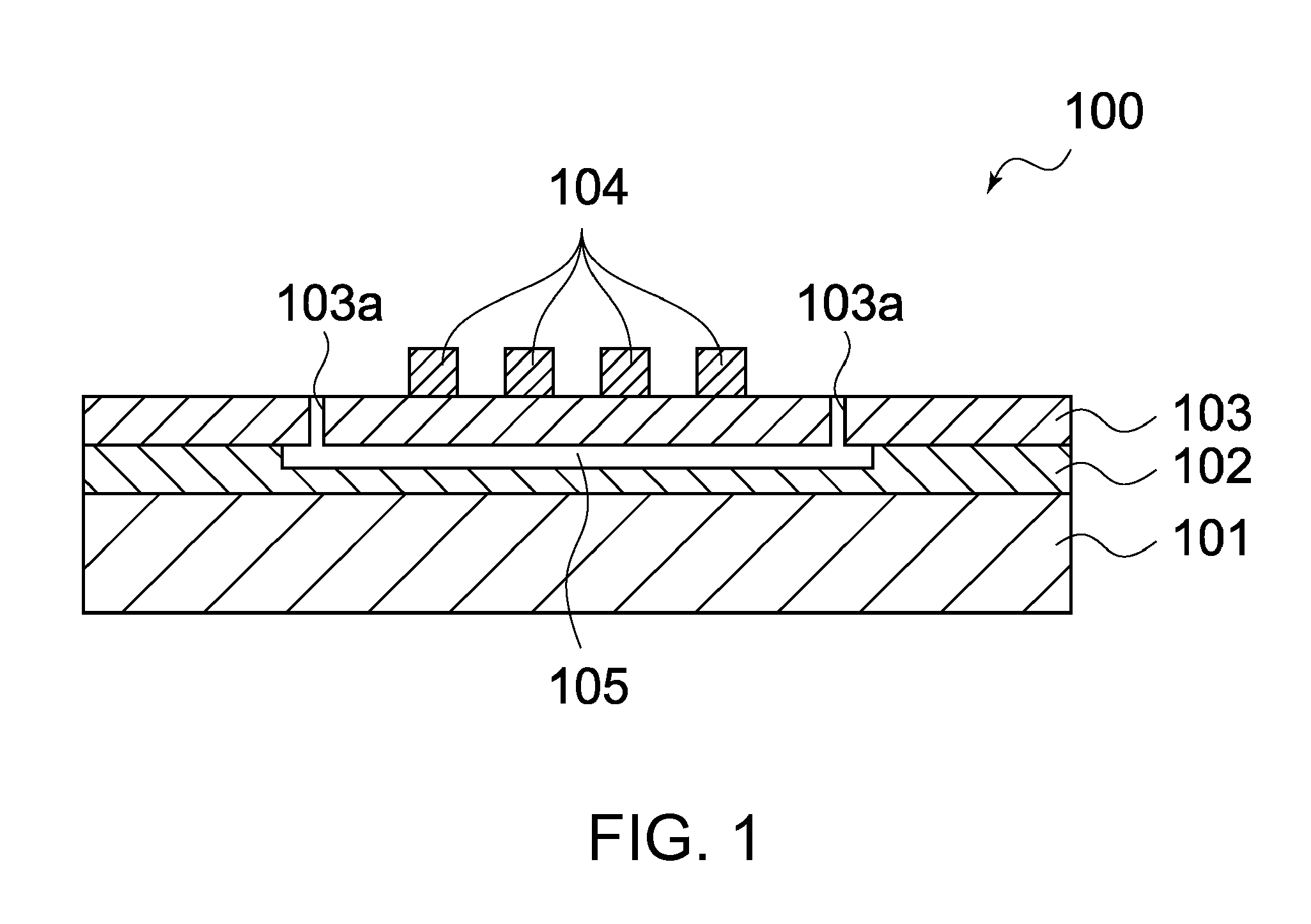
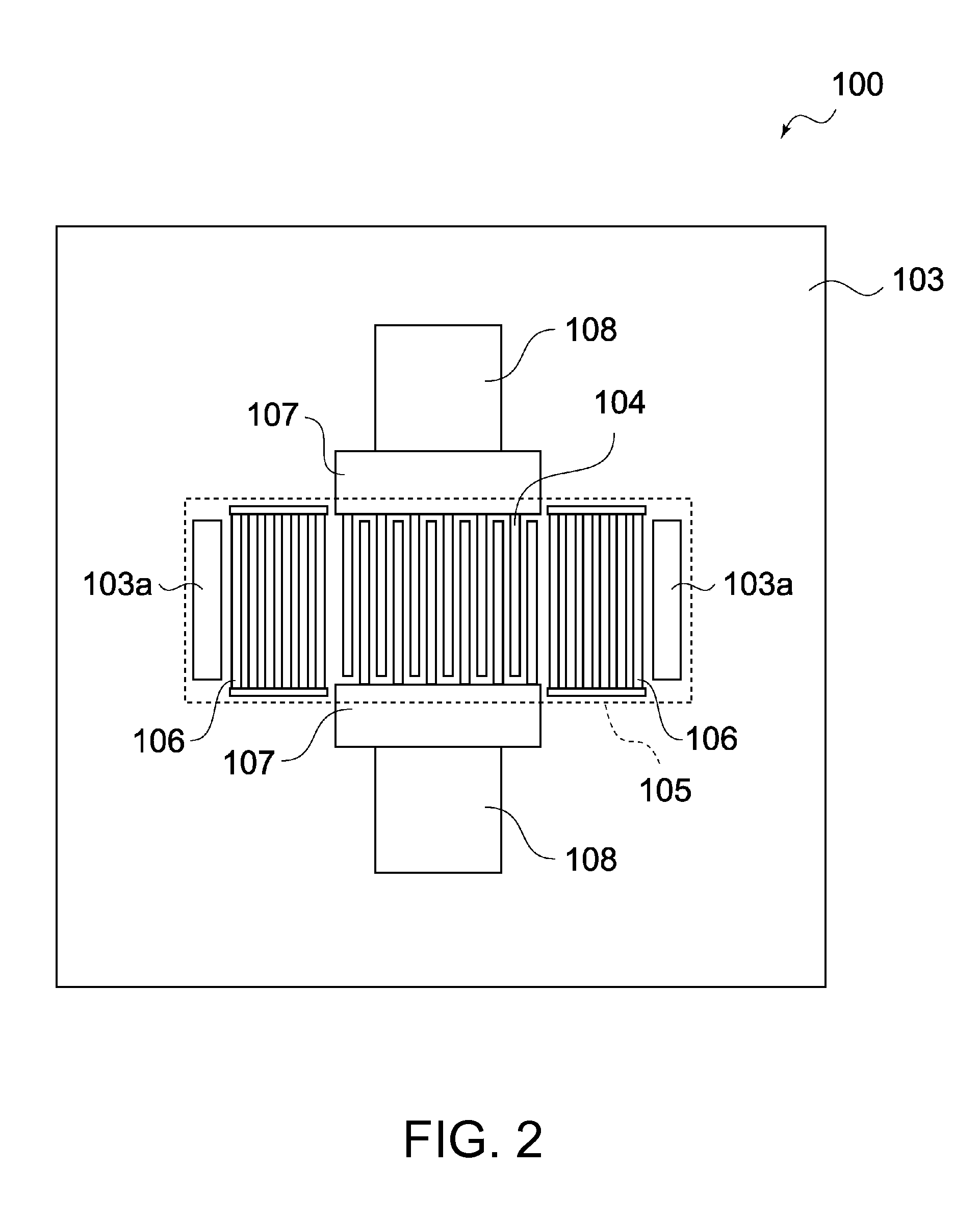
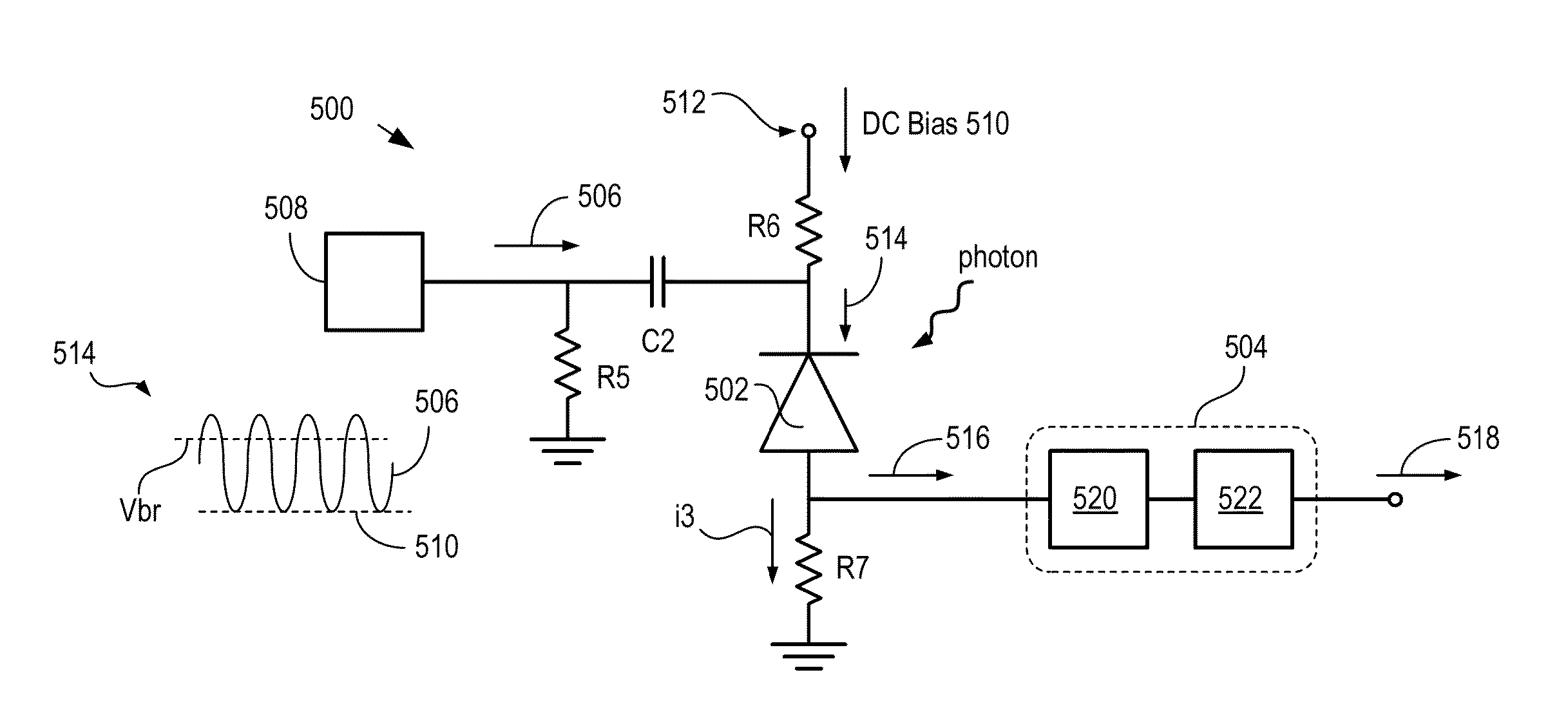
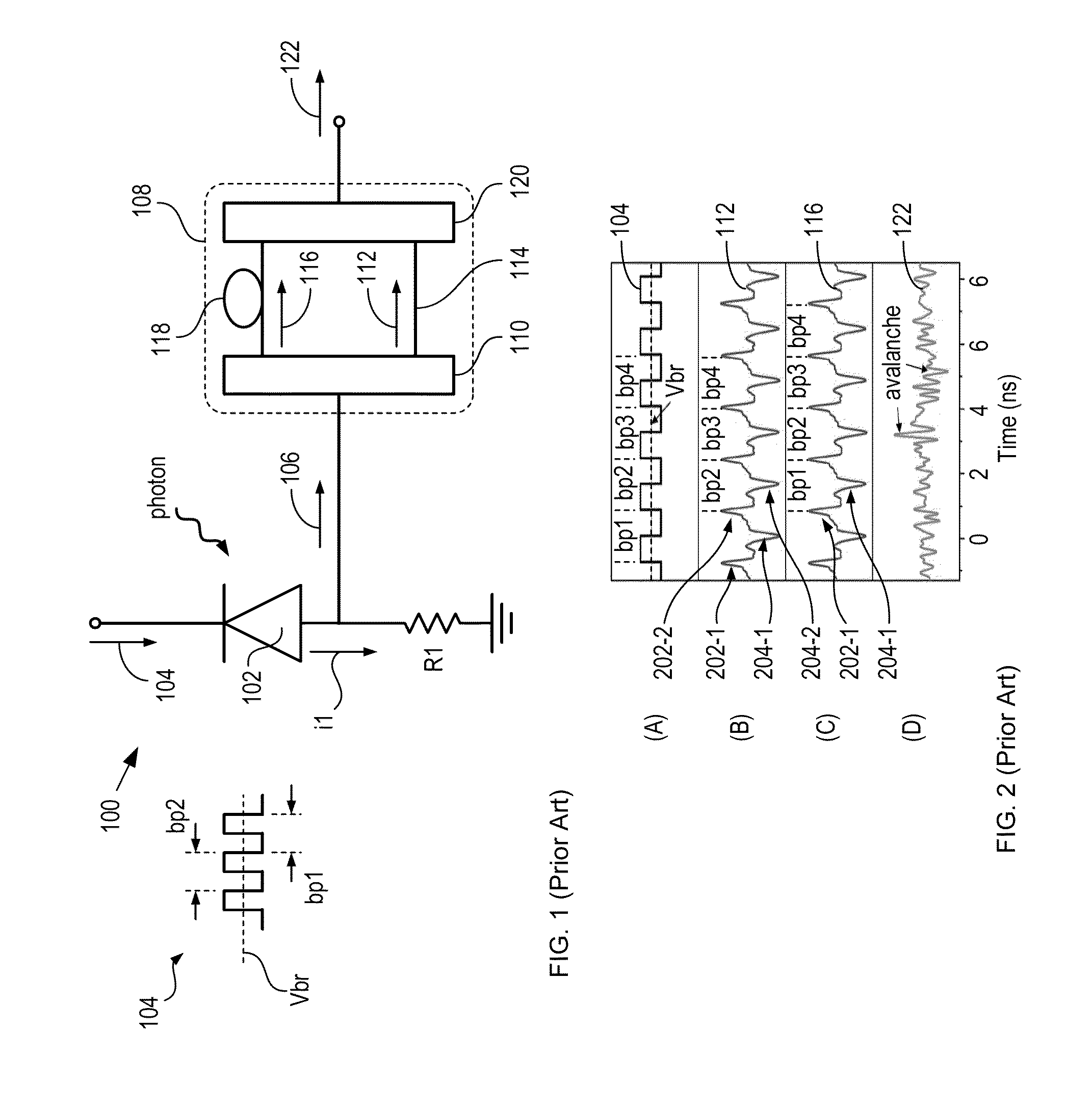
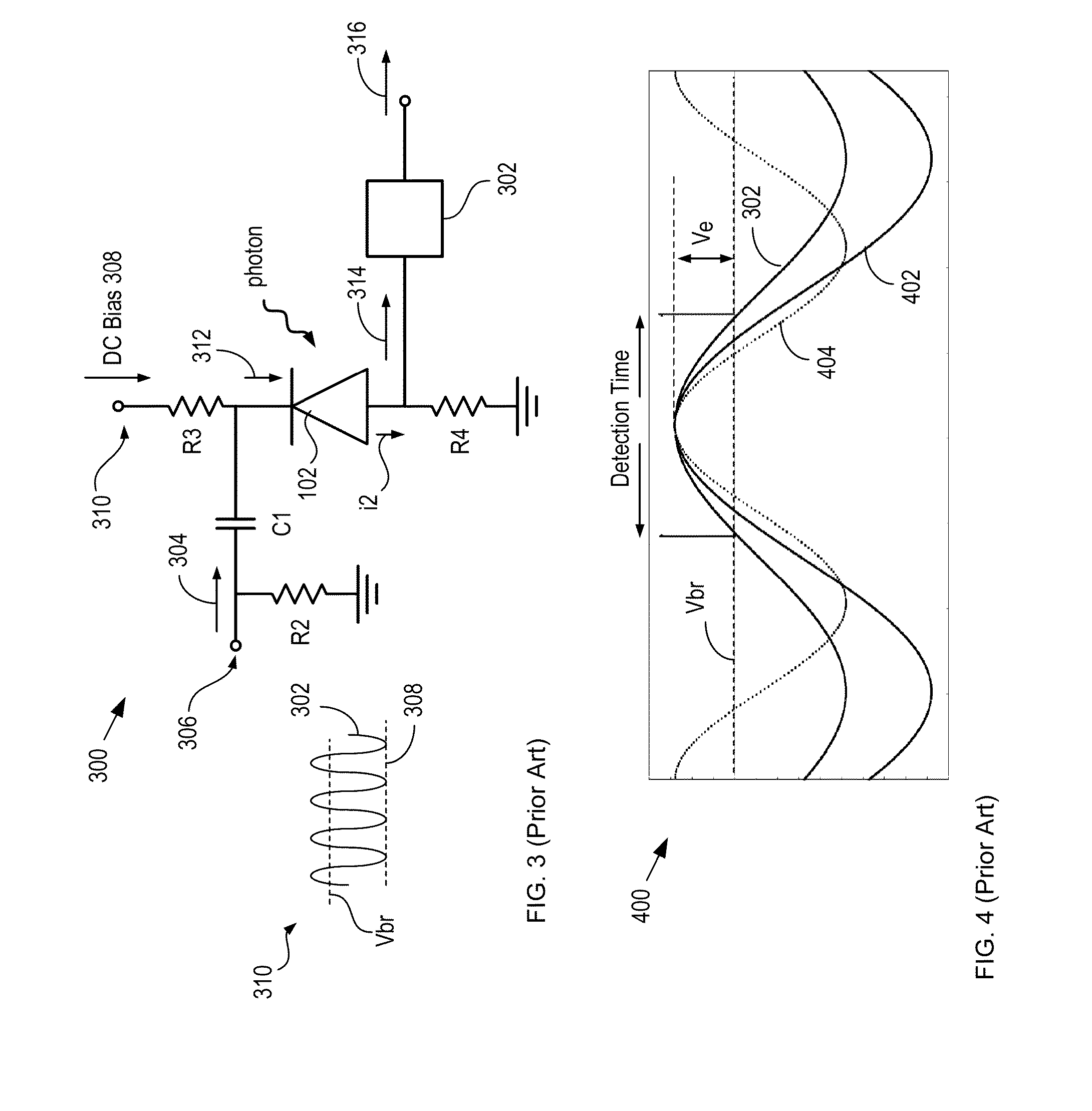
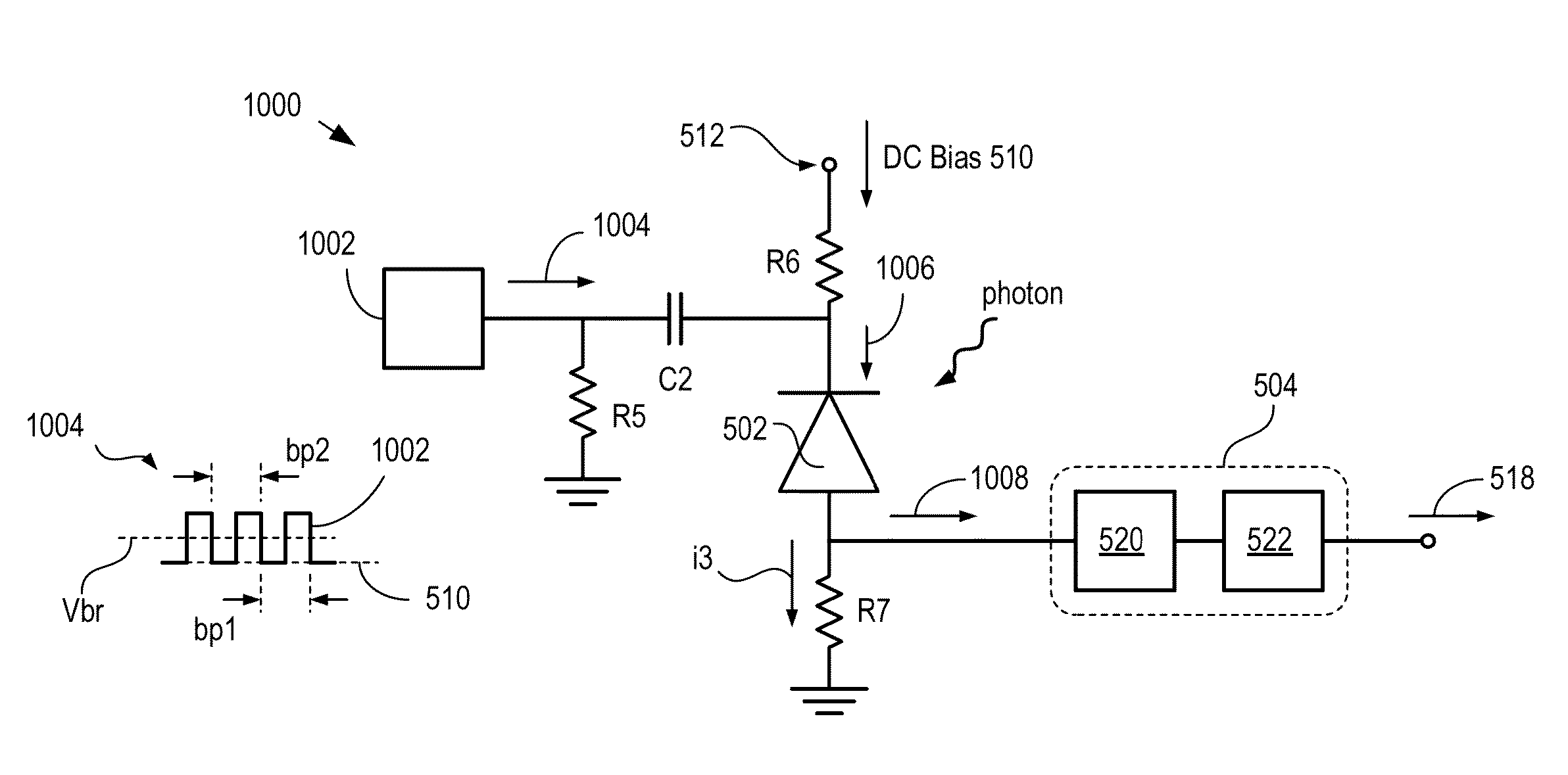
High-repetition-rate single-photon receiver and method therefor
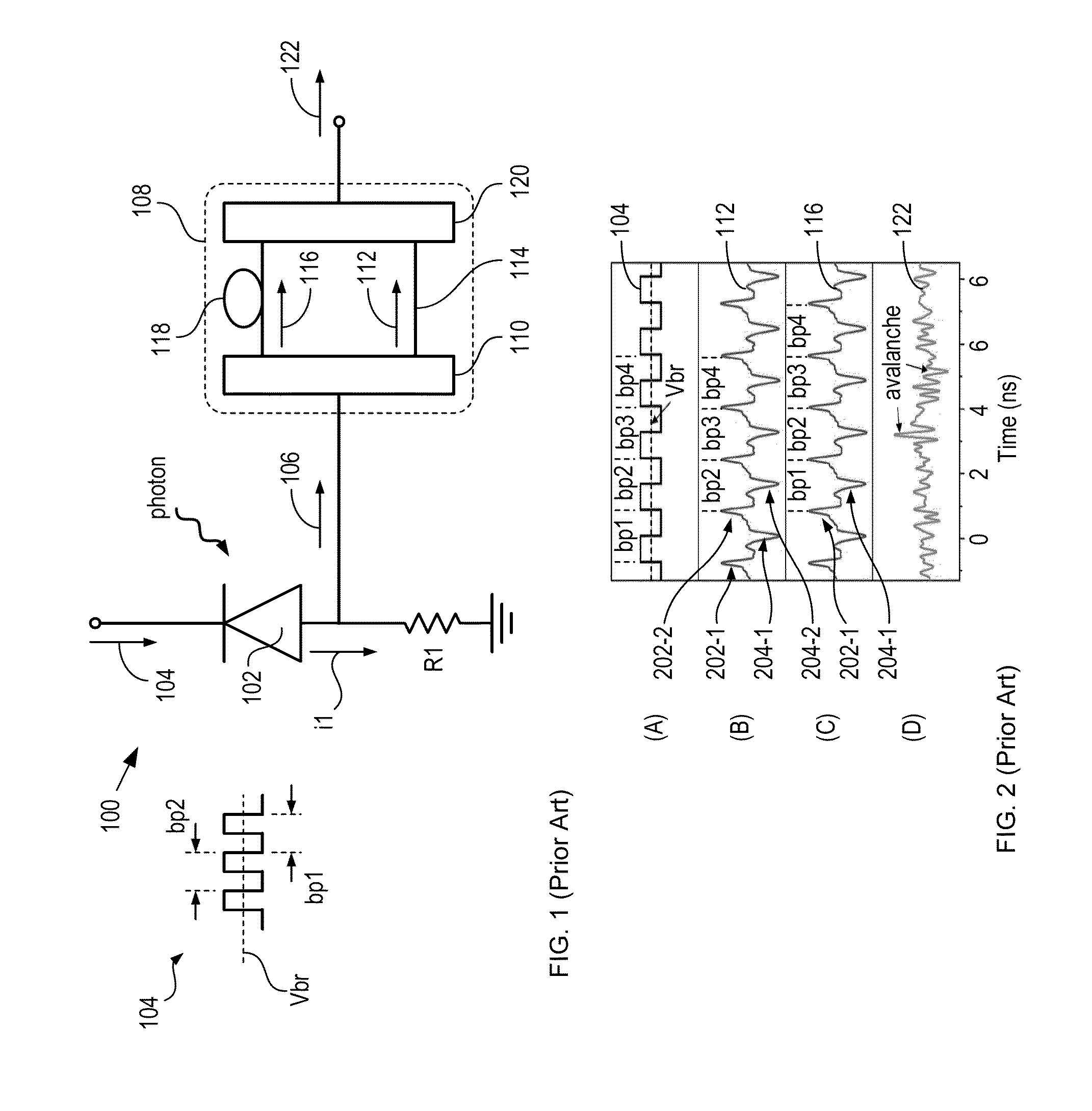
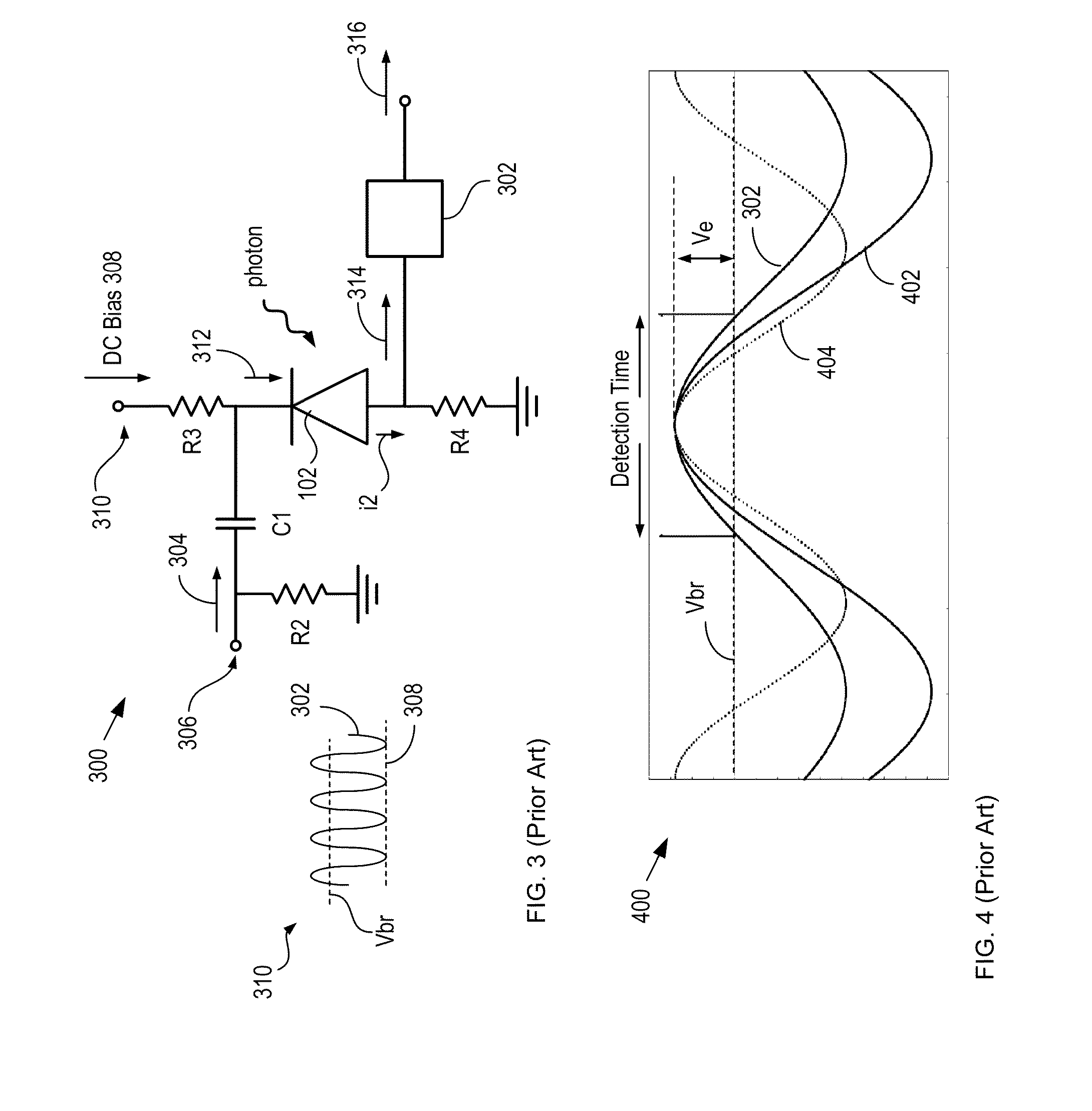
ActiveUS8796605B2Material analysis by optical meansElectronic switchingSignal qualityLow-pass filter
A single-photon receiver and method for detecting a single-photon are presented. The receiver comprises a SPAD that receives a gating signal having a fundamental frequency in the 100 MHz to multiple GHz range. The receiver further comprises a two-stage frequency filter for filtering the output of the SPAD, wherein the filter has: (1) a notch filter response at the fundamental frequency; and (2) a low-pass filter response whose cutoff frequency is less than the first harmonic of the fundamental frequency. As a result, the frequency filter removes substantially all the frequency components in the SPAD output without significant degradation of the signal quality but with reduced complexity, cost, and footprint requirement relative to receivers in the prior art.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Magnetic sensor having a frequency filter coupled to an output of a magnetoresistance element
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistance element having a peak of a thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization under a magnetic field having a certain frequency, a frequency filter connected to the magnetoresistance element and having its transmittance decreased or increased in substantially the frequency of the magnetic field to output a signal corresponding substantially to the peak of the thermal fluctuation strength of magnetization, and a detector connected to the frequency filter to detect the magnetic field based on the signal of the frequency filter.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for thickness decomposition of complicated layer structures
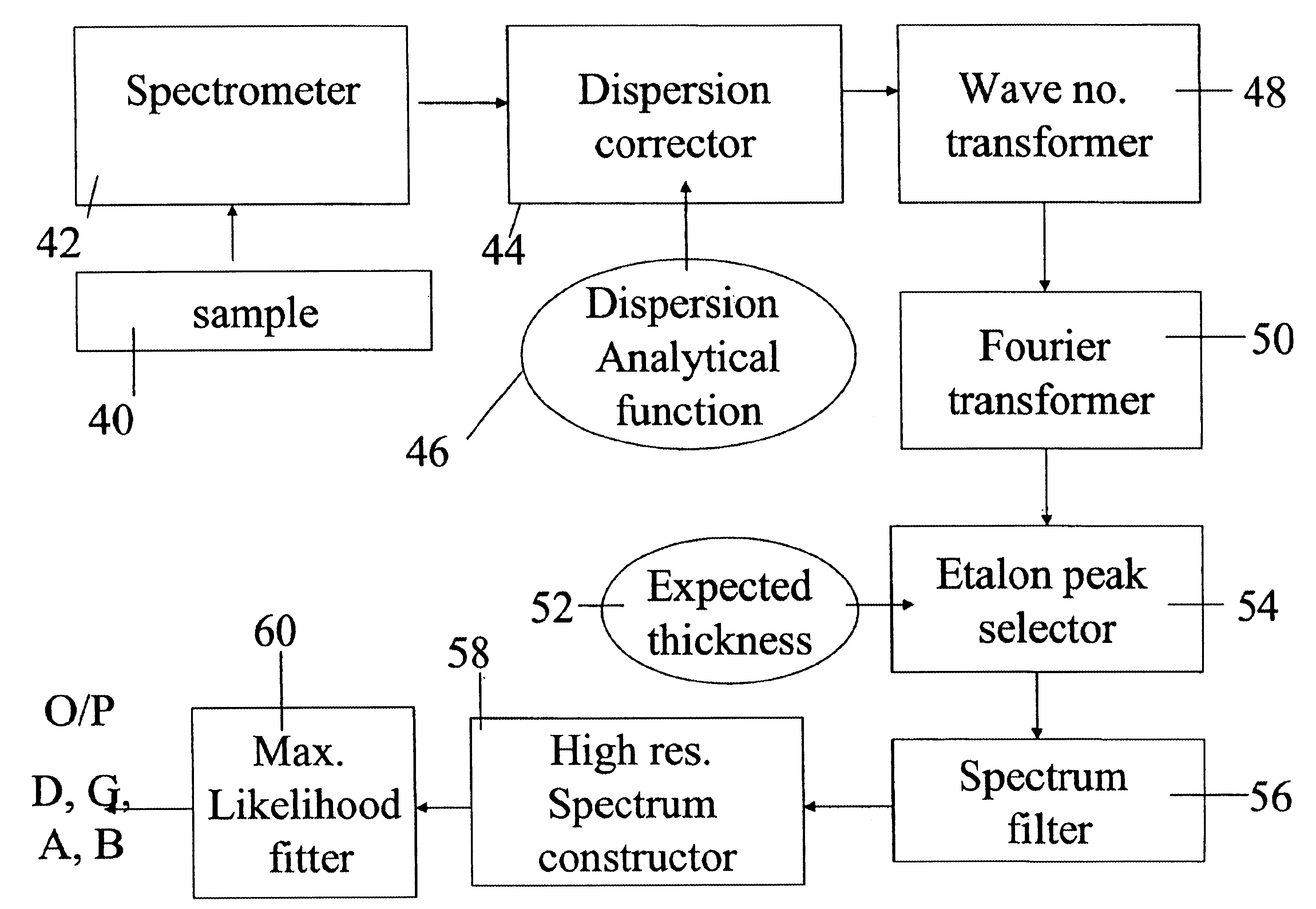
ActiveUS6885467B2Provide controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon real timeFrequency spectrum
Thickness measurement apparatus for measuring layer thicknesses on patterned areas of a semiconductor wafer, comprises: a spectrum analyzer for obtaining reflection data taken from a patterned area and obtaining therefrom a frequency spectrum, a peak detector for searching the spectrum to find peak frequencies within said spectrum, the search being restricted to regions corresponding to peak frequencies found in an earlier learning stage, a frequency filter, associated with the peak detector, for filtering the spectrum about said peak frequencies, and a maximum likelihood fitter for using parameters obtained in the learning stage to carry out maximum likelihood fitting of said filtered spectrum to obtain the desired layer thicknesses. By carrying out maximum likelihood fitting using parameters obtained beforehand in a high resolution non-real time learning stage, it is possible to provide high resolution results in real time.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Digital beamforming for an electronically scanned radar system
ActiveUS7474262B2Improve performanceLow costParticular array feeding systemsRadio transmissionRadar systemsEngineering
Digital beamforming is provided for use with electronically scanned radar. In an aspect, the present invention provides enhanced sensitivity, wide angle or field of view (FOV) coverage with narrow beams, minimized number of receivers, reduced sidelobes, eliminated grating lobes and beam compensation for target motion. In an aspect, the present invention employs a uniform overlapped subarray feed network, a time multiplexed switch matrix, and a restructured digital signal processor. Antenna channels share a receiver, rather than maintain a dedicated receiver for each antenna element, as in conventional systems. In an aspect, Doppler / frequency filtering is performed on each antenna element or subarray output prior to digital beamforming. Further, Doppler compensation is employed following Doppler / frequency filtering, followed by digital beamforming.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
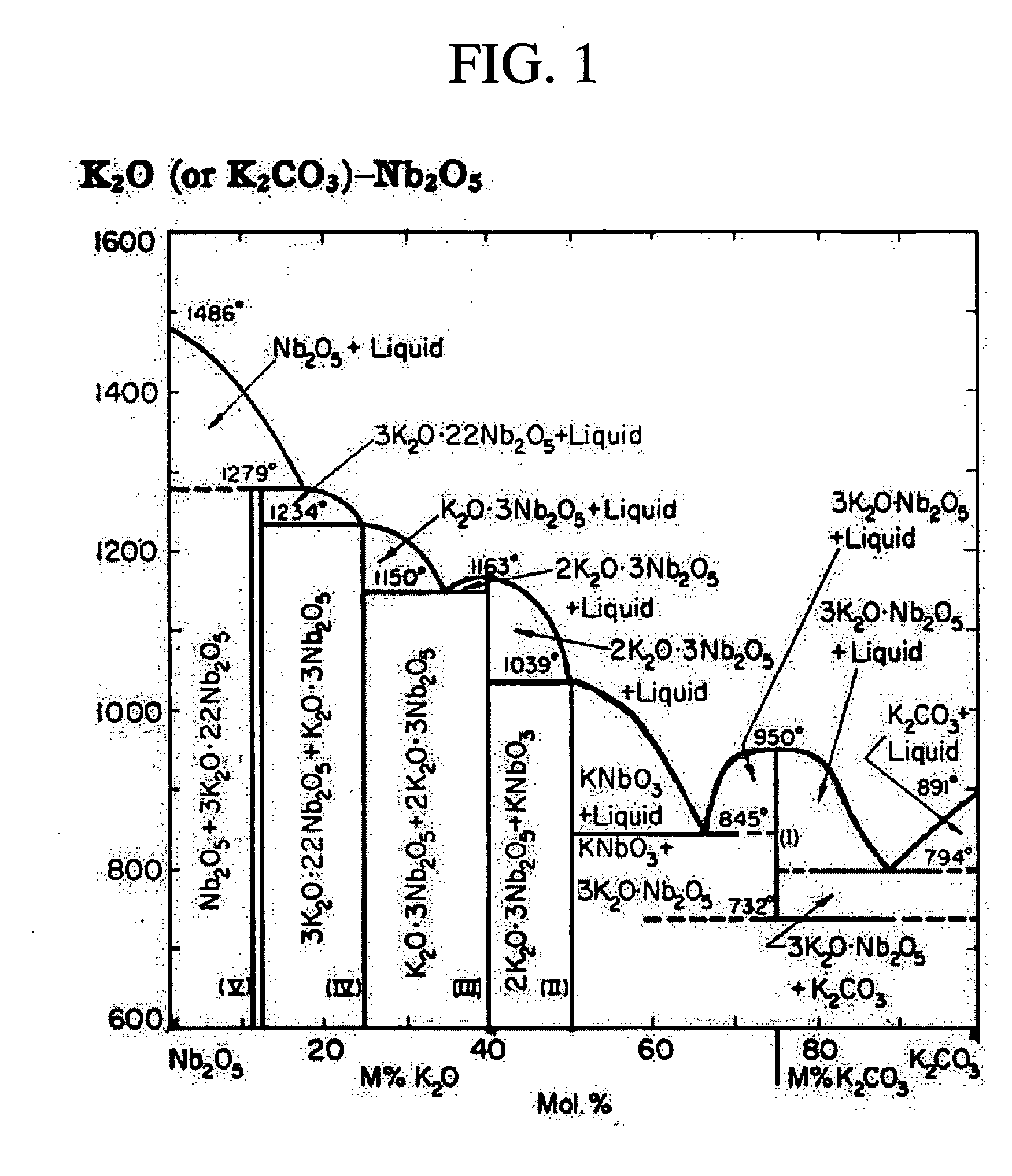
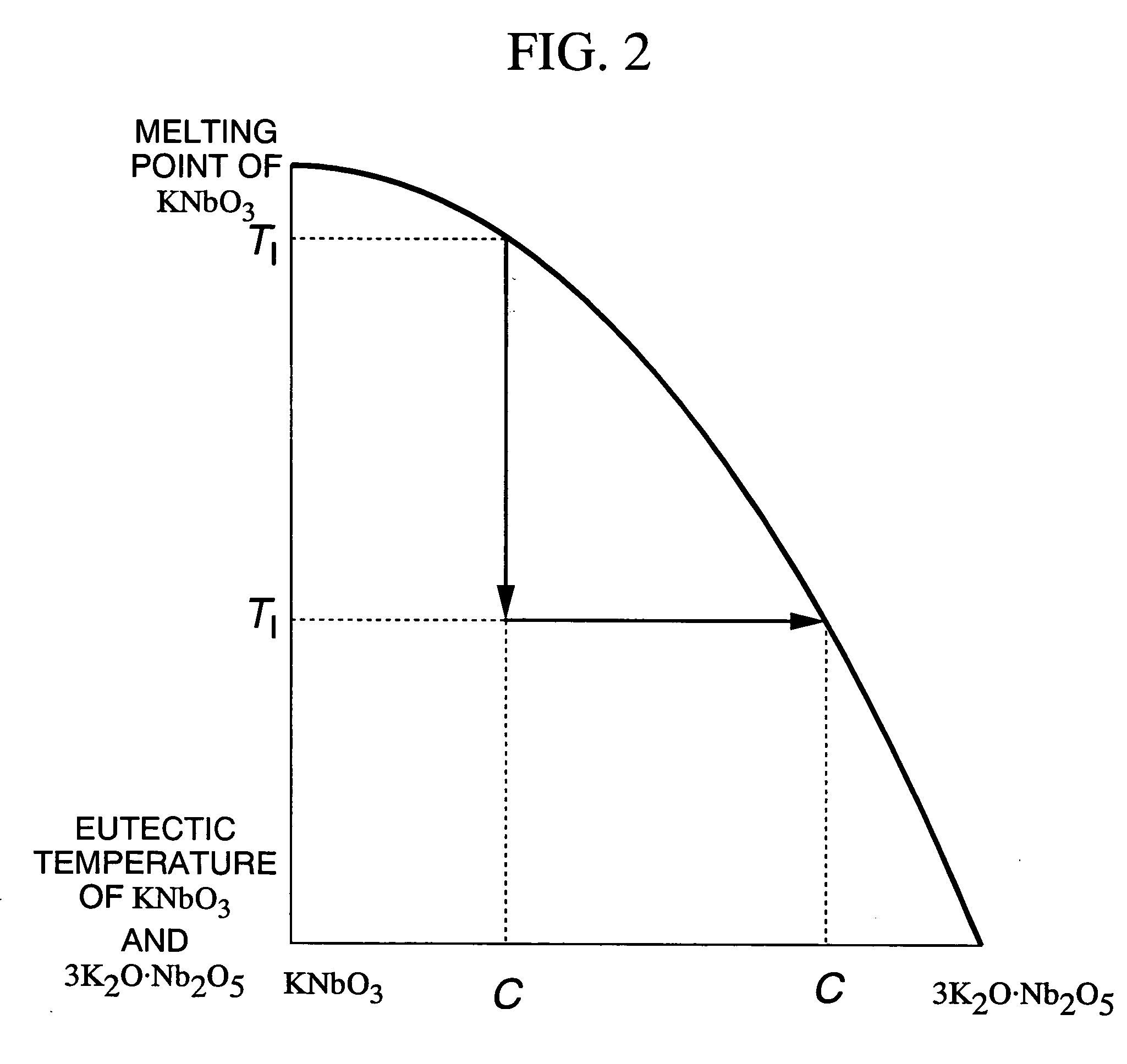
Method of manufacturing potassium niobate single crystal thin film, surface acoustic wave element, frequency filter, frequency oscillator, electric circuit, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20040197599A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseSingle crystal
A method of manufacturing a potassium niobate (KNbO3) single crystal thin film, includes the steps of maintaining the substrate under a predetermined oxygen partial pressure; maintaining the substrate within a temperature region which is equal to or higher than an eutectic temperature of KNbO3 and 3K2O.Nb2O5 and is equal to or lower than complete melting temperature of KNbO3 and 3K2O.Nb2O5 so that a solid phase of KNbO3 and a liquid phase can coexist on the substrate; depositing a vapor phase material on the substrate in a state in which a solid phase and a liquid phase coexist; and precipitating KNbO3 on the substrate from the liquid phase as a solid phase to grow a KNbO3 single crystal thin film. The composition of a starting material to be vaporized to generate the vapor phase material is from K2O.Nb2O5=50:50 to K2O.Nb2O5=65:35.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
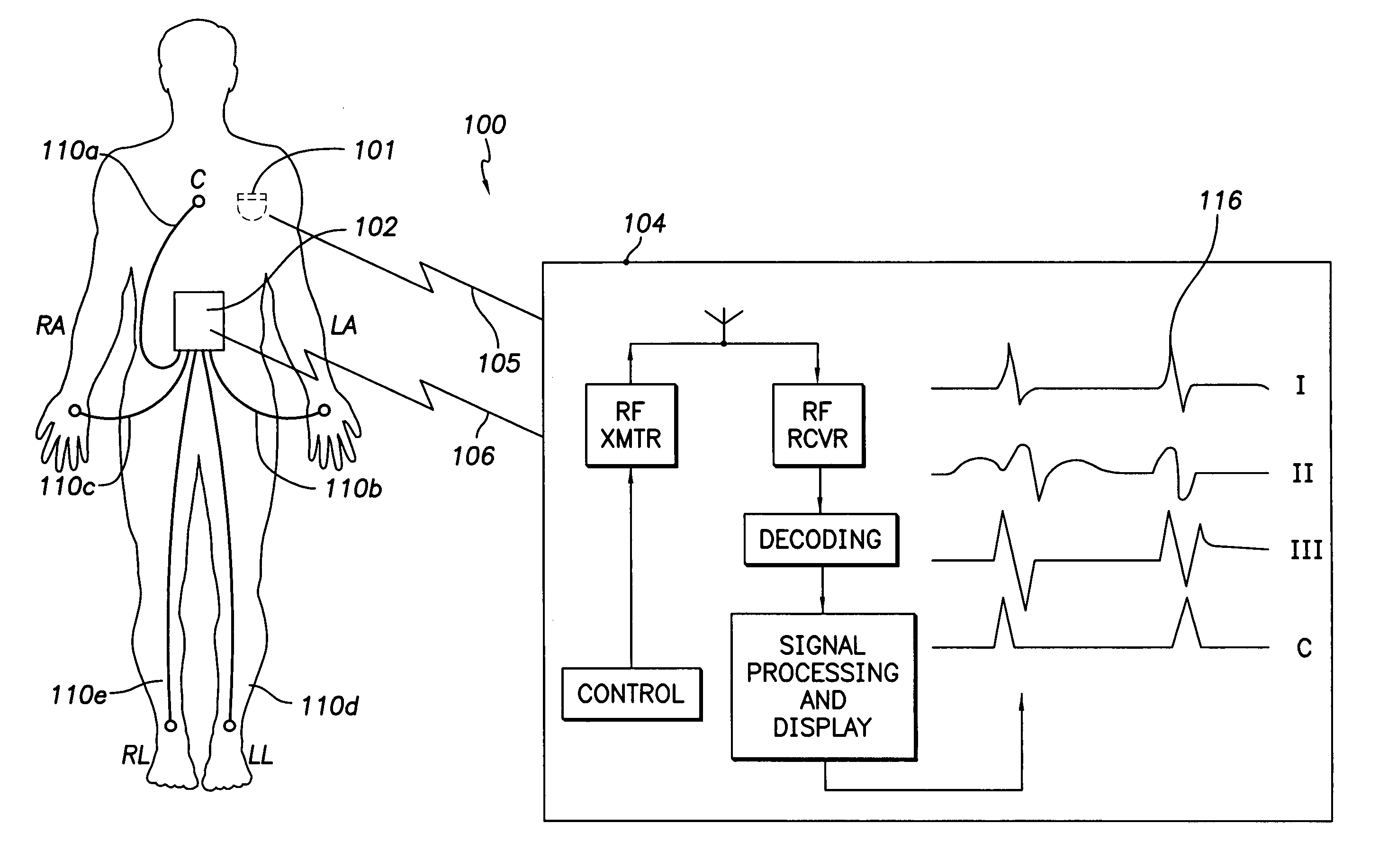
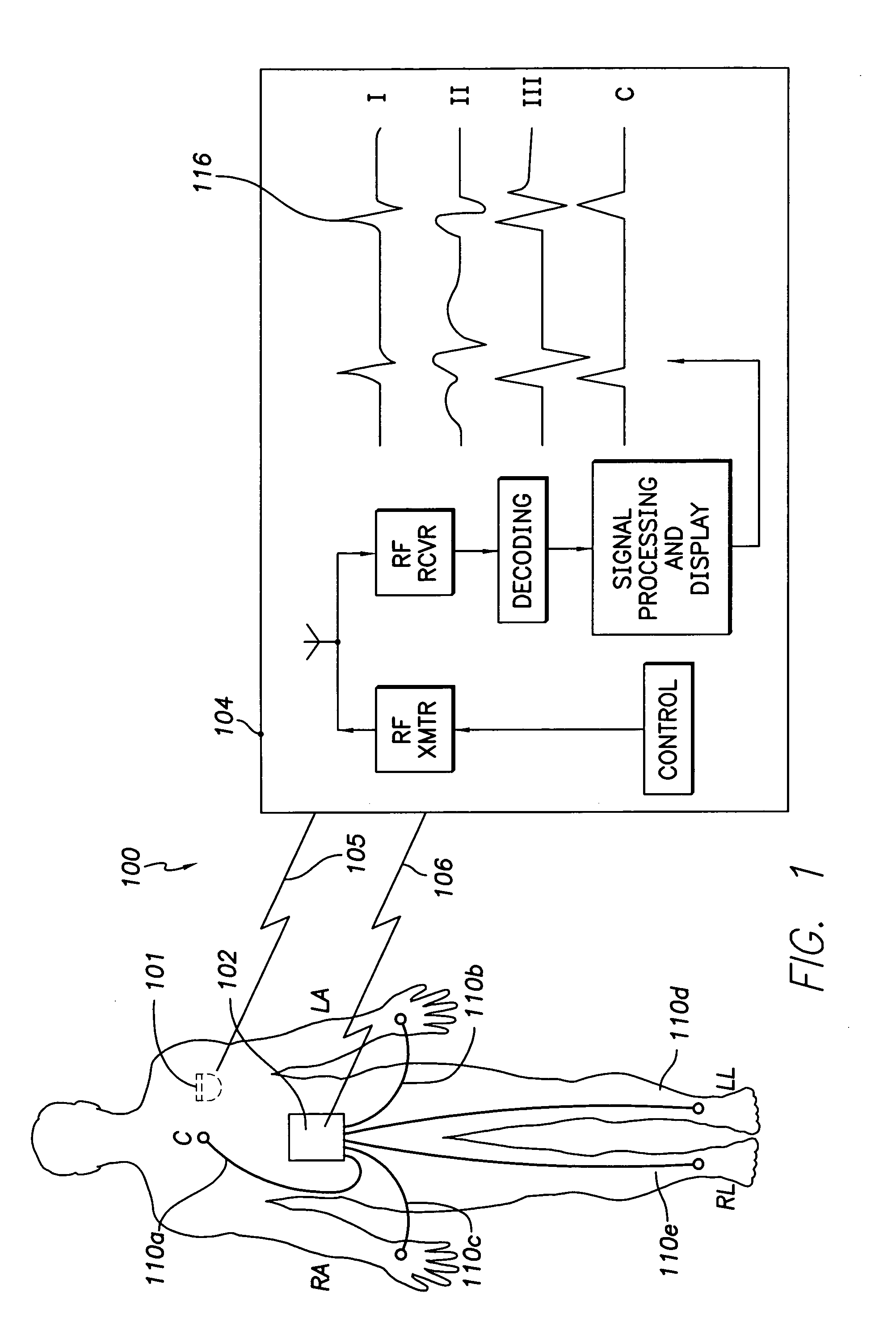
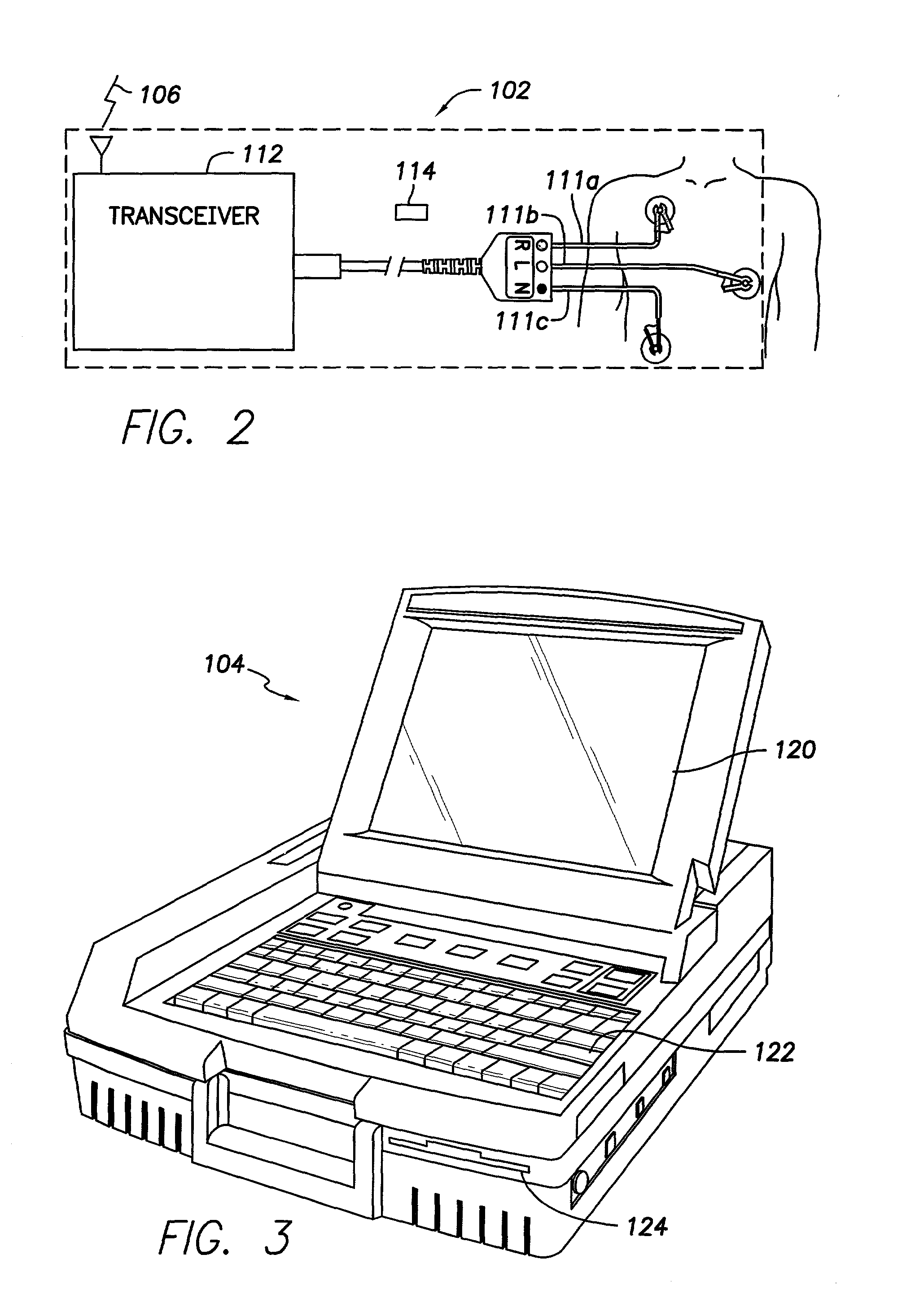
Programmer and surface ECG system with wireless communication
A programmer for implantable stimulation devices and surface ECG system in wireless communication with each other. A self-powered ECG monitor with conventional surface electrodes transceives signals from and to a programmer provided with a radio frequency transceiver to eliminate hardwiring between the surface electrodes and the programmer. The system reduces the need for supply line frequency filtering and isolation circuitry to protect against high voltage defibrillation shocks.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Noise Reduction Apparatus, Systems, and Methods
InactiveUS20090136104A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFrequency spectrumNoise reduction
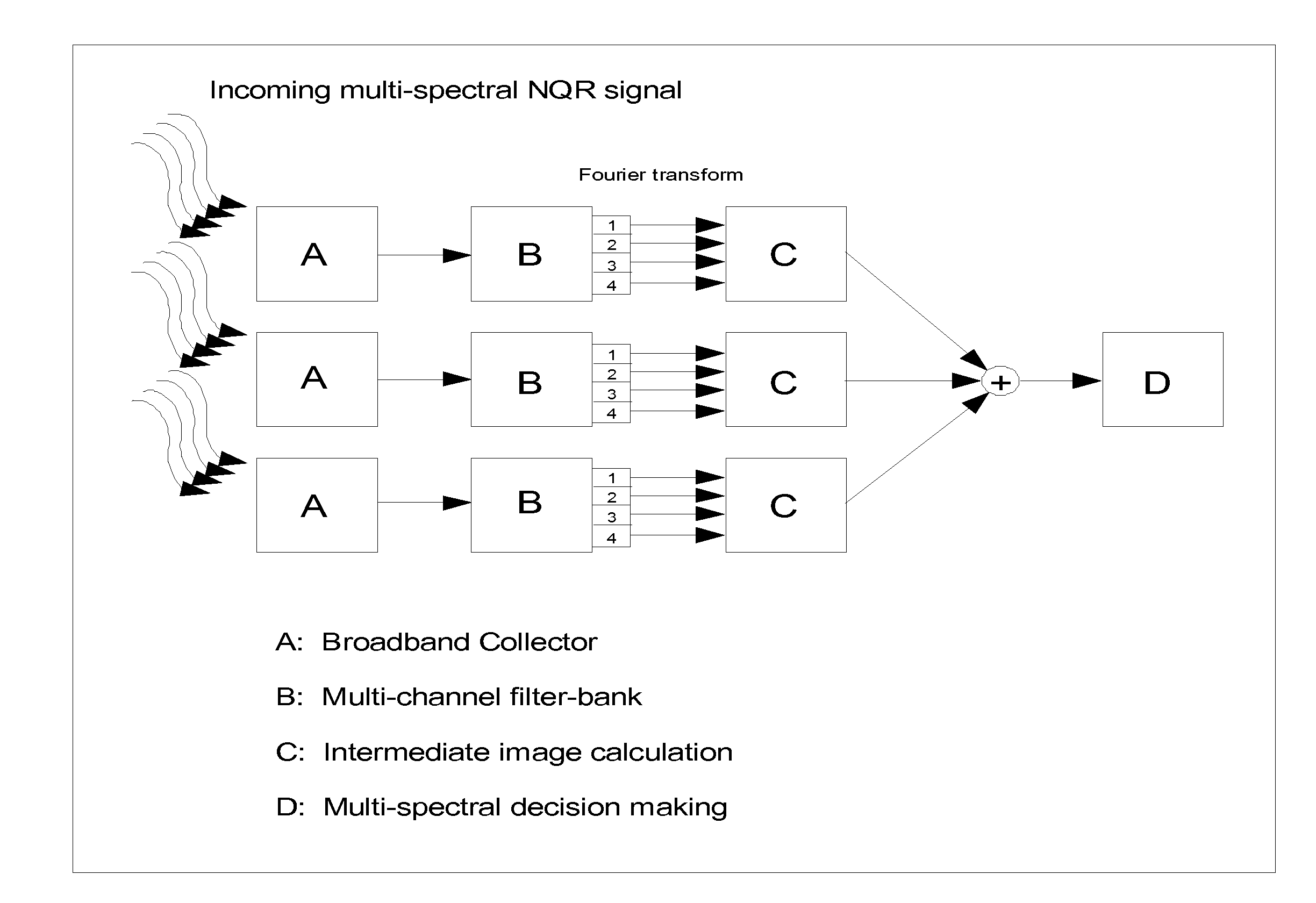
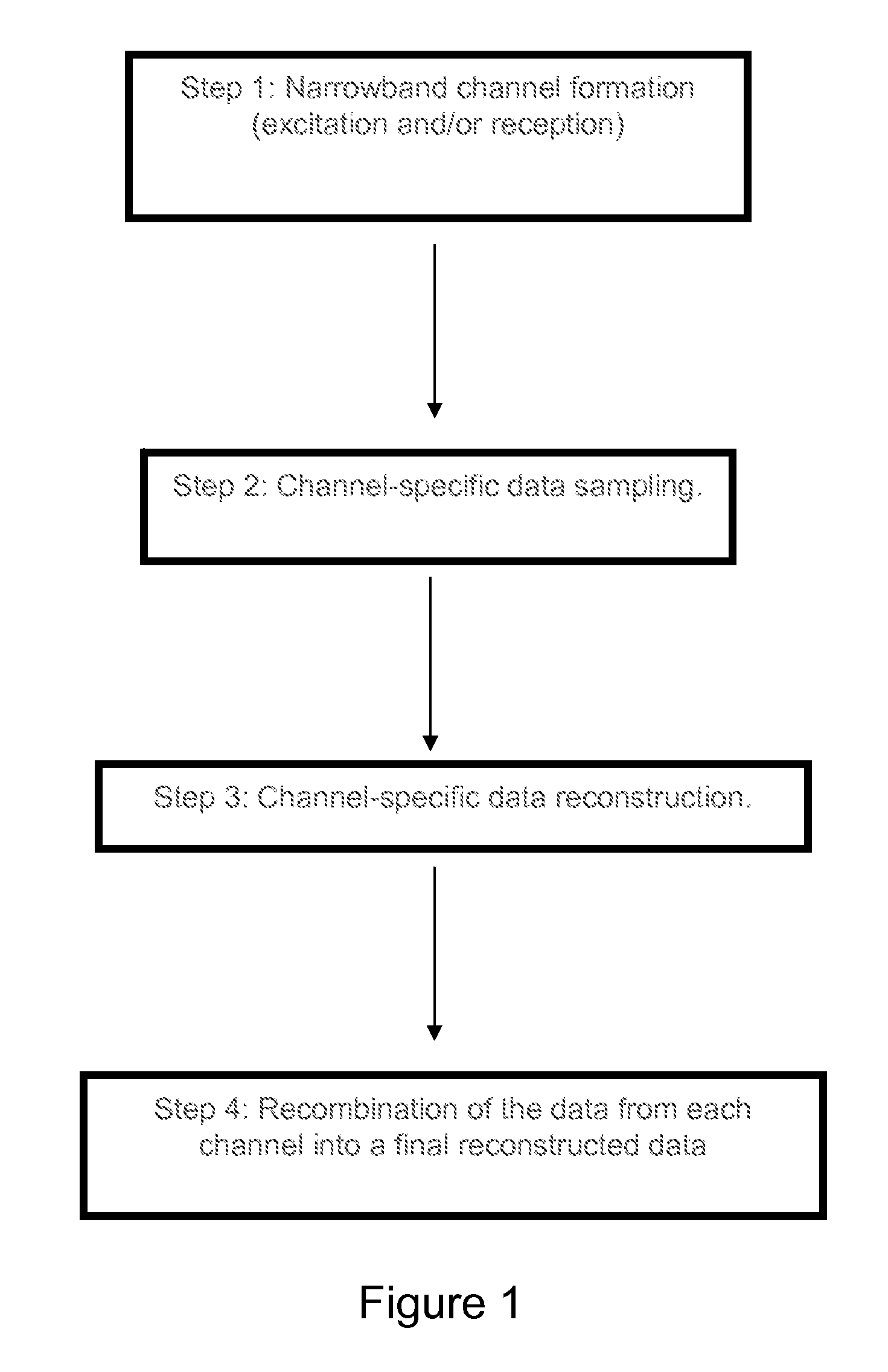
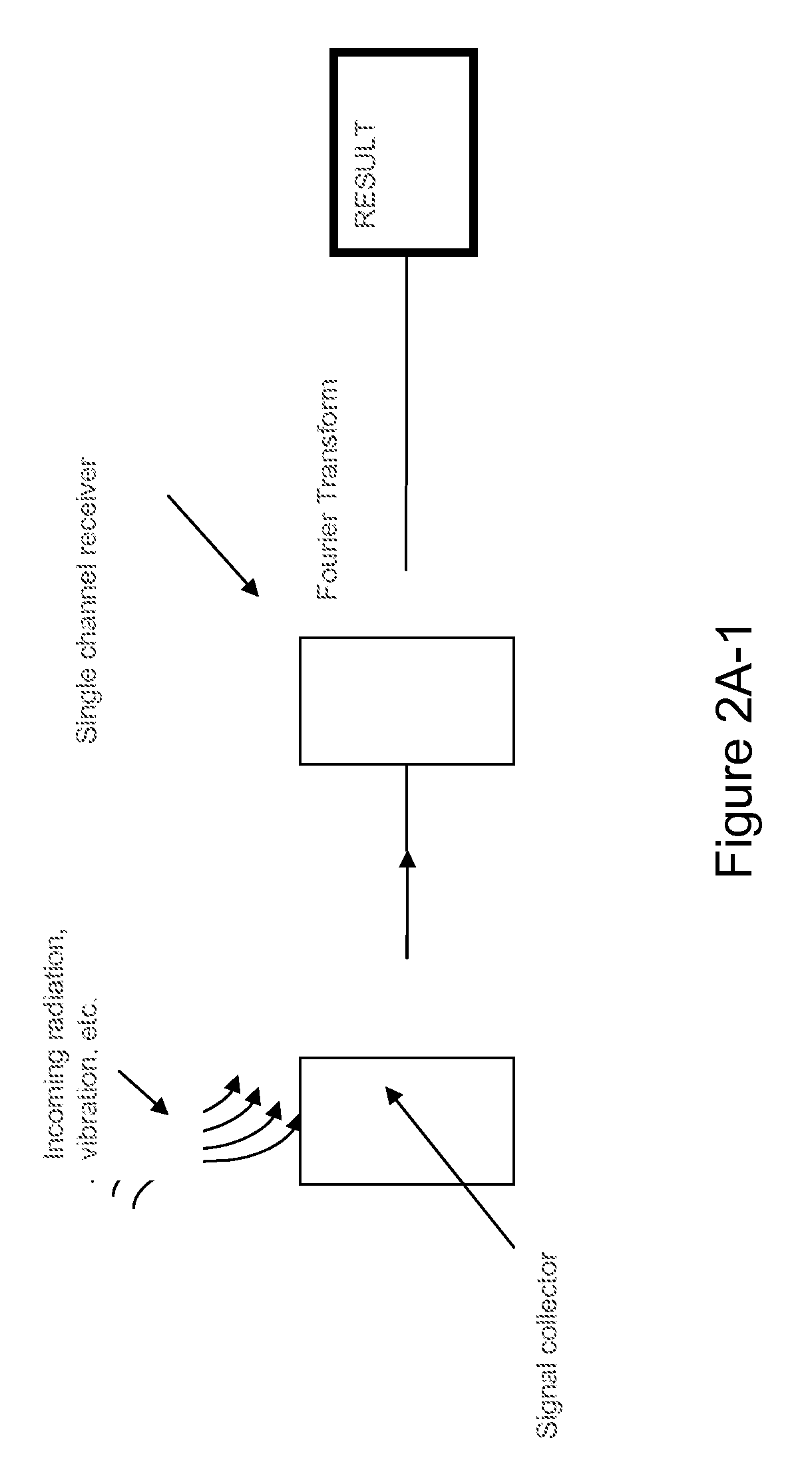
This document describes a general system for noise reduction, as well as a specific system for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR). The general system, which is called Calculated Readout by Spectral Parallelism (CRISP), involves reconstruction and recombination of frequency-limited broadband data using separate narrowband data channels to create images or signal profiles. A multi-channel CRISP system can perform this separation using (1) frequency tuned hardware, (2) a frequency filter-bank (or equivalent), or (3) a combination of implementations (1) and (2). This system significantly reduces what we call cross-frequency noise, thereby increasing signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR). A multi-channel CRISP system applicable to MRI and NQR are described.
Owner:ARJAE SPECTRAL ENTERPRISES
Methods of processing magnetotelluric signals
InactiveUS6950747B2Improve the display effectAid in its interpretationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCurrent/voltage measurementFrequency filteringRemote sensing
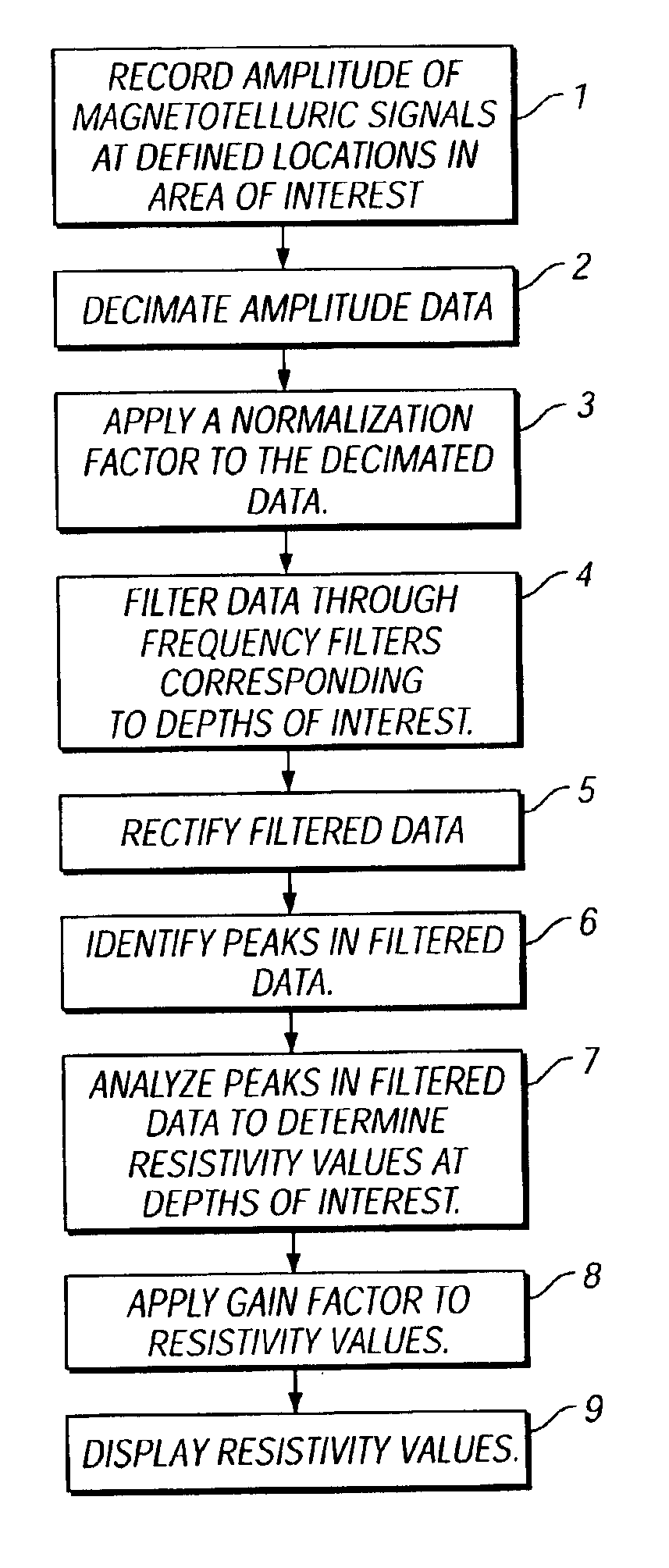
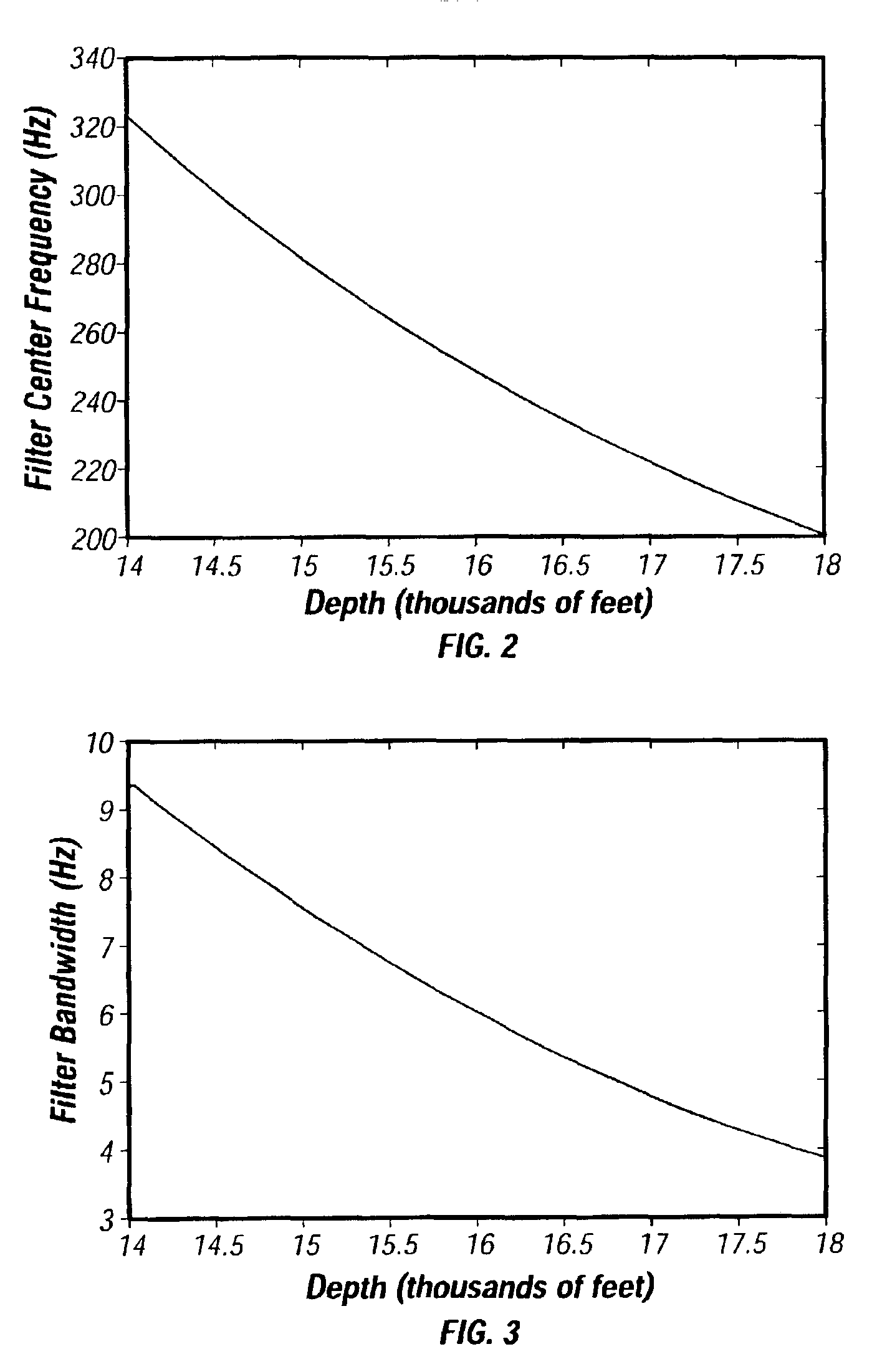
A method for processing magnetotelluric signals to identify subterranean deposits is provided for. The methods comprise obtaining magnetotelluric data from an area of interest. The magnetotelluric data comprises the amplitude of magnetotelluric signals recorded over time at one or more defined locations in the area of interest. The data for each location then is filtered through a set of frequency filters. The frequency filters correspond to subterranean depths over a range of interest. Amplitude peaks in the filtered data then are identified and analyzed to determine a value correlated to the resistance of the earth at each frequency and location. The resistance values are indicative of the presence or absence of deposits at the corresponding subterranean depth. Preferably, the amplitude data is power normalized across all locations in the survey, a gain factor is applied to the resistance values to scale the values for depth variation, and the resistance values are displayed as a depth-location plot for interpretation.
Owner:BYERLY KENT
Sensor-Activated Transponder
InactiveUS20130194100A1Long detection rangeGood directionMountaineeringBuilding rescueFrequency filteringControl signal
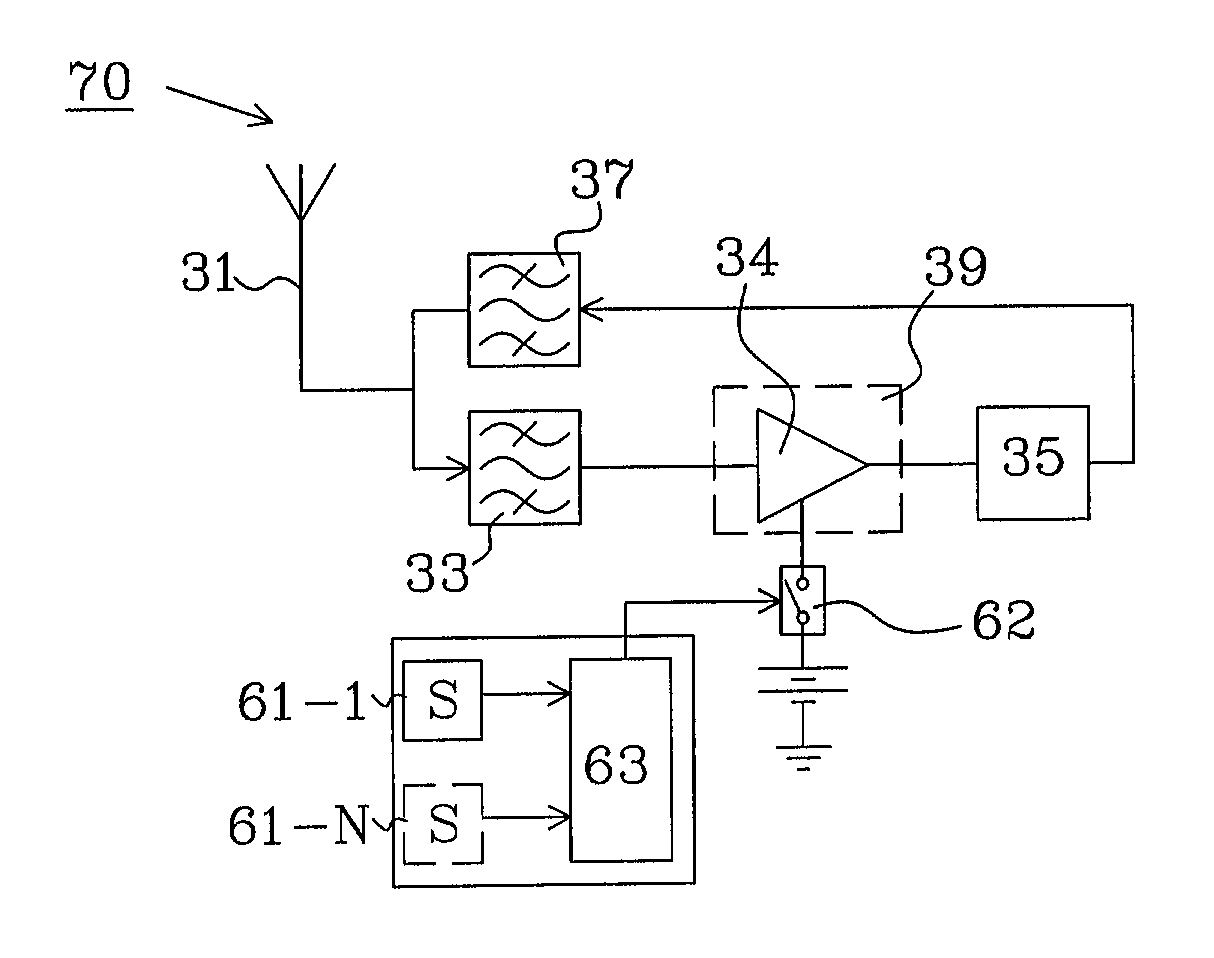
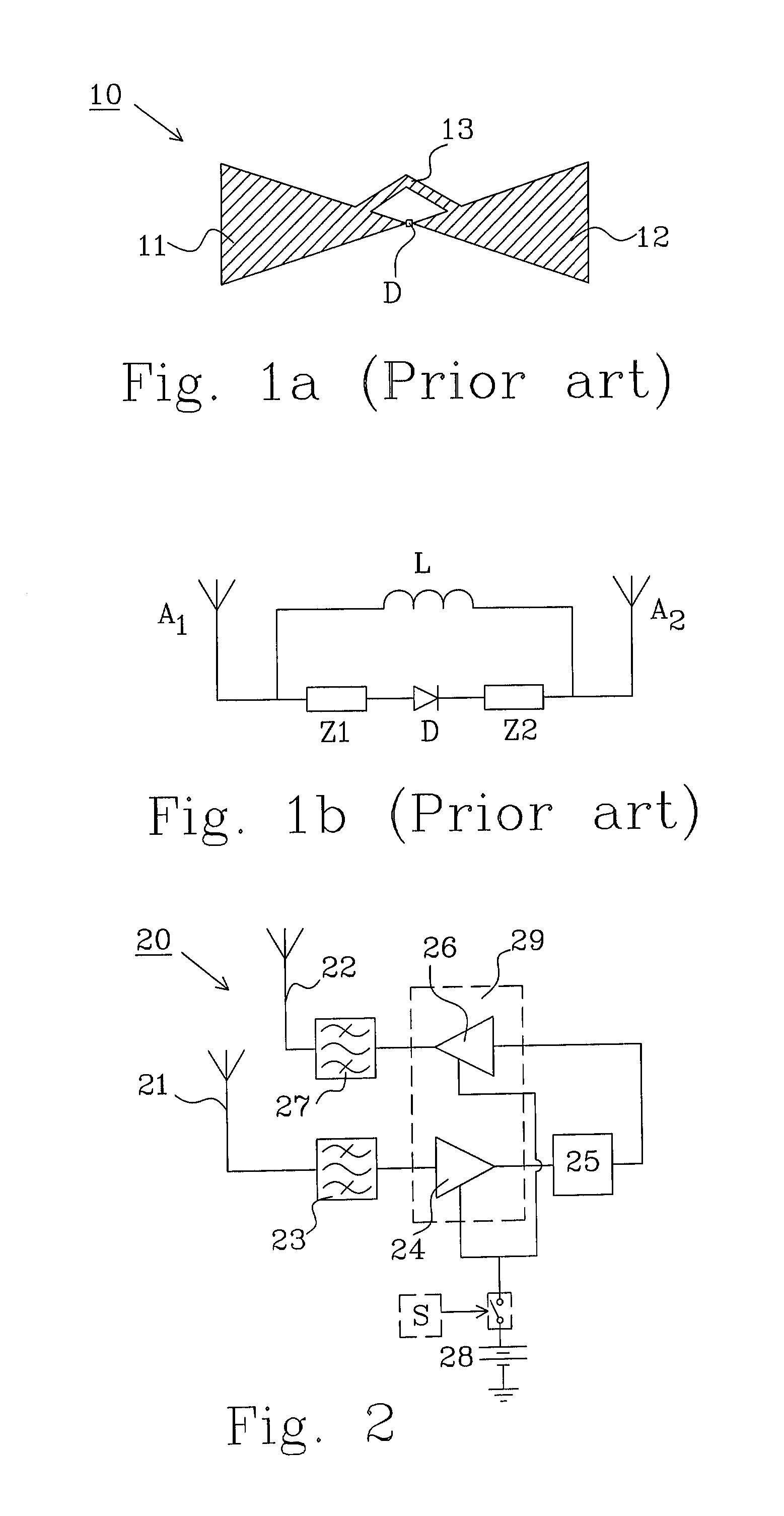
The present invention relates to a transponder comprising an antenna structure (31) configured to receive an incoming signal with RF power of a first frequency f1 and to retransmit the incoming signal as a transparent output signal with RF power of a second frequency f2 when hit by the incoming signal. The transponder further comprises: an amplifier (39) configured to provide an amplified transparent output signal based on the incoming signal; a frequency converter (35) configured to frequency convert the incoming signal into the transparent output signal; and a first frequency filter (33) connected to the antenna structure. The first frequency filter is tuned to the first frequency f1 to avoid amplifying incoming signals with RF power of frequencies other than the first frequency f1. The transponder further comprises a sensor (S) configured to respond to physical stimulus for generating a control signal as output response, and an activator for selectively activating or deactivating the possibility to retransmit based on the control signal of the sensor.
Owner:RECCO INVEST
Multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device
ActiveCN103117767AEasy to changeEasy to adjustSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionLow noiseSignal processing circuits
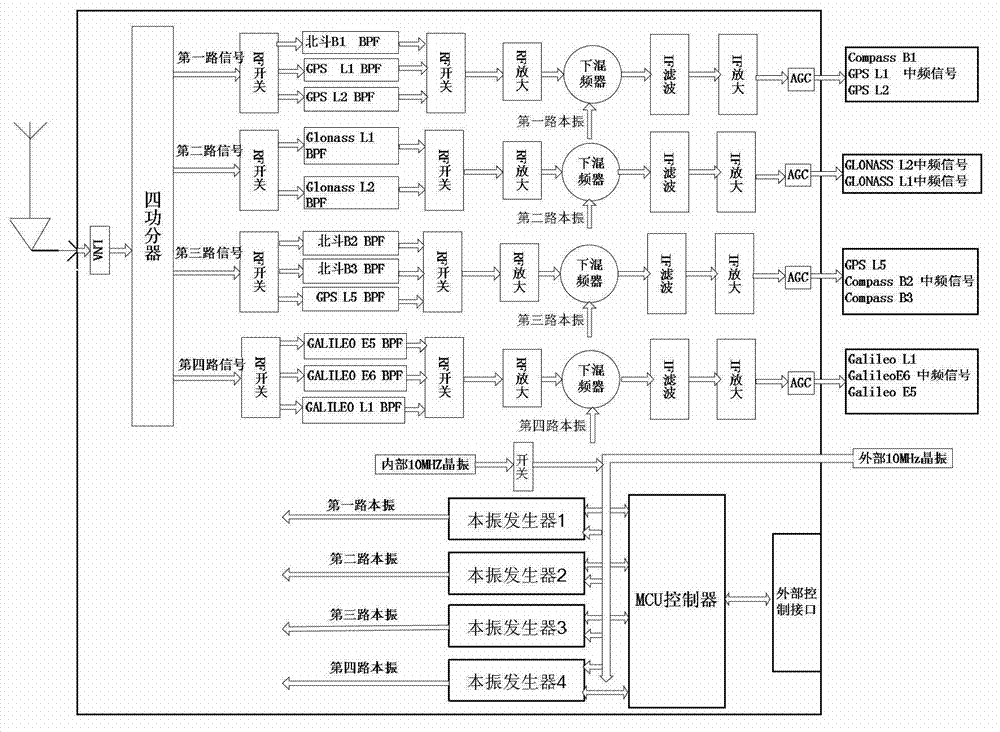
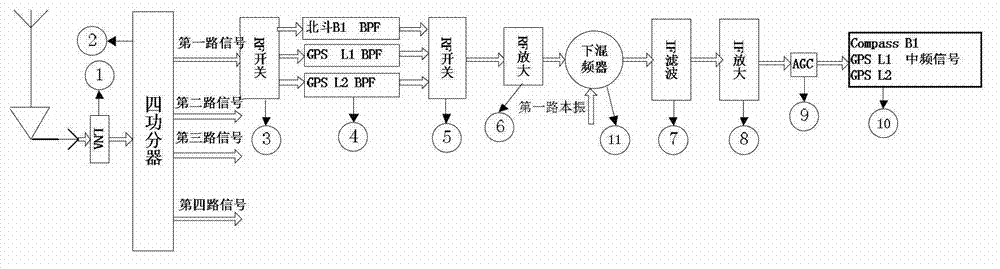
The invention discloses a multi-mode multi-frequency global navigational satellite system receiver radio frequency front end device. The device comprises a low-noise amplifier, a power divider, and multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits, wherein the low-noise amplifier, the power divider, and the multiple radio-frequency signal processing circuits are connected in sequence. Each radio-frequency signal processing circuit comprises a first radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency filter bank, a second radio-frequency switch, a radio-frequency amplifying module, a lower frequency mixing module, an intermediate frequency filter module, an intermediate frequency amplifying module, and an automatic gain control unit, wherein the first radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency filter bank, the second radio-frequency switch, the radio-frequency amplifying module, the lower frequency mixing device, the intermediate frequency filter module, the intermediate frequency amplifying module, and the automatic gain control unit are connected in sequence. The lower frequency mixing module comprises a lower frequency mixing device and a local oscillating generating module which are connected with each other. A control unit is connected with the first radio-frequency switch and the second radio-frequency switch of each radio-frequency signal processing circuit and the local oscillating generating module of the lower frequency mixing module. The device can flexibly select intermediate frequency inputting from various combination frequency ranges of a quad-mode 11 frequency range, and therefore functions of collecting in the same module and processing navigation system intermediate frequency signals of four system satellites are realized, namely a global position system (GPS), Glonass, Galileo, and Big Dipper.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
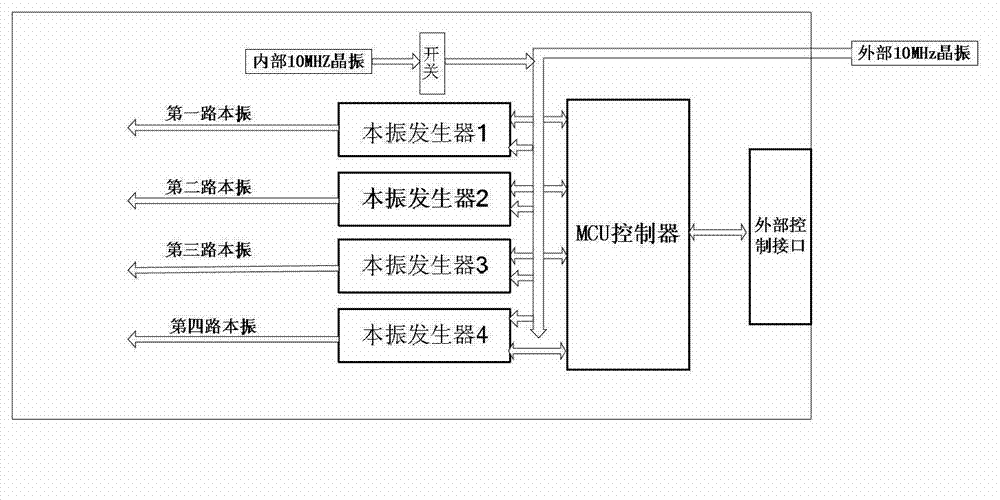
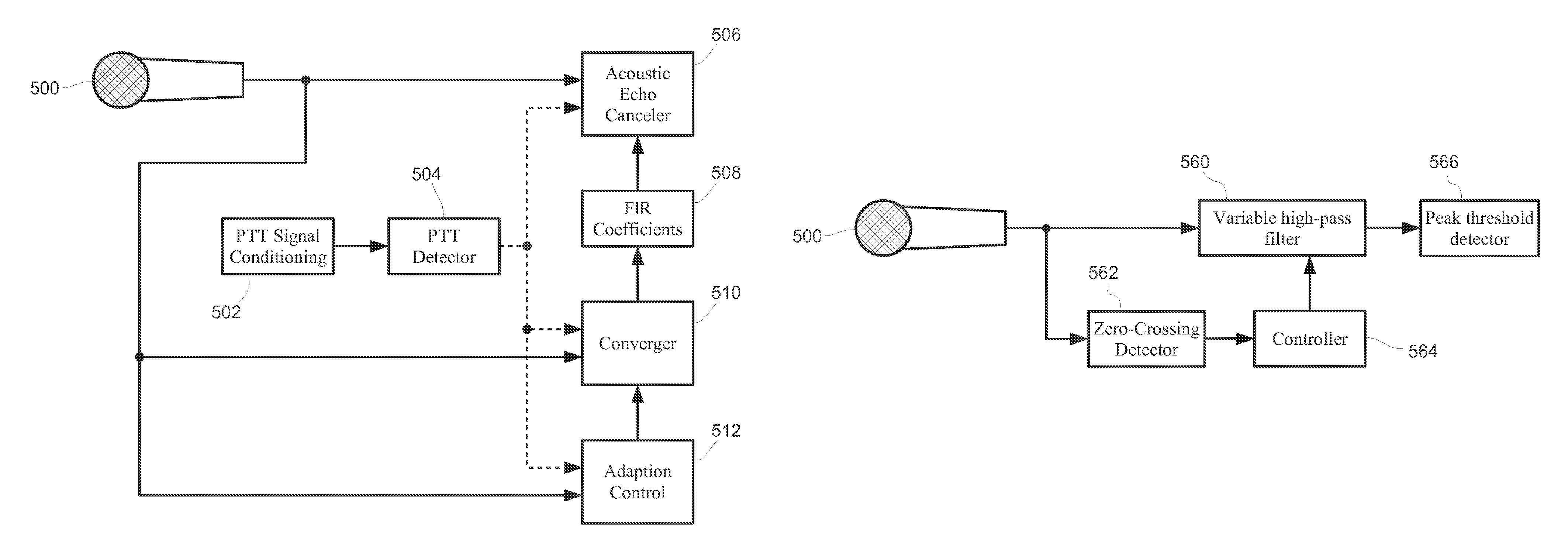
Conferencing system implementing echo cancellation and push-to-talk microphone detection using two-stage frequency filter
ActiveUS8199927B1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsPublic address systemsFrequency filteringPush-to-talk
Disclosed herein are conferencing products implementing an acoustic echo cancellation system that utilizes converging coefficients and a detector of turn-off and / or turn-on events of push-to-talk microphones, and, further, that mitigates against divergence and / or drift of coefficients and other variables of an echo canceller. A push-to-talk detector may be used that includes a high-pass filter, a transient detector, or an adjustable high-pass filter. An echo canceller may be disabled as to a push-to-talk microphone that has been turned off.
Owner:CLEARONCE COMM INC
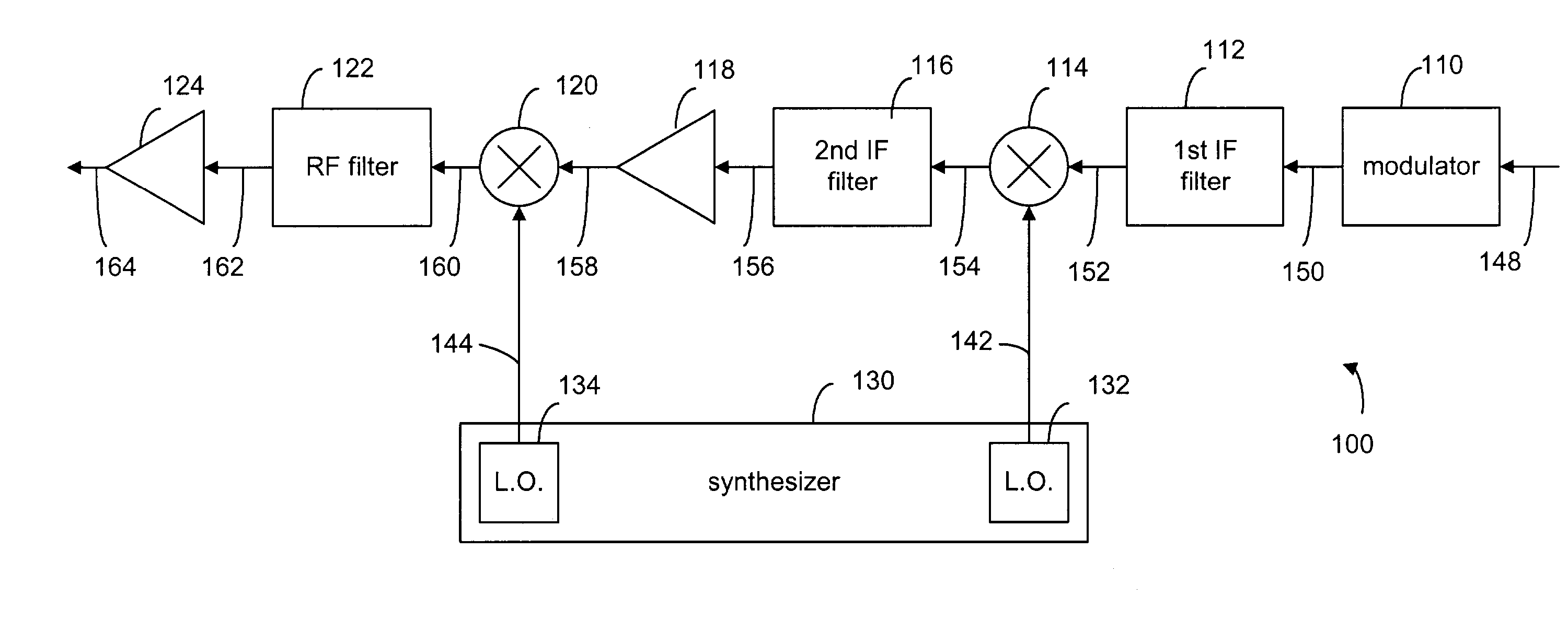
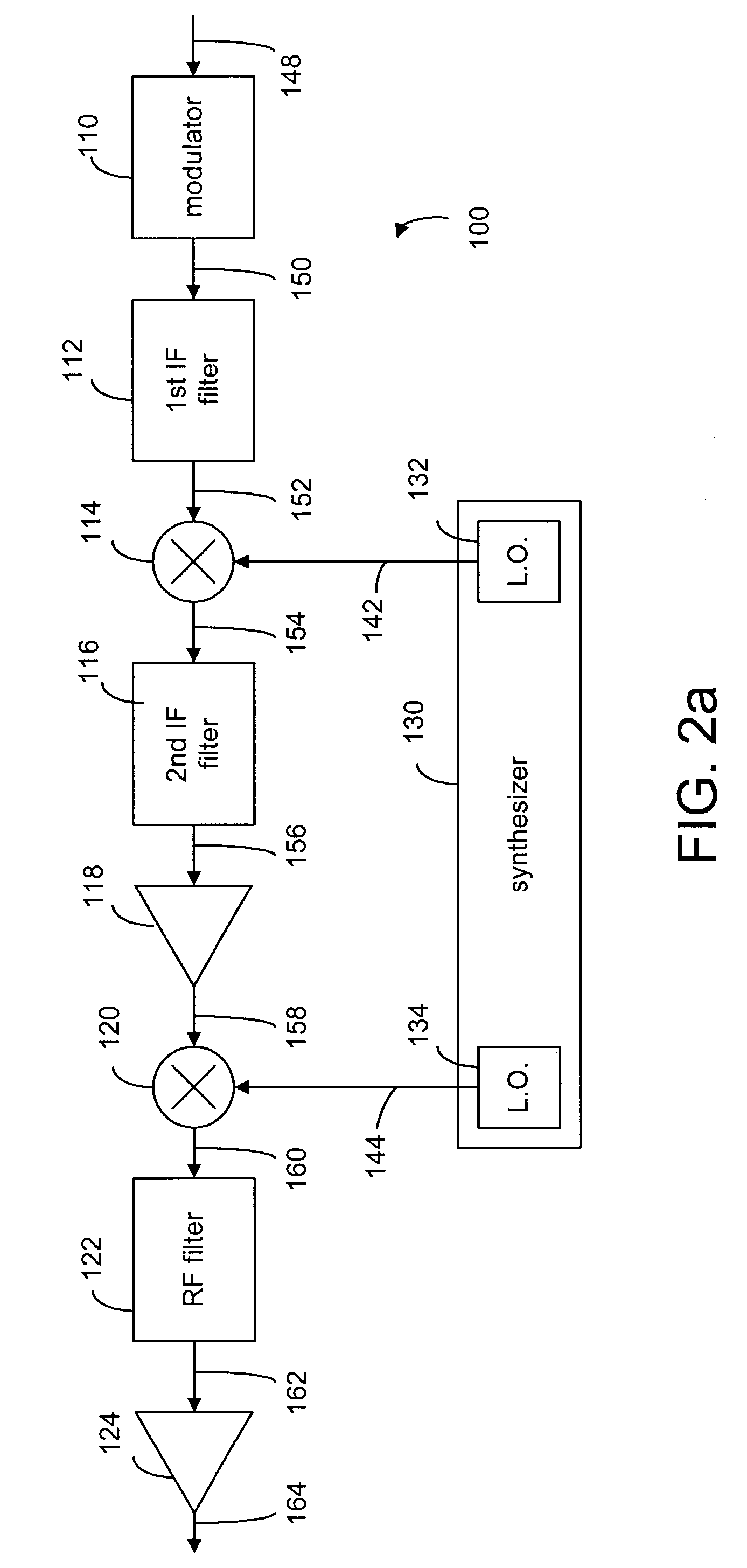
Method and device for frequency translation in powerline communications
InactiveUS6985715B2Enhance communication signalHigh selectivitySystems using filtering and bypassingInterconnection arrangementsLocal oscillator signalModem device
A method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving RF signals for broadband communications using power lines as communication medium. A super-heterodyne structure is used to translate the signals from one frequency to another so as to avoid interference sources, which may corrupt the communication signals. In the heterodyne structure, a plurality of local oscillators are used to mix the local oscillator signals with the communication signals for frequency translation. A plurality of frequency filters are used to filtered out unwanted signals. The communication signals are imparted onto or received from the power lines via couplers operatively connected to modems.
Owner:AMPERION
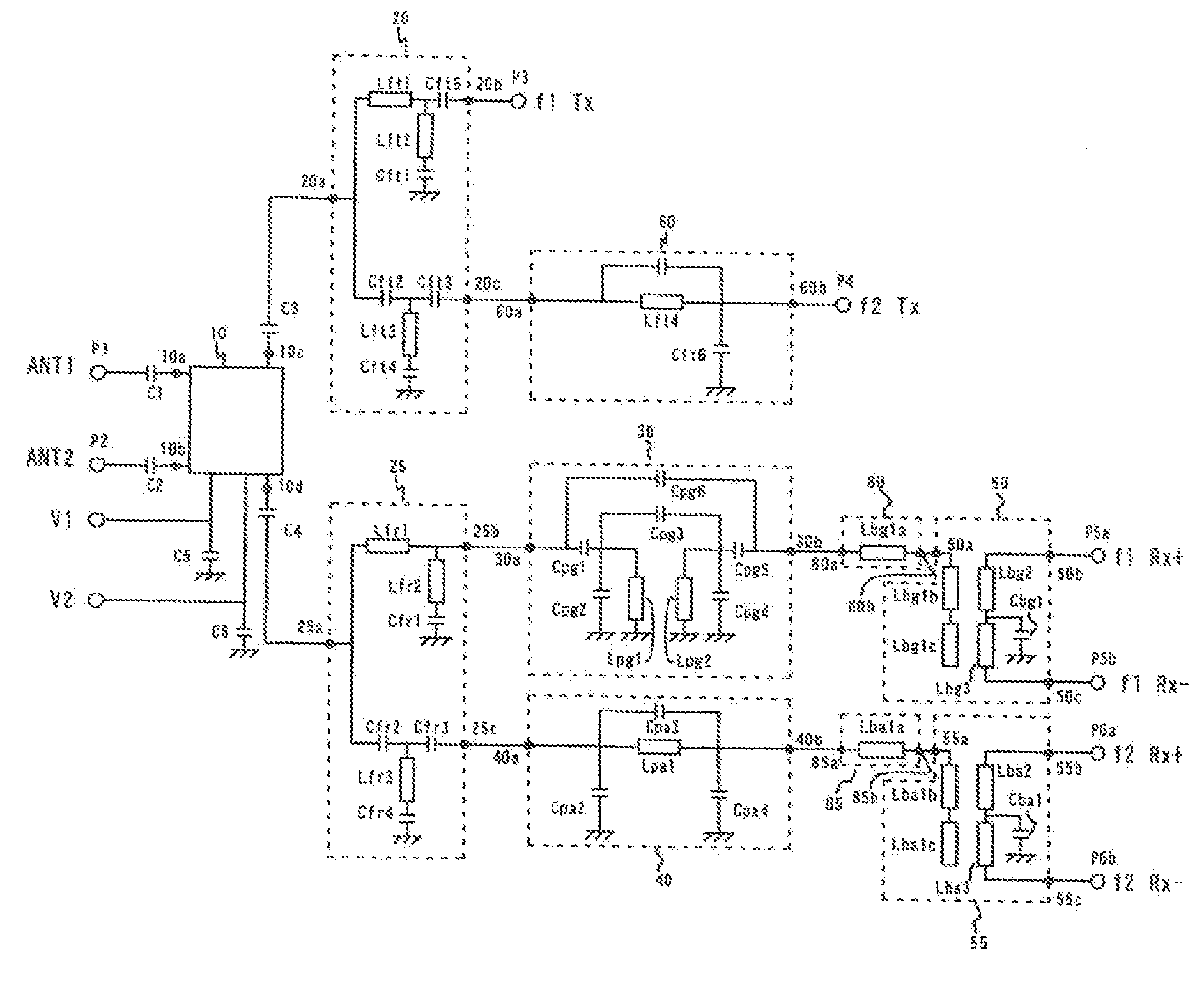
Multi-band high-frequency circuit, multi-band high-frequency circuit component and multi-band communication apparatus using same
ActiveUS20070075803A1Reduce in quantityImprove featuresMultiple-port networksTransmissionBandpass filteringMulti band
A multi-band high-frequency circuit for performing wireless communications among pluralities of communication systems having different communication frequencies, comprising a high-frequency switch circuit comprising switching elements for switching the connection of pluralities of multi-band antennas to transmitting circuits and receiving circuits; a first diplexer circuit disposed between the high-frequency switch circuit and transmitting circuits for branching a high-frequency signal into frequency bands of the communication systems; a second diplexer circuit disposed between the high-frequency switch circuit and receiving circuits for branching a high-frequency signal into frequency bands of the communication systems; the first and second diplexer circuits each comprising a lower-frequency filter circuit and a higher-frequency filter circuit, a bandpass filter circuit being used as the lower-frequency filter circuit in the second diplexer circuit, or disposed between the lower-frequency filter circuit in the second diplexer circuit and the receiving circuit, so that there is a bandpass filter between the second diplexer circuit and a lower-frequency receiving circuit; the high-frequency switch circuit comprising first to fourth ports, the first port being connected to a first multi-band antenna, the second port being connected to a second multi-band antenna, the third port being connected to the first diplexer circuit, and the fourth port being connected to the second diplexer circuit; and the switching elements being controlled in an ON or OFF state to select a multi-band antenna for performing wireless communications and to switch the connection of the selected multi-band antenna to the transmitting circuit or the receiving circuit.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
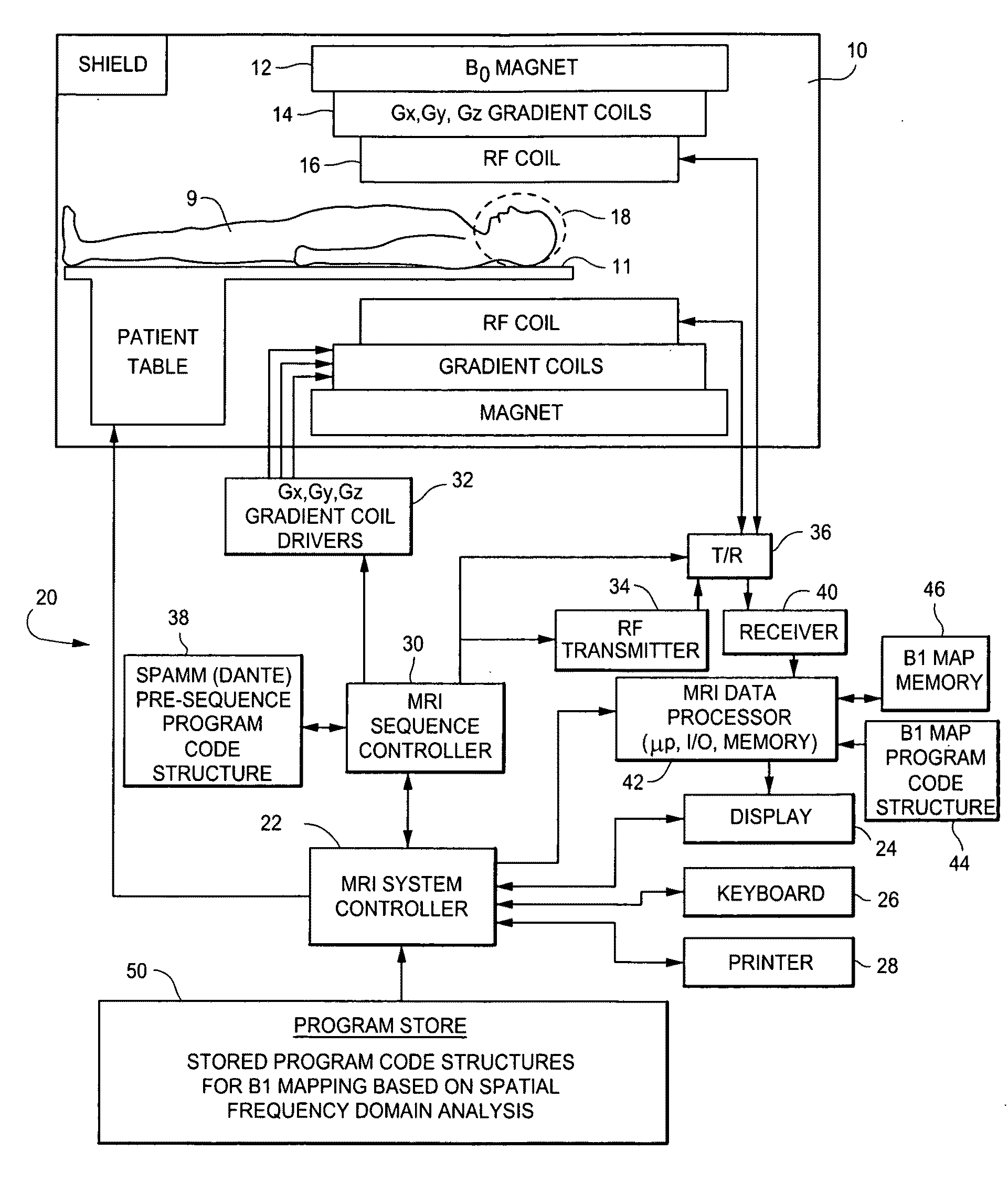
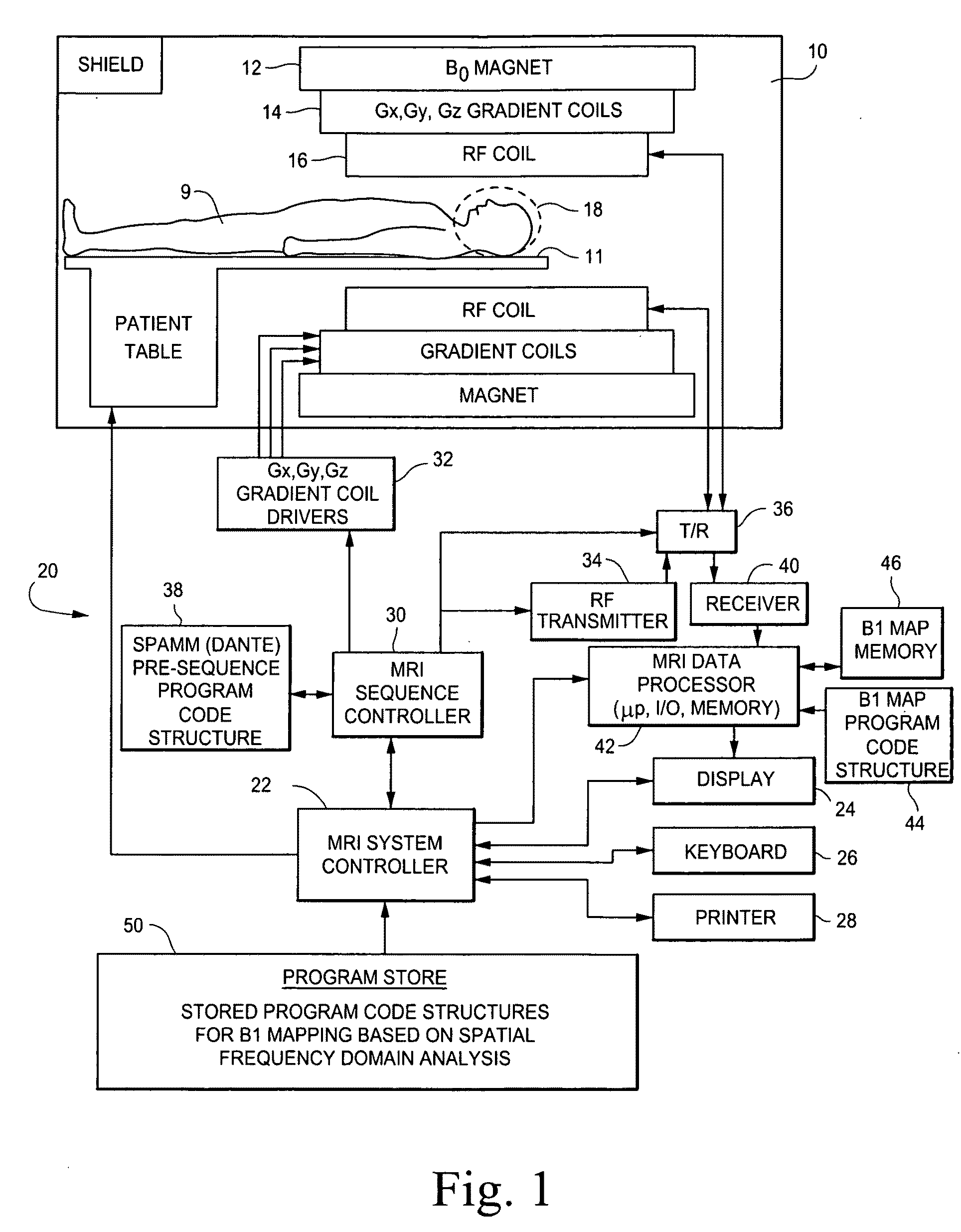
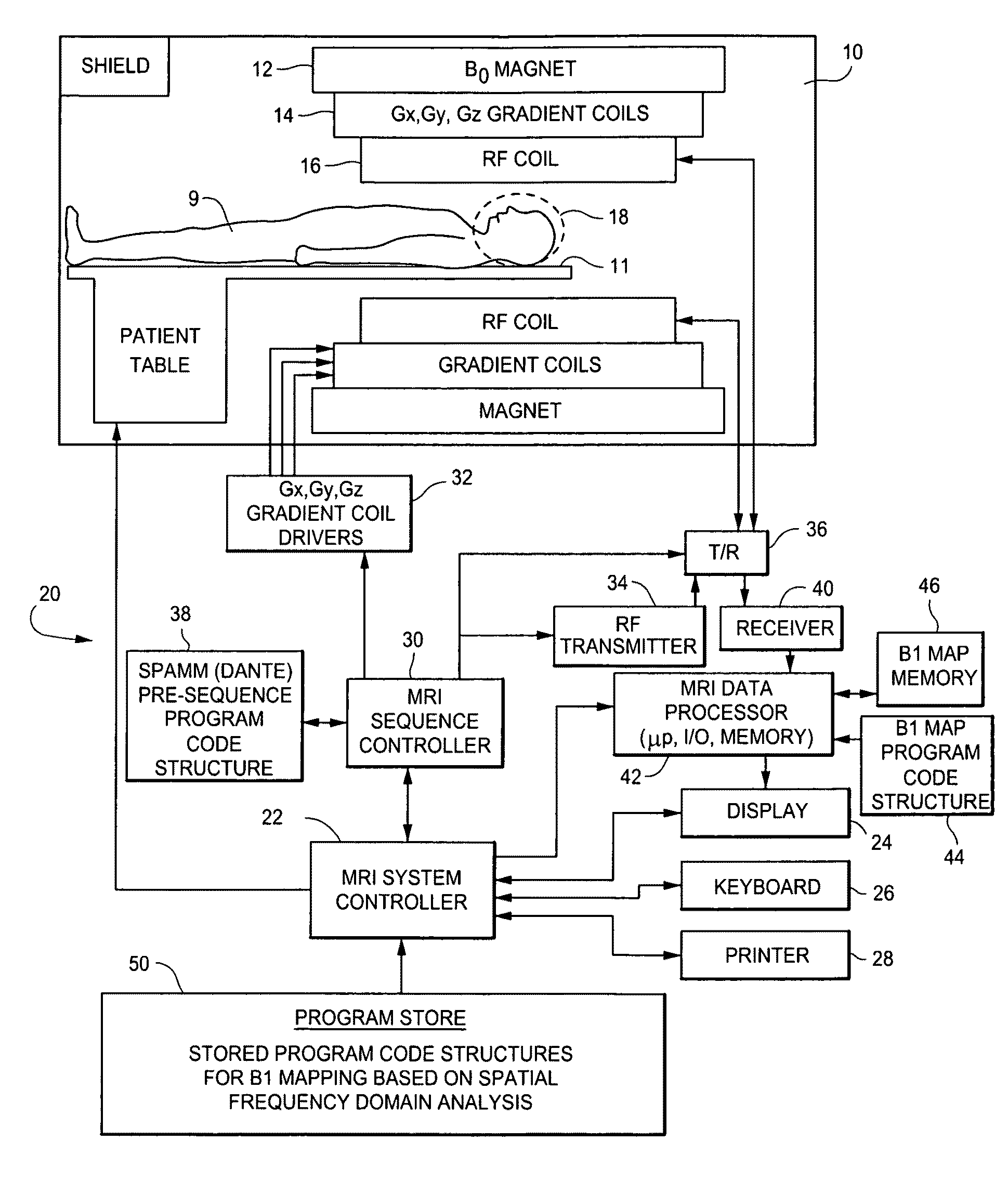
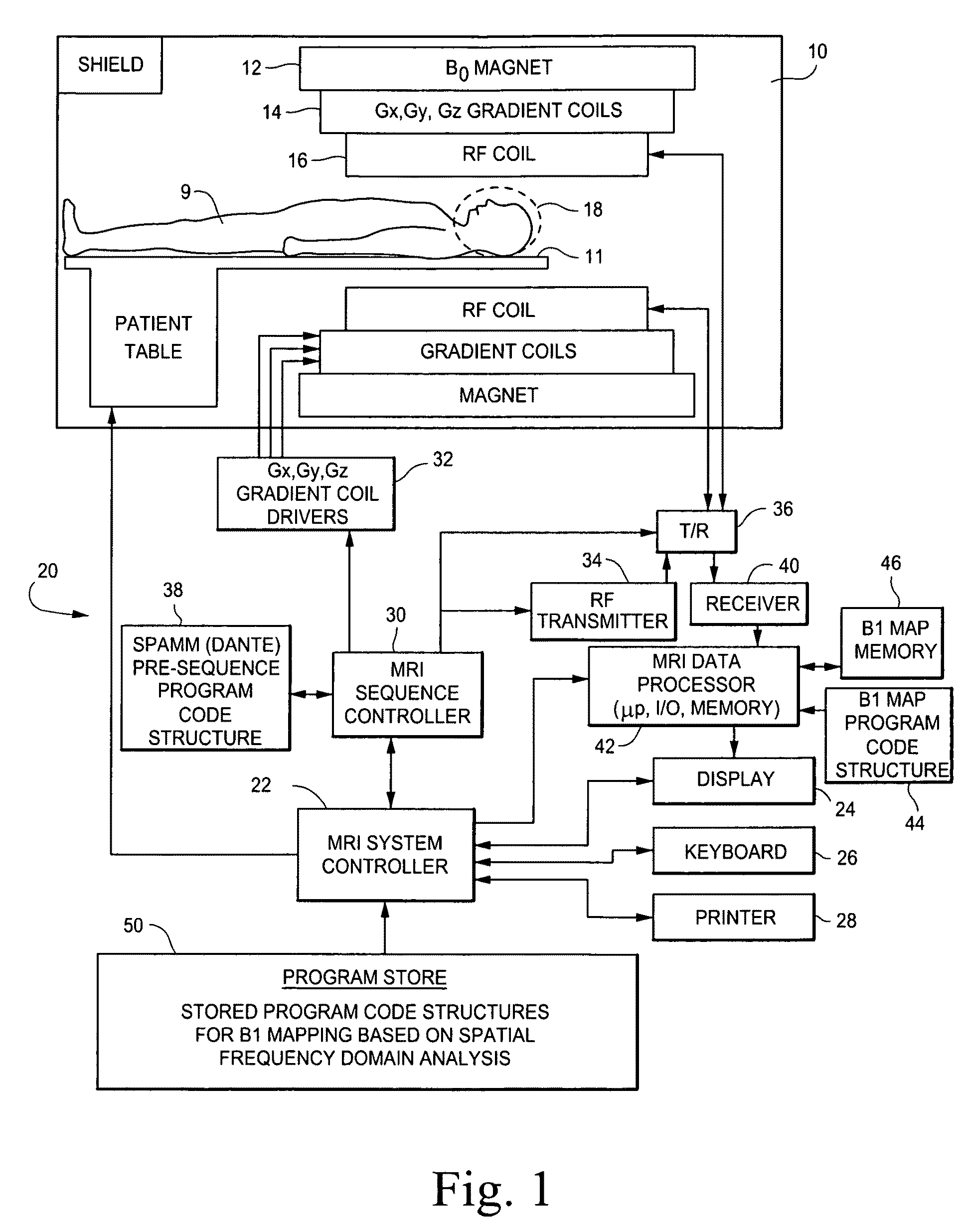
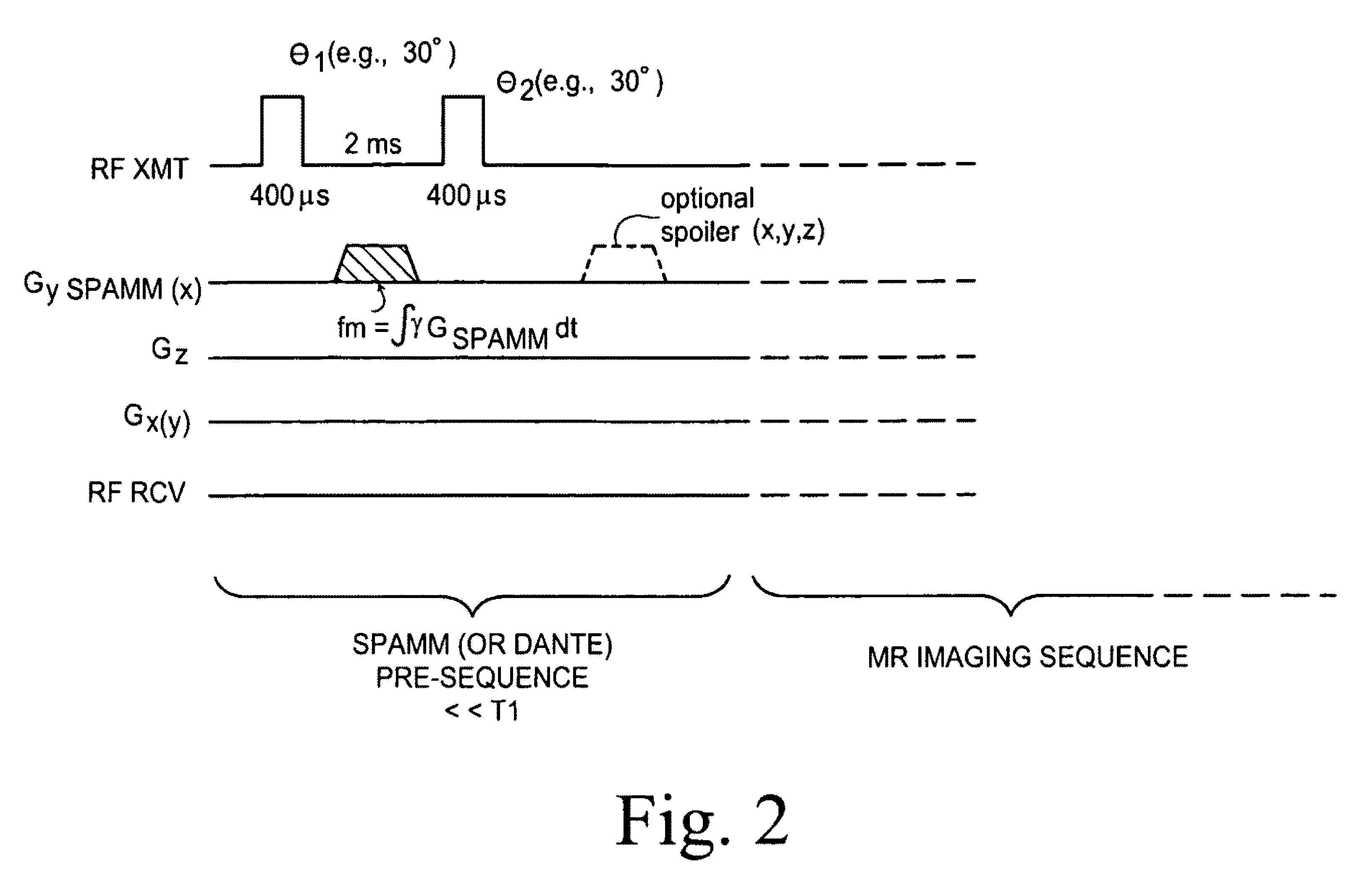
B1 mapping in MRI system using k-space spatial frequency domain filtering
ActiveUS20100239142A1High resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency filteringCondensed matter physics
Frequency filtering of spatially modulated or “tagged” MRI data in the spatial frequency k-space domain with subsequent 2DFT to the spatial domain and pixel-by-pixel arithmetic calculations provide robust ratio values that can be subjected to inverse trigonometric functions to derive B1 maps for an MRI system.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
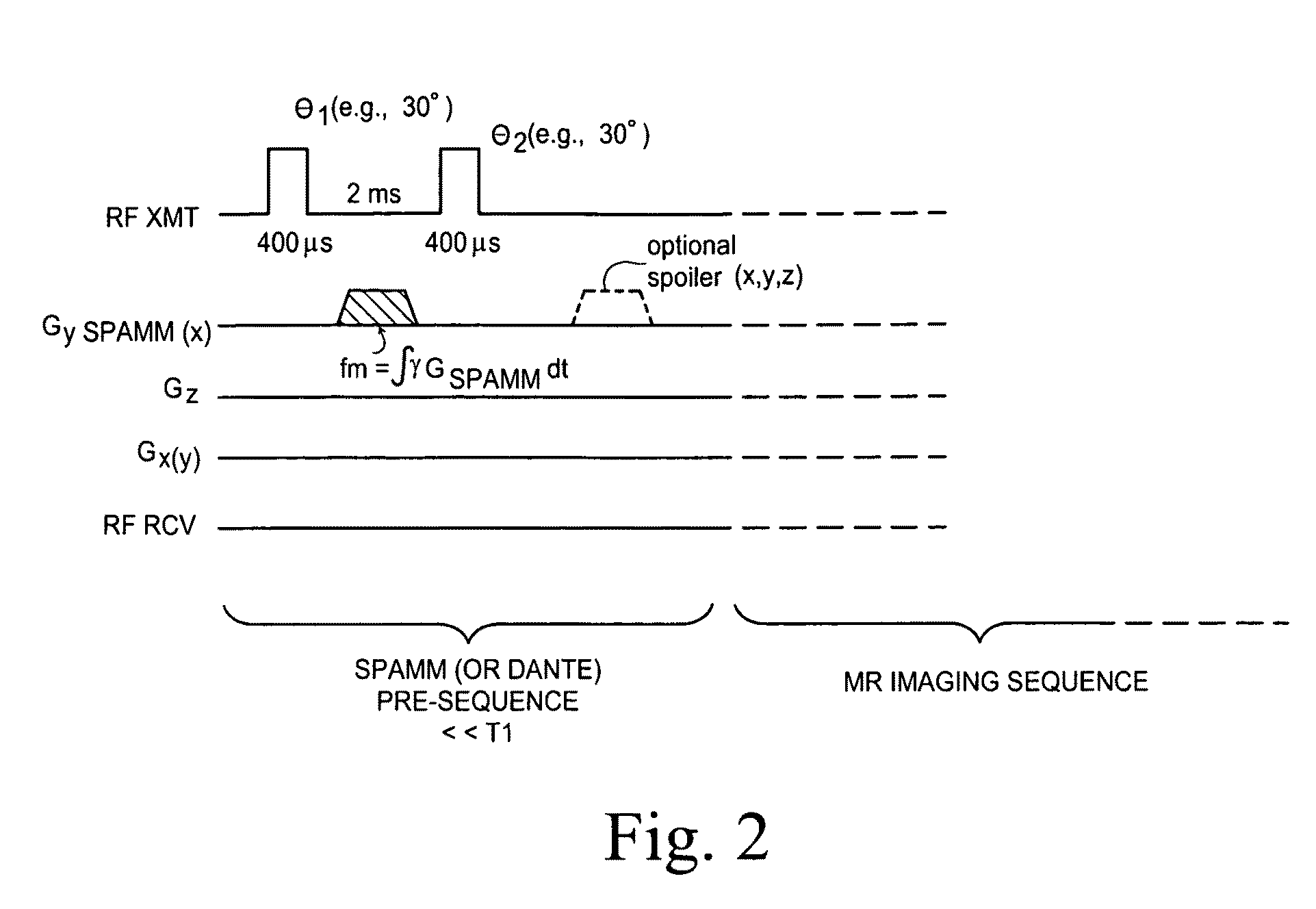
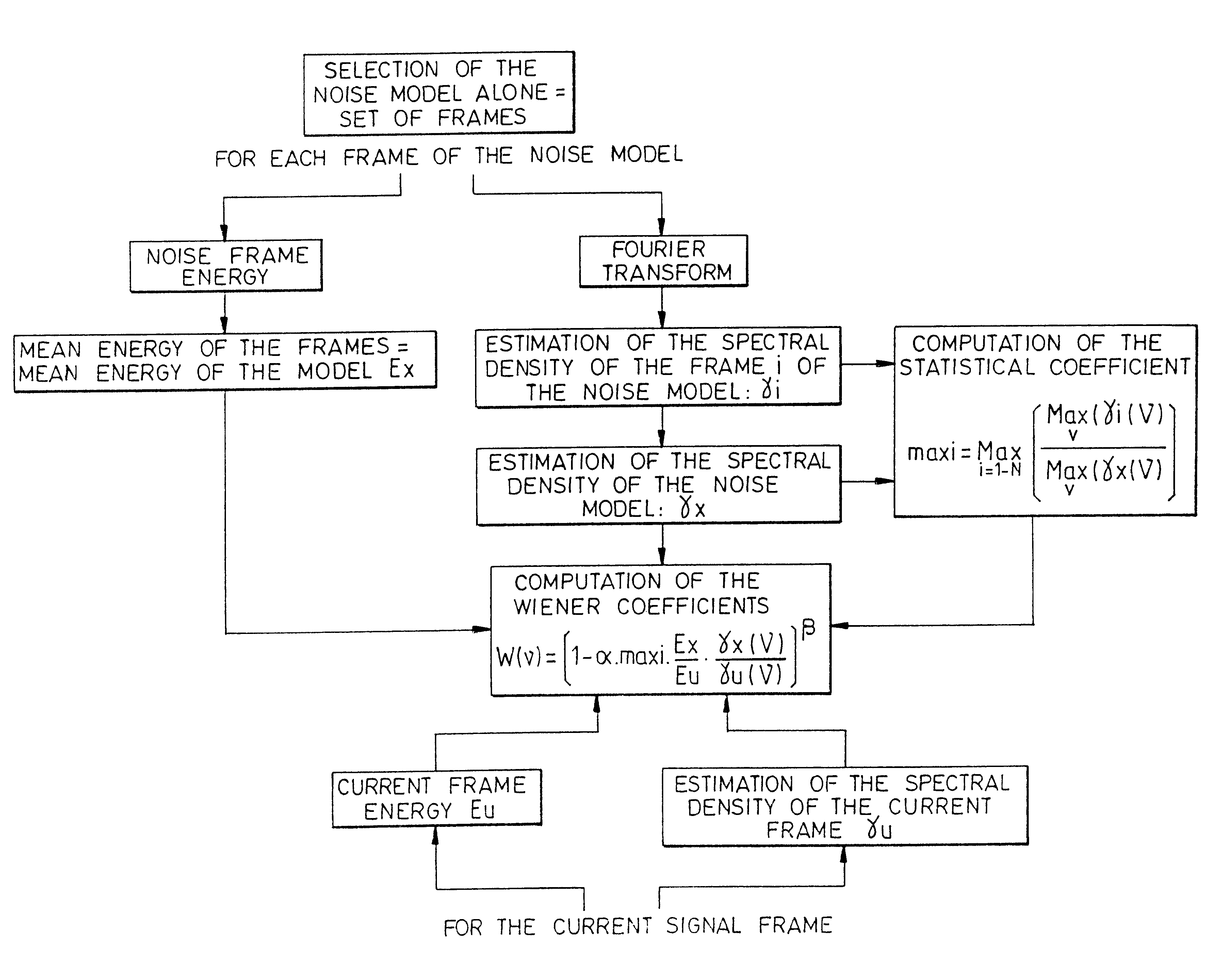
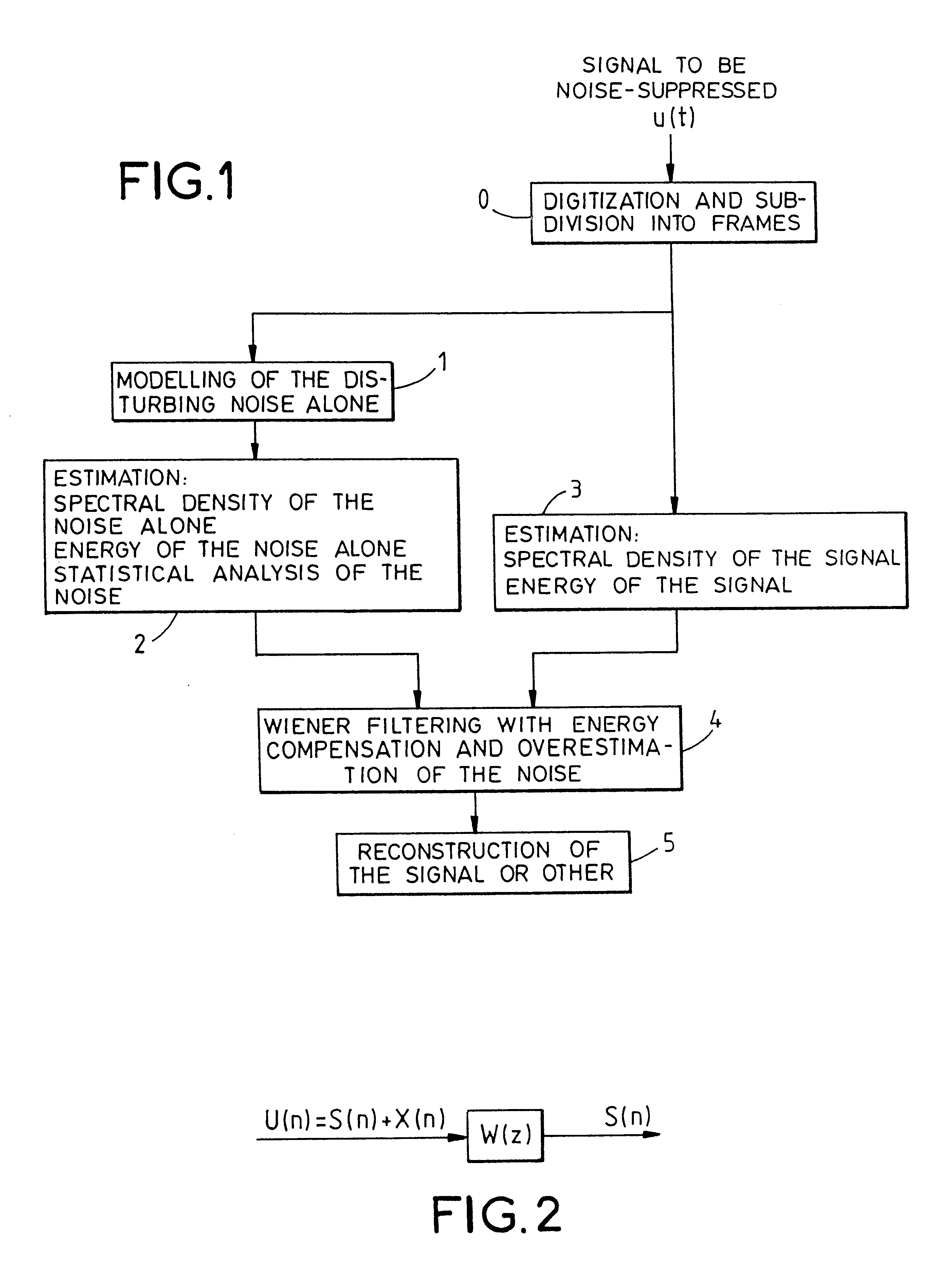
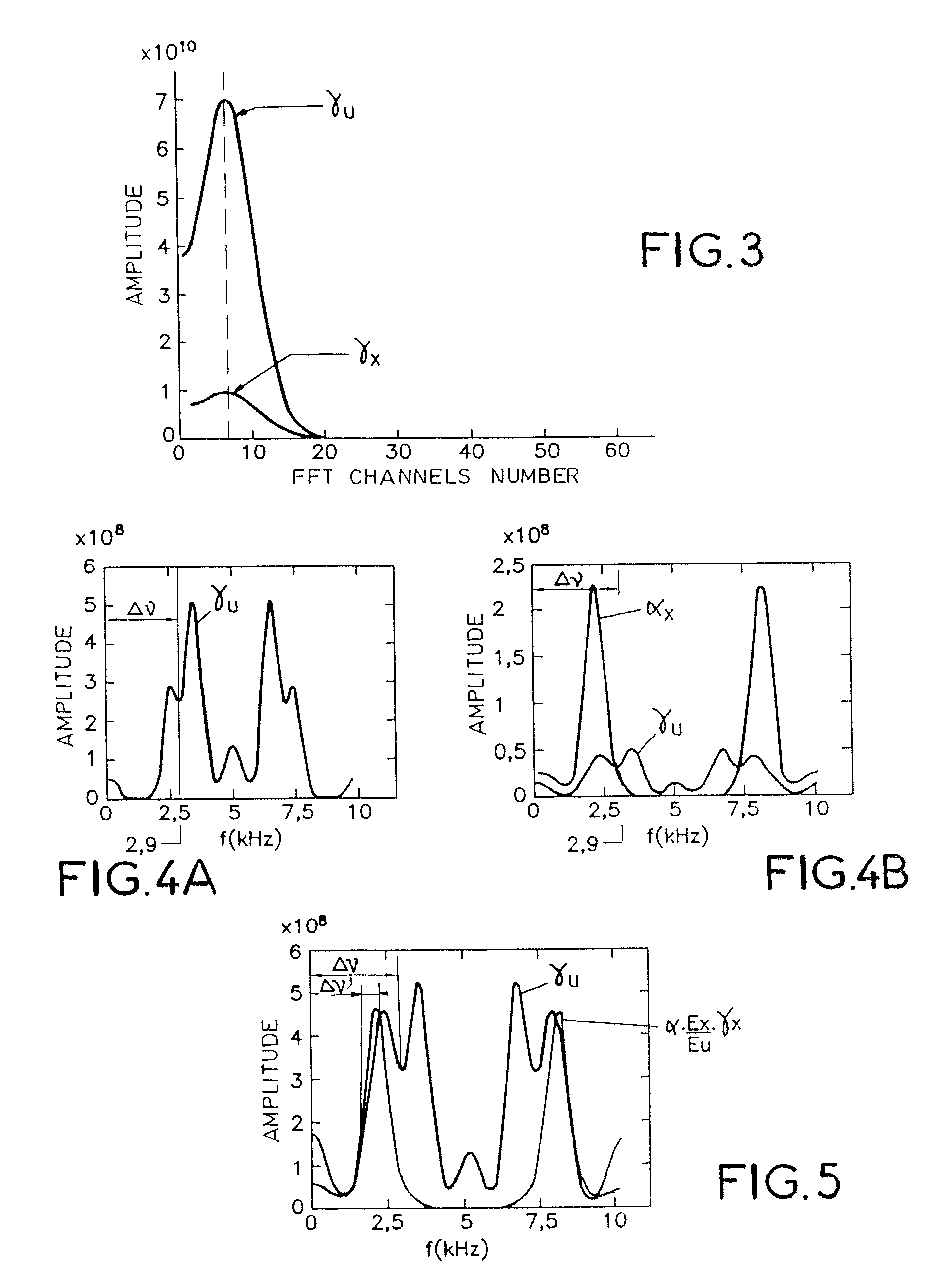
Method of frequency filtering applied to noise suppression in signals implementing a wiener filter
The disclosed method uses the Wiener frequency filtering to suppress noise in noisy sound signals (u(t)). This method includes a preliminary step in which the sound signals (u(t)) to be noise-suppressed are digitized by sampling and subdivided into frames. The method then includes a first series of steps including the creation of a noise model on N frames, the estimating of the spectral density of the noise and of the energy of the noise model and the computing of a coefficient that reflects the statistical dispersion of the noise. It also includes a second series of steps including the computation of the spectral density of the signals to be noise-suppressed fore each frame. The coefficients of the Wiener filter are modified for each successively processed frame, by the parameters determined at the end of the two series of steps, so as to introduce an energy compensation and an adaptive overestimation of the noise.
Owner:SEXTANT AVIONIQUE
Surface acoustic wave device, method for manufacturing, and electronic circuit device
InactiveUS6969945B2Low costImprove reliabilityImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityFrequency filtering
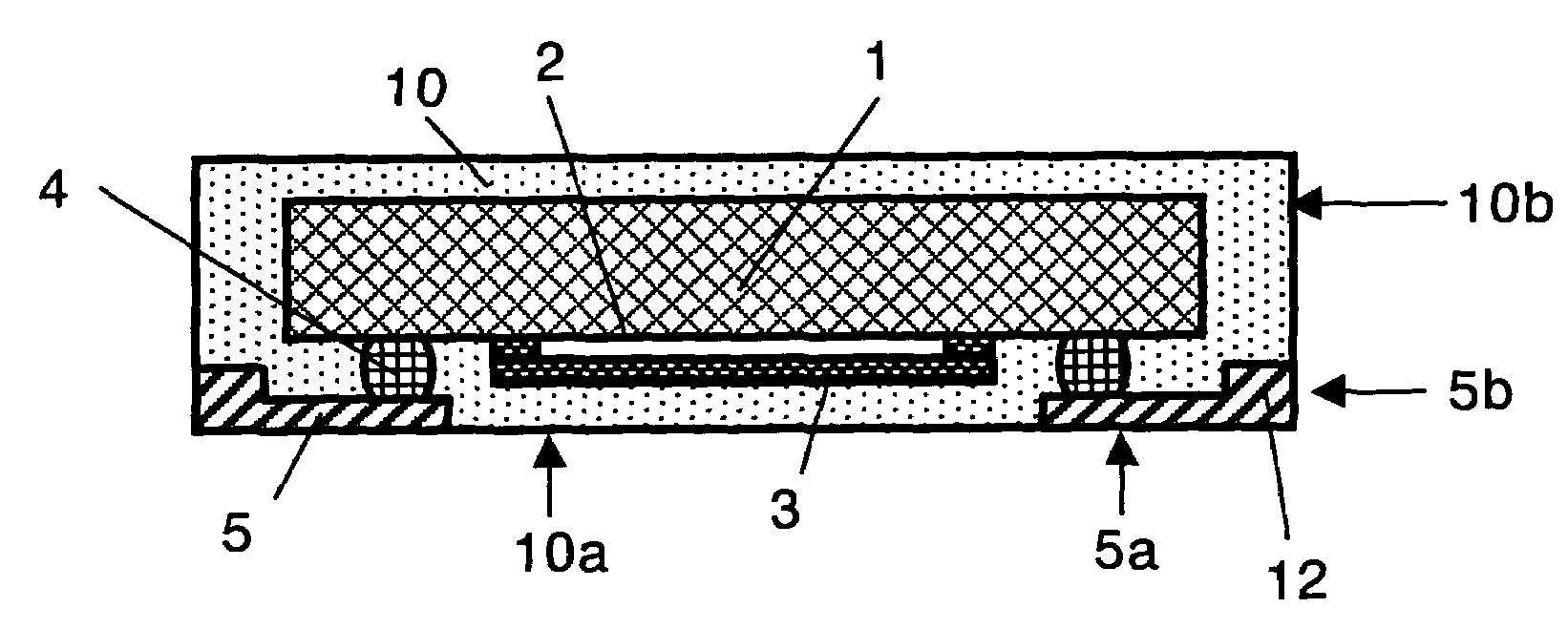
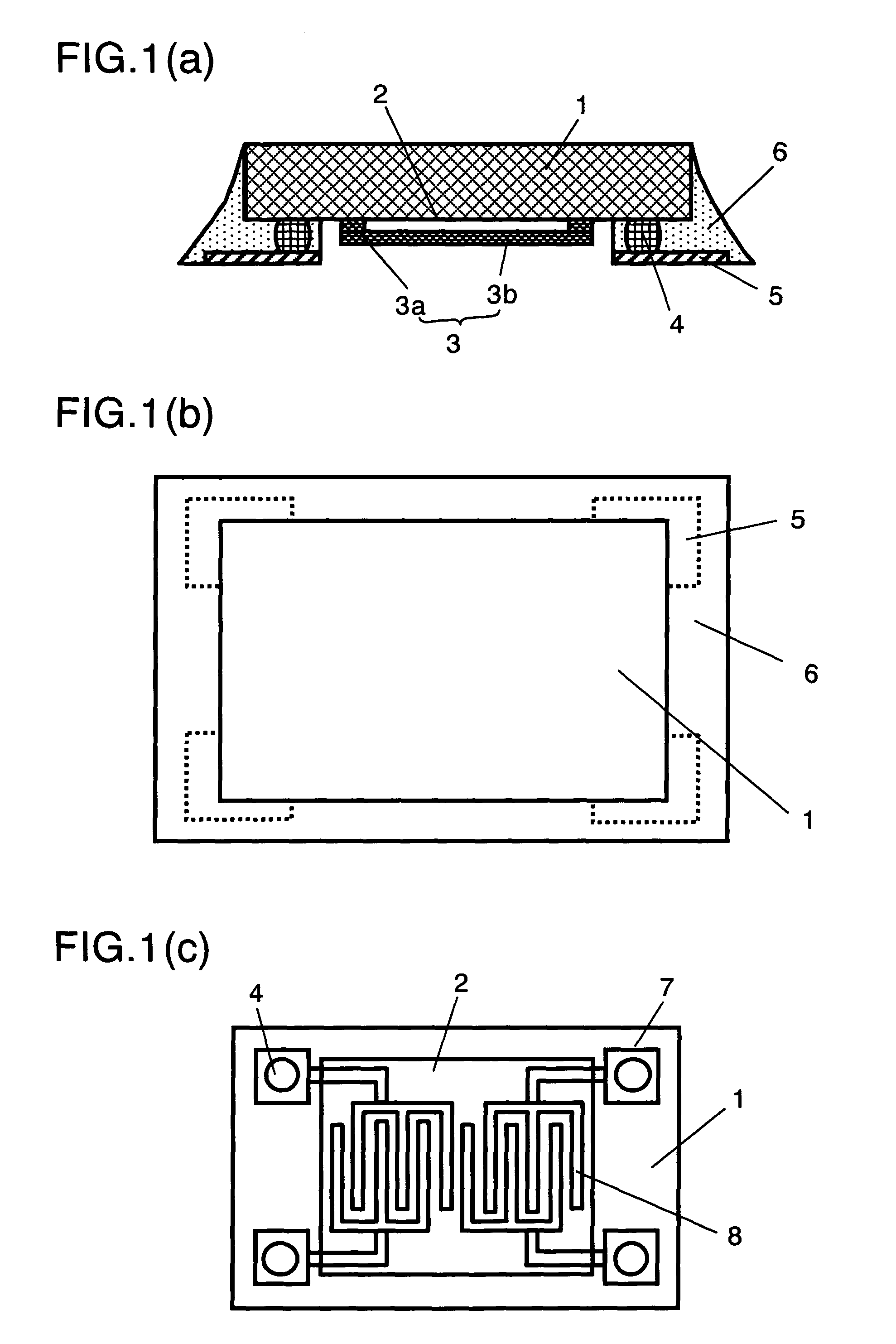
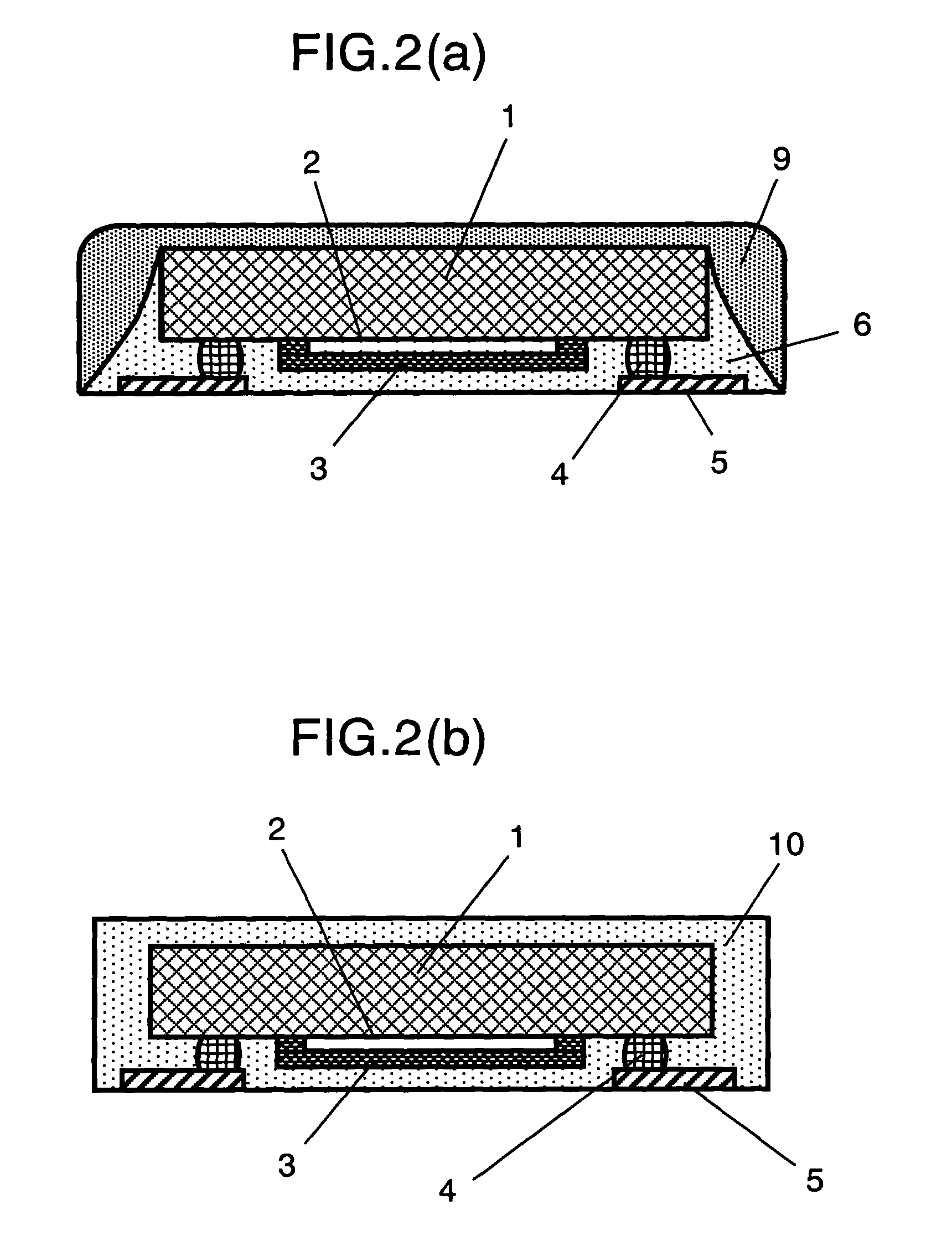
A surface acoustic wave device which occupies a small mounting area and has a low profile, yet having an improved reliability, and can be made available at low cost. The surface acoustic wave device comprises a piezoelectric substrate, a function region formed of comb-like electrodes for exciting surface acoustic wave provided on a main surface of the piezoelectric substrate, a space formation member covering the function region, a plurality of bump electrodes provided on a main surface of the piezoelectric substrate and a terminal electrode provided opposed to the main surface of piezoelectric substrate. The bump electrode and the terminal electrode are having a direct electrical connection, and a space between piezoelectric substrate and terminal electrode is filled with resin. When the above-configured acoustic wave device is applied for a frequency filter, a resonator, in a portable telephone unit, a keyless entry or the like communication apparatus, the overall size of such apparatus can be reduced and a higher reliability is implemented.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Method, system, and computer code for finding spots defined in biological microarrays
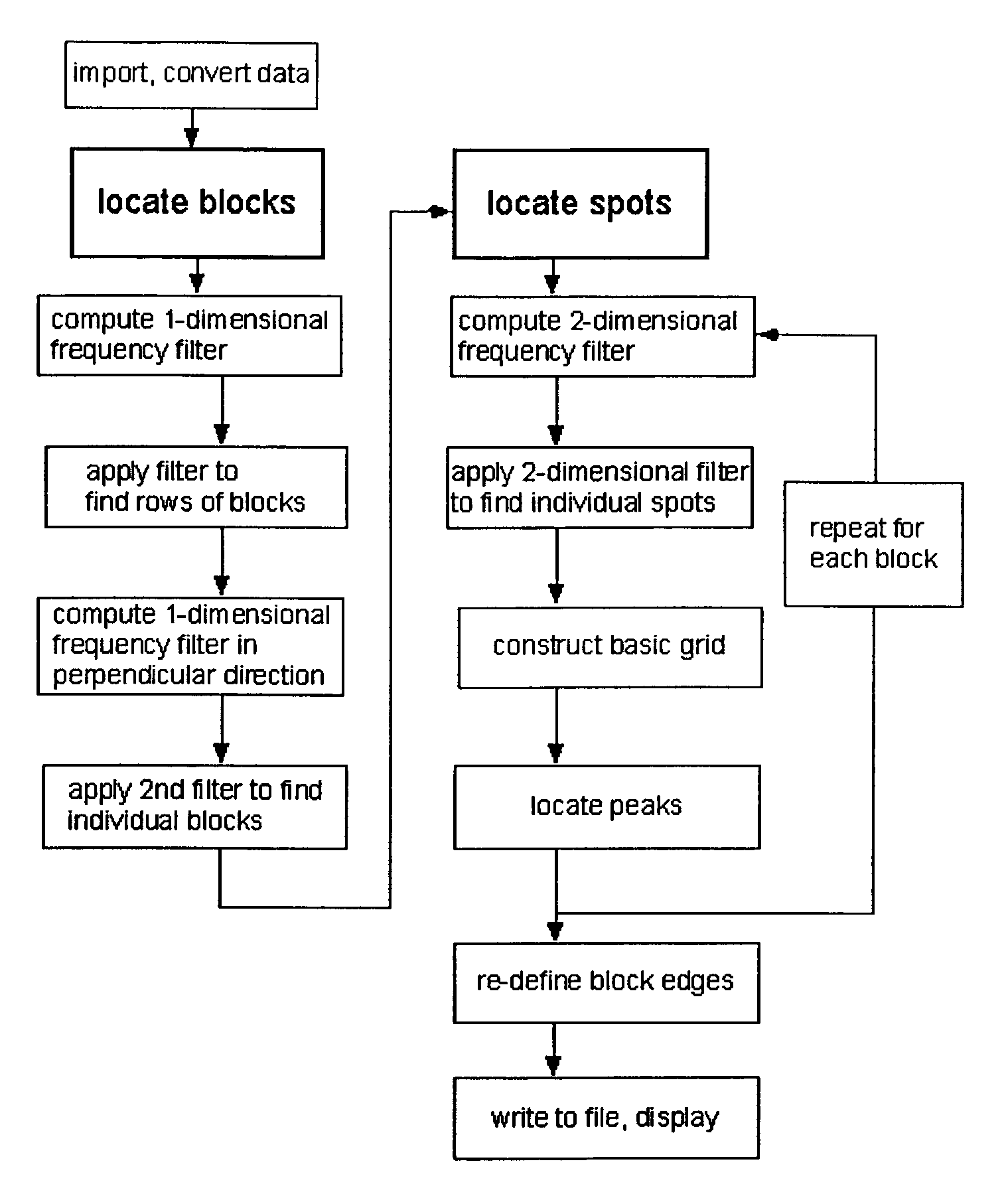
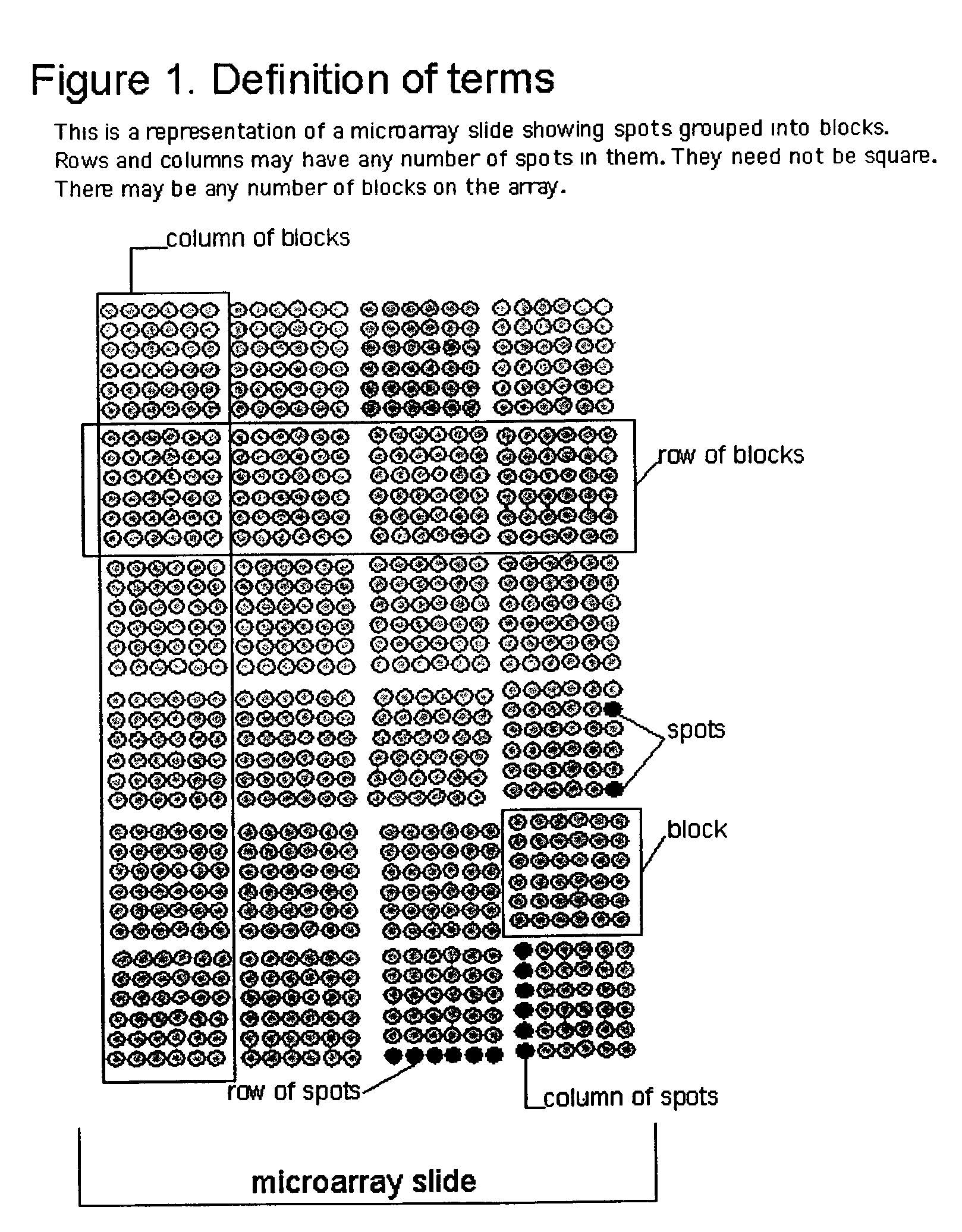
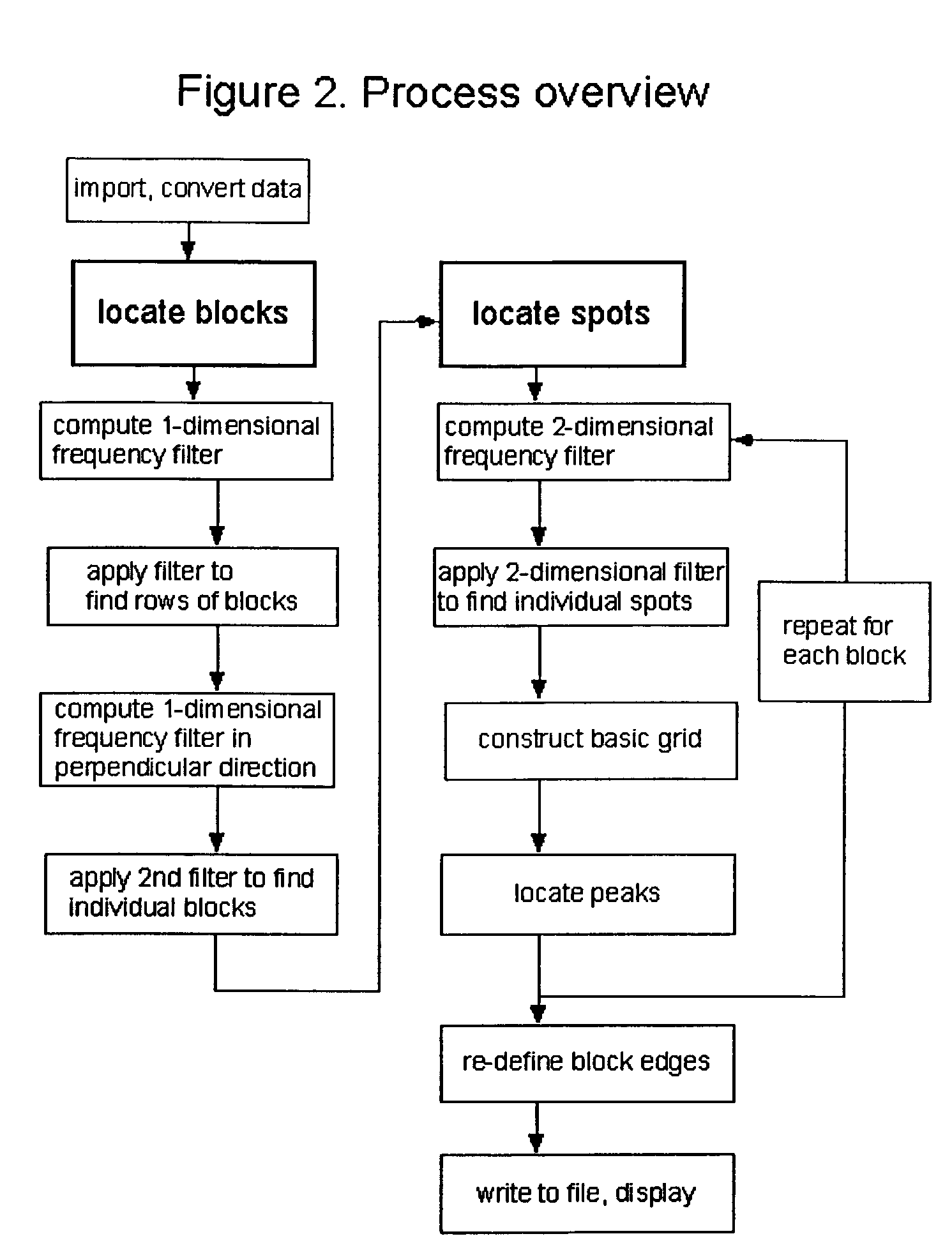
InactiveUS6980677B2Wide rangeEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisMathematical ComputingFrequency filtering
A method (and system) for using information contained within the scanned image to create, in an automated (or semi-automated) process, an accurate data grid. The process has steps: enhance the image; locate blocks of spots; and find each individual spot in each of the blocks. Preferably, the method makes use of image filtering using a“Principal Frequency Filter” based on a mathematical determination of major periodic elements in the image to eliminate noisy, non-periodic signals, and of smoothed intensity profiles of the filtered image data. Here, the term Principal Frequency Filter is used to indicate an image-enhancing filter based upon a mathematical operation which identifies the major periodic components of the image.
Owner:NILES SCI
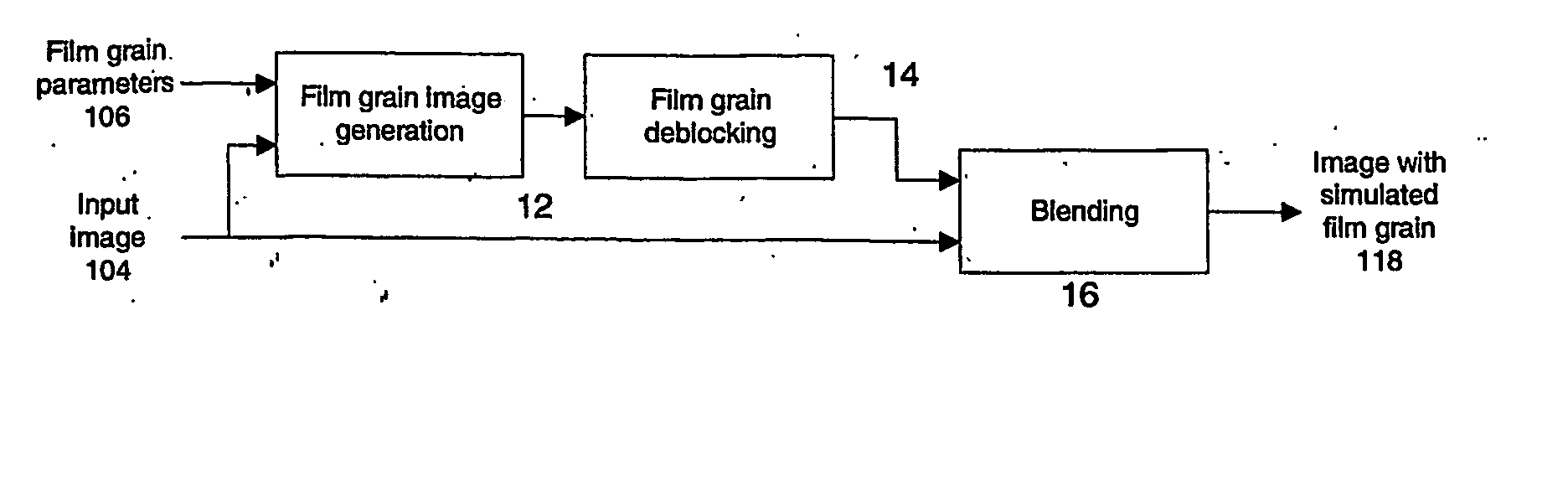
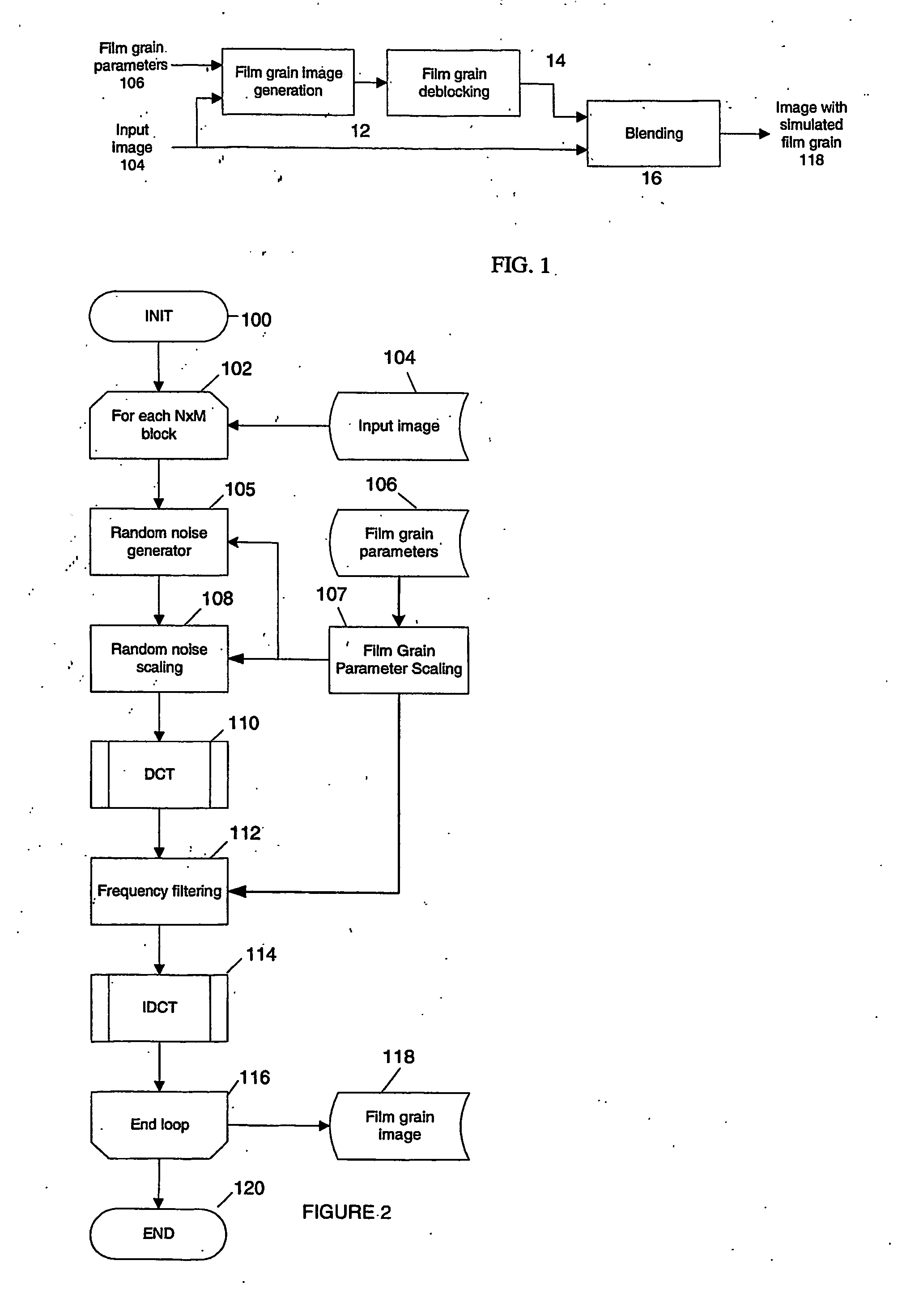
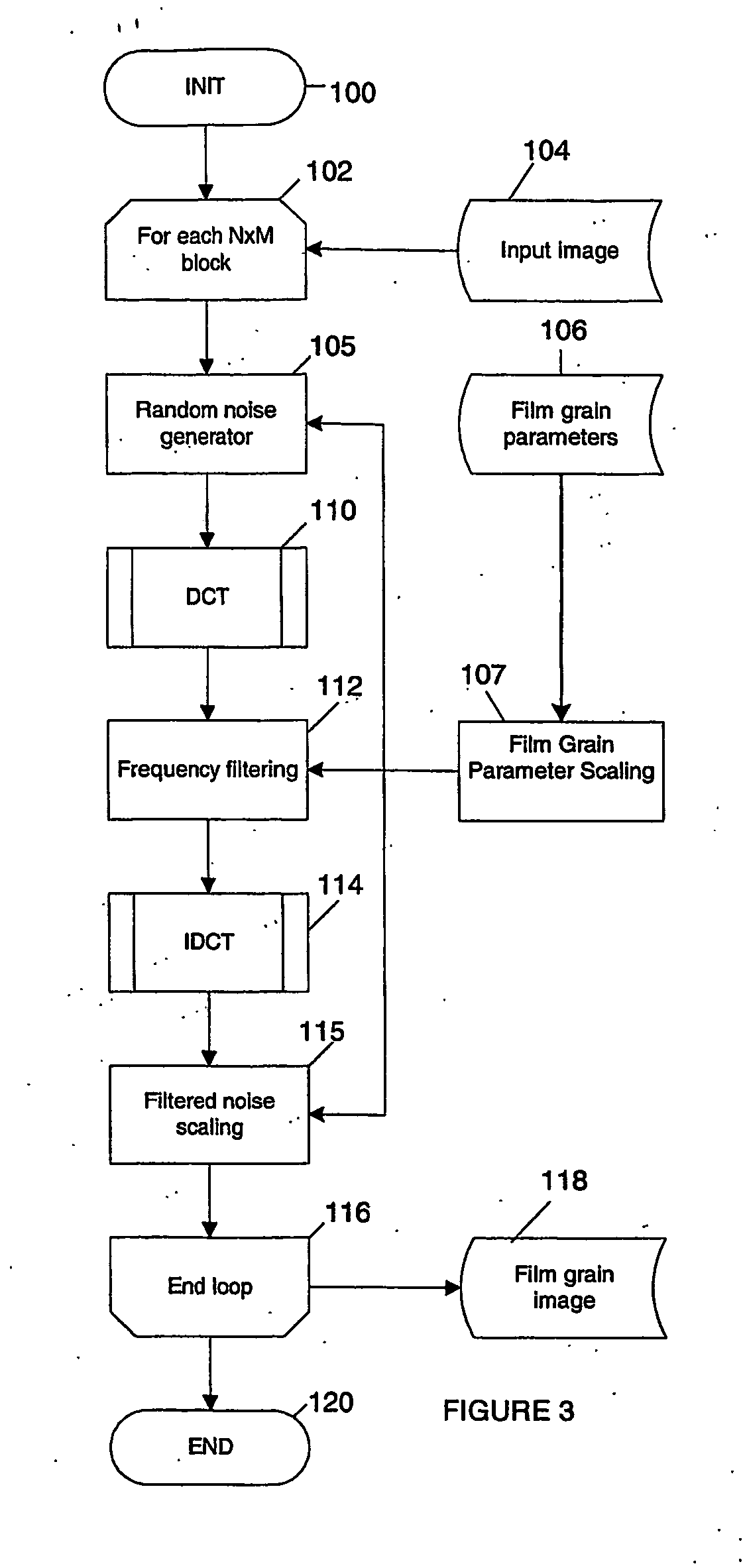
Technique for simulating film grain using frequency filtering
Simulation of film grain in an image can occur by compressing a video image, then transmitting compressed video together with a message containing at least one parameter indicative of the original film grain, to a decoder, and restoring the original grainy appearance of images by having the decoder simulating film grain based on the content of the film grain message. To improve efficiency, one or more parameters of film grain information undergo scaling in accordance with a target pixel block size for pixel blocks in the image. Such scaling allows for the use of conventional circuitry for performing block-based operations in connection with the film grain simulation.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Digital wireless narrow band radio
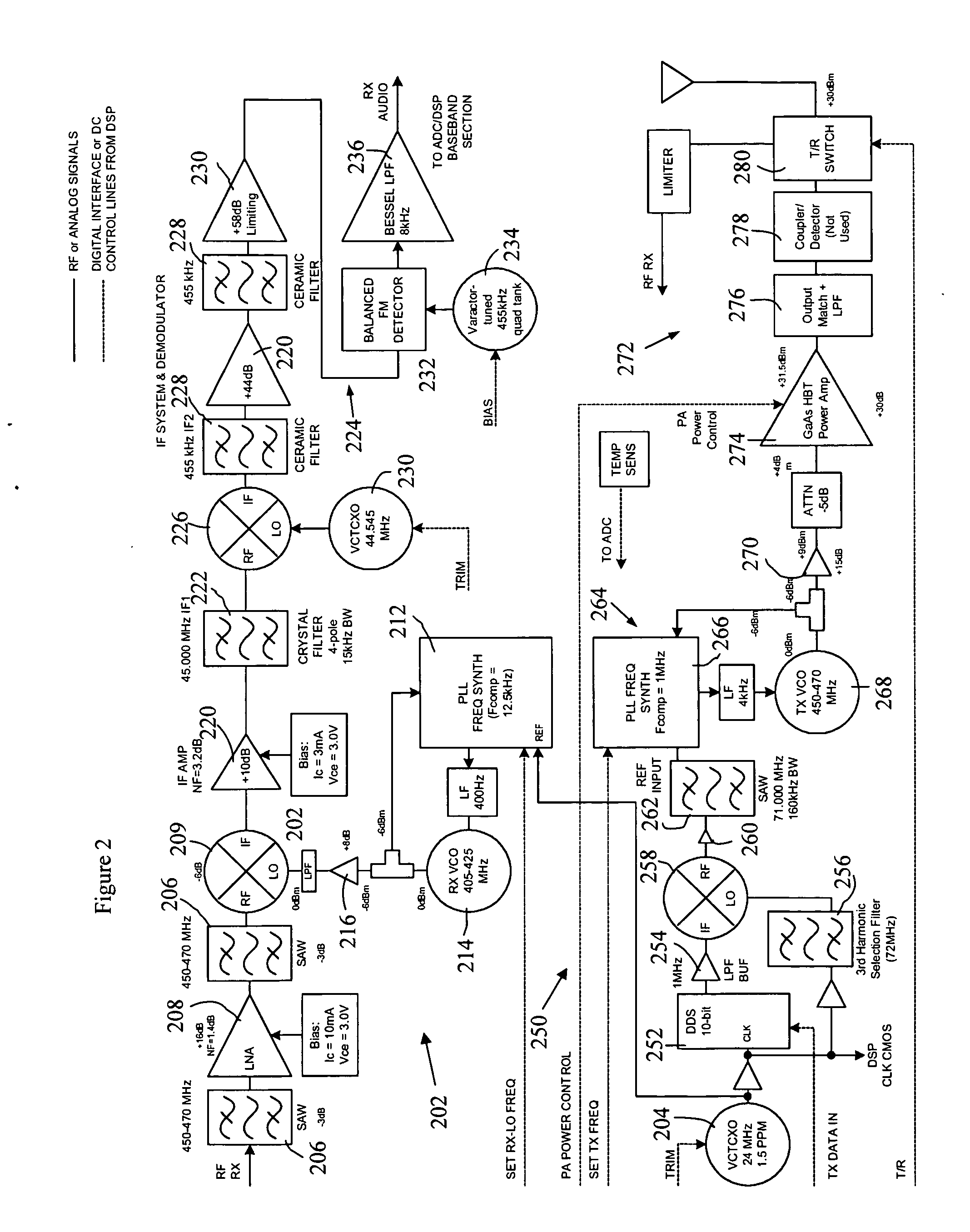
ActiveUS20060199622A1Improve accuracyHigh frequencyCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsCarrier signalEngineering
A network communication card is provided for facilitating ultra high frequency (UHF) radio communication between a terminal and a base station, the network communication card being in communication with an antenna and comprising a double-sided multilayer printed circuit board (PCB). The PCB comprises a digital interface, a receiver and a transmitter. The digital interface provides communication between the PCB and the terminal. The receiver receives incoming radio signals from the base station and processes the received signals for communication to the terminal via the digital interface. The transmitter transmits outgoing radio signals from the terminal via the digital interface to the base station and includes the following components. A digital synthesizer provides a highly accurate modulated carrier signal. An upconversion circuit increases the frequency of the carrier signal. A filter filters spurious content from the carrier signal. A phase locked loop (PLL) comprising a synthesizer and a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) generates a transmission signal from the filtered carrier signal. A transmission circuit transmits the transmission signal via the antenna.
Owner:PSION
B1 mapping in MRI system using k-space spatial frequency domain filtering
ActiveUS8077955B2High resolutionReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency filteringCondensed matter physics
Frequency filtering of spatially modulated or “tagged” MRI data in the spatial frequency k-space domain with subsequent 2DFT to the spatial domain and pixel-by-pixel arithmetic calculations provide robust ratio values that can be subjected to inverse trigonometric functions to derive B1 maps for an MRI system.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
High-Repetition-Rate Single-Photon Receiver and Method Therefor
ActiveUS20140027607A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesSignal qualityFrequency filtering
A single-photon receiver and method for detecting a single-photon are presented. The receiver comprises a SPAD that receives a gating signal having a fundamental frequency in the 100 MHz to multiple GHz range. The receiver further comprises a two-stage frequency filter for filtering the output of the SPAD, wherein the filter has: (1) a notch filter response at the fundamental frequency; and (2) a low-pass filter response whose cutoff frequency is less than the first harmonic of the fundamental frequency. As a result, the frequency filter removes substantially all the frequency components in the SPAD output without significant degradation of the signal quality but with reduced complexity, cost, and footprint requirement relative to receivers in the prior art.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting combustion knock from the ionic current in an internal combustion engine
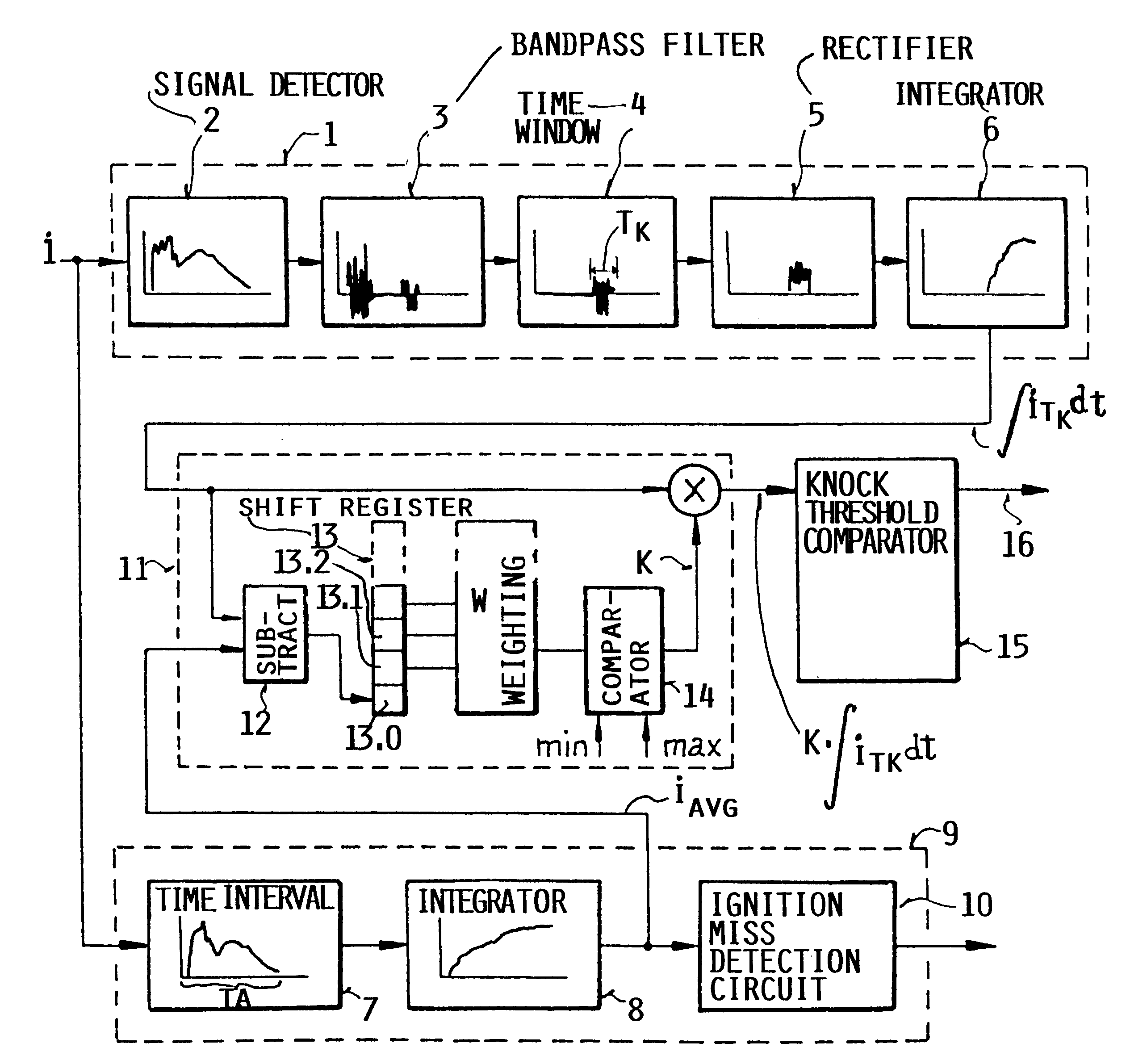
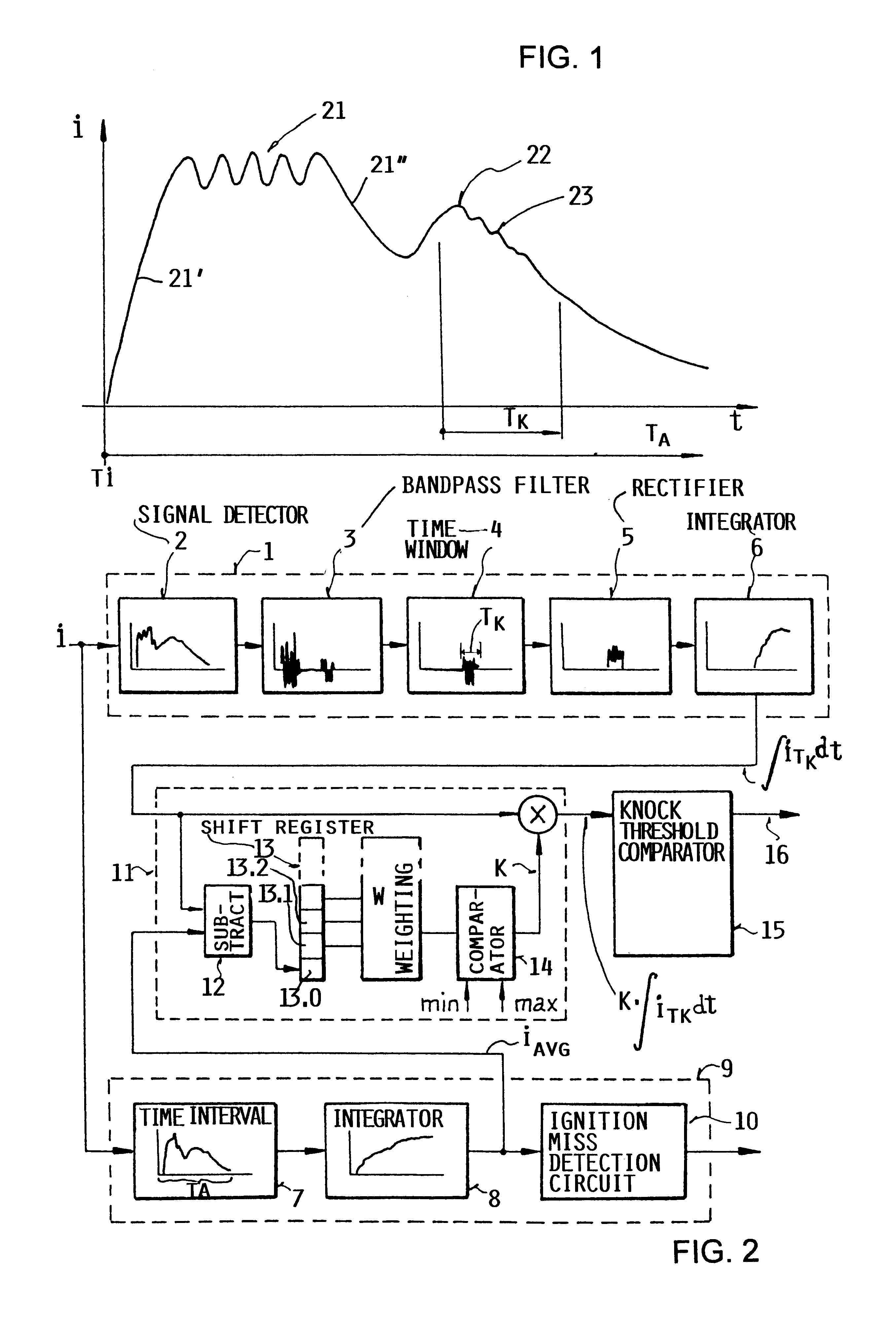
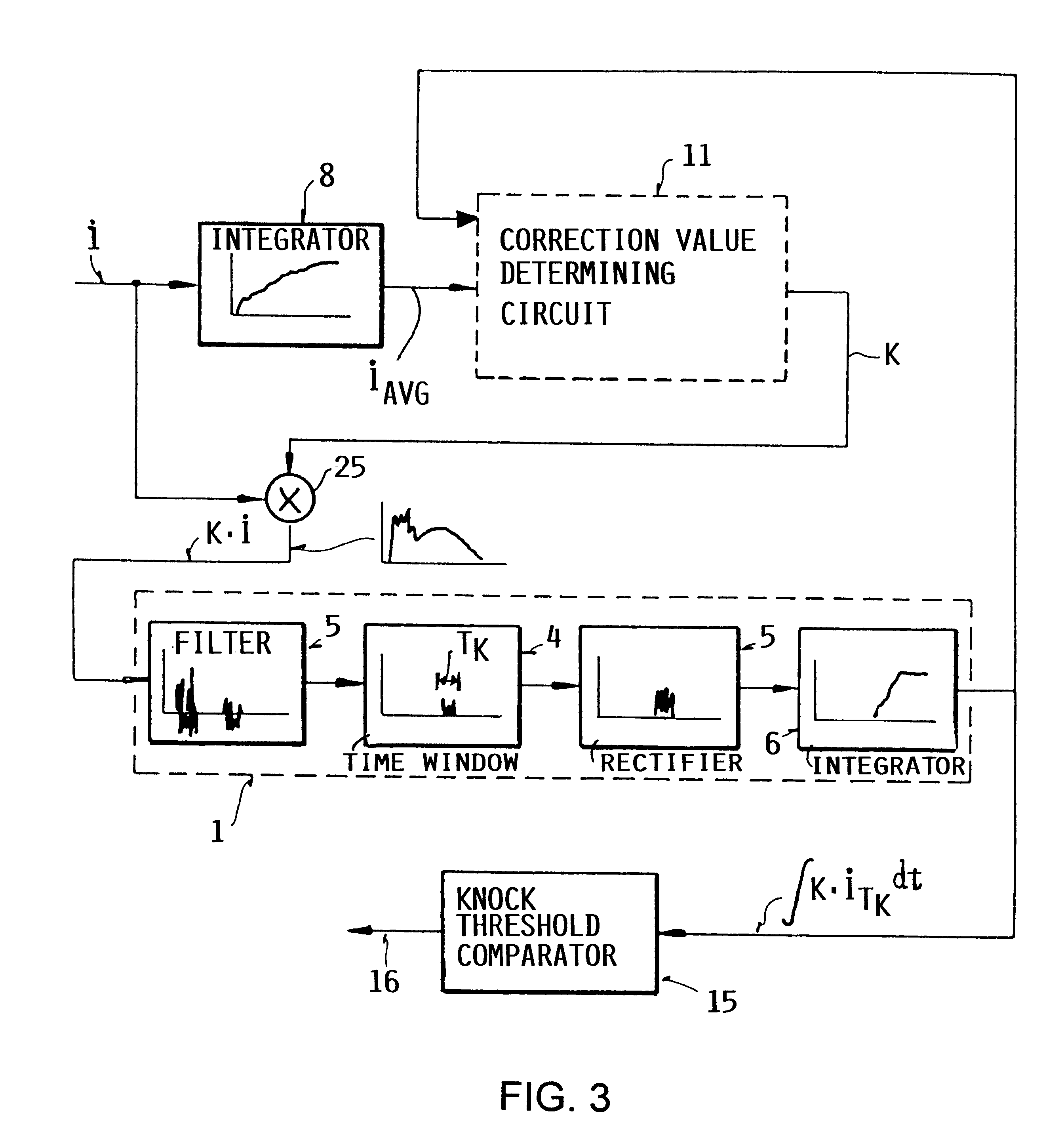
InactiveUS6230546B1Delay variationMinimize biasMachines/enginesAdvancing/retarding ignitionShift registerCombustion chamber
A method and an apparatus for detecting knocking combustion in an internal combustion engine, by evaluating the ionic current signal sensed in the combustion chamber, is especially adapted to correct or compensate the ionic current signal for longterm variations arising therein, for example due to variations in the composition of the fuel as a result of contamination with metallic components or the like. Thereby, erroneous knock recognition is prevented. To achieve this, a frequency-filtered time-sampled knocking component integral of the ionic current signal generated in the present combustion cycle is multiplied by a correction value determined from at least one integral value of the ionic current signal generated during at least one prior combustion cycle. The correction value is preferably a time-weighted combination of plural difference values that are respectively determined by subtracting an average integrated value of the ionic current signal from the knocking component integral of the ionic current signal in plural prior combustion cycles, and that are stored in successive positions of a shift register. If the final corrected knocking component integral falls outside of an allowable range, a knock recognition signal is released.
Owner:DAIMLER AG +1
Duplexer and communication apparatus with first and second filters, the second filter having plural switch selectable saw filters
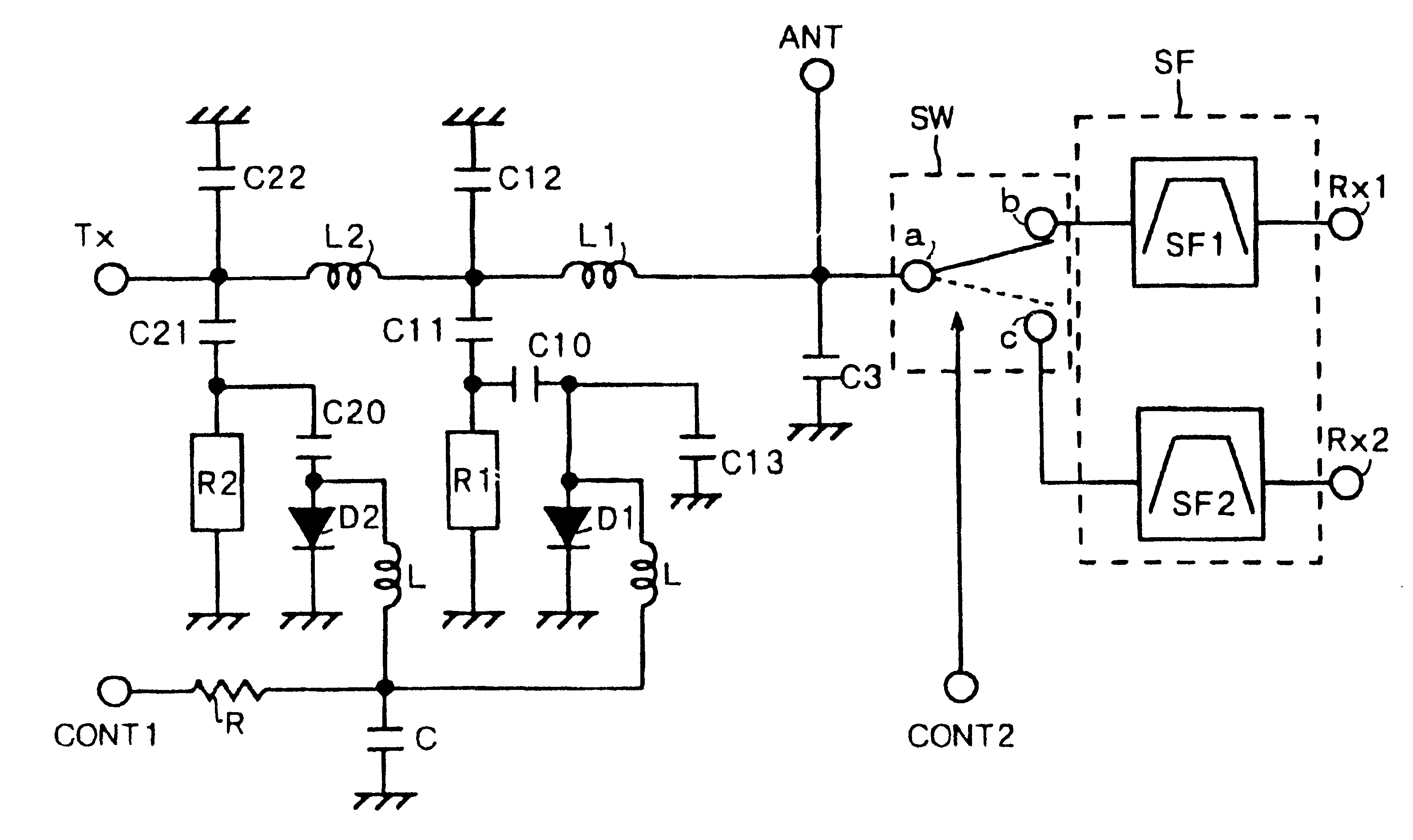
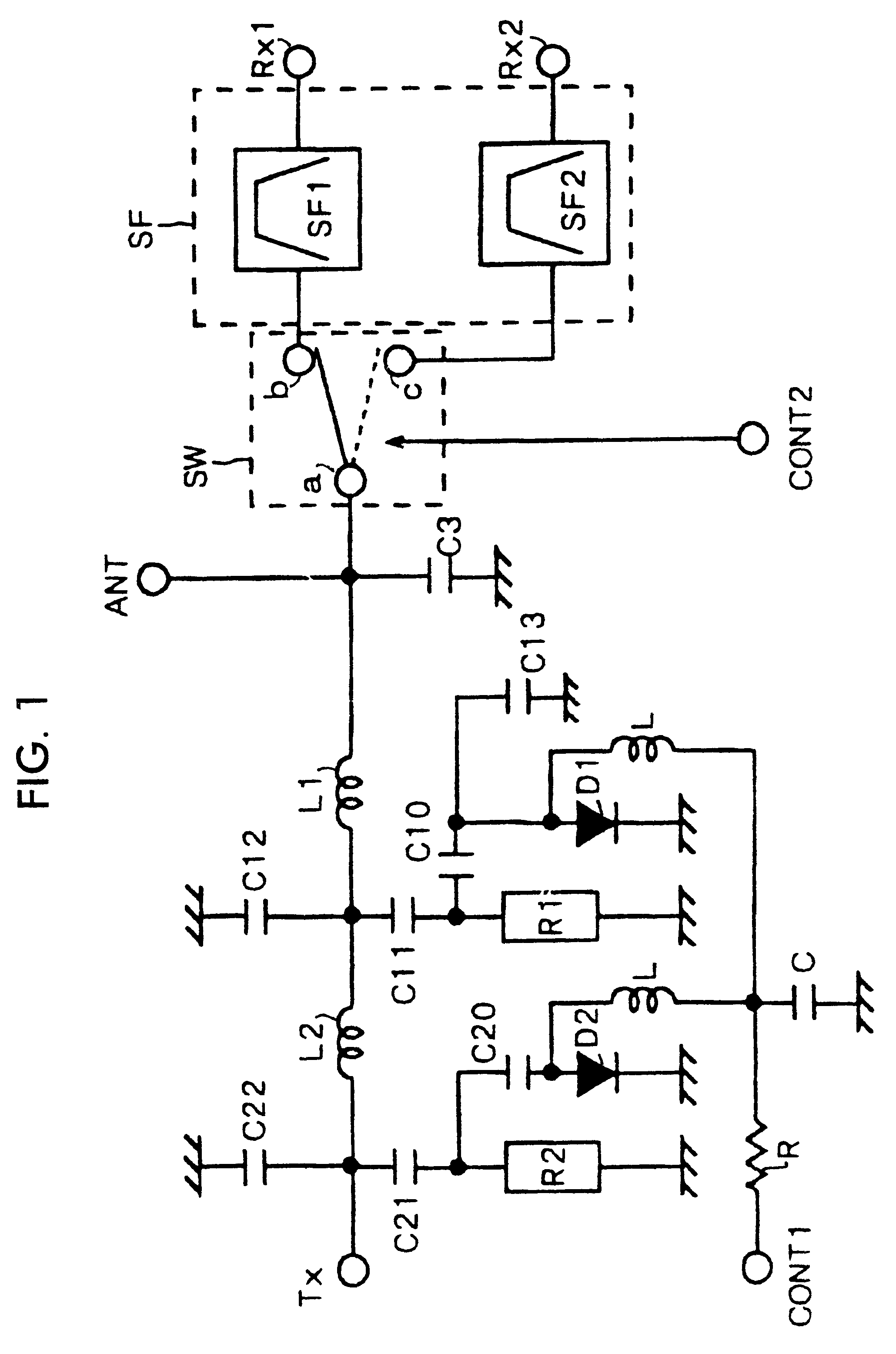
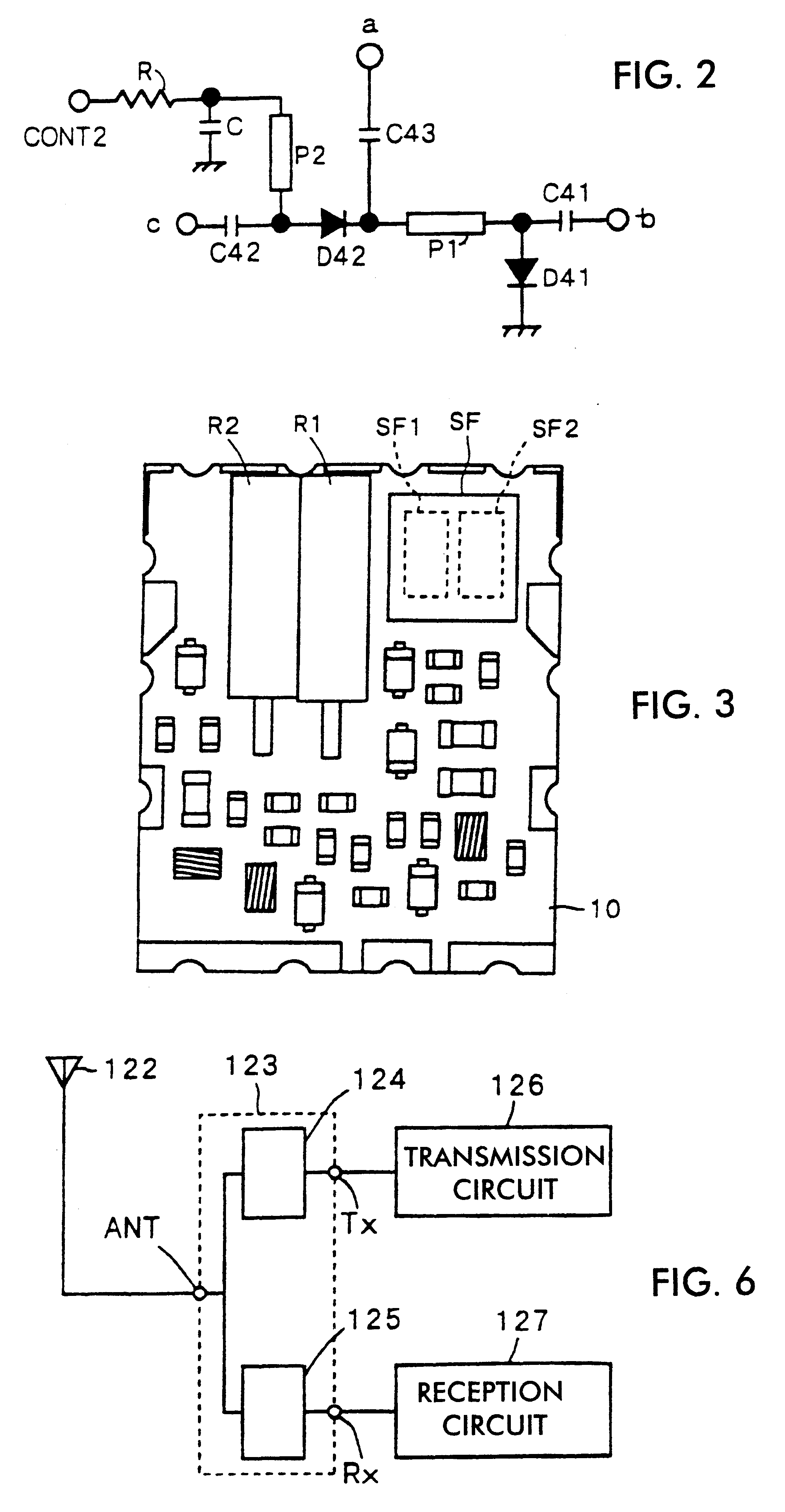
InactiveUS6483399B1Reduce the amount requiredSatisfactory characteristicMultiple-port networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesCommunications systemFrequency filtering
A duplexer and a communication apparatus incorporating the same which are suitable for use in communication systems with wide frequency bands and narrow separations, and which can be miniaturized while having satisfactory characteristics. The duplexer has a transmission filter constituted of a variable frequency filter in which PIN diodes are connected to dielectric resonators and a reception filter constituted of two surface acoustic wave filters and a switching circuit. In the transmission filter, one of the higher and lower sides of a transmission frequency band can be selected according to a voltage applied to a first voltage control terminal. In addition, in the reception filter, one of the two surface acoustic wave filters can be selected according to a voltage applied to a second voltage control terminal.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Methods for generating and transmitting frequency hopped signals
InactiveUS20050025220A1Easy to manufactureInadequate filteringPolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationFrequency filteringEngineering
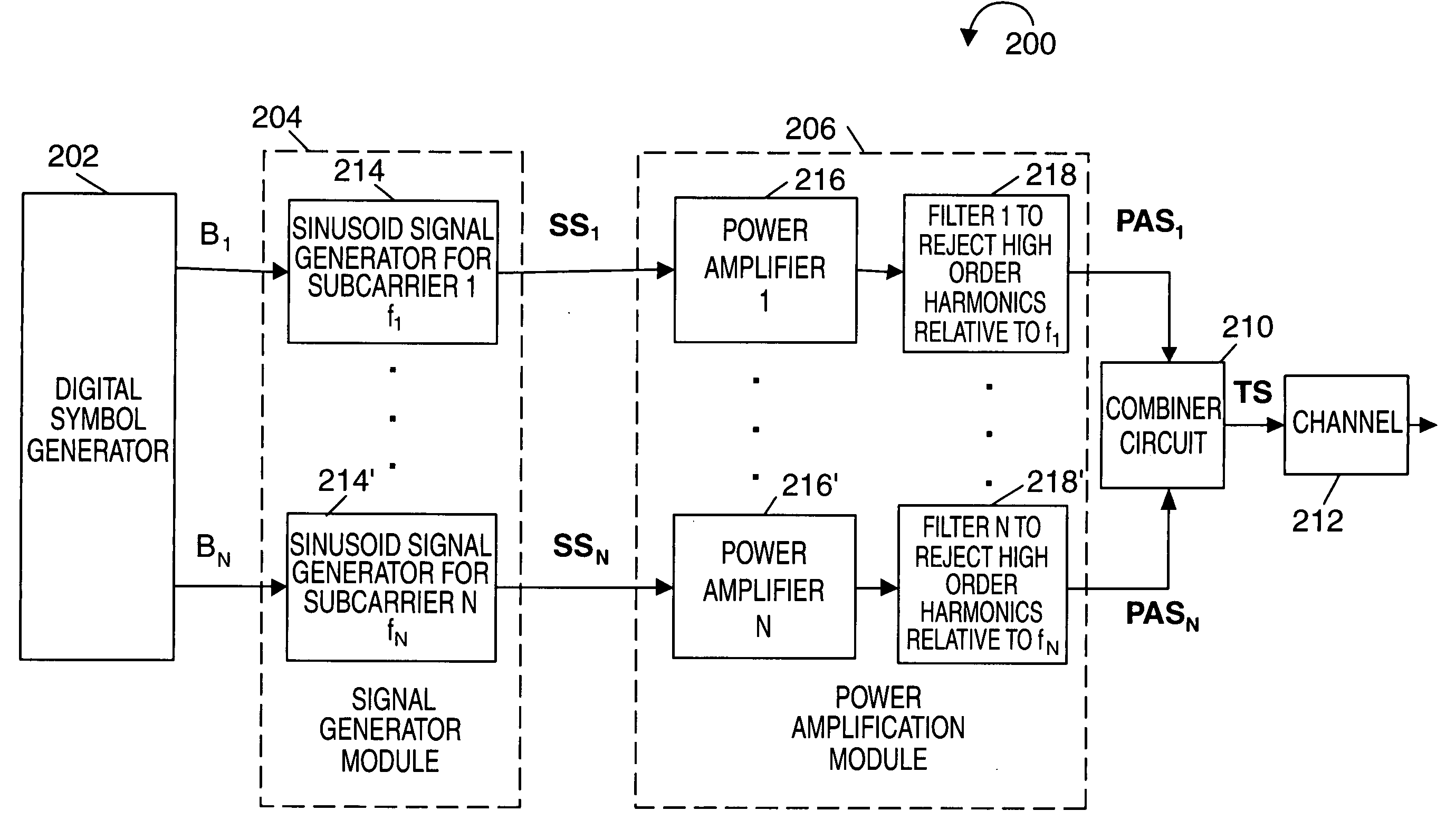
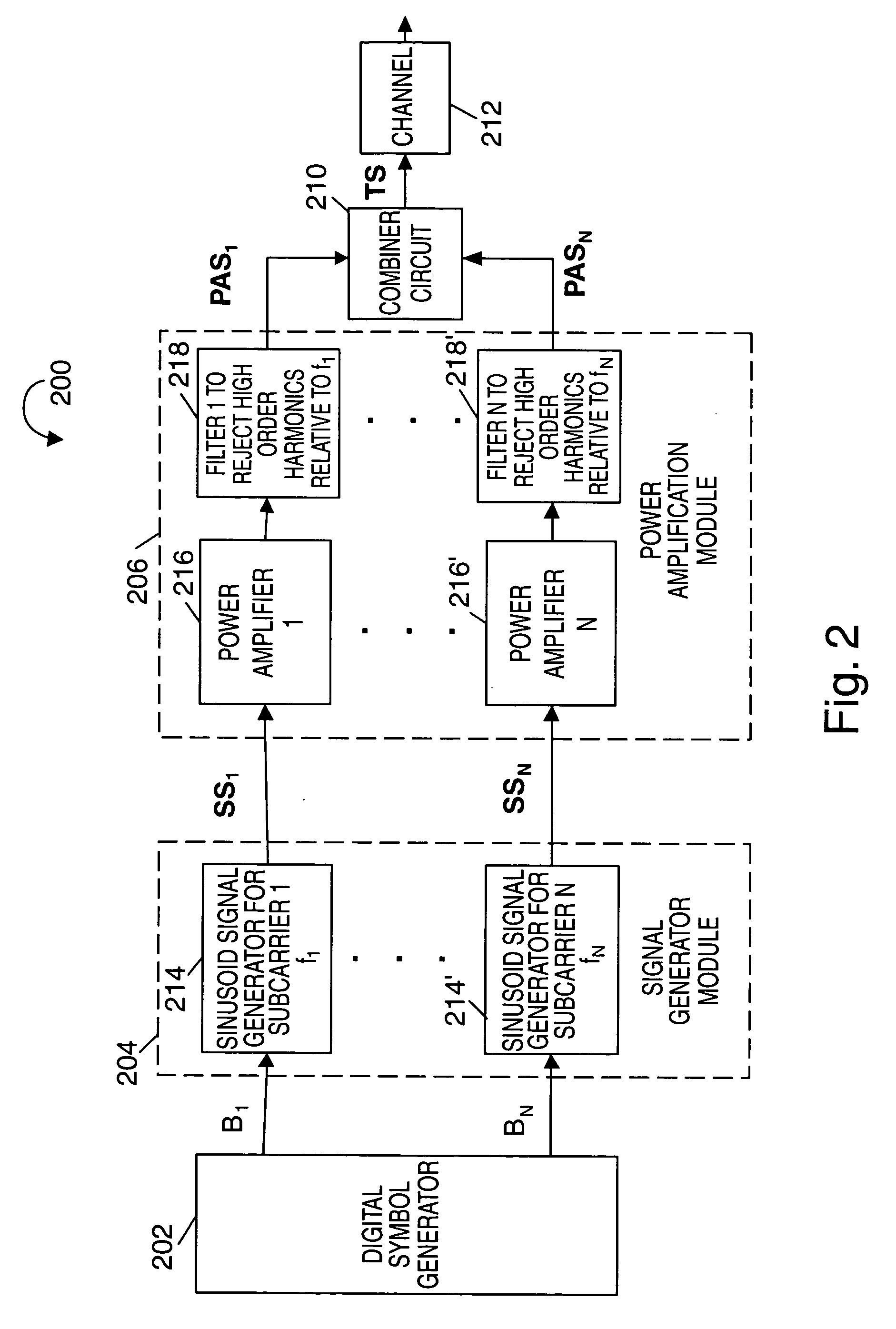
Methods and apparatus for generating and transmitting frequency division multiplexed signals are described. The methods are well suited for use where a device uses a small subset, M, of a larger set of N subcarrier frequencies at any given time. Each transmitted FDM signal is generated by combining a plurality of individual analog subcarrier signals whose frequency may change, e.g., be hopped as a function of time. Each generated analog subcarrier signal is amplified, e.g., power amplified, and filtered prior to being combined with other analog subcarrier signals. Filters are used to compensate for or correct signal distortions and / or reduce interference between subcarriers. Fixed frequency filters are used in an exemplary frequency hopping OFDM system. In another embodiment, the filters are programmable and change, e.g., in terms of center frequency, to match the selected subcarrier frequency as frequency hopping occurs. The bandwidth of the programmable filters may remain constant.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Audio spectral noise reduction method and apparatus
InactiveUS7742914B2Improve intelligibilityAdd featureSpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumRelative energy
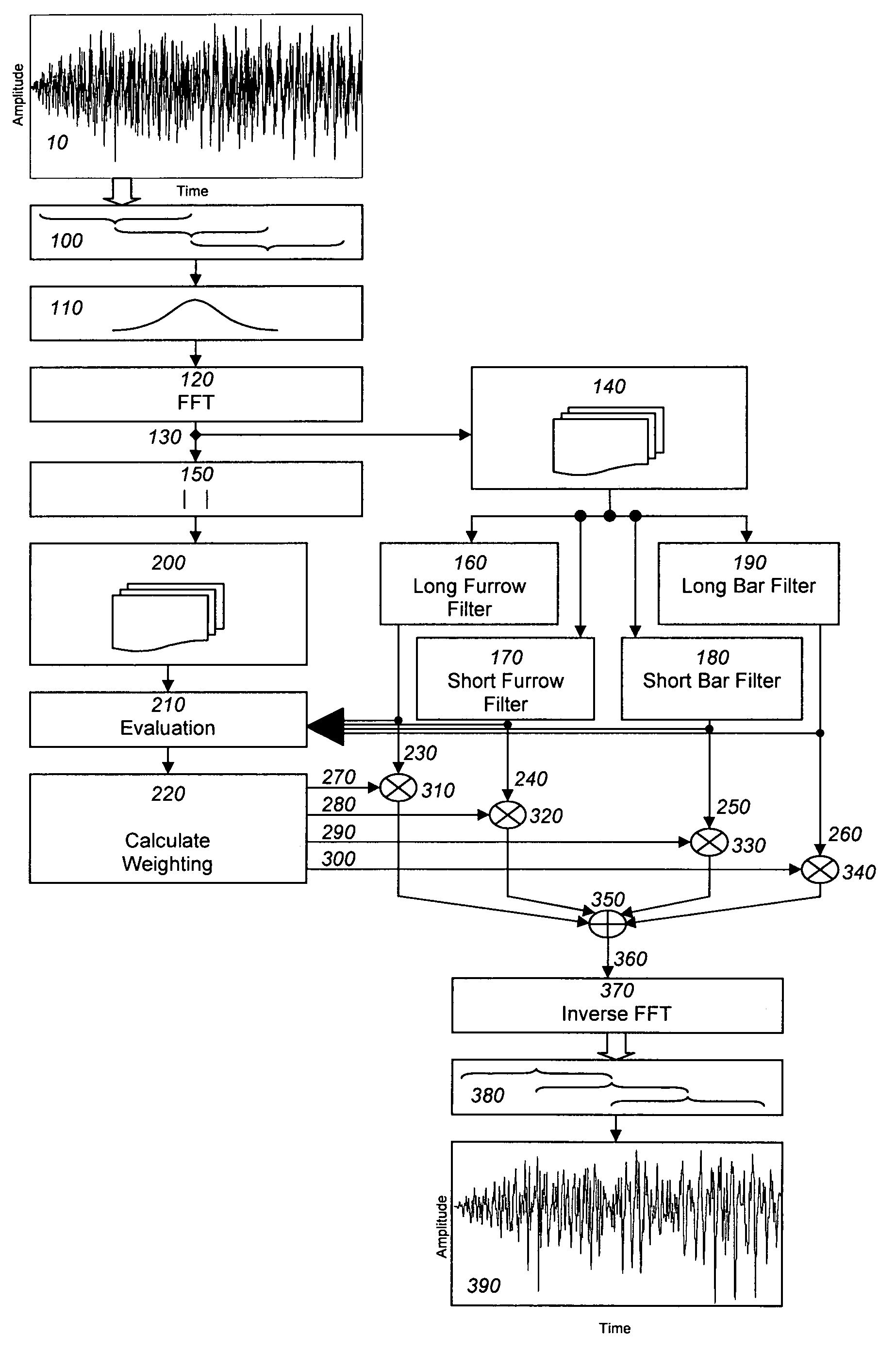
A method of reducing noise in an audio signal, comprising the steps of: using a furrow filter to select spectral components that are narrow in frequency but relatively broad in time; using a bar filter to select spectral components that are broad in frequency but relatively narrow in time; analyzing the relative energy distribution between the output of the furrow and bar filters to determine the optimal proportion of spectral components for the output signal; and reconstructing the audio signal to generate the output signal. A second pair of time-frequency filters may be used to further improve intelligibility of the output signal. The temporal relationship between the furrow filter output and the bar filter output may be monitored so that the fricative components are allowed primarily at boundaries between intervals with no voiced signal present and intervals with voice components. A noise reduction system for an audio signal.
Owner:KOSEK DANIEL A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com